Patents
Literature
5932results about How to "High frequency" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
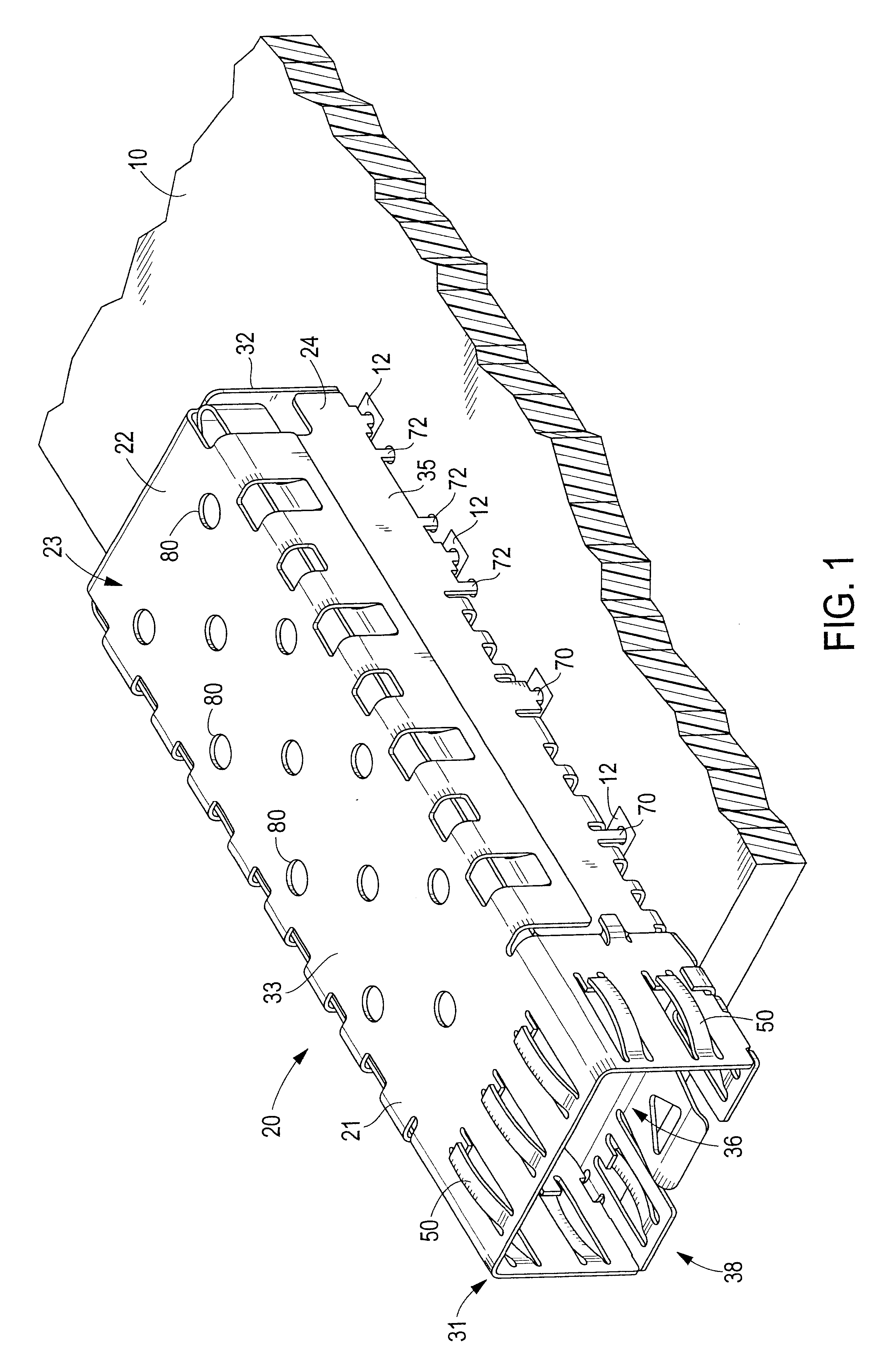
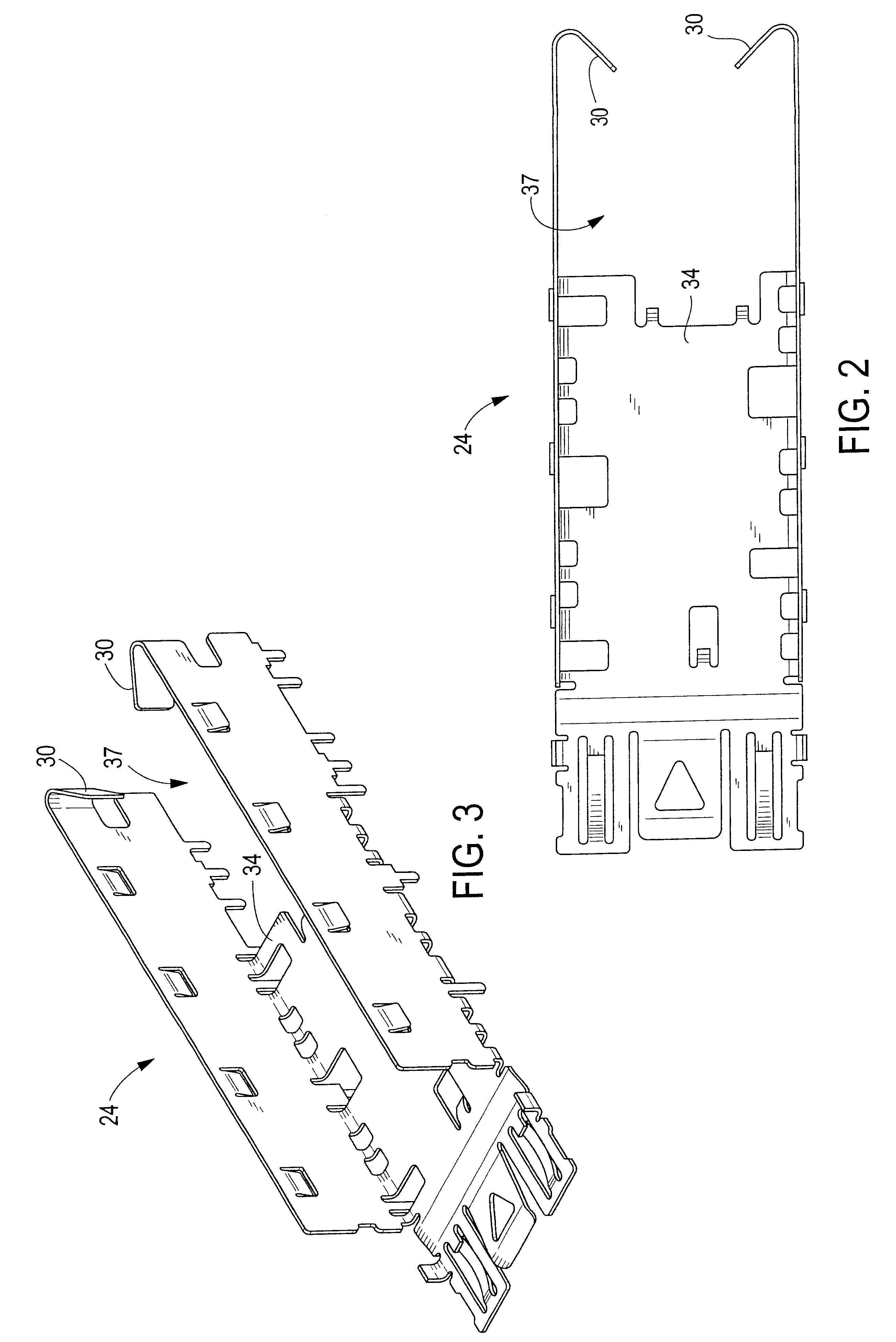
Endoscope having detachable imaging device and method of using
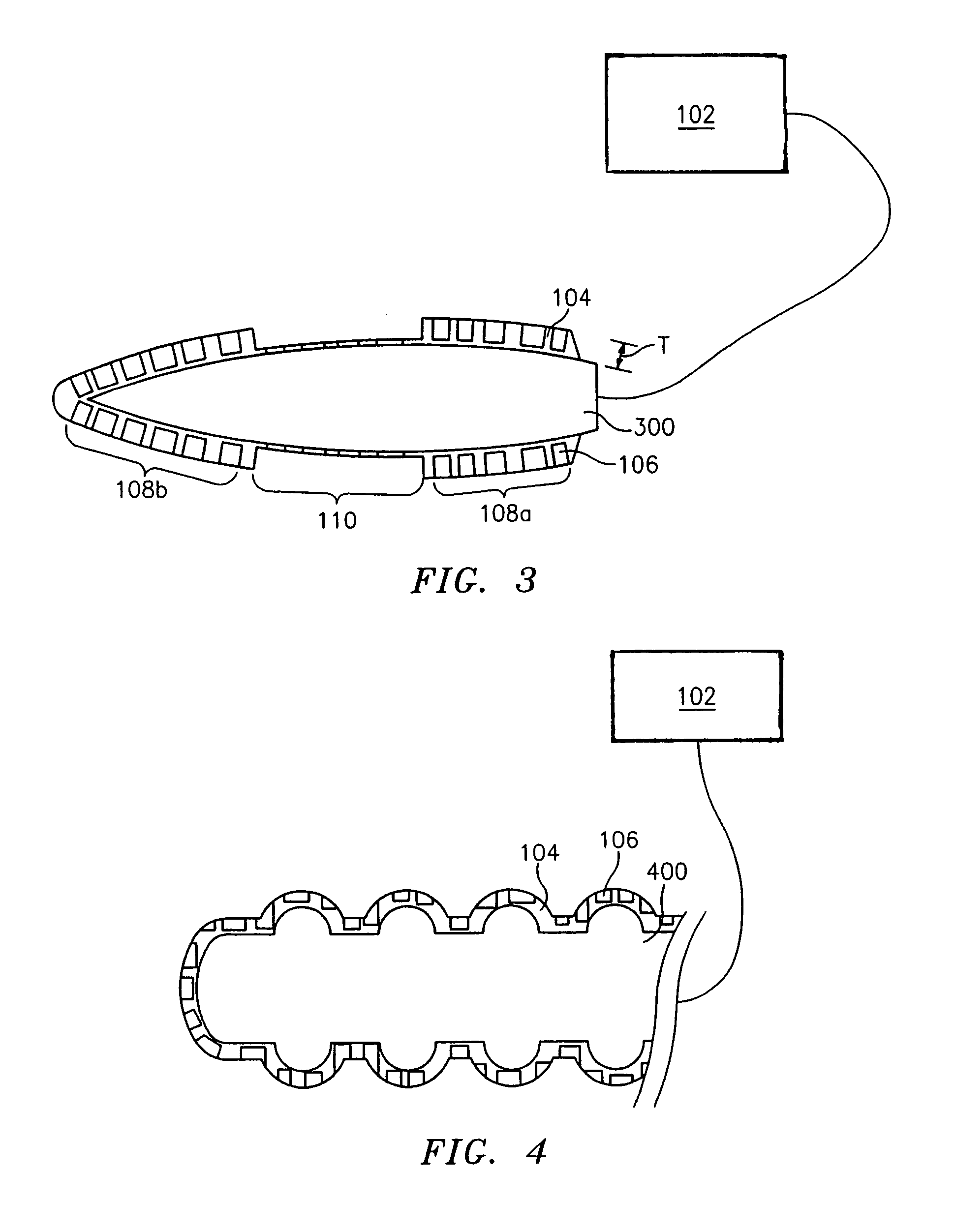
An endoscope assembly with a main imaging device and a first light source is configured to provide a forward view of a body cavity, and further includes a detachable imaging device with an attachment member engageable with the distal end region of the endoscope, a linking member connected to the attachment member, and an imaging element with a second light source, wherein the detachable imaging device provides a retrograde view of the body cavity and the main imaging device. Light interference is reduced by using polarizing filters or by alternating the on / off state of the main imaging device, the first light source, the imaging element and the second light source so that the main imaging device and first light source are on when the imaging element and second light source are off and the main imaging device and first light source are off when the imaging element and second light source are on.
Owner:PSIP LLC
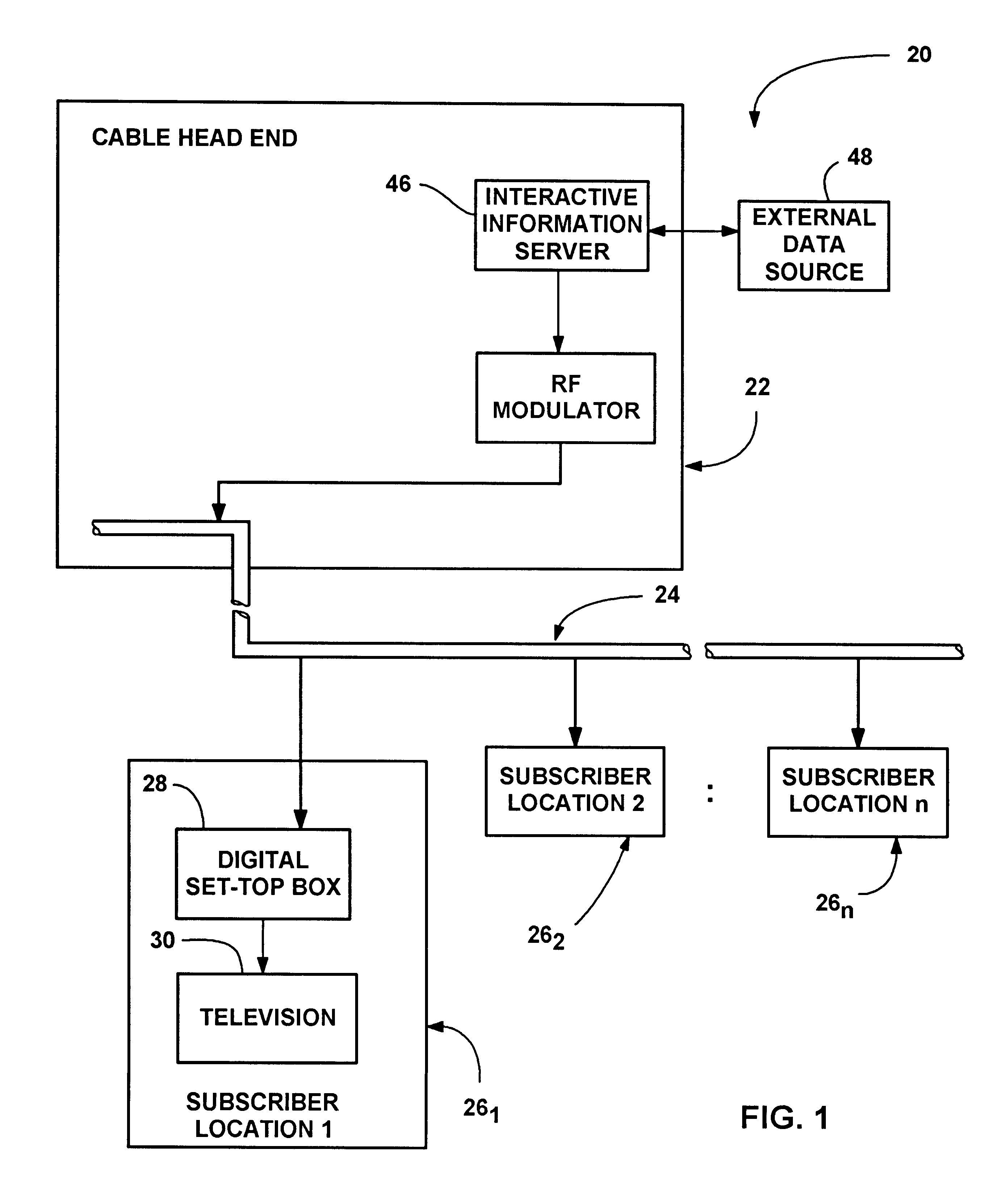
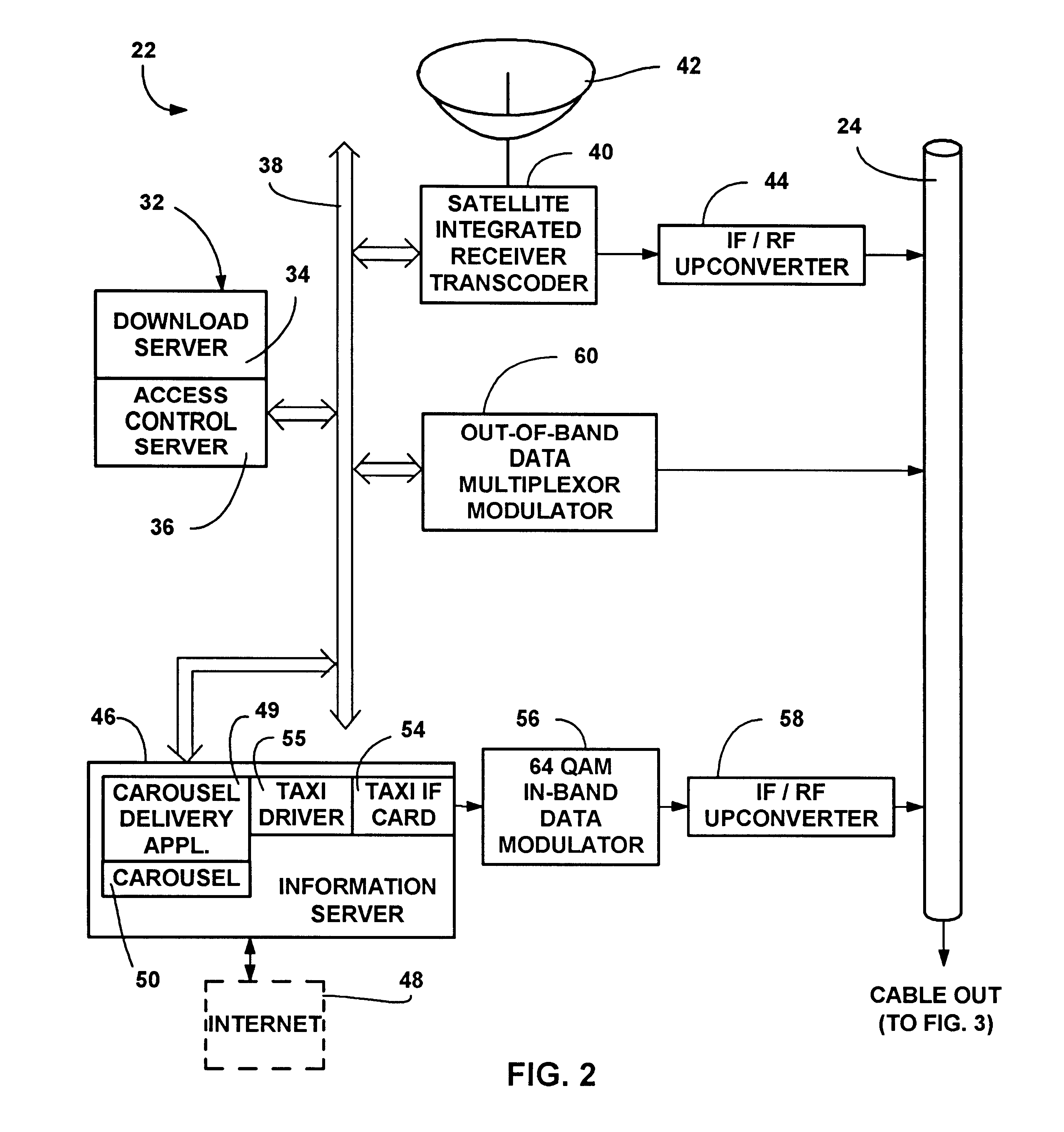
Interactive entertainment and information system using television set-top box
InactiveUS6317885B1SpeedNot much bandwidthTelevision system detailsAnalogue secracy/subscription systemsInformation systemControl equipment
An interactive entertainment and information system using a television set-top box, wherein pages of information are periodically provided to the set-top box for user interaction therewith. The pages include associated meta-data defining active locations on each page. When a page is displayed, the user interacts with the active locations on the page by entering commands via a remote control device, whereby the system reads the meta-data and takes the action associated with the location. Actions include moving to other active locations, hyperlinking to other pages, entering user form data and submitting the data as a form into memory. The form data may be read from memory, and the pages may be related to a conventional television program, thereby providing significant user interactivity with the television.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
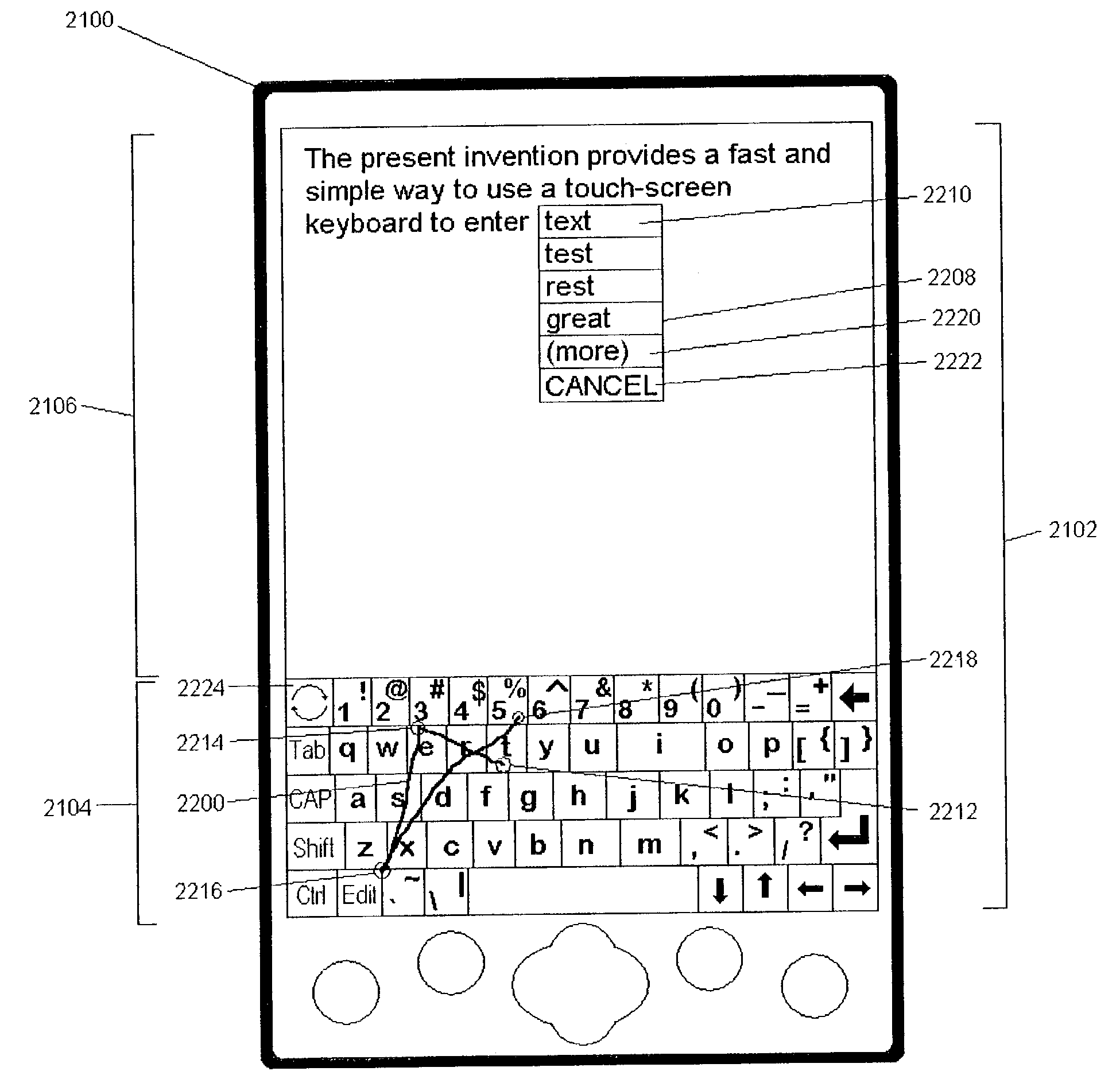
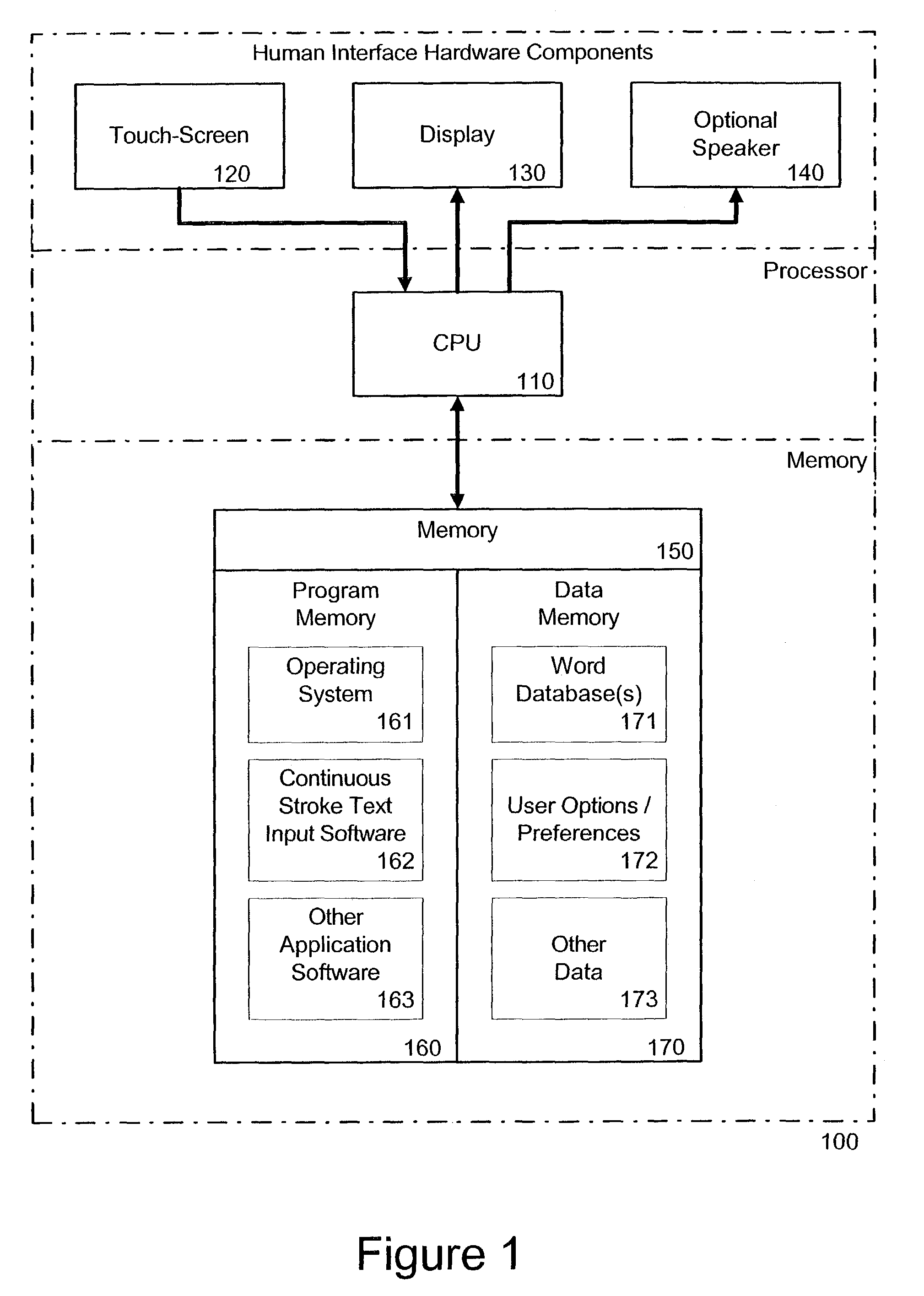
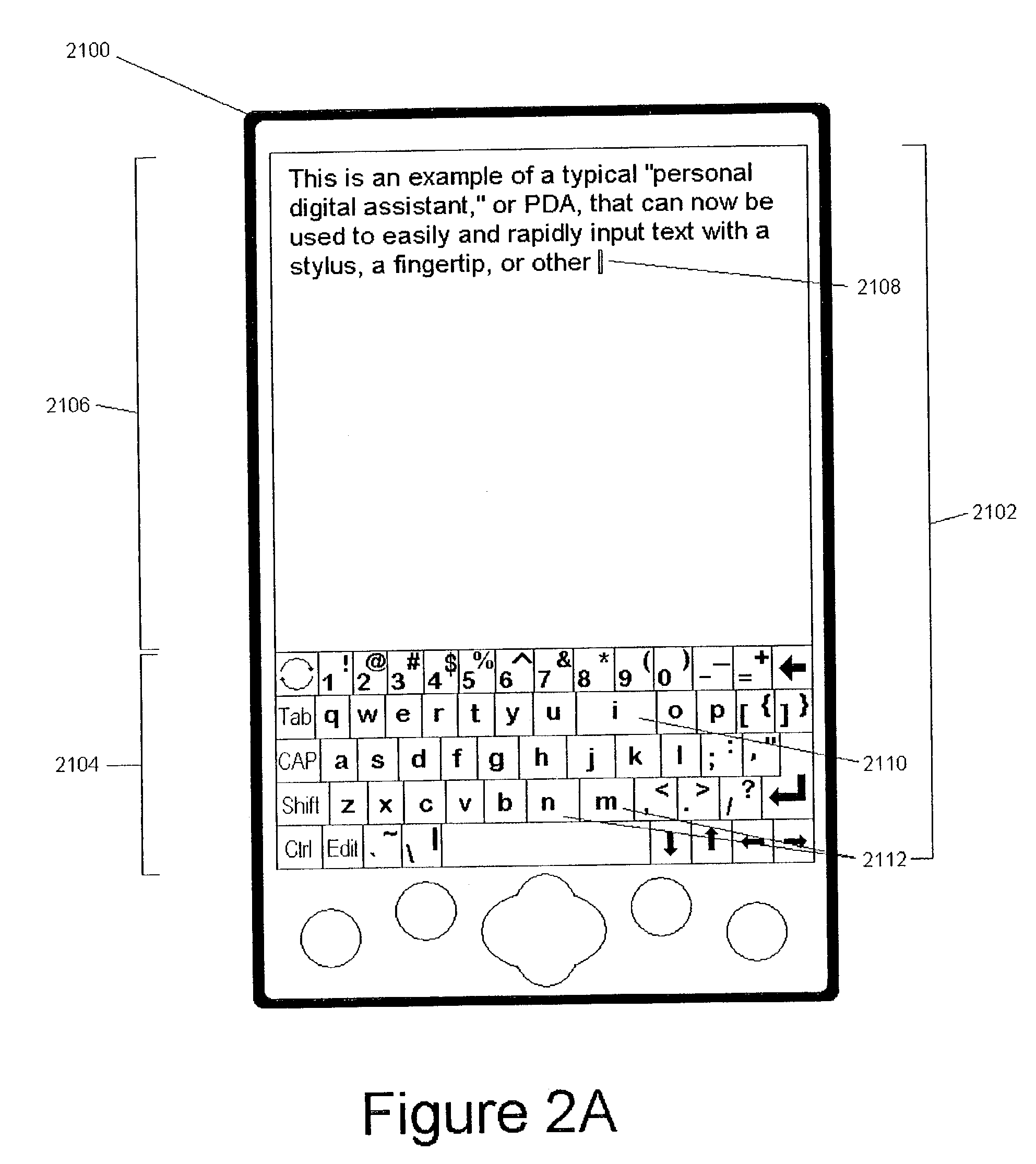
System and method for continuous stroke word-based text input
ActiveUS7098896B2Reduce in quantityIncrease text entry speedInput/output for user-computer interactionCathode-ray tube indicatorsText entryLettering
A method and system of inputting alphabetic text having a virtual keyboard on a touch sensitive screen. The virtual keyboard includes a set of keys where an each letter of alphabet is associated with at least one key. The present invention allows someone to use the virtual keyboard with continuous contact of the touch sensitive screen. The user traces an input pattern for word by starting at or near the first letter in a decided word and then tracing through or near each letter in sequence. The present invention then generates a list of possible words associated with the entered part and presents it to user for selection.
Owner:CERENCE OPERATING CO
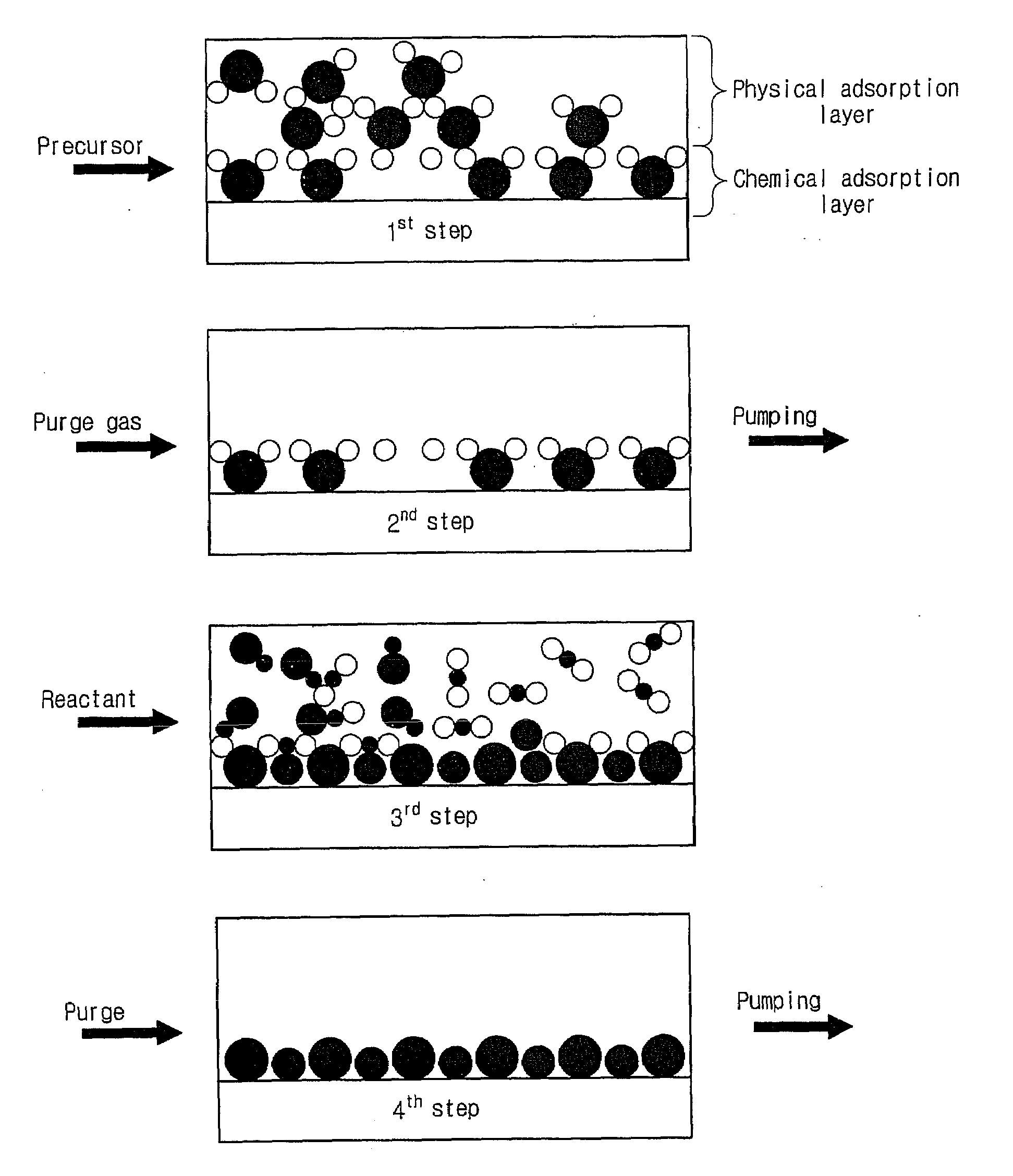
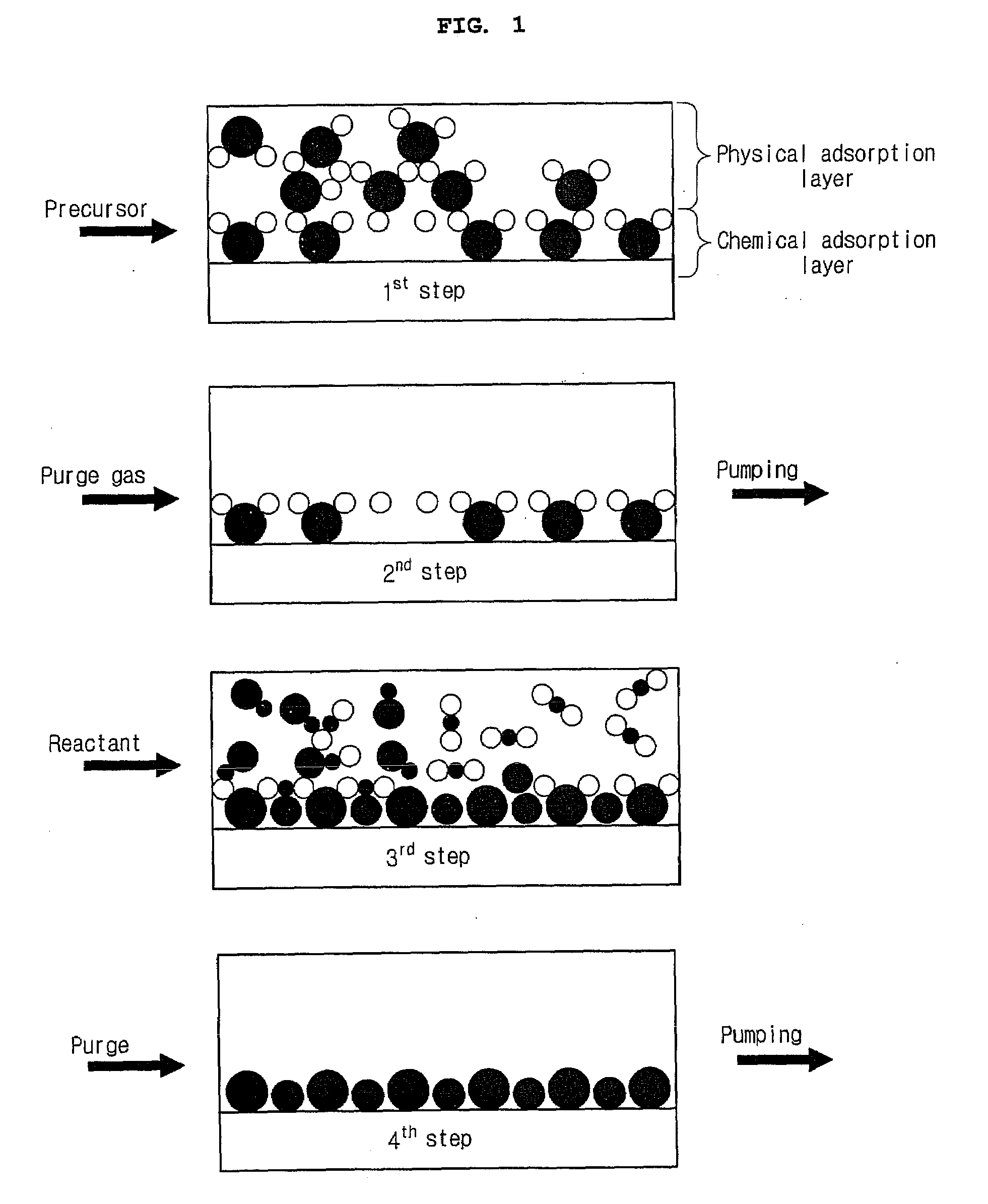
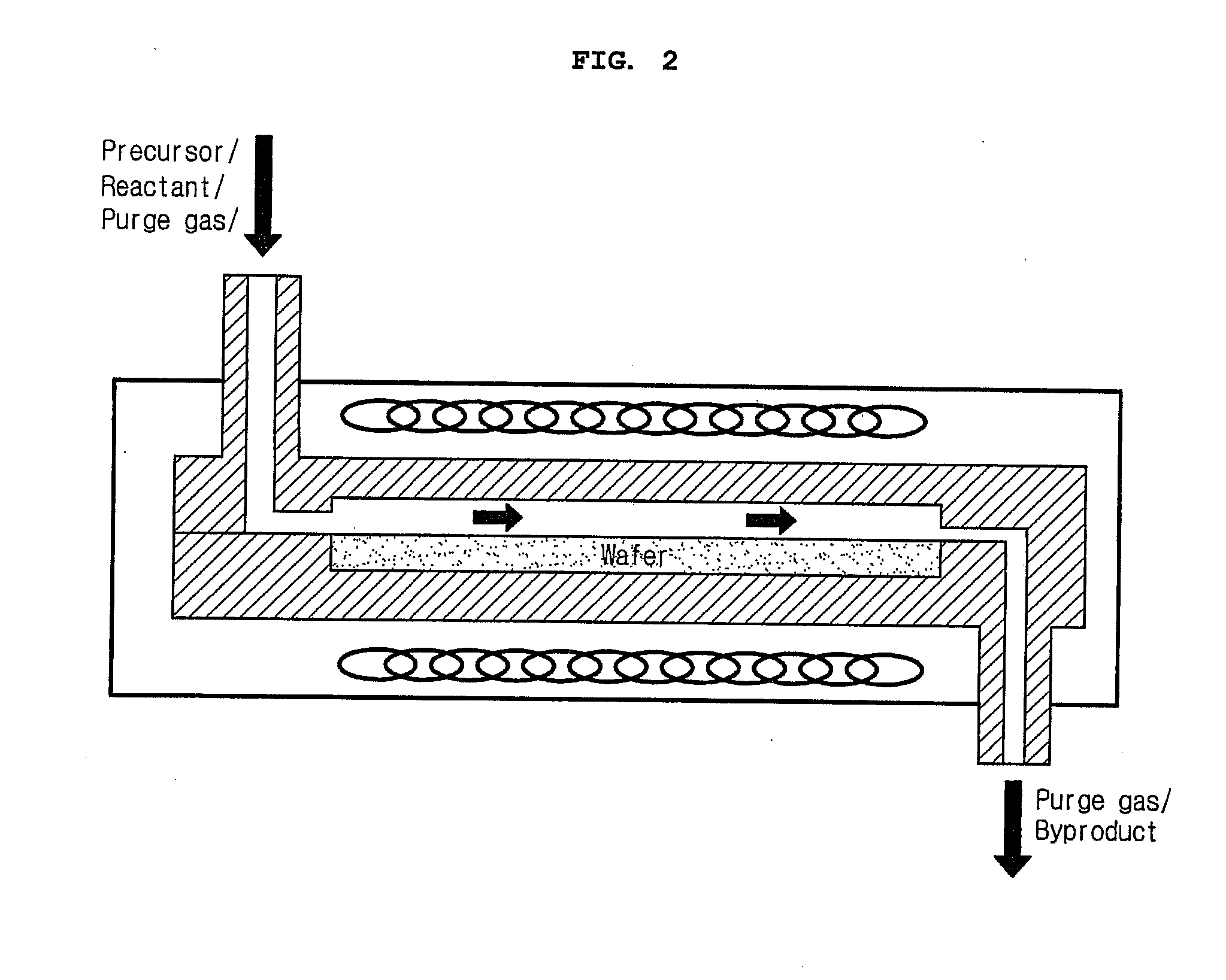
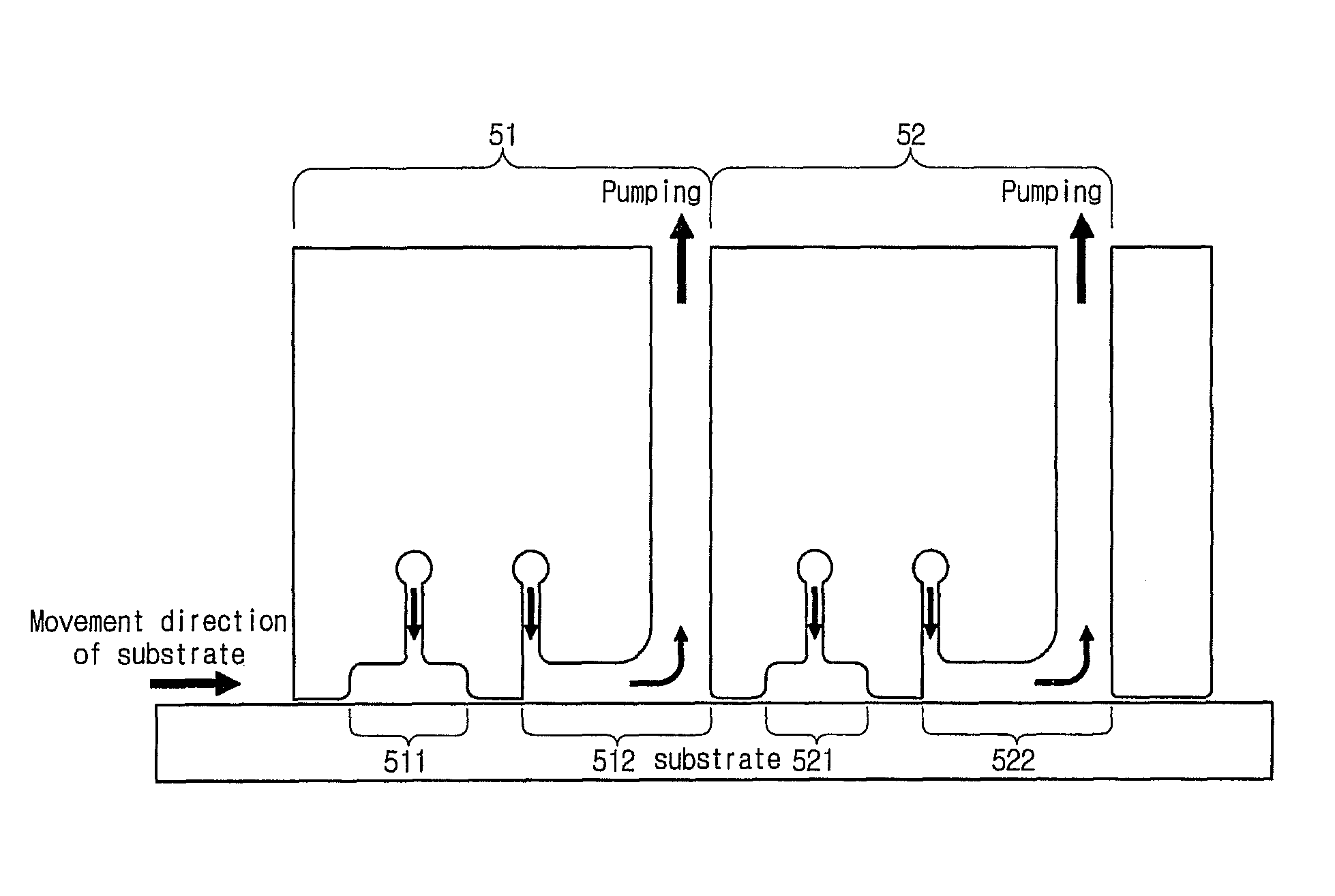
Vapor deposition reactor
InactiveUS20090165715A1Improve deposition efficiencyShorten the timeChemical vapor deposition coatingRemote plasmaMicrowave
A vapor deposition reactor has a configuration where a substrate or a vapor deposition reactor moves in a non-contact state with each other to allow the substrate to pass by the reactor and an injection unit and an exhaust unit are installed as a basic module of the reactor for receiving a precursor or a reactant and for receiving and pumping a purge gas, respectively. With the use of a small-size inlet for the reactor, homogeneous film properties are obtained, the deposition efficiency of precursors is improved, and an amount of time required for a purge / pumping process can be reduced. In addition, since the reactor itself is configured to reflect each step of ALD, it does not need a valve. Moreover, the reactor makes it easier for users to apply remote plasma, use super high frequencies including microwave, and UV irradiation.
Owner:VEECO ALD
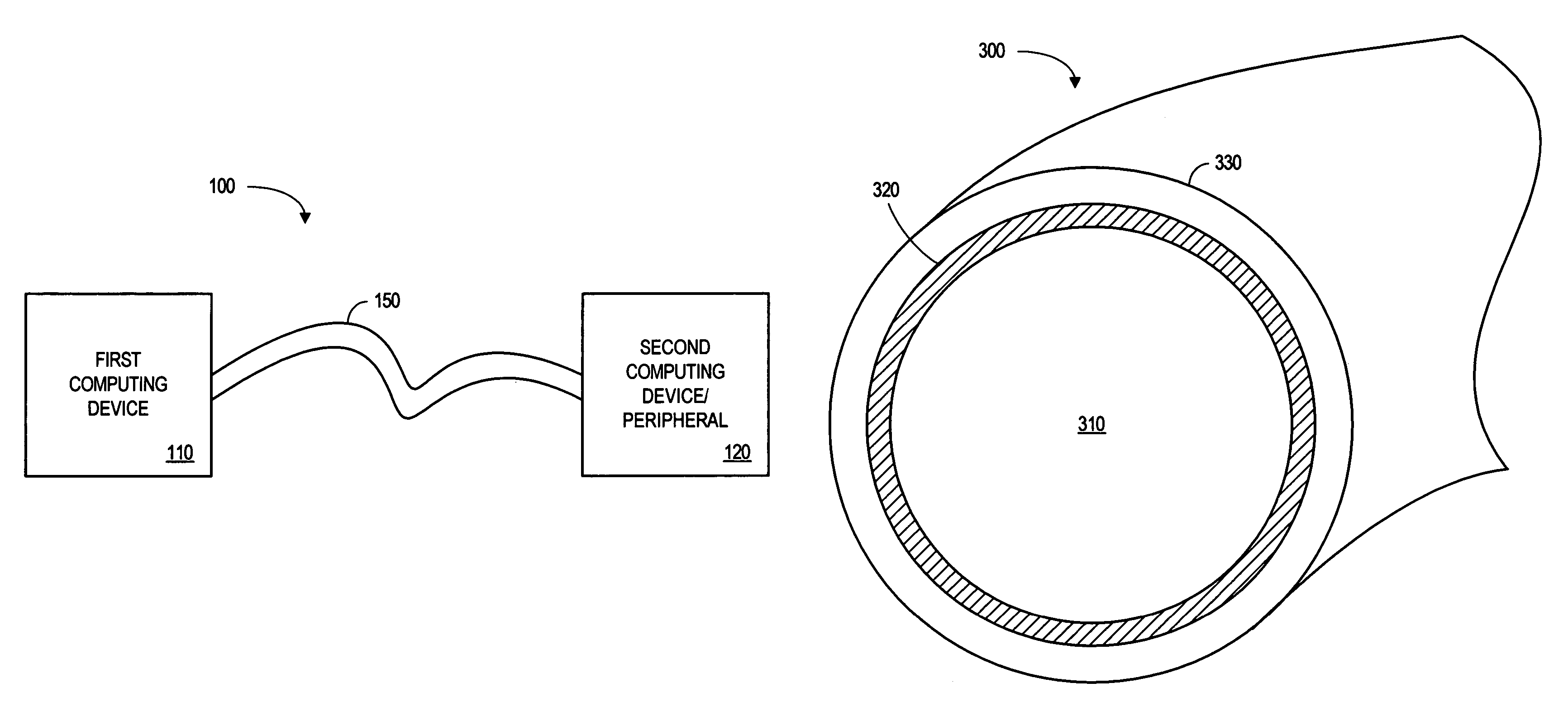
Coaxial cable-connector termination
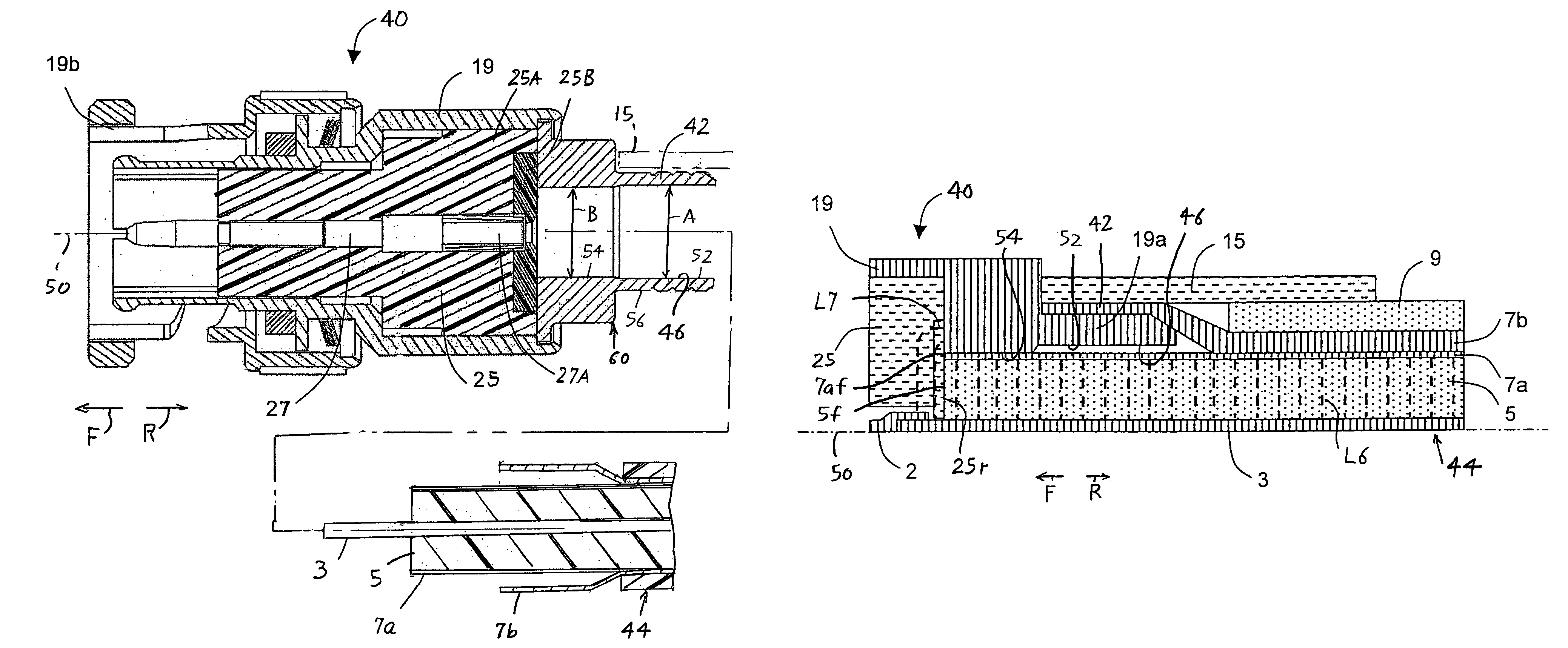
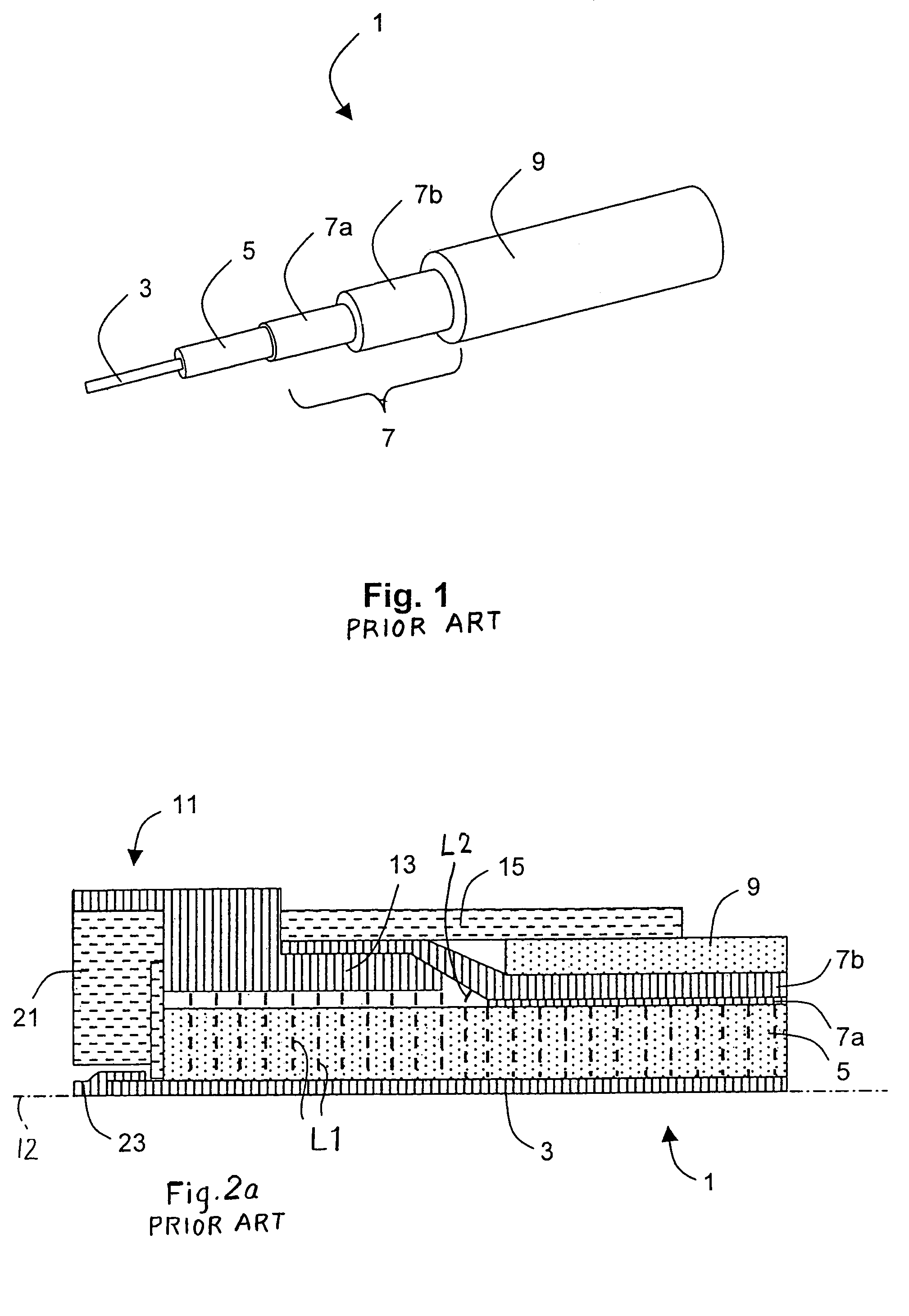
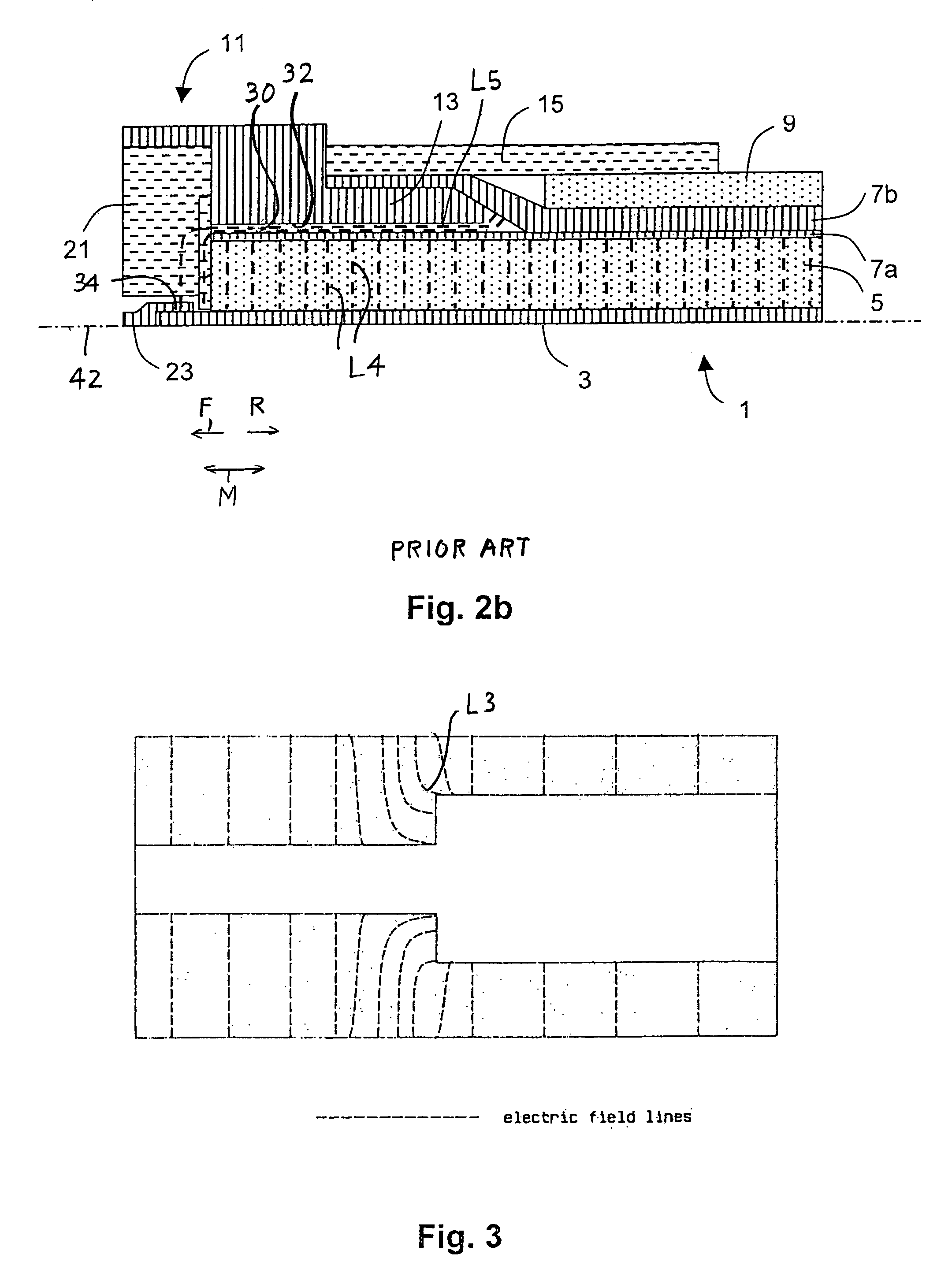
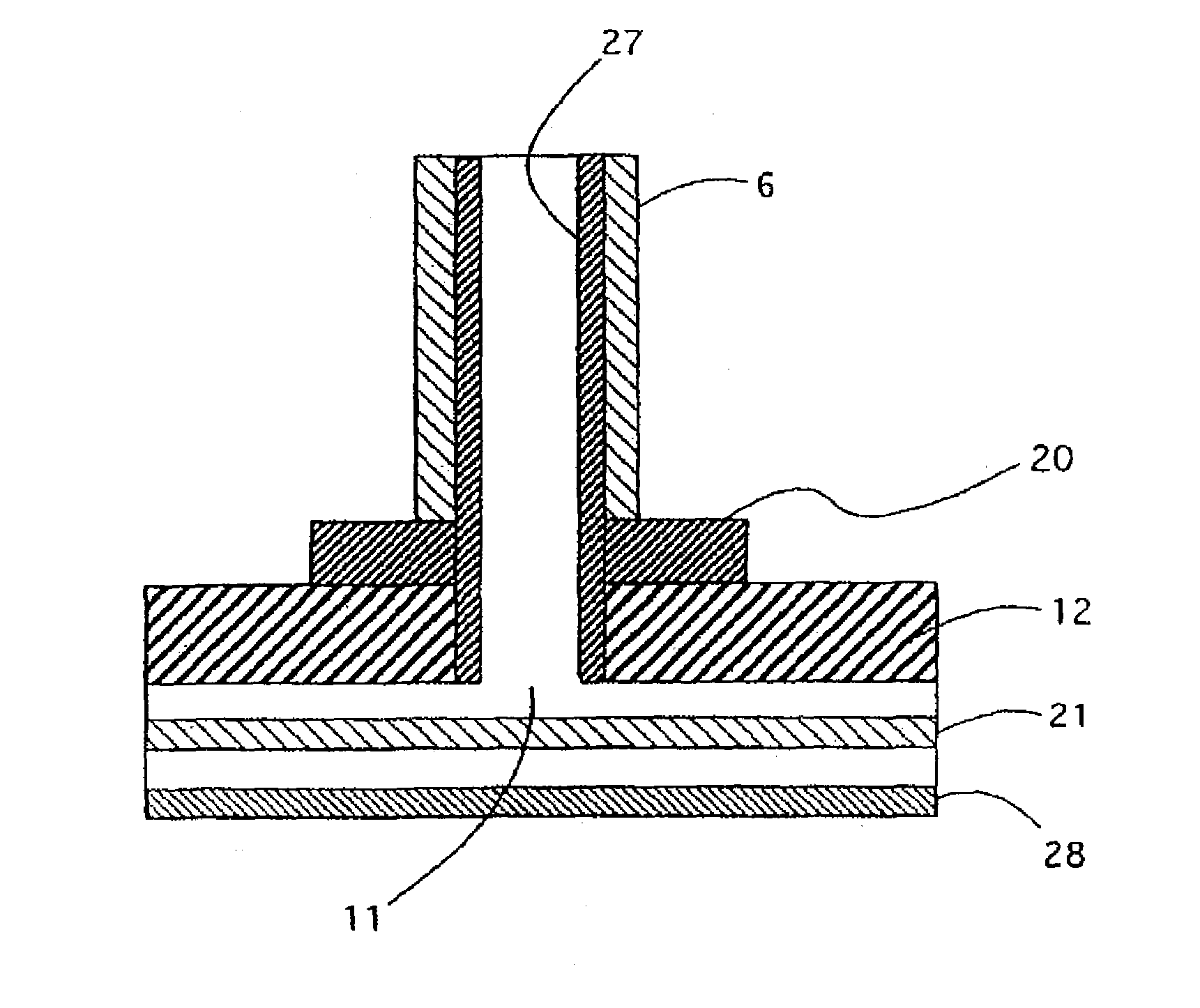
InactiveUS7381089B2Eliminate spaceEliminates a longitudinal electric fieldElectrically conductive connectionsCoupling device detailsInterference fitElectrical conductor
A high frequency coaxial cable having a foil (7a) between the cable insulator (5) and cable braid (7b), is terminated to a coaxial connector (40) in a manner that allows fast and easy cable preparation and results in a termination with minimal axial electric field lines that cause a high insertion loss and a high VSWR (voltage standing wave ratio). A bore (46) at the rear portion of the connector outer conductor, receives the cable insulator with foil around the cable insulator. The bore has a front part (54) that forms an interference fit around the foil, to avoid an axially-extending gap which might contain axially-extending field lines. The front of cable insulator and foil are flush and both abut the insulation (25) of the connector.
Owner:ITT MFG ENTERPRISES LLC
Plasma processing apparatus with insulated gas inlet pore
ActiveUS7712435B2Low reliabilityReduce throughputElectric discharge tubesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingGas passingProduct gas
A plasma processing apparatus includes: a reaction chamber; two electrodes provided inside the reaction chamber for generating a plasma therebetween, wherein at least one of the electrodes has at least one gas inlet pore through which a gas is introduced into the reaction chamber; and a gas inlet pipe coupled to the gas inlet pore for introducing the gas into the reaction chamber. The gas inlet pipe is grounded and insulated from the gas inlet pore, wherein an insulation member is placed inside the gas inlet pipe and the gas inlet pore.
Owner:ASM JAPAN
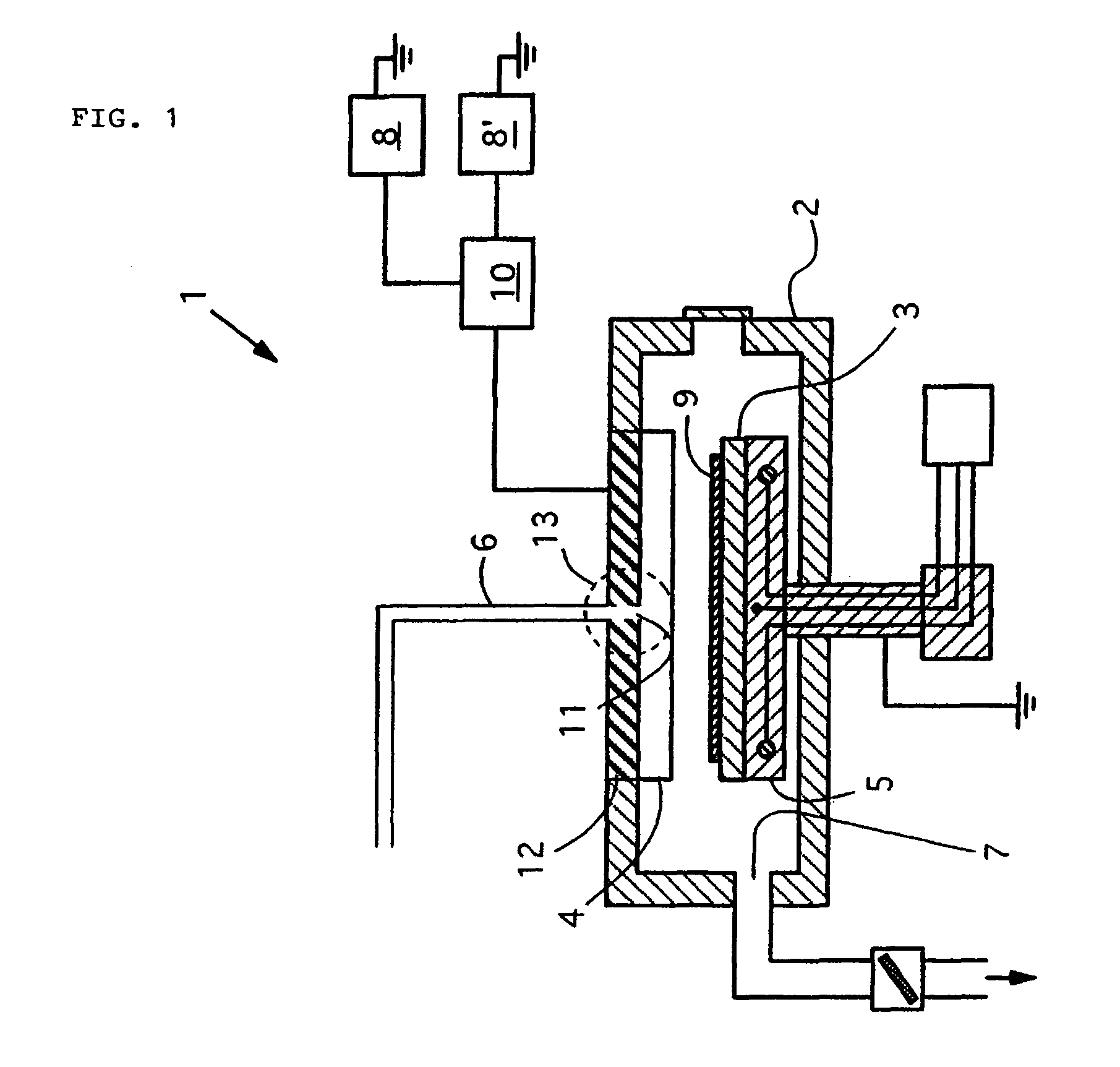
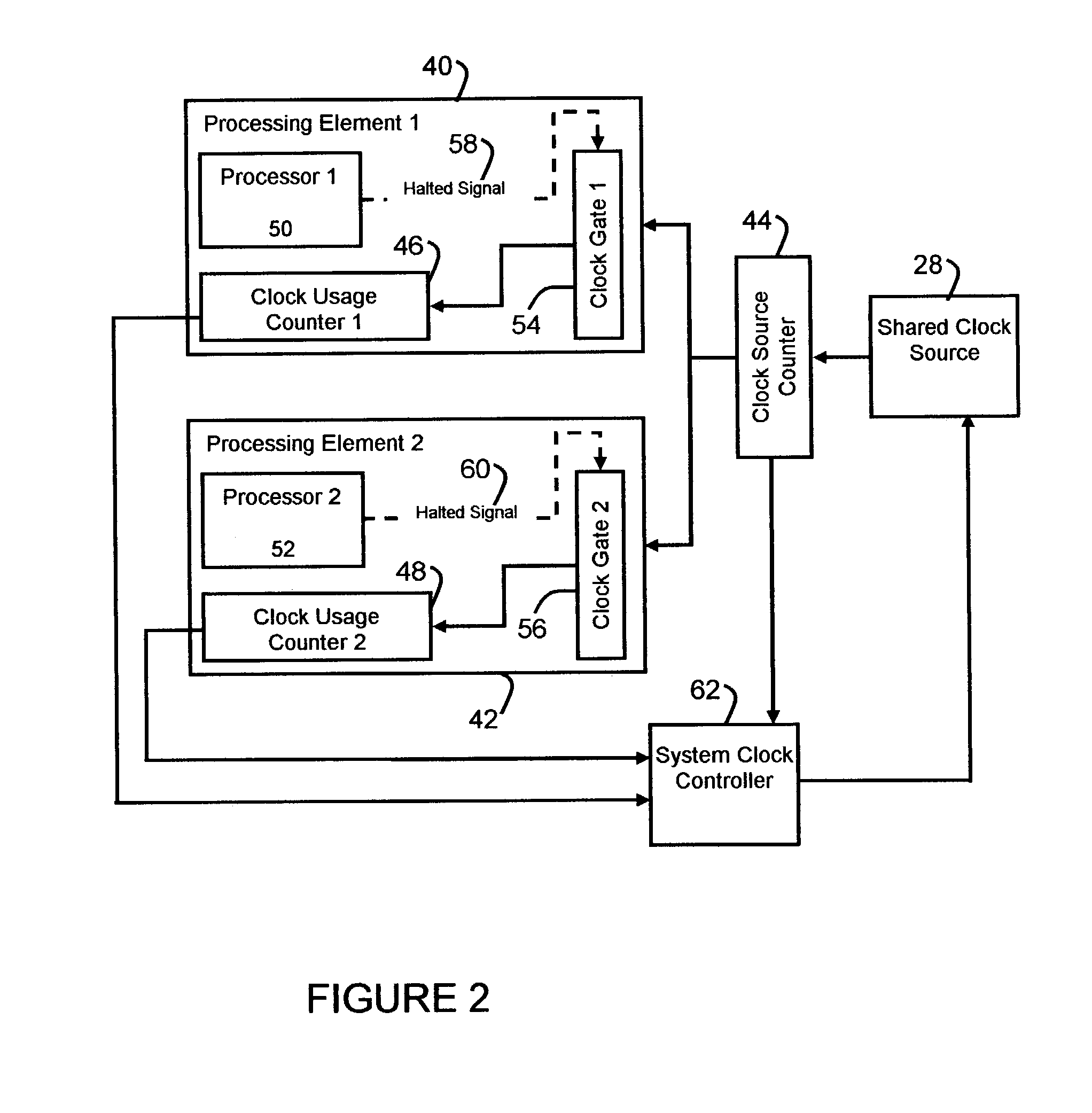
System clock power management for chips with multiple processing modules
ActiveUS7043649B2Reduce power consumptionEasy to operateEnergy efficient ICTPower supply for data processingProcessing elementComputer science
A system and method are disclosed for controlling the frequency of a common clock which is shared by a plurality of processing elements. The usage of the common clock by each of the plurality of processing elements is measured, and the common clock is controlled to have a frequency determined as a function of the measured common clock usage by the plurality of processing elements.
Owner:NVIDIA CORP
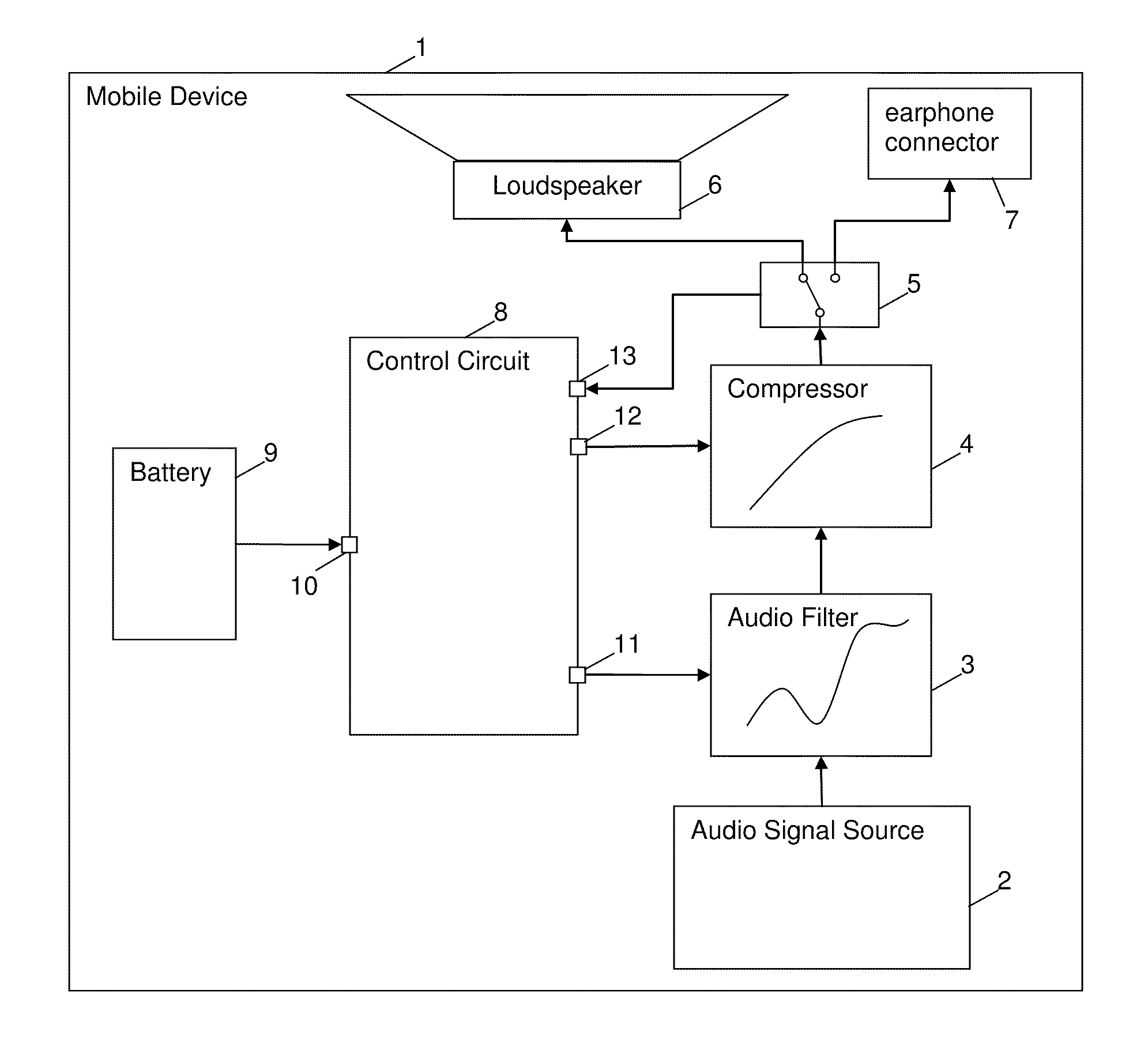
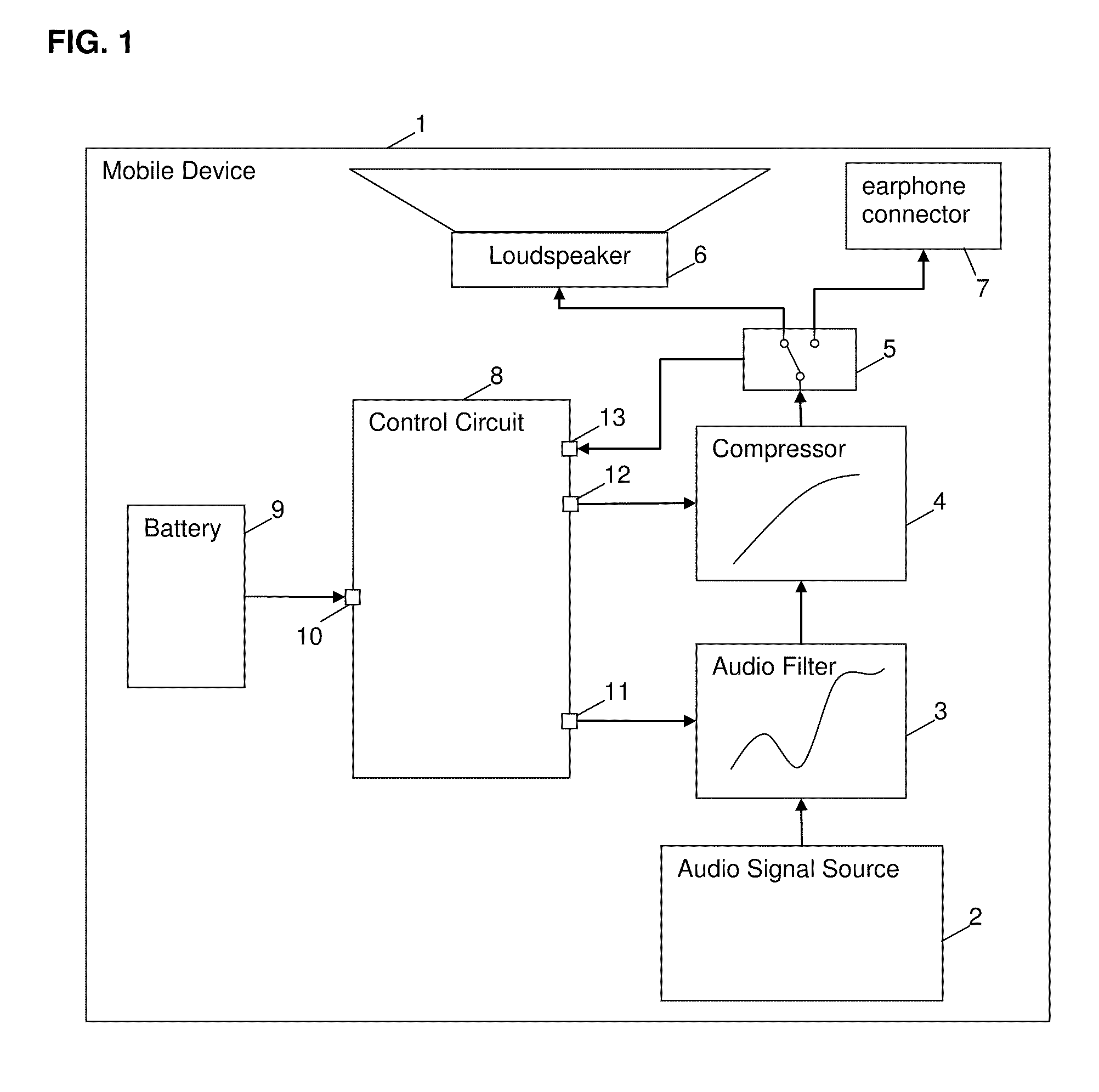
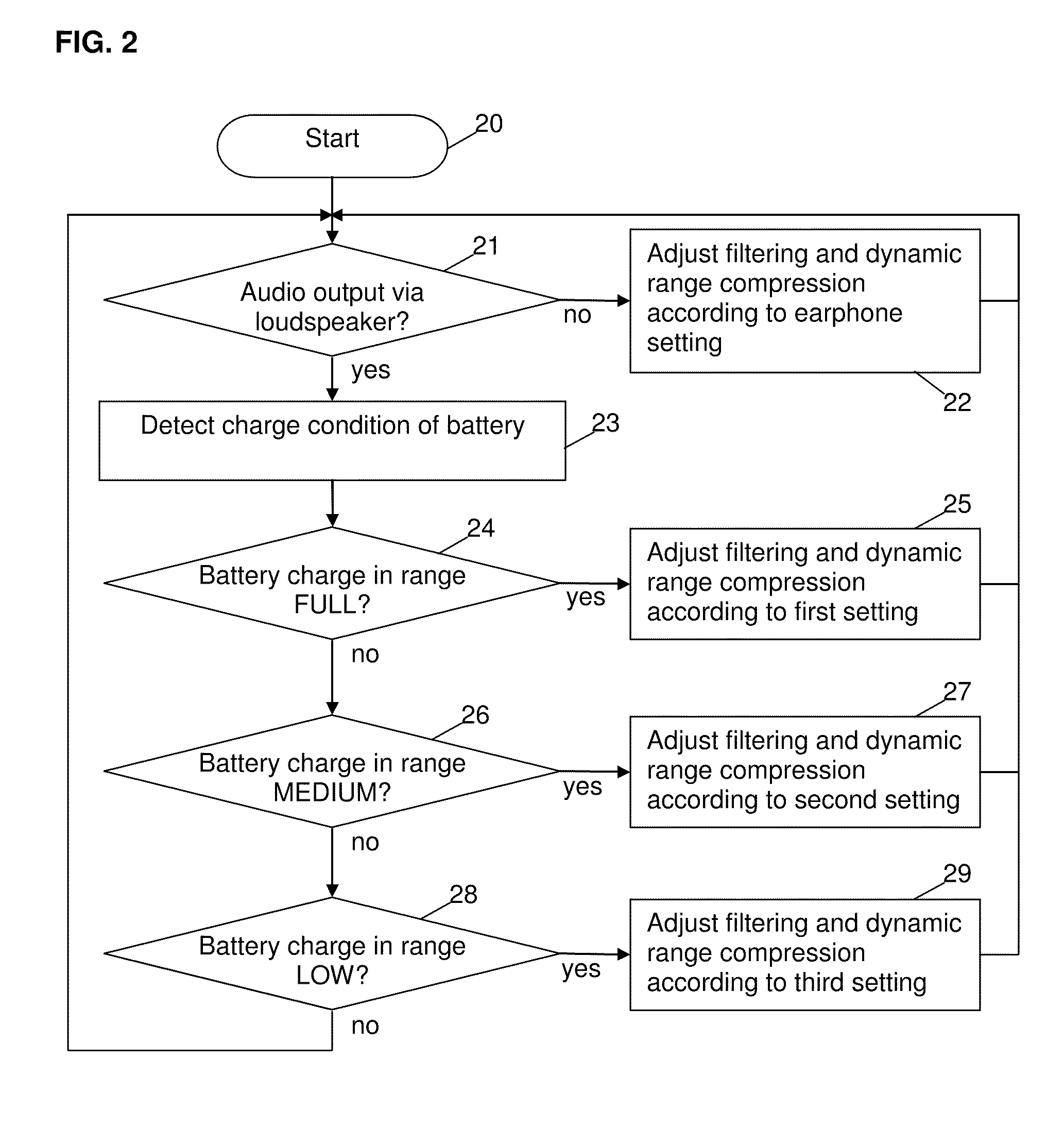
Method and circuit for controlling an output of an audio signal of a battery-powered device
ActiveUS20100322438A1Shorten the timeHigh power consumptionSupply voltage controlEarpiece/earphone attachmentsEngineeringControl circuit
A method and a control circuit for controlling an output of an audio signal of a battery-powered device are described.
Owner:SONY CORP
Flexible waveguide cable with a dielectric core
According to some embodiments, a waveguide cable includes a dielectric core and a conducting layer surrounding the dielectric core. A first antenna may be provided at a first end of the waveguide cable to receive a digital signal and to propagate an electromagnetic wave through the dielectric core. A second antenna may be provided at a second end of the waveguide cable, opposite the first end, to receive the electromagnetic wave from the dielectric core and to provide the digital signal.
Owner:INTEL CORP
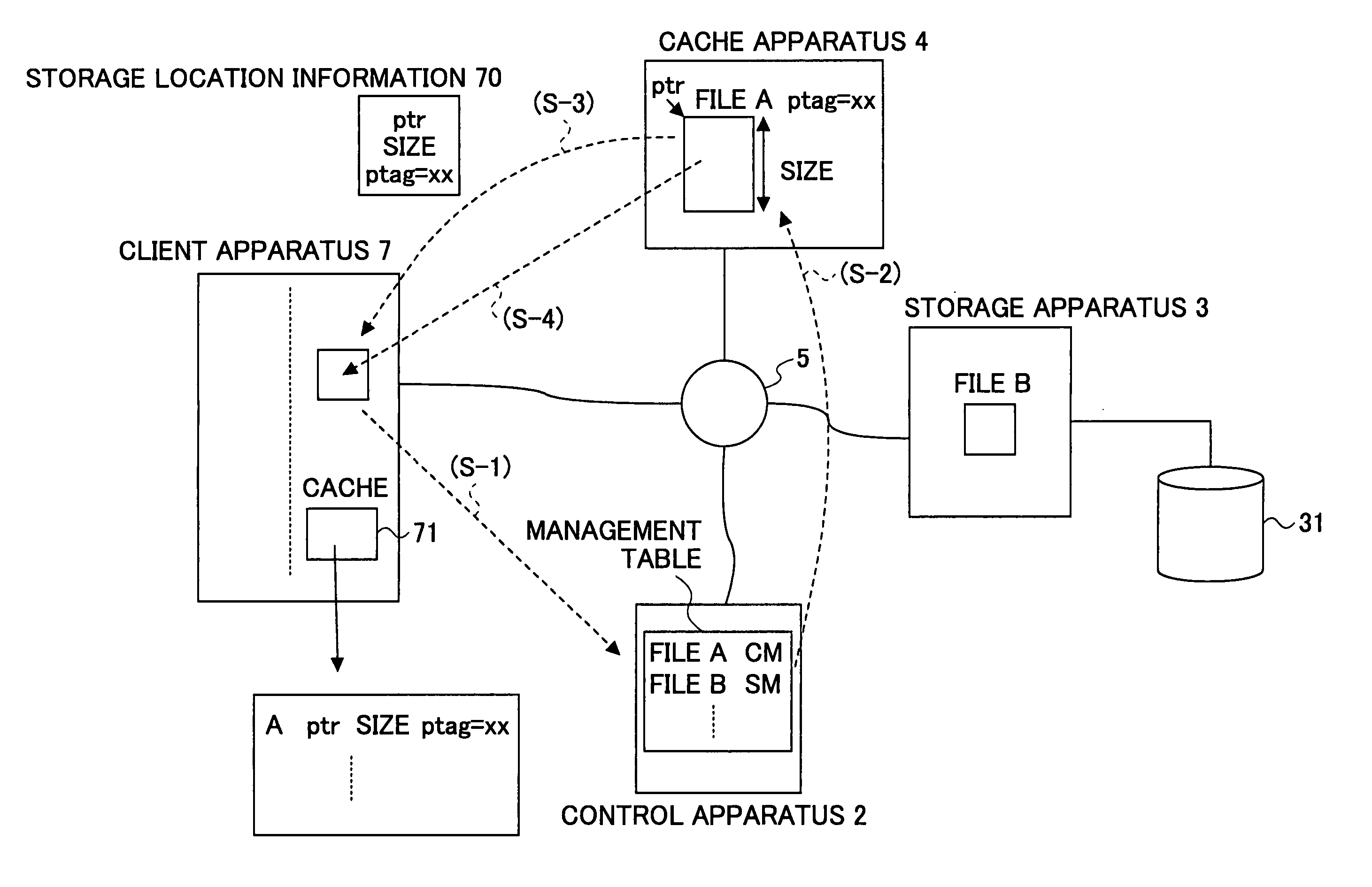
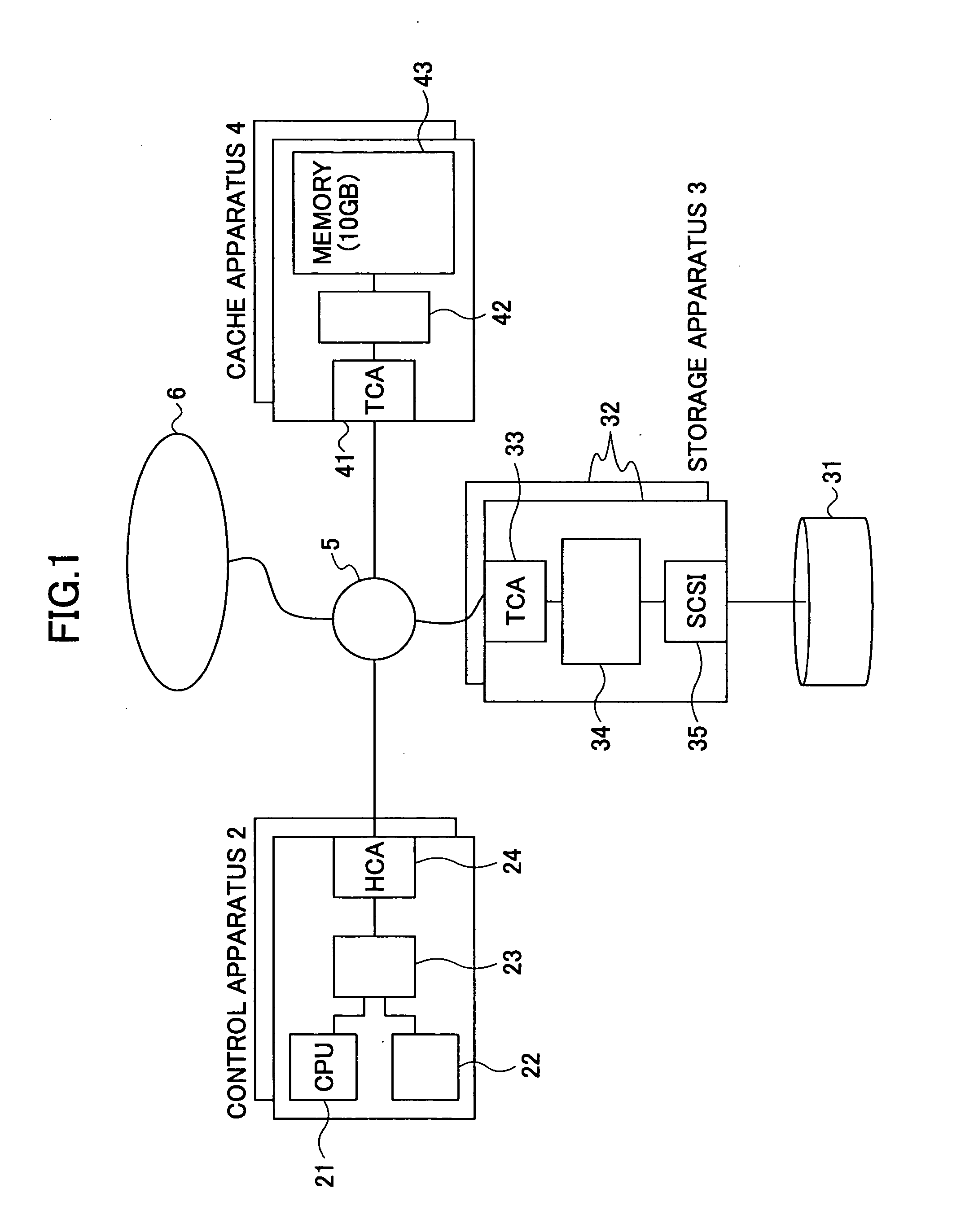
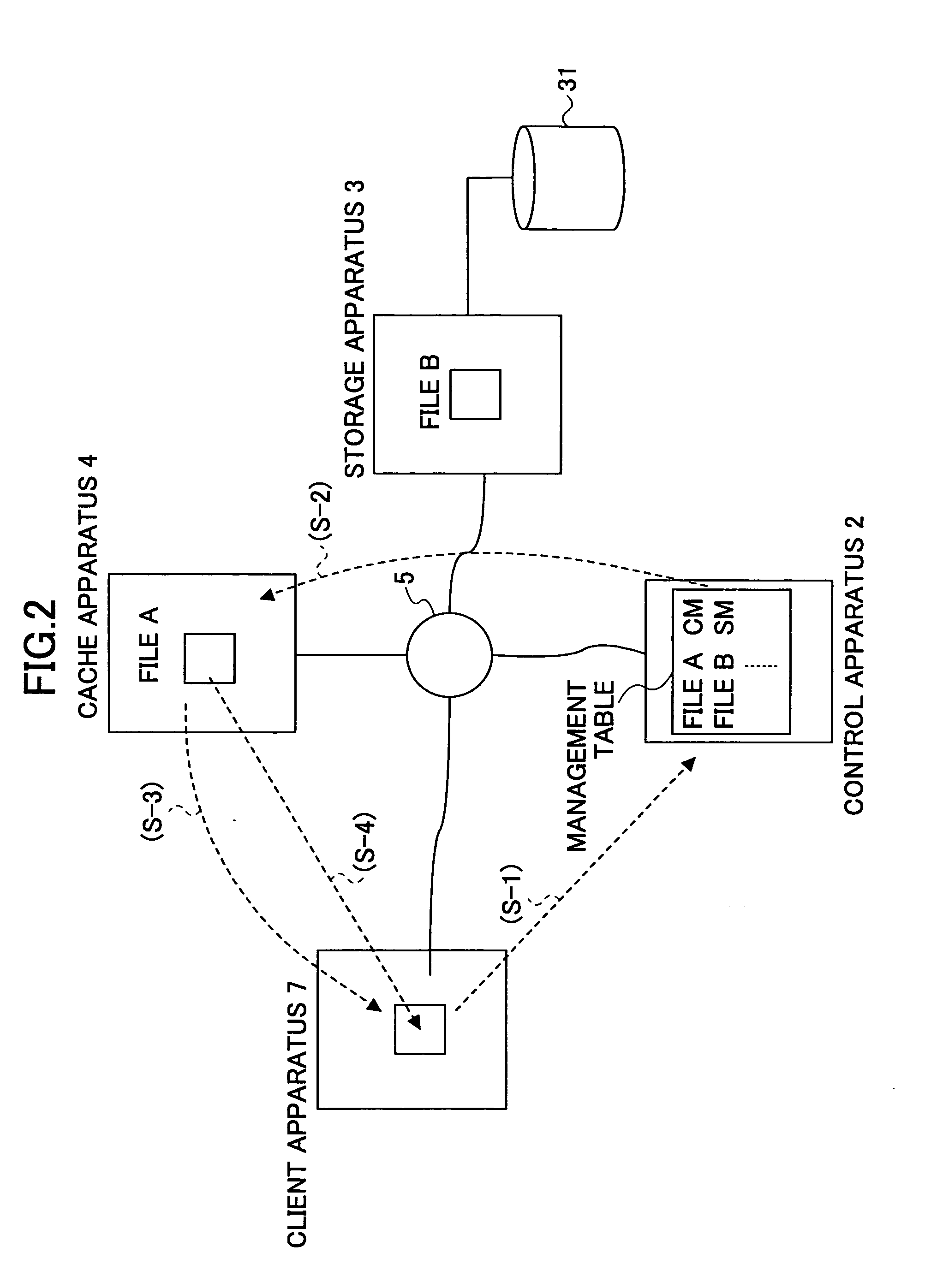
Data access responding system, storage system, client apparatus, cache apparatus, and method for accessing data access responding system
InactiveUS20060041614A1Lower latencyHigh access frequencyMemory architecture accessing/allocationInput/output to record carriersData accessClient-side
A control apparatus provides a transfer instruction to one of storage apparatus and a cache apparatus, in which relevant data is stored, when receiving an access request from a client apparatus for the data for which the storage location is managed; and the one of the storage apparatus and the cache apparatus receiving the transfer instruction directly returns a reply message, to the client apparatus, having information of the storage location of the data added thereto, which data the access request requests.
Owner:FUJITSU LTD
Electrosurgical electrode having a non-conductive porous ceramic coating
ActiveUS7033354B2Minimizing and preventing thermal damageHigh frequencySurgical instruments for heatingCoatingsElectrosurgeryPorous ceramics
An electrosurgical electrode and electrosurgical generator system utilizing the same are disclosed capable of controlling or limiting the current per arc in real-time during an electrosurgical procedure. The conductive electrosurgical electrode is configured for being connected to an electrosurgical generator system and has a non-conductive, porous ceramic coating that “pinches” or splits the arc current generated by the electrosurgical generator system into the smaller diameter pores of the coating, effectively keeping the same current and voltage, but creating several smaller diameter arcs from one larger diameter arc. This has the effect of separating the arc current, effectively increasing the current frequency, resulting in a finer cut or other surgical effect. That is, the non-conductive, porous ceramic coating enables a low frequency current to achieve surgical results indicative of a high frequency current, while minimizing or preventing thermal damage to adjacent tissue.
Owner:COVIDIEN AG
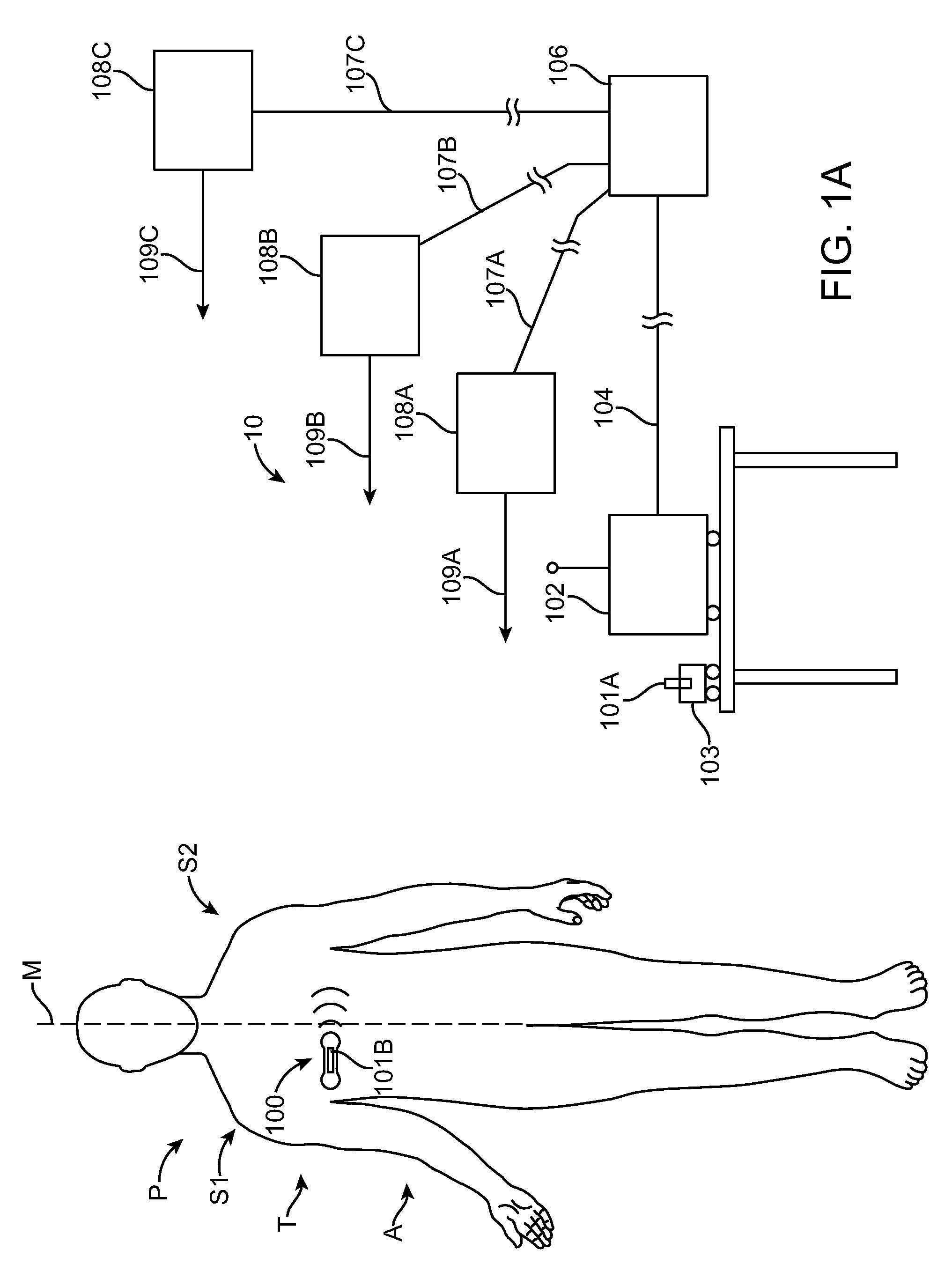
Method and Apparatus to Measure Bioelectric Impedance of Patient Tissue
ActiveUS20090264792A1Time-consume to manufactureMinimizing memory resourceElectrocardiographyAuscultation instrumentsEngineeringBioelectric Impedance
A device to measure tissue impedance comprises drive circuitry coupled to calibration circuitry, such that a calibration signal from the calibration circuitry corresponds to the current delivered through the tissue. Measurement circuitry can be coupled to measurement electrodes and the calibration circuitry, such that the tissue impedance can be determined in response to the measured calibration signal from the calibration circuitry and the measured tissue impedance signal from the measurement electrodes. Processor circuitry comprising a tangible medium can be configured to determine a complex tissue impedance in response to the calibration signal and the tissue impedance signal. The processor can be configured to select a frequency for the drive current, and the amount of drive current at increased frequencies may exceed a safety threshold for the drive current at lower frequencies.
Owner:MEDTRONIC MONITORING
Data communications systems and methods using different wireless links for inbound and outbound data
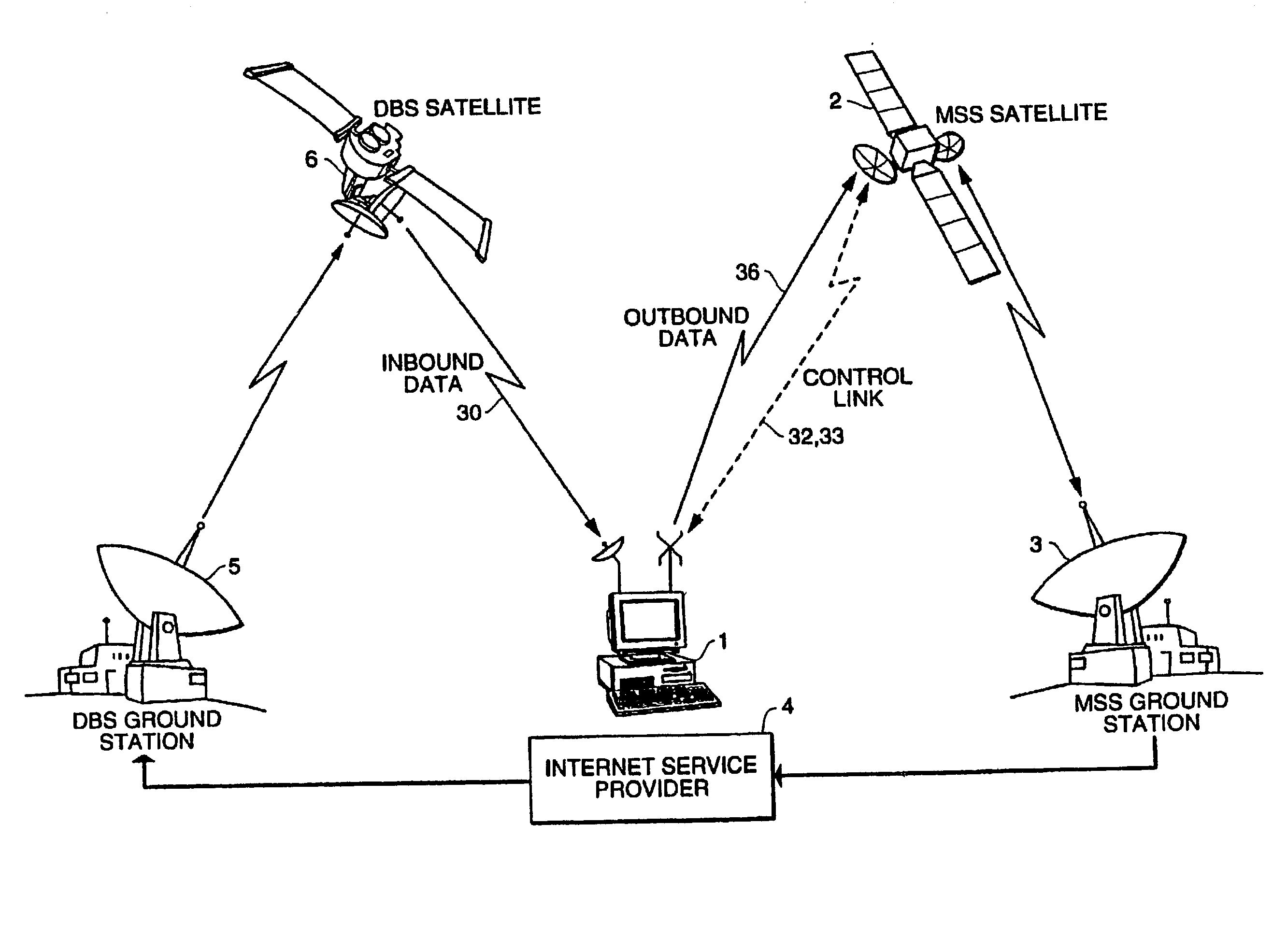
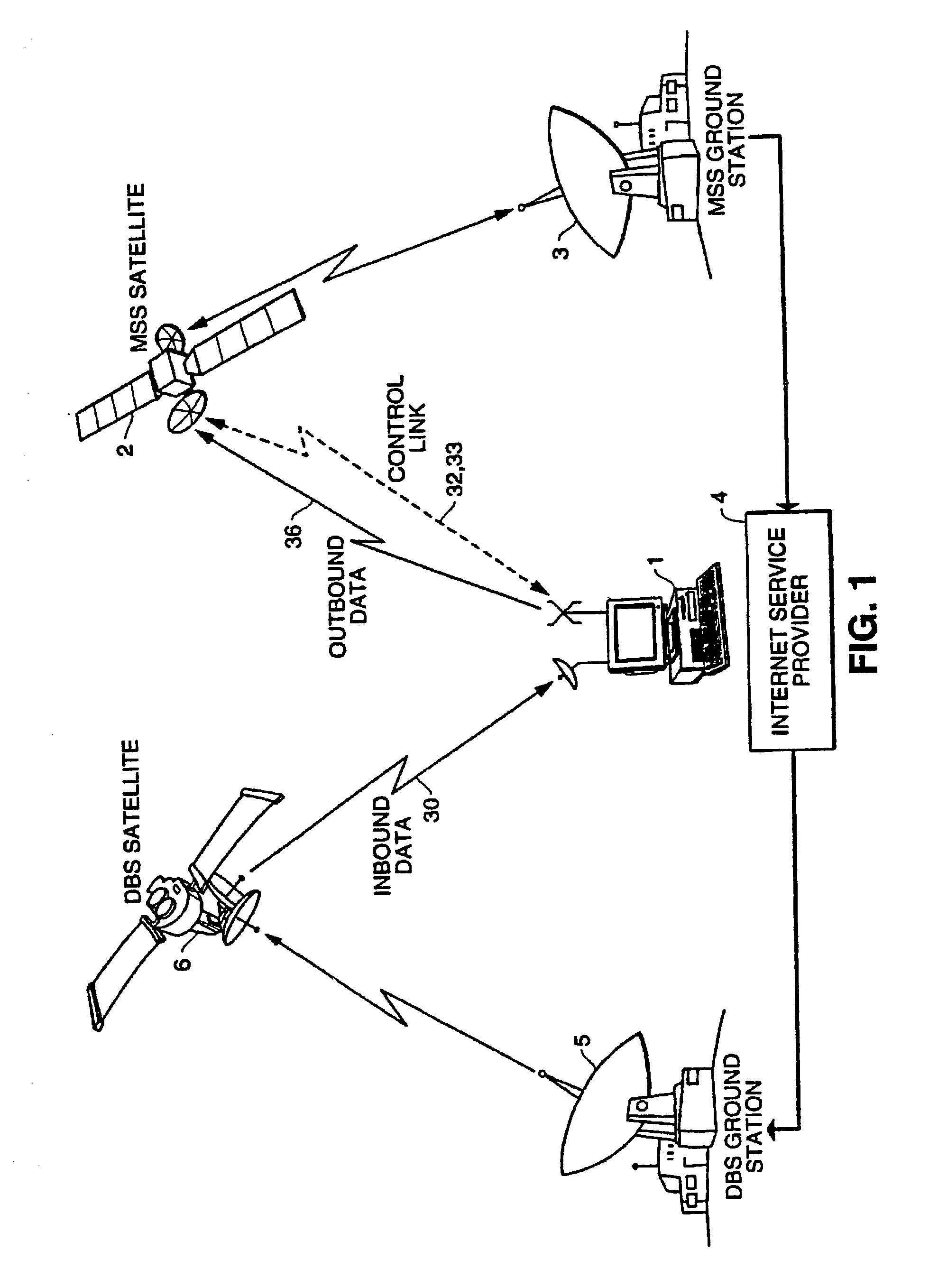
InactiveUS7174127B2High frequencyRadio/inductive link selection arrangementsRadio transmissionSatelliteTransceiver
A hybrid satellite communications system provides communications, particularly Internet access, to computer users. The hybrid satellite communications system includes a satellite system and a terrestrial communications system. The satellite system includes two transceivers. The first transceiver receives and transmits a first set of signals received from the terrestrial communications system to a plurality of user units. In reverse fashion, the satellite systems second transceiver receives a second set of signals in a second frequency band from the user units and transmits those signals back to the terrestrial communications system. The first set of signals (downlink signals) are of much higher frequency than the second set of signals (uplink signals). Preferably, the first set of signals are relayed by a Direct Broadcast System (DBS) satellite in a frequency band between 12.2 GHz and 12.9 GHz, while the second set of signals are relayed by a Mobile Satellite System (MSS) satellite operating between 1.0 GHz and 3.0 Ghz, or relayed by a terrestrial node operating between 0.8 and 2.0 Ghz. The differences in frequency between the first set of signals and second set of signals is considered optimal for the transmission and receipt of communications between a computer user with the Internet. Moreover, the present invention is capable of using the present communications infrastructures dedicated to the satellite transmission of television via DBS satellites, satellite cellular communications via MSS satellites, and radio communications via terrestrial cellular systems.
Owner:ATC TECH LLC
Method and apparatus to measure bioelectric impedance of patient tissue
ActiveUS8412317B2Minimizing memory resourceReduce gainElectrocardiographyAuscultation instrumentsDriving currentPower flow
A device to measure tissue impedance comprises drive circuitry coupled to calibration circuitry, such that a calibration signal from the calibration circuitry corresponds to the current delivered through the tissue. Measurement circuitry can be coupled to measurement electrodes and the calibration circuitry, such that the tissue impedance can be determined in response to the measured calibration signal from the calibration circuitry and the measured tissue impedance signal from the measurement electrodes. Processor circuitry comprising a tangible medium can be configured to determine a complex tissue impedance in response to the calibration signal and the tissue impedance signal. The processor can be configured to select a frequency for the drive current, and the amount of drive current at increased frequencies may exceed a safety threshold for the drive current at lower frequencies.
Owner:MEDTRONIC MONITORING
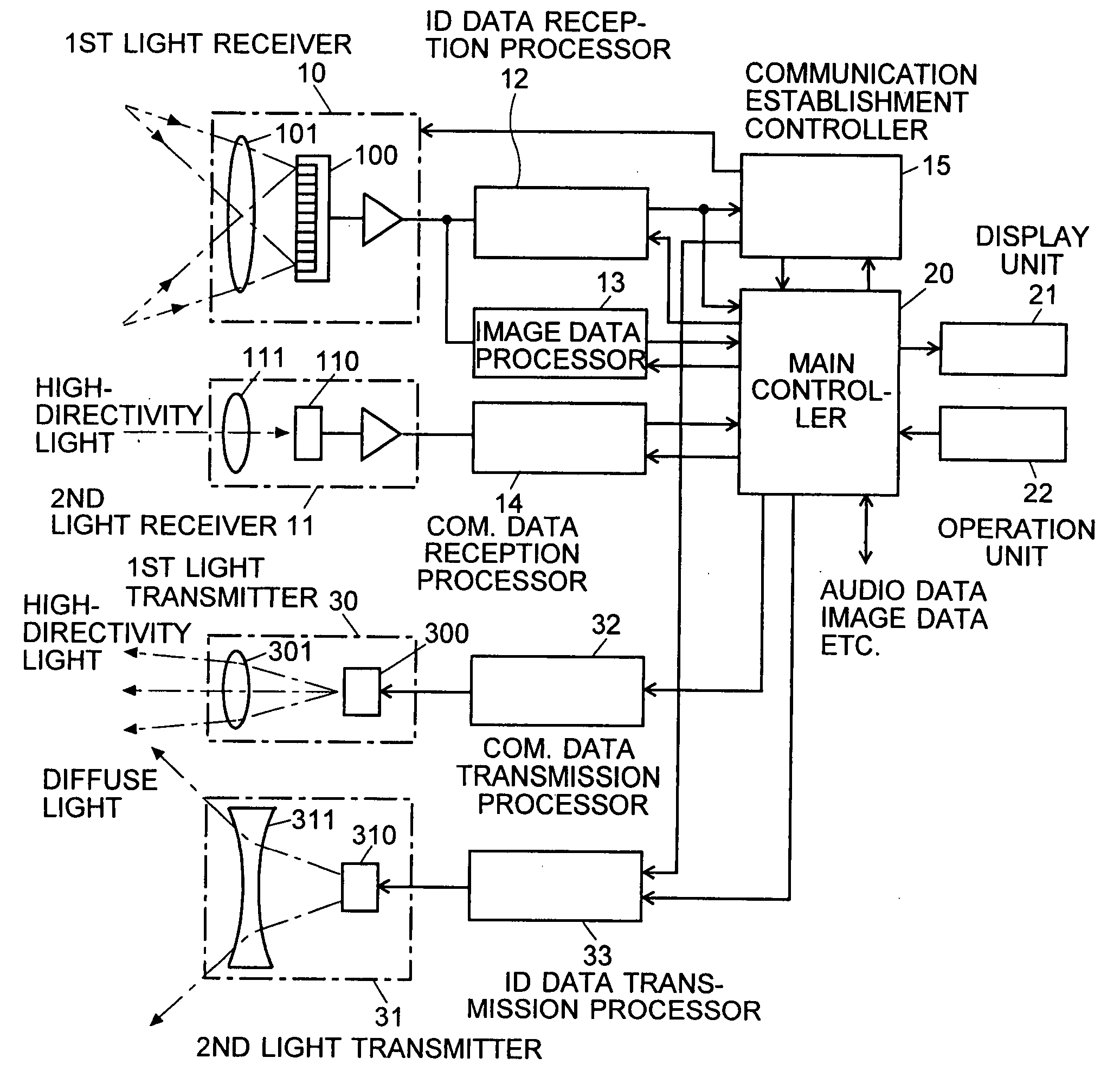
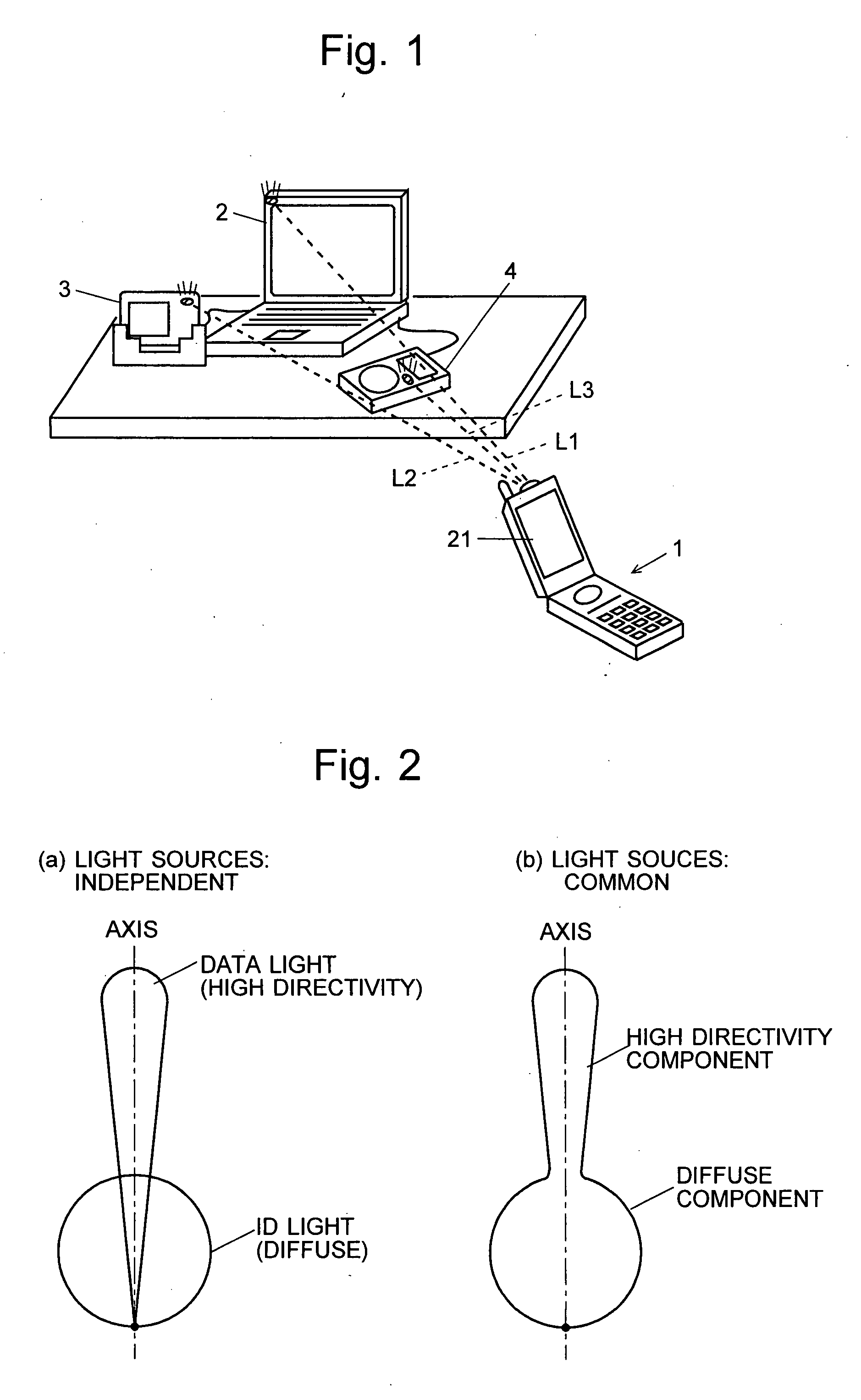
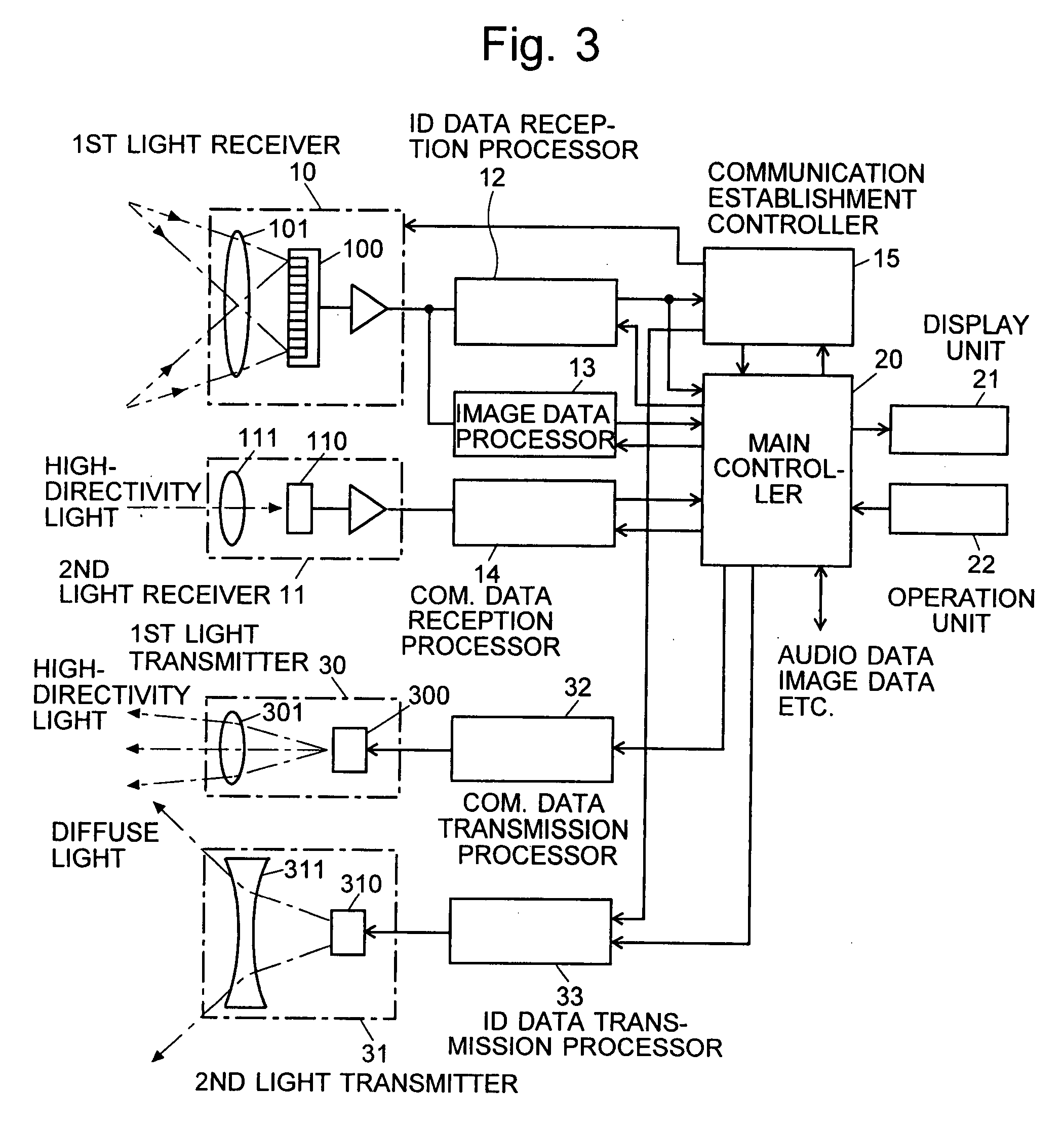
Information-Processing System Using Free-Space Optical Communication and Free-Space Optical Communication System
InactiveUS20080044188A1Suppress power consumptionSmall sizeNetwork topologiesConnection managementLight sourceHigh frequency
In a system for data communication between an information terminal to be operated by a user and remote communication nodes, the present invention intends to suppress the power consumption of the information terminal. For that purpose, communication nodes 2, 3 and 4 each emit diffuse light carrying a pilot signal blinking at a low frequency to notify the presence of the communication node and an ID signal belonging to a higher frequency range, the ID signal containing inherent address etc. for identifying each communication node. A mobile phone 1 as the information terminal captures an image and processes the image data to detect the pilot signal of each communication node. Then, determining the position of each node and setting a limited range for reading the pixels around that position, the mobile phone 1 reads the detection signals of the pixels within the limited range at high speed and obtains identification information. This information is used to identify each node and eliminate influences of any other light source that apparently resembles the pilot signal.
Owner:JAPAN SCI & TECH CORP +1
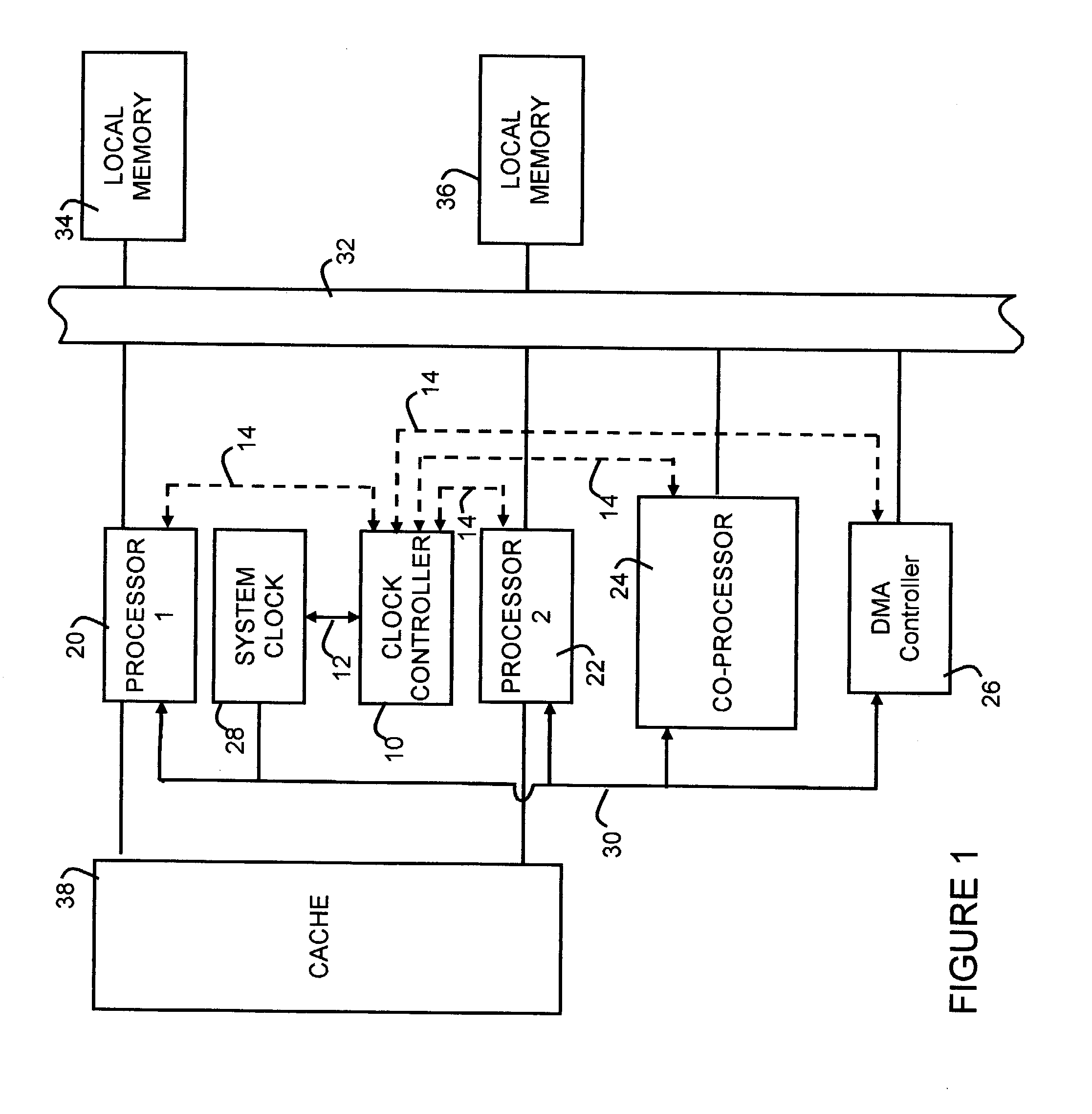
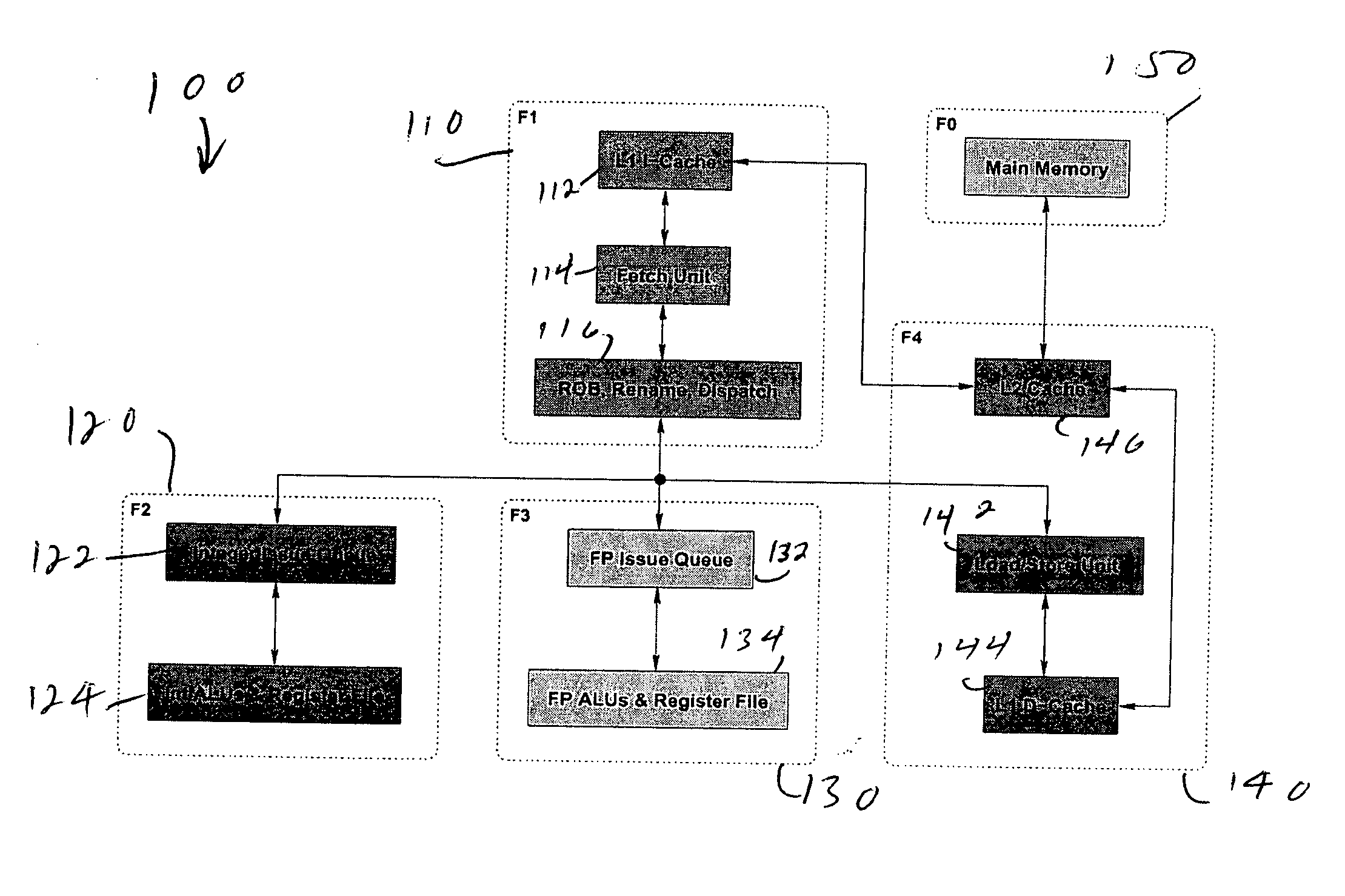
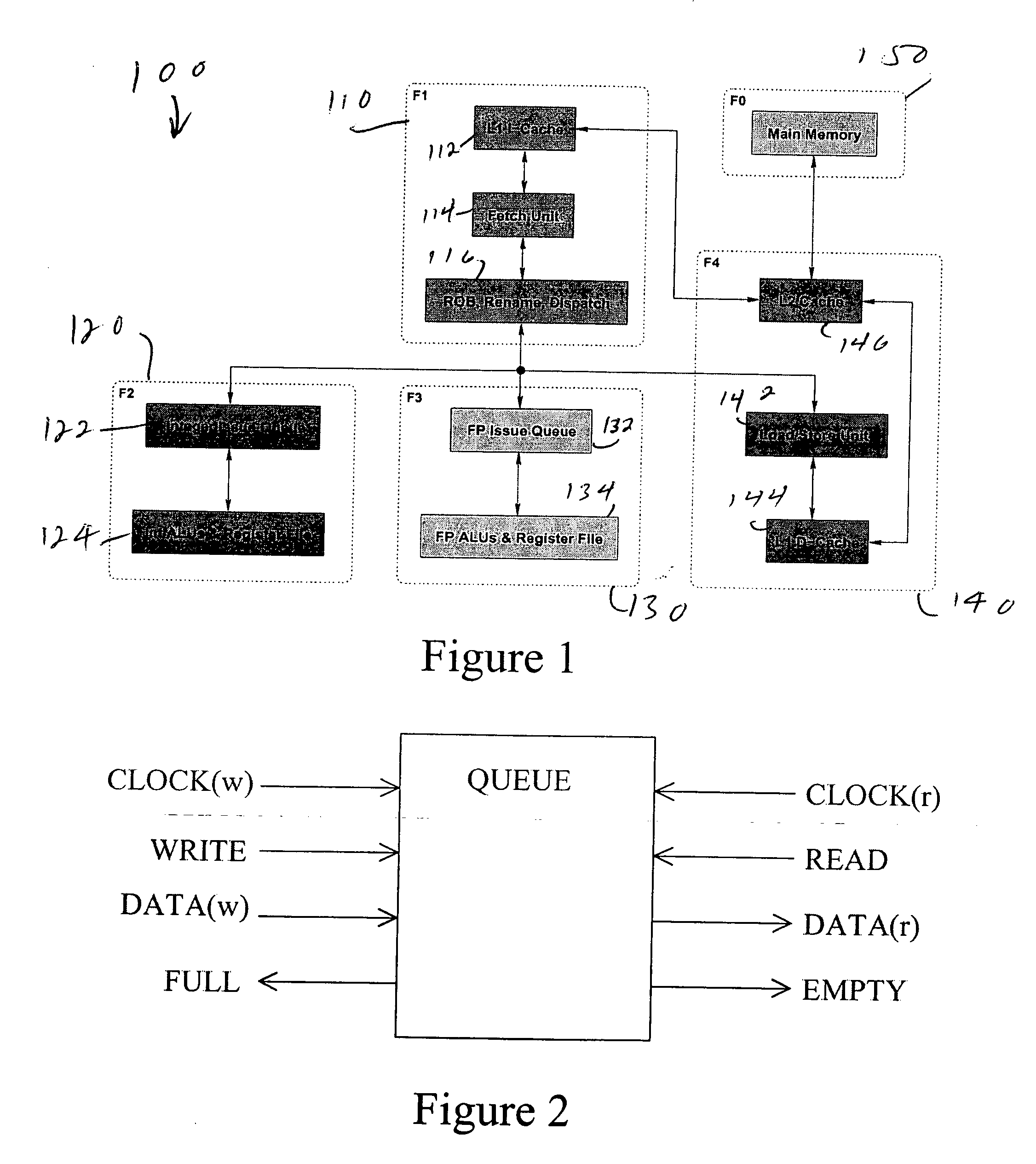
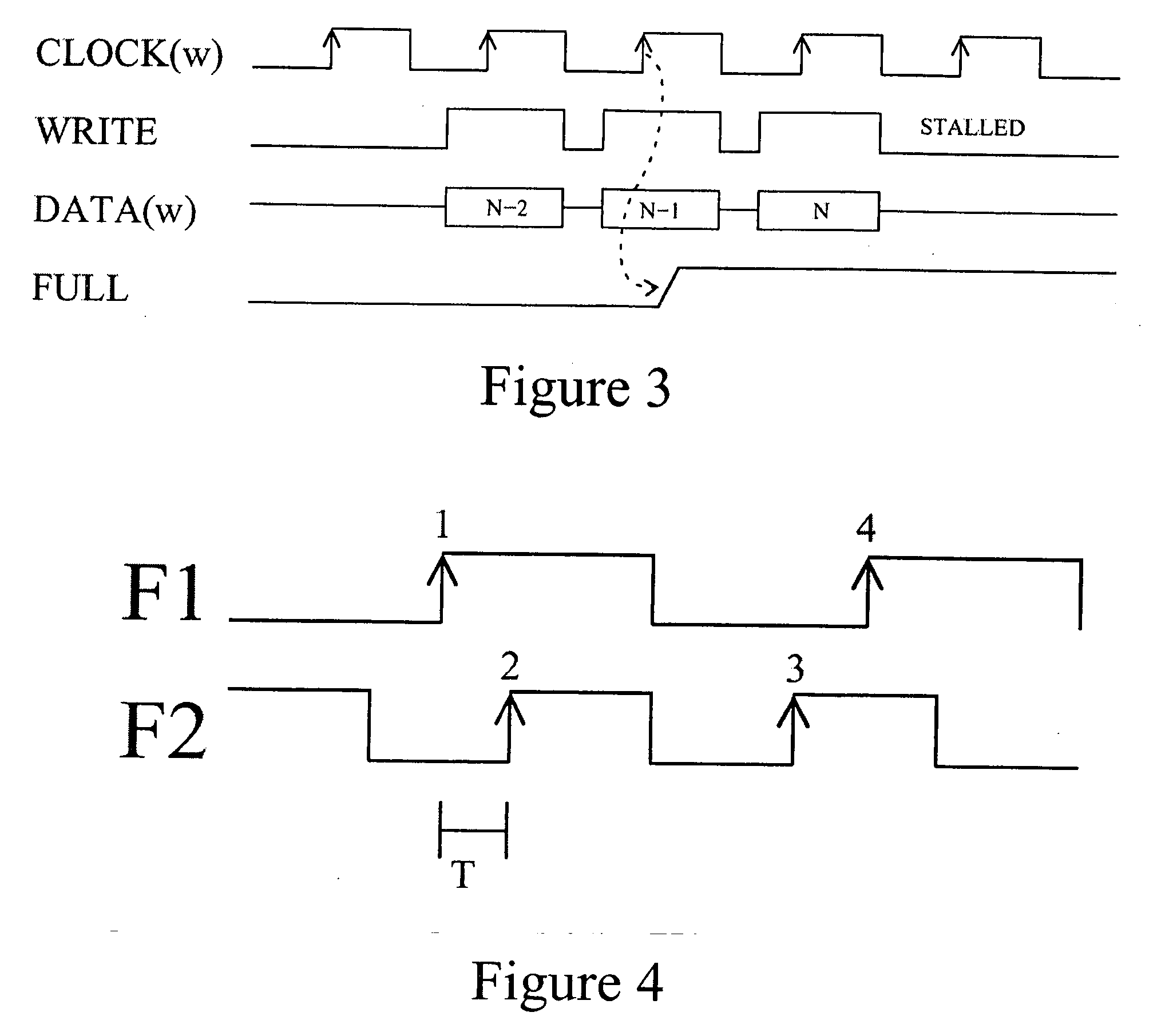
Multiple clock domain microprocessor
ActiveUS20070016817A1High frequencyImprove good performanceEnergy efficient ICTPower supply for data processingComputer scienceInter-domain
A multiple clock domain (MCD) microarchitecture uses a globally-asynchronous, locally-synchronous (GALS) clocking style. In an MCD microprocessor each functional block operates with a separately generated clock, and synchronizing circuits ensure reliable inter-domain communication. Thus, fully synchronous design practices are used in the design of each domain.
Owner:ALBONESI DAVID +5
Vapor deposition reactor
InactiveUS8333839B2Improve deposition efficiencyShorten the timeChemical vapor deposition coatingMicrowaveRemote plasma
A vapor deposition reactor has a configuration where a substrate or a vapor deposition reactor moves in a non-contact state with each other to allow the substrate to pass by the reactor and an injection unit and an exhaust unit are installed as a basic module of the reactor for receiving a precursor or a reactant and for receiving and pumping a purge gas, respectively. With the use of a small-size inlet for the reactor, homogeneous film properties are obtained, the deposition efficiency of precursors is improved, and an amount of time required for a purge / pumping process can be reduced. In addition, since the reactor itself is configured to reflect each step of ALD, it does not need a valve. Moreover, the reactor makes it easier for users to apply remote plasma, use super high frequencies including microwave, and UV irradiation.
Owner:VEECO ALD
Pluggable module and receptacle
InactiveUS6517382B2High frequencyHighly miniaturizedMagnetic/electric field screeningContact members penetrating/cutting insulation/cable strandsElectrical connectionConductive materials
A receptacle for a pluggable module includes a housing having a front, a back wall, a top wall, a bottom wall, and side walls and defining a cavity for receiving a module. The bottom wall has a bottom opening to receive a receptacle connector, and the front has a front opening to receive the module. The walls of the housing are made from a conductive material. A plurality of elongated members extend down from the housing past the bottom wall. The elongated members are adapted for electrical connection to a host circuit board such that the walls of the housing are electrically connected to the host circuit board.
Owner:TE CONNECTIVITY CORP
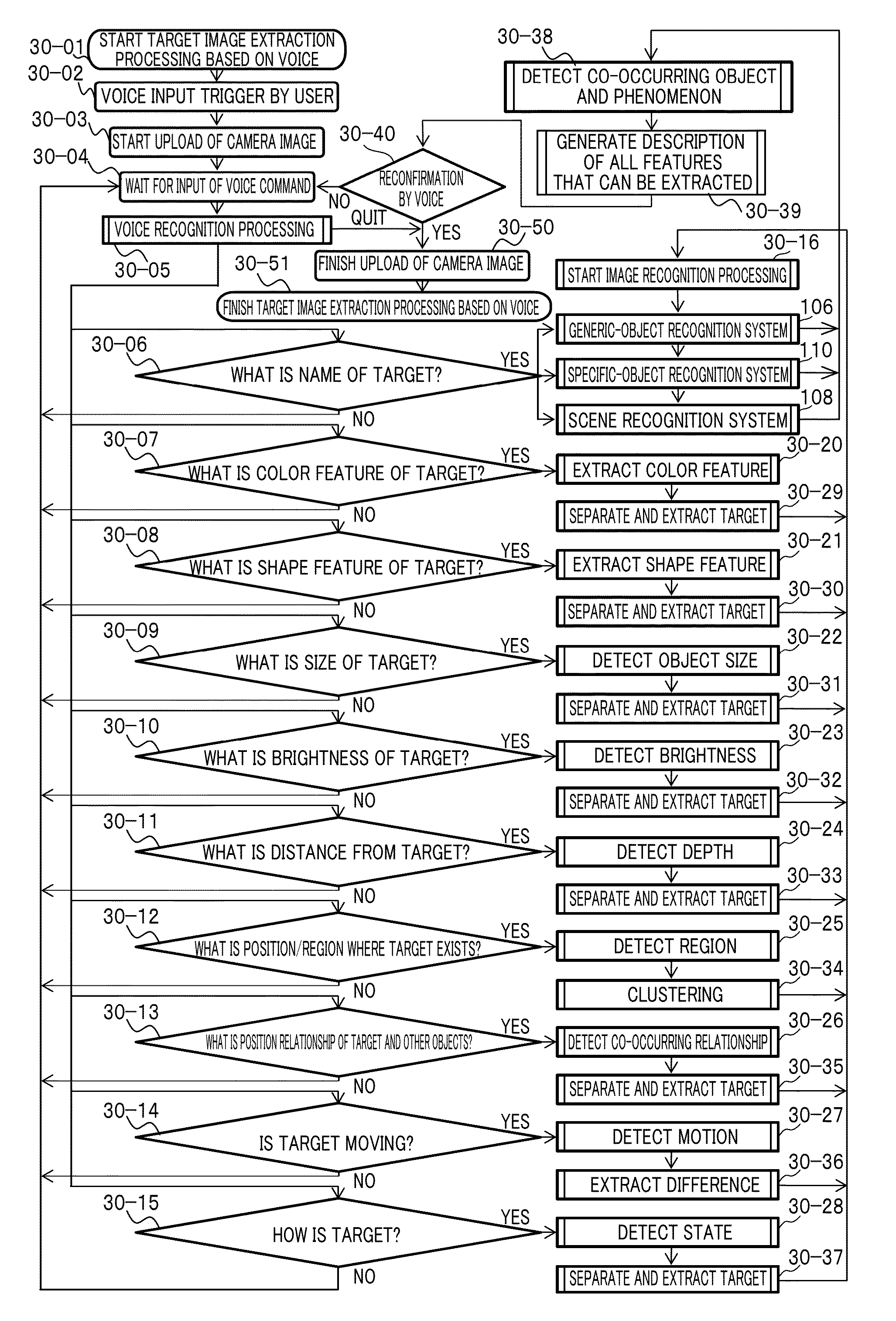
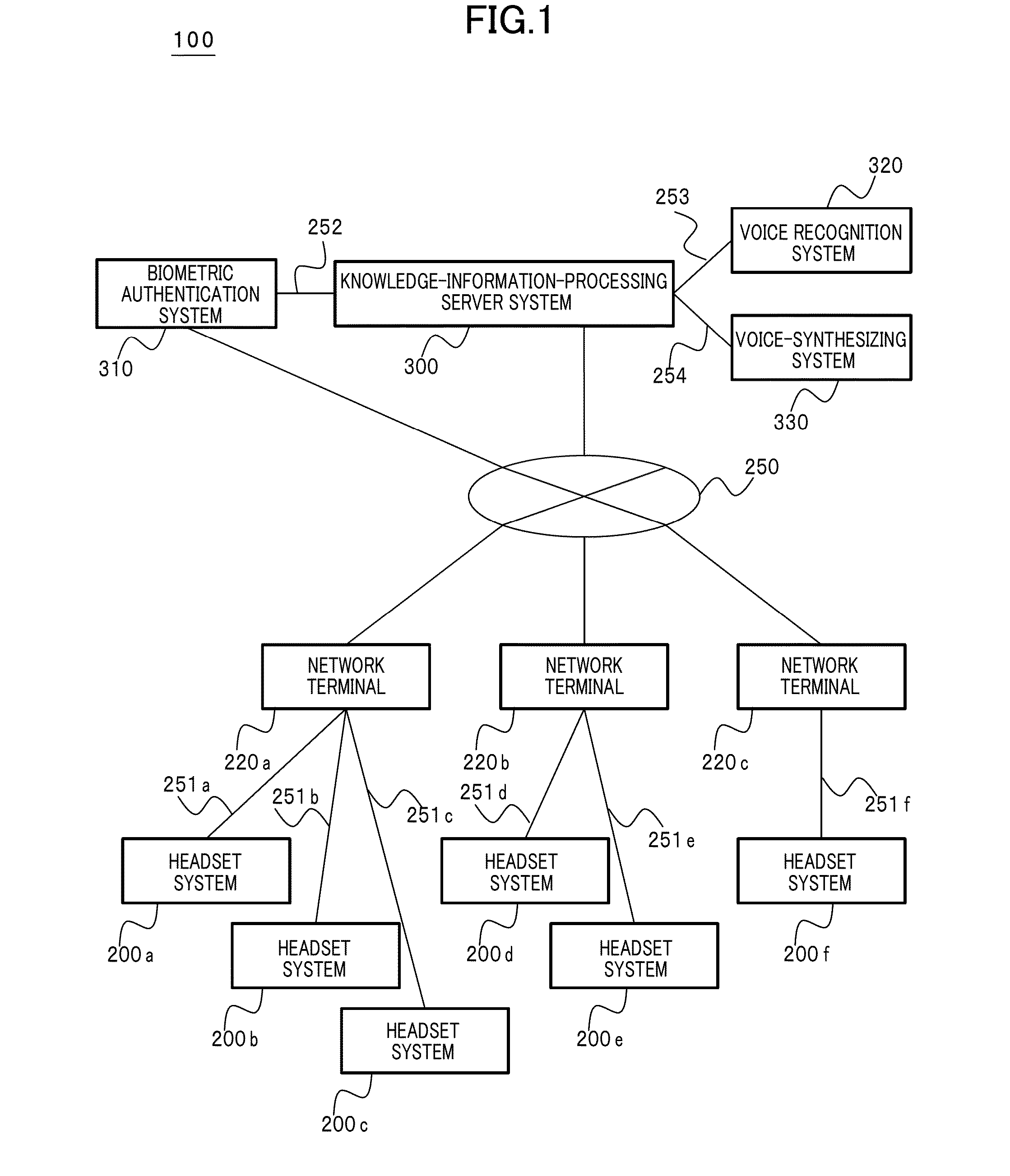
Knowledge-information-processing server system having image recognition system
InactiveUS20140289323A1Improve image recognition rateHigh frequencyData processing applicationsDigital data information retrievalNetwork terminationInformation processing
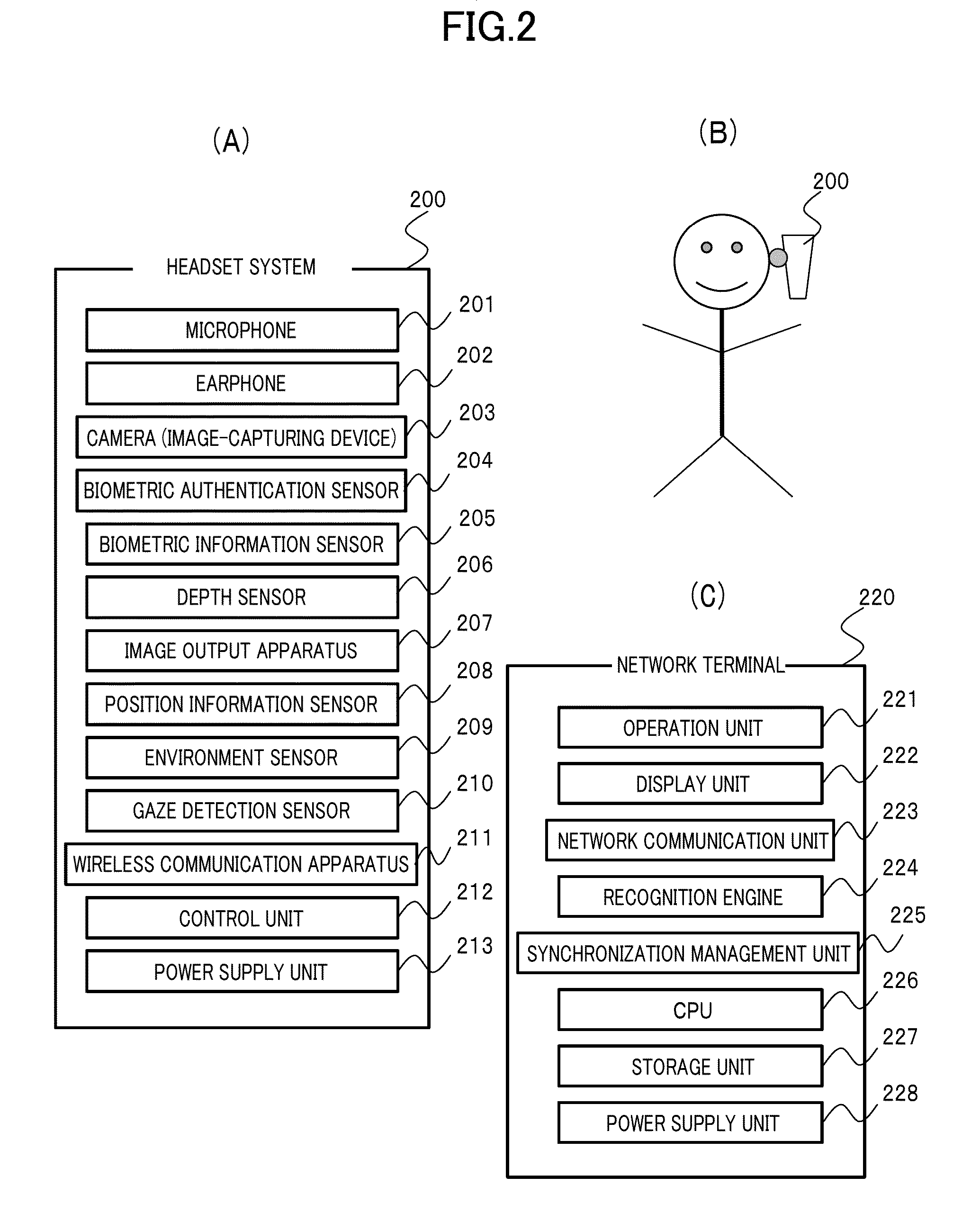
Extensive social communication is induced. Connection is made with a network terminal capable of connecting to the Internet, and an image and voice signal reflecting the subjective visual field of the user and the like which can be obtained from the headset system that can be worn by the user on the head is uploaded via the network terminal to a knowledge-information-processing server system, and specifying and selecting of an attention-given target by the voice of the user himself / herself are enabled on the server system with collaborative operation with the voice recognition system with regard to a specific object and the like to which the user gives attention and which is included in the image, and with regard to the series of image recognition processes and image recognition result made by the user, image recognition result and recognition processes thereof are notified as voice information to an earphone incorporated into the headset system of the user by way of the user's network terminal via the Internet by the server system with collaborative operation with a voice-synthesizing system, so that user's message or tweet can be extensively shared by users.
Owner:CYBER AI ENTERTAINMENT
End-to-end design of superresolution electro-optic imaging systems
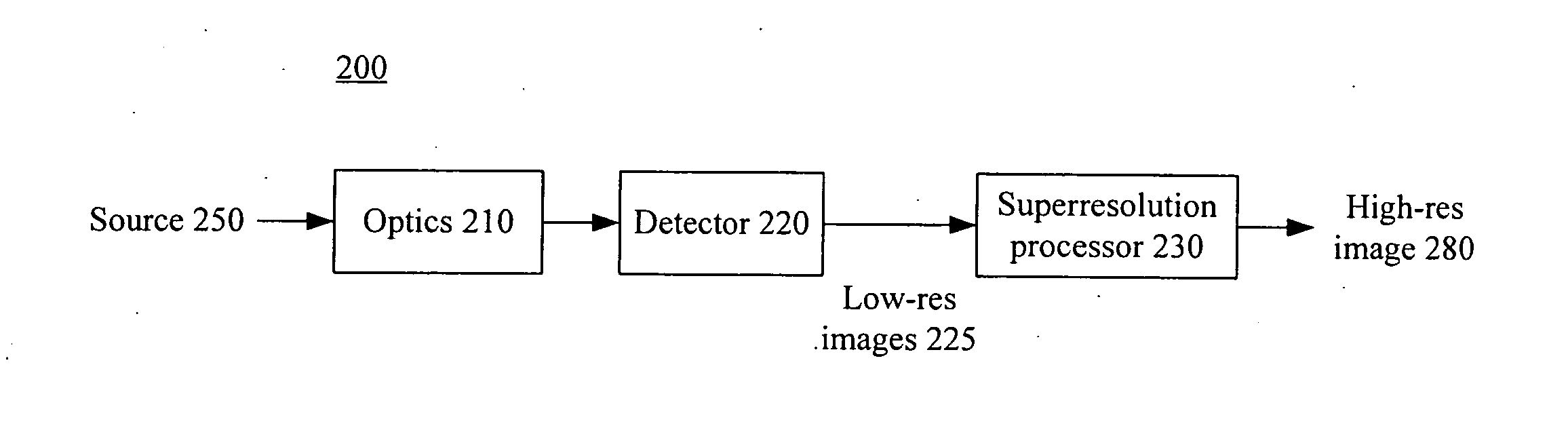
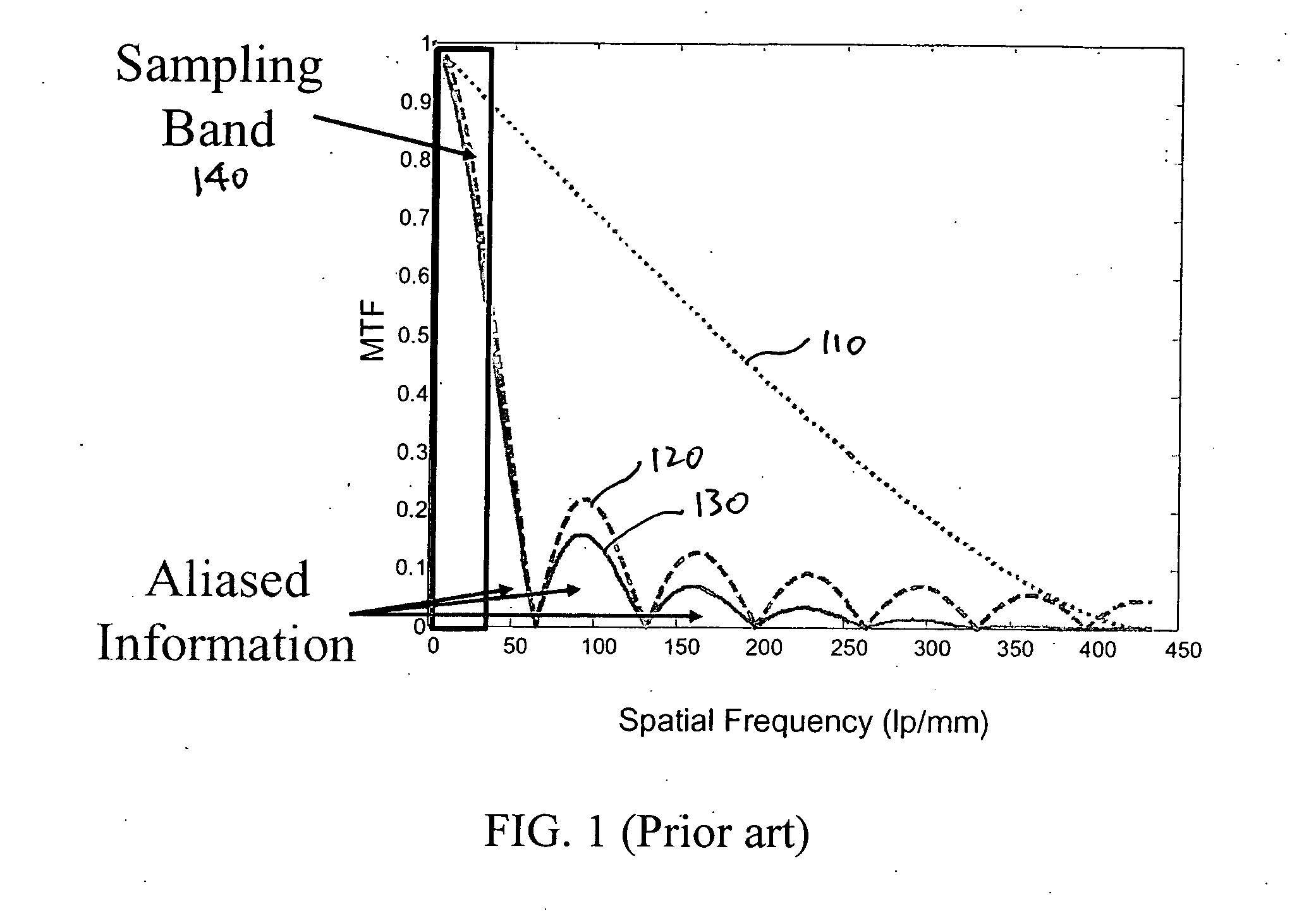
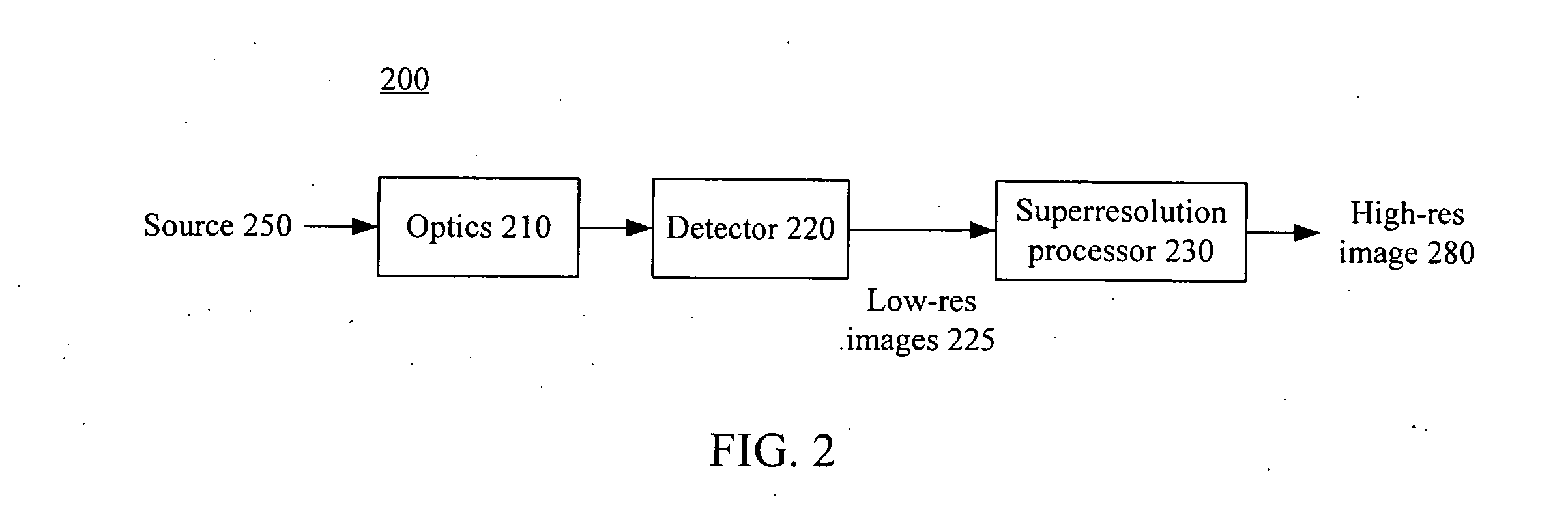
ActiveUS20070268374A1Reduces aliasing effectOvercome limitationsTelevision system detailsTelevision system scanning detailsEngineeringElectro-optics
A superresolution electro-optic imaging system operates in a manner that takes into account the different subsystems. For example, rather than designing the optical subsystem to be diffraction-limited, the optical subsystem can be designed in a manner that is better suited for subsequent superresolution processing and / or that reduces aliasing effects.
Owner:RICOH KK
Providing enhanced haptic feedback effects
InactiveUS7218310B2Enhanced tactile sensationStrong tactile effectInput/output for user-computer interactionCathode-ray tube indicatorsTactile sensationEngineering
Method and apparatus for providing high strength, low frequency tactile sensations using an inertial actuator in a haptic feedback interface device, such as an actuator driving an oscillating inertial mass. A commanded low frequency is modulated or combined with a higher frequency at which the tactile sensations feel stronger, where the resulting signal is used to output a tactile sensation at the higher frequency and convey the commanded low frequency to the user. One embodiment provides higher frequency pulse bursts at the desired low frequency wherein the higher frequency pulse bursts are at or near a resonant frequency of the actuator; other embodiments modulate or otherwise vary the amplitude of the higher frequency signal according to the desired low frequency.
Owner:IMMERSION CORPORATION
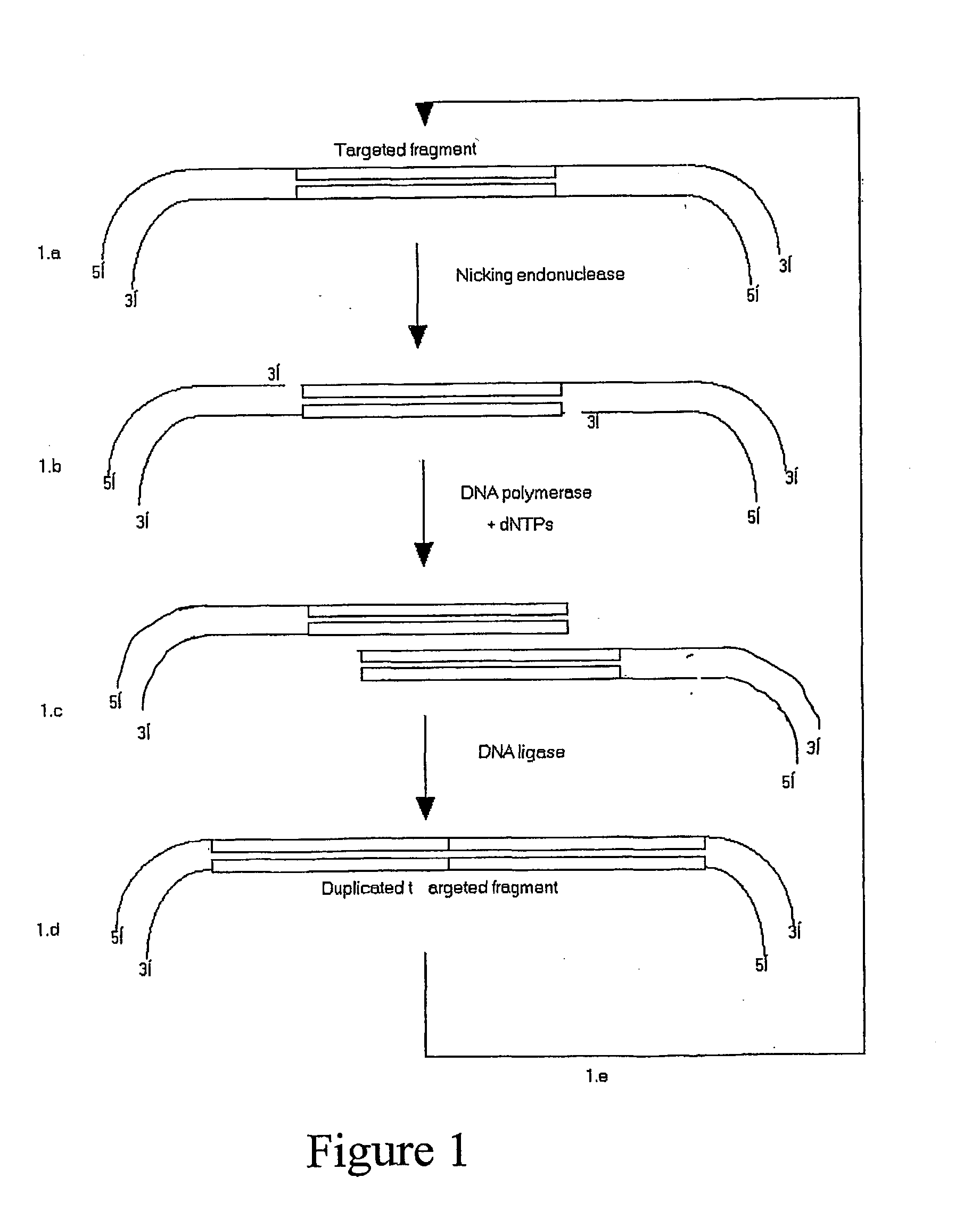
Concatenated nucleic acid sequence
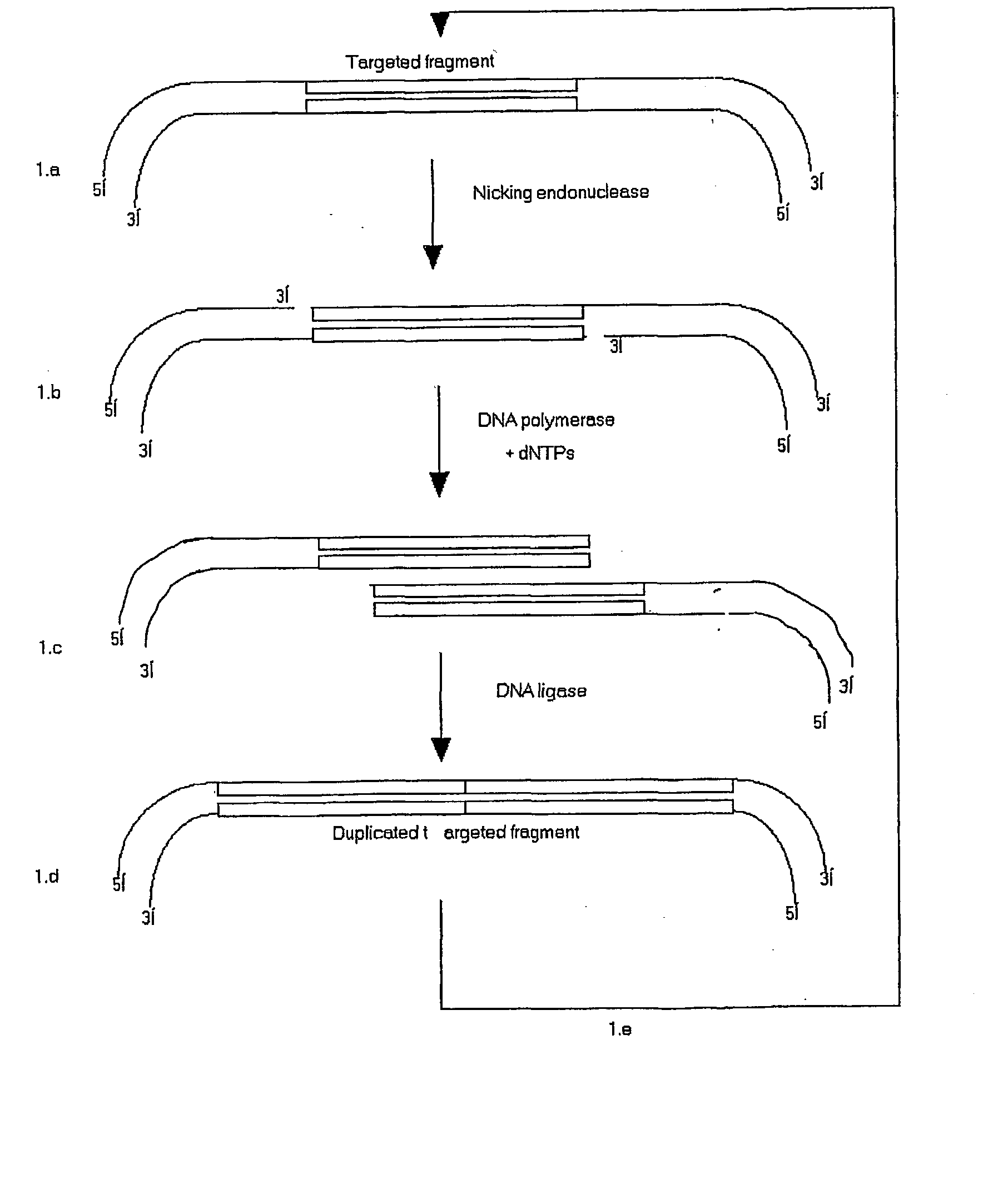
InactiveUS20040009507A1High frequencyDesigning can be facilitatedSugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementNucleic acid sequencingDNA
An in vitro method for constructing a concatenated head-to-tail repertoire of target nucleic acid sequences is revealed. In particular, the method relates to cycles of concatenation whereby after a single cycle of concatenation, not more than two identical copies of each target nucleic acid sequence are linked together head-to-tail on the same molecule of DNA. The present method ensures that each molecule of a concatenated repertoire is derived from a single template target sequence of the starting repertoire.
Owner:DORMANTIS LTD
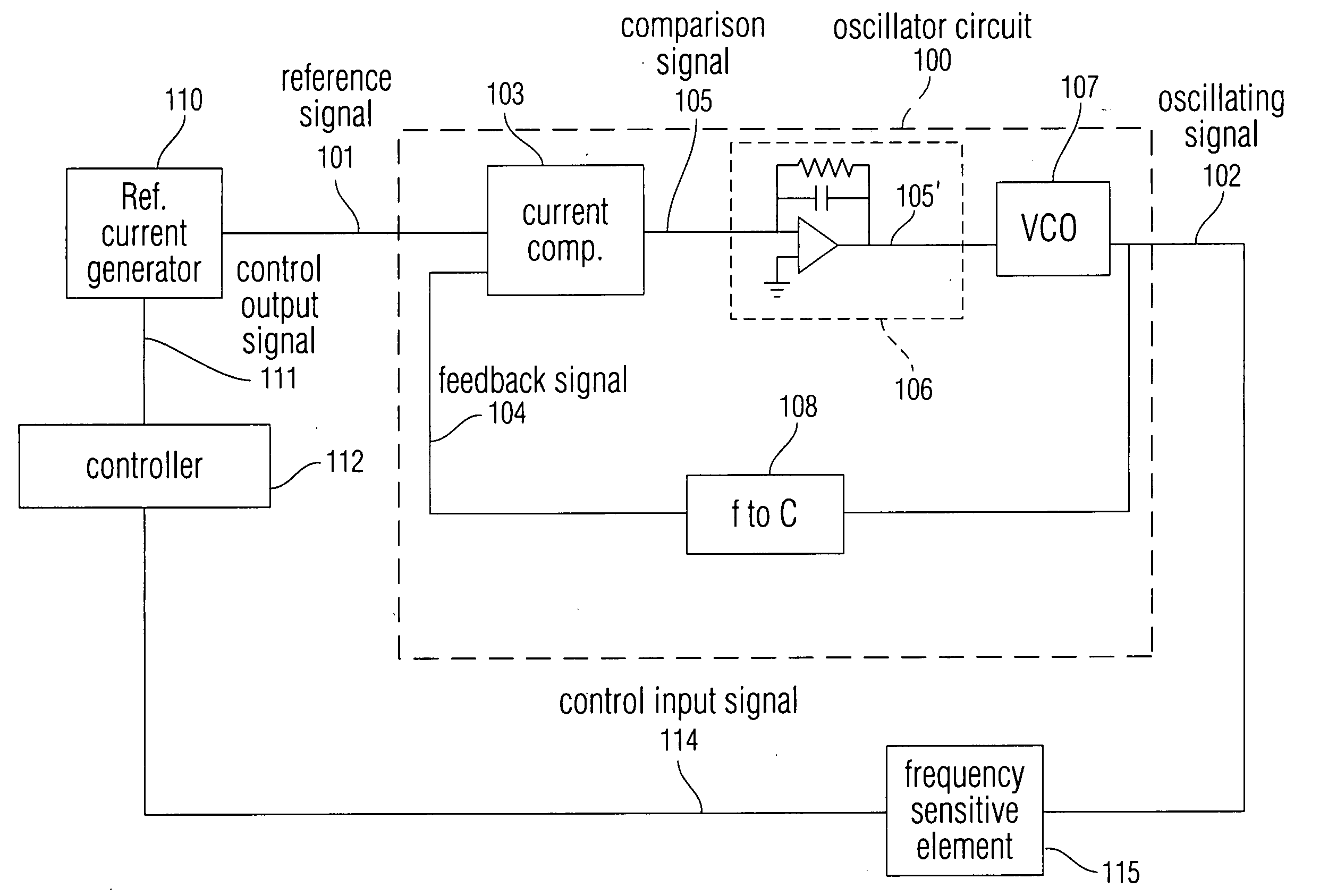
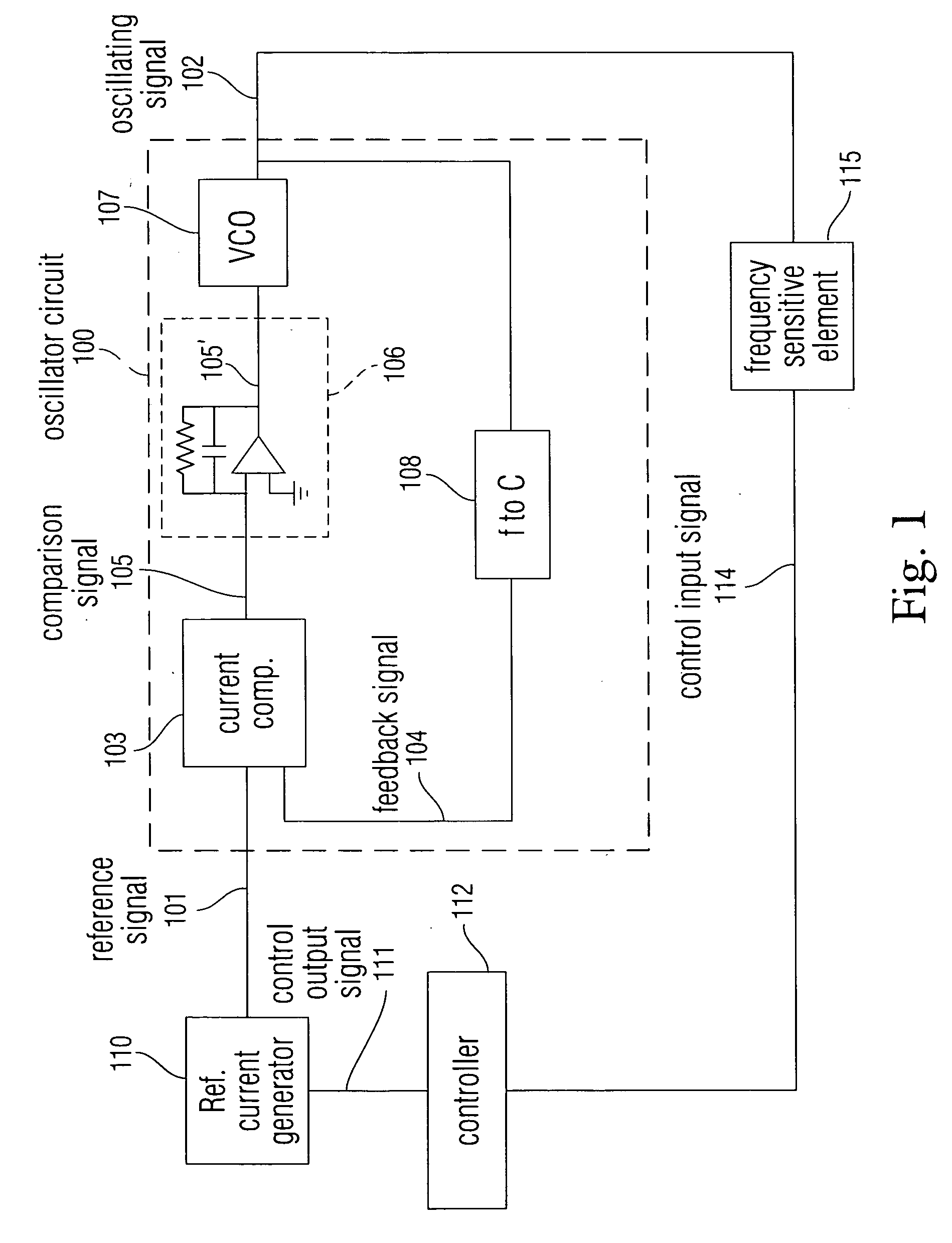
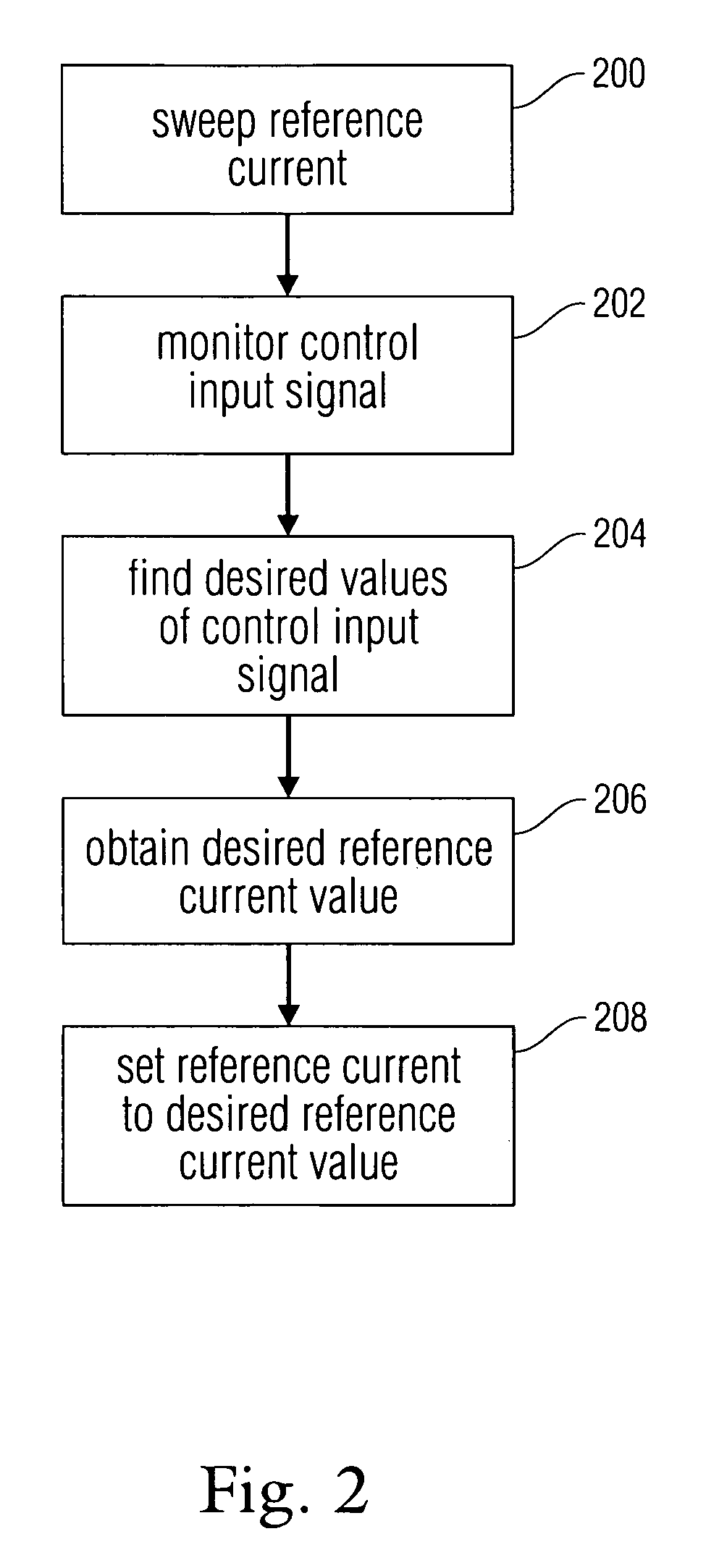
Noise reduction within an electronic device using automatic frequency modulation
ActiveUS20080157893A1High frequencyLimitation to input signalPulse automatic controlFrequency analysisEngineeringNoise reduction
Disclosed is a system and method for providing an oscillating signal of relatively precise frequency without using a signal provided by a crystal as a reference. Disclosed is a feedback oscillator circuit configured to output an oscillating signal having a frequency defined by a reference signal. The oscillating signal can be sent to one or more circuits including at least one frequency sensitive element. The frequency sensitive element produces an output signal which depends on the frequency of the oscillating signal. A controller controls the reference signal in order to cause an attribute of the output signal to have a value within a desired range.
Owner:APPLE INC
Multi-sector in-building repeater
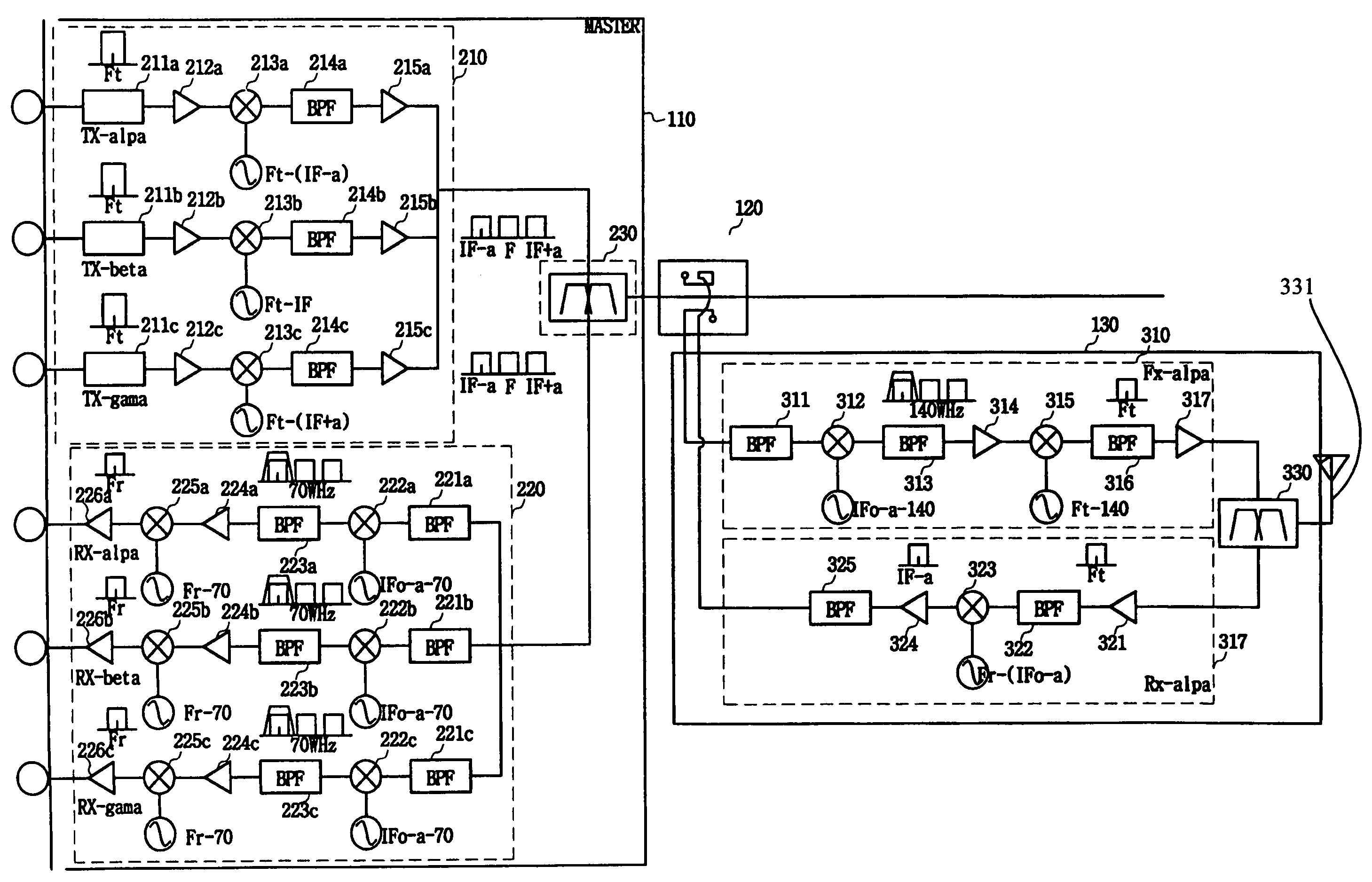
InactiveUS7272362B2Maximize transfer efficiencyHigh frequencyPower distribution line transmissionRepeater/relay circuitsIntermediate frequencyCarrier signal
A multi-sector in-building repeater, including: a master transmitting unit for receiving multi-sector signals of a carrier from a base station, mixing the multi-sector signals with different transmission intermediate frequency signals, and outputting mixed multi-sector signals to a same transmission line; a plurality of slave transmitting units for extracting sector signals assigned to the multi-sector signals from the master transmitting unit, converting extracted sector signals into high frequency signals, and transmitting converted high frequency signals through an antenna to a mobile terminal.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
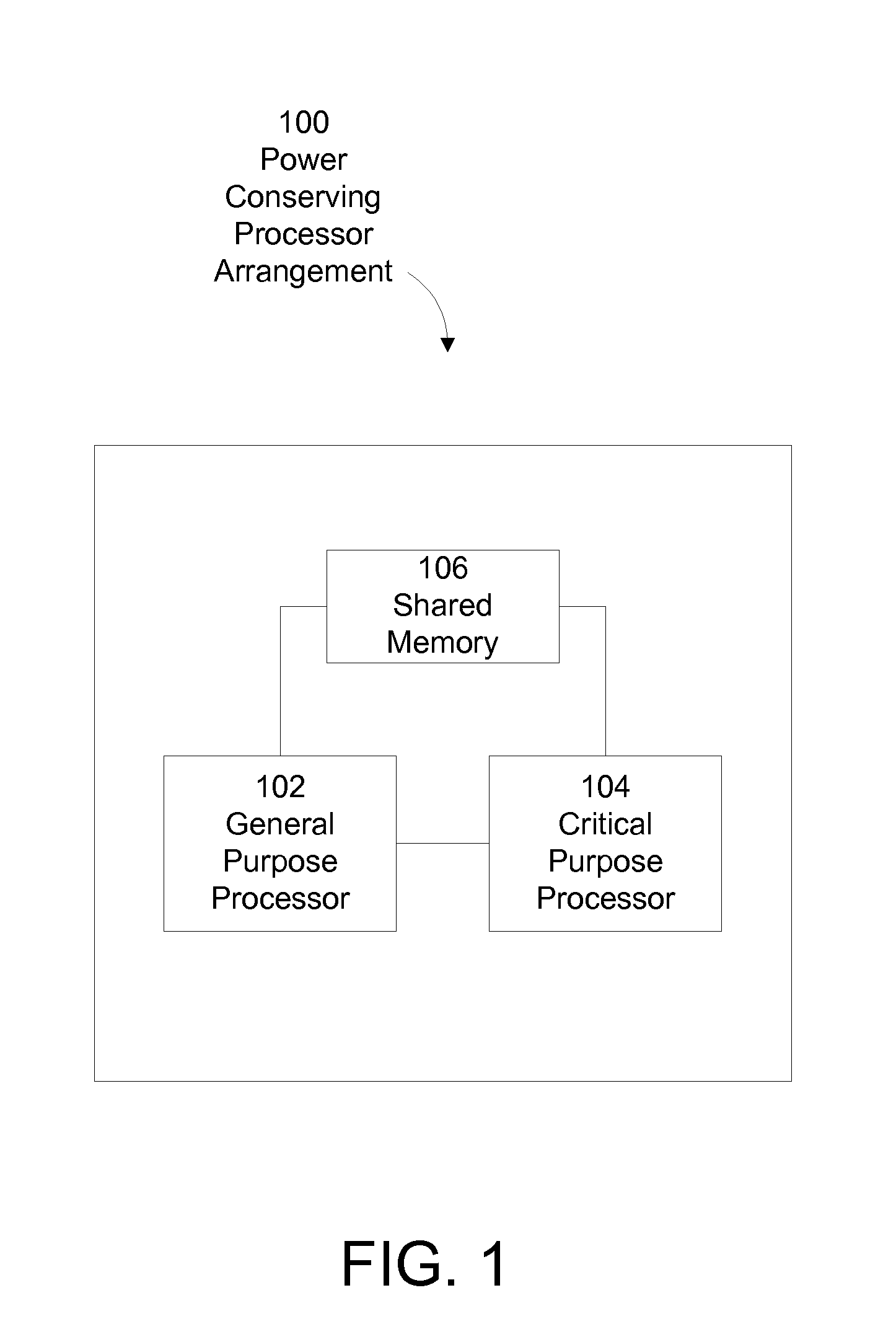
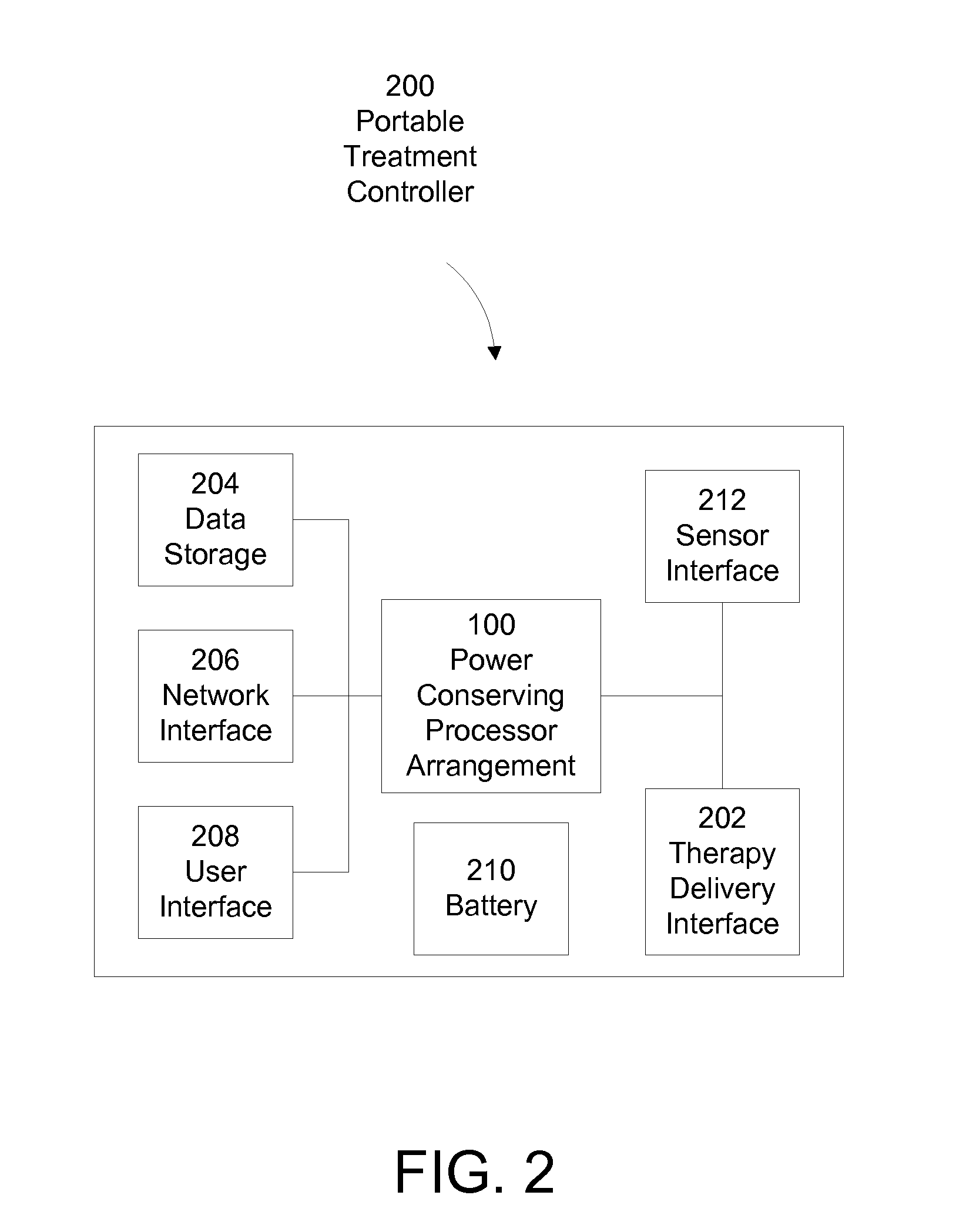
System and method for conserving power in a medical device
ActiveUS20120011382A1Useful lifespan of batteryEfficient treatment methodEnergy efficient ICTElectrotherapyCritical functionMedical device
A system and method for conservation of battery power in a portable medical device is provided. In one example, a processor arrangement that includes a plurality of processors is implemented. At least one of these processors is configured to execute the critical functions of the medical device, while one or more other processors assume a reduced service level, thereby drawing significantly less power. According to this arrangement, the medical device conserves energy by drawing the additional electrical power needed to activate the additional processing power only when needed.
Owner:ZOLL MEDICAL CORPORATION
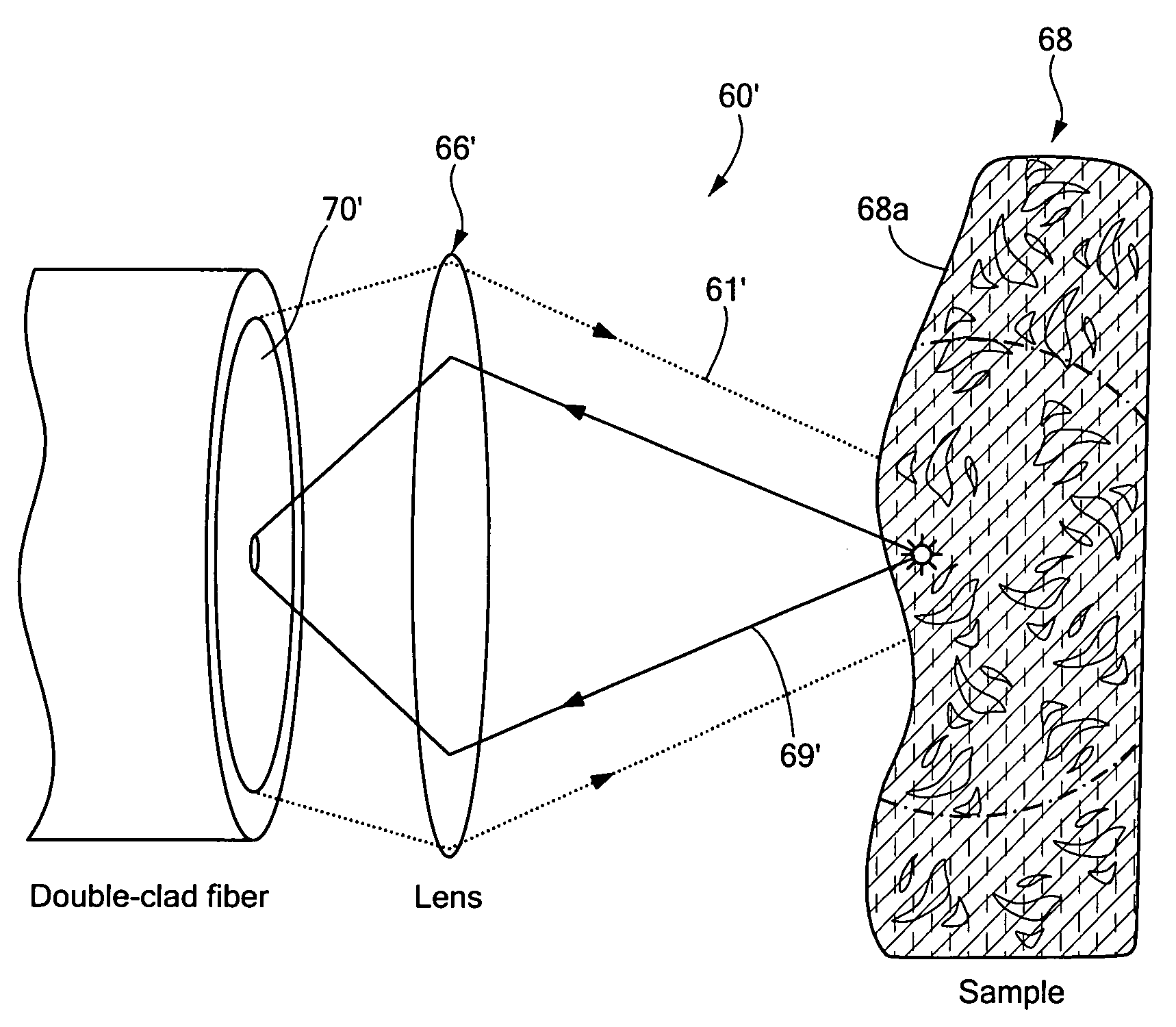
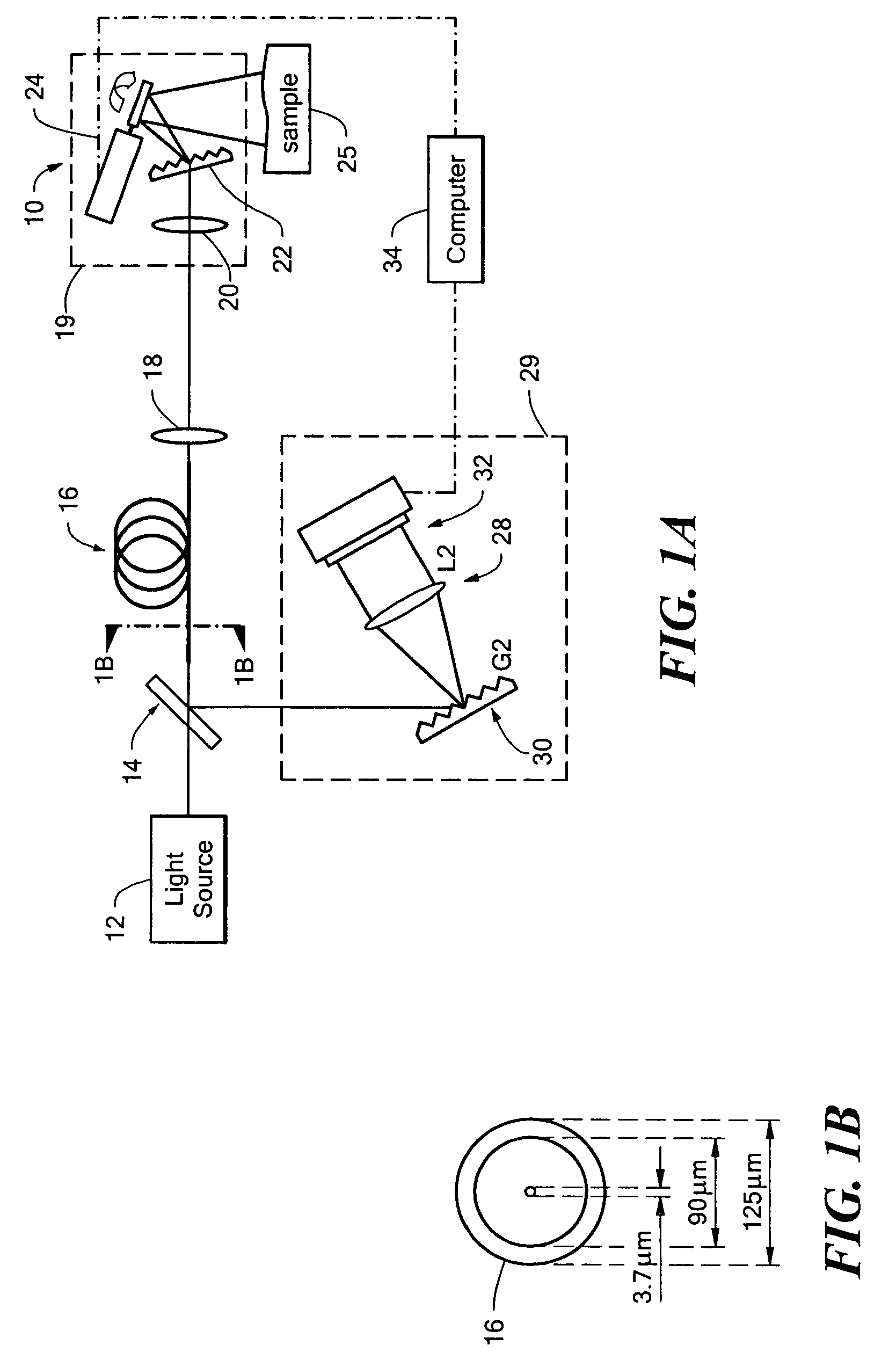
Imaging system and related techniques
ActiveUS7447408B2Reduces image speckleAdd depthRadiation pyrometrySpectrum investigationDouble-clad fiberComputer science
Owner:THE GENERAL HOSPITAL CORP
Antenna coil and rfid-use tag using it, transponder-use antenna
InactiveUS20050007296A1Improve rigidityHigh frequencyLoop antennas with ferromagnetic coreOther printing matterAir coreNon magnetic
An antenna coil includes an air-core coil wound helically in a plane and a plate magnetic core member inserted in the air-core coil to be approximately parallel with a plane of the air-core coil. The magnetic core member is formed by a soft magnetic metal, an amorphous or ferrite, or a composite member of a powder, flake and plastic, or rubber. The magnetic core member is formed by performing an injection molding operation or a compressing molding operation of the composite member. Alternatively, the magnetic core member is a magnetic coating formed by applying and drying the composite member. A non-magnetic conductive plate that has a conductivity is layered on a surface of the air-core coil through which the magnetic core member is inserted. The conductive plate is made of a copper, a copper alloy, an aluminum or an aluminum alloy having 0.01 to 2 mm thickness. The antenna coil is operated by relatively high frequency while it is rigid relatively.
Owner:MITSUBISHI MATERIALS CORP
Transformer structure
InactiveUS6867678B2Reduce manufacturing costLow costTransformers/inductances coils/windings/connectionsCoilsConductor CoilPrinted circuit board
The present invention describes a planar transformer having a plurality of juxtaposed magnetic cores as well as a two-layer printed circuit board for spiralling a plurality of windings. Each arm of a plurality of juxtaposed magnetic cores respectively goes through a corresponding hole in the middle of these windings, to magnetically couple the current in the main winding to the other windings.
Owner:ENTRUST POWER CO LTD
Optical sensor unit and procedure for the ultrasensitive detection of chemical or biochemical analytes
InactiveUS6346376B1High sensitivitySelective retentionBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsSpecific detectionNon-covalent interactions
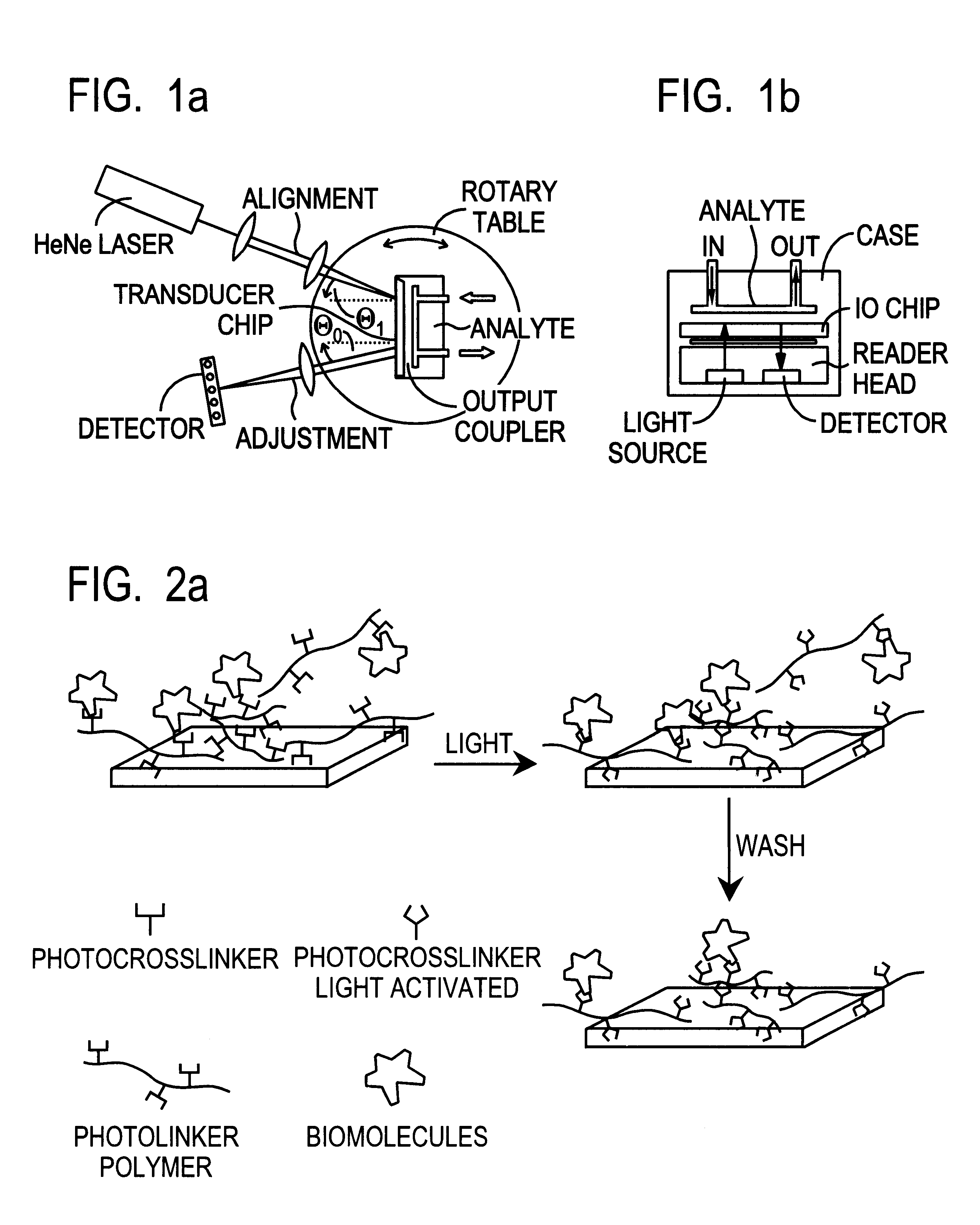
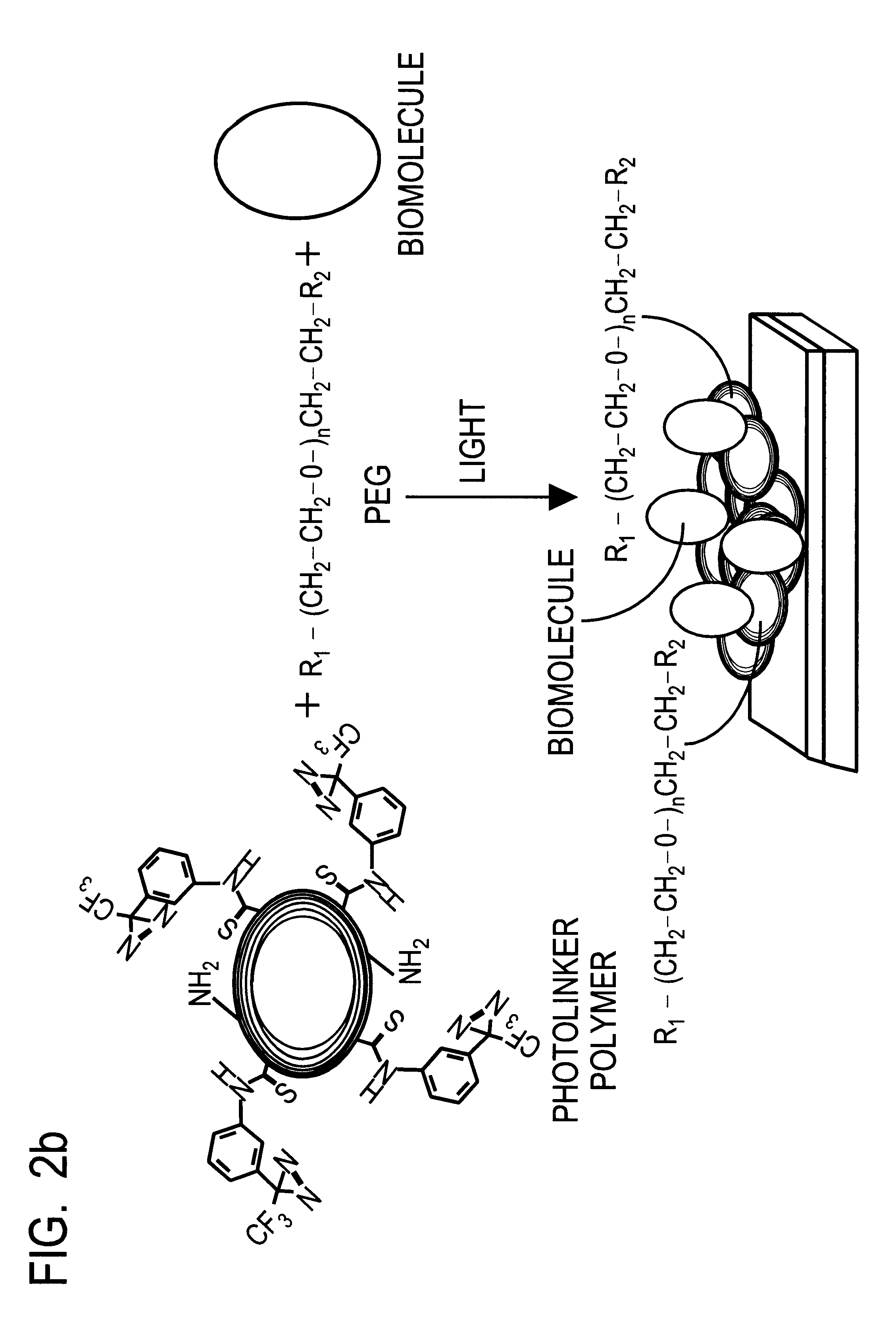
This document describes an optical sensor unit and a procedure for the specific detection and identification of biomolecules at high sensitivity in real fluids and tissue homogenates. High detection limits are reached by the combination of i) label-free integrated optical detection of molecular interactions, ii) the use of specific bioconstituents for sensitive detection and iii) planar optical transducer surfaces appropriately engineered for suppression of non-specific binding, internal referencing and calibration. Applications include the detection of prion proteins and identification of those biomolecules which non-covalently interact with surface immobilized prion proteins and are intrinsically involved in the cause of prion related disease.
Owner:CSEM CENT SUISSE DELECTRONIQUE & DE MICROTECHNIQUE SA RECH & DEV
Product including power supply circuit board
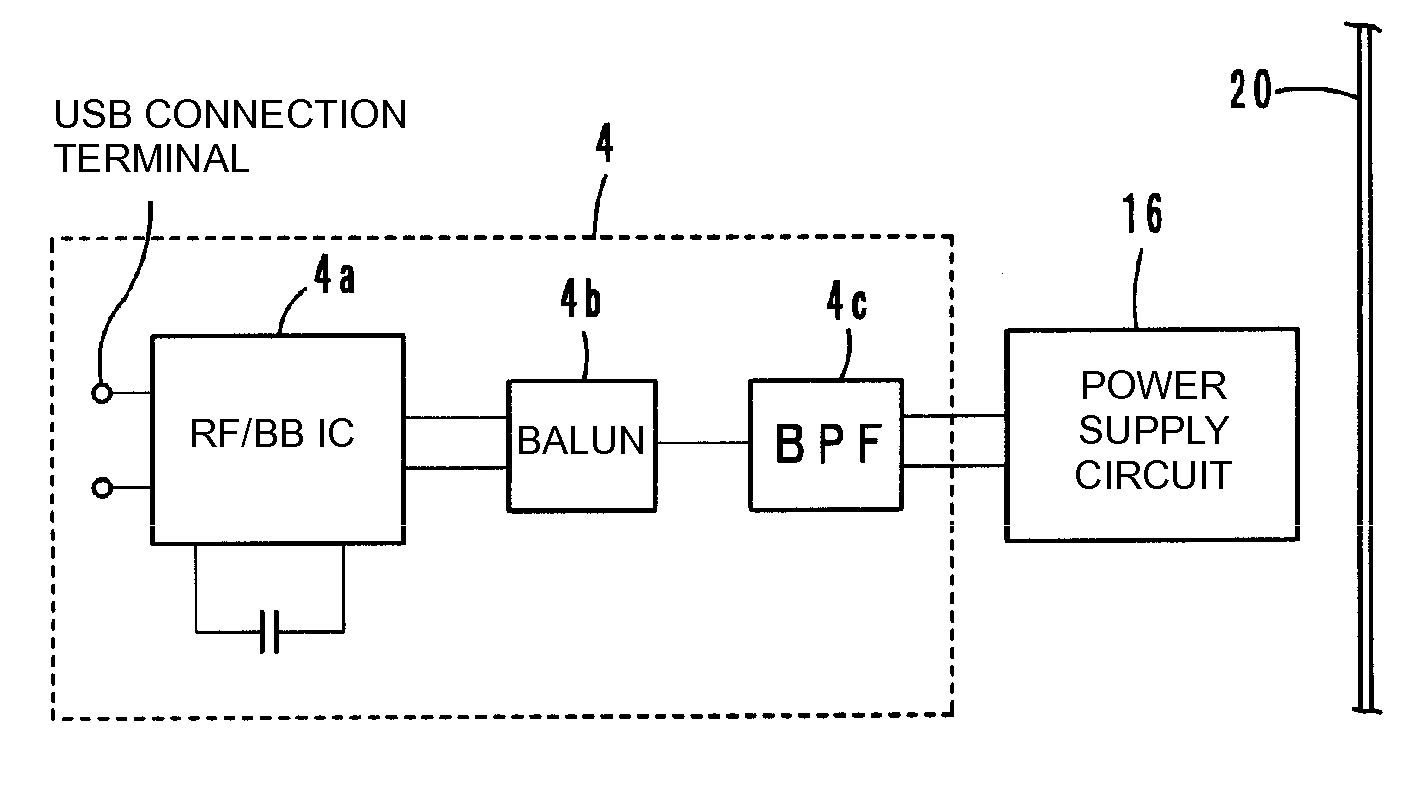
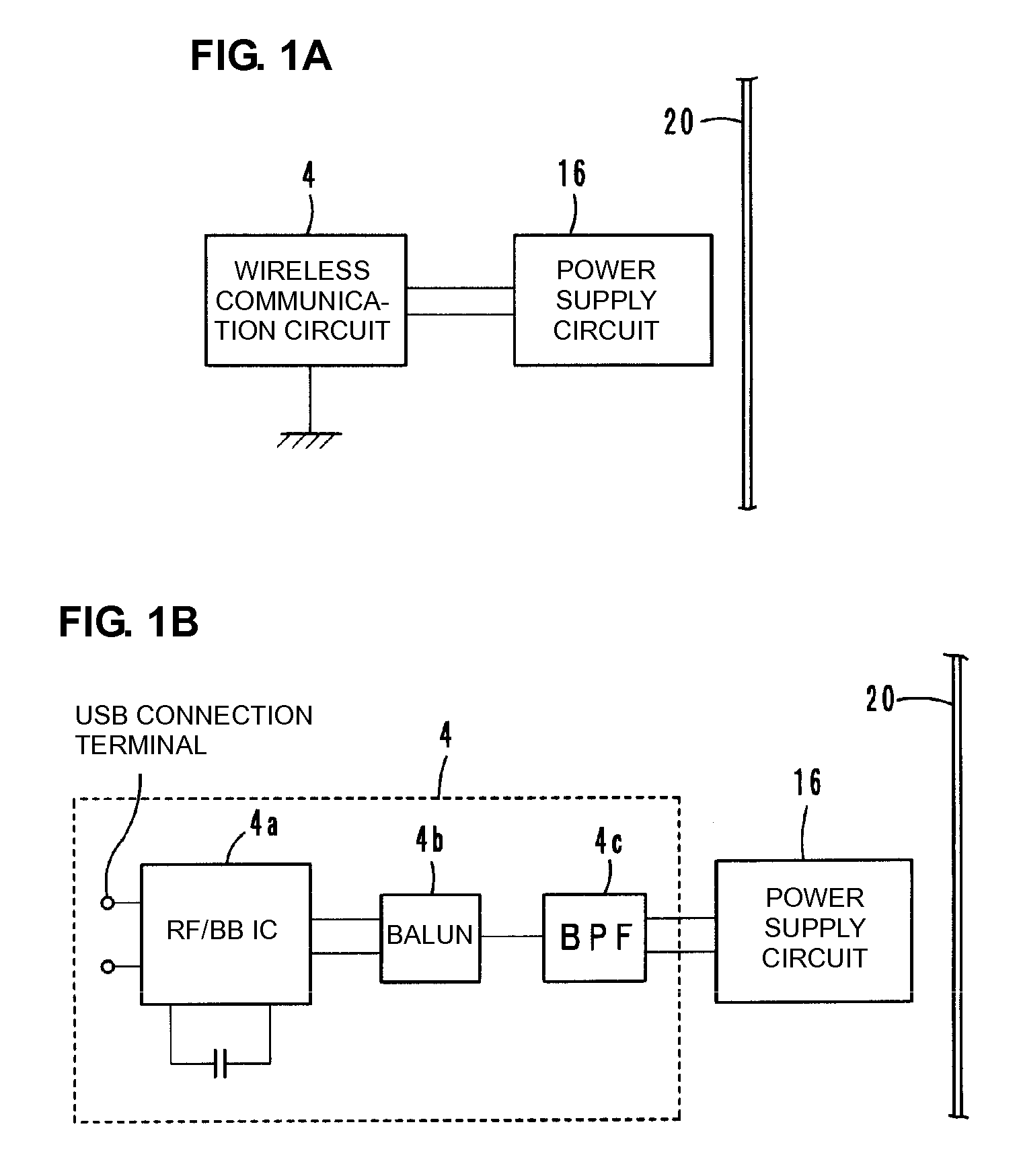
ActiveUS20090009007A1Frequency stabilityEnhanced signalAntenna supports/mountingsSolid-state devicesElectricityElectromagnetic field coupling
A product includes a power supply circuit board, which includes a power supply circuit having a stable frequency characteristic which enables communication among various products to be obtained. The product includes a power supply circuit board including a power supply circuit arranged thereon having an inductance element, and a wireless communication circuit board electrically connected to the power supply circuit. The wireless communication circuit board is mounted on the power supply circuit board. The product further includes a radiation plate which emits a transmission signal which is supplied from the power supply circuit through electromagnetic field coupling and which has a frequency substantially determined in accordance with a resonant frequency of the power supply circuit, and which is used to supply a reception signal to the power supply circuit through electromagnetic field coupling.
Owner:MURATA MFG CO LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com