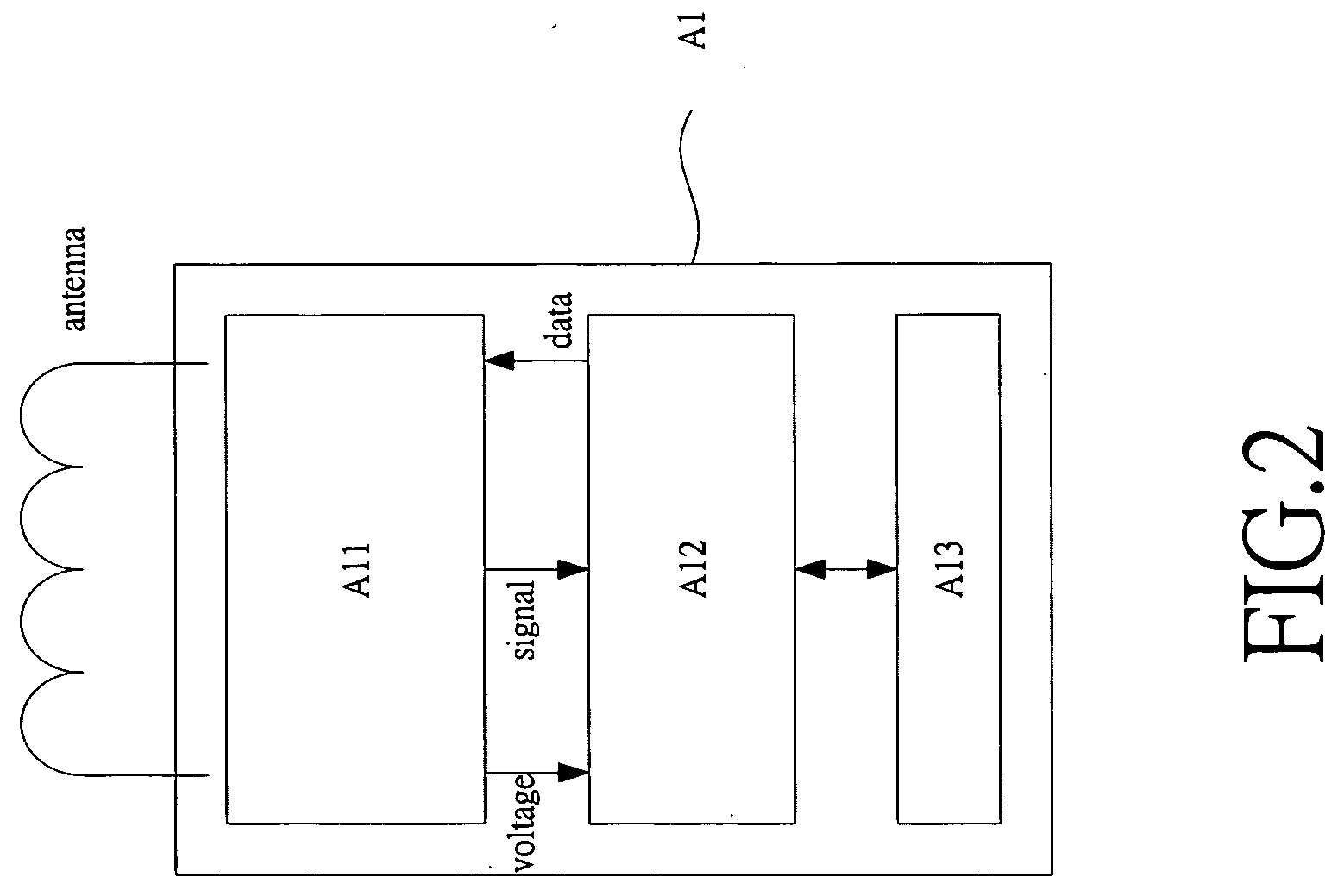
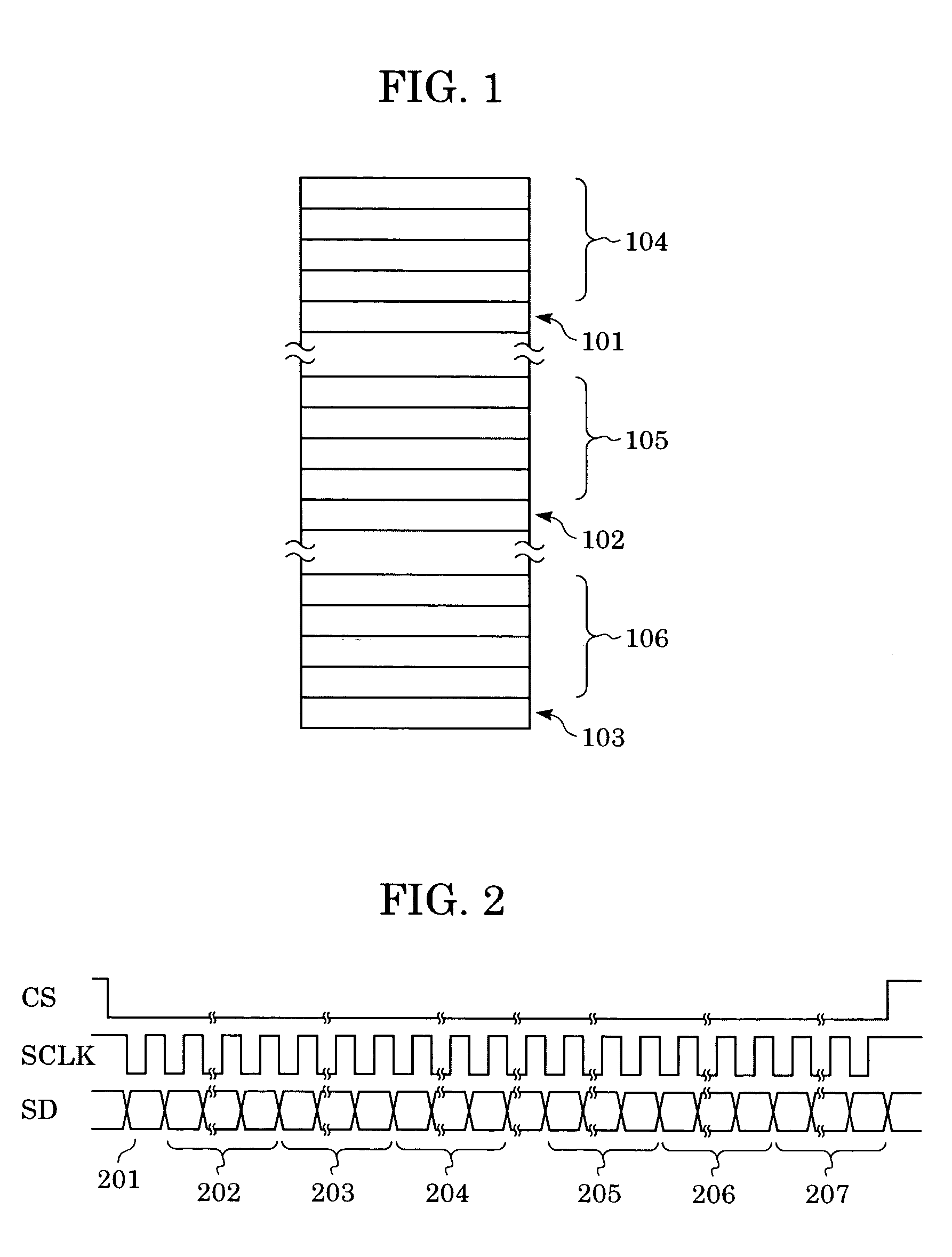
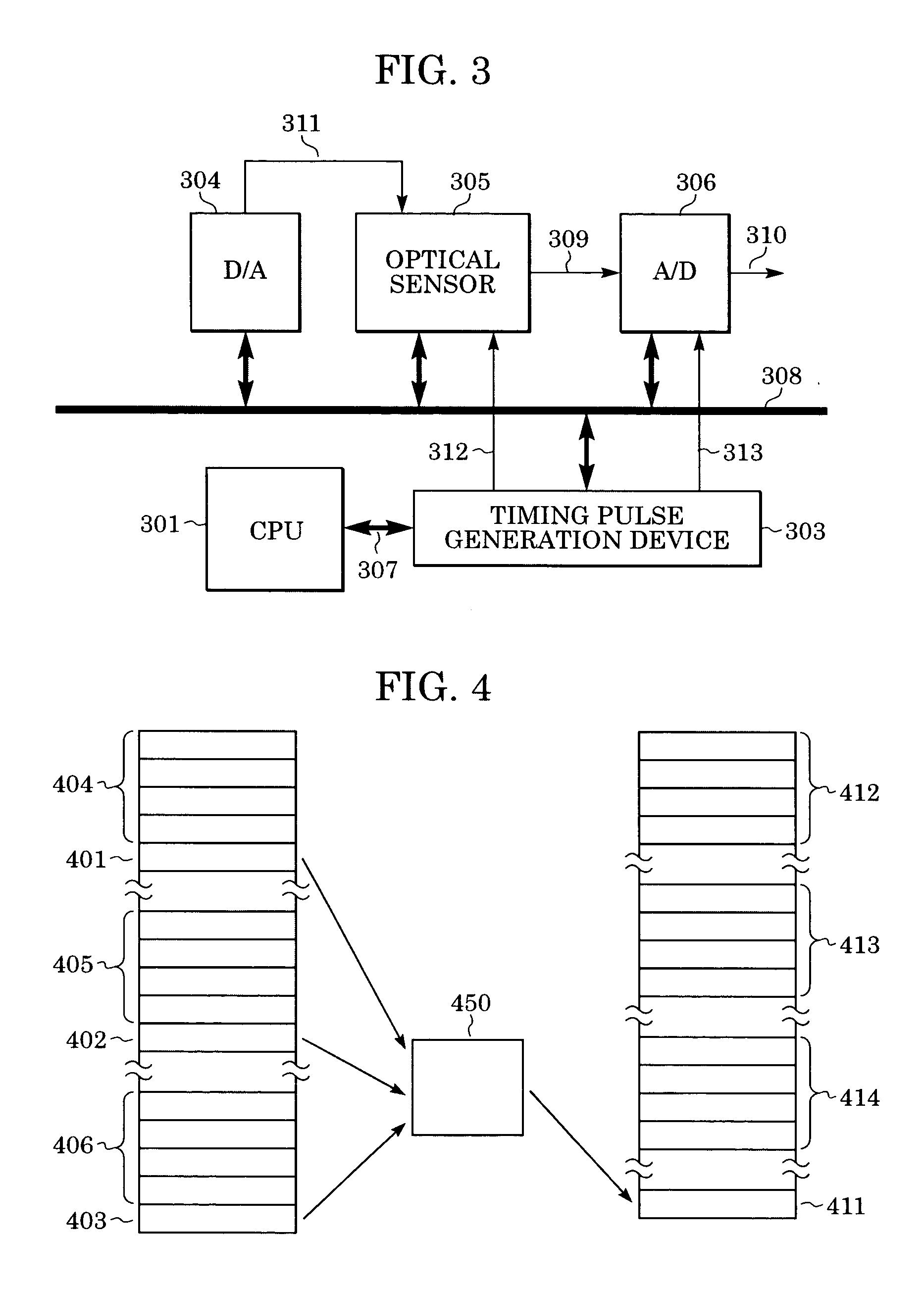
Patents
Literature
7689 results about "Trunking" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
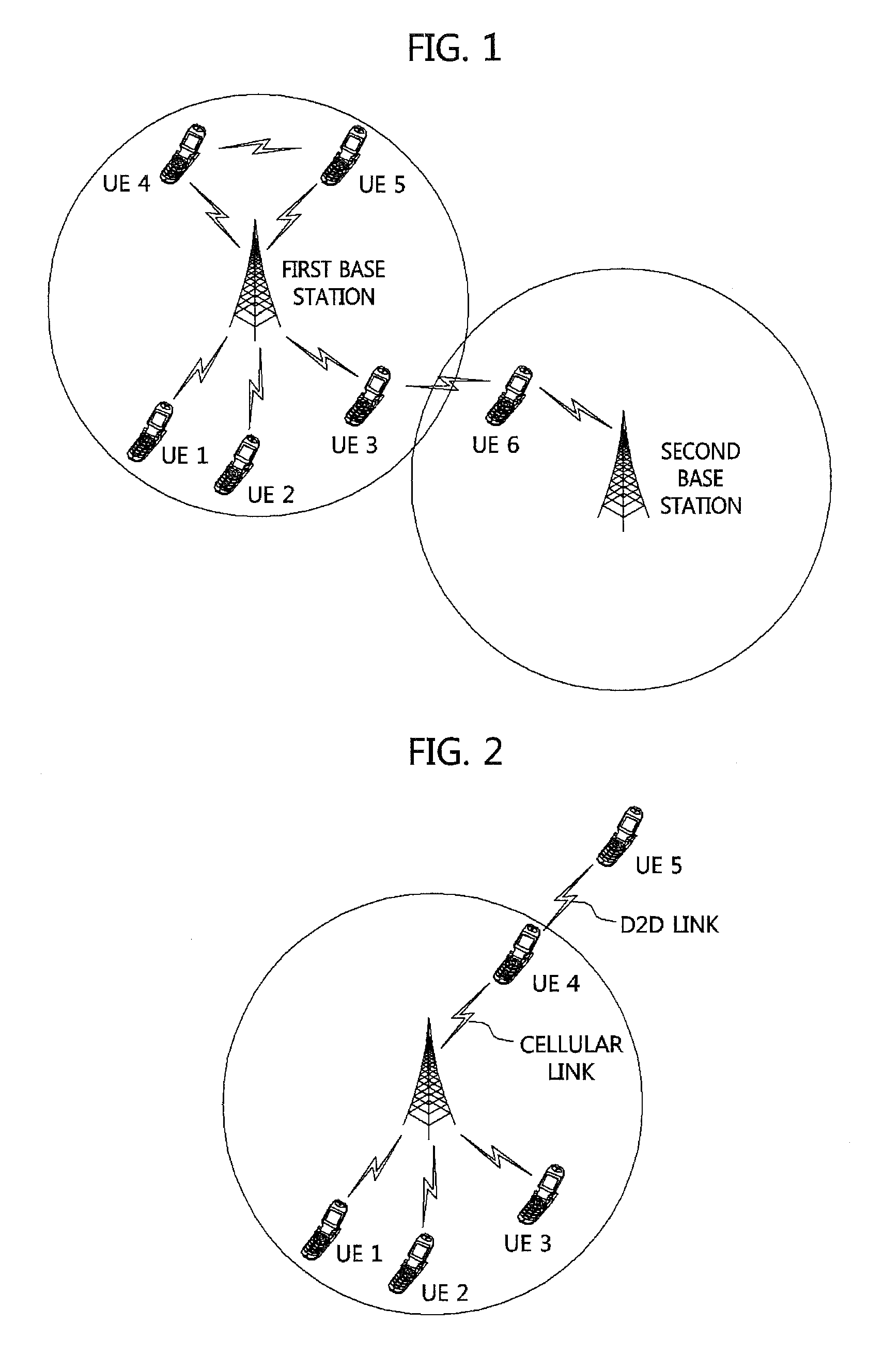
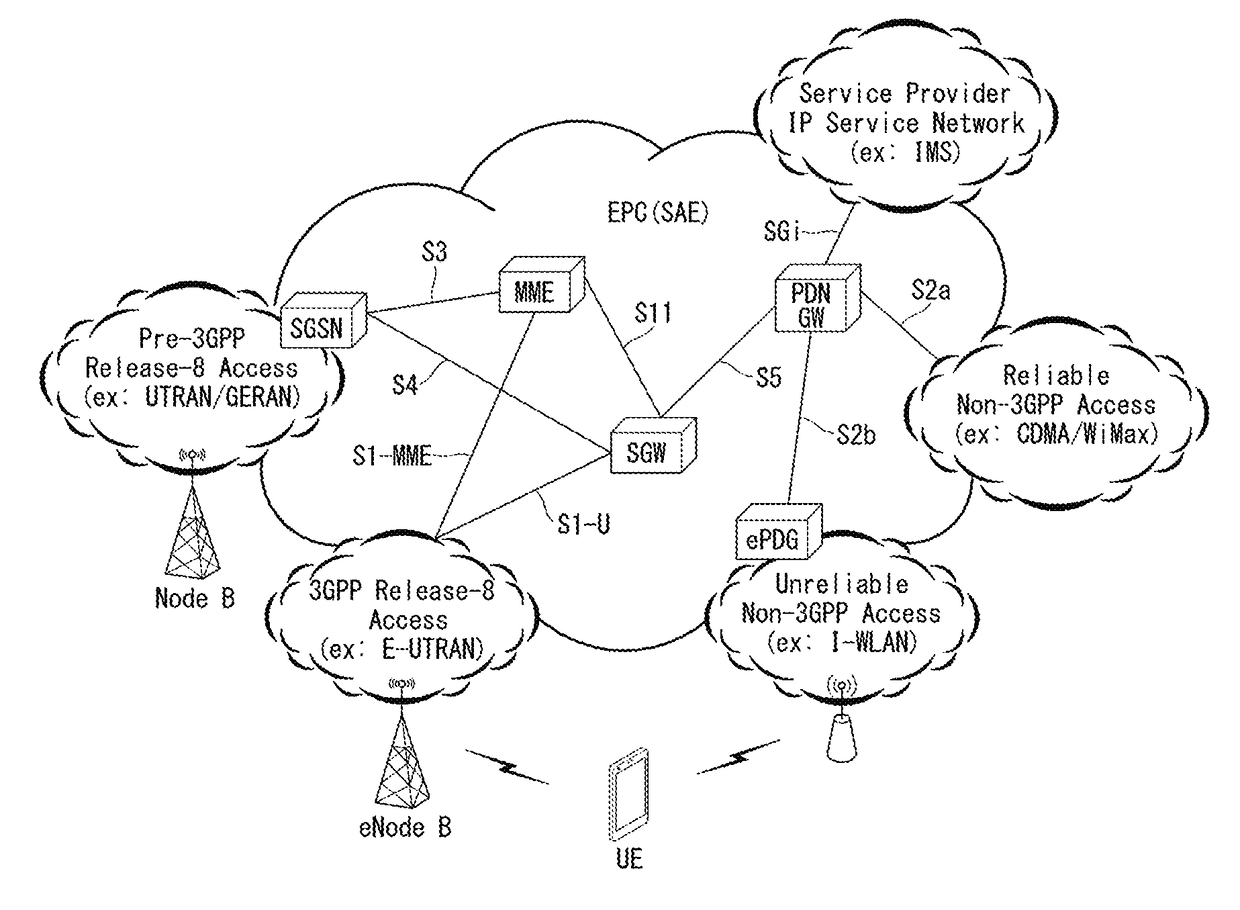
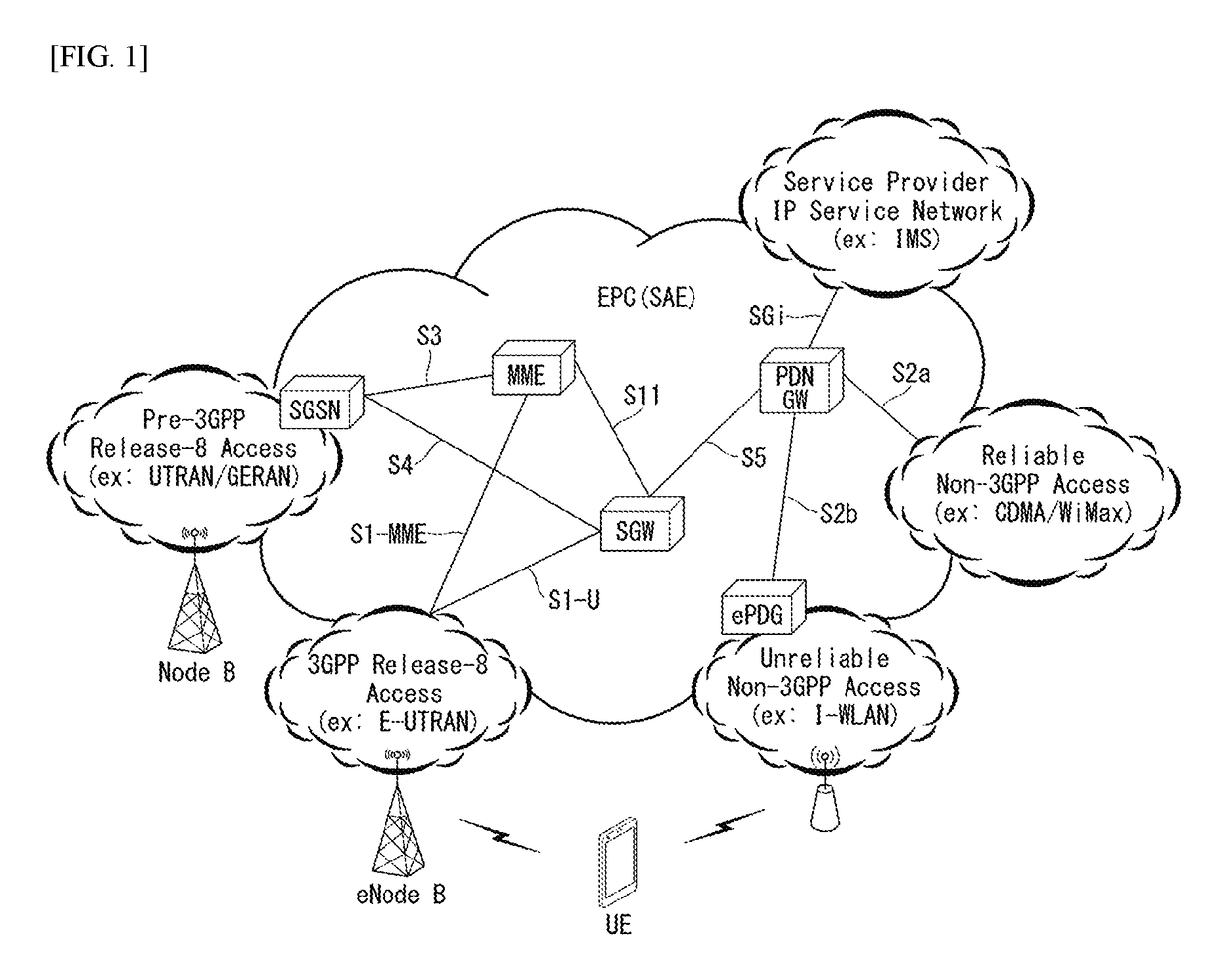
In telecommunications, trunking is a method for a system to provide network access to many clients by sharing a set of lines or frequencies instead of providing them individually. This is analogous to the structure of a tree with one trunk and many branches. Examples of this include telephone systems and the two-way radios commonly used by police agencies. Trunking, in the form of link aggregation and VLAN tagging, has been applied in computer networking as well.
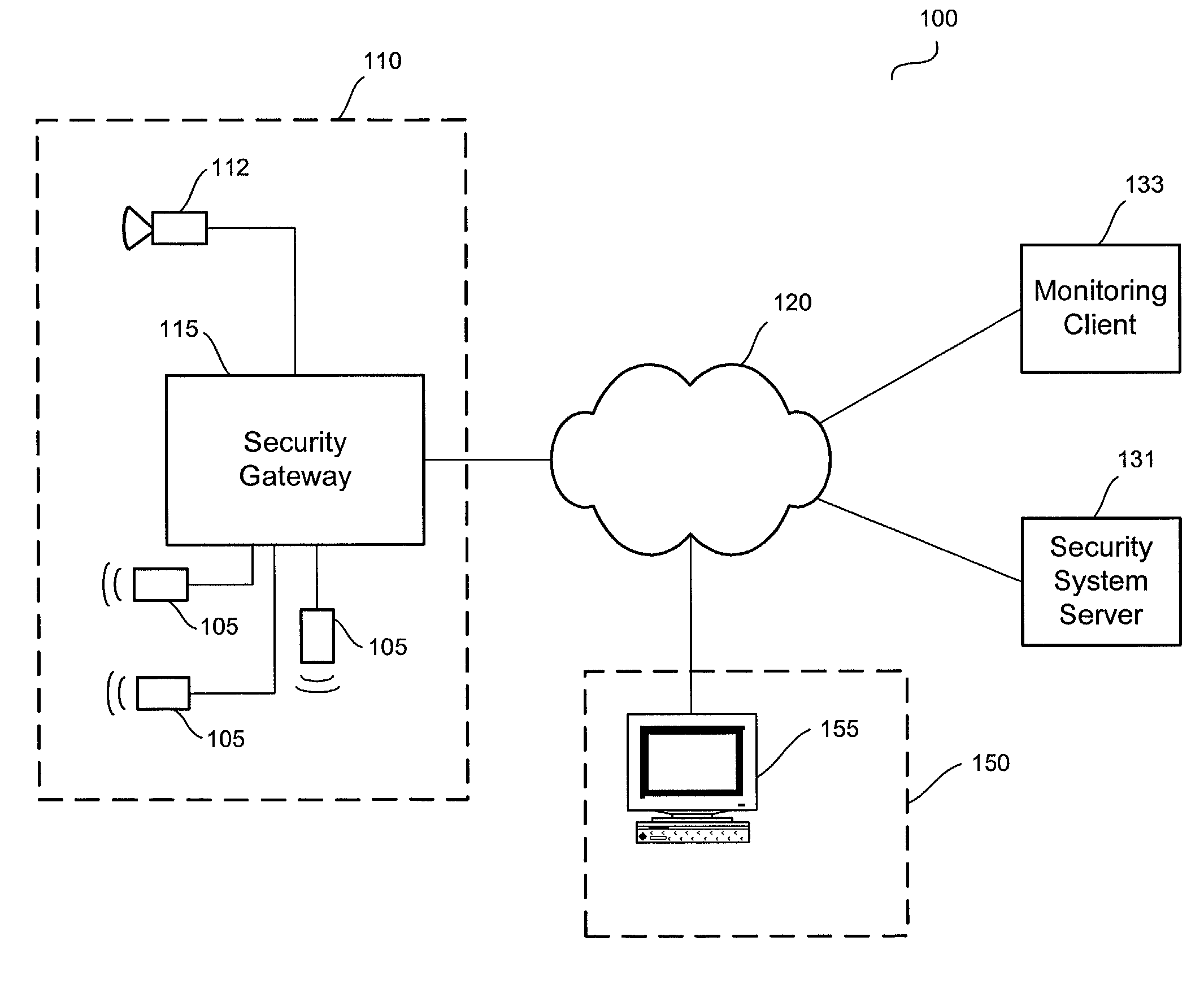
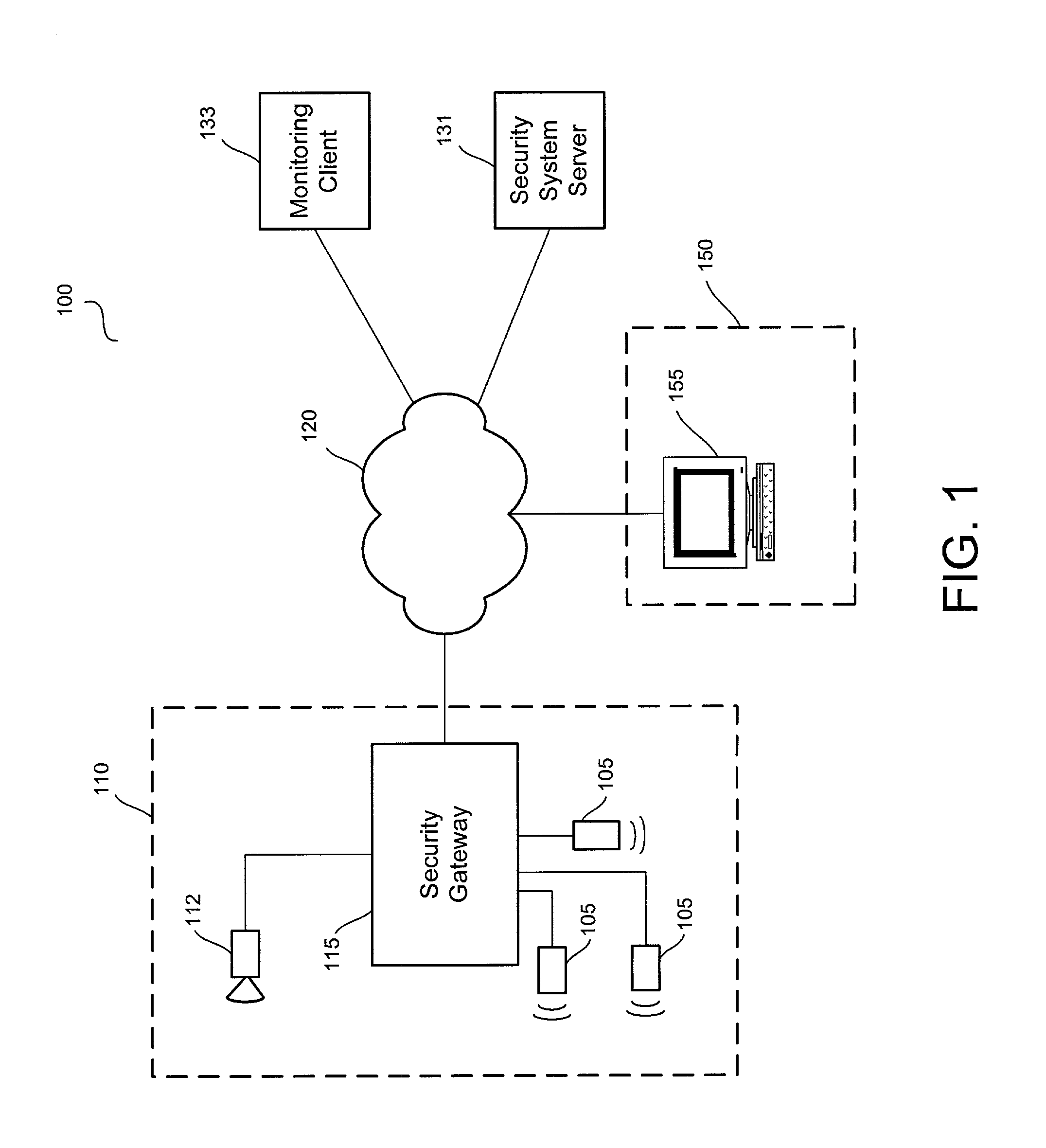
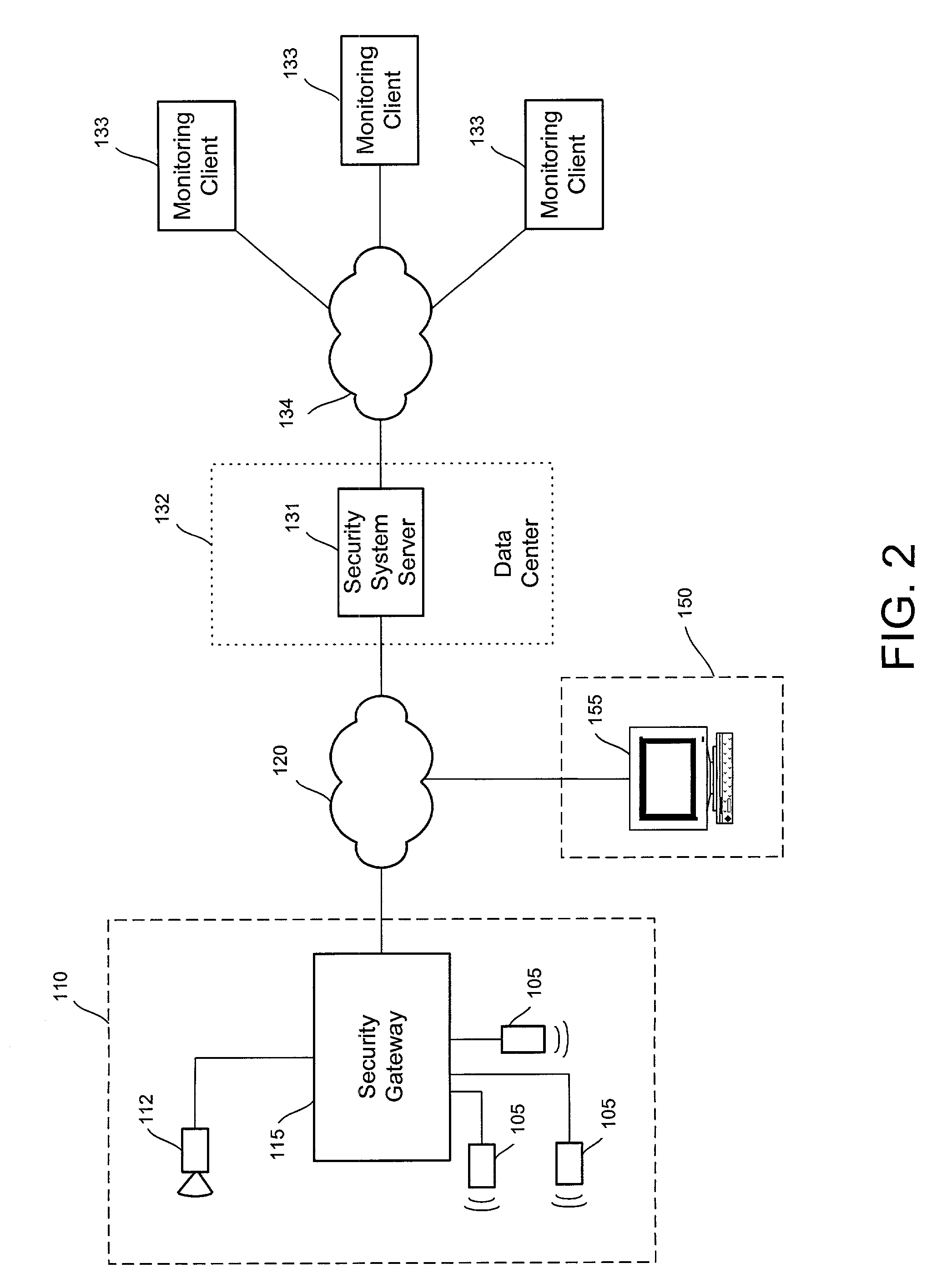
Distributed monitoring for a video security system
A system and method for distributed monitoring and remote verification of conditions surrounding an alarm condition in a security system. A security gateway detects alarm conditions at a premises and records video relating to the alarm condition. The security gateway transmits an alarm notification and the video across a network to a security system server in substantially real time. The security system server relays information to one or more distributed monitoring clients using rules-based routines for verification of the alarm condition. An operator at a monitoring client determines whether the alarm condition represents an actual alarm event and activates an appropriate response.
Owner:COMCAST CABLE COMM LLC
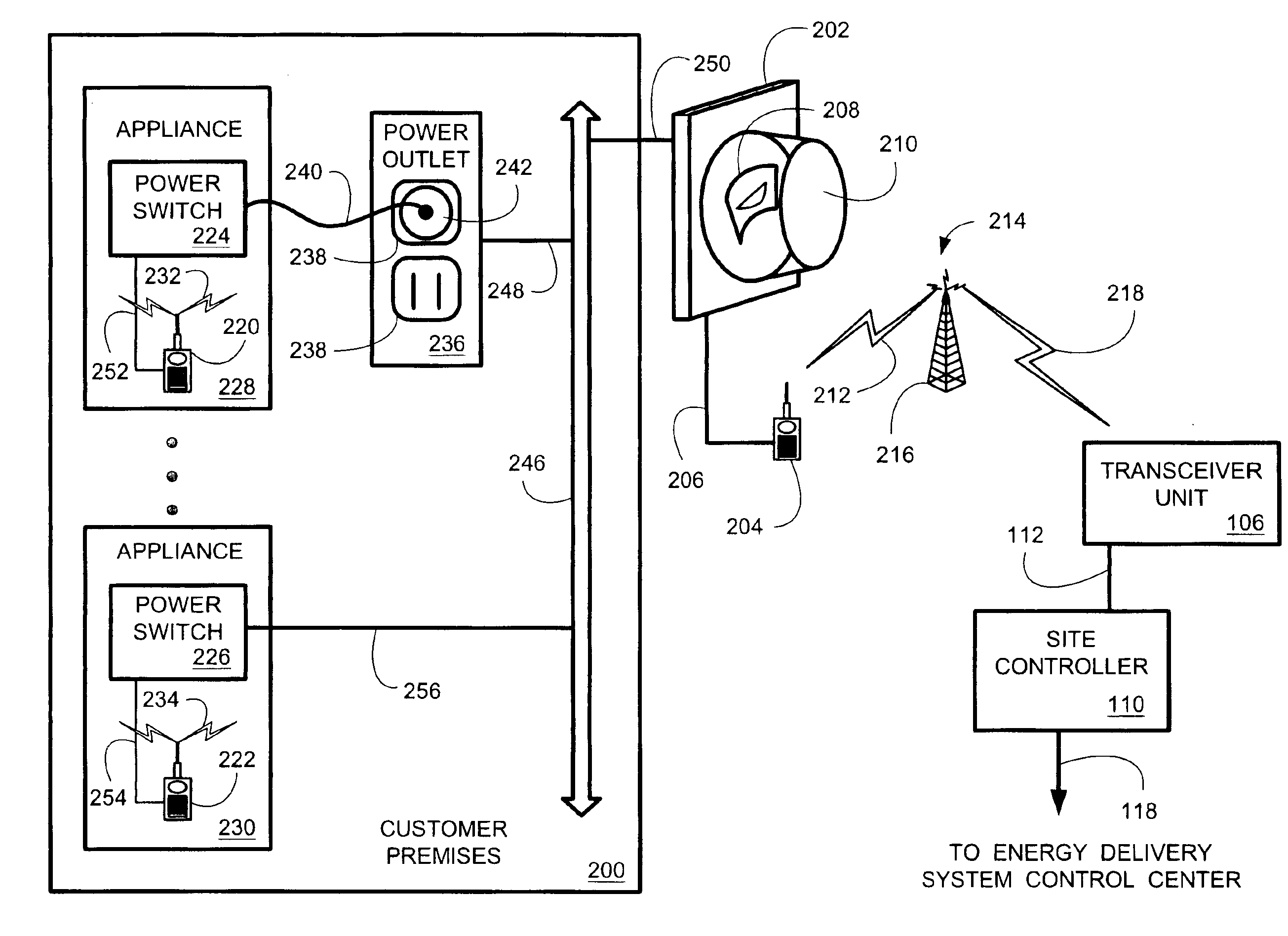
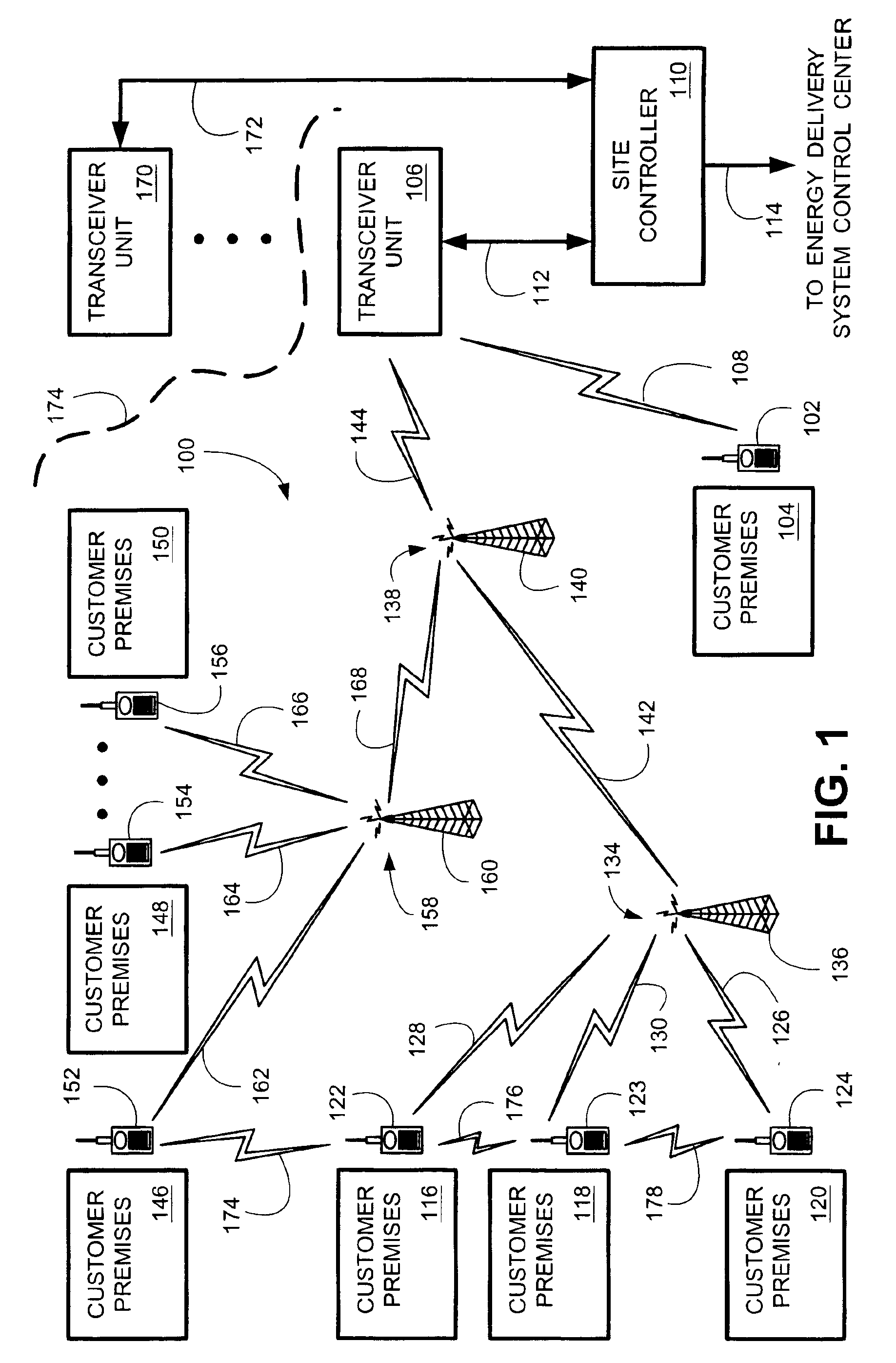
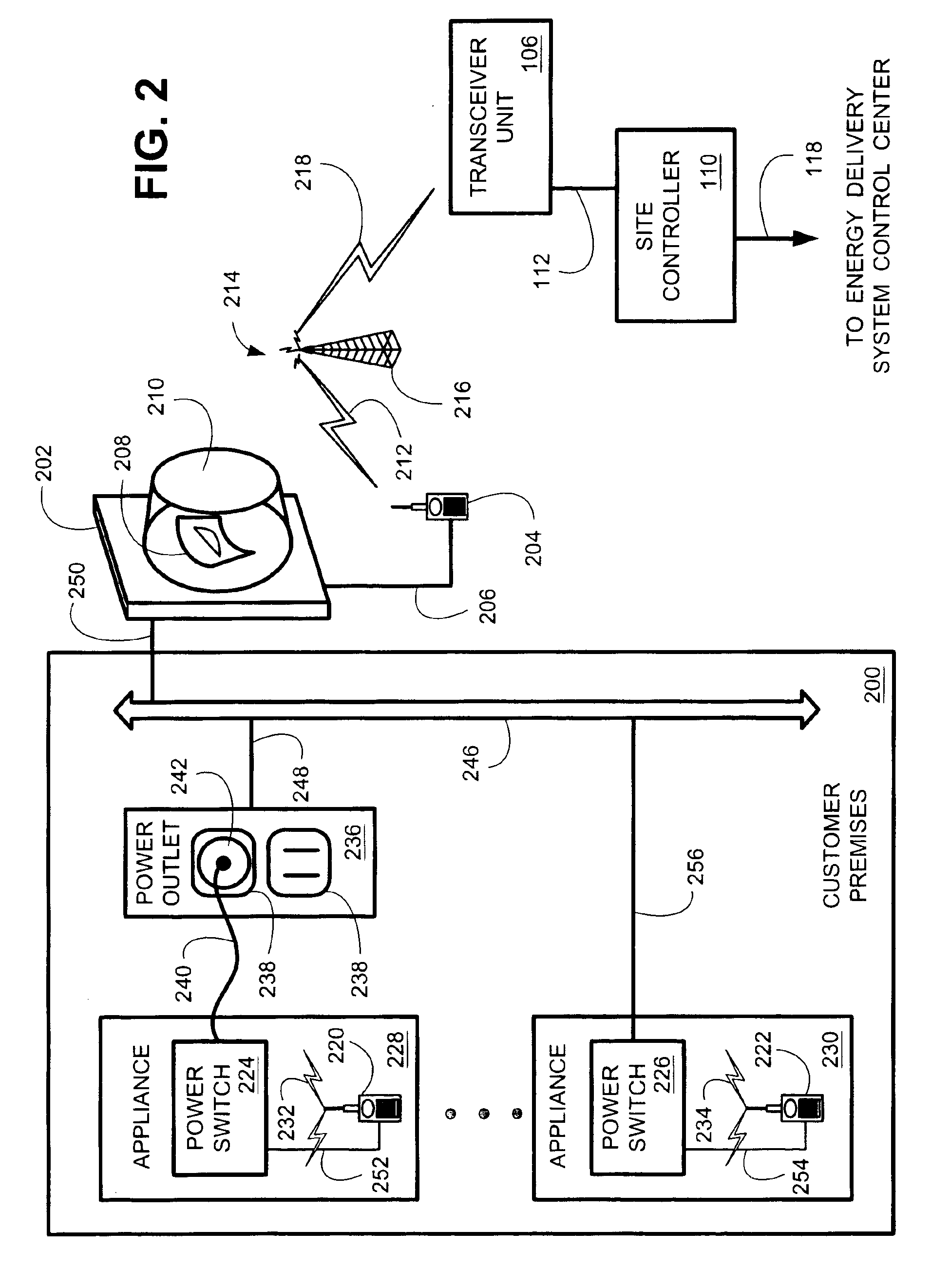
System and method for controlling power demand over an integrated wireless network
An intelligent network demand control system provides a system and method for controlling demand in an energy delivery system. Various embodiments of the intelligent network demand control system employs a transceiver network with a plurality transceivers coupled to meters and appliances residing at a plurality of customer premises. Control room operators instruct a customer premises (CP) energy management controller to implement a reduction in system demand. A demand reduction control signal is relayed out to a predefined group of transceivers to bring their respective controlled generators on line. The predefined transceivers, identified by their identification codes, are specified in the demand reduction control signal. The actual demand reduction is metered and relayed back to the CP energy management controller. In some embodiments, the total demand reduction is aggregated into a single number and then communicated to the operators.
Owner:LANDISGYR TECH
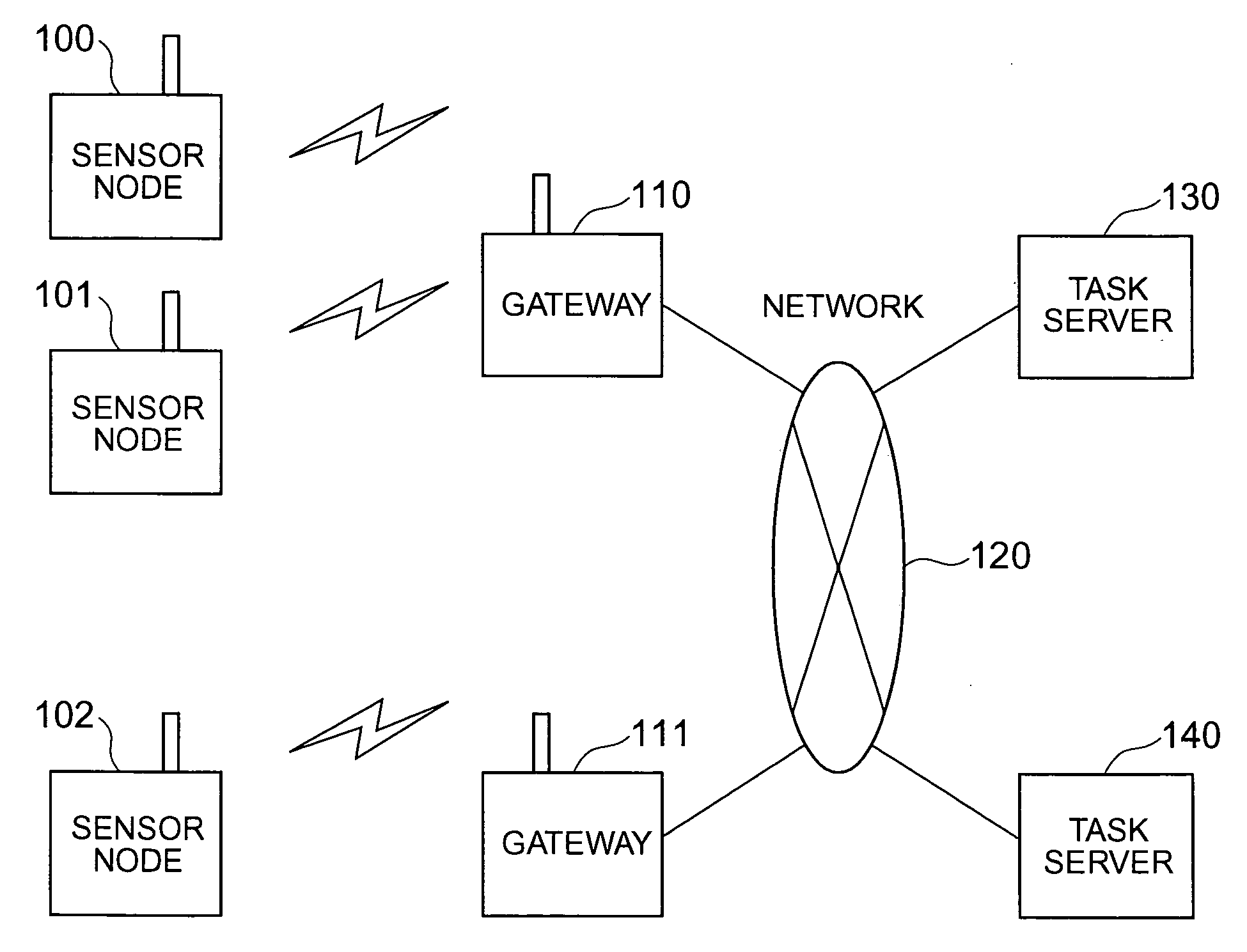
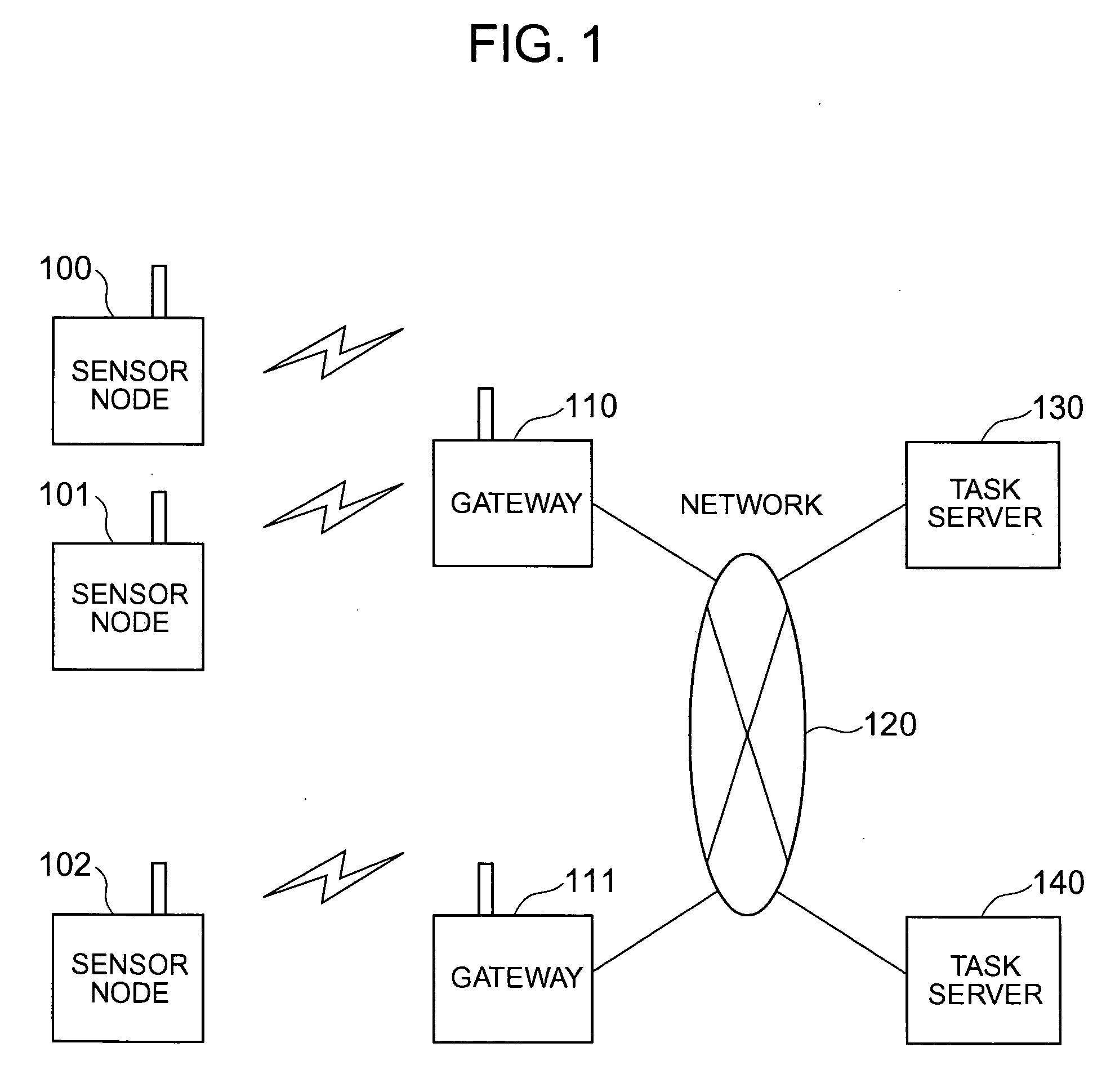
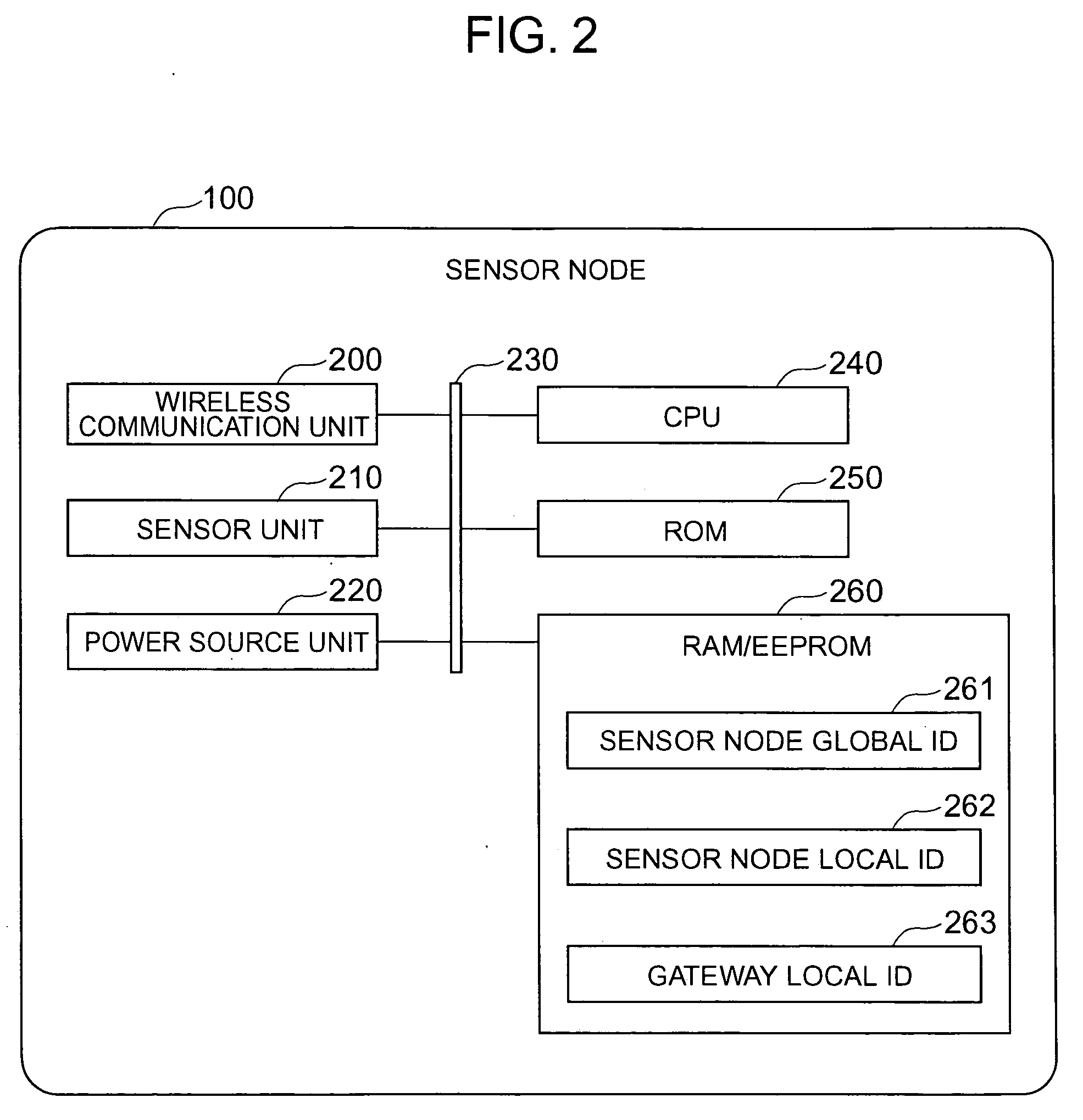
Sensor network management system
InactiveUS20060190458A1Easily lookIncrease freedomDigital data processing detailsActive radio relay systemsTrunkingNetwork management
An attribute value of a matter accompanied by a sensor is transmissibly accessible in a sensor node system constituted by wireless terminal computers having the sensor, the wireless communication base stations and server computers. The wireless terminal computer reports at the time of wireless communication an identification number of a wireless communication base station with which it communicates previously. A relay processing service is dynamically constituted so that when a wireless communication base station different from itself is reported, the wireless base station as the communication counter-part can transmissbly look up the wireless terminal computer from a host computer.
Owner:HITACHI LTD
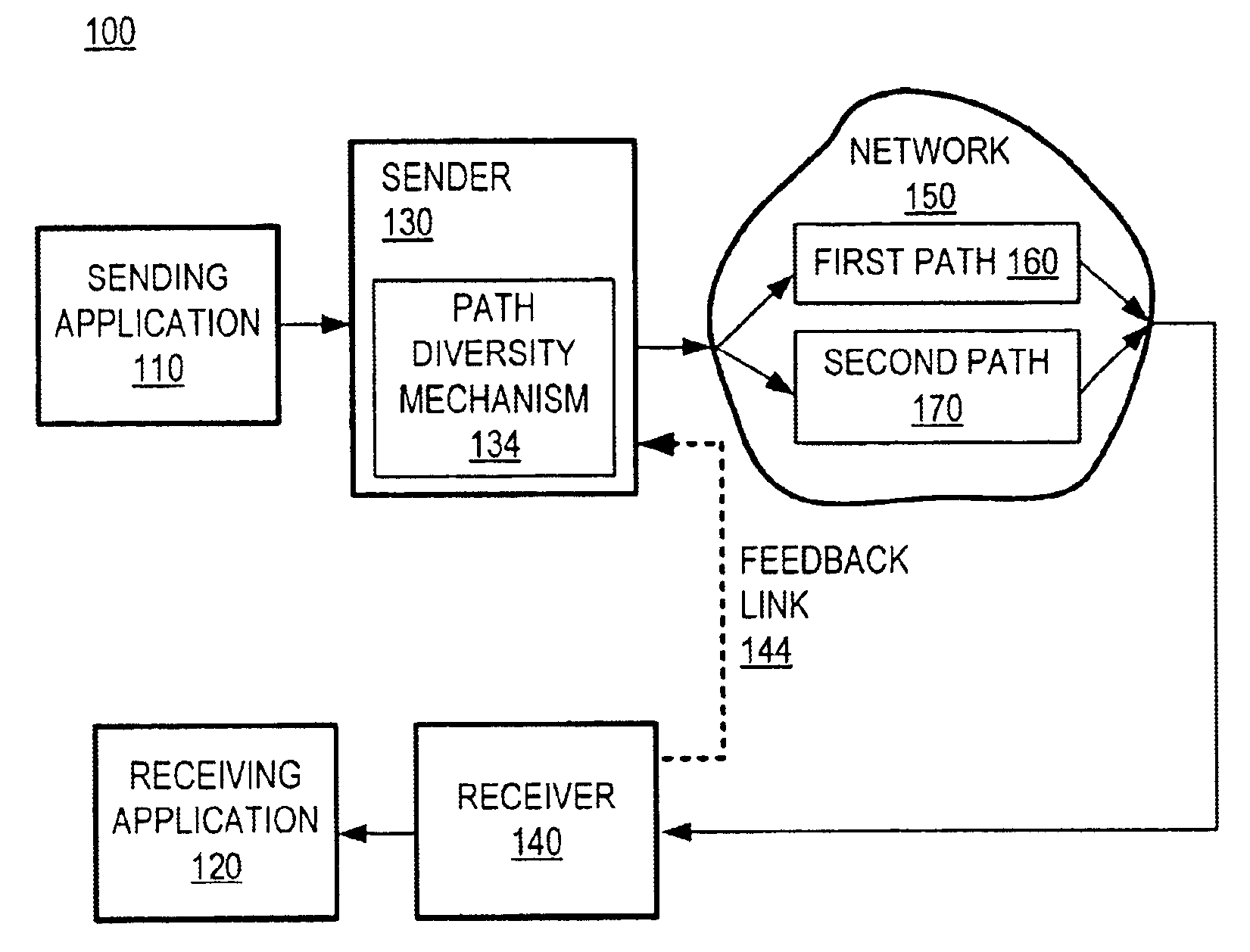
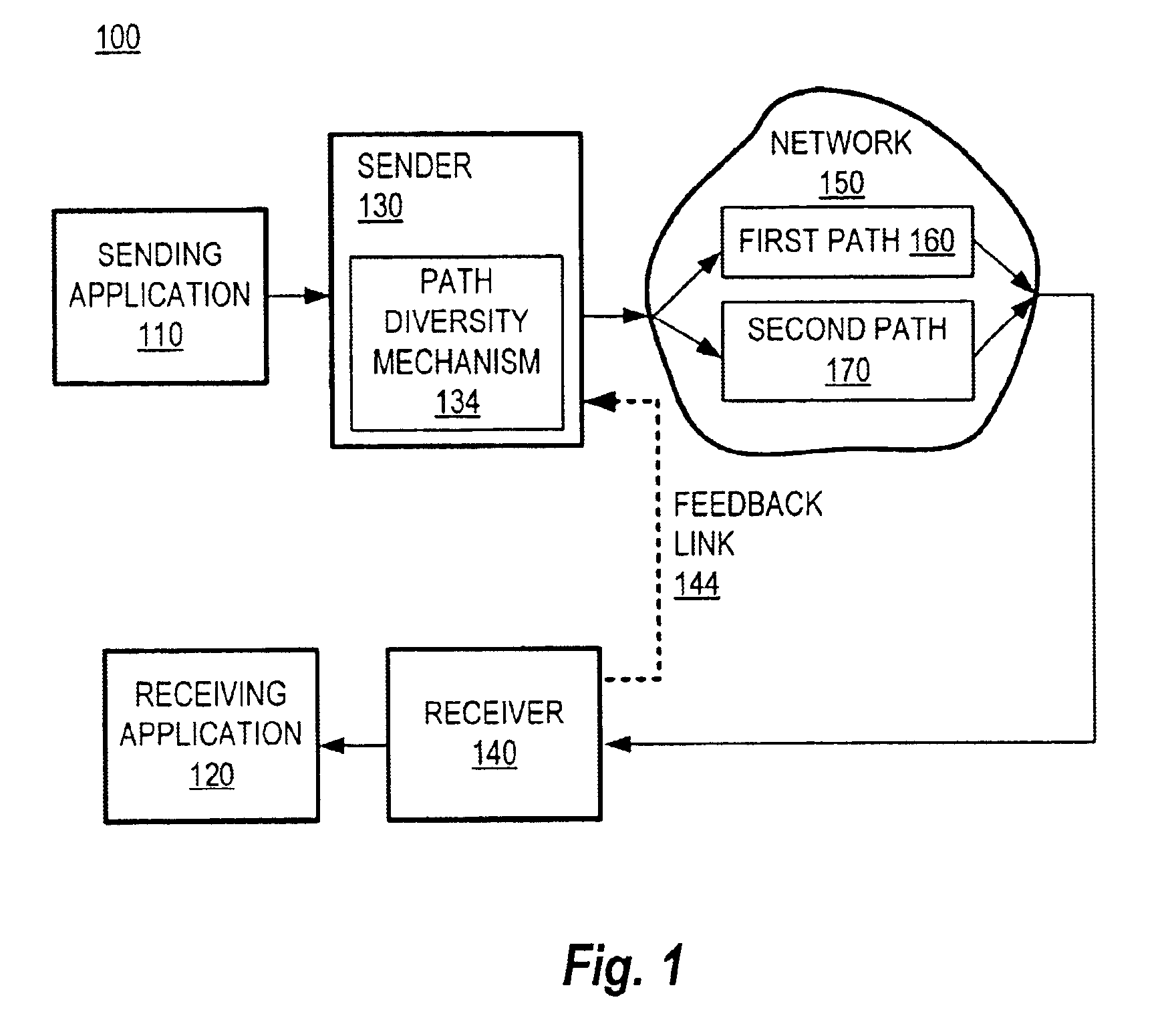
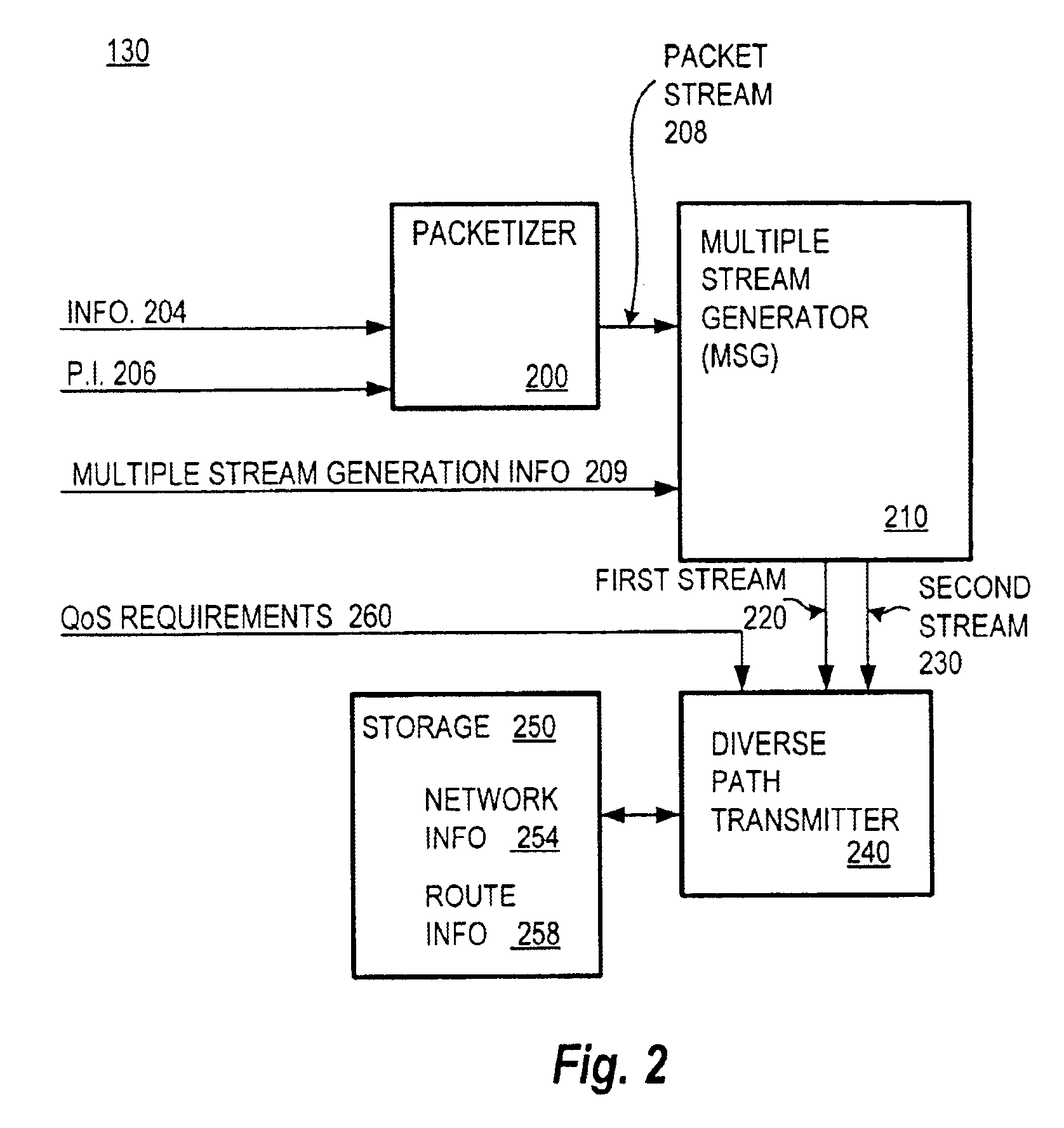
Method and system for packet communication employing path diversity
InactiveUS6868083B2Error preventionFrequency-division multiplex detailsPacket communicationPacket loss
Communication over lossy packet networks such as the Internet is hampered by limited bandwidth and packet loss. The present invention provides a path diversity transmission system for improving the quality of communication over a lossy packet network. The path diversity transmission system explicitly sends different subsets of packets over different paths, thereby enabling the end-to-end application to effectively see an average path behavior. Generally, seeing this average path behavior provides better performance than seeing the behavior of any individual random path. For example, the probability that all of the multiple paths are simultaneously congested is much less than the probability that a single path is congested. The resulting path diversity can provide a number of benefits, including enabling real-time multimedia communication and simplifying system design (e.g., error correction system design). Two exemplary architectures for achieving path diversity are described herein. The first architecture is based on source routing, and the second architecture is based on a relay infrastructure. The second architecture routes traffic through semi-intelligent nodes at strategic locations in the Internet, thereby providing a service of improved reliability while leveraging the infrastructure of the Internet.
Owner:VALTRUS INNOVATIONS LTD
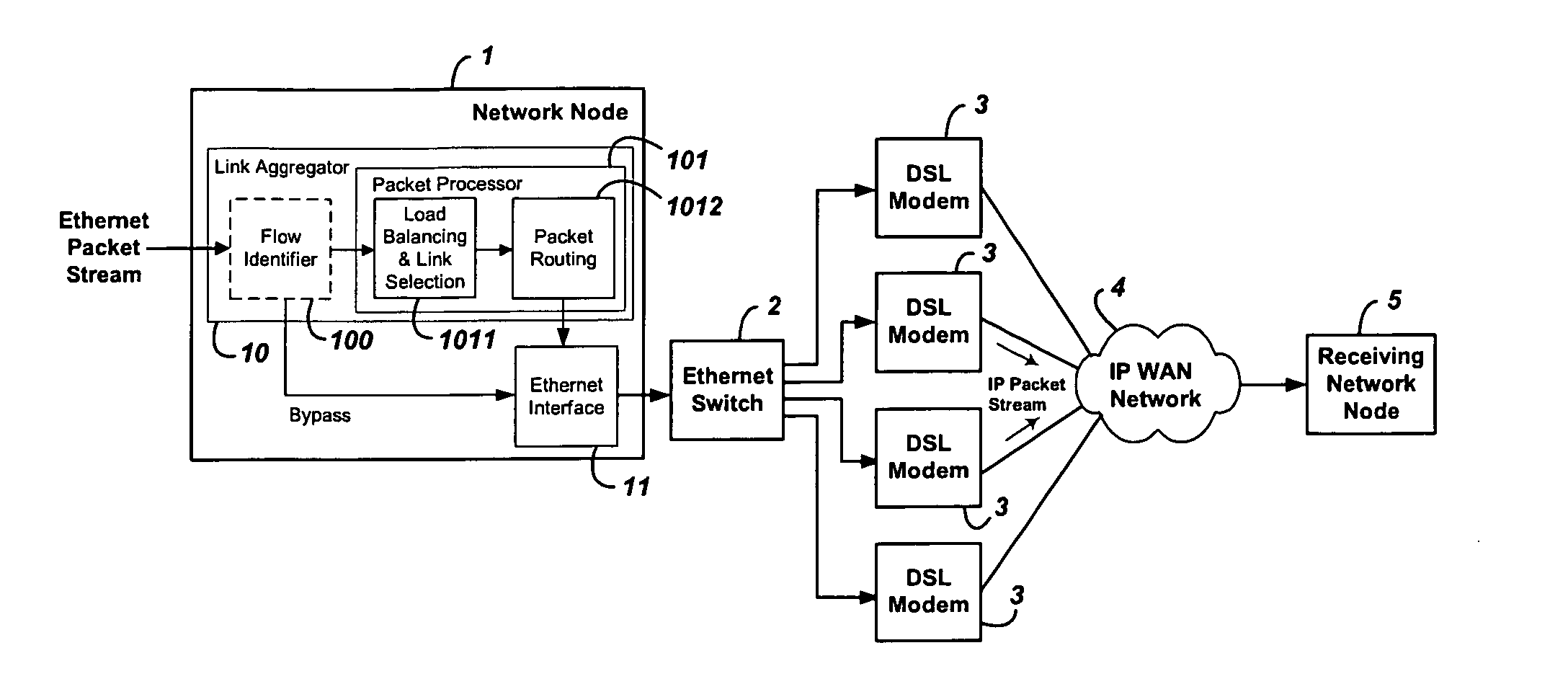
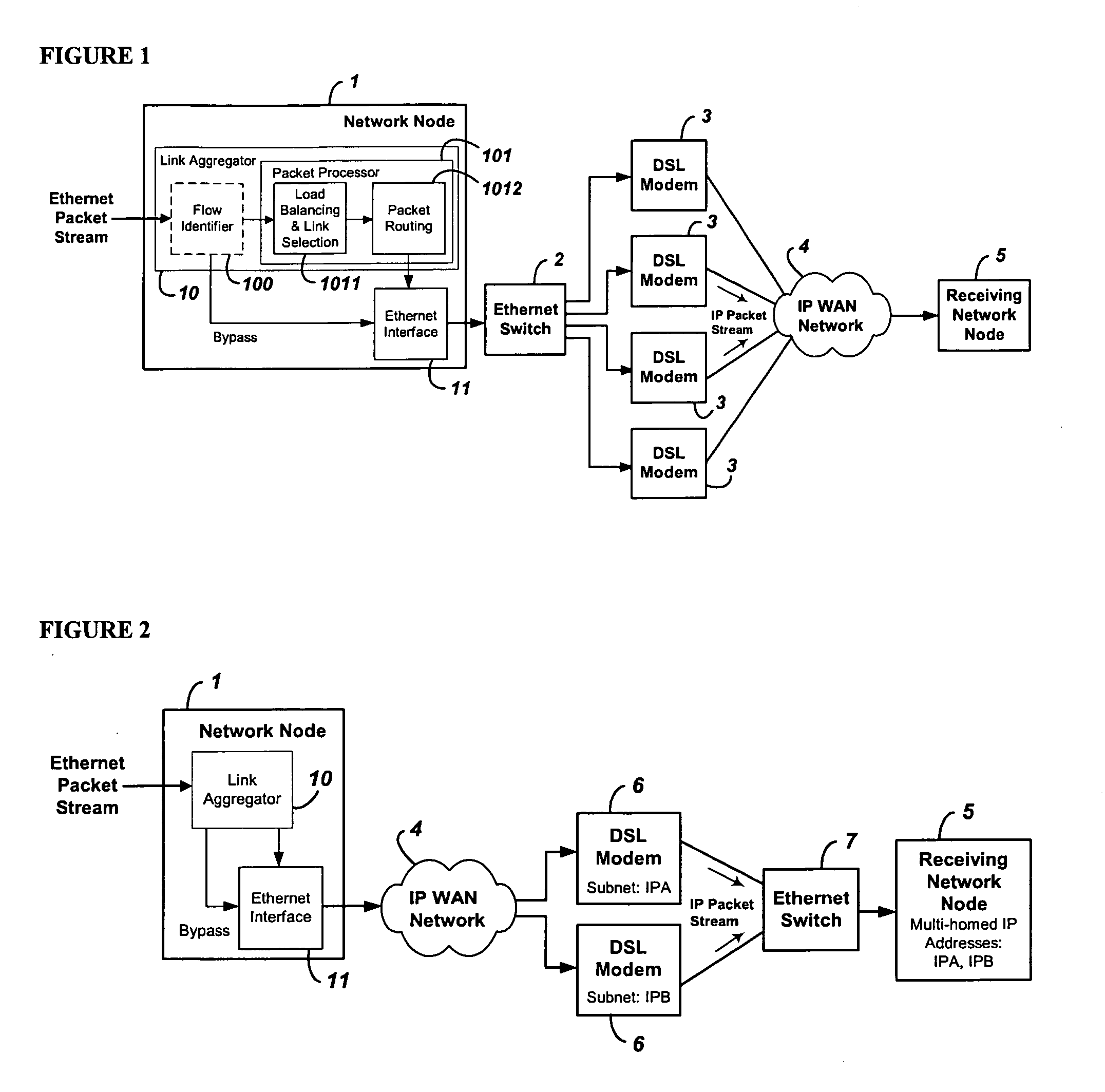
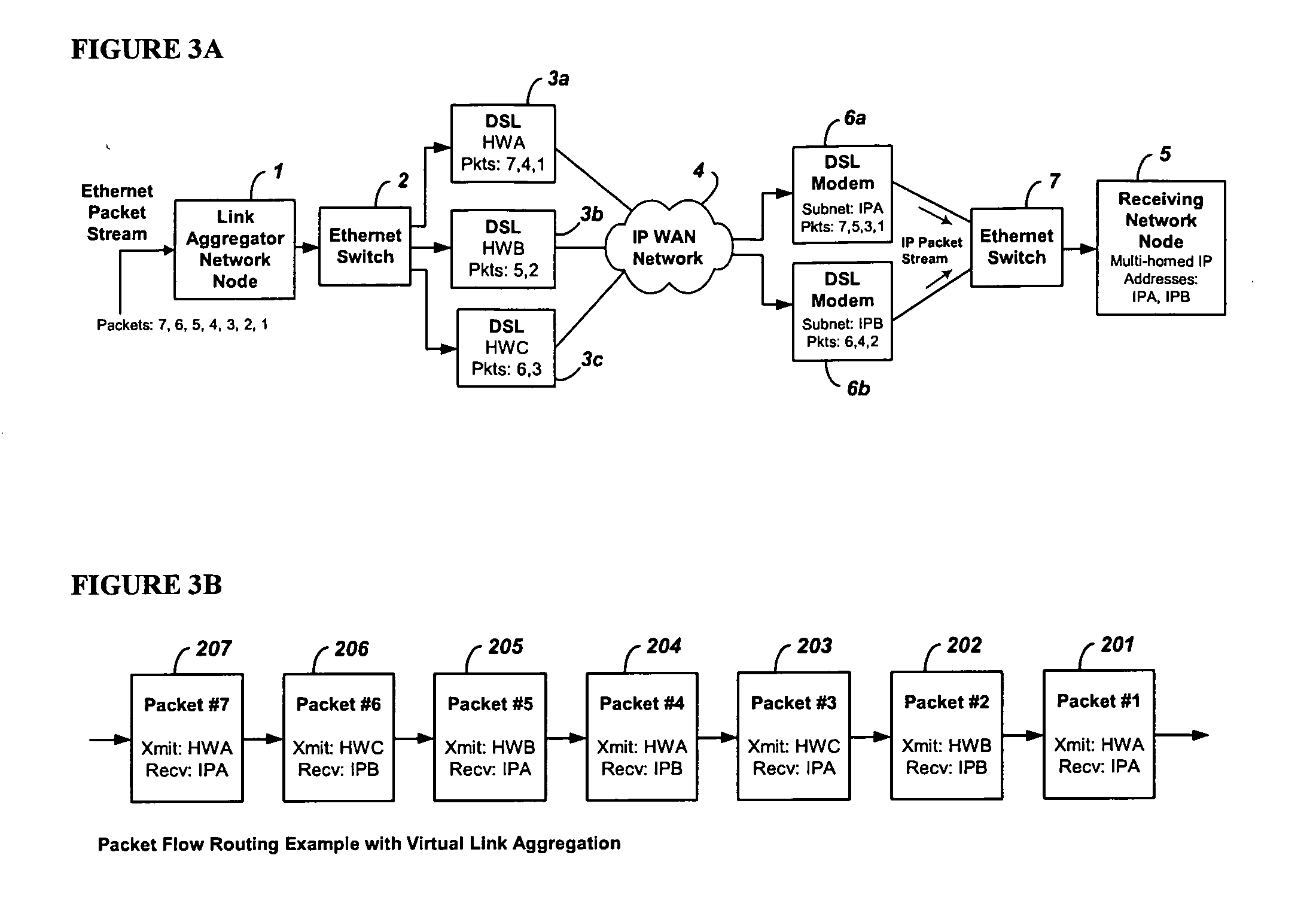
System and method for the virtual aggregation of network links
InactiveUS20060098573A1Improve throughputImprove reliabilityEnergy efficient ICTError preventionNetwork linkRewriting
A system and method for virtual link aggregation for combining network links of various types and speeds to increase throughput and reliability for packetized transport. In contrast with physical port trunking, the system does not require direct control over ports or network interfaces. Instead, the system rewrites packet addresses and works through existing networking equipment, without requiring any new or special protocols, processing, or equipment within the network. The system works through low-level rerouting by rewriting hardware addresses and / or high-level routing by rewriting logical addresses. Thus packets are redirected through multiple routes to a common destination via alternate gateways and links. Different algorithms may be employed to balance the load on each link and determine an optimal route for each packet. Embodiments may also employ packet flow or stream identification and thereby only provide link aggregation for a specified set of packet flows.
Owner:QVIDIUM TECH
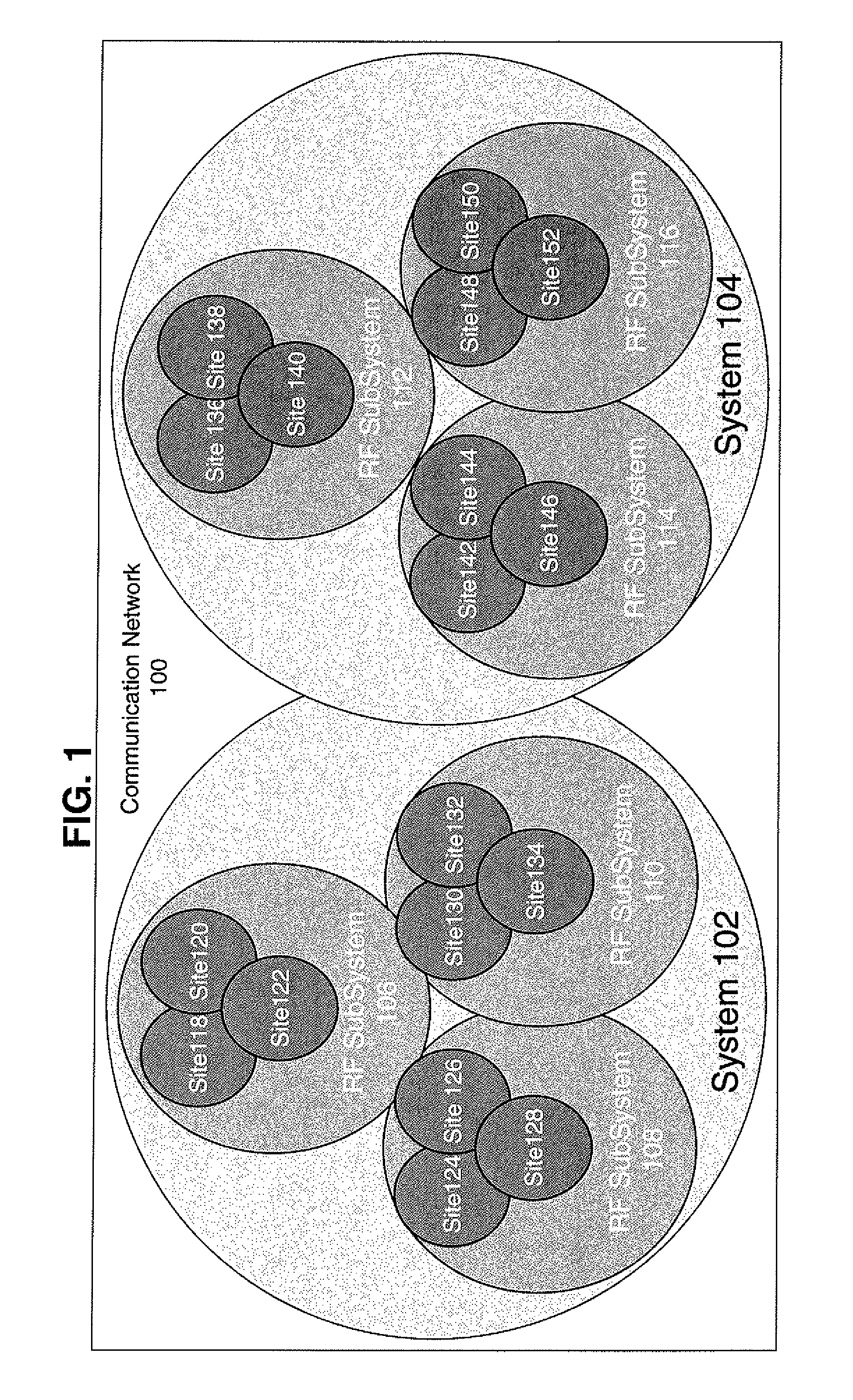
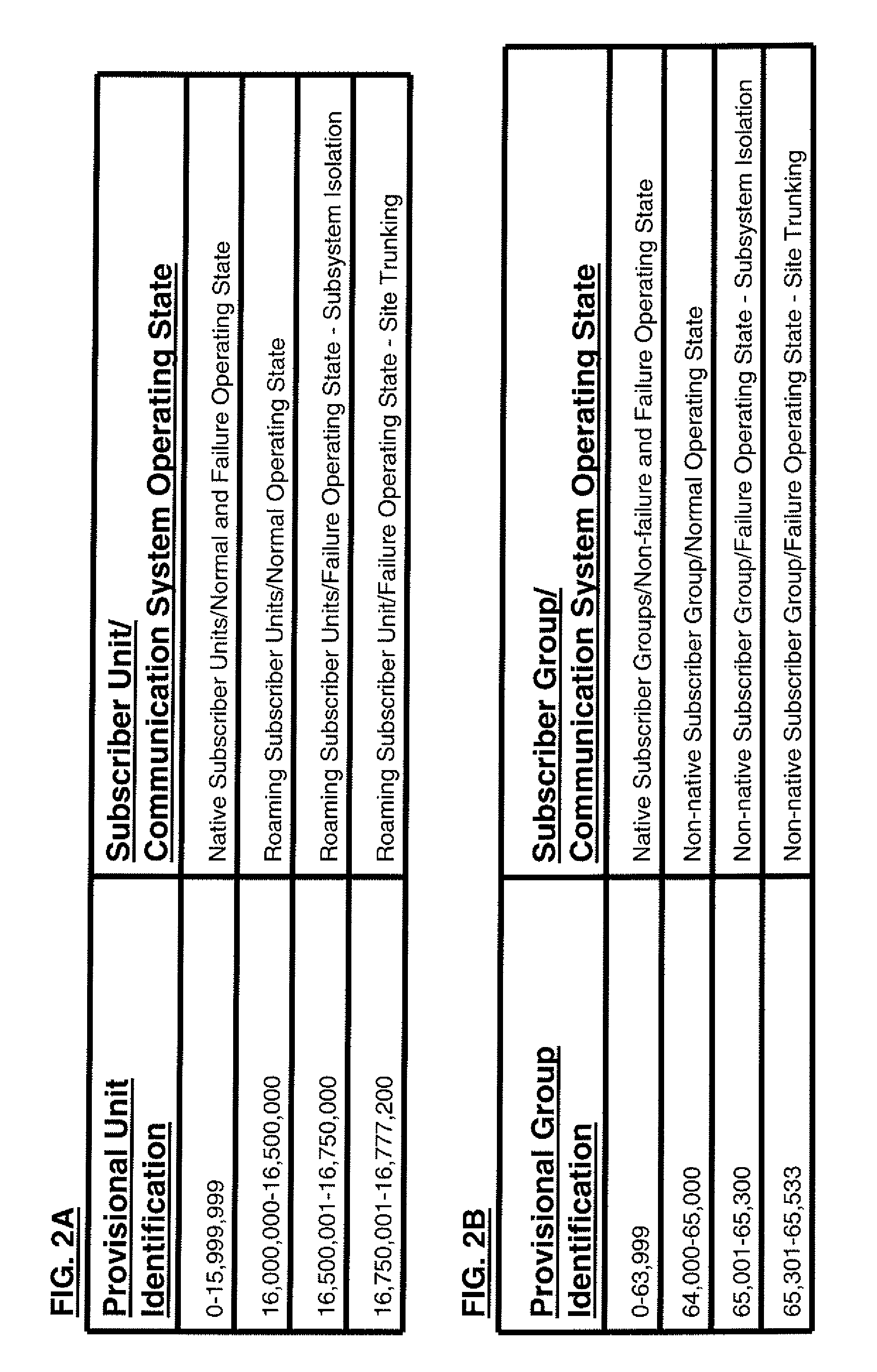
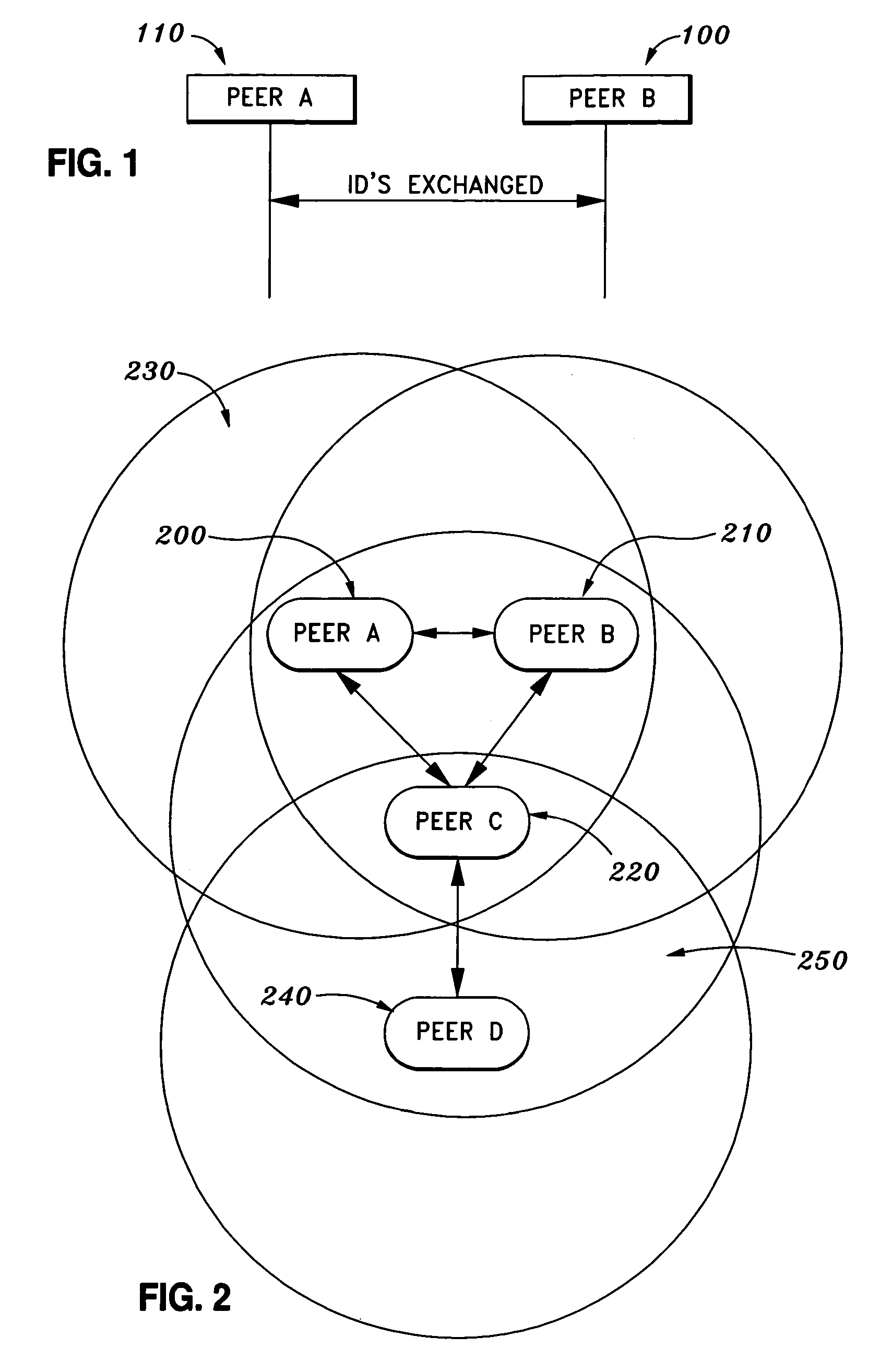
Method of assigning provisional identification to a subscriber unit and group
ActiveUS7970426B2Network traffic/resource managementBroadcast service distributionCommunications systemTrunking
Owner:MOTOROLA SOLUTIONS INC
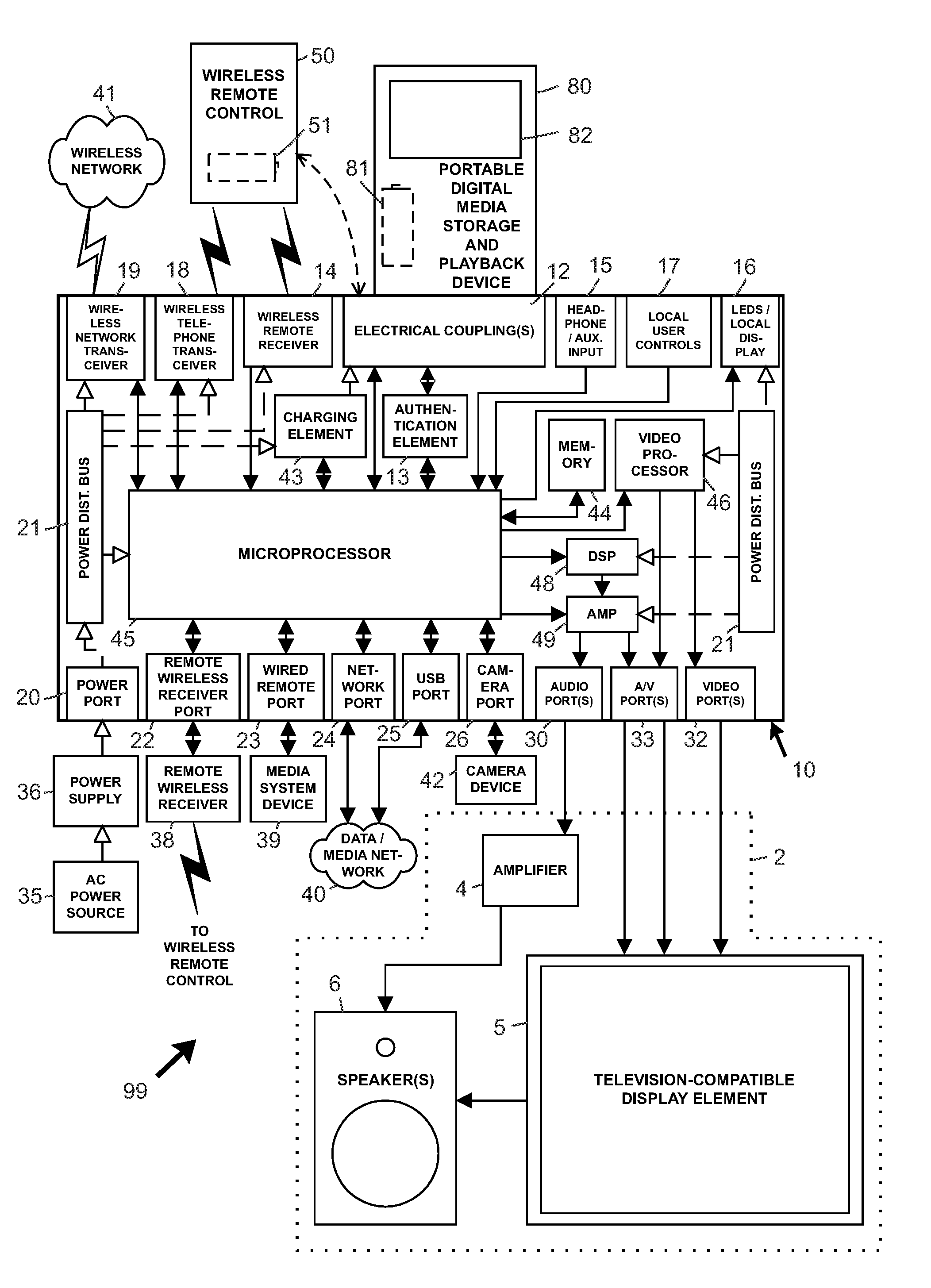
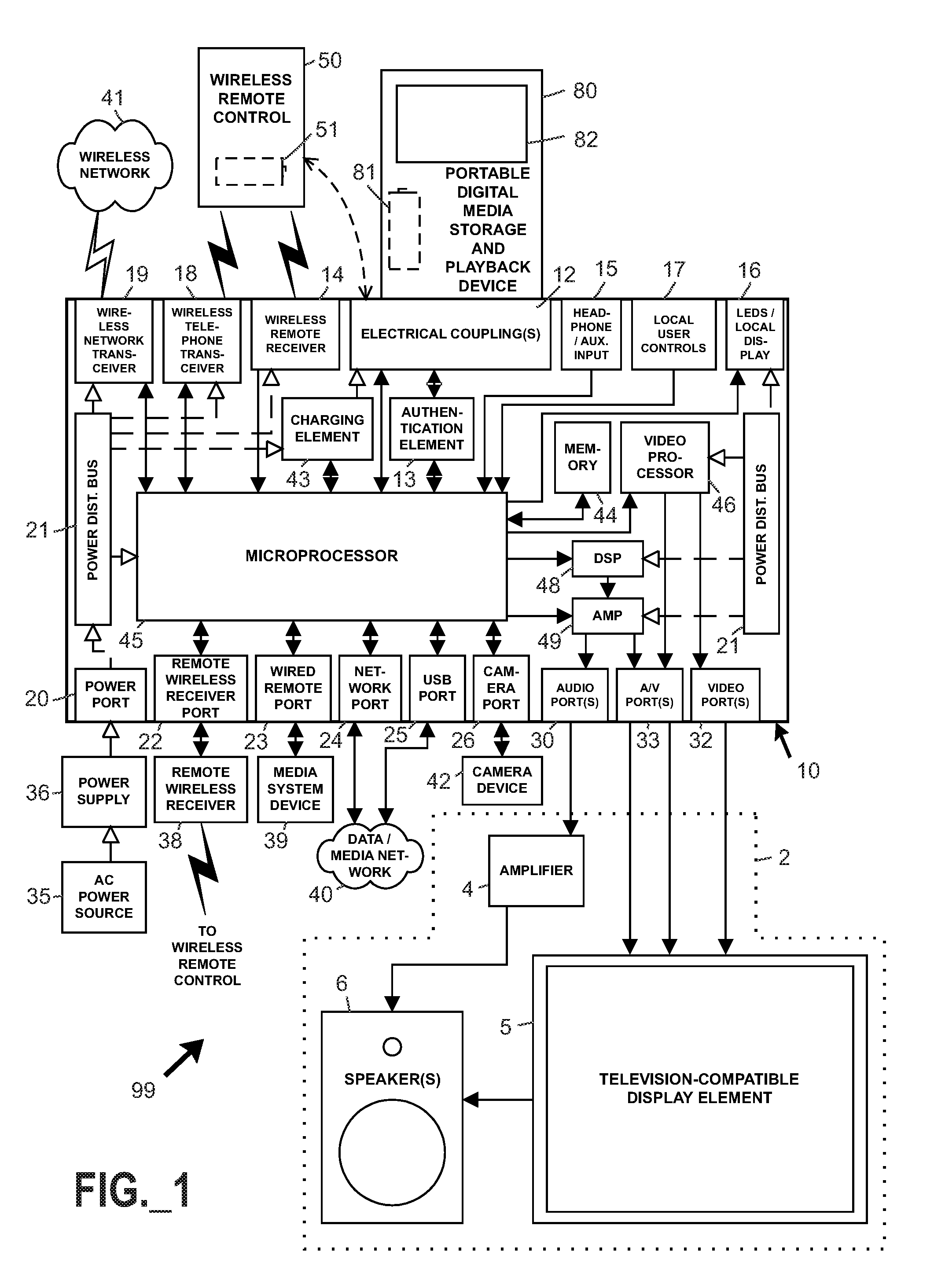
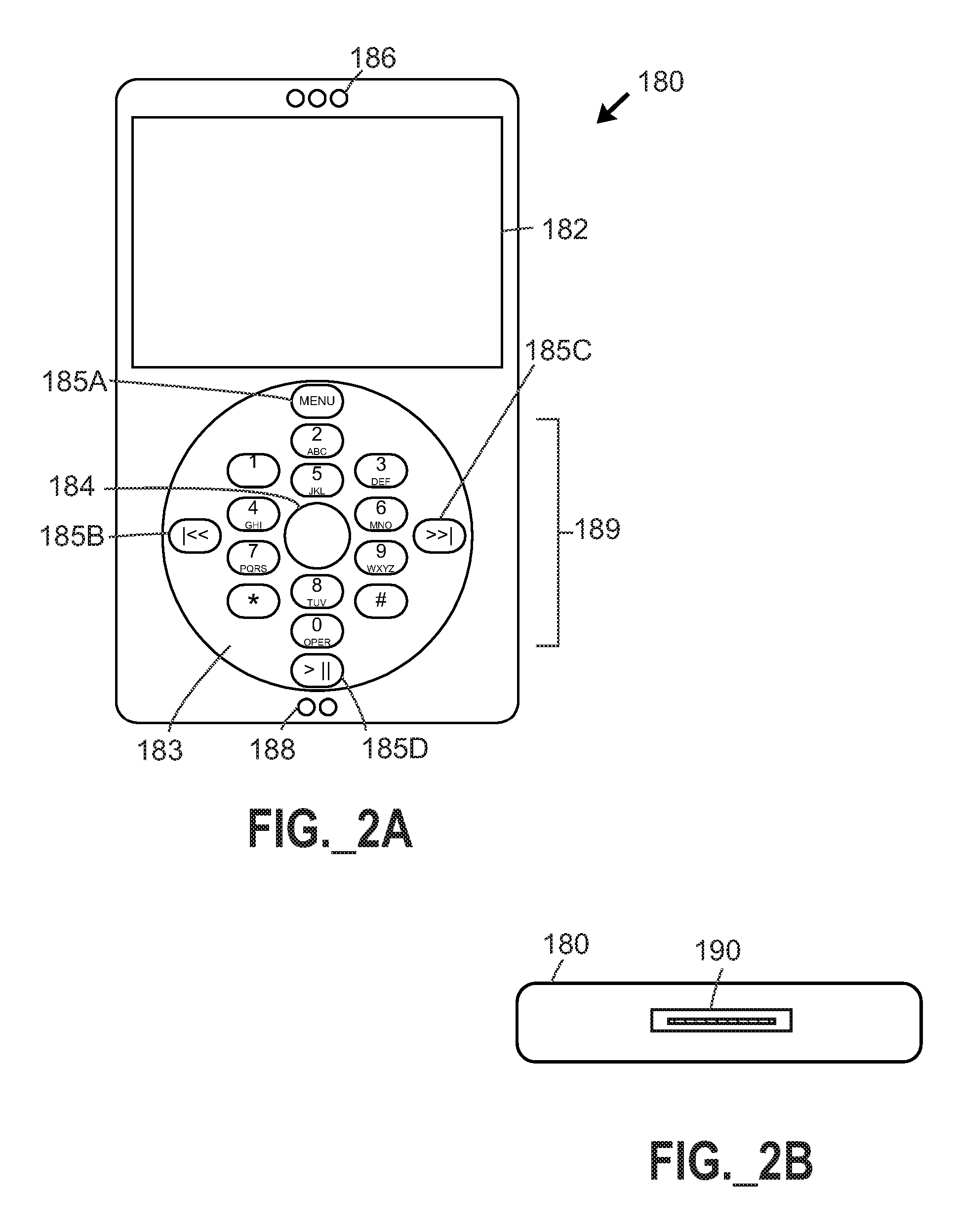
Interface systems for portable digital media storage and playback devices
A docking assembly serves as an interface between (1) a portable digital media storage and playback (PDMSP) device, and (2) a media reproduction system. A remote controller preferably controls the docking assembly and PDMSP device, which may receive electric charge from the assembly. Media reproduction systems may reproduce audio and video signals in user-perceptible form. Telephonic relay capability is further provided between a telephonic PDMSP playback device and a telephonic remote controller by way of a telephone rebroadcast receiver associated with the docking assembly. Methods for downloading digital media files, and for creating or modifying playlists with a remotely controllable docking assembly adapted to provide a television-compatible video output signal, are further provided.
Owner:PHILIPS ELECTRONICS NORTH AMERICA
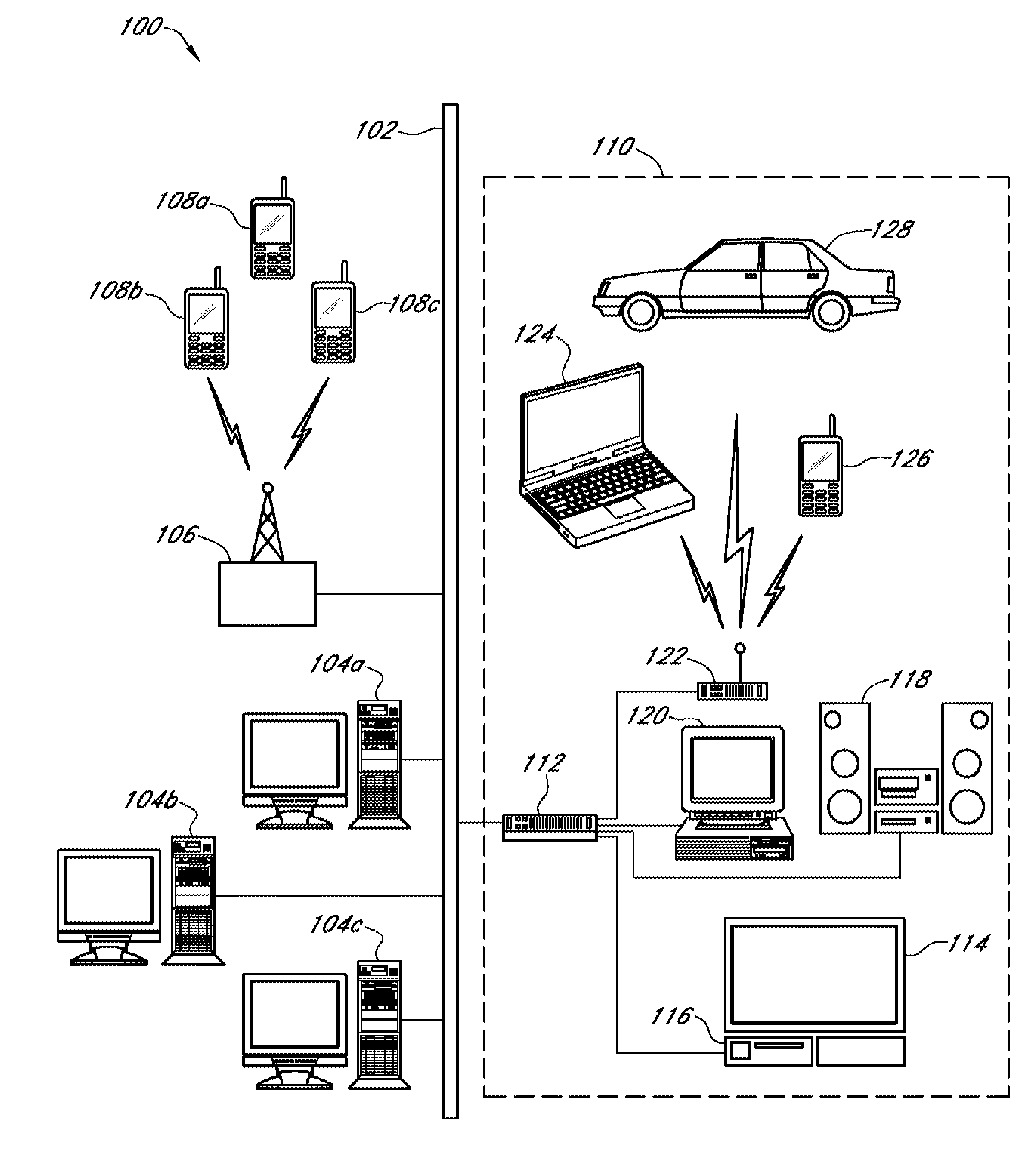
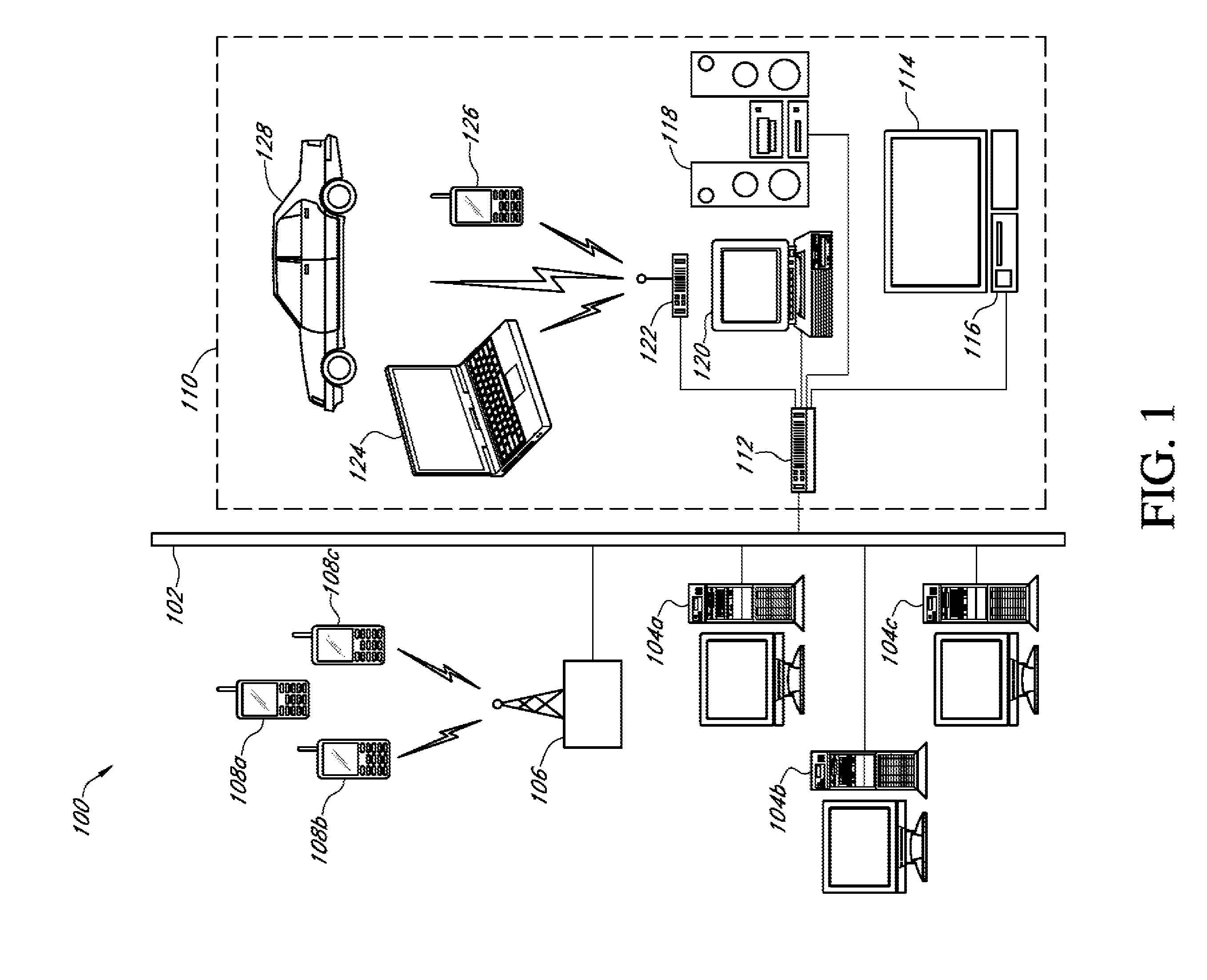
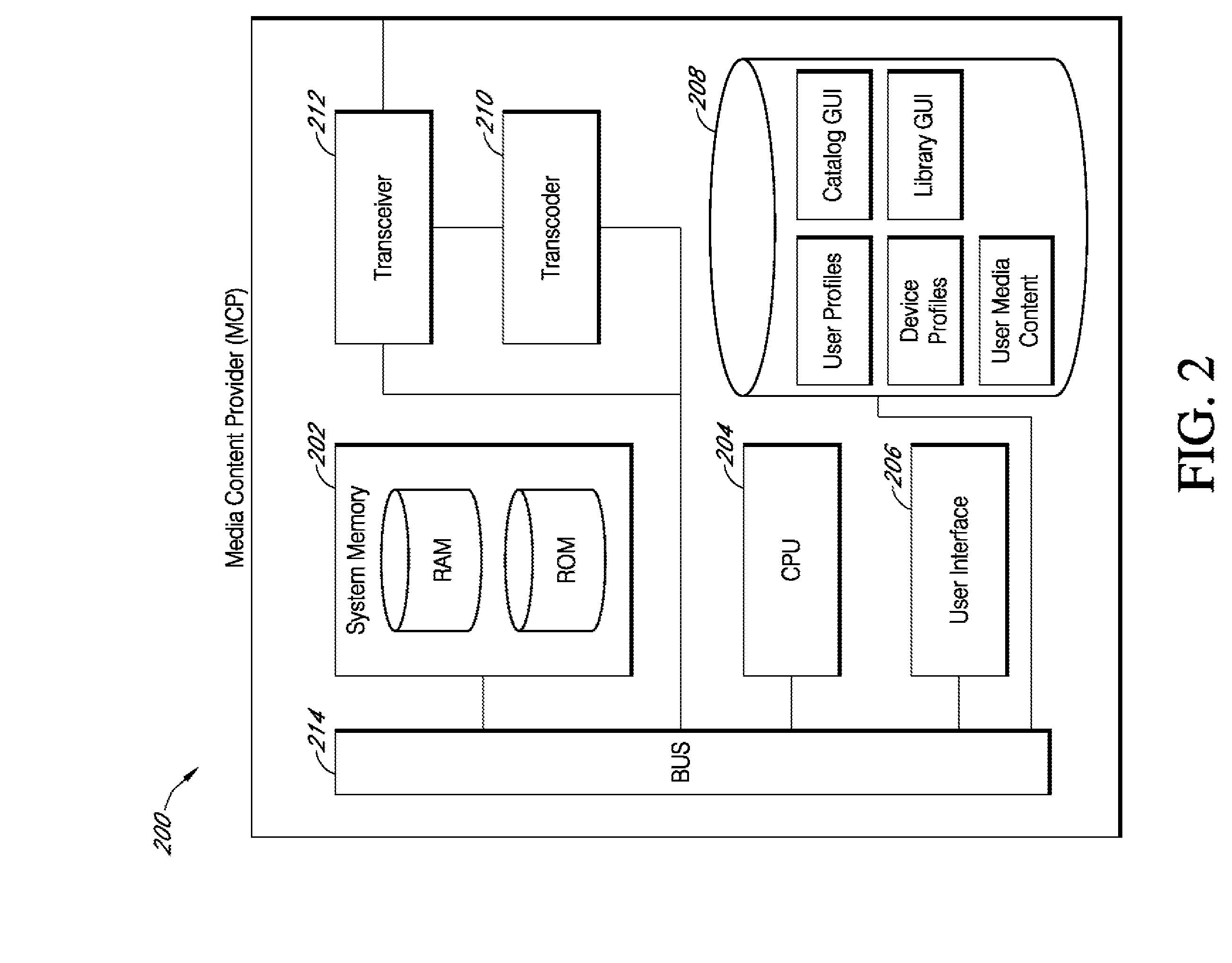
Systems and methods for device dependent media content delivery in a local area network
InactiveUS20100031299A1Special service provision for substationClosed circuit television systemsDistribution systemWorld Wide Web
A media distribution system that includes a media content provider, a relay device, a data communications network, and multiple media playback devices that each have distinct device-dependent media playback capabilities. The relay device receives a media content from the media content provider over a remote portion of the data communications network, and in response to a received instruction from either the media content provider or a local media playback device, the relay device determines whether or not to reformat the received media content to be compatible with one or more media playback devices. After the reformatting determination and instruction processing, the relay device transfers the media content to designated media playback devices over a local portion of the data communications network.
Owner:OPANGA NETWORKS
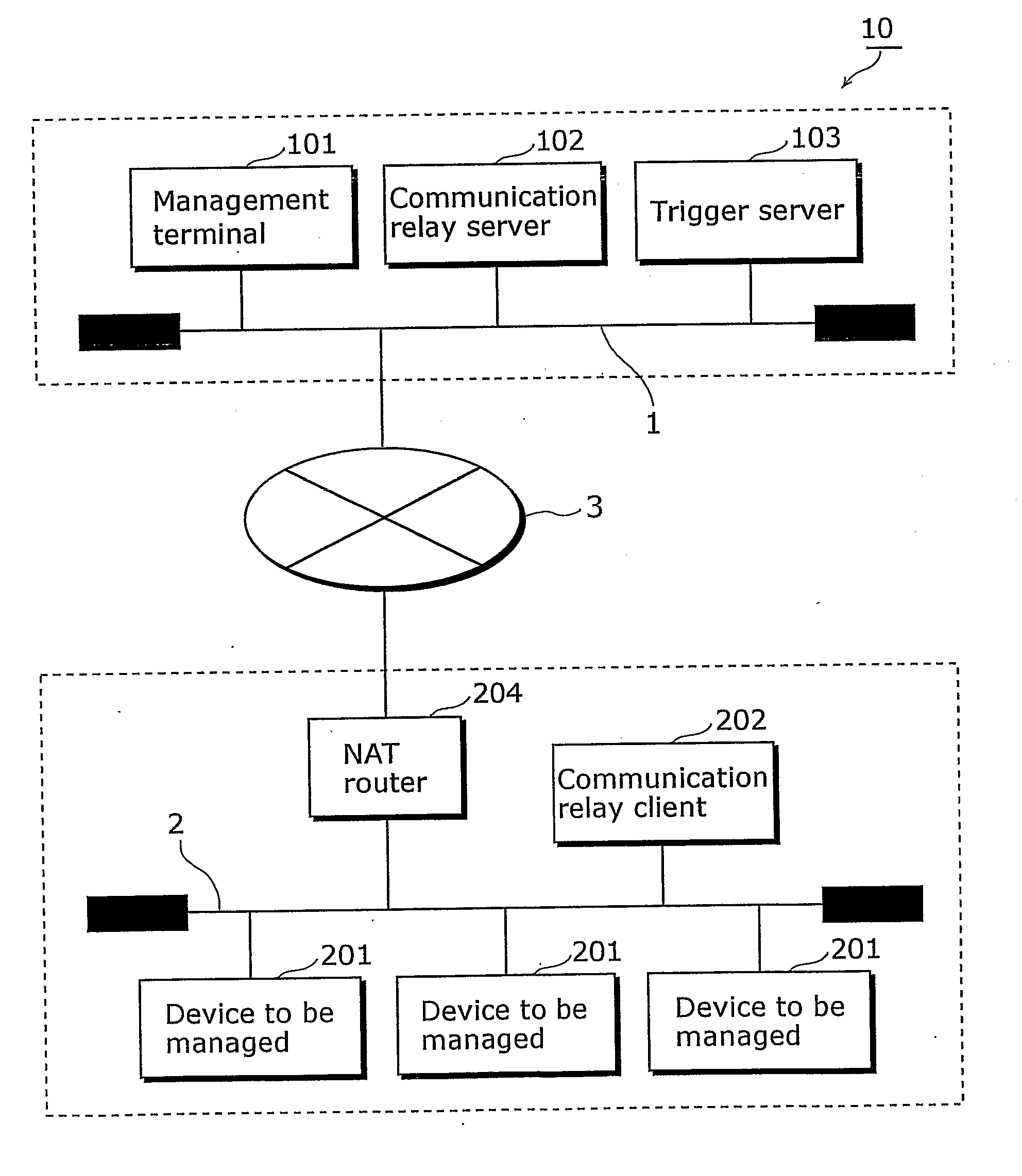
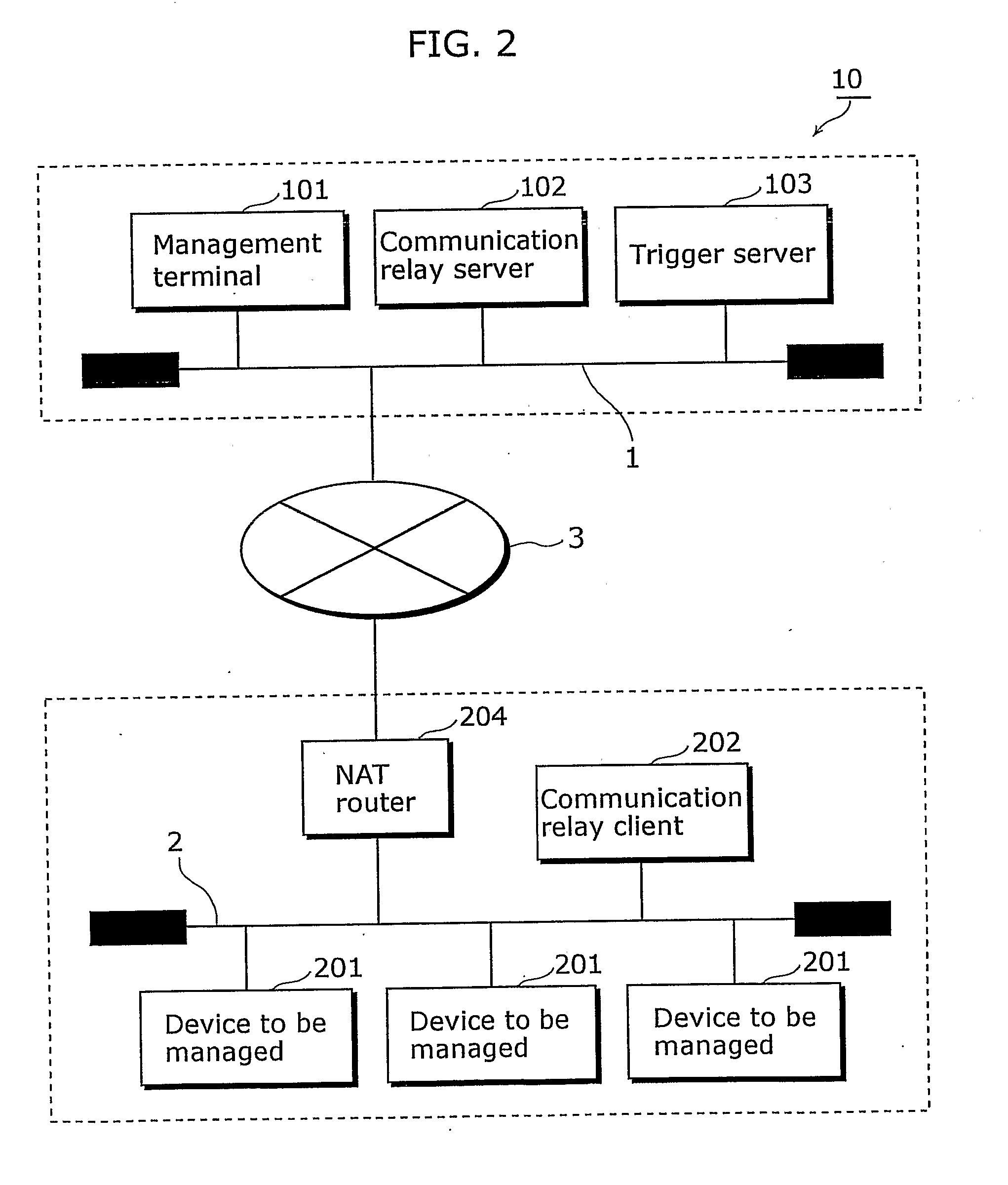
Communication network system and communication apparatus
InactiveUS20070147419A1Secure performanceSpecial service provision for substationTime-division multiplexNetwork onNetworked system
The present invention provides a communication network system in which communication can be securely performed via a global network from an existing terminal apparatus to an existing device connected to a local network without needing a special gateway function in a router and without performing a special setting in the router. In the communication network system (10), a communication relay client (202) performs polling on a management center network (1) via a NAT router (204); a communication relay server (102) converts a packet transmitted from a management terminal (101); and the communication relay client (202) receives the converted packet as a response to the polling via the NAT router (204) from the side of the management center network (1). The communication relay client (202) converts the converted packet to the original packet, and transmits the original packet to a device to be managed (201).
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
Method and system for peer-to-peer wireless communication over unlicensed communication spectrum
InactiveUS7342895B2Avoid collisionData switching by path configurationRadio transmissionTrunkingManet routing
Owner:SERPA MARK
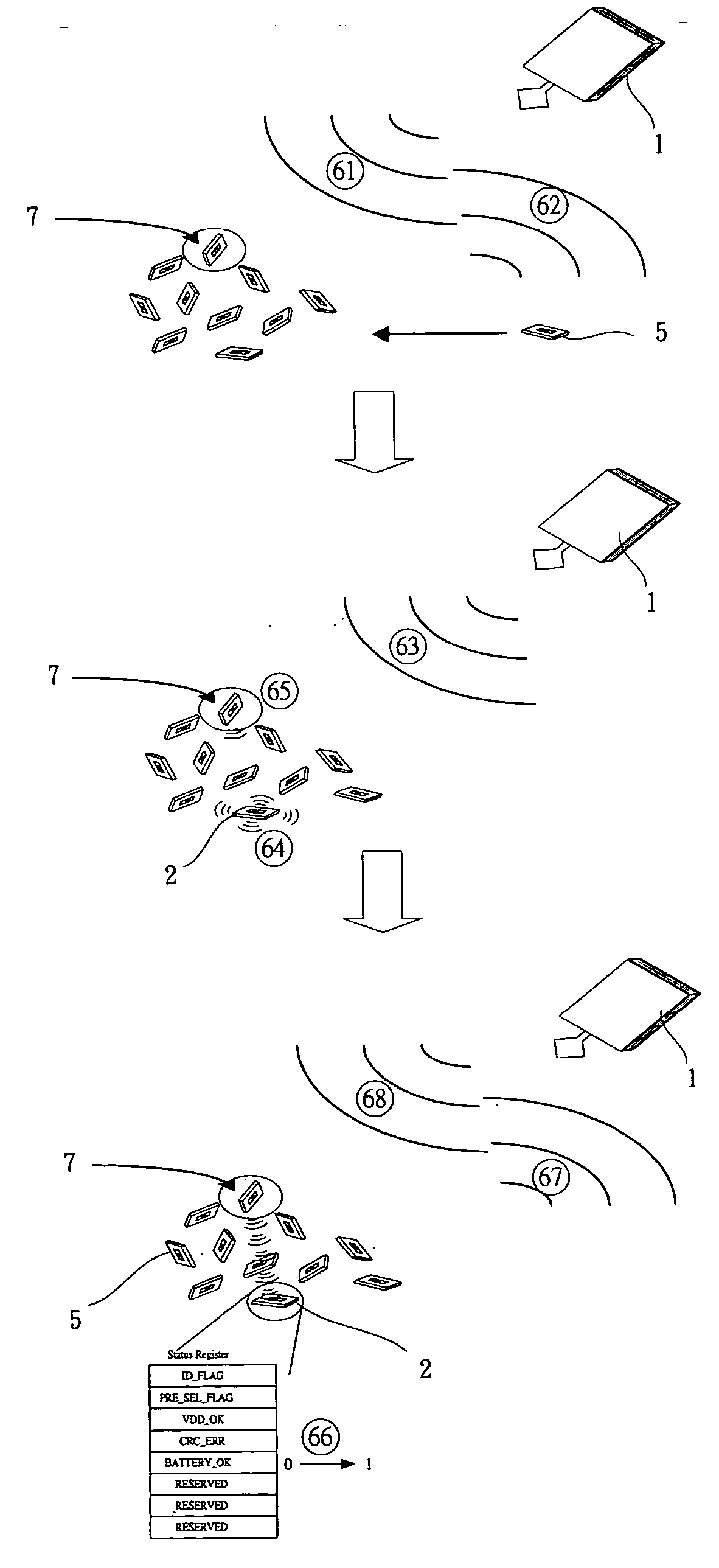
High performance RFID system and operating method thereof
InactiveUS20060114102A1Improve performanceMemory record carrier reading problemsSubscribers indirect connectionSemi activeTrunking
A high performance Radio Frequency Identification (RFID) system and the operating method thereof. The RFID system includes a reader, a plurality of passive tags, and at least one local reader to communicate with nearby passive tags and further forward results to the reader. A repeater tag or a semi-active tag can serve as a local reader. An operating method of the high performance RFID system, a repeater tag operating method, a semi-active tag electric power detecting method, and an operating method for searching for no electric power tags are further provided.
Owner:IND TECH RES INST
Layer two tunneling protocol (L2TP) merging and management
InactiveUS6094437AEasy to implementReduce complexityData switching detailsNetworks interconnectionDistributed computingEdge device
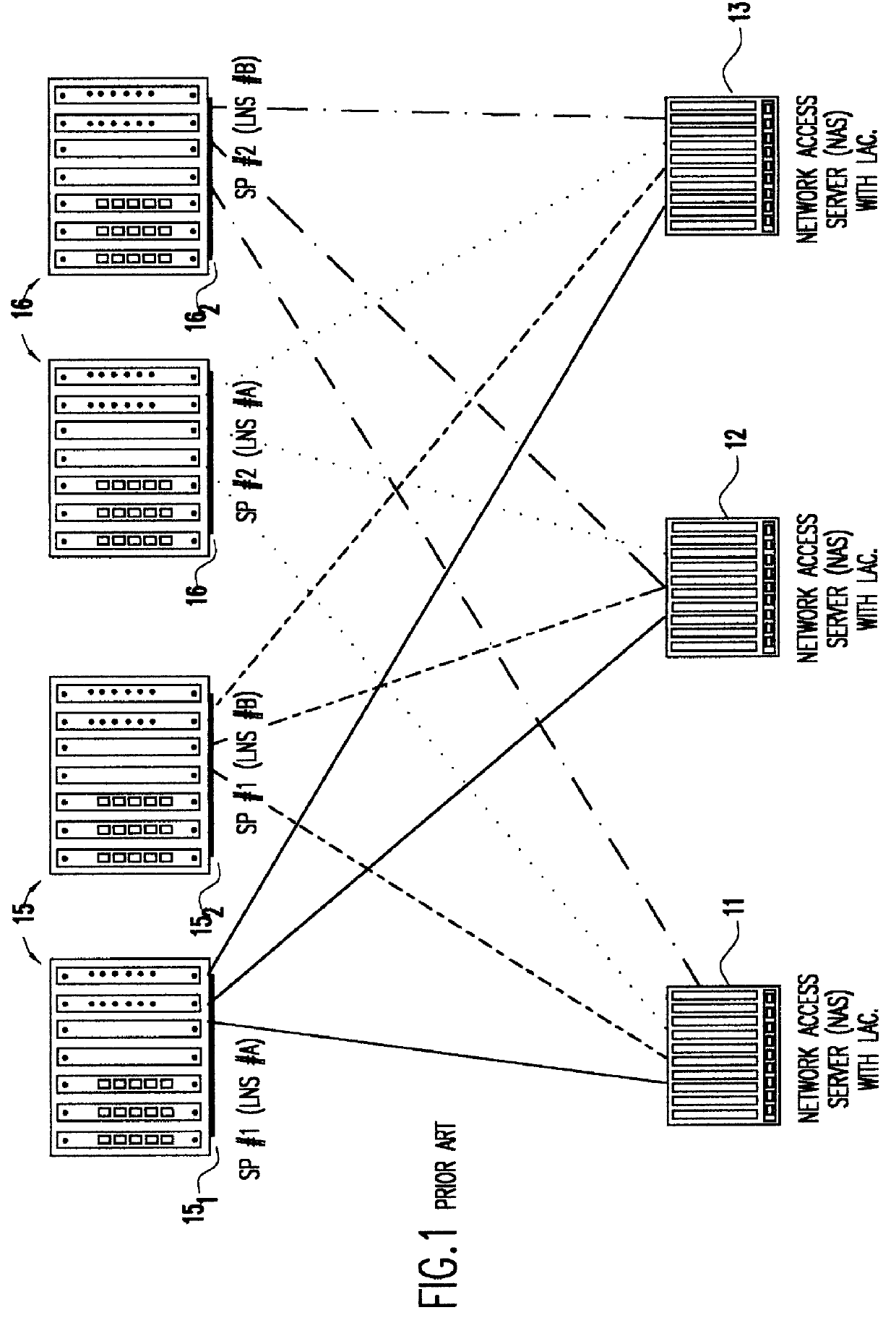
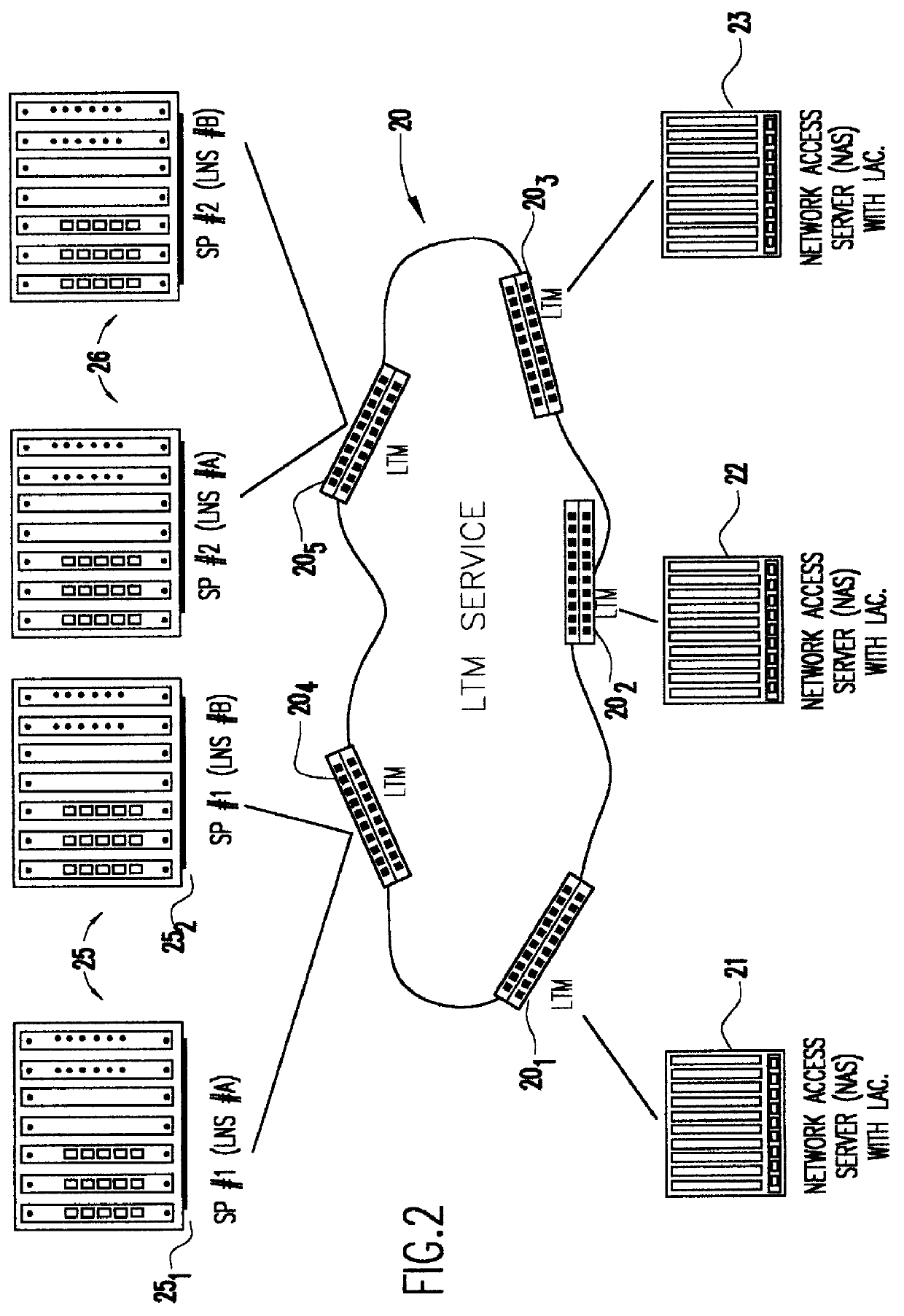
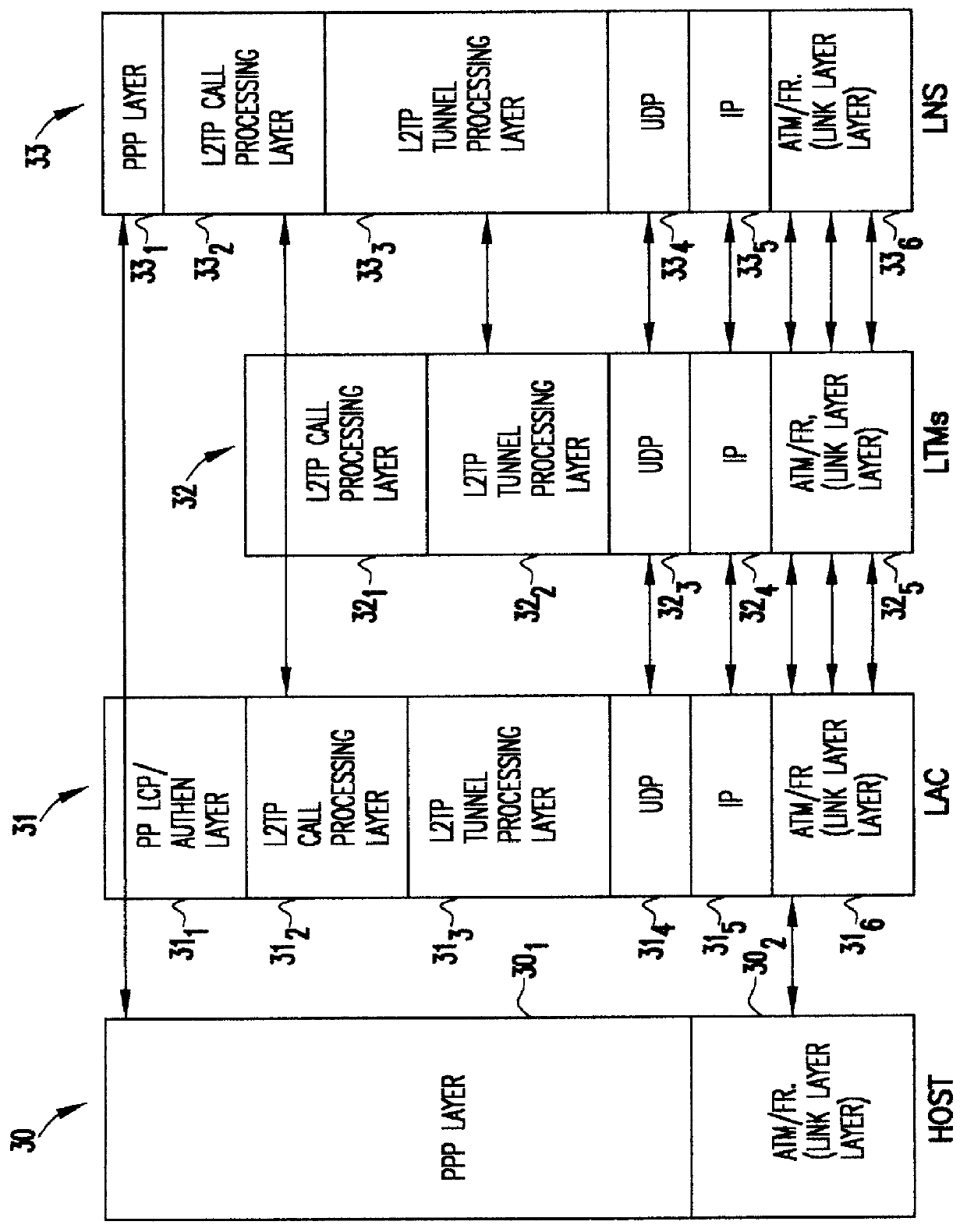
A system is provided for creating a tunneling service from the use of a traditional tunneling protocol, such as the layer two tunneling protocol (L2TP). In particular, the L2TP tunneling protocol, which is designed to go point-to-point between an L2TP Access Concentrator (LAC) and an L2TP Network Server (LNS), is abstracted so that L2TP becomes an access protocol to a tunneling service. A new L2TP tunnel merger and management (LTM) service is created which severs the tight configuration relationships between LAC and LNSs. Only a tight configuration between an LAC and its LTM edge device and between an LNS and its LTM edge device is required. An internal trunk protocol (INT protocol) carries needed information between LTM edge devices to establish ingress / egress L2TP access calls inside of separate L2TP access tunnels on opposite LTM edge devices. The addition of another LAC is accomplished by re-routing L2TP tunnels within the LTM service without reconfiguration of the LNSs, and the addition of another LNS is accomplished by re-routing L2TP tunnels within the LTM service without reconfiguration of the LACs. The LTM service determines the need for both additional trunk and access resources and establishes both new trunk / access tunnels to provide additional resources. The LTM service also determines excess resources on both trunk and access entities and releases trunk / access tunnels to provide the needed additional resources.
Owner:TDC THE
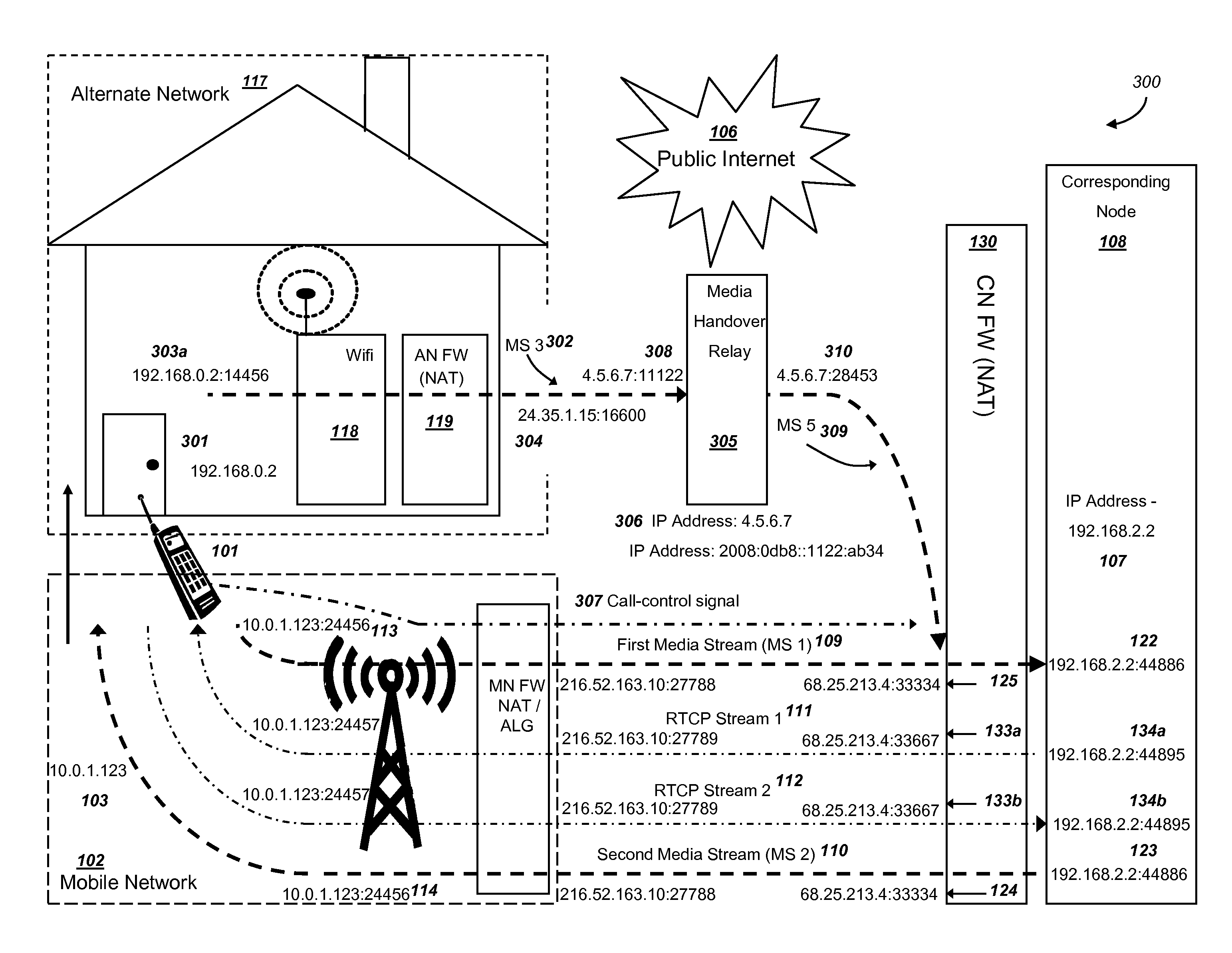
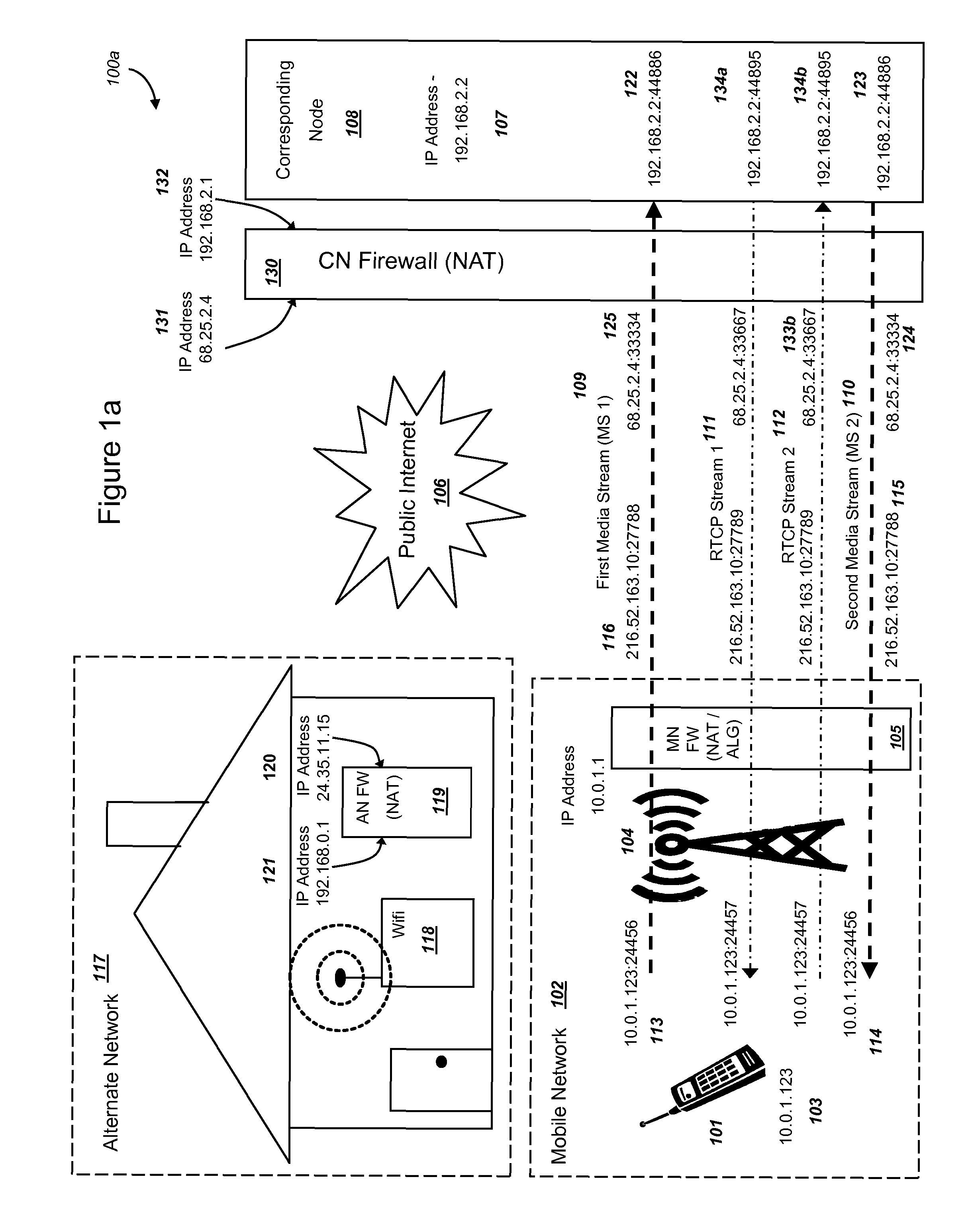
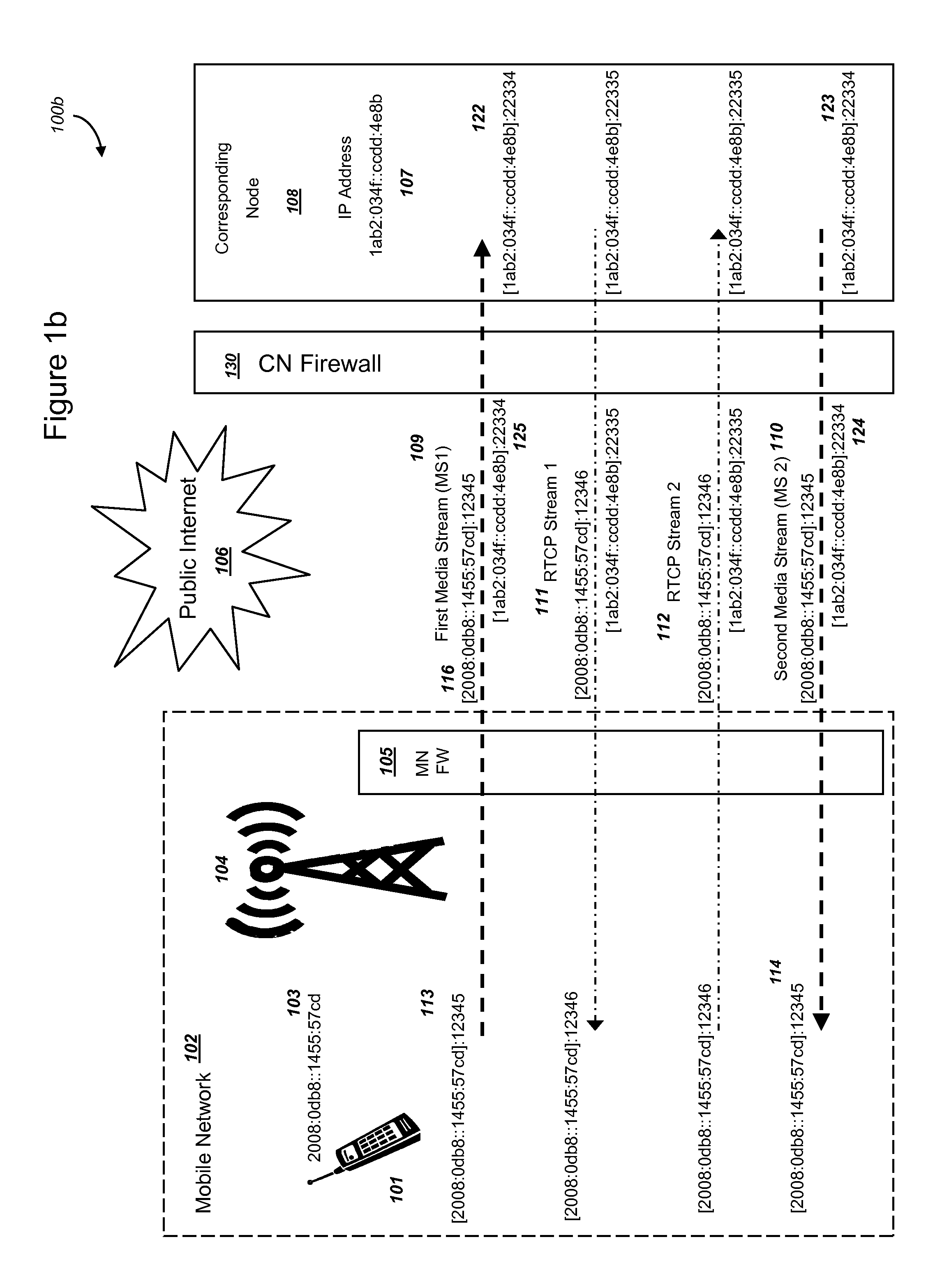
Efficient handover of media communications in heterogeneous IP networks using handover procedure rules and media handover relays
ActiveUS8228861B1Reduce complexityIncrease speedError detection/prevention using signal quality detectorChannel coding adaptationMedia controlsCable Internet access
Methods and systems are provided for efficient handover of a media session between heterogeneous Internet Protocol (IP) networks. A mobile device with Internet access can operate a software program to communicate with a corresponding node. The corresponding node may access the Internet through a firewall which may include Network Address Translation (NAT)-routing functionality. The mobile device establishes a media session with a corresponding node via the transmission of a first media stream and receipt of a second media stream, and a media-control channel can optionally be implemented. The mobile device can acquire Internet access through a second IP address, and packets routed between the second IP address and the Internet may traverse a firewall. The mobile device can evaluate a set of network parameters at the second IP address from a stored Local Area Network (LAN) profile. A software routine can (i) evaluate that handover of the media session from the first IP address to the second IP address is preferred and (ii) select an efficient handover procedure according to handover procedure rules.
Owner:GOOGLE LLC
Relay apparatus for relaying communication from CPU to peripheral device
InactiveUS20050132098A1Reduce CPU overheadReduce overheadInput/output processes for data processingComputer hardwareTrunking
In order to reduce overhead of a CPU, a relay apparatus for relaying communication from a CPU to a peripheral device includes communication information holding sections for holding information required for communication with the peripheral devices inside the relay apparatus; and command holding sections, which are provided adjacent to the communication information holding section, for holding commands used to communicate desired information inside the communication information holding section to the peripheral device. The CPU writes desired information in the communication information holding section and the command holding section inside the relay apparatus by burst-mode communication, and the relay apparatus performs communication with the peripheral devices in accordance with instructions from the command holding section after the writing of the desired information in the communication holding section and the command holding section is completed.
Owner:CANON KK
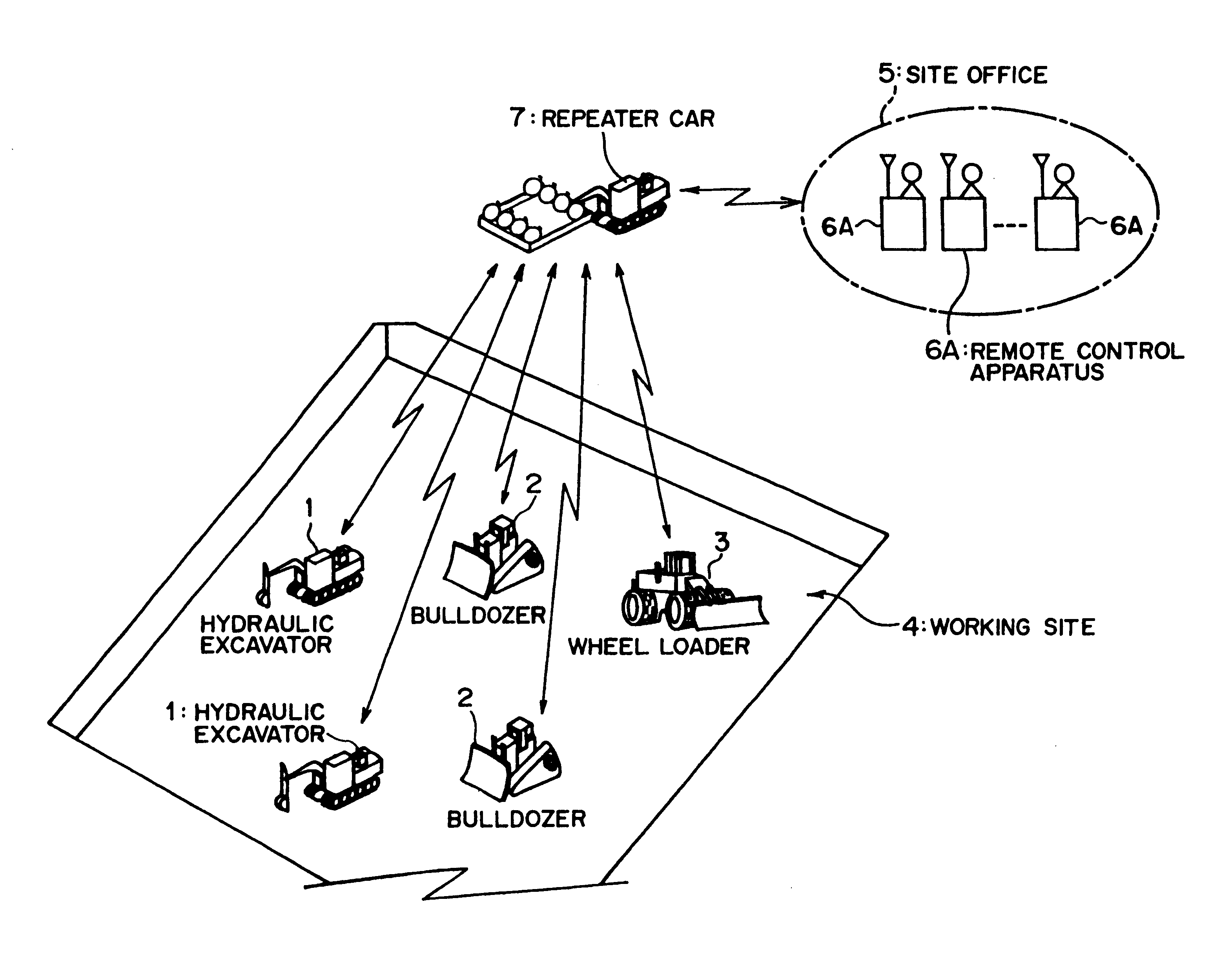
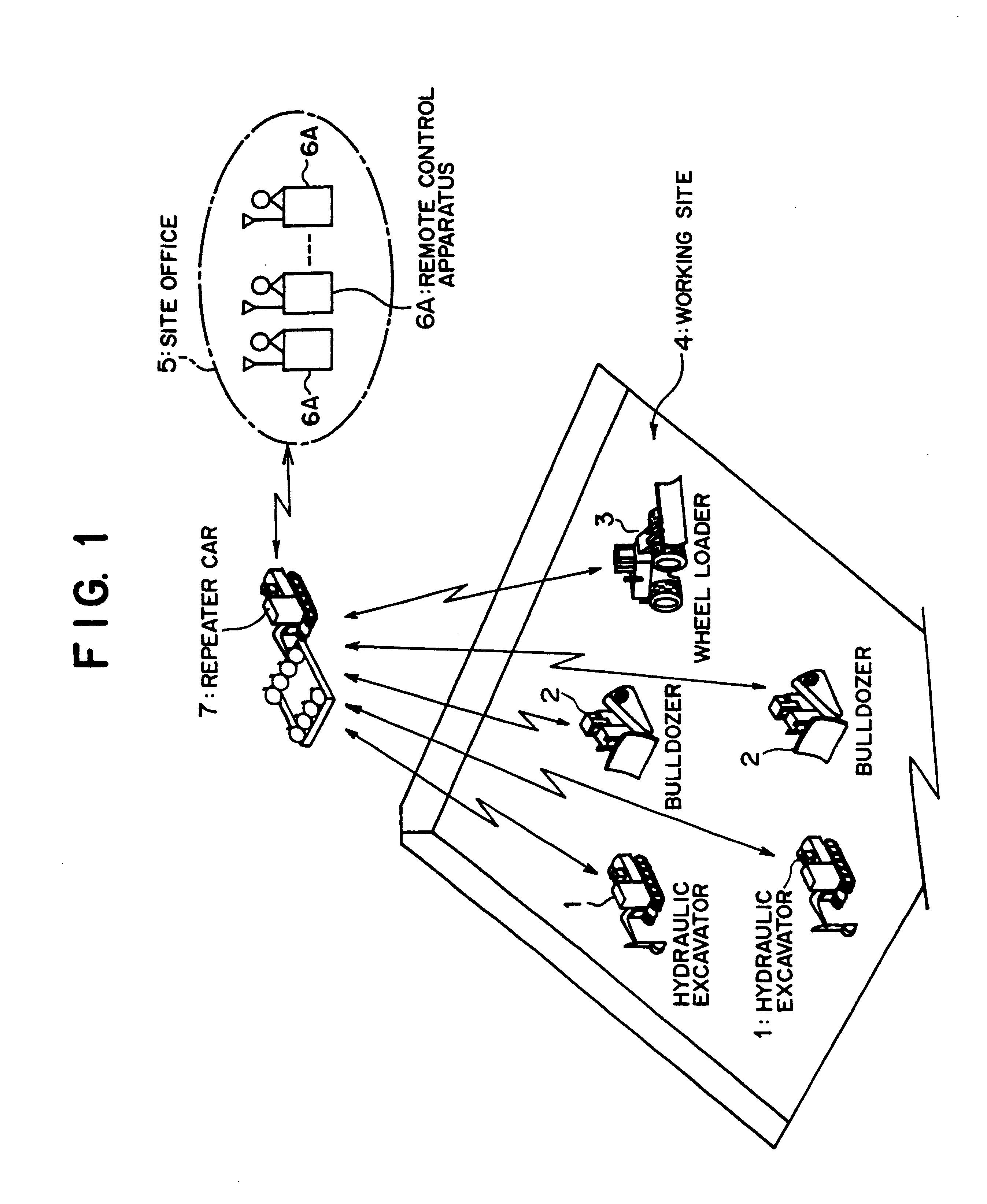
Remote radio operating system, and remote operating apparatus, mobile relay station and radio mobile working machine
InactiveUS6778097B1Improve reliabilityShort working hoursElectric signal transmission systemsDigital data processing detailsMobile relayRemote control
The present invention relates to remote radio control technology, and a remote radio control system includes a radio movable working machine (1), a remote control apparatus (6A), and a movable repeater station (7). First bidirectional communication means (31, 71) having a high radio wave directionality and first automatic tracking means (32, 71A) are provided between the working machine (1) and the repeater station (7), and second bidirectional communication means (63, 76) having a high radio wave directionality, second automatic tracking means (63A, 76A), and emergency spread spectrum bidirectional communication means (64, 87) for enabling bidirectional communication between the remote control apparatus (6A) and the repeater station (7) when communication by the second bidirectional communication means (63, 76) is impossible are provided between the remote control apparatus (6A) and the repeater station (7). Consequently, even if communication between the working machine (1) and the movable repeater station (7) is disabled, each of the working machine (1) and the repeater station (7) is permitted to perform a minimum necessary operation, and any other person than those skilled in actual controlling operation of the working machine (1) can perform remote control easily.
Owner:CATEPILLAR SARL
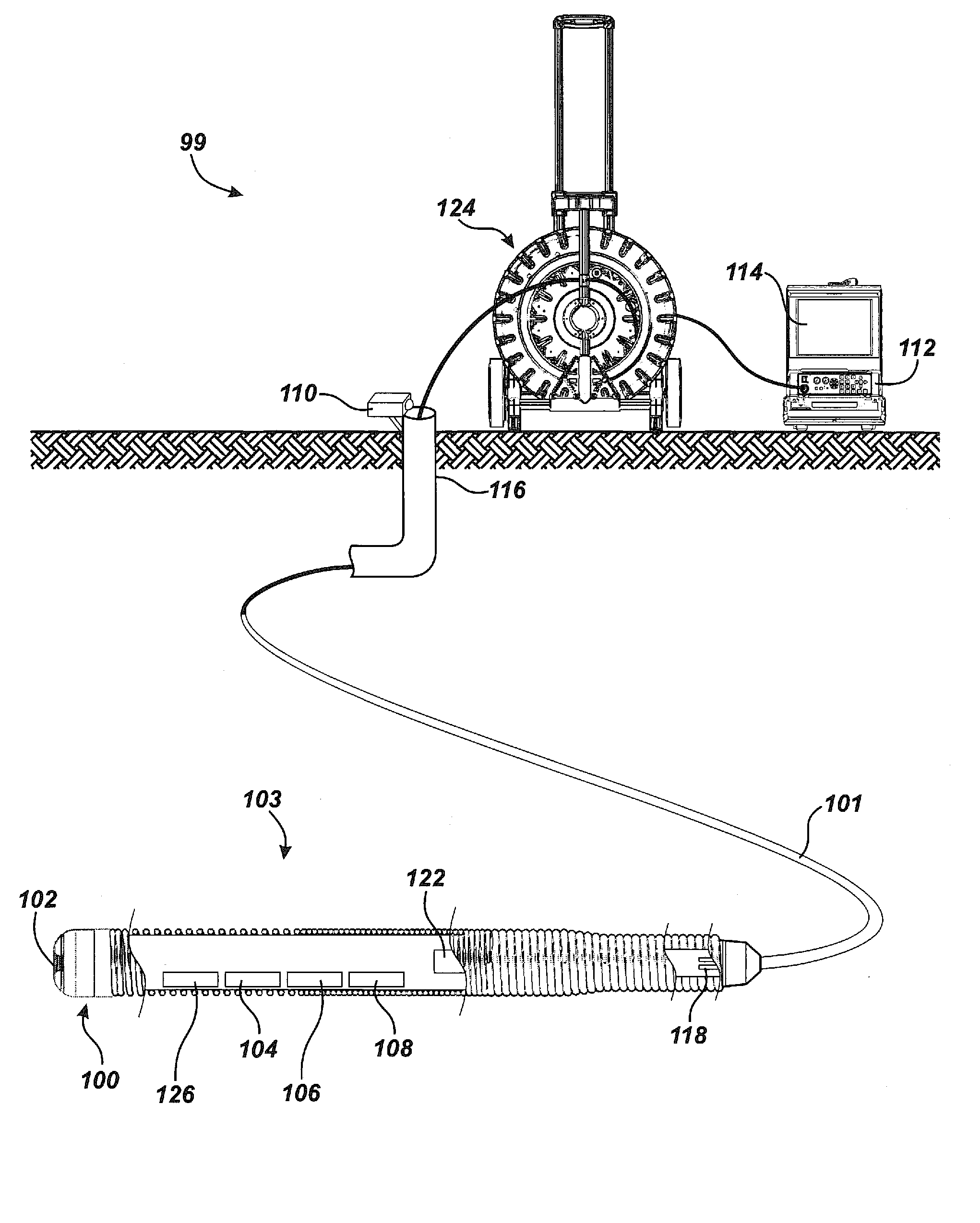
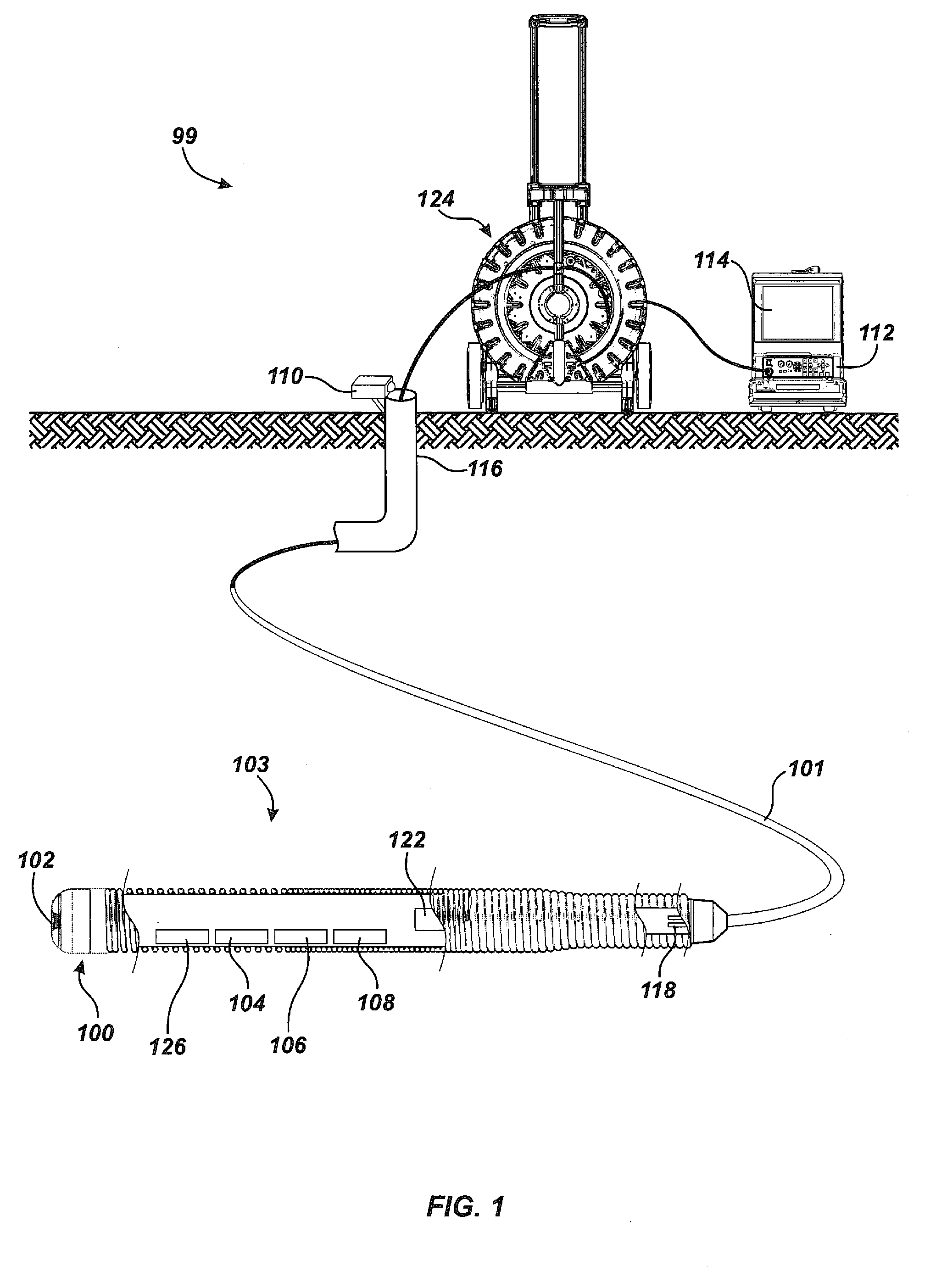
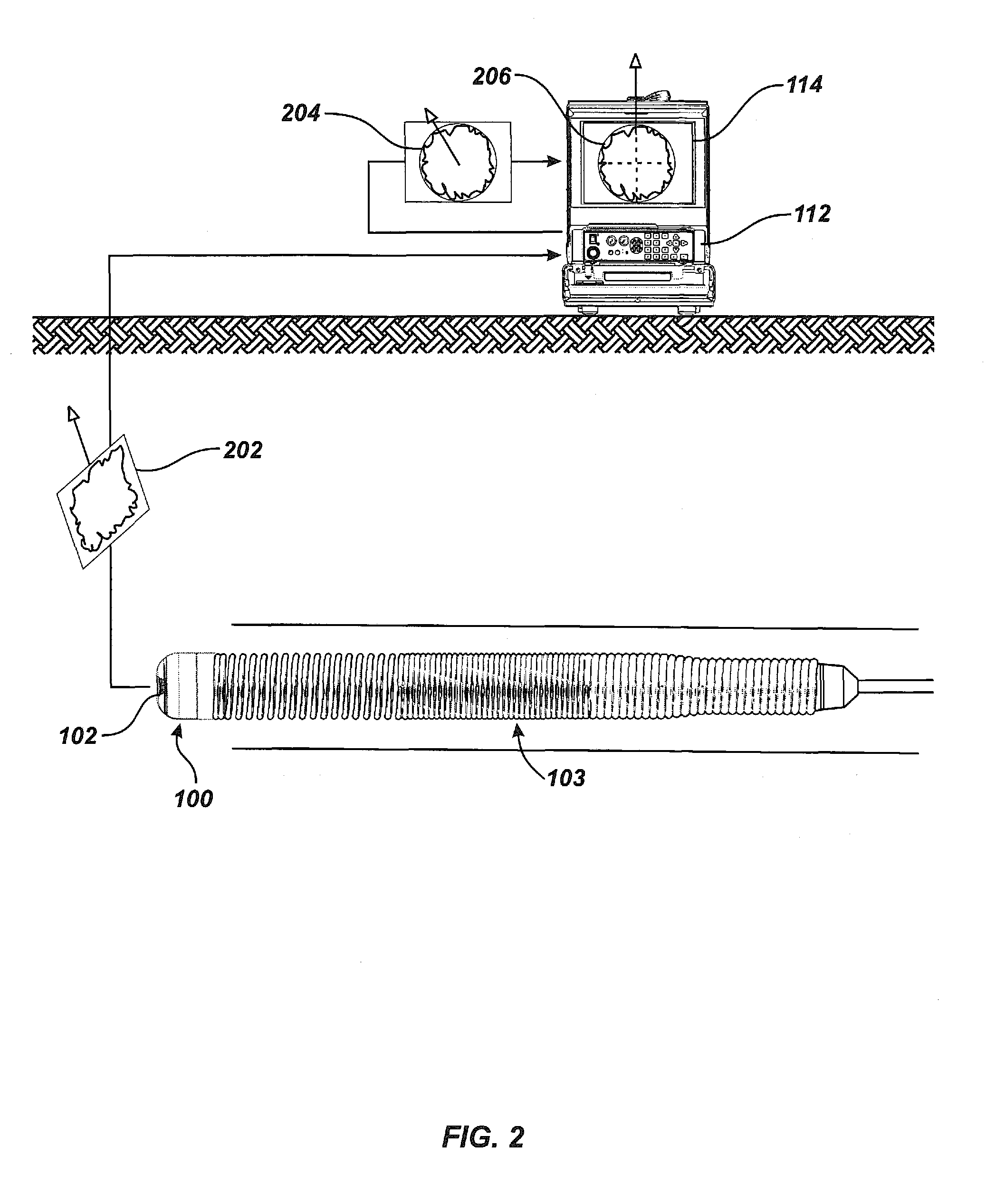
Pipe mapping system
ActiveUS8547428B1Simple methodTelevision system detailsImage enhancementData connectionThree axis accelerometer
A pipe inspection system employing a camera head assembly incorporating multiple local condition sensors, an integral dipole Sonde, a three-axis compass, and a three-axis accelerometer. The camera head assembly terminates a multi-channel push-cable that relays local condition sensor and video information to a processor and display subsystem. A cable storage structure includes data connection and wireless capability with tool storage and one or more battery mounts for powering remote operation. During operation, the inspection system may produce a two- or three-dimensional (3D) map of the pipe or conduit from local condition sensor data and video image data acquired from structured light techniques or LED illumination.
Owner:SEESCAN
Wireless repeater with intelligent signal display
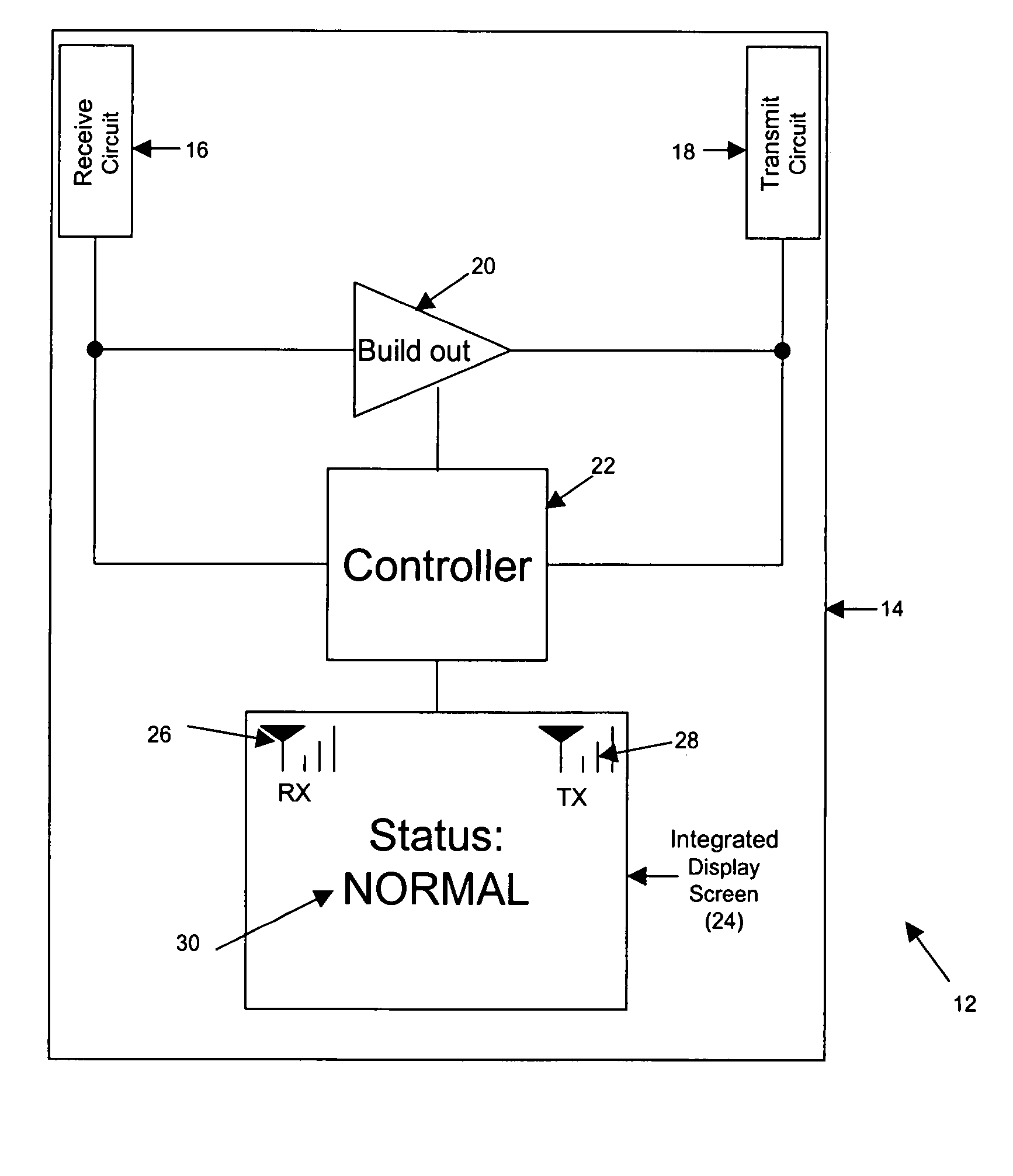
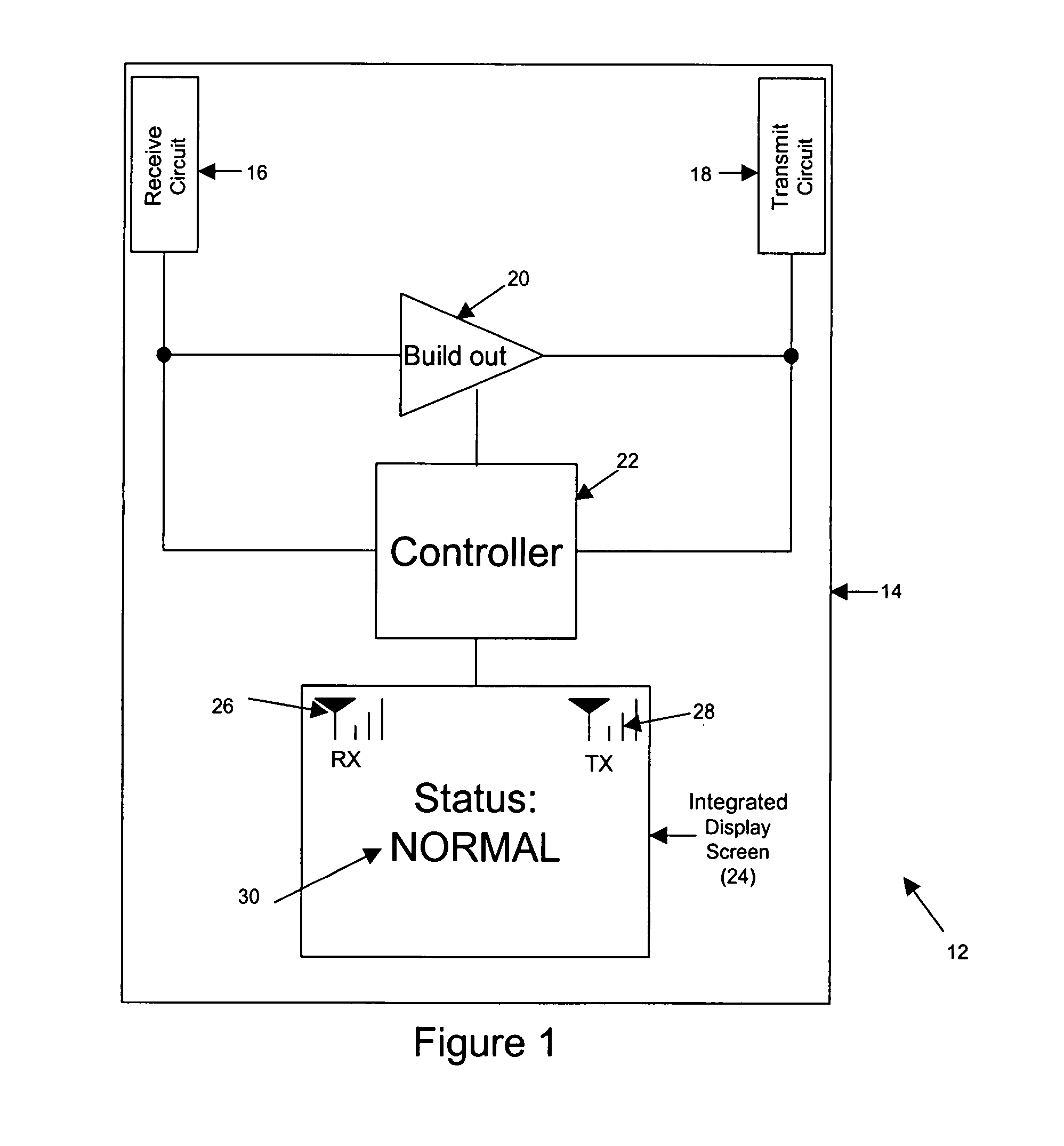
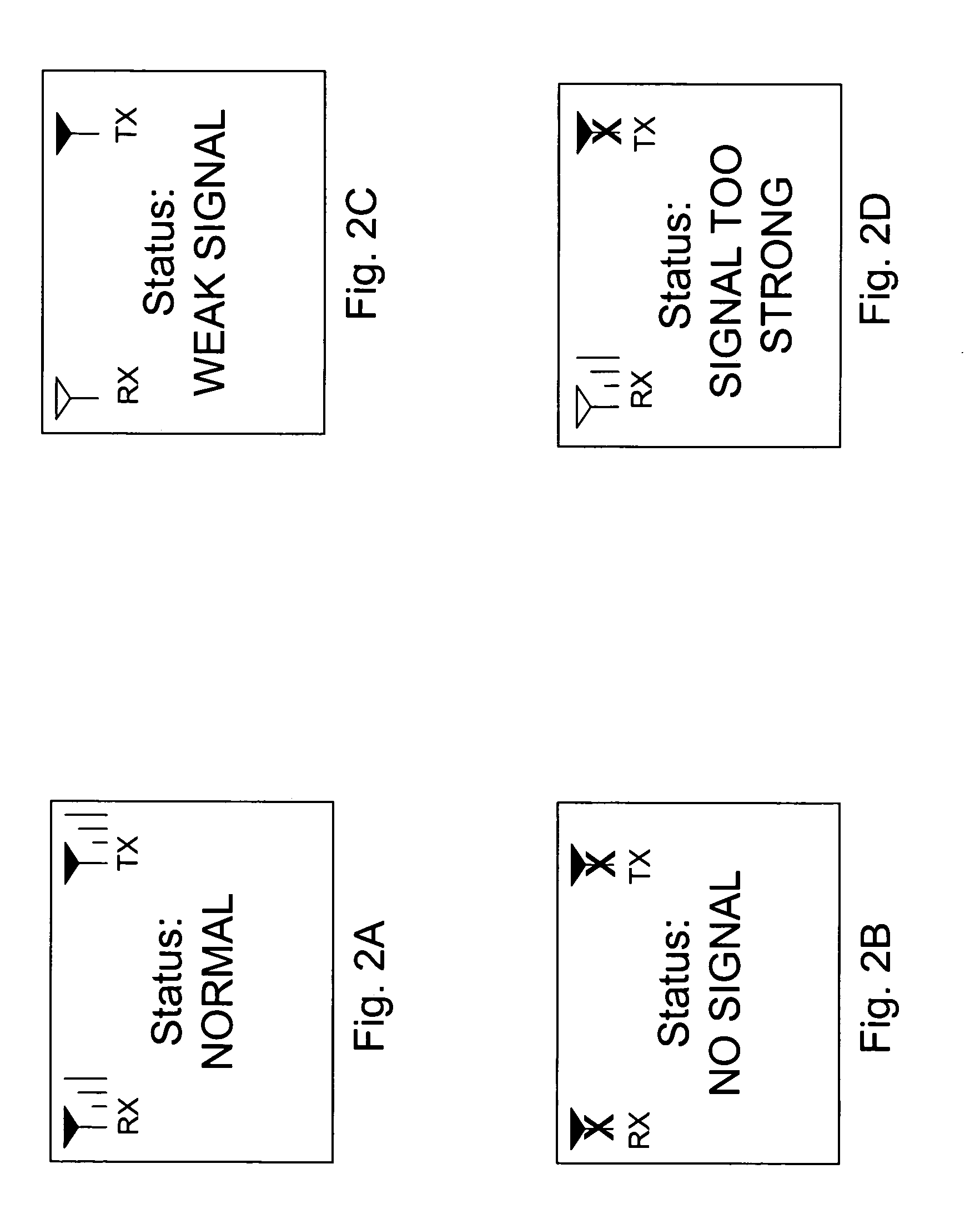
InactiveUS6990313B1Improve wireless signal qualityQuality improvementReceivers monitoringActive radio relay systemsSignal qualityDisplay device
A wireless signal repeater having an integrated display that concurrently displays a receive signal level, a transmit signal level, and a textual indication of signal quality, reflecting how well the repeater is currently operating to repeat wireless signals. By reference to the integrated display, a user can readily determine whether the repeater is well positioned to function as desired. And if the display indicates that the repeater is not functioning optimally, the user can then conveniently move the repeater around until the repeater reflects an acceptable level of operation.
Owner:SPRINT SPECTRUM LLC
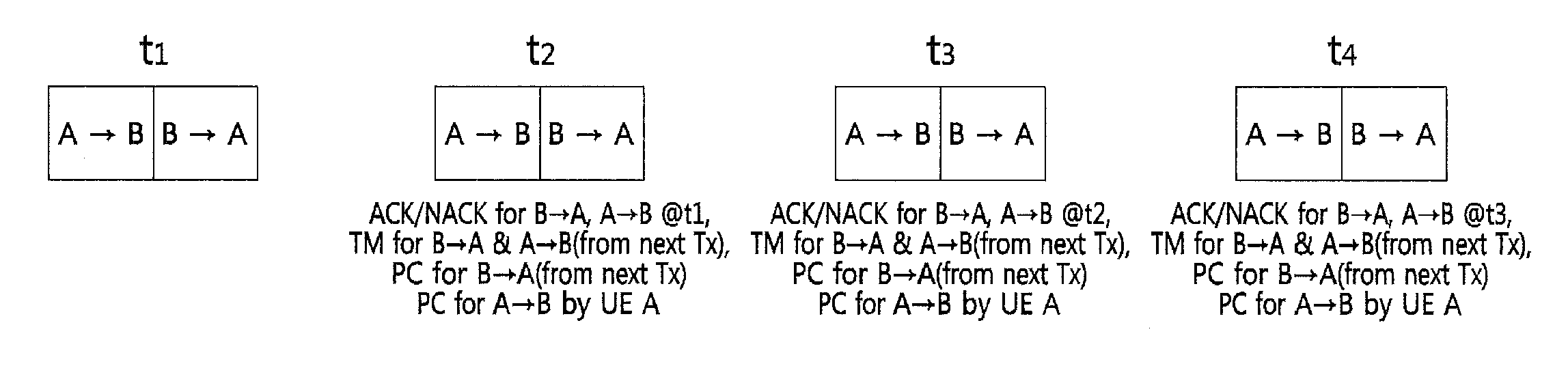
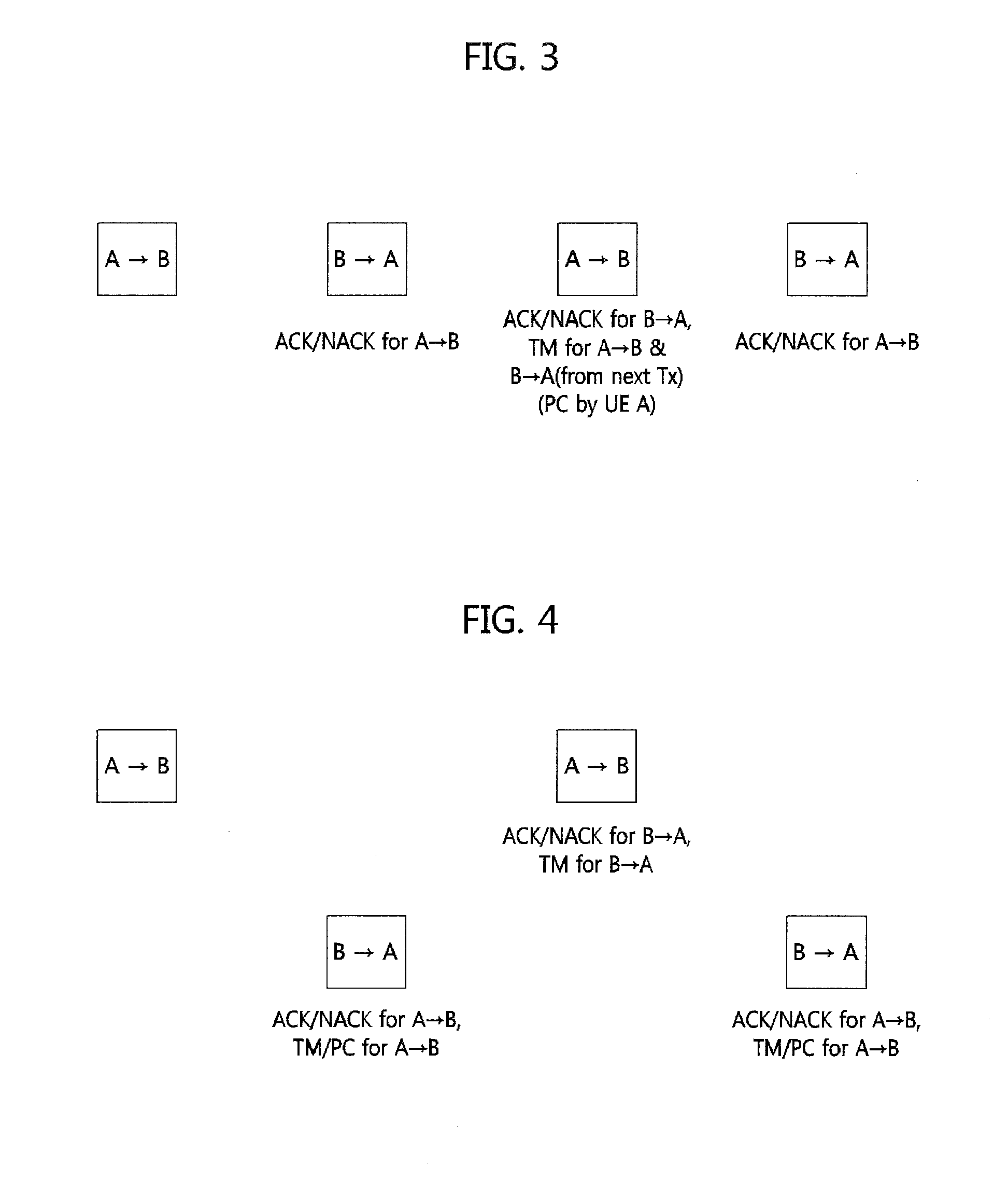
Method for HARQ and link adaptation of device to device link in direct communication between user equipments and relaying by user equipment
Provided is a method of processing hybrid automatic repeat request (HARQ) and adaptive transmission of a device-to-device (D2D) link. In the method, an operation method of user equipment (UE) includes (a) receiving an initial transmission mode (TM) and transmission power for the D2D link from a base station, and performing data transmission through the D2D link, (b) determining, at the UE, a TM and transmission power of a succeeding subframe, or receiving a TM control value and a transmission power control value from counterpart UE of the D2D link and determining the TM and the transmission power of the succeeding subframe, and (c) performing the data transmission to the counterpart UE using the determined TM and transmission power. Here, (b) and (c) are repeated.
Owner:ELECTRONICS & TELECOMM RES INST
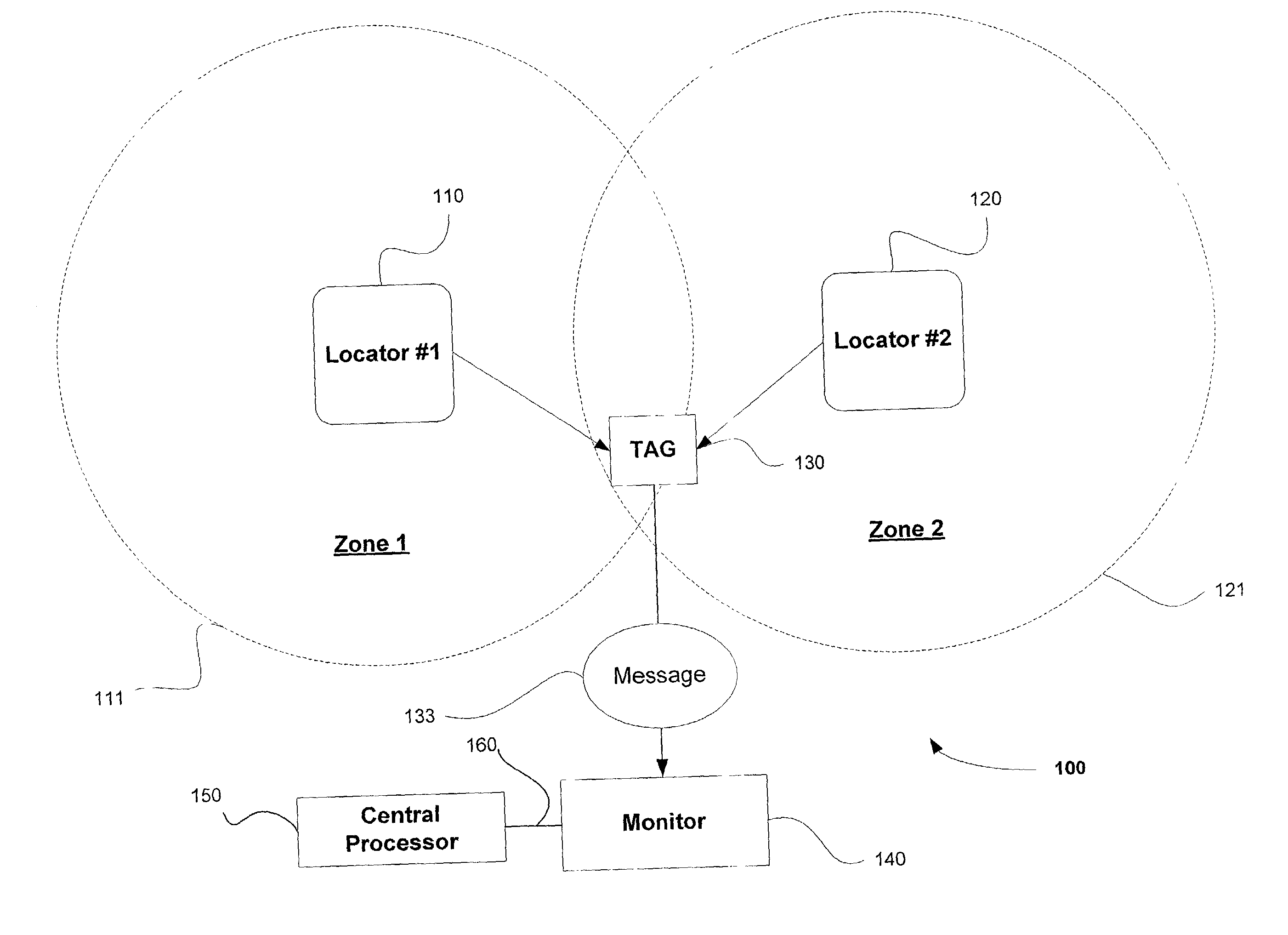
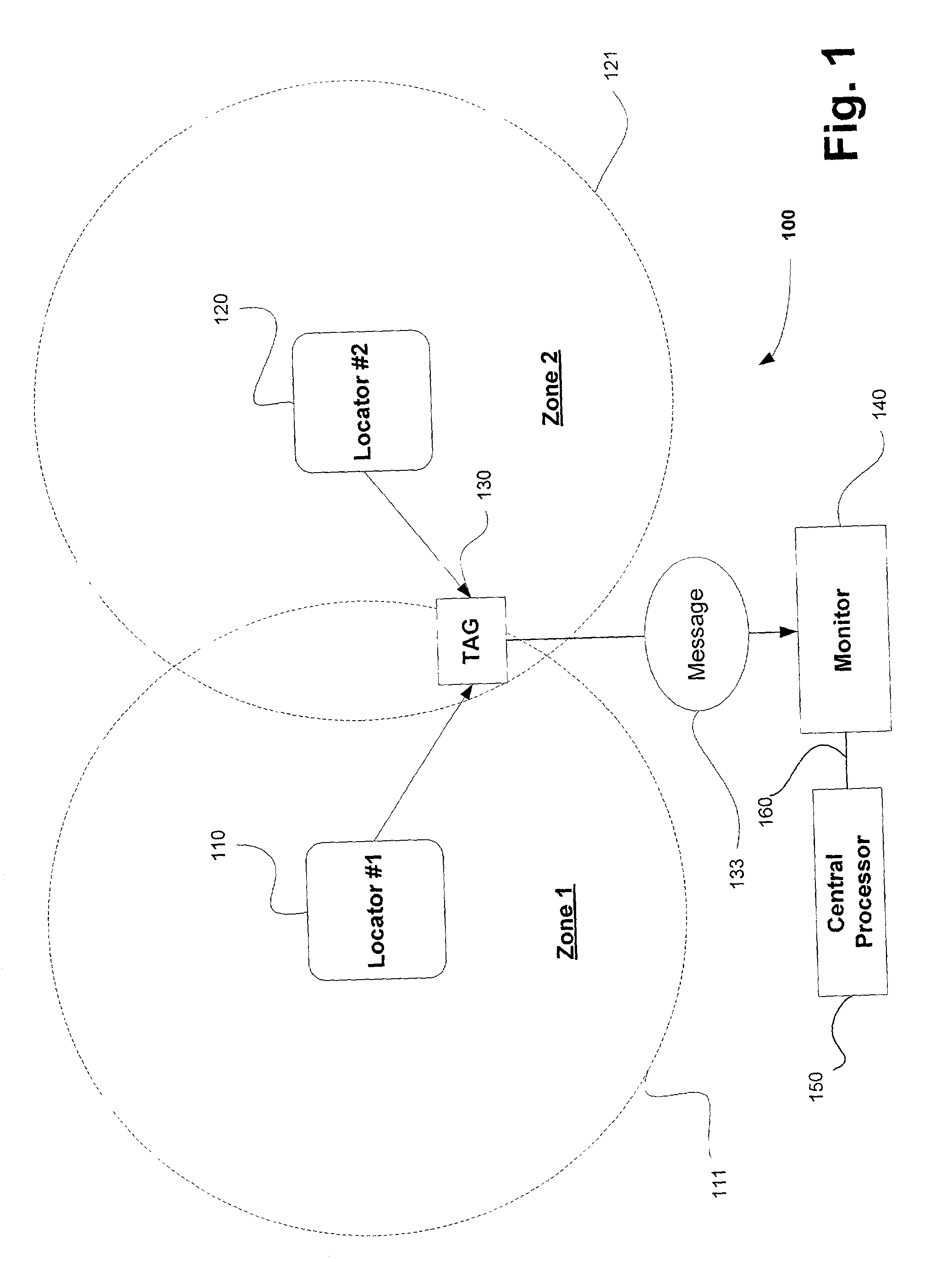
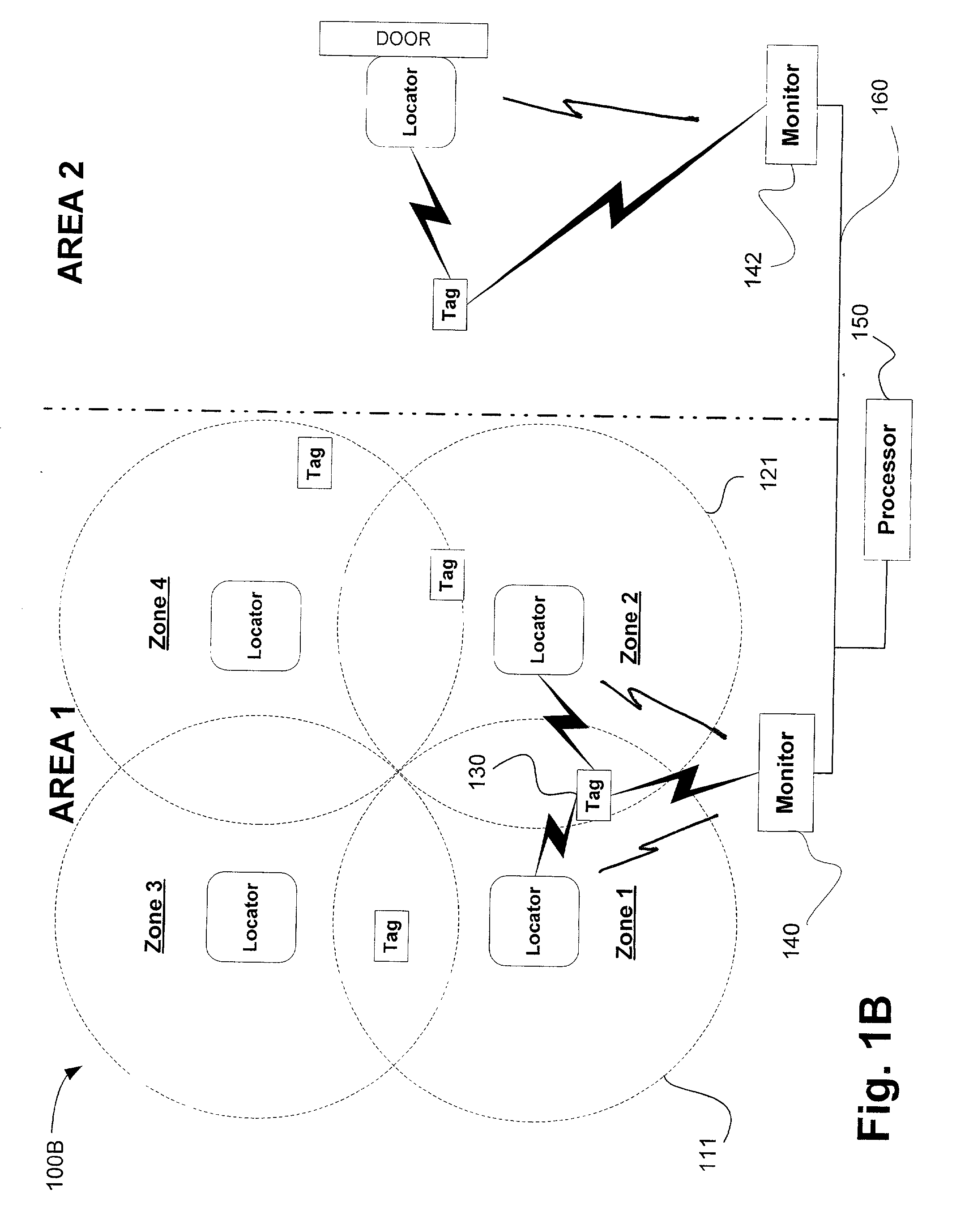
Wireless identification systems and protocols
InactiveUS20030030568A1Electric signal transmission systemsError preventionLocation detectionMonitoring system
Monitoring systems and protocols are disclosed that are flexible in mode operation and format depending on the environment in which they are used. Such monitoring systems and protocols are able to change their utilization automatically, or by received instruction to do so. A location detection system includes one or more low frequency transmitters, one or more radio frequency monitoring tags and one or more receiving devices. The low frequency transmitter transmits location identification information, such as the transmitter ID, to a tag in the vicinity of the transmission. The tag relays the transmitter ID using a higher frequency transmission sent from the tag to the receiver. Communication protocols are disclosed that enable deciphering of multiple tag transmissions starting simultaneously.
Owner:RF CODE
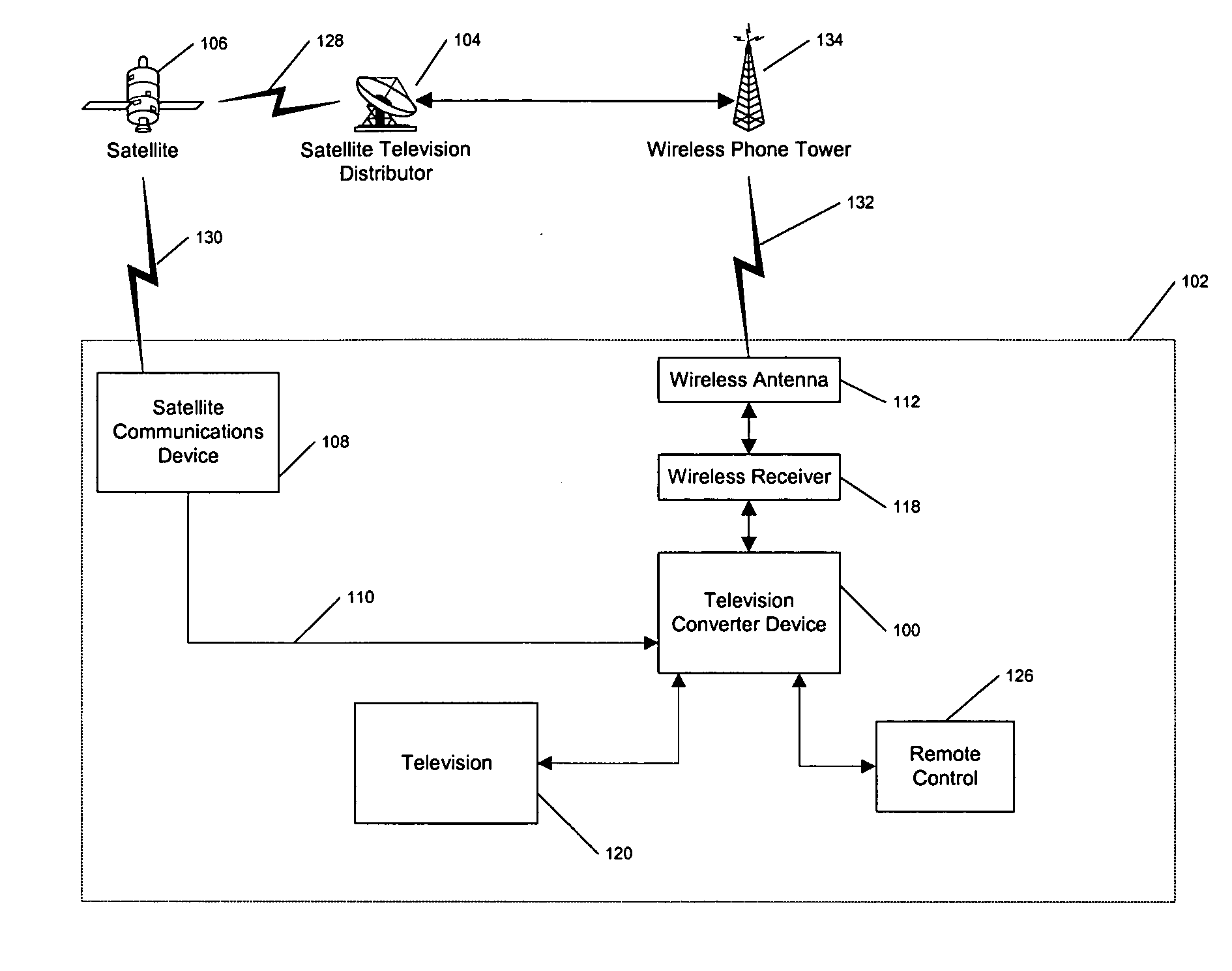
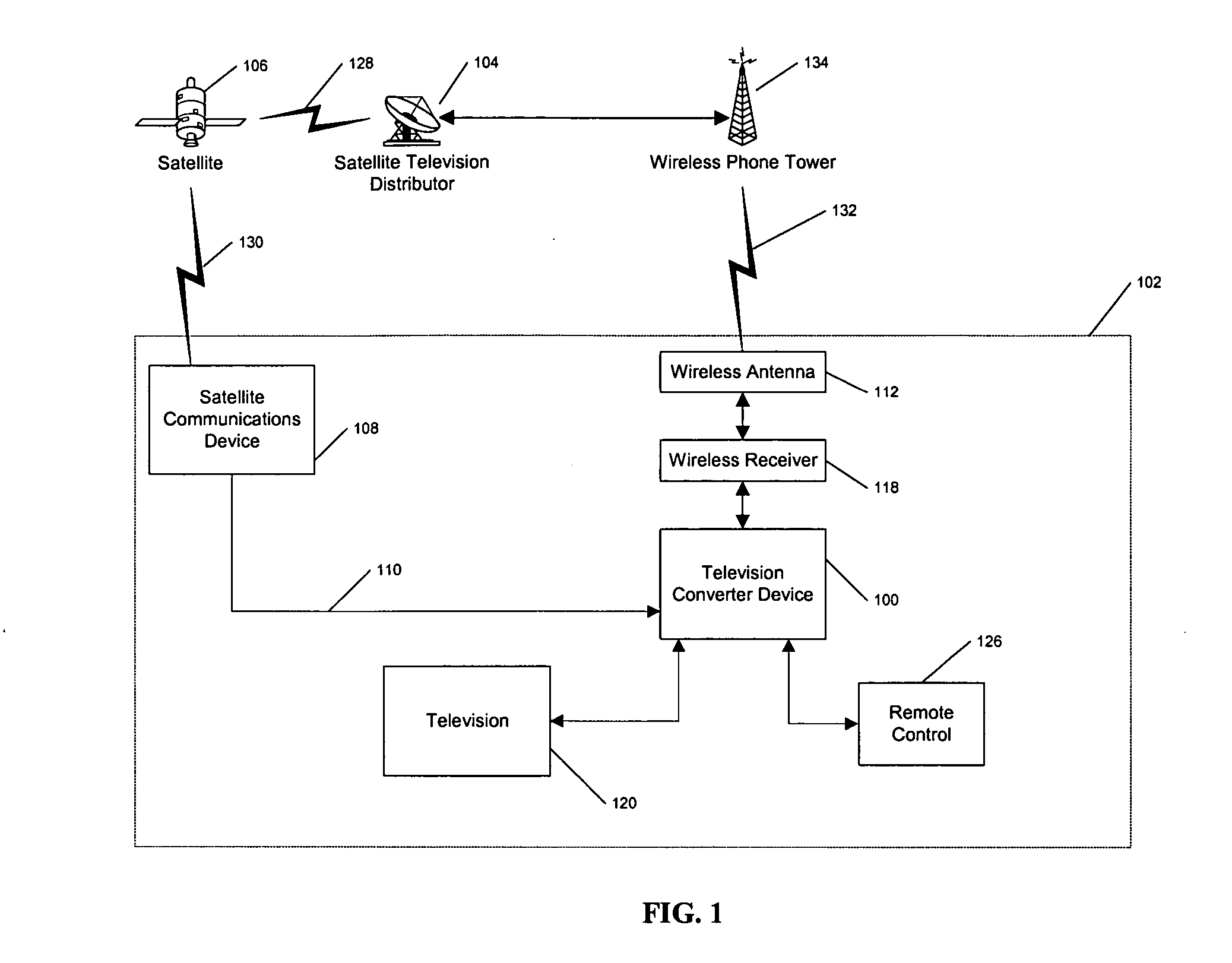
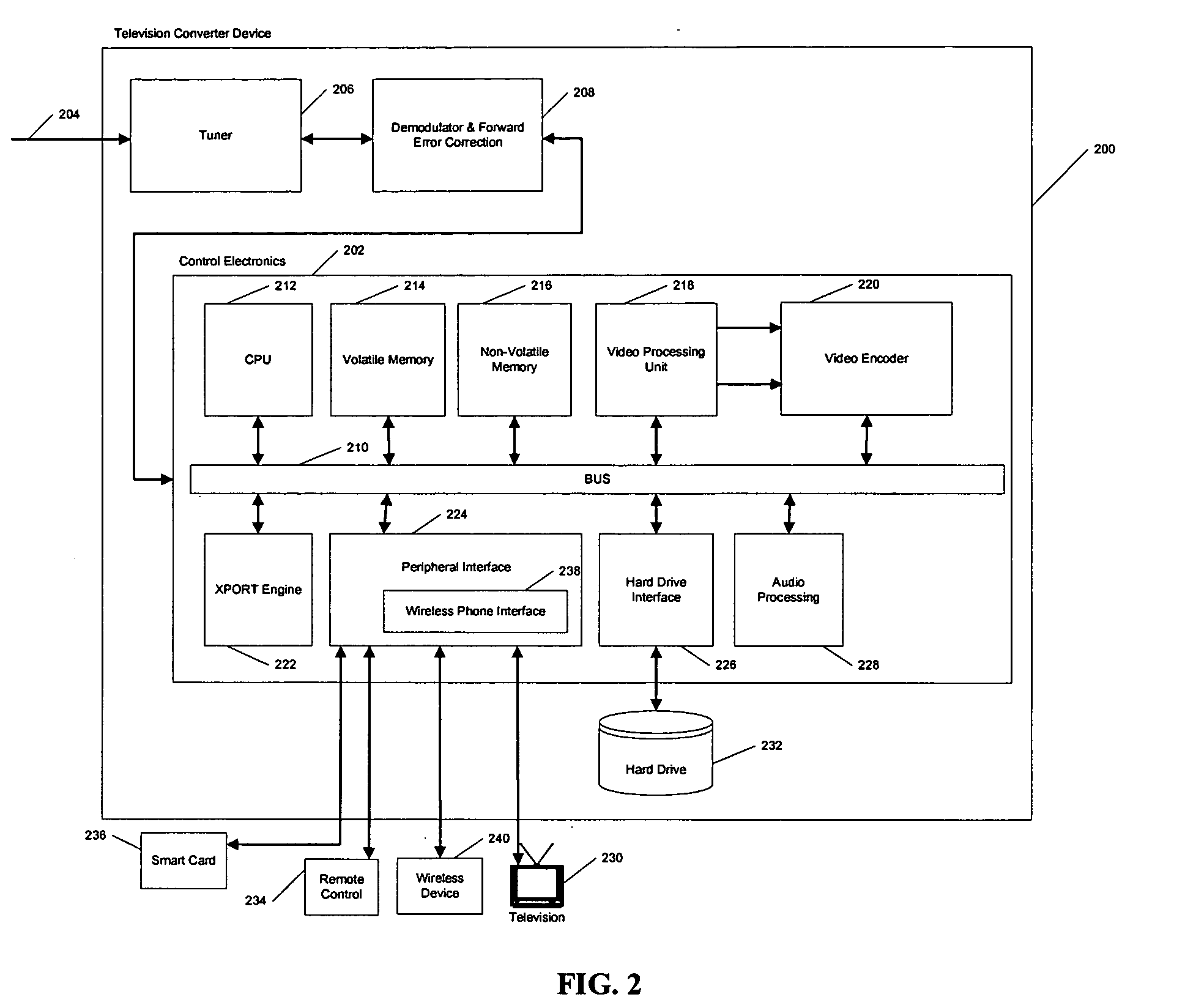
Wireless back channel for satellite television system
InactiveUS20060053436A1GHz frequency transmissionAnalogue secracy/subscription systemsModem deviceSatellite television
The present invention solves the above problems by attaching a cellular phone receiver to the set-top-box. This cellular phone receiver has a modem to transmit data between the subscriber's box and a cellular network. The cellular network may relay the data to the pay-television distributor. Other features and advantages of the present invention will become apparent from the following detailed description of the invention and the accompanying drawings.
Owner:ECHOSTAR TECH LLC
Relay communication method for an OFDMA-based cellular communication system
InactiveUS20060193280A1Expand coverageRemove shaded areasFrequency-division multiplex detailsModulated-carrier systemsCommunications systemTrunking
A relay communication method in an orthogonal frequency division multiple access (OFDMA) communication system including at least one base station for providing a multiple access service to a plurality of mobile stations frame by frame. The relay communication method includes dividing a cell defined by transmission power of the base station into a plurality of sectors on the basis of the base station; dividing the cell into an inner area where a first service is supported and an outer area where a second service is supported, on the basis of the base station; arranging at least one relay station in a second service area of each sector; and allocating a partial resource of the frame for communication between the base station and the mobile station through the relay station.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
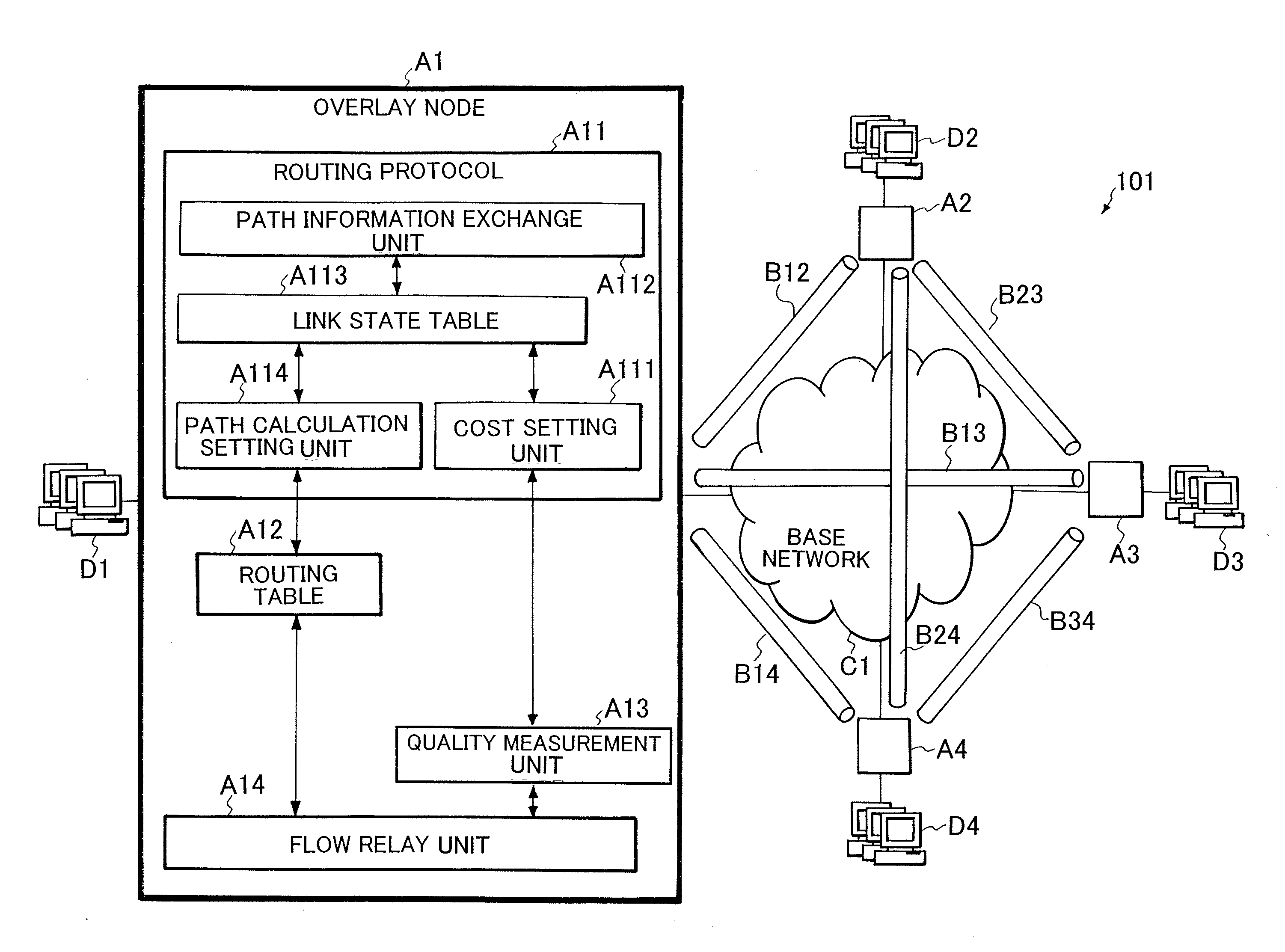
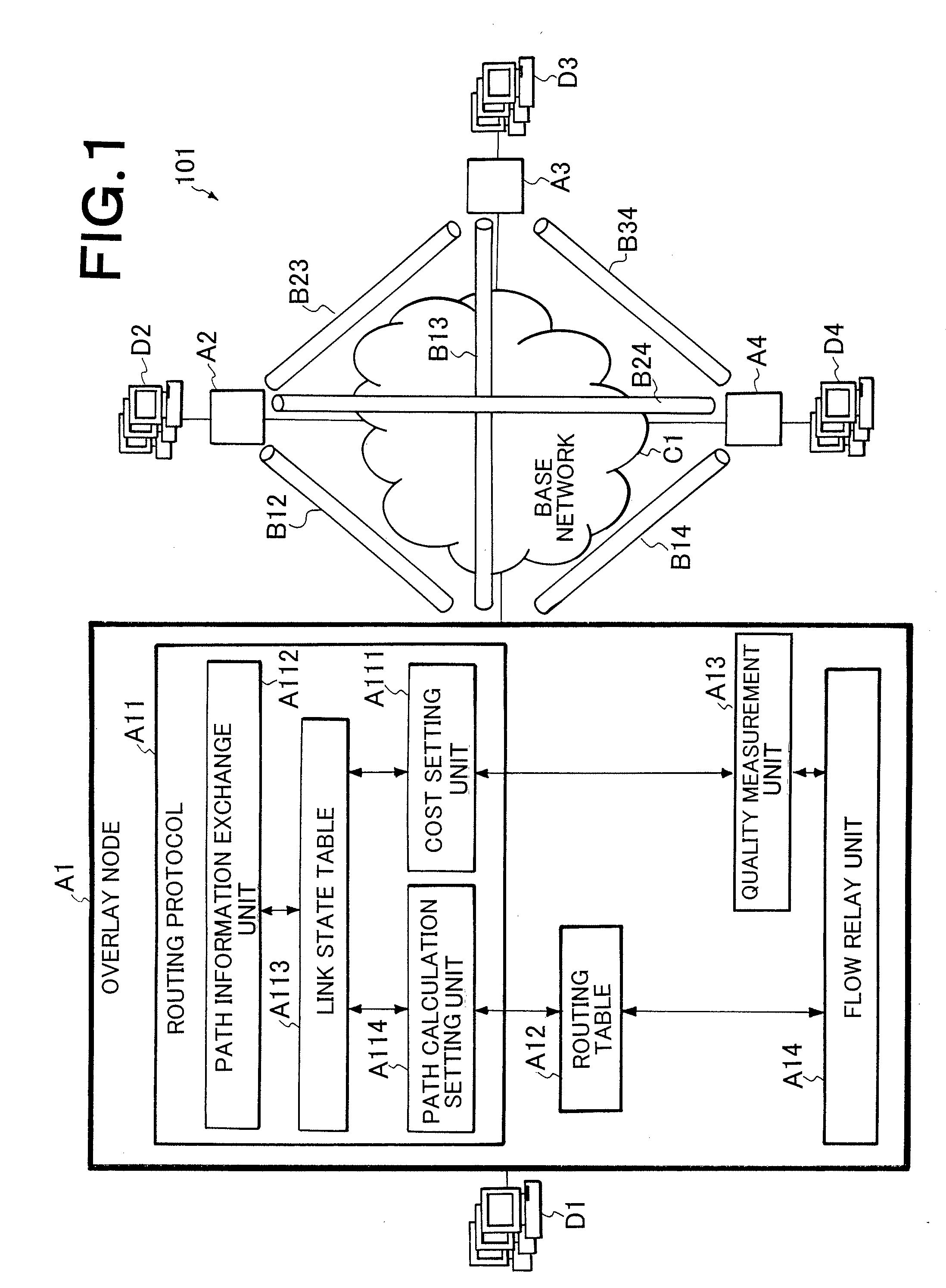
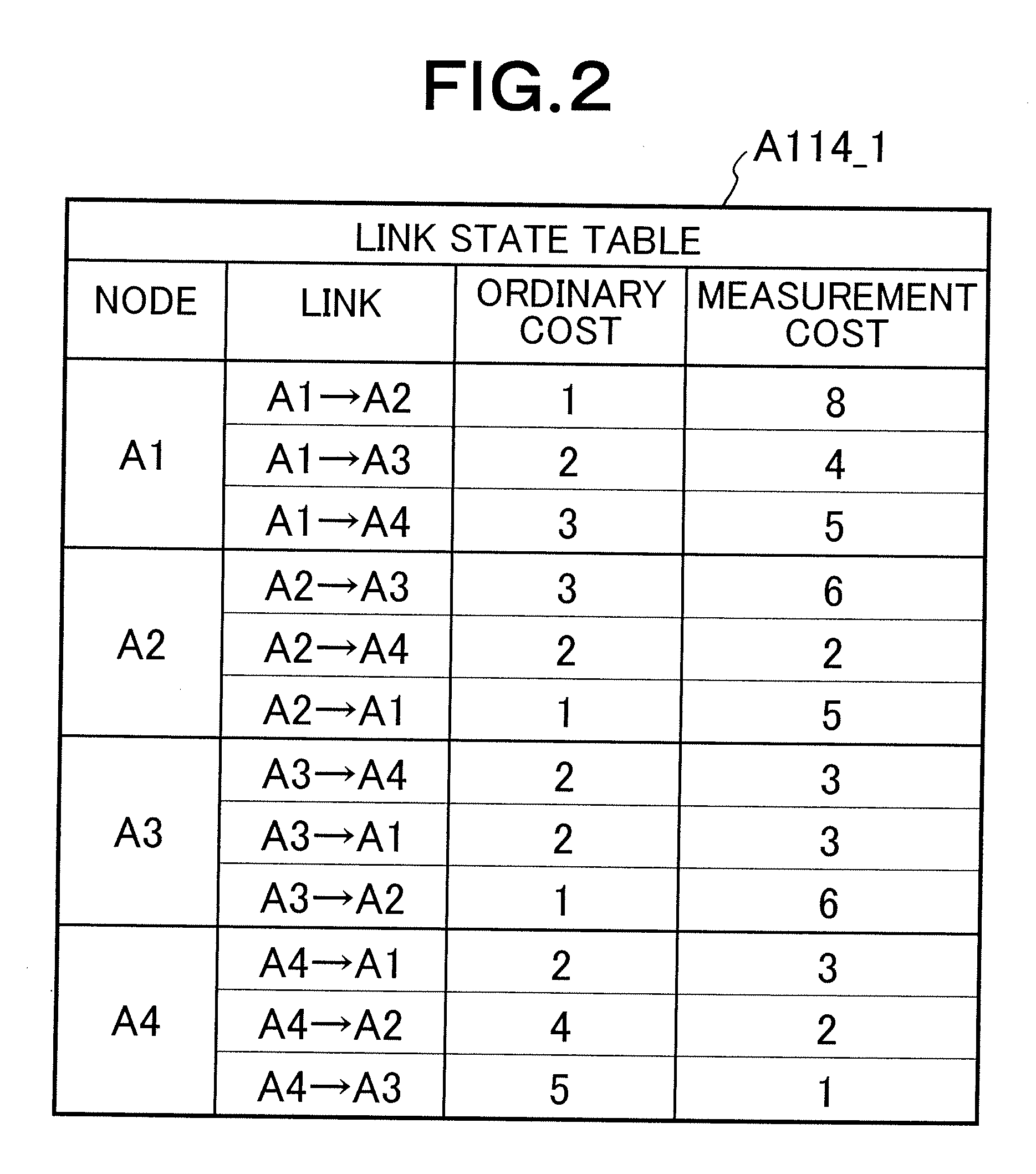
QoS ROUTING METHOD AND QoS ROUTING APPARATUS
ActiveUS20080101227A1Reduced measurement accuracyHigh measurement accuracyError preventionFrequency-division multiplex detailsData packPathPing
A QoS routing apparatus as a node of a logical network to transmit data communicated between user's terminals comprises a relay unit discriminating whether or not flows of received data are measurement flows and transmitting said received data, a quality measurement unit measuring communication quality of links connected the own apparatus using the measurement flows, a quality accuracy setting unit determining measurement accuracy of the communication qualities of the respective links and a path setting unit prescribing transmission amounts of the measurement flows to the respective links. When the path setting unit prescribes the transmission amounts of the measurement flows, it applies a higher rate to a link which has been determined a lower measurement accuracy.
Owner:NEC CORP
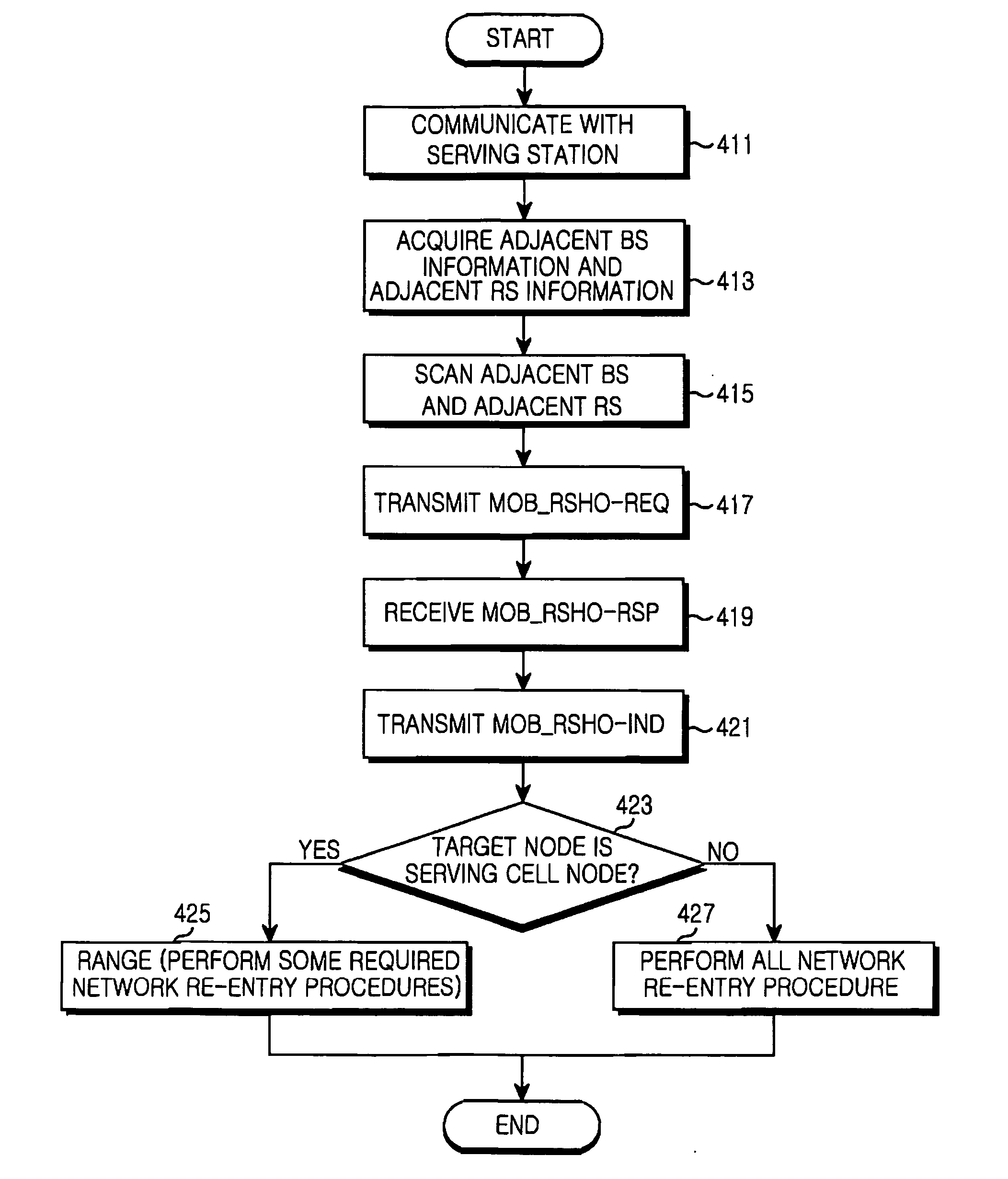
Apparatus and method of processing handover of a mobile relay station in broadband wireless access (BWA) communication system using multihop relay scheme
InactiveUS20070104148A1Broadcast service distributionRadio/inductive link selection arrangementsCommunications systemMobile relay
An apparatus and method of processing handover of a mobile relay station (MRS) in a cellular communication system using a multihop relay scheme is provided. The handover processing method includes transmitting, by the MRS, a handover request message containing child node information to a serving BS when handover is required; making, by the serving BS, an adjacent node list by collecting handover-related information from adjacent nodes to which the MRS is able to be handed over when the handover request message is received; transmitting, by the serving BS, a handover response message containing the adjacent node list to the MRS; and determining, by the MRS, a handover target node based on information contained in the handover response message and transmitting a handover indication message containing the target node to the serving BS. By suggesting the handover method of the MRS in the multihop relay system, it is possible to provide uninterrupted communication to the MRS and its child node in the service area of the MRS.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
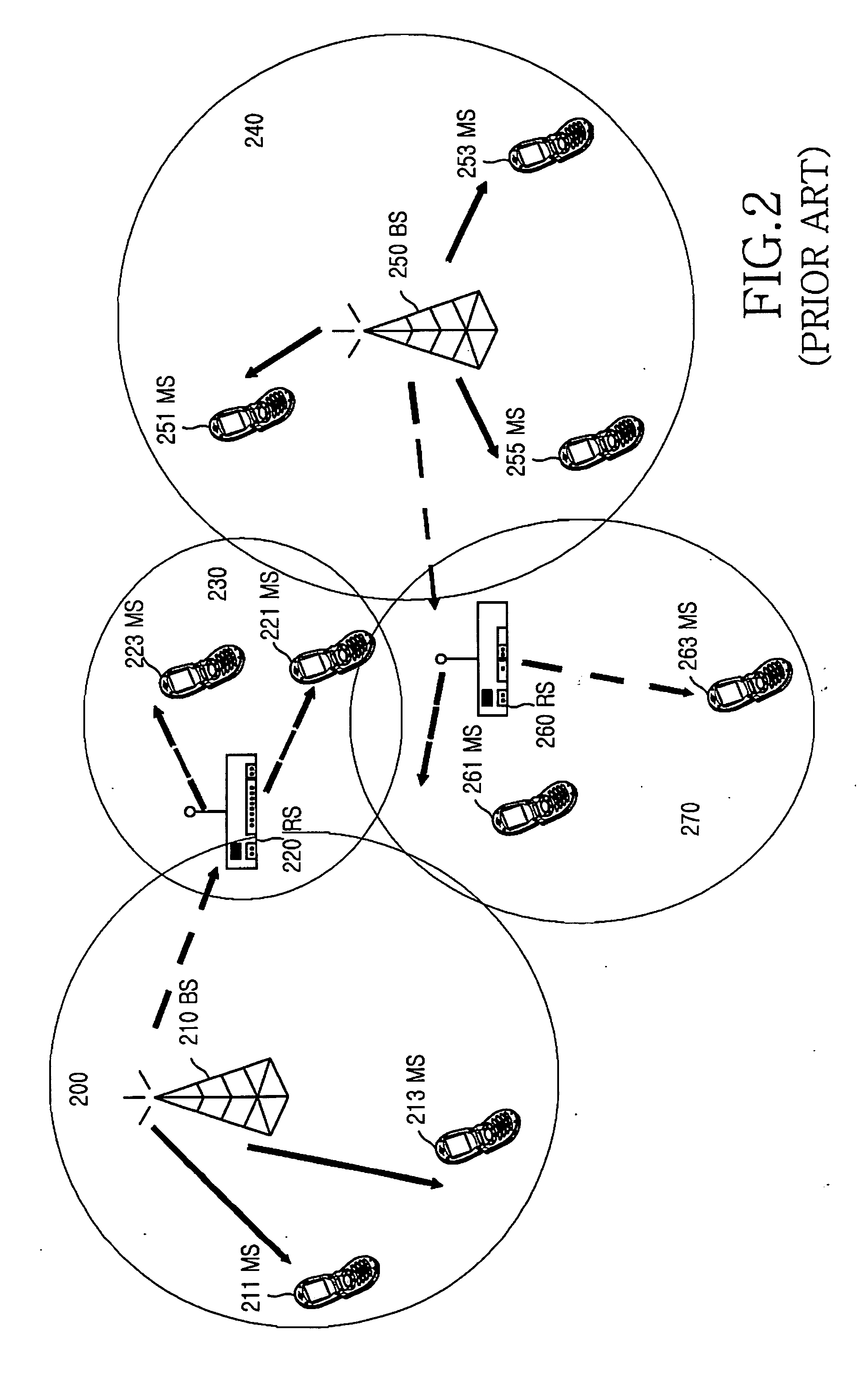
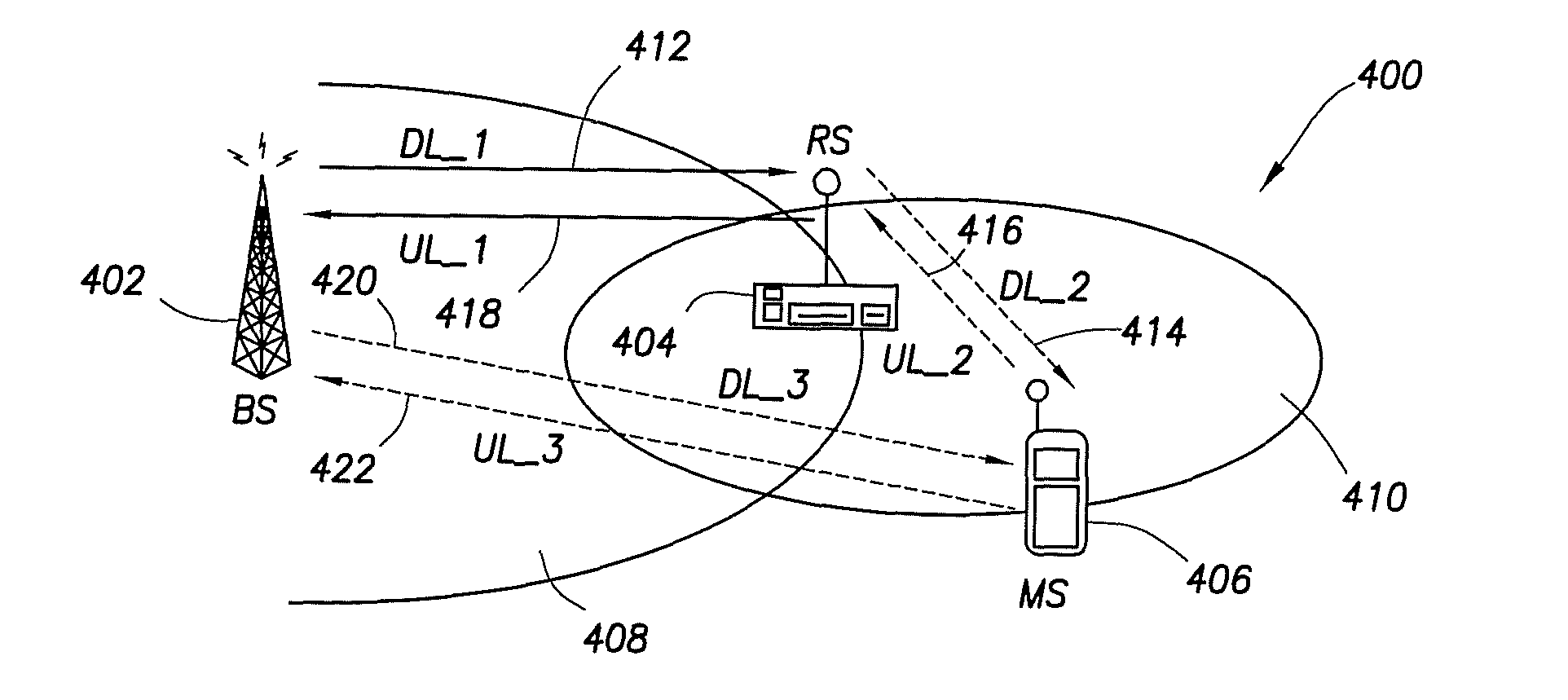
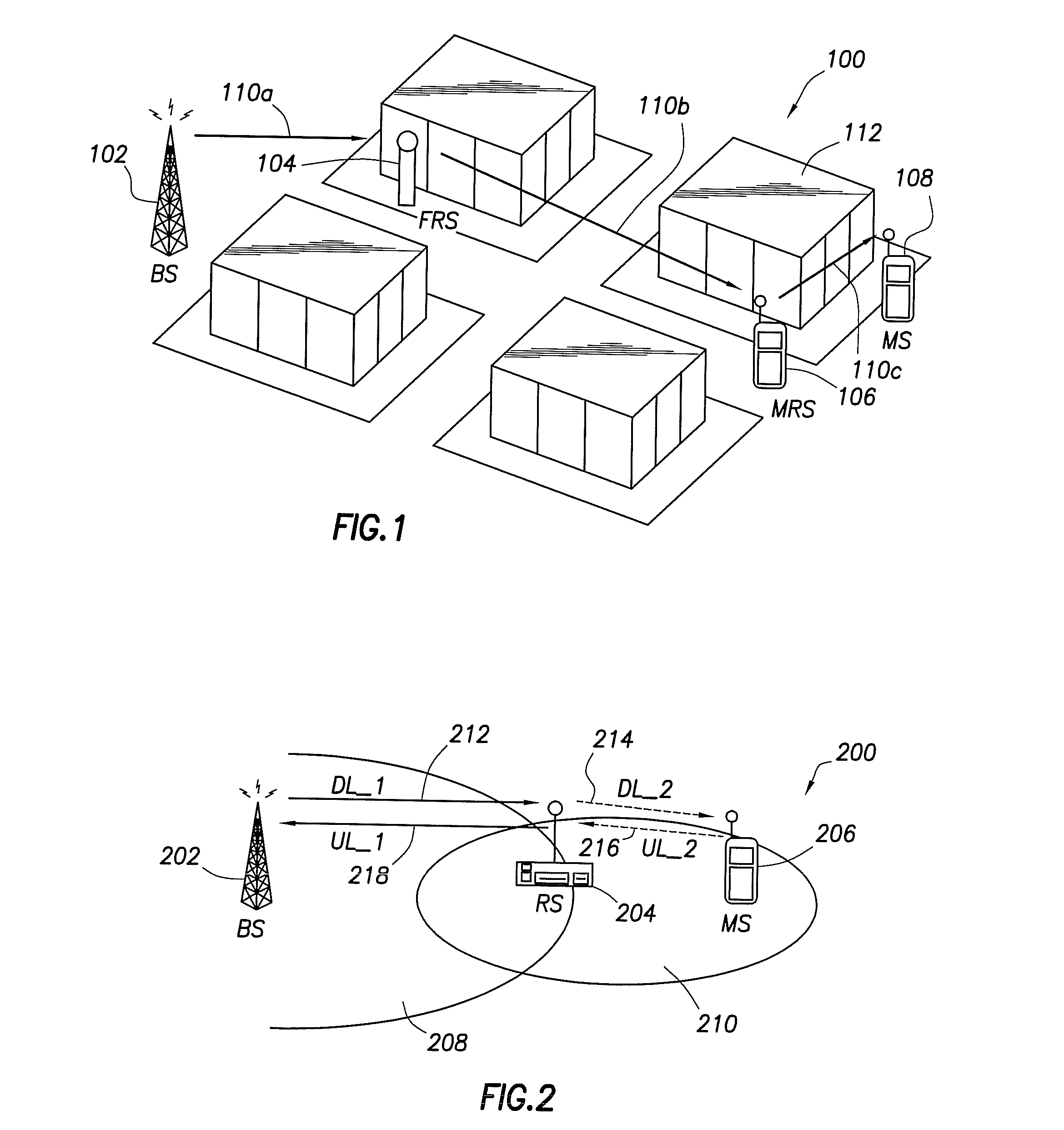
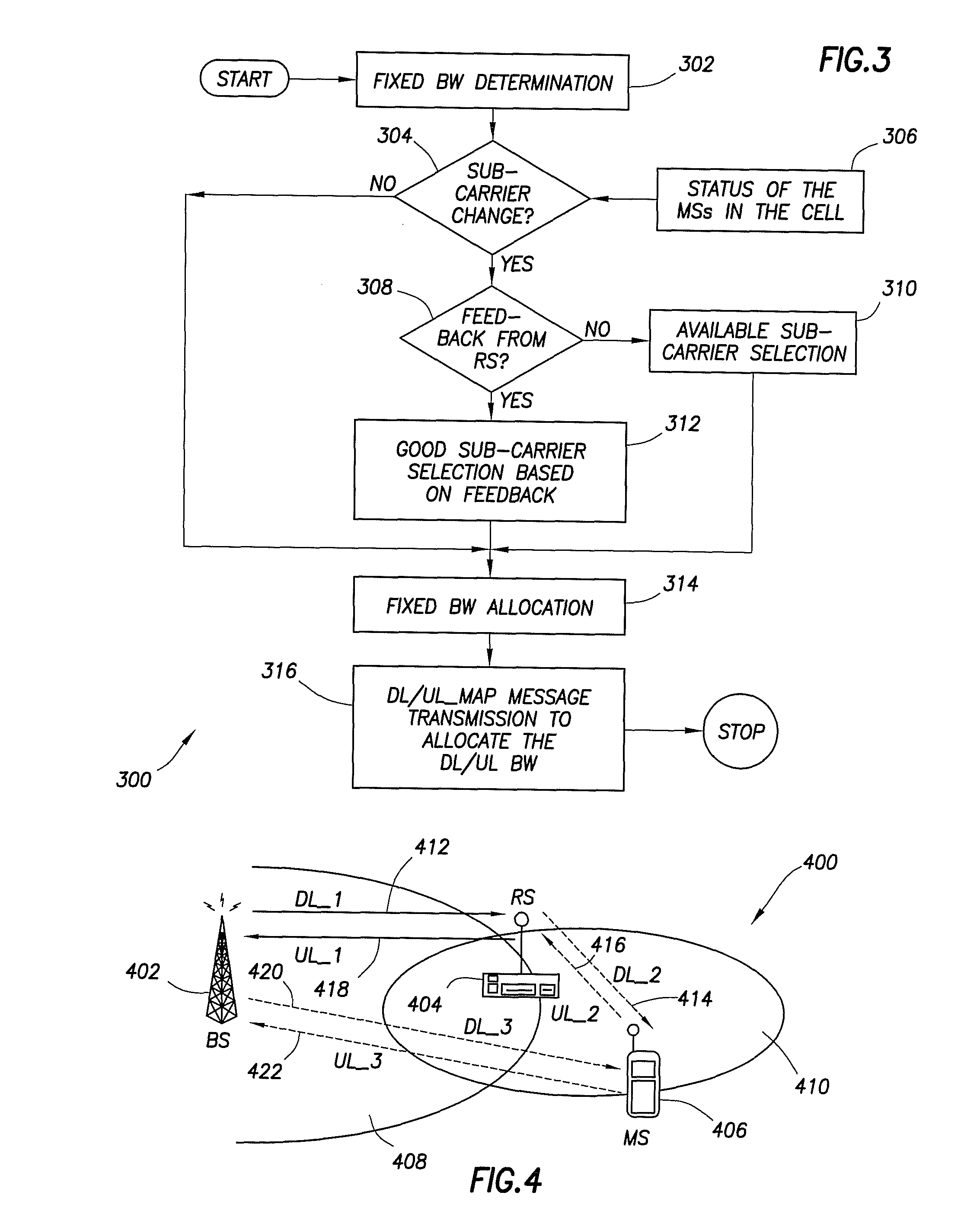
Channel configuration and bandwidth allocation in multi-hop cellular communication networks
ActiveUS20070081507A1Allocate bandwidthFrequency-division multiplex detailsNetwork traffic/resource managementCommunication unitSignal on
A multi-hop wireless communication network is disclosed, which includes a fixed communication unit, at least one mobile communication unit, and a relay communication unit. The relay communication unit is operable to relay a plurality of signals bi-directionally between the fixed communication unit and the at least one mobile communuication unit, by receiving a first signal on at least one of a dedicated sub-carrier and a dynamic sub-carrier in a first downlink channel segment from the fixed communication unit, and transmitting the received first signal to the at least one mobile communication unit on a dynamic sub-carrier in a second downlink channel segment. Also, the relay communication unit is operable to receive a second signal on a dynamic sub-carrier in a first uplink channel segment from the at least one mobile communication unit, and transmit the received second signal to the fixed communication unit on at least one of a dedicated sub-carrier and a dynamic sub-carrier in a second uplink channel segment. Also, the fixed communication unit can allocate bandwidth dynamically or in a fixed amount in the first downlink channel segment, the relay communication unit can allocate bandwidth dynamically in the second downlink channel segment based on at least one Quality of Service value received from the at least one mobile communication unit, the relay communication unit can allocate bandwidth dynamically for the at least one mobile communication unit in the first uplink channel segment, and the fixed communication unit can allocate bandwidth dynamically or in a fixed amount for the relay communication unit in the second uplink channel segment.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
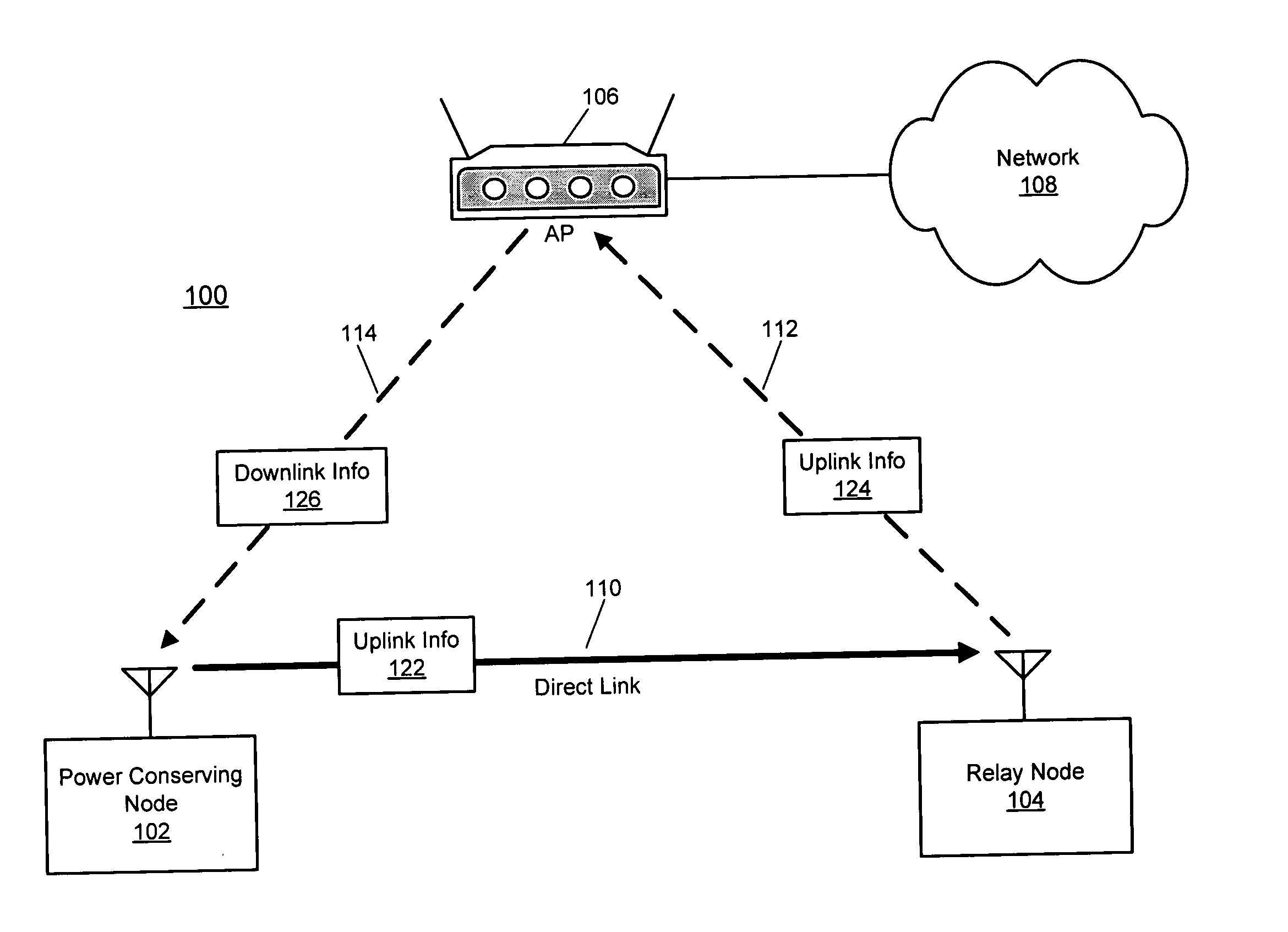
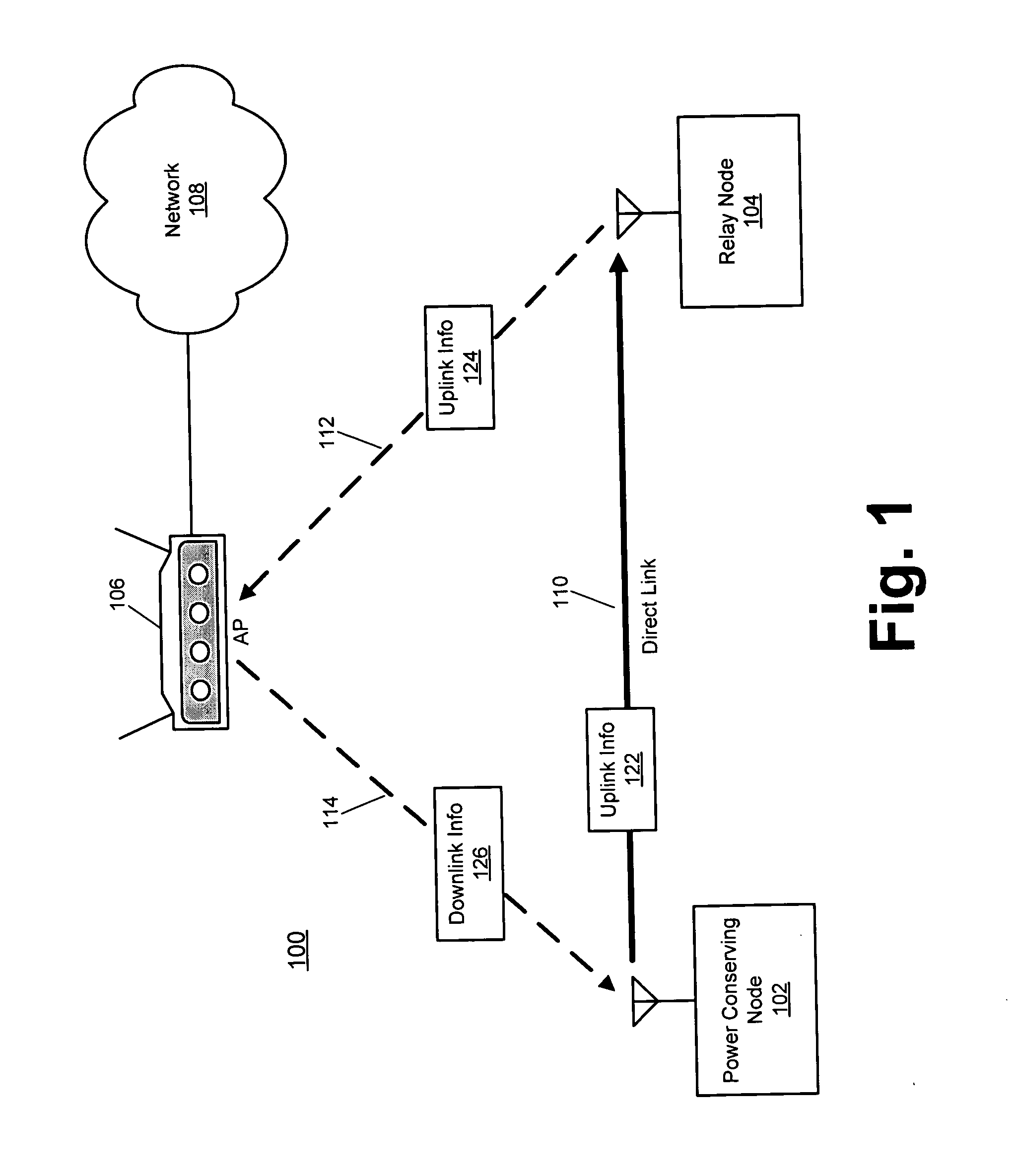
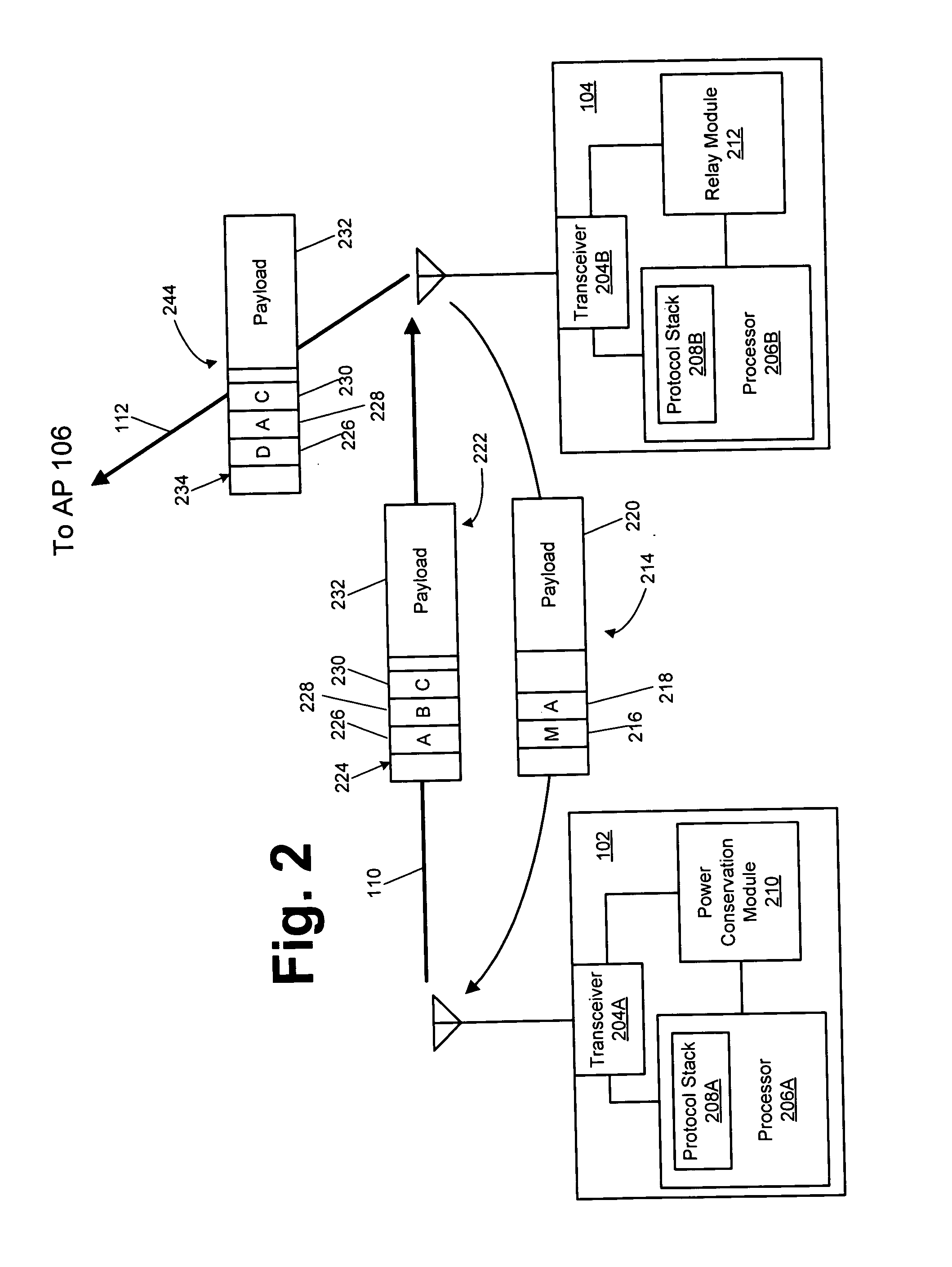
Direct link relay in a wireless network
ActiveUS20050094588A1Transparent operationLow costPower managementFrequency-division multiplex detailsTransmitted powerTrunking
Disclosed herein are exemplary techniques for power conservation in a wireless network. A wireless device identifies another wireless device suitable to act as a relay node. Uplink information is transmitted to the other wireless device, which is in turn relayed to an access point for transmission to its destination. Downlink information may be transmitted directly from the access point to the wireless device. The use of a relay node may reduce transmit power consumption as the relay node may be closer to, or support a higher transmit rate, than the access point with which the wireless device is associated.
Owner:INTELLECTUAL VENTURES I LLC
Mapping of control information to control channel elements
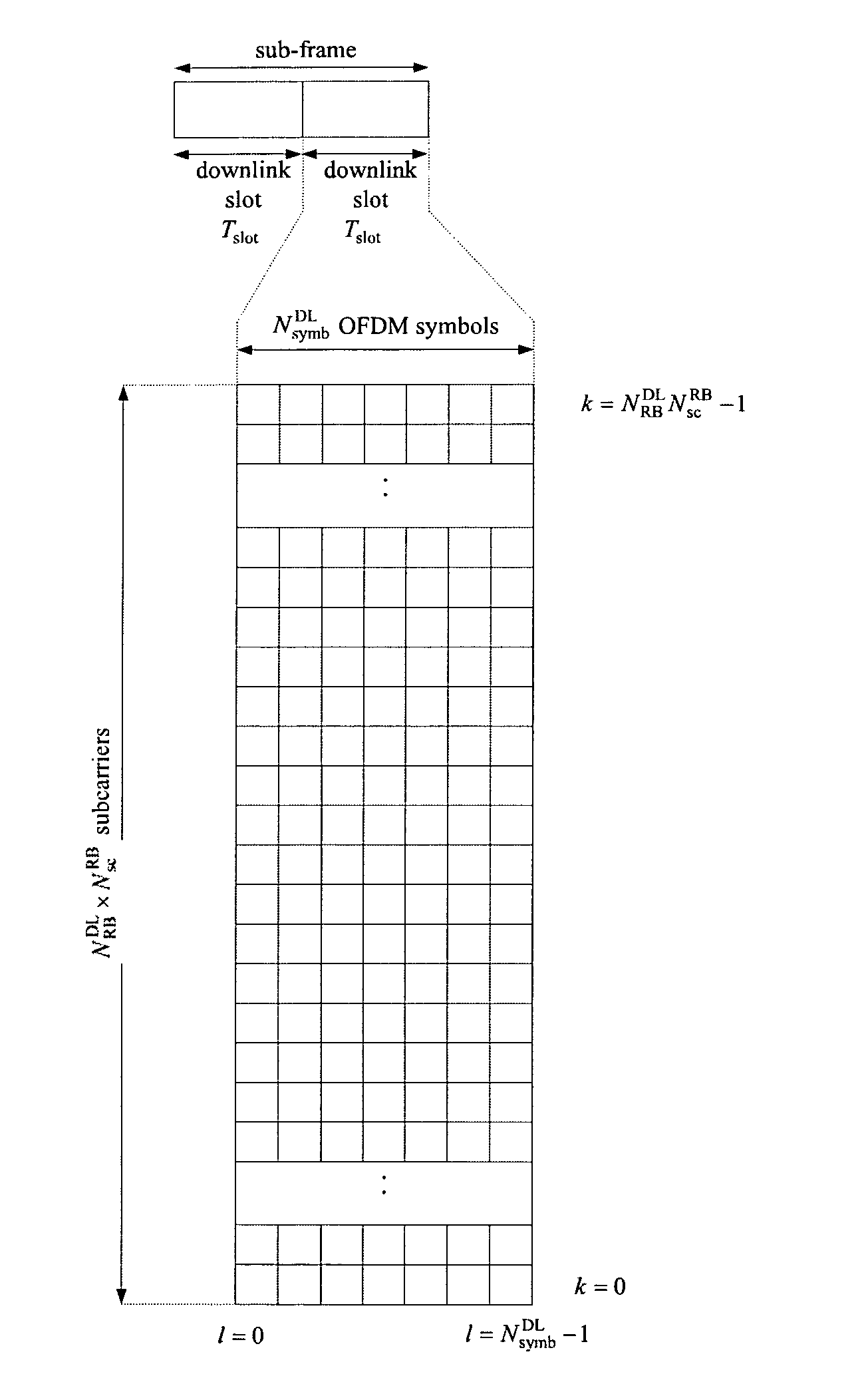
ActiveUS20130223402A1Increase system bandwidthWider transmission bandwidthTransmission path divisionSignal allocationTime domainCommunications system
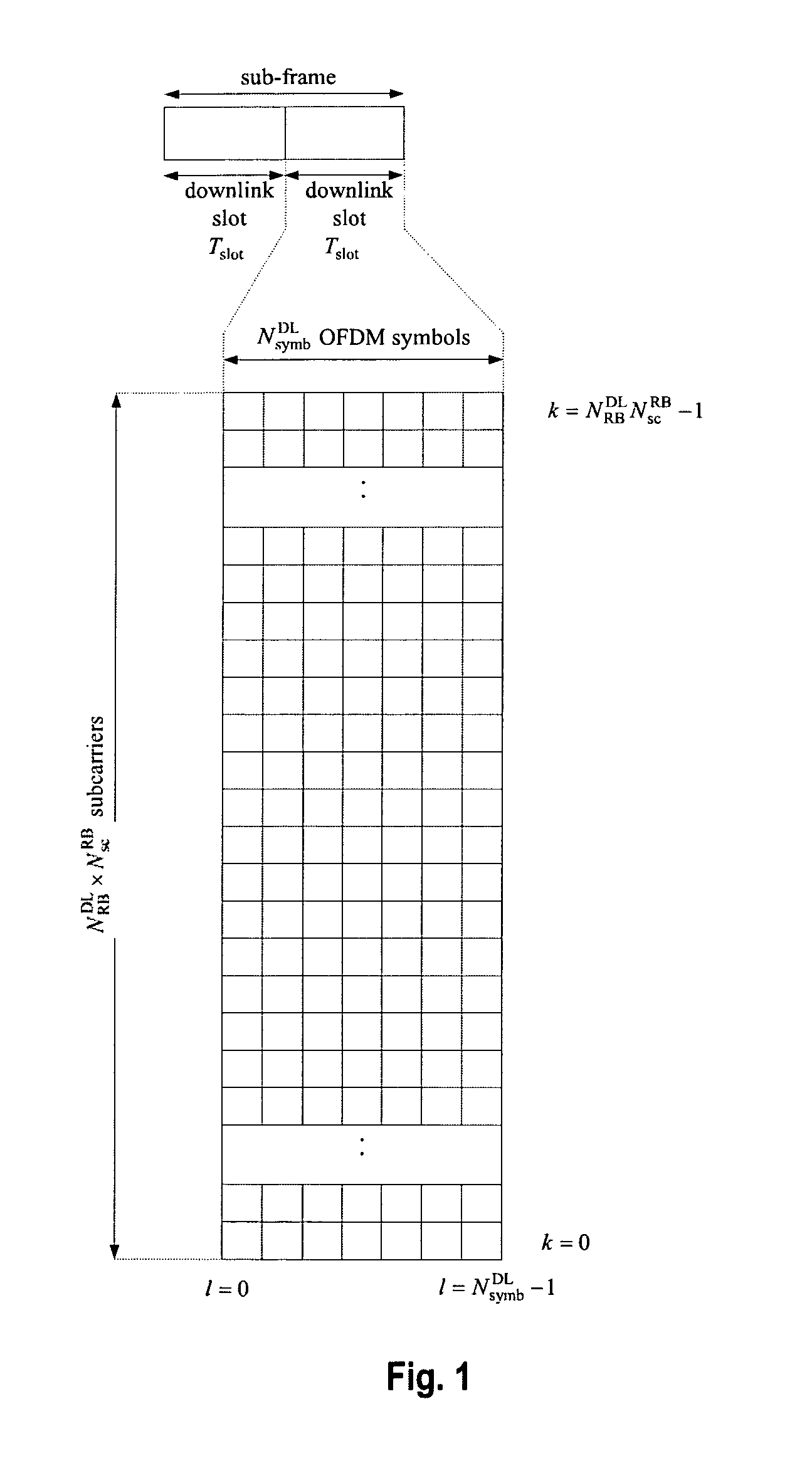
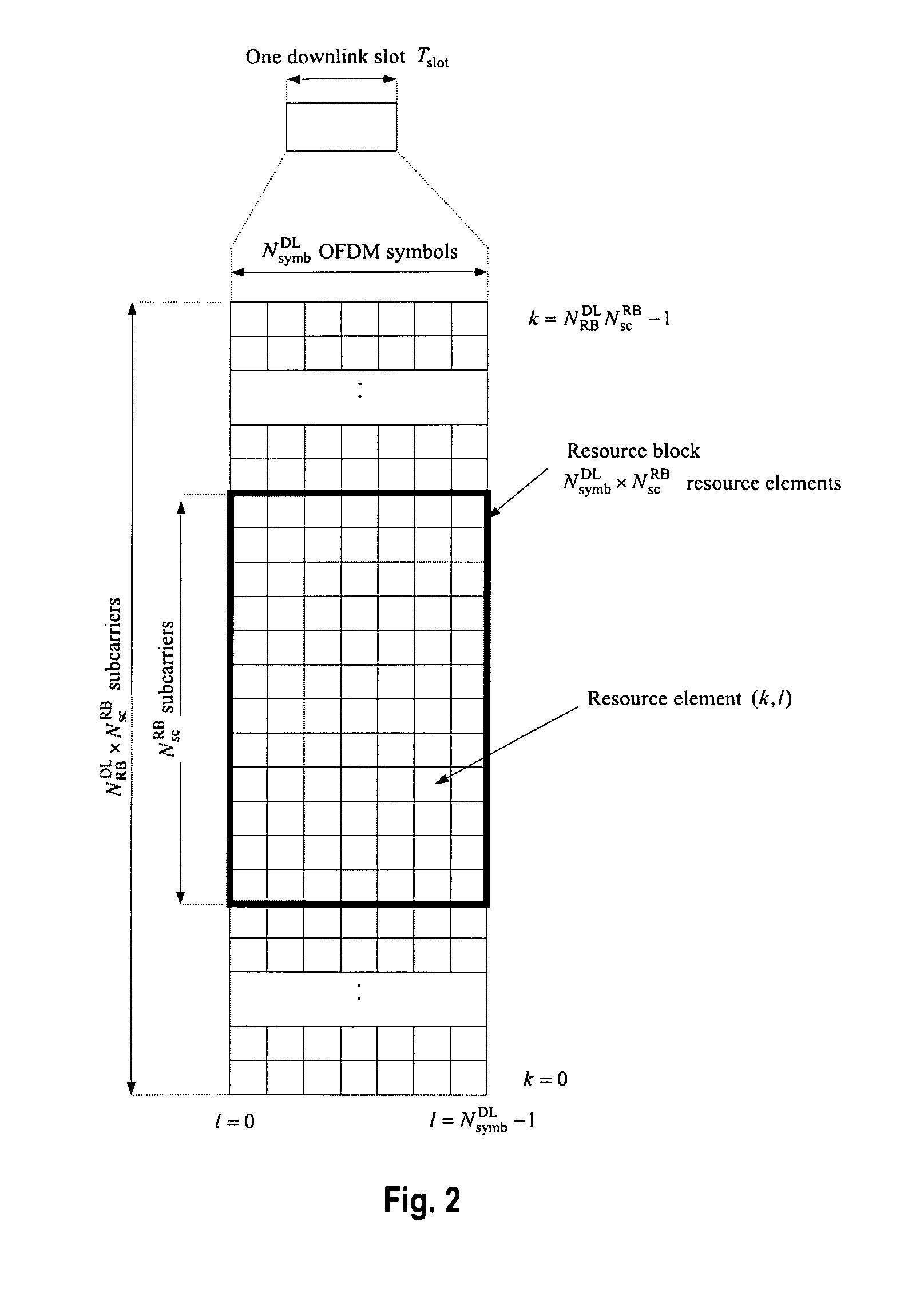
The invention relates to a new structure of a control channel region within a sub-frame of a 3GPP-based based communication system using OFDM in the downlink. This new structure of a control channel region is inter alia particularly suitable for conveying physical downlink control channel information from a donor eNodeB to a relay node. The control channel region is divided in CCEs that have equal size irrespective of the presence of further cell-specific and / or UE-specific reference signals within the control channel region. This is achieved by dividing the control channel region in plural sub-CCEs that are combined to CCEs all having equal size (in terms of resource elements that can be used for the signaling of control information). The control channel region is divided in the frequency domain and / or time domain in a FDM respectively TDM fashion in order to obtain the sub-CCEs
Owner:SUN PATENT TRUST
Optical network subscriber access architecture
InactiveUS7171121B1Provides redundancyMultiplex system selection arrangementsOptical multiplexConnection typeFiber
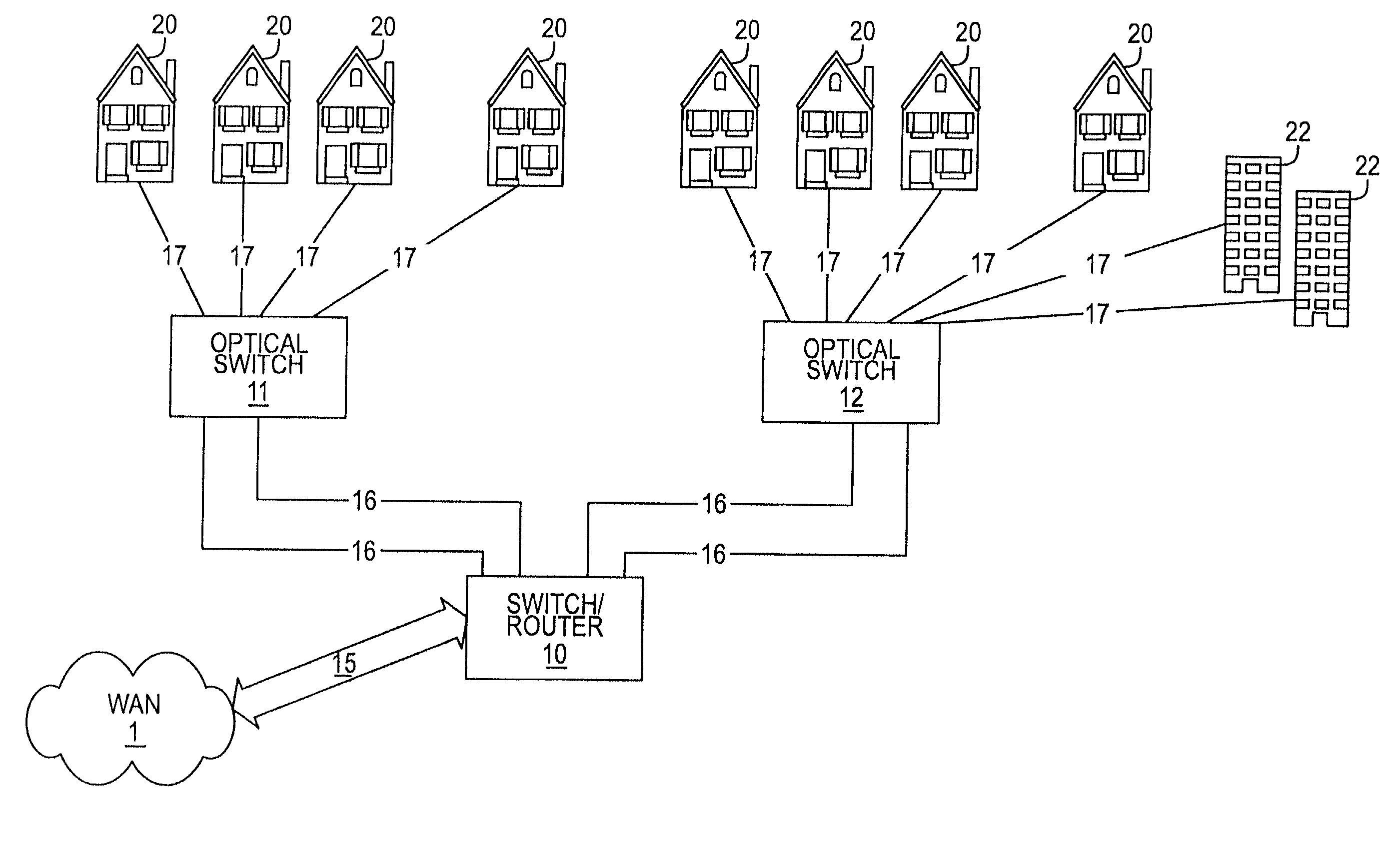
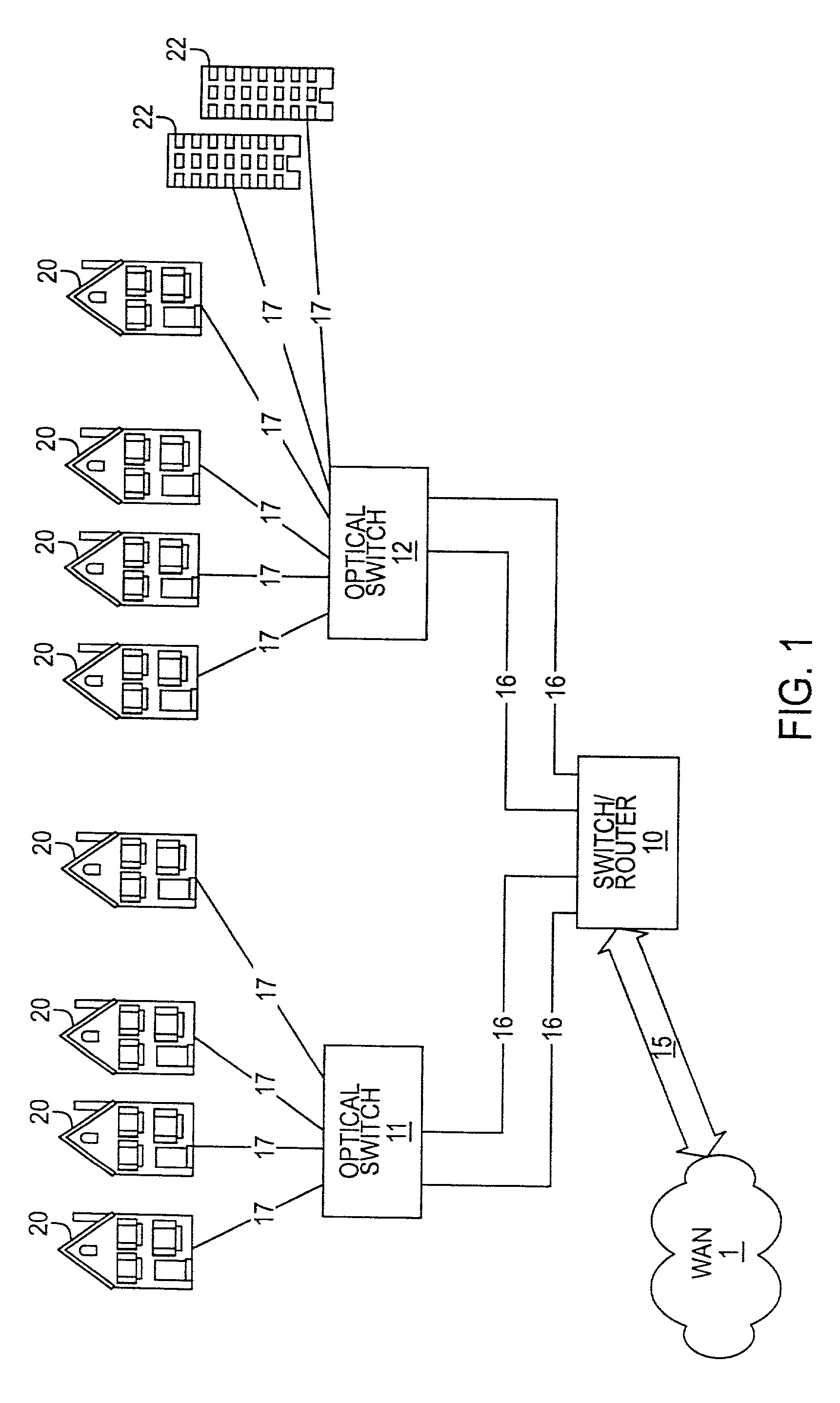
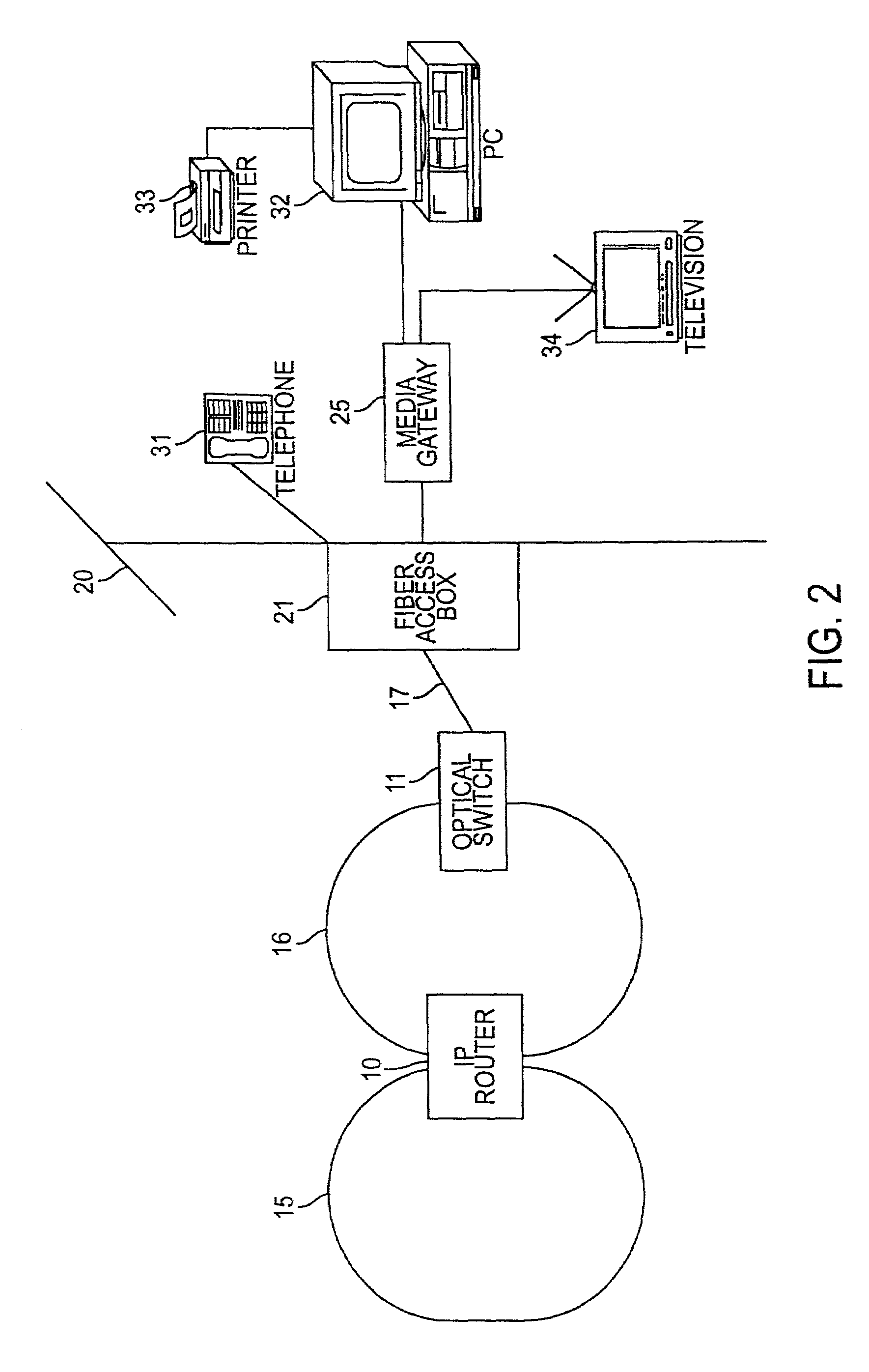
A technique for providing an optical signal to a destination. In one embodiment, the technique is realized through the use of an environmentally hardened, modular switch and a fiber distribution methodology. The modular switch may include fiber access ports, power access ports, dual power supply modules, dual switch fabric modules, dual optical trunking modules, and multiple subscriber service modules that house subscriber service ports and serve a total of up to 96 end points. The dual optical trunking modules may act as an interface between an optical network and the dual switch fabrics, and provide redundancy and variable optical transmission distance between the modular switch and the optical network to which the modular switch is connected. The dual switch fabrics are used for switching and aggregating signals and providing redundancy. Each subscriber service module acts as an interface between one or more subscriber end points and the dual switch fabrics of the modular switch. The subscriber service modules may be coupled to one or both of the dual switch fabrics and a total of up to 96 subscriber end points. Subscriber end point connectivity may be achieved via subscriber service ports (housed within a subscriber service module), one or more of the fiber access ports, external fiber optic splice cabinet, fiber optic trunk cable, and one or more fiber breakout points (housed by pedestals). The subscriber end points may consist of one or more optical or electrical subscriber connection types.
Owner:RPX CLEARINGHOUSE
Cellular communication system
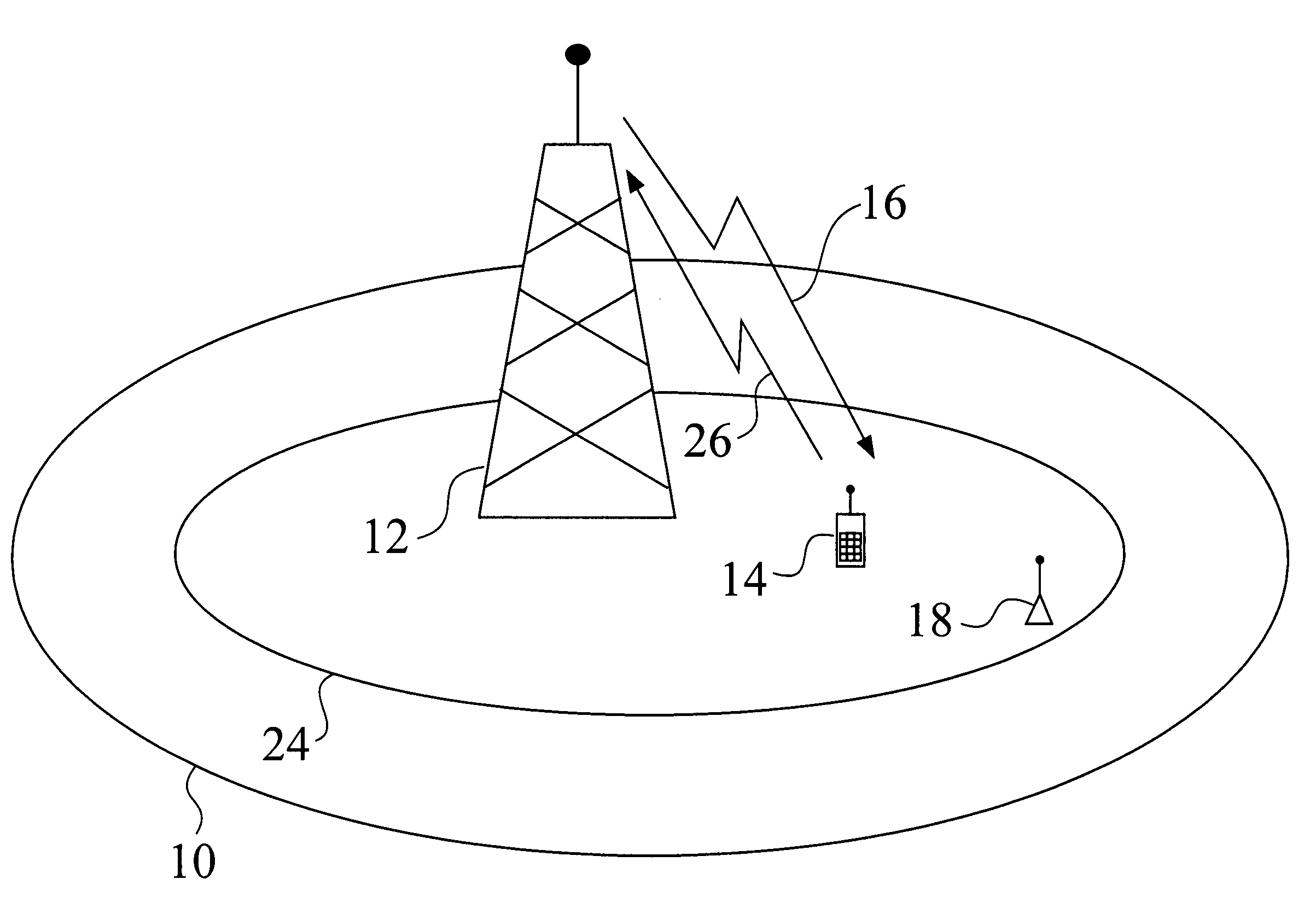
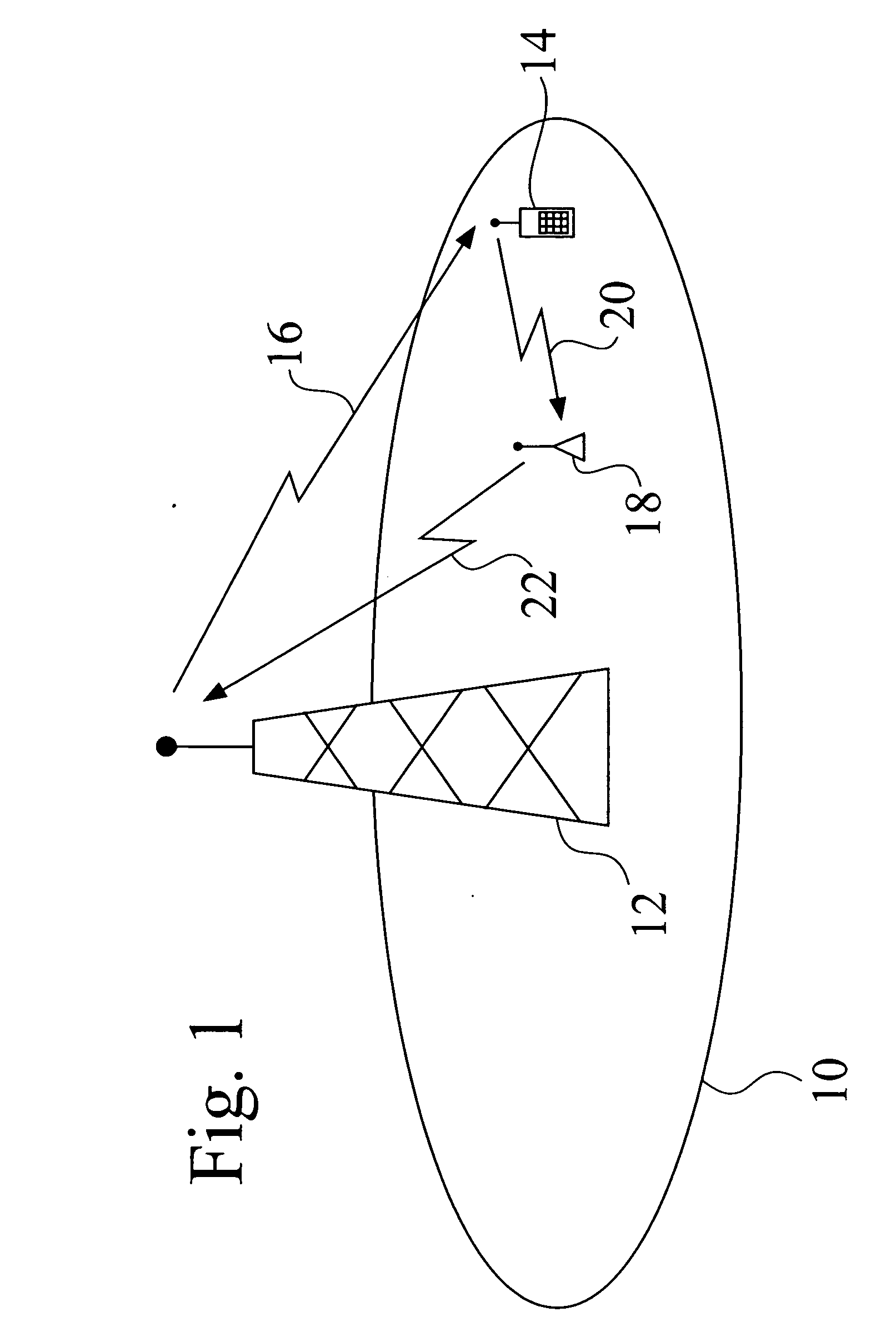
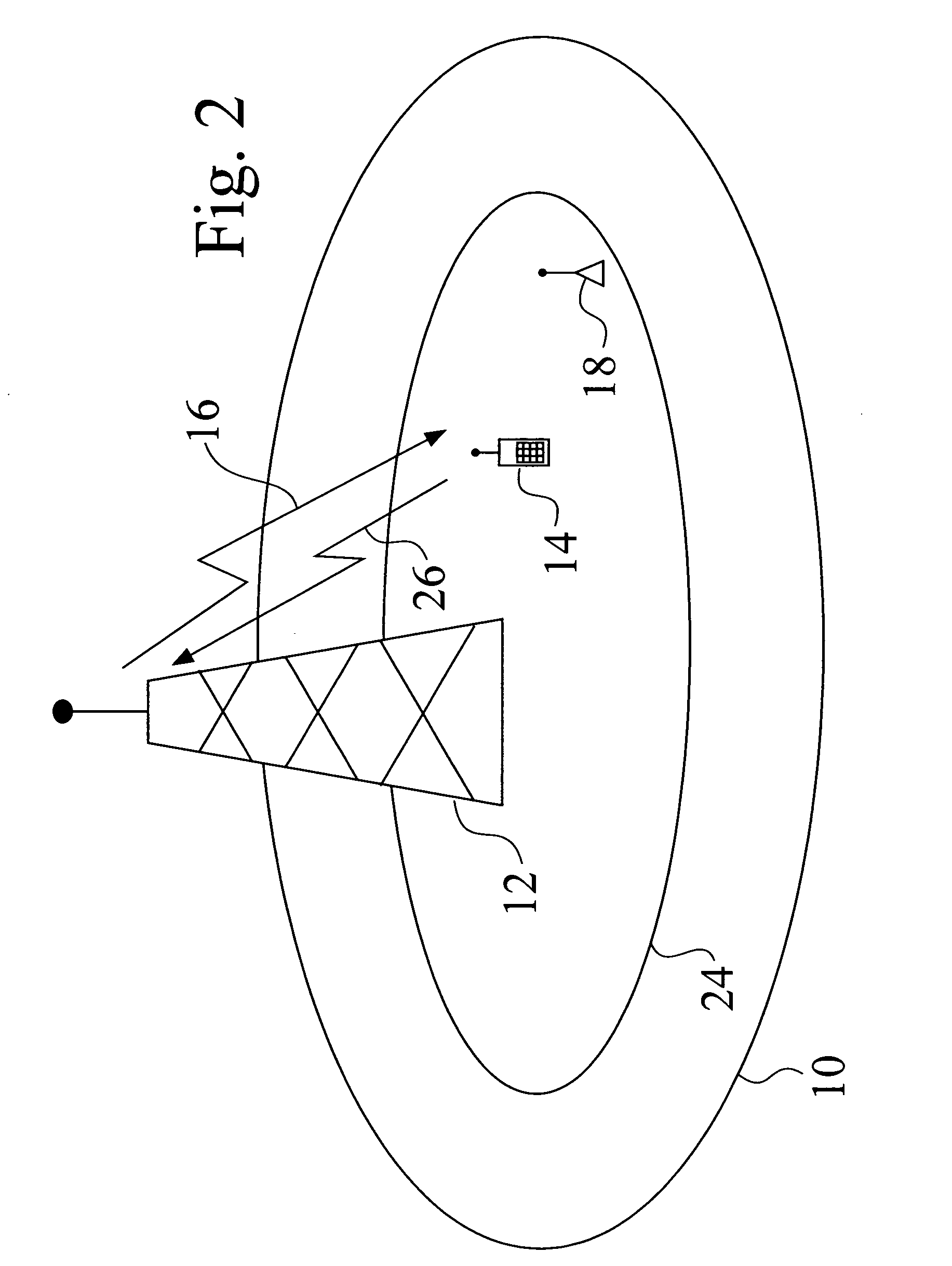
InactiveUS20060141929A1Improve performanceActive radio relay systemsNetwork planningTransceiverTrunking
Methods and apparatus for improving the performance of a conventional cellular telephone system. In a conventional system, a base station (12) located in a cell (10) both sends and receives signals to and from handheld phones (14). In one embodiment, the present invention employs a relay transceiver (18) located in the cell (10) to relay signals (20) from handheld phones (14) to the a base station (12). The handheld (14) still receives signals (16) directly from the base station (12), but the return signal (22) back to the base station (12) is accomplished through the relay transceiver (18).
Owner:GIGABEAM CORP
METHOD OF TRANSMITTING AND RECEIVING MESSAGE FOR COMMUNICATION BETWEEN UEs IN WIRELESS COMMUNICATION SYSTEM AND APPARATUS USING METHOD
ActiveUS20170245245A1Minimize collisionReliably and efficiently transmittedTransmissionWireless communicationCommunications systemTrunking
Disclosed is a method of transmitting and receiving a message for a communication between UEs in a wireless communication system and an apparatus using the method. Specifically, in a method of relaying a V2X message by a first UE (User Equipment) in a wireless communication system supporting V2X (Vehicle-to-Everything) communication, the method may comprise steps of receiving the V2X message from a second UE, calculating a resource usage rate of a direct link between UEs, determining a relay scheme of the V2X message, by comparing the calculated resource usage rate and a predetermined threshold, and transferring the V2X message to a third UE based on the determined relay scheme.
Owner:LG ELECTRONICS INC
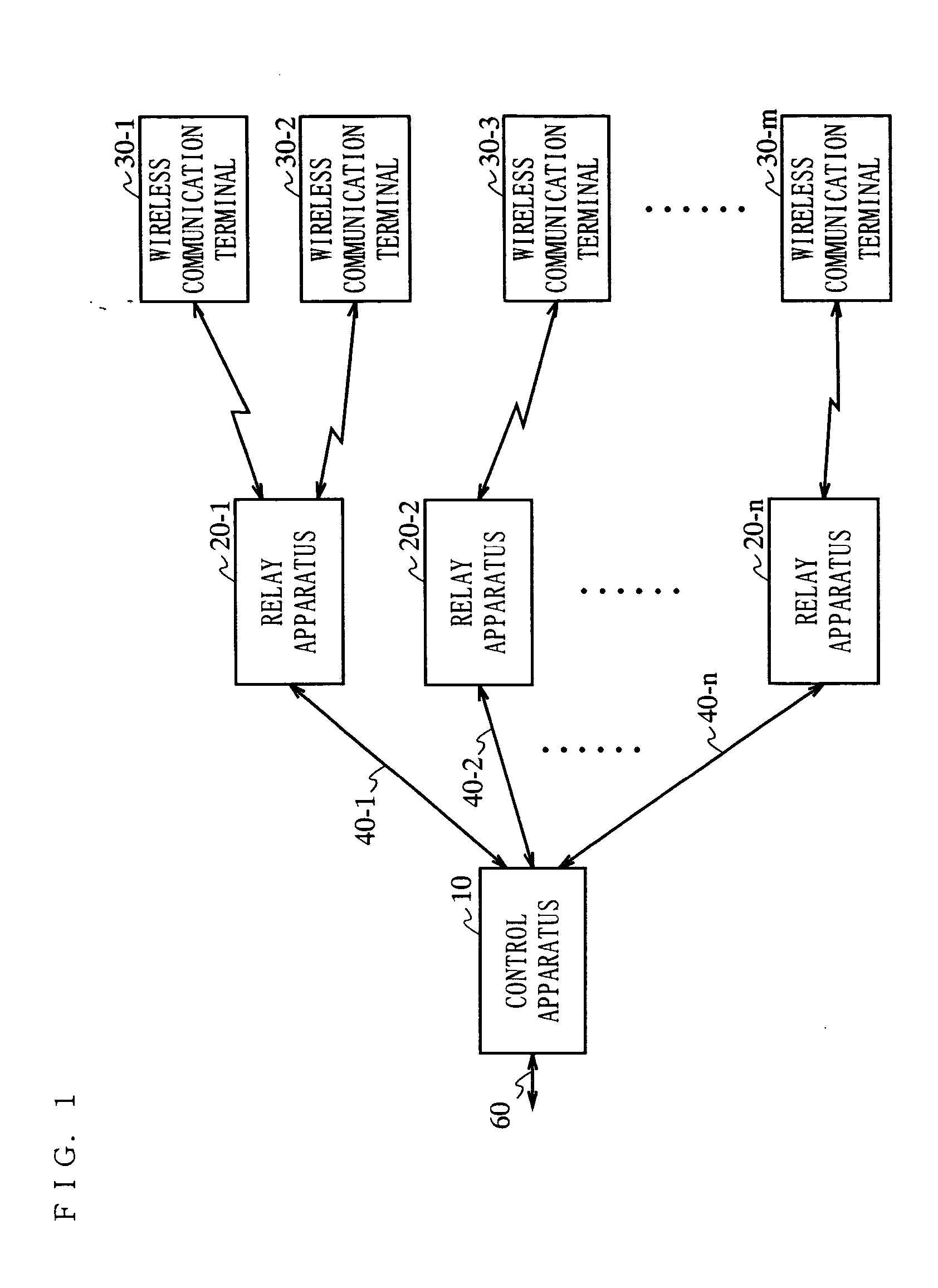
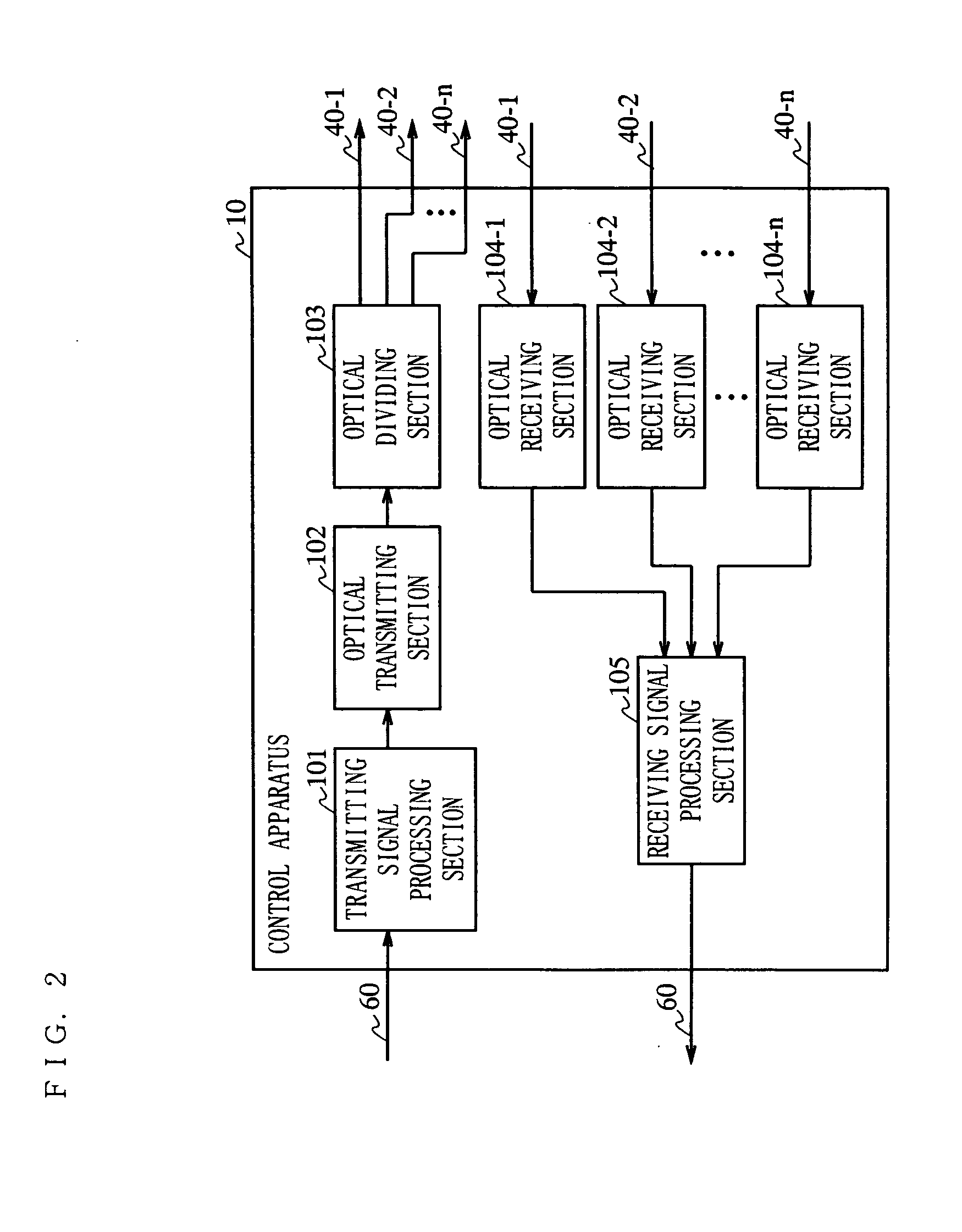
Radio communication system
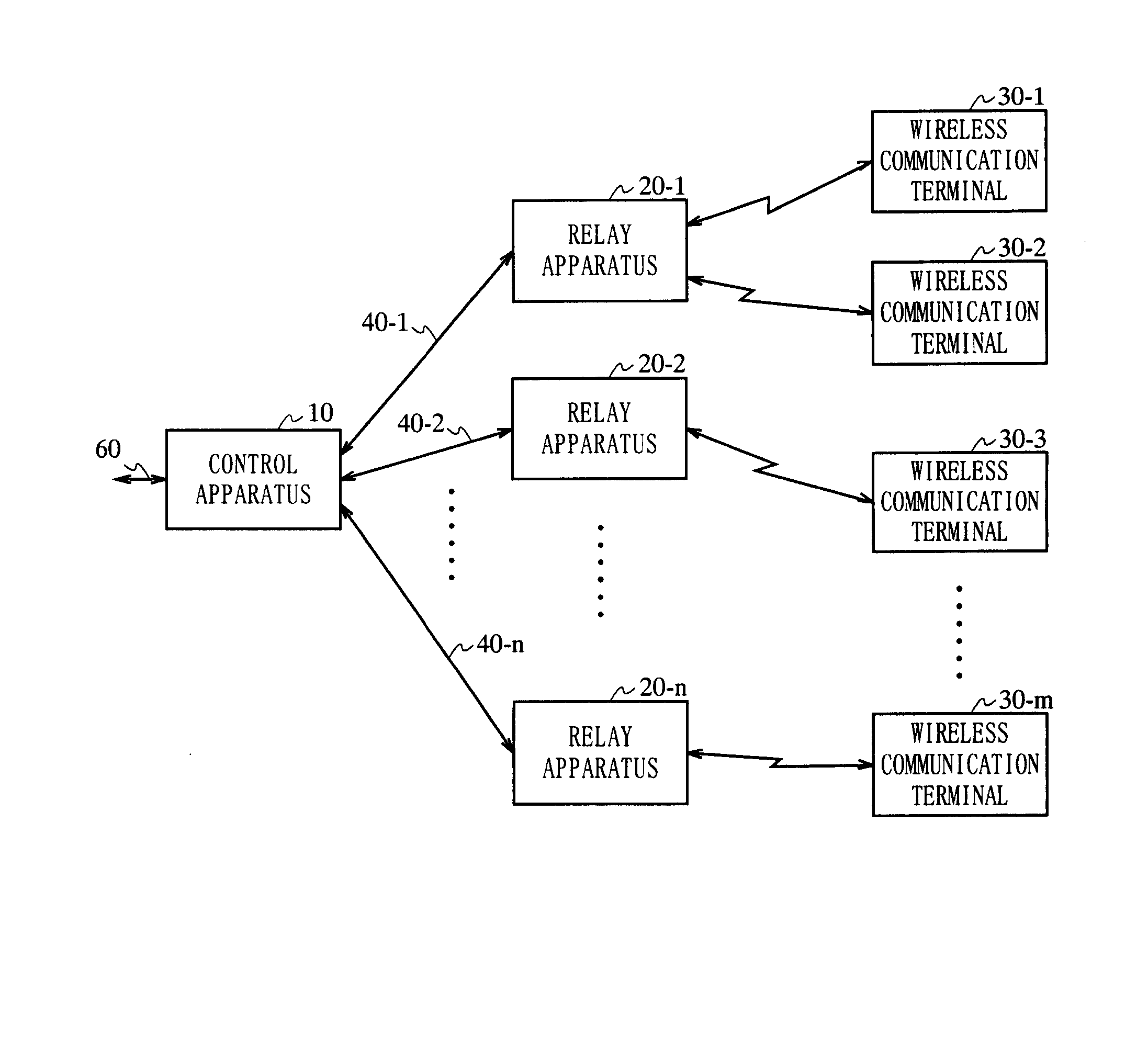
InactiveUS20050266797A1Quality improvementAvoid reflectionsPower managementTransmission control/equalisingCommunications systemEngineering
The present invention is directed to a wireless communication system capable of keeping a level of a wireless signal received by a relay apparatus (20) within a predetermined dynamic range. In a control apparatus (10), a transmitting section (102) converts a downstream electric signal into a downstream optical signal and transmits the downstream optical signal to the relay apparatus (20) via an optical transmission path (40). The relay apparatus (20) converts the received downstream optical signal into a downstream electric signal and transmits the downstream electric signal as a wireless signal to a wireless communication terminal (30) from a transmitting / receiving antenna section (204). In the relay apparatus (20), a level adjustment section (207) adjusts the level of the wireless signal transmitted by the relay apparatus (20) such that the receiving level of the wireless signal received by the relay apparatus is kept within a predetermined range.
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com