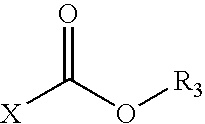
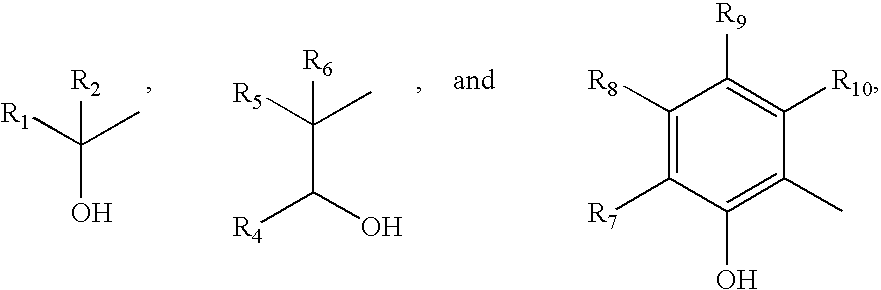
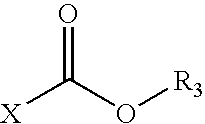
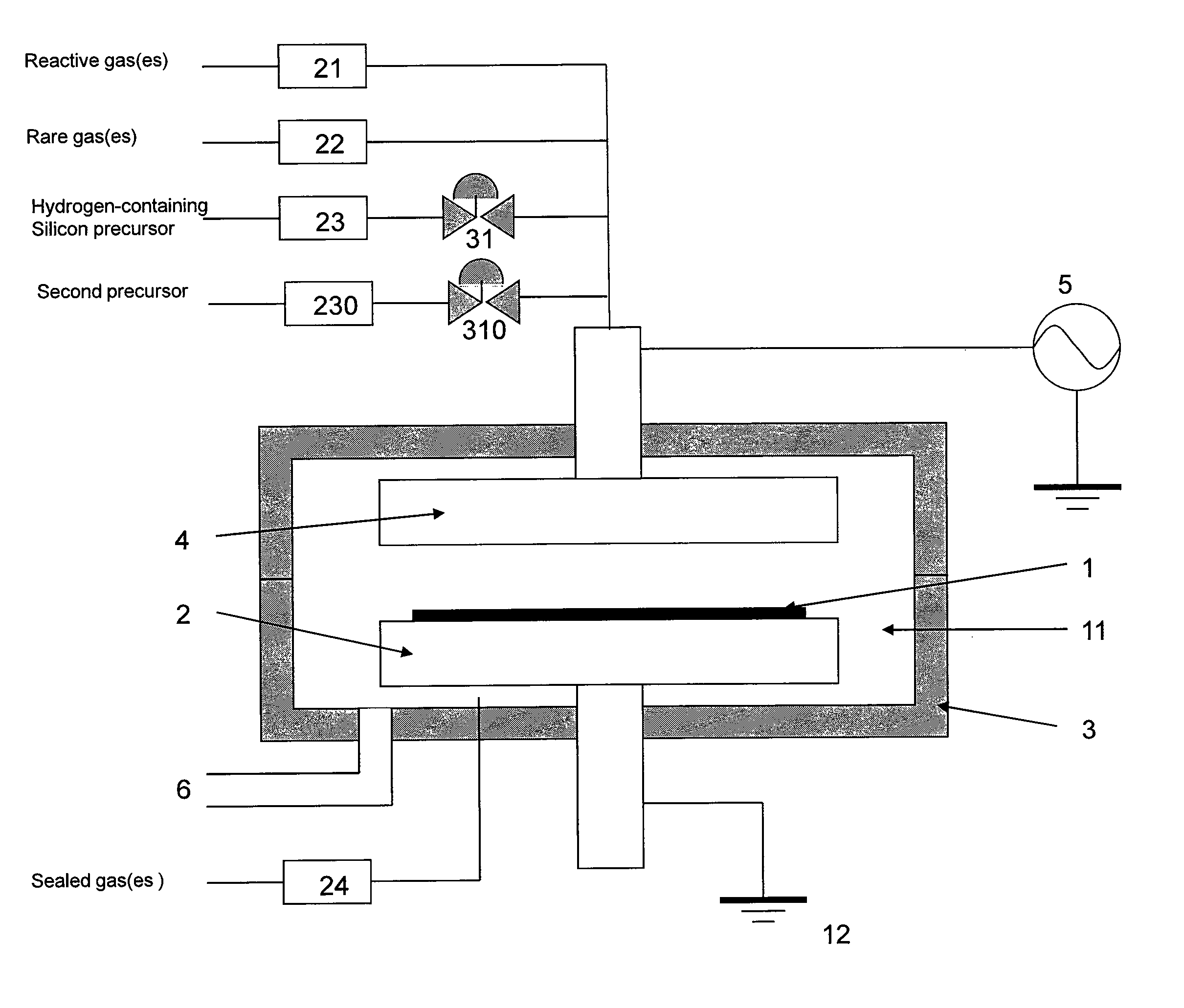
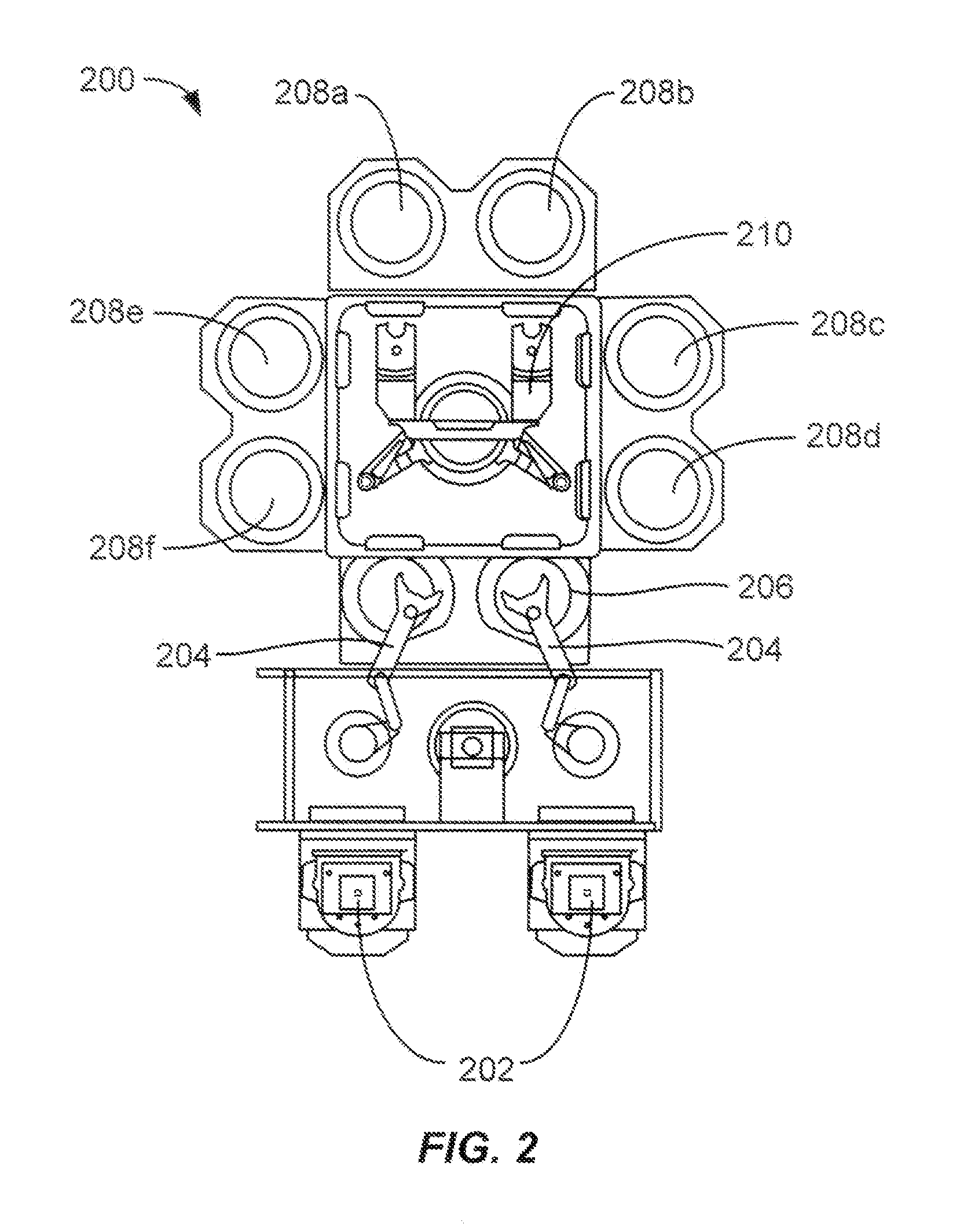
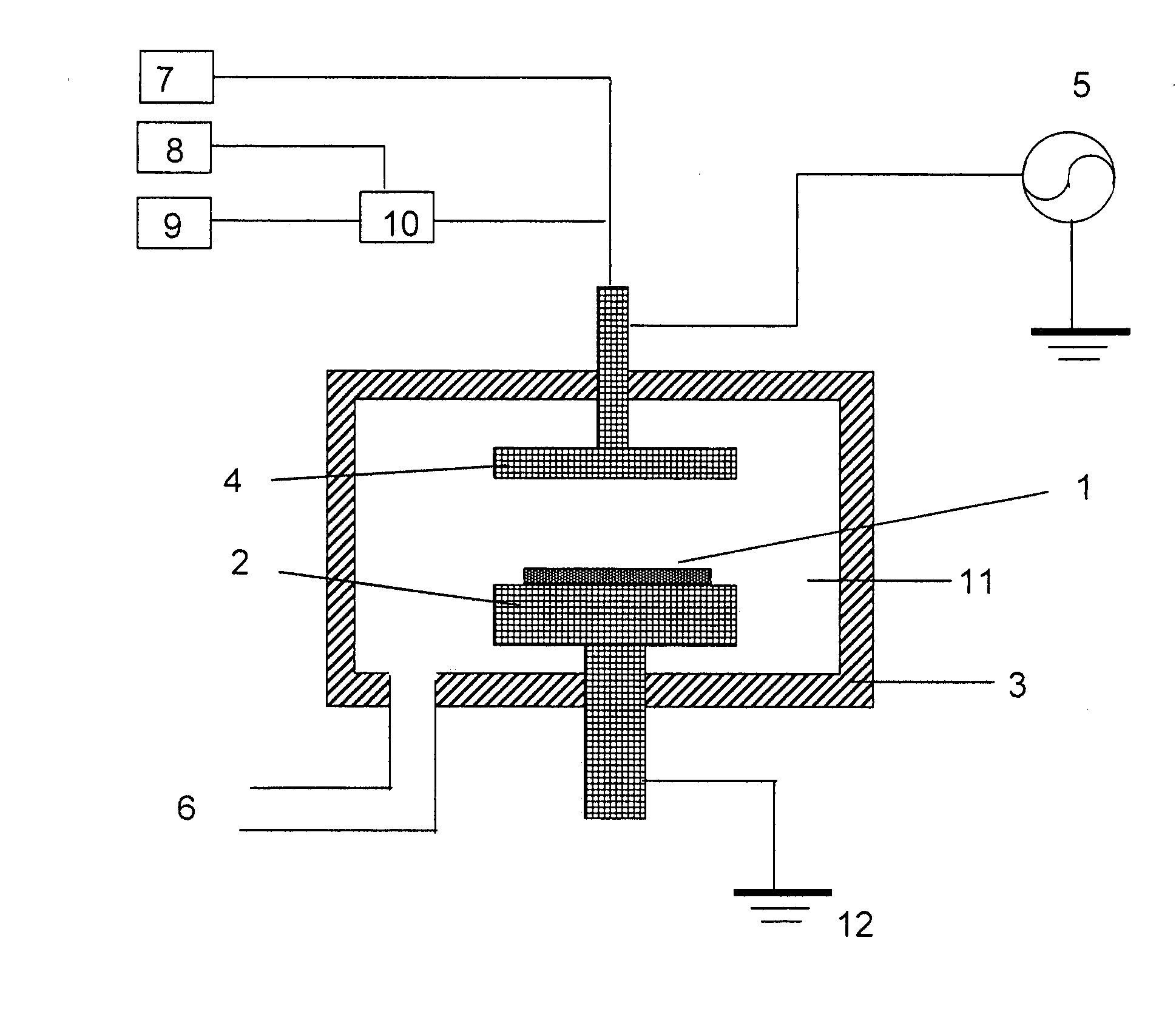
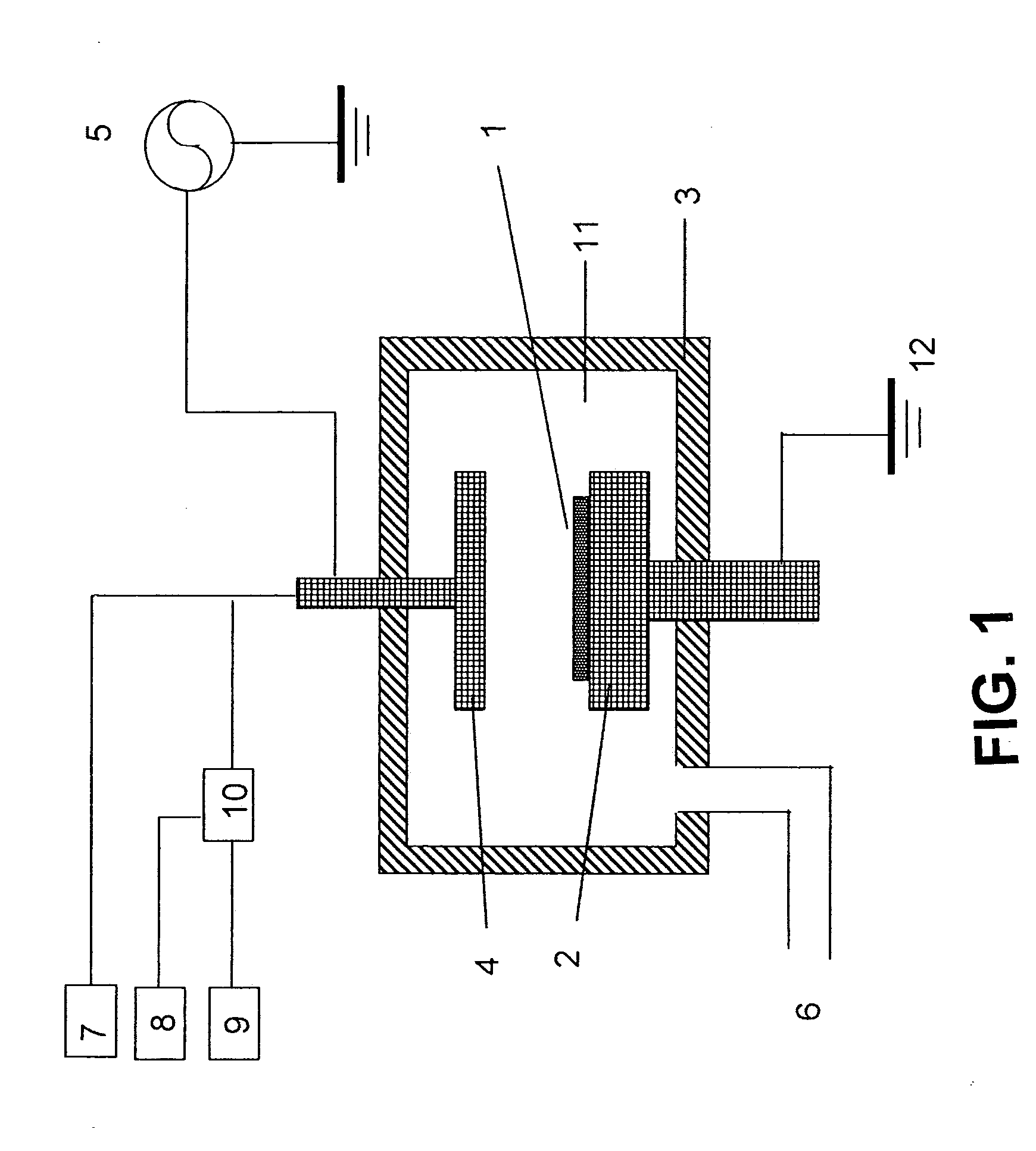
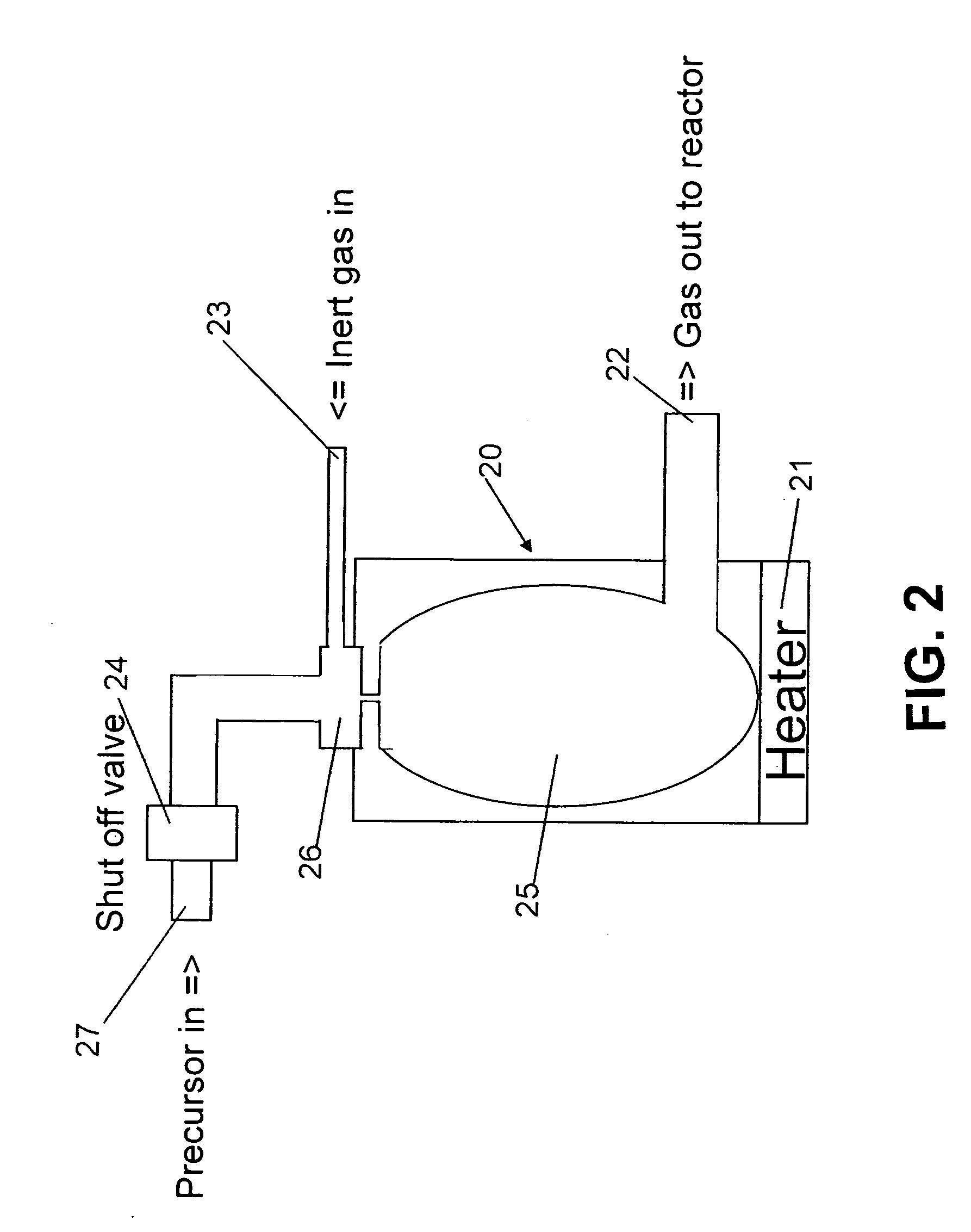
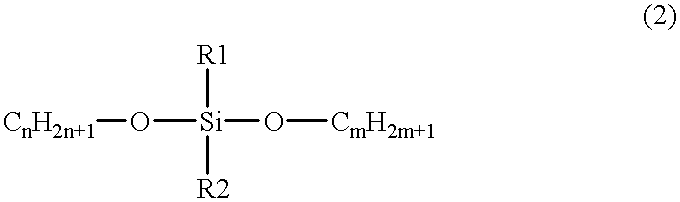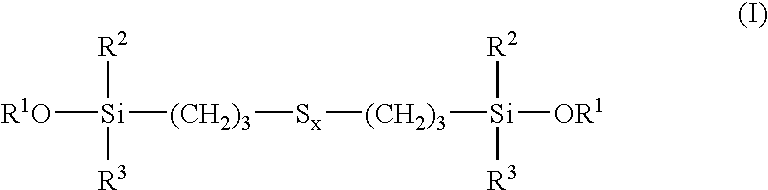Patents
Literature
32371 results about "Hydrocarbon" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
In organic chemistry, a hydrocarbon is an organic compound consisting entirely of hydrogen and carbon. Hydrocarbons are examples of group 14 hydrides. Hydrocarbons from which one hydrogen atom has been removed are functional groups called hydrocarbyls. Because carbon has 4 electrons in its outermost shell (and because each covalent bond requires a donation of 1 electron, per atom, to the bond) carbon has exactly four bonds to make, and is only stable if all 4 of these bonds are used.
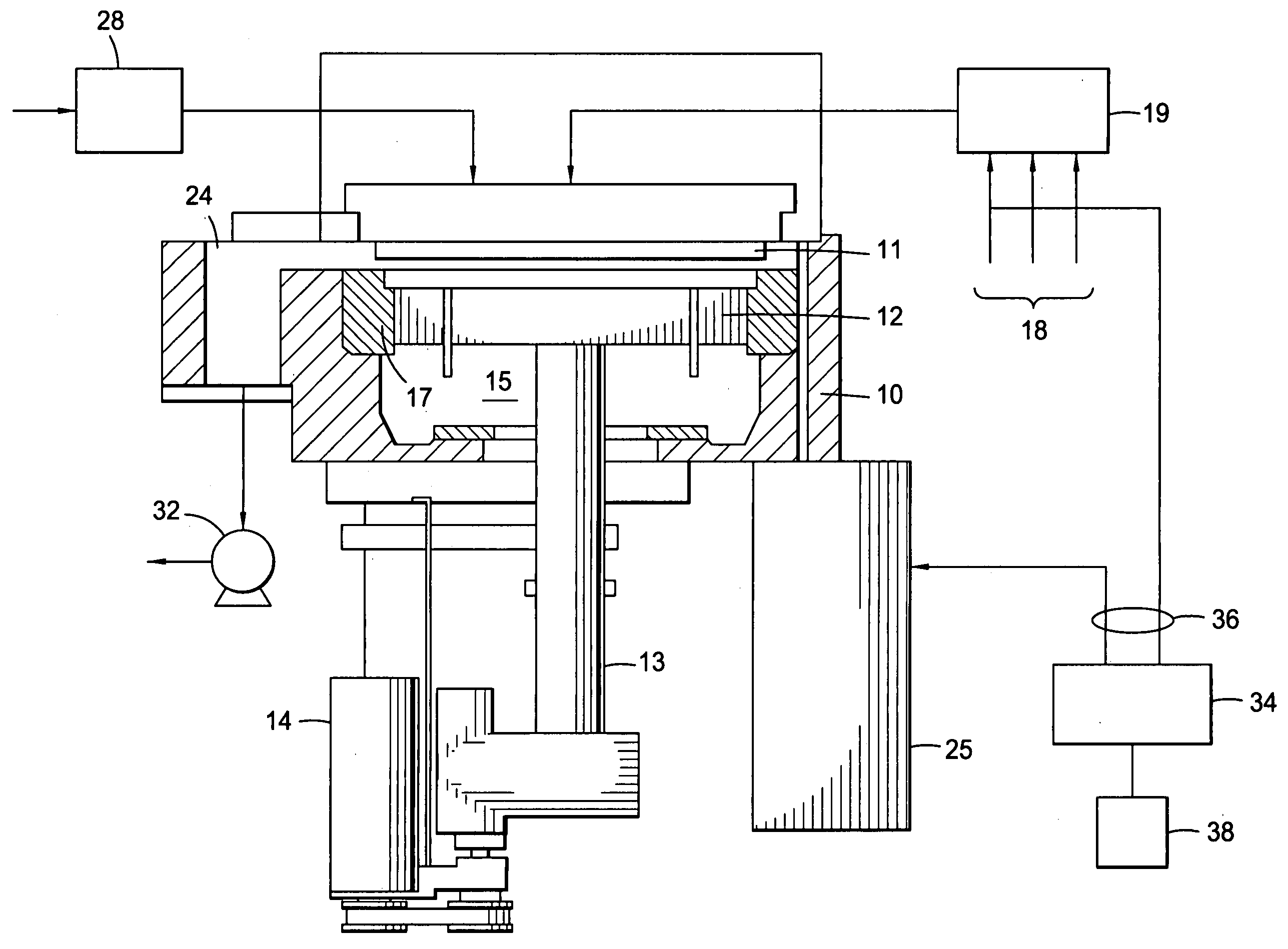
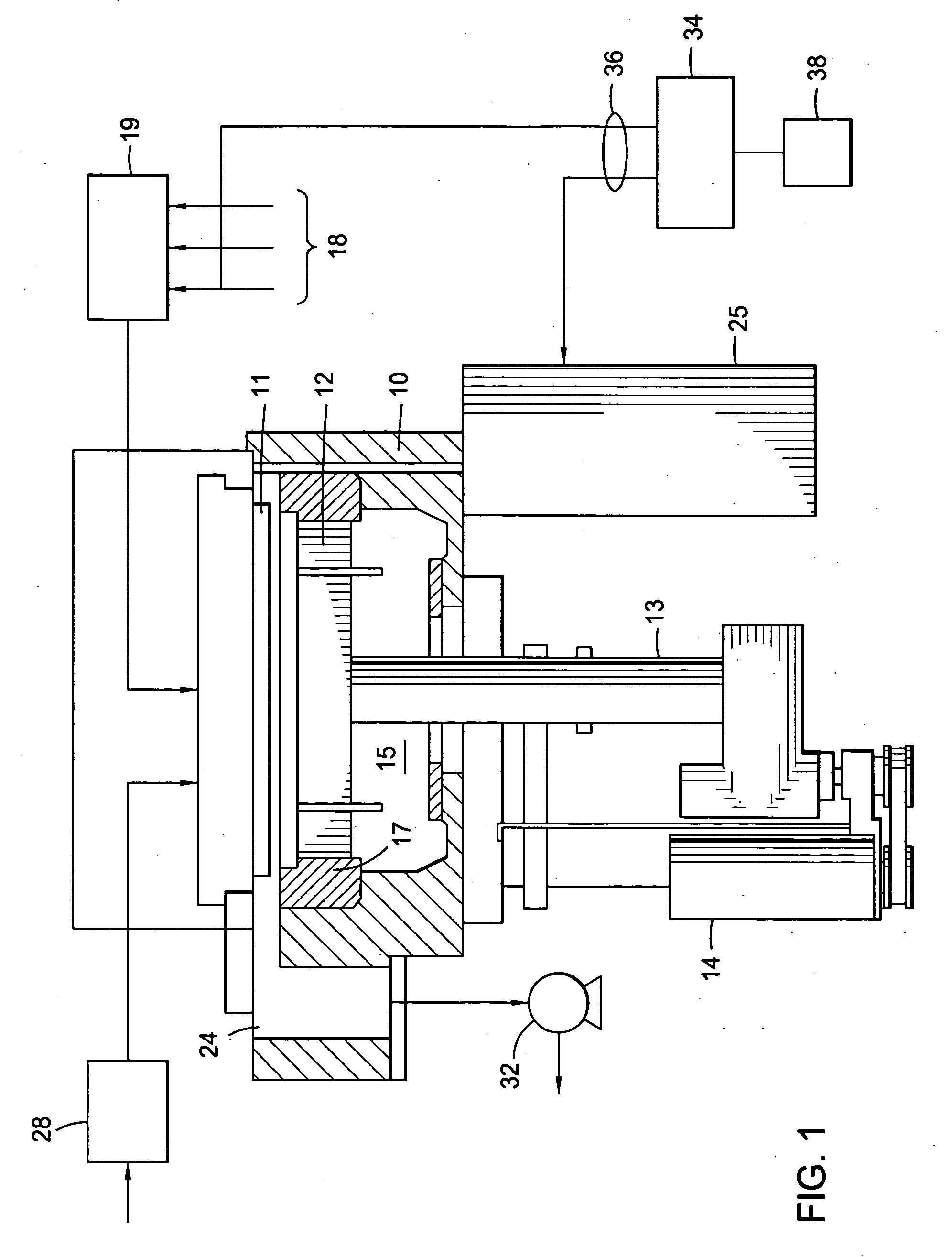
Dry etching method for oxide semiconductor film
InactiveUS20070287296A1Improve processing accuracyIncrease etch rateDecorative surface effectsSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingDry etchingSemiconductor
Provided is a dry etching method for an oxide semiconductor film made of In—Ga—Zn—O, in which an etching gas containing a hydrocarbon is used in a dry etching process for the oxide semiconductor film made of In—Ga—Zn—O formed on a substrate.
Owner:CANON KK
Silicone polymer insulation film on semiconductor substrate and method for forming the film
InactiveUS6352945B1Low dielectric constantImprove thermal stabilityLiquid surface applicatorsSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsPolymer scienceHigh humidity
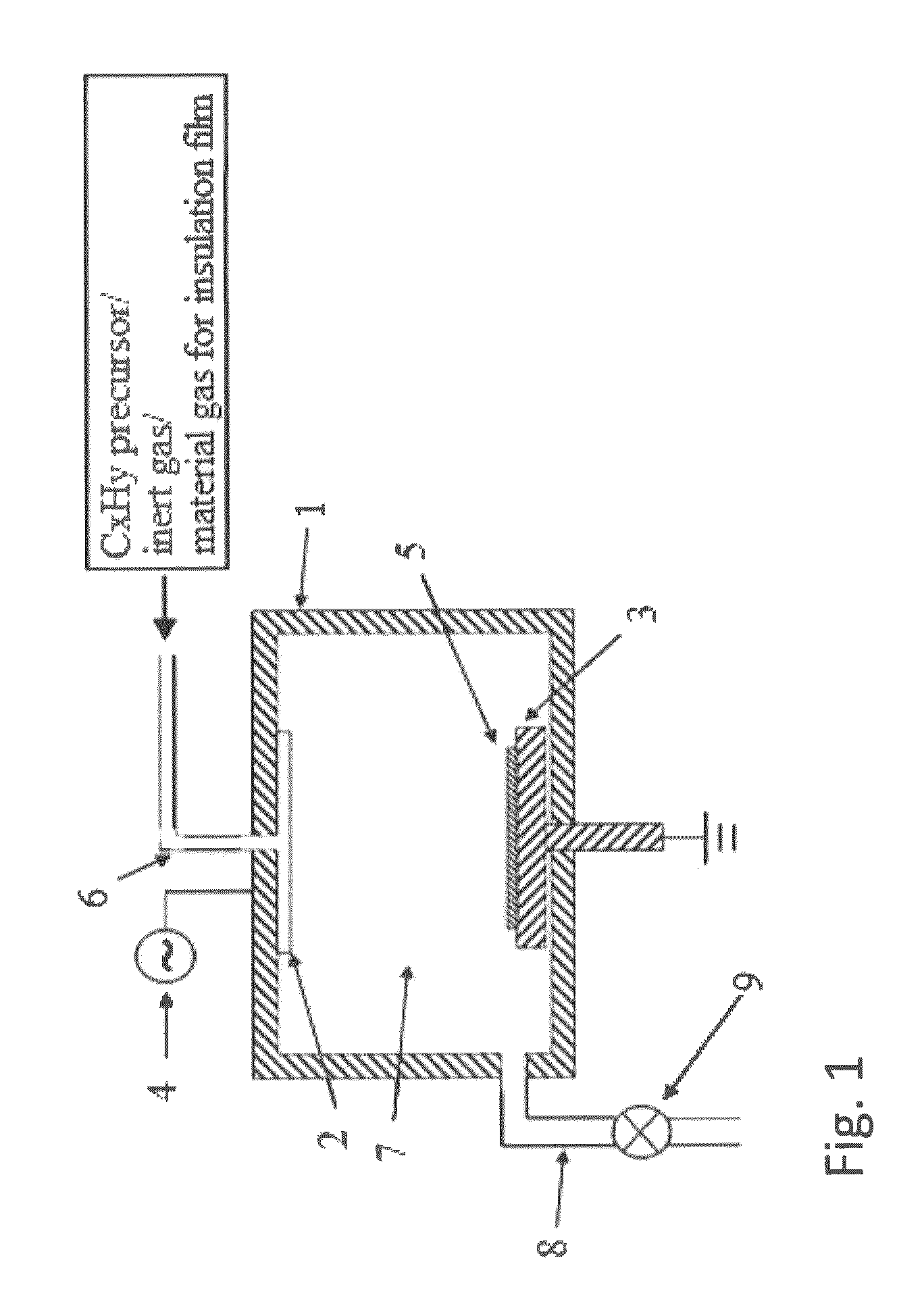
A method for forming a silicone polymer insulation film having a low relative dielectric constant, high thermal stability and high humidity-resistance on a semiconductor substrate is applied to a plasma CVD apparatus. The first step is introducing a silicon-containing hydrocarbon compound expressed by the general formula SialphaObetaCxHy (alpha, beta, x, and y are integers) to the reaction chamber of the plasma CVD apparatus. The silicon-containing hydrocarbon compound has at most two O-CnH2n+1 bonds and at least two hydrocarbon radicals bonded to the silicon. The residence time of the material gas is lengthened by, for example, reducing the total flow of the reaction gas, in such a way as to form a silicone polymer film having a micropore porous structure with a low relative dielectric constant.
Owner:ASM JAPAN
Process for producing a hydrocarbon component of biological origin
ActiveUS20040230085A1Improve performanceLow densityLiquid hydrocarbon mixture productionHydrocarbonsIsomerizationHydrocarbon
The invention relates to a process for producing a hydrocarbon component of biological origin. The process comprises at least two steps, the first one of which is a HDO step and the second one is an isomerization step operated using the counter-current flow principle. A biological raw material containing fatty acids and / or fatty acid esters serves as the feed stock.
Owner:OYJ NESTE OIL +1
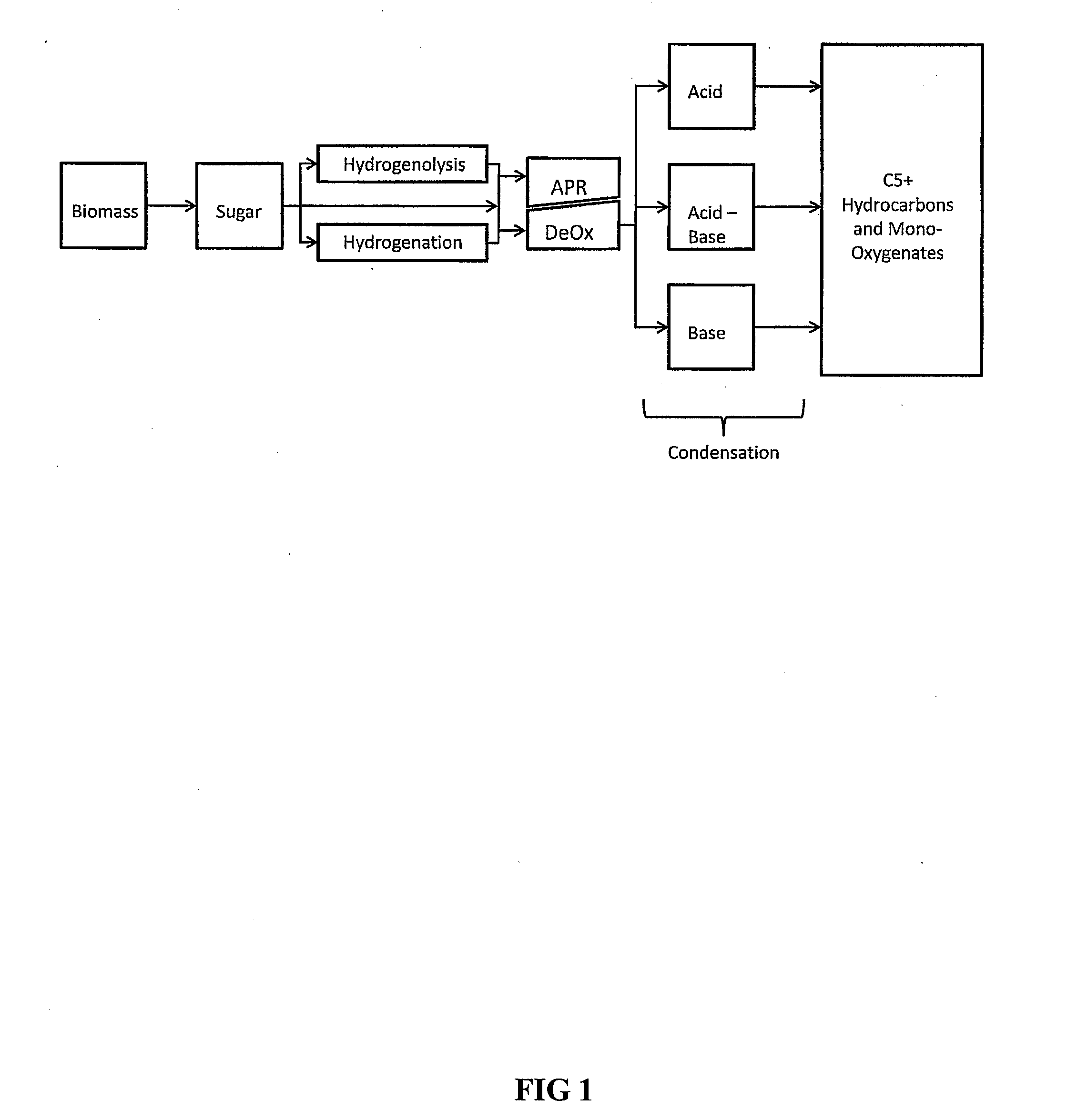
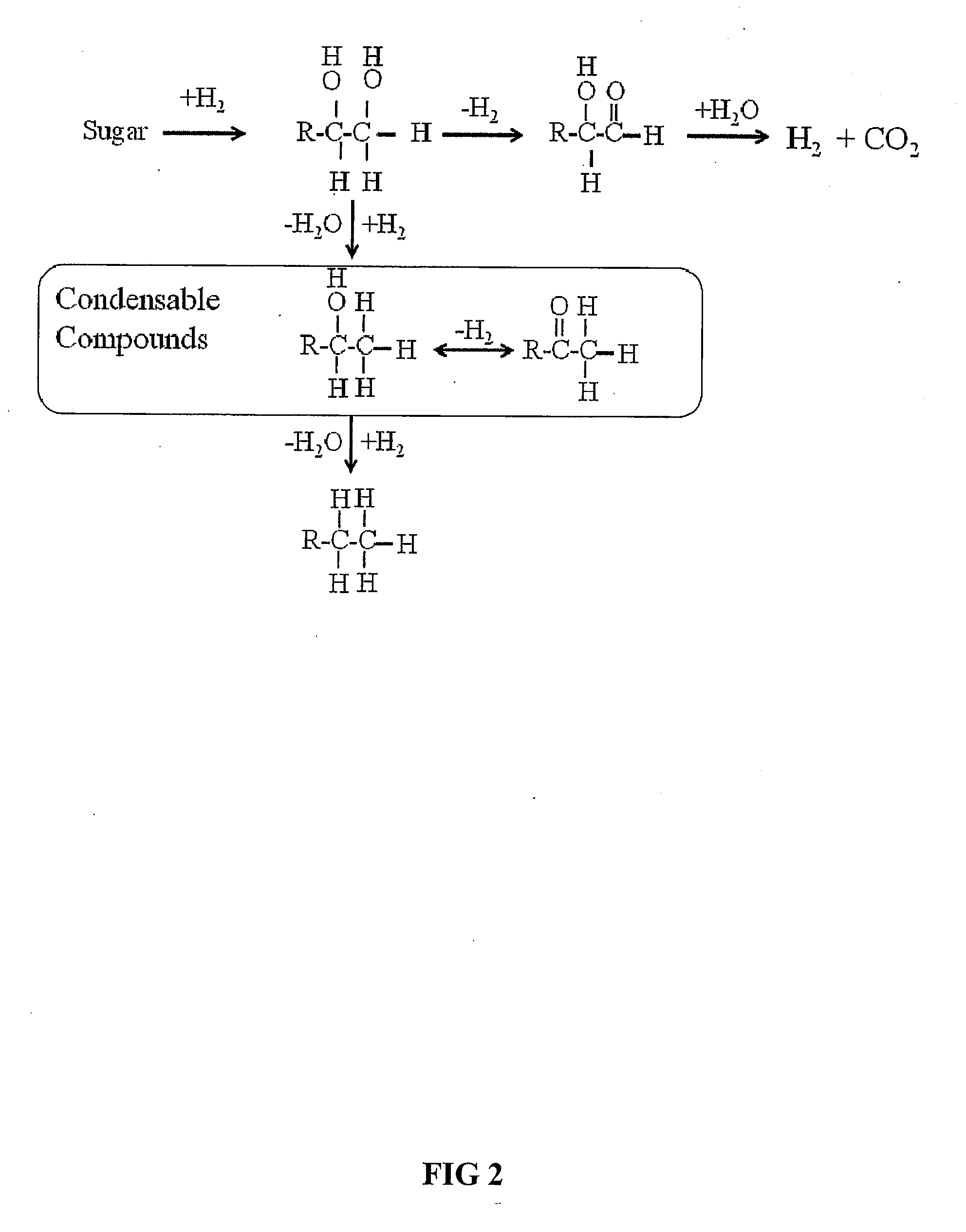
Synthesis of liquid fuels and chemicals from oxygenated hydrocarbons
ActiveUS20080216391A1Organic compound preparationHydrocarbon from oxygen organic compoundsFuranLiquid fuel
Processes and reactor systems are provided for the conversion of oxygenated hydrocarbons to hydrocarbons, ketones and alcohols useful as liquid fuels, such as gasoline, jet fuel or diesel fuel, and industrial chemicals. The process involves the conversion of mono-oxygenated hydrocarbons, such as alcohols, ketones, aldehydes, furans, carboxylic acids, diols, triols, and / or other polyols, to C4+ hydrocarbons, alcohols and / or ketones, by condensation. The oxygenated hydrocarbons may originate from any source, but are preferably derived from biomass.
Owner:VIRENT
Method for Sealing Pores at Surface of Dielectric Layer by UV Light-Assisted CVD
InactiveUS20110159202A1Improve controllabilityReduce throughputPretreated surfacesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingOptoelectronicsIrradiation
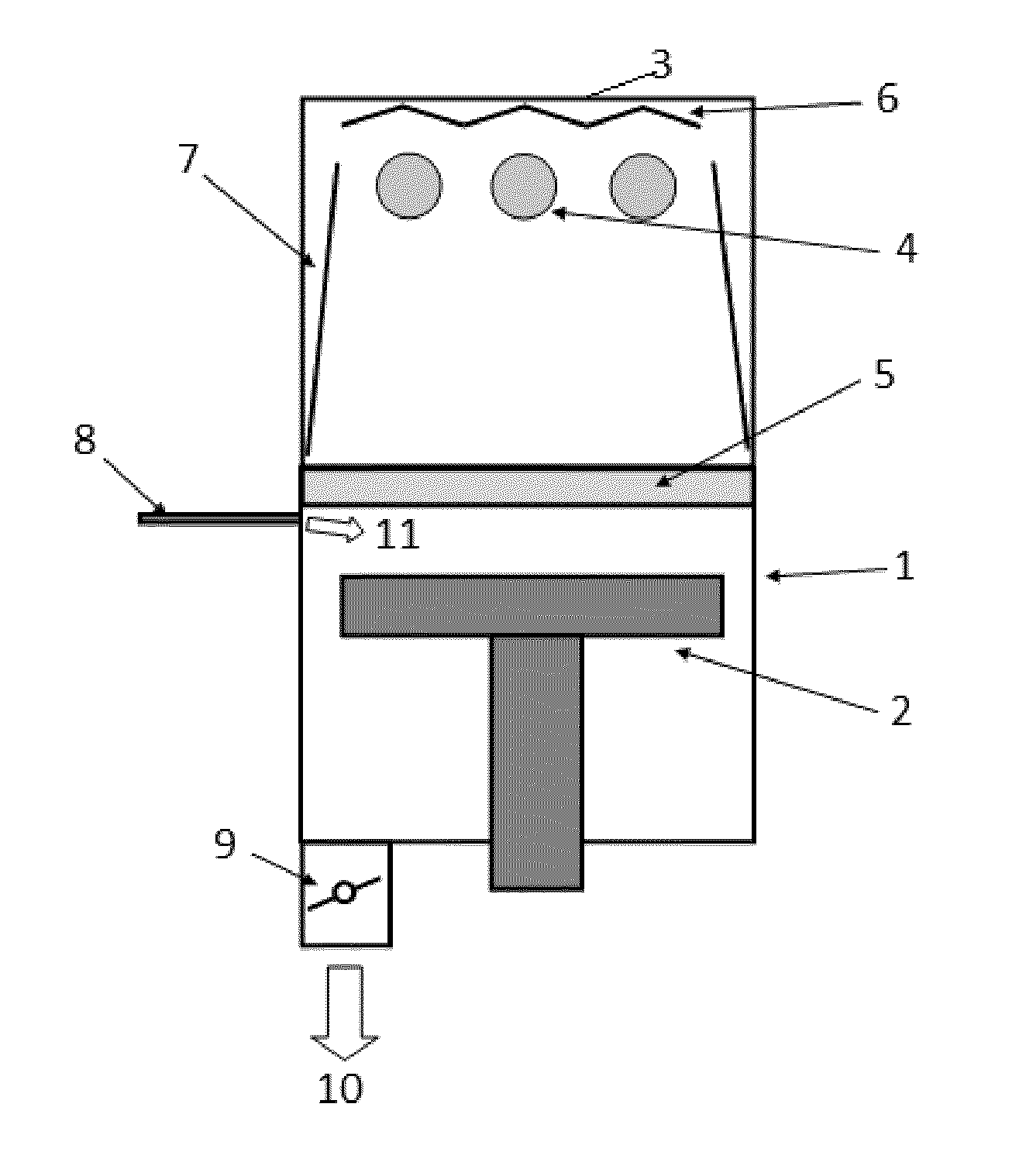
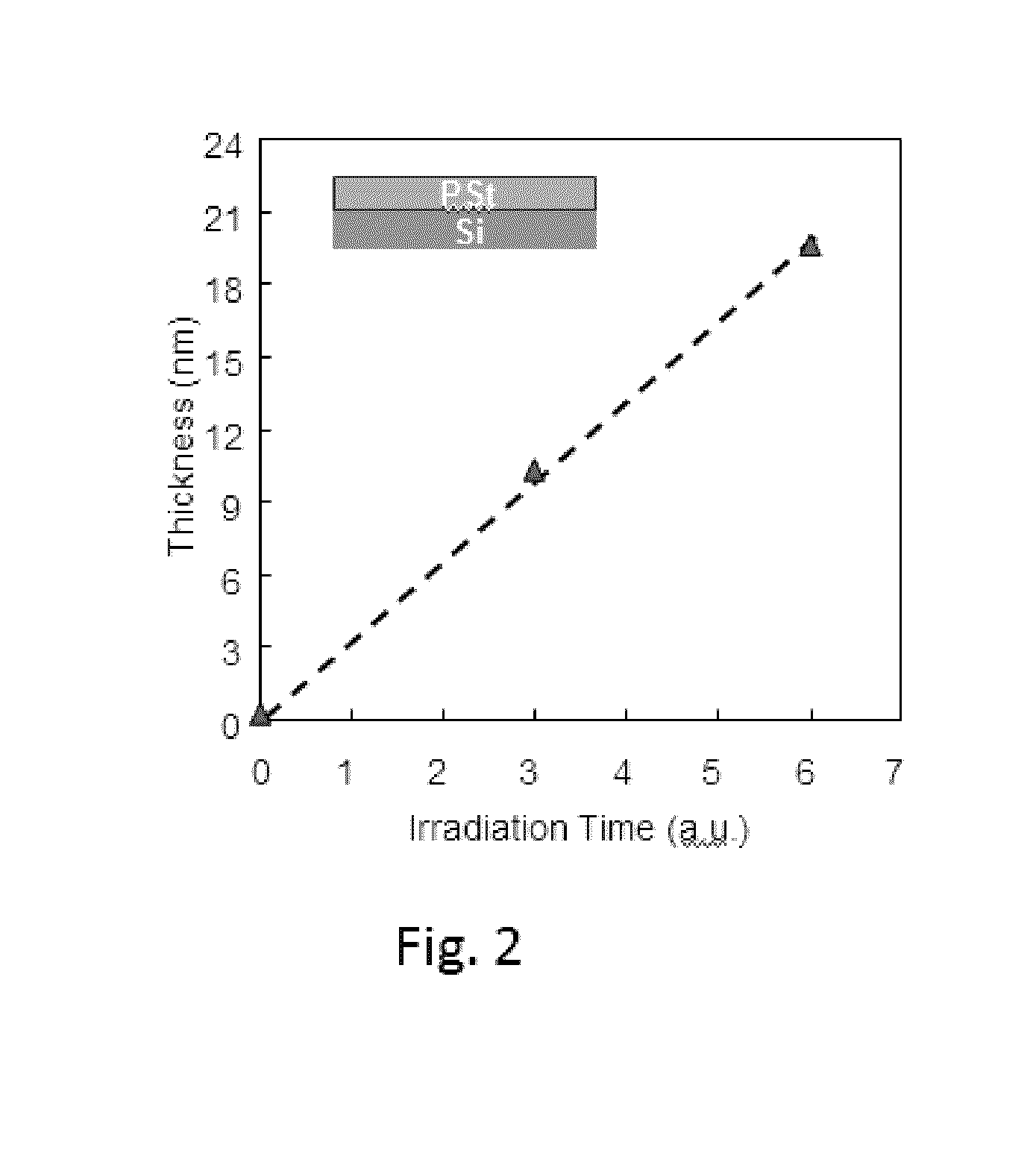
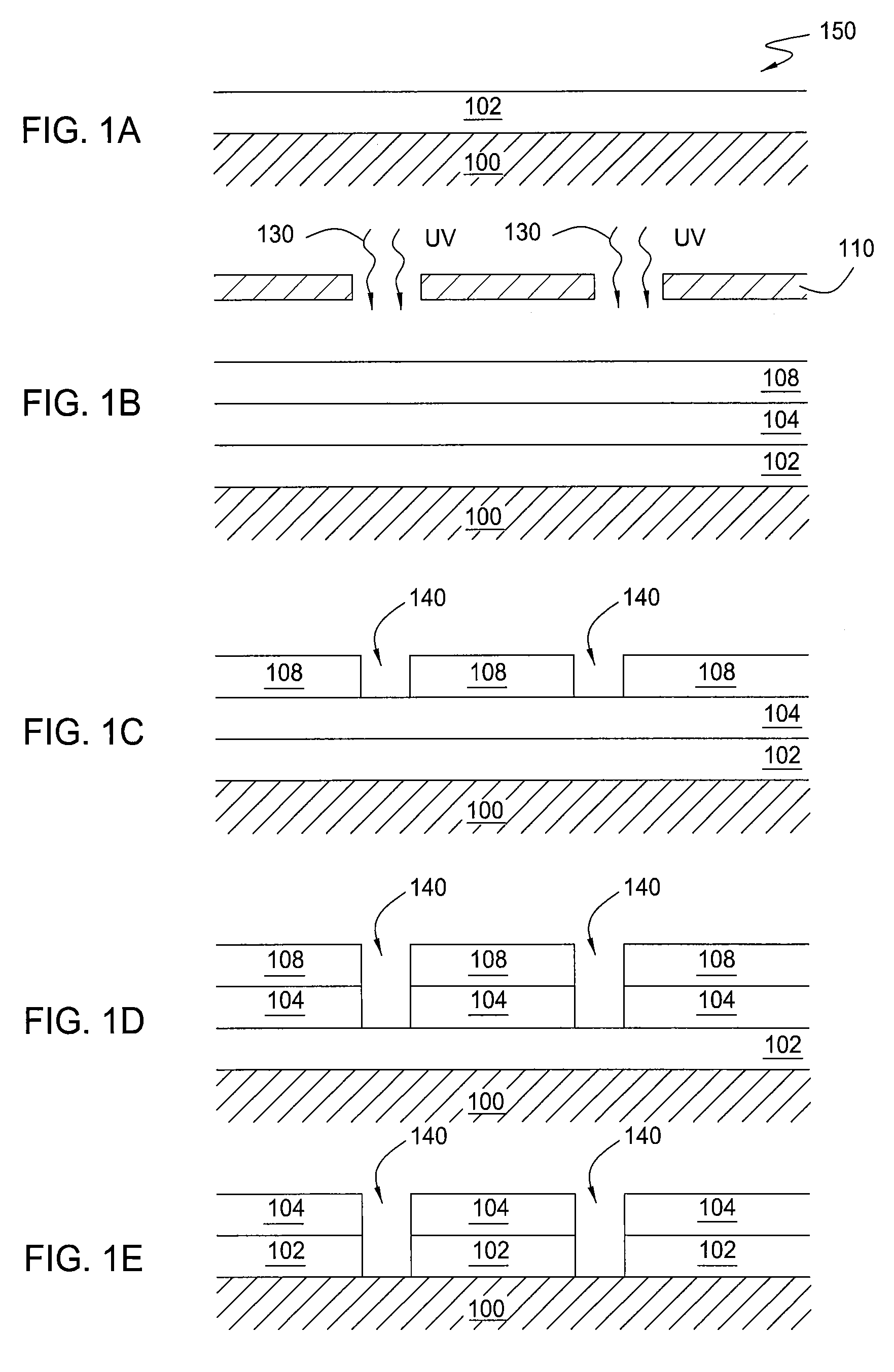
A method for sealing pores at a surface of a dielectric layer formed on a substrate, includes: providing a substrate on which a dielectric layer having a porous surface is formed as an outermost layer; placing the substrate in an evacuatable chamber; irradiating the substrate with UV light in an atmosphere of hydrocarbon and / or oxy-hydrocarbon gas; sealing pores at the porous surface of the dielectric layer as a result of the irradiation; and continuously irradiating the substrate with UV light in the atmosphere of hydrocarbon and / or oxy-hydrocarbon gas until a protective film having a desired thickness is formed on the dielectric layer as a result of the irradiation.
Owner:ASM JAPAN
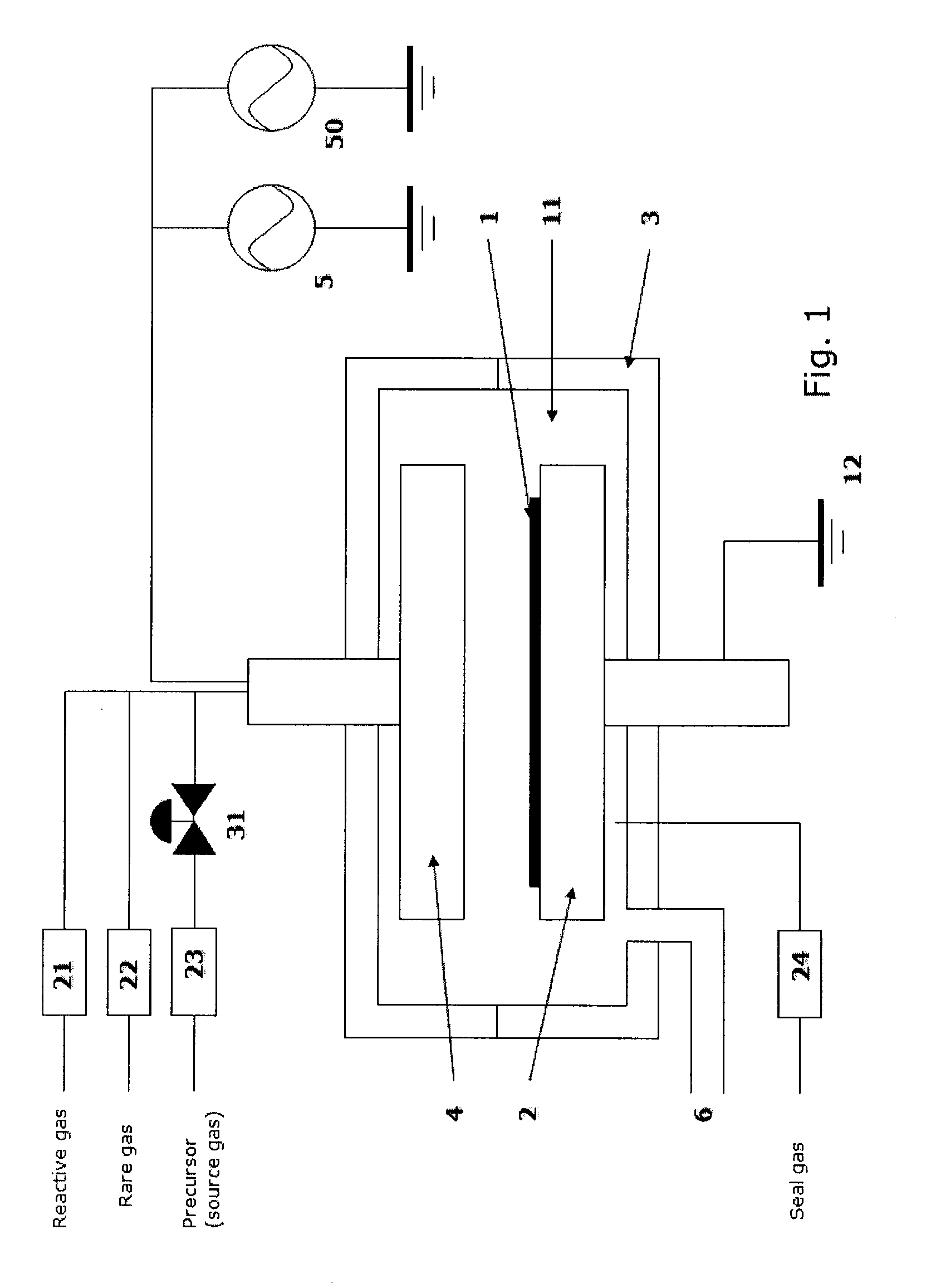
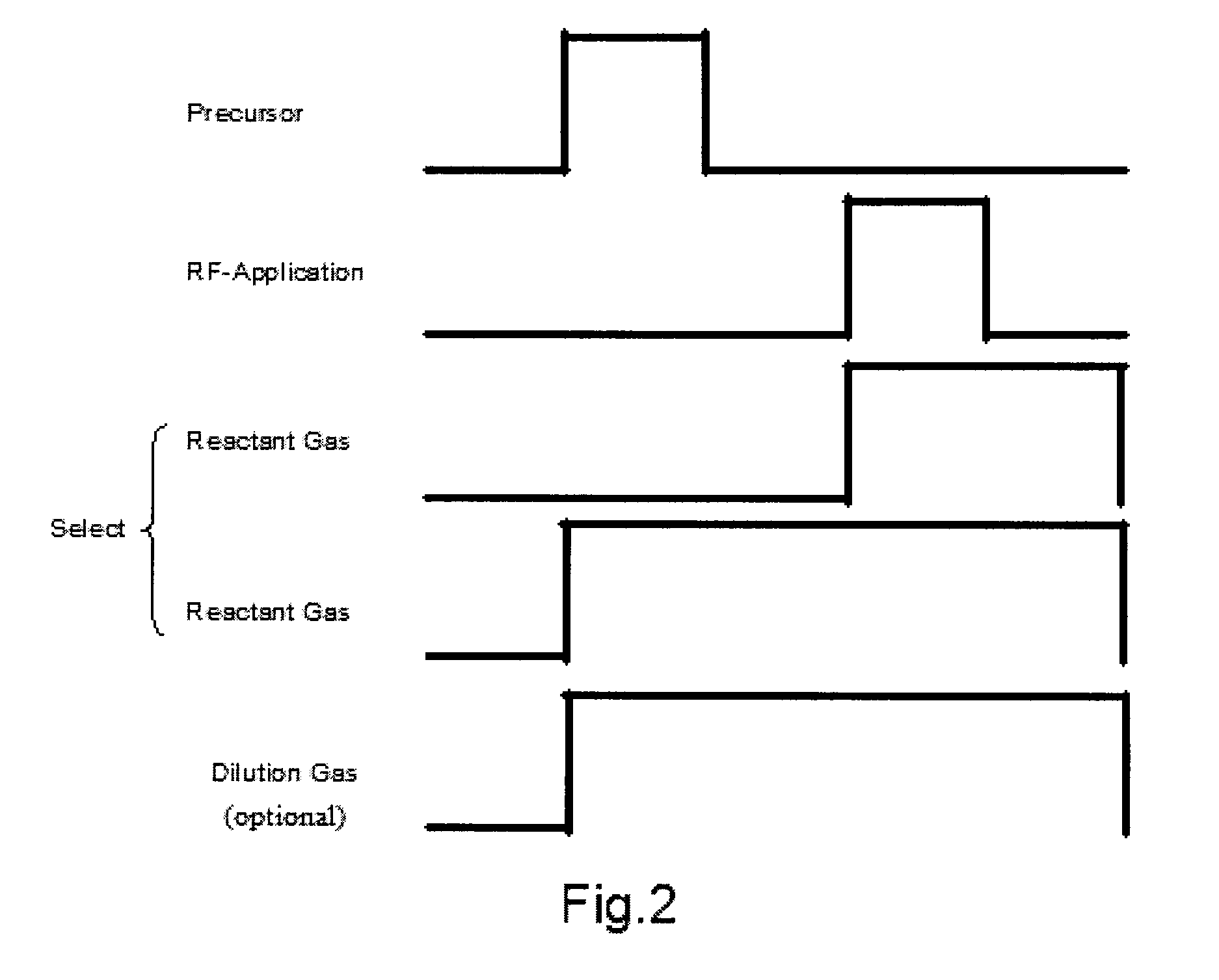
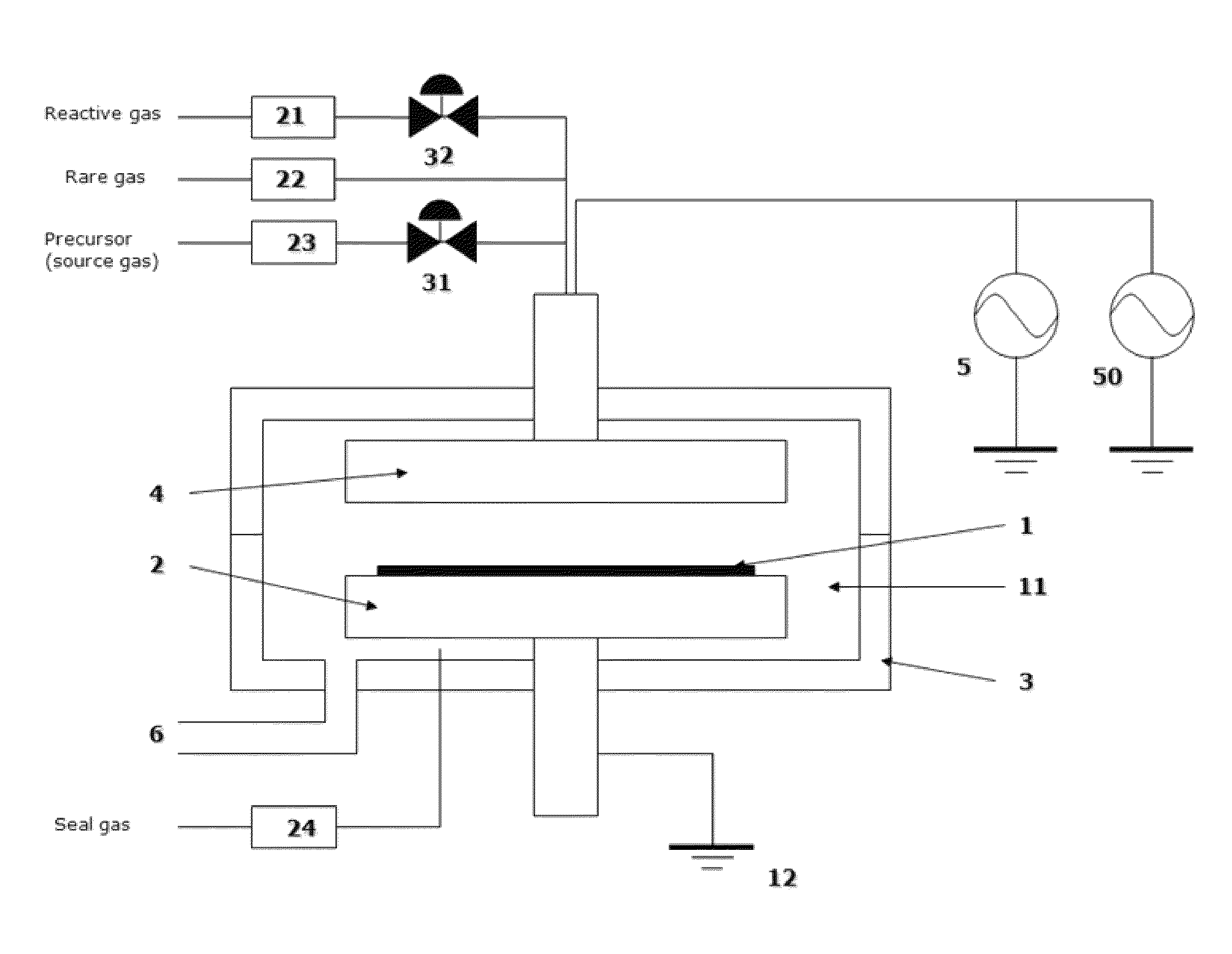
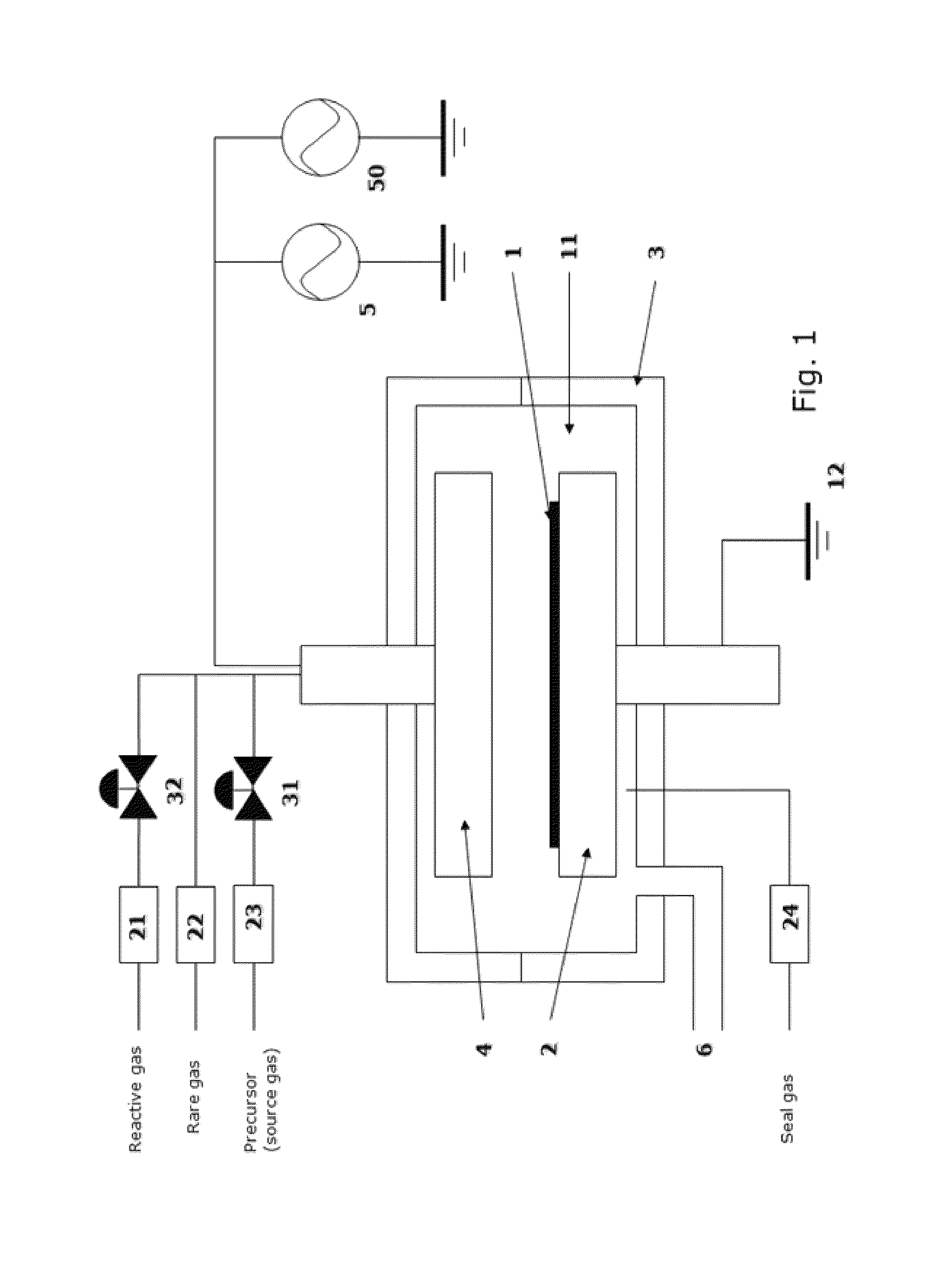
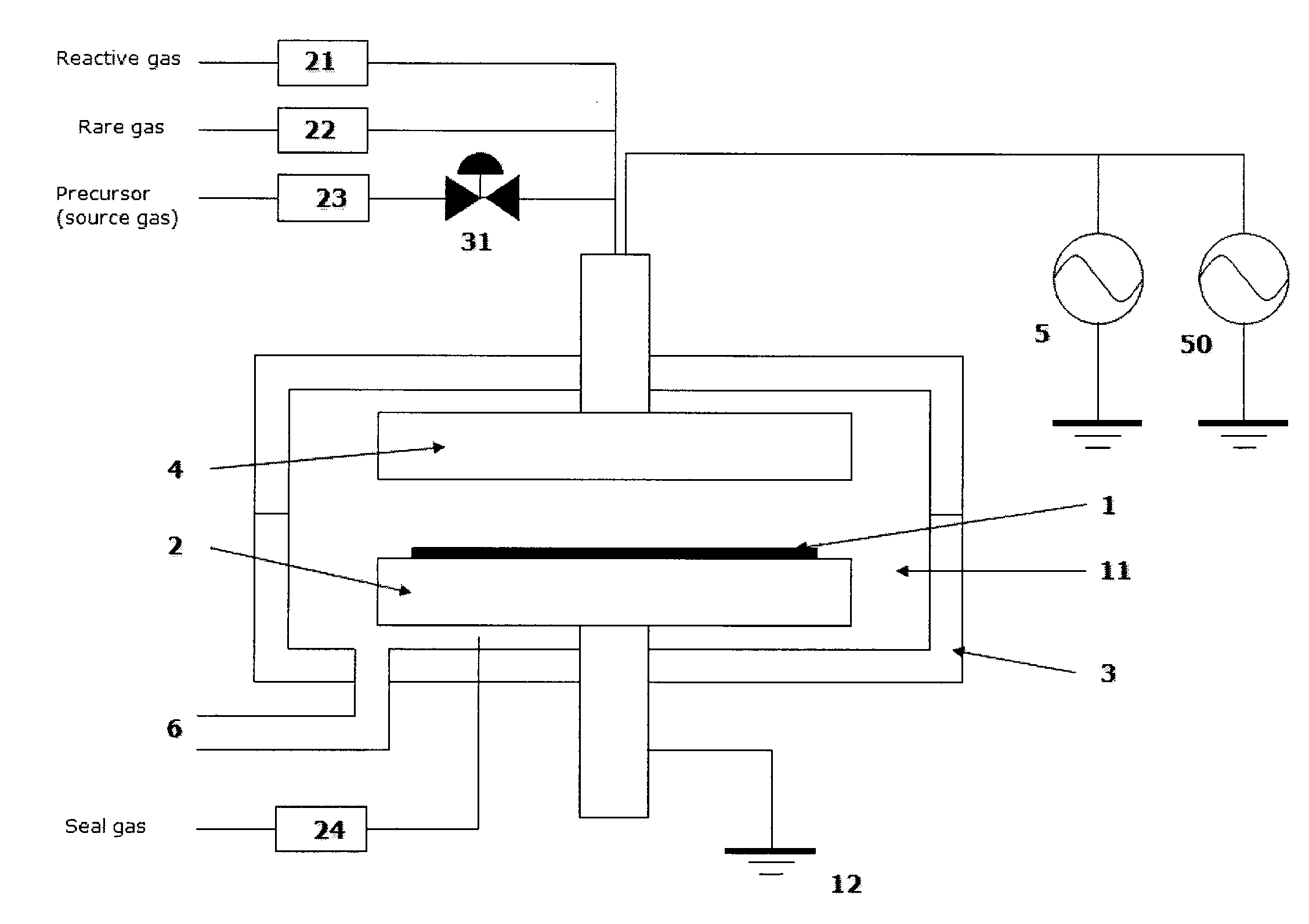
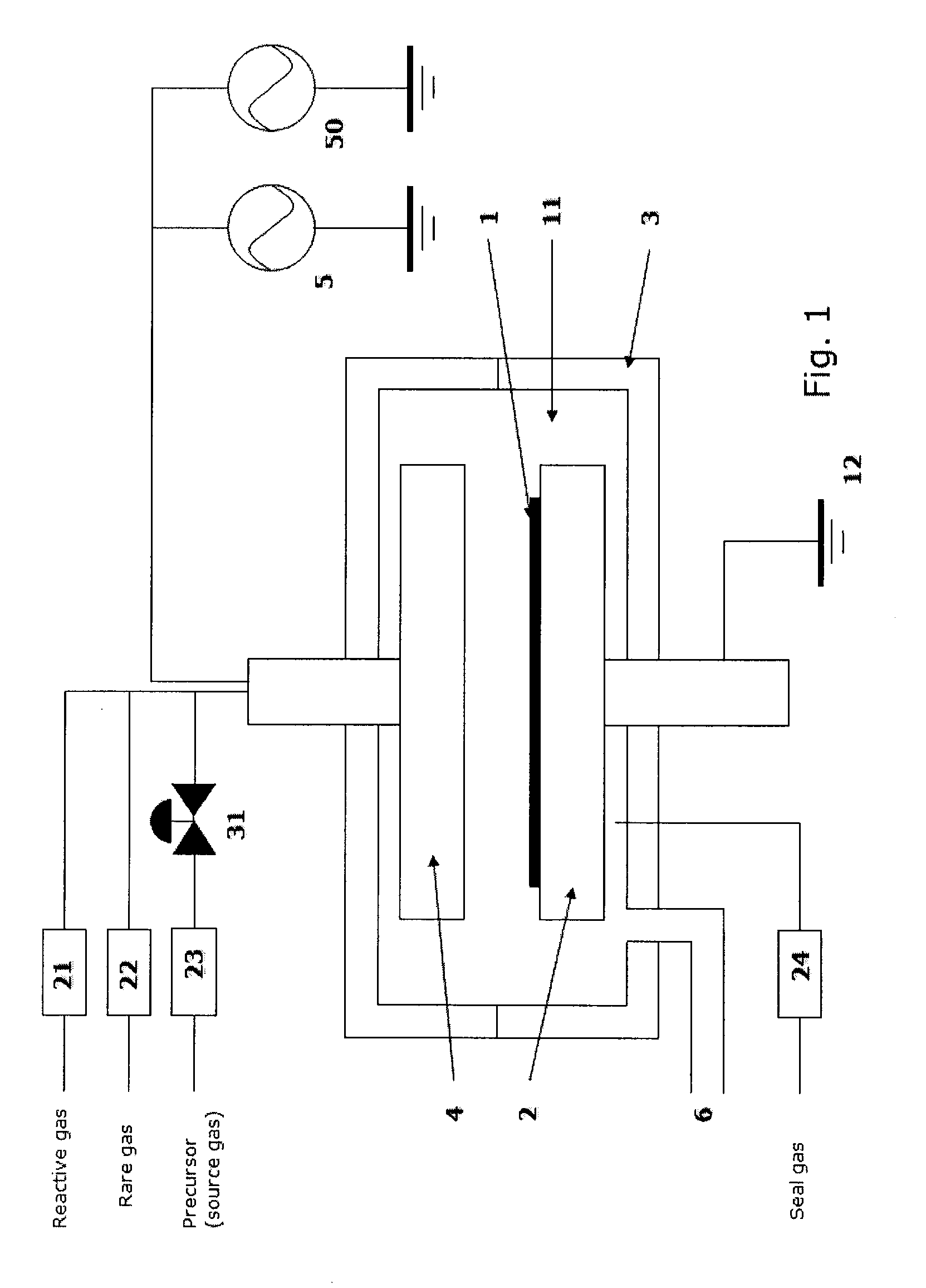
Method of depositing dielectric film by ALD using precursor containing silicon, hydrocarbon, and halogen
ActiveUS8329599B2Accelerates the carbonization processHigh conformalitySemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingChemical vapor deposition coatingDielectricHalogen
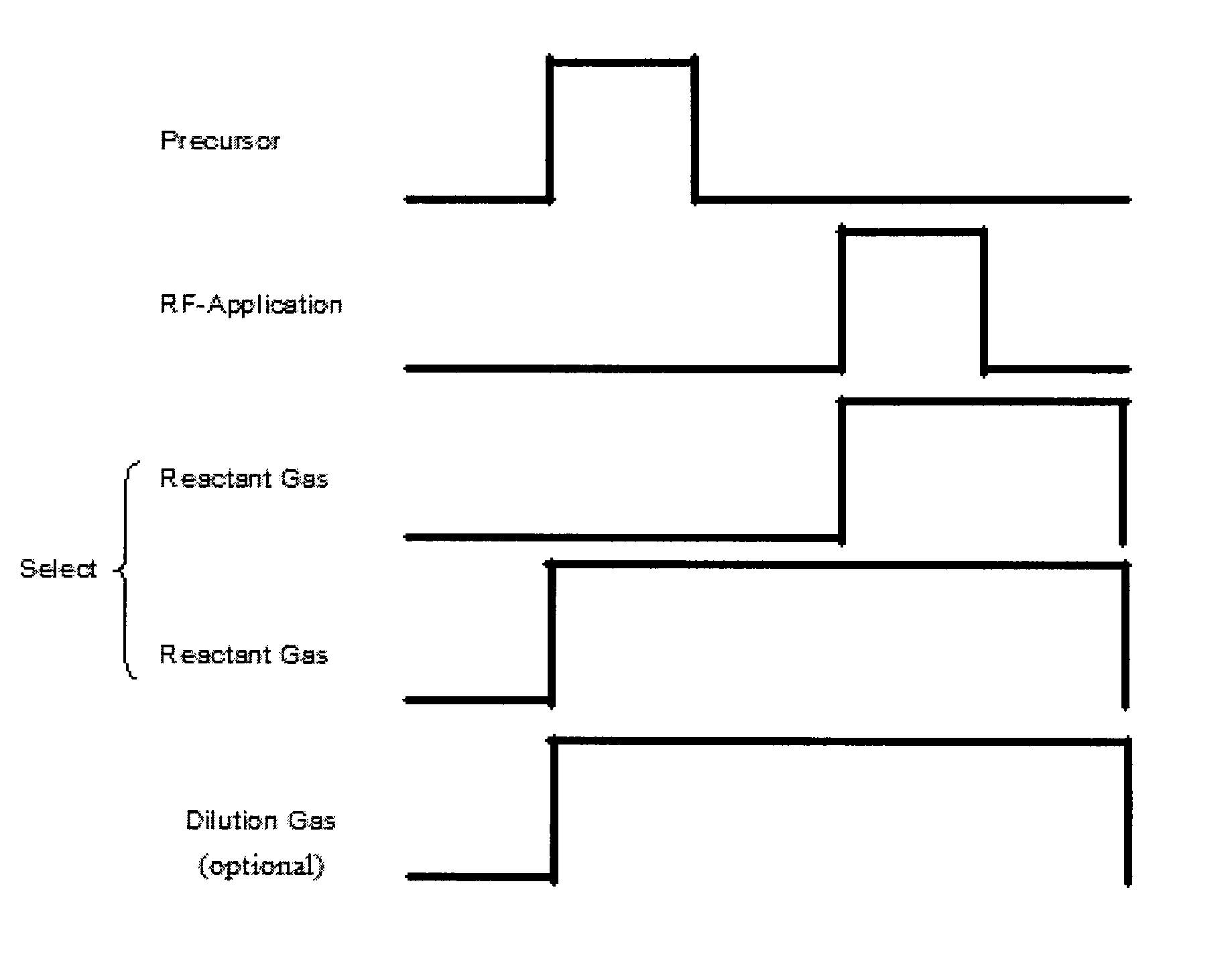
A method of forming a dielectric film having at least Si—N, Si—C, or Si—B bonds on a semiconductor substrate by atomic layer deposition (ALD), includes: adsorbing a precursor on a surface of a substrate; supplying a reactant gas over the surface; reacting the precursor and the reactant gas on the surface; and repeating the above steps to form a dielectric film having at least Si—N, Si—C, or Si—B bonds on the substrate. The precursor has at least one Si—C or Si—N bond, at least one hydrocarbon, and at least one halogen attached to silicon in its molecule.
Owner:ASM JAPAN
Method for Depositing Conformal Amorphous Carbon Film by Plasma-Enhanced Chemical Vapor Deposition (PECVD)
ActiveUS20100093187A1Good shape retentionHighly conformalSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingChemical vapor deposition coatingCarbon layerNitrogen gas
Methods and apparatus for depositing an amorphous carbon layer on a substrate are provided. In one embodiment, a deposition process includes positioning a substrate in a substrate processing chamber, introducing a hydrocarbon source having a carbon to hydrogen atom ratio of greater than 1:2 into the processing chamber, introducing a plasma initiating gas selected from the group consisting of hydrogen, helium, argon, nitrogen, and combinations thereof into the processing chamber, with the hydrocarbon source having a volumetric flow rate to plasma initiating gas volumetric flow rate ratio of 1:2 or greater, generating a plasma in the processing chamber, and forming a conformal amorphous carbon layer on the substrate.
Owner:APPLIED MATERIALS INC
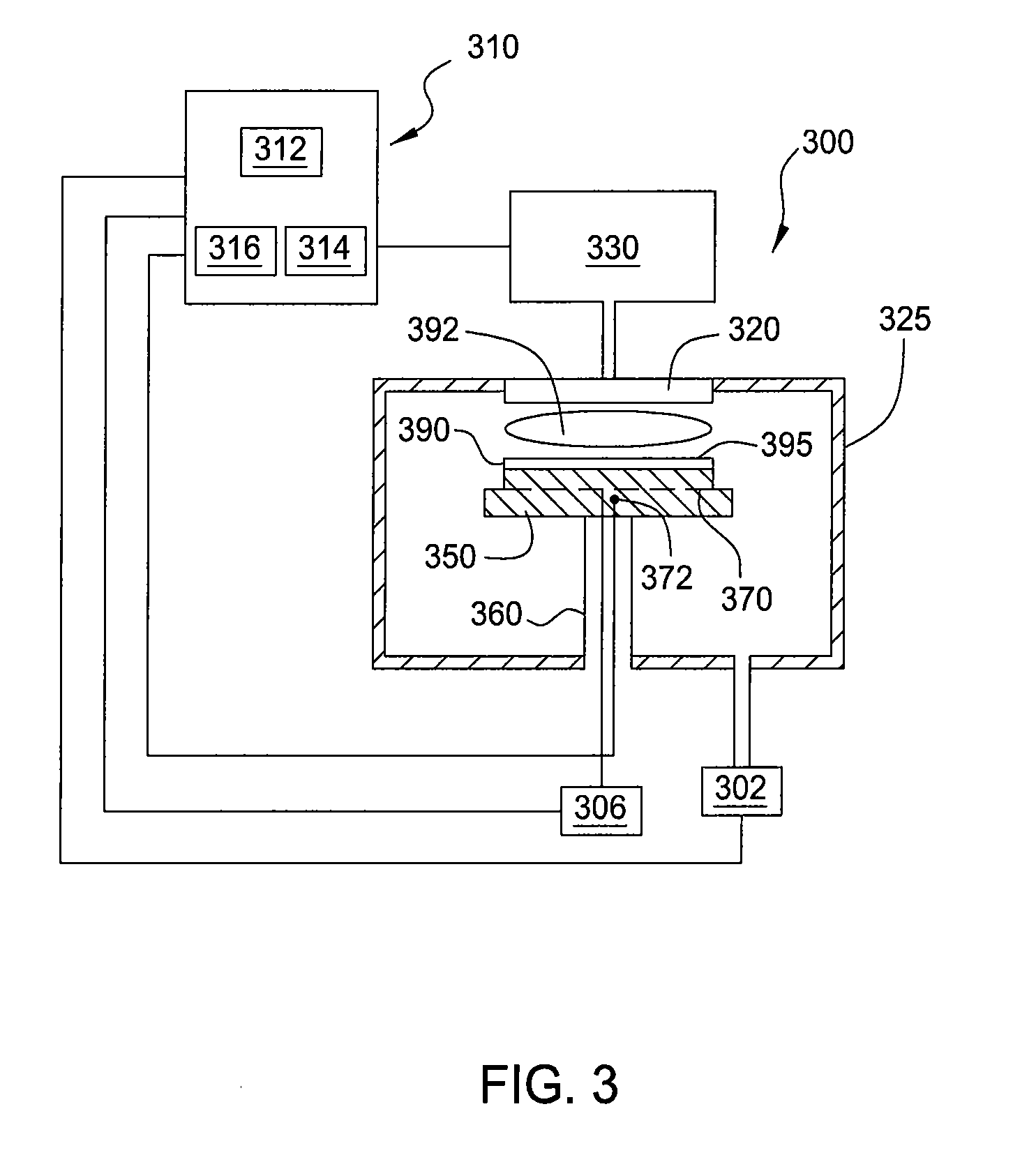
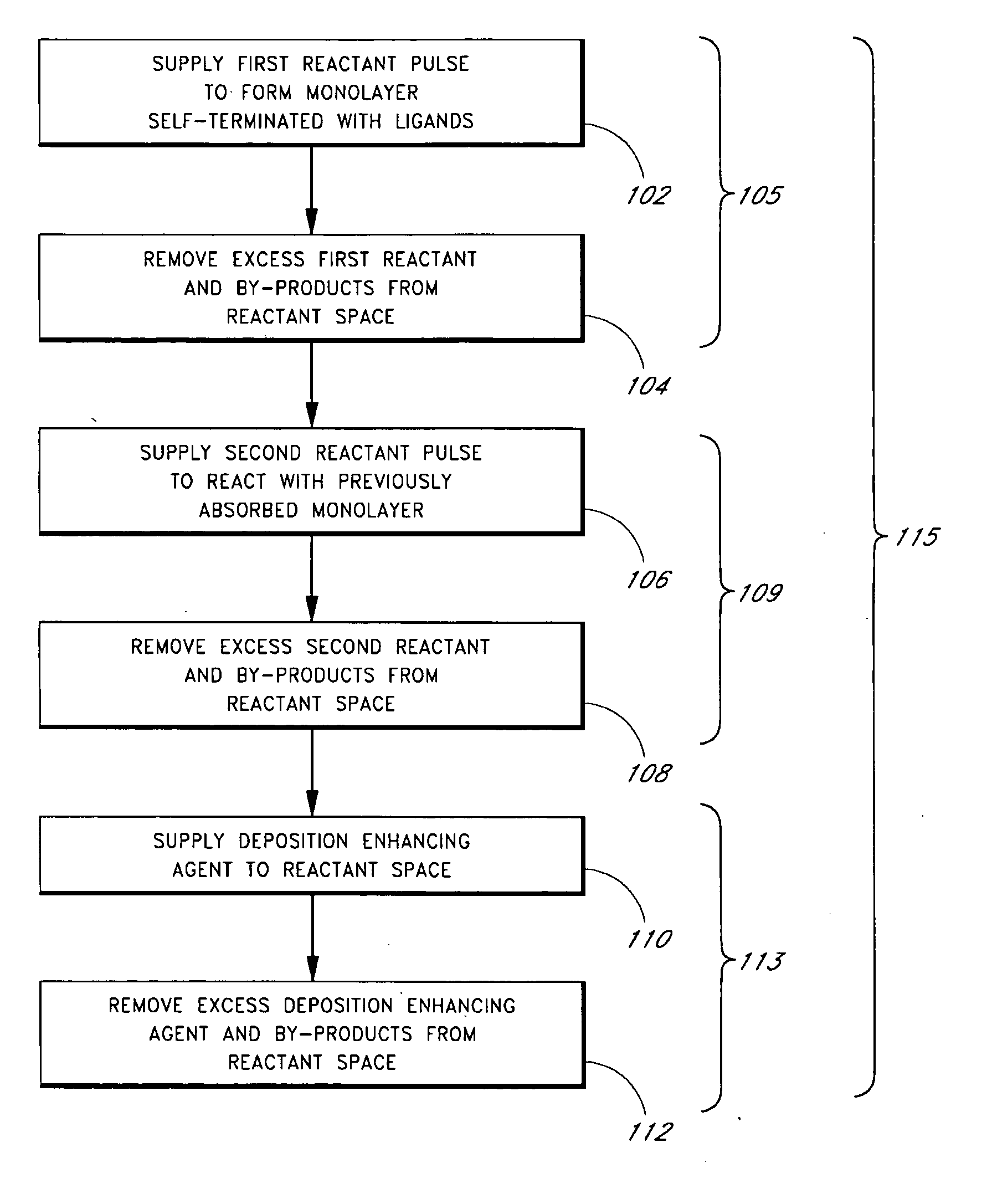
Enhanced thin film deposition
ActiveUS20070148350A1Semiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingChemical vapor deposition coatingSilanesNitrogen
Methods of producing metal-containing thin films with low impurity contents on a substrate by atomic layer deposition (ALD) are provided. The methods preferably comprise contacting a substrate with alternating and sequential pulses of a metal source chemical, a second source chemical and a deposition enhancing agent. The deposition enhancing agent is preferably selected from the group consisting of hydrocarbons, hydrogen, hydrogen plasma, hydrogen radicals, silanes, germanium compounds, nitrogen compounds, and boron compounds. In some embodiments, the deposition-enhancing agent reacts with halide contaminants in the growing thin film, improving film properties.
Owner:ASM INTERNATIONAL
Lubricant and fuel compositions containing hydroxy carboxylic acid and hydroxy polycarboxylic acid esters
InactiveUS20050198894A1Reduce the amount requiredWithout diminishing anti-wear performanceOrganic chemistryLiquid carbonaceous fuelsCarboxylic acidMedicinal chemistry
Disclosed herein is a composition comprising: (A) a lubricant or a hydrocarbon fuel; (B) at least one hydroxy carboxylic acid ester or hydroxy polycarboxylic acid ester having the generic formula defined herein; and (C) at least one phosphorus-containing additive.
Owner:CHEMTURA CORP
Method of forming conformal dielectric film having Si-N bonds by PECVD
ActiveUS7972980B2Increase deposition rateHigh conformalitySemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesDielectricNoble gas
Owner:ASM JAPAN
Thermal processes for subsurface formations
A process may include providing heat from one or more heaters to at least a portion of a subsurface formation. Heat may transfer from one or more heaters to a part of a formation. In some embodiments, heat from the one or more heat sources may pyrolyze at least some hydrocarbons in a part of a subsurface formation. Hydrocarbons and / or other products may be produced from a subsurface formation. Certain embodiments describe apparatus, methods, and / or processes used in treating a subsurface or hydrocarbon containing formation.
Owner:SHELL OIL CO
Production of synthetic lubricant and lubricant base stock without dewaxing
InactiveUS6103099AThermal non-catalytic crackingRefining to change hydrocarbon structural skeletonAutomatic transmissionBoiling point
A lubricating base stock useful for forming lubricants such as a multigrade automotive oils, automatic transmission oils, greases and the like is prepared by hydroisomerizing a waxy hydrocarbon feed fraction having an initial boiling point in the 650-750 DEG F. range and an end point of at least 1050 DEG F., synthesized by a slurry Fischer-Tropsch hydrocarbon synthesis process. The hydroisomerization forms a hydroisomerate containing the desired base stock which is recovered, without dewaxing the hydroisomerate. The hydroisomerization is conducted at conditions effective to convert at least 67 wt. % of the 650-750 DEG F.+ waxy feed hydrocarbons to lower boiling hydrocarbons. When combined with a standard lubricant additive package, these base stocks have been formed into multigrade automotive crankcase oils, transmission oils and hydraulic oils meeting the specifications for these oils.
Owner:EXXON RES & ENG CO
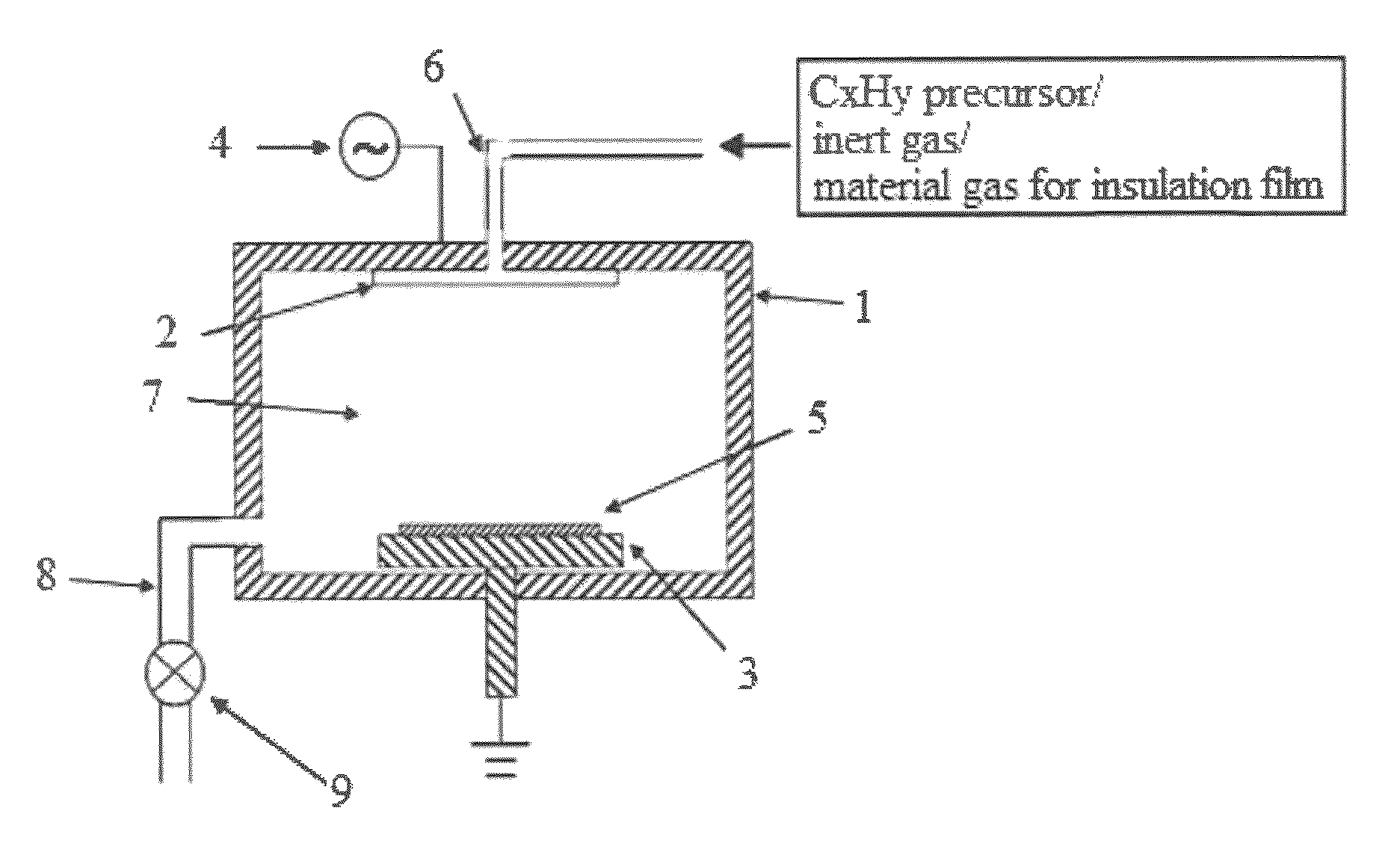
Sealing pores of low-k dielectrics using CxHy
A semiconductor method of manufacturing involving porous and / or carbon containing, low-k dielectrics is provided. The method includes forming a hydrocarbon of the general composition CxHy on the surface of the low-k dielectric. The hydrocarbon layer includes depositing a precursor material, preferably C2H4 or (CH3)2CHC6H6CH3. In accordance with embodiments of this invention, carbon diffuses into the low-k dielectric, thereby reducing carbon depletion damage caused by plasma processing or etching. Surface dielectric pores damaged by plasma processing are also repaired by sealing them with the CXHY layer. Embodiments include semiconductor devices, such as devices having damascene interconnect structures, manufacturing using methods provided.
Owner:TAIWAN SEMICON MFG CO LTD
Deposition of low dielectric constant films by N2O addition
InactiveUS20050214457A1Semiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingChemical vapor deposition coatingOxygenHydrocarbon
A method for depositing a low dielectric constant film includes providing a gas mixture including a cyclic organosiloxane and N2O as an oxidizing gas to a chamber and applying RF power to the gas mixture to deposit a low dielectric constant film. The gas mixture may also include oxygen and / or a linear hydrocarbon. In one aspect, the gas mixture includes N2O and oxygen as oxidizing gases, and a ratio of the flow rate of the N2O to a total flow rate of the N2O and the oxygen is between about 0.1 and about 0.5.
Owner:APPLIED MATERIALS INC
Method For Depositing an Amorphous Carbon Film with Improved Density and Step Coverage
ActiveUS20080003824A1High densityLower thermal budgetPretreated surfacesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingCarbon layerKrypton
A method for depositing an amorphous carbon layer on a substrate includes the steps of positioning a substrate in a chamber, introducing a hydrocarbon source into the processing chamber, introducing a heavy noble gas into the processing chamber, and generating a plasma in the processing chamber. The heavy noble gas is selected from the group consisting of argon, krypton, xenon, and combinations thereof and the molar flow rate of the noble gas is greater than the molar flow rate of the hydrocarbon source. A post-deposition termination step may be included, wherein the flow of the hydrocarbon source and the noble gas is stopped and a plasma is maintained in the chamber for a period of time to remove particles therefrom.
Owner:APPLIED MATERIALS INC
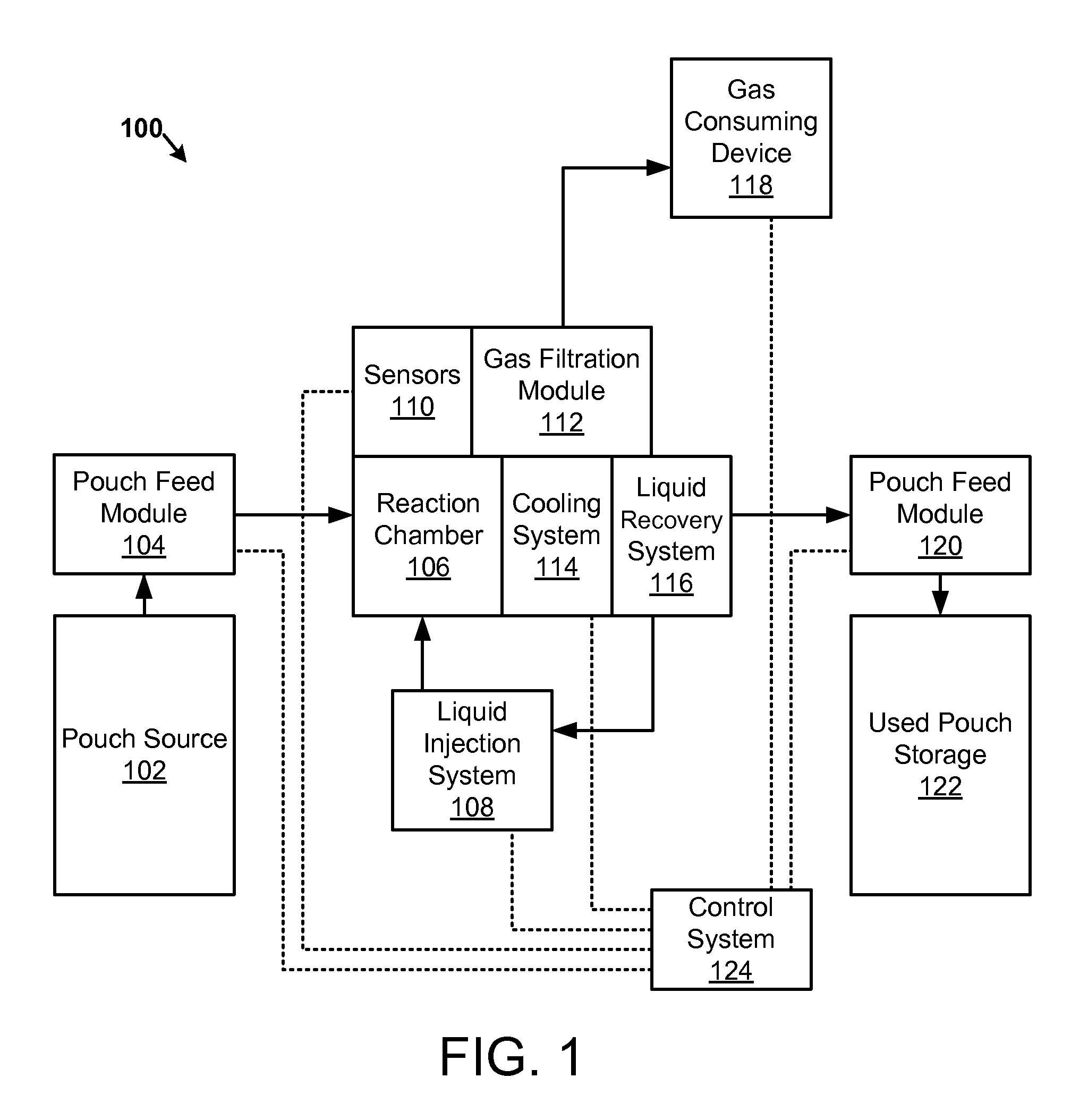
Apparatus, system, and method for generating a gas from solid reactant pouches
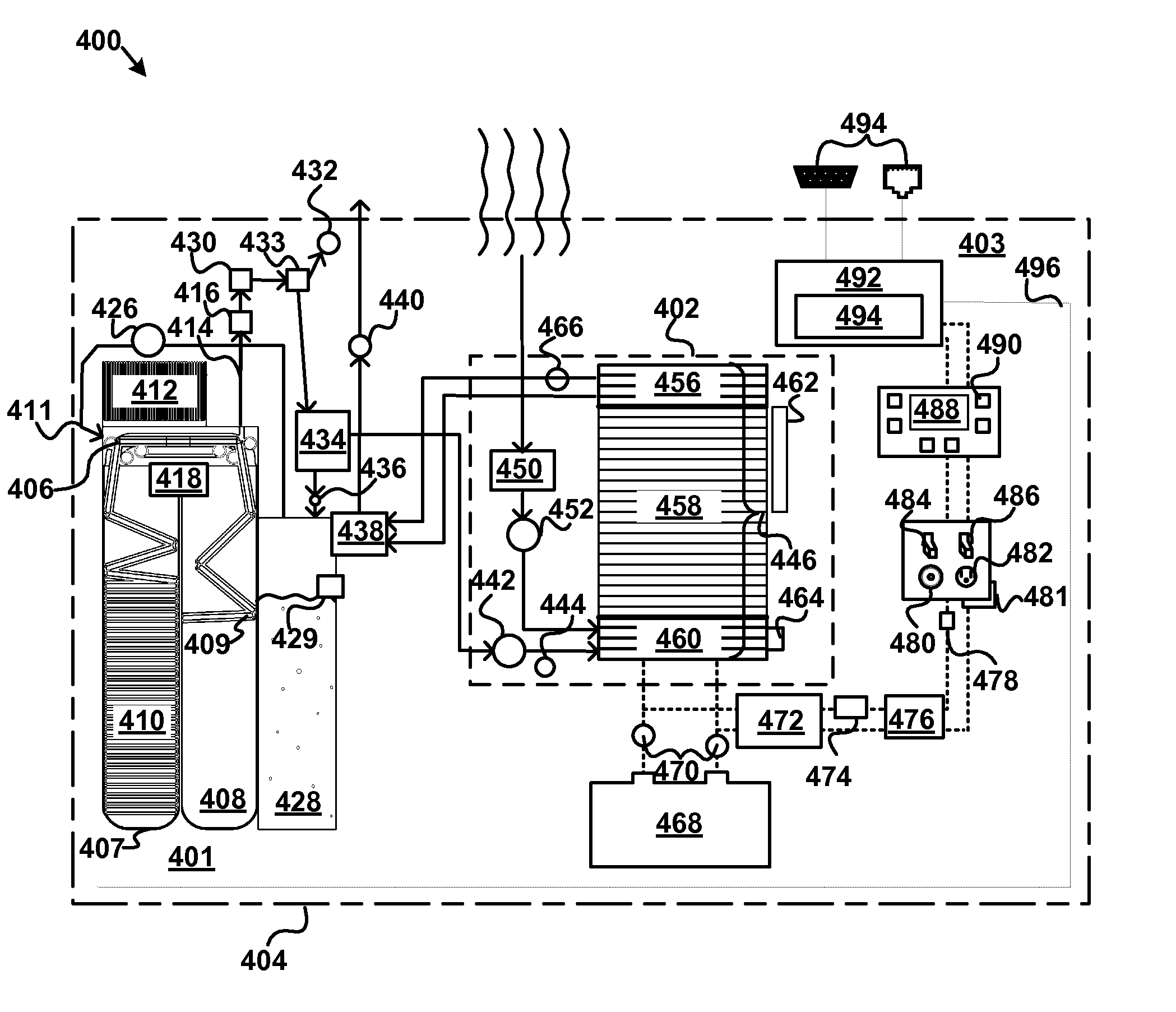
An apparatus, system, and method are disclosed for generating a gas. One or more liquid permeable pouches each define a cavity that contains a solid anhydrous reactant, such as a chemical hydride. A reaction chamber made of a heat, chemical and / or pressure resistant material receives the one or more pouches from a pouch feeder that transfers the one or more pouches into the reaction chamber successively at a feed rate. One or more liquid sources inject a liquid reactant into the reaction chamber so that the liquid reactant contacts a portion of the one or more pouches. The one or more liquid sources inject the liquid reactant at an injection rate that corresponds to the feed rate. A gas outlet releases a gas, such as hydrogen, oxygen, ammonia, borazine, nitrogen, or a hydrocarbon, that is produced by a reaction between the solid reactant and the liquid reactant.
Owner:TRULITE INC
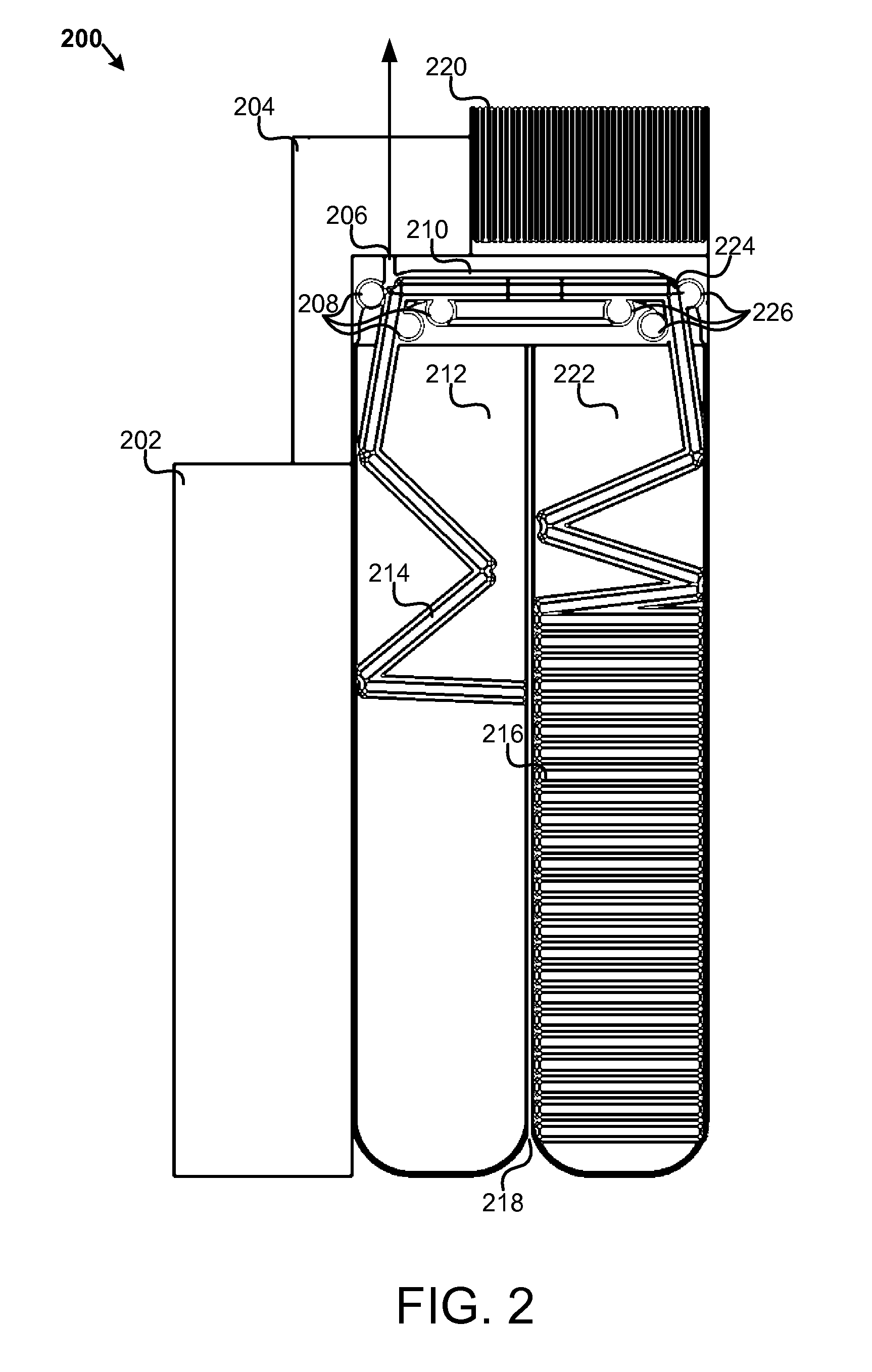
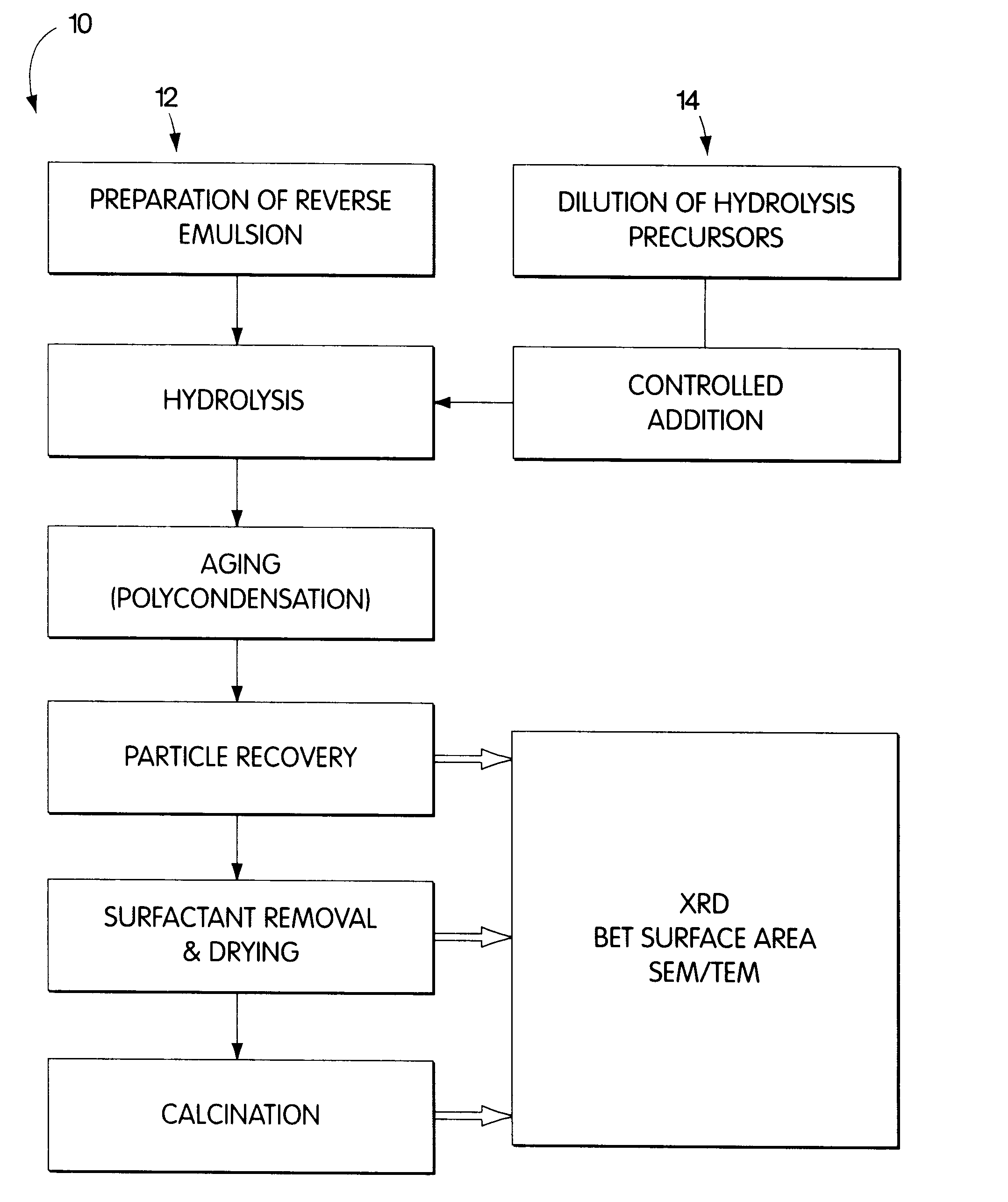
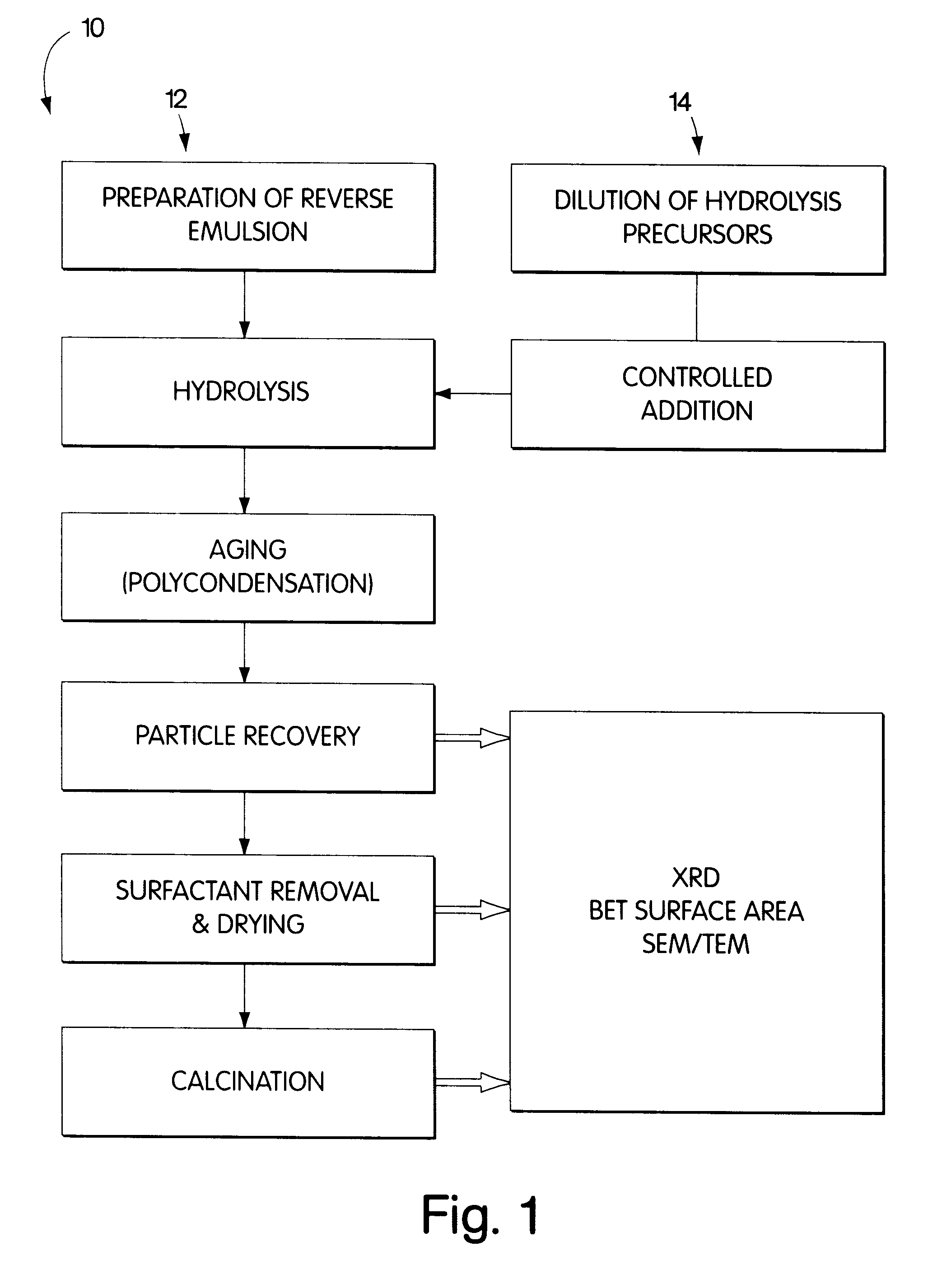
Synthesis of nanometer-sized particles by reverse micelle mediated techniques
The present invention relates to a method of producing particles having a particle size of less than 100 nm and surface areas of at least 20 m2 / g where the particles are free from agglomeration. The method involves synthesizing the particles within an emulsion having a 1-40% water content to form reverse micelles. In particular, the particles formed are metal oxide particles. The particles can be used to oxidize hydrocarbons, particularly methane.
Owner:MASSACHUSETTS INST OF TECH
Purine derivative
PCT No. PCT / JP97 / 02310 Sec. 371 Date Mar. 3, 1998 Sec. 102(e) Date Mar. 3, 1998 PCT Filed Jul. 3, 1997 PCT Pub. No. WO98 / 01448 PCT Pub. Date Jan. 15, 1998This invention relates to novel purine derivatives of formula (I): where R2 and R9 are hydrocarbon groups, R6 is an amino group and R8 is a hydroxyl, or acyloxy group. These purine derivatives are effective at promoting secretion of interferon in patients, and can be used to treat diseases against which interferon is effective.
Owner:SUMITOMO DAINIPPON PHARMA CO LTD
Method of depositing dielectric film by ALD using precursor containing silicon, hydrocarbon, and halogen
ActiveUS8563443B2Accelerates the carbonization processHigh conformalitySemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingChemical vapor deposition coatingDielectricHalogen
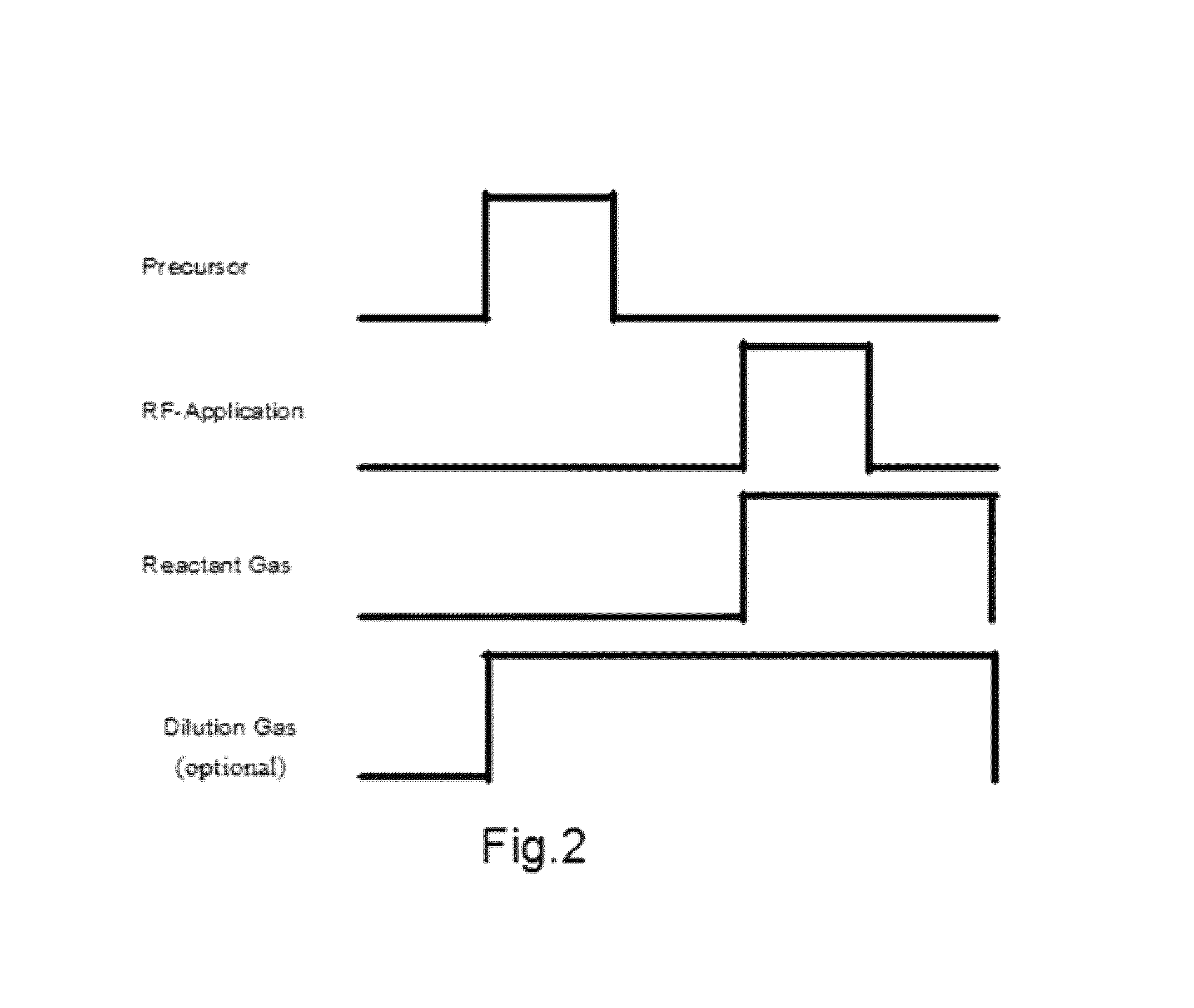
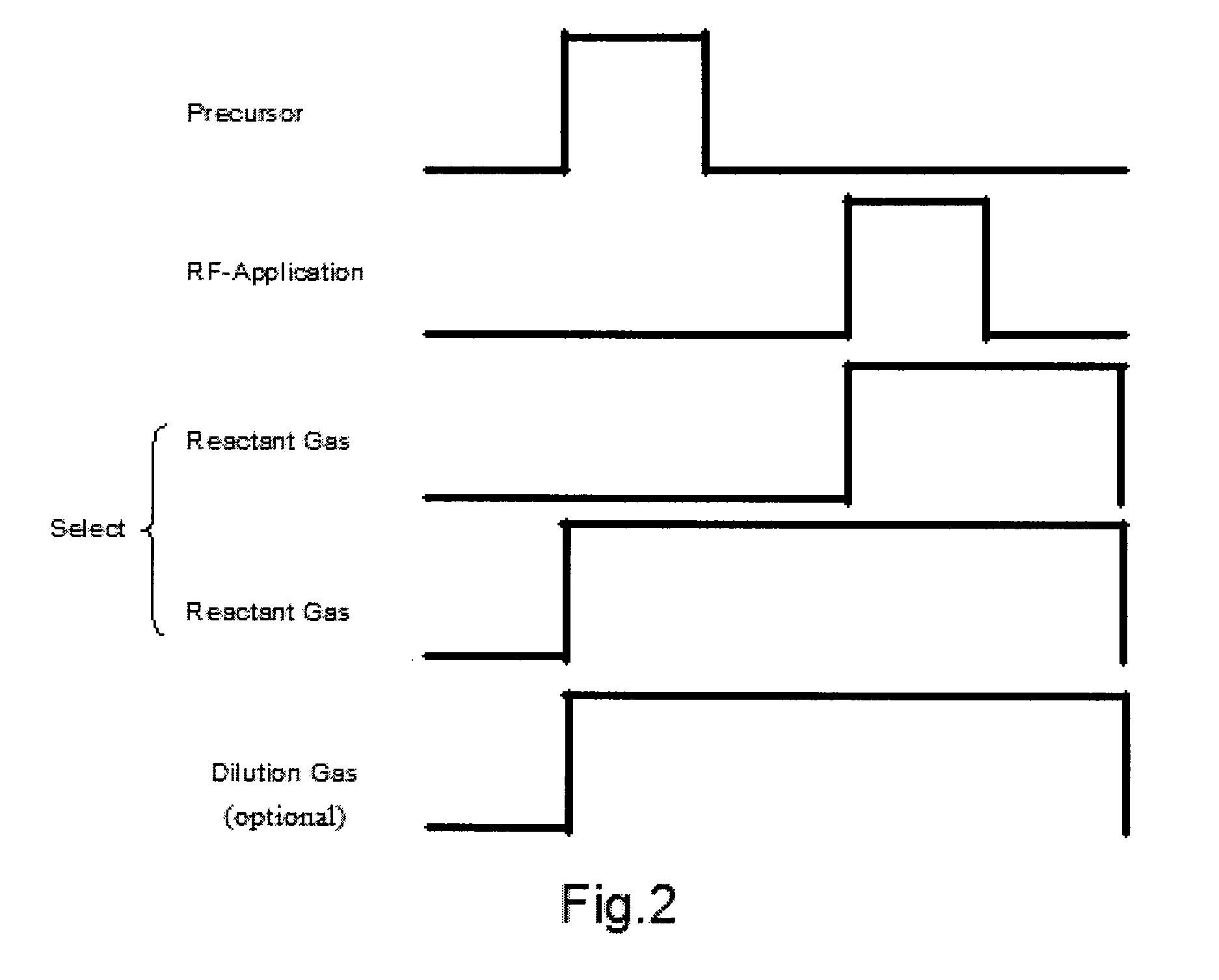
A method of forming a dielectric film having at least Si—N, Si—C, or Si—B bonds on a semiconductor substrate by atomic layer deposition (ALD), includes: supplying a precursor in a pulse to adsorb the precursor on a surface of a substrate; supplying a reactant gas in a pulse over the surface without overlapping the supply of the precursor; reacting the precursor and the reactant gas on the surface; and repeating the above steps to form a dielectric film having at least Si—N, Si—C, or Si—B bonds on the substrate. The precursor has at least one Si—C or Si—N bond, at least one hydrocarbon, and at least two halogens attached to silicon in its molecule.
Owner:ASM JAPAN
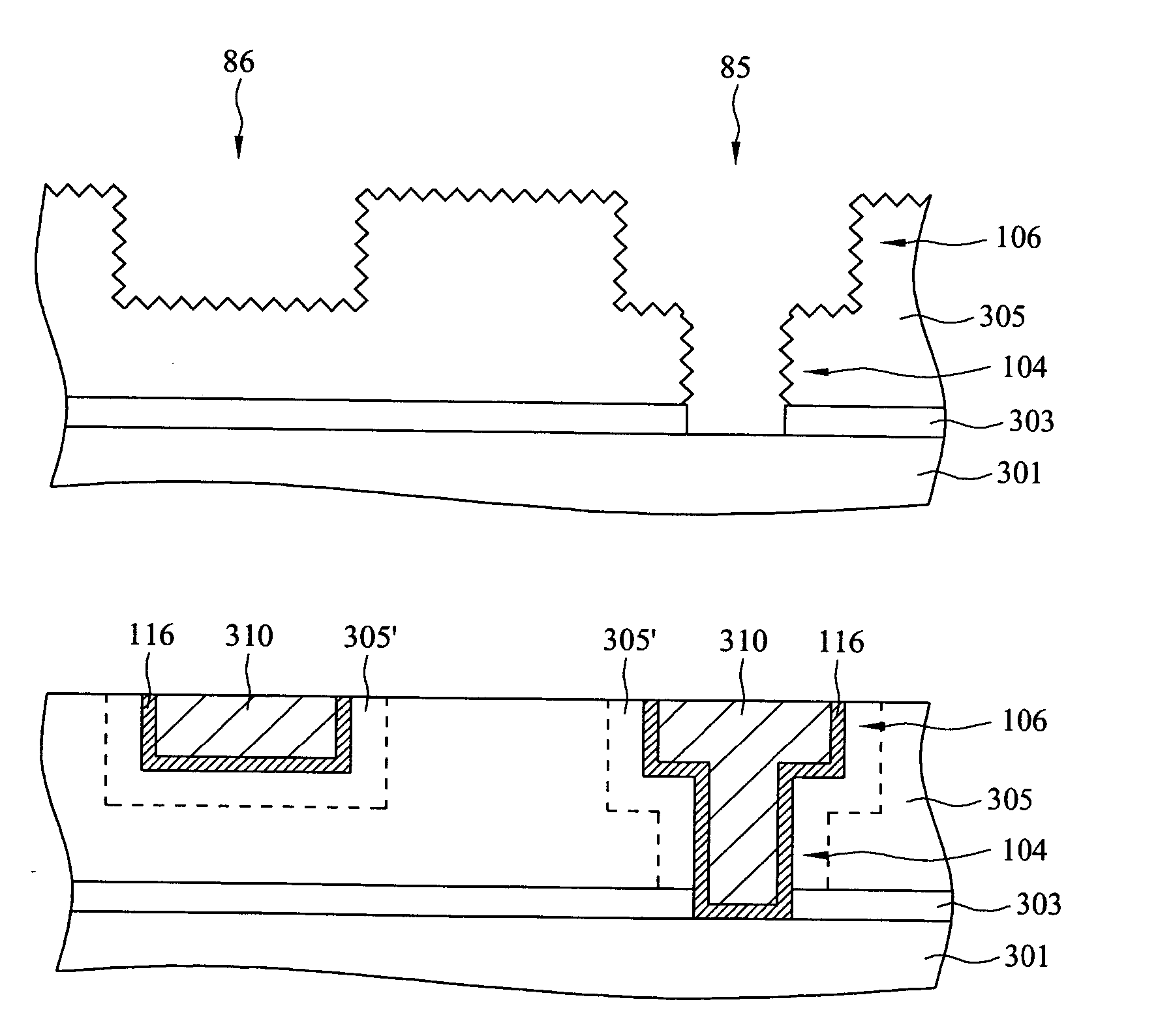
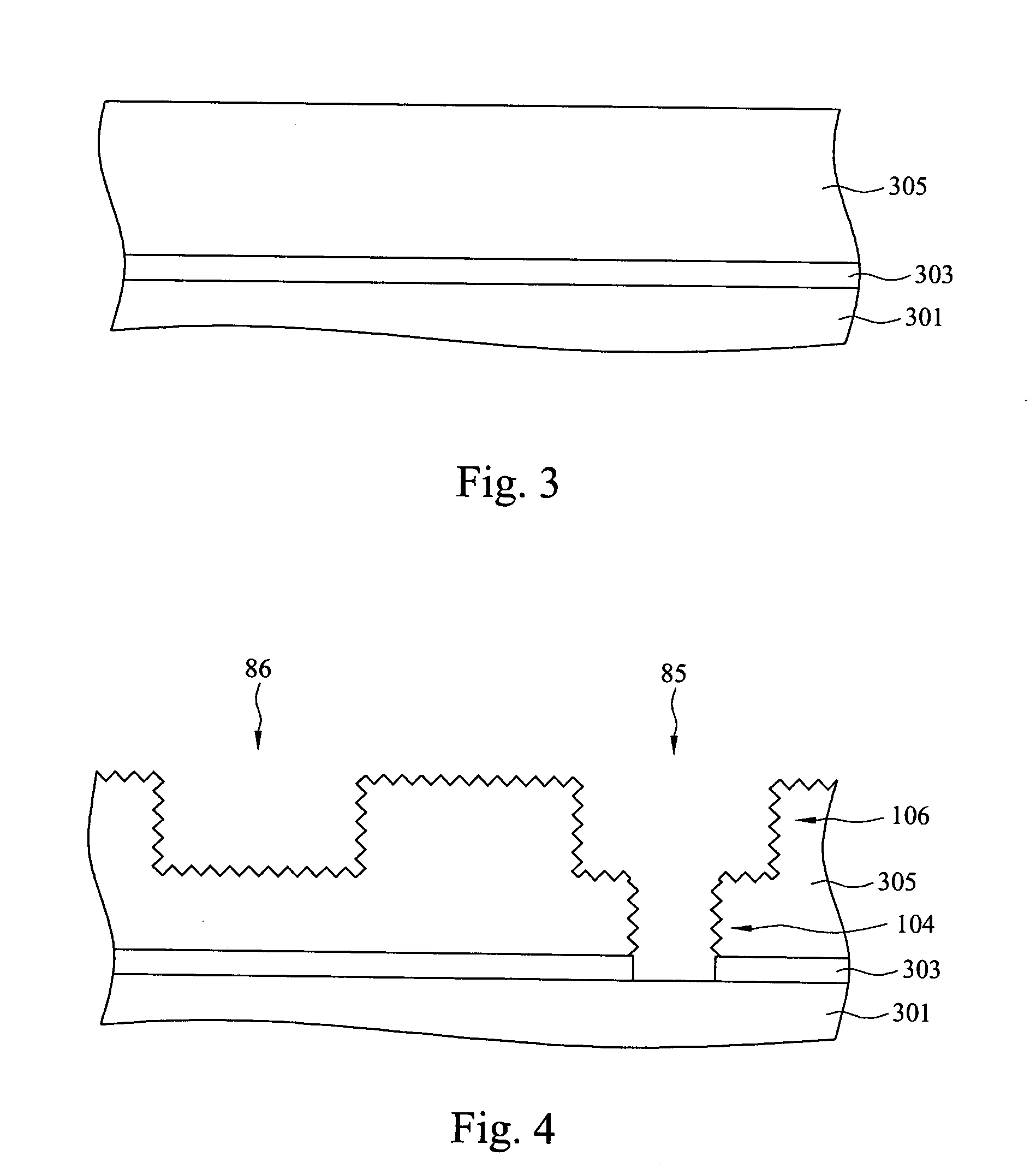
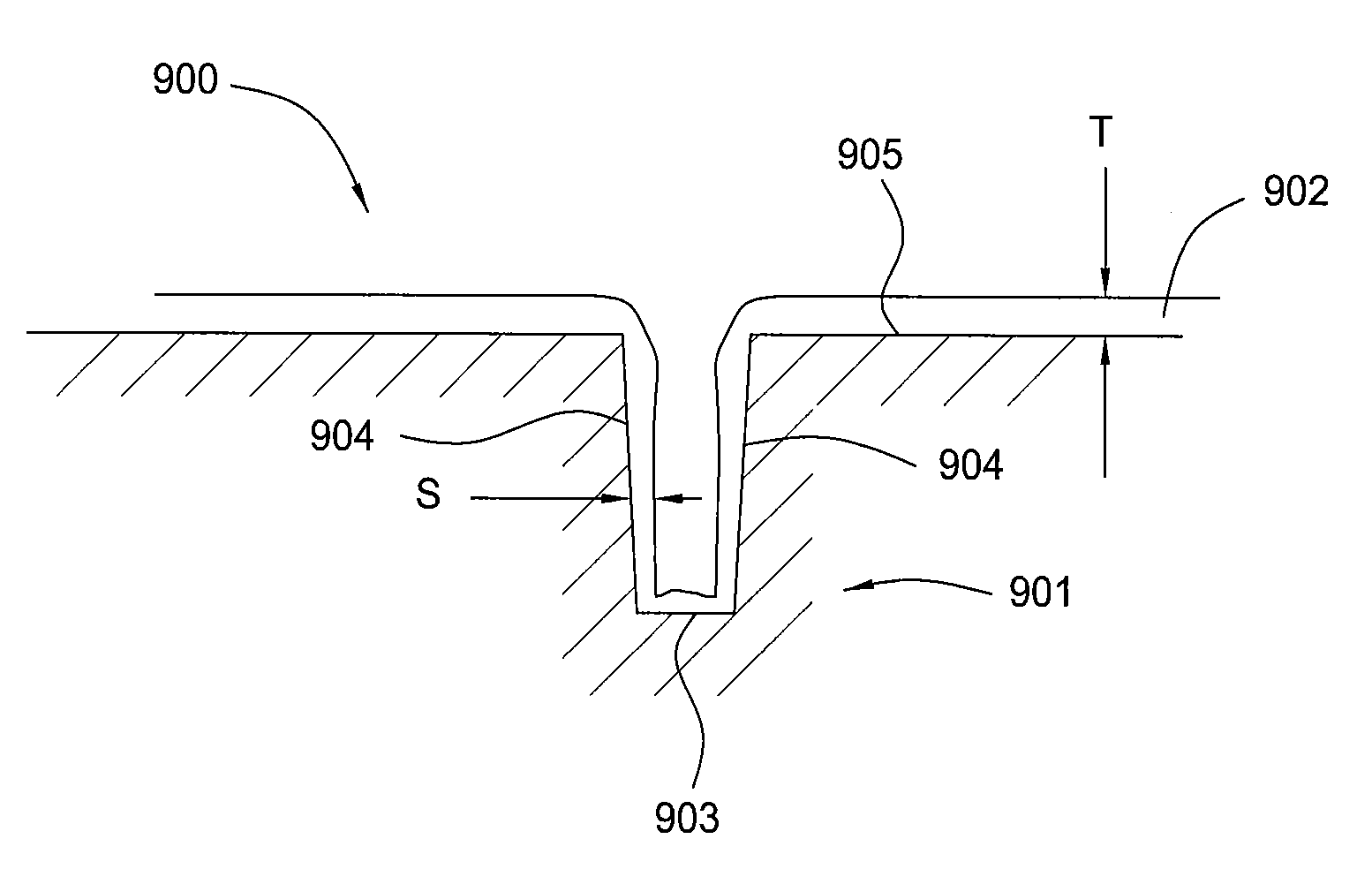
Method for filling recesses using pre-treatment with hydrocarbon-containing gas
ActiveUS9117657B2Improve flatnessHighly effectiveSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingChemical vapor deposition coatingPre treatmentPre deposition
A method for filling recesses of a substrate with an insulation film includes: (i) exposing surfaces of the recesses of the substrate to a pre-deposition gas in a reactive state in a reaction space to treat the surfaces with reactive hydrocarbons generated from the pre-deposition gas without filling the recesses; and (ii) depositing a flowable insulation film using a process gas other than the pre-deposition gas on a surface of the substrate to fill the recesses treated in step (i) therewith by plasma reaction. The pre-deposition gas has at least one hydrocarbon unit in its molecule.
Owner:ASM IP HLDG BV
Tire and tread comprising a bis-alkoxysilane tetrasulfide as coupling agent
Owner:MICHELIN & CO CIE GEN DES ESTAB MICHELIN
Method of forming a high transparent carbon film
ActiveUS7632549B2Improve featuresRich varietyLiquid surface applicatorsSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingCarbon filmProduct gas
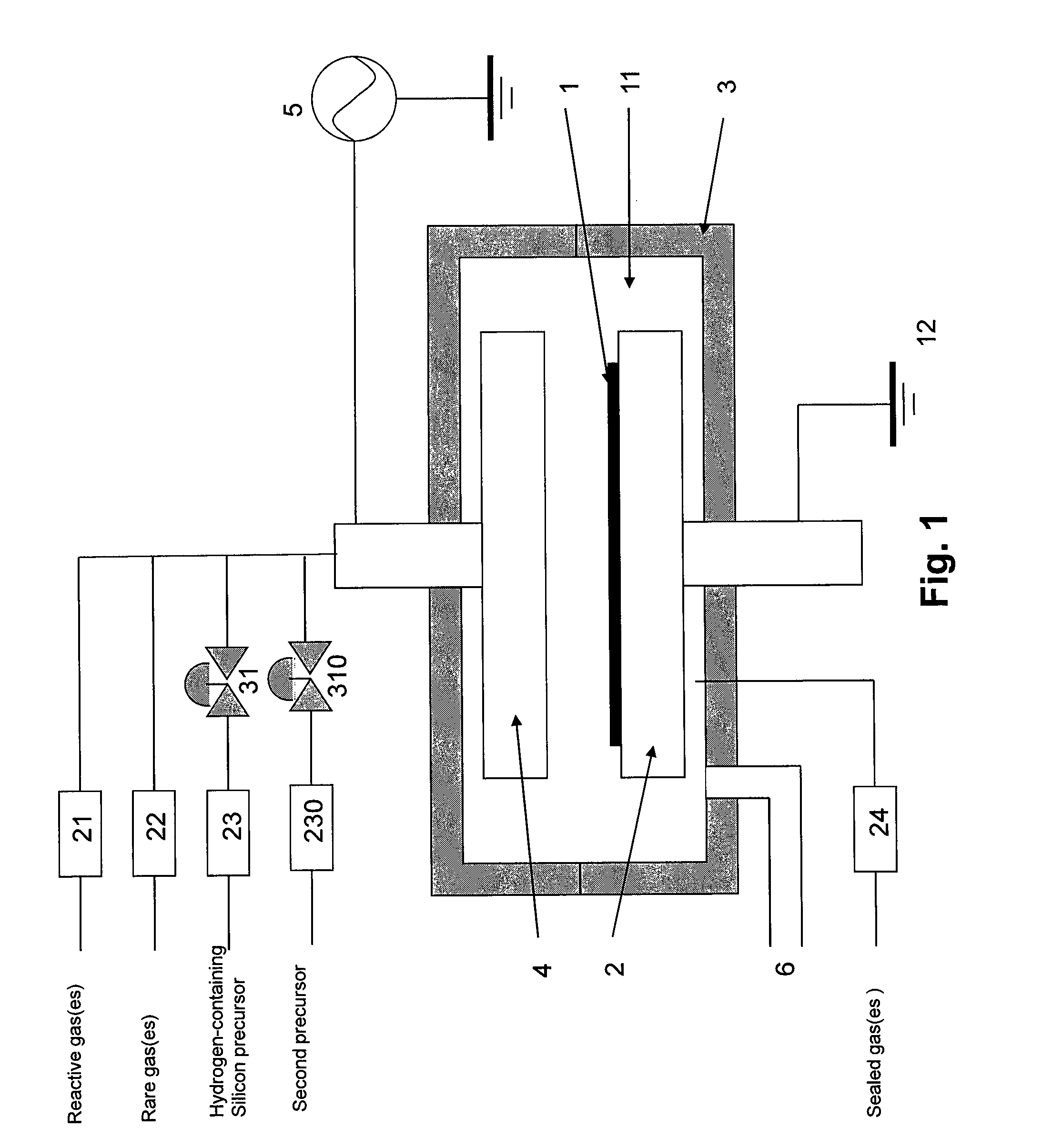
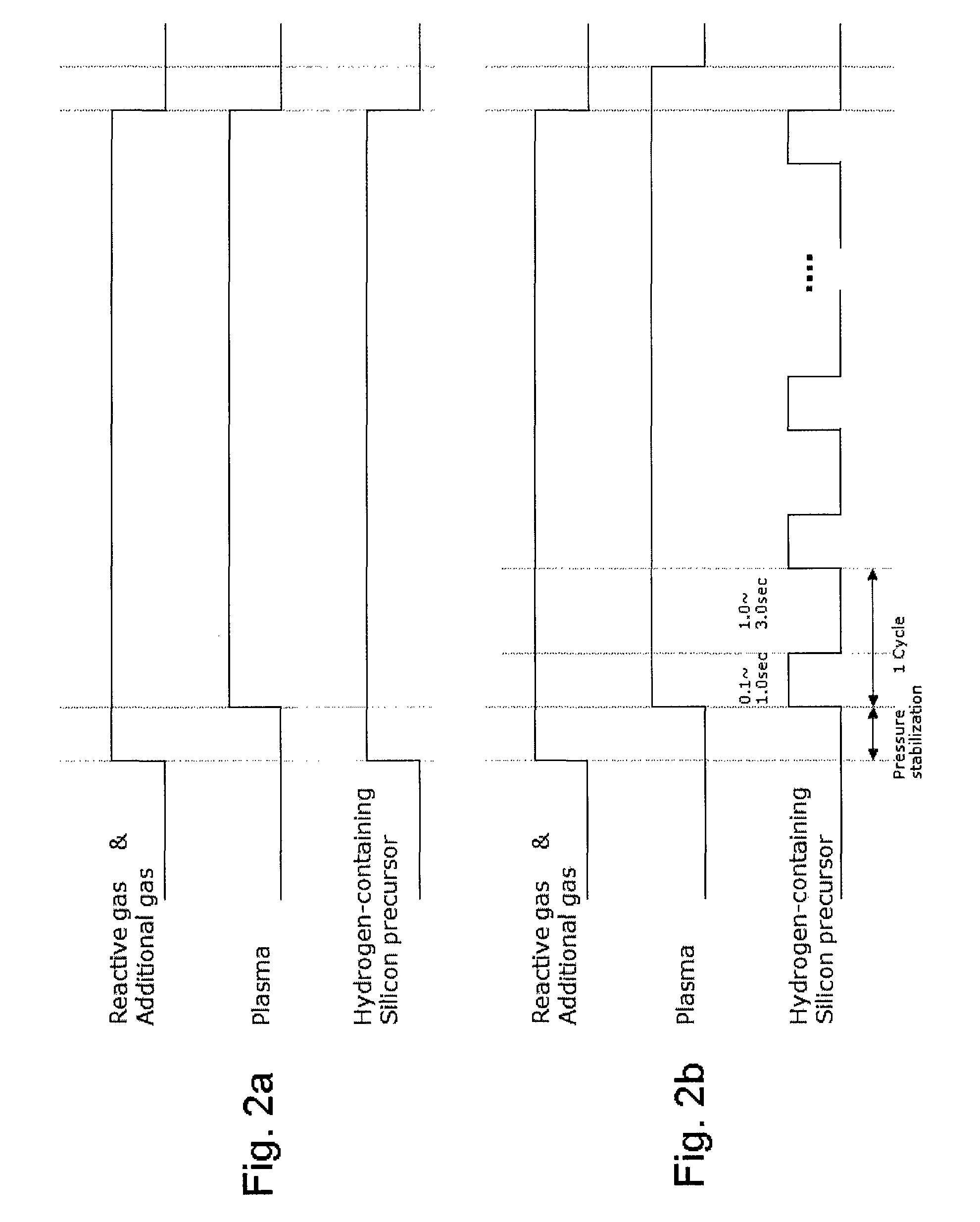
A method of forming a transparent hydrocarbon-based polymer film on a substrate by plasma CVD includes: introducing a main gas consisting of a hydrocarbon gas (CαHβ, wherein α and β are natural numbers) and an inert gas at a flow ratio (R) of CαHβ / inert gas of 0.25 or less into a CVD reaction chamber inside which a substrate is placed; and forming a hydrocarbon-based polymer film on the substrate by plasma polymerization of the gas at a processing temperature (T) wherein T≦(−800R+500).
Owner:ASM JAPAN
Method of forming highly conformal amorphous carbon layer
ActiveUS7842622B1Easily ionizedReduce riskSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingChemical vapor deposition coatingCarbon layerSemiconductor
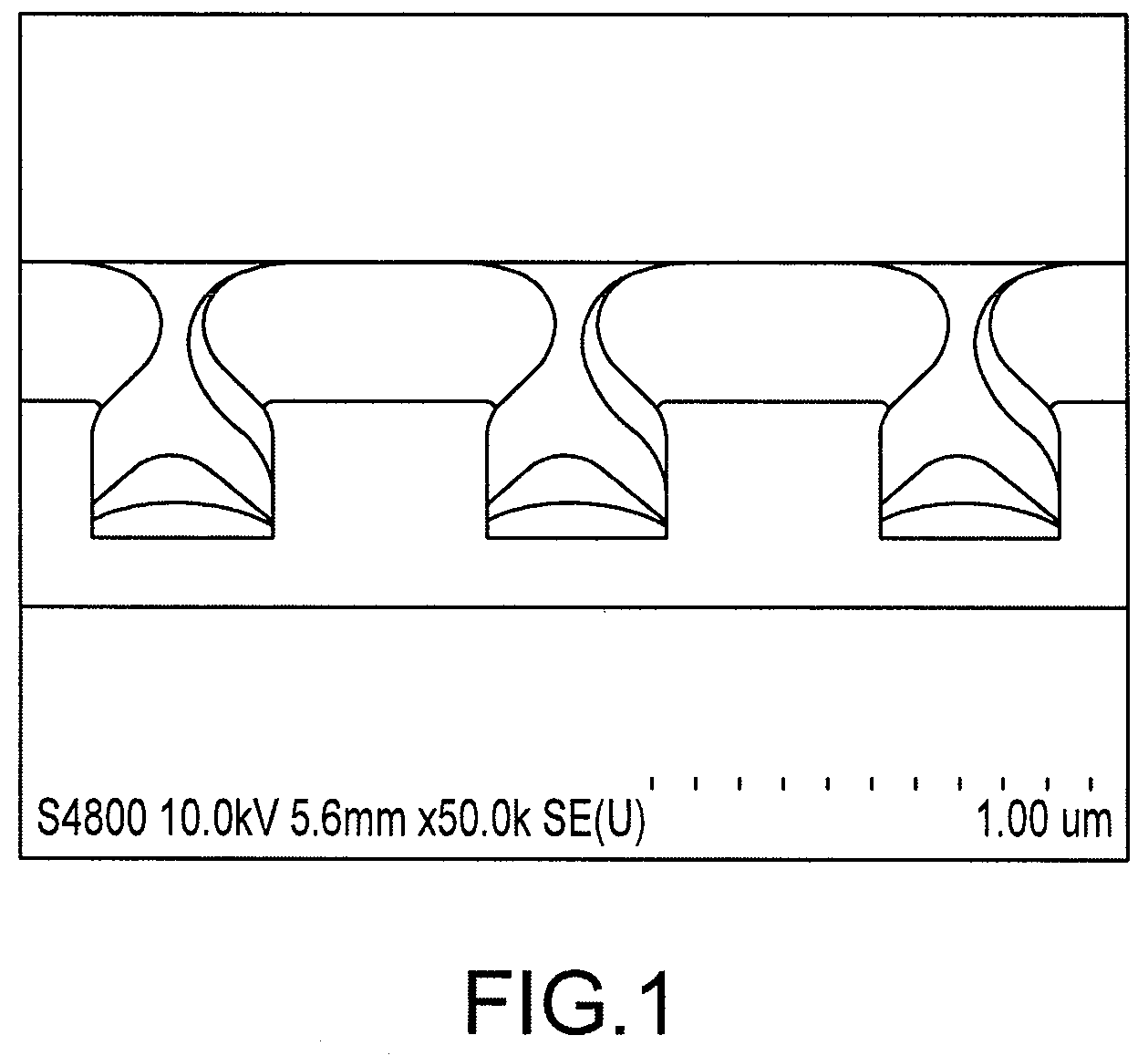
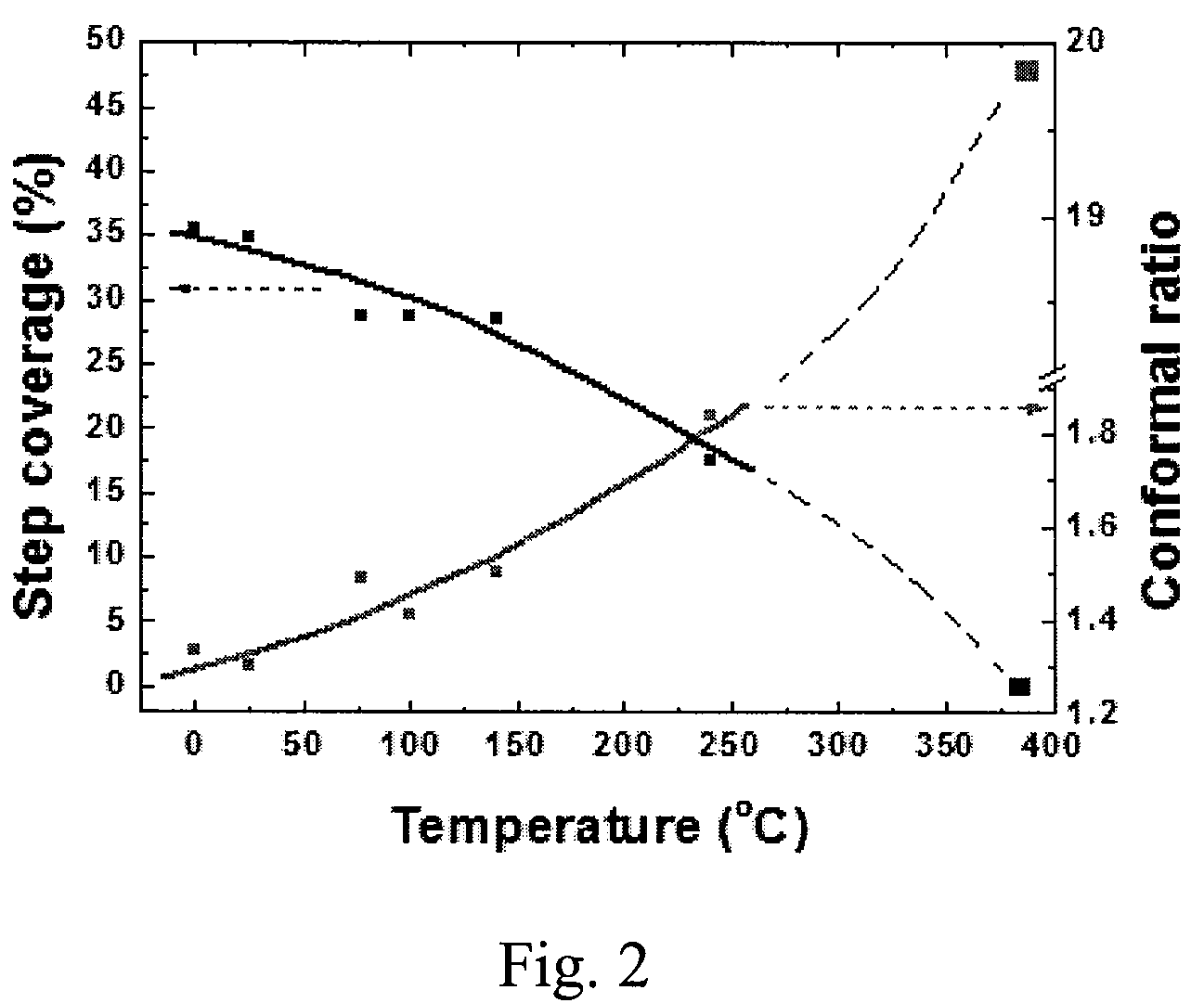
A method of forming a conformal amorphous hydrogenated carbon layer on an irregular surface of a semiconductor substrate includes: vaporizing a hydrocarbon-containing precursor; introducing the vaporized precursor and an argon gas into a CVD reaction chamber inside which the semiconductor substrate is placed; depositing a conformal amorphous hydrogenated carbon layer on the irregular surface of the semiconductor substrate by plasma CVD; and controlling the deposition of the conformal ratio of the depositing conformal amorphous hydrogenated carbon layer. The controlling includes (a) adjusting a step coverage of the conformal amorphous hydrogenated carbon layer to about 30% or higher as a function of substrate temperature, and (b) adjusting a conformal ratio of the conformal amorphous hydrogenated carbon layer to about 0.9 to about 1.1 as a function of RF power and / or argon gas flow rate.
Owner:ASM JAPAN
Flowable silicon-and-carbon-containing layers for semiconductor processing
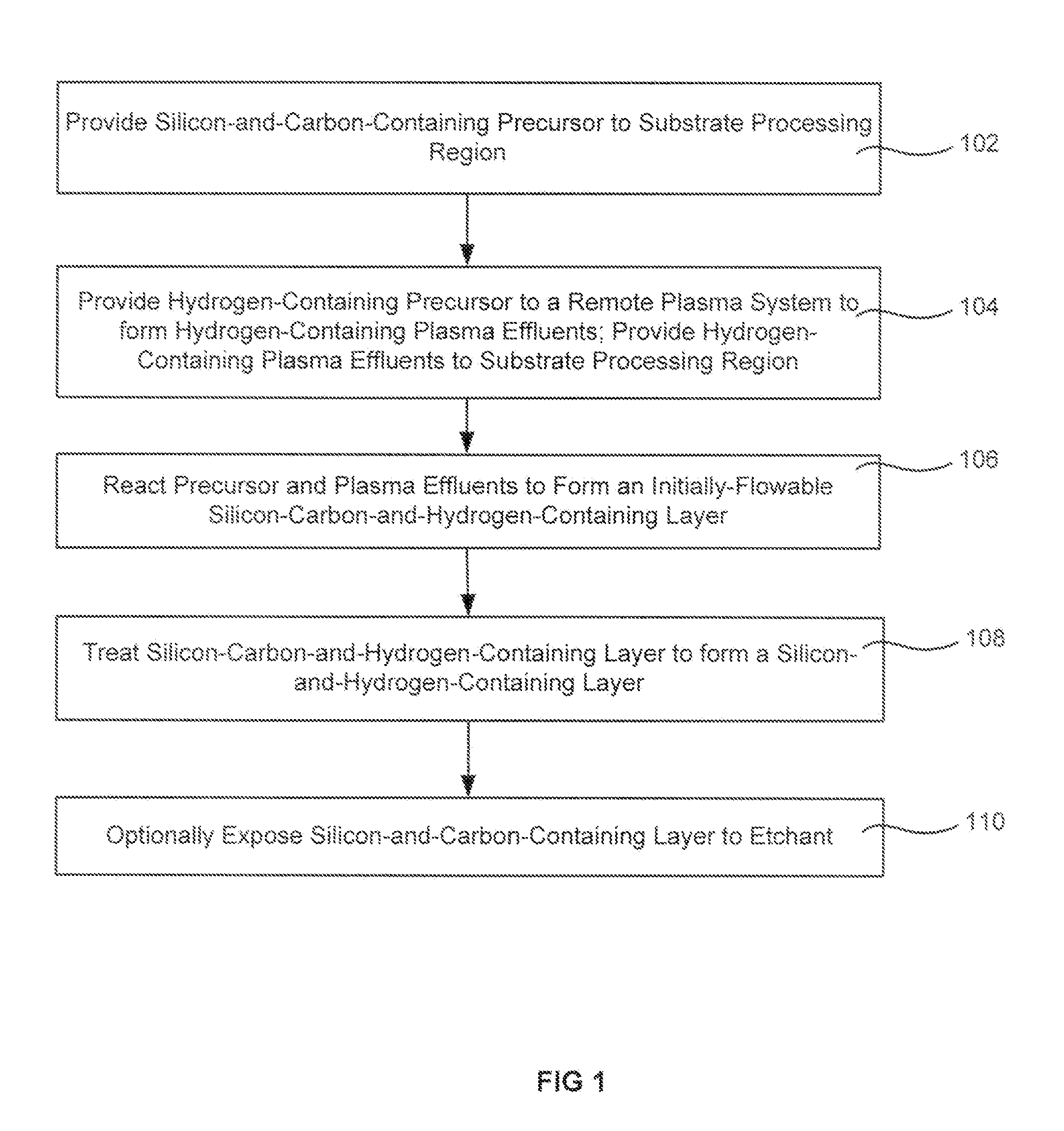
InactiveUS20130217239A1Decreases beneficially low wet etch rateReduce hydrogen contentSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingCarbon layerHydrogen
Methods are described for forming and curing a gapfill silicon-and-carbon-containing layer on a semiconductor substrate. The silicon and carbon constituents may come from a silicon-and-carbon-containing precursor excited by a radical hydrogen precursor that has been activated in a remote plasma region. Exemplary precursors include 1,3,5-trisilapentane (H3Si—CH2—SiH2—CH2—SiH3) as the silicon-and-carbon-containing precursor and hydrogen (H2) as the hydrogen-containing precursor. The hydrogen-containing precursor may also be a hydrocarbon, such as acetylene (C2H2) or ethylene (C2H4). The hydrogen-containing precursor is passed through a remote plasma region to form plasma effluents (the radical hydrogen precursor) which are flowed into the substrate processing region. When the silicon-and-carbon-containing precursor combines with the plasma effluents in the substrate processing region, they form a flowable silicon-carbon-and-hydrogen-containing layer on the semiconductor substrate.
Owner:APPLIED MATERIALS INC
Method of forming a carbon polymer film using plasma CVD
ActiveUS20070218705A1Improve featuresFunction increaseLiquid surface applicatorsPhotomechanical apparatusCapacitanceBoiling point
A method forms a hydrocarbon-containing polymer film on a semiconductor substrate by a capacitively-coupled plasma CVD apparatus. The method includes the steps of: vaporizing a hydrocarbon-containing liquid monomer (CαHβXγ, wherein α and β are natural numbers of 5 or more; γ is an integer including zero; X is O, N or F) having a boiling point of about 20° C. to about 350° C.; introducing the vaporized gas into a CVD reaction chamber inside which a substrate is placed; and forming a hydrocarbon-containing polymer film on the substrate by plasma polymerization of the gas.
Owner:ASM JAPAN
Compositions with Improved Adhesion to Low Surface Energy Substrates
InactiveUS20080113094A1Excellent low surface energyImprove adhesionSynthetic resin layered productsOrganic dyesOligomerEnd-group
Acrylic-based pressure sensitive adhesives are modified with a telechelic hydrocarbon oligomer. The oligomer comprises a hydrocarbon polymer chain or backbone and a functional end group, e.g., an oligomer prepared from a mono hydroxyl polybutadiene polymer and toluene diisocyanate. The oligomer attaches to the acrylic backbone of the polymer as a pendant group and in a preferred embodiment, the oligomer is mixed with the PSA shortly before the PSA is coated.
Owner:BRADY WORLDWIDE INC
Method of Depositing Dielectric Film by ALD Using Precursor Containing Silicon, Hydrocarbon, and Halogen
ActiveUS20120214318A1Accelerates the carbonization processHigh conformalitySemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingChemical vapor deposition coatingDielectricHalogen
A method of forming a dielectric film having at least Si—N, Si—C, or Si—B bonds on a semiconductor substrate by atomic layer deposition (ALD), includes: adsorbing a precursor on a surface of a substrate; supplying a reactant gas over the surface; reacting the precursor and the reactant gas on the surface; and repeating the above steps to form a dielectric film having at least Si—N, Si—C, or Si—B bonds on the substrate. The precursor has at least one Si—C or Si—N bond, at least one hydrocarbon, and at least one halogen attached to silicon in its molecule.
Owner:ASM JAPAN
Method for forming low-carbon CVD film for filling trenches
ActiveUS20100143609A1Semiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSolid state diffusion coatingBoiling pointSilicon membrane
A method of forming a low-carbon silicon-containing film by CVD on a substrate having trenches includes: introducing a silicon-containing compound having three or less hydrocarbon units in its molecule and having a boiling temperature of 35° C. to 220° C.; applying RF power to the gas; and depositing a film on a substrate having trenches wherein the substrate is controlled at a temperature such that components of the silicon-containing compound are at least partially liquidified on the substrate, thereby filling the trenches with the film.
Owner:ASM JAPAN
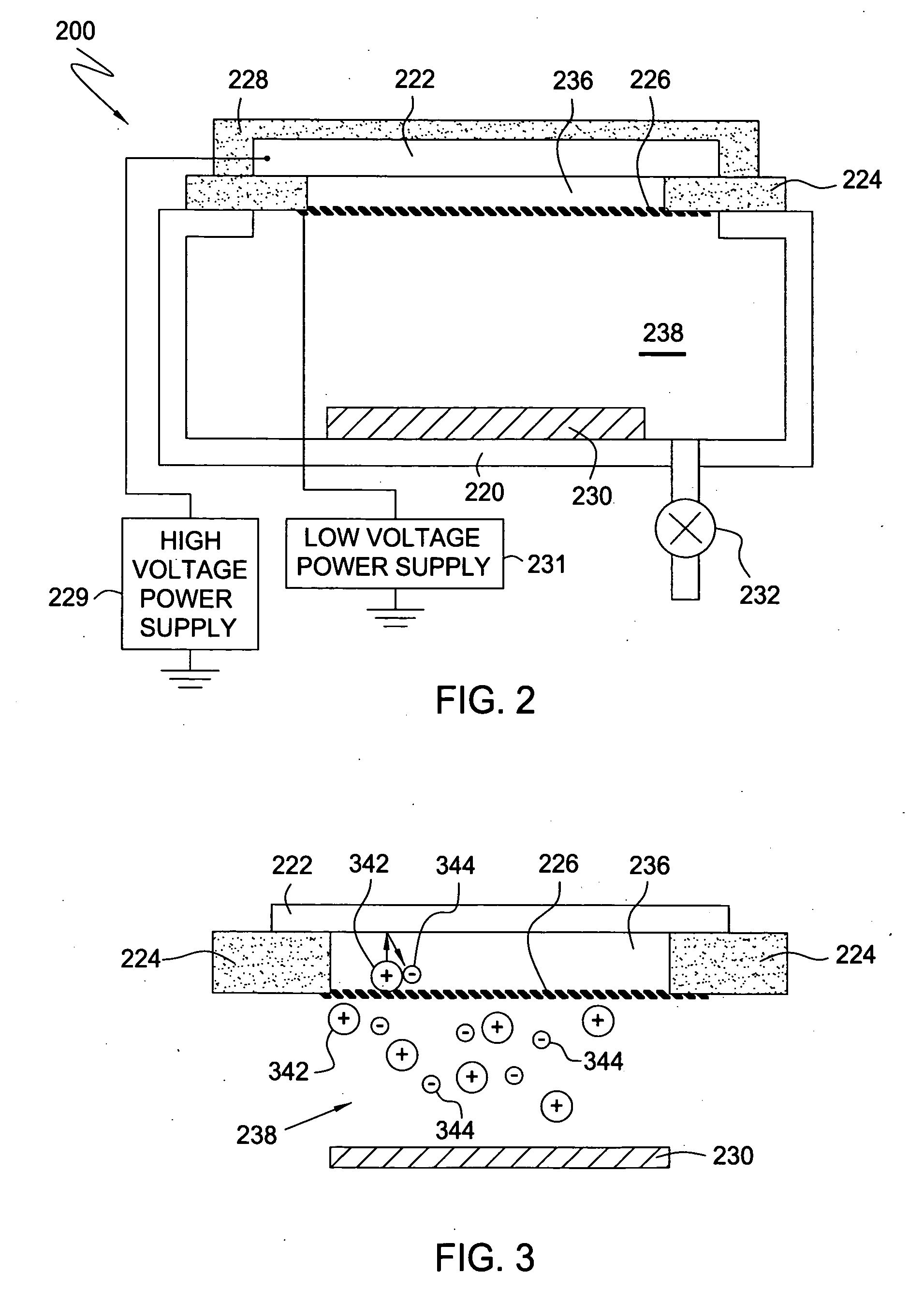
Surface coating method for hydrophobic and superhydrophobic treatment in atmospheric pressure plasma
The present invention relates to a method of coating fluorocarbon or hydrocarbon on the surface of a workpiece using atmospheric pressure plasma. More particularly, the present invention relates to a method of coating hydrocarbon or fluorocarbon on the surface of a workpiece using plasma generated under atmospheric pressure such that the workpiece can have a hydrophobic or super-hydrophobic surface.The method of coating a surface of a workpiece with fluorocarbon to be hydrophobic or super-hydrophobic according to the present invention comprises the steps of generating first atmospheric pressure glow plasma by supplying a reaction gas into a discharge space formed between a first electrode and a second electrode, the reaction gas containing hydrogen gas, fluorocarbon gas and inert gas, the first and second electrodes being connected to an RF power supply of an atmospheric pressure plasma generator; and approaching the workpiece to the first electrode downstream of a reaction gas flow passing through the discharge space, such that the plasma created in the discharge space is transferred into a space between the first electrode and the workpiece to generate a second atmospheric pressure glow plasma therein, whereby a fluorocarbon coating layer can be formed on the surface of the workpiece.
Owner:KANG BANG KWON
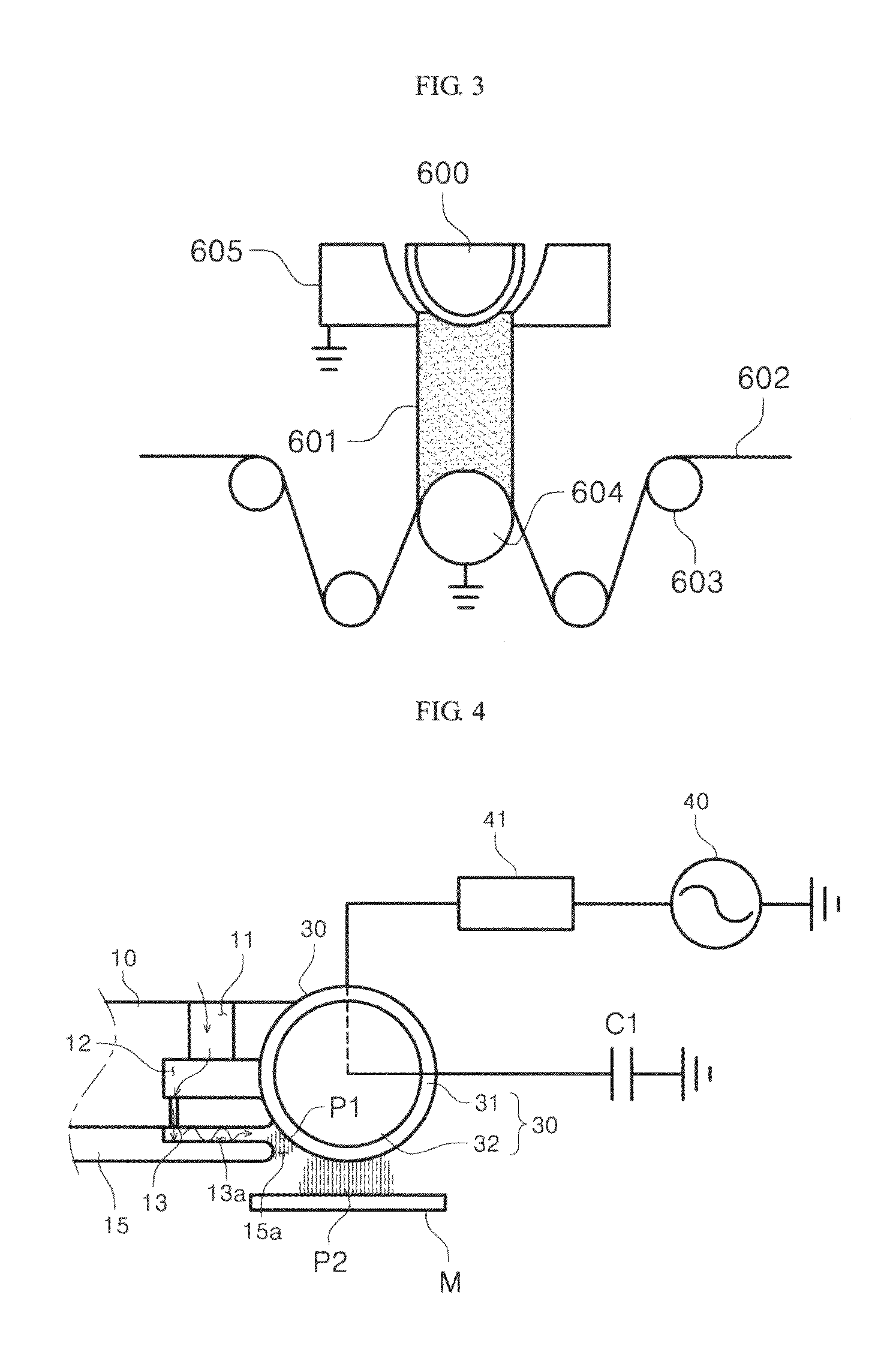
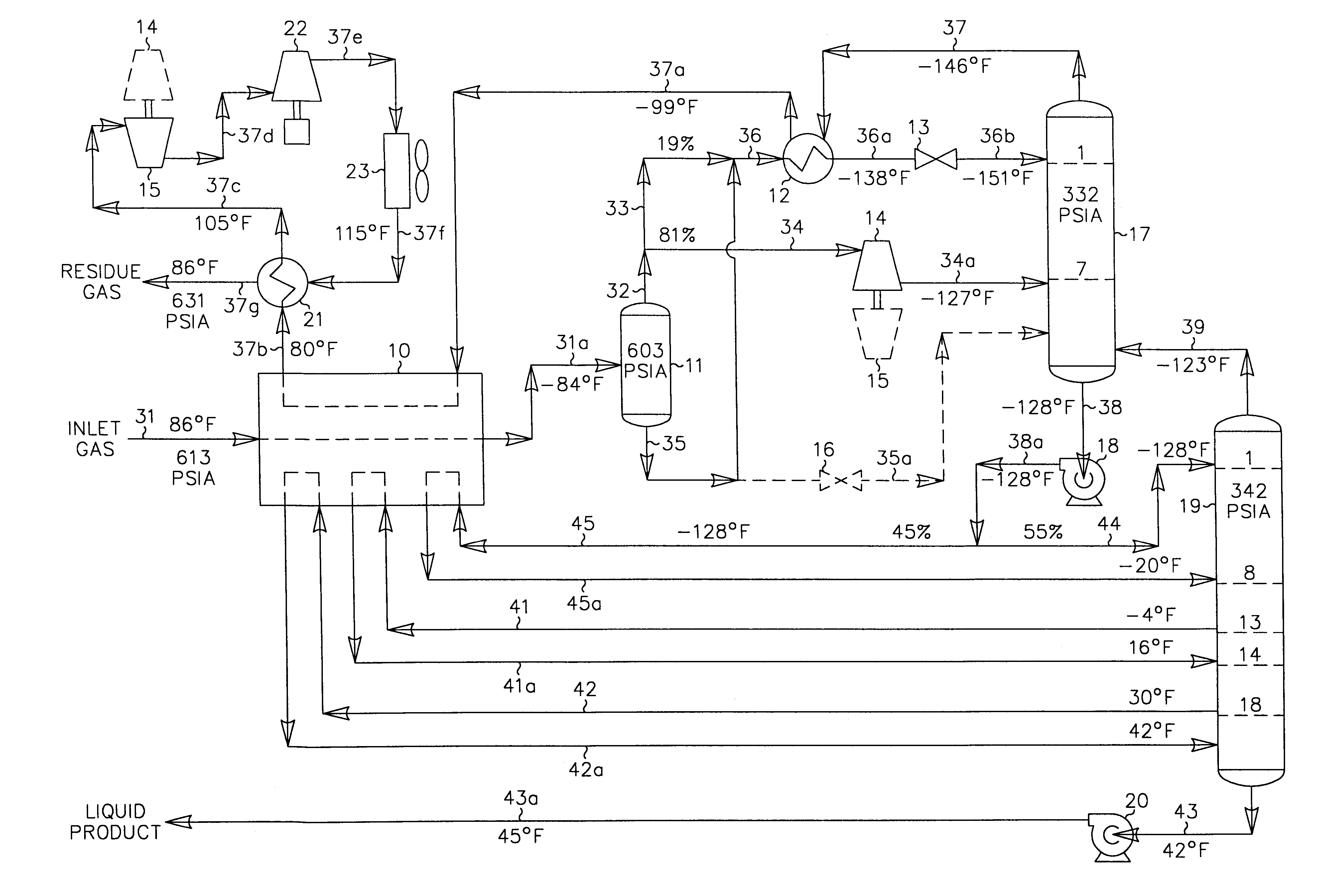
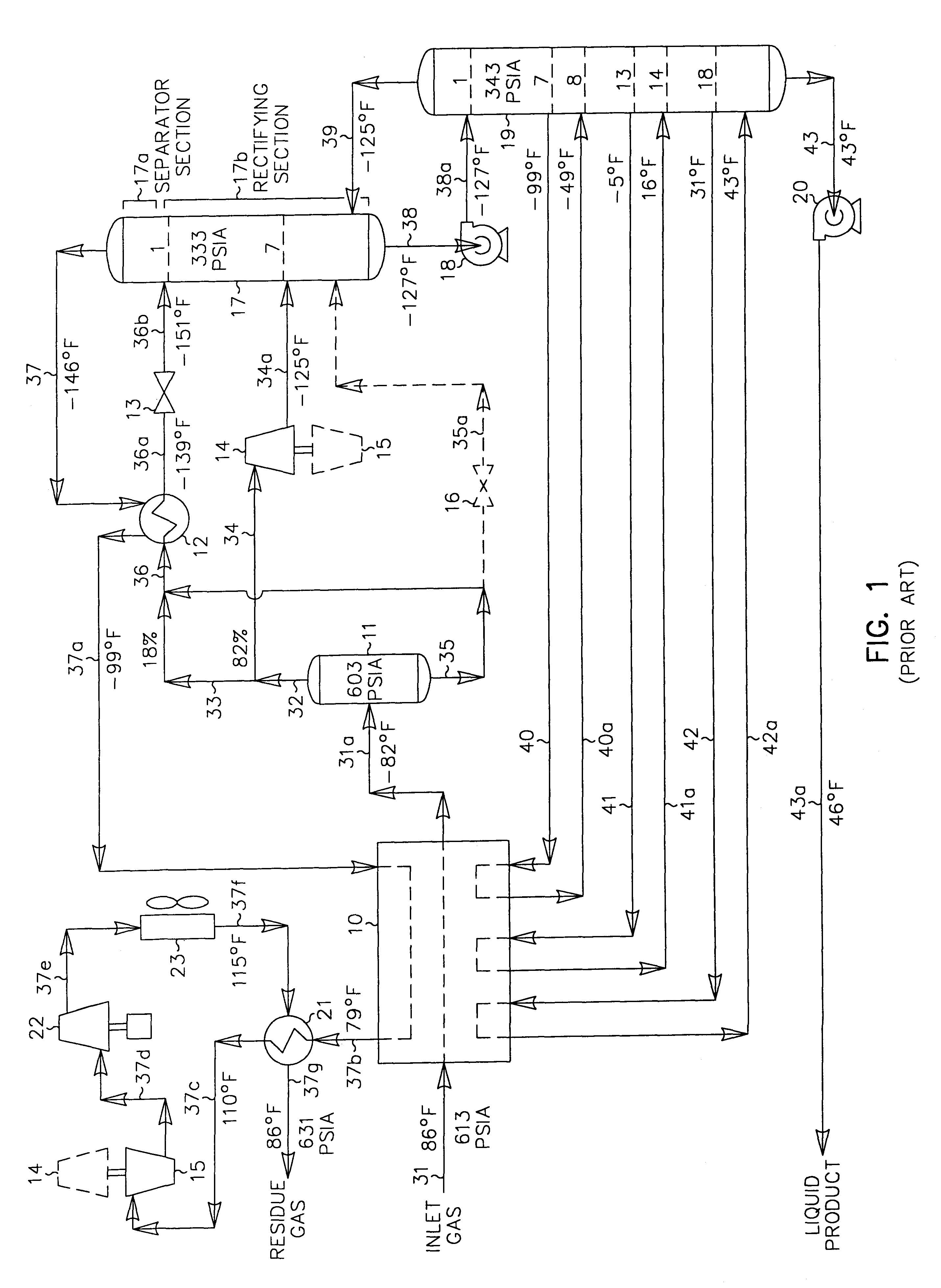
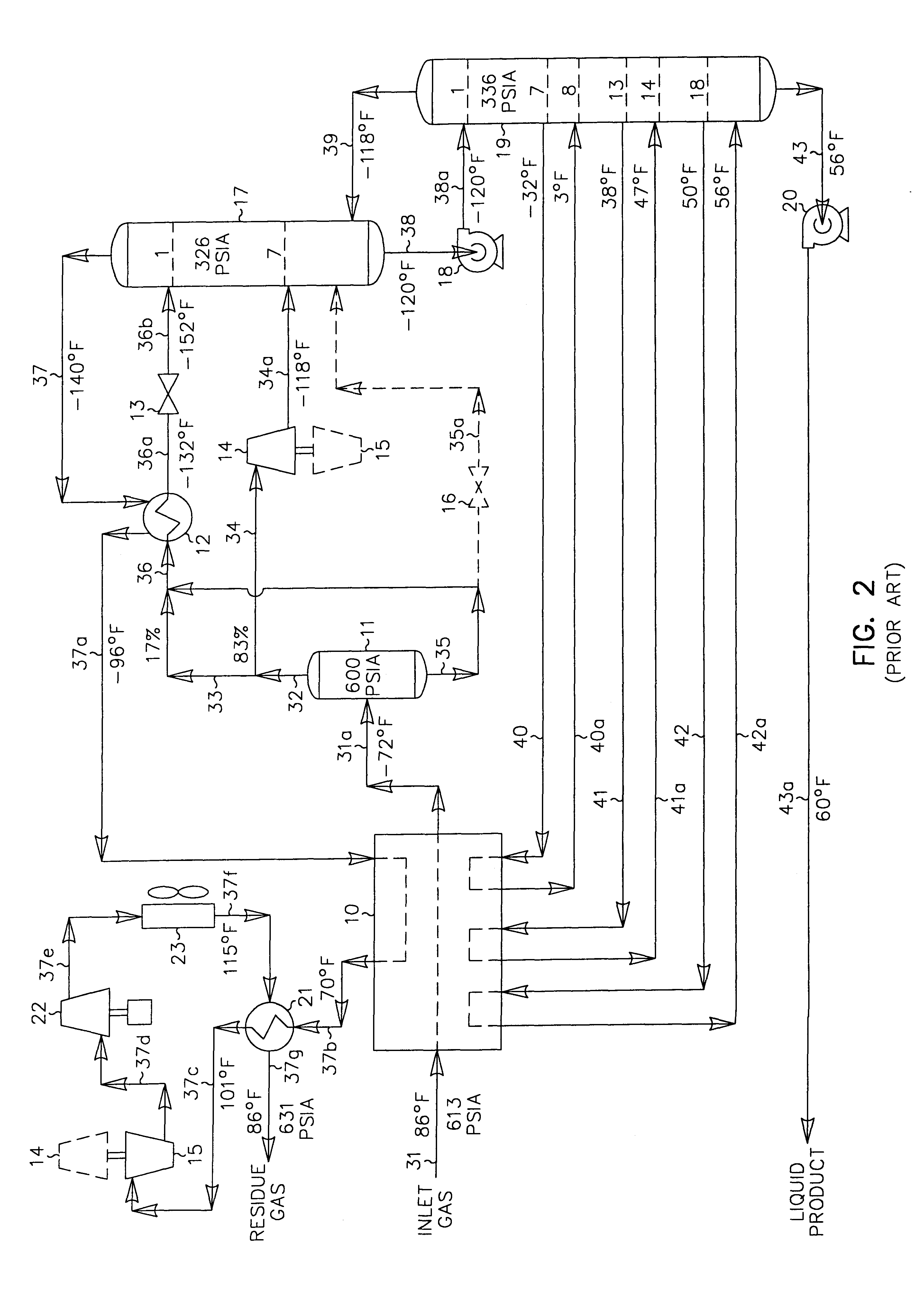
Hydrocarbon gas processing
A process for the recovery of ethane, ethylene, propane, propylene and heavier hydrocarbon components from a hydrocarbon gas stream is disclosed. In recent years, the preferred method of separating a hydrocarbon gas stream generally includes supplying at least portions of the gas stream to a fractionation tower having at least one reboiler, and often one or more side reboilers, to supply heat to the column by withdrawing and heating some of the tower liquids to produce stripping vapors that separate the more volatile components from the desired components. The reboiler and side reboilers (if any) are typically integrated into the feed stream cooling scheme to provide at least a portion of the refrigeration needed to condense the desired components for subsequent fractionation in the distillation column. In the process disclosed, the tower reboiling scheme is modified to use one or more tower liquid distillation streams from a point higher in the column than is used in the conventional reboiling scheme, providing colder stream(s) for the reboiler(s) that allow more effective cooling of the feed streams and thereby improve the efficiency with which the desired components are recovered. In addition, the tower liquid streams withdrawn from a higher point in the column contain larger quantities of the more volatile components, which when vaporized provide better stripping of undesirable components like carbon dioxide without reducing the recovery of the desired components. The heated distillation stream is returned to a lower point on the fractionation tower that is separated from the withdrawal point by at least one theoretical stage.
Owner:UOP LLC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com