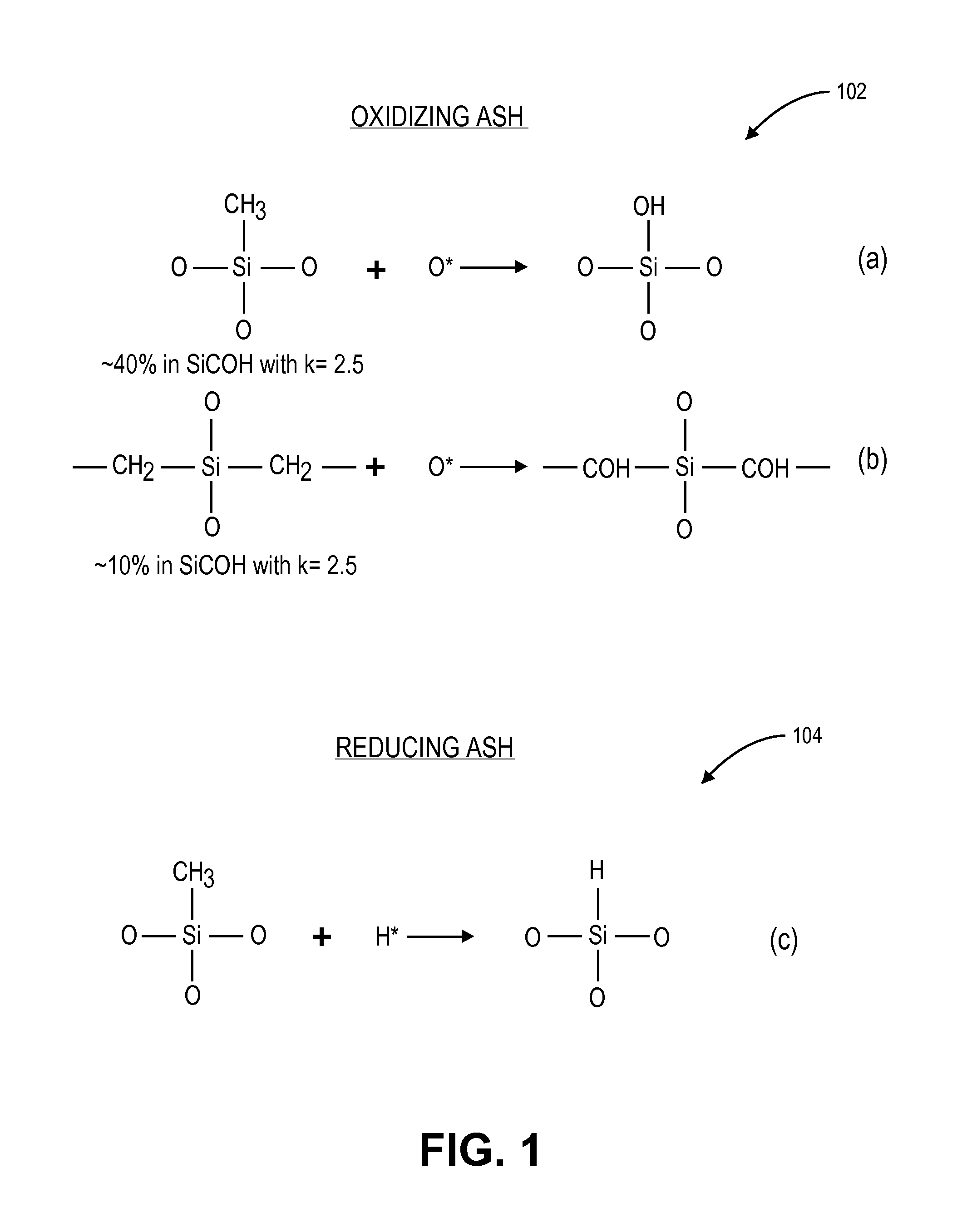Patents
Literature
157 results about "Multiple patterning" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
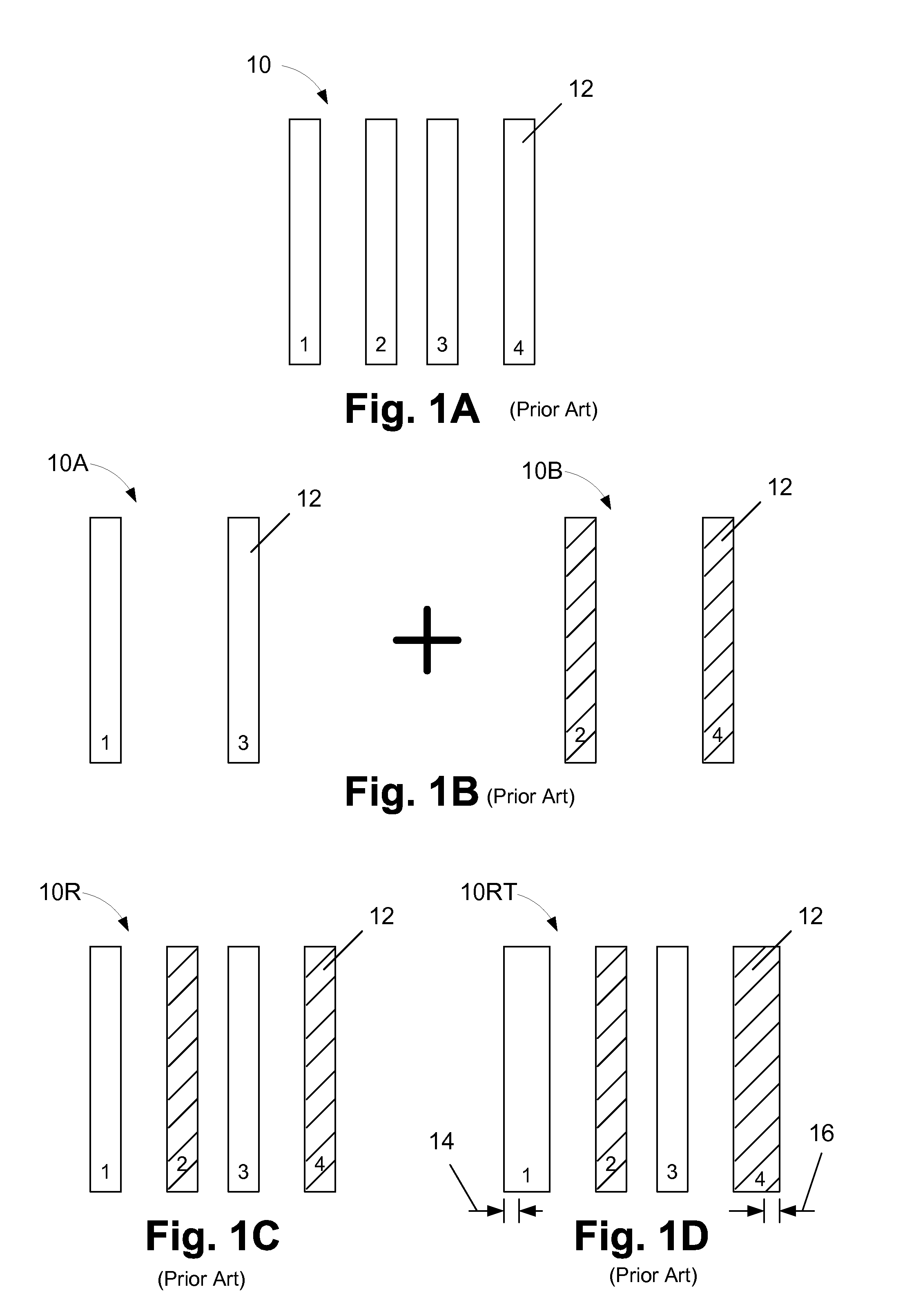
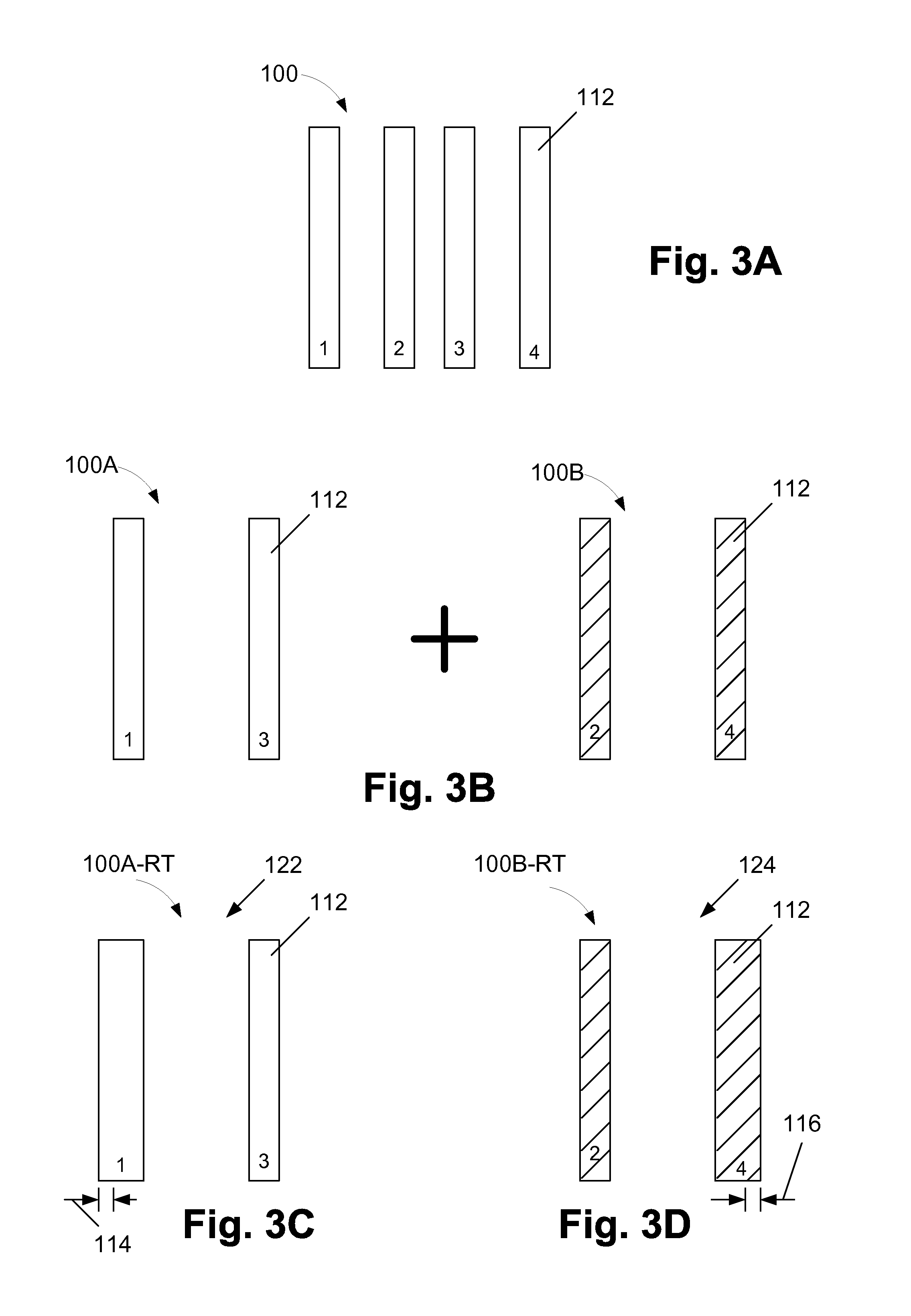
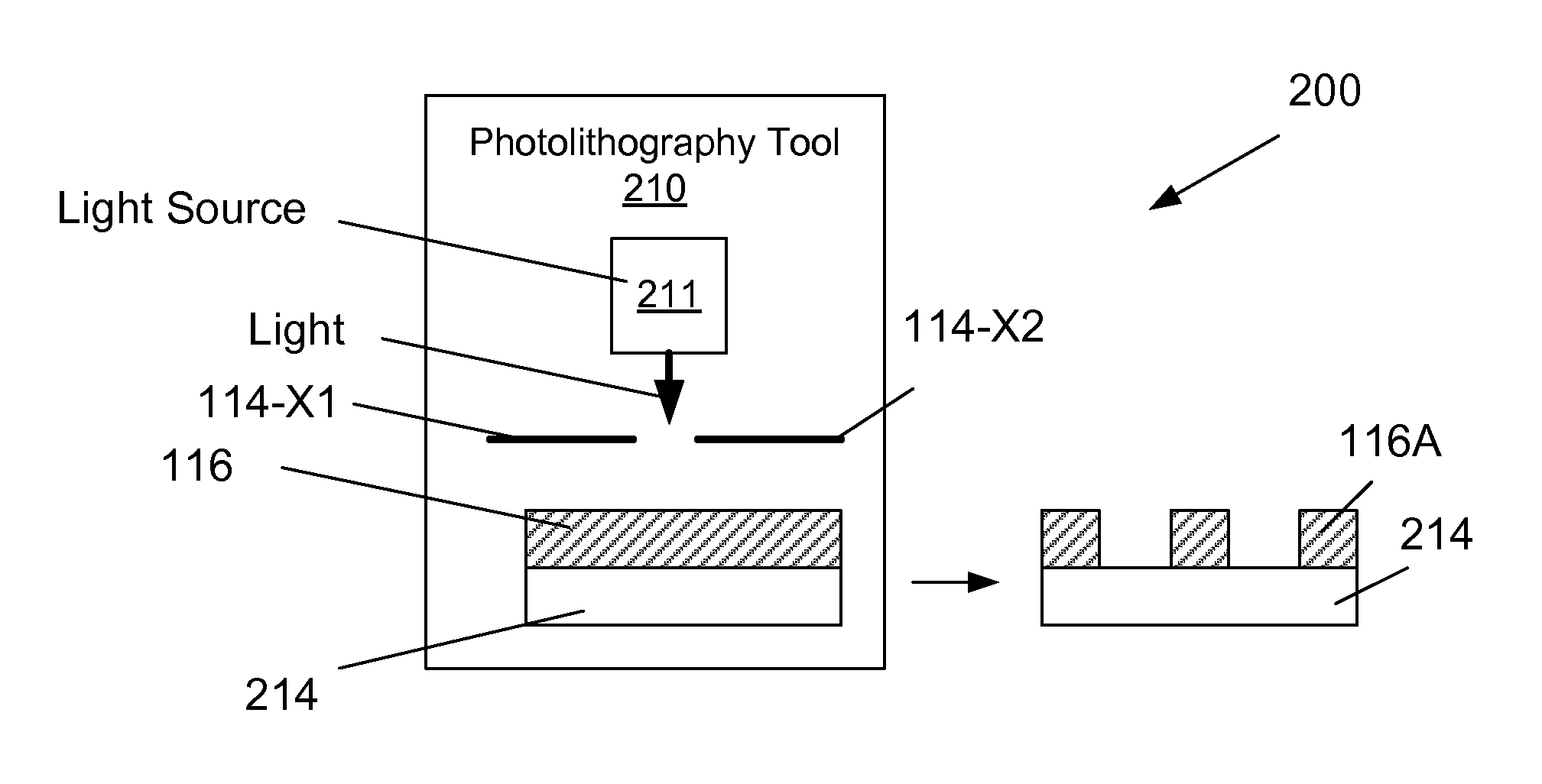
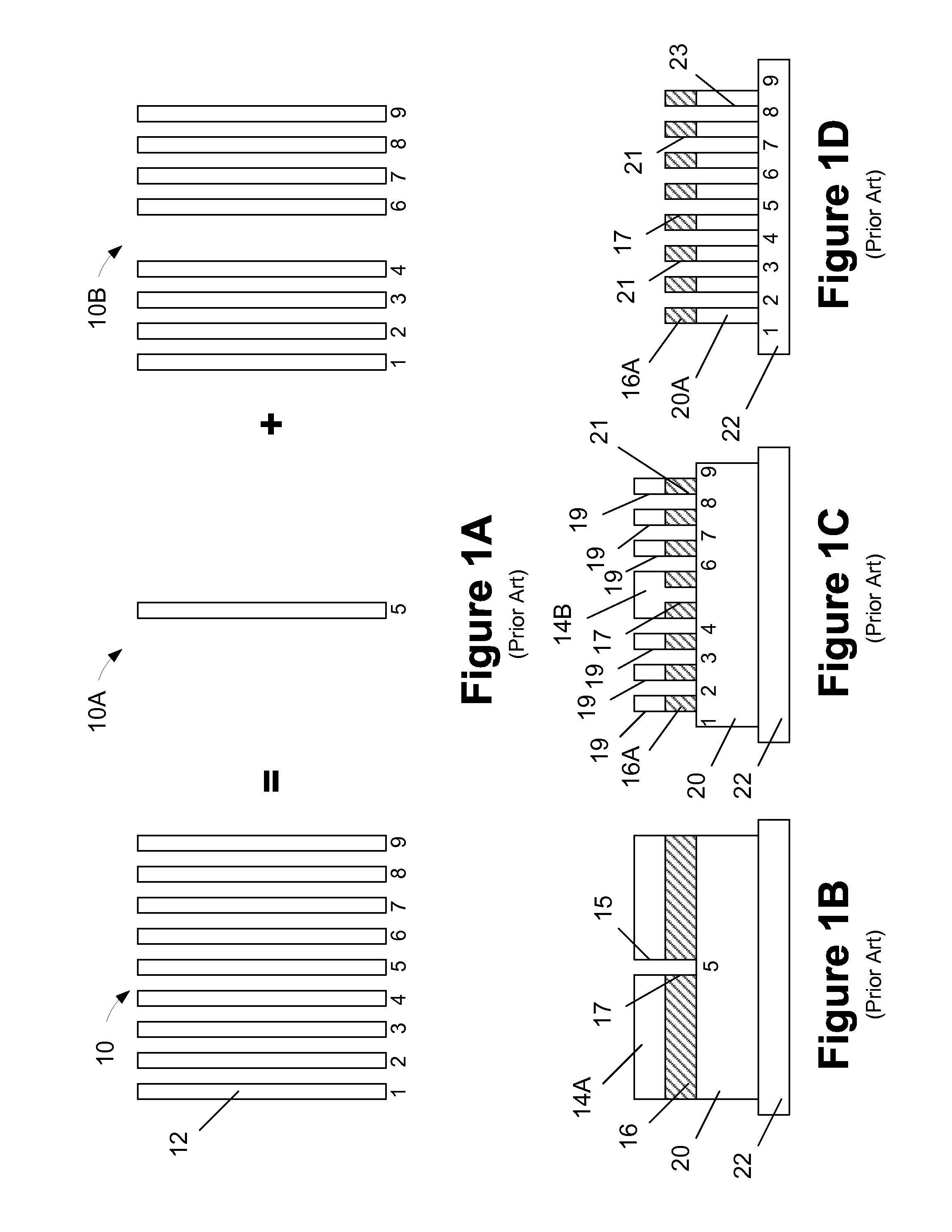
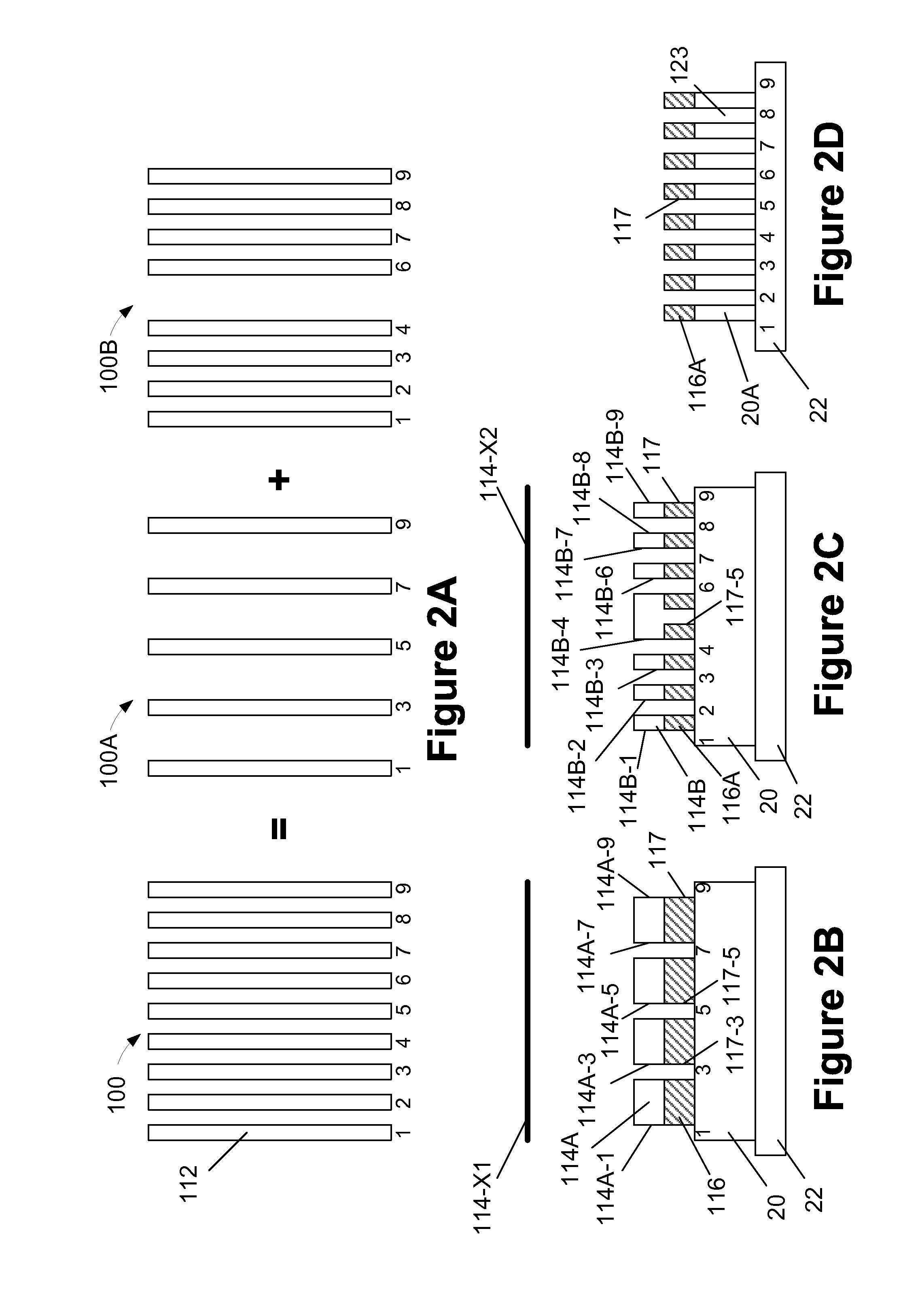
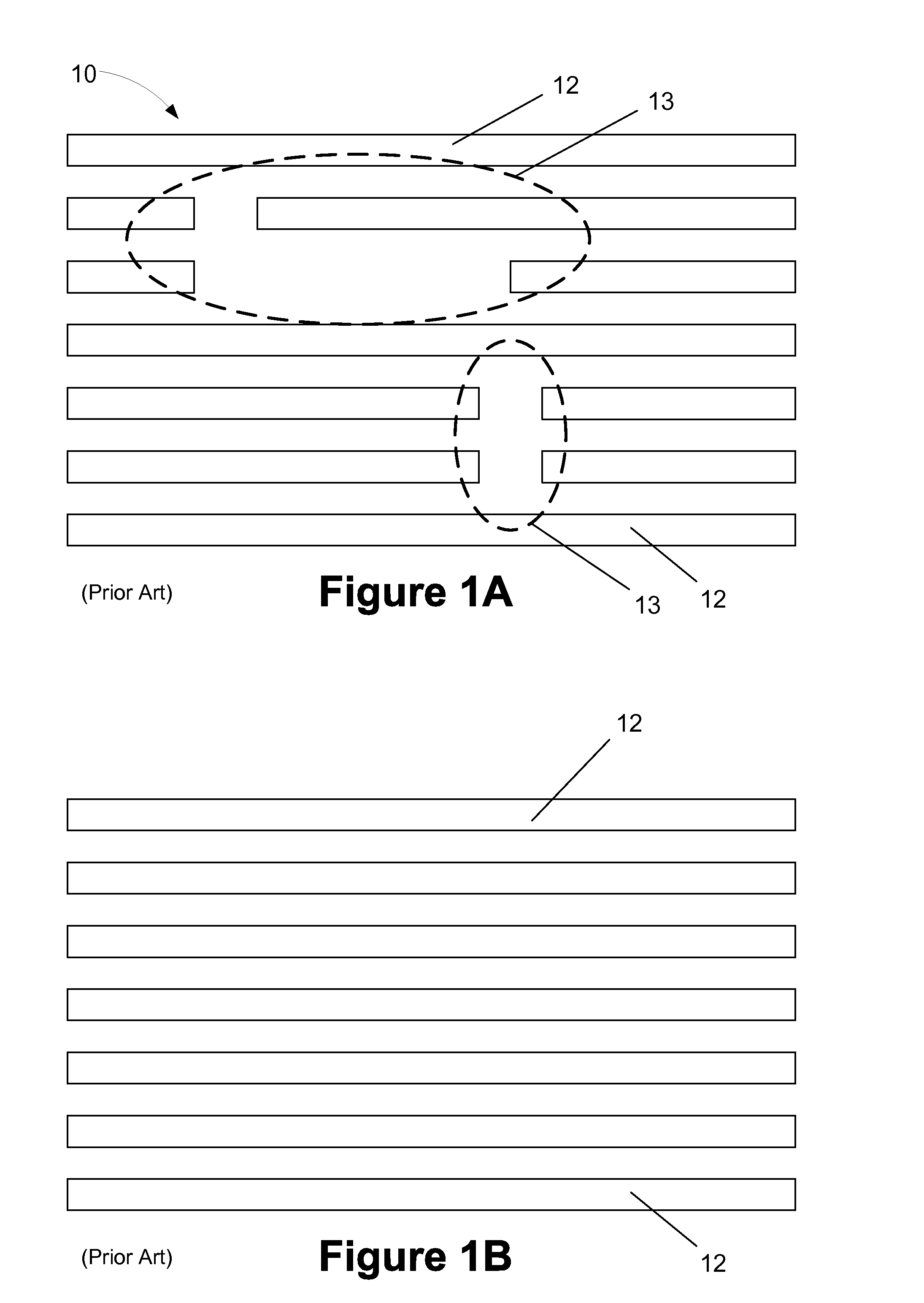
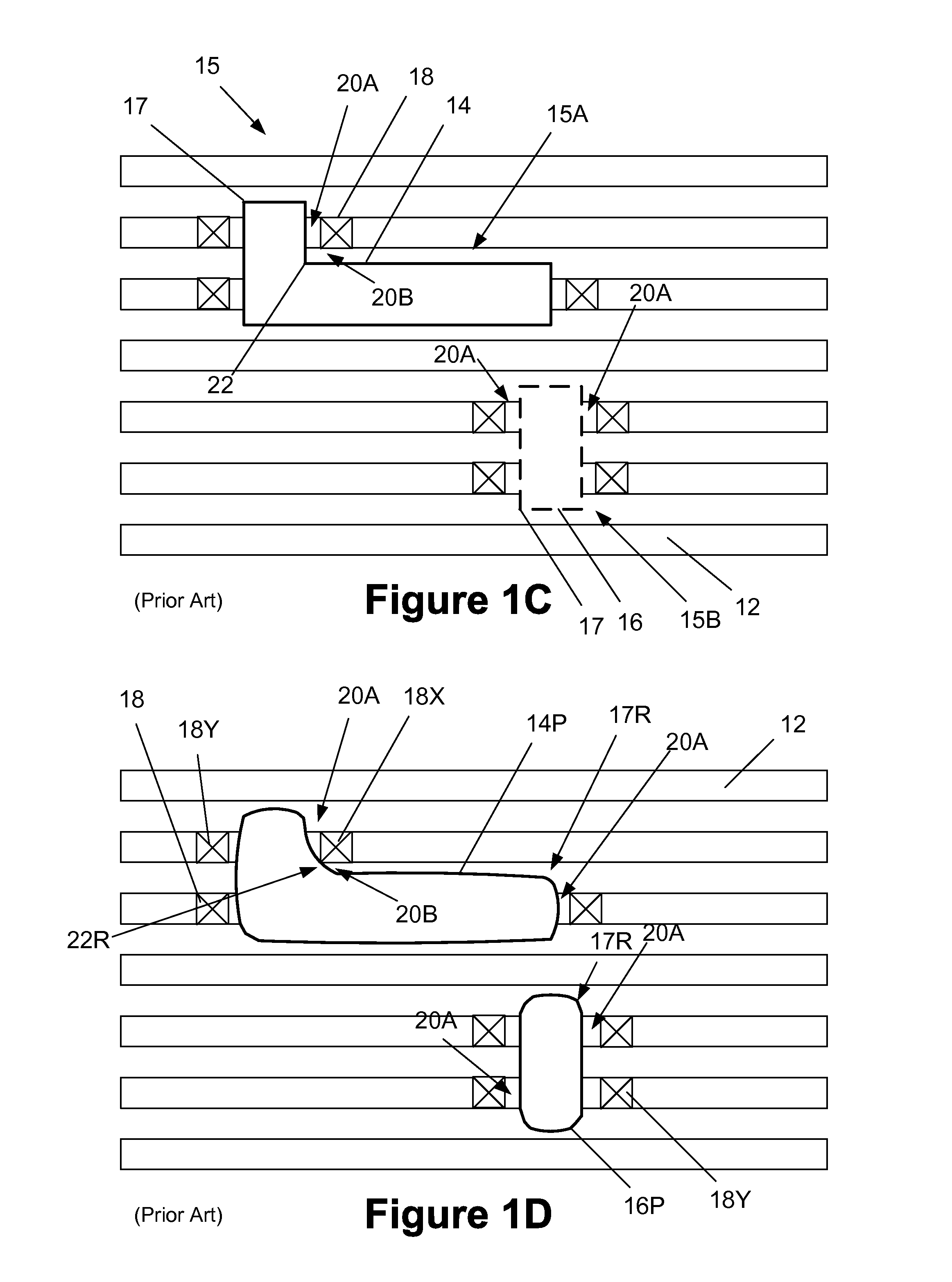
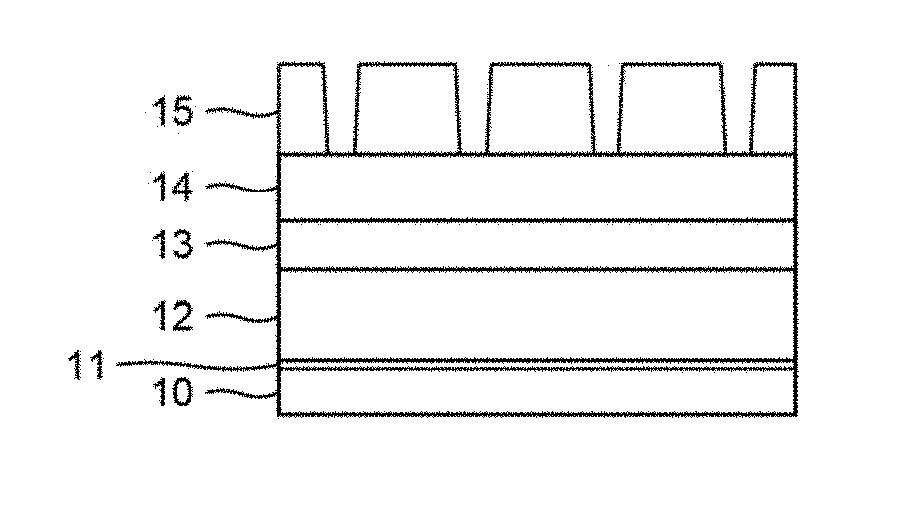
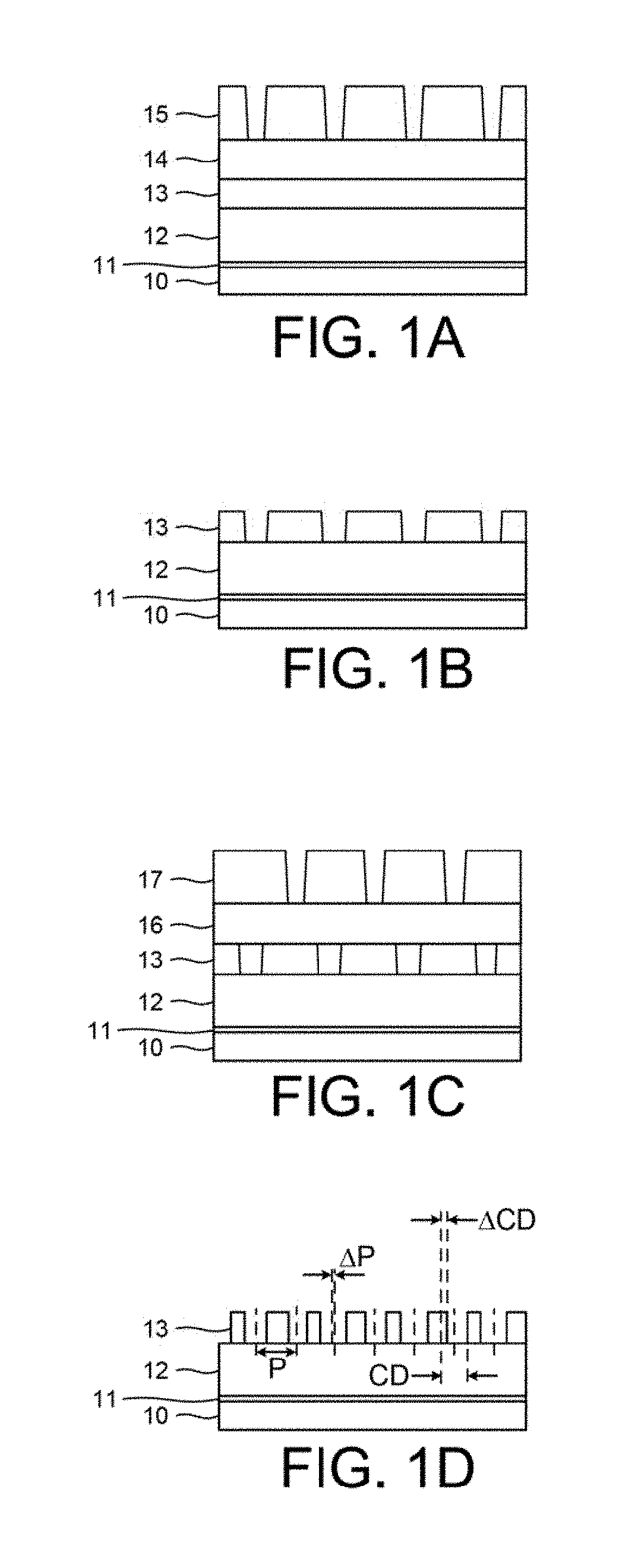
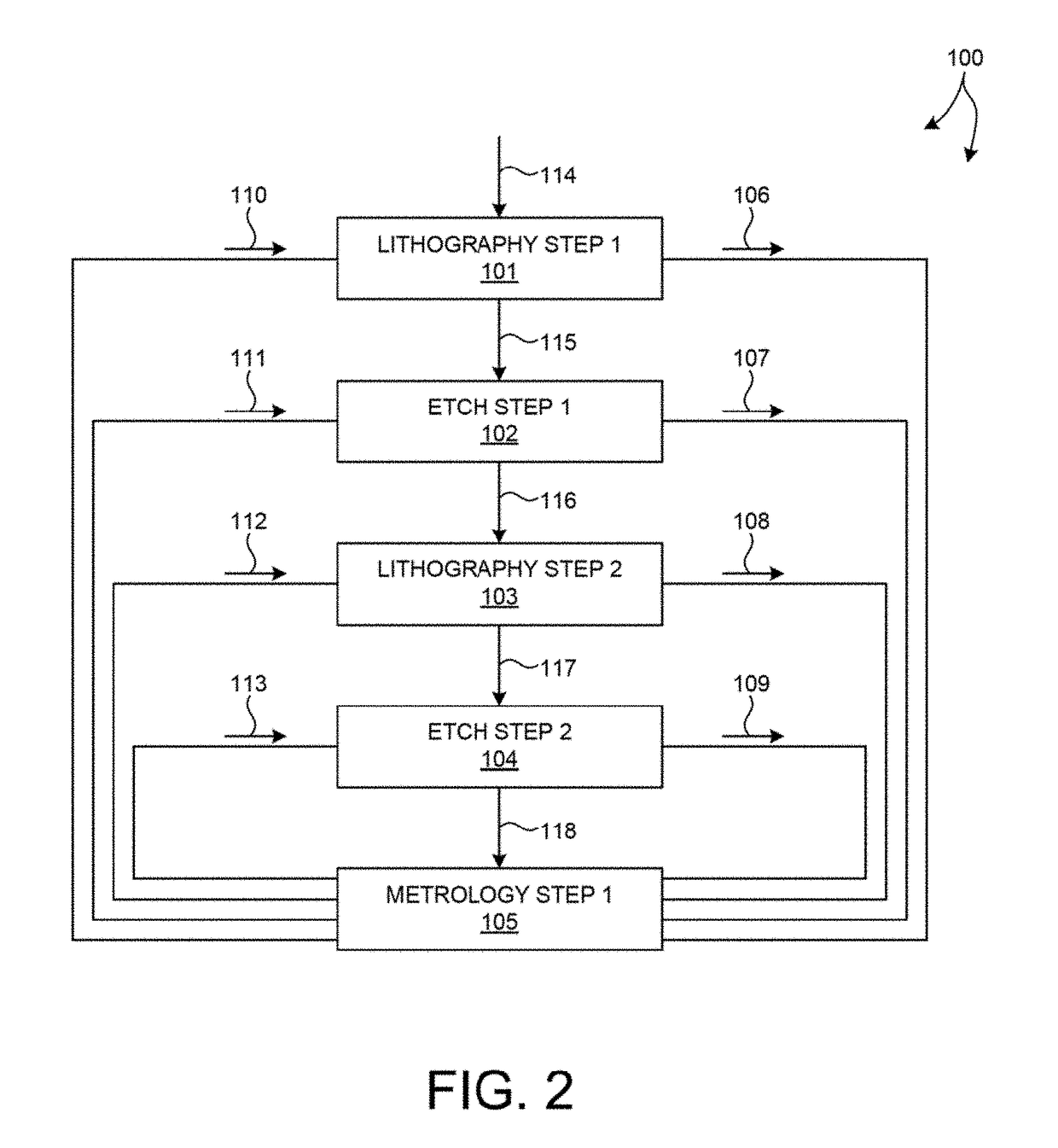
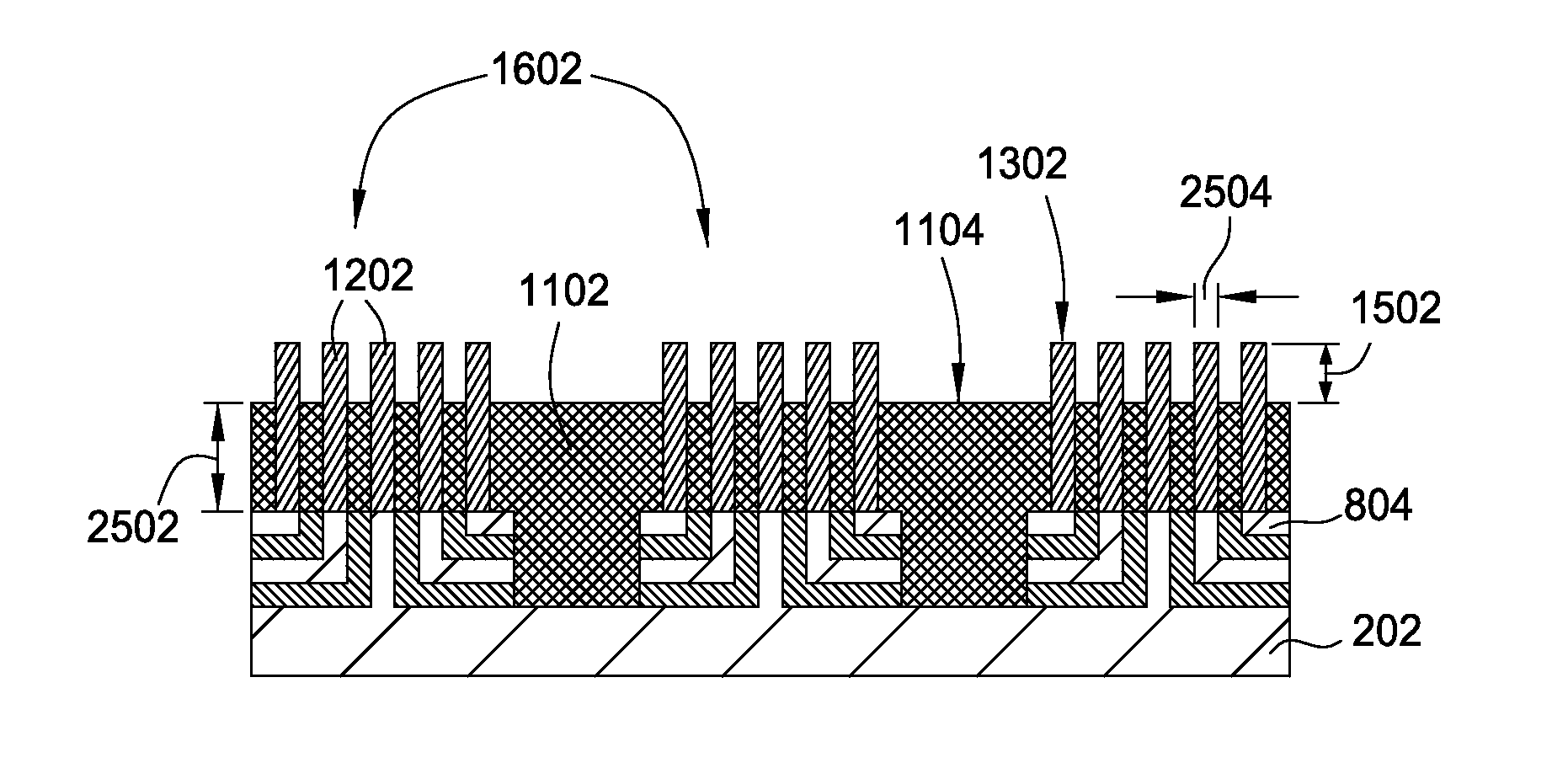
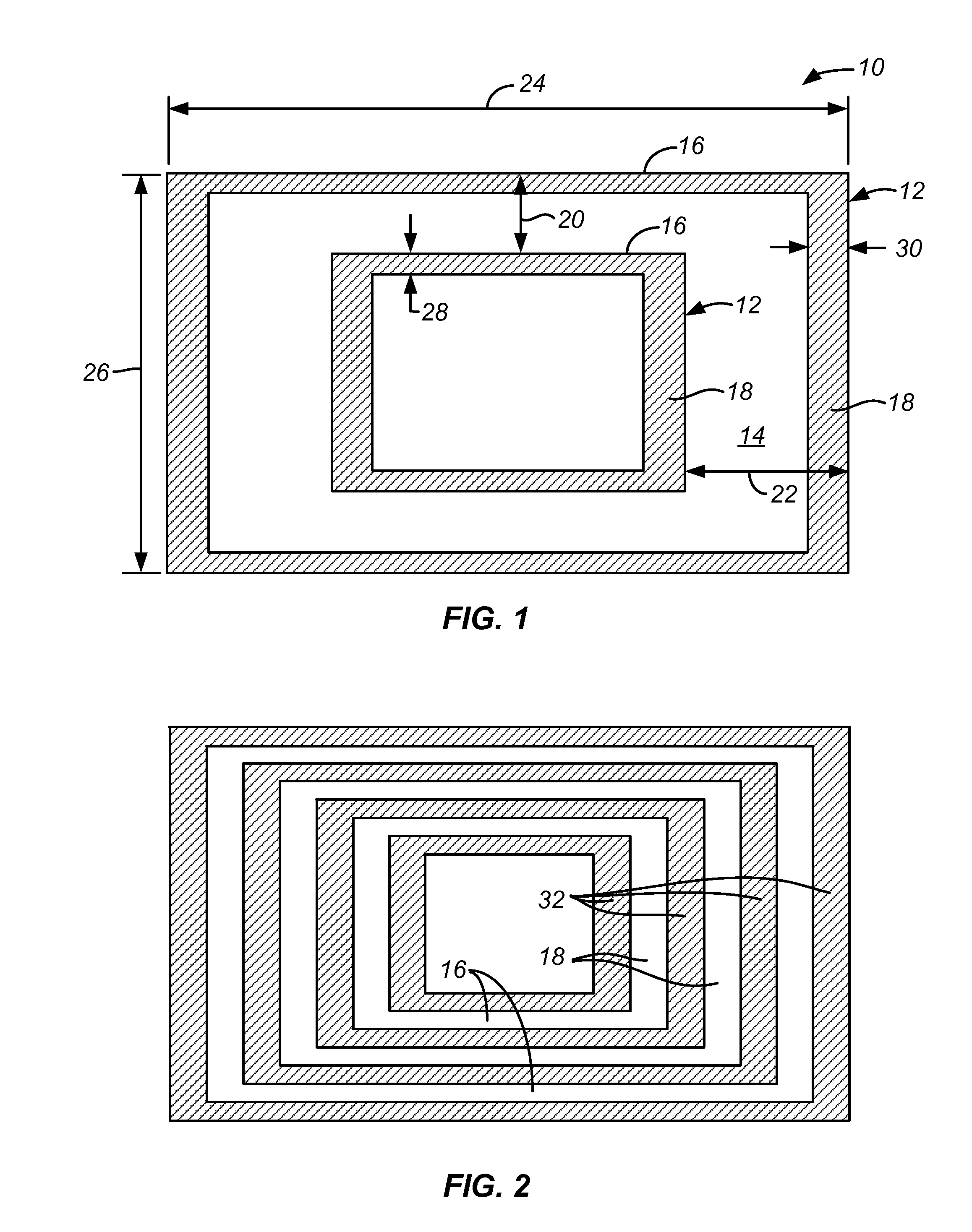
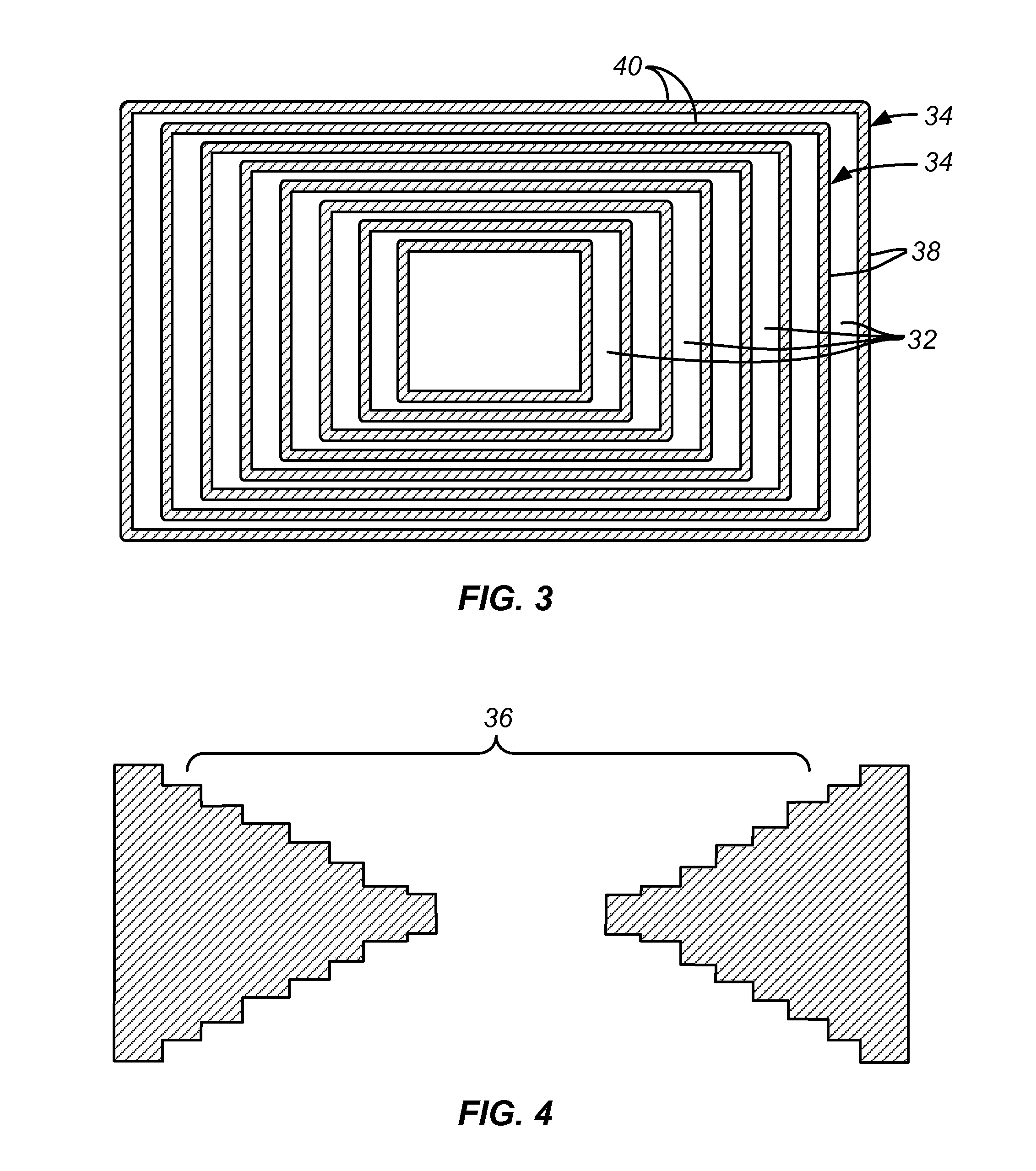
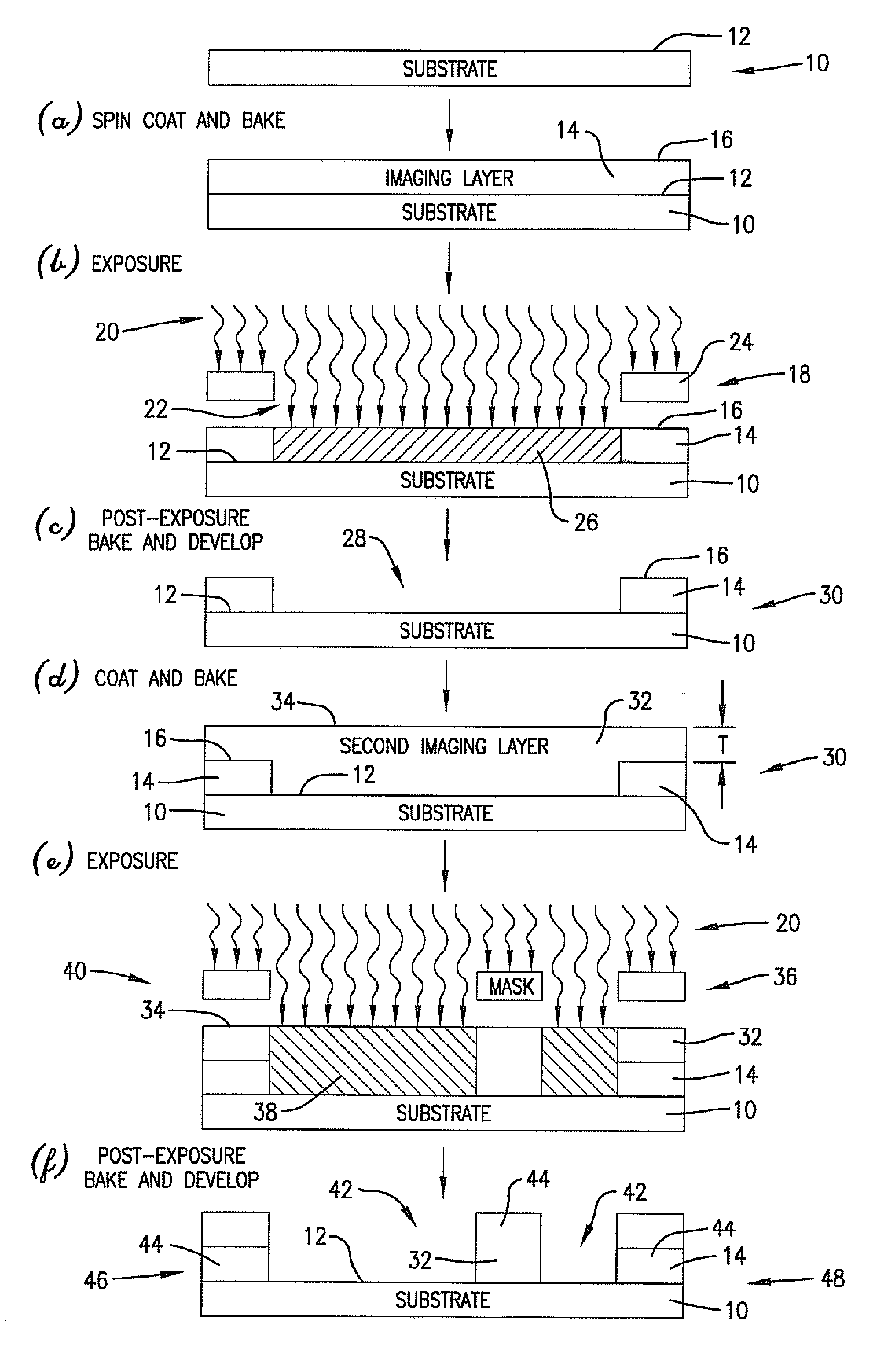
Multiple patterning (or multi-patterning) is a class of technologies for manufacturing integrated circuits (ICs), developed for photolithography to enhance the feature density. It is expected to be necessary for the 10 nm and 7 nm node semiconductor processes and beyond. The premise is that a single lithographic exposure may not be enough to provide sufficient resolution. Hence additional exposures would be needed, or else positioning patterns using etched feature sidewalls (using spacers) would be necessary.
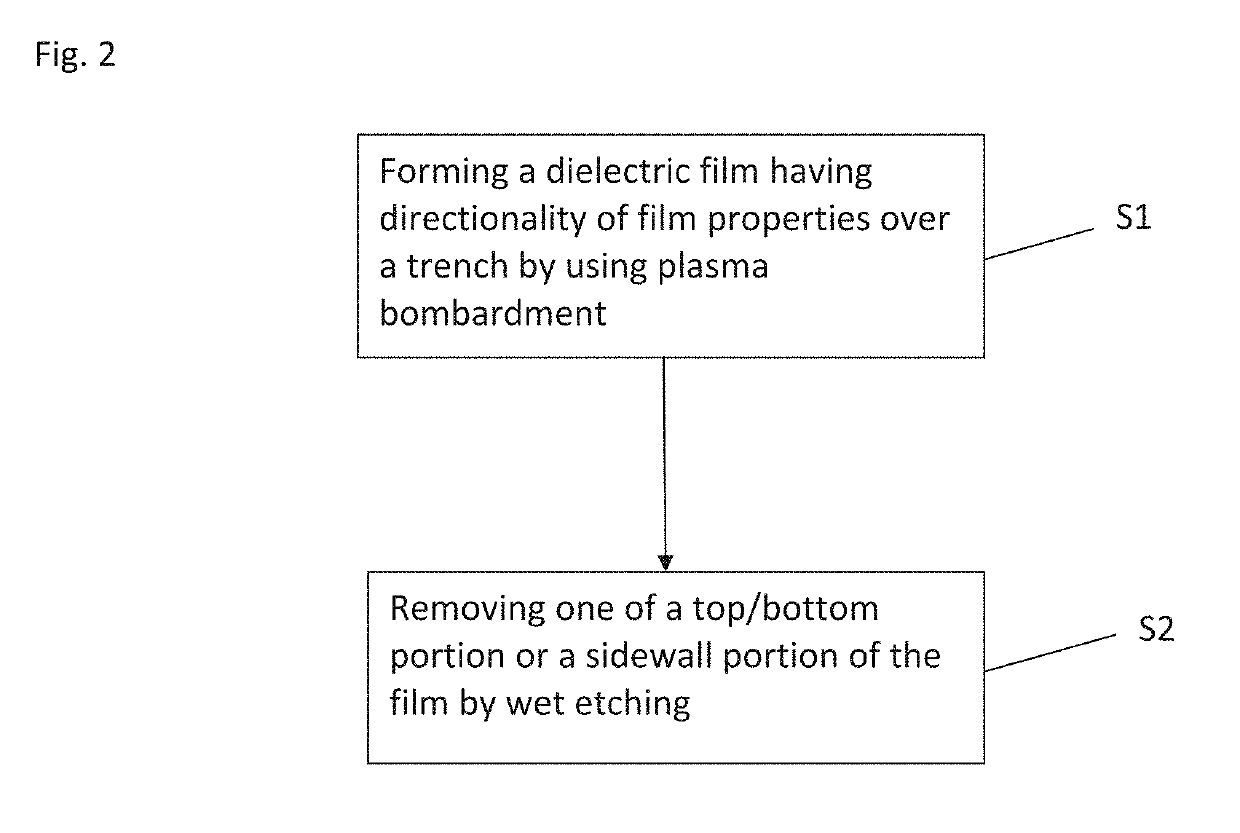
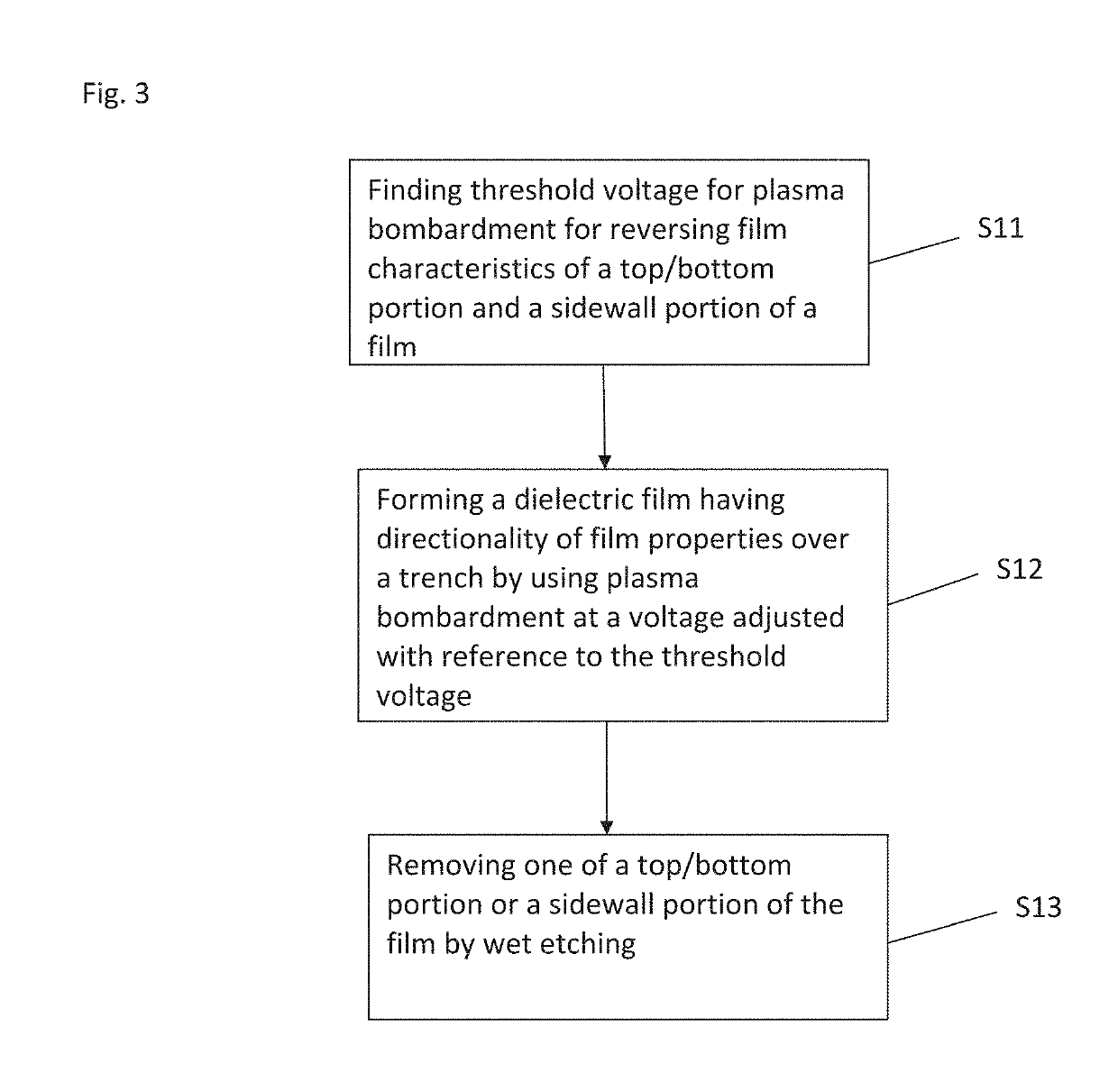
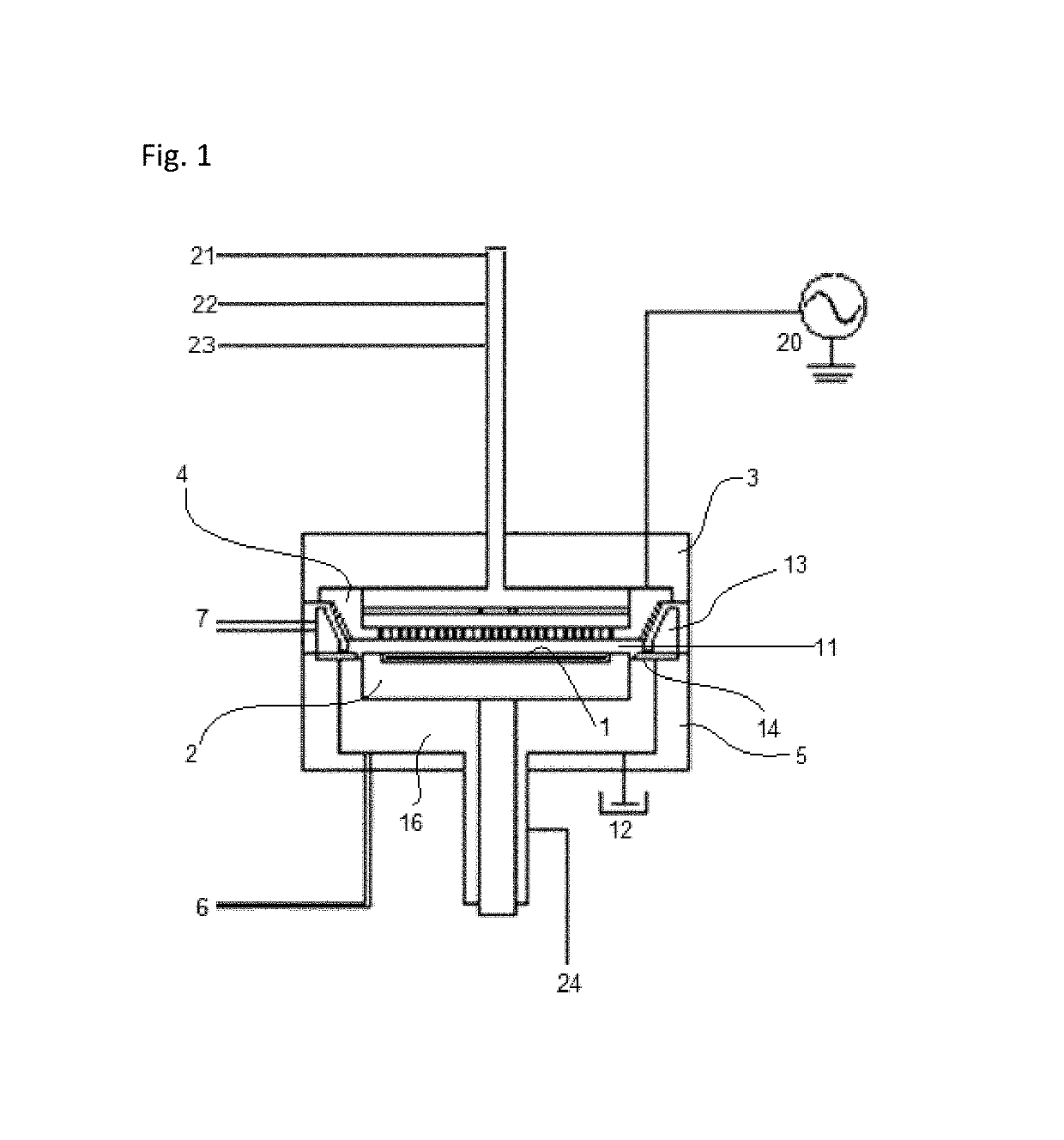
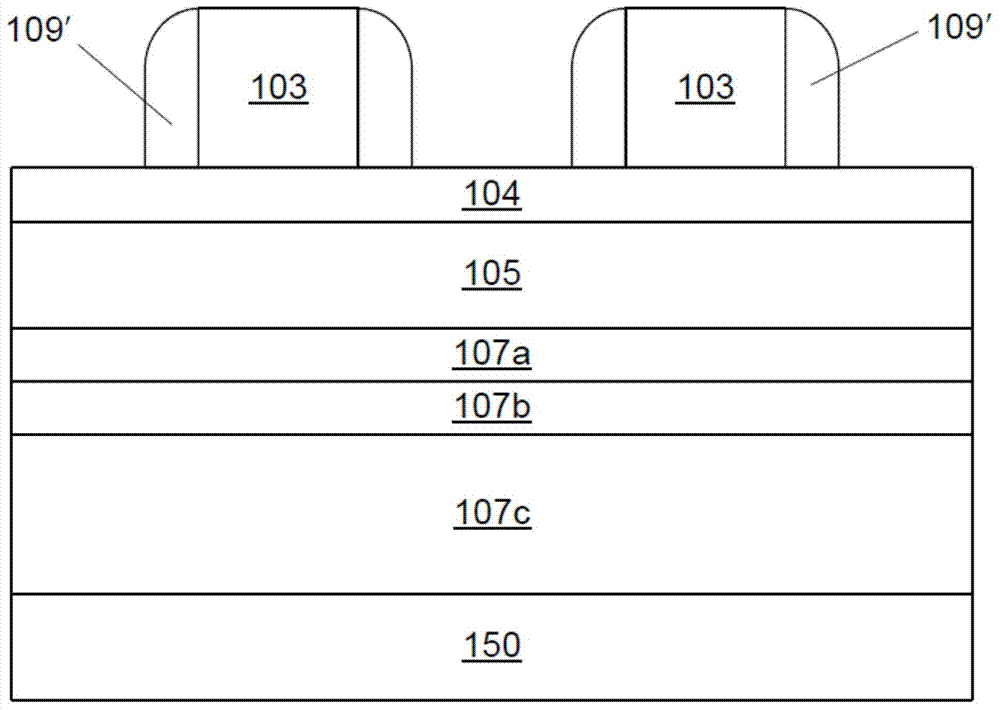
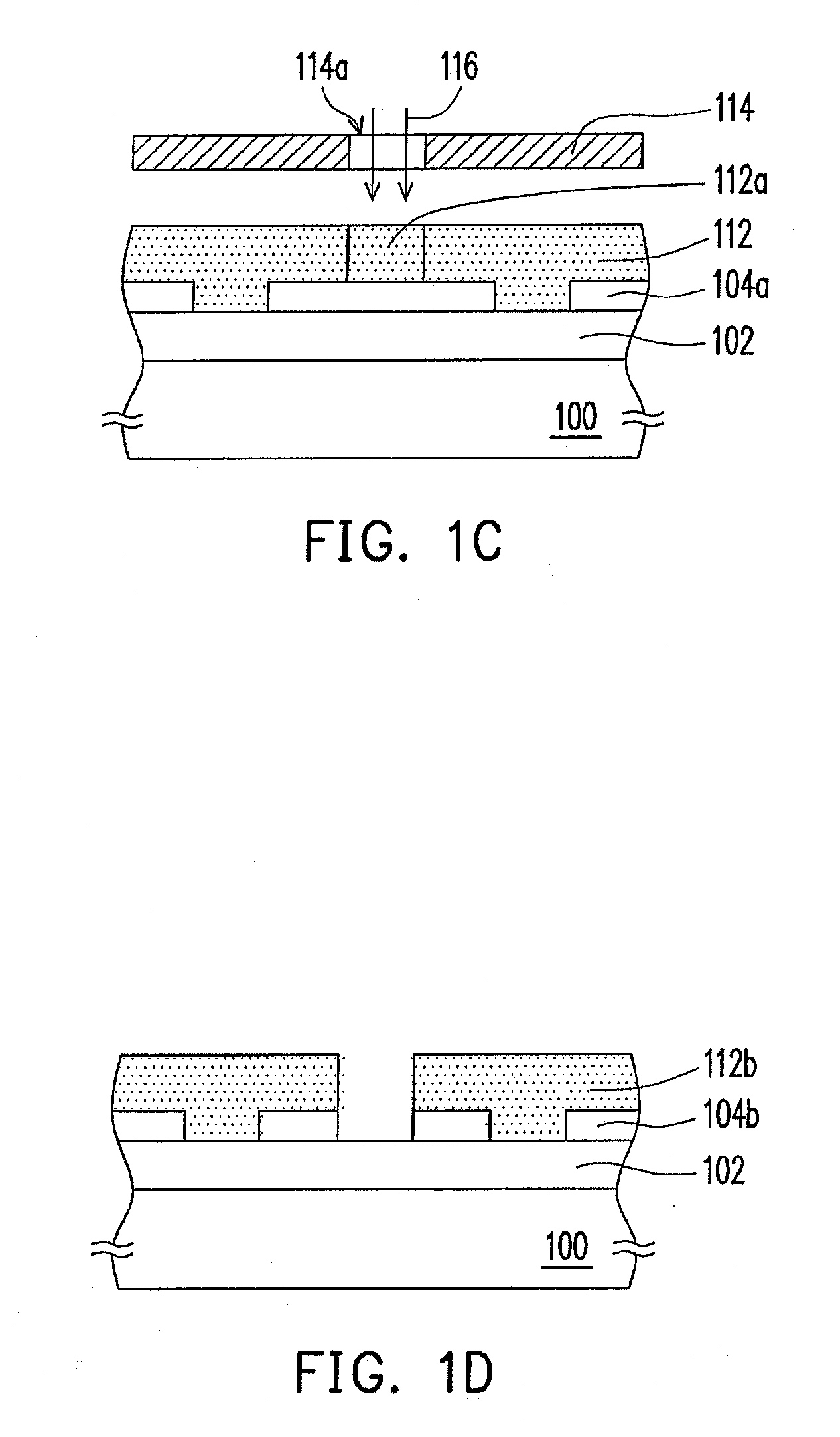
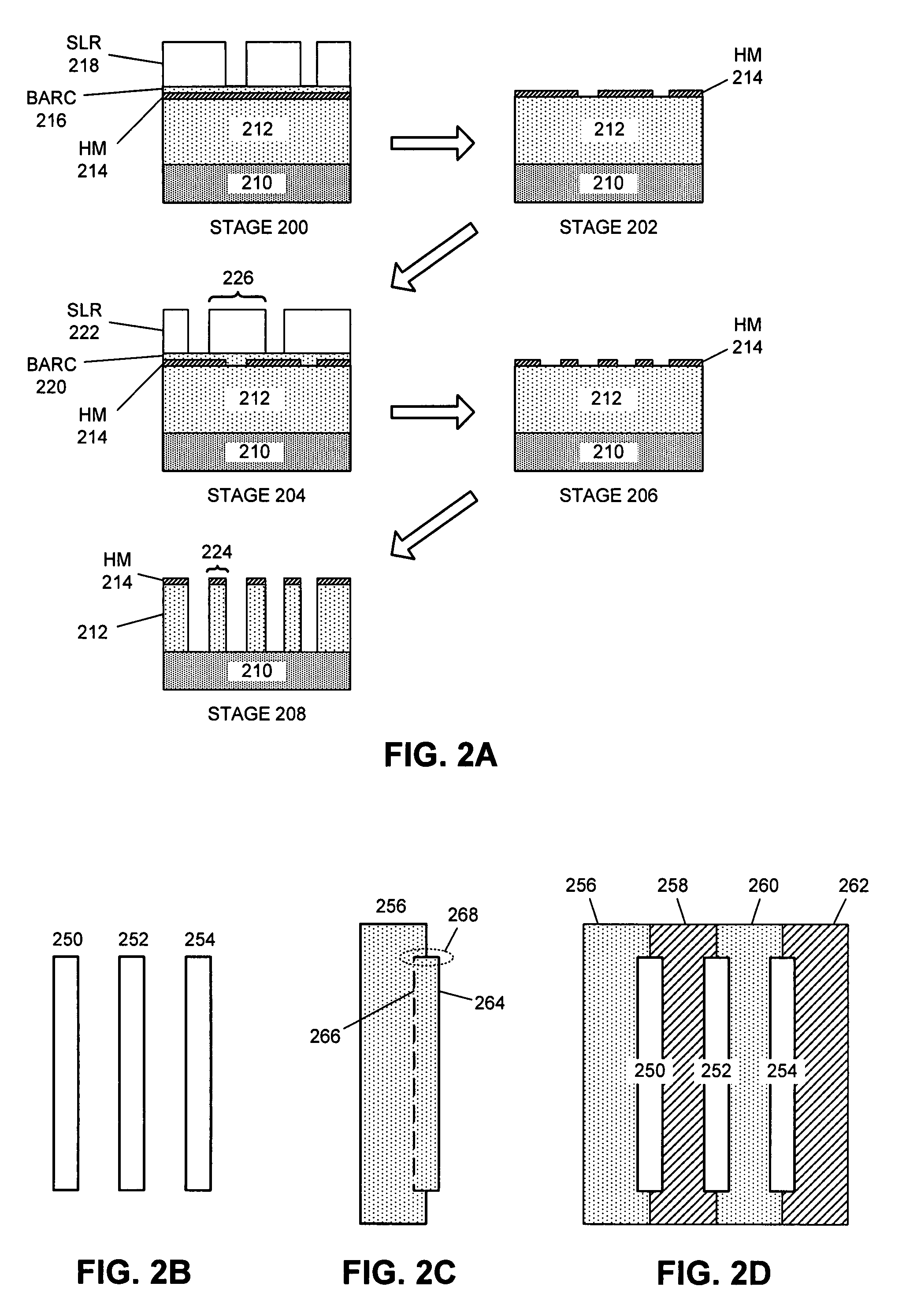
Method for forming spacers using silicon nitride film for spacer-defined multiple patterning
ActiveUS20170316940A1Semiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingChemical vapor deposition coatingSurface patternSilanes
A method of forming spacers for spacer-defined multiple pattering (SDMP), includes: depositing a pattern transfer film by PEALD on the entire patterned surface of a template using halogenated silane as a precursor and nitrogen as a reactant at a temperature of 200° C. or less, which pattern transfer film is a silicon nitride film; dry-etching the template using a fluorocarbon as an etchant, and thereby selectively removing a portion of the pattern transfer film formed on a top of a core material and a horizontal portion of the pattern transfer film while leaving the core material and a vertical portion of the pattern transfer film as a vertical spacer, wherein a top of the vertical spacer is substantially flat; and dry-etching the core material, whereby the template has a surface patterned by the vertical spacer on a underlying layer.
Owner:ASM IP HLDG BV
Method for forming spacers using silicon nitride film for spacer-defined multiple patterning
ActiveUS10468251B2Semiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingChemical vapor deposition coatingFluorocarbonDry etching
A method of forming spacers for spacer-defined multiple pattering (SDMP), includes: depositing a pattern transfer film by PEALD on the entire patterned surface of a template using halogenated silane as a precursor and nitrogen as a reactant at a temperature of 200° C. or less, which pattern transfer film is a silicon nitride film; dry-etching the template using a fluorocarbon as an etchant, and thereby selectively removing a portion of the pattern transfer film formed on a top of a core material and a horizontal portion of the pattern transfer film while leaving the core material and a vertical portion of the pattern transfer film as a vertical spacer, wherein a top of the vertical spacer is substantially flat; and dry-etching the core material, whereby the template has a surface patterned by the vertical spacer on a underlying layer.
Owner:ASM IP HLDG BV
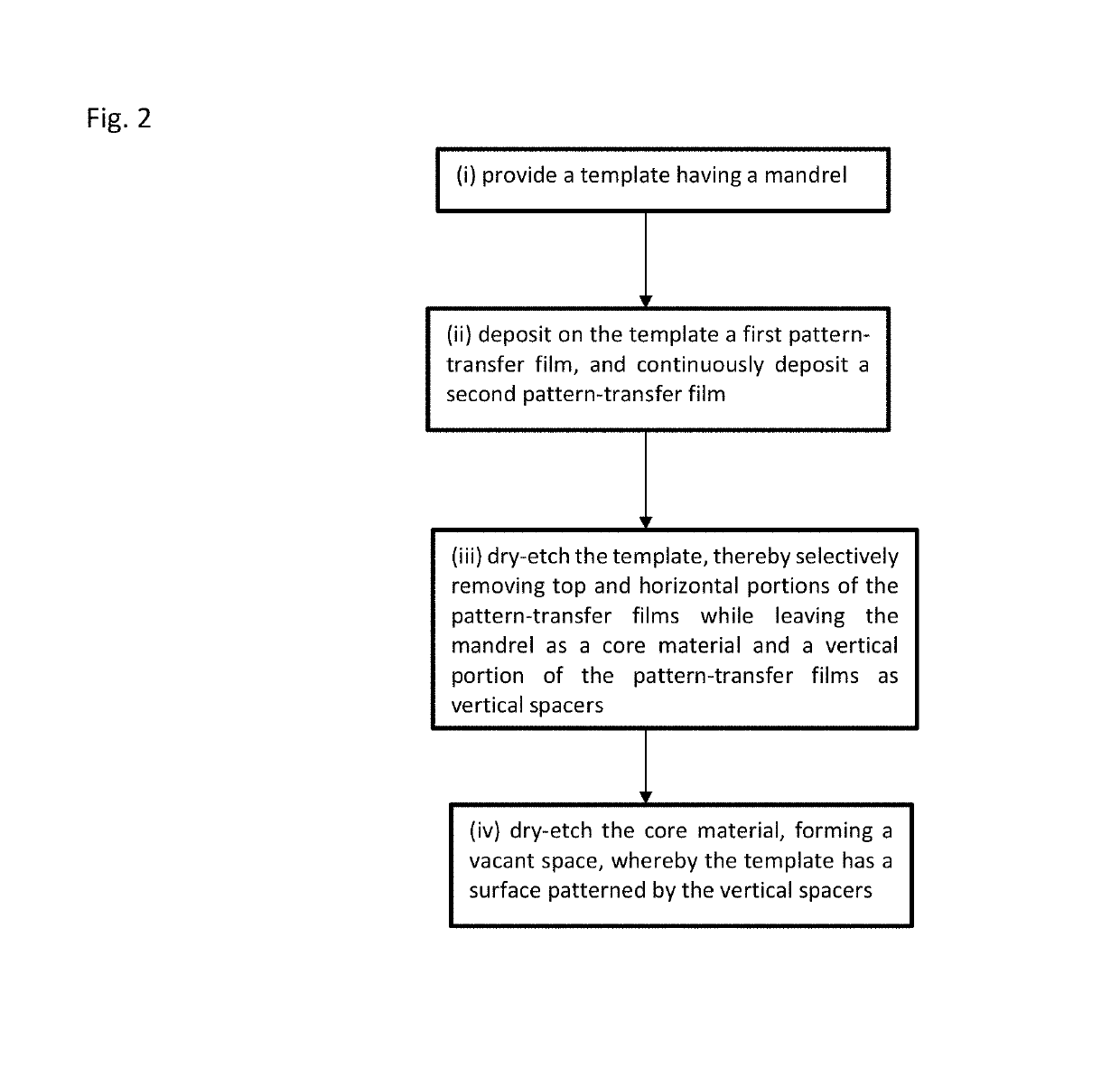
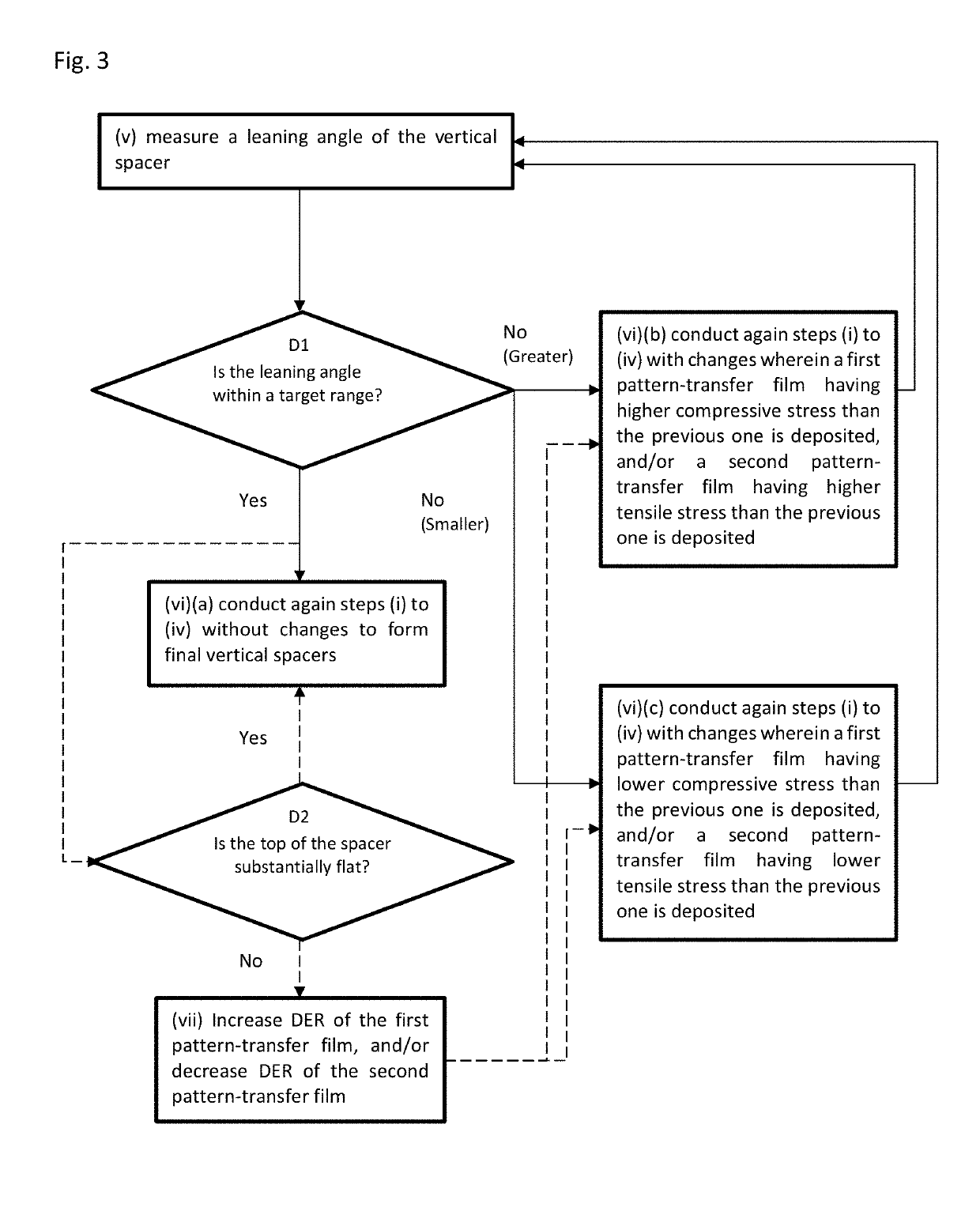
Method for forming vertical spacers for spacer-defined patterning
ActiveUS10290508B1Easy to adjustTop profile of the spacer can be manipulatedPhotomechanical apparatusSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingEngineeringDry etching
A method of forming vertical spacers for spacer-defined multiple patterning, includes: depositing a first conformal pattern-transfer film having a first film stress, and continuously depositing a second conformal pattern-transfer film having a second film stress on a template; dry-etching the template except for a core material and a vertical portion of the first and second pattern-transfer films to form vertical spacers; and dry-etching the core material, forming a vacant space between the vertical spacers, wherein by adjusting the difference in film stress between the first and second pattern-transfer films, the leaning angle of the spacers is adjusted.
Owner:ASM IP HLDG BV
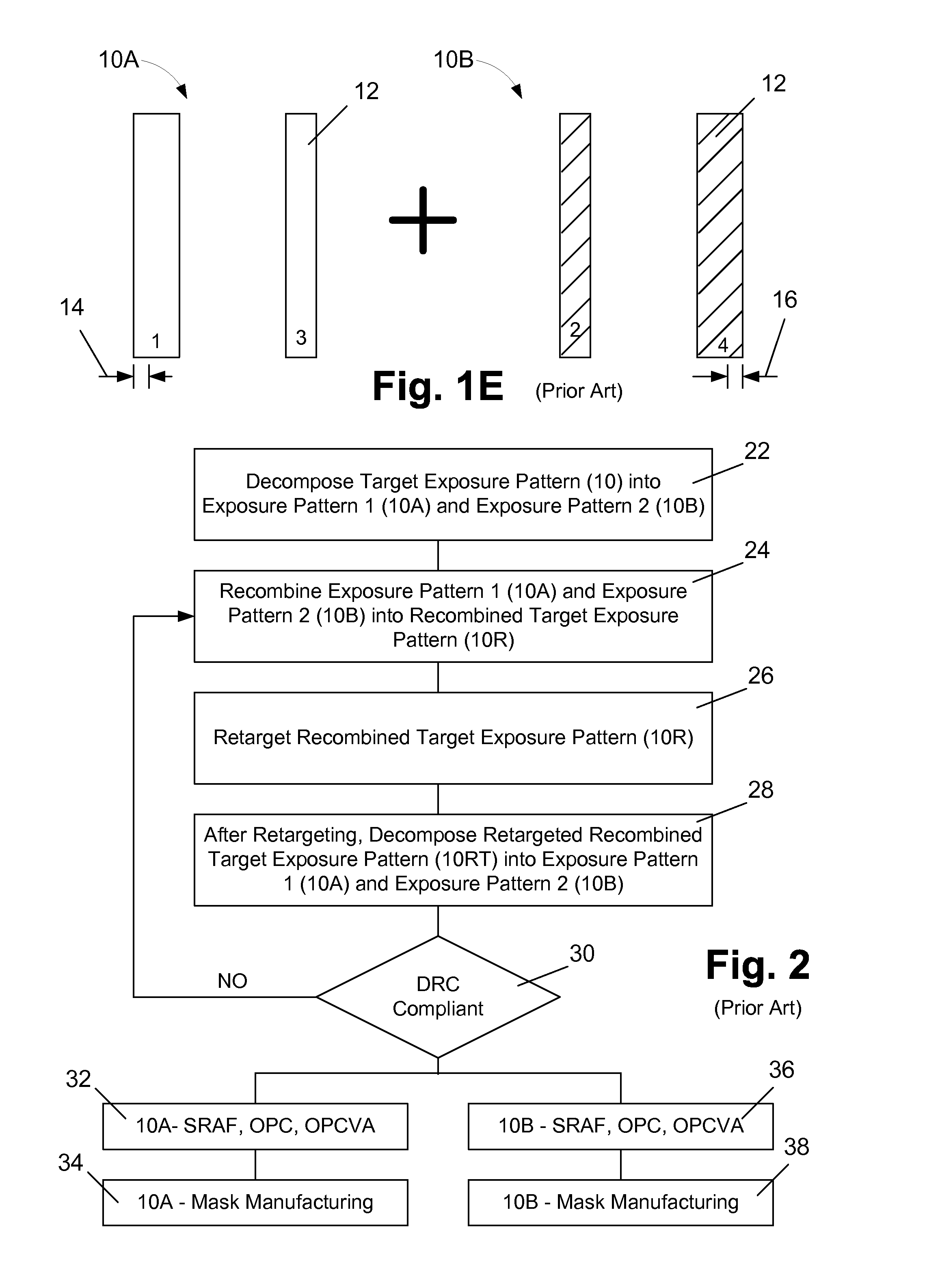
Methods involving color-aware retargeting of individual decomposed patterns when designing masks to be used in multiple patterning processes
InactiveUS8921016B1Originals for photomechanical treatmentSpecial data processing applicationsAlgorithmRetargeting
One illustrative method disclosed herein includes the steps of decomposing an initial overall target exposure pattern into at least a first decomposed sub-target pattern and a second decomposed sub-target pattern, performing first and second retargeting processes on the first and second decomposed sub-target patterns while using the other sub-target pattern as a reference layer, respectively, to thereby define retargeted first and second decomposed sub-target patterns, respectively, and, after performing the first and second retargeting processes, performing at least one process operation to determine if each of the retargeted first decomposed sub-target pattern and the retargeted second decomposed sub-target pattern is in compliance with at least one design rule.
Owner:GLOBALFOUNDRIES INC
Measurement Of Multiple Patterning Parameters
ActiveUS20150176985A1High measurement sensitivitySignificant changeSemiconductor/solid-state device testing/measurementPhotomechanical apparatusDiffraction orderComputational physics
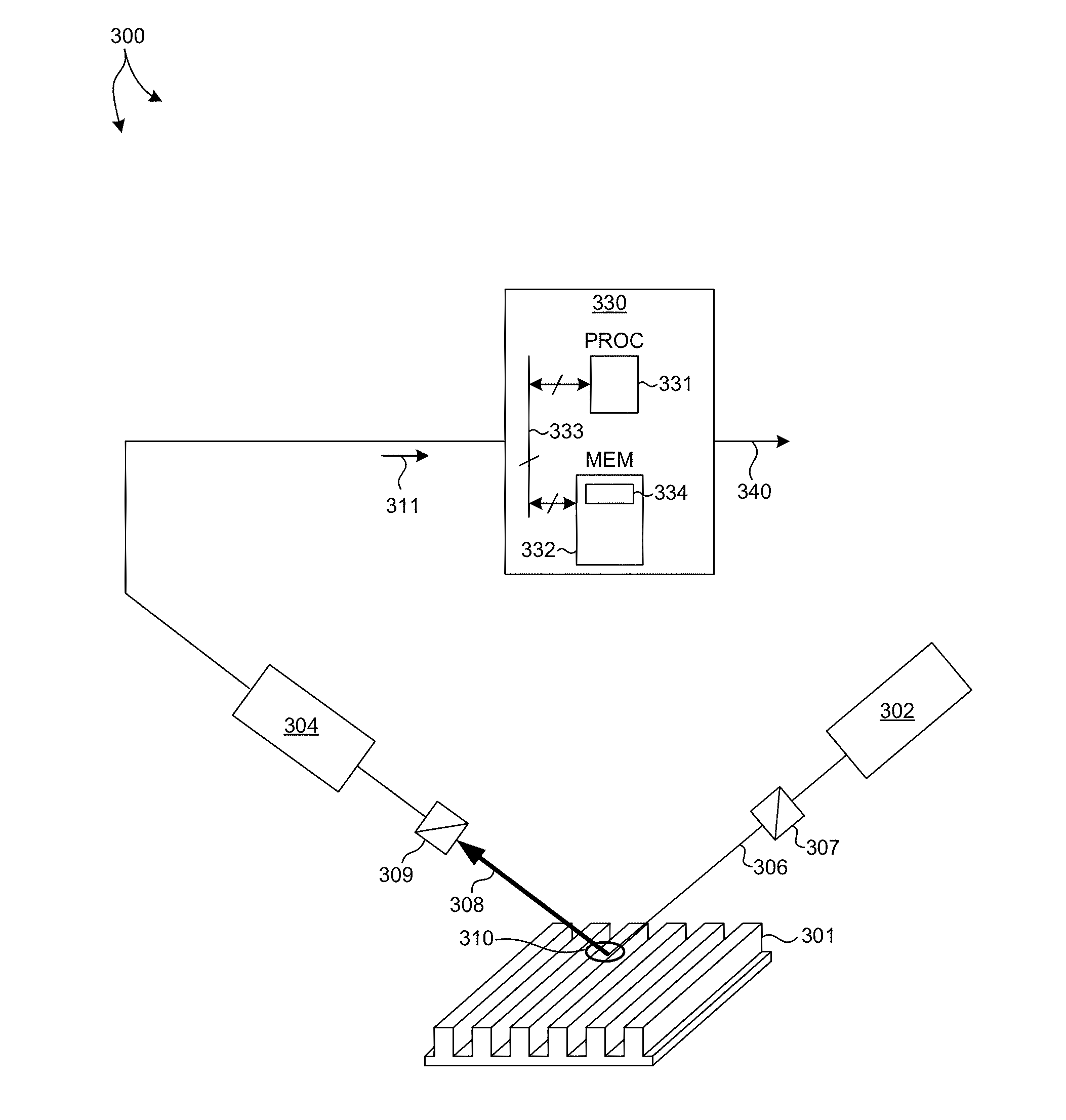
Methods and systems for evaluating the performance of multiple patterning processes are presented. Patterned structures are measured and one or more parameter values characterizing geometric errors induced by the multiple patterning process are determined. In some examples, a single patterned target and a multiple patterned target are measured, the collected data fit to a combined measurement model, and the value of a structural parameter indicative of a geometric error induced by the multiple patterning process is determined based on the fit. In some other examples, light having a diffraction order different from zero is collected and analyzed to determine the value of a structural parameter that is indicative of a geometric error induced by a multiple patterning process. In some embodiments, a single diffraction order different from zero is collected. In some examples, a metrology target is designed to enhance light diffracted at an order different from zero.
Owner:KLA TENCOR CORP
Patterning a Substrate Using Grafting Polymer Material
Patterning methods for creating sub-resolution trenches, contact openings, lines, and other structures at smaller dimensions as compared to using conventional self-aligned multiple patterning and sequential litho-etch deposition patterning approaches. Techniques herein include patterning using a grafting polymer material that has been modified to provide little or no etch resistance (fast etching). The grafting polymer material is deposited as spacer material on a substrate having mandrels. The spacer material selectively adheres to mandrel surfaces without adhering to exposed portions of an underlying layer. The spacer material also adheres up to a specific length so that sidewall spacers are formed. Openings between spacers are filled with a filler material, and then the sidewall spacers, made of the grafting material, are etched thereby creating antispacers. Etch transfer to a memorization layer and / or using additional relief patterns can be incorporated for creating various features.
Owner:TOKYO ELECTRON LTD
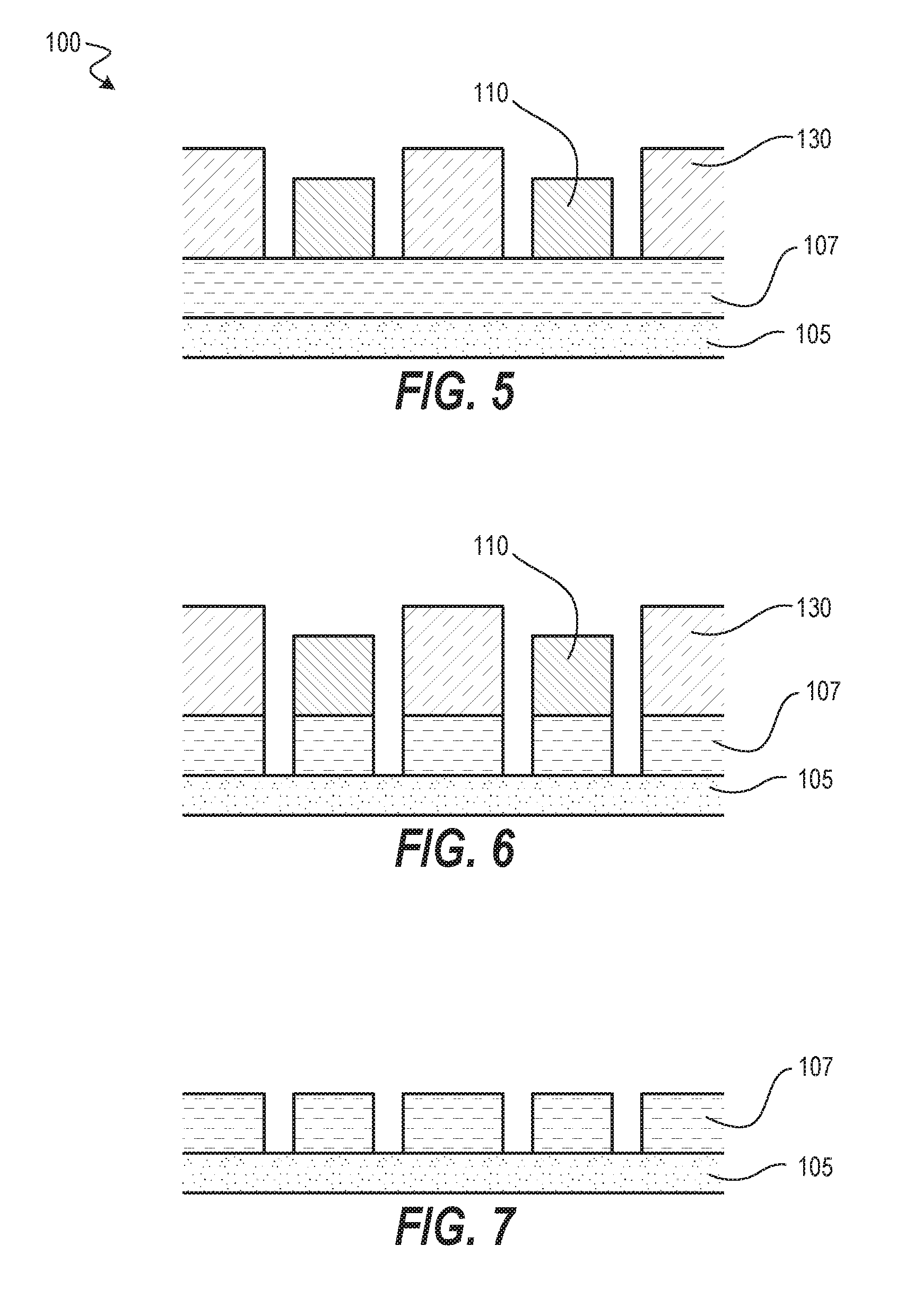
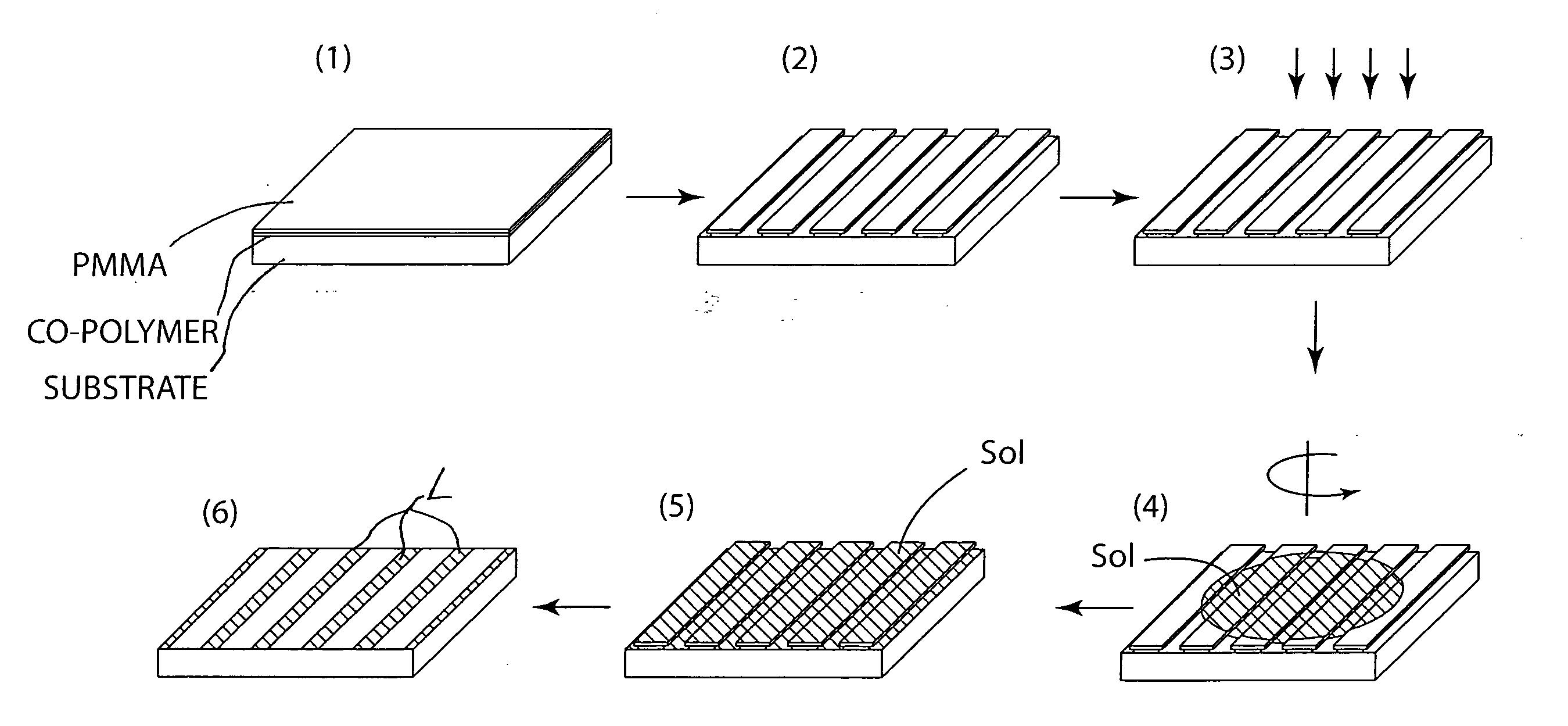
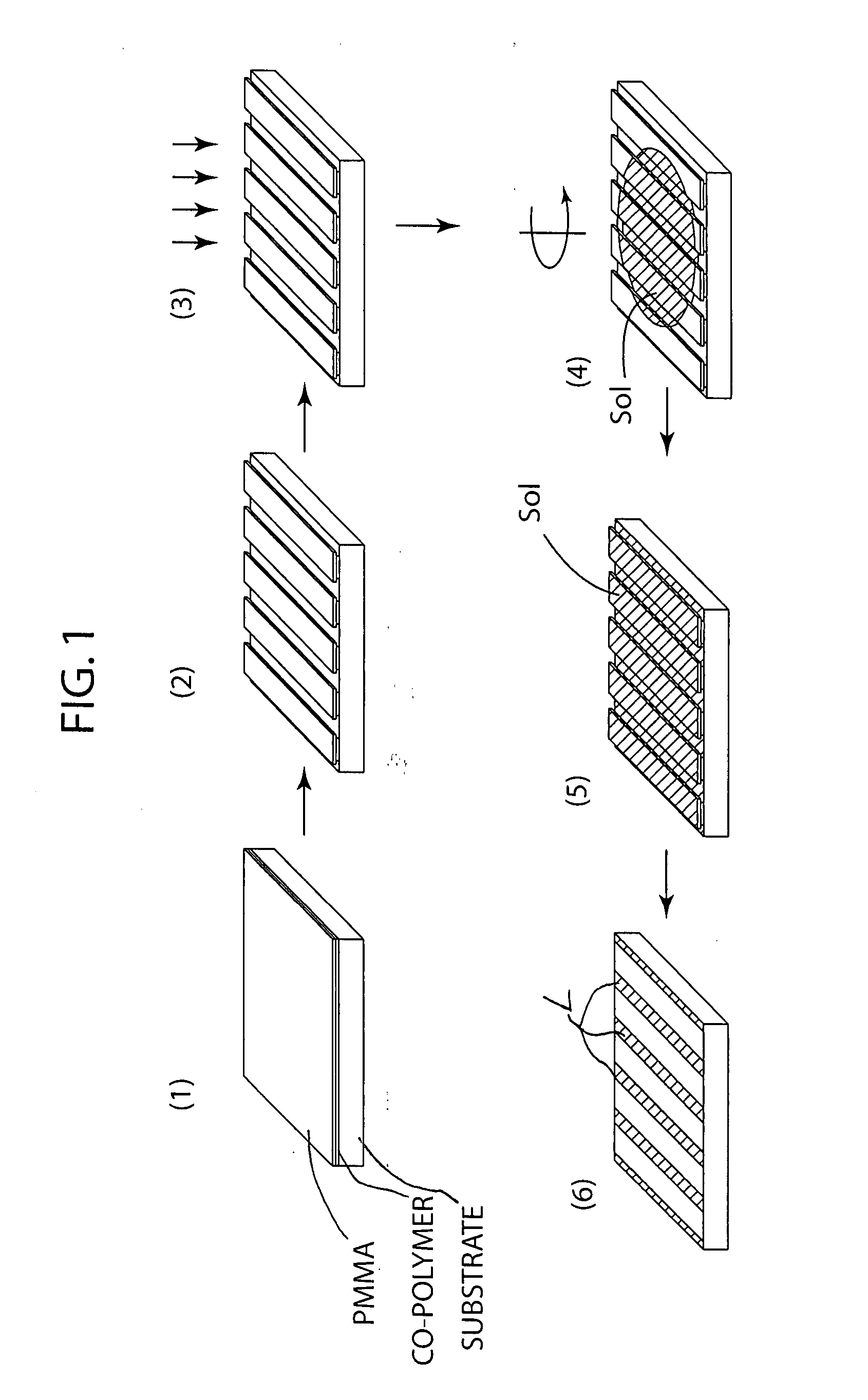
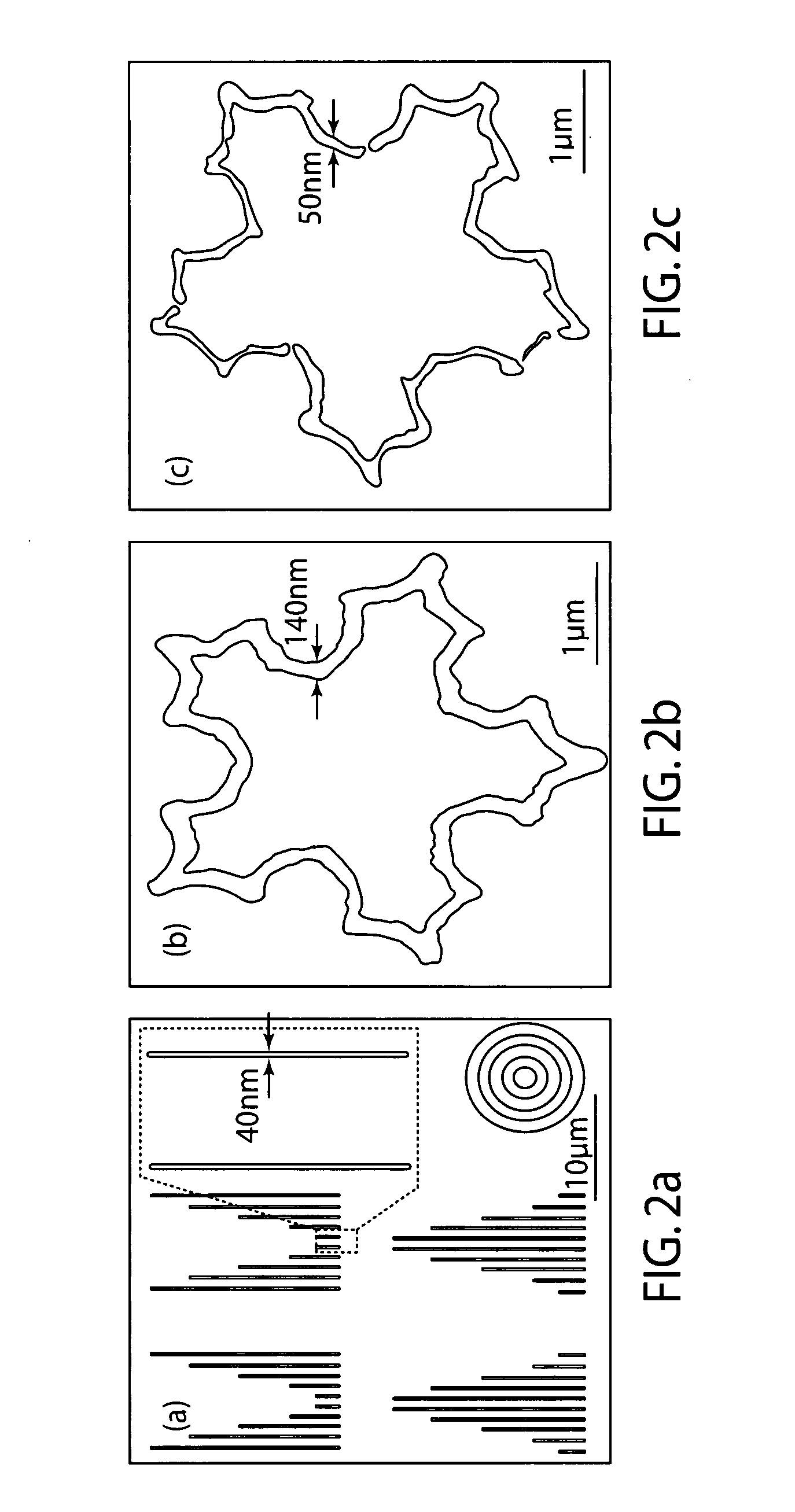
Method of making nanopatterns and nanostructures and nanopatterned functional oxide materials
InactiveUS20080070010A1High patterning speedHigh-throughput processingElectric discharge tubesDecorative surface effectsMulti materialNanostructure
Method for nanopatterning of inorganic materials, such as ceramic (e.g. metal oxide) materials, and organic materials, such as polymer materials, on a variety of substrates to form nanopatterns and / or nanostructures with control of dimensions and location, all without the need for etching the materials and without the need for re-alignment between multiple patterning steps in forming nanostructures, such as heterostructures comprising multiple materials. The method involves patterning a resist-coated substrate using electron beam lithography, removing a portion of the resist to provide a patterned resist-coated substrate, and spin coating the patterned resist-coated substrate with a liquid precursor, such as a sol precursor, of the inorganic or organic material. The remaining resist is removed and the spin coated substrate is heated at an elevated temperature to crystallize the deposited precursor material.
Owner:NORTHWESTERN UNIV
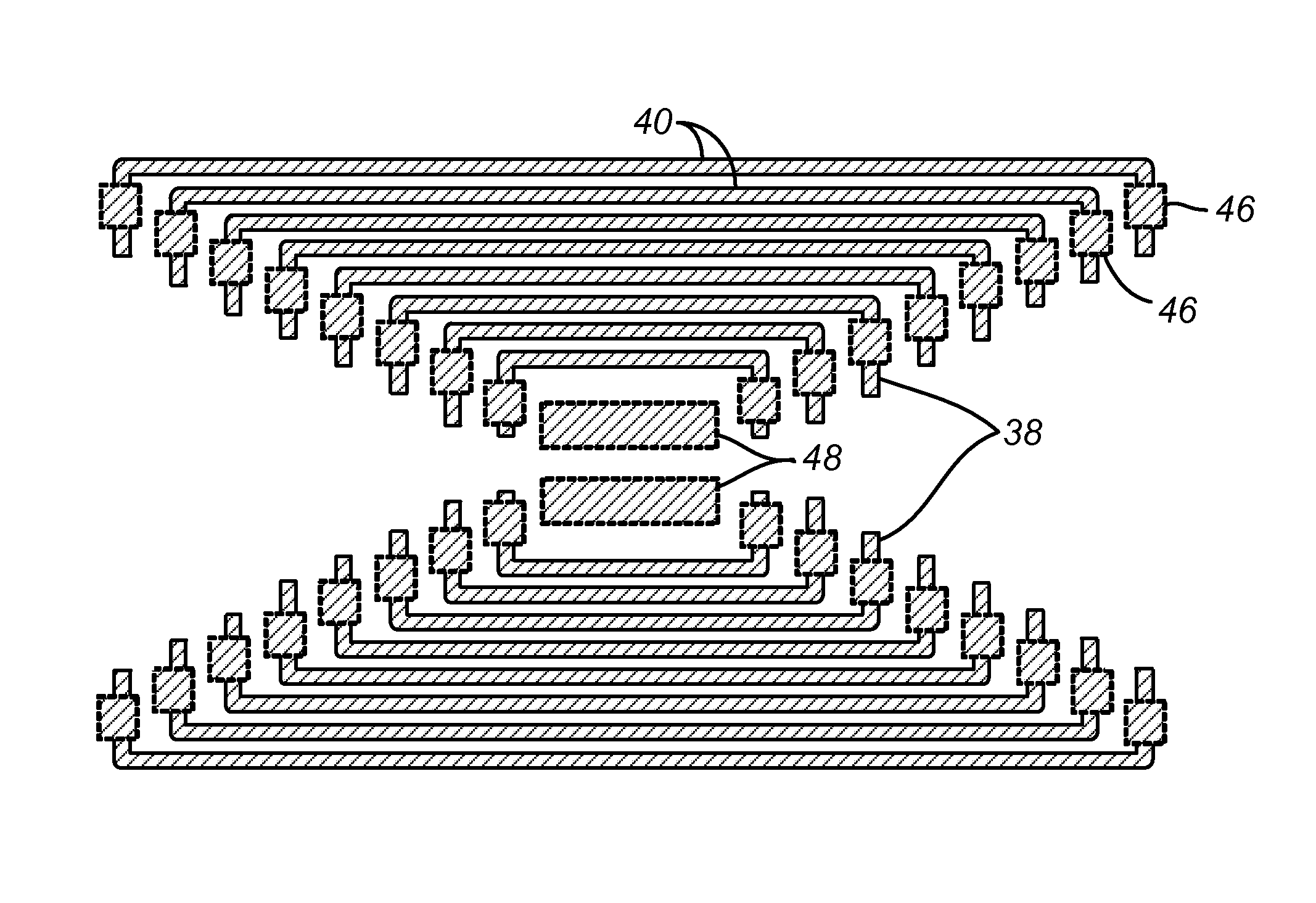
Self-aligned multi-patterning mask layer and formation method thereof
InactiveCN103515197ADoes not affect electrical performancePhotomechanical apparatusSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingElectrical performanceSemiconductor
The invention relates to a self-aligned multi-patterning mask layer and a formation method thereof. The formation method comprises the following steps that: a semiconductor substrate is provided and a to-be-etched material layer is formed at the surface of the semiconductor substrate; a sacrificial material layer is formed at the surface of the to-be-etched material layer; etching is carried out on the sacrificial material layer to form a sacrificial layer, wherein the dimension of the portion, approaching the to-be-etched material layer, of the sacrificial layer is smaller than that of the portion, far away from the to-be-etched material layer, of the sacrificial layer; and a side wall is formed at the surface of the side wall of the sacrificial layer, wherein the portions of the two sides of the side wall are inclined towards the middle portion of the side wall from a position at the surface of the to-be-etched material layer to a position far away from the surface of the to-be-etched material layer. Because the portions of the two sides of the side wall are inclined towards the middle portion of the side wall and the profile shapes of the portions of the two sides of the side wall are identical with each other, the shapes of side walls of the to-be-etched material layer formed by etching by using the side wall as the mask subsequently are identical, so that the electrical performance of the semiconductor device that is formed subsequently is not influenced.
Owner:SEMICON MFG INT (SHANGHAI) CORP
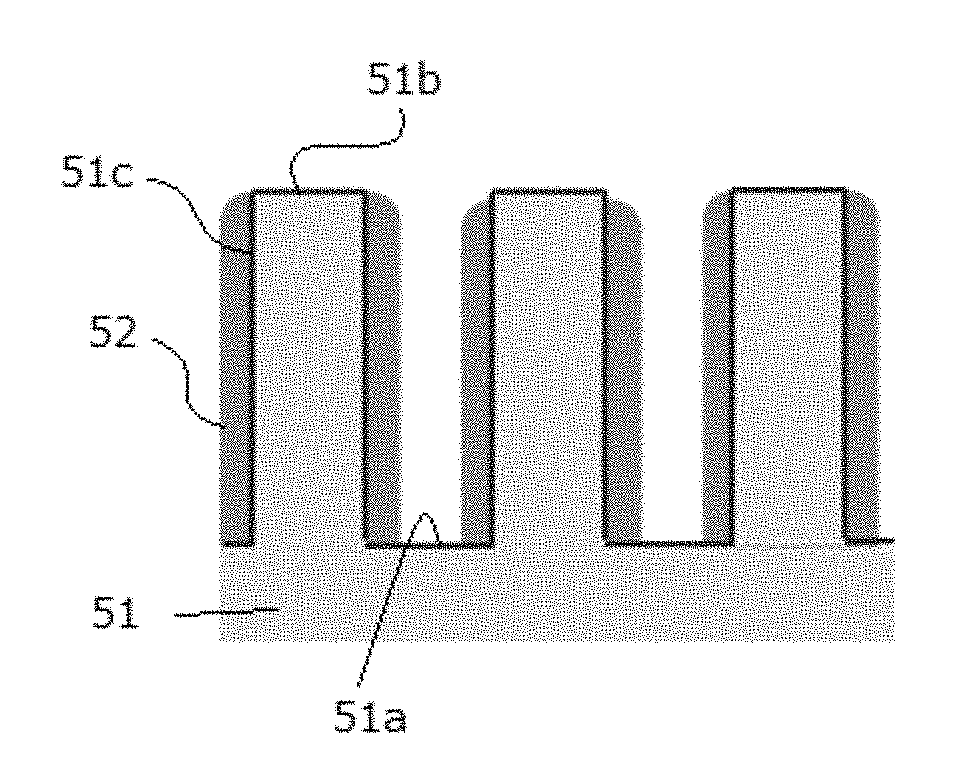
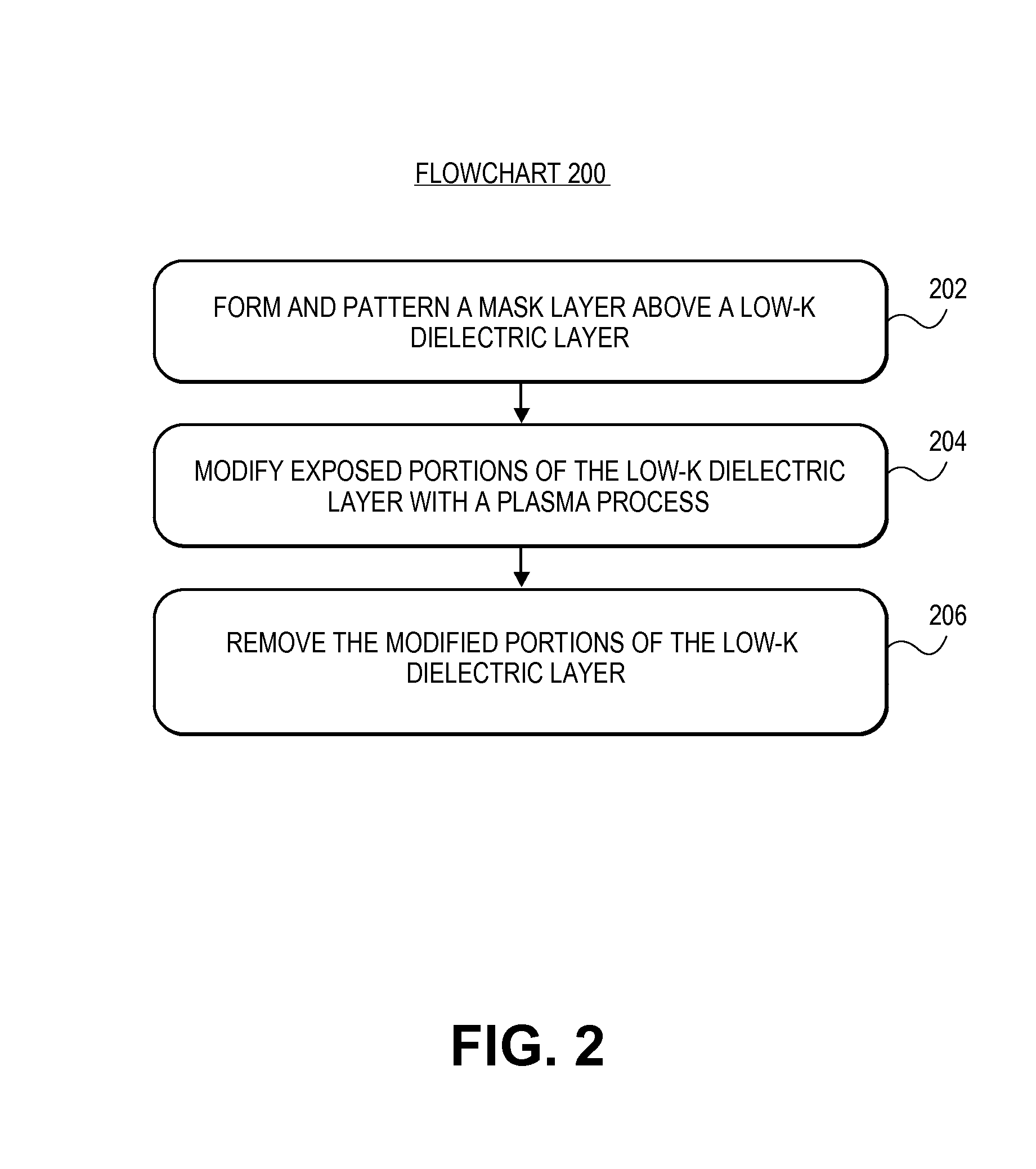
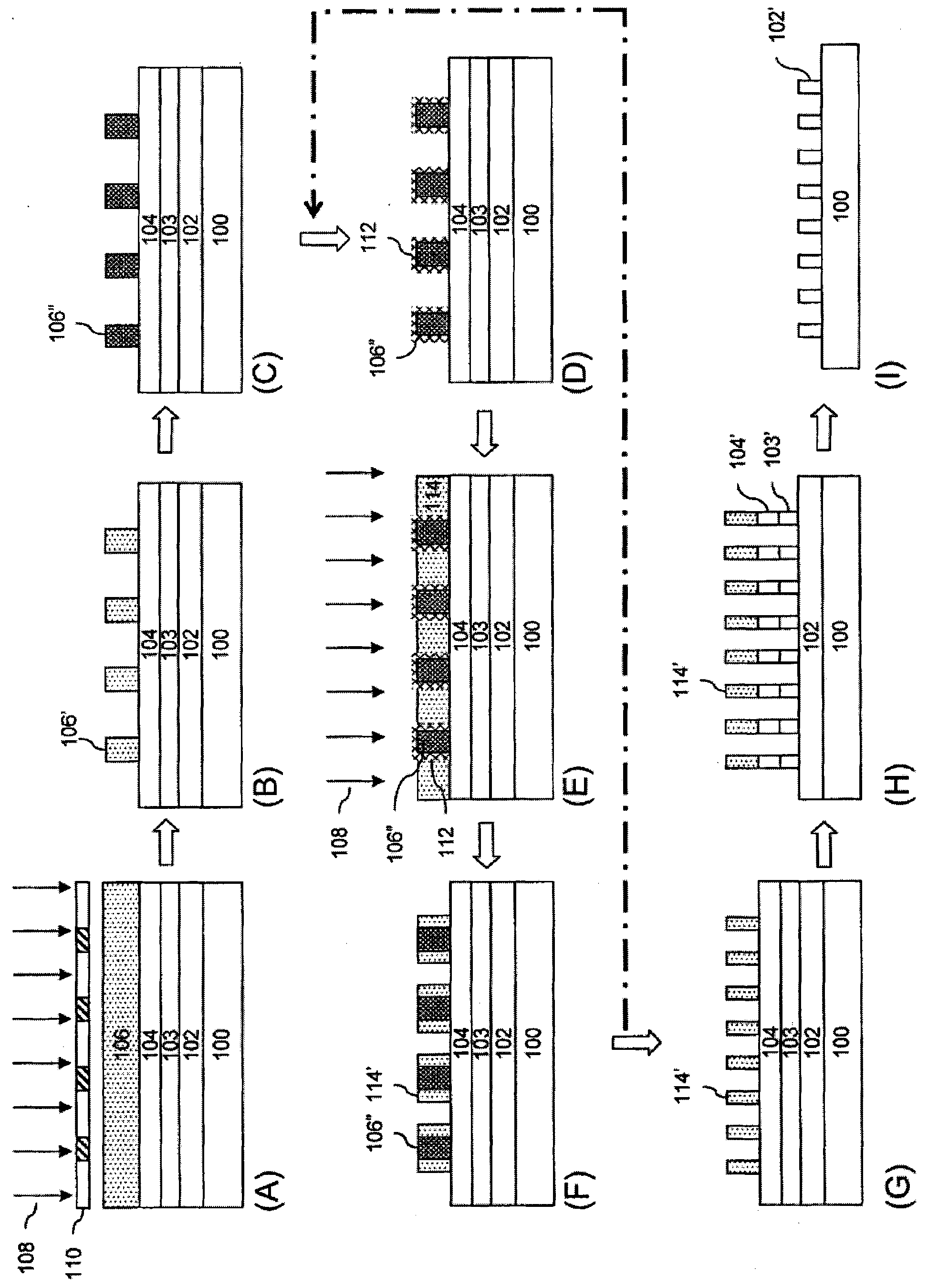
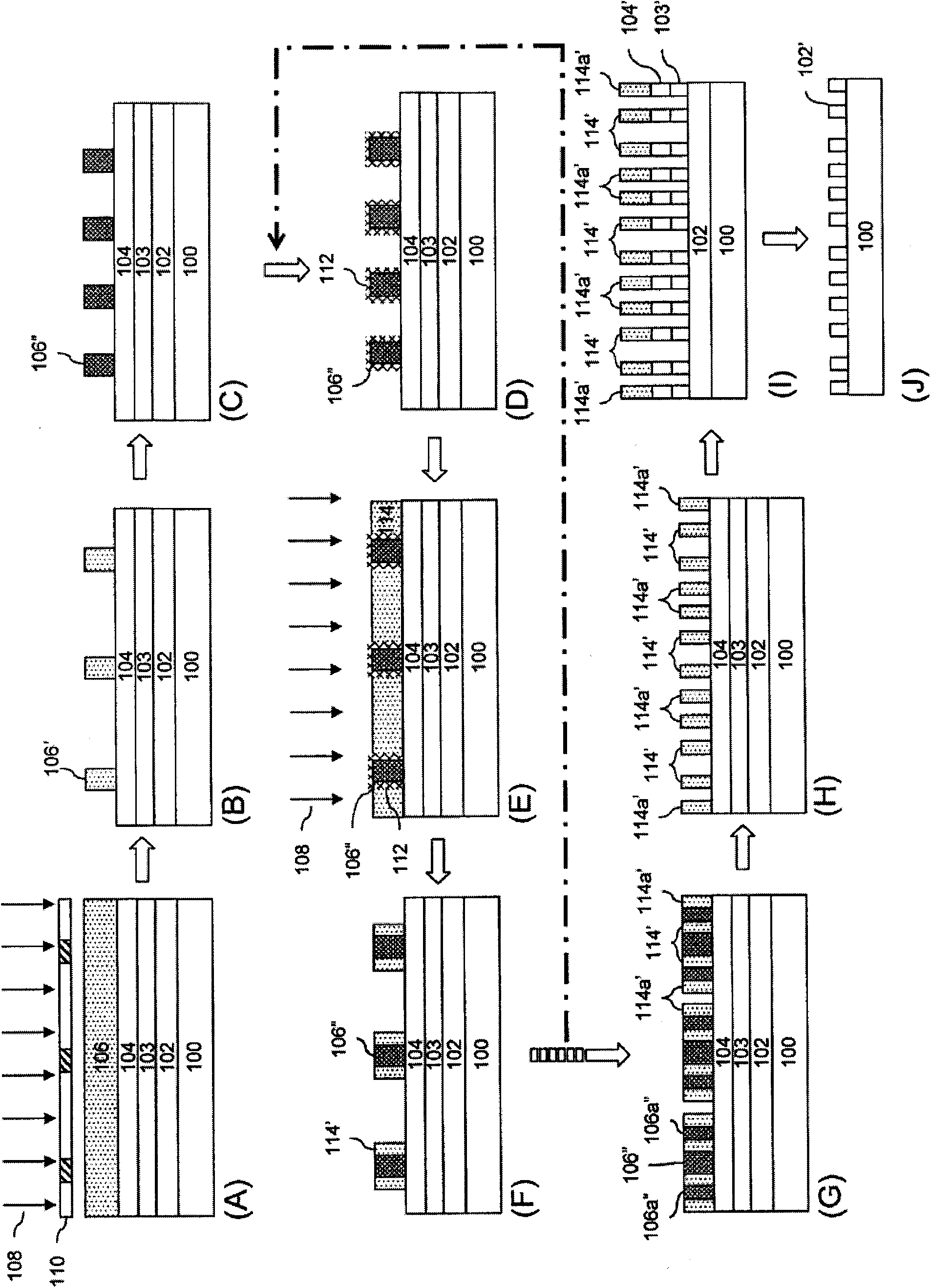
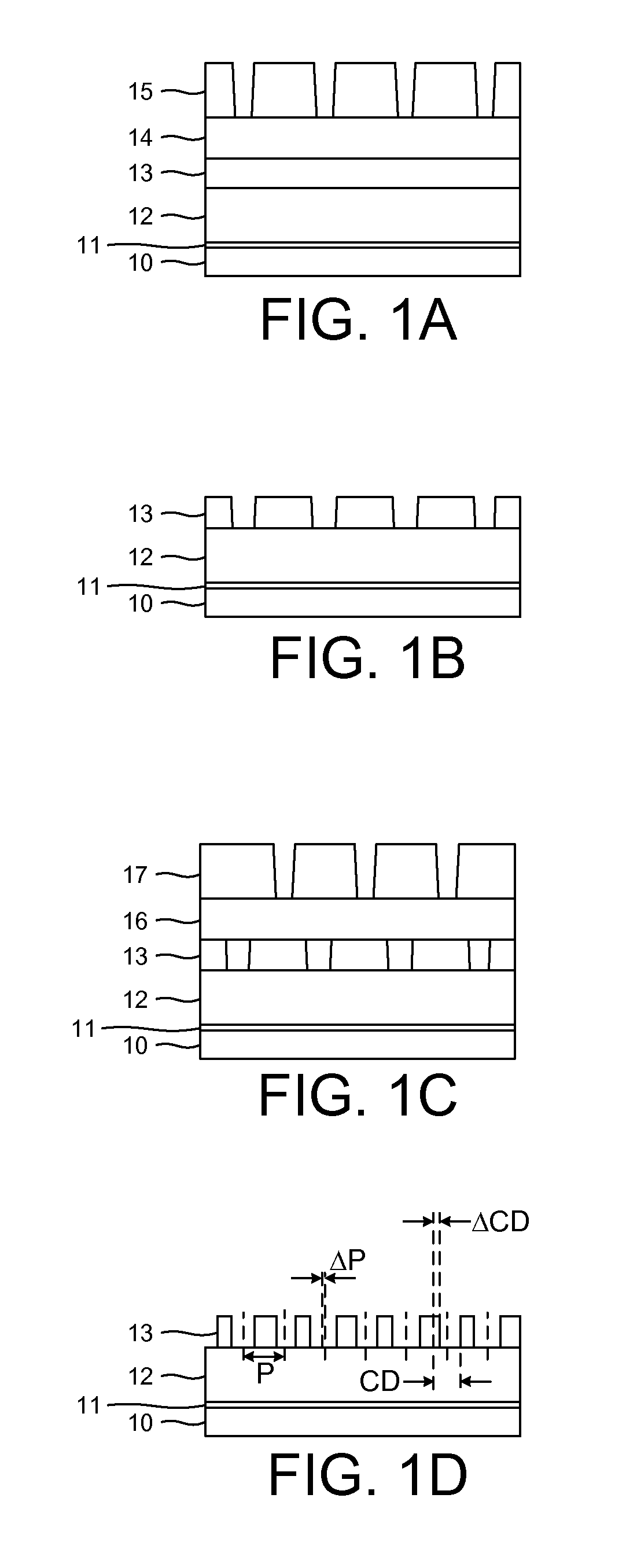
Method of multiple patterning of a low-k dielectric film
InactiveUS20130023122A1Semiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingComputational physicsMask layer
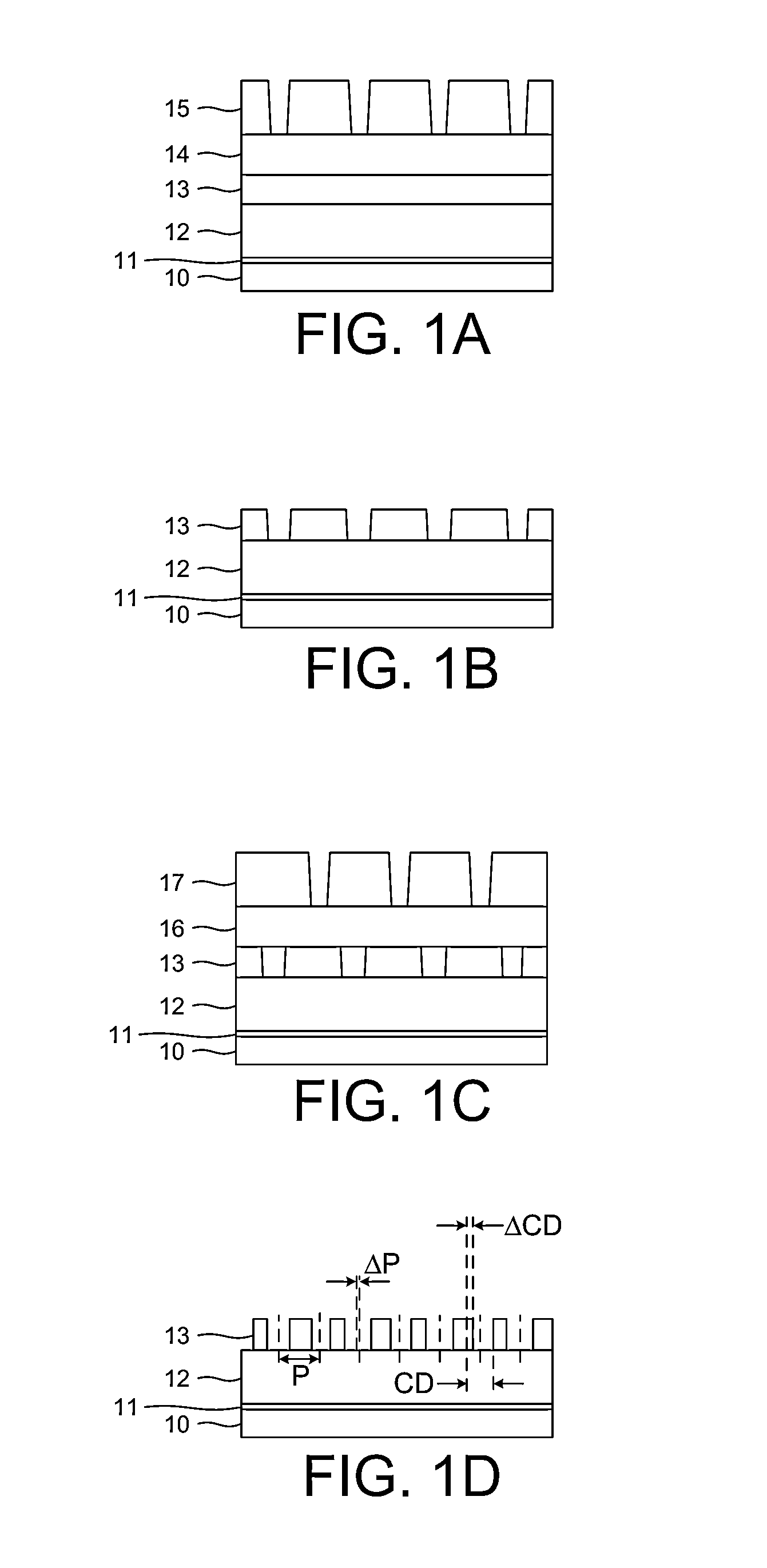
Methods of multiple patterning of low-k dielectric films are described. For example, a method includes forming and patterning a first mask layer above a low-k dielectric layer, the low-k dielectric layer disposed above a substrate. A second mask layer is formed and patterned above the first mask layer. A pattern of the second mask layer is transferred at least partially into the low-k dielectric layer by modifying first exposed portions of the low-k dielectric layer with a first plasma process and removing the modified portions of the low-k dielectric layer. Subsequently, a pattern of the first mask layer is transferred at least partially into the low-k dielectric layer by modifying second exposed portions of the low-k dielectric layer with a second plasma process and removing the modified portions of the low-k dielectric layer.
Owner:APPLIED MATERIALS INC
Self-aligned spacer multiple patterning methods
InactiveCN101963755ASolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingHigh densityPhotoresist
Self-aligned spacer multiple patterning method are provided. The methods involve alkaline treatment of photoresist patterns and allow for the formation of high density resist patterns. The methods find particular applicability in semiconductor device manufacture.
Owner:ROHM & HAAS ELECTRONICS MATERIALS LLC
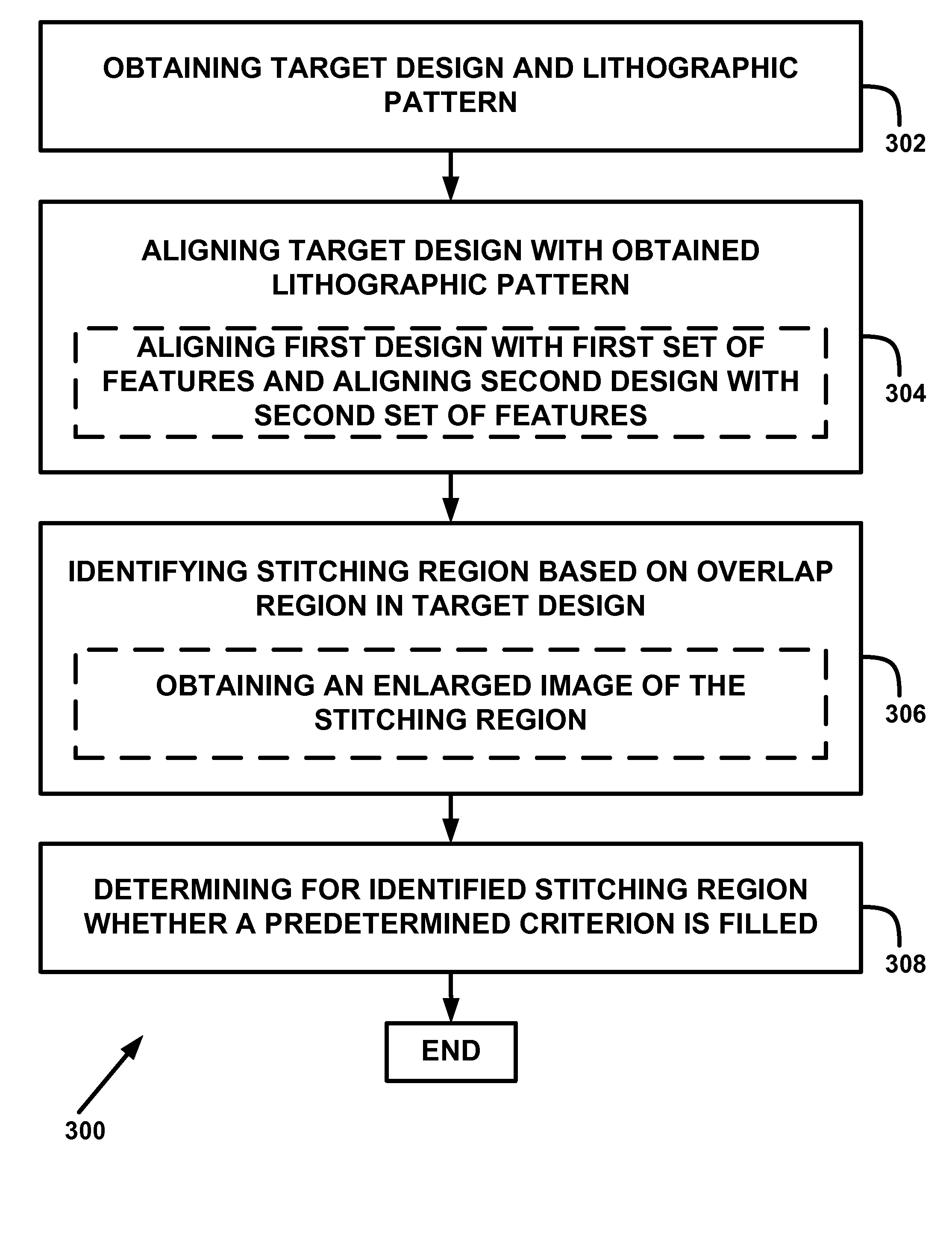
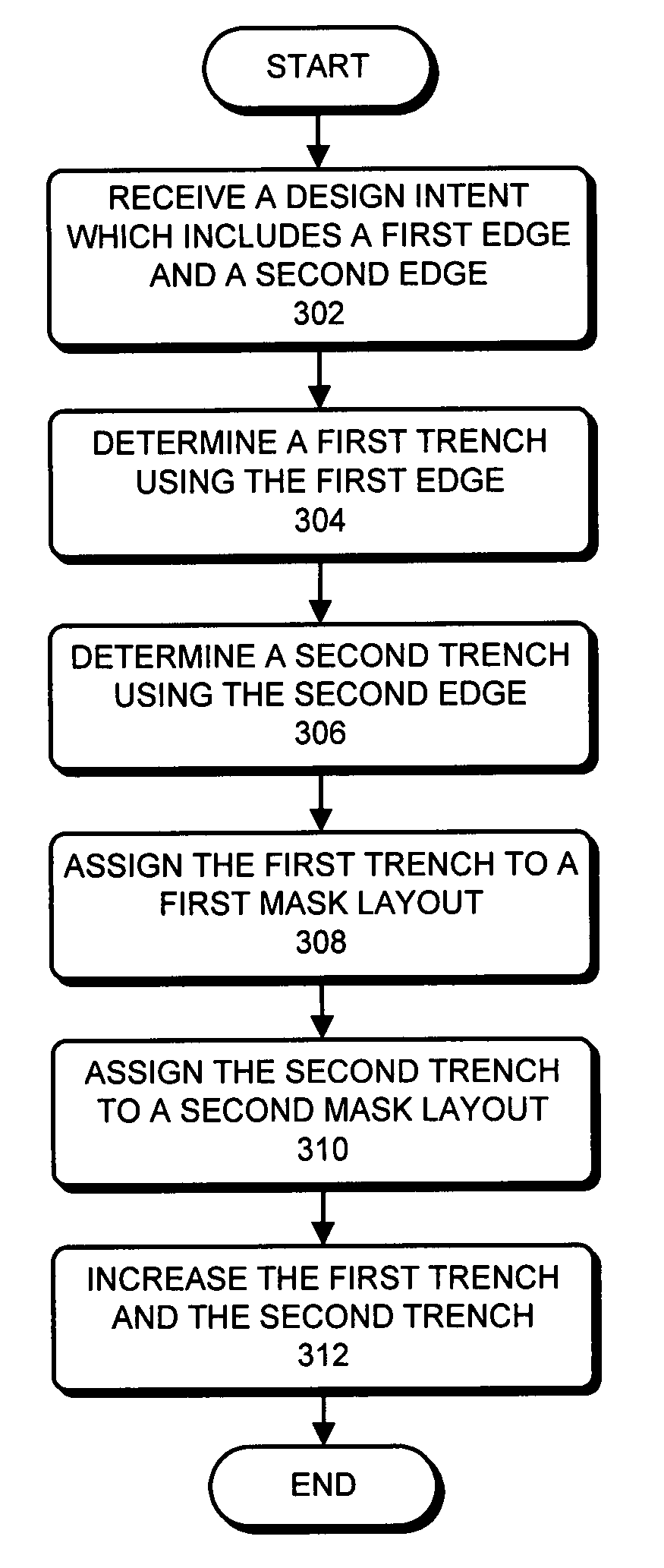
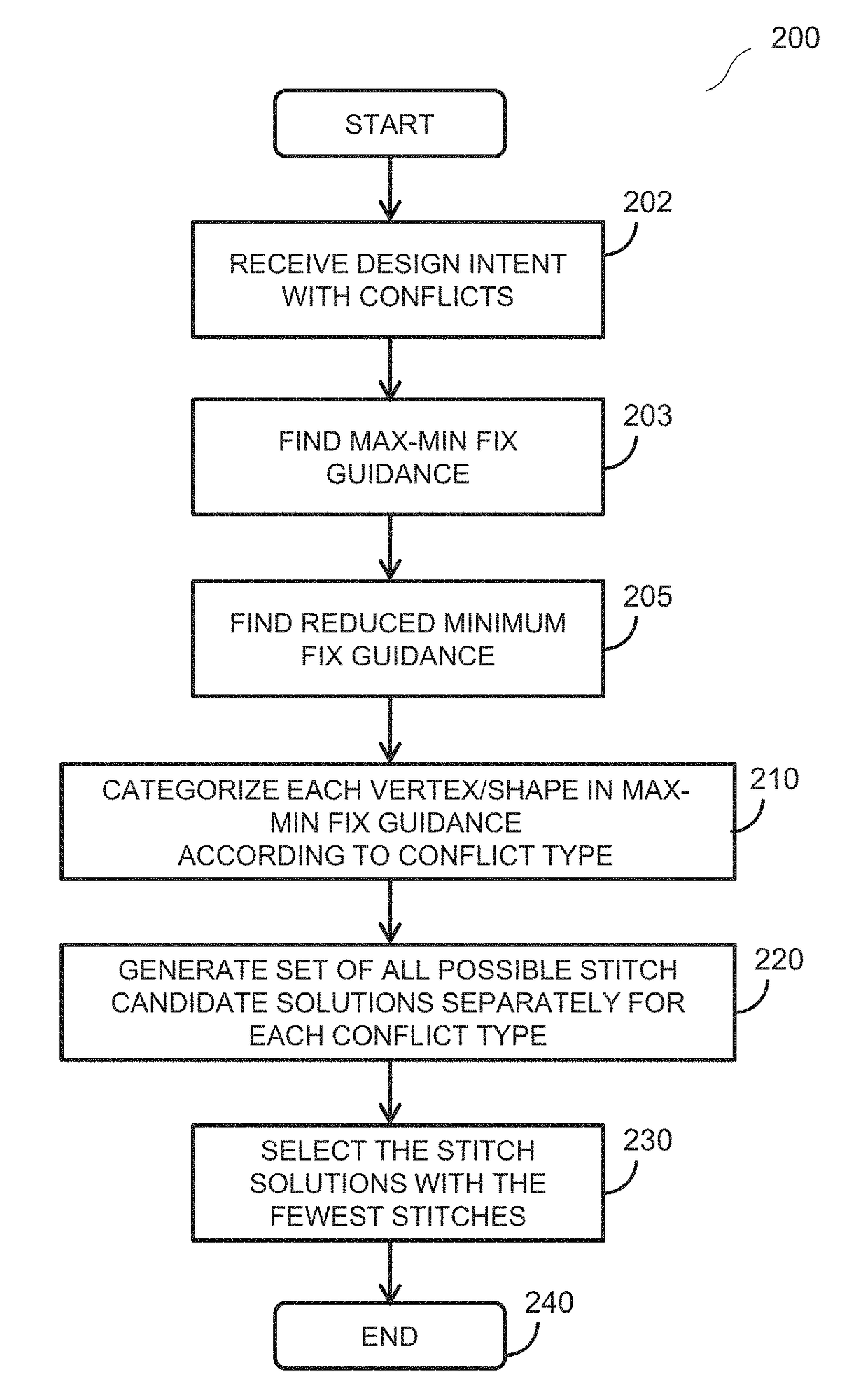
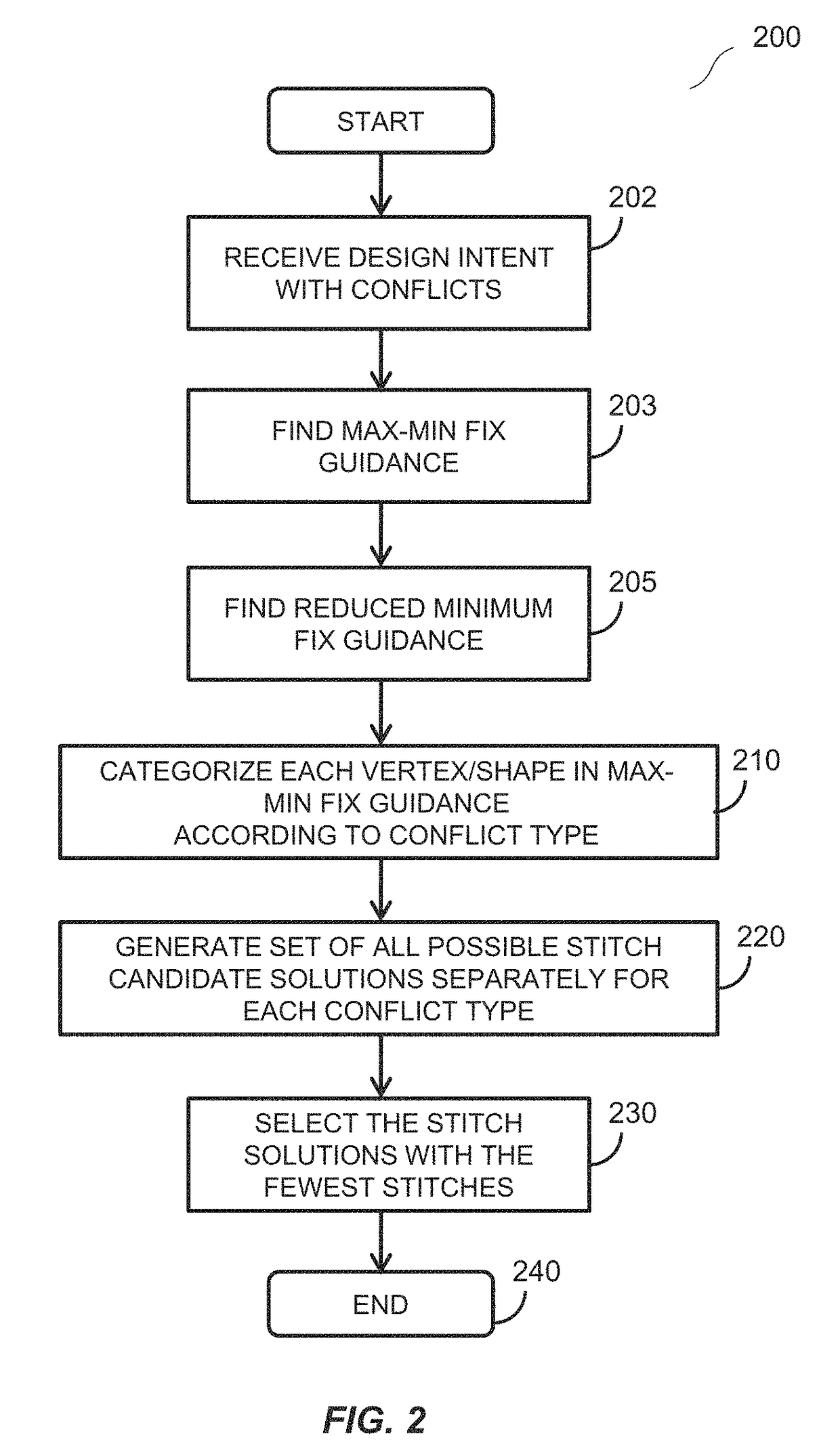
Method and apparatus for determining mask layouts for a multiple patterning process
ActiveUS20080244504A1Improve toleranceIncreasing trenchOriginals for photomechanical treatmentSpecial data processing applicationsEngineeringDesign intent
One embodiment provides a method for determining mask layouts. During operation, the system can receive a design intent. Next, the system can determine a set of critical edges in the design layout, and select a first edge and a second edge. The system can then determine a first trench and a second trench using the first edge and the second edge, respectively. Note that an edge of the first trench may substantially overlap with the first edge, and an edge of the second trench may substantially overlap with the second edge. Next, the system may assign the first trench and the second trench to the first mask layout and the second mask layout, respectively. The system can then increase the first trench and the second trench, thereby improving pattern fidelity. The resulting mask layouts may be used in a double patterning process.
Owner:SYNOPSYS INC
Multiple patterning process for forming trenches or holes using stitched assist features
ActiveUS20130236836A1Well formedPhotomechanical exposure apparatusMicrolithography exposure apparatusPattern recognitionData information
One illustrative method disclosed herein involves identifying an overall target pattern comprised of at least one hole-type feature, decomposing the overall target pattern into at least a first sub-target pattern and a second sub-target pattern, wherein the first sub-target pattern and the second sub-target pattern each comprise at least one common hole-type feature, generating a first set of mask data information corresponding to the first sub-target pattern, and generating a second set of mask data information corresponding to the second sub-target pattern.
Owner:GLOBALFOUNDRIES US INC
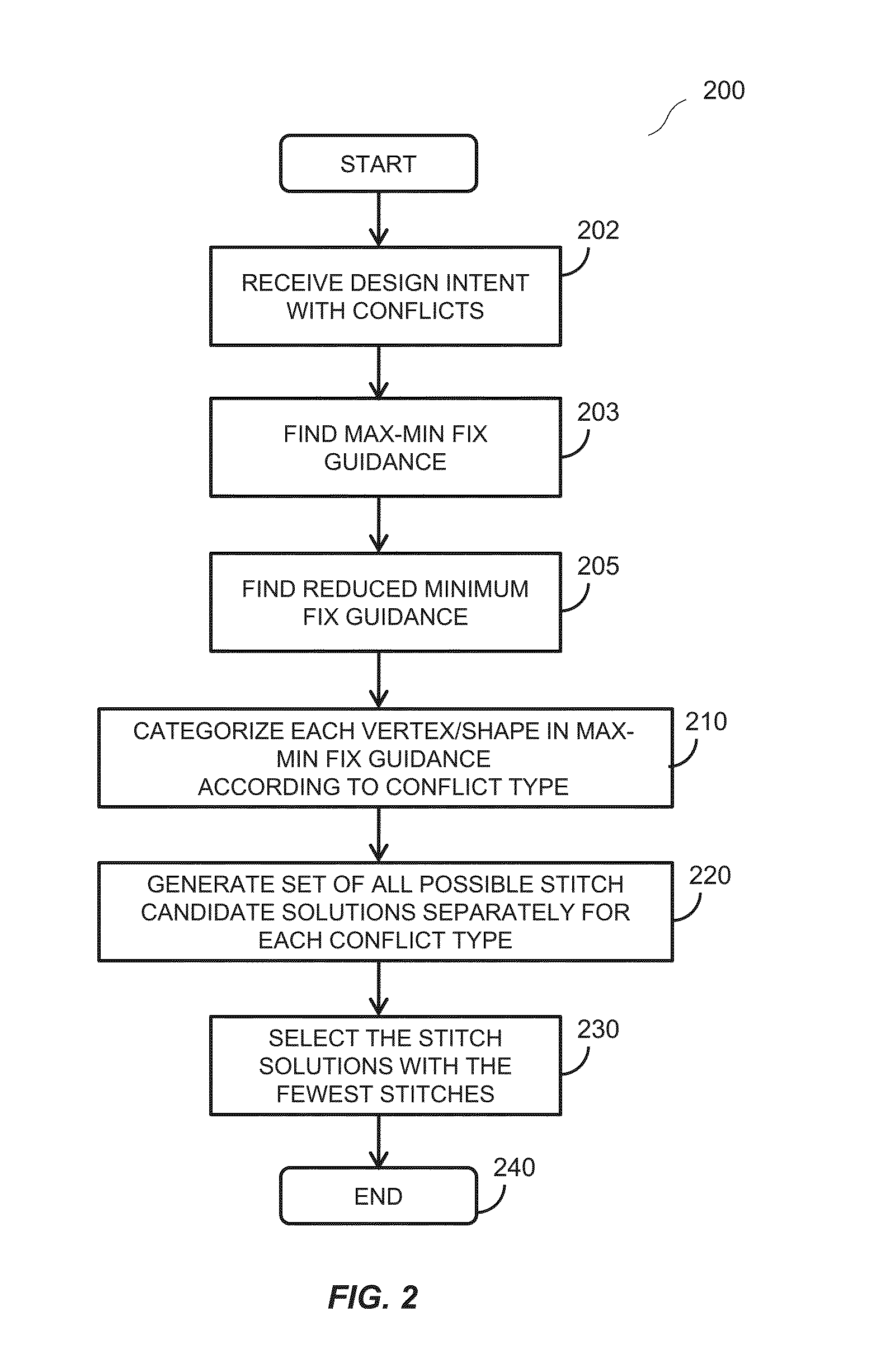
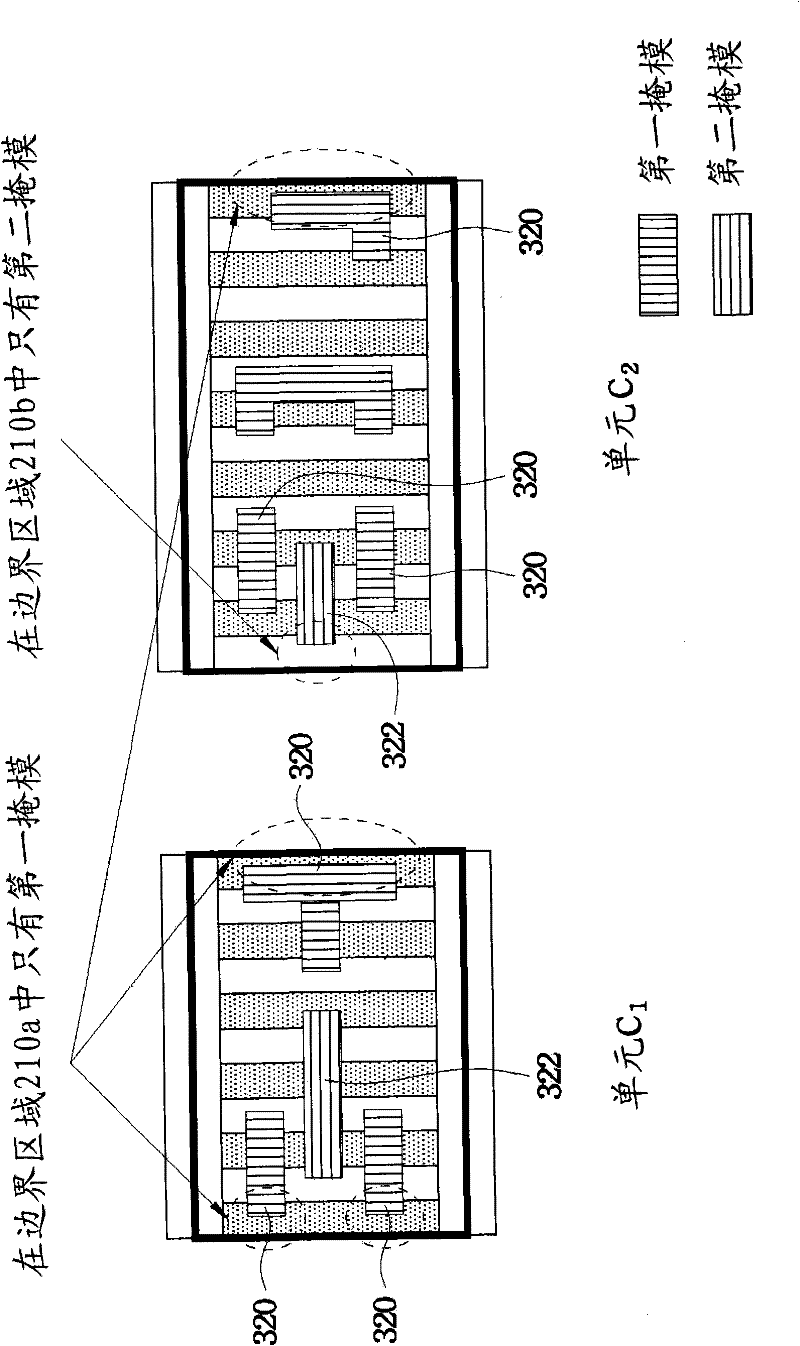
Categorized stitching guidance for triple-patterning technology
ActiveUS20150286771A1Microlithography exposure apparatusOriginals for photomechanical treatmentDecompositionTheoretical computer science
A computer-implemented method for validating a design is disclosed. The method includes receiving, with the computer, the design, where the design is printable using a multiple-patterning process when the computer is invoked, and where the design includes a plurality of shapes and at least one conflict preventing decomposition of the design into a plurality of multiple-patterning masks. The method also includes forming a subset of the shapes, the subset including the shapes associated with the at least one conflict, categorizing each of the shapes of the subset into one of a plurality of topology types generating one or more stitch candidate solutions for each of the plurality of topology types, and decomposing the design into a plurality of masks.
Owner:SYNOPSYS INC
Metrology Of Multiple Patterning Processes
Methods and systems for evaluating the performance of multiple patterning processes are presented. Patterned structures are measured and one or more parameter values characterizing geometric errors induced by the multiple patterning process are determined. In some examples, a primary, multiple patterned target is measured and a value of a parameter of interest is directly determined from the measured data by a Signal Response Metrology (SRM) measurement model. In some other examples, a primary, multiple patterned target and an assist target are measured and a value of a parameter of interest is directly determined from the measured data by a Signal Response Metrology (SRM) measurement model. In some other examples, a primary, multiple patterned target is measured at different process steps and a value of a parameter of interest is directly determined from the measured data by a Signal Response Metrology (SRM) measurement model.
Owner:KLA TENCOR CORP
Integrated circuit cell library for multiple patterning
A method is disclosed for defining a multiple patterned cell layout for use in an integrated circuit design. A layout is defined for a level of a cell in accordance with a dynamic array architecture so as to include a number of layout features. The number of layout features are linear-shaped and commonly oriented. The layout is split into a number of sub-layouts for the level of the cell. Each of the number of layout features in the layout is allocated to any one of the number of sub-layouts. Also, the layout is split such that each sub-layout is independently fabricatable. The sub-layouts for the level of the cell are stored on a computer readable medium.
Owner:RPX CORP
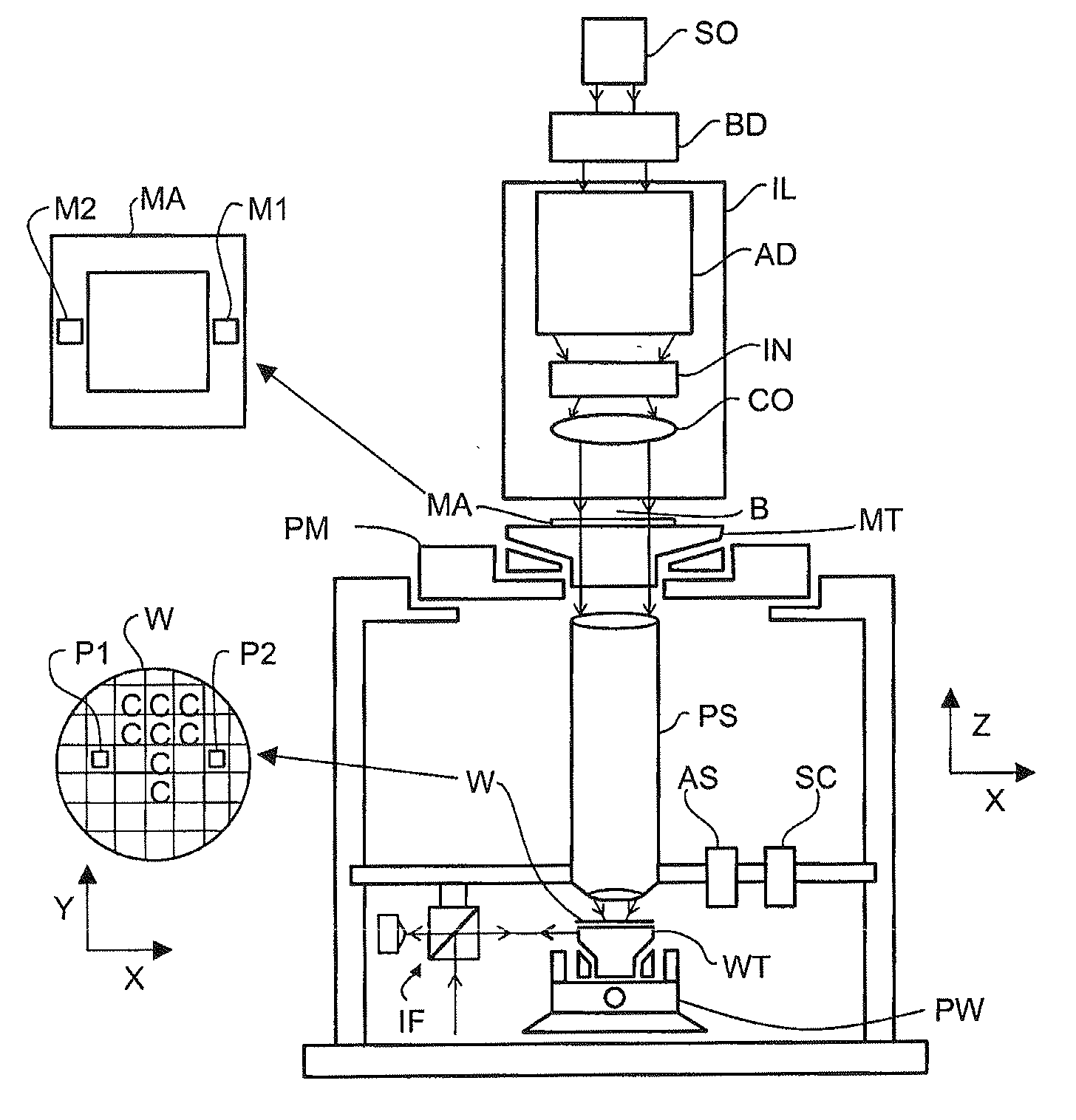
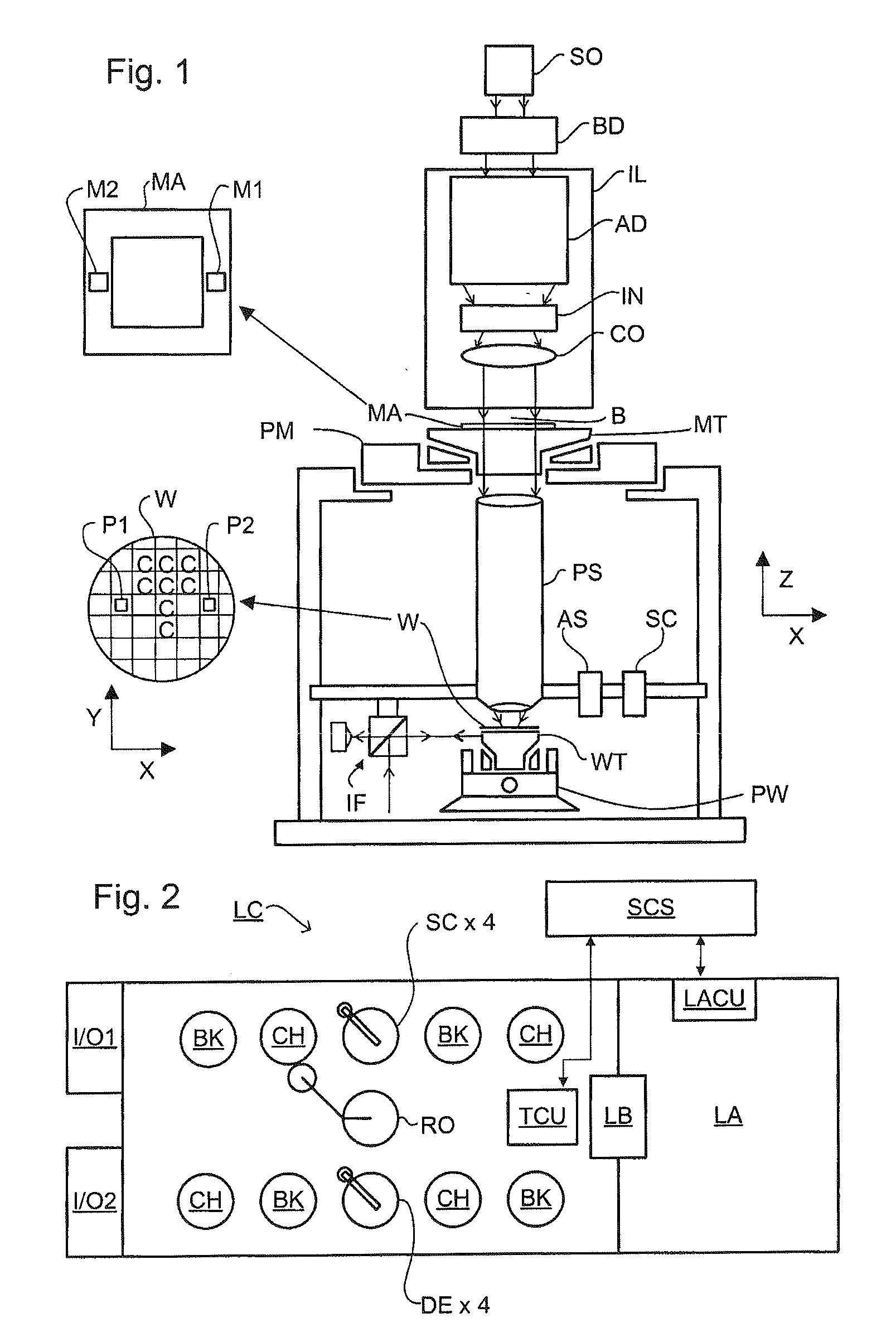
Lithographic Apparatus and Device Manufacturing Method
InactiveUS20110003256A1Simple methodPhotomechanical exposure apparatusMicrolithography exposure apparatusMetrologyEngineering
A method for providing temporary measurement targets during a multiple patterning process which can be removed in the completion of the process. The metrology target is defined in either the first or the second exposure of a multiple exposure process and whether or not it is temporary or made permanent is selected according to whether or not the area of the target is covered or cleared out in the other exposure. The use of temporary targets reduces the amount of space on the substrate that must be devoted to targets.
Owner:ASML NETHERLANDS BV
Methods of patterning line-type features using a multiple patterning process that enables the use of tighter contact enclosure spacing rules
ActiveUS20150243515A1Photomechanical apparatusSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingEngineeringMultiple patterning
A method involving identifying a pattern for an overall target cut mask to be used in patterning line-type features that includes a target non-rectangular opening feature having an inner, concave corner, decomposing the overall target cut mask pattern into first and second sub-target patterns, wherein the first sub-target pattern comprises a first rectangular-shaped opening feature corresponding to a first portion, but not all, of the target non-rectangular opening feature and the second sub-target pattern comprises a second rectangular-shaped opening feature corresponding to a second portion, but not all, of the target non-rectangular opening feature, the first and second openings overlapping adjacent the inner, concave corner, and generating first and second sets of mask data corresponding to the first and second sub-target patterns, wherein at least one of the first and second sets of mask data is generated based upon an identified contact-to-end-of-cut-line spacing rule.
Owner:GLOBALFOUNDRIES US INC
Soft landing nanolaminates for advanced patterning
InactiveCN104752199ASemiconductor/solid-state device testing/measurementSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSilicon oxideOptoelectronics
Methods for depositing nanolaminate protective layers over a core layer to enable deposition of high quality conformal films over the core layer for use in advanced multiple patterning schemes are provided. In certain embodiments, the methods involve depositing a thin silicon oxide or titanium oxide film using plasma-based atomic layer deposition techniques with a low high frequency radio frequency (HFRF) plasma power, followed by depositing a conformal titanium oxide film or spacer with a high HFRF plasma power.
Owner:NOVELLUS SYSTEMS
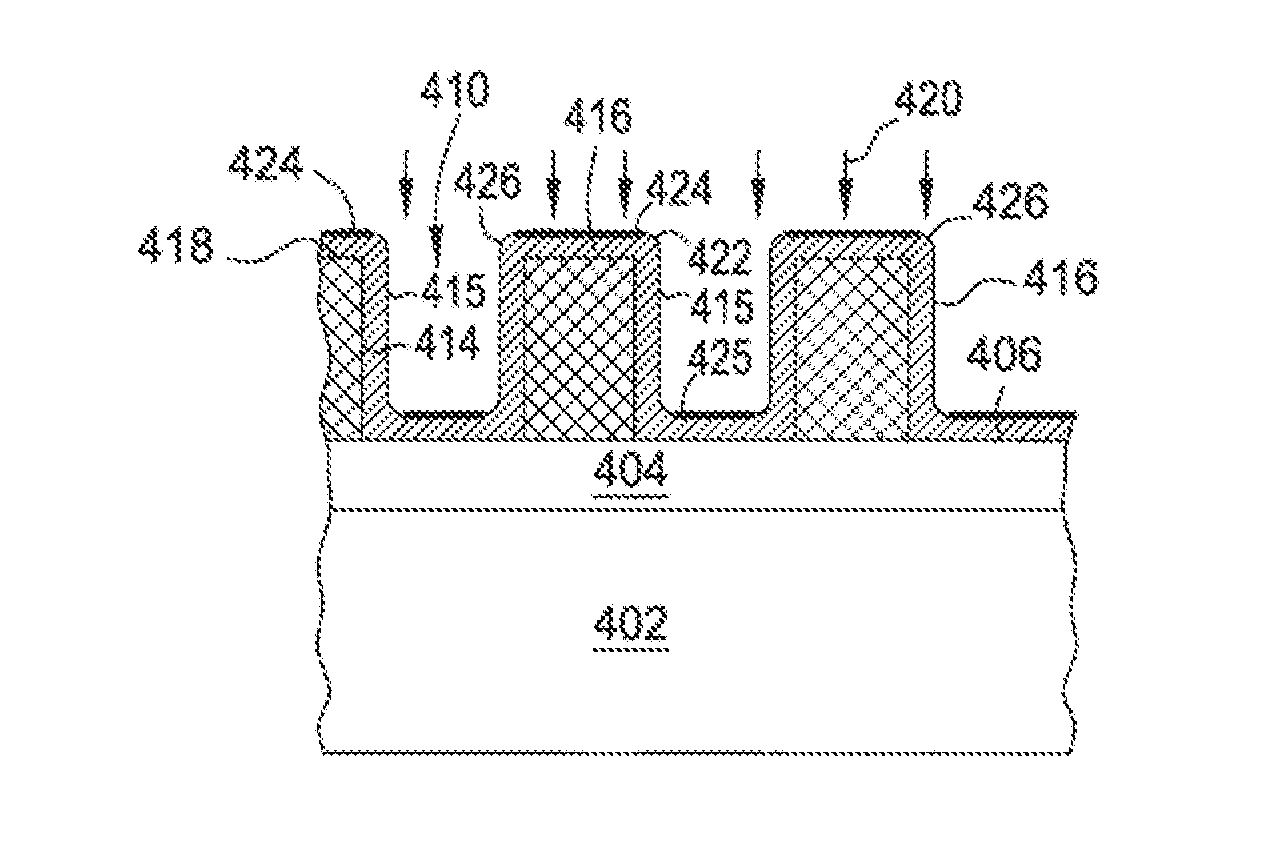
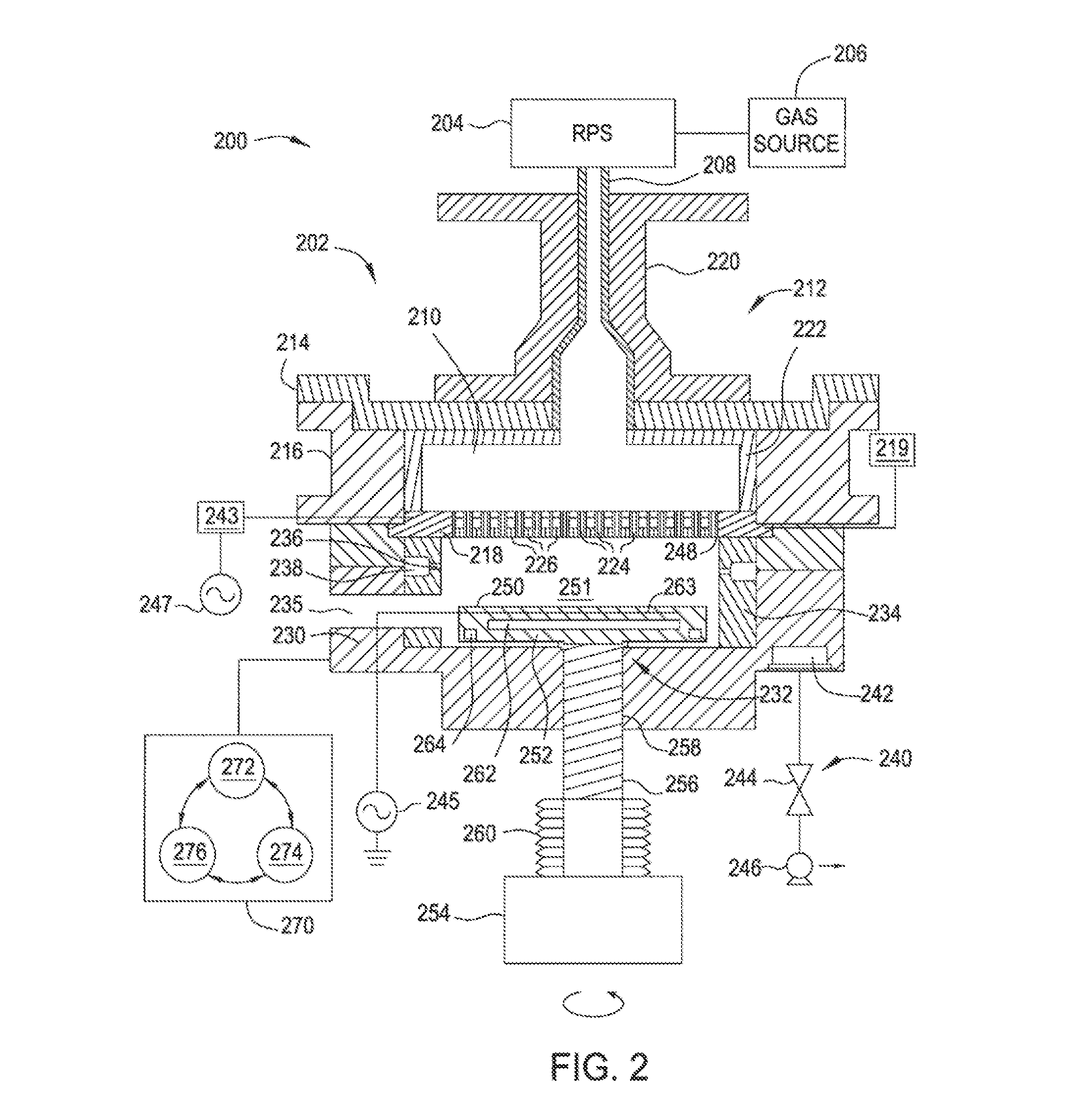
Apparatus and methods for spacer deposition and selective removal in an advanced patterning process
ActiveUS9484202B1Good profile controlSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingEngineeringMultiple patterning
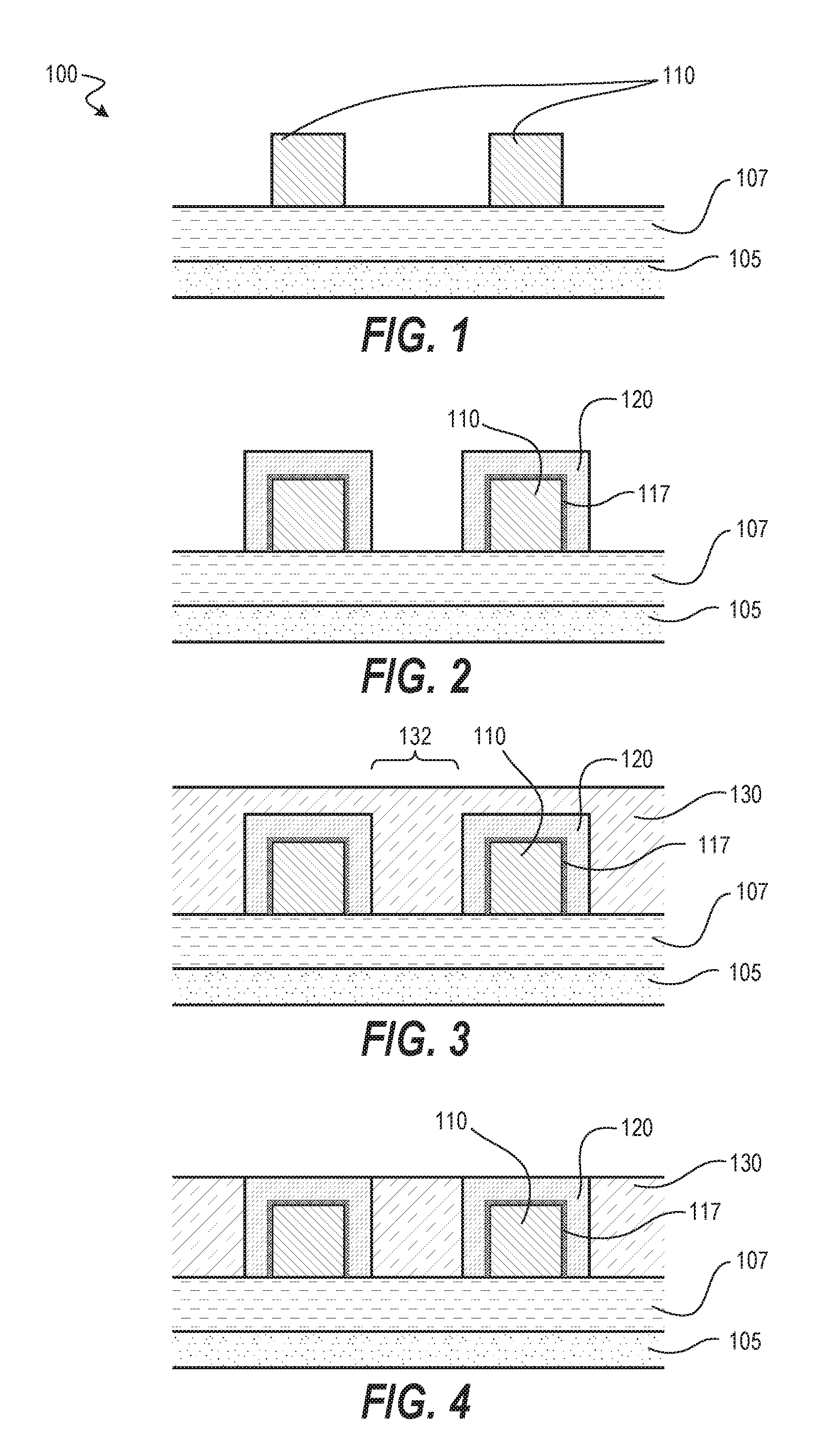
Embodiments herein provide apparatus and methods for performing a deposition and a patterning process on a spacer layer with good profile control in multiple patterning processes. In one embodiment, a method for depositing and patterning a spacer layer during a multiple patterning process includes conformally forming a spacer layer on an outer surface of a patterned structure disposed on a substrate, wherein the patterned structure has a first group of openings defined therebetween, selectively treating a first portion of the spacer layer formed on the substrate without treating a second portion of the spacer layer, and selectively removing the treated first portion of the spacer layer.
Owner:APPLIED MATERIALS INC
Semiconductor Metrology With Information From Multiple Processing Steps
ActiveUS20170287751A1Easy to processSemiconductor/solid-state device testing/measurementPhotomechanical apparatusMetrologyProcess information
Owner:KLA TENCOR TECH CORP
Fin structure formation by selective etching
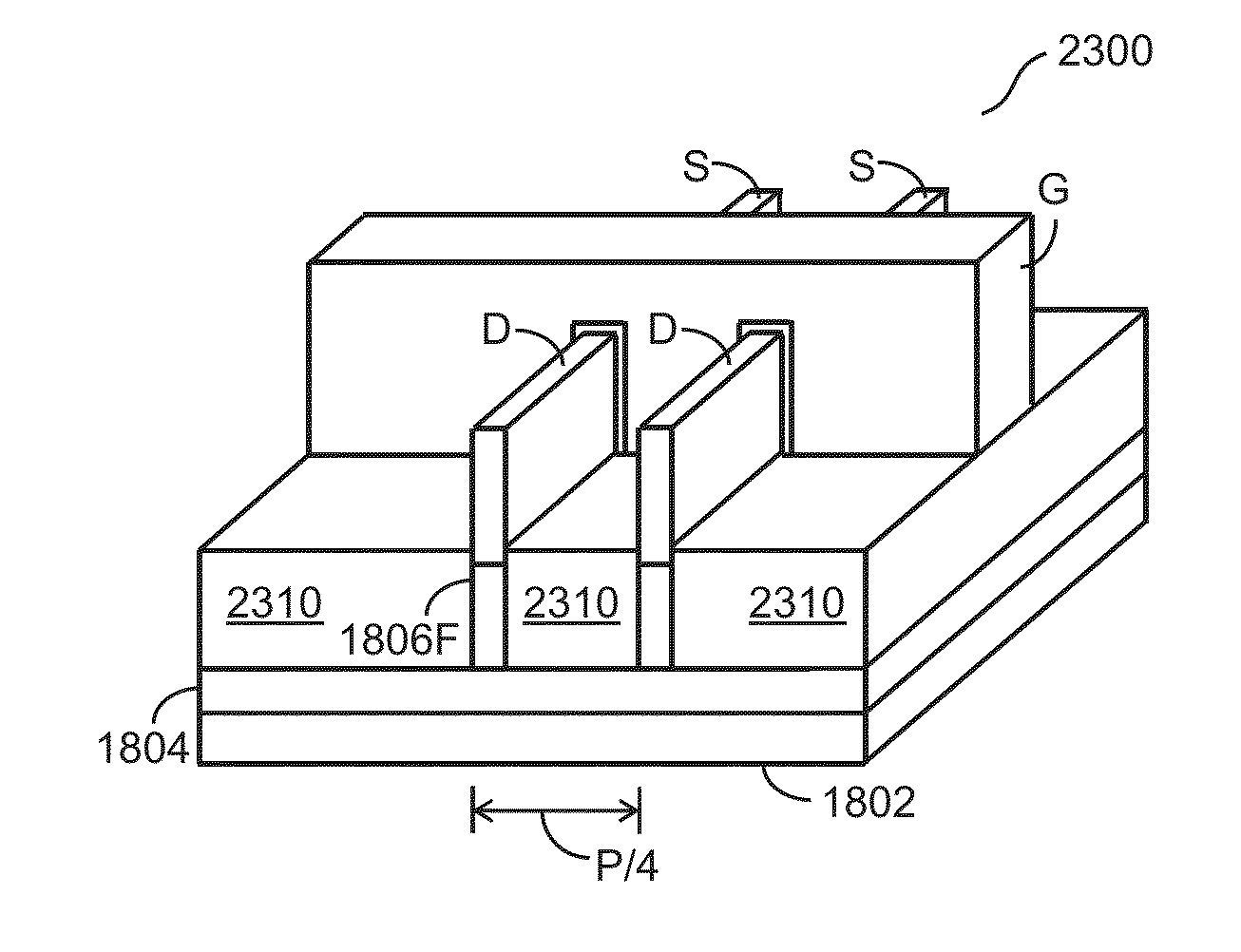
ActiveUS20160099178A1Semiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSemiconductor devicesEtchingDeposition process
Methods and apparatus for forming FinFET structures are provided. Selective etching and deposition processes described herein may provide for FinFET manufacturing without the utilization of multiple patterning processes. Embodiments described herein also provide for fin material manufacturing methods for transitioning from silicon to III-V materials while maintaining acceptable crystal lattice orientations of the various materials utilized. Further embodiments provide etching apparatus which may be utilized to perform the methods described herein.
Owner:APPLIED MATERIALS INC
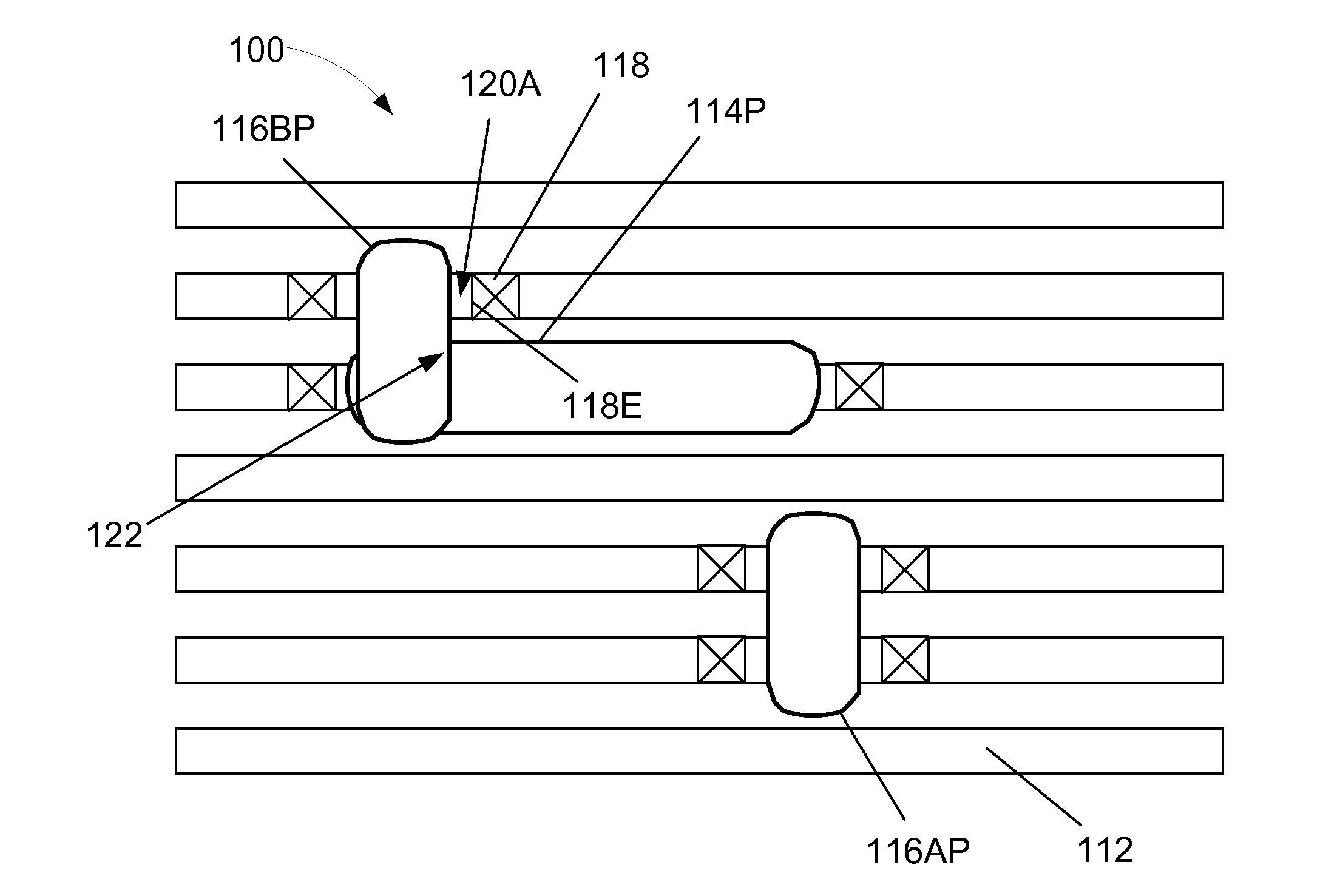
Multiple Patterning Method
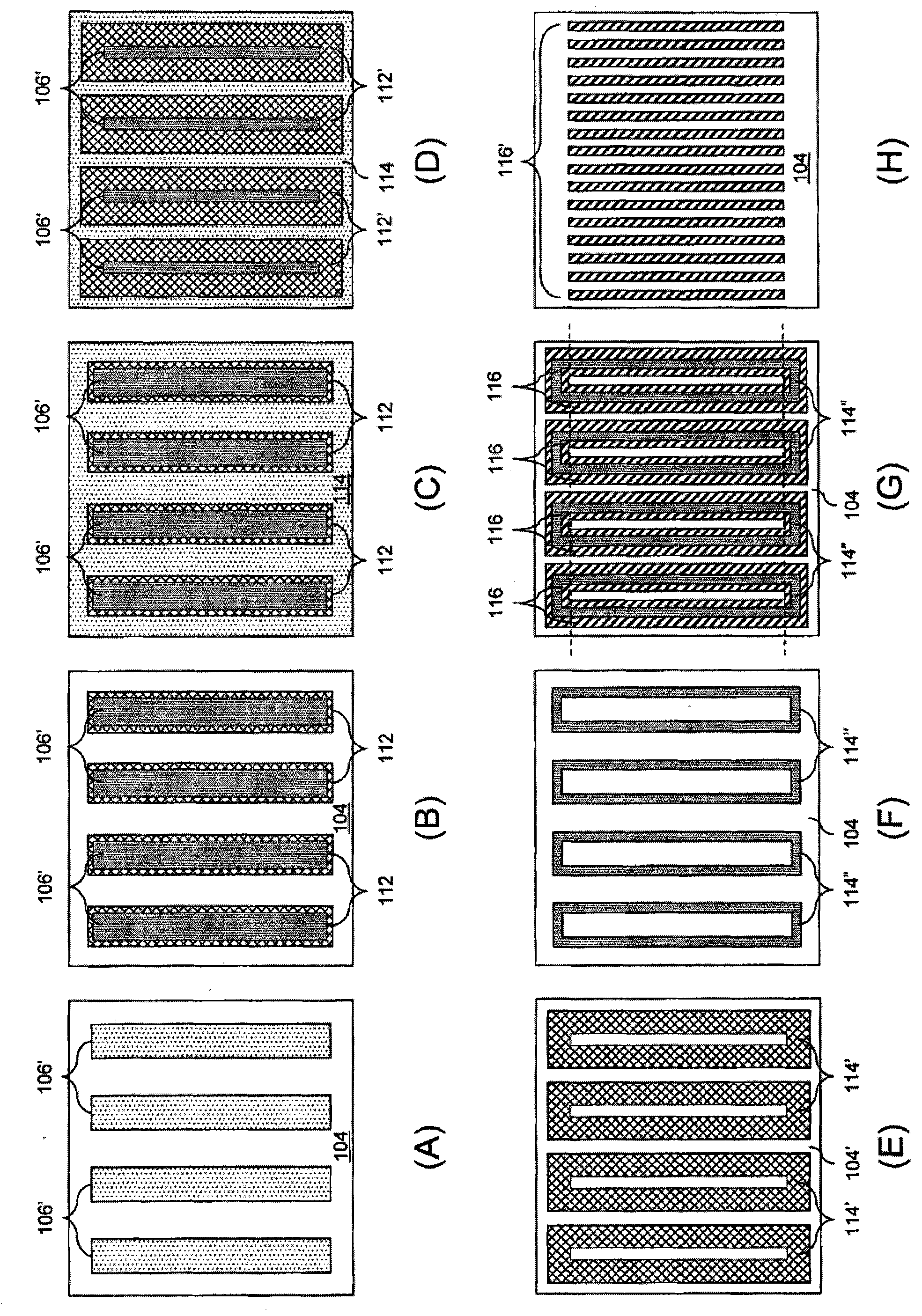
An integrated circuit memory comprises a set of lines each line having parallel X direction line portions in a first region and Y direction line portions in a second region. The second region is offset from the first region. The lengths of the X direction line portions are substantially longer than the lengths of the Y direction line portions. The X direction and Y direction line portions have respective first and second pitches with the second pitch being at least 3 times larger than the first pitch. Contact pickup areas are at the Y direction line portions. In some examples, the lines comprise word lines or bit lines. The memory can be created using multiple patterning methods to create lines of material and then the parallel X direction line portions and parallel Y direction line portions.
Owner:MACRONIX INT CO LTD
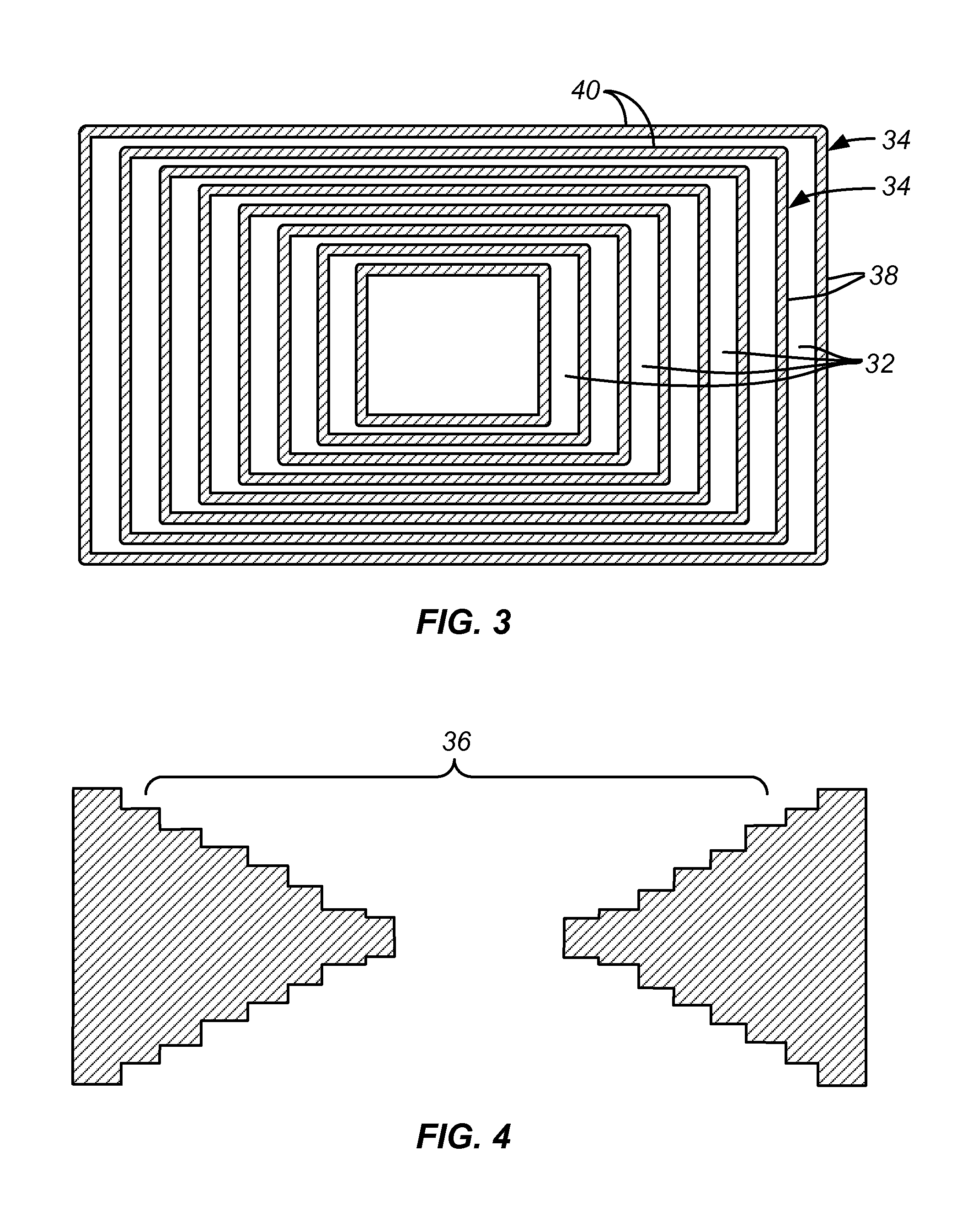
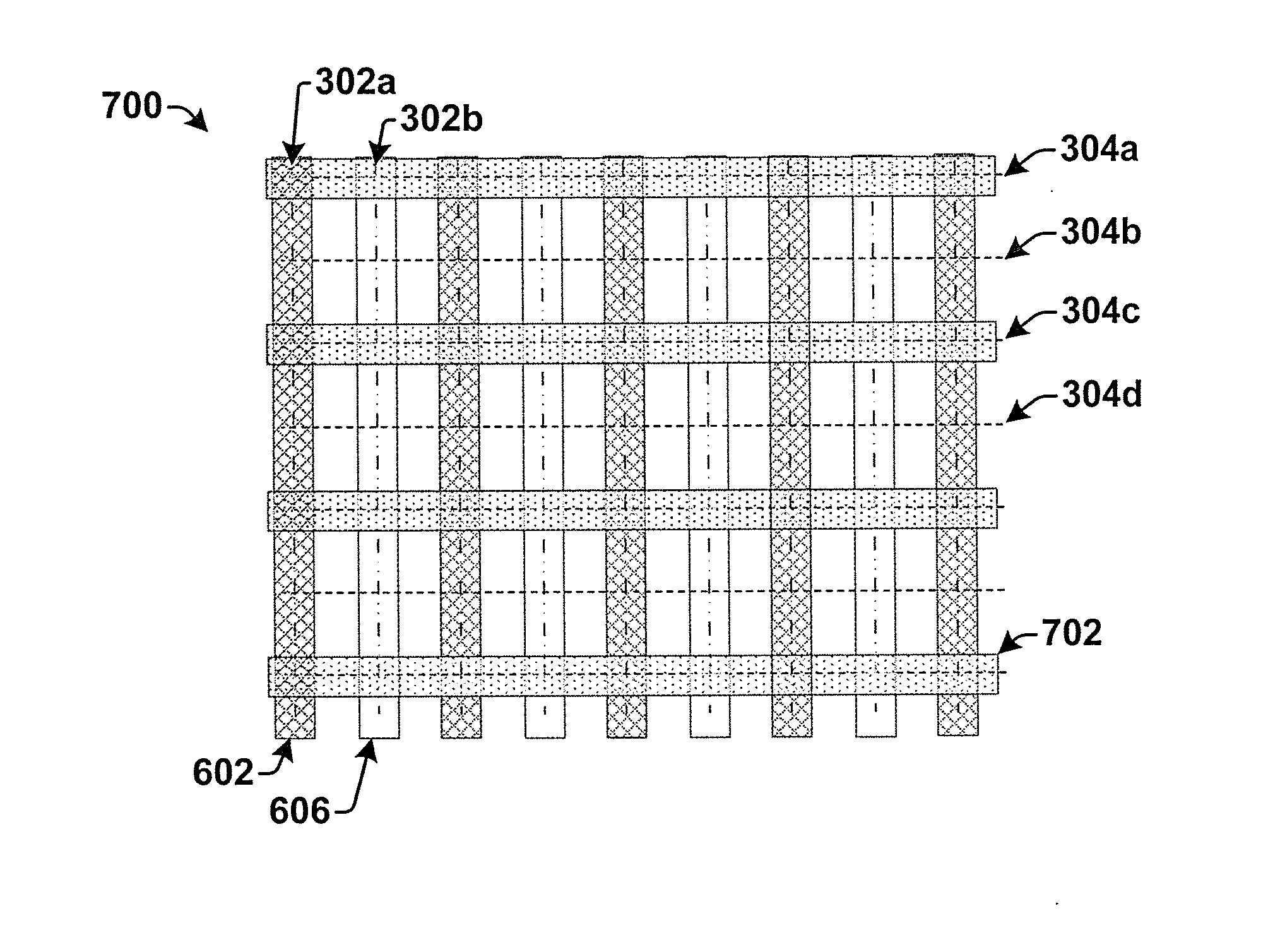
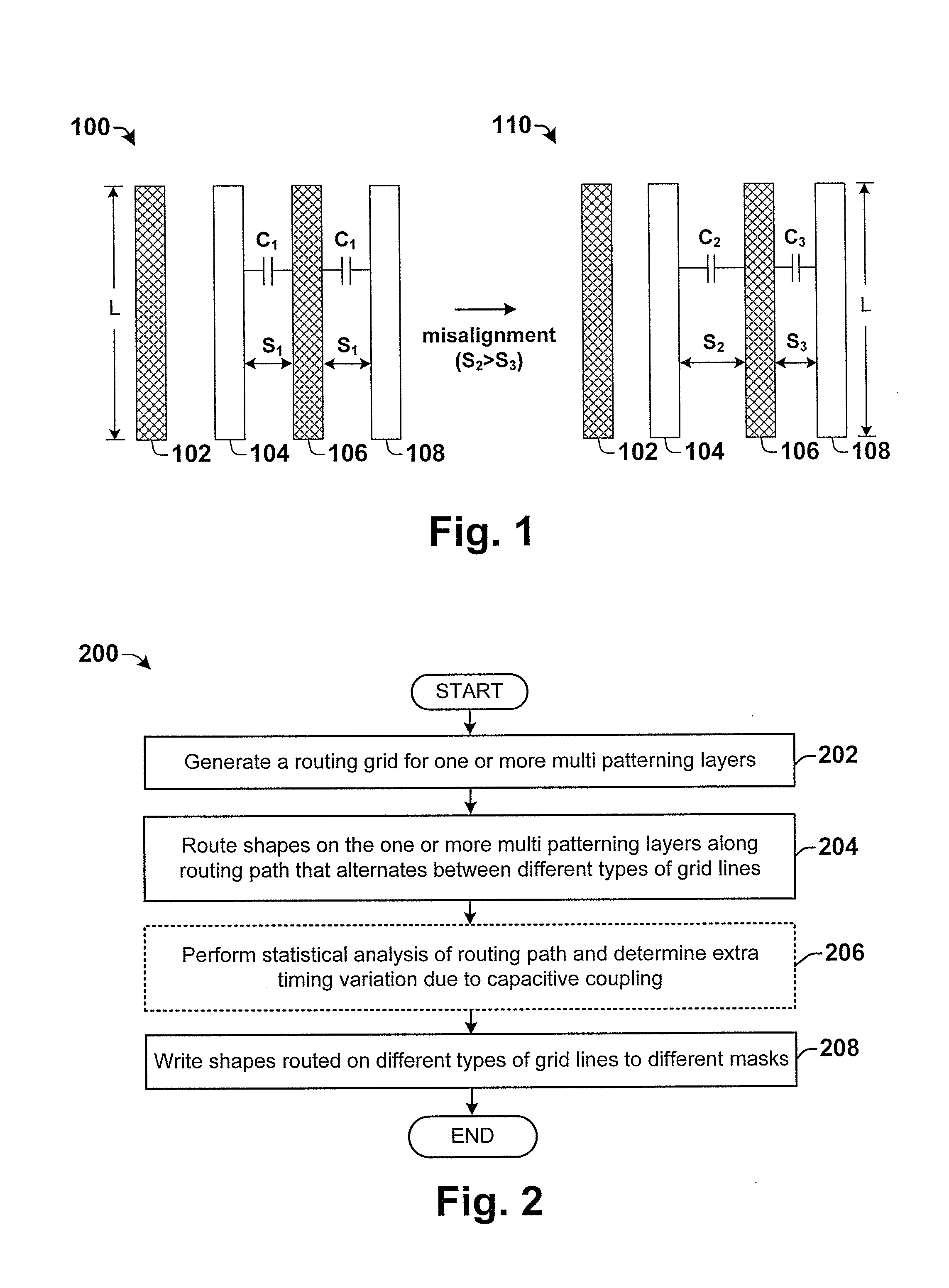
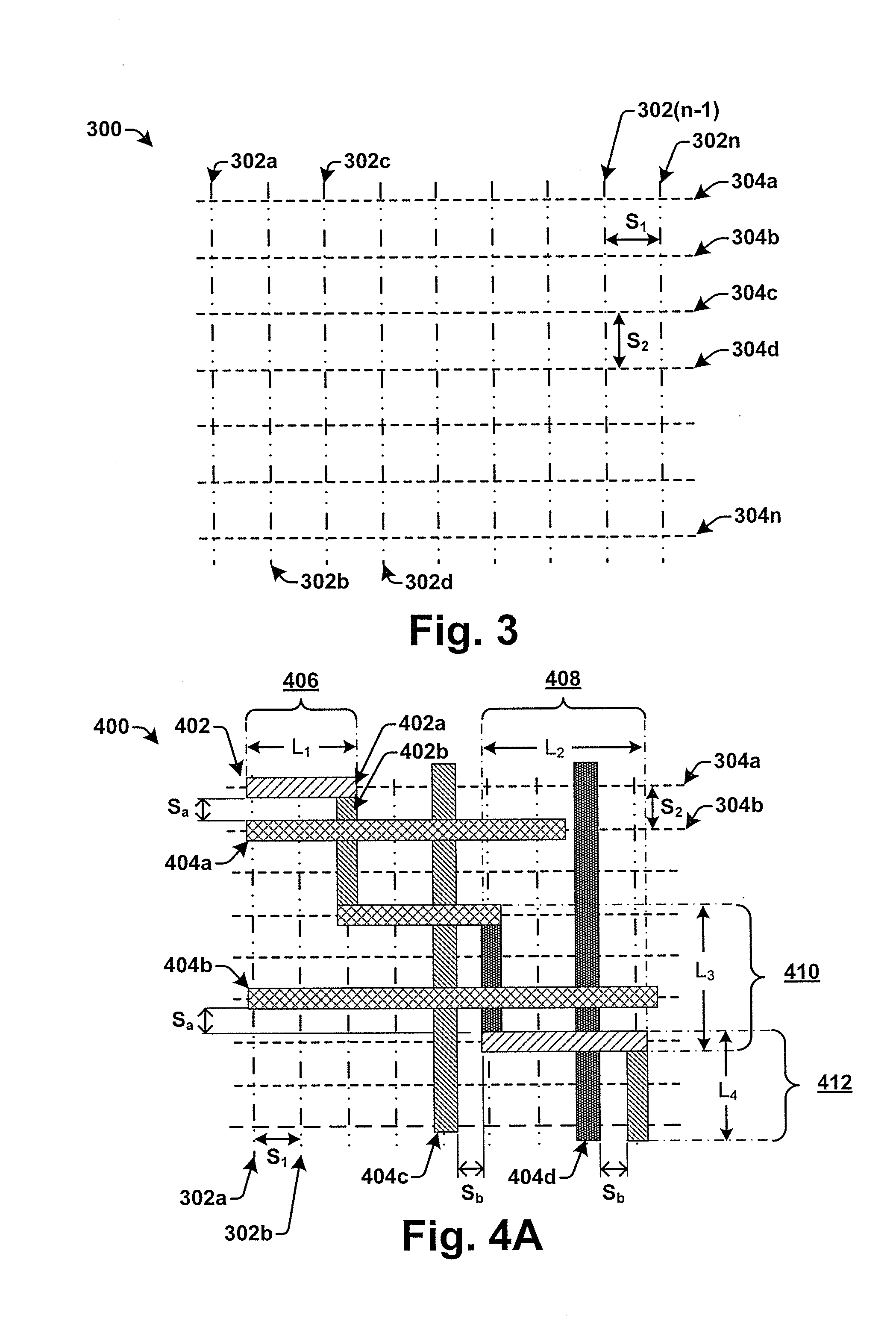
Automatic Misalignment Balancing Scheme for Multi-Patterning Technology
ActiveUS20140038085A1Photomechanical apparatusOriginals for photomechanical treatmentCapacitanceCapacitive coupling
Some aspects of the present disclosure provide for a method of automatically balancing mask misalignment for multiple patterning layers to minimize the consequences of mask misalignment. In some embodiments, the method defines a routing grid for one or more double patterning layers within an IC layout. The routing grid has a plurality of vertical grid lines extending along a first direction and a plurality of horizontal grid lines extending along a second, orthogonal direction. Alternating lines of the routing grid in a given direction (e.g., the horizontal and vertical direction) are assigned different colors. Shapes on the double patterning layers are then routed along the routing grid in a manner that alternates between different colored grid lines. By routing in such a manner, variations in capacitive coupling caused by mask misalignment are reduced.
Owner:TAIWAN SEMICON MFG CO LTD
Integrated Circuit Pattern and Method
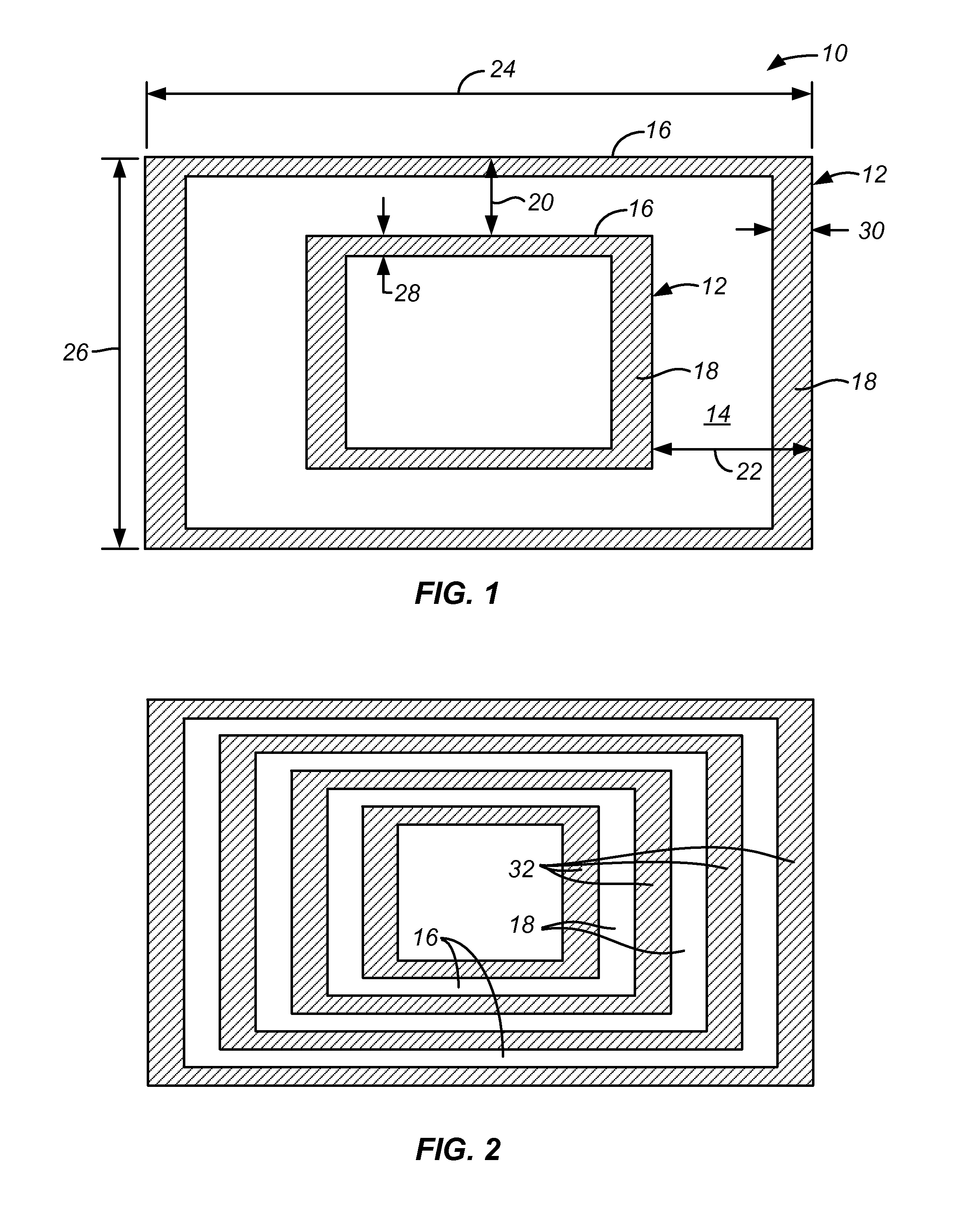
ActiveUS20120168955A1Increase in sizeSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesElement spaceTransfer procedure
An integrated circuit pattern comprises a set of lines of material having X and Y direction portions. The X and Y direction portions have first and second pitches, the second pitch being larger, such as at least 3 times larger, than the first pitch. The X direction portions are parallel and the Y direction portions are parallel. The end regions of the Y direction portions comprise main line portions and offset portions. The offset portions comprise offset elements spaced apart from and electrically connected to the main line portions. The offset portions define contact areas for subsequent pattern transferring procedures. A multiple patterning method, for use during integrated circuit processing procedures, provides contact areas for subsequent pattern transferring procedures.
Owner:MACRONIX INT CO LTD
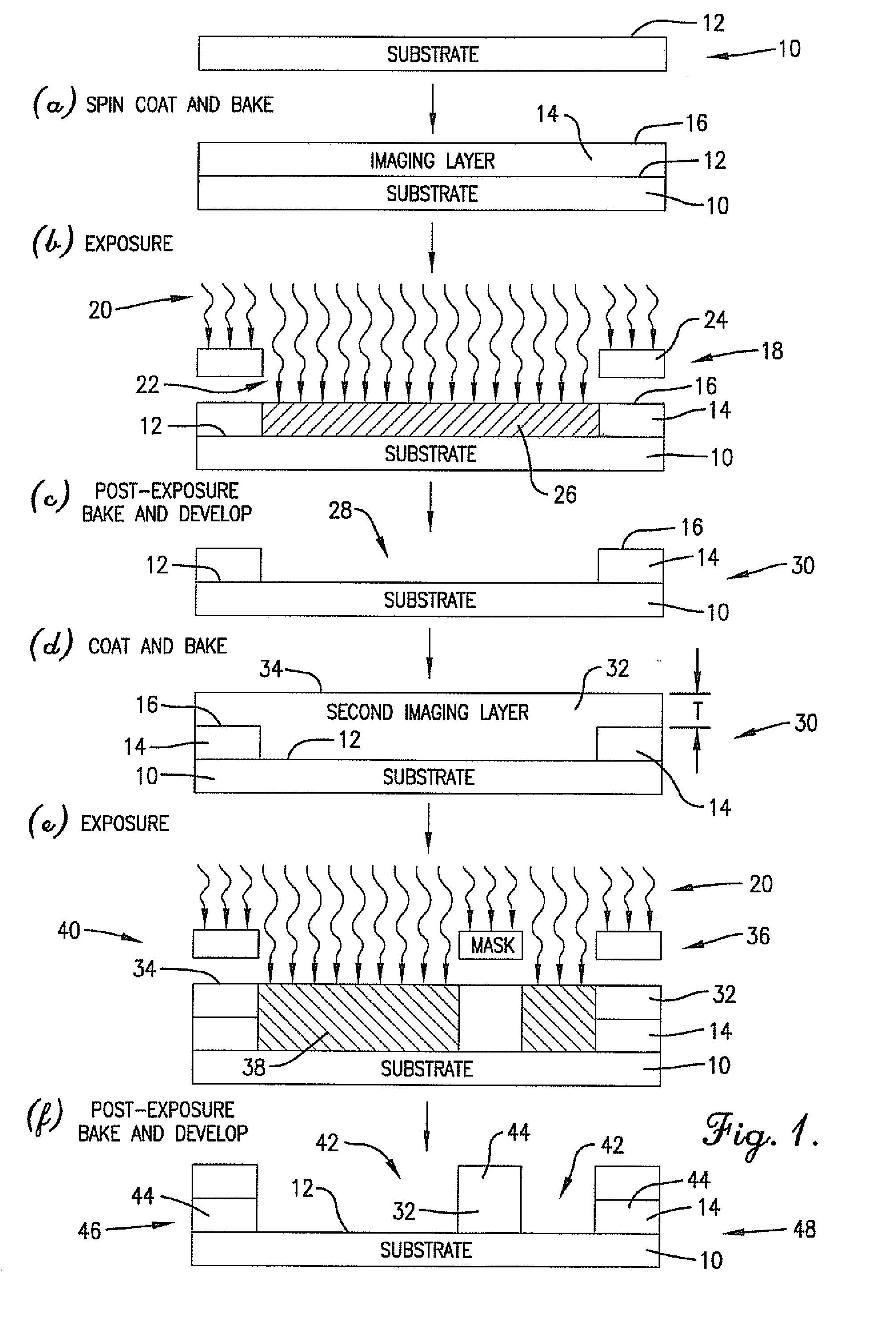
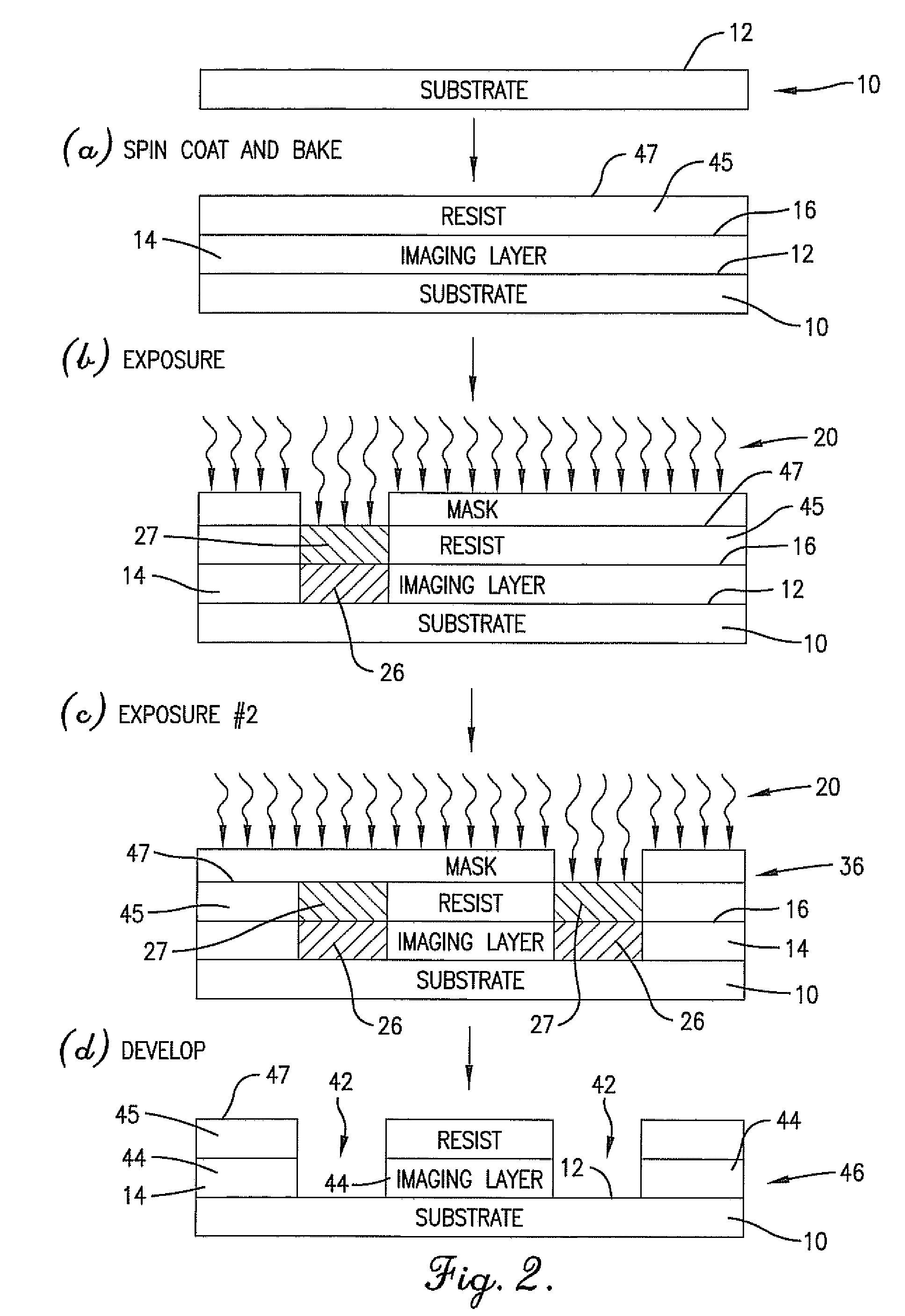
Anti-reflective imaging layer for multiple patterning process
ActiveUS20080044772A1Semiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingPhotomechanical exposure apparatusOligomerCrosslinked polymers
Novel methods of double patterning a photosensitive resin composition are provided. The methods involve applying the photosensitive composition to a substrate and thermally crosslinking the composition. The crosslinked layer can be used to provide reflection control. Upon exposure to light, the crosslinked polymer (or oligomer or monomer) in the compositions will decrosslink, rendering the light-exposed portions soluble in typical photoresist developing solutions (e.g., alkaline developers). Advantageously, the crosslinked portions of the composition remain insoluble in the solvent used to form the photosensitive composition. As a result, the coating, lithographic, and or developing steps can be repeated multiple times in varying order, depending upon the particular process, without destroying earlier-formed patterns.
Owner:BREWER SCI
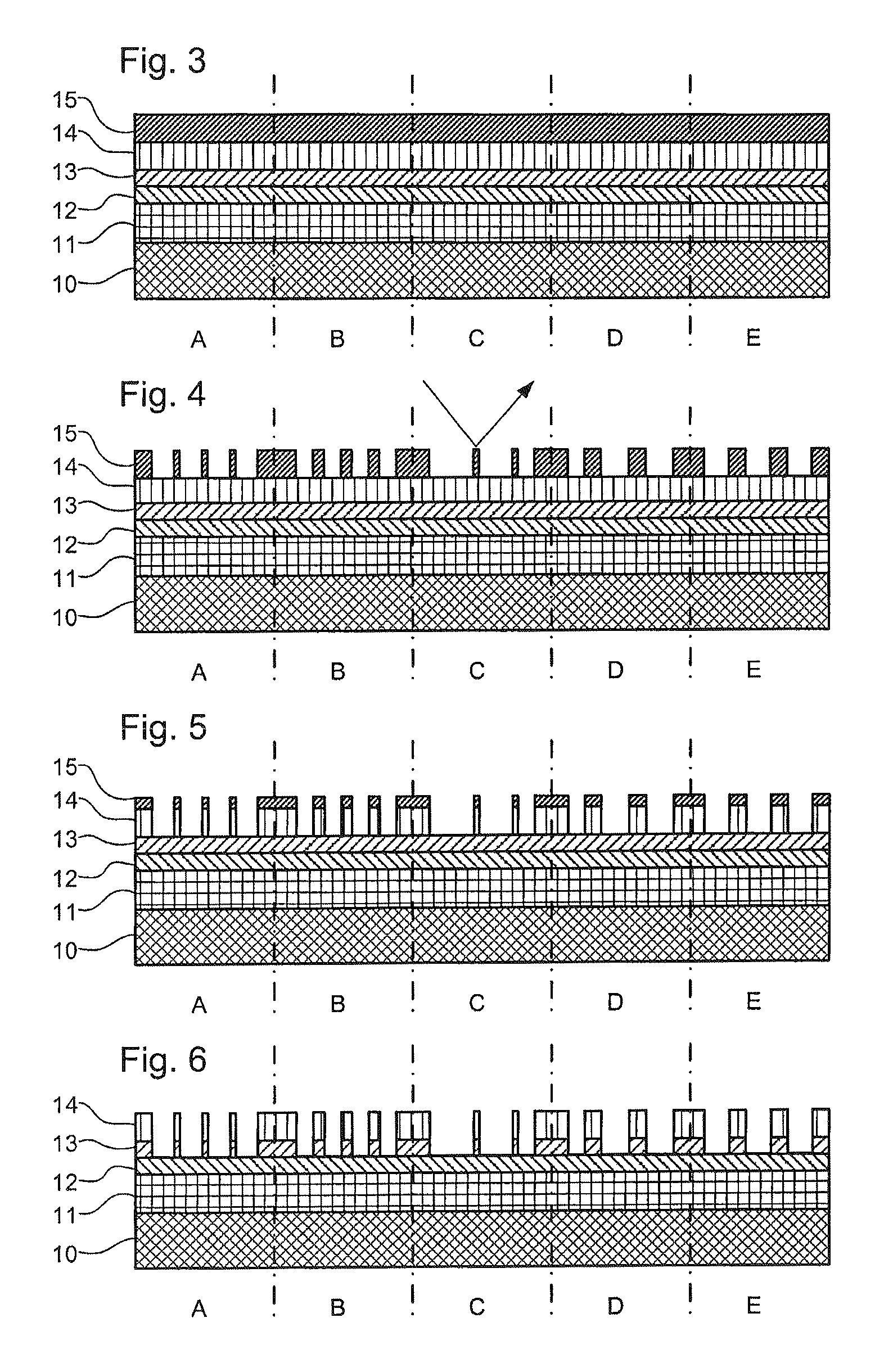
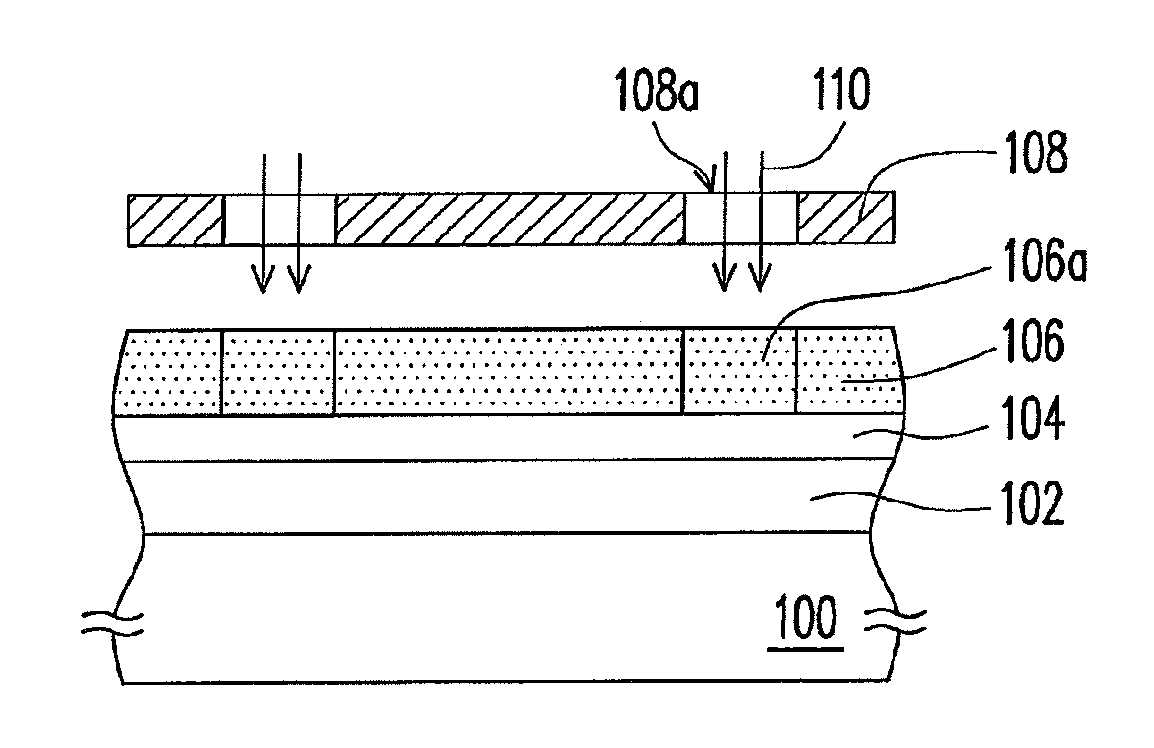
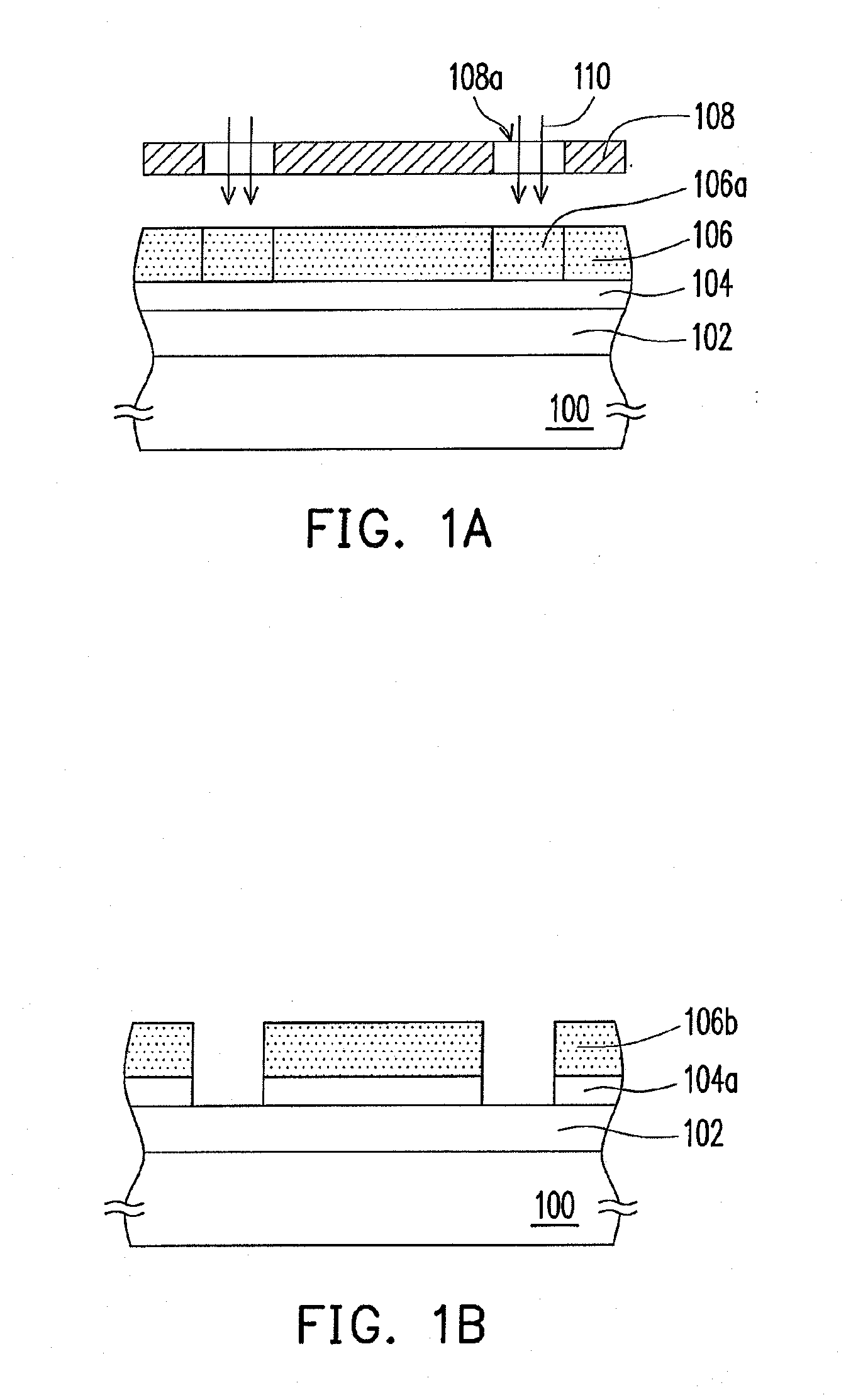
Patterning process
InactiveUS20090104564A1Easy to processReduce spacingPhotomechanical apparatusSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingComputational physicsPhotoresist
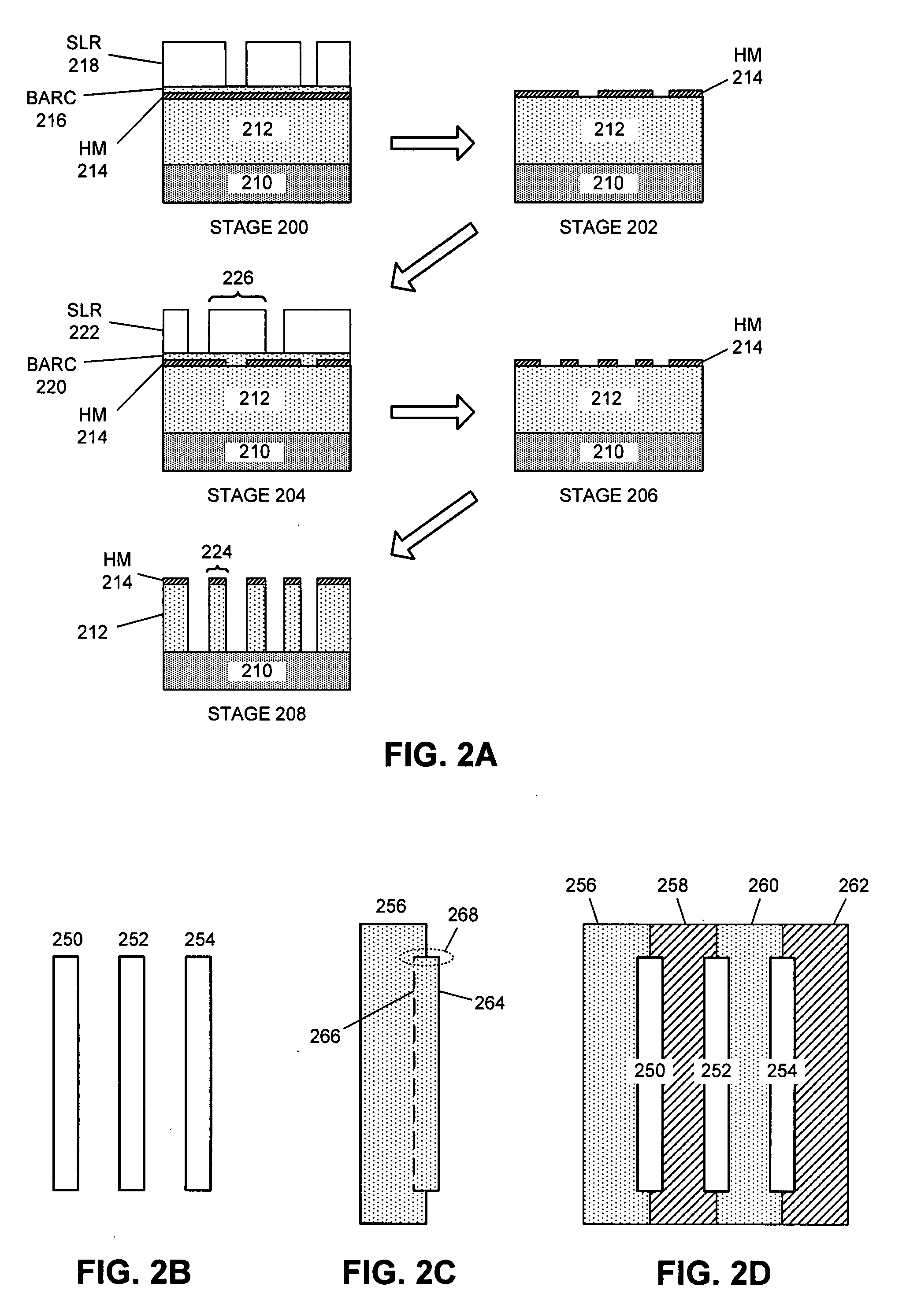
The invention is directed to a method for patterning a material layer. The method comprises steps of forming a mask layer on the material layer. A multiple patterning process is performed on the mask layer for transferring at least a first pattern from a first photomask through a first photoresist and a second pattern from a second photomask from a second photoresist layer into the mask layer without performing any etching process. The mask layer exposes a portion of the material layer and the mask layer is patterned at the time that the first photoresist layer and the second photoresist layer are developed respectively. An etching process is performed to pattern the material layer by using the mask layer as an etching mask.
Owner:MACRONIX INT CO LTD
Method and System for Wafer Inspection
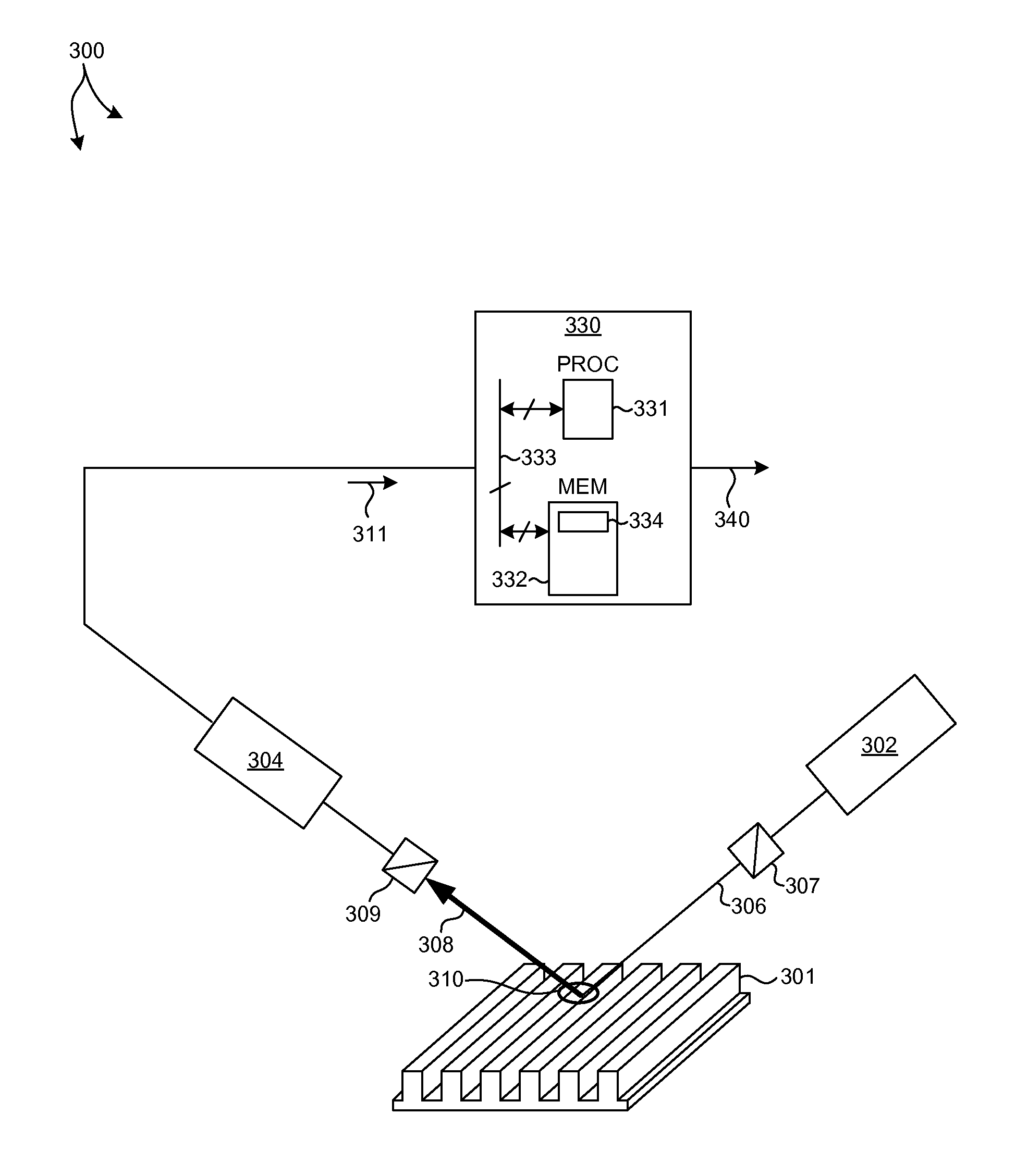
InactiveUS20110096309A1Accurate measurementPrecise positioningPhotomechanical apparatusPhotographic printingEngineeringMultiple patterning
A method and system for evaluating a lithographic pattern obtained using multiple-patterning lithographic processing are presented. In one aspect, the method includes aligning a target design with a lithographic pattern. The target design may comprise a first design and a second design. The method further comprises identifying in the lithographic pattern a stitching region based on a region of overlap between the first design and the second design. The method further comprises determining for the identified stitching region whether a predetermined criterion is fulfilled. In some embodiments, determining whether a predetermined criterion is fulfilled may comprise determining a line or trench minimum width. Alternately or additionally, determining whether a predetermined criterion is fulfilled may comprise determining a stitching metric for the identified stitching region, and evaluating whether or not the stitching metric fulfills the predetermined criterion.
Owner:INTERUNIVERSITAIR MICRO ELECTRONICS CENT (IMEC VZW) +1
Method and apparatus for determining mask layouts for a multiple patterning process
ActiveUS8028253B2Increasing trenchImprove toleranceOriginals for photomechanical treatmentSpecial data processing applicationsEngineeringDesign intent
One embodiment provides a method for determining mask layouts. During operation, the system can receive a design intent. Next, the system can determine a set of critical edges in the design layout, and select a first edge and a second edge. The system can then determine a first trench and a second trench using the first edge and the second edge, respectively. Note that an edge of the first trench may substantially overlap with the first edge, and an edge of the second trench may substantially overlap with the second edge. Next, the system may assign the first trench and the second trench to the first mask layout and the second mask layout, respectively. The system can then increase the first trench and the second trench, thereby improving pattern fidelity. The resulting mask layouts may be used in a double patterning process.
Owner:SYNOPSYS INC
Cell layout for multiple patterning technology
ActiveCN102542099APhotomechanical apparatusSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingEngineeringBoundary region
A system and method for providing a cell layout for multiple patterning technology is provided. An area to be patterned is divided into alternating sites corresponding to the various masks. During a layout process, sites located along a boundary of a cell are limited to having patterns in the mask associated with the boundary site. When placed, the individual cells are arranged such that the adjoining cells alternate the sites allocated to the various masks. In this manner, the designer knows when designing each individual cell that the mask pattern for one cell will be too close to the mask pattern for an adjoining cell.
Owner:TAIWAN SEMICON MFG CO LTD
Categorized stitching guidance for triple-patterning technology
ActiveUS9747407B2Photomechanical exposure apparatusMicrolithography exposure apparatusTheoretical computer scienceMultiple patterning
A computer-implemented method for validating a design is disclosed. The method includes receiving, with the computer, the design, where the design is printable using a multiple-patterning process when the computer is invoked, and where the design includes a plurality of shapes and at least one conflict preventing decomposition of the design into a plurality of multiple-patterning masks. The method also includes forming a subset of the shapes, the subset including the shapes associated with the at least one conflict, categorizing each of the shapes of the subset into one of a plurality of topology types generating one or more stitch candidate solutions for each of the plurality of topology types, and decomposing the design into a plurality of masks.
Owner:SYNOPSYS INC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com