Radio communication system
a radio communication and system technology, applied in the field of radio communication systems, can solve the problems of affecting the quality of optical signals, the inability to separate signals to be received and noise from each other, and the inability to prevent optical signal deterioration, so as to prevent the quality deterioration of optical signals
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
embodiment 1
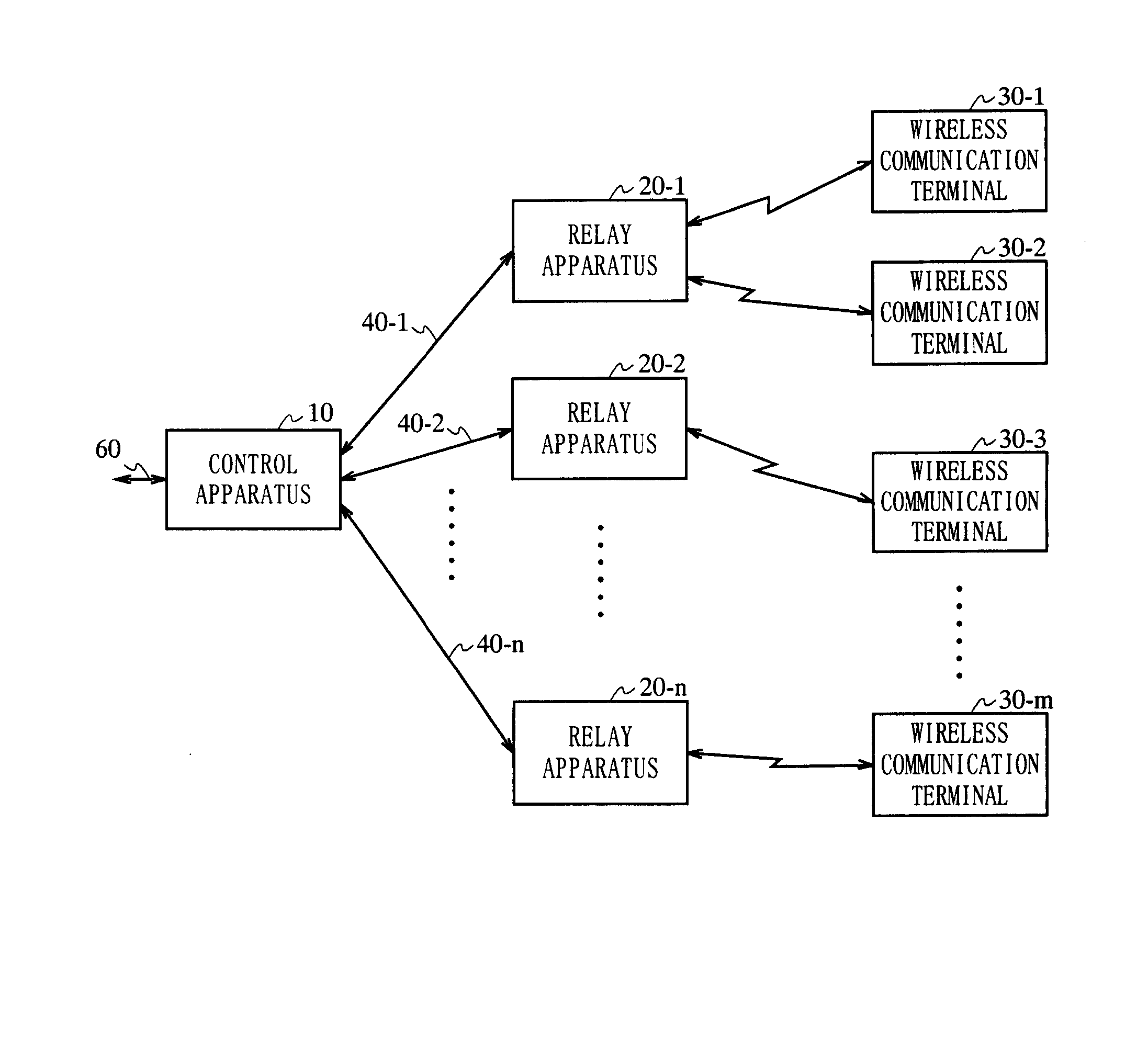
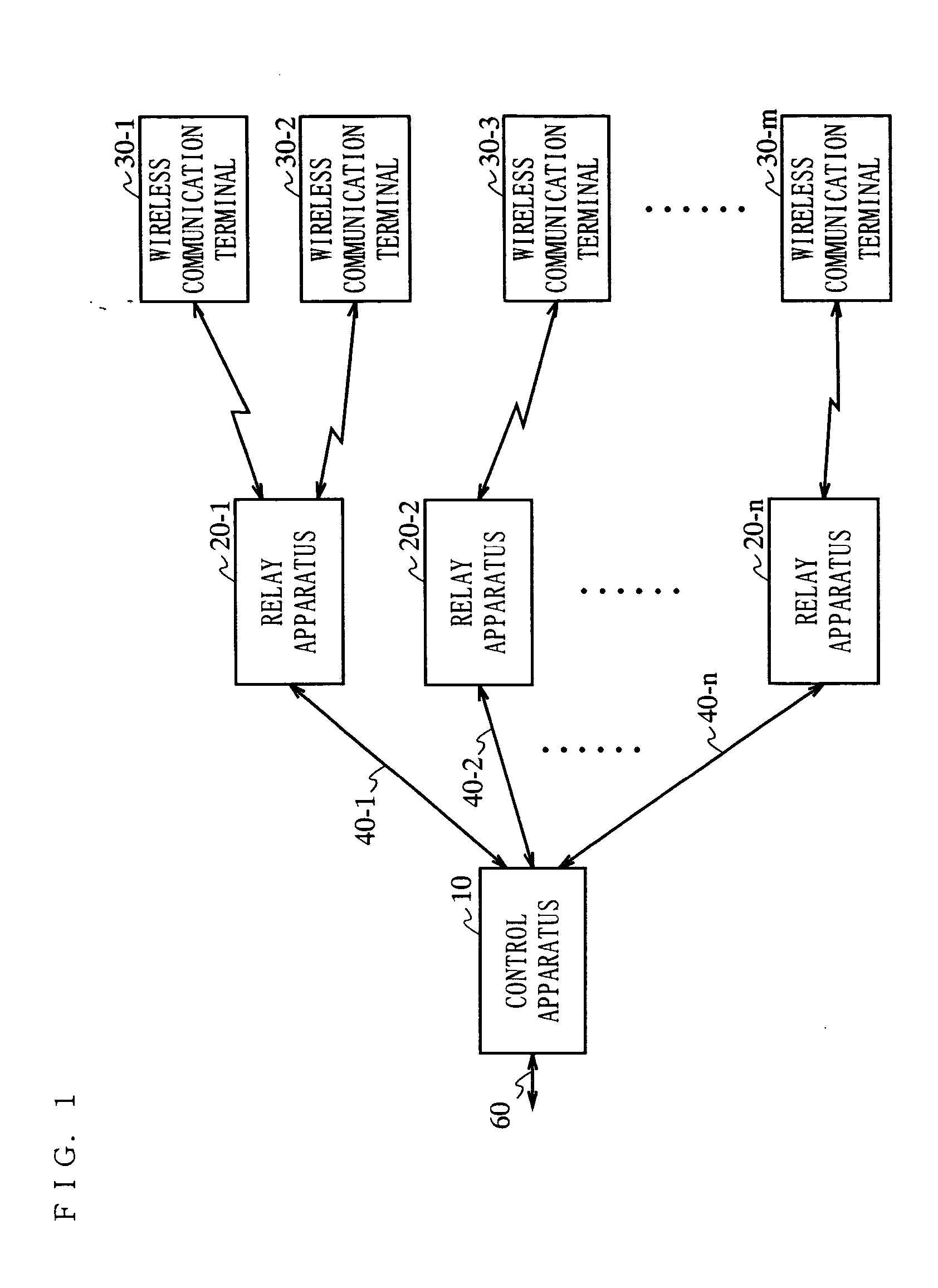
[0171]FIG. 1 is a block diagram showing a structure of a wireless communication system according to Embodiment 1 of the present invention.
[0172] In FIG. 1, the wireless communication system includes a control apparatus 10, relay apparatuses 20-1 through 20-n (n: a natural number of 1 or greater), and wireless communication terminals 30-1 through 30-m. The control apparatus 10 and the relay apparatuses 20-1 through 20-n are connected to each other via optical transmission paths 40-1 through 40-n, respectively. The relay apparatuses 20-1 through 20-n and the wireless communication terminals 30-1 through 30-m are connected to each other wirelessly. The optical transmission paths are, for example, optical fibers.
[0173] The control apparatus 10 and an external network (not shown) are connected to each other via an Ethernet (registered trademark) cable 60. The control apparatus 10 and the external network may be connected to each other via a cable other than the Ethernet (registered tra...
embodiment 2
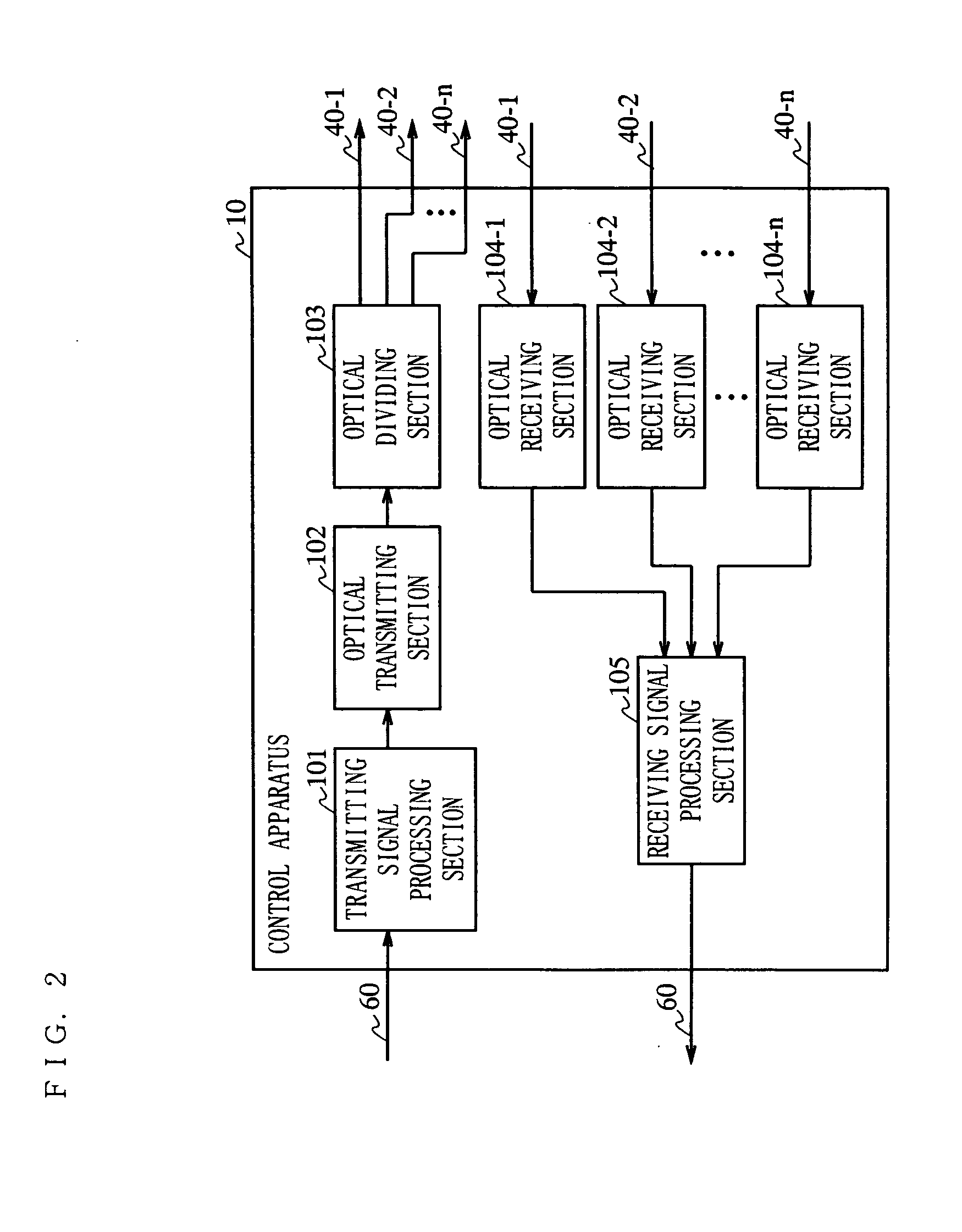
[0218]FIG. 8 is a block diagram showing a structure of a control apparatus 10b included in a wireless communication system according to Embodiment 2 of the present invention.
[0219] The control apparatus 10b shown in FIG. 8 is different from the control apparatus 10 shown in FIG. 2 in including a transmitting signal dividing section 107 instead of the optical dividing section 103. The other parts of the structure are substantially the same as those of Embodiment 1, and elements which are substantially the same as those of FIG. 2 bear identical reference numerals thereto and descriptions thereof will be omitted. In this embodiment, the relay apparatus 20 has the structure shown in FIG. 3 except that the level control section 207 is not included.
[0220] In the control apparatus 10b, the transmitting signal processing section 101 modulates a signal transmitted from an external network and outputs the modulated signal to the transmitting signal dividing section 107.
[0221] The transmitt...
embodiment 3
[0263] Hereinafter, a wireless communication system according to Embodiment 3 of the present invention will be described. The wireless communication system according to this embodiment, upon detecting that the quality of an optical signal is deteriorated, stops transmission of the wireless signal from a relay apparatus. When a wireless signal with deteriorated quality is transmitted or received, other communication devices or human body may possibly be adversely influenced. Therefore, when communicating using a wireless signal, the quality of the wireless signal transmitted by a communication device needs to fulfill the public conditions regulated by the Radio Law. In this embodiment, an exemplary case where the wireless communication system evaluates the quality of an optical signal will be described.
[0264]FIG. 14 is a block diagram showing a structure of a relay apparatus 20b included in a wireless communication system according to this embodiment. In FIG. 14, the relay apparatus...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com