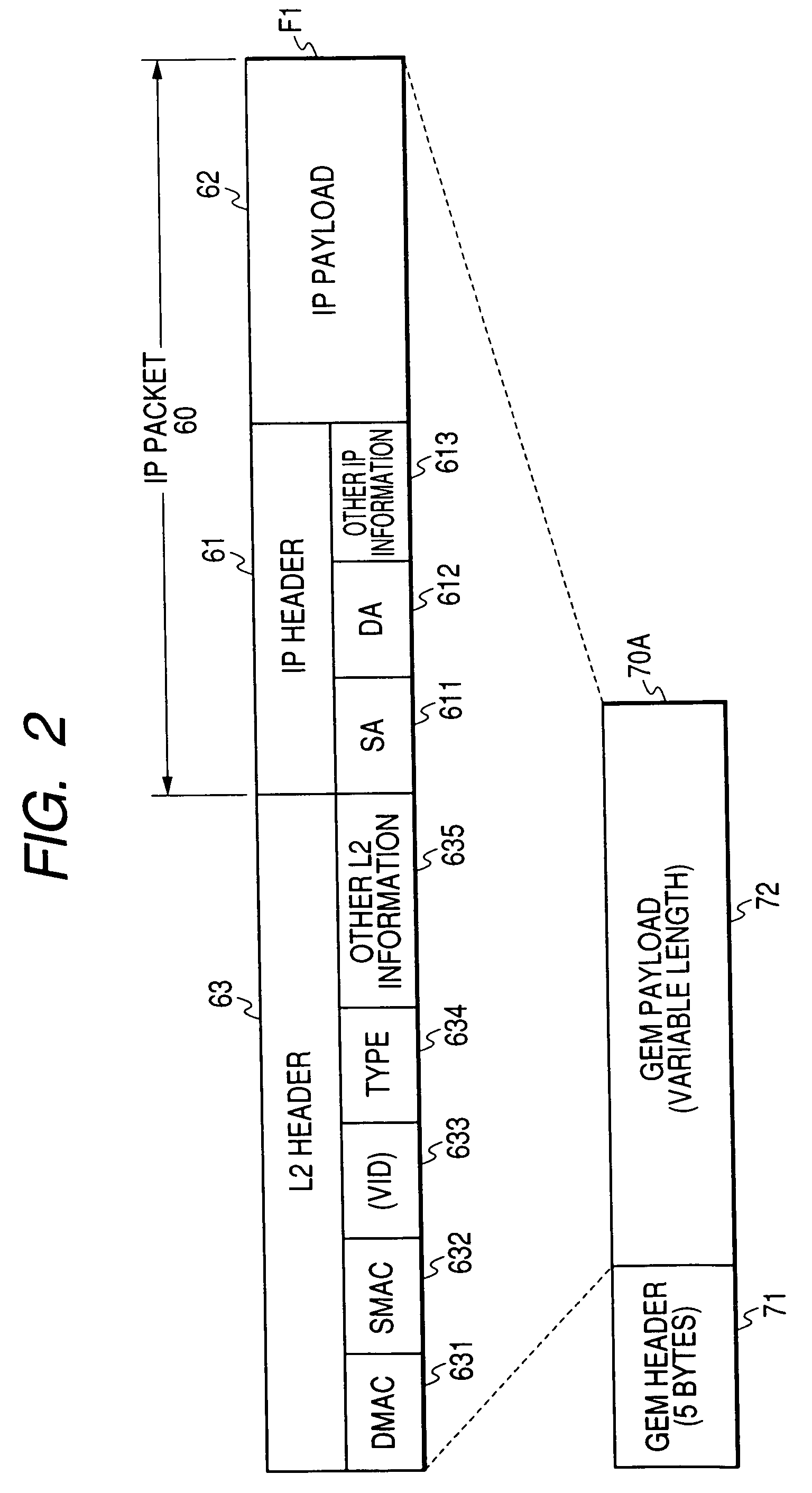
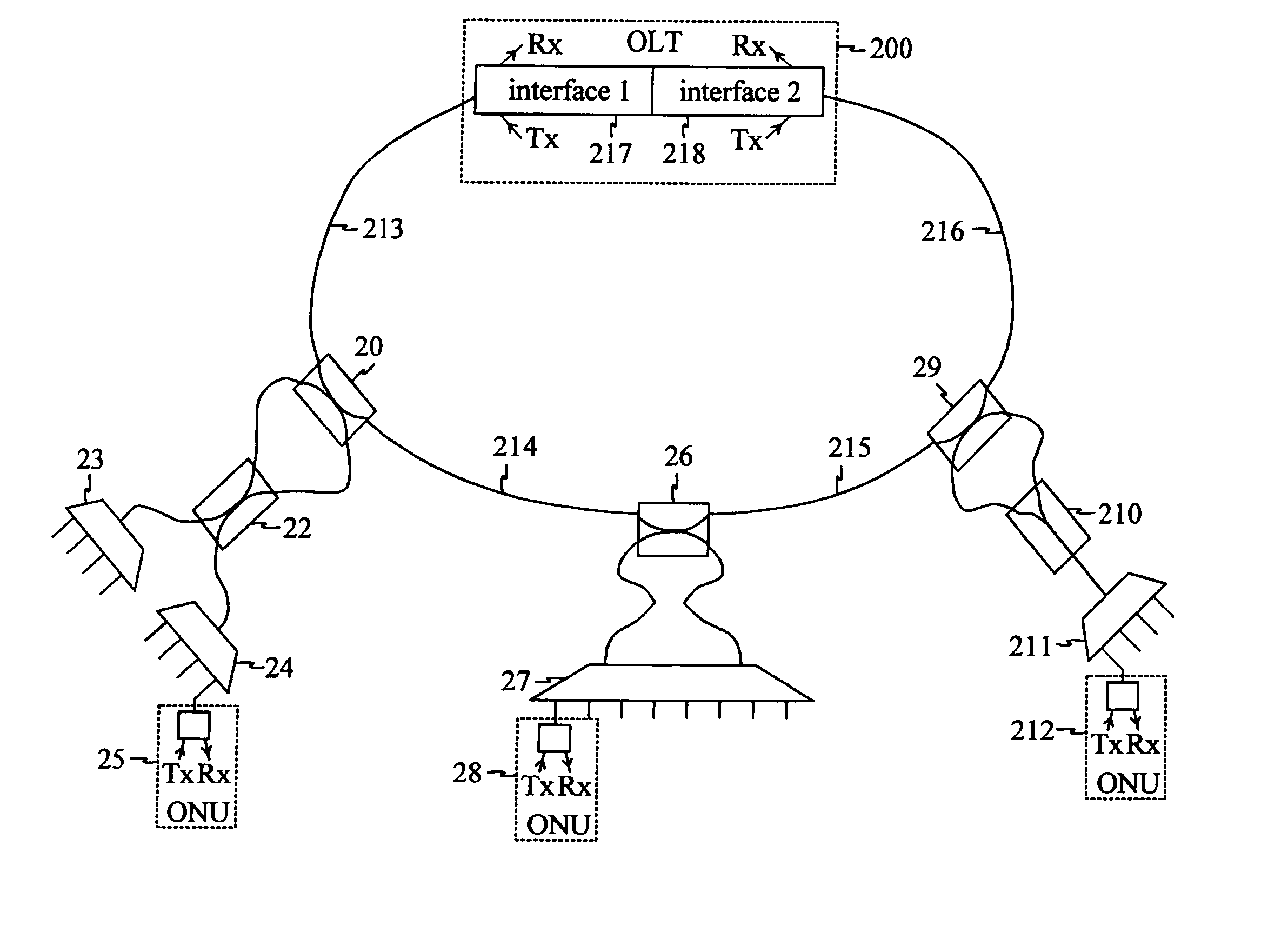
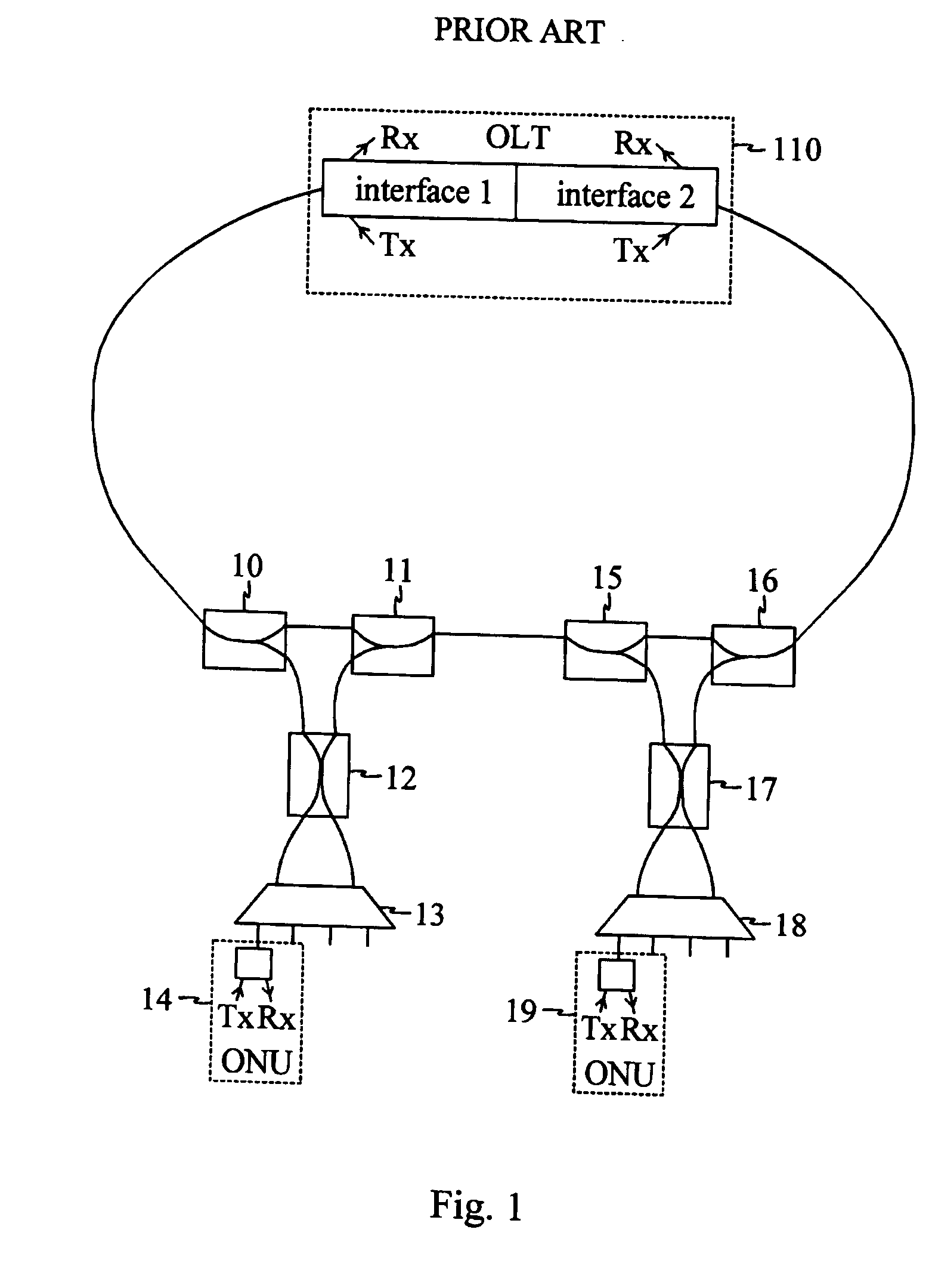
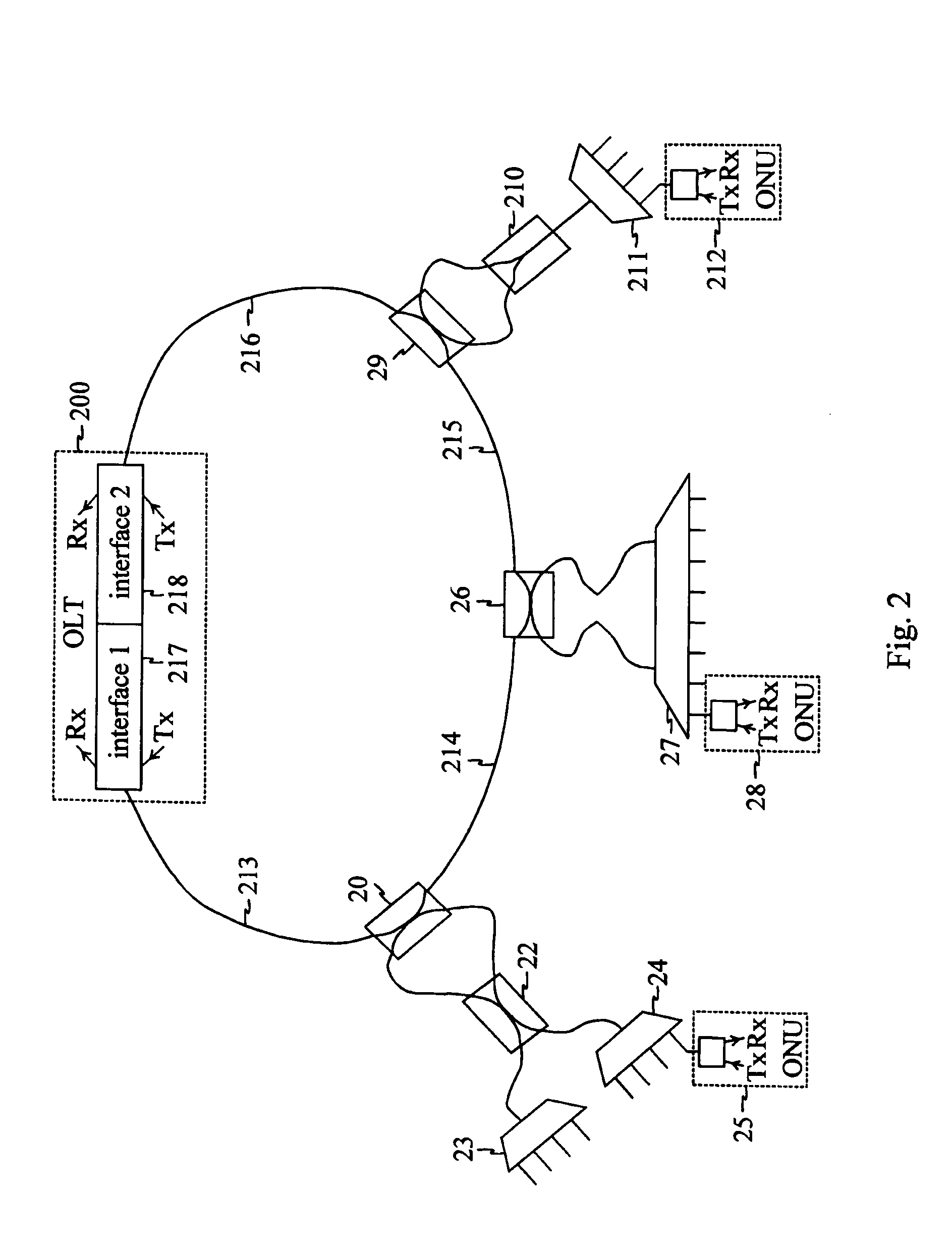
Patents
Literature
1712 results about "Passive optical network" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
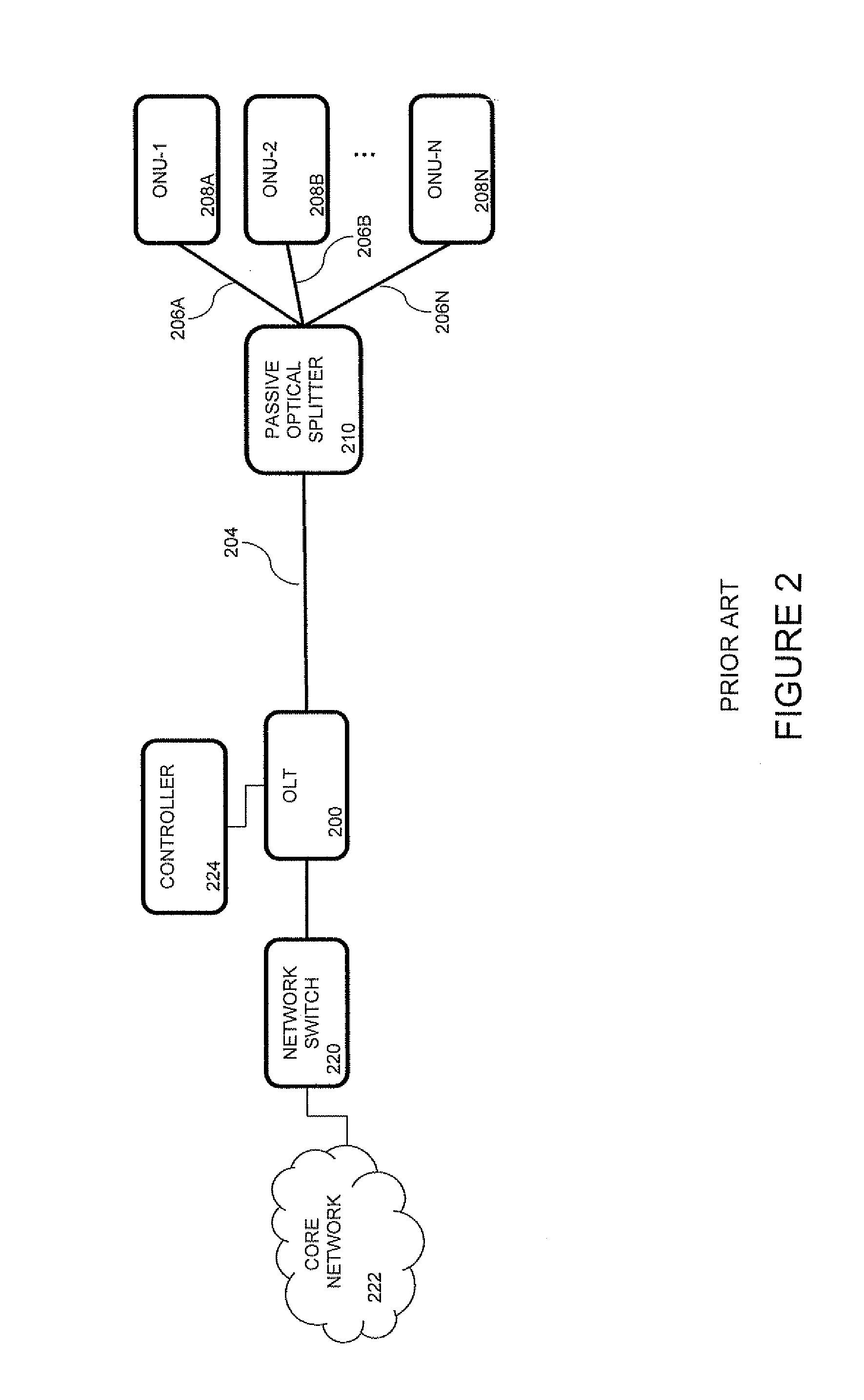
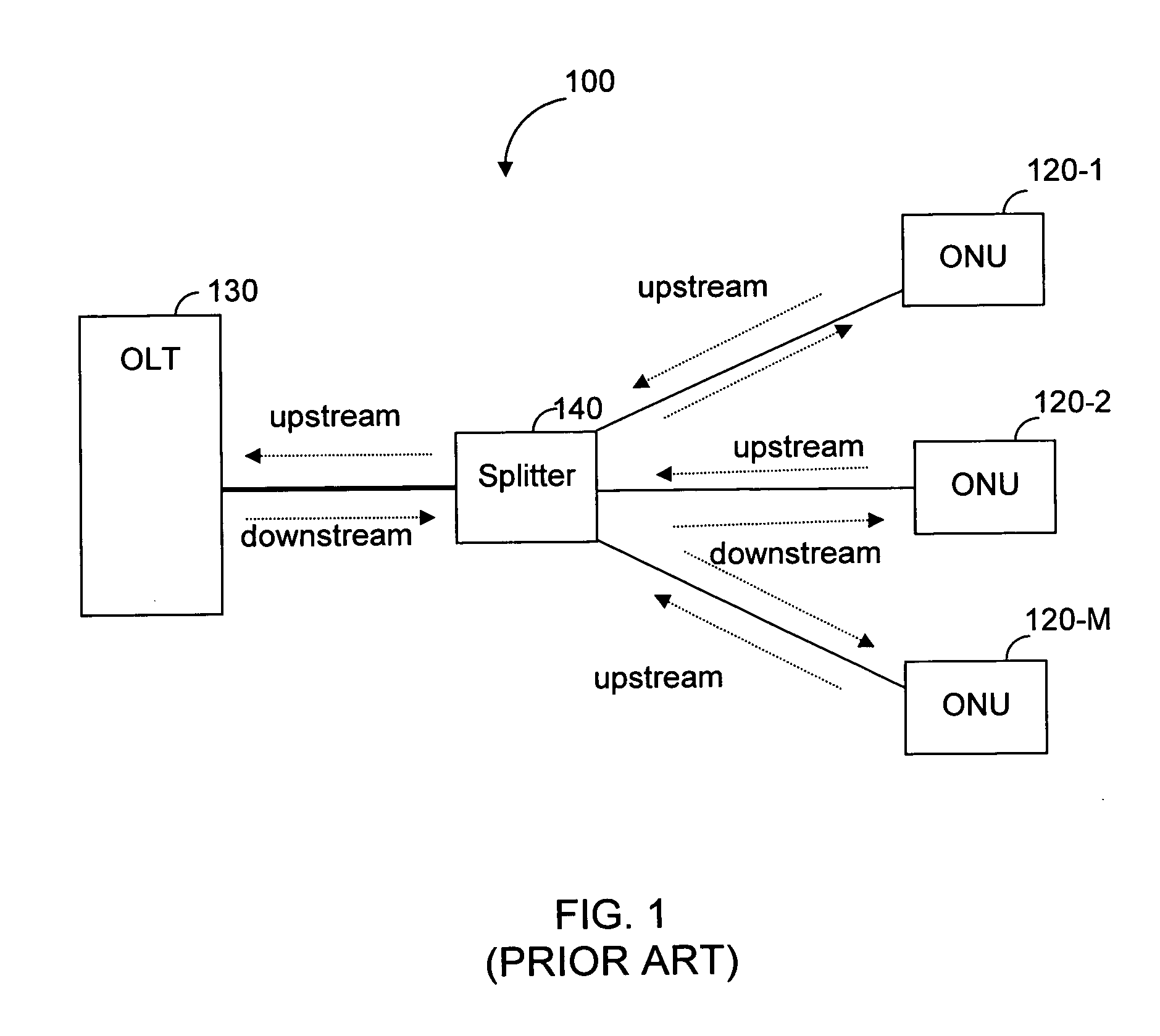
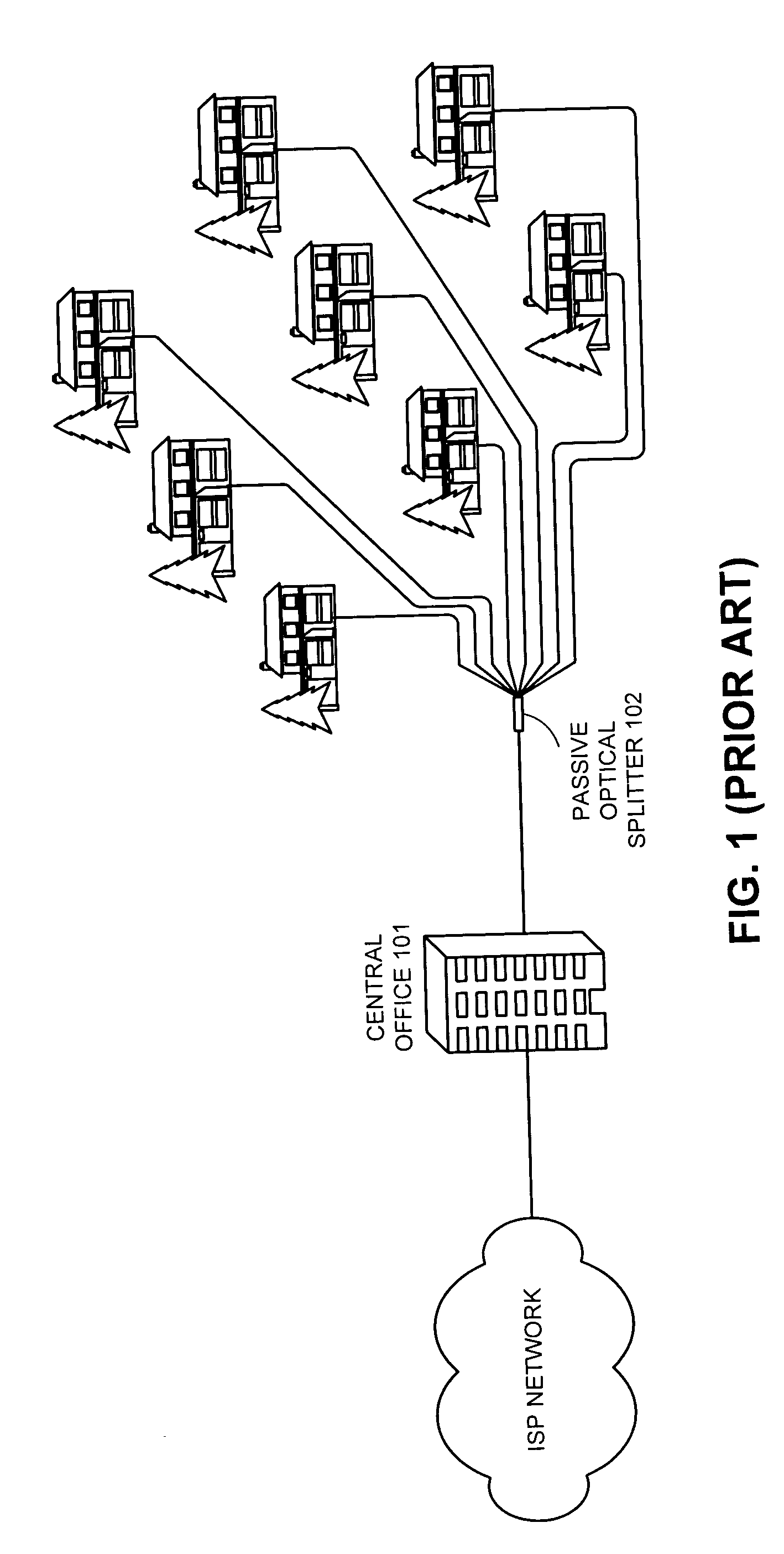
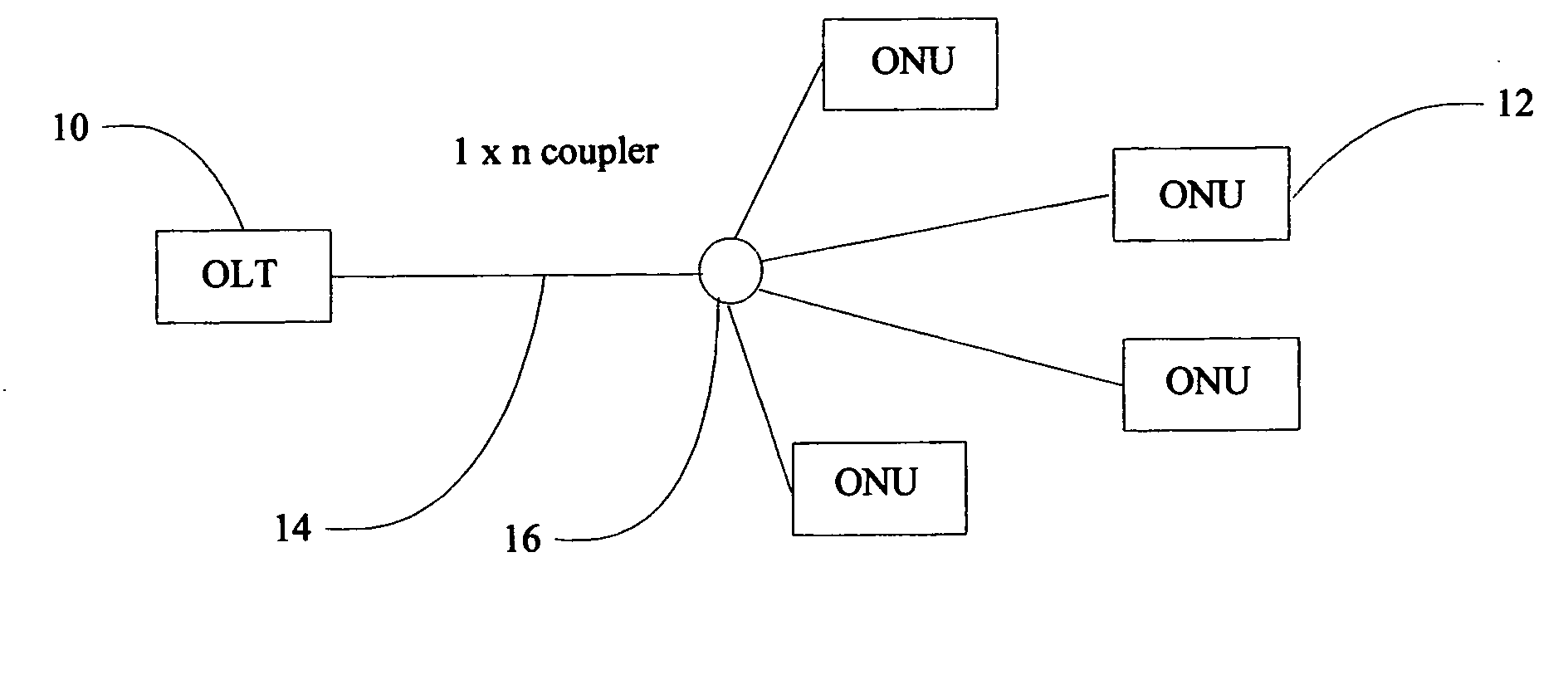
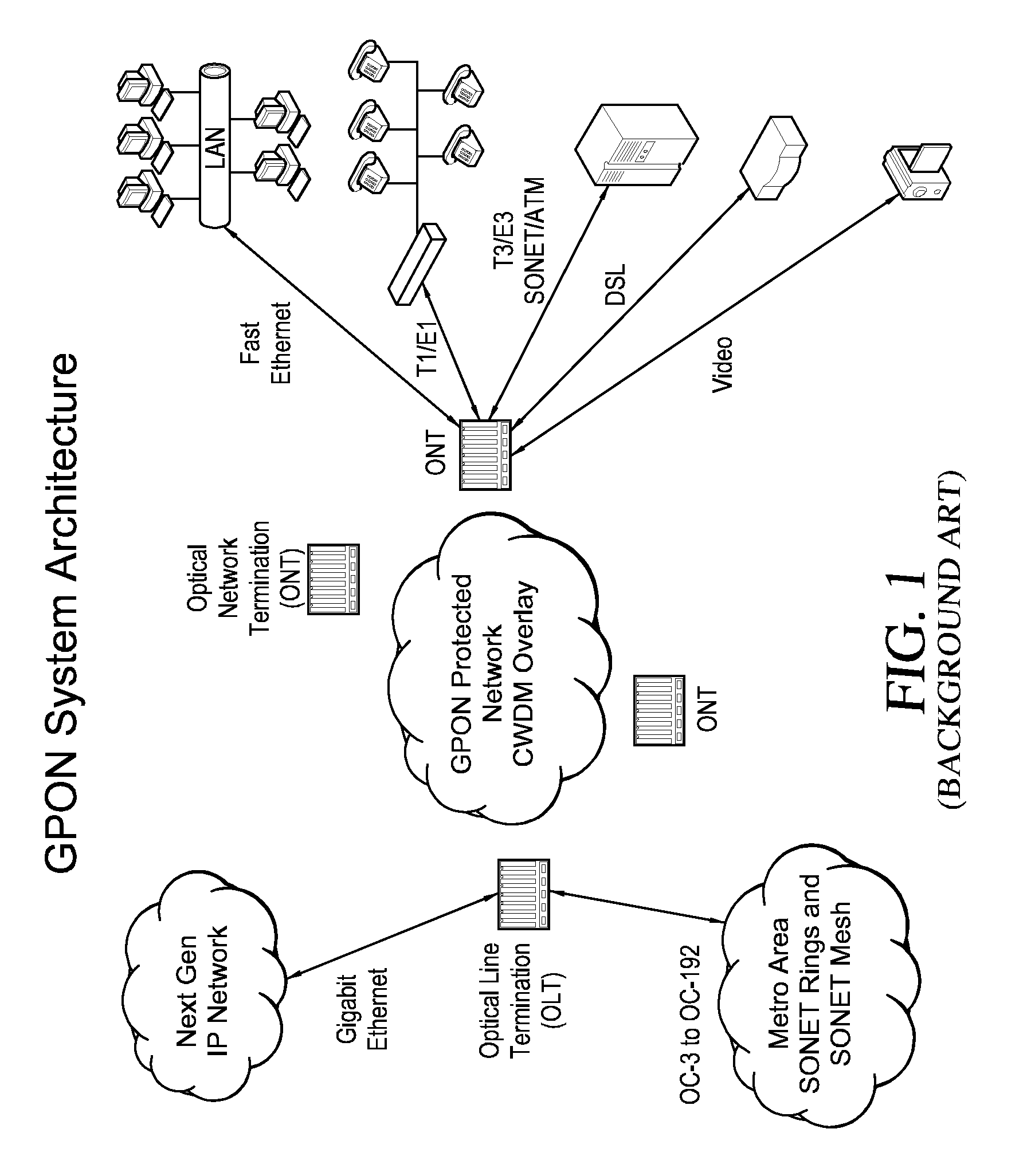
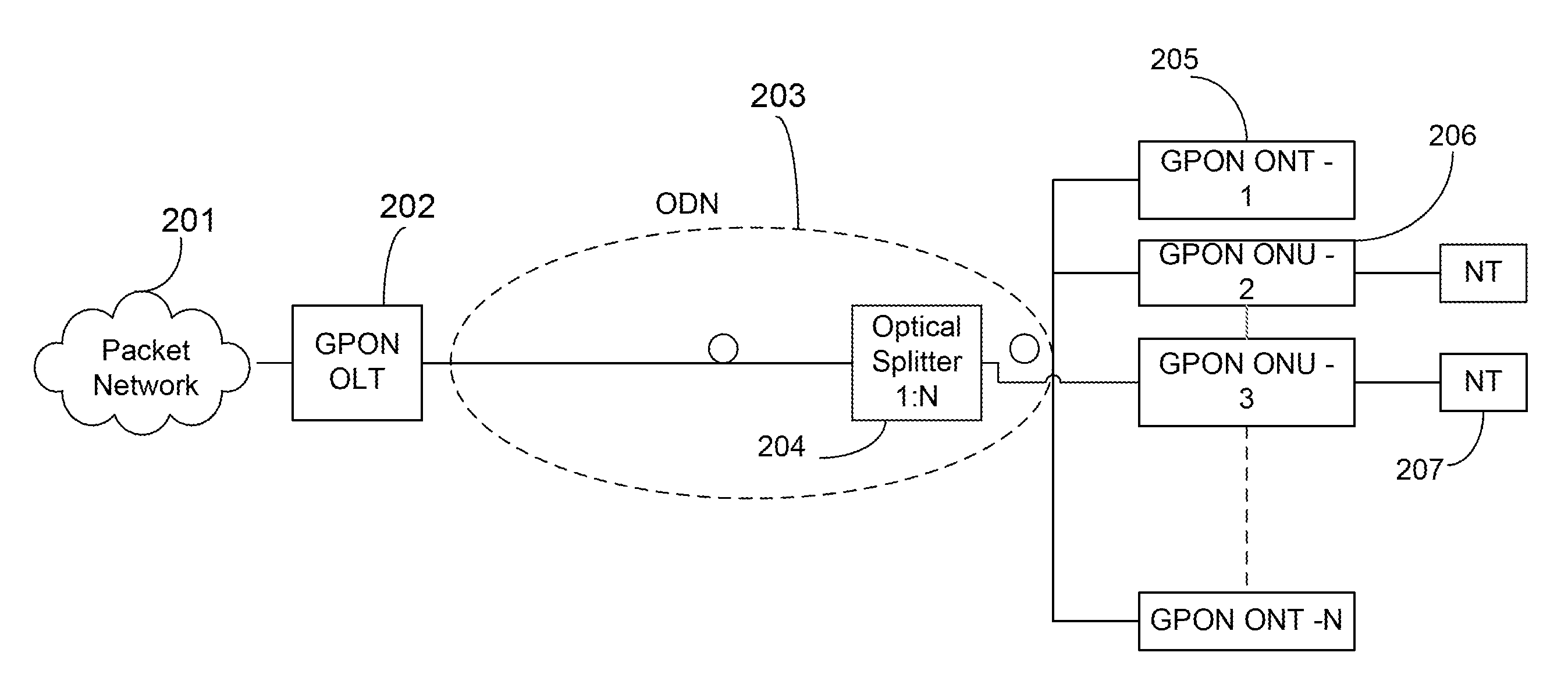
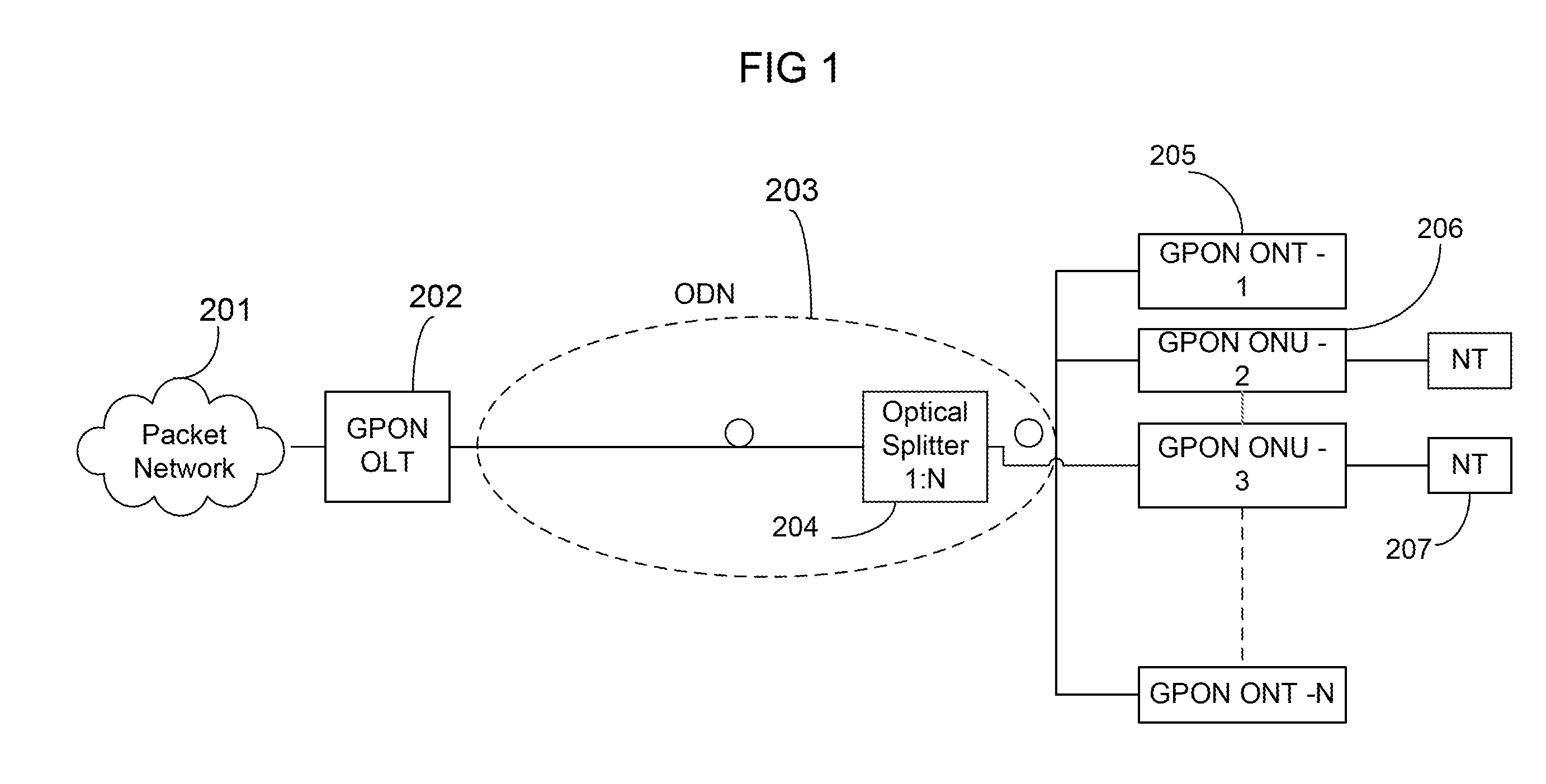
A passive optical network (PON) is a fiber-optic telecommunications technology for delivering broadband network access to end-customers. Its architecture implements a point-to-multipoint topology, in which a single optical fiber serves multiple endpoints by using unpowered (passive) fiber optic splitters to divide the fiber bandwidth between multiple access points. Passive optical networks are often referred to as the "last mile" between an Internet service provider (ISP) and its customers.
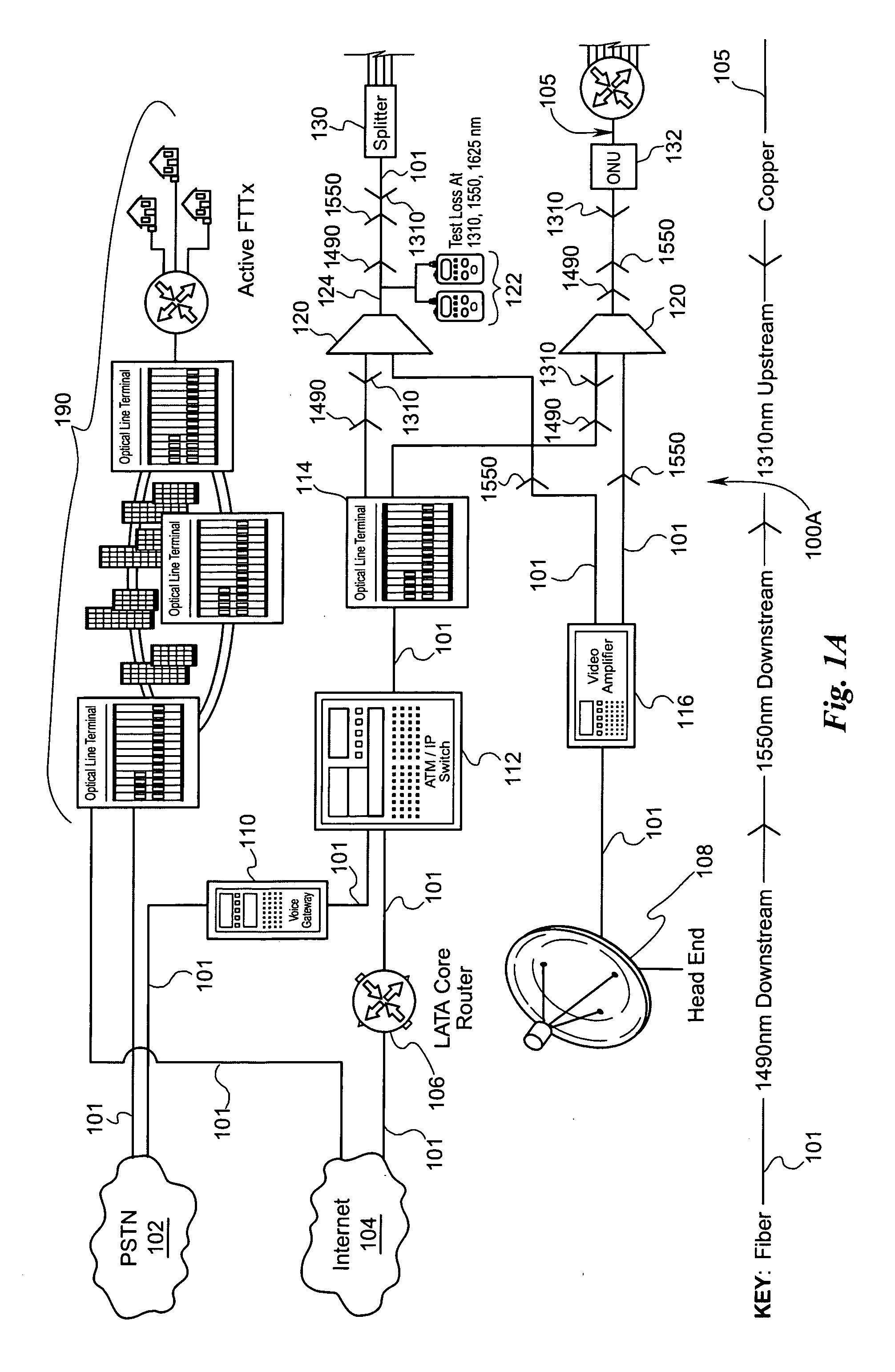
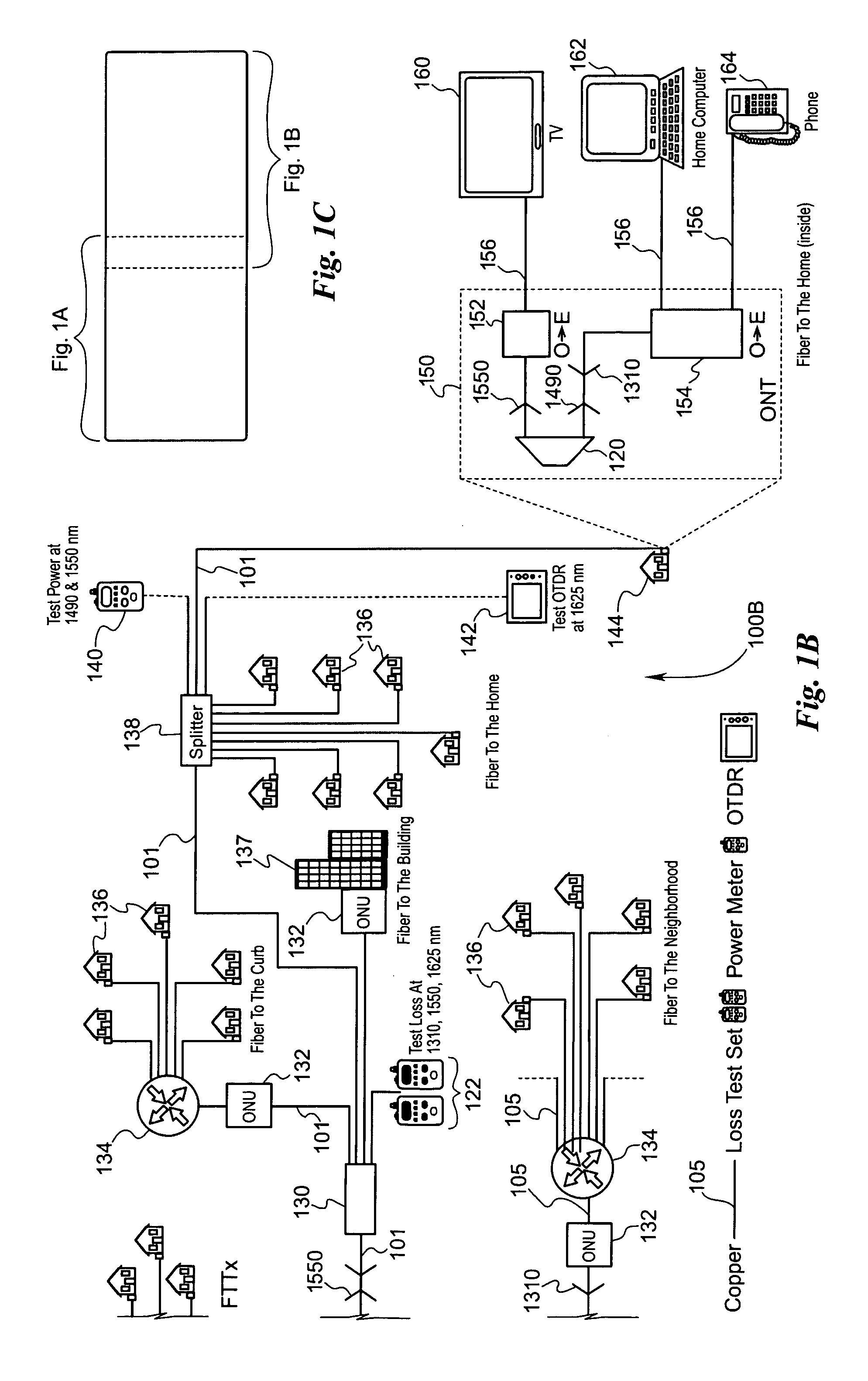
Fiber to the home (FTTH) multimedia access system with reflection PON
InactiveUS20020063924A1Inexpensive, easy-to-serviceEasy to scaleBroadband local area networksWavelength-division multiplex systemsMultiplexingData signal
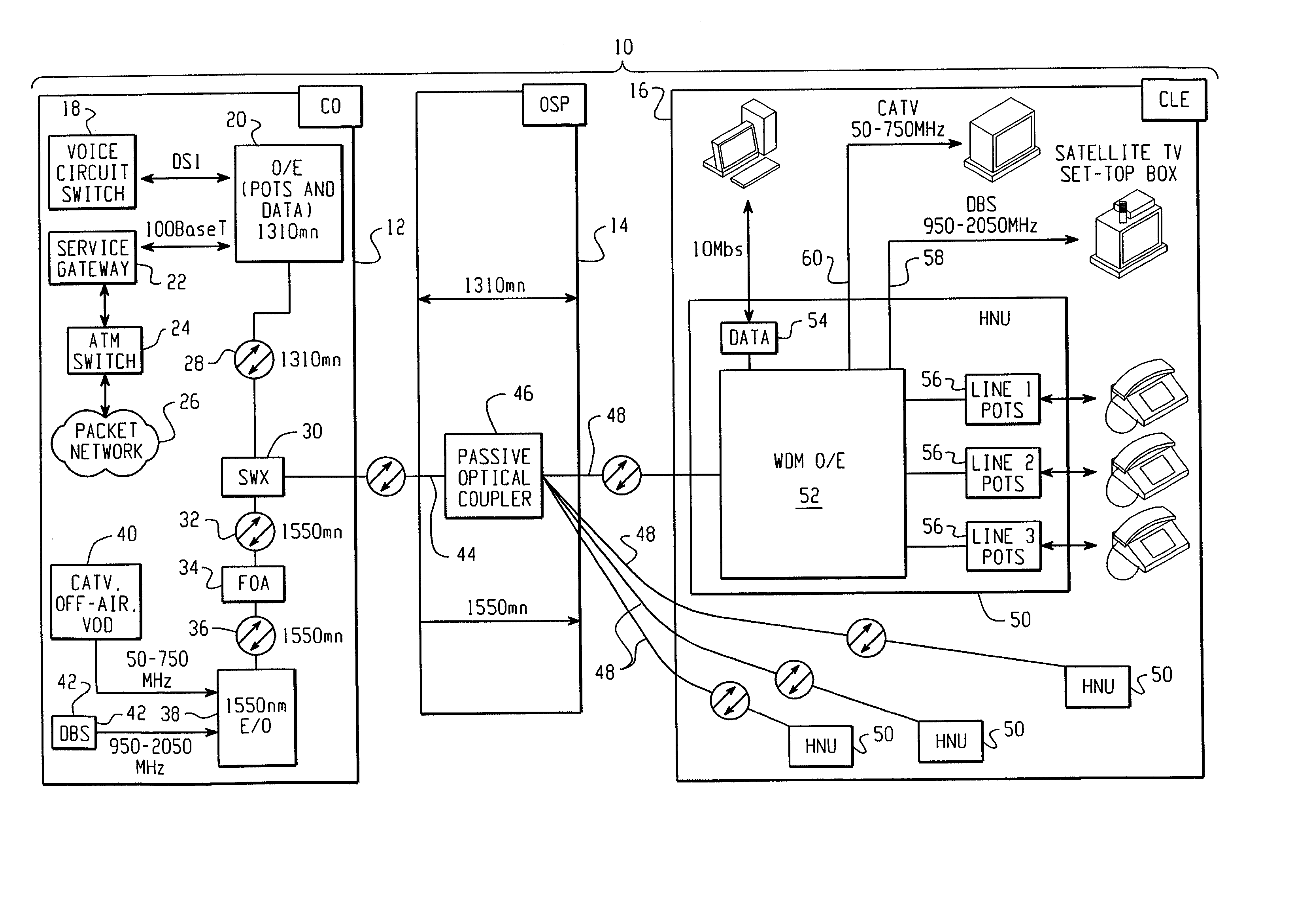
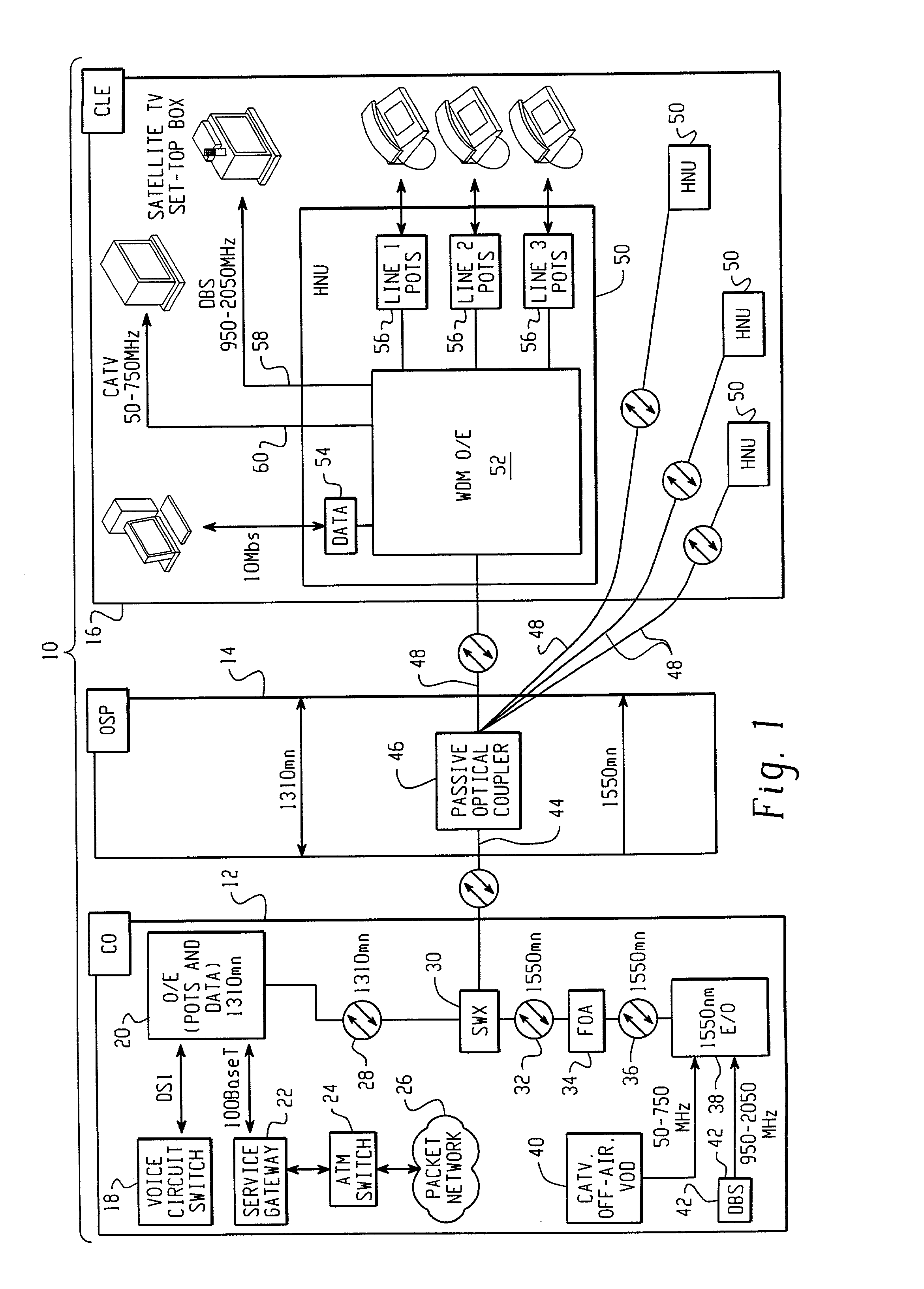
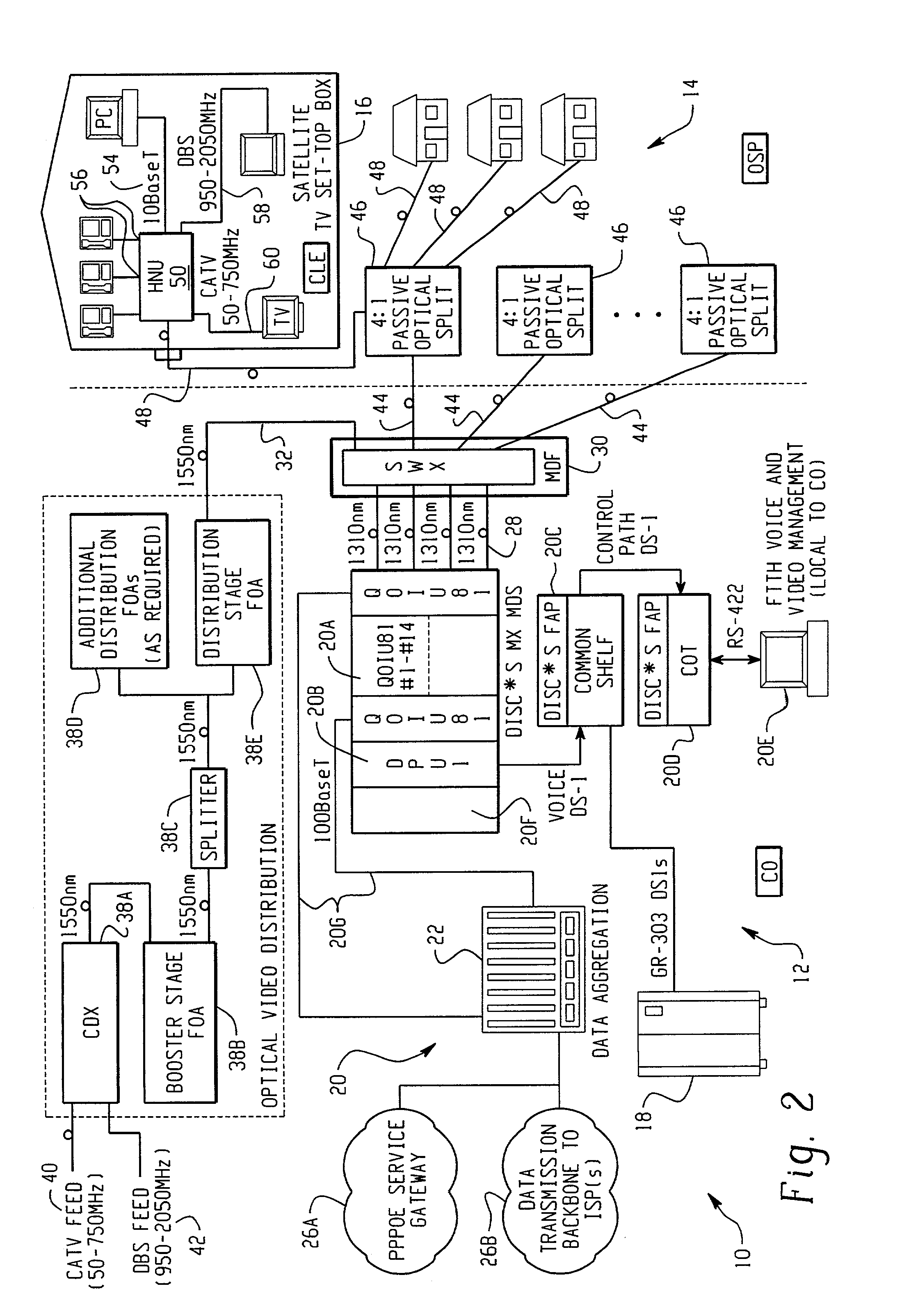
A Fiber-to-the-Home (FTTH) multi-media access system and method are provided in which voice, video and data signals are transported over a passive optical network (PON) between a central office location and a plurality of subscriber home network units (HNUs). Optical video distribution circuitry and telephony / data distribution circuitry at the central office location are included in the system and operate to send and receive CATV video, PBS video television, telephony and Packet data signals to and from the HNUs via the PON. Optical multiplexing / demultiplexing circuitry operating at the central office combines the video signals, which are operating at one optical wavelength, with the telephony / data signals, which are operating at a second, distinct optical wavelength. These combined optical signals are then transported over the PON to the HNUs. The PON includes a plurality of distribution fibers coupled to a plurality of passive optical splitters, which are each coupled to a plurality of drop fibers that connect to the HNUs. The HNUs receive the combined optical signals, demultiplex and convert the optical signals into corresponding electrical signals, which are in turn coupled through the HNU to the video, data and telephony networks within the home. The HNUs also receive upstream electrical signals from devices within the home, multiplex and convert these electrical signals into upstream optical signals, and transmit these upstream optical signals to the central office.
Owner:ADVANCED FIBER ACCESS CORP
System and method for providing wireless over a passive optical network (PON)
ActiveUS20080063397A1Maximize utilizationConvenient supplementMultiplex system selection arrangementsTime-division optical multiplex systemsService provisionNetworked system
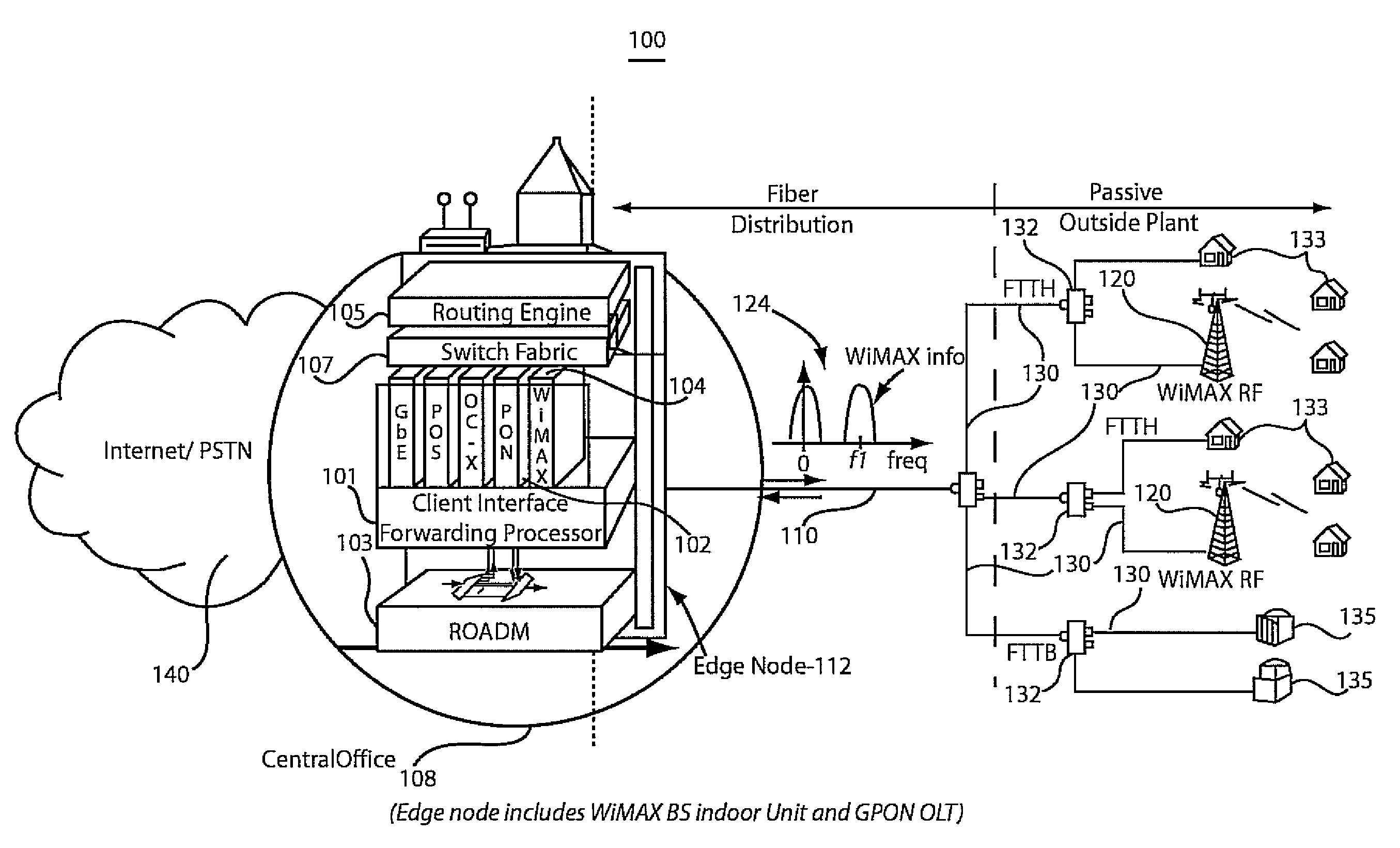
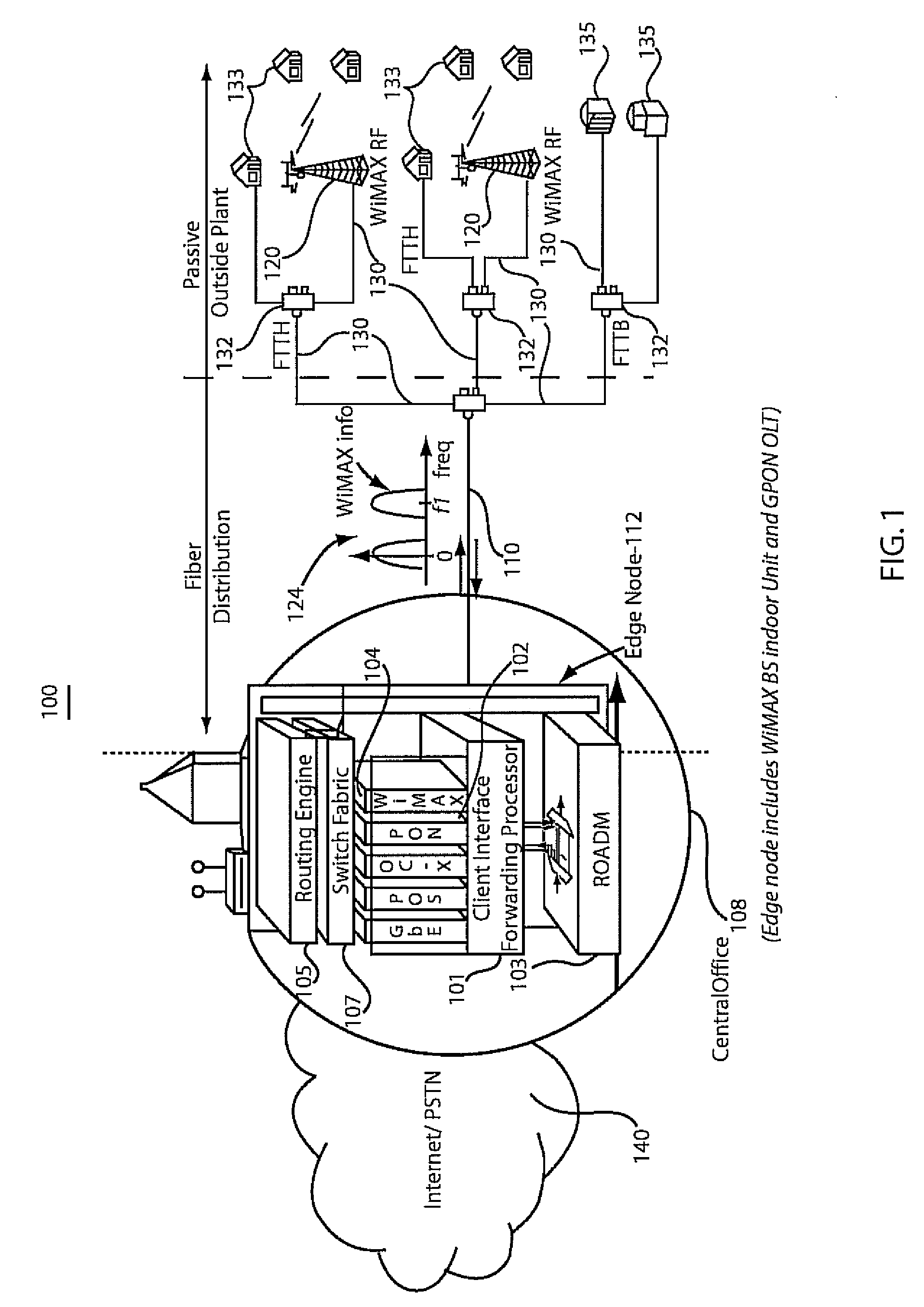
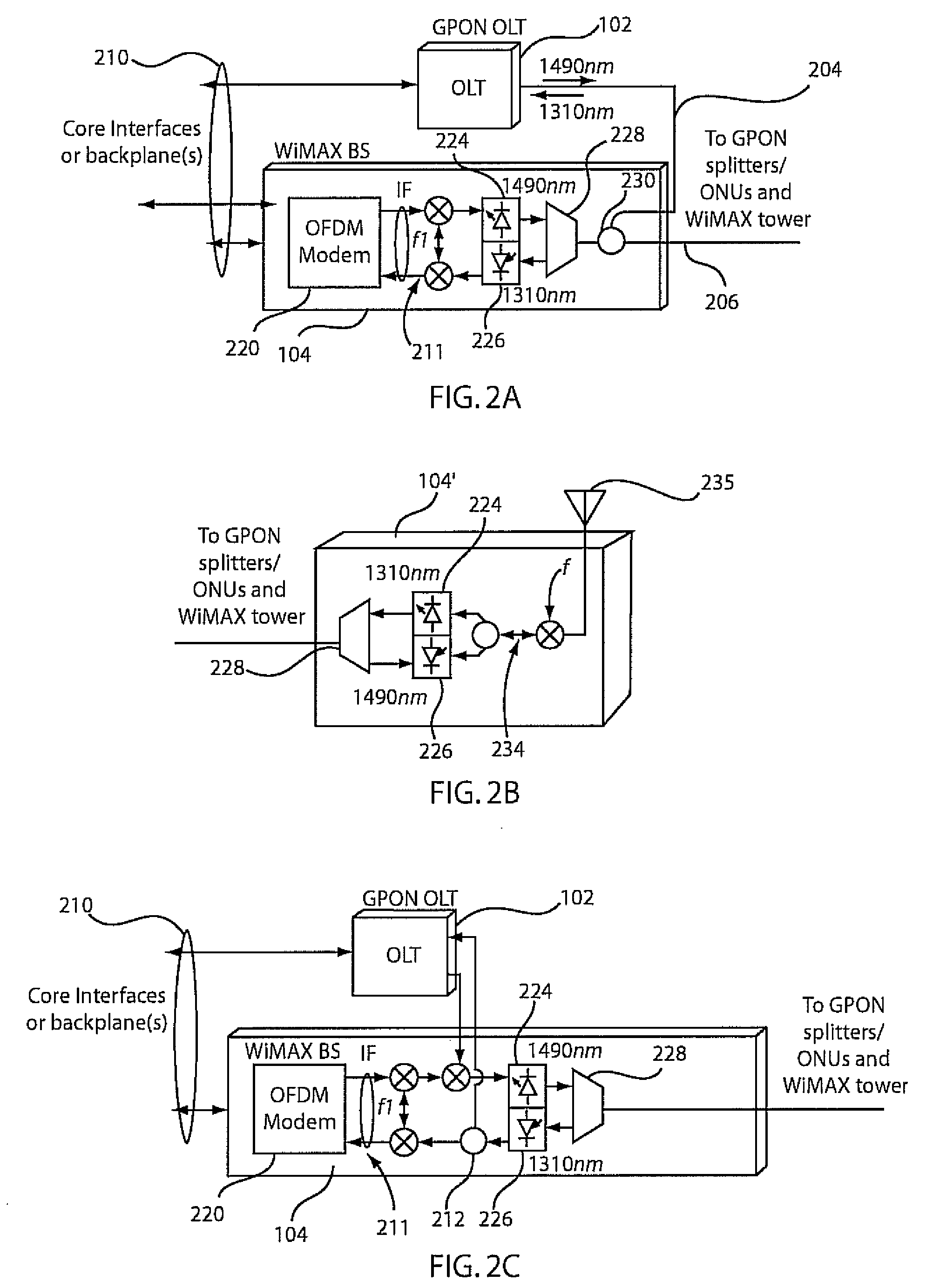
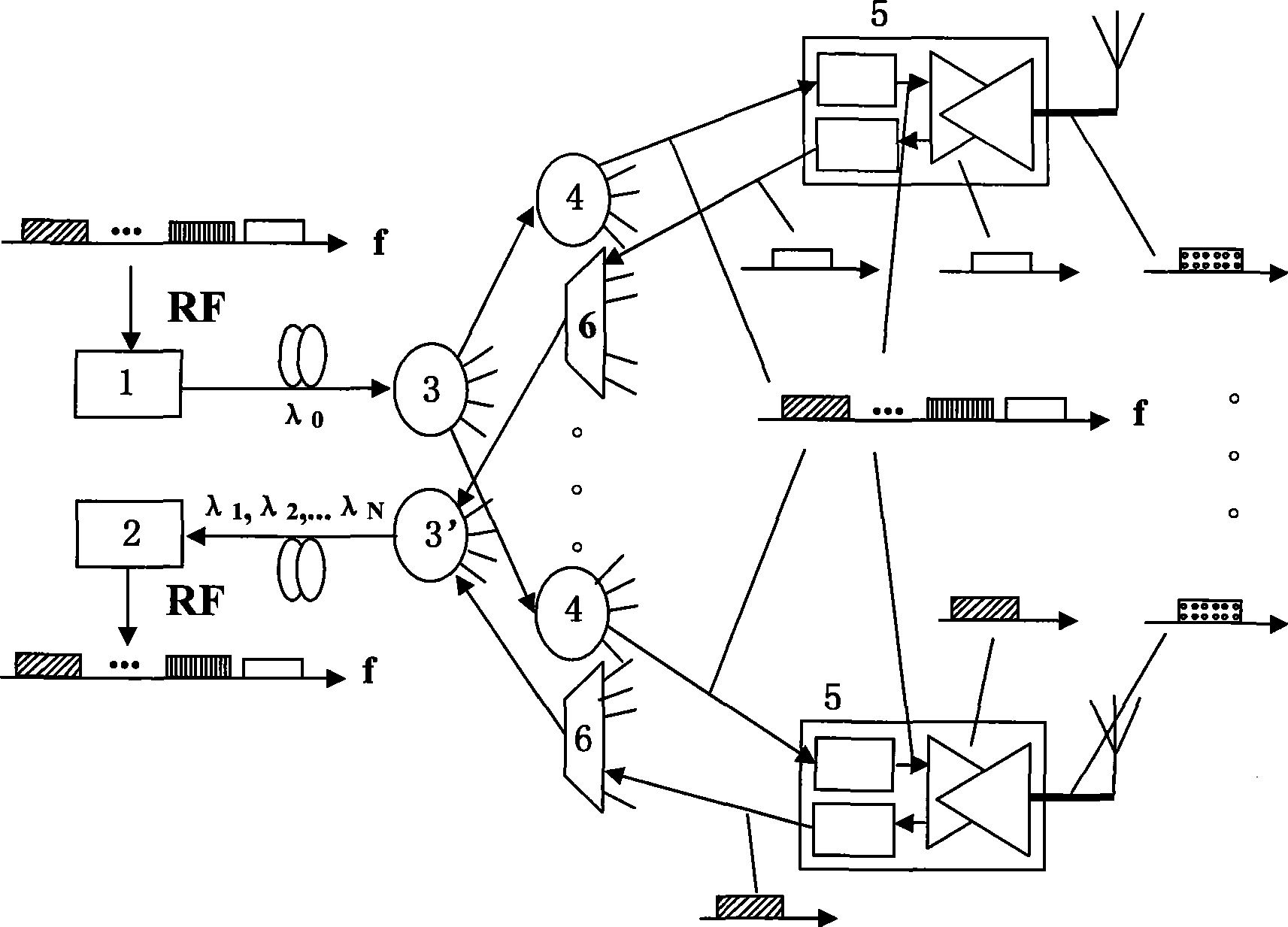
A network system and method include a wireless base station integrated at a central office of a service provider. The wireless base station is configured to provide portable and fixed services to customers. A passive optical network is coupled to the wireless base station at the central office to provide a link to extend an antenna for wireless operations of the wireless base station to a remote site such that a wireless signal from the wireless base station is transmitted in parallel with a passive fiber network signal through the link.
Owner:NEC CORP
WDM type passive optical network
InactiveUS20070092256A1Increasing ONUs easierImprove communication bandwidthWavelength-division multiplex systemsStar/tree networksLength waveOptical transmitter
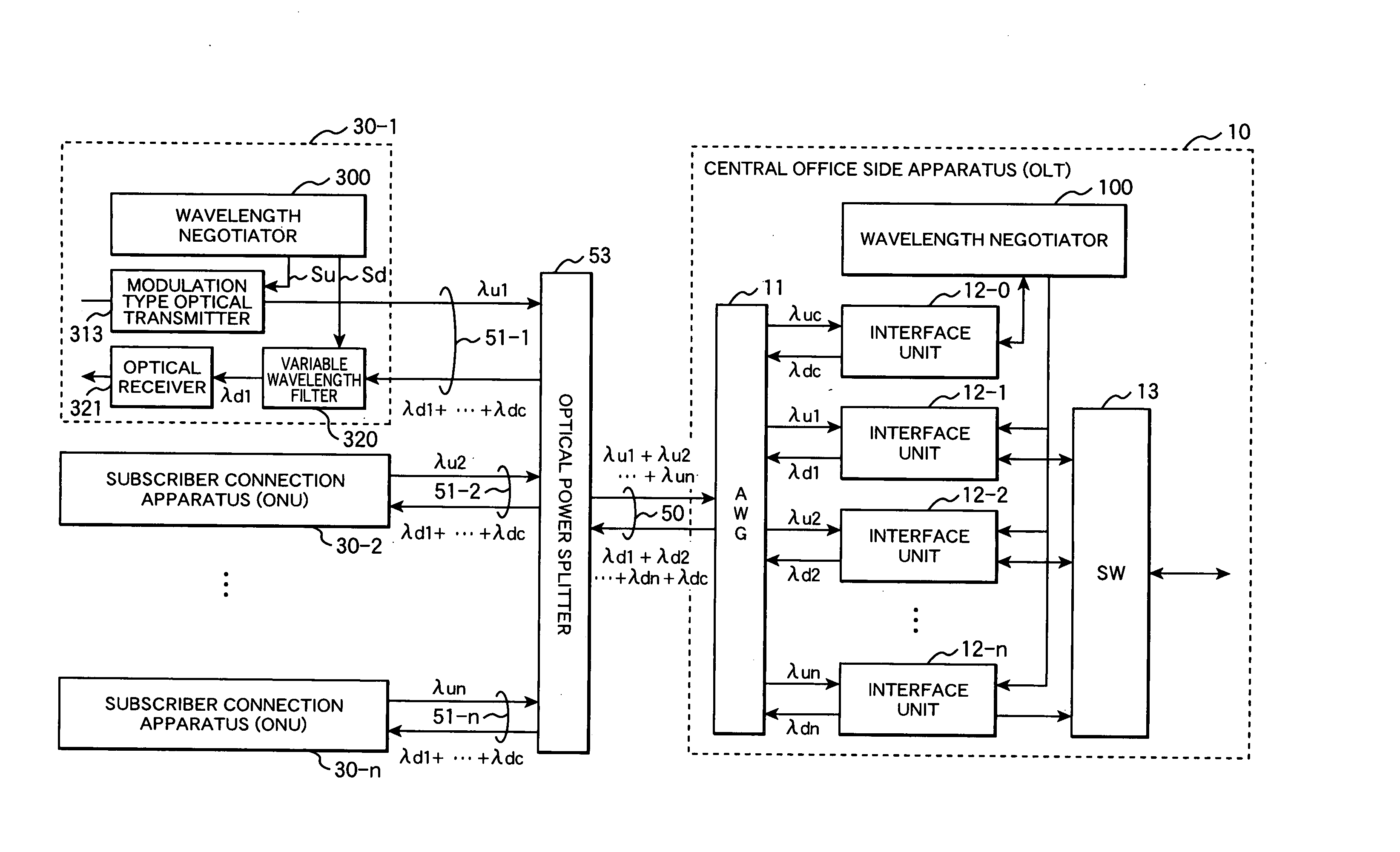
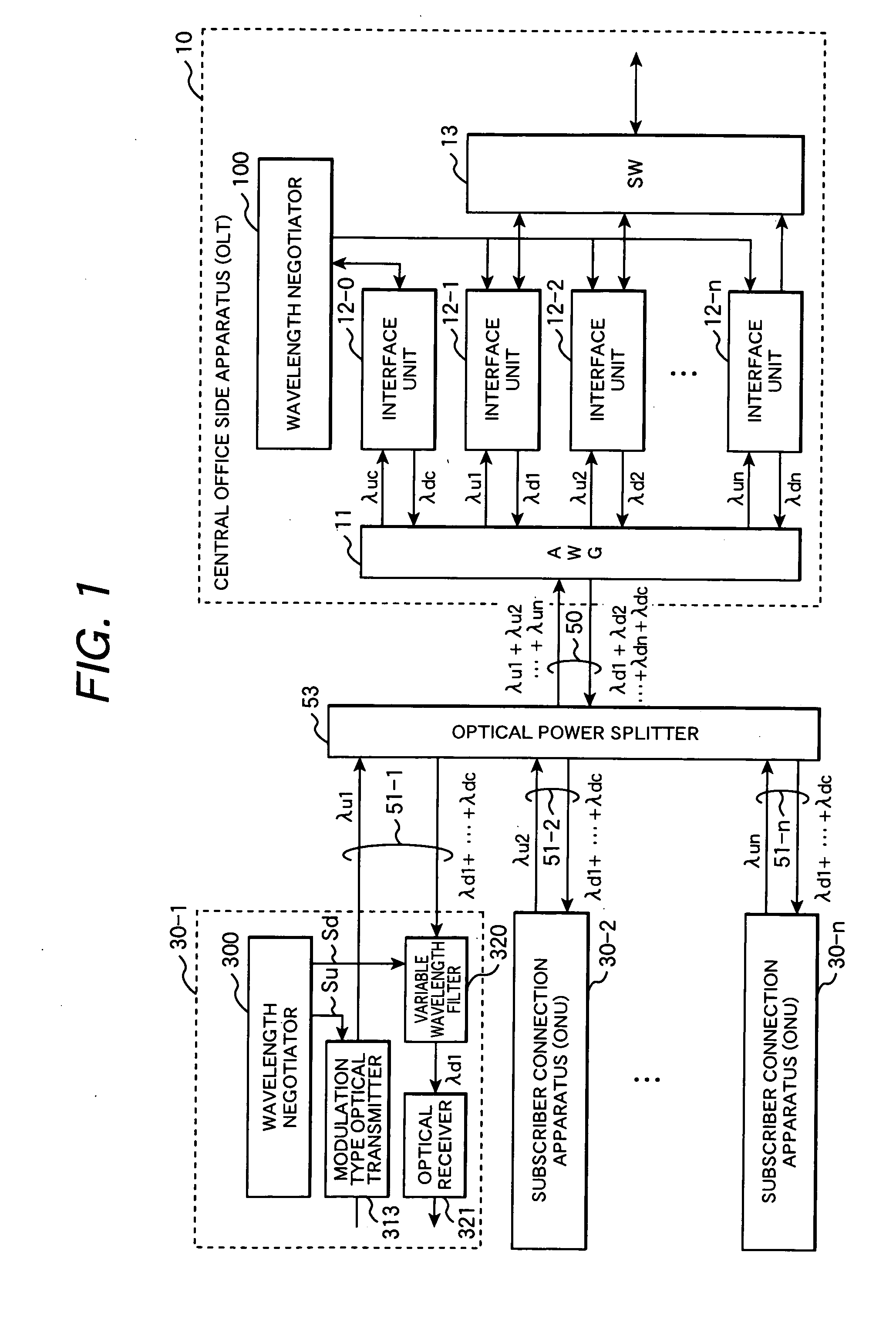
In a WDM type PON system, each ONU comprises an optical transmitter capable to transmit optical signals with variable wavelengths, an optical signal receiving filter variable its receiving wavelength, and a control unit. An OLT selects in response to a wavelength allocation request from each ONU, a transmitting wavelength and a receiving wavelength out of currently free wavelengths and allocates these wavelengths to the requester ONT. The control unit of the ONU switches the transmitting wavelength of the optical transmitter and the receiving wavelength of the optical signal receiving filter to the wavelengths specified in a response message from the OLT and starts data communication.
Owner:HITACHI LTD
Low-cost WDM source with an incoherent light injected fabry-perot laser diode
InactiveUS20010004290A1Semiconductor laser arrangementsWavelength-division multiplex systemsPeak valueBroadband
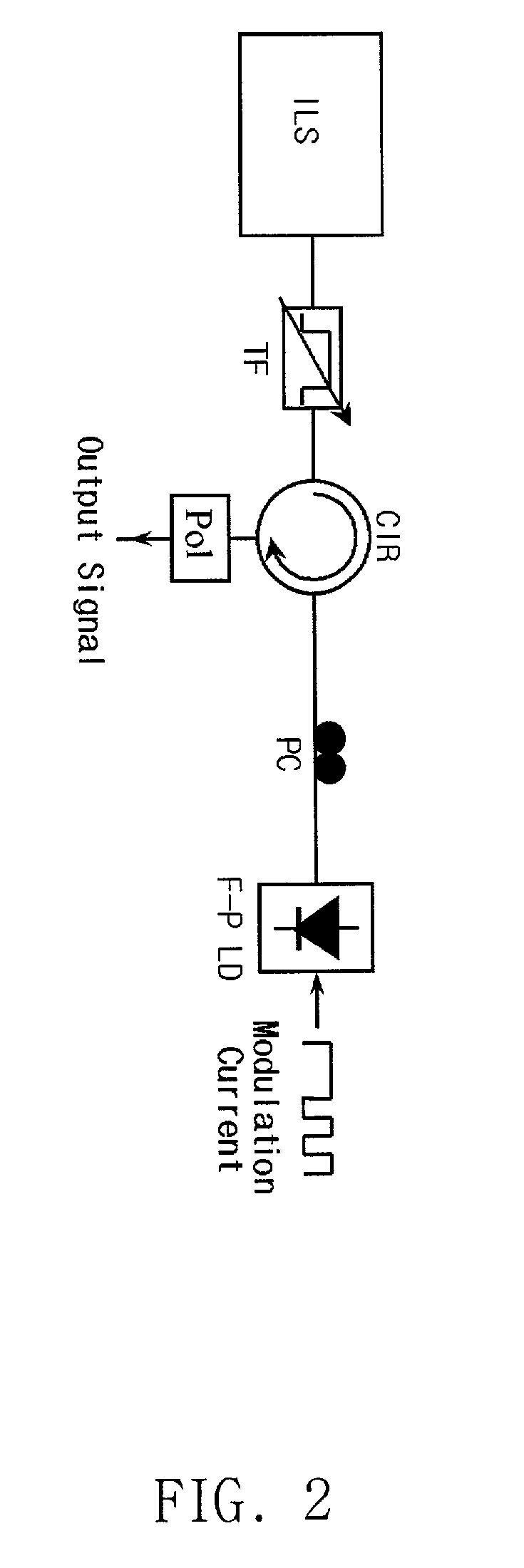
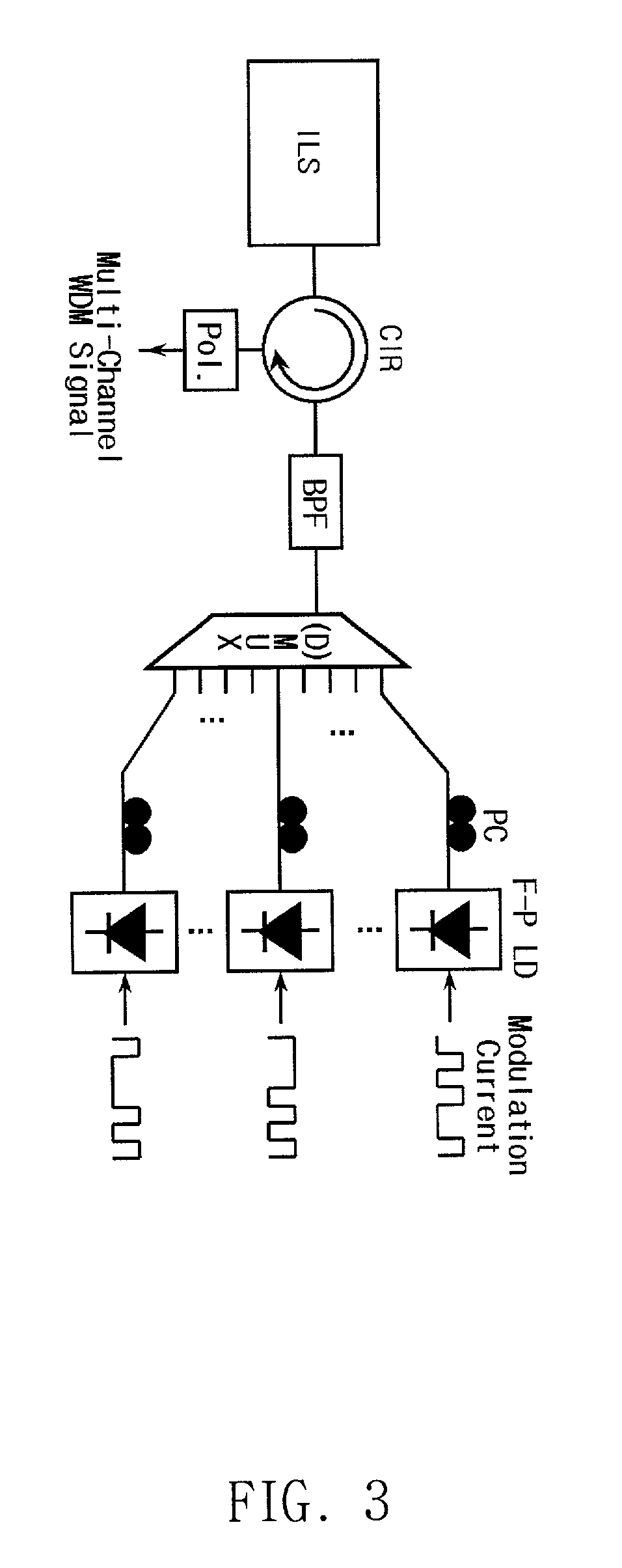
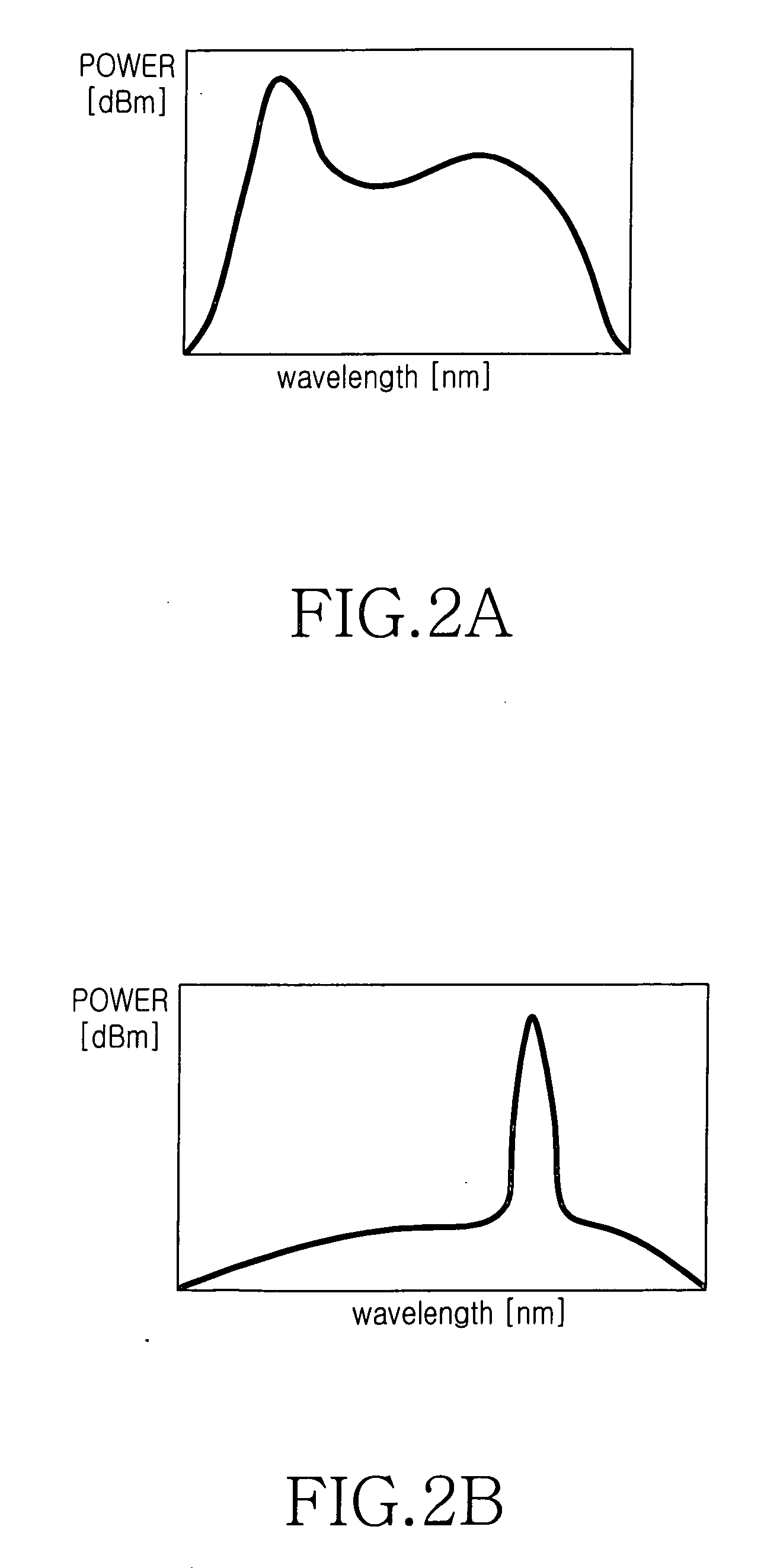
The present invention discloses a low-cost light source for optical transmission systems and optical networks based on wavelength-division multiplexing (WDM) technology. A light source in accordance with the present invention is implemented by externally injecting a narrow-band incoherent light into a Fabry-Perot laser diode (F-P LD). After injection of narrow-band incoherent light, the output of F-P LD becomes wavelength-selective rather than multi-mode and the output wavelength of F-P LD coincide with the peak wavelength of the injected incoherent light. Multi-channel WDM light sources according to the present invention can be implemented using a single broadband incoherent light source and plurality of F-P LDs. An optical transmission system for upstream signal transmission in an passive optical network using the light source according the present invention is also disclosed.
Owner:KOREA ADVANCED INST OF SCI & TECH
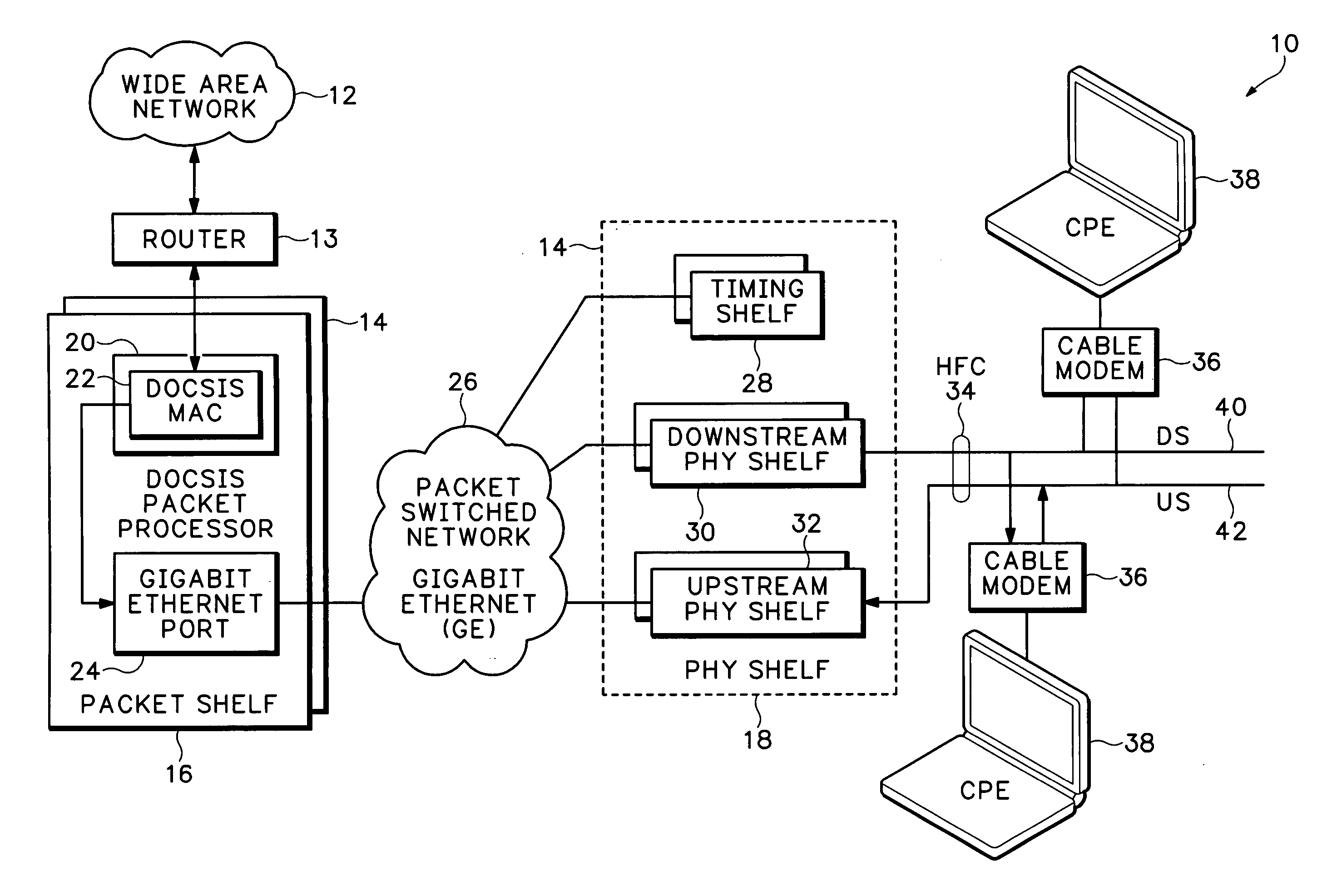
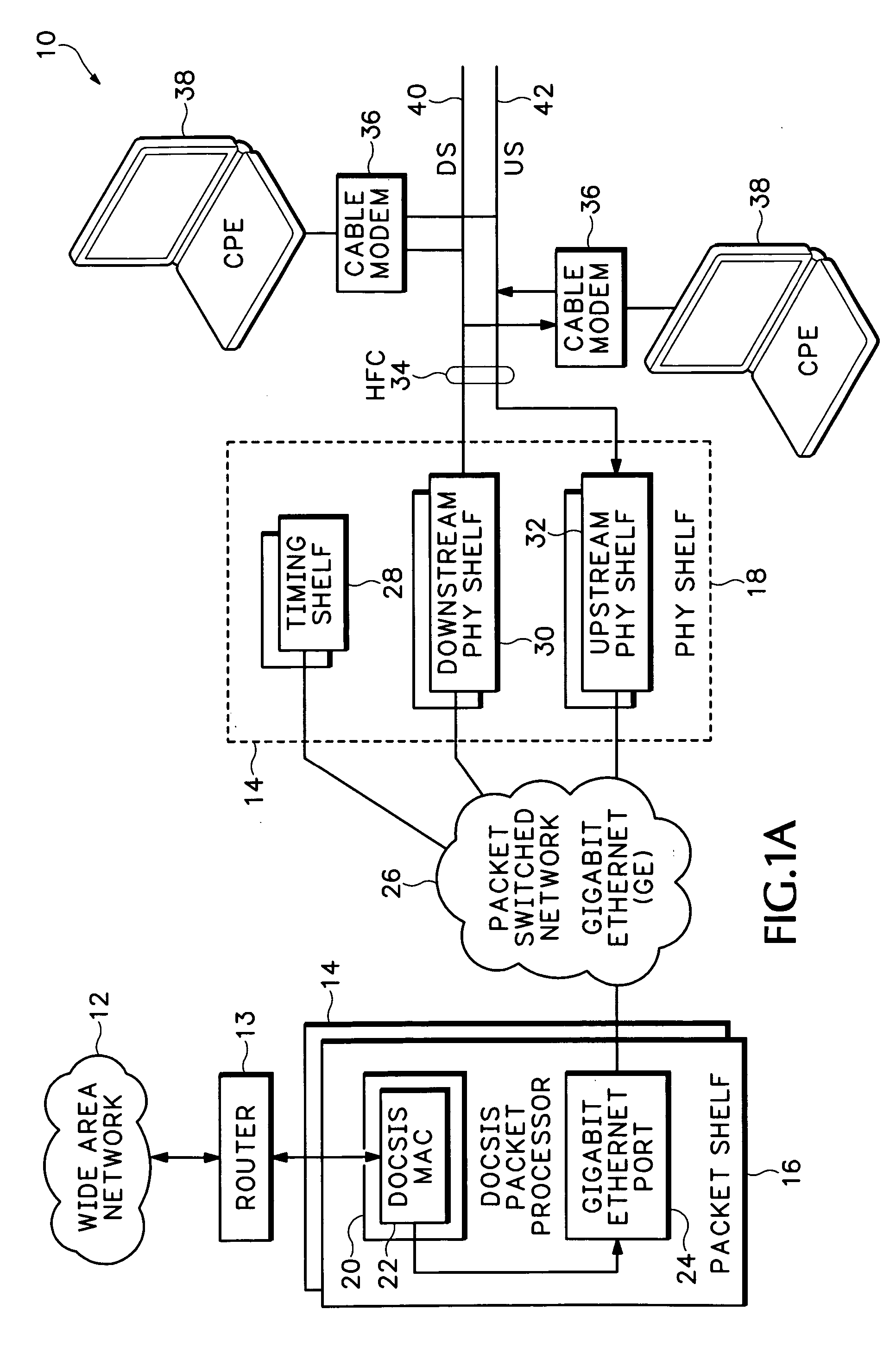
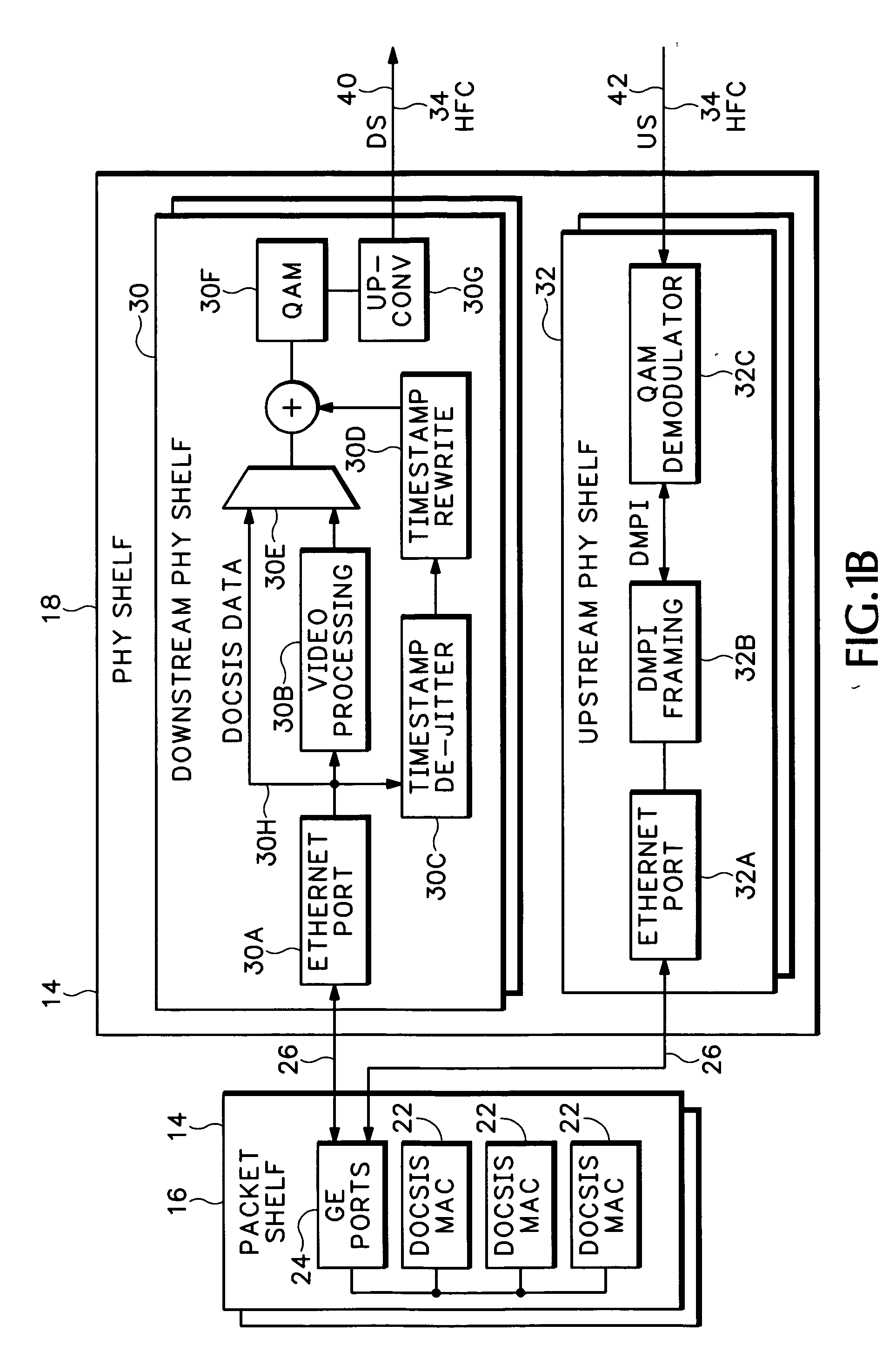
Timing system for modular cable modem termination system
InactiveUS20060168612A1Synchronisation information channelsBroadcast transmission systemsDigital subscriber lineModem device
A modular Cable Modem Termination System (CMTS) includes a packet shelf operating a Data Over Cable Service Interface Specifications (DOCSIS) Media Access Control (MAC) framer. One or more downstream Physical Interface (PHY) shelves receive DOCSIS data from the packet shelf over a packet switched network and modulate the DOCSIS data for sending on a downstream path of a cable plant. One or more upstream PHY shelves send DOCSIS data received from an upstream path of the cable plant over the packet switched network to the packet shelf. By separating the PHY components from the MAC and from the system software, the PHY components for a Hybrid Fiber Coax (HFC) plant may be replaced with different PHY components for other access technologies such as wireless, Digital Subscriber Lines (DSL), Ethernet-to-the-Home, Fiber-to-the-Home, or fiber Passive Optical Networks (PONs).
Owner:CISCO TECH INC
Optical access network of wavelength division method and passive optical network using the same
InactiveUS20060045525A1Low investment costWavelength-division multiplex systemsStar-type electromagnetic networksAccess networkWireless data services
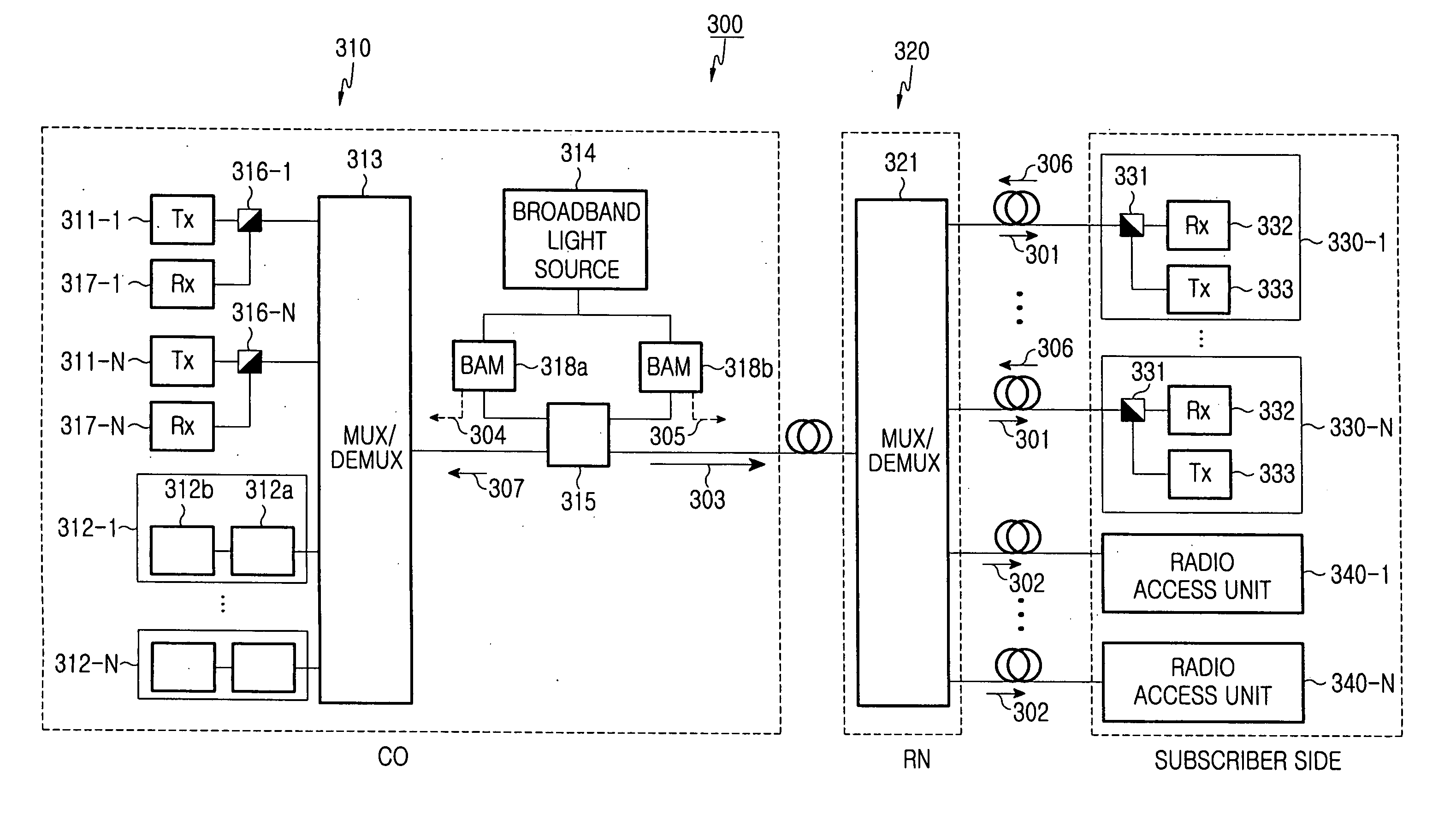
A wavelength division multiplexed optical access network including a central office for multiplexing first optical signals used for transmitting a high-speed wire data service to a subscriber side and second optical signals used for transmitting a wireless data service to a remote subscriber terminal, a remote node connected to the central office through an optical fiber and for de-multiplexing a multiplexed optical signal received from the central office, a plurality of subscribers connected to the remote node, each subscriber receiving a first optical signal having a corresponding wavelength from among the de-multiplexed first optical signals, and a plurality of radio access units connected to the remote node, each radio access unit converting a second optical signal having a corresponding wavelength from among the de-multiplexed second optical signals into a wireless electric signal and wirelessly transmitting the wireless electric signal.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
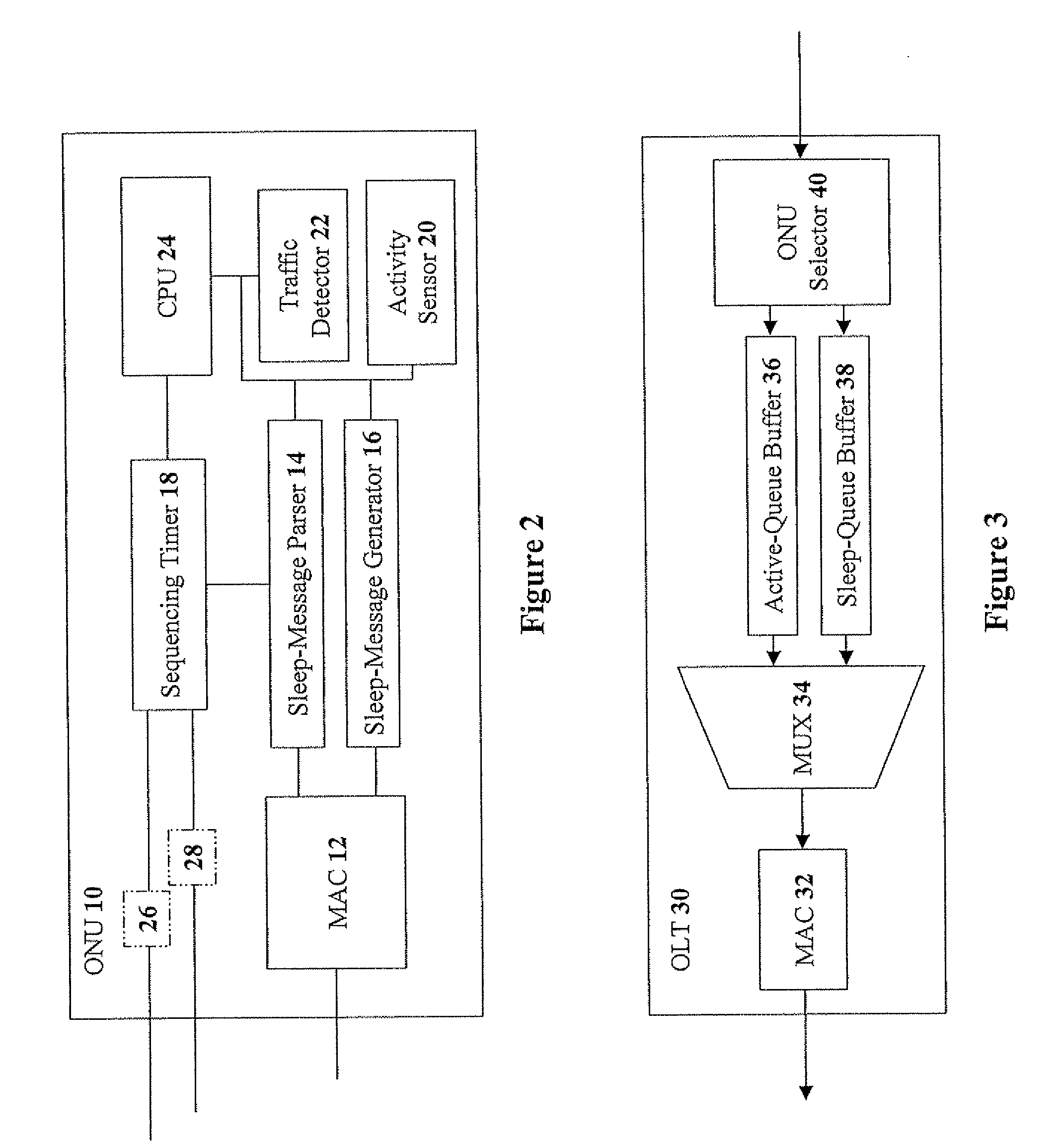
Methods and devices for reducing power consumption in a passive optical network while maintaining service continuity
ActiveUS20090263127A1Reduce power consumptionMaintain continuityMultiplex system selection arrangementsTransmission monitoringData trafficComputer science
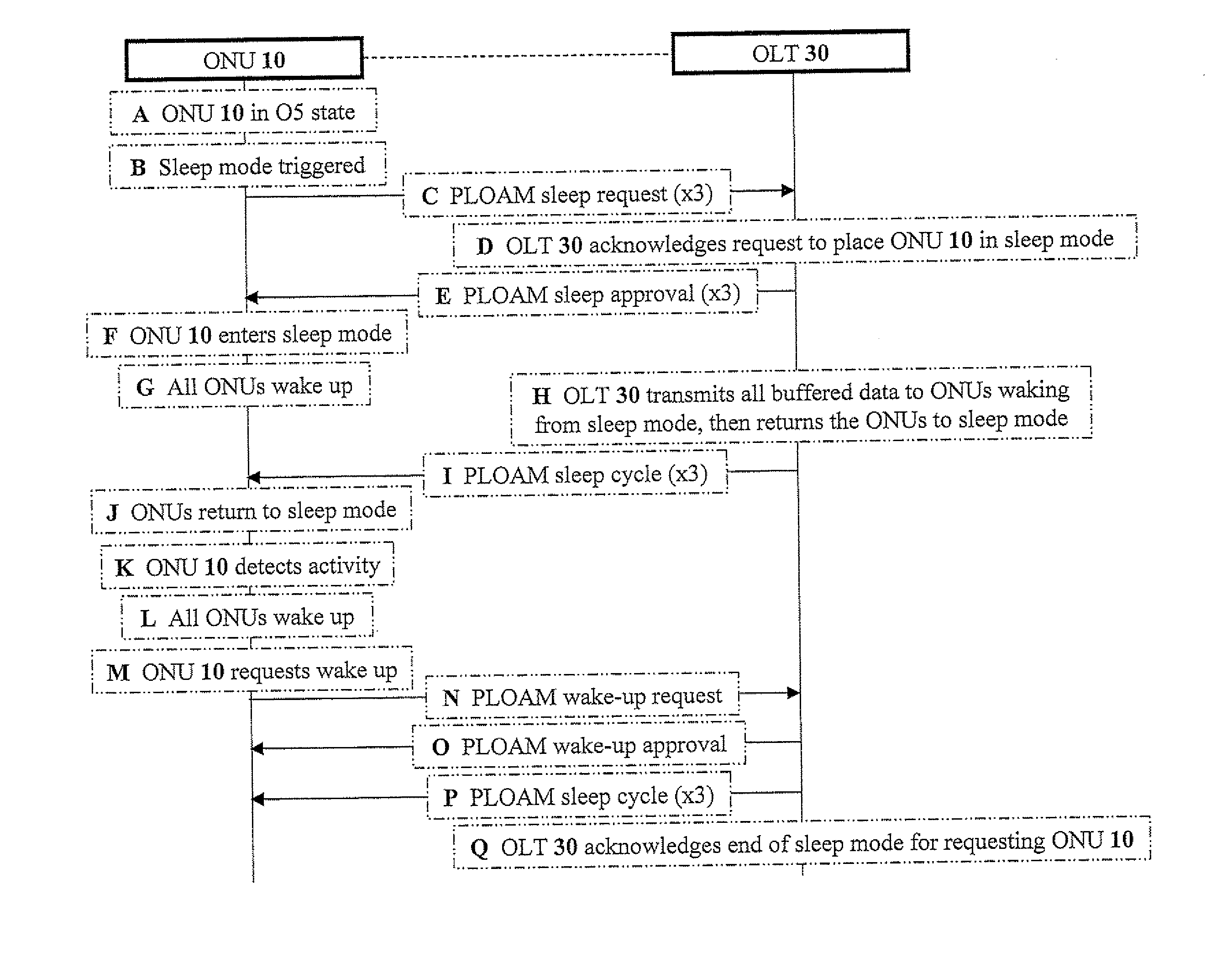
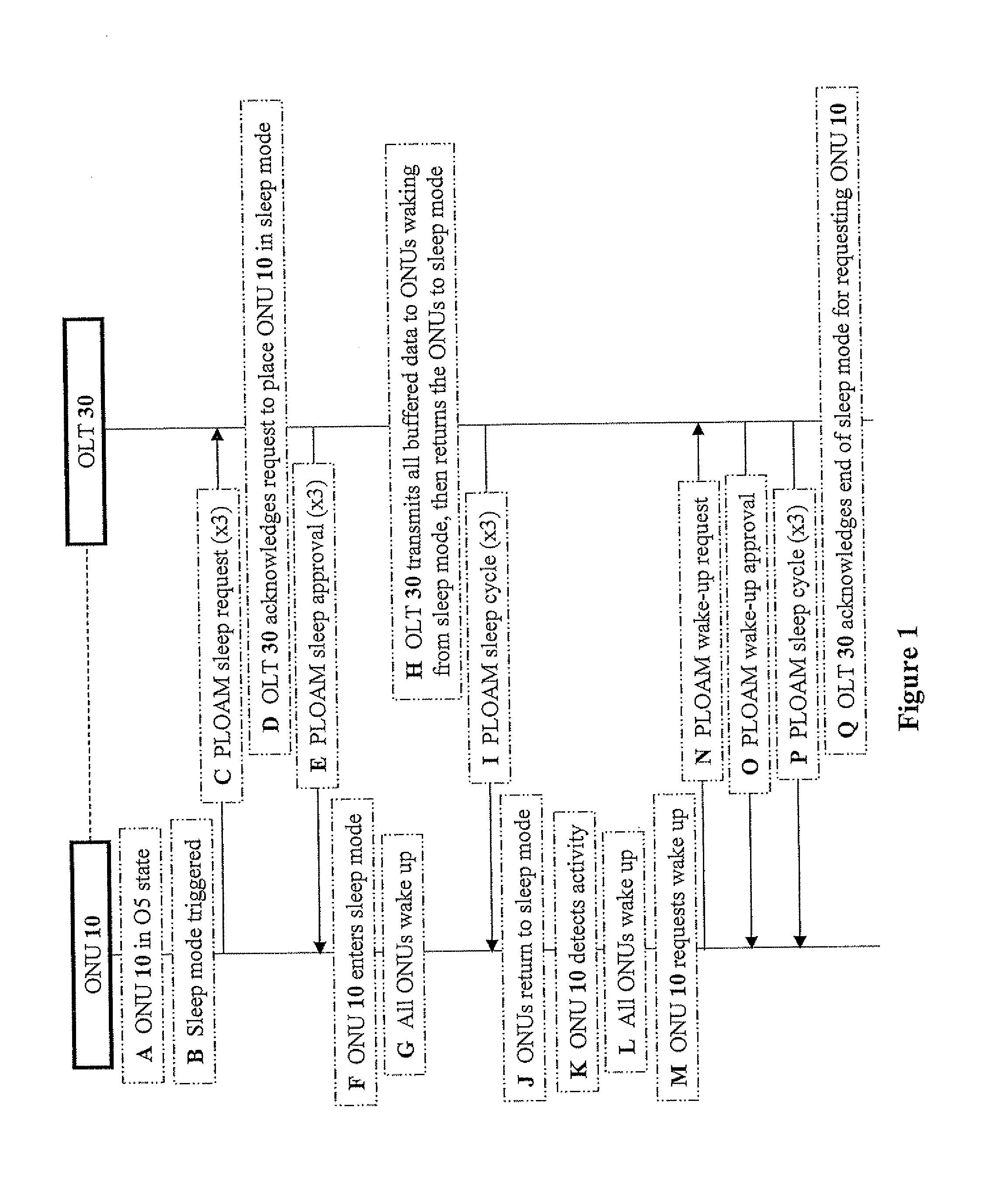
The present invention discloses methods for reducing power consumption in a PON while maintaining service continuity, the method including the steps of: providing an OLT operationally connected to at least one ONU; triggering a sleep request for at least one requesting ONU; upon receiving a sleep acknowledgement, activating a sleep mode for at least one requesting ONU according to a sleep period designated in the sleep request; and terminating the sleep mode according to the sleep period. Preferably, the sleep acknowledgement is transmitted from the OLT to the requesting ONU. Preferably, the sleep period is executed by a sleep command in the sleep acknowledgement. Preferably, the method further includes the step of: upon completion of the sleep period, transmitting buffered data traffic from the OLT to a sleeping ONU. Preferably, the step of transmitting is performed without the sleeping ONU being re-registered and without causing packet reordering.
Owner:MICROSEMI ISRAEL STORAGE SOLUTIONS LTD
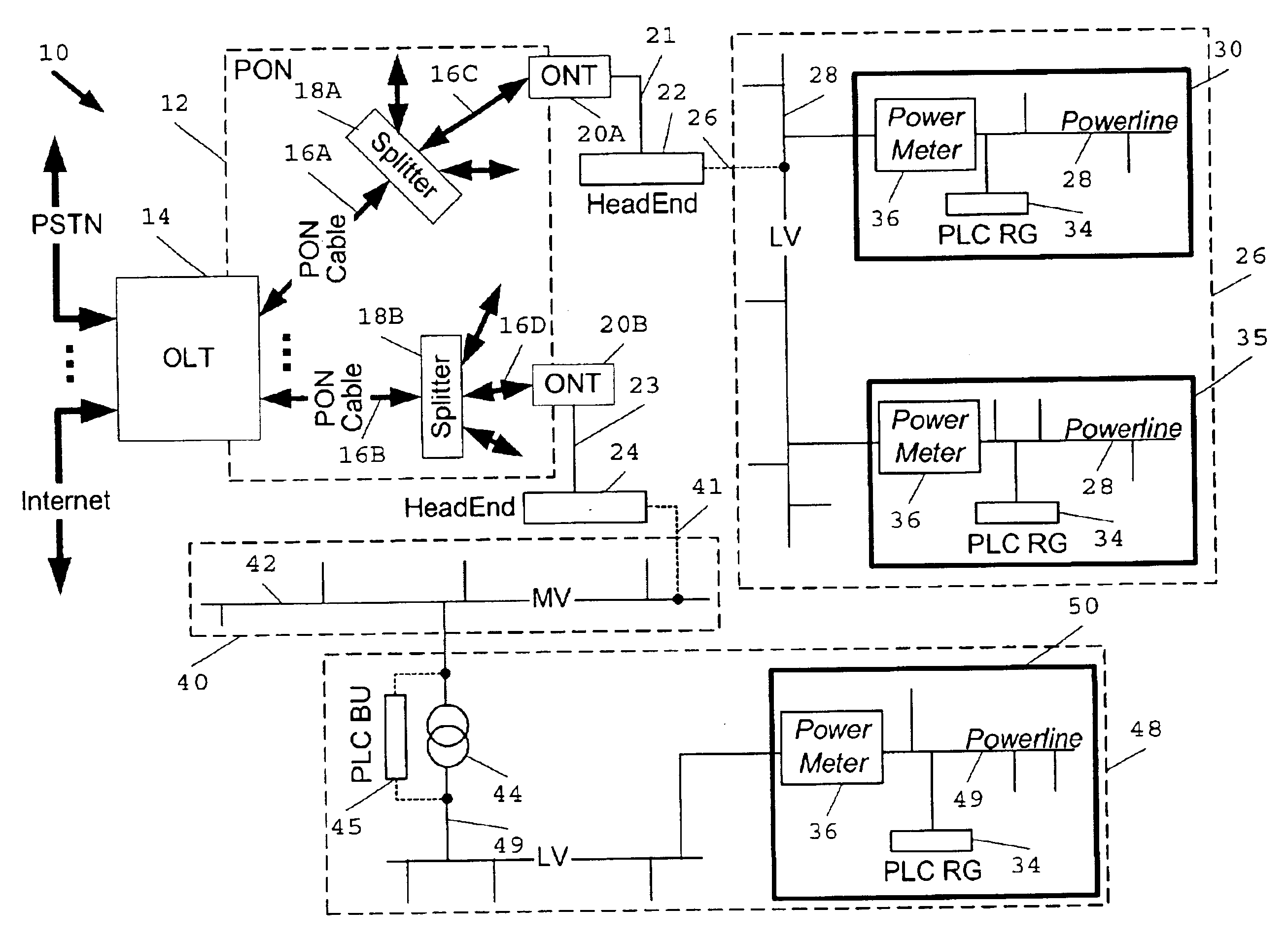
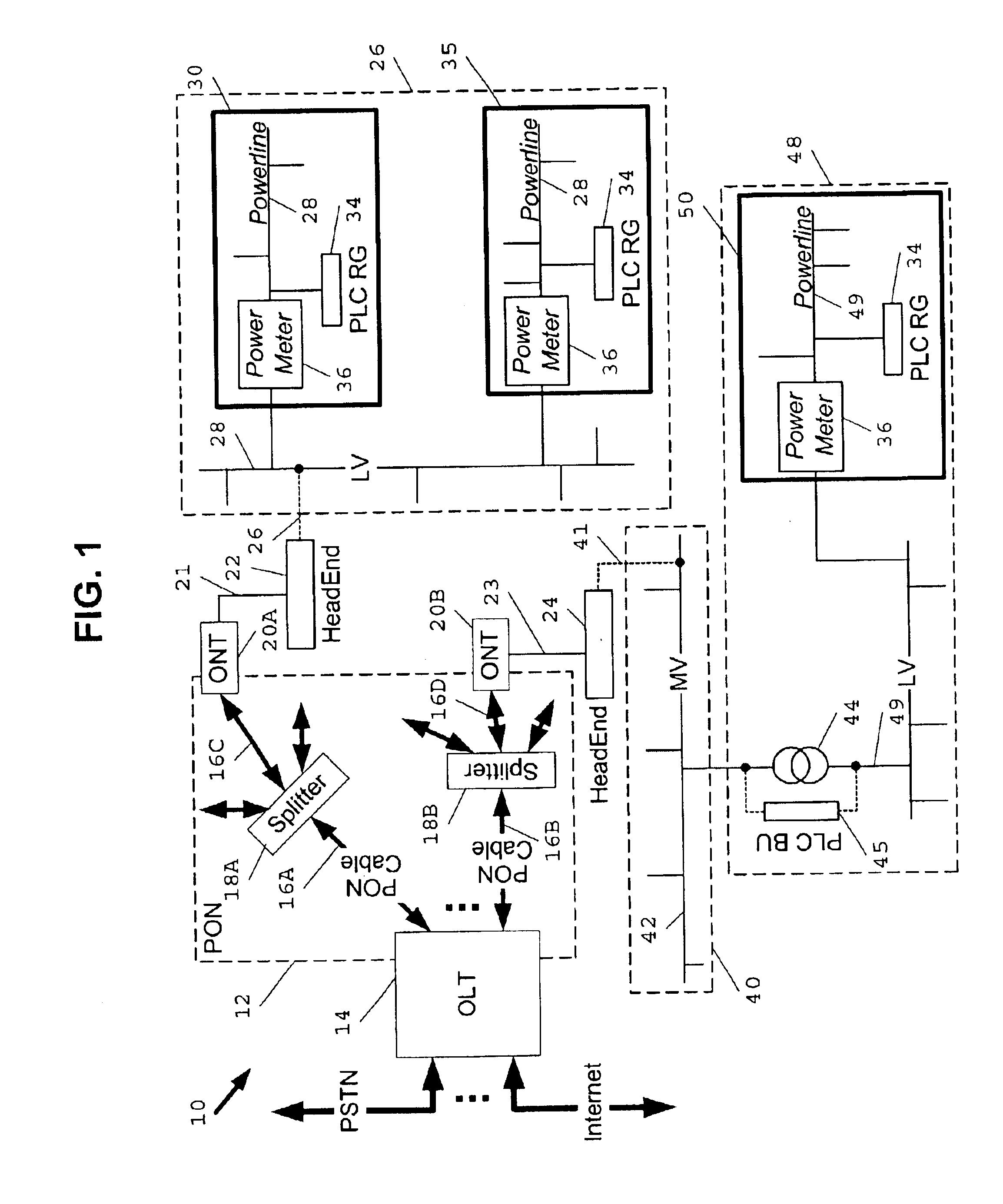
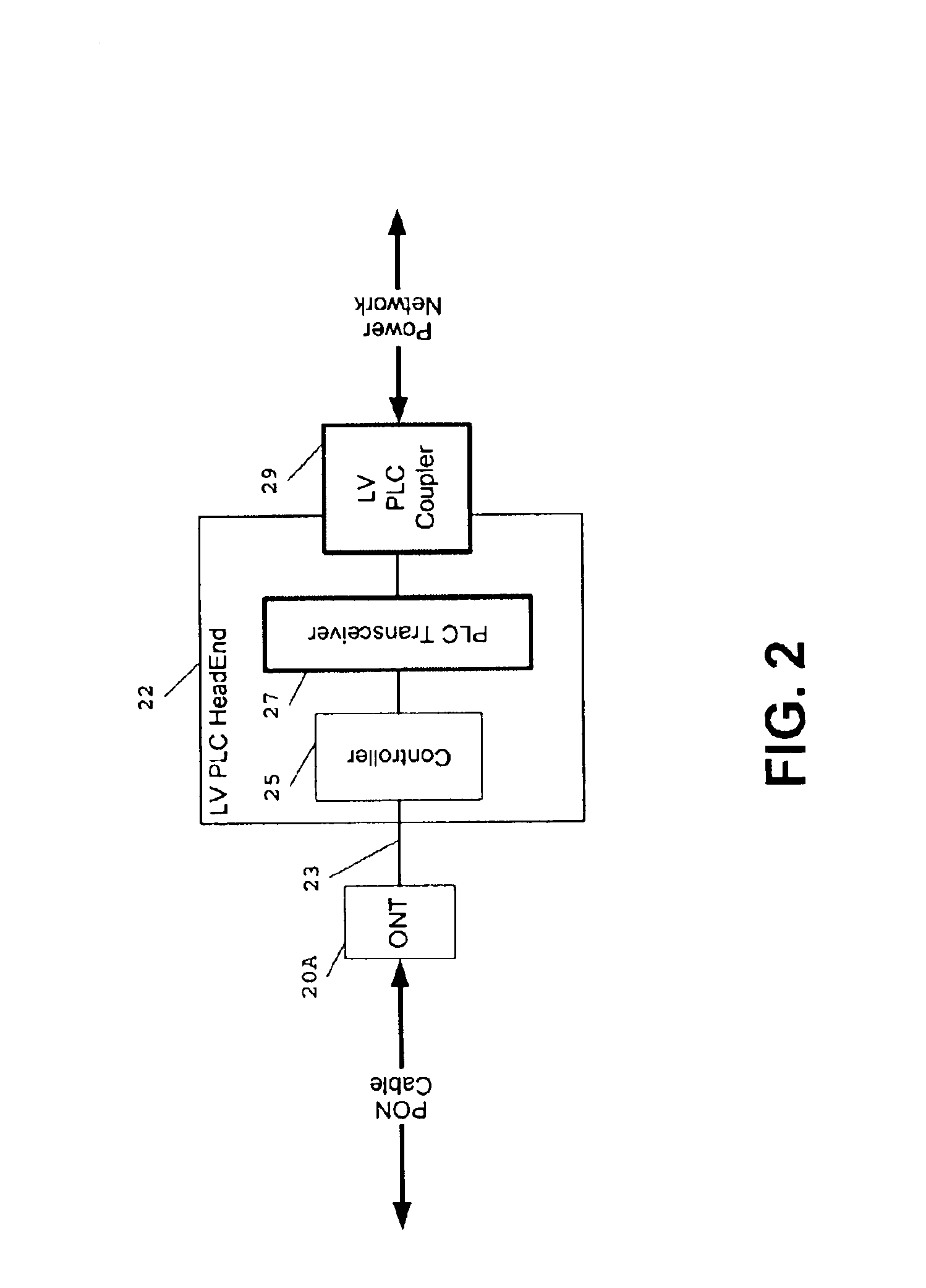
Passive optical network backhaul for powerline communications
InactiveUS6844809B2Quick and easy and inexpensive couplingIncrease speedElectric signal transmission systemsFrequency-division multiplexCommunications systemLow voltage
System, apparatus and method for connecting a passive optical network (“PON”) to a power line communications (“PLC”) network using a PLC HeadEnd installed at the PON to provide for distribution of high speed, broadband data communications services available on the PON to the PLC network using high speed, broadband PLC data signals. Where the PLC HeadEnd is installed on a medium voltage power distribution network, a PLC bypass unit is installed at a medium voltage / low voltage power transformer in the PLC network to provide PLC signal connectivity between the MV and LV networks. A PLC residential gateway is installed at each end user facility, such as a home or business, desiring broadband service available on the PON.
Owner:ENIKIA
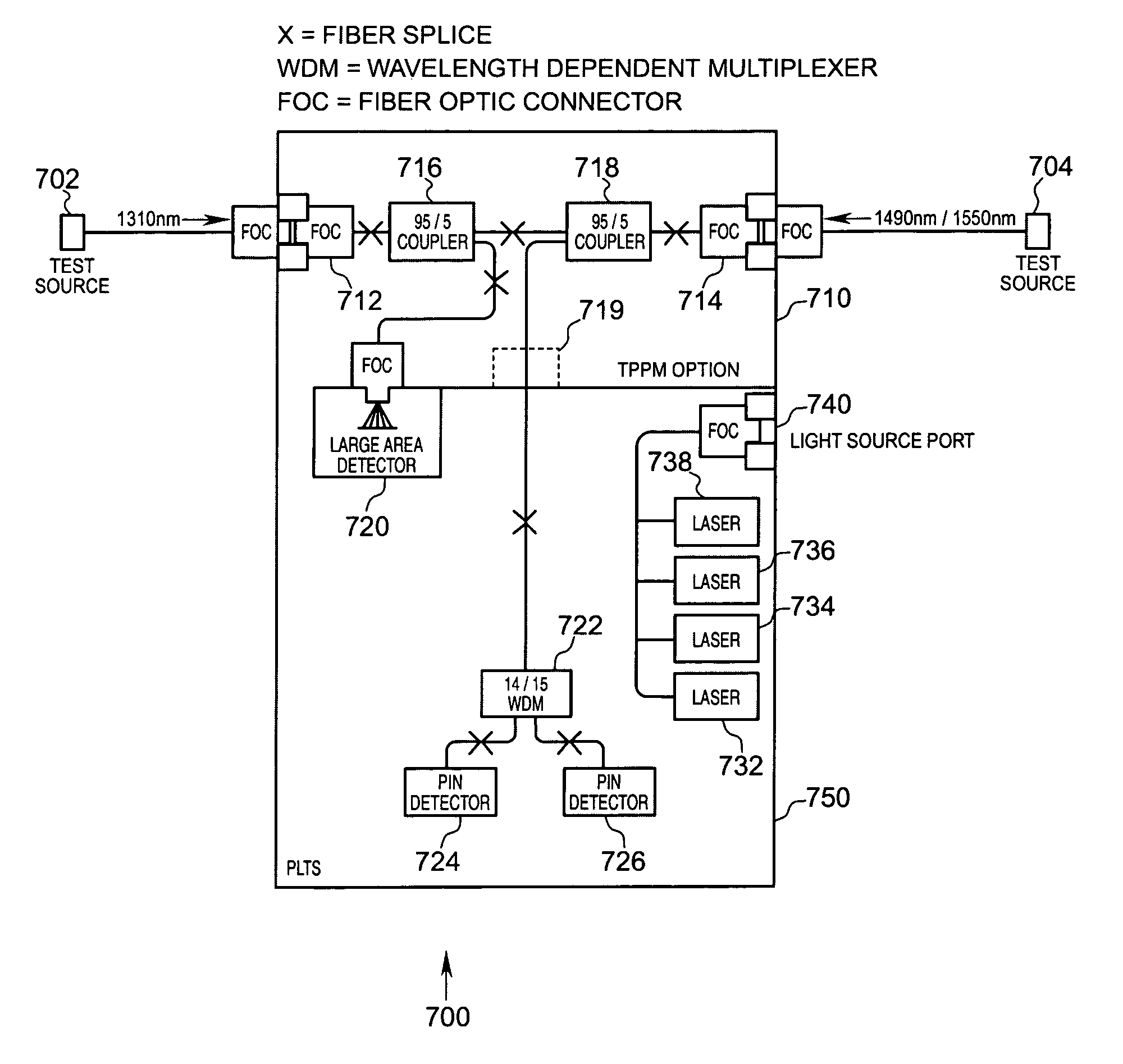
Passive optical network loss test apparatus and method of use thereof
ActiveUS20060198634A1Material analysis by optical meansTransmission monitoringAttenuation lossElectrical and Electronics engineering
An apparatus and methods for testing a passive optical network with regard to fiber connectivity and attenuation losses, and with regard to the proper operation of packet-based communication protocols thereon.
Owner:ANRITSU CORP
Passive optical network arrangement
InactiveUS6351582B1High loss pathPoint of failureMultiplex system selection arrangementsWavelength-division multiplex systemsEngineeringDual-homed
A passive optical network having a plurality of optical splitters / combiners each comprising first and second through ports and at least one drop port. The through ports of the plurality of splitters / combiners are concatenated to form a linear arrangement having two end through ports. Optical signals may be transmitted between the end through ports by means of the linear arrangement; and signals may be transmitted between at least one of the end through ports and one of the drop ports by means of the linear arrangement. The splitter / combiners can be inserted to form drop points in a ring or dual-homed passive optical network to provide flexibility in provision of protection and network reconfiguration.
Owner:CIENA
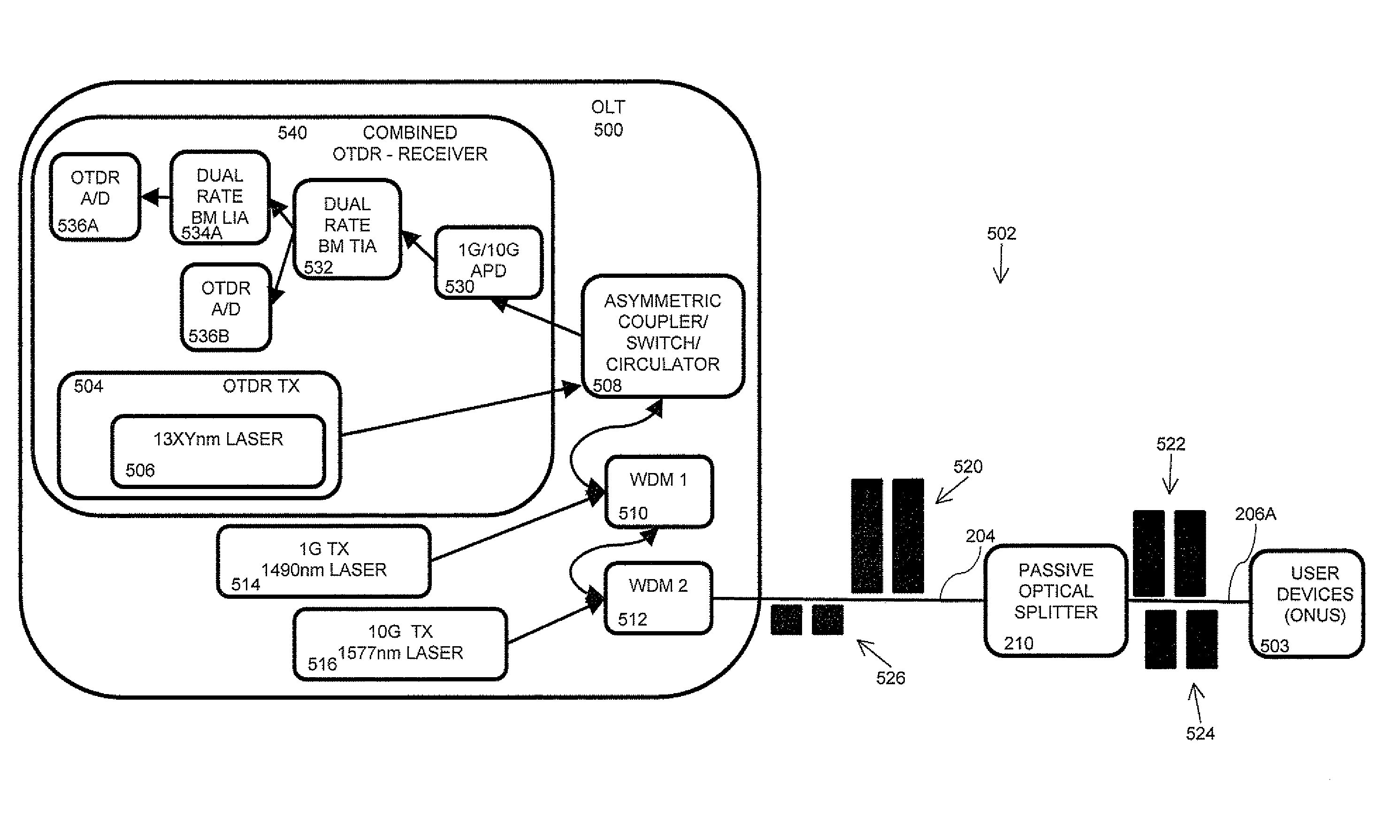
Passive optical network (PON) in-band optical time domain reflectometer (OTDR)
ActiveUS20110013904A1Material analysis by optical meansTransmission monitoringSignal onNetwork Communication Protocols
An in-band OTDR uses a network's communication protocols to perform OTDR testing on a link. Because the OTDR signal (probe pulse) is handled like a data signal, the time required for OTDR testing is typically about the same as the time required for other global network events, and is not considered an interruption of service to users. A network equipment includes an optical time domain reflectometry (OTDR) transmitter and receiver, each operationally connected to a link to transmit and receive, respectively, an OTDR signal. When an OTDR is to be performed, a network device operationally connected to the link actuates the OTDR transmitter to transmit the OTDR signal on the link during a determined test time based on a communications protocol of the link, during which data signals are not transmitted to the network equipment. A processing system processes the OTDR signal to provide OTDR test results.
Owner:MICROSEMI ISRAEL STORAGE SOLUTIONS LTD
Passive optical network system and wavelength assignment method
InactiveUS20080166127A1Easy to useEasy to installWavelength-division multiplex systemsStar/tree networksLength waveLight source
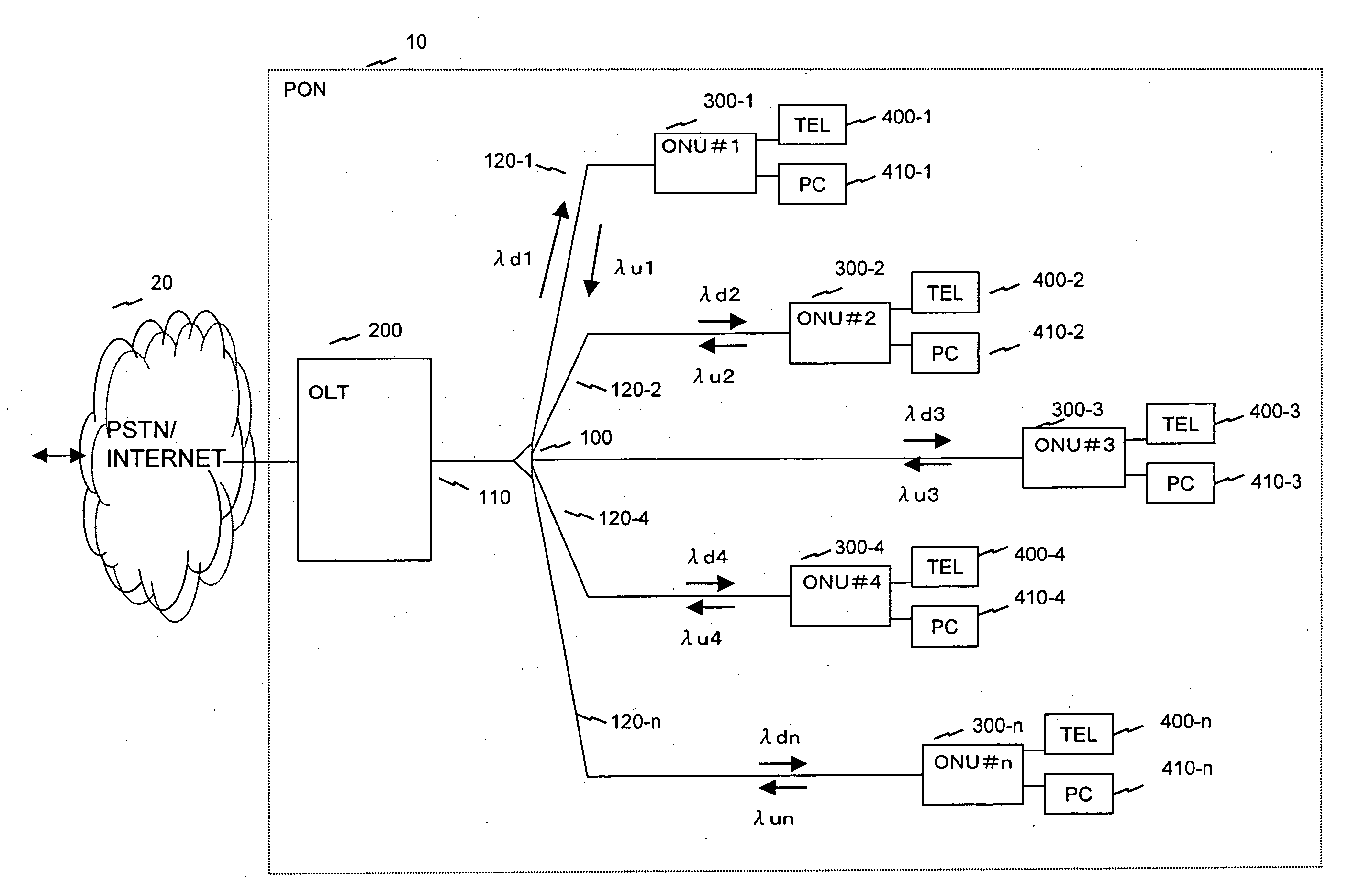
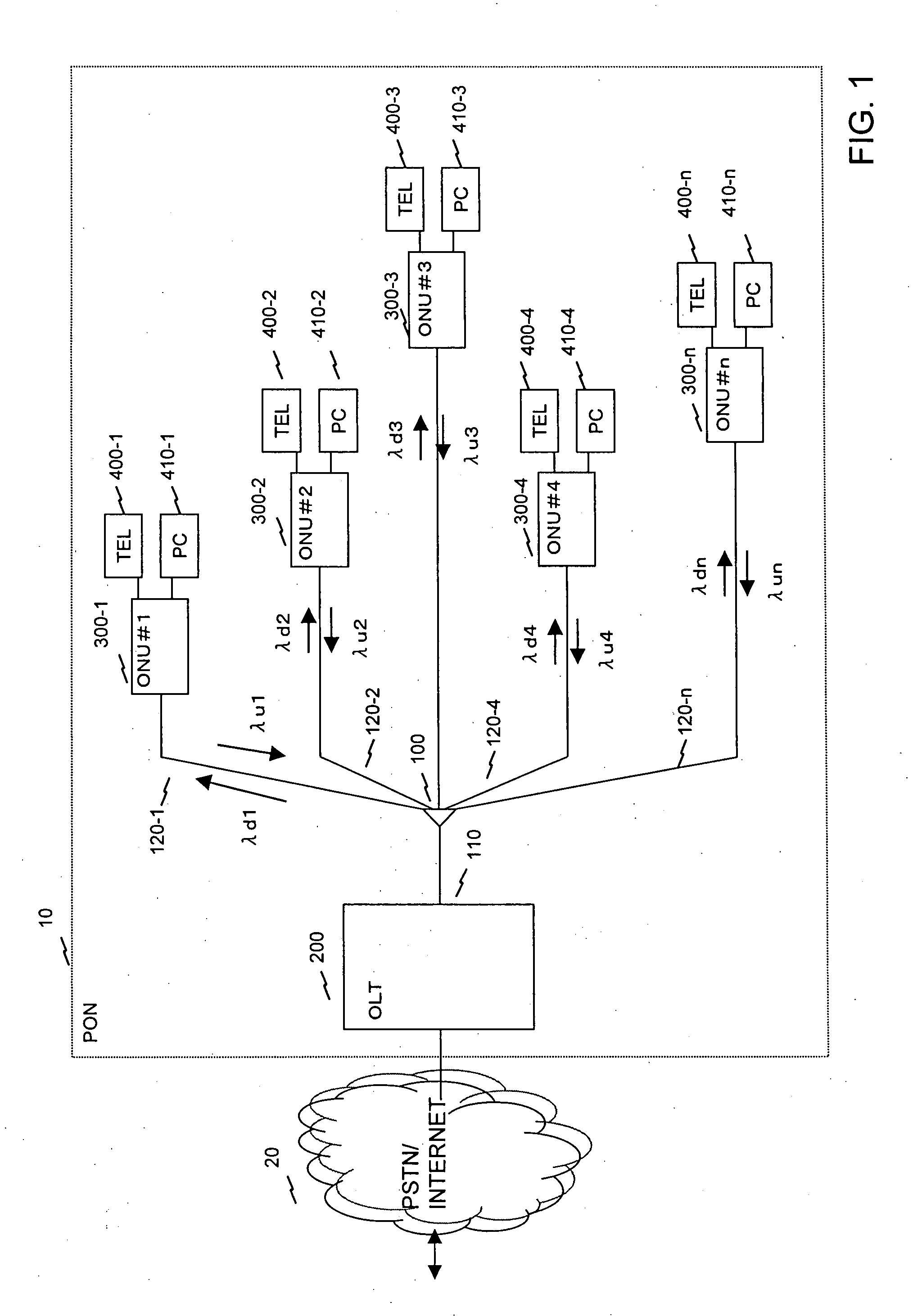
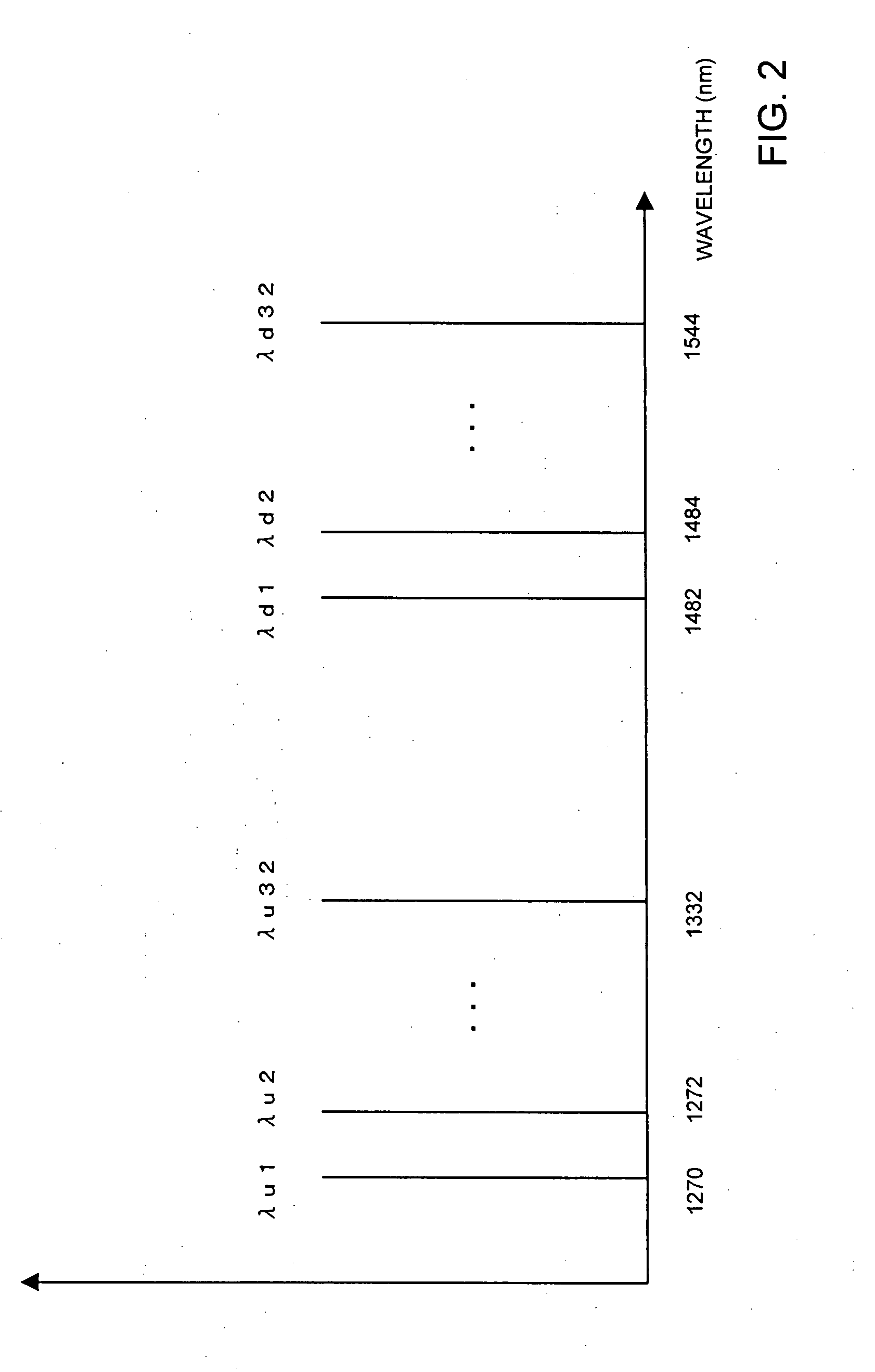
In a PON system with WDM, at the time of initial setting, each ONU negotiates with an OLT, and automatically acquires a wavelength which can be used by the ONU. One wavelength for negotiation of assigned wavelength is fixed as a default, and a newly connected ONU first uses the wavelength. The OLT 200 includes a plurality of light sources for downstream communication. The ONU 300 includes a wavelength variable filter selectively receiving one of wavelengths of downstream communication, and a wavelength variable light source selectively emitting light of one of plural wavelengths for upstream communication. The ONU 300 uses a transmission wavelength (for example, λu32) for negotiation and transmits a wavelength assignment request 1000 to the OLT 200. The OLT 200 selects a wavelength λu1 to be assigned from unused wavelengths, and transmits wavelength information to the ONU 300. The OLT 200 and the ONU 300 communicates using the notified wavelengths.
Owner:HITACHI LTD
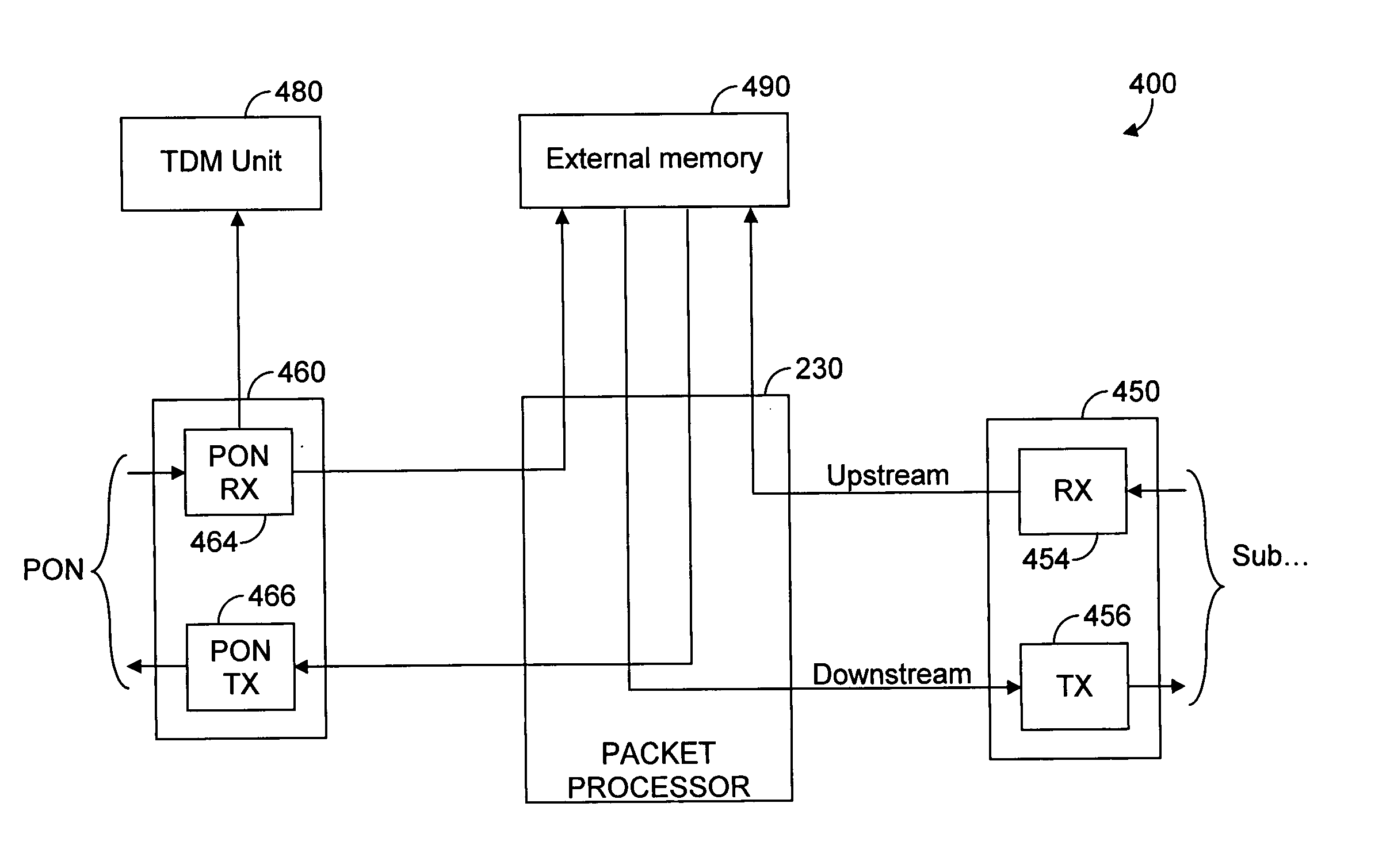
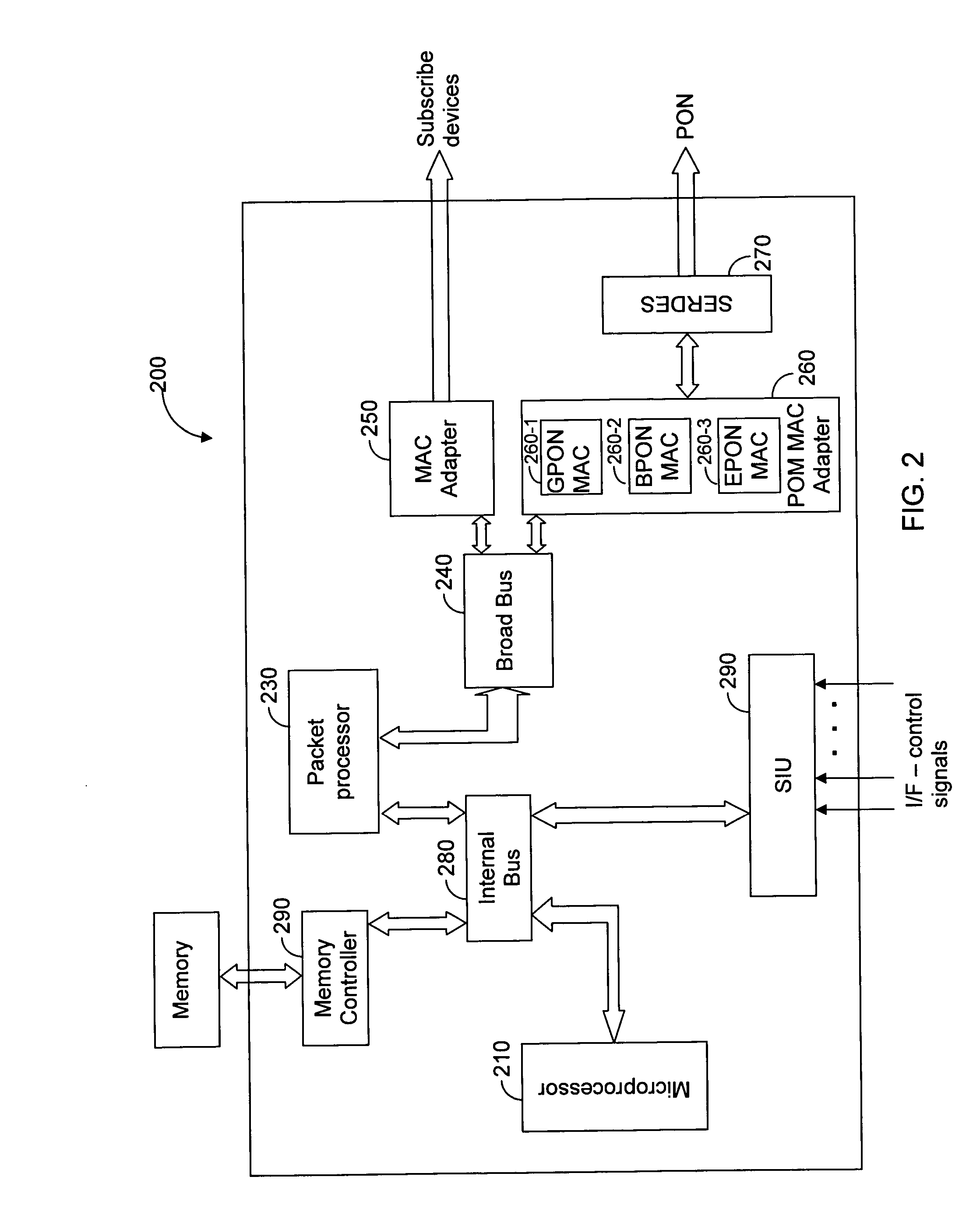
Enhanced passive optical network (PON) processor
InactiveUS20070070997A1Multiplex system selection arrangementsData switching by path configurationGigabitBroadband
An enhanced passive optical network (PON) processor adapted to serve a plurality of PON applications is disclosed. The PON processor is a highly integrated communications processor that can operate in different PON modes including, but not limited to, a gigabit PON (GPON), a broadband PON (BPON), an Ethernet PON (EPON), or any combination thereof. In an embodiment of the present invention the provided PON is fabricated on a single integrated circuit (IC).
Owner:AVAGO TECH INT SALES PTE LTD
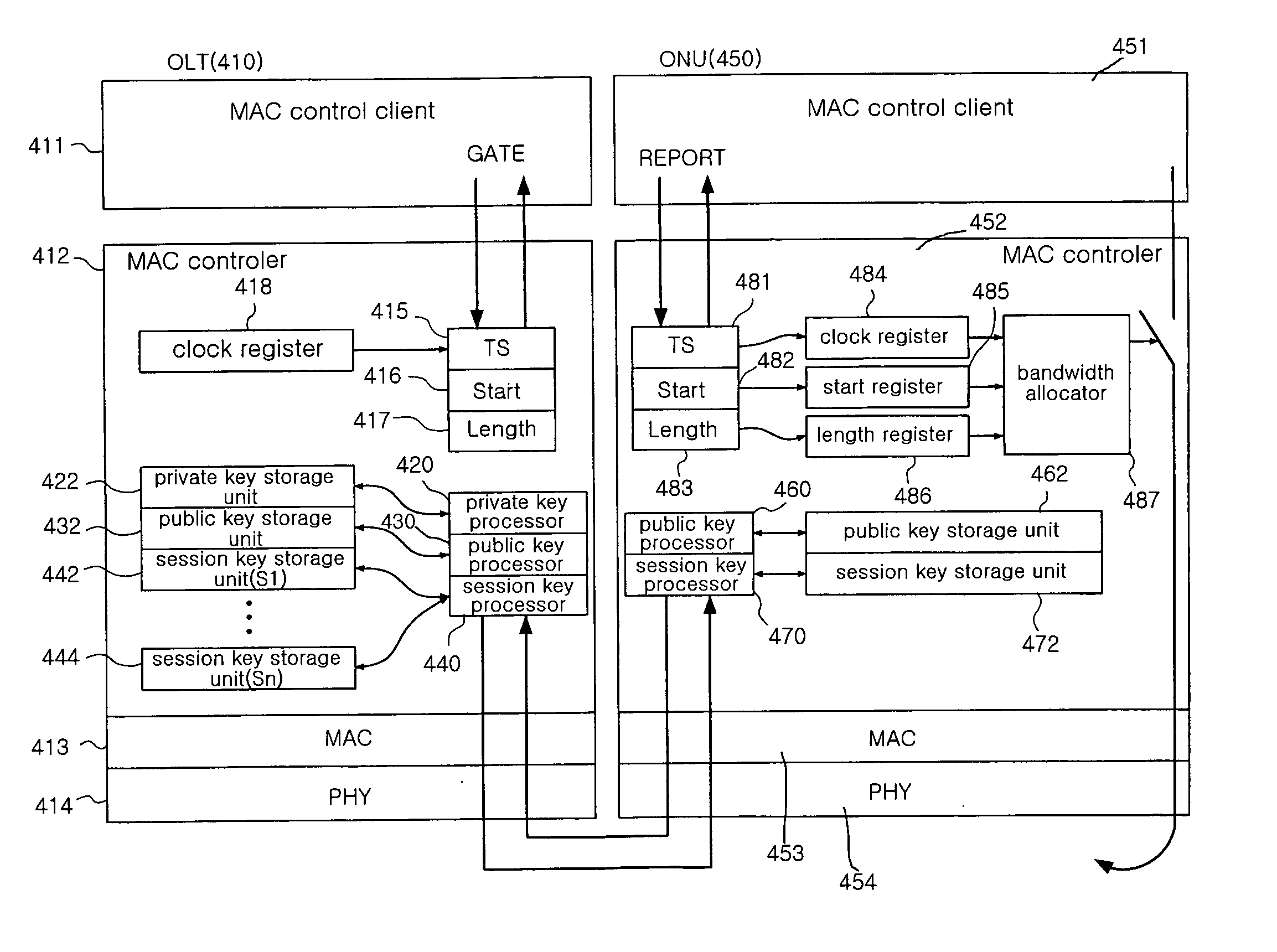
Key management device and method for providing security service in ethernet-based passive optical network
InactiveUS20050008158A1Key distribution for secure communicationDigital computer detailsDistribution functionEthernet
A key management device and method which is required for provision of a security service in an EPON vulnerable to security breaches due to characteristics of Ethernet. A session key distribution function is performed in such a manner that, during the process of communication setup between an OLT and an ONU, the OLT multicasts a public key and the ONU receives the public key from the OLT and then distributes a corresponding session key to the OLT. A session key update function is performed in such a manner that an existing session key is updated with a new one through a periodic MPCP general gate message and an ONU report message.
Owner:ELECTRONICS & TELECOMM RES INST
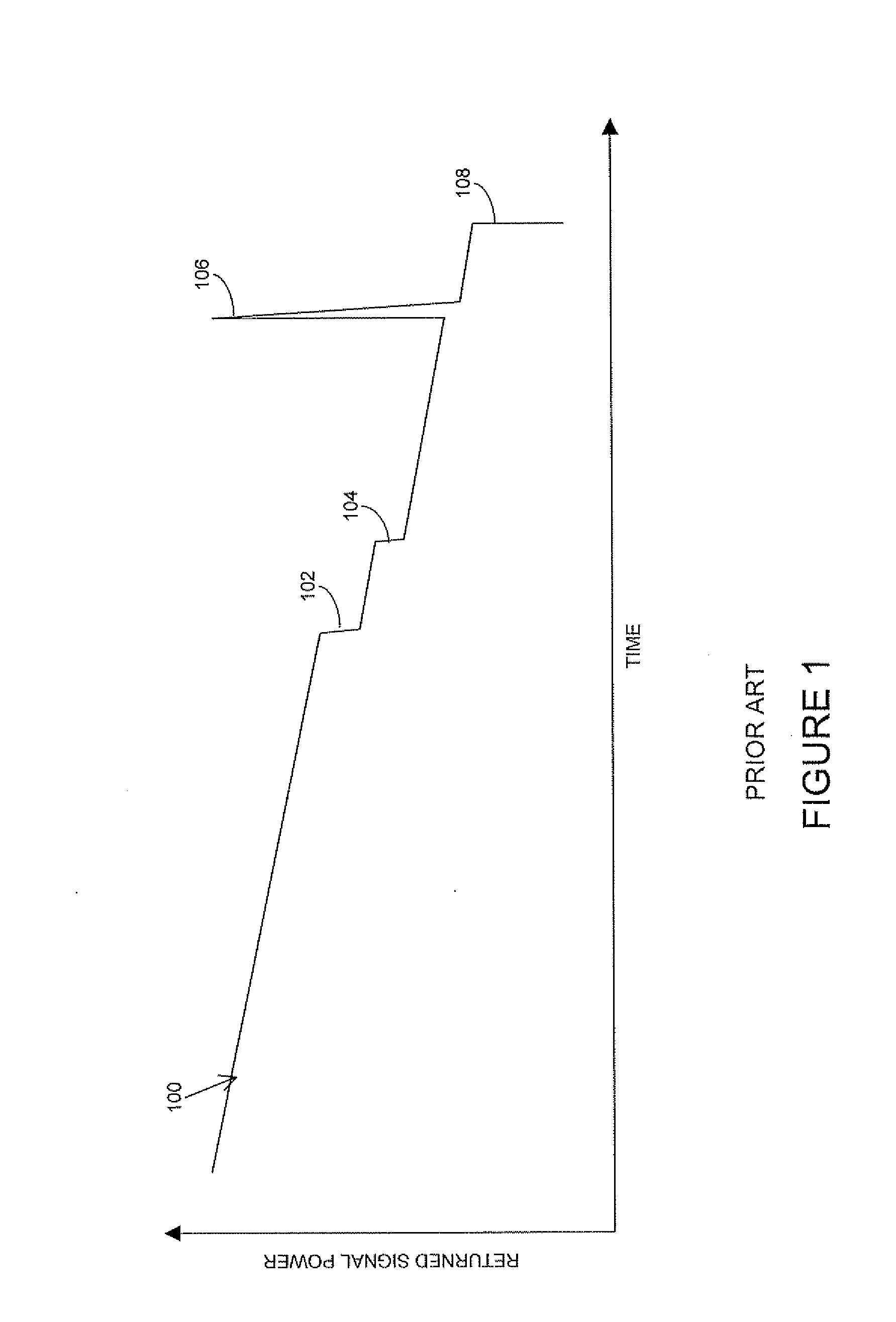
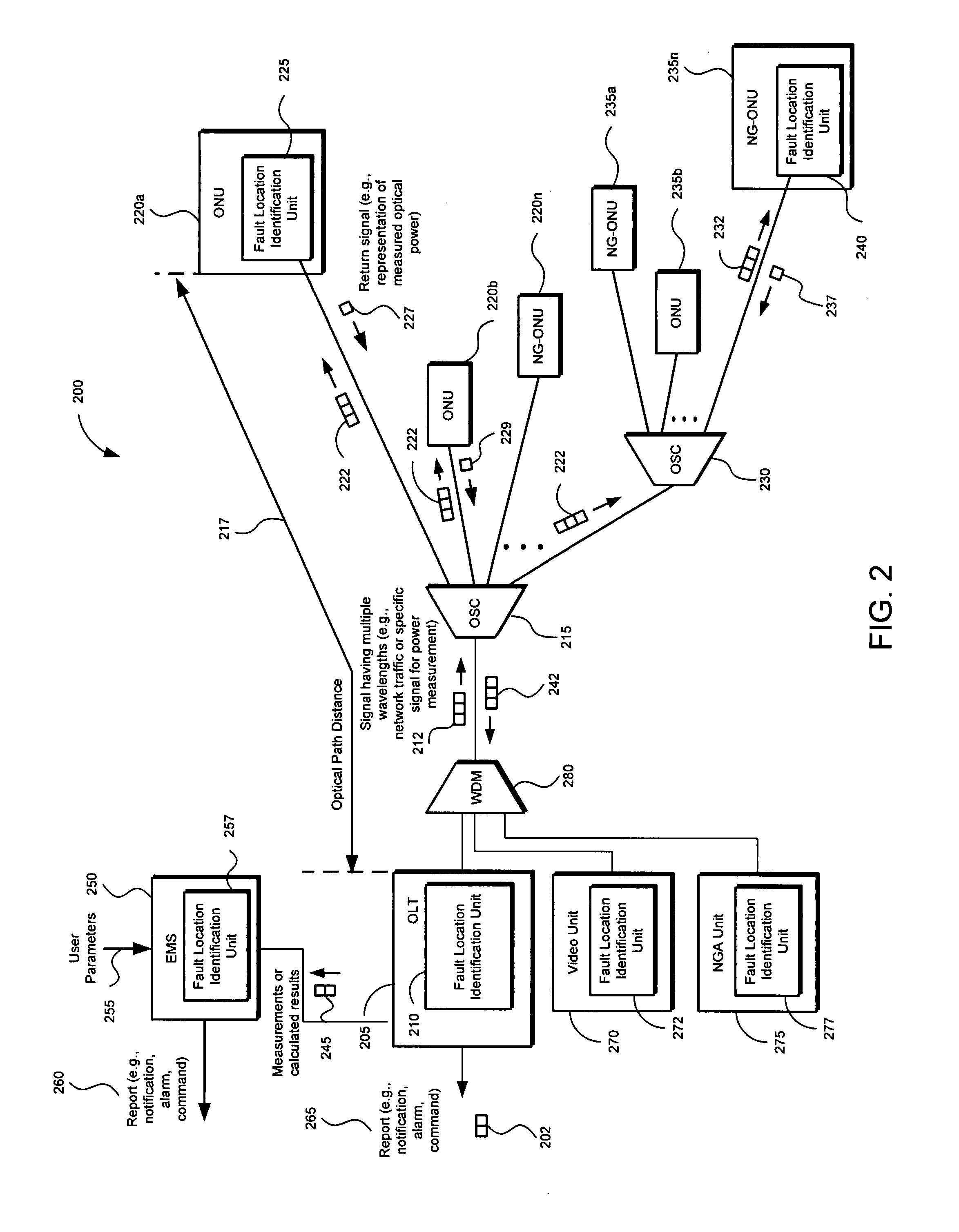
Method and apparatus for isolating a location of a fault in a passive optical network
A method and apparatus of isolating a location of a fault in an optical network may include using communications traffic signals and network nodes to determine excess power losses without interrupting service or requiring additional external test equipment. A transmit optical network node is configured to measure the transmit power of multiple wavelengths of a transmitted optical signal. A receive optical network node is configured to measure the receive power of the same multiple wavelengths. Power differentials of the transmit and receive optical power for each wavelength may be calculated. Optical power losses as a function of the optical path distance between the transmit and receive optical network nodes my be determined. The data may be used to isolate the location of a fault in a passive optical network based on the differences between the optical power losses of the multiple wavelengths thereby reducing troubleshooting time and network downtime.
Owner:TELLABS PETALUMA
Optical access network of wavelength division method and passive optical network using the same
InactiveUS20060045524A1Minimize investmentLow costWavelength-division multiplex systemsMultimode transmissionAccess networkWired communication
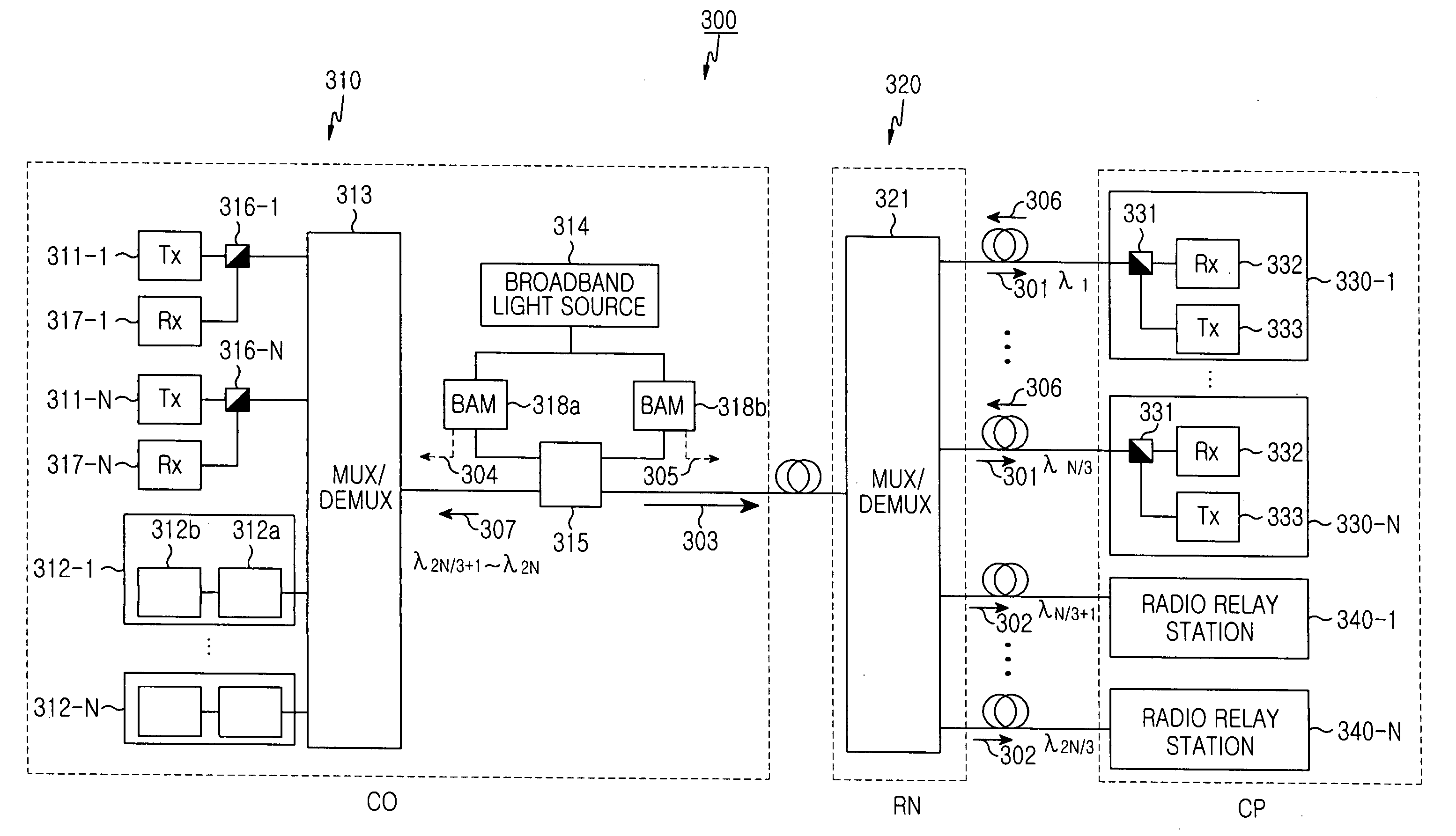
An optical access network of wavelength division method and passive optical network using the same are disclosed. The wavelength division multiplexed optical access network includes a central office for multiplexing first optical signals for wire communication and second optical signals for wireless communication and a remote node connected to the central office through an optical fiber and for demultiplexing a multiplexed optical signal received from the central office. A plurality of subscribers may be connected to the remote node. Each subscriber receives a first optical signal having a corresponding wavelength from among the demultiplexed first optical signals. The network also includes a plurality of radio relay stations connected to the remote node, each radio relay station converting a second optical signal having a corresponding wavelength from among the demultiplexed second optical signals into a radio electric signal and wirelessly transmitting the radio electric signal.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Broadband wireless signal covering network based on passive optical network structure
The invention relates to a broadband wireless signal covering network based on a passive optical network structure. The network comprises a first fiber power divider / wave combiner, a plurality of user terminal units, an optical wavelength multiplexing / de-multiplexing device, a second fiber power divider / wave combiner and a broadband photoreceiver, wherein the first fiber power divider / wave combiner allocates light carrier signals of a light emitter to a plurality of fiber power dividers; a plurality of the user terminal units correspondingly receive the light carrier signals of the fiber power dividers, emit the light carrier signals to air and receive user uplink RF signals through antennas; the optical wavelength multiplexing / de-multiplexing device collects user uplink optical signals of a plurality of the user terminal units and transmits the signals to the uplink direction; the second fiber power divider / wave combiner collects the user uplink optical signals and transmits the signals to the uplink direction; and the broadband photoreceiver converts the received multi-wavelength user uplink optical signals into multi-bandwidth broadband RF signals and sends the signals to upper layer equipment. The broadband wireless signal covering network solves the problem of realizing broadband wireless communication for large-scale indoor multiuser, strengthens the adaptability to the horizontal dynamic change of uplink optical signal power and can adapt to the functional requirement of various wireless communication systems.
Owner:GUANGXUN SCI & TECH WUHAN
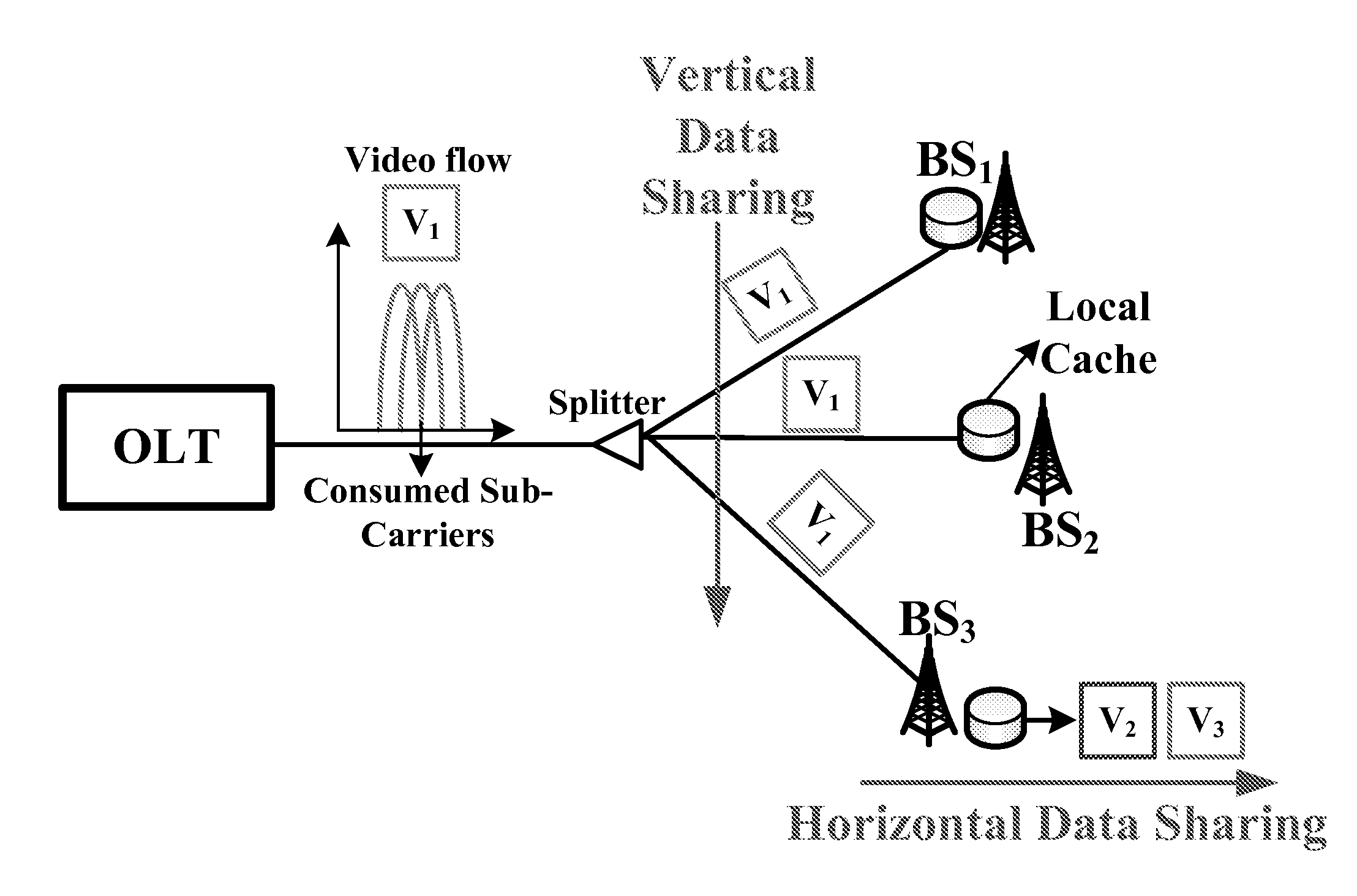
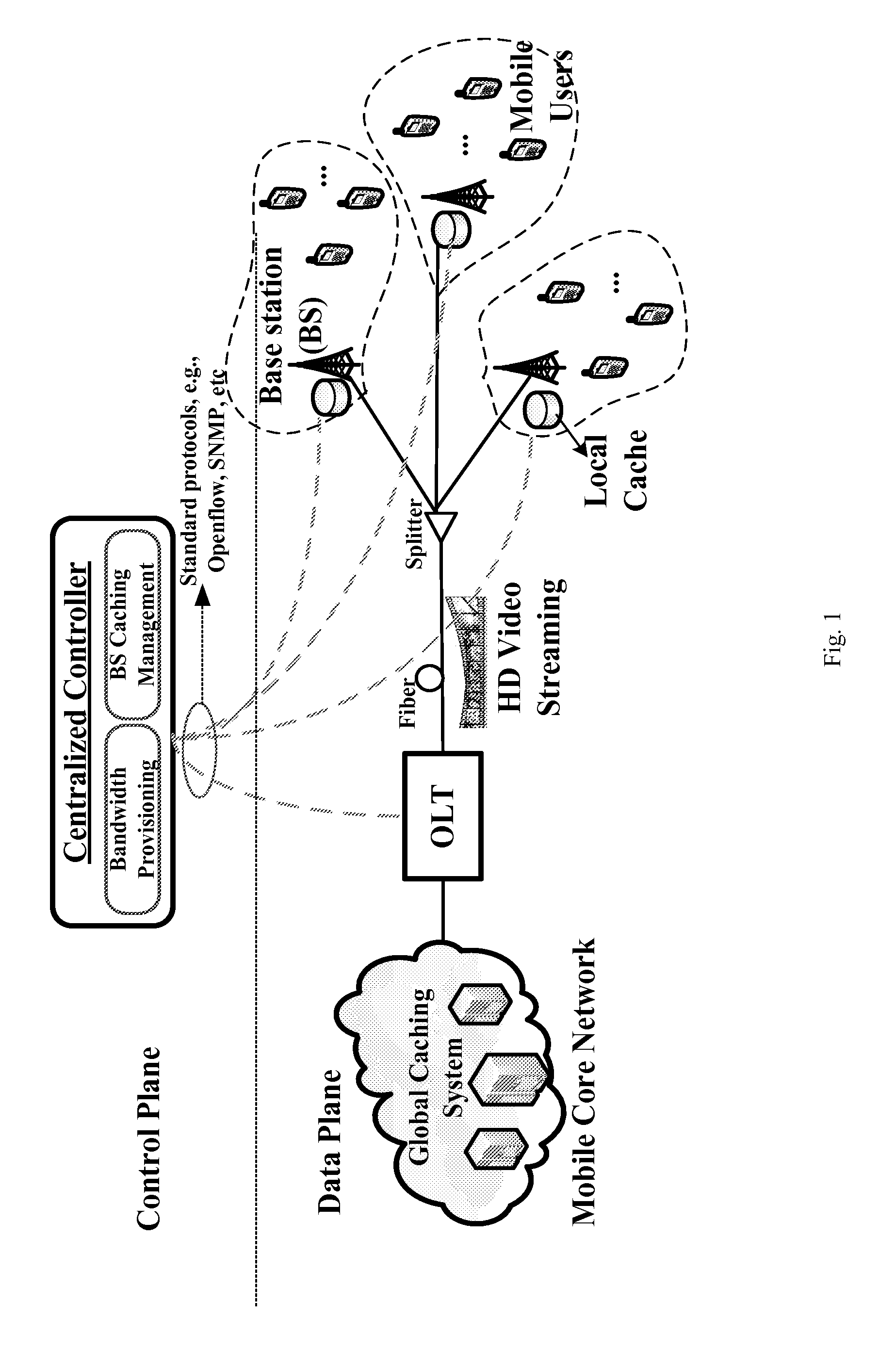
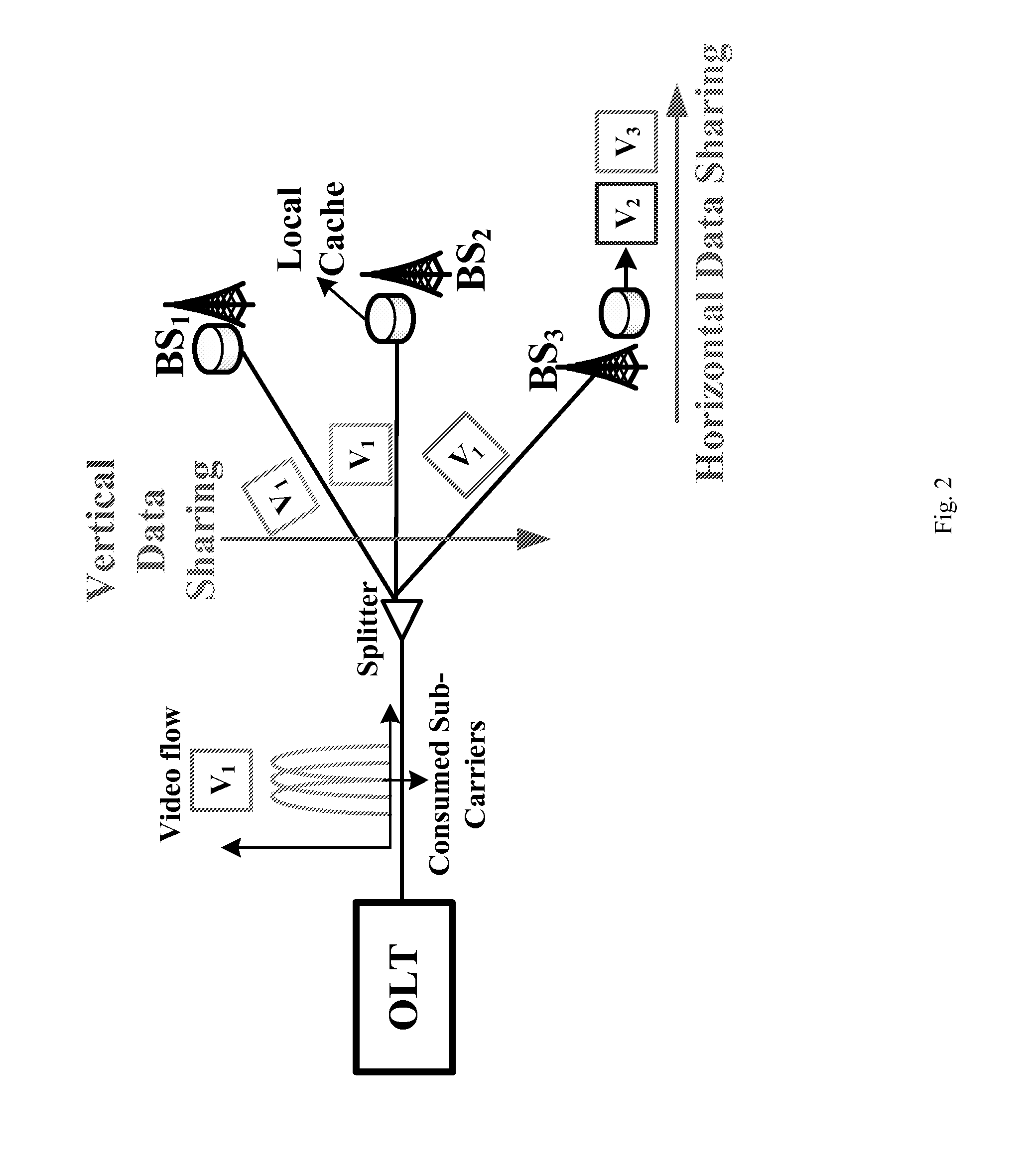
Software defined joint bandwidth provisioning and cache management for mbh video traffic optimization
ActiveUS20150106864A1Raise priorityTwo-way working systemsRadio-over-fibreVideo deliveryTraffic optimization
A method includes provisioning joint bandwidth in a software defined passive optical network PON based mobile backhaul MBH and cache management on base stations for video delivery across the network, the provisioning in each time unit includes grouping bandwidth utilization in the network into a first category used to support video requests which cannot directly be served by caches on base stations, the first category video requests being high priority, and if bandwidth remains after the high priority requests remaining bandwidth being used to deliver some videos that are low priority to caches.
Owner:NEC CORP
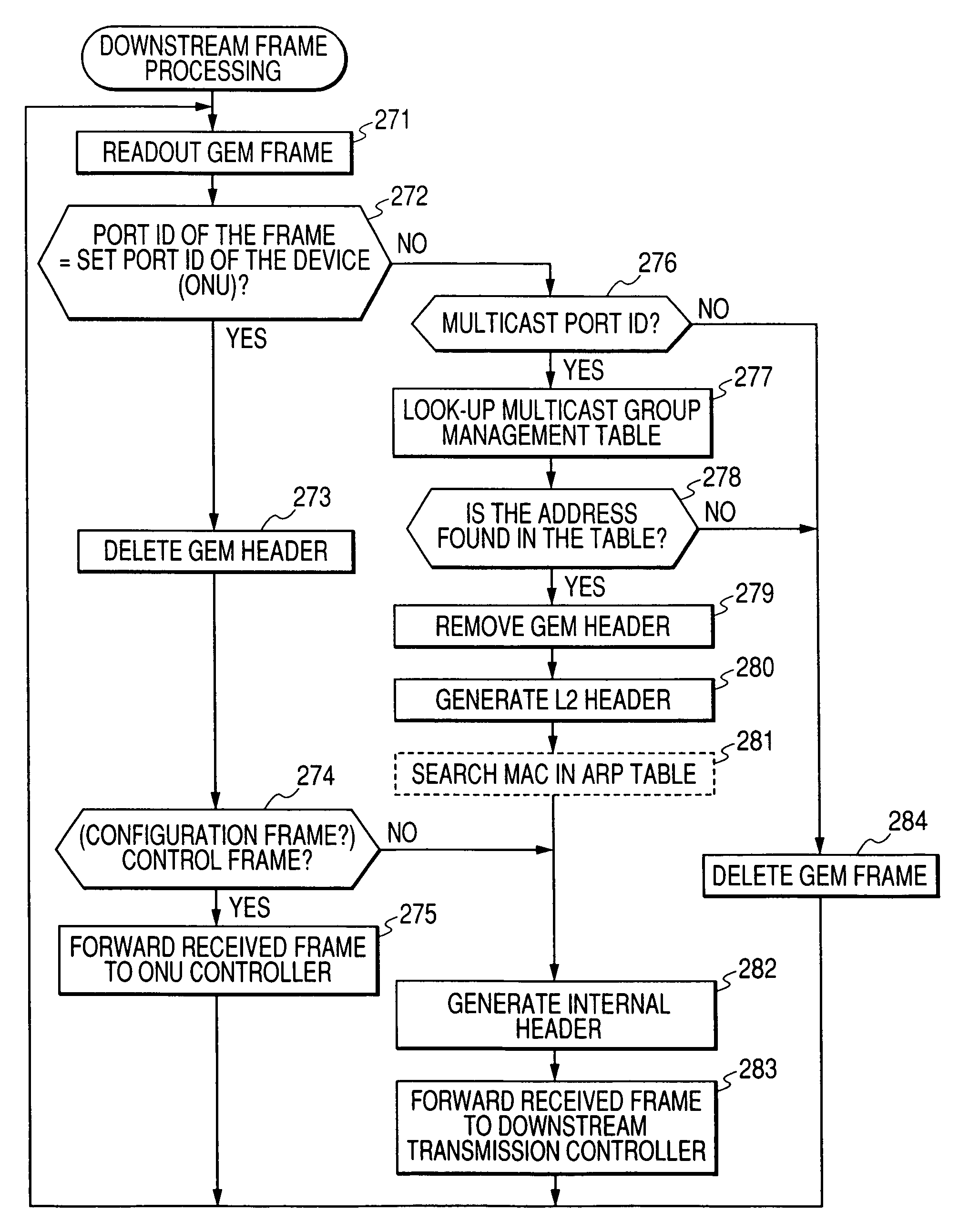
Passive optical network (PON) system
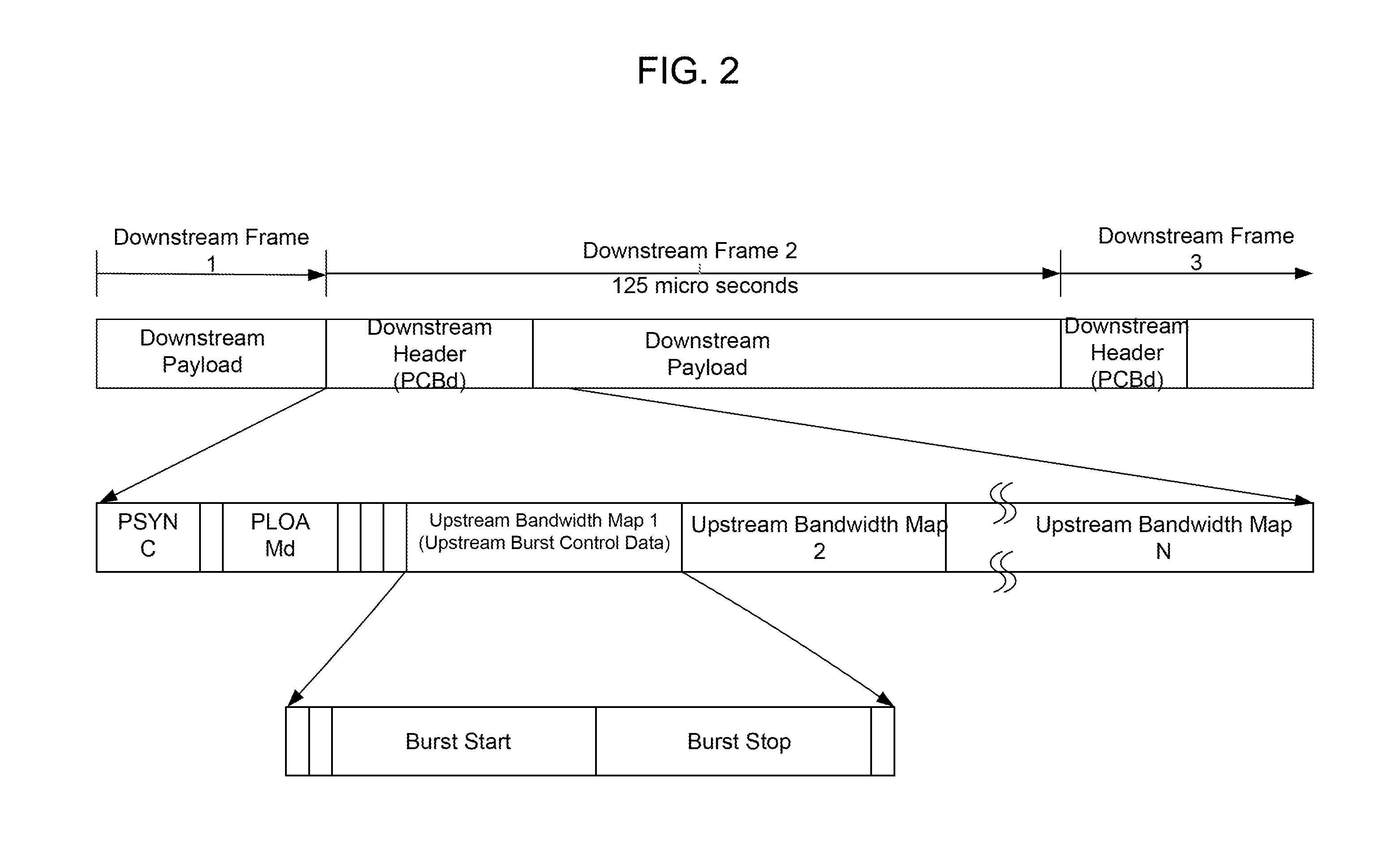
InactiveUS7675936B2Shorten the lengthEfficient use ofMultiplex system selection arrangementsTime-division multiplexTransmission channelEmbedded system
A PON system capable of utilizing the bandwidth of an optical transmission channel in the PON section. In a PON system including an OLT and a plurality of ONUs, the OLT has: a downstream frame processing unit that removes at least part of the header information in a layer 2 header from a downstream frame received from a wide area network, and converts the remaining frame portion into a frame having a header specific to the PON section; and a downstream frame processing unit that extracts a downstream frame portion to be transferred to a user terminal, from a received frame from a PON, and adds the layer 2 header information deleted in the OLT.
Owner:HITACHI LTD
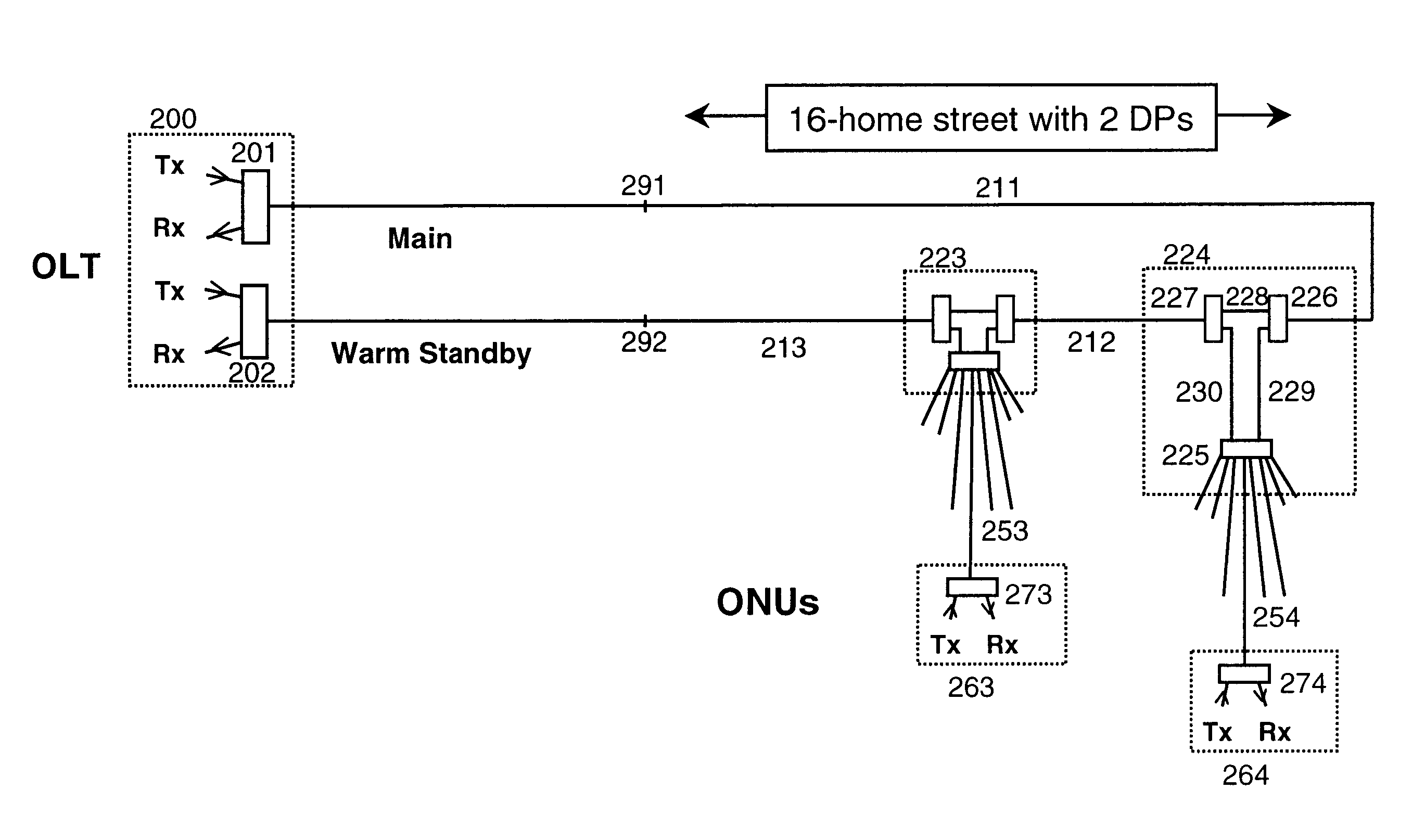
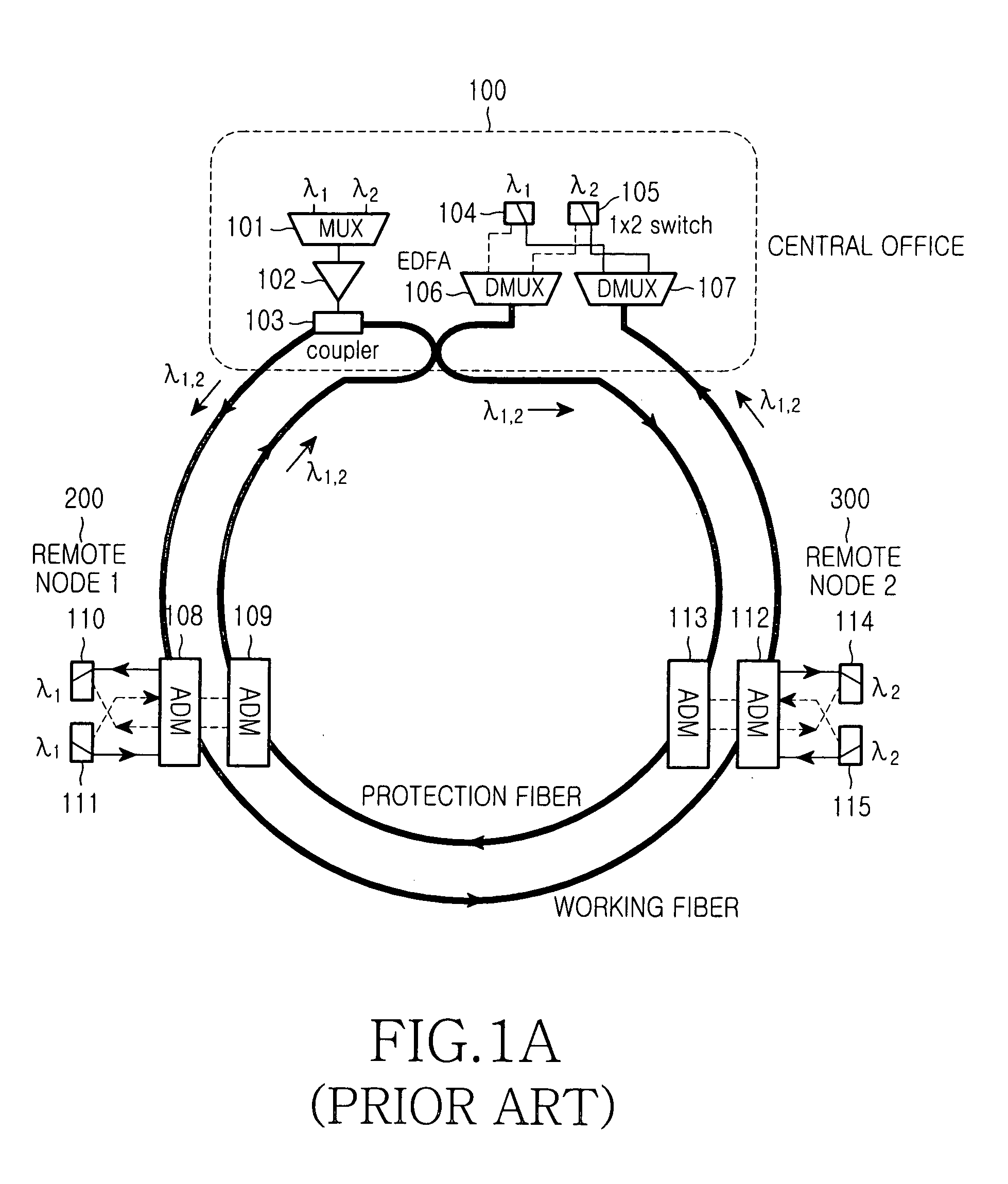
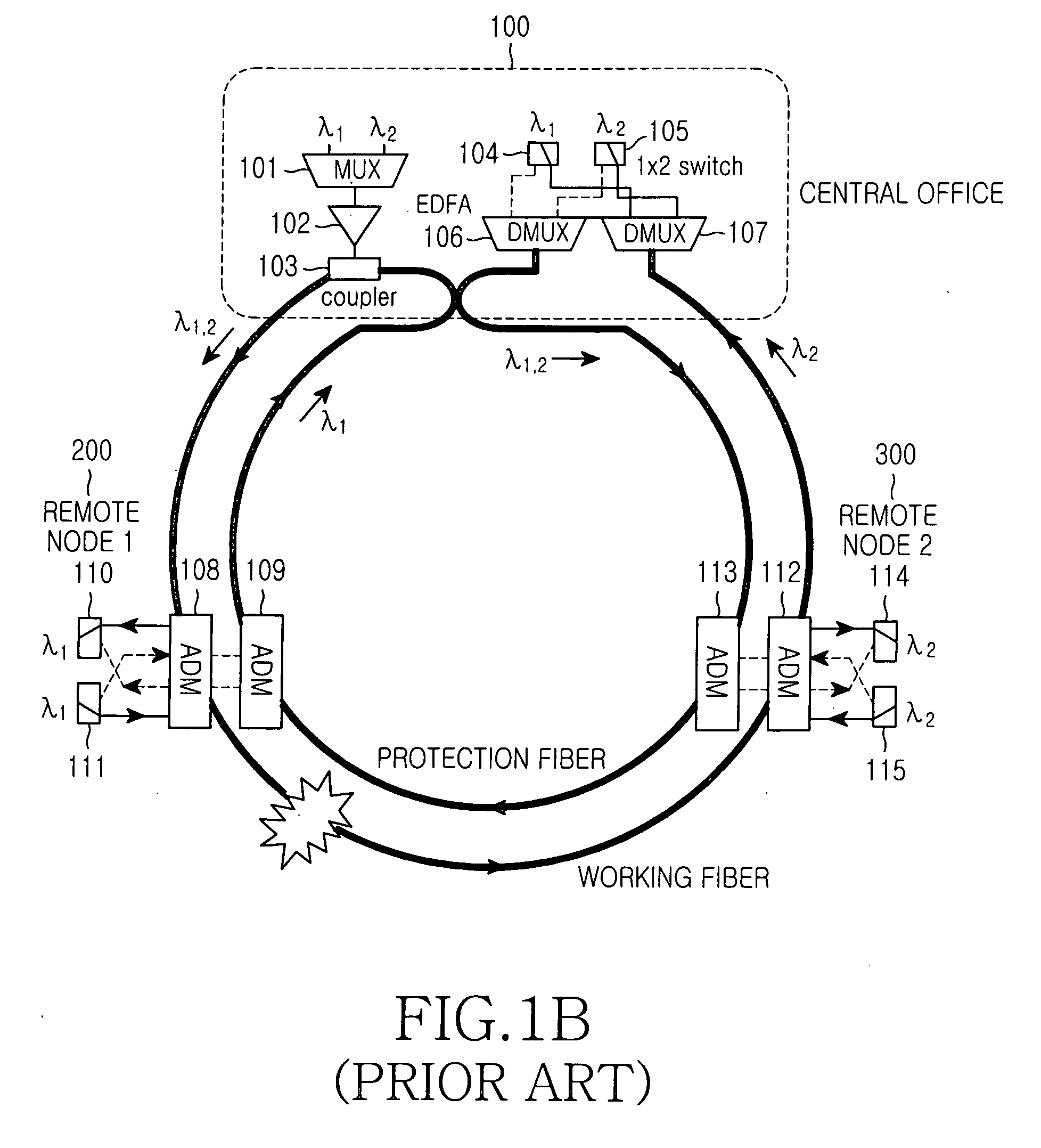
Single-fiber protection in telecommunications networks
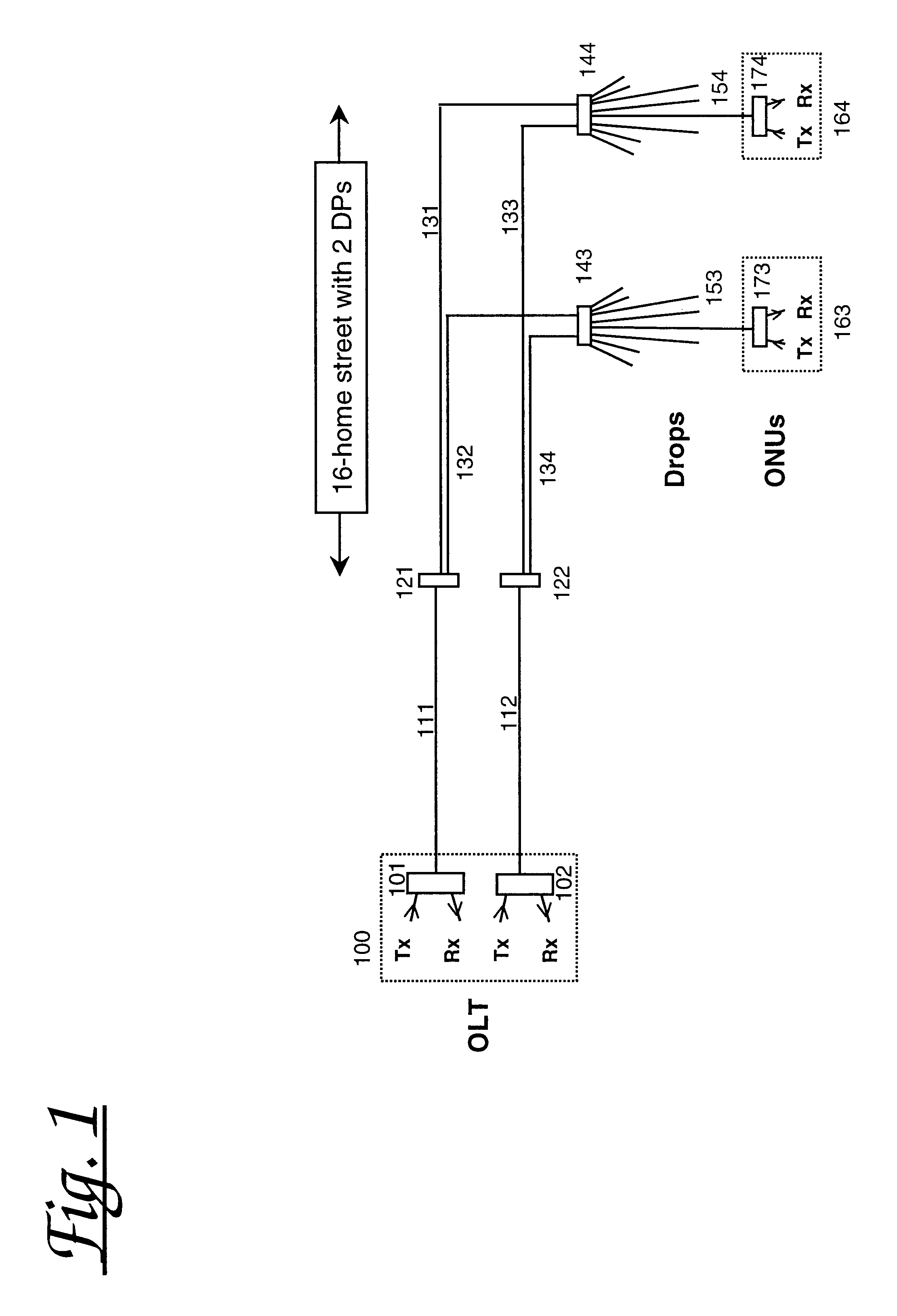
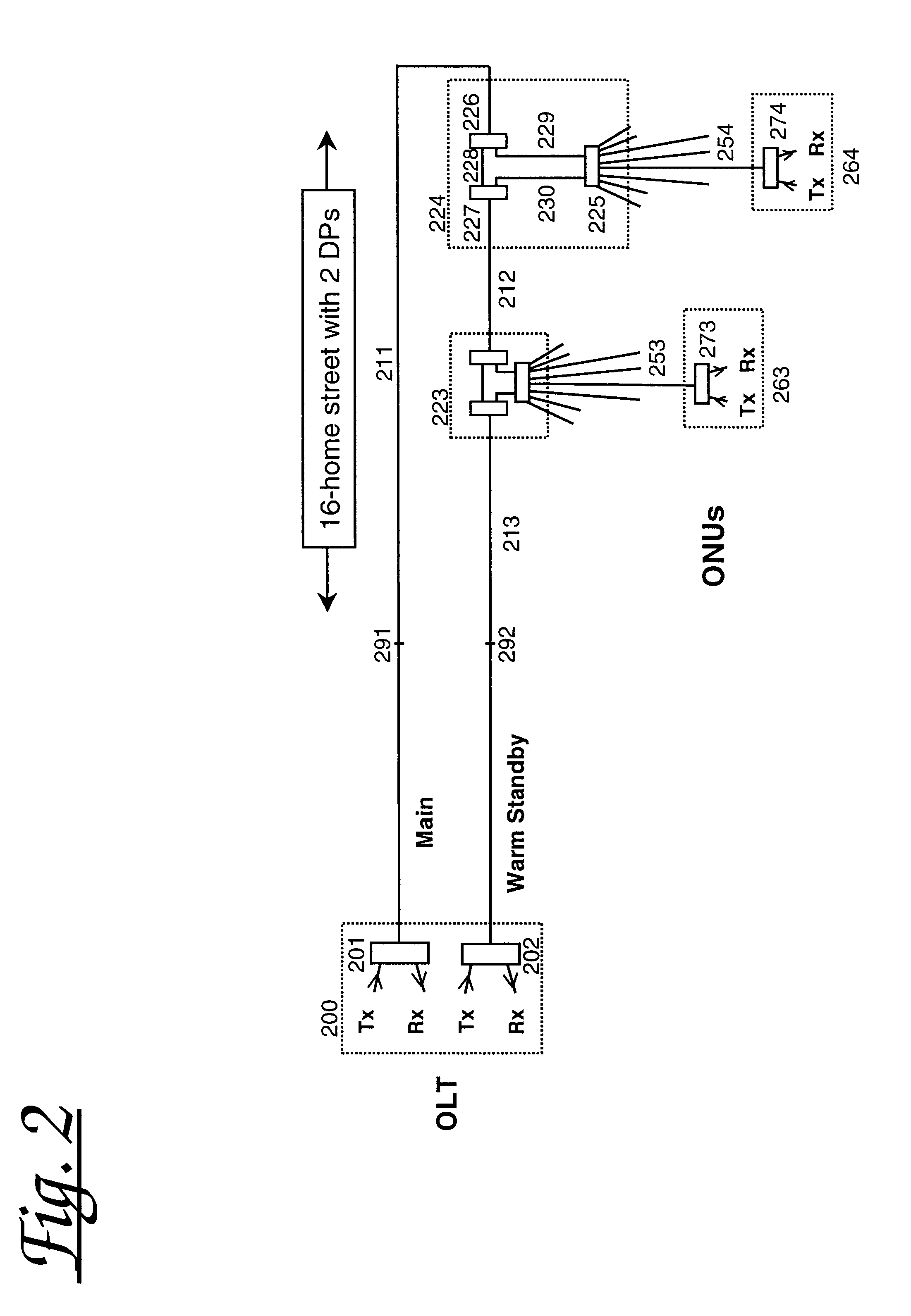
ActiveUS20050019031A1Efficient solutionCost-effectiveRing-type electromagnetic networksLaser detailsTelecommunications networkOptical power
A solution for detecting and recovering from a failure in a protected single-fiber passive optical network. A detector is used to detect the degradation in power level of optical signals. Furthermore, the invention discloses a variable symmetric split ratio approach to improve the number of splits (e.g. the number of ONUs). A single-fiber passive optical network is disclosed that uses a plurality of passive nodes connected in the optical fiber between the interfaces, wherein in the passive nodes 2-by-2 splitters / combiners are used to couple optical power from and into the optical fiber at a predetermined split ratio.
Owner:SCHOFIELD TECH
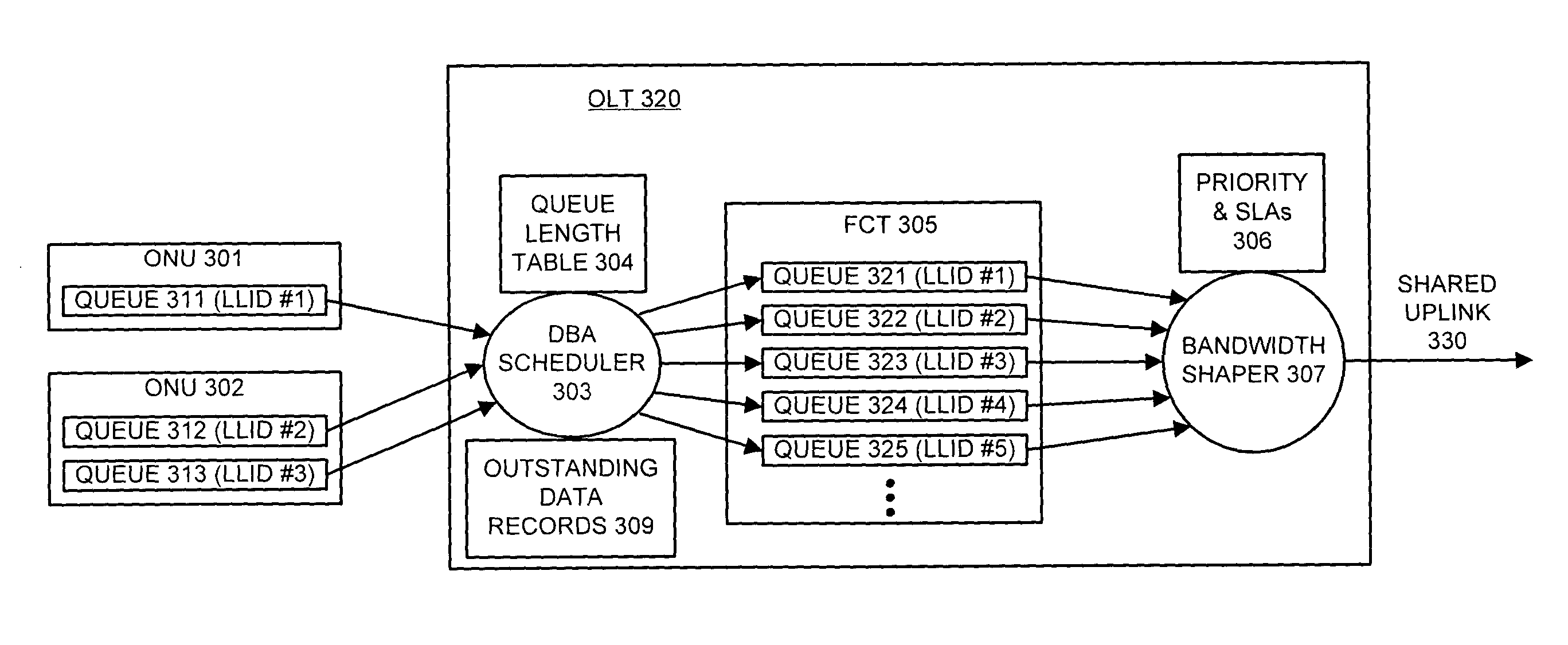
Method and apparatus for dynamically allocating upstream bandwidth in passive optical networks
InactiveUS20050058135A1Facilitates dynamic allocationData switching by path configurationDistributed computingCentral node
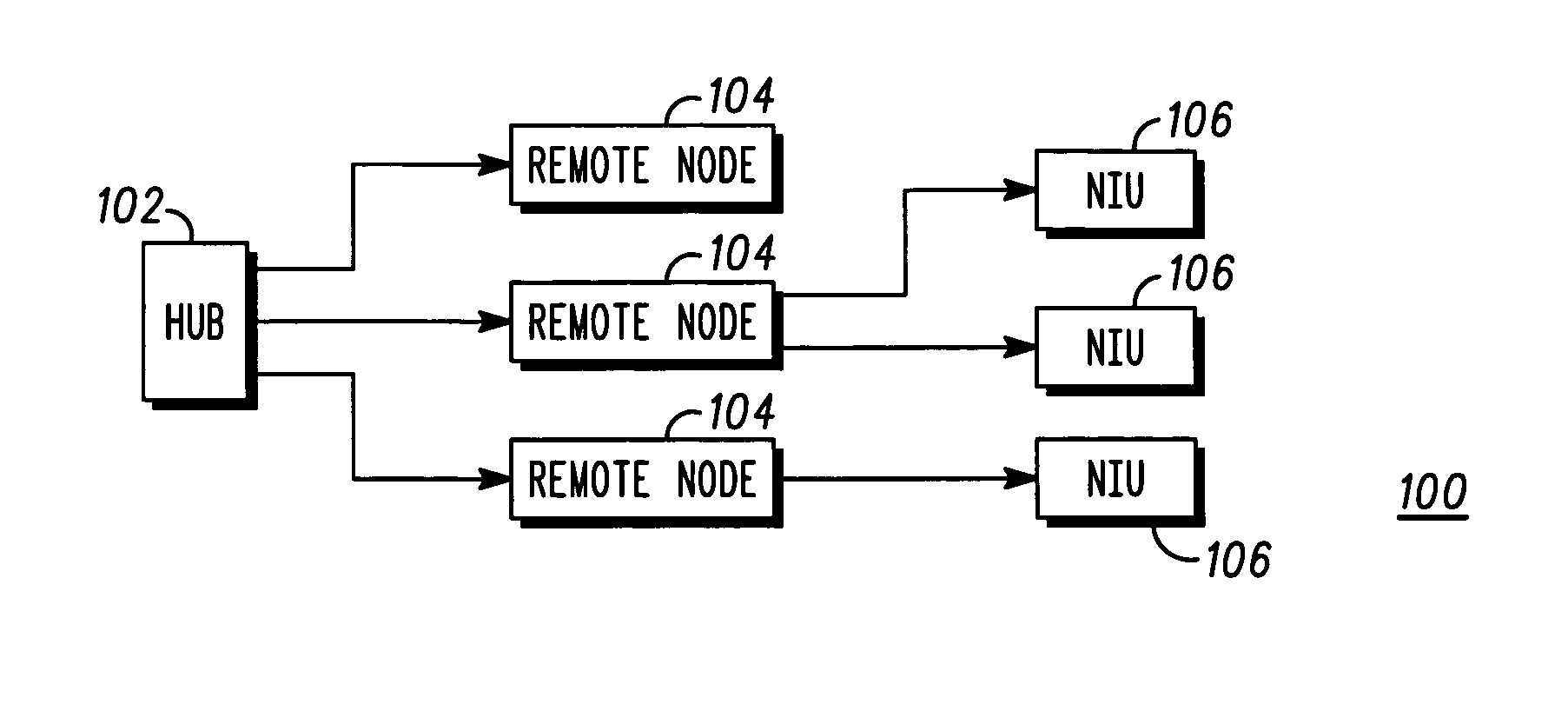
One embodiment of the present invention provides a system that facilitates dynamic allocation of upstream bandwidth in a passive optical network which includes a central node and at least one remote node. Each remote node is coupled to at least one logical entity, which corresponds to a device or a user, that transmits upstream data to the central node and receives downstream data from the central node. The central node is coupled to an external network outside of the passive optical network through a shared out-going uplink.
Owner:AVAGO TECH INT SALES PTE LTD
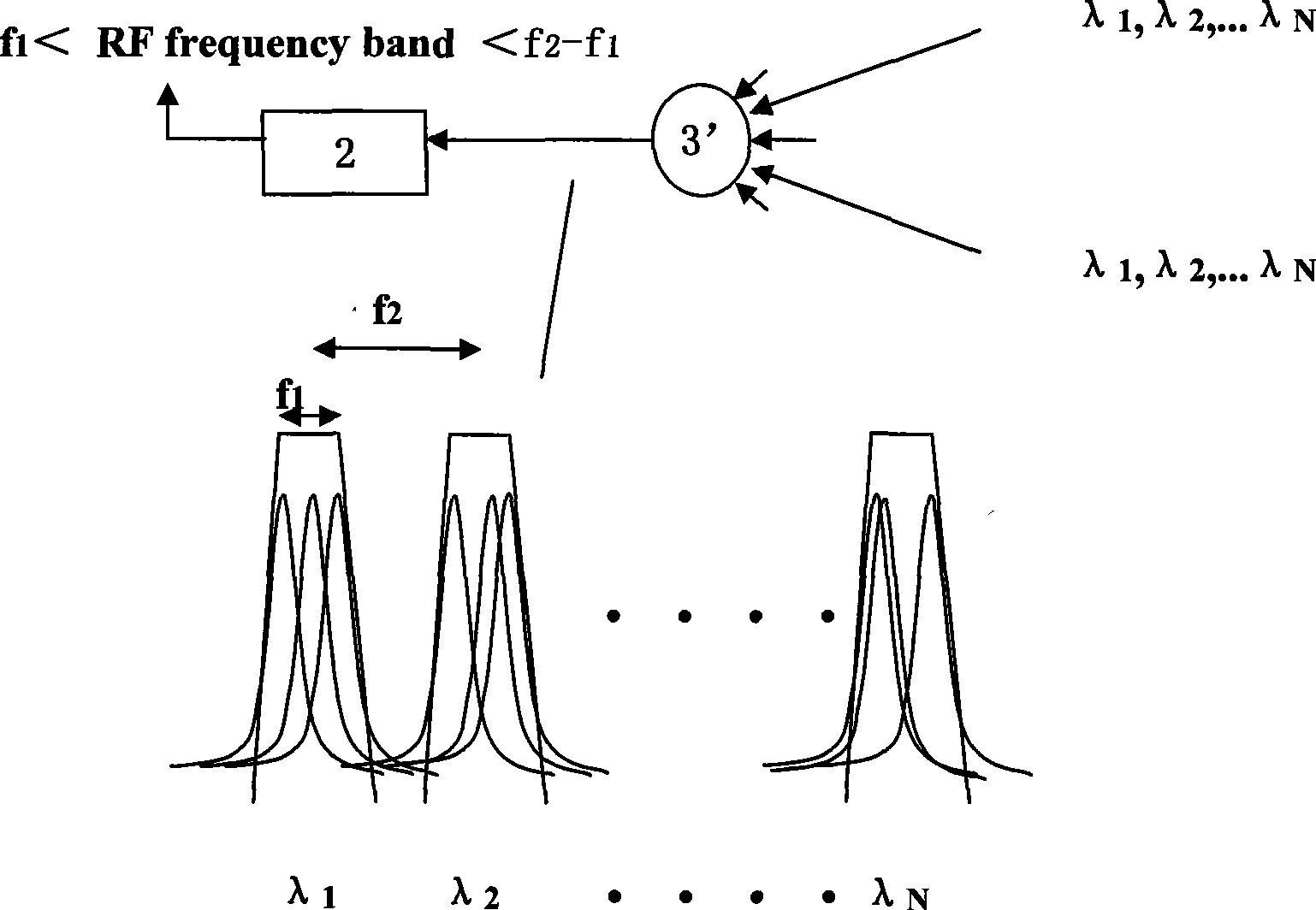
System and apparatus for a carrier class WDM PON accommodating multiple services or protocols
InactiveUS20050175344A1Wavelength-division multiplex systemsMultimode transmissionMultiplexerEngineering
A Passive Optical Network (PON) is provided with capability for multiple protocols and service suppliers by employing Wavelength Division Multiplexer (WDM) elements in combination with optical couplers at optical distribution nodes (ODN) intermediate a local exchange office and a customer node. The local exchange office node transmitting and receiving signals from a single optical fiber through a WDM providing M / 2 wavelength pairs for use with differing protocols and each customer node connected to one leg of an optical coupler in the ODN with a WDM associated with one of the wavelength pairs for received and transmitted signals.
Owner:UTSTARCOM INC
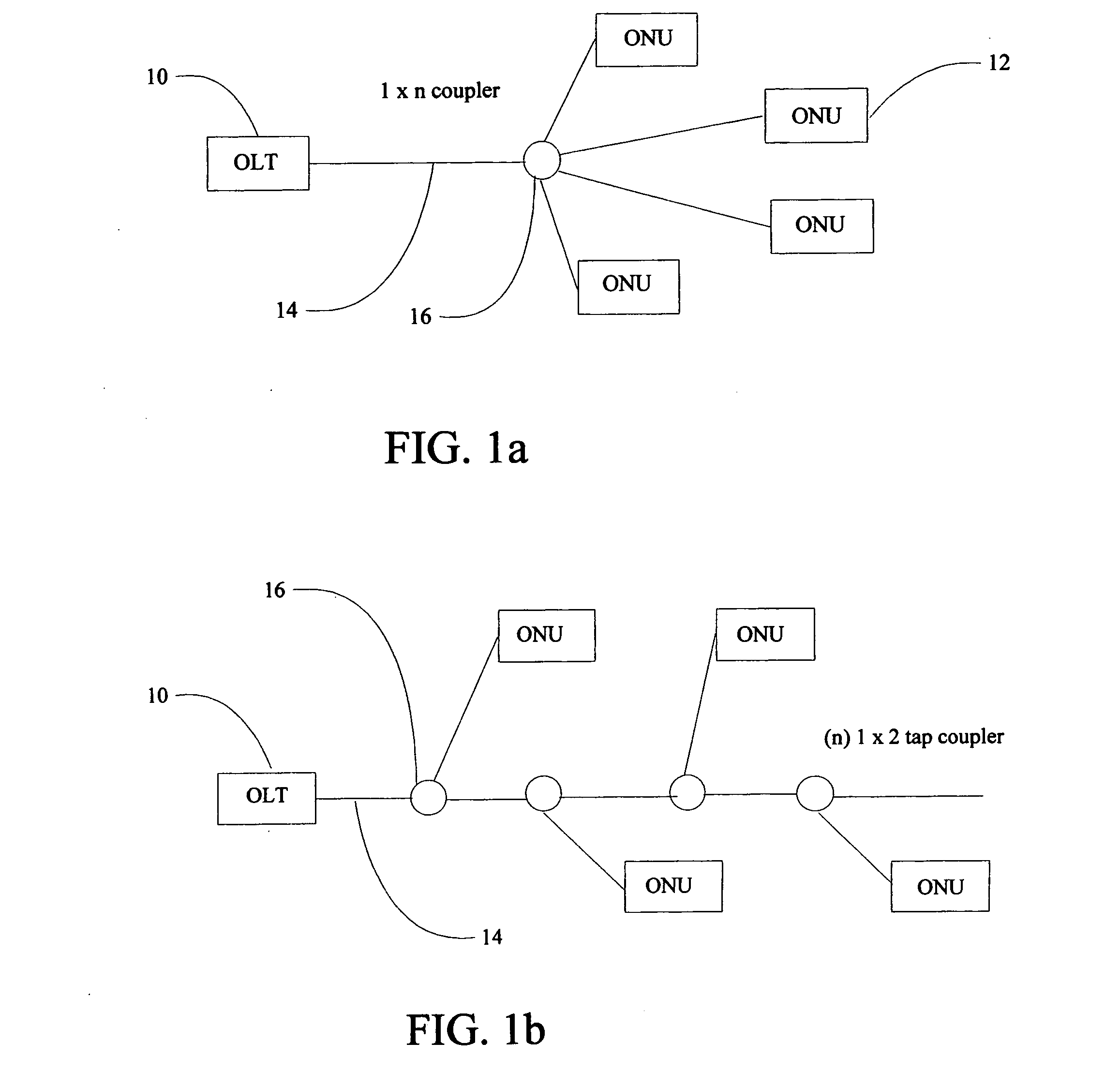
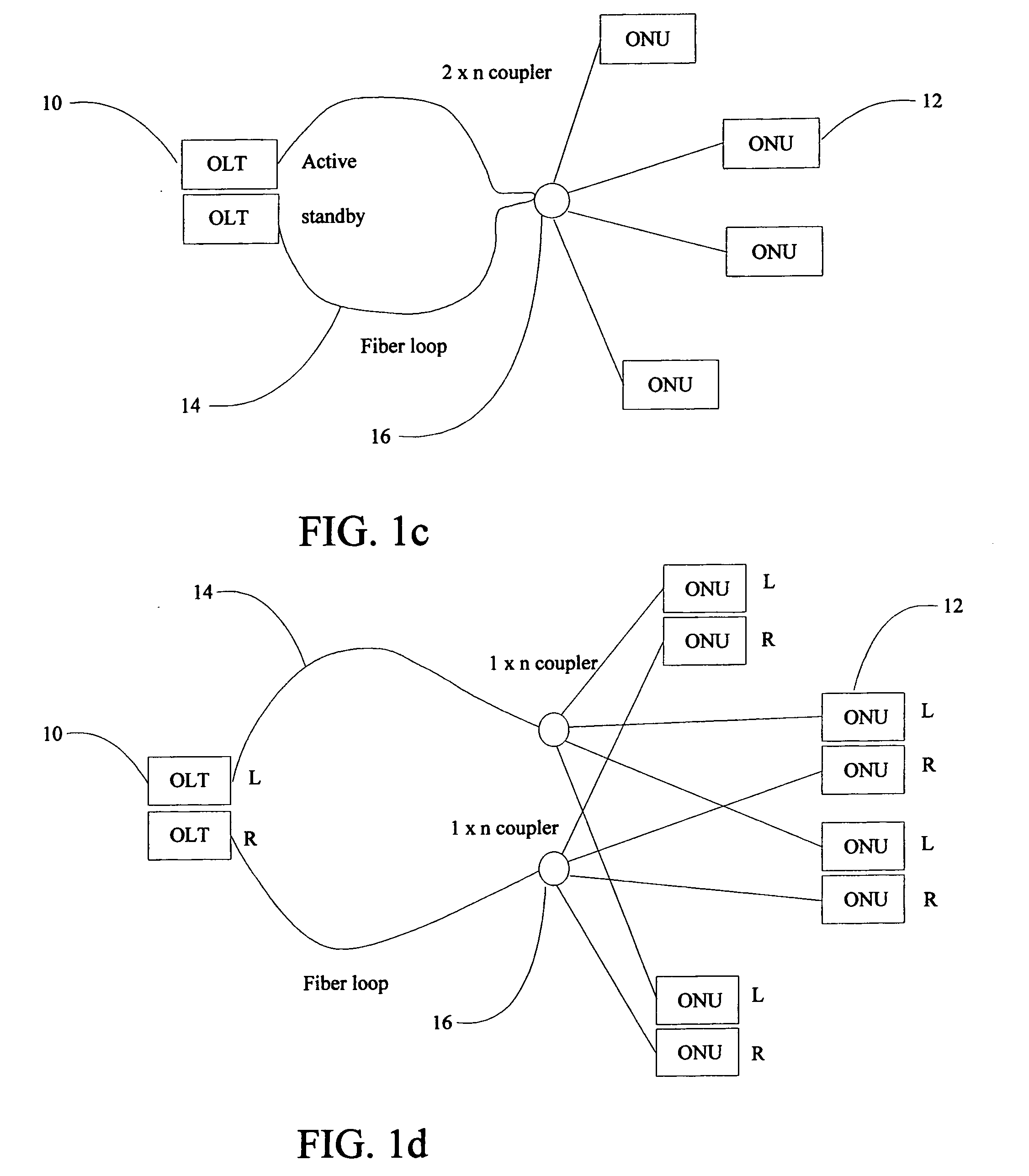
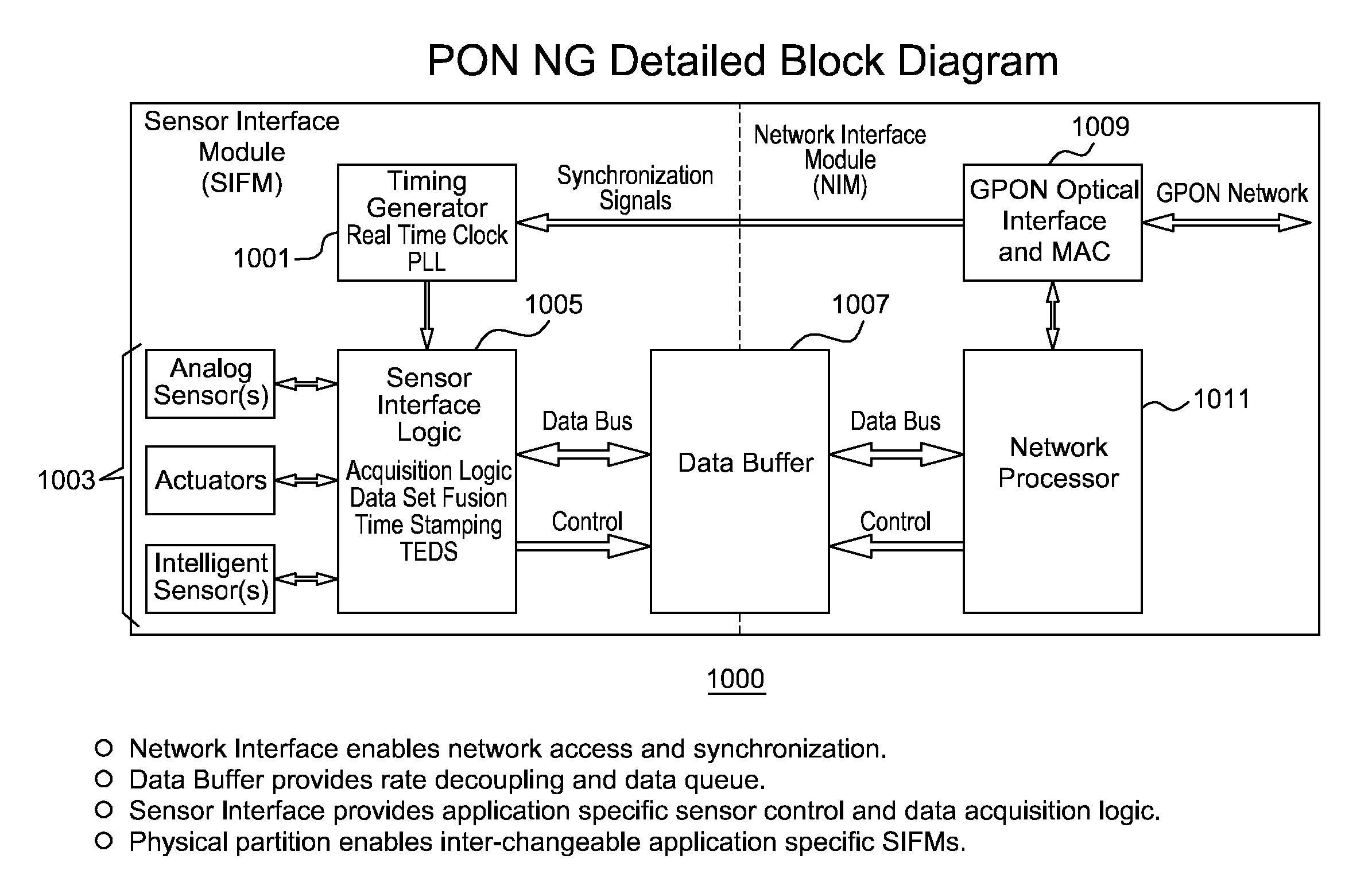
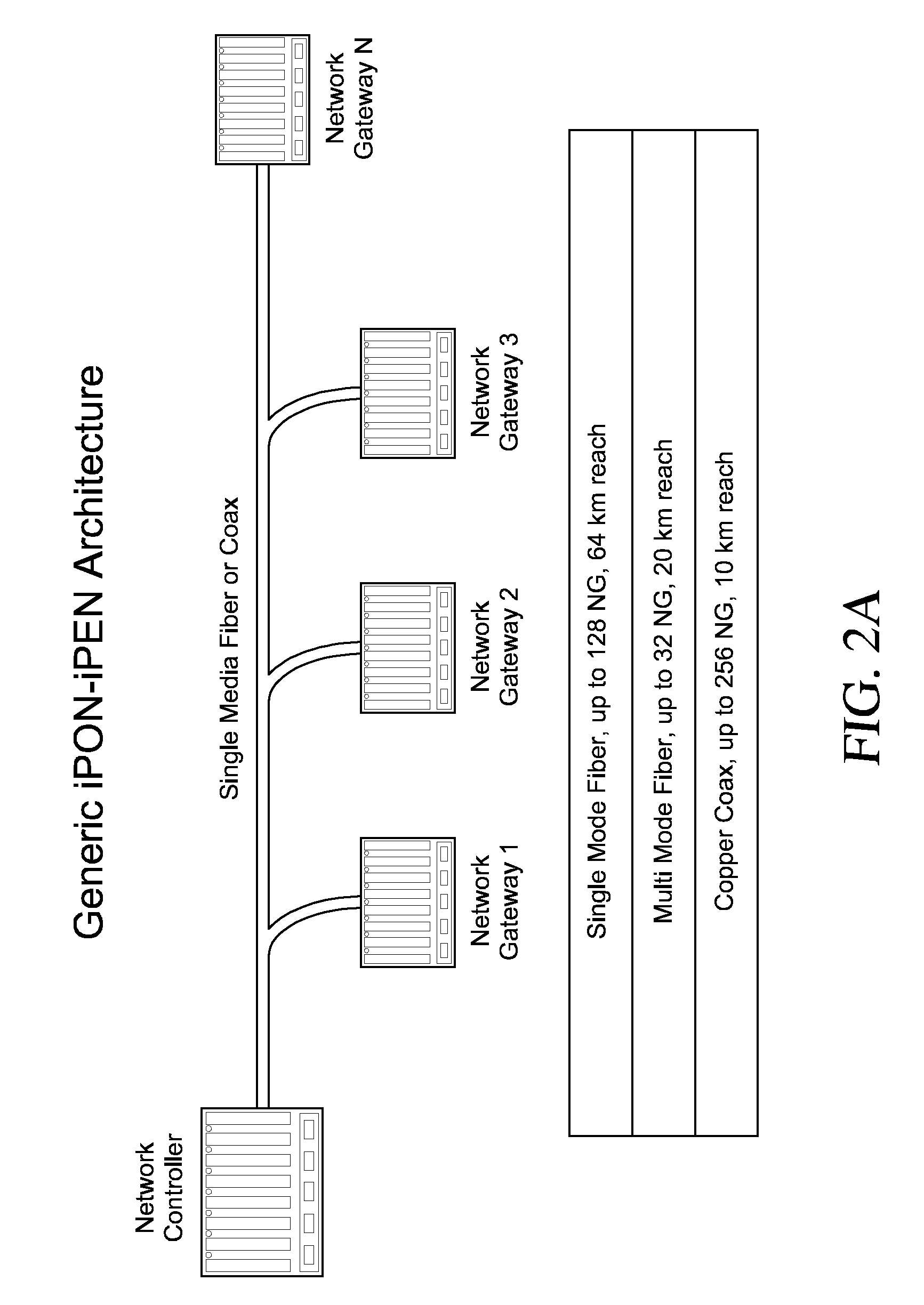
Inverted Passive Optical Network/inverted Passive Electrical Network (iPON/iPEN) Based Data Fusion and Synchronization System
InactiveUS20070291777A1Easy to integrateEasy to fuseTime-division multiplexData switching by path configurationTelecommunications linkLine rate
The present invention is an apparatus, method and system for time synchronizing data from various sensor types that enables data fusion and transport. To provide this capability, the present invention utilizes an inverted Passive Optical Network (PON) approach for synchronous communication. Further, the present invention introduces an inverted Passive Electrical Network (iPEN) that extends the iPON approach. Data that are in a common format with embedded time synchronization information can easily be integrated or fused and transported over such communication links. The present invention provides the ability to merge and aggregate data from a wide range of disparate sensors and systems while maintaining close synchronization. The present invention is appropriate for synchronization of data, voice, and video onto a single network and / or multi-tiered networks and can also handle signal processing and control technologies at line rates well into the Gigabits per second (Gbps) range.
Owner:3 PHOENIX
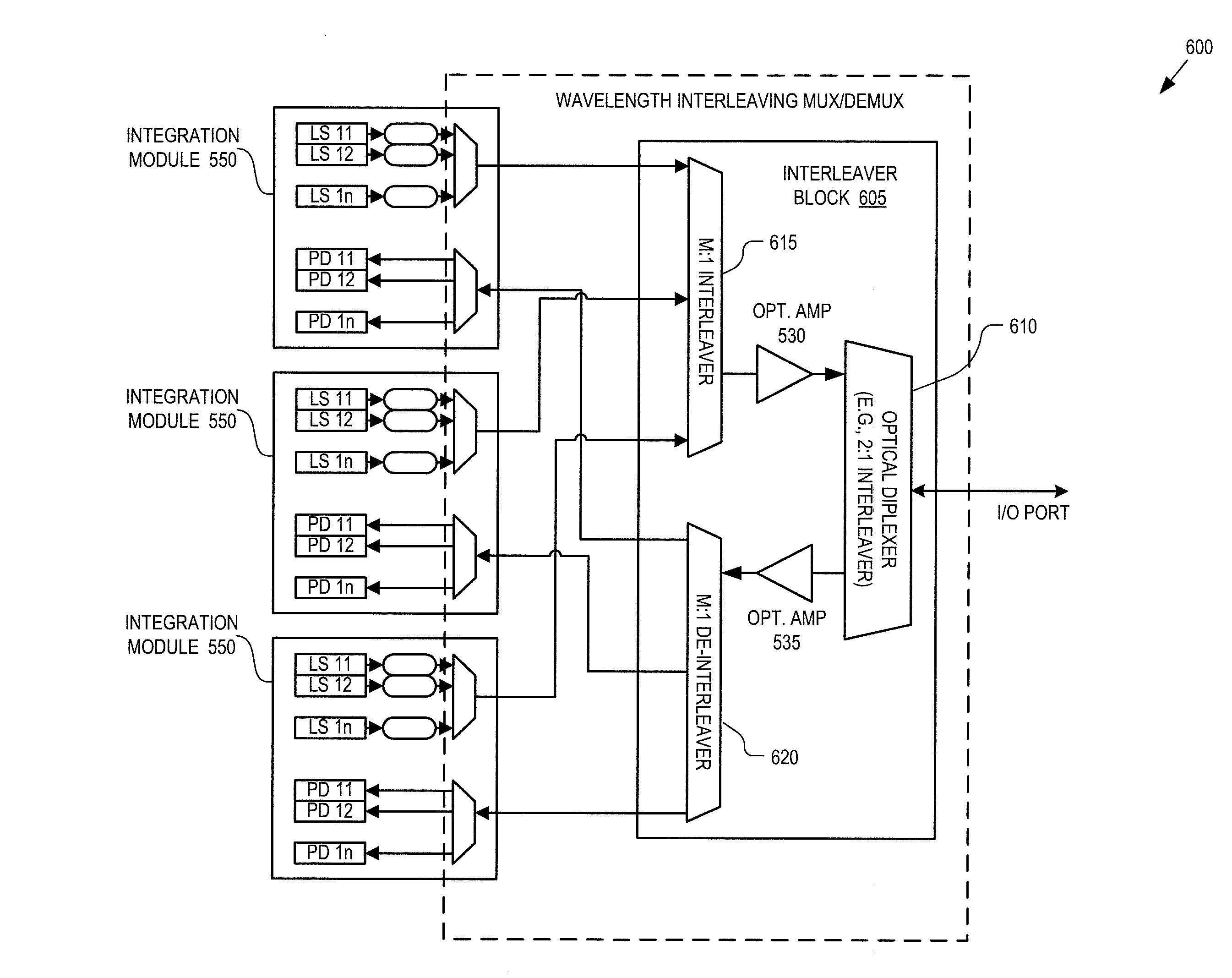
Passive optical network with asymmetric modulation scheme
A passive optical network couples a WDM optical line terminal (“OLT”) to WDM optical network units (“ONUs”). The WDM OLT includes an optical transmitter array with coherent transmitters to generate downstream WDM signals encoded using phase modulation, an optical receiver array with direct detection photo-detectors to receive upstream WDM signals encoded with amplitude modulation, and an optical diplexer optically coupled to the optical transmitter array and the optical receiver array. The WDM ONU includes a tunable optical transmitter having a first tunable laser source coupled to generate a selectable upstream carrier wavelength and direct amplitude modulation circuitry coupled to amplitude modulate the first tunable laser source and a tunable optical receiver having coherent detection circuitry to demodulate phase information from the downstream WDM signals and a second tunable laser source operated as a local oscillator and coupled to tune to a selectable downstream carrier wavelength.
Owner:GOOGLE LLC
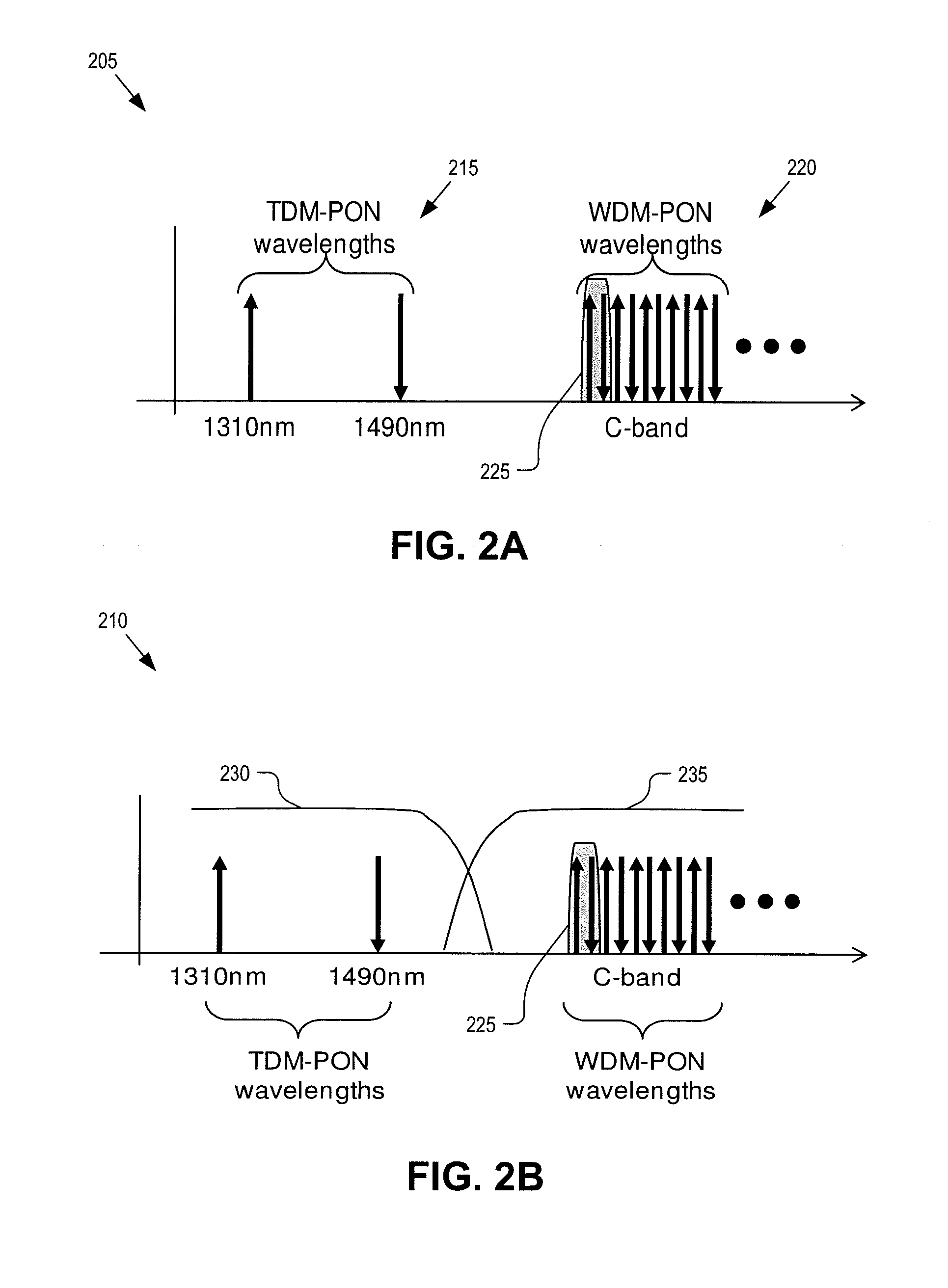
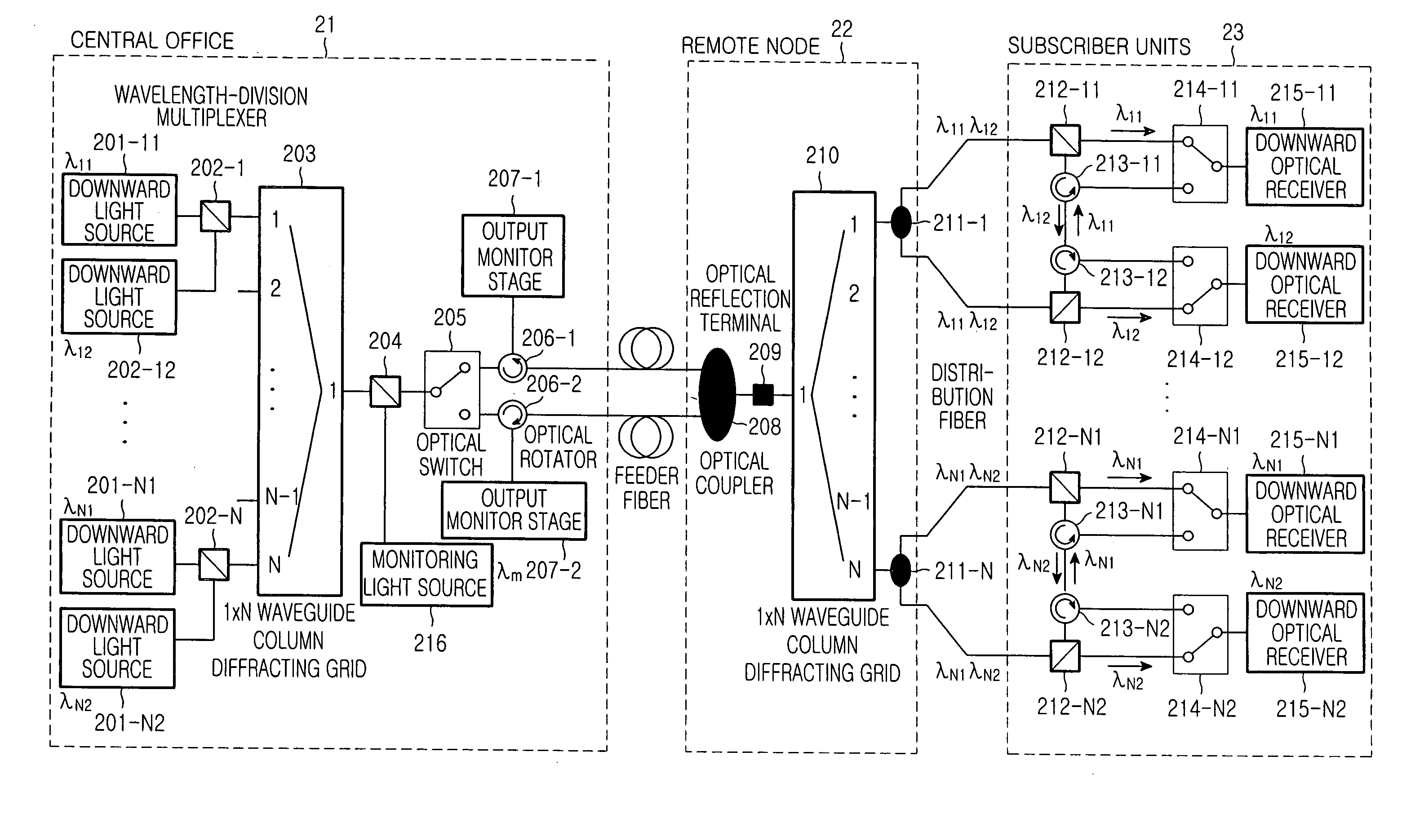
Wavelength-division multiplexed self-healing passive optical network
InactiveUS20050141892A1Detected accidentallyRing-type electromagnetic networksLaser detailsTelecommunicationsControl signal
A wavelength-division multiplexed self-healing passive optical network is capable of detecting cut-off and deterioration of feeder fiber and distribution fiber and restoring a network with a star structure. The network includes a central office, a remote node, and a plurality of subscriber units. Working and protection feeder fibers connect the central office to the remote node. A reflection unit at an end of the remote node connects to the central office for reflecting a monitoring optical signal transmitted from the central office. An output monitor stage at an end of the central office connects to the remote node for detecting the reflected monitoring optical signal and generating a control signal based on the presence of abnormality of the working and protection feeder fibers.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
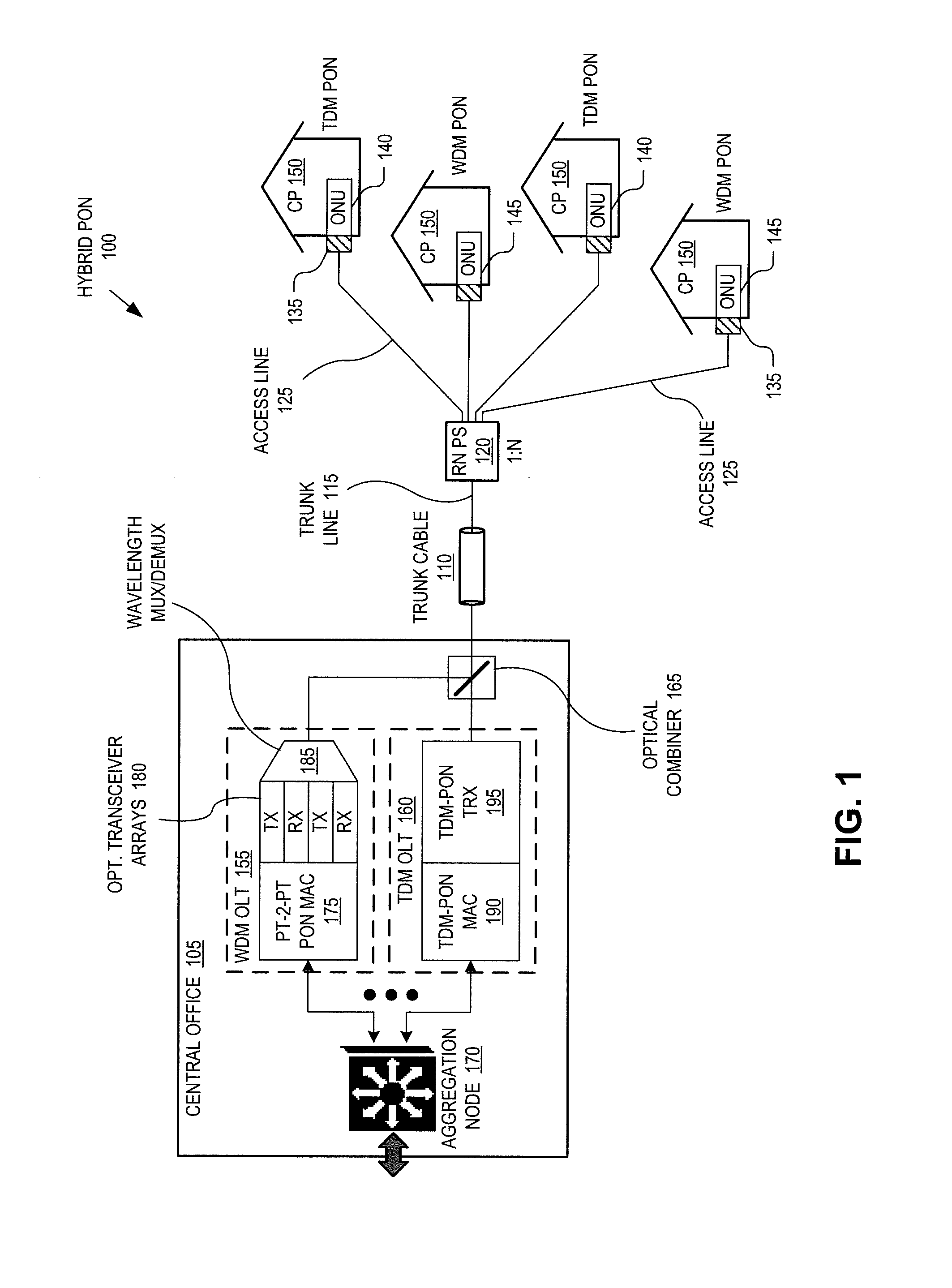
System and Method for Optical-Electrical-Optical Reach Extension in a Passive Optical Network
InactiveUS20120141139A1Multiplex system selection arrangementsStar-type electromagnetic networksControl dataPhotoelectric conversion
A system and method are disclosed in which an optical network may include an optical-electrical converter module within an OEO (Optical Electrical Optical) reach extension system (OEO RE system), the OEO RE system having an OEO port and including a downstream frame regeneration block; and a downstream control data extraction block including a GPON operating parameter extraction module (GOPEM), wherein the GOPEM is operable to extract at least one OEO-port operating parameter from data frames arriving at the GOPEM module.
Owner:ALPHION
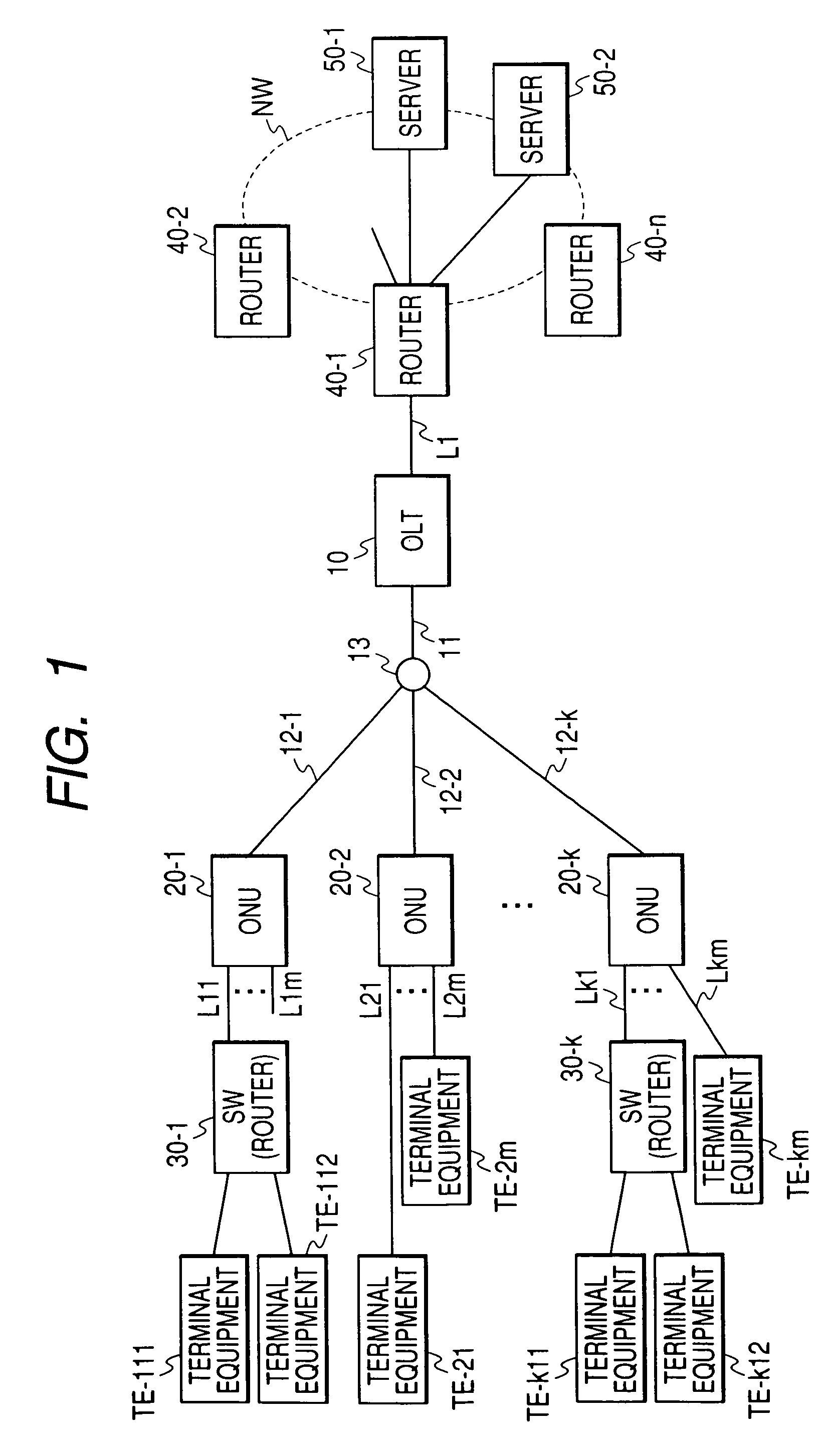
System and method for transfer of IP data in an optical communication networks
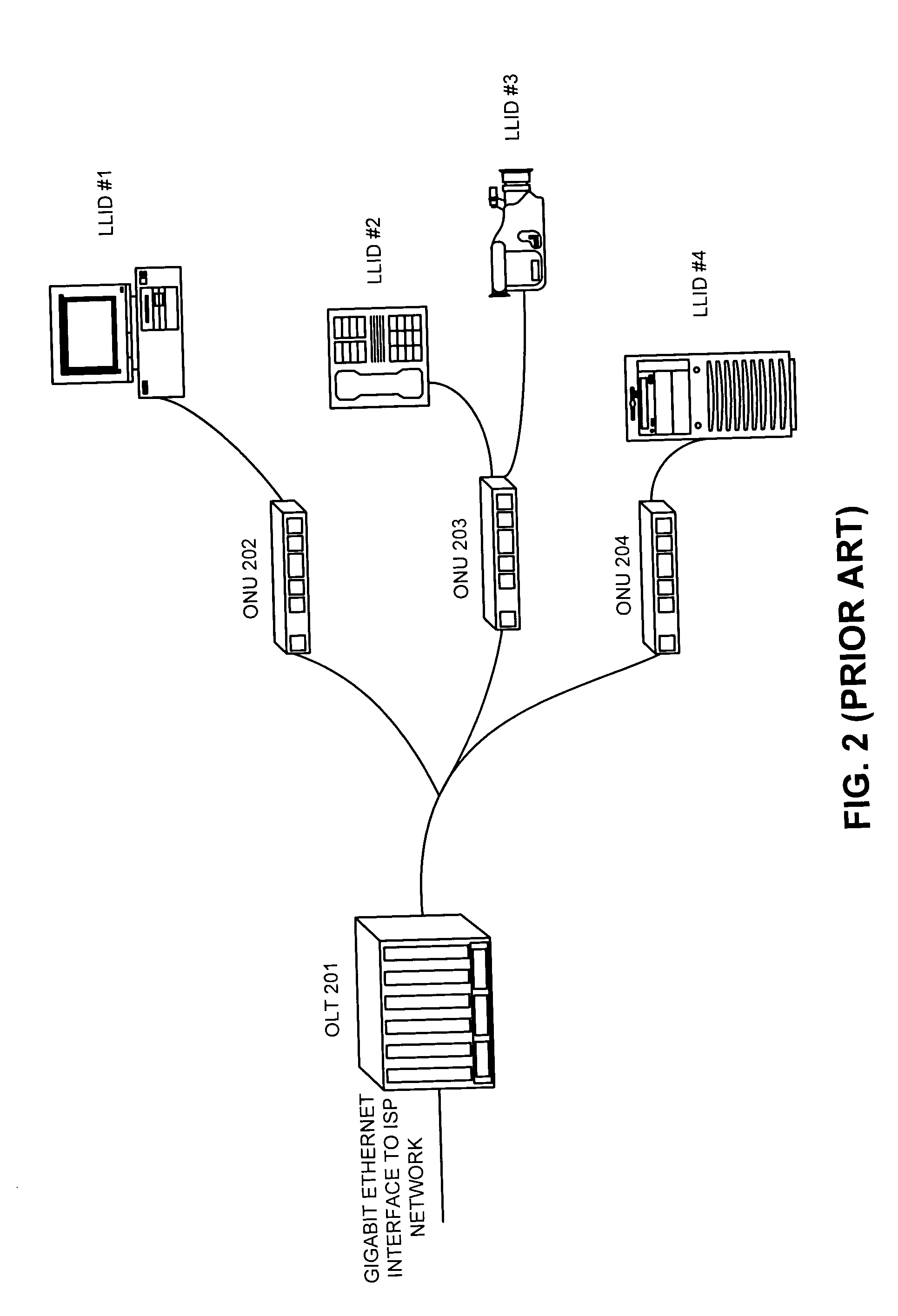
InactiveUS6870836B1Reduce complexityHigh complexityMultiplex system selection arrangementsTime-division optical multiplex systemsCollision detectionMedia access control
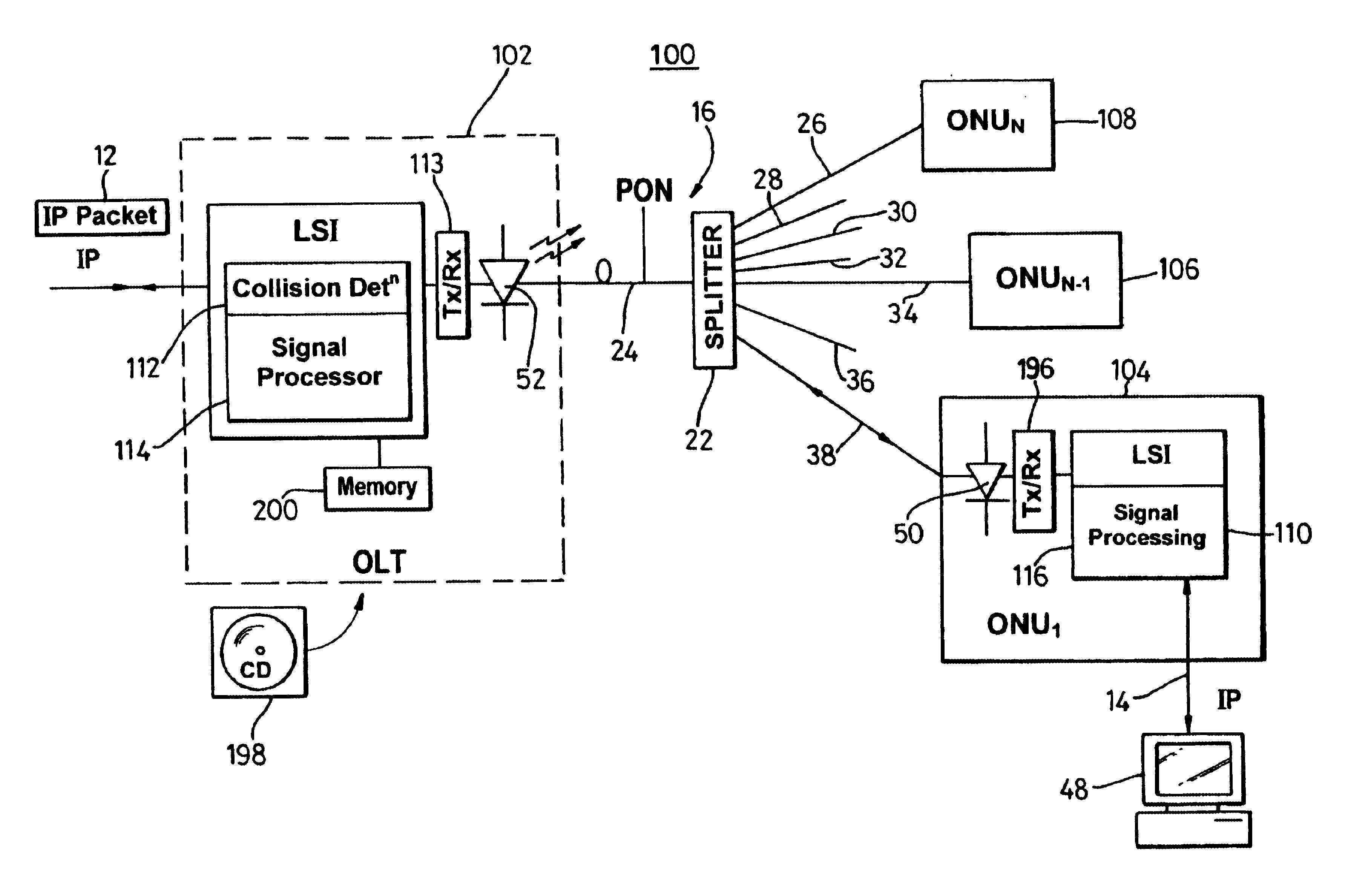
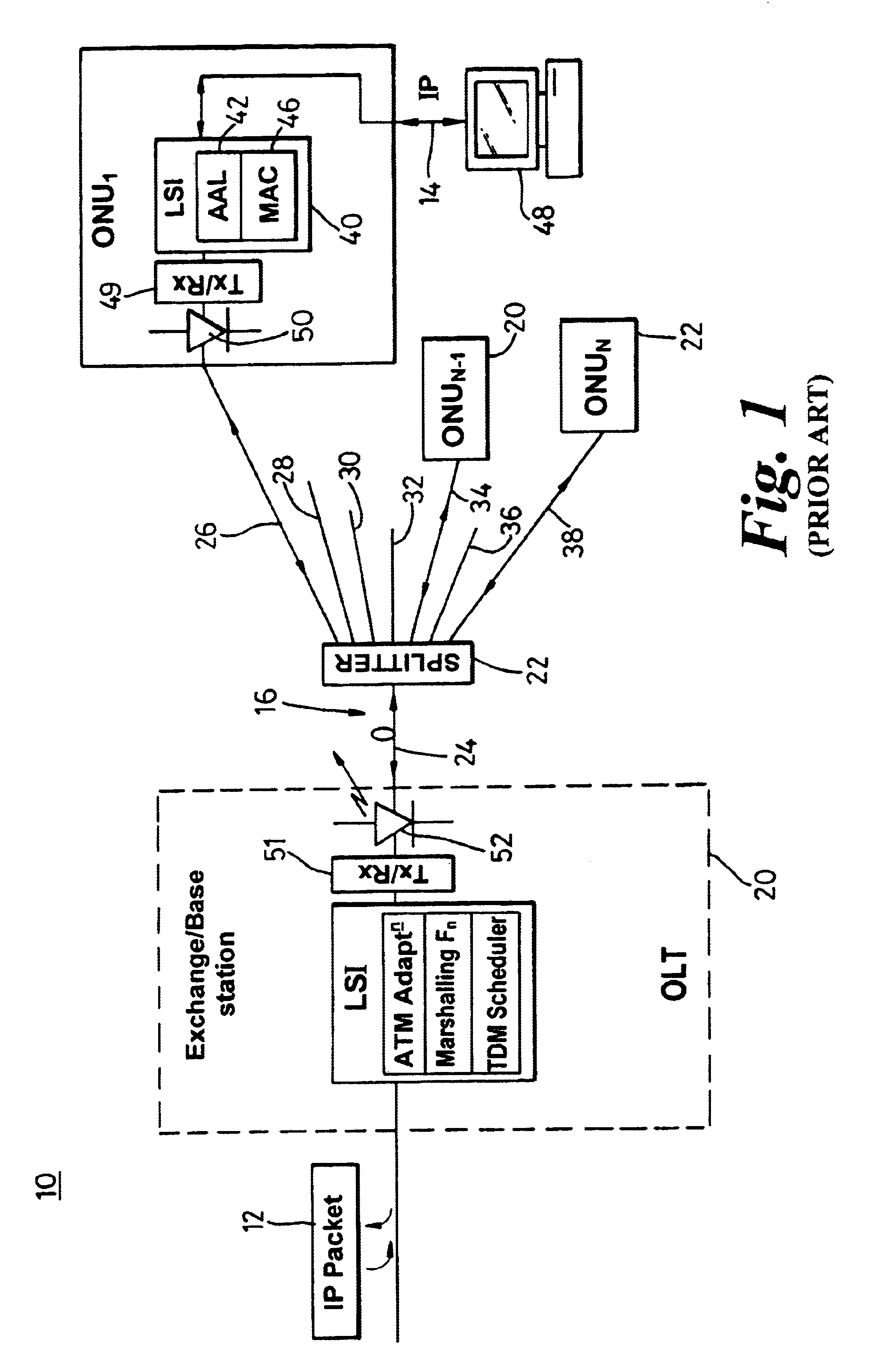
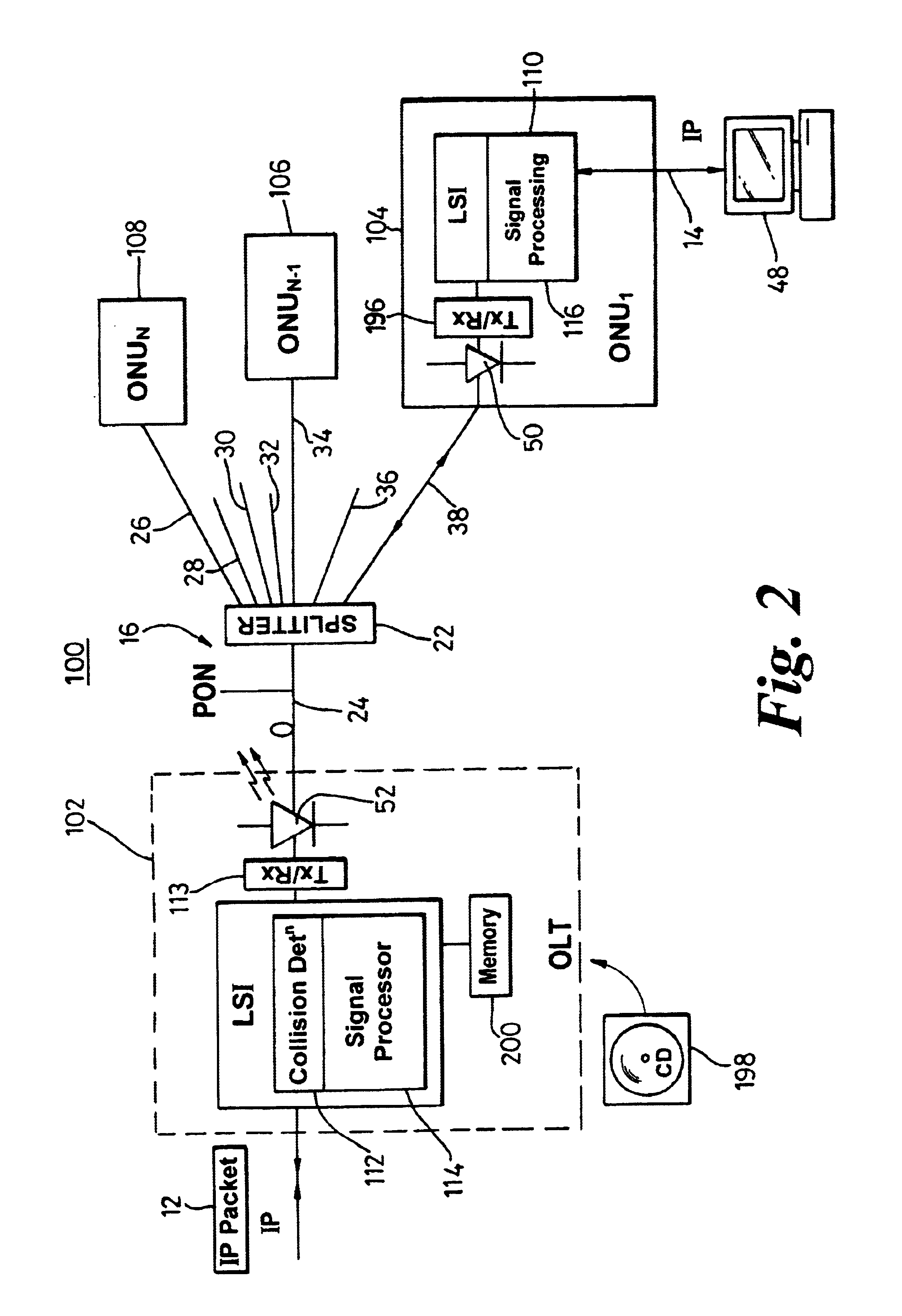
A system (100) to enable the transfer of Internet protocol (IP) format data (12, 14) over a point-to-multipoint passive optical network (PON, 16) is illustrated in FIG. 2. An exchange (102) is connected to a plurality of outstations (104-108) via an optical communication resource (24, 26-38) including a passive optical splitter (22) providing isolation to individual outstations. Media access control of the plurality of outstations is administered by the exchange (102), with collision detection logic (112) in the exchange determining collision (158) of Internet protocol (IP) encoded data communicated thereto through the PON (16). The IP encoded data realises a transport mechanism through the PON. Each of the plurality of outstations (104-108) and the exchange (102) is adapted to pass data in an IP format to and from the optical communication resource such that IP encoded data is transported, in use, directly between the outstation and the exchange.
Owner:RPX CLEARINGHOUSE
Subscriber authentication method for passive optical network
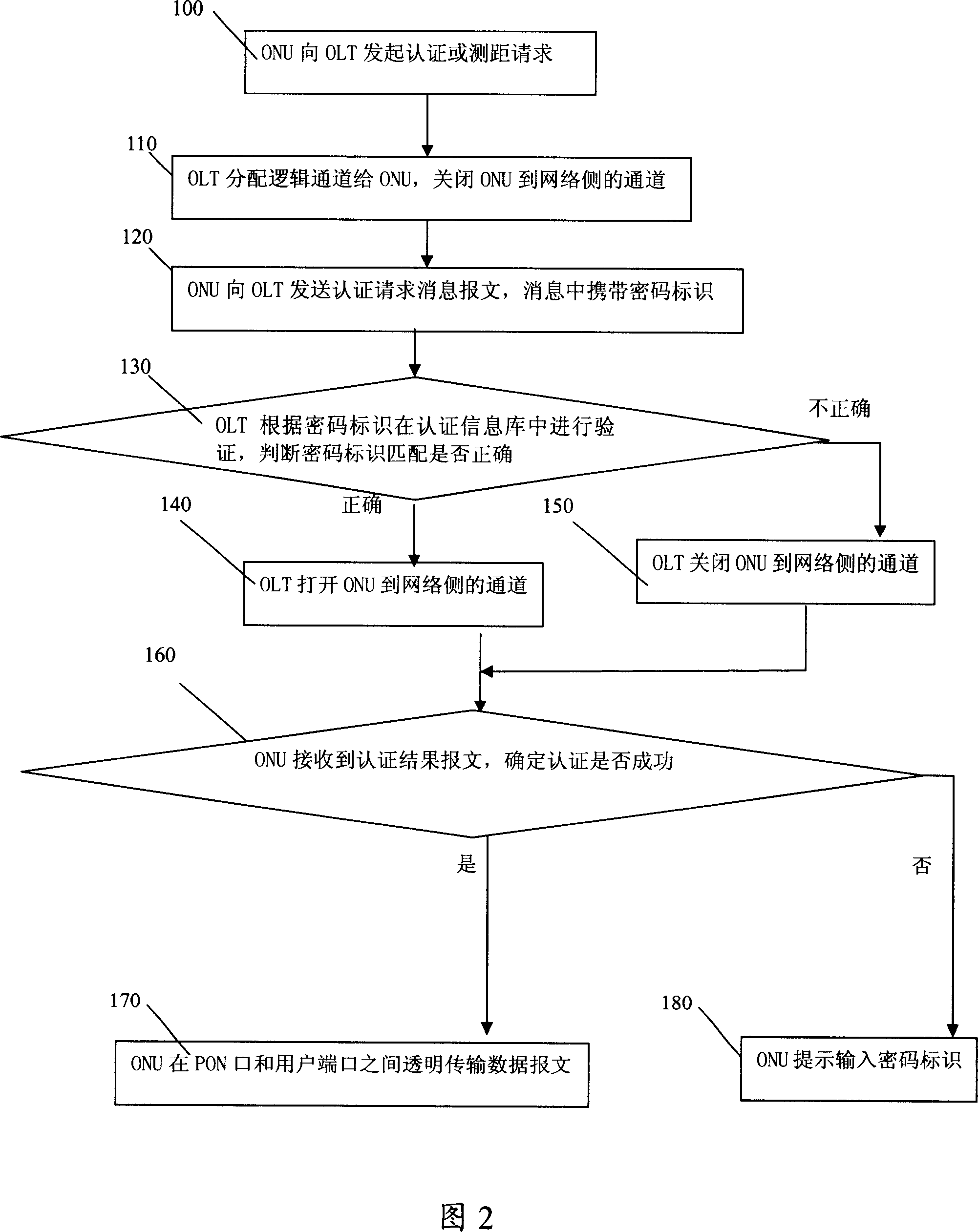
InactiveCN1968089ASimple and convenient managementEasy maintenanceUser identity/authority verificationData switching networksAccess networkPassword
The invention relates to a user identification method of inactive light network, wherein said method comprises that: light network unit ONU initializes register or ranging request to the light terminal OLT; OLT distributes relative logic channel to ONU, and sets the ONU mark as registered but not identified state, closing the channel from ONU to network; ONU initializes user identification request to the OLT, with carried password mark; OLT based on said password mark identifies, to switch the channel from ONU to network. The invention can improve user safety, while new ONU can access network via password mark.
Owner:HUAWEI TECH CO LTD
Dynamic bandwidth allocation device and method of passive optical network
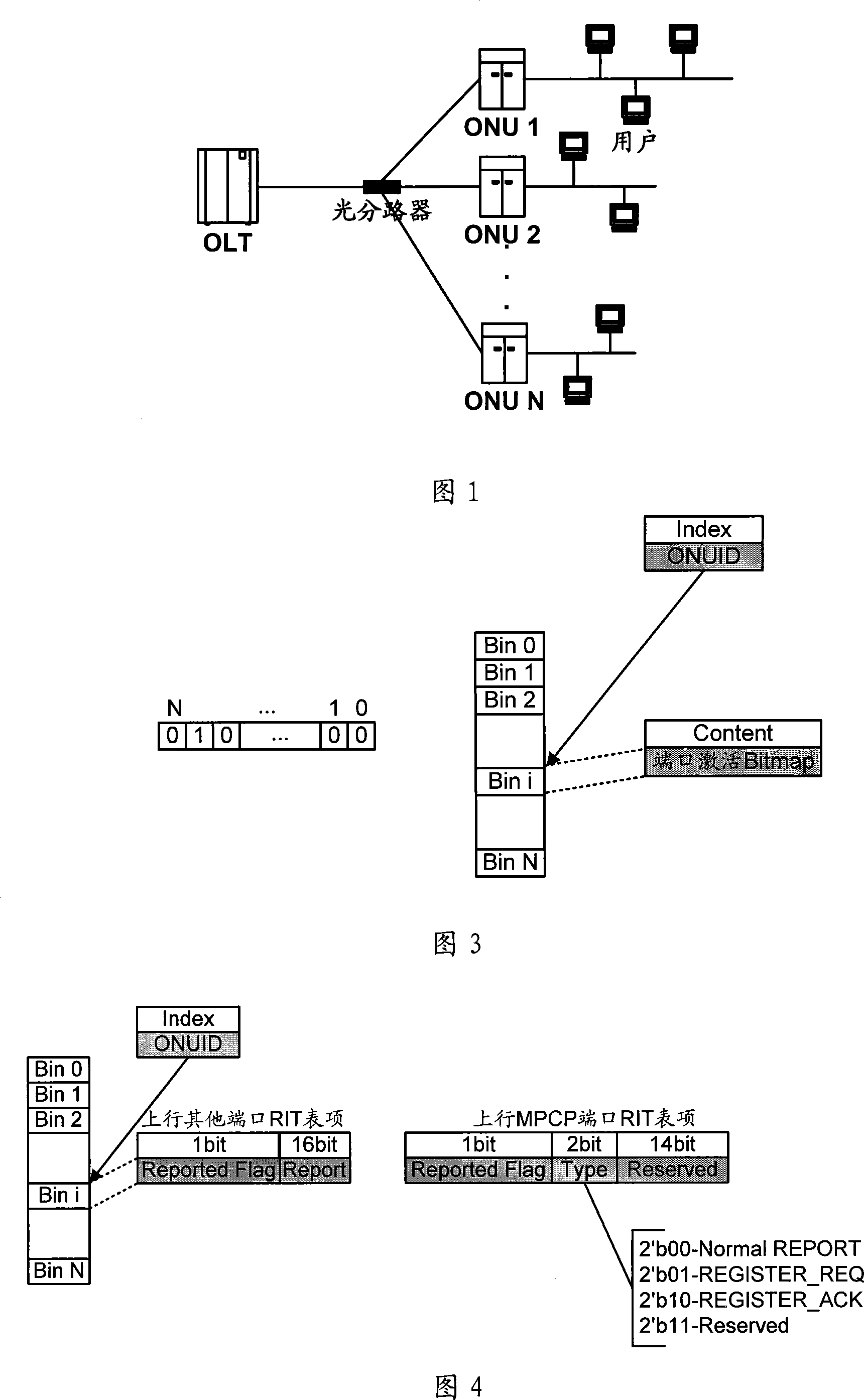
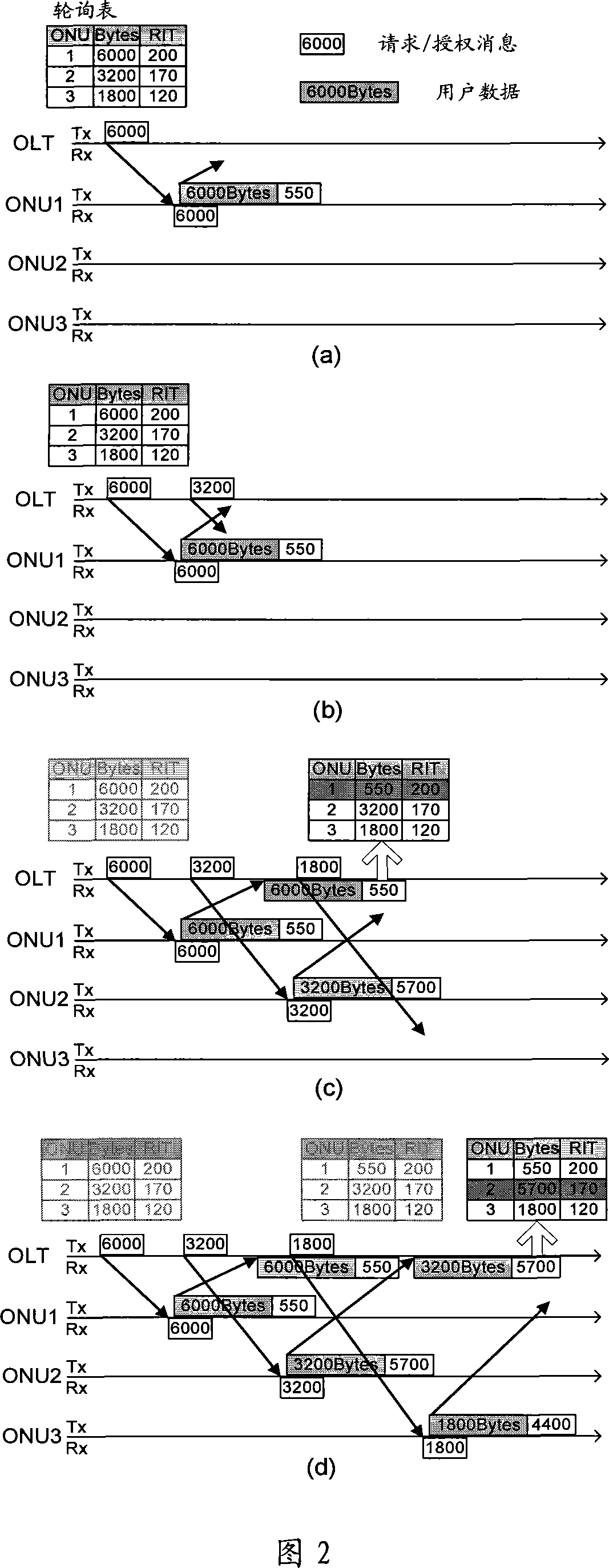
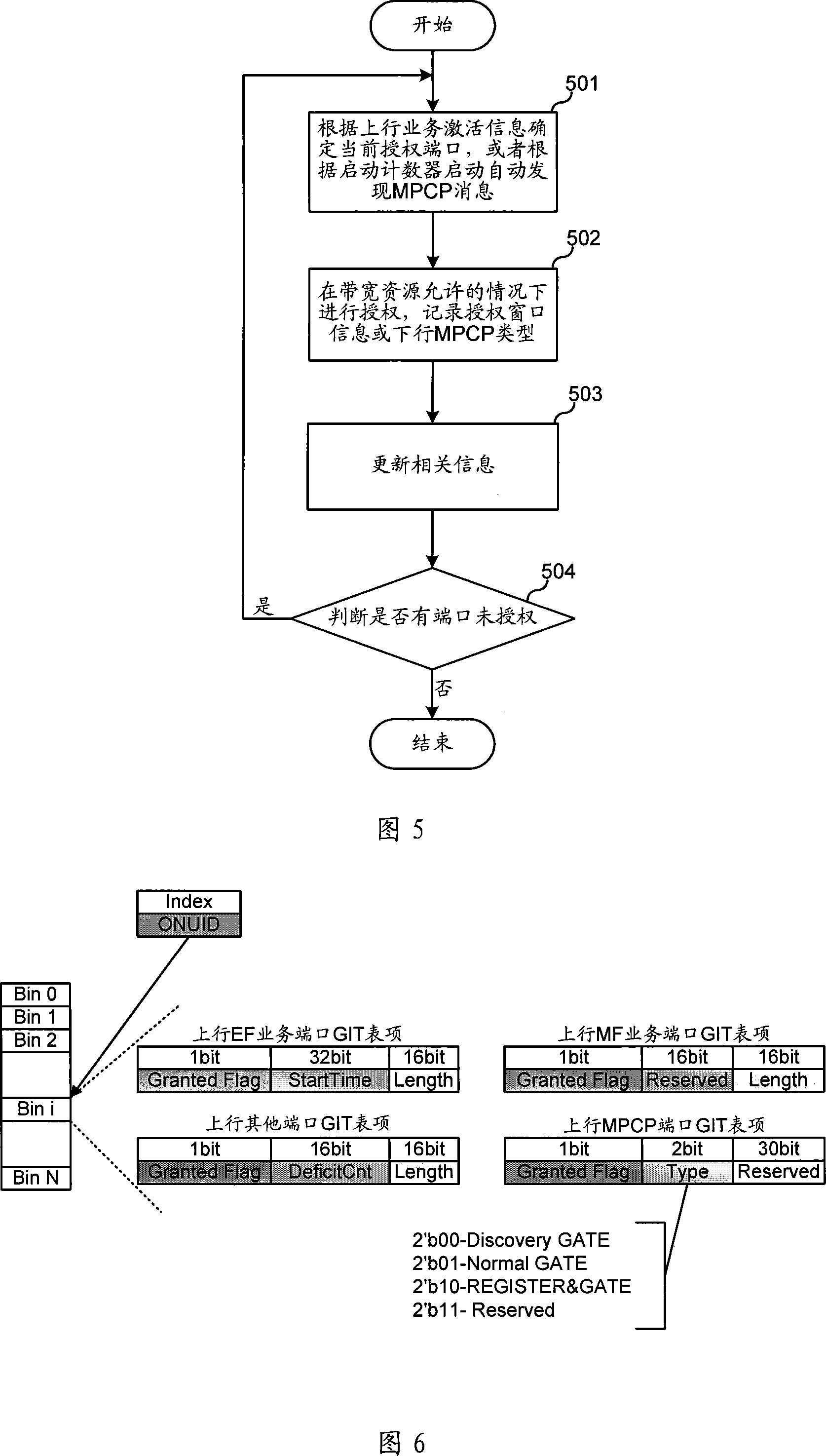
ActiveCN101087238AIncrease profitEfficient use ofMultiplex system selection arrangementsStore-and-forward switching systemsService flowOptical communication
The invention relates to optical communication field, discloses a collating device and method for dynamic bandwidth in source-free optical network, and the distribution method for dynamic bandwidth is transparent, which can satisfy the requirement for different service, improve the utilization rate of bandwidth, realize the fair distribution for bandwidth, good haleness, real time, and can distribute bandwidth for different port, and support to release offline bandwidth of ONU. The distributing device for dynamic bandwidth in source-free optical network includes ascending service active fiber network unit bit-mapping register, ascending service active port bit-mapping table, ascending virtual media accessing control sub-layer information table, descending virtual media accessing control sub-layer authorization information table; said distributing device for dynamic bandwidth, consults said fiber network unit active information, port active information and length information of sending data, according to preset priority of different service, process the service flow according to priority according to preset priority, and distributes the dynamic bandwidth for ports.
Owner:HUAWEI TECH CO LTD
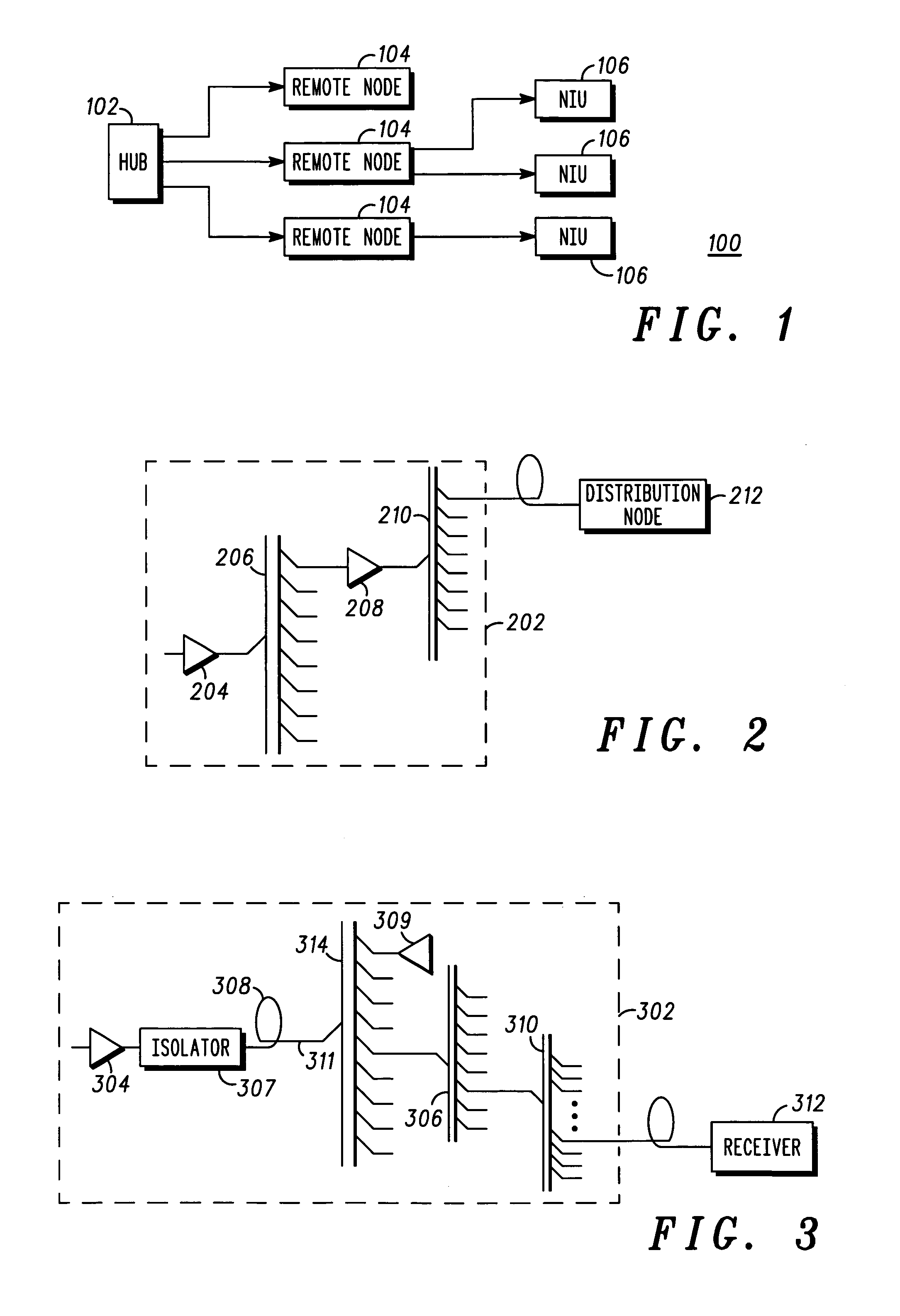
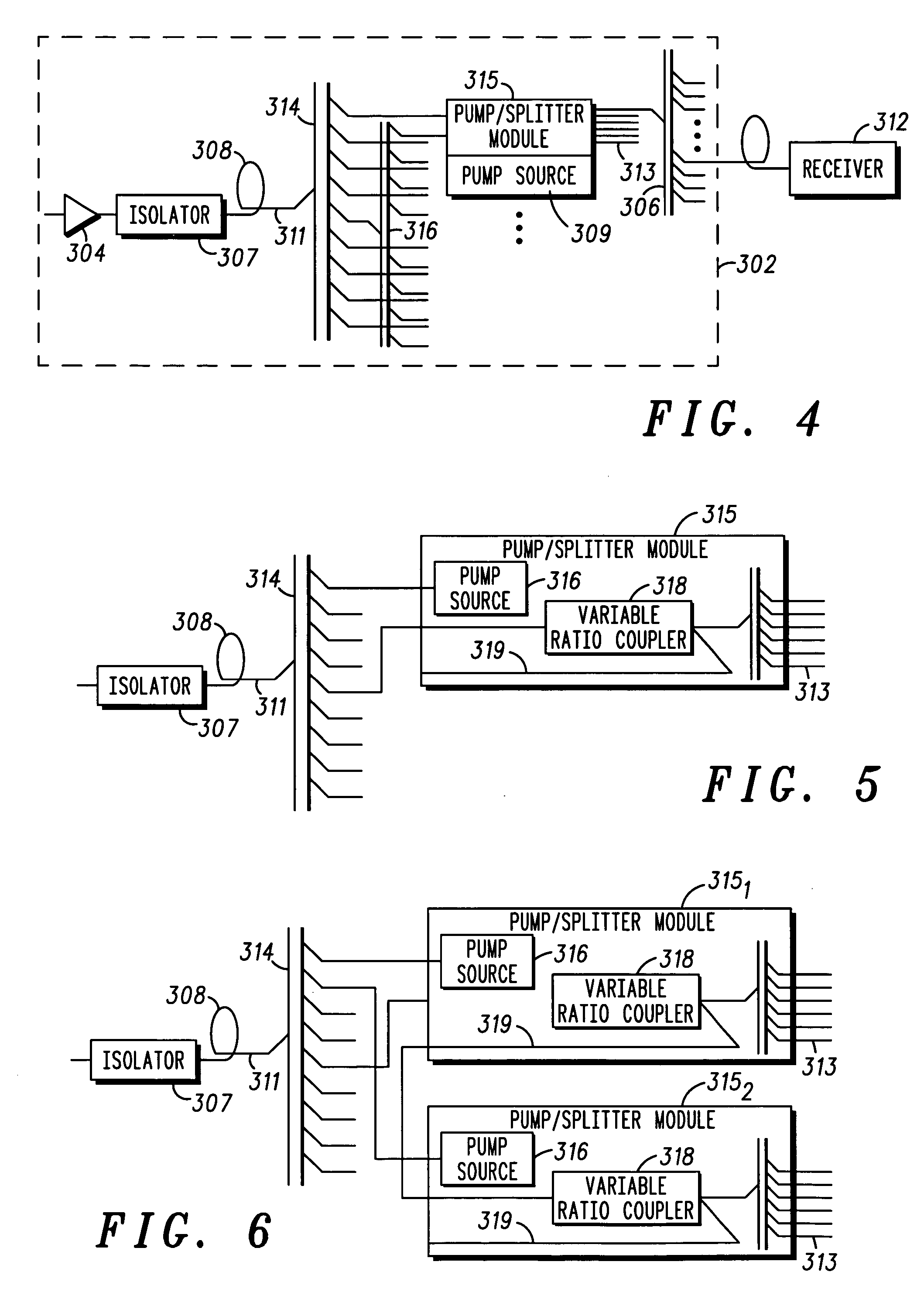
Hub for a passive optical network hub
ActiveUS20050036786A1Wavelength-division multiplex systemsCoupling light guidesOptical pumpingRare earth
A hub for use in a passive optical network (PON) includes a transmission fiber on which an information-bearing optical signal is received, a double-cladded, rare-earth doped fiber located along the transmission fiber for imparting gain to the information-bearing optical signal, and a combiner having an output coupled to the transmission fiber and a plurality of inputs. The output is coupled to the transmission fiber such that optical energy at pump energy wavelengths but not signal wavelengths are communicated therebetween. At least one pump source is optically coupled to one of the inputs of the combiner for providing optical pump energy to the double-cladded, rare-earth doped fiber. An optical splitter is also provided. The optical splitter has an input coupled to the transmission fiber for receiving an amplified, information-bearing optical signal and a plurality of outputs for directing portions of the amplified, information-bearing optical signal to remote nodes in the PON.
Owner:GOOGLE TECH HLDG LLC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com