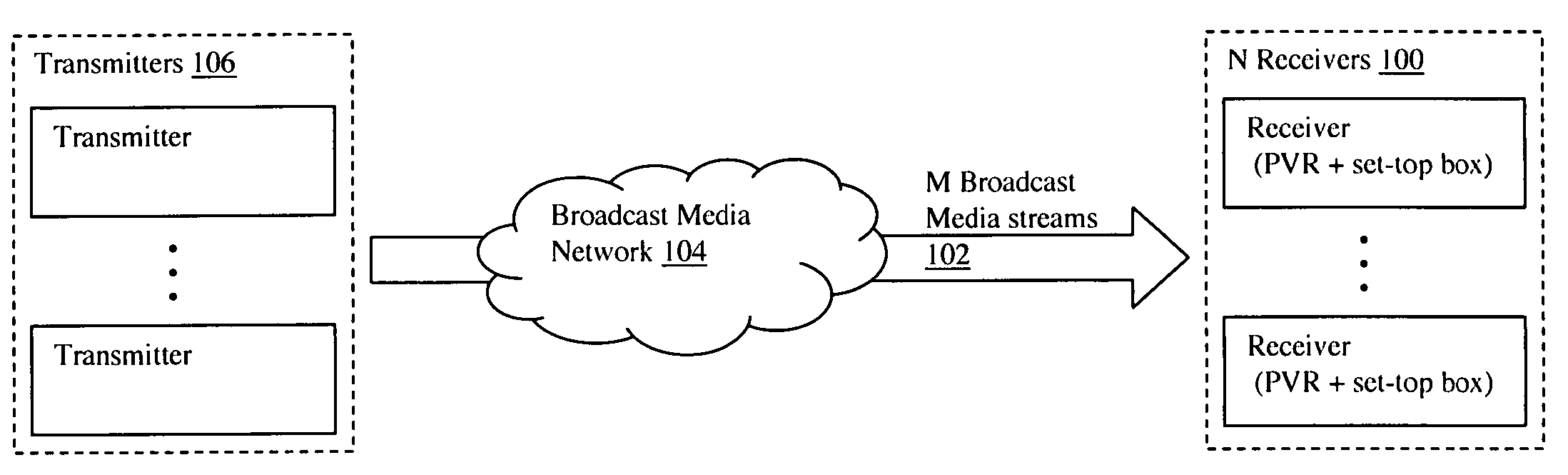Patents
Literature
1846 results about "Network termination" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
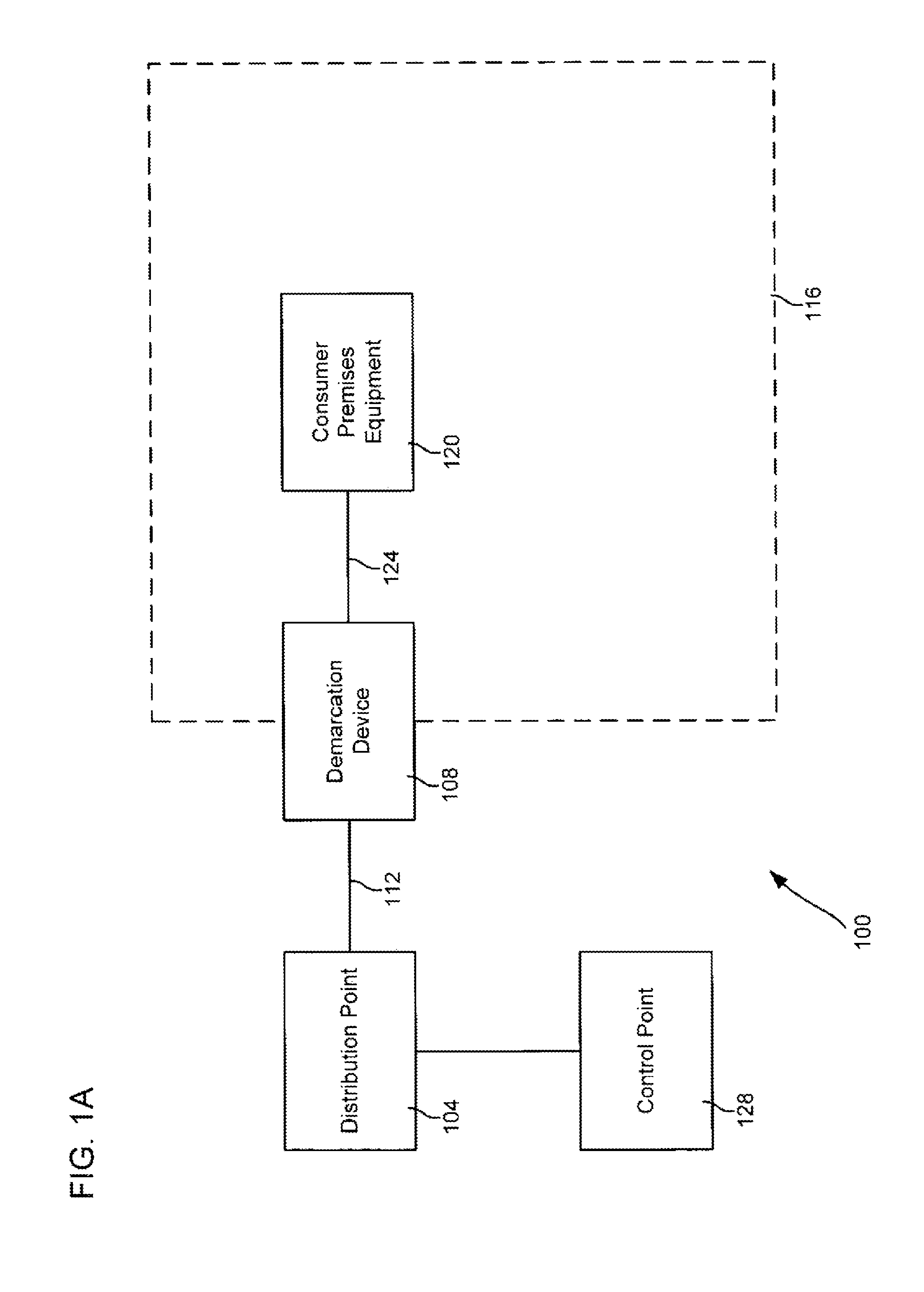
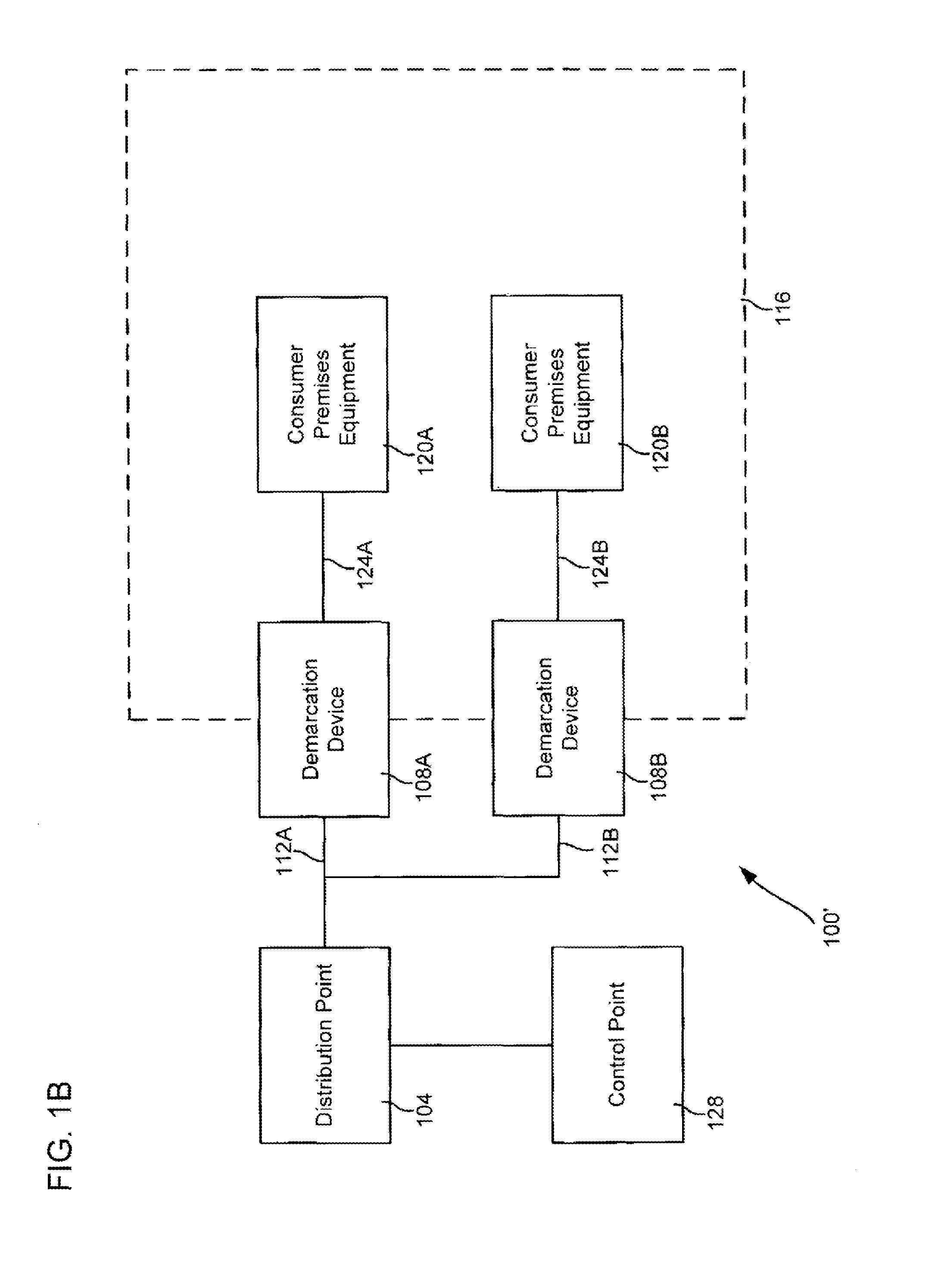
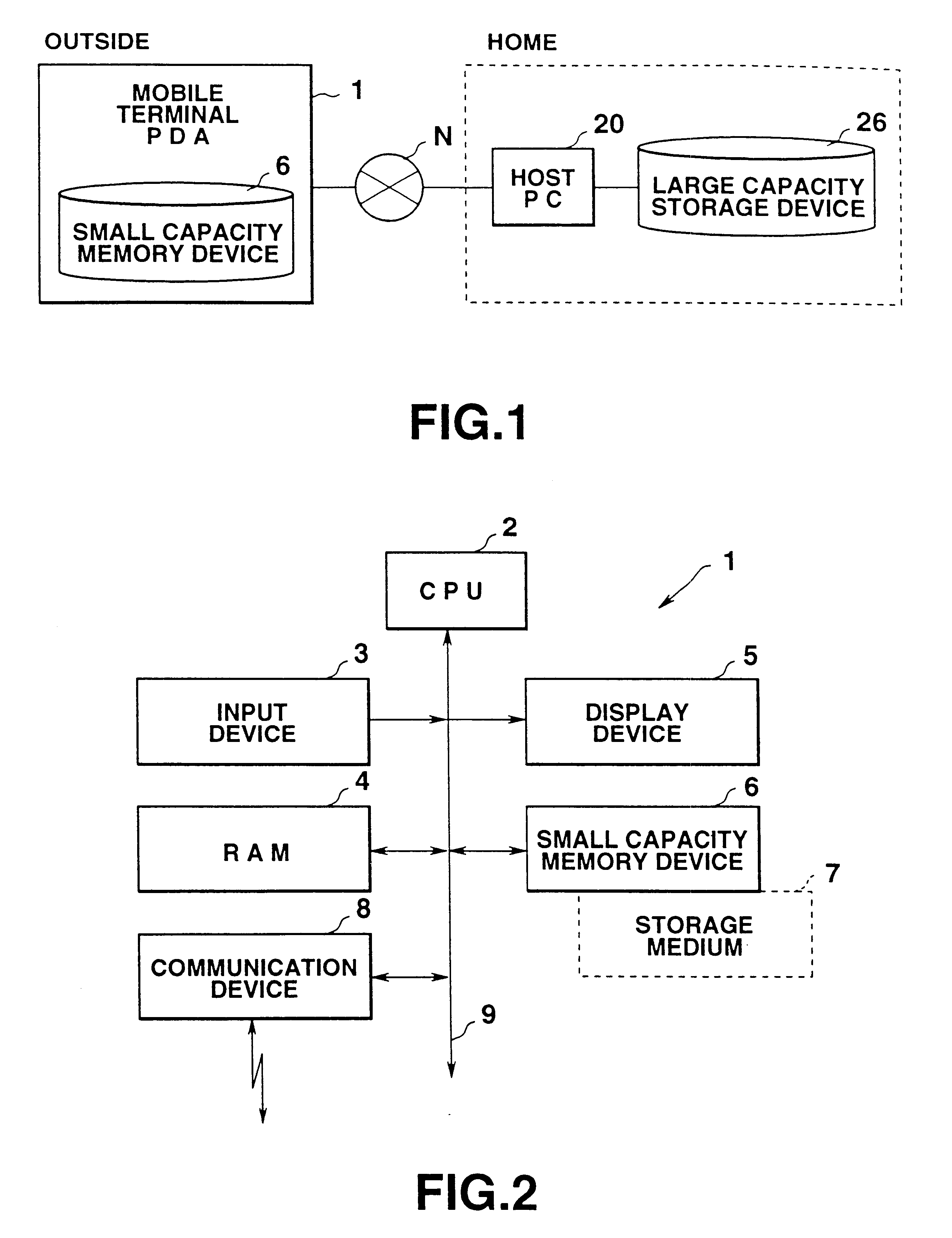
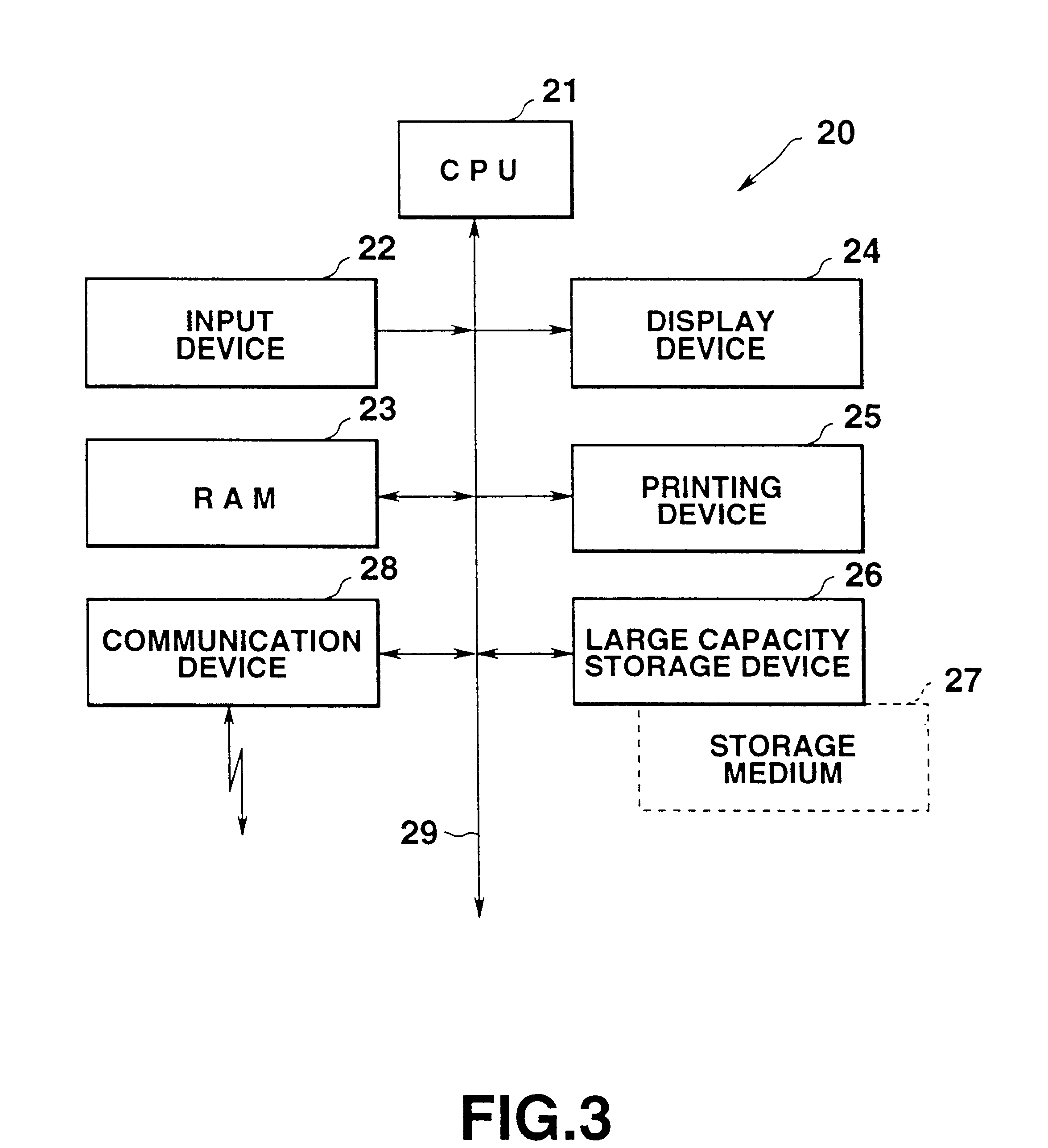
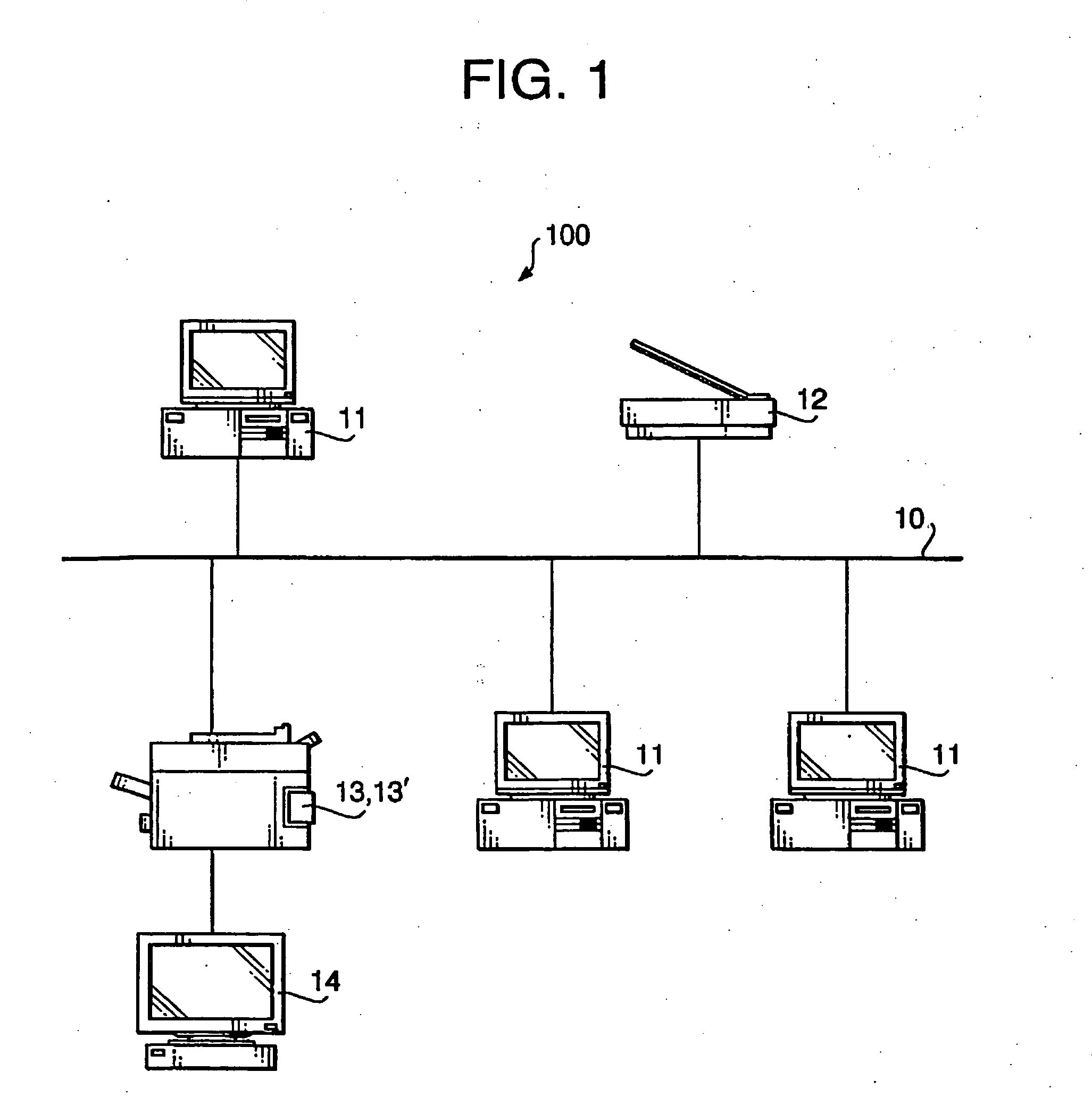
A network termination (NT) (also NTE for network termination equipment) is a device that connects the customer's data or telephone equipment to a carrier's line that comes into a building or an office. The NT device provides a connection for terminal equipment (TE) and terminal adapter (TA) equipment to the local loop.
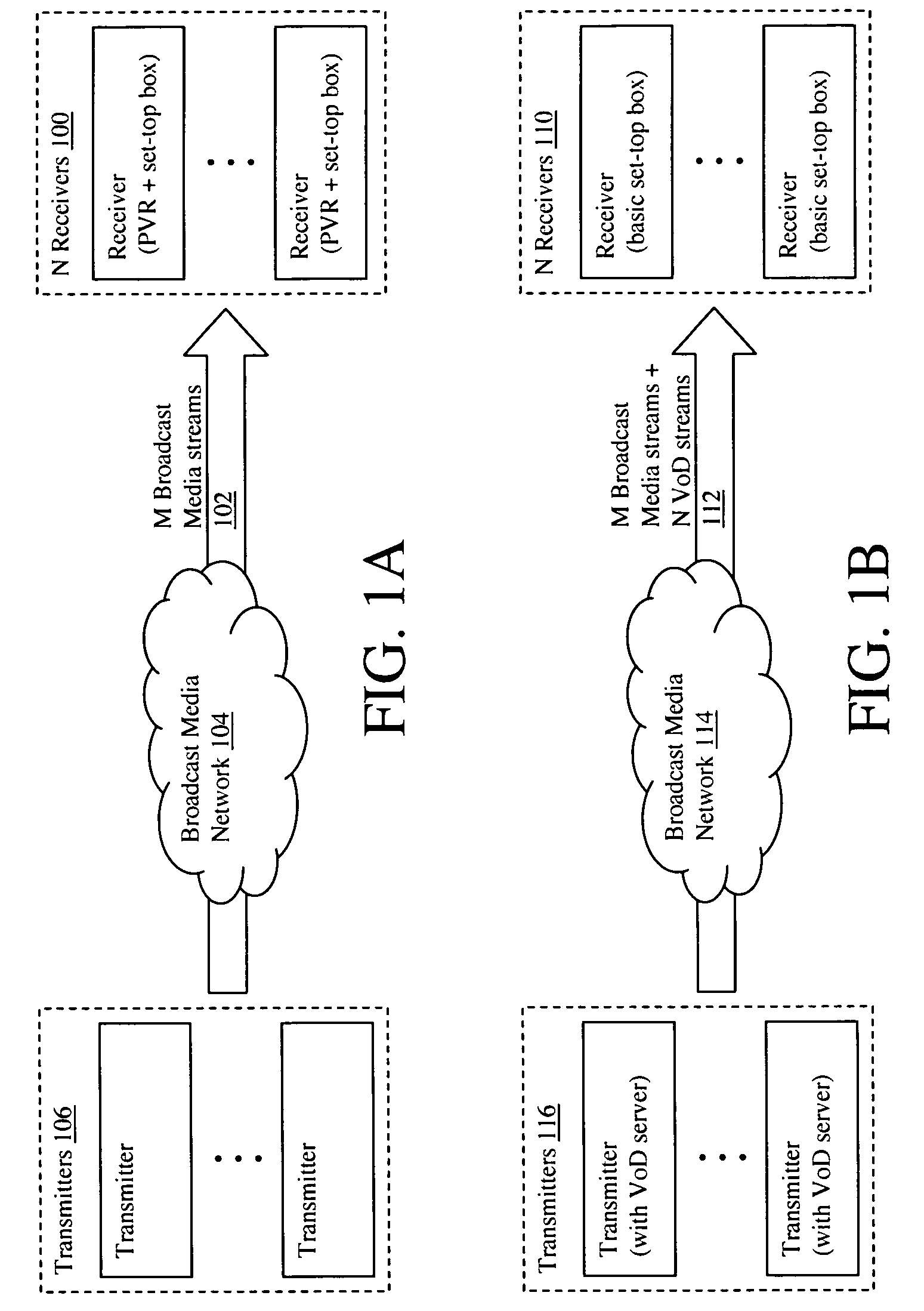
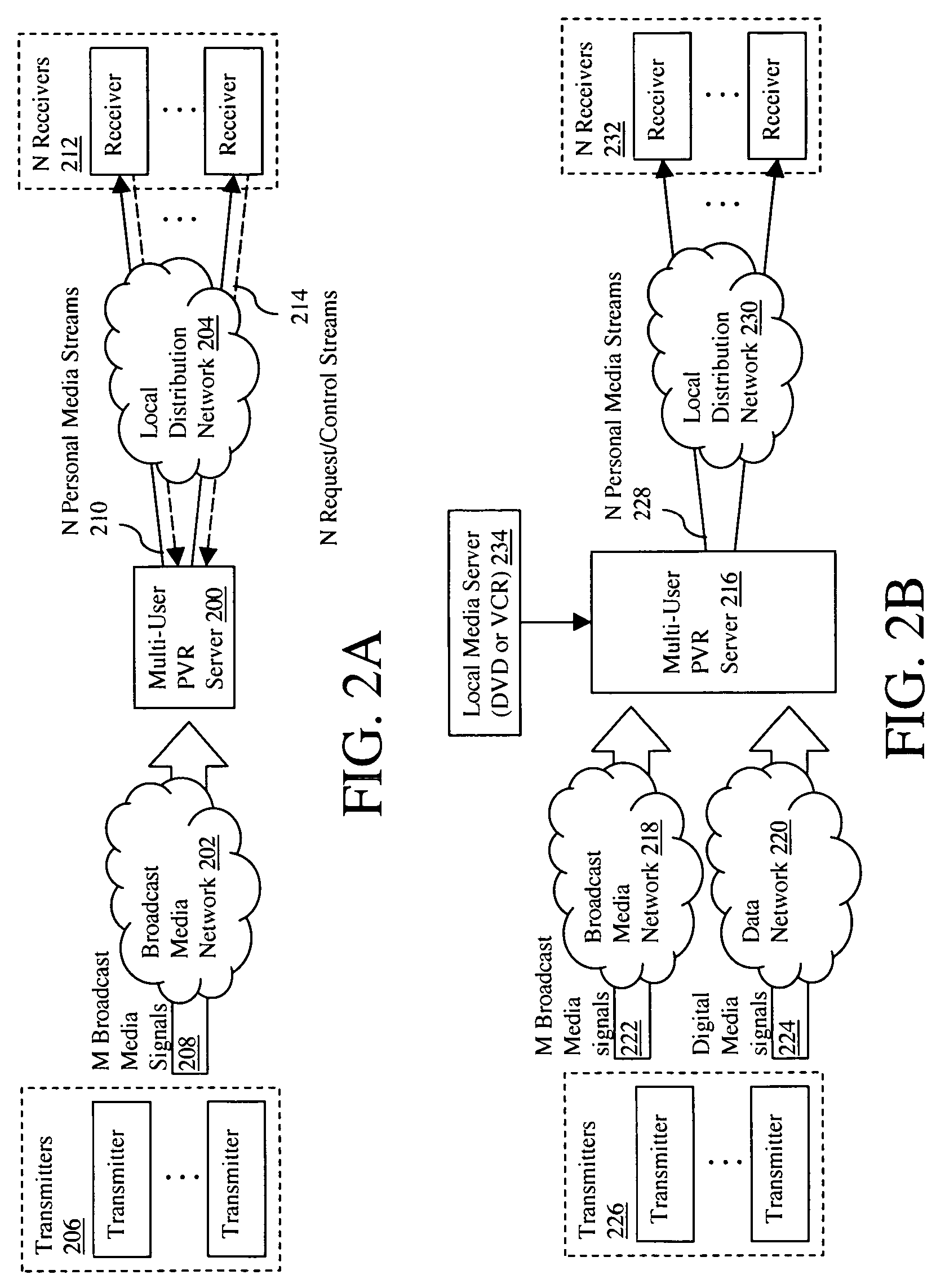
Multi-user personalized digital multimedia distribution methods and systems
InactiveUS20050183120A1Communication securityTelevision system detailsColor television detailsPersonalizationNetwork termination
A media distribution technique employs a multi-user server positioned at the terminal end of a broadcast media network. The server receives broadcast media signals and selectively captures a portion of the signals for live personalized media streaming and / or storage for later personalized media streaming and / or download over a local distribution network to a collection of user receivers. Request / control streams sent from the receivers to the server control real-time personalization of the media streams such as trick-play functions and channel selection. Buffering and data storage segmentation techniques are used to provide highly responsive personal video recorder-like functionality to the multiple end users.
Owner:IP VIDEO SYST
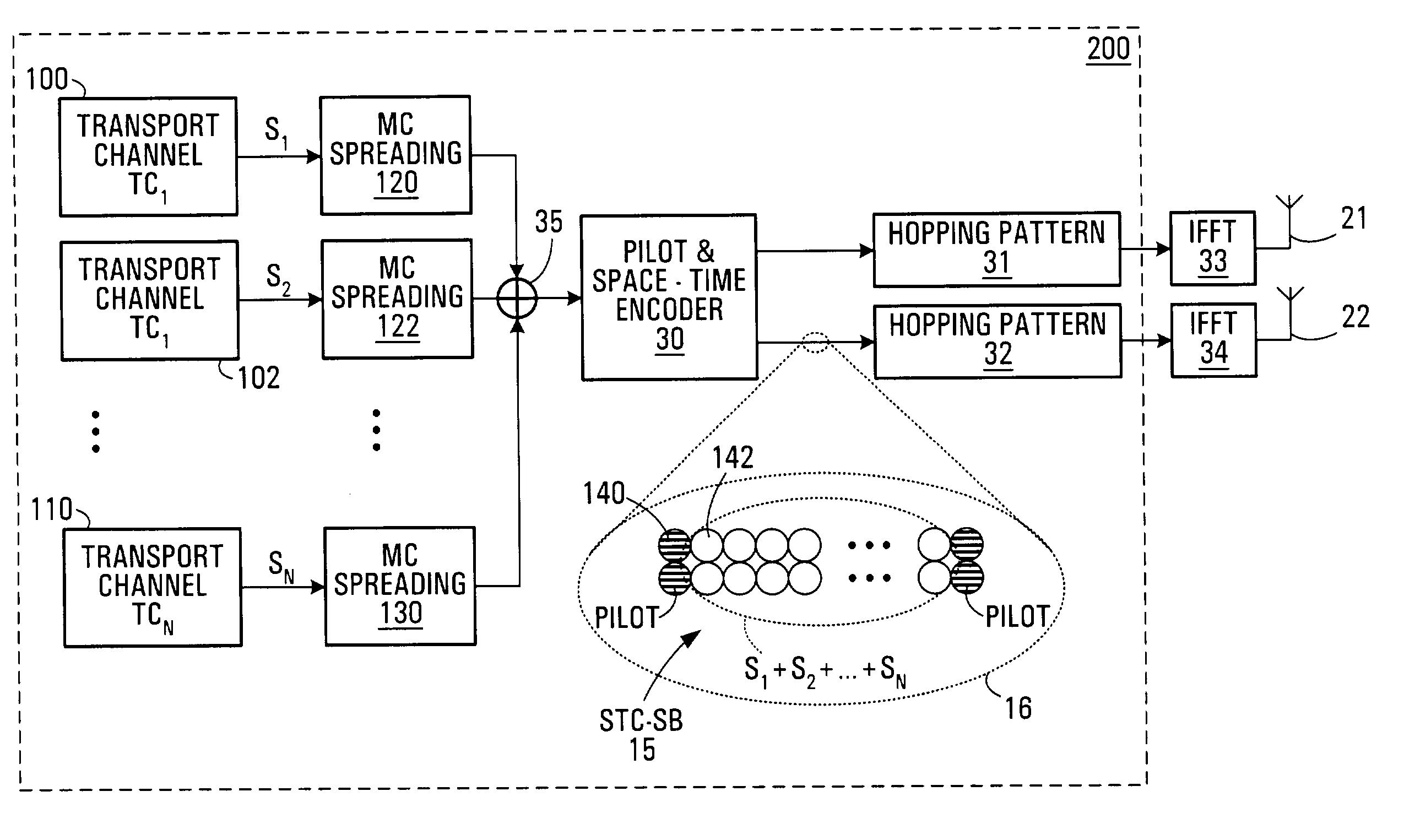
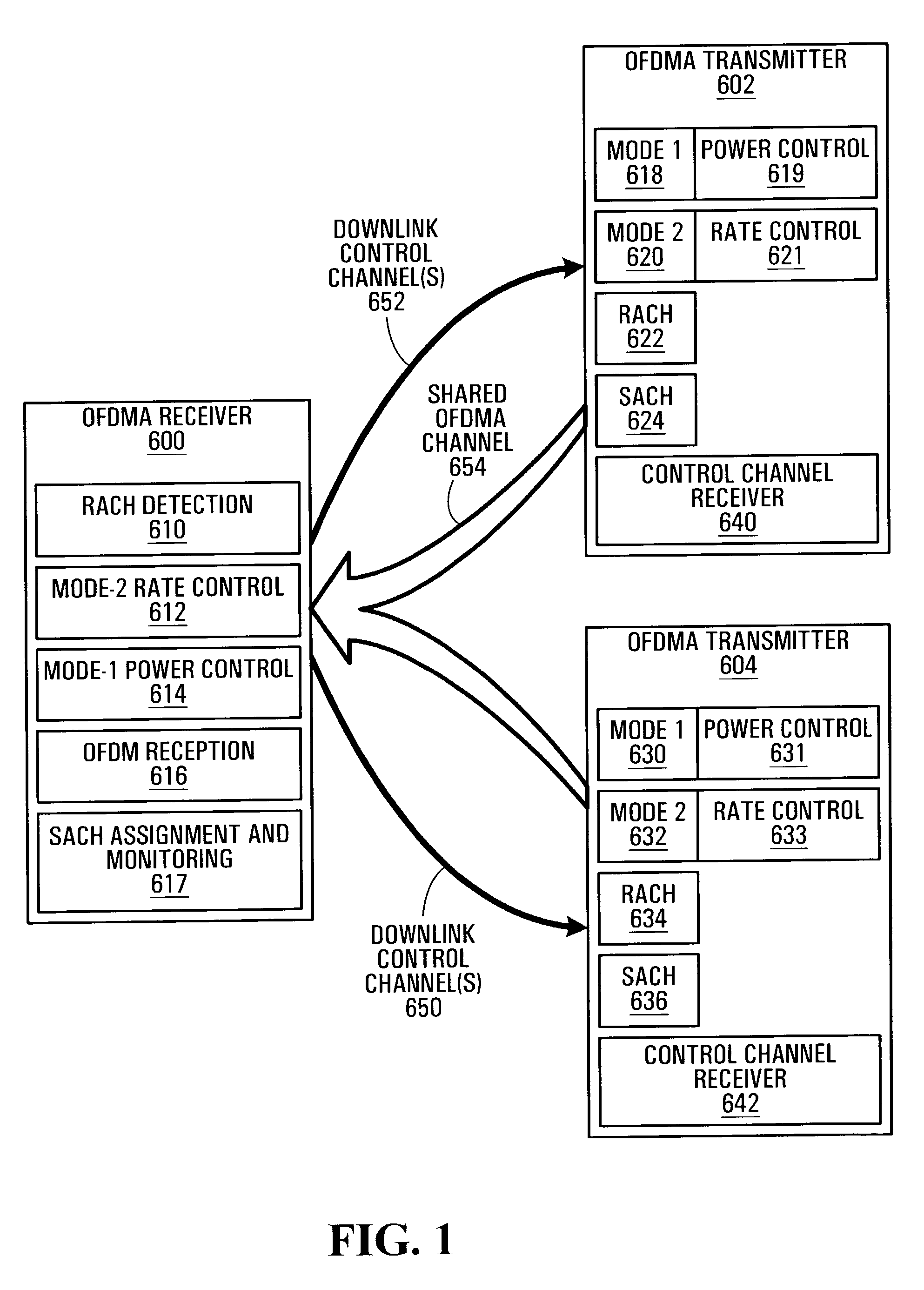
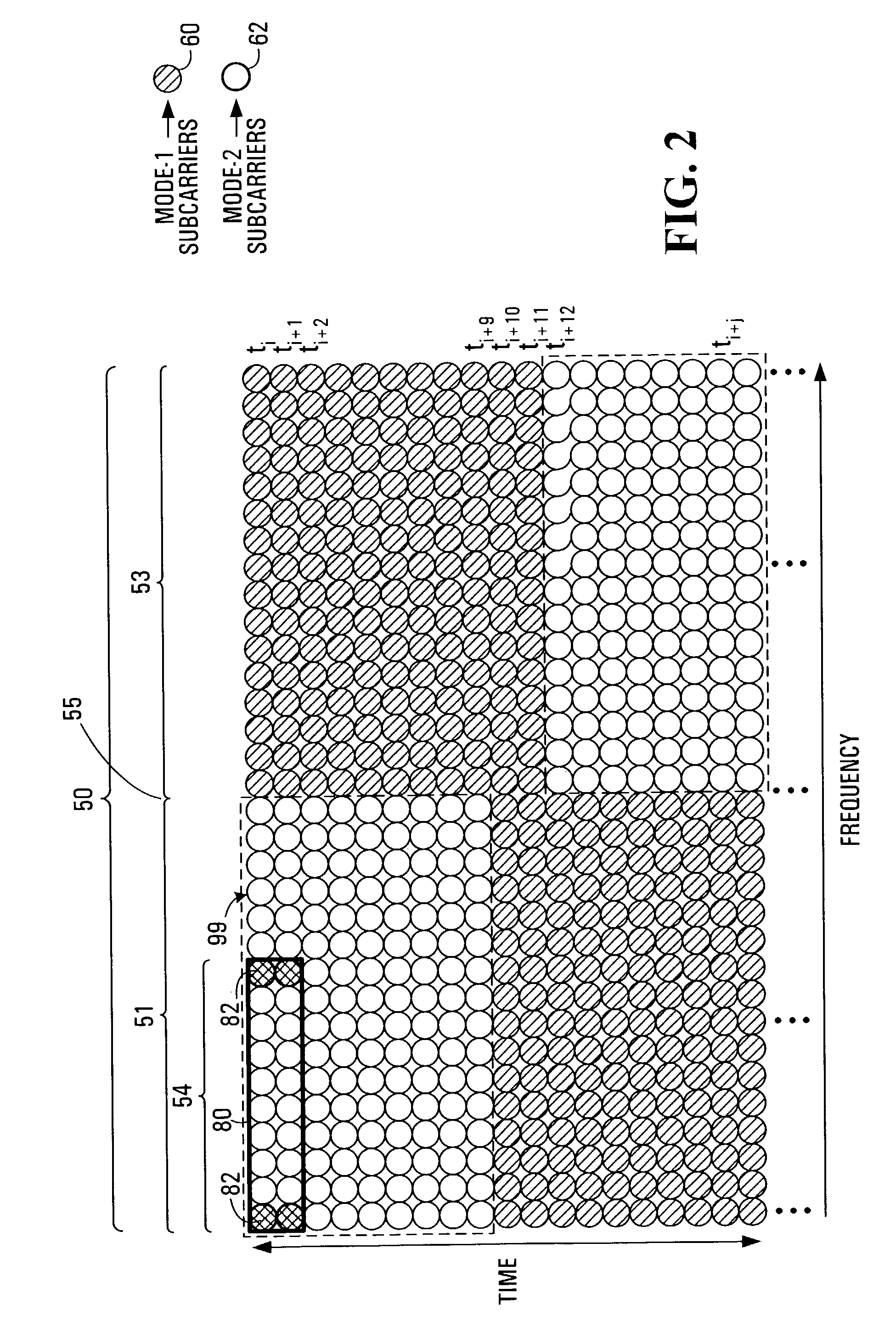
Dual-mode shared OFDM methods/transmitters, receivers and systems
ActiveUS7551546B2Network traffic/resource managementData switching by path configurationNetwork terminationDual mode
A wireless terminal and network terminal are provided for implementing a new uplink OFDM protocol. In the new protocol, the wireless terminal has a first transmit chain for generating and transmitting a low rate mode OFDM transmission in a first frequency band of the OFDM band; and a second transmit chain for generating and transmitting a burst-mode transmission in a second frequency band of the OFDM band, the first frequency band being distinct from the second frequency band. An access channel is provided which is overlaid over the low rate mode transmissions of other users.
Owner:APPLE INC
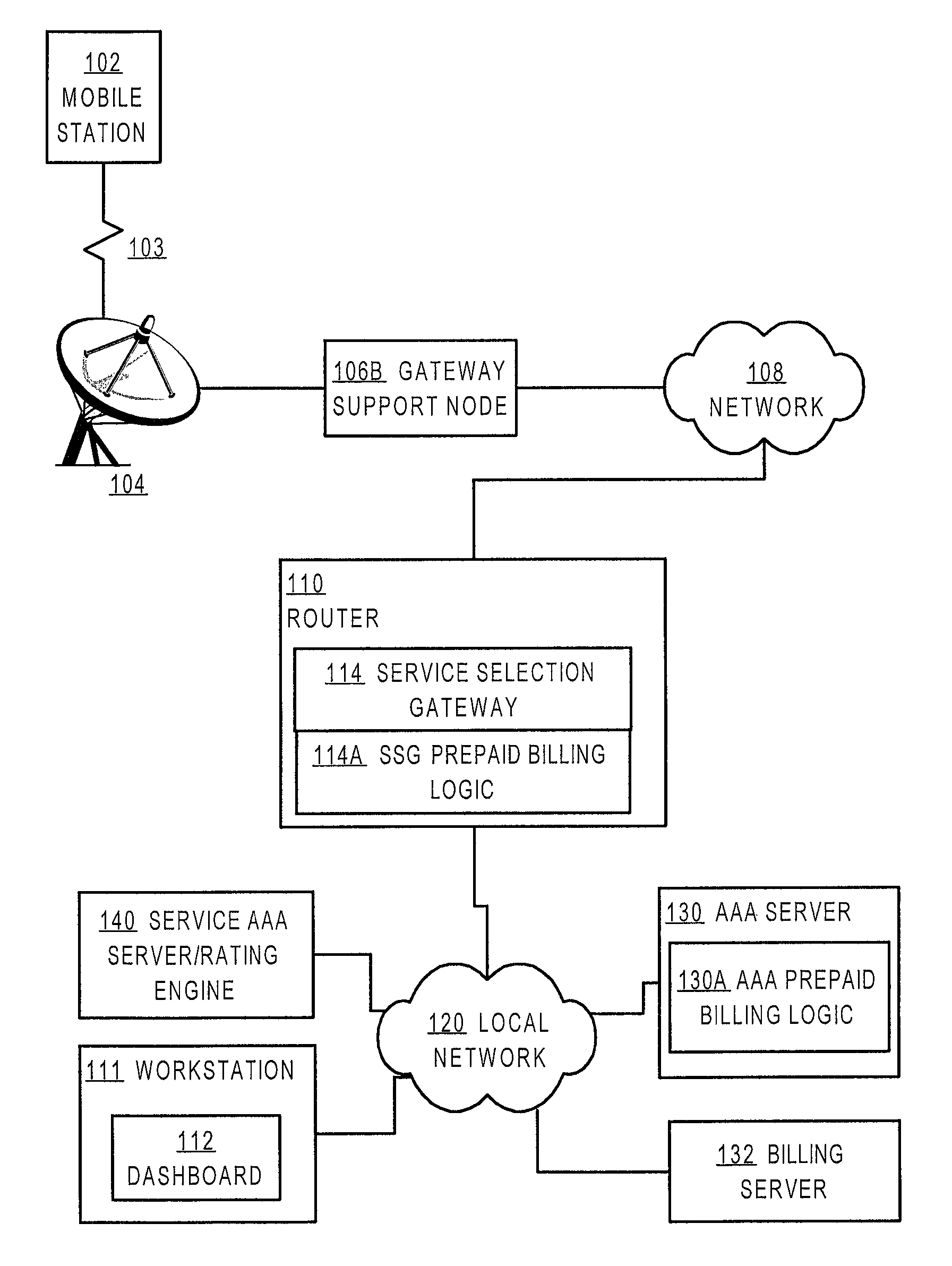
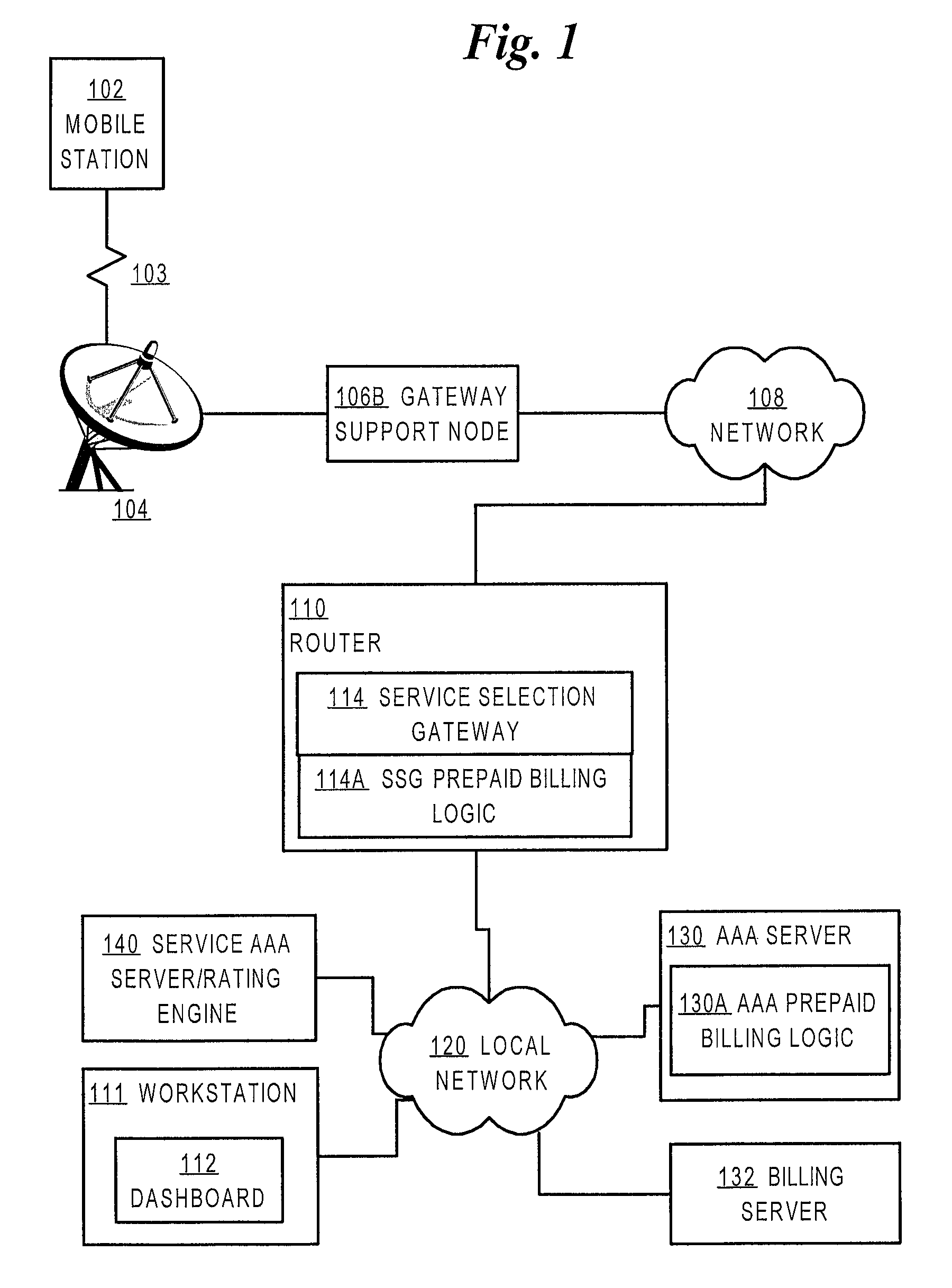
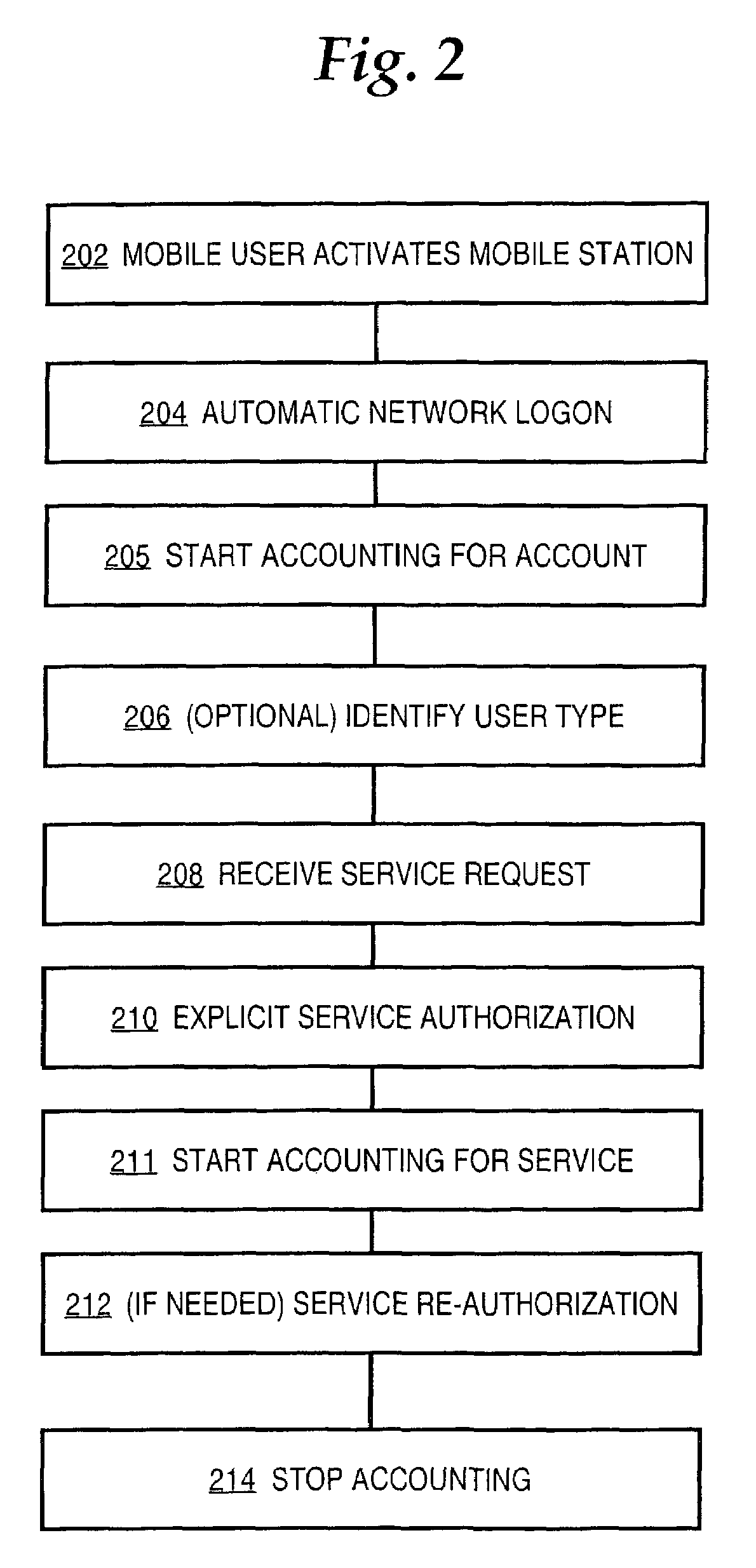
Method and apparatus providing prepaid billing for network services using explicit service authorization in an access server
ActiveUS7720960B2Complete banking machinesAccounting/billing servicesNetwork terminationTraffic capacity
A method is disclosed for authorizing a prepaid network service in a data network. A network end station issues a request for a prepaid network service. At a network node, such as a router serving as a gateway for selecting services, a determination is made about whether a user associated with the end station is authorized to access the prepaid network service. Network traffic from the end station is forwarded to a service provider only when the user is authorized to use the prepaid network service. Specific embodiments provide message flows among a mobile station, gateway support node, router, and authentication server that support providing prepaid services in a packet-switched network for mobile communication. In certain embodiments, a connection is held open for an end station while a prepaid quota value is refreshed at a portal, thereby reducing overhead and precluding the need to repeat user logon steps. Further, unused quota amounts can be returned to the authentication server for use in association with multiple concurrent connections of the same device.
Owner:CISCO TECH INC
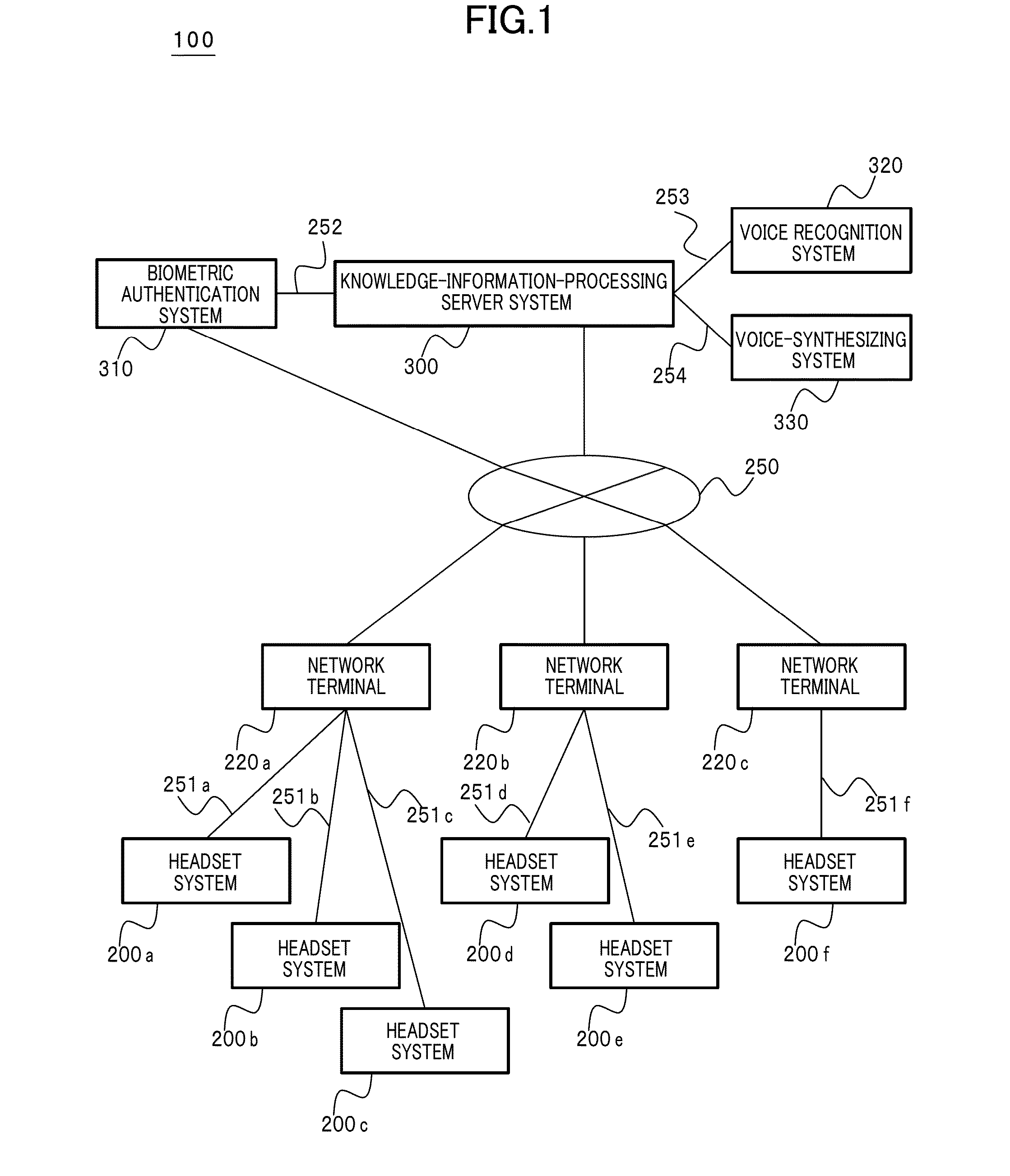
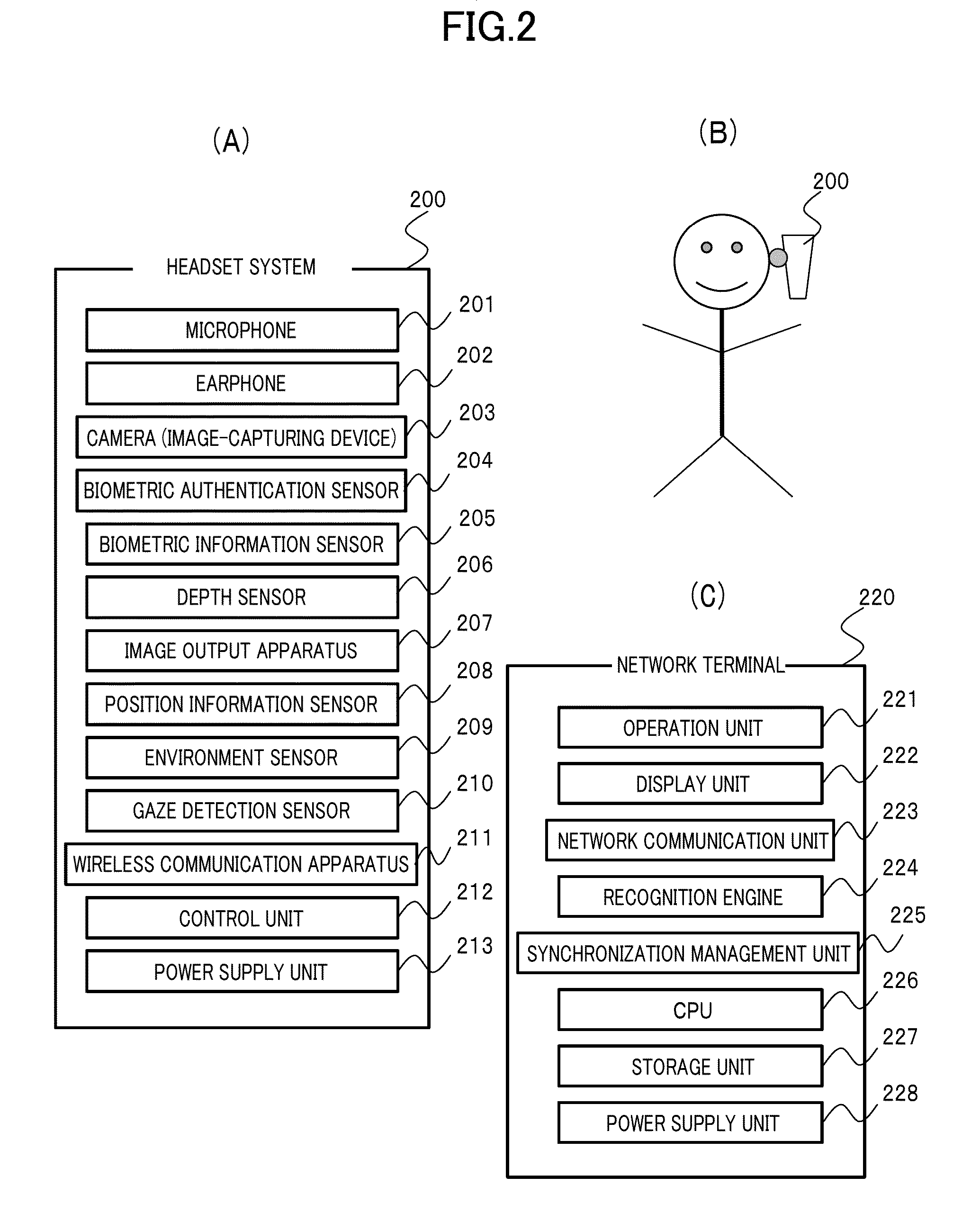
Knowledge-information-processing server system having image recognition system
InactiveUS20140289323A1Improve image recognition rateHigh frequencyData processing applicationsDigital data information retrievalNetwork terminationInformation processing
Extensive social communication is induced. Connection is made with a network terminal capable of connecting to the Internet, and an image and voice signal reflecting the subjective visual field of the user and the like which can be obtained from the headset system that can be worn by the user on the head is uploaded via the network terminal to a knowledge-information-processing server system, and specifying and selecting of an attention-given target by the voice of the user himself / herself are enabled on the server system with collaborative operation with the voice recognition system with regard to a specific object and the like to which the user gives attention and which is included in the image, and with regard to the series of image recognition processes and image recognition result made by the user, image recognition result and recognition processes thereof are notified as voice information to an earphone incorporated into the headset system of the user by way of the user's network terminal via the Internet by the server system with collaborative operation with a voice-synthesizing system, so that user's message or tweet can be extensively shared by users.
Owner:CYBER AI ENTERTAINMENT
Systems and methods for presentation of preferred program selections
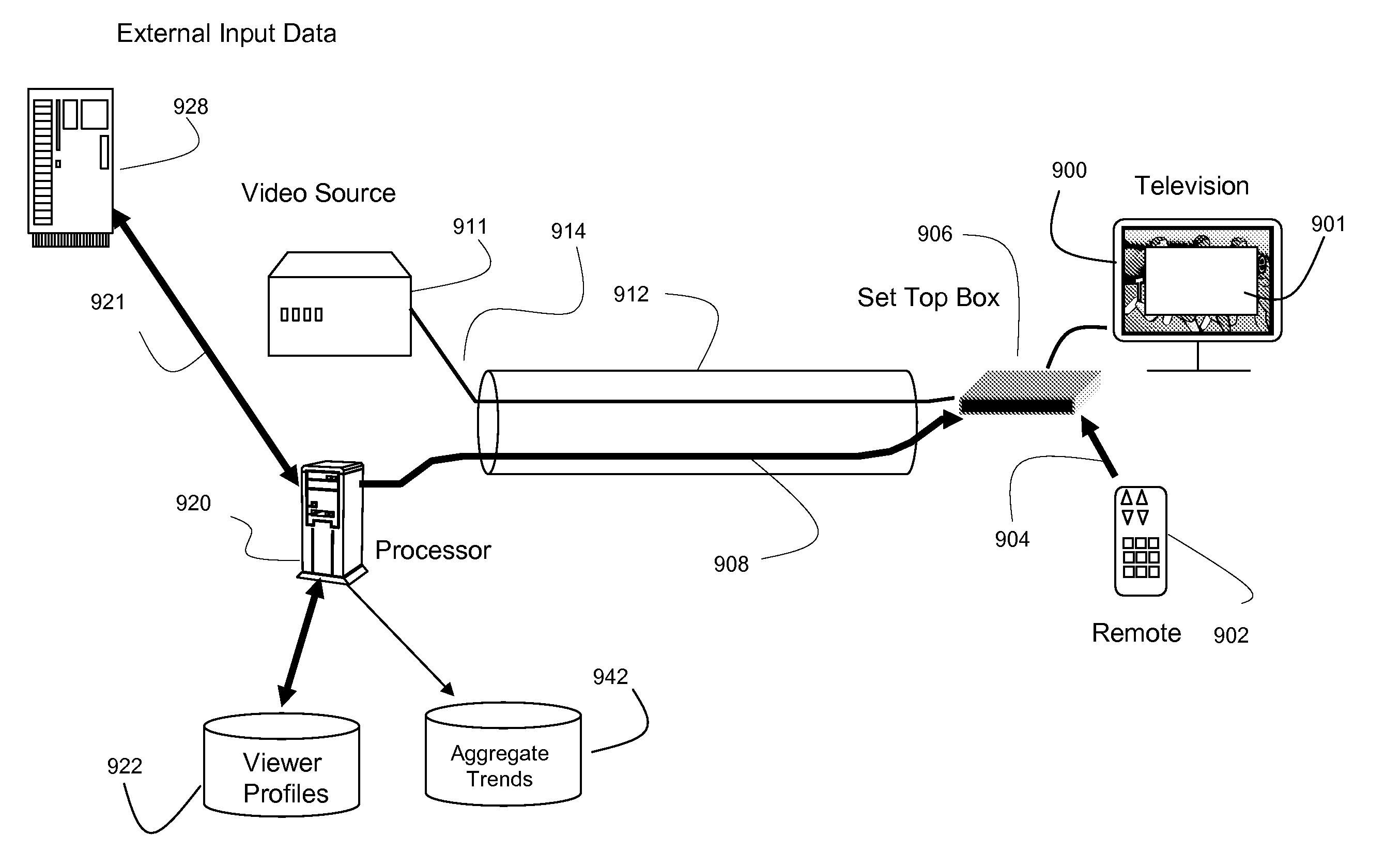
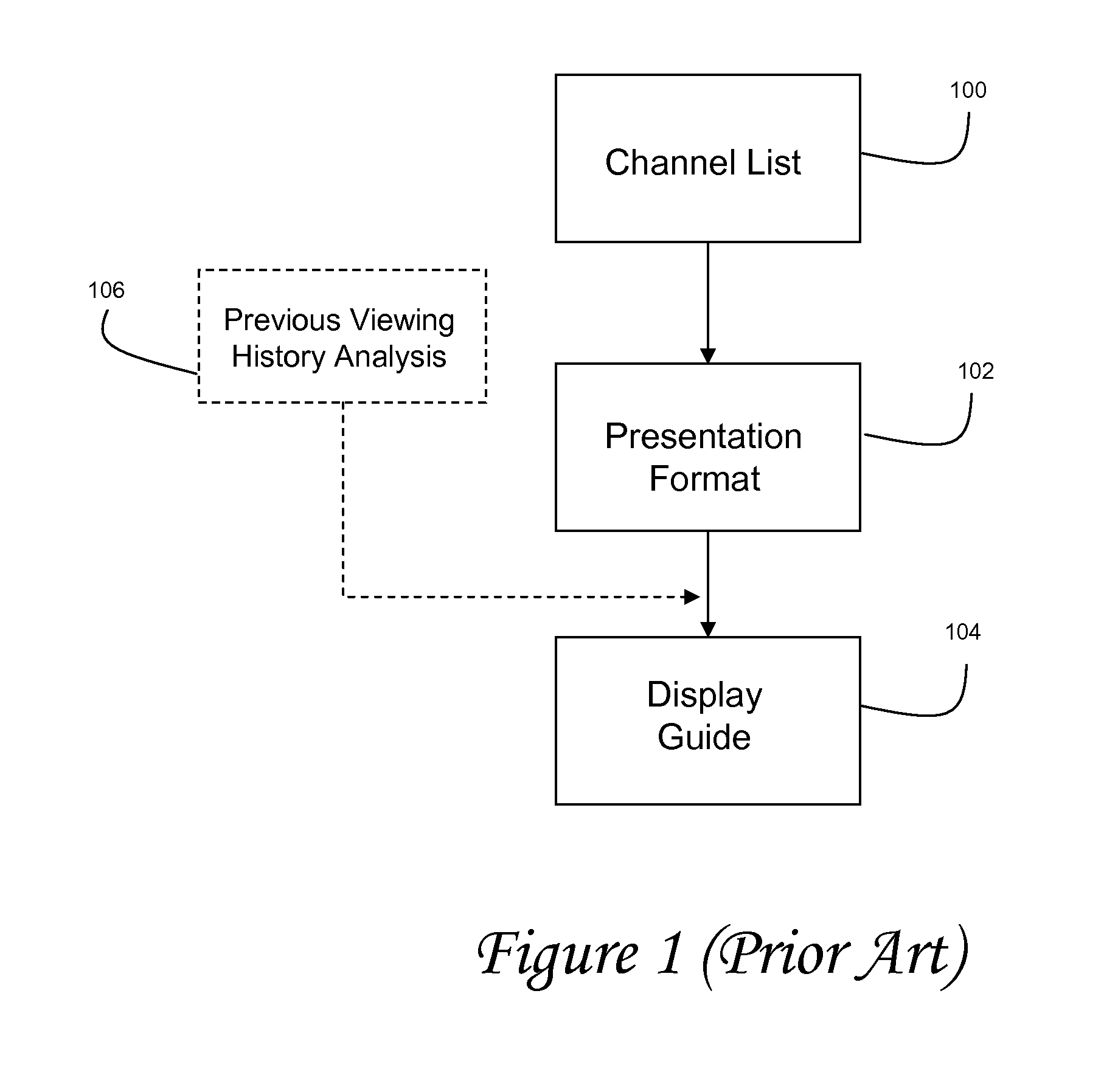
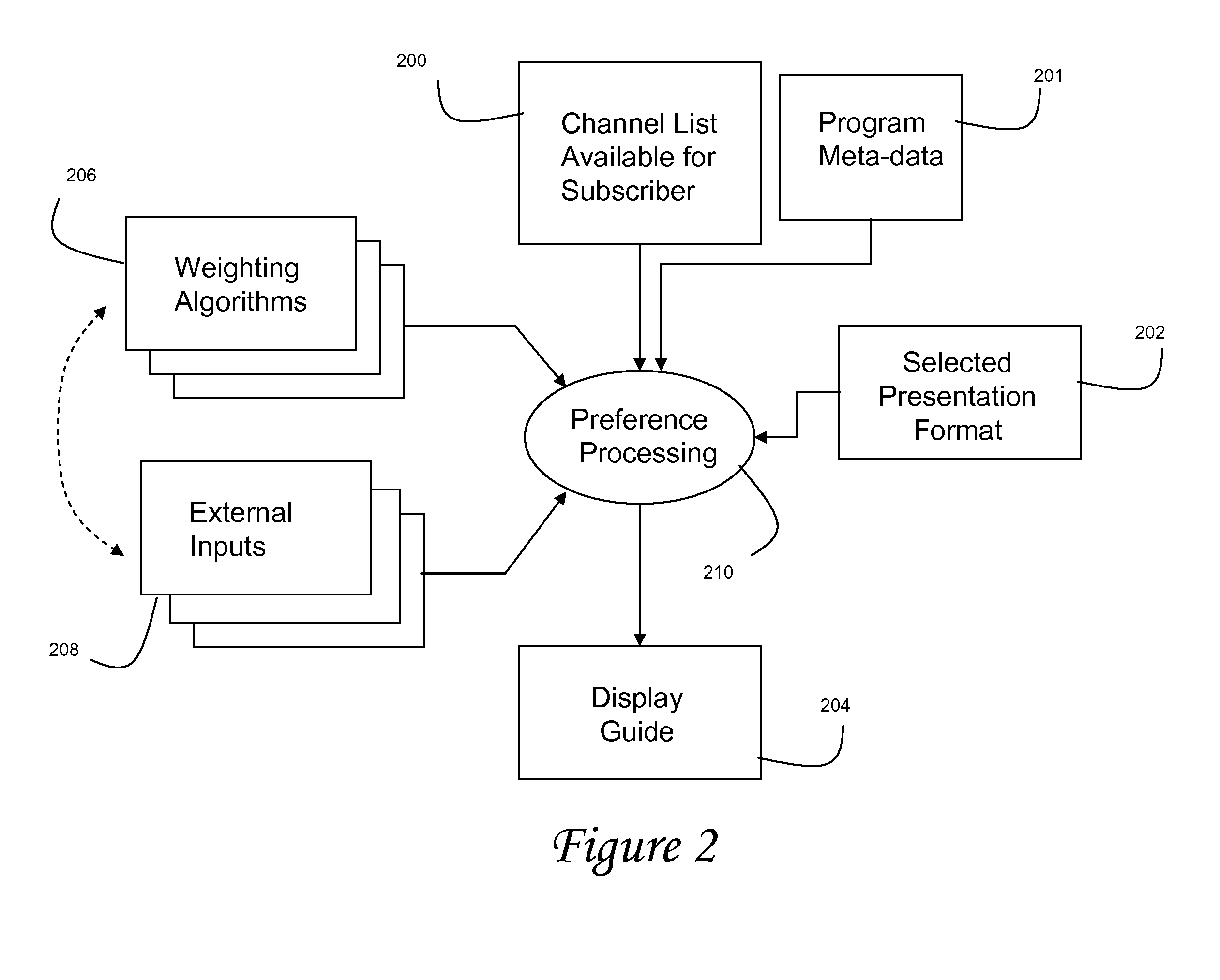
ActiveUS20080148317A1Television system detailsColor television detailsNetwork terminationExternal data
Preferred systems and methods are disclosed for navigating among a group or lists of programs, such as in a network terminal (such as a set top box) in a video program distribution system which presents a viewer with an electronic program guide comprising a plurality of program titles wherein the order is determined by a program score used to predict a level of interest for the viewer based in part on extrinsic data provided to the network terminal regarding the viewer's characteristics and attributes. The extrinsic data could be obtained based on the individual viewer's specific attributes, or the demographic attributes of similarly situated viewers. The extrinsic data, as well as intrinsic data is processed to provide an ordered list of program which are more reflective of that viewer's interests that a linear listing of programs. The system and method can apply for other applications involving prioritizing selection information.
Owner:VERIZON PATENT & LICENSING INC
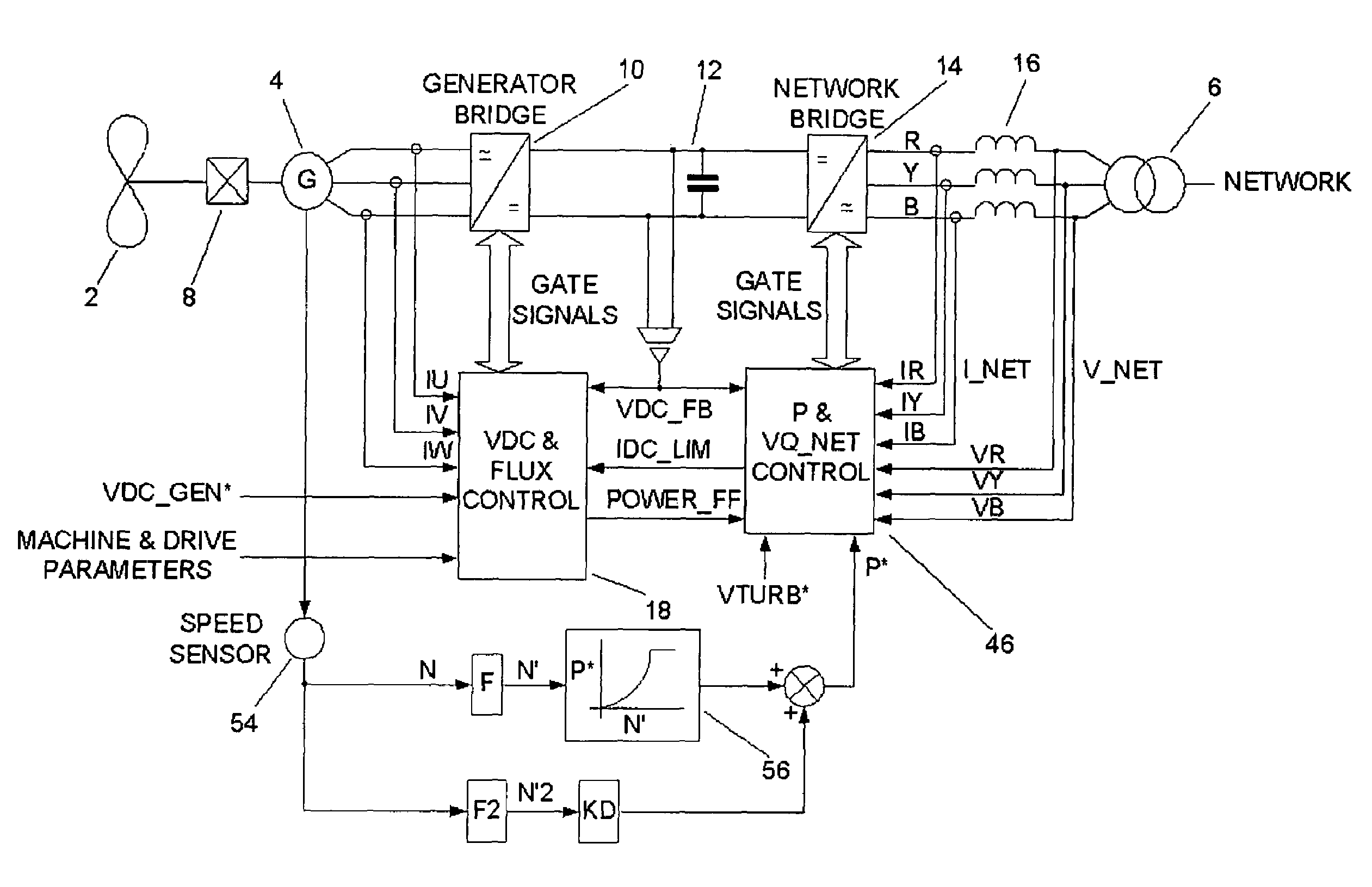
Power converters
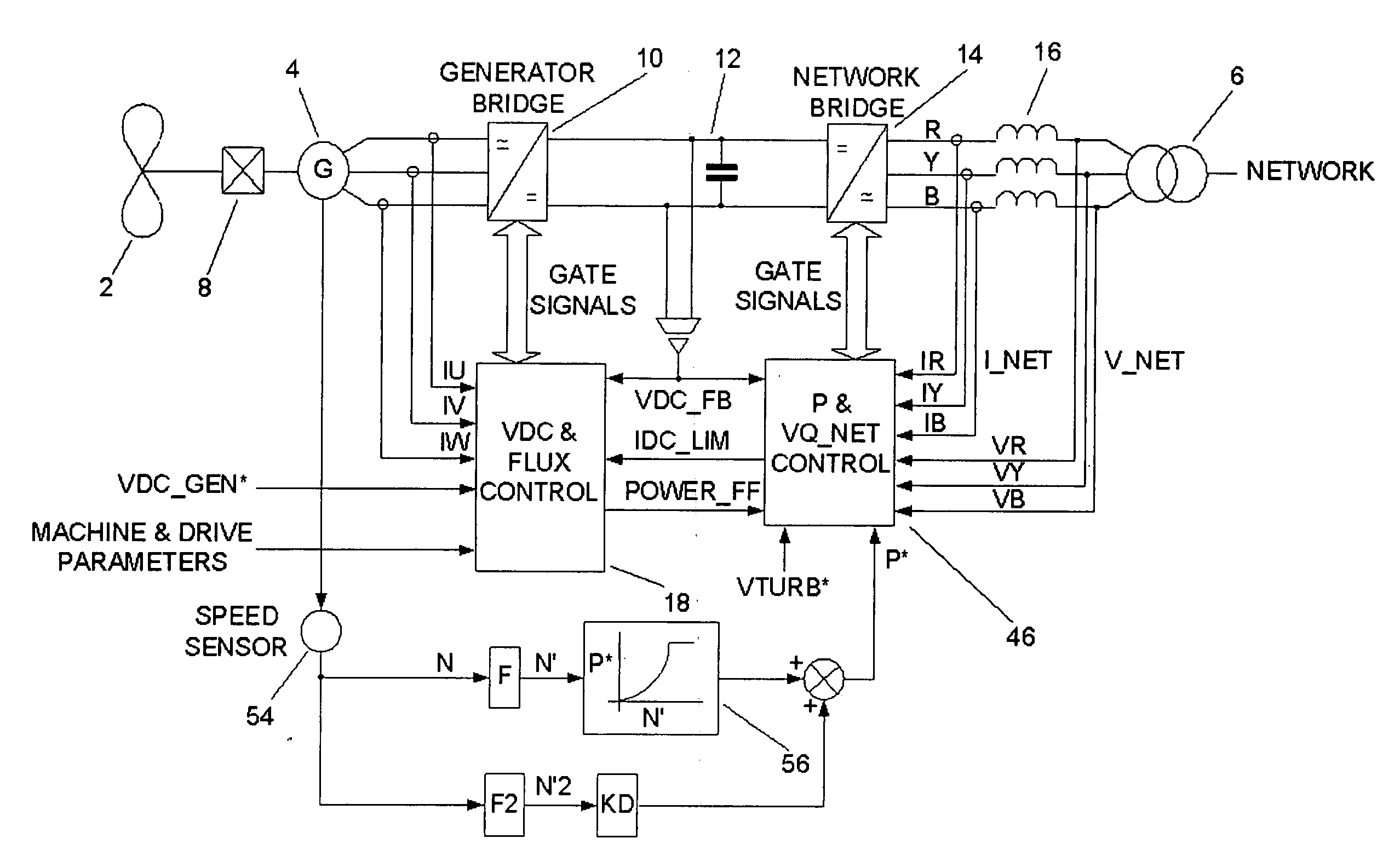
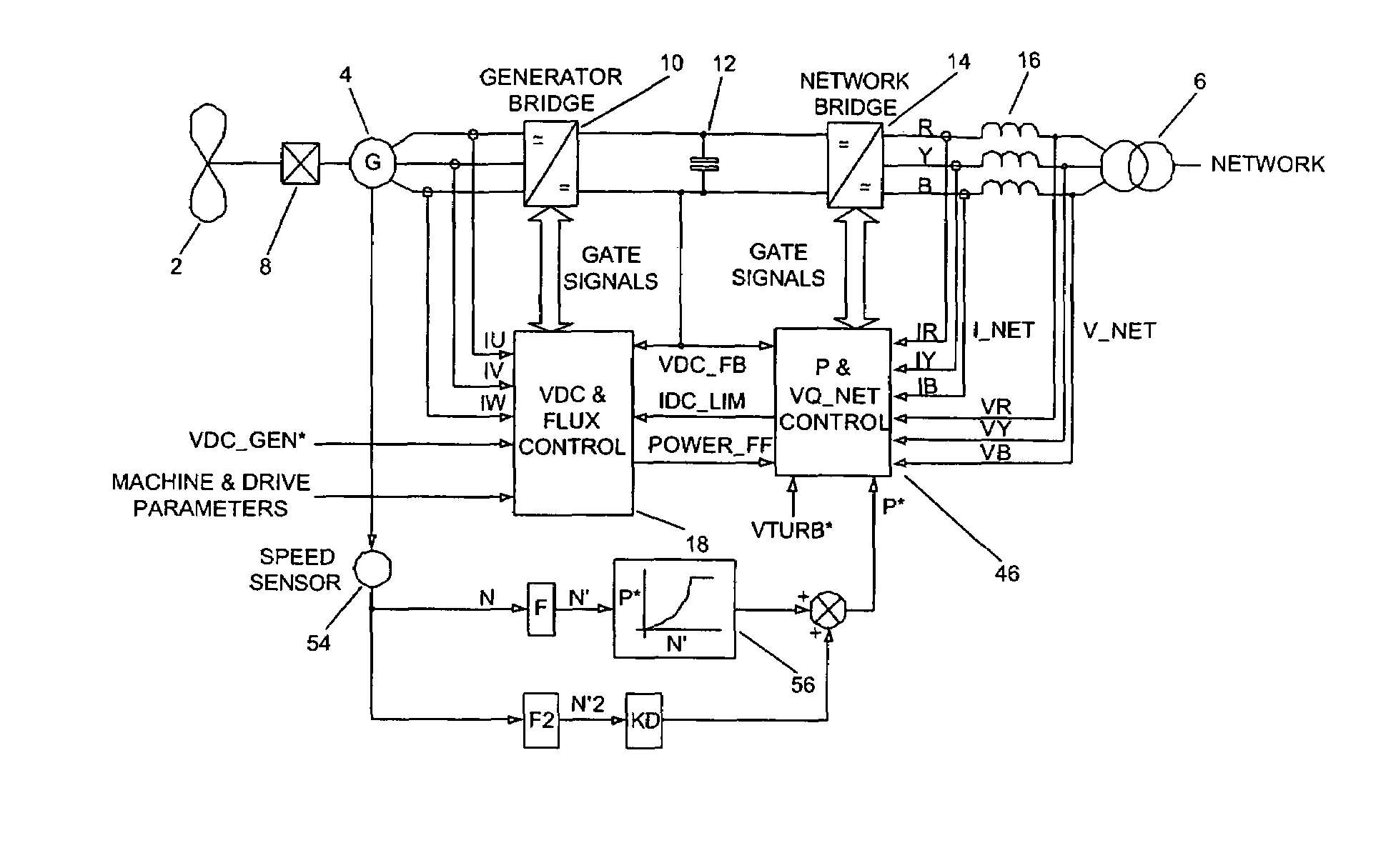
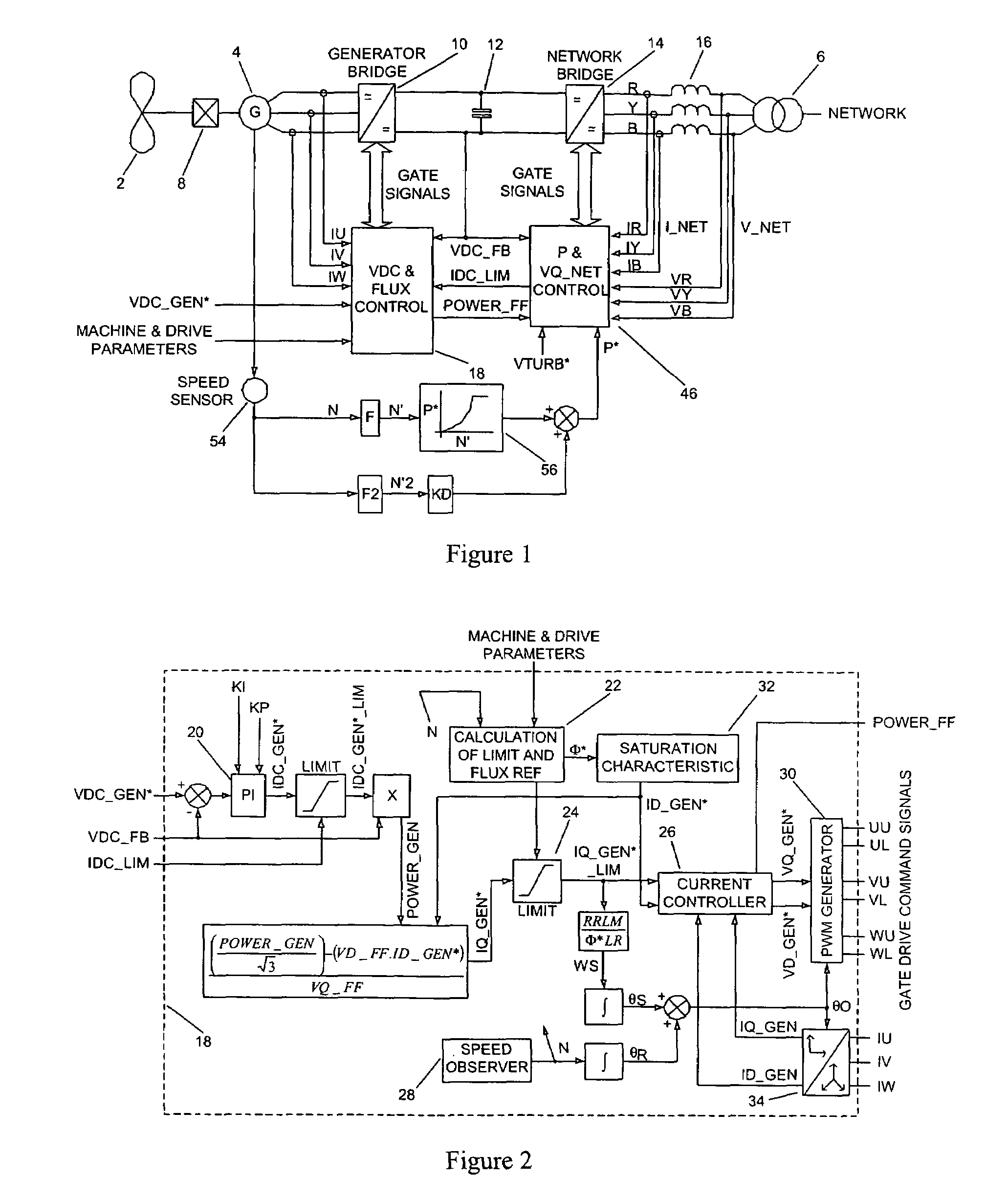
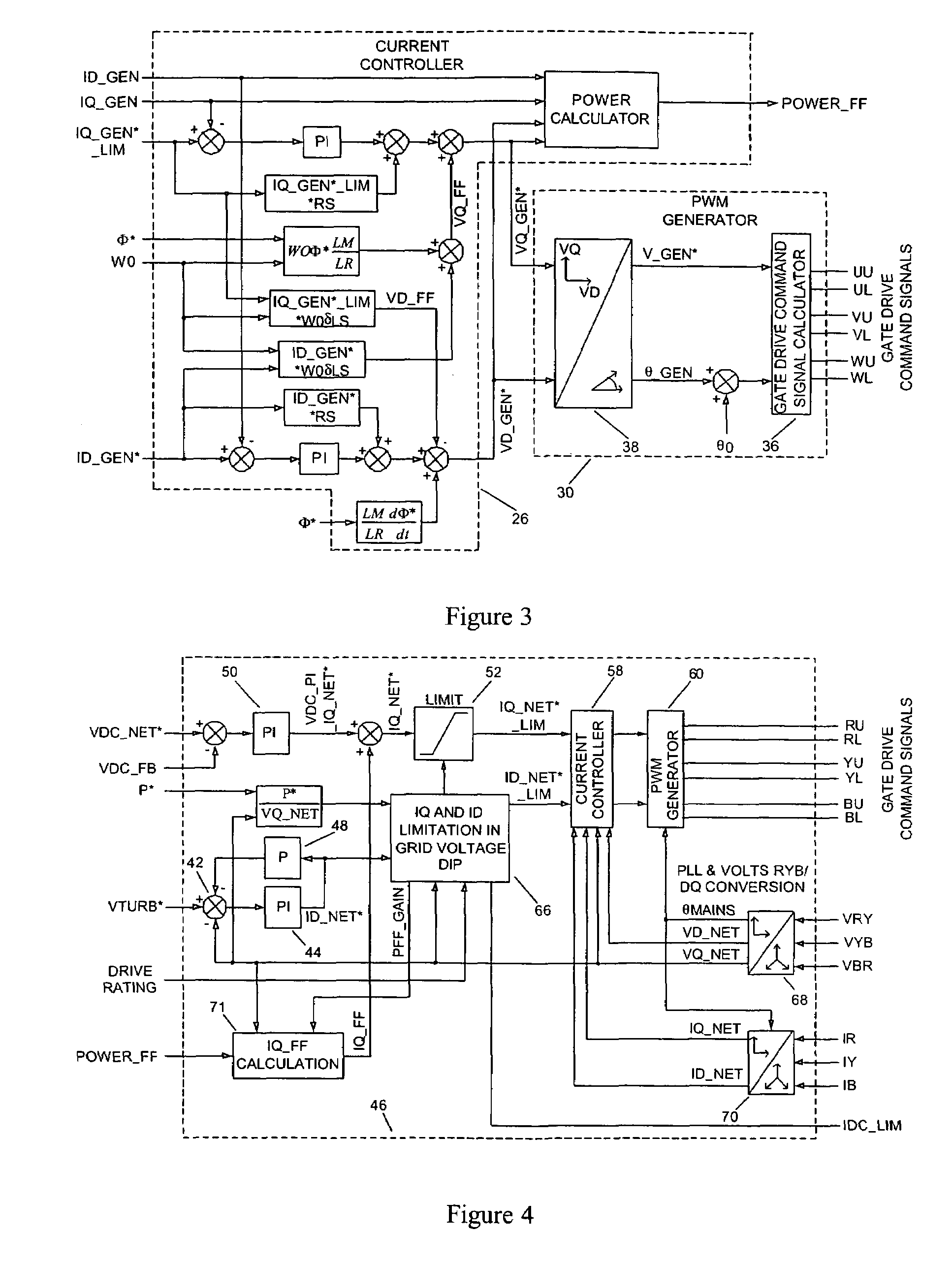
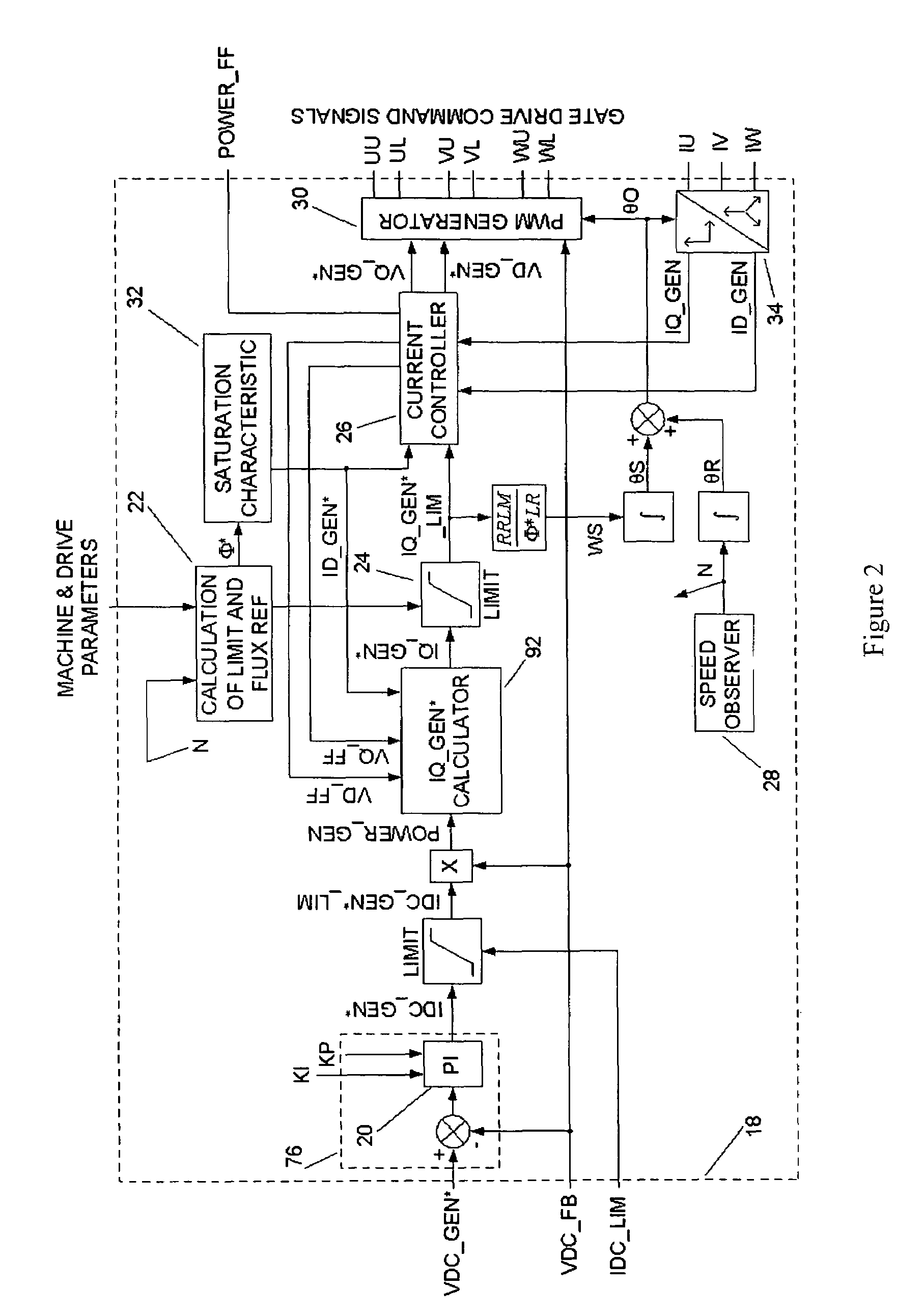
ActiveUS20070121354A1Ac-dc conversion without reversalWind motor combinationsNetwork terminationPower switching
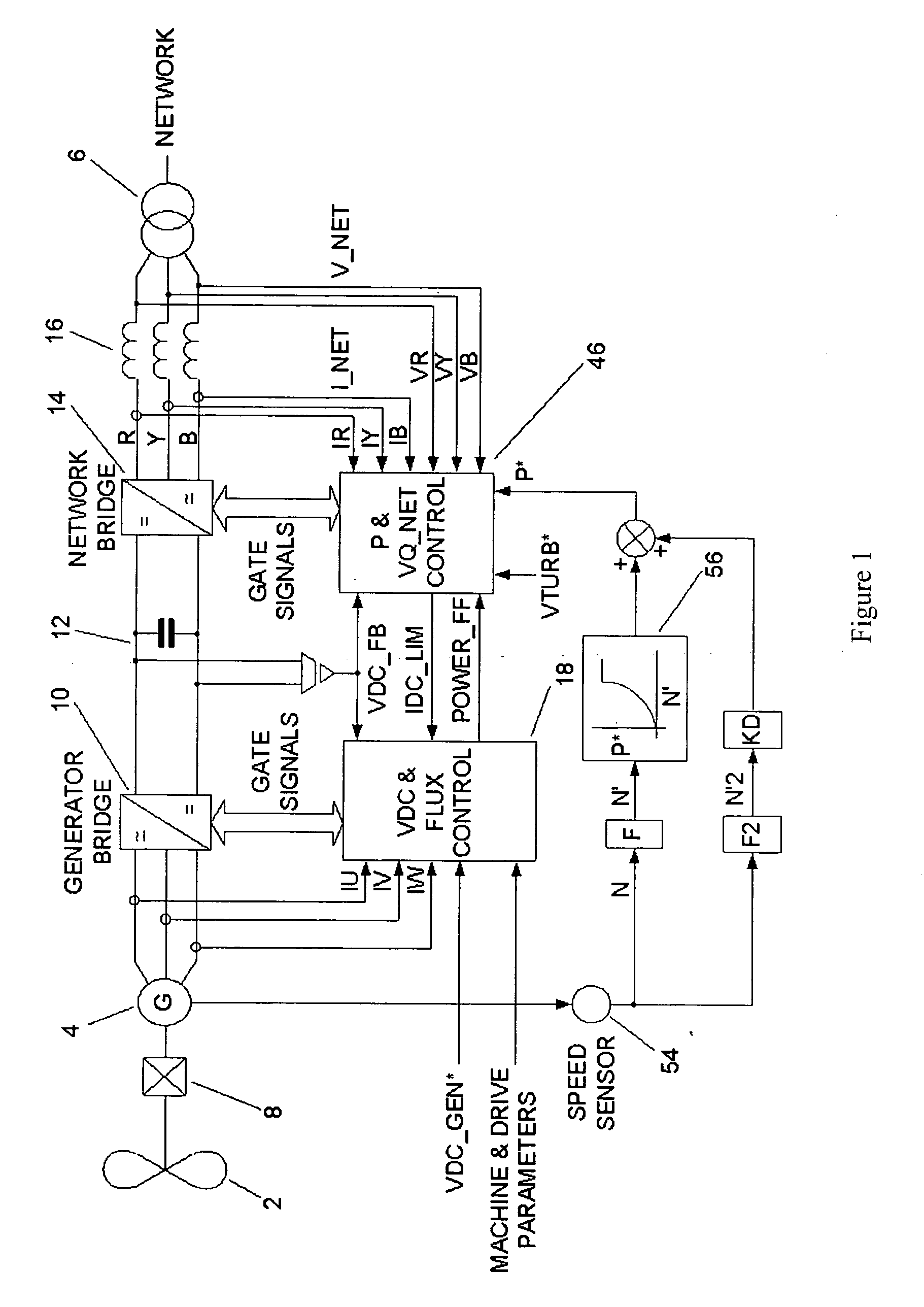
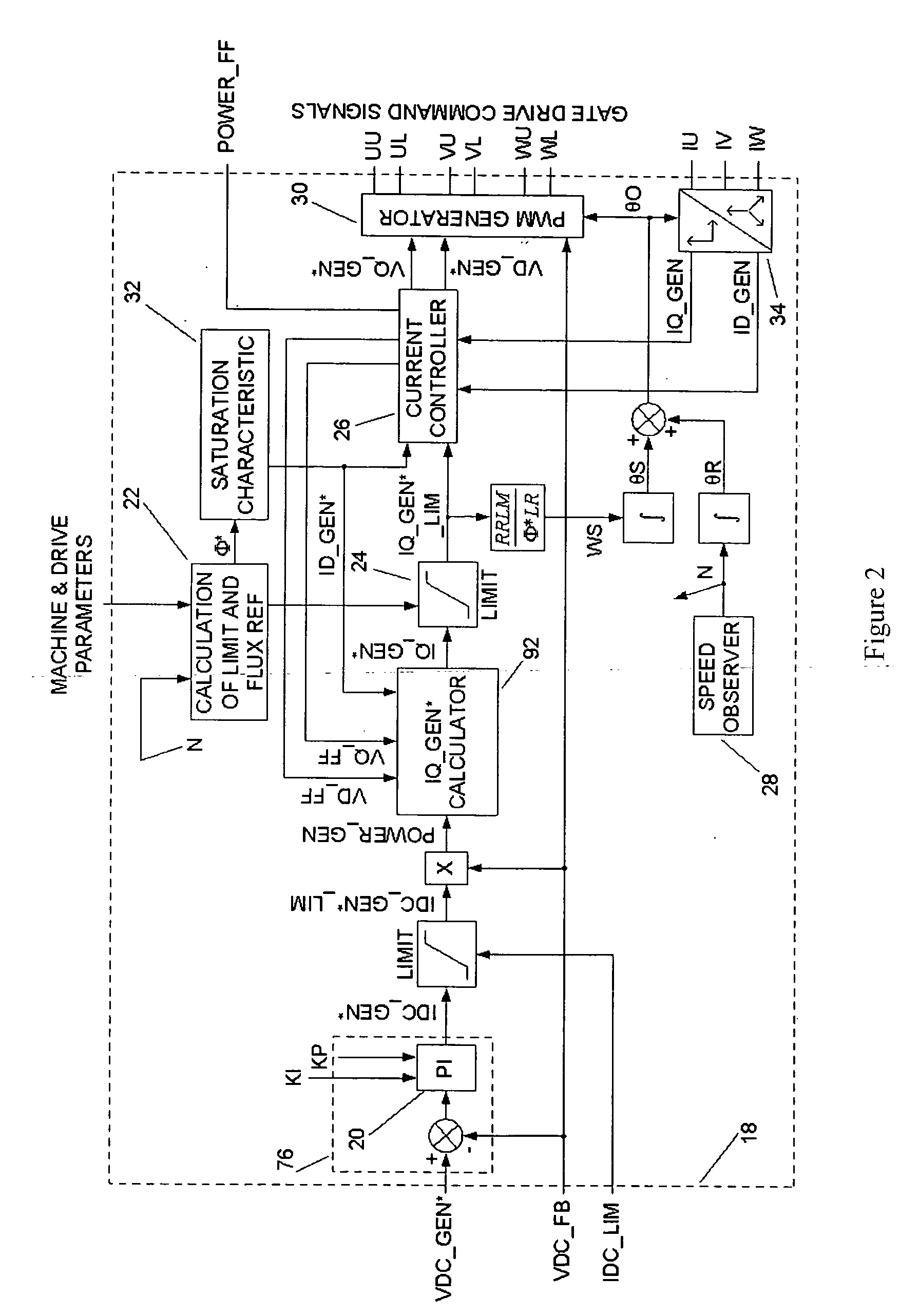
The present invention provides_a power converter that can be used to interface a generator (4) that provides variable voltage at variable frequency to a supply network operating at nominally fixed voltage and nominally fixed frequency and including features that allow the power converter to remain connected to the supply network and retain control during supply network fault and transient conditions. The power converter includes a generator bridge (10) electrically connected to the stator of the generator (4) and a network bridge (14). A dc link (12) is connected between the generator bridge (10) and the network bridge (14). A filter (16) having network terminals is connected between the network bridge (14) and the supply network. A first controller (18) is provided for controlling the operation of the semiconductor power switching devices of the generator bridge (14). Similarly, a second controller (46) is provided for controlling the operation of the semiconductor power switching devices of the network bridge (14). The first controller (18) uses a dc link voltage demand signal (VDC13 GEN*) indicative of a desired dc link voltage to control the semiconductor power switching devices of the network bridge (10) to achieve the desired level of dc link voltage that corresponds to the dc link voltage demand signal (VDC13 GEN*). The second controller (46) uses a power demand signal (P*) indicative of the level of power to be transferred from the dc link to the supply network through the network bridge (14), and a voltage demand signal (VTURB*) indicative of the voltage to be achieved at the network terminals of the filter (16) to control the semiconductor power switching devices of the network bridge (14) to achieve the desired levels of power and voltage that correspond to the power and voltage demand signals (P* and VTURB*).
Owner:GE POWER CONVERSION
System comprising a publish/subscribe broker for a remote management of end-user devices, and respective end-user device
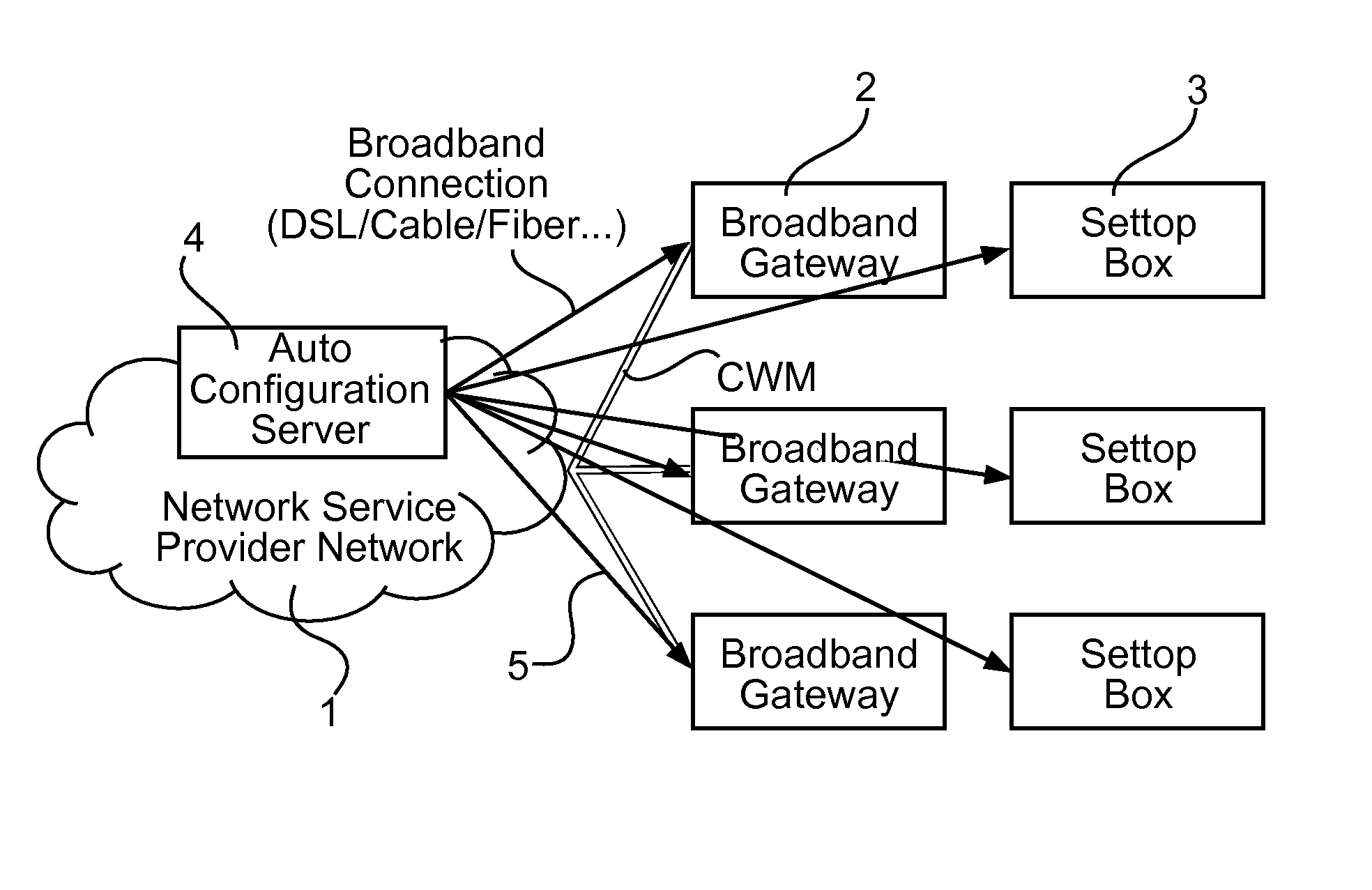
The present invention provides a method for sending a message to a network device with a specific MAC address, in an IP network implementing a internet group management protocol IGMP, comprising: sending, by a network terminal, to the network device, a multicast group management status message including a destination address set as the specific MAC address A system comprises a multitude of end-user devices coupled via a broadband connection with a service provider network, a publish / subscribe broker adapted to communicate with the multitude of end-user devices and at least a first back-end entity coupled with the service provider network. The first back-end entity includes a first client software application for connecting to the publish / subscribe broker and publishes control data via a control data channel for a device management of the end-user devices. The end-user devices include a second client software application for connecting to the publish / subscribe broker for subscribing to the control data channel and for receiving the control data, and for publishing device data and action data as instructed by the control data. The backend entity authorization is validated in particular by using a control data signature.
Owner:INTERDIGITAL CE PATENT HLDG
Method and system for conditional acceptance to a group
InactiveUS20050149443A1Easy accessData processing applicationsAssess restrictionNetwork terminationApplication server
In one embodiment, a method and system allows management of restricted group access based upon credentials associated with network terminals. Location information from a location server and capability information from a profile server may provide the credentials that are checked by an application server for compliance with predefined access requirements to the group. Additionally, performance during, for example, a gaming activity may provide performance related credentials that are required for access to performance related groups.
Owner:NOKIA CORP
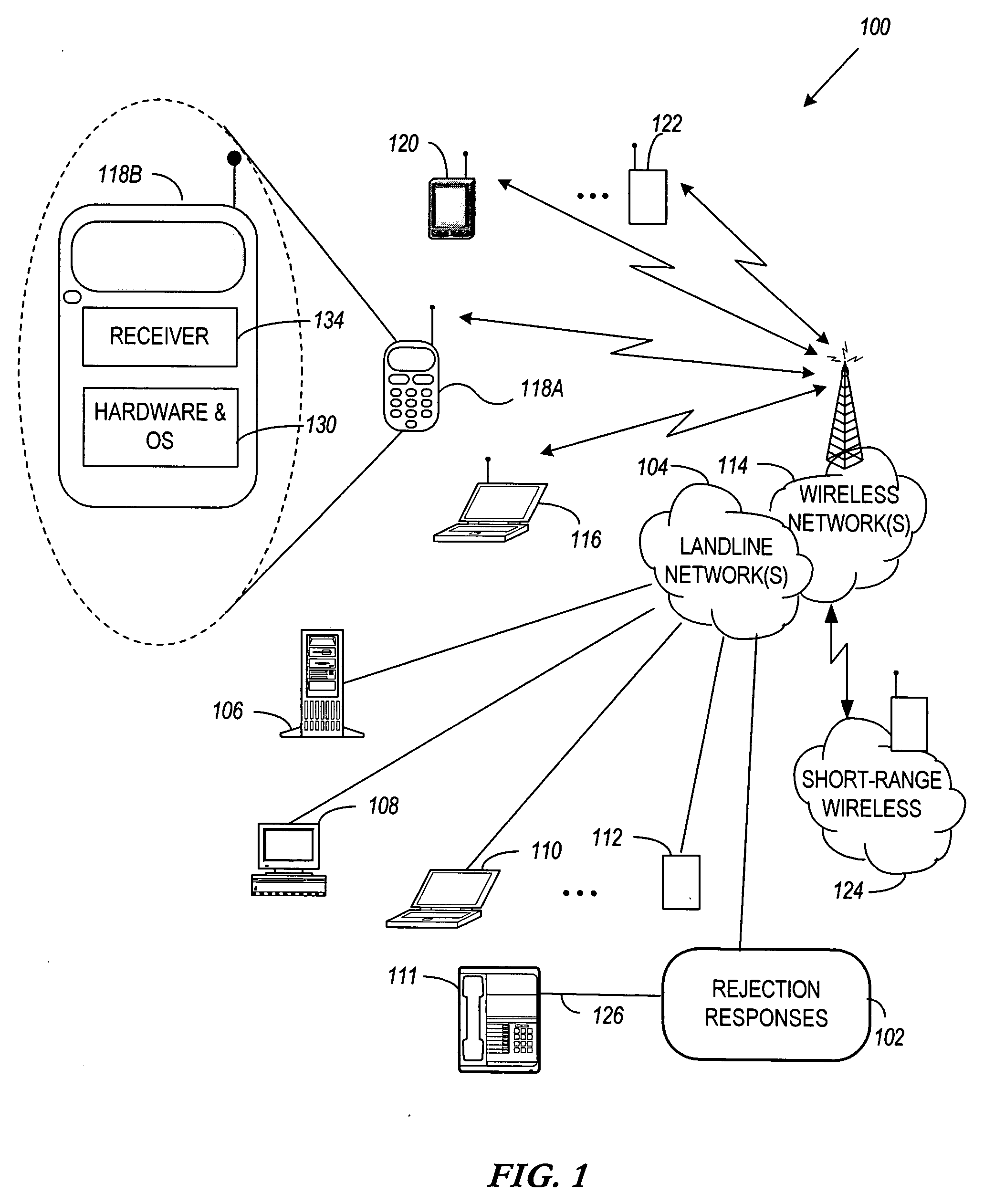
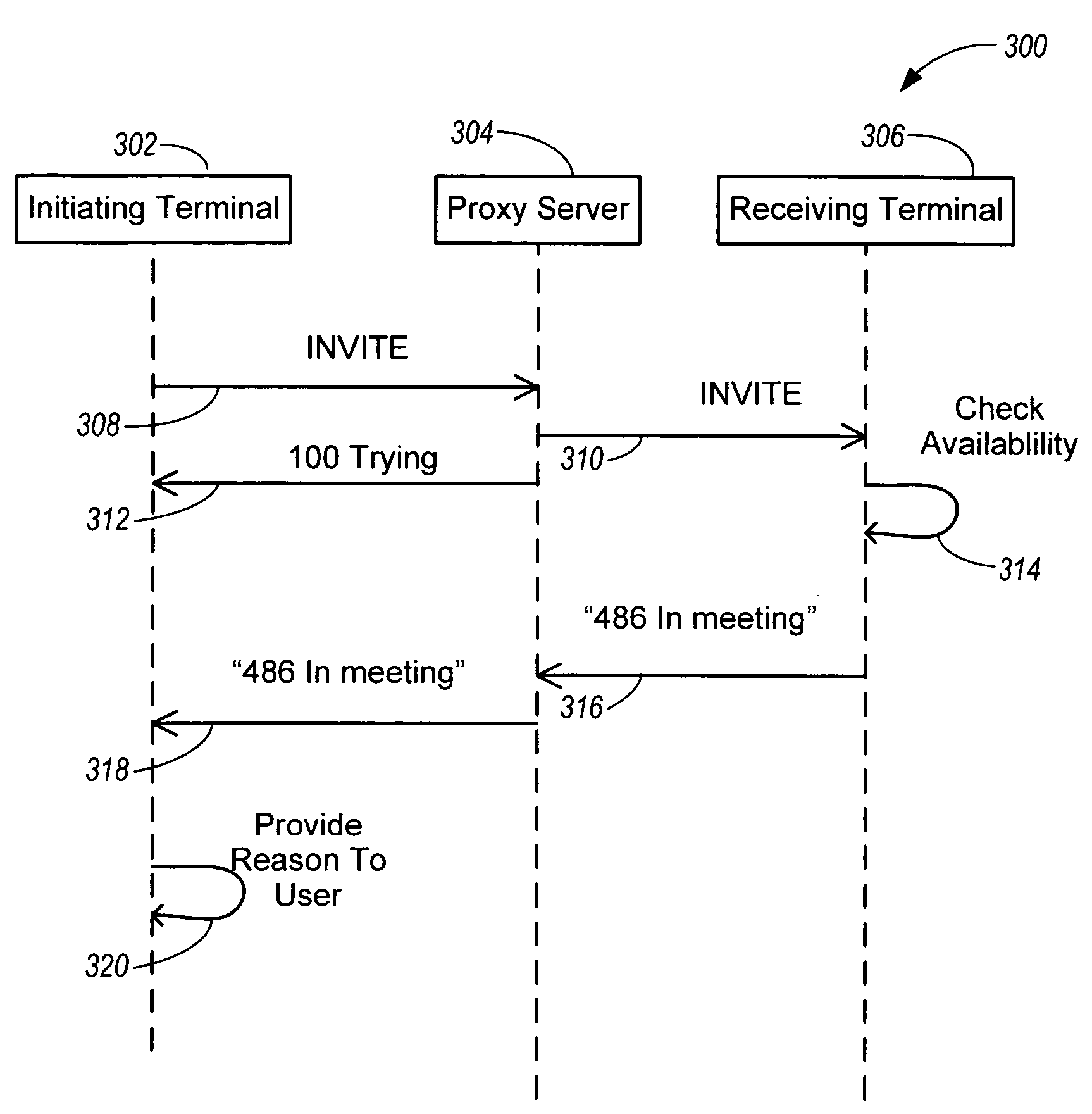
Apparatus, system, and method for rejecting a session establishment request
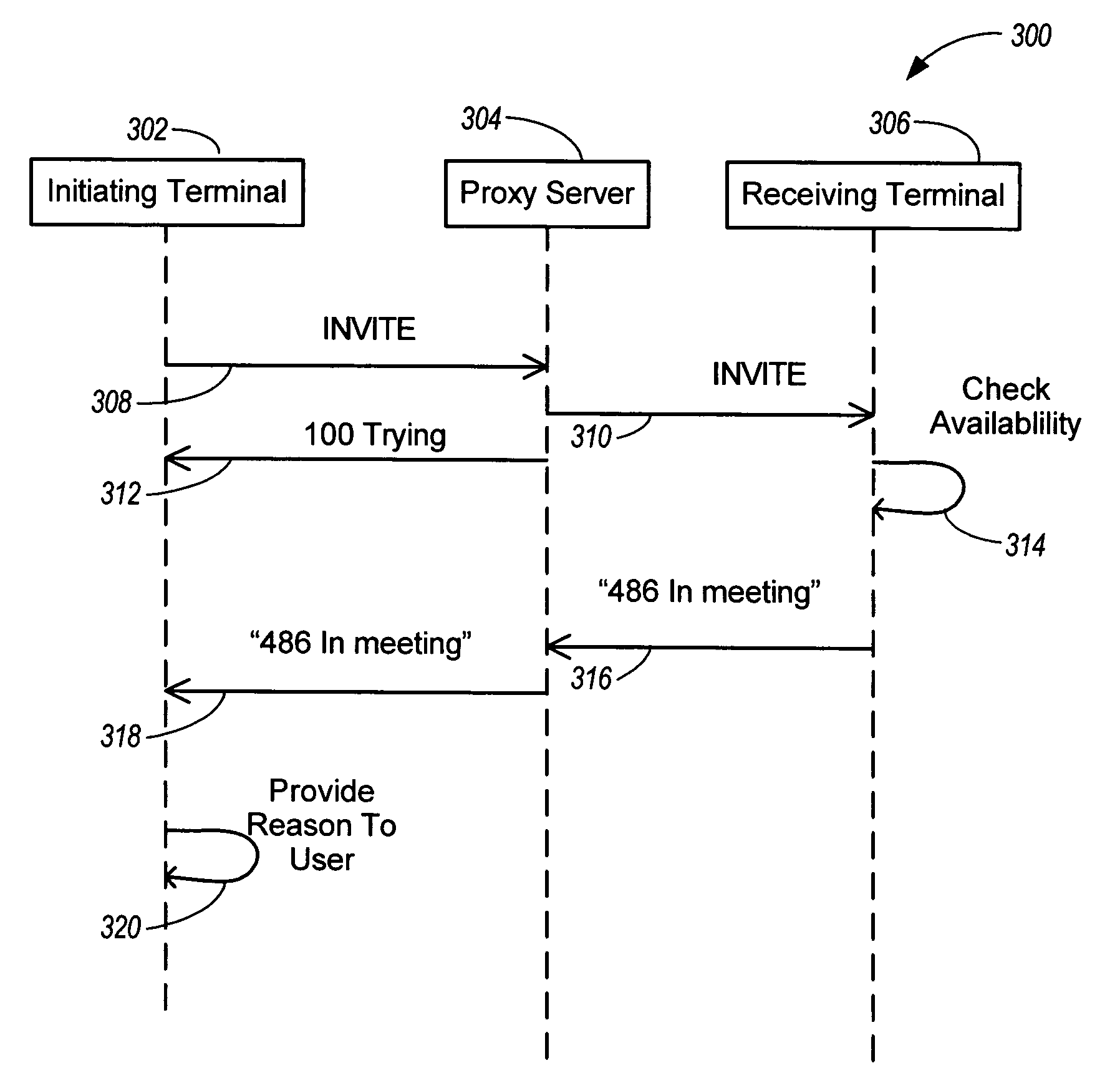
InactiveUS20050265318A1Connection managementData switching by path configurationComputer hardwareNetwork termination
Rejecting a session request initiated via a session establishment protocol involves receiving, at a first network terminal, a session initiation request sent from a second network terminal via the session establishment protocol. A rejection message of the session establishment protocol is formed based on a presence state of the first network terminal. The rejection message is sent via the session establishment protocol targeted for the second network terminal.
Owner:NOKIA CORP
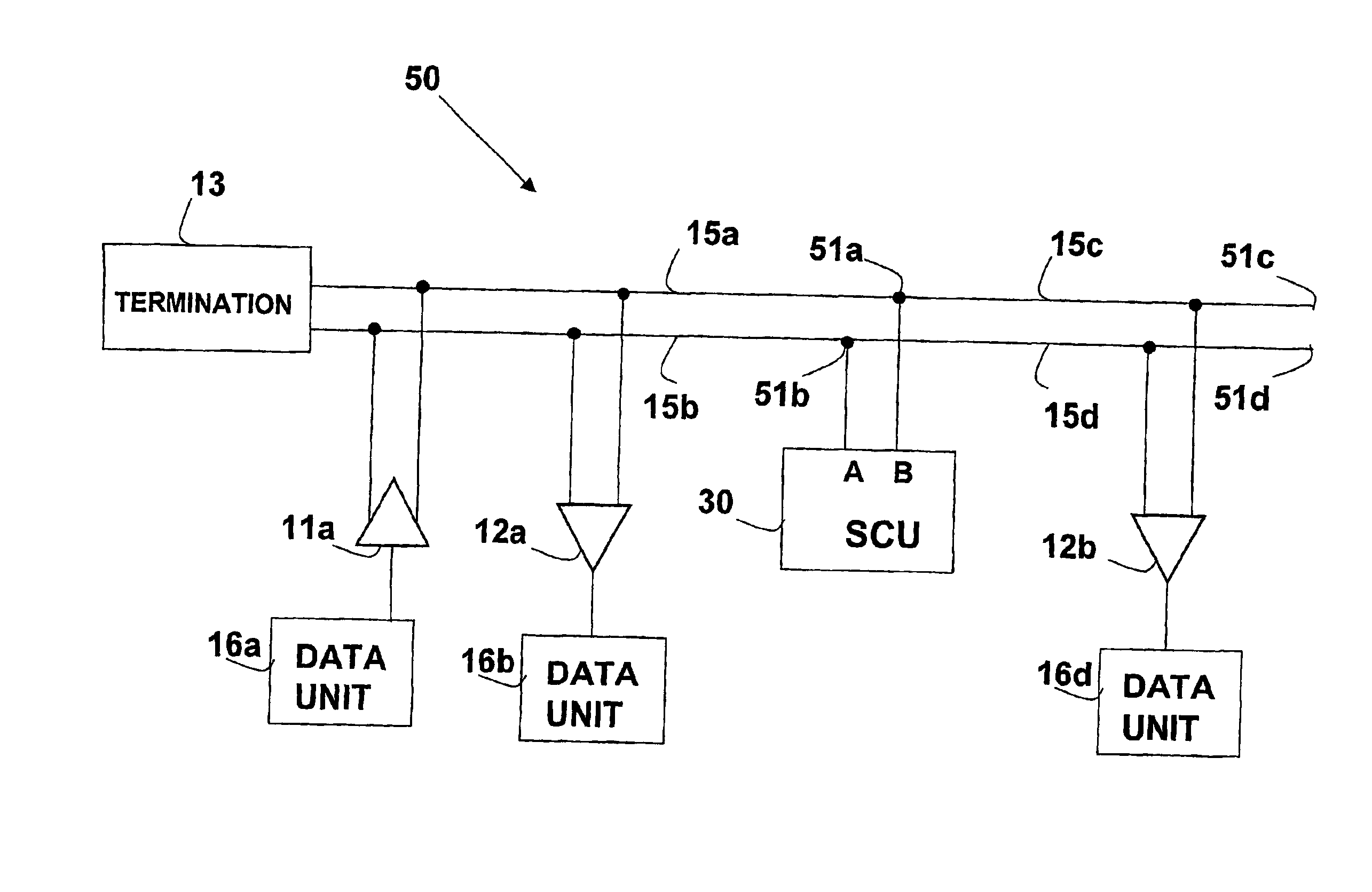
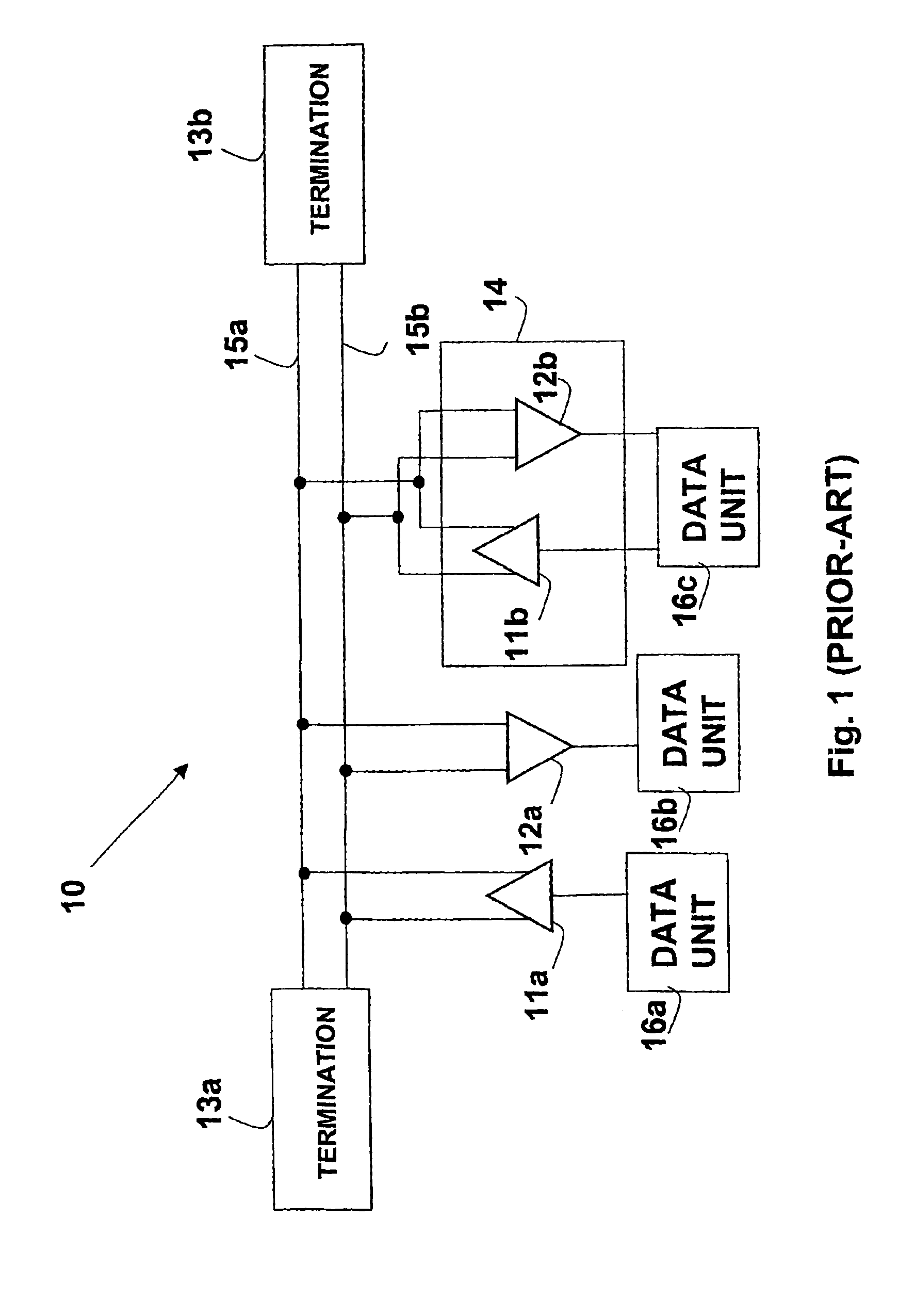
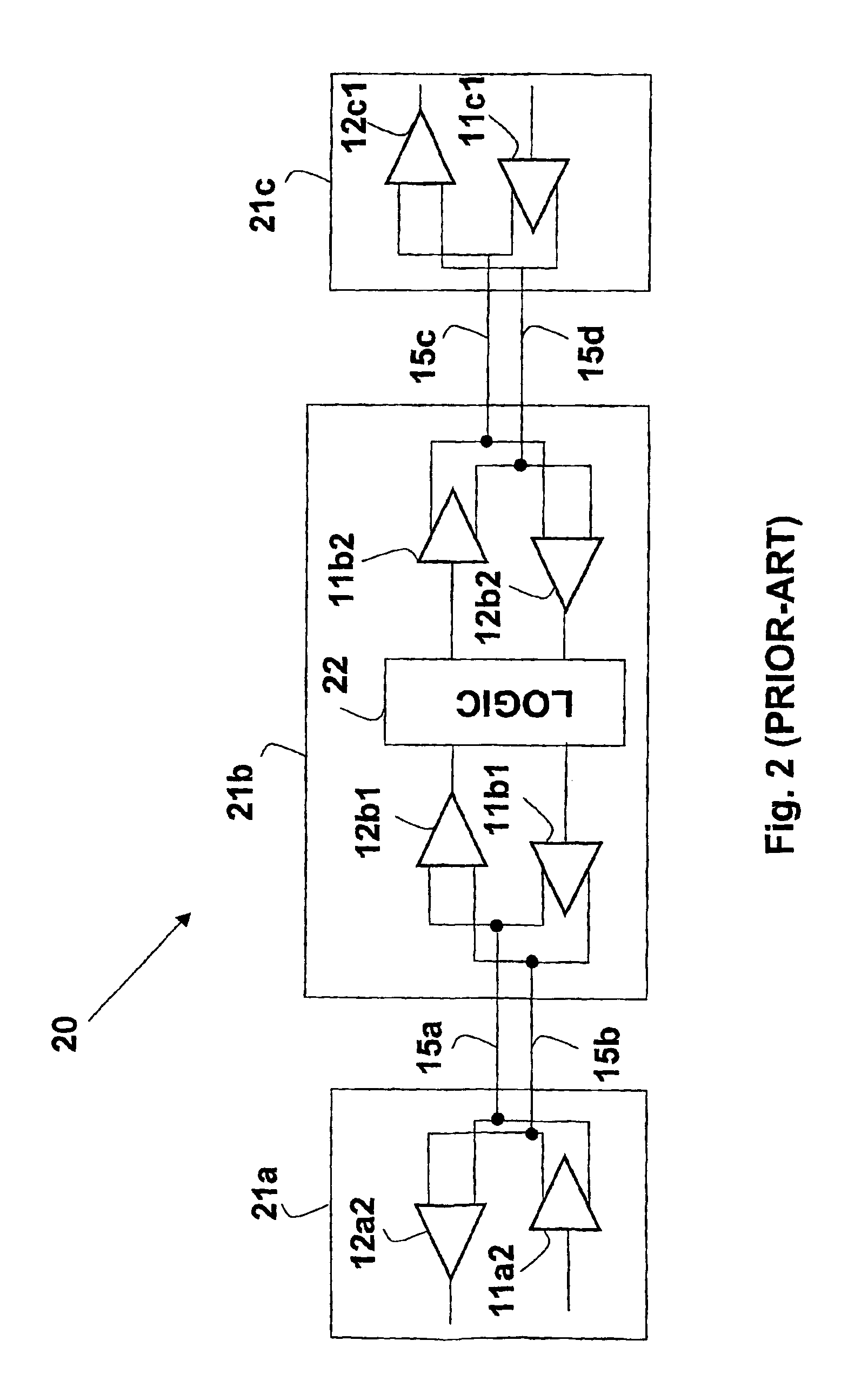
System and method for transmission-line termination by signal cancellation, and applications thereof
InactiveUS6937056B2Effective segmentationInput/output impedence modificationReliability increasing modificationsElectric power transmissionNetwork termination
An active terminating device (30) for an electrical transmission line with optional line-receiving and line-driving capabilities. The basic device is a two-terminal unit, denoted as a Signal Canceling Unit (SCU), which sensesthe signal available at its terminals (34a, 34b), and applies negative feedback in order to cancel and absorb the signal. When applied to the end of a transmission line (15a, 15b) as part of wired communication network, the SCU functions as a terminator. When connected in the middle of such wired transmission line, the SCU splits the transmission line into two separate and isolated segments. In such a configuration, the SCU can be used to isolate a portion of a network from signal degradation due to noise or bridge-tap. Furthermore, the two isolated segments may each employ independent communications, such that no interference exists between the segments. In another embodiment, line receiver functionality is integrated into the SCU, designated as a Signal Canceling and Receiving Unit (SCRU) (90). The SCRU can perform all the SCU functions, and also serves as a line receiver in the communication network. In yet another embodiment, line driver functionality is integrated into the SCRU, designated as a Signal Canceling, Receiving and Transmitting Unit (SCRTU) (120). The SCRTU can perform all the SCRU functions, and also serves as a line driver in the communication network. Upon connecting multiple SCRTU's to a continuous transmission line, terminated independent point-to-point communication segments are formed.
Owner:CONVERSANT INTPROP MANAGEMENT INC
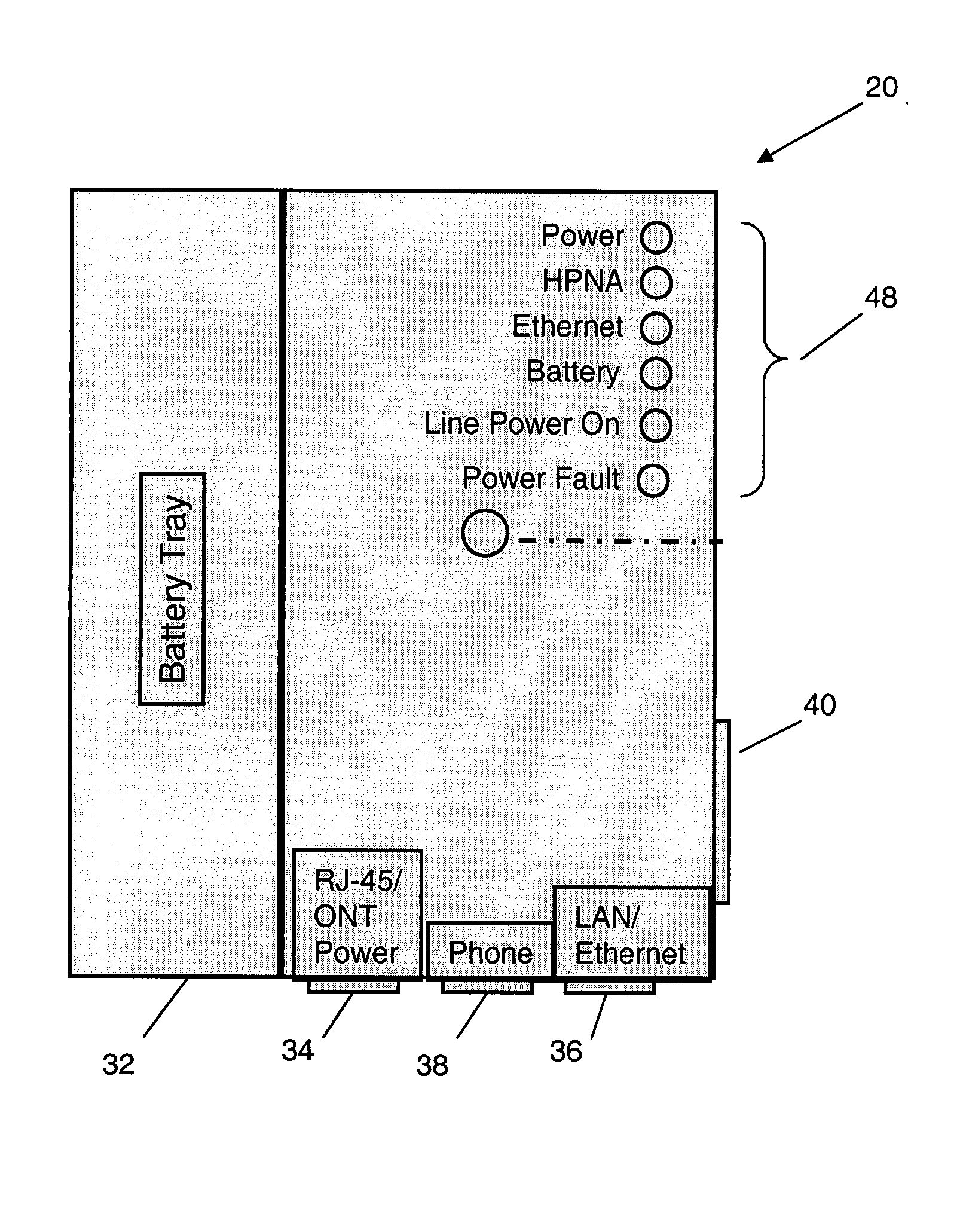
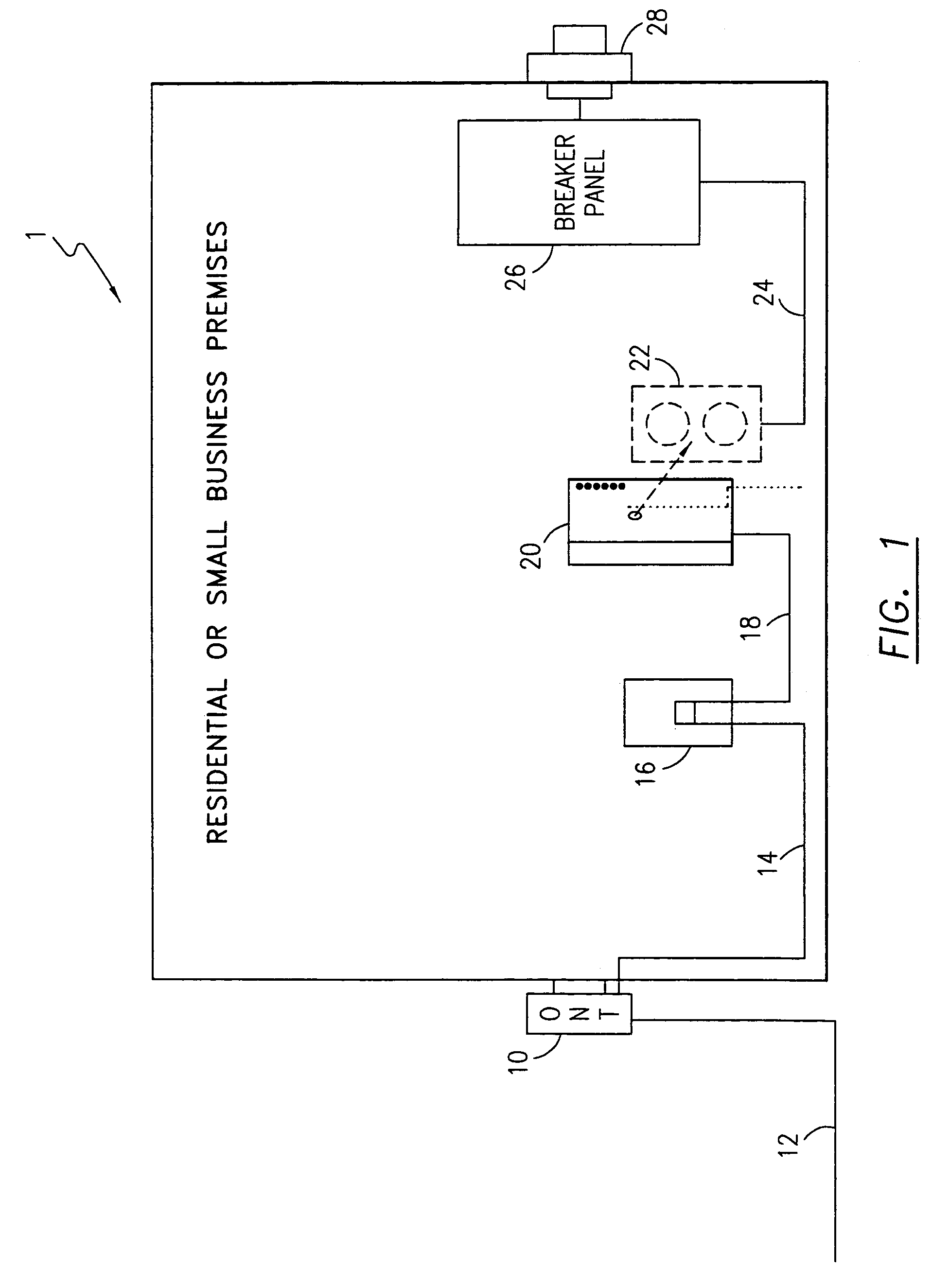
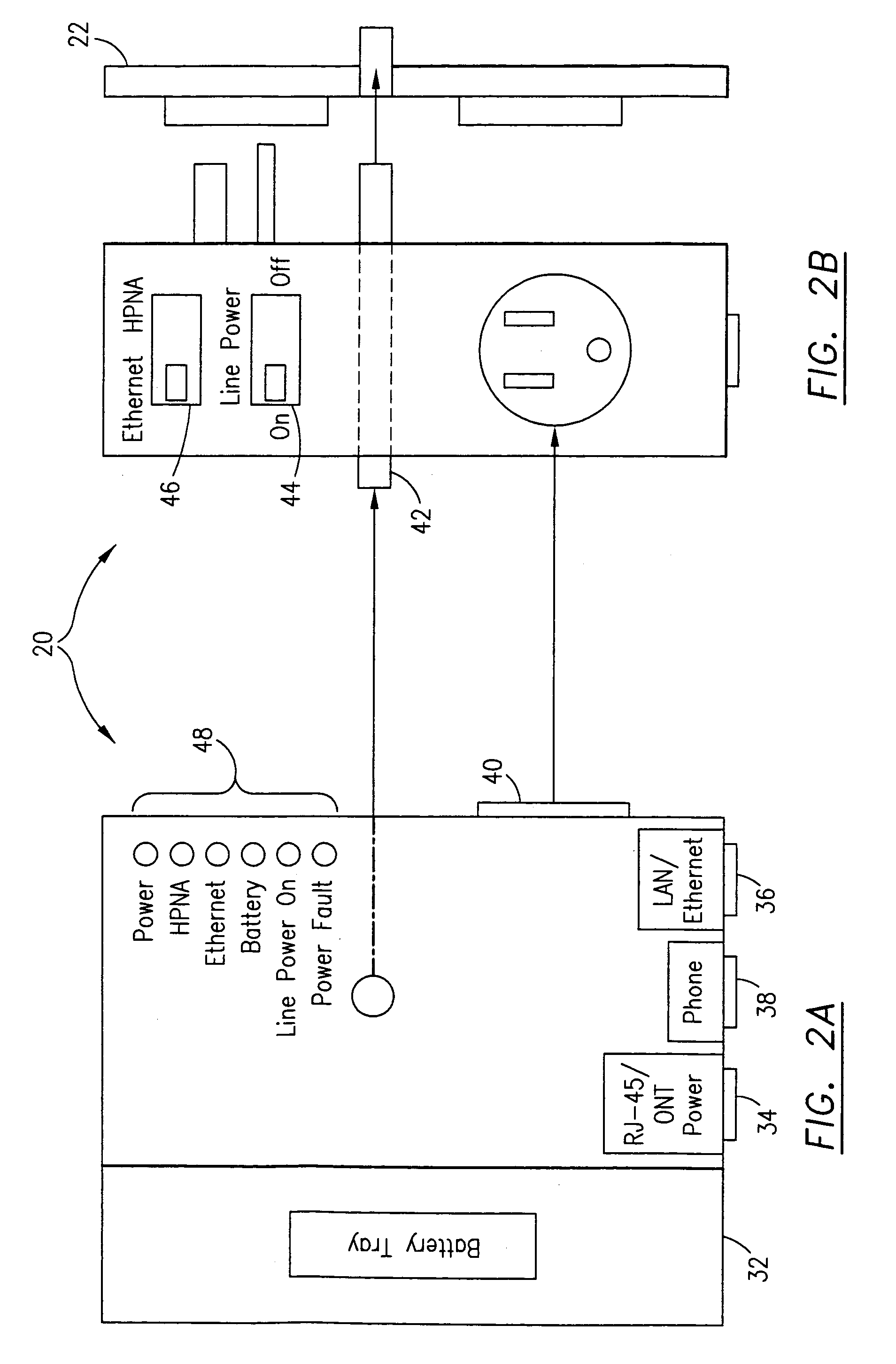
Power adapter and broadband line extender system and method
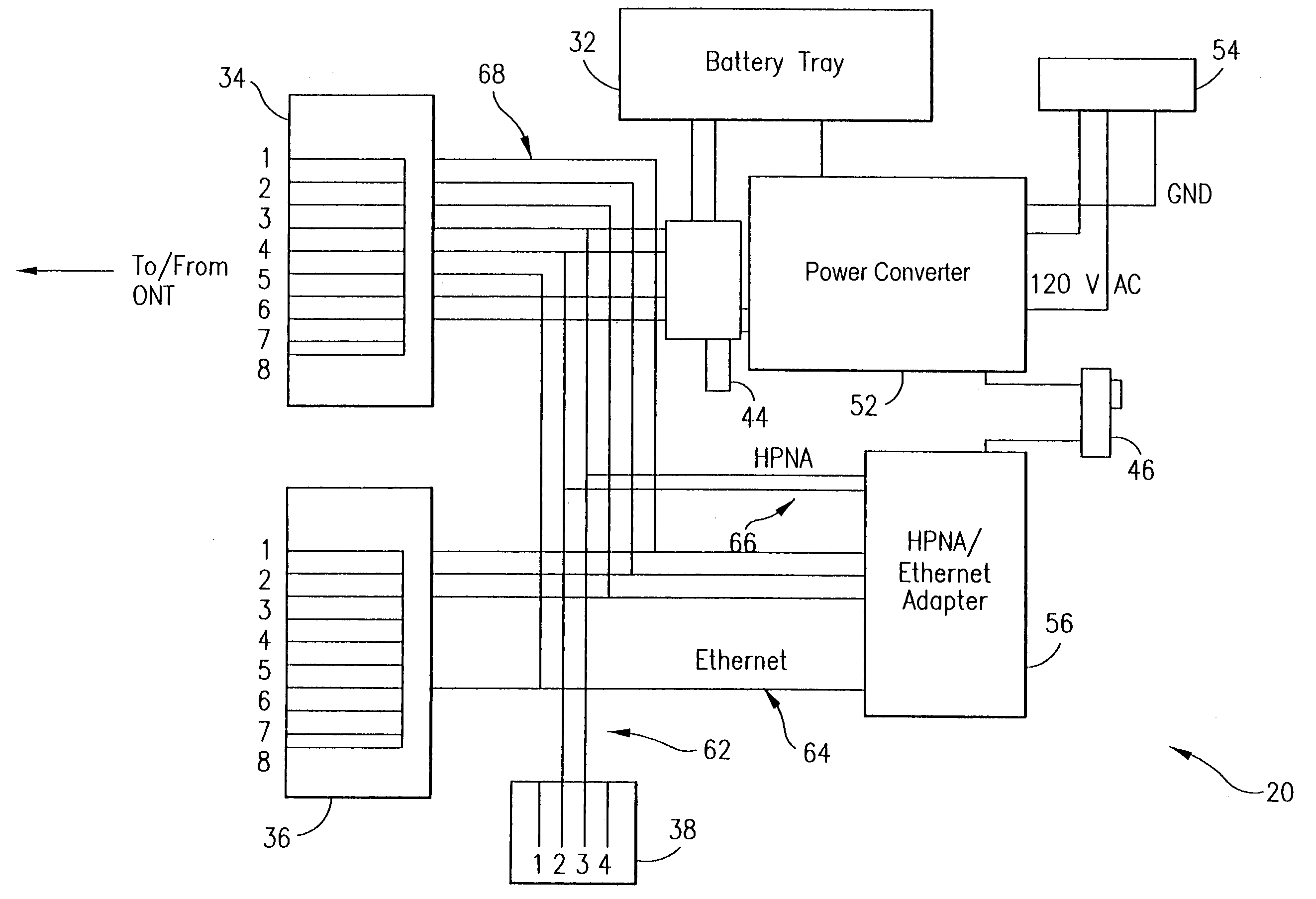
ActiveUS20040268160A1Volume/mass flow measurementTwo-part coupling devicesNetwork terminationData port
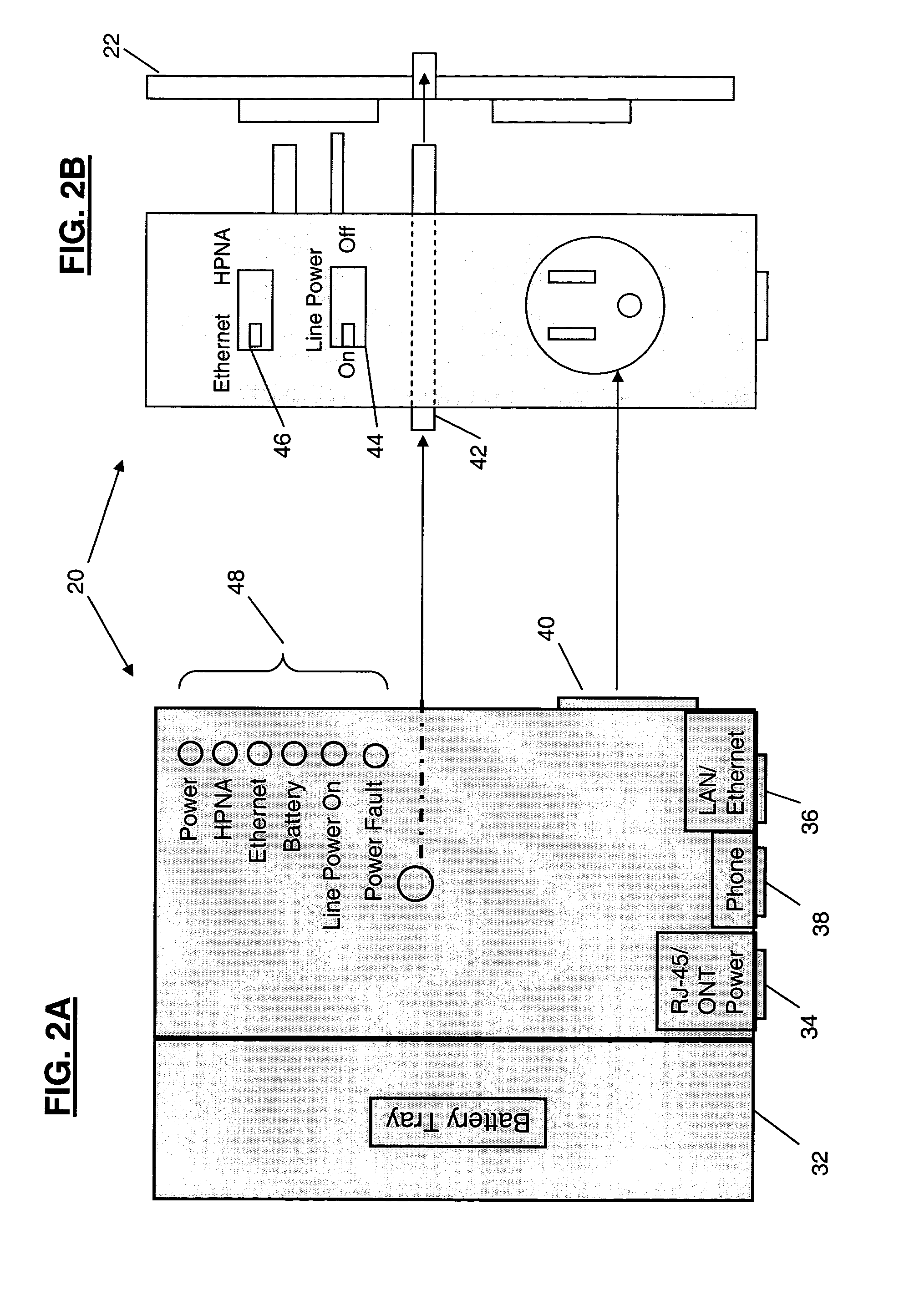
A power adapter, in a presently preferred embodiment, includes a power converter and multiple data ports, and is configured for ease of coupling the power converter into pre-existing premises power connectors. Thus, premises power can be supplied from the power converter and a first data port, via data cabling, to a network terminating device for an external network. Multi-protocol adapters, such as an HPNA (Home Phoneline Network Alliance protocol compliant) / Ethernet adapter, may also be included to provide extension of a protocol (such as Ethernet) over pre-existing premises wiring. A back-up battery is optionally provided, as well as appropriate switches and indicators. Specialized male-female connectors may also be used.
Owner:TELLABS VIENNA
Antenna System and Methods for Wireless Optical Network Termination
ActiveUS20140233951A1Television system detailsOptical transmission adaptationsNetwork terminationTransport medium
Optical network termination systems, devices and methods including an optical network terminal (ONT) having a processor in communication with an external optical fiber. The ONT processors further in communication with a wireless access point and at least one electrically conductive internal transport medium, both providing for the communication of telecommunication signals with devices located within a customer premises. The wireless access point and in certain instances the processor are back powered over the electrically conductive internal transport medium from AC power within the premises. In certain embodiments, the wireless access point communicates with devices within the premises over a distributed antenna.
Owner:CENTURYLINK INTPROP
Method and system for controlling and auditing content/service systems
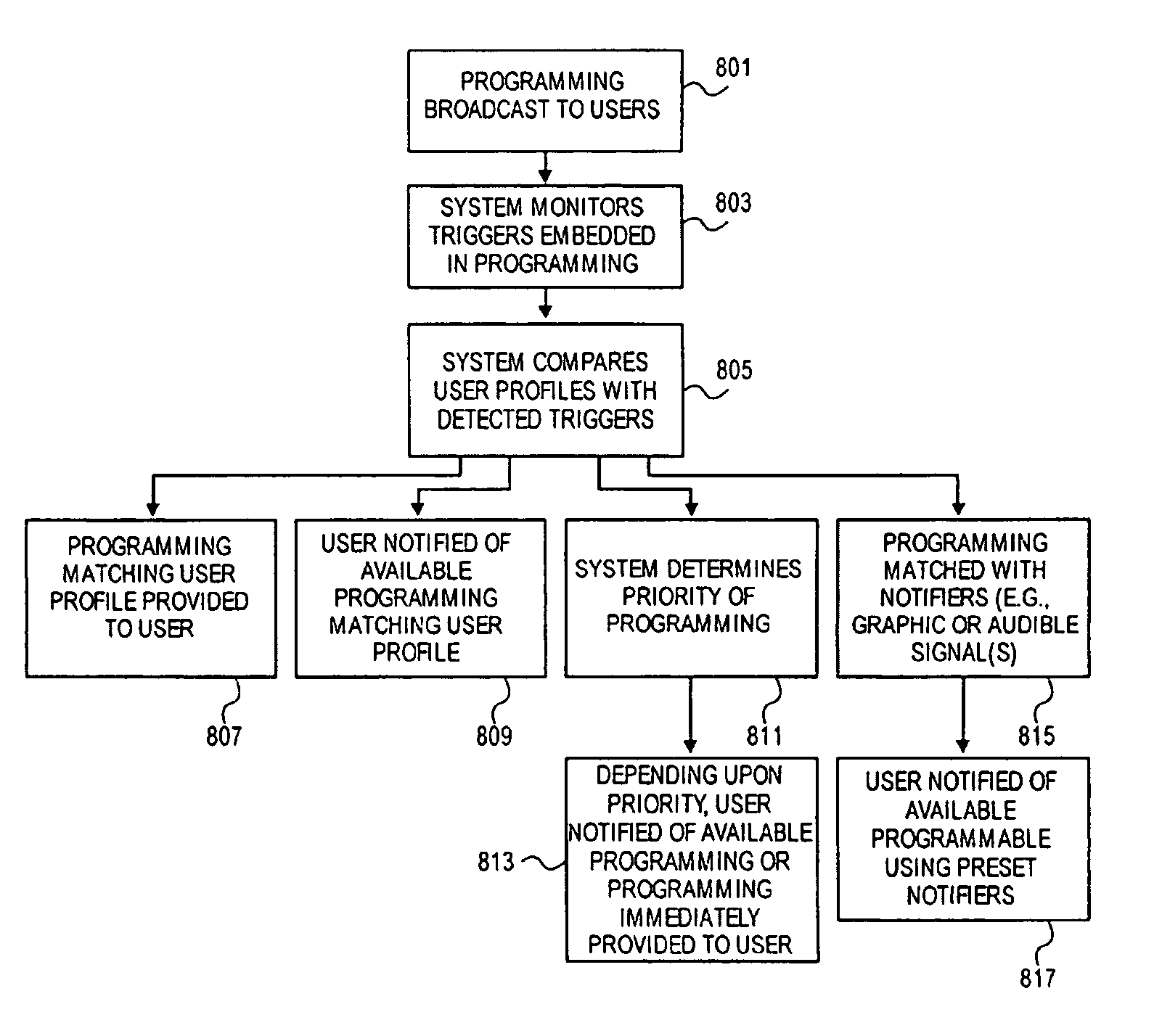
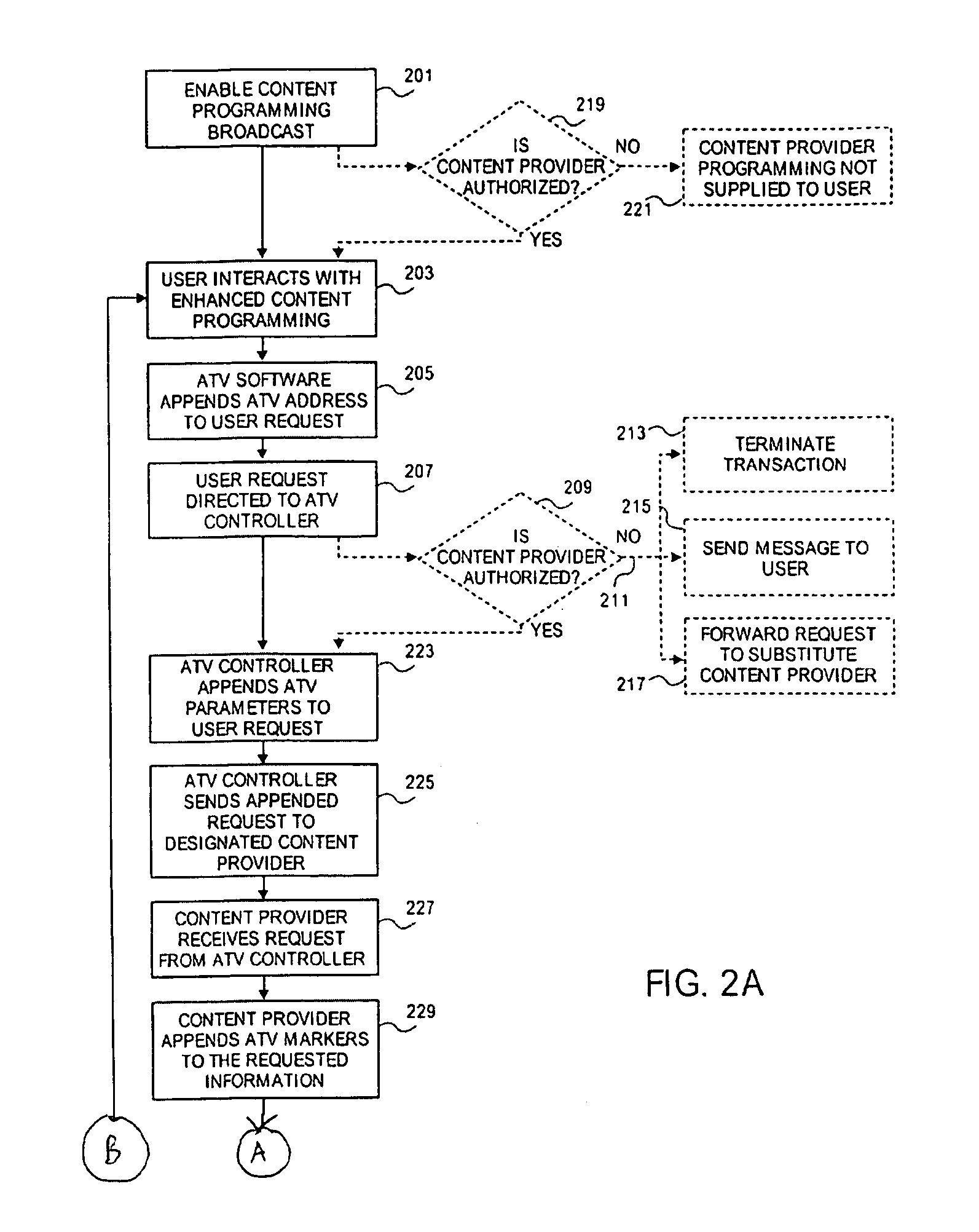
ActiveUS7426558B1Efficiently garnerEasily enforceFinanceAnalogue secracy/subscription systemsThird partyGraphics
An improved interactive network system is provided that allows the Network Operator to control the transfer of information to and from the network end users, the system preferably using triggers or markers embedded within the programming broadcast to users via the network. As a consequence of this system, the Network Operator is able to efficiently garner revenues from third parties transacting business over the network and to control the look and feel of programming offered to network users. Additionally the system can be used as a means of limiting network access, filtering programming, providing on-screen graphics or audible signals for particular programming types or providers, bookmarking programming, profiling network users, targeting advertising, and simplifying network transactions.
Owner:INTERDIGITAL MADISON PATENT HLDG
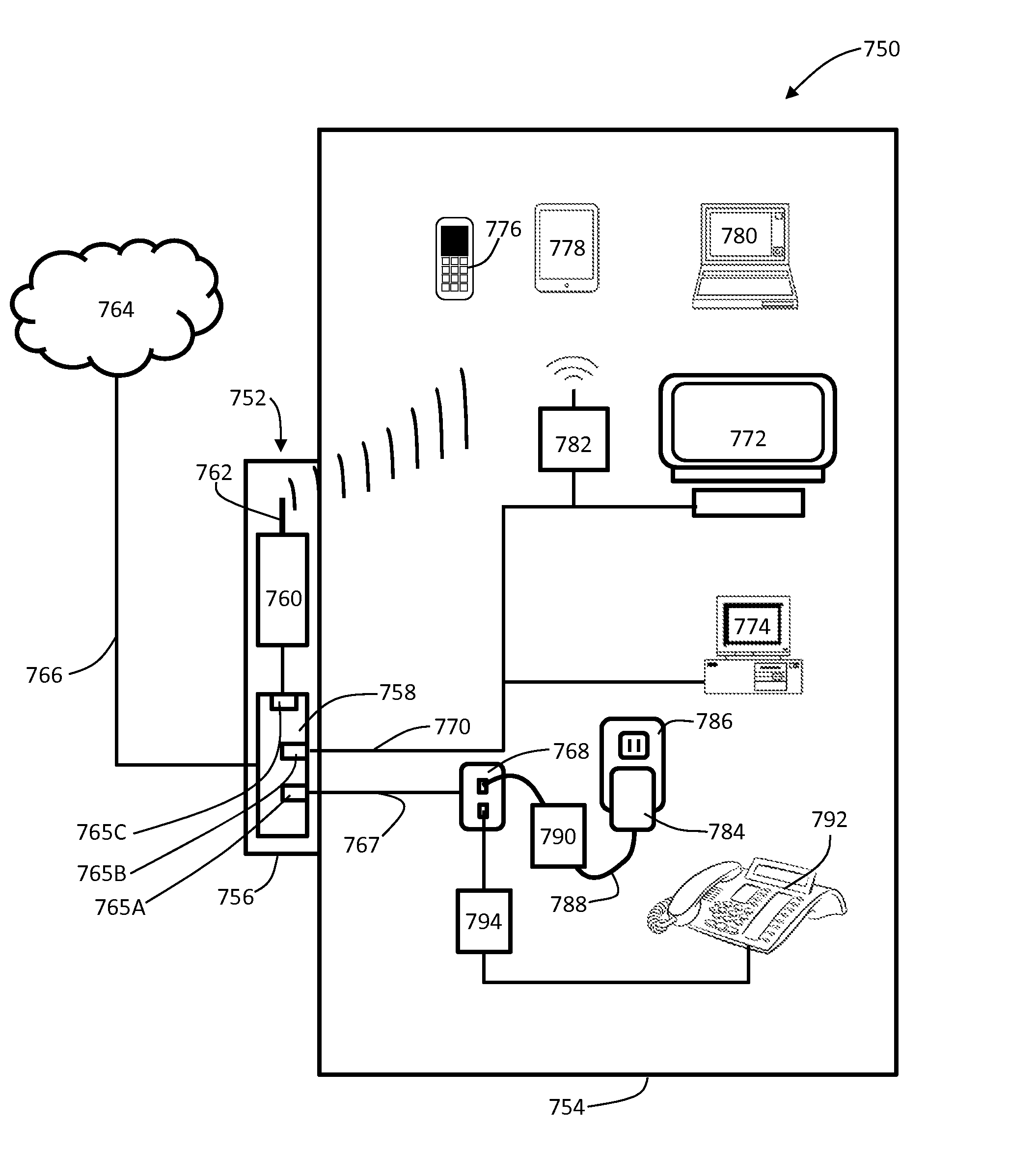
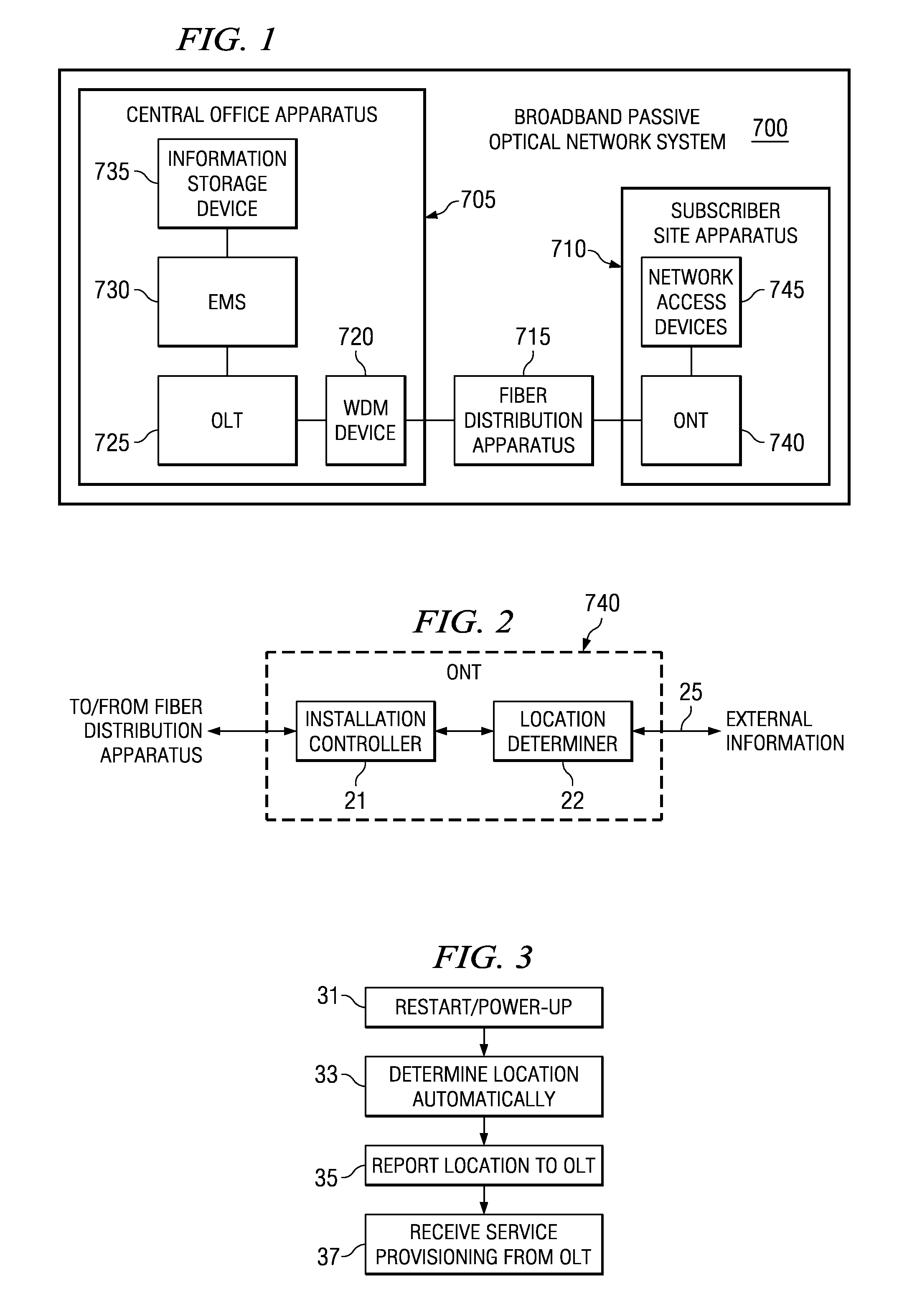
Optical network termination with automatic determination of geographic location
An optical network termination (ONT) apparatus can determine its own geographic location information automatically, thereby permitting the ONT to report its geographic location to a management entity in a passive optical network (PON) automatically, without manual intervention.
Owner:ALCATEL LUCENT SAS
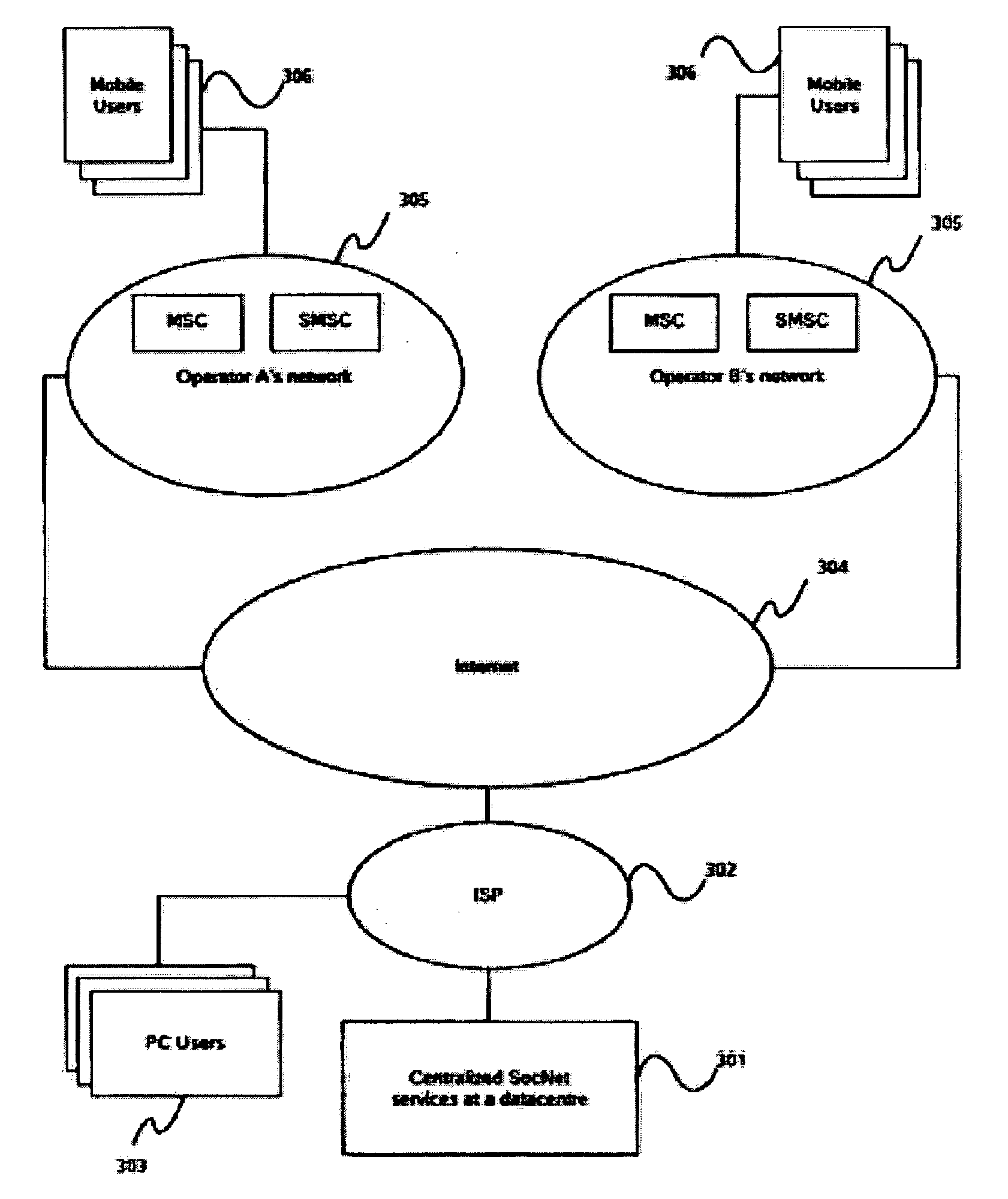
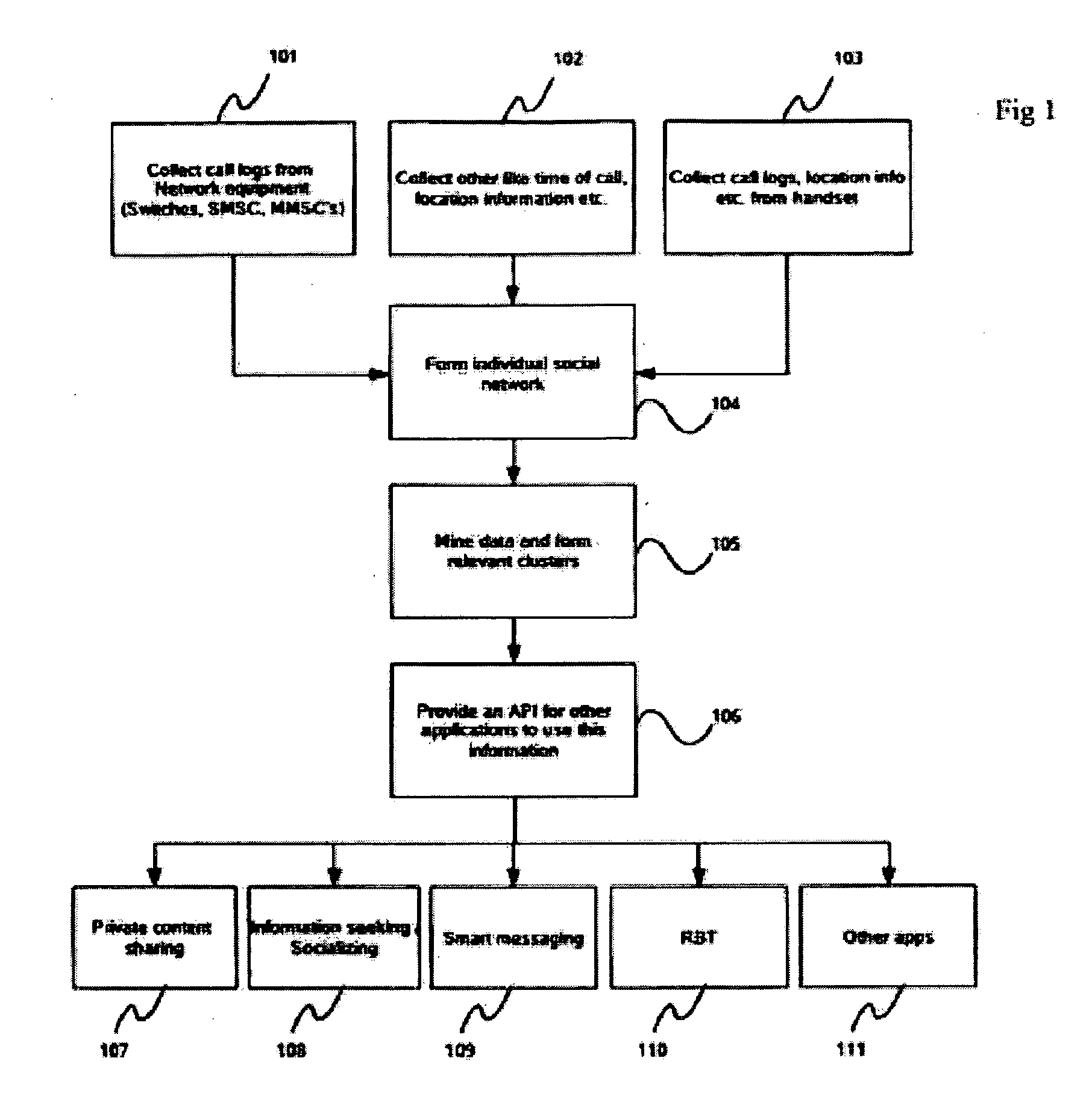
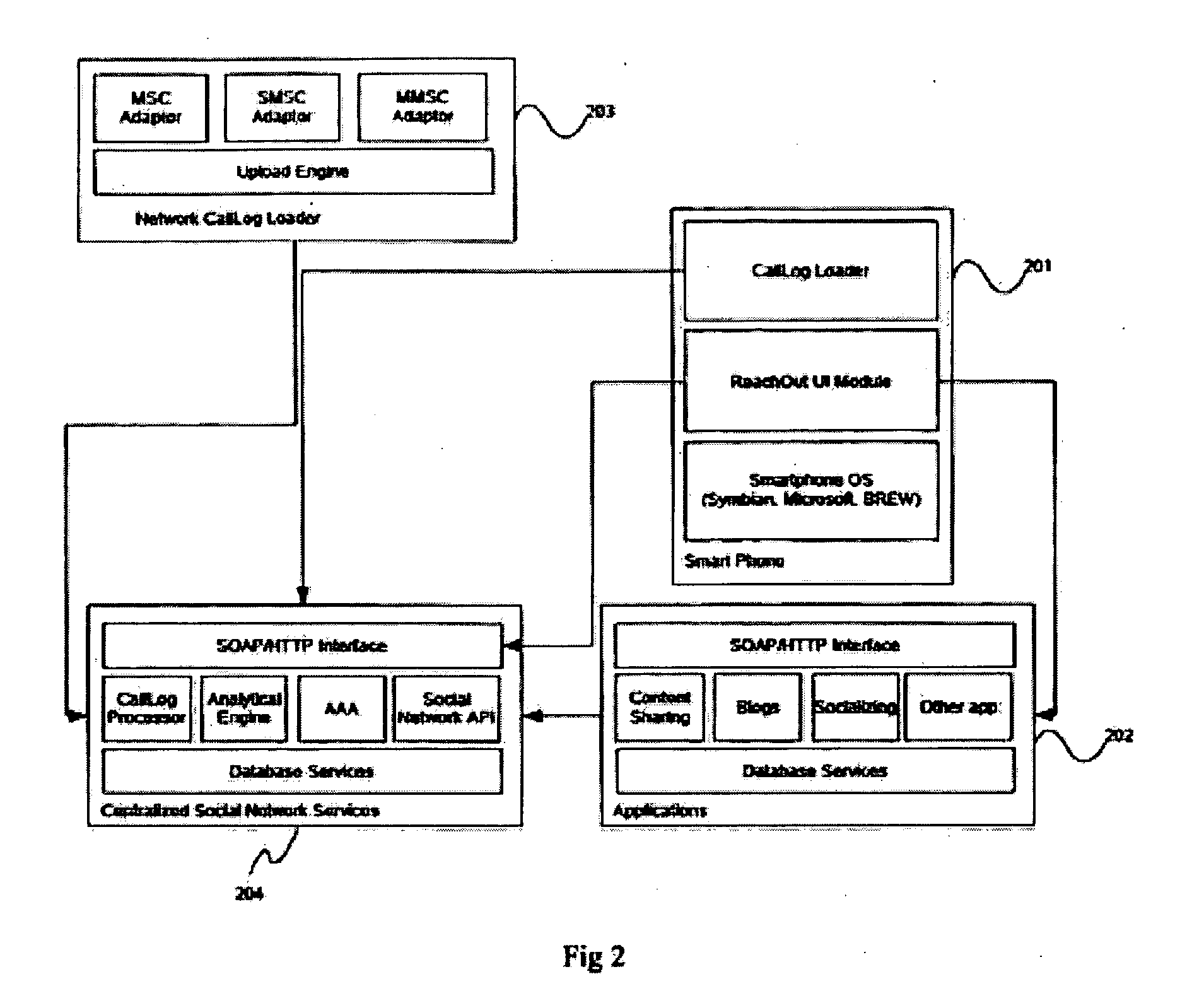
System and method for facilitating a ready social network
ActiveUS20100049802A1Increase contentImprove effectivenessDigital data information retrievalError detection/correctionNetwork terminationClustered data
The invention provides system and method wherein the system collects user activity data including call log information from network equipment, handset and other context specific user activity data including time of call and location information to enable various applications to use the information collected and build social network. In accordance with the method of the invention, the user activity data collected is used to form individual social networks. The networks are formed based on clusters identified by mining the data collected. Furthermore, various applications are provided access to the clustered data to assist in individual social networking. The system of the invention comprises of an application server comprising a centralized data center providing social networking services through a plurality of networks, the networks in-turn connecting a plurality of users through their individual network terminal stations to the application server.
Owner:ONMOBILE GLOBAL LTD
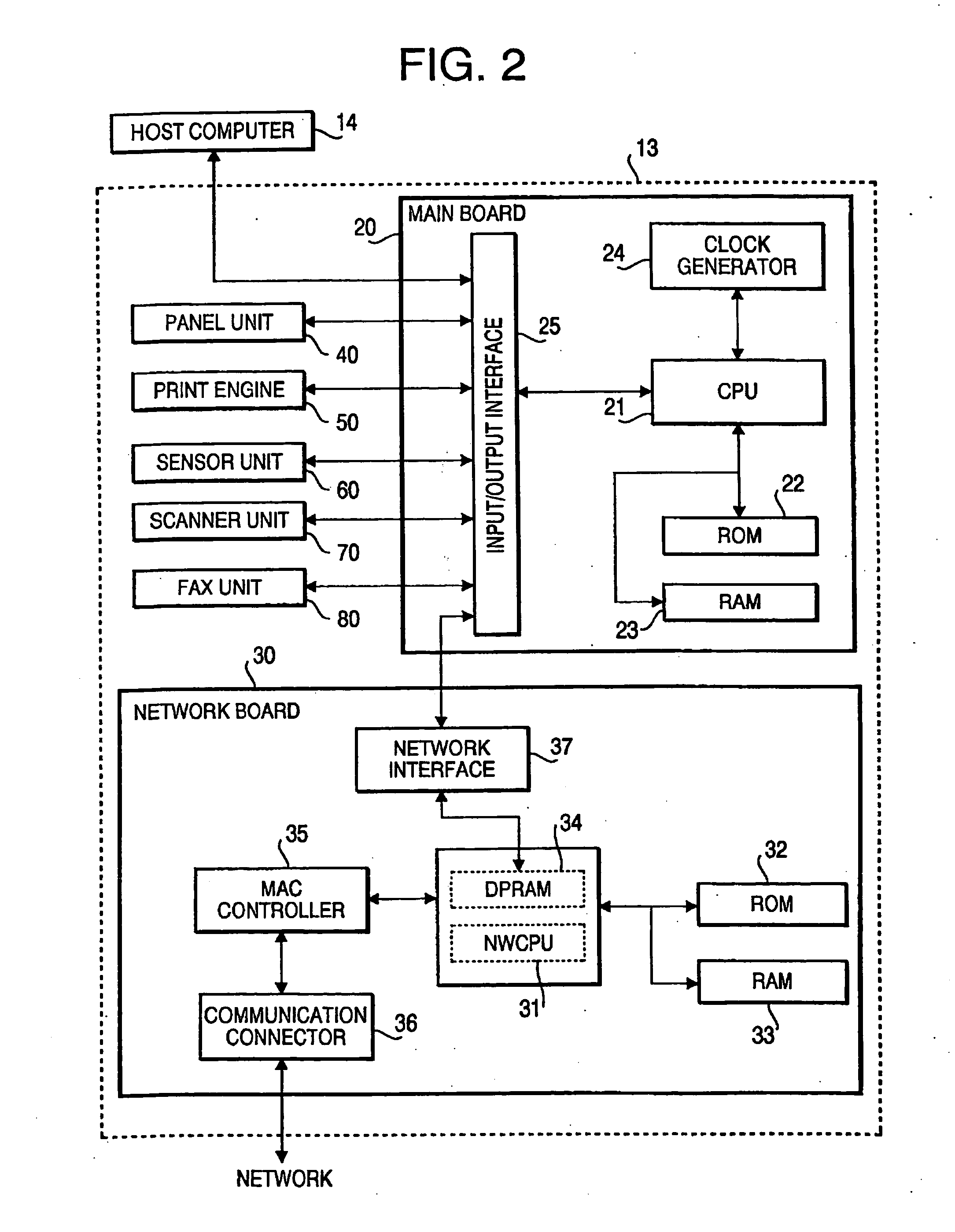
Communication network terminal supporting a plurality of applications
InactiveUS7088990B1Current supply arrangementsSubstation equipmentNetwork terminationComputer terminal
Owner:NOKIA MOBILE PHONES LTD
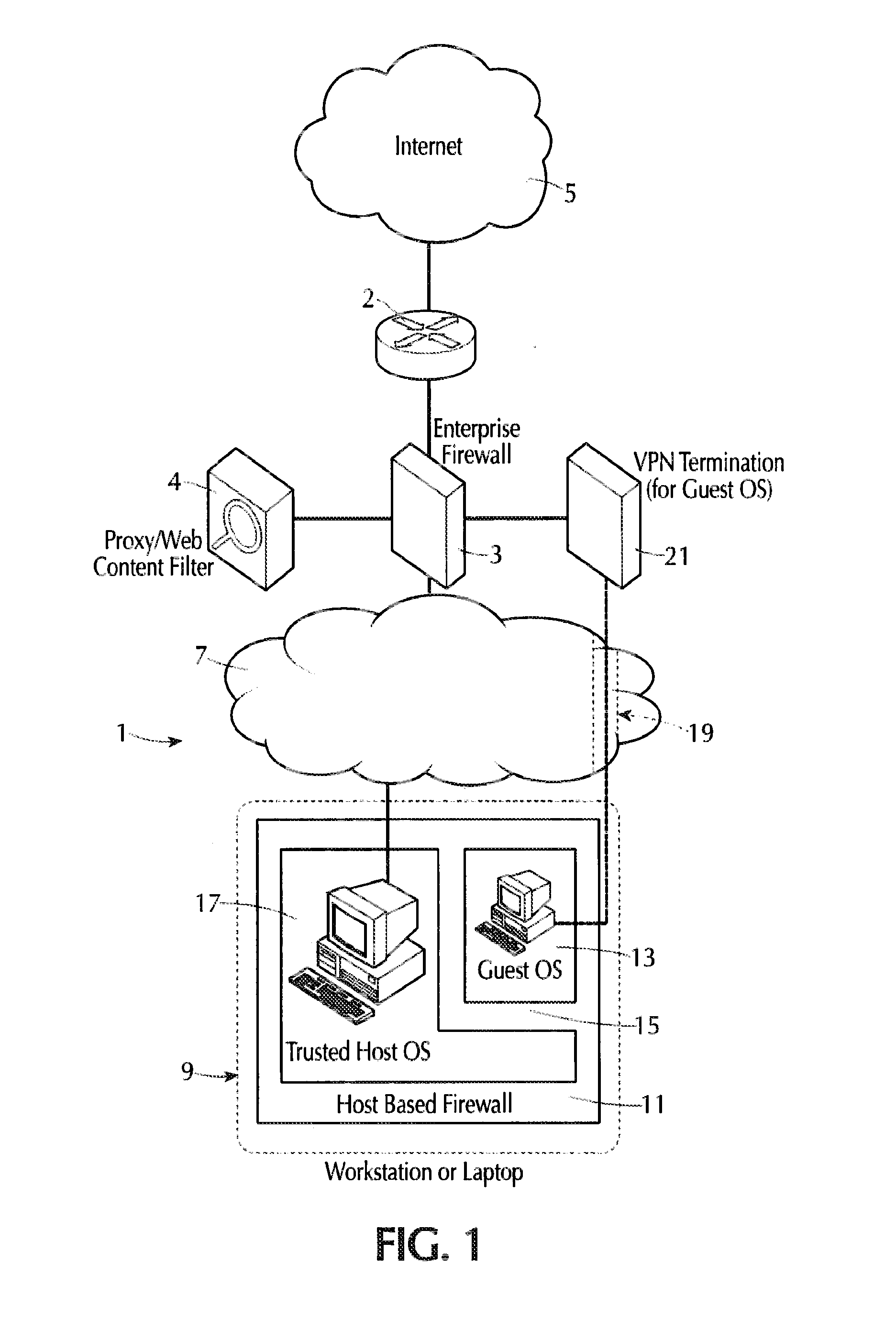
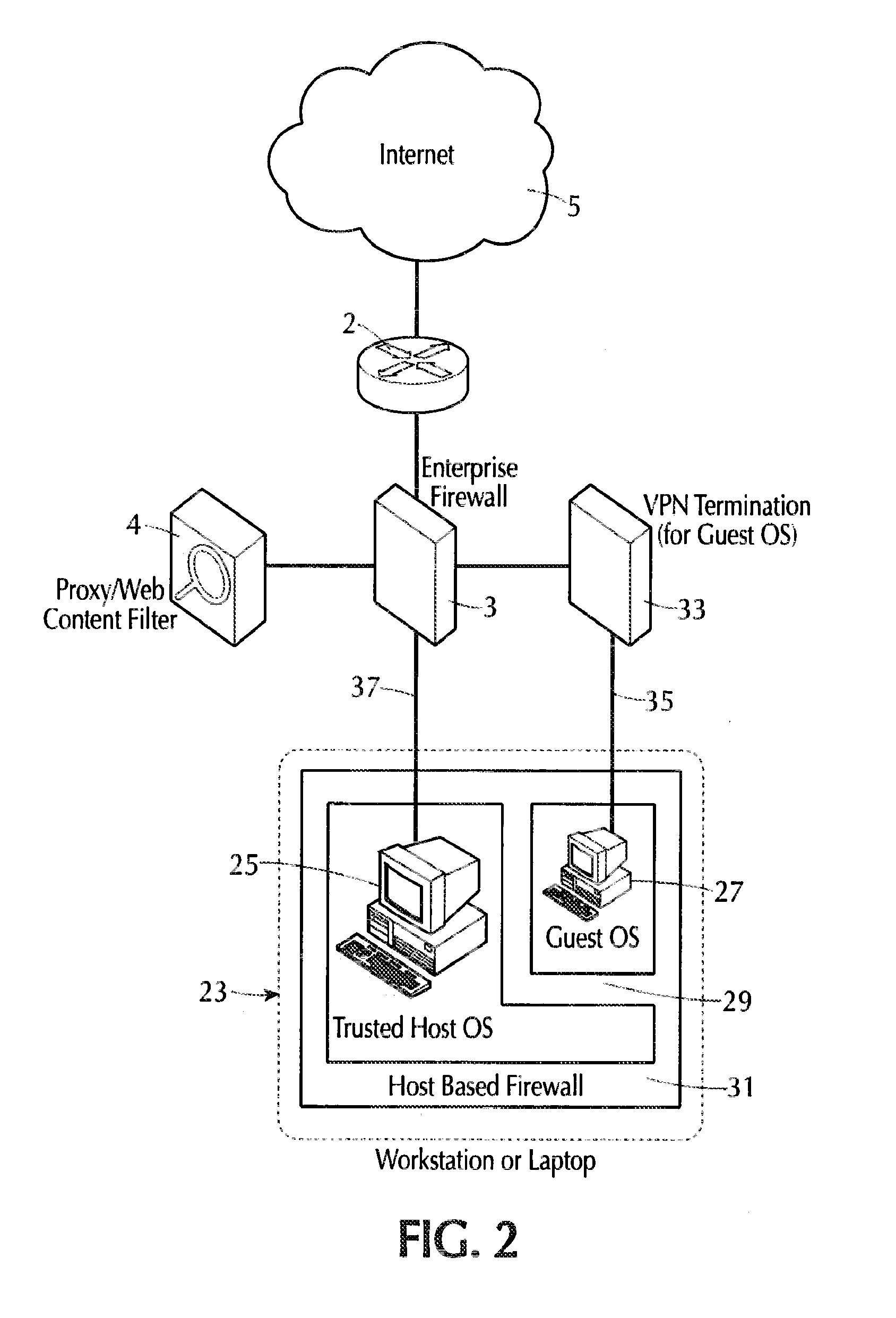
Internet isolation for avoiding internet security threats
ActiveUS20130318594A1Obviates abilityReduce the possibilityMultiple digital computer combinationsPlatform integrity maintainanceNetwork terminationPrivate network
A host computer supports a virtual guest system running thereon. The host system has a firewall that prevents it from communicating directly with the Internet, except with predetermined trusted sites. The virtual guest runs on a hypervisor, and the virtual guest comprises primarily a browser program that is allowed to contact the Internet freely via an Internet access connection that is completely separate from the host computer connection, such as a dedicated network termination point with its specific Internet IP address, or by tunneling through the host machine architecture to reach the Internet without exposing the host system. The virtual guest system is separated and completely isolated by an internal firewall from the host, and the guest cannot access any of the resources of the host computer, except that the guest can initiate cut, copy and paste operations that reach the host, and the guest can also request print of documents. The host can transfer files to and from a virtual data storage area accessible by the guest by manual operator action. No other transfer of data except these user initiated actions is permitted.
Owner:L3 TECH INC
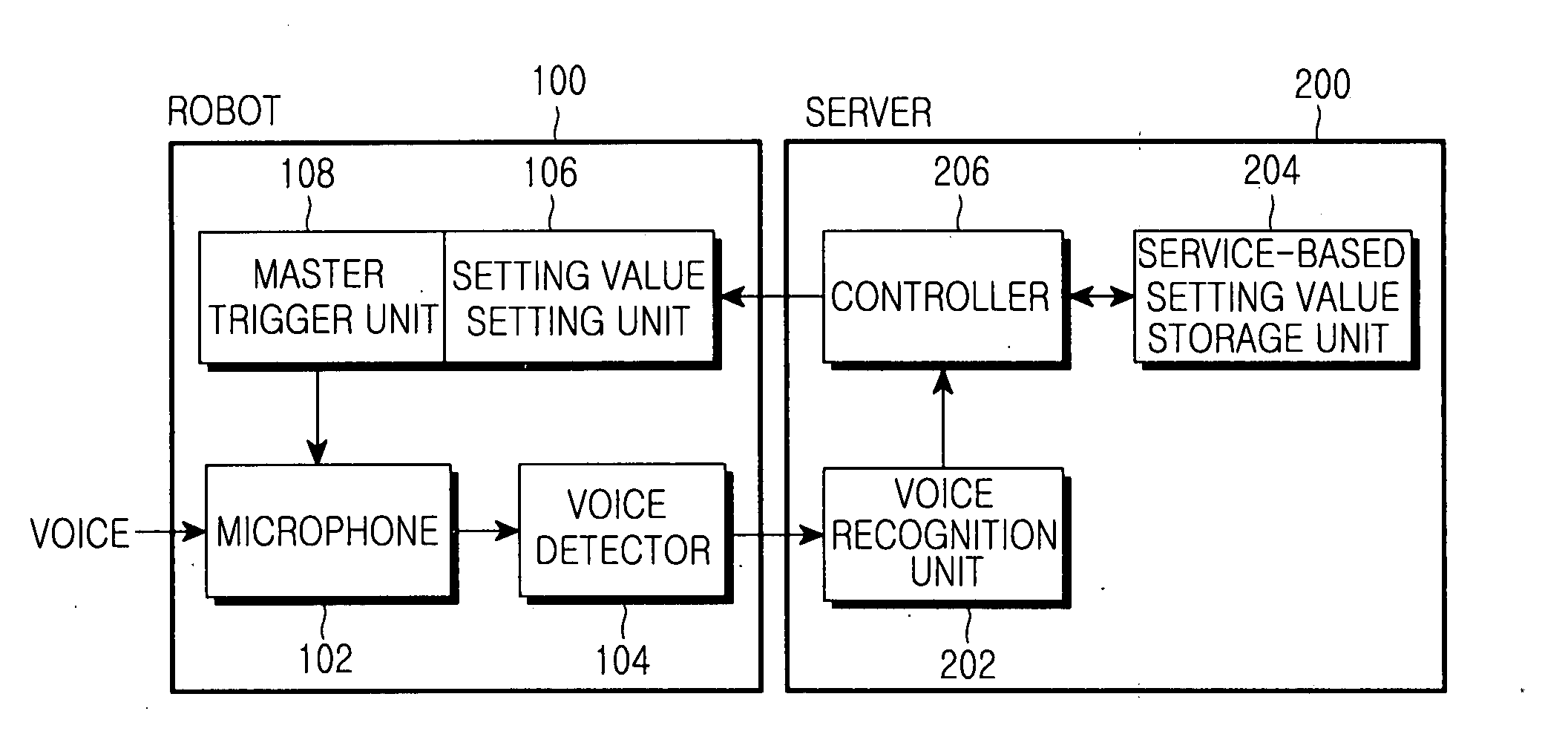
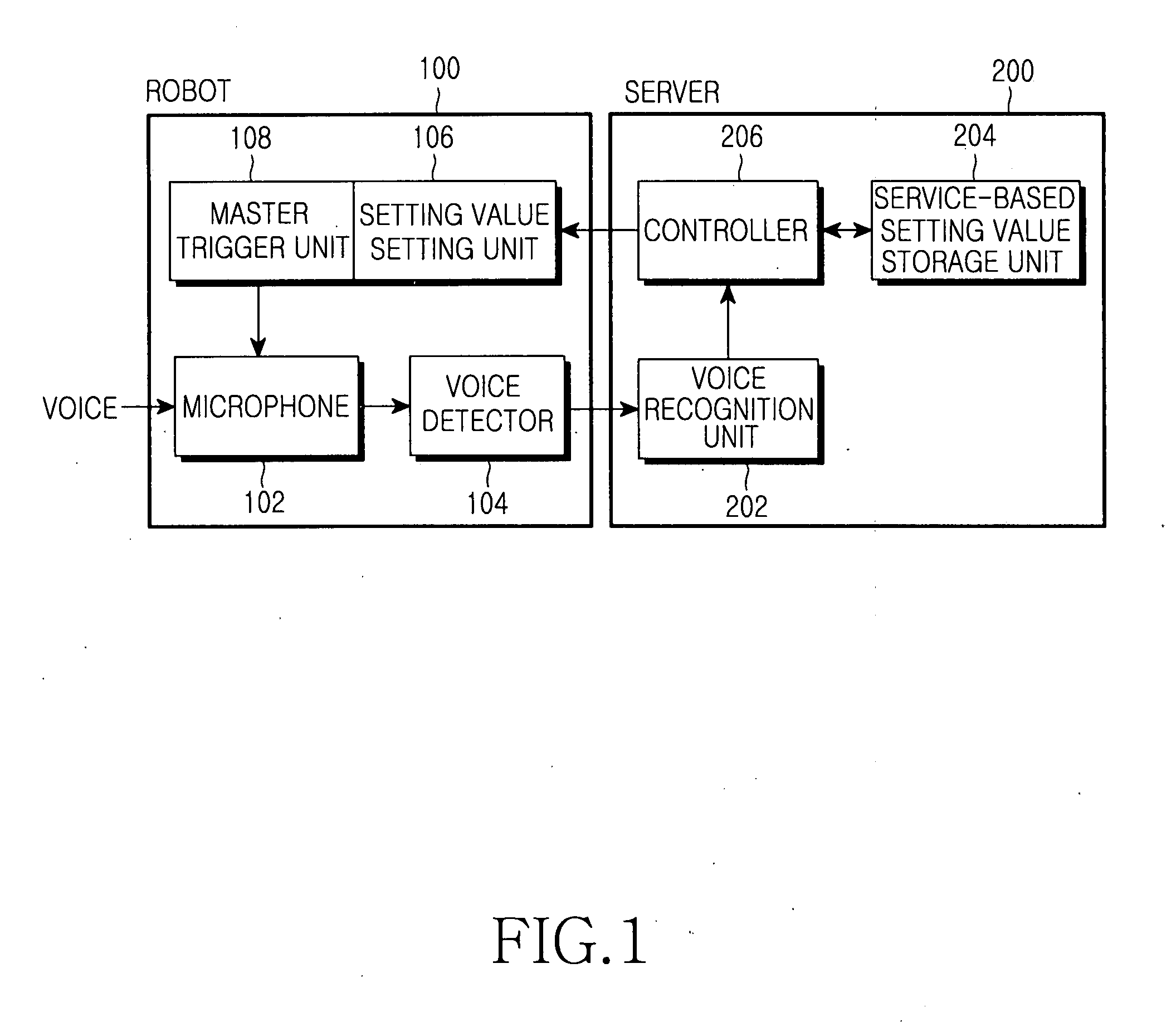
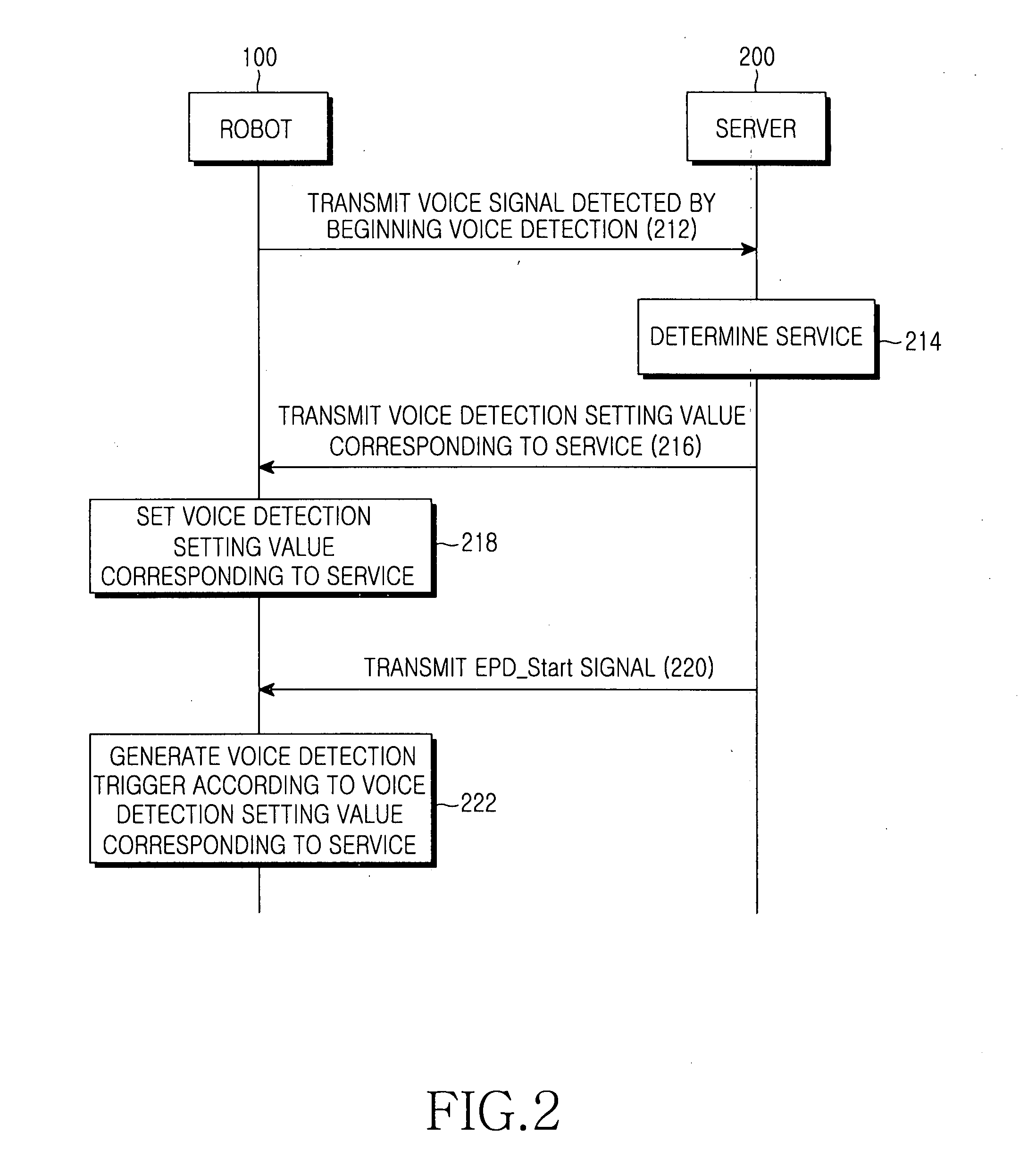
System and method for controlling voice detection of network terminal
InactiveUS20070201639A1Telephonic communicationSubstation remote connection/disconnectionNetwork terminationService control
Provided is a system and method for controlling voice detection of a network terminal. The system includes the network terminal for, if detection of a voice signal is requested, detecting voice by receiving and setting a voice detection setting value corresponding to a predetermined service and generating a trigger signal for the voice detection according to the voice detection setting value corresponding to the service; and a server for determining the service of the network terminal and transmitting the voice detection setting value corresponding to the service to the network terminal. Accordingly, by controlling to commence voice detection according to a service, voice detection optimized to a relevant service can commence.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
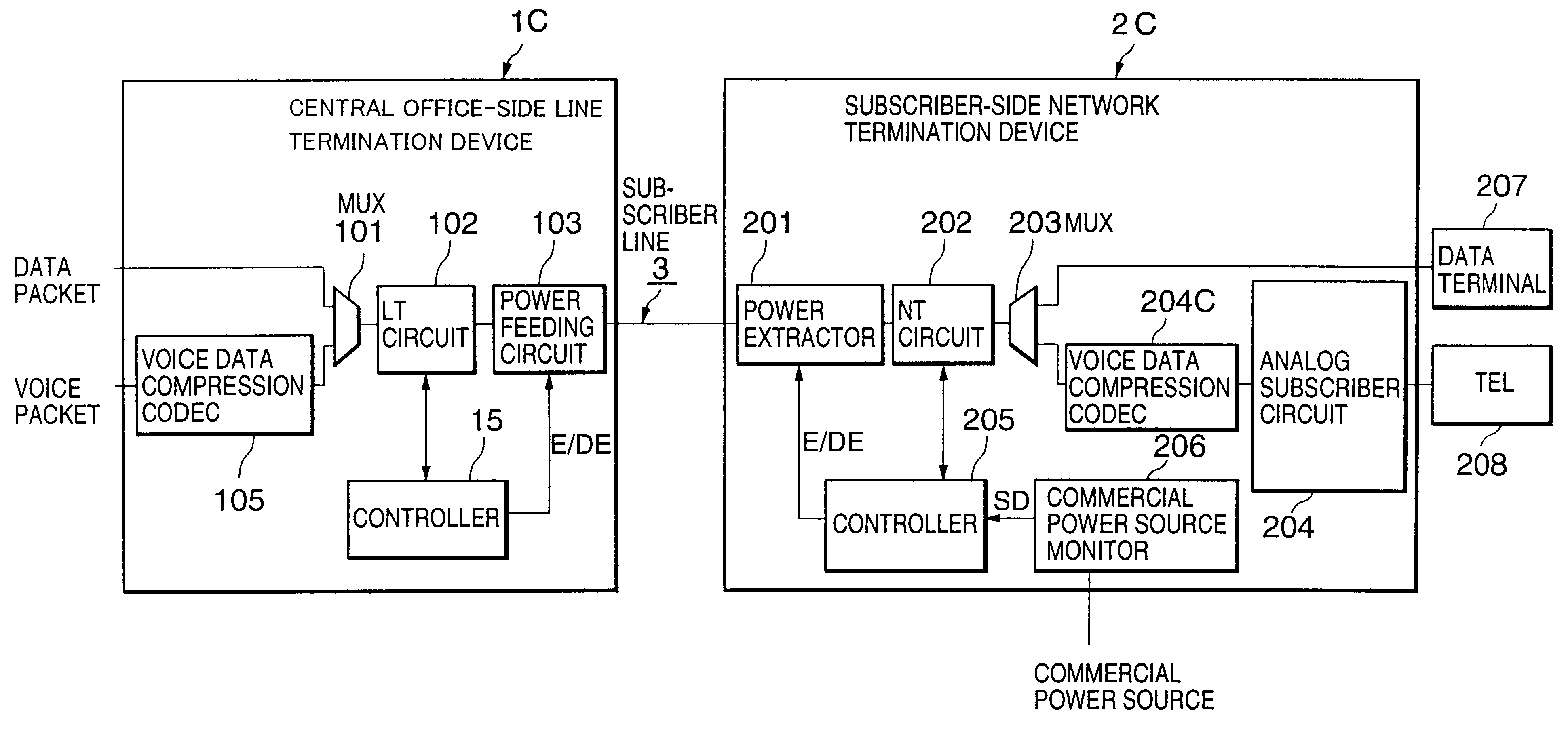
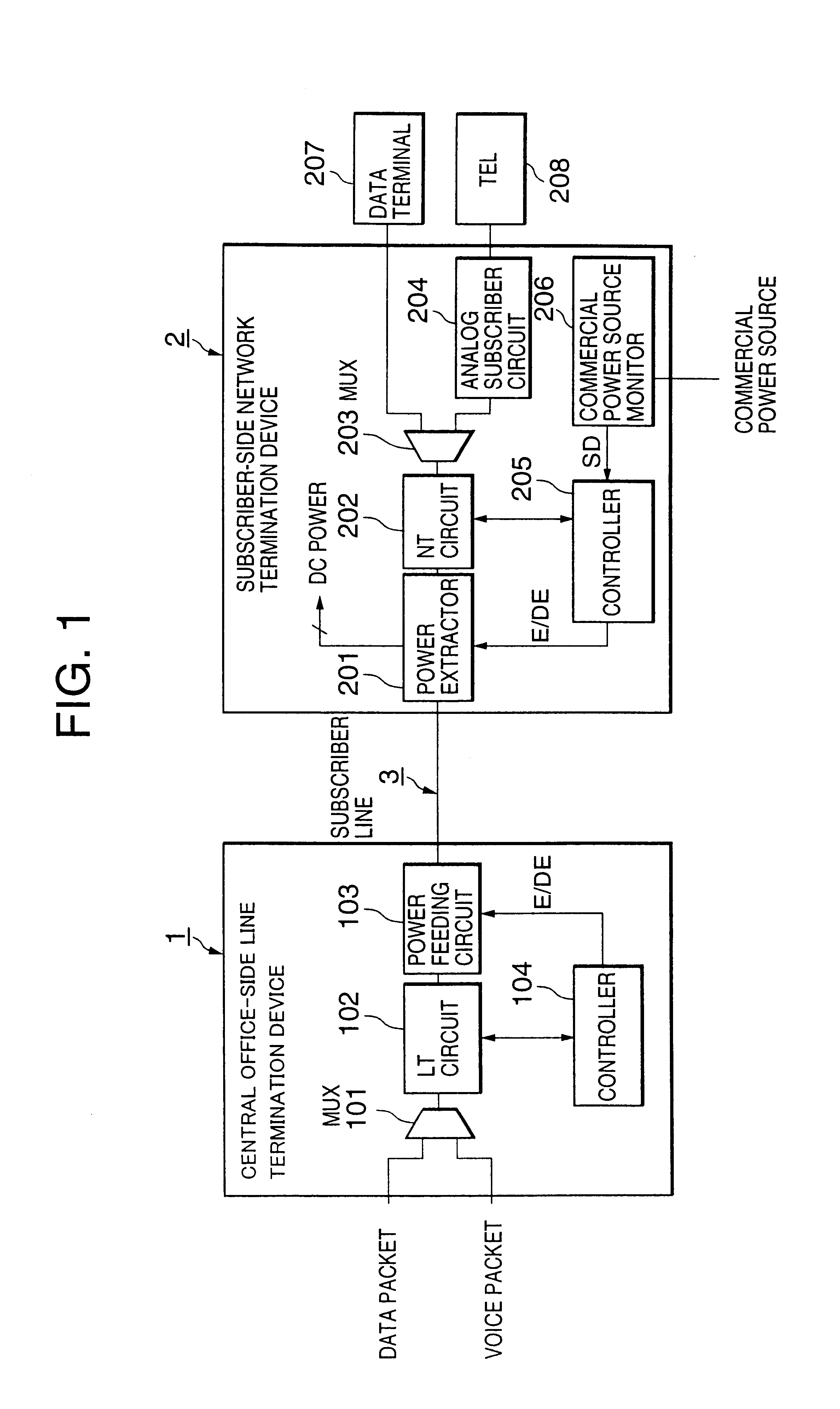
Remote power feed method and system
InactiveUS6847718B1Power feeding efficiency can be increasedImprove feeding efficiencyInterconnection arrangementsLevel controlNetwork terminationVoice communication
A remote power feeding method allowing efficient remote power feeding into a network termination device in the event of a commercial power failure at a subscriber site is disclosed. When the commercial power failure occurs, a power failure signal is transmitted from the subscriber-side network termination device to the central office-side line termination device. The central office-side line termination device, when receiving the power failure signal, starts DC power feeding to the subscriber-side network termination device via the subscriber line. During the power failure, only voice communication is permitted using previously selected good channels.
Owner:NEC CORP
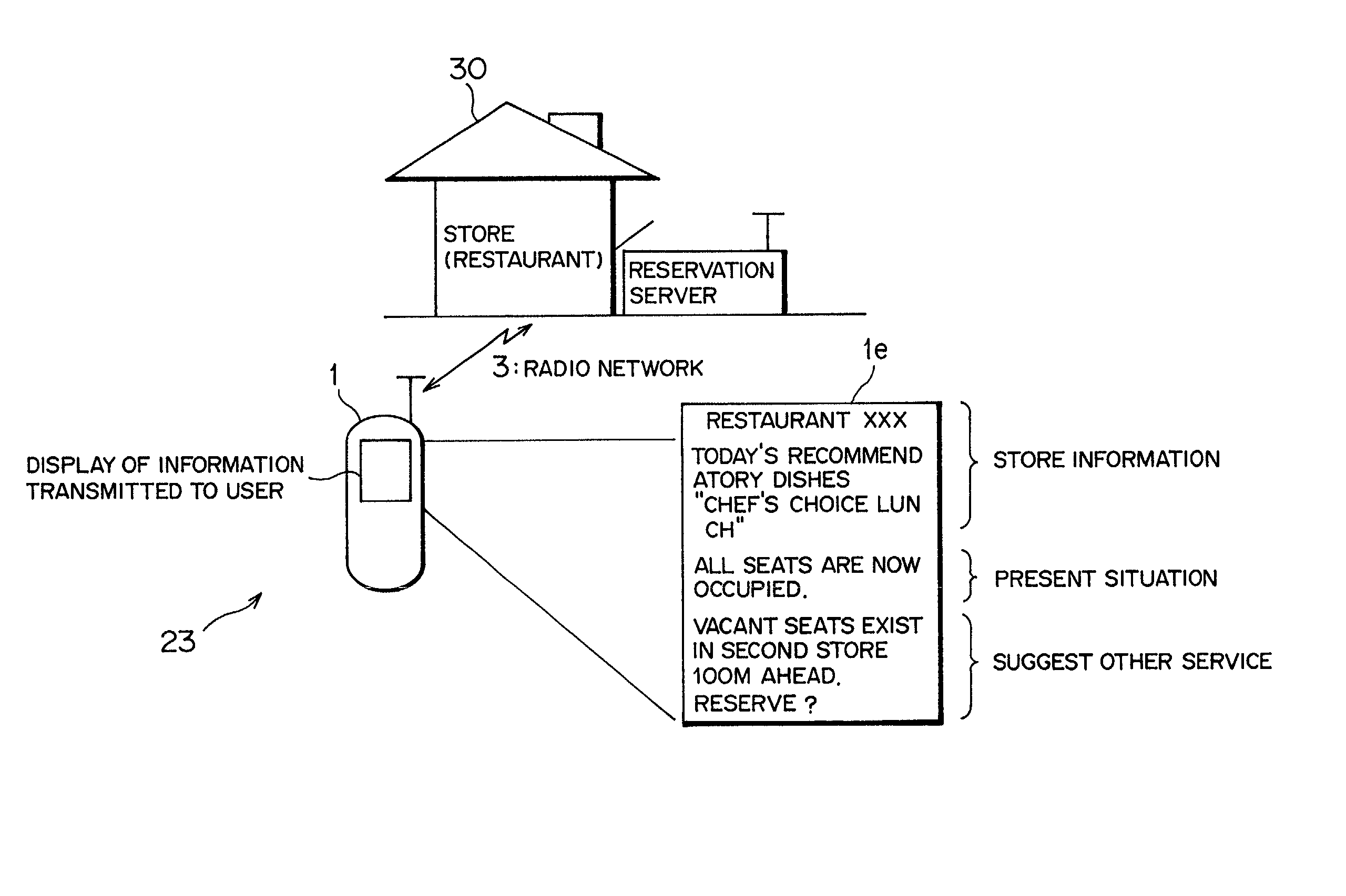
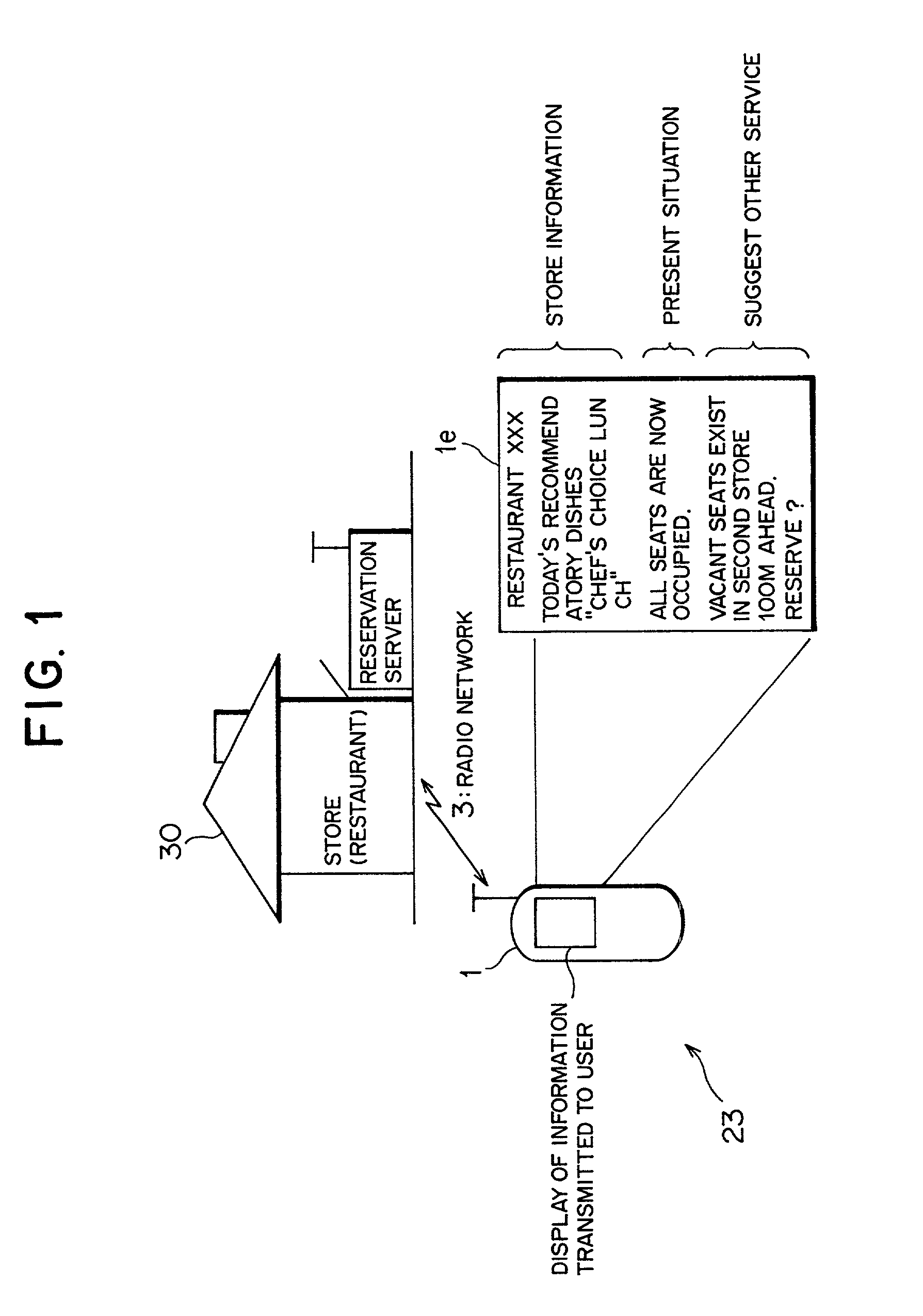
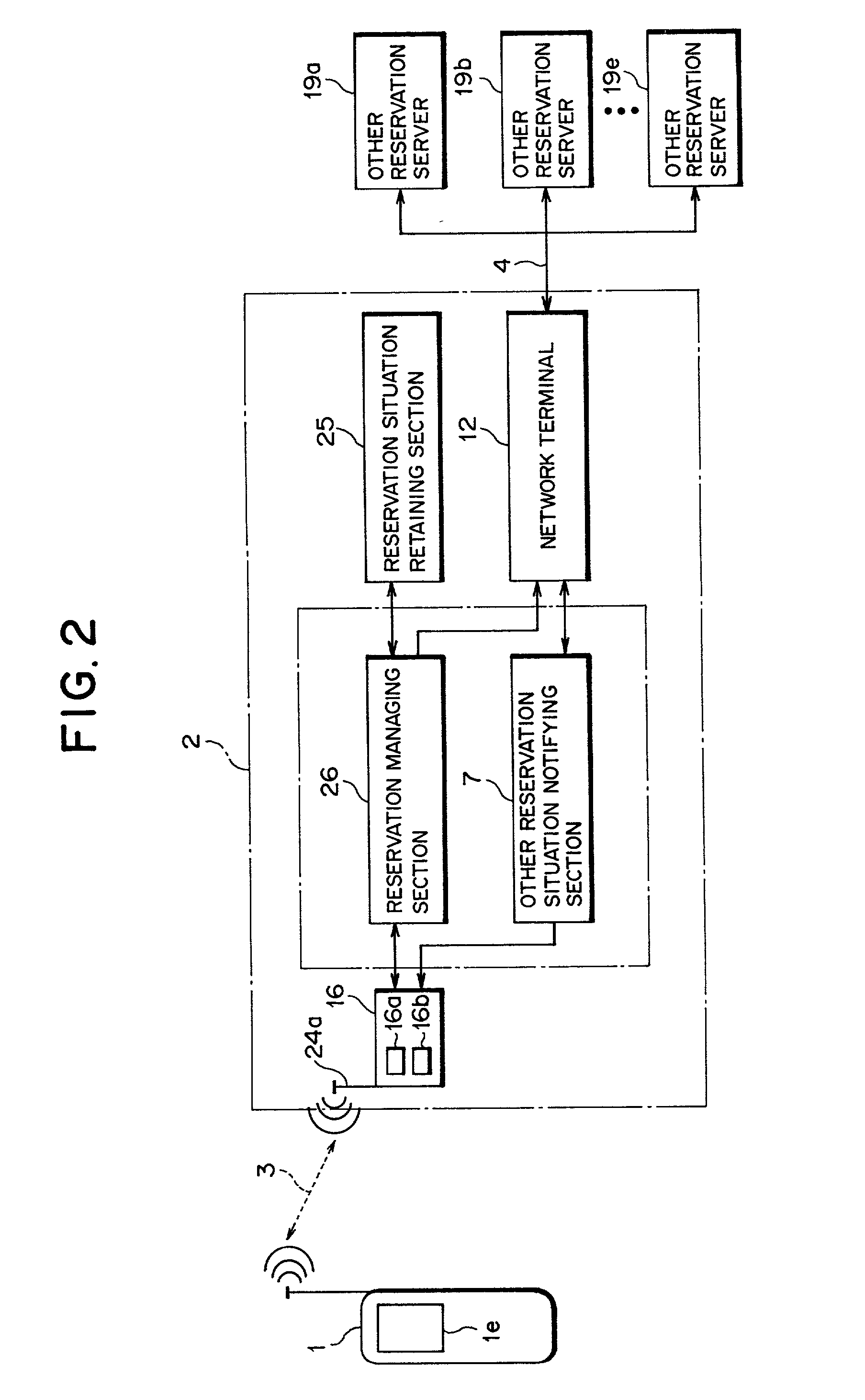
Reservation server, user terminal, reservation system, and reservation method
InactiveUS20020062236A1Promoting an increase of customersReservationsOffice automationNetwork terminationService provision
The present invention relates to a reservation server which comprises a retaining section for retaining store / facility information including a reservation-needed service and a reservation situation, a network terminal for outputting alternative event substituting for the service, a receiving section for receiving a desired service, a reservation managing section for selectively reading out the store / facility information and the alternative event, and a transmitting section for transmitting the information and event. Accordingly, a service provider can notify a user of a service and reservation situation of a store-near the user or the start / end time of the service, and the time to be taken for the service and can suggest an alternative event in a time zone convenient to the user.
Owner:FUJITSU LTD
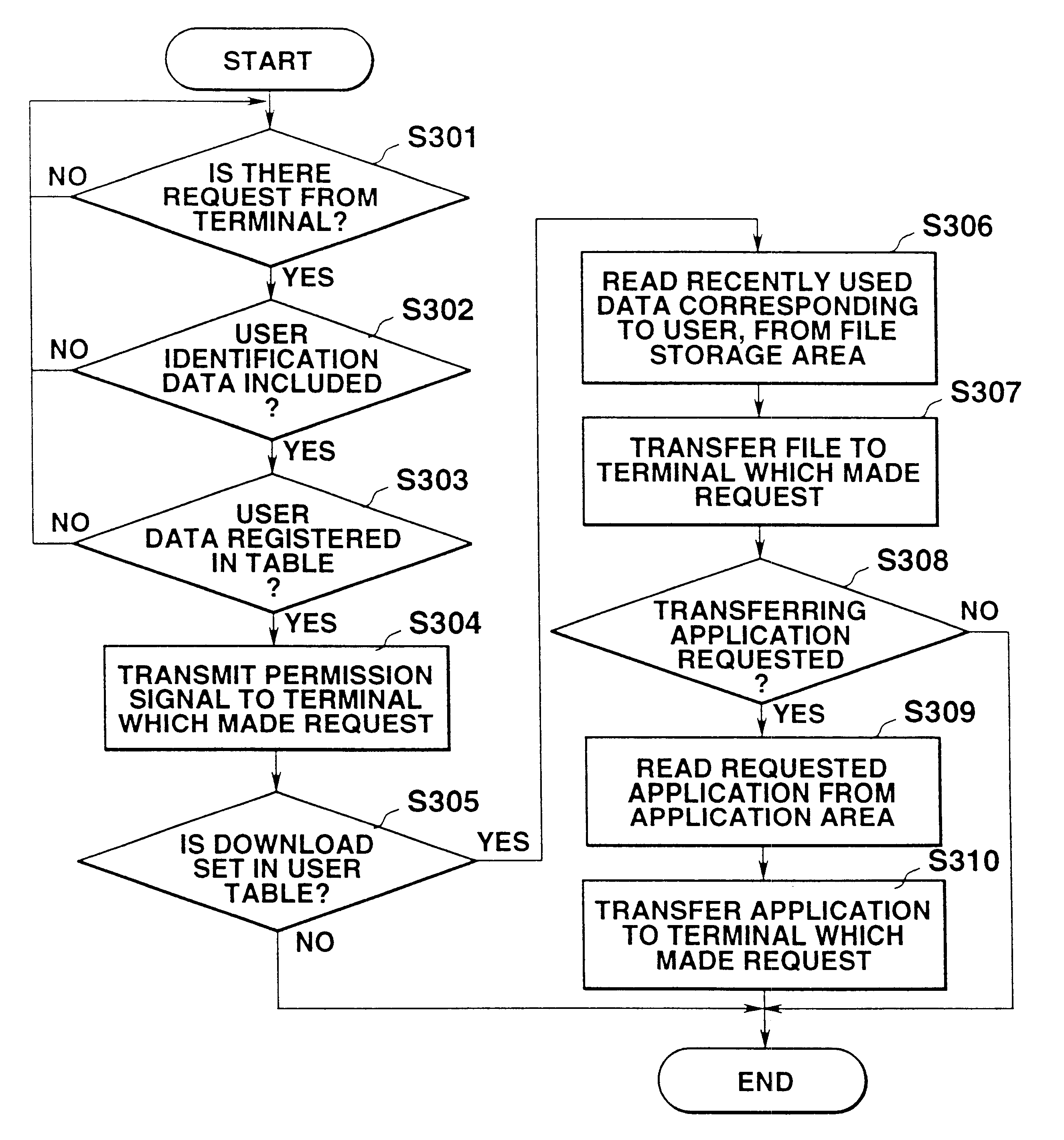
PDA workspace interface using application icons for downloading remote user file
InactiveUS6493743B2Digital data information retrievalMultiple digital computer combinationsNetwork terminationComputer hardware
In the network terminal device (200), the computer main body (202) transmits a download request containing user identification data to the host device (300) via a network (100) at the time of starting the terminal device (200). In the host device (300), of various types of files corresponding to the user identification data, a designated file which is set by the user table in advance, is selected from the user management file which stores various types of files corresponding to each and individual user, in reply to the download request, and the designated file is transferred to the network terminal device (200) which made the request. The designated file is a recently used data file.
Owner:HANGER SOLUTIONS LLC
Method for processing acoustic frequency flow playback in network terminal buffer
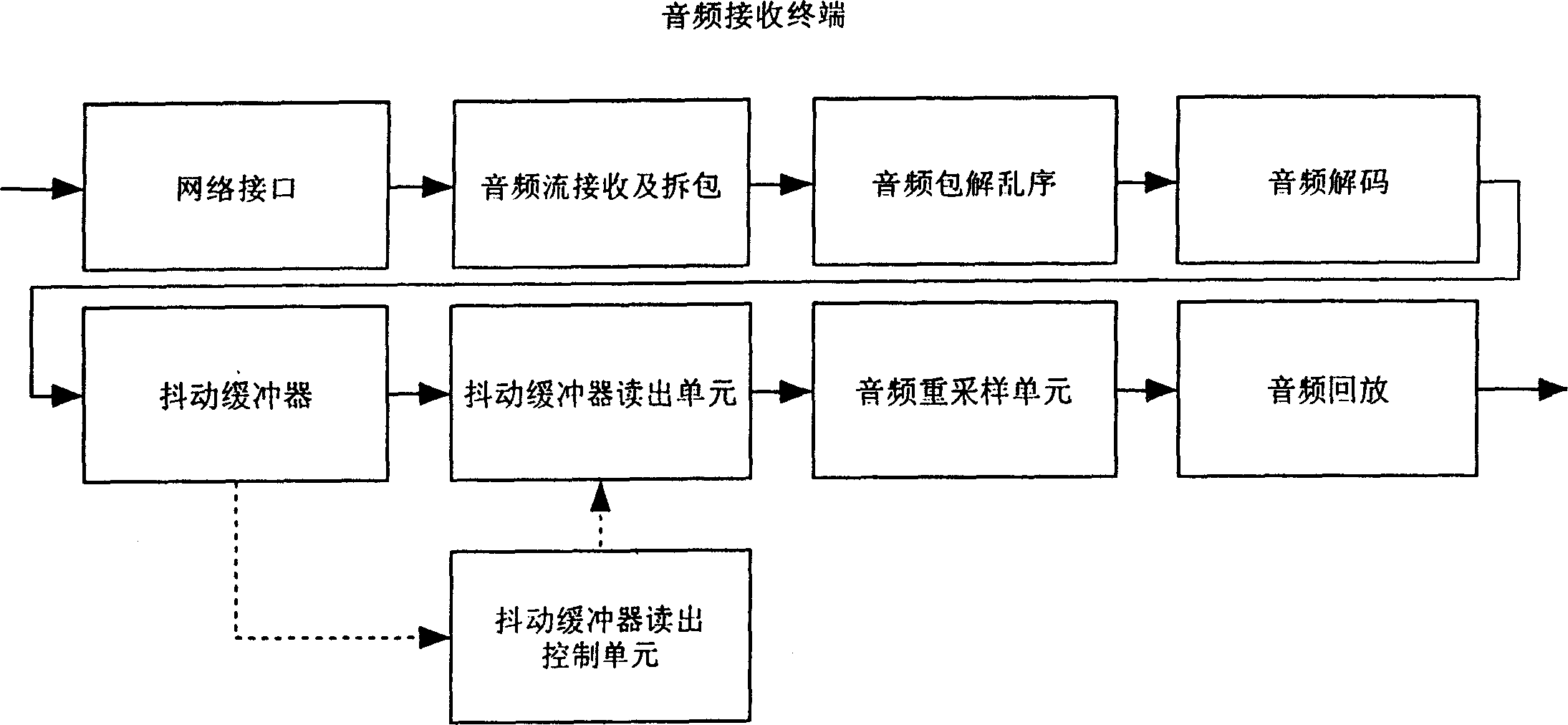
InactiveCN1464685ASpeed up or slow down playbackContinuous and smooth playbackSpecial service provision for substationTelephonic communicationComputer hardwareNetwork termination
The invention discloses a method for processing audio stream playback in the network terminal buffer zone for solving the problem of voice pausing and jamming in the network communication. The aim of the invention is achieved by performing real time audio (e.g. voice) communication on the packet-switching network (e.g. IP network), arranging a shake buffer zone on the receiving end, after the receiving end receives the audio package, it first performs decoding based on the normal sequence, then places it into the shake buffer zone, when the shake buffer zone is to be filled, lower the sampling rate to the audio data to realize the fast playback of the audio data stream, when the shake buffer zone is to be empty, raise the sampling rate to the audio data to realize the low speed playback of the audio data stream, when the audio data in the shake buffer is within the normal range, playback the audio stream with the original sampling rate.
Owner:优创科技(深圳)有限公司
Login administration method and server
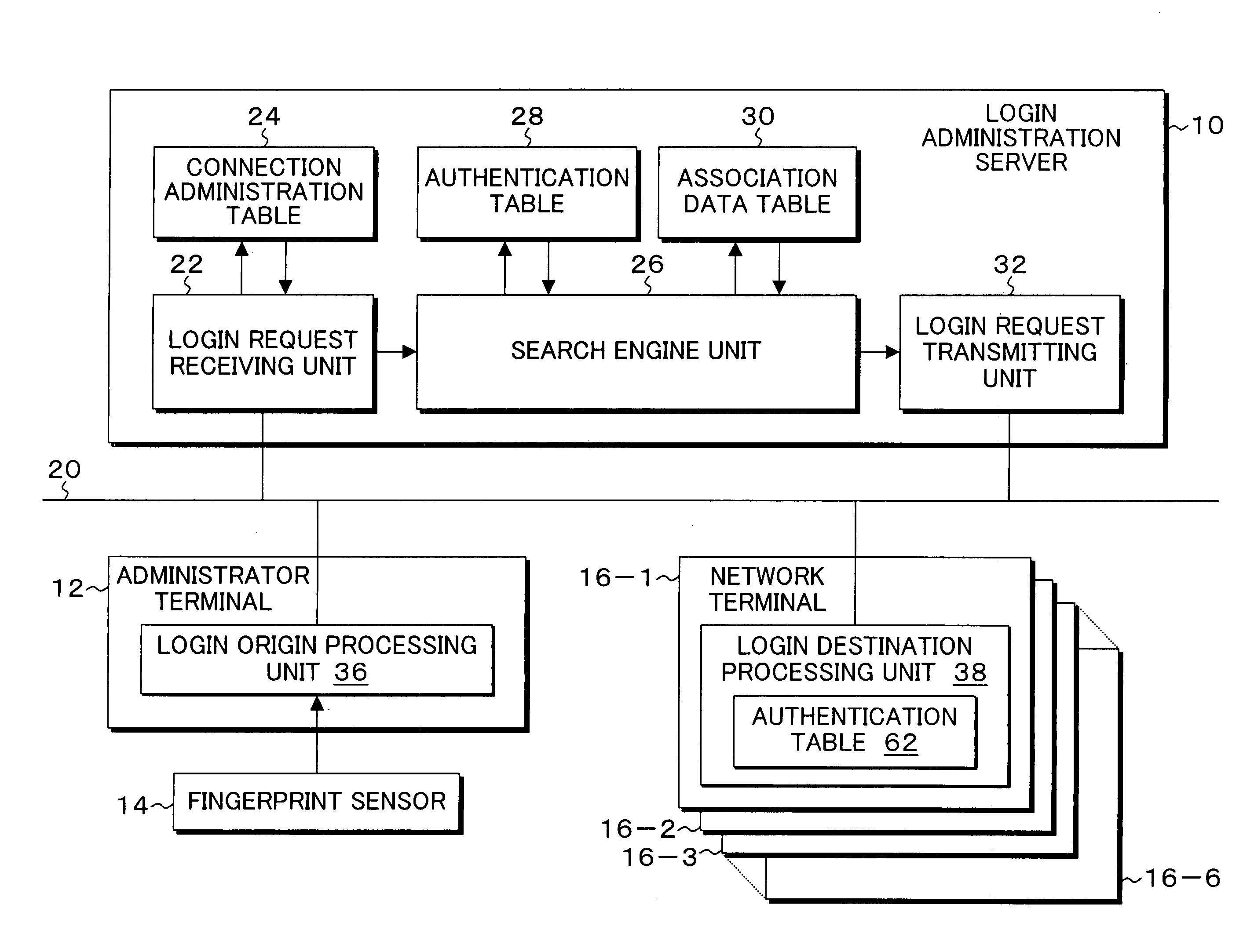
InactiveUS20080034411A1Simply and readily and reliably performedRandom number generatorsUser identity/authority verificationNetwork terminationComputer terminal
When a login request in which a network terminal serves as a login destination is received from an administrator terminal, a login request receiving unit of a login administration server causes the administrator terminal to transmit a shared account and fingerprint information. A search engine unit performs a search in an authentication table by using the account and the user fingerprint information as a key, and, when the authentication succeeds, acquires association data including a right upon successful authentication and a login permitted terminal (in this case, a terminal) from an association data table. A login request transmitting unit transmits a login request to the network terminal of the login destination so as to achieve login and imparts the right upon successful authentication. Furthermore, the login request transmitting unit transmits a login request to the unprocessed network terminal of the login permitted terminal of the association data so as to achieve login and imparts the right upon successful authentication.
Owner:FUJITSU LTD
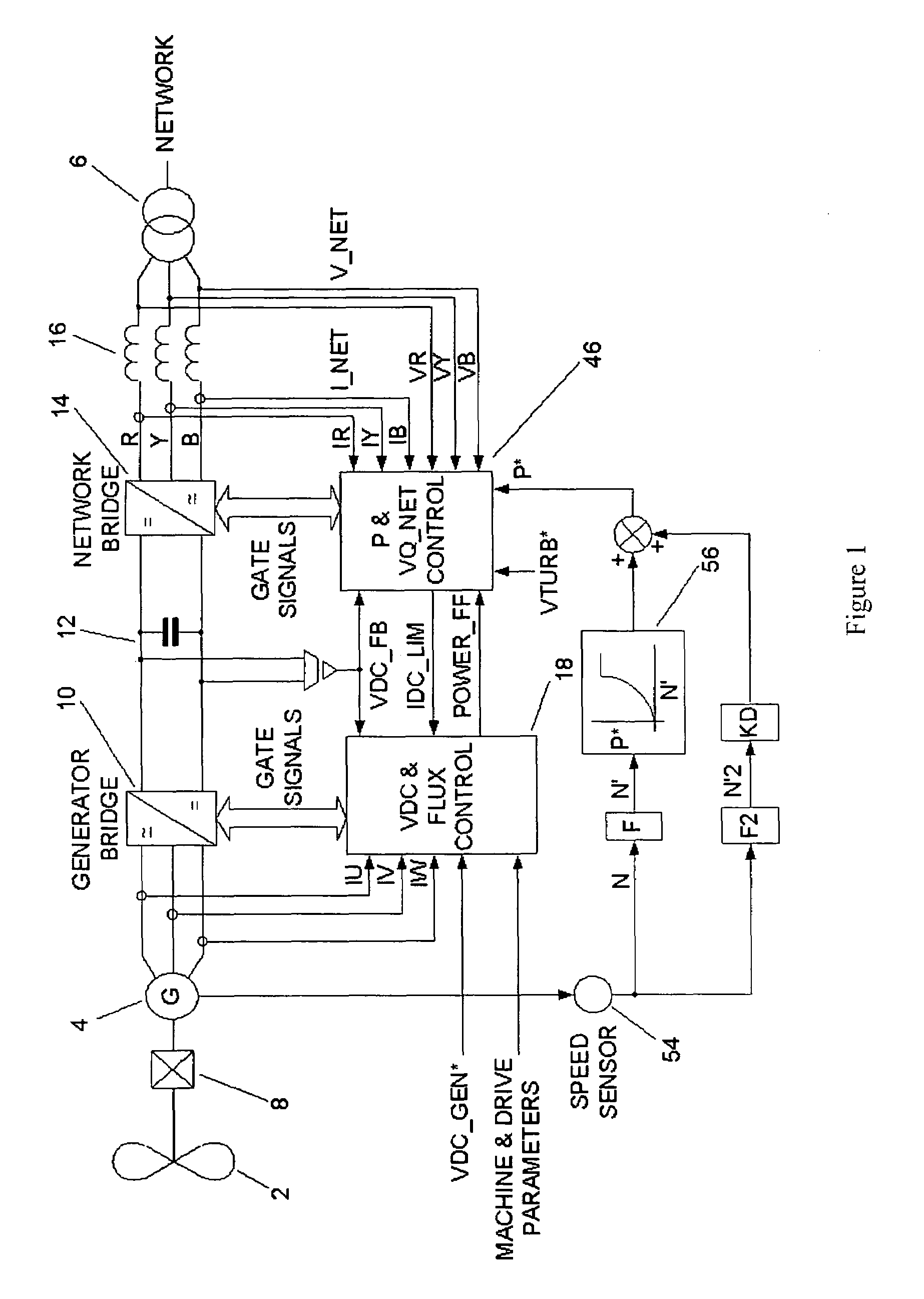
Power converters
ActiveUS7372174B2Emergency protective circuit arrangementsDynamo-electric converter controlNetwork terminationConverters
The present invention provides a power converter that can be used to interface a generator that provides variable voltage at variable frequency to a supply network operating at nominally fixed voltage and nominally fixed frequency and including features that allow the power converter to remain connected to the supply network and retain control during supply network fault and transient conditions. The power converter includes a generator bridge electrically connected to the stator of the generator and a network bridge. A dc link is connected between the generator bridge and the network bridge. A filter having network terminals is connected between the network bridge and the supply network. A first controller is provided for controlling the operation of the semiconductor power switching devices of the generator bridge. Similarly, a second controller is provided for controlling the operation of the semiconductor power switching devices of the network bridge. The first controller uses a dc link voltage demand signal VDC_NET* indicative of a desired dc link voltage to control the semiconductor power switching devices of the network bridge to achieve the desired level of dc link voltage that corresponds to the dc link voltage demand signal VDC_NET*. The second controller uses a power demand signal P* indicative of the level of power to be transferred from the dc link to the supply network through the network bridge, and a voltage demand signal VTURB* indicative of the voltage to be achieved at the network terminals of the filter to control the semiconductor power switching devices of the network bridge to achieve the desired levels of power and voltage that correspond to the power and voltage demand signals P* and VTURB*.
Owner:GE POWER CONVERSION
Power adapter and broadband line extender system and method
ActiveUS7194639B2Digital data processing detailsTwo-part coupling devicesNetwork terminationData port
A power adapter, in a presently preferred embodiment, includes a power converter and multiple data ports, and is configured for ease of coupling the power converter into pre-existing premises power connectors. Thus, premises power can be supplied from the power converter and a first data port, via data cabling, to a network terminating device for an external network. Multi-protocol adapters, such as an HPNA (Home Phoneline Network Alliance protocol compliant) / Ethernet adapter, may also be included to provide extension of a protocol (such as Ethernet) over pre-existing premises wiring. A back-up battery is optionally provided, as well as appropriate switches and indicators. Specialized male-female connectors may also be used.
Owner:TELLABS VIENNA
Power converters
ActiveUS7511385B2Ac-dc conversion without reversalWind motor combinationsNetwork terminationPower switching
Owner:GE POWER CONVERSION
Battery charging system for electric vehicle
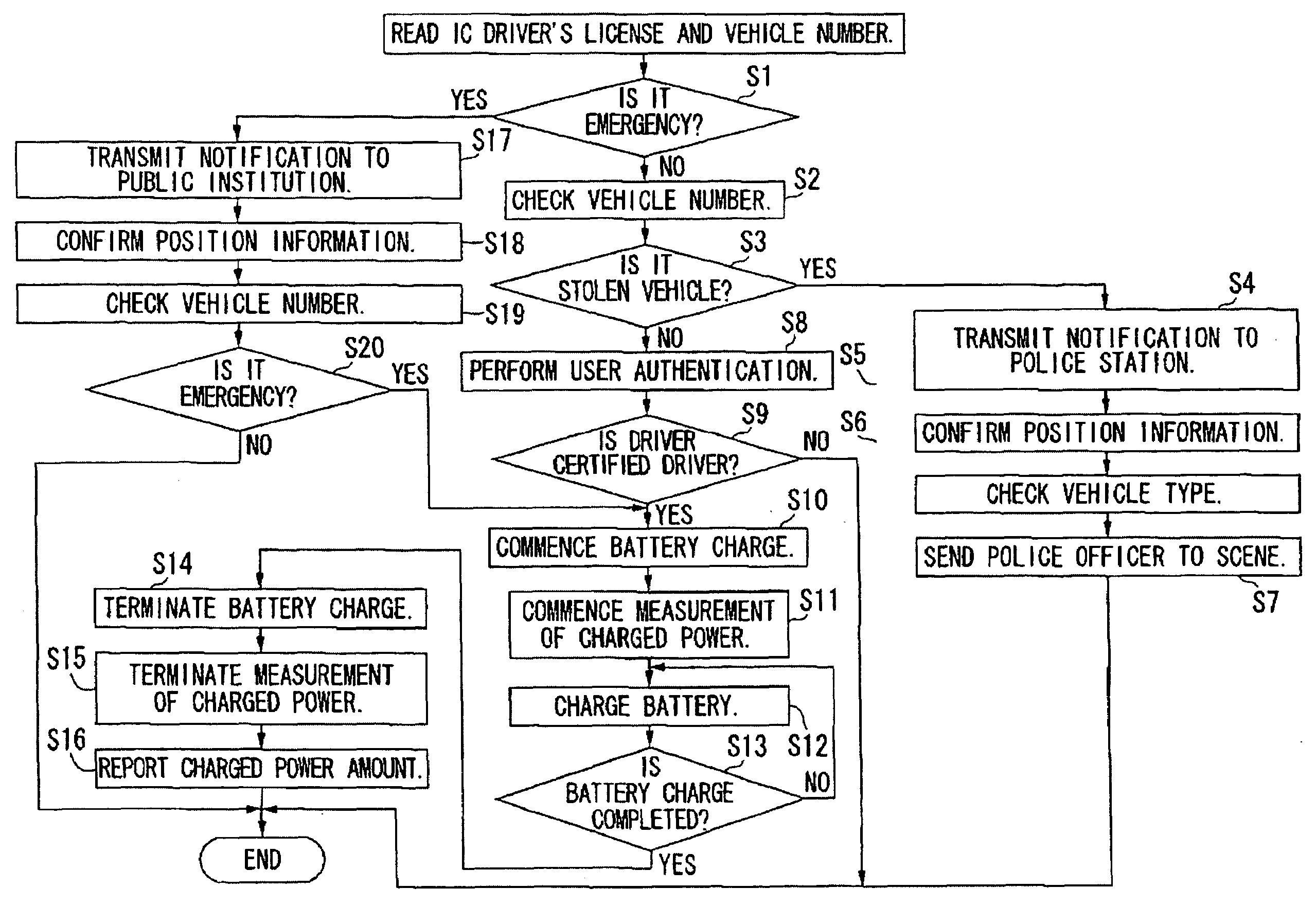
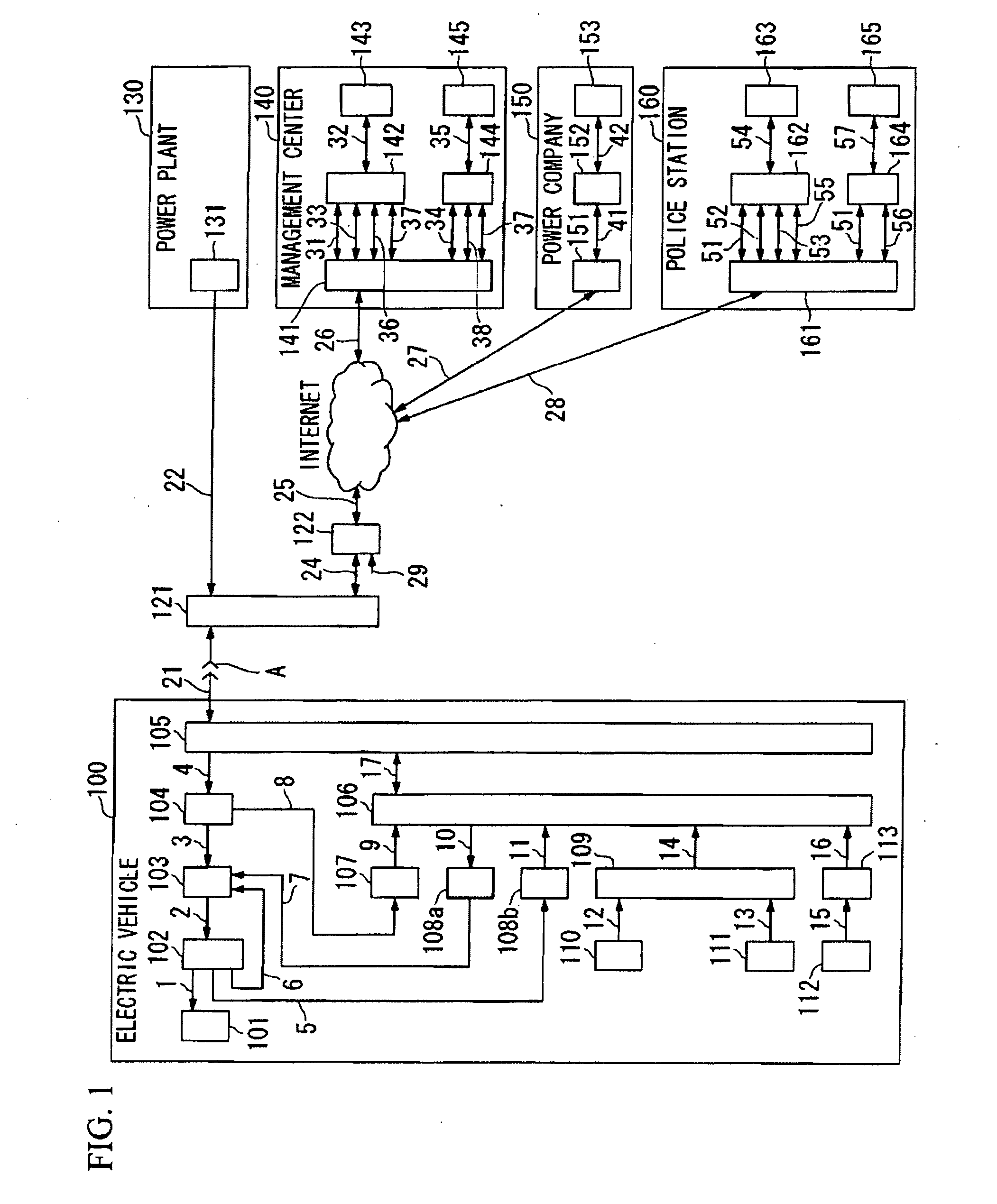
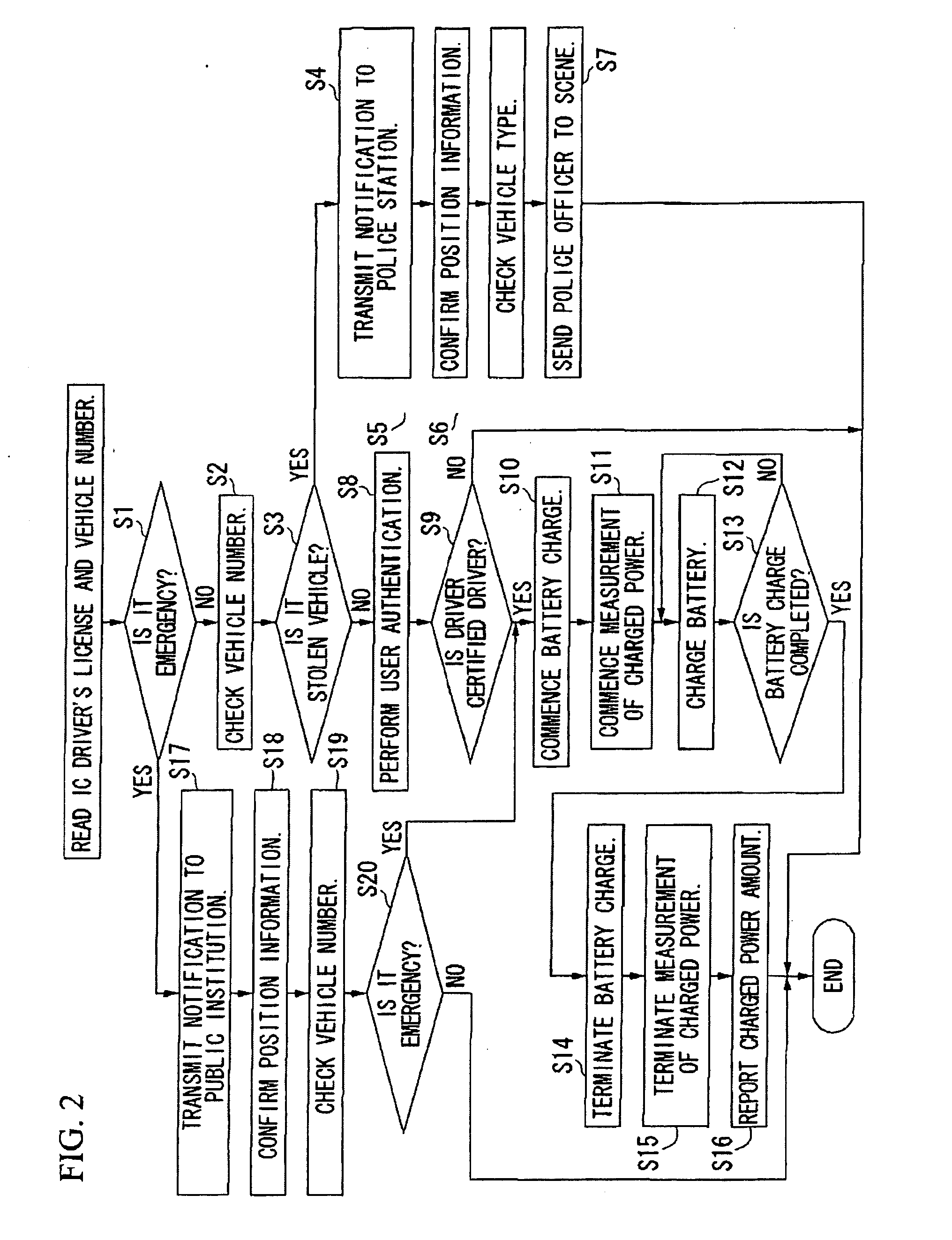
ActiveUS20090251300A1Quick searchDigital data processing detailsAnti-theft devicesNetwork terminationBattery charge
A battery charging system includes: an electric vehicle; a network termination unit connectable to the electric vehicle through a power line cable for supplying electric power to the electric vehicle; and a first server that transmits a control signal indicative of permission or forbiddance of power supply from the network termination unit to the electric vehicle to the electric vehicle through the network termination unit. The electric vehicle transmits identification information for identifying the electric vehicle and the user thereof to the first server through the network termination unit. The network termination unit transmits position information concerning the position of the network termination unit to the first server. The first server determines permission or forbiddance of the power supply based on the identification information and the position information.
Owner:NEC CORP
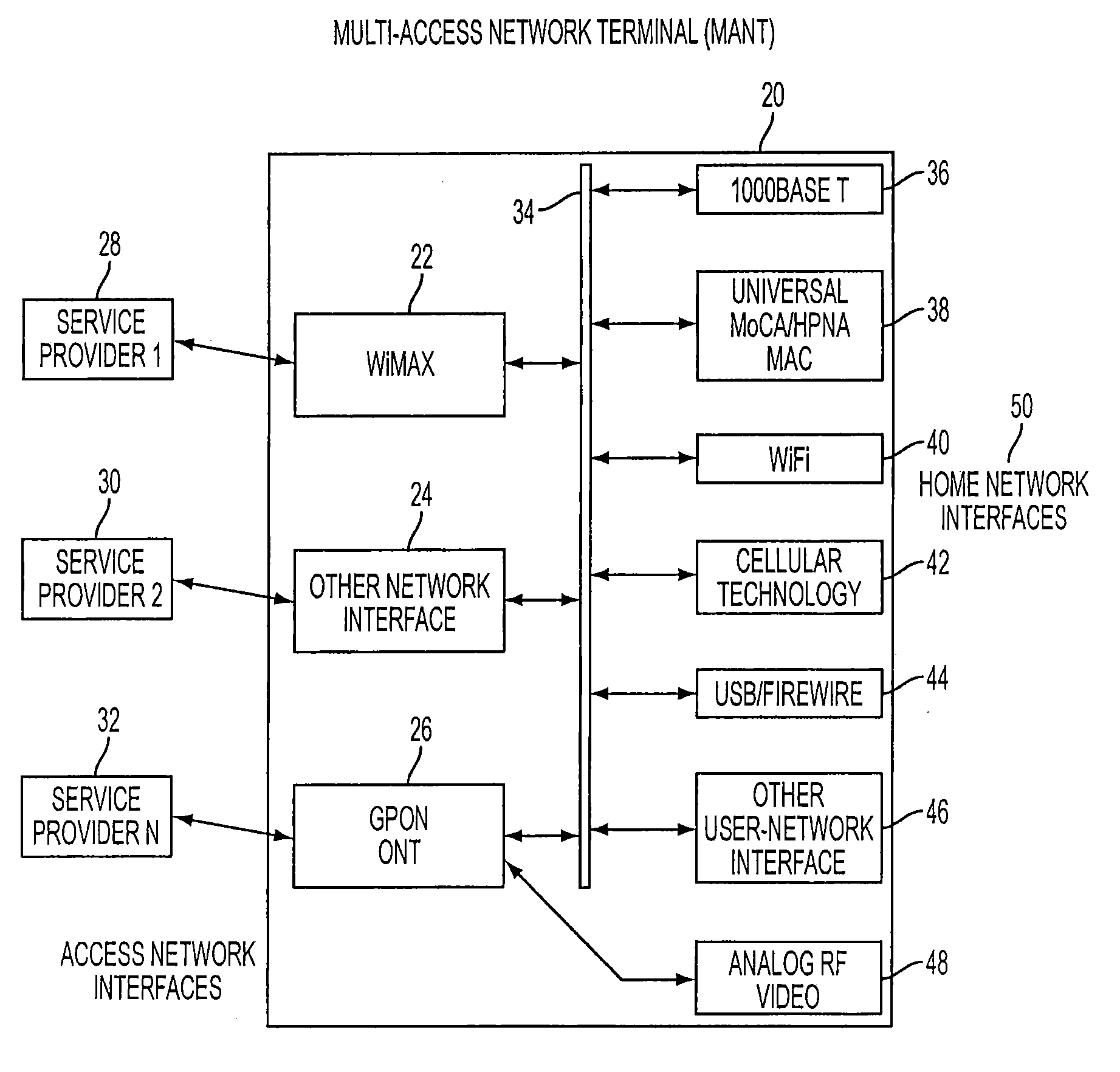
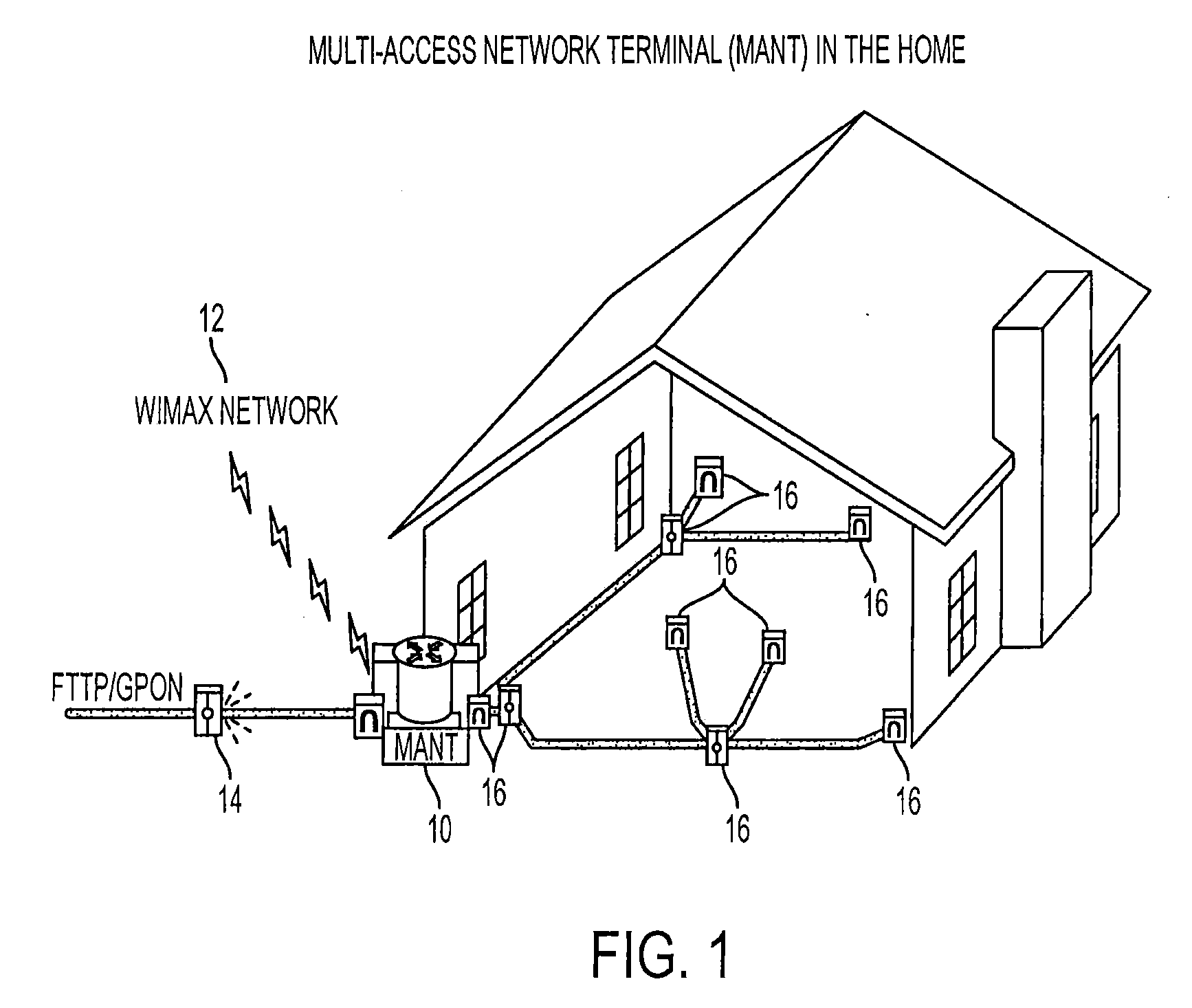
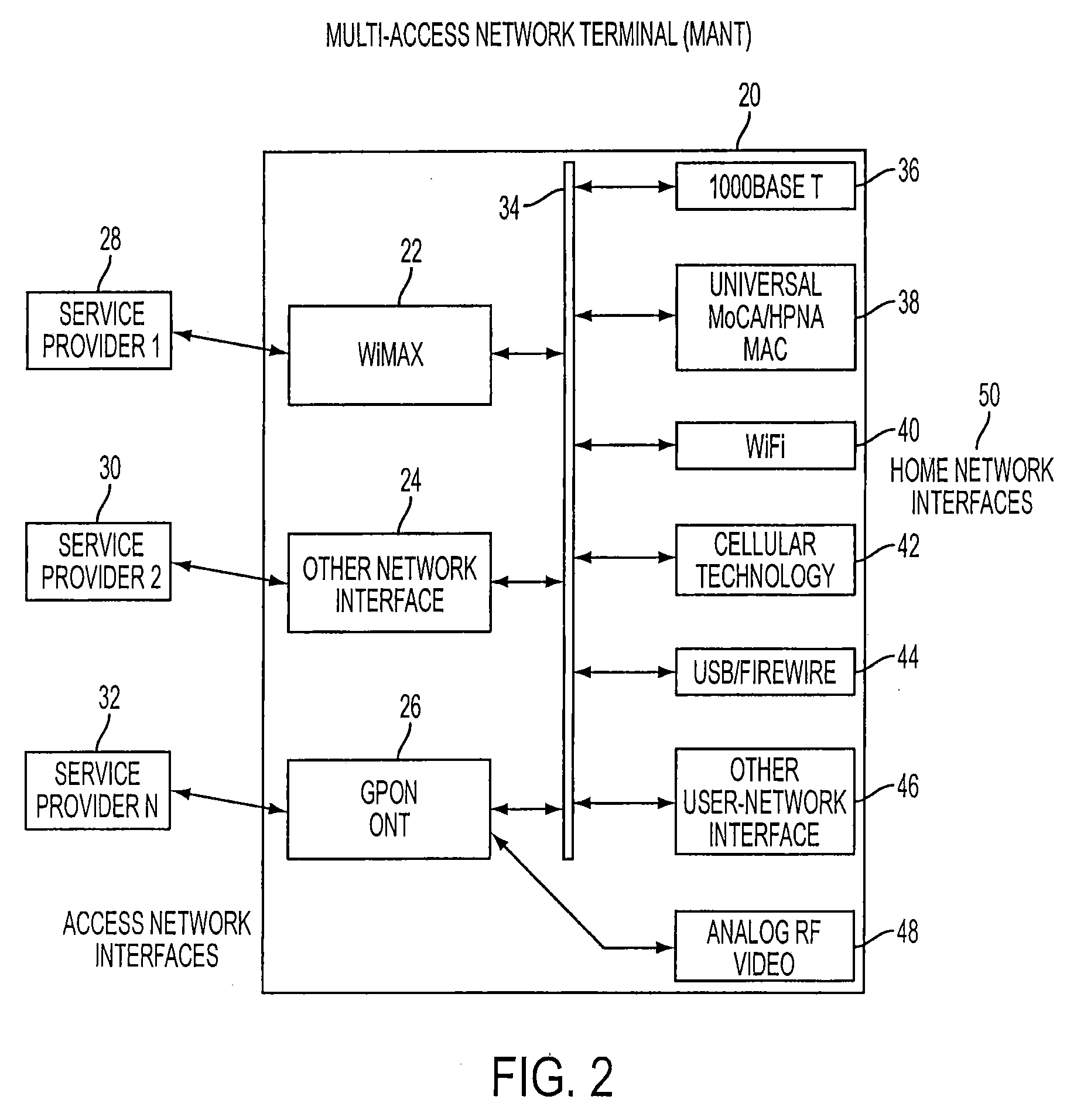
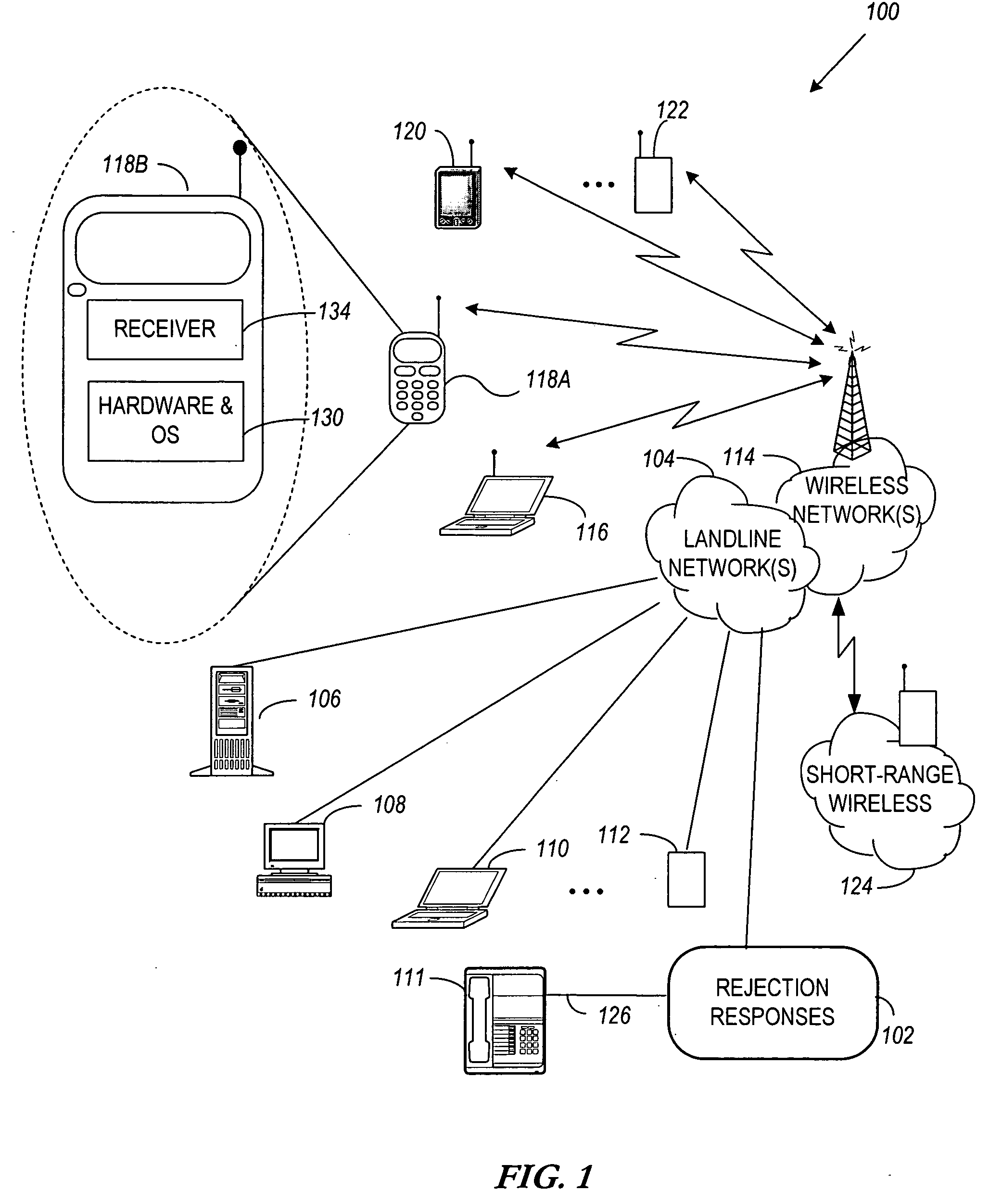
Multi-access network terminal, communication method, service-providing method, and revenue-receiving method
InactiveUS20090047016A1Solve problemsOptical multiplexData switching networksCommunication interfaceNetwork termination
A multi-access network terminal includes first and second communication interfaces. The first interface is configured to communicate with a first service provider providing services to a user through the first interface with a first type of signal and / or a first type of communications protocol. The second interface is configured to communicate with the first service provider providing services to the user through the second communication interface using a second type of signal and / or a second type of communications protocol. Alternatively, the second interface is configured to communicate with a second service provider providing services to the user through the second communication interface using the first or second type of signal and / or the first or second different type of communications protocol.
Owner:TELLABS OPERATIONS
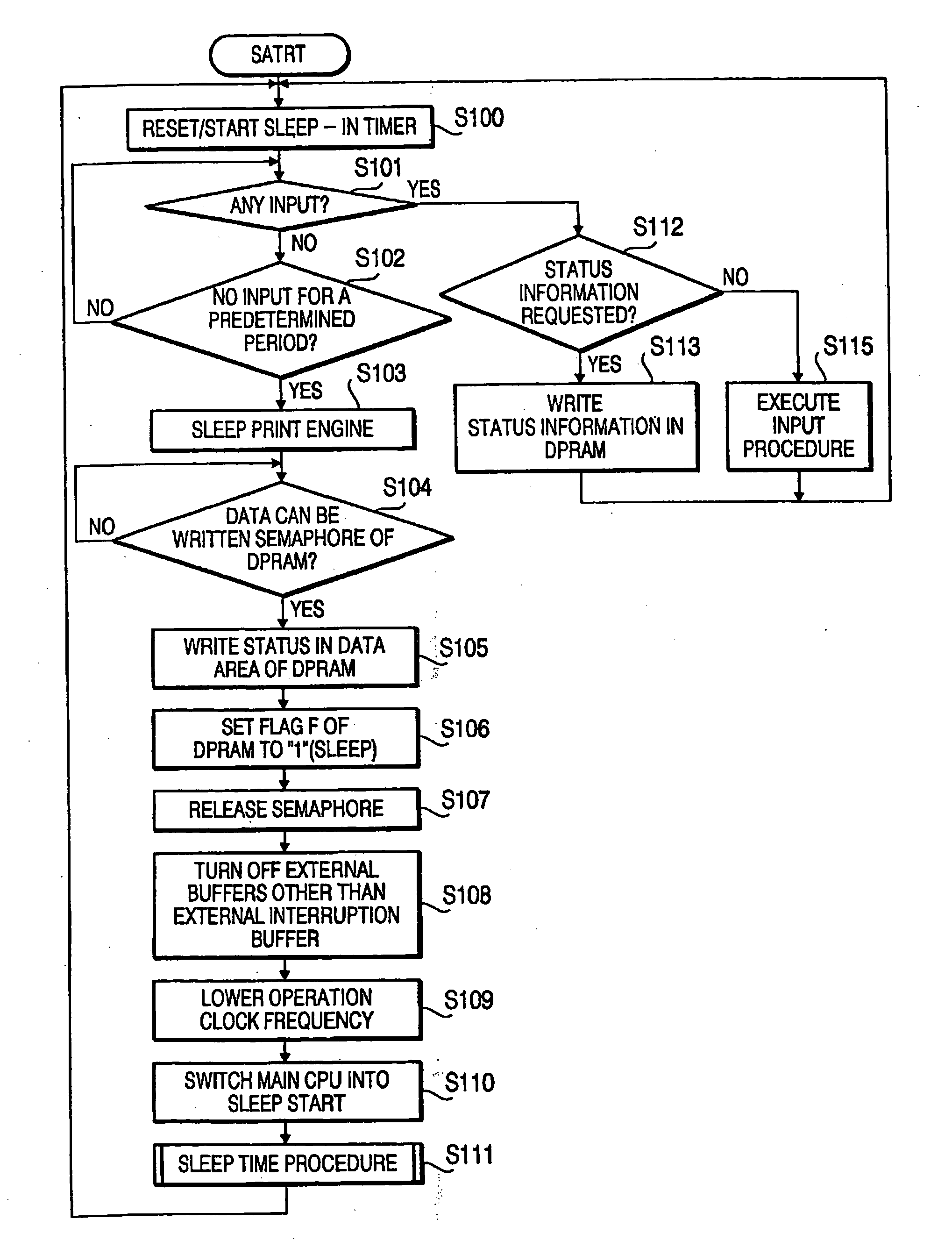
Status information notification system
InactiveUS20050021728A1Reduce power consumptionEnergy efficient ICTMultiple digital computer combinationsNetwork terminationControl system
A status information notification system includes a network terminal device and a communication processing device that enables the network terminal device to communicate with another terminal device through a communication network. The network terminal device includes a terminal controlling system that controls processing of functional units and outputs status information representing operational status of the network terminal device, and a sleeping system that lowers a power consumption of the terminal control system when a predetermined condition is satisfied. The communication processing device has an examining system that examines whether a request for the status information is received from the another terminal device. A communication controlling system obtains the status information from a storing system or the terminal controlling system, and transmits the obtained status information to the communication network. The status information is obtained from the storing system when the terminal control system is in the sleep status.
Owner:BROTHER KOGYO KK
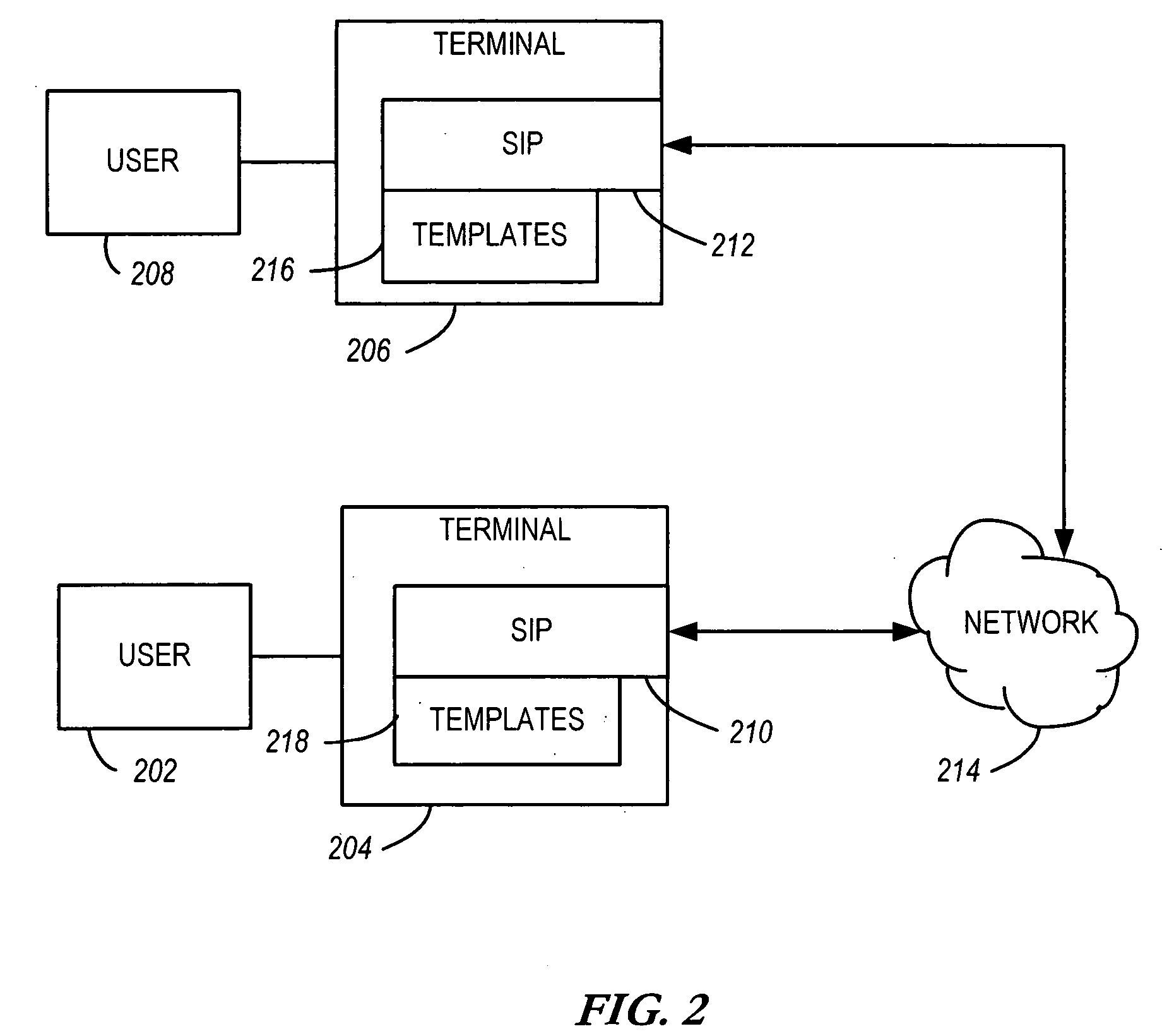
Apparatus, system, and method for rejecting a session establishment request
InactiveUS20050154793A1Connection managementData switching by path configurationComputer hardwareNetwork termination
A system, apparatus and method for rejecting a session request is disclosed. The session establishment request is initiated via a session establishment protocol operable via a network. In one configuration, a first network terminal receives a session establishment request sent from a second network terminal via the session establishment protocol. A message template is selected from one or more message templates of the first network terminal. Each message template includes a reason descriptor describing reasons the session cannot be established. A rejection message of the session establishment protocol is formed based on the selected message template. The rejection message is sent via the session establishment protocol targeted for the second network terminal. The reason descriptor is communicated to a user of the second network terminal.
Owner:NOKIA CORP
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com