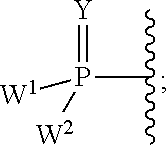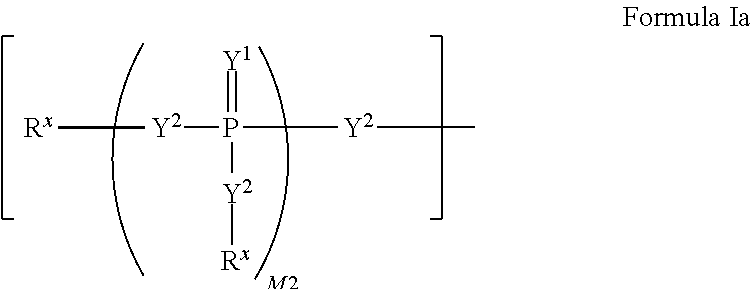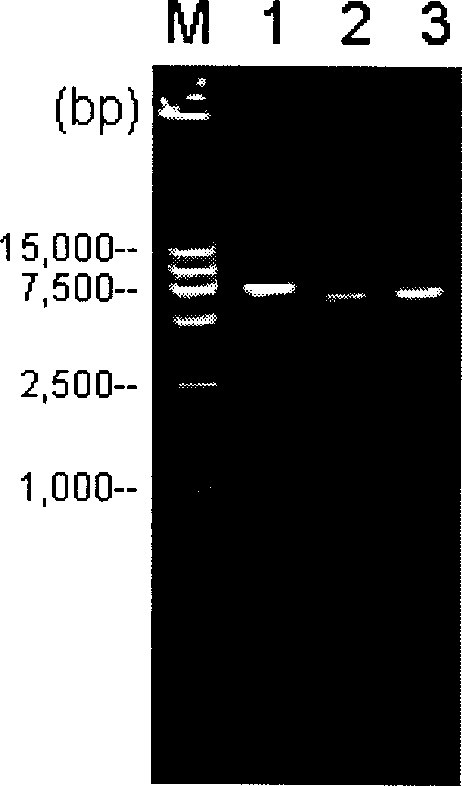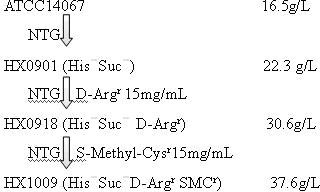Patents
Literature
1946 results about "Mutant strain" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
(myo͞ot′nt) n. 1. An organism, cell, virus, or gene resulting from genetic mutation. 2. Slang One that is suggestive of a genetic mutant, as in bizarre appearance or inaptitude. adj. 1. Resulting from genetic mutation: a mutant strain of bacteria.
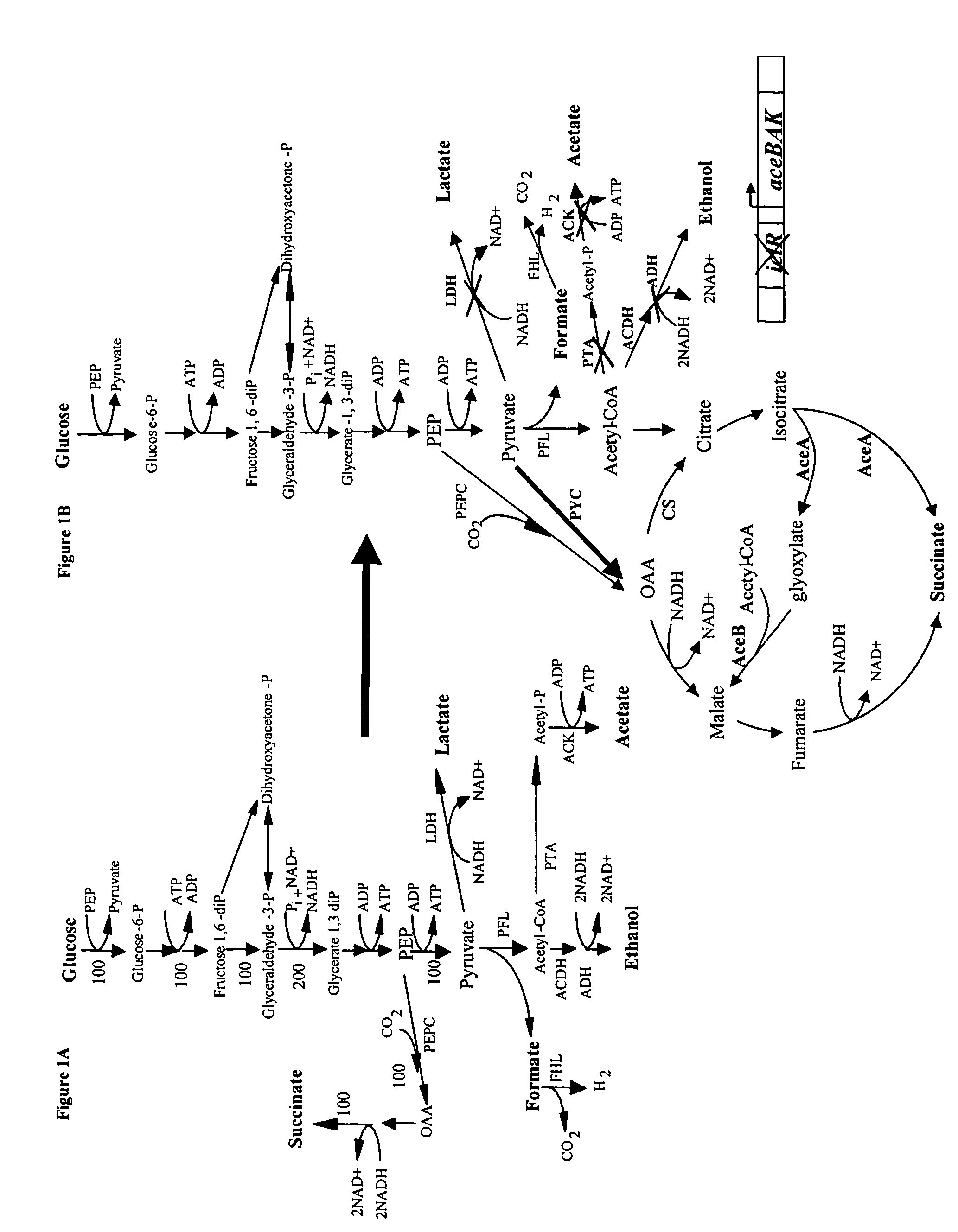
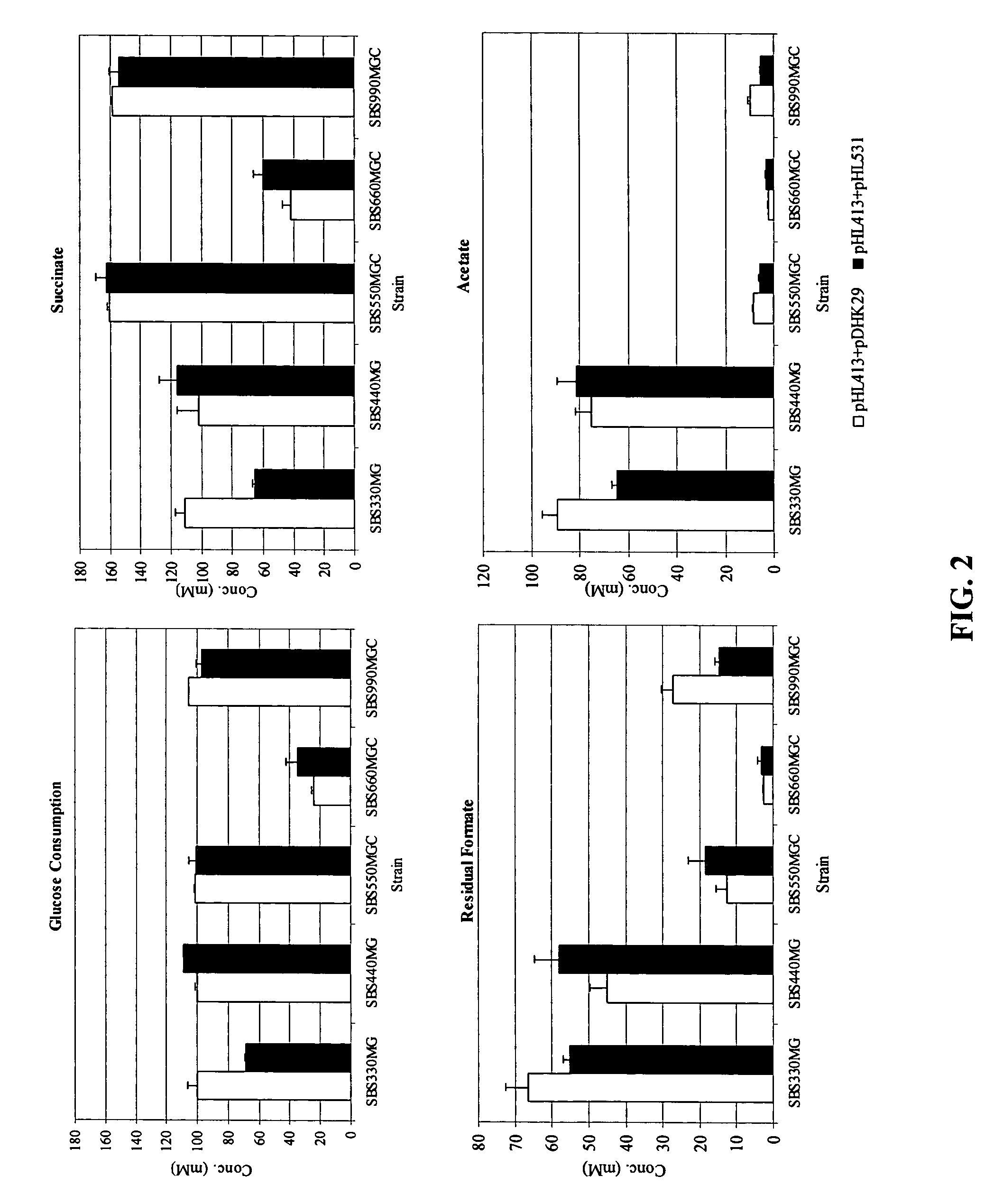
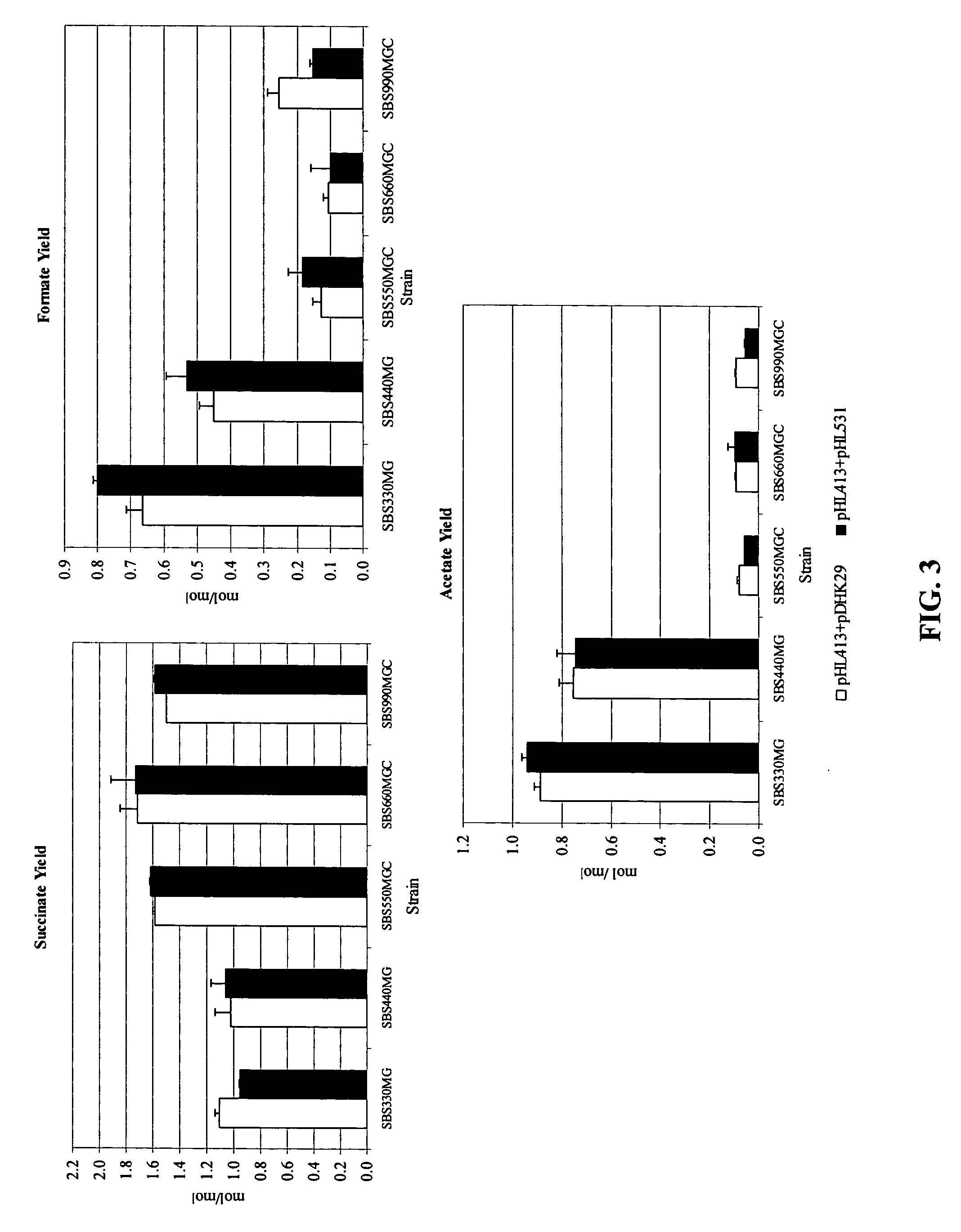
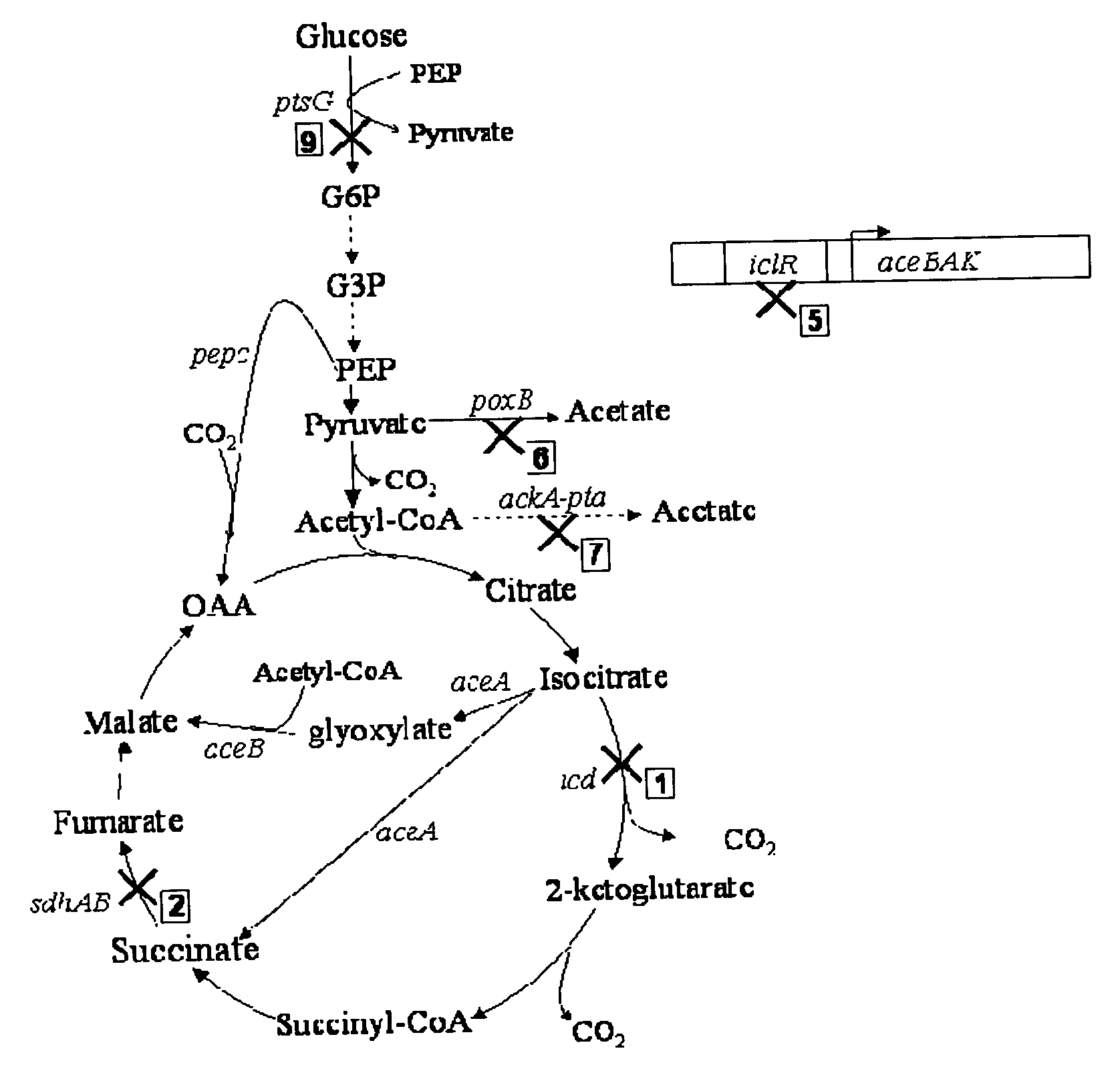
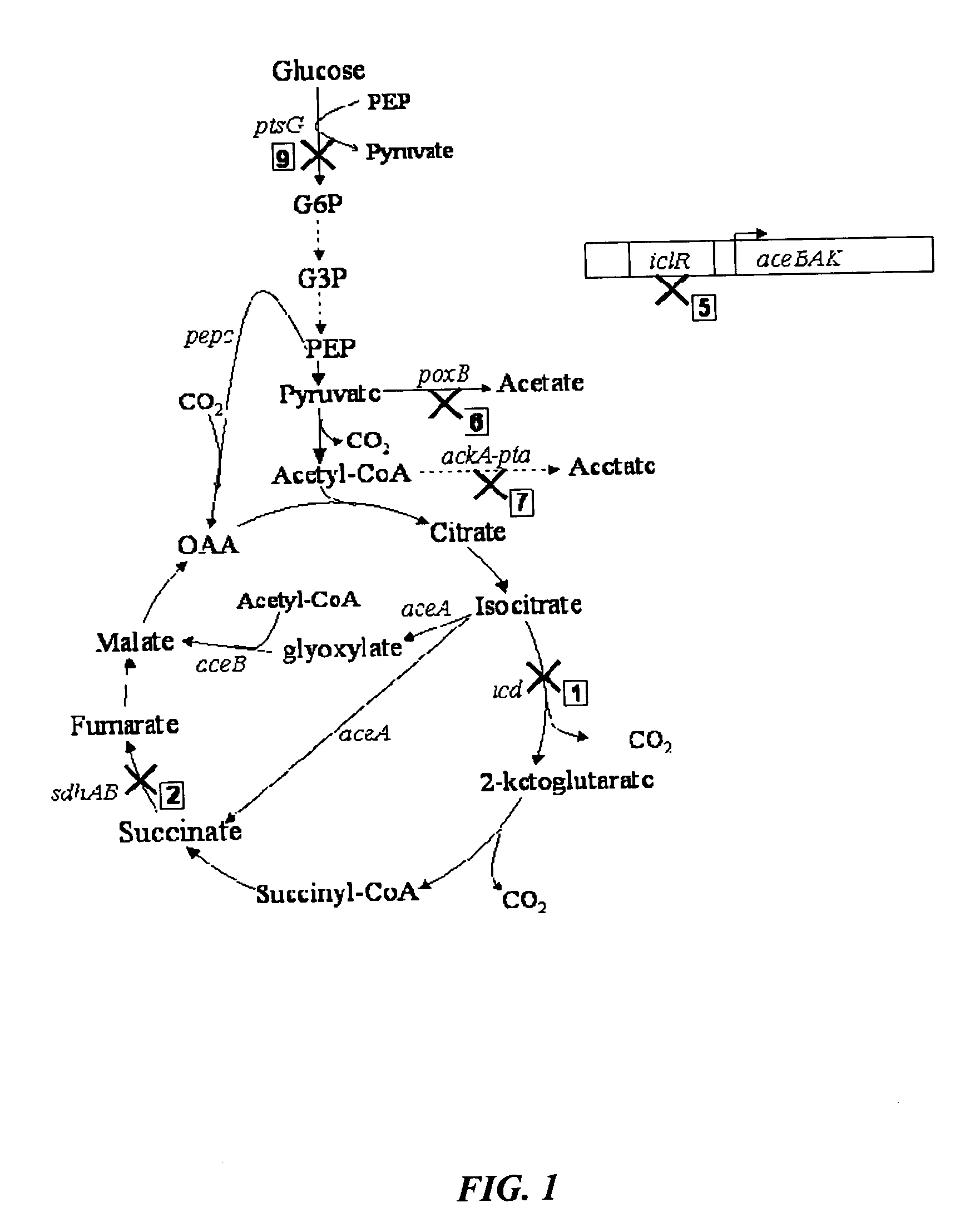
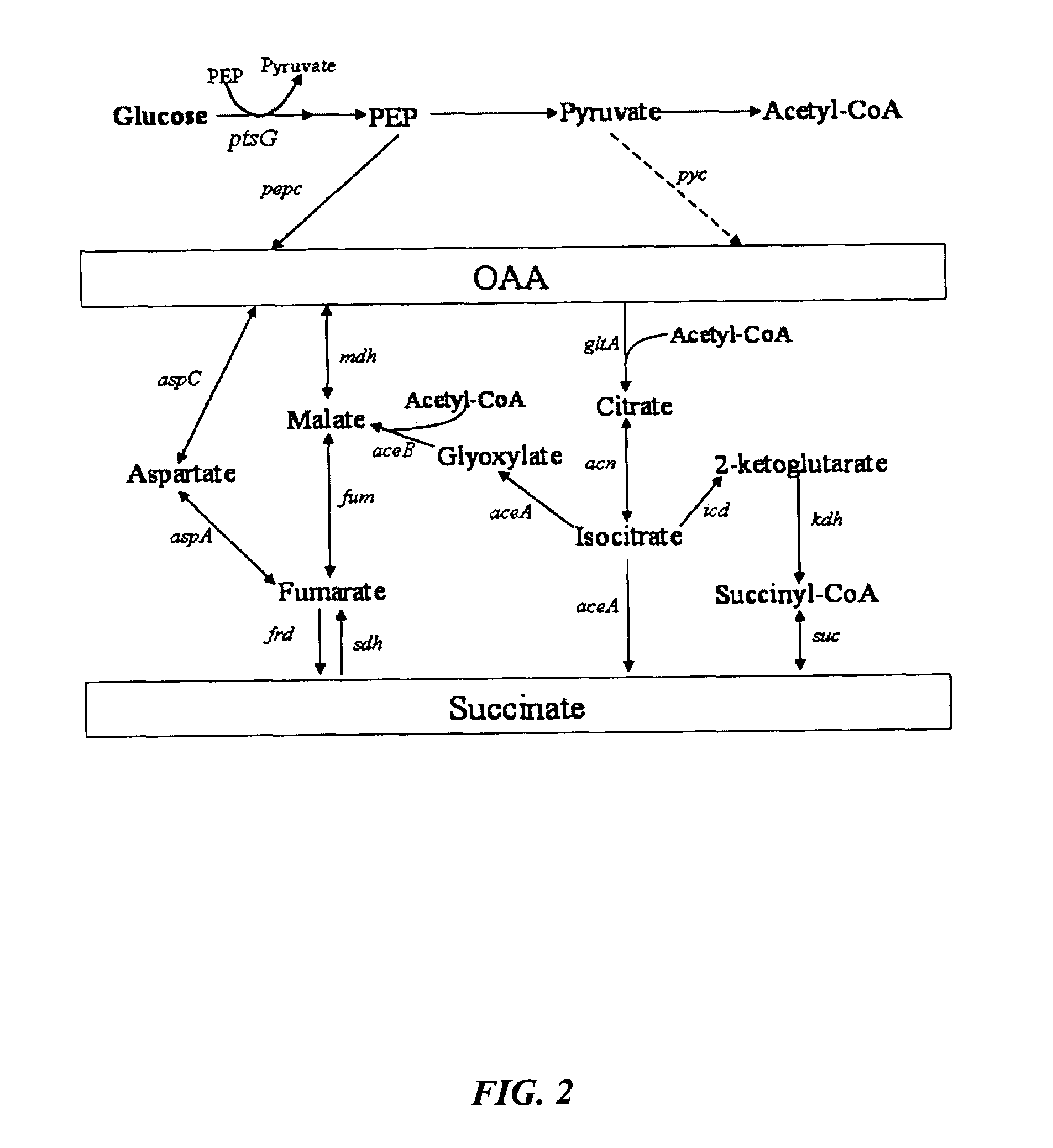
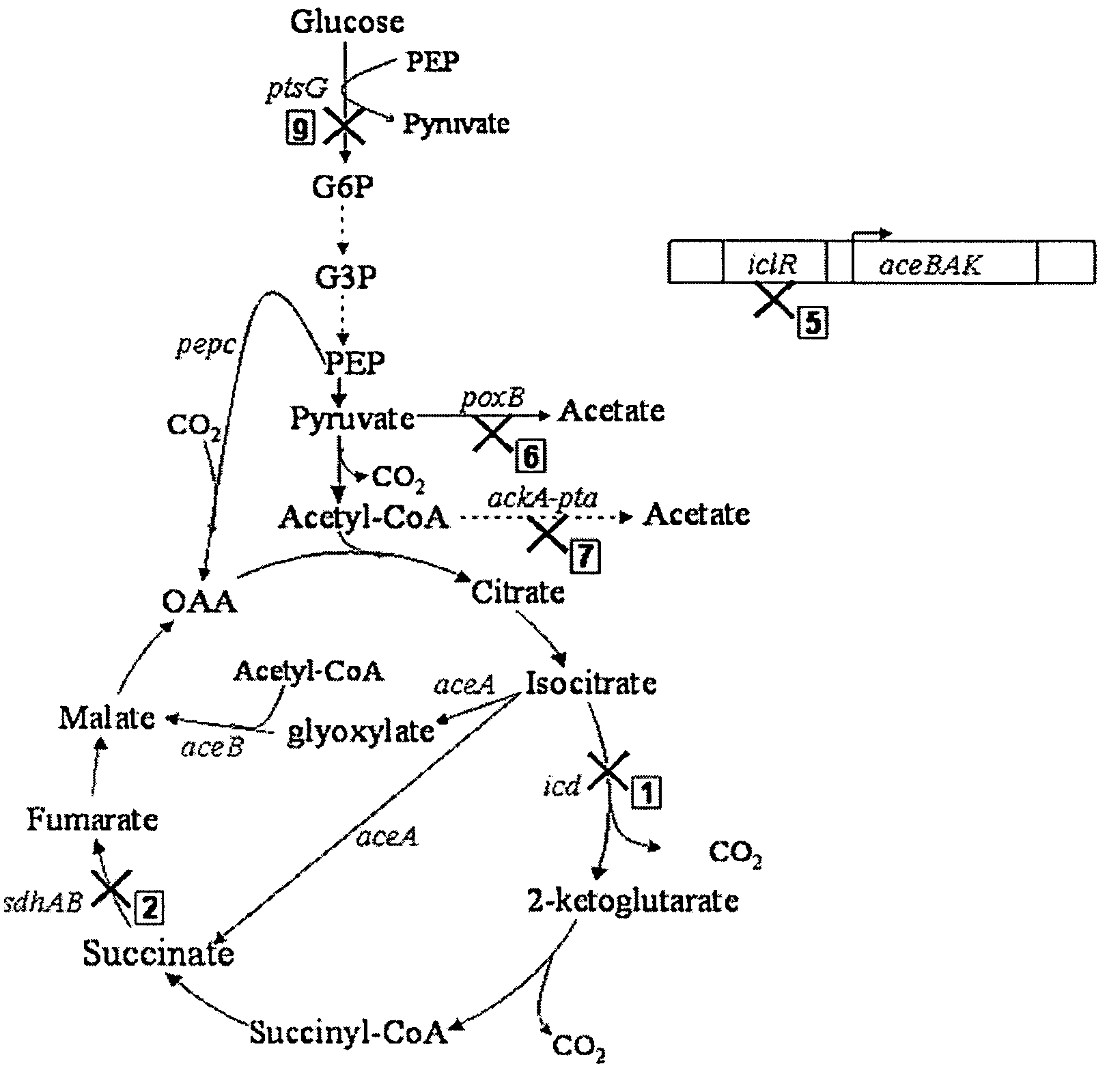
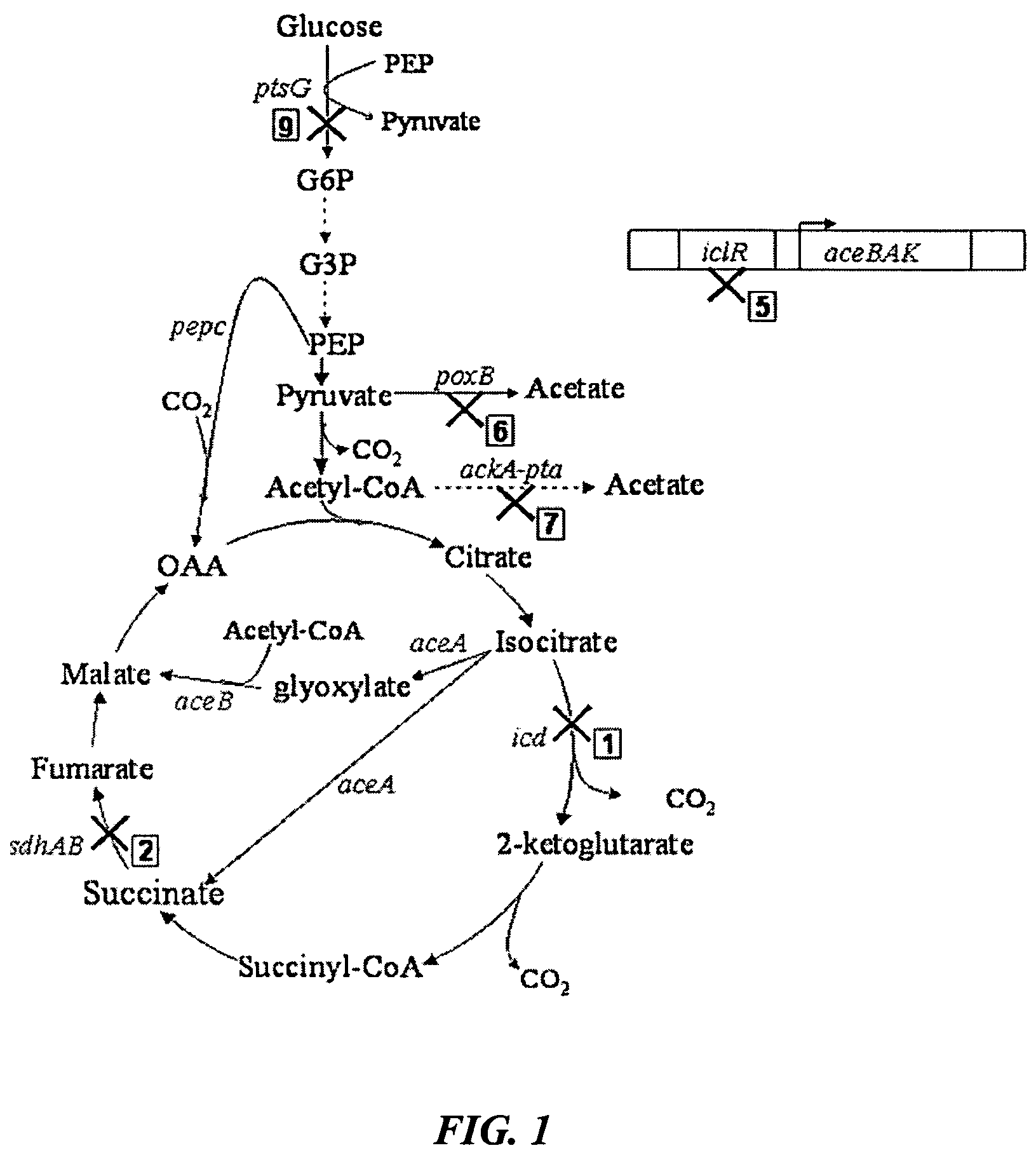
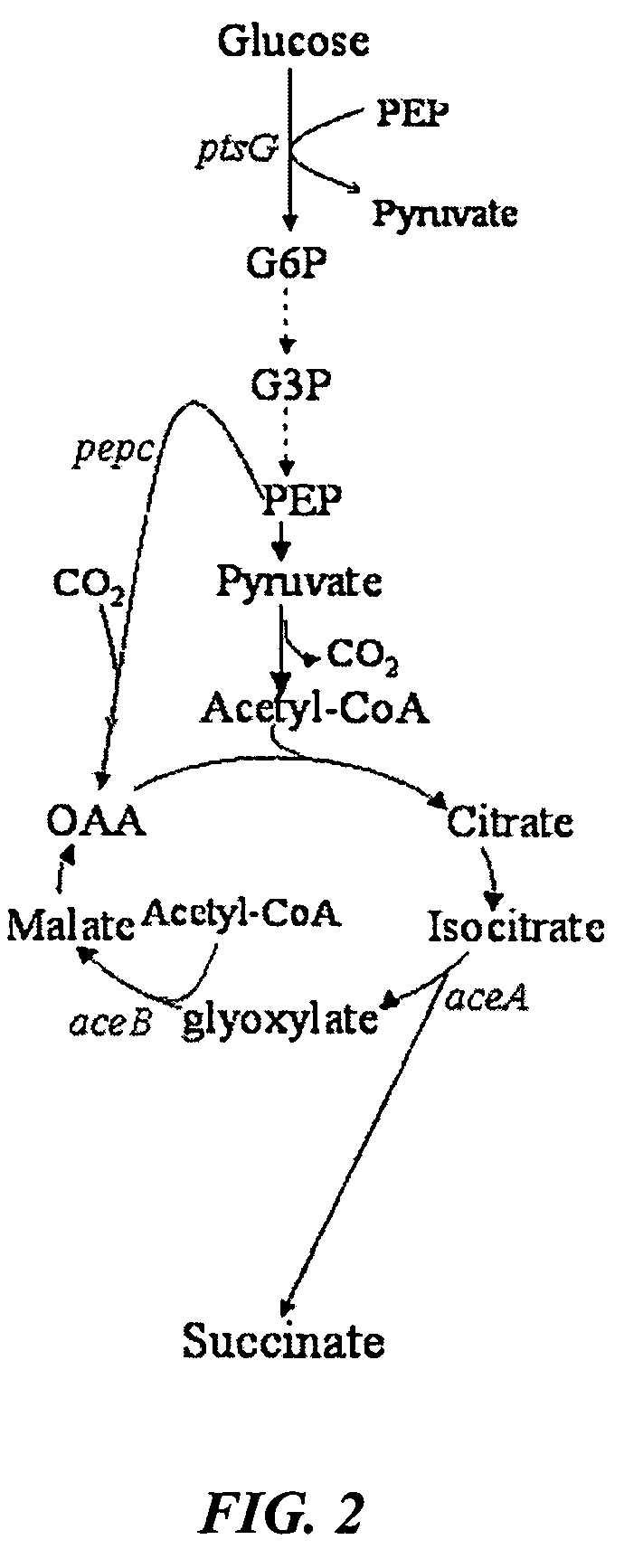
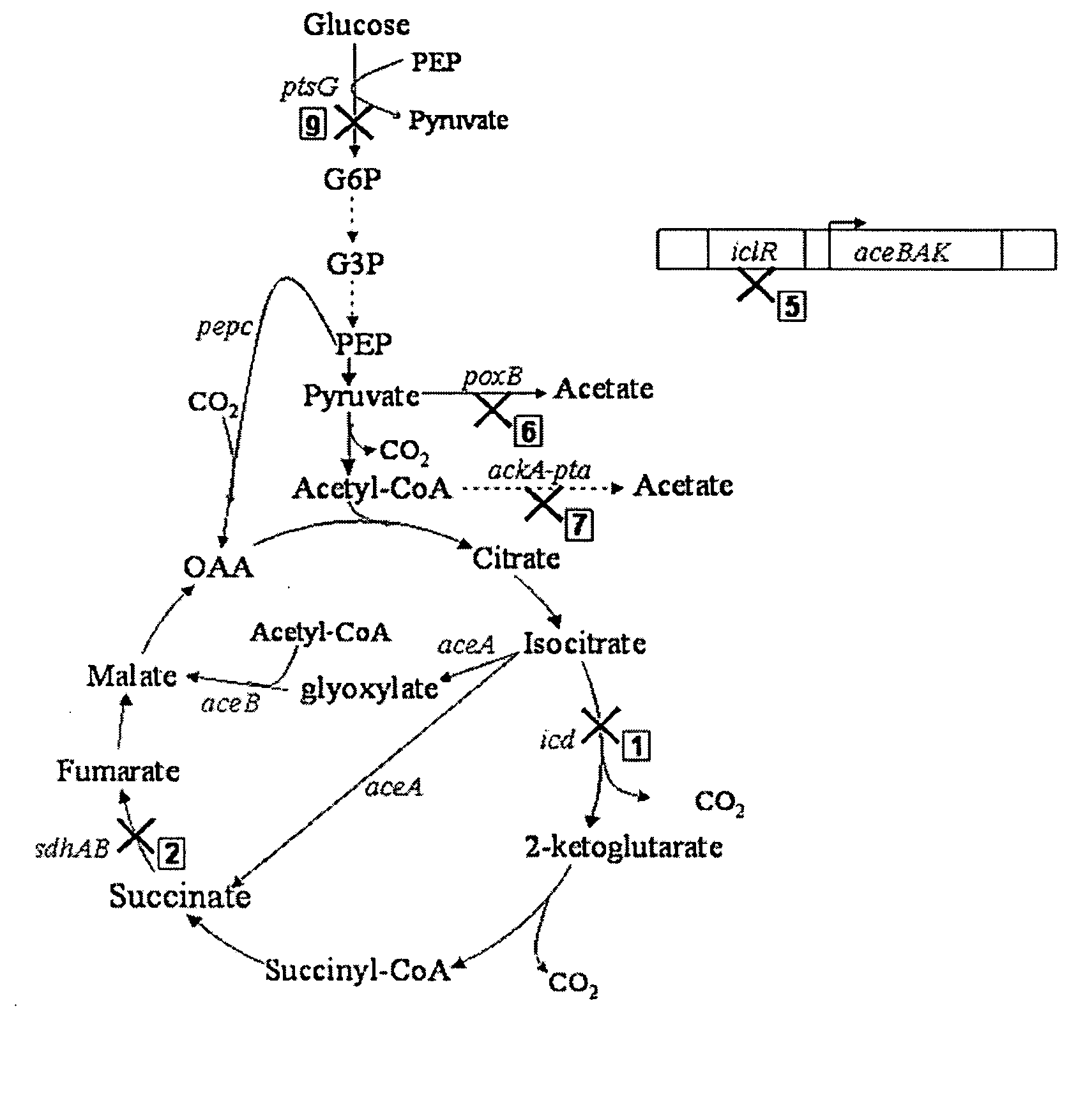
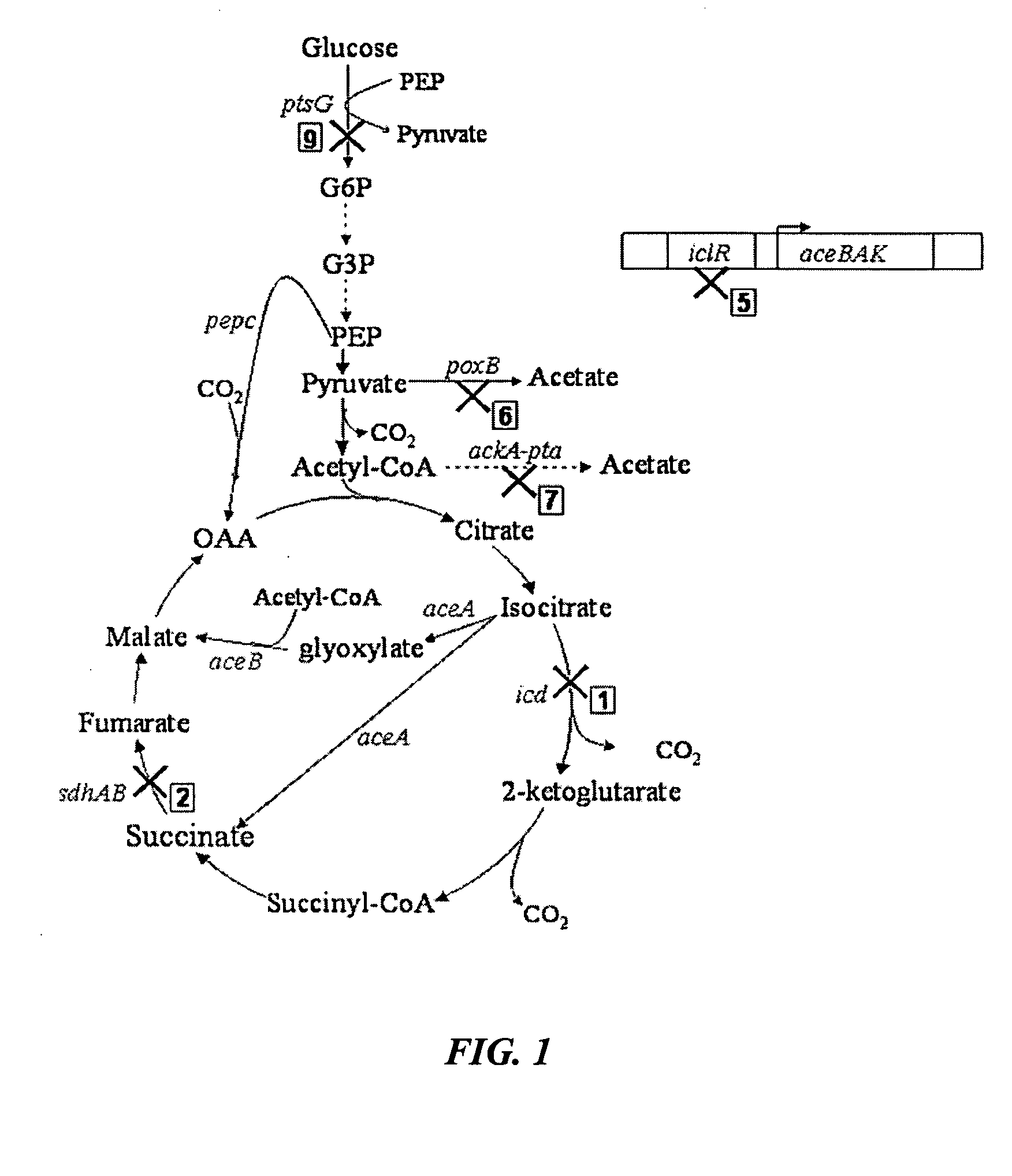
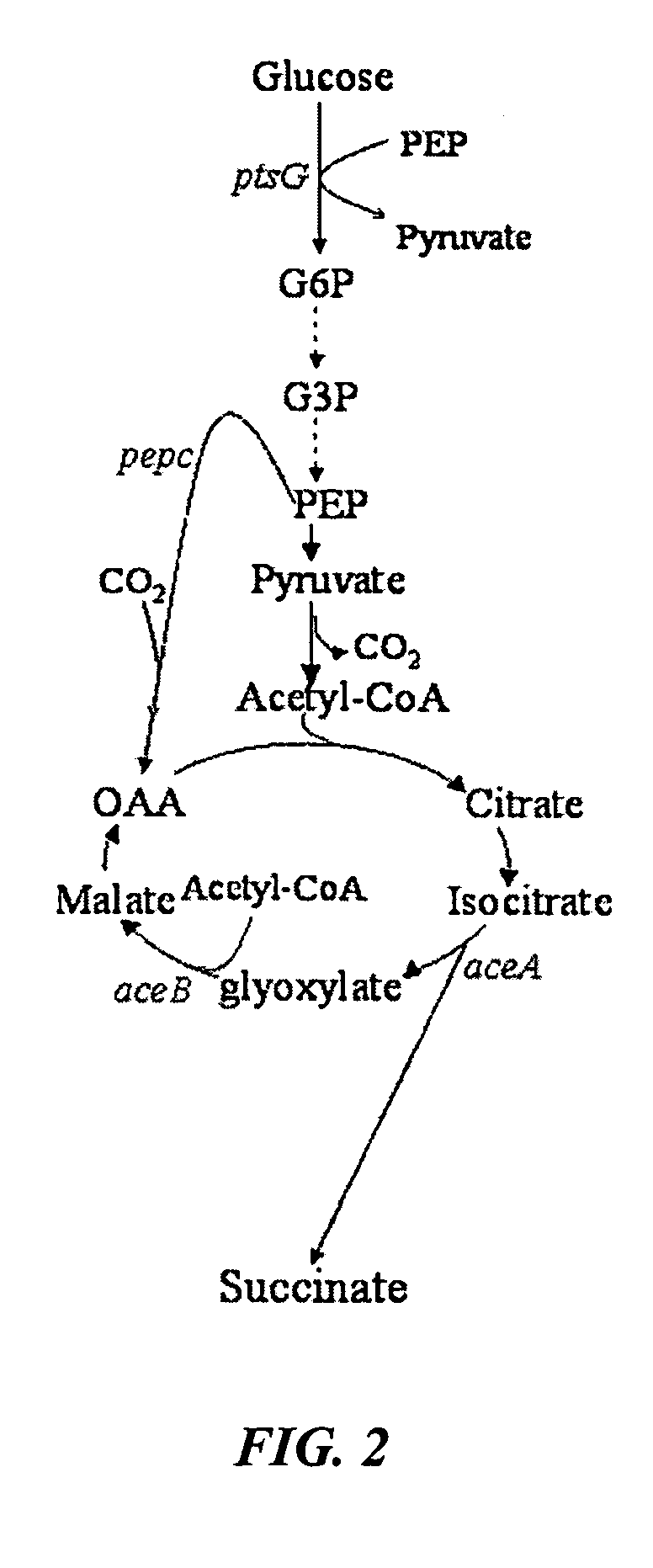
Mutant E. coli strain with increased succinic acid production
The invention relates to a mutant strain of bacteria, which either lacks or contains mutant genes for several key metabolic enzymes, and which produces high amounts of succinic acid under anaerobic conditions.
Owner:RICE UNIV
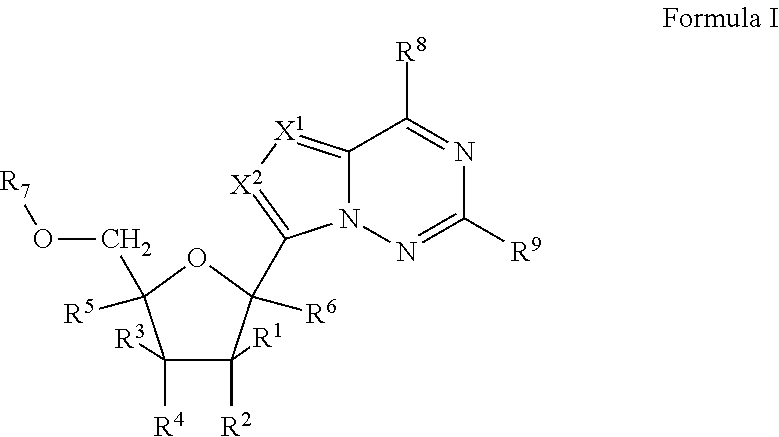
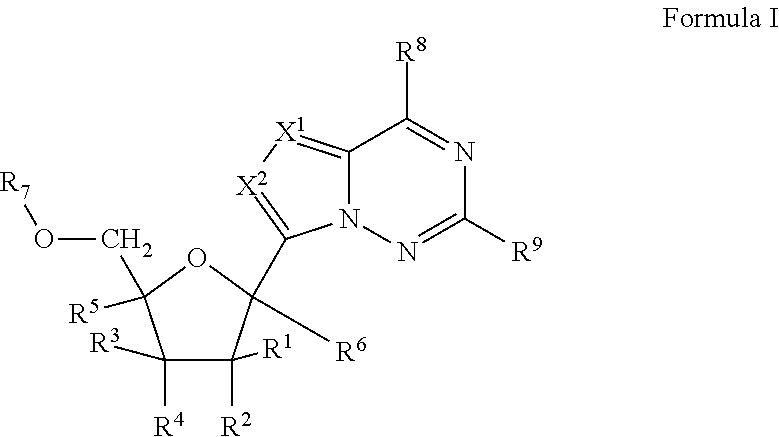
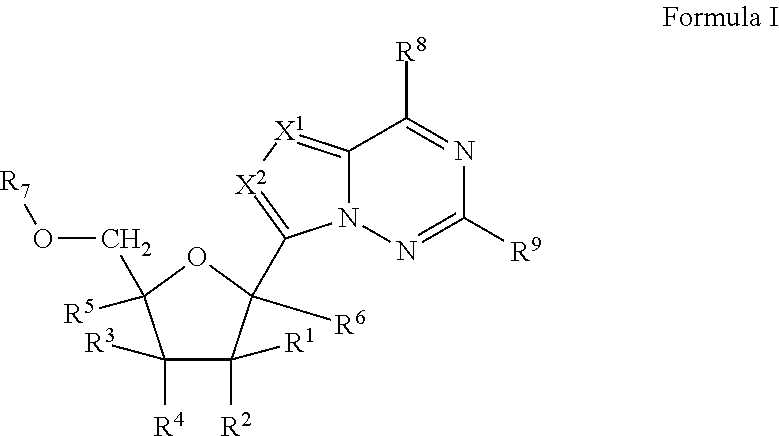
2'-fluoro substituted carba-nucleoside analogs for antiviral treatment
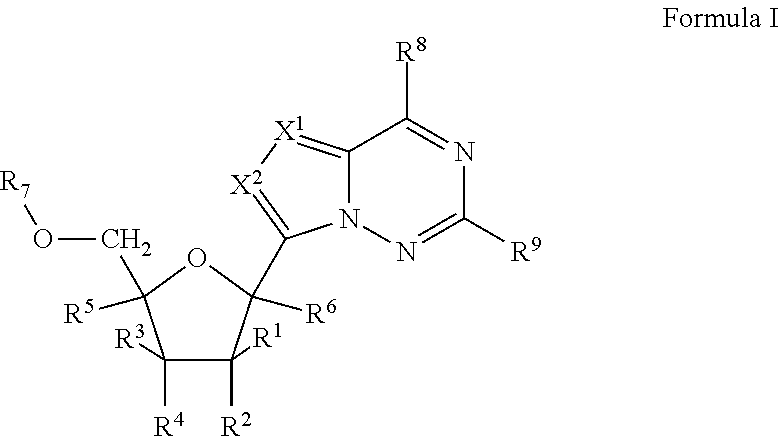
Provided are select imidazo[1,2-f][1,2,4]triazinyl nucleosides, nucleoside phosphates and prodrugs thereof, wherein the 2′ position of the nucleoside sugar is substituted with halogen and carbon substituents. The compounds, compositions, and methods provided are useful for the treatment of Flaviviridae virus infections, particularly hepatitis C infections caused by both wild type and mutant strains of HCV.
Owner:GILEAD SCI INC
Aerobic succinate production in bacteria
Methods of increasing yields of succinate using aerobic culture methods and a multi-mutant E. coli strain are provided. Also provided is a mutant strain of E. coli that produces high amounts of succinic acid.
Owner:RICE UNIV
2'-fluoro substituted carba-nucleoside analogs for antiviral treatment
ActiveUS7973013B2Esterified saccharide compoundsSaccharide with heterocyclic radicalsHalogenPhosphate
Owner:GILEAD SCI INC
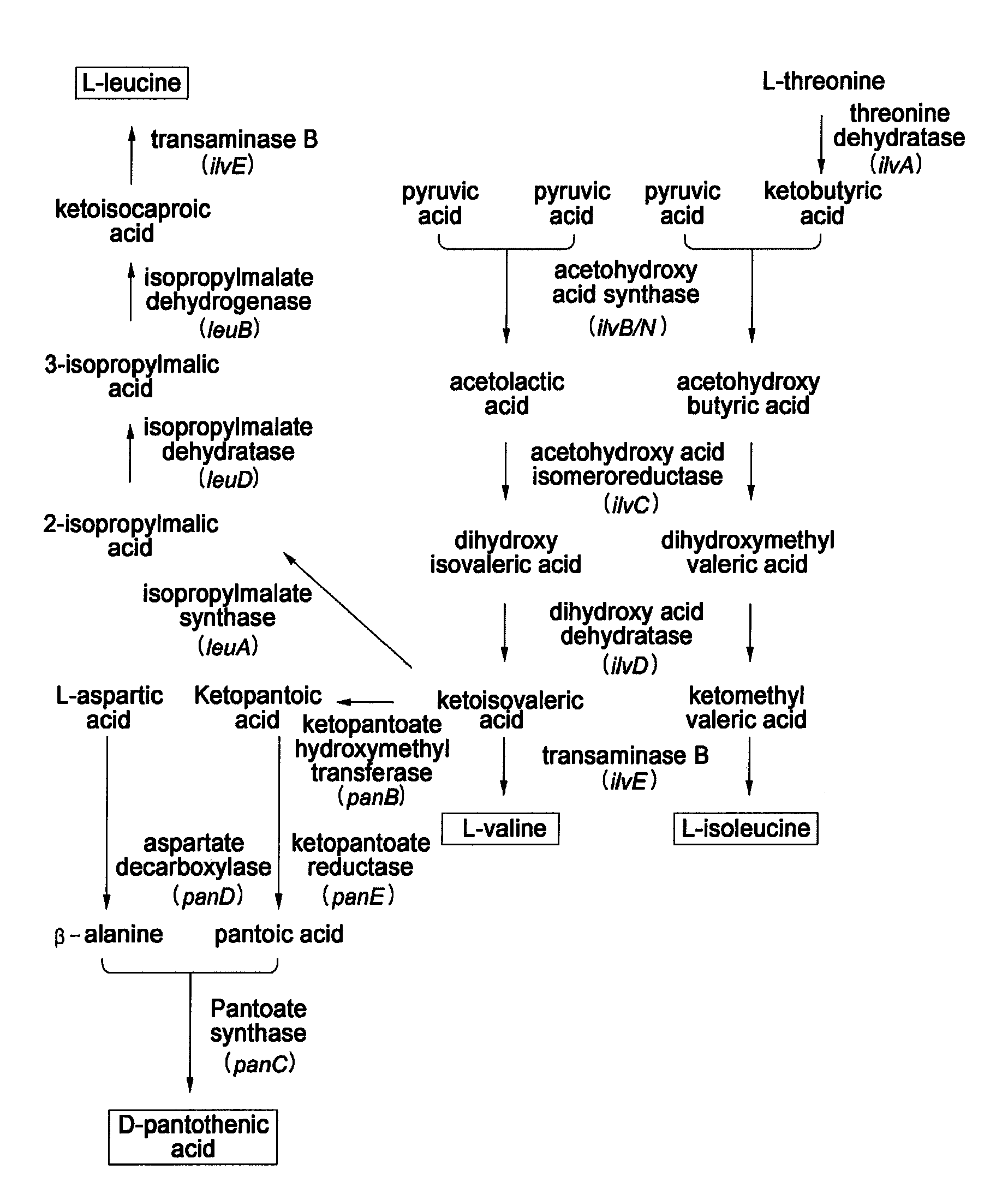
Microorganism having enhanced L-valine productivity and method for producing L-valine using the same
The present invention relates to a microorganism having an enhanced L-valine productivity and a method for producing L-valine using the same. More particularly, the present invention relates to a Corynebacterium glutamicum mutant strain that has resistance to L-valine and derivatives thereof so as to have an enhanced L-valine productivity, and a method for producing L-valine using the same.
Owner:CJ CHEILJEDANG CORP
2'-fluoro substituted carba-nucleoside analogs for antiviral treatment
Owner:GILEAD SCI INC
Aerobic succinate production in bacteria
Methods of increasing yields of succinate using aerobic culture methods and a multi-mutant E. coli strain are provided. Also provided is a mutant strain of E. coli that produces high amounts of succinic acid.
Owner:RICE UNIV
2′-branched nucleosides and Flaviviridae mutation
ActiveUS7824851B2High sensitivityReduce Flaviviridae infectionBiocideSsRNA viruses positive-senseAmino acidMutant strain
The present invention discloses a method for the treatment of Flaviviridae infection that includes the administration of a 2′-branched nucleoside, or a pharmaceutically acceptable prodrug and / or salt thereof, to a human in need of therapy in combination or alternation with a drug that directly or indirectly induces a mutation in the viral genome at a location other than a mutation of a nucleotide that results in a change from seine to a different amino acid in the highly conserved consensus sequence, XRXSGXXXT (Sequence ID No. 63), of domain B of the RNA polymerase region, or is associated with such a mutation. The invention also includes a method to detect a mutant strain of Flaviviridae and a method for its treatment.
Owner:INDENIX PHARM LLC
L-arginine producing strain and its mutation method and usage in producing L-arginine
InactiveCN1441055AHigh genetic stabilityGood genetic stabilityBacteriaFermentationBiotechnologyArginine
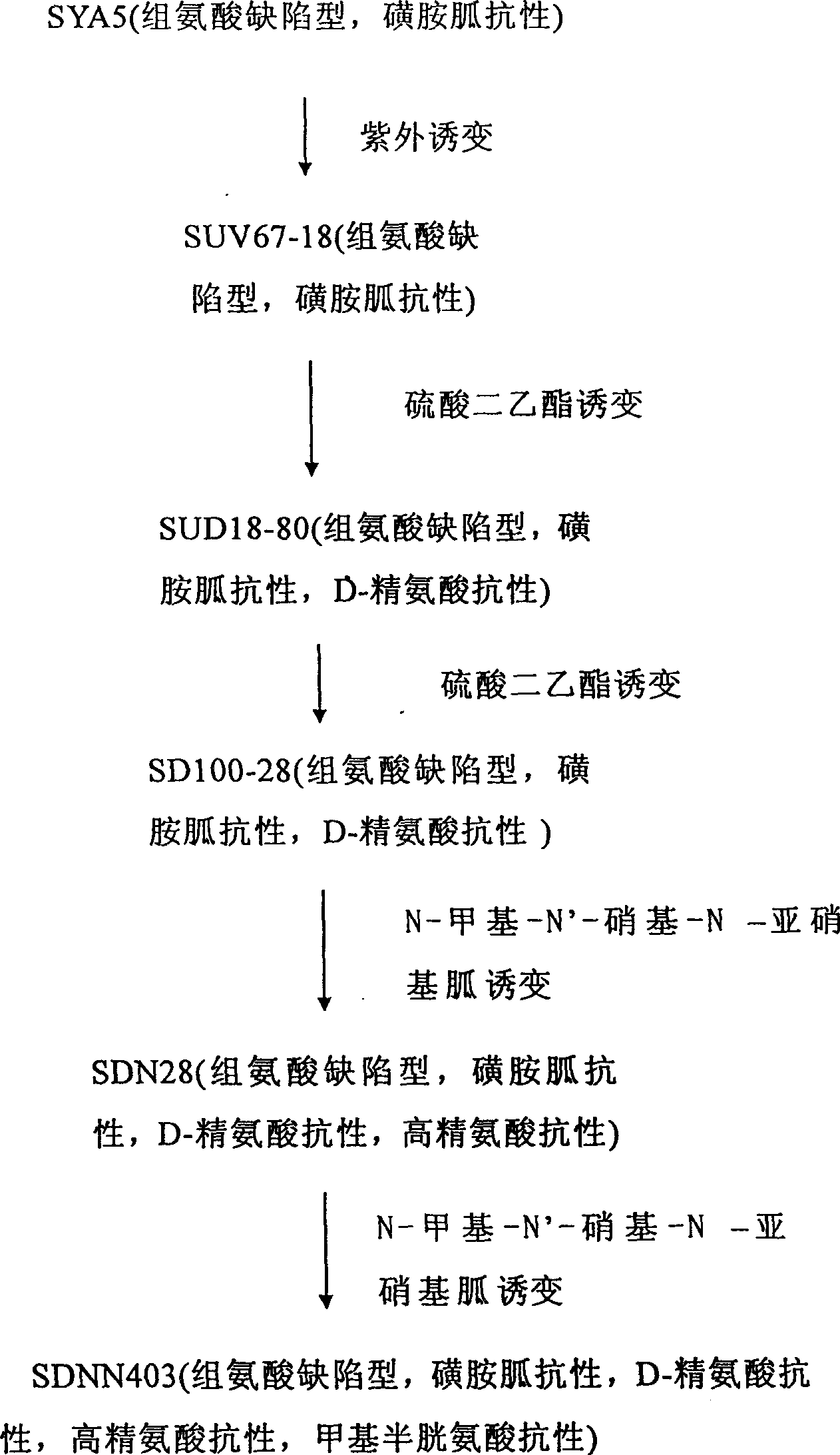
The present invention relates to the fermentation process of producing L-arginine. By using Corynebacterium crenatum SYA5 screened and preserved by the present lab as parent and through conventional physical and chemical mutation process and multiple structural analog resistance screening, mutant strain SDNN403 is obtained. Through culturing of the mutant strain under optimized condition, L-arginine is produced in the yield level of 30-35 g / L. The strain has high genetic stability, stable yield characteristic, high L-arginine yield level, less produced hetero acids and easy technological amplification, and is suitable four industrial production.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
Aerobic succinate production in bacteria
Methods of increasing yields of succinate using aerobic culture methods and a multi-mutant E. coli strain are provided. Also provided is a mutant strain of E. coli that produces high amounts of succinic acid.
Owner:RICE UNIV
2'-fluoro substituted carba-nucleoside analogs for antiviral treatment
Provided are pyrrolo[1,2-f][1,2,4]triazinyl, imidazo[1,5-f][1,2,4]triazinyl, imidazo[1,2-f][1,2,4]triazinyl, and [1,2,4]triazolo[4,3-f][1,2,4]triazinyl nucleosides, nucleoside phosphates and prodrugs thereof, wherein the 2′ position of the nucleoside sugar is substituted with halogen and carbon substitutents. The compounds, compositions, and methods provided are useful for the treatment of Flaviviridae virus infections, particularly hepatitis C infections caused by both wild type and mutant strains of HCV.
Owner:GILEAD SCI INC
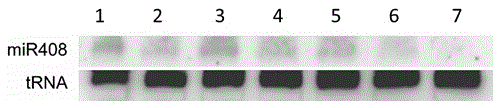
Application of gene miR408 and UCL in cultivating high-yielding rice
ActiveCN105112422ARegulatoryIncrease productionVector-based foreign material introductionAngiosperms/flowering plantsBiotechnologyGrain weight
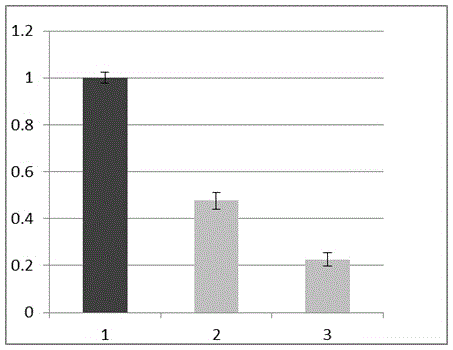
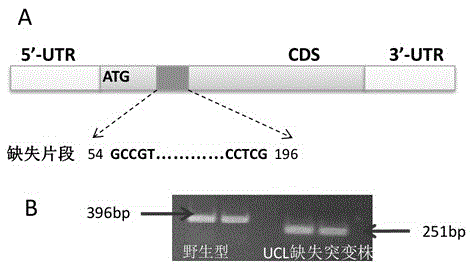
The invention discloses application of gene miR408 and UCL (uclacyanin) in cultivating high-yielding rice. By analyzing miRNA in charge of specific expression in rice grains and embryos, it is found that the gene miR408 has an important regulating effect in rice grain growth, and the function is achieved by lowering the target gene UCL of the gene miR408. According to the application, rice mutant strains over-expressing miR408 and UCL-RNA interference and UCL-CRISPR knockout are respectively constructed. The research shows that the three types of mutant strains all have the phenomenon of rapid growth, and the drooping phenomenon of rice ears at the maturation stage is more obvious compared with that of a wild type; in addition, the fruiting rate is increased, ears are larger in size, the number of grains per ear is much larger compared with the wild type, and the thousand grain weight and the yield are also remarkably increased. According to the application, a brand-new, simple and effective method is provided for cultivation of high-yielding rice and can be applied and popularized on a large scale; besides, the application will not pollute the environment, and the rice is safe to eat.
Owner:SUN YAT SEN UNIV
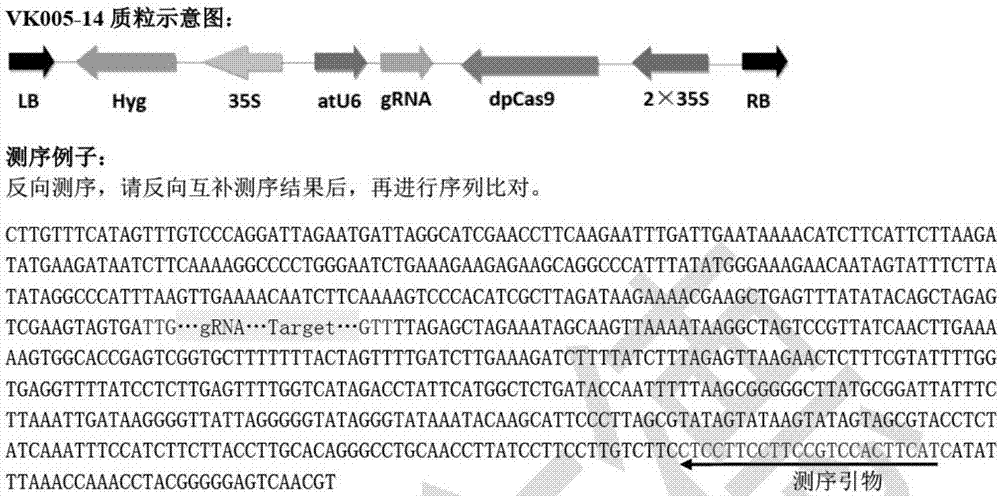
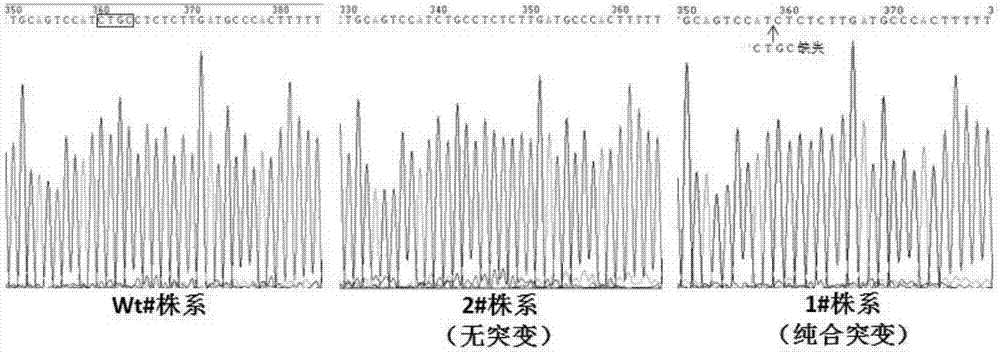
Gene editing method using CRISPR/Cas9 system to create pink fruit tomato
InactiveCN107312795AOvercoming the problem of being unable to knock out genes in a targeted mannerGenetic stabilityHorticulture methodsPlant tissue cultureEscherichia coliCompetent cell
The invention relates to construction of a tomato transgenic material, and aims to provide a gene editing method using a CRISPR / Cas9 system to mutate a tomato SlMYB12 gene in order to transform red fruit tomato into pink fruit tomato. The method includes the following steps: designing an oligo primer corresponding to the gRNA target site of the SlMYB12 gene, and recombining and connecting an oligo dimer with a Cas9 / gRNA vector; transforming Escherichia Coli competent cells, transforming a plasmid with a correct sequencing result into Agrobacterium tumefaciens, and mediating and transforming tomato calluses to obtain a transgenic plant in order to obtain a transgenic positive strain; and carrying out gene sequencing and phenotype observation to determine a pure mutant strain which is an SlMYB12 function completely lost tomato mutant for pink fruits. The method can effectively knock out the transcriptional translation of the SlMYB12 gene, and is an ideal gene editing system for successfully transforming the tomato red fruits into the pink fruits.
Owner:ZHEJIANG ACADEMY OF AGRICULTURE SCIENCES
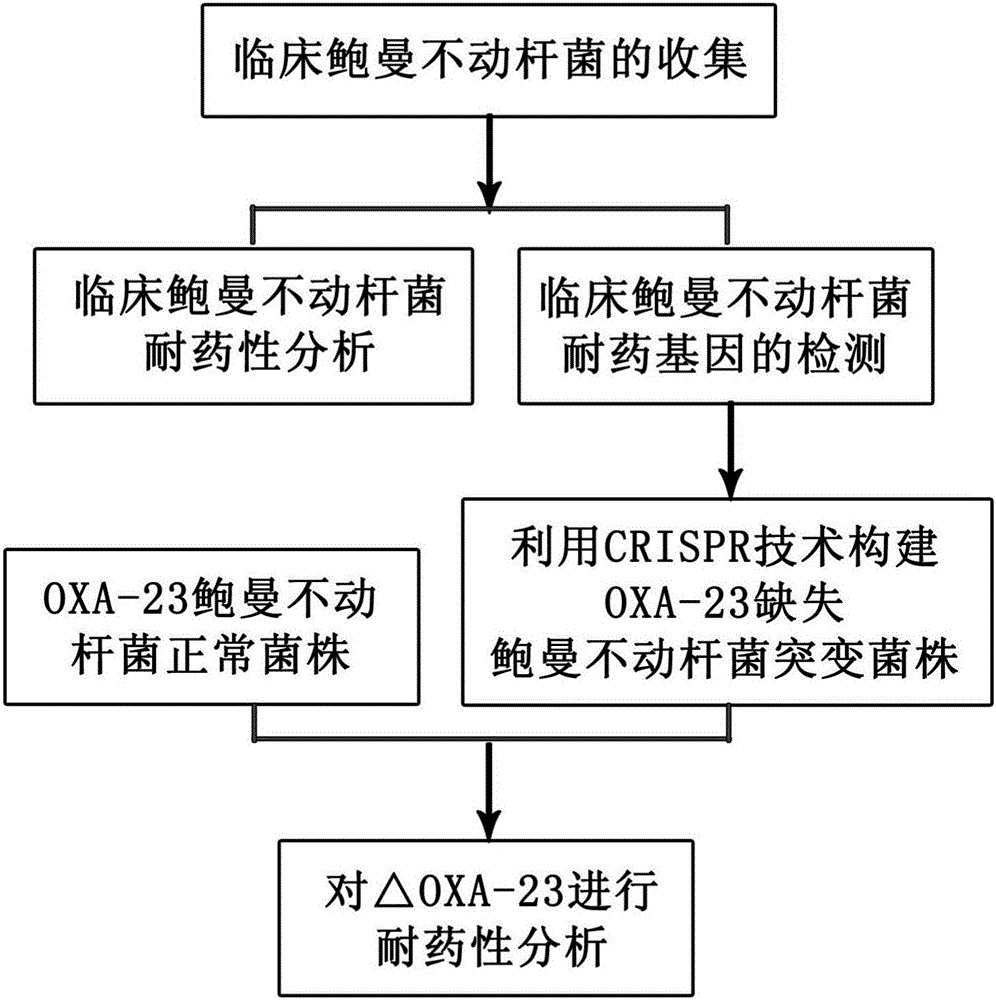
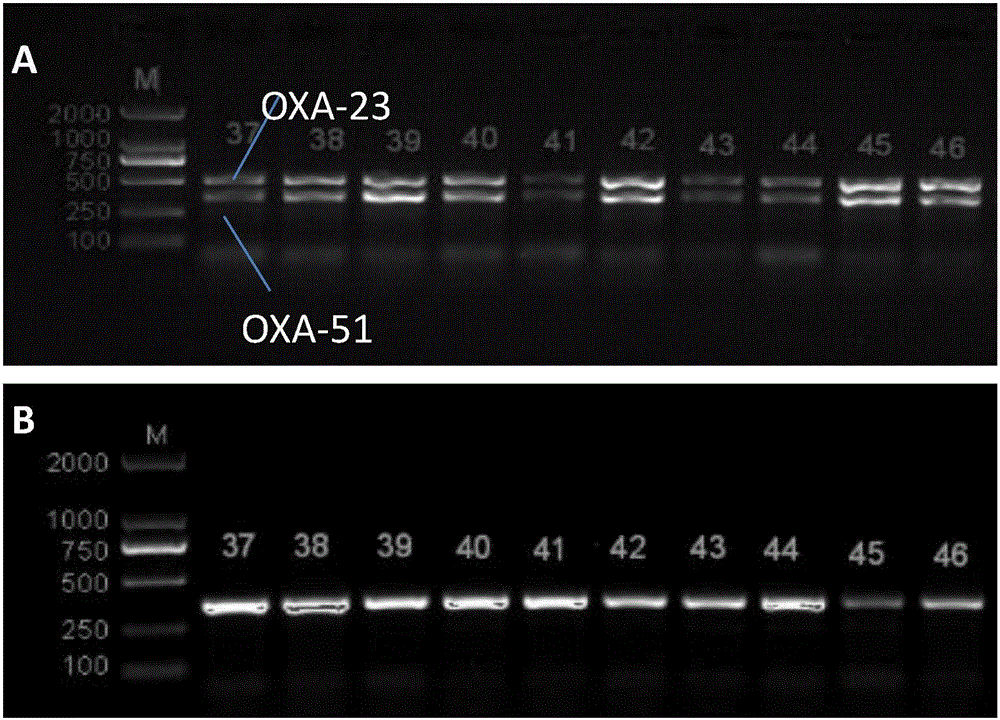
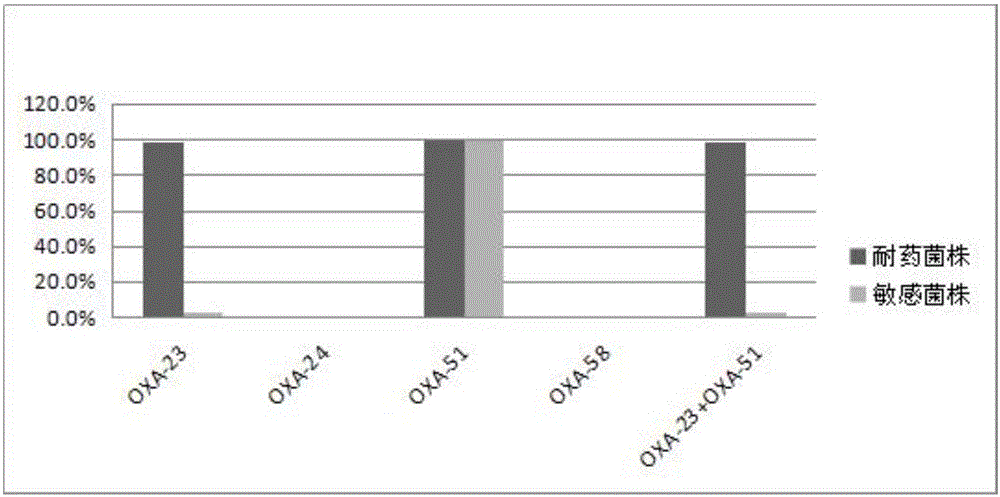
Method for deleting drug resistant genes of acinetobacter baumannii (AB) through CRISPR-Cas9
InactiveCN106544353ASensitivity reversalEasy to operateVectorsMicroorganism based processesBacteroidesMulti drug resistant
The invention discloses a method for deleting drug resistant genes of acinetobacter baumannii (AB) through CRISPR-Cas9. The method comprises the steps that firstly, AB is collected clinically, and drug resistance analysis and statistics are conducted after the AB is subjected to drug resistance measurement through a drug sensitive slip method; secondly, the multi-drug resistant AB is subjected to DNA extraction through a lysis-boiling method, and then amplification analysis is conducted by mean of well designed drug resistant gene primers of the AB; and thirdly, according to drug resistant gene detection in the former step, the AB containing an OXA-23 gene is selected, CRISPR / Cas9 and sgRNA plasmids are established and transferred into the AB containing the OXA-23 gene, an OXA-23 gene deletion AB mutant strain is established, and drug resistance analysis is conducted on the OXA-23 gene deletion AB mutant strain. The method is easy to operate and high in knocking-out efficiency, and a novel method and a novel concept are provided for preventing spreading of the drug resistant genes and treating drug resistant bacteria.
Owner:GENERAL HOSPITAL OF NINGXIA MEDICAL UNIV
Novel Strain of Schizochytrium limacinum useful in the production of lipids and Extracellular Polysaccharides and process thereof
The present disclosure provides a novel mutant strain of Schizochytrium limacinum having the Accession No. MTCC 5249, which produces lipids and extracellular polysaccharide (EPS) simultaneously. The disclosure further provides a process for simultaneous production of lipids and extracellular polysaccharide (EPS) from the novel mutant strain of Schizochytrium limacinum. The lipids produced from the novel mutant strain of Schizochytrium limacinum comprises docosahexaenoic acid (DHA). The disclosure also provides a food, feed, cosmetic, nutritional or therapeutic supplement for humans or animals comprising the cell biomass and extracellular polysaccharides (EPS) of the mutant strain of Schizochytrium limacinum. A cosmetic composition comprising the extracellular polysaccharides (EPS) of Schizochytrium limacinum is also provided that is useful as a base for cosmetics for topical application. The present disclosure further provides a pickle composition and a fat product having improved nutritive value.
Owner:ABL BIOTECH
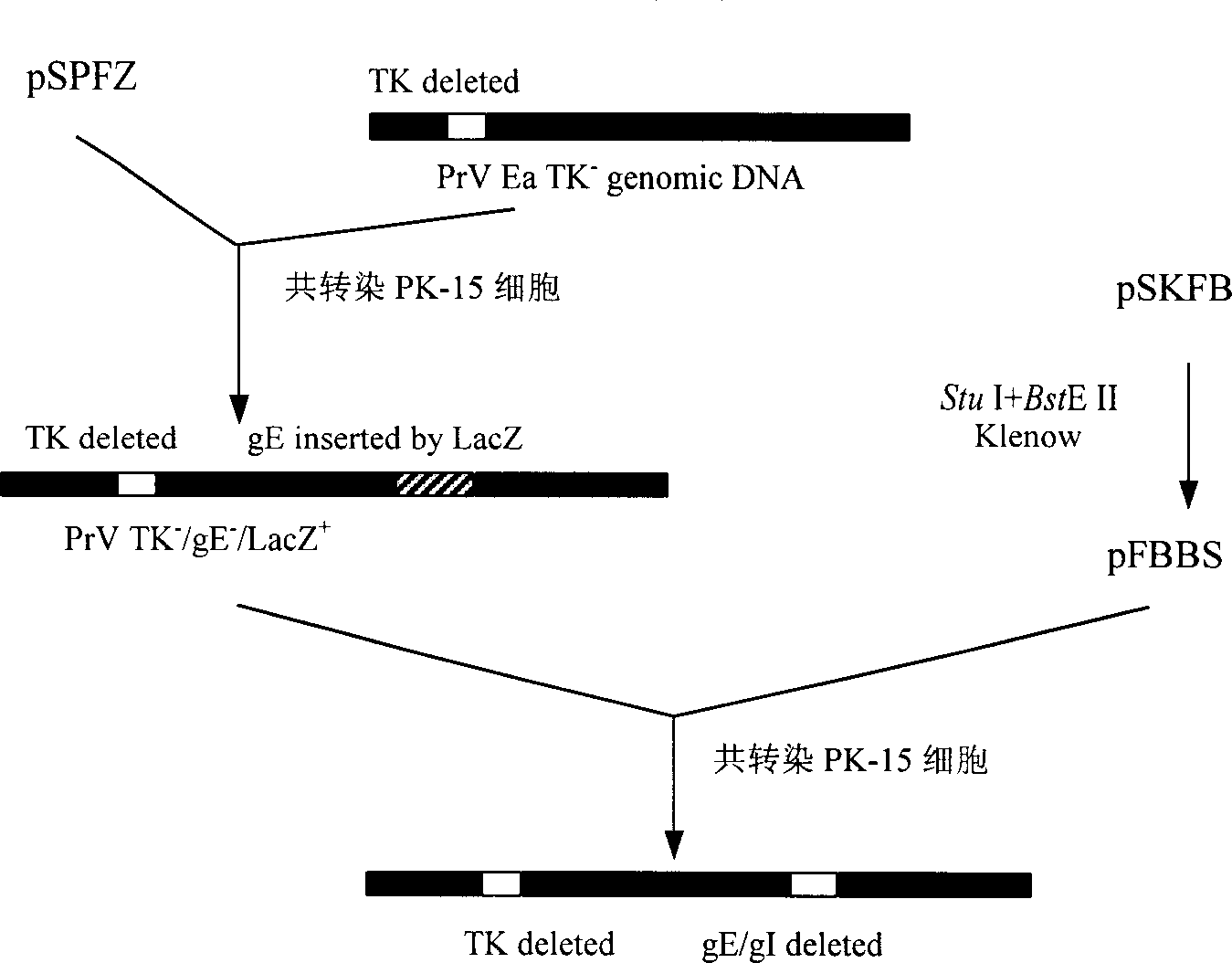
Pseudorabies TK*/gE*/gI* gene dificiency mark live vaccine and preparation method thereof
The present invention discloses a construction of three-gene defected recombinant pseudorabies virus (PrV) strain, vaccine prepared by said strain, method for constructing said strain and method for preparing said vaccine. The described recombinant pseudorabies virus strain defects genes of TK.gE ang gI, and contains no exogenous gene. The described vacine belongs to the freeze-dried live vaccine made up by virus liquid containing said invention and gelatin. Said invented live vaccine can be inoculated on the piglet, slaughter pig and sow with farrow, and can obtain obious immune effect. Said vaccine has good biological safety, and can be used for preventing and curing pseudorabies.
Owner:HUAZHONG AGRI UNIV
Strain used for fermenting rice bran and wheat bran extracts for producing grifolan
InactiveCN102816701AReduce use costHigh polysaccharide yieldFungiMicroorganism based processesMyceliumMicrobiology
The invention belongs to the fields of microbe application technologies and food biotechnologies, and discloses a strain used for fermenting rice bran and wheat bran extracts for producing grifolan. The grifola frondosa strain is collected in China Center for Type Culture Collection (CCTCC) in Wuhan University in Wuhan, China on Aprial 7th, 2011, and has a strain collection number of CCTCC No: M2011113. The name of the strain is Grifolasp. JSU10-2. According to the invention, through protoplast laser mutation, the strain with high yield of mycelium polysaccharide produced from cheap raw materials is obtained. When the strain and an original strain are respectively used in liquid fermentation of a rice bran and wheat bran composite culture medium, the dry weight and polysaccharide of the mutant strain are respectively increased by 31.7% and 32.6% compared with those of the original strain.
Owner:JIANGSU UNIV
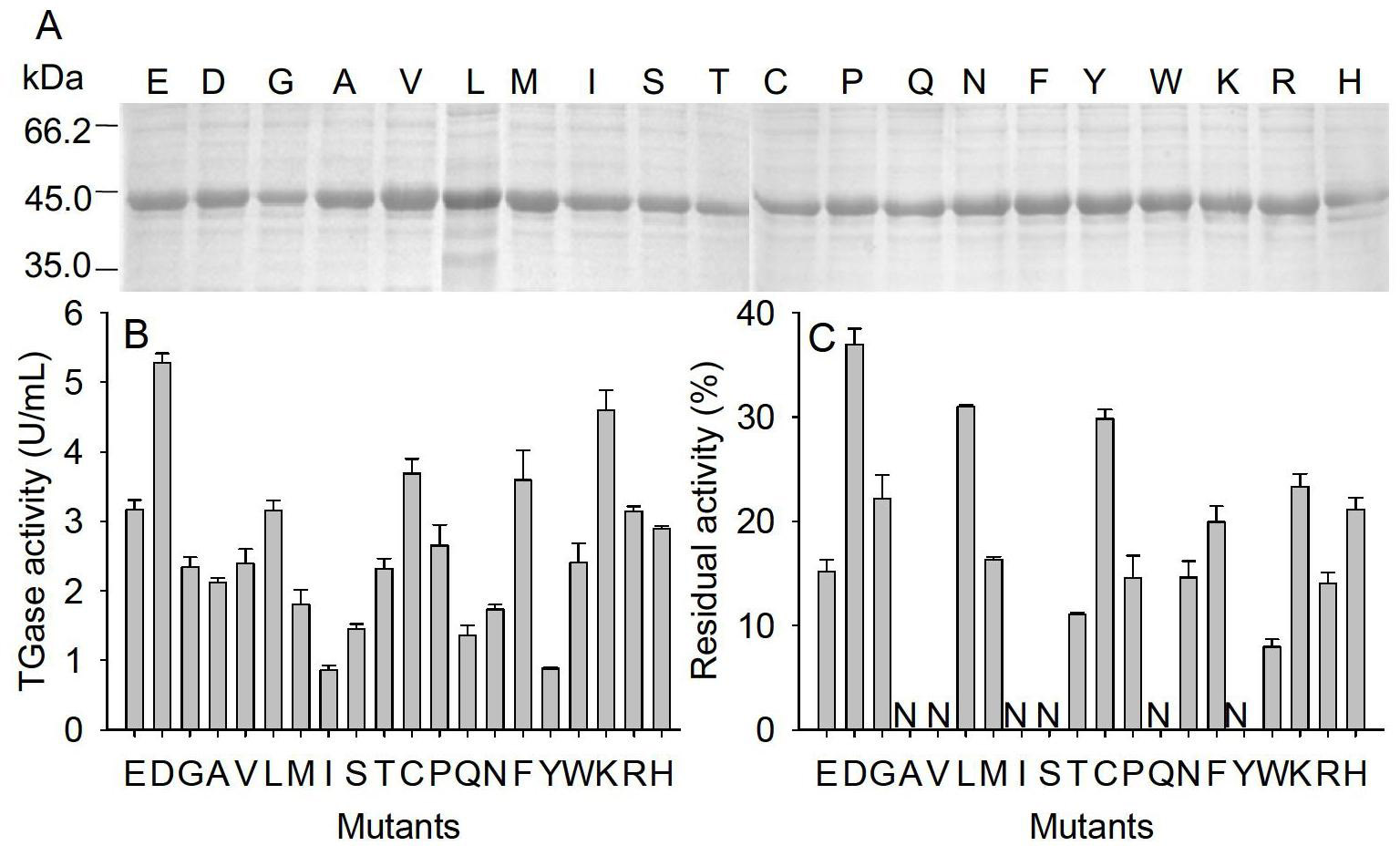
Glutamine transaminase with improved enzymatic activity and thermal stability
InactiveCN102660515AGood enzymatic propertiesImprove thermal stabilityTransferasesMicroorganism based processesMutant strainEnzyme
The invention provides glutamine transaminase with improved enzymatic activity, wherein the amino acid sequence is shown as SEQ ID NO.1. According to the invention, amino acid at the N end of MTG (Microbial Transglutaminase) maturase is subjected to deficiency and saturation mutation by taking the efficient expression of MTG in colibacillus as an improvement platform, and a mutant strain with good enzymatic property is obtained. The enzyme activity is improved by 1.85 times, and the thermal stability is improved by 2.7 times. The modified enzyme is more suitable for industrial applications, the production cost can be lowered, and the production efficiency can be improved.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
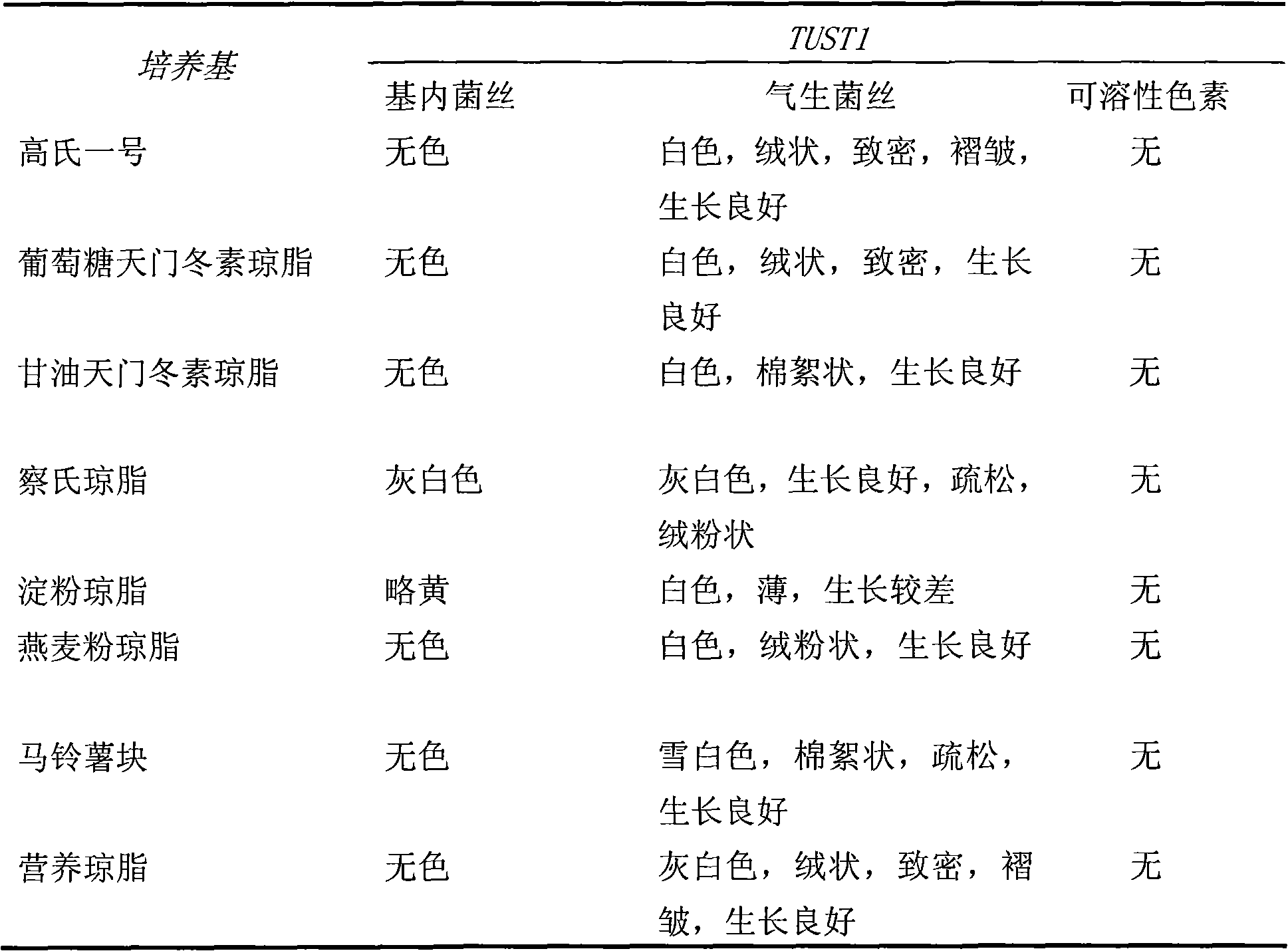
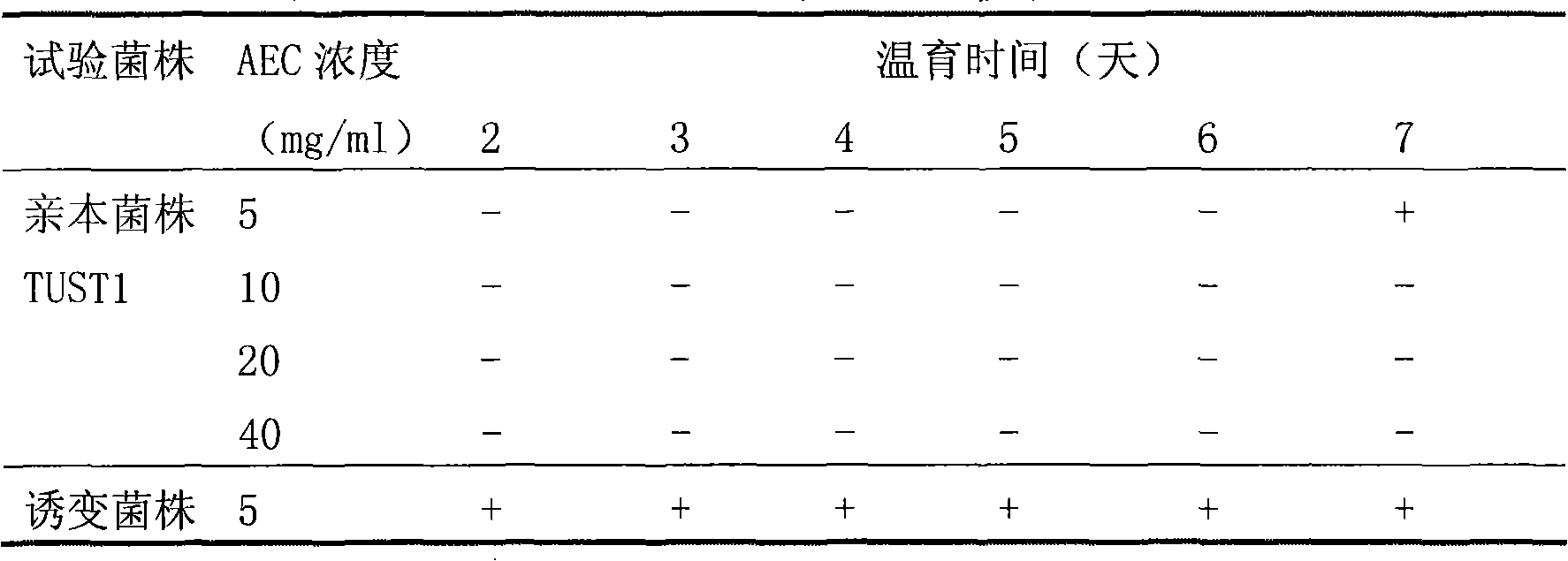
Mutant strain streptomyces albus TUST2 and process for producing epsilon-polylysine and salts thereof by using the mutant strain
InactiveCN101285046AHigh yieldImprove generation effectBacteriaMicroorganism based processesEpsilon-PolylysineUltrafiltration
The invention relates to a mutagenized strain of streptomyces albus TUST2, and a method for using the same to produce epsilon-polylysine and a salt of the epsilon-epsilon. The strain is a high-yield mutagenized strain of epsilon-polylysine selected and bred by means of ultraviolet mutagenesis, ultraviolet-chemical mutagenesis, N ion injection mutagenesis, etc from a strain of streptomyces albus TUST2 which is capable of producing epsilon-polylysine and is screened from the earth in Hainan province of China; the mutagenized strain is resistant to 10mg / ml or above S-(2 Aminoethyl )-L-Cysteine and can generate 10 to 30 g / L acid under optimal conditions; zymotic fluid is removed of the streptomyces albus by configuration and is filtered by diatomaceous earth to obtain clear filtrate and to weak acid type ion exchange resin to obtain coarse epsilon-polylysine products which is subjected to ultrafiltration and purification to get epsilon-polylysine and the salt of the epsilon-epsilon. The distribution of molecular weight of epsilon-polylysine is between 4000 and 6500Da.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIVERSITY OF SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY
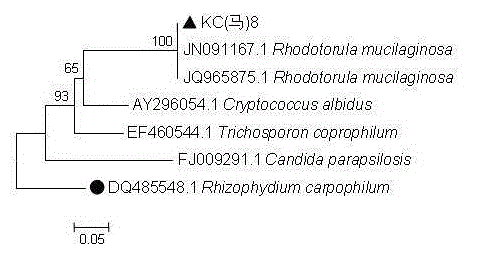
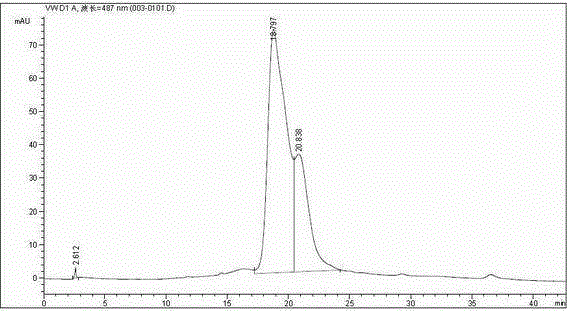
Rhodotorula mucilaginosa and application in fermentation production of carotenoid and oils
The invention discloses a Rhodotorula mucilaginosa strain and application in fermentation production of carotenoid and oils. The main point of the technical scheme involved in the invention lies in that: the Rhodotorula mucilaginosa strain is preserved in China General Microbiological Culture Collection Center with a preservation number of CGMCC No.8926. The Rhodotorula mucilaginosa provided by the invention can be used for fermentation production of carotenoid and oils. According to the invention, Rhodotorula mucilaginosa is utilized to produce carotenoid and oils at the same time, multi-round ARTP (atmospheric and room temperature plasma) mutagenesis is carried out on the production strain so as to obtain a high yield mutant strain, thus providing good application prospects and economic benefits for industrial production of carotenoid and oils.
Owner:HENAN NORMAL UNIV
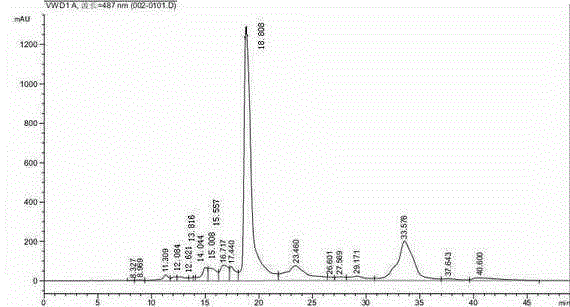
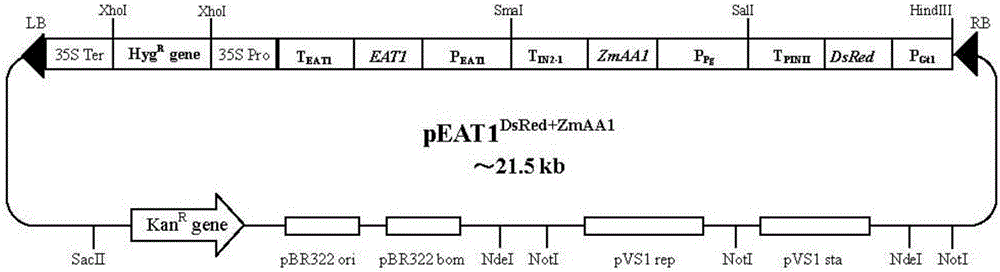
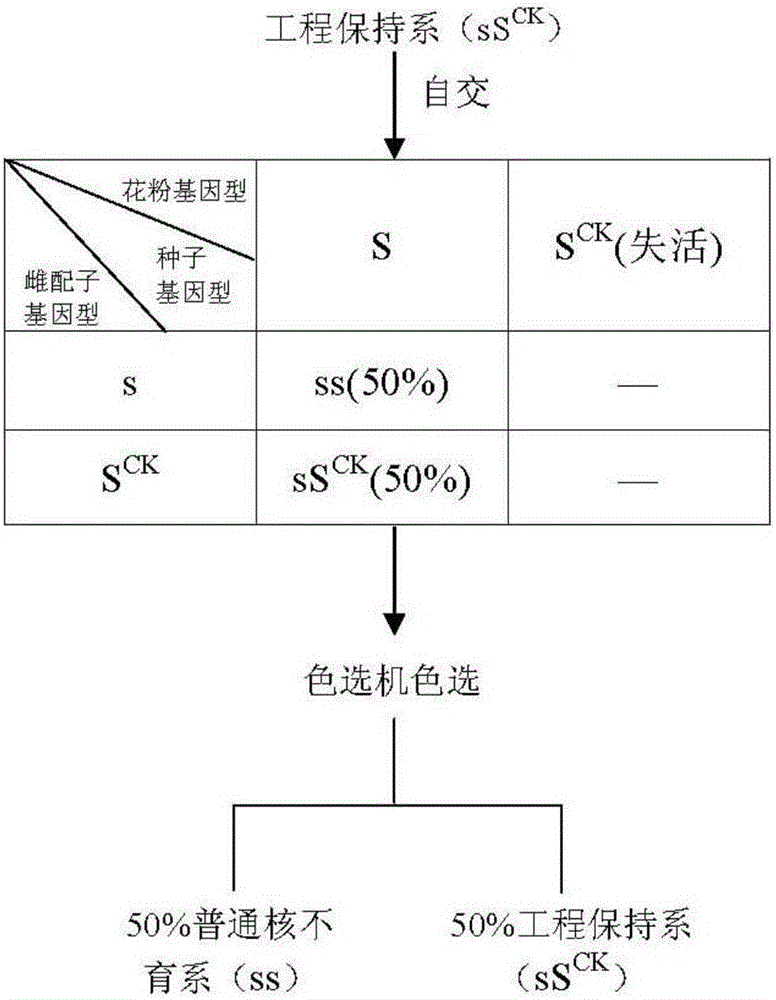
Propagation method for rice normcore sterile line
InactiveCN106544358AHigh reproductive outputReduce the cost of seed productionPlant peptidesGlycosylasesAgricultural scienceColor marker
The invention provides a propagation method for a rice normcore sterile line. The propagation method comprises the following steps of establishing an expression vector containing a color marker gene C, a normcore sterile fertility recovery gene S and a pollen inactivation gene K; converting the expression vector into rice normcore sterile mutant strains to obtain T0 generation transgenic plants; selecting fertile plants, having the three genes of the color marker gene C, the normcore sterile fertility recovery gene S and the pollen inactivation gene K, from the T0 generation transgenic plants; performing self-fertilized propagation on the fertile plants, and separating out engineering maintainer line seeds and normcore sterile line seeds from the seeds obtained from self-fertilized propagation offspring; and taking the normcore sterile line seeds as a female parent while taking the engineering maintainer line seeds as a male parent, performing hybridization on the female parent and the male parent, and obtaining seeds from female parent plants, namely normcore sterile line seeds without transgenic components. The propagation method has the advantages of high occupation proportion of the sterile line seeds, low production cost and the like.
Owner:HUNAN HYBRID RICE RES CENT
Method for producing target substance by fermentation
InactiveUS20030077764A1Improve abilitiesMicroorganism based processesDepsipeptidesMicroorganismGlucose polymers
In a method for producing a target substance by utilizing a microorganism, which comprises culturing the microorganism in a medium to produce and accumulate the target substance in the medium and collecting the target substance from the culture, there is used, as the microorganism, a mutant strain or recombinant strain of a microorganism in which maltose assimilation is controlled by an interaction between IIA.sup.Glc protein of glucose PTS and a protein involved in non-PTS uptake of maltose, and the interaction between the IIA.sup.Glc protein and the protein involved in non-PTS uptake of maltose is reduced or eliminated in the mutant strain or recombinant strain.
Owner:AJINOMOTO CO INC
Method for producing target substance using microorganisms with reduced interactions between MalK and IIAGlc
InactiveUS7097999B2Improve abilitiesMicroorganism based processesDepsipeptidesSubstance useMicroorganism
The present invention describes a method for producing a target substance by utilizing a microorganism comprising culturing the microorganism in a medium, allowing the target substance to accumulate, and collecting the target substance from the medium. Also the microorganism used in the present invention is a mutant strain whereby maltose assimilation is controlled by the interaction between IIAGlc protein of glucose PTS and MalK.
Owner:AJINOMOTO CO INC
Method for producing heptadecanedioic acid by fermenting and converting n-heptadecane
ActiveCN102115765AScale upImprove conversion rateMicroorganism based processesFermentationCandida tropicalisCarboxylic acid
The invention discloses a method for producing long-chain alpha,omega-dicarboxylic acid by fermenting and converting an n-alkane with microbes, particularly a method for producing high-yield heptadecanedioic acid, which comprises the following steps: inoculating seed liquor, which is cultured from a Candida tropicalis mutant strain ly-7 which is obtained by mutagenesis by an N<+> injection technique and subjected to oxidase activity screening and culture, into mixed liquor of an n-alkane and a fermentation medium; fermenting and converting at 25-32 DEG C for 48-168 hours; and separating and purifying the generated long-chain alpha,omega-dicarboxylic acid. When n-heptadecane is fermented and converted to produce the heptadecanedioic acid in a 5-ton fermentation tank for 144 hours, the content of the heptadecanedioic acid can reach 163 g / l.
Owner:青岛智库生物科技有限公司
Strain of Schizochytrium limacinum useful in the production of lipids and extracellular polysaccharides and process thereof
The present disclosure provides a novel mutant strain of Schizochytrium limacinum having the Accession No. MTCC 5249, which produces lipids and extracellular polysaccharide (EPS) simultaneously. The disclosure further provides a process for simultaneous production of lipids and extracellular polysaccharide (EPS) from the novel mutant strain of Schizochytrium limacinum. The lipids produced from the novel mutant strain of Schizochytrium limacinum comprises docosahexaenoic acid (DHA). The disclosure also provides a food, feed, cosmetic, nutritional or therapeutic supplement for humans or animals comprising the cell biomass and extracellular polysaccharides (EPS) of the mutant strain of Schizochytrium limacinum. A cosmetic composition comprising the extracellular polysaccharides (EPS) of Schizochytrium limacinum is also provided that is useful as a base for cosmetics for topical application. The present disclosure further provides a pickle composition and a fat product having improved nutritive value.
Owner:ABL BIOTECH
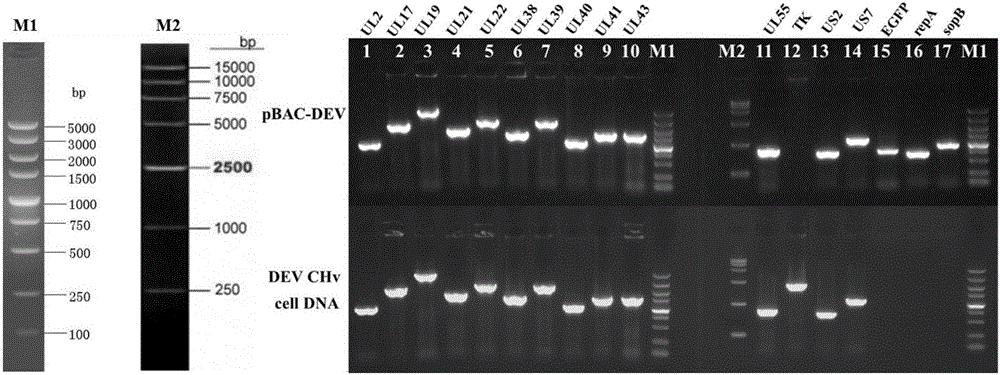
Establishing method of bacterial artificial chromosome recombinant duck plague virus rescue system platform and application
InactiveCN105802922ALower titerDoes not affect the replication cycleVirus peptidesNucleic acid vectorBacteroidesRecombinant vaccines
The invention discloses an establishing method of a bacterial artificial chromosome recombinant duck plague virus rescue system platform and application of the platform. A bacterial artificial chromosome recombinant duck plague virus is obtained by inserting a recombinant duck plague virus transfer vector pUC18 / EGFP-TKAB-BAC11 in a TK domain, wherein the recombinant duck plague virus transfer vector contains a TK gene left-right homologous arm, a reporter gene EGFP and a bacterial artificial chromosome core function component. By means of the platform, the in-vitro biologics characteristics of a UL55 gene-deleted strain established through an inside-bacterium two-step RED recombination method and a back mutation strain and parent strain of the UL55 gene-deleted strain are quite close; the functions are not related to positioning of a UL26.5 gene in a cell. The method is beneficial to development of pathogenic mechanism and gene function research of DPV CHv and is beneficial to the duck plague virus prevention and the research and application of recombinant duck plague virus vaccines of other poultry infectious diseases based on the platform; in addition, due to the fact that the recombinant virus carries a TK deletion mark and an EGFP gene, a mark vaccine can be developed to clinically distinguish a wild virus and a recombinant vaccine virus.
Owner:SICHUAN AGRI UNIV
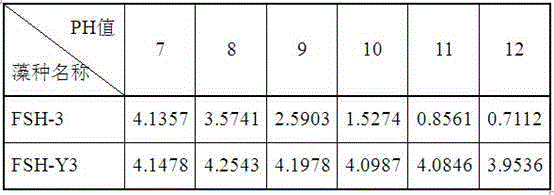
Parachlorella kessleri with tolerance to high pH and culture and applications of parachlorella kessleri
ActiveCN106467896AImprove solubilityEasy to fixUnicellular algaeMutant preparationSolubilityMicroorganism
The invention discloses parachlorella kessleri with the tolerance to a high pH and culture and applications of parachlorella kessleri. A parachlorella kessleri mutant strain FSH-Y3 with the tolerance to the high pH is obtained through the method adopting ultraviolet mutagenesis and acclimation screening utilizing step-by-step pH increase, the classification name is Parachlorella Kessleri, and the parachlorella kessleri strain FSH-Y3 is prepared in the China General Microbiological Culture Collection Center (CGMCC) on May 26, 2014, and is assigned with the accession number of CGMCC No.9238. The bred parachlorella kessleri FSH-Y3 can well absorb and utilize carbon dioxide at the high pH, and rapidly grow and reproduce, therefore, the problems that the existing parachlorella kessleri only can grow at the neutral pH, but the solubility of carbon dioxide is low, and the carbon dioxide fixing efficiency is low under the neutral pH condition are solved.
Owner:CHINA PETROLEUM & CHEM CORP +1
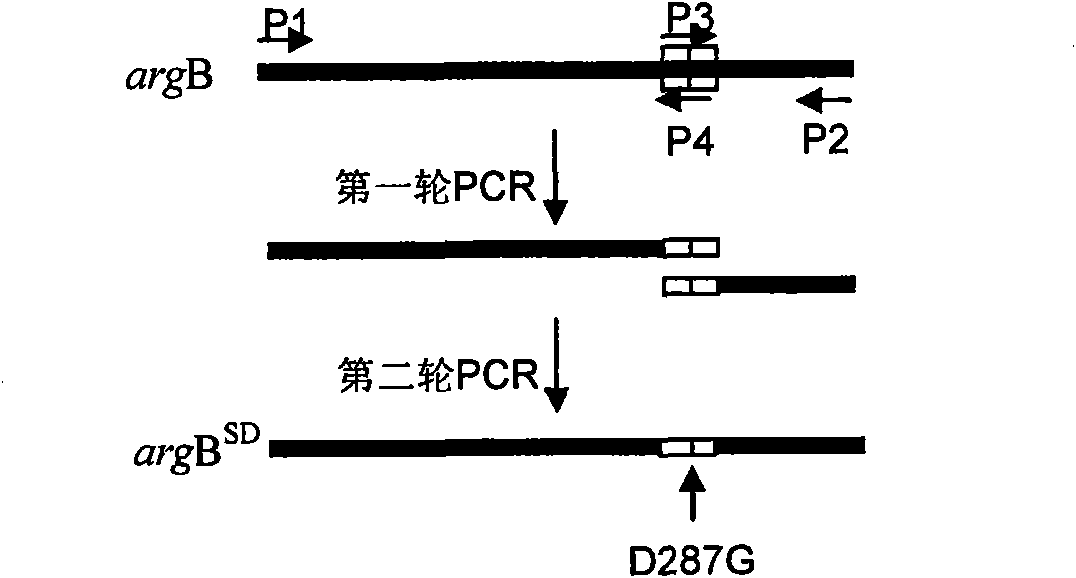
Method for improving yield of arginine by mutation of Corynebacterium crenatum N-acetyl glutamic acid kinase
The invention relates to a method for improving the yield of arginine by the mutation of Corynebacterium crenatum N-acetyl glutamic acid kinase. L-arginine is one of semi-essential basic amino acids for a human body, and has various particular physiology and pharmacology functions. High-yield arginine mutant strain C. crenatum SYPA5-5 is compounded into the arginine through a circulating way, and N-acetyl glutamic acid kinase (NAGK) is a key enzyme in the compounding way and is subject to the feedback inhibition of the product arginine. By using an overlapping PCR (Polymerase Chain Reaction) technique, a GAT (glycerol phosphate acyl transferase) codon used for coding aspartic acid is used for substituting a GGA (General Gonadotropic activity) codon used for coding glycine at the site 287 in the coding NAGK albumen, and the NAGK which has high activity and arginine with obviously reduced by the feedback inhibition can be obtained after the mutation. An argBSD gene is brought into the Corynebacterium crenatum of the high-yield arginine through pJCl-tac, and the expression volume of the key enzyme is further improved. The final acid yield is increased to 36.3g / L from original 28g / L, and the yield of the L-arginine is increased by 29.7 percent.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
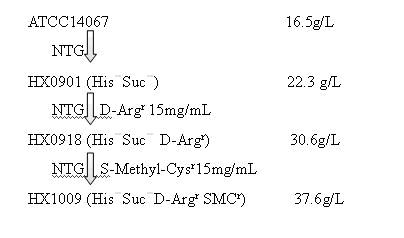
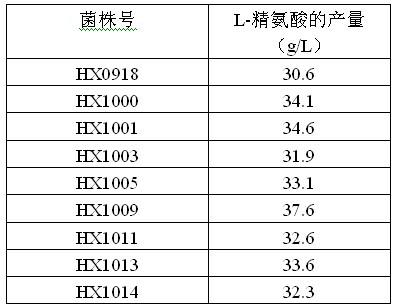
Strain capable of producing L-arginine and method for producing L-arginine by same
The invention relates to a strain capable of producing L-arginine and a method for producing the L-arginine by the strain and belongs to the technical field of biological engineering. For the strain, Brevibacterium flavum ATCC 14067 is used as a starting strain; nitrosoguanidine is adopted to carry out mutagenesis step by step; mutant strains with histidine and succinic acid auxotrophic strains are screened out so as to cut off a competitive metabolic pathway; and mutant strains (His-, Suc-, D-Argr, SMCr) with resistances of arginine structural analogs and cysteine structural analogs are screened out. The strain is named as Brevibacterium flavum HX1009, is preserved in the China general microbiological culture collection center, has the preservation number of CGMCC No.4464 and has the genetic characters of histidine auxotroph His-, succinic acid auxotroph Suc-, D-arginine resistance D-Argr and S-methyl cysteine resistance SMCr for improving the yield of the L-arginine. Under the optimized condition, the L-arginine is produced by fermentation on a fermentation tank with the volume of 5L to 5M3 and the arginine production level achieves 50 to 70g / L.
Owner:FUJIAN GUTIAN PHARMA
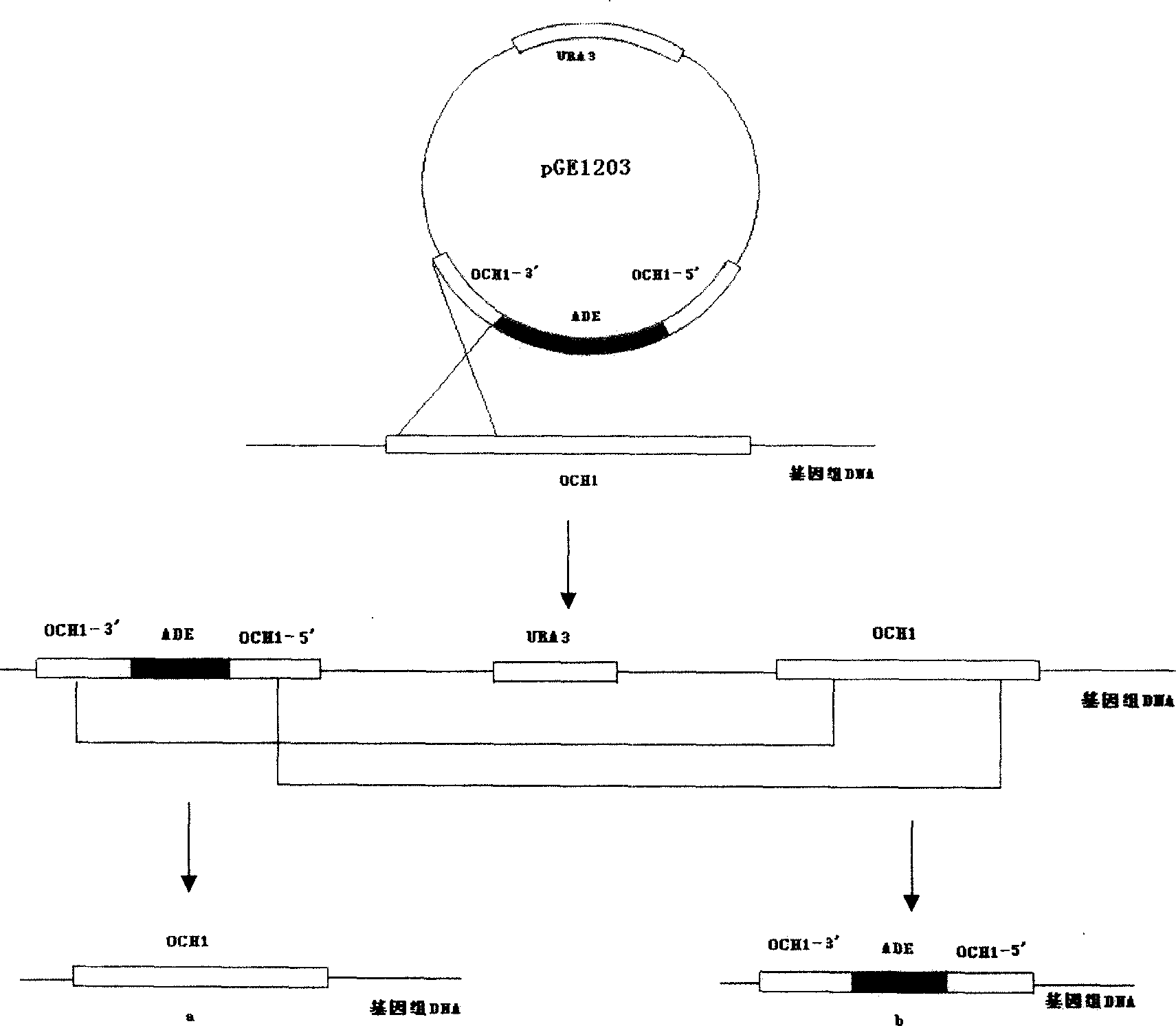
Pichia pastoris strain with deletion of alpha-1,6-mannose transferase and construction method thereof
ActiveCN101195809ALow immunogenicityEasy to getFungiMicroorganism based processesBio engineeringPichia
The invention discloses Pichia pastoris strain with alpha-1, 6-mannosyl transferase absent and the establishing method, which belongs to the biological engineering field. The collection number of the Pichia pastoris strain with alpha-1, 6-mannosyl transferase absent is CGMCC No.1853. The invention has the advantages that the Pichia pastoris strain with alpha-1, 6-mannosyl transferase absent built by the invention can prevent the generation of excessive manna saccharify, when expressing extrinsic glucoprotein, reduce the immunogenicity of the pressed protein, and therefore, the invention has important application value in the biomedical field, and other fields; simultaneously, the strain can also be applied to the further gene knockout or the metabolic engineering reconstruction. The invention also builds a method for knocking out the alpha-1, 6-mannosyl transferase gene through secondary homologous recombination, mutant strain can be relatively easily obtained through the method, therefore the sieving workload is greatly reduced, and the success ratio is improved.
Owner:INST OF BIOENG ACAD OF MILITARY MEDICAL SCI OF THE CHINESE
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com