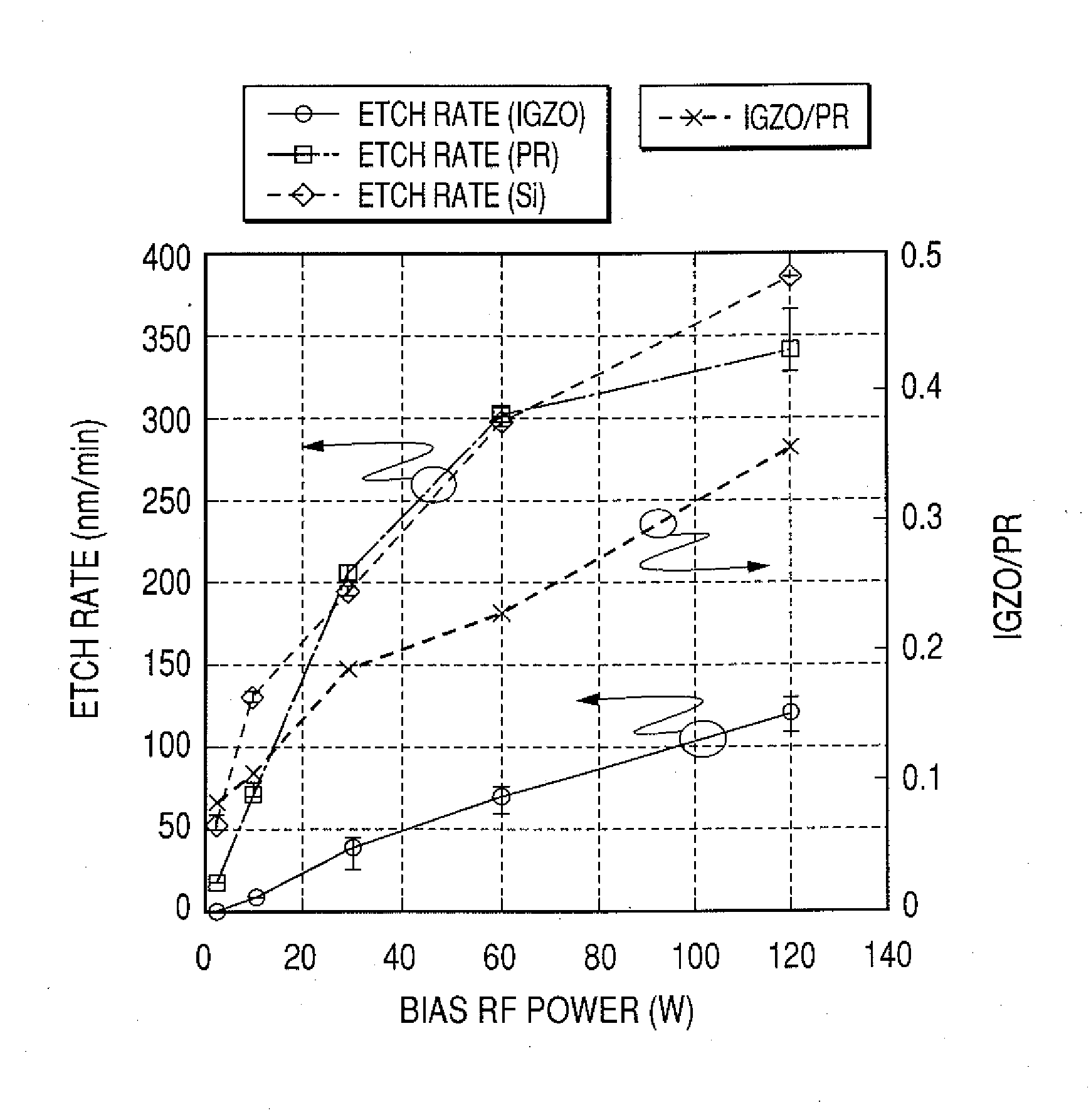
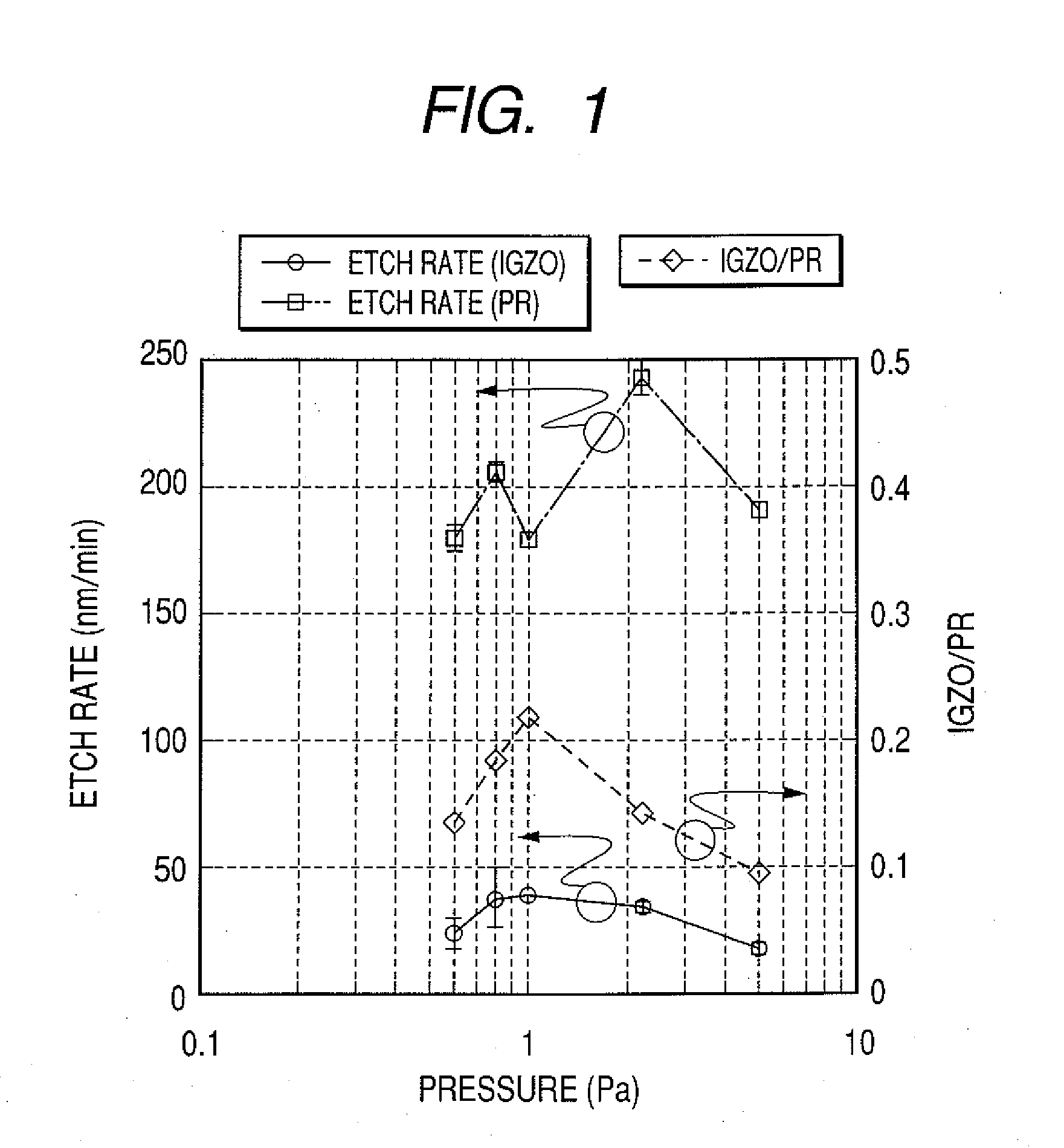
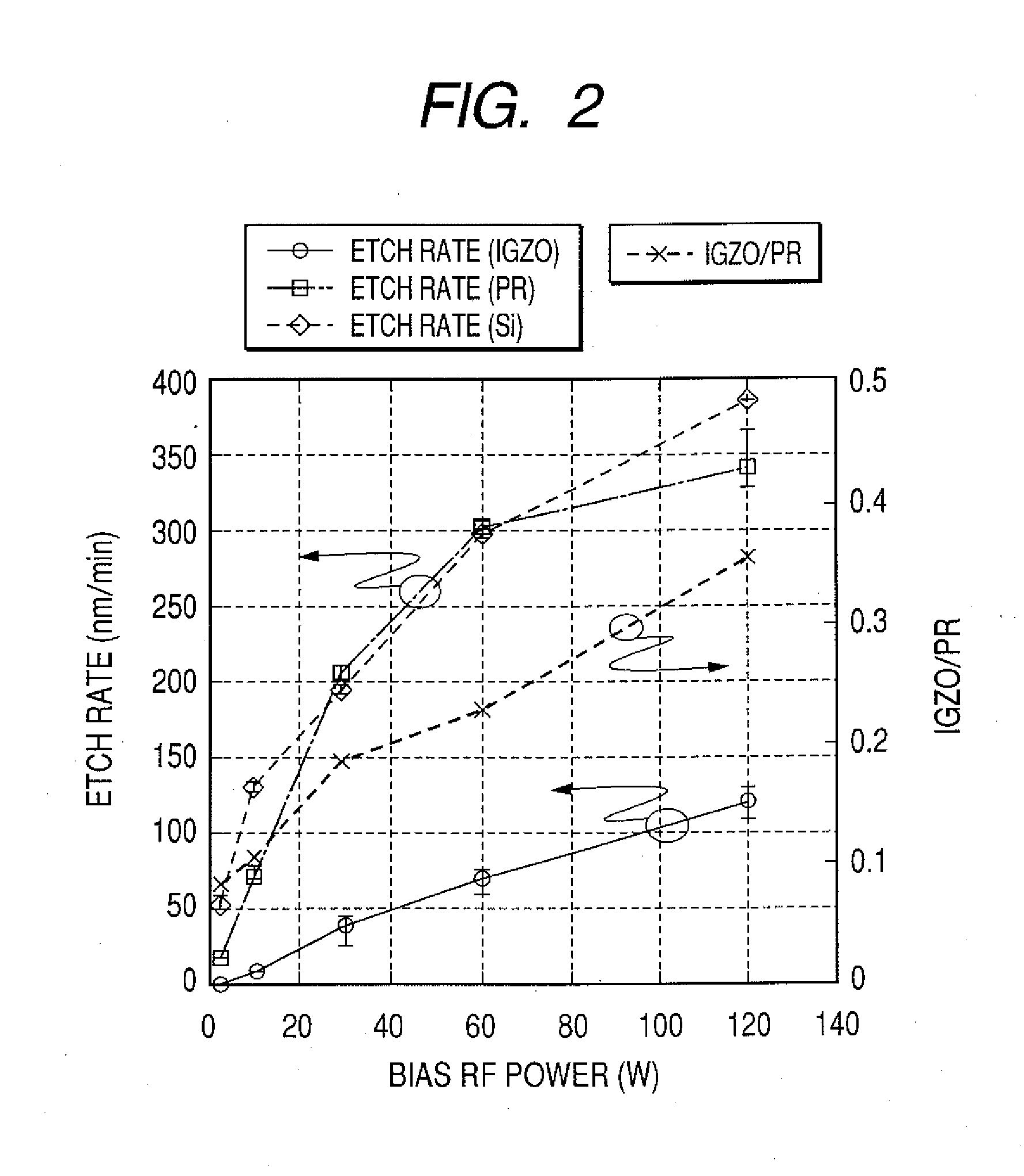
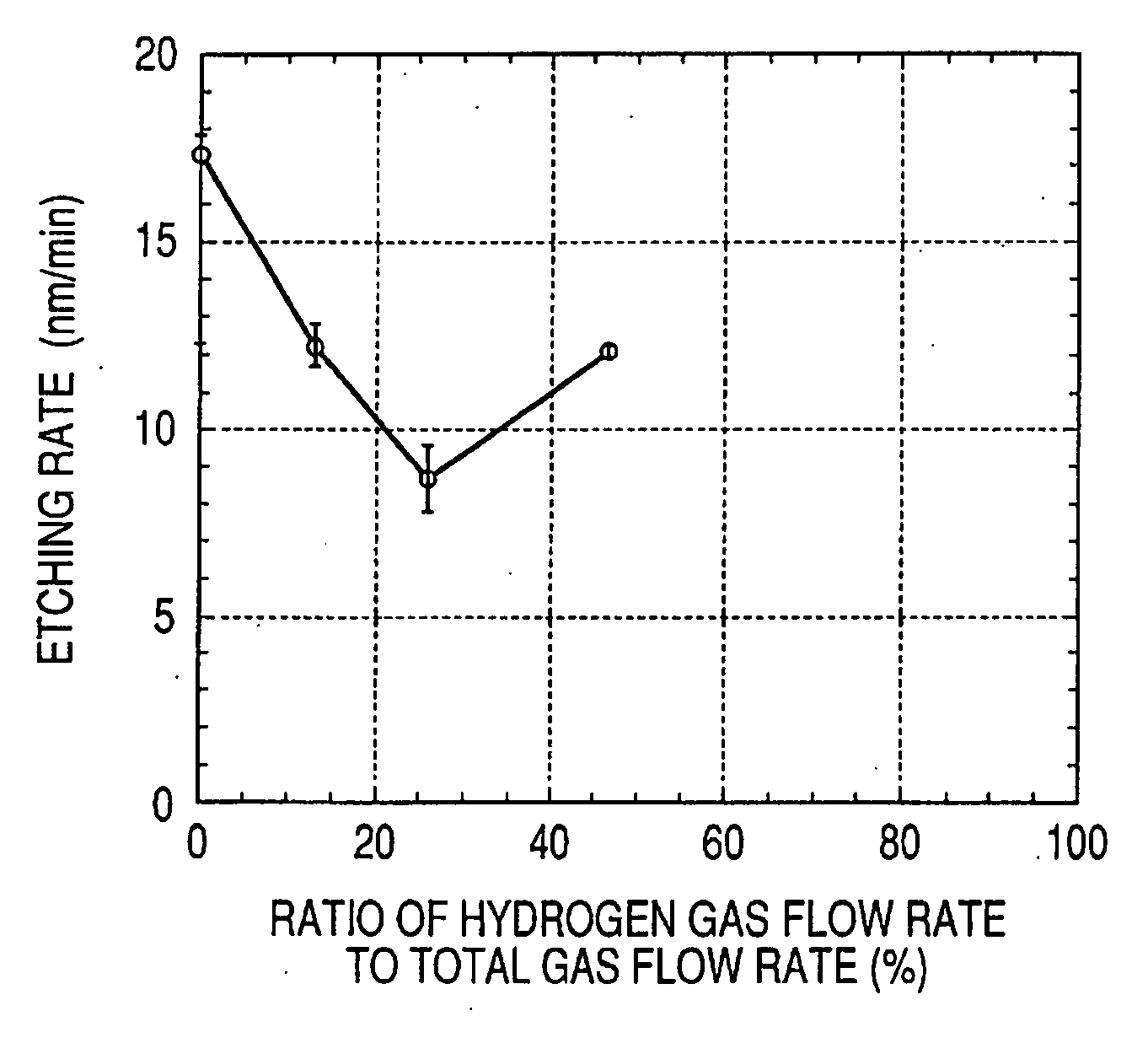
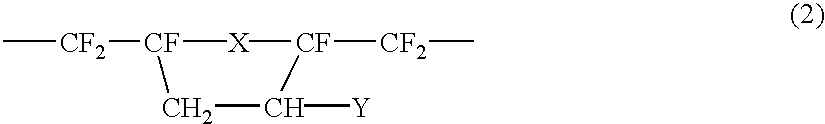Patents
Literature
5563 results about "Dry etching" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
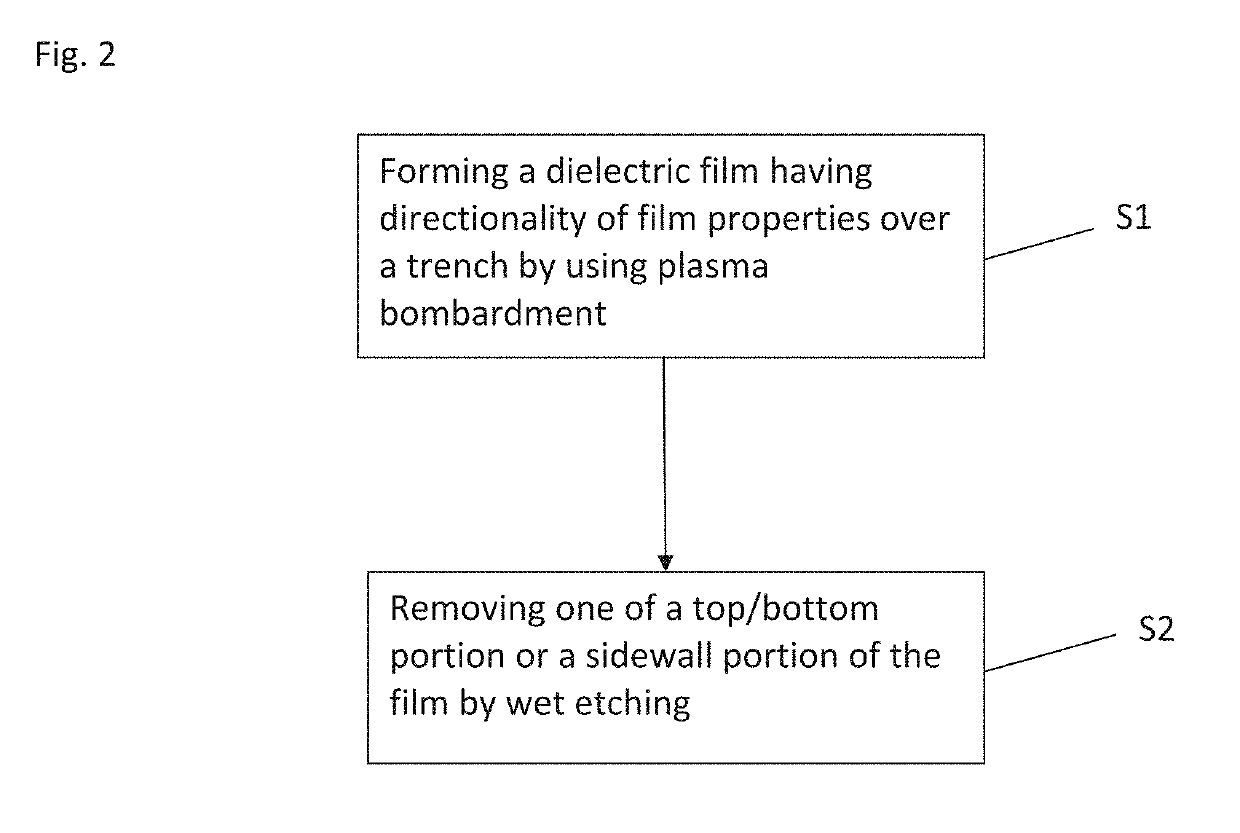
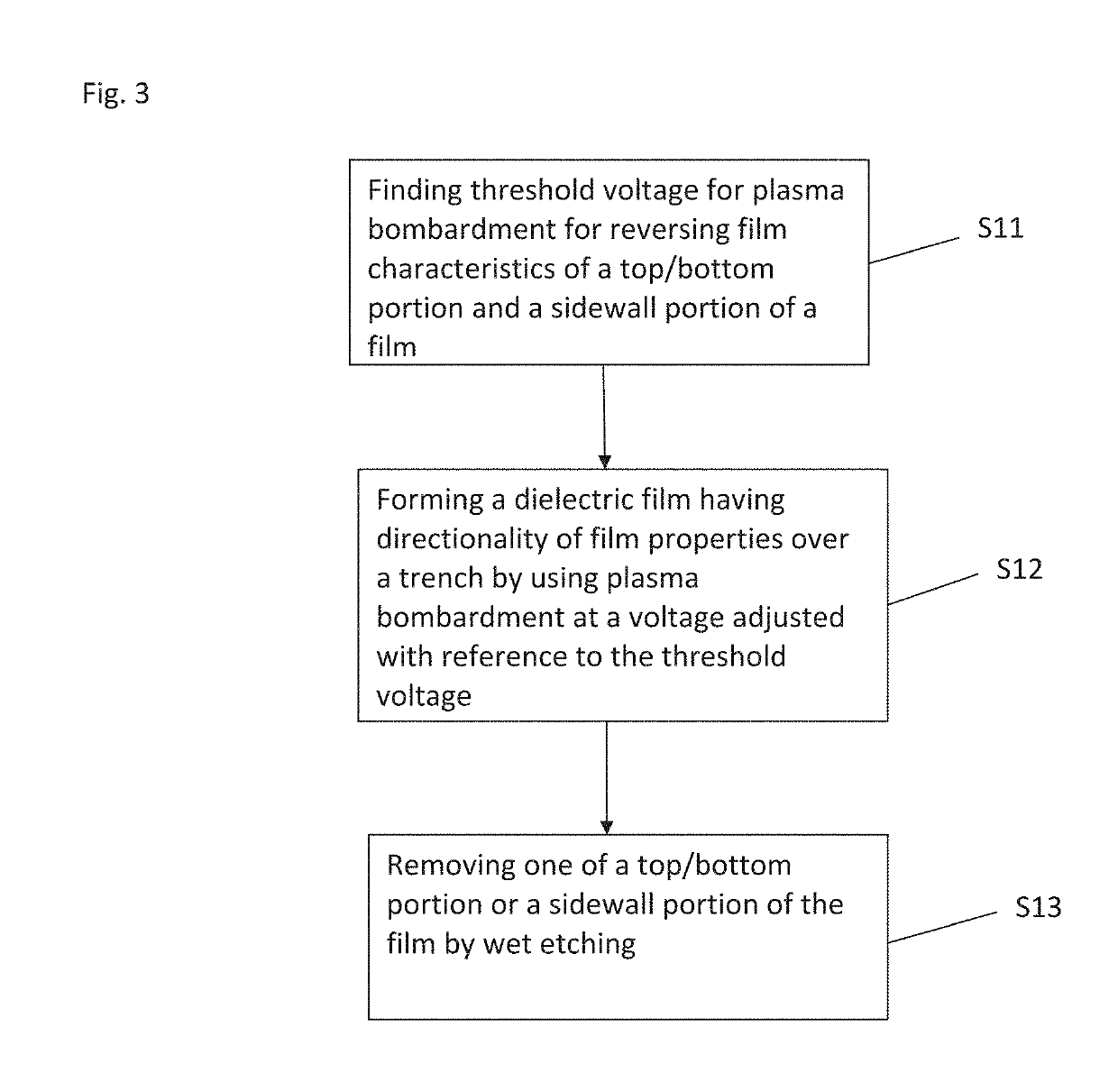
Dry etching refers to the removal of material, typically a masked pattern of semiconductor material, by exposing the material to a bombardment of ions (usually a plasma of reactive gases such as fluorocarbons, oxygen, chlorine, boron trichloride; sometimes with addition of nitrogen, argon, helium and other gases) that dislodge portions of the material from the exposed surface. A common type of dry etching is reactive-ion etching. Unlike with many (but not all, see isotropic etching) of the wet chemical etchants used in wet etching, the dry etching process typically etches directionally or anisotropically.
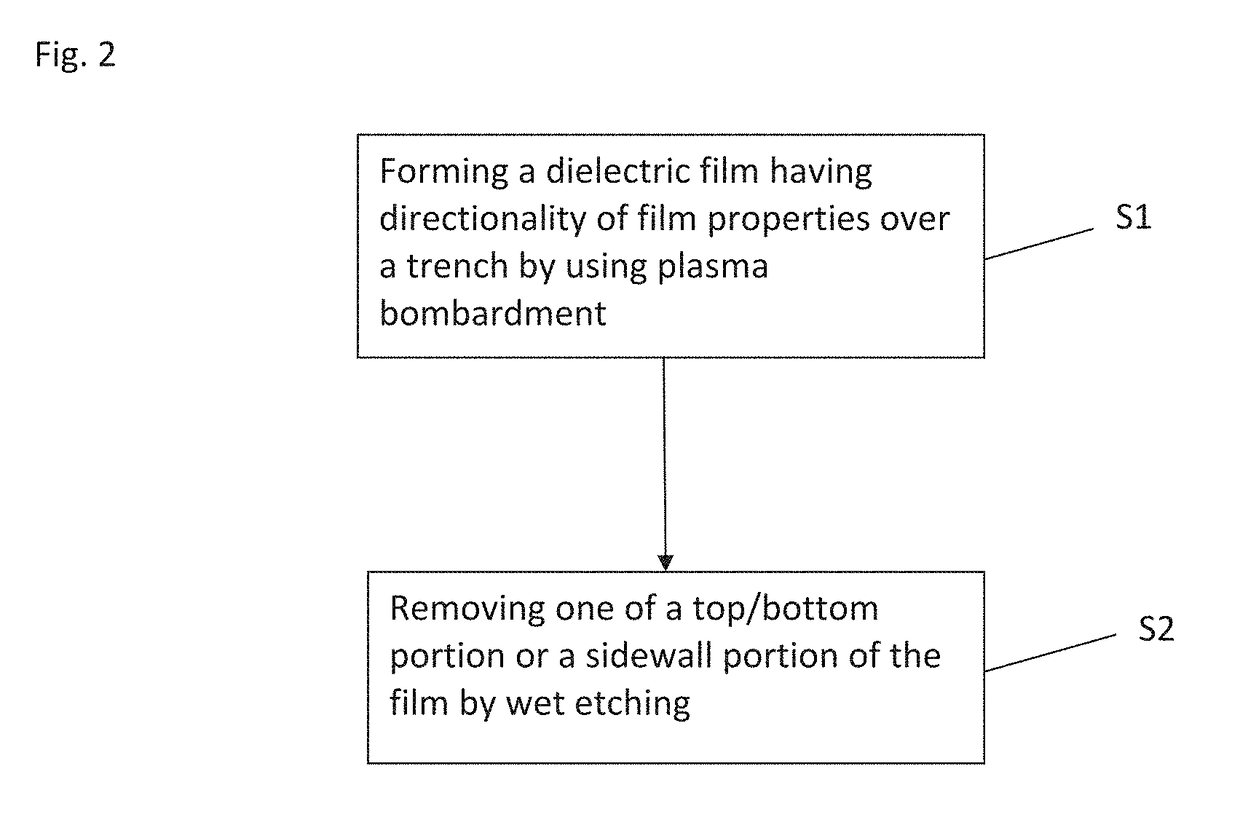
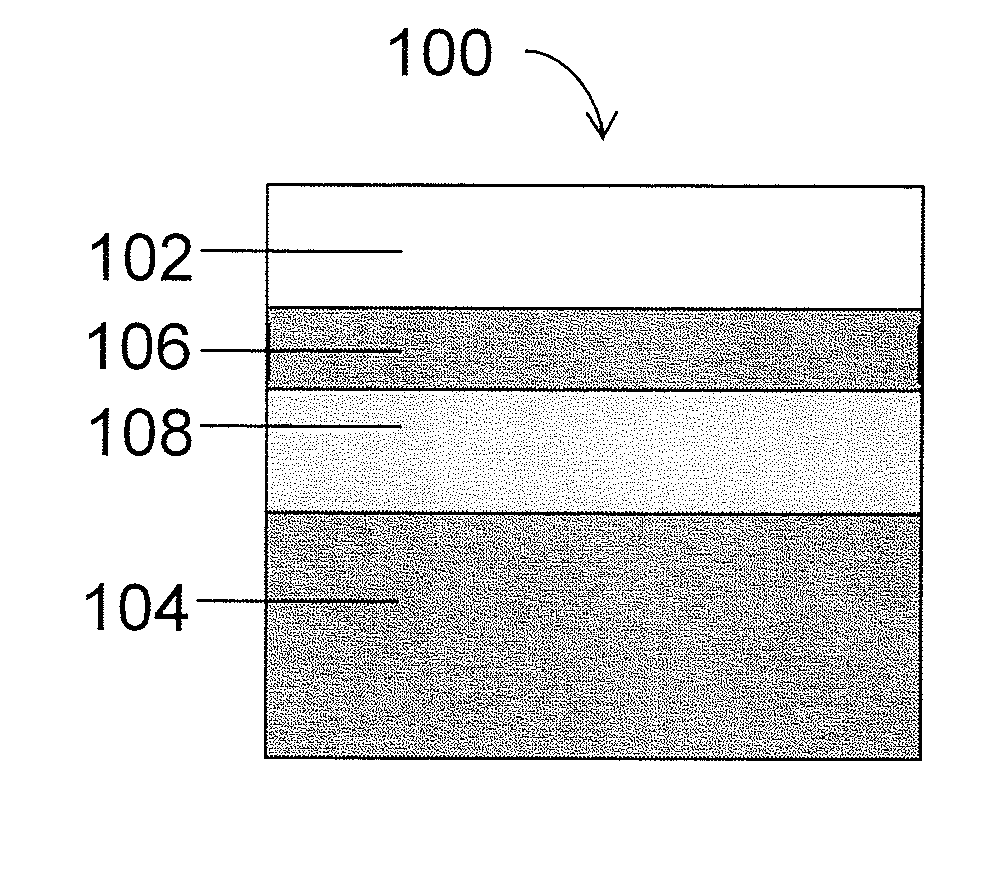
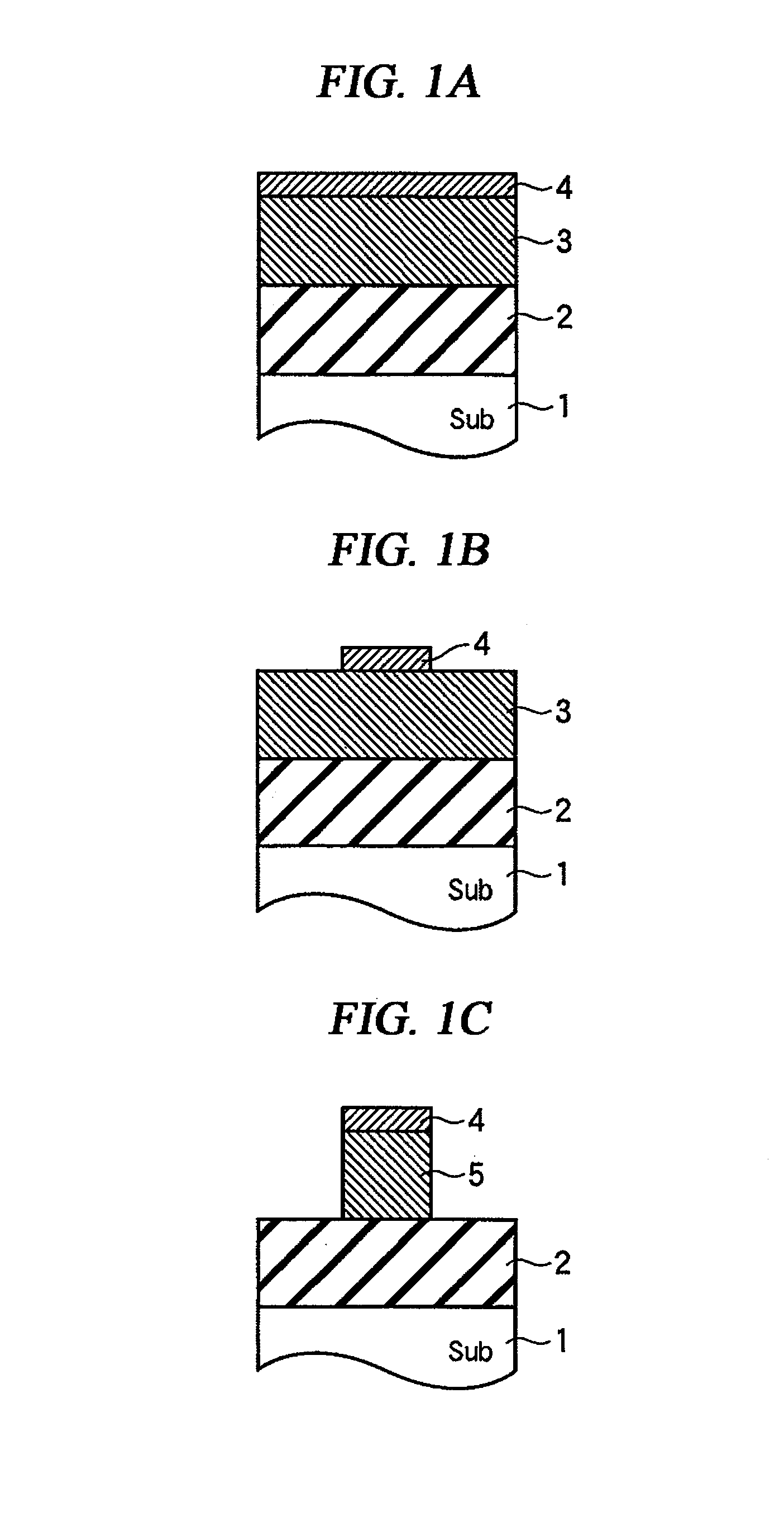
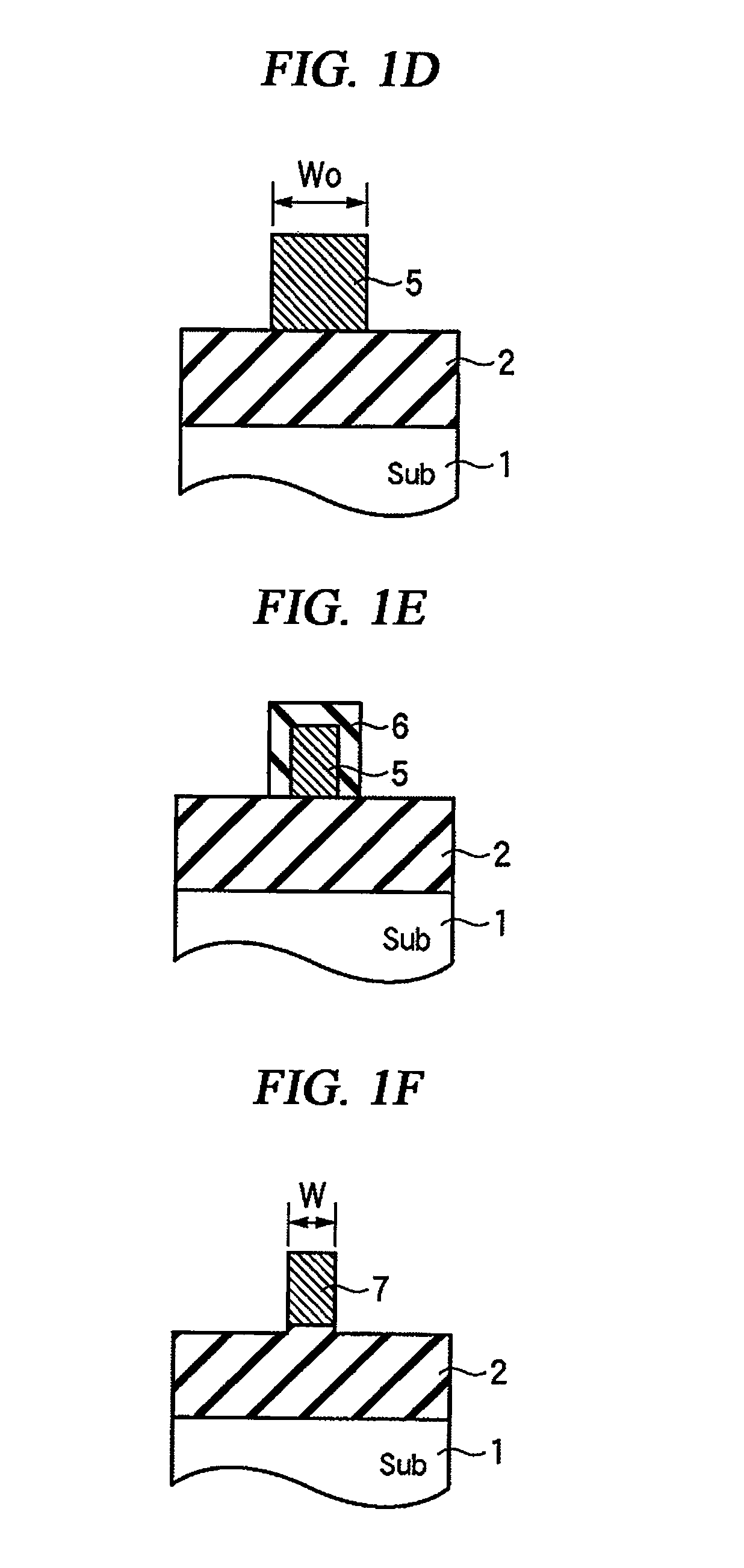
Method of dry etching oxide semiconductor film
InactiveUS20080038929A1Improve processing accuracyIncrease etch rateDecorative surface effectsSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSemiconductorDry etching
Provided is a dry etching method for an oxide semiconductor film containing at least In, Ga, and Zn, which includes etching an oxide semiconductor film in a gas atmosphere containing a halogen-based gas.
Owner:CANON KK
Dry etching method for oxide semiconductor film
InactiveUS20070287296A1Improve processing accuracyIncrease etch rateDecorative surface effectsSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingDry etchingSemiconductor
Provided is a dry etching method for an oxide semiconductor film made of In—Ga—Zn—O, in which an etching gas containing a hydrocarbon is used in a dry etching process for the oxide semiconductor film made of In—Ga—Zn—O formed on a substrate.
Owner:CANON KK
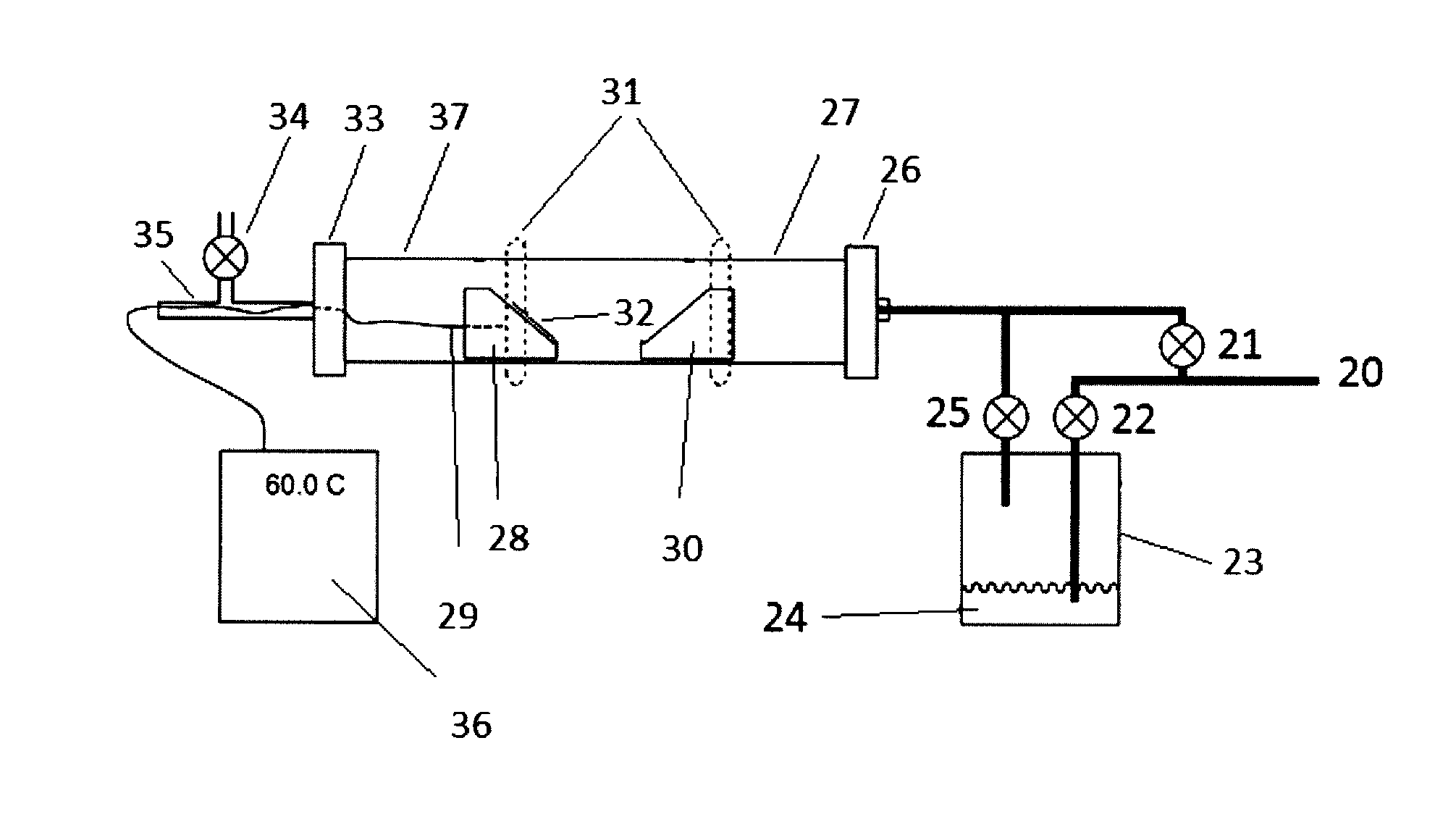
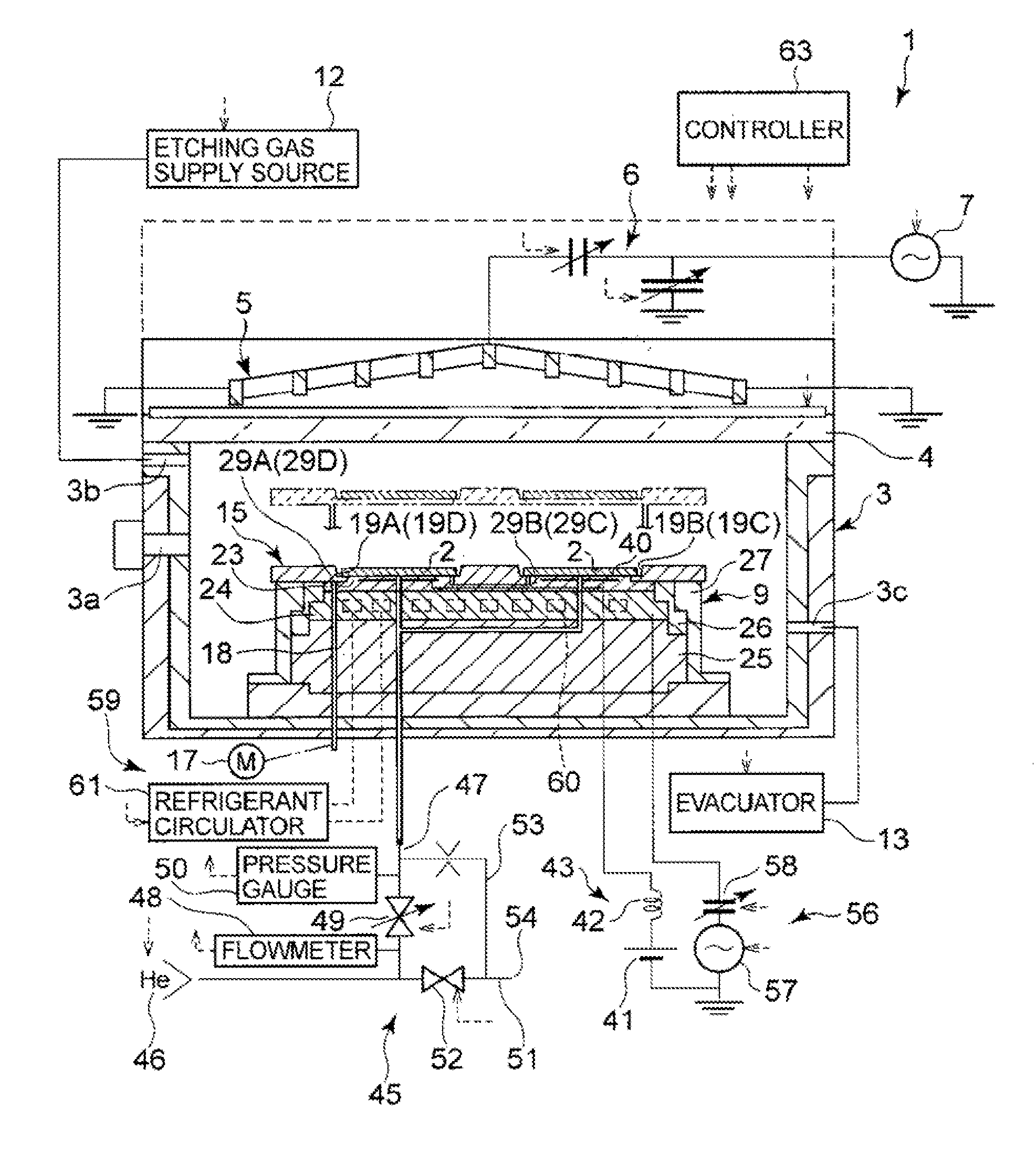
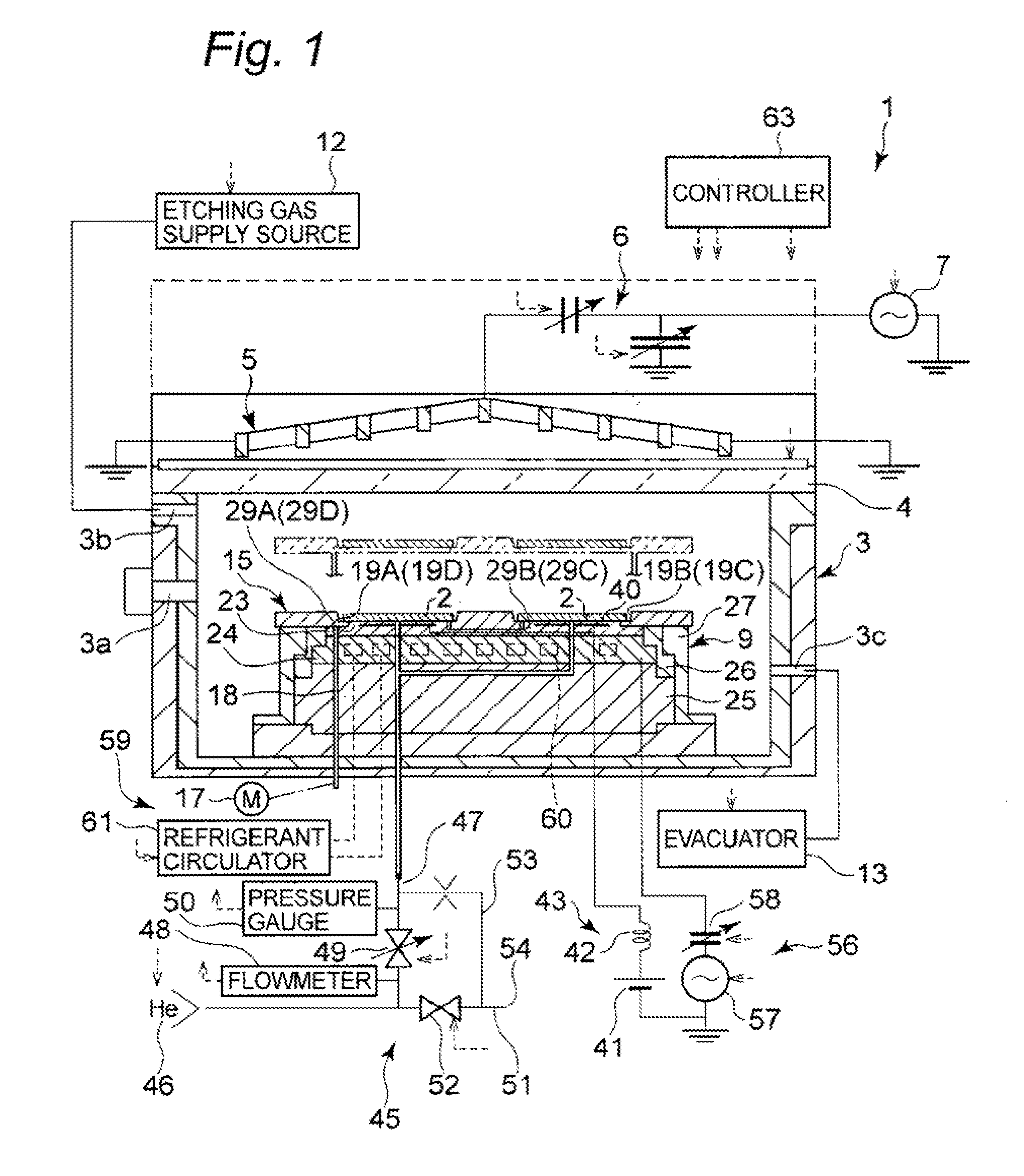
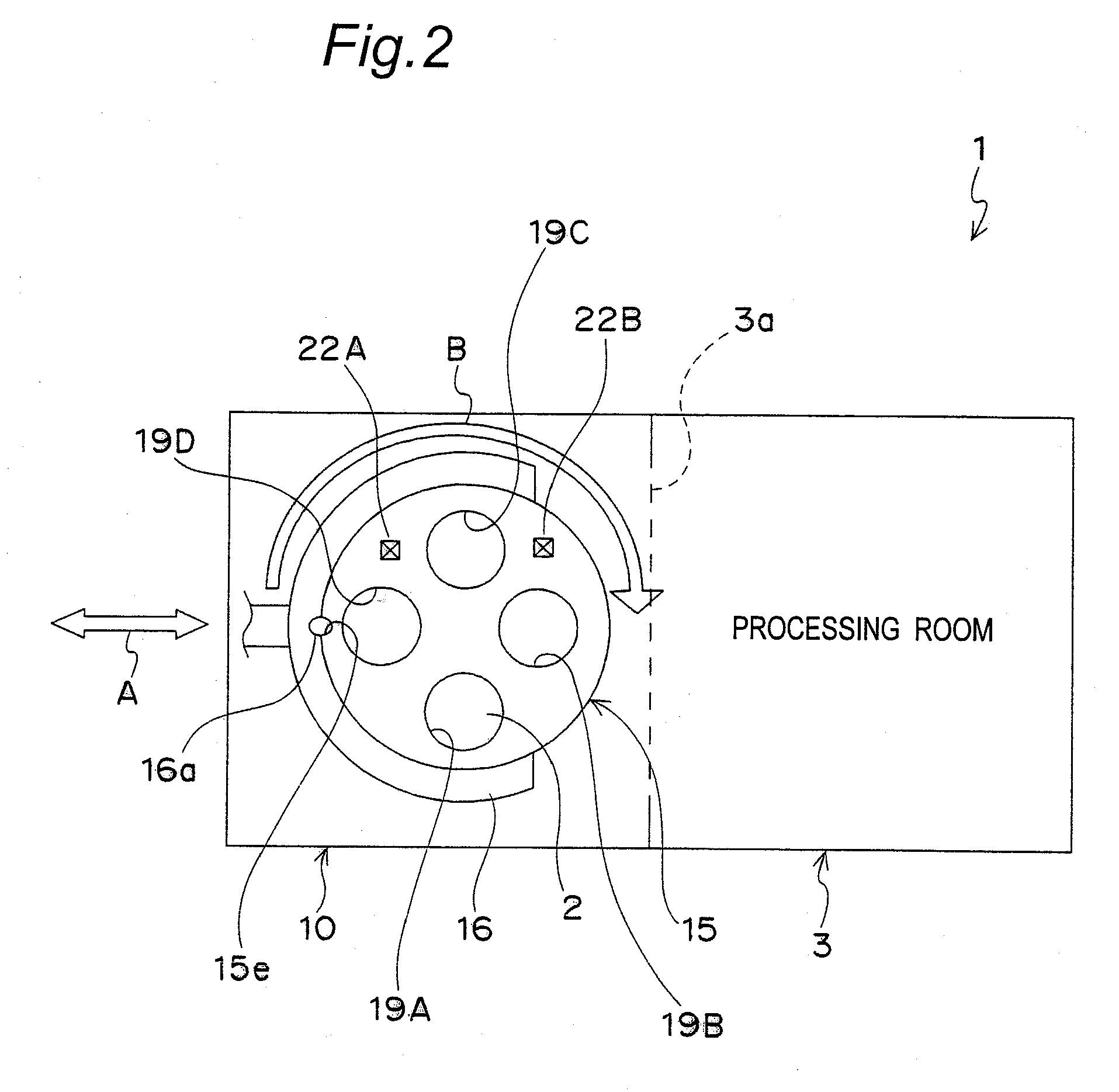
Plasma processing apparatus, plasma processing method, and tray
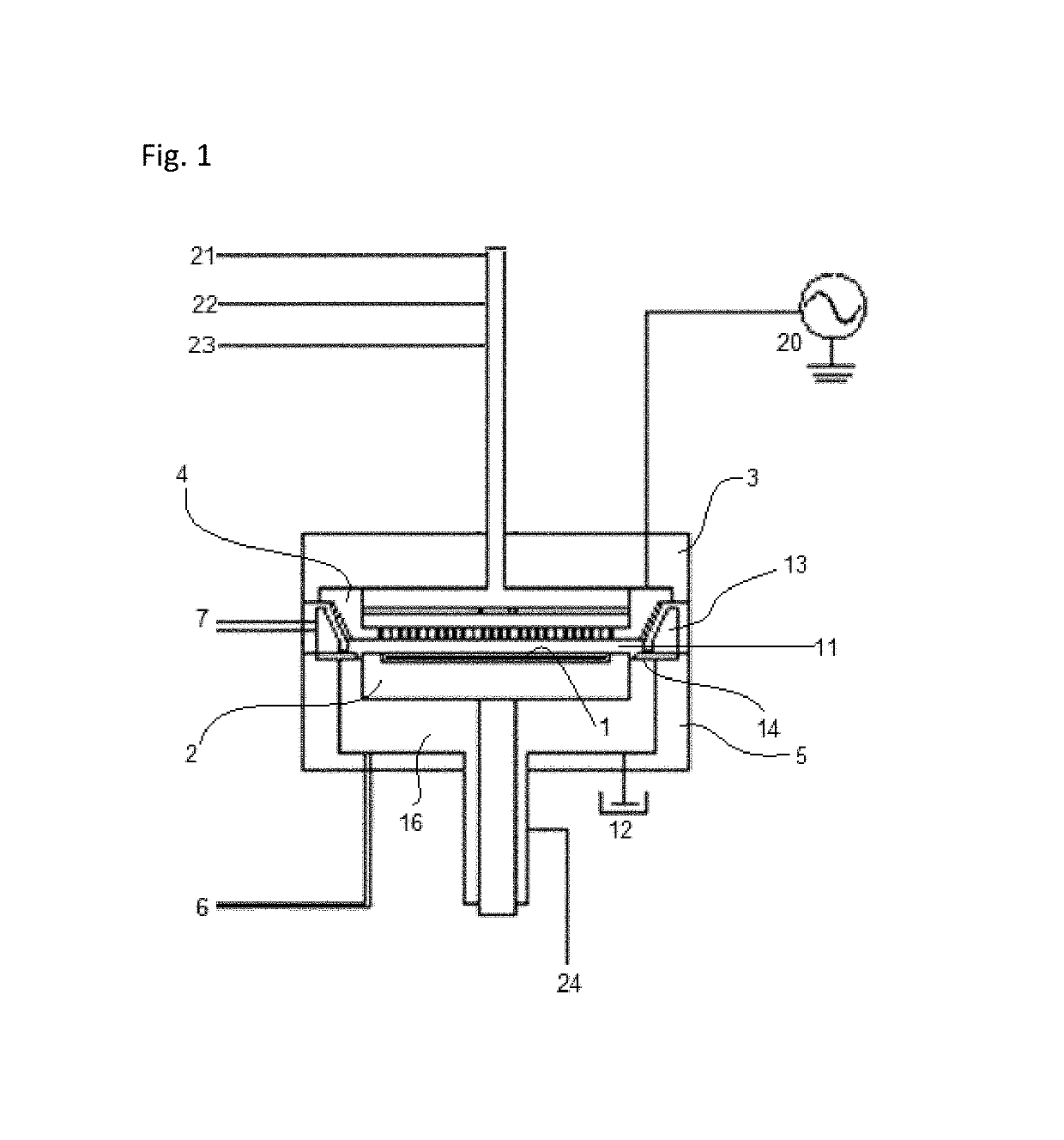
ActiveUS20090255901A1Uniform plasma treatmentImprove adhesionElectric discharge tubesDecorative surface effectsDielectric plateEngineering
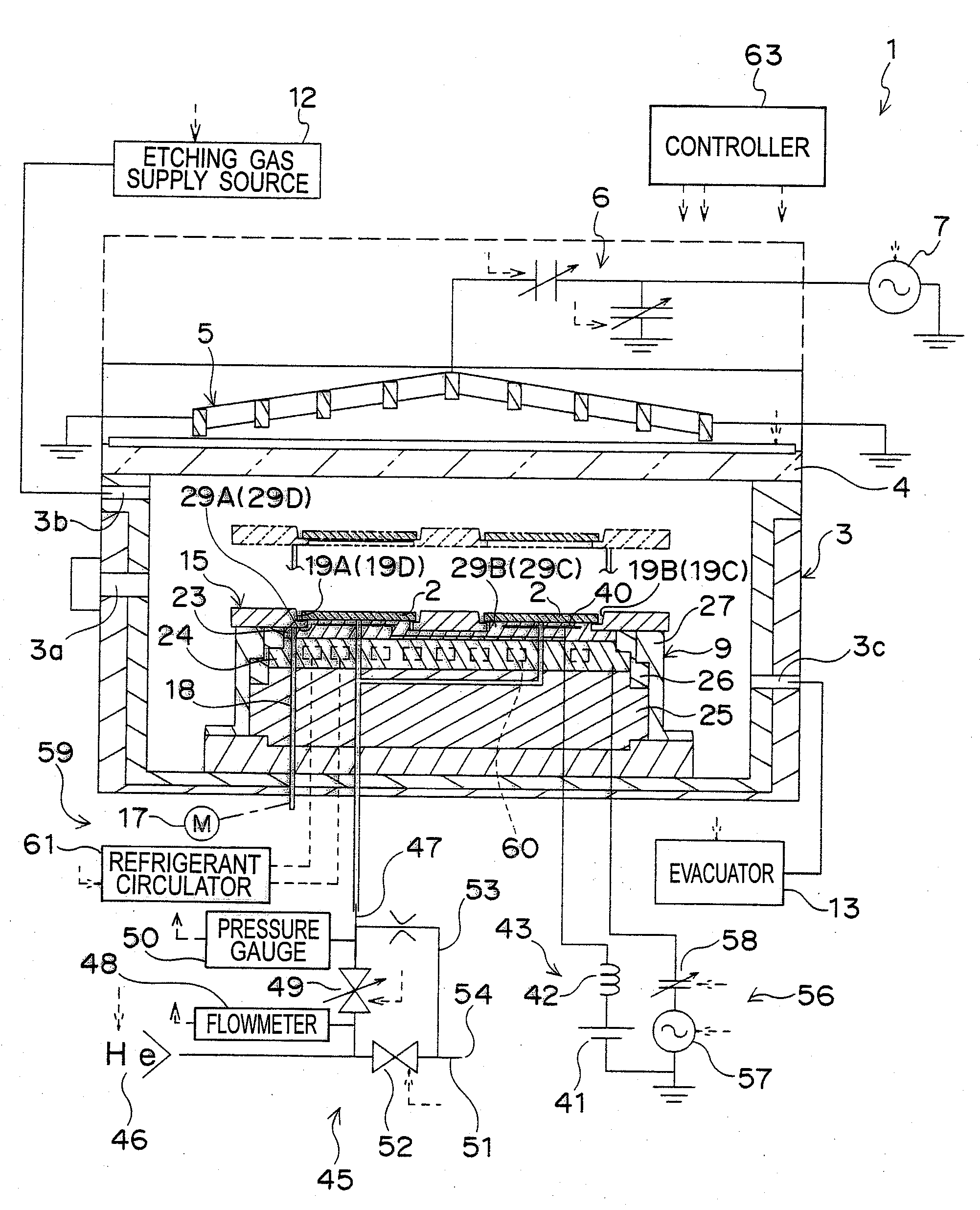
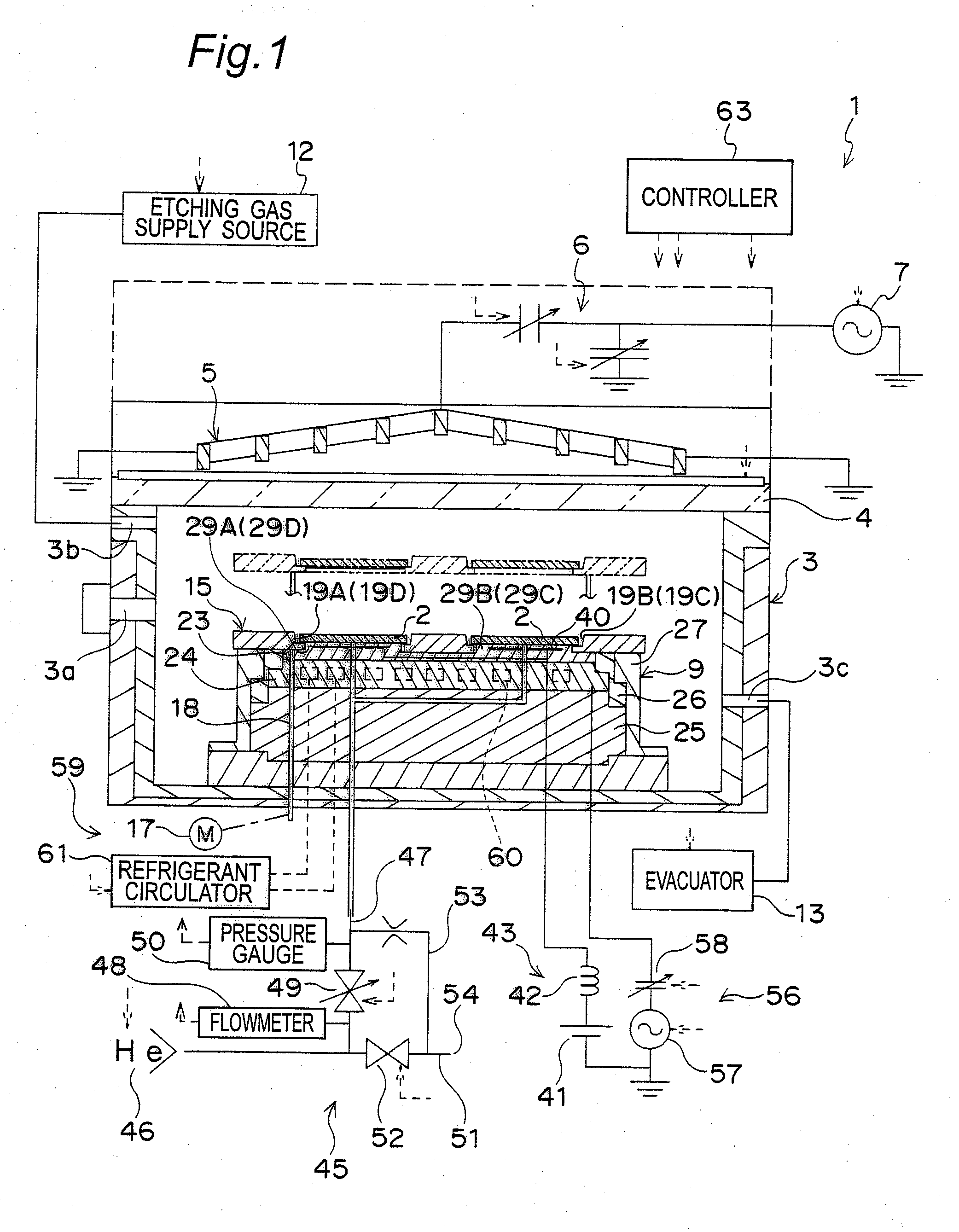
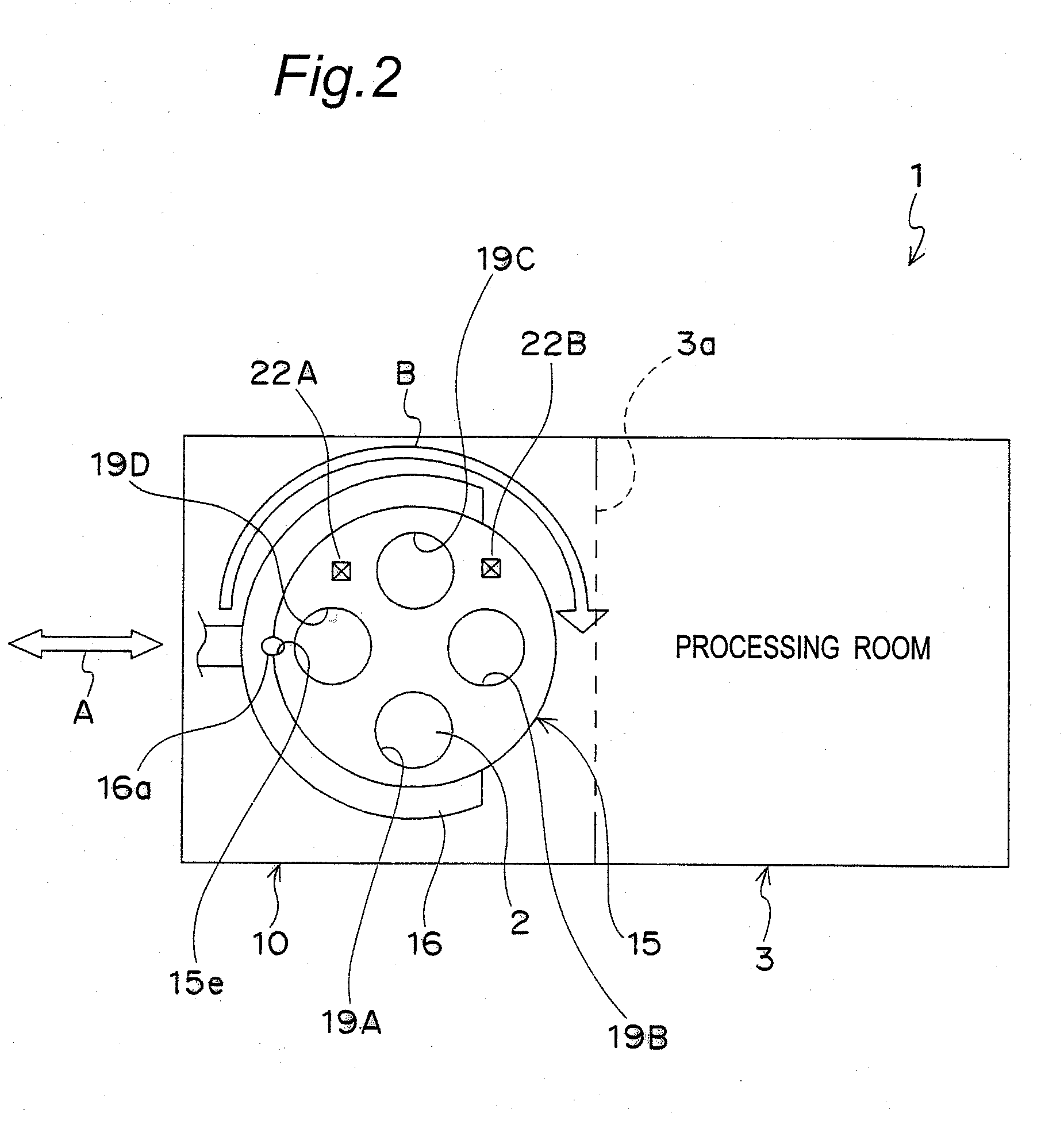
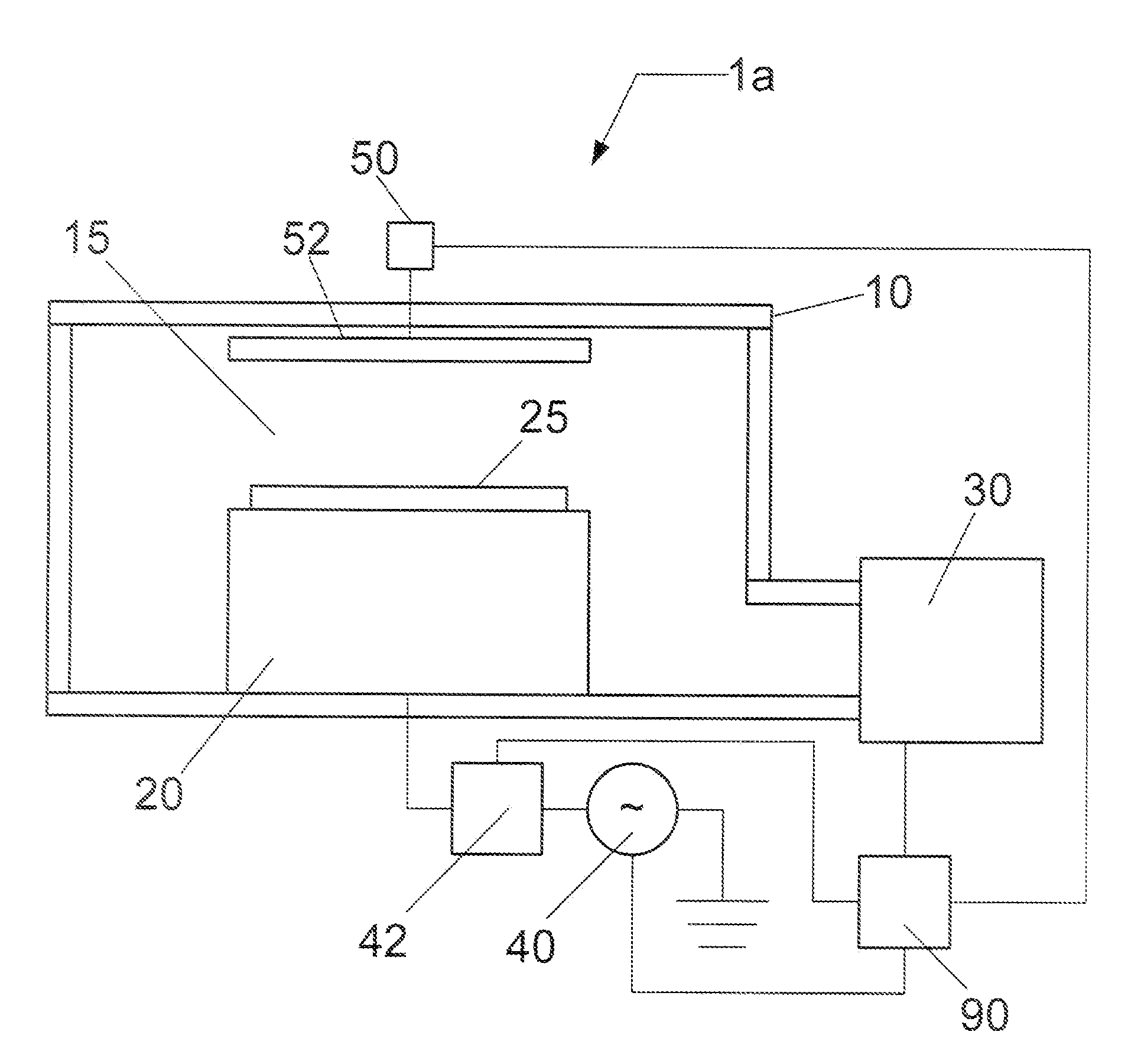
A tray 15 for a dry etching apparatus 1 has substrate accommodation holes 19A to 19D penetrating thickness direction and a substrate support portion 21 supporting an outer peripheral edge portion of a lower surface 2a of a substrate 2. A dielectric plate 23 has a tray support surface 28 supporting a lower surface of the tray 15, substrate placement portions 29A through 29D inserted from a lower surface side of the tray 15 into the substrate accommodation holes 19A through 19D and having a substrate placement surface 31 at its upper end surface for placing the substrate 2. A dc voltage applying mechanism 43 applies a dc voltage to an electrostatic attraction electrode 40. A heat conduction gas supply mechanism 45 supplies a heat conduction gas between the substrate 2 and substrate placement surface 31. The substrate 2 can be retained on the substrate placement surface 31 with high degree of adhesion. This results in that the cooling efficiency of the substrate 2 is improved and processing is uniformed at the entire region of the substrate surface including the vicinity of the outer peripheral edge.
Owner:PANASONIC INTELLECTUAL PROPERTY MANAGEMENT CO LTD
Nitride-based transistors and fabrication methods with an etch stop layer
InactiveUS20070018199A1Reduce harmSolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingEngineeringField-effect transistor
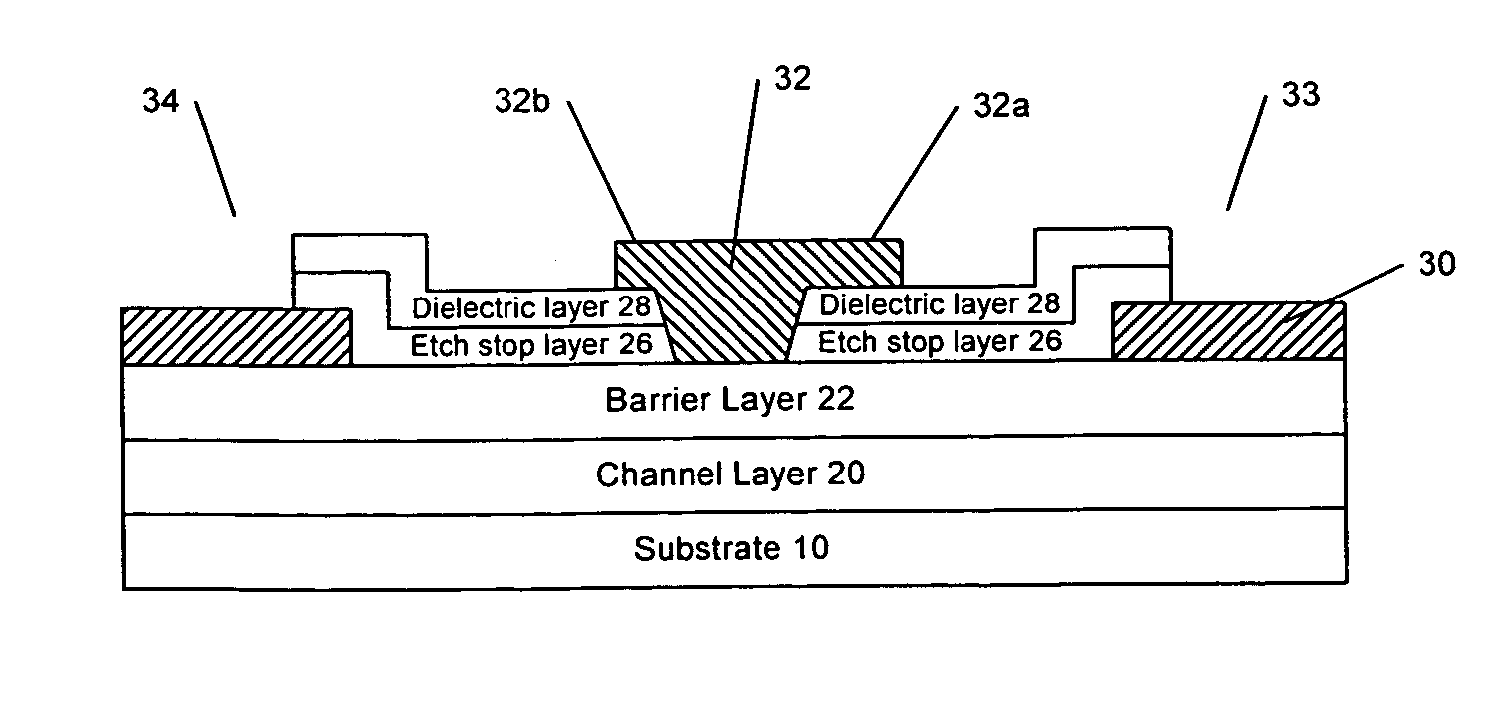
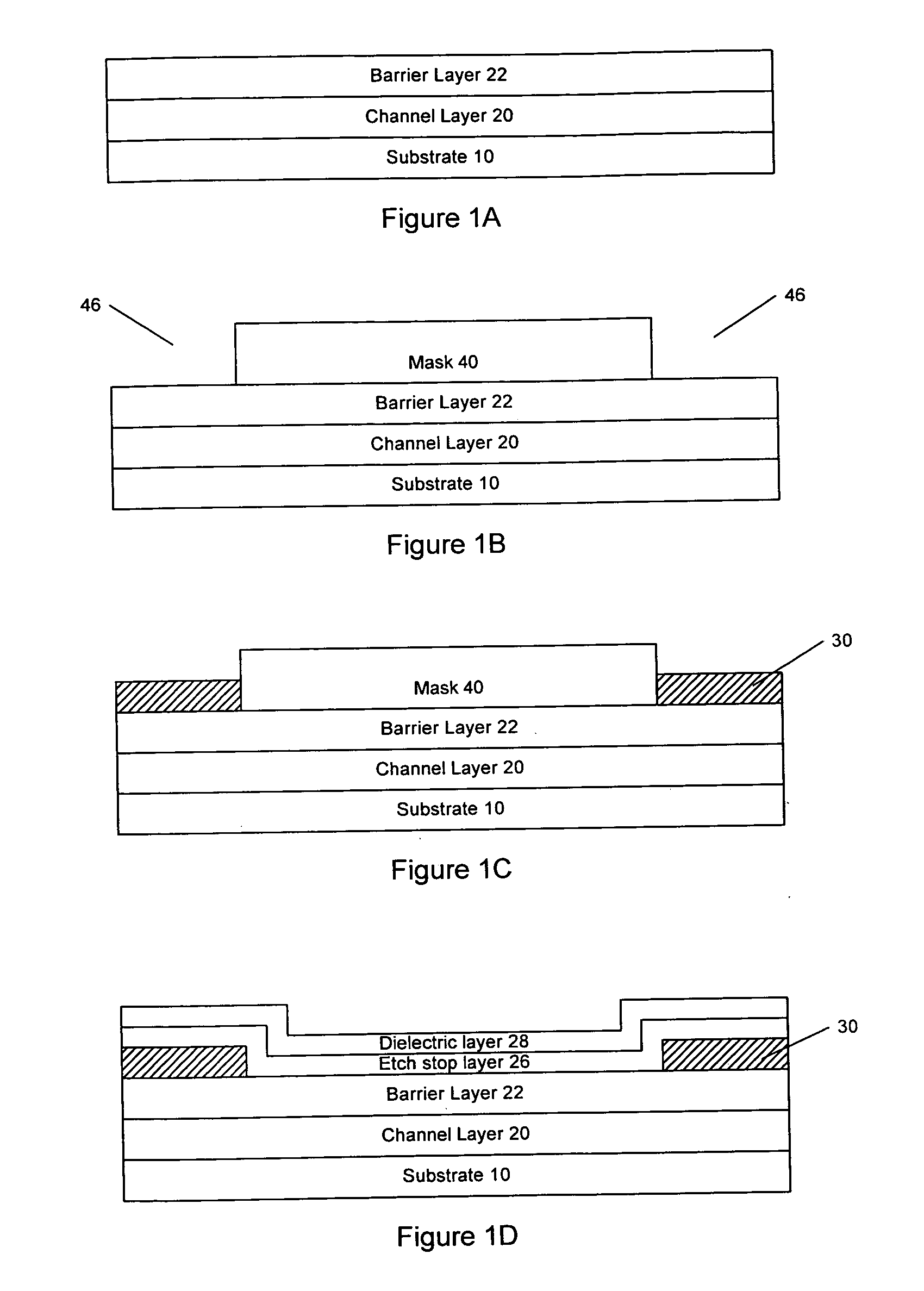
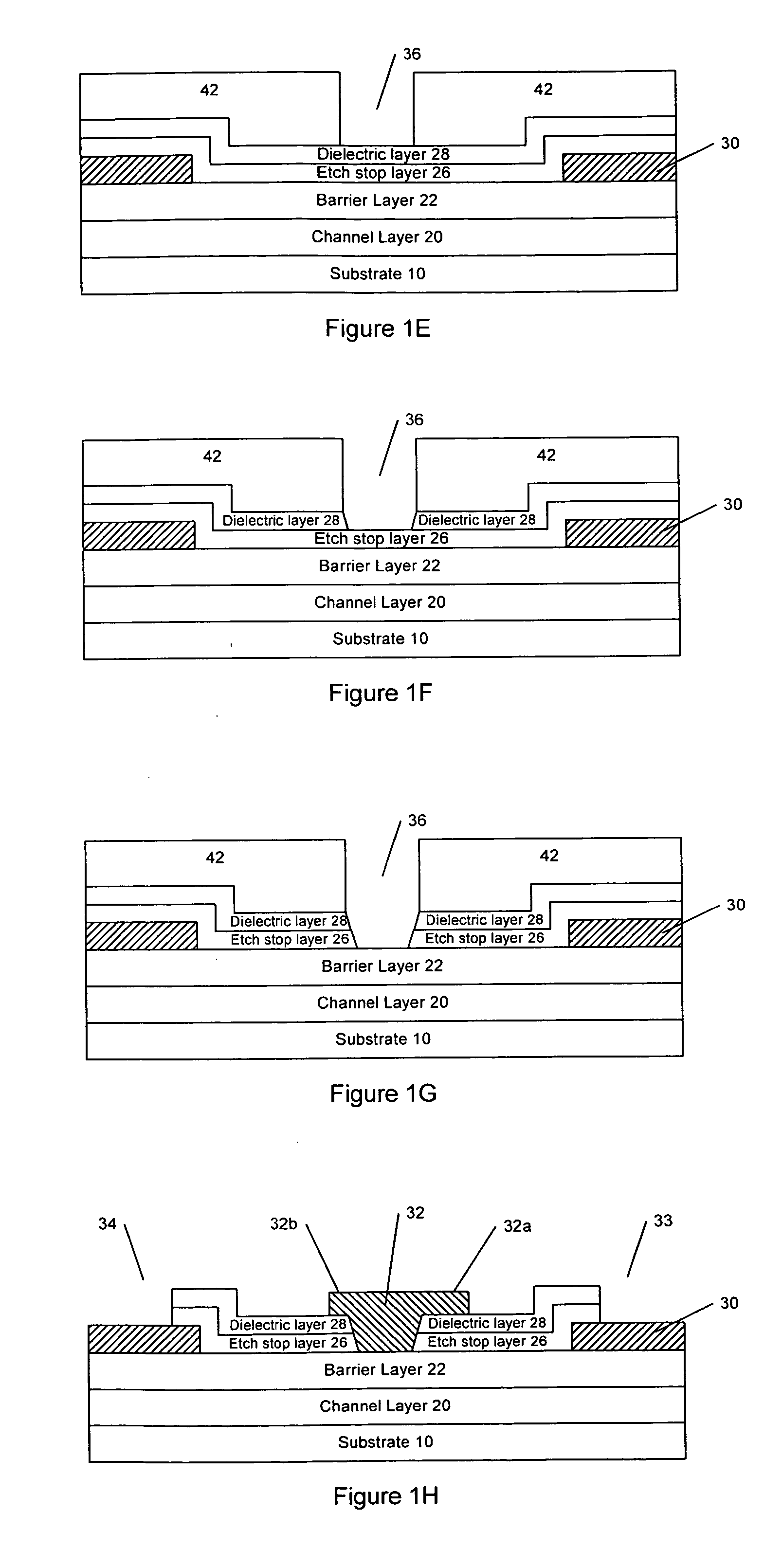
A III-Nitride field-effect transistor, specifically a HEMT, comprises a channel layer, a barrier layer on the channel layer, an etch stop layer on the cap layer, a dielectric layer on the etch stop layer, a gate recess that extends to the barrier layer, and a gate contact in the gate recess. The etch stop layer may reduce damage associated with forming the recessed gate by not exposing the barrier layer to dry etching. The etch stop layer in the recess is removed and the remaining etch stop layer serves as a passivation layer.
Owner:CREE INC
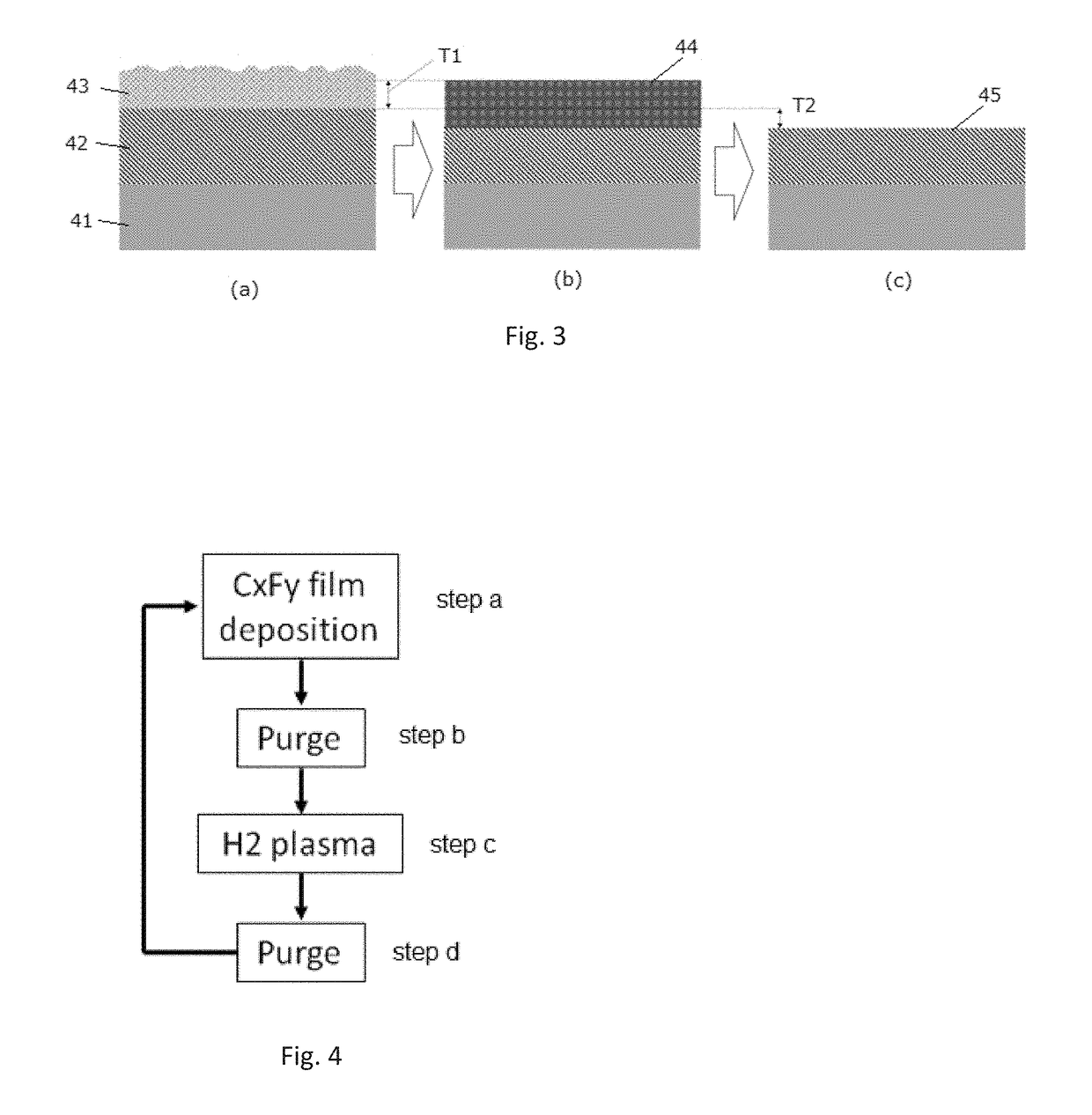
Process and method for in-situ dry cleaning of thin film deposition reactors and thin film layers
ActiveUS20150218695A1Efficient dry etching.Easy to useLighting and heating apparatusVacuum evaporation coatingHalogenChemical vapor deposition
The invention relates to the use of thionyl chloride and related materials for dry etching of internal surfaces of metalorganic vapour phase epitaxy (MOVPE) reactors to remove deposits. The method is also useful for the dry etching of process substrates within such reactors for cleaning and processing of those substrates. The invention may be particularly adaptable to chemical vapor deposition reactors used in the manufacture of high brightness LED's based on III-V semiconductors such as GaN and related materials. Features of the process include thermal, UV, and plasma activated dry cleaning, and the use of etchant gases such as COCl2, COBr2, COl2, SOl2, SOCl2, SOBr2, SO2Cl2, SO2Br2, NOCI, NOBr, NOl, S2Cl2, S2Br2, SCI2, SBr2, SOClBr, SOClF and SOFBr, either formed from neat materials or combinations of constituent gases such as CO, SO, SO2 or NO with halogens, to achieve the desired effect.
Owner:SEASTAR CHEM
Method of cyclic dry etching using etchant film
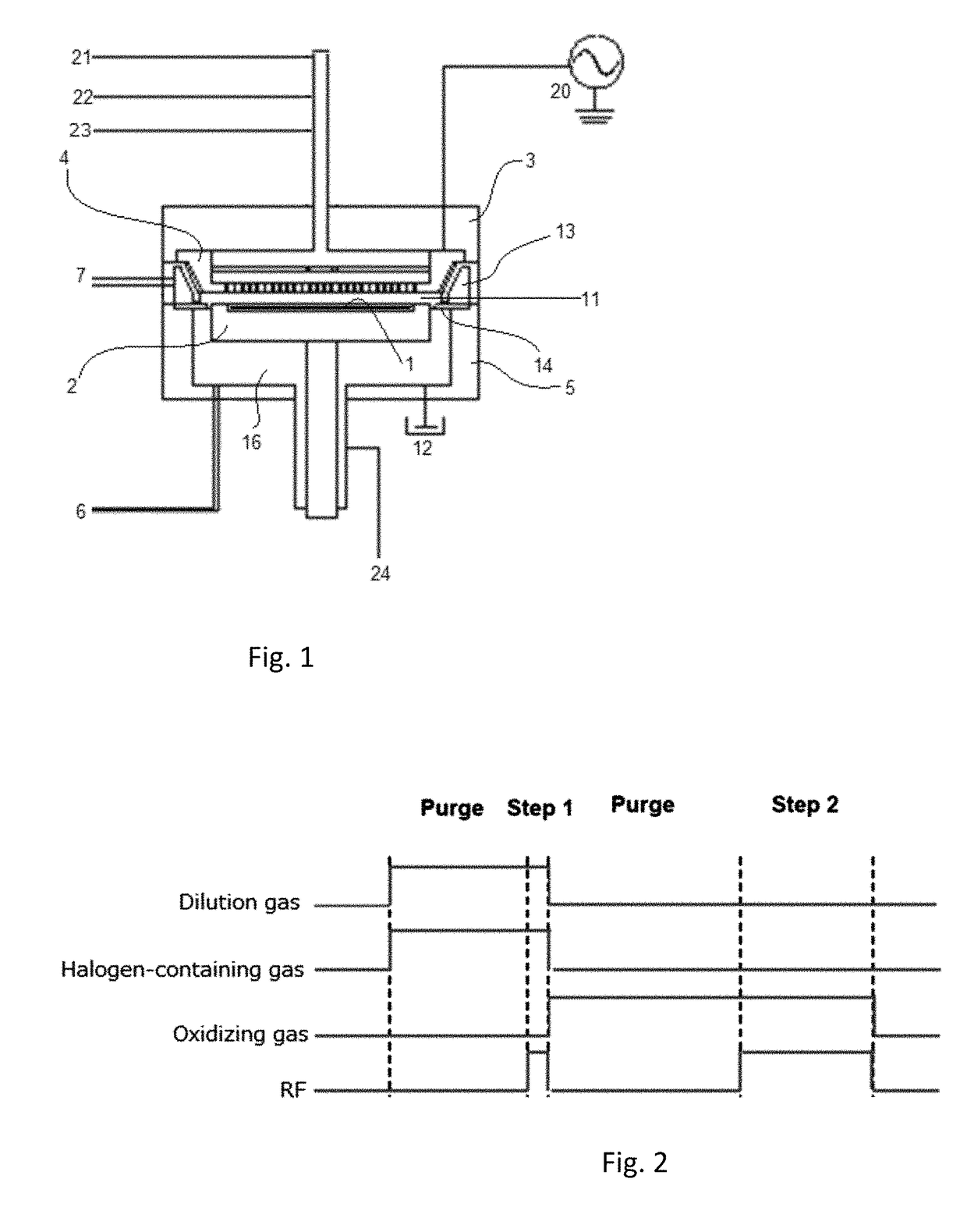
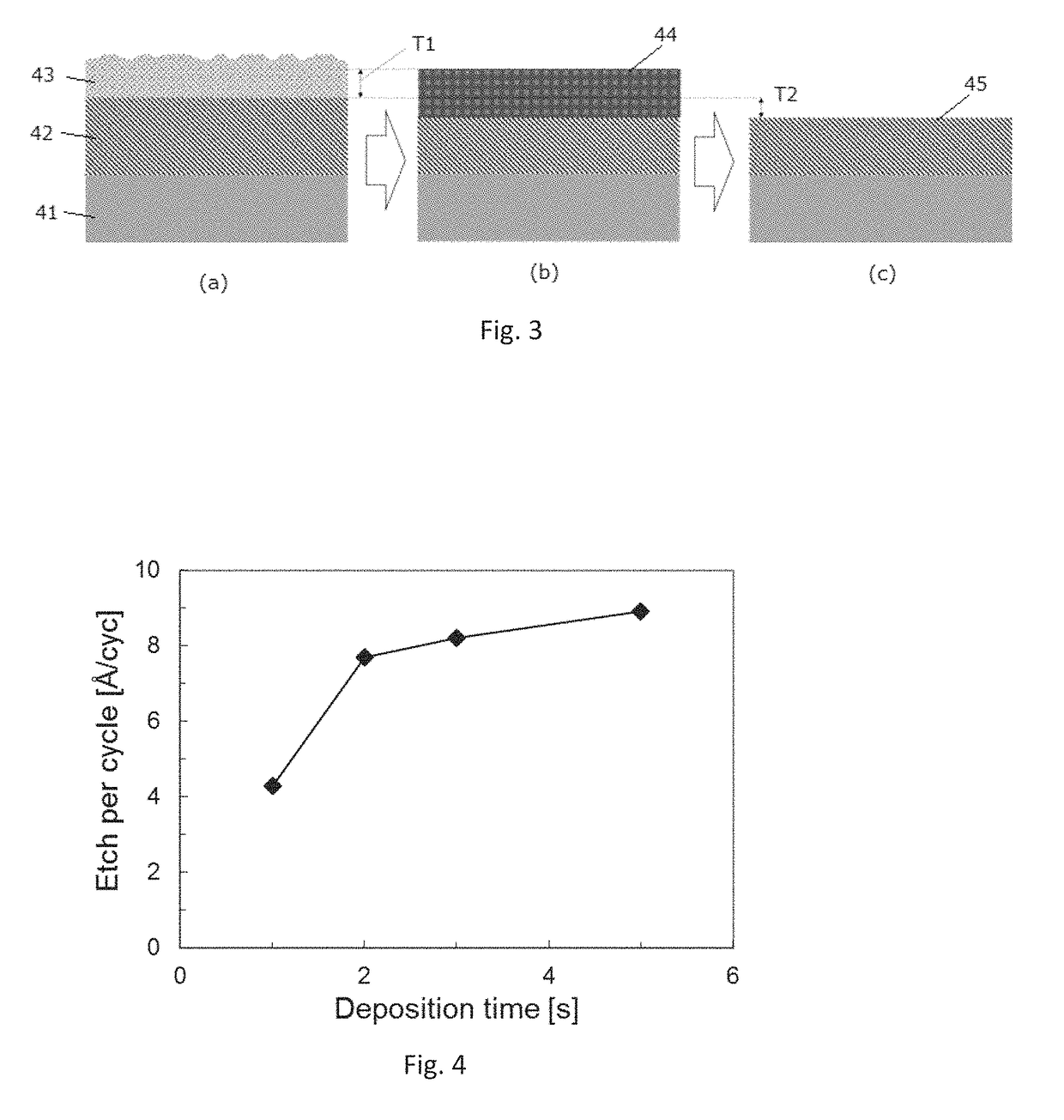
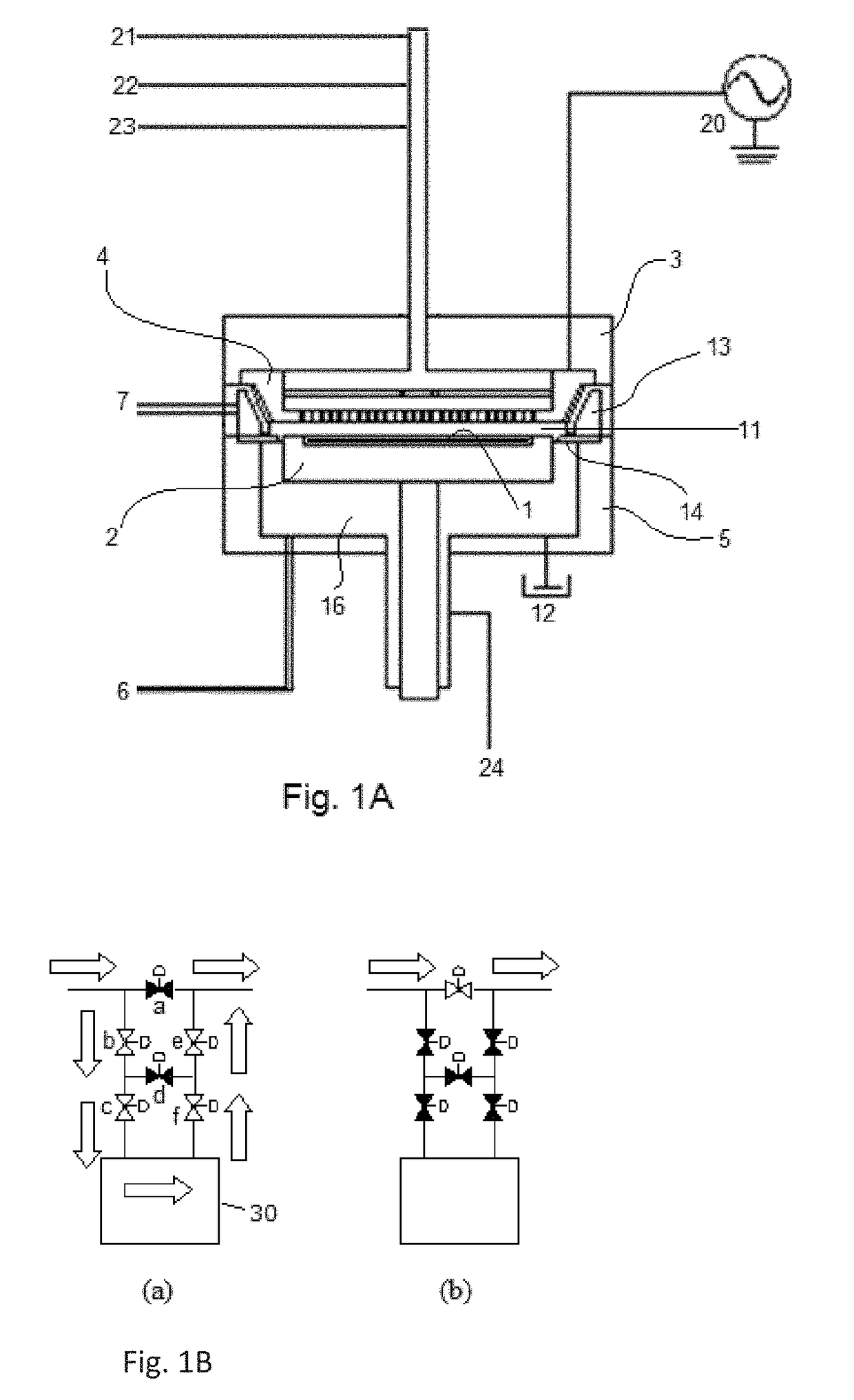
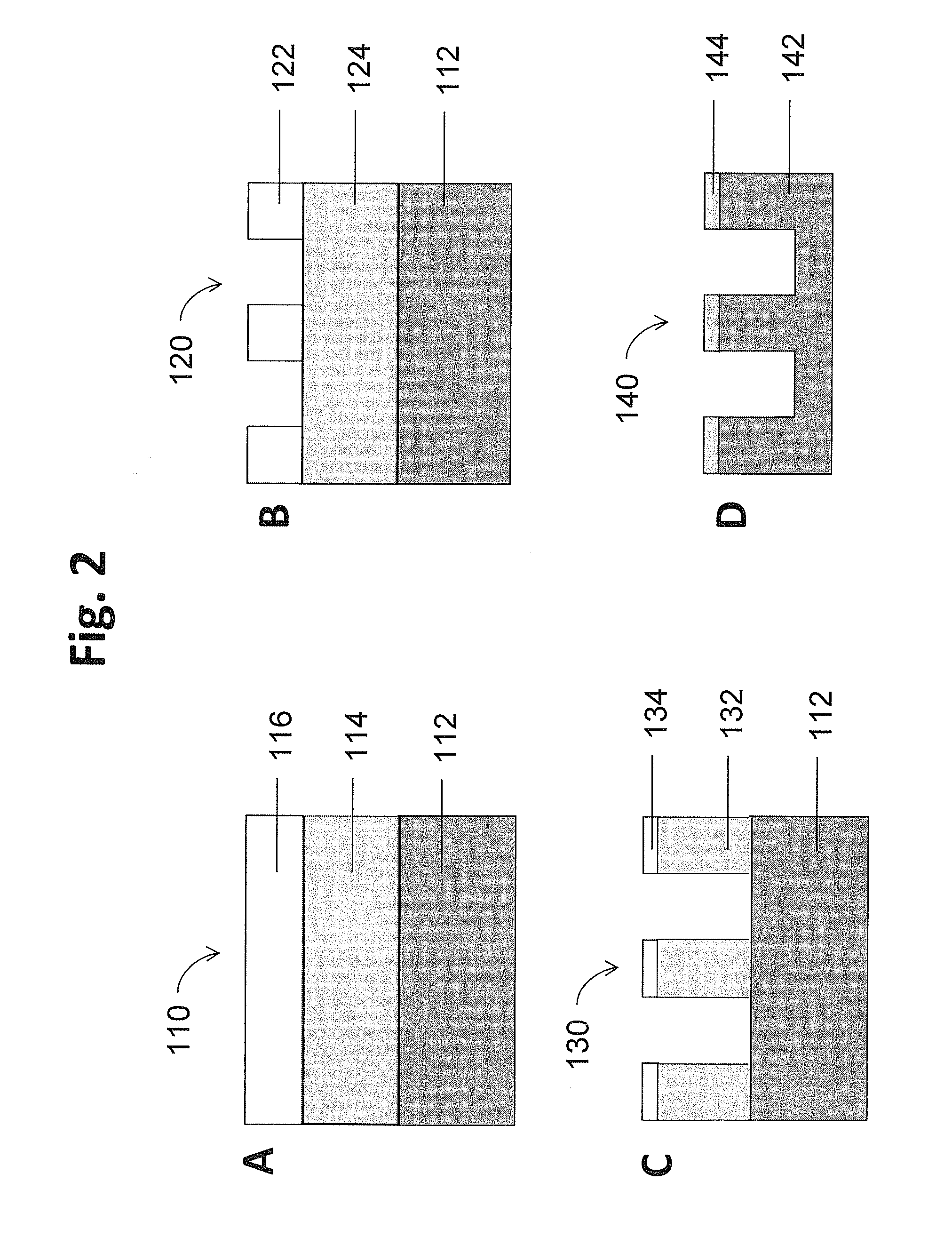
ActiveUS9793135B1Improve controllabilityEasy to operateSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingOptoelectronicsBoundary region
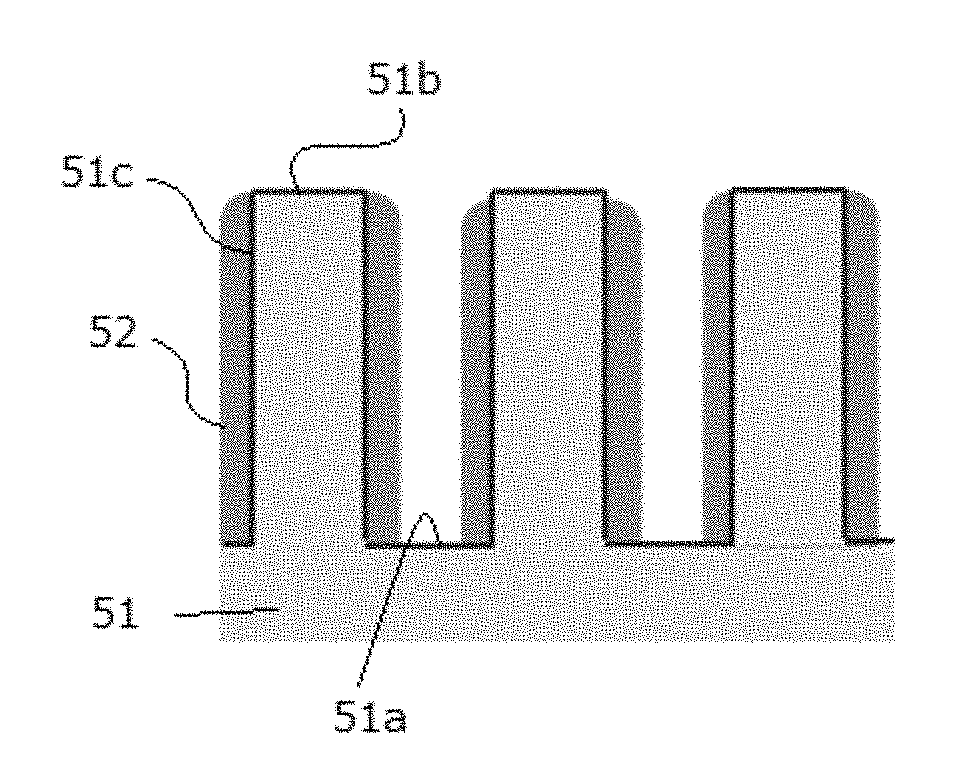
A method for etching a target layer on a substrate by a dry etching process includes at least one etching cycle, wherein an etching cycle includes: depositing a halogen-containing film using reactive species on the target layer on the substrate; and etching the halogen-containing film using a plasma of a non-halogen etching gas, which plasma alone does not substantially etch the target layer, to generate etchant species at a boundary region of the halogen-containing film and the target layer, thereby etching a portion of the target layer in the boundary region.
Owner:ASM IP HLDG BV
Method for forming spacers using silicon nitride film for spacer-defined multiple patterning
ActiveUS20170316940A1Semiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingChemical vapor deposition coatingSurface patternSilanes
A method of forming spacers for spacer-defined multiple pattering (SDMP), includes: depositing a pattern transfer film by PEALD on the entire patterned surface of a template using halogenated silane as a precursor and nitrogen as a reactant at a temperature of 200° C. or less, which pattern transfer film is a silicon nitride film; dry-etching the template using a fluorocarbon as an etchant, and thereby selectively removing a portion of the pattern transfer film formed on a top of a core material and a horizontal portion of the pattern transfer film while leaving the core material and a vertical portion of the pattern transfer film as a vertical spacer, wherein a top of the vertical spacer is substantially flat; and dry-etching the core material, whereby the template has a surface patterned by the vertical spacer on a underlying layer.
Owner:ASM IP HLDG BV
Plasma processing apparatus and plasma processing method
ActiveUS20100051584A1Improve adhesionImprove cooling efficiencyElectric discharge tubesDecorative surface effectsDielectric plateEngineering
A tray 15 for a dry etching apparatus 1 has substrate accommodation holes 19A to 19D penetrating thickness direction and a substrate support portion 21 supporting an outer peripheral edge portion of a lower surface 2a of a substrate 2. A dielectric plate 23 has a tray support surface 28 supporting a lower surface of the tray 15, substrate placement portions 29A through 29D inserted from a lower surface side of the tray 15 into the substrate accommodation holes 19A through 19D and having a substrate placement surface 31 at its upper end surface for placing the substrate 2. A dc voltage applying mechanism 43 applies a dc voltage to an electrostatic attraction electrode 40. A heat conduction gas supply mechanism 45 supplies a heat conduction gas between the substrate 2 and substrate placement surface 31. The substrate 2 can be retained on the substrate placement surface 31 with high degree of adhesion. This results in that the cooling efficiency of the substrate 2 is improved and processing is uniformed at the entire region of the substrate surface including the vicinity of the outer peripheral edge.
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
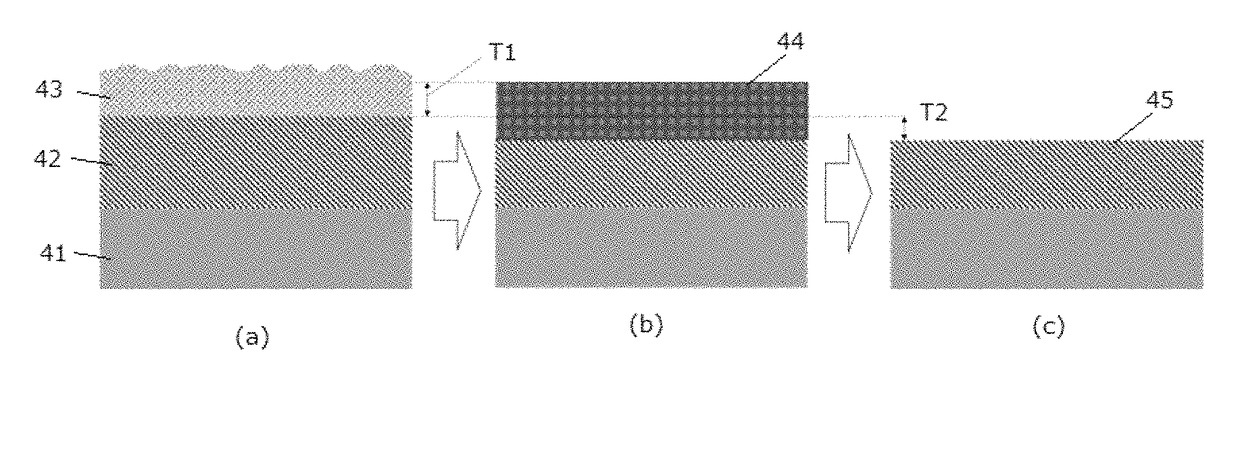
Solution processible hardmasks for high resolution lithography
Solution processible hardmasks are described that can be formed from aqueous precursor solutions comprising polyoxometal clusters and anions, such as polyatomic anions. The solution processible metal oxide layers are generally placed under relatively thin etch resist layers to provide desired etch contrast with underlying substrates and / or antireflective properties. In some embodiments, the metal oxide hardmasks can be used along with an additional hardmask and / or antireflective layers. The metal oxide hardmasks can be etched with wet or dry etching. Desirable processing improvements can be obtained with the solution processible hardmasks.
Owner:INPRIA CORP
Method of atomic layer etching using hydrogen plasma
ActiveUS20180350620A1High selectivityImprove controllabilitySemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingHydrogen halideHydrogen
A method for etching a target layer on a substrate by a dry etching process includes at least one etching cycle, wherein an etching cycle includes: depositing a carbon halide film using reactive species on the target layer on the substrate; and etching the carbon halide film using a plasma of a non-halogen hydrogen-containing etching gas, which plasma alone does not substantially etch the target layer, thereby generating a hydrogen halide as etchant species at a boundary region of the carbon halide film and the target layer, thereby etching a portion of the target layer in the boundary region.
Owner:ASM IP HLDG BV
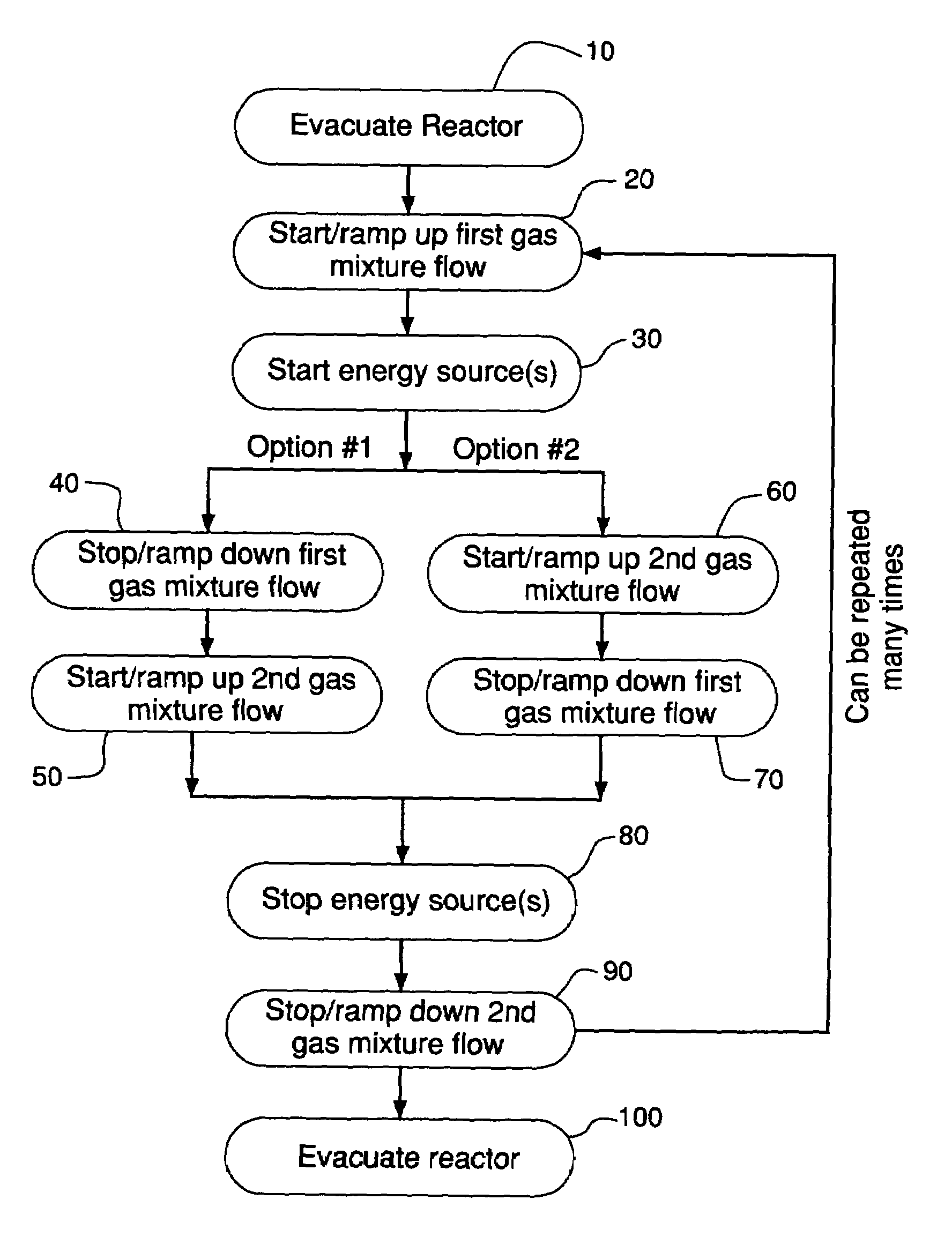
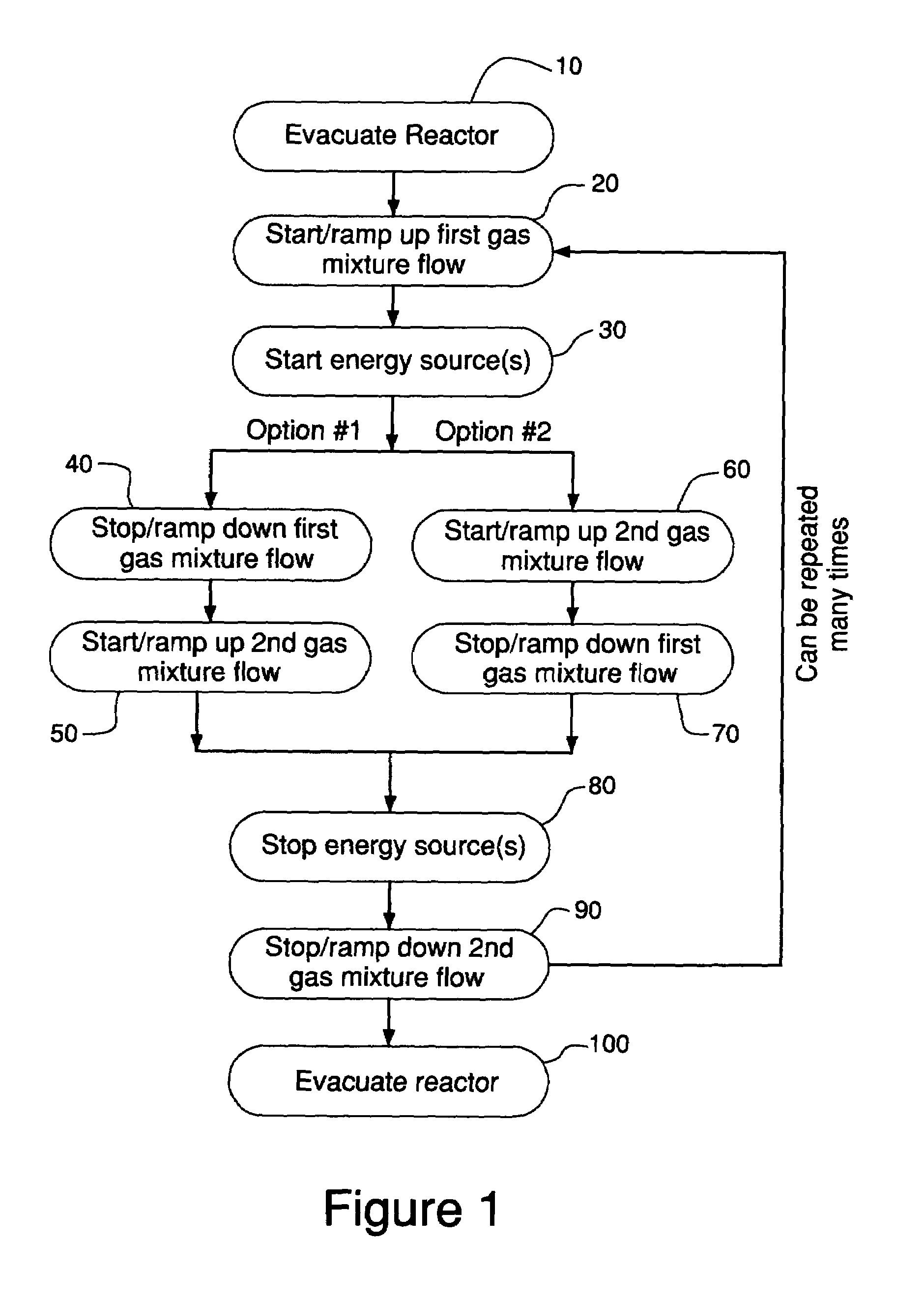
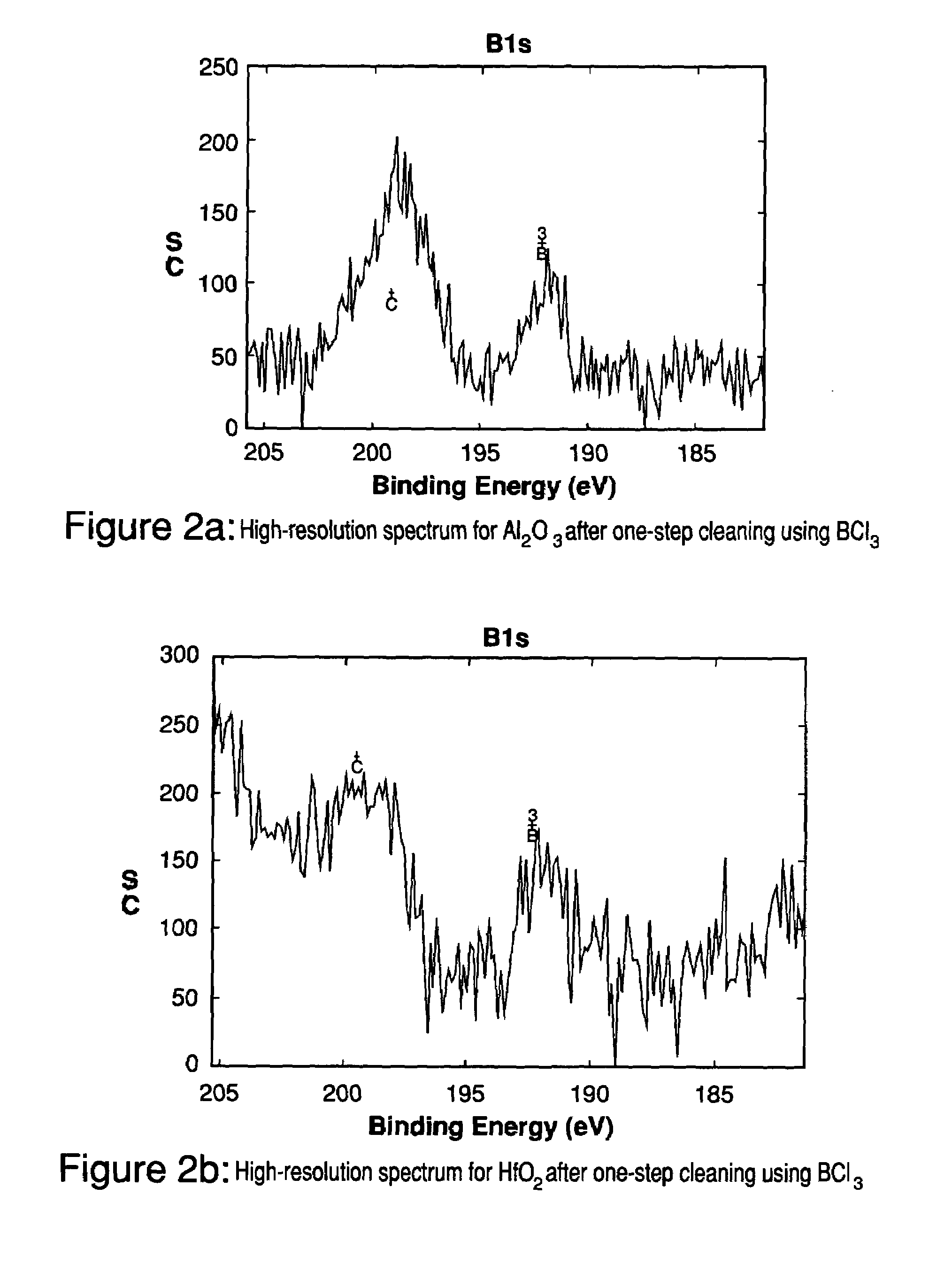
Method for cleaning deposition chambers for high dielectric constant materials
A method for dry etching and chamber cleaning high dielectric constant materials is disclosed herein. In one aspect of the present invention, there is provided a process for cleaning a substance comprising a dielectric constant greater than the dielectric constant of silicon dioxide from at least a portion of a surface of a reactor comprising: introducing a first gas mixture comprising a boron-containing reactive agent into the reactor wherein the first gas mixture reacts with the substance contained therein to provide a volatile product and a boron-containing by-product; introducing a second gas mixture comprising a fluorine-containing reactive agent into the reactor wherein the second gas mixture reacts with the boron-containing by-product contained therein to form the volatile product; and removing the volatile product from the reactor.
Owner:AIR PROD & CHEM INC
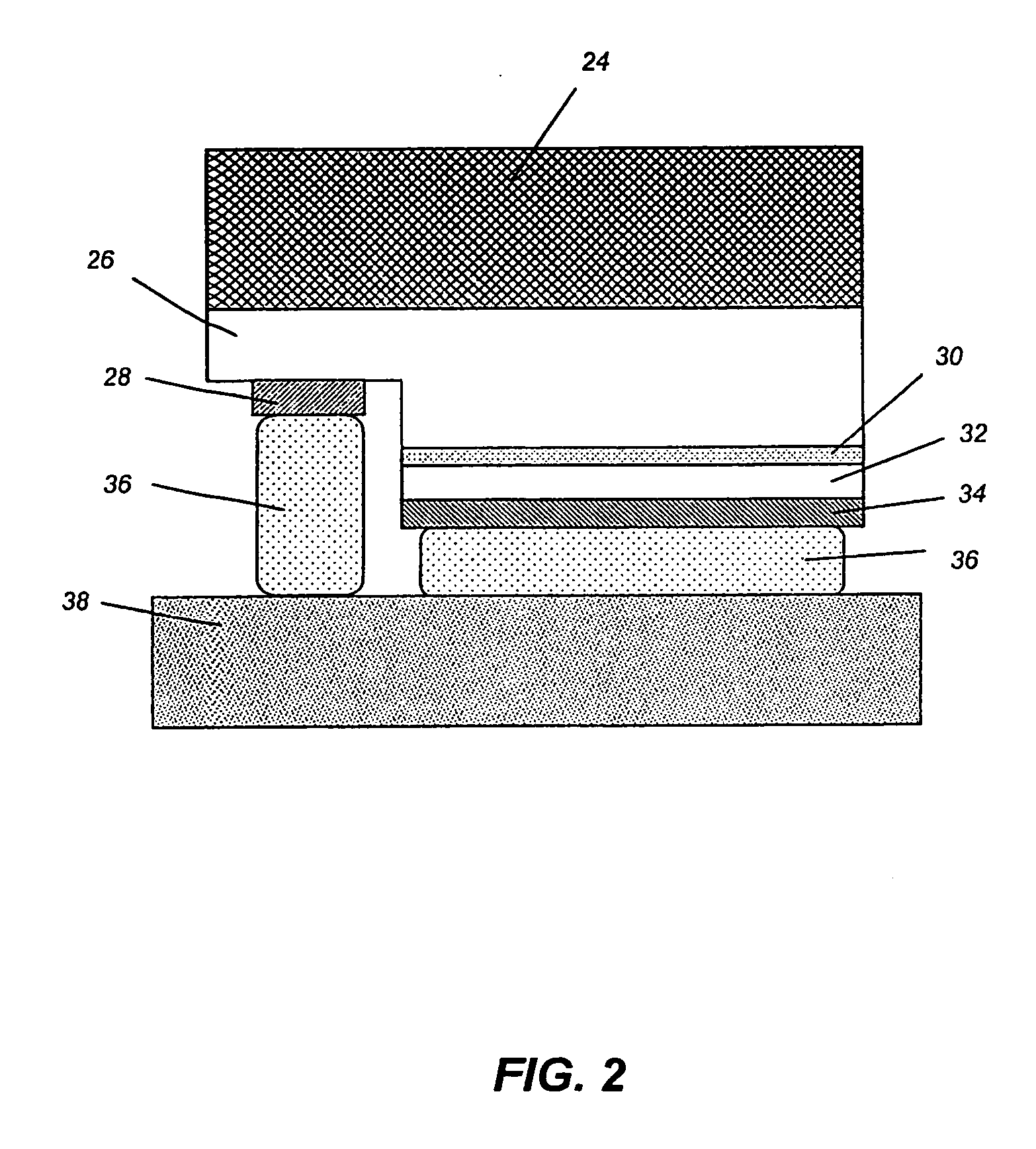
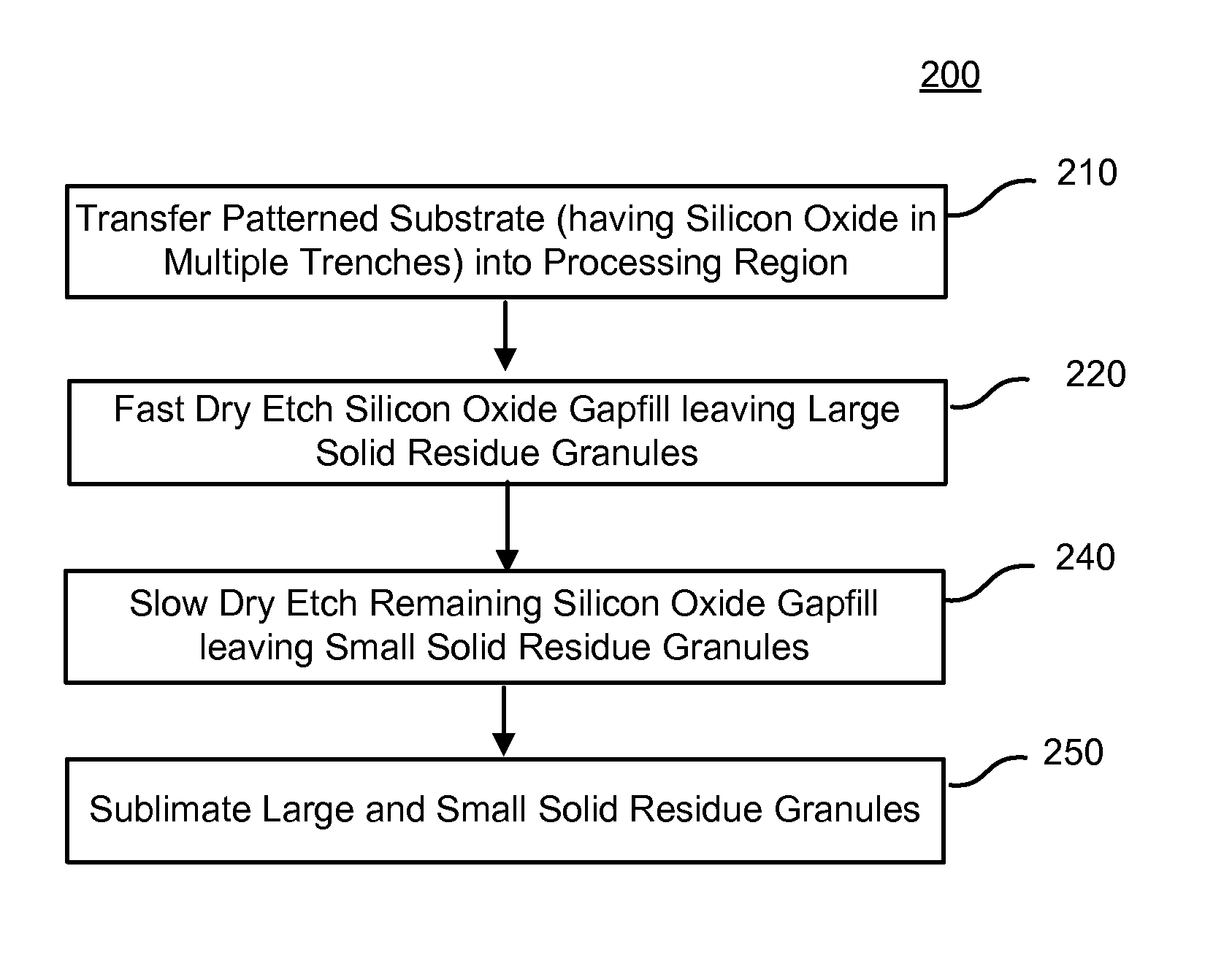
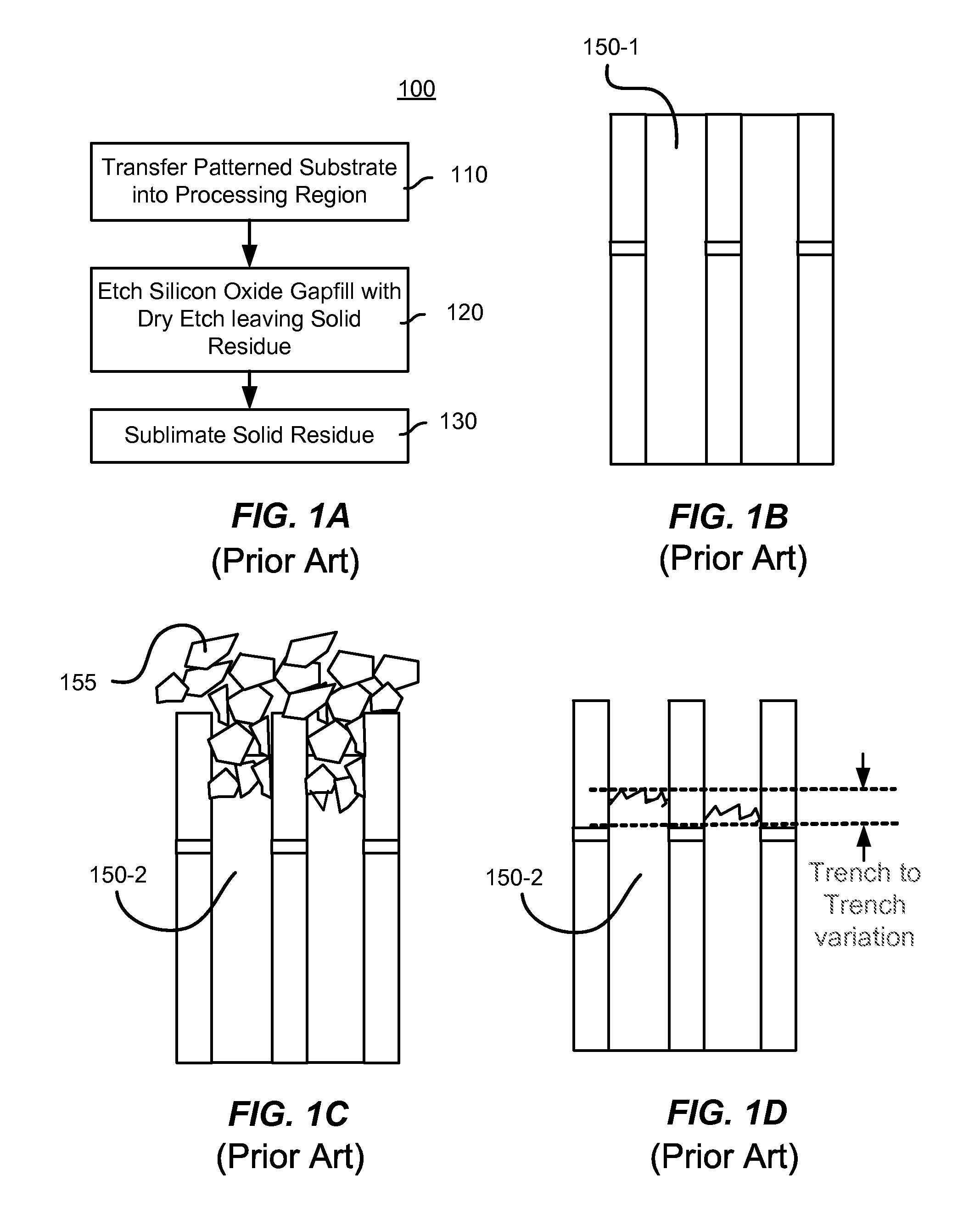
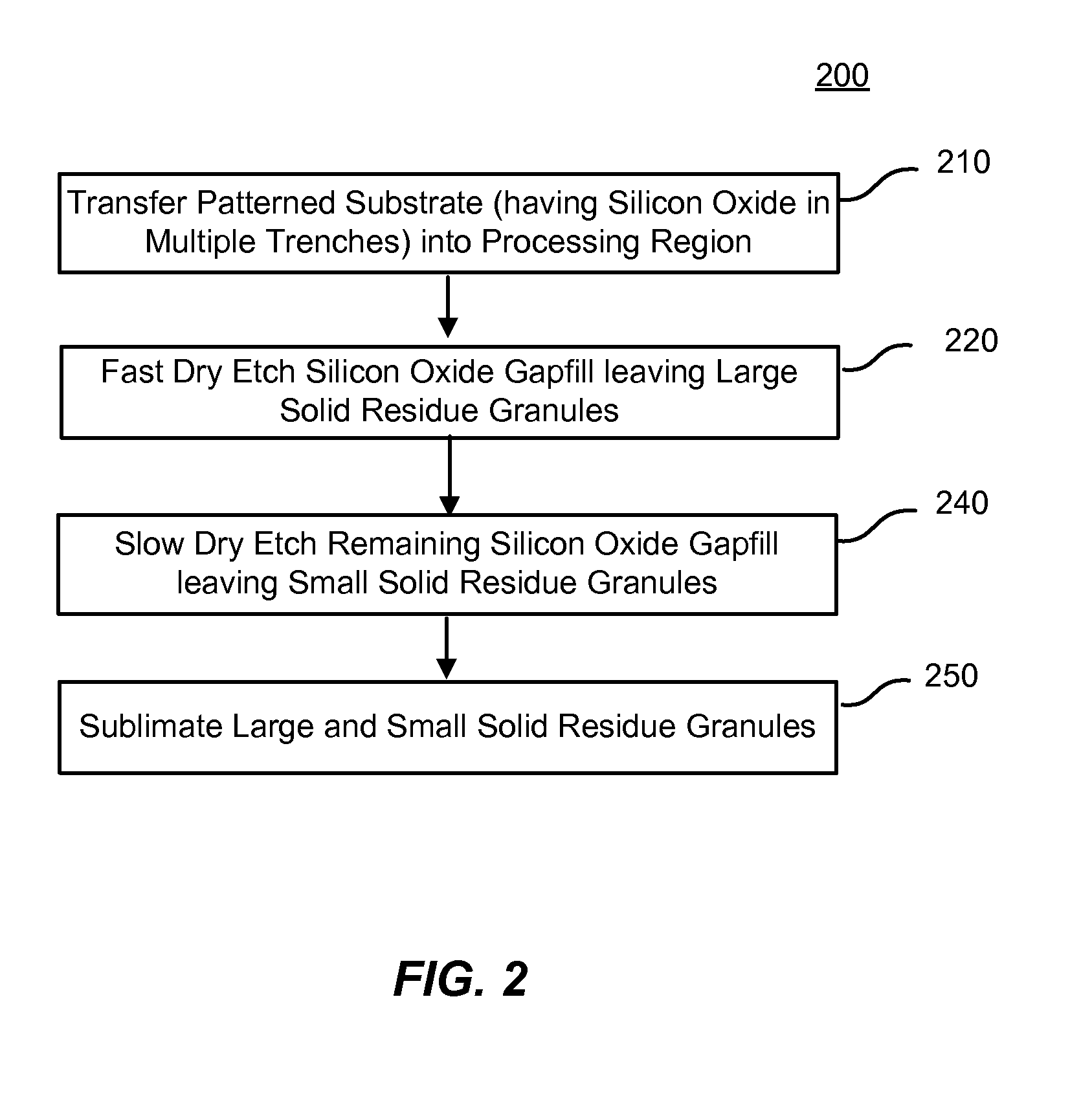
Uniform dry etch in two stages
ActiveUS20120196447A1Flat surfaceEasy to removeSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSilicon oxideDry etching
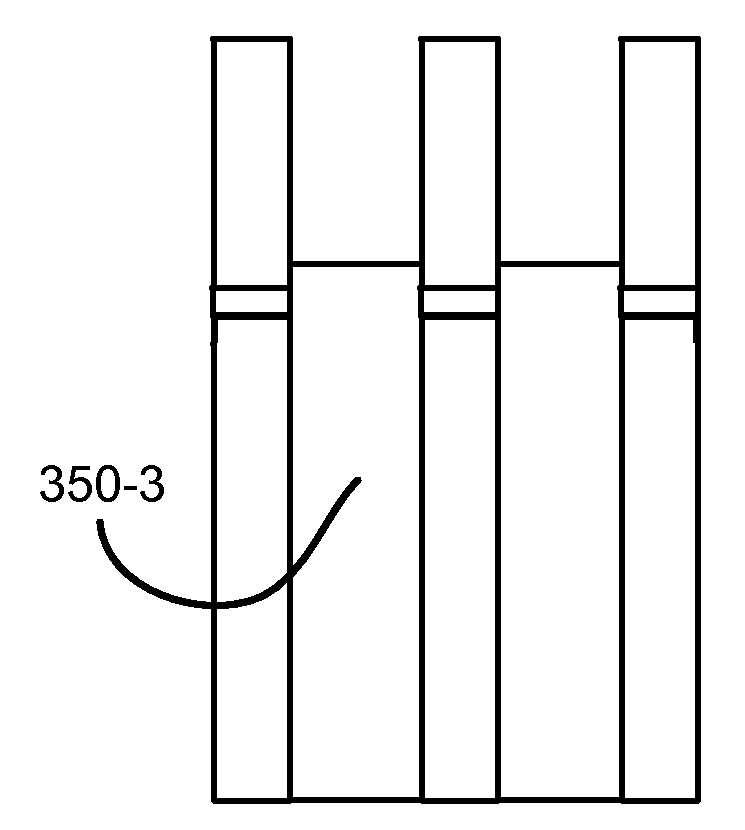
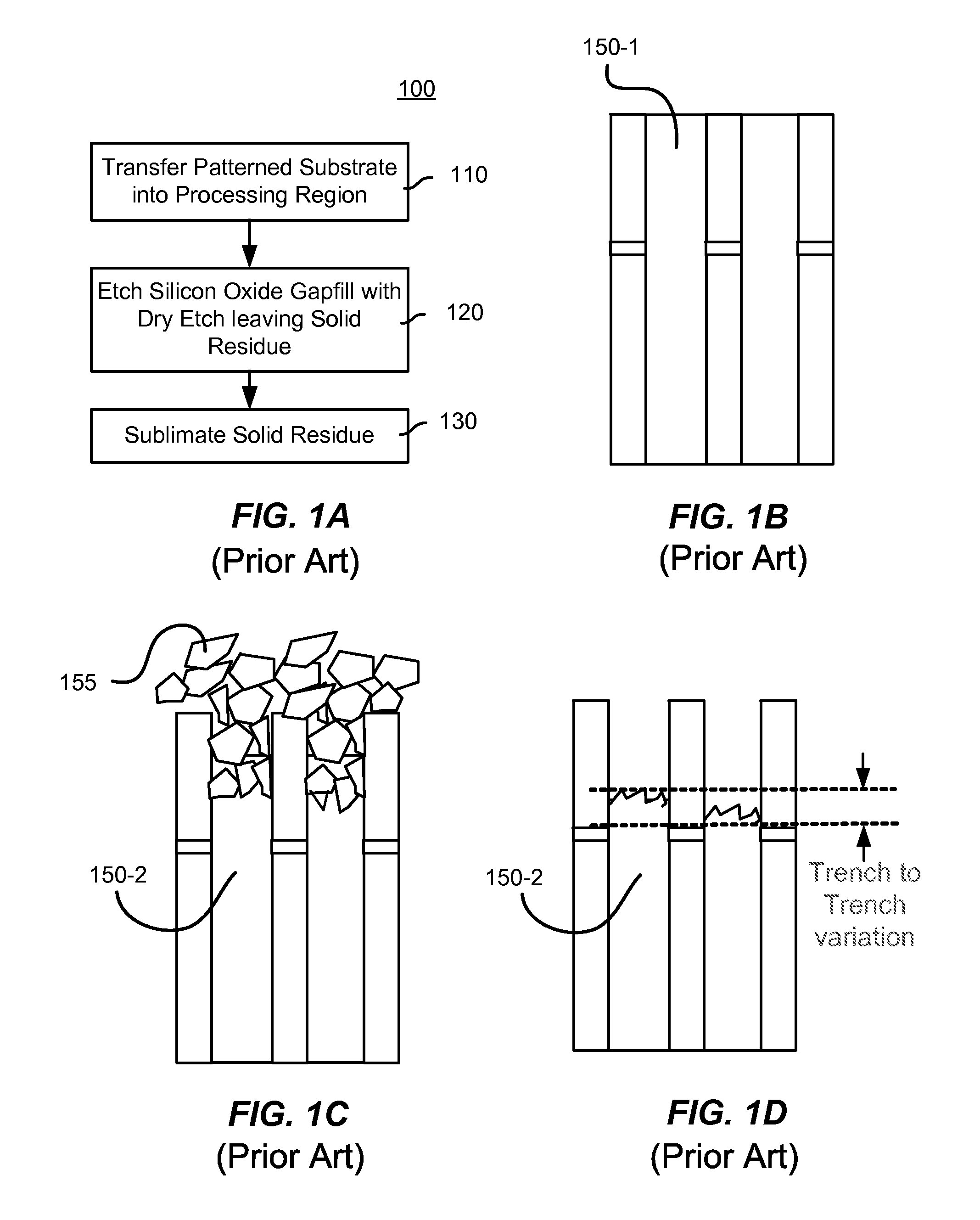
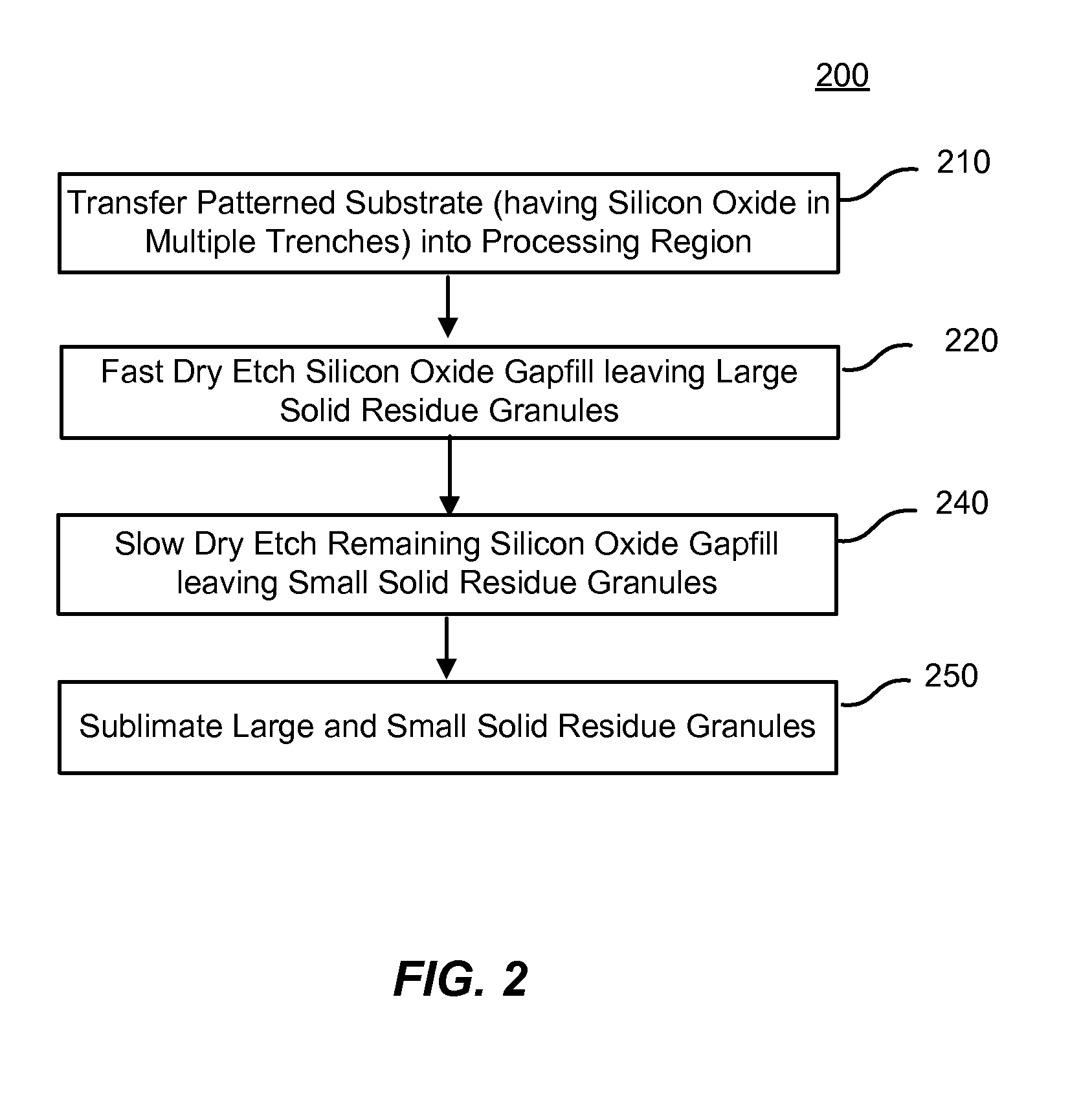
A method of etching silicon oxide from a multiple trenches is described which allows more homogeneous etch rates among trenches. The surfaces of the etched silicon oxide within the trench following the etch may also be smoother. The method includes two dry etch stages followed by a sublimation step. The first dry etch stage removes silicon oxide quickly and produces large solid residue granules. The second dry etch stage remove silicon oxide slowly and produces small solid residue granules in amongst the large solid residue granules. Both the small and large solid residue are removed in the ensuing sublimation step. There is no sublimation step between the two dry etch stages.
Owner:APPLIED MATERIALS INC
Method for forming spacers using silicon nitride film for spacer-defined multiple patterning
ActiveUS10468251B2Semiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingChemical vapor deposition coatingFluorocarbonDry etching
A method of forming spacers for spacer-defined multiple pattering (SDMP), includes: depositing a pattern transfer film by PEALD on the entire patterned surface of a template using halogenated silane as a precursor and nitrogen as a reactant at a temperature of 200° C. or less, which pattern transfer film is a silicon nitride film; dry-etching the template using a fluorocarbon as an etchant, and thereby selectively removing a portion of the pattern transfer film formed on a top of a core material and a horizontal portion of the pattern transfer film while leaving the core material and a vertical portion of the pattern transfer film as a vertical spacer, wherein a top of the vertical spacer is substantially flat; and dry-etching the core material, whereby the template has a surface patterned by the vertical spacer on a underlying layer.
Owner:ASM IP HLDG BV
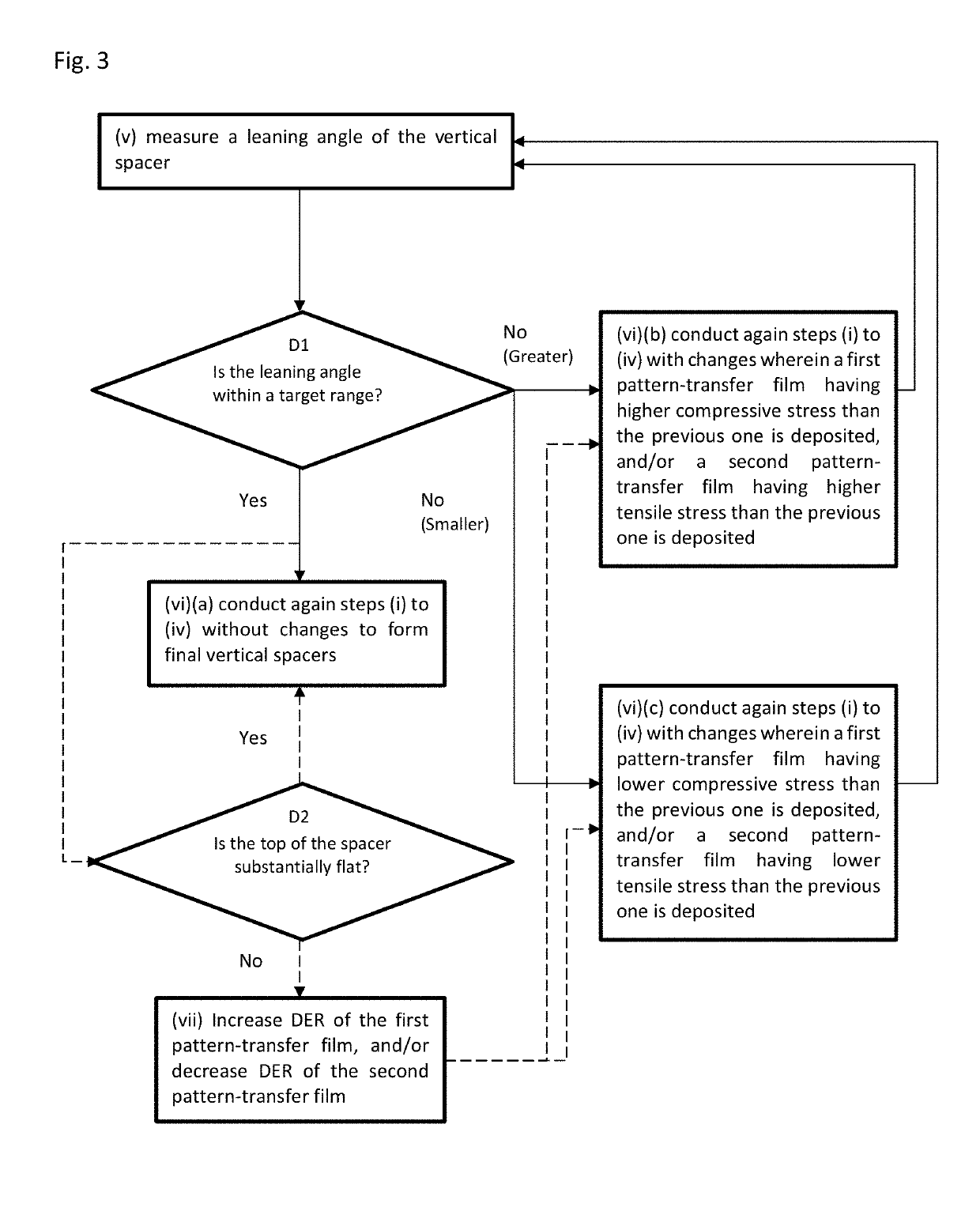
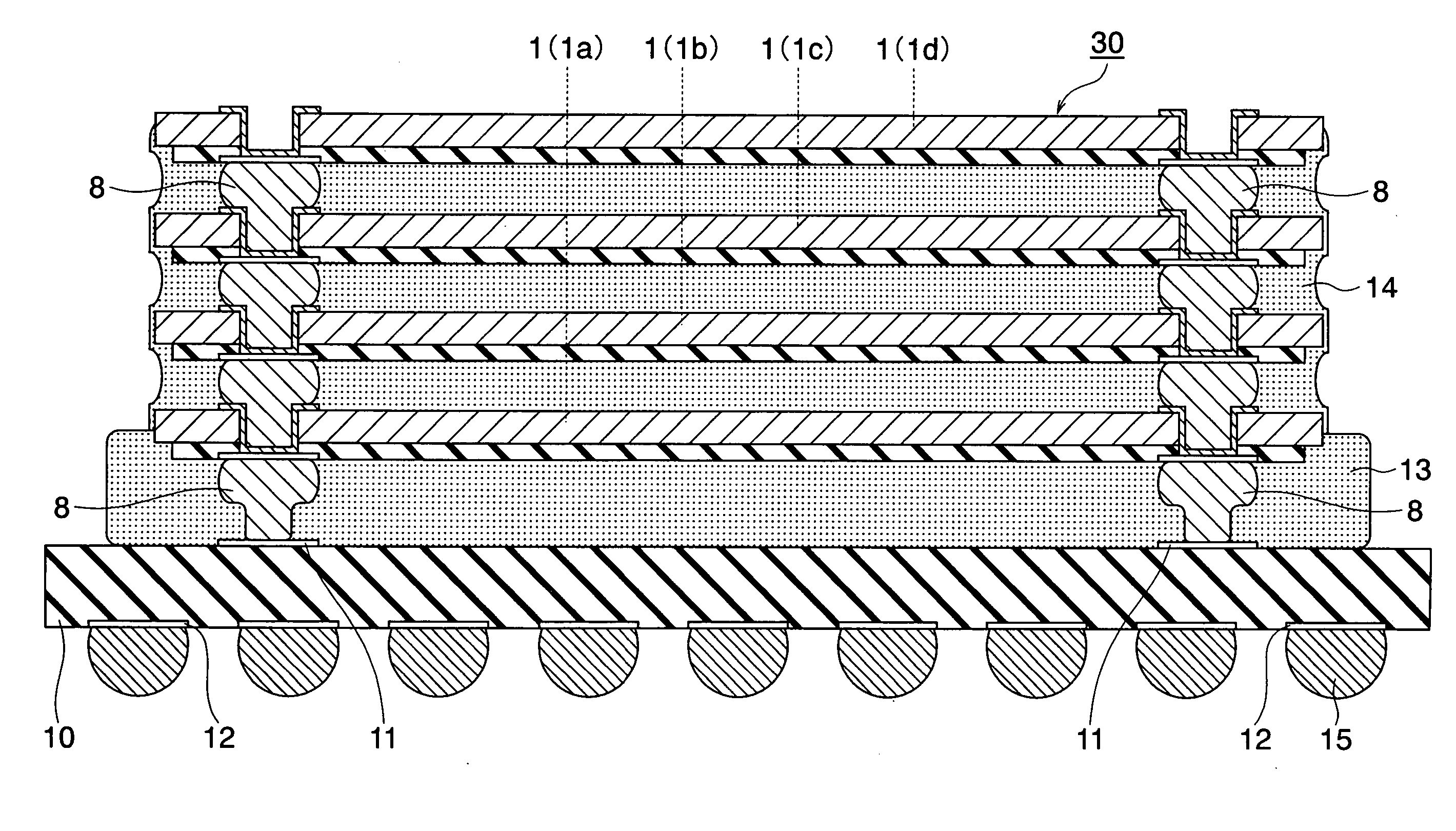
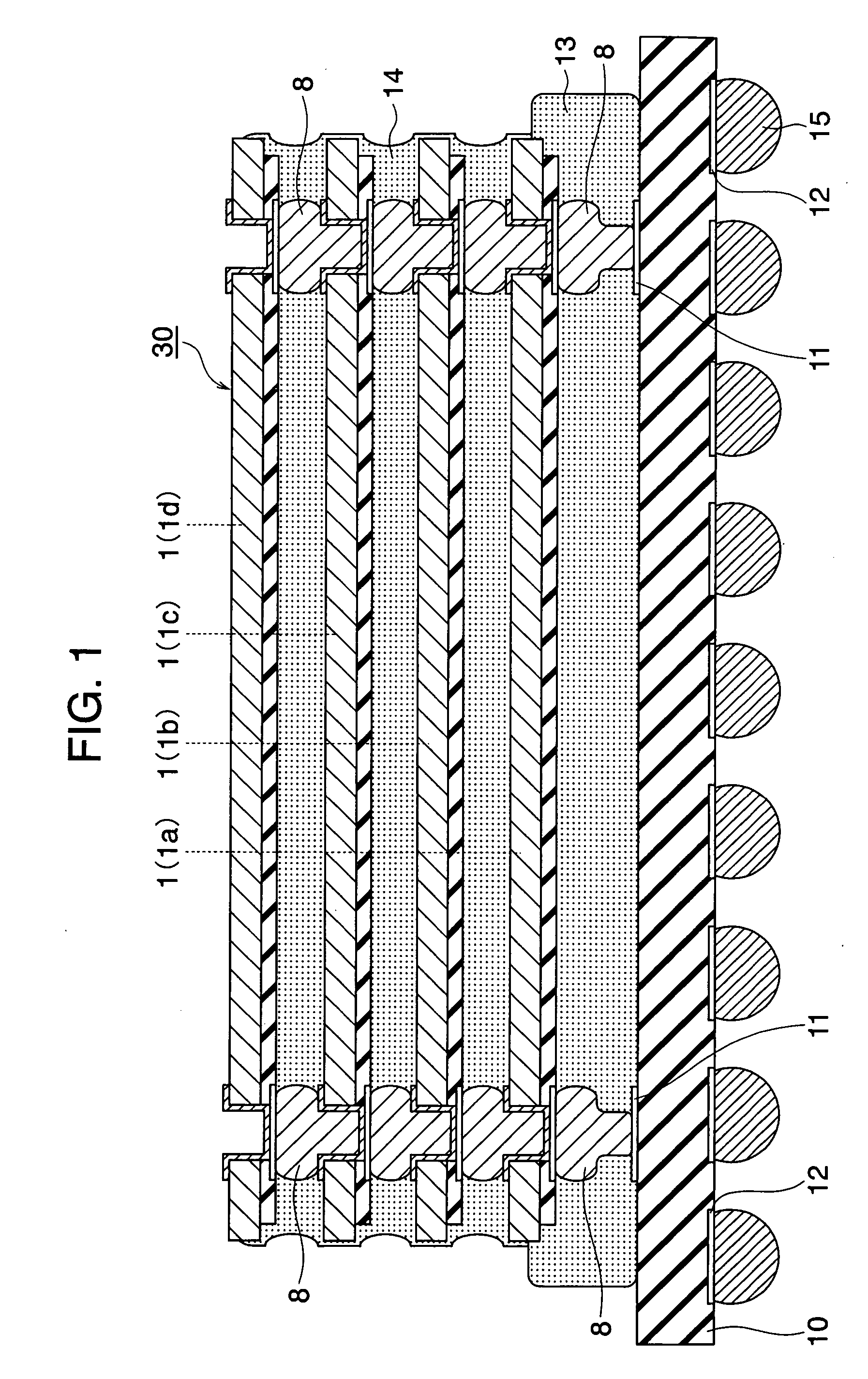
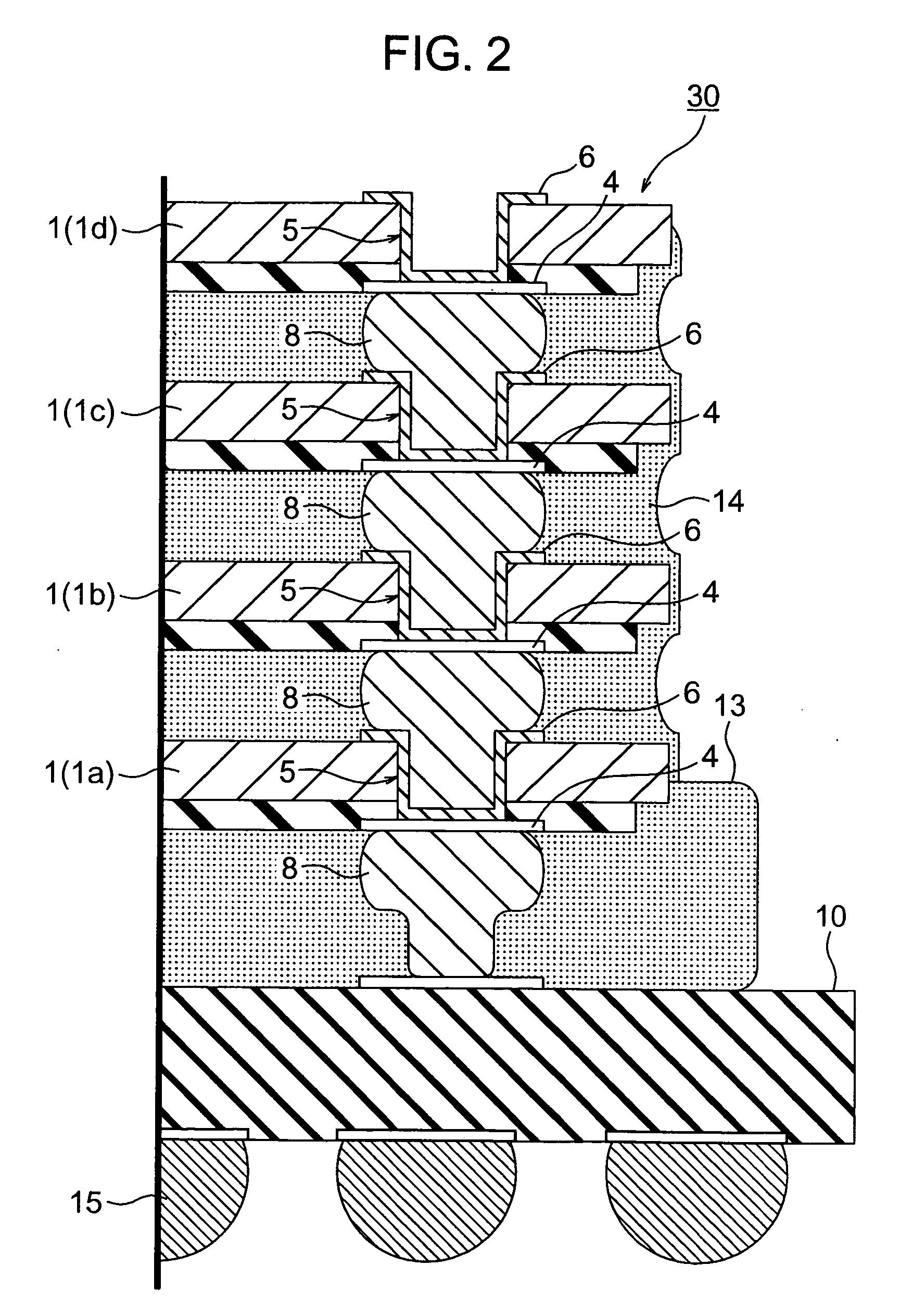
Method for forming vertical spacers for spacer-defined patterning
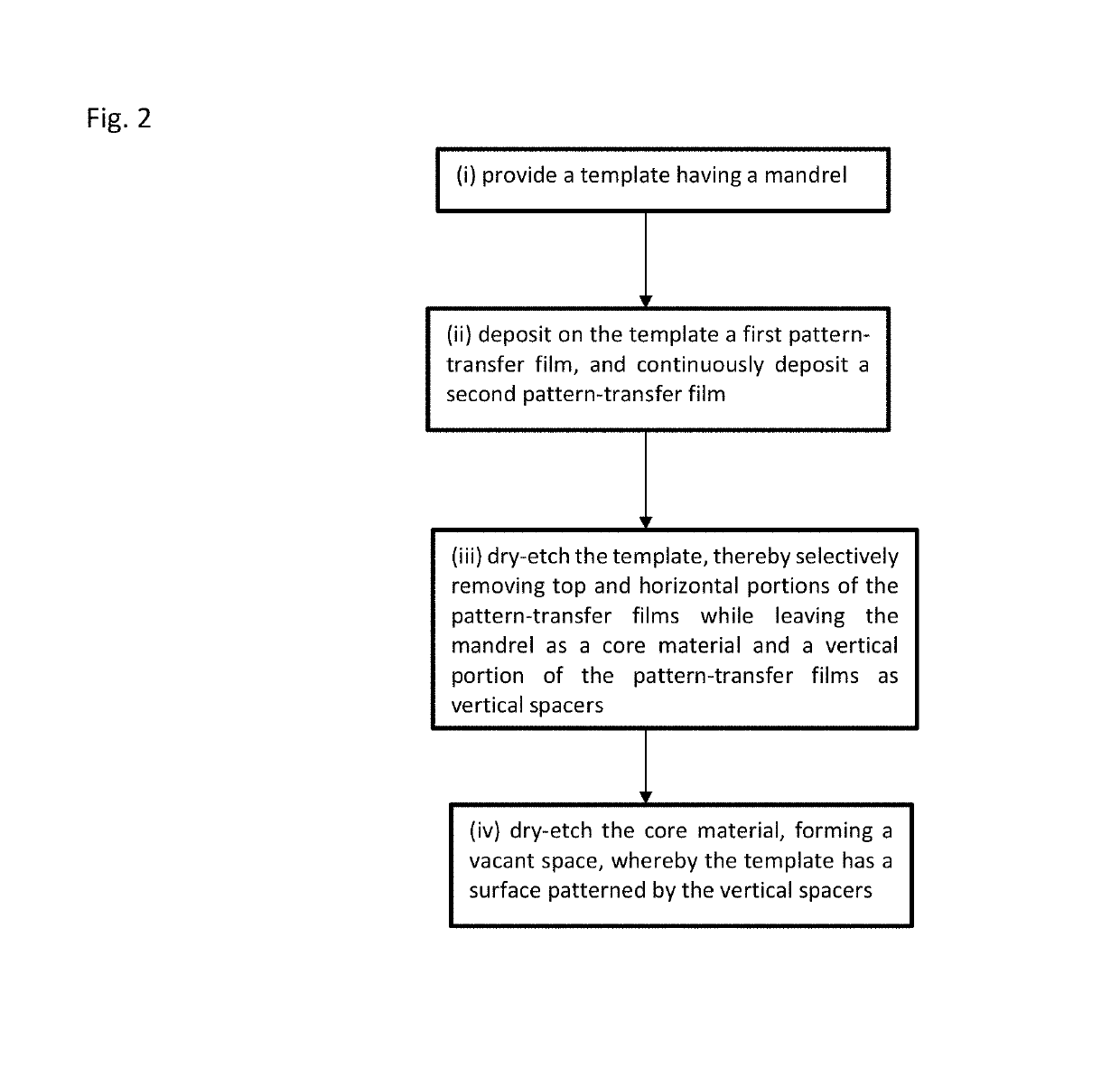
ActiveUS10290508B1Easy to adjustTop profile of the spacer can be manipulatedPhotomechanical apparatusSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingEngineeringDry etching
A method of forming vertical spacers for spacer-defined multiple patterning, includes: depositing a first conformal pattern-transfer film having a first film stress, and continuously depositing a second conformal pattern-transfer film having a second film stress on a template; dry-etching the template except for a core material and a vertical portion of the first and second pattern-transfer films to form vertical spacers; and dry-etching the core material, forming a vacant space between the vertical spacers, wherein by adjusting the difference in film stress between the first and second pattern-transfer films, the leaning angle of the spacers is adjusted.
Owner:ASM IP HLDG BV
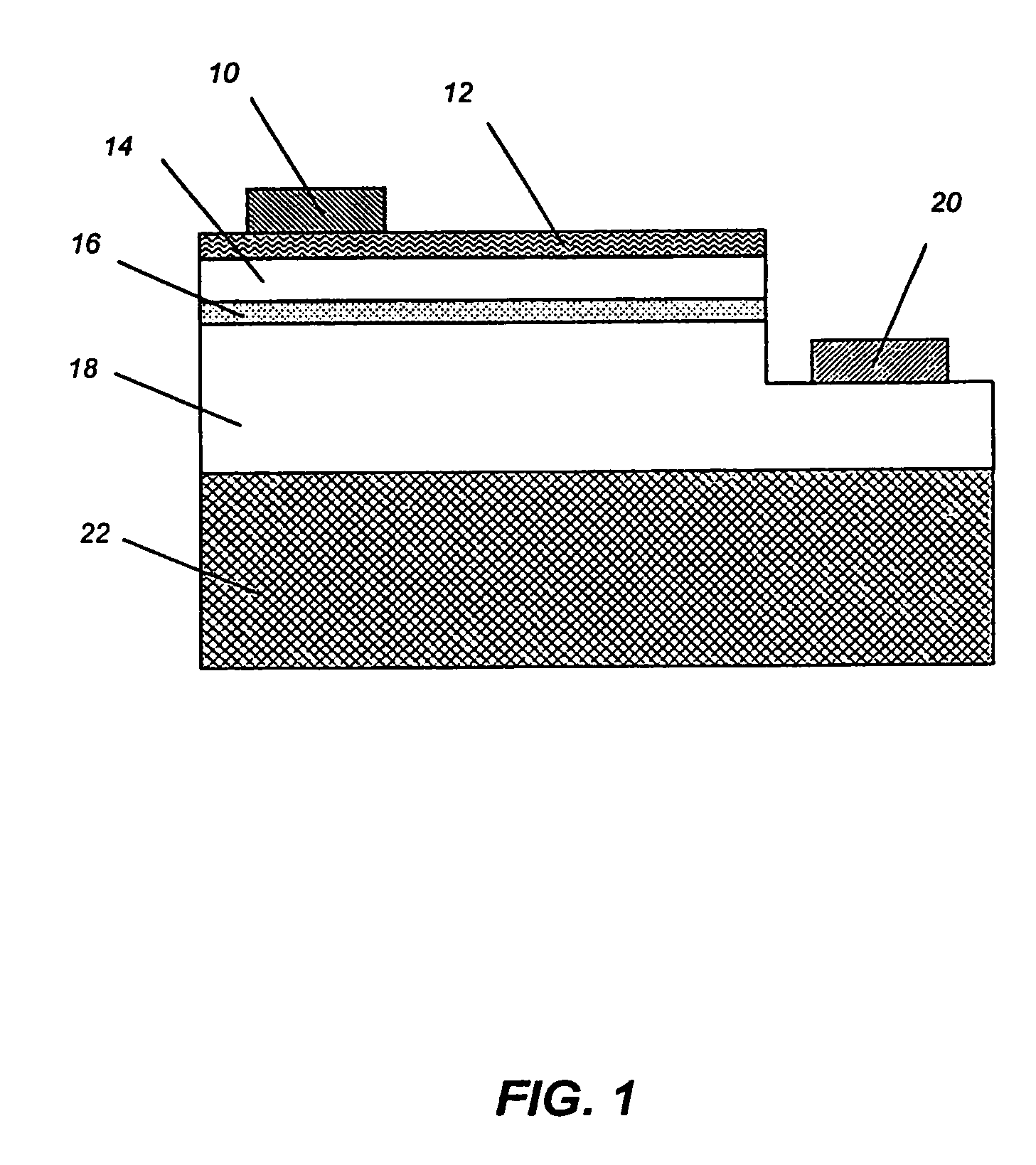
Semiconductor device and manufacturing process therefor
InactiveUS20050263869A1Improve reliabilityHigh practicabilitySemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesManufacturing technologySurface layer
To provide a very-low-cost and short-TAT connection structure superior in connection reliability in accordance with a method for three-dimensionally connecting a plurality of semiconductor chips at a shortest wiring length by using a through-hole electrode in order to realize a compact, high-density, and high-function semiconductor system. The back of a semiconductor chip is decreased in thickness up to a predetermined thickness through back-grinding, a hole reaching a surface-layer electrode is formed at a back position corresponding to a device-side external electrode portion through dry etching, a metallic deposit is applied to the sidewall of the hole and the circumference of the back of the hole, a metallic bump (protruded electrode) of another semiconductor chip laminated on the upper side is deformation-injected into the through-hole by compression bonding, and the metallic bump is geometrically caulked and electrically connected to the inside of a through-hole formed in an LSI chip. It is possible to realize a unique connection structure having a high reliability in accordance with the caulking action using the plastic flow of a metallic bump in a very-low-cost short-TAT process and provide a three-dimensional inter-chip connection structure having a high practicability.
Owner:RENESAS TECH CORP
Method for anisotropic plasma-chemical dry etching of silicon nitride layers using a gas mixture containing fluorine
InactiveUS6569773B1Improve uniformityHigh atomic weightSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSilicon oxideOxygen
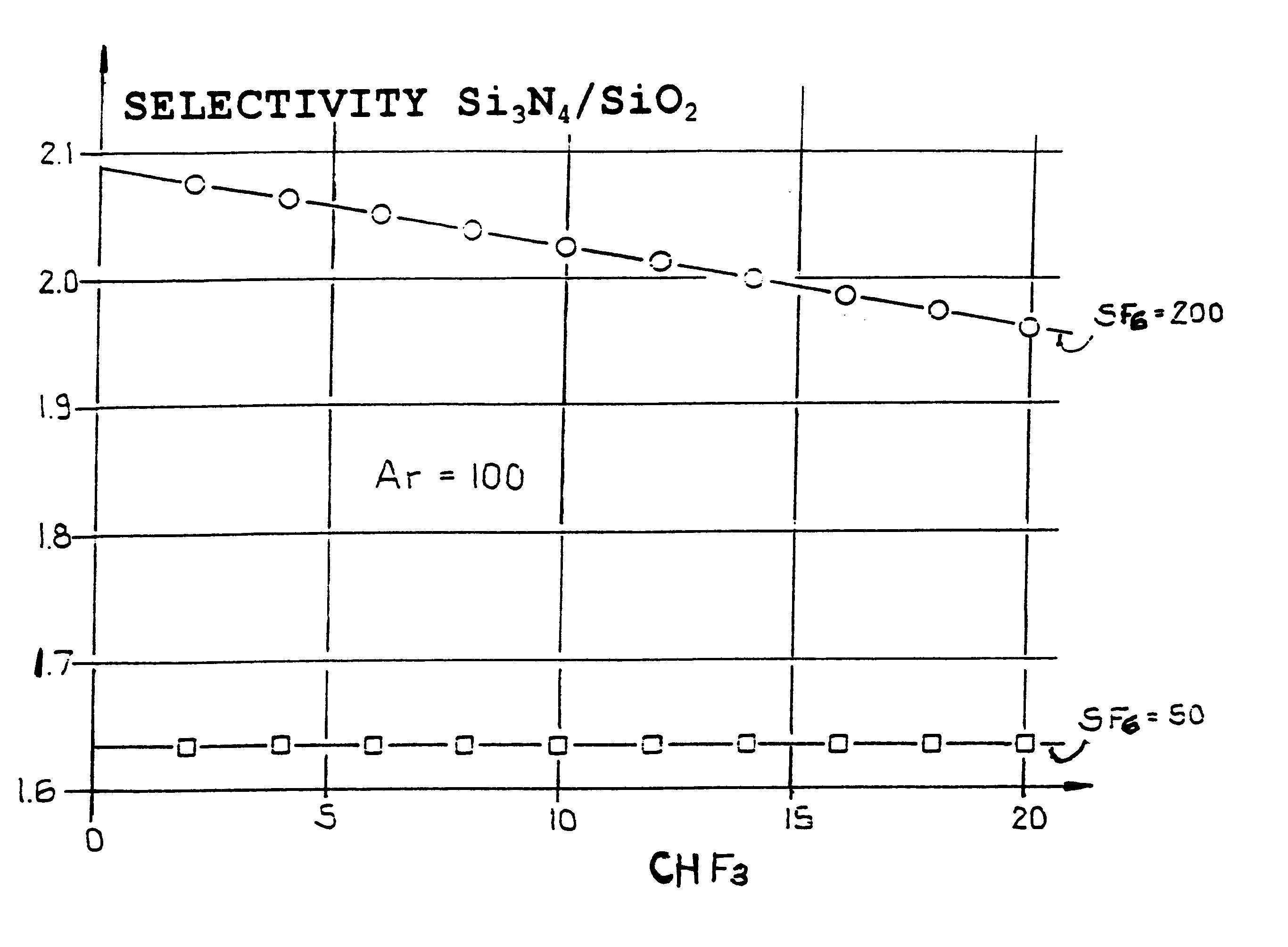
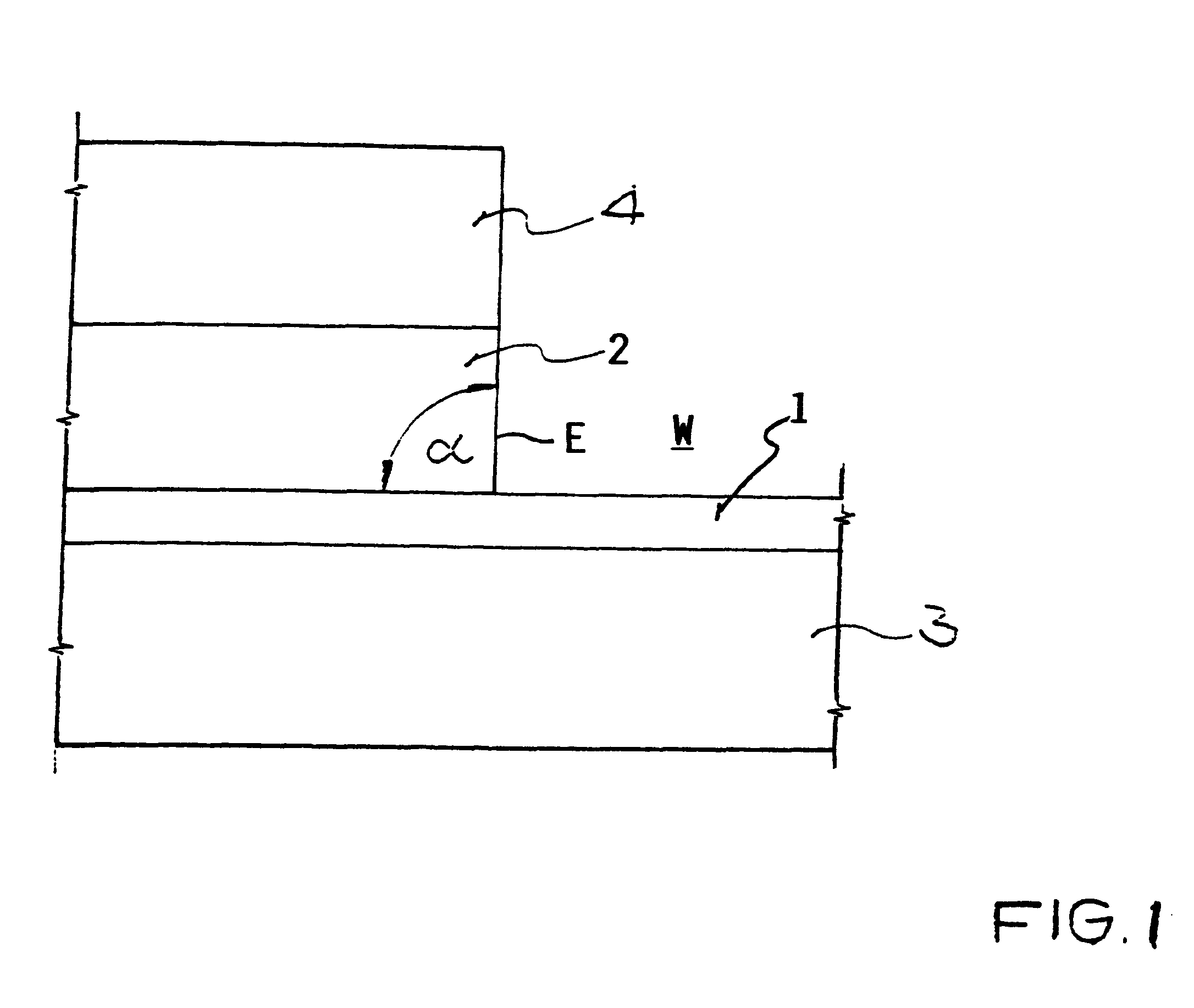
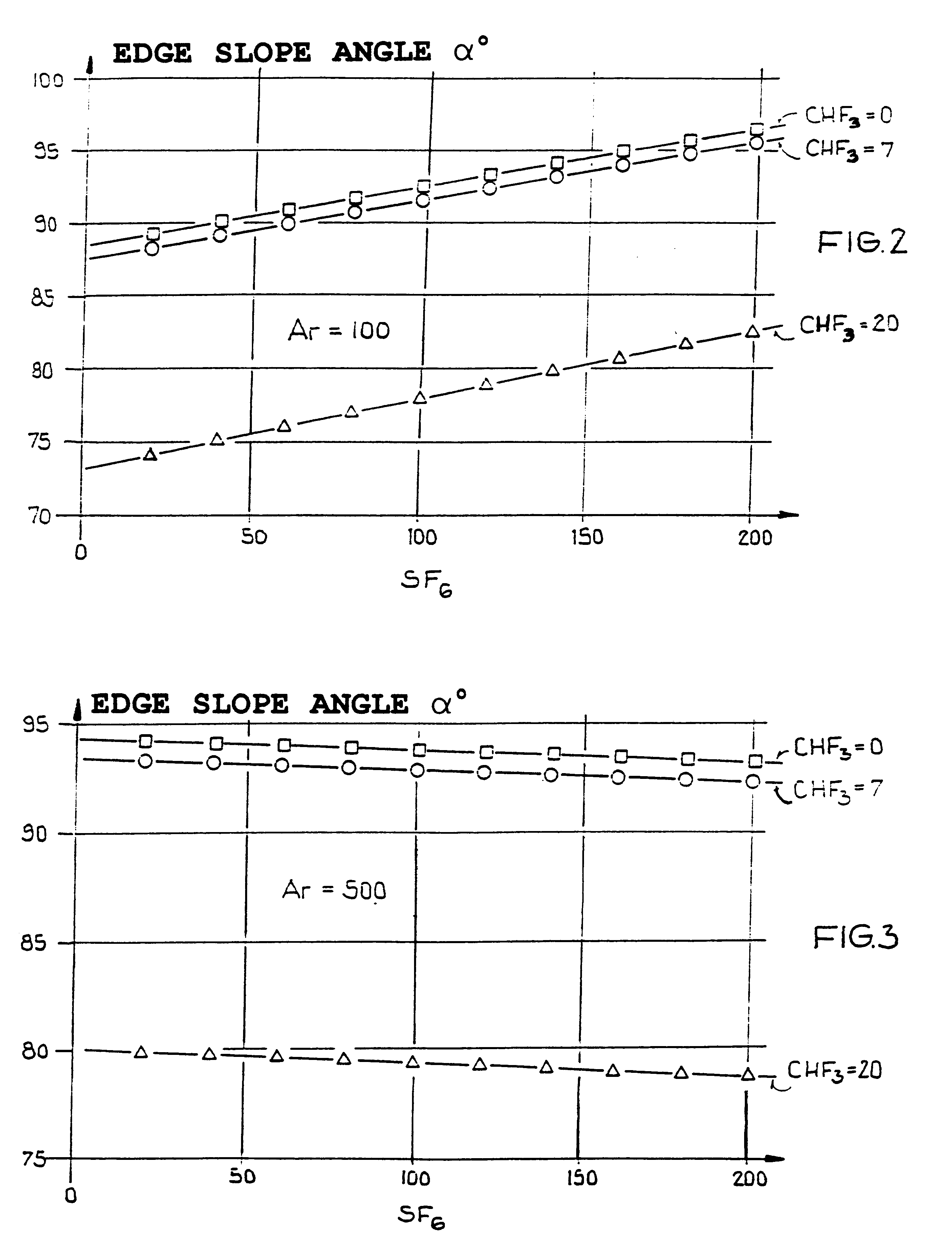
An etching gas mixture containing CHF3, SF6 and a non-oxidizing gas such as Ar is used as an etching gas mixture for the anisotropic plasma-chemical dry-etching of a silicon nitride layer differentially or selectively relative to a silicon oxide layer. The gas mixture does not contain oxygen, chlorine, bromine, iodine or halides in addition to the above mentioned constituents, so that the process can be carried out in reactor systems equipped with oxidizable electrodes. By adjusting the gas flow rates or composition ratios of CHF3, SF6, and argon in the etching gas mixture, it is possible to adjust the resulting etching selectivity of silicon nitride relative to silicon oxide, and the particular edge slope angle of the etched edge of the remaining silicon nitride layer. A high etch rate for the silicon nitride is simultaneously achieved.
Owner:ATMEL CORP +1
Manufacturing method of a silicon carbide semiconductor device
InactiveUS8071482B2Smooth curveImprove breakdown voltageSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesSemiconductorDry etching
A manufacturing method for a silicon carbide semiconductor device is disclosed. It includes an etching method in which an Al film and Ni film are laid on an SiC wafer in this order and wet-etched, whereby a two-layer etching mask is formed in which Ni film portions overhang Al film portions. Mesa grooves are formed by dry etching by using this etching mask.
Owner:FUJI ELECTRIC CO LTD
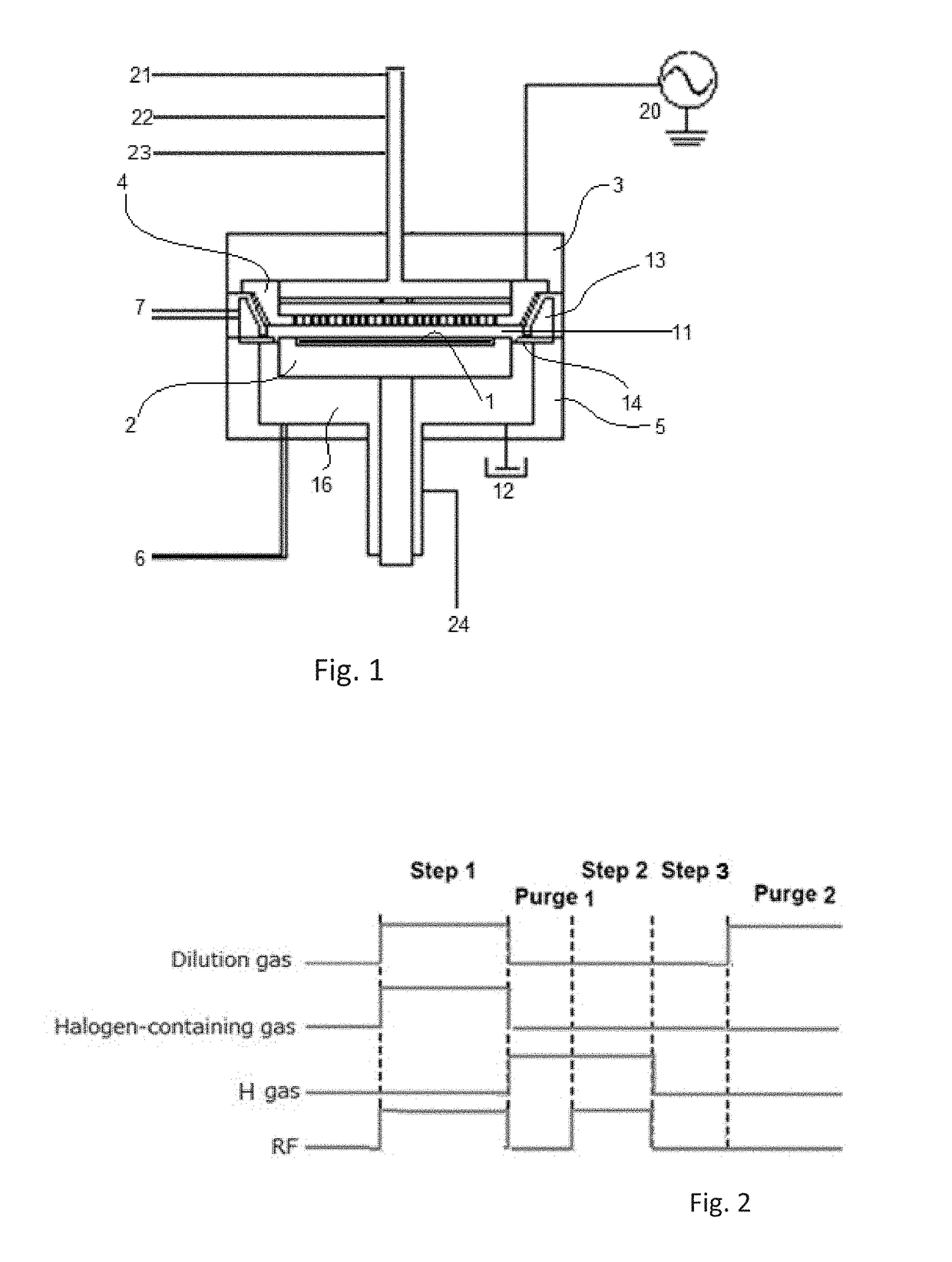
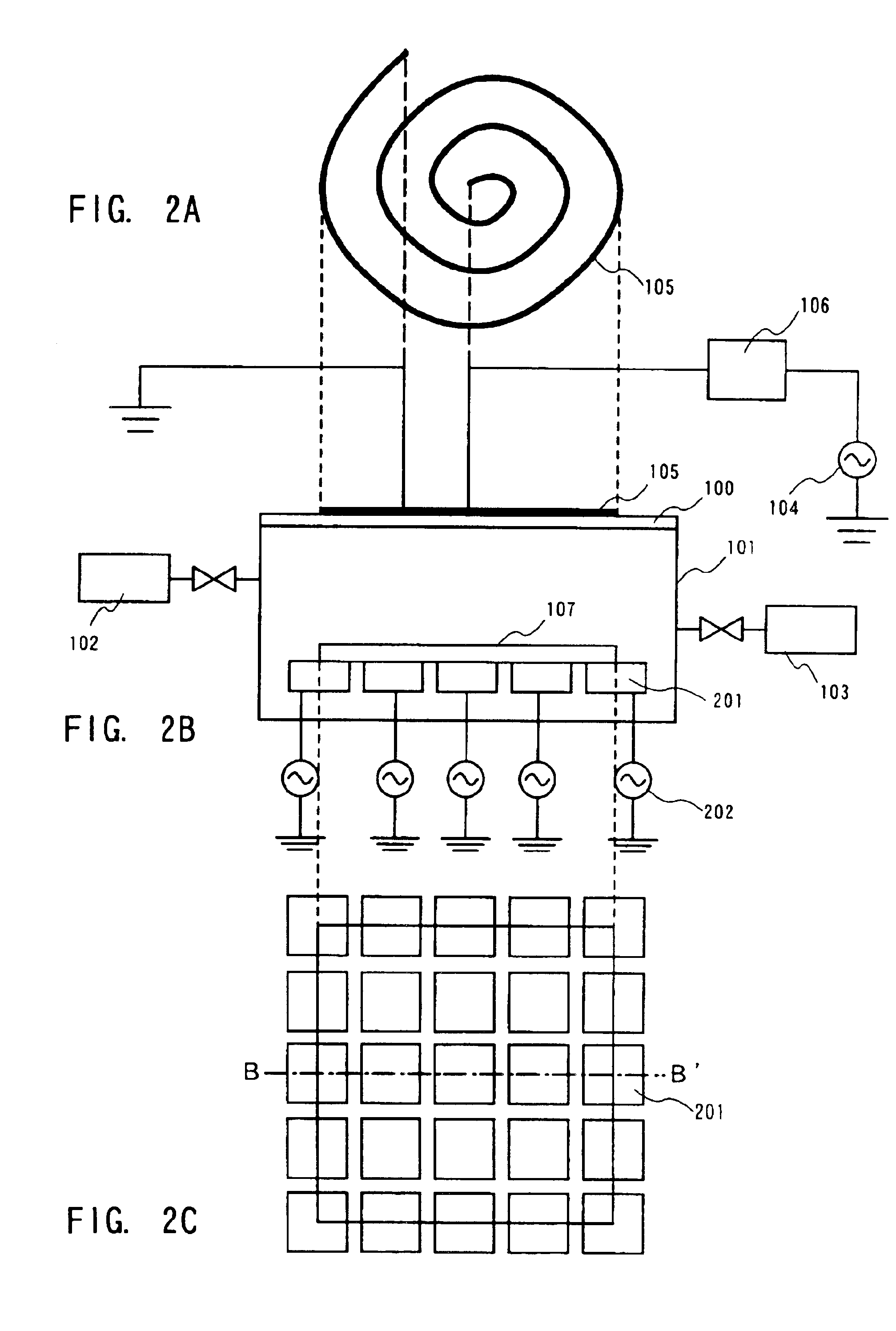
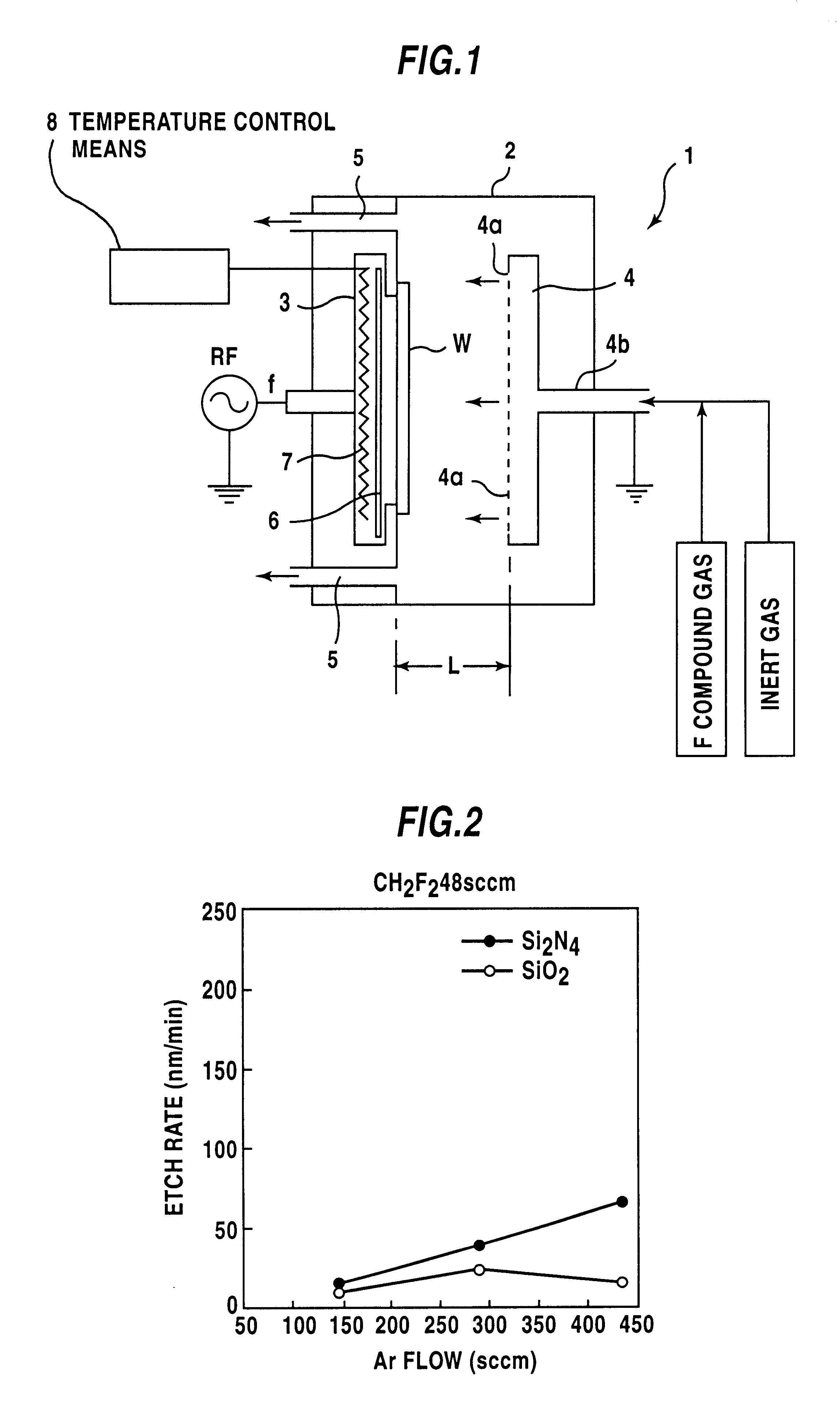
Dry etching apparatus, etching method, and method of forming a wiring
InactiveUS6930047B2Improve in-plane uniformityUniformity of selection ratioTransistorElectric discharge tubesIn planeHigh frequency power
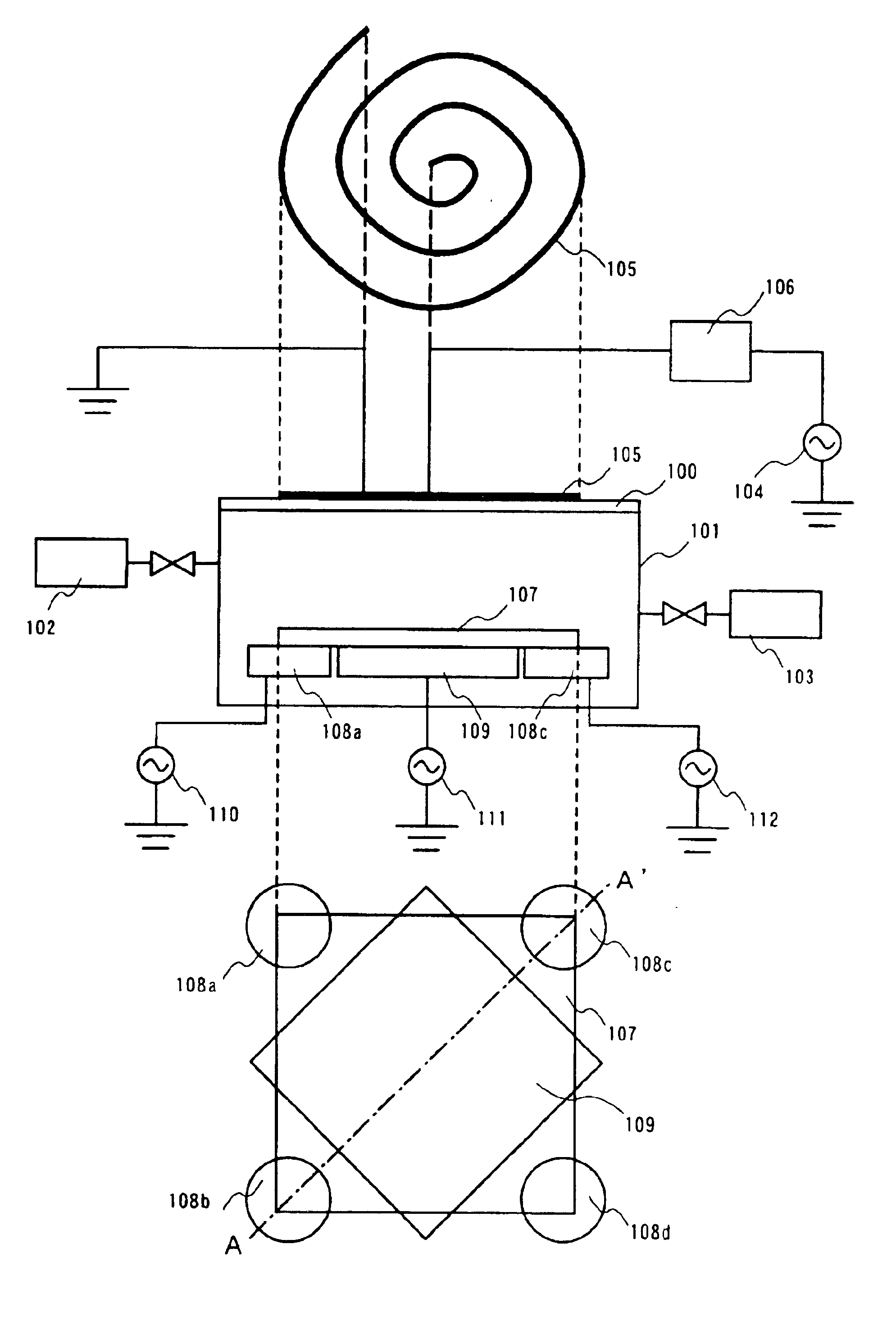
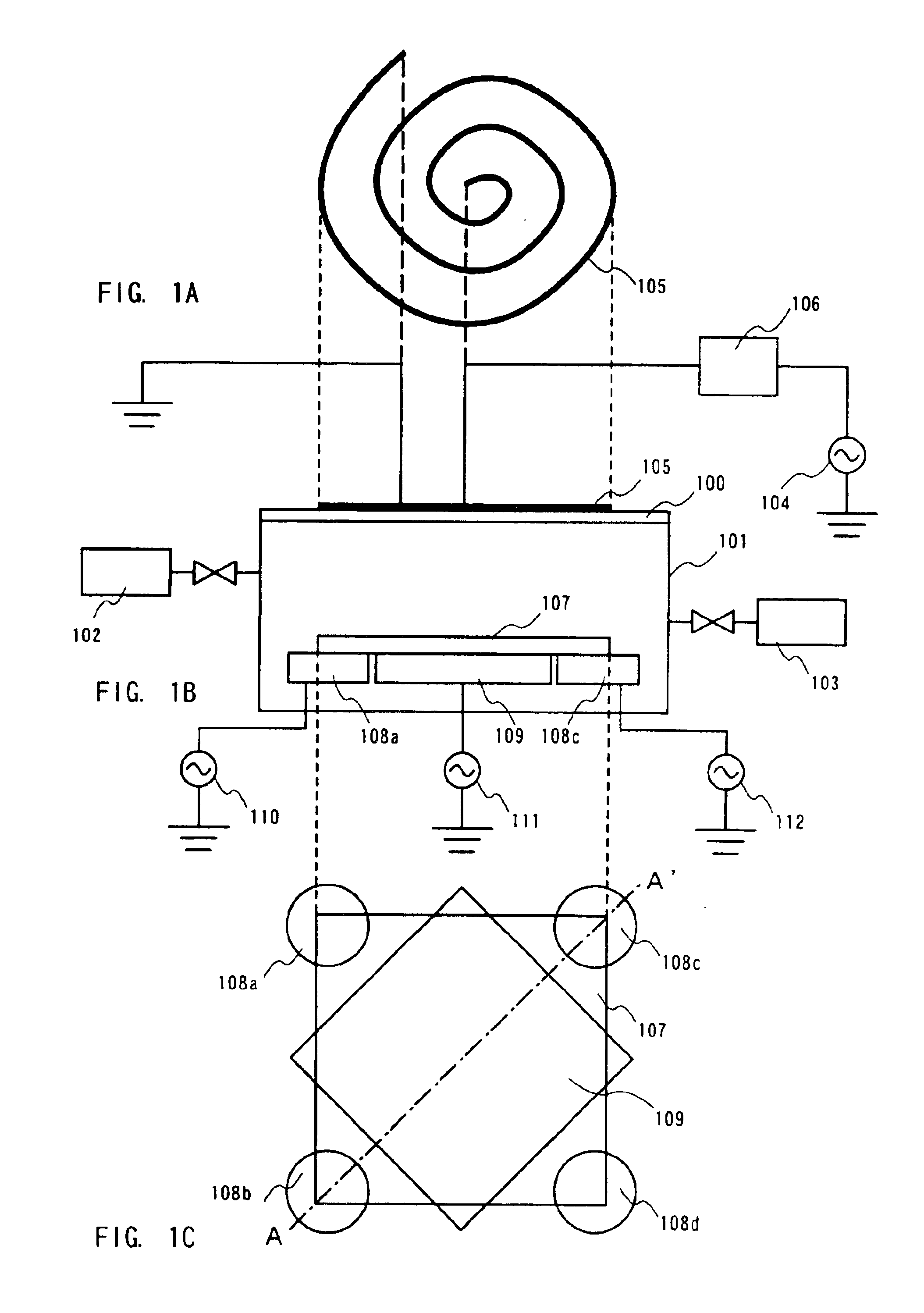
An etching apparatus is provided, in which a plurality of electrodes are disposed for placing a substrate, high-frequency power sources as many as electrodes are provided, and the electrodes and the high-frequency power sources are connected to each other independently. Among a plurality of electrodes, a high-frequency power applied to an electrode disposed below the central portion of the substrate and a high-frequency power applied to electrodes disposed below comer portions of the substrate are controlled respectively, whereby in-plane uniformity of etching can be enhanced.
Owner:SEMICON ENERGY LAB CO LTD
Method and system for dry etching a metal nitride
InactiveUS20080230519A1Decorative surface effectsSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingTitanium nitrideProcess composition
A method and system of etching a metal nitride, such as titanium nitride, is described. The etching process comprises introducing a process composition having a halogen containing gas, such as Cl2, HBr, or BCl3, and a fluorocarbon gas having the chemical formula CxHyFz, where x and z are equal to unity or greater and y is equal to 0 or greater.
Owner:TOKYO ELECTRON LTD
Resist composition
The following resist composition which is excellent particularly in transparency to light beams and dry etching properties and gives a resist pattern excellent in sensitivity, resolution, evenness, heat resistance, etc., as a chemical amplification type resist, is presented. A resist composition which comprises a fluoropolymer (A) having repeating units represented by a structure formed by the cyclopolymerization of one molecule of a fluorinated diene and one molecule of a monoene, in which the monoene unit in each repeating unit has a blocked acid group capable of regenerating the acid group by the action of an acid, an acid-generating compound (B) which generates an acid upon irradiation with light, and an organic solvent (C).
Owner:ASAHI GLASS CO LTD
Etching method, low-temperature polysilicon thin film transistor and AMOLED panel
ActiveCN108389798AEasy to handlePrevent dark spotsTransistorSolid-state devicesSulfur hexafluorideOxygen
Owner:TRULY HUIZHOU SMART DISPLAY
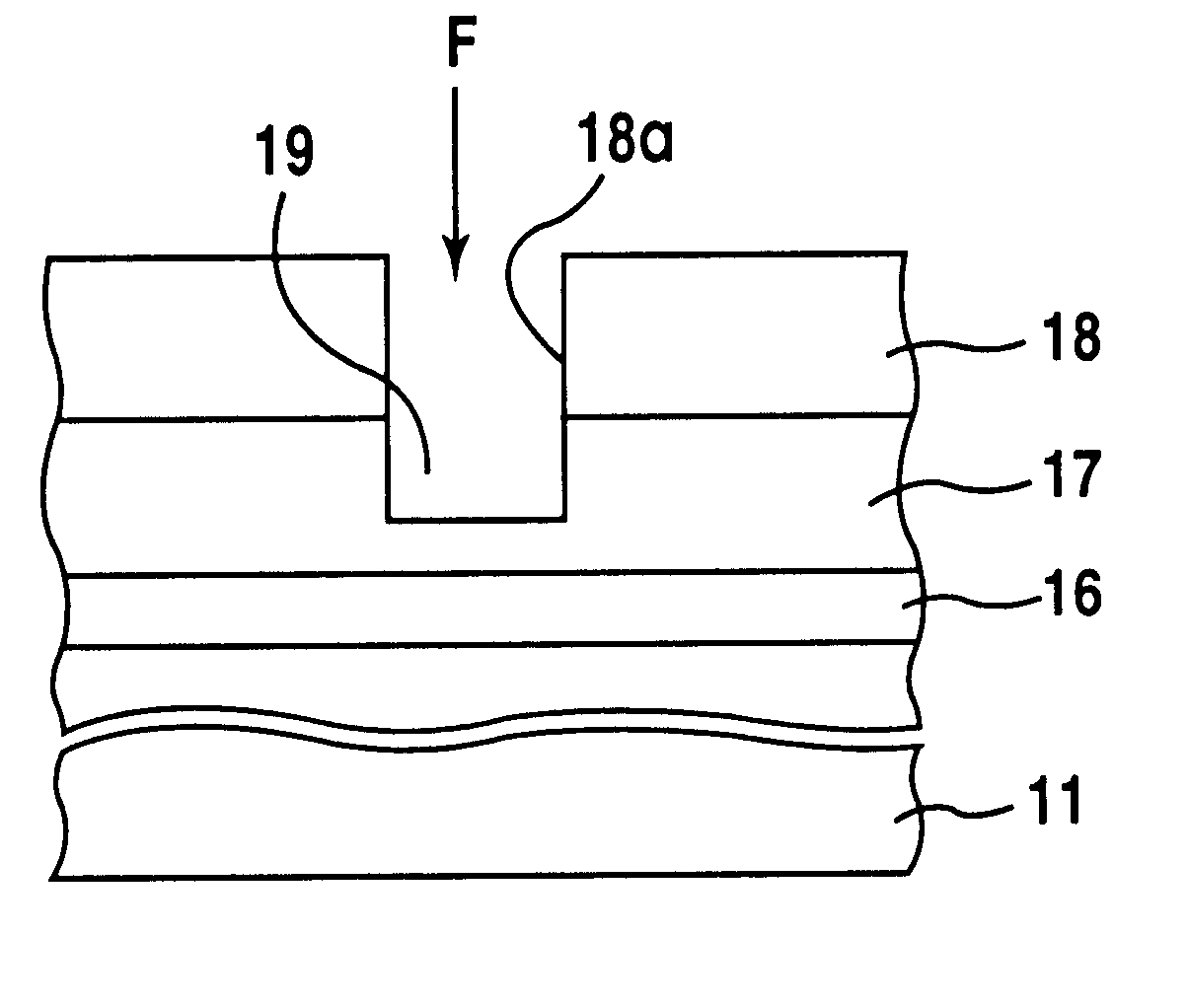
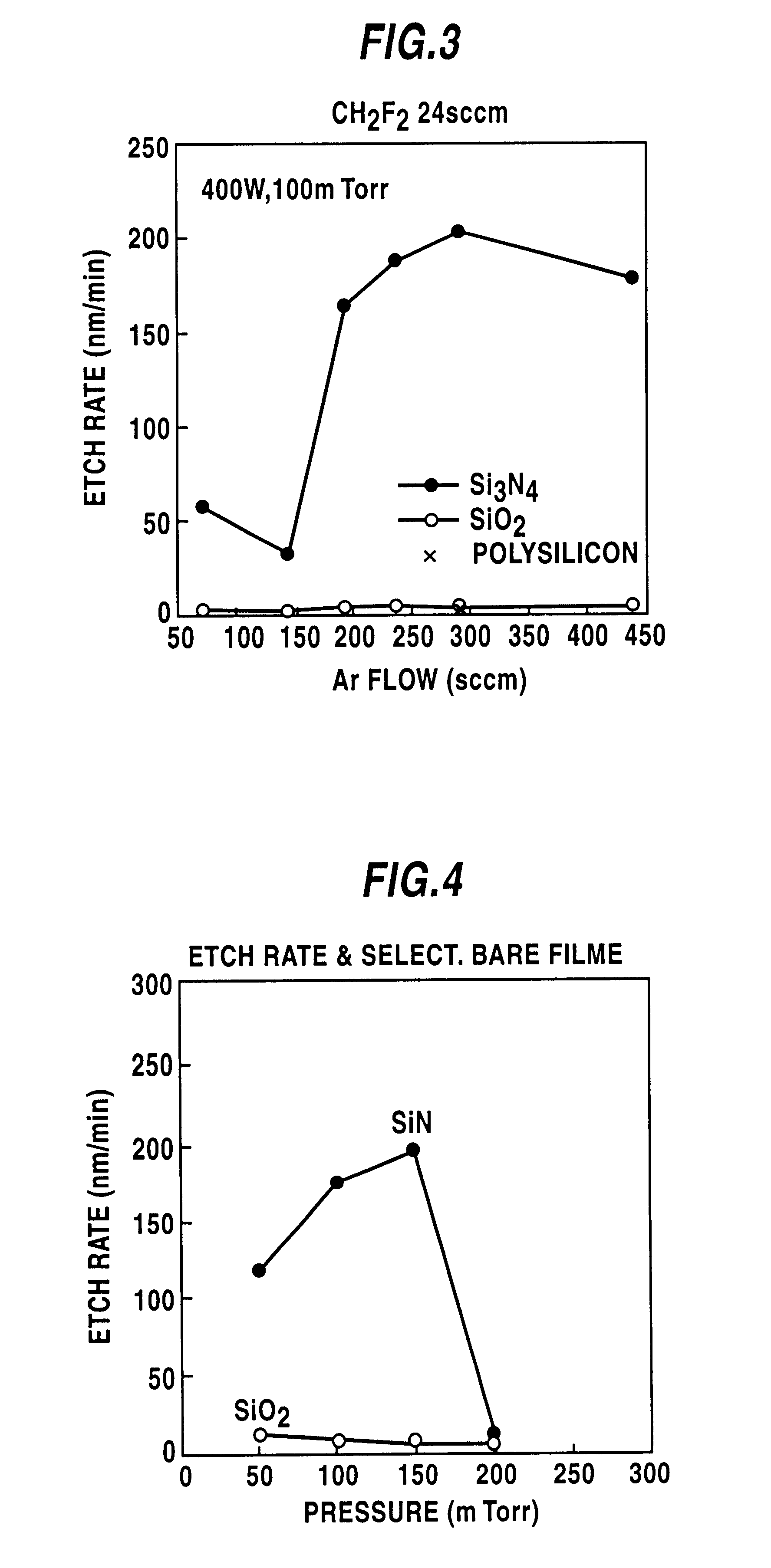
Method of etching silicon nitride by a mixture of CH2 F2, CH3F or CHF3 and an inert gas
InactiveUS6376386B1Solid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSilicon oxideDry etching
There are included steps of forming a silicon nitride layer on a silicon layer or a silicon oxide layer, loading the silicon layer or the silicon oxide layer and the silicon nitride layer in a dry etching atmosphere, and selectively etching the silicon nitride layer with respect to the silicon layer or the silicon oxide layer by flowing a fluorine gas consisting of any one of CH2F2, CH3F, or CHF3 and an inert gas to the dry etching atmosphere. Hence, in the etching process of the silicon nitride layer, the etching selectivity of the silicon nitride layer to Si or SiO2 can be enhanced and also etching anisotropy can be enhanced.
Owner:FUJITSU SEMICON LTD
Plasma for patterning advanced gate stacks
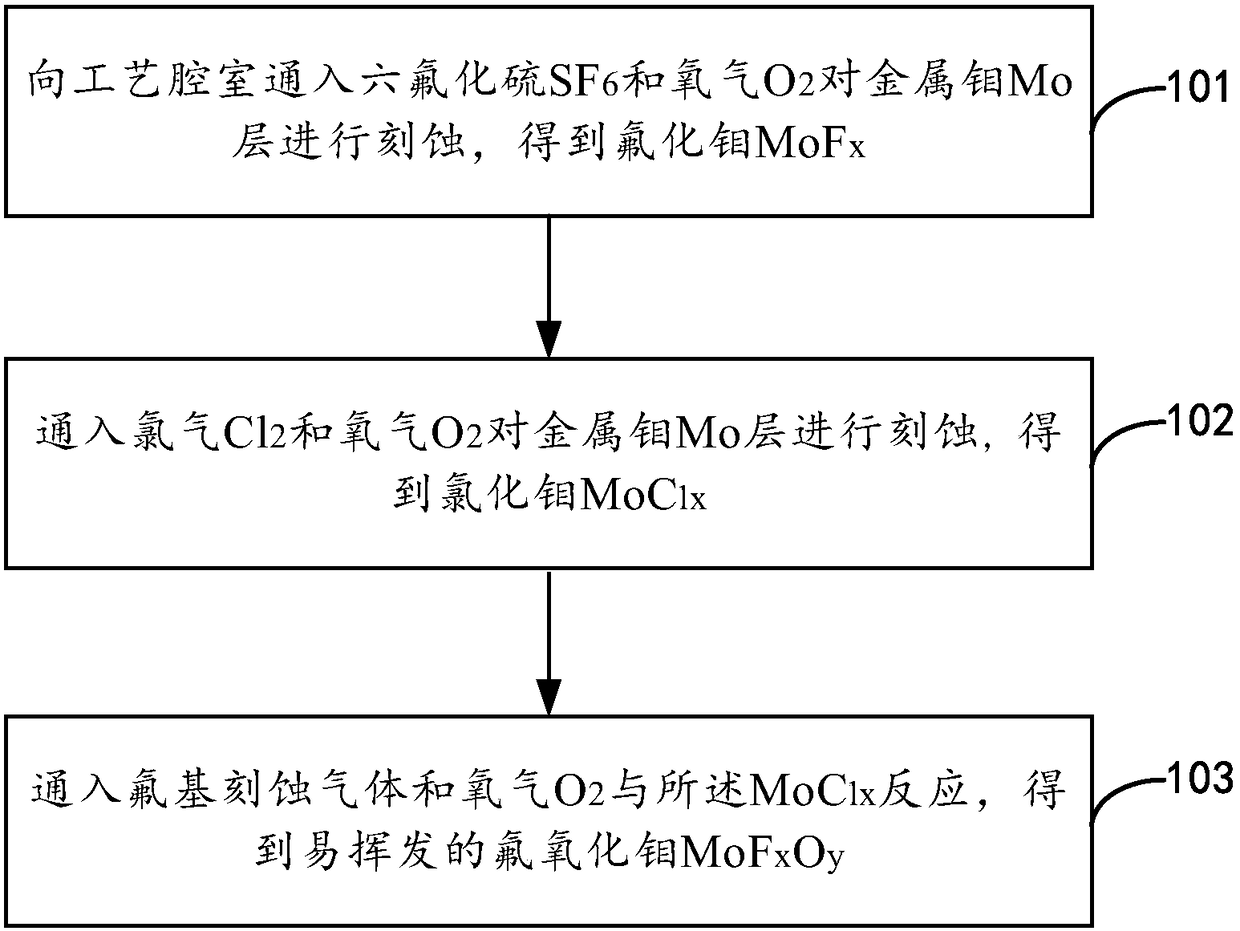
InactiveUS20070099428A1Avoid attackSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSemiconductor devicesPlasma compositionNitrogen
A plasma composition and its use in a method for the dry etching of a stack of at least one material chemically too reactive towards the use of a Cl-based plasma are provided. Small amounts of nitrogen (5% up to 10%) can be added to a BCl3 comprising plasma and used in an anisotropical dry etching method whereby a passivation film is deposited onto the vertical sidewalls of stack etched for protecting the vertical sidewalls from lateral attack such that straight profiles can be obtained.
Owner:INTERUNIVERSITAIR MICRO ELECTRONICS CENT (IMEC VZW)
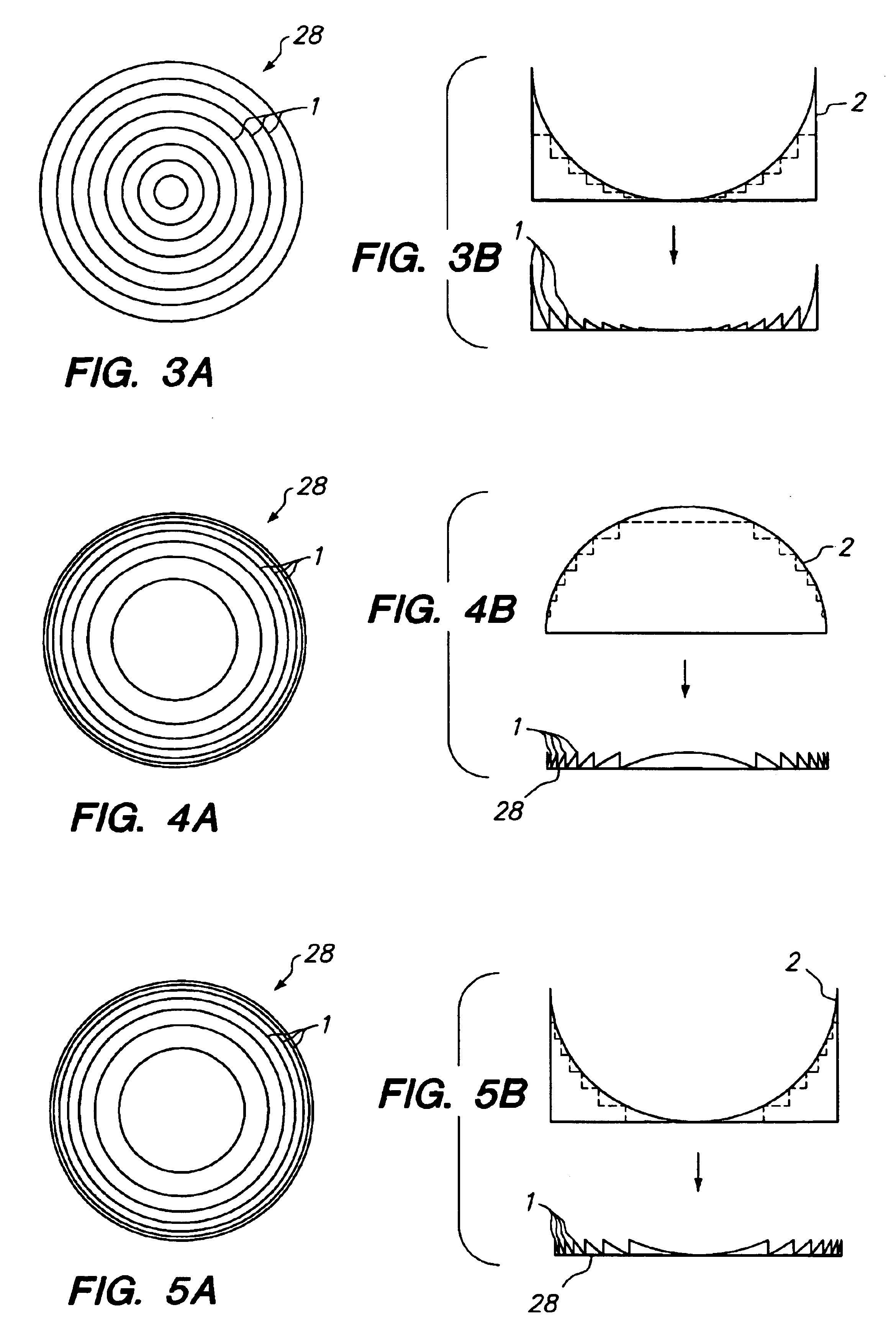
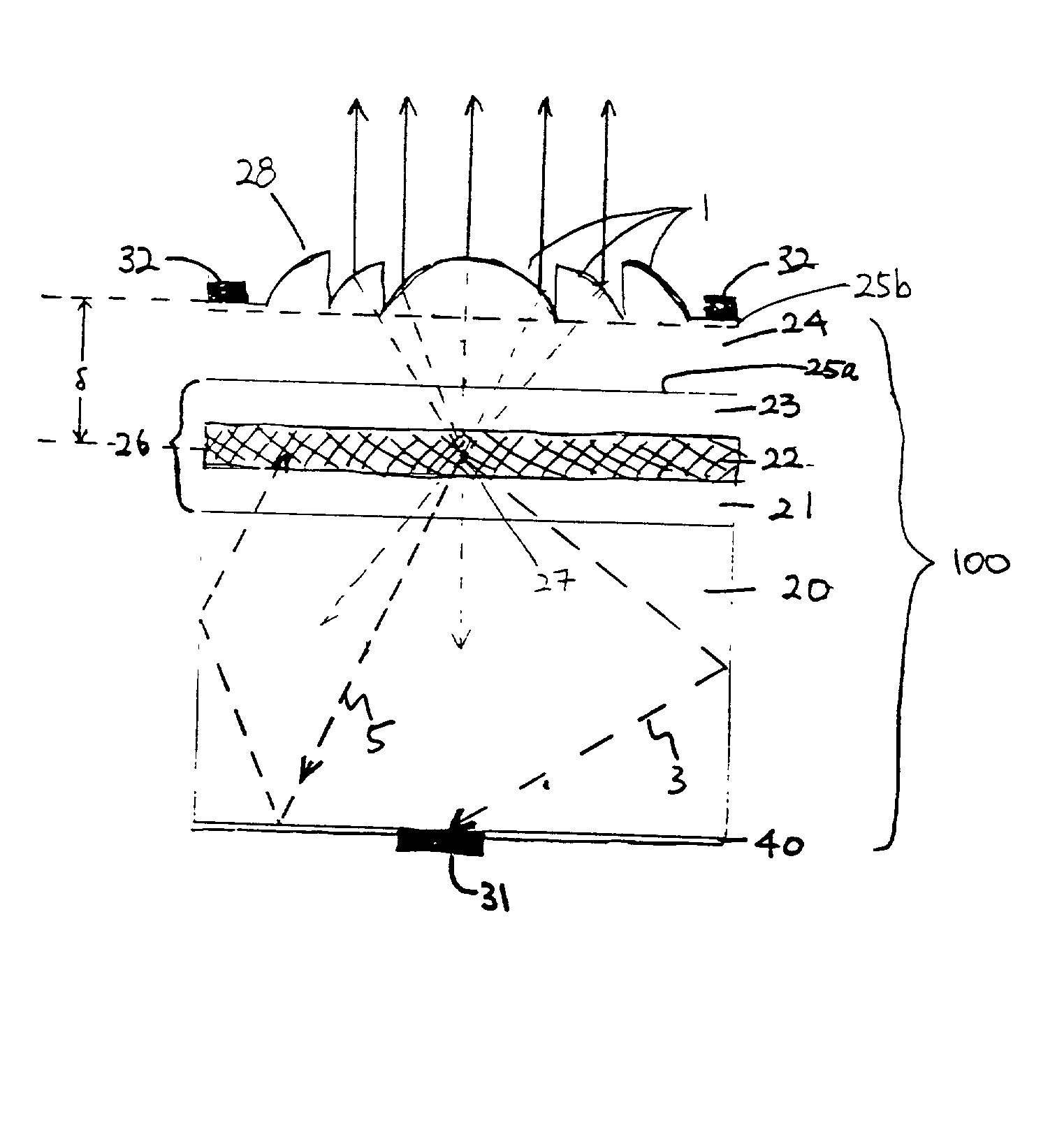
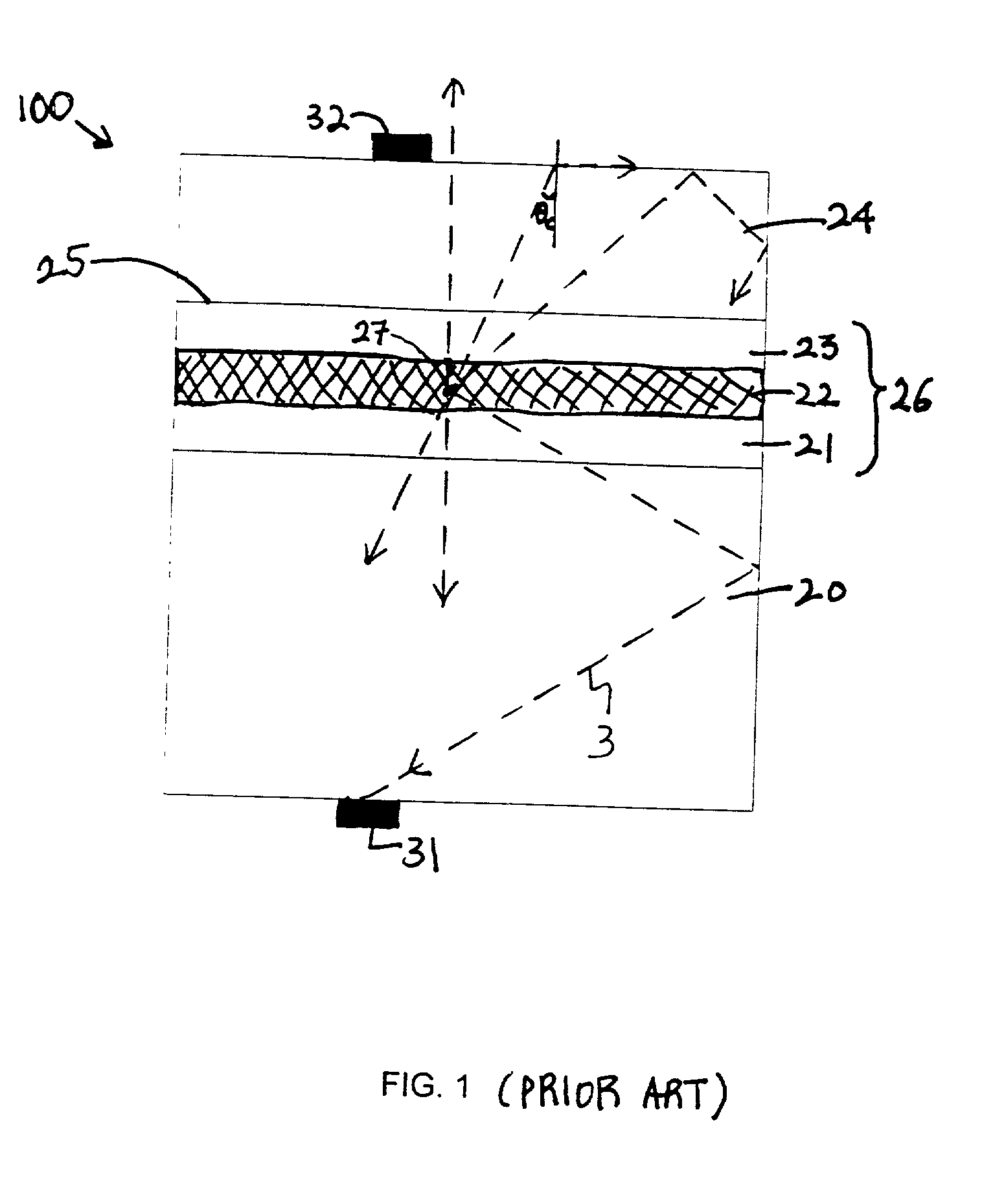
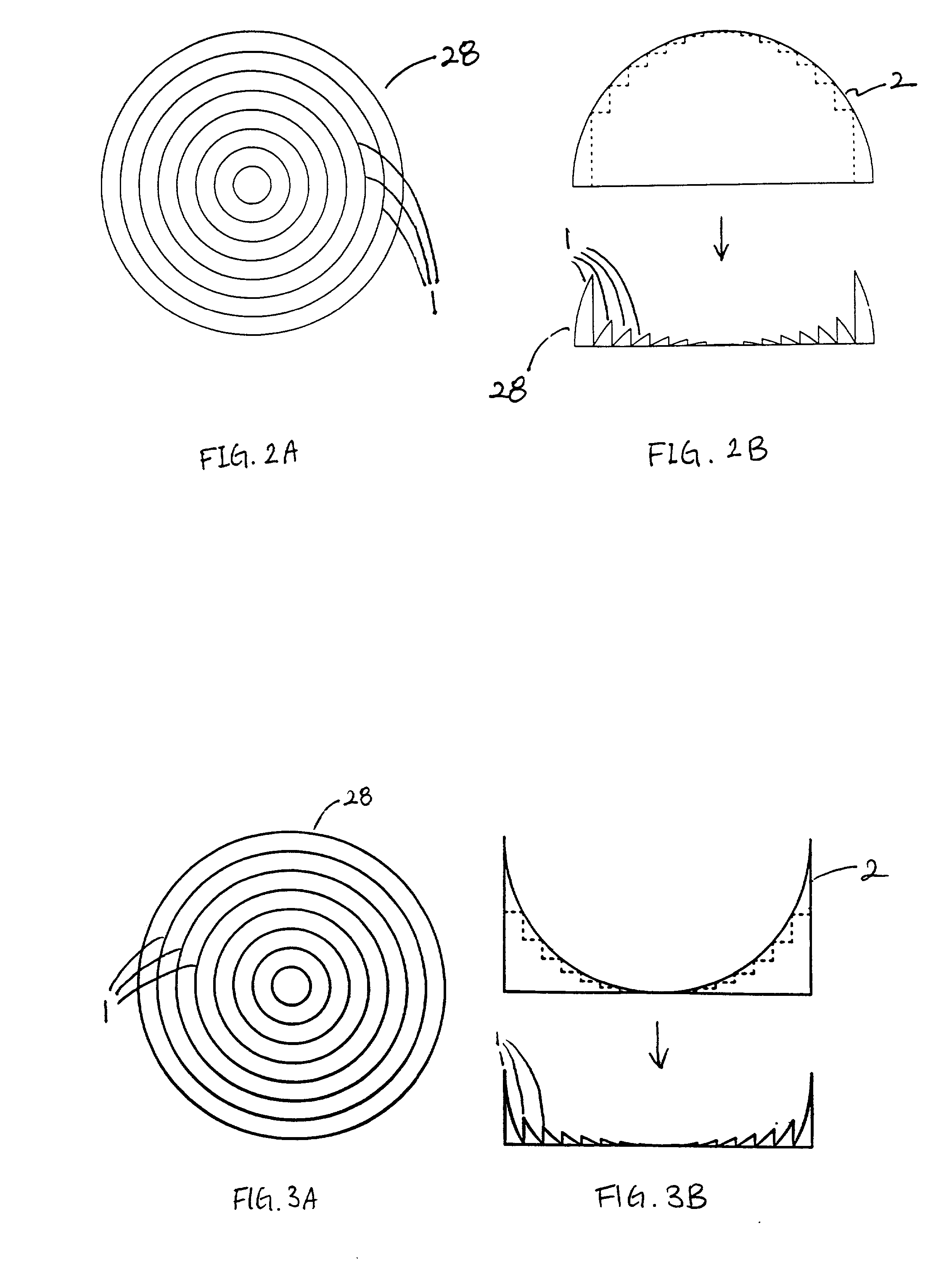
Forming an optical element on the surface of a light emitting device for improved light extraction
InactiveUS6987613B2Easy to integrateMaximize production efficiencyDiffraction gratingsSemiconductor devicesWafer bondingAlternative methods
Provided is a light emitting device including a Fresnel lens and / or a holographic diffuser formed on a surface of a semiconductor light emitter for improved light extraction, and a method for forming such light emitting device. Also provided is a light emitting device including an optical element stamped on a surface for improved light extraction and the stamping method used to form such device. An optical element formed on the surface of a semiconductor light emitter reduces reflective loss and loss due to total internal reflection, thereby improving light extraction efficiency. A Fresnel lens or a holographic diffuser may be formed on a surface by wet chemical etching or dry etching techniques, such as plasma etching, reactive ion etching, and chemically-assisted ion beam etching, optionally in conjunction with a lithographic technique. In addition, a Fresnel lens or a holographic diffuser may be milled, scribed, or ablated into the surface. Stamping, an alternative method for forming an optical element, can also be used to form a Fresnel lens or a holographic diffuser on the surface of a semiconductor light emitter. Stamping includes pressing a stamping block against the surface of a light emitting diode. The stamping block has a shape and pattern that are the inverse of the desired optical element. Optionally, stamping can be done before, after, or concurrently with wafer-bonding. Alternatively, a material can be stamped and later bonded to the semiconductor light emitter.
Owner:LUMILEDS
Forming an optical element on the surface of a light emitting device for improved light extraction
Provided is a light emitting device including a Fresnel lens and / or a holographic diffuser formed on a surface of a semiconductor light emitter for improved light extraction, and a method for forming such light emitting device. Also provided is a light emitting device including an optical element stamped on a surface for improved light extraction and the stamping method used to form such device. An optical element formed on the surface of a semiconductor light emitter reduces reflective loss and loss due to total internal reflection, thereby improving light extraction efficiency. A Fresnel lens or a holographic diffuser may be formed on a surface by wet chemical etching or dry etching techniques, such as plasma etching, reactive ion etching, and chemically-assisted ion beam etching, optionally in conjunction with a lithographic technique. In addition, a Fresnel lens or a holographic diffuser may be milled, scribed, or ablated into the surface. Stamping, an alternative method for forming an optical element, can also be used to form a Fresnel lens or a holographic diffuser on the surface of a semiconductor light emitter. Stamping includes pressing a stamping block against the surface of a light emitting diode. The stamping block has a shape and pattern that are the inverse of the desired optical element. Optionally, stamping can be done before, after, or concurrently with wafer-bonding. Alternatively, a material can be stamped and later bonded to the semiconductor light emitter.
Owner:LUMILEDS
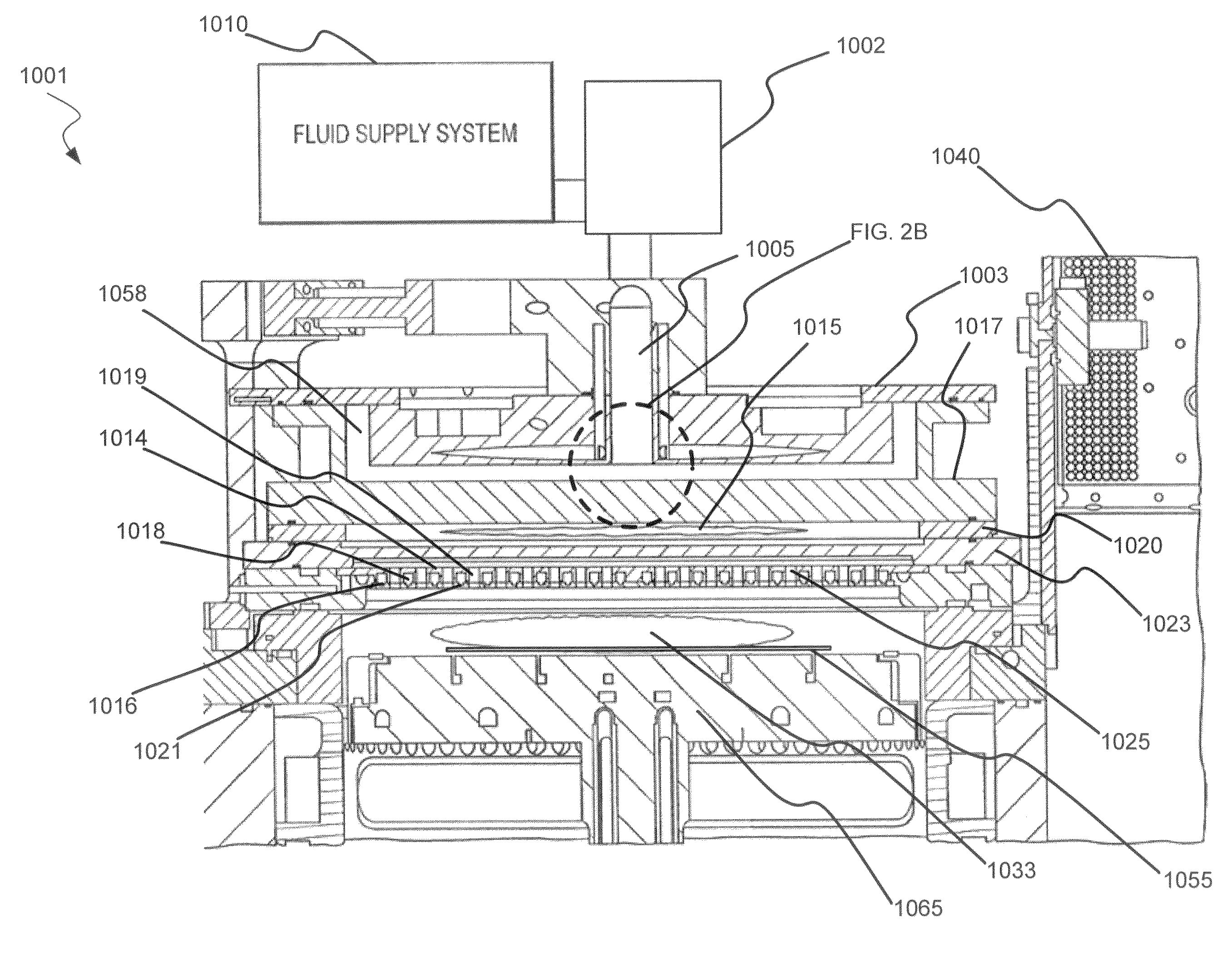
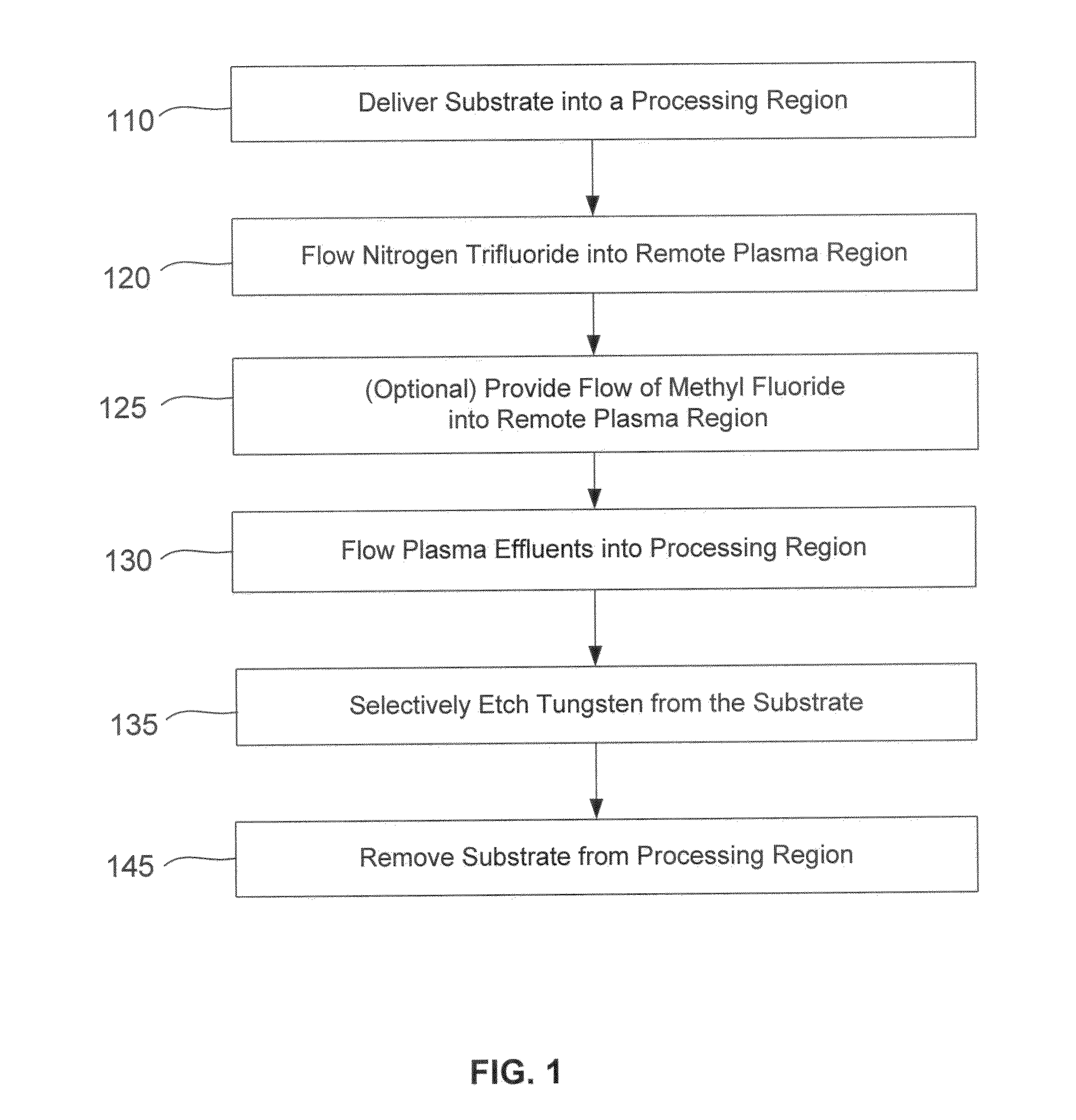
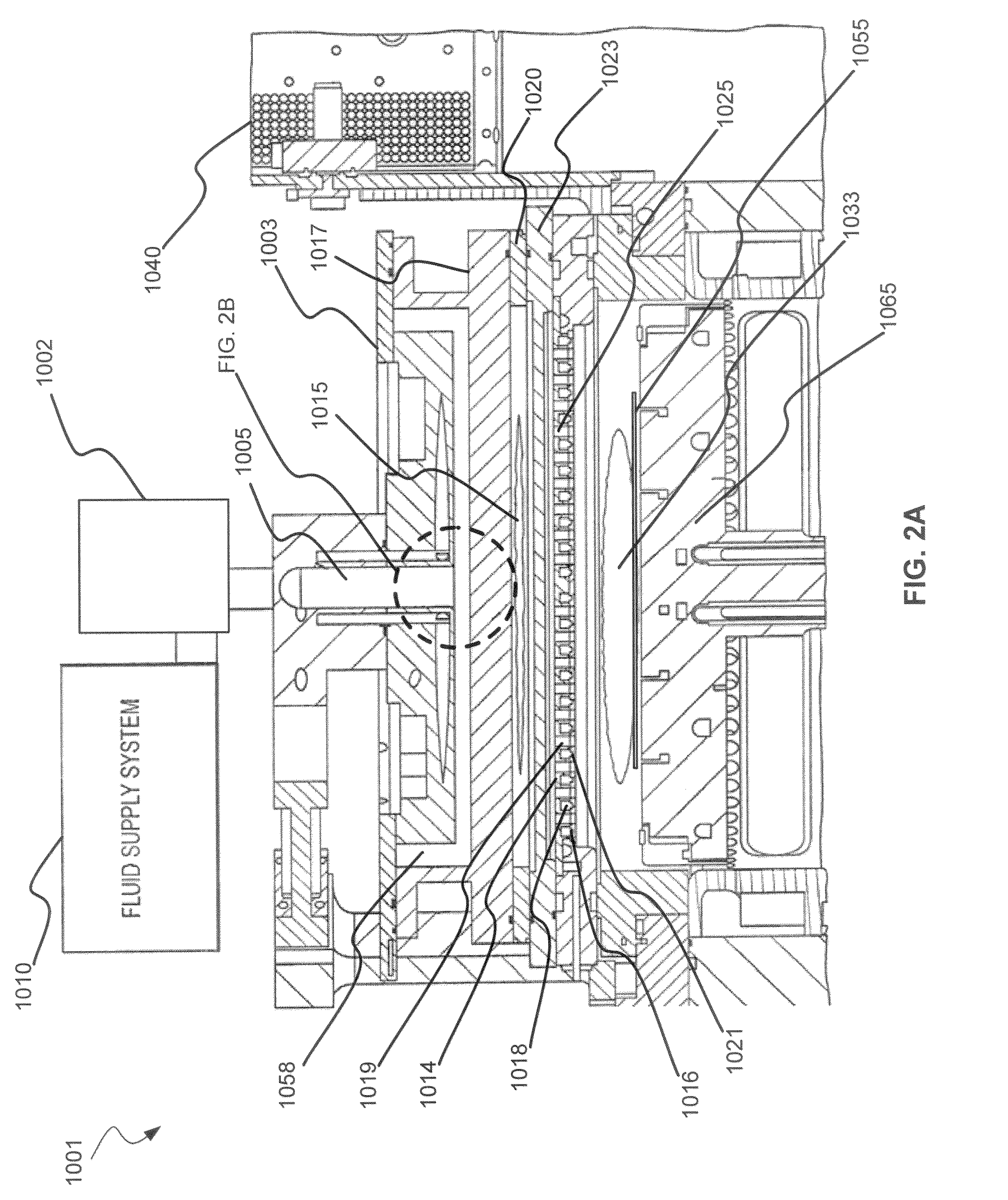
Dry-etch for selective tungsten removal
Methods of selectively etching tungsten relative to silicon-containing films (e.g. silicon oxide, silicon carbon nitride and (poly)silicon) as well as tungsten oxide are described. The methods include a remote plasma etch formed from a fluorine-containing precursor and / or hydrogen (H2). Plasma effluents from the remote plasma are flowed into a substrate processing region where the plasma effluents react with the tungsten. The plasma effluents react with exposed surfaces and selectively remove tungsten while very slowly removing other exposed materials. Sequential and simultaneous methods are included to remove thin tungsten oxide which may, for example, result from exposure to the atmosphere.
Owner:APPLIED MATERIALS INC
Manufacturing method of fin-type field effect transistor
InactiveUS20080171407A1Inhibition formationIncrease etch rateSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSemiconductor devicesEngineeringField-effect transistor
A method for manufacturing a fin-type field effect transistor simply and securely by using a SOI (Silicon On Insulator) wafer, capable of suppressing an undercut formation, is disclosed. The method includes forming a fin-shaped protrusion by selectively dry-etching a single crystalline silicon layer until an underlying buried oxide layer is exposed; forming a sacrificial oxide film by oxidizing a surface of the protrusion including a damage inflicted thereon; and forming a fin having a clean surface by removing the sacrificial oxide film by etching, wherein an etching rate r1 of the sacrificial oxide film is higher than an etching rate r2 of the buried oxide layer during the etching.
Owner:TOKYO ELECTRON LTD
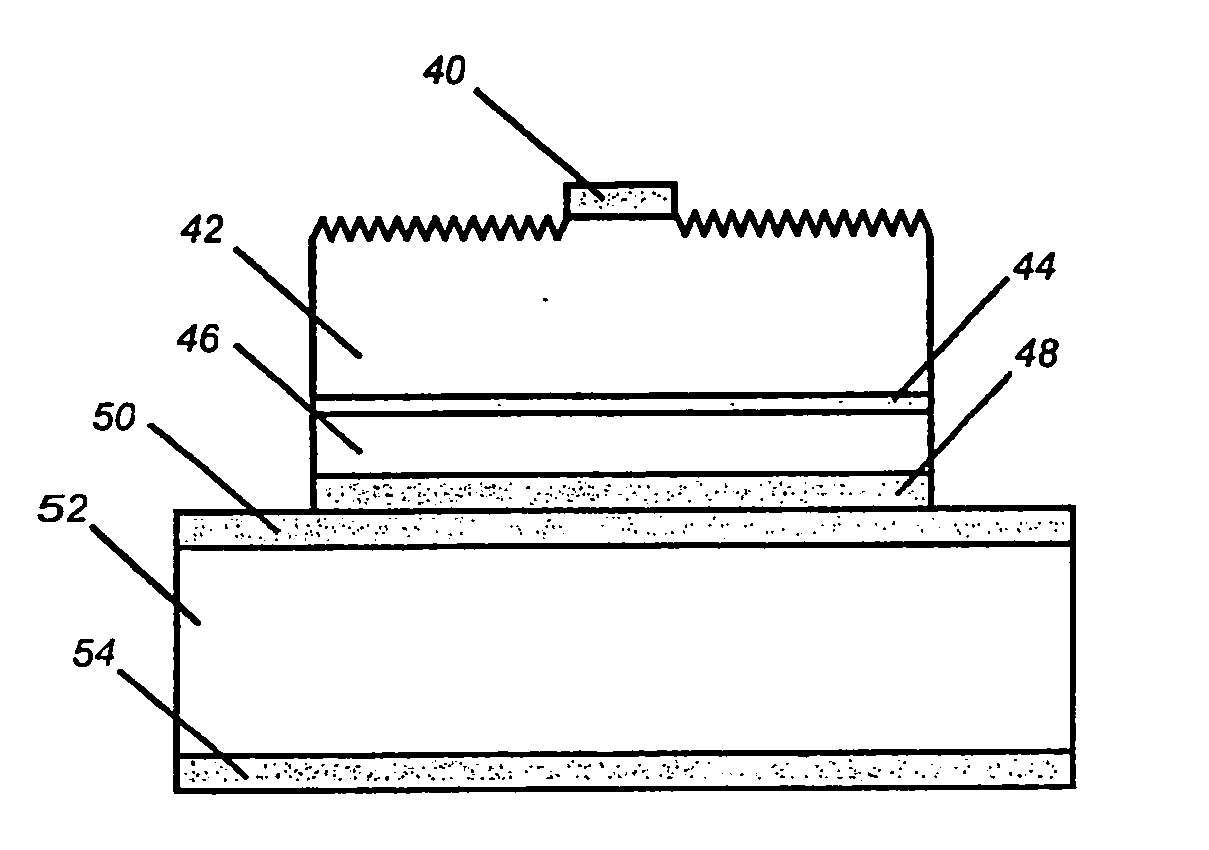
Highly efficient gallium nitride based light emitting diodes via surface roughening
ActiveUS20070121690A1Solid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingNitrogenLight reflection
A gallium nitride (GaN) based light emitting diode (LED), wherein light is extracted through a nitrogen face (N-face) (42) of the LED and a surface of the N-face (42) is roughened into one or more hexagonal shaped cones. The roughened surface reduces light reflections occurring repeatedly inside the LED, and thus extracts more light out of the LED. The surface of the N-face (42) is roughened by an anisotropic etching, which may comprise a dry etching or a photo-enhanced chemical (PEC) etching.
Owner:JAPAN SCI & TECH CORP
Uniform dry etch in two stages
ActiveUS8741778B2Flat surfaceEasy to removeDecorative surface effectsSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSilicon oxideDry etching
Owner:APPLIED MATERIALS INC
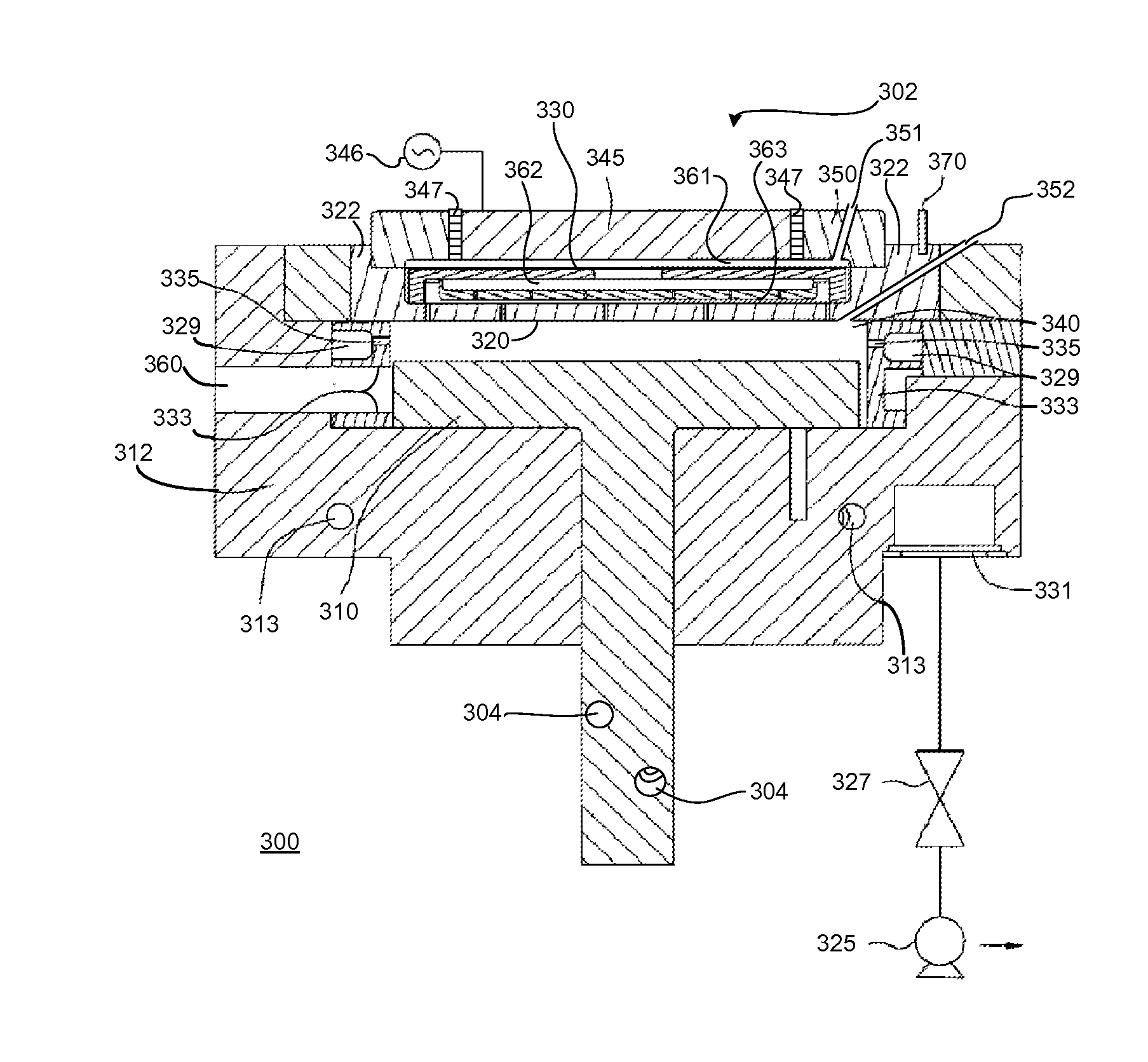
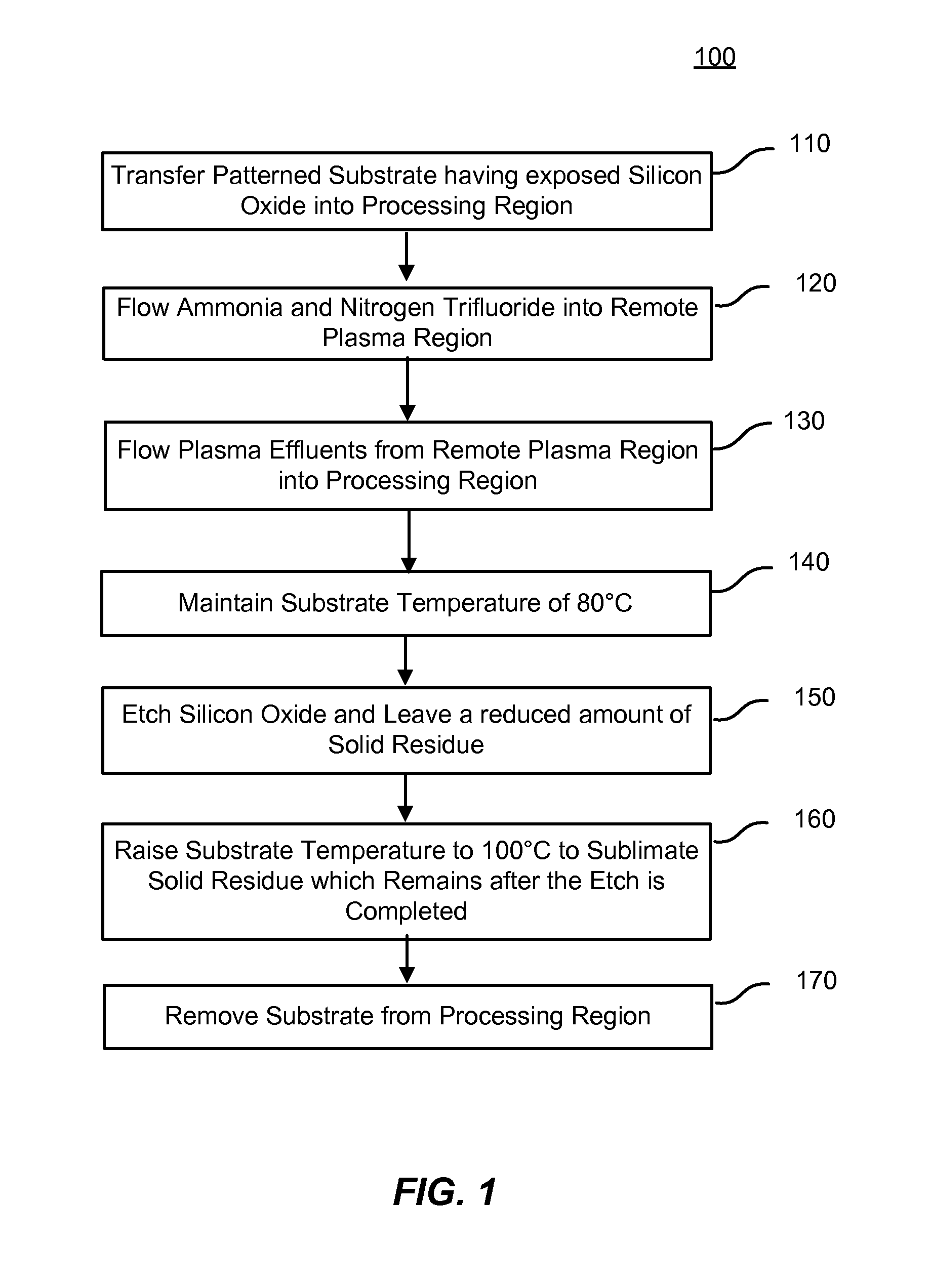
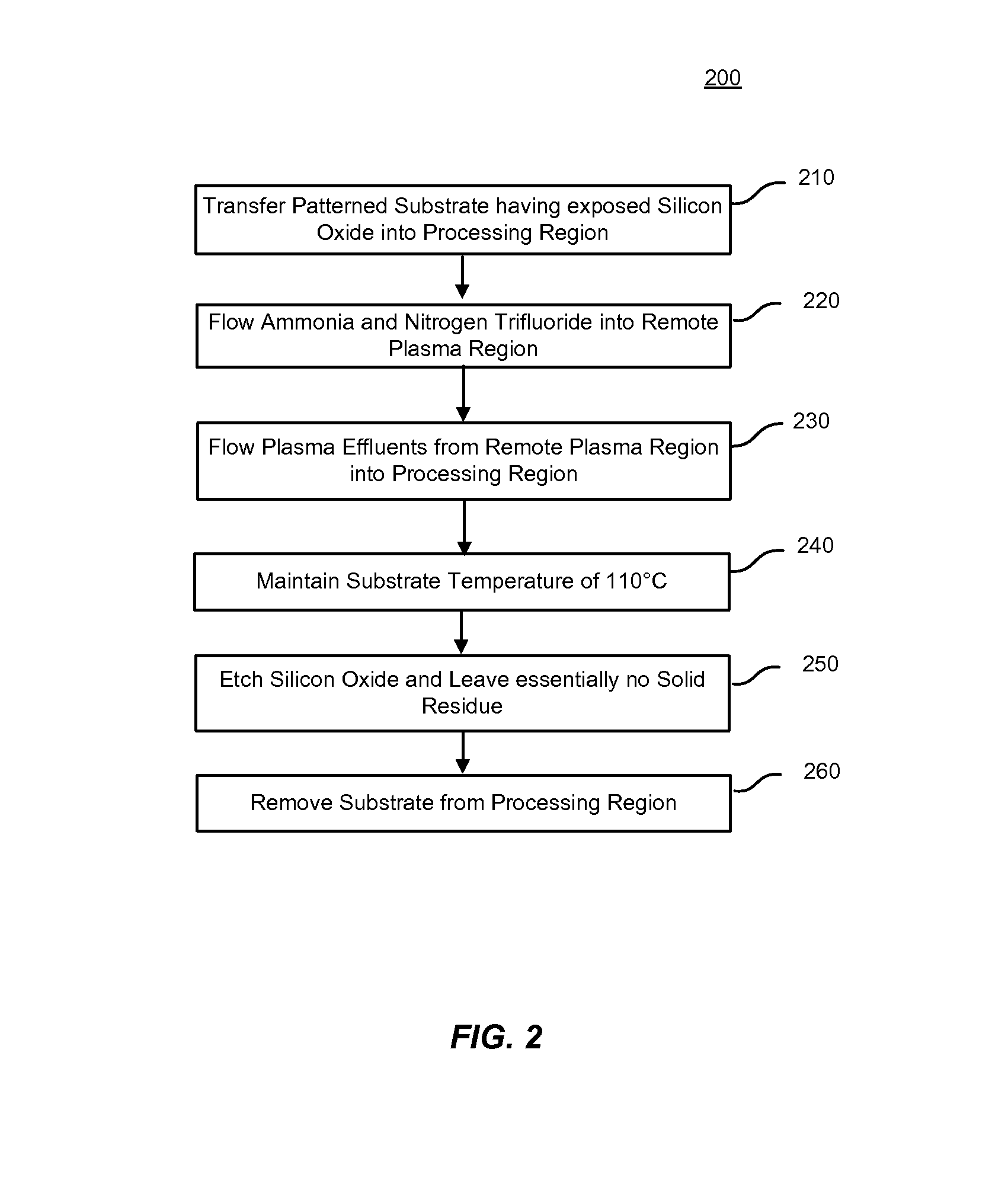
High-temperature selective dry etch having reduced post-etch solid residue
ActiveUS8475674B2Residue reductionHigh temperature of the dielectric filmsElectric discharge tubesDecorative surface effectsDielectricDry etching
Methods of dry etching silicon-containing dielectric films are described. The methods include maintaining a relatively high temperature of the dielectric films while etching in order to achieve reduced solid residue on the etched surface. Partially or completely avoiding the accumulation of solid residue increases the etch rate.
Owner:APPLIED MATERIALS INC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com