Patents
Literature
1051 results about "Boundary region" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
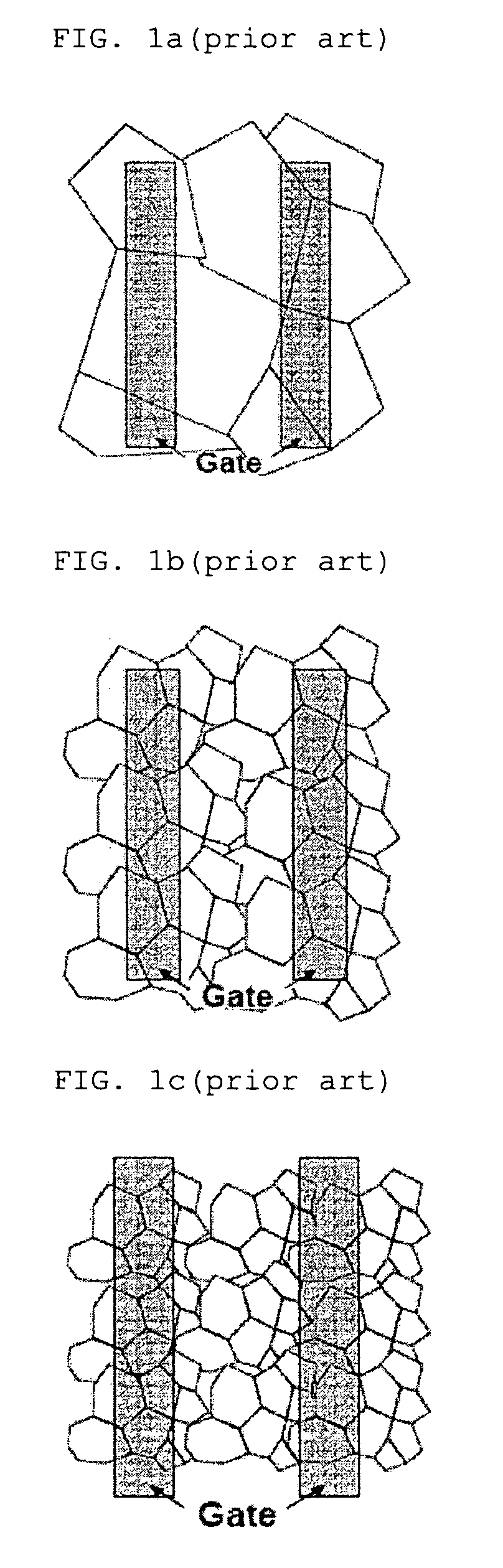
The boundary regions contain a large amount of trap centers. As there are very few free charge carriers in the region, it is virtually “non-conductive”. The trap centers in the boundary regions cause a potential barrier between neighboring grains and cause depletion layers in the surface region of the grains.
Apparatus and method for forming polycrystalline silicon thin film
ActiveUS20070054499A1Increase the rate of crystallizationDecrease in crystallization temperatureAfter-treatment apparatusSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingGas phaseAmorphous silicon
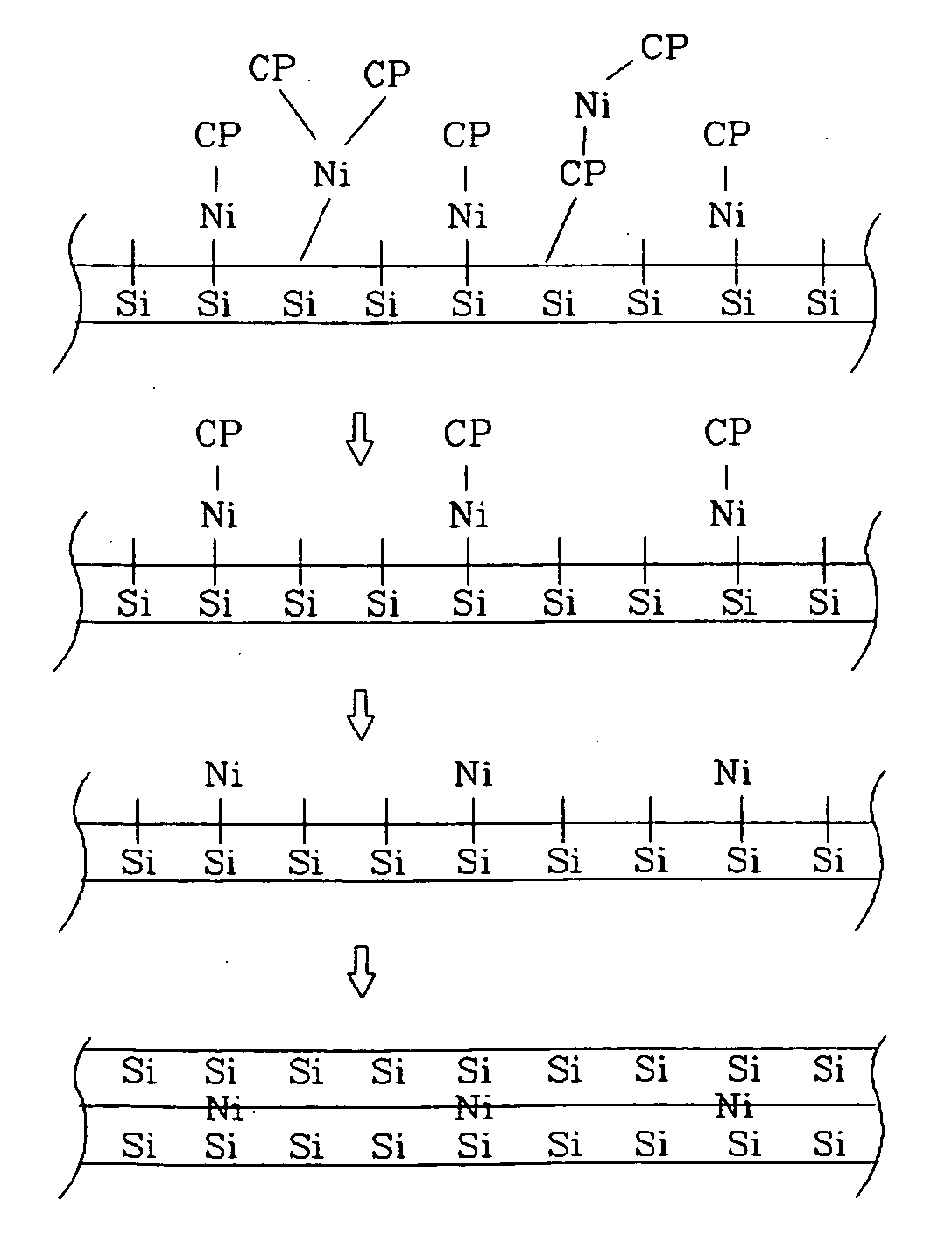
Apparatus and method for forming a polycrystalline silicon thin film by converting an amorphous silicon thin film into the polycrystalline silicon thin film using a metal are provided. The method includes: a metal nucleus adsorbing step of introducing a vapor phase metal compound into a process space where the glass substrate having the amorphous silicon formed thereon is disposed, to adsorb a metal nucleus contained in the metal compound into the amorphous silicon layer; a metal nucleus distribution region-forming step of forming a community region including a plurality of silicon particles every metal nucleus in a plane boundary region occupied by the metal compound by a self-limited mechanism due to the adsorption of the metal nucleus; and an excess gas removing step of purging and removing an excess gas which is not adsorbed in the metal nucleus distribution region-forming step.
Owner:WONIK IPS CO LTD
Method of cyclic dry etching using etchant film
ActiveUS9793135B1Improve controllabilityEasy to operateSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingOptoelectronicsBoundary region
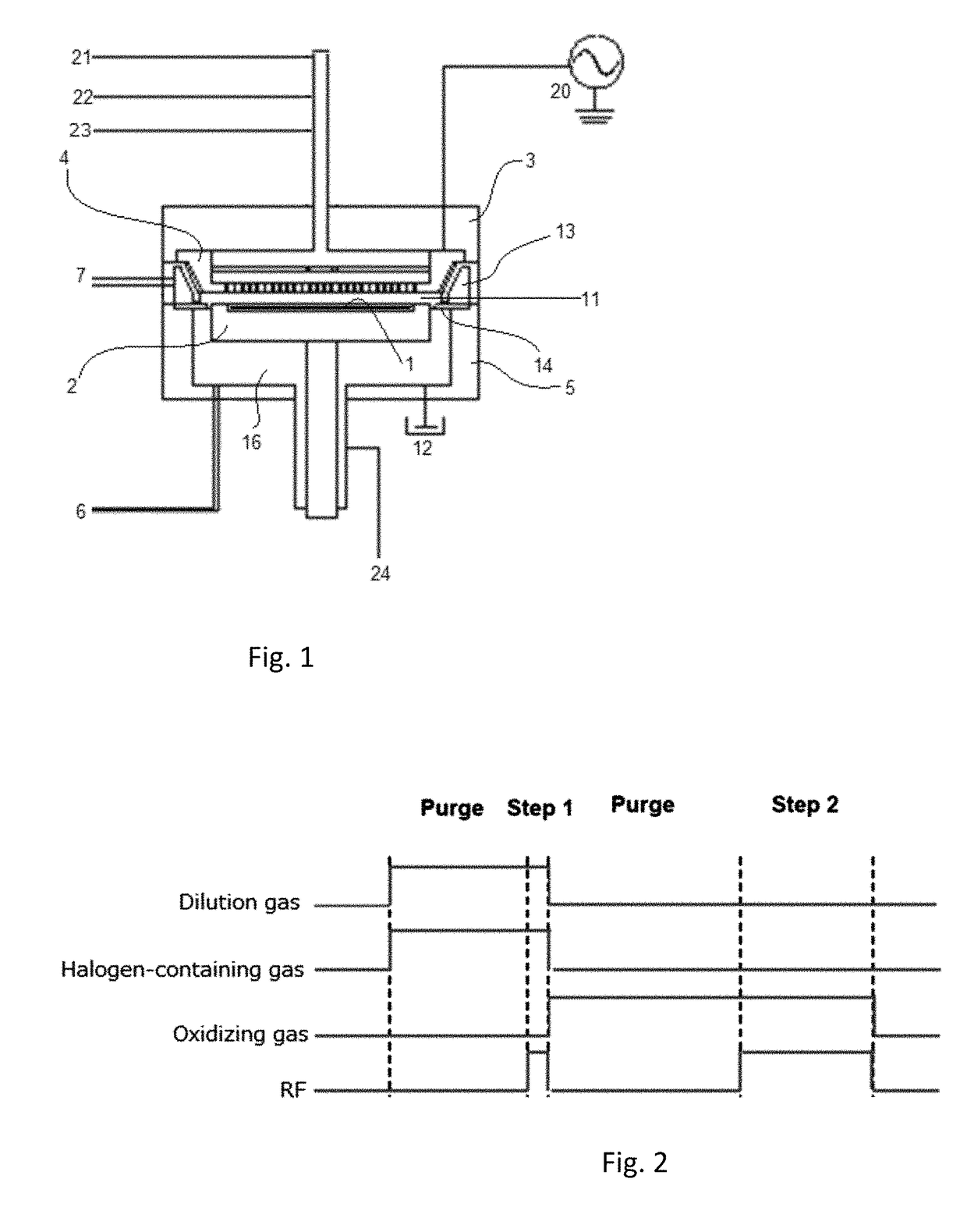
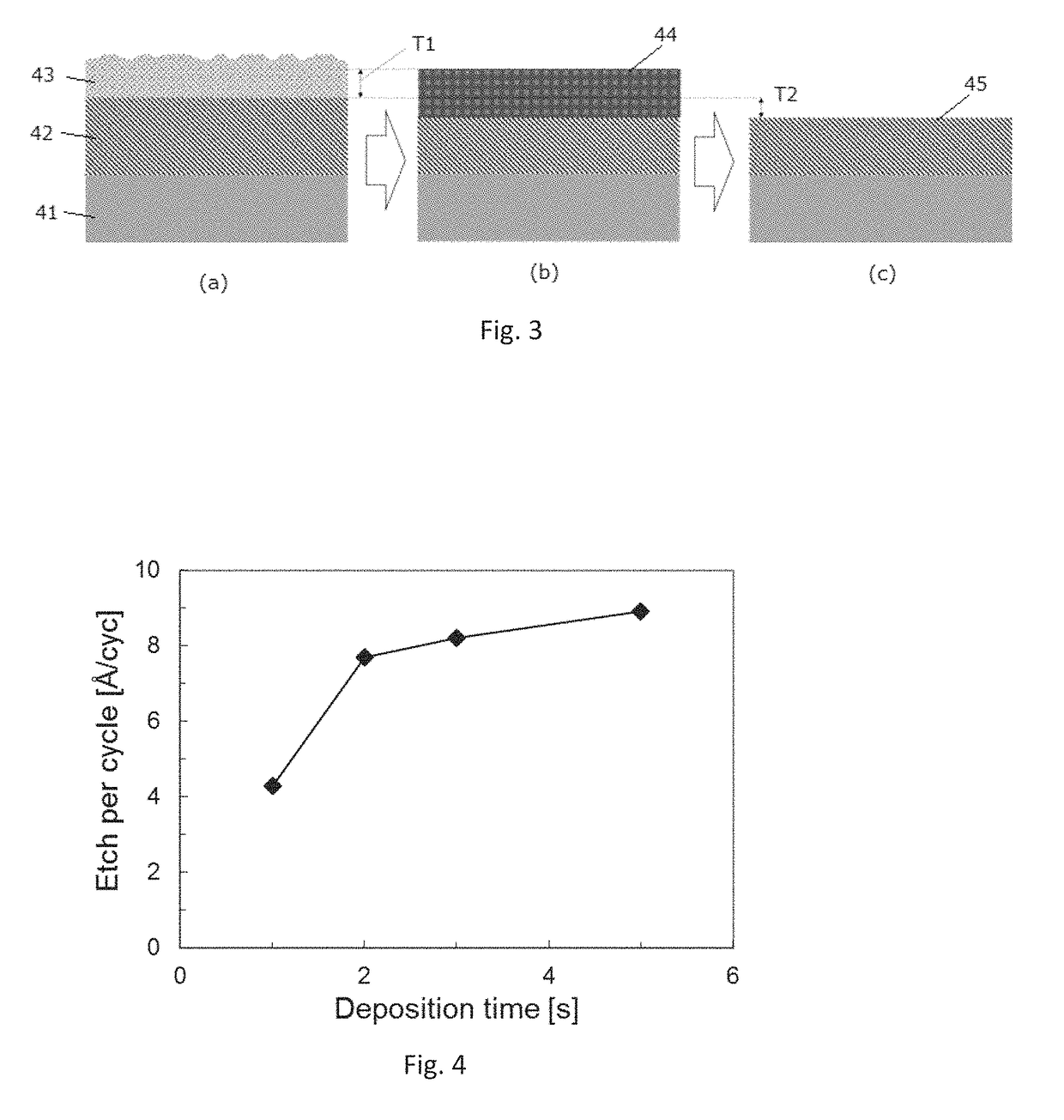
A method for etching a target layer on a substrate by a dry etching process includes at least one etching cycle, wherein an etching cycle includes: depositing a halogen-containing film using reactive species on the target layer on the substrate; and etching the halogen-containing film using a plasma of a non-halogen etching gas, which plasma alone does not substantially etch the target layer, to generate etchant species at a boundary region of the halogen-containing film and the target layer, thereby etching a portion of the target layer in the boundary region.
Owner:ASM IP HLDG BV
Method of atomic layer etching using hydrogen plasma
ActiveUS20180350620A1High selectivityImprove controllabilitySemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingHydrogen halideHydrogen
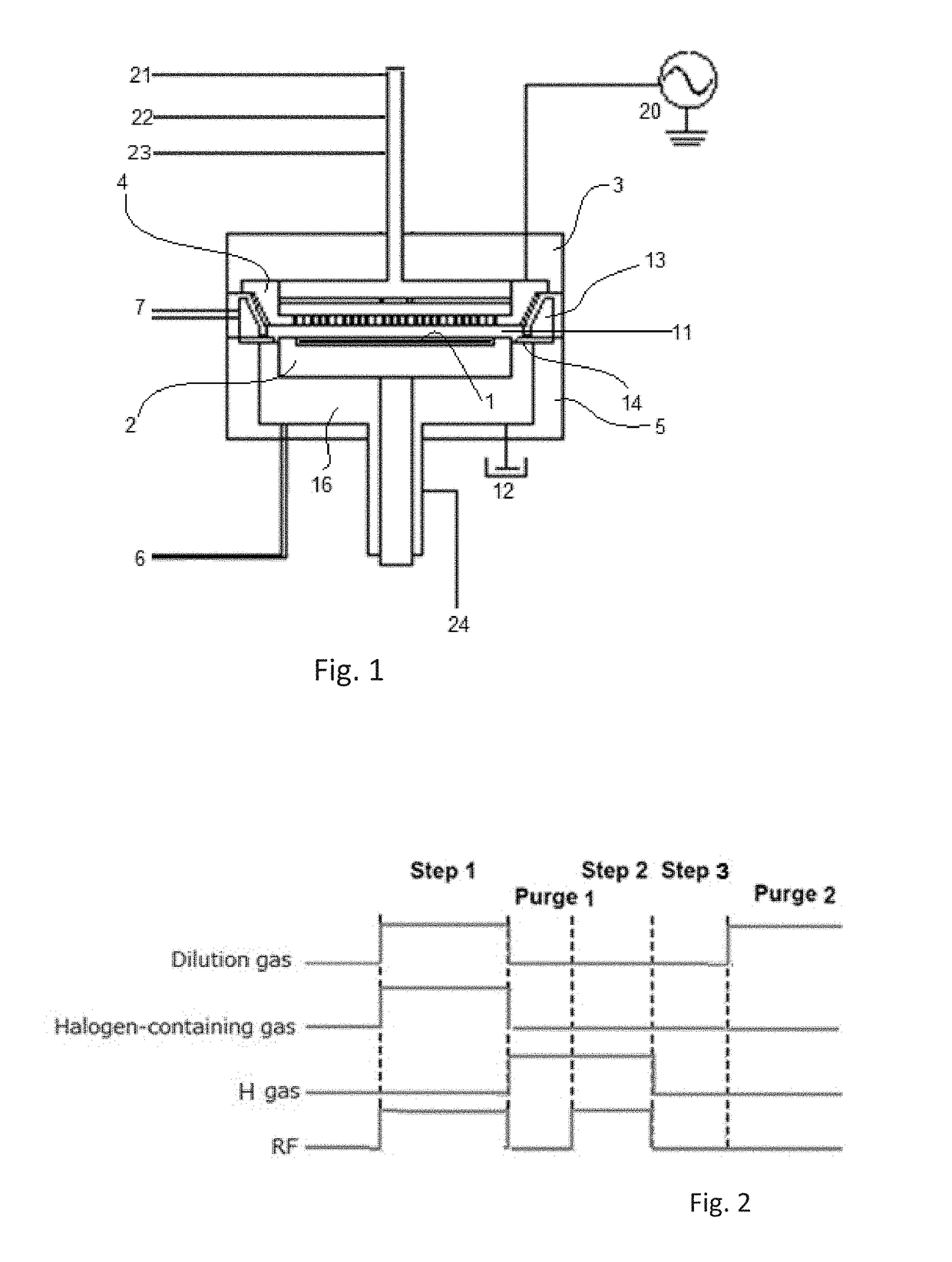
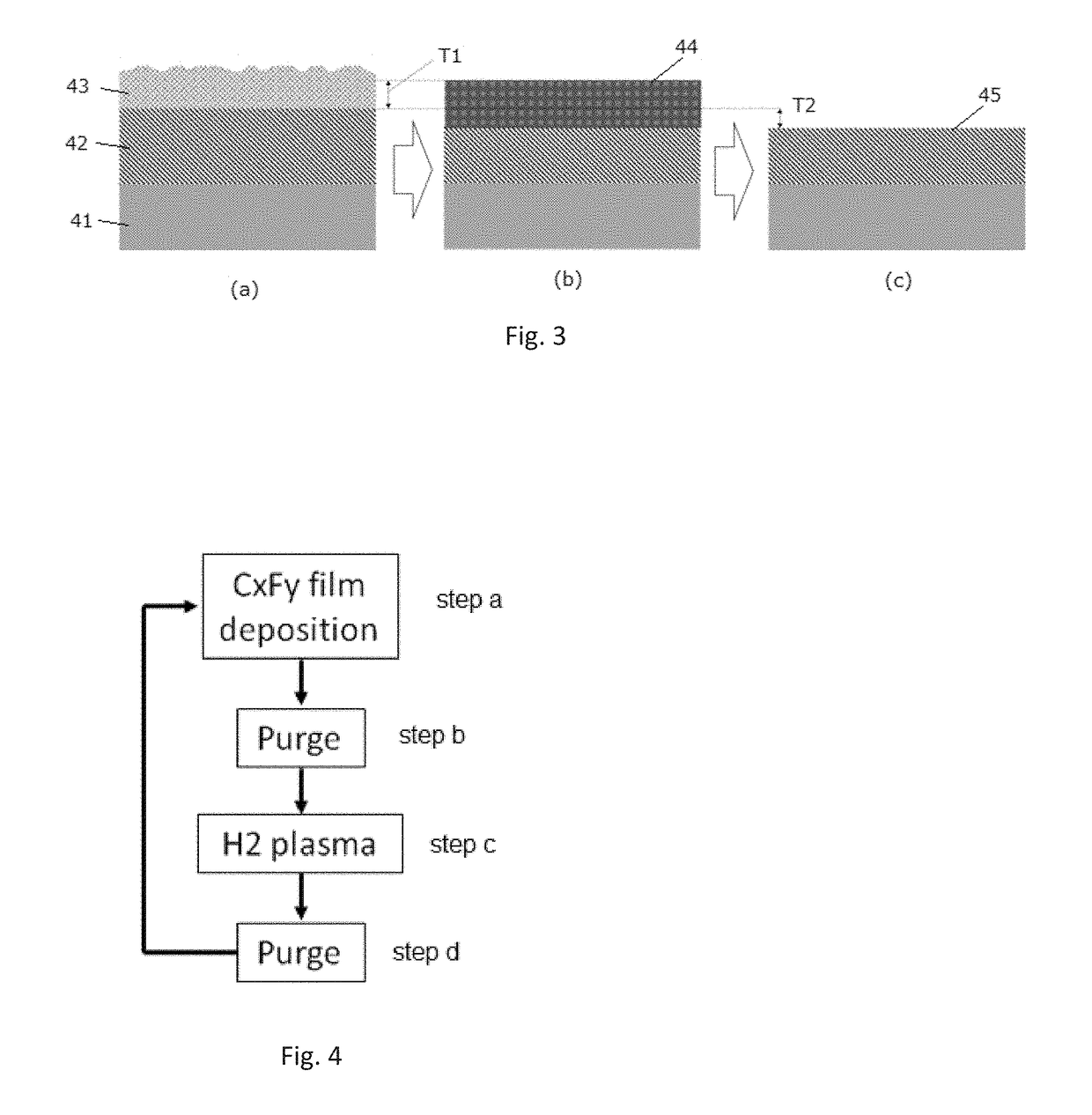
A method for etching a target layer on a substrate by a dry etching process includes at least one etching cycle, wherein an etching cycle includes: depositing a carbon halide film using reactive species on the target layer on the substrate; and etching the carbon halide film using a plasma of a non-halogen hydrogen-containing etching gas, which plasma alone does not substantially etch the target layer, thereby generating a hydrogen halide as etchant species at a boundary region of the carbon halide film and the target layer, thereby etching a portion of the target layer in the boundary region.
Owner:ASM IP HLDG BV
Data-driven global boundary optimization
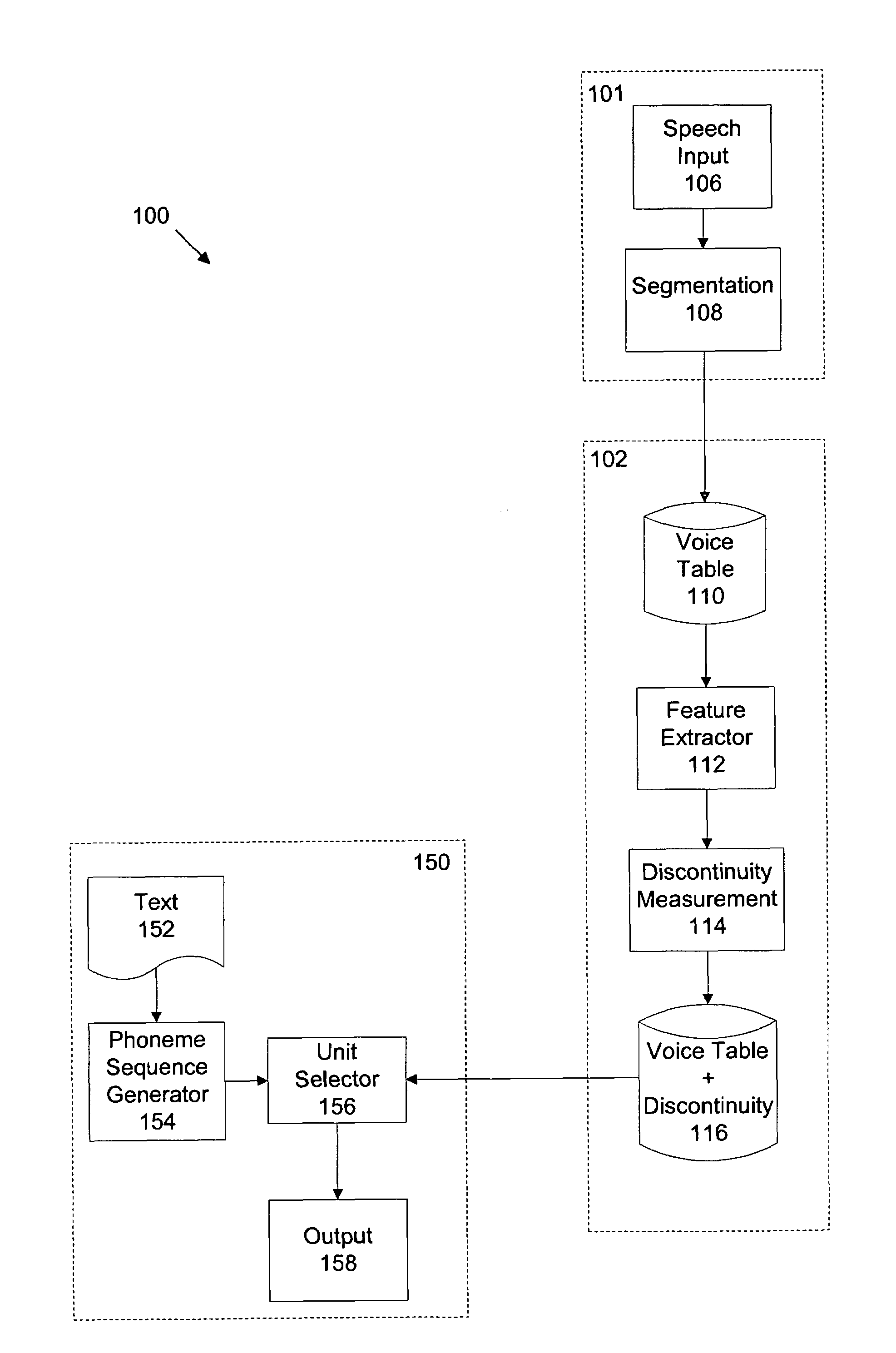
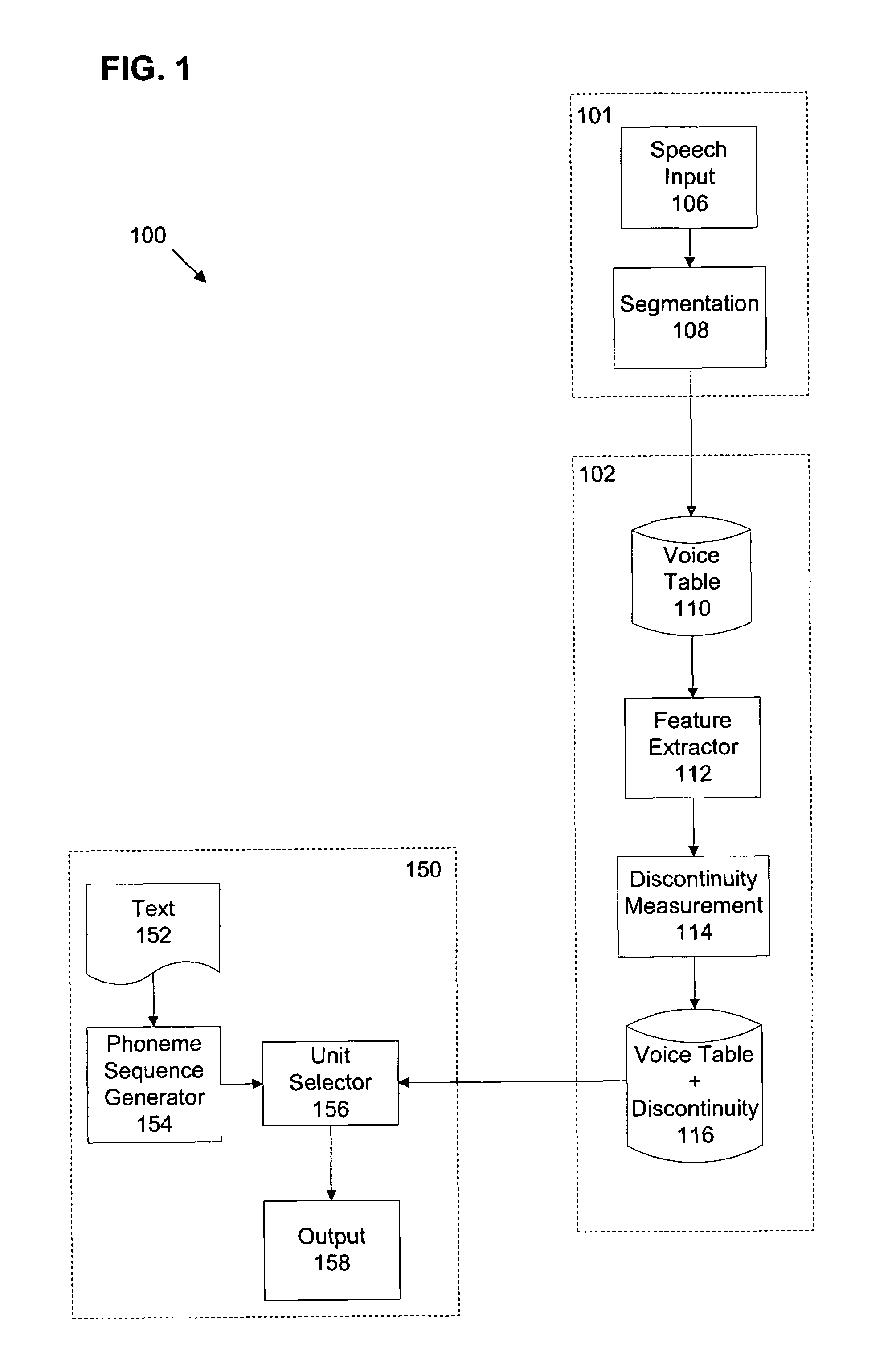
Portions from segment boundary regions of a plurality of speech segments are extracted. Each segment boundary region is based on a corresponding initial unit boundary. Feature vectors that represent the portions in a vector space are created. For each of a plurality of potential unit boundaries within each segment boundary region, an average discontinuity based on distances between the feature vectors is determined. For each segment, the potential unit boundary associated with a minimum average discontinuity is selected as a new unit boundary.
Owner:APPLE INC
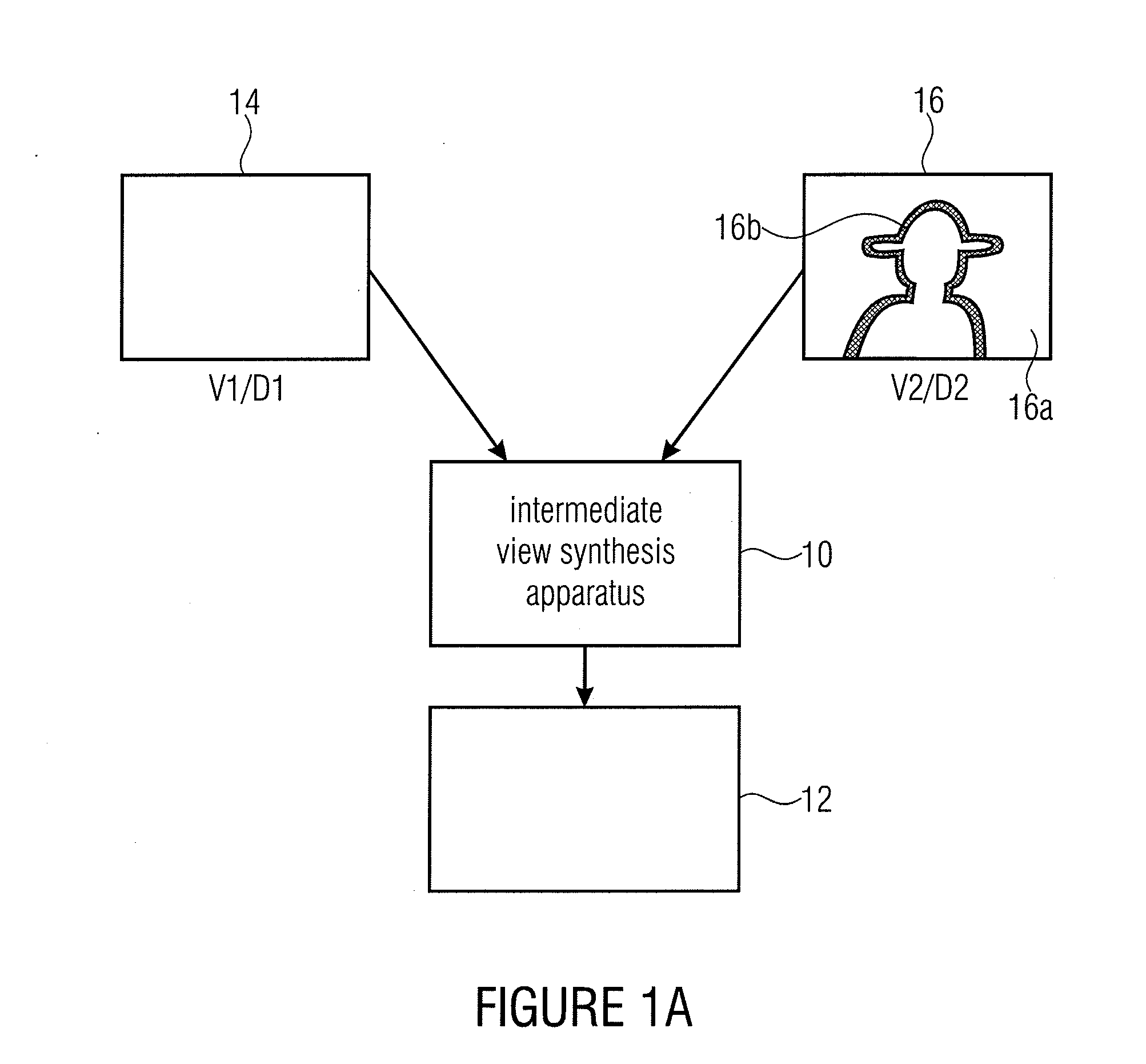
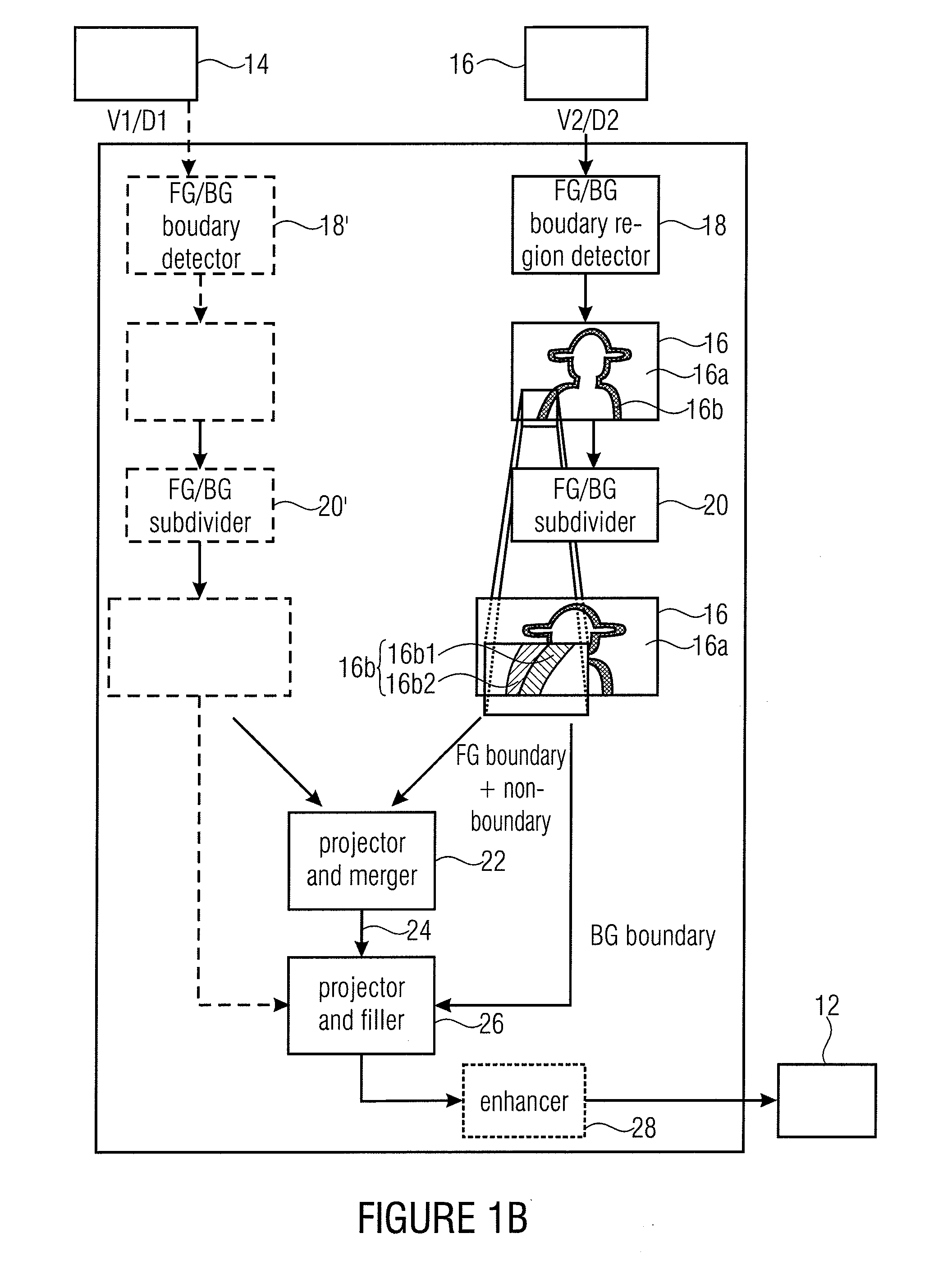
Intermediate View Synthesis and Multi-View Data Signal Extraction
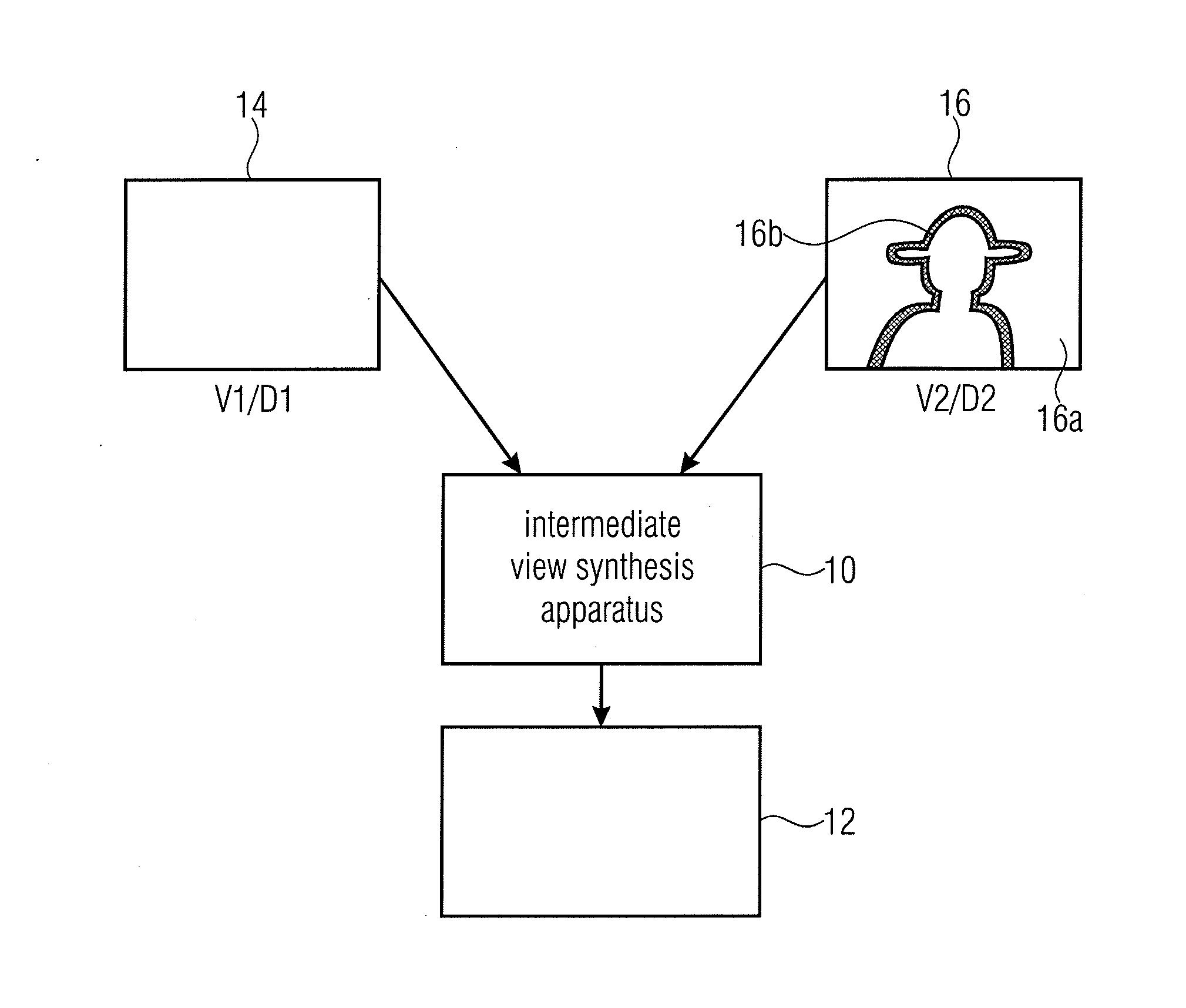
ActiveUS20110261050A1Avoid and reduce artifactImage codingCathode-ray tube indicatorsComputer visionBoundary region
An intermediate view synthesis apparatus for synthesizing an intermediate view image from a first image corresponding to a first view and a second image corresponding to a second view different from the first view, the first and second images including depth information, wherein the second image being is divided-up into a non-boundary portion, and a foreground / background boundary region, wherein the intermediate view synthesis apparatus is configured to project and merge the first image and the second image into the intermediate view to obtain an intermediate view image, with treating the foreground / background boundary region subordinated relative to the non-boundary portion. A multi-view data signal extraction apparatus for extracting a multiview data signal from a multi-view representation including a first image corresponding to a first view and a second image corresponding to a second view being different from the first view is also described, the first and second images including depth information.
Owner:FRAUNHOFER GESELLSCHAFT ZUR FOERDERUNG DER ANGEWANDTEN FORSCHUNG EV
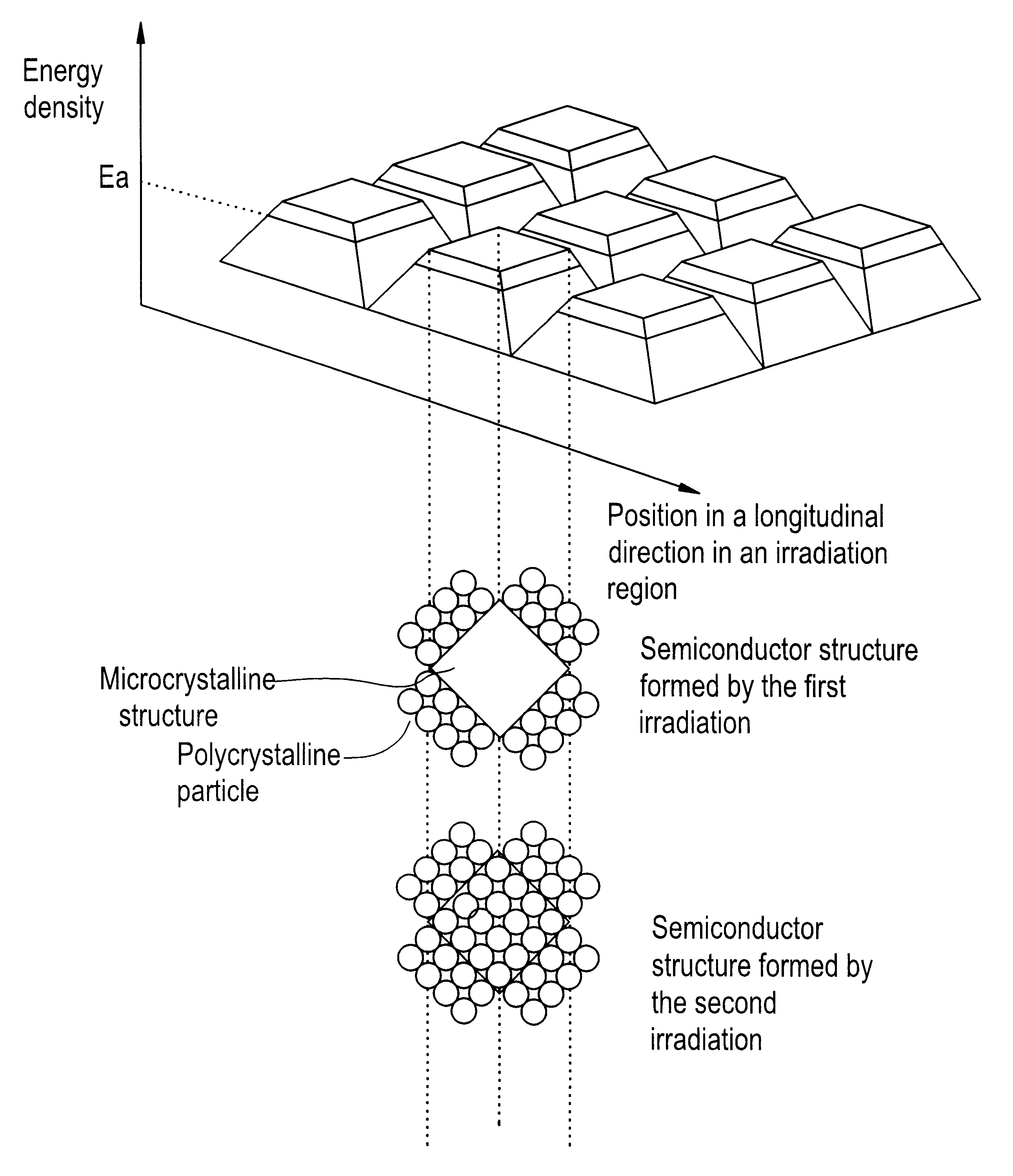
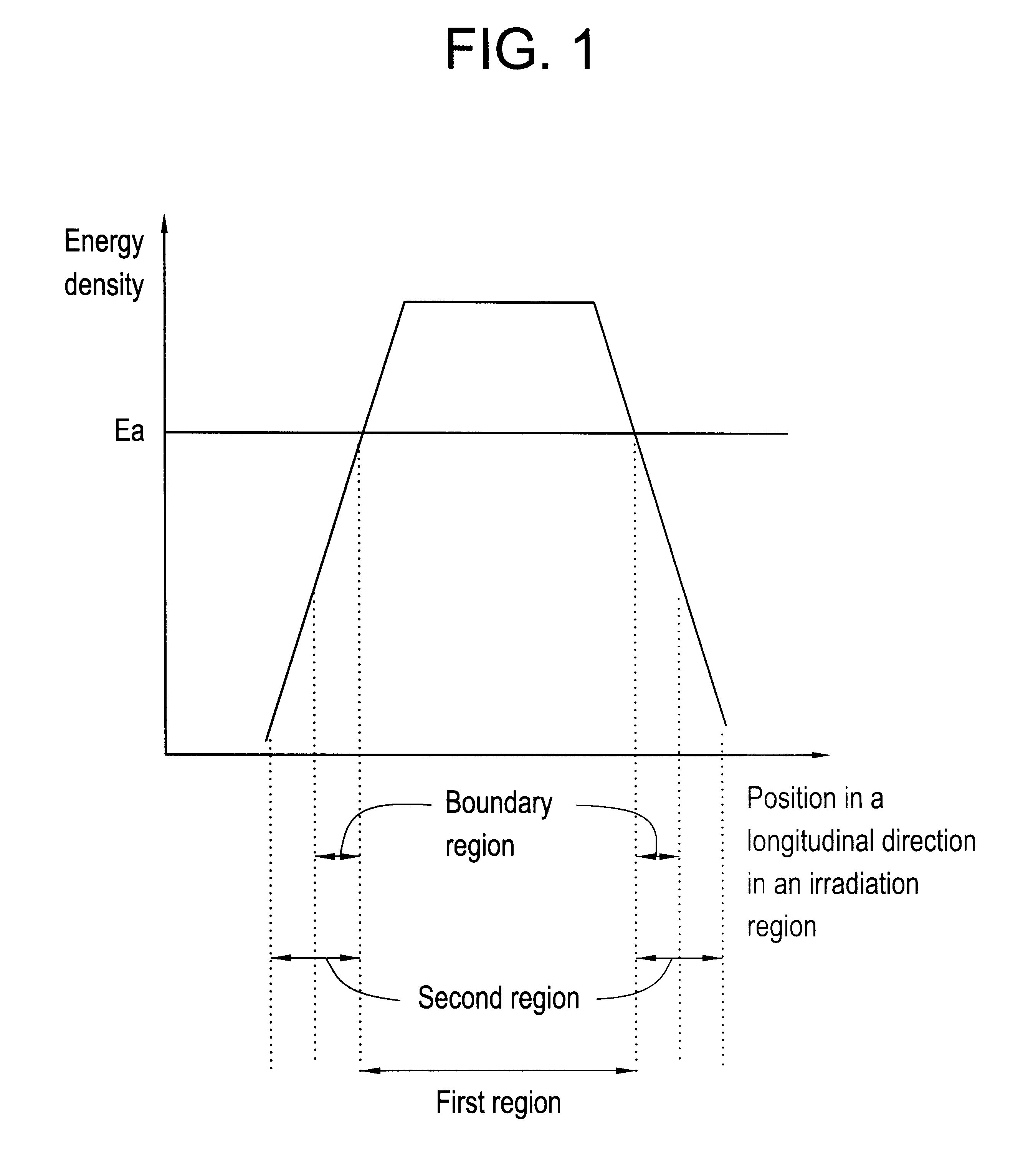
Laser irradiation process
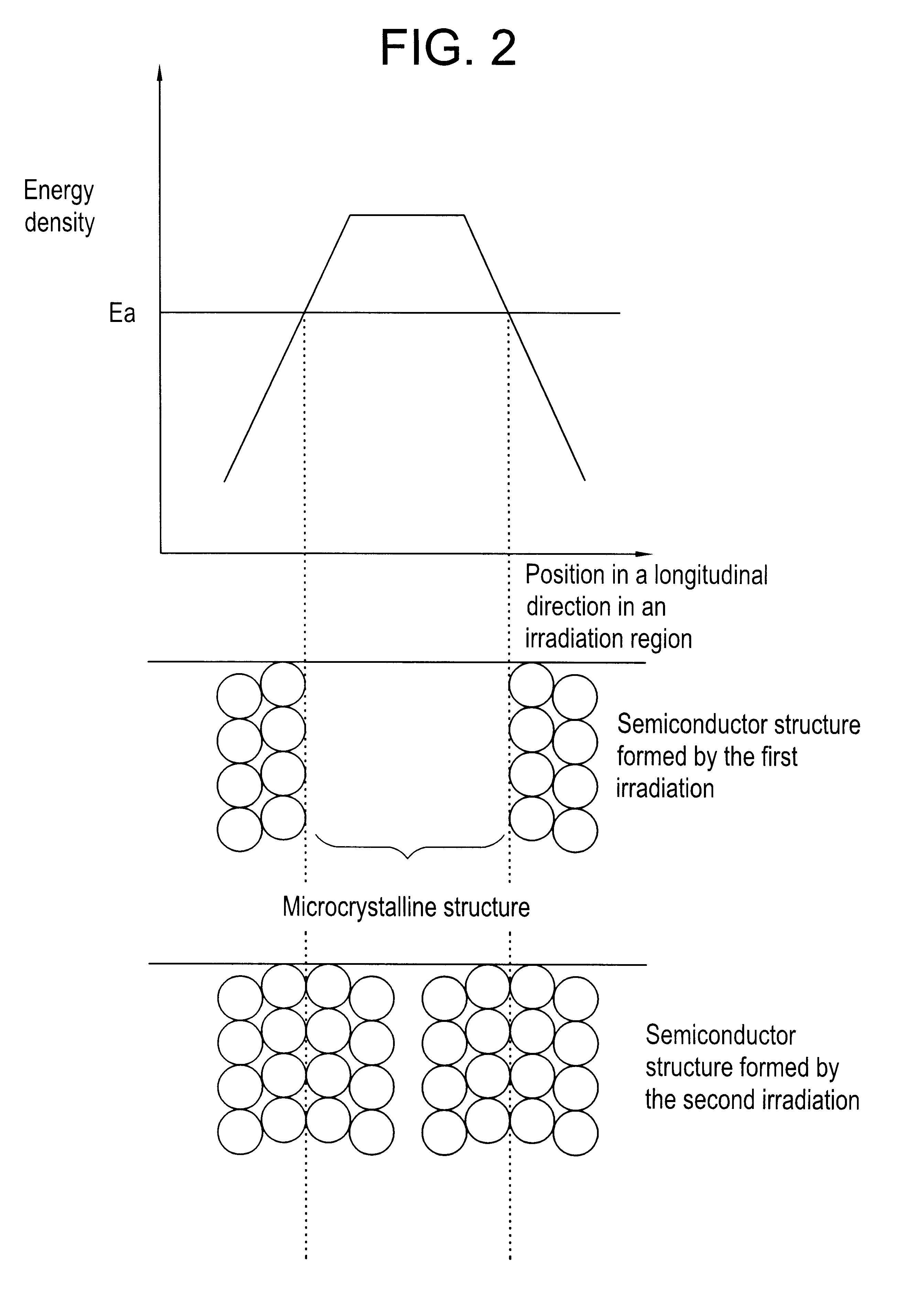
A pulse laser beam having a rectangular irradiation region is irradiated on the same point in a non-single crystal semiconductor film multiple times. The pulse laser beam has an energy profile in a longitudinal direction in the beam irradiation region as follows: (a) there are the first region having an energy density of Ea or higher and the second regions on both sides of the first region having an energy density of less than Ea, and (b) an energy density slope has an absolute value of 20 to 300 J / cm3 in a boundary region extending to 1 mum from the boundary line between the first and the second regions.
Owner:GOLD CHARM LTD
Semiconductor device
InactiveUS20070272979A1Reduce doping concentrationSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingDiodeHigh resistanceDopant
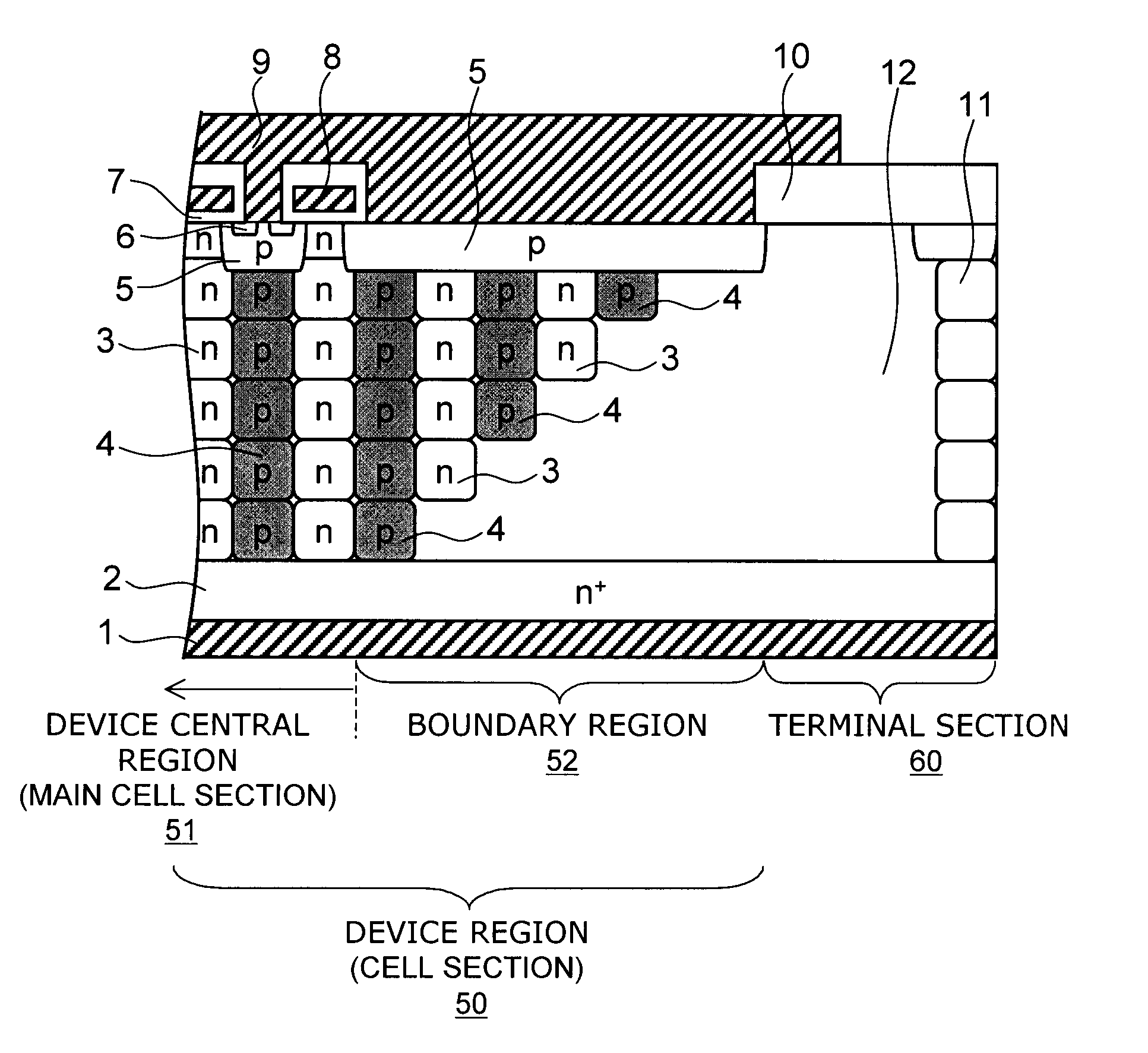
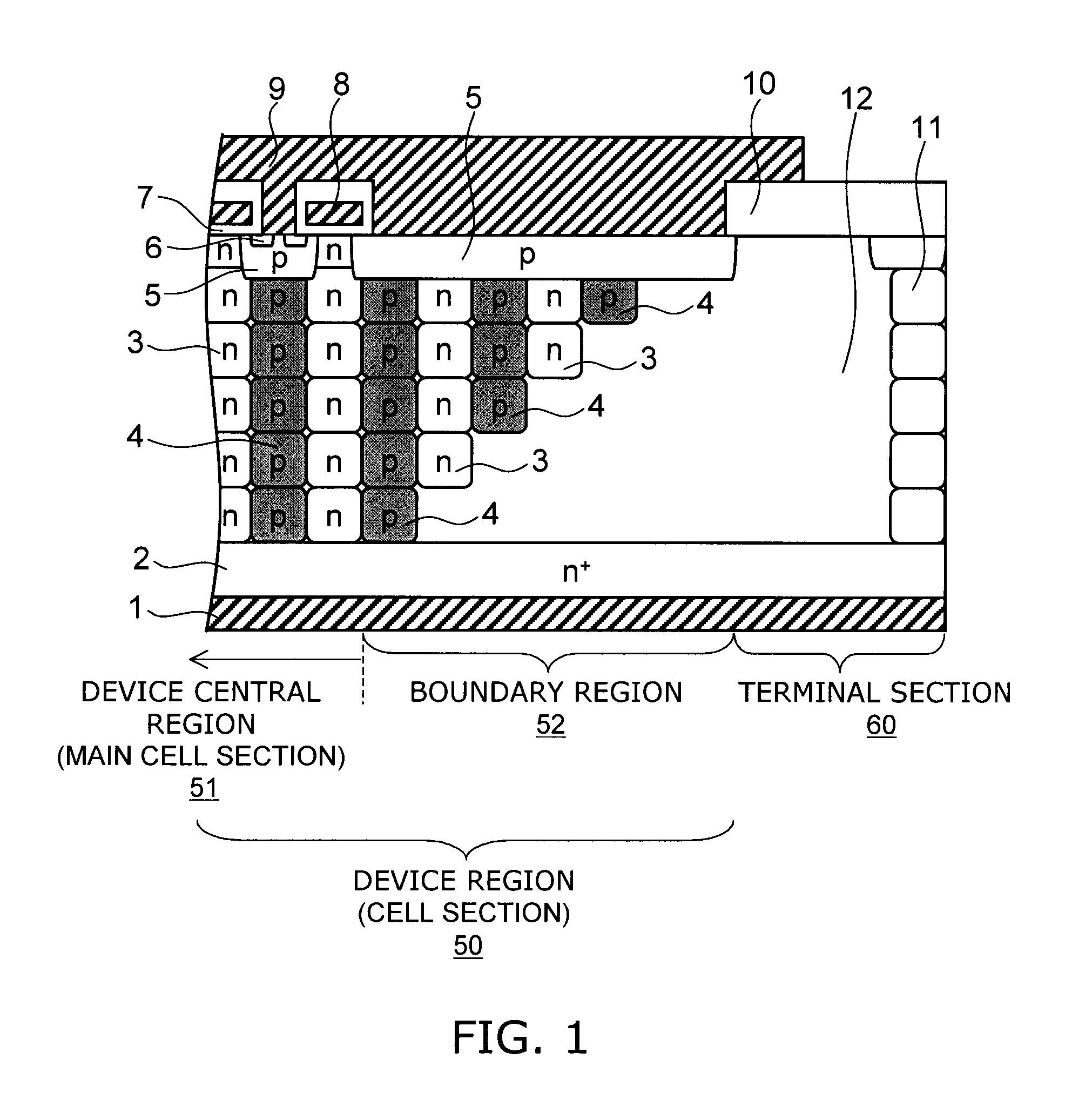
A semiconductor device includes: a semiconductor layer of a first conductivity type; a first semiconductor pillar region of the first conductivity type provided on a major surface of the semiconductor layer; a second semiconductor pillar region of a second conductivity type provided adjacent to the first semiconductor pillar region on the major surface of the semiconductor layer, the second semiconductor pillar region forming a periodic arrangement structure substantially parallel to the major surface of the semiconductor layer together with the first semiconductor pillar region; a first main electrode; a first semiconductor region of the second conductivity type; a second semiconductor region of the first conductivity type; a second main electrode; a control electrode; and a high-resistance semiconductor layer provided on the semiconductor layer in an edge termination section surrounding the first semiconductor pillar region and the second semiconductor pillar region. The high-resistance semiconductor layer has a lower dopant concentration than the first semiconductor pillar region. A boundary region is provided between a device central region and the edge termination section. The first semiconductor pillar region and the second semiconductor pillar region adjacent to the high-resistance semiconductor layer in the boundary region have a depth decreasing stepwise toward the edge termination section.
Owner:KK TOSHIBA
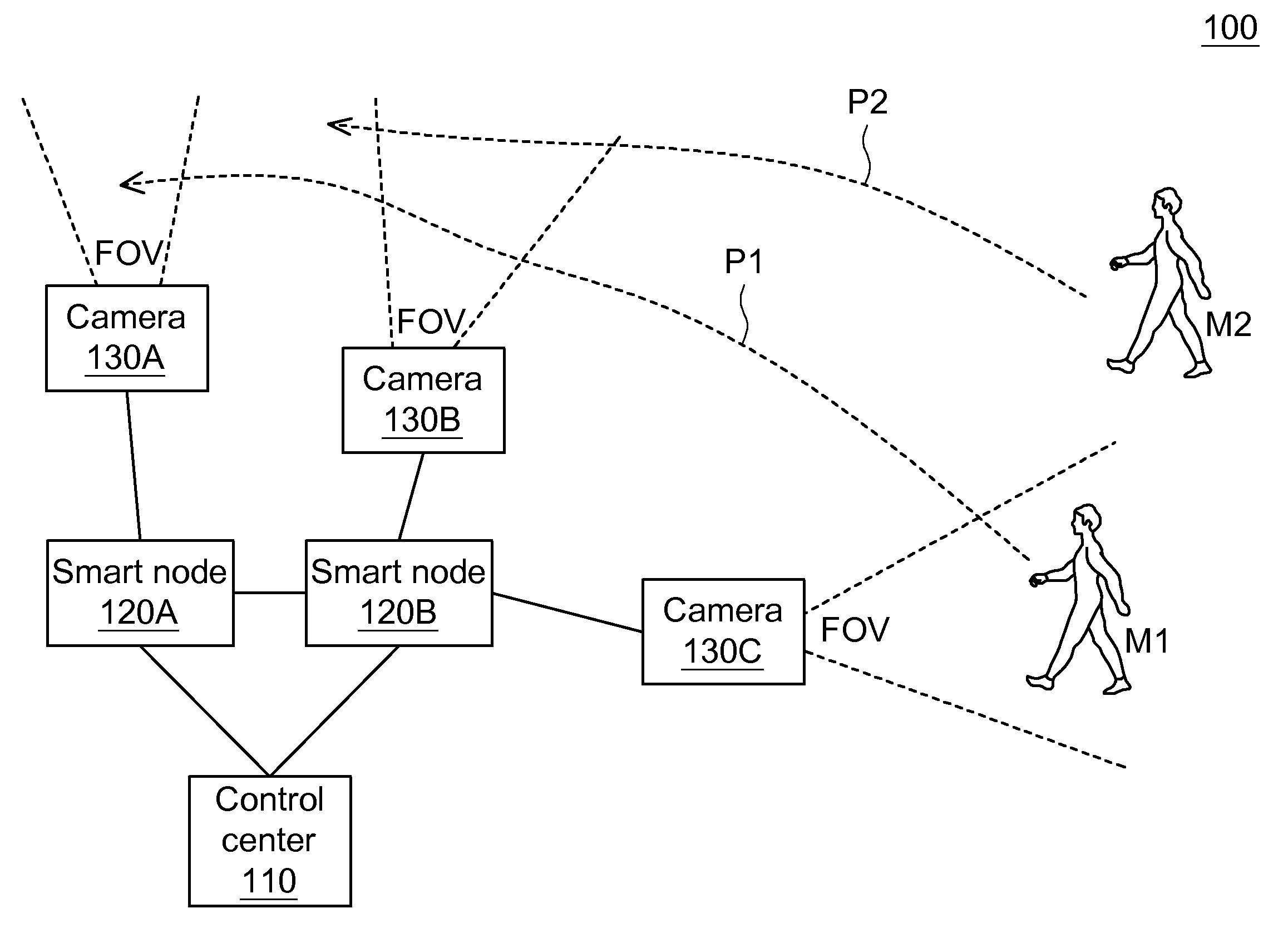
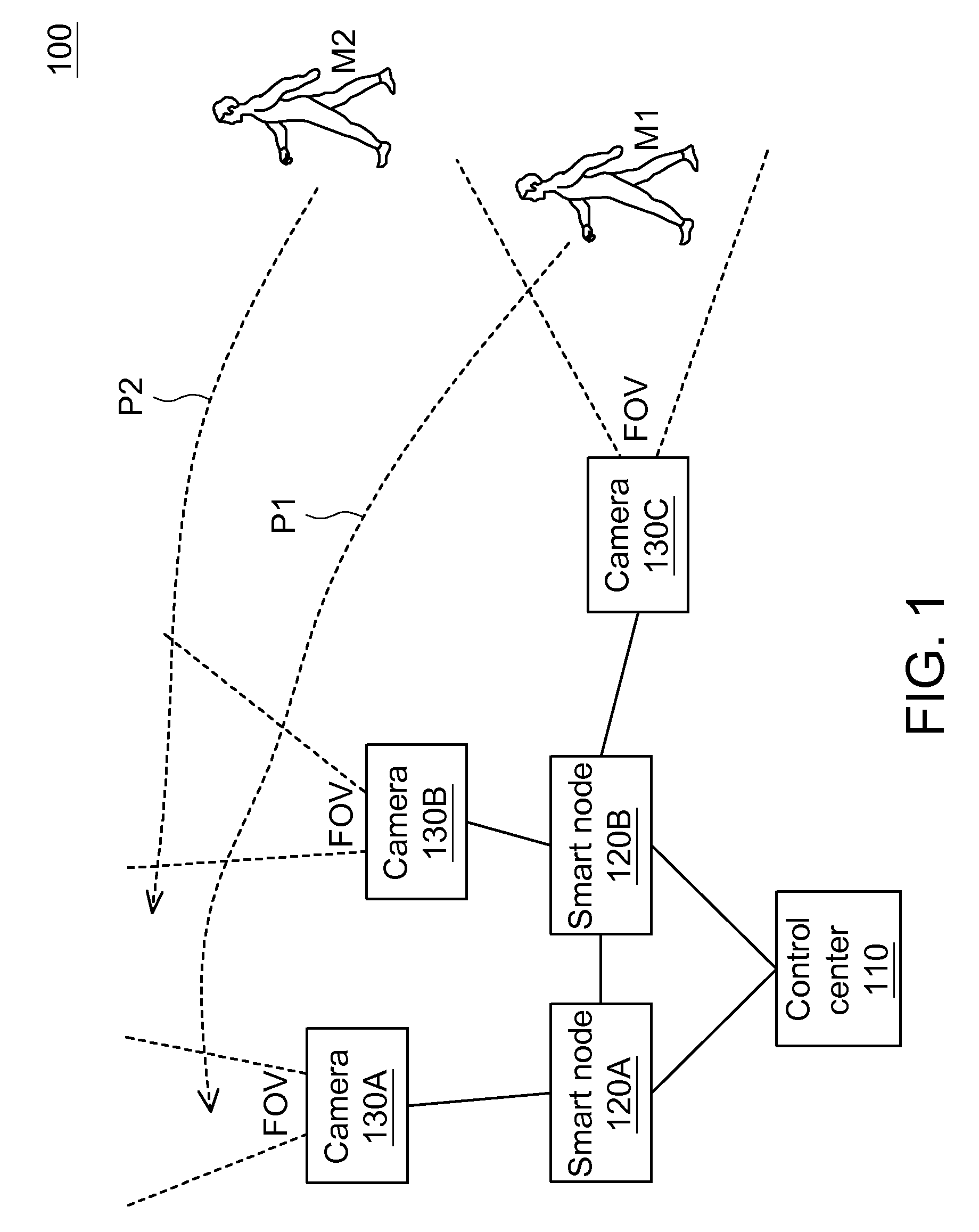
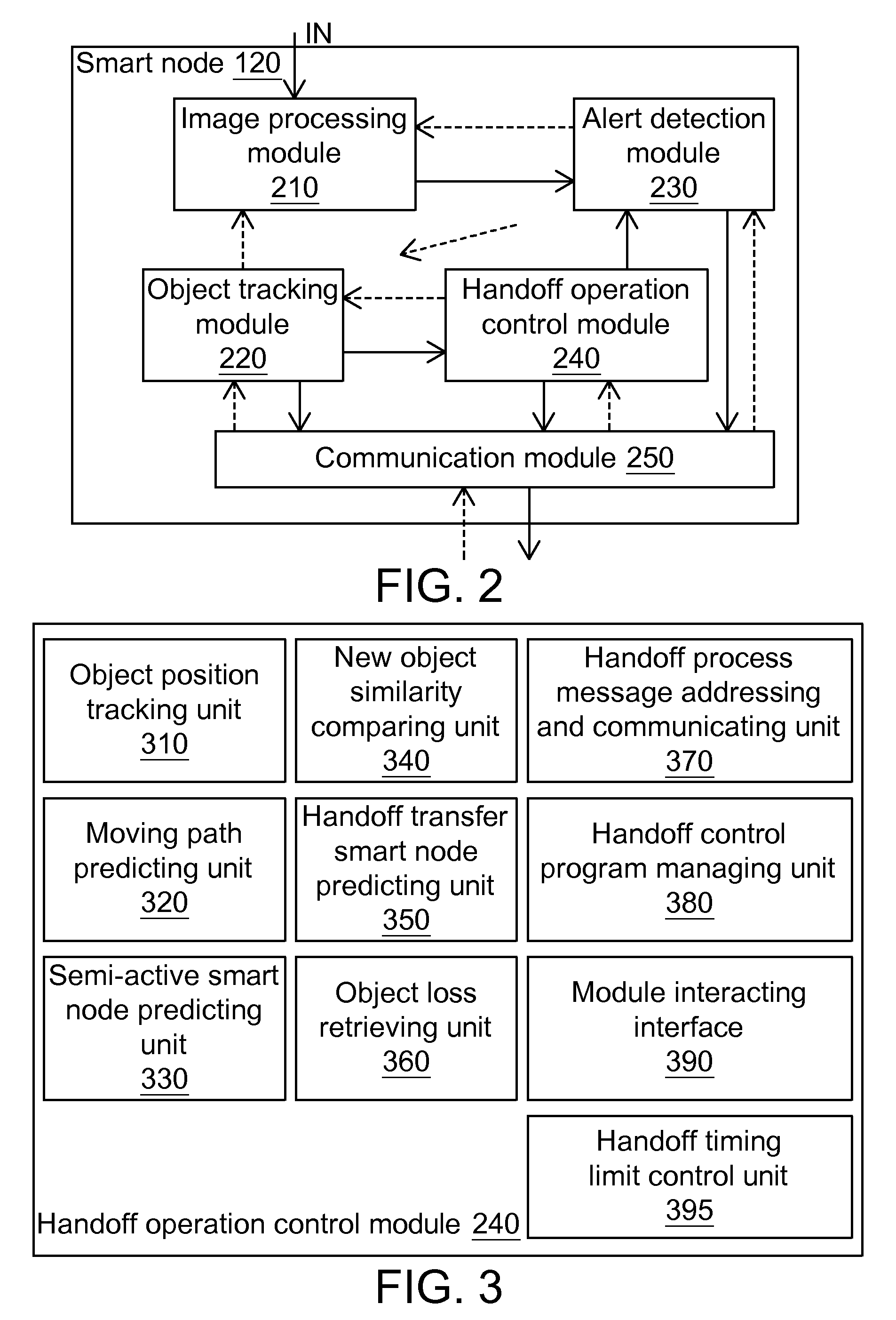
Object tracking system, method and smart node using active camera handoff
If an active smart node detects that an object leaves a center region of a FOV for a boundary region, the active smart node predicts a possible path of the object. When the object gets out of the FOV, the active smart node predicts the object appears in a FOV of another smart node according to the possible path and a spatial relation between cameras. The active smart node notifies another smart node to become a semi-active smart node which determines an image characteristic similarity between the object and a new object and returns to the active smart node if a condition is satisfied. The active smart node compares the returned characteristic similarity, an object discovery time at the semi-active smart node, and a distance between the active smart node and the semi-active smart node to calculate possibility.
Owner:IND TECH RES INST
Silicon carbide substrate, epitaxial layer provided substrate, semiconductor device, and method for manufacturing silicon carbide substrate
InactiveUS20120119225A1Lower on-resistanceSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSemiconductor devicesSingle crystal substrateSingle crystal
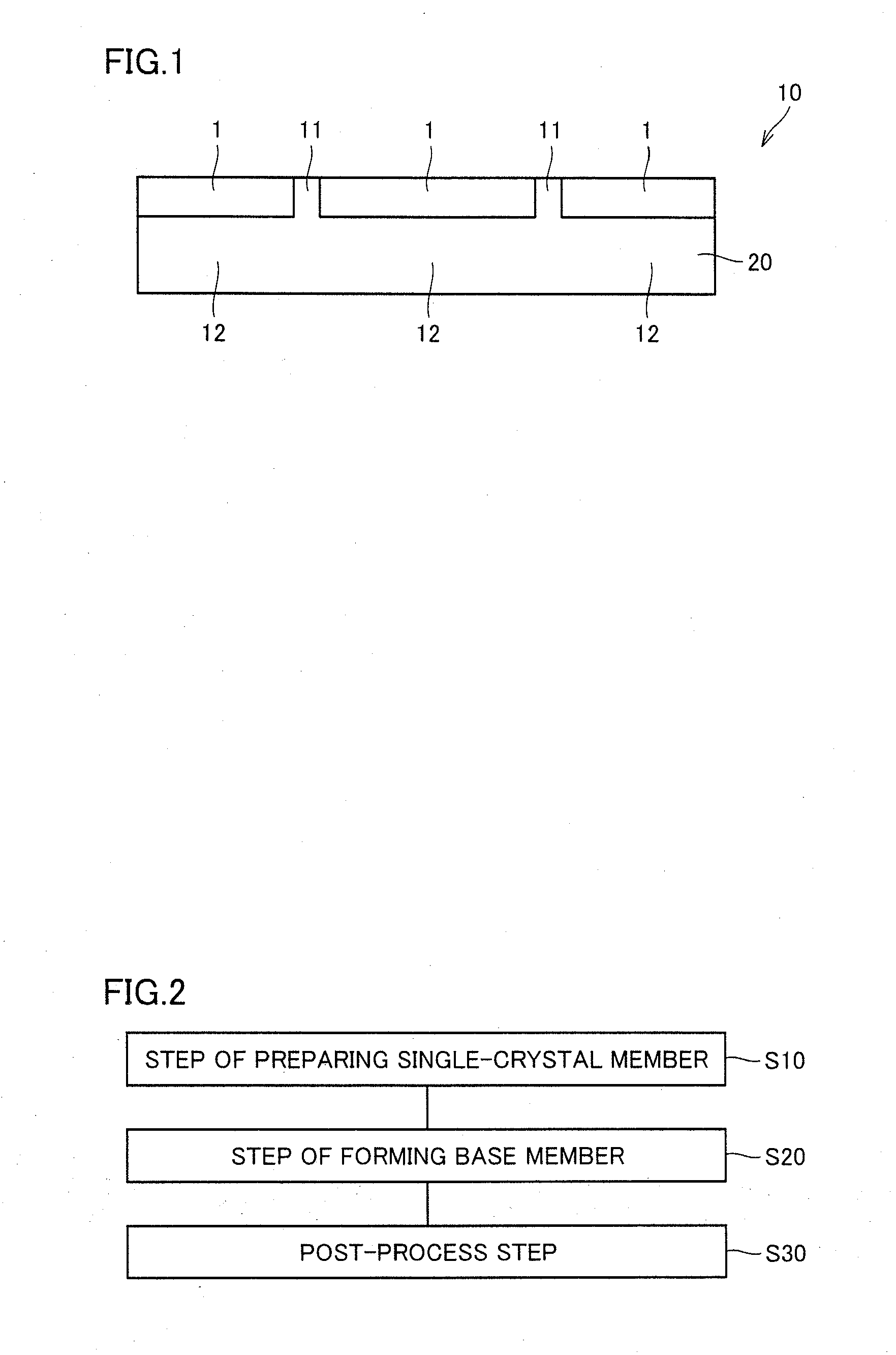
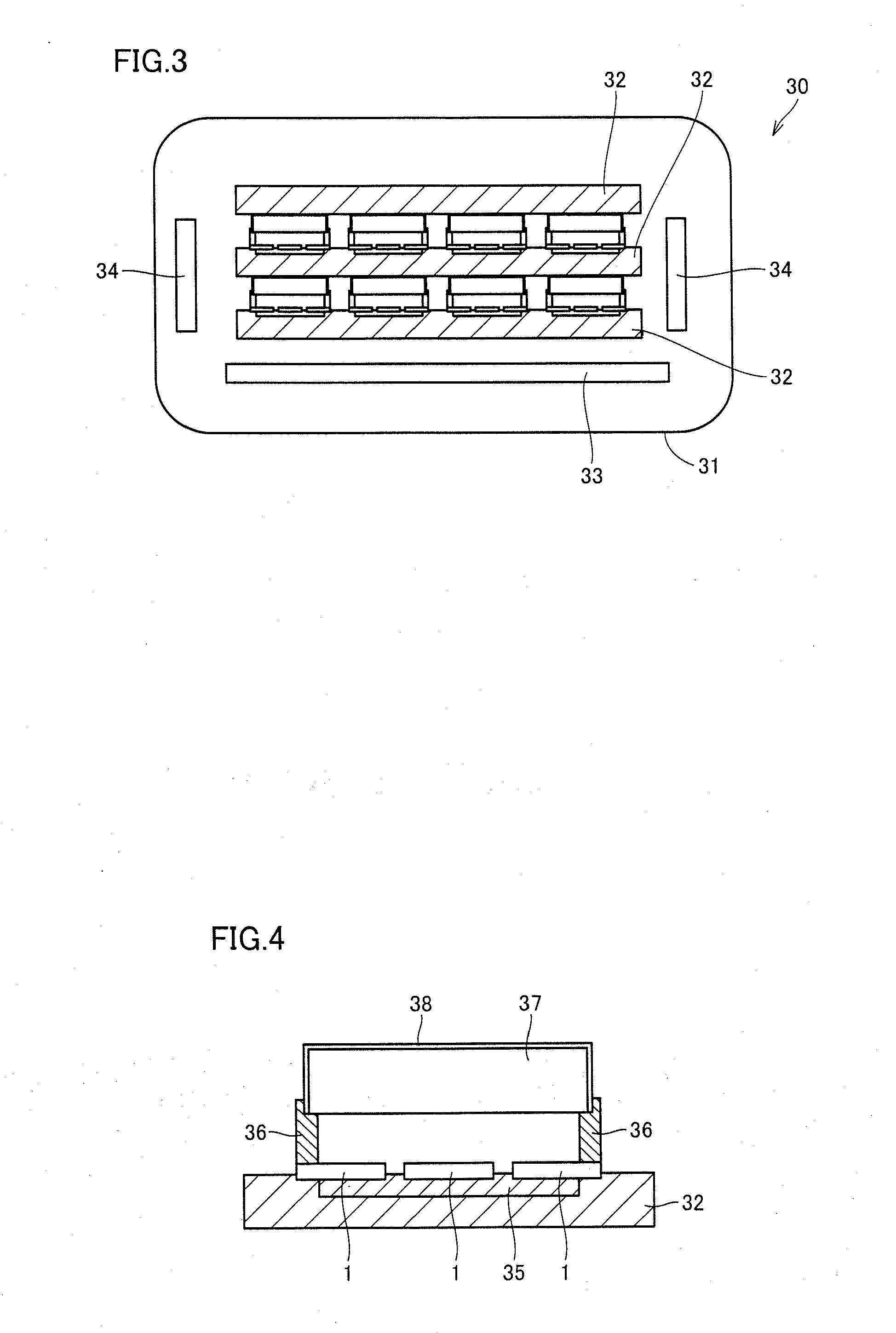
The present invention provides a silicon carbide substrate, an epitaxial layer provided substrate, a semiconductor device, and a method for manufacturing the silicon carbide substrate, each of which achieves reduced on-resistance. The silicon carbide substrate is a silicon carbide substrate having a main surface, and includes: a SiC single-crystal substrate formed in at least a portion of the main surface; and a base member disposed to surround the SiC single-crystal substrate. The base member includes a boundary region and a base region. The boundary region is adjacent to the SiC single-crystal substrate in a direction along the main surface, and has a crystal grain boundary therein. The base region is adjacent to the SiC single-crystal substrate in a direction perpendicular to the main surface, and has an impurity concentration higher than that of the SiC single-crystal substrate.
Owner:SUMITOMO ELECTRIC IND LTD
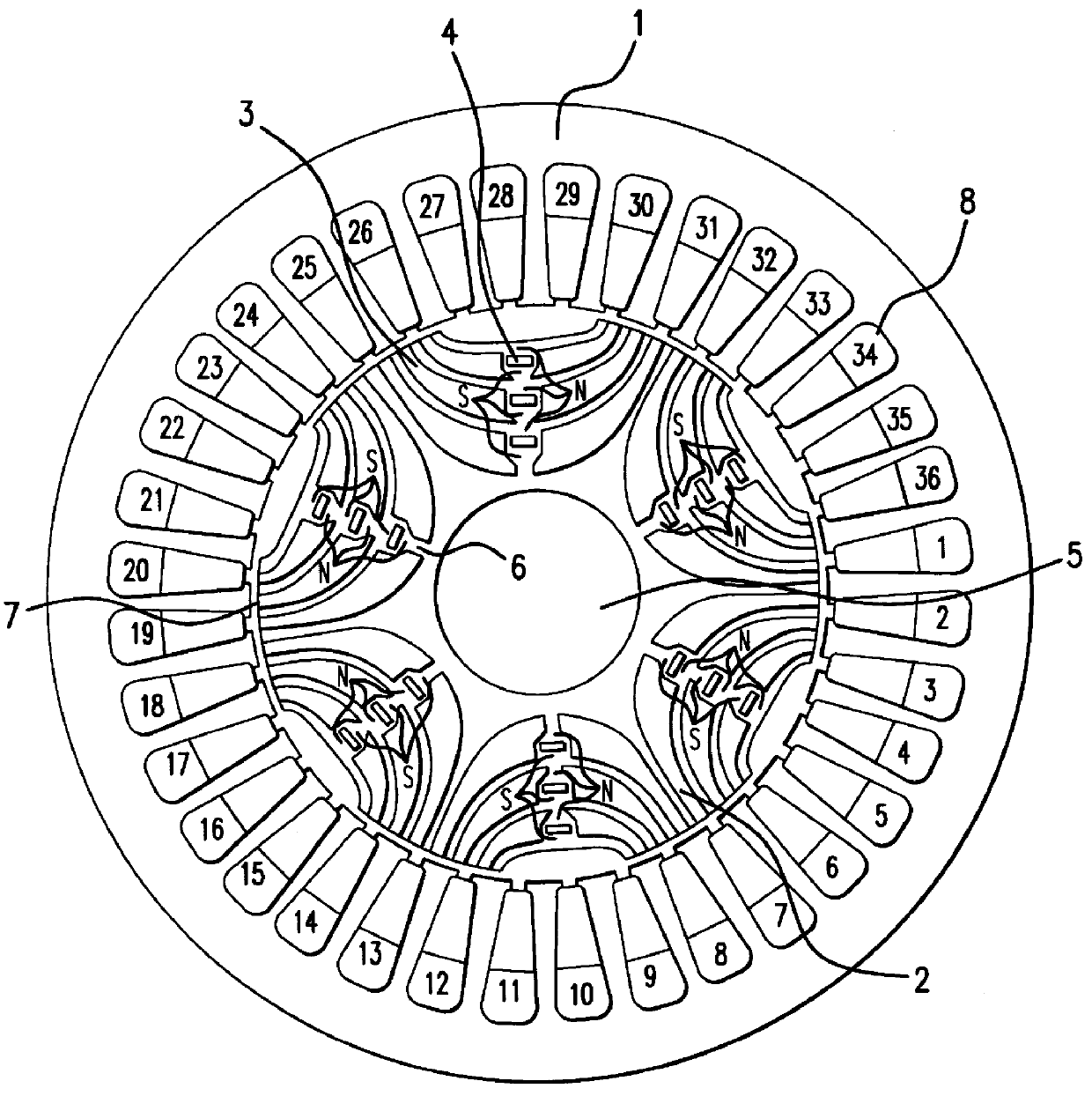
Reluctance motor
InactiveUS6121706ASynchronous generatorsMagnetic circuit rotating partsMagnetic polesReluctance motor
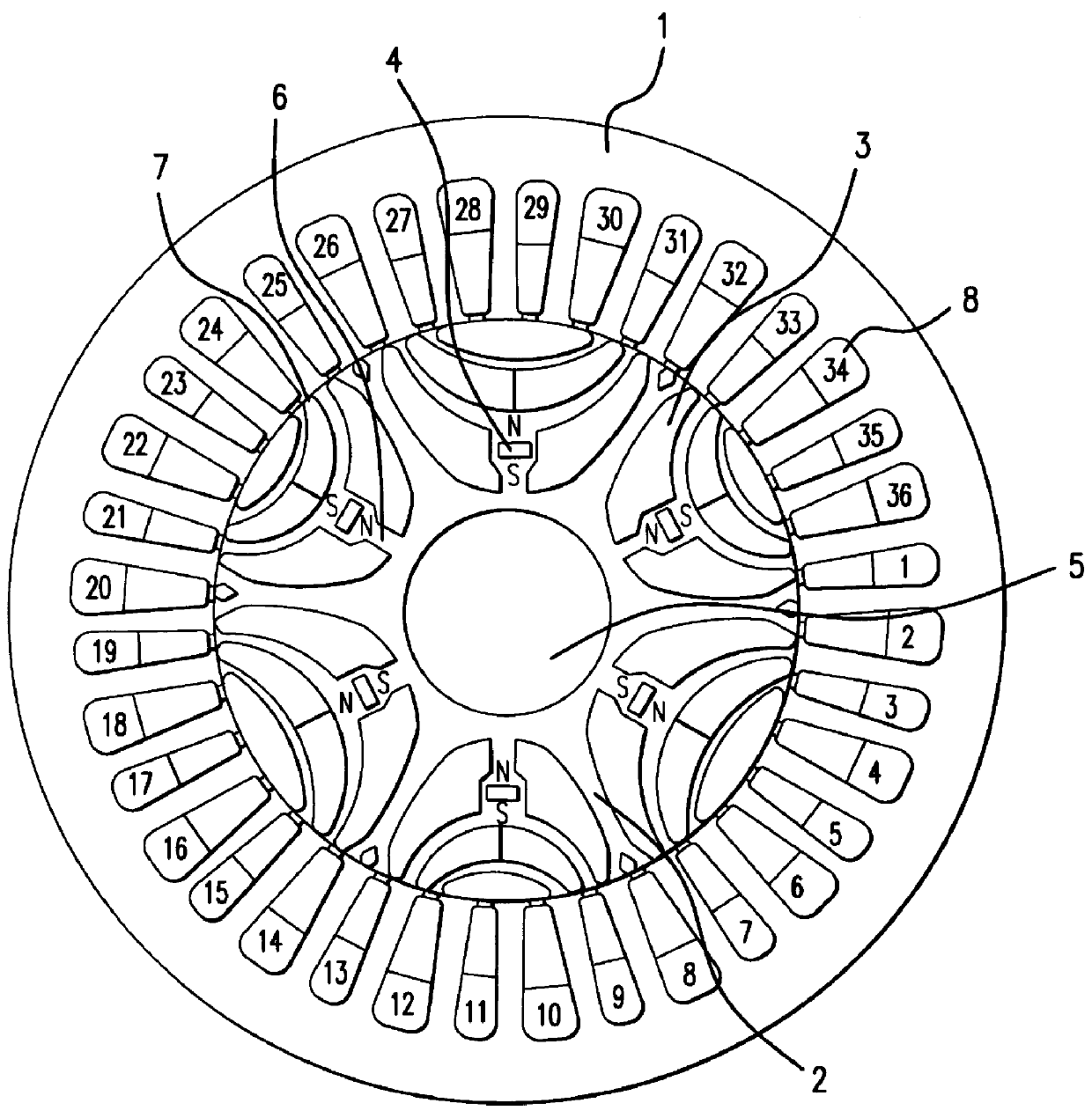
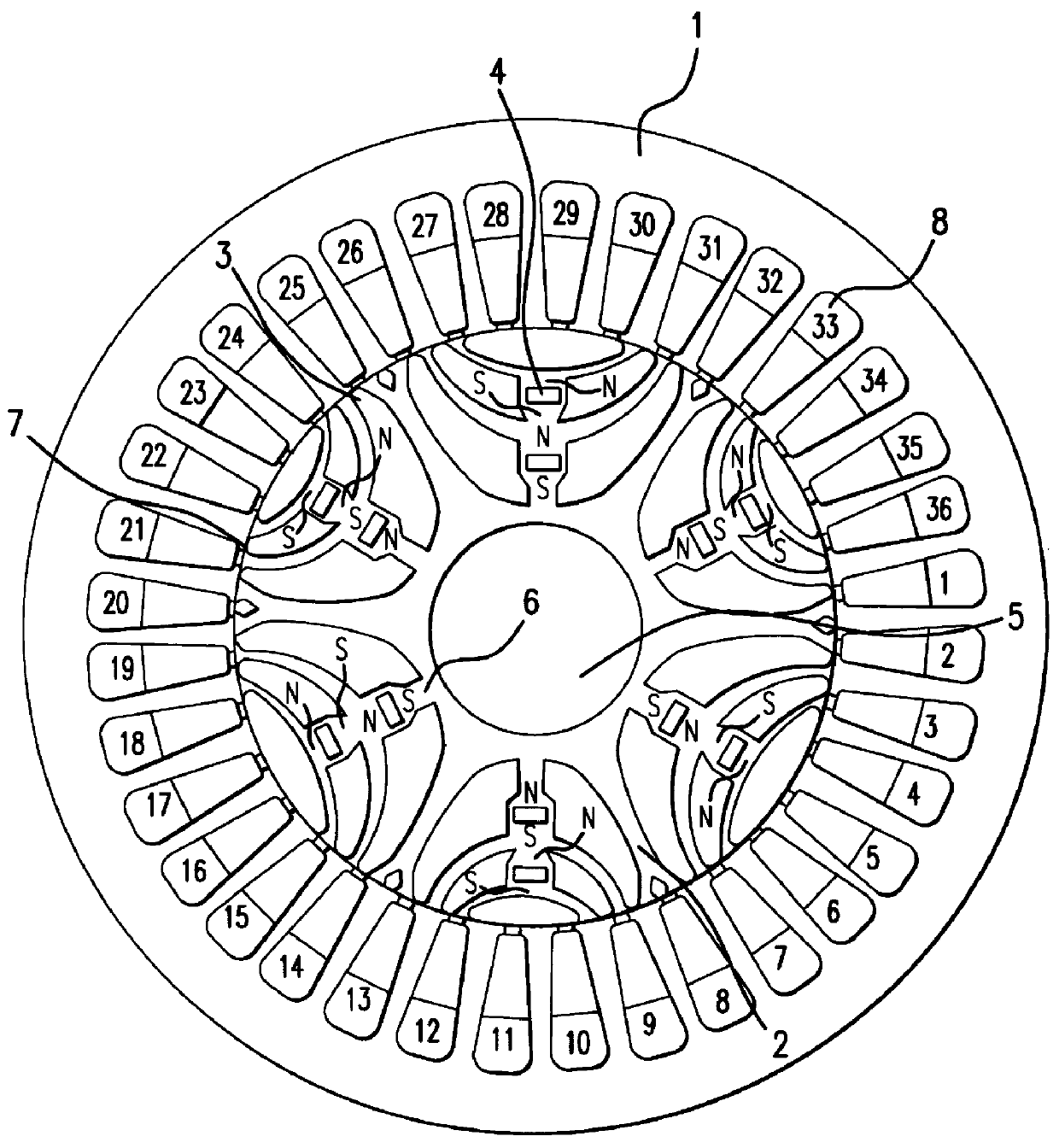
A reluctance motor is provided that reduces leaking magnetic flux. To generate magnetic flux between adjacent magnetic poles in a rotor 2, permanent magnets 4 are disposed in approximate centers of split magnetic paths near a borderline area between two magnetic poles in an internal portion of the rotor. Further, each of slots 8 in a stator 1 is wound with a coil of a corresponding phase such that the vector phase and amplitude expressed by the products of the number of coil turns and the amount of passing current, namely, ampere-turns, become almost identical for each of the slots. By reducing leaking magnetic flux according to this arrangement, generated torque can be increased. As the rotor mechanical strength is enhanced, the rotor can be safely driven at a higher speed. A practical motor is obtained that simultaneously achieves improved motor characteristics and reduced torque ripples.
Owner:OKUMA CORP
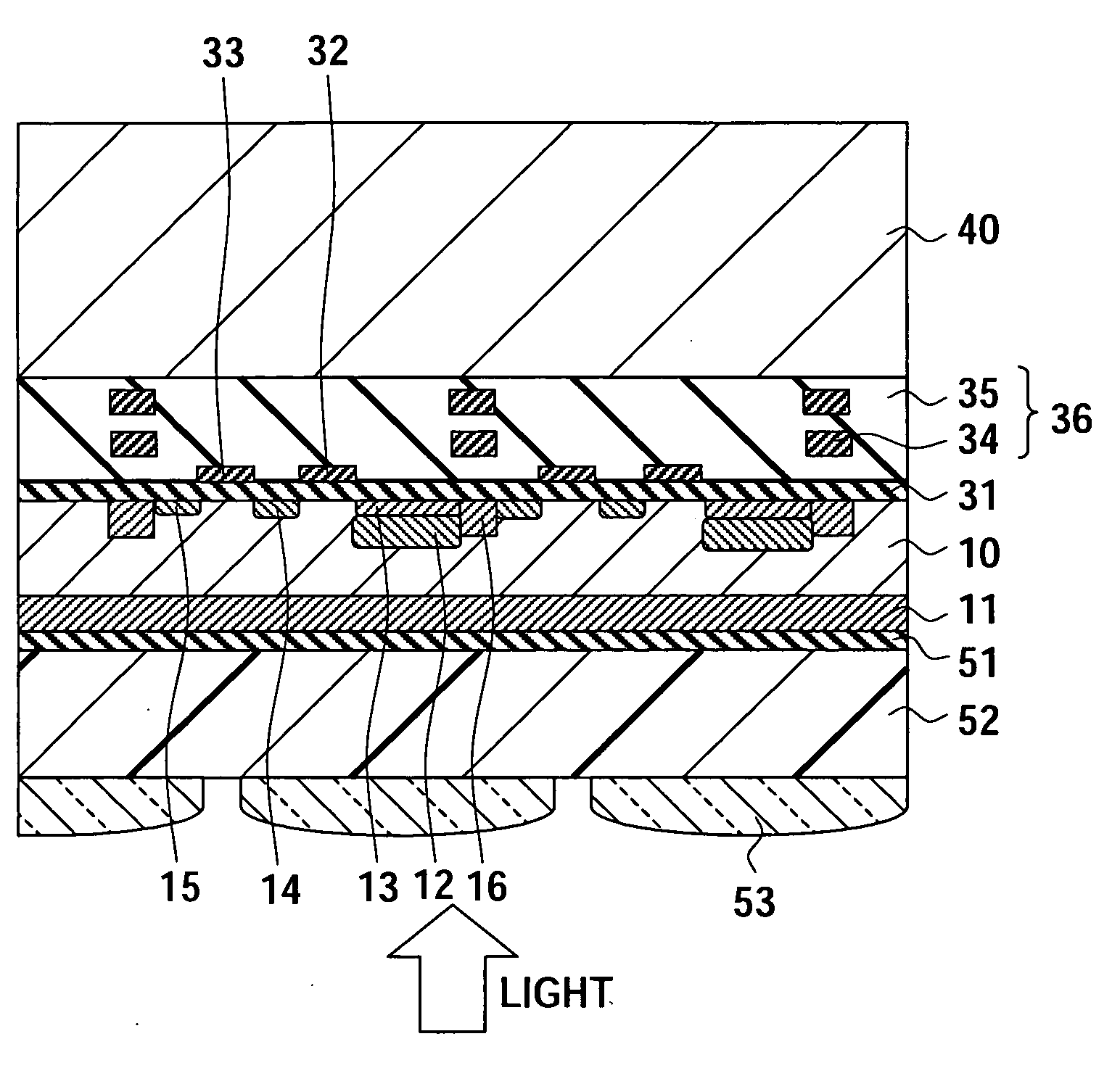
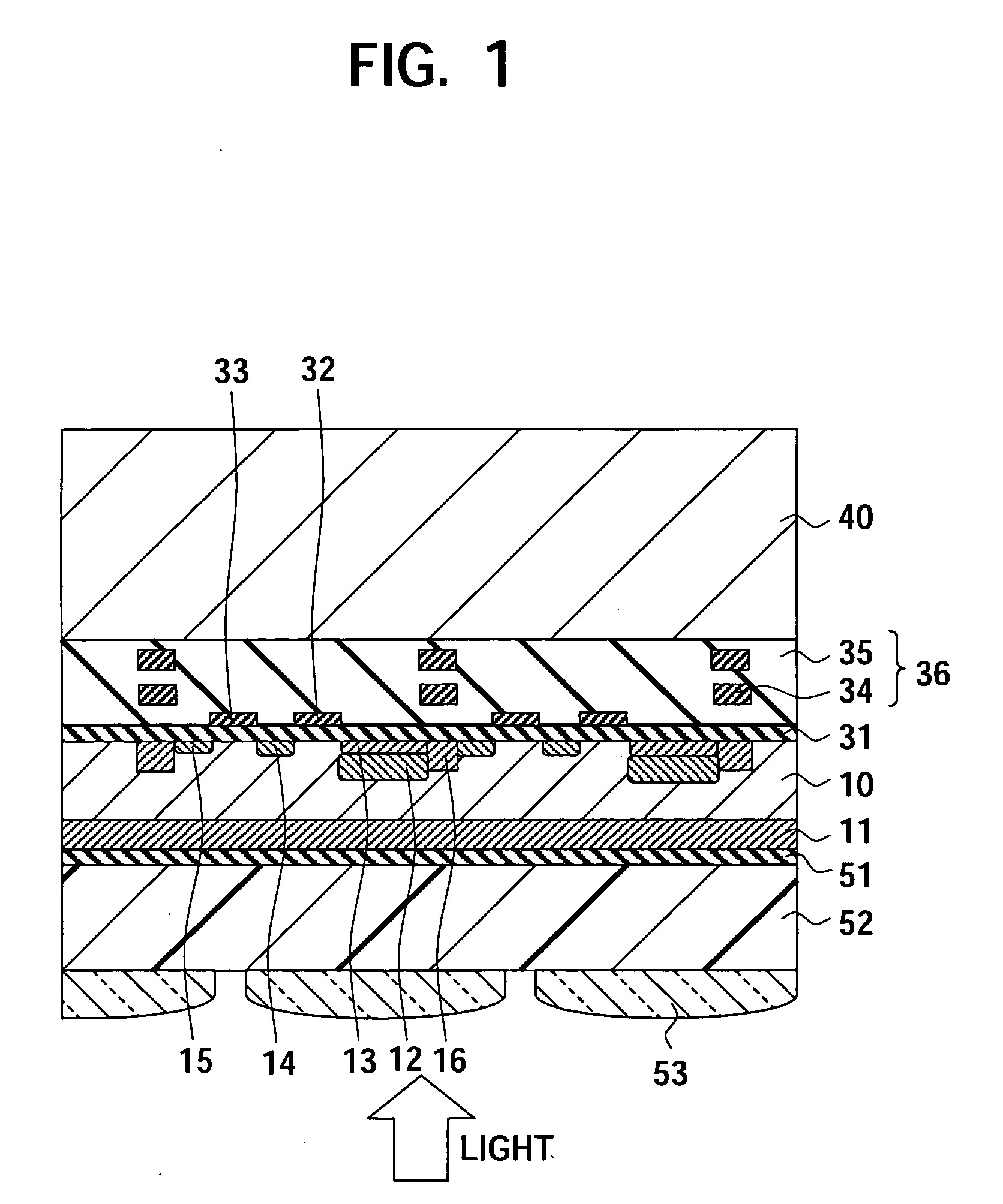
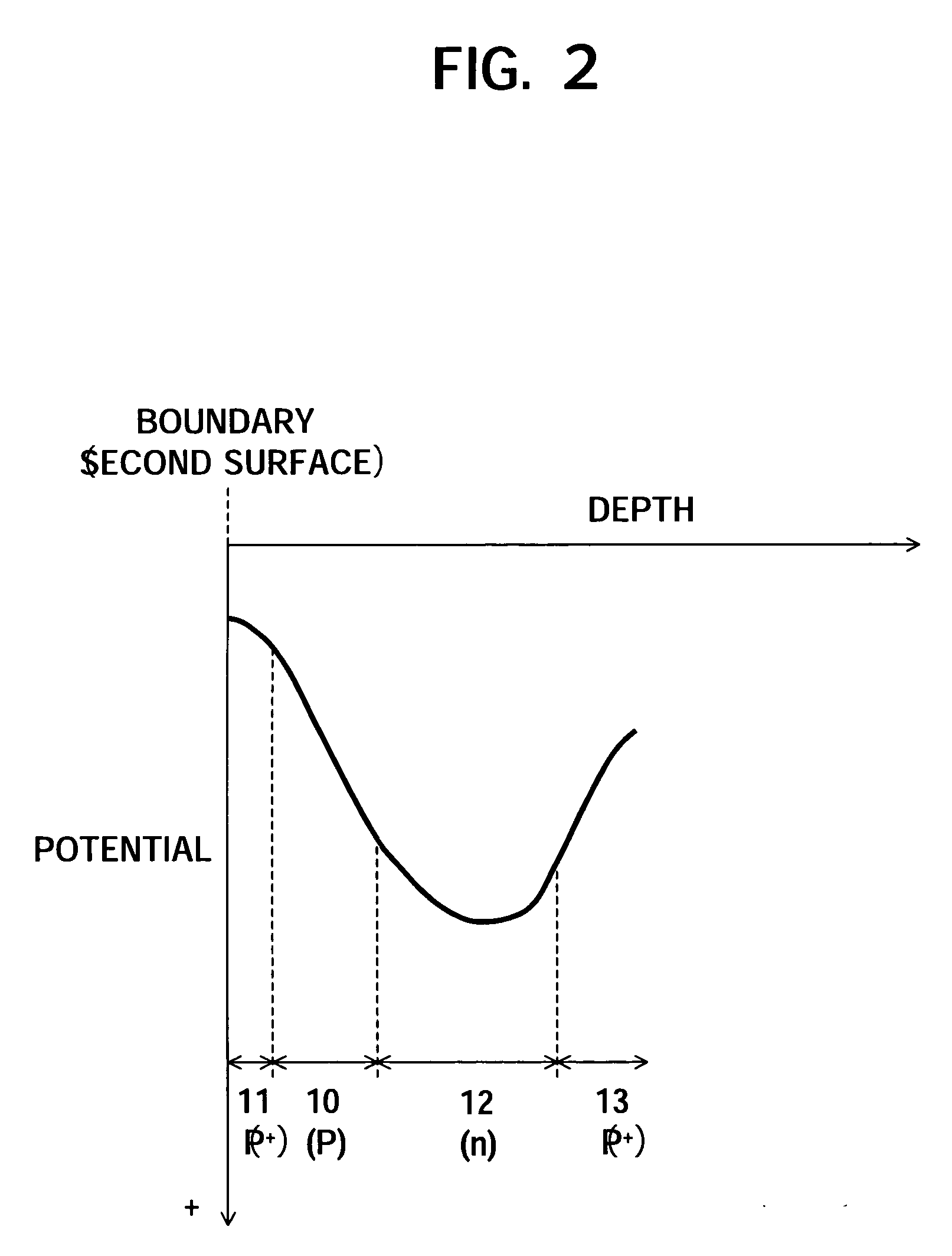
Solid-state imaging device, camera and method of producing the solid-state imaging device
InactiveUS20060006488A1High sensitivityInhibit currentTelevision system detailsSolid-state devicesQuantum efficiencyInterconnection
To provide a back-illuminated solid-state imaging device able to suppress a crystal defect caused by a metal contamination in a process and to suppress a dark current to improve quantum efficiency, a camera including the same and a method of producing the same, having the steps of forming a structure including a substrate, a first conductive type epitaxial layer and a first conductive type impurity layer, the first conductive type epitaxial layer being formed on the substrate to have a first impurity concentration, and the first conductive type impurity layer being formed in a boundary region to have a second impurity concentration higher than the first impurity concentration of the epitaxial layer; forming a second conductive type region storing a charge generated by a photoelectric conversion in the epitaxial layer; forming an interconnection layer on the epitaxial layer; and removing the substrate.
Owner:SONY CORP
Natural gas desulfurization process suitable for offshore floating platform
InactiveCN108034466AFast regenerationImprove oxidation regeneration efficiencyGaseous fuelsChemical industryChemical reaction
The invention relates to the field of natural gas chemical industry, in particular to a natural gas desulfurization process suitable for an offshore floating platform. The natural gas desulfurizationprocess comprises a reactor, a re-reactor and a centrifugal machine; acid gas coming from a boundary region is directly introduced into the reactor, a trivalent complex iron catalyst enters the re-reactor, the trivalent complex iron catalyst at the bottom of the re-reactor enters the reactor under the control of a valve and a pipeline, a chemical reaction is then carried out, divalent complex ironobtained by means of the reaction is centrifuged, the divalent complex iron is conveyed to an electrochemical regeneration device by means of a regenerative feed pump so as to complete the regeneration, and the regenerated trivalent complex iron catalyst is returned to the re-reactor by means of a circulation pump. The natural gas desulfurization process is simple in technological process, smallin equipment size and compact in structure, and adapts to the condition limit of limited production space of offshore floating liquefied natural gas (FLNG).
Owner:SICHUAN HENGRI GAS ENG CO LTD
Semiconductor device
InactiveUS20100290292A1Improve access efficiencySmall sizeRead-only memoriesDigital storageHemt circuitsData access
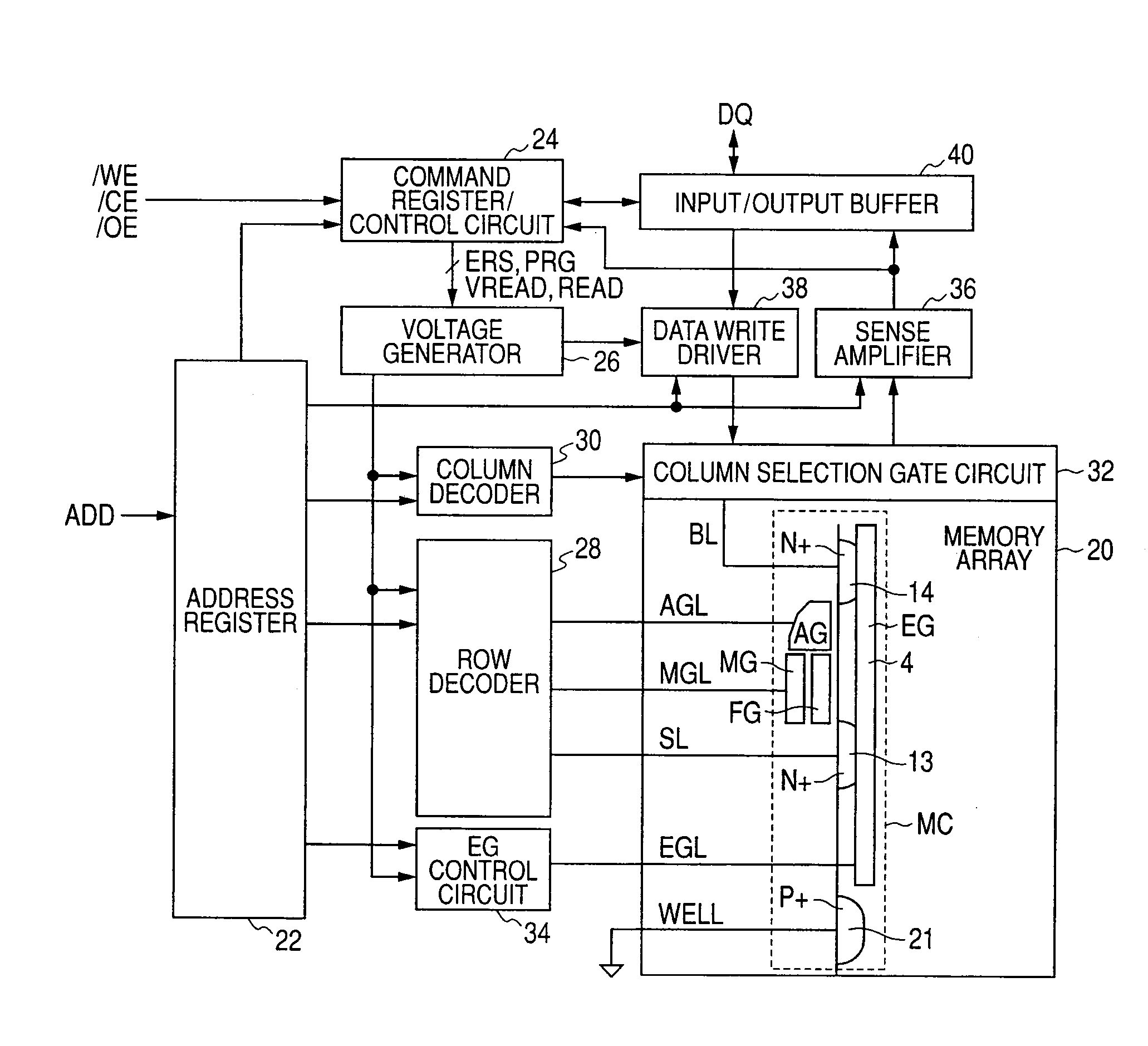
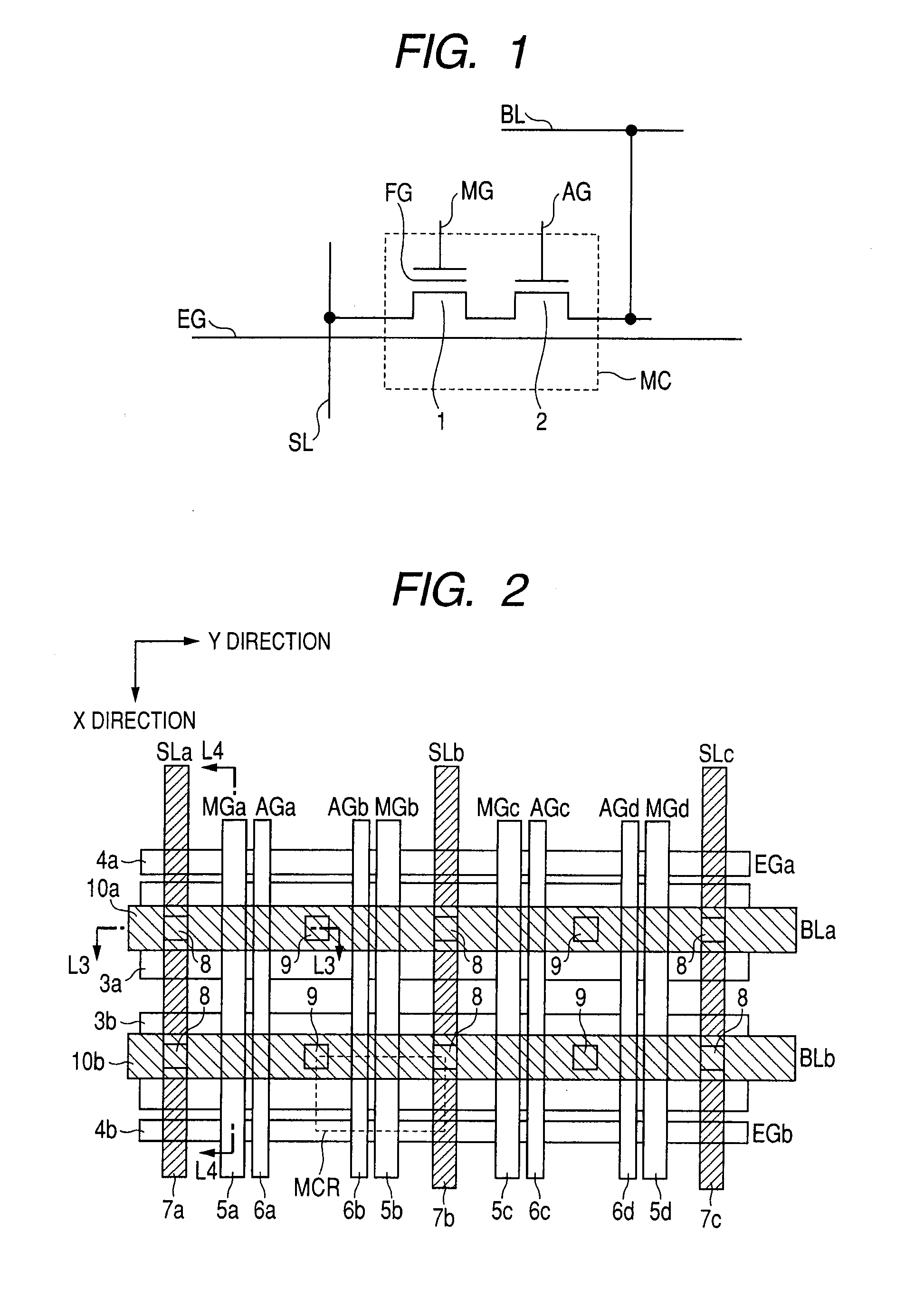
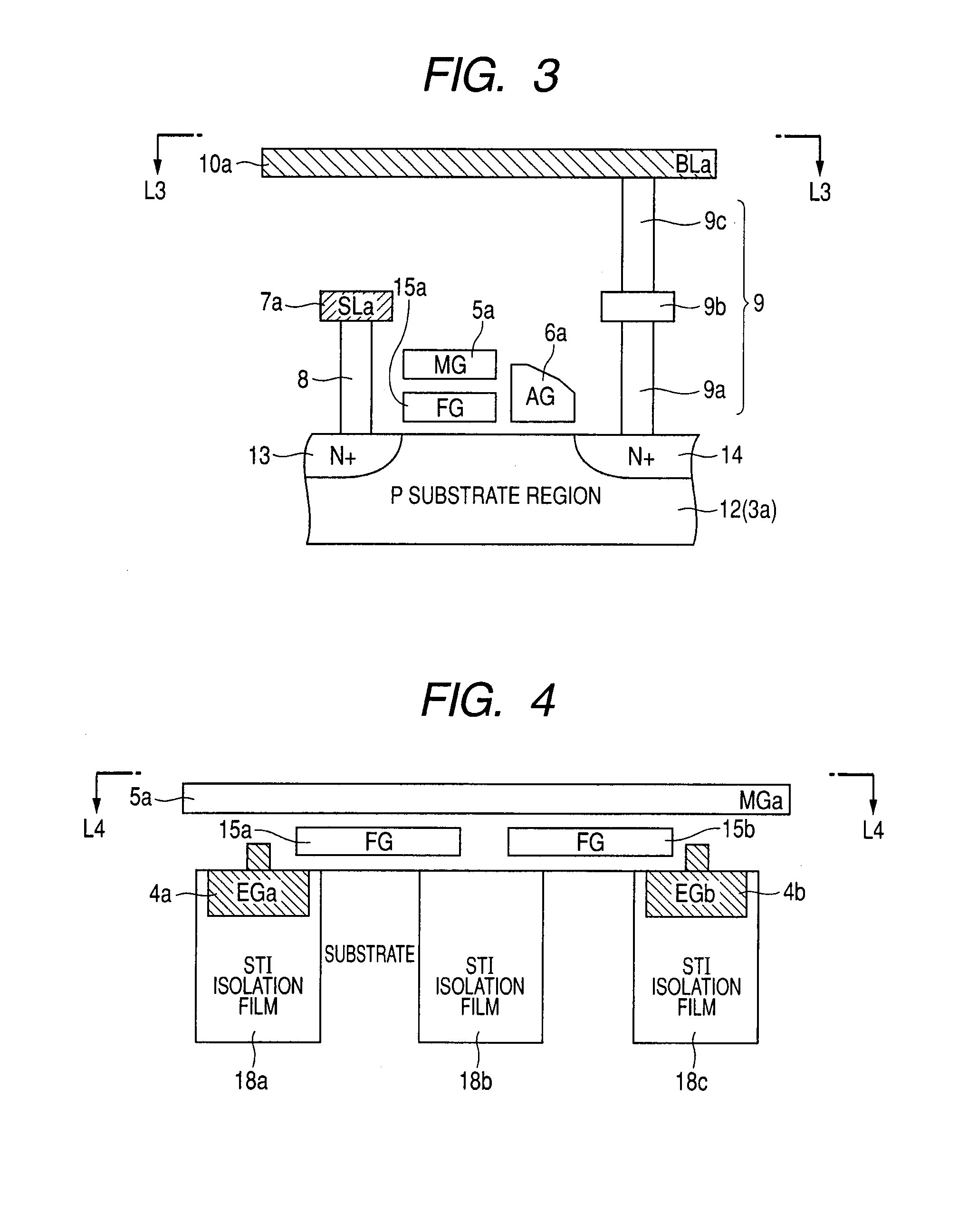
The present invention provides a semiconductor device having a nonvolatile memory function capable of shortening an erase time and executing data access efficiently. When, under the control of a command register / control circuit, an erase voltage is applied to an embedded erase gate wiring disposed in a memory cell boundary region, and an electrical charge is transferred between a floating gate and an embedded erase gate to thereby perform an erase operation, a read selection voltage is applied to a memory gate line and an assist gate line during the application of the erase voltage to thereby carry out the reading of data.
Owner:RENESAS ELECTRONICS CORP
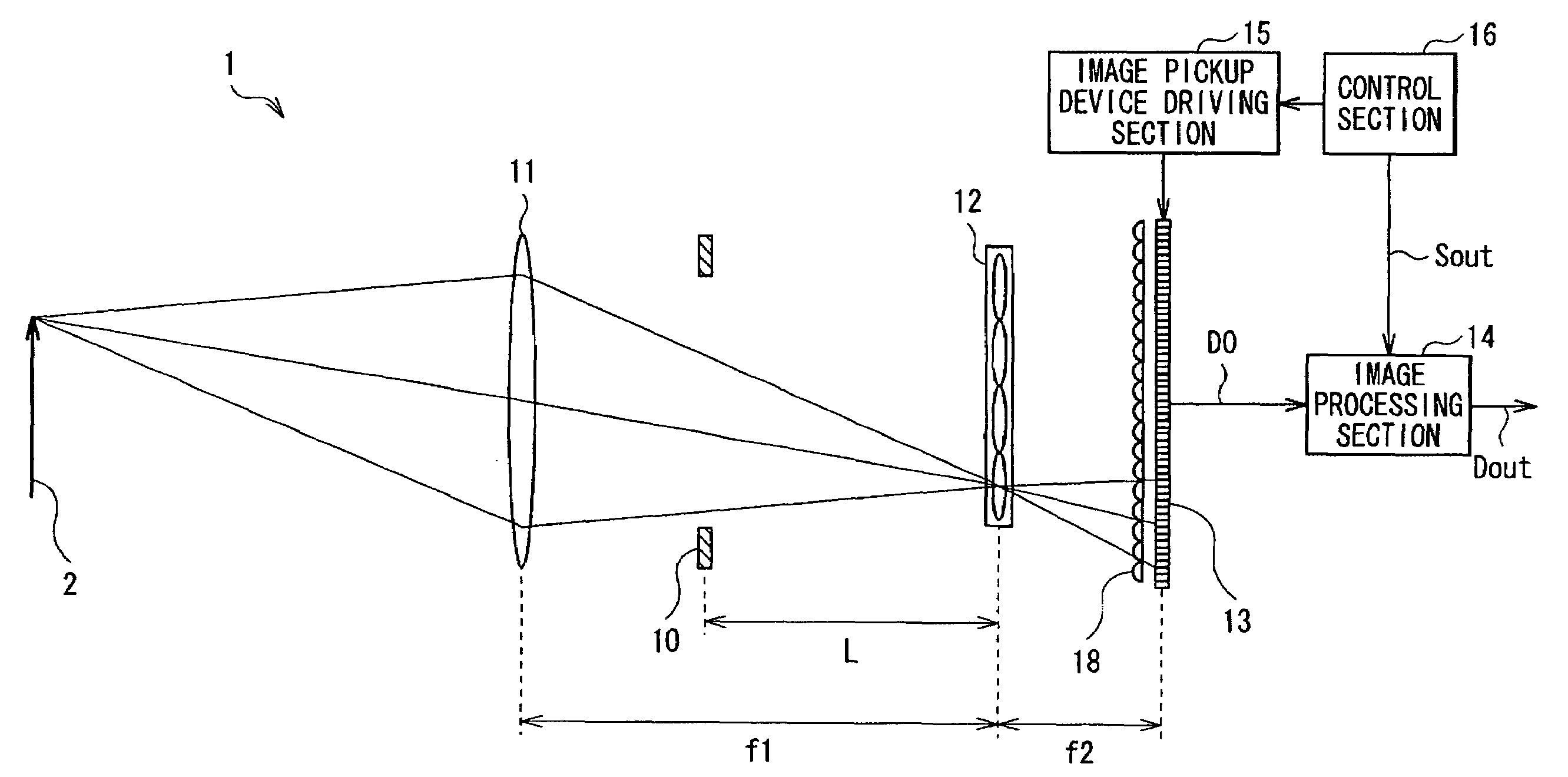
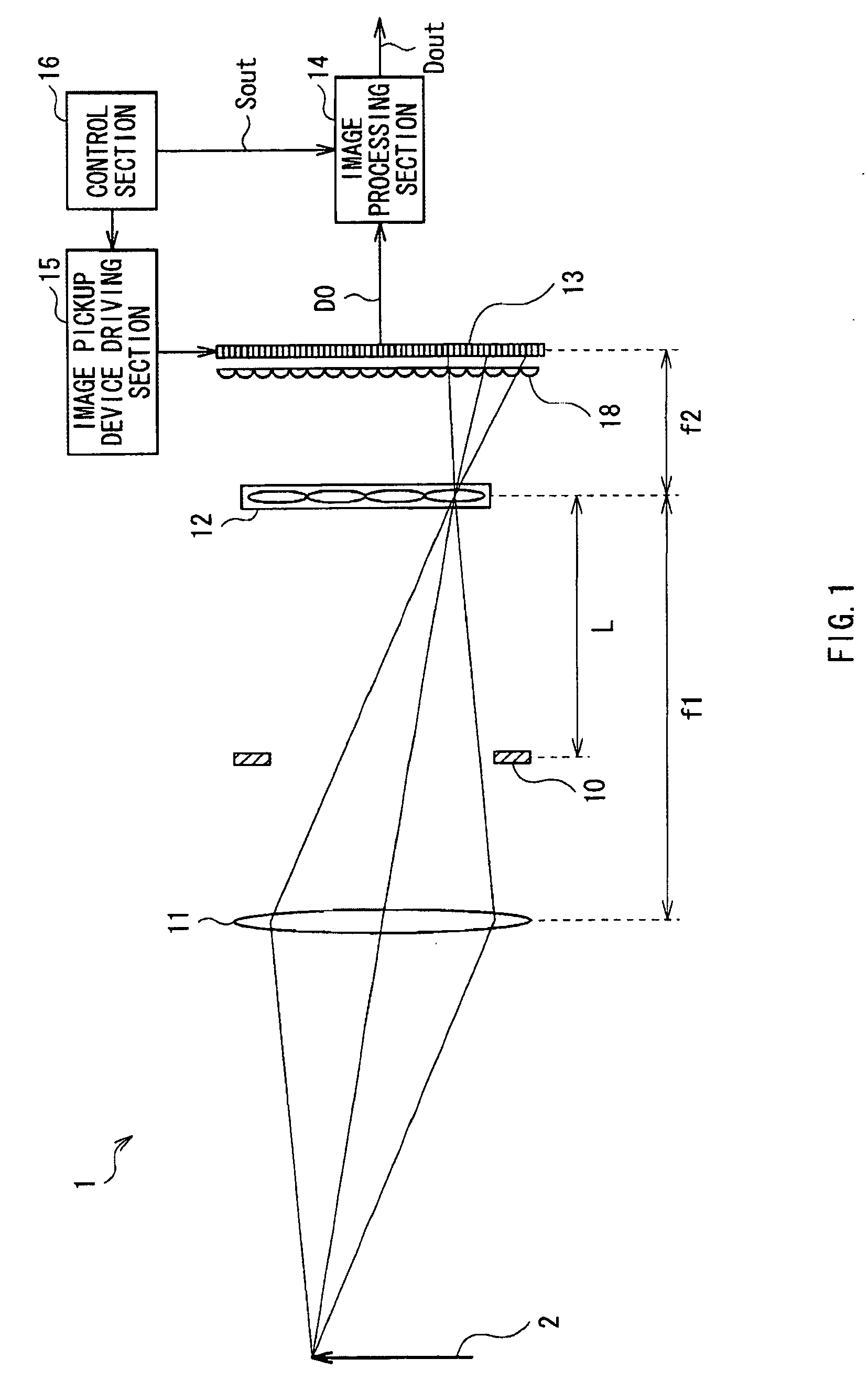
Image pickup apparatus
InactiveUS20090190022A1Reduce signal to noise ratioDegradation of image qualityTelevision system detailsTelevision system scanning detailsBoundary regionComputer vision
An image pickup apparatus includes: an image pickup lens section; an image pickup device obtaining image pickup data on the basis of light detected; a microlens array section arranged on a focal plane of the image pickup lens section, and including a plurality of microlenses, each of the microlenses being provided corresponding to a plurality of image pickup pixels of the image pickup device; and a light-condensing section configured of a plurality of light-condensing elements, each of the light-condensing elements condensing light entering into each of the image pickup pixels of the image pickup device, wherein on the image pickup device, in a pixel region corresponding to each microlens, the pitch between the light-condensing elements is smaller than the pixel size, and in a boundary region between pixel regions corresponding to microlenses, respectively, the pitch between the light-condensing elements is larger than the pixel size.
Owner:SONY CORP
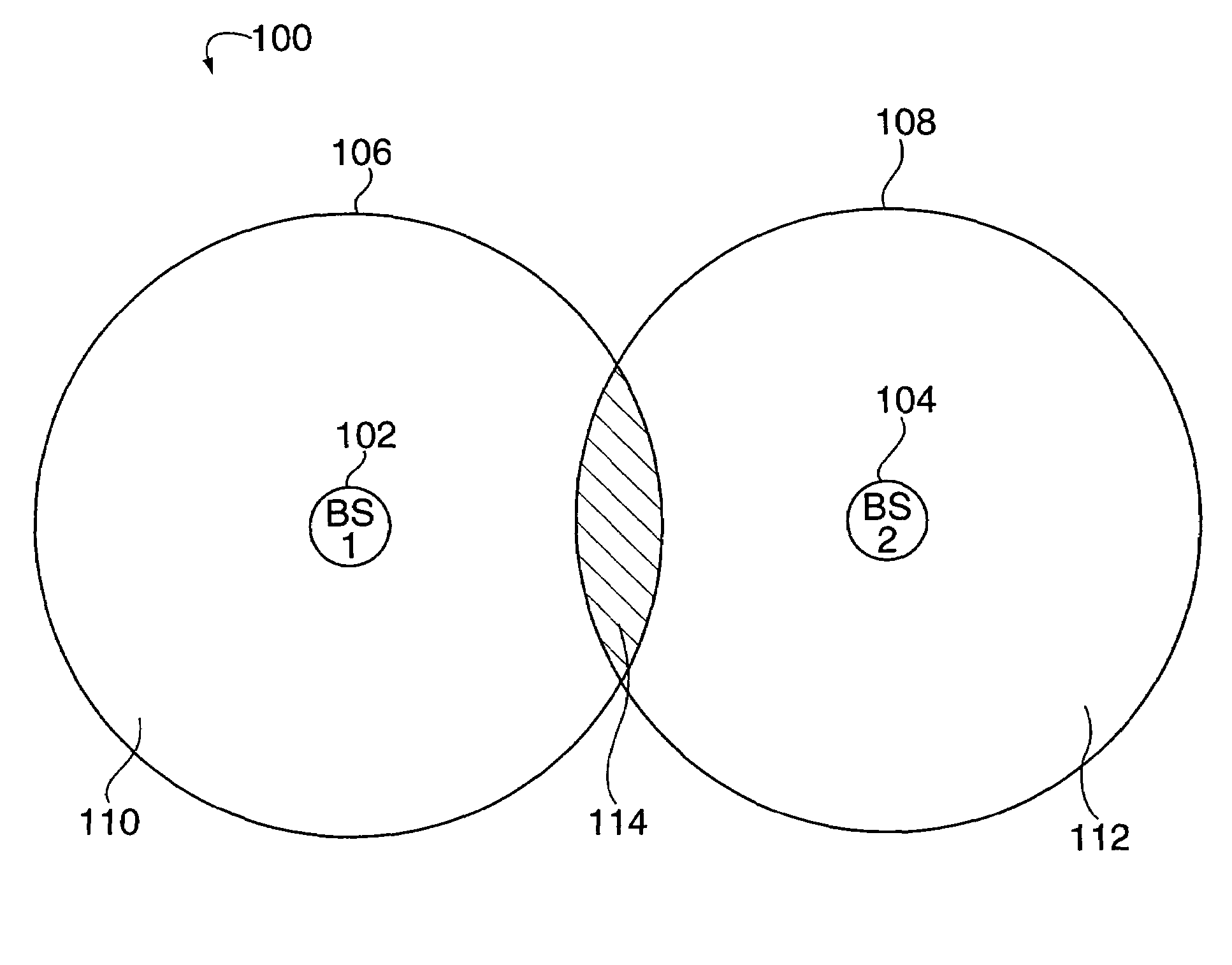
Method of creating and utilizing diversity in multiple carrier communication system
InactiveUS7363039B2Low reliabilityReduce quality problemsEnergy efficient ICTPower managementFrequency spectrumCommunications system
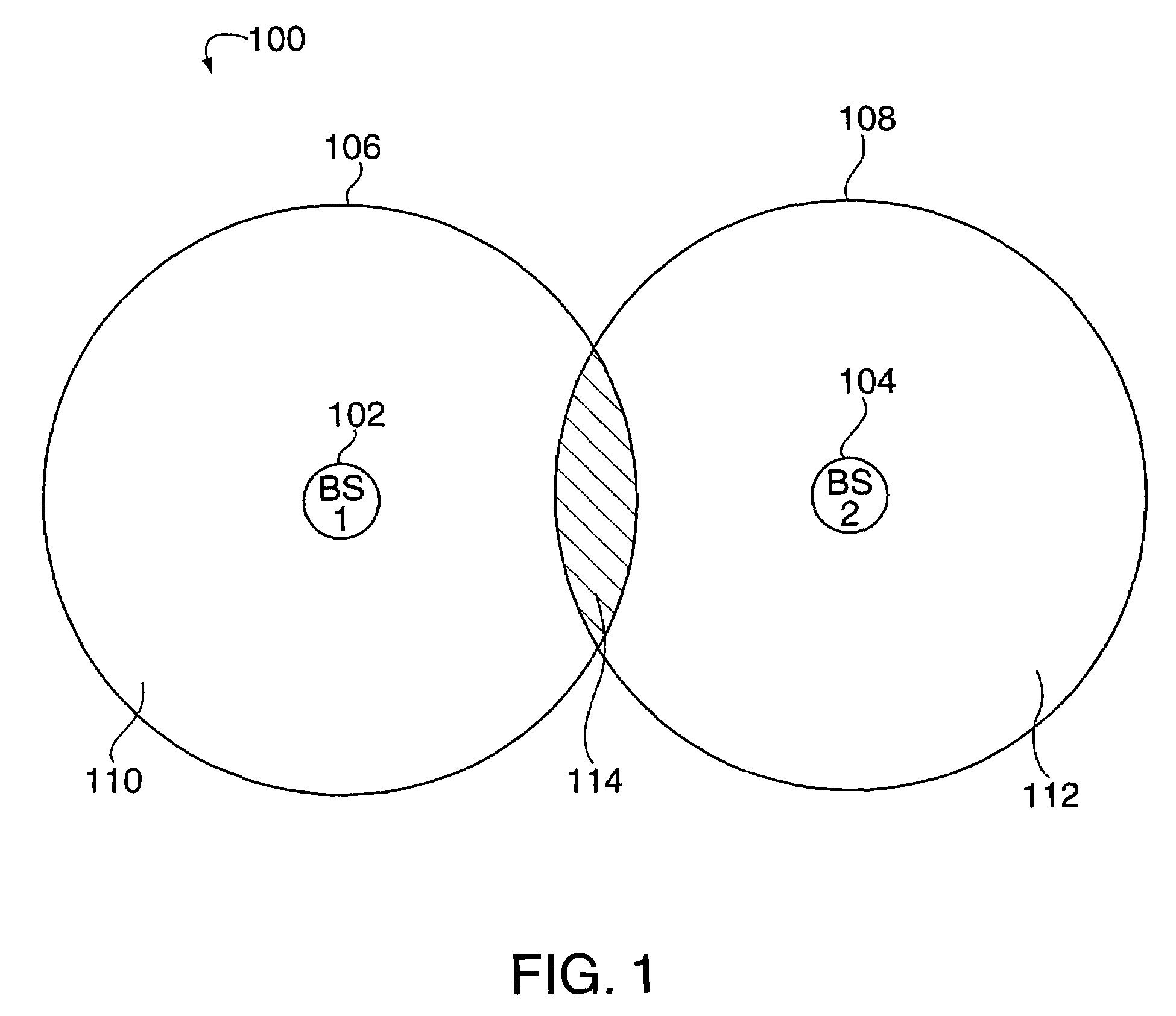
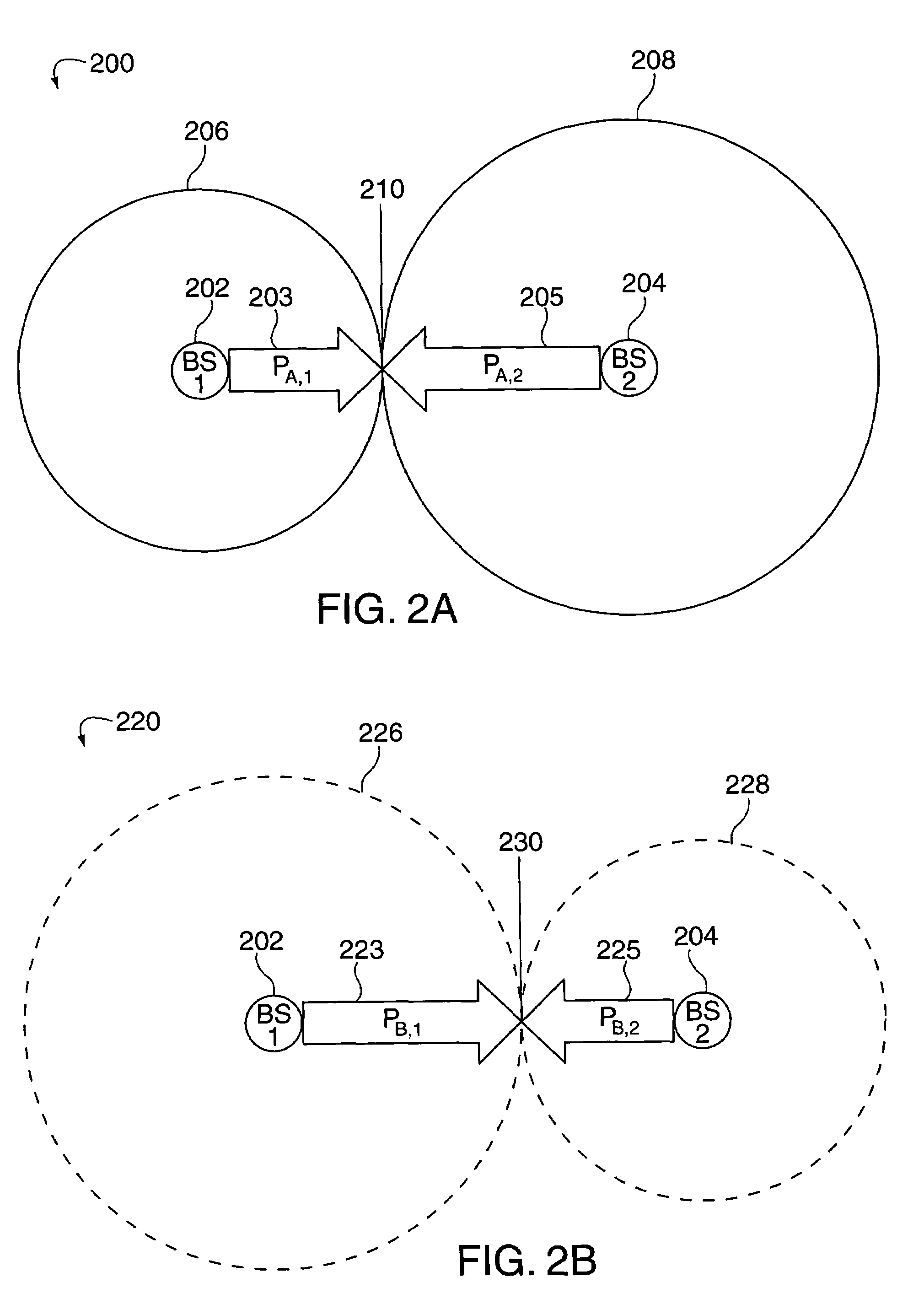
In many cellular systems, reusing spectrum bandwidth, creates problems in boundary regions between the cells and sectors where the signal strength received from adjacent base stations or adjacent sector transmissions of a single base station may be nearly equivalent. The invention creates a new type of diversity, referred to as multiple carrier diversity by utilizing multiple carriers, assigning different power levels to each carrier frequency at each base station, and / or offsetting sector antennas. The cell and / or sector coverage areas can be set so as to minimize or eliminate overlap between cell and / or sector boundary regions of different carrier frequencies. Mobile nodes traveling throughout the system can exploit multiple carrier diversity by detecting carriers and selecting to use a non-boundary carrier based on other system criteria in order to improve performance. Boundary carriers may, but need not be, identified and excluded from consideration for use by a wireless terminal.
Owner:QUALCOMM INC
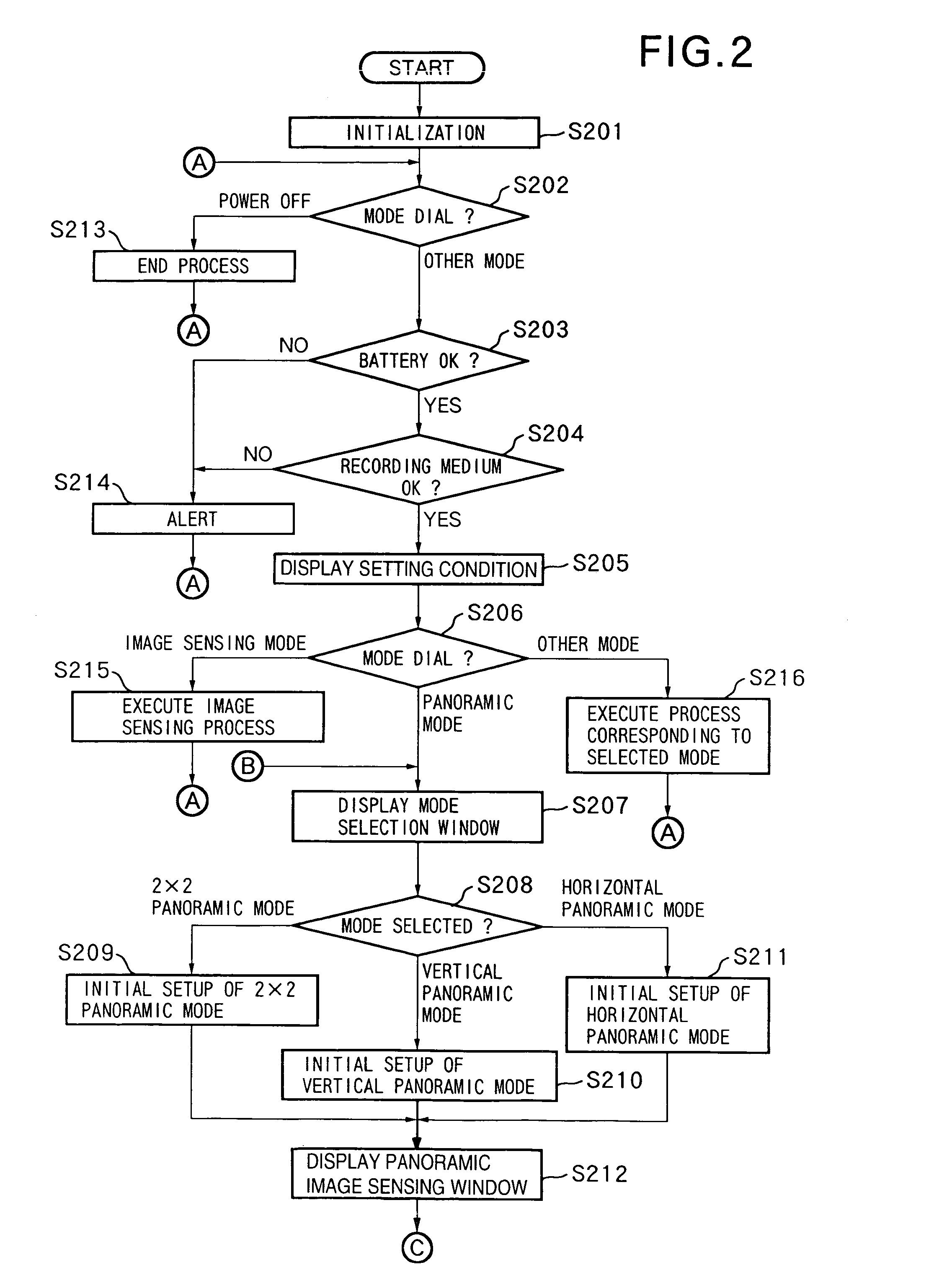
Image processing method and apparatus, control method therefor, and storage medium
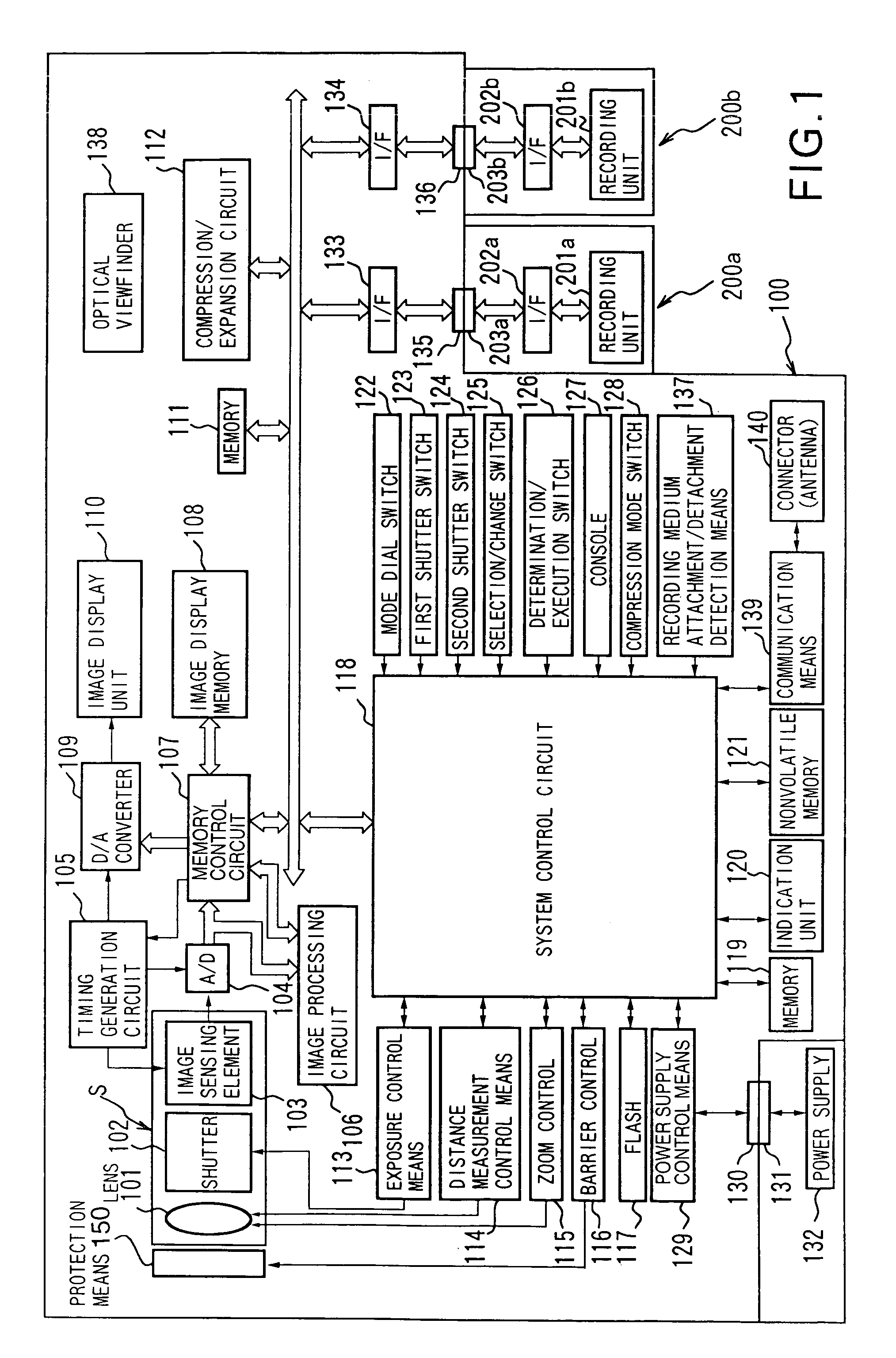
InactiveUS7136096B1Stable controlTelevision system detailsColor television detailsImaging processingComputer graphics (images)
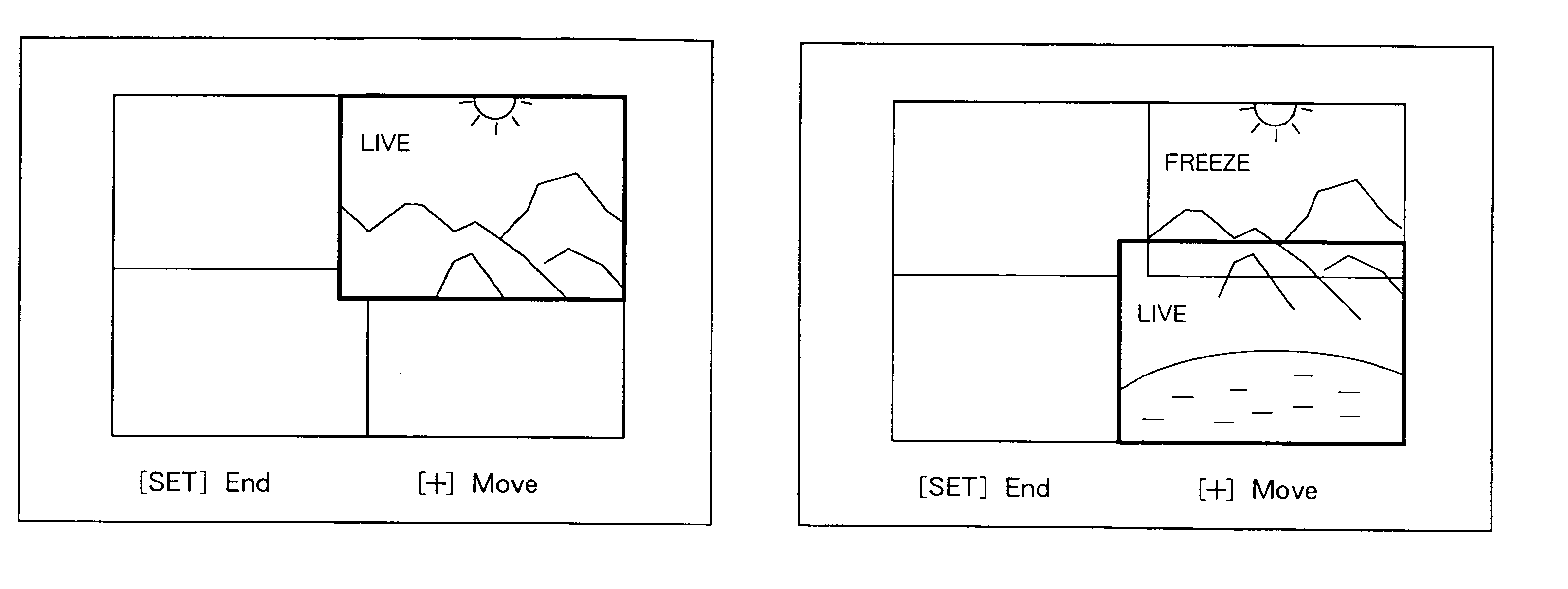
This invention has as its object to provide a convenient image processing apparatus which does not limit image sensing purposes. To achieve this object, an image processing apparatus has a recording medium for recording and playing back an image sensed by an image sensing unit, and an image display unit for playing back and displaying at least an image sensed before the current image. The image display unit has a display layout mode for displaying the current image sensing signal and at least the image sensed before the current image sensing signal with their partial boundary regions overlapping each other.
Owner:CANON KK
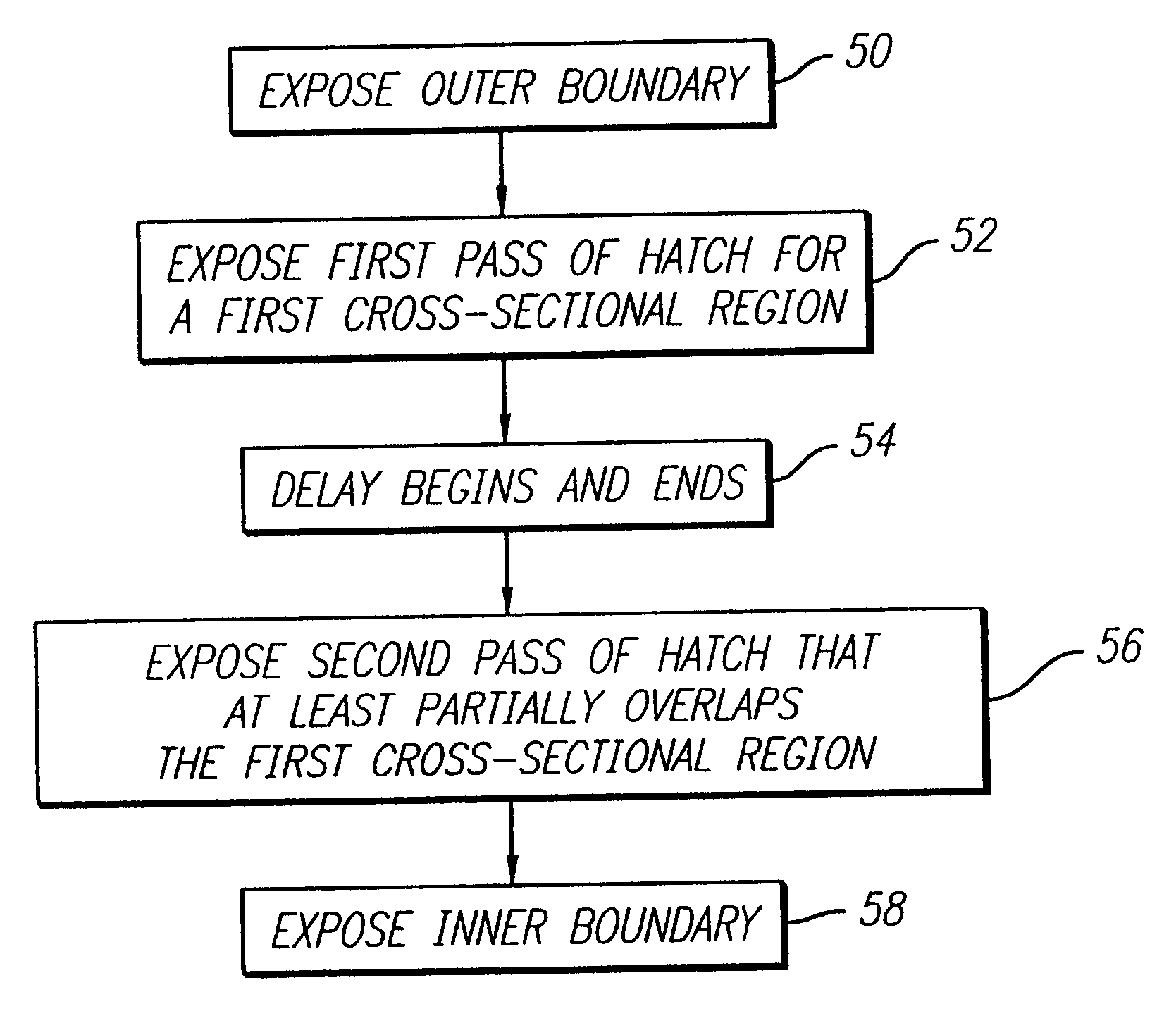
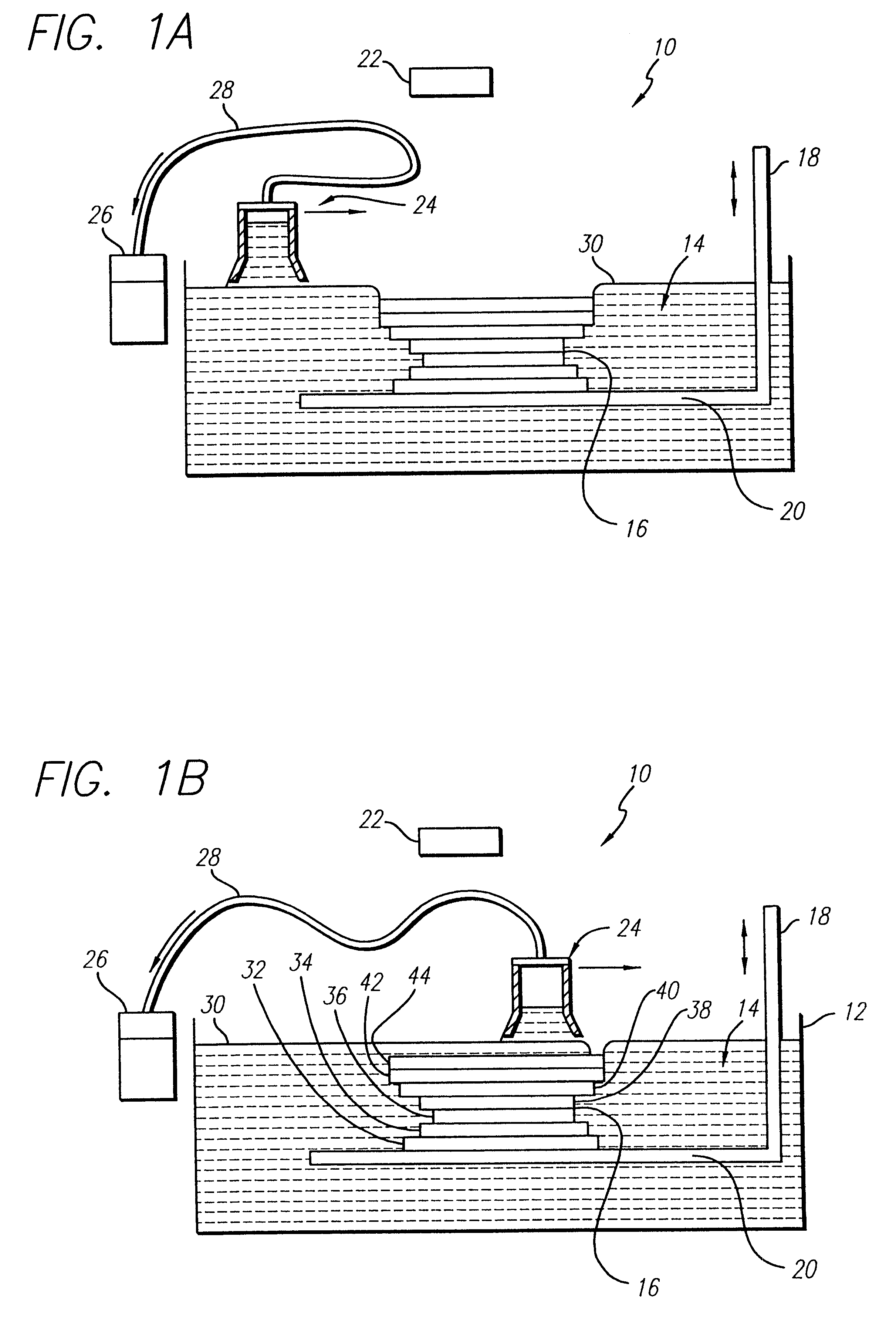
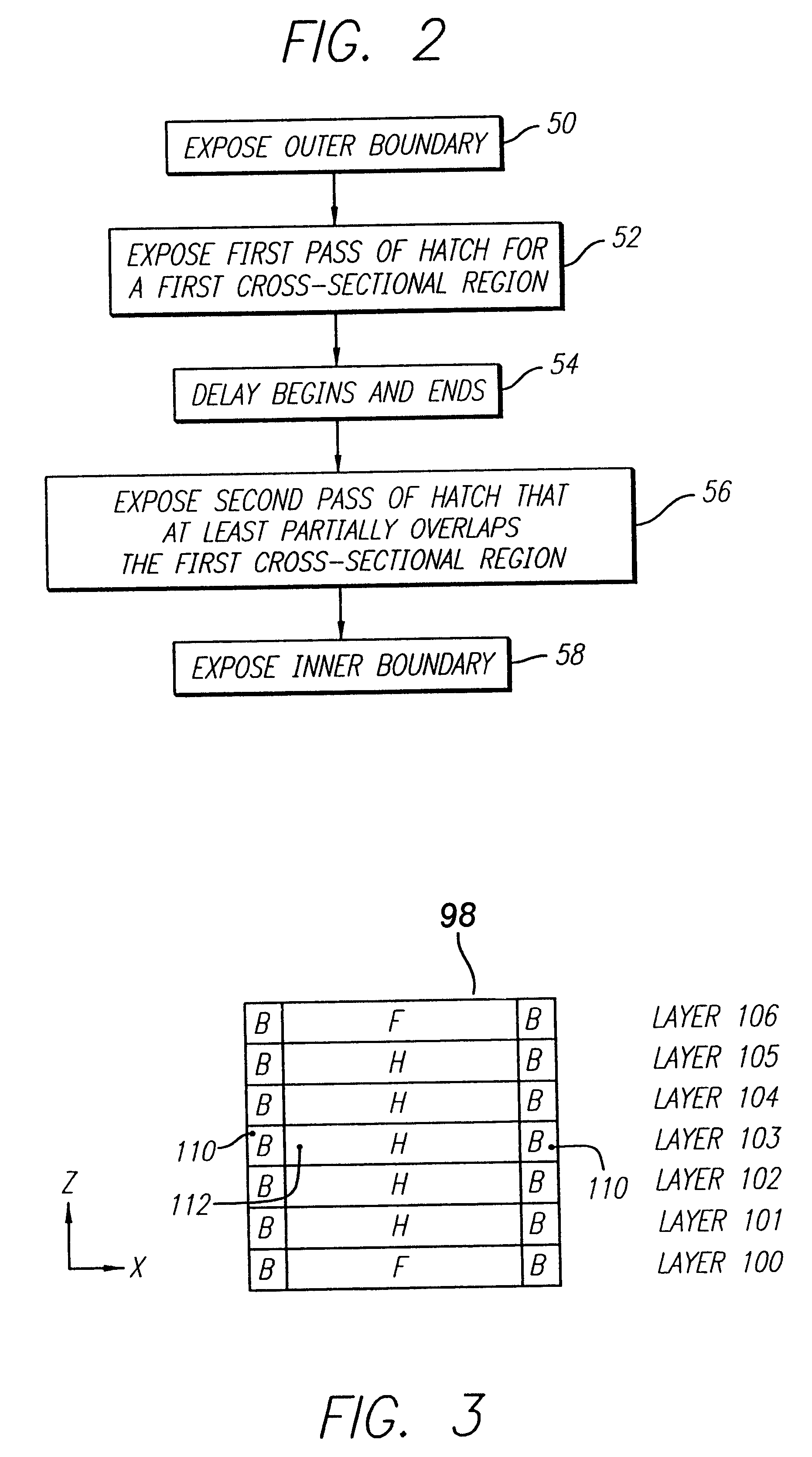
Method and apparatus for stereolithographically forming three dimensional objects with reduced distortion
A rapid prototyping and manufacturing (e.g. stereolithography) method and apparatus for making three-dimensional objects on a layer-by-layer basis by selectively exposing layers of material to prescribed synergistic stimulation including forming portions of a lamina using a first exposure, allowing a time delay, and then applying a second exposure. The time delay is sufficient to allow shrinkage of the material to occur that results from the first exposure. It is preferred that the solidified portion resulting from the first exposure does not adhere to the previously formed lamina. It is also preferred that the portion solidified by this first exposure does not adhere to any boundary region that may have been exposed and adhered to the previously formed lamina. The time delay associated with a given cross-sectional region may be occupied by exposing other cross-sectional regions. The delay may occur between two exposures of overlaying hatch or fill vectors. The delay may alternatively occur between exposure of hatch vectors and boundary vectors. The time delay may be determined by a clock, or alternatively, the time delay may be considered to have lapsed upon certain physical conditions being met, such as detecting the amount of shrinkage and determining that it has progressed far enough for the second exposure to occur.
Owner:3D SYST INC
Method and device for inspecting pipelines
InactiveUS6848313B2Avoid bouncingImprove resilientAnalysing solids using sonic/ultrasonic/infrasonic wavesUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic wave generationEngineeringBoundary region
The invention concerns a method and a device for inspecting pipelines, in particular for detecting defects in pipelines by means of ultrasound. Towards this end, measuring sensors transmit ultrasound signals during passage through a pipeline. The signals reflected on boundary regions of a pipeline wall, e.g. surfaces or defects, are then measured and evaluated. The invention is characterized in that partial regions of the measuring sensors (virtual sensors) formed of a plurality of neighboring sensor elements irradiate ultrasound signals into the pipe wall at at least one radiation angle which is inclined with respect to the normal to the pipe wall and the signals reflected at boundary regions of the pipe wall are received by same and / or other partial regions of the respective measuring sensors, wherein defects in the pipe wall are determined by evaluation of the acoustical signals reflected by different boundary regions.
Owner:PII PIPETRONIX
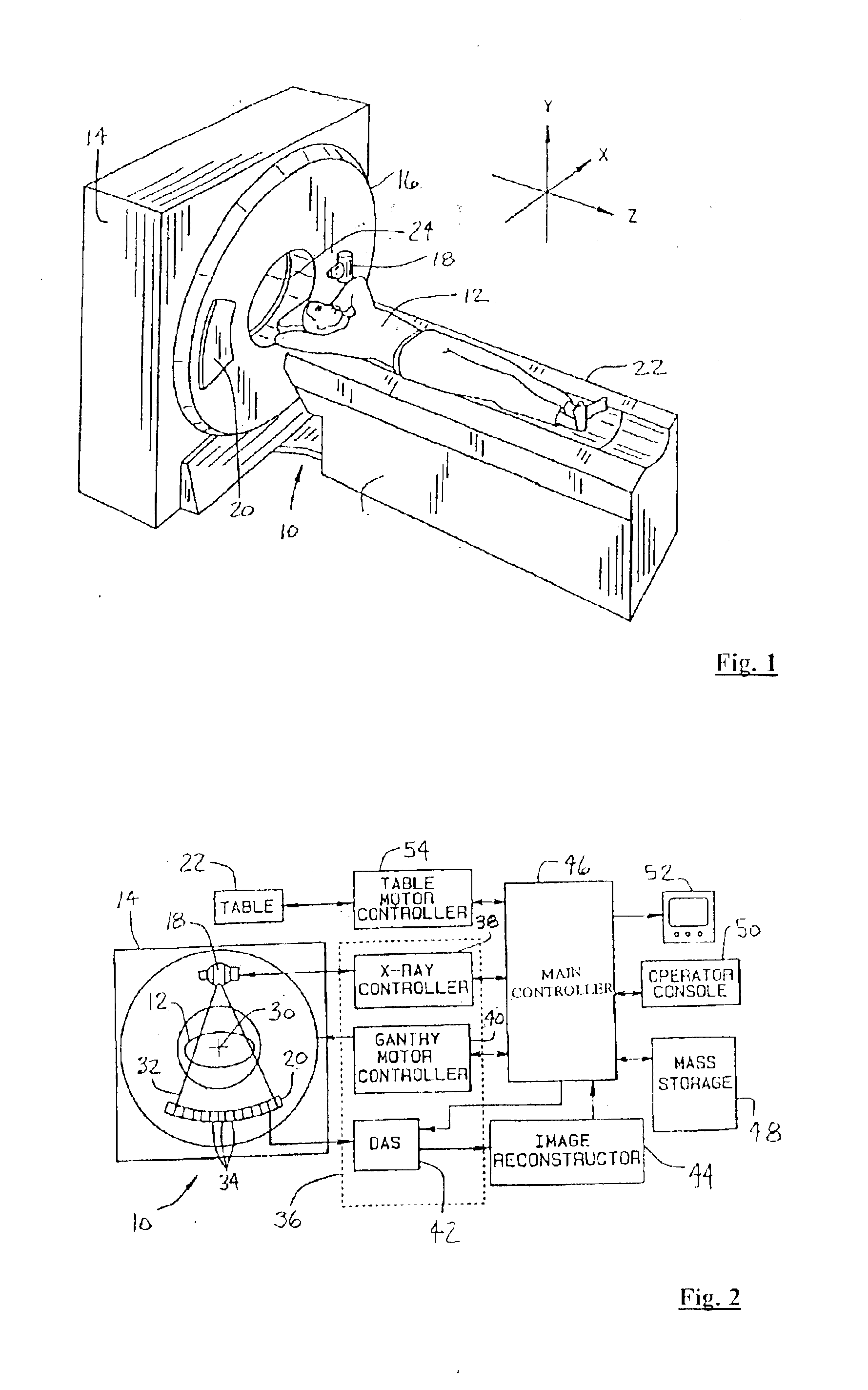
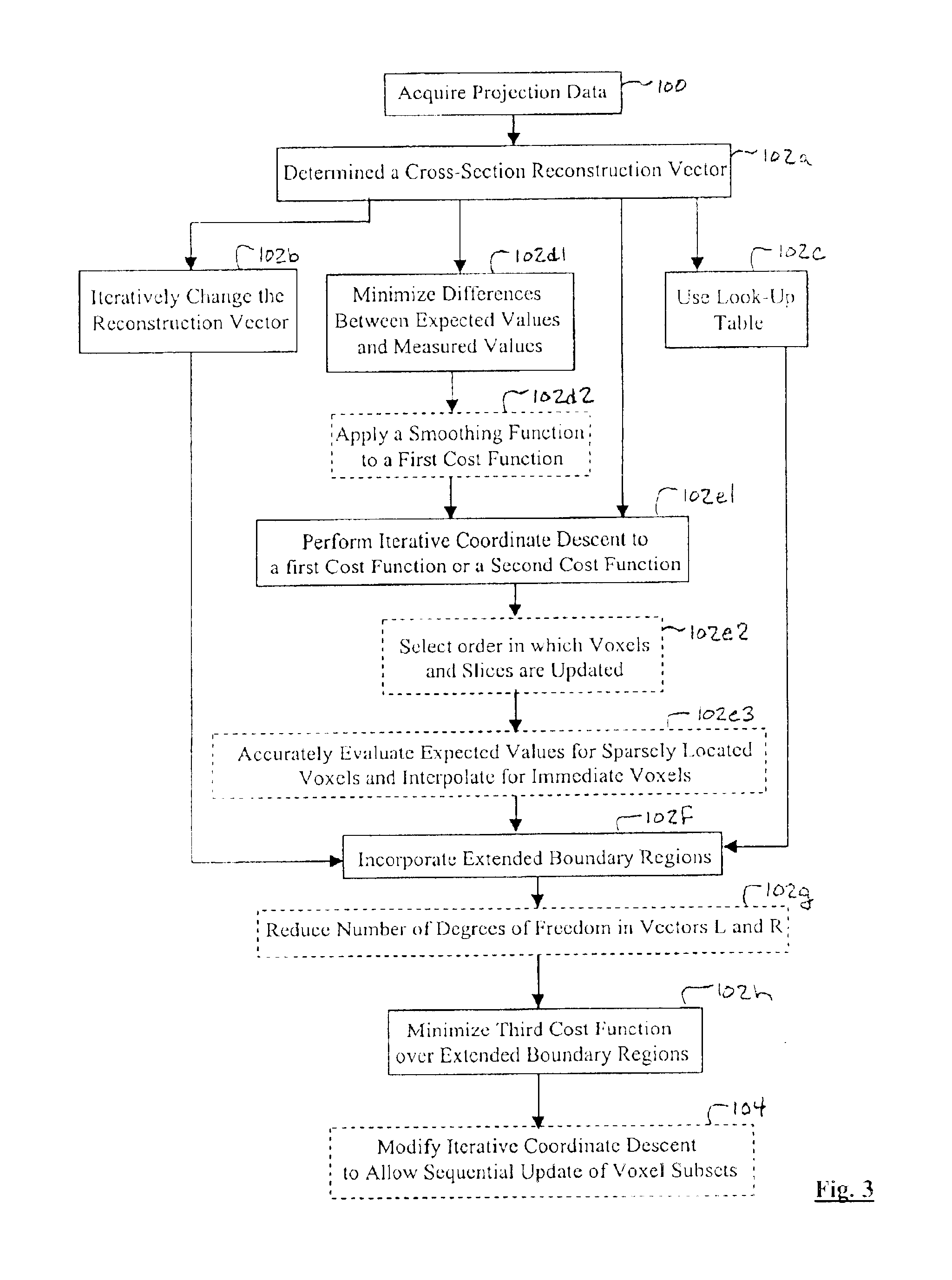
Iterative reconstruction methods for multi-slice computed tomography
InactiveUS6907102B1Avoid warpingError minimizationReconstruction from projectionMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationHelical scanMulti slice
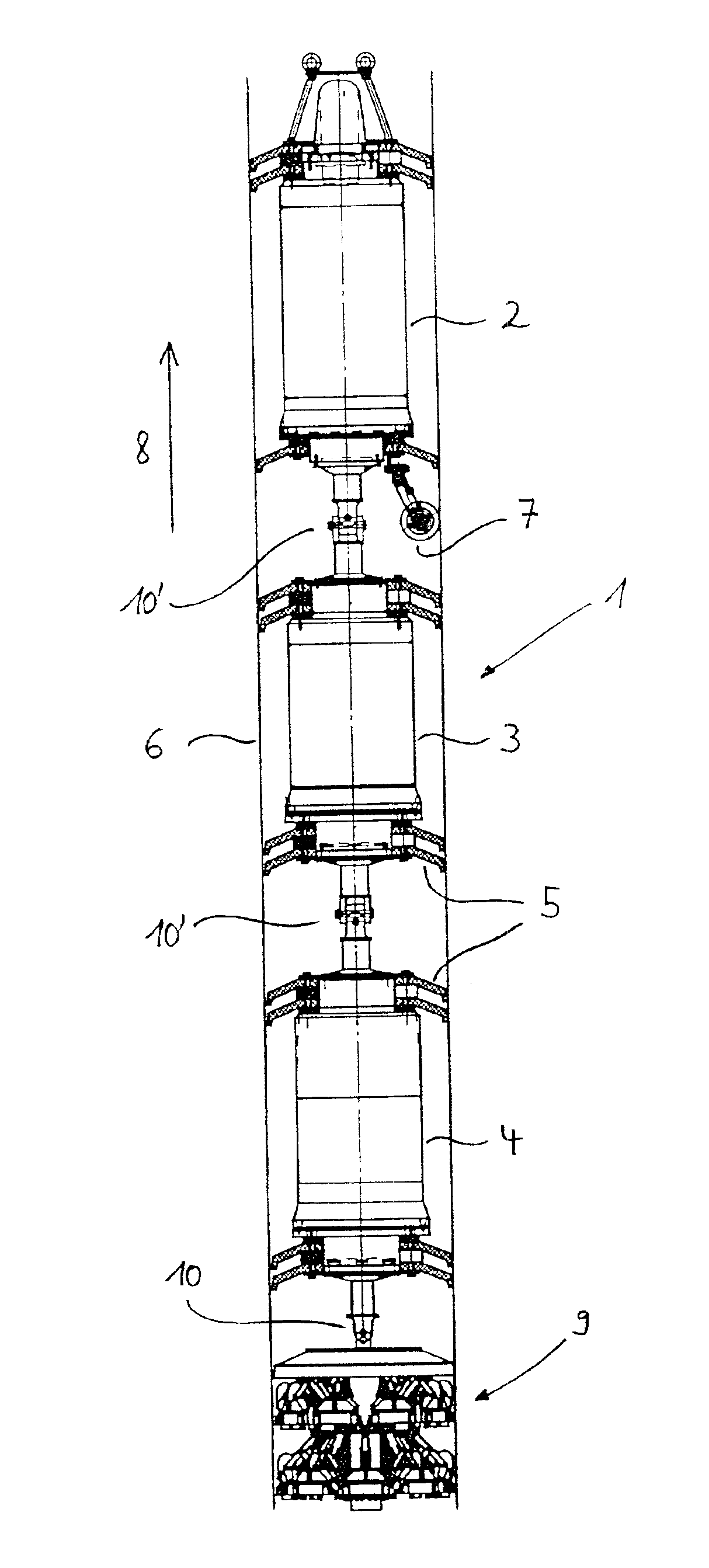
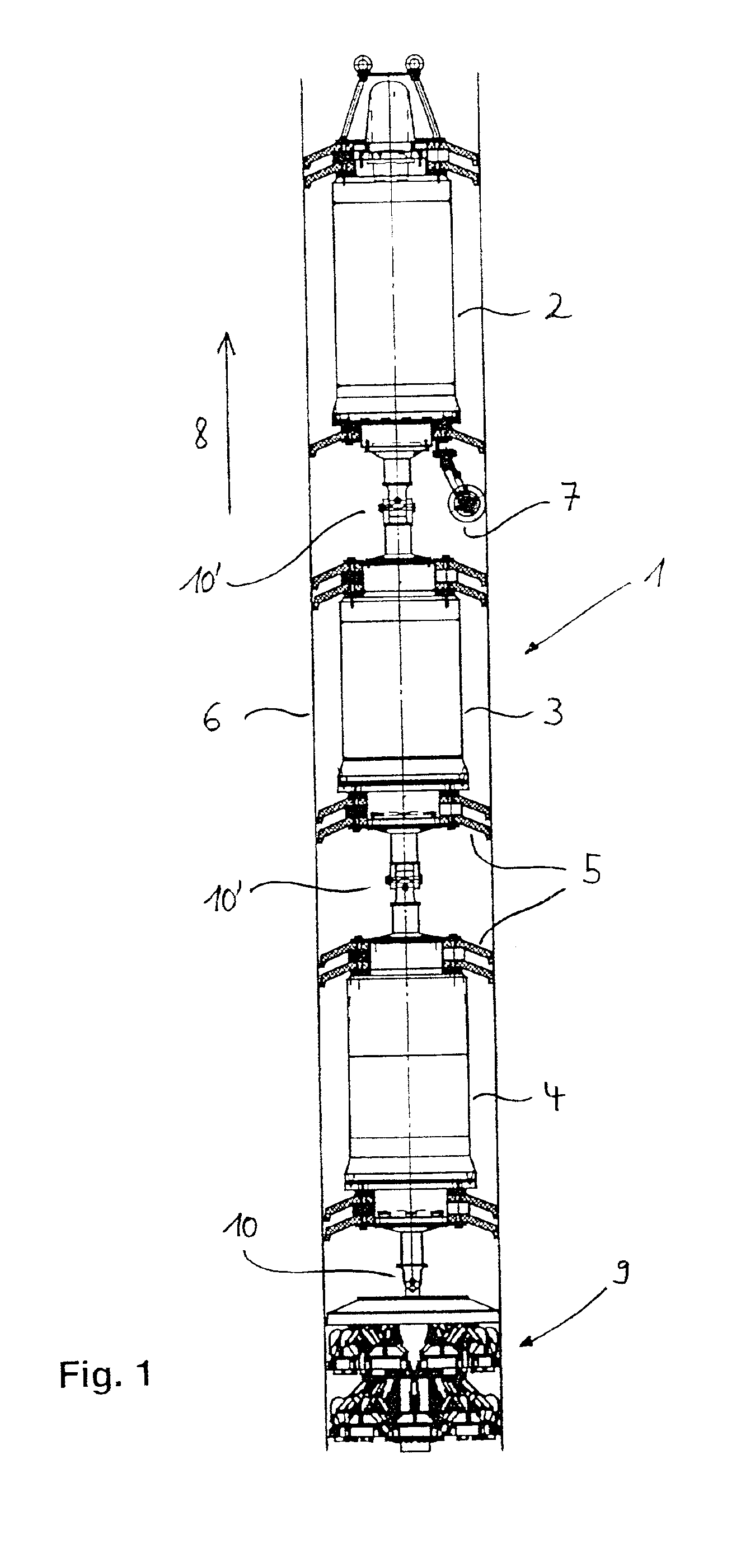
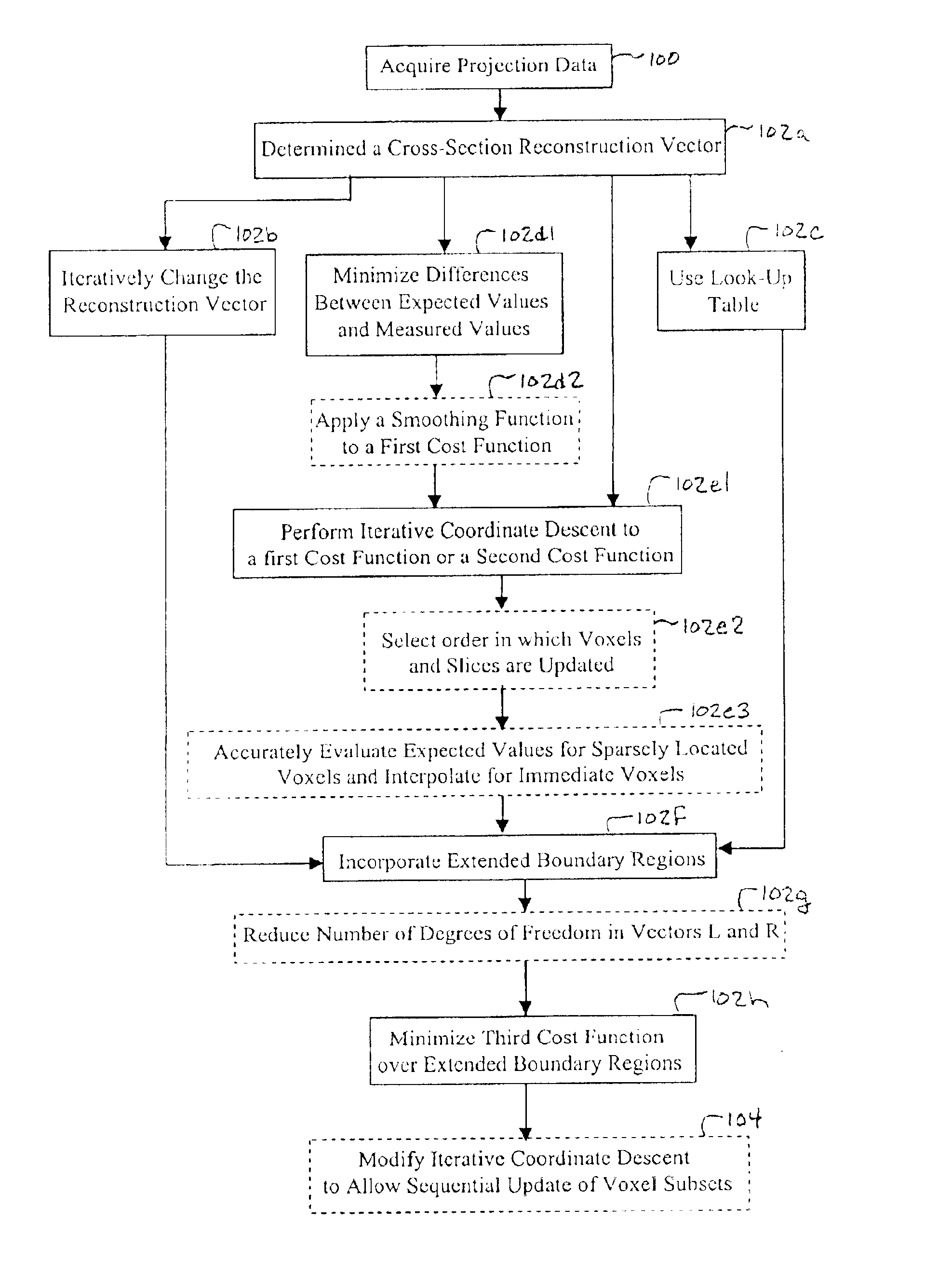
A multi-slice computed tomography imaging system is provided including a source that generates an x-ray beam and a detector array that receives the x-ray beam and generates projection data. A translatable table has an object thereon and is operable to translate in relation to the source and the detector array. The source and the detector array rotate about the translatable table to helically scan the object. An image reconstructor is electrically coupled to the detector array and reconstructs an image in response to the projection data using a computed tomography modeled iterative reconstruction technique. The iterative reconstruction technique includes determining a cross-section reconstruction vector, which approximately matches the projection data via a computed tomography model. Methods for performing the same are also provided including accounting for extended boundary regions.
Owner:PURDUE RES FOUND INC +2
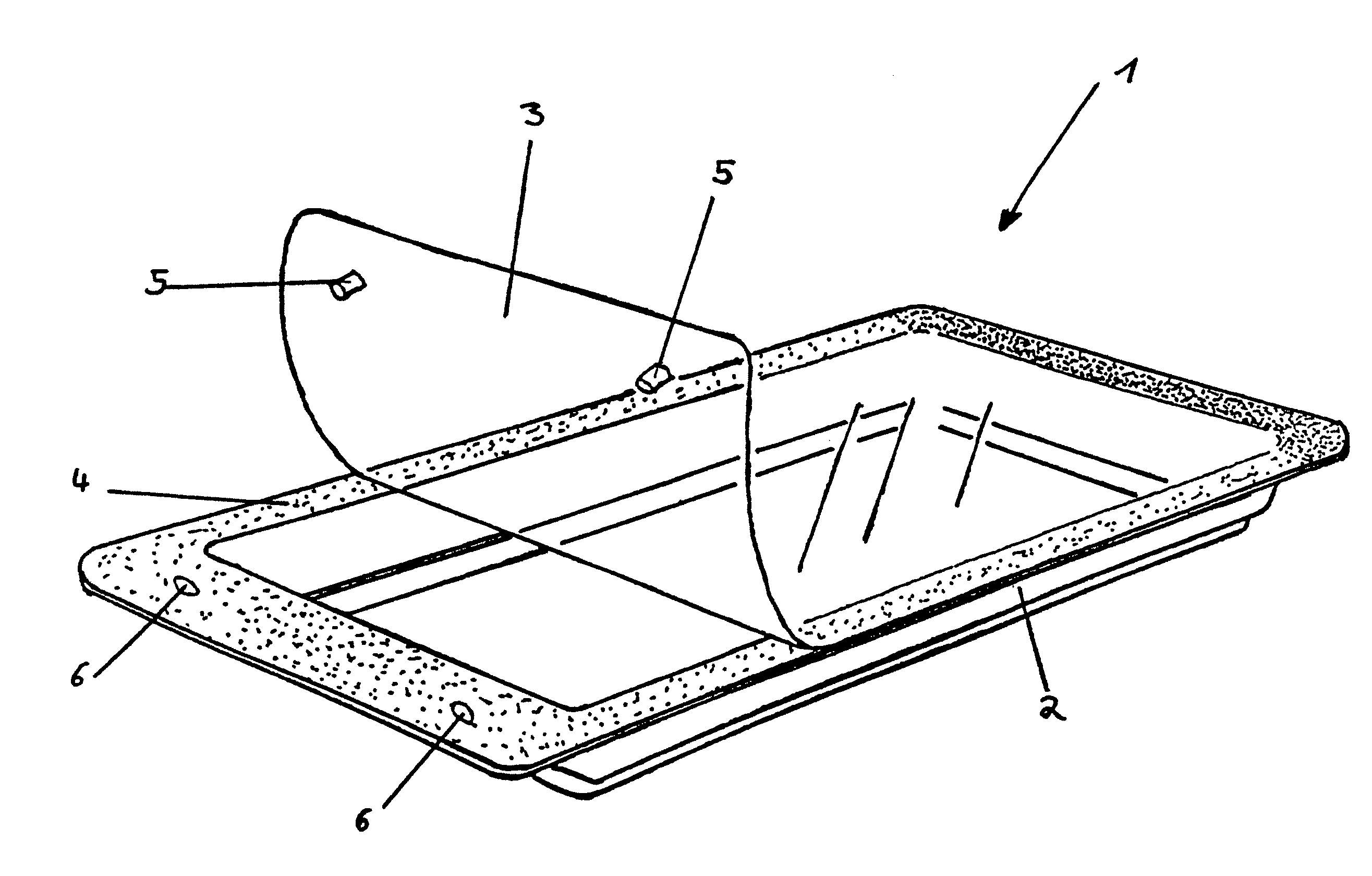
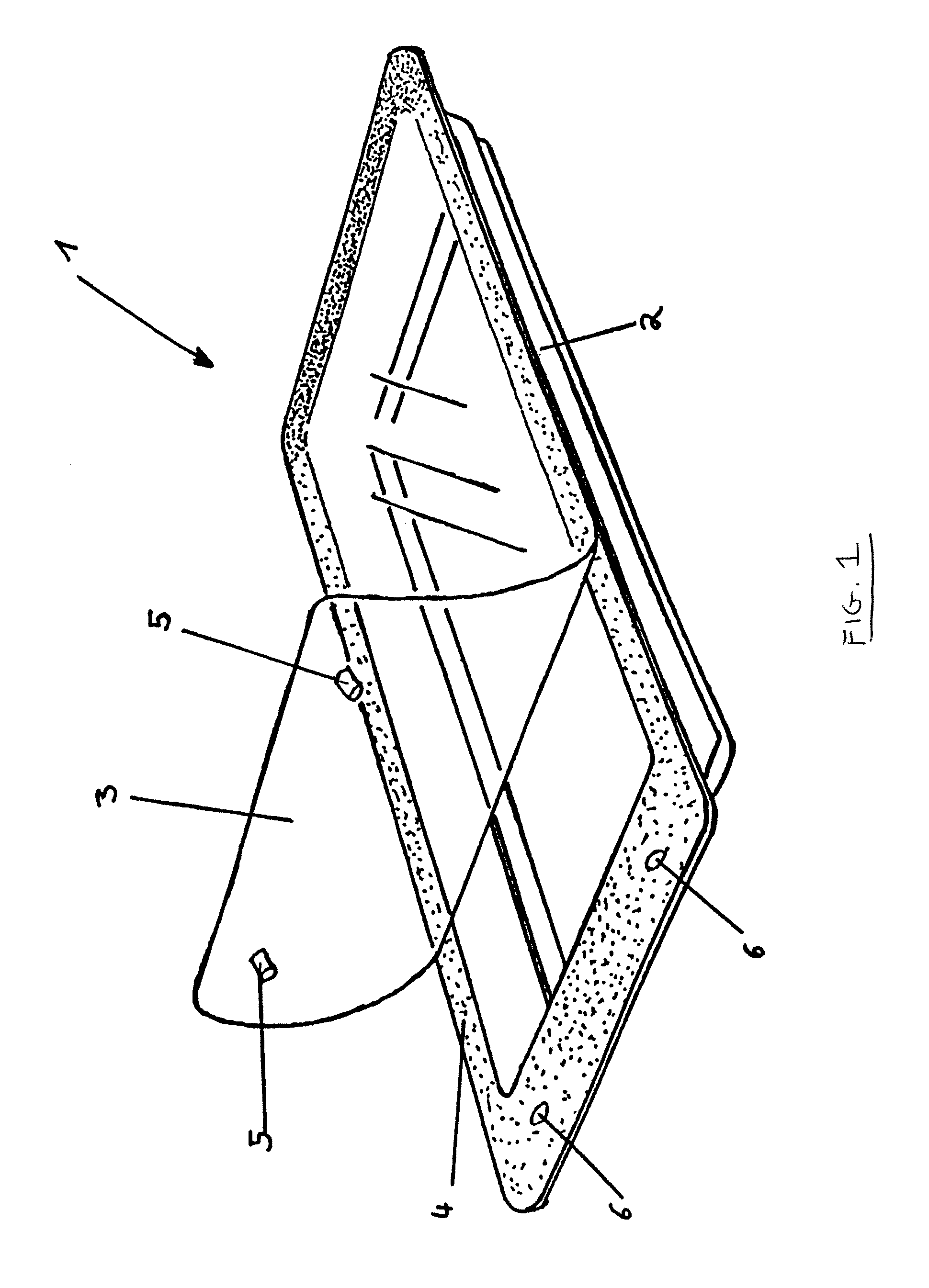
Plastic packaging with at least one welded knob
InactiveUS7322473B2Firmly connectedReadily feltOther accessoriesContainer/bottle contructionPlastic packagingBoundary region
The invention relates to a plastic packaging (1) made from a packaging dish (2) and a cover lid (3). The cover lid (3) is at least partially sealed to the packaging dish (2) in a peelable manner and the cover lid (3), or the packaging dish (2), comprises at least one knob (5) and complementary to the above the packaging dish (2) or the cover lid (3) comprises a recess (6), through which the knob(s) is / are pressed on sealing the plastic packaging (1). At least a partial region of at least one knob is provided with a sealing material (95) or preferably at least one partial region of at least one knob (5) and the boundary region of the complementary recess (7) is connected to a sealing material (9), which on first opening of the packaging (1) is damaged. The invention further relates to methods for the production of said packages.
Owner:CONVENIENCE FOOD SYST WALLAU
Semiconductor device
A semiconductor device includes a first insulating layer provided above a semiconductor substrate. The first insulating layer includes a layer consisting essentially of a material having a relative dielectric constant smaller than 3. The first insulating layer includes a first integral structure consisting of a plug and wiring. The upper surface of the wiring is flush with the upper surface of the first insulating layer, and the lower surface of the plug is flush with the lower surface of the first insulating layer. A region protective member is formed of a second integral structure consisting of a plug and wiring. The second integral structure extends from the upper surface of the first insulating layer to the lower surface of the first insulating layer. The region protective member surrounds one of first to n-th regions (n being a natural 2 or more) partitioned by a boundary region on a horizontal plane.
Owner:KK TOSHIBA
Multiple focussing image fusion method based on block dividing
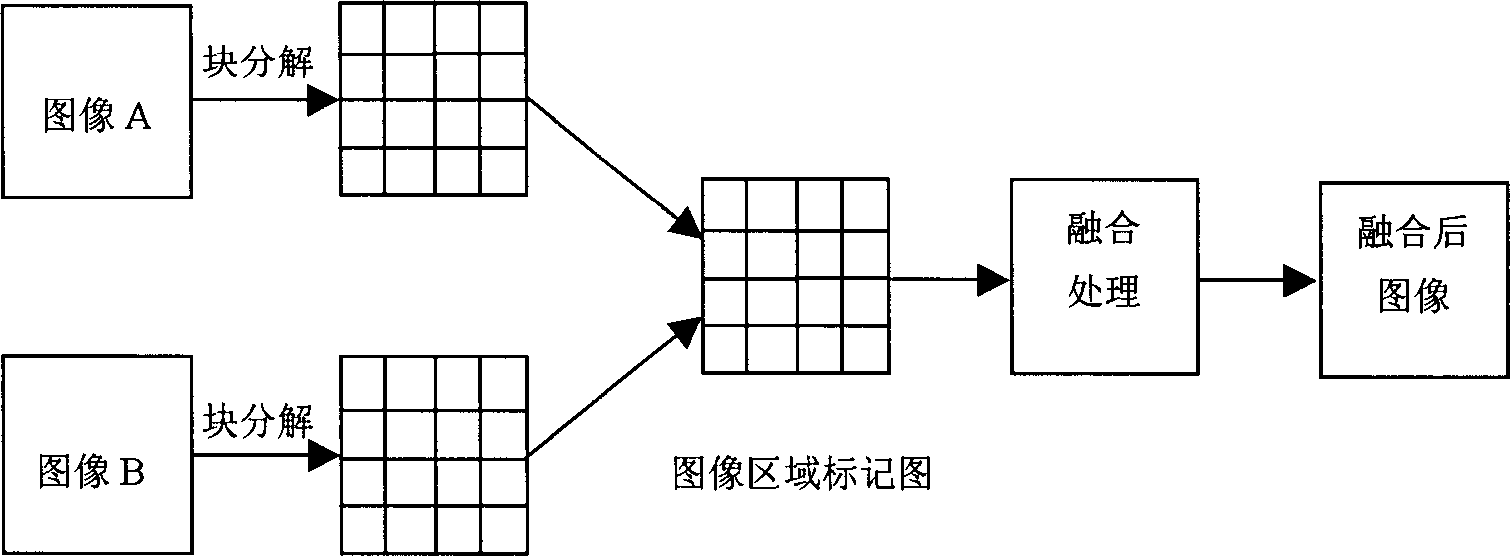
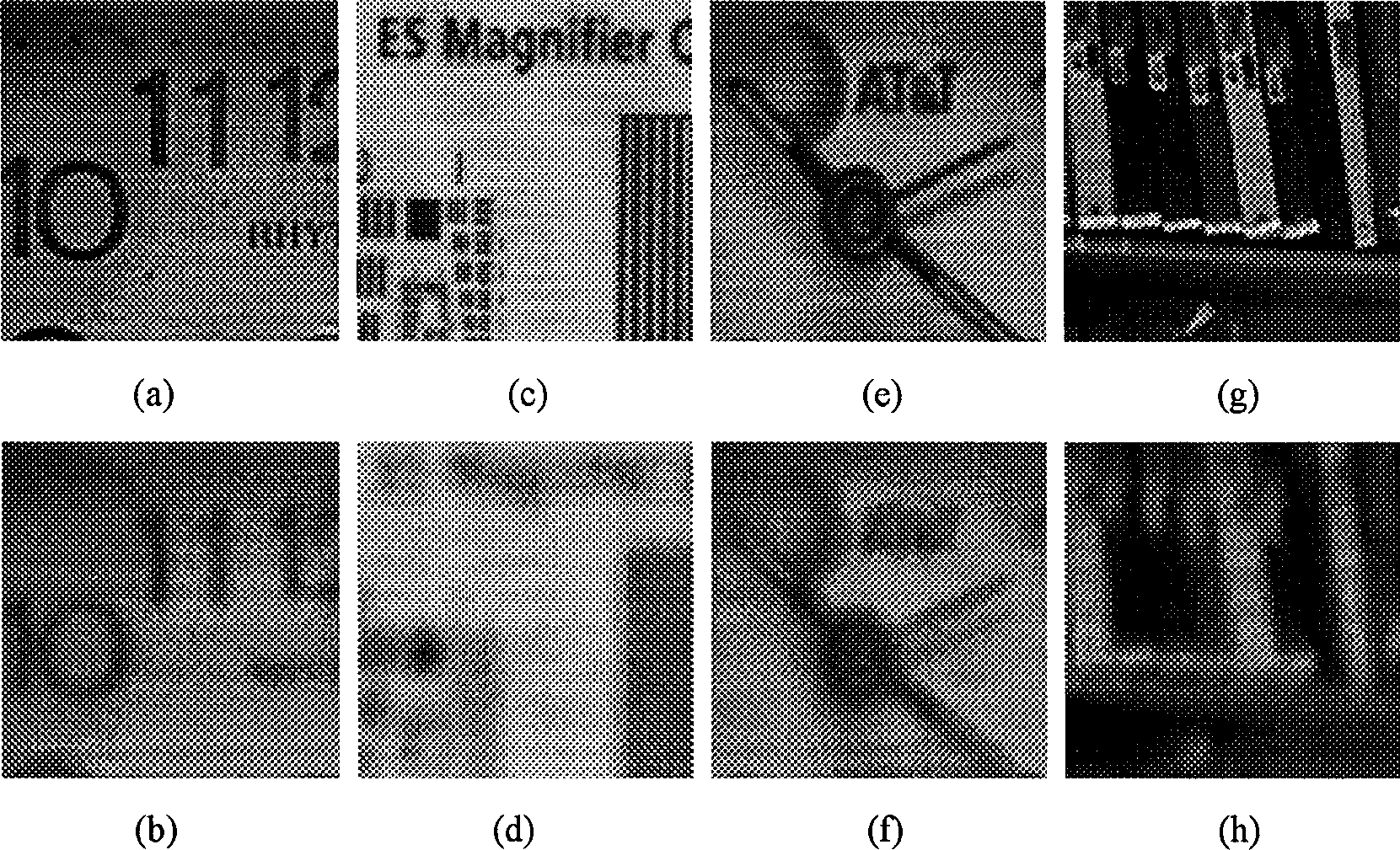
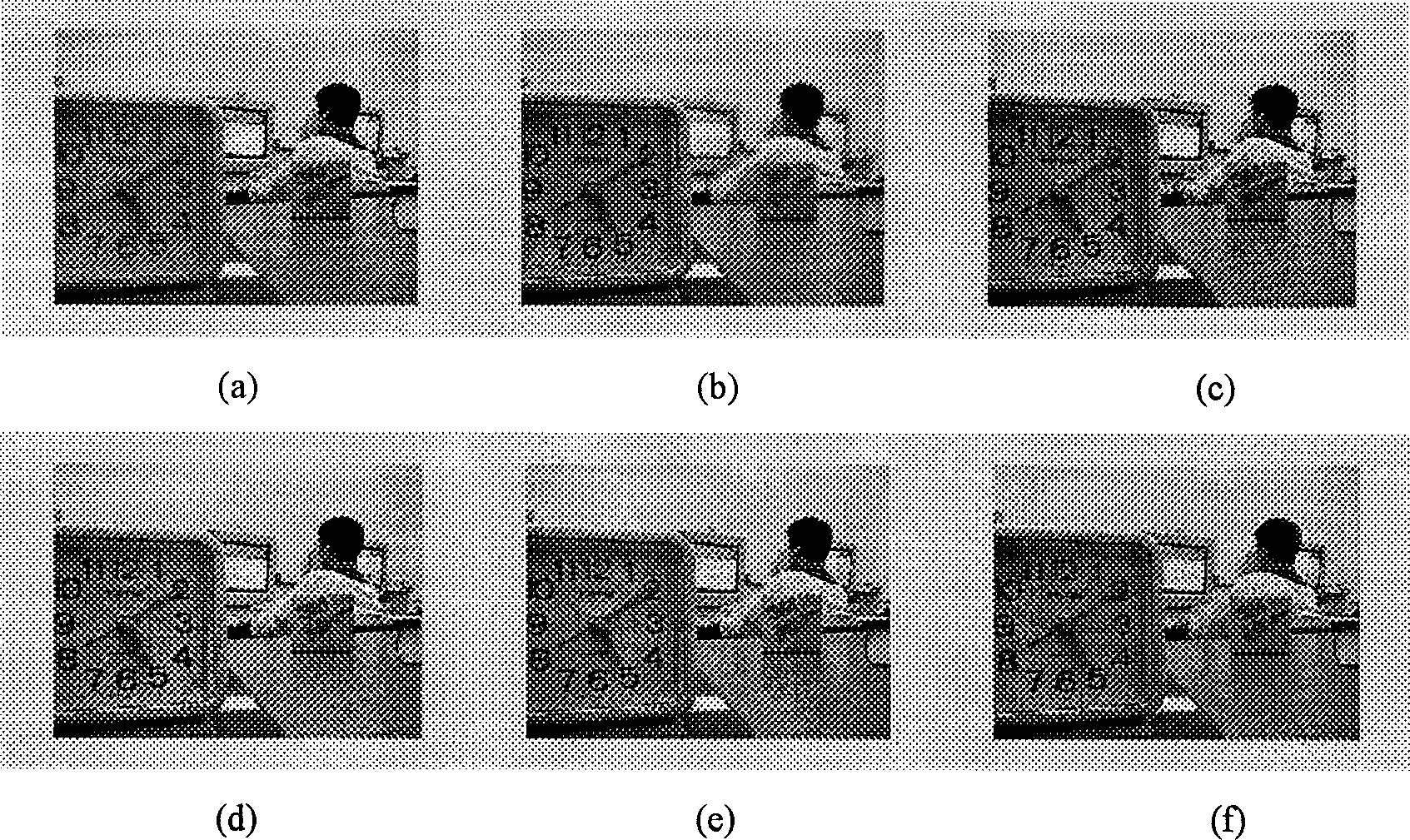
InactiveCN1402191APreserve edge informationIdeal Fusion ResultsImage analysisImaging qualityImage segmentation
A method based on block division for the fusion of multiple focused images includes dividing the original focused images into blocks with same sizes, finding out the local contrast of each block to reflect the difference between clear focusing area and fuzzy focusing area, dividing an image into clear region and fuzzy region, defining the blocks adjacent to the clear region and fuzzy region as boundary region, expressing said three regions, directly using the clear region as the fused region and using pixel fusion method to fuse the boundary region. Its advantage is high image quality.
Owner:SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV
Boundary configurations for multi-material print-forming
InactiveUS20100009133A1Distribute pressureMinimise concentrationAdditive manufacturing apparatusLiquid surface applicatorsMulti materialEngineering
A print-forming method is disclosed which provides a method to engineer and design boundaries between the materials used in devices. The boundary includes primarily a first material on one side and primarily a second material on the other side. At least some of the second material is located on the first material side of the boundary and at least some of the first material is located on the second material side of the boundary in a precise pattern that achieve the objectives of the design. This approach is then extended to 3-dimensional shapes with any number of materials. Material properties that differ from each other thus do not exhibit an abrupt transition within the overall structure, but rather are accommodated within the boundary region. Various different exemplary boundary region configurations are disclosed, as well as techniques for optimizing this print-forming manufacturing within boundary regions.
Owner:EOPLEX
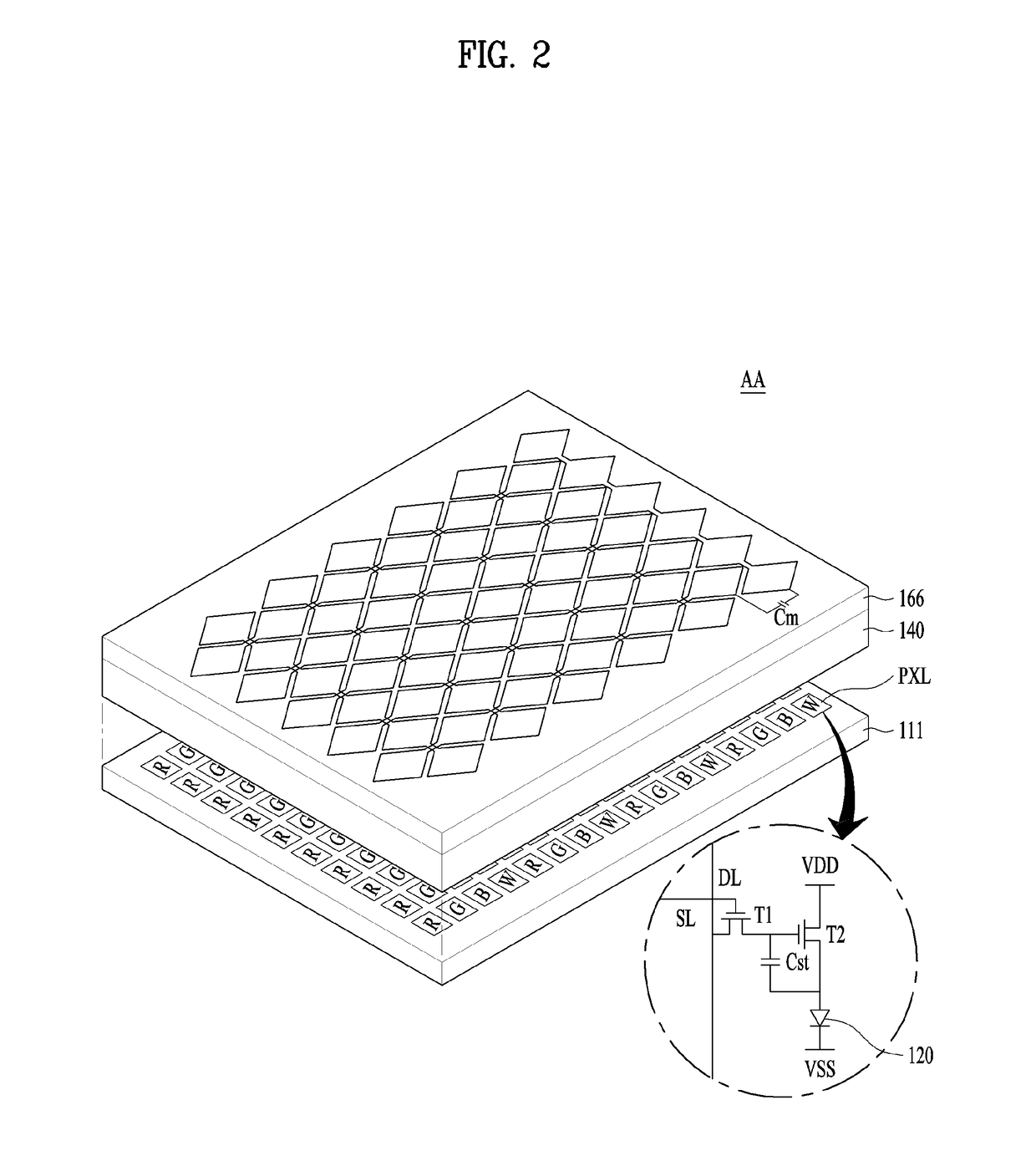
Organic Light Emitting Display Having Touch Sensor and Method of Fabricating the Same
ActiveUS20180061899A1Simple processLow costSolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingDisplay deviceOptoelectronics
Disclosed are an organic light emitting display having a touch sensor, which may achieve process simplification and cost reduction, and a method of fabricating the same. The organic light emitting display includes a compensation film having a flat surface and formed to cover dams forming a boundary with an organic encapsulation layer and the compensation film has a planarized surface between a region above the dams and a boundary region between the dams and the organic encapsulation layer (144) and may prevent cut and short-circuit of routing lines cutting across the same. Further, touch sensors are disposed on an encapsulation unit including the organic encapsulation layer and thus a separate attachment process is not required, thereby simplifying the overall process and reducing manufacturing costs of the organic light emitting display.
Owner:LG DISPLAY CO LTD
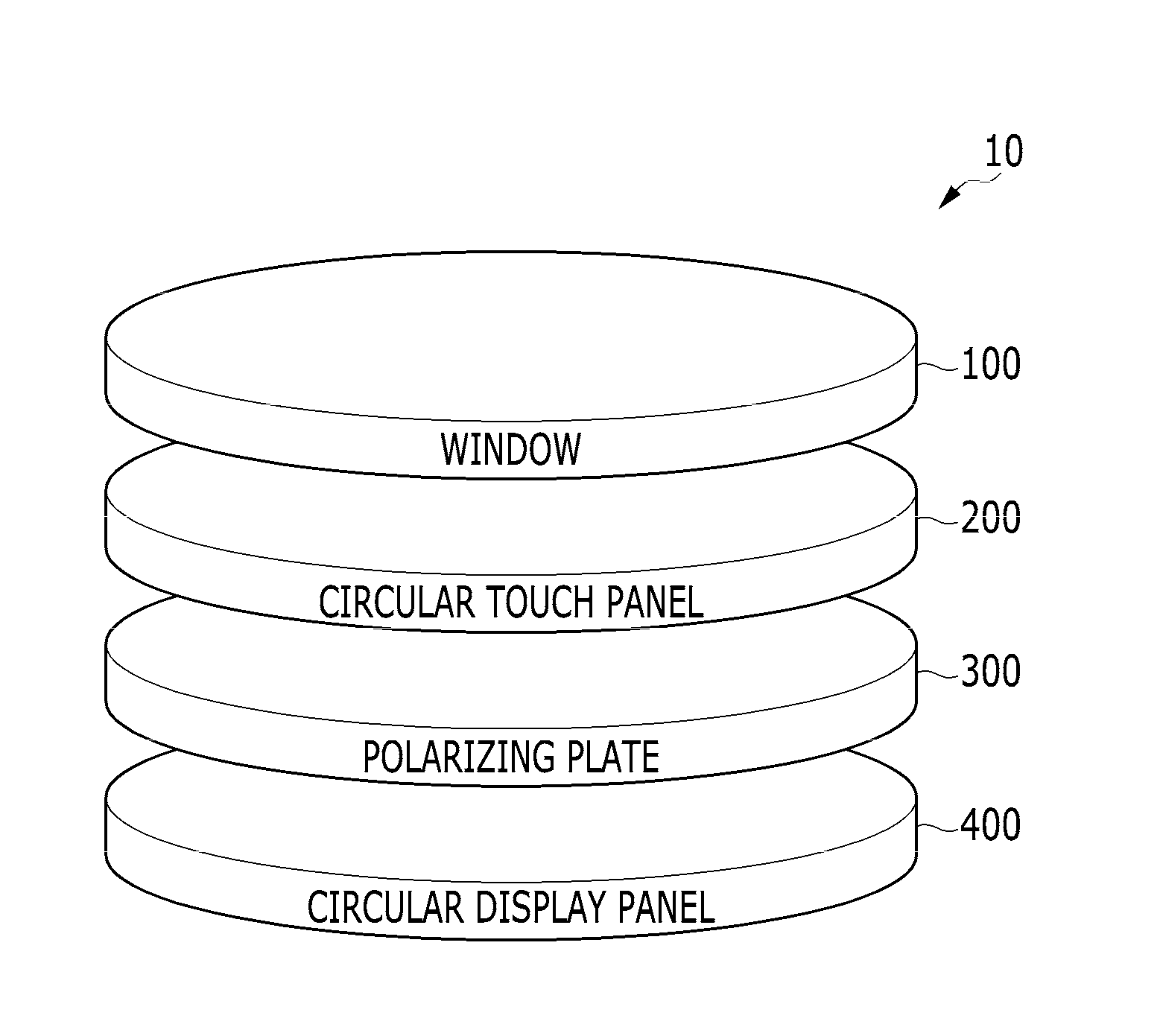
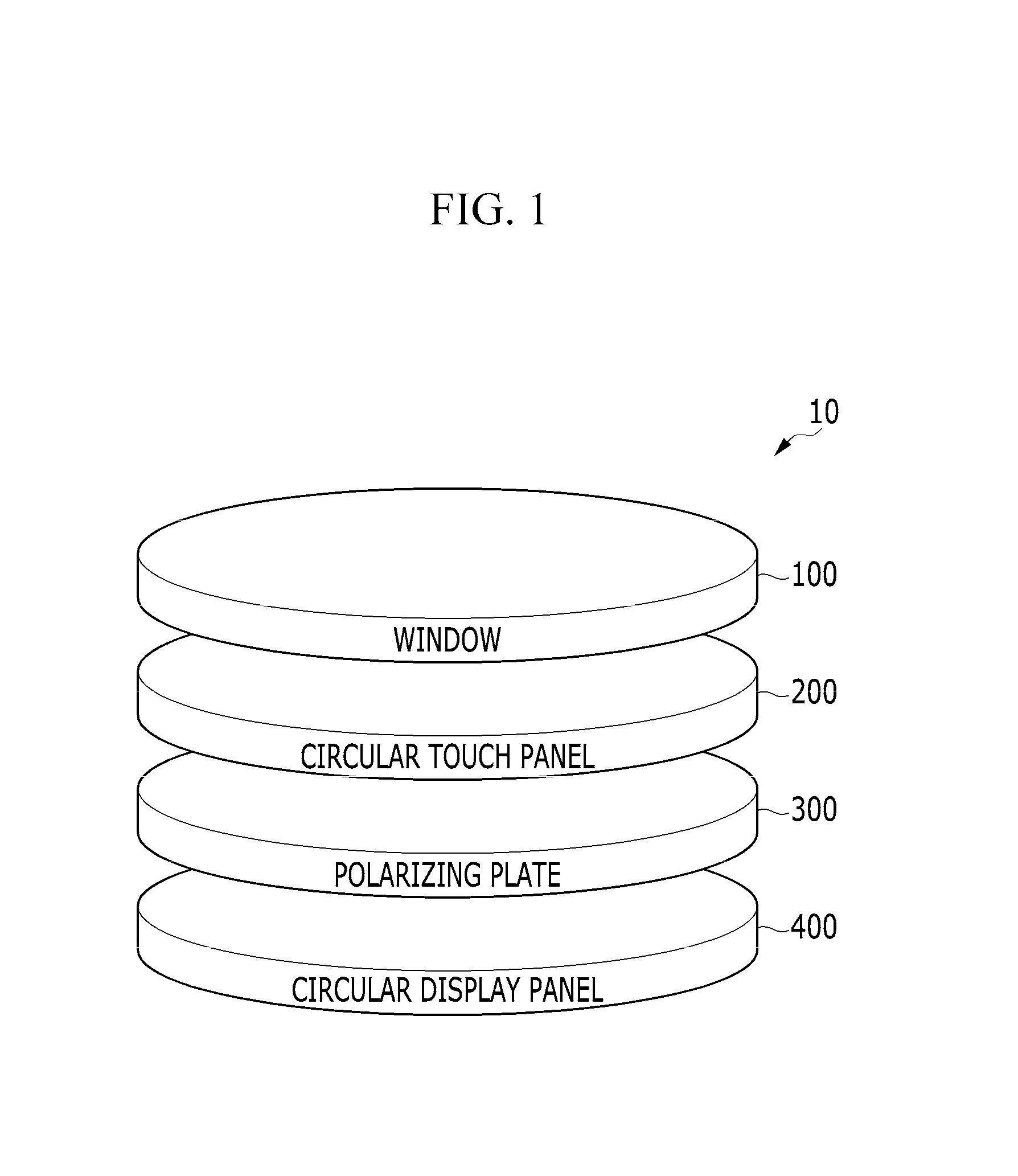
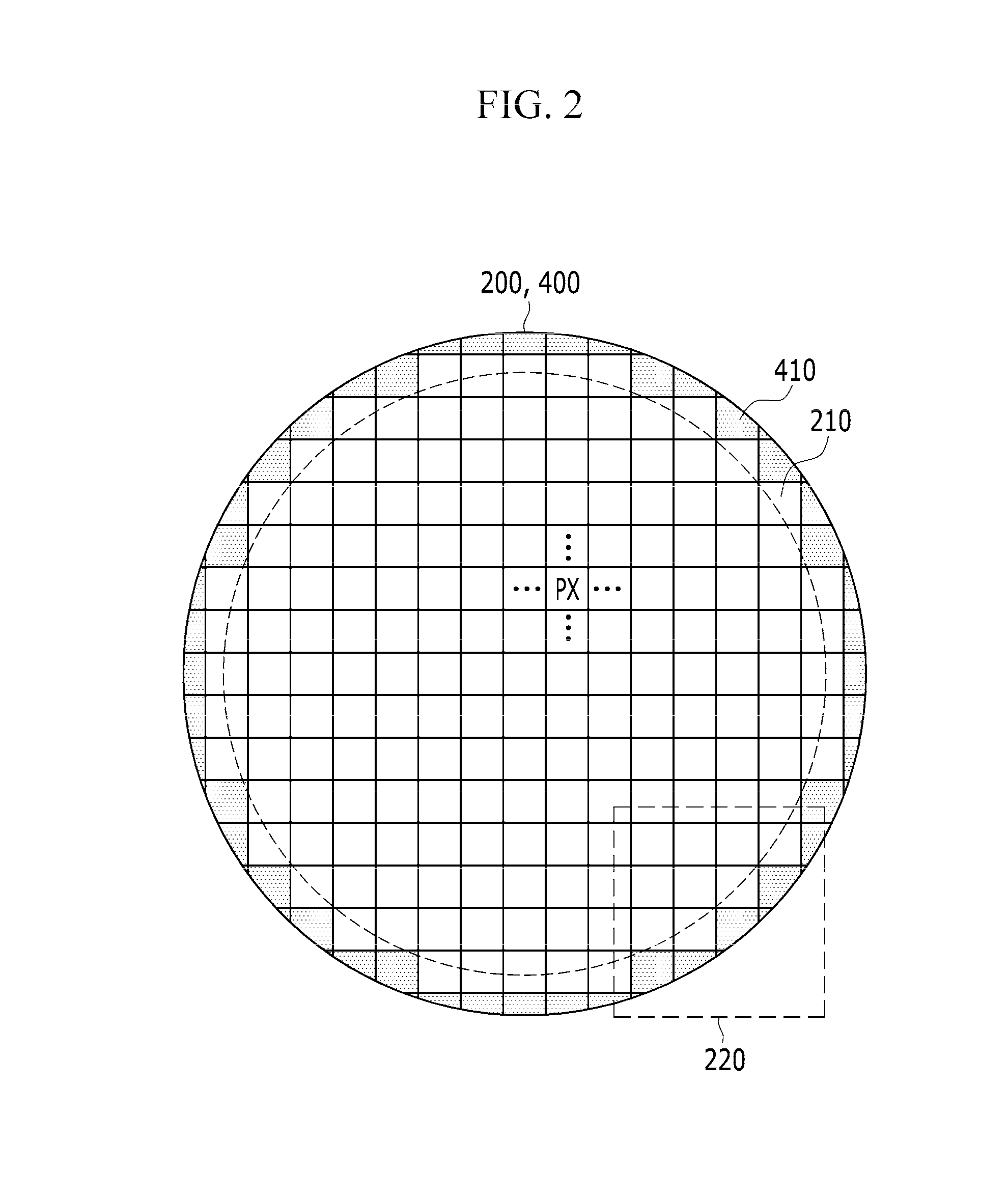
Circular touch panel and manufacturing method of the same
InactiveUS20160239131A1Input/output processes for data processingSignal processing circuitsEngineering
A circular touch panel disposed on a circular display panel including a plurality of pixels, the circular touch panel including: a plurality of sensing electrodes; a plurality of connection wirings connecting the plurality of sensing electrodes to a signal processing circuit; and an insulator insulating the plurality of sensing electrodes from each other. The circular touch panel includes a circular boundary region patterned in an optical pattern.
Owner:SAMSUNG DISPLAY CO LTD
Solar cell and method of manufacturing the same
ActiveUS20150144183A1Improve efficiencyMaximizing conversionFinal product manufactureSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingBoundary regionSolar cell
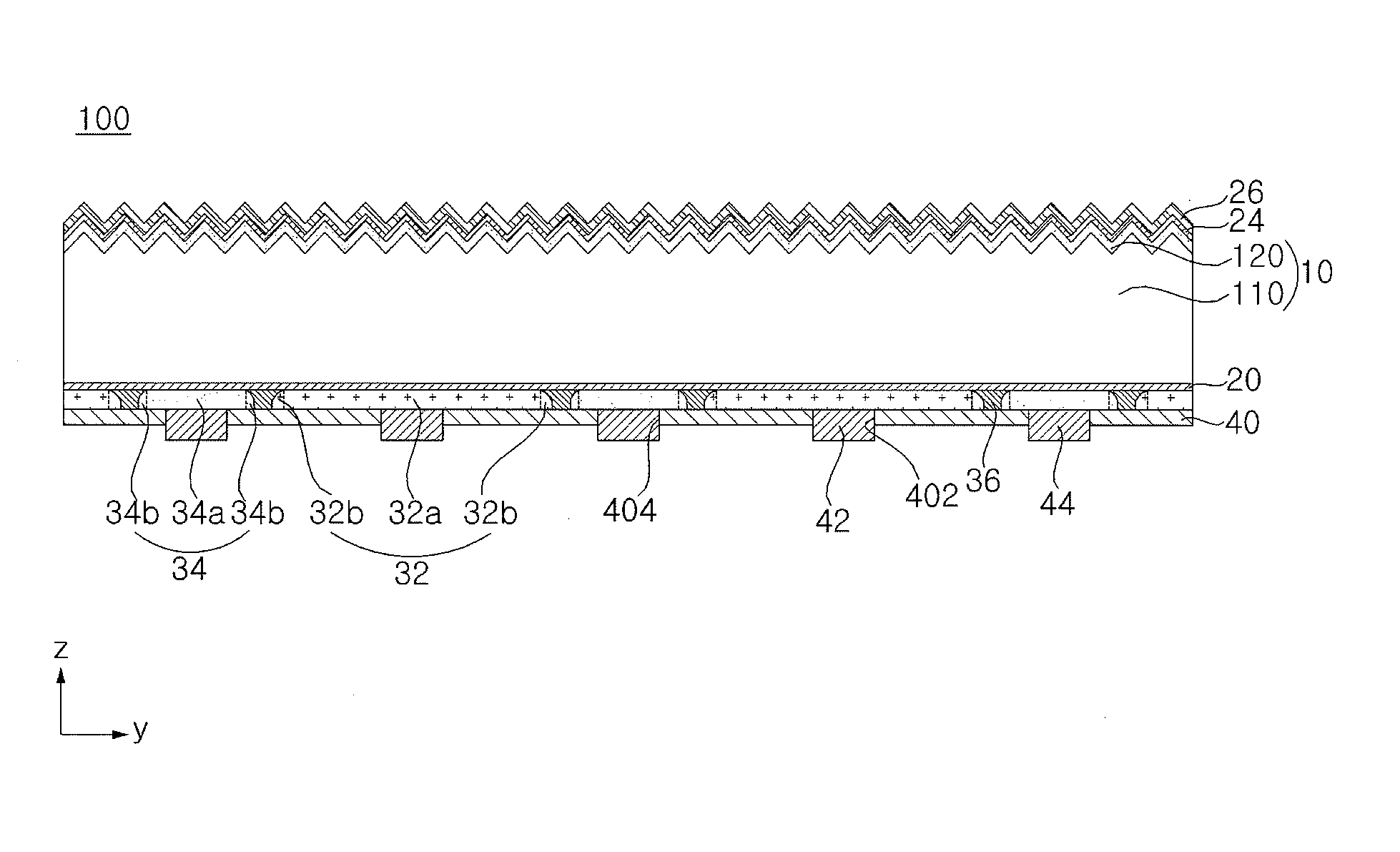
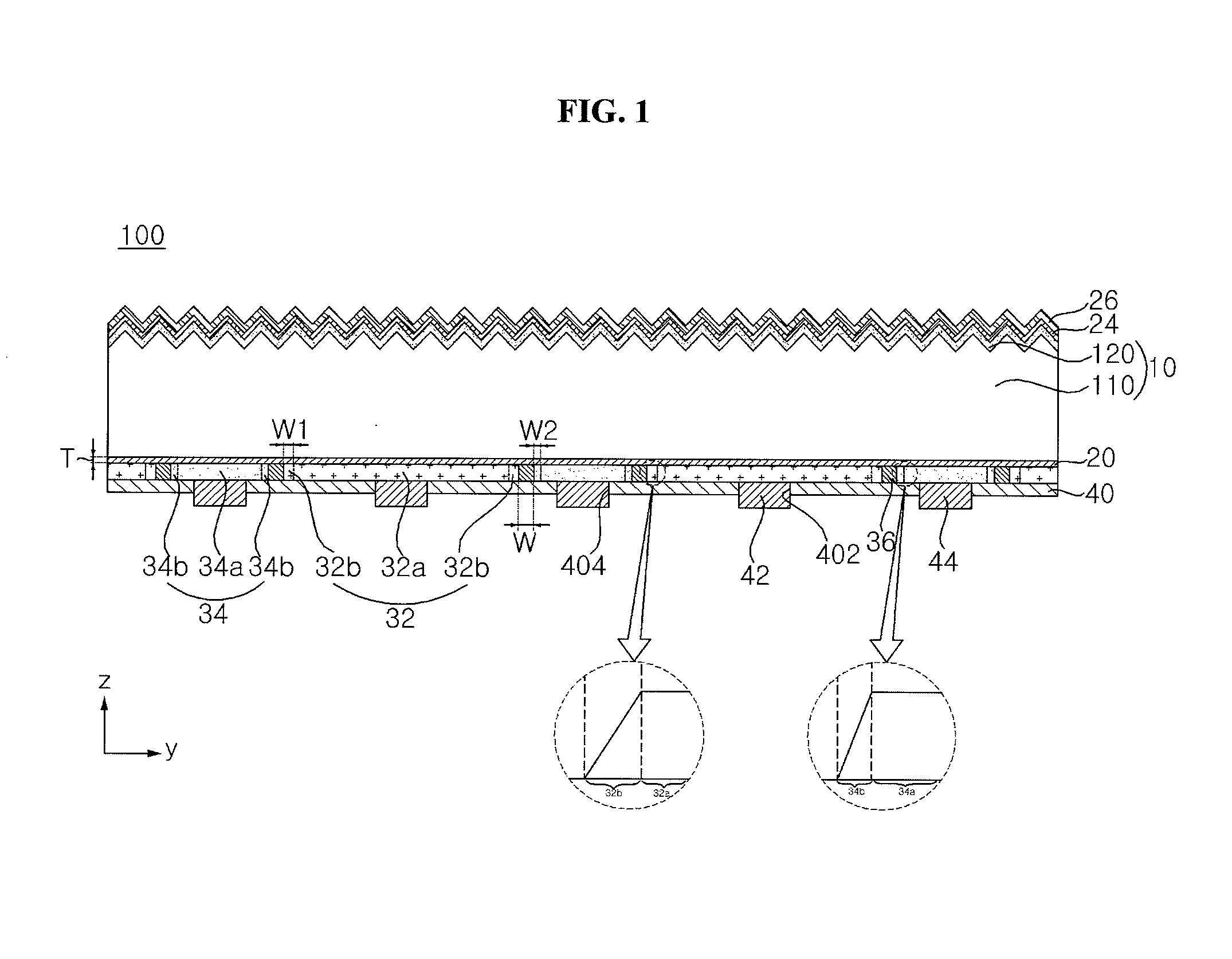
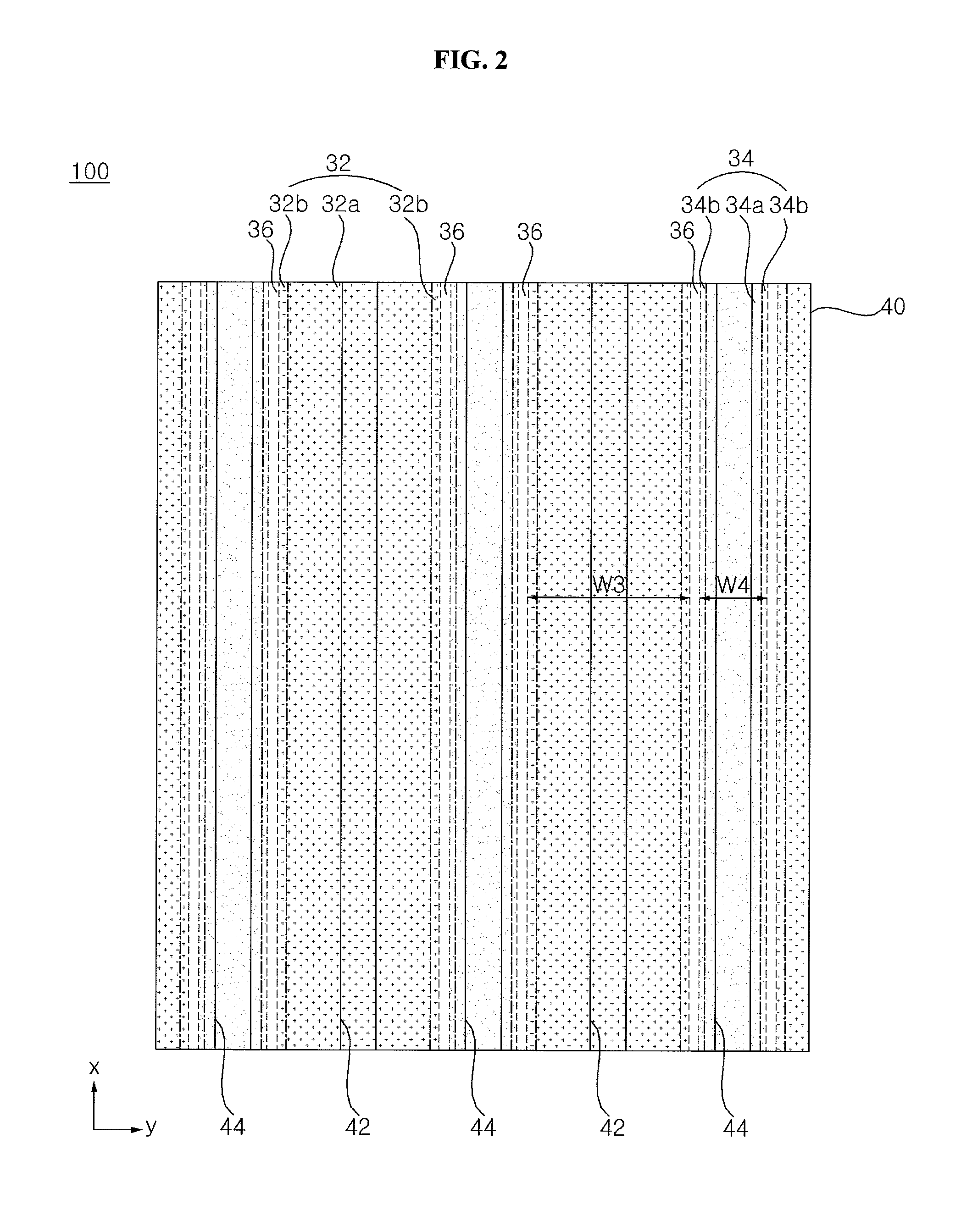
A solar cell is discussed. The solar cell according to an embodiment includes a semiconductor substrate, a first conductive type region and a second conductive type region disposed on the same side of the semiconductor substrate, wherein at least one of the first and second conductive type regions includes a main region and a boundary region disposed at a peripheral portion of the main region, and the boundary region has at least one of a varying doping concentration and a varying doping depth.
Owner:SHANGRAO JINKO SOLAR TECH DEV CO LTD
Lane line detection method based on monocular vision
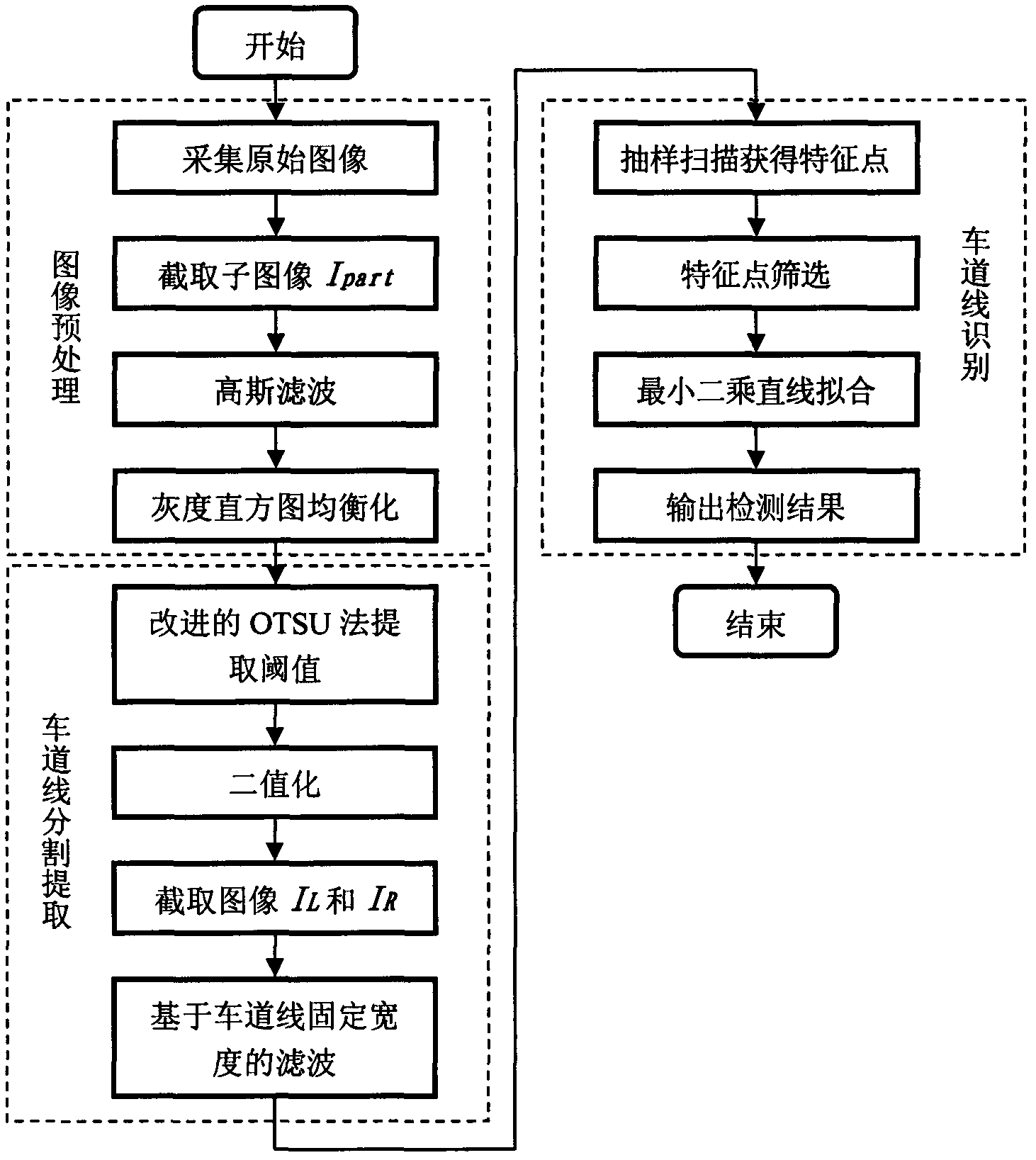
InactiveCN102629326AGood split extractionSmall amount of calculationCharacter and pattern recognitionActive safetyPattern recognition
The invention belongs to the technical field of vehicle active safety and relates to a lane line detection method based on monocular vision. The lane line detection method comprises the following steps: acquiring an original image of a road condition in front of a vehicle; intercepting subimages of boundary regions at the two sides, wherein the subimages include the original image; removing the high-frequency noise of the subimages and carrying out grey level histogram equalization and binaryzation; intercepting left and right lane line detection region images; filtering based on the fixed width range of a lane line according to the features of low grey value pavements at the two sides of the lane line; preliminarily determining feature points of the lane line in a sampling line scanning manner and screening; and carrying out lane detection. The lane line detection method has the characteristics of good real time and high reliability.
Owner:TIANJIN POLYTECHNIC UNIV
Light emitting device and method for fabricating the same
ActiveUS20100006881A1Solve deteriorationTransistorSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsMetallic materialsBoundary region
There is provided a light emitting device, which comprises compound semiconductor layers including a first conductive semiconductor layer, an active layer and a second conductive semiconductor layer; a metal reflection layer formed on a region of the second conductive semiconductor layer; an insulating structure formed at least in a boundary region of the second conductive semiconductor layer; a metal material structure formed to cover the second conductive semiconductor layer having the metal reflection layer and the insulating structure formed; and a substrate bonded to the metal material structure, wherein the boundary region of the second conductive semiconductor layer includes an outer region of the second conductive semiconductor layer along an outer circumference of the second conductive semiconductor layer.
Owner:SEOUL VIOSYS CO LTD
Geographic coding method, position inquiring system and position inquiring method
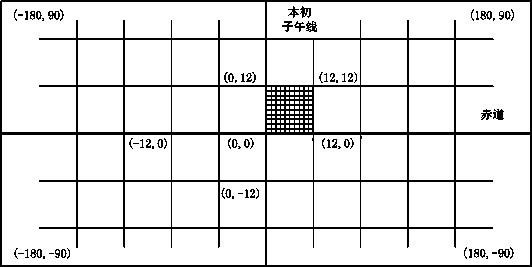
InactiveCN103810194ASolve the boundary point problemEliminate regional errorsGeographical information databasesSpecial data processing applicationsGeolocationBoundary region
The invention discloses a geographic coding method, which comprises the steps that a, the coding precision is determined according to the preset inquiring range; b, the ith division is carried out, the earth surface is divided into a plurality of sub regions, in addition, the numbering is carried out, and each sub region is continuously subjected to number division until each divided region is relevant to the coding precision; c, the fall corresponding sub region number of the specified geographic position is obtained, in addition, whether the number falls in the boundary region of the corresponding sub region or not is judged, and through coding, the one-dimensional ith geographic code and the ith boundary identification are obtained; the steps b to c are repeated for N times so that any specified geographic position at least has the boundary identification of one center region; d, N geographic codes and boundary identifications are combined. The invention also discloses a position inquiring system and a position inquiring method adopting the geographic coding method. The position inquiring system and the position inquiring method are suitable for real-time and massive inquiry of any specified position in the preset inquiring range or the approximate inquiry of nearby positions without the inquiring range.
Owner:刘龙
Noise-reducing transistor arrangement
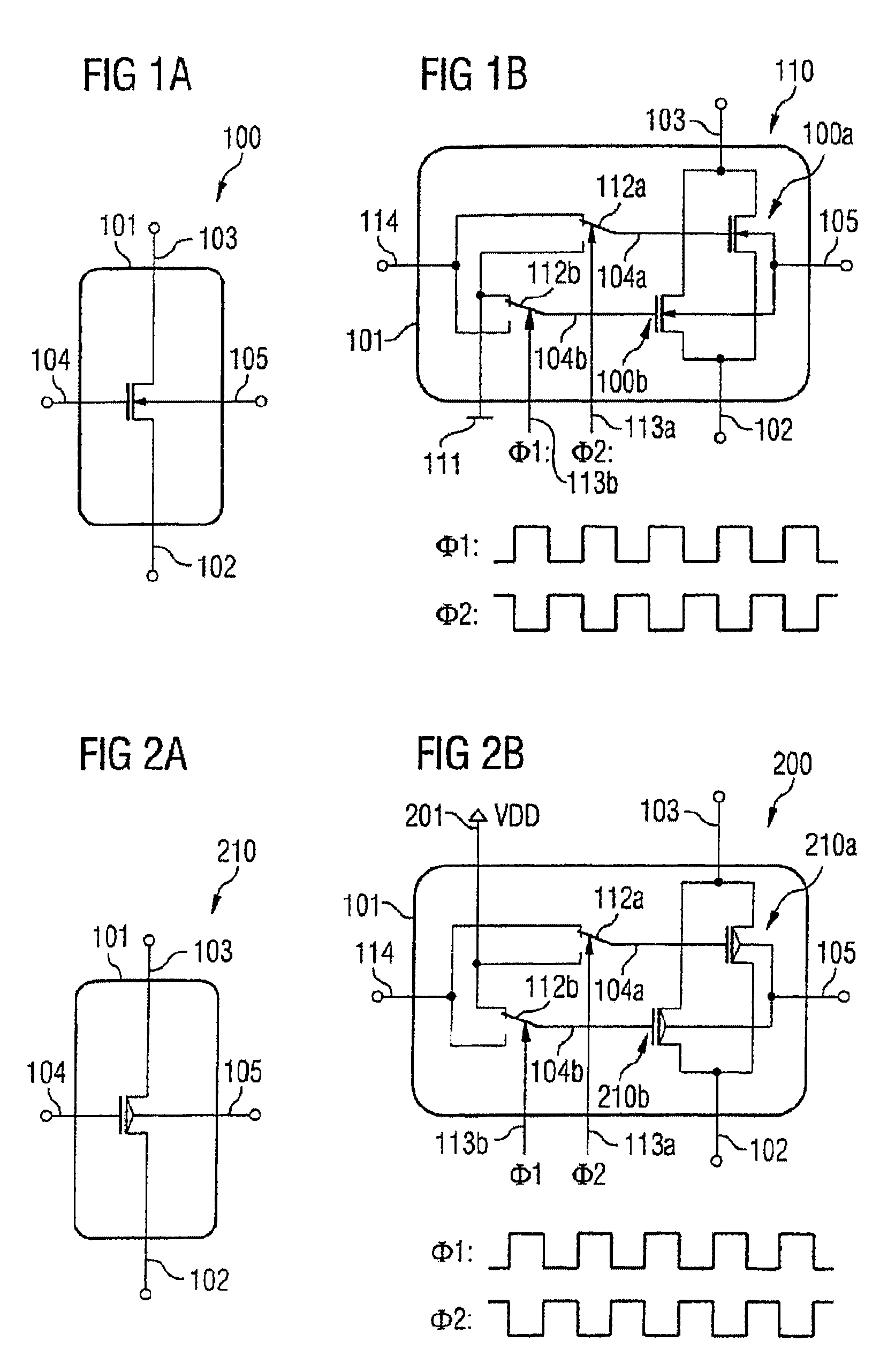
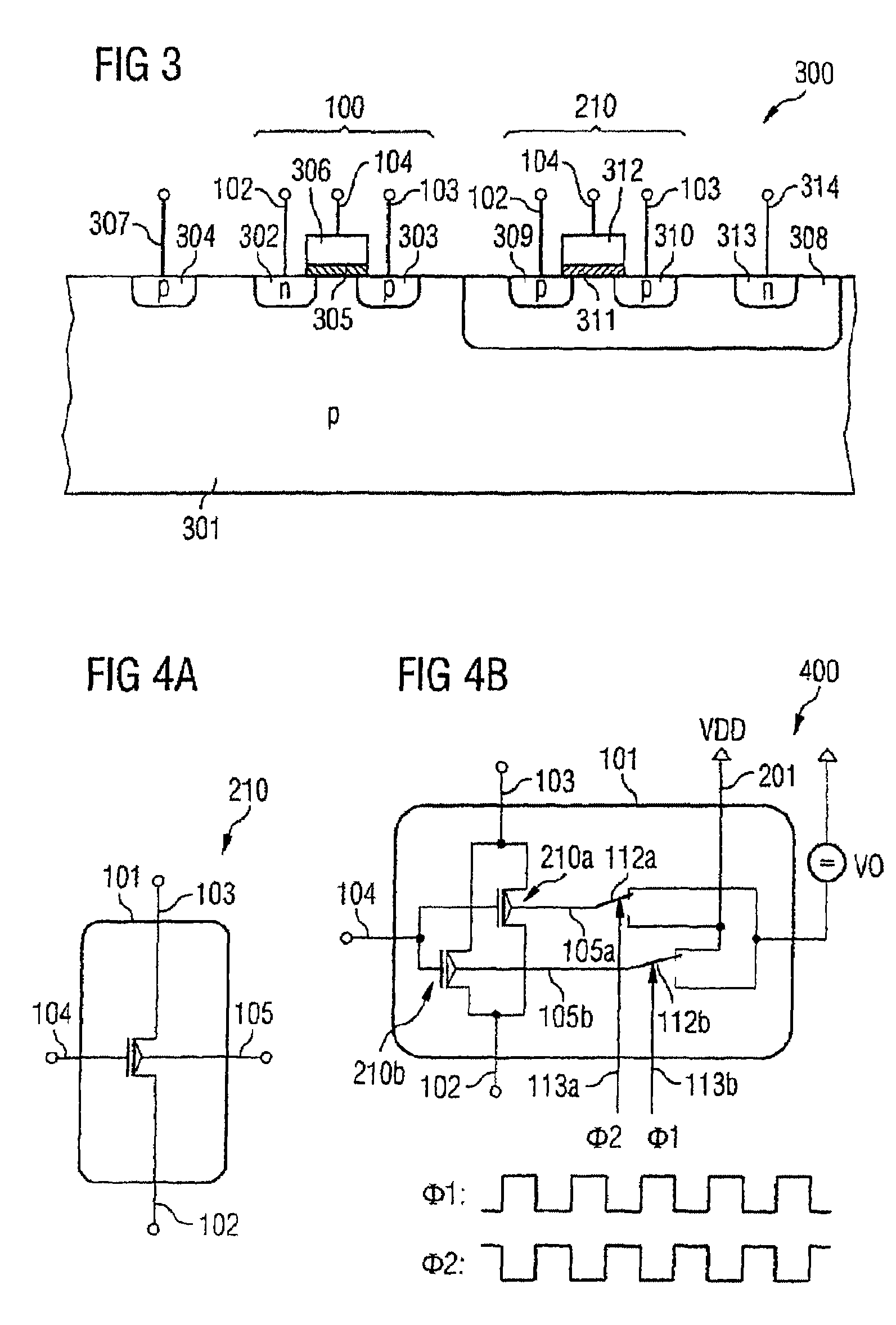
Noise-reducing transistor arrangement having first and second field effect transistors (FETs) having source terminals coupled together, drain terminals coupled together, and control terminals for application of a first or second signal. A clock generator unit is configured to provide the first and second signals alternately to the FETs with an alternating frequency which is at least as great as the cut-off frequency of the noise characteristic of the FETs, or with a reciprocal alternating frequency which is less than a mean lifetime of an occupation state of a defect in the boundary region between channel region and gate insulating layer of the FETs. The first signal is applied to the control terminal of the first FET and, simultaneously, the second signal to the control terminal of the second FET. The second signal is applied to the control terminal of the first FET and, simultaneously, the first signal to the control terminal of the second FET.
Owner:INFINEON TECH AG
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com