Patents
Literature
586results about "From gel state" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
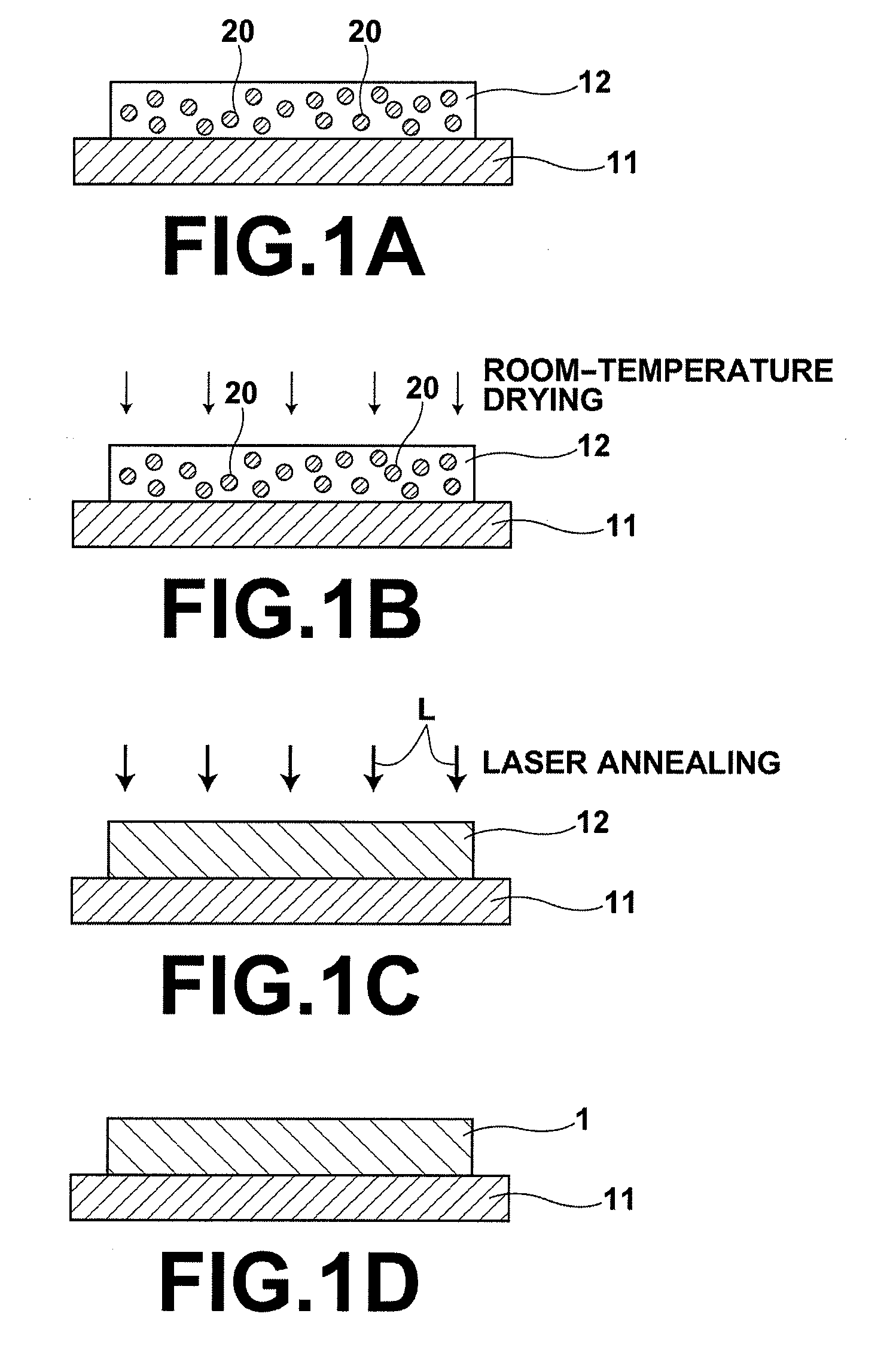
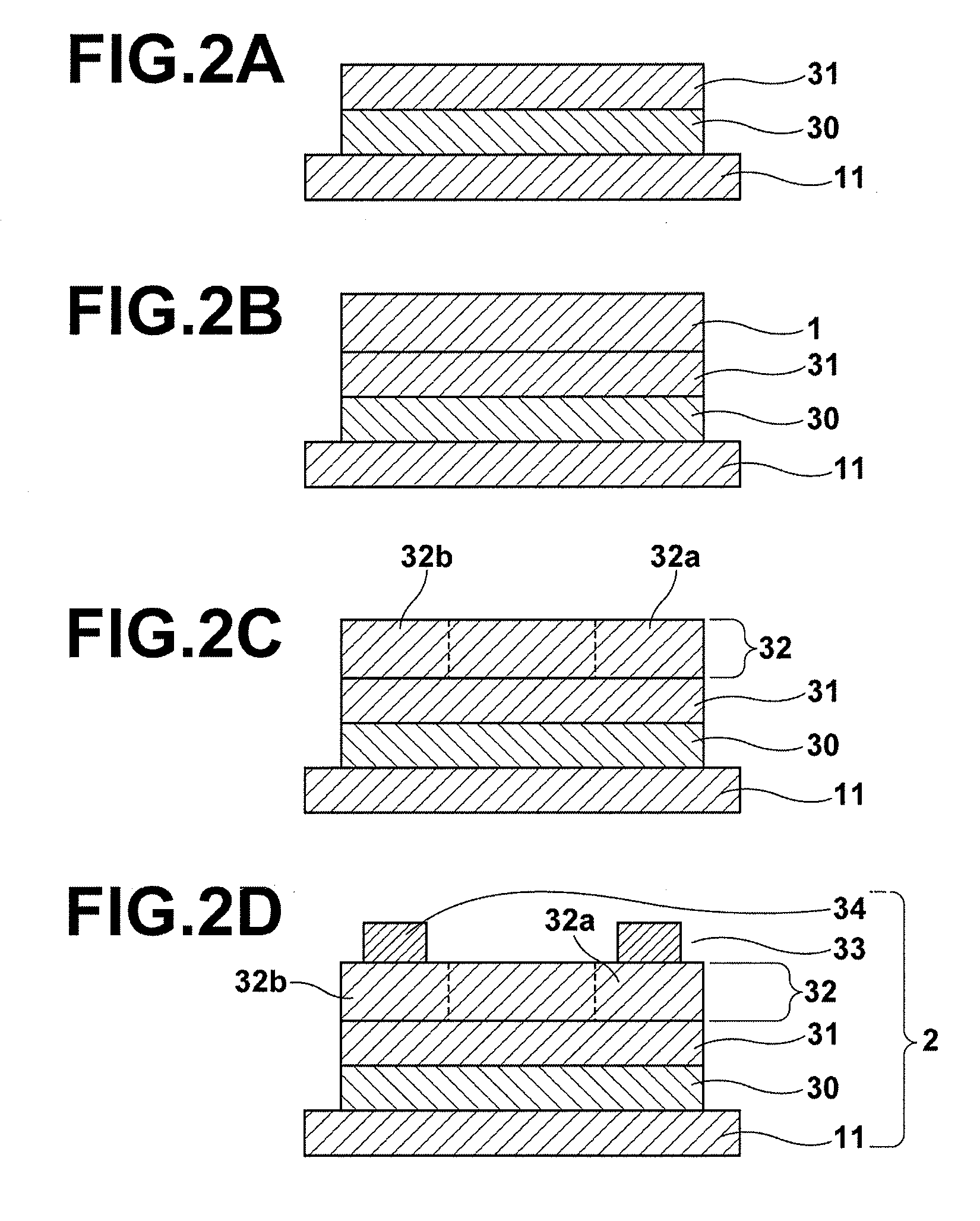
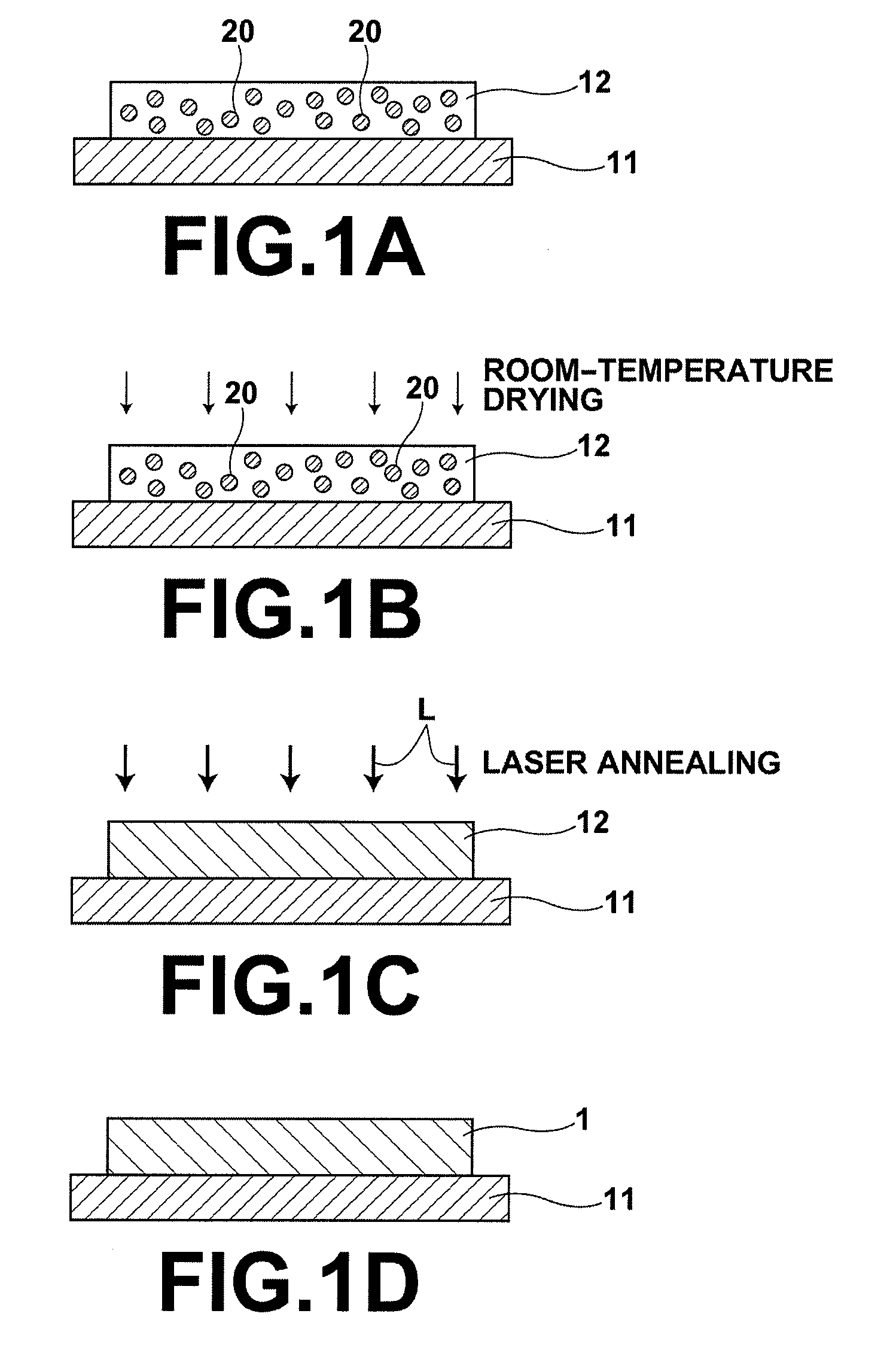
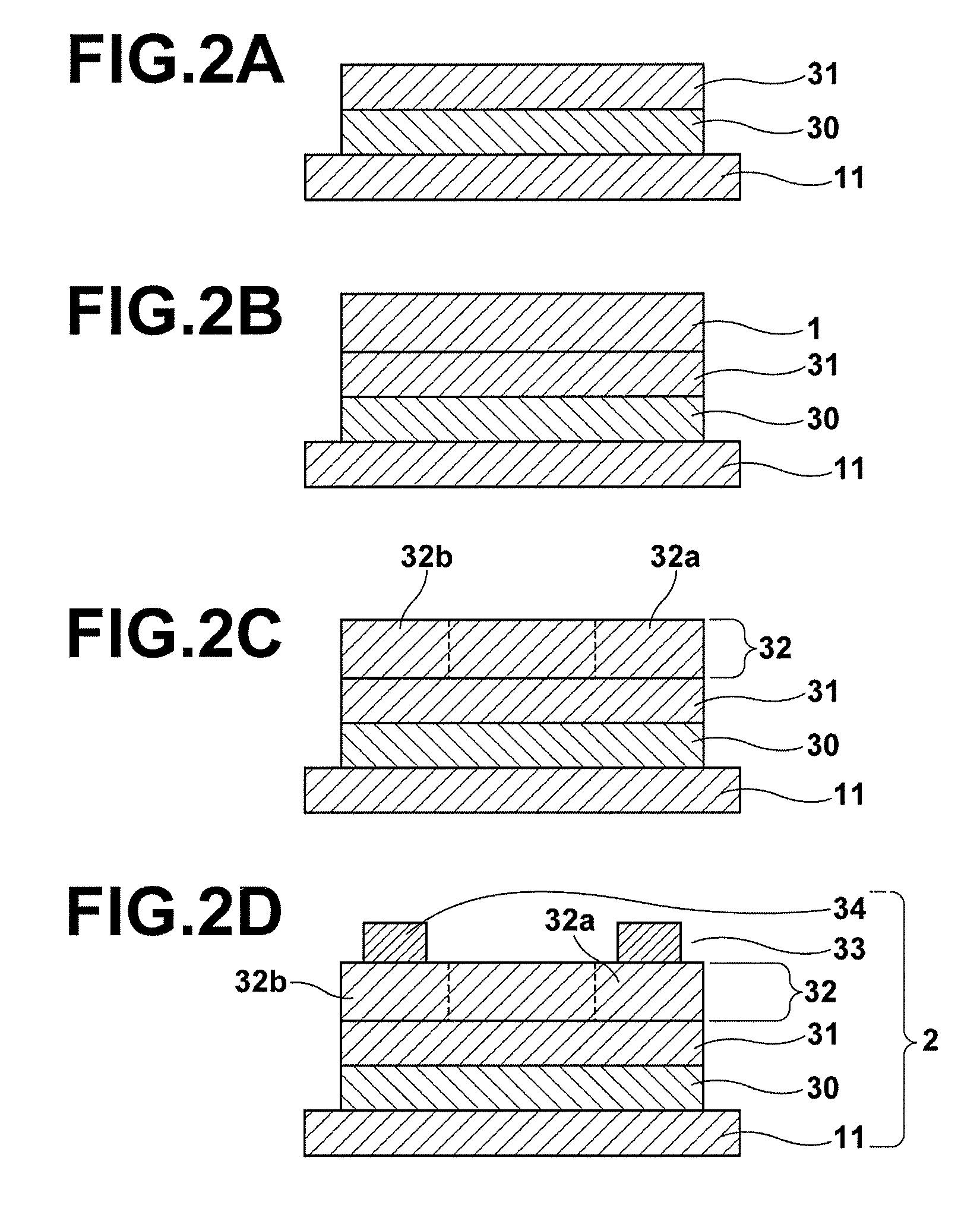
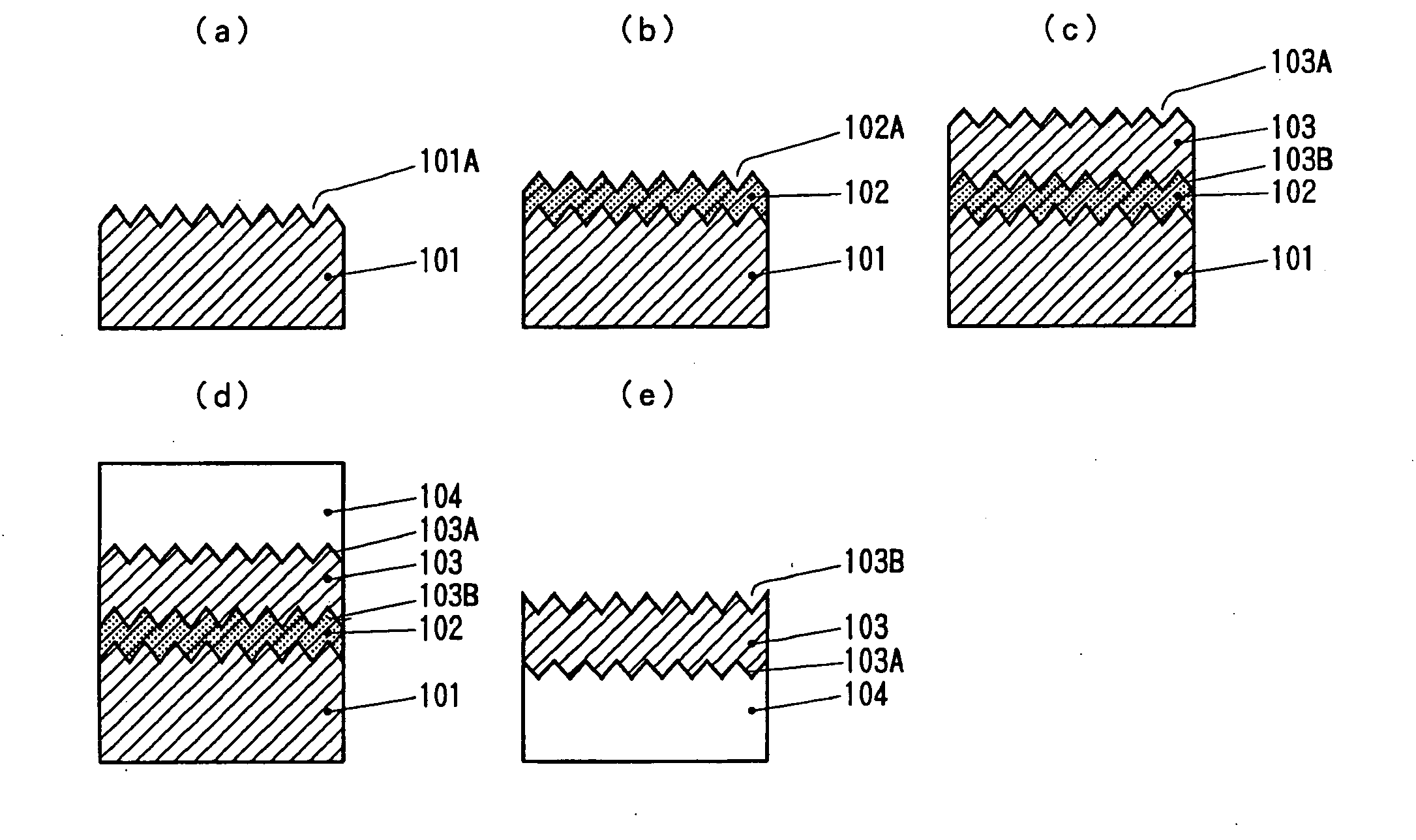
Process for producing oriented inorganic crystalline film, and semiconductor device using the oriented inorganic crystalline film
ActiveUS20090152506A1Orientation can be controlledLow costFrom gel stateFrom solid stateOrganic solventDevice material
In a process for producing an oriented inorganic crystalline film, a non-monocrystalline film containing inorganic crystalline particles is formed on a substrate by a liquid phase technique using a raw-material solution which contains a raw material and an organic solvent, where the inorganic crystalline particles have a layered crystal structure and are contained in the raw material. Then, the non-monocrystalline film is crystallized by heating the non-monocrystalline film to a temperature equal to or higher than the crystallization temperature of the non-monocrystalline film so that part of the inorganic crystalline particles act as crystal nuclei.
Owner:FUJIFILM CORP
Process for producing oriented inorganic crystalline film, and semiconductor device using the oriented inorganic crystalline film
ActiveUS8202365B2Orientation can be controlledLow costFrom gel stateFrom solid stateOrganic solventCrystal structure
In a process for producing an oriented inorganic crystalline film, a non-monocrystalline film containing inorganic crystalline particles is formed on a substrate by a liquid phase technique using a raw-material solution which contains a raw material and an organic solvent, where the inorganic crystalline particles have a layered crystal structure and are contained in the raw material. Then, the non-monocrystalline film is crystallized by heating the non-monocrystalline film to a temperature equal to or higher than the crystallization temperature of the non-monocrystalline film so that part of the inorganic crystalline particles act as crystal nuclei.
Owner:FUJIFILM CORP
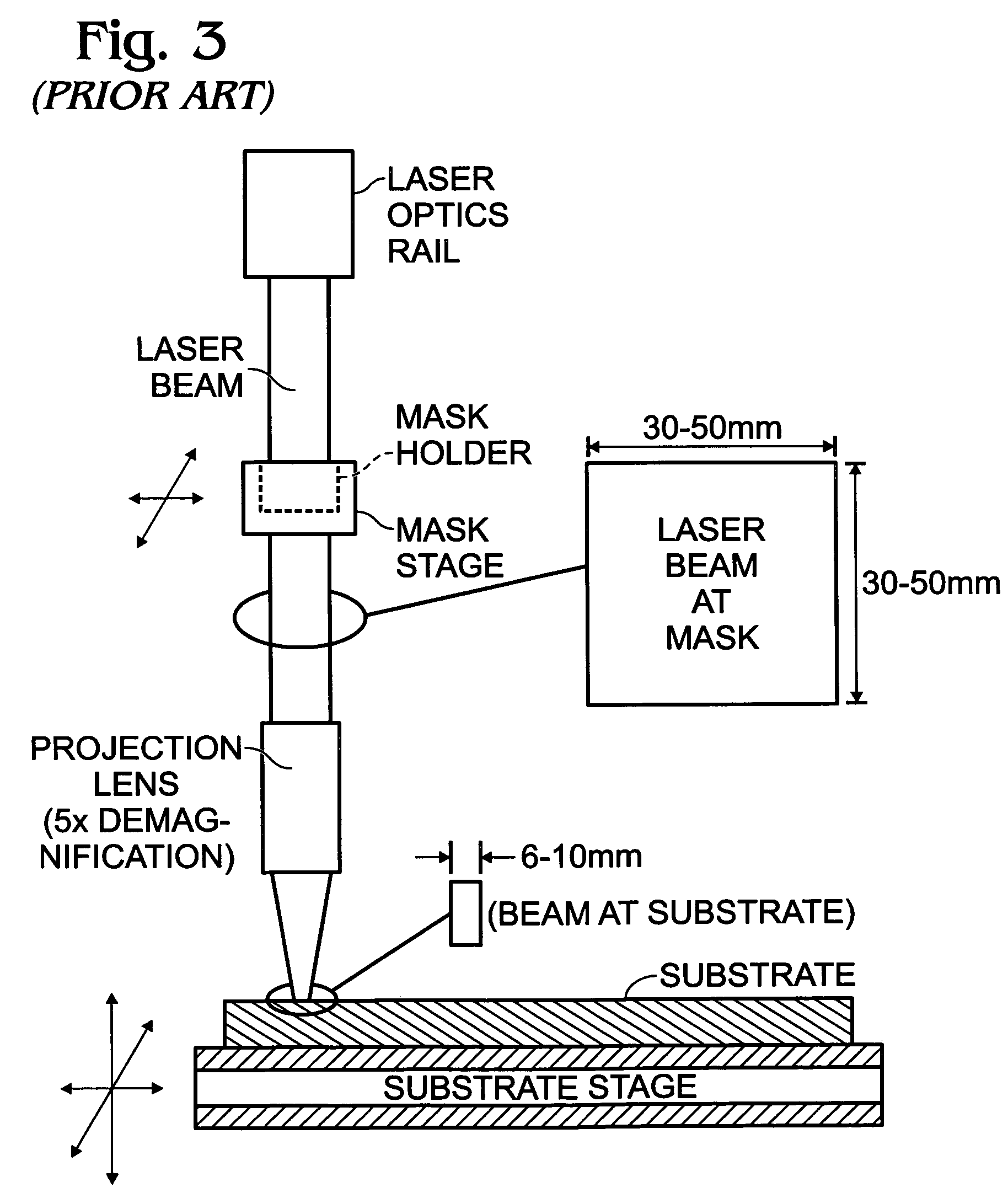
Laser irradiation process
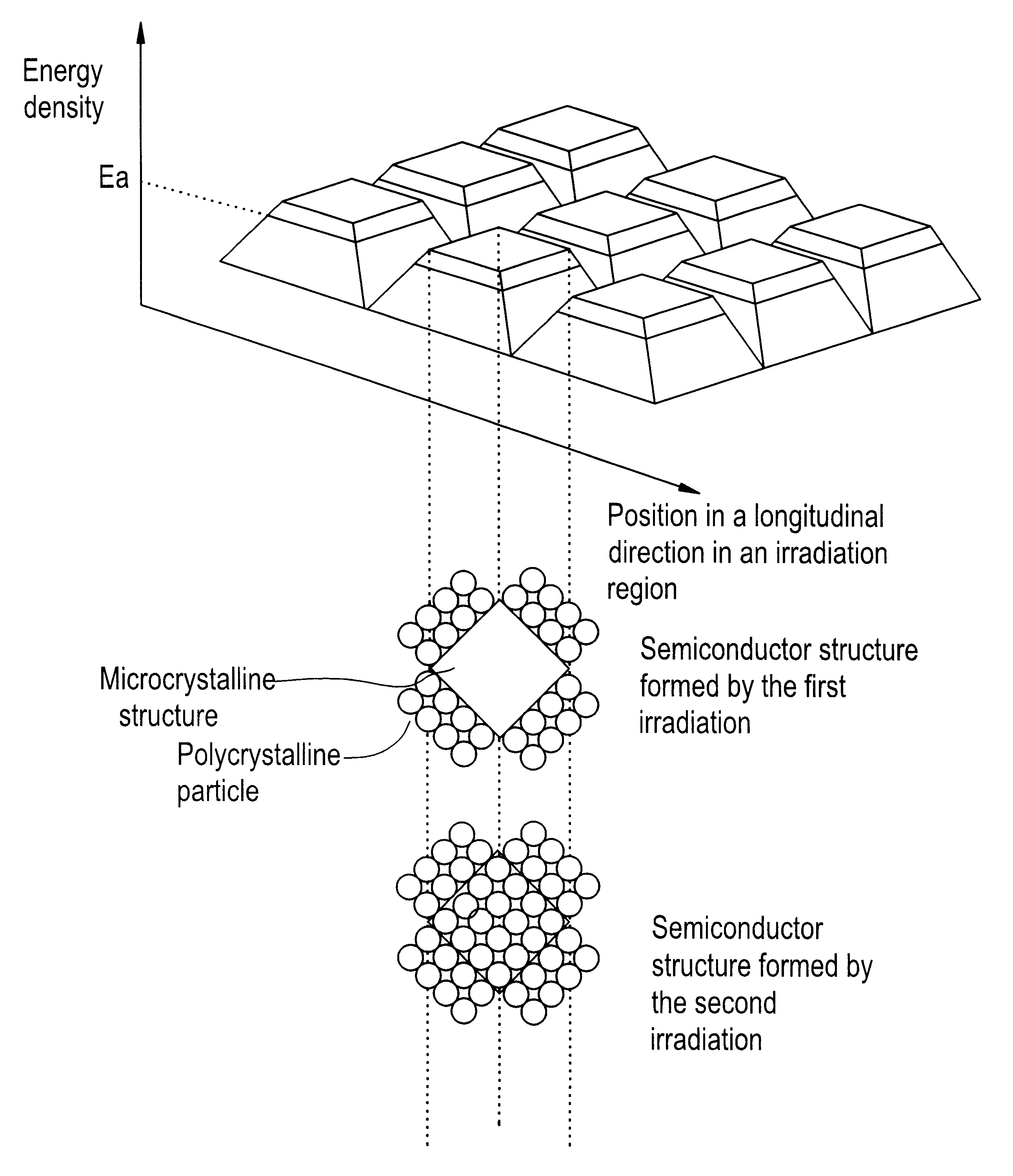
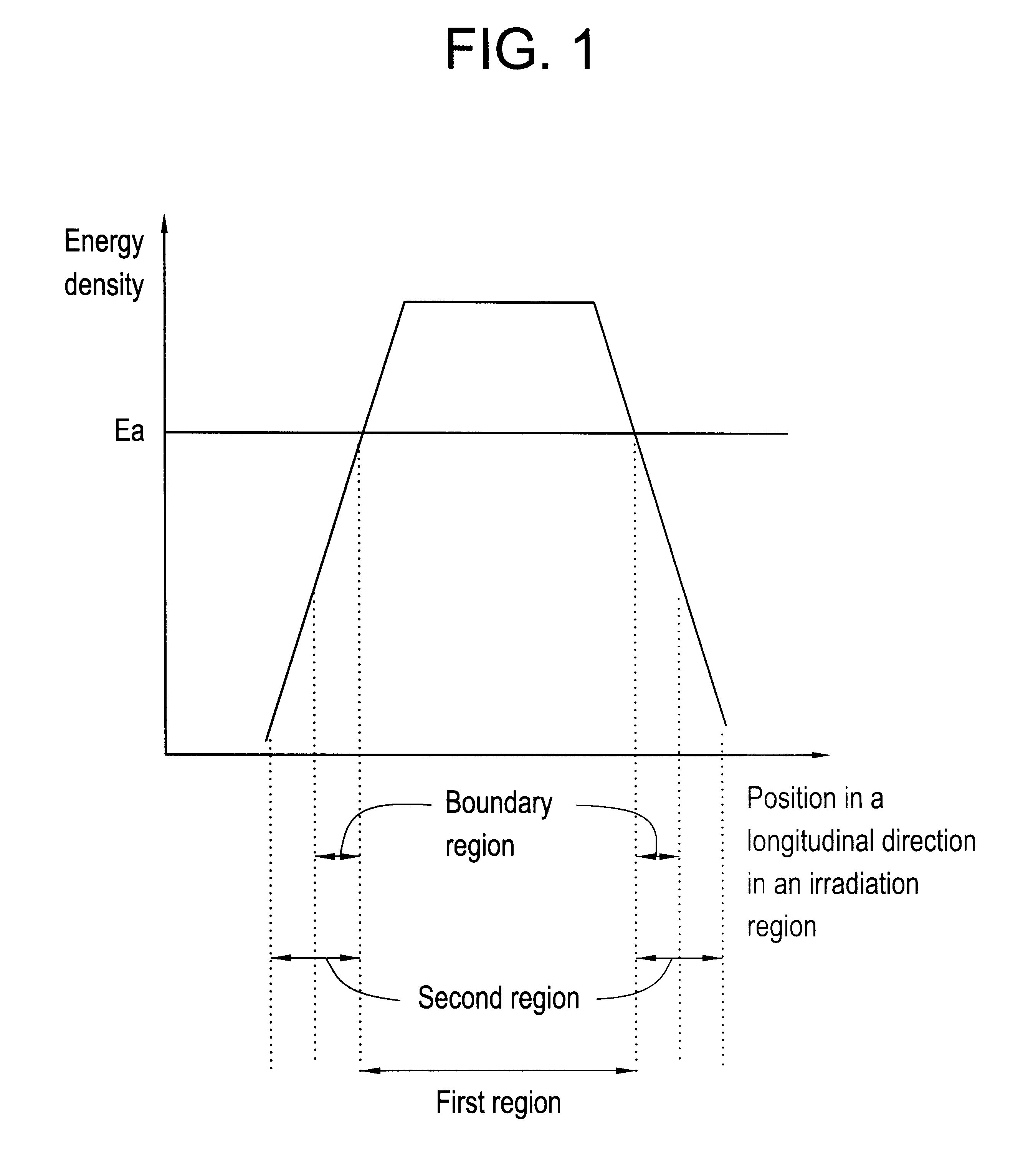
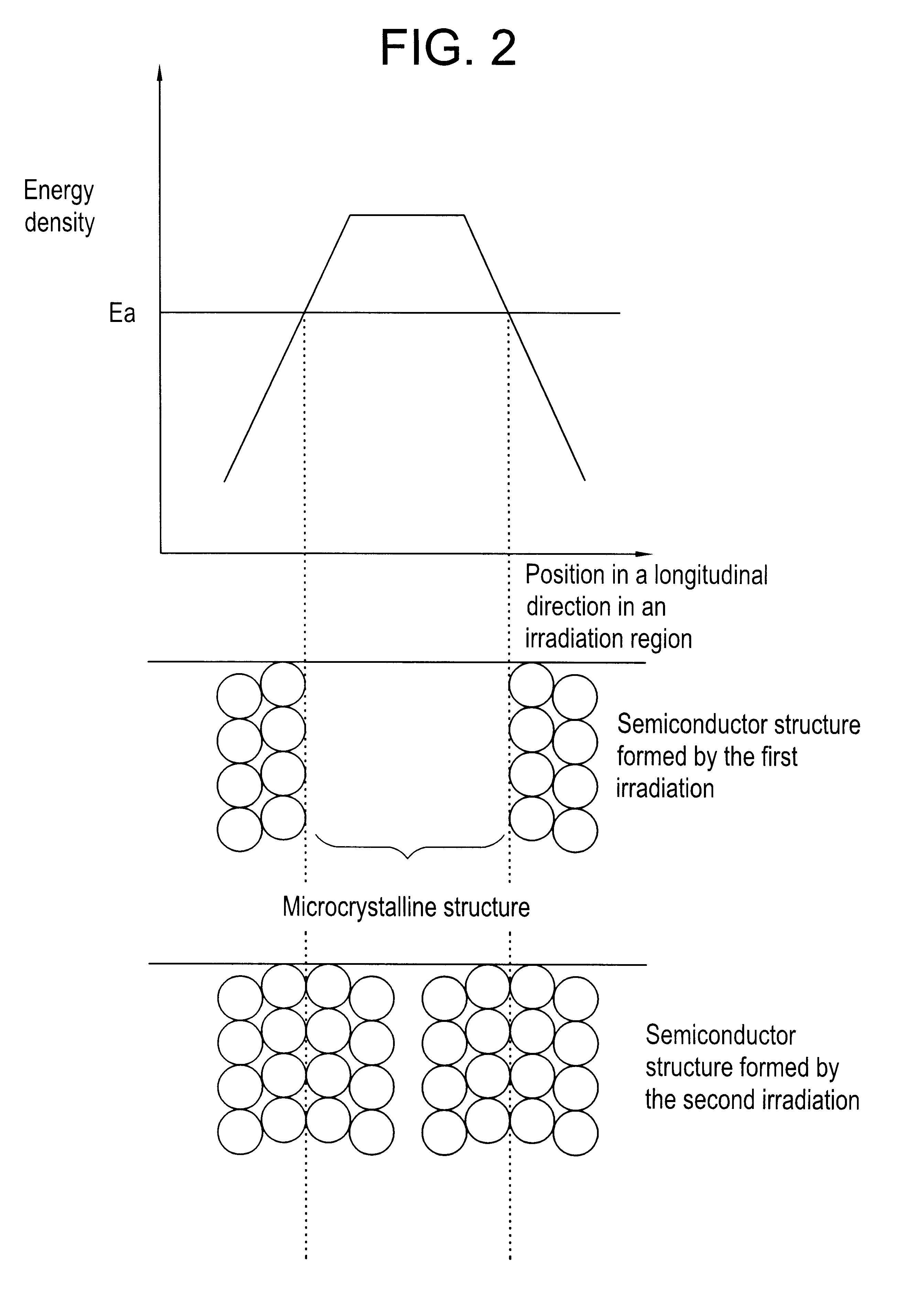
A pulse laser beam having a rectangular irradiation region is irradiated on the same point in a non-single crystal semiconductor film multiple times. The pulse laser beam has an energy profile in a longitudinal direction in the beam irradiation region as follows: (a) there are the first region having an energy density of Ea or higher and the second regions on both sides of the first region having an energy density of less than Ea, and (b) an energy density slope has an absolute value of 20 to 300 J / cm3 in a boundary region extending to 1 mum from the boundary line between the first and the second regions.
Owner:GOLD CHARM LTD
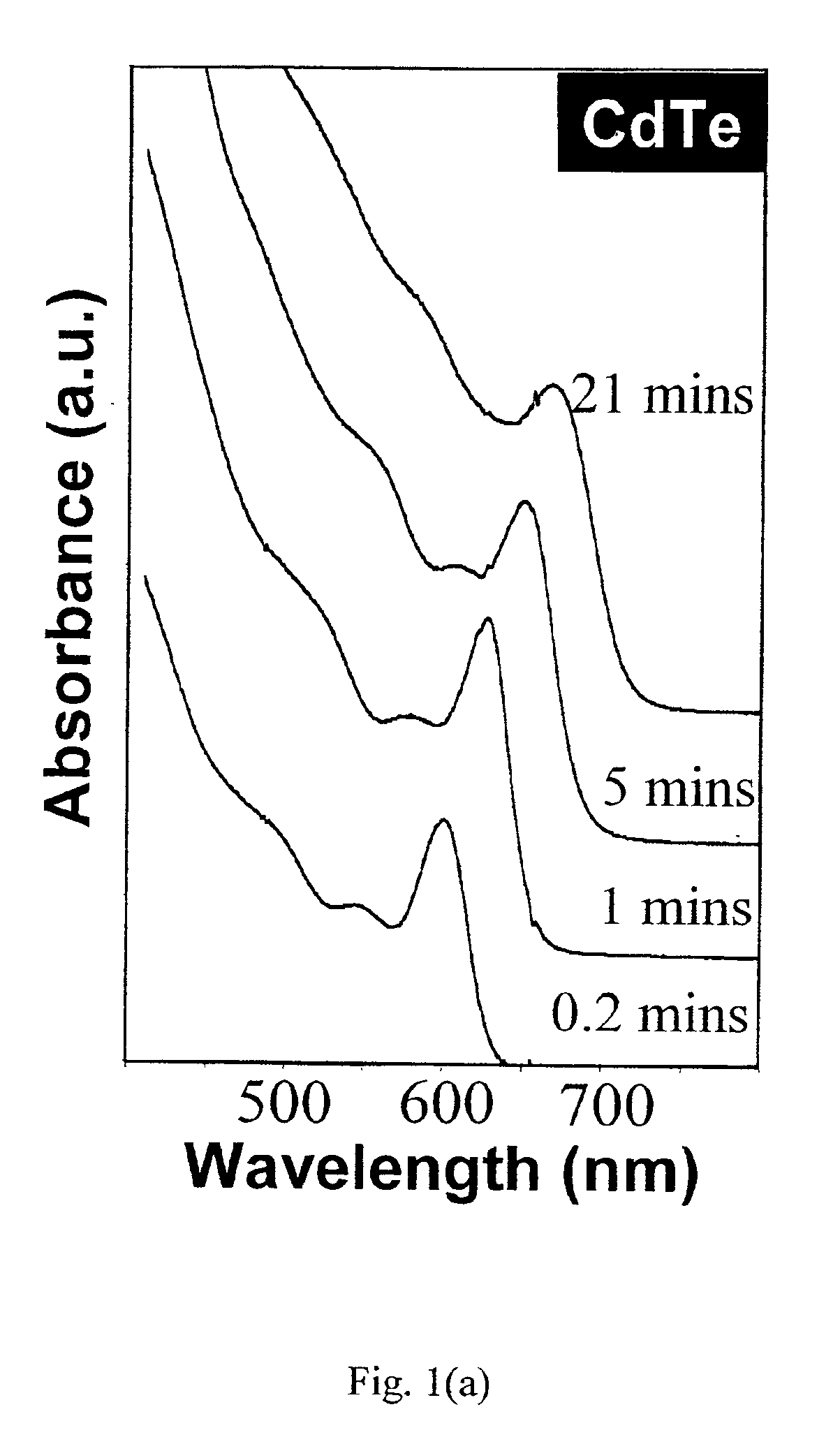
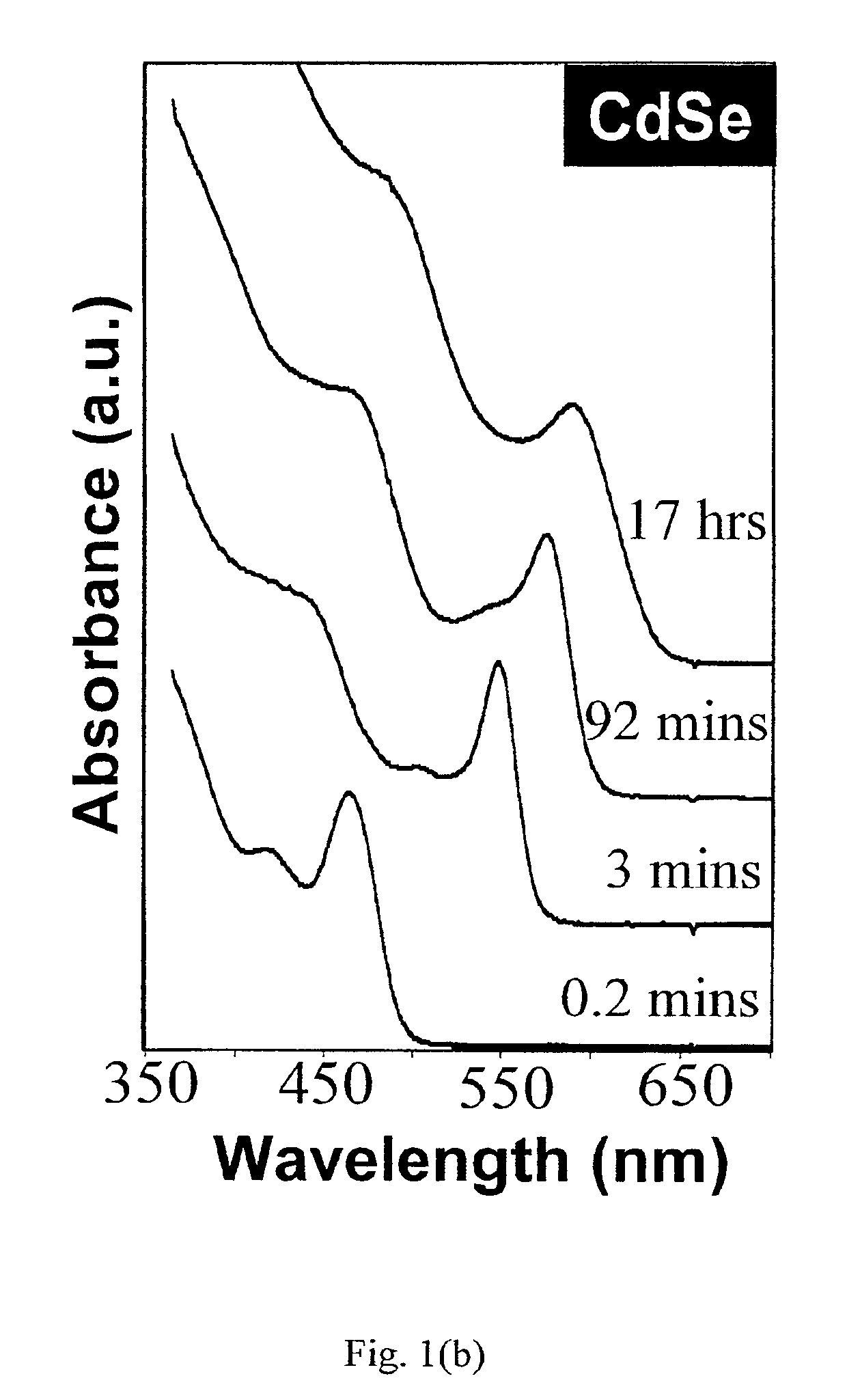
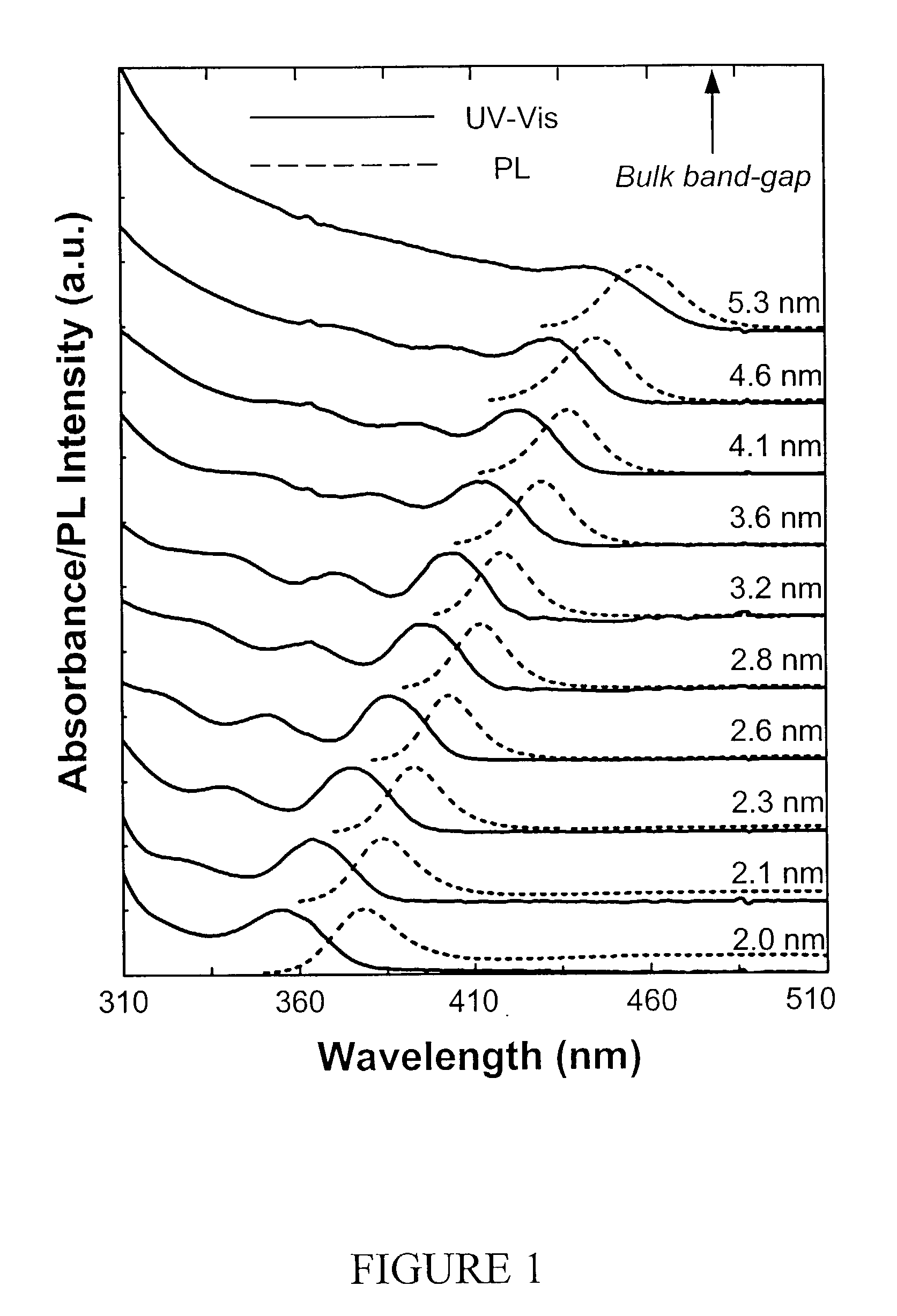
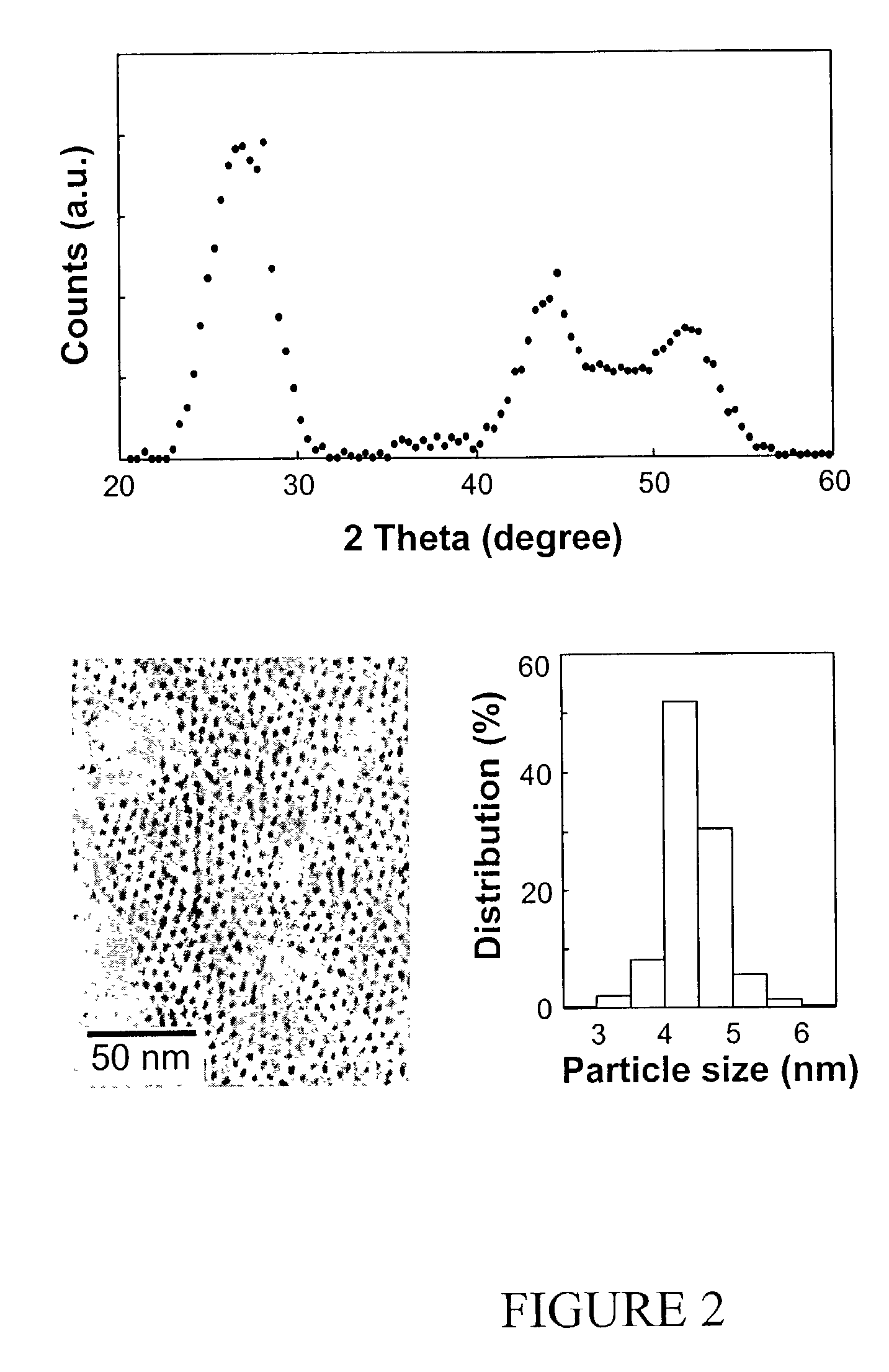
Synthesis of colloidal nanocrystals
InactiveUS6872249B2High crystallinityGood monodispersityFrom gel stateMaterial nanotechnologyPresent methodSulfur
A method of synthesizing colloidal nanocrystals is disclosed using metal oxides or metal salts as a precursor. The metal oxides or metal salts are combined with a ligand and then heated in combination with a coordinating solvent. Upon heating, the metal oxides or salts are converted to stable soluble metal complexes. The metal complexes are formed by cationic species combining with the ligands and / or with the coordinating solvent. Finally, an elemental chalcogenic precursor, for example, Se, Te, or S, is introduced into the soluble metal complex to complete the formation of the nanocrystals at a controllable rate. High-quality CdSe, CdTe, and CdS nanocrystals are produced when CdO is used as the cadmium precursor. With the present method, the size, size distribution, and shape (dots or rods) of the resulting nanocrystals can be controlled during growth. For example, the resulting nanocrystals are nearly monodisperse without any size separation. Further, the method represents a major step towards a green chemistry approach for synthesizing high-quality semiconductor nanocrystals.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE UNIV OF ARKANSAS
Single crystalline graphene sheet and process of preparing the same
A single-crystal graphene sheet includes a polycyclic aromatic molecule wherein a plurality of carbon atoms are covalently bound to each other, the single-crystal graphene sheet comprising between about 1 layer to about 300 layers; and wherein a peak ratio of a Raman D band intensity to a Raman G band intensity is equal to or less than 0.2. Also described is a method for preparing a single-crystal graphene sheet, the method includes forming a catalyst layer, which includes a single-crystal graphitizing metal catalyst sheet; disposing a carbonaceous material on the catalyst layer; and heat-treating the catalyst layer and the carbonaceous material in at least one of an inert atmosphere and a reducing atmosphere. Also described is a transparent electrode including a single-crystal graphene sheet.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Ternary oxide nanostructures and methods of making same
InactiveUS20070138459A1Suitable for preparationFrom gel stateAlkaline earth titanatesNanostructureDislocation
A single crystalline ternary nanostructure having the formula AxByOz, wherein x ranges from 0.25 to 24, and y ranges from 1.5 to 40, and wherein A and B are independently selected from the group consisting of Ag, Al, As, Au, B, Ba, Br, Ca, Cd, Ce, Cl, Cm, Co, Cr, Cs, Cu, Dy, Er, Eu, F, Fe, Ga, Gd, Ge, Hf, Ho, I, In, Ir, K, La, Li, Lu, Mg, Mn, Mo, Na, Nb, Nd, Ni, Os, P, Pb, Pd, Pr, Pt, Rb, Re, Rh, Ru, S, Sb, Sc, Se, Si, Sm, Sn, Sr, Ta, Tb, Tc, Te, Ti, Ti, Tm, U, V, W, Y, Yb, and Zn, wherein the nanostructure is at least 95% free of defects and / or dislocations.
Owner:THE RES FOUND OF STATE UNIV OF NEW YORK
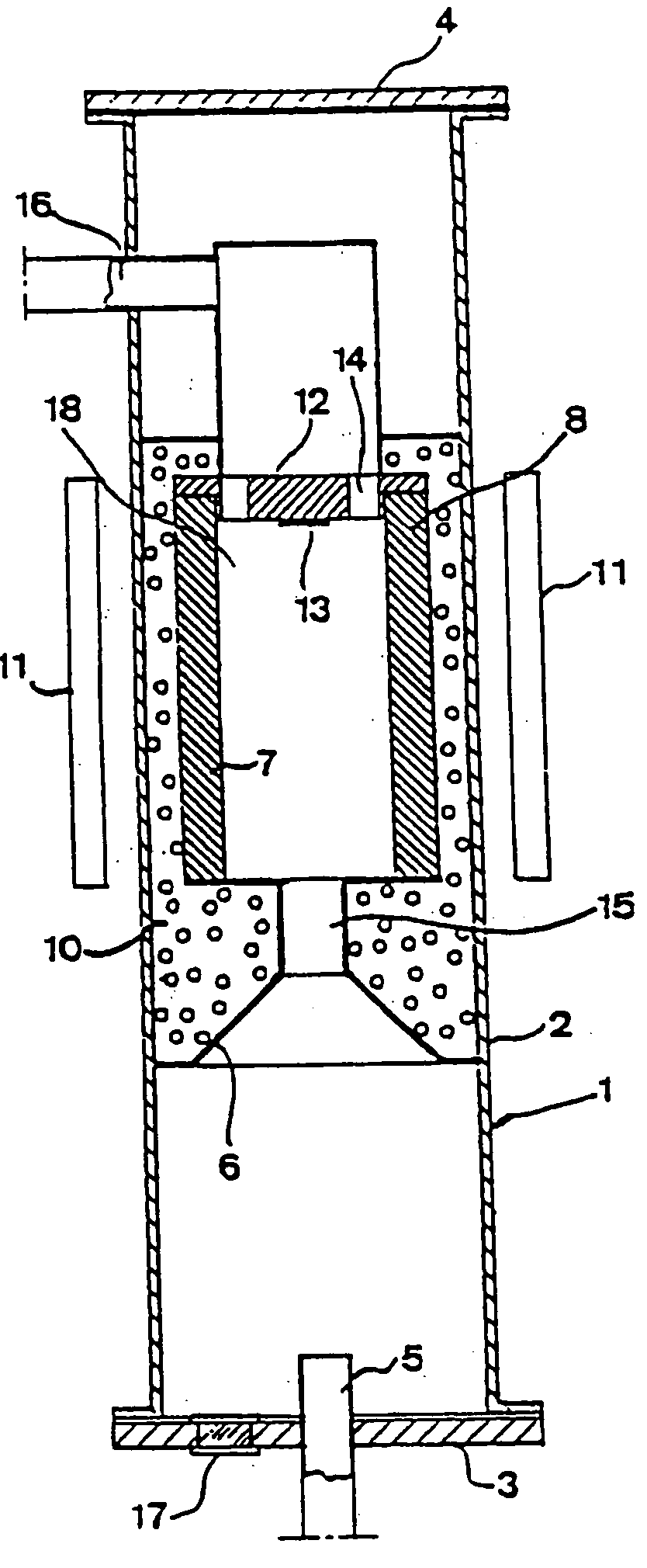
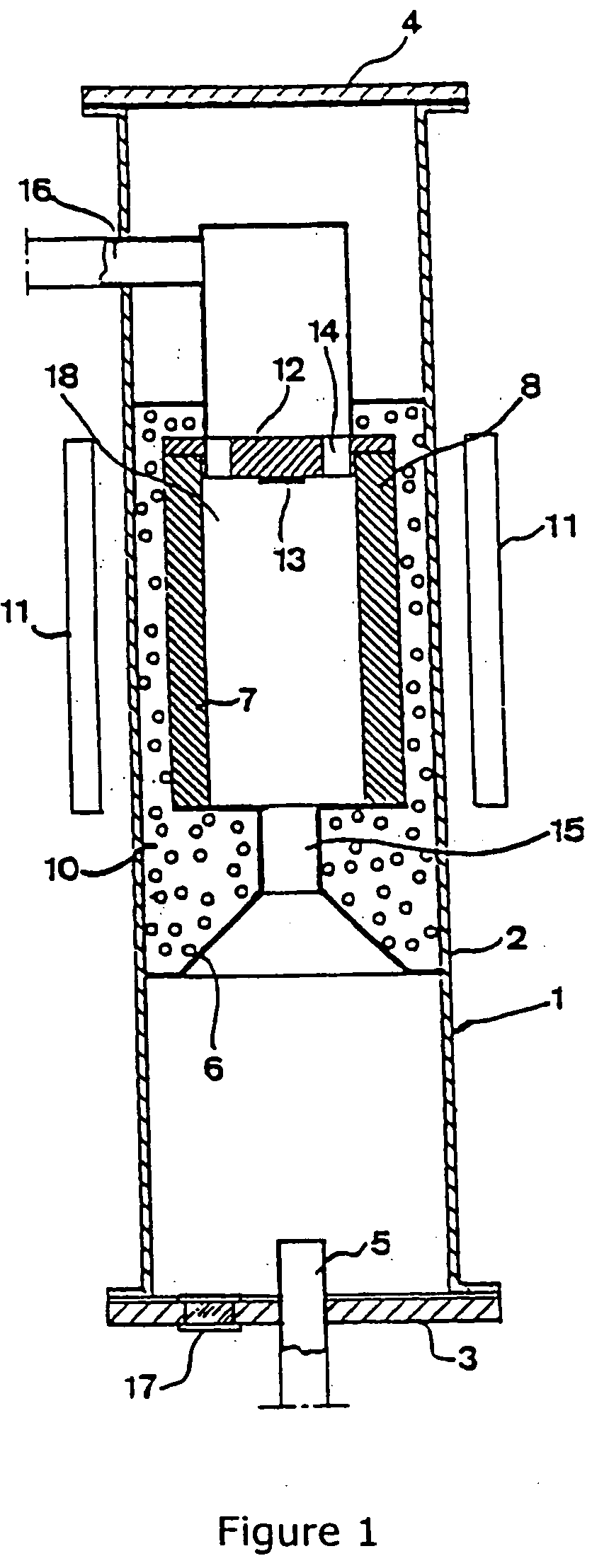
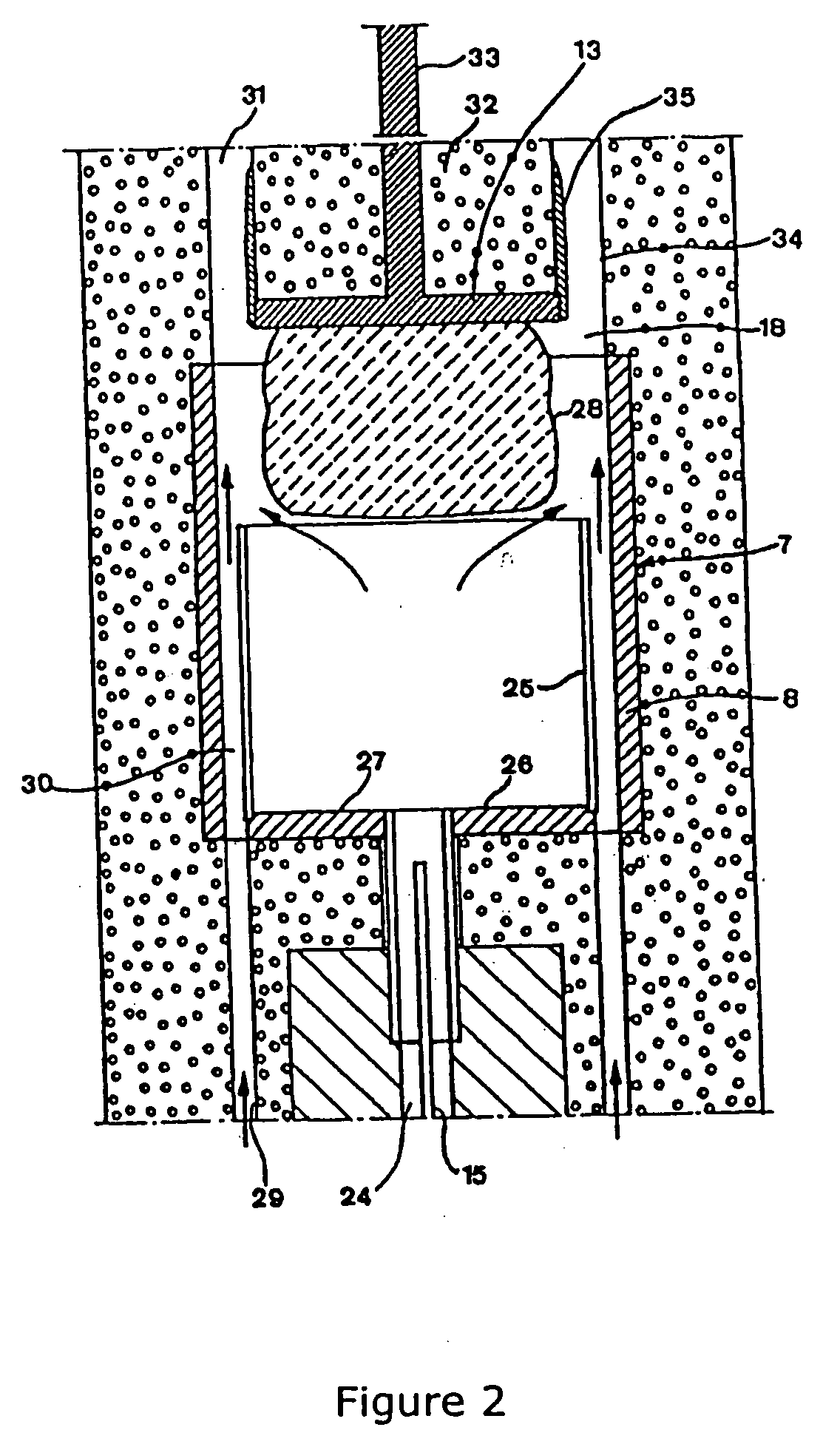
Pressure vessel
InactiveUS20030140845A1Prevent escapeAvoid creatingFrom gel statePolycrystalline material growthTemperature controlPressure transmission
A pressure vessel for processing at least one material in a supercritical fluid. The pressure vessel includes a self-pressurizing capsule for containing at least one material and the supercritical fluid in a substantially air-free environment, a pressure transmission medium surrounding the capsule for maintaining an outer pressure on the capsule, at least one heating element insertable in the pressure transmission medium such that the heating element surrounds the capsule, a temperature measurement means for measuring a temperature of the capsule, a temperature controller for controlling the temperature and providing power to the heating element, a restraint to contain and hold in place the capsule, the pressure transmission medium, and the heating element, and at least one seal between the restraint and the pressure transmission medium for preventing escape of the pressure transmission medium. Methods of using the pressure vessel, processing a material at high temperature and high pressure in the presence of a supercritical fluid within the capsule are also described.
Owner:SORAA
Nitride semiconductor growth method, nitride semiconductor substrate, and nitride semiconductor device
InactiveUS20020046693A1From gel statePolycrystalline material growthCrystallographic defectNitride semiconductors
A method of growing a nitride semiconductor crystal which has very few crystal defects and can be used as a substrate is disclosed. This invention includes the step of forming a first selective growth mask on a support member including a dissimilar substrate having a major surface and made of a material different from a nitride semiconductor, the first selective growth mask having a plurality of first windows for selectively exposing the upper surface of the support member, and the step of growing nitride semiconductor portions from the upper surface, of the support member, which is exposed from the windows, by using a gaseous Group 3 element source and a gaseous nitrogen source, until the nitride semiconductor portions grown in the adjacent windows combine with each other on the upper surface of the selective growth mask.
Owner:NICHIA CORP
Anneal of epitaxial layer in a semiconductor device
InactiveUS7416605B2From gel statePolycrystalline material growthCharge carrier mobilityDegree Celsius
An anneal of an epitaxially grown crystalline semiconductor layer comprising a combination of group-IV elements. The layer contains at least one of the group of carbon and tin. The layer of epitaxially grown material is annealed at a temperature substantially in a range of 1,000 to 1,400 degrees Celsius for a period not to exceed 100 milliseconds within 10% of the peak temperature. The anneal is performed for example with a laser anneal or a flash lamp anneal. The limited-time anneal may improve carrier mobility of a transistor.
Owner:NORTH STAR INNOVATIONS
Fabrication of nanoparticle arrays
The self-assembly of a close-packed, highly-ordered monolayers of molecularly protected nanoparticles on an assembly surface is disclosed. Also disclosed is the transfer of a nanoparticle monolayer from an assembly surface to a transfer surface. The transfer of a monolayer or multilayer structure of nanoparticles from a transfer surface to a substrate by conformal contact of the transfer surface with the substrate is disclosed. Also disclosed is the removal of protective molecules from nanoparticle cores by exposure to an oxidizing atmosphere (optionally in the presence of UV radiation). The exchange of protective molecules in molecularly protected nanoparticles with other molecules is also disclosed.
Owner:PURDUE RES FOUND INC
High quality colloidal nanocrystals and methods of preparing the same in non-coordinating solvents
InactiveUS7105051B2Good monodispersityIncrease in sizeFrom gel statePolycrystalline material growthSemiconductor materialsSynthesis methods
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE UNIV OF ARKANSAS
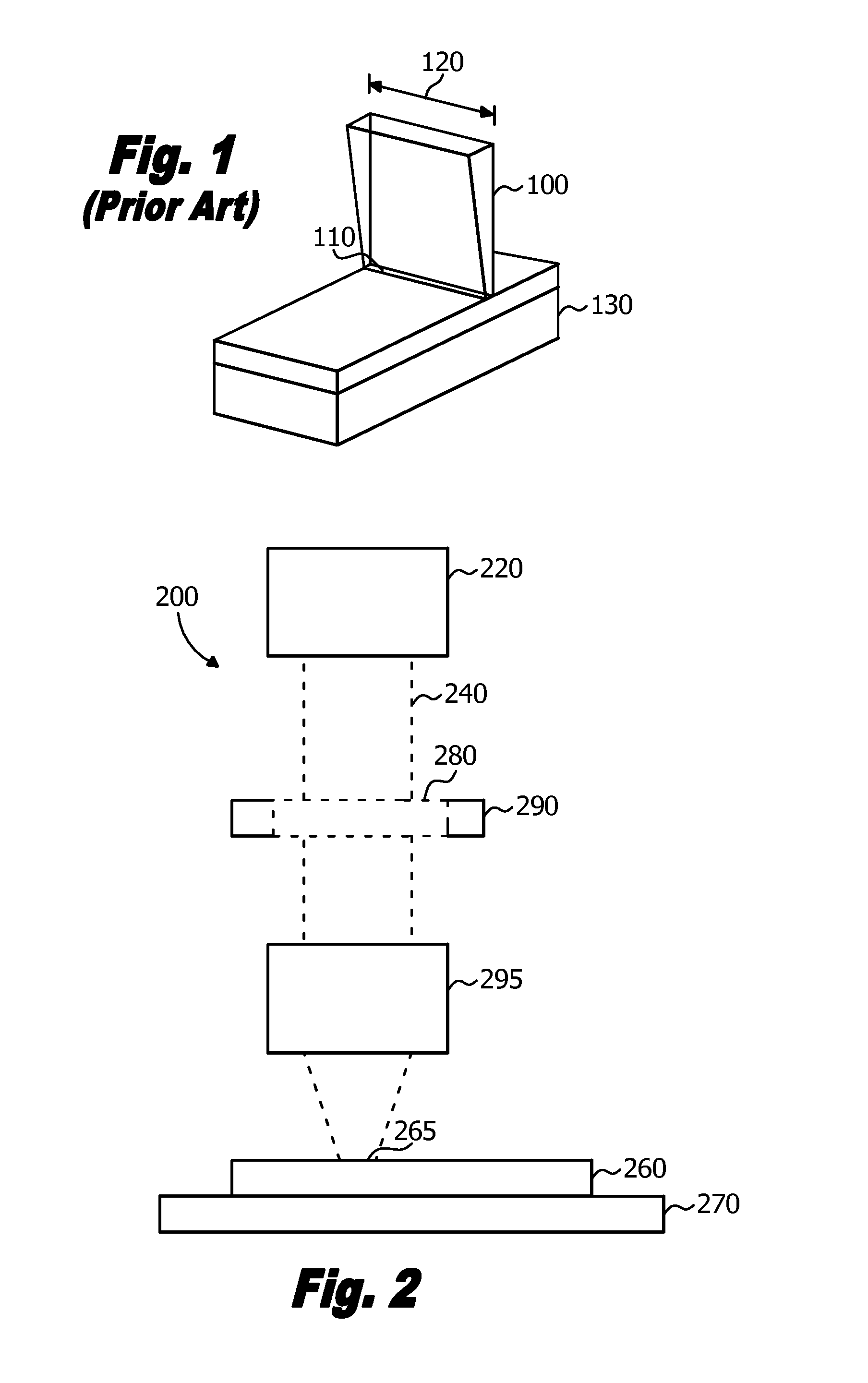
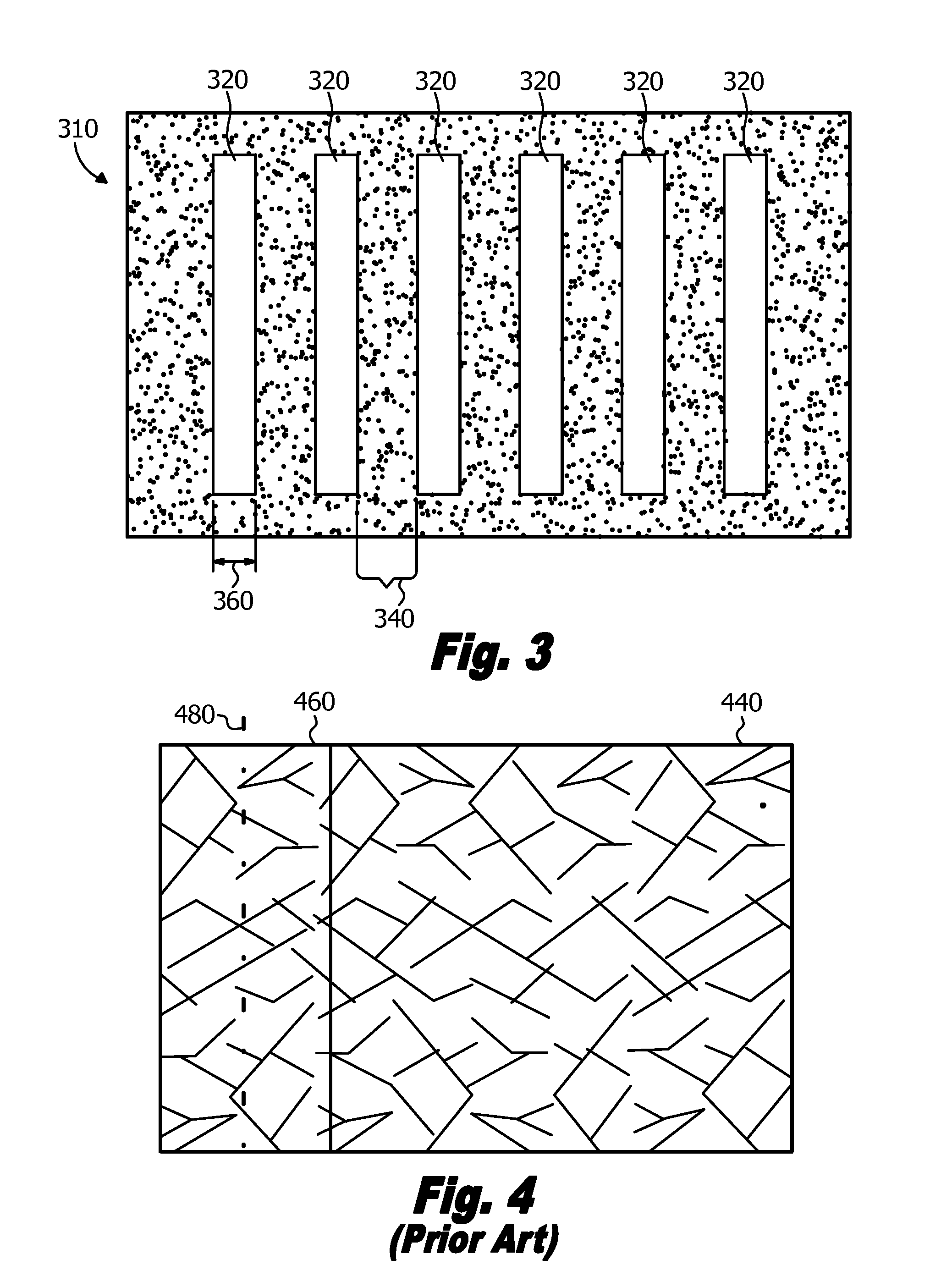
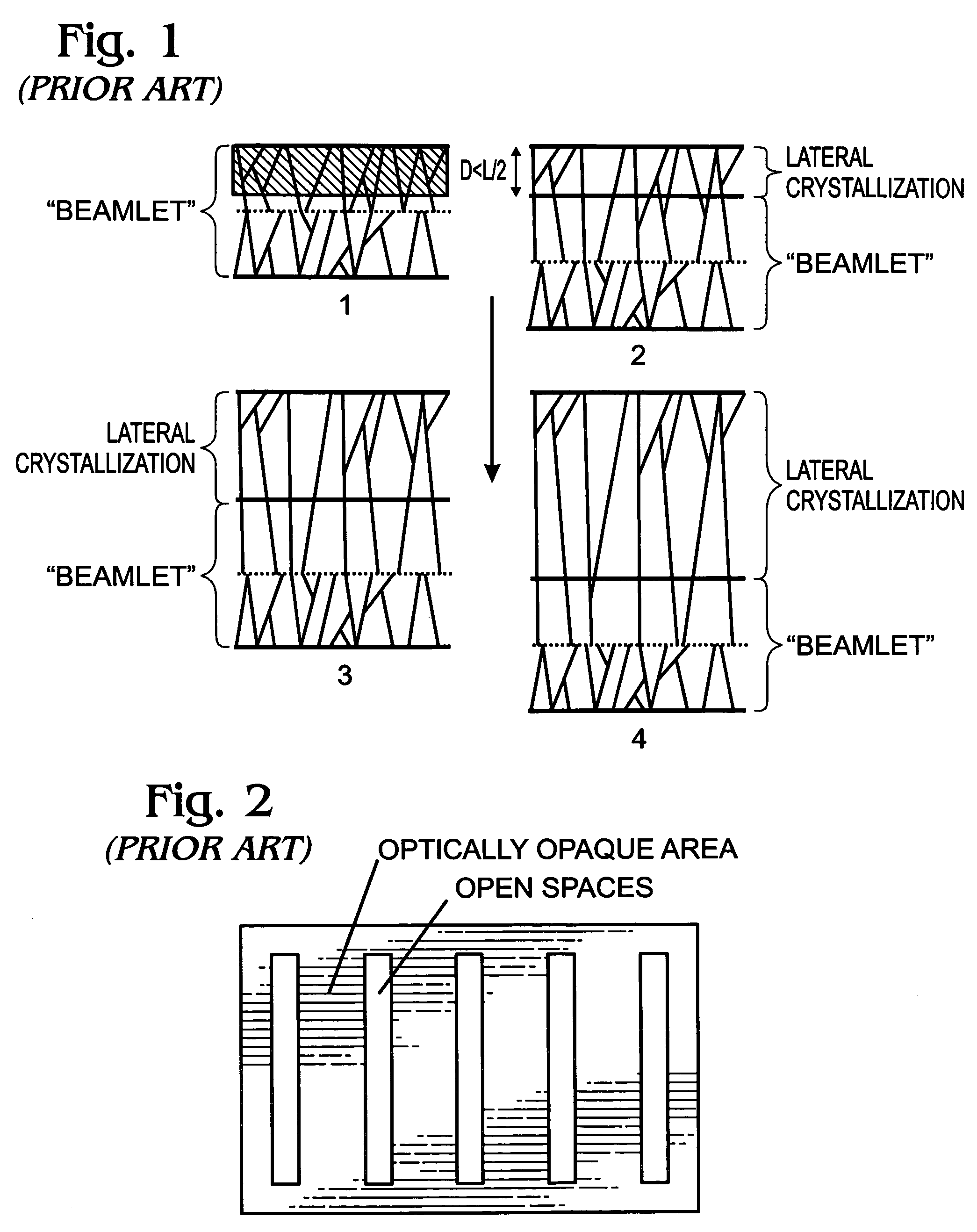
Line scan sequential lateral solidification of thin films
ActiveUS20060254500A1Improve uniformityReduce sharpnessFrom gel statePolycrystalline material growthOptoelectronicsNucleation
A polycrystalline film is prepared by (a) providing a substrate having a thin film disposed thereon, said film capable of laser-induced melting, (b) generating a sequence of laser pulses having a fluence that is sufficient to melt the film throughout its thickness in an irradiated region, each pulse forming a line beam having a predetermined length and width, said width sufficient to prevent nucleation of solids in a portion of the thin film that is irradiated by the laser pulse, (c) irradiating a first region of the film with a first laser pulse to form a first molten zone, said first molten zone demonstrating a variation in width along its length to thereby define a maximum width (Wmax) and a minimum width (Wmin), wherein the first molten zone crystallizes upon cooling to form one or more laterally grown crystals, (d) laterally moving the film in the direction of lateral growth a distance that is greater than about one-half Wmax and less than Wmin; and (e) irradiating a second region of the film with a second laser pulse to form a second molten zone having a shape that is substantially the same as the shape of the first molten zone, wherein the second molten zone crystallizes upon cooling to form one or more laterally grown crystals that are elongations of the one or more crystals in the first region.
Owner:THE TRUSTEES OF COLUMBIA UNIV IN THE CITY OF NEW YORK
Ordered vertically oriented porous inorganic films produced through solution processing
InactiveUS20060278158A1Easy to produceFrom gel statePhotosensitive materialsPatterned substrateSelf-assembly
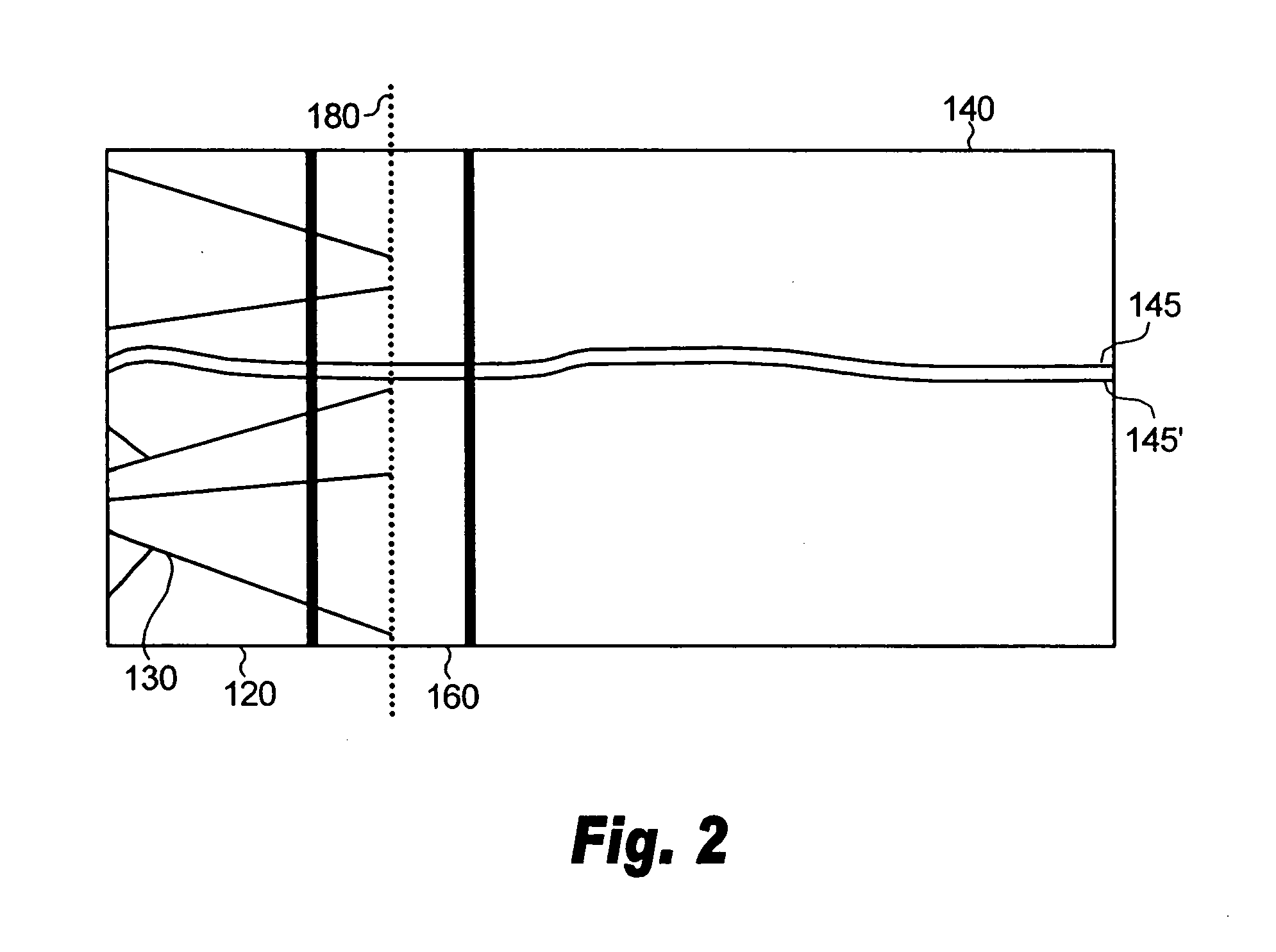
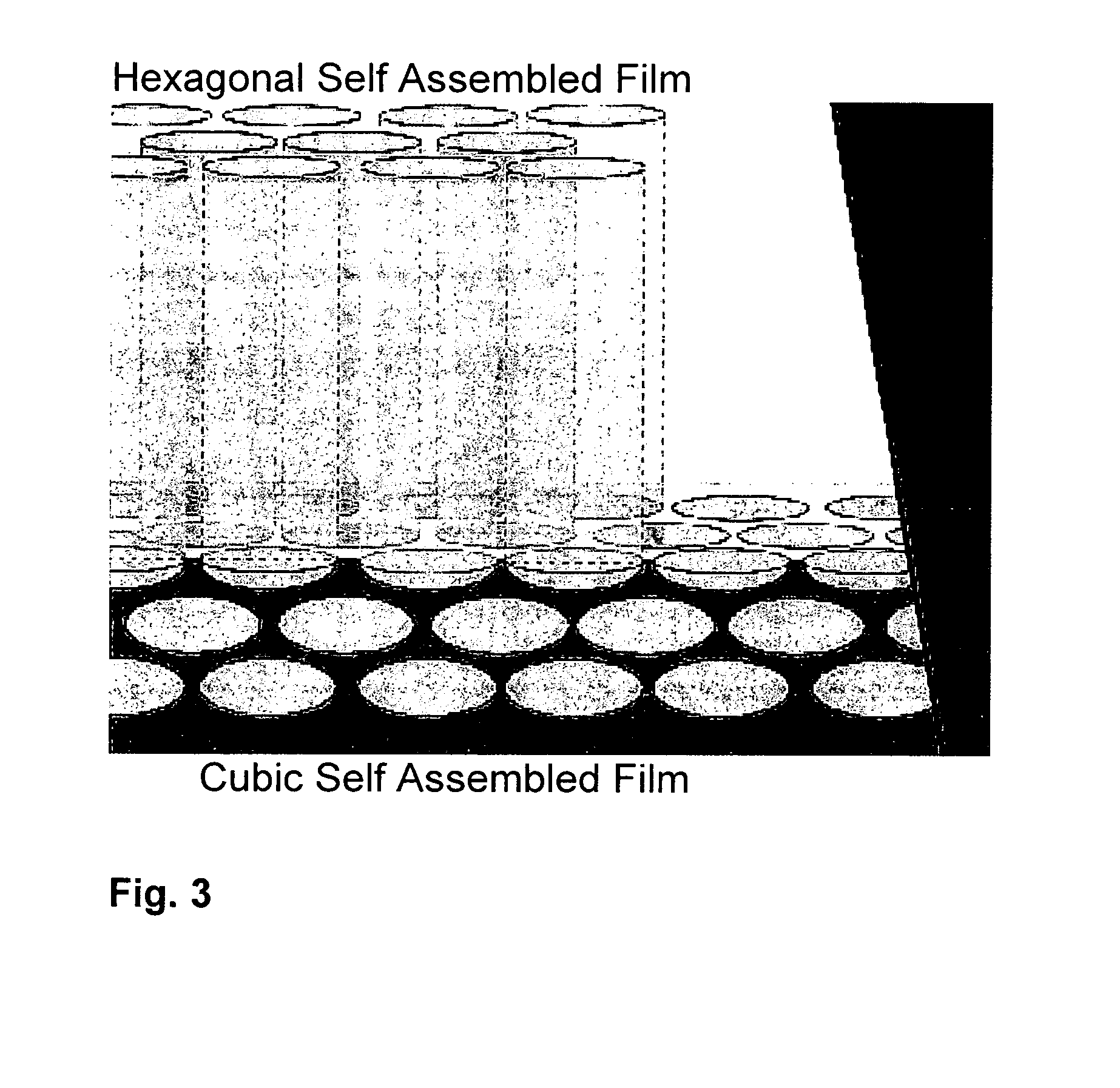
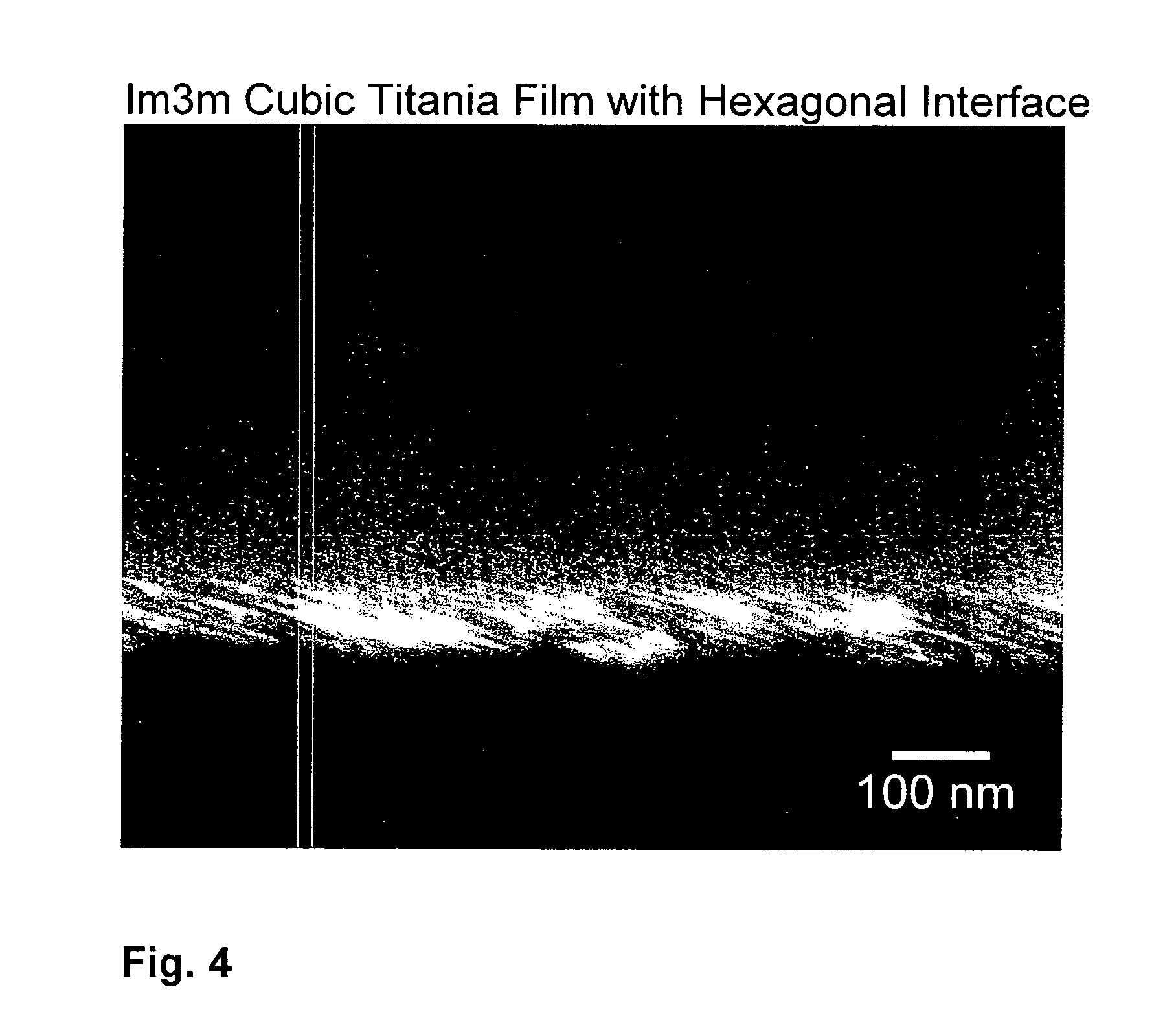
Porous films with straight pores oriented normal to the plane of the films are produced through solution processing techniques. The production takes advantage of inorganic-surfactant or inorganic-polymer co-assembly and a patterned substrate. The patterned substrate, which is also produced via solution phase self-assembly, forces vertical orientation in a hexagonal cylinder system with no practical limits in substrate size or type. This provides a route to vertically oriented inorganic pores with a pitch ranging from 3 nm to over 15 nm and pore sizes ranging from 2 nm to over 12 nm. The size is tuned by choice the choice of organic templating agents and the deposition conditions. The pores can be produced with or without a capping layer which can be used to seal the nanopores.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
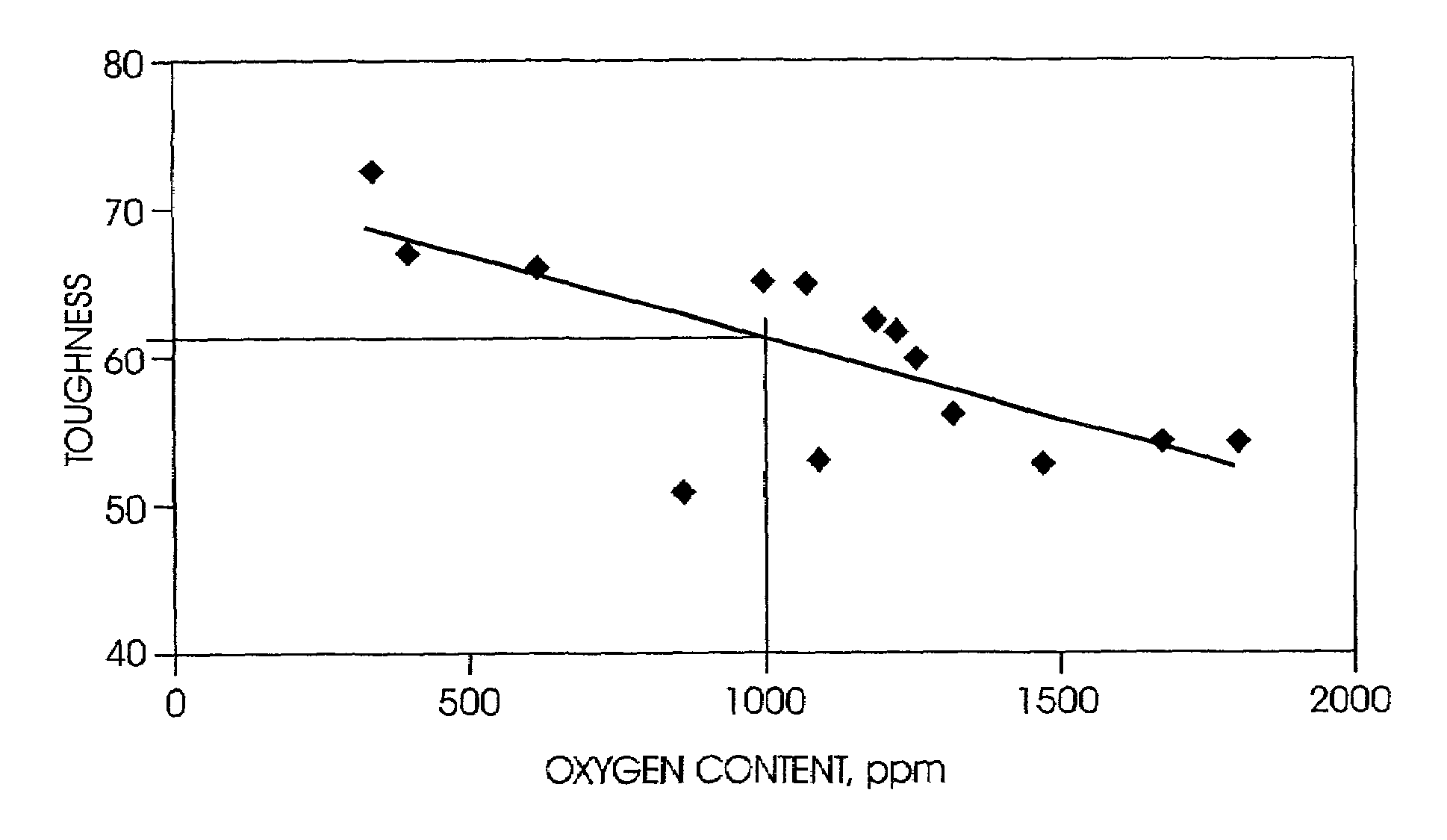
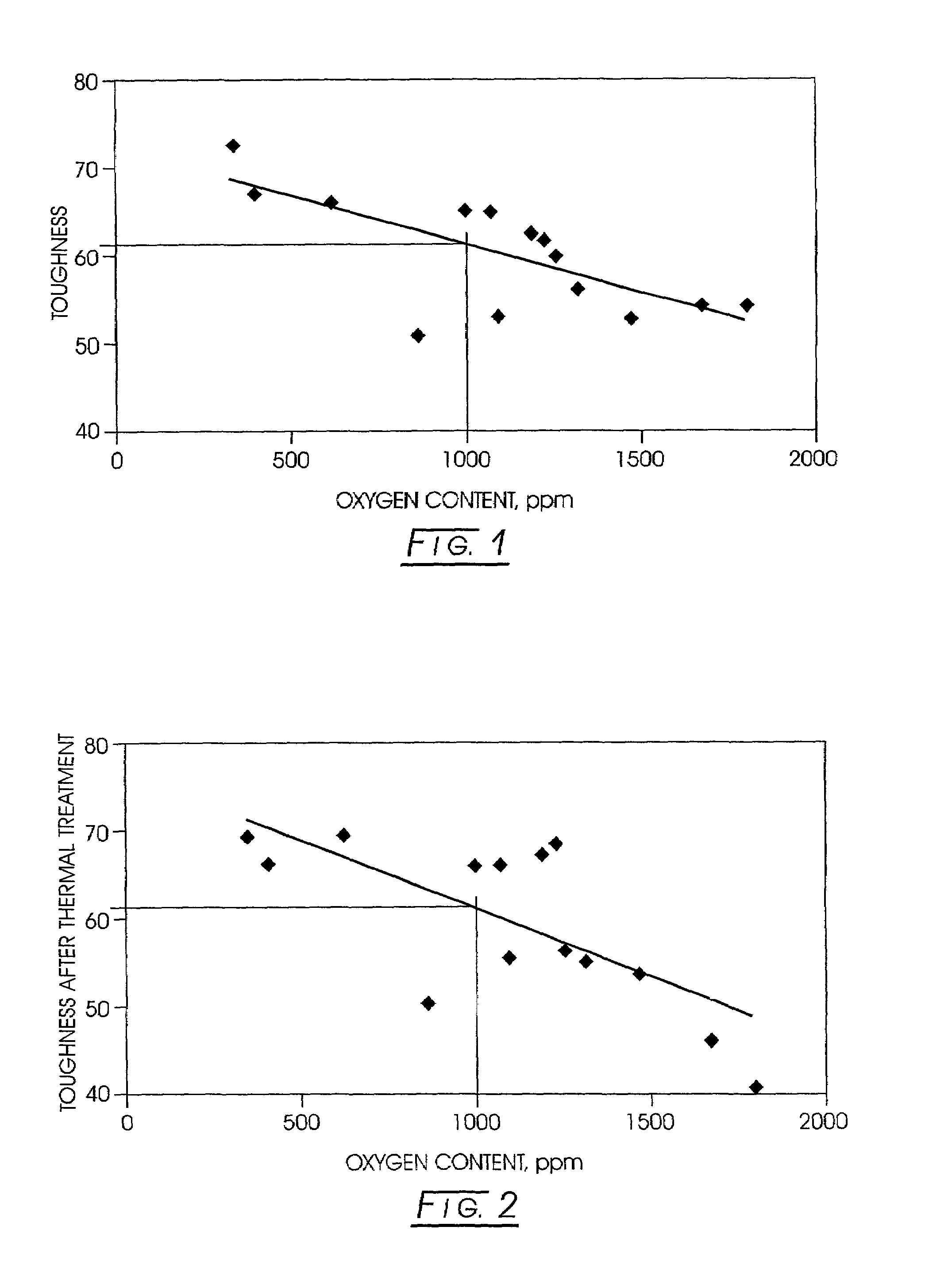
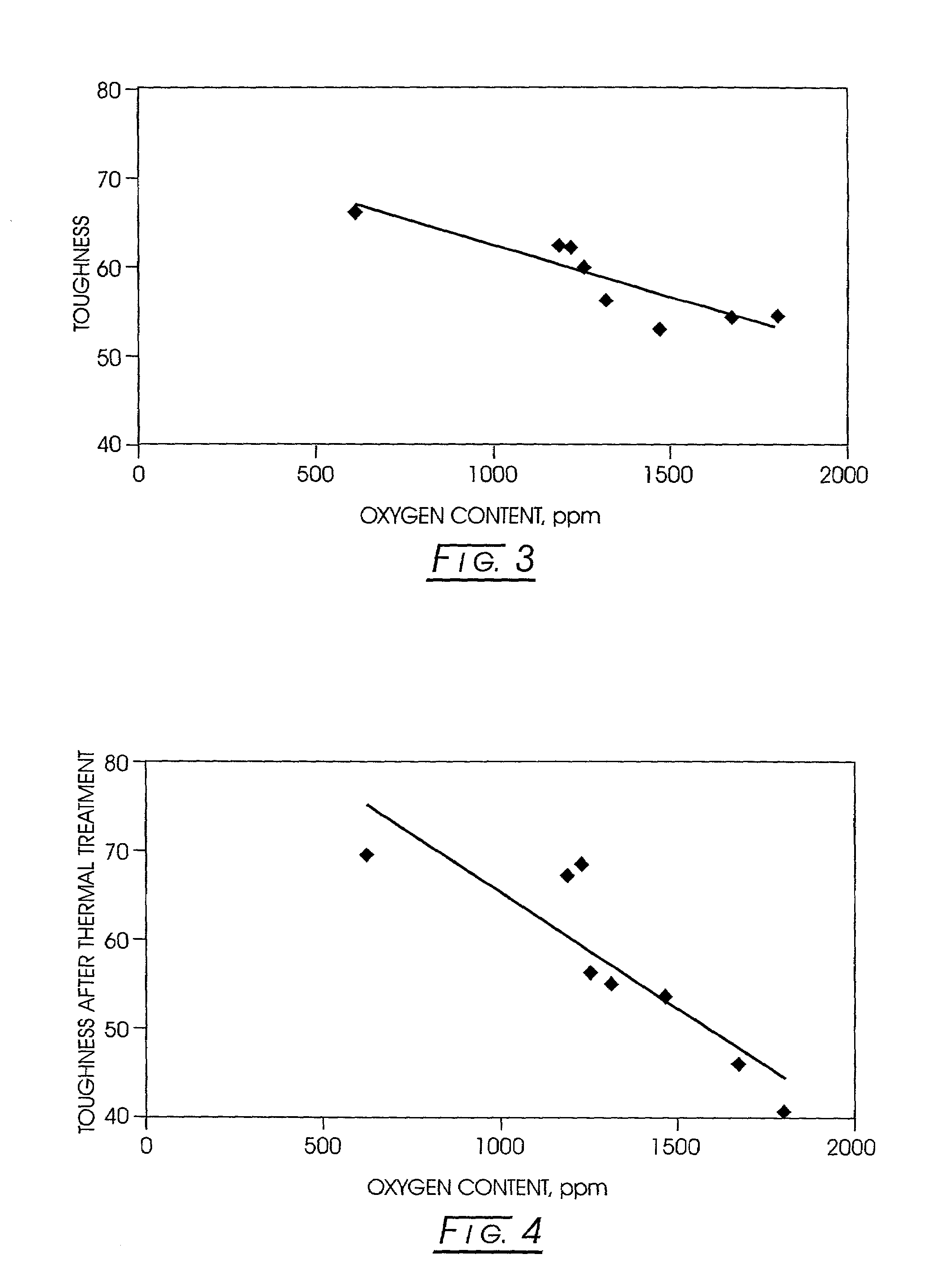
Low oxygen cubic boron nitride and its production
InactiveUS7001577B2Increased toughness indexImprove toughnessFrom gel statePolycrystalline material growthBoron nitrideHigh pressure
A method for improving the toughness of a CBN product made by a high temperature / high pressure (HP / HT) process commences by forming a blend of an oxygen getter and CBN product-forming feedstock. The blend is subjected to a CBN high temperature / high pressure (HP / HT) process for forming a CBN product. The amount of oxygen getter in the blend is sufficient to improve the toughness of the CBN product. The resulting CBN product desirably has an oxygen content of less than about 300 ppm. Oxygen getters include Al, Si, and Ti. The HP / HT process is conducted in the absence or presence of catalytic materials.
Owner:DIAMOND INNOVATIONS INC
High quality colloidal nanocrystals and methods of preparing the same in non-coordinating solvents
InactiveUS20060130741A1Increase in sizeGood monodispersityFrom gel statePolycrystalline material growthSemiconductor materialsSynthesis methods
The present invention provides substantially monodisperse colloidal nanocrystals and new preparative methods for the synthesis of substantially monodisperse colloidal nanocrystals. These synthetic methods afford the ability to tune nanocrystal size and size distribution. By using non-coordinating solvents in the synthetic process, these procedures constitute easier, less expensive, safer, and more environmentally “green” methods than those currently in use. This invention is generally applicable to any II-VI or III-V semiconductor material, and may be useful in generating metal-nonmetal compounds involving transition metals as well.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE UNIV OF ARKANSAS
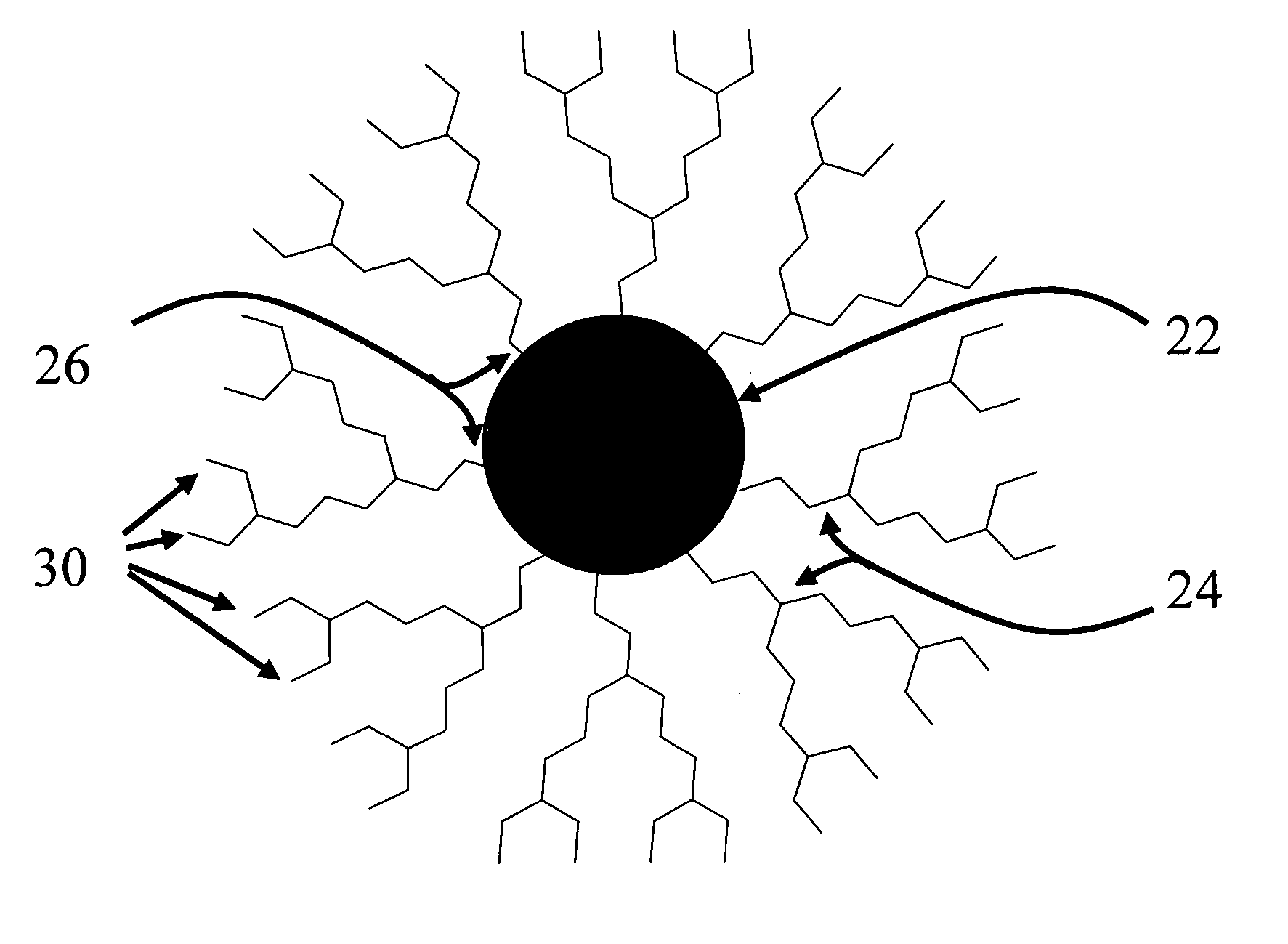
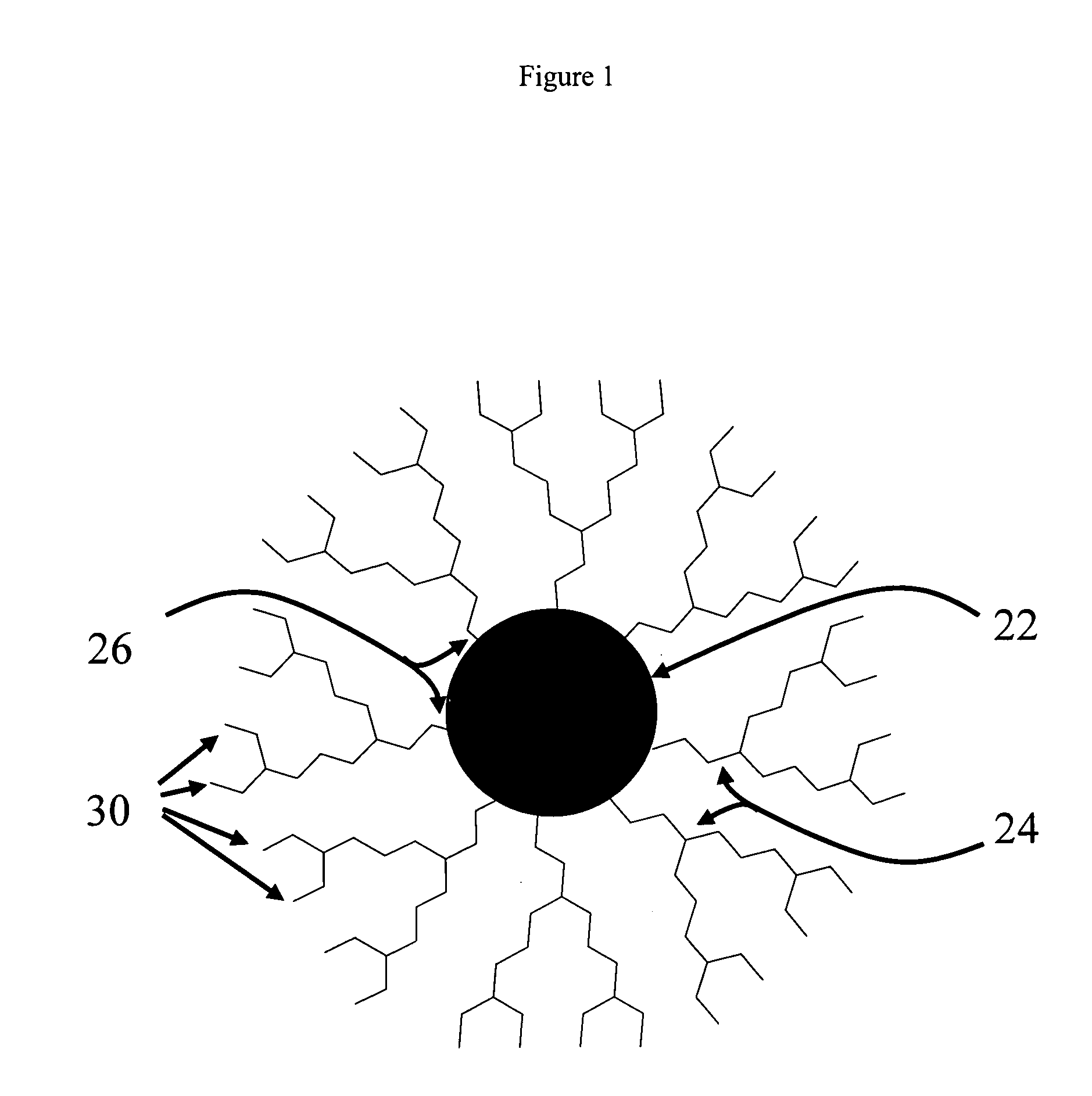
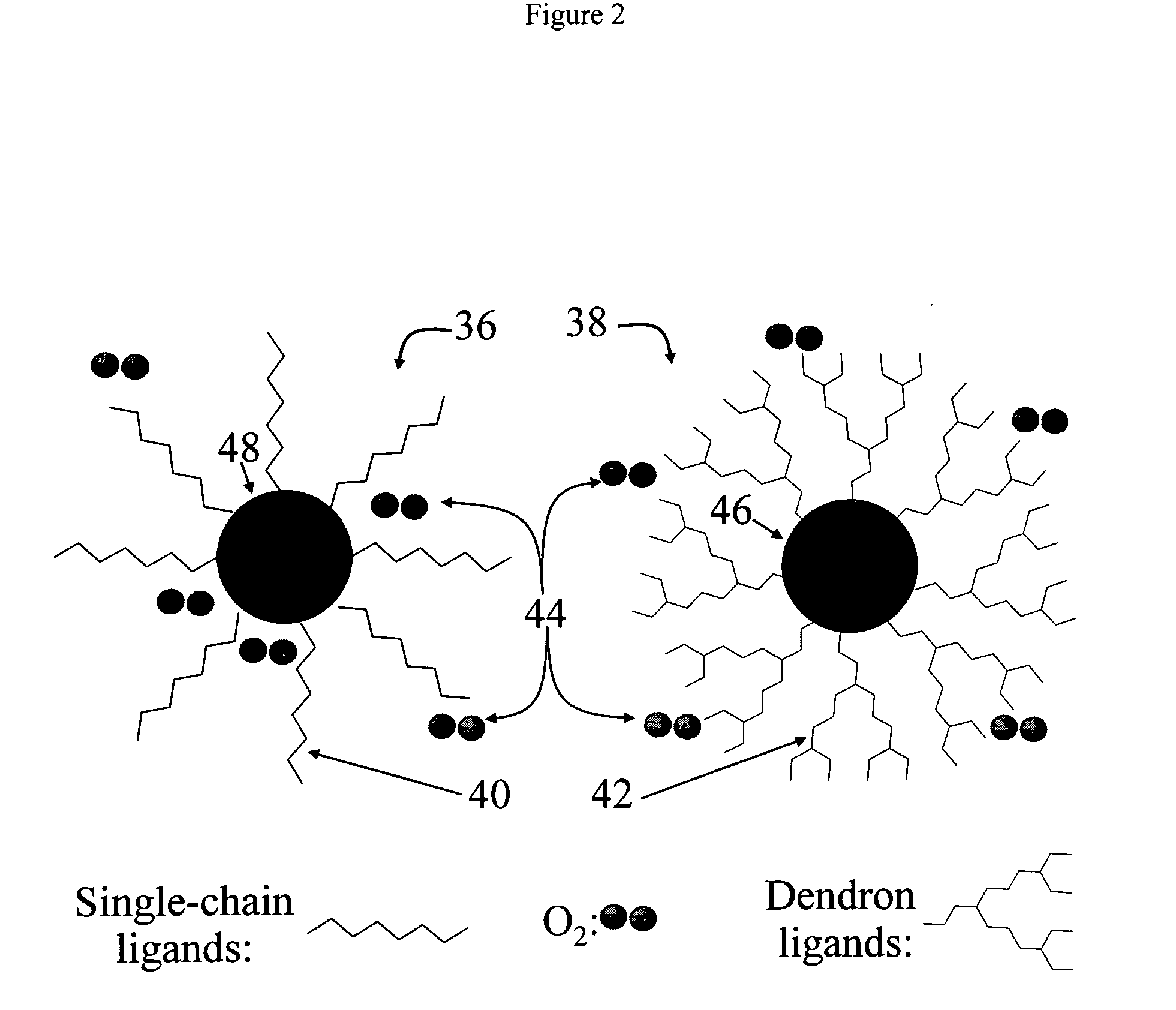
Synthesis of stable colloidal nanocrystals using organic dendrons
ActiveUS7153703B2Enhances protection against oxidationIncrease the number ofFrom gel statePolycrystalline material growthCross-linkNanoparticle
A method for stabilizing colloidal suspensions of nanocrystals or nanoparticles in a solvent or solid matrix is provided by coating the nanocrystals with bulky organic molecules, specifically dendrons. By coating nanocrystals with a dense organic dendron coat and further cross-linking the dendron ligands, oxidation of the nanocrystals and dissociation of the ligands are avoided. This invention allows nanocrystals to undergo rigorous purification and processing. It may regularly be applied to a variety of nanocrystals.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE UNIV OF ARKANSAS +1
Device and method for producing single crystals by vapor deposition
ActiveUS20050000406A1Down and eliminate formationPreventing structural defect generationFrom gel statePolycrystalline material growthGas phaseSingle crystal
A method and a device to grow from the vapor phase, a single crystal of either SiC, a group III-nitride, or alloys thereof, at a growth rate and for a period of time sufficient to produce a crystal of preferably several centimeters length. The diameter of the growing crystal may be controlled. To prevent the formation of undesirable polycrystalline deposits on surfaces in the downstream vicinity of the single crystal growth area, the local supersaturation of at least one component of the material grown is lowered by introducing a separate gas flow comprising at least one halogen element or a combination of said halogen and hydrogen species.
Owner:NORSTEL
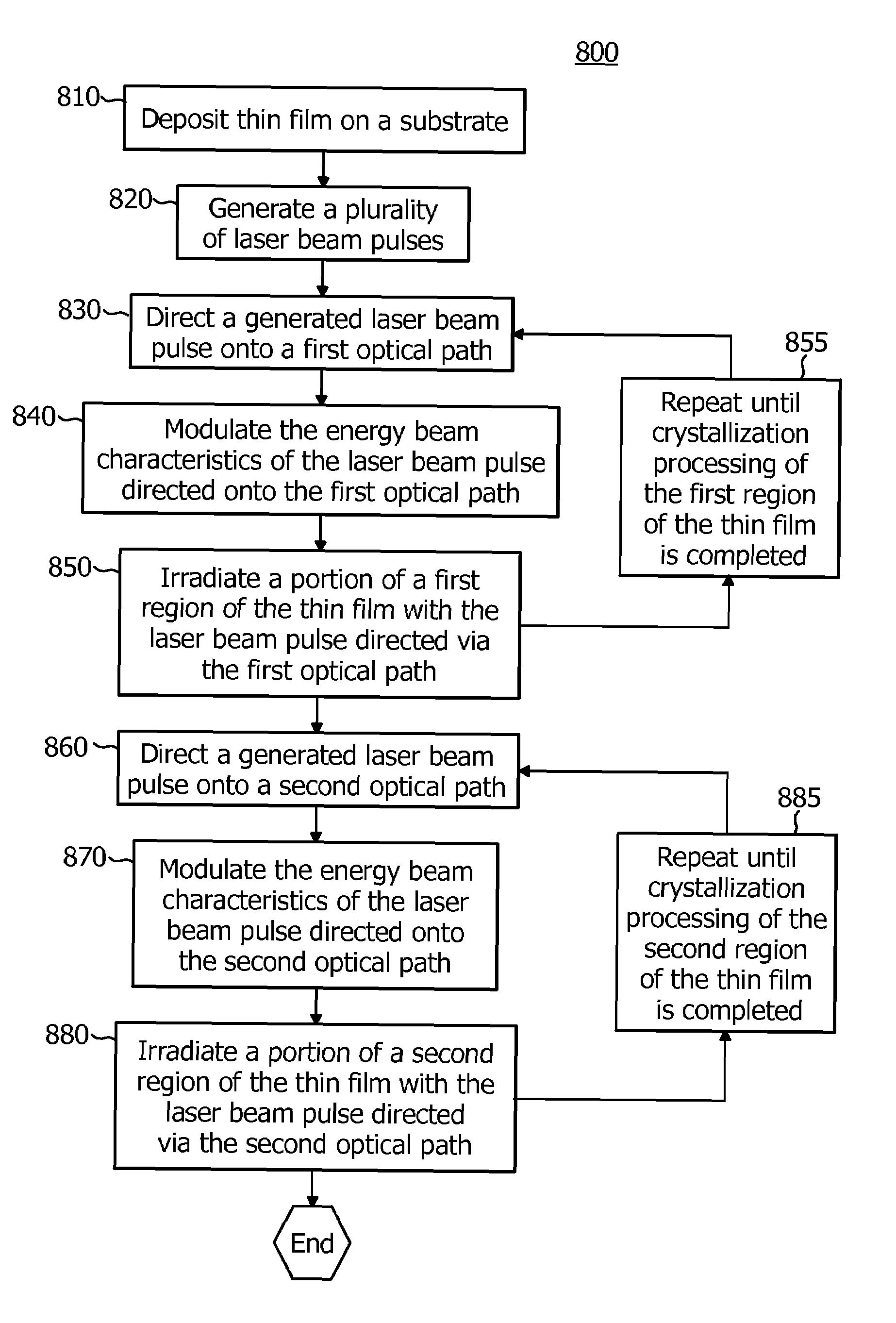
Systems and methods for inducing crystallization of thin films using multiple optical paths
InactiveUS7318866B2Promote crystallizationReduce the amount requiredAfter-treatment apparatusFrom gel stateLight beamBeam steering
The present invention is directed to systems and methods for irradiating regions of a thin film sample(s) with laser beam pulses having different energy beam characteristics that are generated and delivered via different optical paths. Exemplary methods include the steps of generating a plurality of laser beam pulses having energy beam characteristics, directing a generated laser beam pulse onto a first optical path, modulating the energy beam characteristics of the first optical path-directed laser beam pulse, irradiating at least a portion of a first region of the thin film with the first optical path-directed laser beam pulse to induce crystallization of the portion of the first region, directing a generated laser beam pulse onto a second optical path, modulating the energy beam characteristics of the second optical path-directed laser beam pulse, wherein the energy beam characteristics of the second optical path-directed laser beam pulse is different from the energy beam characteristics of the first optical path-directed laser beam pulse, and irradiating at least a portion of a second region of the thin film with the second optical path-directed laser beam pulse to induce crystallization of the portion of the second region. An exemplary system includes a first optical path, a second optical path, a beam steering element for directing laser beam pulses onto the first optical path and the second optical path; and a handling stage for controlling the position of a thin film relative to the laser beam pulses being directed via the first and second optical paths.
Owner:THE TRUSTEES OF COLUMBIA UNIV IN THE CITY OF NEW YORK
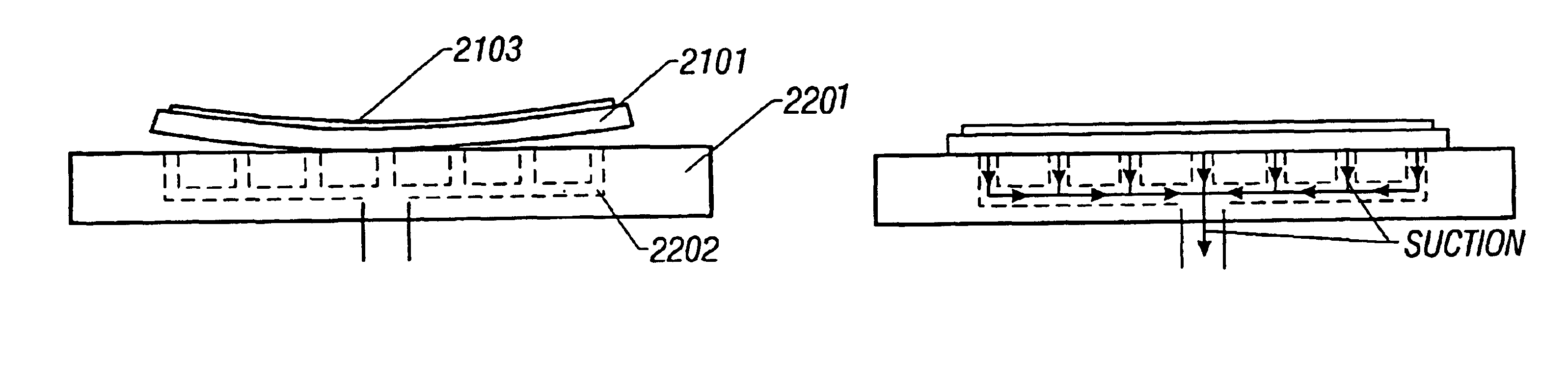
Method and apparatus for producing semiconductor device
InactiveUS6902616B1Correct warpingGood effectFrom gel statePolycrystalline material growthLiquid-crystal displayCrystallinity
A liquid crystal display device is manufactured by first forming a crystalline semiconductor film 2103, of silicon for example, over an insulating substrate 2101, such as glass. The substrate is warped in the process. The warpage is corrected by suction against a stage 2201. The film crystallinity is enhanced by scanning with a linear laser beam.
Owner:SEMICON ENERGY LAB CO LTD
Laser annealing mask and method for smoothing an annealed surface
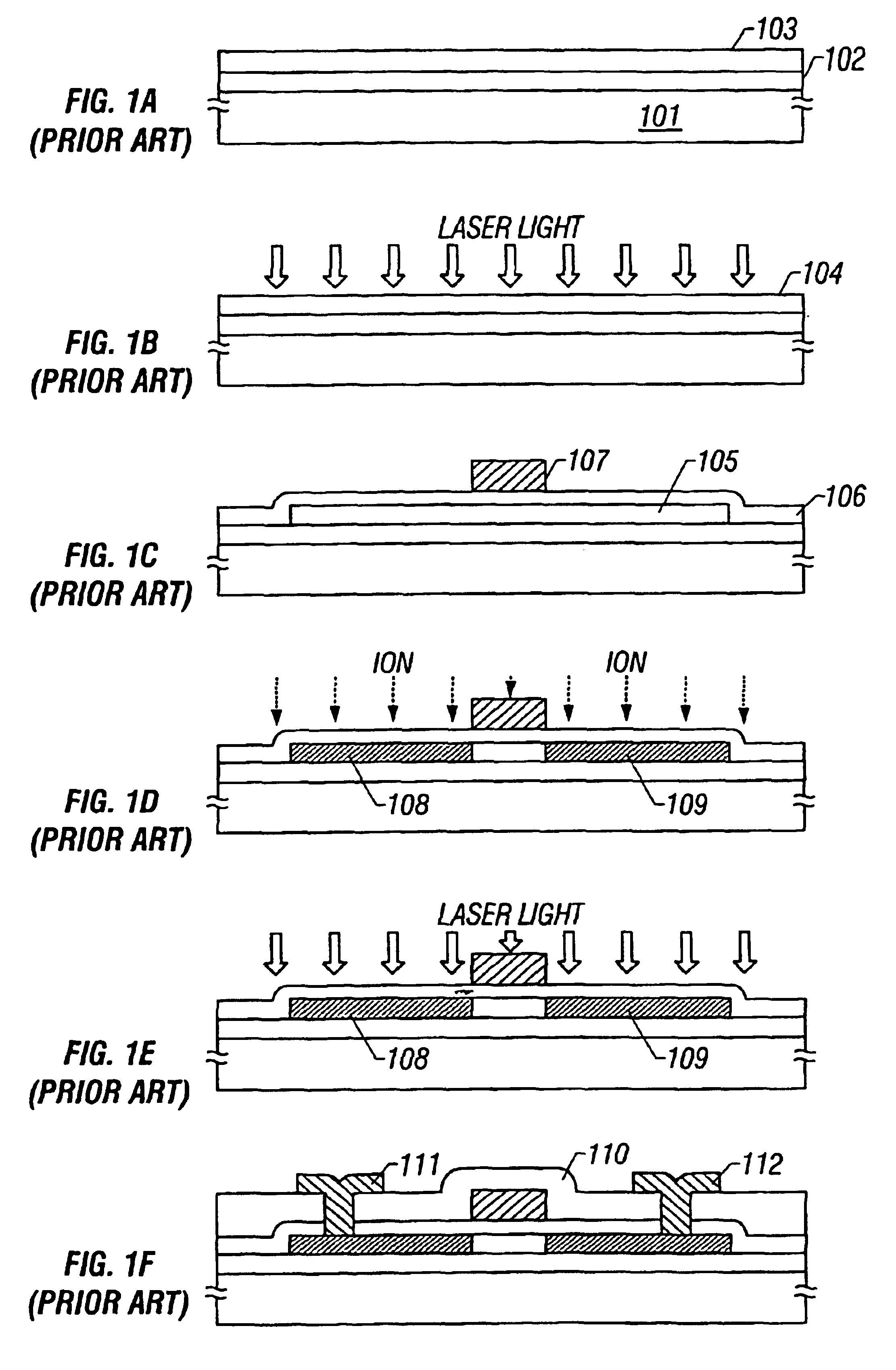
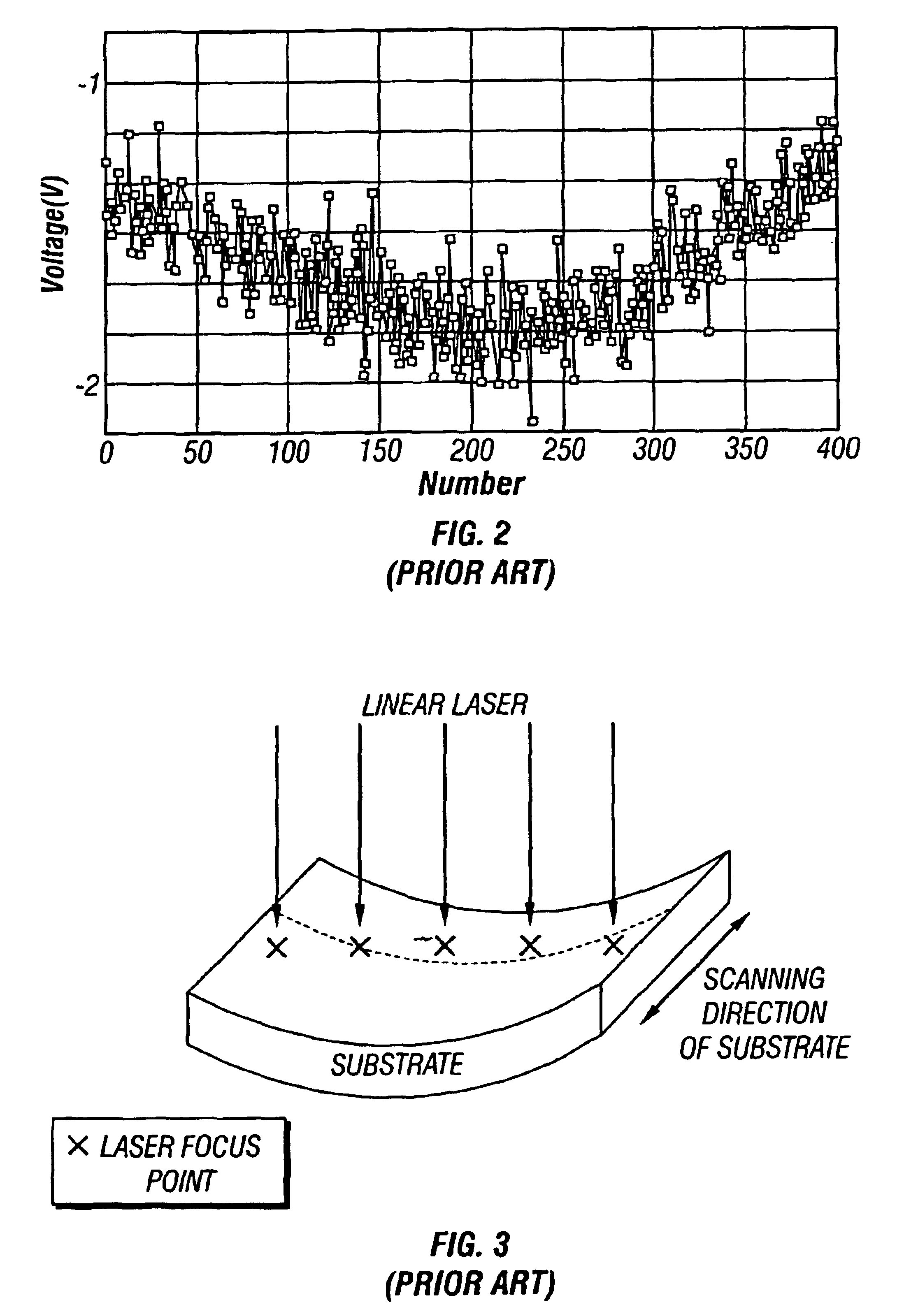
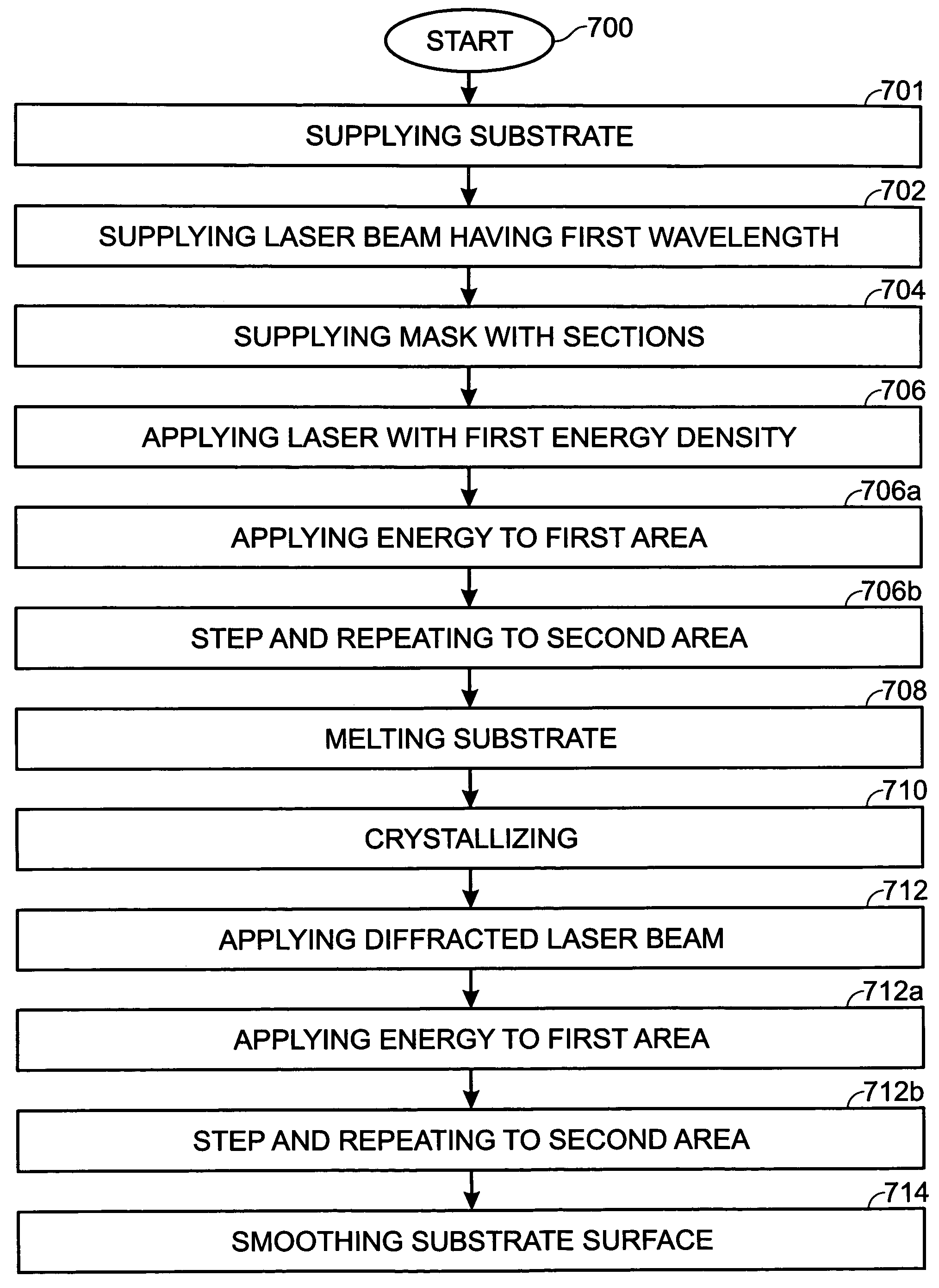
ActiveUS7192479B2Improve TFT performanceImprovement in TFT reliabilityFrom gel stateFrom solid stateLaser annealingEnergy density
A mask with sub-resolution aperture features and a method for smoothing an annealed surface using a sub-resolution mask pattern are provided. The method comprises: supplying a laser beam having a first wavelength; supplying a mask with a first mask section having apertures with a first dimension and a second mask section with apertures having a second dimension, less than the first dimension; applying a laser beam having a first energy density to a substrate region; melting a substrate region in response to the first energy density; crystallizing the substrate region; applying a diffracted laser beam to the substrate region; and, in response to the diffracted laser beam, smoothing the substrate region surface. In some aspects of the method, applying a diffracted laser beam to the substrate area includes applying a diffracted laser beam having a second energy density, less than the first energy density, to the substrate region. The second energy density is in the range of 40% to 70% of the first energy density, and preferably in the range of 50% to 60% of the first energy density.
Owner:SHARP KK
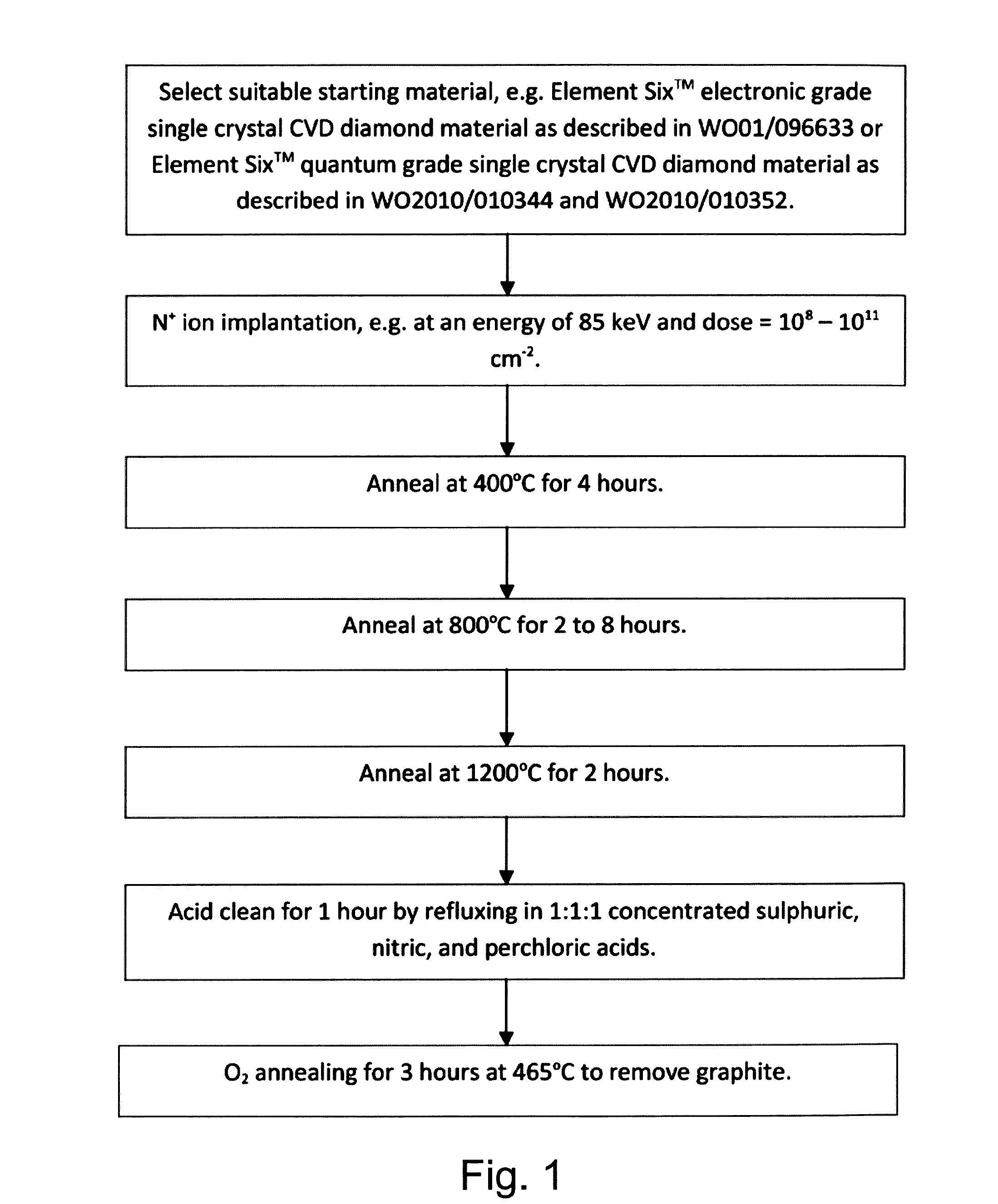
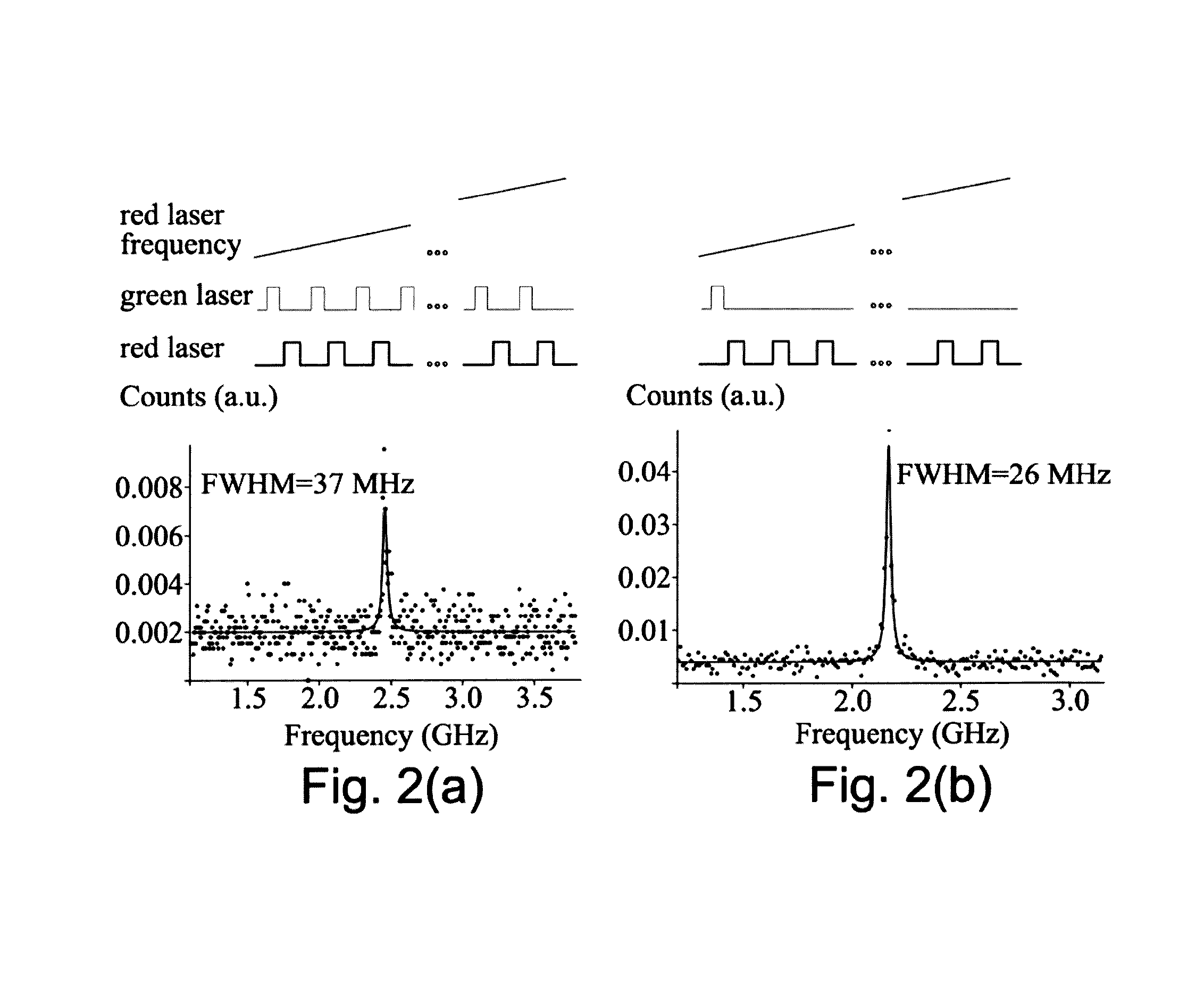
Synthetic diamond materials for quantum and optical applications and methods of making the same
A synthetic diamond material comprising one or more spin defects having a full width half maximum intrinsic inhomogeneous zero phonon line width of no more than 100 MHz. The method for obtain such a material involves a multi-stage annealing process.
Owner:PRESIDENT & FELLOWS OF HARVARD COLLEGE
Semiconductor, semiconductor device, and method for fabricating the same
InactiveUS6997985B1Improve continuityImprove solubilityTransistorFrom gel stateGlass transition pointCobalt
Method of fabricating semiconductor devices such as thin-film transistors by annealing a substantially amorphous silicon film at a temperature either lower than normal crystallization temperature of amorphous silicon or lower than the glass transition point of the substrate so as to crystallize the silicon film. Islands, stripes, lines, or dots of nickel, iron, cobalt, or platinum, silicide, acetate, or nitrate of nickel, iron, cobalt, or platinum, film containing various salts, particles, or clusters containing at least one of nickel, iron, cobalt, and platinum are used as starting materials for crystallization. These materials are formed on or under the amorphous silicon film.
Owner:SEMICON ENERGY LAB CO LTD
Nitride semiconductor heterostructures and related methods
InactiveUS20090283028A1Easy to manufactureGood chemical compatibilityFrom gel statePolycrystalline material growthSemiconductor structureSemiconductor heterostructures
Semiconductor structures and devices based thereon include an aluminum nitride single-crystal substrate and at least one layer epitaxially grown thereover. The epitaxial layer may comprise at least one of AlN, GaN, InN, or any binary or tertiary alloy combination thereof, and have an average dislocation density within the semiconductor heterostructure is less than about 106 cm−2.
Owner:CRYSTAL
Light emitting photonic crystals
InactiveUS20030148088A1Increase brightnessUniform lightFrom gel statePolycrystalline material growthPhotonic bandgapCrystal orientation
The invention relates to processes for the synthesis of 2-D and 3-D periodic porous silicon structures and composites with improved properties having the advantages of porous silicon and photonic bandgap materials. Photonic crystals comprise a two dimensionally periodic or three dimensionally periodic microporous structural matrix of interconnecting, crystallographically oriented, monodispersed members having voids between adjacent members, and said members additionally having randomly nanoporous surface porosity. The silicon nanofoam material shows enhanced and spectrally controlled / tunable photoluminescence and electroluminesce and finds use as transparent electrodes, high-lumonosity light emitting diodes (LEDs), wavelength division multiplexors, high-active-area catalyst supports, photonic bandgap lasers, silicon-based UV detectors, displays, gas sensors, and the like.
Owner:HONEYWELL INT INC
Passivated nanoparticles, method of fabrication thereof, and devices incorporating nanoparticles
A plurality of semiconductor nanoparticles having an elementally passivated surface are provided. These nanoparticles are capable of being suspended in water without substantial agglomeration and substantial precipitation on container surfaces for at least 30 days. The method of making the semiconductor nanoparticles includes reacting at least a first reactant and a second reactant in a solution to form the semiconductor nanoparticles in the solution. A first reactant provides a passivating element which binds to dangling bonds on a surface of the nanoparticles to passivate the surface of the nanoparticles. The nanoparticle size can be tuned by etching the nanoparticles located in the solution to a desired size.
Owner:RENESSELAER POLYTECHNIC INST
Unitary graphene layer or graphene single crystal
ActiveUS20140147648A1Improve thermal conductivityImproves Structural IntegrityFrom gel stateMaterial nanotechnologySingle crystalFilm material
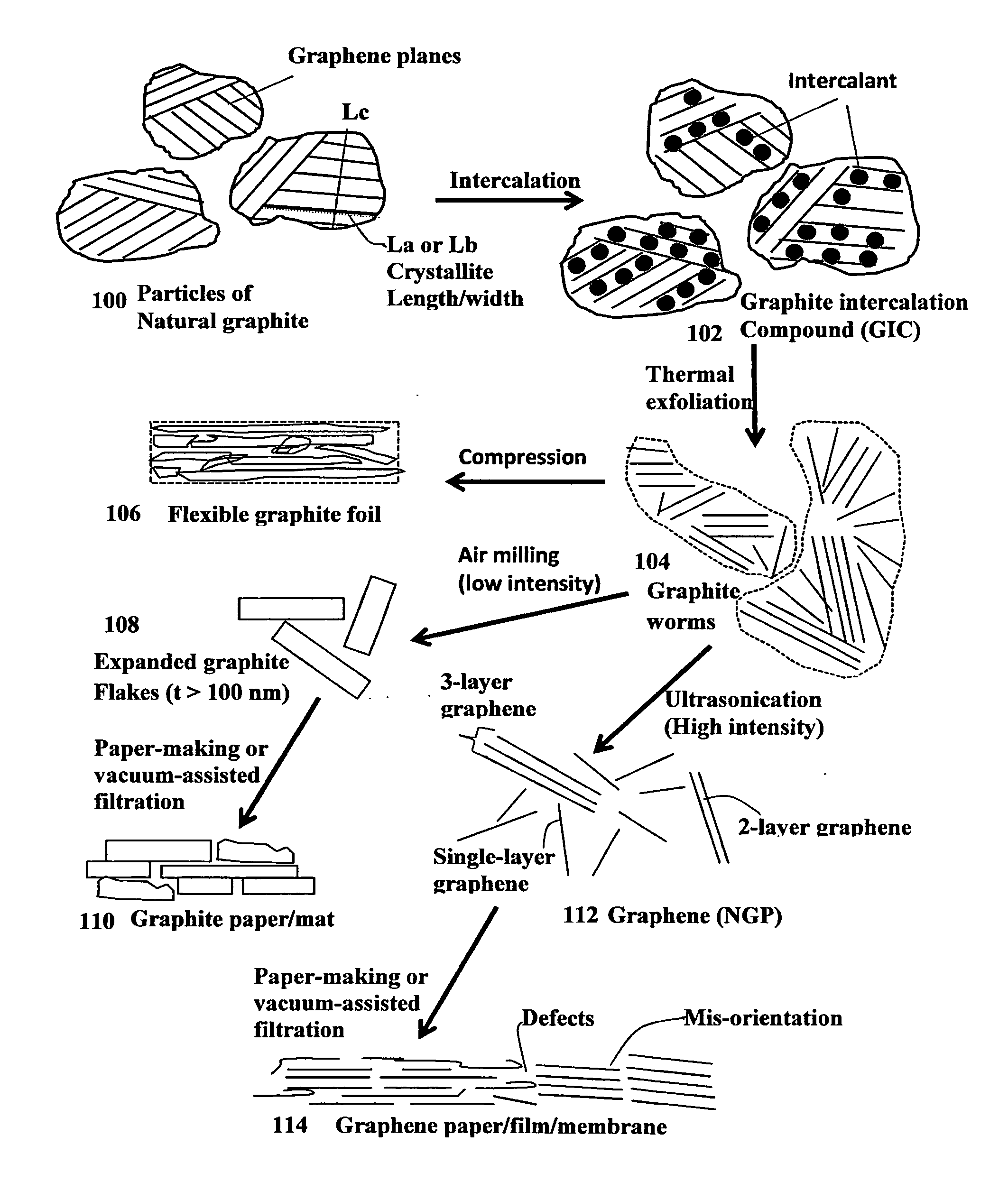
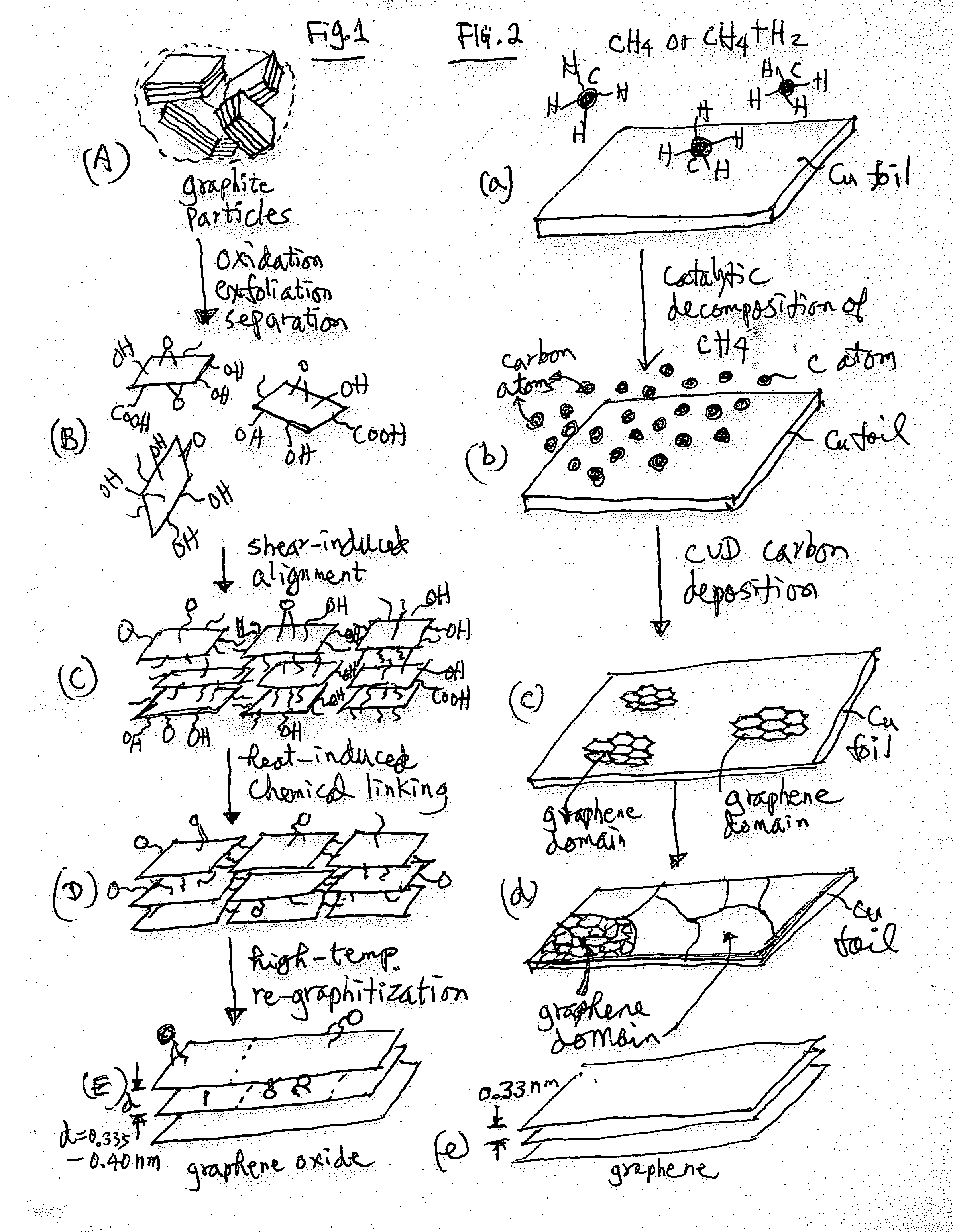
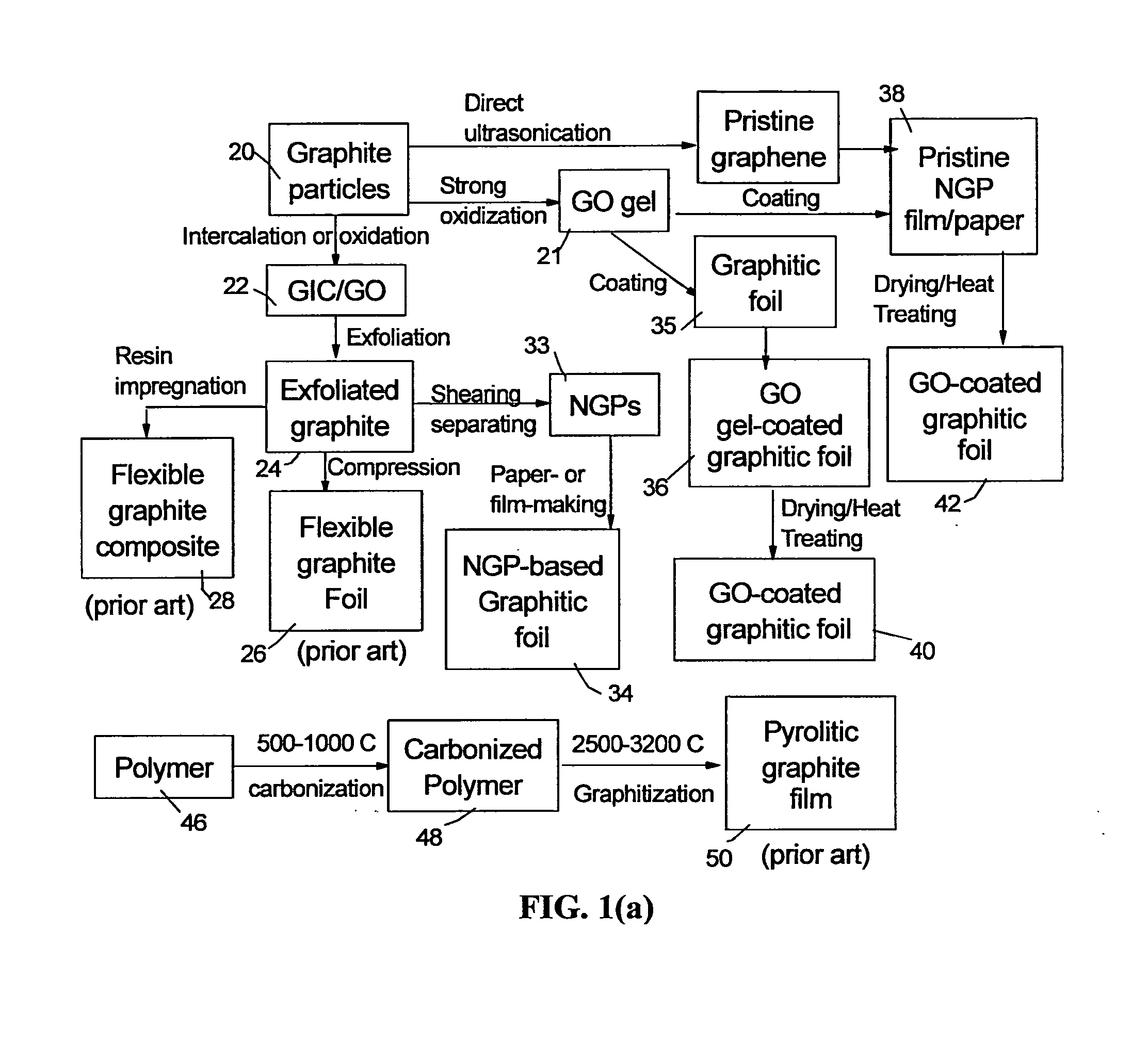
A unitary graphene layer or graphene single crystal containing closely packed and chemically bonded parallel graphene planes having an inter-graphene plane spacing of 0.335 to 0.40 nm and an oxygen content of 0.01% to 10% by weight, which unitary graphene layer or graphene single crystal is obtained from heat-treating a graphene oxide gel at a temperature higher than 100° C., wherein the average mis-orientation angle between two graphene planes is less than 10 degrees, more typically less than 5 degrees. The molecules in the graphene oxide gel, upon drying and heat-treating, are chemically interconnected and integrated into a unitary graphene entity containing no discrete graphite flake or graphene platelet. This graphene monolith exhibits a combination of exceptional thermal conductivity, electrical conductivity, mechanical strength, surface smoothness, surface hardness, and scratch resistance unmatched by any thin-film material of comparable thickness range.
Owner:GLOBAL GRAPHENE GRP INC
System and high pressure, high temperature apparatus for producing synthetic diamonds
An apparatus for growing a synthetic diamond comprises a growth chamber, at least one manifold allowing access to the growth chamber, and a plurality of safety clamps positioned on opposite sides of the growth chamber; wherein the growth chamber and the plurality of safety clamps are comprised of a material having a tensile strength of about 120,000-200,000 psi, a yield strength of about 100,000-160,000 psi, an elongation of about 10-20%, an area reduction of about 40-50%, an impact strength of about 30-40 ft-lbs, and a hardness greater than 320 BHN.
Owner:THE GEMESIS CORP
Single scan irradiation for crystallization of thin films
InactiveUS20050235903A1Improve propertiesSimple processFrom gel stateFrom solid stateLight beamOptoelectronics
A method of processing a polycrystalline film on a substrate includes generating a plurality of laser beam pulses, positioning the film on a support capable of movement in at least one direction, directing the plurality of laser beam pulses through a mask to generate patterned laser beams; each of said beams having a length l′, a width w′ and a spacing between adjacent beams d′, irradiating a region of the film with the patterned beams, said beams having an intensity that is sufficient to melt an irradiated portion of the film to induce crystallization of the irradiated portion of the film, wherein the film region is irradiated n times; and after irradiation of each film portion, translating either the film or the mask, or both, a distance in the x- and y-directions, where the distance of translation in the y-direction is in the range of about 1′ / n-δ, where δ is a value selected to form overlapping the beamlets from the one irradiation step to the next, and where the distance of translation in the x-direction is selected such that the film is moved a distance of about λ′ after n irradiations, where λ′=w′+d′.
Owner:THE TRUSTEES OF COLUMBIA UNIV IN THE CITY OF NEW YORK
Single scan irradiation for crystallization of thin films
InactiveUS7311778B2Improve propertiesSimple processFrom gel stateFrom solid stateLight beamOptoelectronics
A method of processing a polycrystalline film on a substrate includes generating a plurality of laser beam pulses, positioning the film on a support capable of movement in at least one direction, directing the plurality of laser beam pulses through a mask to generate patterned laser beams; each of said beams having a length l′, a width w′ and a spacing between adjacent beams d′, irradiating a region of the film with the patterned beams, said beams having an intensity that is sufficient to melt an irradiated portion of the film to induce crystallization of the irradiated portion of the film, wherein the film region is irradiated n times; and after irradiation of each film portion, translating either the film or the mask, or both, a distance in the x- and y-directions, where the distance of translation in the y-direction is in the range of about 1′ / n-δ, where δ is a value selected to form overlapping the beamlets from the one irradiation step to the next, and where the distance of translation in the x-direction is selected such that the film is moved a distance of about λ′ after n irradiations, where λ′=w′+d′.
Owner:THE TRUSTEES OF COLUMBIA UNIV IN THE CITY OF NEW YORK
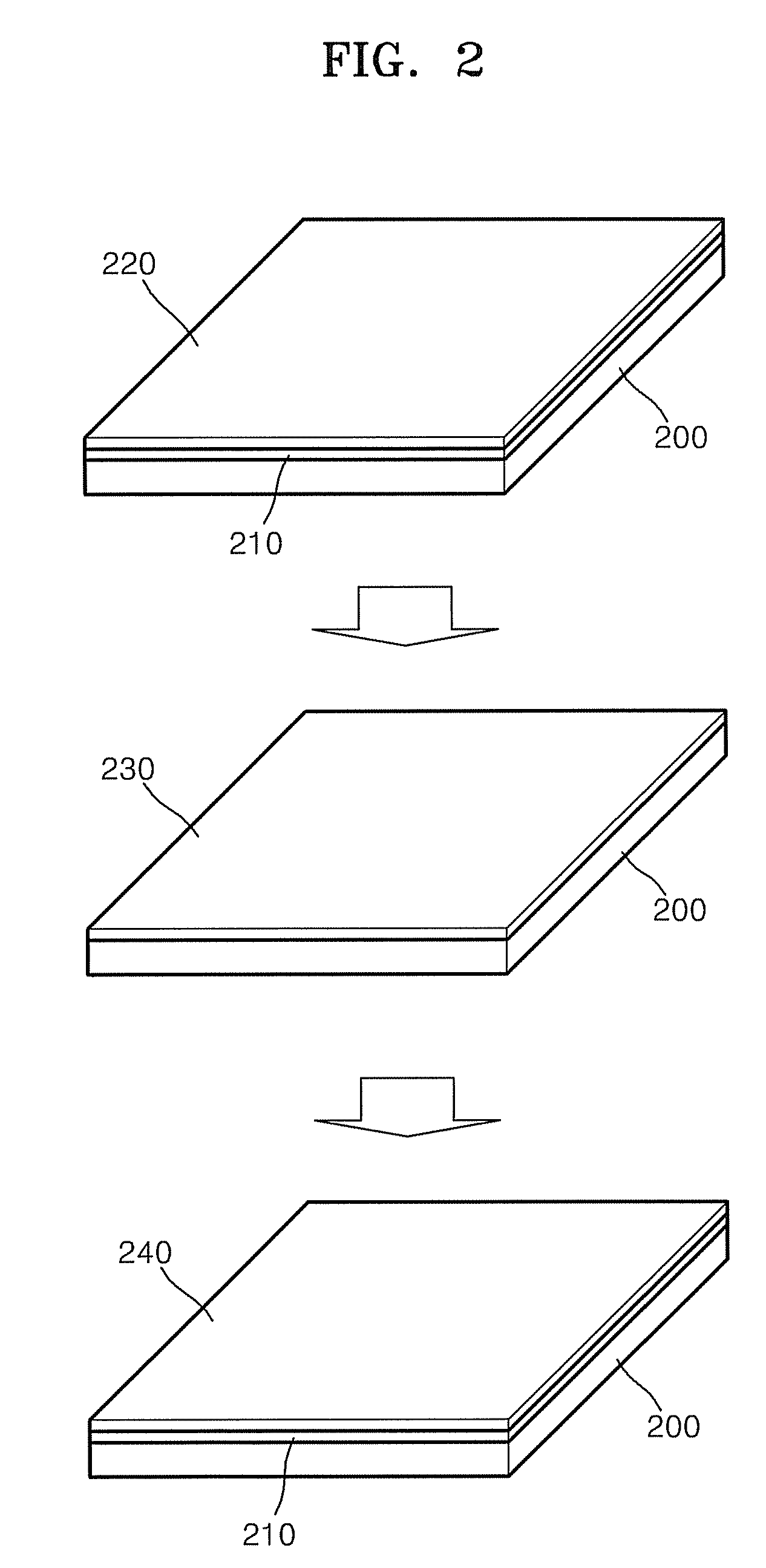
Process for Producing Monocrystal Thin Film and Monocrystal Thin Film Device
The present invention provides a method for manufacturing a monocrystalline film and a device formed by the above method, and according to the method mentioned above, lift-off of the monocrystalline silicon film is preferably performed and a high-purity monocrystalline silicon film can be obtained. A monocrystalline silicon substrate (template Si substrate) 201 is prepared, and on this monocrystalline silicon substrate 201, an epitaxial sacrificial layer 202 is formed. Subsequently, on this sacrificial layer 202, a monocrystalline silicon thin film 203 is rapidly epitaxially-grown using a RVD method, followed by etching of the sacrificial layer 202, whereby a monocrystalline silicon thin film 204 used as a photovoltaic layer of solar cells is formed.
Owner:JAPAN SCI & TECH CORP
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com