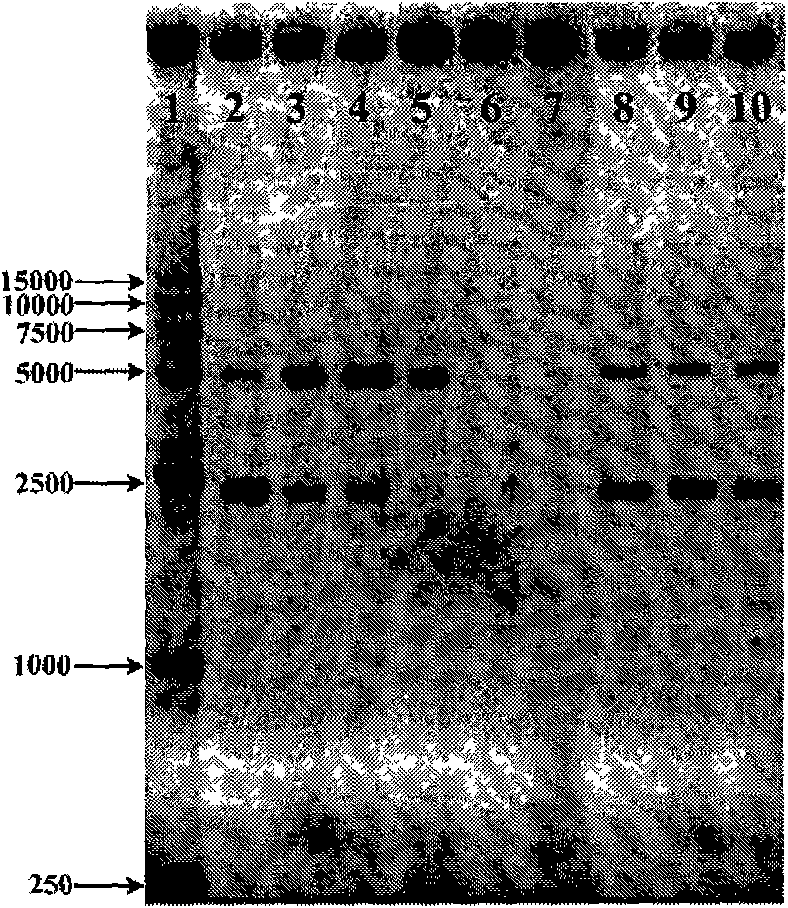
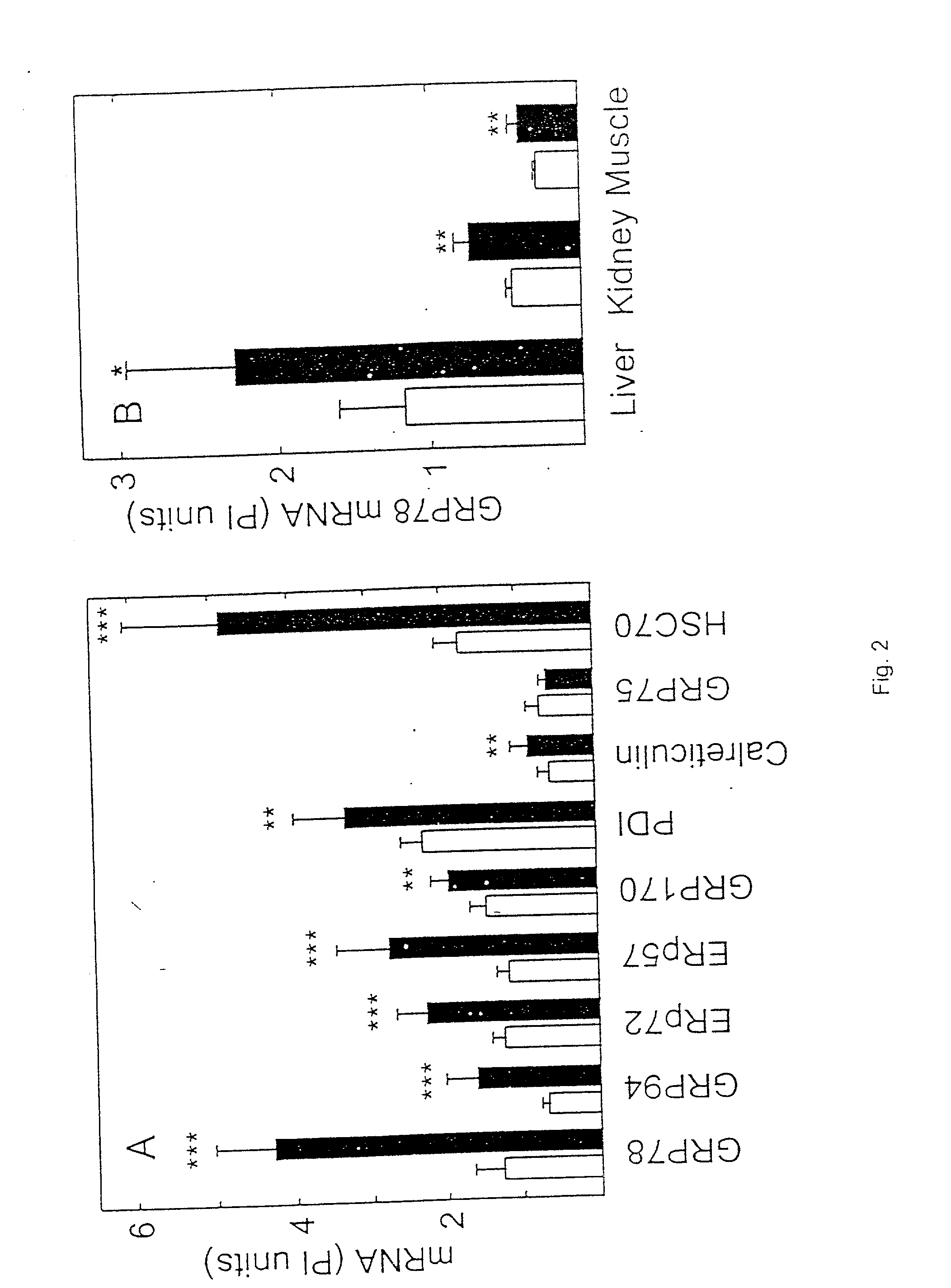
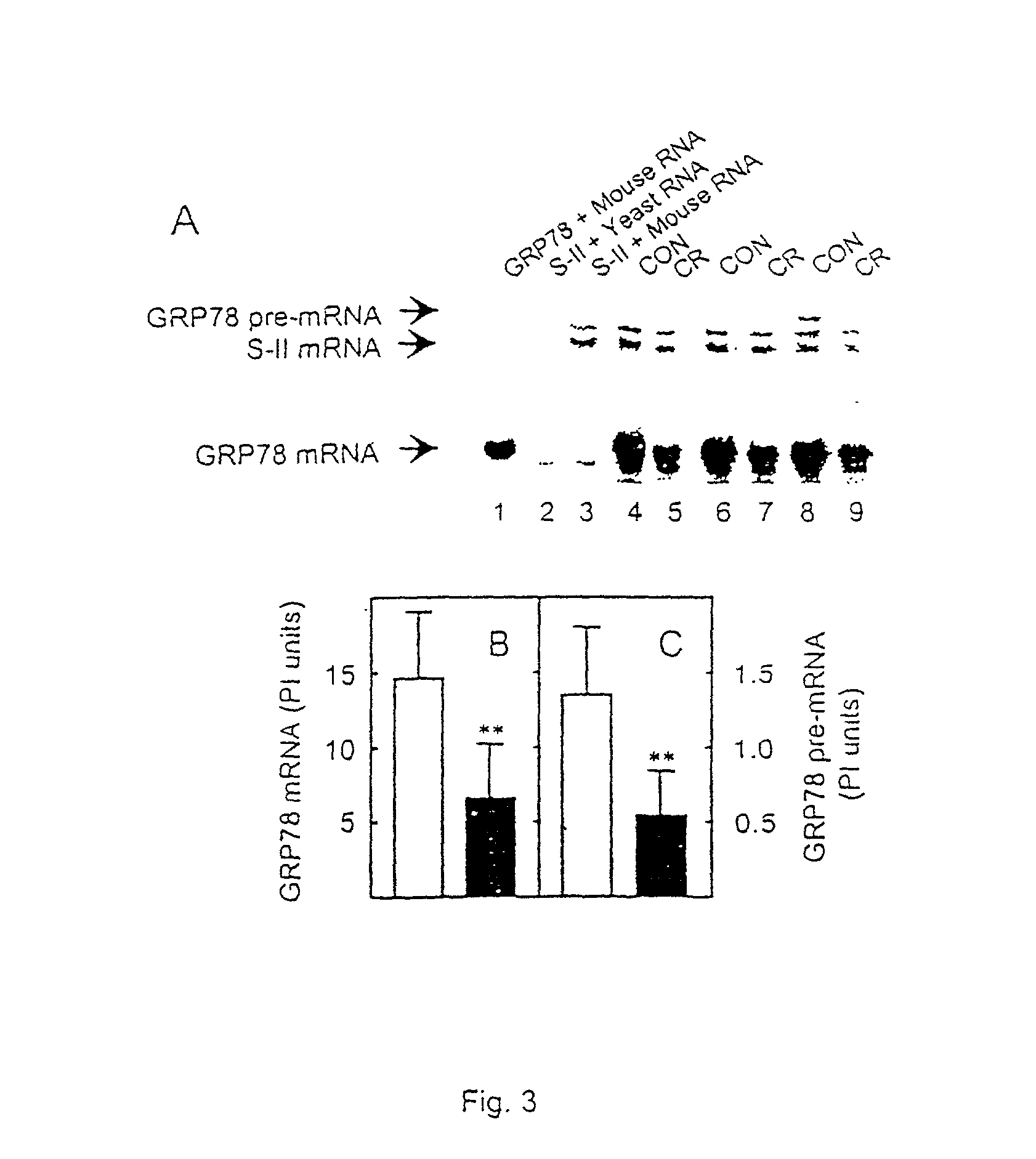
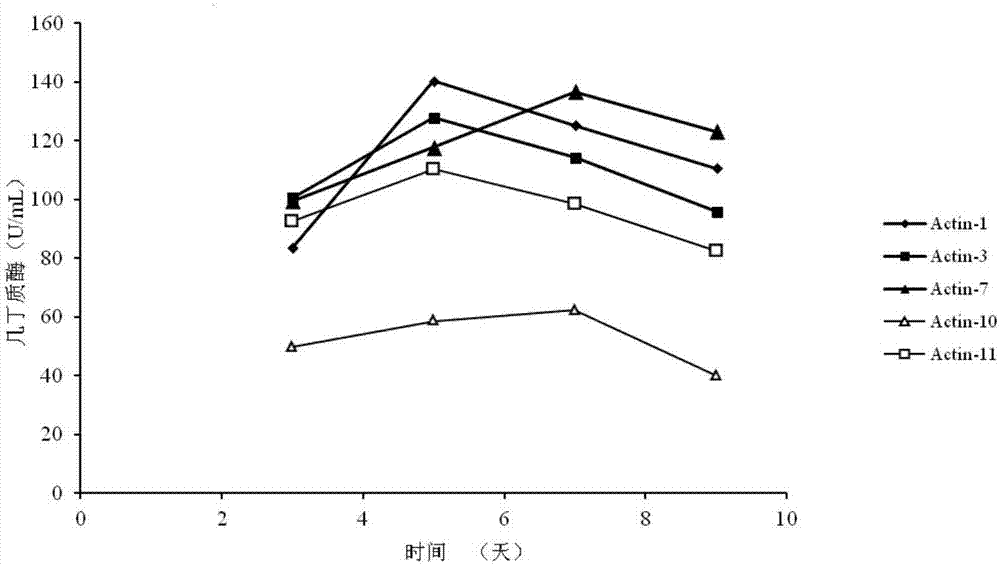
Patents
Literature
215results about How to "High genetic stability" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
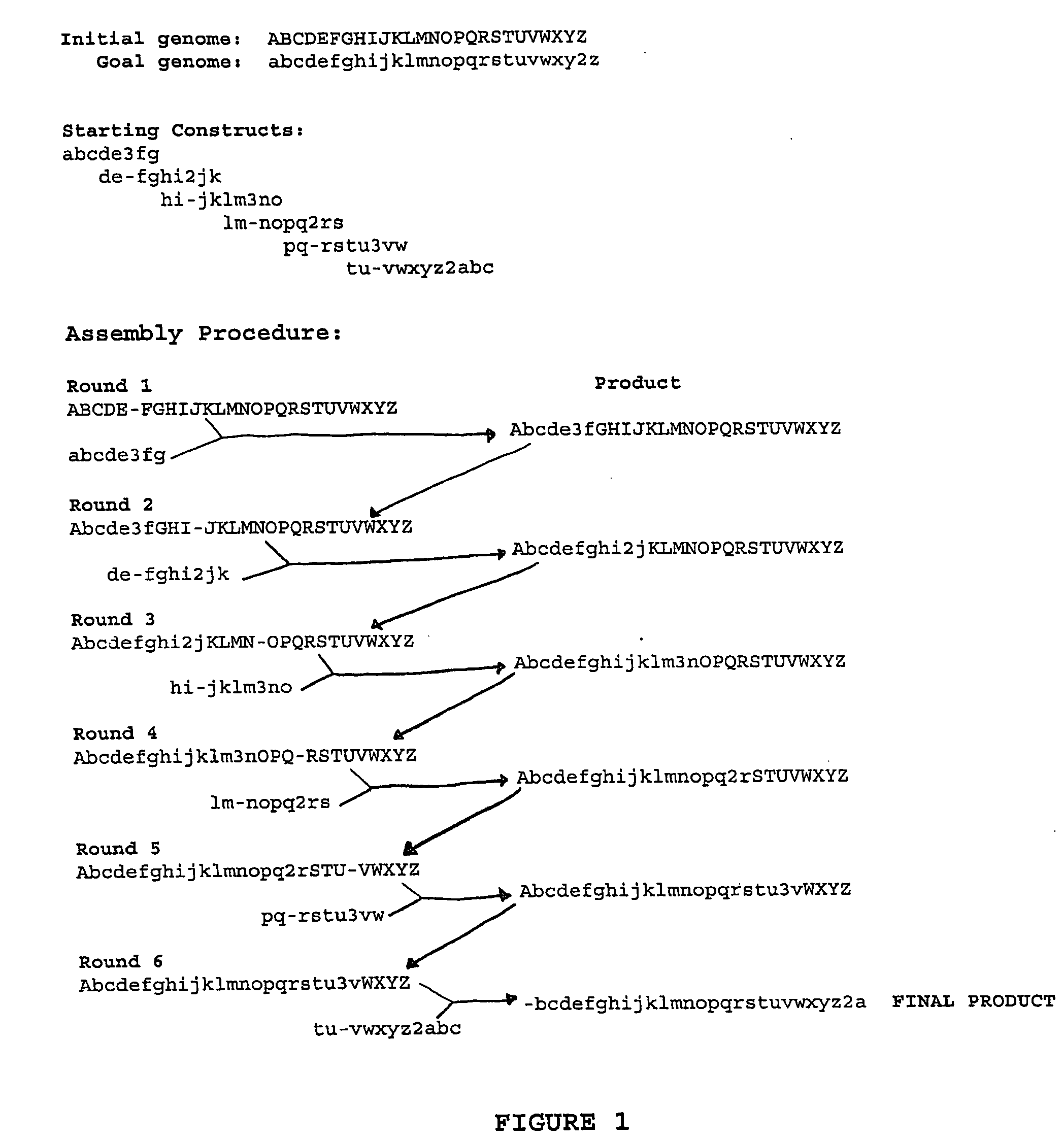
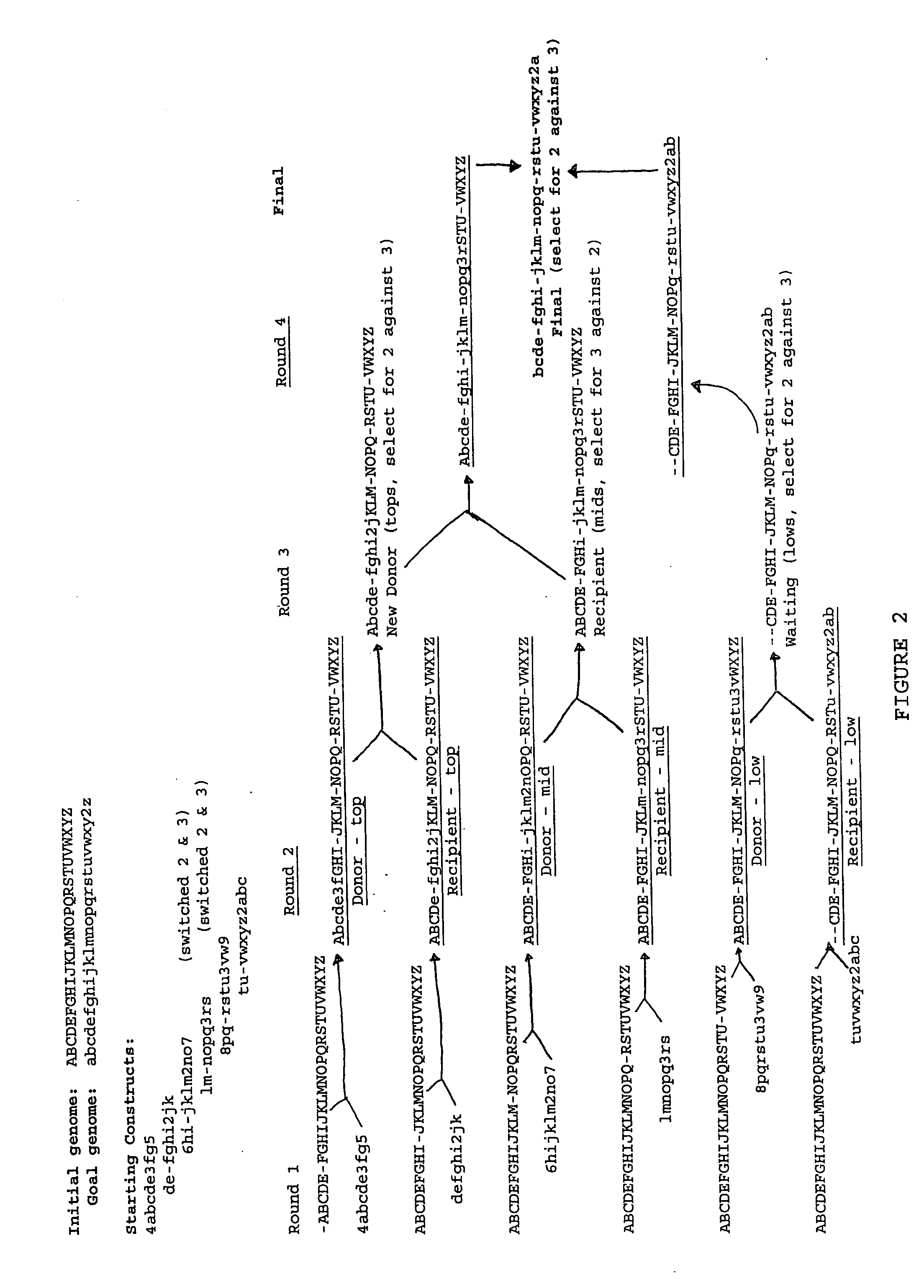
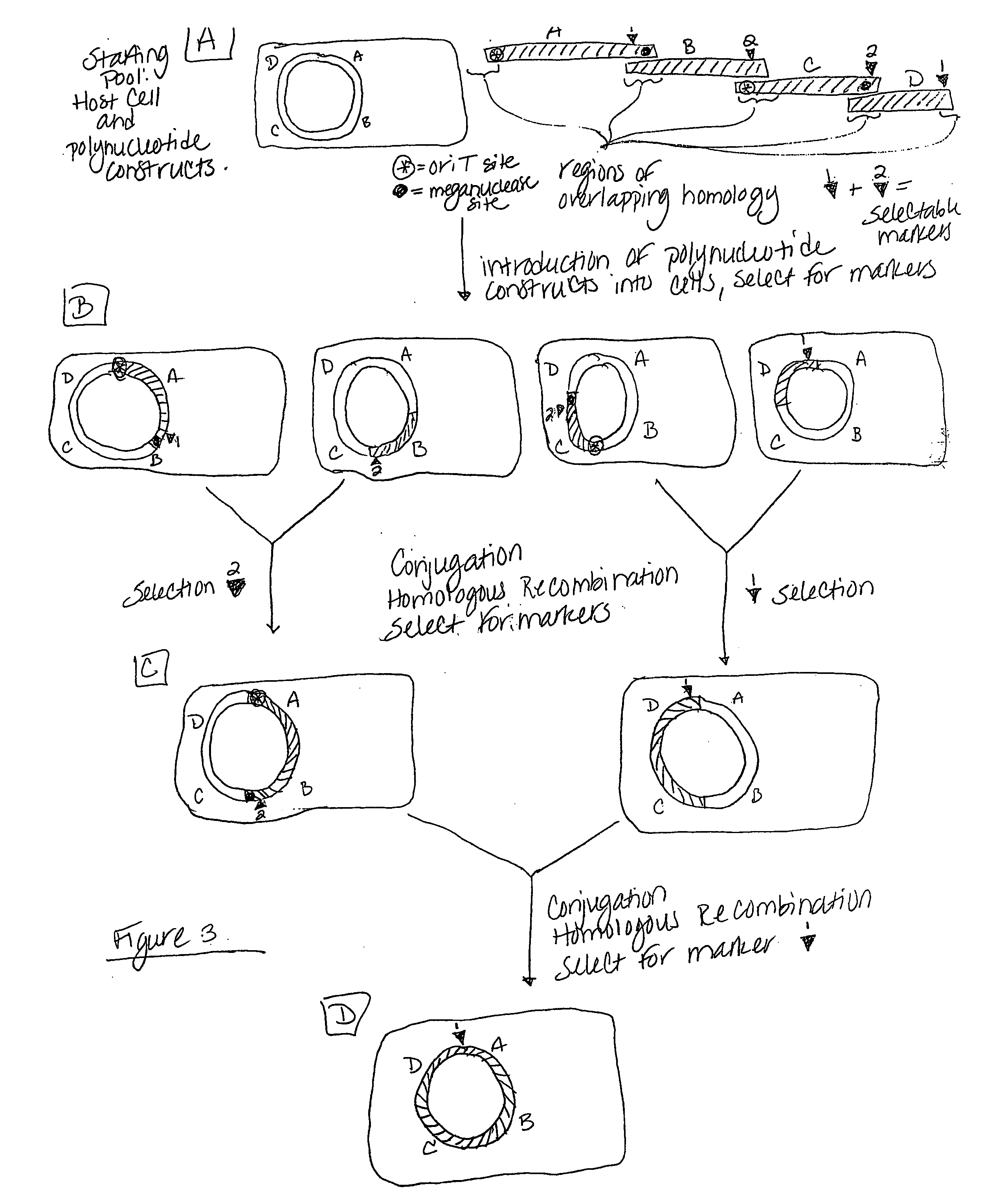
Heirarchical assembly methods for genome engineering
InactiveUS20070004041A1Improve securityImprove propertiesStable introduction of DNAFermentationBiological bodyGenomic Stability
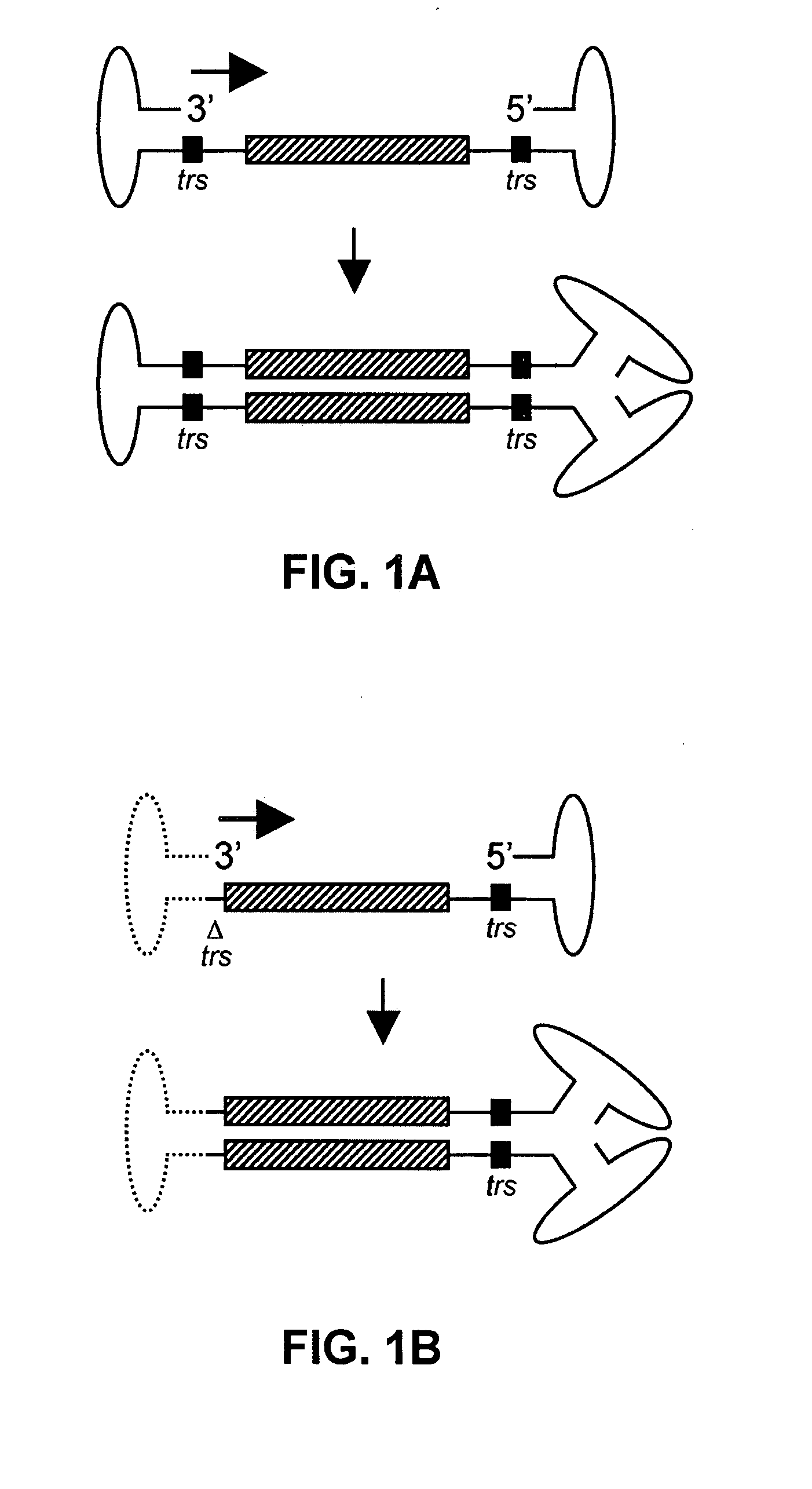
The present invention provides recombination based methods for assembling nucleic acids. In certain aspects the present invention provides hierarchical assembly methods for producing genome sized polynucleotide constructs. The methods may be used for assembling large polynucleotide constructs, for synthesizing synthetic genomes, or for introducing a plurality of nucleotide changes throughout the genome of an organism. In another aspect, the invention provides cells having increased genomic stability. For example, cells comprising alterations in at least a substantial portion of the transposons in the genome are provided.
Owner:CODON DEVICES
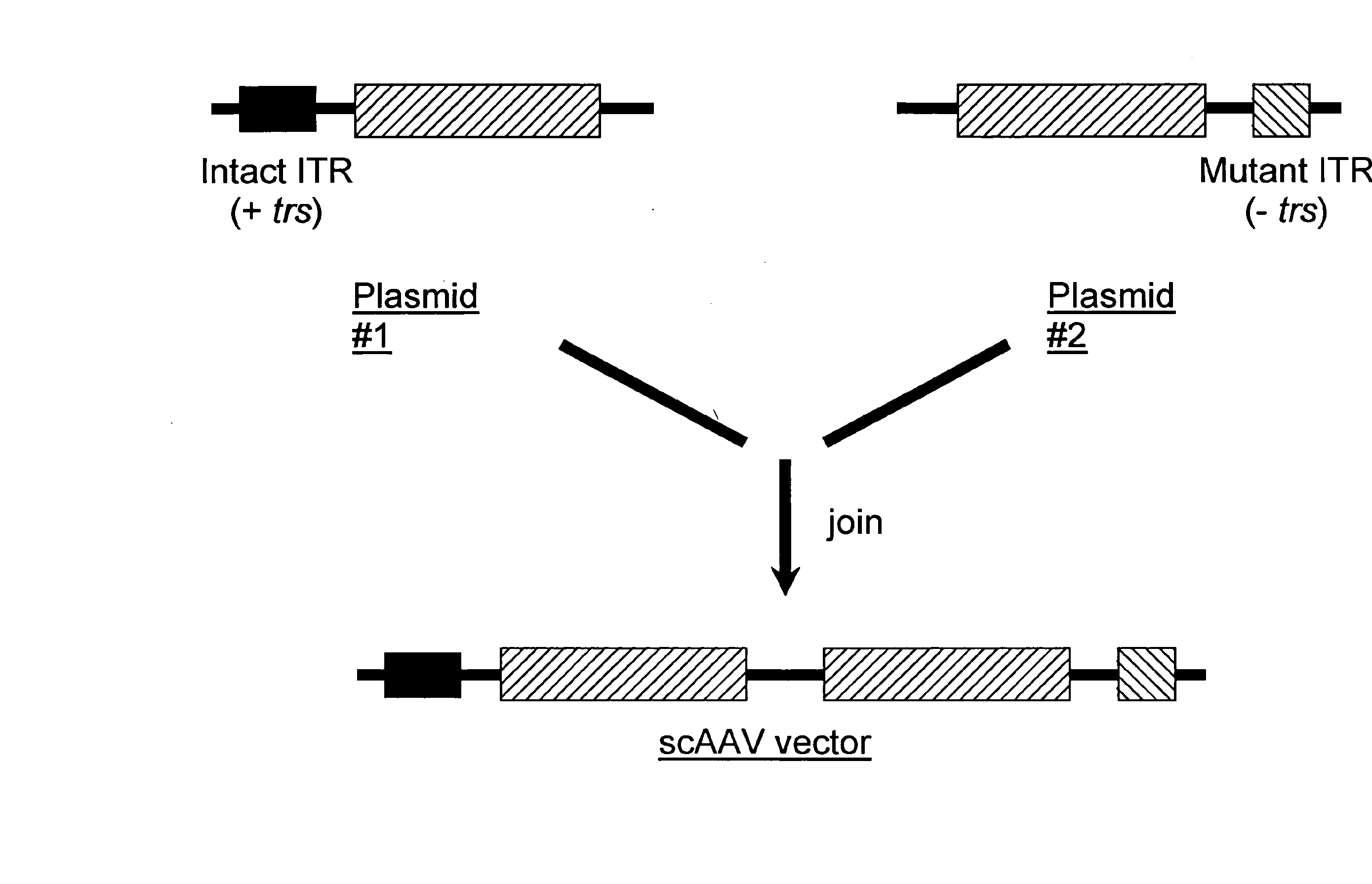
Self-complementary parvoviral vectors, and methods for making and using the same
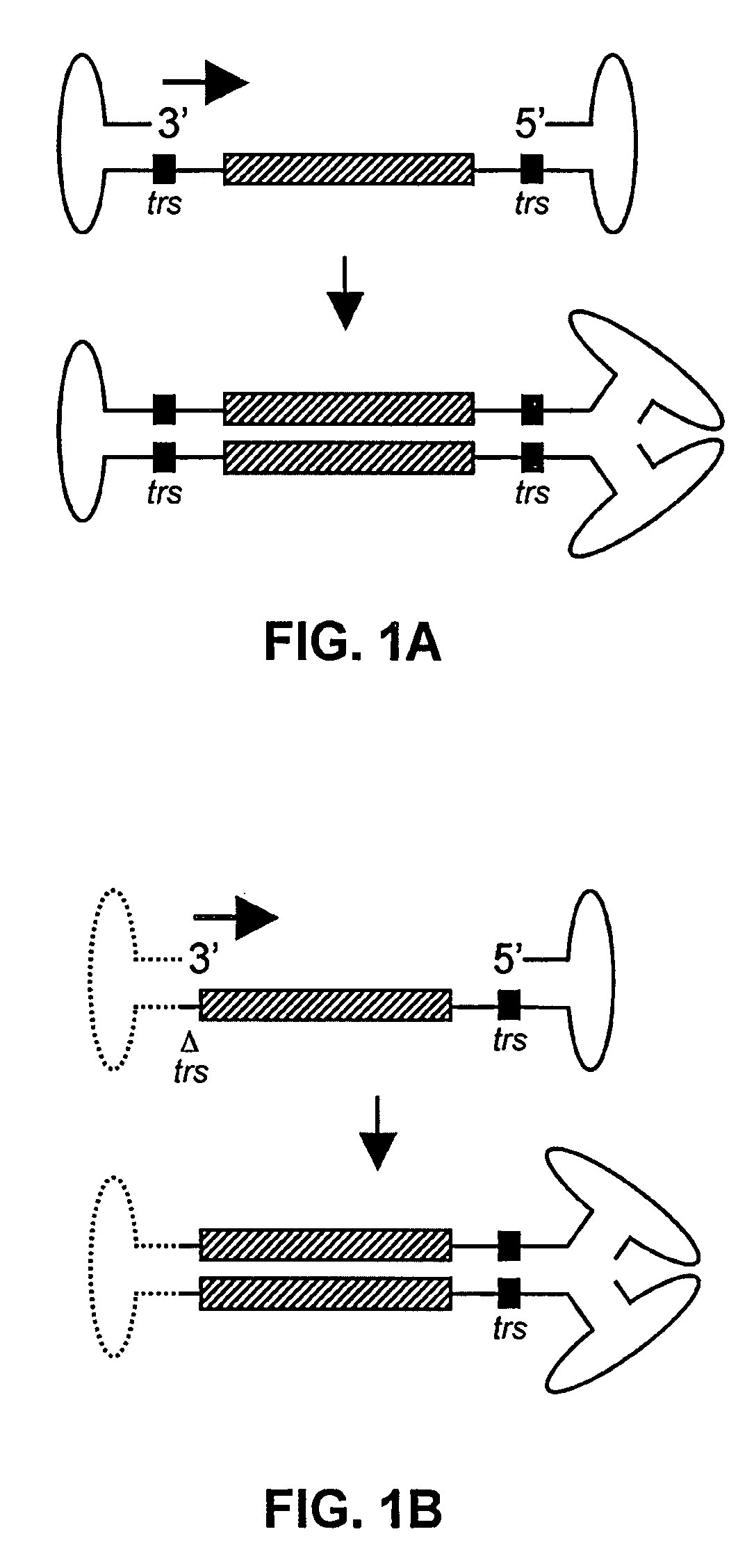
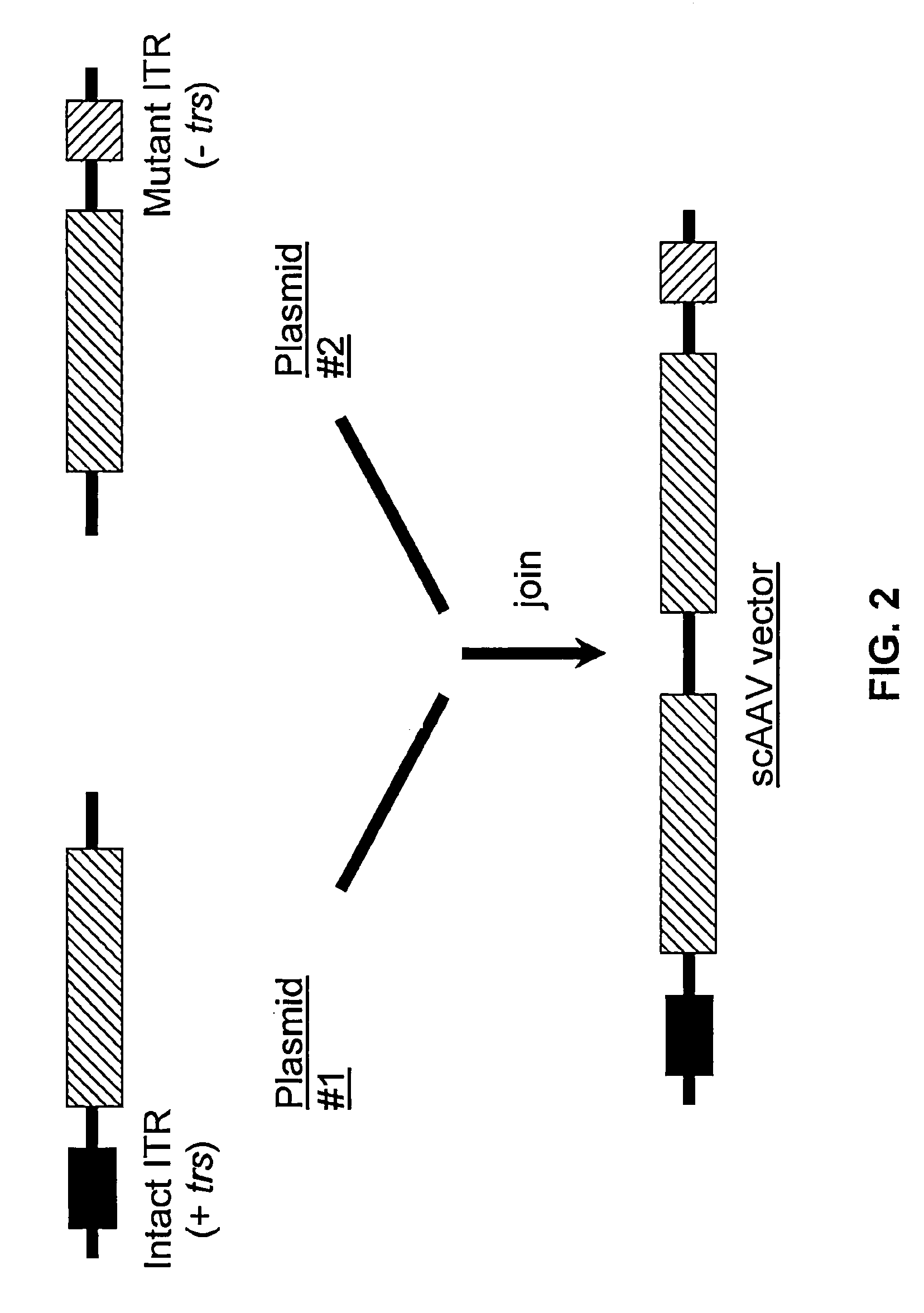
ActiveUS20070253936A1High genetic stabilityStabilized parvovirus vector is more stableBiocideAnimal repellantsGene transferTiter
The teachings herein are generally directed to a method of enhancing the genetic stability of parvovirus vectors. The stability of conventional ss or dsAAV vector constructs can be enhanced, for example, to obtain a concurrent increase in vector titer and purity, as well as an improvement in vector safety, due at least in part to the elimination of stuffer DNA from the AAV vector. The method is broadly applicable to all gene transfer / therapy applications, such as those requiring delivery of foreign DNA containing recombinant gene expression cassettes. Such foreign DNA can range, for example, from about 0.2 up to about 5.2 kb in length. The enhanced vector constructs are highly flexible, user-friendly, and can be easily modified (via routine DNA cloning) and utilized (via standard AAV vector technology) by anyone skilled in the art.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE LELAND STANFORD JUNIOR UNIV
Quick breeding method for butterfly orchid high quality sprout
InactiveCN1586165AHigh genetic stabilityRapid emergenceHorticulture methodsPlant tissue culturePhalaenopsisBud
The present invention relates to the quick breeding method of high quality seedling of Phalaenopsis, known as 'queen orchid' and the culture medium therewith. The present invention uses the flower stem section of Phalaenopsis as explant and induces flower stem seedling with unique culture medium and performs proliferation with fascicular bud stem tip or stem section to produce high quality seedling of Phalaenopsis. The method is simple, practical, feasible and high in application value.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA BOTANICAL GARDEN CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCI
Gene recombination bacillus amyloliquefaciens and microbial inoculum preparation method
InactiveCN101717744AProtect environmentIncreased spore contentBacteriaMicroorganism based processesBiotechnologyEcological environment
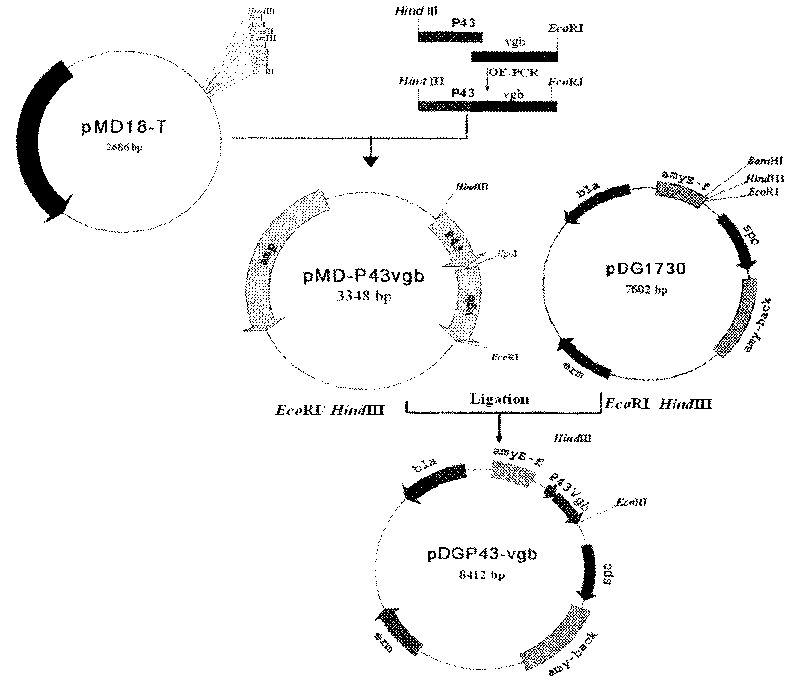
The invention discloses gene recombination bacillus amyloliquefaciens and a microbial inoculum preparation method. A bacillus amyloliquefaciens FZB42 strain is taken as a host bacterium to construct the gene recombination bacillus amyloliquefaciens XLV09-1 with transparent vitreoscilla hemoglobin which is regulated and controlled by a P43 strong promoter by contrasting a gene recombination vector. The produced spore number of microbial inoculum prepared by fermenting the bacillus amyloliquefaciens can reach more than 100 hundred millions per milliliter, the overall yield of antibacterial lipopeptid reaches more than 1 gram per liter and prevention effect on various fungal plant diseases is improved by over 30 percent. The microbial inoculum is a green microecological preparation, of no toxic residue, safe to human and livestock, and favorable for protecting the ecological environment.
Owner:HUNAN NORMAL UNIVERSITY
High quality germchit tissure culturing and rapid breeding method of Dendrobium sp.
InactiveCN1631109AStable traitsHigh genetic stabilityPlant tissue cultureHorticulture methodsBudZoology
Disclosed is the high quality germchit tissure culturing and rapid breeding method of Dendrobium sp., wherein a large amount of test tube seedlings with stabilized performance are obtained through fine breed tissue culture by adopting the path of clumping buds. The produced Dendrobium sp. has the advantages of high genetic stability, quick emergence of seedlings, strong seedlings, good seedling quality, strong resistance, and fine growth status.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA BOTANICAL GARDEN CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCI
High-temperature resistant saccharomyces cerevisiae strain and breeding method thereof
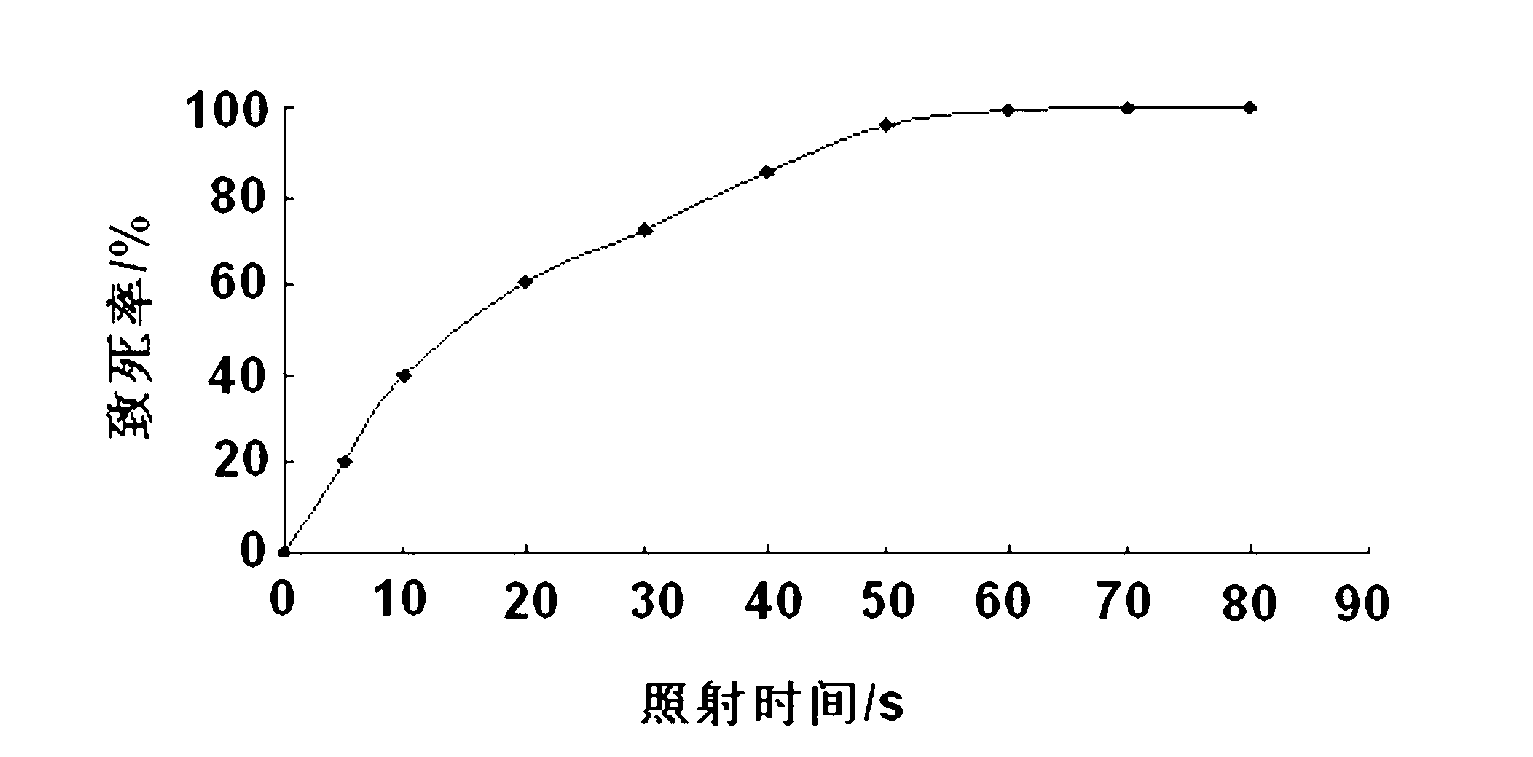
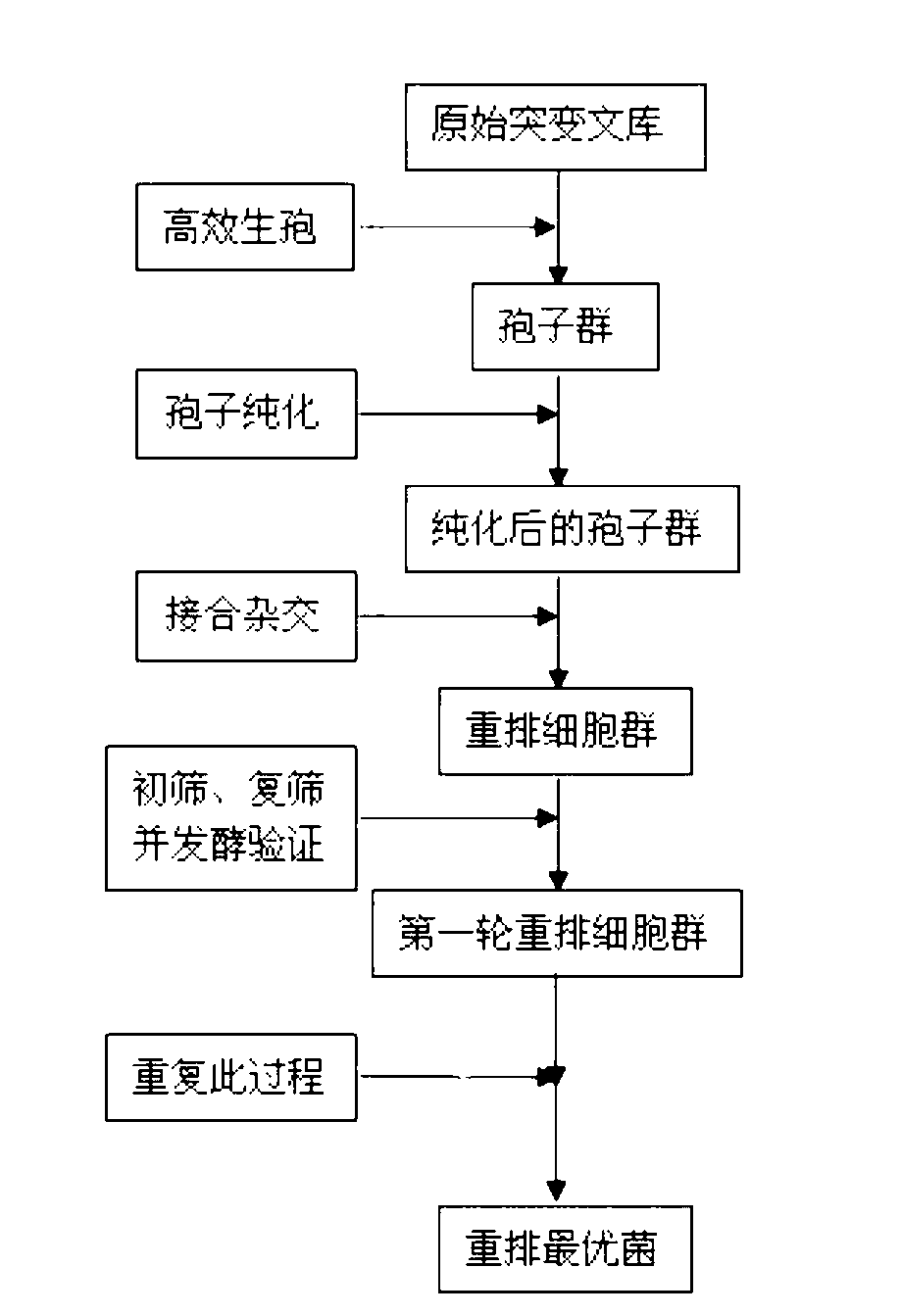
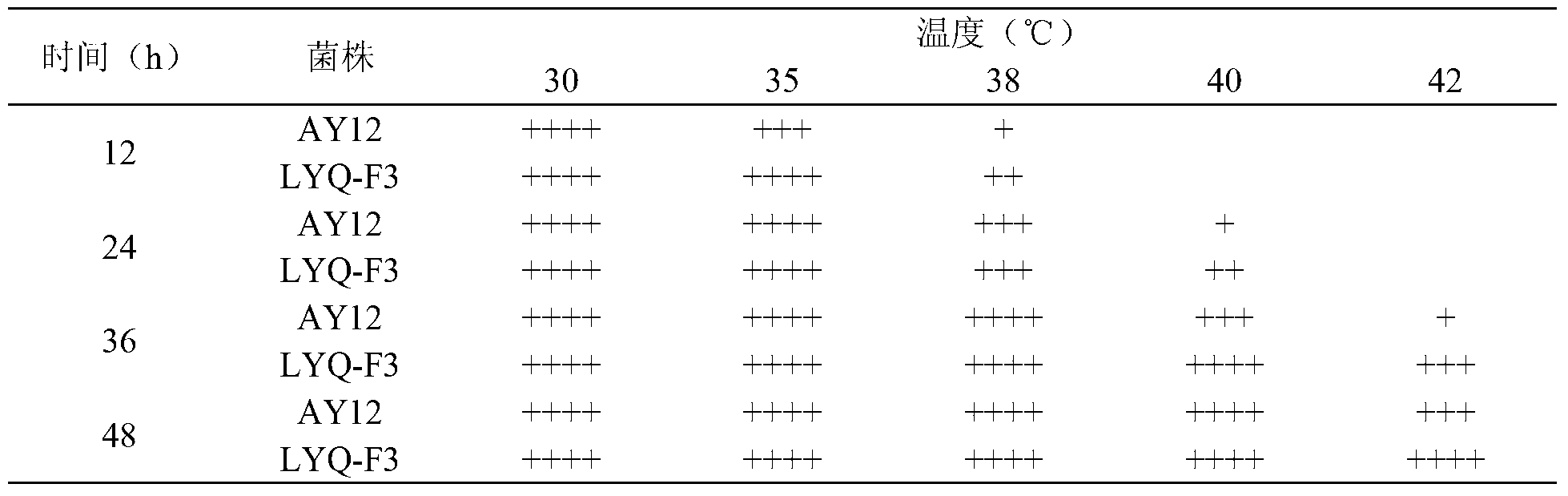
ActiveCN103232948AHigh genetic stabilityBack mutationFungiMutant preparationBiotechnologyEthanol yield
The invention provides a high-temperature resistant saccharomyces cerevisiae strain and a breeding method of the high-temperature resistant saccharomyces cerevisiae strain. The saccharomyces cerevisiae (Saccharomyces cerevisiae) SY-5-11L has a preservation number of CGMCC No.7377. The strain is characterized in that the ethanol yield is 13.9% (v / v) at a condition of fermenting at high temperature of 38 DEG C on the premise that other fermenting performances are not influenced, the yield is improved by 17.8% as compared with that of a parent strain. The ethanol output at the condition of fermenting at high temperature of 40 DEG C is 12.2% (v / v), and is improved by 34.1% as compared with that of the parent strain. The breeding method comprises the following steps of: performing artificial ultraviolet mutagenesis on an initial strain of the saccharomyces cerevisiae; screening out 23 forward mutant strains as a genome rearrangement library, wherein the ethanol output of the forward mutant strains are obviously raised on the condition of fermenting at a high temperature; and performing the genome rearrangement at three rounds, thus gaining the mutant strains with the maximum ethanol output under the high-temperature fermenting condition. The finally bred saccharomyces cerevisiae strain can be subjected to alcoholic fermentation at the high-temperature fermenting condition, brings no special requirements to fermenting equipment and technological conditions, and can be put into service with the equipment and conditions of general plants, thus having a wide application prospect.
Owner:贵州钓鱼台国宾酒业有限公司
Method for cultivating subcultured bud of upright crown tissue culture seedling of fir wood
ActiveCN104145824AGrowth inhibitionRemove position effectClimate change adaptationAfforestationSocial benefitsEconomic benefits
The invention discloses a method for cultivating a subcultured bud of an upright crown tissue culture seedling of fir wood. The method comprises the following steps: an excellent clonal annual burgeon of the fir wood is used as an explant, a breeding bud is obtained through disinfection, sterilization and tissue culture, the breeding bud is innoculated in a proliferation culture medium comprising 1 / 2MS, 1.0mg / L of 6-BA and 0.5mg / L of IBA for inducing the cluster buds to sprout, the subcultured bud which is germinated at the base of the breeding bud and is healthy in growth is selected and is cut in a common rooting culture medium, seedlings are exercised and transplanted, and when the height of the seedlings of the fir wood is 15-30 cm, the seedlings are taken out of a garden for forestation. When the method is used, the proliferation rate of the subcultured bud of the fir wood is as high as 4-6, the breeding speed is high, the seedling culturing number is large, the tissue culture subcultured bud with high genetic stability, 100% of the upright crown rate of the tissue culture seedling and more than 96% of the rooting rate can be in batch production in a short period, and the requirements of the construction and the development of a fir wood reserving base of China for good seedlings can be met, so that the method has better economic benefits, social benefits and ecological benefits.
Owner:GUANGXI FORESTRY RES INST
Method for modifying hybrid matching strains of Sansui duck
InactiveCN102783456AQuality improvementHigh genetic stabilityAnimal husbandryDiseaseGenetic stability
The invention discloses a method for modifying hybrid matching strains of Sansui duck. The method includes firstly, selecting breeding female and male ducks; secondly, feeding the breeding female and male ducks; thirdly, establishing and managing a feeding area; fourthly, hybridizing; and fifthly, feeding in the laying stage. By optimized purification and hybridization, genetic stability of fine characters of the Sansui duck such as meat quality and the like is improved, and growth speed and feed reward of the Sansui duck are increased. The strains are established and are propagated, and accordingly the related contradiction between low growth speed and meat quality is overcome. Hybridization experiments are performed, hybrid vigor of the Sansui duck is taken advantage, the strains are selected and bred selectively, and breeding value of the Sansui duck is increased. By strain selection and selective breeding, feeding management condition improvement and the like, fertilizing rate andhatching rate are increased, breeding egg quality is improved while reproduction rate is increased, and disease resistance of Sansui duck is improved. The method is applicable to strain modification for Sansui duck.
Owner:GUIZHOU QIANLISHAN ECOLOGICAL FOOD CO LTD
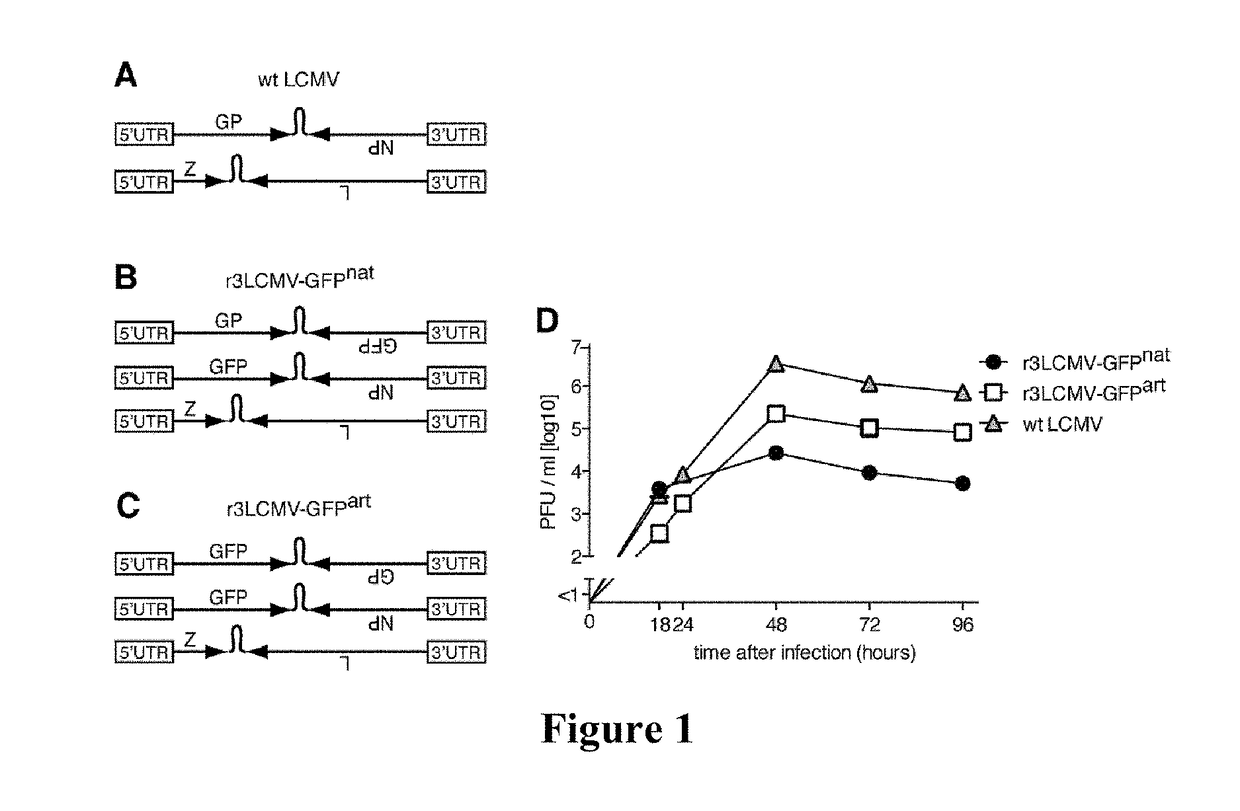
Tri-segmented arenaviruses as vaccine vectors
ActiveUS20170319673A1High genetic stabilitySsRNA viruses negative-senseVectorsGenomic SegmentDisease
The present application relates to arenaviruses with rearrangements of their open reading frames (“ORF”) in their genomes. In particular, described herein is a modified arenavirus genomic segment, wherein the arenavirus genomic segment is engineered to carry a viral ORF in a position other than the wild-type position of the ORF. Also described herein are trisegmented arenavirus particles comprising one L segment and two S segments or two L segments and one S segment. The arenavirus, described herein may be suitable for vaccines and / or treatment of diseases and / or for the use in immunotherapies.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF GENEVA
In-vitro culture method for catalpa bungei
ActiveCN105010143AHigh genetic stabilityHigh reproductive coefficientPlant tissue cultureHorticulture methodsGermplasmEmbryo
An in-vitro culture method for catalpa bungei comprises 1) inducing callus, concretely, putting catalpa bungei on a callus induction medium for inducing callus, wherein the callus induction medium is obtained by adding 6-benzyladenine (6-BA) and 2,4-dichlorophenoxyacetic acid (2,4-D) on the basis of 1 / 2 MS basal medium; 2) propagating callus, concretely putting callus on a propagation medium for propagation, wherein the propagation medium is obtained by adding 6-benzyladenine (6-BA) and alpha-naphthalene acetic acid (NAA) on the basis of 1 / 2 MS basal medium; 3) inducing embryonic callus and differentiating somatic embryo, concretely putting propagated callus on an induction differentiation medium, wherein the induction differentiation medium is obtained by adding 6-benzyladenine (6-BA) and alpha-naphthalene acetic acid (NAA) on the basis of 1 / 2 MS basal medium; and 4) regenerating a plant, concretely putting somatic embryo obtained through differentiation on a regeneration medium for inducing somatic embryo to germinate, so as to obtain a catalpa bungei regeneration plant. The method aims at expanding catalpa bungei propagation coefficient and providing conditions for germplasm preservation and genetic transformation.
Owner:CHINA THREE GORGES UNIV
Pollen-mediated method for transformation of maize, tomato or melon
InactiveUS6806399B1Speed up the processHigh-frequencyOther foreign material introduction processesFermentationPollenGenotype
Owner:CARMEL HAIFA UNIV ECONOMIC
Attenuated influenza viruses and vaccines
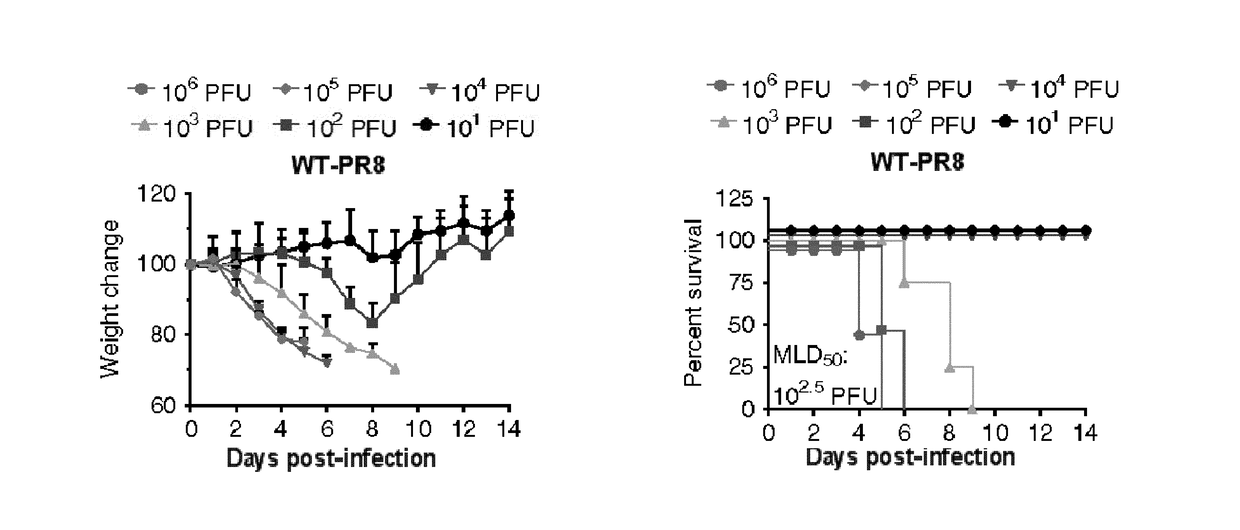
InactiveUS20120269849A1High genetic stabilityMaximum safetySsRNA viruses negative-senseSugar derivativesNucleotideProtection sex
The present provides attenuated influenza viruses comprising a modified viral genome containing a plurality of nucleotide substitutions. The nucleotide substitutions result in the rearrangement of preexisting codons of one or more protein encoding sequences and changes in codon pair bias. Substitutions of non-synonymous and synonymous codons may also be included. The attenuated influenza viruses enable production of improved vaccines and are used to elicit protective immune responses.
Owner:THE RES FOUND OF STATE UNIV OF NEW YORK
Watermelon tissue culture seedling grafting method
ActiveCN103782686AHigh genetic stabilityLow costSeed and root treatmentHorticultureField cropPlant roots
The invention discloses a watermelon tissue culture seedling grafting method, comprising the following steps: stock preparation, scion preparation, grafting, grafted seedling culturing, grafted seedling transpiration and the like. Stock seeds are sowed in a nutrition disc after pregermination, and can be grafted after two leaves and one bud grow; 2-3cm-high watermelon tissue culture seedlings are domesticated and subjected to scion ingraftment, and grafted through a top grafting method; the grafted seedlings are subjected to timely heat preservation, humidity preservation, shading culturing, and shoots of stock are timely removed; and the grafted seedlings with two leaves and one bud can be transplanted into the land for growing field crops and subjected to field management as same as common grafted seedlings. According to the invention, rooting is avoided in the tissue culture seeding culturing, the problem of difficulty in rooting or instability can be overcome by directly obtaining the watermelon grafted seedlings; the method can be carried out all the year round with artificially controlling conditions, is short in period, high in rate of survival, simple and feasible and convenient to operate, the production cost of the watermelon grafted seedlings is reduced, and the problems of imperfect regeneration plant rooting effect and low transportation survival rate during watermelon tissue culturing are solved.
Owner:武汉市农业科学技术研究院作物科学研究所 +1
Method for breeding microorganisms by plasma-induced mutation
InactiveCN101624591ARich varietySimplified typesMutant preparationMicroorganism based processesPlasma jetActive particles
The invention discloses a method for breeding microorganisms by plasma-induced mutation, which radiates microorganisms to be induced to mutate with a plasma jet flow that uses neutral active particles as acting particles to obtain mutated microorganisms. The method in which the neutral active particles in the plasma jet flow play a main induction role has the advantages of: ensuring the high activity of forward mutant strains and the high capability and genetic stability of produced target products, reducing mutagenesis period and improving mutagenesis efficiency, inducing a great variety of microorganisms such as prokaryotic microorganisms, eukaryotic microorganisms and archaebacteria in form of microbial community, bacterial suspension or spore suspension, simplifying experimental operation by avoiding culturing the processed microorganisms in the dark, having the characteristics of simple, safe and pollution-free whole operation, low equipment and experiment cost and the like and having great potential role in the field of industrial microorganism induced mutation breeding.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
Interventions to mimic the effects of calorie restriction
InactiveUS20030124540A1Affecting responseLess in CRBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsCaloric restrictionsIntervention measures
Long term calorie restriction has the benefit of increasing life span. Methods to screen interventions that mimic the effects of calorie restriction are disclosed. Extensive analysis of genes for which expression is statistically different between control and calorie restricted animals has demonstrated that specific genes are preferentially expressed during calorie restriction. Screening for interventions which produce the same expression profile will provide interventions that increase life span. In a further aspect, it has been discovered that test animals on a calorie restricted diet for a relatively short time have a similar gene expression profile to test animals which have been on a long term calorie restricted diet.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Streptomyces albidoflavus and application thereof in apple tree rot prevention and treatment
ActiveCN106906172AConducive to long-term colonizationStrong antibacterial active substanceBiocideBacteriaActive matterTherapeutic effect
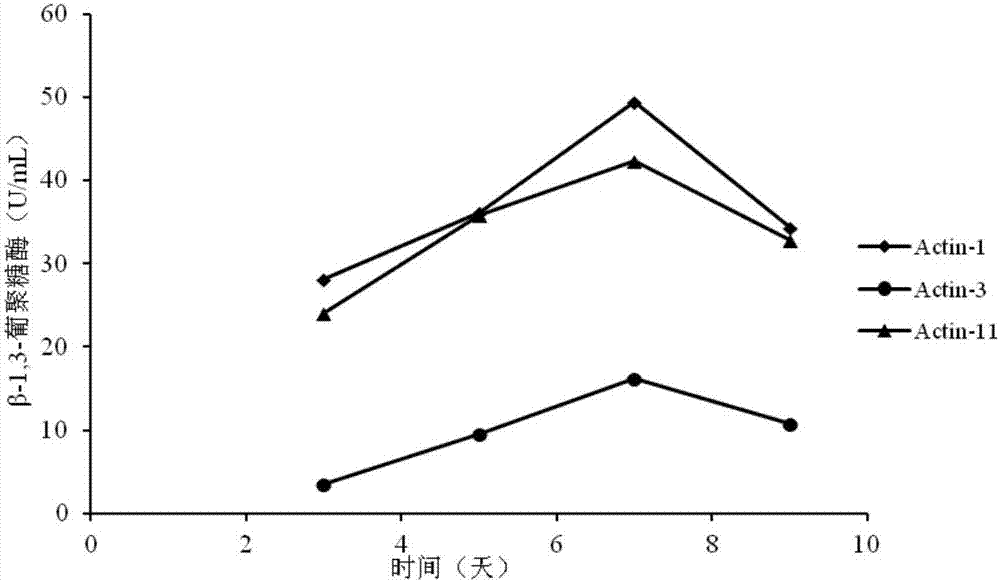
The invention discloses streptomyces albidoflavus Actin-1. The streptomyces albidoflavus Actin-1 can grow and propagate with apple tree rot pathogenic bacterium mycelium as nutrition, long-term colonization of biocontrol bacteria on apple tree rot scabs is promoted, a long-term biological prevention and treatment function is achieved, meanwhile, the streptomyces albidoflavus Actin-1 is induced to generate multiple ectoenzyme cell wall hydrolytic enzymes, and pathogenic bacterium cells disintegrate in combination with the enzyme dissolving function; high antibacterial active matter can be generated, the bacteriostasis rate on the apple rot pathogenic bacteria is 89.82%, a good antibacterial effect is achieved on botryosphaeria berengeriana and other pathogenic bacteria, the bacteriostasis rate ranges from 76.08% to 87.10%, and broad spectrum bacteriostasis performance is achieved. The streptomyces albidoflavus Actin-1 is adopted as main biocontrol bacteria for preventing and treating the apple tree rot and other fruit and vegetable pathogenic bacteria, and the advantages of being good in prevention and treatment effect (100%), high in efficiency, low in recurrence rate (0), high in environment adaption capacity, high in stability, not likely to generate resistance to drugs and the like are achieved. Important significance is achieved on improving the prevention and treatment effect on the apple tree rot and other fruit and vegetable pathogenic bacteria, preventing pathogenic bacterium relapse and protecting the environment.
Owner:陕西枫丹百丽生物科技有限公司
Cutting propagation method for splash-ink dendrobe old stems
ActiveCN106106103ASimple means of reproductionBlooming fastGrowth substratesCulture mediaHigh humiditySeedling
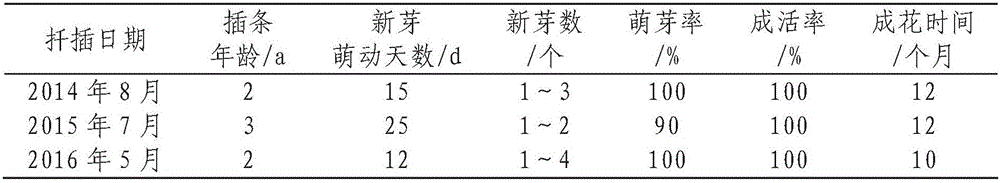
The invention discloses a cutting propagation method for splash-ink dendrobe old stems. The method comprises following steps: utilizing two-year or perennial splash-ink dendrobe pseudobulb as material; utilizing a high-temperature high-humidity condition for drought stress, forming buds induced on old stems, carrying out final-period management and seedling transplant to culture new excellent parental plant. The method is utilized for obtaining cuttage seedlings with excellent parental characters. From March to May, seedlings grow. From October to December, flowers bloom. New stem sprouts germinate for 12 to 25 days. Each pseudobulb has 1 to 4 buds of more than 90% germination rate. Compared with the aseptic sowing and tissue culture propagation, the method has following beneficial effects: the method is stable in inheritance, short in culture period, fast in florescence, low in production cost, easy in operation and easy in promotion; new plants can be cultured by effective utilization of aging pseudobulb so that nutrient consumption of new pseudobulb by utilizing aging pseudobulb is reduced and service lifetime of seedlings is prolonged; and therefore, a new way is provided for splash-ink dendrobe seedling propagation and effective utilization of old stems.
Owner:GUANGXI FORESTRY RES INST
Tissue culture method for Vaccinium bracteatum Thunb
ActiveCN103404440ASolve difficult breeding problemsHigh multiplication ratePlant tissue cultureHorticulture methodsVaccinium bracteatumPlant cultivation
The invention relates to plant tissue culture and discloses a tissue culture method for Vaccinium bracteatum Thunb, belonging to the field of plant cultivation. The method comprises the following four steps: explant sterilization; induction culture; propagation culture; and rooting culture. The method has the advantages of a high propagation rate, a fast growth rate and high hereditary stability, overcomes the problem of difficult breeding of Vaccinium bracteatum Thunb, can realize large-scale production and industrial large-scale supply of finished seedlings, protects excellent wild plant resources and brings about good economic values.
Owner:江苏九久环境科技有限公司
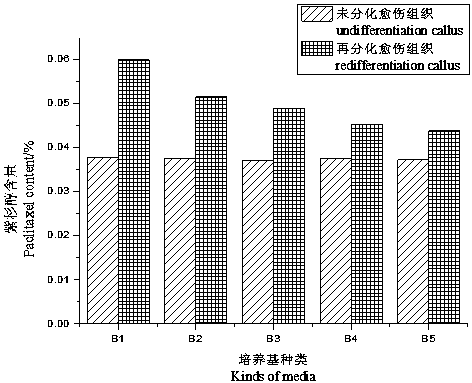
Induced redifferentiation method for improving paclitaxel content in calluses of Taxus wallichiana var. mairei
InactiveCN103651139APaclitaxel content increasedGood genetic stabilityHorticulture methodsPlant tissue cultureSecondary metaboliteTaxus species
The invention provides a technology for inducing the redifferentiation of calluses of Taxus wallichiana var. mairei to improve or maintain the genetic stability of the cellular metabolism of the Taxus wallichiana var. mairei and improve the content of paclitaxel as a secondary metabolite of the Taxus wallichiana var. mairei. The technology comprises four steps of explant preprocessing, induced culture of calluses, calluses subculture and calluses redifferentiation induction. In the step of induced culture of calluses, subculture is performed four times with 20-35 days for each culture, the calluses with good color and right texture are transferred to an improved MS (Murashige & Skoog) culture medium in which 0.05-0.20mg / L6 of BA, 0.2-2.0mg / L of NAA, 0.1mg / L of KT and 0.5mg / L of CH are added for redifferentiation induction culture, after 45-75 days of the induction culture, tiny sprouts grow from the calluses of the Taxus wallichiana var. mairei, the calluses are harvested at the time, after samples are subjected to drying, weighing and a series of preprocessing, HPLC (High Performance Liquid Chromatography) is adopted to measure the content of the paclitaxel, and a result shows that the content of the paclitaxel is one time higher than that of the calluses which are not subjected to differentiation. In the improved MS culture medium, ammoniacal nitrogen is 2000-2600 mg / L and the nitrate nitrogen is 800-1000mg / L.
Owner:JISHOU UNIVERSITY
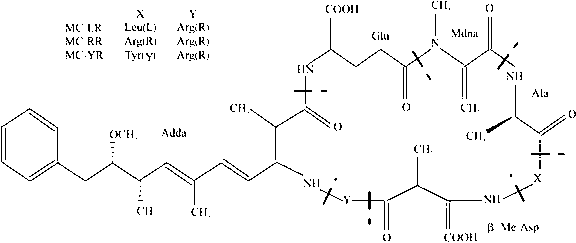
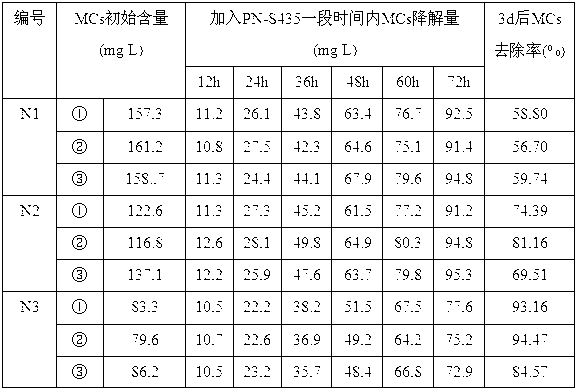
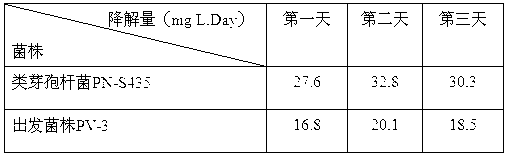
Paenibacillus sp. PN-S435 and application thereof in microcystins (MCs) degradation
InactiveCN103074279AIncreased degradation rateAvoid serious threatsBacteriaWater contaminantsBacilliAlgal bloom
The invention discloses a Paenibacillus sp. PN-S435, with the preservation number: CCTCC M 2012422, microcystins (MCs) are the only carbon source and nitrogen source, and MCs can be effectively degraded. The Paenibacillus sp. PN-S435 can be obtained through the performing combination of compound mutation of low-energy N+-LiCl with compound mutation of UV-LiCl for original strain PV-3, and then performing preliminary screening and secondary screening. According to the invention, the capability of the strain degrading MCs reaches 30.2 mg / L per day, which is improved by 64.1percent compared with original strain; and the strain greatly improves the capability of degrading MCs in a water body, hereditary stability tests prove that the Paenibacillus sp. PN-S435 can be applied to practical application, controls water body with serious algal bloom, removes even avoids danger of algal toxin to drinking water safety.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF TECH
Mutations that confer genetic stability to additional genes in influenza viruses
ActiveUS10053671B2High genetic stabilityImprove stabilitySsRNA viruses negative-senseViral antigen ingredientsVirus influenzaValine
The disclosure provides for an isolated recombinant influenza virus having at least one of: a PA gene segment encoding PA with a residue at position 443 that is not arginine, a PB1 gene segment encoding PB1 with a residue at position 737 that is not lysine, a PB2 gene segment encoding PB2 with a residue at position 25 that is not valine or a residue at position 712 that is not glutamic acid, a NS gene segment encoding a NS1 with a residue at position 167 that is not proline, a HA gene segment encoding a HA with a residue at position 380 that is not threonine, or any combination thereof, and methods of making and using the virus.
Owner:WISCONSIN ALUMNI RES FOUND
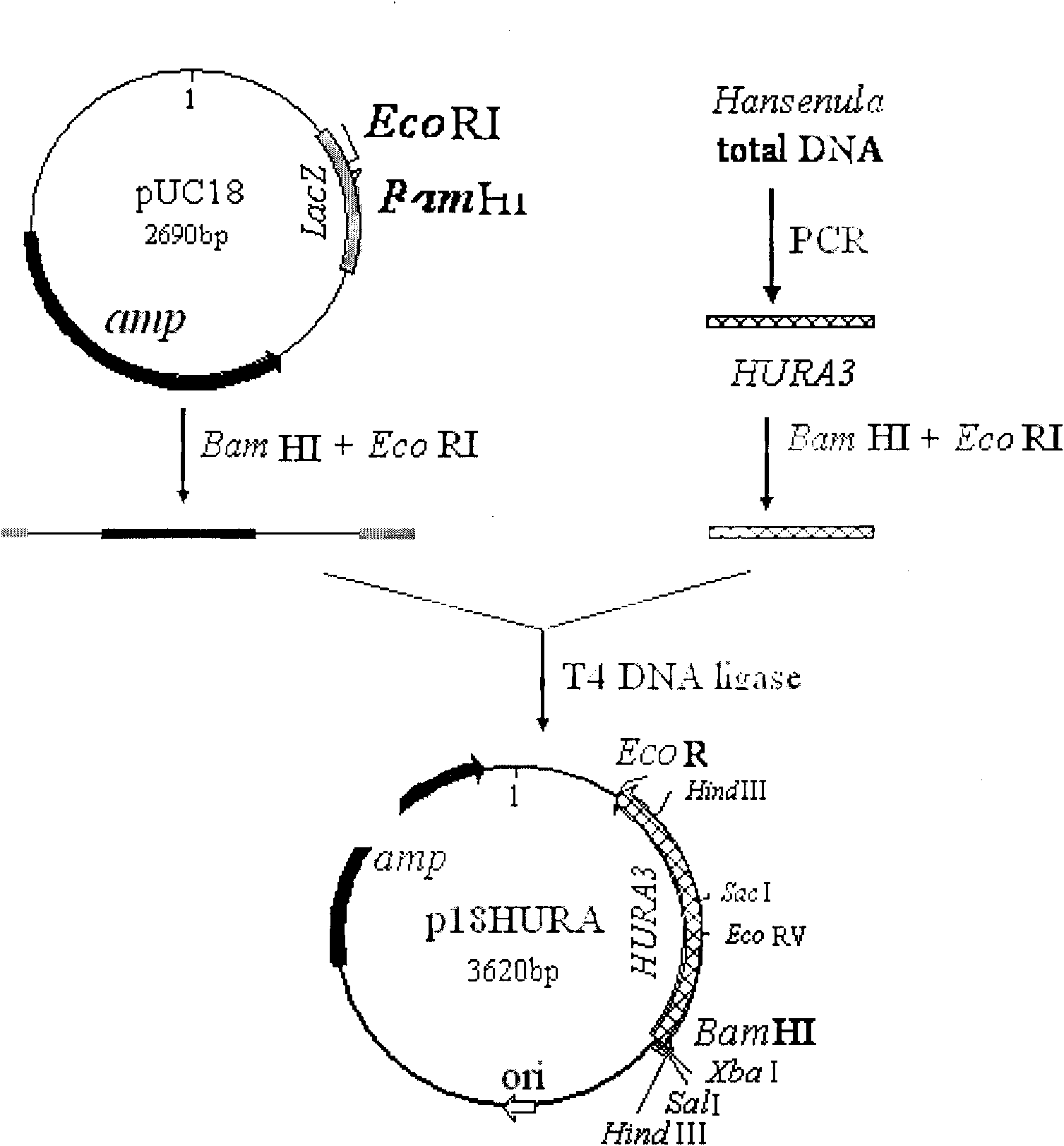
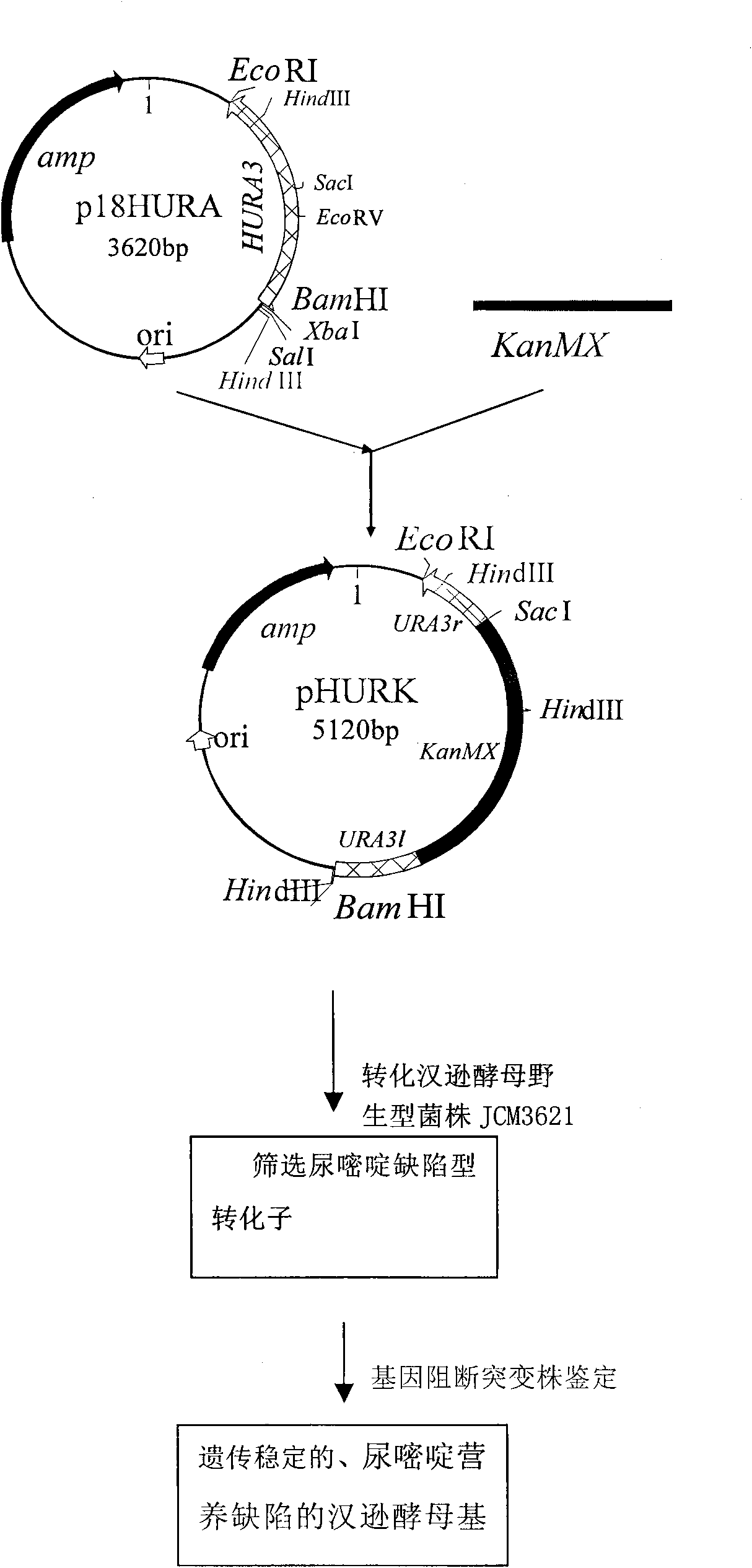
Uracil auxotroph Hansenula yeast, construction method thereof and application thereof
The invention discloses uracil auxotroph Hansenula yeast gene engineering host strain Hansenula yeast YH-11 CGMCC NO.2976 with stable heredity, and simultaneously provides a construction method for the Hansenula yeast. The construction method comprises the following steps: 1) constructing recombinant plasmid p18HURA containing orotidine-5-phosphate decarboxylase gene (HURA3) of the Hansenula yeast; and 2) constructing recombinant plasmid pHURK for the HURA3 with disrupted gene; and converting the plasmid pHURK of step 2) into the Hansenula yeast by using a yeast whole cell conversion method, and obtaining the uracil auxotroph strain through screening. The invention further discloses application of the constructed uracil auxotroph Hansenula yeast gene engineering host strain Hansenula yeast in producing foreign protein.
Owner:元昊
Antibiological inoculant for controlling apple tree canker, and application of antibiological inoculant
ActiveCN106942279AInhibition of reproductionConducive to long-term colonizationBiocideDead animal preservationDiseaseCell wall
The invention discloses an antibiological inoculant for controlling apple tree canker, and application of the antibiological inoculant. The antibiological inoculant can grow and propagate directly by using pathogenic mycelium as nutrition, and can induce the self to produce multiple extracellular enzyme capable of degrading cell walls of pathogenic bacteria; a streptomyces albidoflavus Actin-1 strain, colonized at disease spots of the apple tree canker for a long time, is activated and subjected to spore production, so that spore suspension is prepared; after that, a fermented seed solution is prepared by continuously carrying out liquid fermentation; finally, the fermented seed solution is inoculated into a solid fermentation medium, and is then fermented, dried in the air, crushed and screened so as to be prepared into spore raw powder; the spore raw powder is then scientifically screened and compounded by using auxiliary agents such as an ultraviolet protective agent, a dispersing agent and a carrier. The antibiological inoculant provided by the invention has the multiple advantages of being good in control effect, high in efficiency, low in recurrence rate and high in environmental adaptability and stability, not easy in producing drug-resistance, and the like, thus being a first choice for biological control; the antibiological inoculant has a great significance for improving the preventing and treating effect of fruit and vegetable pathogenic bacteria such as the apple tree canker, preventing pathogen recurrence and protecting environment.
Owner:陕西枫丹百丽生物科技有限公司
Self-complementary parvoviral vectors, and methods for making and using the same
InactiveUS9150882B2High genetic stabilityStabilized parvovirus vector is more stableBiocideInactivation/attenuationGene transferTiter
The teachings herein are generally directed to a method of enhancing the genetic stability of parvovirus vectors. The stability of conventional ss or dsAAV vector constructs can be enhanced, for example, to obtain a concurrent increase in vector titer and purity, as well as an improvement in vector safety, due at least in part to the elimination of stuffer DNA from the AAV vector. The method is broadly applicable to all gene transfer / therapy applications, such as those requiring delivery of foreign DNA containing recombinant gene expression cassettes. Such foreign DNA can range, for example, from about 0.2 up to about 5.2 kb in length. The enhanced vector constructs are highly flexible, user-friendly, and can be easily modified (via routine DNA cloning) and utilized (via standard AAV vector technology) by anyone skilled in the art.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE LELAND STANFORD JUNIOR UNIV
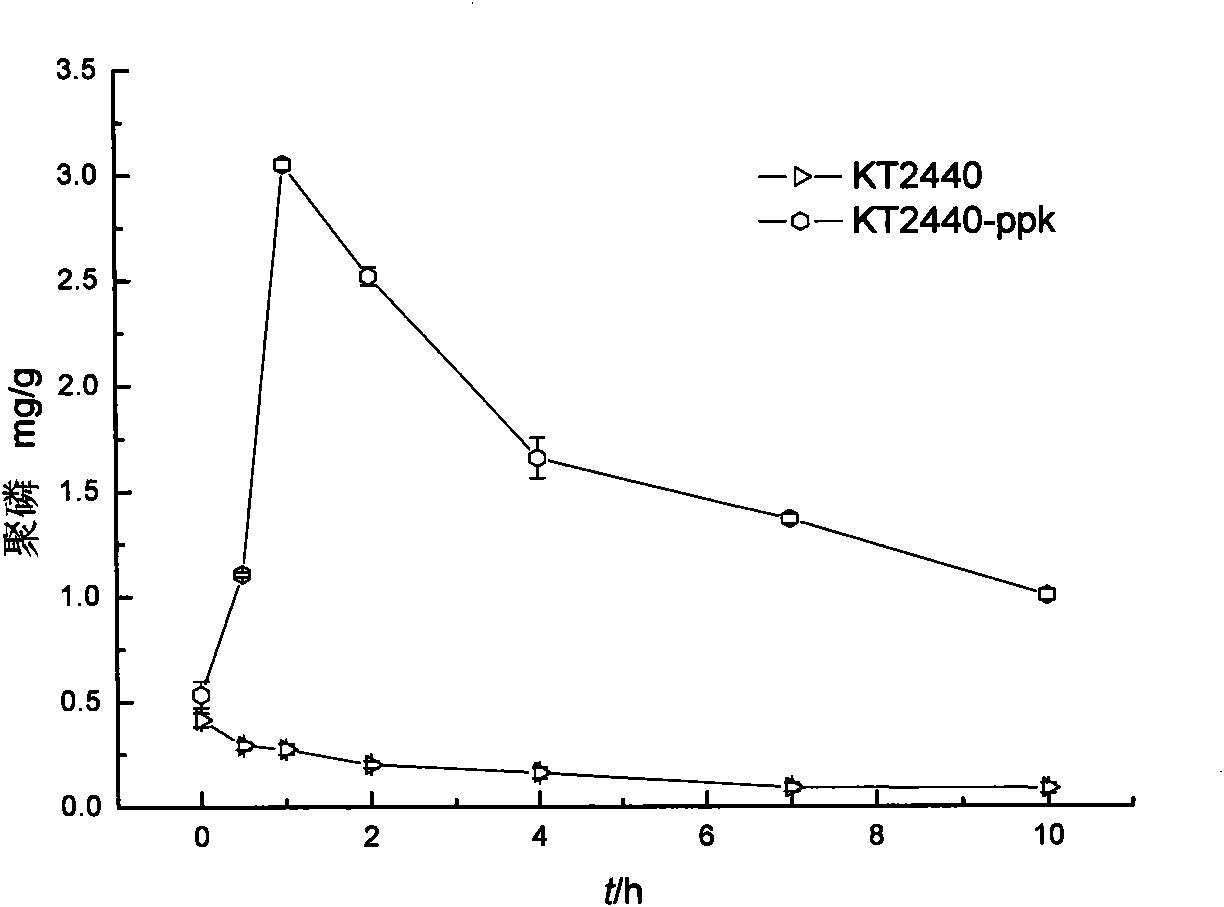
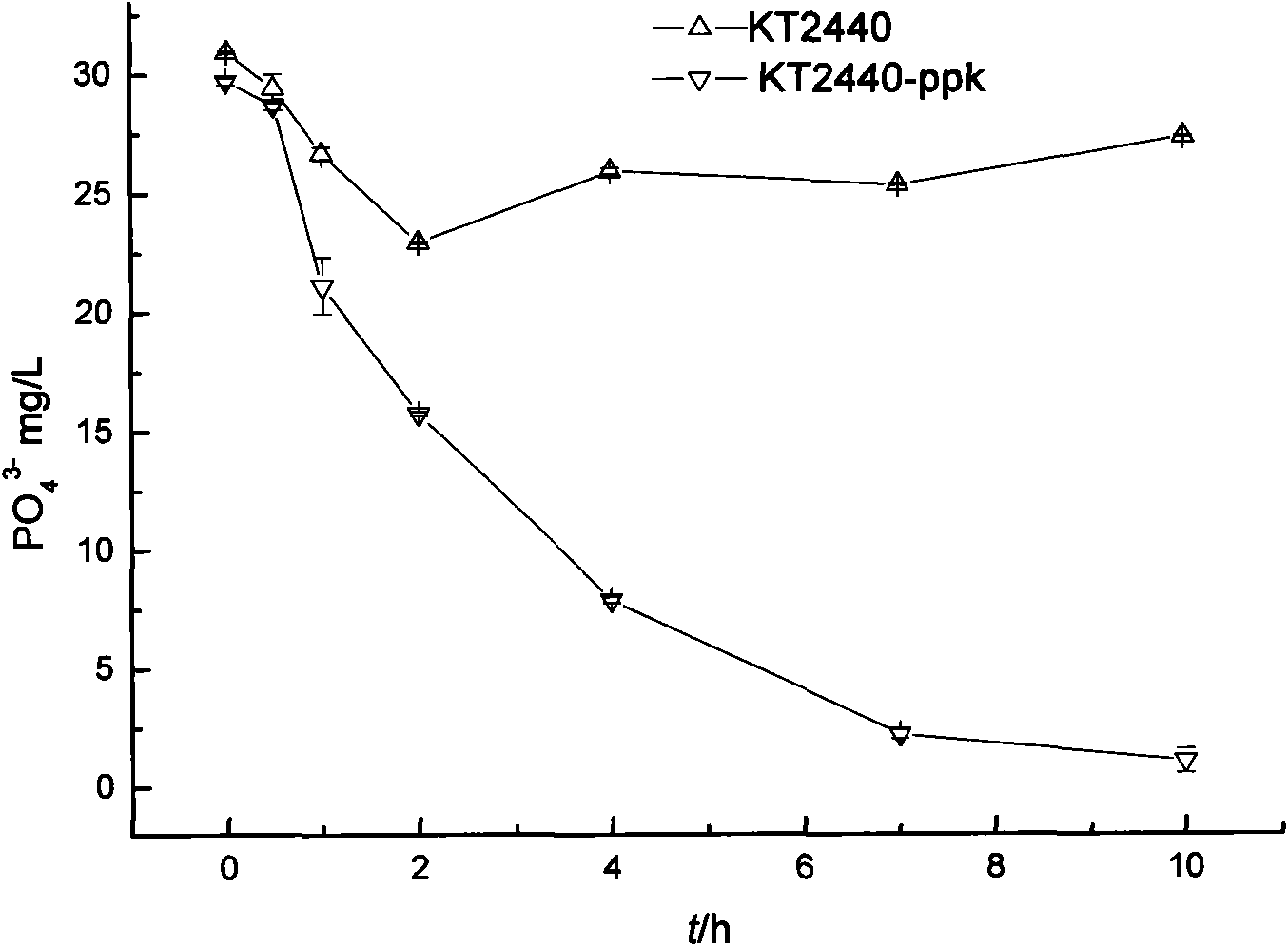
Recombinant pseudomonas putida, and construction method and application thereof
InactiveCN101899413AReduce the burden onConditions affecting growth and reproductionBacteriaWater contaminantsDNA IntegrationPseudomonas putida
The invention discloses recombinant pseudomonas putida, which is expressed on the basis of DNA integration. The invention also discloses a construction method for the recombinant pseudomonas putida, and the application of the recombinant pseudomonas putida in phosphorus removal from wastewater. The method of the invention is simple, and obtained genetically engineered bacteria have high-efficiency phosphorus removal capacity.
Owner:NANJING UNIV +1
Polymorphic hansenula polymorpha mutant strain and application of polymorphic hansenula polymorpha mutant strain in glutathione biosynthesis
The invention provides a polymorphic hansenula polymorpha mutant strain and application of the polymorphic hansenula polymorpha mutant strain in glutathione biosynthesis. Firstly, low-energy ions N+ serve as a mutagenesis source, mutagenesis treatment for Hansenula polymorpha DL-1 is achieved, a glutathione (GSH) high-producing strain (DL-18) is obtained, the temperature remains 37 DEG C, the speed remains 180 r / min, shake flask fermentation remains for 42 hours, the dry cell weight (DCW) in end products is 7.04 g / L, the total quantity of the GSH is 420.46 mg / L, and the DCW in the end products and the total quantity of the GSH are respectively improved by 1.73 times and 1.94 times compared with the original mutant strain. Hereditary stability of the DL-18 is detected through subculture, yatsushiro is cultivated, content changes of the GSH are not significant, and therefore, the hereditary stability of the mutant strain is high.
Owner:SHAANXI UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Method for rapid propagation of zephyr lily
Owner:ZHENGZHOU NORMAL UNIV BIOLOGY ENG RES
Recombination strain for producing trans-4-hydroxy-L-proline and building and application of recombination strain
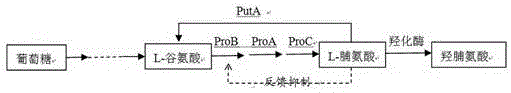
ActiveCN105483069AHigh genetic stabilityOvercoming plasmid lossBacteriaMicroorganism based processesHydroxyprolineGenetic engineering
The invention relates to a recombination strain for producing trans-4-hydroxy-L-proline and building and application of the recombination strain and belongs to the technical field of genetic engineering. The recombination strain for producing the trans-4-hydroxy-L-proline is identified as escherichia coli HJ which is preserved in China Center for Type Culture Collection on September 17th, 2015, and the preservation number of the escherichia coli HJ is CCTCC No. M2015550. The recombination strain has the advantages that wild glutamate kinase controlled by feedback regulation is used to enhance expression, three to-be-expressed genes and expression elements such as related initiators are integrated to the chromosome of the escherichia coli, the to-be-expressed genes can be constantly replicated along with the replication of the chromosome, extremely-high genetic stability is kept, the problem of plasmid loss is solved, effective fermentation cycle is prolonged, and the yield of hydroxyproline is increased.
Owner:ZHEJIANG LVCHUANG BIOTECHNOLOGY CO LTD
RECOVERY OF RECOMBINANT HUMAN PARAINFLUENZA VIRUS TYPE 2 (HPIV2) FROM cDNA AND USE OF RECOMBINANT HPIV2 IN IMMUNOGENIC COMPOSITIONS AND AS VECTORS TO ELICIT IMMUNE RESPONSES AGAINST PIV AND OTHER HUMAN PATHOGENS
ActiveUS20080286848A1Reduce expressionNovel phenotypicSsRNA viruses negative-senseSugar derivativesMammalPolynucleotide
Recombinant human parainfluenza virus type 2 (HPIV2) viruses and related immunogenic compositions and methods are provided. The recombinant HPIV2 viruses, including HPIV2 chimeric and chimeric vector viruses, provided according to the invention are infectious and attenuated in permissive mammalian subjects, including humans, and are useful in immunogenic compositions for eliciting an immune responses against one or more PIVs, against one or more non-PIV pathogens, or against a PIV and a non-PIV pathogen. Also provided are isolated polynucleotide molecules and vectors incorporating a recombinant HPIV2 genome or antigenome.
Owner:UNITED STATES OF AMERICA
Rapid propagation method for plateaus of alliums
ActiveCN105265316ABreed fastProliferation time is shortHorticulture methodsPlant tissue cultureBiotechnologyShoot
The invention discloses a rapid propagation method for plateaus of alliums. The method comprises the following steps: cleaning and disinfecting central parts of the alliums; transversely cutting the central parts 3-5 millimeters away from bottom ends to remove upper scales; longitudinally partitioning into four parts along a vertical tangent line of a main growth point; removing the main growth point and the plateau where the main growth point is positioned; inducing multiple shoots; culturing into seedlings. Through optimization of the culturing process, a rapid propagation system for the plateaus of the alliums is established and a large quantity of virus-free tube seedlings are obtained. The system has the advantages of short proliferation time, large proliferation coefficient and high genetic stability. Through the system, rapid propagation of the alliums can be realized. Industrialized production of allium virus-free tube seedlings can be ensured with a low price cost and a low time cost, and development of the allium industry is promoted.
Owner:吉林省蔬菜花卉科学研究院
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com