Patents
Literature
297 results about "DOCSIS" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
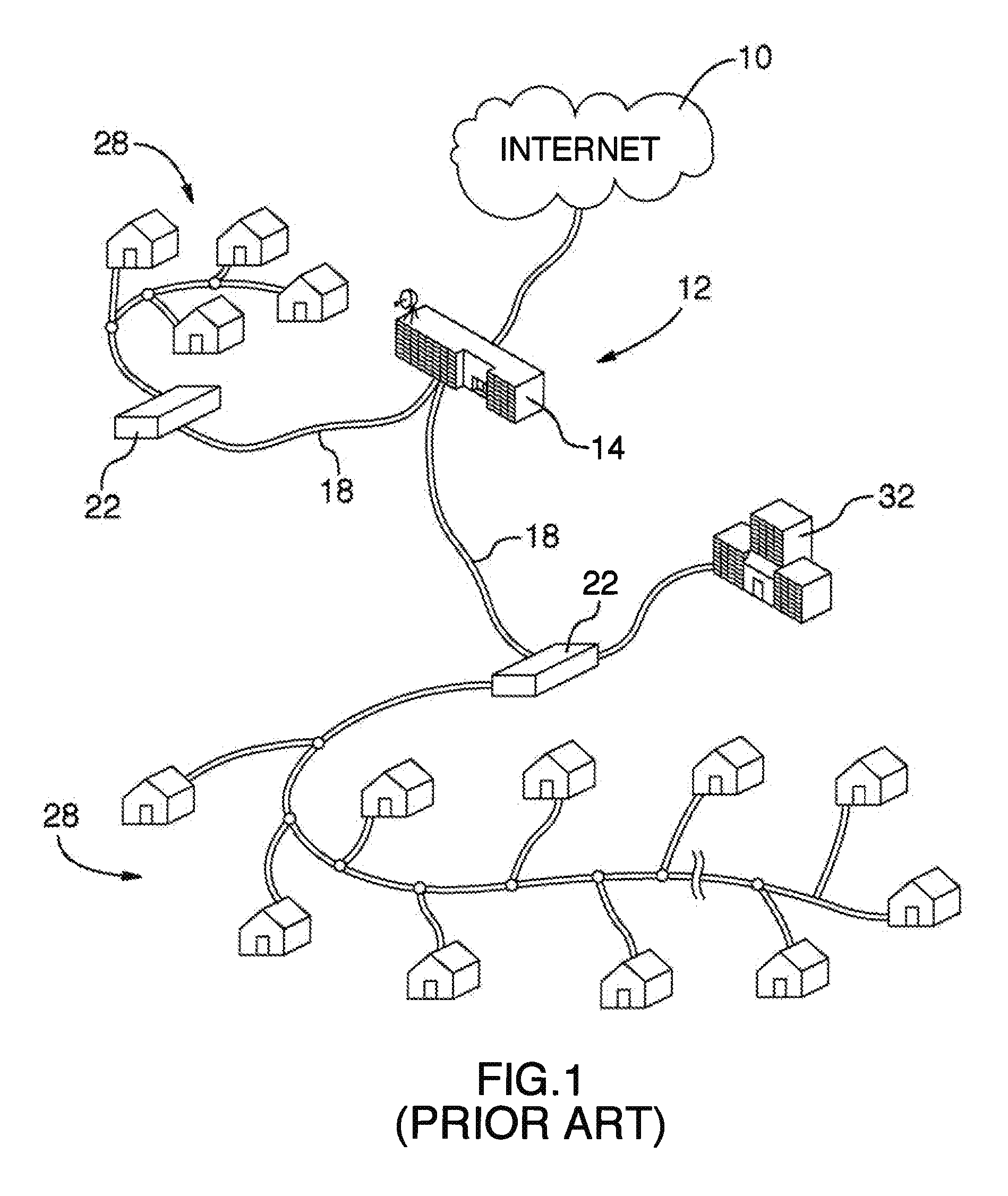
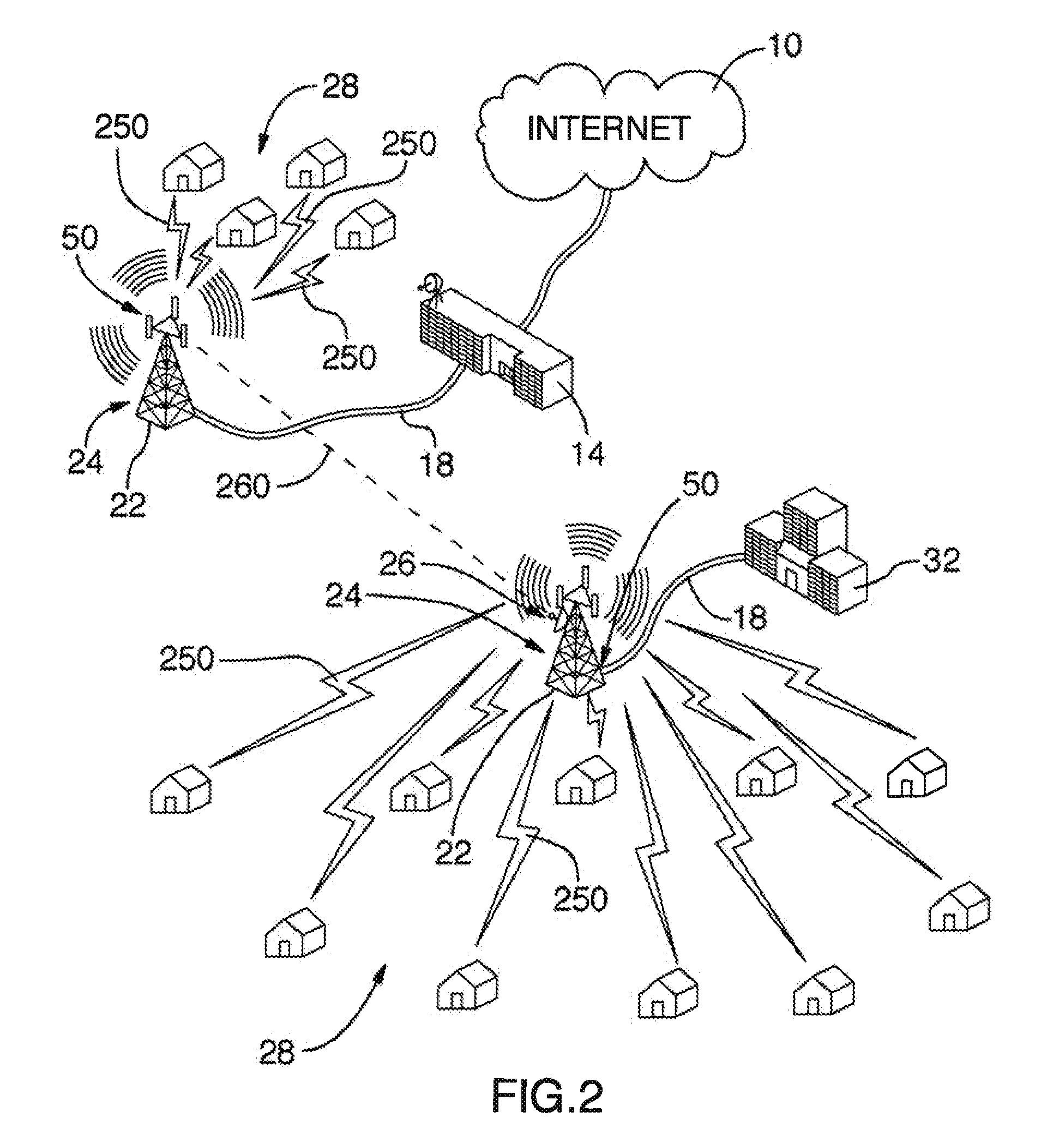
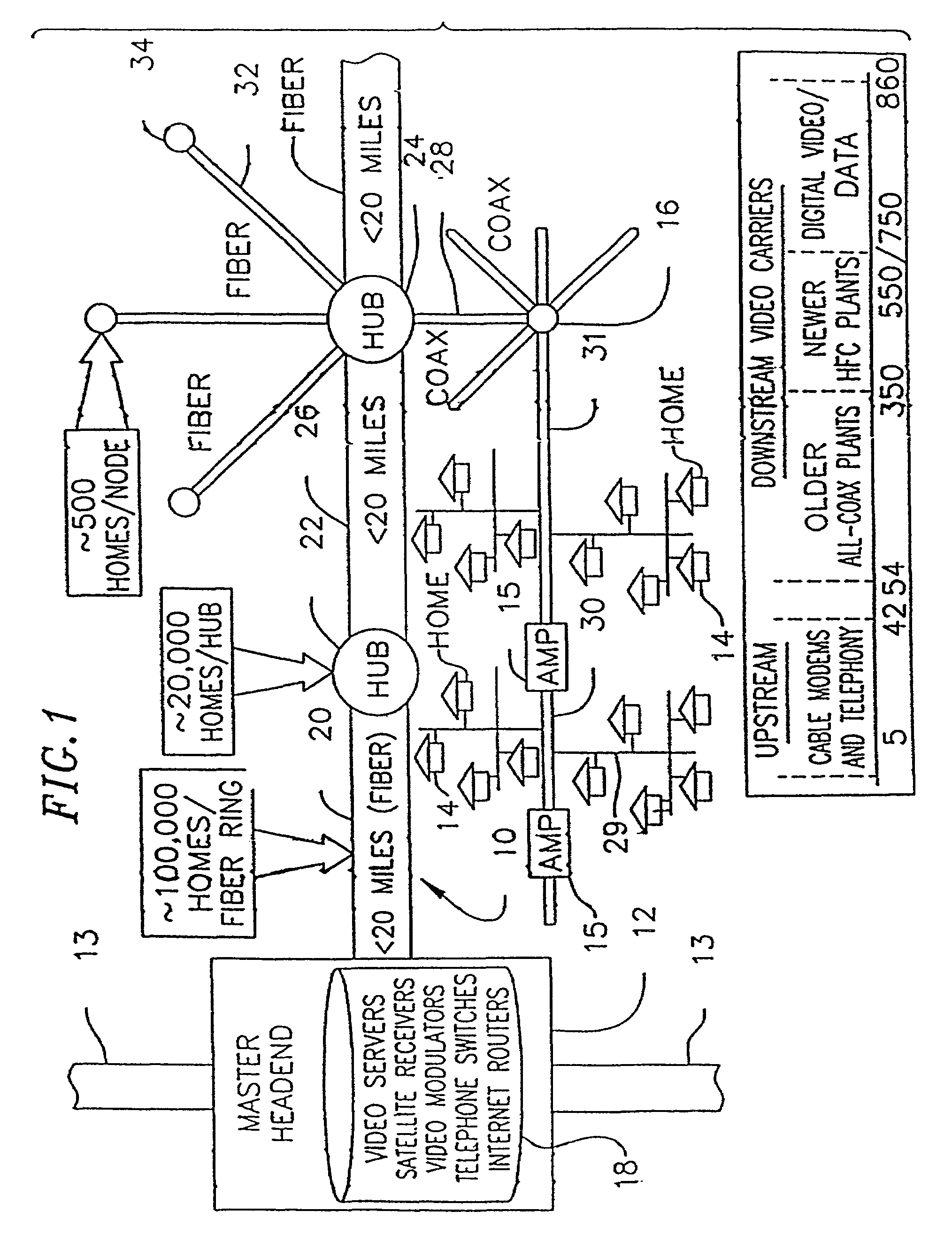
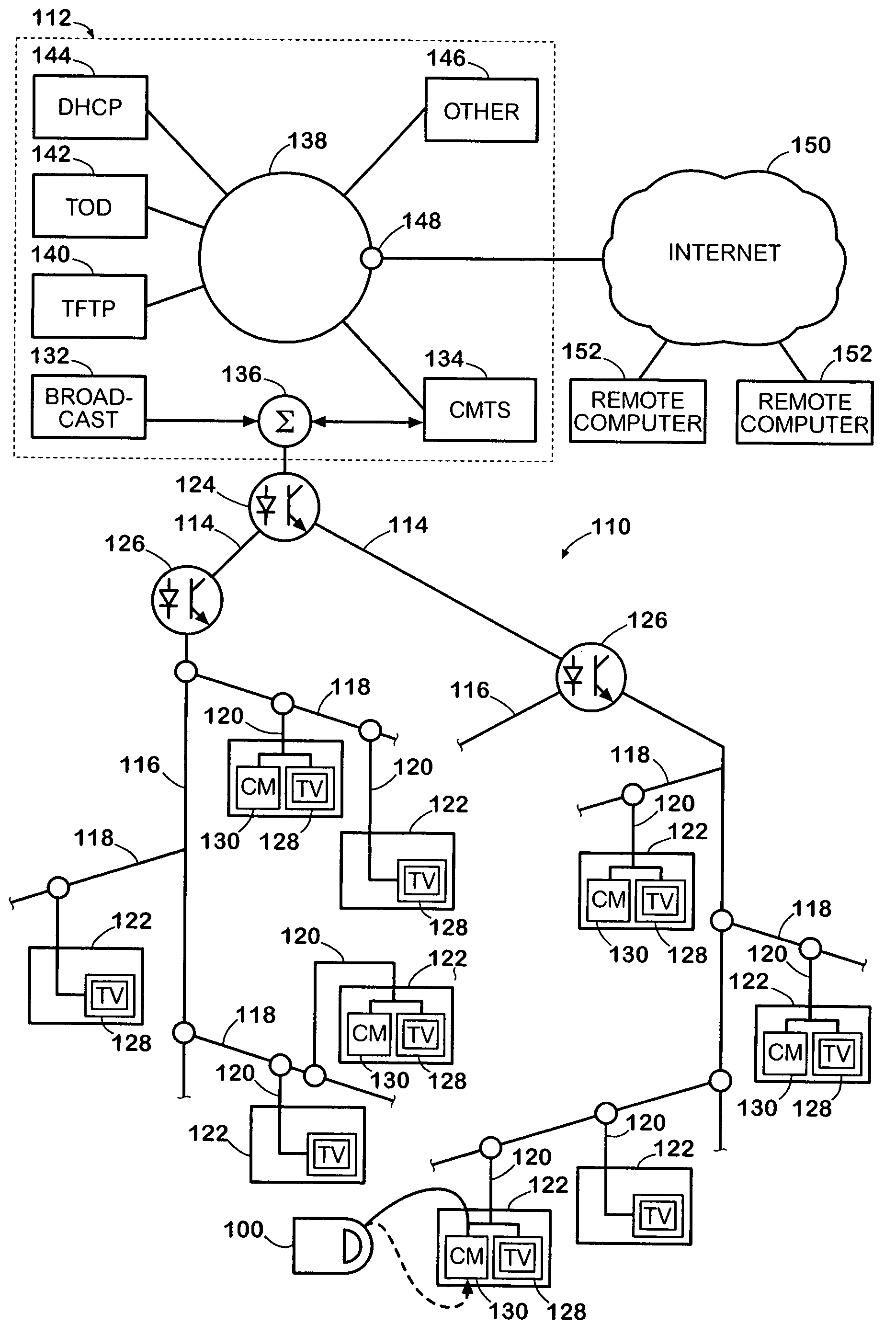
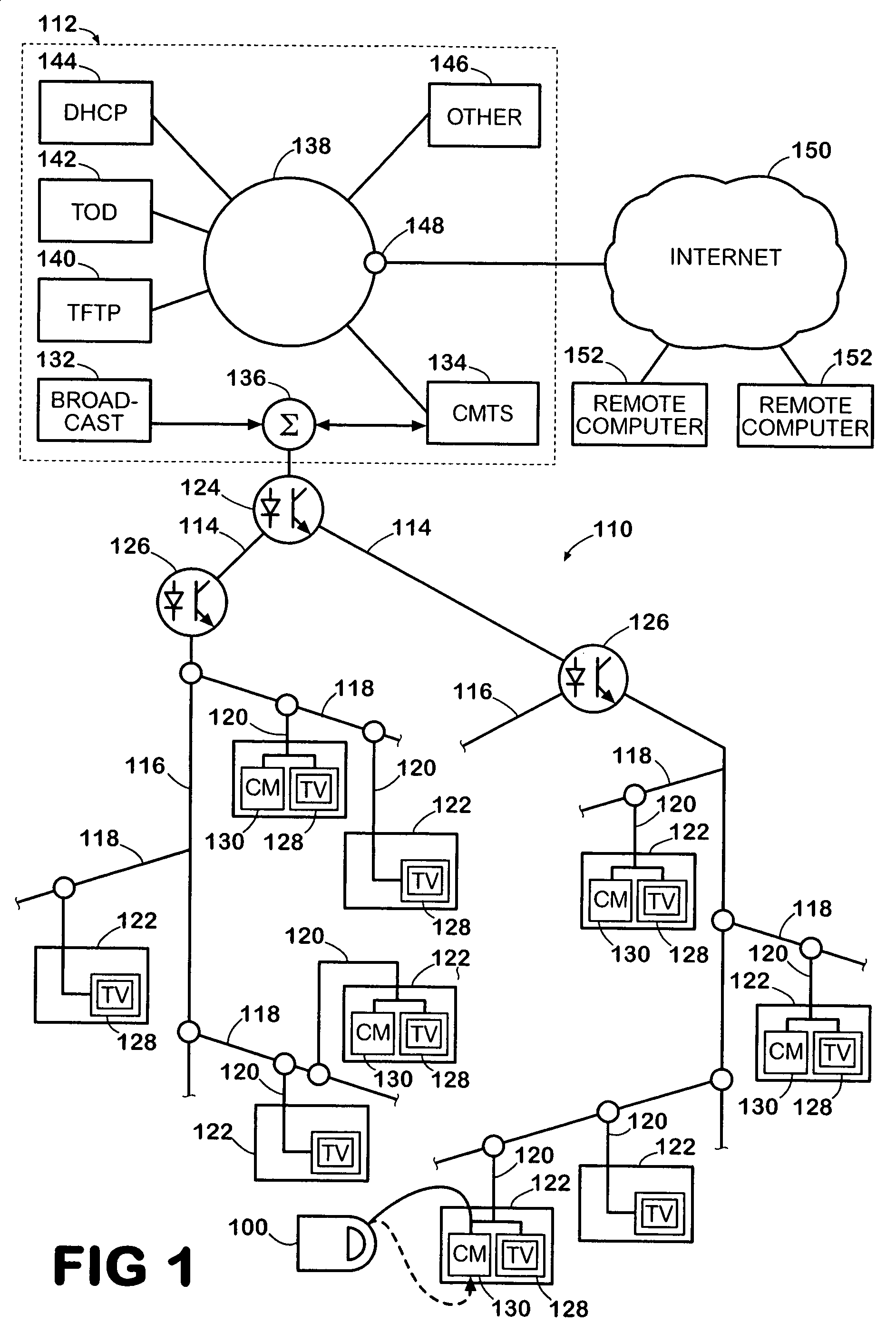
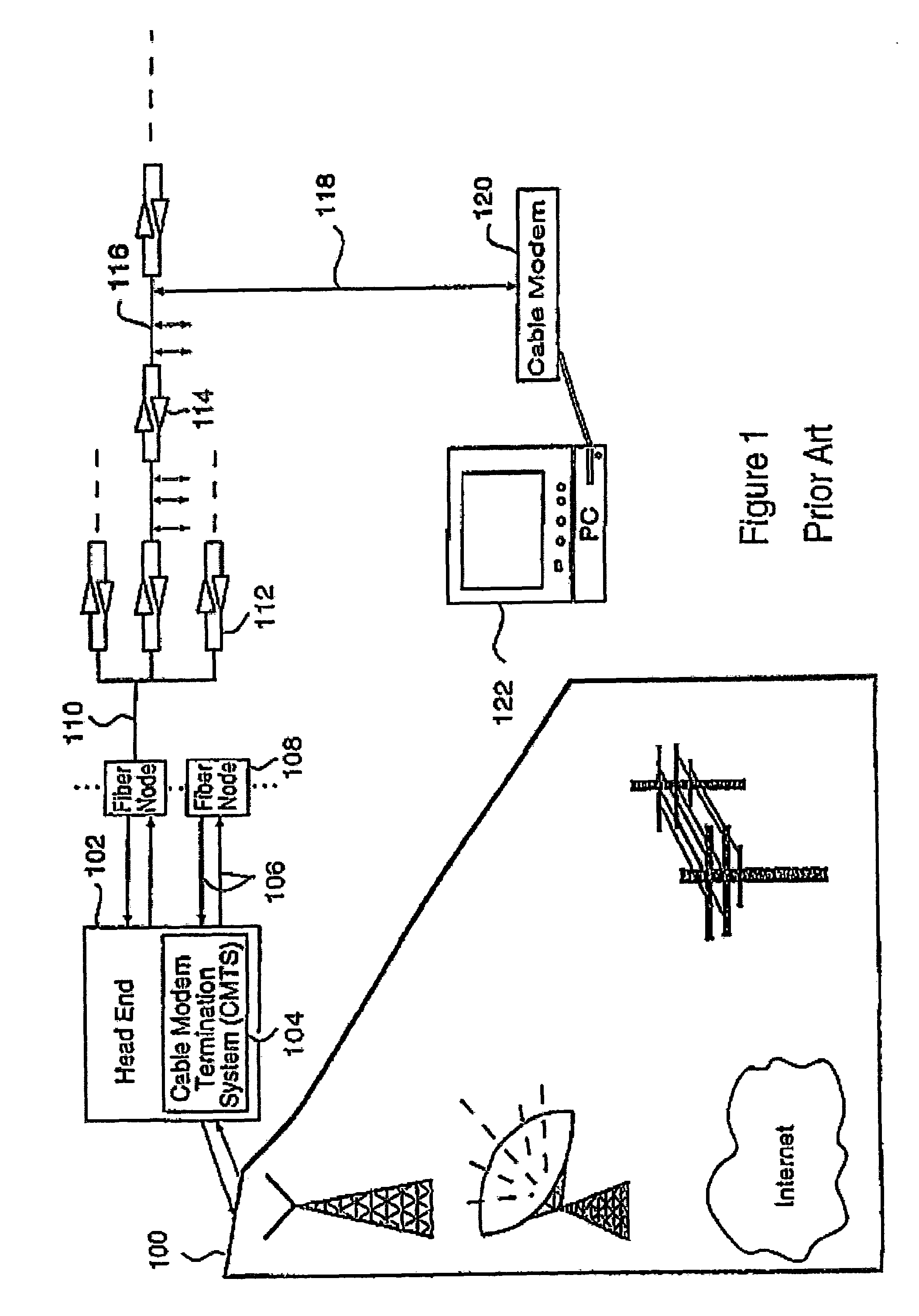
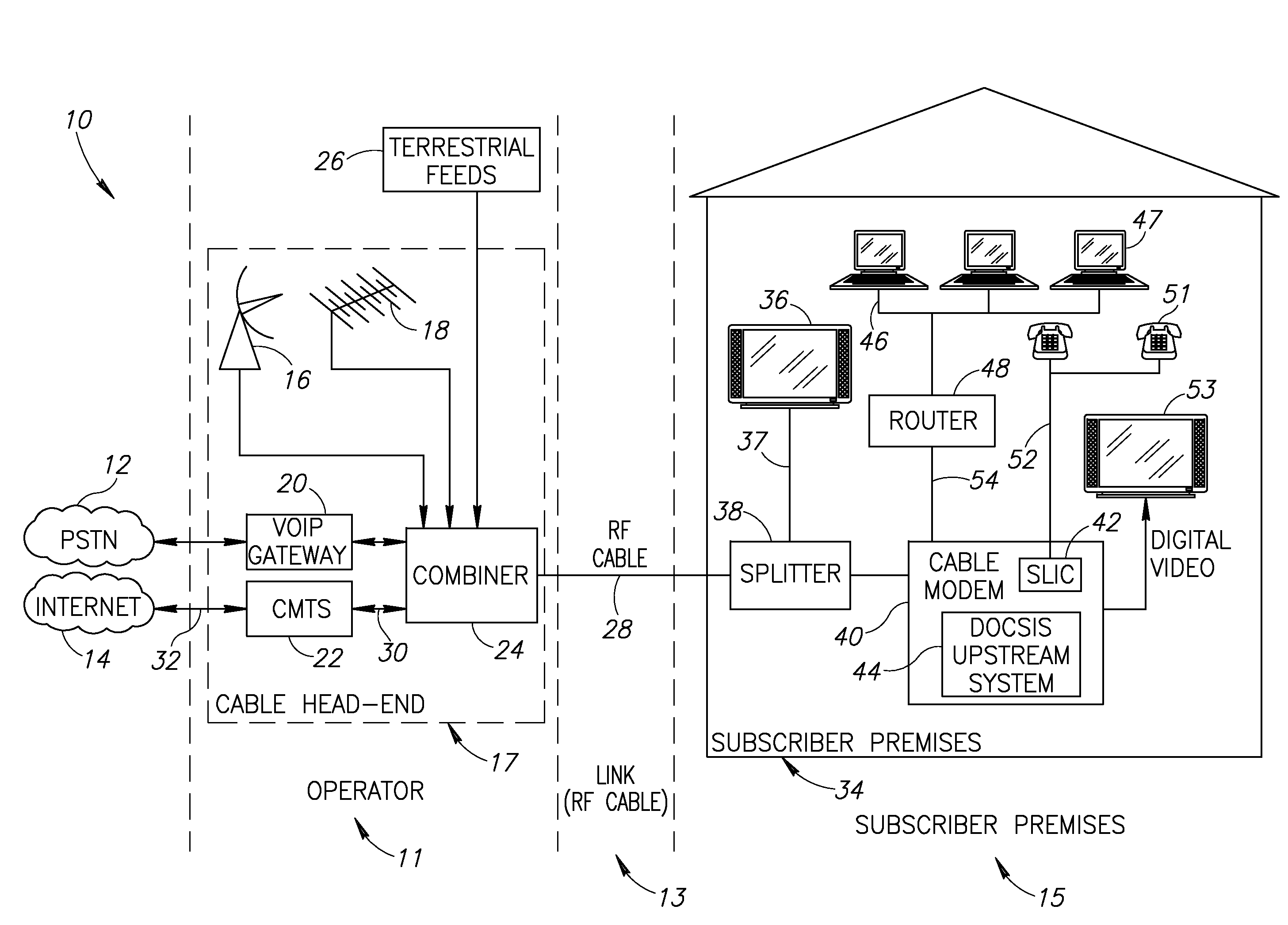
Data Over Cable Service Interface Specification (DOCSIS /ˈdɒksɪs/) is an international telecommunications standard that permits the addition of high-bandwidth data transfer to an existing cable television (CATV) system. It is used by many cable television operators to provide Internet access (see cable Internet) over their existing hybrid fiber-coaxial (HFC) infrastructure. The version numbers are sometimes prefixed with simply "D" instead of "DOCSIS" (e.g. D3 for DOCSIS 3).
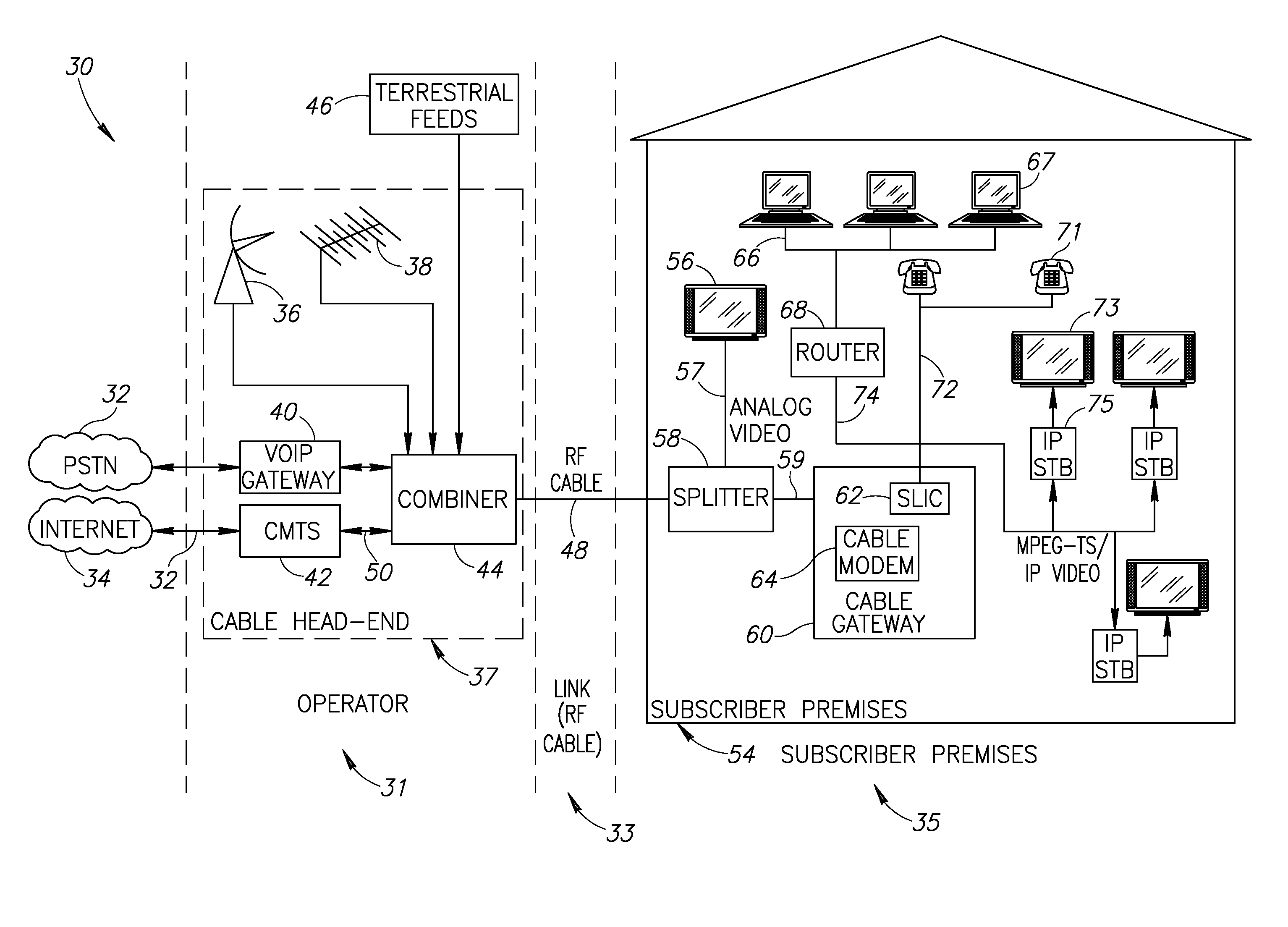
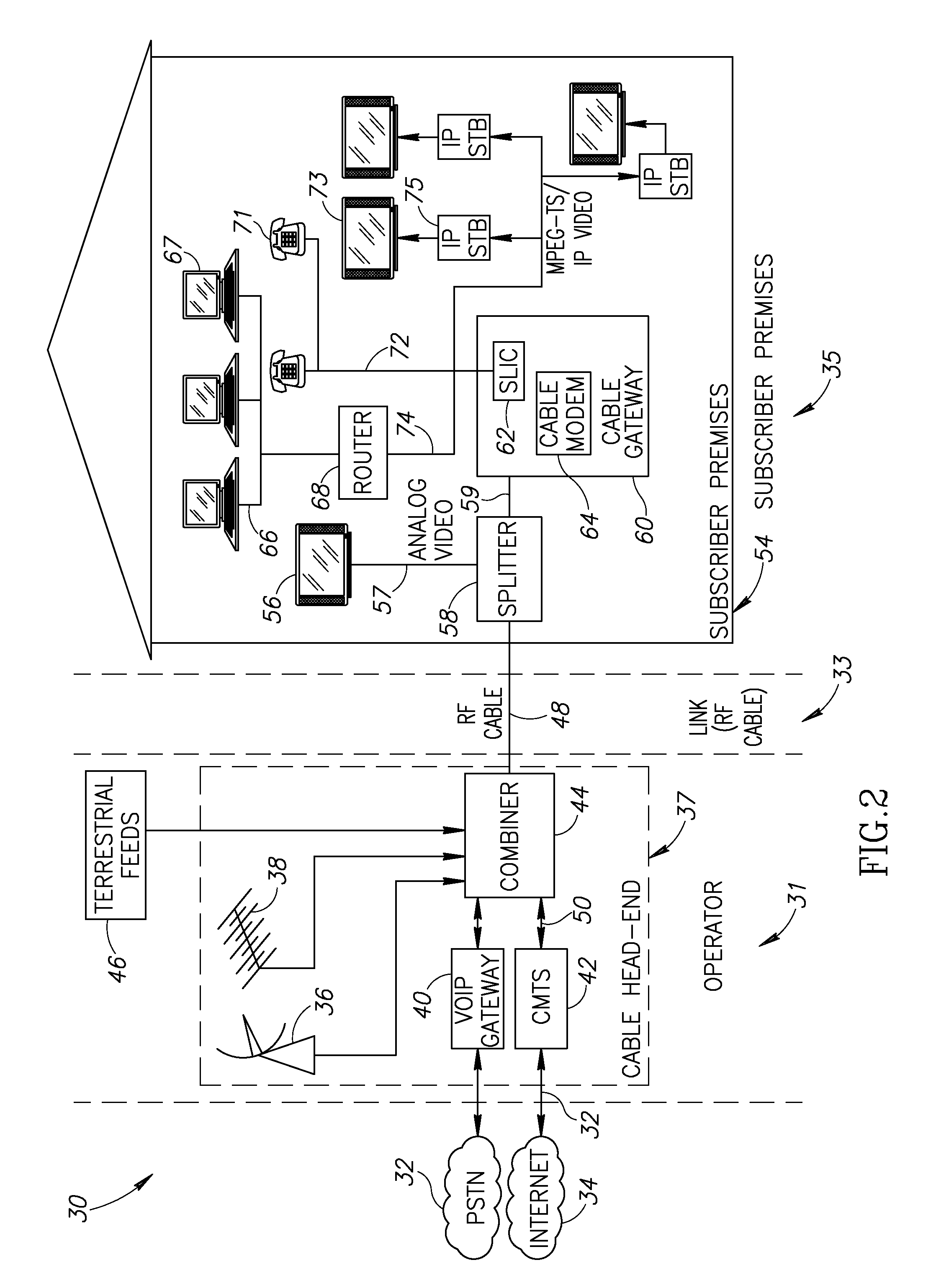
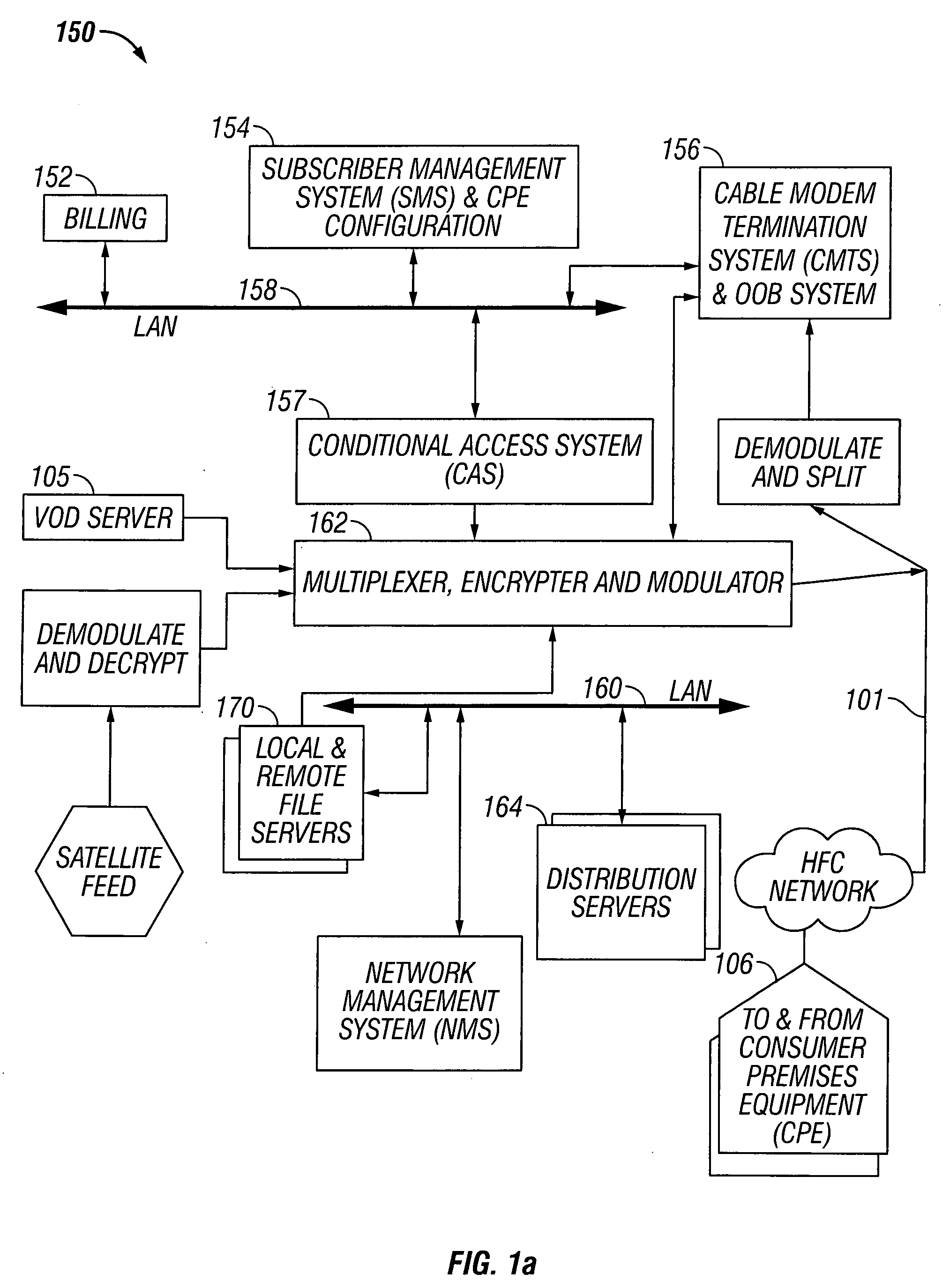
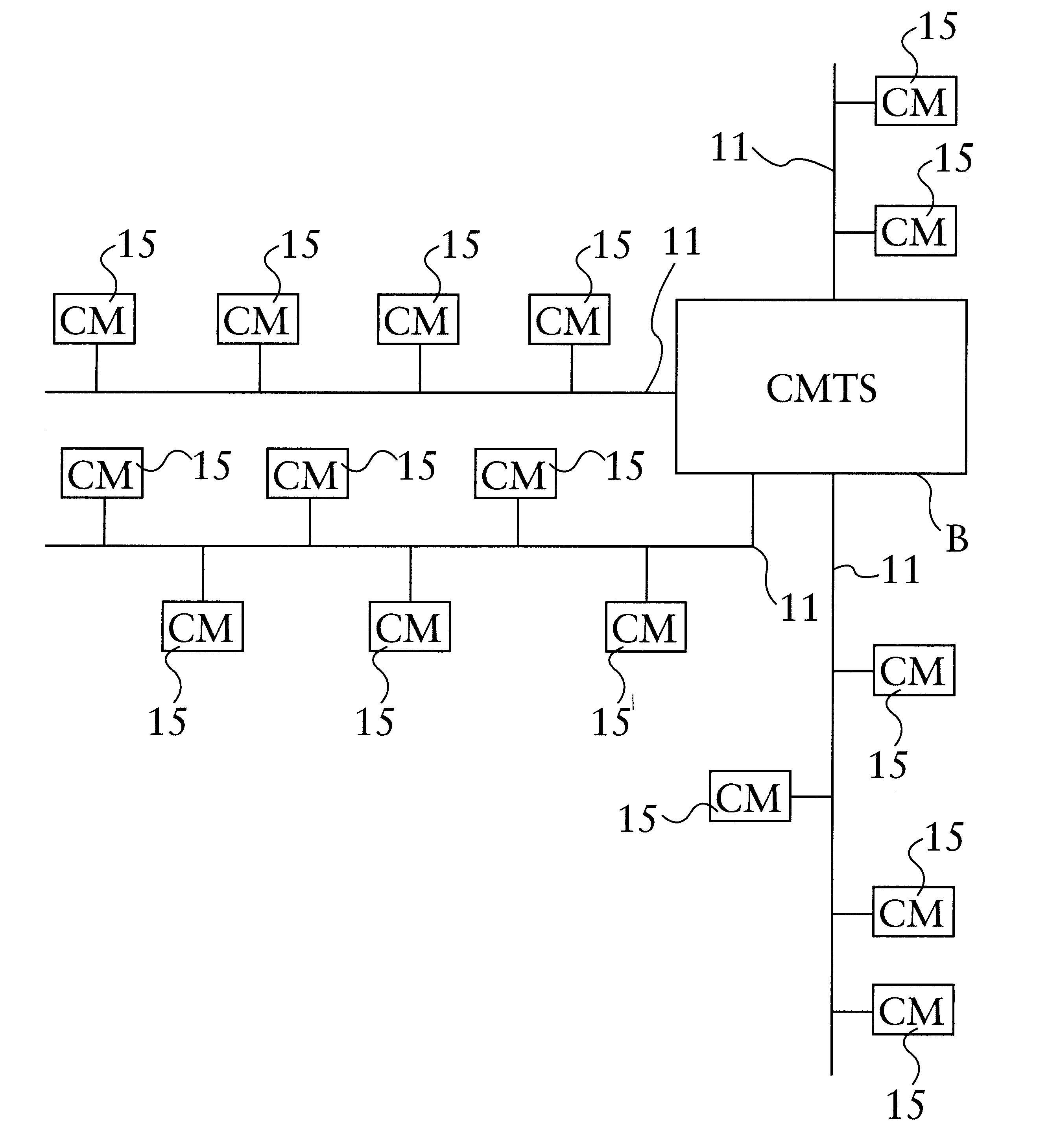
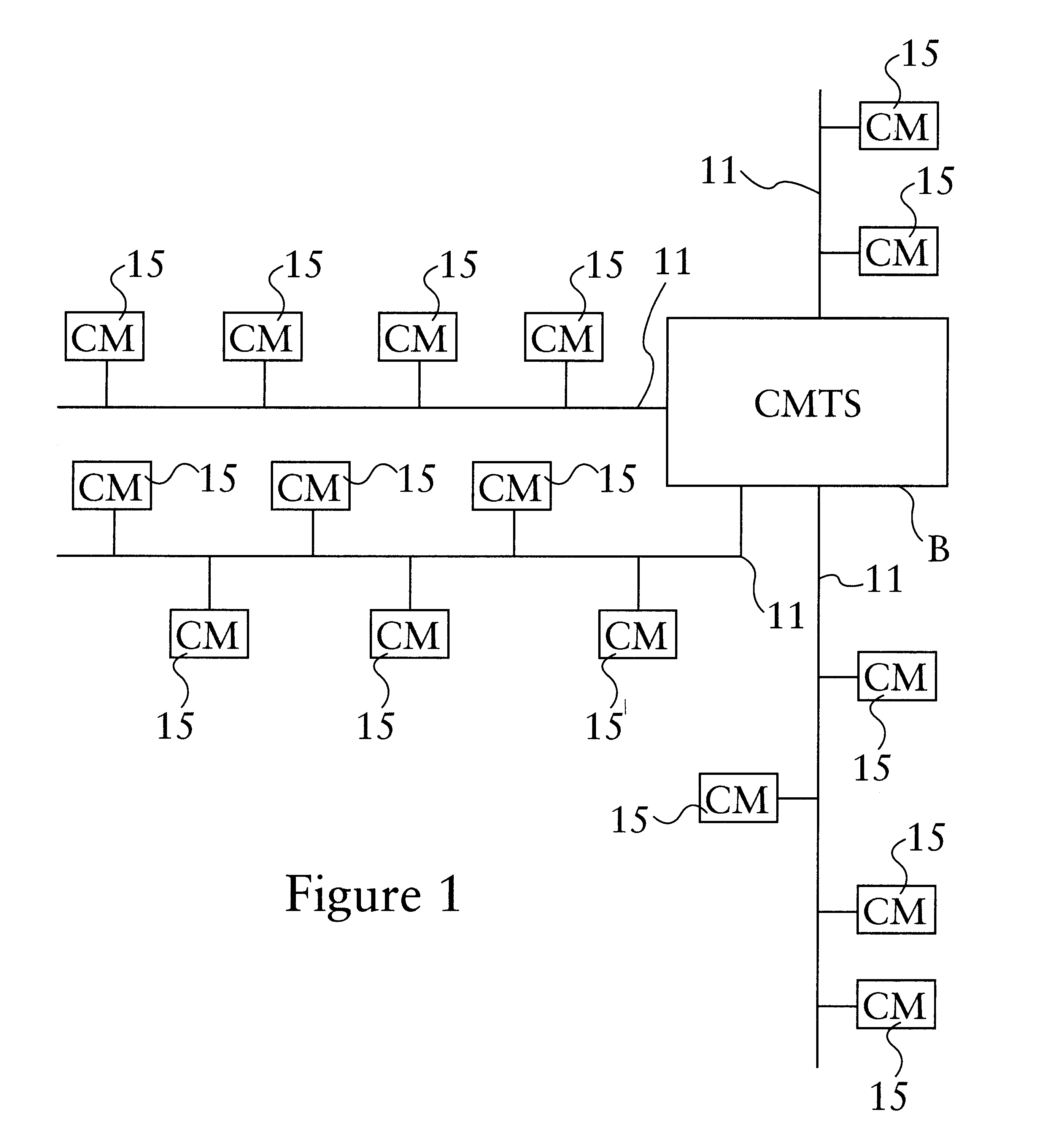
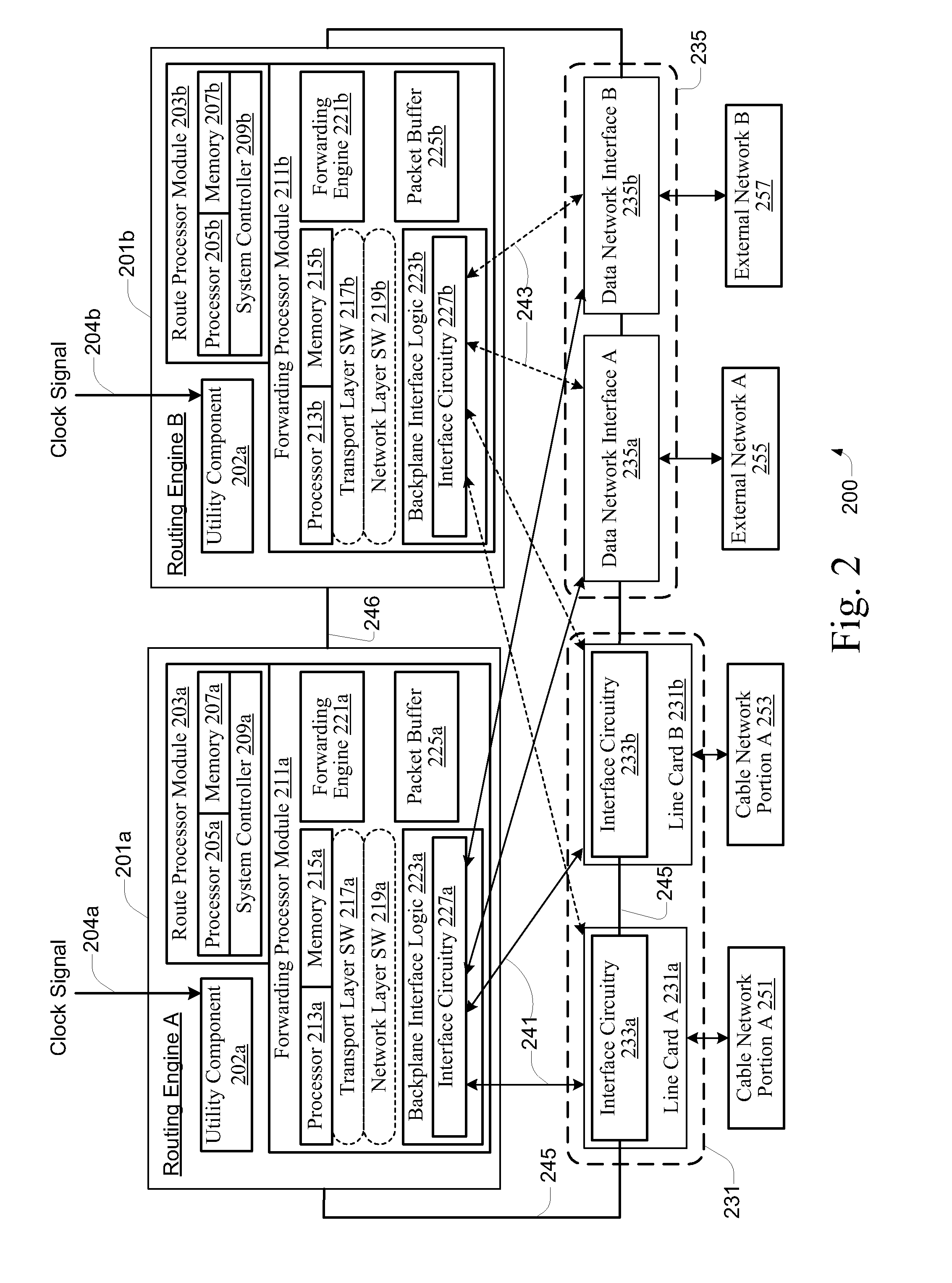
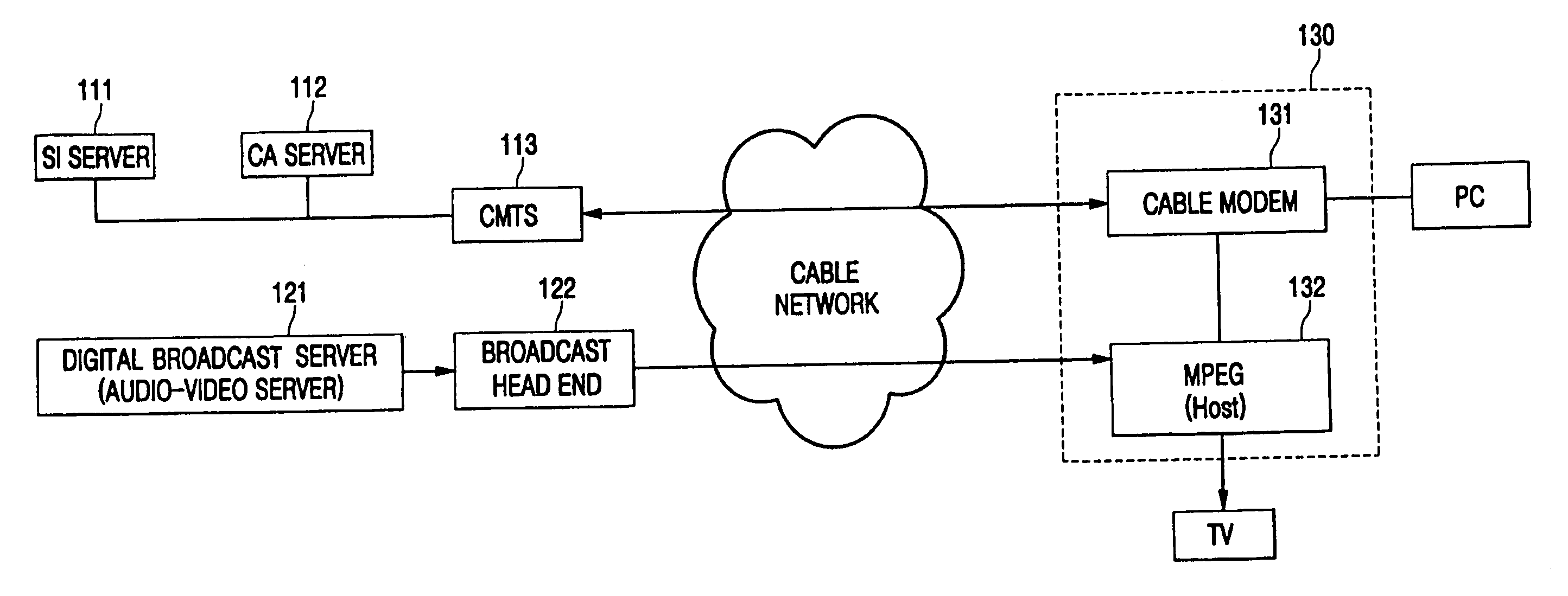
Hybrid mpeg/ip digital cable gateway device and architecture associated therewith
A novel cable gateway system and architecture incorporating a hybrid digital video transceiver. The digital cable system architecture combines reception of legacy video such as MPEG-TS based DVB-C streams with that of original IP video over DOCSIS channels. The system comprises a hybrid DVB / IP cable gateway STB capable of receiving both legacy DVB-C video and original IP video streams. The cable gateway device performs the front-end functionality (including QAM receiver, tuner and broadband connection) while the back-end functionality of video decoding and display is performed by one or more standard IP-STBs connected to the cable gateway device over a network (e.g., home LAN). Legacy MPEG-TS based DVB-C video is captured and encapsulated into packets for distribution over the network to the IP-STBs. The cable gateway distributes the original IP video received over the CATV source and the encapsulated legacy video as video over IP packets over the network.
Owner:INTEL CORP
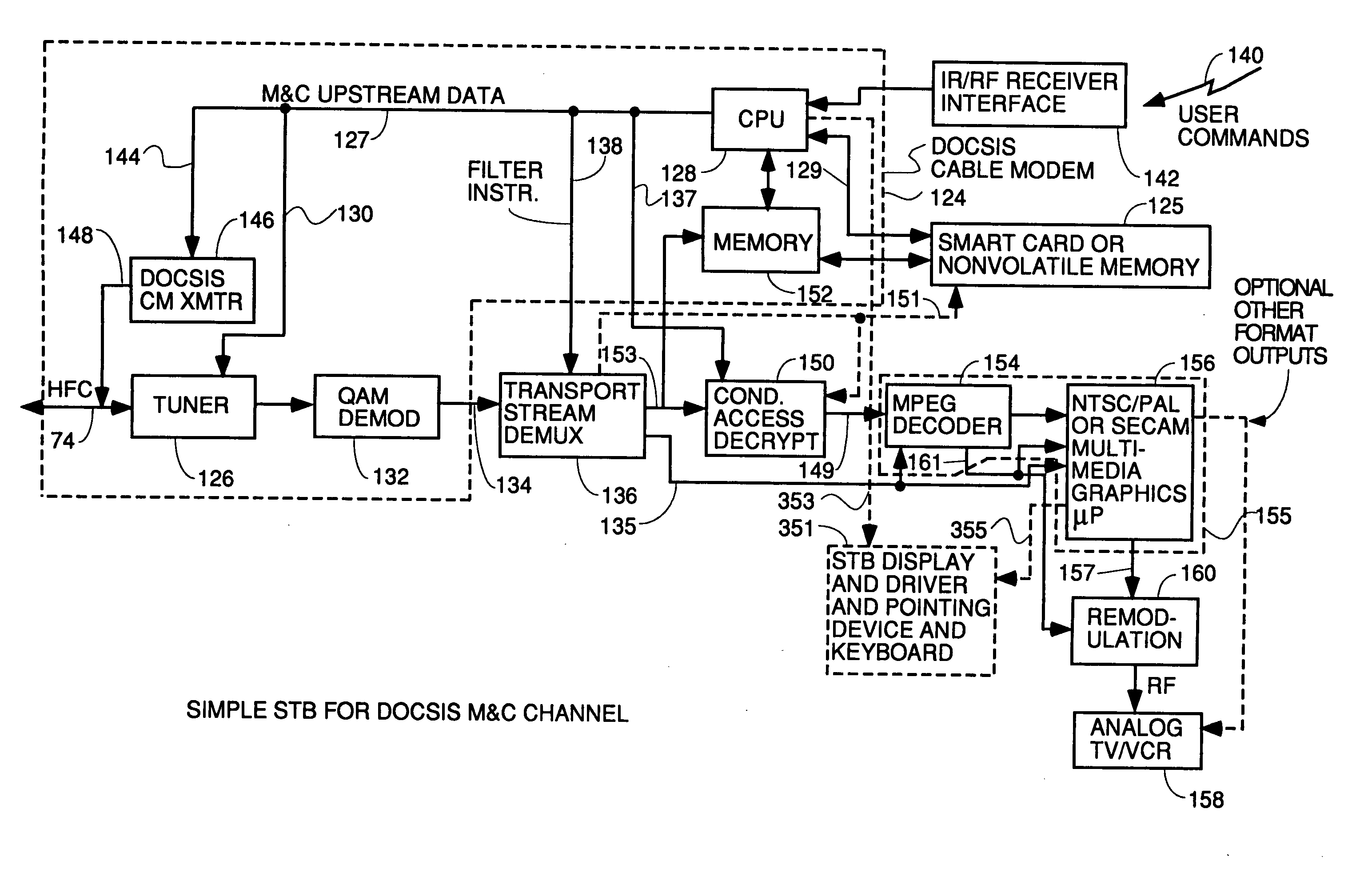
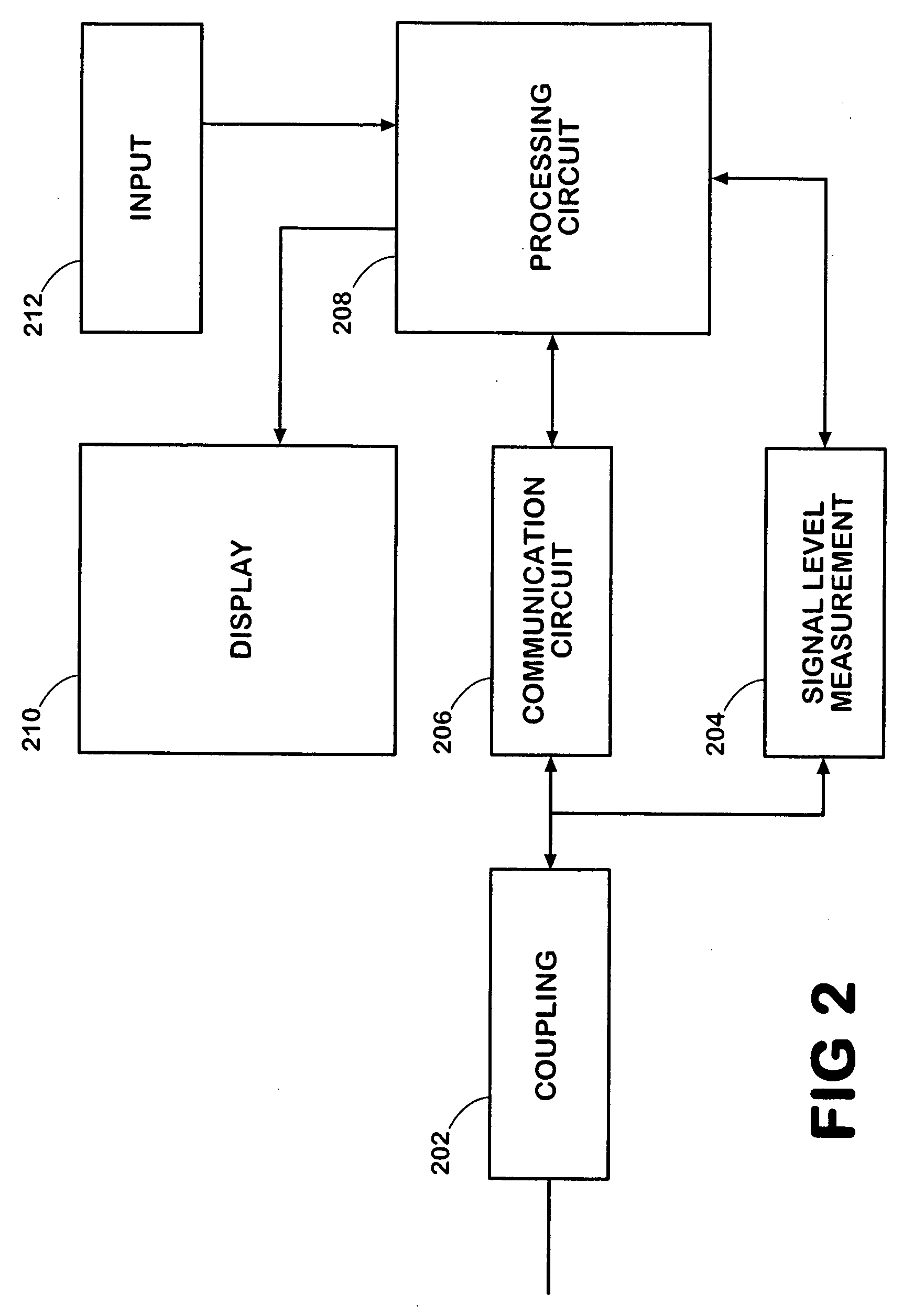
Thin DOCSIS in-band management for interactive HFC service delivery
InactiveUS20040181800A1Simple processLess-expensive to buildAnalogue secracy/subscription systemsTwo-way working systemsModem deviceConditional access
Circuitry and processes carried out thereby are disclosed for implementing simple single tuner set top box decoders which do not require a separate tuner for an out of band management and control channel. Removable smart card conditional access circuitry and replaceable modules having decoding circuitry for different compression schemes and encoding circuitry for different format television circuits is disclosed. An embodiment with a single tuner and a full DOCSIS compatible modem which can interface to personal computers, etc. is also disclosed to make the set top box a simple, inexpensive home gateway is also disclosed.
Owner:TERAYON COMM SYST
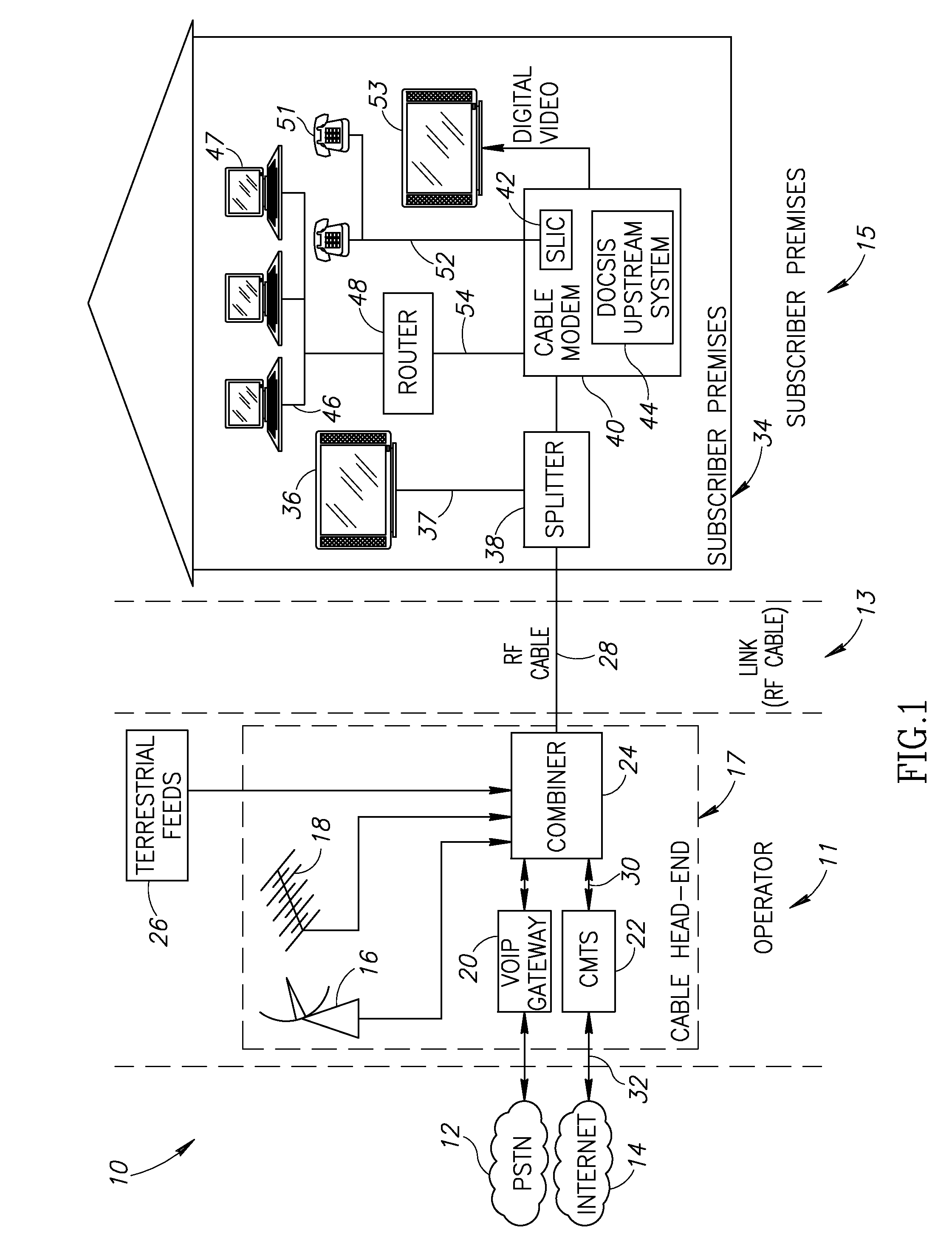
Premises gateway apparatus and methods for use in a content-based network
ActiveUS20080313691A1Satisfies needColor television signals processingNetwork topologiesDigital videoComputer network
Apparatus and methods for premises gateway functions that integrate or unify functions typically distributed across multiple devices within a content-based network. In one embodiment, the out-of-band (OOB) signaling functionality normally provided in each of a set-top-box (STB) and digital video recorder (DVR) are unified into a common OOB (e.g., DOCSIS) capable premises gateway device, thereby obviating OOB tuners and related components from each device. In another variant, the premises gateway is adapted for all-IP operation, such as for use with IP-based computers and IP set-top boxes, etc. Fully unified variants are also disclosed, wherein the DVR and / or STB functions are physically integrated within the premises gateway.
Owner:TIME WARNER CABLE ENTERPRISES LLC
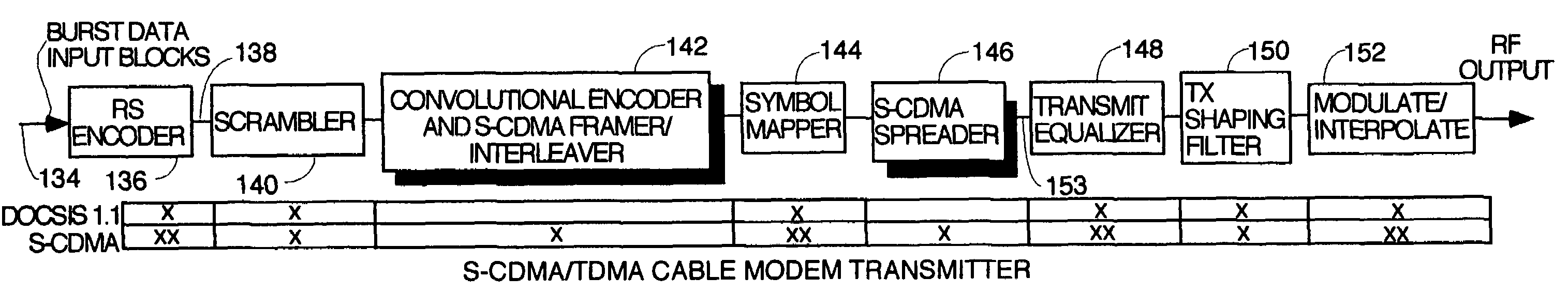
Head end receiver for digital data delivery systems using mixed mode SCDMA and TDMA multiplexing
InactiveUS7050419B2Improve performance(SNR) ratioTransmission control/equlisationMultiple modulation transmitter/receiver arrangementsDigital dataDOCSIS
A pipelined digital data receiver for a cable TV headend which is capable of receiving DOCSIS 1.0 or 1.1 or advanced PHY TDMA or SCDMA bursts having programmable symbol rates and programmable modulation types as well as a host of other burst parameters such at Trellis code modulation on or off, scrambling on or off, various values for Reed-Solomon T number and codeword length. The receiver has an RF section to filter and digitize incoming RF signals. It also has an input section to detect impulse noise and do match filtering and despread SCDMA bursts. A timing recovery section recovers the symbol clock and detects the start of bursts and collisions. A rotational amplifier and equalizer calculate and track gain, phase and frequency offsets and correct symbols and calculates equalization coefficients. A decoder section decodes TCM and non TCM bursts, and a Reed-Solomon decoder section reconstructs RS codewords and uses them to error correct the payload data.
Owner:GOOGLE TECH HLDG LLC
System for low noise aggregation in DOCSIS contention slots in a shared upstream receiver environment
InactiveUS20080170853A1Reduce the amount requiredMore noise tolerantBroadband local area networksTime-division multiplexLow noiseModem device
A cable modem termination system is disclosed with flexible mapping of upstreams to downstreams and flexible mapping of downstreams to optical nodes and optical nodes to upstream receivers and the ability to add singe upstreams or downstreams as needed for load balancing. Multiple downstreams can share the same upstream. Multiple receivers can be coupled to the same upstream. Monitoring of upstream performance for overperforming or underperforming modems can be carried out, and new upstreams with higher and / or lower throughtput can be created to service the overperformers and / or underperformers. Modems can be grouped into logical groups with different performance levels and serviced by different upstreams or different upstream logical channels on the same upstream physical channel. An upstream linecard with a digital crosspoint switch is disclosed with the switch operated during contention intervals to allow reception with or without aggregation of noise where multiple upstream share the same receiver.
Owner:GOOGLE TECH HLDG LLC
Active cable modem outside customer premises servicing multiple customer premises
InactiveUS7007296B2Affect numberAvoiding inefficiency of collisionTwo-way working systemsElectrical cable transmission adaptationDigital dataModem device
A signal distribution system to save on the cost of cable modems for cable TV headend operators who wish to deliver broadband digital data services, DSL, video-on-demand or POTS service over their HFC CATV delivery networks. All species within the genus have a shared cable modem and a filtration and combining circuit comprised of a plurality of diplexer filters or junction boxes or both which mix baseband packet data with analog CATV signals onto coax drop lines coupled to the various subscribers and connect POTS or DSL signals onto twisted pair portions of siamese cables. Various species have the cable modem feeding digital data or packets of DOCSIS or other data or digitized DSL signals sent over the HFC to the cable modem or digitized POTS signals send over the HFC to the cable modem to either a packet switch, a DSL concentrator, a voice-over-IP gateway or some combination of the above. This data is either delivered to each subscriber as LAN packets or analog POTS signals or DSL signals or some combination of the above using coaxial cable or siamese cable drop lines.
Owner:GOOGLE TECH HLDG LLC
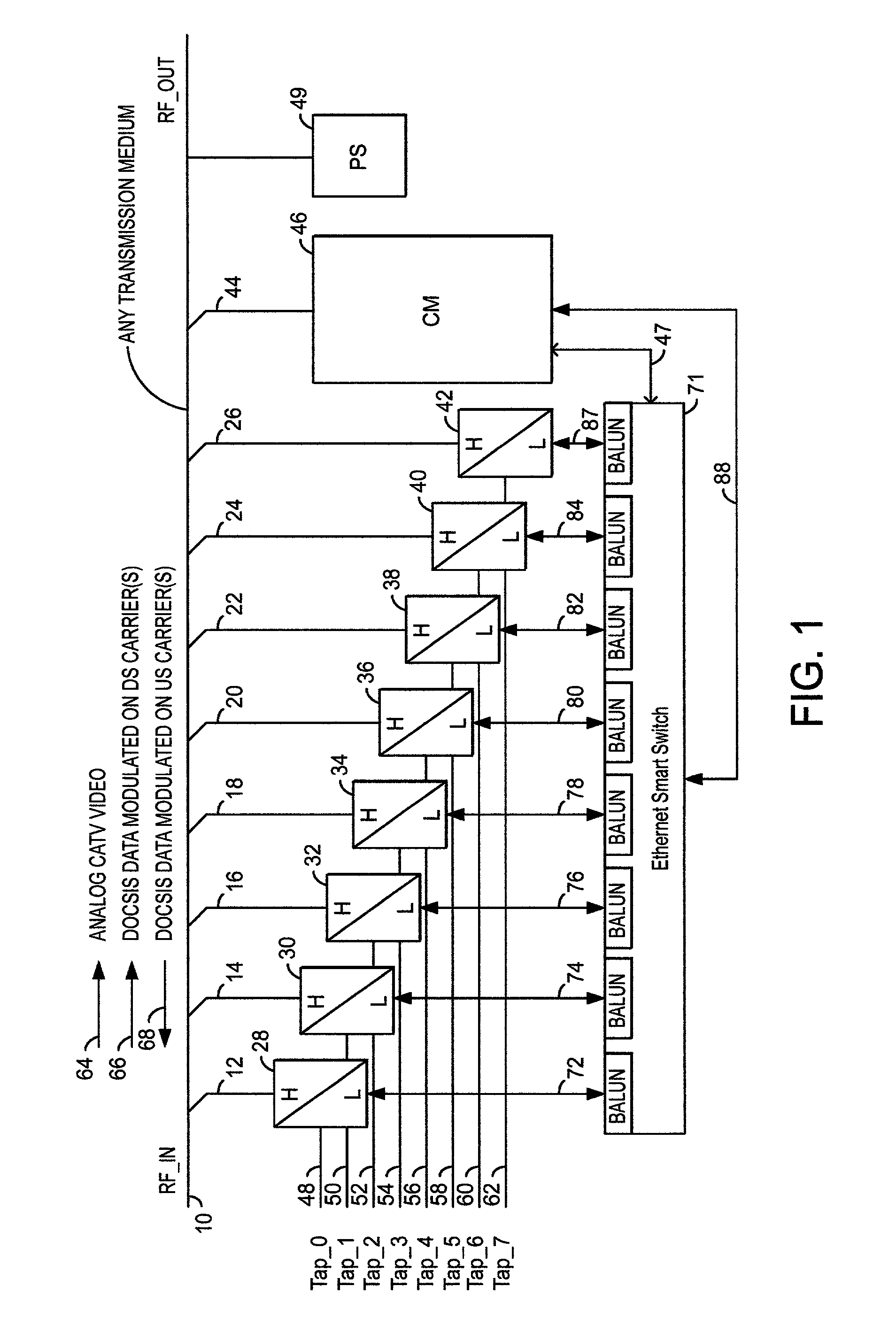
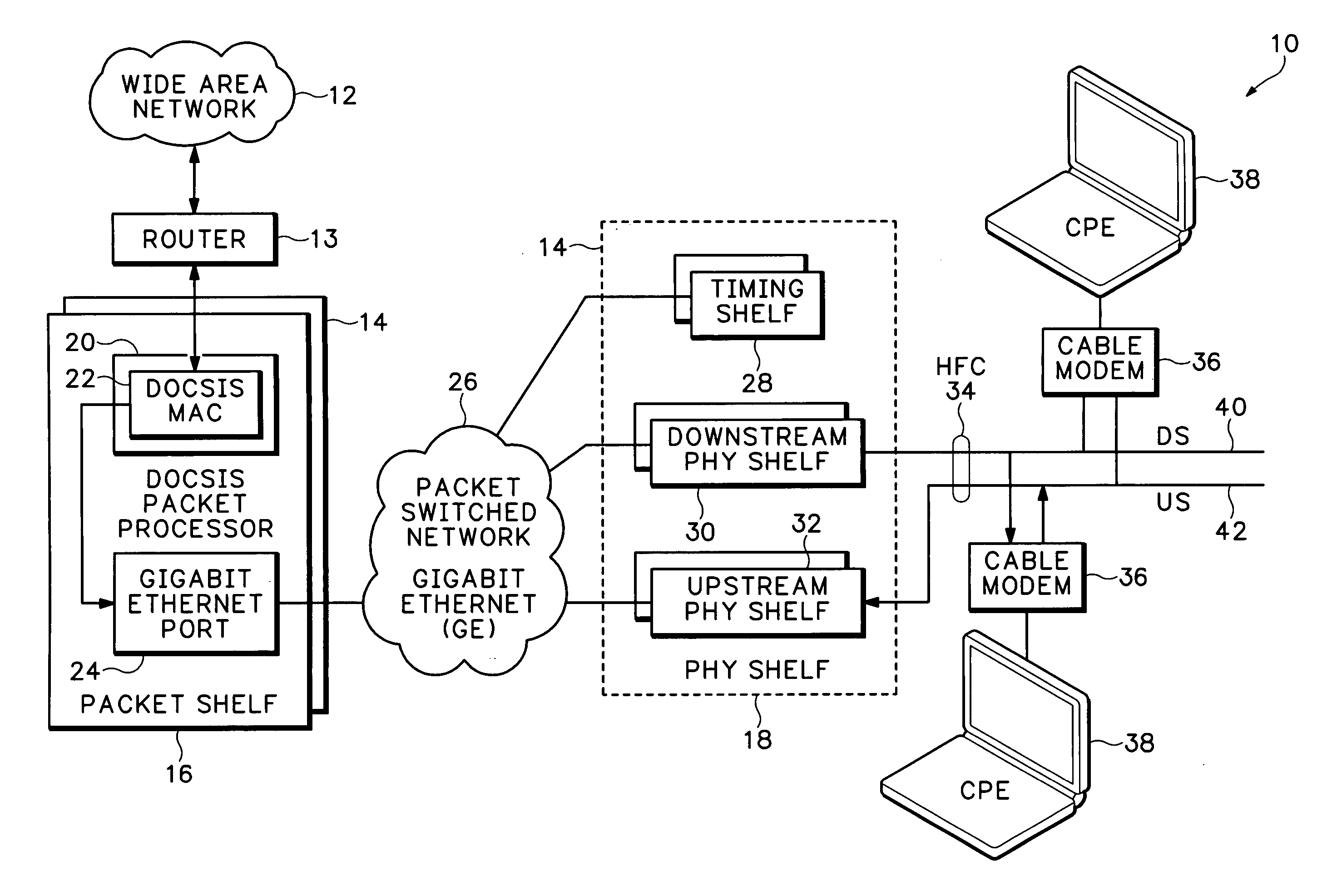
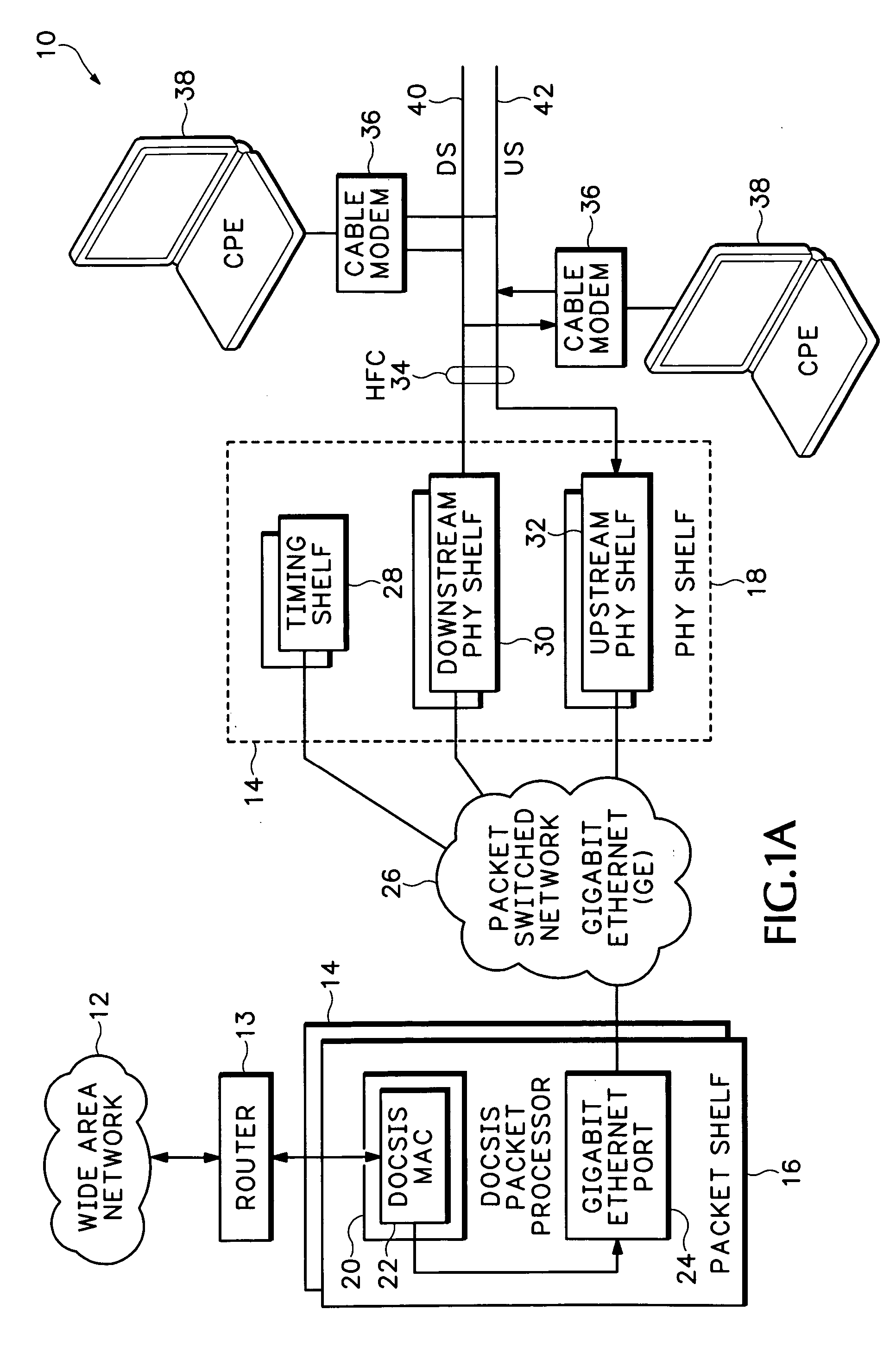
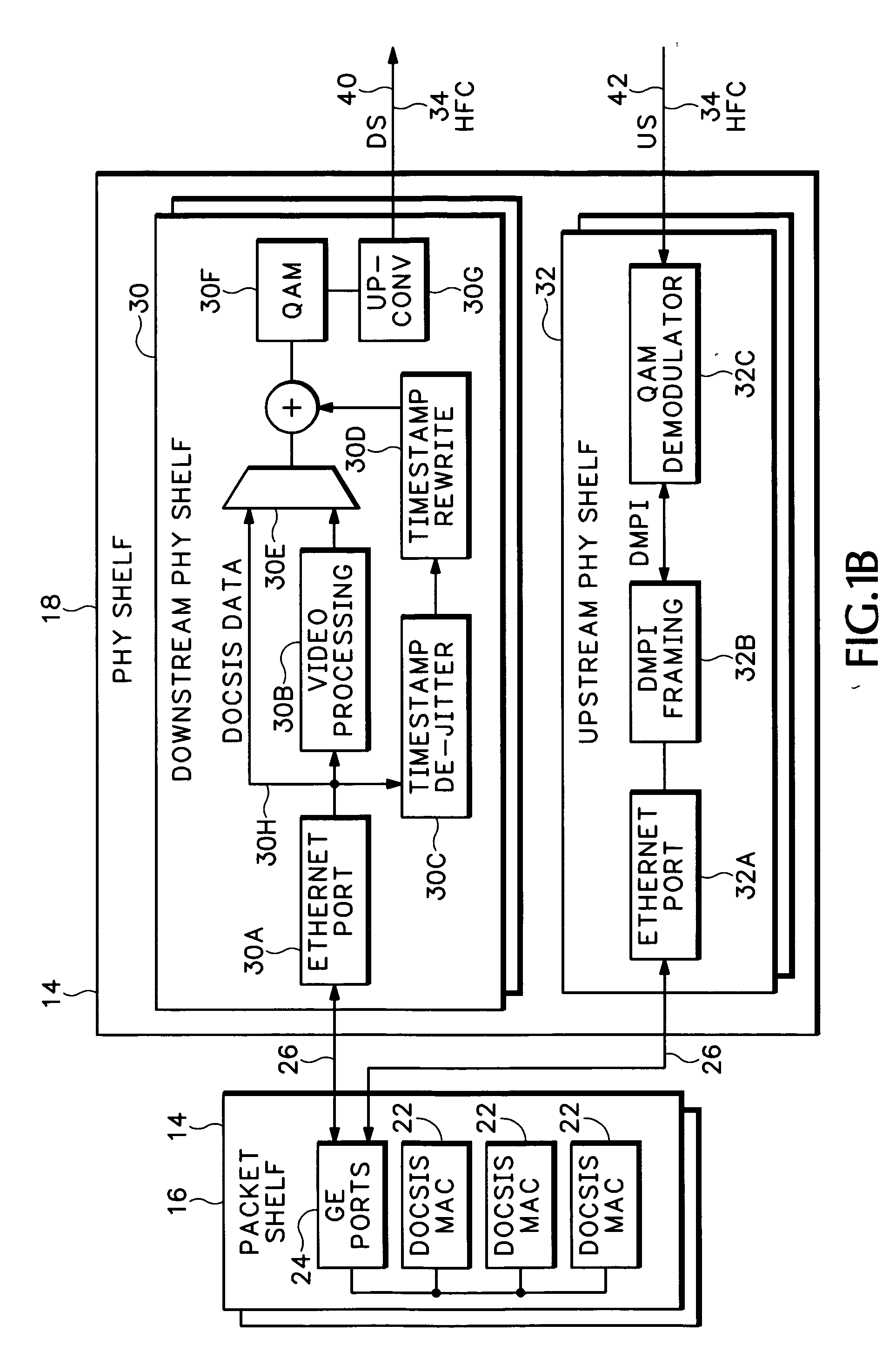
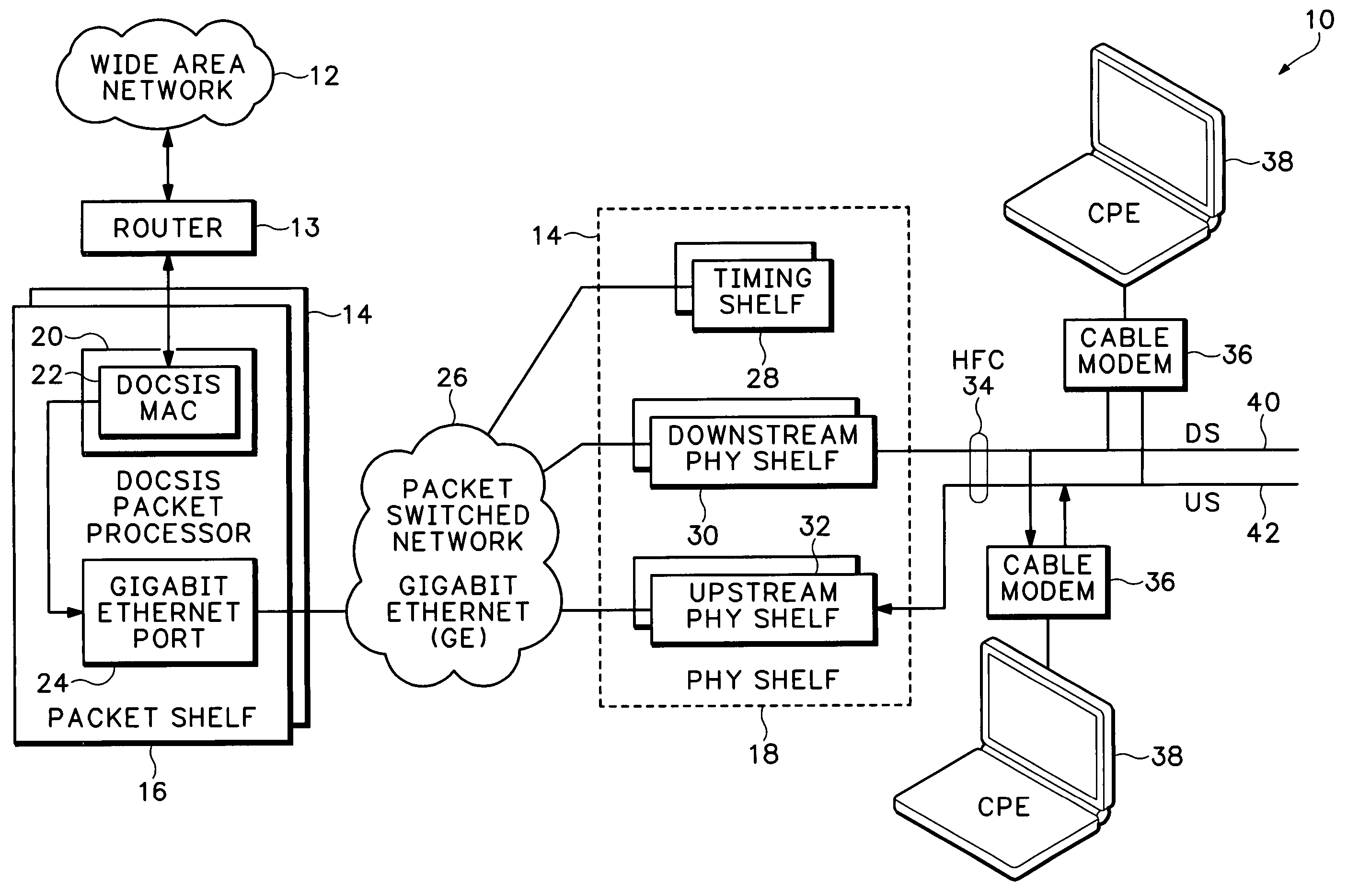
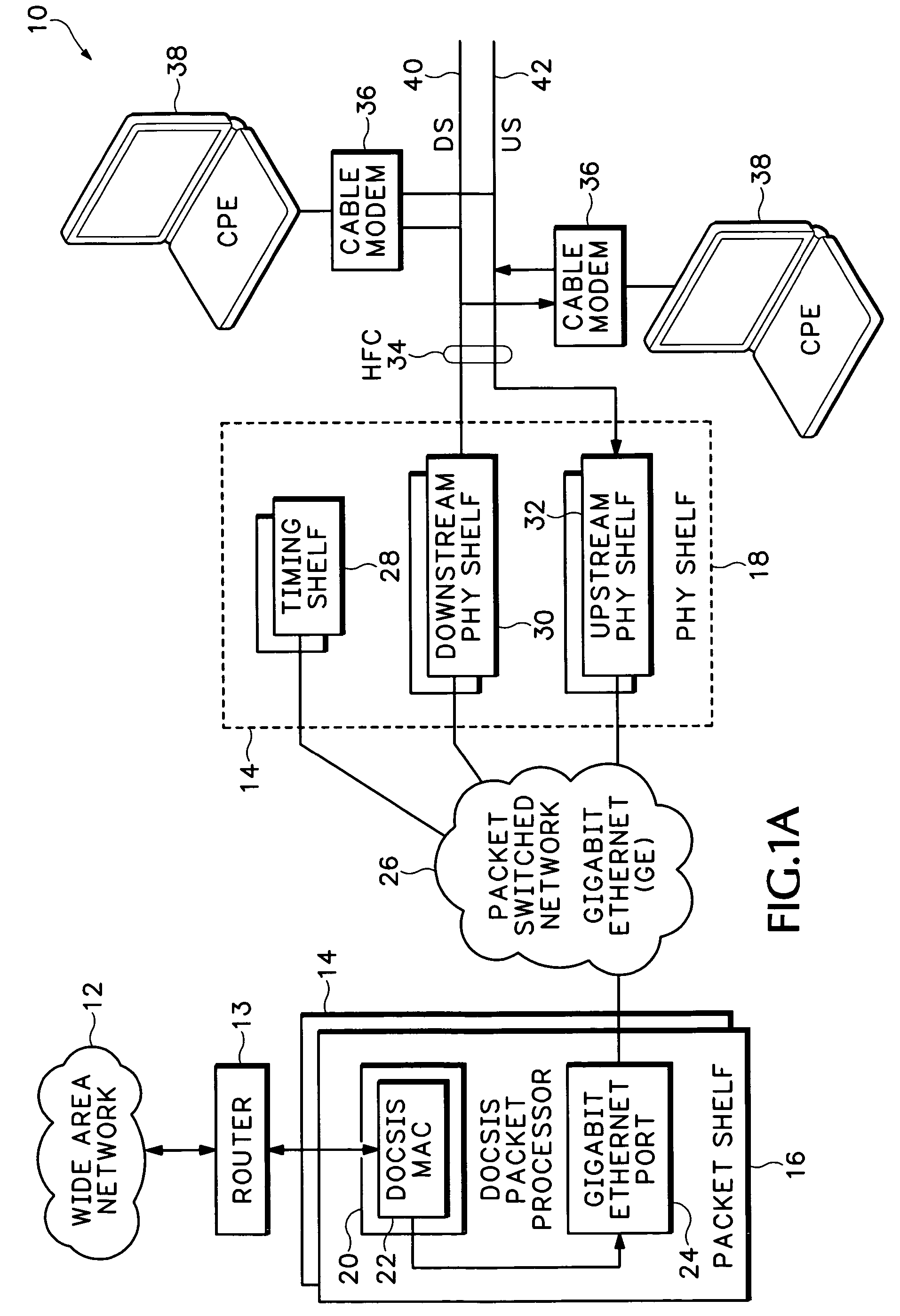
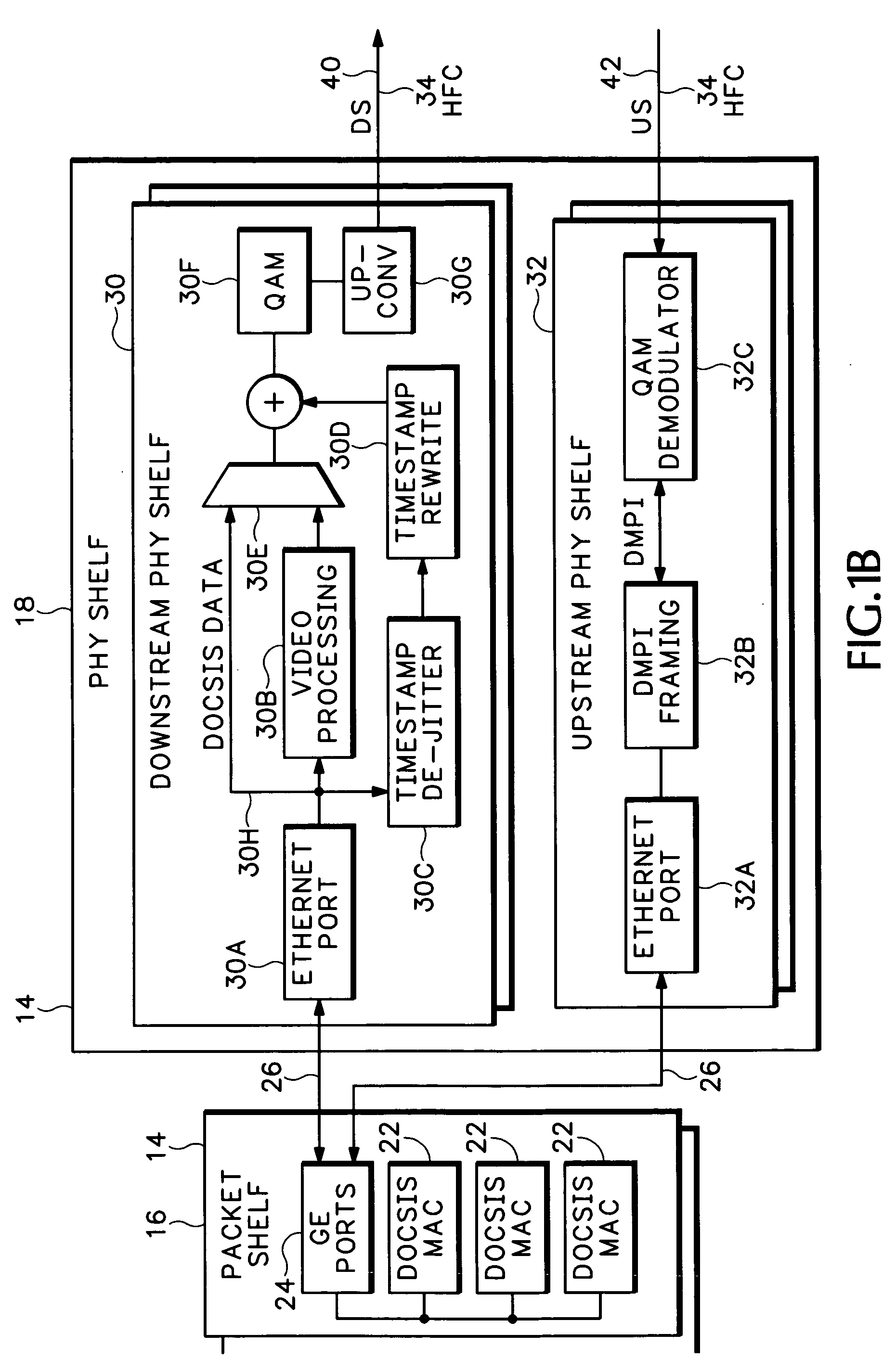
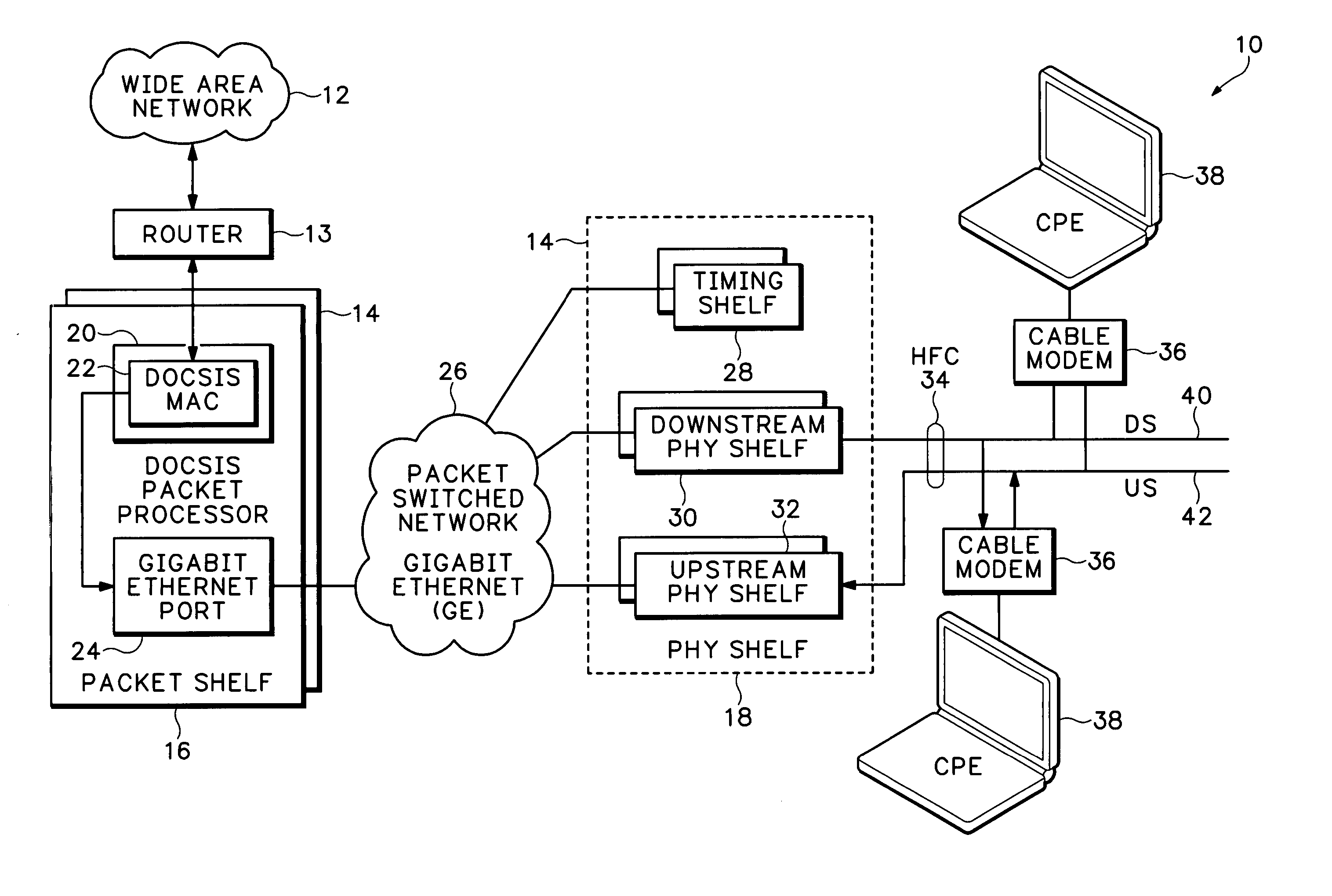
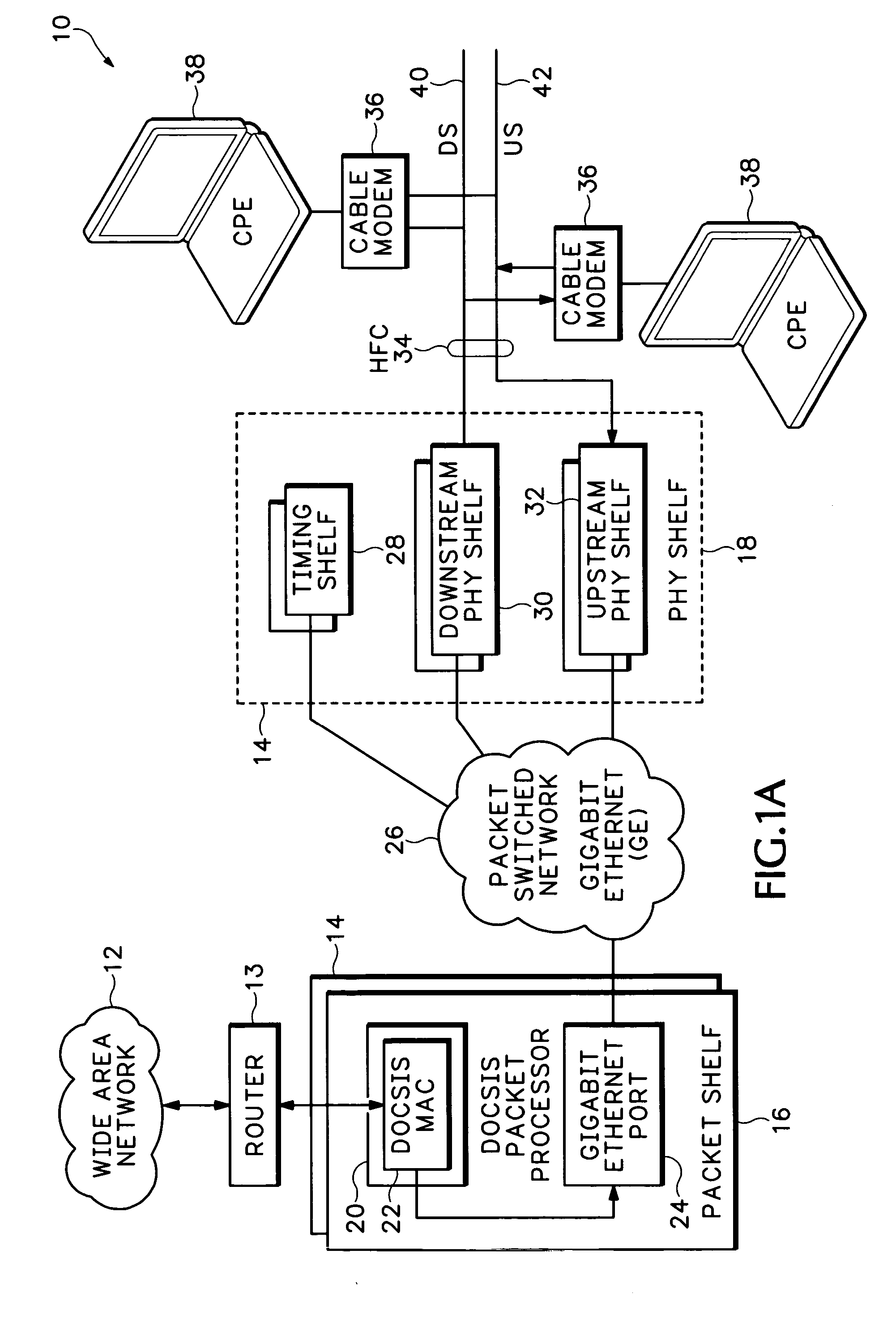
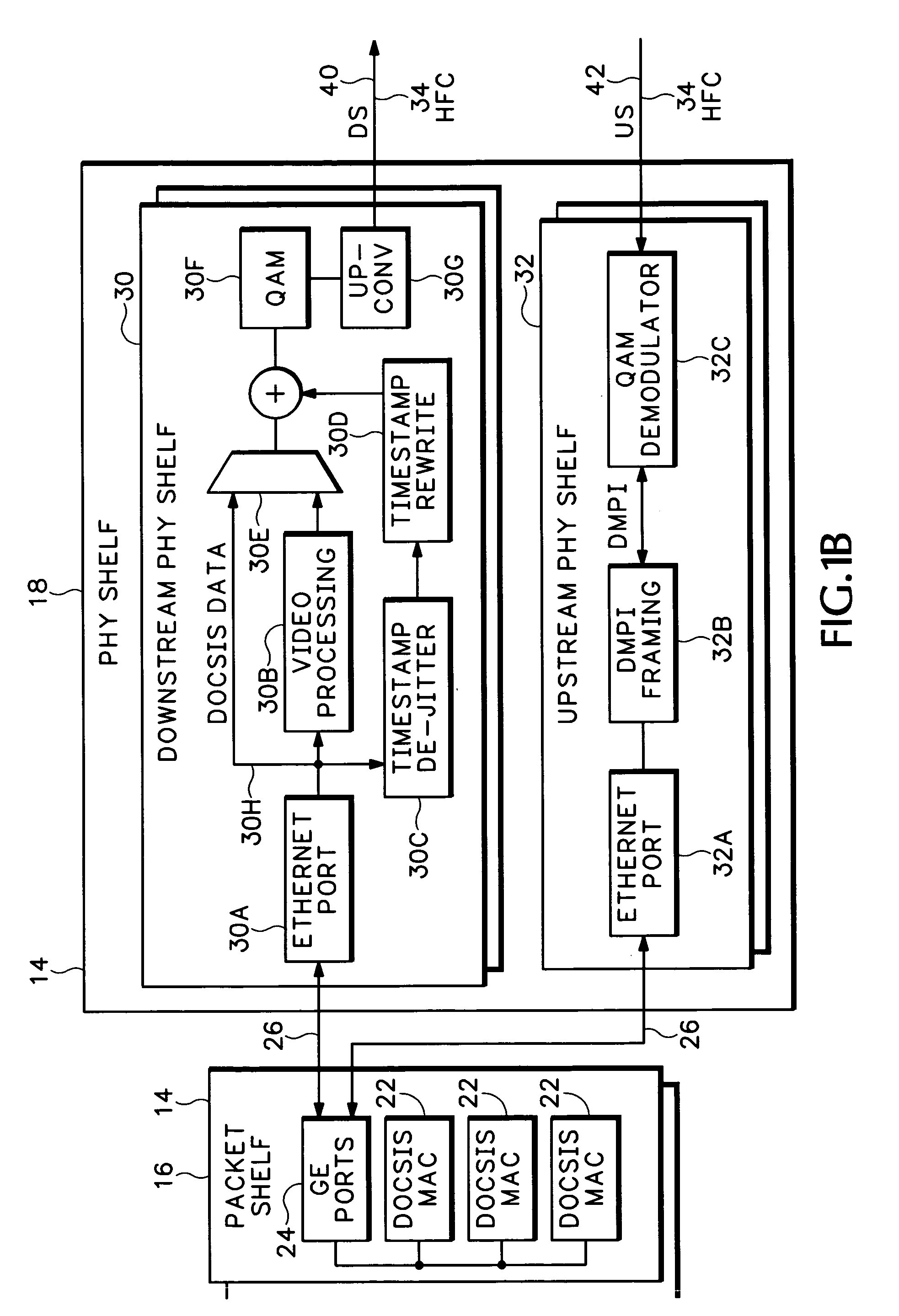
Timing system for modular cable modem termination system
InactiveUS20060168612A1Synchronisation information channelsBroadcast transmission systemsDigital subscriber lineModem device
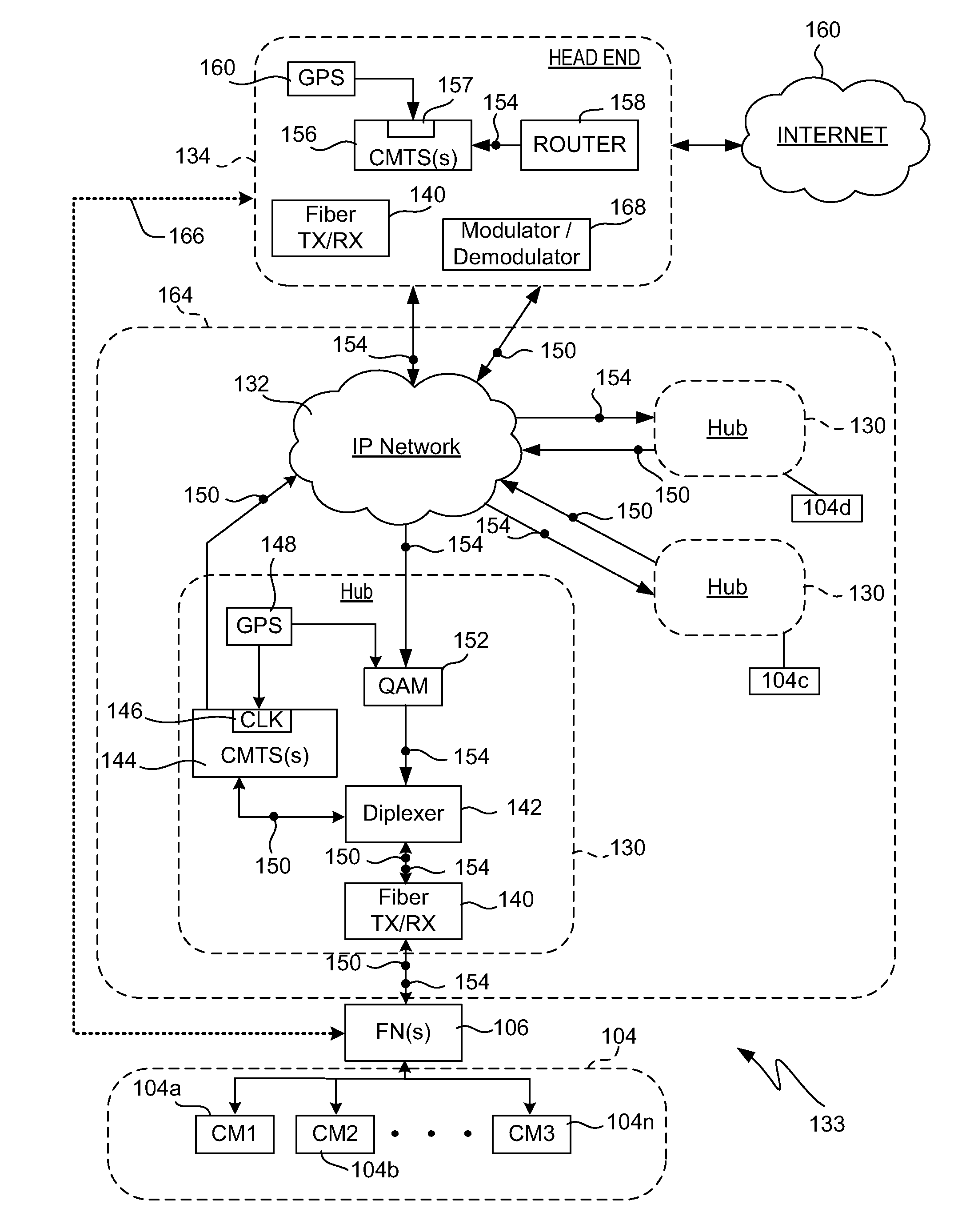
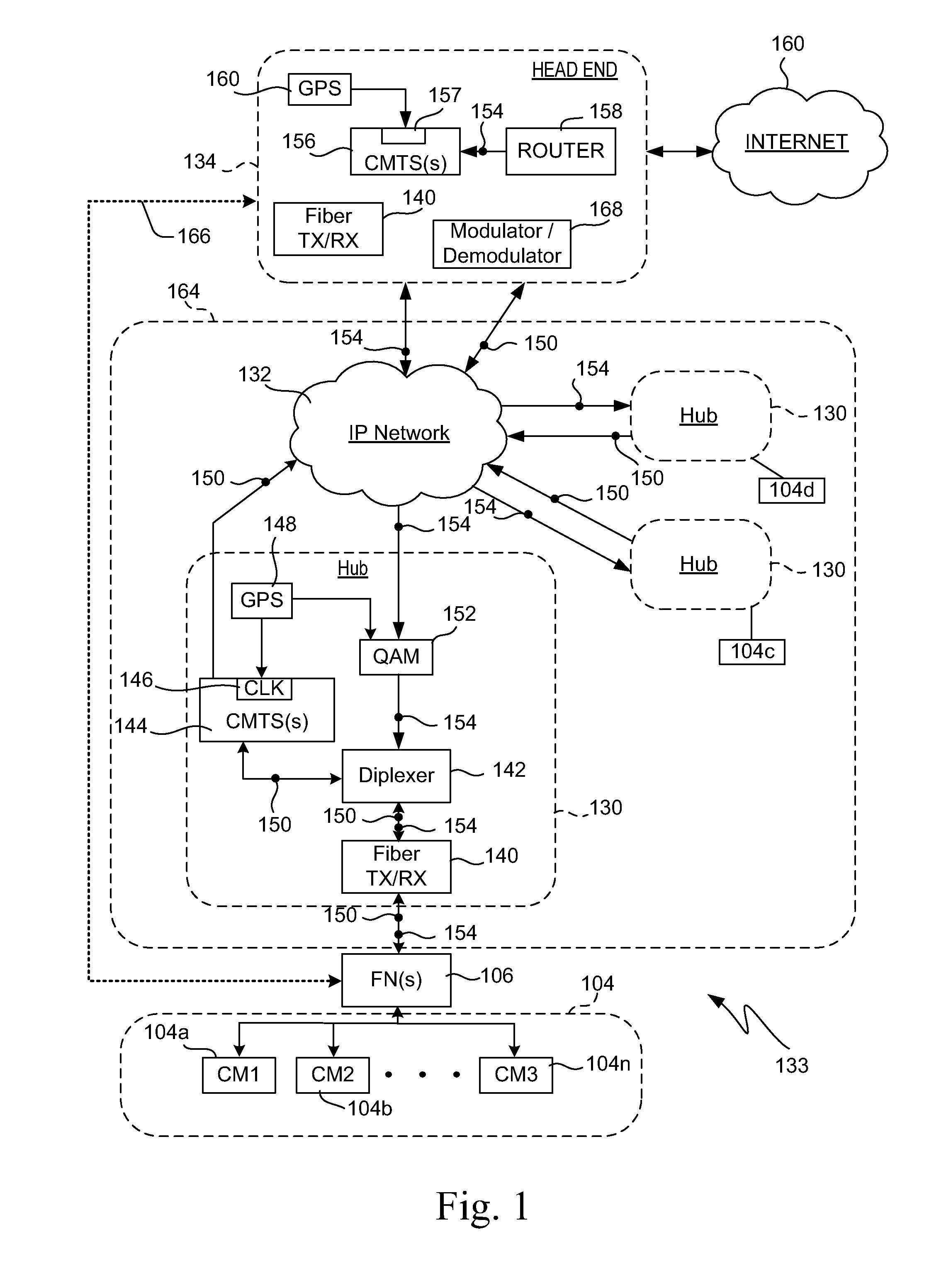
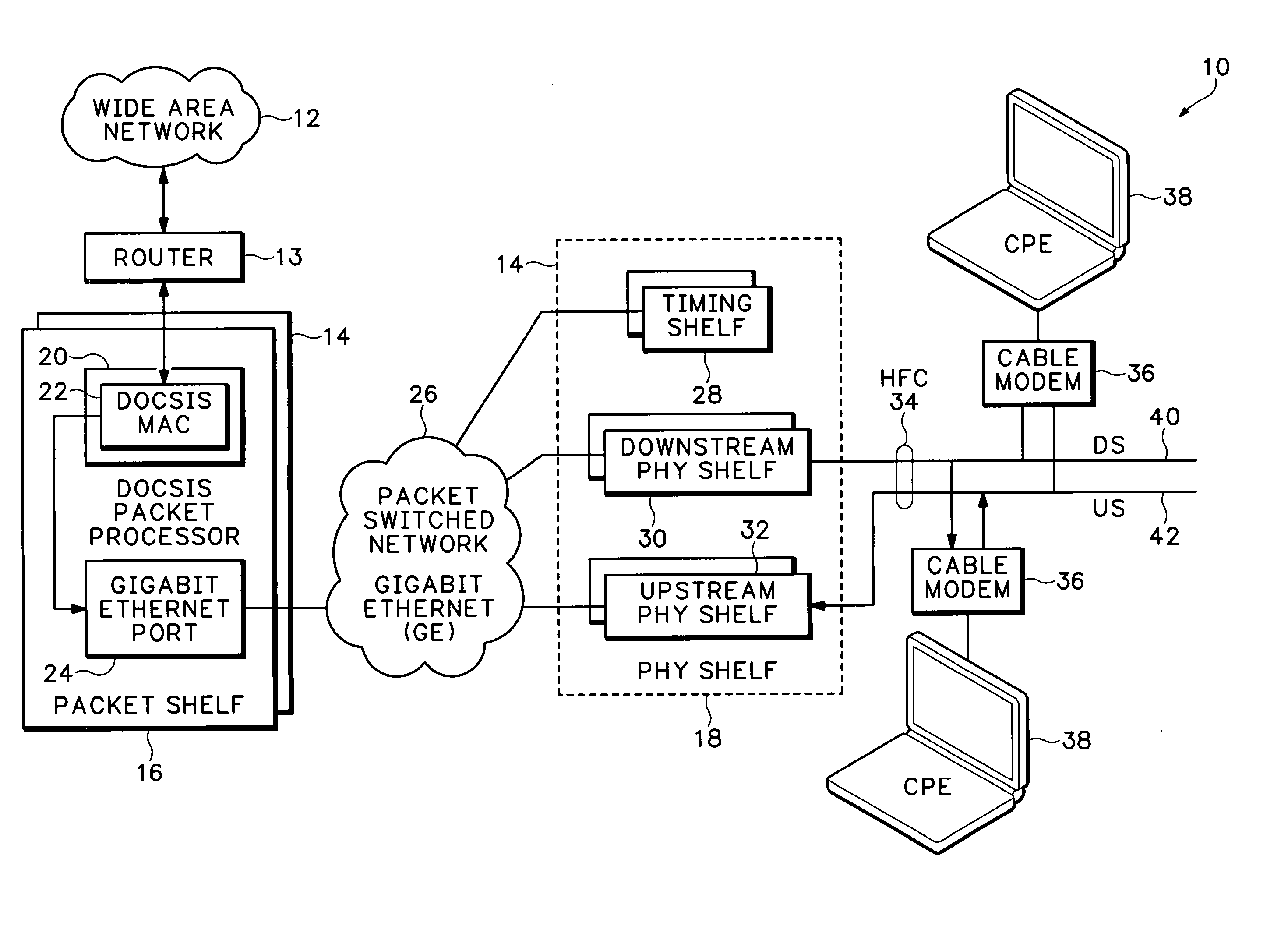
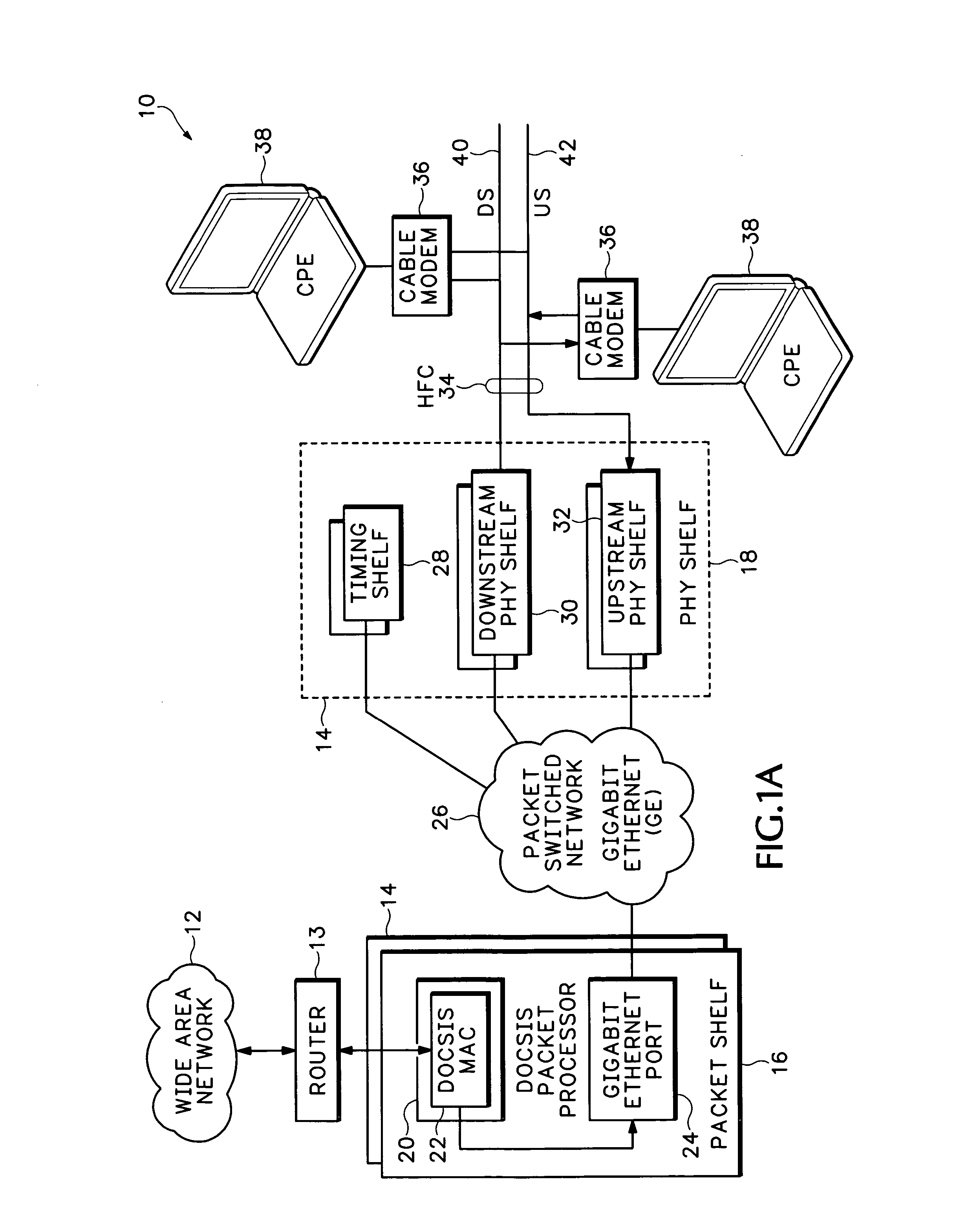
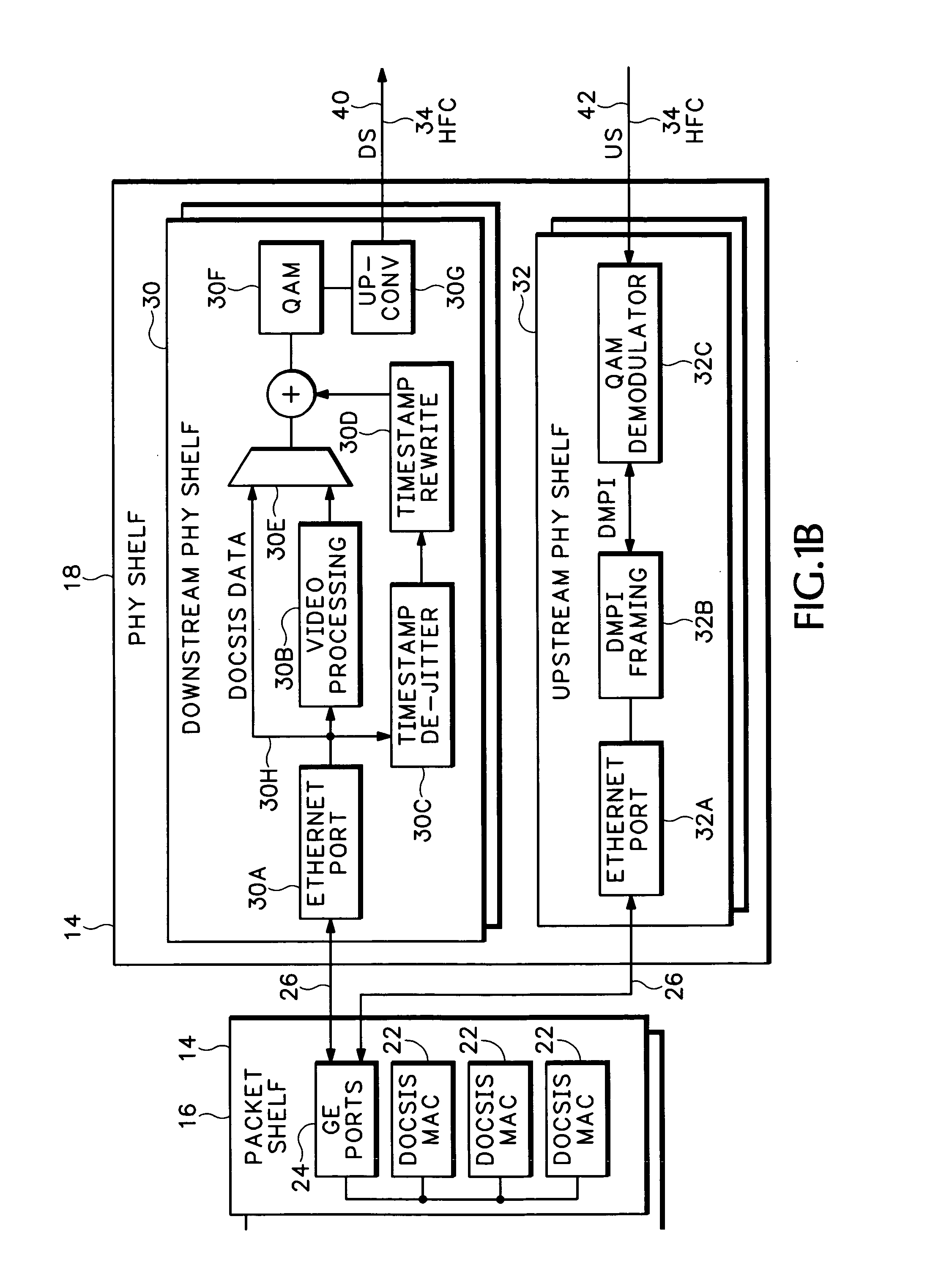
A modular Cable Modem Termination System (CMTS) includes a packet shelf operating a Data Over Cable Service Interface Specifications (DOCSIS) Media Access Control (MAC) framer. One or more downstream Physical Interface (PHY) shelves receive DOCSIS data from the packet shelf over a packet switched network and modulate the DOCSIS data for sending on a downstream path of a cable plant. One or more upstream PHY shelves send DOCSIS data received from an upstream path of the cable plant over the packet switched network to the packet shelf. By separating the PHY components from the MAC and from the system software, the PHY components for a Hybrid Fiber Coax (HFC) plant may be replaced with different PHY components for other access technologies such as wireless, Digital Subscriber Lines (DSL), Ethernet-to-the-Home, Fiber-to-the-Home, or fiber Passive Optical Networks (PONs).
Owner:CISCO TECH INC
Upstream physical interface for modular cable modem termination system
A modular Cable Modem Termination System (CMTS) includes a packet shelf operating a Data Over Cable Service Interface Specifications (DOCSIS) Media Access Control (MAC) framer. One or more downstream Physical Interface (PHY) shelves receive DOCSIS data from the packet shelf over a packet switched network and modulate the DOCSIS data for sending on a downstream path of a cable plant. One or more upstream PHY shelves send DOCSIS data received from an upstream path of the cable plant over the packet switched network to the packet shelf. By separating the PHY components from the MAC and from the system software, the PHY components for a Hybrid Fiber Coax (HFC) plant may be replaced with different PHY components for other access technologies such as wireless, Digital Subscriber Lines (DSL), Ethernet-to-the-Home, Fiber-to-the-Home, or fiber Passive Optical Networks (PONs).
Owner:CISCO TECH INC
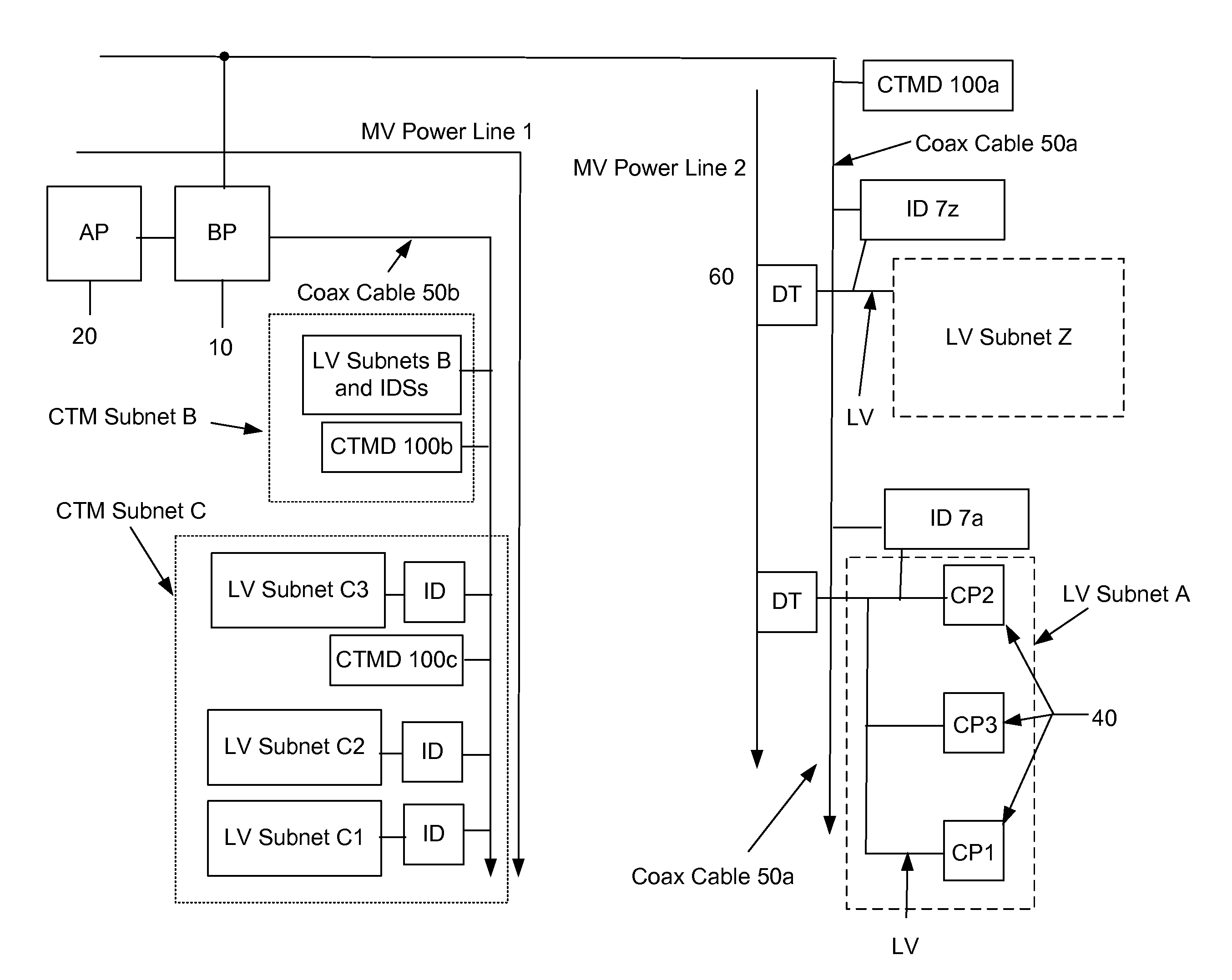
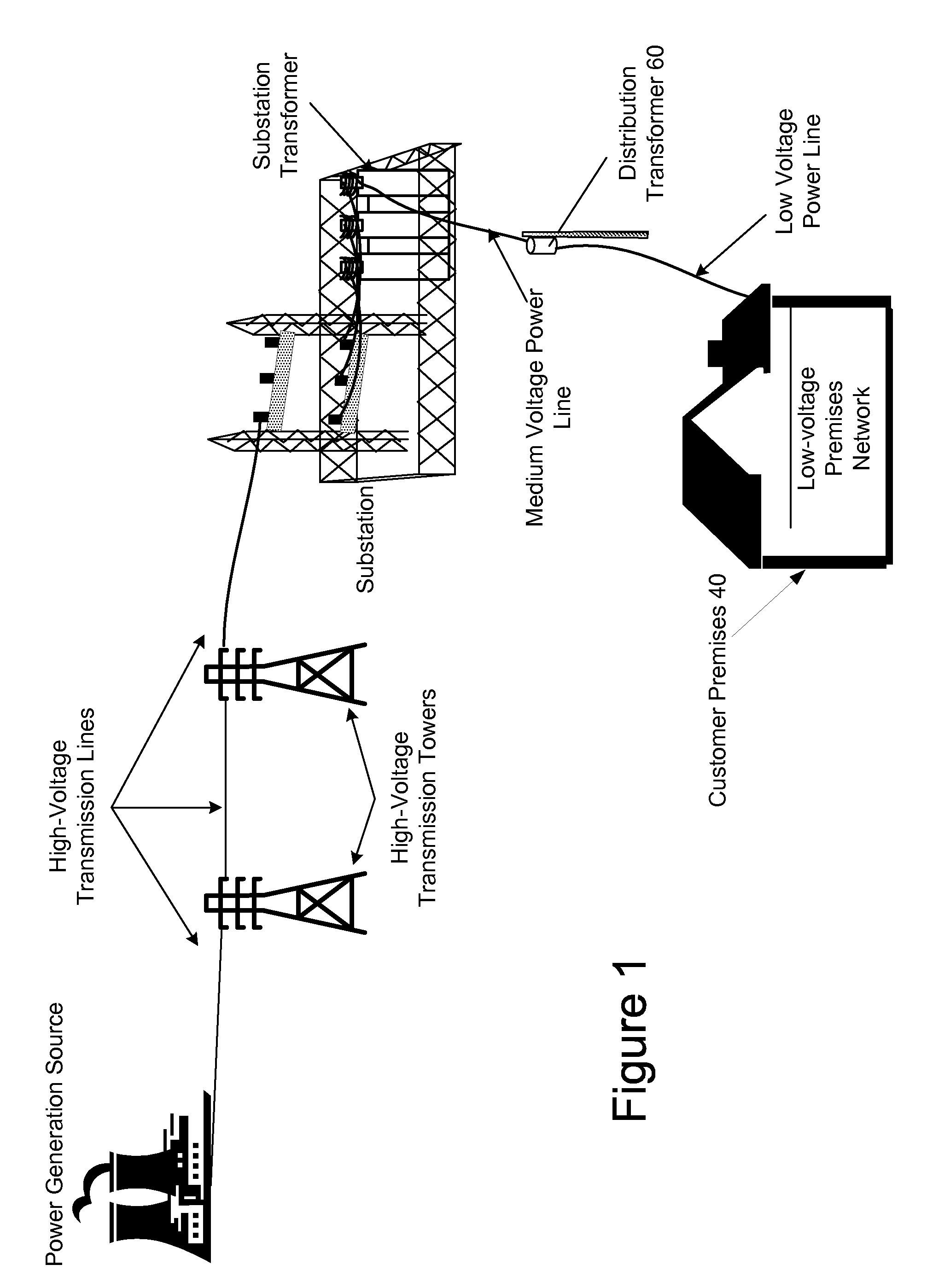
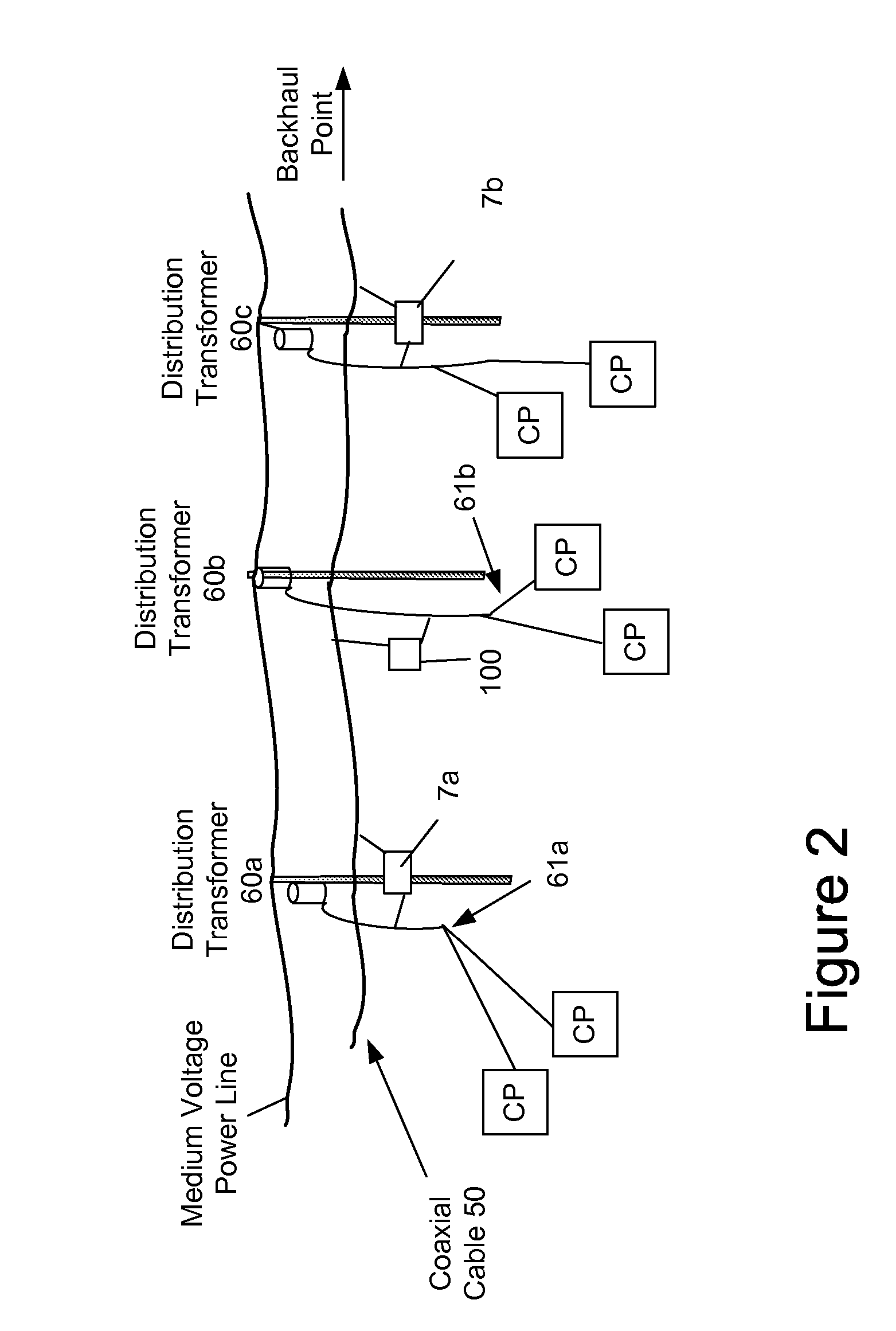
Power Line Communication System and Method
InactiveUS20060291575A1Power distribution line transmissionFrequency-division multiplexCommunications systemModem device
A power line communications system for providing communications for one or more user devices via one or more low voltage power line is provided. In one embodiment the system includes a plurality of first communication devices, each comprising a first modem configured to communicate using a DOCSIS protocol, and a first low voltage power line interface configured to communicate with a plurality of user devices via a low voltage power line. A second communication device includes a backhaul link interface configured to communicate over a backhaul link and a downstream interface configured to communicate with the first modems of the plurality of first communication devices. The plurality of first communication devices transmit upstream data signals in a first frequency band and receive downstream data signals in a second frequency band different from the first frequency band.
Owner:CURRENT TECH
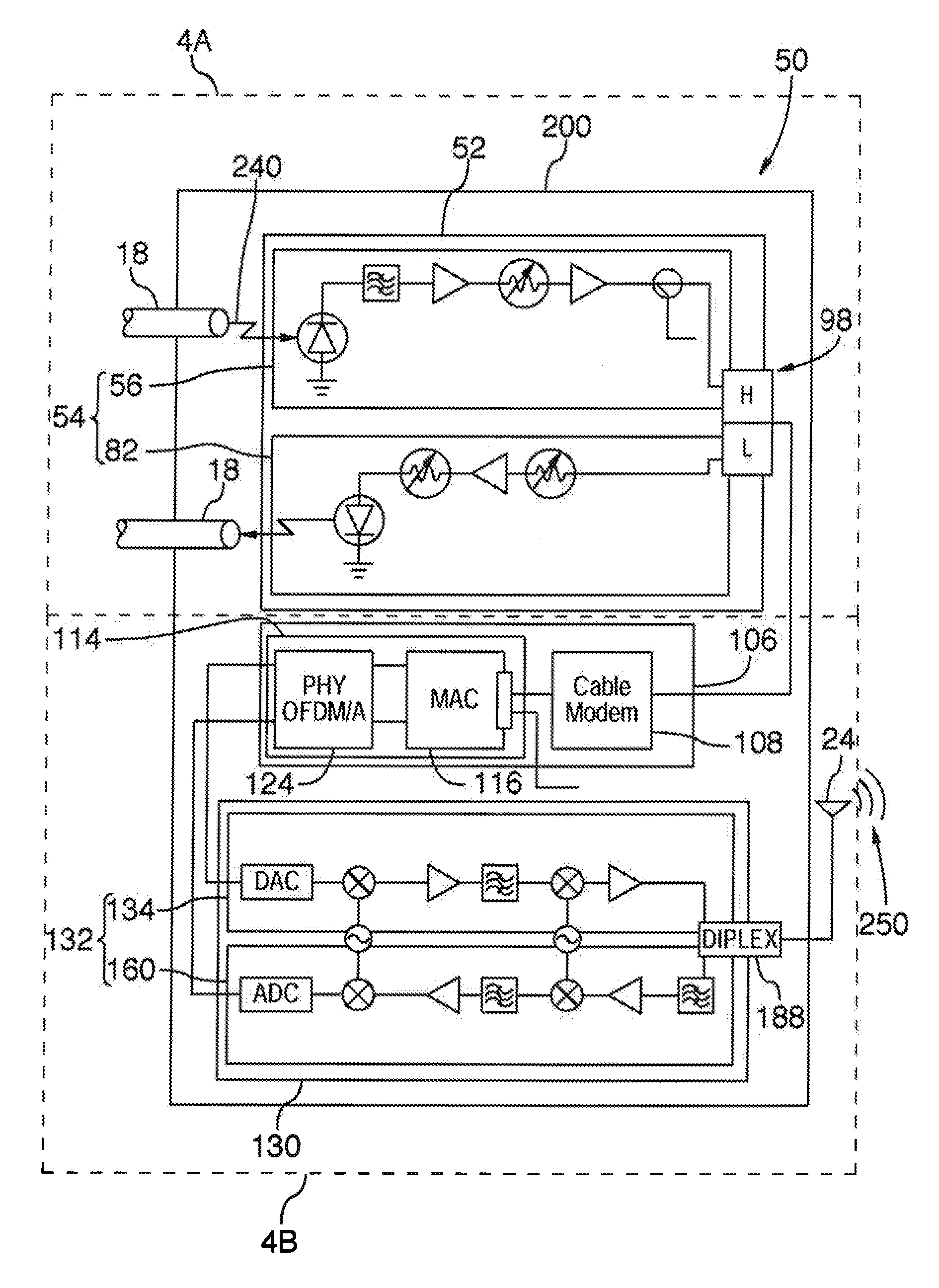
Apparatus and method for transferring signals between a fiber network and a wireless network antenna
An apparatus and method transfers signals between a fiber network and a wireless network antenna. In a fiber to wireless stage, fiber signals are optically transferred from the fiber network and converted into RF signals compatible with the DOCSIS interface standard. The RF signals are electronically converted into data packets, the data packets are electronically converted into baseband digital signals, and the digital signals are converted into analog signals, before being transferred to the network antenna for wireless transmission. The data packets, digital signals, and analog signals are compatible with the IEEE 802.l6 wireless networking standard. Conversely, in a wireless to fiber stage, the analog signals are transferred from the antenna, and converted into digital signals, which are then electronically converted into data packets. The data packets are electronically converted into RF signals, which are next converted into fiber signals, before being optically transferred to the fiber network.
Owner:LOGUS BROADBAND WIRELESS SOLUTIONS
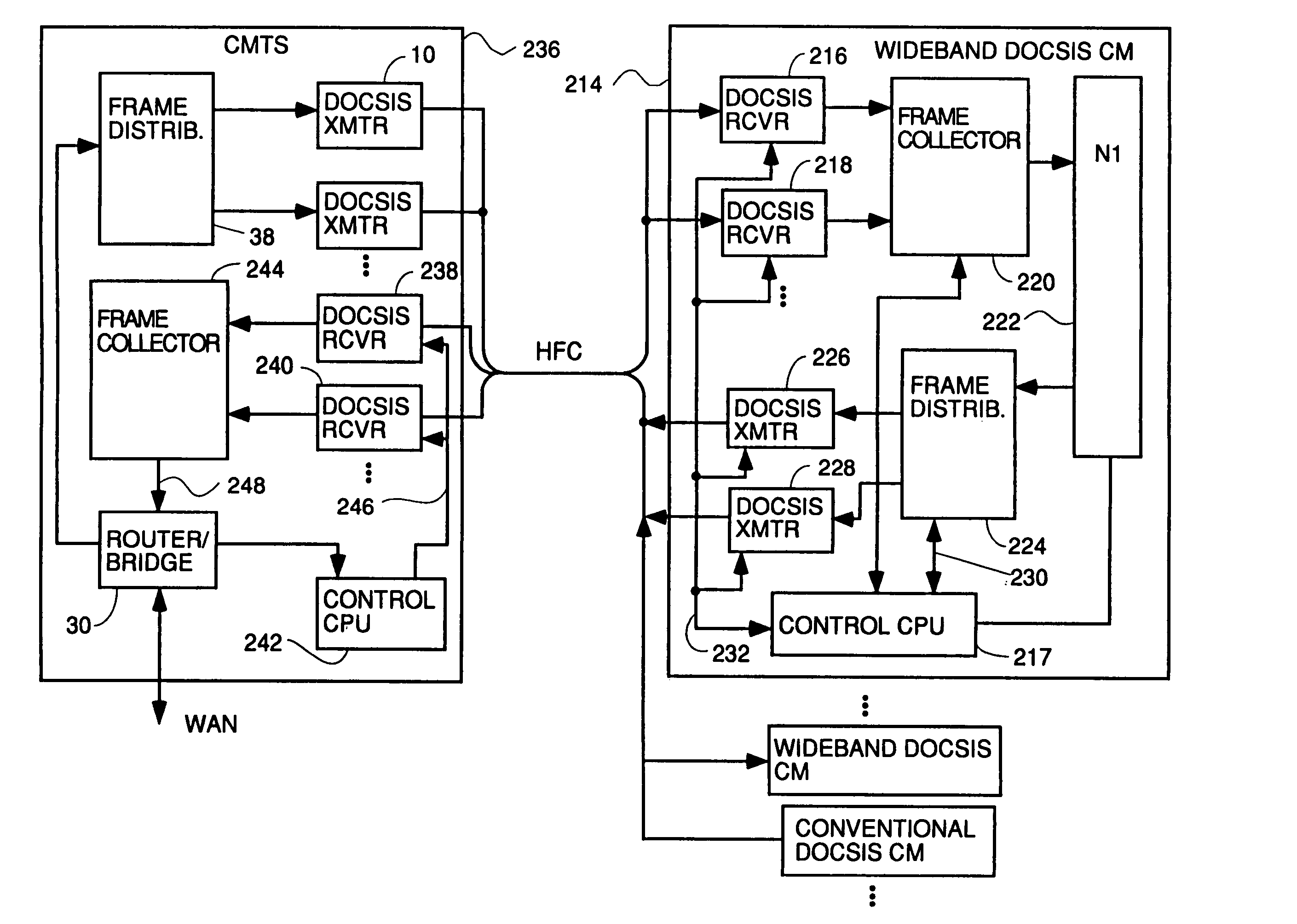
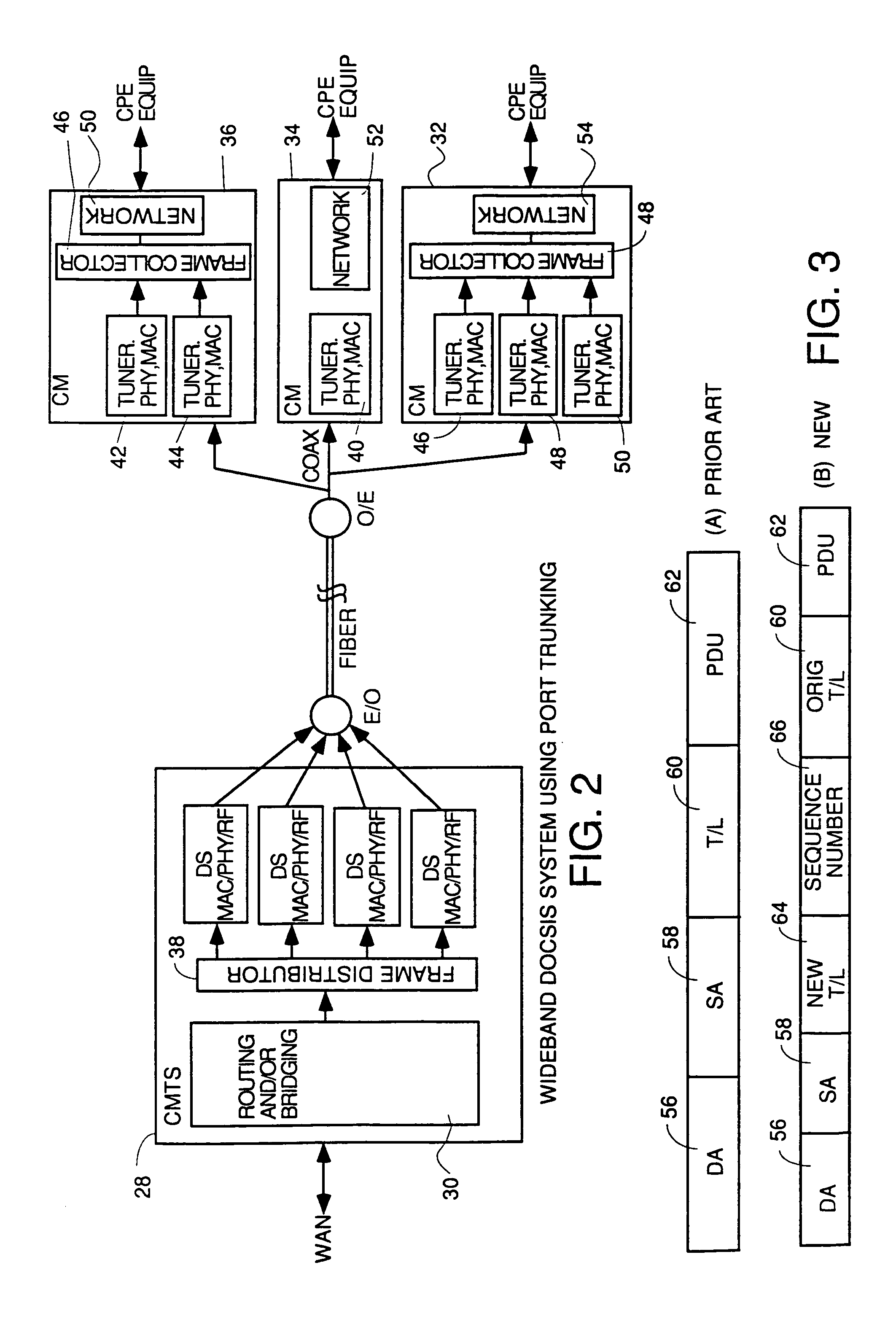
Wideband DOCSIS on catv systems using port-trunking
Method and apparatus to carry out wideband DOCSIS both upstream and downstream in a point-to-multipoint environment of an HFC system using port trunking concepts. For the downstream, each CMTS has a frame distributor which distributes frames to various transmitters transmitting on downstream channels to be used to transmit downstream data simultaneously to a CM using wideband DOCSIS. The frame distributor adds sequence numbers in some embodiments to guarantee proper order of frames can be restored at the CM, and schedules transmissions according to quality of service considerations to meet guaranteed and committed portions of constant bit rate and variable bit rate flows. The CMTS sends and Extended Channel Enable (ECE) message to wideband capable CMs telling them which downstreams to enable. Each CM has a frame collector to which all frames received on various downstream channels are sent. The frame collector makes sure they are all there, puts them into the proper order and delivers them to a NI. Upstream wideband DOCSIS works the same way with a frame distributor in each CM and a frame collector in the CMTS. The CMTS receives bandwidth requests and controls upstream wideband DOCSIS transmissions by sending downstream UCD and MAP and ECE messages to the CMs instructing them which upstream channels to use, describing the parameters of the channel and assigning times for transmission which are simultaneous on multiple channels for upstream wideband capable CMs.
Owner:GOOGLE TECH HLDG LLC
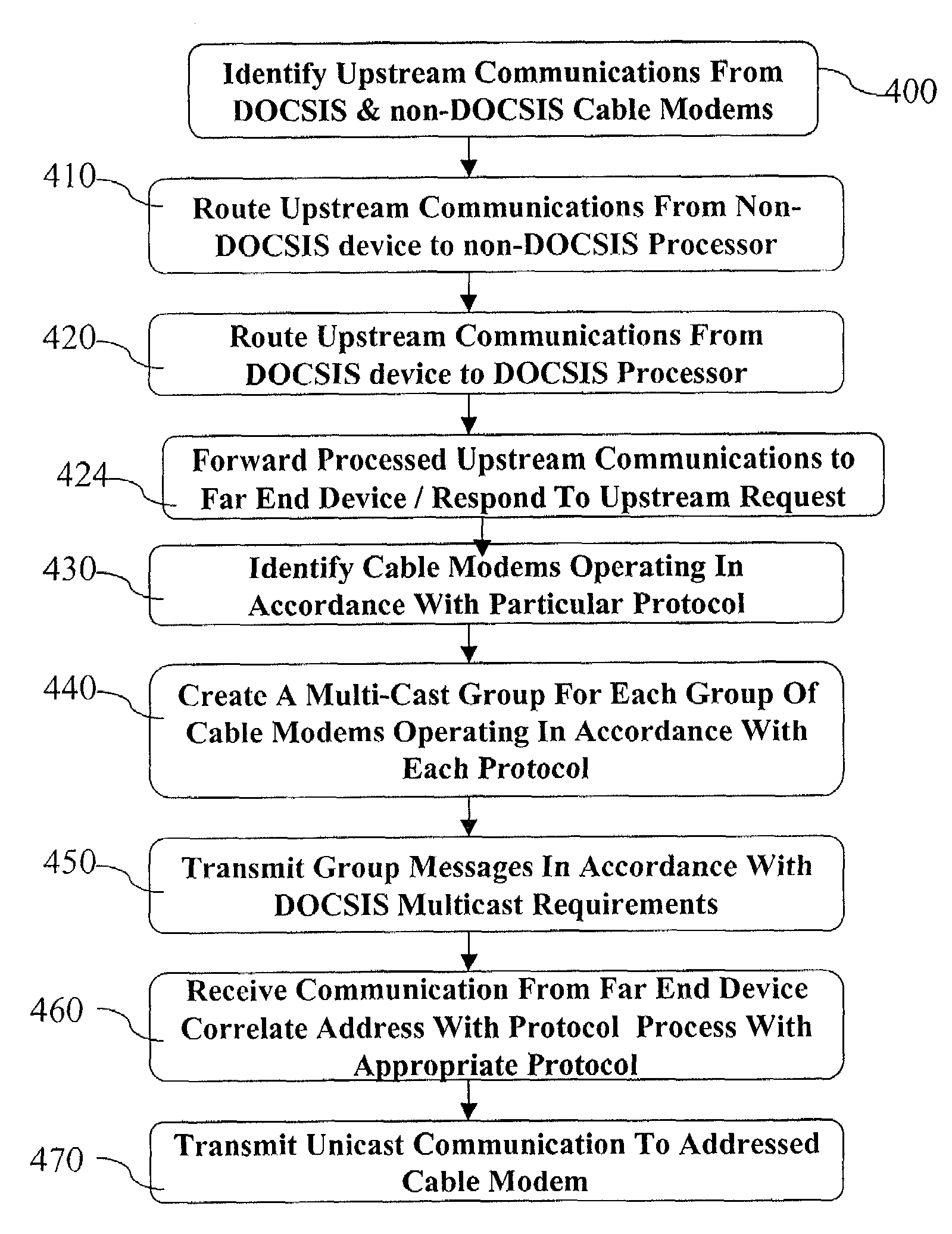
Method for opening a proprietary MAC protocol in a non-DOCSIS modem compatibly with a DOCSIS modem
InactiveUS7164690B2Broadband local area networksTime-division multiplexCommunications systemProtocol processing
A two way communication system is adapted for compatible inter-operation of a plurality of devices operating in accordance with a plurality of protocols. The communication system includes a first group of one or more remote devices that interface with a local host in accordance with a first protocol and a second group of one or more remote devices that interface wit the local host in accordance with a second protocol. The local host includes a protocol processor that identifies transmissions from the first and second groups of remote devices and routes transmissions from the first group of remote devices to a first processor operating in accordance with the first protocol and also routes transmissions from the second group of remote devices to a second processor operating in accordance with the second protocol.
Owner:AVAGO TECH WIRELESS IP SINGAPORE PTE
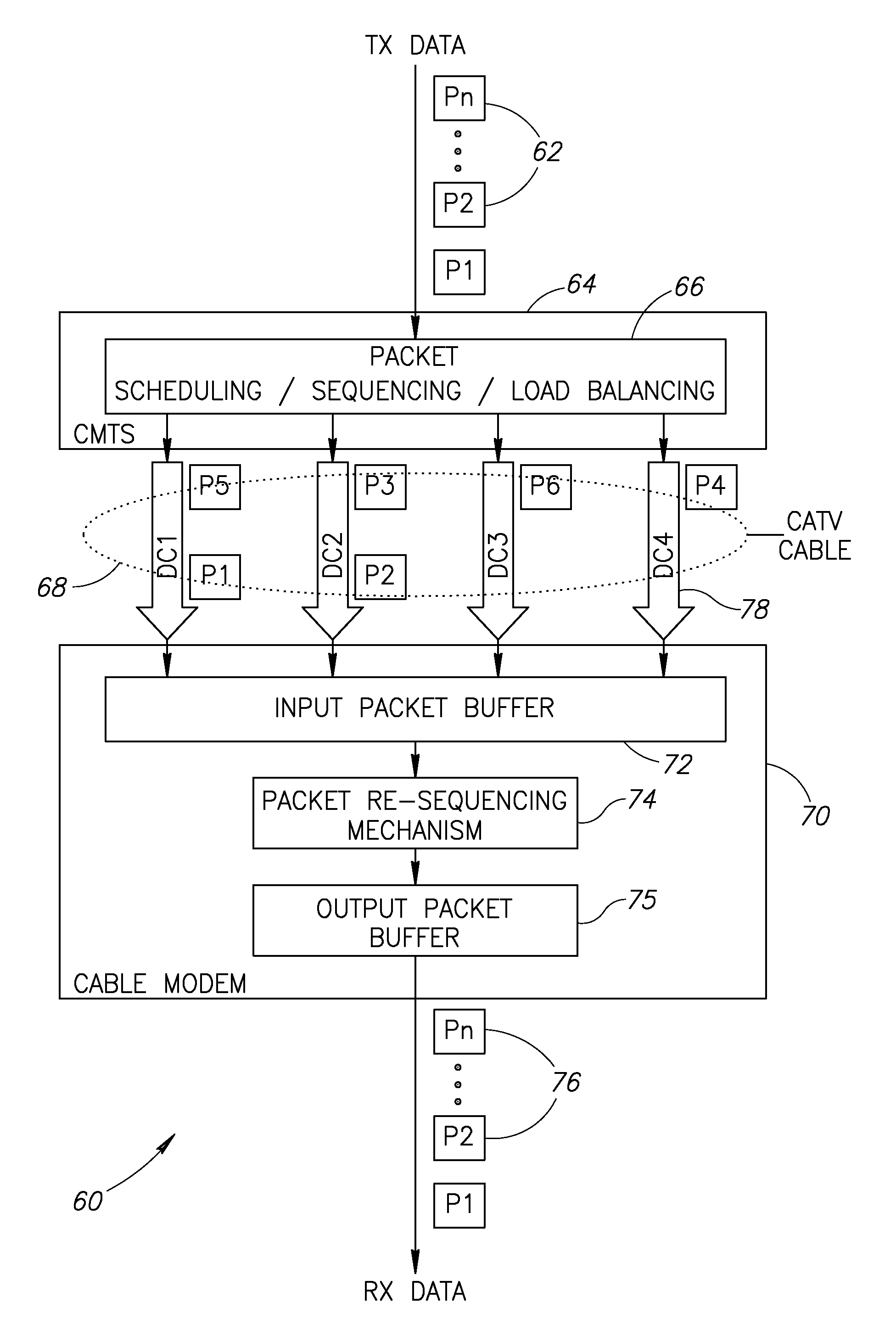
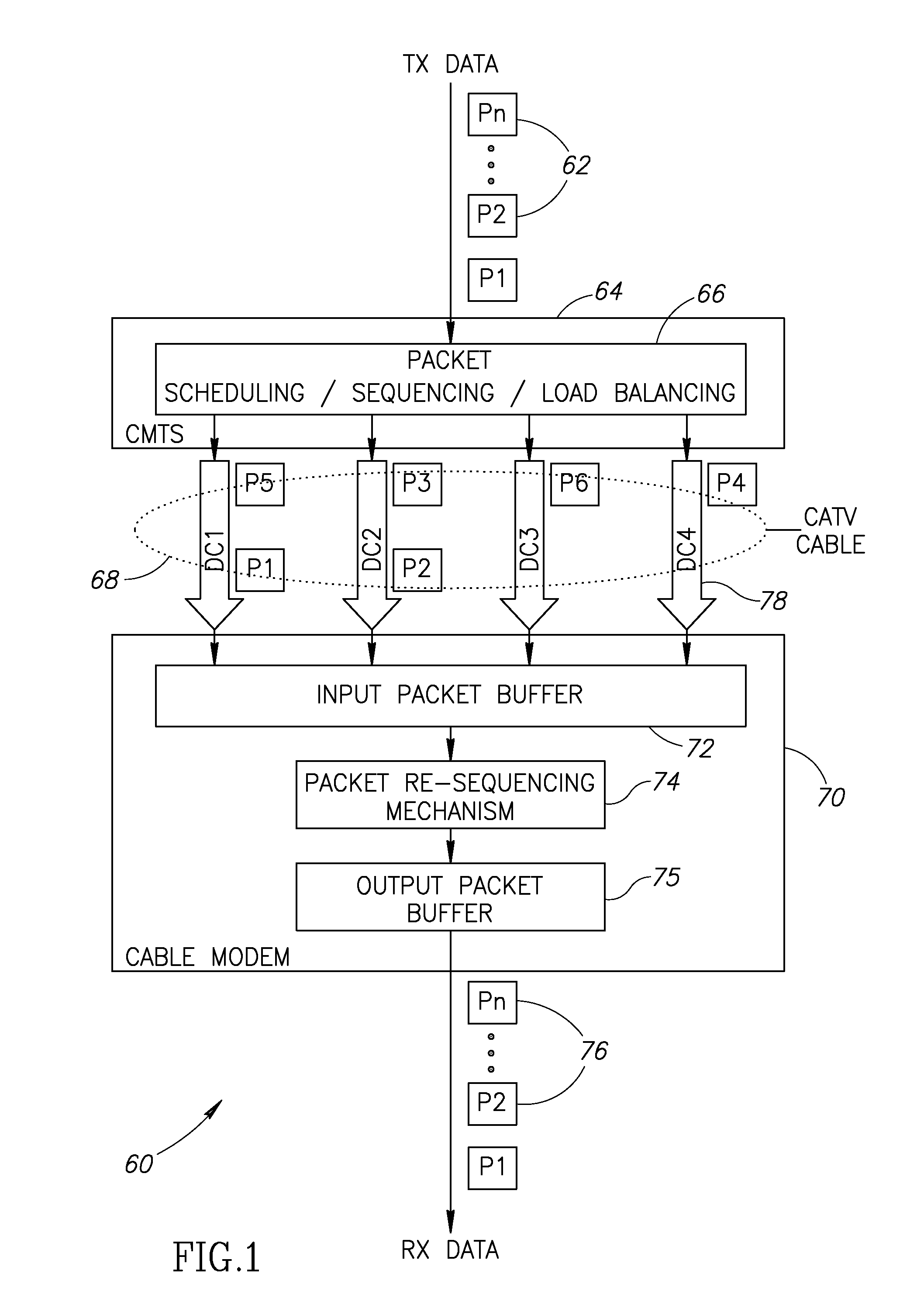
Cable Modem Downstream Channel Bonding Re-sequencing Mechanism
ActiveUS20070206600A1Broadband local area networksStore-and-forward switching systemsRe sequencingComputer hardware
A novel apparatus and method of packet re-sequencing applicable to systems wherein packets are assigned sequence numbers and transmitted over multiple channels with the requirement they be re-ordered at the receiving side. The mechanism is particularly suitable for use in cable systems adapted to implement the DOCSIS 3.0 specification which permits the bonding of a plurality of downstream channels into a single virtual high data rate pipe. In operation, received packets are stored in a memory whereby a pointer to the memory storage location is written into a context table diagram in accordance with the sequence number extracted from the packet. Packets are released in sequence order regardless of the order in which they were received.
Owner:MAXLINEAR INC
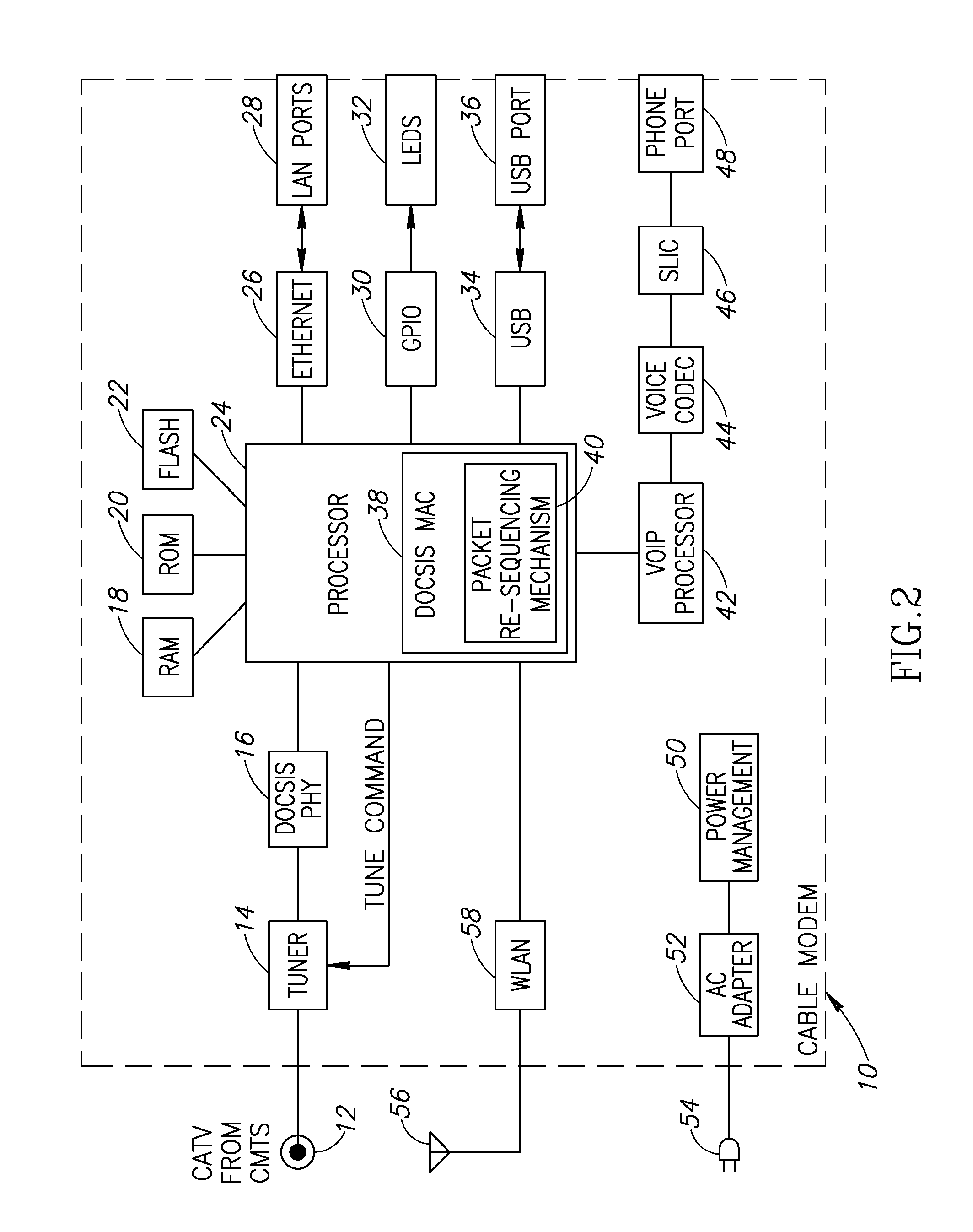
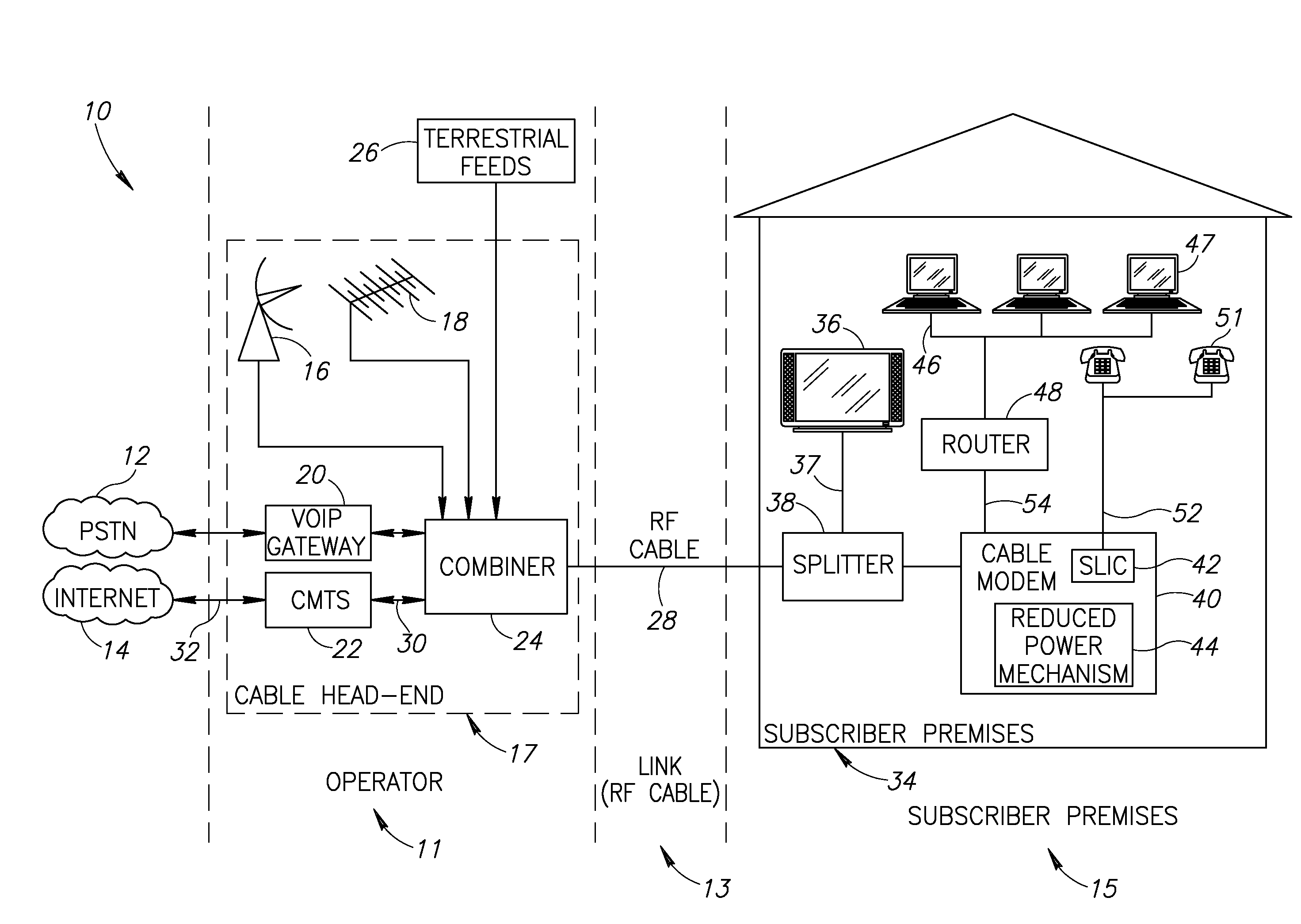
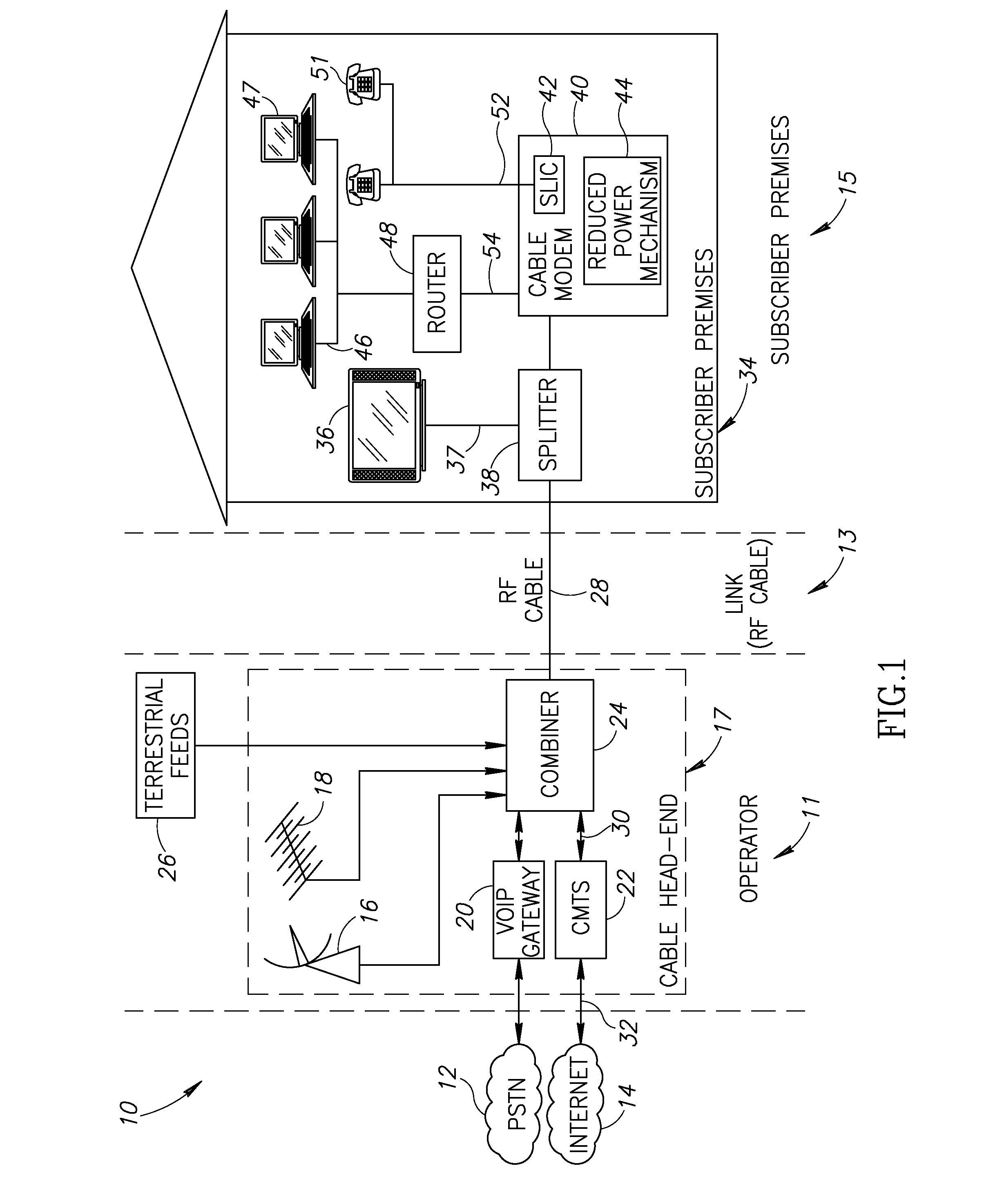
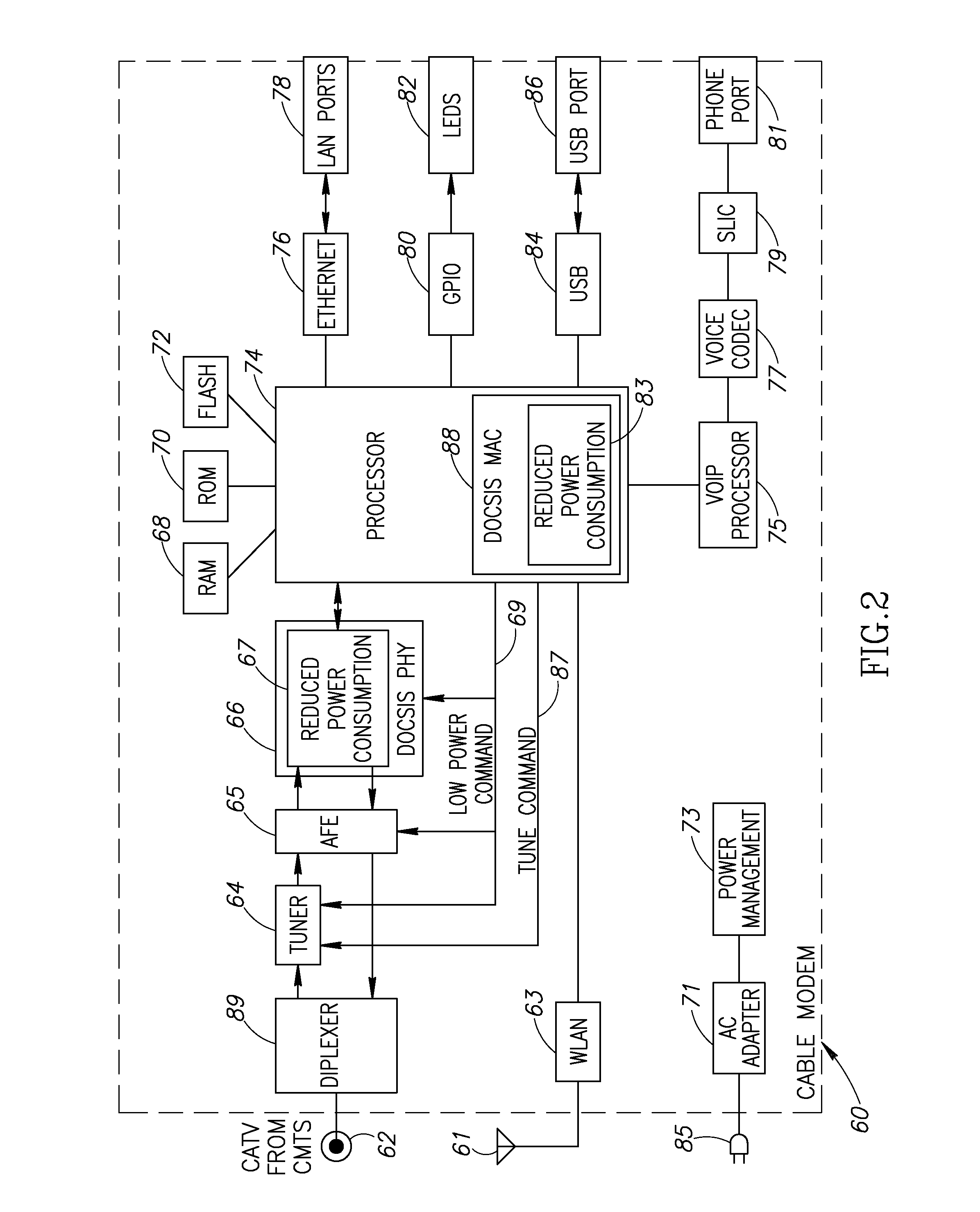
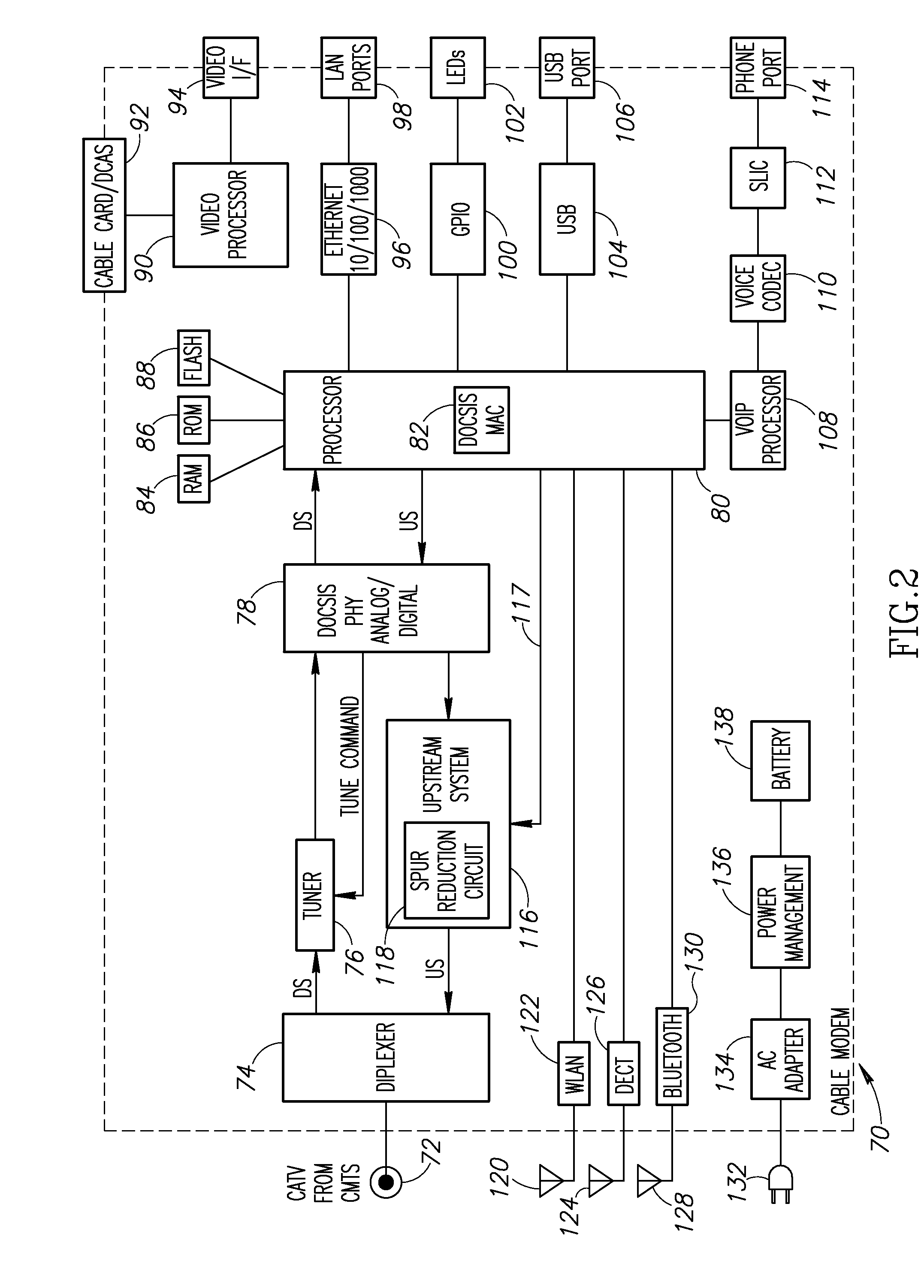
Apparatus for and method of reducing power consumption in a cable modem
ActiveUS20080018427A1Reduce power consumptionReduce MechanismsError preventionFrequency-division multiplex detailsDOCSISBandwidth requirement
A novel apparatus and method of reduced power consumption for battery backup operation of a communication device such as a cable modem. When the cable modem senses a failure of the external power source it requests from the cable head-end to switch from multi-channel DOCSIS 3.0 operation to single-channel DOCSIS 2.0 operation. In response to approval by the cable head-end, the cable modem shuts down multi-channel circuits in the PHY such as the wideband analog to digital converter (ADC) which is normally used during multi-channel operation. In its place, it activates narrowband circuitry such as a narrowband ADC which consumes far less power. Tuner filter circuits are also swapped to match the reduced bandwidth requirements of battery backup operation. To further reduce power, the narrower bandwidth requirements during battery backup operation permit the linearity of a programmable gain amplifier (PGA) in the upstream path to be reduced.
Owner:MAXLINEAR INC
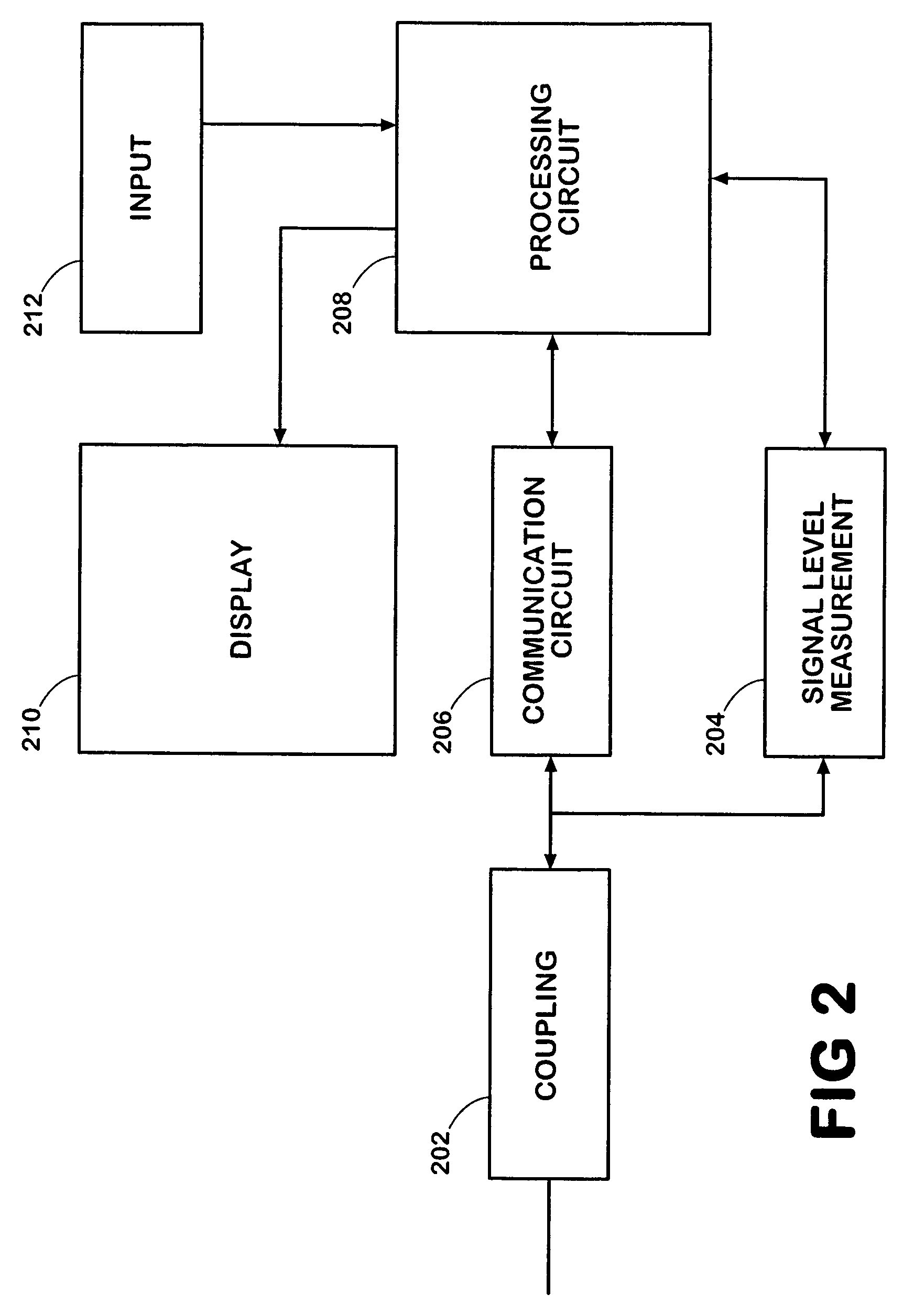
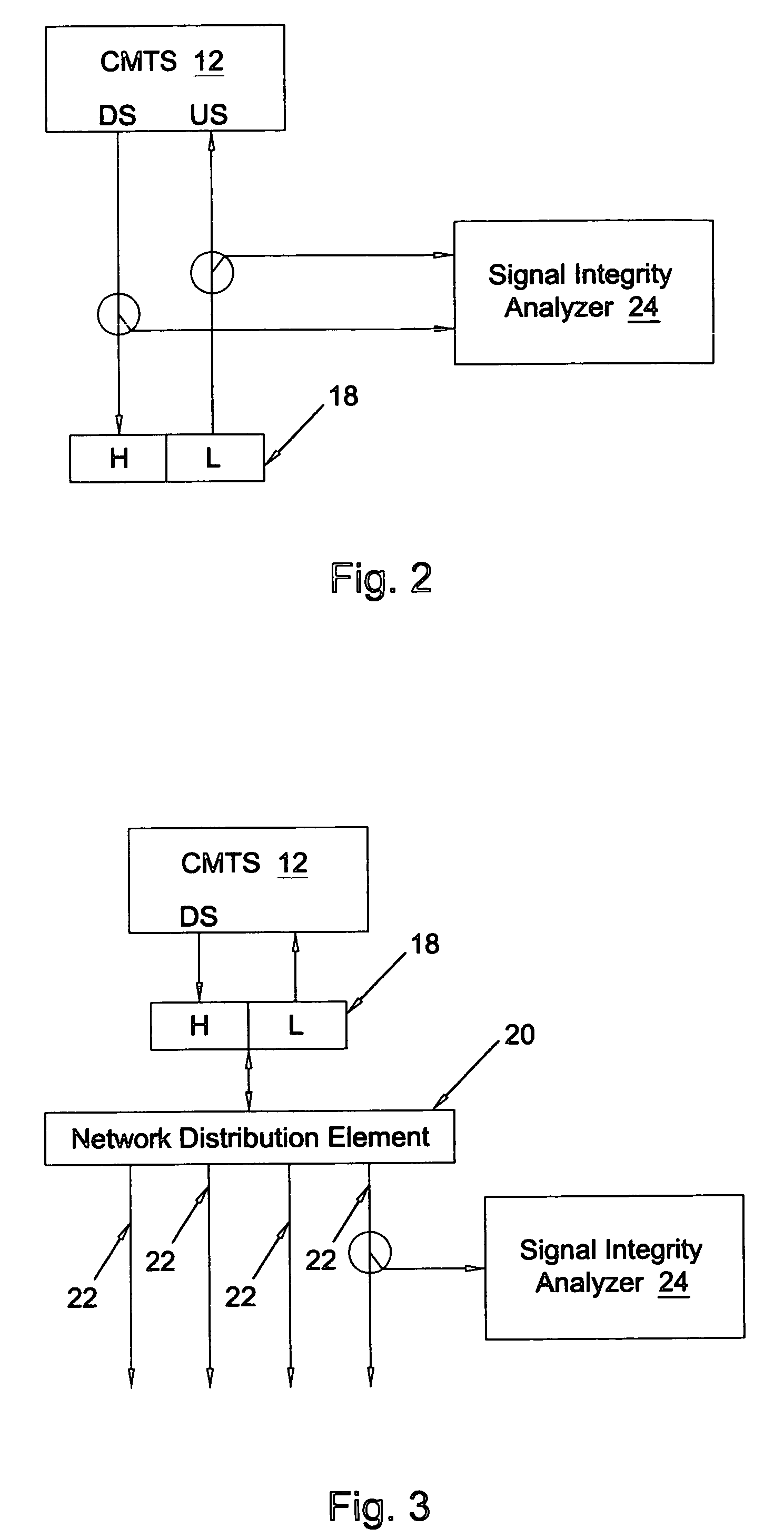
Data connection quality analysis apparatus and methods
ActiveUS20060250967A1Prevents priorityError preventionFrequency-division multiplex detailsData connectionPacket generator
A test device enables DOCSIS link testing in a HFC network without requiring the CMTS or other router at the headend of the HFC network to respond to ICMP messages. The test device includes a test packet generator for generating test packets having a destination Internet protocol (IP) address associated with a test device, a memory for storing transmission parameters of the test packets, and a test packet evaluator associated with the IP address in the generated test packets. The test packet evaluator receives the generated test packets after the test packets have been routed through a router at a head end of a HFC network and compares reception parameters for the received test packets to the transmission parameters stored in the memory.
Owner:VIAVI SOLUTIONS INC
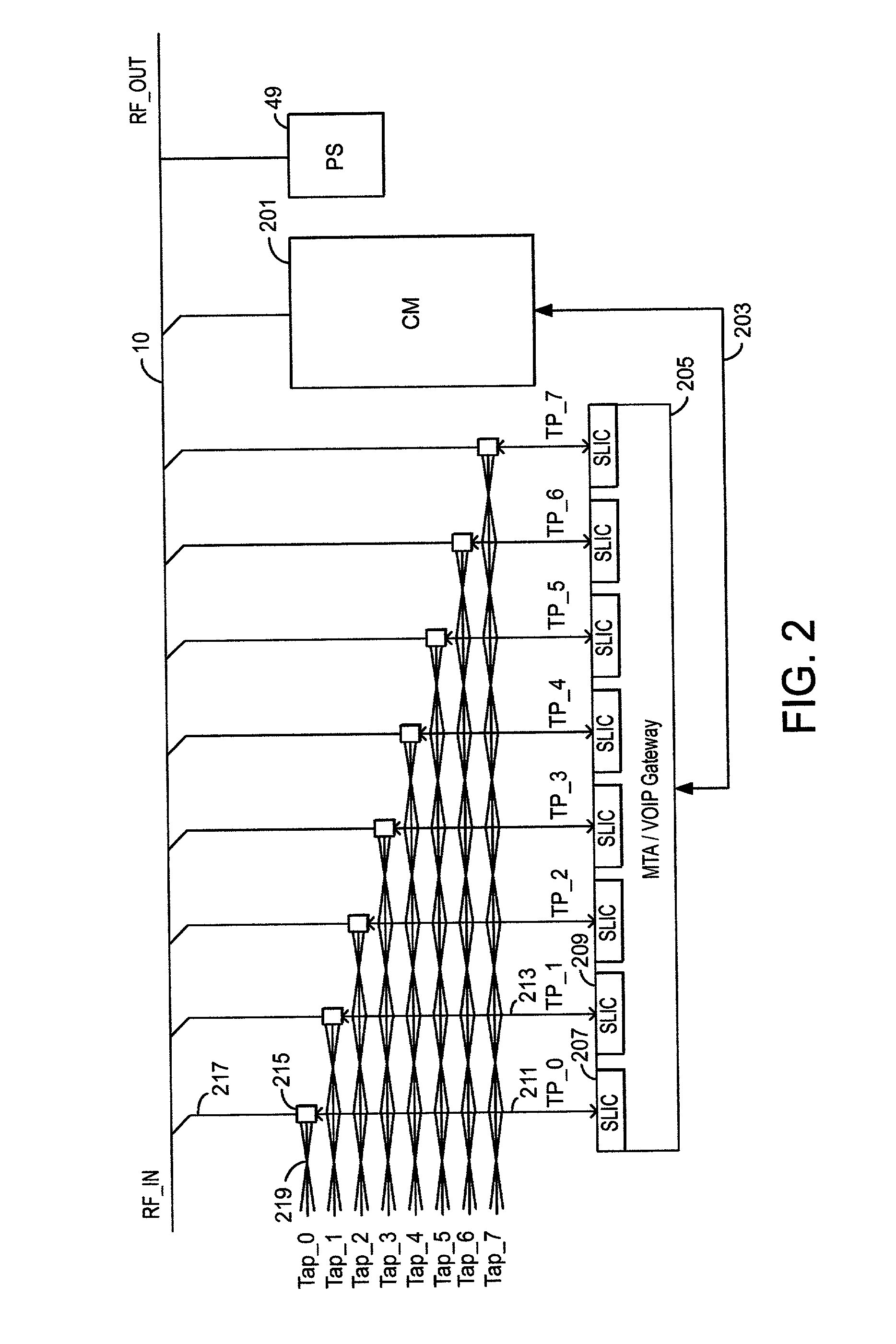
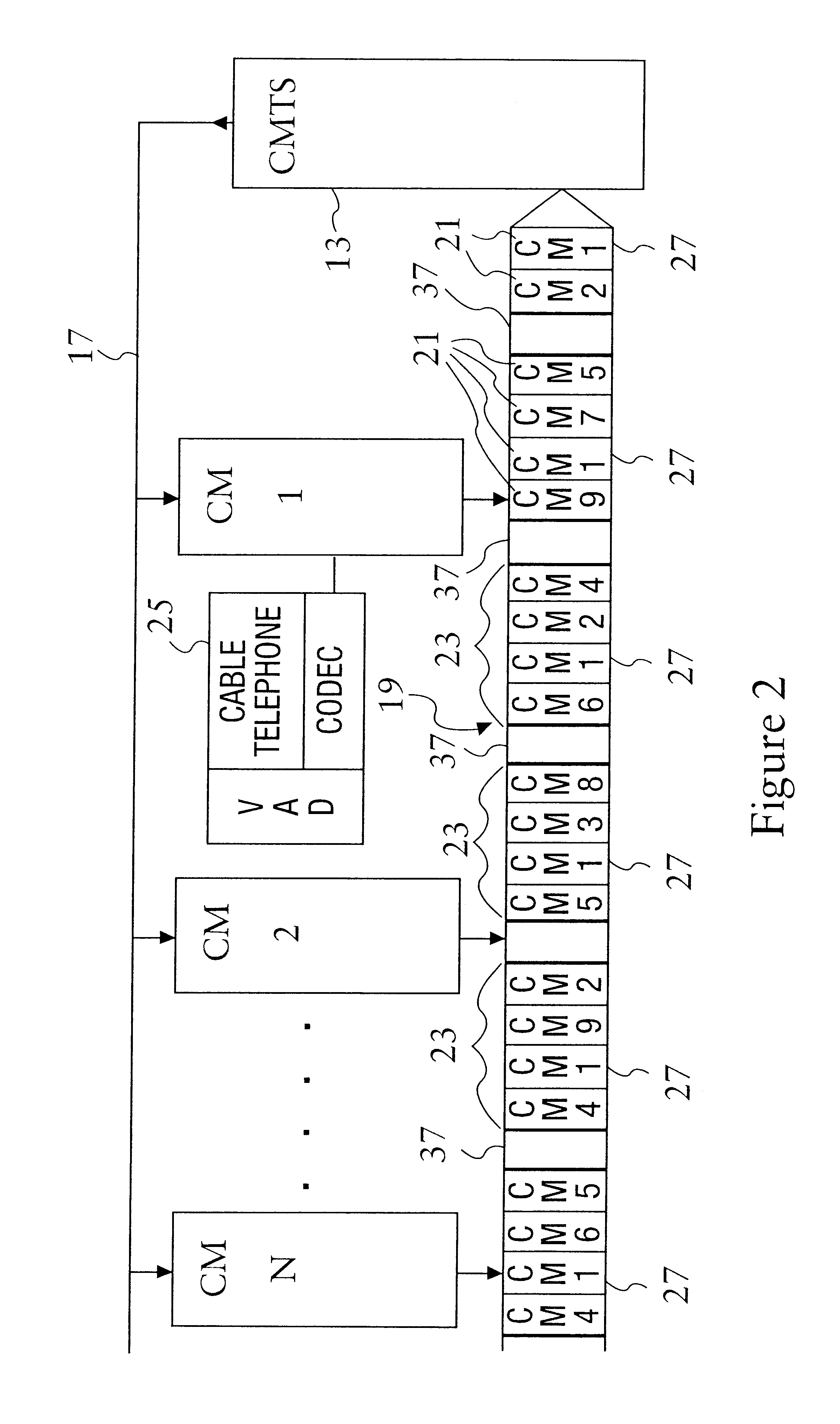
Method to transmit silence compressed voice over IP efficiently in DOCSIS cable networks
InactiveUS6847635B1Accurately and quickly transmitSent very quickly and very accuratelyBroadband local area networksTwo-way working systemsModem deviceNetwork packet
A method to use the data packet carrying ability of cable TV networks as described in DOCSIS to accurately and quickly transmit a voice call from a cable user to another user over a cable TV cable. The cable telephone, or cable modem, is given the ability to detect when voice activity from the subscriber is above and below a predetermined value. When the cable modem has voice activity, the cable modem knows that it will have a continuous stream of voice data packets which need to be sent very quickly and very accurately to the CMTS. Therefore, the cable modem requests a periodic stream of time slots from the CMTS. When the cable modem detects no voice activity or a silence period from the subscriber, the cable modem indicates that the periodic stream of time slots is no longer needed and the CMTS stops providing the periodic stream of time slots. When voice activity of the subscriber resumes, the cable modem again request the periodic stream of time slots, and transmits the voice data packets or cells in these time slots.
Owner:HEWLETT-PACKARD ENTERPRISE DEV LP +1
Tunneling scheme for transporting information over a cable network
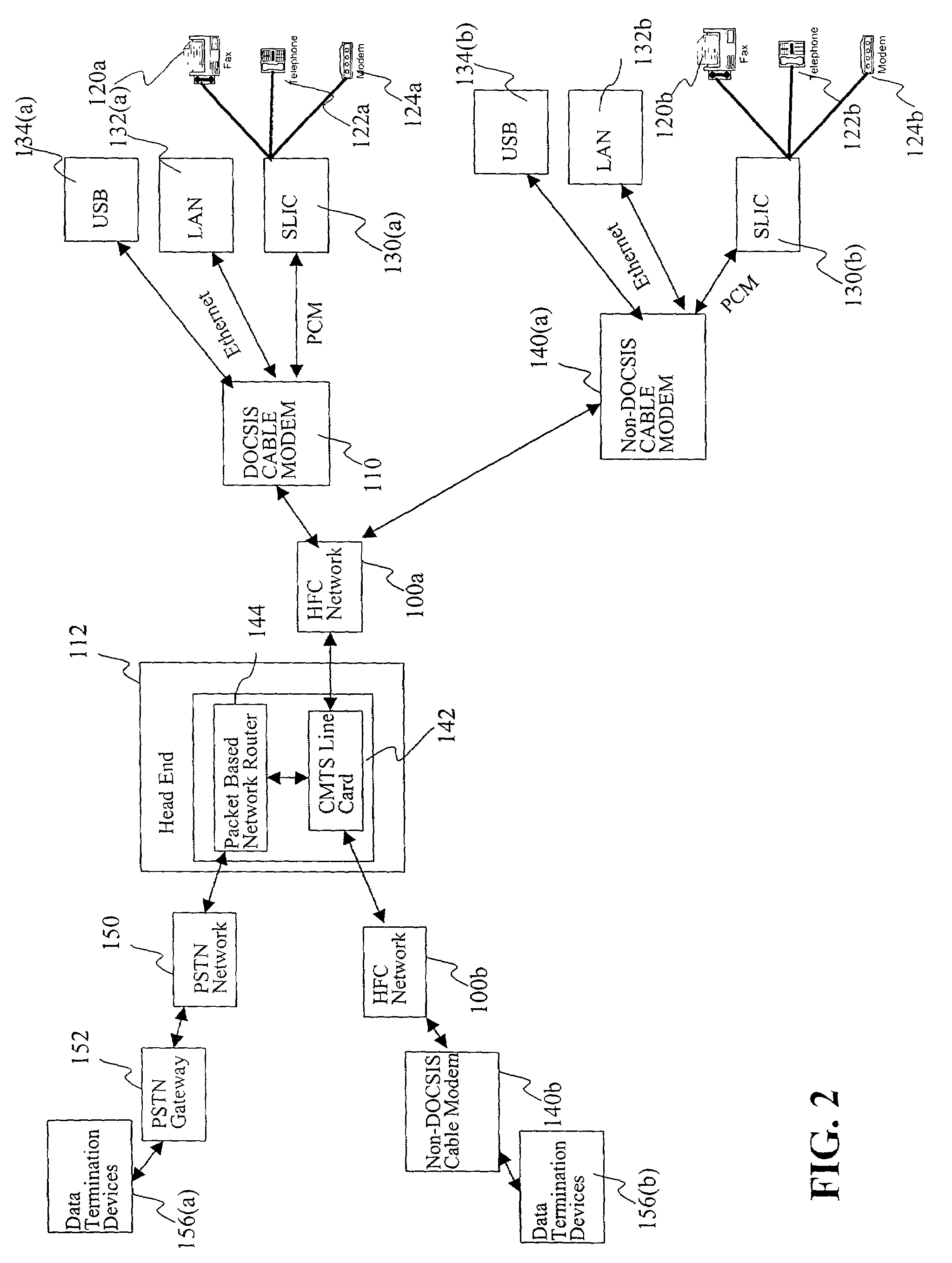
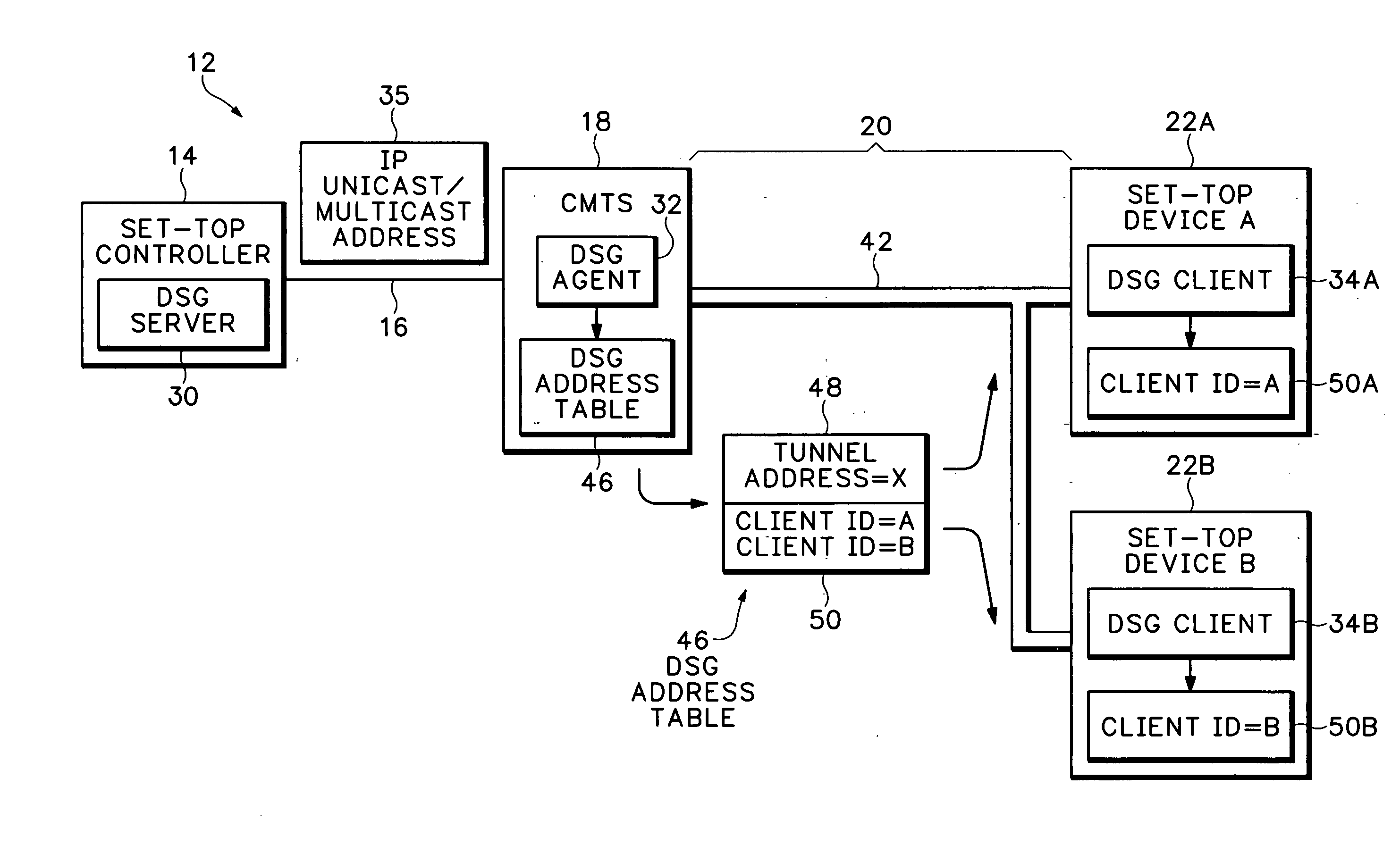
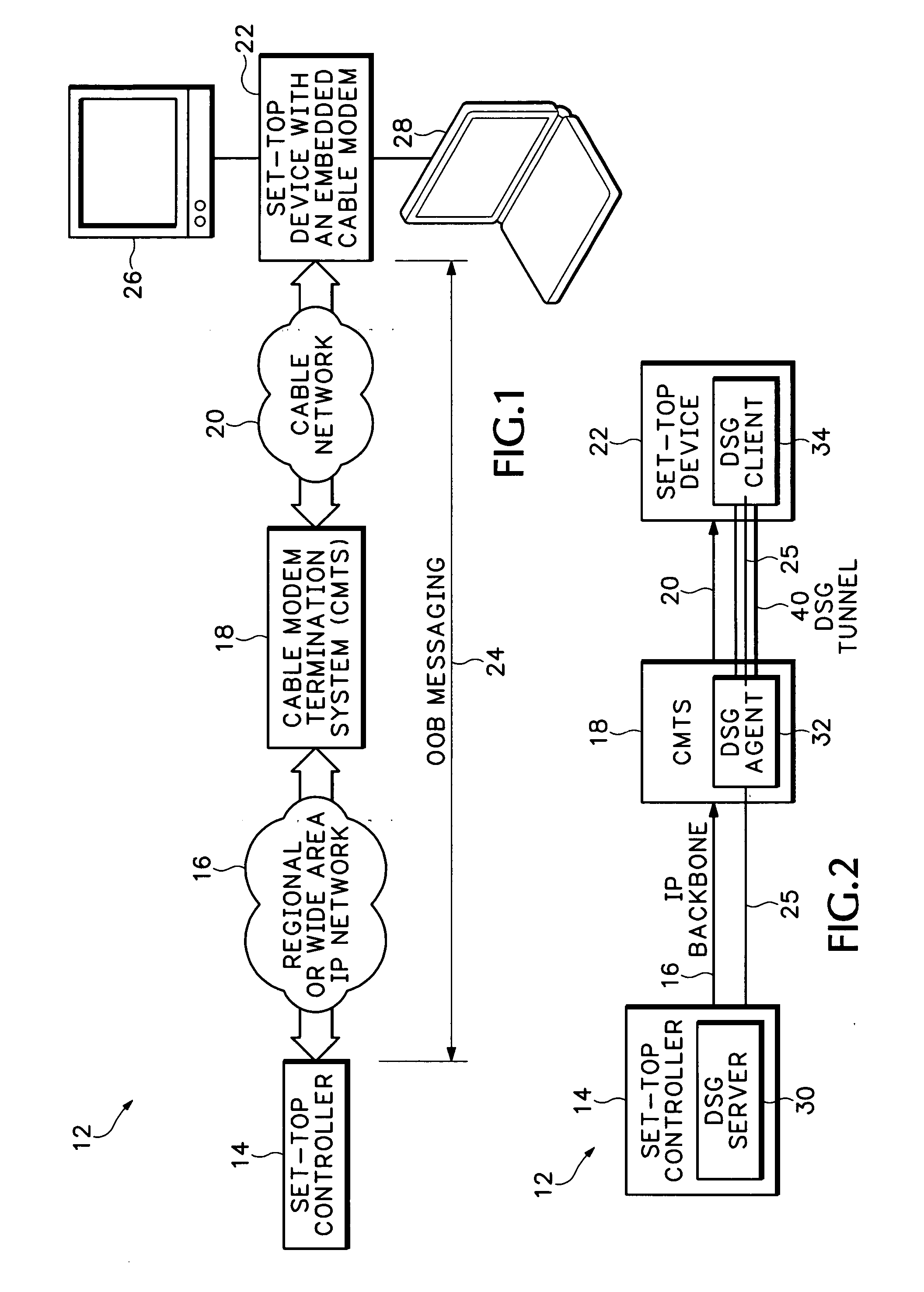
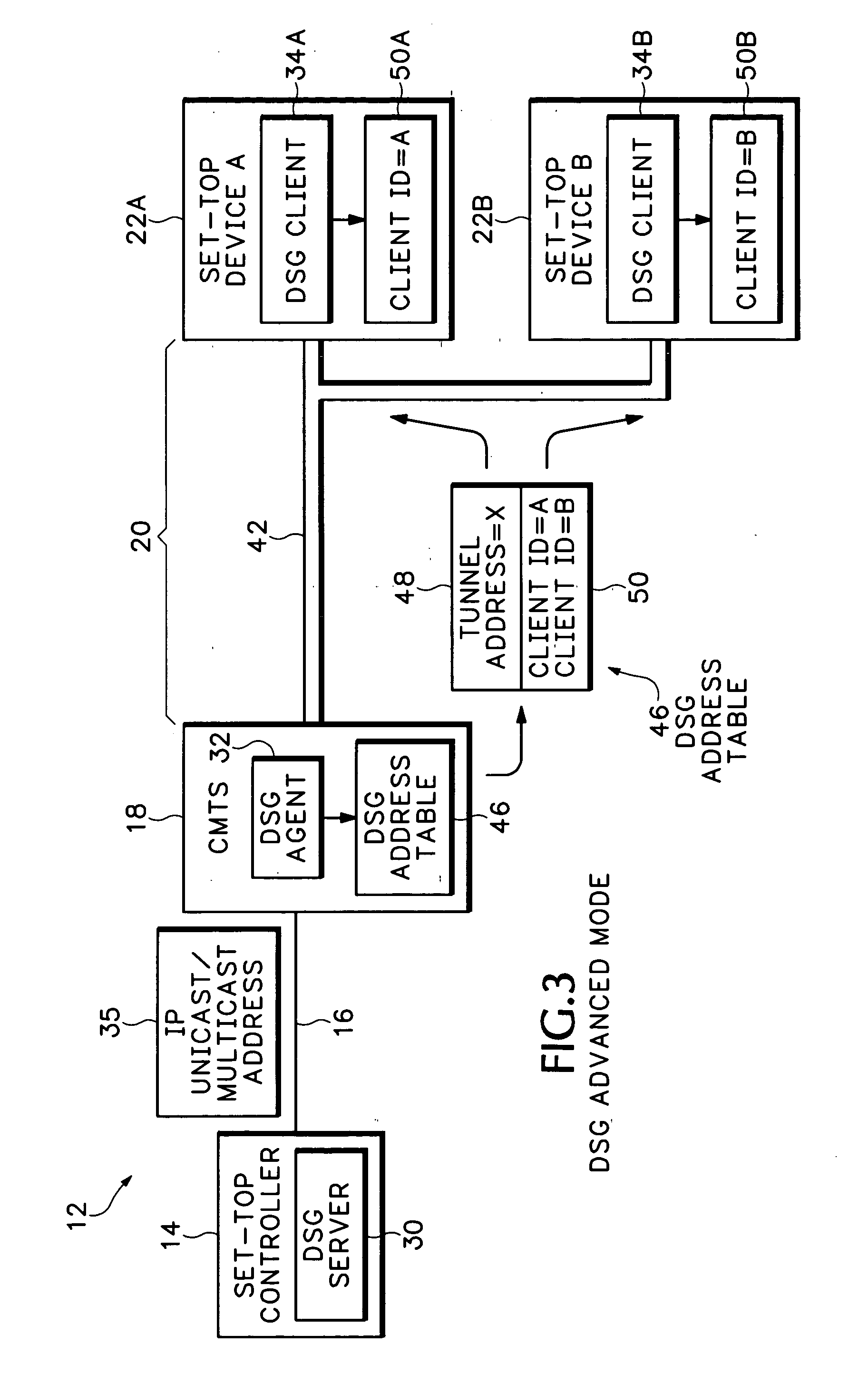
ActiveUS20050265398A1Readily apparentSpecial service provision for substationError preventionClient agentModem device
A cable network includes a Data Over Cable Service Interface Specifications (DOCSIS) set-top gateway (DSG) server connected to an Internet Protocol (IP) network and a DSG client operating in a set-top device connected to a cable network. A DSG agent operates in a cable modem termination system (CMTS) coupled between the IP network and the cable network. The DSG agent receives data from the DSG server and sends the data to the DSG client over dynamically assigned DSG tunnels.
Owner:CISCO TECH INC
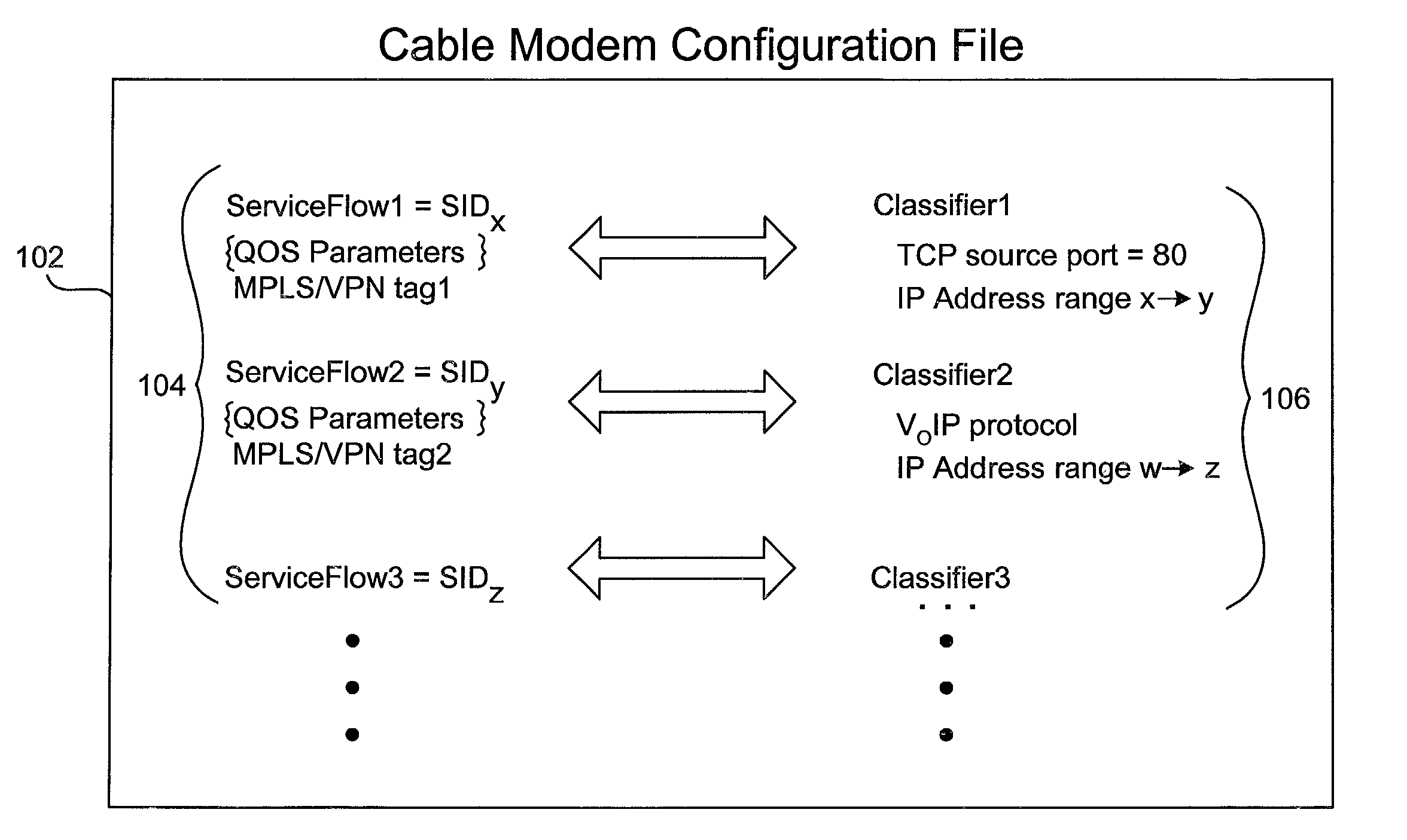
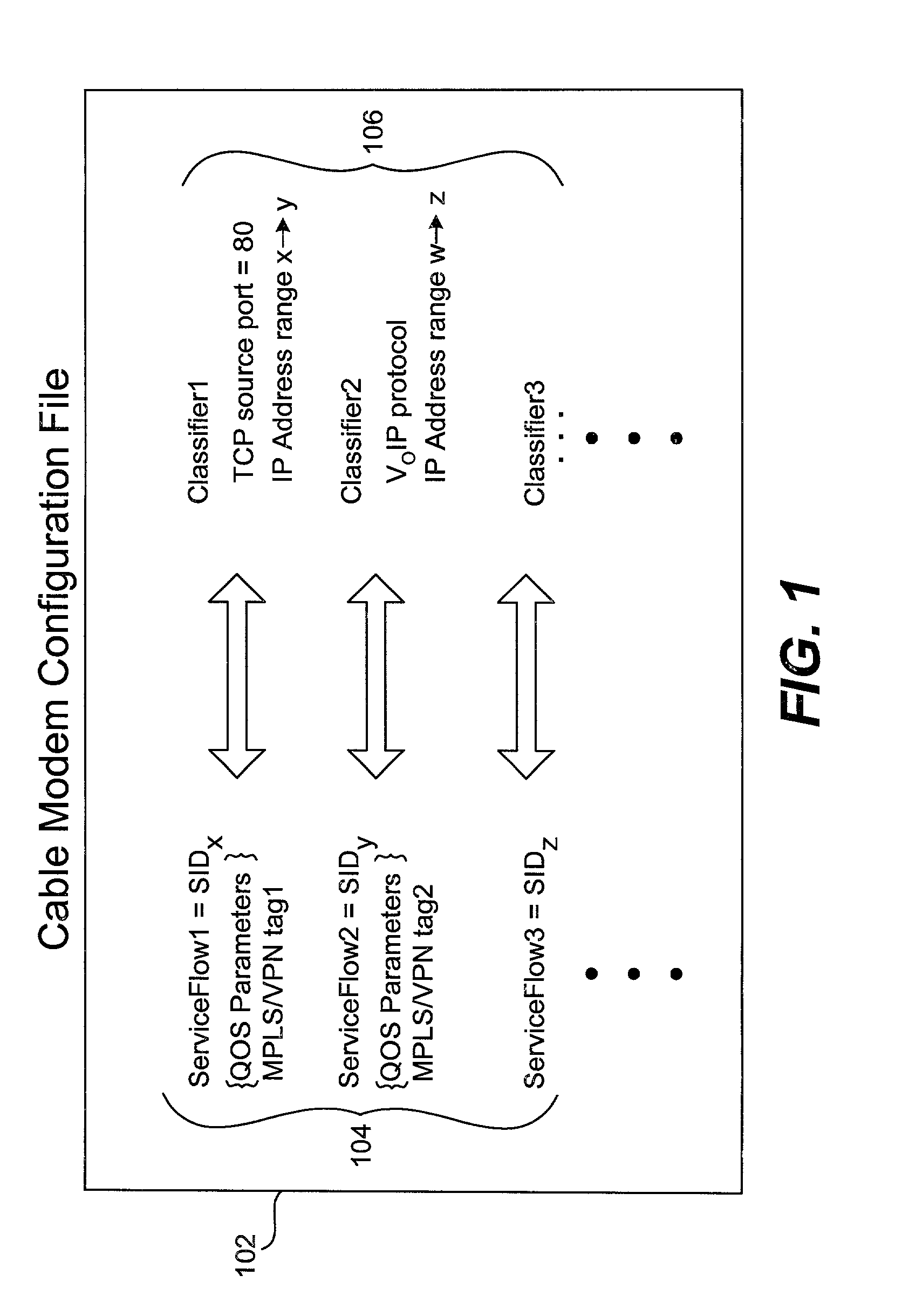
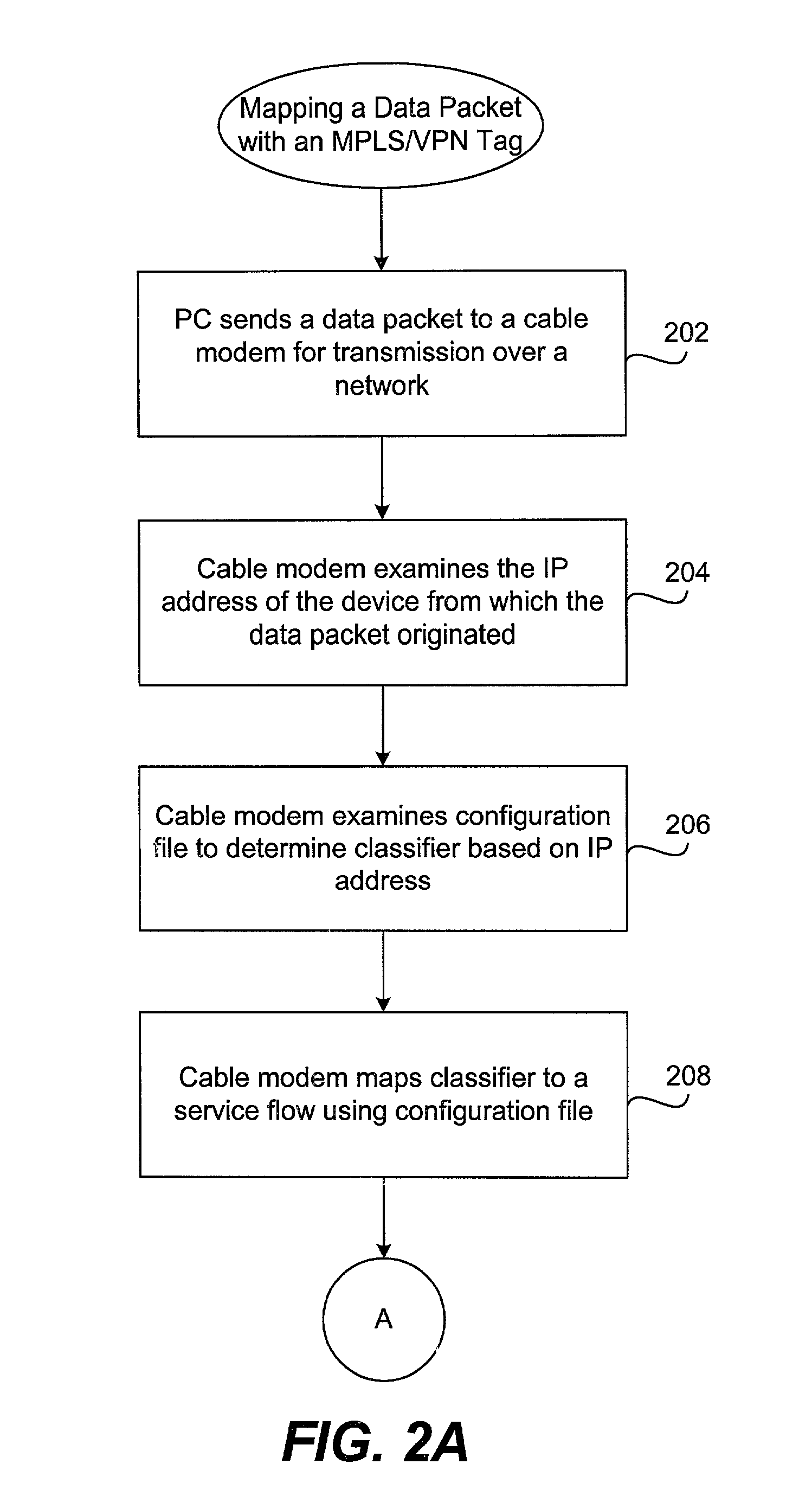
Method and apparatus for mapping an MPLS tag to a data packet in a headend
A method of using DOCSIS 1.1 features to allow the addition of ISPs and QOS levels to a single cable modem without having to modify the CMTS is described in the various figures. Instead of using the SID of a data packet to determine the VPN tag of a data packet (DOCSIS 1.0), a service flow is used to identify the appropriate tag. This is done using the DOCSIS 1.1 configuration file. By doing so, the need for creating additional sub-interfaces in the cable modem interface does not arise. Instead, the configuration is modified at the provisioning server, i.e., the DHCP / TFTP server.
Owner:CISCO TECH INC
Traffic Flow Scheduling Techniques Implemented on Bonded Channels of a Shared Access Cable Network
Owner:CISCO TECH INC
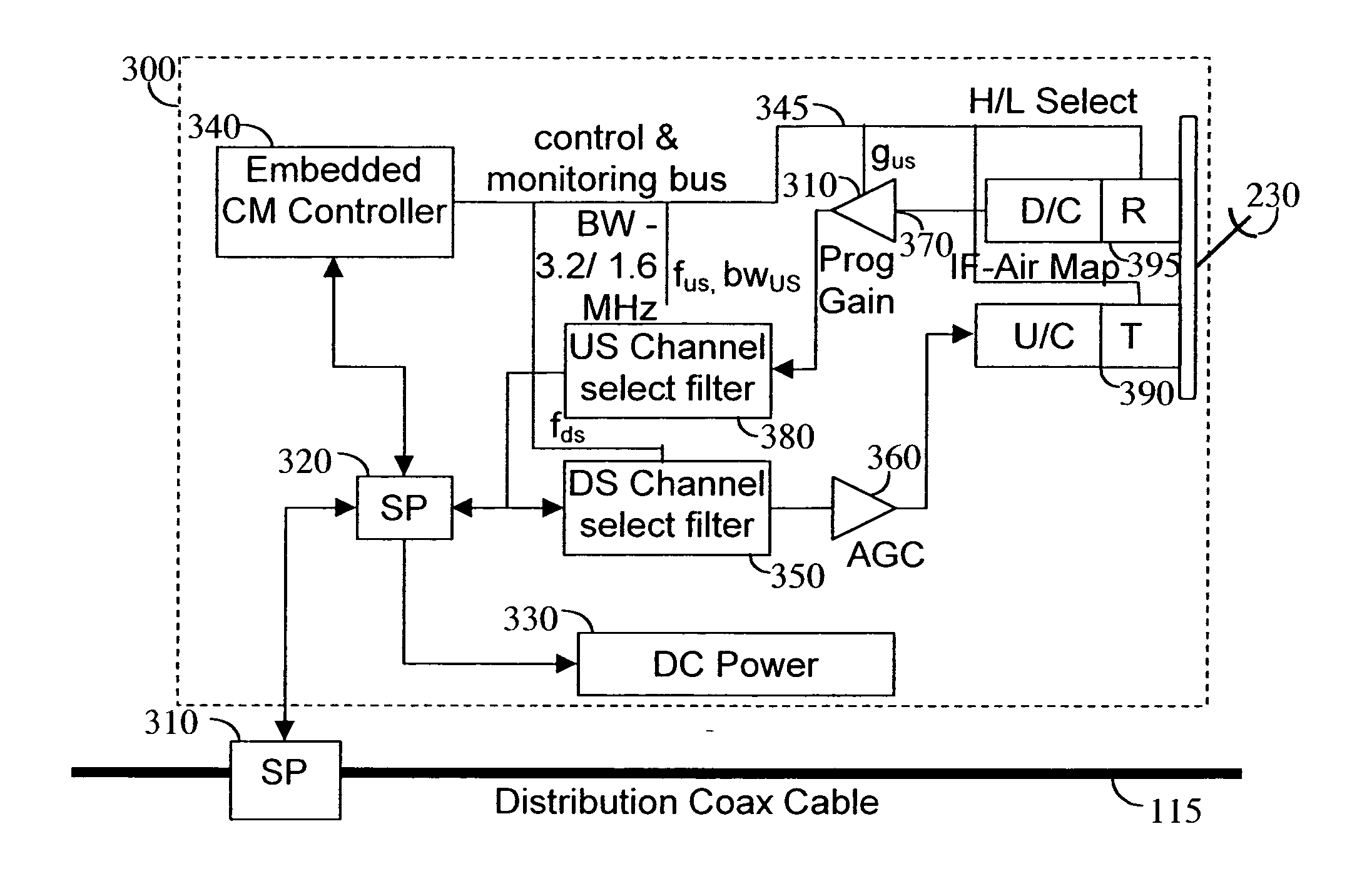
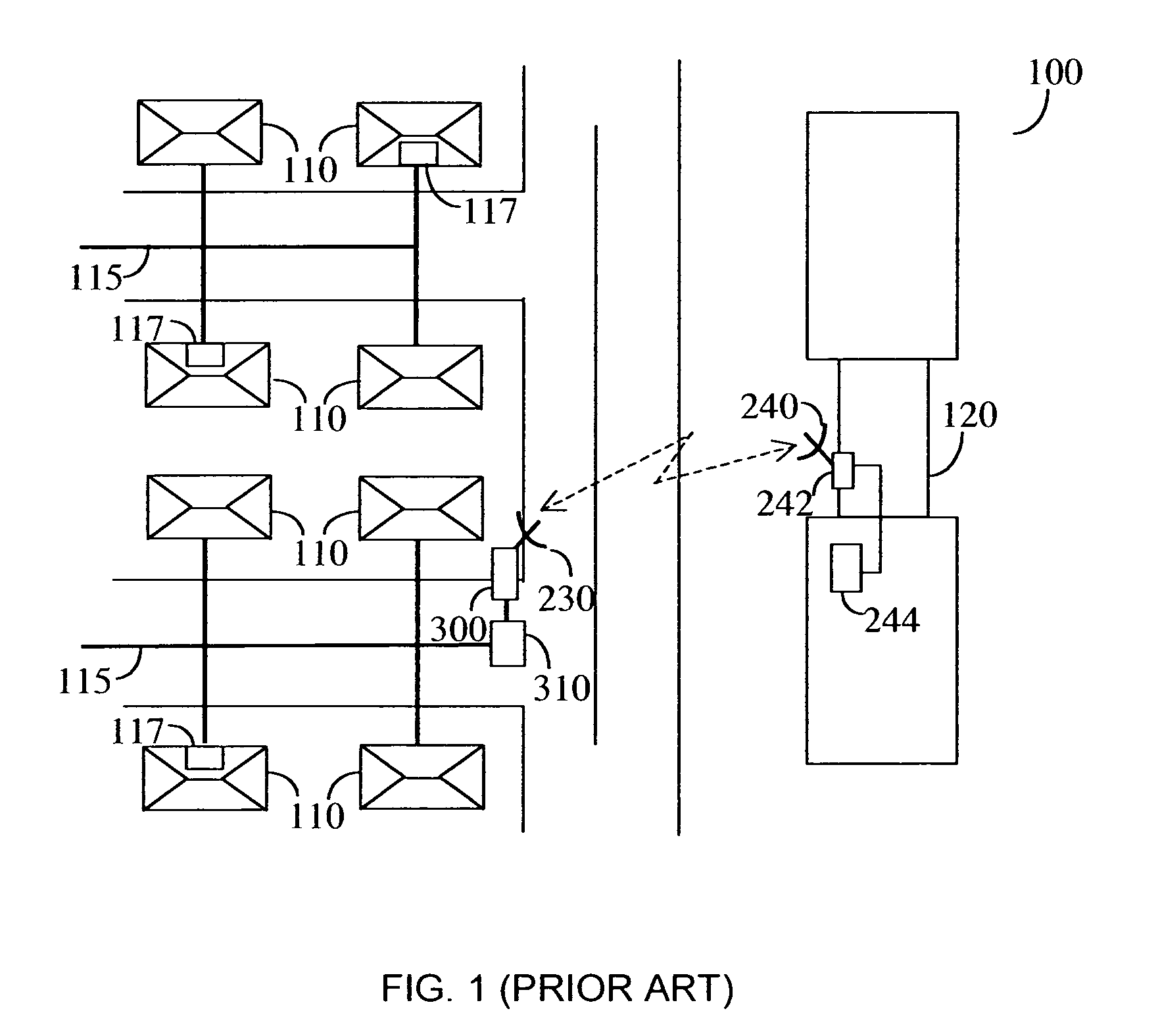
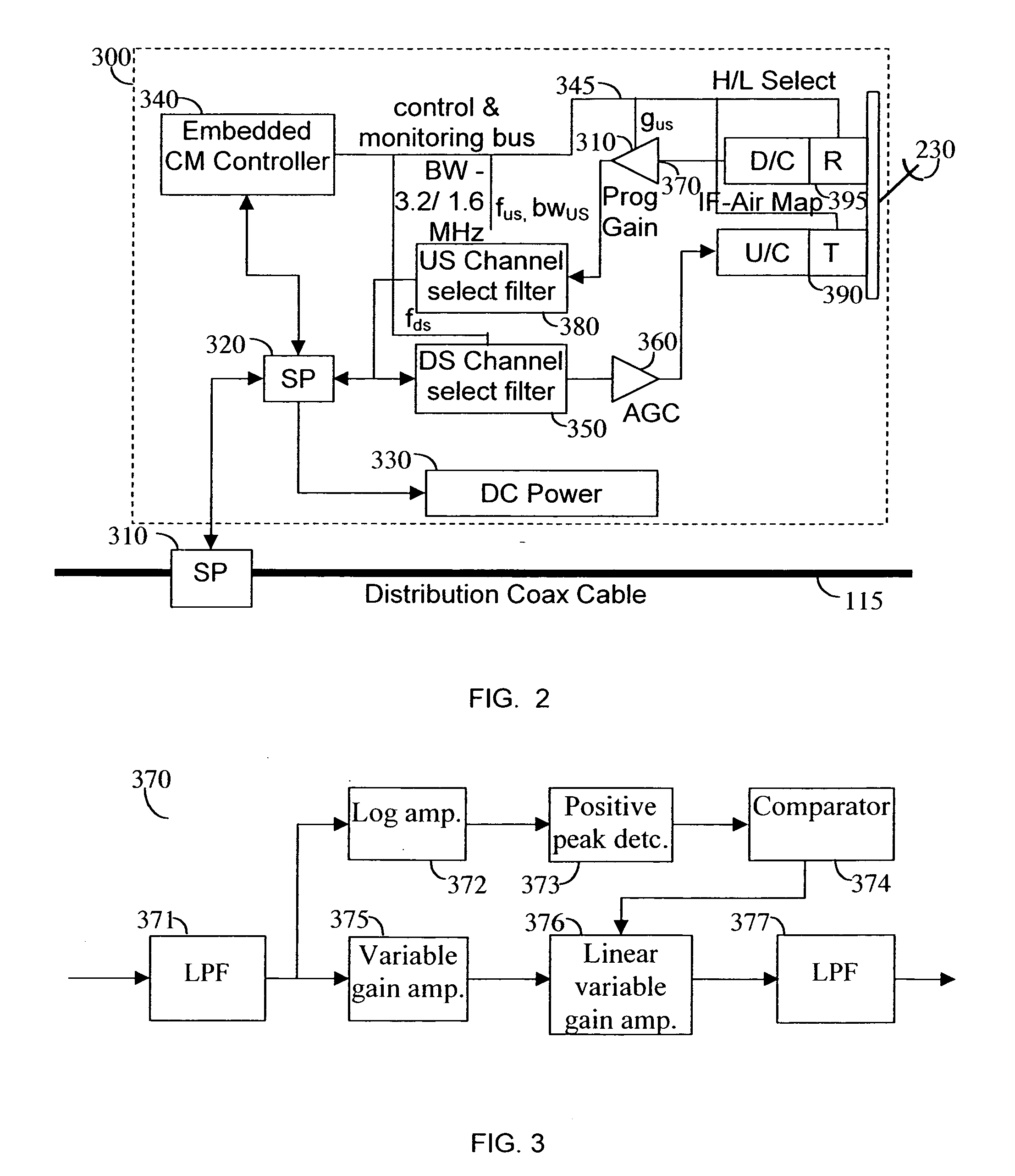
Apparatus and method for reduction of wireless links noise injection to a DOCSIS cable modem service
InactiveUS20050144649A1Reducing overall noise injectionReduce noiseError preventionTransmission systemsTransceiverCoaxial cable
A DOCSIS cable modem service can be extended by providing wireless links that connect users that are beyond the physical reach of the system. This may require that the downstream data are transferred over a wireless link to a remote subscriber radio frequency (RF) unit connected to a cable modem that provides the downstream data to the subscriber. Similarly, upstream data are sent from the subscriber cable modem over the wireless link to the wireless hub transceiver, where such data are inserted back to the distribution coax cable. This insertion causes the injection of noise into the DOCSIS cable modem system. Connecting a plurality of such devices can cause noise beyond the system limitations. By using a burst detect system, the RF receiver portion of the device is connected to the DOCSIS cable only when injecting data upstream, thereby reducing the overall noise injection.
Owner:ARCWAVE +1
Data connection quality analysis apparatus and methods
ActiveUS7489641B2Prevents priorityError preventionBroadband local area networksData connectionTTEthernet
A test device enables DOCSIS link testing in a HFC network without requiring the CMTS or other router at the headend of the HFC network to respond to ICMP messages. The test device includes a test packet generator for generating test packets having a destination Internet protocol (IP) address associated with a test device, a memory for storing transmission parameters of the test packets, and a test packet evaluator associated with the IP address in the generated test packets. The test packet evaluator receives the generated test packets after the test packets have been routed through a router at a head end of a HFC network and compares reception parameters for the received test packets to the transmission parameters stored in the memory.
Owner:VIAVI SOLUTIONS INC
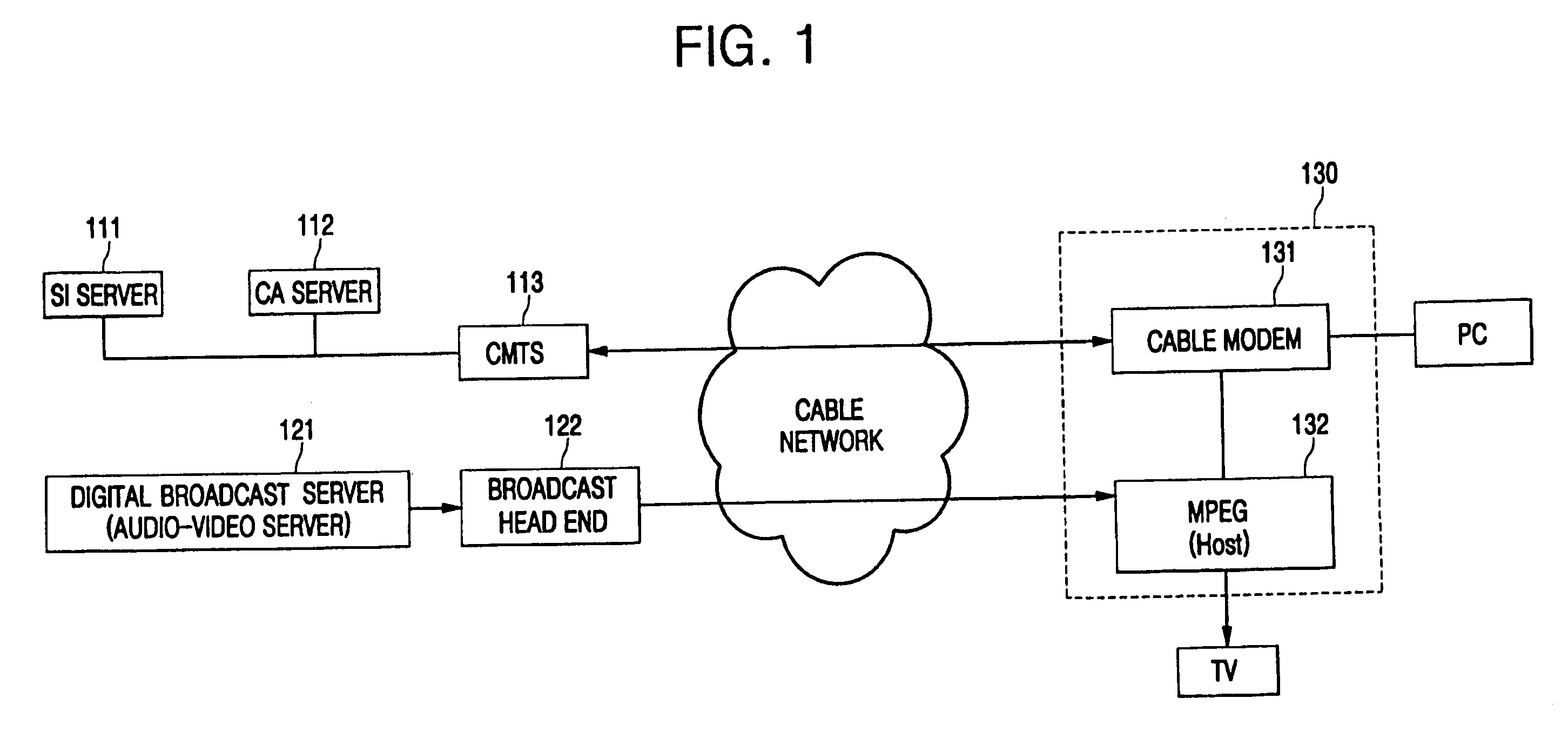
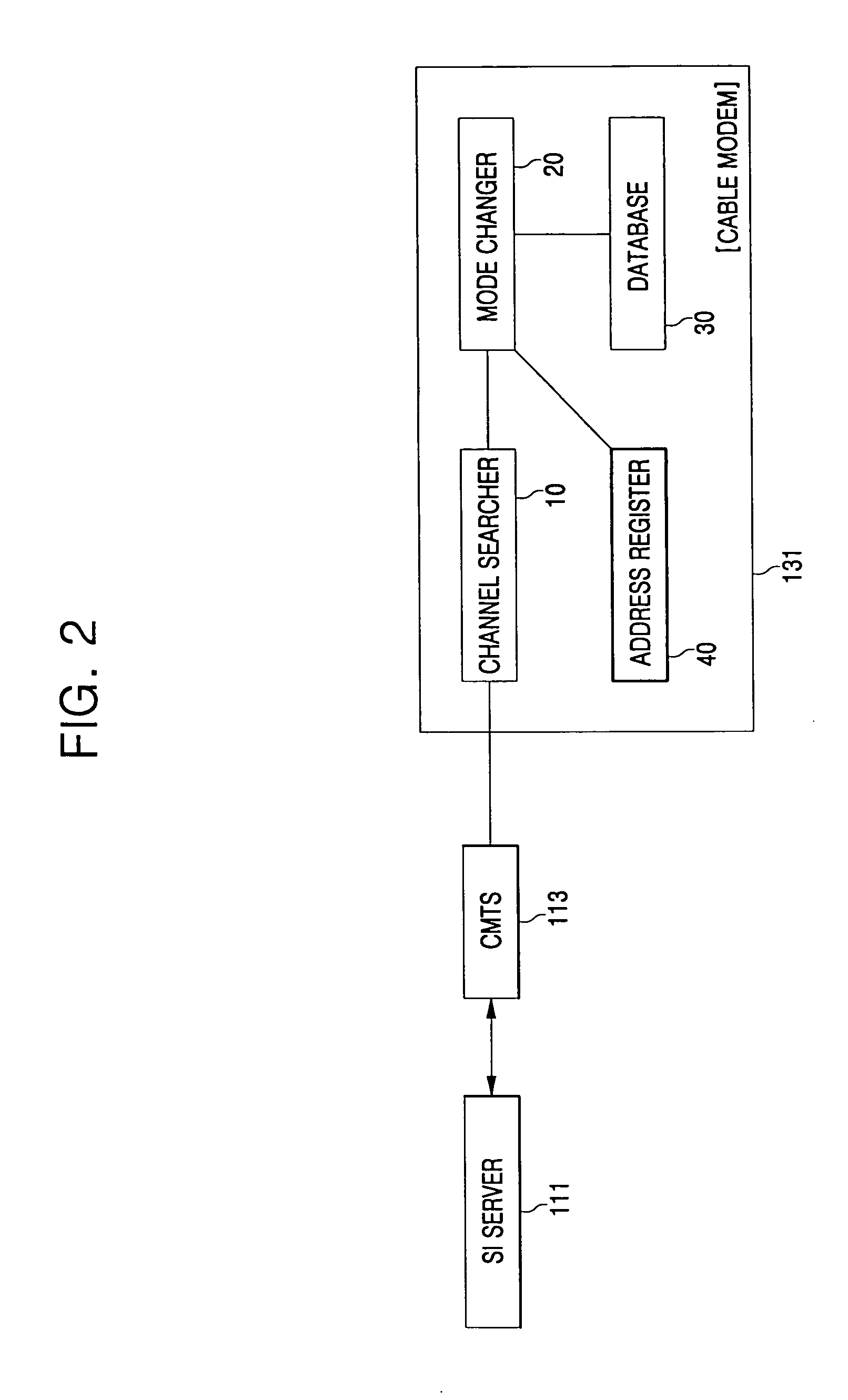
Changing mode in digital broadcast receiver
A method of changing between a Data over Cable Service Interface Specifications (DOCSIS) mode and a DOCSIS Set-top box Gateway (DSG) mode in a digital broadcast receiver, includes: performing channel searching to change into the DSG mode, and detecting a cause of a failure in securing a channel via a database upon failing to secure the channel in response to a user requesting a change of mode via a host; and recovering the DSG mode as a result of detecting the failure cause upon receiving DSG data. It is therefore possible to change from the DOCSIS mode to the DSG mode according to the state of the OpenCable digital broadcast receiver, thereby improving its capability of coping with a field.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Efficiently transmitting RTP protocol in a network that guarantees in order delivery of packets
ActiveUS20020106029A1Increased bandwidth capacityAvoid changeNetwork traffic/resource managementBroadband local area networksTransmission protocolTelecommunications
A method and computer program product for providing RTP suppression across a DOCSIS network. An index number and a set of rules are sent to a receiver. The index number indicates the type of header suppression technique (i.e., RTP header suppression) to be performed, and the set of rules define how to recreate the RTP packets on the receiving end. At least one complete RTP packet is transmitted upstream for enabling a receiver to learn the RTP header. Subsequent RTP packets are transmitted upstream for reconstruction at the receiving end. The subsequent RTP packets are comprised of delta values representing fields that dynamically change from packet to packet in an RTP header.
Owner:AVAGO TECH INT SALES PTE LTD
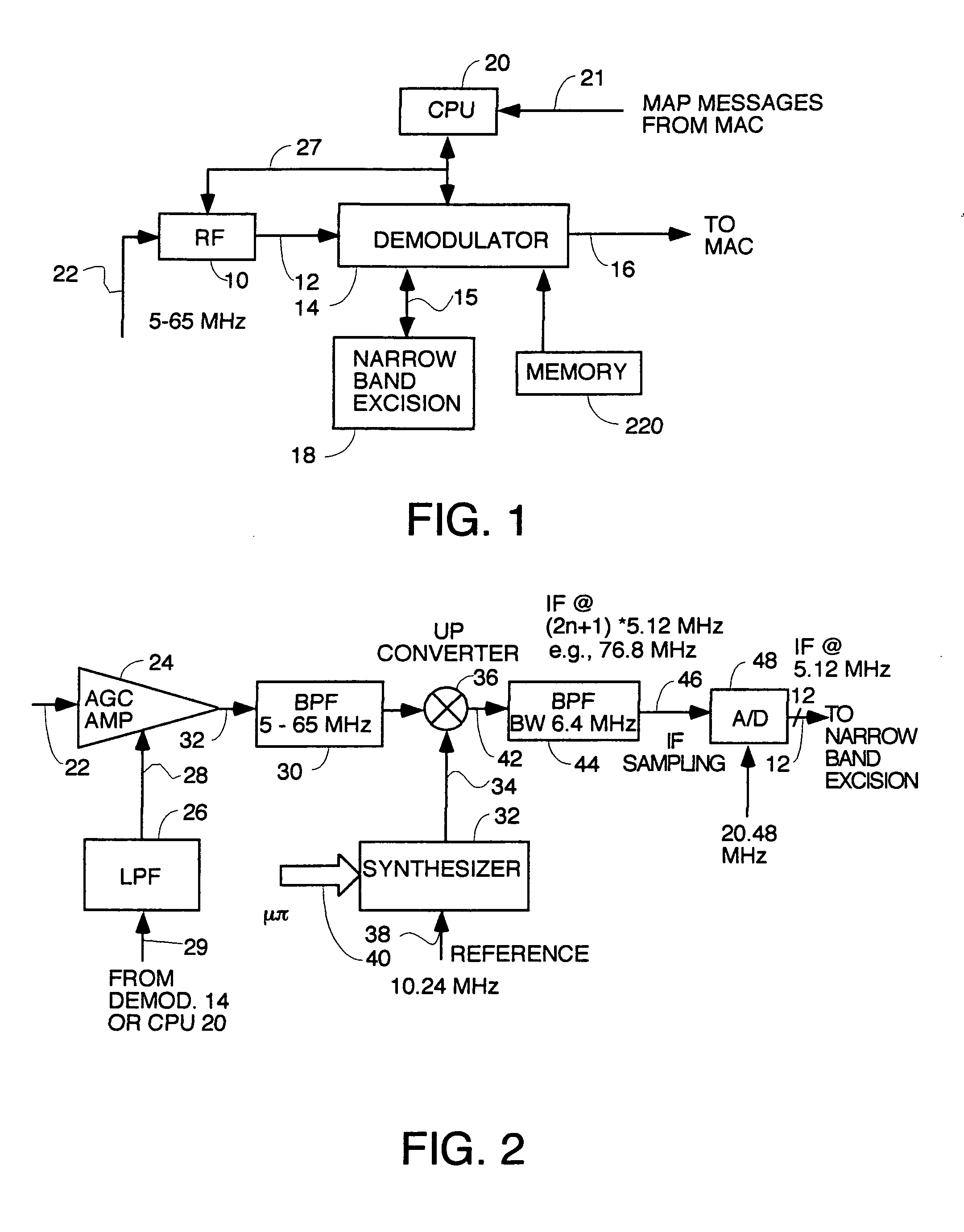
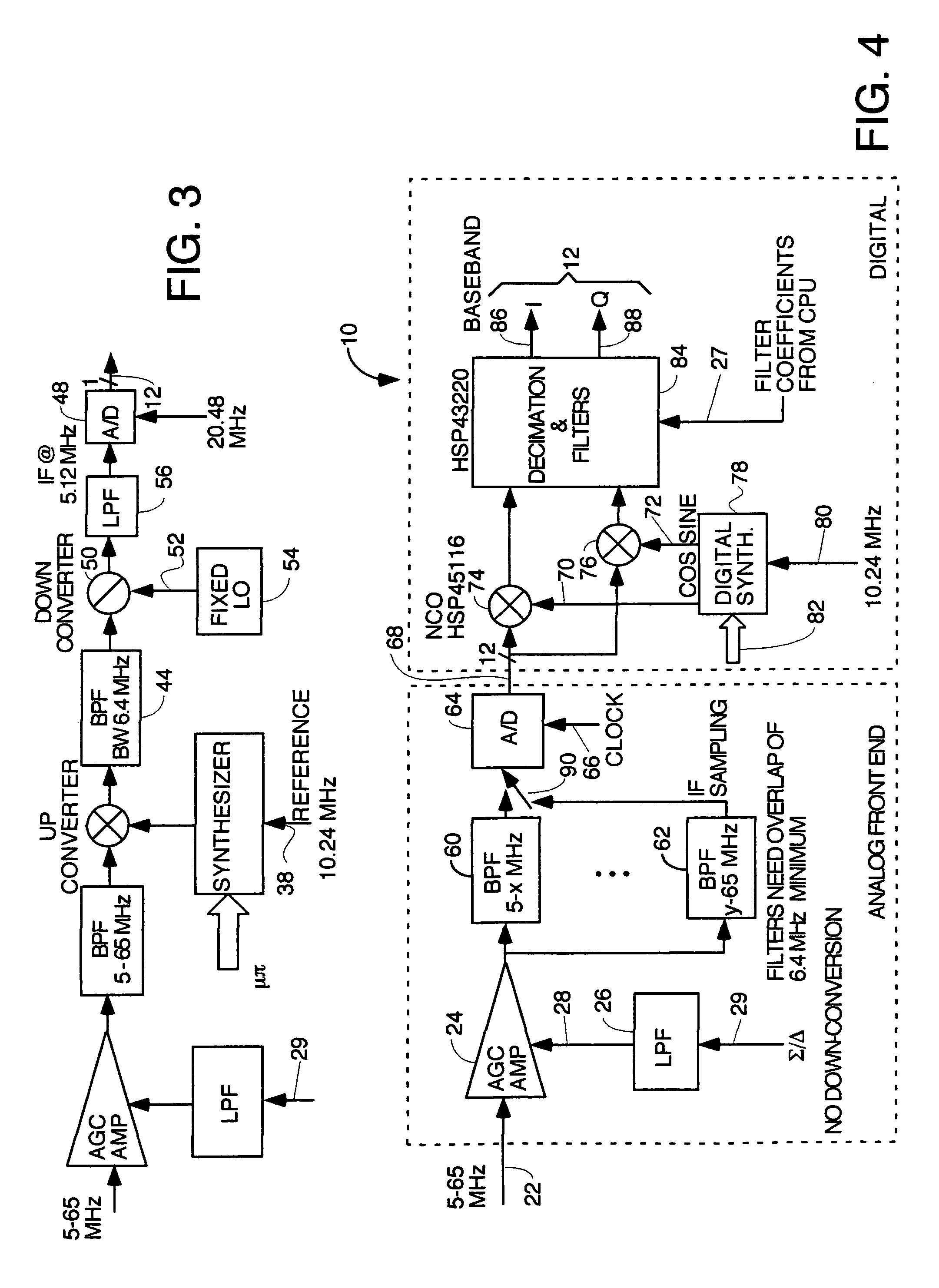
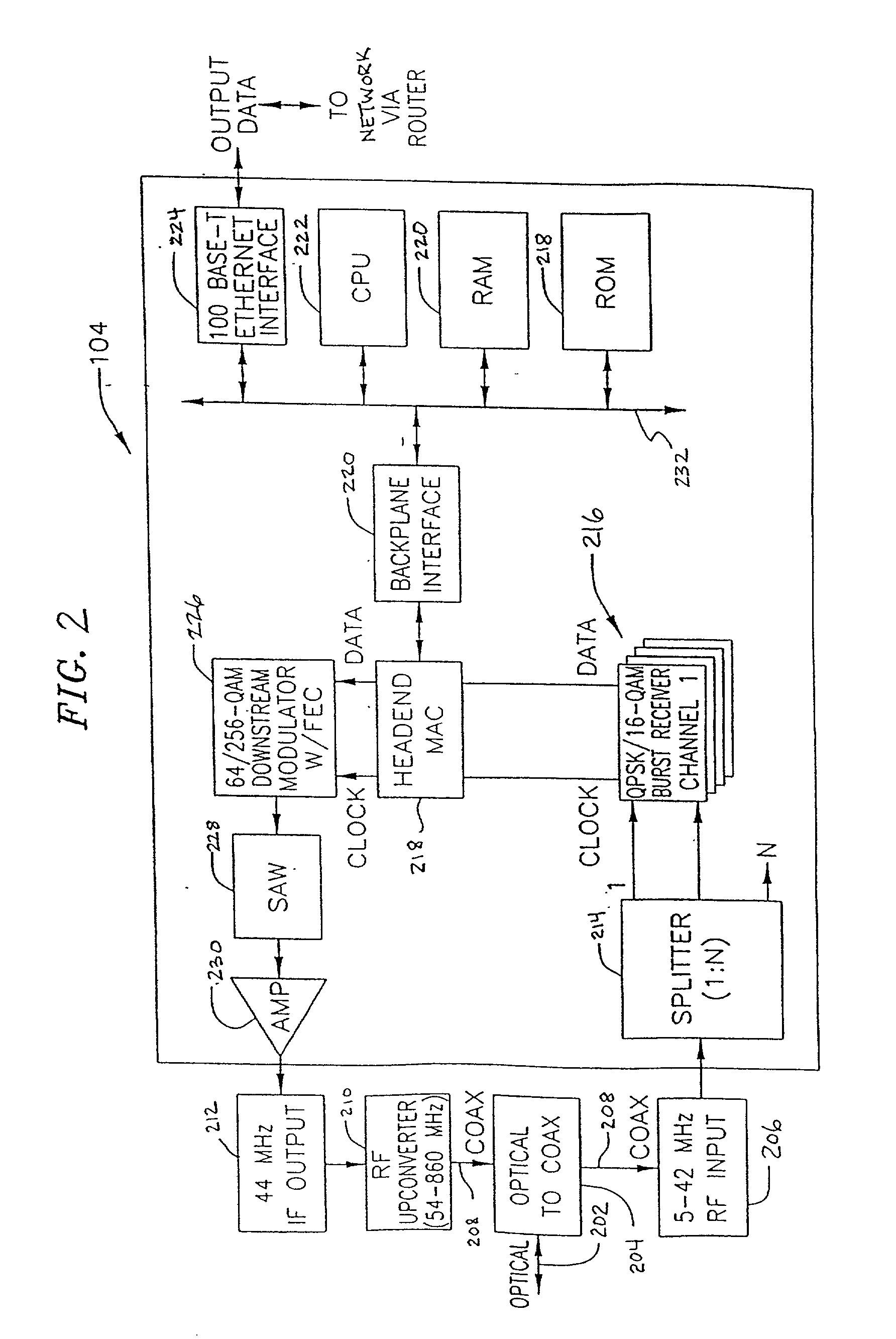
Method and apparatus for collectively and selectively analyzing the signal integrity of individual cable modems on a DOCSIS network
InactiveUS20050047442A1Error detection/prevention using signal quality detectorBroadband local area networksEngineeringDOCSIS
A method and apparatus is provided for quantifying the upstream communication signals transmitted by remotely deployed CMs, and particularly cable modems operated consistent with the DOCSIS specification. Specifically, the method and apparatus provides the capability to capture, demodulate, and analyze the digital transmission originating from a CM source of known or unknown origin, and determine the unique MAC address or SID of the source CM that is measured. Additionally, the method and apparatus has the ability to analyze in the presence of many CMs, a specific user defined or user defined range of CMs by the implementation of real-time filtering either by method of pre-determination of the arrival time of the CM signal or by real-time filtering and analysis of the captured CM signal.
Owner:FILTRONIC SIGTEK
Upstream physical interface for modular cable modem termination system
Owner:CISCO TECH INC
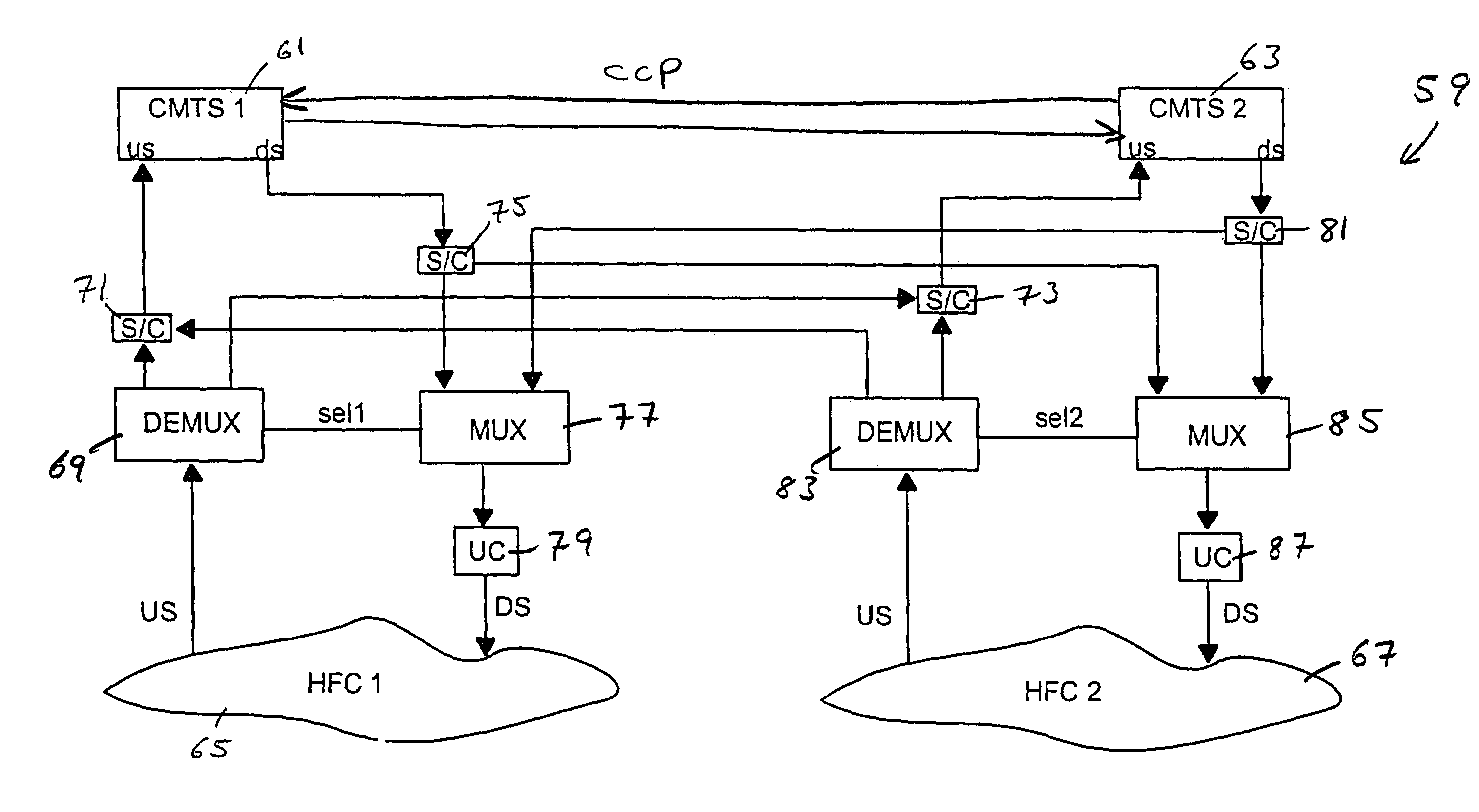
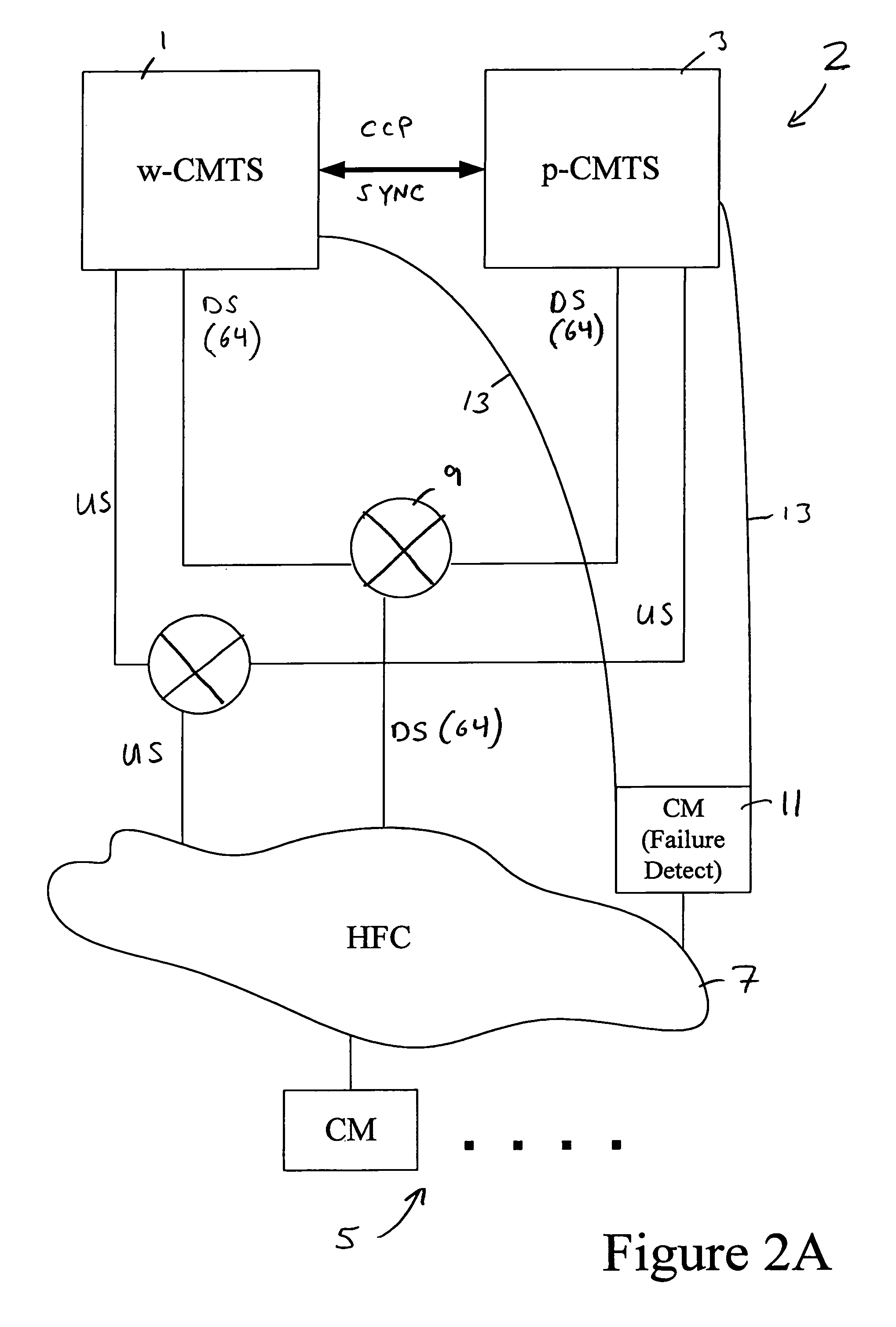
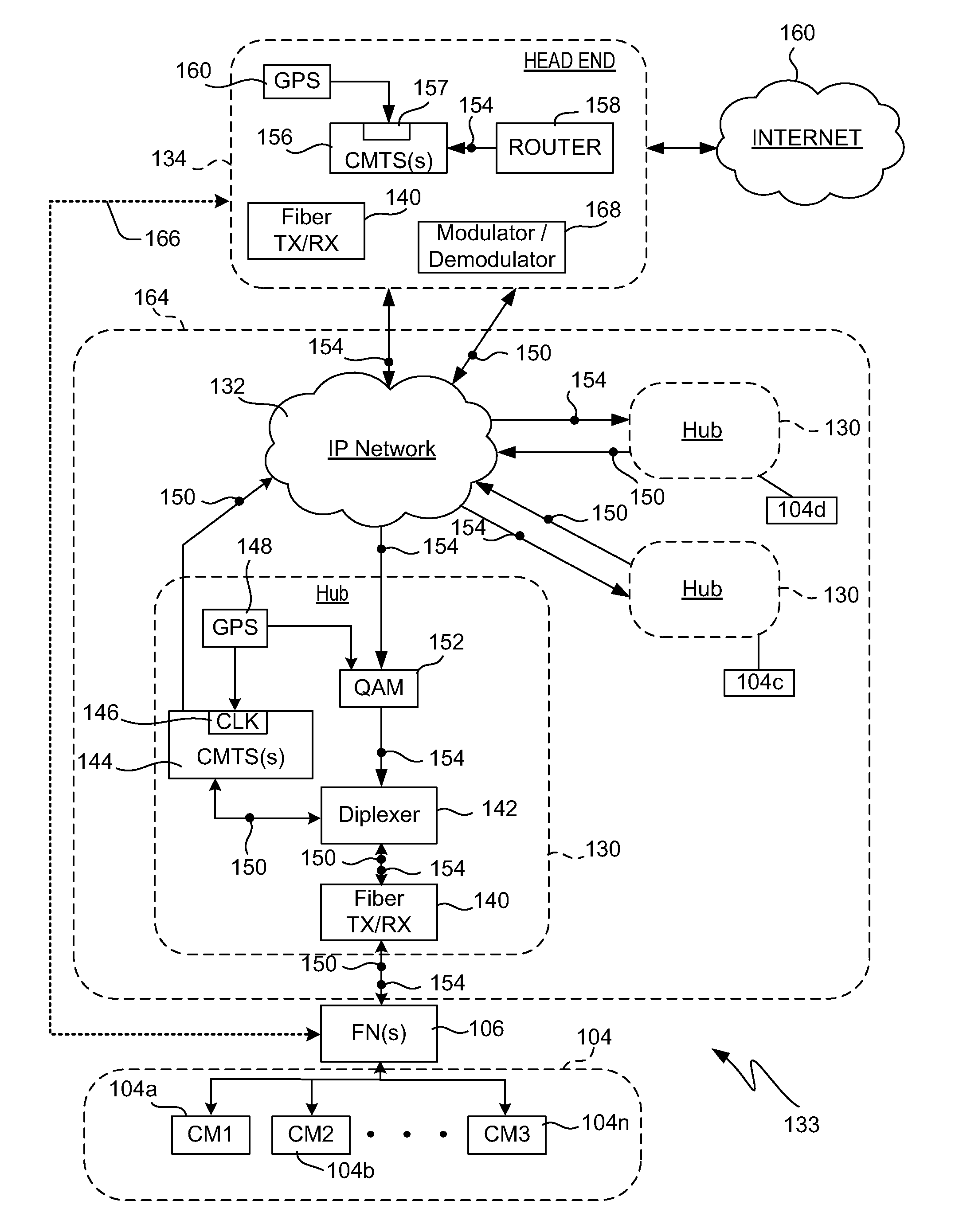
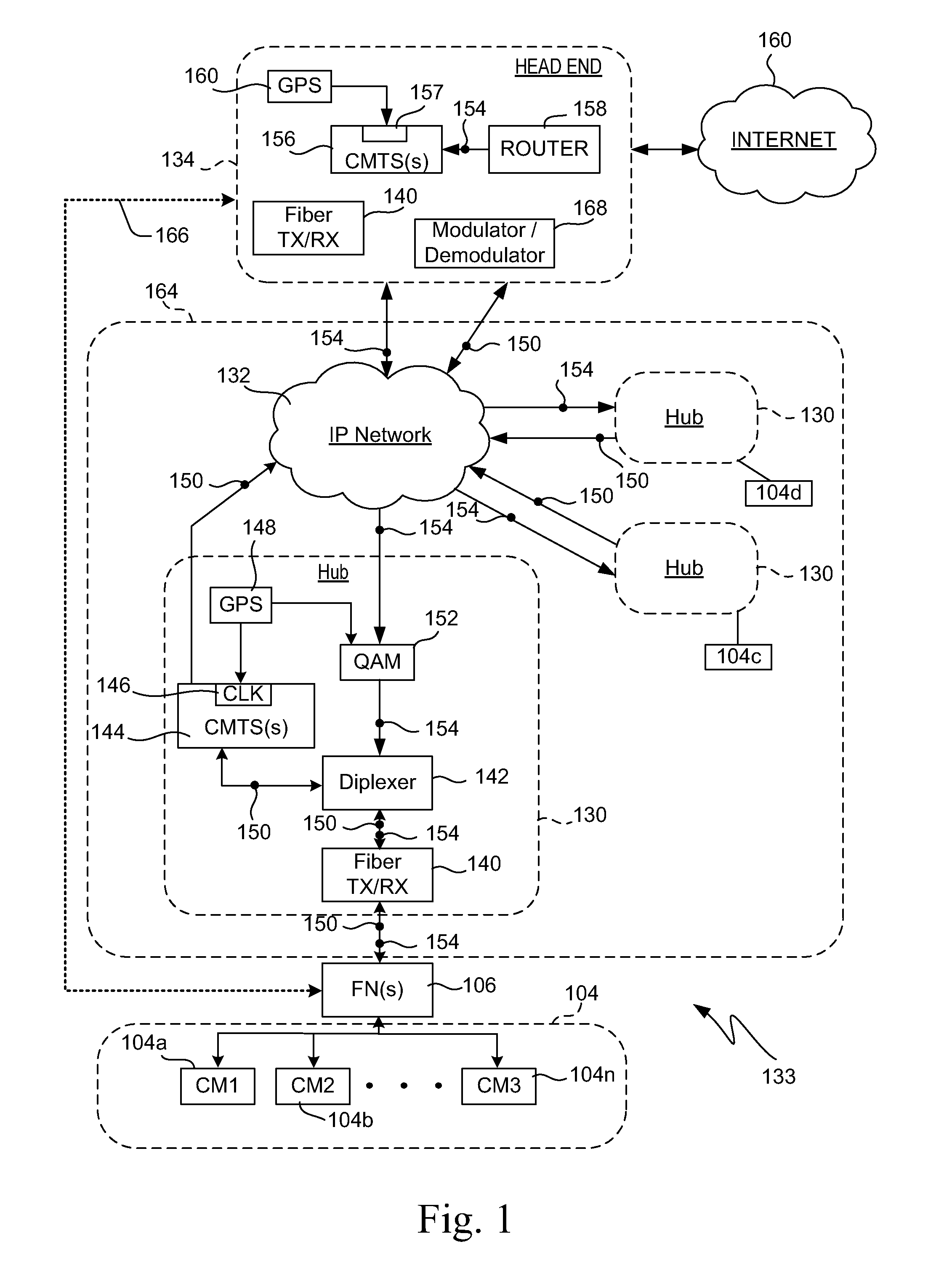
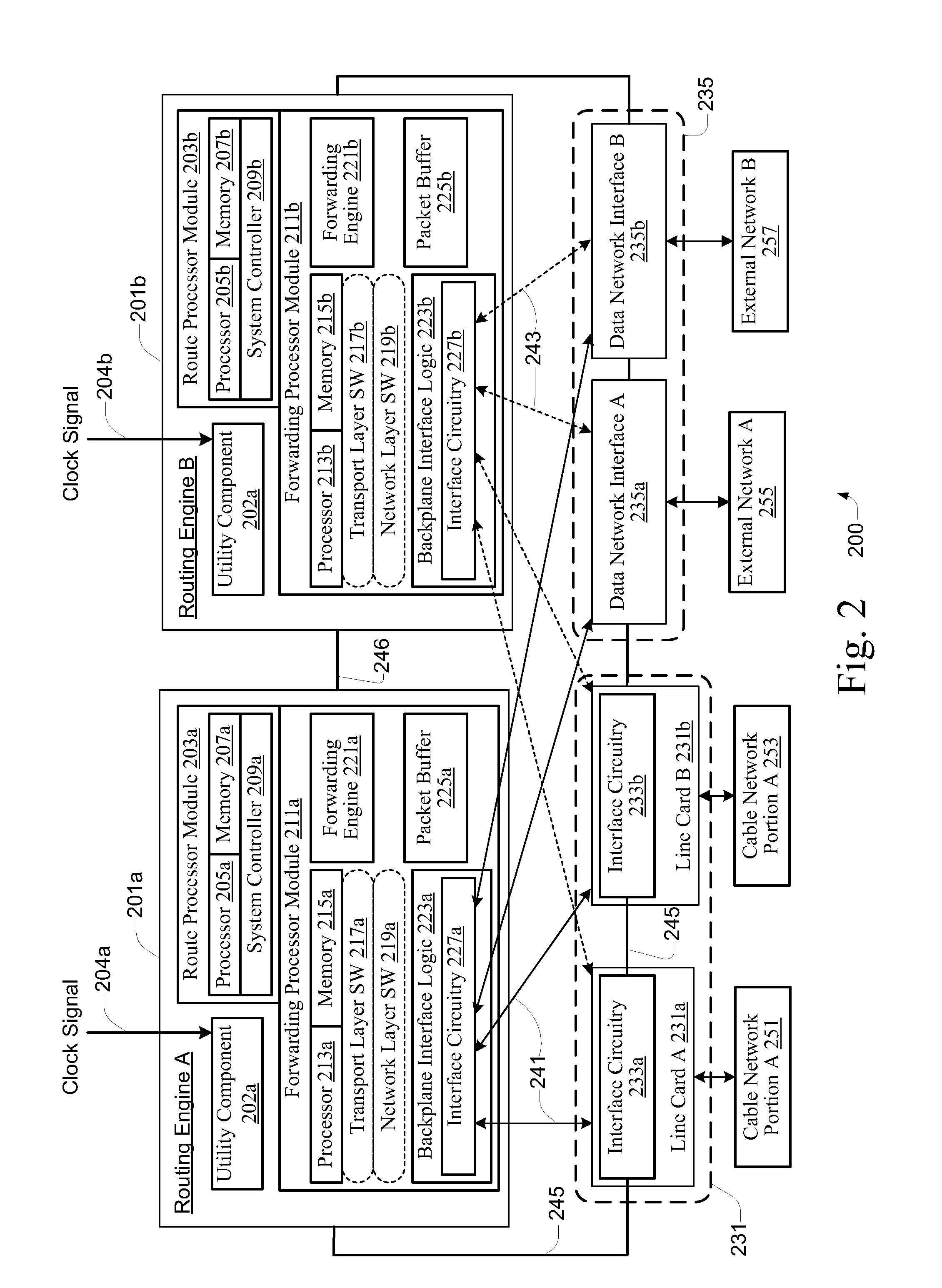
Cable network redundancy architecture
InactiveUS7068712B1Error detection/correctionTelevision systemsLine cardNetwork Communication Protocols
A CMTS redundancy technique requires at least two CMTS interfaces (e.g., line cards) on one or more CMTS chassis at the head end of a cable network. One of the CMTSs serves as a backup or “protecting” CMTS. When another CMTS (a “working” CMTS) becomes unavailable to service its group of cable modems, the protecting CMTS takes over service to those cable modems. The SWITCHOVER takes place transparently (or nearly transparently) to the cable modems. The protecting CMTS provides service on the same downstream channel as used by the working CMTS. The cable modems need not modify any settings pursuant to their cable modem communication protocol (e.g., DOCSIS ranging). This transparency to the cable modems is realized by keeping the working and protecting CMTSs in synchronization regarding service parameters for the cable modems. In other words, the protecting CMTS maintains a list of current parameters for allowing service to the cable modems.
Owner:CISCO TECH INC
Downstream remote physical interface for modular cable modem termination system
A modular Cable Modem Termination System (CMTS) includes a packet shelf operating a Data Over Cable Service Interface Specifications (DOCSIS) Media Access Control (MAC) framer. One or more downstream Physical Interface (PHY) shelves receive DOCSIS data from the packet shelf over a packet switched network and modulate the DOCSIS data for sending on a downstream path of a cable plant. One or more upstream PHY shelves send DOCSIS data received from an upstream path of the cable plant over the packet switched network to the packet shelf. By separating the PHY components from the MAC and from the system software, the PHY components for a Hybrid Fiber Coax (HFC) plant may be replaced with different PHY components for other access technologies such as wireless, Digital Subscriber Lines (DSL), Ethernet-to-the-Home, Fiber-to-the-Home, or fiber Passive Optical Networks (PONs).
Owner:CISCO TECH INC
QOS on Bonded Channels of a Shared Access Cable Network
Various techniques are disclosed for managing traffic flow for transport over a plurality of communication channels of a shared access cable network. According to various embodiments, one or more devices of the cable network (such as, for example, a Cable Modem Termination System (CMTS)), may be operable to implement at least a portion of the traffic flow management techniques. In at least one embodiment, one or more aspects of the traffic flow management techniques disclosed herein may be used for performing real-time shaping of traffic flows across multiple different channels of a DOCSIS channel bonding group. In some embodiments, various different traffic shaping and / or traffic scheduling techniques may be employed (e.g., in DOCSIS 3.0 compatible cable networks) to reduce and / or mitigate issues which, for example, may arise as a result of an inability to represent traffic schedulers as tree-based hierarchies. Other aspects are disclosed for implementing quality of service (QoS) procedures on shared access network(s), such as for example hybrid fiber / coaxial (HFC) cable networks.
Owner:CISCO TECH INC
Discrete spurious leakage cancellation for use in a cable modem
InactiveUS20100266000A1Reduced frequency spur energyLow costTwo-way working systemsSelective content distributionPhase shiftedDOCSIS
A novel apparatus for and method of discrete spurious frequency leakage cancellation for use in a cable modem. The spurious leakage cancellation mechanism is particularly suitable for use in cable modem systems adapted to implement the DOCSIS 2.0 specification which specifies both downstream and upstream channels. In one embodiment, the spurious emission cancellation mechanism cancels the spurious emissions by first creating a replica of the aggressor clock signal having the same amplitude but 180 degree phase shift as the spurious signal. The phase shifted spurious replica is added to the original spurious signal thus cancelling the spurious signal. In another embodiment, an RF switch is used to couple the upstream path signal to the CATV cable only during transmission bursts. In between transmission bursts, the upstream signal is disconnected from the CATV cable. This embodiment takes advantage of the less stringent spurious requirements in the DOCSIS 2.0 specification for transmission bursts. In between transmission bursts, when stricter spurious requirements apply, the upstream signal is disconnected from the CATV cable.
Owner:TEXAS INSTR INC
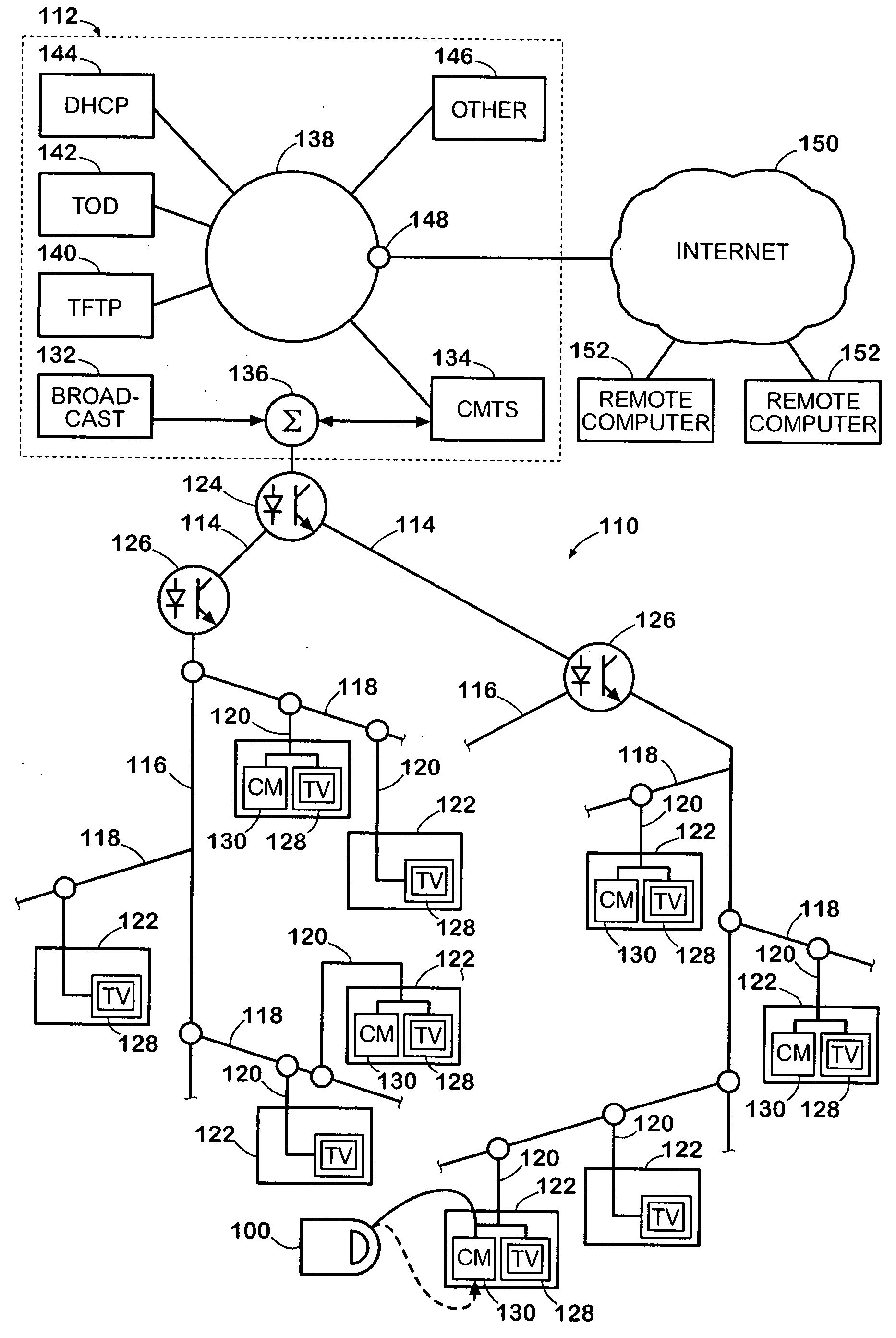
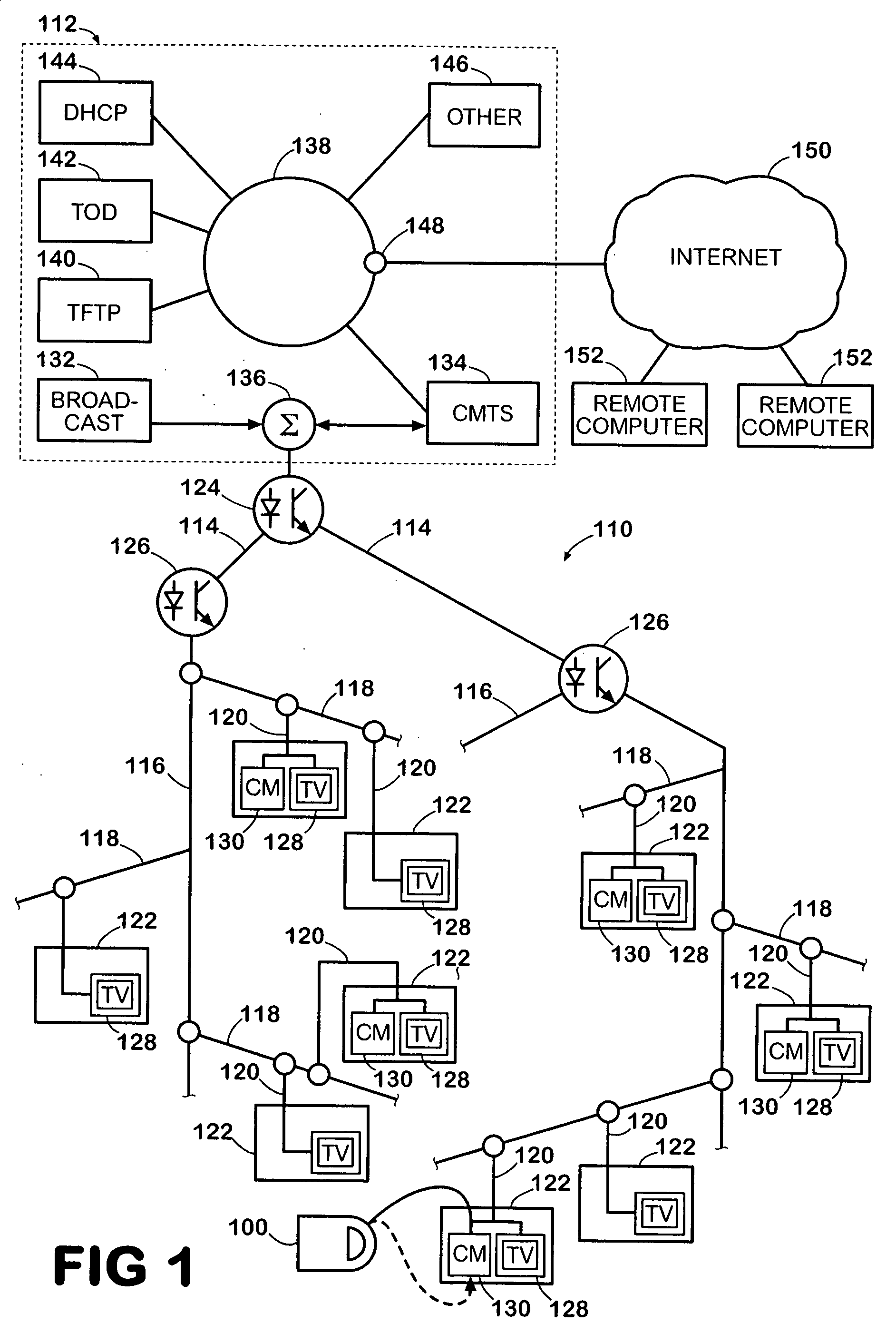
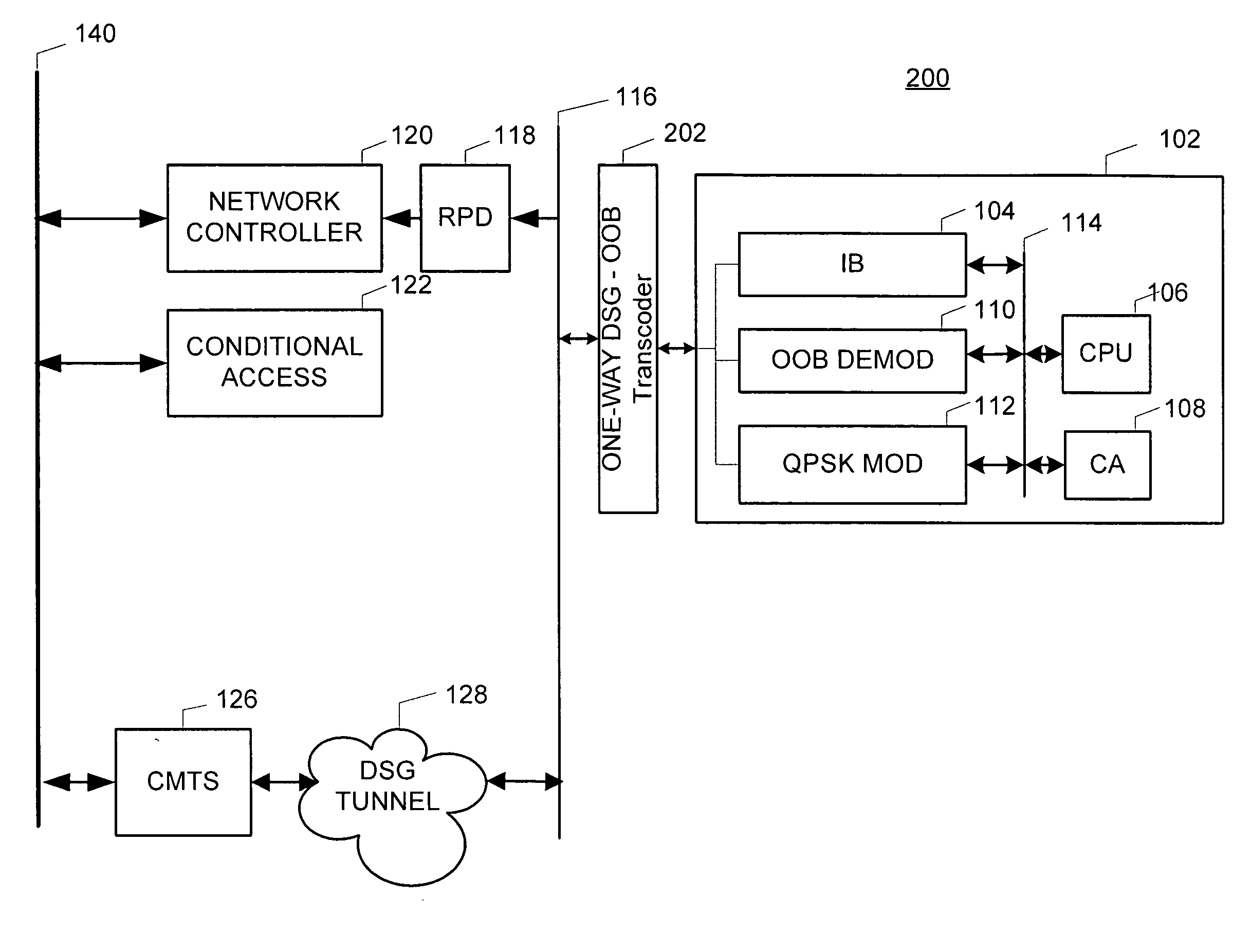
Method and apparatus for providing a DSG to an OOB transcoder
InactiveUS20050198684A1Free up bandwidthBroadband local area networksAnalogue secracy/subscription systemsComputer hardwareTelevision system
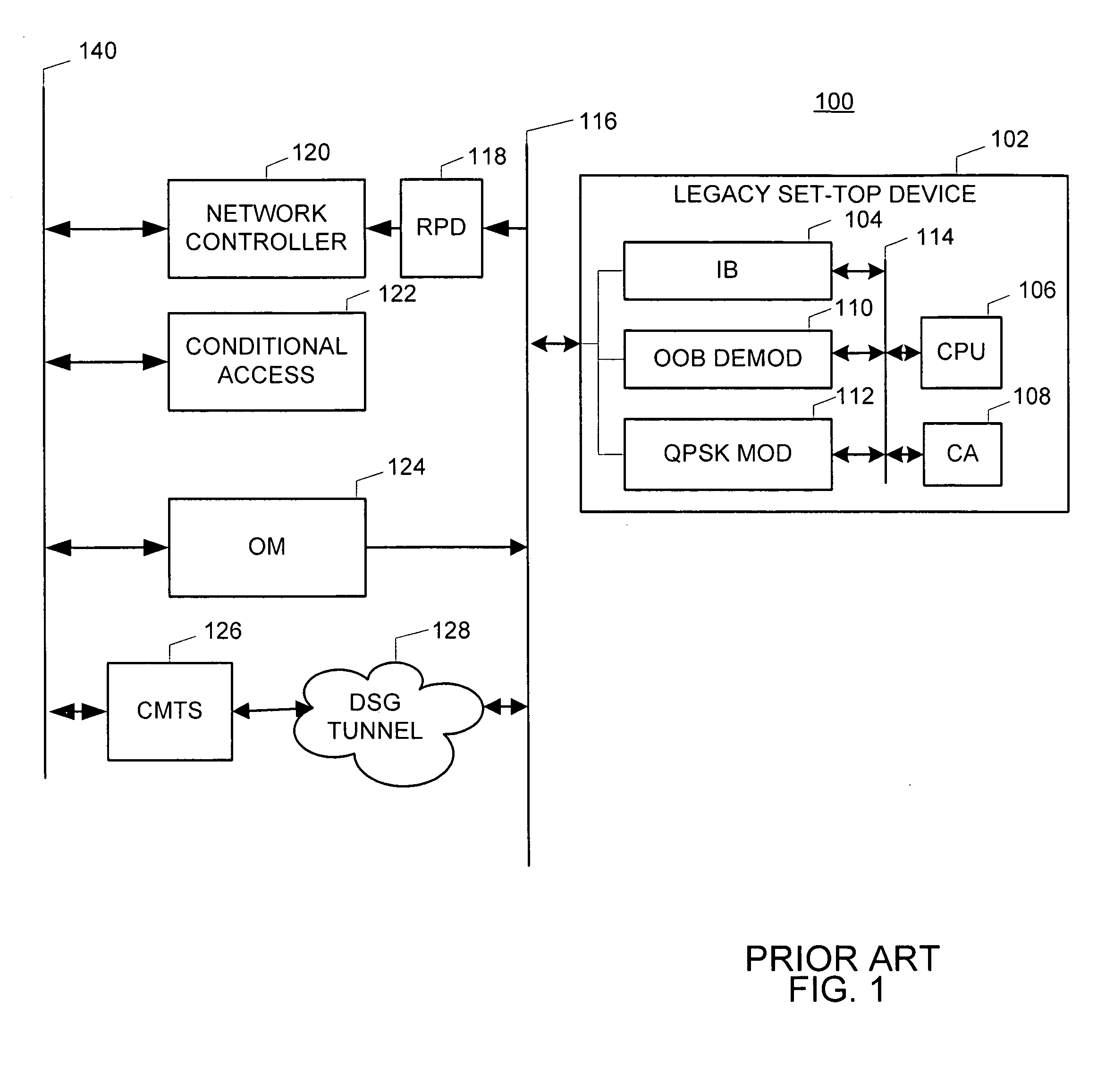
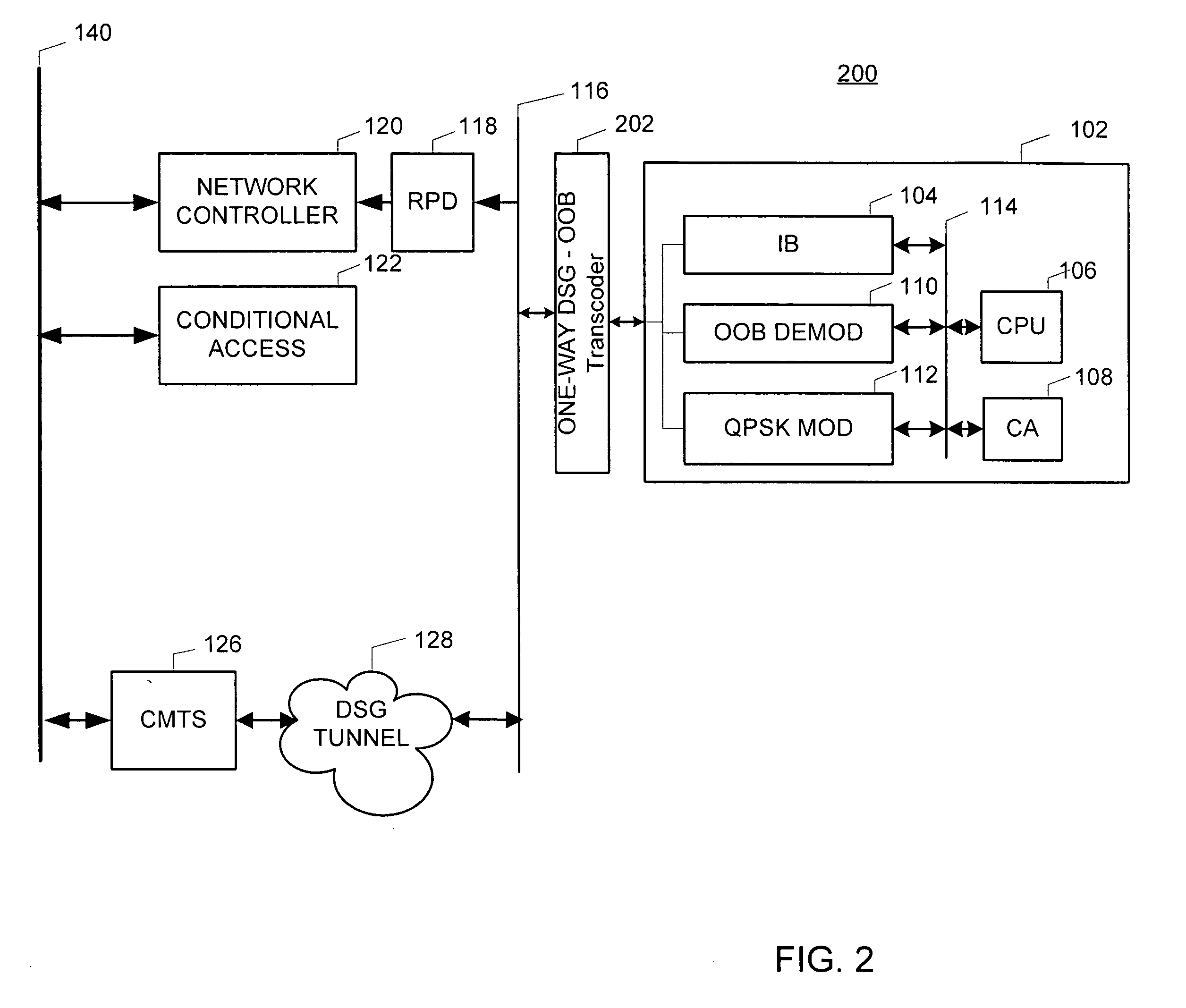
The present invention is a method and apparatus for providing a DSG to OOB transcoder in a cable television system comprising a legacy set-top device 102. In the first embodiment, a one-way DSG to OOB transcoder 202 acts as a proxy device for OOB messages to the DSG tunnel 128. Once an OOB message is generated, the OOB message is transmitted to the DSG tunnel 128. The DSG to OOB transcoder 202 of the present invention then captures the OOB message, and communicates the OOB message to the legacy set-top device 102. In a second embodiment of the invention, the legacy set-top device 102 may communicate return communications to the DSG to OOB transcoder 402 by generating a QPSK message. The QPSK message is then translated to an OOB message comprising DOCSIS content.
Owner:GENERAL INSTR CORP
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com