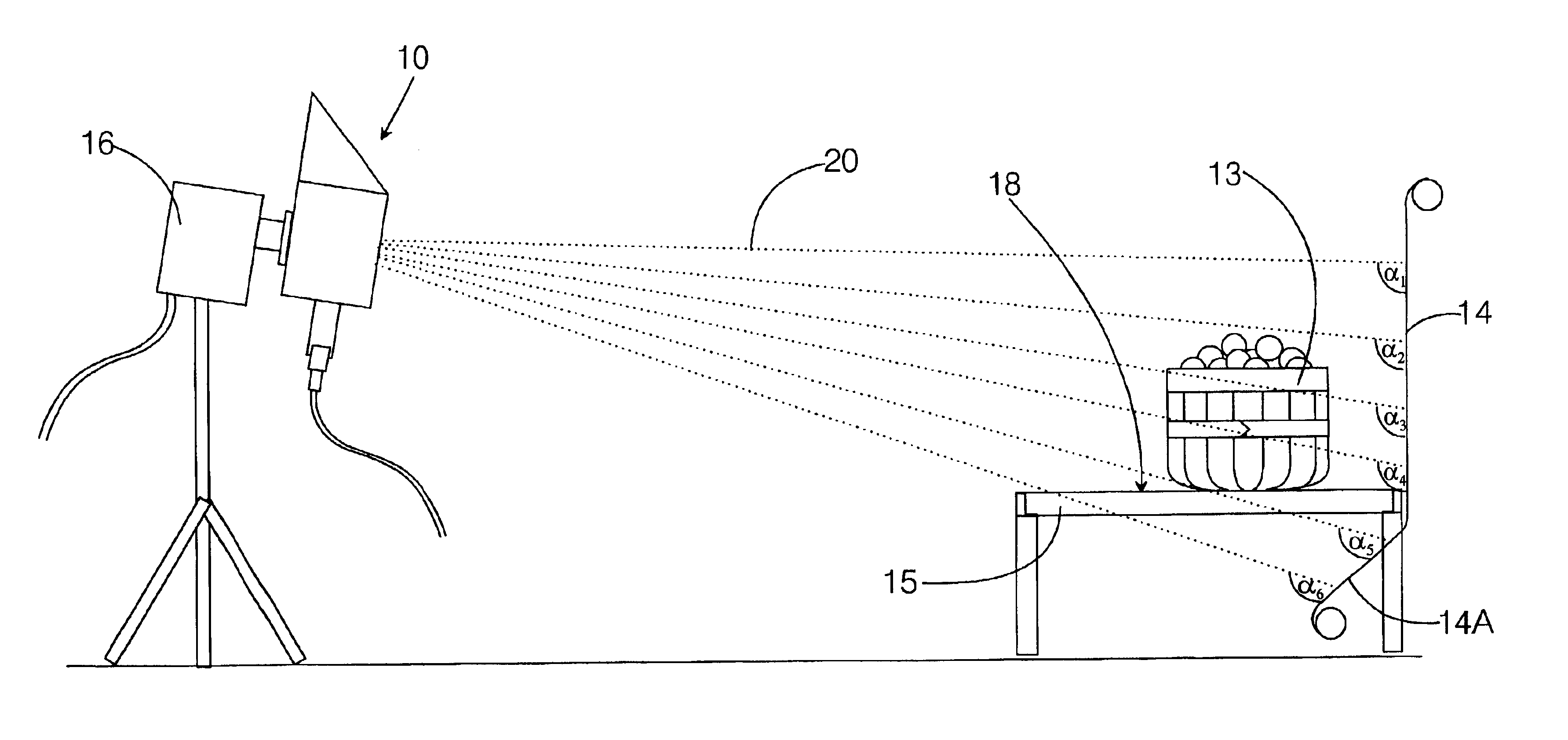
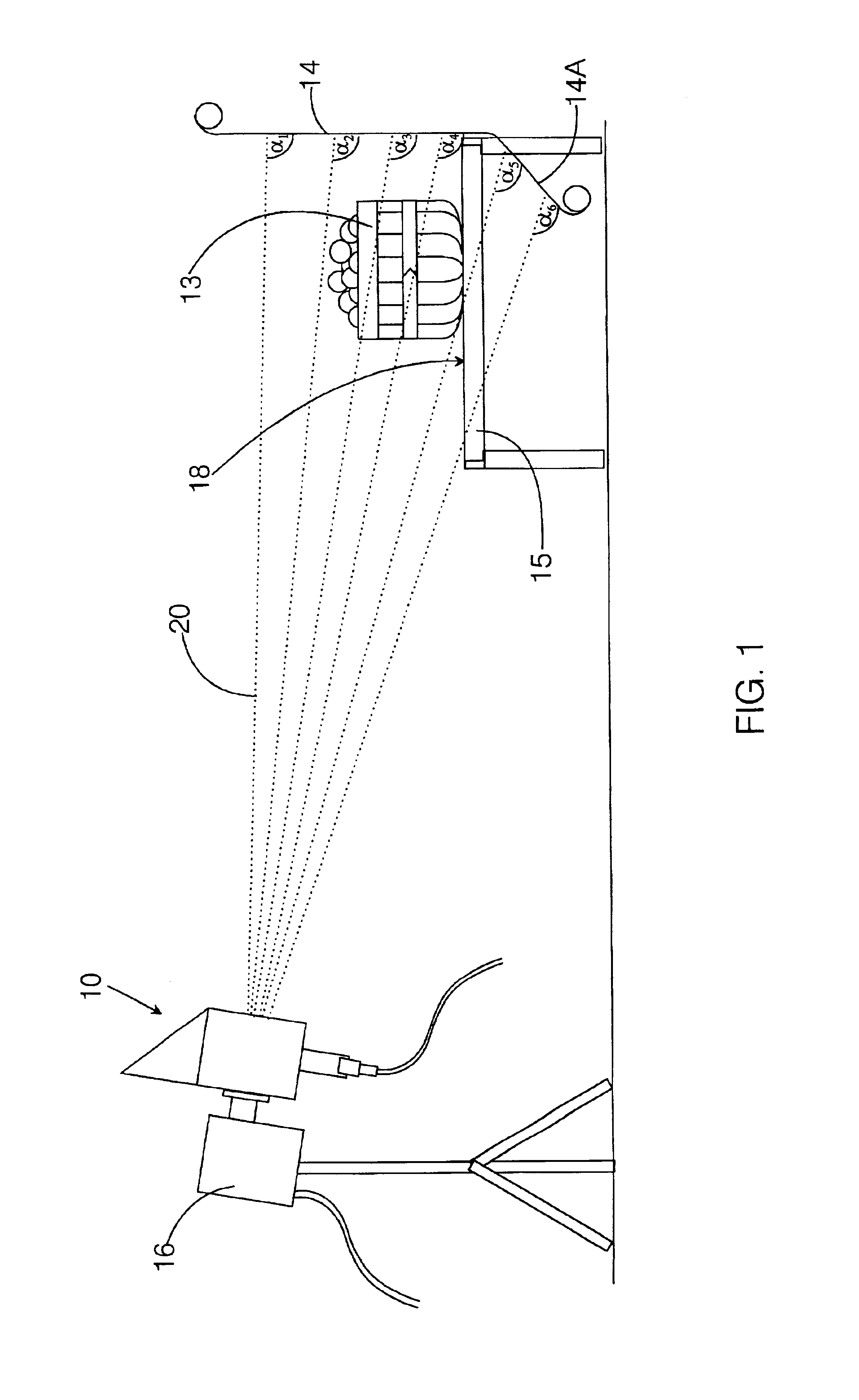
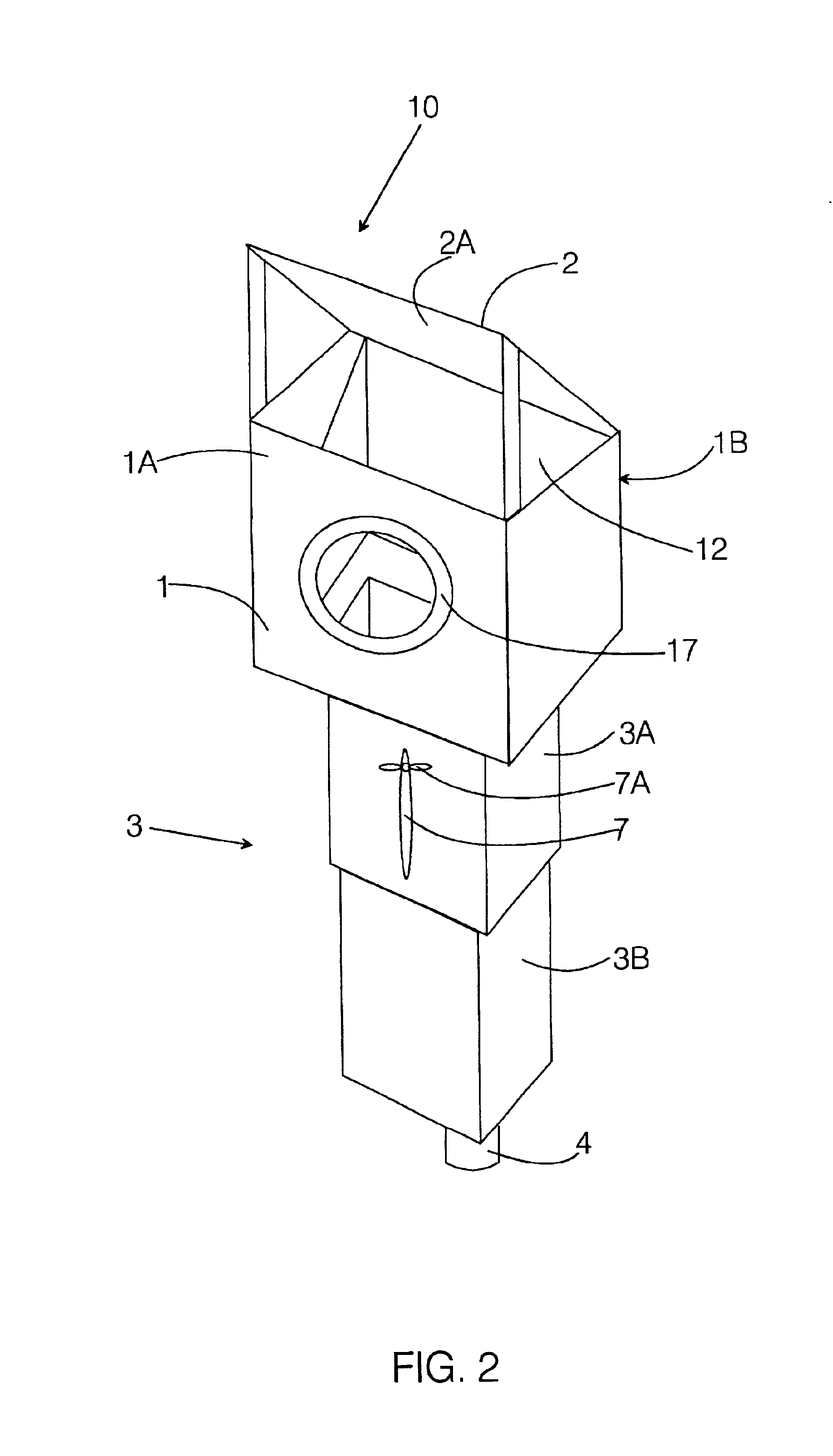
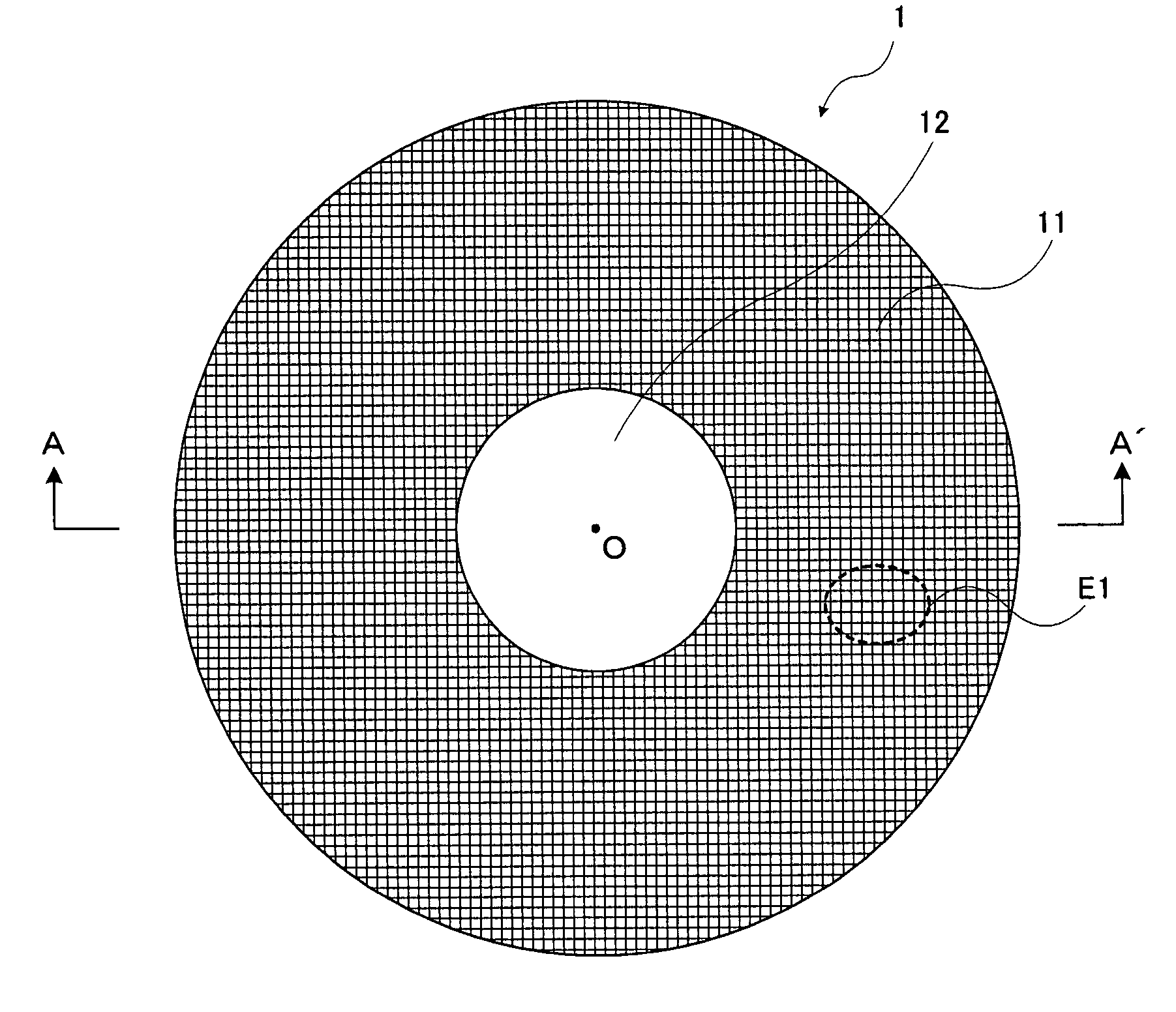
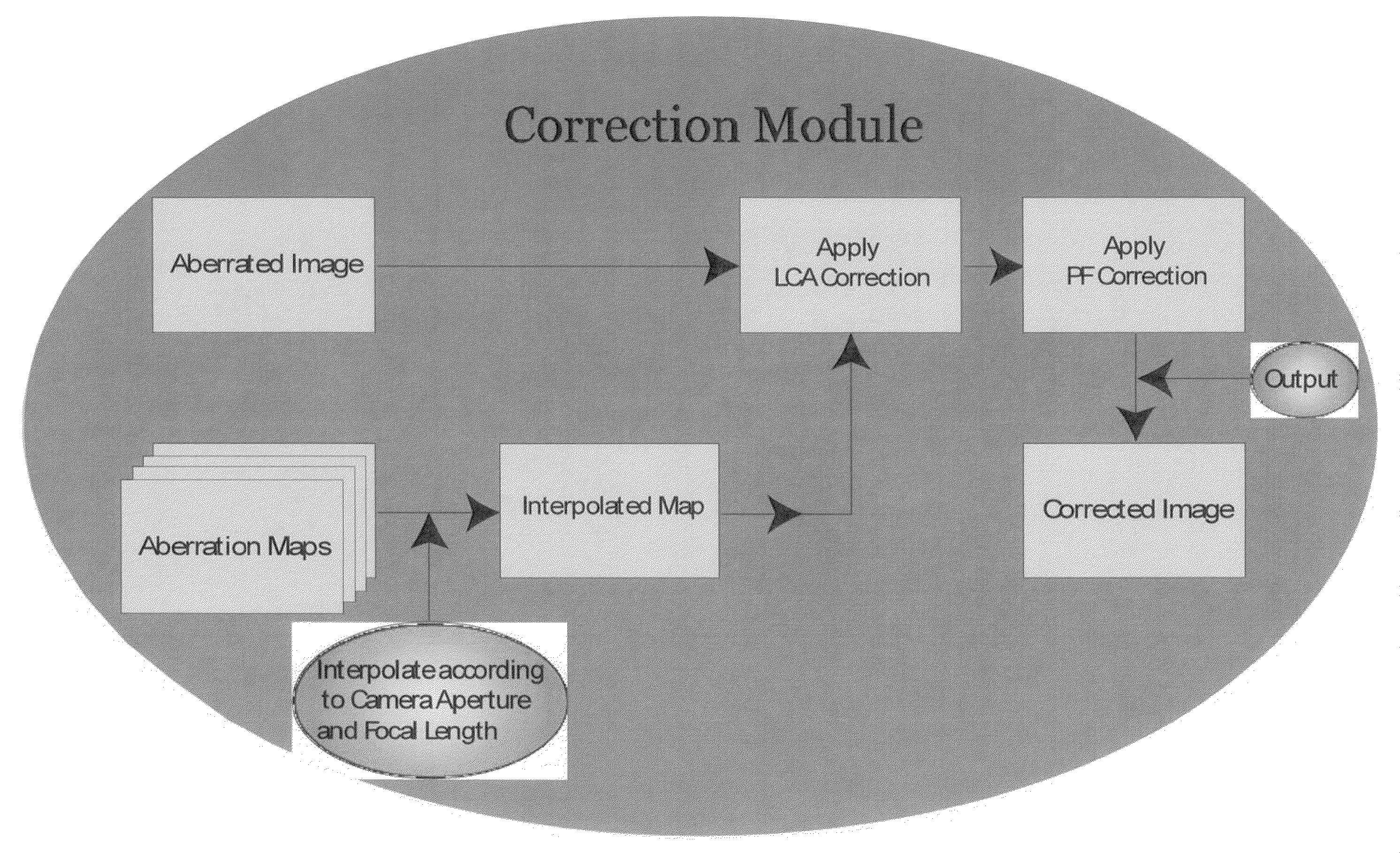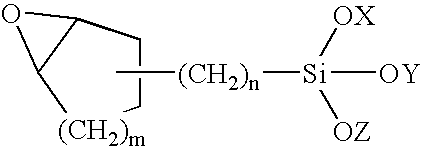Patents
Literature
442results about How to "Reduce sharpness" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
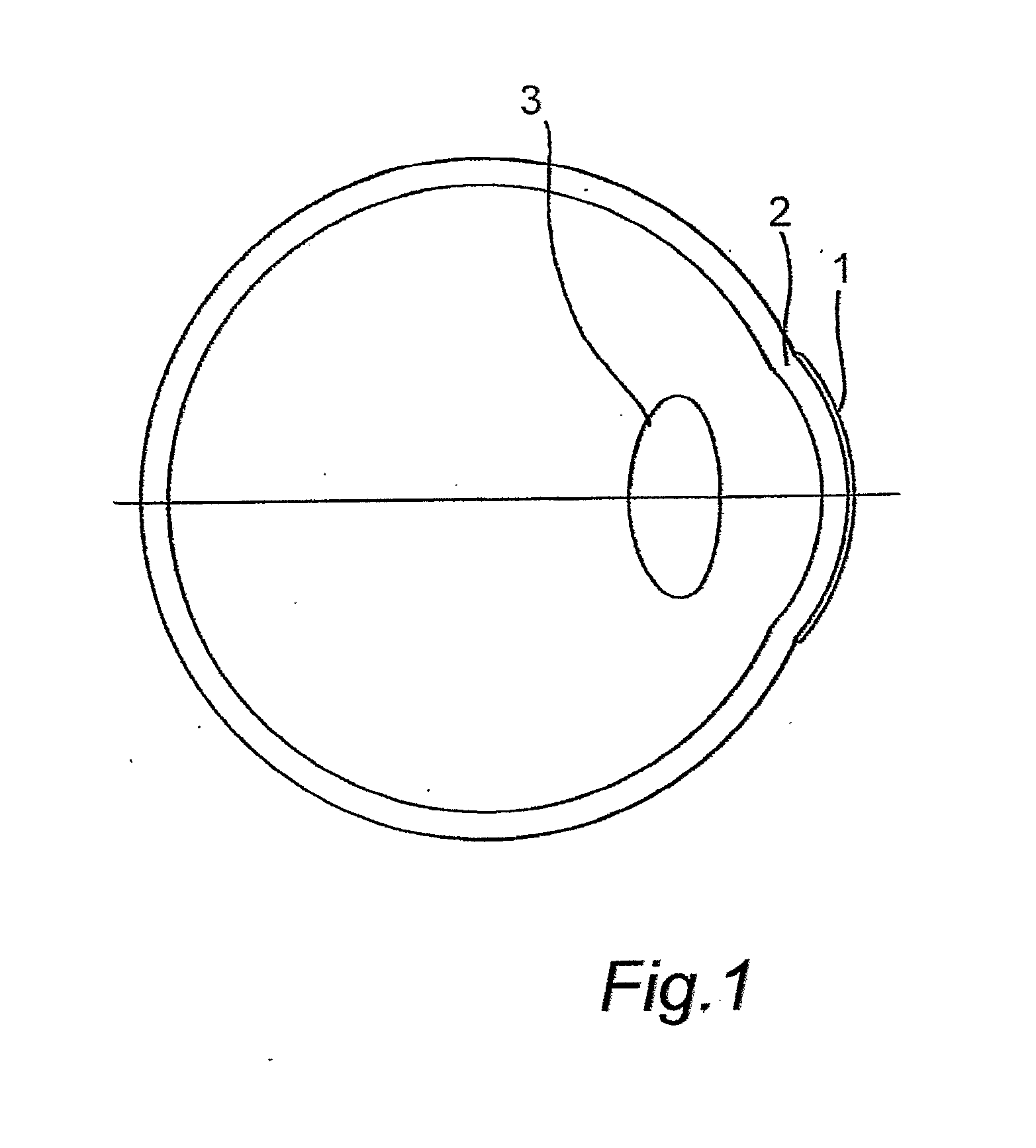
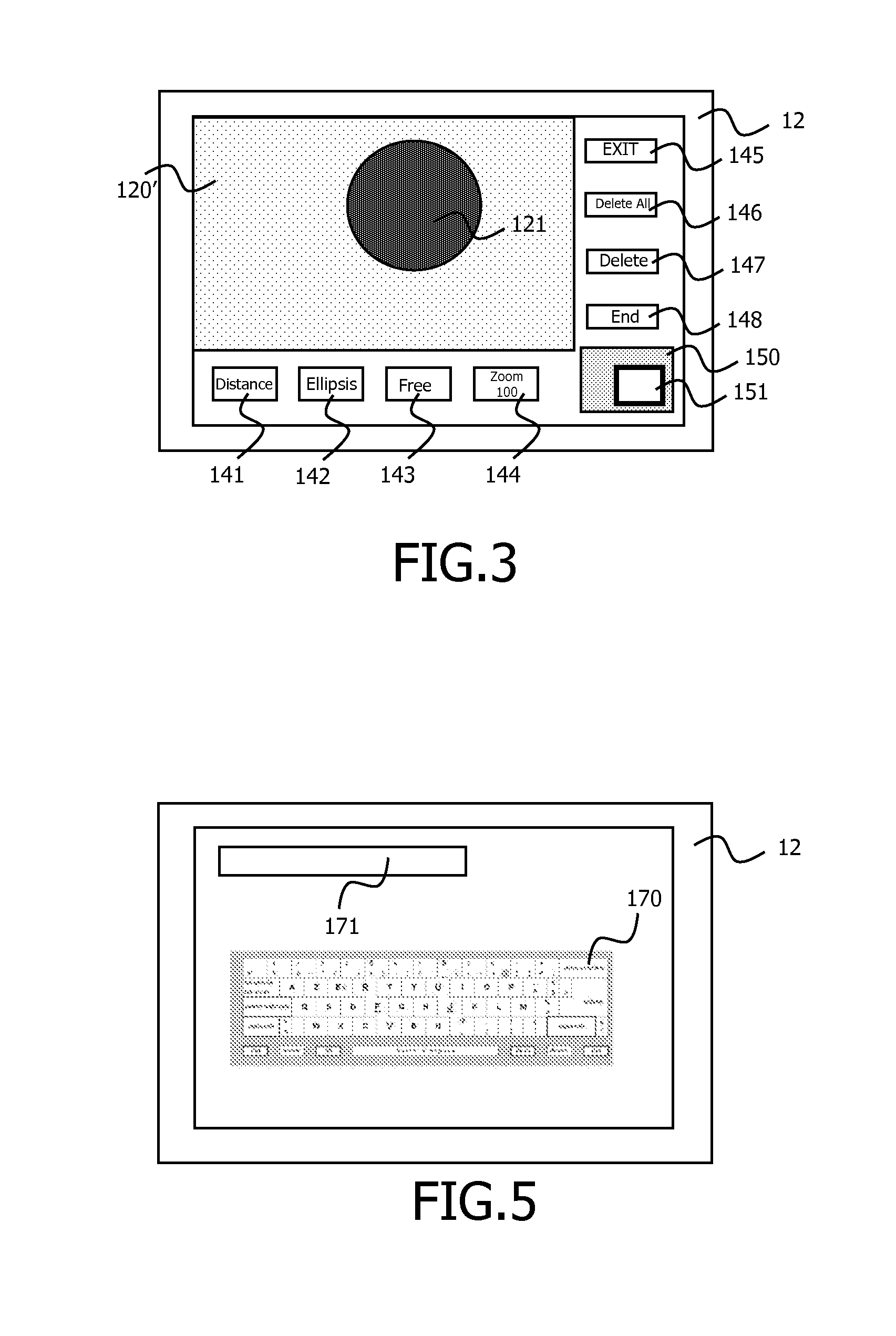
Imaging modification, display and visualization using augmented and virtual reality eyewear
ActiveUS20190011703A1Improve clarityReduce sharpnessInput/output for user-computer interactionMechanical/radiation/invasive therapiesDisplay deviceUser perception
A display system can include a head-mounted display configured to project light to an eye of a user to display augmented reality image content to the user. The display system can include one or more user sensors configured to sense the user and can include one or more environmental sensors configured to sense surroundings of the user. The display system can also include processing electronics in communication with the display, the one or more user sensors, and the one or more environmental sensors. The processing electronics can be configured to sense a situation involving user focus, determine user intent for the situation, and alter user perception of a real or virtual object within the vision field of the user based at least in part on the user intent and / or sensed situation involving user focus. The processing electronics can be configured to at least one of enhance or de-emphasize the user perception of the real or virtual object within the vision field of the user.
Owner:MAGIC LEAP
Line scan sequential lateral solidification of thin films
ActiveUS20060254500A1Improve uniformityReduce sharpnessFrom gel statePolycrystalline material growthOptoelectronicsNucleation
A polycrystalline film is prepared by (a) providing a substrate having a thin film disposed thereon, said film capable of laser-induced melting, (b) generating a sequence of laser pulses having a fluence that is sufficient to melt the film throughout its thickness in an irradiated region, each pulse forming a line beam having a predetermined length and width, said width sufficient to prevent nucleation of solids in a portion of the thin film that is irradiated by the laser pulse, (c) irradiating a first region of the film with a first laser pulse to form a first molten zone, said first molten zone demonstrating a variation in width along its length to thereby define a maximum width (Wmax) and a minimum width (Wmin), wherein the first molten zone crystallizes upon cooling to form one or more laterally grown crystals, (d) laterally moving the film in the direction of lateral growth a distance that is greater than about one-half Wmax and less than Wmin; and (e) irradiating a second region of the film with a second laser pulse to form a second molten zone having a shape that is substantially the same as the shape of the first molten zone, wherein the second molten zone crystallizes upon cooling to form one or more laterally grown crystals that are elongations of the one or more crystals in the first region.
Owner:THE TRUSTEES OF COLUMBIA UNIV IN THE CITY OF NEW YORK
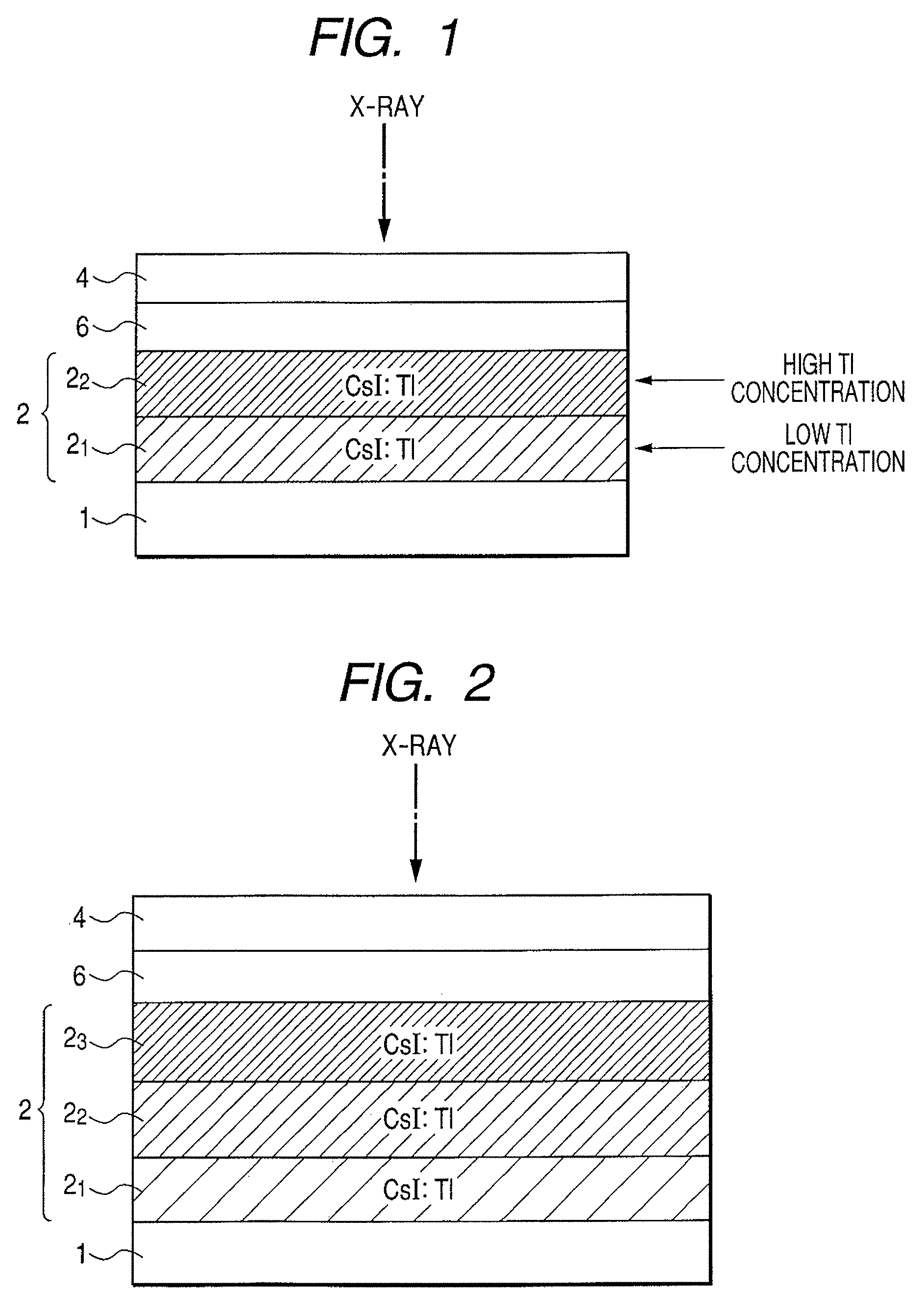
Radiation detection apparatus and scintillator panel
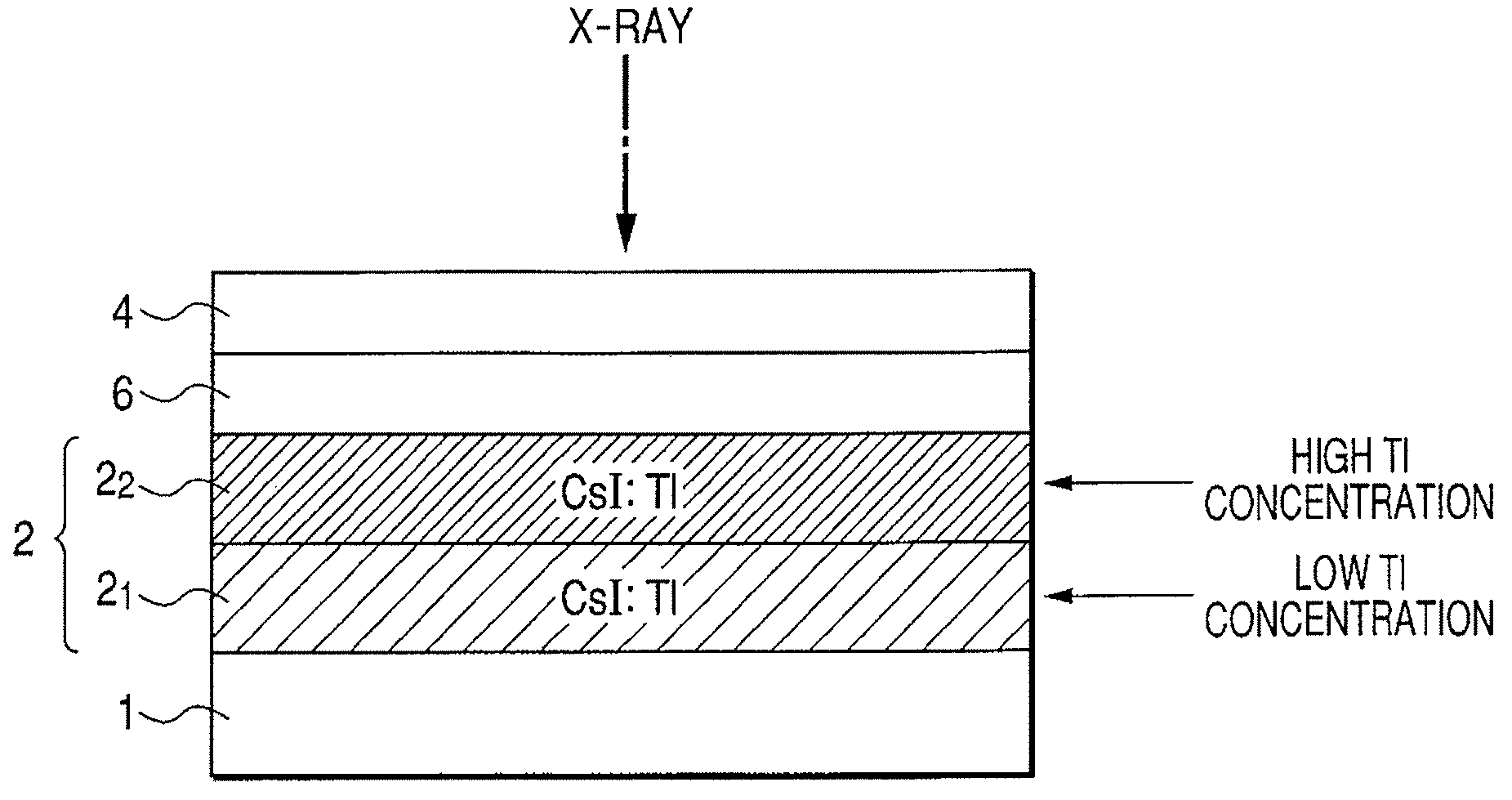
InactiveUS20080083877A1Increase the amount of lightReduce sharpnessMaterial analysis by optical meansRadiation intensity measurementCrystal structurePhotoelectric conversion
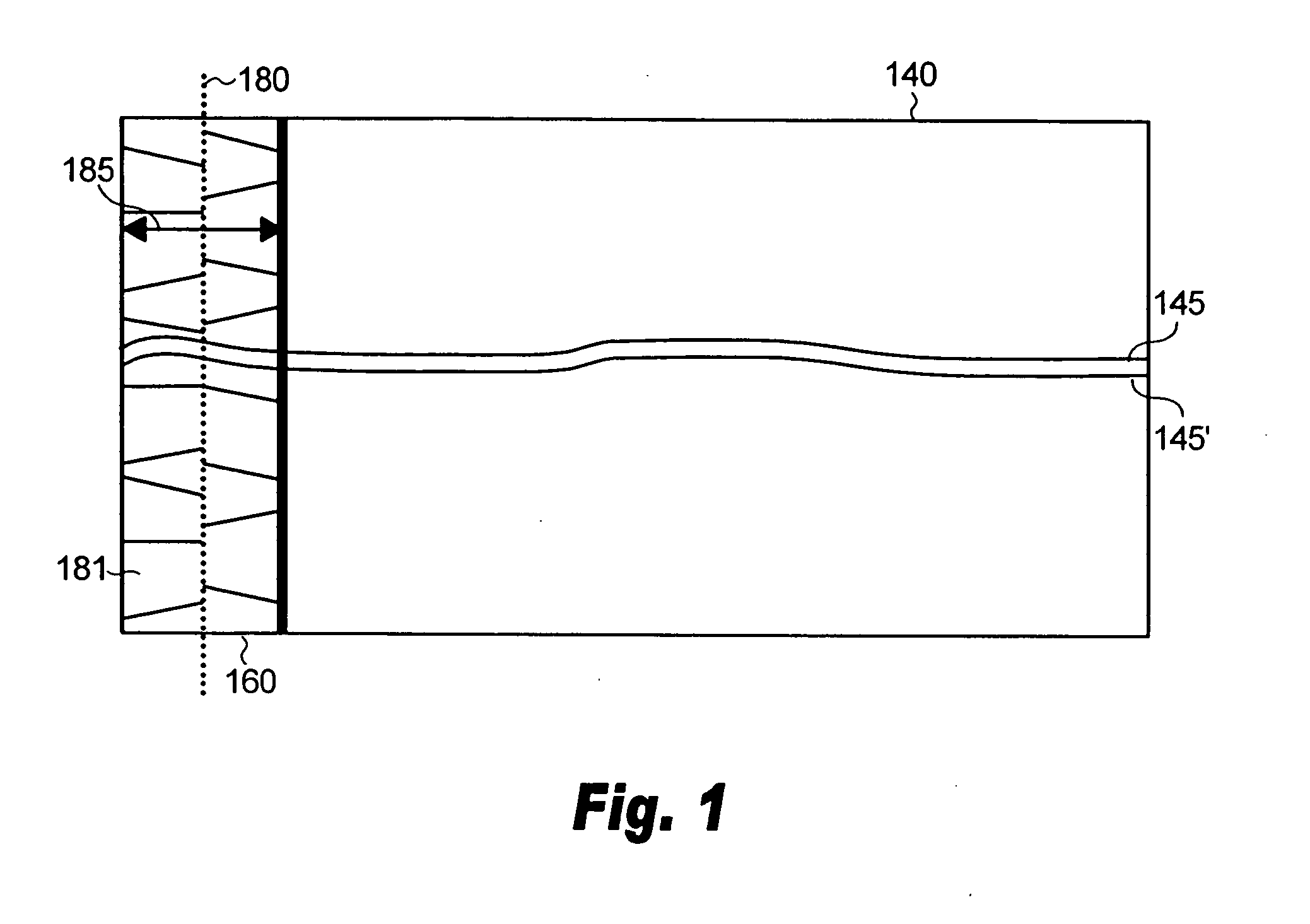
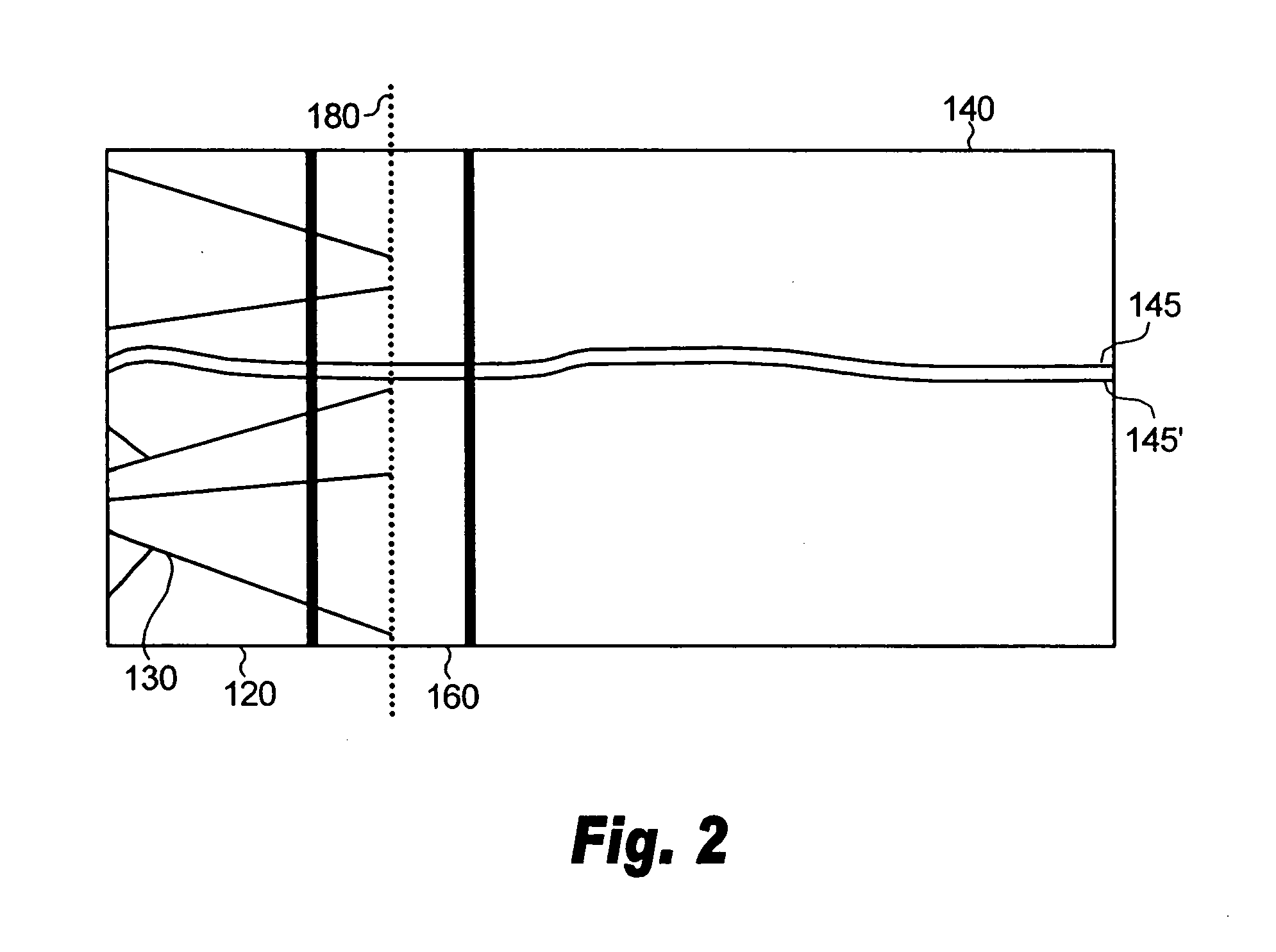
A radiation detection apparatus of the present invention includes an optical detector disposed on a substrate and having a plurality of photoelectric conversion elements which convert light into an electrical signal, and a scintillator layer disposed on the optical detector and having a columnar crystal structure which converts radiation into light, wherein the concentration of an activator of the scintillator layer is higher at the radiation incident side opposite the optical detector and is lower at the optical detector side. The scintillator panel of the present invention includes the substrate and the scintillator layer disposed on the substrate, wherein the concentration of the activator of the scintillator layer is higher at the radiation incident side and is lower at the light emission side.
Owner:CANON KK
Methods and Apparatuses for Addressing Chromatic Abberations and Purple Fringing
InactiveUS20090189997A1Limit performanceReduce sharpnessImage enhancementTelevision system detailsColor planePurple fringing
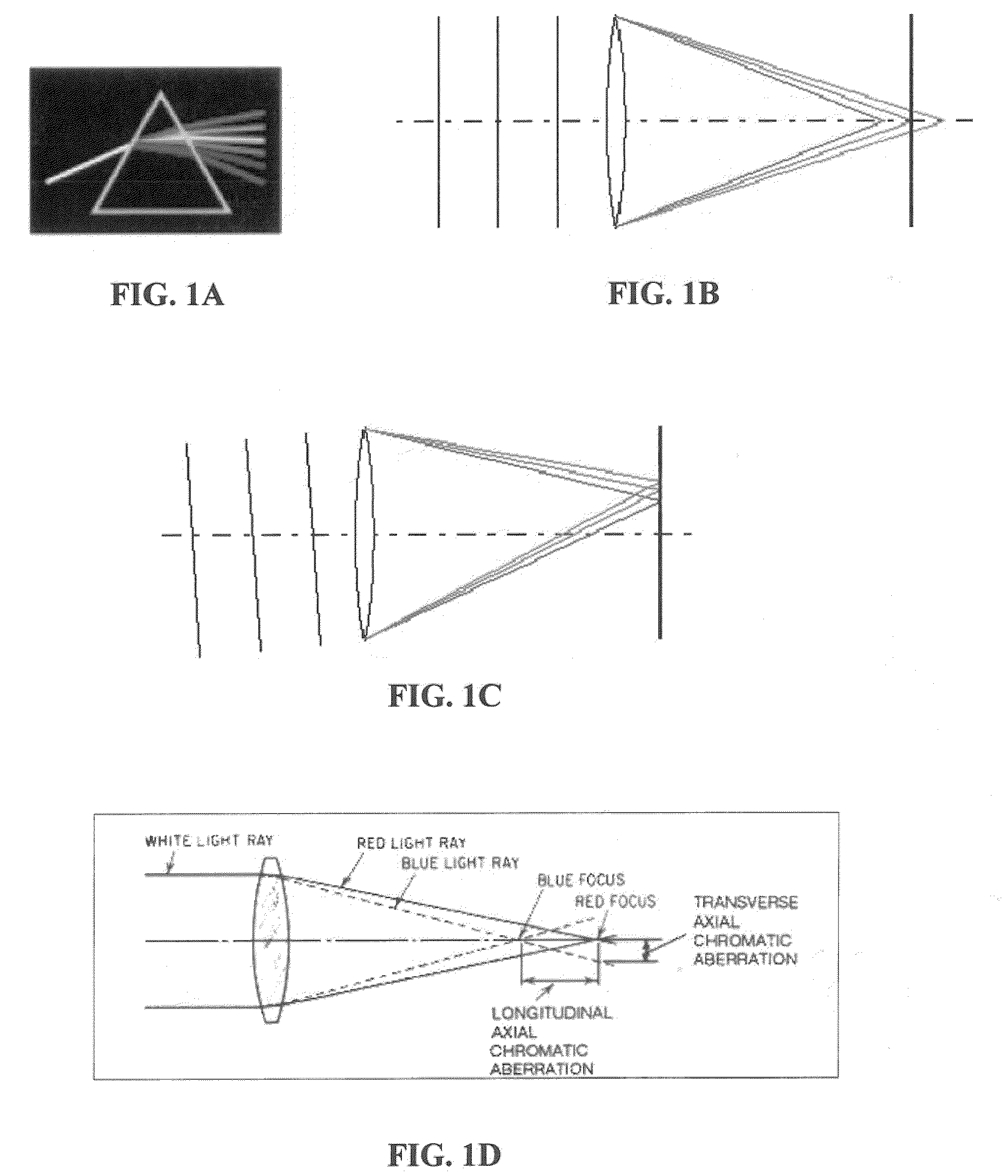
Methods and systems for detecting and correcting chromatic aberration and purple fringing are disclosed. Chromatic aberration can be addressed by separating an image into color planes and then adjusting these to reduce chromatic aberration by using a specific calibration image (calibration chart) as an empirical method to calibrate the image acquisition device. Purple fringing can be corrected by initially addressing color aberration resulting from the lateral chromatic aberration (LCA). The LCA is first removed and then the correction is extended to purple fringing. A discovery is relied upon that the purple fringing is created in the direction of the chromatic aberration and is more pronounced in the direction of the chromatic aberration.
Owner:FOTONATION LTD
Contact Lenses
ActiveUS20080055545A1Confer rotational and translational stabilitySimplify fitting and makingSpectales/gogglesEye diagnosticsLayer thicknessLandform
Disclosed is a method of designing a soft contact lens, the method comprising the steps of: (a) measuring or defining a wavefront generated by passage of light through a selected eye and using the wavefront to generate a computer model of the optical characteristics of the selected eye; (b) measuring or defining the topography of the cornea of the selected eye; (c) incorporating into the computer model a soft contact lens, the posterior surface topography of which is defined by the topography of the cornea, offset by an arbitrary amount intended to represent the tear layer thickness of the selected eye, said lens having a defined thickness at a selected locus on the anterior surface; (d) calculating a desired topography for the anterior surface of the lens such that the wavefront will be corrected to assume a desired pattern (for example, preferably planar, the plane of which is perpendicular to the optical axis of the lens) when passing through the computer model eye / lens combination; (e) remodelling the lens off-eye by adapting the posterior topography of the lens to a desired posterior topography to be manufactured; and (f) recalculating a modified anterior topography required as a result of adapting the posterior topography, the modified anterior topography being intended to preserve the desired wavefront pattern defined in (d) when the lens is in situ on the selected eye.
Owner:CONTACT LENS PRECISION LAB
Twin-monitor electronic display system
ActiveUS20110043434A1Easy to operateReduce sharpnessUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsImage enhancementGraphicsUltrasound imaging
The invention concerns an electronic display system, intended to be coupled with ultrasound imaging equipment capable of capturing an image of a medium, said system comprising a first monitor to display an ultrasound image such as captured by the ultrasound imaging equipment and image processing means. According to the invention, the system further comprises a second touch-screen monitor, means to duplicate the ultrasound image, means to send this duplicate to the second monitor on which at least part therefore is displayed, means to display at least one graphical element which, by means of the tactility of the screen, is used to perform at least one processing operation on the ultrasound image, means for instant application of all processing operations performed using the second monitor to the duplicate ultrasound image displayed on the second monitor, and means for instant or deferred application to the ultrasound image displayed on the first monitor of all or part of the processing operations performed on the duplicate ultrasound image by means of the second monitor.
Owner:SUPER SONIC IMAGINE
Screen display method in mobile terminal and mobile terminal using the method
ActiveUS20140143725A1Improve visual effectsReduce sharpnessMultimedia data retrievalRecord information storageOn-screen displayMobile media
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Image exposure device
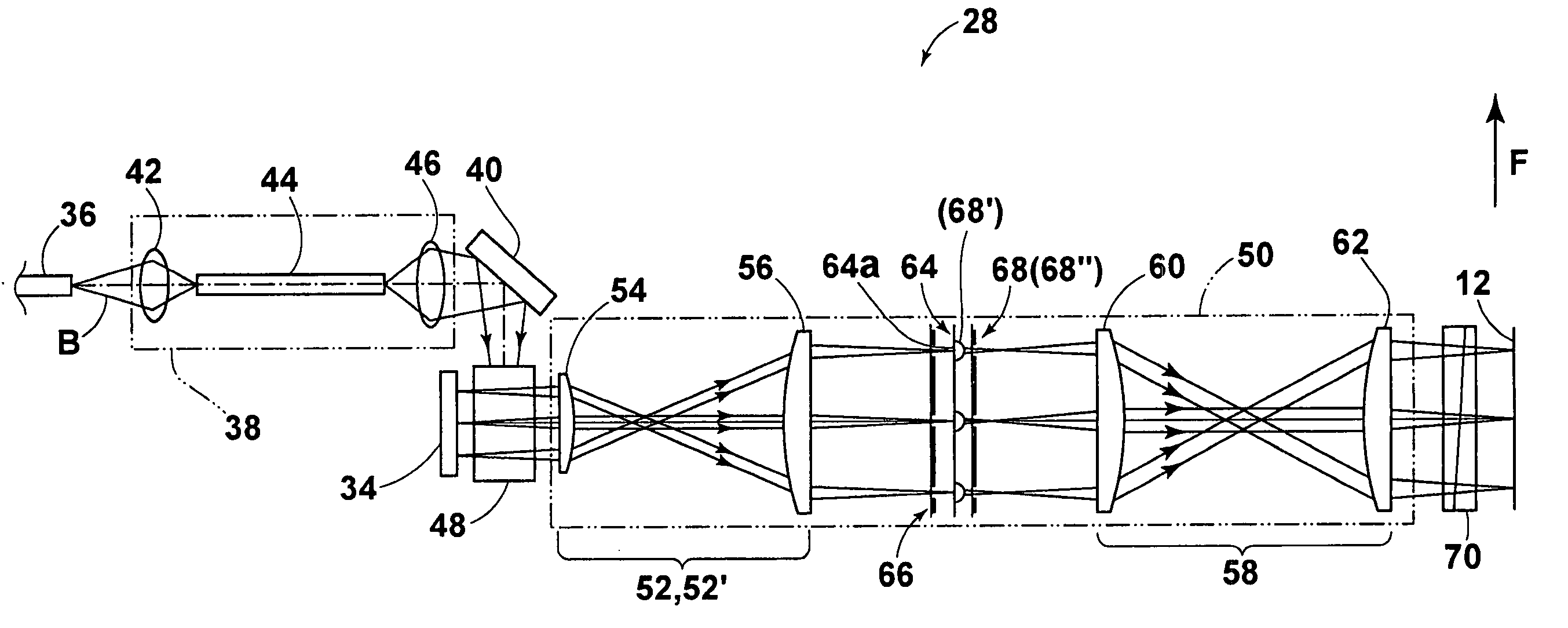
InactiveUS20050213068A1Reduce sharpnessEasy alignmentPhotomechanical exposure apparatusMicrolithography exposure apparatusSpatial light modulatorLight beam
An image exposure device includes an exposure head for forming a desired pattern on a photosensitive material. The exposure head is equipped with a light source for emitting a great number of light beams, a spatial light modulator in which a great number of pixel portions are arranged for independently modulating the light beams emitted from the light source, a micro lens array in which a great number of micro lenses are arranged for individually converging the great number of light beams modulated by the pixel portions, and a total of two or more aperture arrays arranged in the stage before the micro lens array and / or the stage after the micro lens array. Each of the aperture arrays has a great number of apertures for individually restricting the light beams.
Owner:FUJIFILM HLDG CORP +1
Double stacked projection
InactiveUS20130093805A1Reduces the visible artefactsReduce componentsPicture reproducers using projection devicesCathode-ray tube indicatorsComputer visionSource image
A method for producing a first output image and a second output image for being projected by a first projector and a second projector, respectively, is disclosed. The method comprises: providing a source image comprising a plurality of pixels, each pixel having a source value, providing a threshold value and an inverted threshold value for each pixel of the plurality of pixels, and generating there from a temporary image comprising a temporary value for each pixel of the plurality of pixels. The method further comprises generating the first output image comprising a first output value for each pixel of the plurality of pixels, the first output value being generated from the temporary value and the source value for each pixel, and generating the second output image comprising a second output value for each pixel of the plurality of pixels, the second output value being generated from the temporary value.
Owner:IMAX THEATERS INT
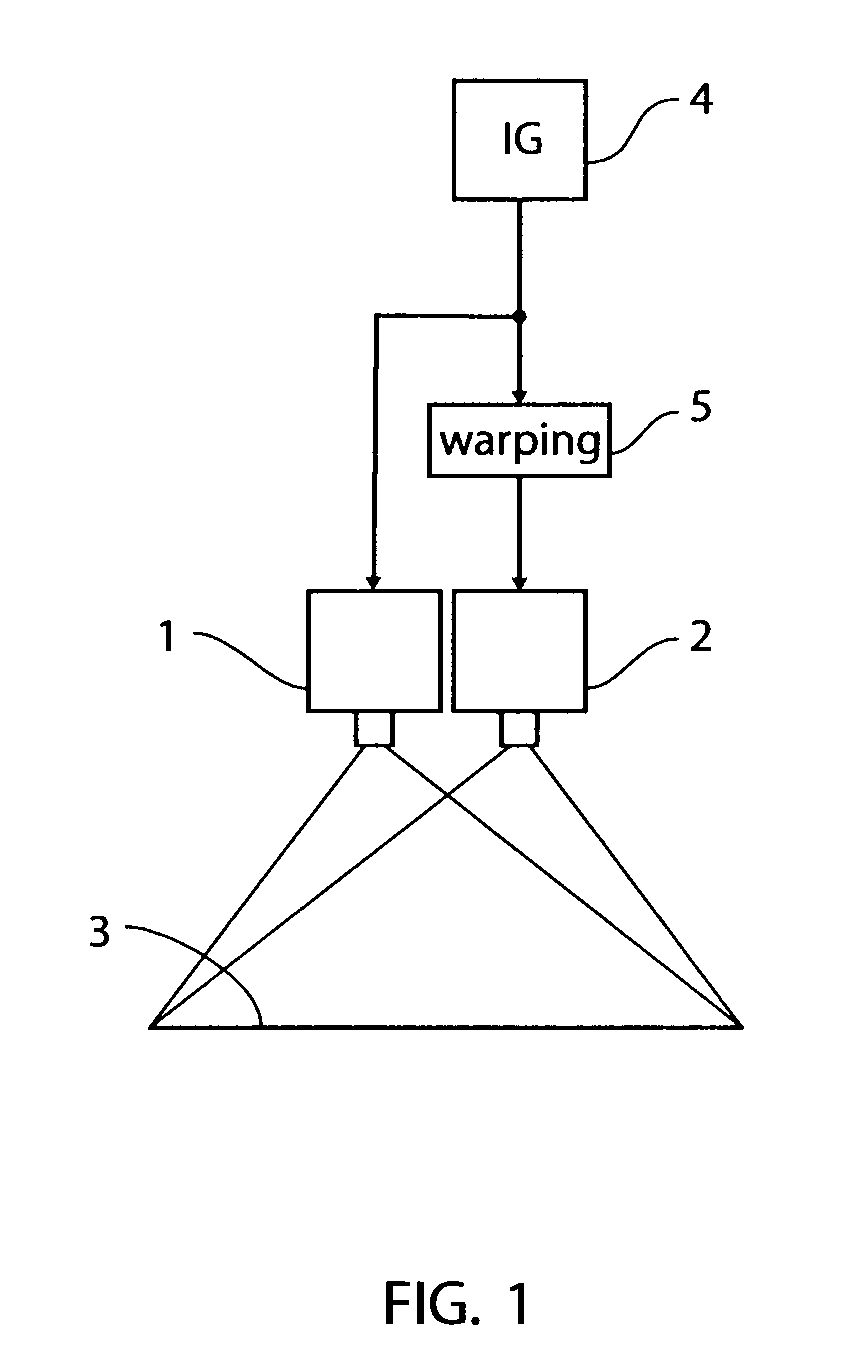
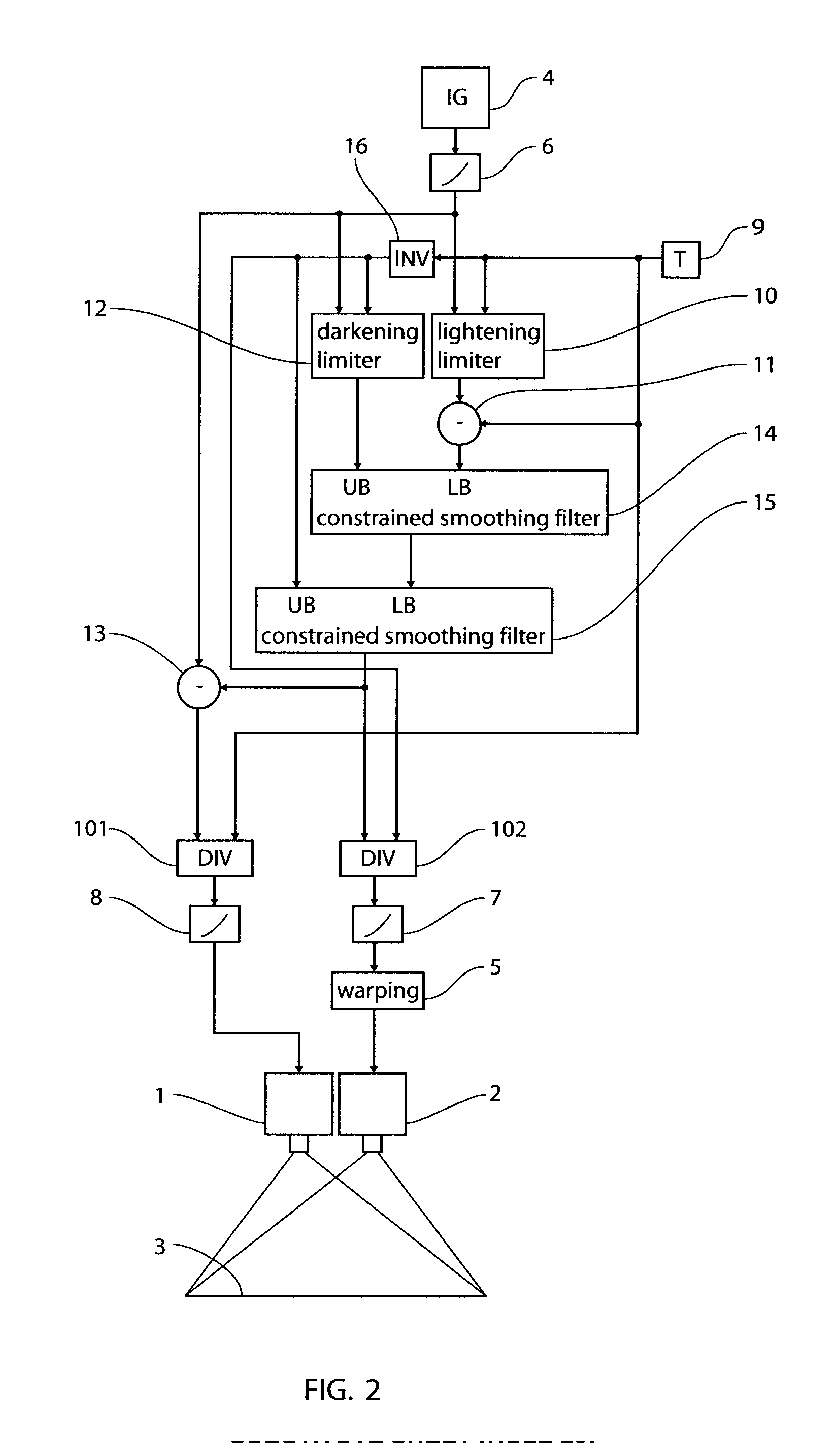
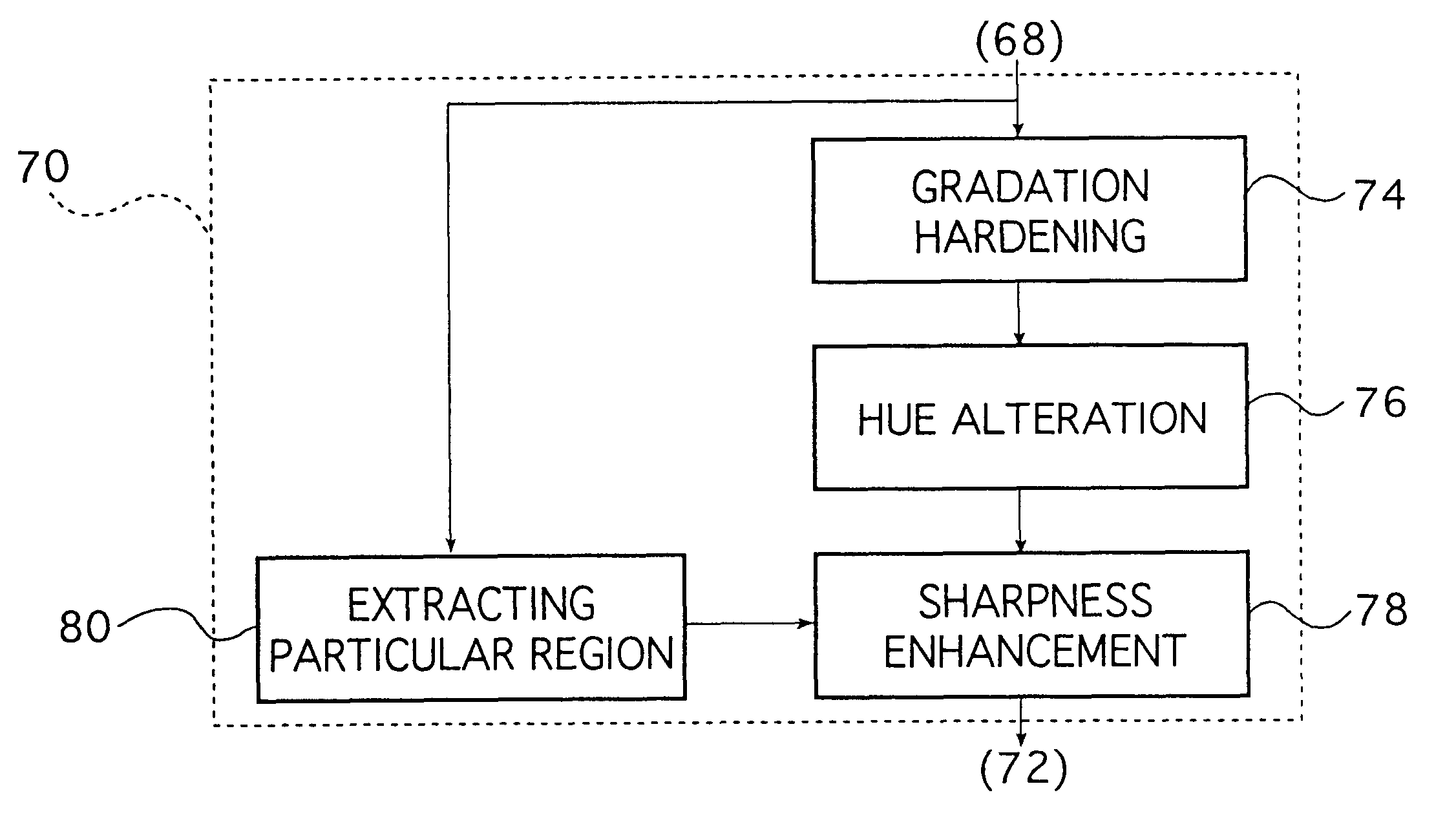
Image processing method
InactiveUS6603878B1Reduce sharpnessImage enhancementCharacter and pattern recognitionImaging processingHue
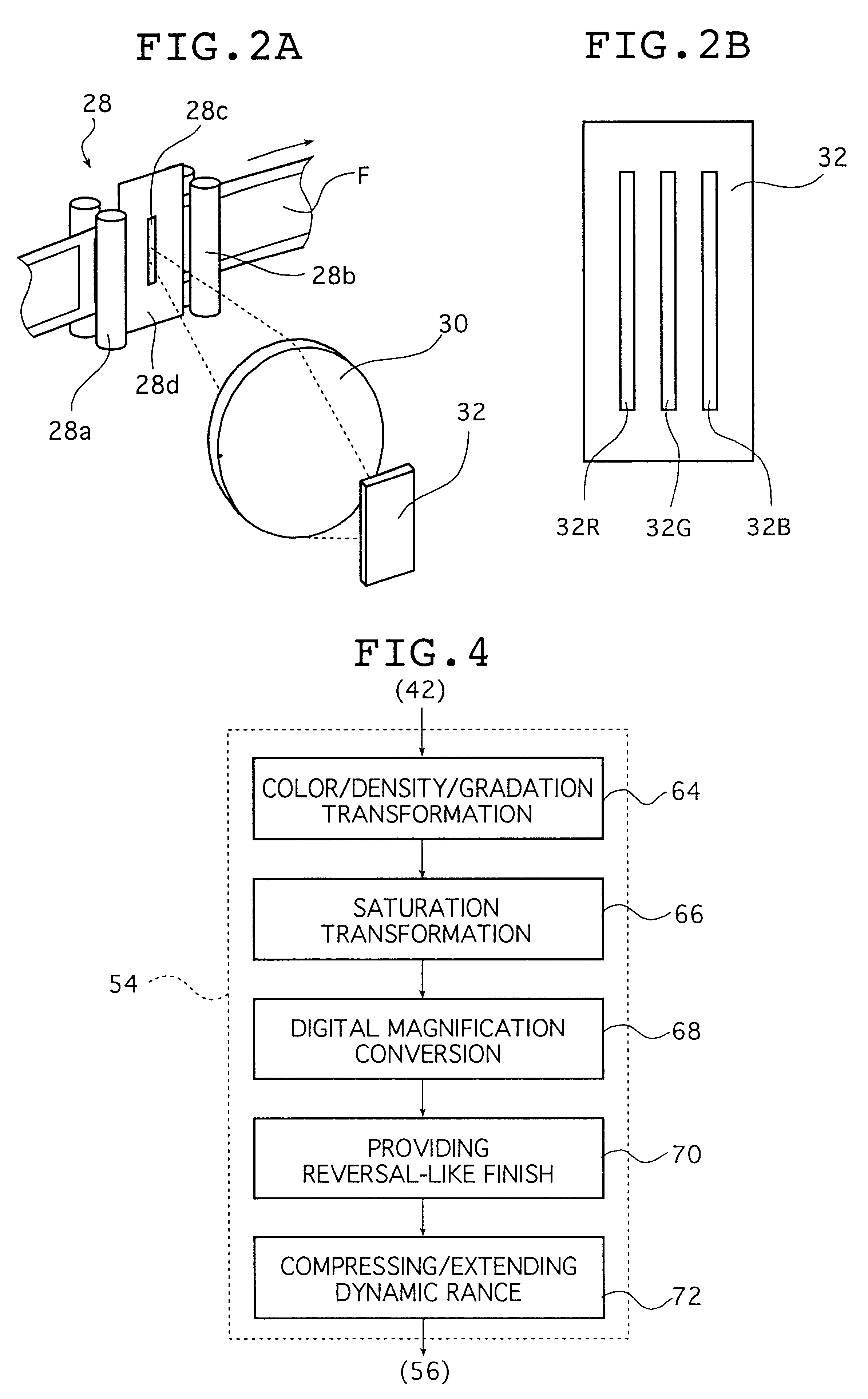
The image processing method subjects color negative image signals read photoelectrically from a color negative image to specified image processing. If the color negative image is designated as representing a particular picture, the method subjects the color negative image signals to gradation hardening process in which the gradation of the designated color negative image is rendered harder and subjects the color negative image signals to a hue altering process in which a particular hue in the designated color negative image is altered to a desired hue. The method is capable of reproducing the color negative image as a color print image that has been processed to a reversal-like finish and which provides good appeal and natural impression in a satisfactory way.
Owner:FUJIFILM CORP
Digital camera with integrated accelerometers
ActiveUS7554578B2Reduce moiré image defectIncrease sharpnessTelevision system detailsTelevision system scanning detailsDigital cameraComputer graphics (images)
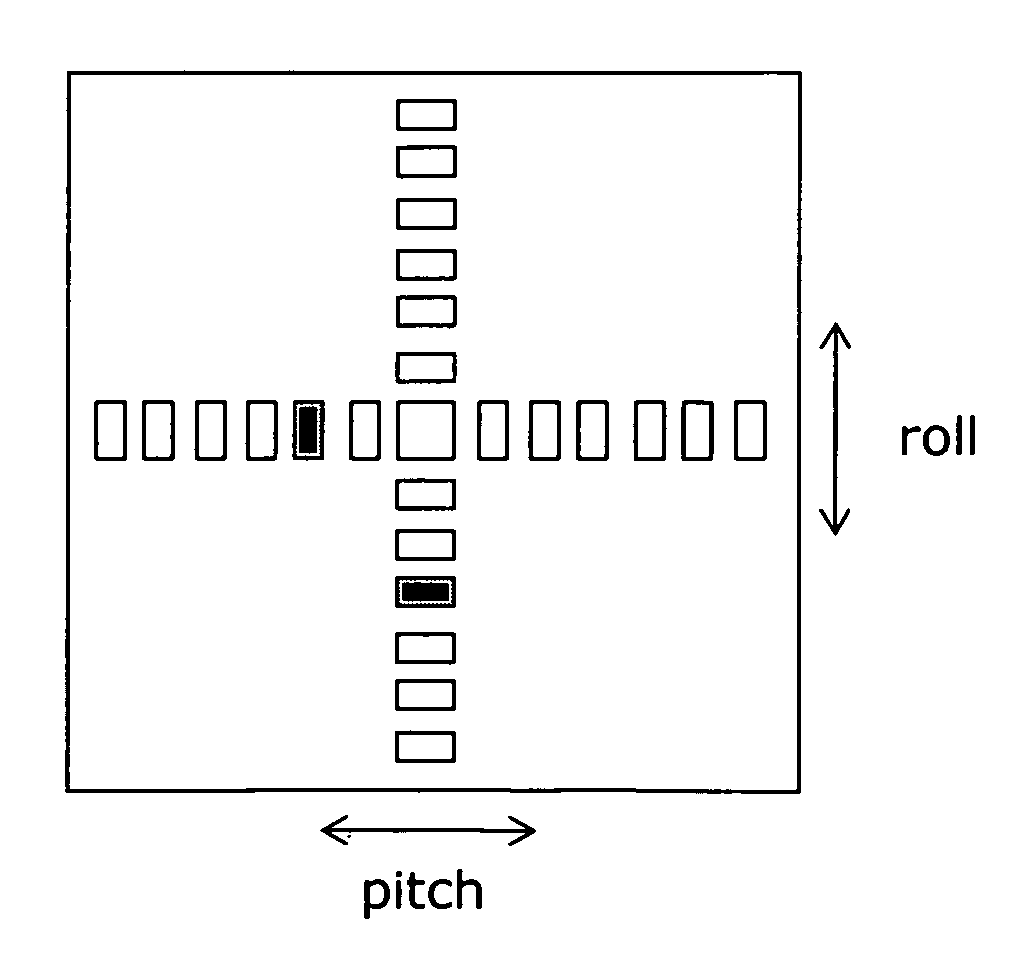
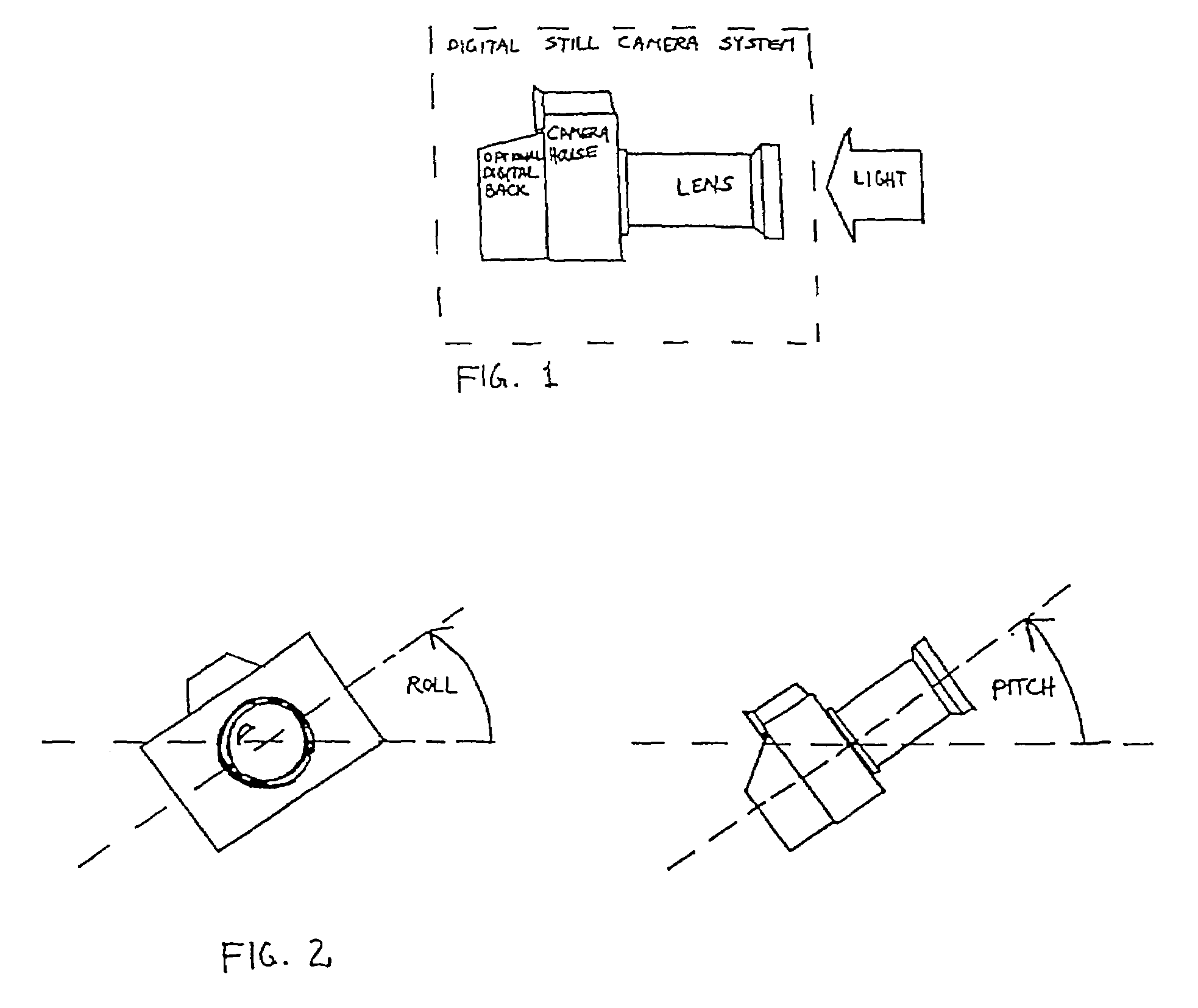
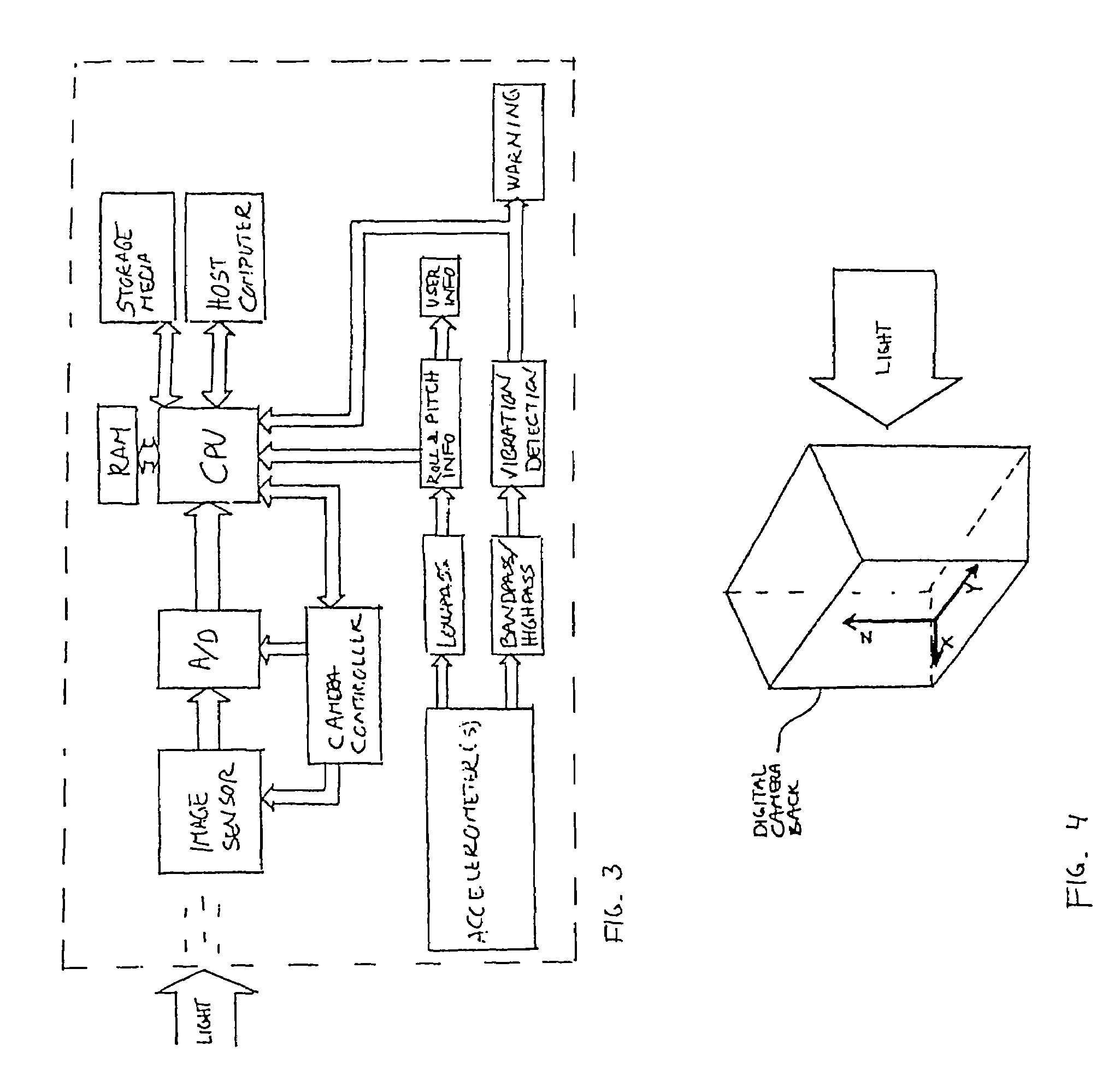
A digital camera system has integrated accelerometers for determining static and dynamic accelerations of the digital camera system. Data relating to static and dynamic accelerations are stored with recorded image data for further processing, such as for correcting image data for roll, pitch and vibrations and for displaying recorded images with a predetermined orientation using information about, e.g., roll. Data may also be used on-the-fly for smear suppression caused by vibrations.
Owner:PHASE ONE
Silhouetting apparatus and method
InactiveUS6885767B1Few processing operationReduce stepsTelevision system detailsCharacter and pattern recognitionComputer graphics (images)Computer science
Owner:HOWELL
Damper for speaker device, speaker device using the damper and manufacturing method therefor
InactiveUS20050254682A1Resistant effectReliable supportTransducer detailsDeaf-aid setsBobbinEngineering
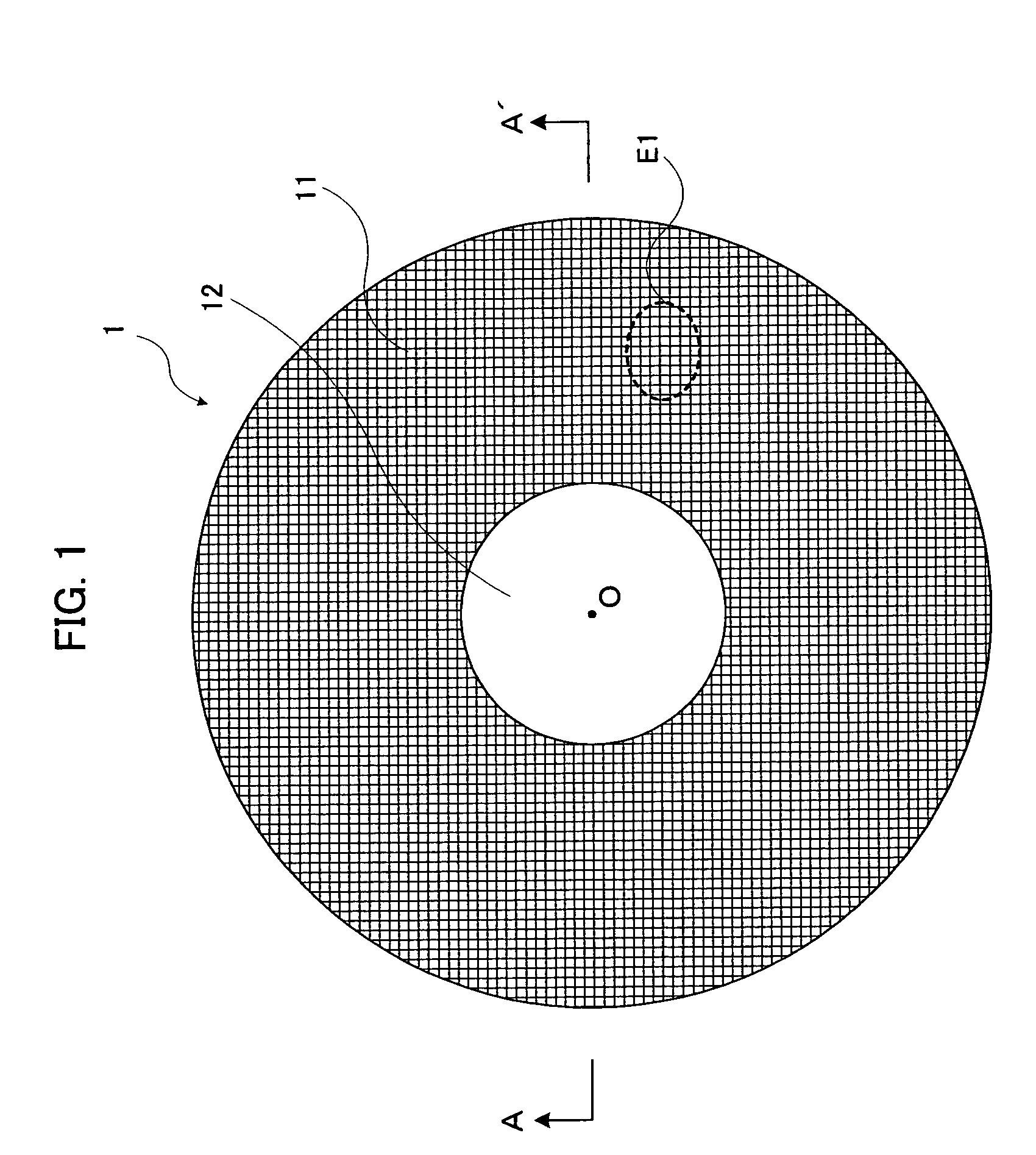
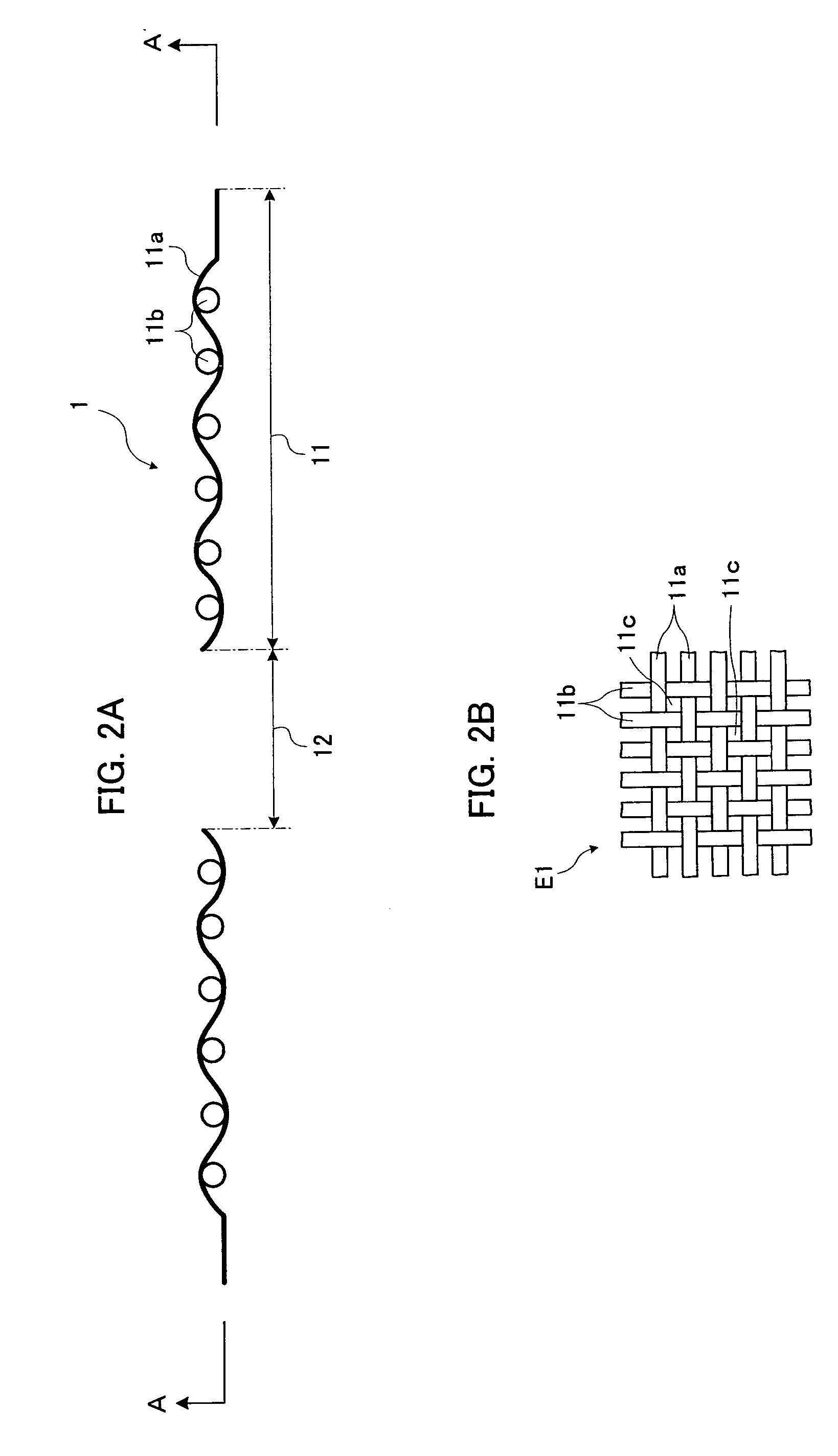
A damper having an annular elastic part is manufactured by stamping out a wire mesh material formed by weaving a plurality of metal wires into a net shape with a press device. The elastic part of the damper thus manufactured has a wire mesh structure. Thereby, a damper with high durability is obtained. Consequently, by applying this damper to the speaker device, the voice coil bobbin, a diaphragm and the like can be restrained / prevented from vibrating more than necessary even when an abnormal large signal is inputted into the speaker device.
Owner:PIONEER CORP +1
Digital fog effect filter method based on dark primary color channel prior principle
InactiveCN102663694AReduce sharpnessReduce image qualityImage enhancement2D-image generationImage extractionPhysical model
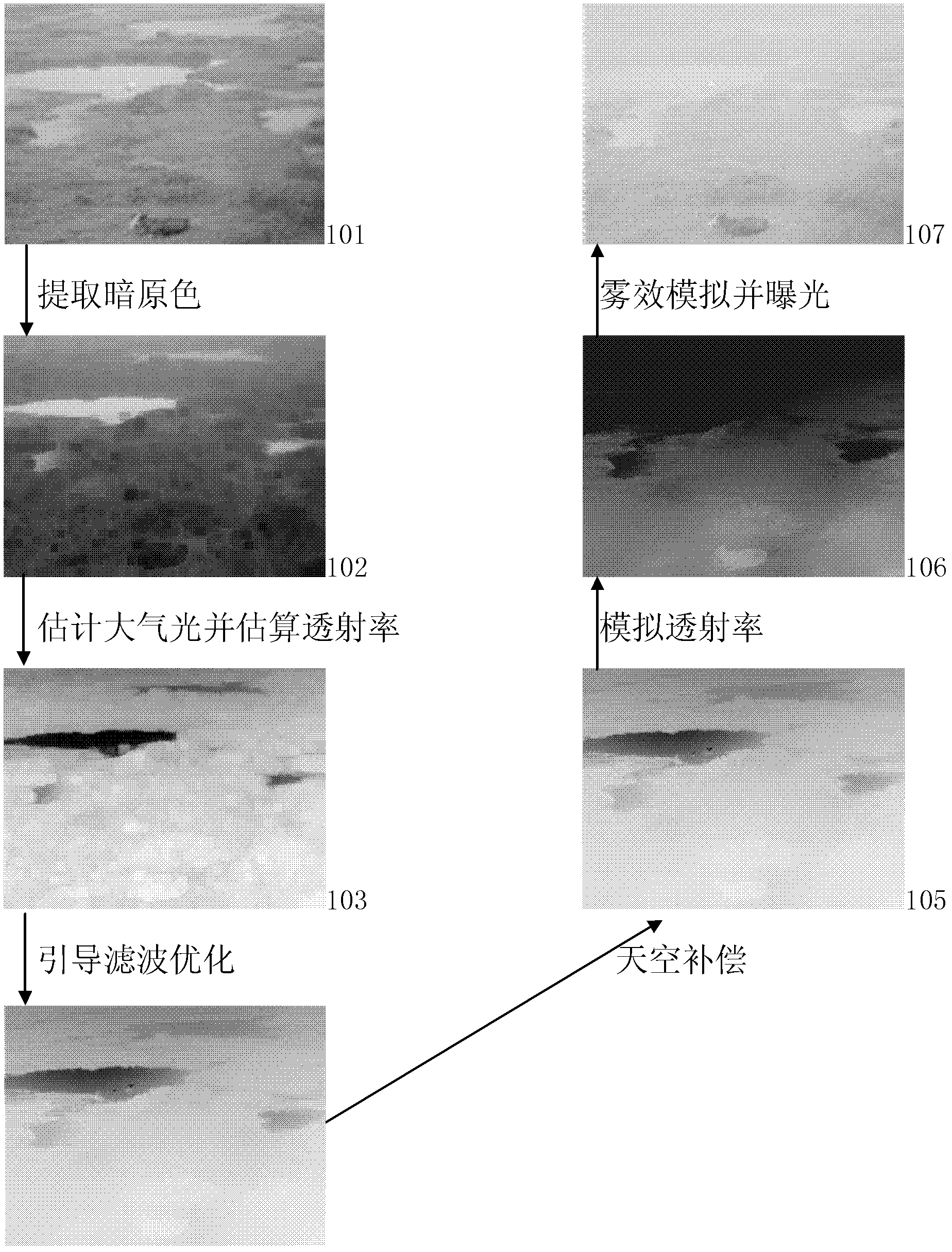
The invention, which belongs to the computer application technology field, relates to a digital fog effect filter method based on dark primary color channel prior principle. A model in which an atmospheric scattering model is applied for defogging in haze weather and a dark primary color channel prior principle is employed to carry out operation on an image, wherein the operation including dark primary image extraction, atmospheric light estimation, transmissivity conversion, optimization compensation and fog effect simulation and the like. According to the invention, a solution scheme is proposed for limitation of an exiting model; on the basis of a perspective concept, a traditional defogging method is changed into a fog effect filter method to obtain foggy / fog-free scenes with different fog effects, so that defects existing in the prior art are overcome. According to the method, only a physical model and data calculation are needed to carry out correction operation on the physical model, thereby substantially reducing time and space and improving generality of the method.
Owner:DALIAN UNIV OF TECH
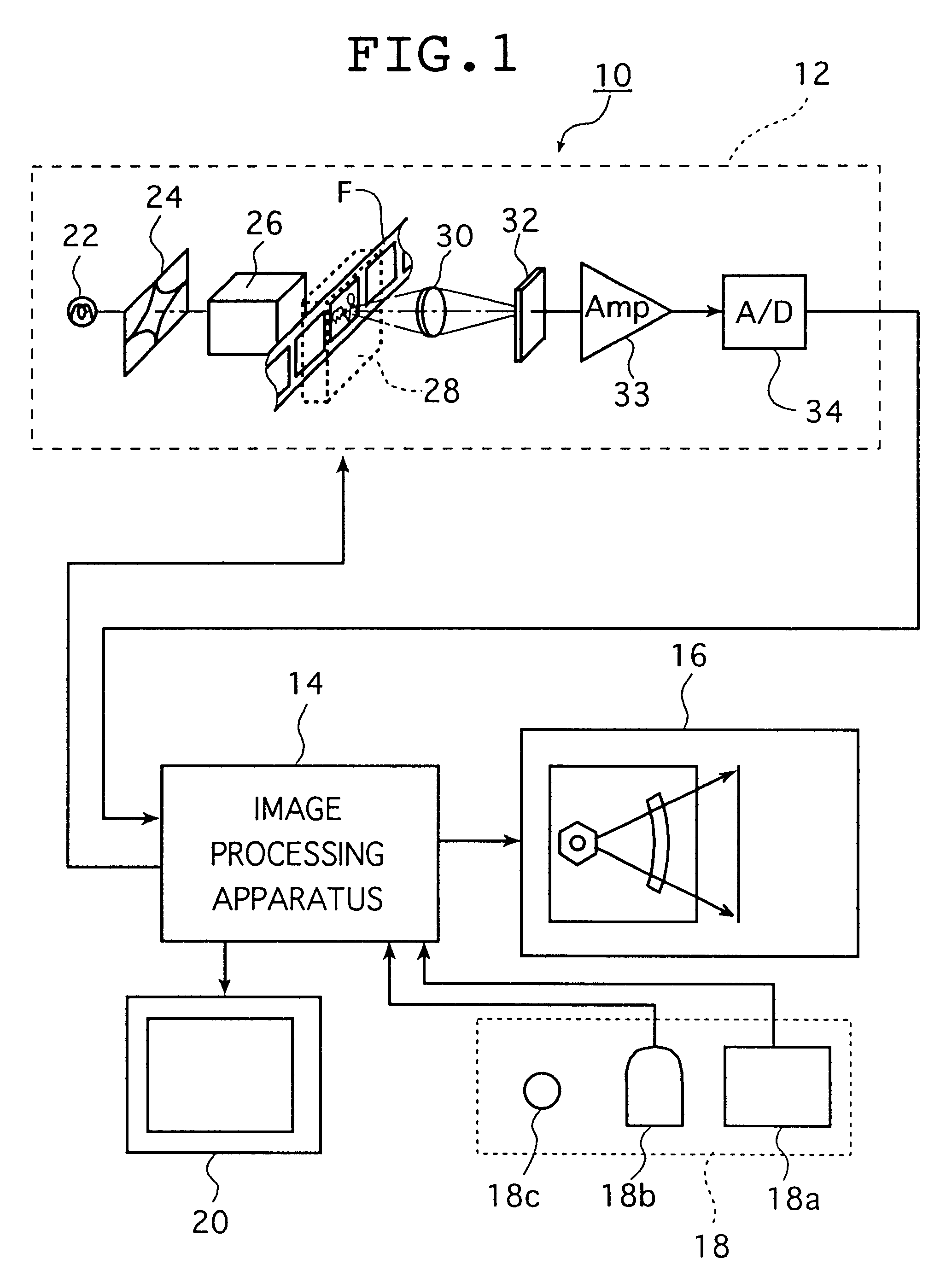
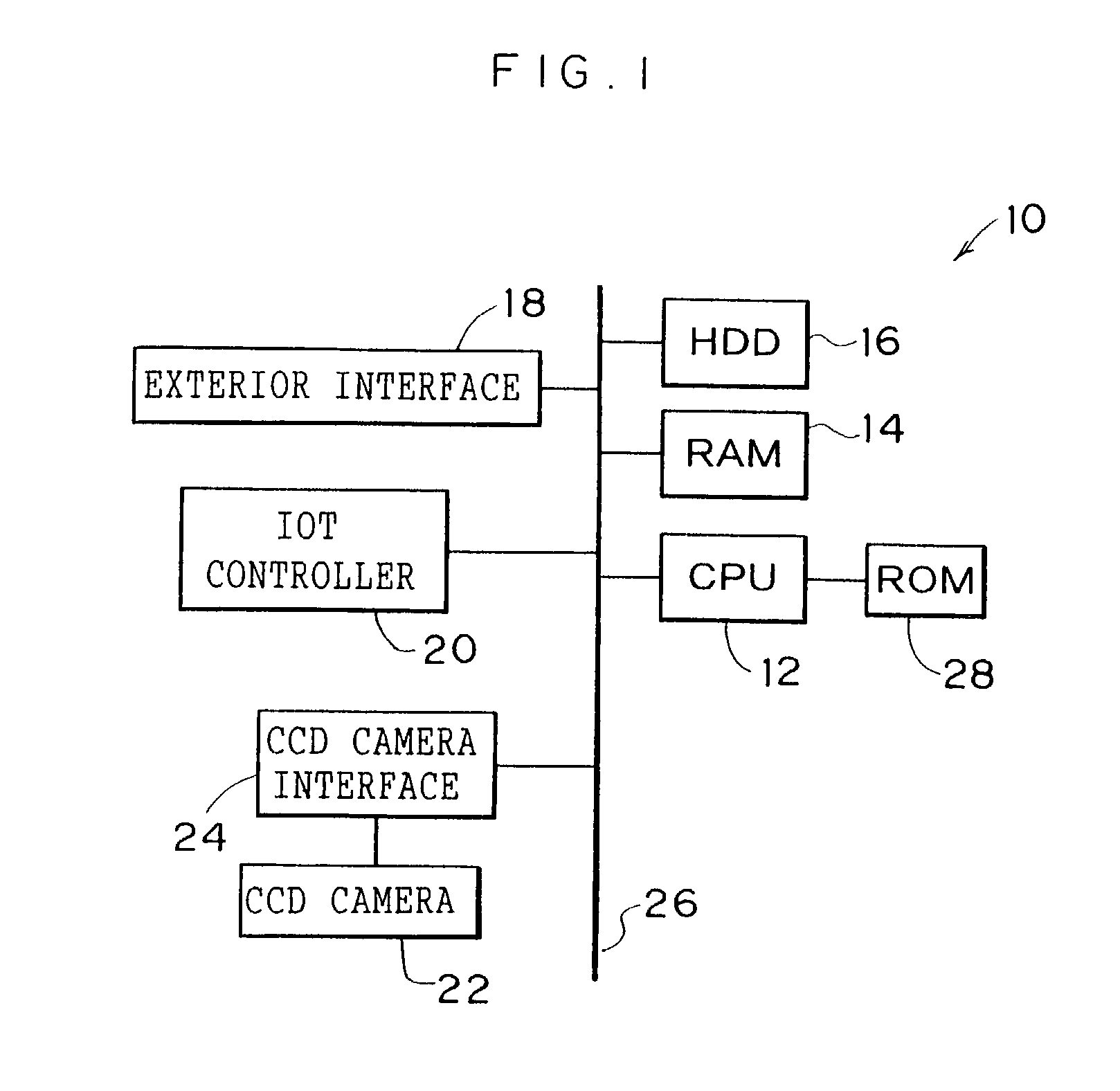
Image inspection device
InactiveUS7076086B2Simplify of output imageEasy to checkImage enhancementDigitally marking record carriersImage InspectionImaging processing
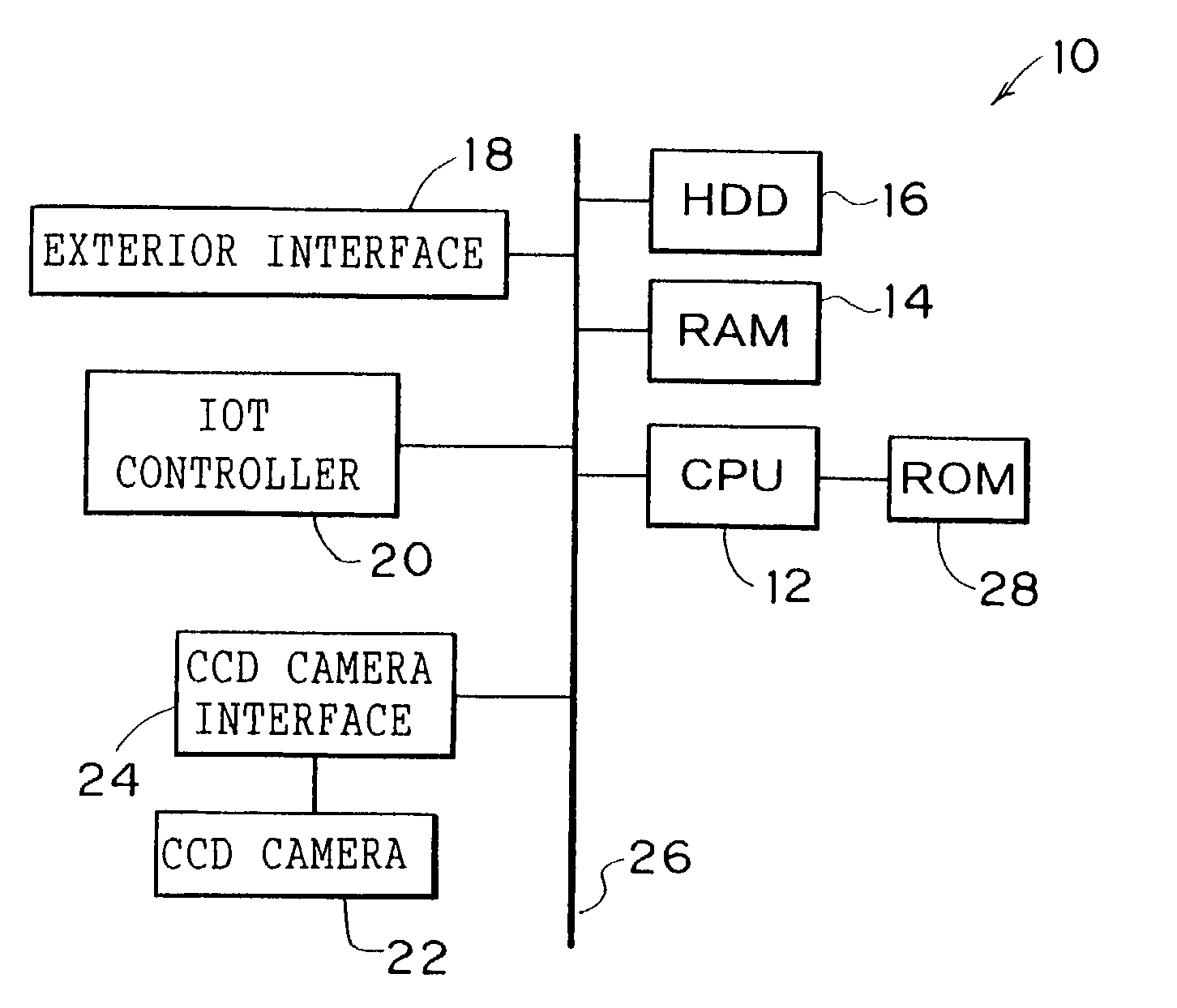
An image inspection device to automate and simplify inspection of an output image. A paper discharge tray of a printer is a different color from paper. A CCD camera is disposed above a paper discharge portion of the printer, at which paper is discharged, and can capture the whole upper face of the paper discharge tray. When, directly after a state in which there is no paper on the paper discharge tray, a print job is received and a first print-processed sheet is outputted to the paper discharge tray, a CPU controls the CCD camera to capture the paper discharge tray in this state. Captured image data including the paper is acquired, corrections are applied to the captured image data and to original image data by image processing, and image characteristics thereof are made substantially the same. Thereafter, the outputted image is inspected by comparison of the two data sets.
Owner:FUJIFILM BUSINESS INNOVATION CORP
Polymer powders, pressure sensitive adhesives and methods of making the same
InactiveUS7019067B2Stable in solutionEnhance sheet feedingCosmetic preparationsLiquid surface applicatorsPressure sensitiveEthyl ester
A method for making hydrophilic homopolymers and copolymers of poly 2-hydroxyethyl methacrylate. Also disclosed are coatings, films, hydrogels, cosmetic compositions, dermatological compositions, pressure sensitive adhesives containing the hydrophilic homopolymers or copolymers of poly 2-hydroxyethylmethacrylate. Further disclosed are methods of coating substrates with the hydrophilic homopolymers and copolymers of poly 2-hydroxyethyl methacrylate and hydrophilic pressure sensitive adhesives.
Owner:AVERY DENNISON CORP
Multilayer coating film-forming method and coated
InactiveUS20140030528A1Increase resistanceImprove sharpnessSynthetic resin layered productsCellulosic plastic layered productsEndcappingPolymer science
The invention provides a multilayer coating film-forming method that allows formation of a multilayer coating film with excellent smoothness, sharpness and water resistance, and which avoids or minimizes pinhole popping. The multilayer coating film-forming method of the invention has the following construction. A multilayer coating film-forming method comprising the following steps (1) to (4): step (1): coating an article to be coated with an aqueous first pigmented coating composition (X), step (2): coating the article to be coated, with an aqueous second pigmented coating composition (Y), step (3): coating the article to be coated, with a clear coating composition (Z), and step (4): heating an uncured first pigmented coating film, uncured second pigmented coating film and uncured clear coating film to cure them, wherein the aqueous first pigmented coating composition (X) contains a blocked polyisocyanate compound with a specific blocked isocyanate group.
Owner:KANSAI PAINT CO LTD
Radiation detection apparatus and scintillator panel
InactiveUS7538330B2Reduce sharpnessIncrease the amount of lightPhotometryFluorescence/phosphorescenceCrystal structurePhotoelectric conversion
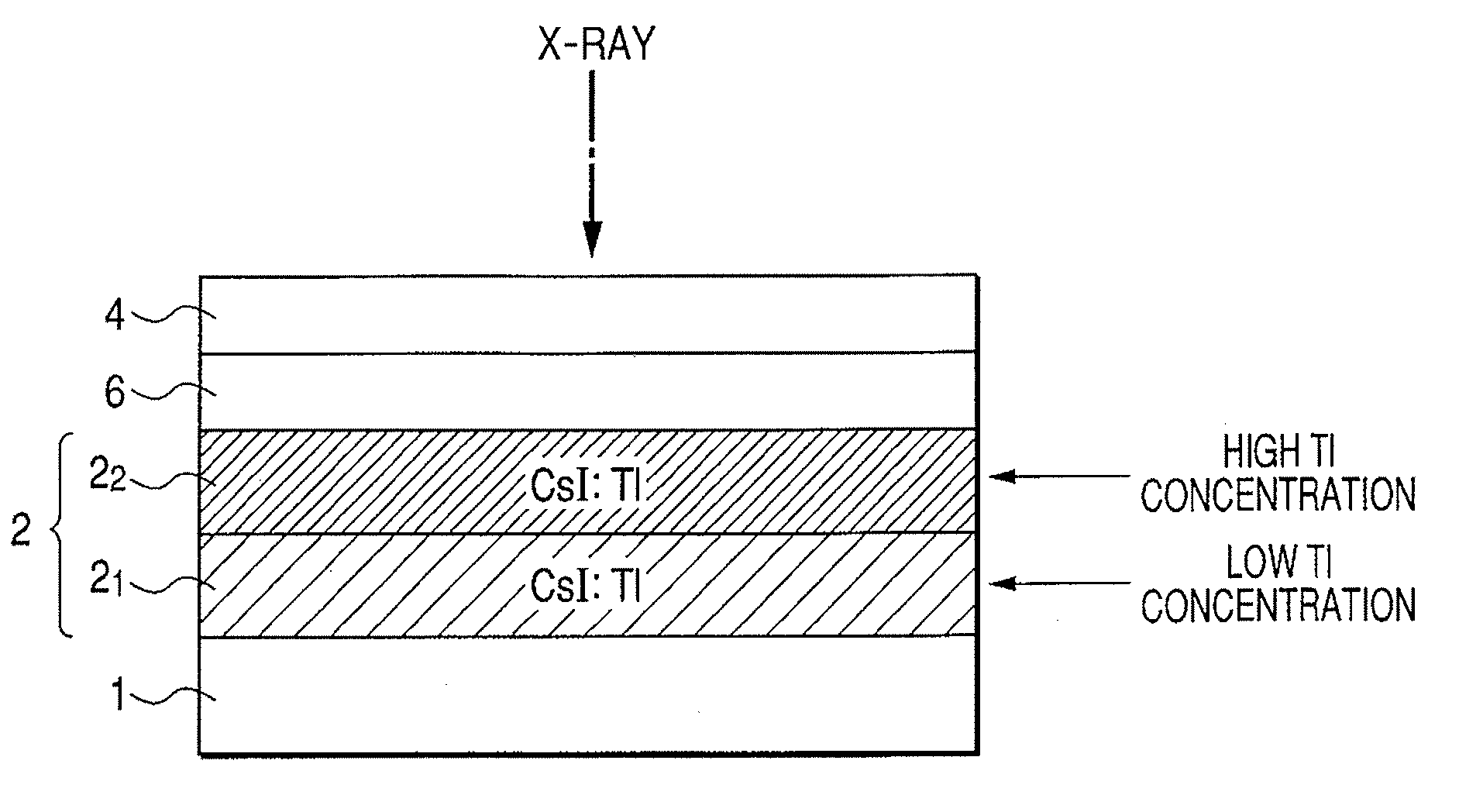
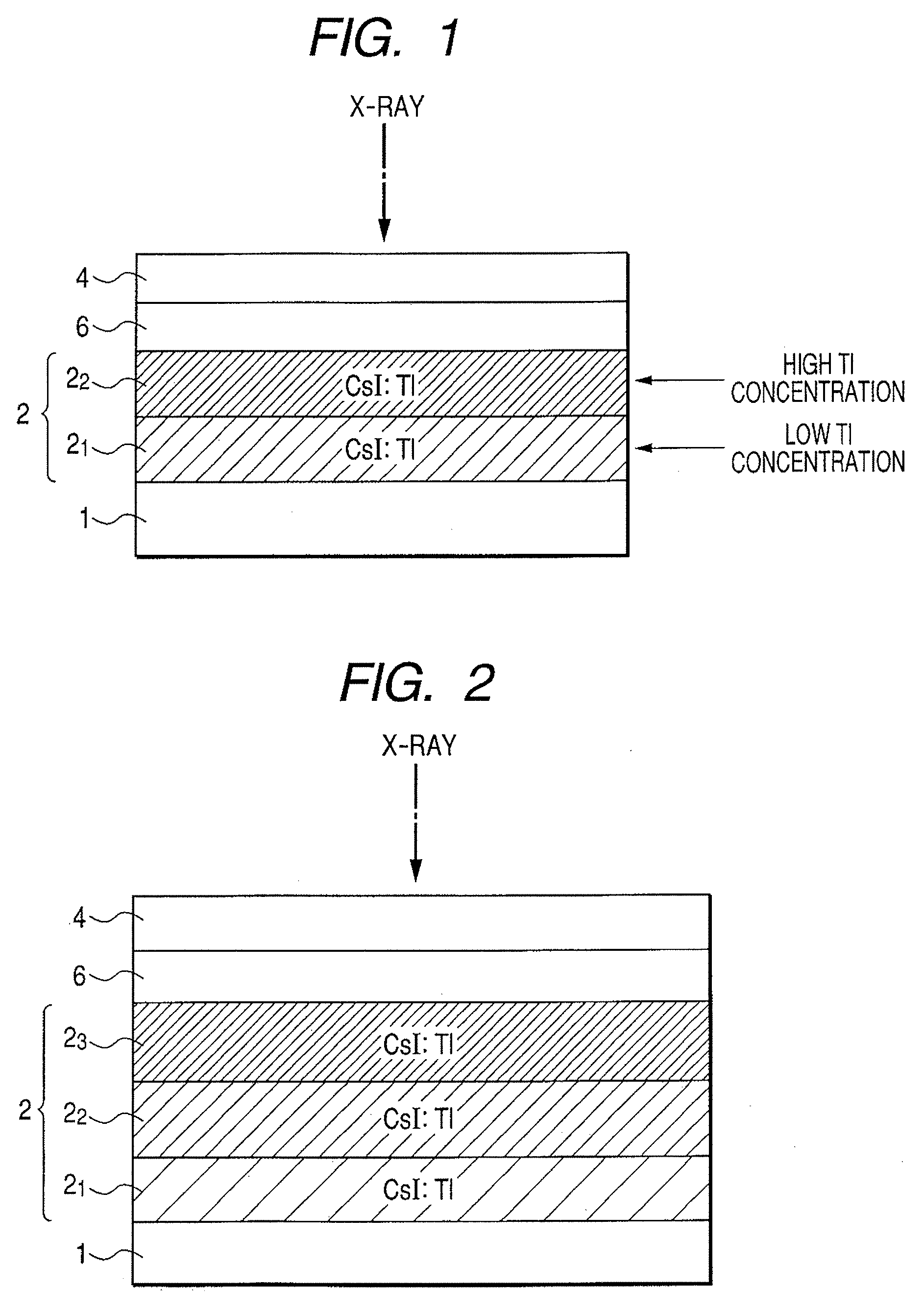
A radiation detection apparatus includes an optical detector disposed on a substrate and having a plurality of photoelectric conversion elements which convert light into an electrical signal, and a scintillator layer disposed on the optical detector and having a columnar crystal structure which converts radiation into light, wherein the concentration of an activator of the scintillator layer is higher at the radiation-incident side opposite the optical detector and is lower at the optical detector side. The scintillator panel includes the substrate and the scintillator layer disposed on the substrate, wherein the concentration of the activator of the scintillator layer is higher at the radiation-incident side and is lower at the light-emission side.
Owner:CANON KK
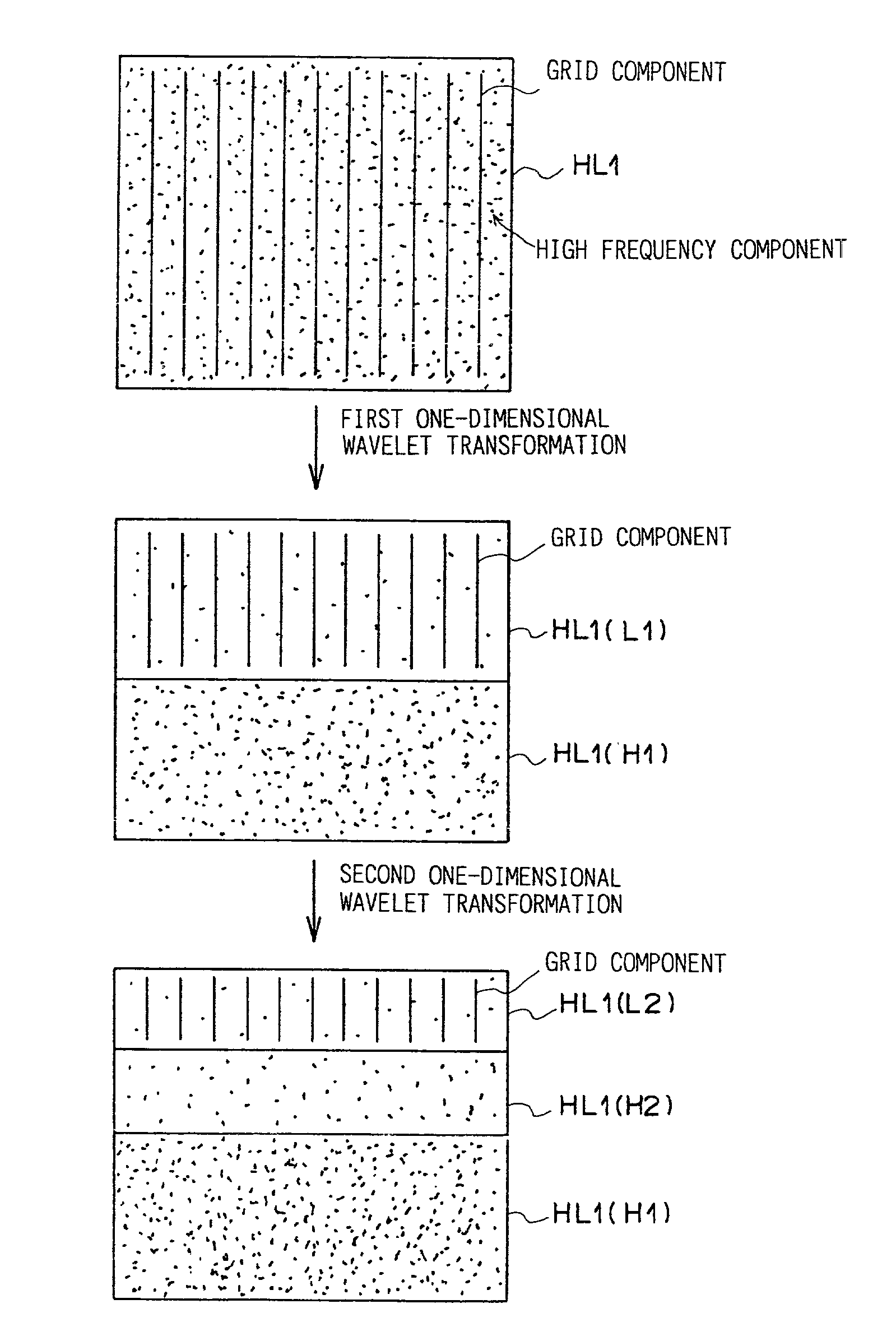
Method and unit for suppressing a periodic pattern
InactiveUS7336811B2Reduce componentsReduce sharpnessImage enhancementImage analysisLow-pass filterSignal restoration
In a wavelet transform section, wavelet-transform coefficient signals are obtained by two-dimensional wavelet transformation, employing a low-pass filter which has a characteristic that its response at a frequency greater than a spatial frequency corresponding to grid pitch is approximately zero. Based on the direction of the grid judged by a direction judging section, a suppressing section applies one-dimensional wavelet transformation to a signal containing a grid component (when a vertical grid is used, signal HL1), in the grid direction. Then, a low frequency transform coefficient signal of the transform coefficient signals is made zero. The signal, made zero, and the remaining signals, are subjected to inverse one-dimensional wavelet transformation. In an inverse wavelet transform section, the original image is restored with a signal having a suppressed grid component.
Owner:FUJIFILM HLDG CORP +1
Transparent polypropylene formulations that become opaque upon exposure to sufficient heat
InactiveUS6561122B1Improve clarityEase of productionThermometer detailsDiffusing elementsRefractive indexEthylene Homopolymers
Unique transparent polypropylene articles that can be tailored to become opaque when exposed to a sufficiently high temperature and which returns to substantially the same transparency level upon cooling. Such formulations include non-polypropylene polymeric constituents that exhibit refractive index measurements similar to the base clarified polypropylene at lower temperatures, as well as melting temperatures well below that for the base clarified polypropylene. Upon exposure to temperatures in close proximity to the melting temperature of the non-polypropylene polymeric constituents, the refractive index for such constituents will then become modified to the extent that the overall article appears at least partially opaque. In particular, the non-polypropylene polymeric constituents should exhibit melting temperatures well below that for the base clarified polypropylene, from about 60 to about 100° C. (well below the typical polypropylene melting temperatures of roughly about 160-190° C. for homopolymer and about 140-170° C. for typical random copolymer, both nucleated or non-nucleated). In this manner, a temperature sensitivity measuring thermoplastic article may be provided, and may be tailored to specific temperature ranges dependent on the melting temperatures exhibited by the non-polypropylene polymeric constituents. Methods of measuring temperature levels via the transformation of transparent polypropylene formulations to at least partially opaque versions thereof are also encompassed within this invention.
Owner:MILLIKEN & CO
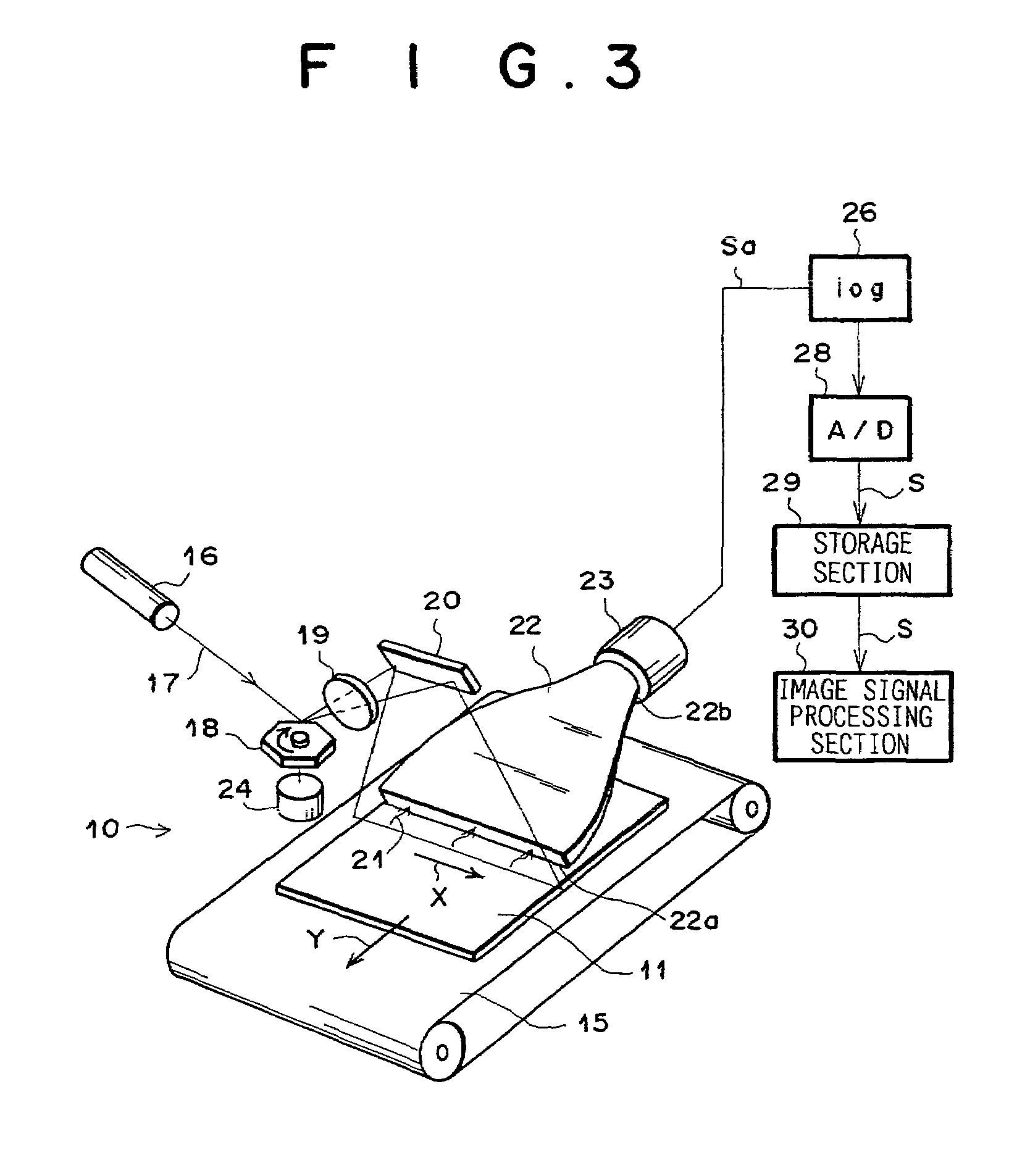
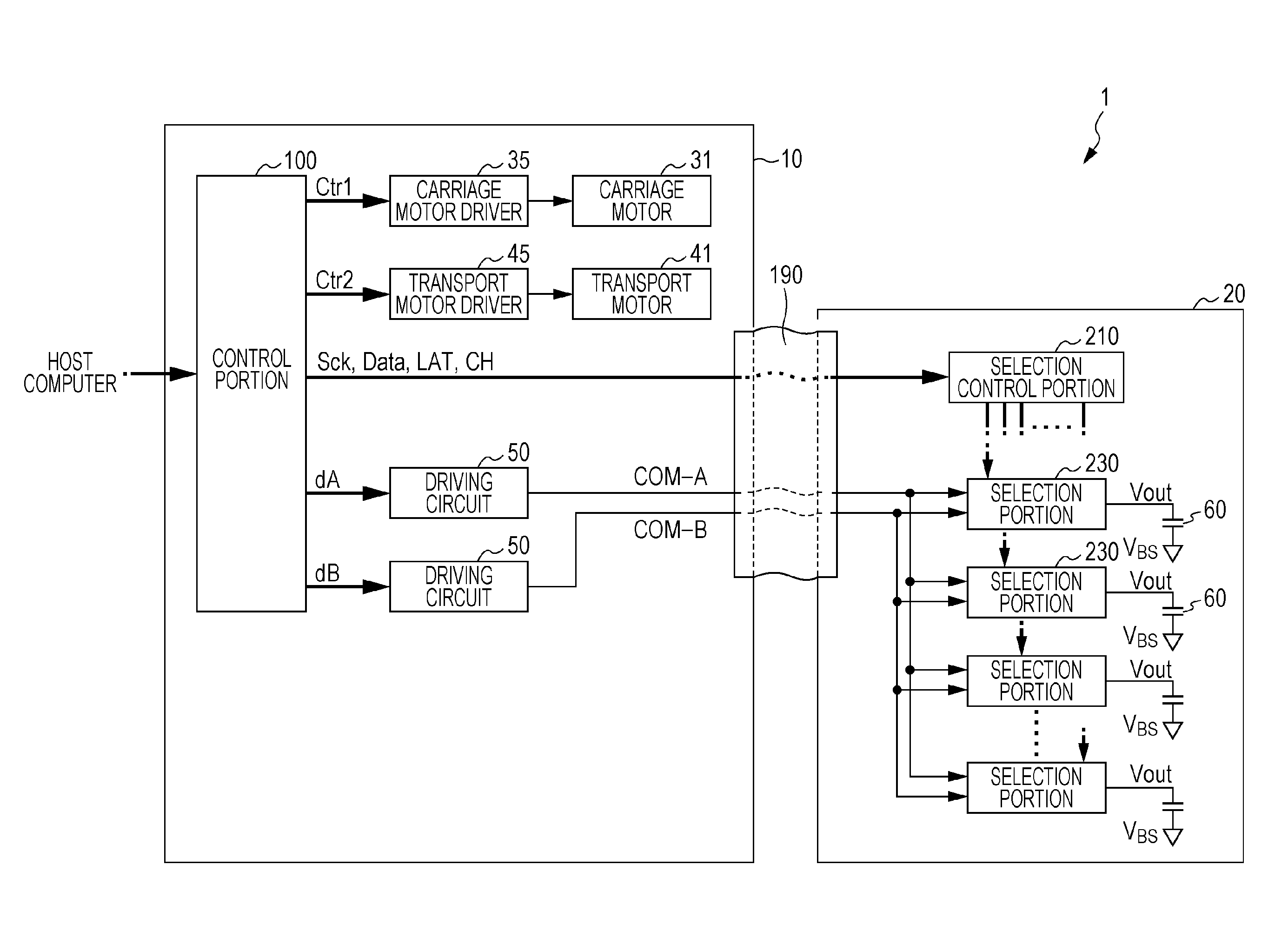
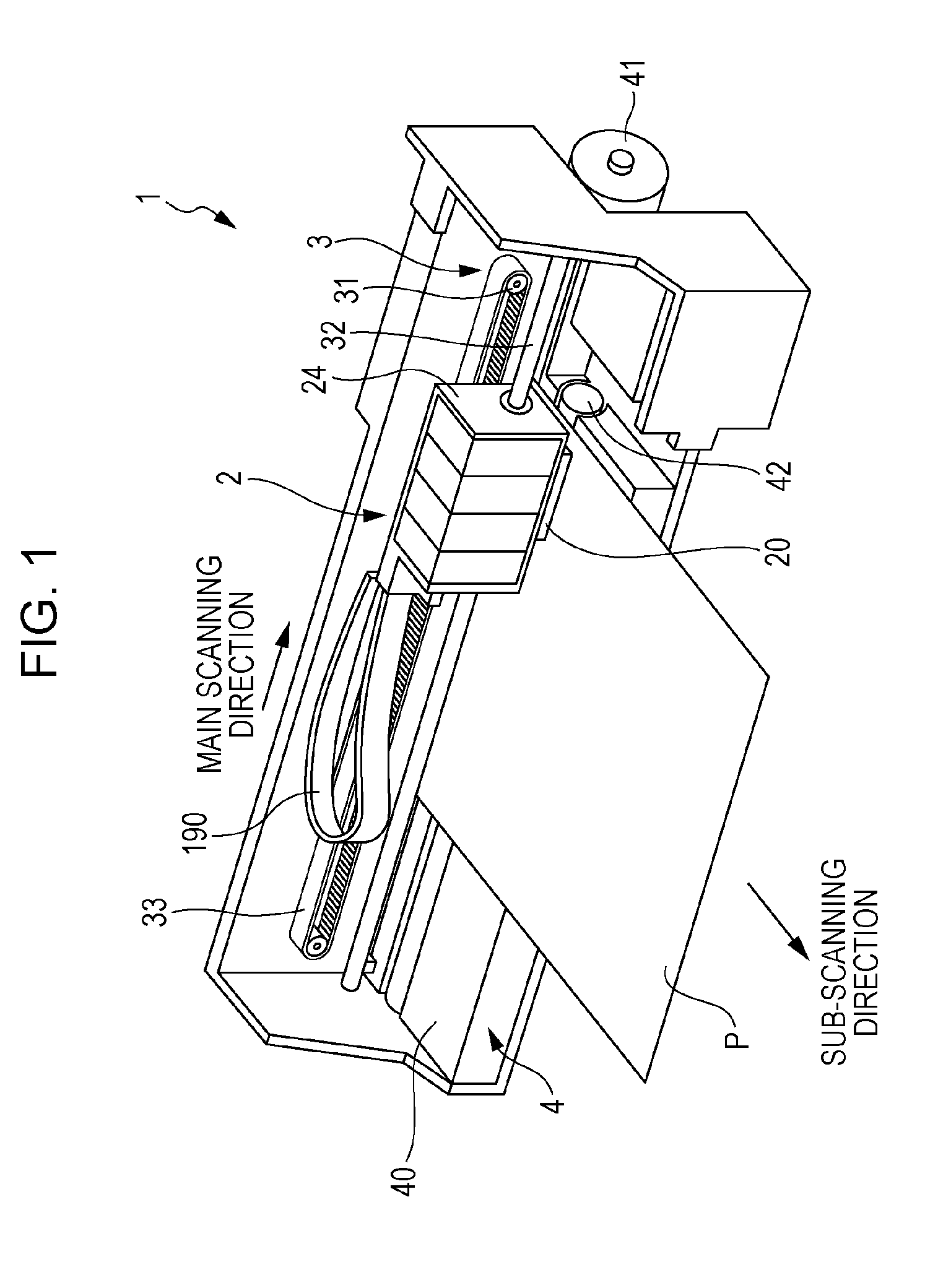
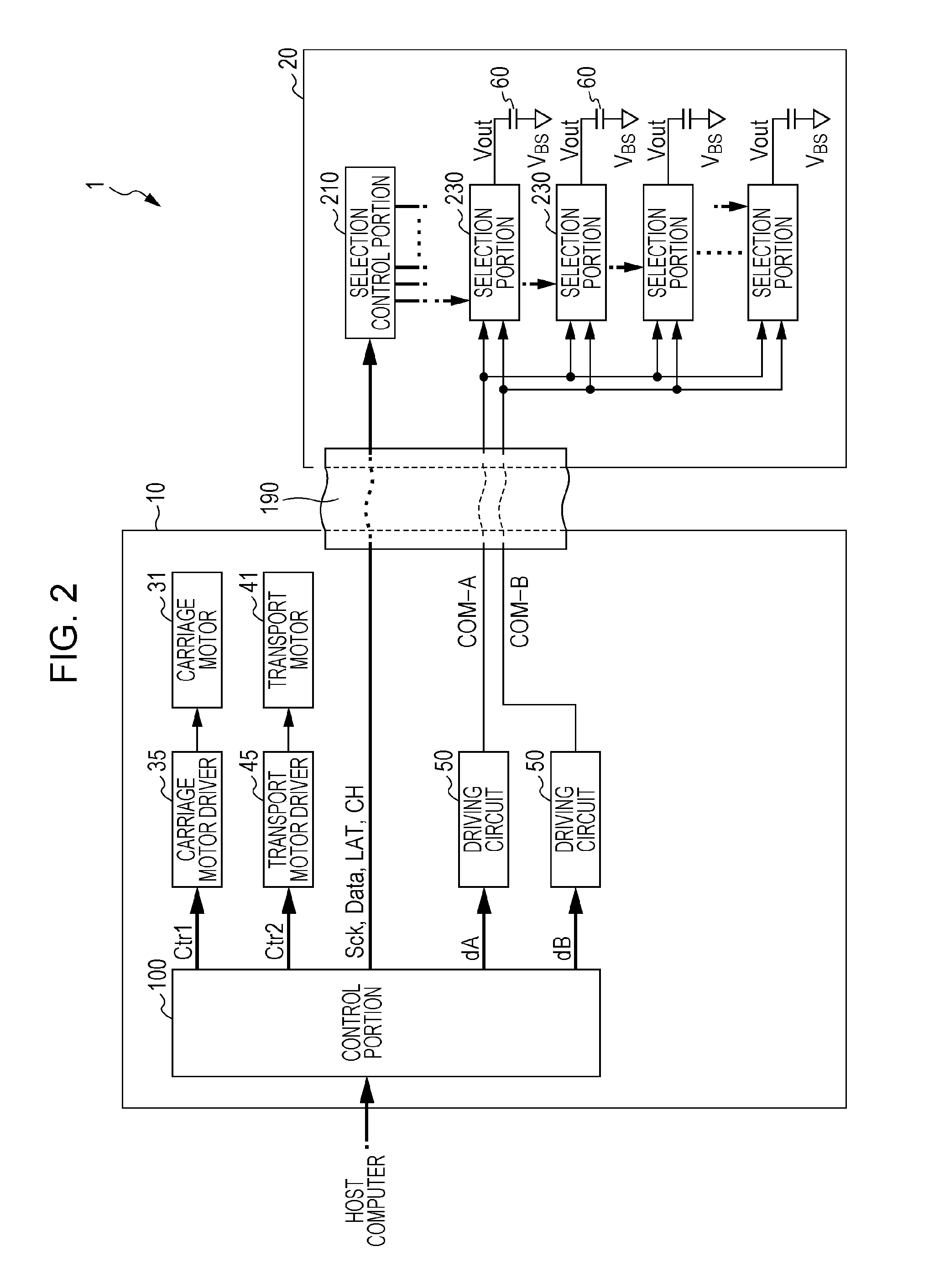
Liquid discharging apparatus, head unit, and control method of liquid discharging apparatus
ActiveUS20150246530A1High speed printingHigh-resolution printingElectronic switchingOther printing apparatusElectricityLow-pass filter
Provided is a liquid discharging apparatus which includes a modulation circuit which generates a modulation signal which is obtained by pulse-modulating a source signal, a transistor which generates an amplified modulation signal by amplifying the modulation signal, a low pass filter which generates a drive signal by smoothening the amplified modulation signal, a piezoelectric element which is displaced by receiving the drive signal, and a circuit substrate on which the transistor is mounted. The transistor includes a first electrode, a second electrode, a third electrode, and a clip which has conductivity, is electrically connected to the first electrode. Furthermore, the circuit substrate has a first land corresponding to the first electrode, a second land corresponding to the second electrode, and a third land corresponding to the third electrode. In addition, a part of the clip is connected to the third land.
Owner:SEIKO EPSON CORP
Printer and image processing apparatus
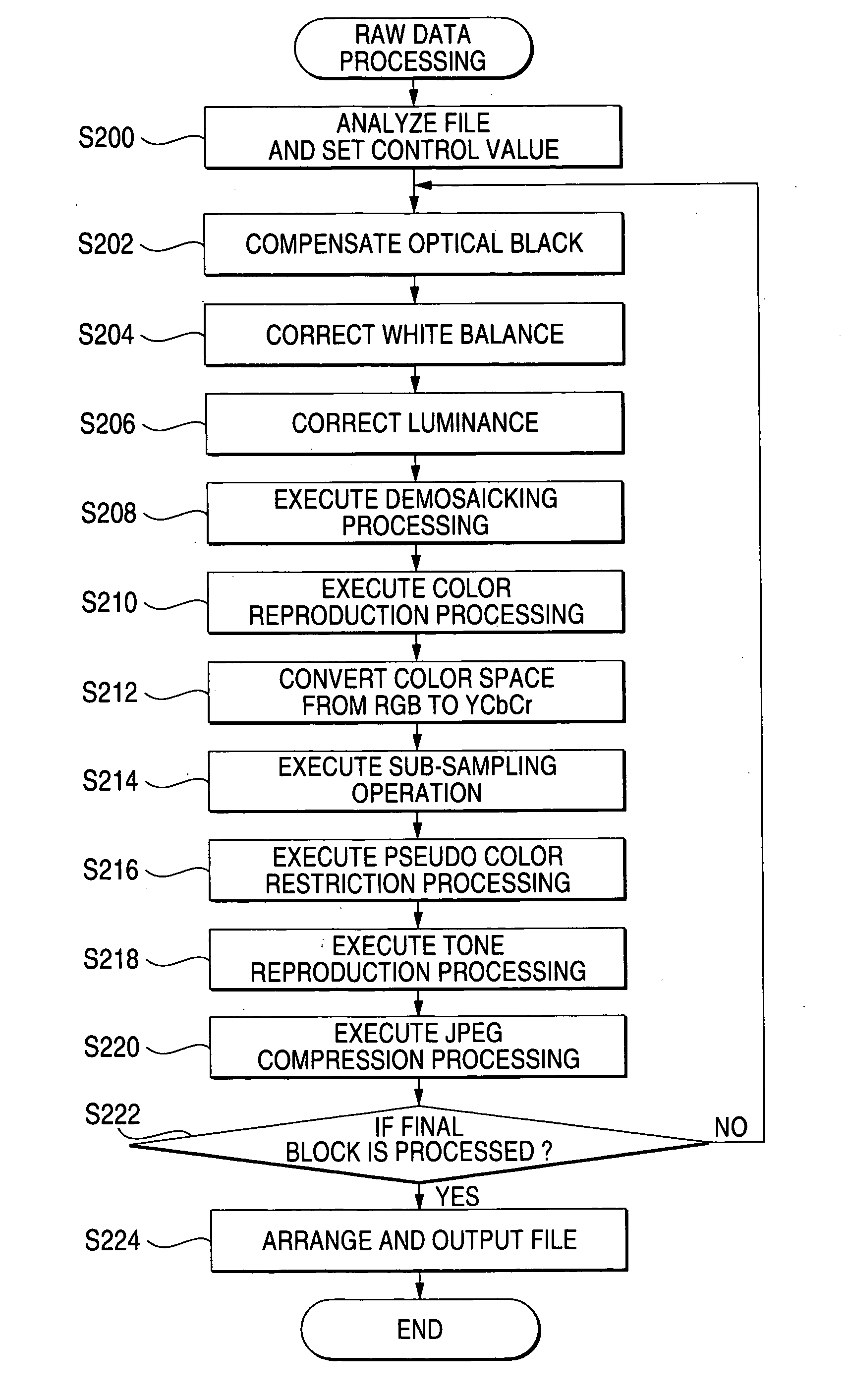
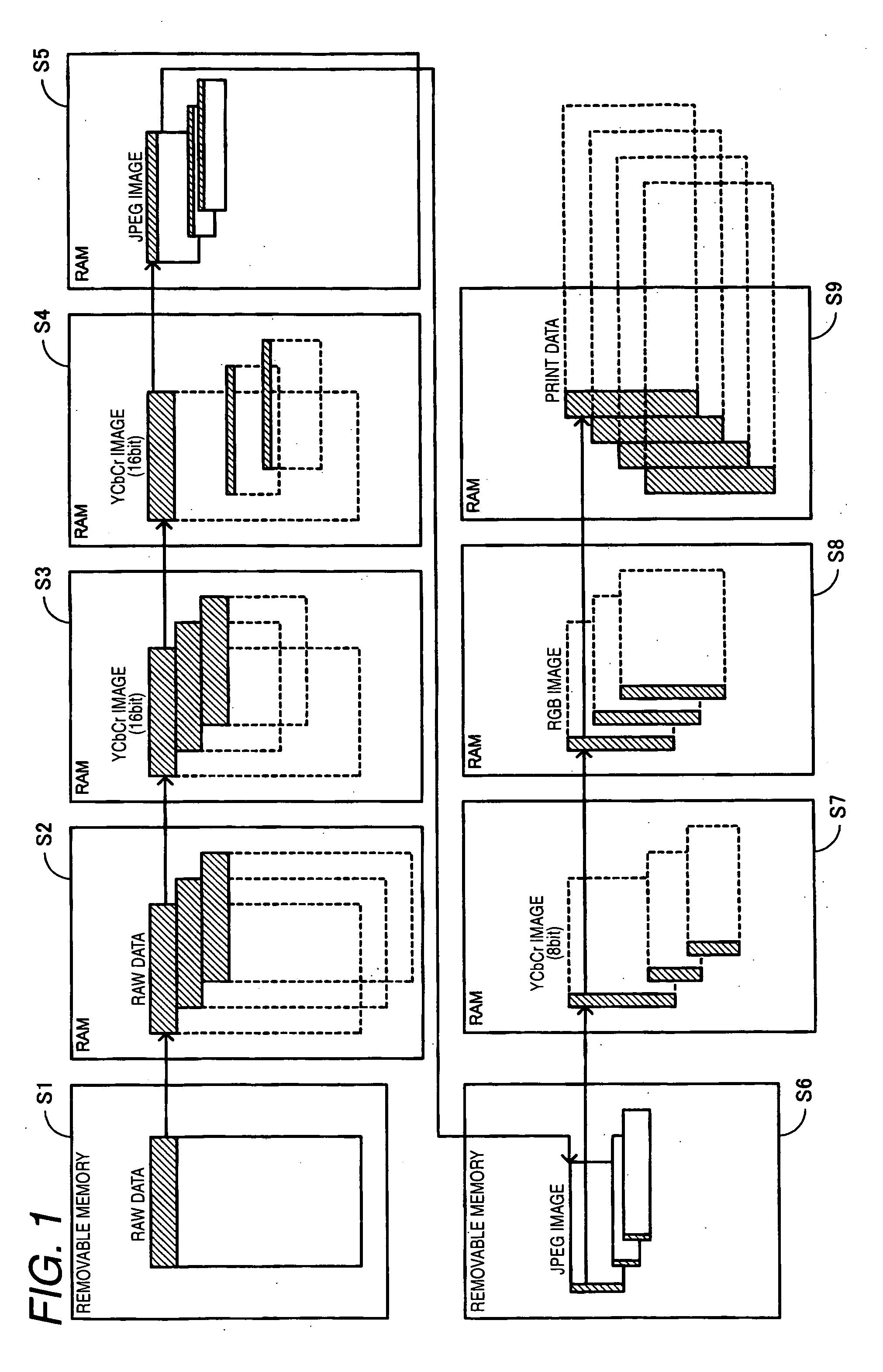
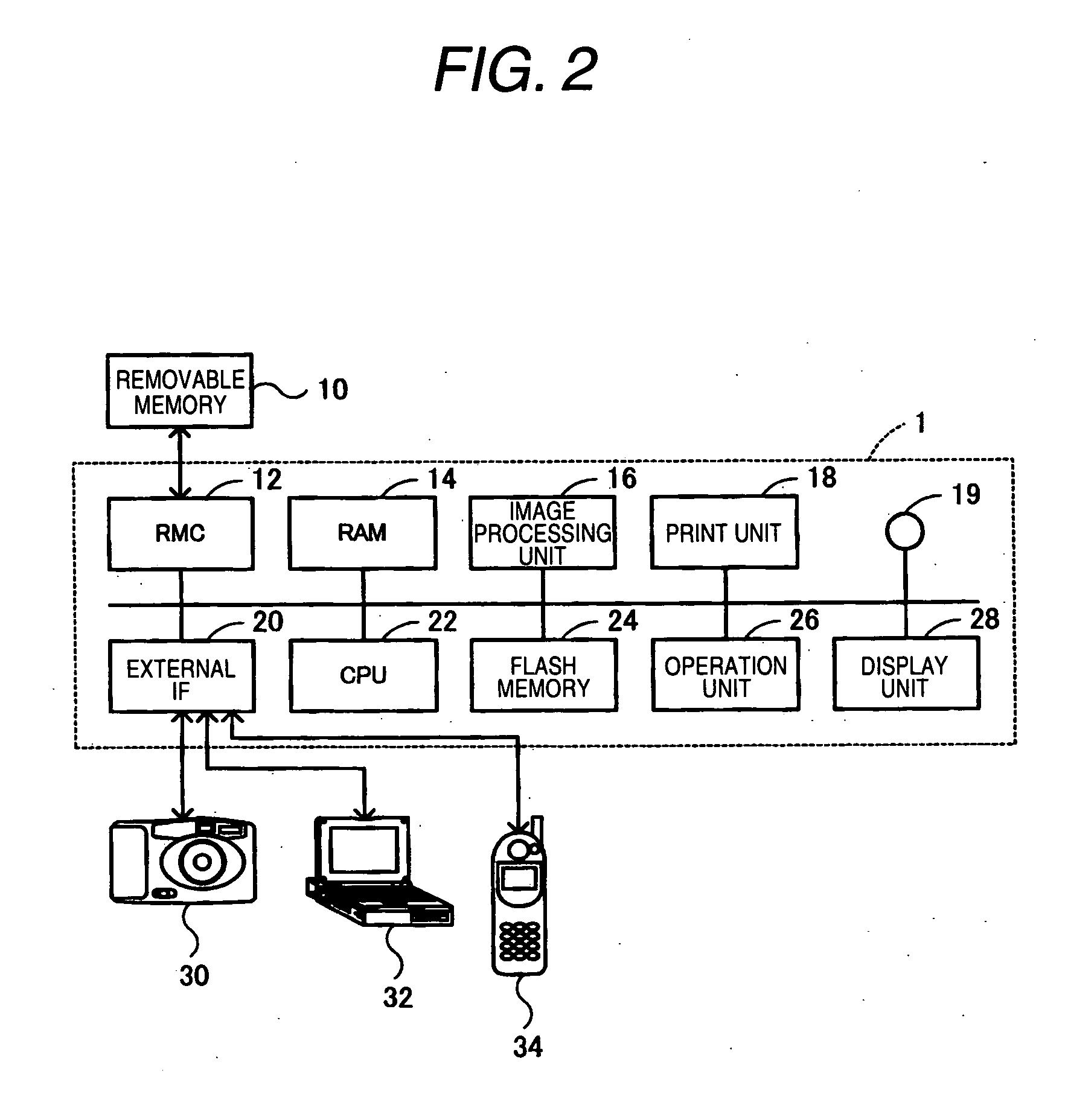
ActiveUS20070081182A1Reduces image sharpnessImprove imaging clarityVisual presentationPictoral communicationImaging processingComputer graphics (images)
An input unit inputs RAW data. An image generating unit generates an image from the RAW data using a demosaicking processing. A print unit that prints the image.
Owner:138 EAST LCD ADVANCEMENTS LTD
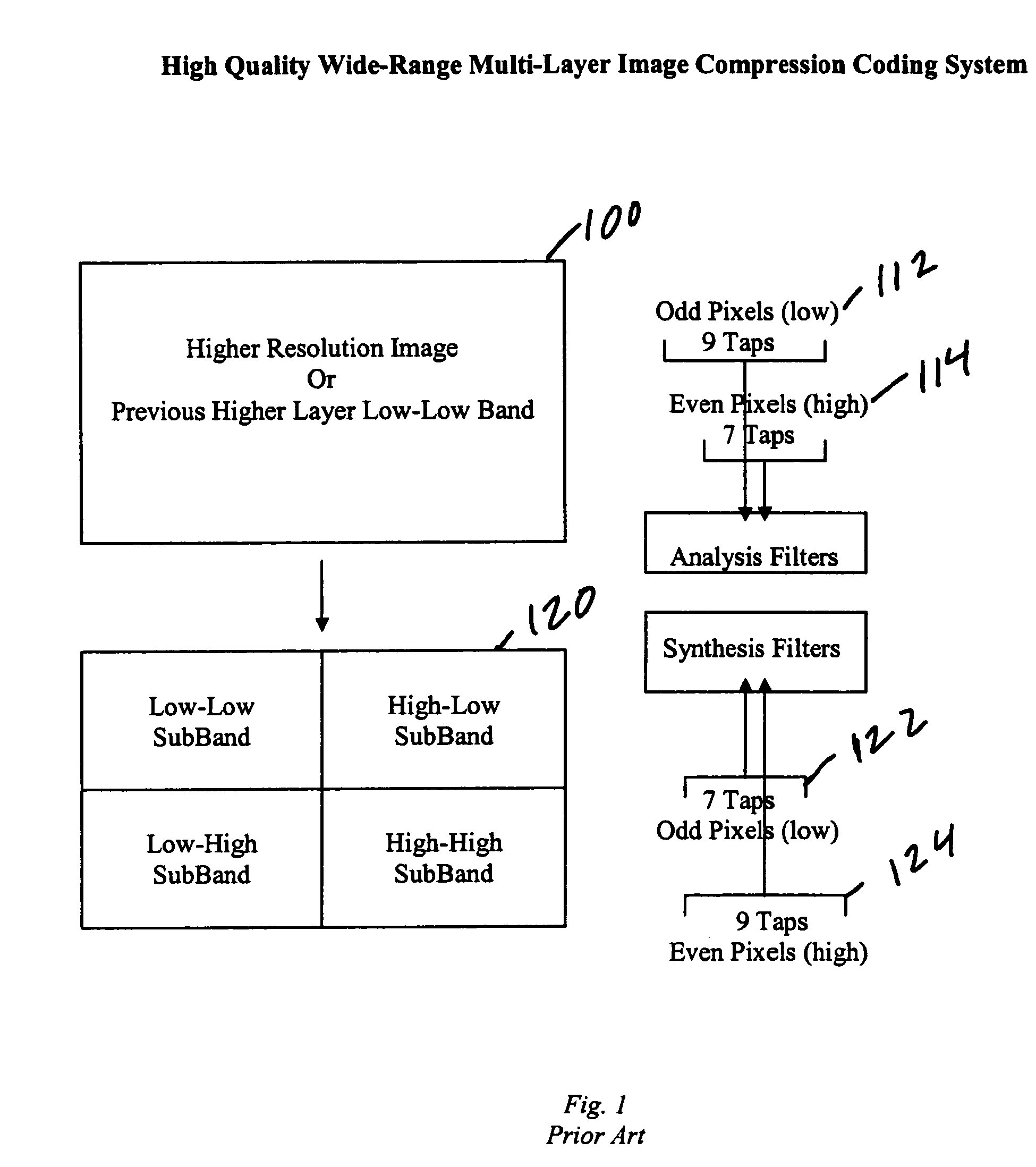
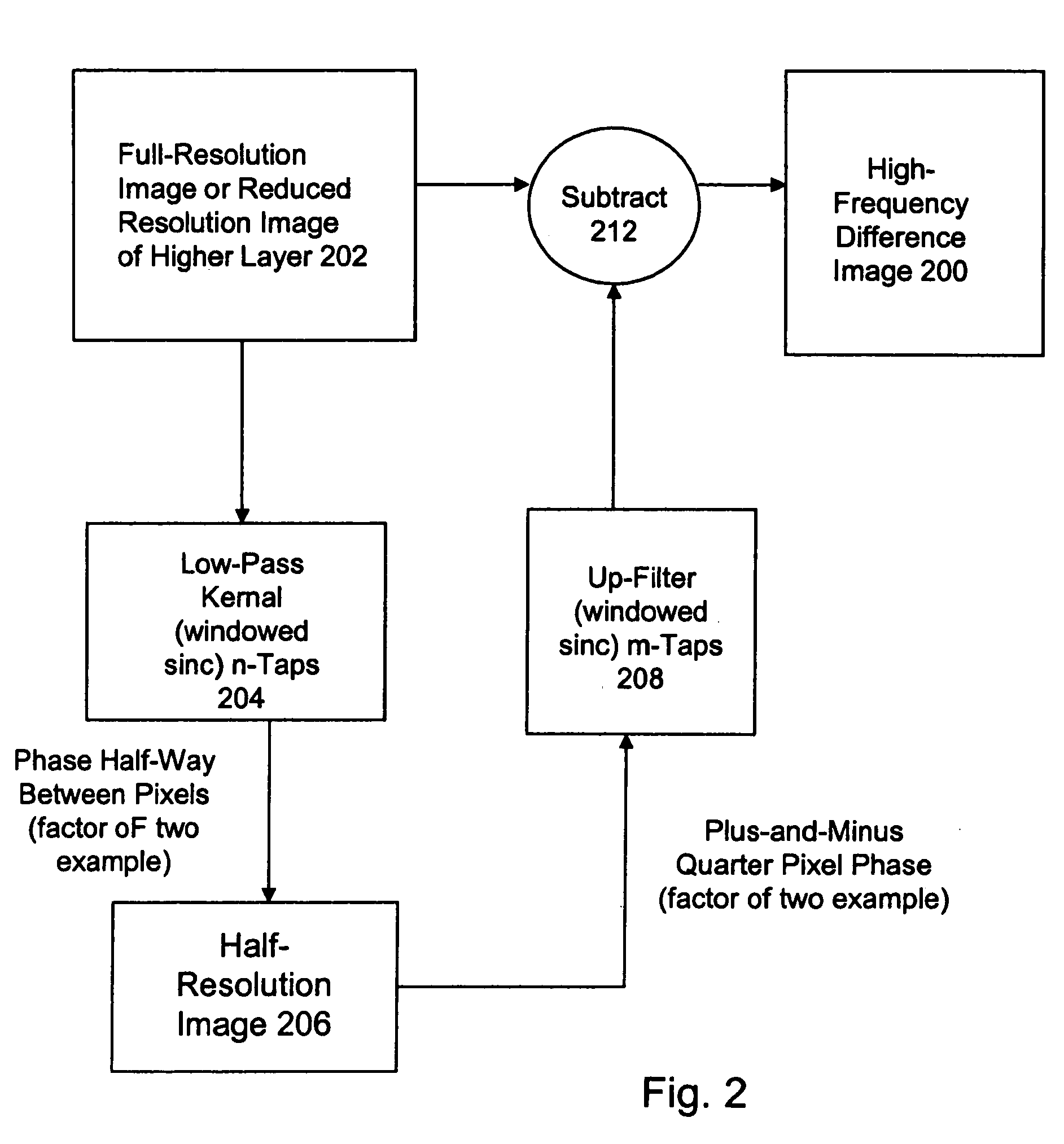
High quality wide-range multi-layer image compression coding system
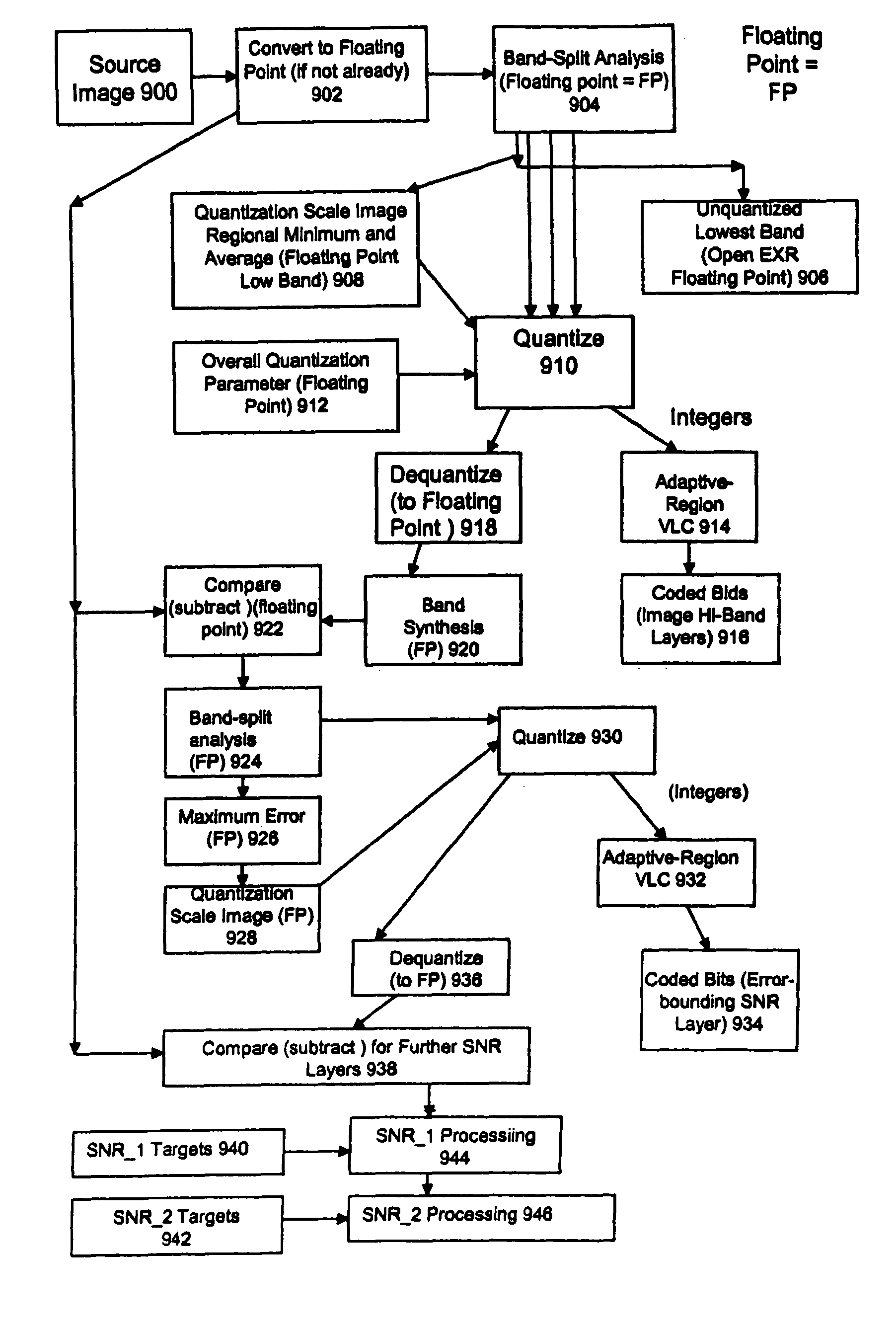
ActiveUS7916952B2Efficient compressionReduce sharpnessCode conversionCharacter and pattern recognitionFloating pointImage compression
Systems, methods, and computer programs for high quality wide-range multi-layer image compression coding, including consistent ubiquitous use of floating point values in essentially all computations; an adjustable floating-point deadband; use of an optimal band-split filter; use of entire SNR layers at lower resolution levels; targeting of specific SNR layers to specific quality improvements; concentration of coding bits in regions of interest in targeted band-split and SNR layers; use of statically-assigned targets for high-pass and / or for SNR layers; improved SNR by using a lower quantization value for regions of an image showing a higher compression coding error; application of non-linear functions of color when computing difference values when creating an SNR layer; use of finer overall quantization at lower resolution levels with regional quantization scaling; removal of source image noise before motion-compensated compression or film steadying; use of one or more full-range low bands; use of alternate quantization control images for SNR bands and other high resolution enhancing bands; application of lossless variable-length coding using adaptive regions; use of a folder and file structure for layers of bits; and a method of inserting new intra frames by counting the number of bits needed for a motion compensated frame.
Owner:DEMOS GARY
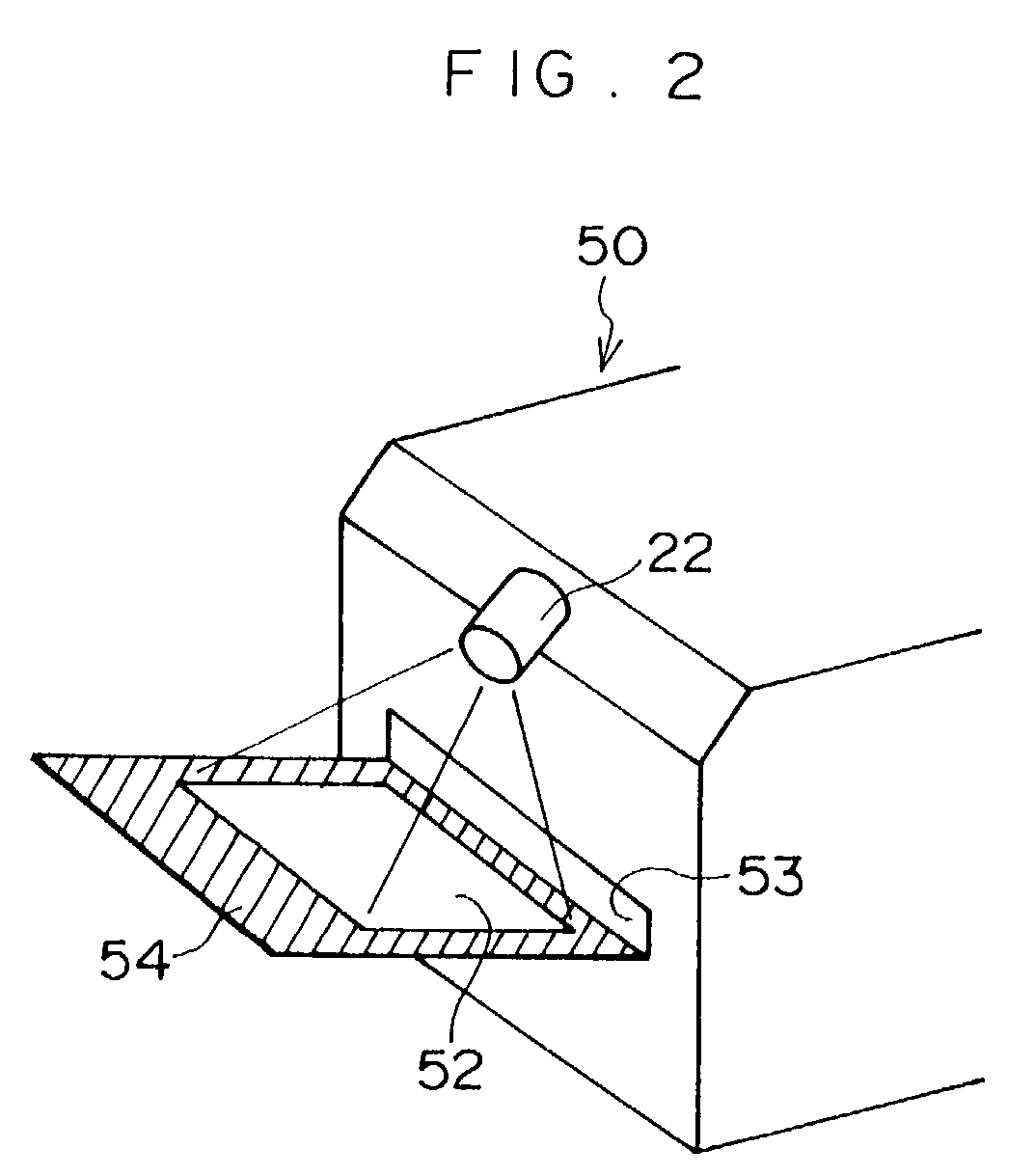
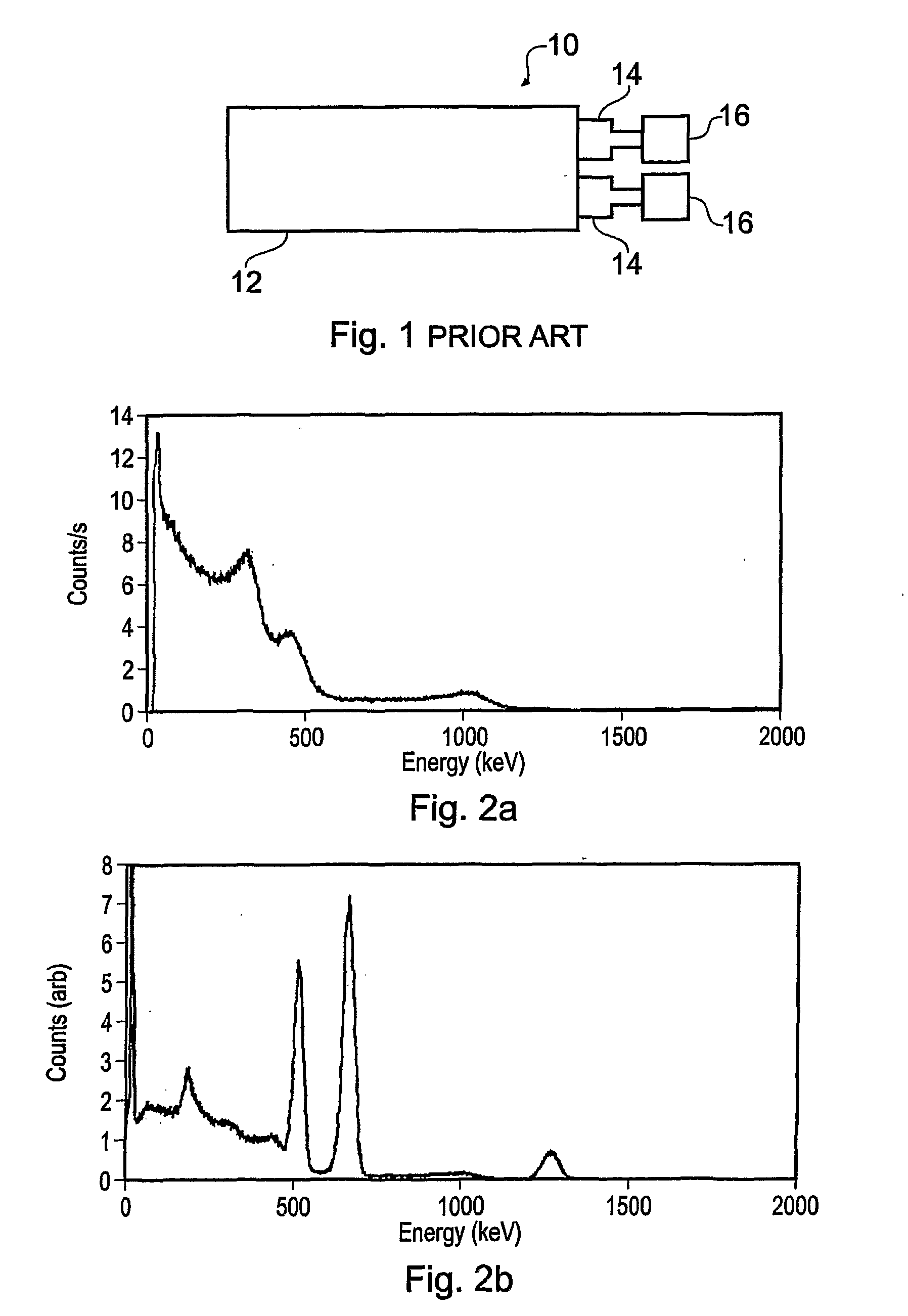
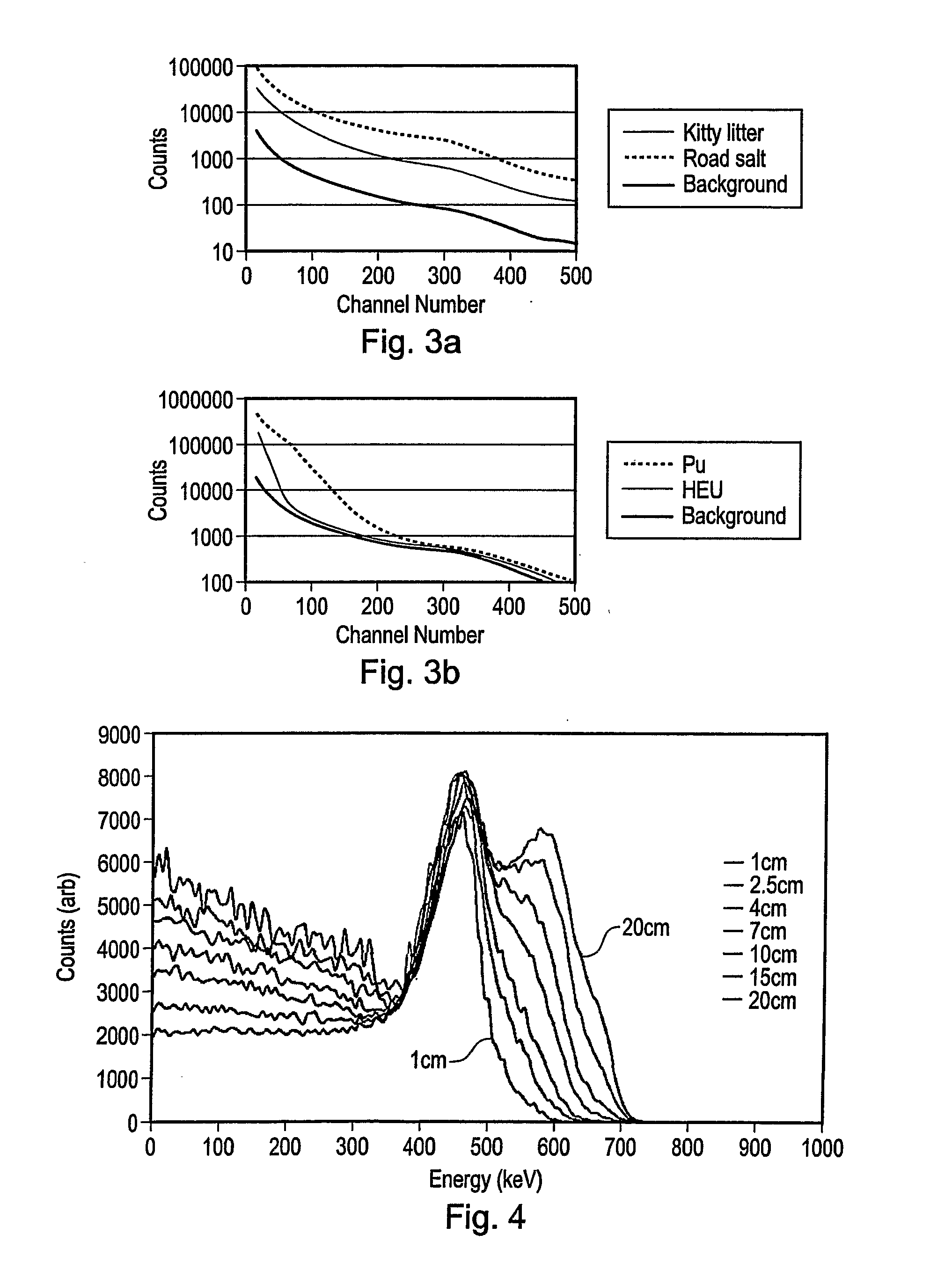
Gamma Ray Detectors
ActiveUS20080067390A1Faster decay timeQuick measurementX-ray spectral distribution measurementMaterial analysis by optical meansPhotovoltaic detectorsPhotodetector
A gamma ray detector (50) comprises a plastic scintillation body (52) arranged to receive incident gamma rays to be detected. Photons are generated in response to the gamma rays by excitation and de-excitation processes in the scintillation body. The photons are detected using at least one photodetector (56) which generates an output signal representative of the energy of the gamma rays. The scintillation body has a detection surface to receive the gamma rays and a thickness in a direction substantially orthogonal to the detection surface that is not greater than 5 cm. Deconvolution techniques can be used to improve the output signal; the thinness of the scintillation body allows sufficiently accurate results to be obtained that individual isotopes can be readily identified. The detector can be usefully employed in portal radiation monitors.
Owner:SYMETRICA
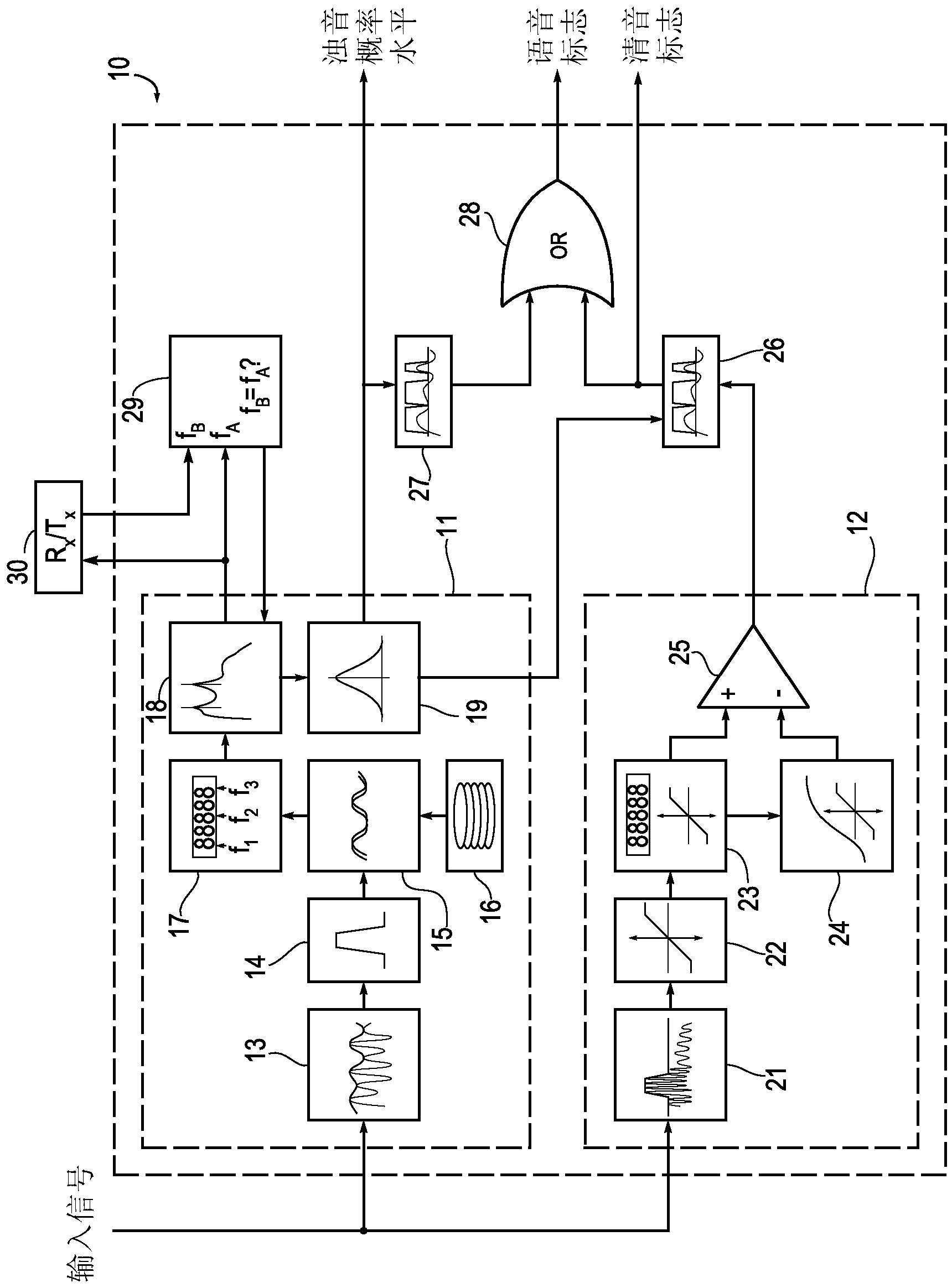
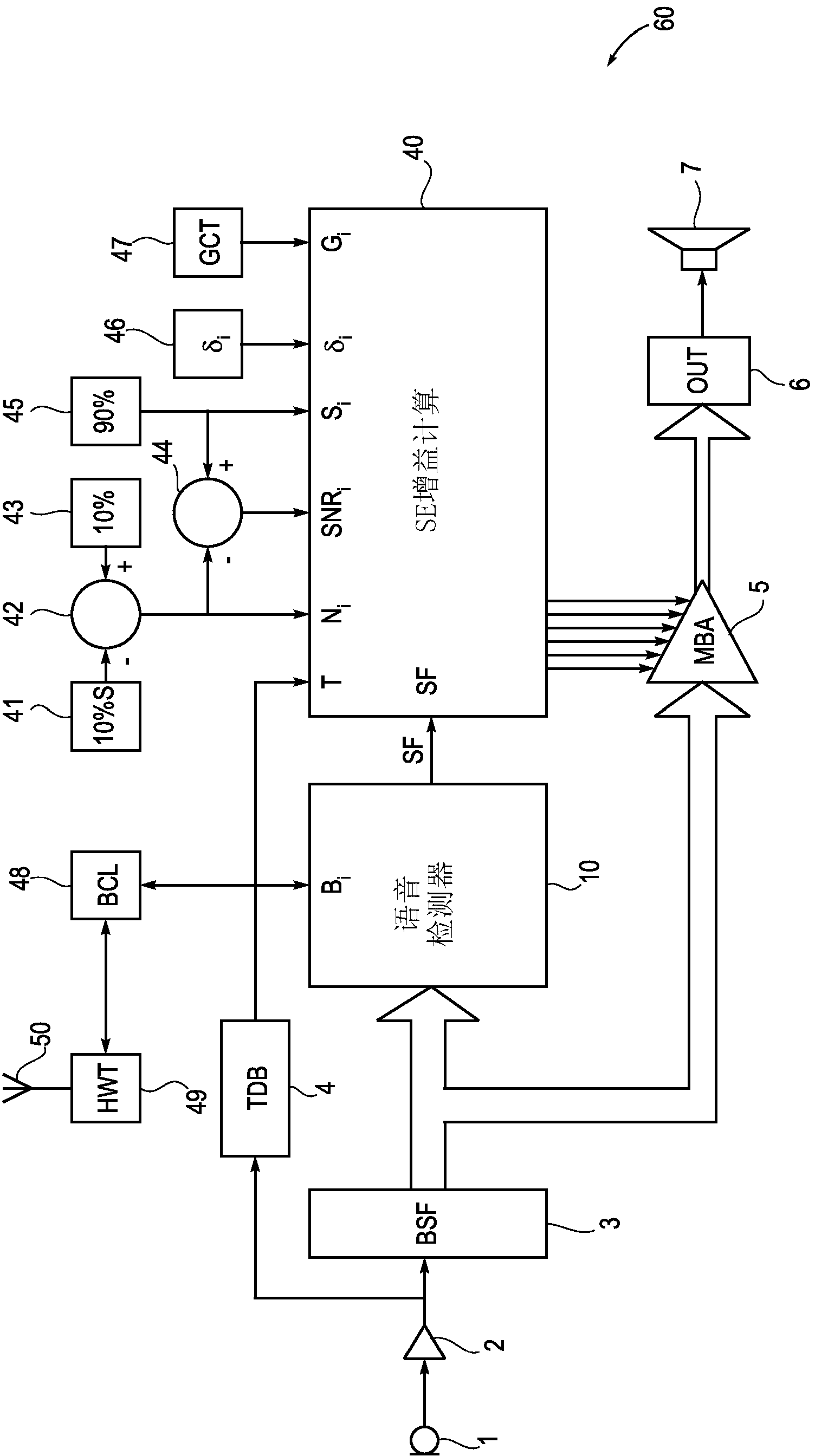
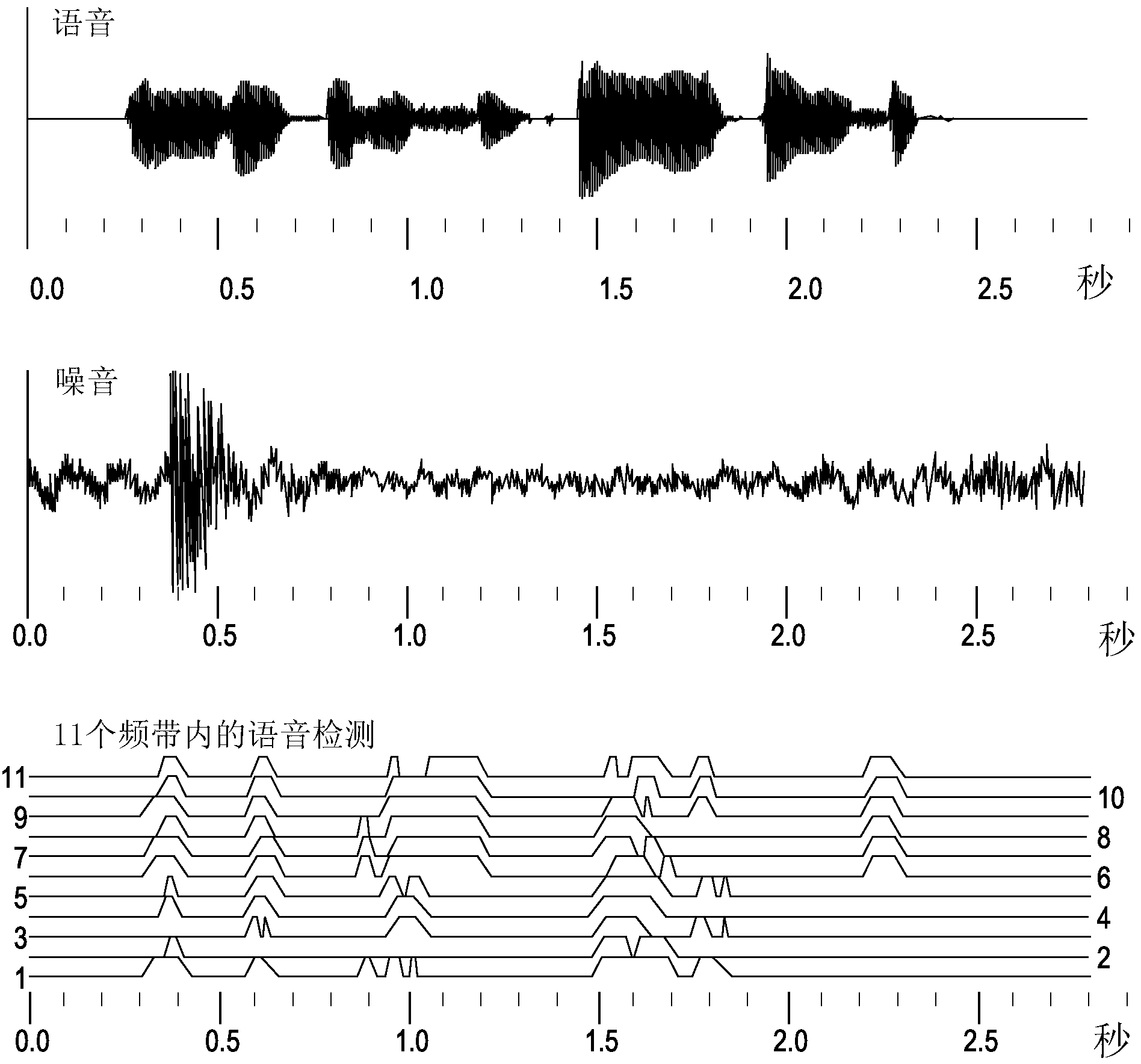
Hearing aid and a method of enhancing speech reproduction
ActiveCN103262577AFaster and more precise gain adjustmentQuick Speech Enhancement Gain AdjustmentSpeech analysisHearing aids signal processingElectrophonic hearingVoice source
A hearing aid (60A) configured to be worn by a hearing-impaired user has a speech detector (10A) and a speech enhancer (40A) for enhancing speech being present in an input signal of the hearing aid (60A). The speech detector (10A) has means (11, 12) for independently detecting the presence of voiced and unvoiced speech in order to allow for the speech enhancer (40A) to increase the gain of speech signals suitably fast to incorporate the speech signals themselves. The hearing aid (60A) has means (49A, 50A) for communicating information regarding the detected speech signals wirelessly to a similar hearing aid (60B) worn contralaterally by the user for the purpose of mutually enhancing speech signals in the two hearing aids (60A, 60B) when speech is detected to be originating from the front of the user, and means (52B) for suppressing speech enhancement in the contralateral hearing aid (60B) when speech is detected to be originating from the ipse-lateral side of the user. The invention further provides a method of enhancing speech in a hearing aid.
Owner:WIDEX AS
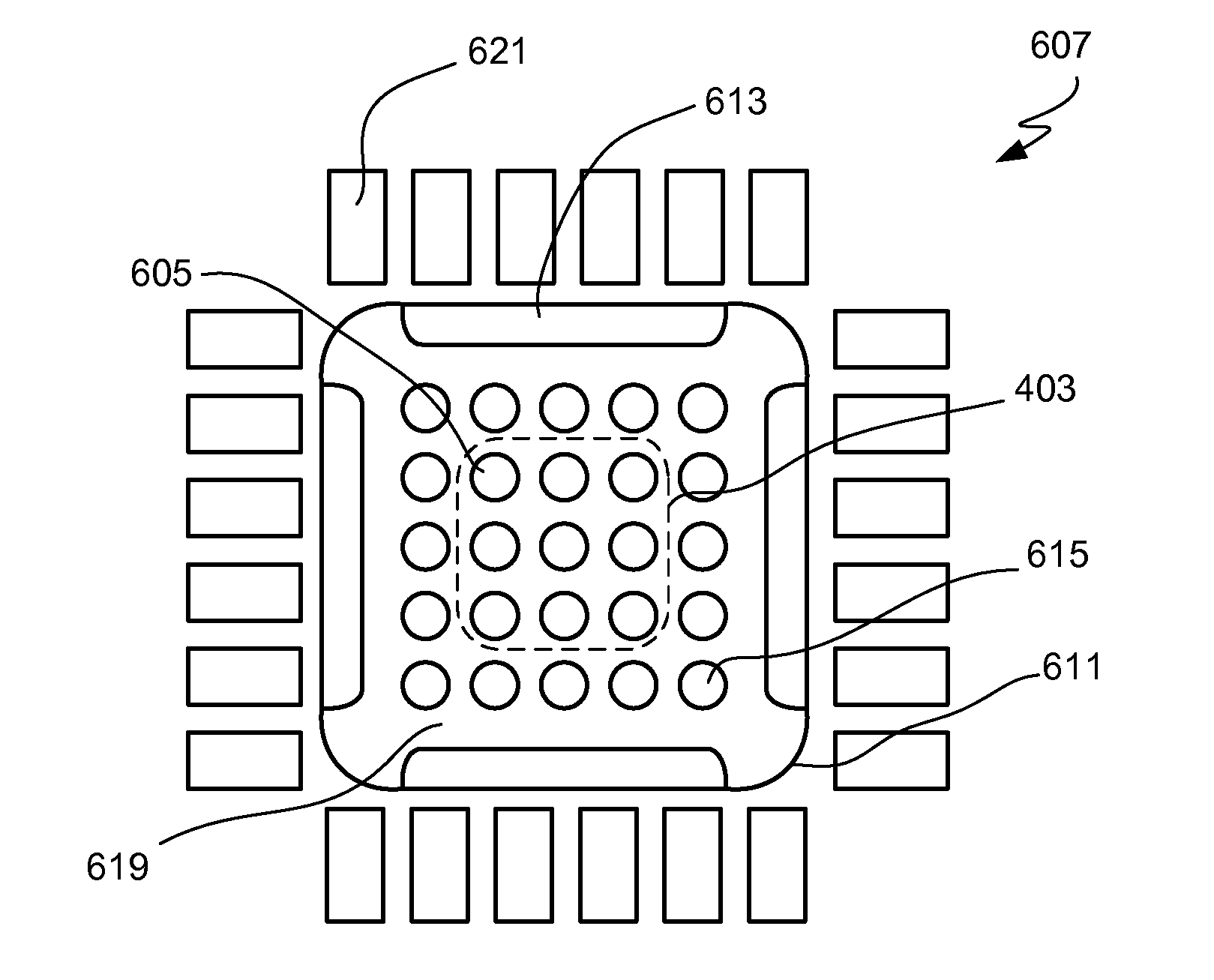
Rounded die configuration for stress minimization and enhanced thermo-mechanical reliability
InactiveUS20090152683A1Reduce stress buildupReduce sharpnessSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesStress minimizationSemiconductor package
One aspect of the invention pertains to a semiconductor die with rounded sidewall junction edge corners. Such rounding reduces stress accumulations at those corners. In other embodiments of the invention, the sharpness of other corners and edges in the die are reduced. For example, reducing the sharpness of the bottom edge corners formed by the intersection of a sidewall and the back surface of a die can further diminish stress accumulations. One embodiment pertains to a wafer carried on a wafer support, where the wafer includes a multiplicity of such dice. Another embodiment involves a semiconductor package containing such dice. Methods of fabricating the dice are also described.
Owner:NAT SEMICON CORP
Crosslinked polyester compositions, method of manufacture, and uses thereof
ActiveUS20080185558A1Effectively crosslinkedImprove scalabilityFibre treatmentSynthetic resin layered productsPolyesterReactive material
A Composition comprises a thermally crosslinked reaction product of a polyester and a carboxy-reactive material. Methods for the manufacture of the composition and articles derived from the composition are also disclosed.
Owner:SABIC GLOBAL TECH BV
Imaging modification, display and visualization using augmented and virtual reality eyewear
ActiveUS20200183171A1Improve clarityReduce sharpnessInput/output for user-computer interactionMechanical/radiation/invasive therapiesDisplay deviceUser perception
A display system can include a head-mounted display configured to project light to an eye of a user to display augmented reality image content to the user. The display system can include one or more user sensors configured to sense the user and can include one or more environmental sensors configured to sense surroundings of the user. The display system can also include processing electronics in communication with the display, the one or more user sensors, and the one or more environmental sensors. The processing electronics can be configured to sense a situation involving user focus, determine user intent for the situation, and alter user perception of a real or virtual object within the vision field of the user based at least in part on the user intent and / or sensed situation involving user focus. The processing electronics can be configured to at least one of enhance or de-emphasize the user perception of the real or virtual object within the vision field of the user.
Owner:MAGIC LEAP INC
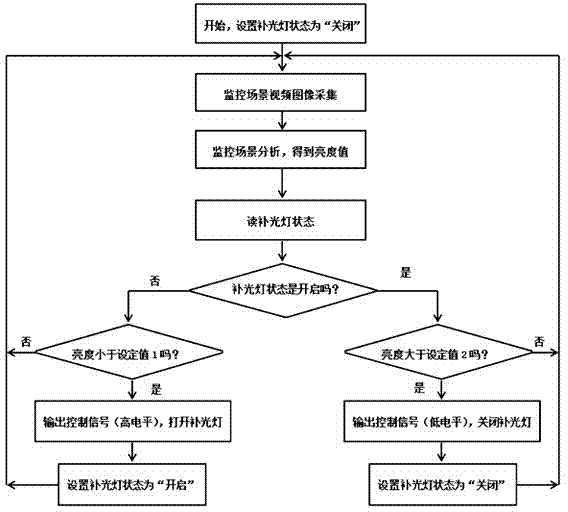
Fill light lamp automatic control method based on video analysis
InactiveCN103491313AAchieving Adaptive ControlBrightness value is accurateTelevision system detailsColor television detailsAutomatic controlLight pollution
The invention discloses a fill light lamp automatic control method based on video analysis. The fill light lamp automatic control method based on the video analysis achieves the automatic control over a fill light lamp according to the changing of brightness values in a monitoring area. The fill light lamp automatic control method based on the video analysis achieves the self-adaptive control over the fill light lamp according to the changing of ambient brightness, avoids electric energy waste and light pollution to the environment by the fill light lamp, avoids the phenomena that the definition of monitoring video images declines due to insufficient light and the fill light lamp may flicker, saves equipment investment, shortens mounting construction cycles, and improves the reliability of system working.
Owner:ANHUI SANLIAN APPLIED TRAFFIC TECH
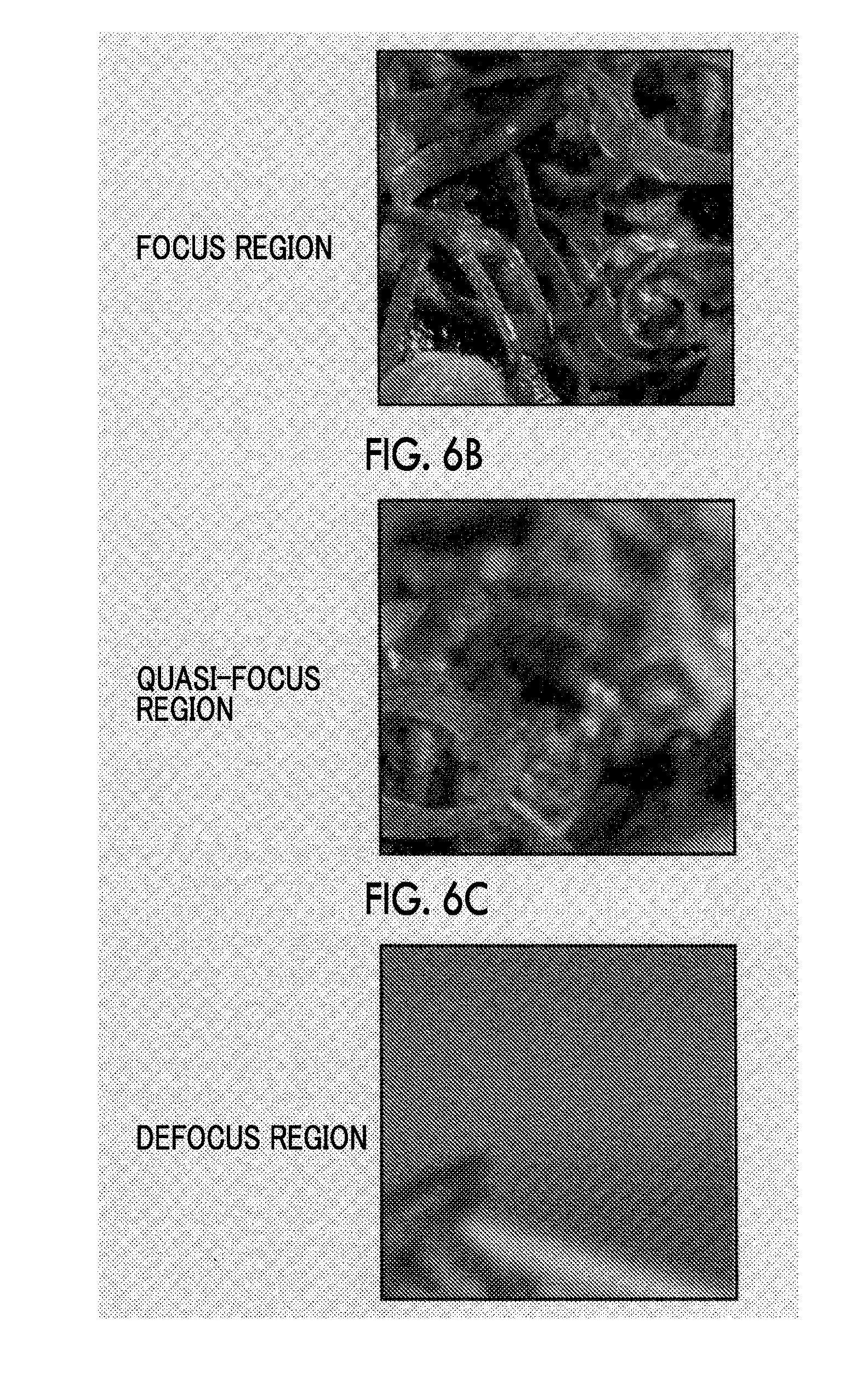
Image processing device, imaging device, image processing method, and image processing program
InactiveUS20170004603A1Avoid over-correctionImprove image qualityImage enhancementImage analysisImaging processingRadiology
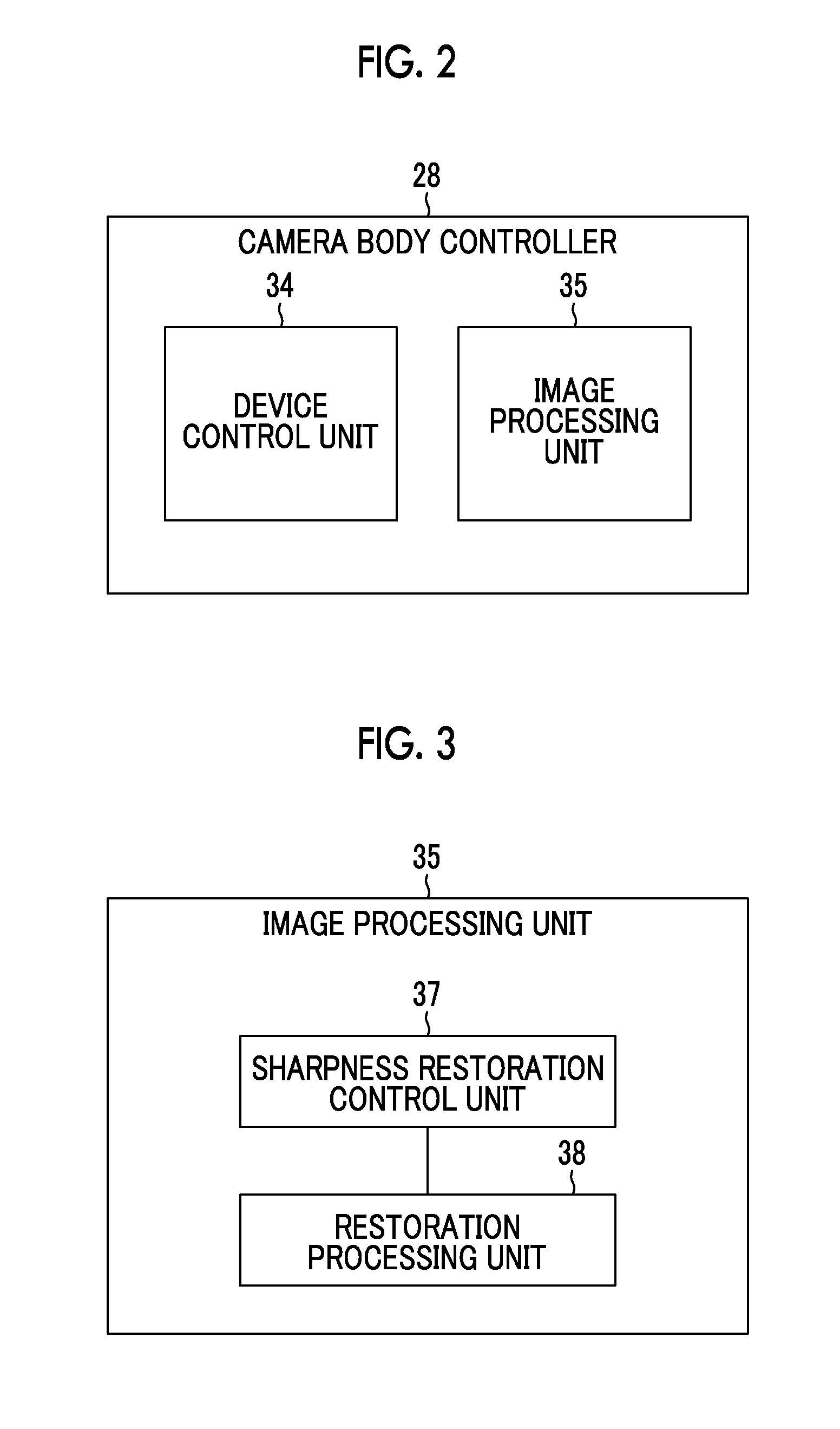
There is provided an image processing device that acquires restored image data by performing restoration processing using a restoration filter based on the PSF of an optical system for original image data acquired by capturing a subject image using the optical system. This device includes a restoration processing unit 38 that performs restoration processing by applying the restoration filter to the original image data, a quasi-focus region detection unit 50 that detects a quasi-focus region in an original image corresponding to the original image data, and a sharpness restoration control unit 37. The sharpness restoration control unit adjusts the restoration strength magnification U for original image data of the detected quasi-focus region so as to be smaller than the restoration strength magnification U for original image data of at least a focus region.
Owner:FUJIFILM CORP
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com