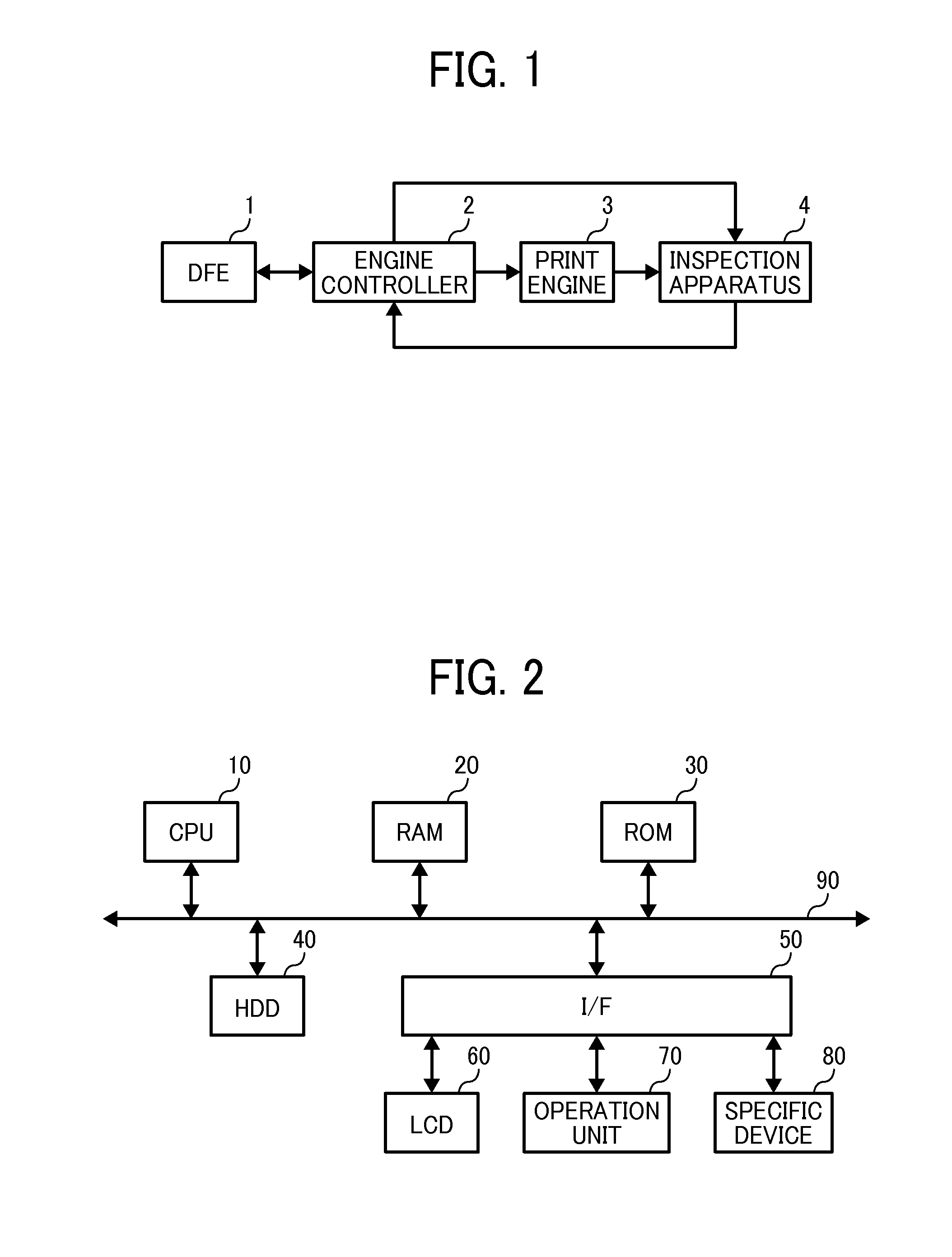
Patents
Literature
651 results about "Image Inspection" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
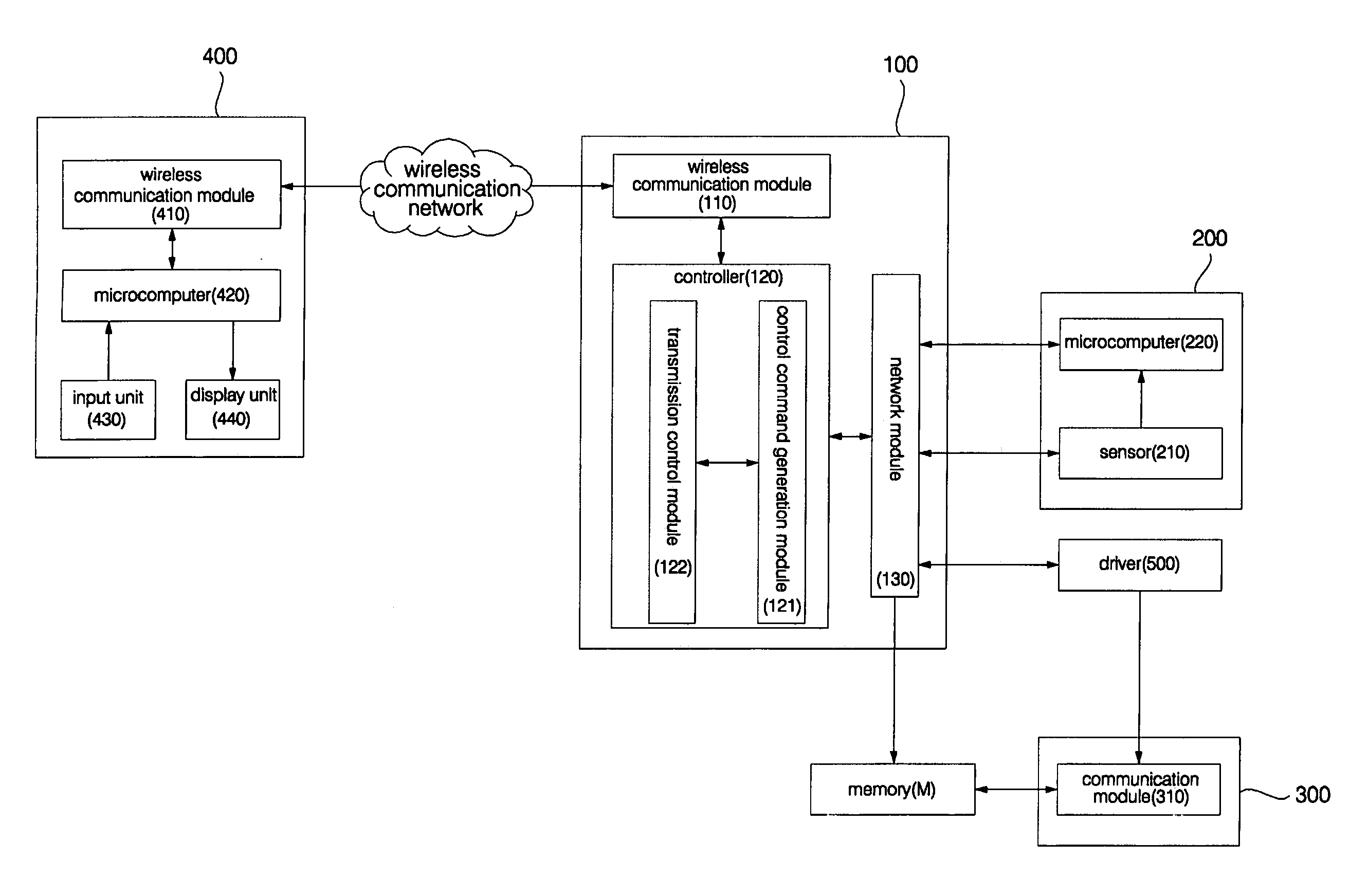
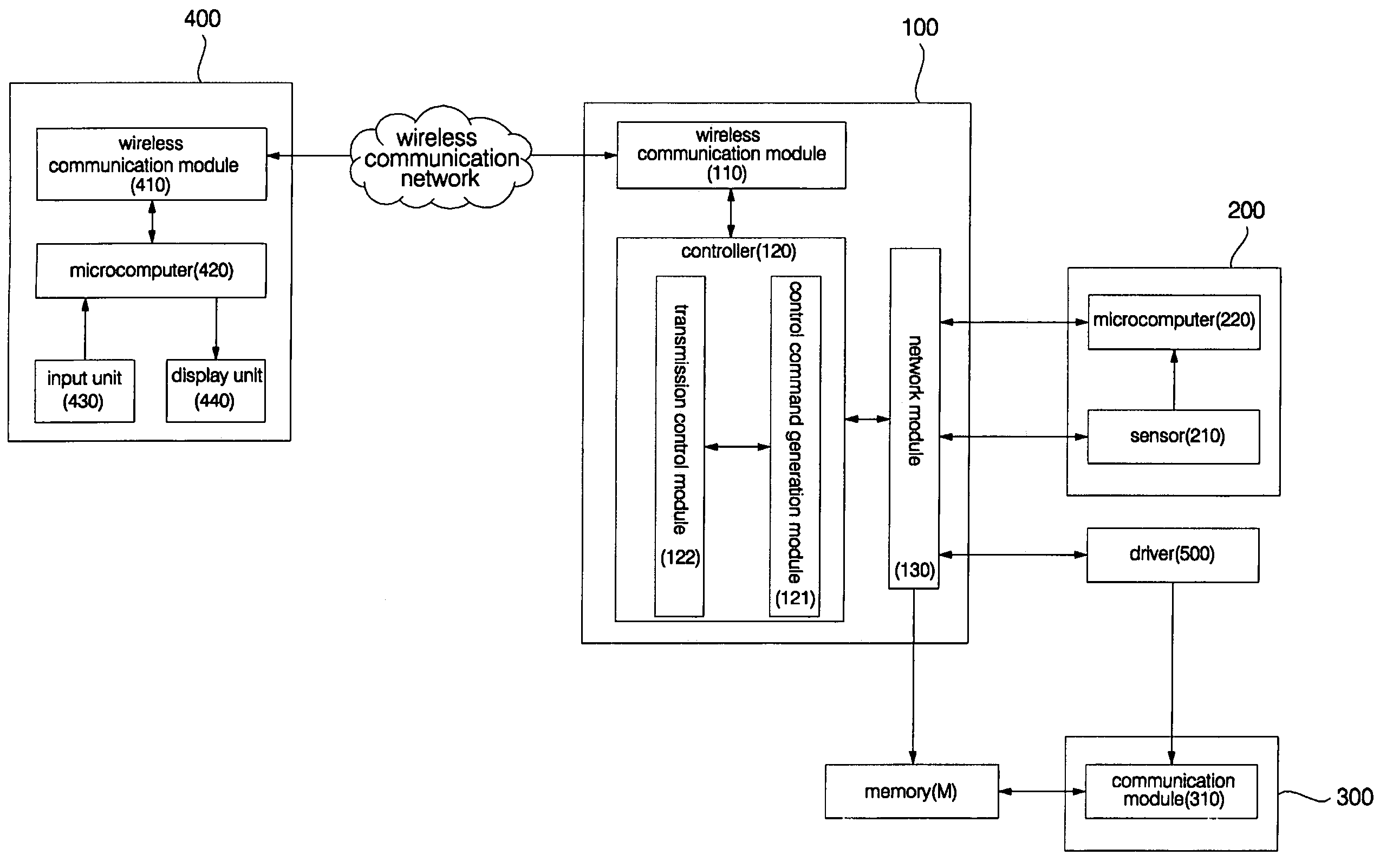
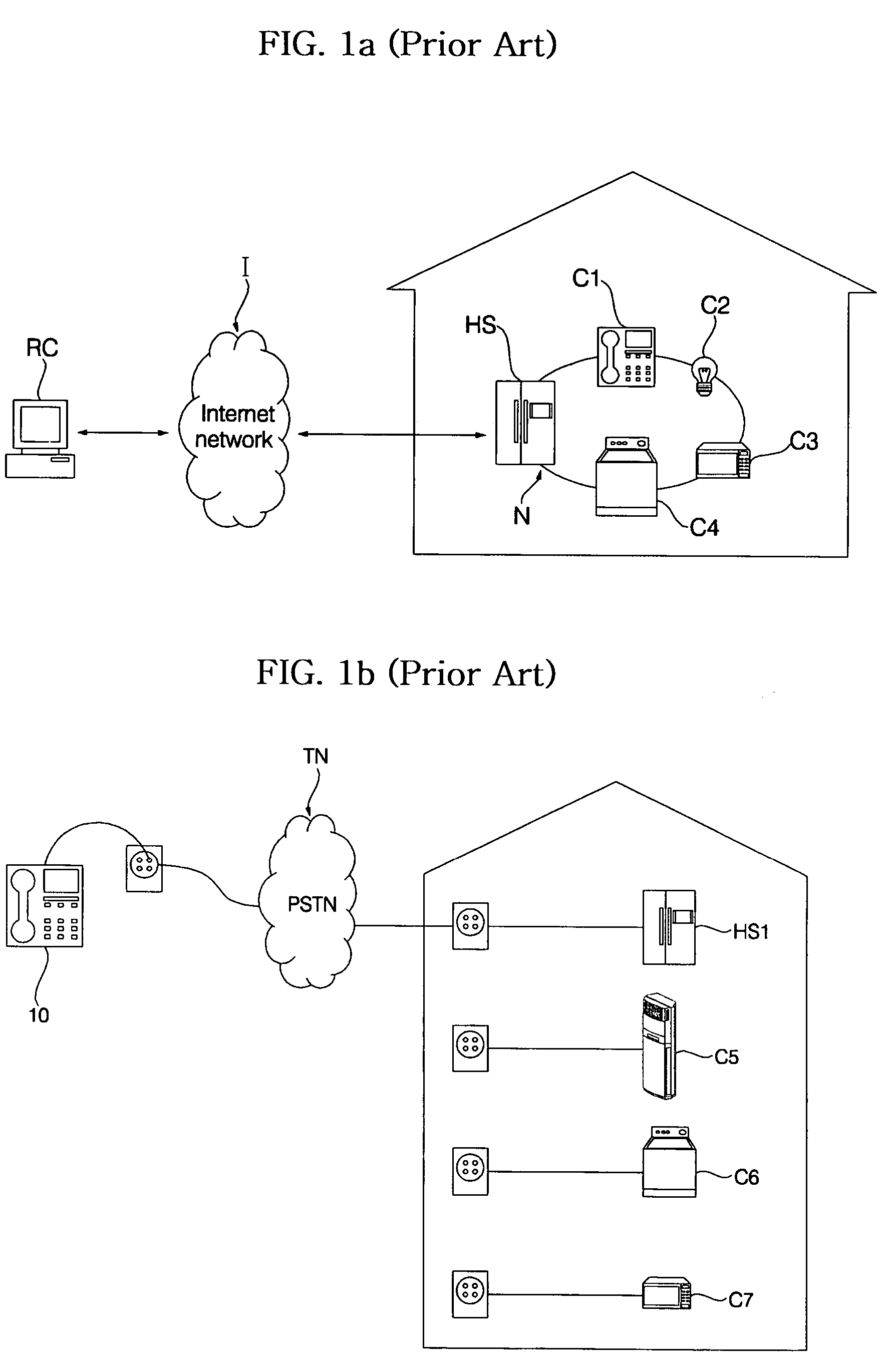
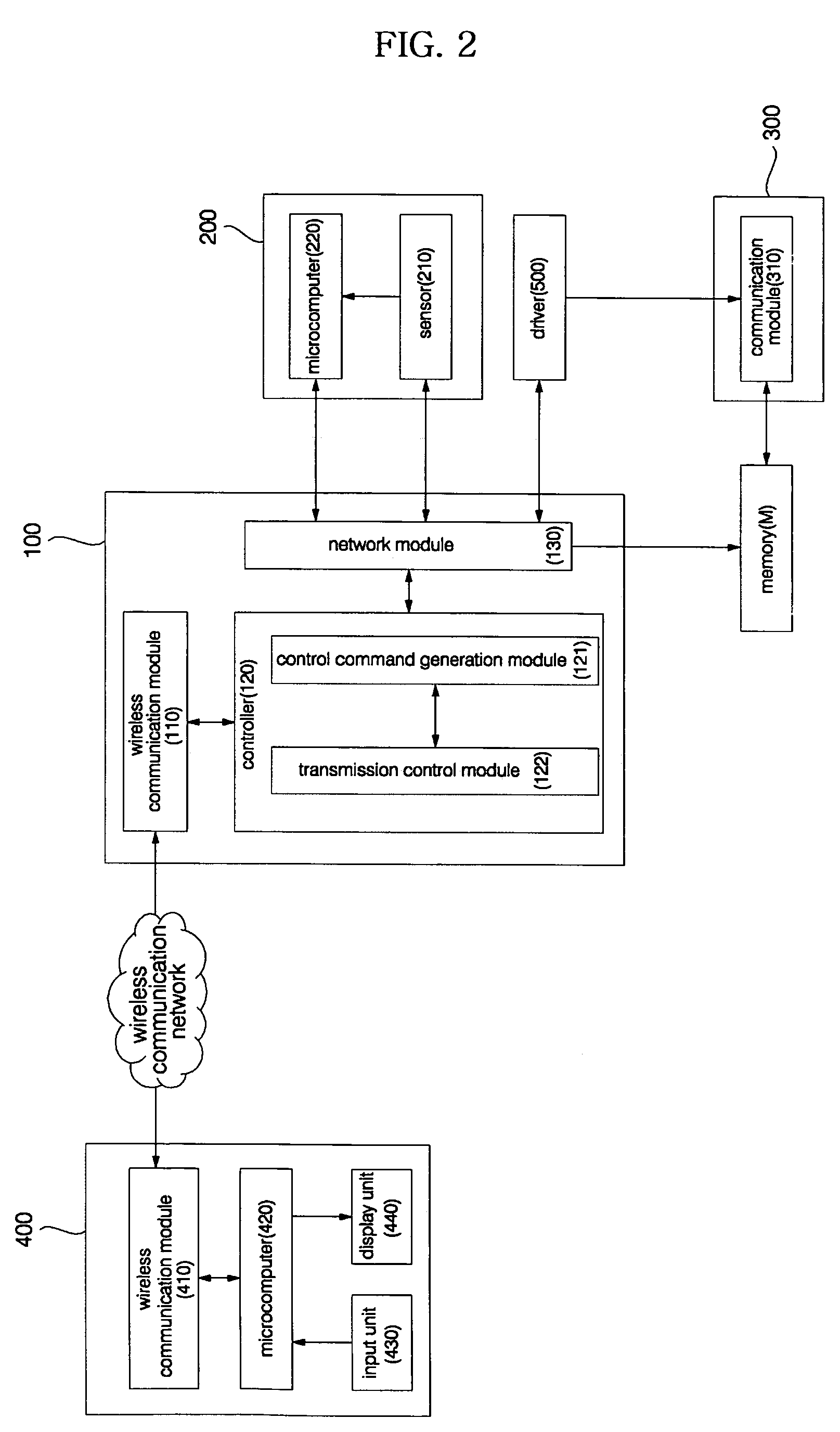
Wireless terminal-interoperable home network system and method controlling the same
ActiveUS20050184865A1Improve control efficiencyImprove ease of useProtective foundationSubstation remote connection/disconnectionImage InspectionTelecommunications
Disclosed herein are a wireless terminal-interoperable home network system and a method for controlling the same. A home server is linked with a security device and camera installed in a building to, when the security device senses entrance / exit of an outsider into / from the building, acquire an internal image of the building from the camera and send the acquired image to a wireless terminal of a user to enable the user to monitor the internal situation of the building in real time. The user can access the home server over a wireless communication network from a remote place outside of the building without separate access to the Internet to receive the internal image of the building and check the internal situation of the building on the basis of the received internal image, resulting in an increase in convenience of use.
Owner:LG ELECTRONICS INC
Pattern inspection apparatus and method
A pattern inspection apparatus is used for inspecting a pattern, such as semiconductor integrated circuit (LSI), liquid crystal panel, and a photomask by using an image of the pattern to-be-inspected and design data for fabricating the pattern to-be-inspected. The pattern inspection apparatus includes a reference pattern generation device for generating a reference pattern represented by one or more lines from design data, an image generation device for generating the image of the pattern to-be-inspected, a detecting device for detecting an edge of the image of the pattern to-be-inspected, and an inspection device for inspecting the pattern to-be-inspected by comparing the edge of the image of the pattern to-be-inspected with the one or more lines of the reference pattern.
Owner:TASMIT INC
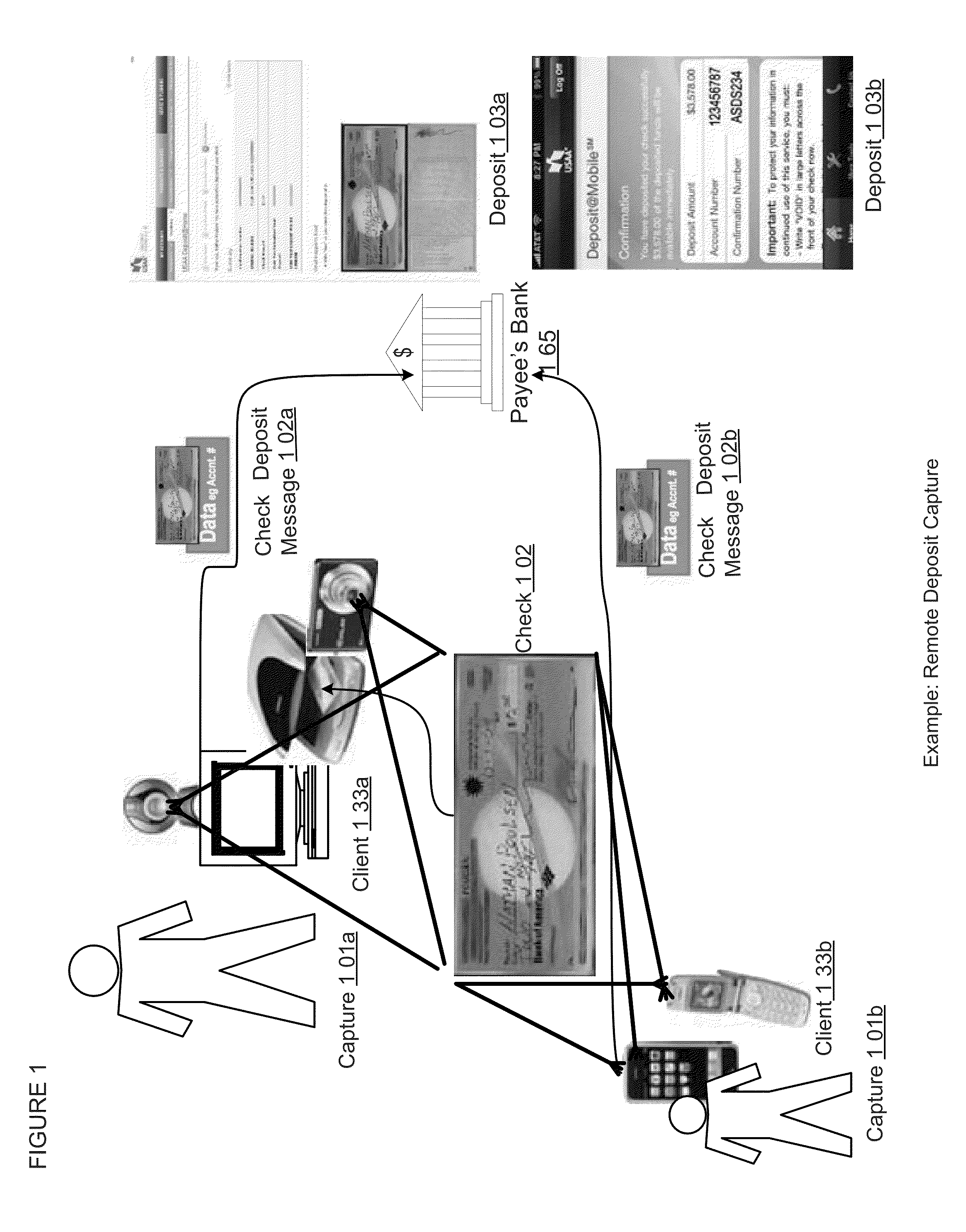
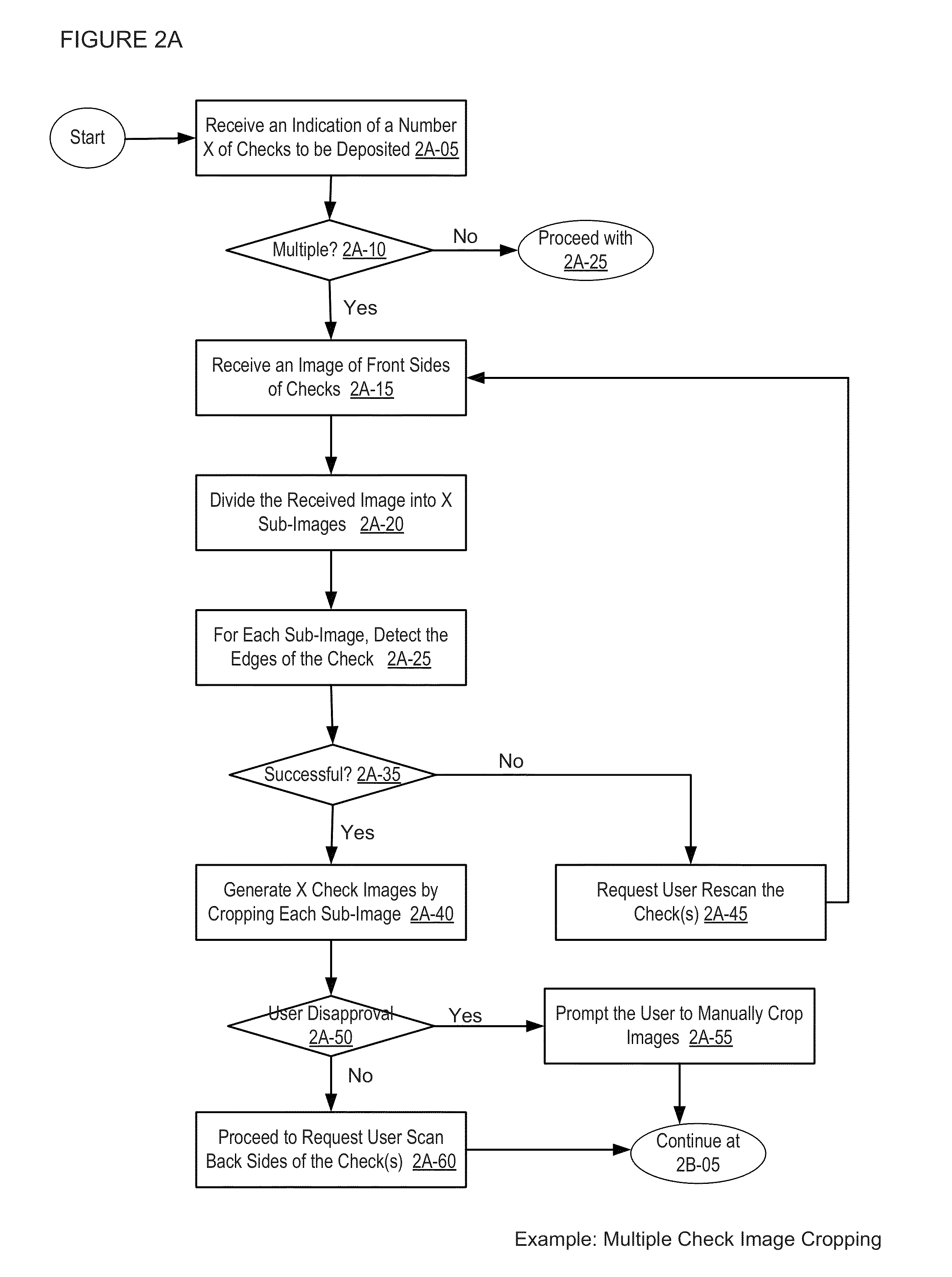
Remote deposit image inspection apparatuses, methods and systems
The REMOTE DEPOSIT IMAGE INSPECTION APPARATUSES, METHODS AND SYSTEMS (hereinafter “ImageInspector”) transforms uploaded check images and check deposit information inputs via ImageInspector components image into deposit confirmation outputs. For example, in one embodiment, a user may employ a personal computer connected to a web camera, and / or a smartphone with a built-in camera to initiate the remote deposit by holding a check in front of the camera, and the ImageInspector may capture images of the check and send them to a financial institution for deposit processing.
Owner:USAA
Image-type intubation-aiding device
InactiveUS20090118580A1Improve medical qualityIncrease spot ratioBronchoscopesTracheal tubesDisplay deviceEndotracheal tube
An image-type intubation-aiding device comprises a small-size image sensor and a light source module both placed into an endotracheal tube to help doctors with quick intubation. Light from light emission devices in the light source module passes through a transparent housing and is reflected by a target and then focused. The optical signal is converted into a digital or analog electric signal by the image sensor for displaying on a display device after processing. Doctors can thus be helped to quickly find the position of trachea, keep an appropriate distance from a patient for reducing the possibility of infection, and lower the medical treatment cost. Disposable products are available to avoid the problem of infection. The intubation-aiding device can be used as an electronic surgical image examination instrument for penetration into a body. Moreover, a light source with tunable wavelengths can be used to increase the spot ratio of nidus.
Owner:MEDICAL INTUBATION TECH CORP
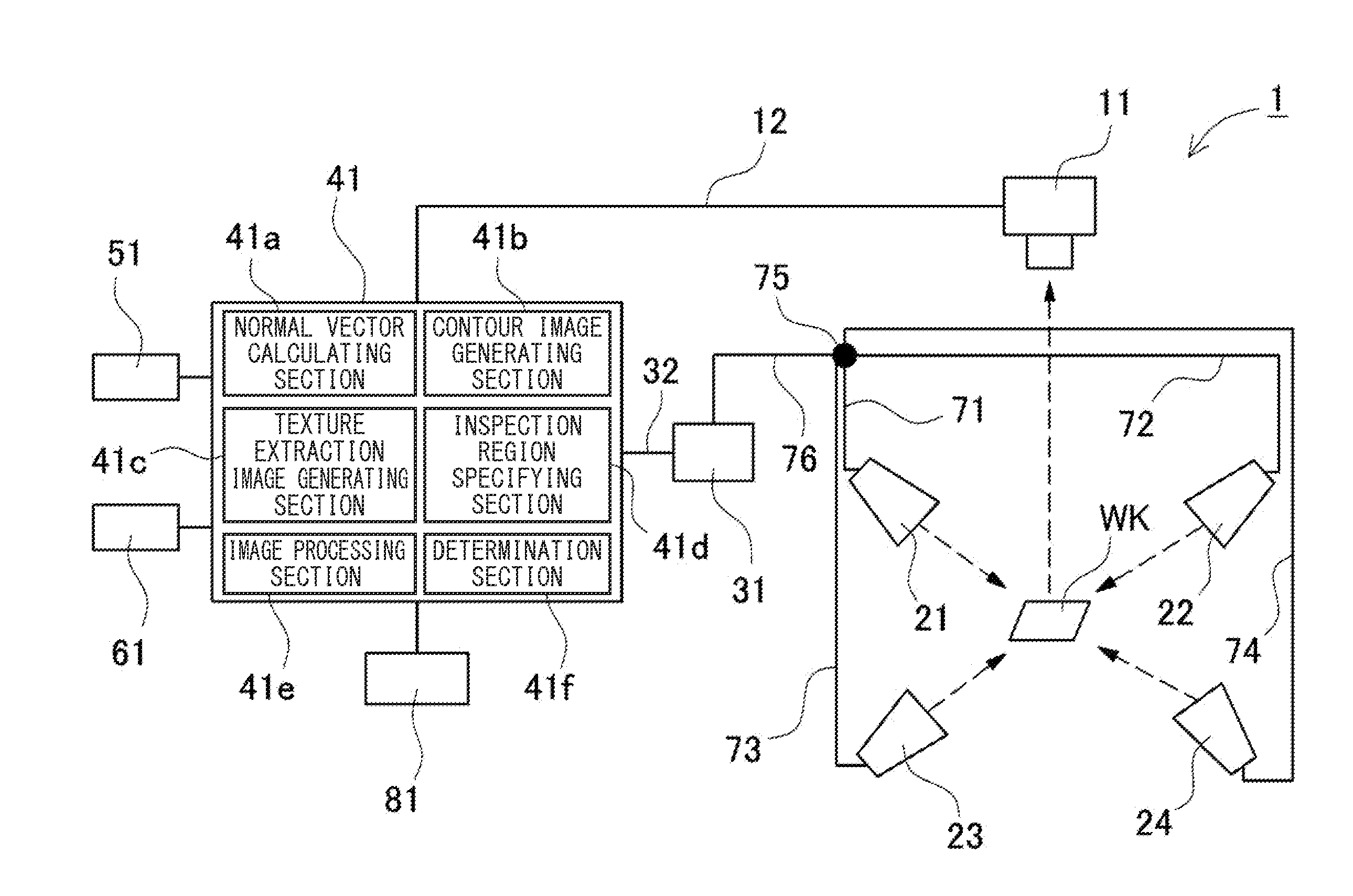
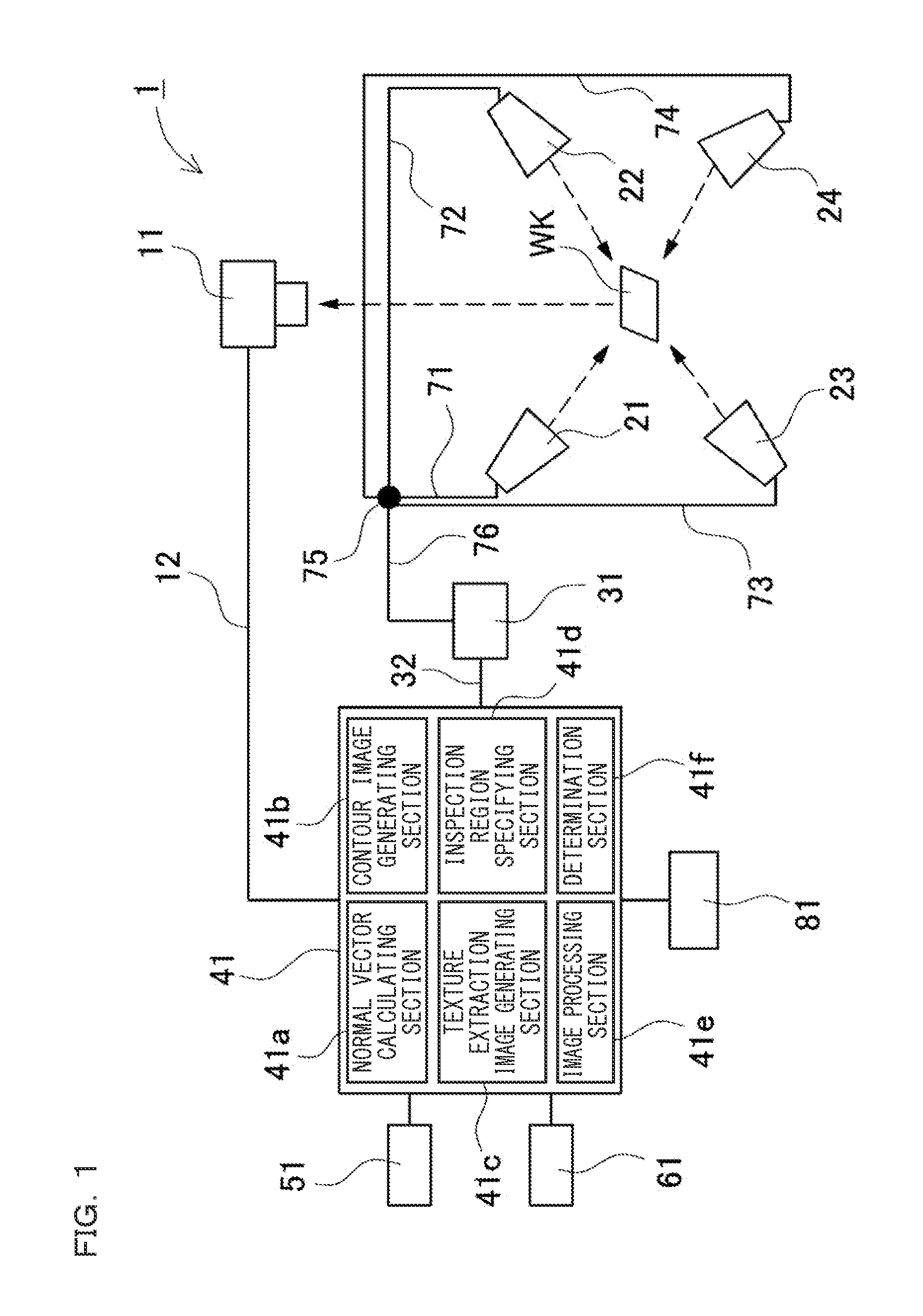
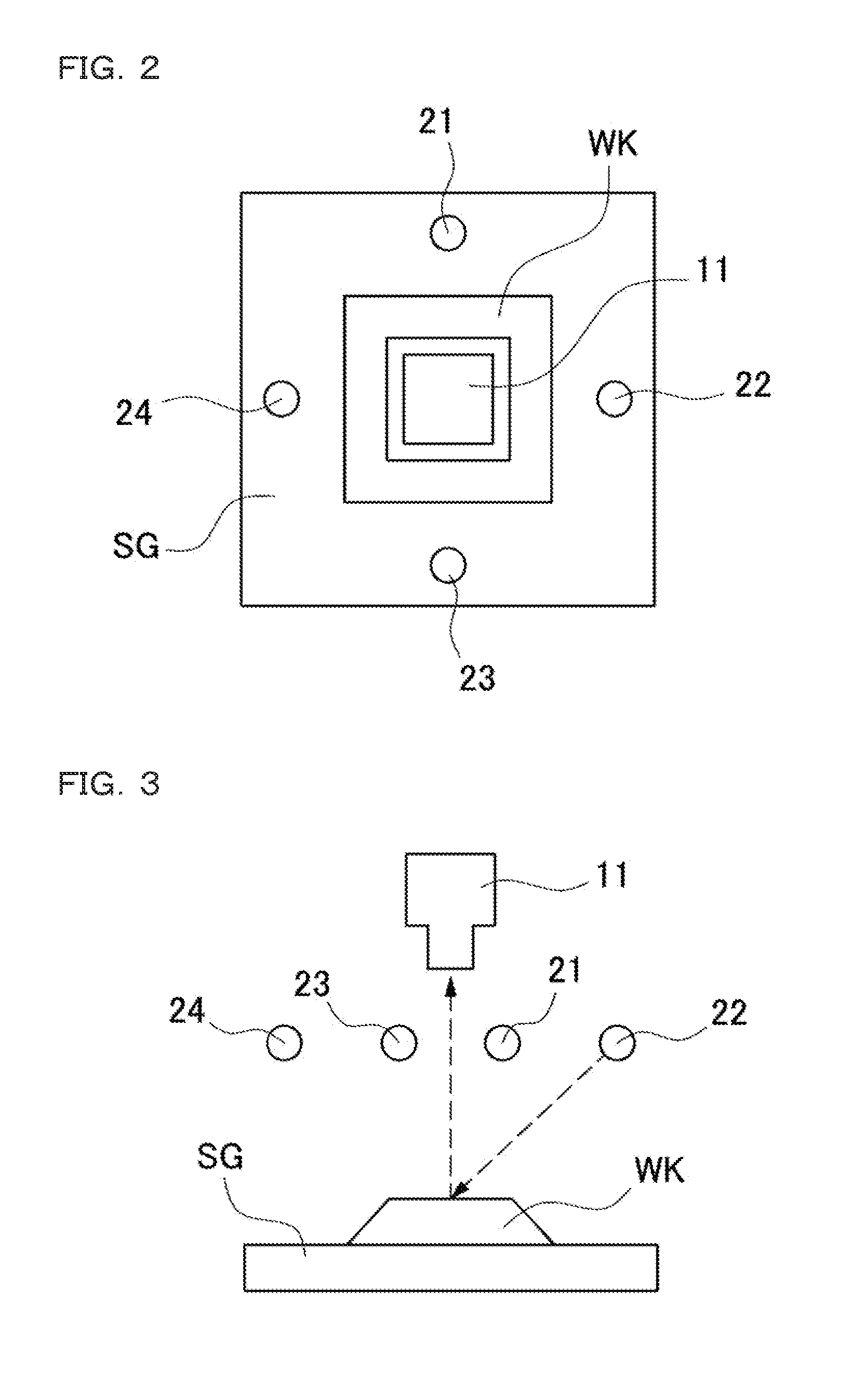
Image Inspection Apparatus, Image Inspection Method, Image Inspection Program, Computer-Readable Recording Medium And Recording Device
ActiveUS20150355101A1Easy to checkImprove accuracyImage enhancementImage analysisImage InspectionRecording media
An image inspection apparatus includes: an imaging section for capturing an image of a workpiece from a certain direction; an illumination section for illuminating the workpiece from different directions at least three times; an illumination controlling section for sequentially turning on the illumination sections one by one; an imaging generating section for driving the imaging section to generate a plurality of images; a normal vector calculating section for calculating a normal vector with respect to the surface of the workpiece at each of pixels by use of a pixel value of each of pixels having a corresponding relation among the plurality of images; and a contour image generating section for performing differential processing in an X-direction and a Y-direction on the calculated normal vector at each of the pixels, to generate a contour image that shows a contour of inclination of the surface of the workpiece.
Owner:KEYENCE
Imaging inspection apparatus
ActiveUS7177391B2Shorten the lengthEnhance shipping of the apparatusConveyorsMaterial analysis by optical meansImage InspectionObject based
An imaging inspection apparatus which utilizes a plurality of individual imaging inspection devices (e.g., X-ray Computer Tomography scanning devices) positioned on a frame for directing beams onto articles having objects therein to detect the objects based on established criteria. The apparatus utilizes a conveyor which is not physically coupled to the frame having the imaging inspection devices to pass the articles along a path of travel to an inspection location within the apparatus, whereupon the inspection devices direct beams onto the article and the beams are detected and output signals provided to a processing and analysis assembly which analyzes the signals and identifies certain objects which meet the criteria.
Owner:SURESCAN CORP
Image inspection result determination apparatus, image inspection system, method of determinating image inspection result, and storage medium
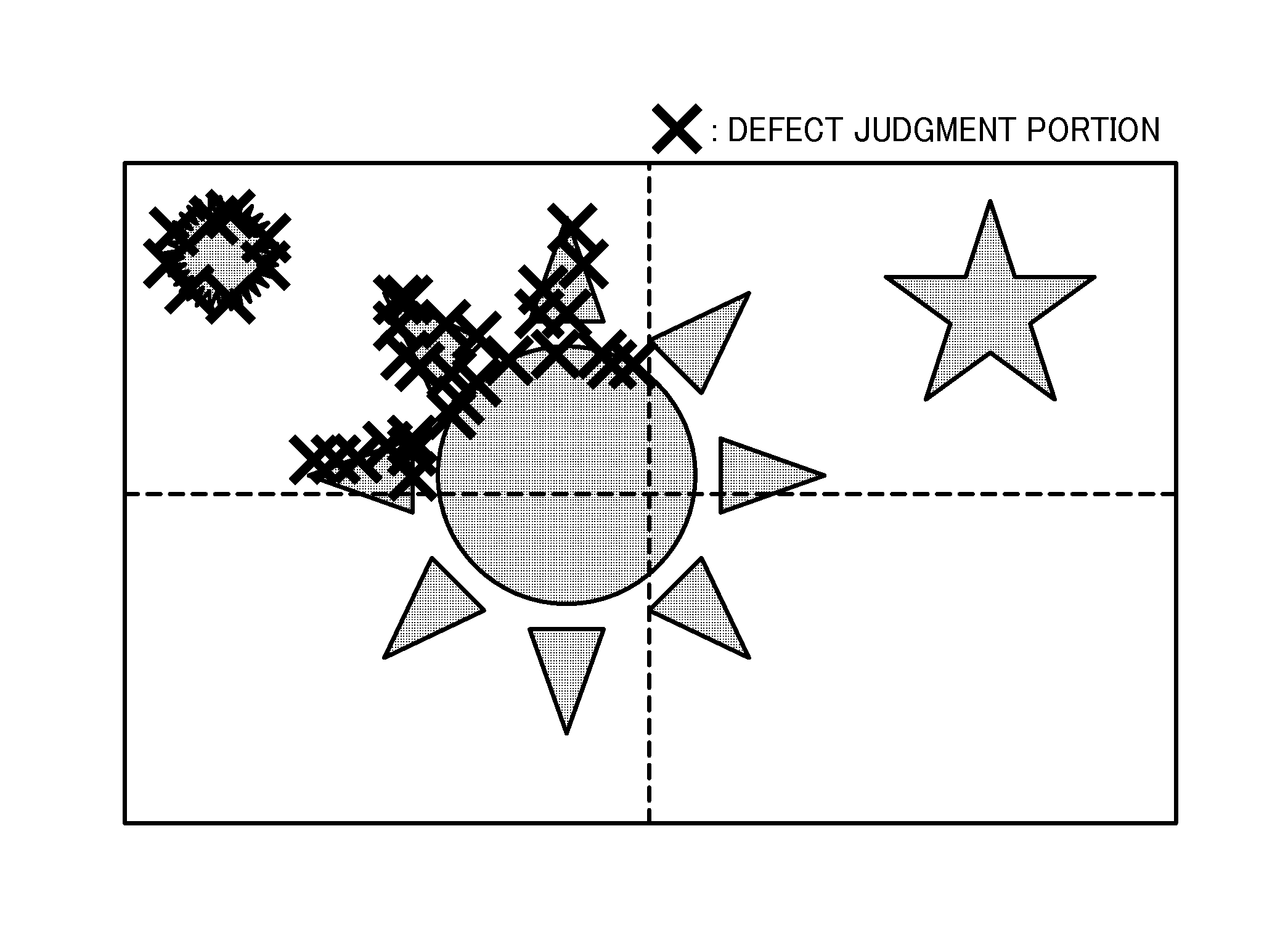
An apparatus for verifying an inspection result includes an inspection result obtaining unit to obtain inspection result indicating defect amount and defect position in a scanned image, from an inspection result of defect judgment of the scanned image with respect to an inspection reference image, the defect judgment being performed through dividing at least one of the scanned image and the inspection reference image and conducting position matching of the scanned image and inspection reference image; and a verification unit to count defect amount occurring to the scanned image, to determine whether a defect pattern occurring to the scanned image matches a pre-set condition corresponding to a false detection condition causable by failure of the position matching, and to determine that defect occurring to the scanned image is a false detection when the counted defect amount is a threshold or more, and the defect pattern matches the false detection condition.
Owner:RICOH KK
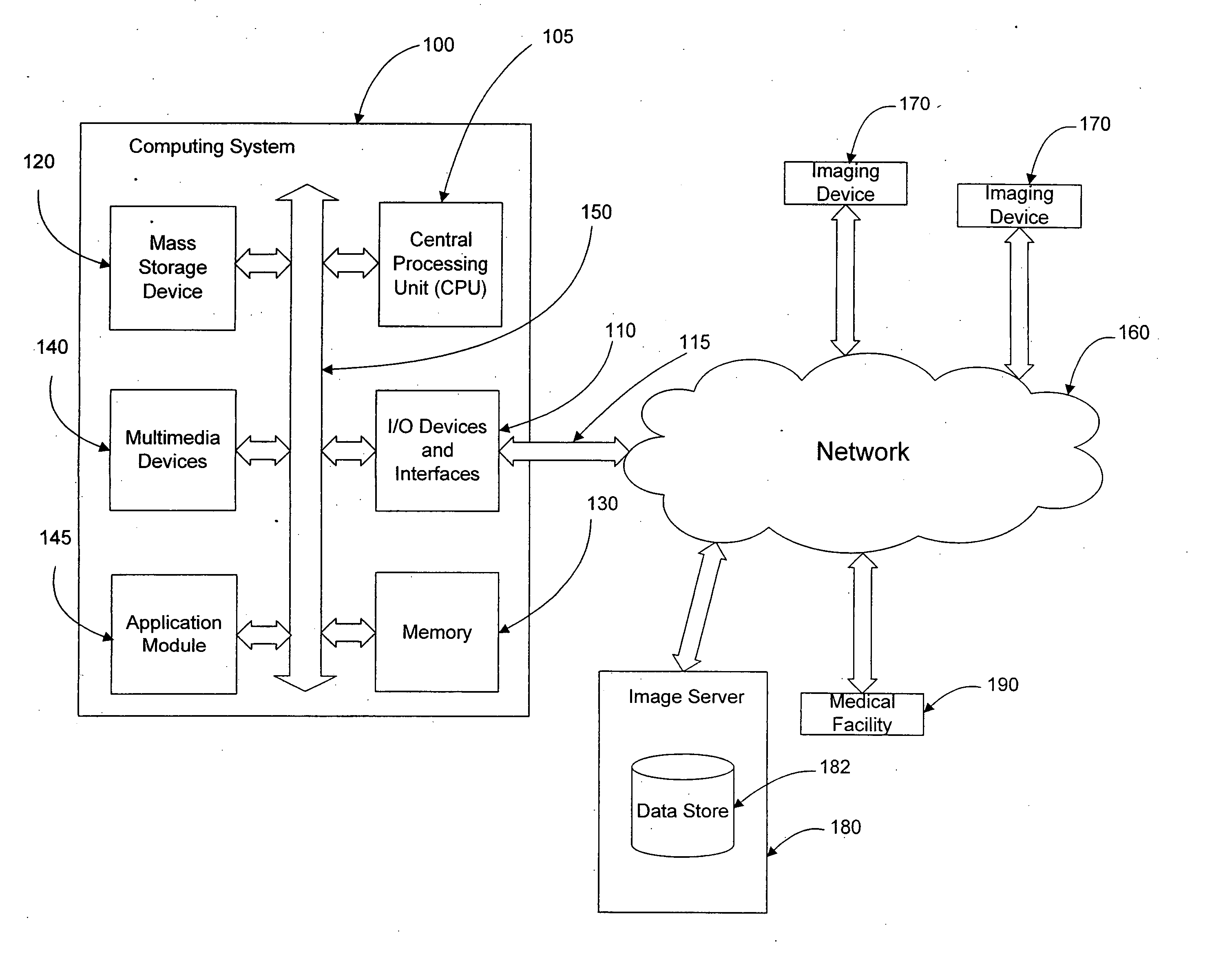
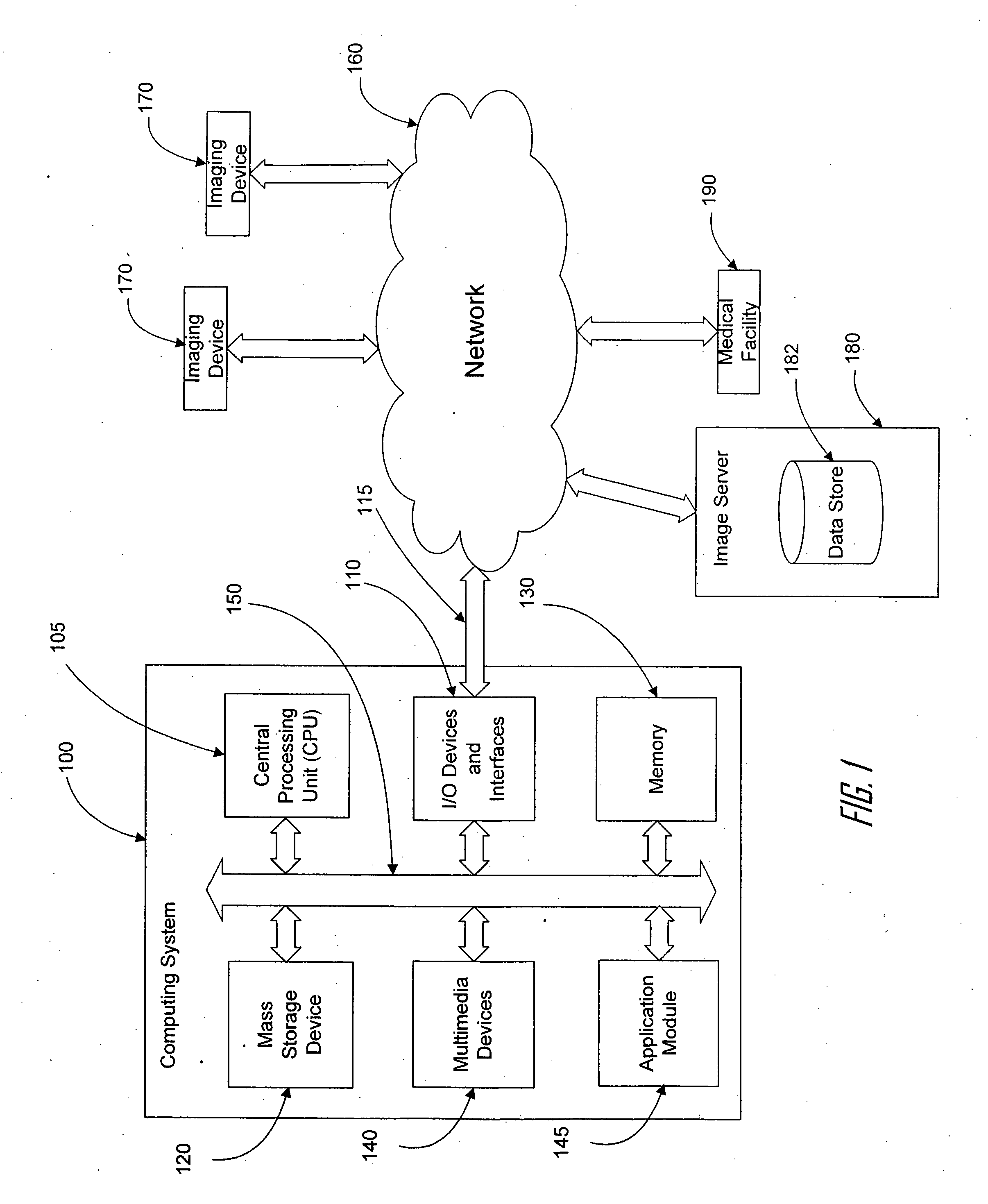
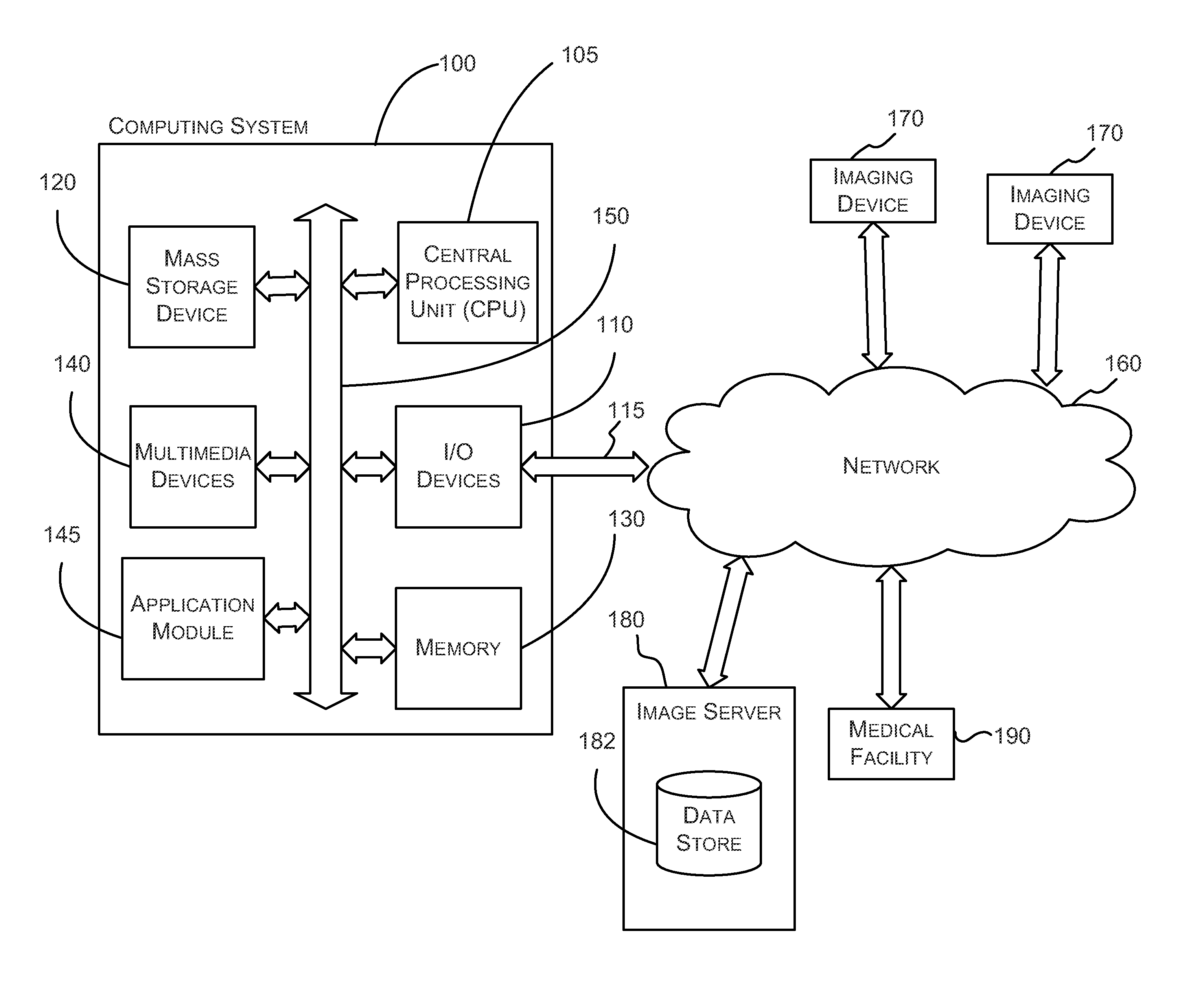
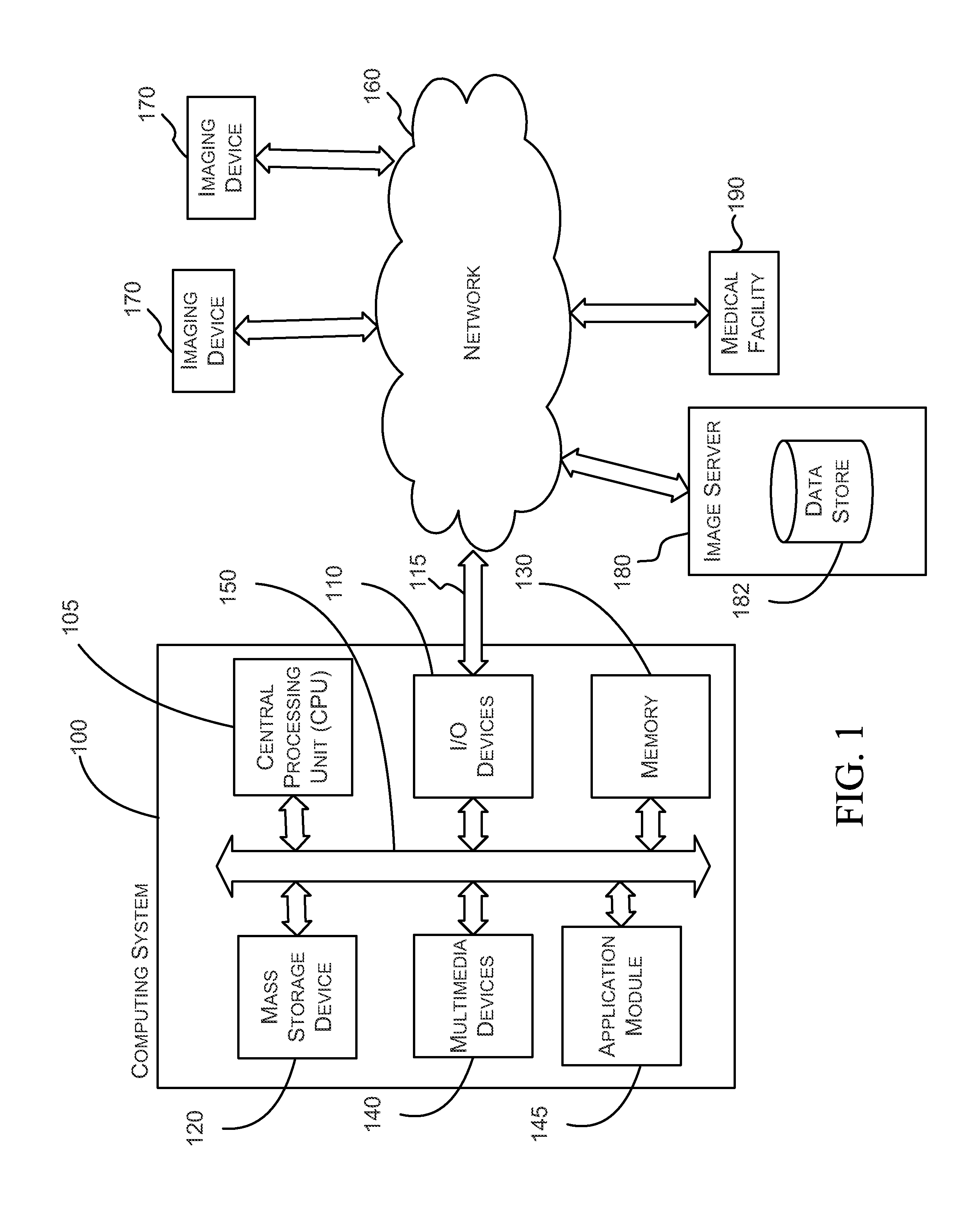
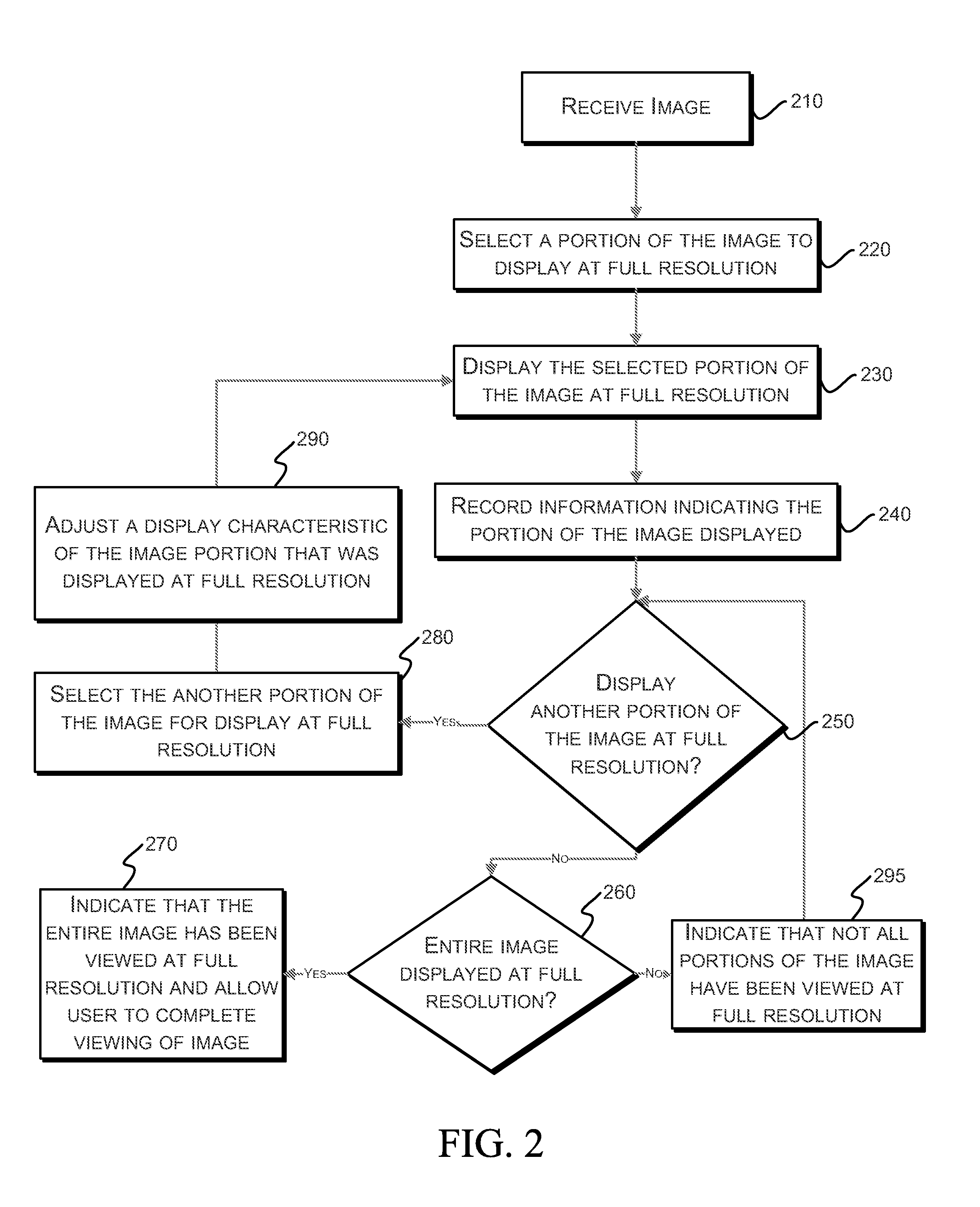
Systems and methods for viewing medical images
ActiveUS20060093207A1Character and pattern recognitionCathode-ray tube indicatorsImage InspectionComputer graphics (images)
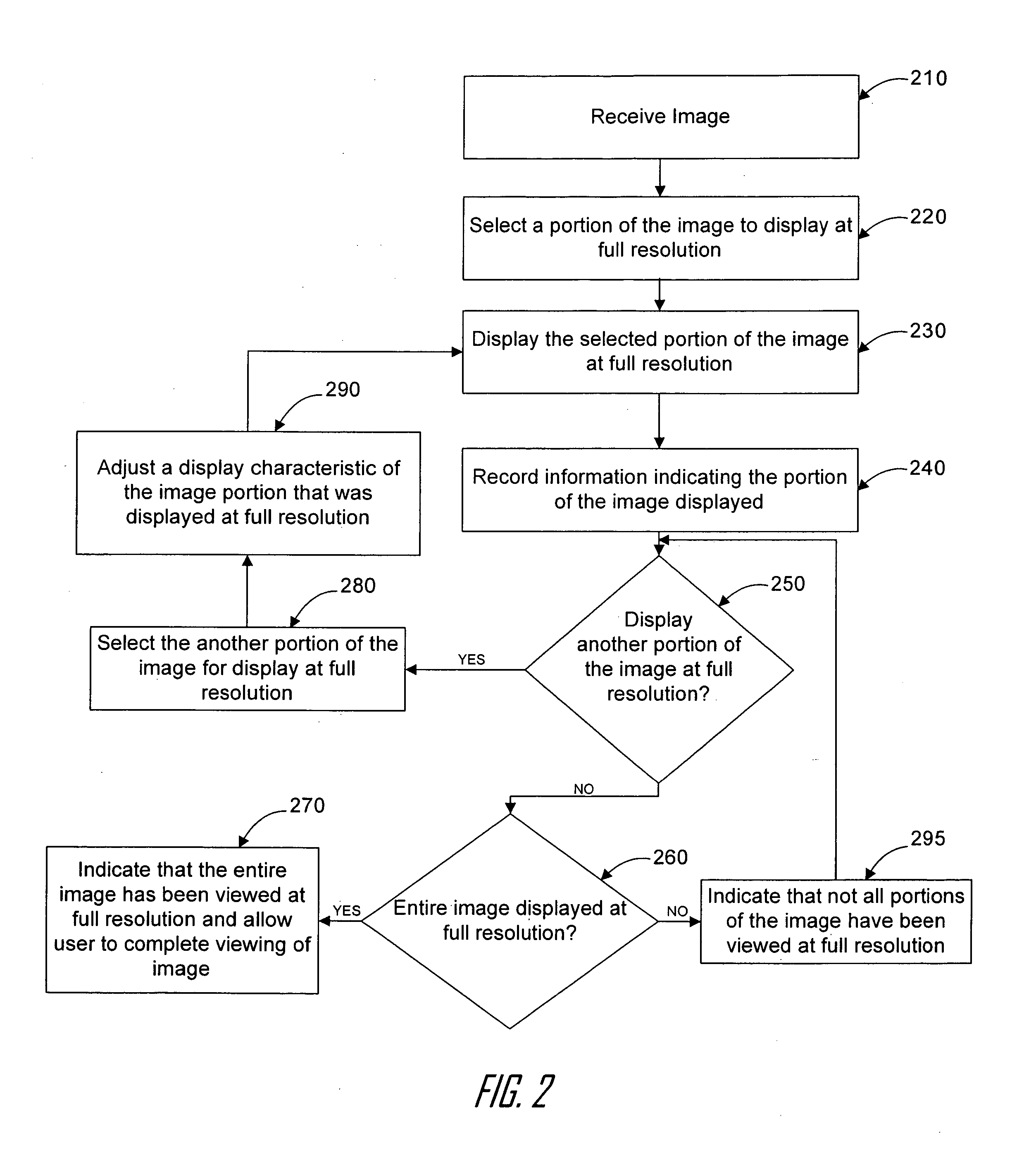
For certain medical images, it is important and / or required that a user view all of a medical image at full resolution so that minute, but important, indicia in the medical image are not missed. A computing systems monitor the portions of the medical image that are displayed on the display device, notates those portions that have been displayed at full resolution (or other user-defined display parameters), and provides the user with information indicating portions that have not been viewed at full resolution and / or provides information indicating for which images of a multiple image examination full pixel display has been accomplished. The process reduces the possibility of missing an abnormality in a medical image due to the viewer not viewing a portion of the image at full resolution or using other user-defined display parameters.
Owner:MERATIVE US LP
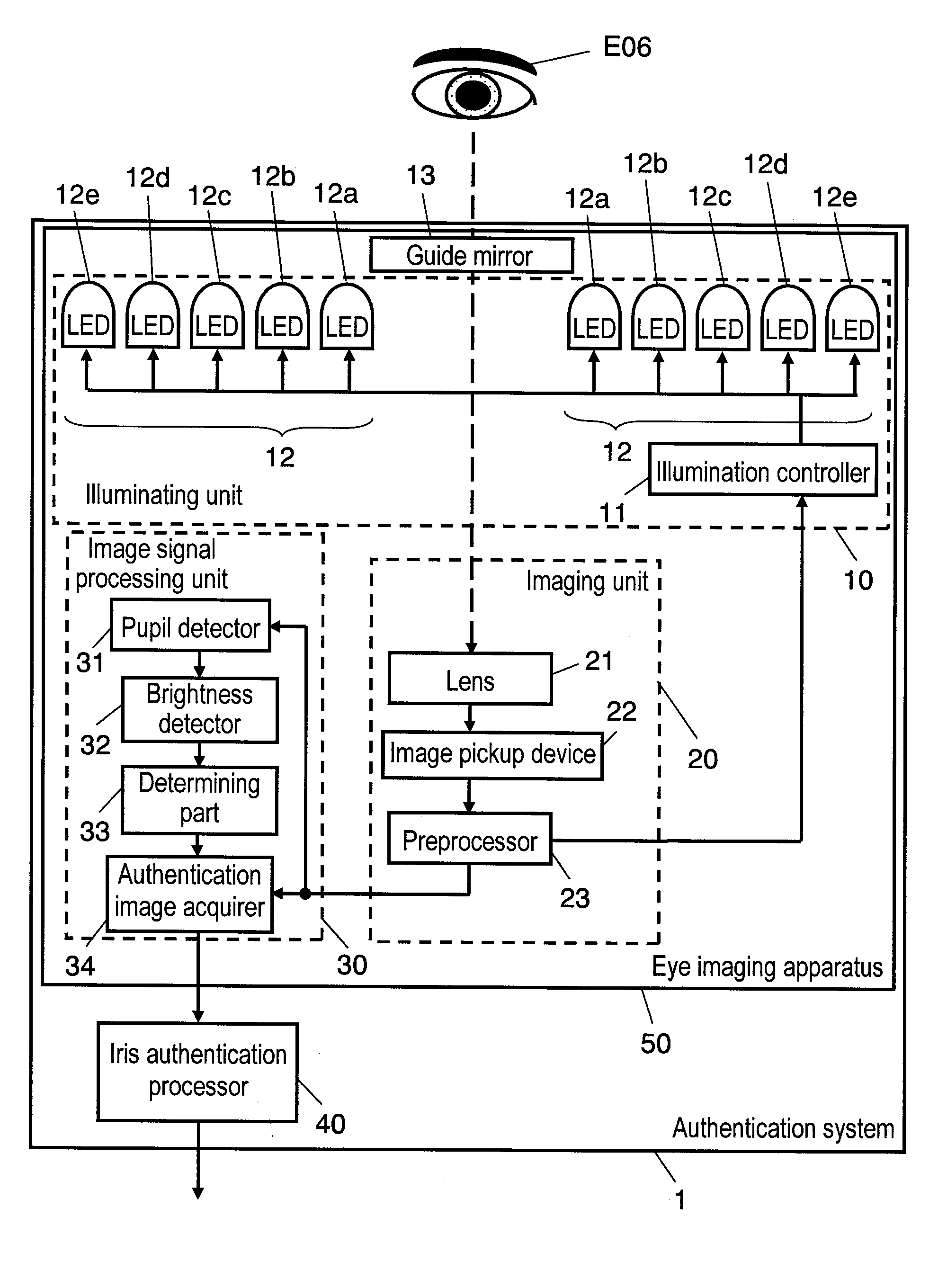
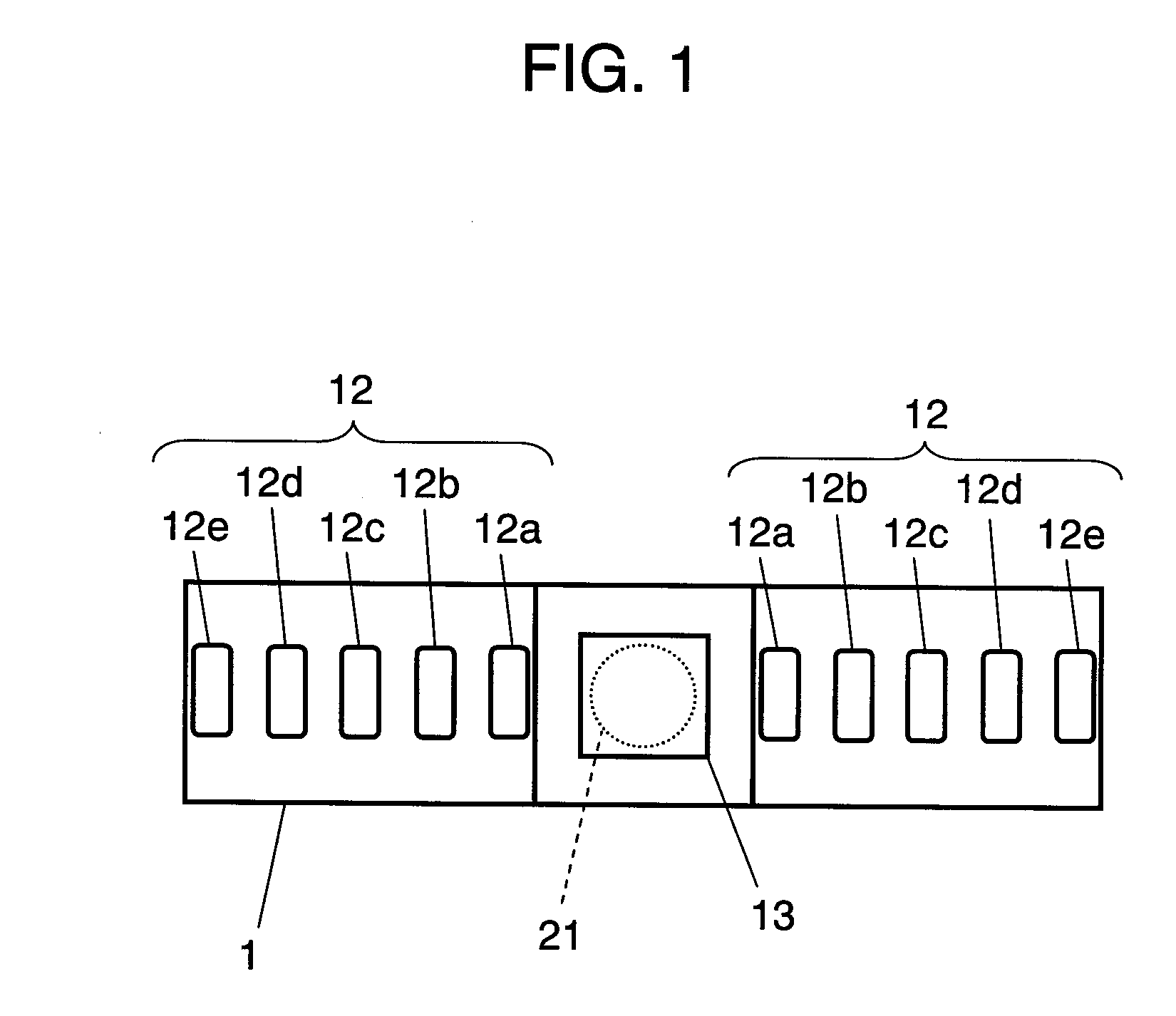
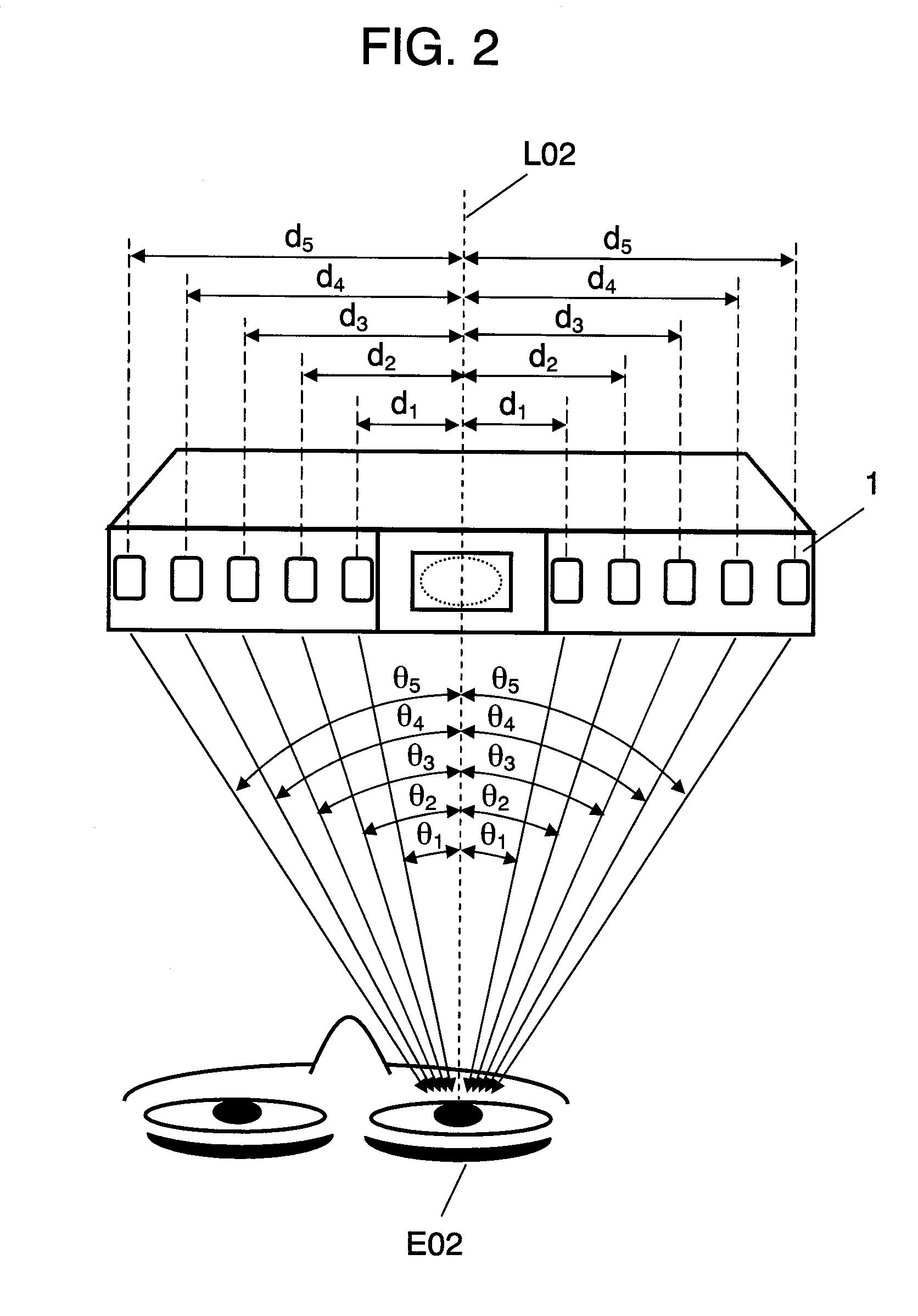
Biometric discrimination device, authentication device, and biometric discrimination method
InactiveUS20090016574A1Improve accuracyReduce the possibilityPerson identificationAcquiring/recognising eyesImage InspectionOptical axis
An authentication system includes the following elements: a guide mirror to be used when a subject checks the position of the eye with an image reflected therefrom during imaging the eye of the subject; a lens disposed behind the mirror; and illuminating LEDs that are disposed symmetrically about the optical axis and can be switched for emitting near infrared rays. With this structure, the authentication system takes a plurality of images of the eye of the subject irradiated with illuminating rays from the illuminating LEDs at different lighting angles to the eye of the subject, determines whether the taken eye images are of a living eye or a forgery, and authenticates the iris.
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
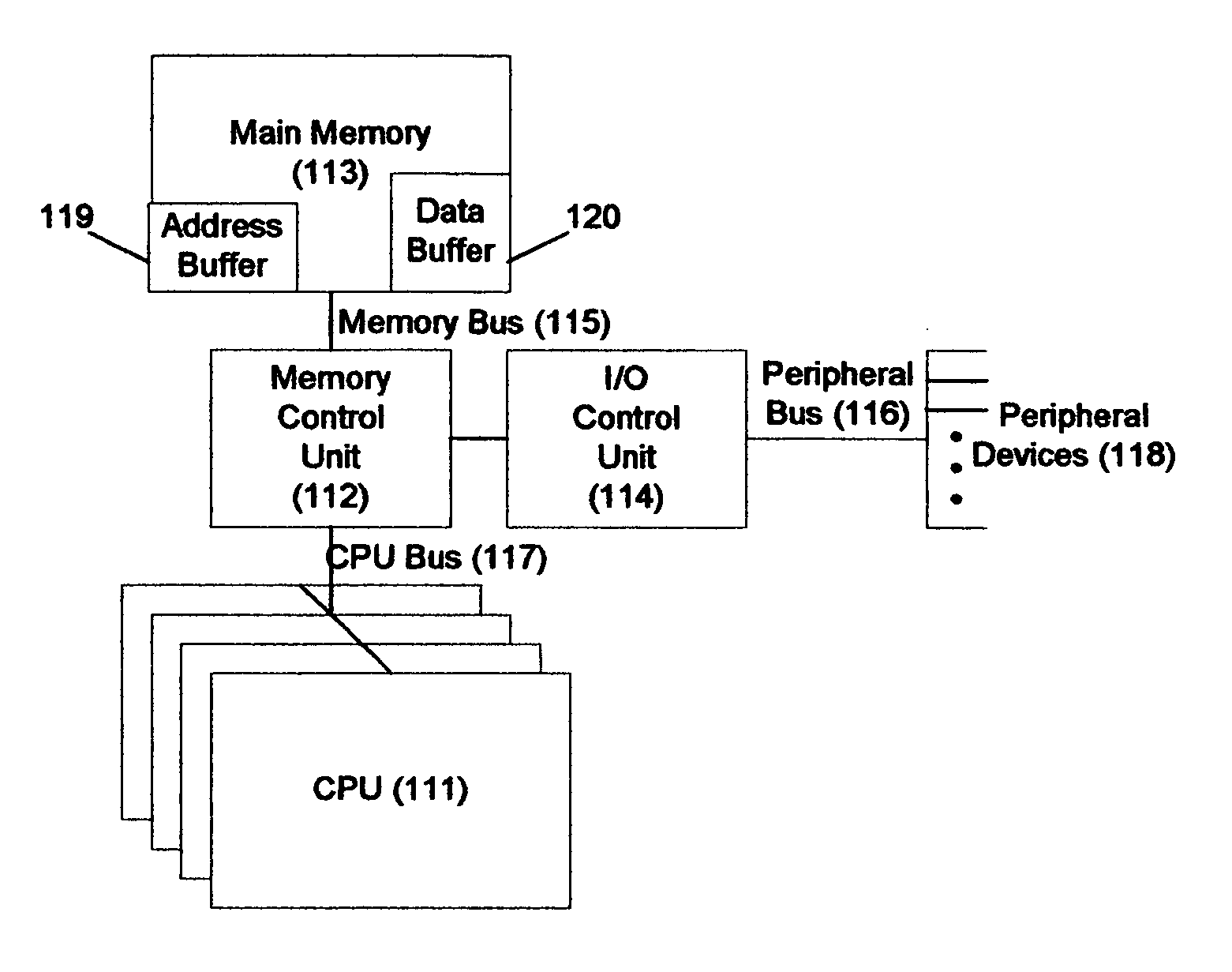
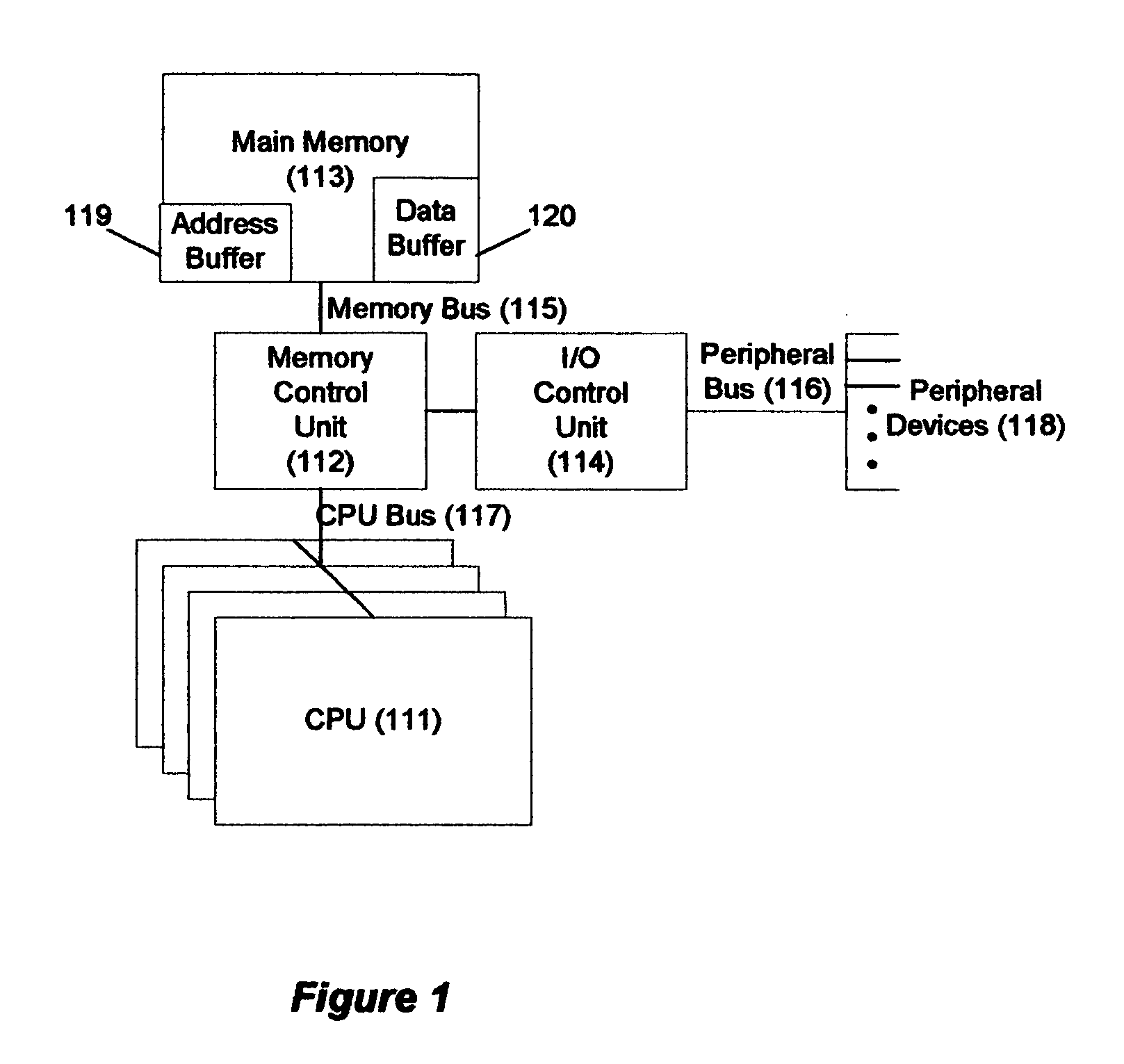
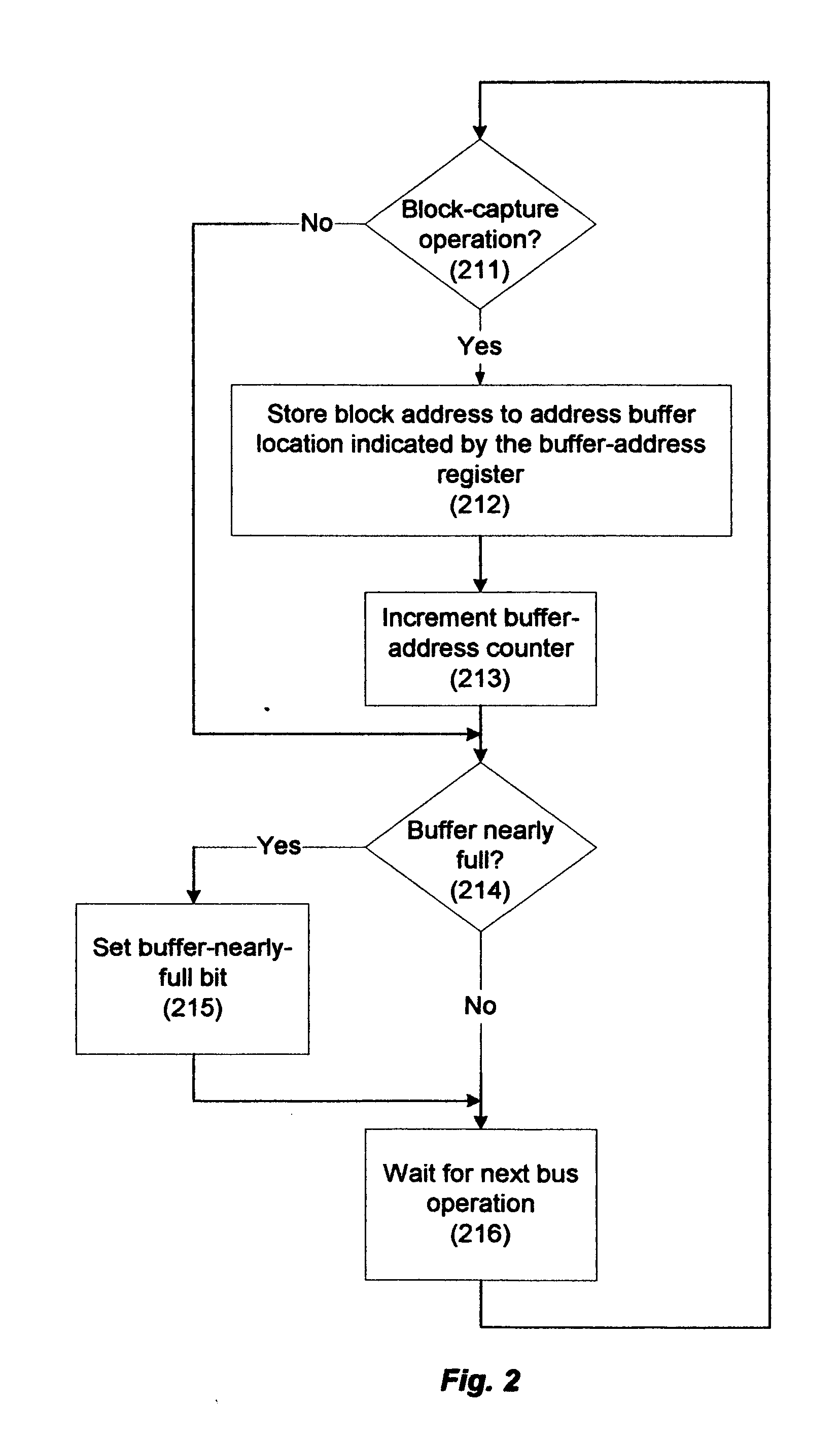
Memory-controller-embedded apparatus and procedure for achieving system-directed checkpointing without operating-system kernel support
InactiveUS20060150010A1Eliminate needMemory controllerError detection/correctionSupporting systemImage Inspection
System-directed checkpointing is enabled in otherwise standard computers through relatively straightforward enhancements to the computer's memory controller. Different embodiments of the invention can be used to support: local and remote post-image checkpointing using a memory-resident address buffer for storing the addresses of modified data blocks, either with or without requiring the processor caches to be flushed at each checkpoint; local and remote post-image checkpointing using either memory- or I / O-resident buffers for both the addresses and the data associated with blocks modified since the last checkpoint and supporting background buffer-to-shadow copying; remote and local post-image checkpointing using bit-map memories thereby avoiding the need for either address or data buffers while still supporting background data copying and either with or without requiring caches to be flushed to effect a checkpoint; local post-image checkpointing using a two-bit-per-memory-block state memory that eliminates the need for any data to be copied from one memory location to another; and pre-image local checkpointing again either with or without requiring caches to be flushed for checkpointing purposes. Since most of these implementations have advantages and disadvantages over the others and since similar mechanisms are used in the memory controller for all of these options, the controller can be implemented to support all of them with a hardwired or settable status register defining which is to be supported in a given situation. Alternatively, since some of these implementations require somewhat less extensive memory controller enhancements, the controller can be designed to support only one or a small subset of these embodiments with a correspondingly smaller perturbation to its more standard implementation.
Owner:OSHANTEL SOFTWARE
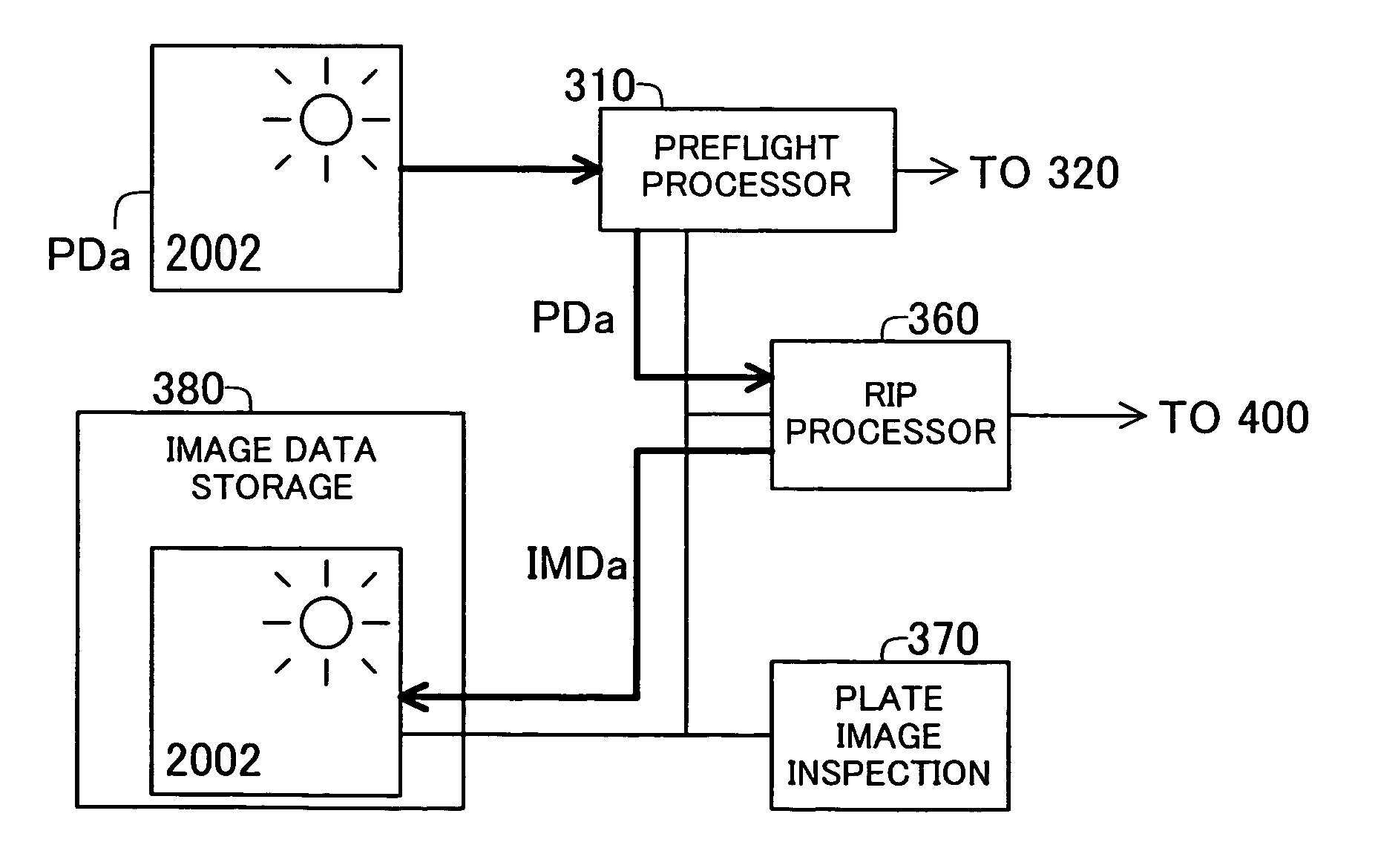
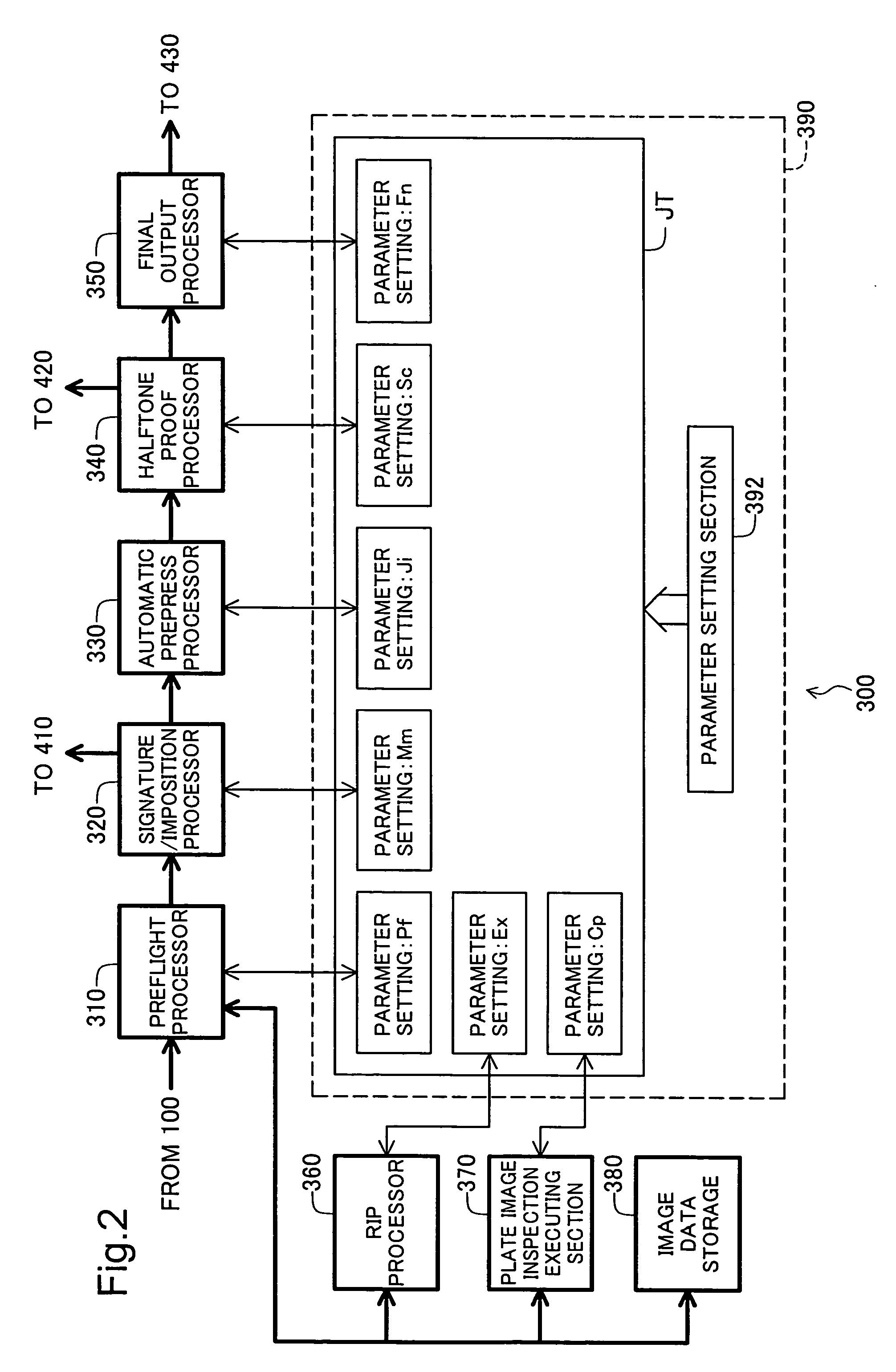
Plate image inspection for printing prepress
InactiveUS20040086156A1Addressing slow performanceImage enhancementImage analysisImage InspectionGrating
A prepress system comprises a raster image processor for developing first print image data to display resolution to create first raster image data, and for developing second print image data to the display resolution to create second raster image data. A plate image inspection processor executes a plate image inspection process by comparing the first and second raster image data, and displays on a display device the result of the plate image inspection process.
Owner:DAINIPPON SCREEN MTG CO LTD
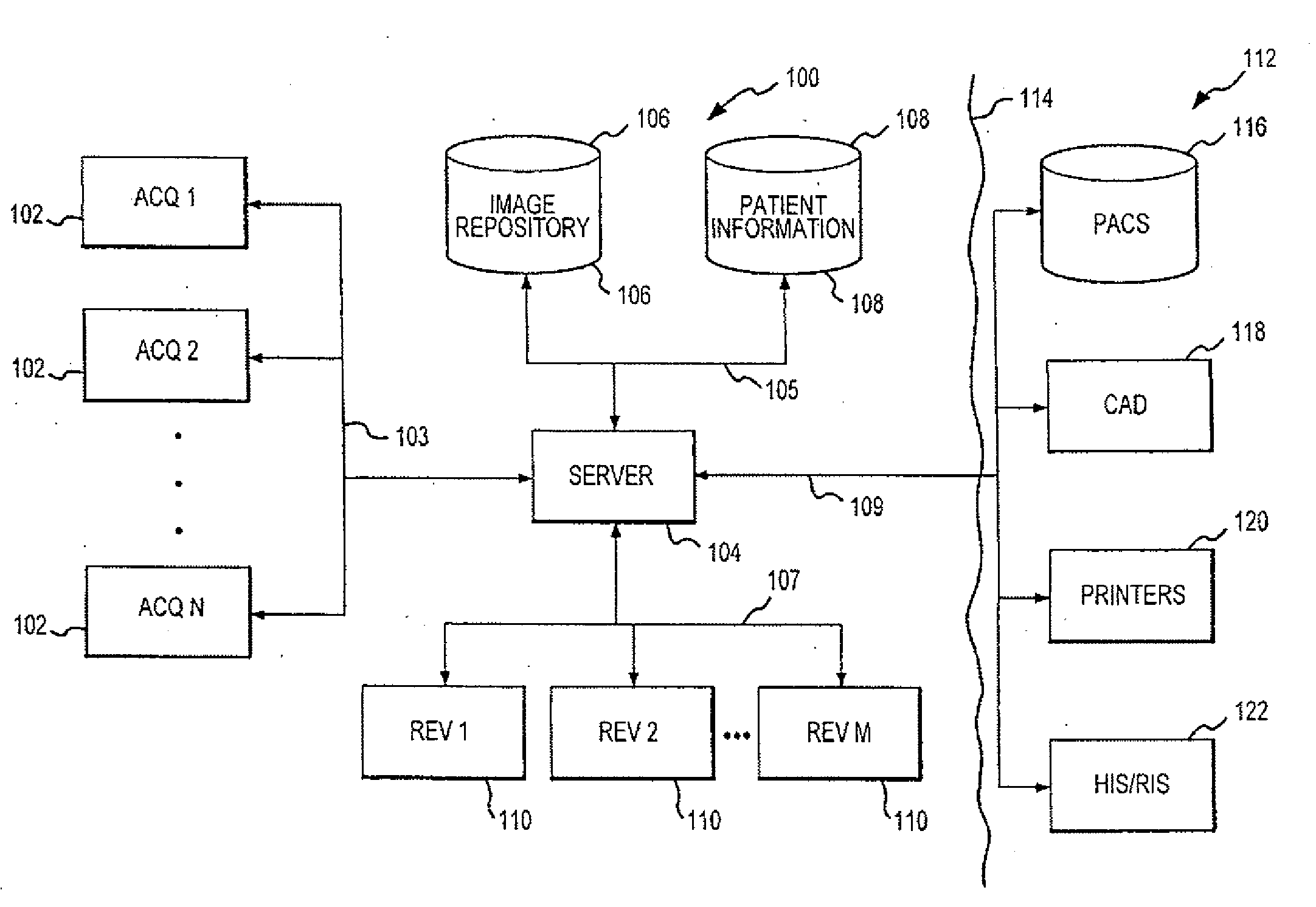
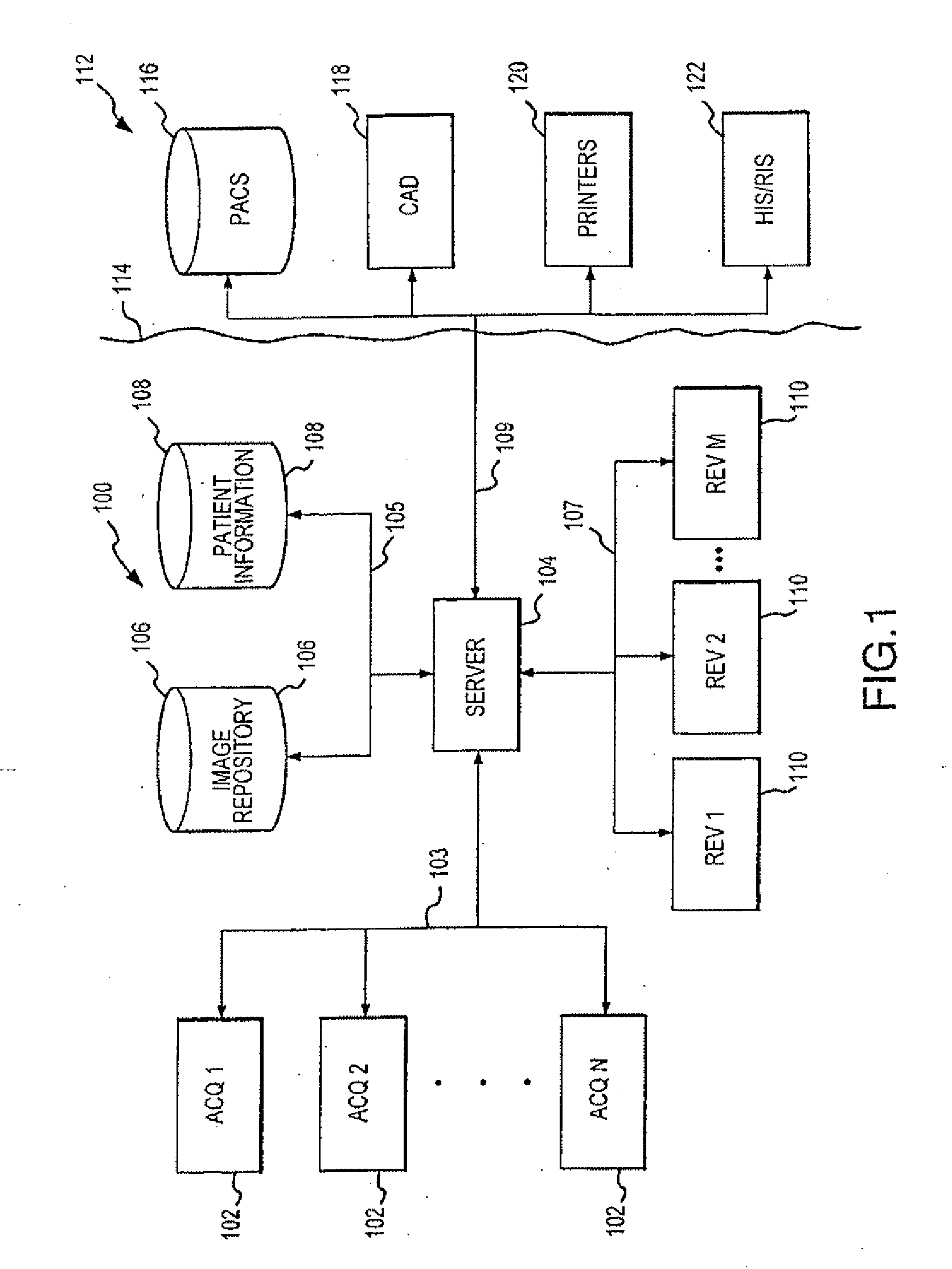
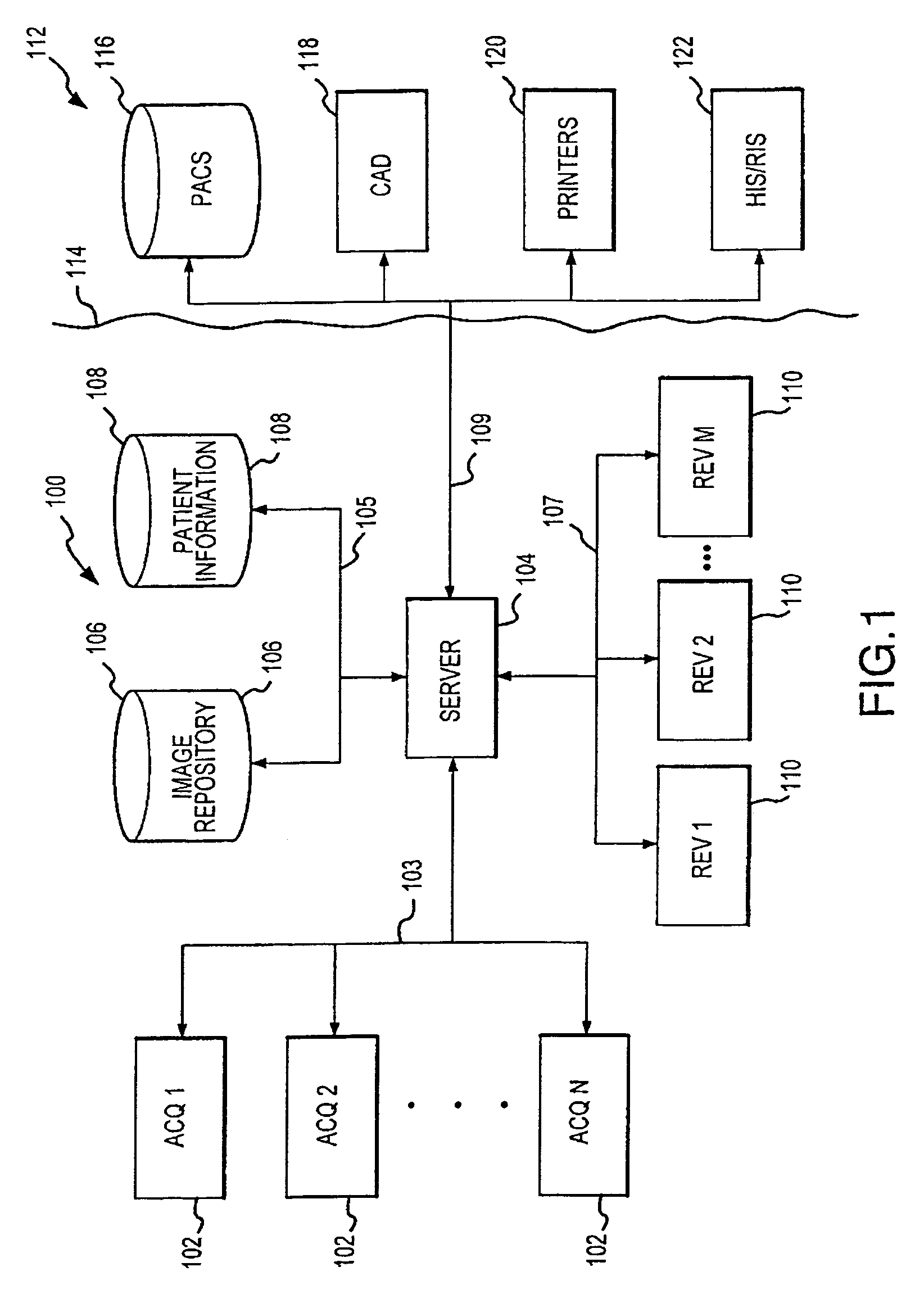
Distributed Architecture for Mammographic Image Acquisition and Processing
InactiveUS20080279439A1Easy to useOrgan movement/changes detectionPatient positioning for diagnosticsImage InspectionDICOM
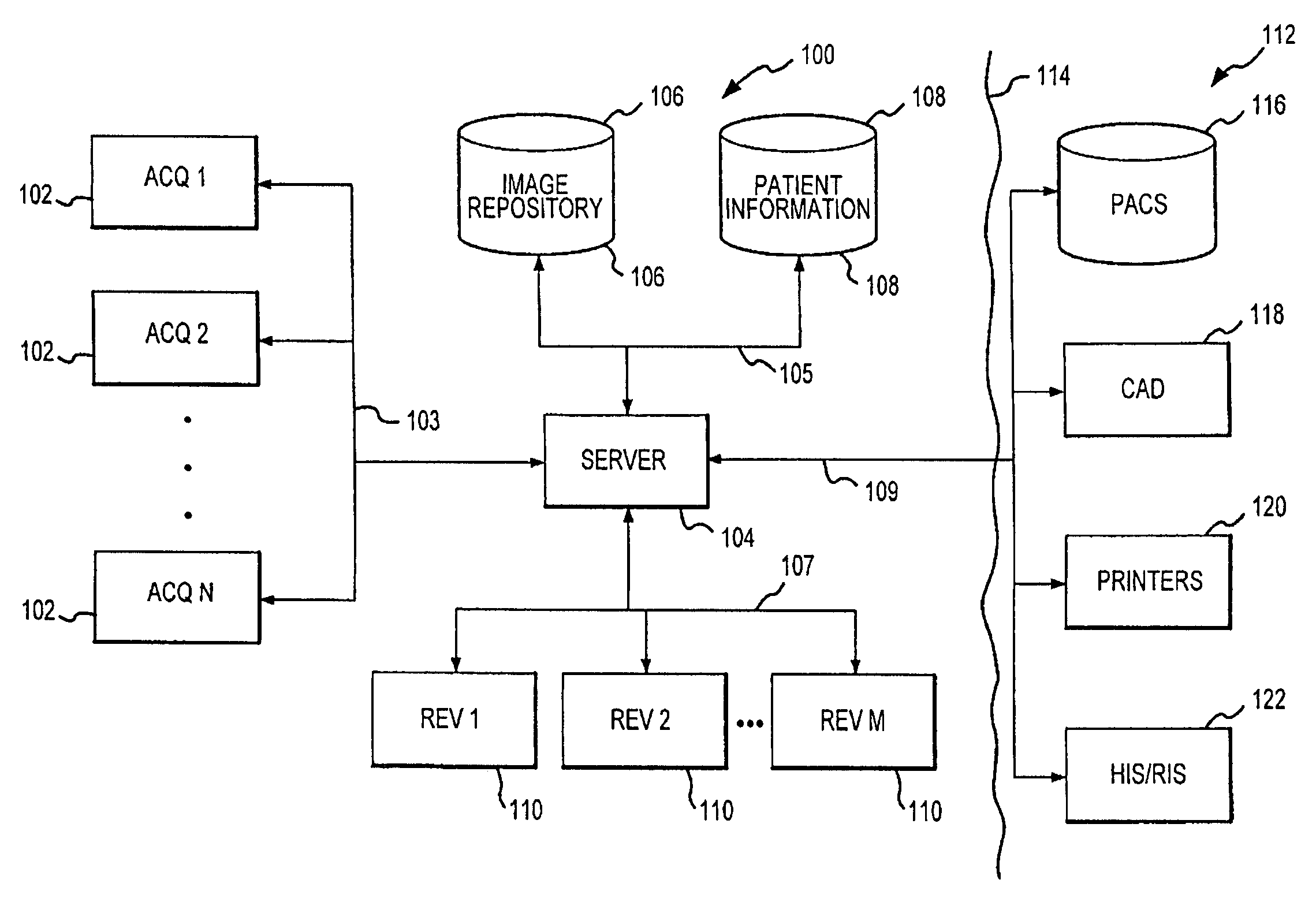
A distributed architecture allows for decoupling of mammographic image acquisition and review, thereby enabling more efficient use of resources and enhanced processing. In one embodiment, the system (100) includes a number of image acquisition stations (102) and a number of image review stations (110) all associated with a central server (104). The server (104) is operative to access an image repository (106), a patient information data base (108) and a number of DICOM tools (112). The invention allows for more efficient and / or more convenient use of the image acquisition equipment and image processing stations. Moreover, the distributed architecture including the central image repository provides certain processing and analysis advantages. The invention also provides certain processing and workflow enhancements that allow for a more full realization of potential digital mammography advantages.
Owner:HOLOGIC INC
Apparatus and method for detecting defect existing in pattern on object
InactiveUS20060133660A1Avoid detectionAccurate detectionImage enhancementImage analysisPattern recognitionImage Inspection
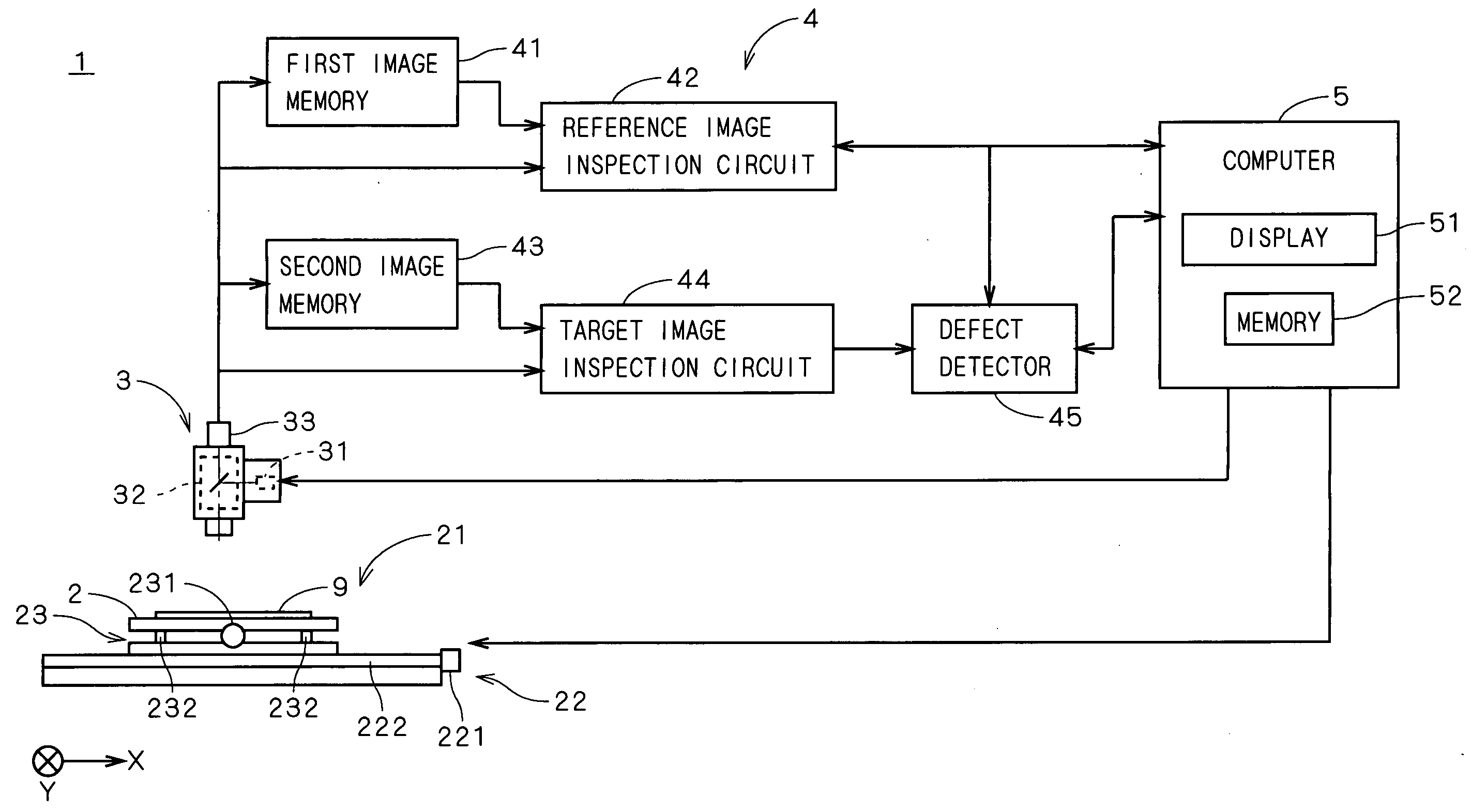
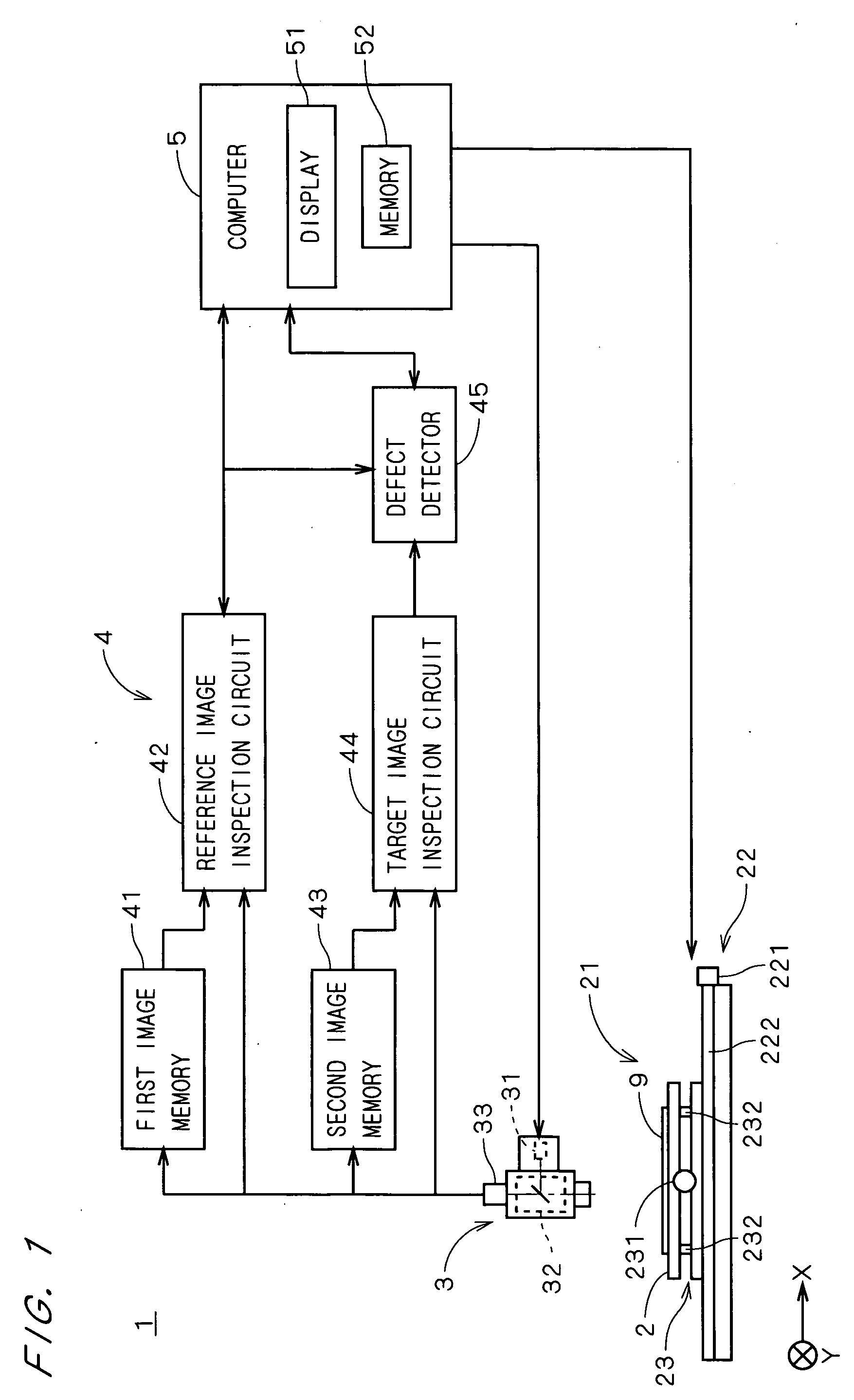
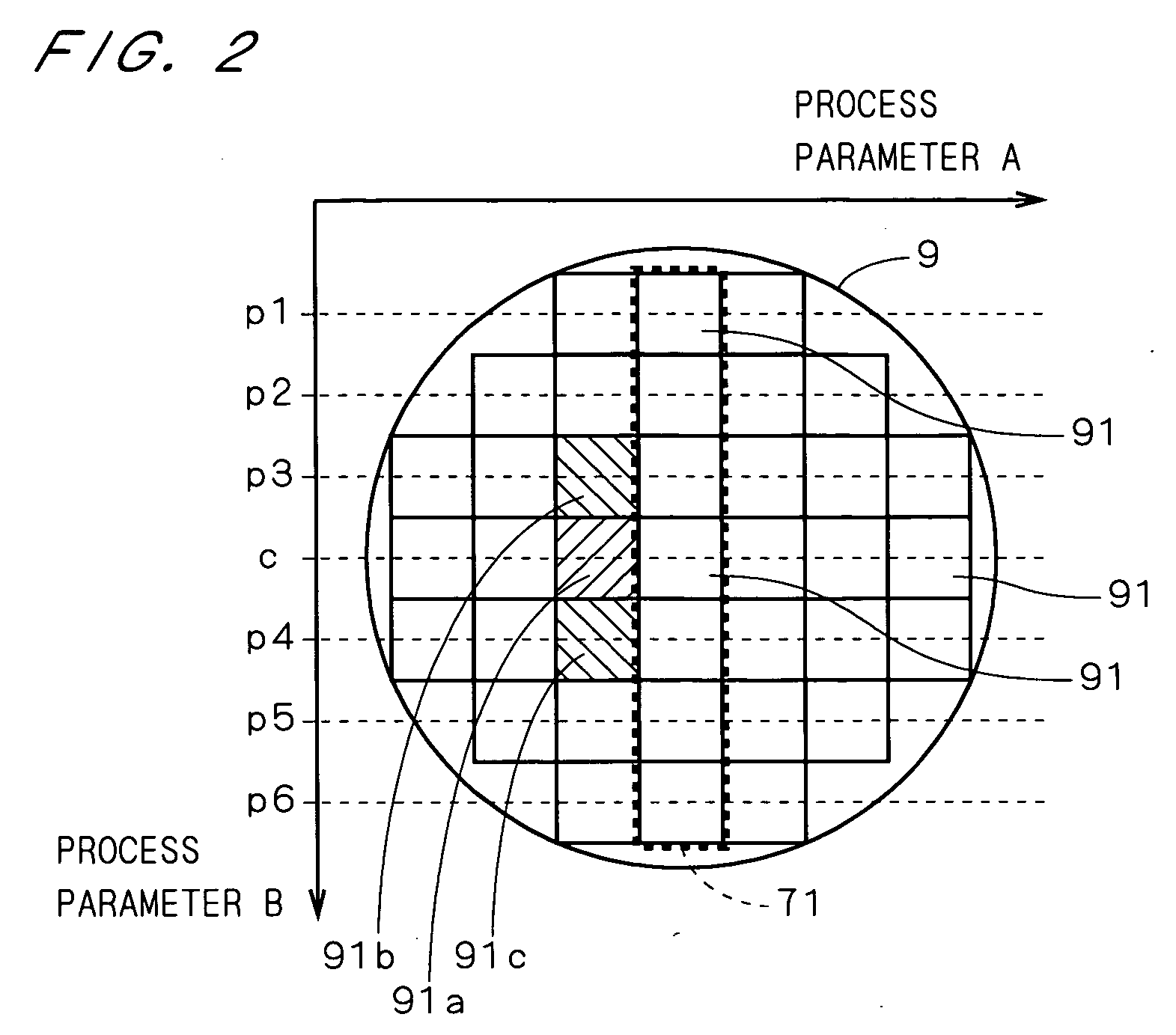
In a defect detection apparatus 1, in a reference image inspection circuit 42 compared are a reference image representing a pattern in a die which is determined as a reference on a substrate 9 and a plurality of supervisory images which represent patterns in selected block areas, respectively, to detect defects included in the reference image. Subsequently, in the target image inspection circuit 44, a target image representing a pattern in another die and the reference image are compared to detect a plurality of defect candidates included in the target image. Then, a defect detector 45 excludes defect candidates overlapping with the defects included in the reference image from the plurality of defect candidates on the basis of at least positional information of the defects included in the reference image. This makes it possible to detect defects existing in the pattern in another die accurately while eliminating effects of the defects existing in the pattern in the die which is determined as the reference.
Owner:DAINIPPON SCREEN MTG CO LTD
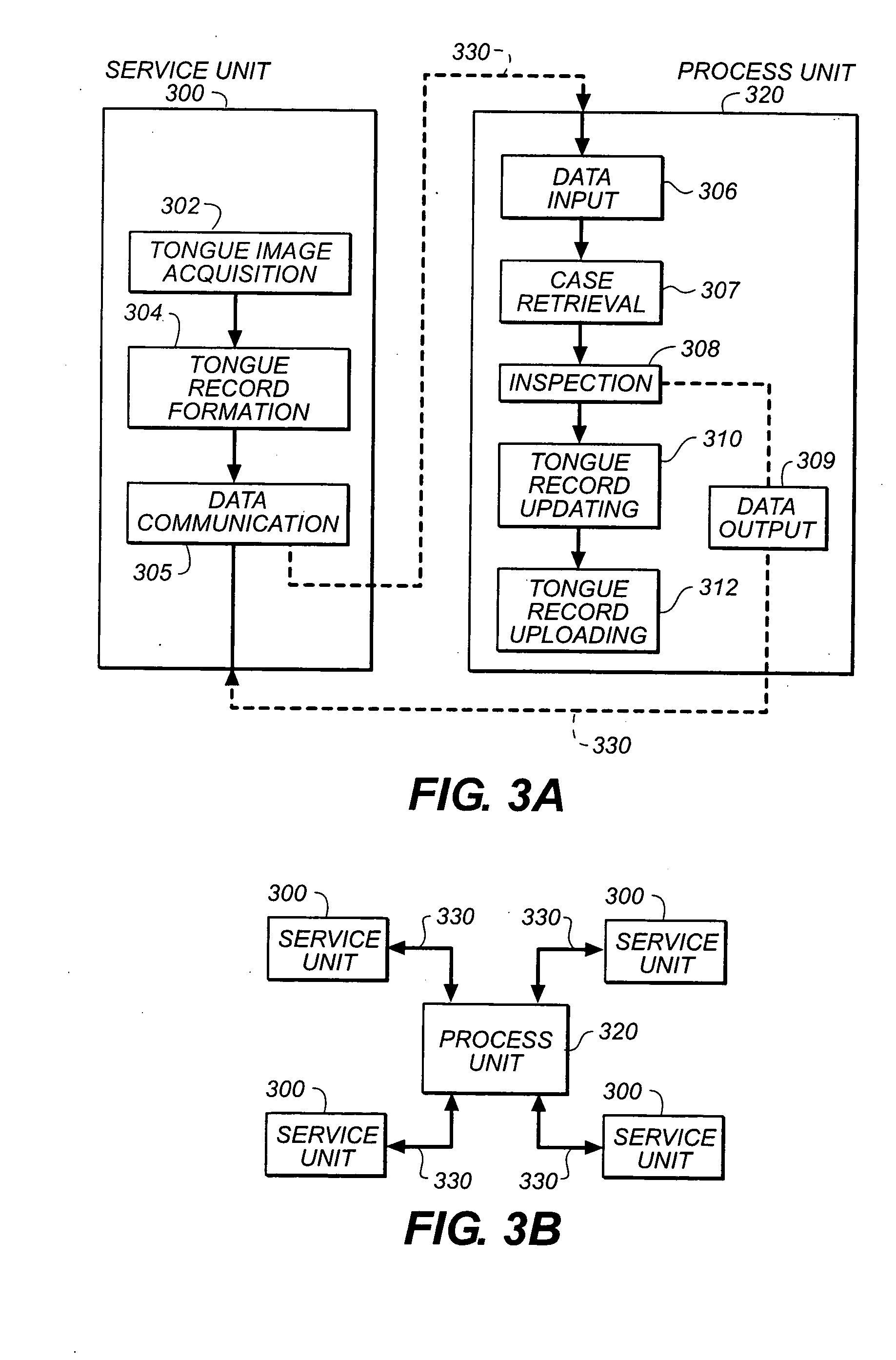
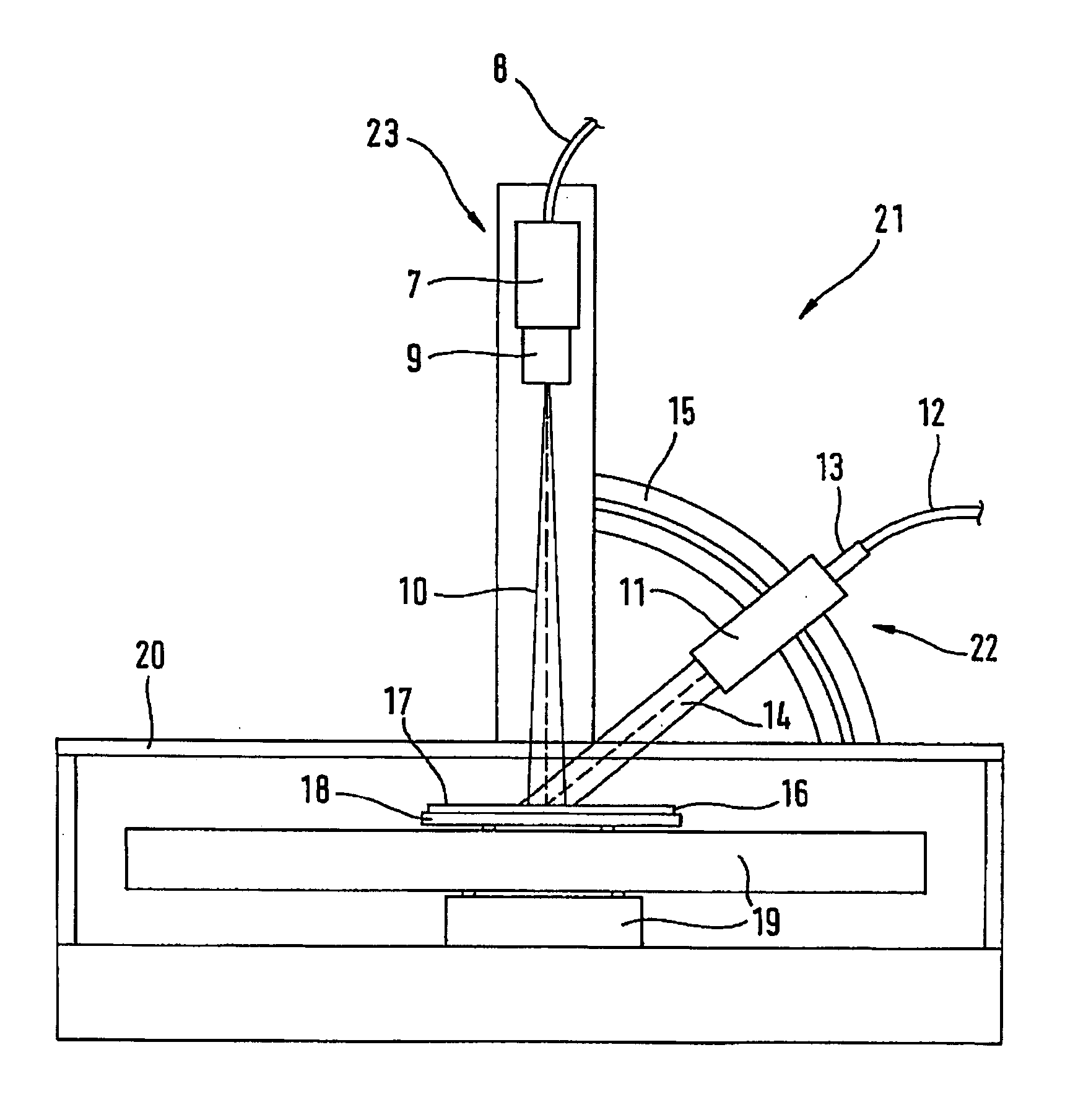
Method for diagnosing disease from tongue image
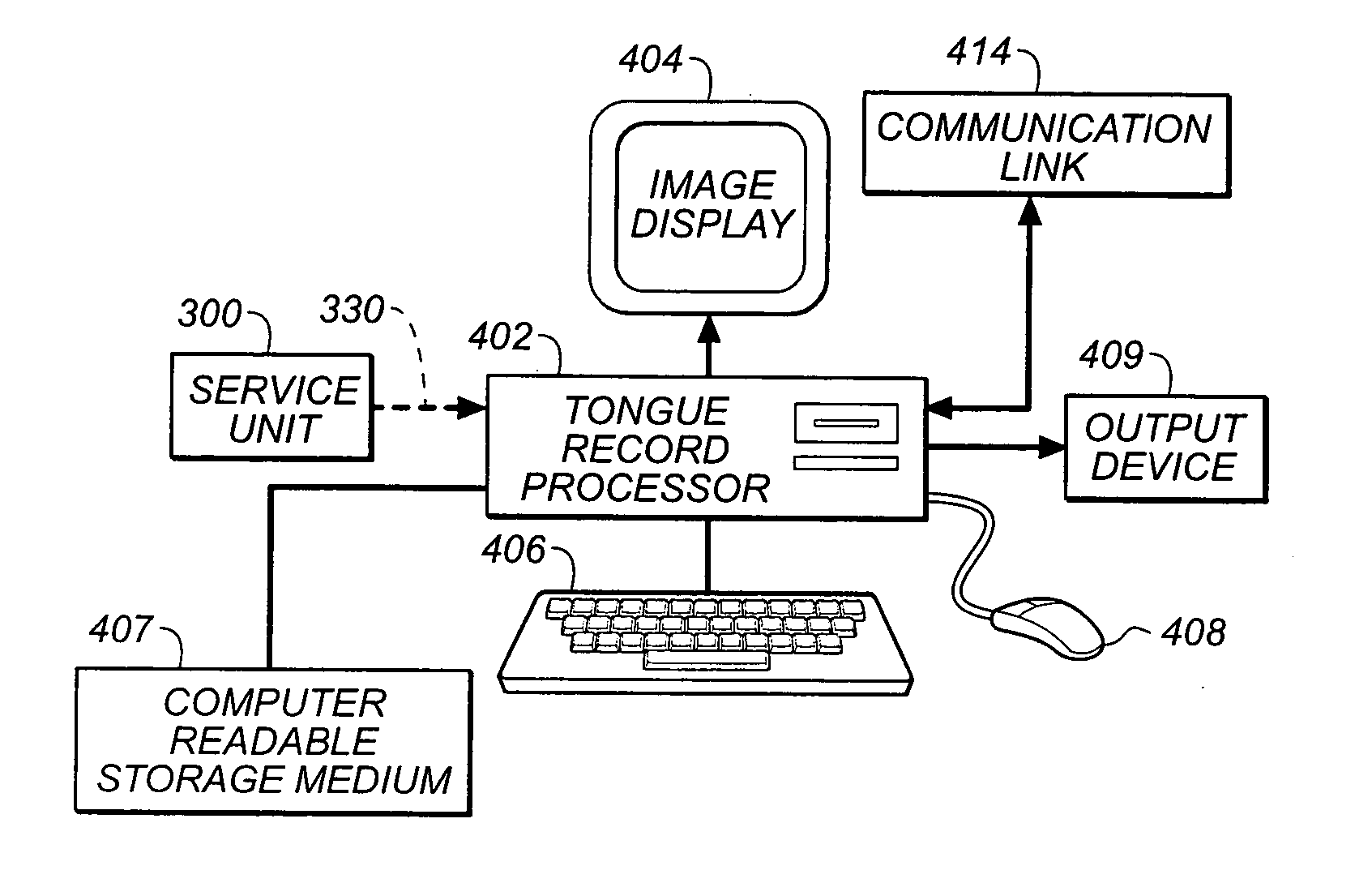
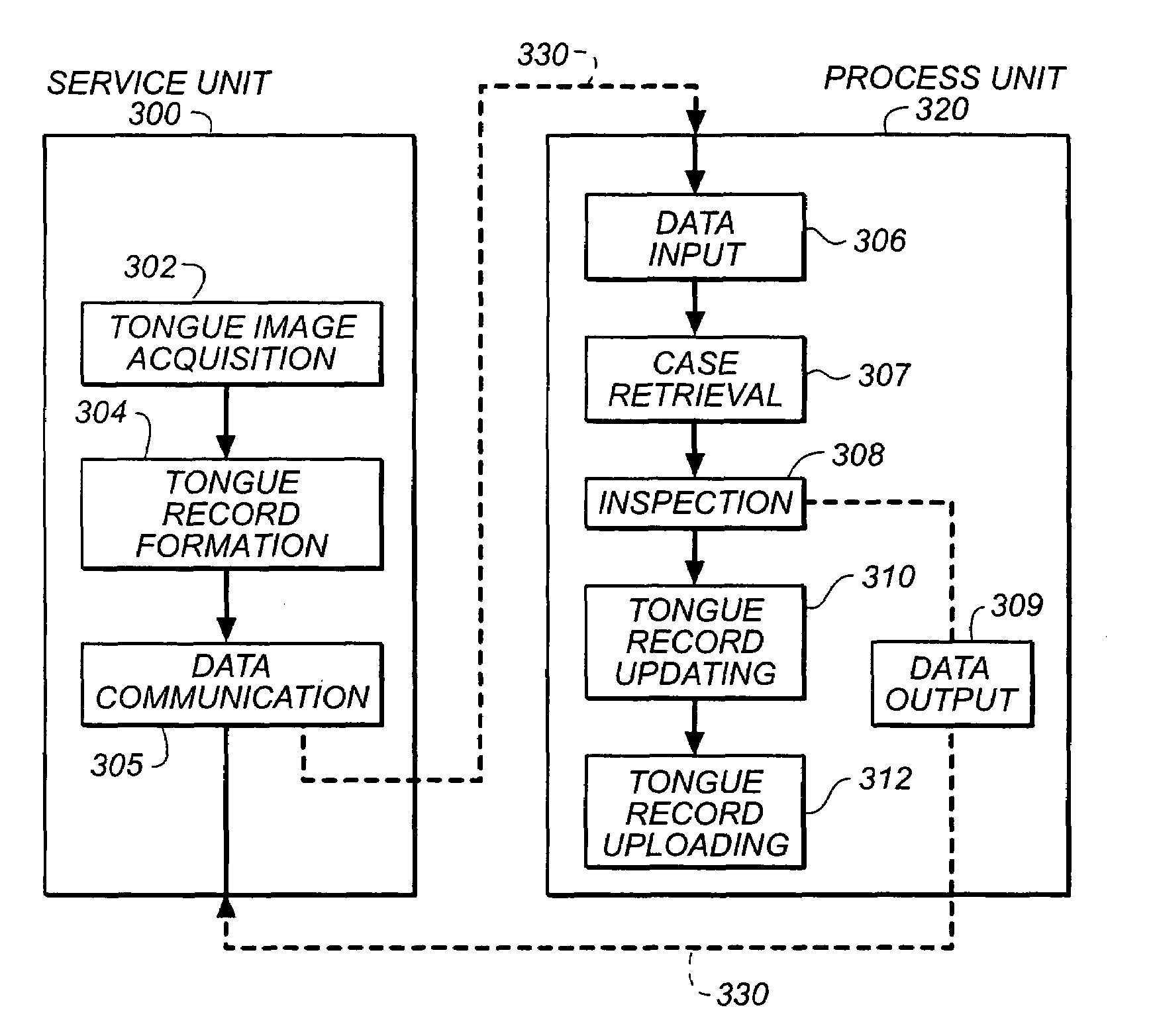
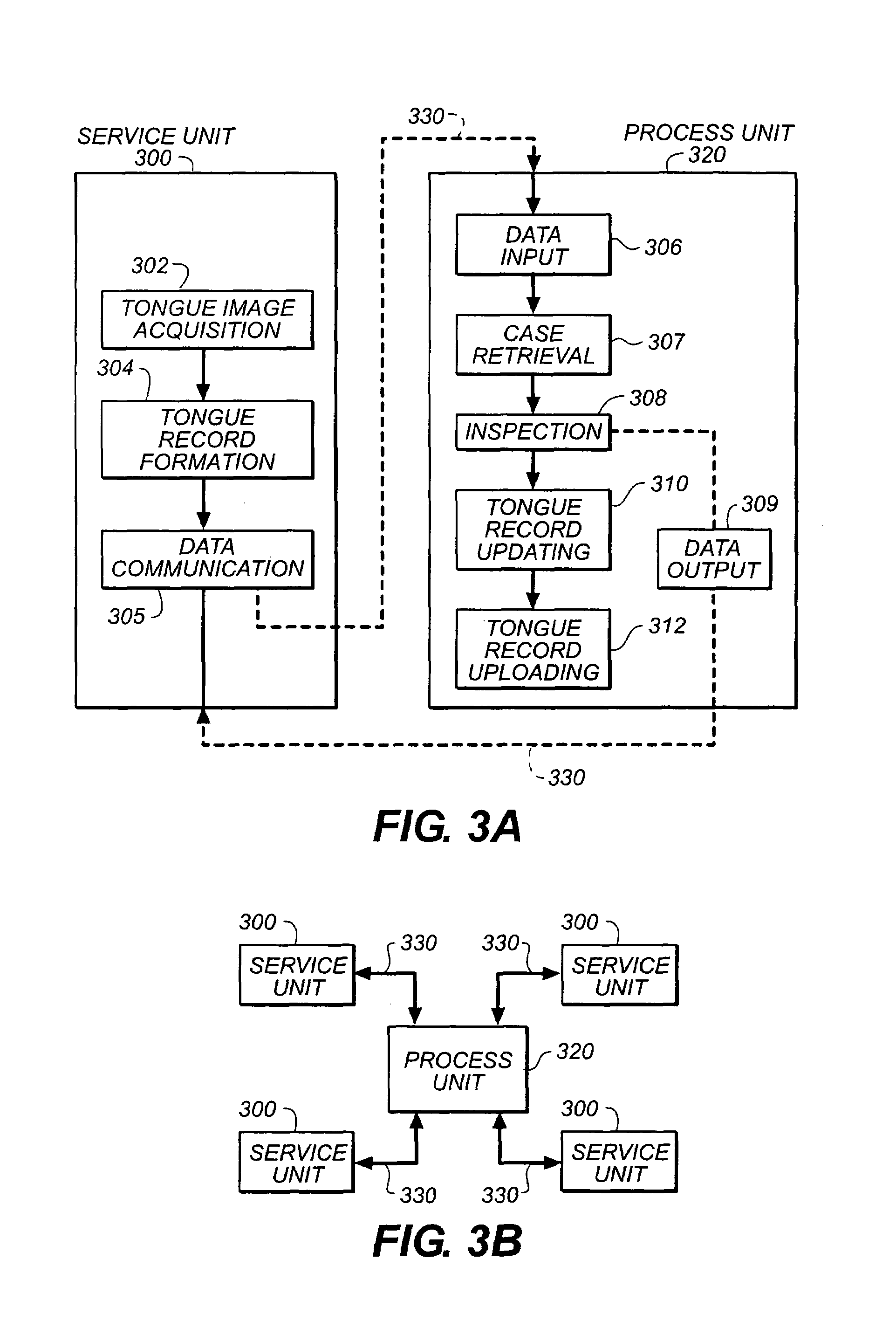
A digital image processing method for a centralized multi-mode medical tongue image inspection system, comprising the steps of: forming at least one service unit (300) for performing tongue record (220) construction; forming a processing unit (320) for tongue record inspection (308); and providing communication links (330) between the service units and the processing unit.
Owner:CARESTREAM HEALTH INC
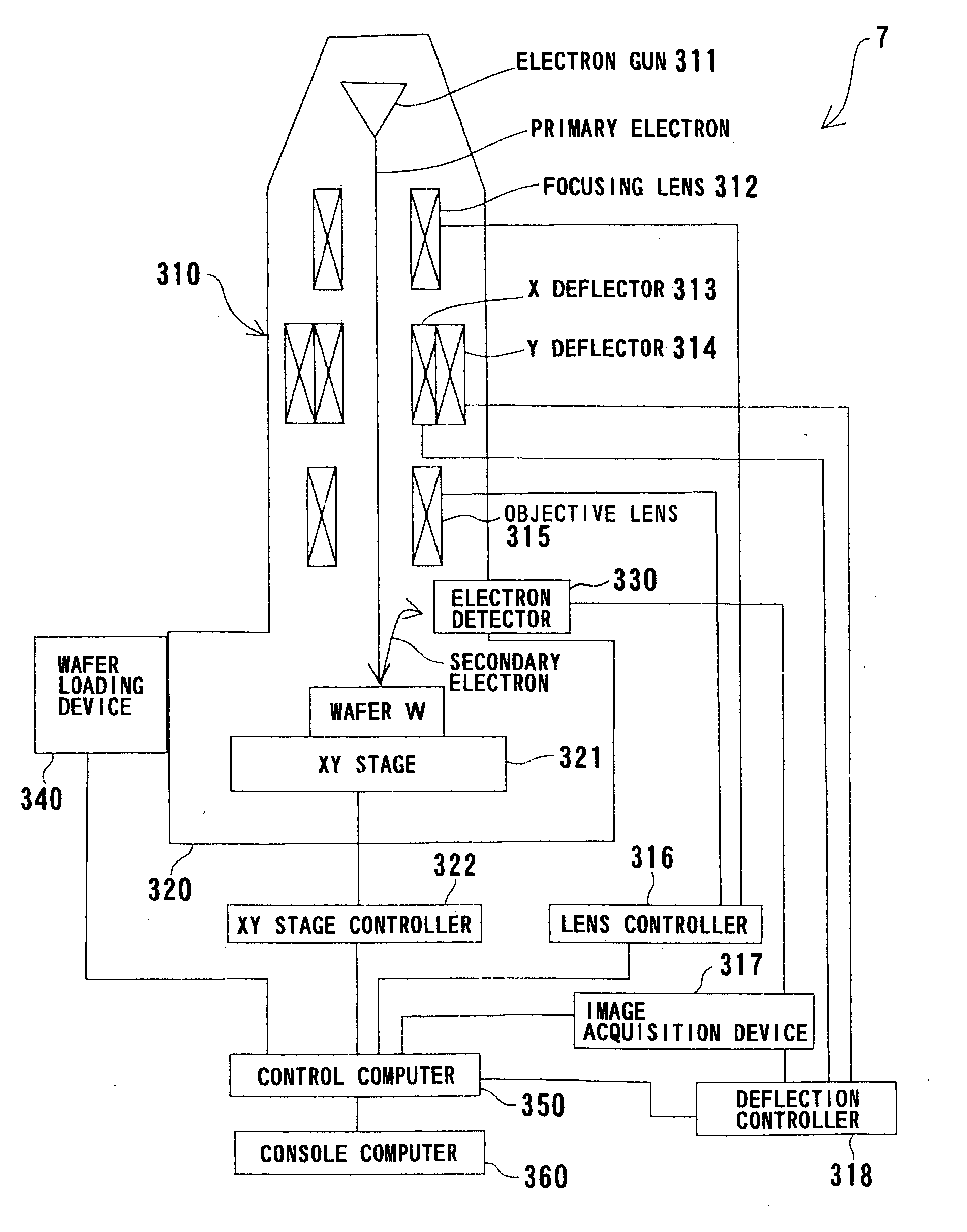
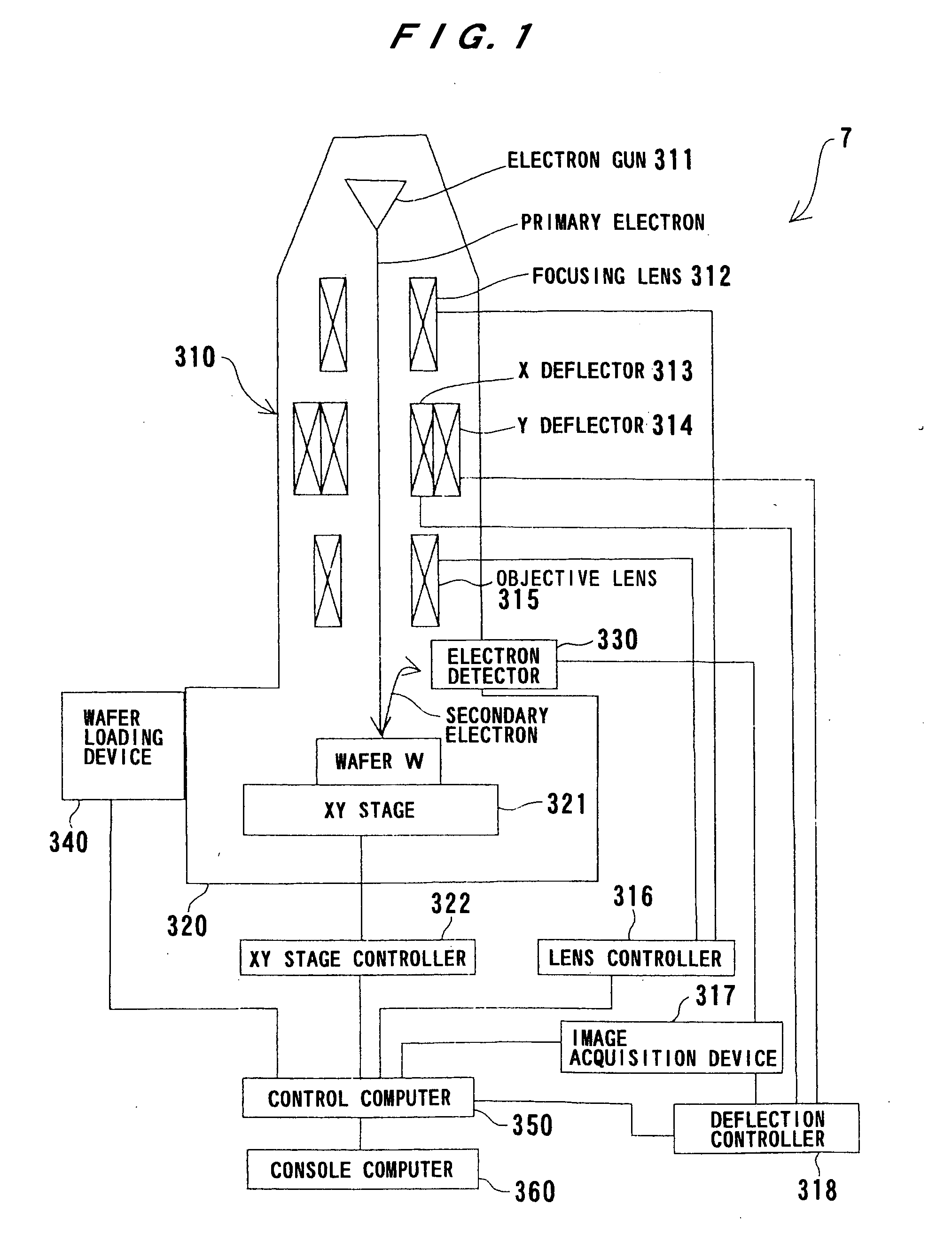
Method and system for inspecting a wafer
InactiveUS20050280808A1Solve lack of contrastOptically investigating flaws/contaminationImage InspectionPhysics
Owner:VISTEC SEMICON SYST
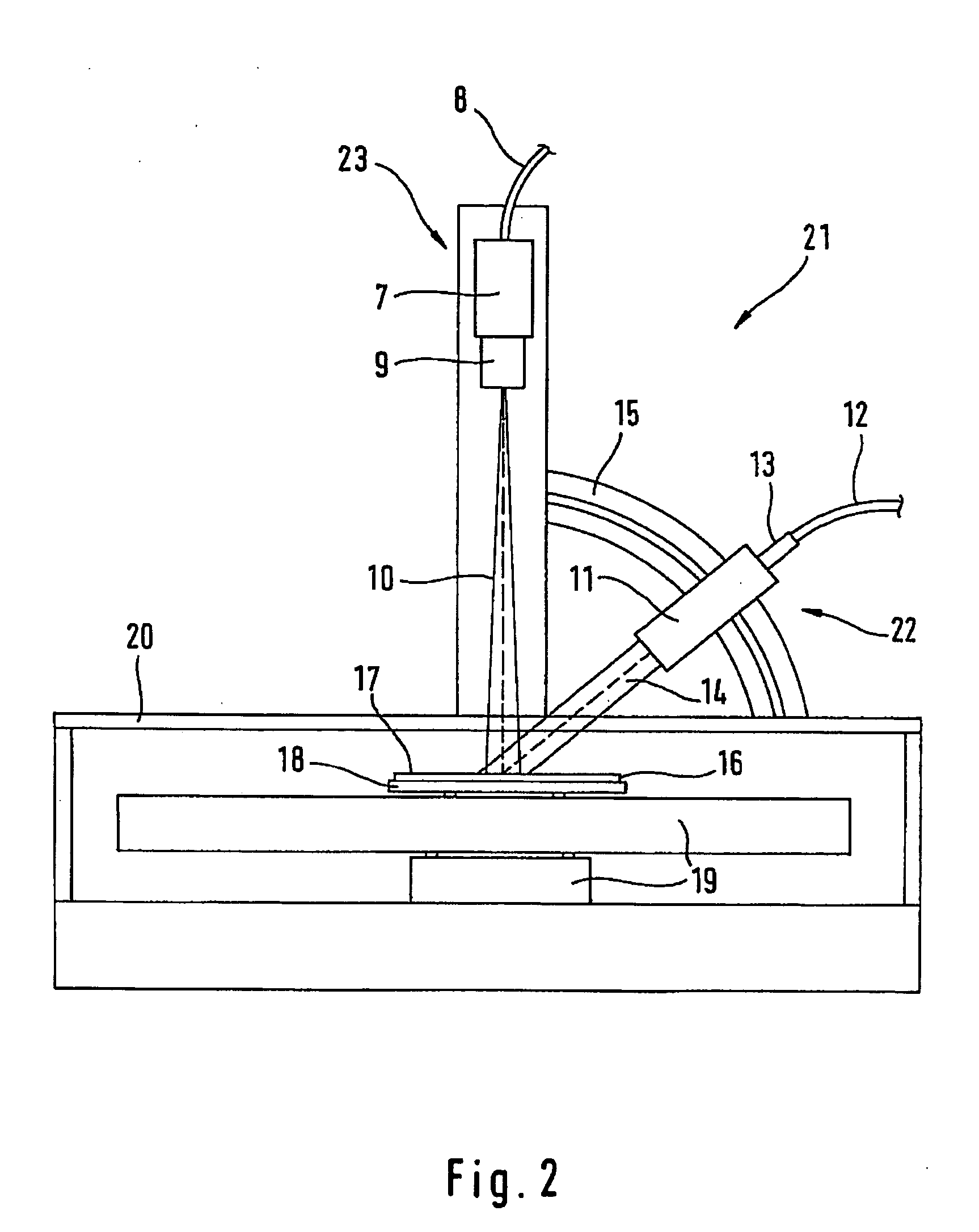
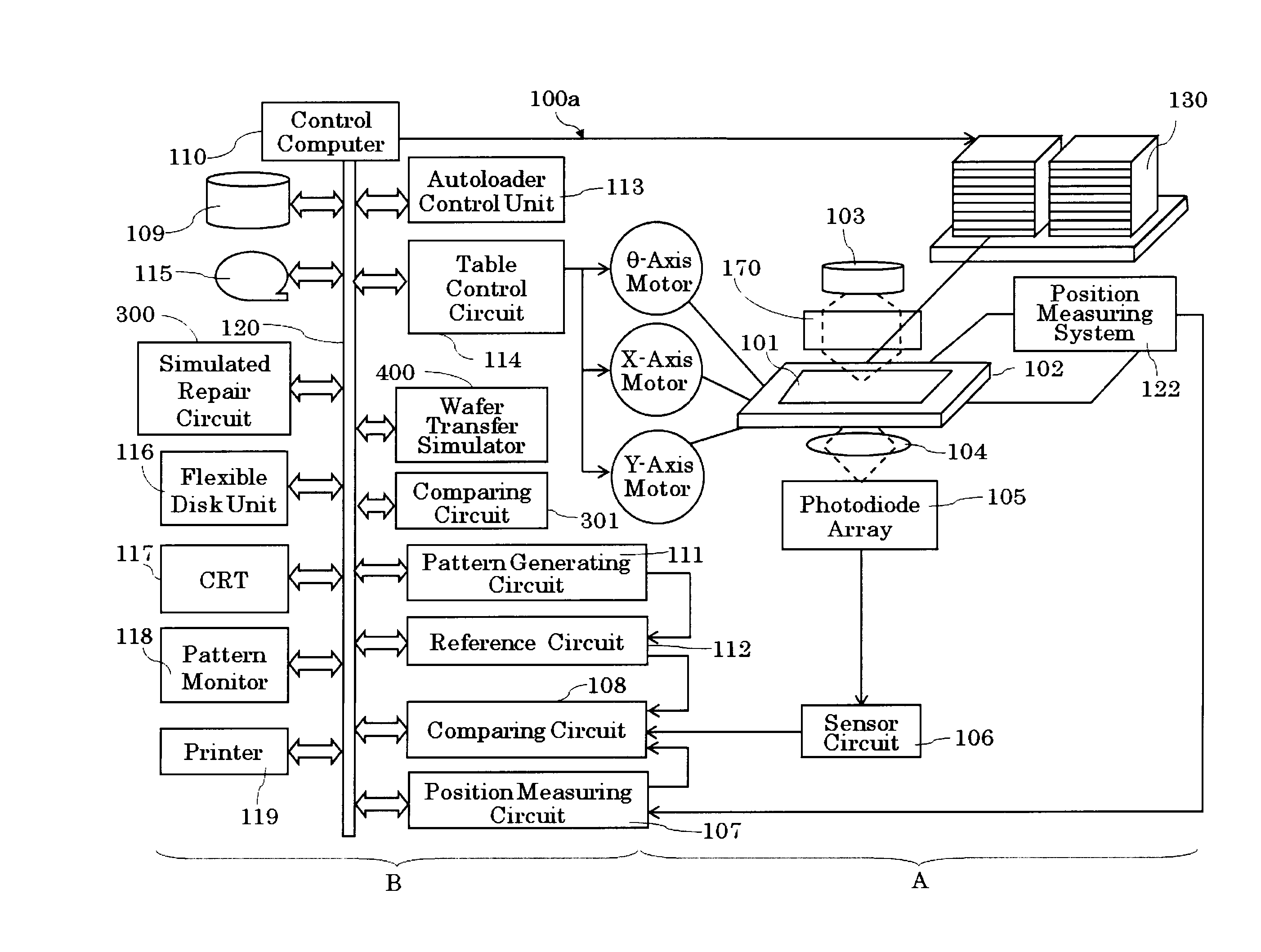
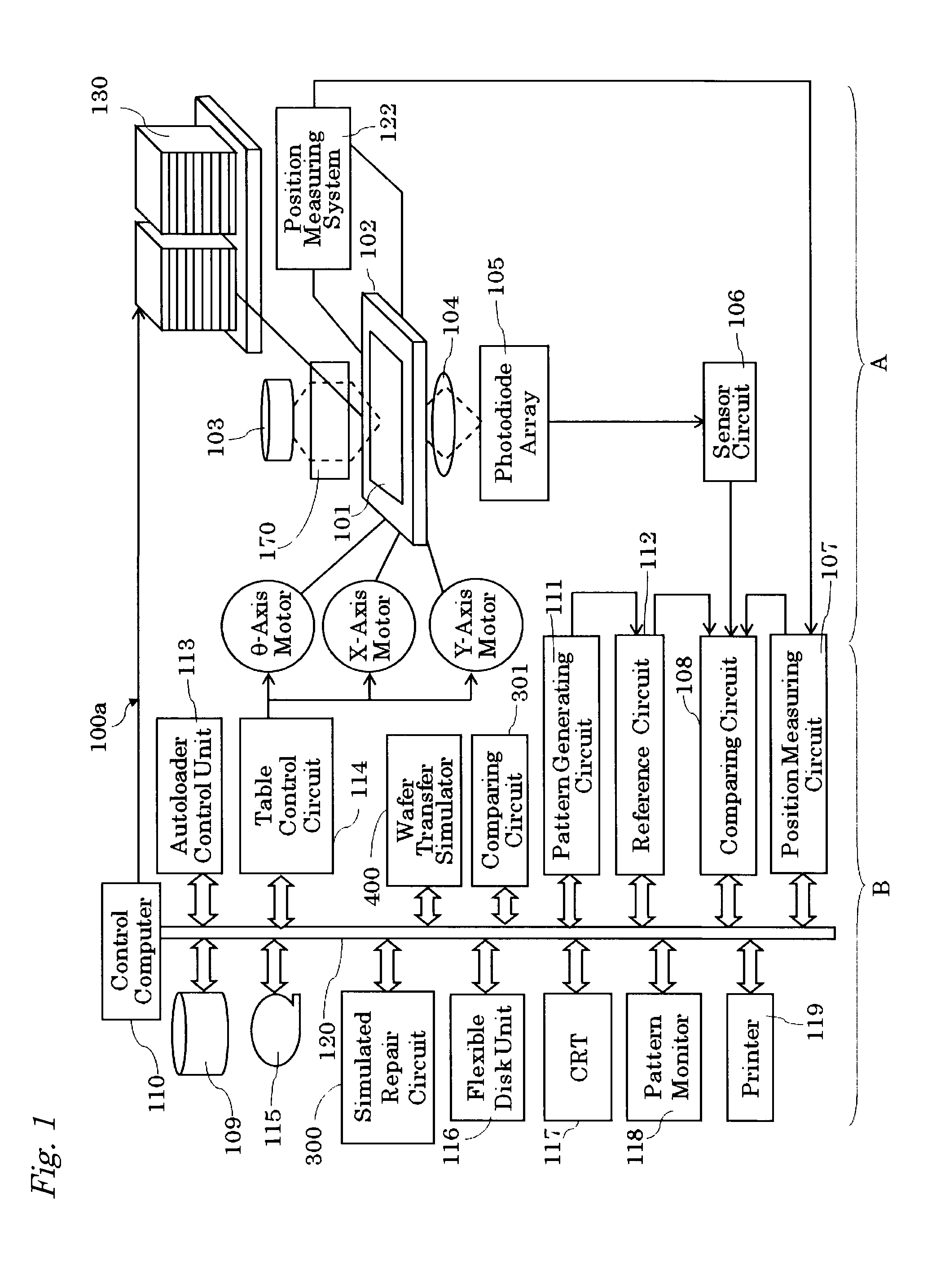
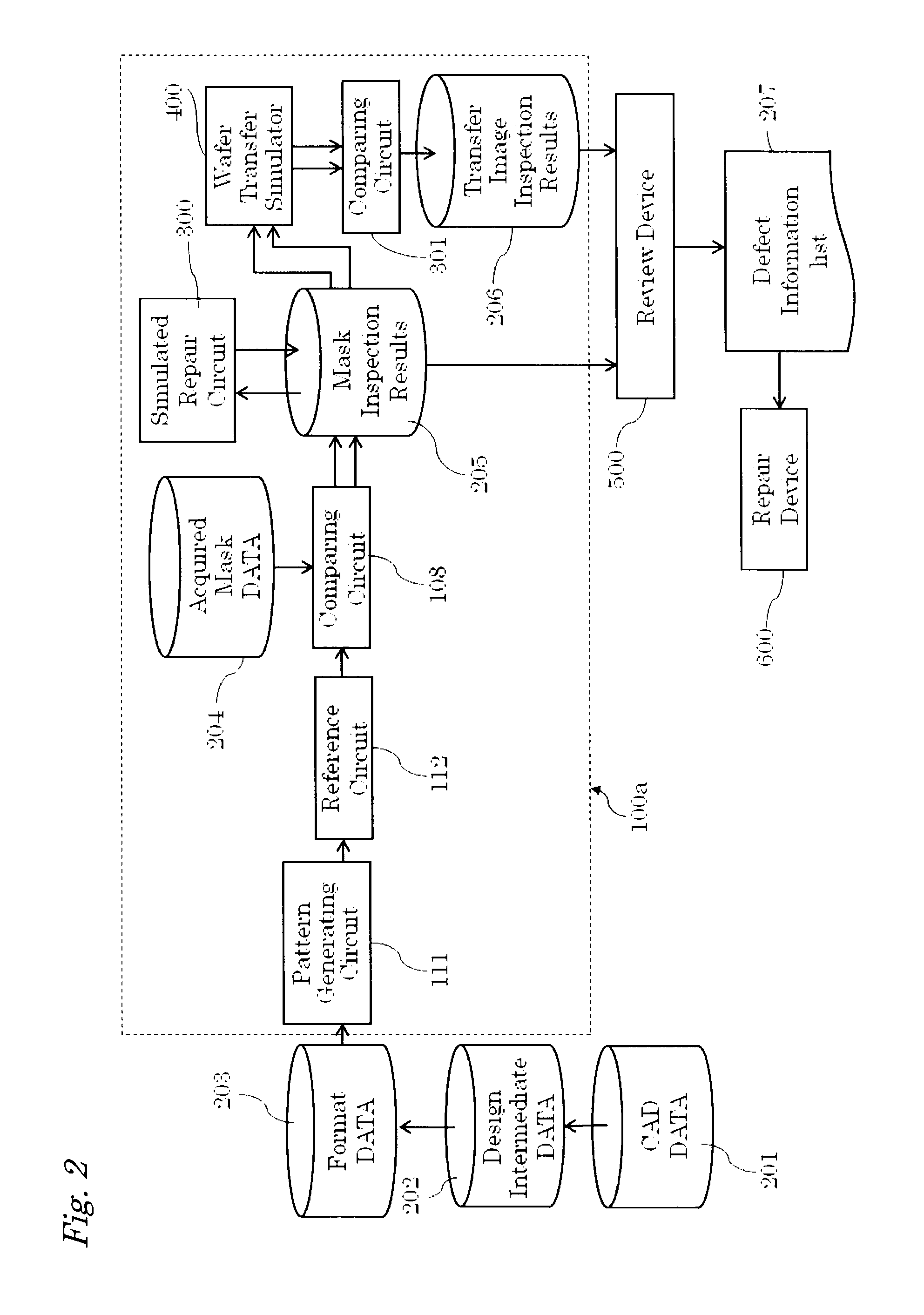
Defect estimation device and method and inspection system and method
Acquired mask data of a defect portion is sent to a simulated repair circuit 300 to be simulated. The simulation of the acquired mask data 204 is returned to the mask inspection results 205 and thereafter sent to a wafer transfer simulator 400 along with a reference image at the corresponding portion. A wafer transfer image estimated by the wafer transfer simulator 400 is sent to a comparing circuit 301. When it is determined that there is a defect in the comparing circuit 301, the coordinates and the wafer transfer image which is a basis for the defect determination are stored as transfer image inspection results 206. The mask inspection results 205 and the transfer image inspection result 206 are then sent to the review device 500.
Owner:NUFLARE TECH INC
Systems and methods for viewing medical images
ActiveUS20100201714A1Character and pattern recognitionCathode-ray tube indicatorsImage InspectionComputer graphics (images)
For certain medical images, it is important and / or required that a user view all of a medical image at full resolution so that minute, but important, indicia in the medical image are not missed. A computing systems monitor the portions of the medical image that are displayed on the display device, notates those portions that have been displayed at full resolution (or other user-defined display parameters), and provides the user with information indicating portions that have not been viewed at full resolution and / or provides information indicating for which images of a multiple image examination full pixel display has been accomplished. The process reduces the possibility of missing an abnormality in a medical image due to the viewer not viewing a portion of the image at full resolution or using other user-defined display parameters.
Owner:MERATIVE US LP
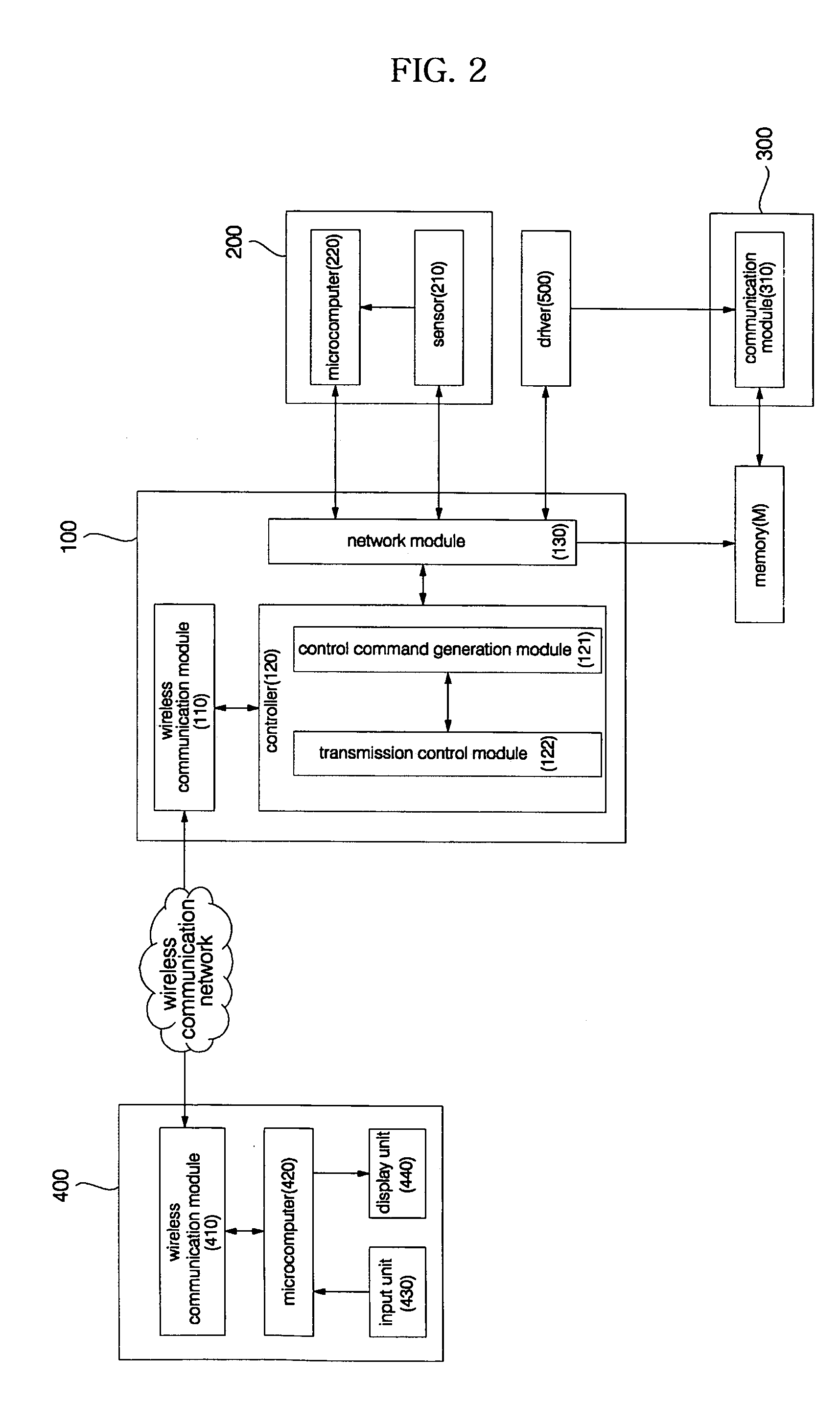
Wireless terminal-interoperable home network system and method controlling the same
ActiveUS7301456B2Improve control efficiencyImprove convenienceProtective foundationSubstation remote connection/disconnectionImage InspectionTelecommunications
Disclosed herein are a wireless terminal-interoperable home network system and a method for controlling the same. A home server is linked with a security device and camera installed in a building to, when the security device senses entrance / exit of an outsider into / from the building, acquire an internal image of the building from the camera and send the acquired image to a wireless terminal of a user to enable the user to monitor the internal situation of the building in real time. The user can access the home server over a wireless communication network from a remote place outside of the building without separate access to the Internet to receive the internal image of the building and check the internal situation of the building on the basis of the received internal image, resulting in an increase in convenience of use.
Owner:LG ELECTRONICS INC
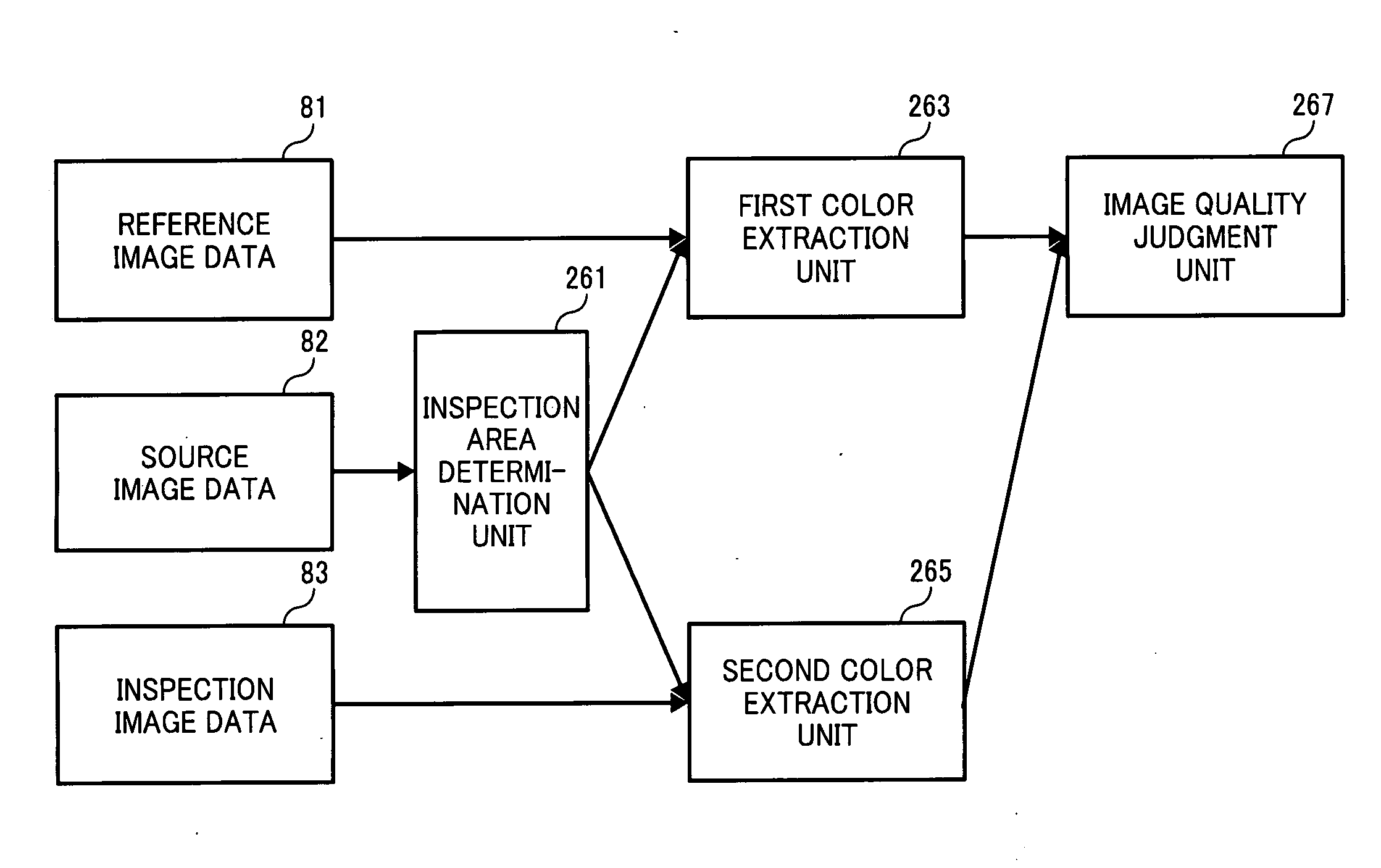
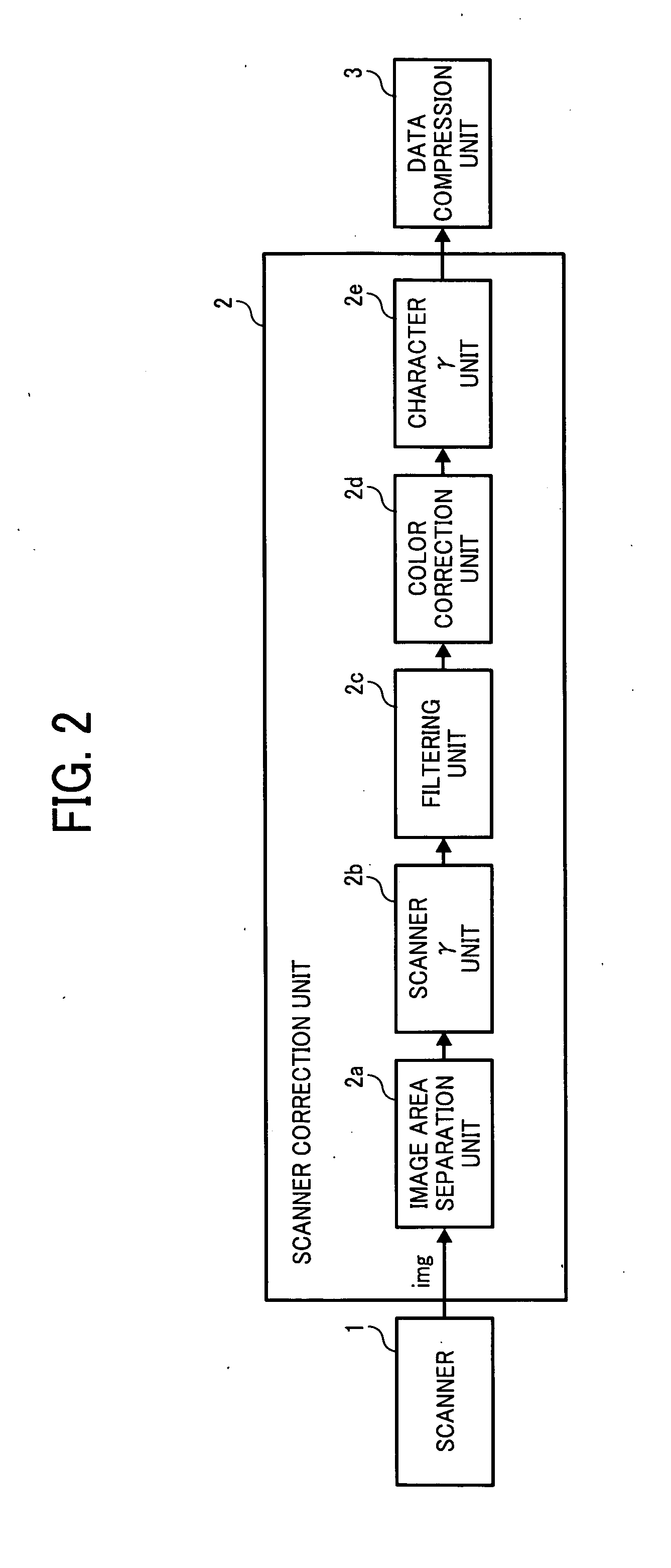
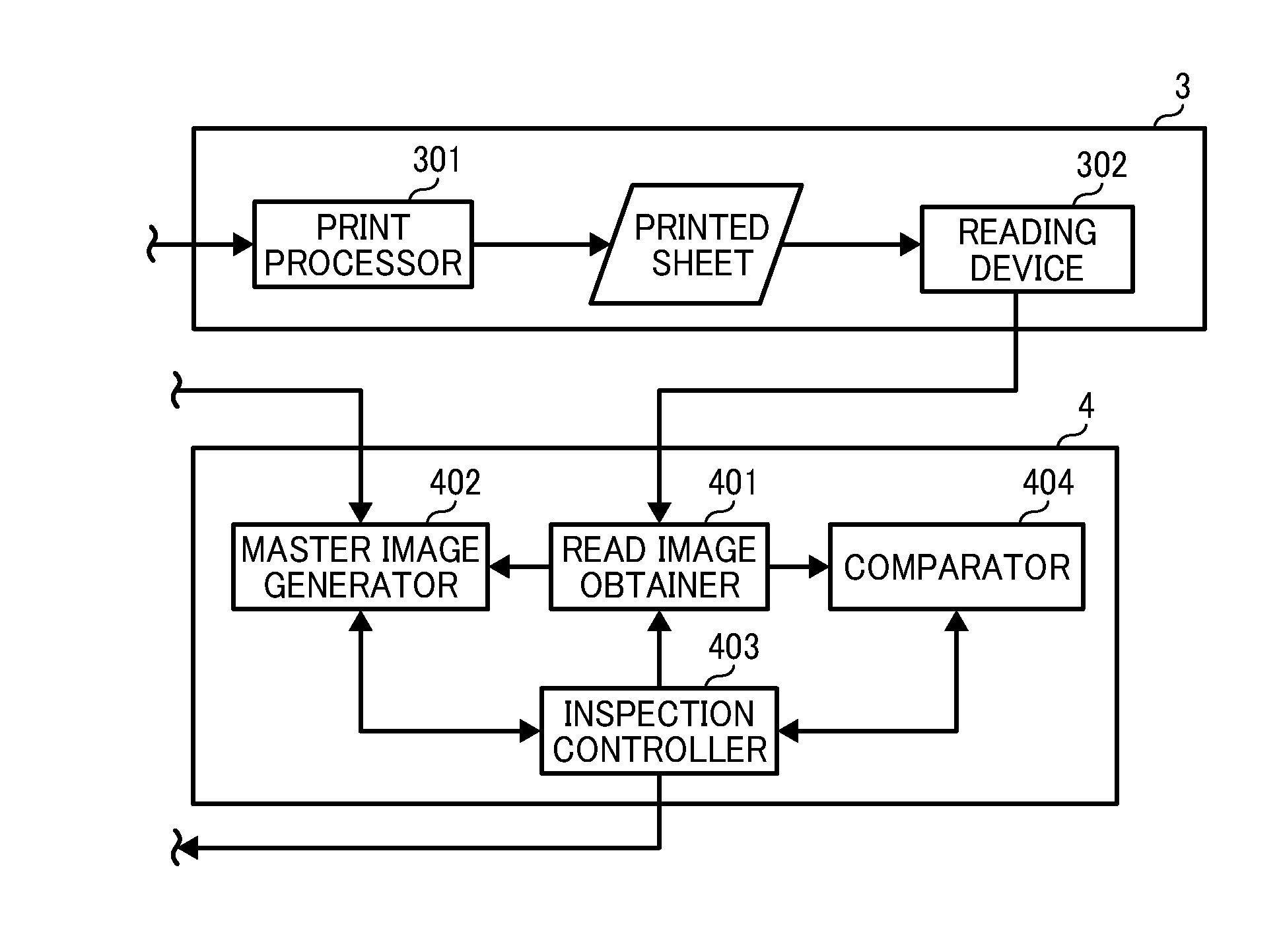
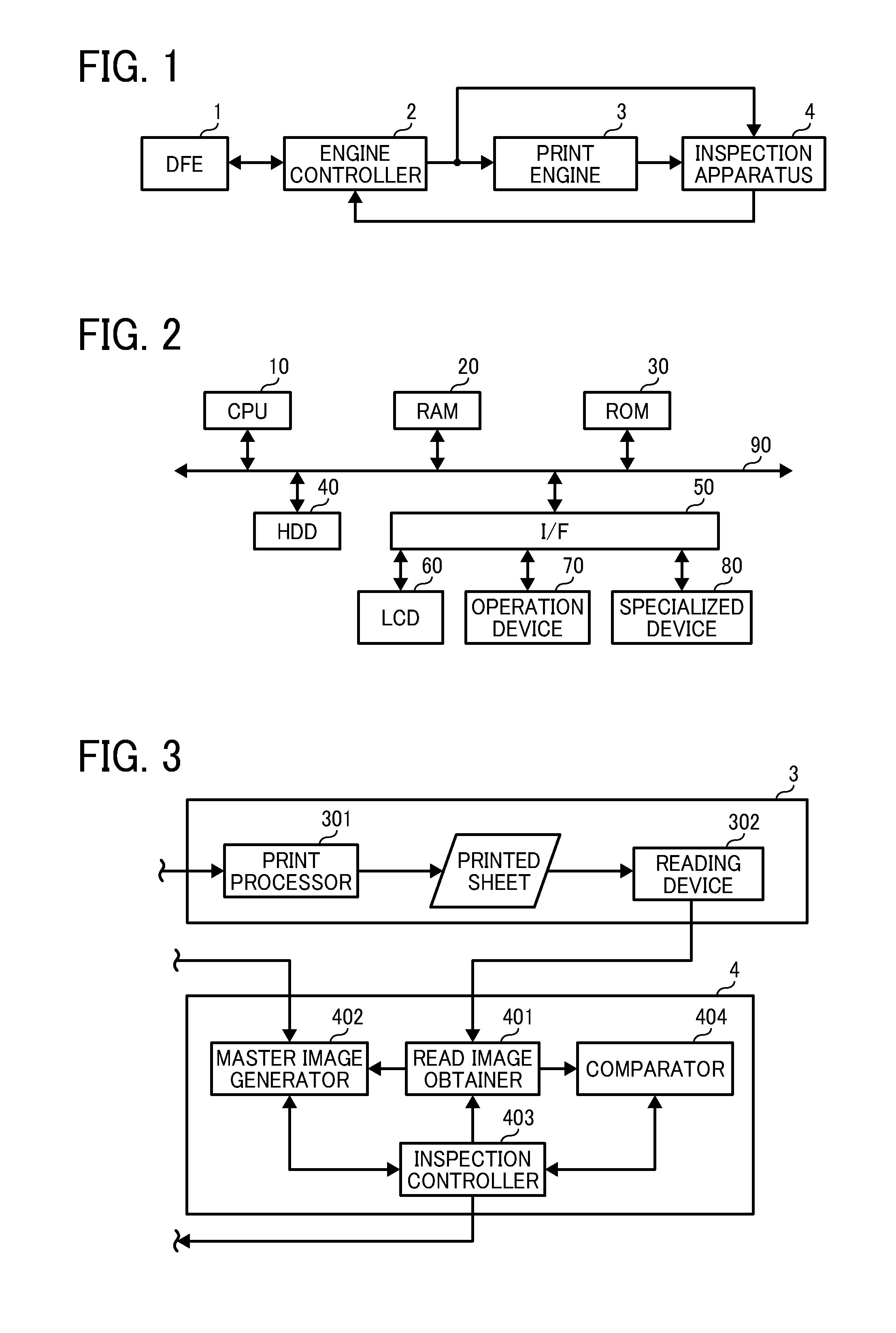
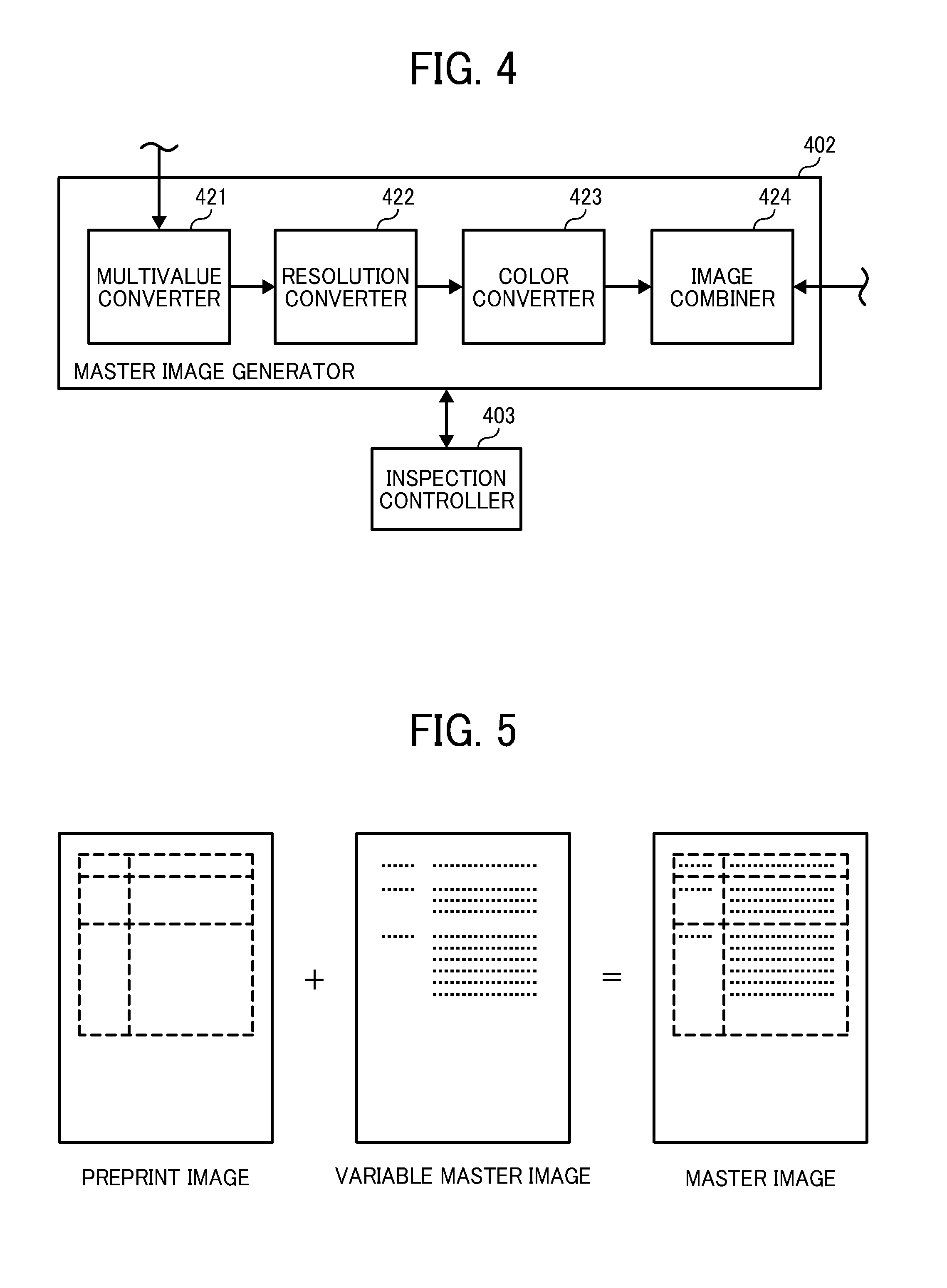
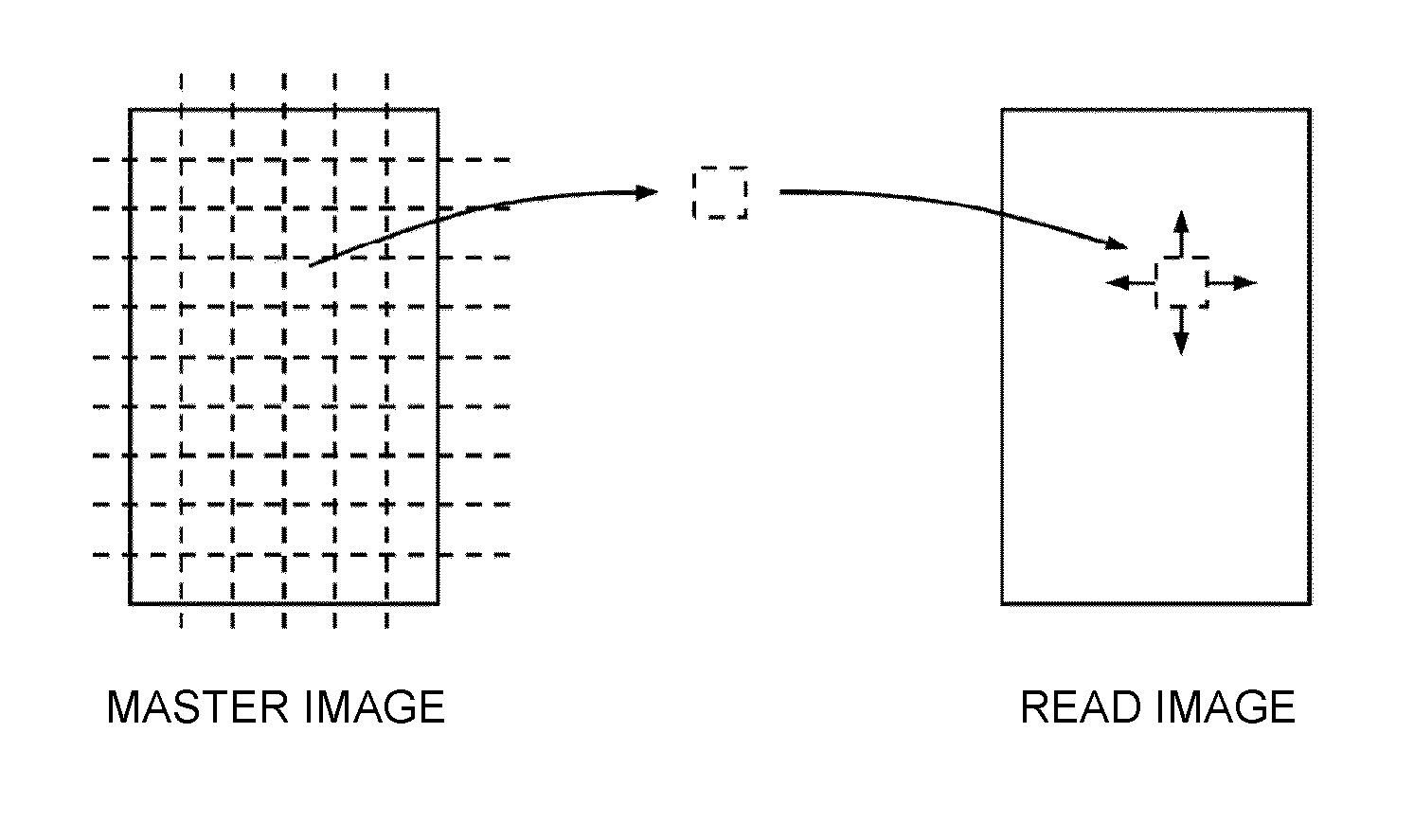
Image inspection system, image inspection method, and computer-readable medium storing an image inspection program
An image inspection system inspects quality of image prepared from source image data by an image forming apparatus. The image inspection system includes a scanner, a storage unit, an inspection color designating unit, an inspection area determination unit, a reference color extraction unit, an inspection color extraction unit, and an image quality judgment unit. The scanner scans reference and inspection document to prepare reference and inspection image data. The inspection color designating unit designates an inspection color. The inspection area determination unit extracts an inspection area having the inspection color from the source image data. The reference color extraction unit extracts an image having first-extracted-color from the reference image data. The inspection color extraction unit extracts an image having a second-extracted-color from the inspection image data. The image quality judgment unit compares the first and second-extracted-colors to determine image quality of the inspection document image.
Owner:RICOH KK
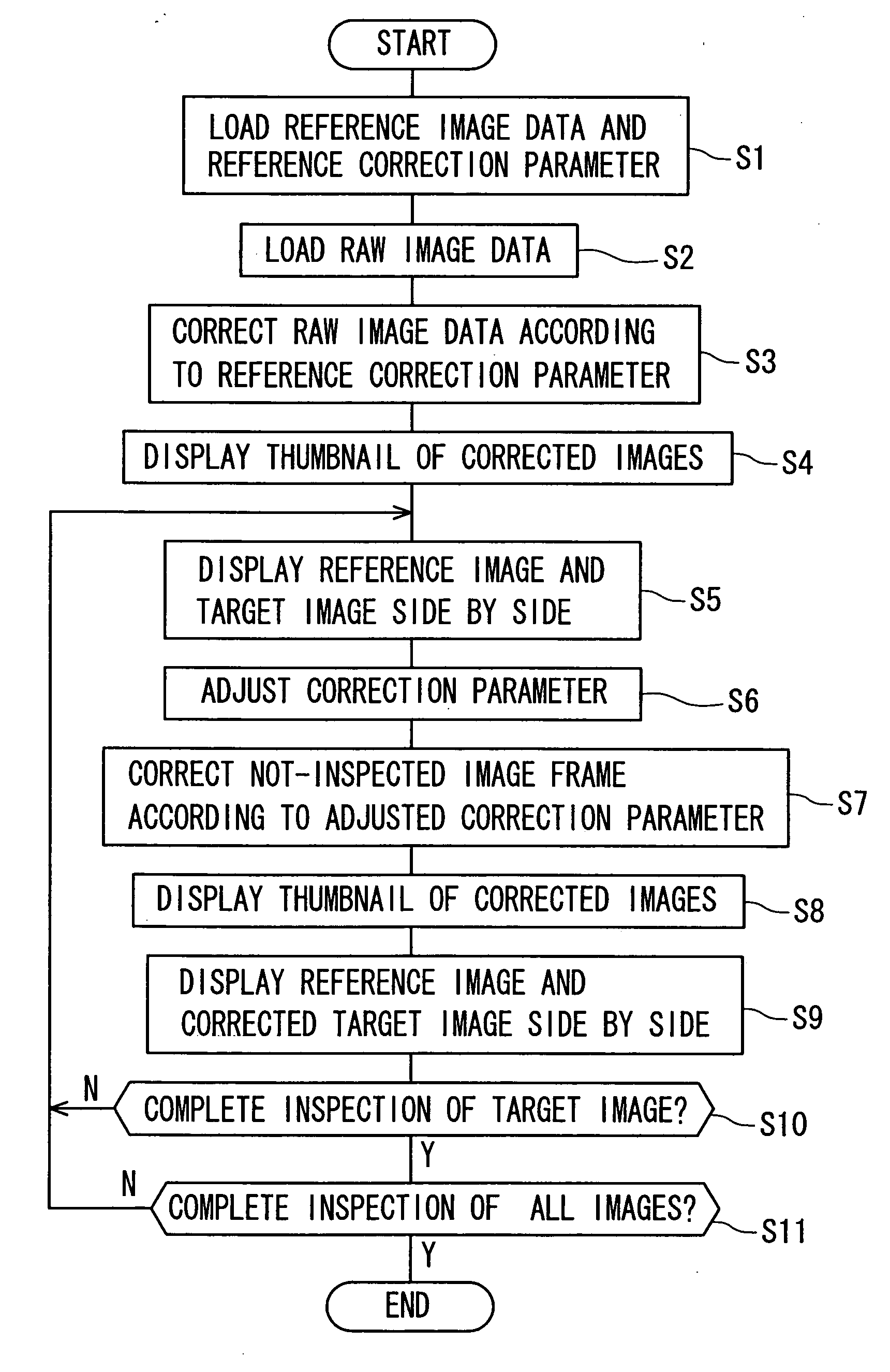
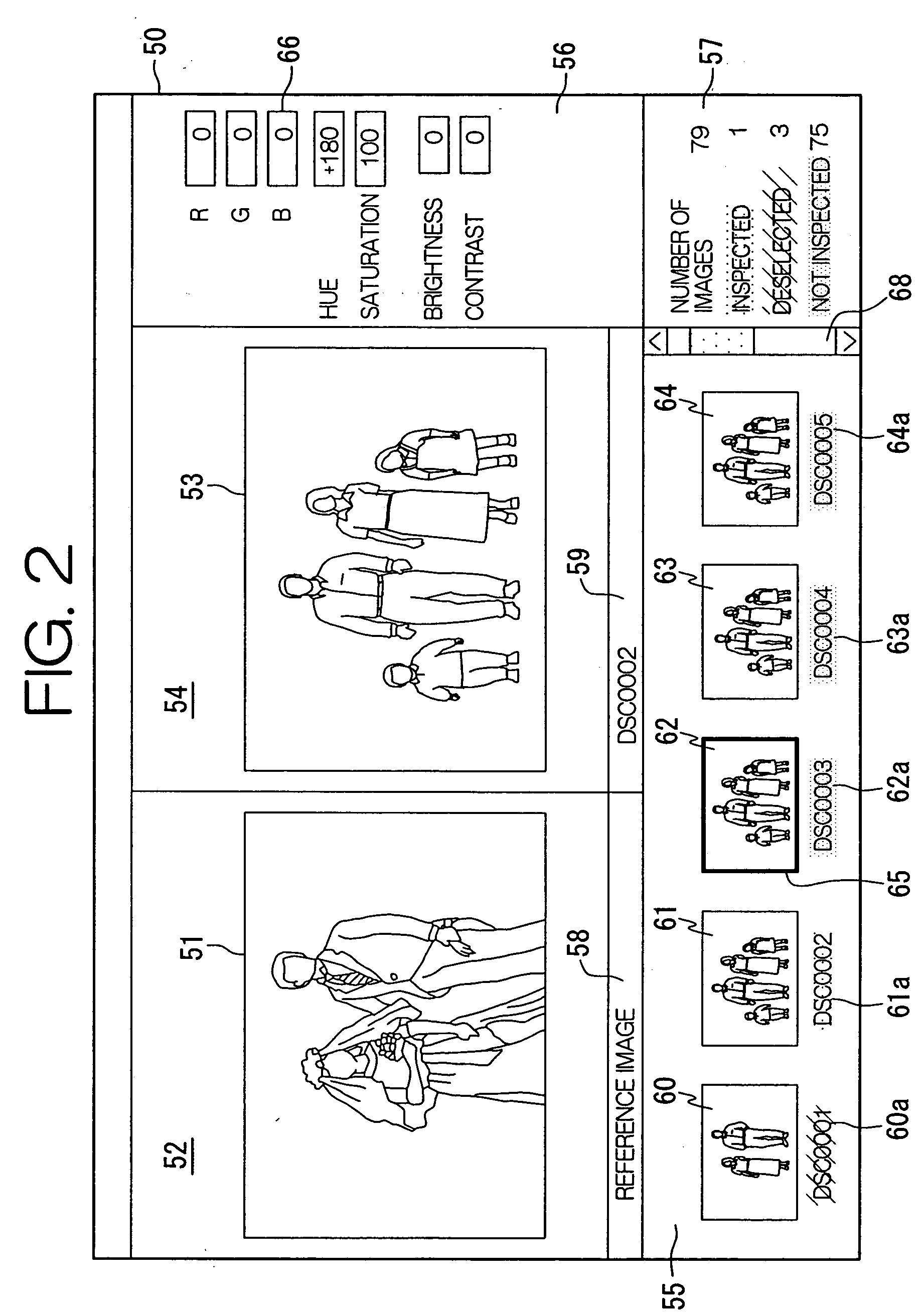
Image reproducing method, image reproducing apparatus and image reproducing program
InactiveUS20050196040A1Uniform finished product qualityImprove efficiencyImage enhancementTelevision system detailsImage InspectionImaging quality
A reference image and a target image for image inspection are displayed side by side in a monitor. The reference image is taken in approximately identical shooting condition to the target image for the image inspection, and corrected with a reference correction parameter. The reference correction parameter and the reference image are stored in a memory. The target image for the image inspection is corrected with the reference correction parameter. The operator determines image quality while comparing the reference image to the target image for the image inspection. When the image quality is unsatisfactory, the target image for the image inspection is corrected. When the correction parameter is changed during the image correction, the changed correction parameter is used for correcting the next image instead of the reference correction parameter.
Owner:FUJIFILM HLDG CORP +1
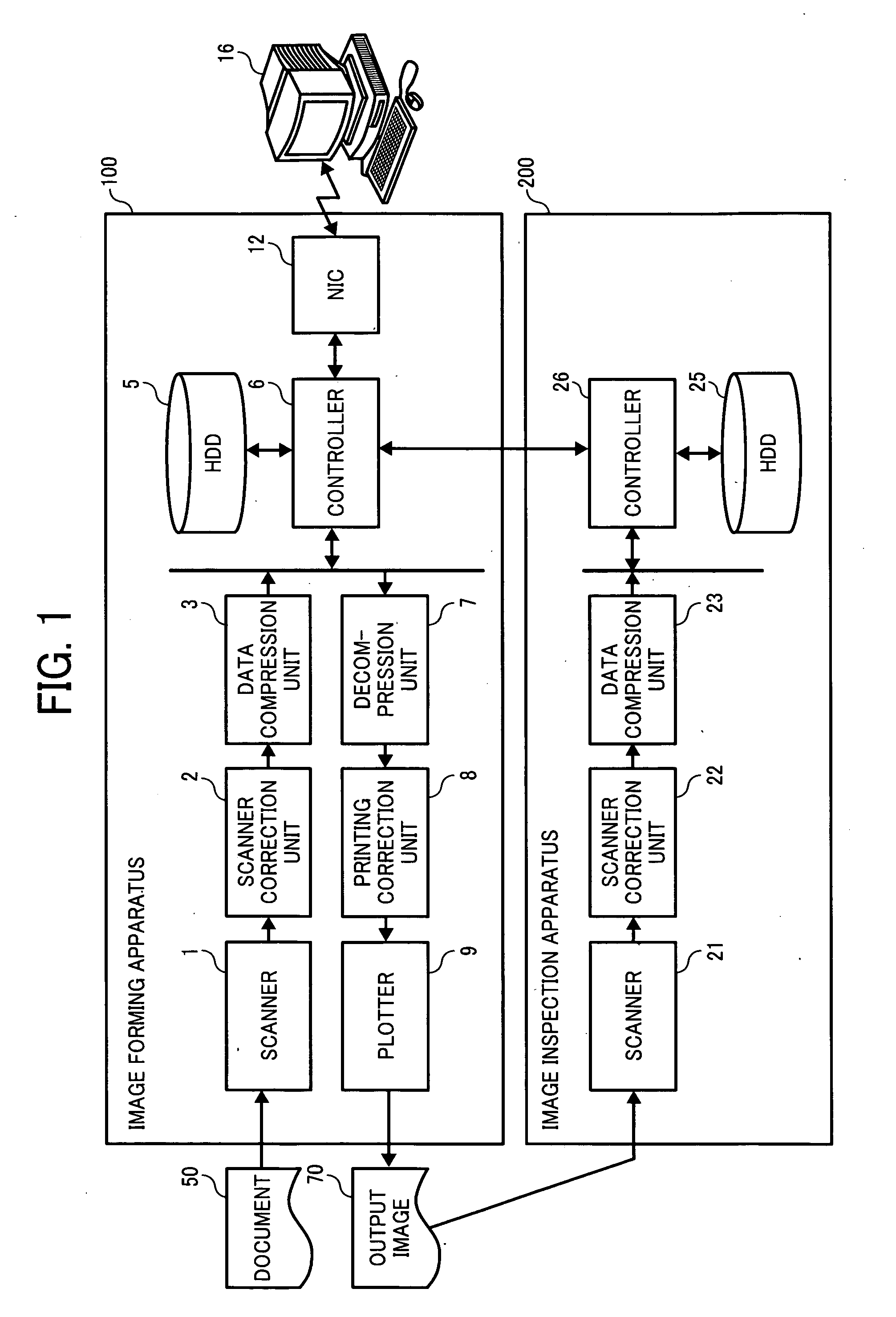
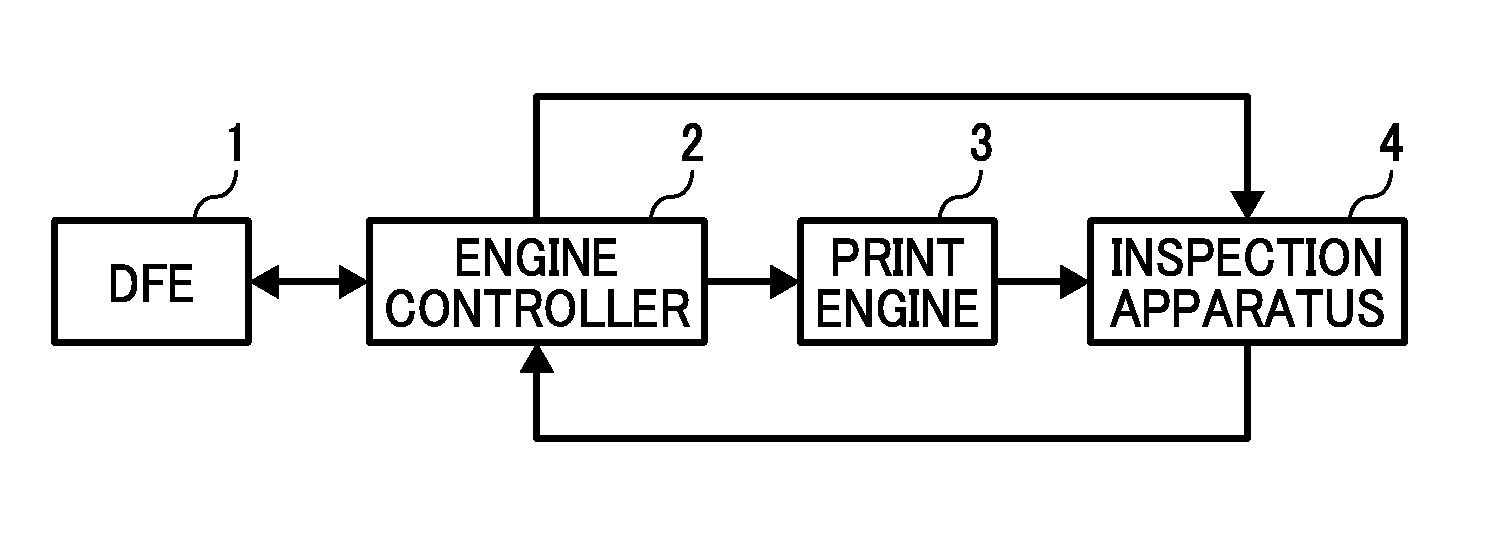
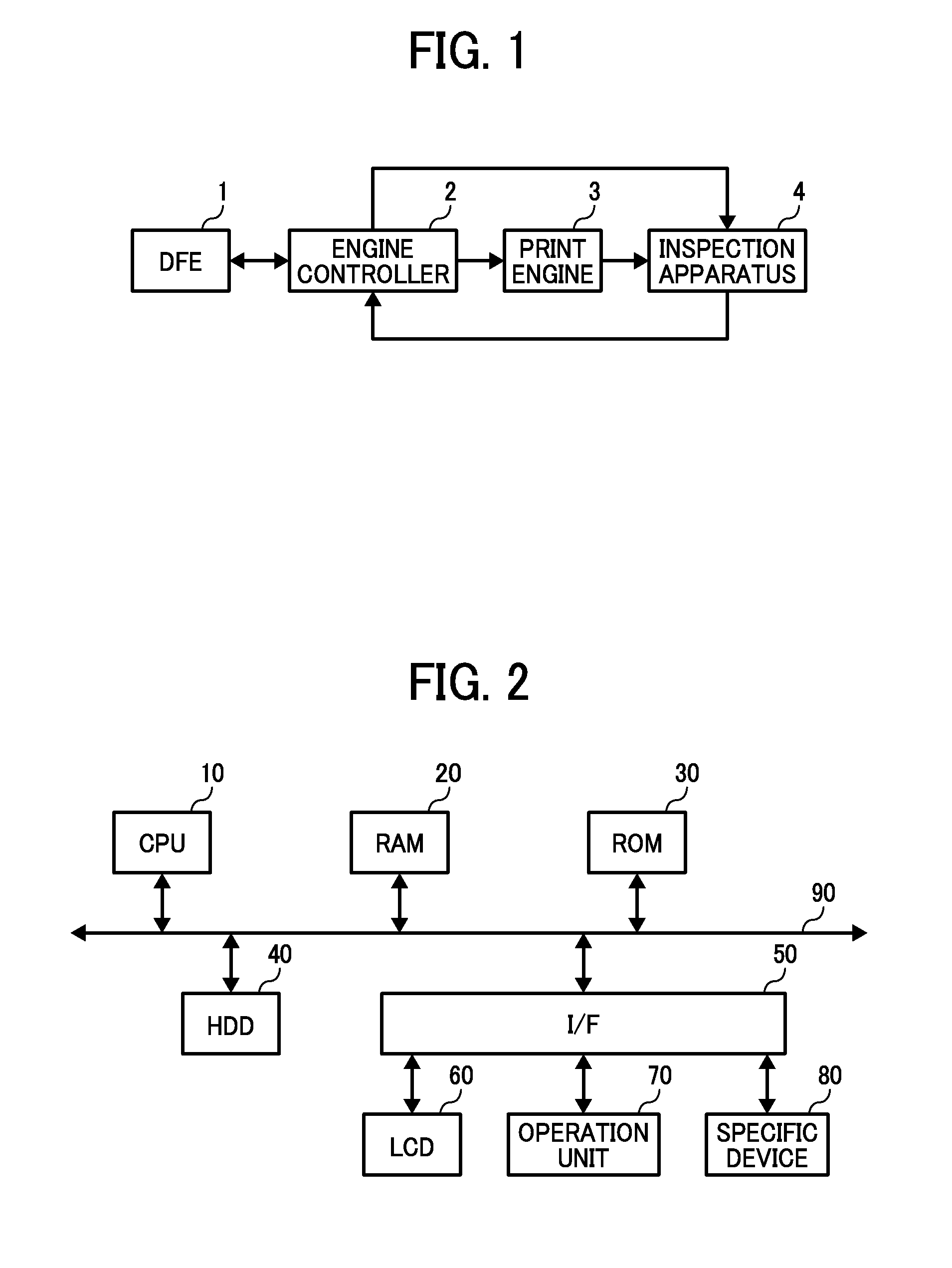
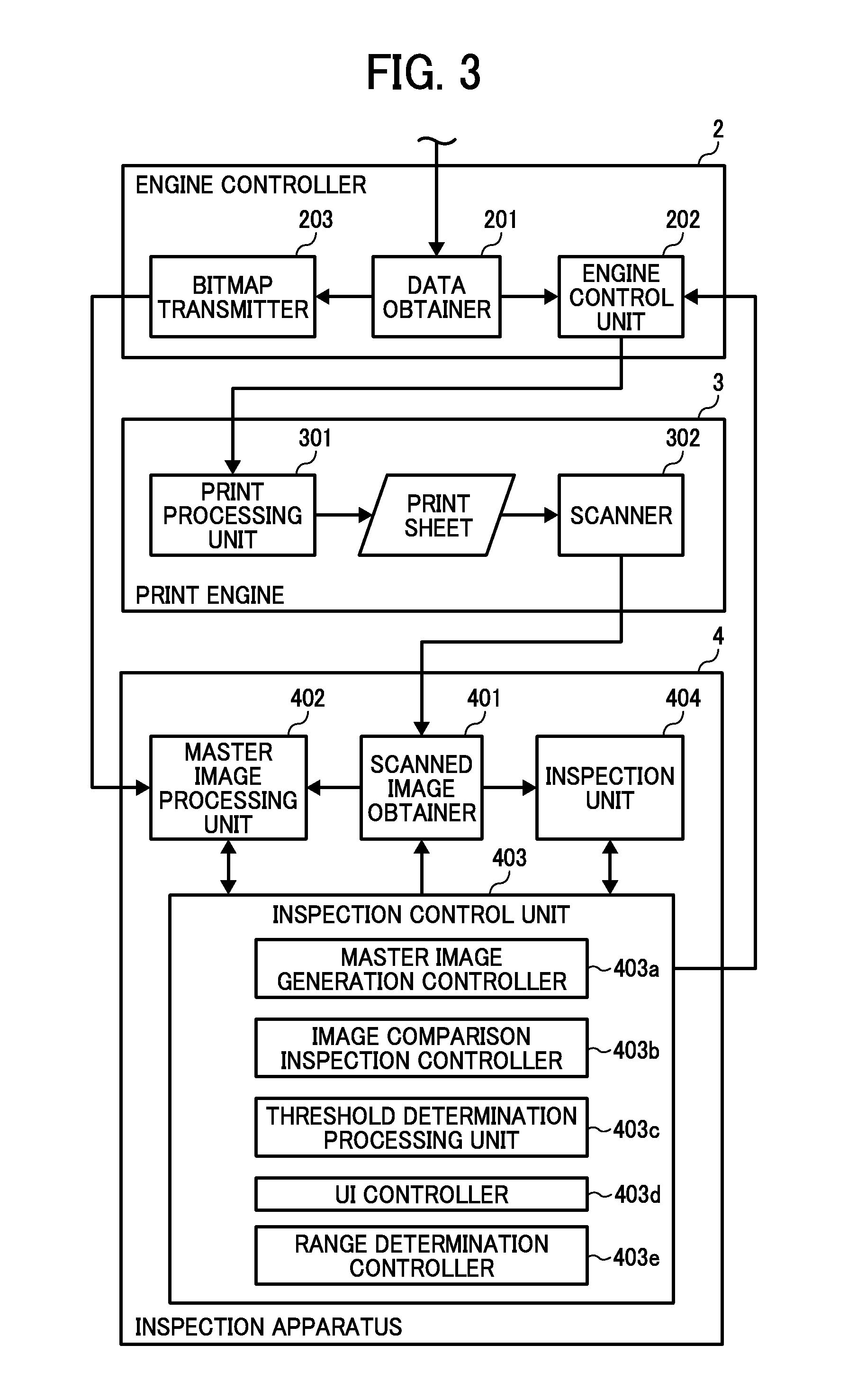
Image inspection apparatus, image inspection system and image inspection method
An image inspection apparatus for inspecting a scanned image of an output image includes an inspection reference image generator to generate an inspection reference image; an image inspection unit to determine a defect by comparing a difference between the inspection reference image and the scanned image with a threshold; a threshold determiner to determine the threshold; and a defect range determiner to determine a range of defect level of a plurality of artificial defects. Based on a difference computed for a defect selected from the plurality of artificial defects, the threshold determiner determines a threshold to be compared with the difference of the selected defect. The defect range determiner conducts a defect determination for the scanned image at the upper and lower limits for a threshold to determine a range of defect level of the plurality of artificial defects.
Owner:RICOH KK
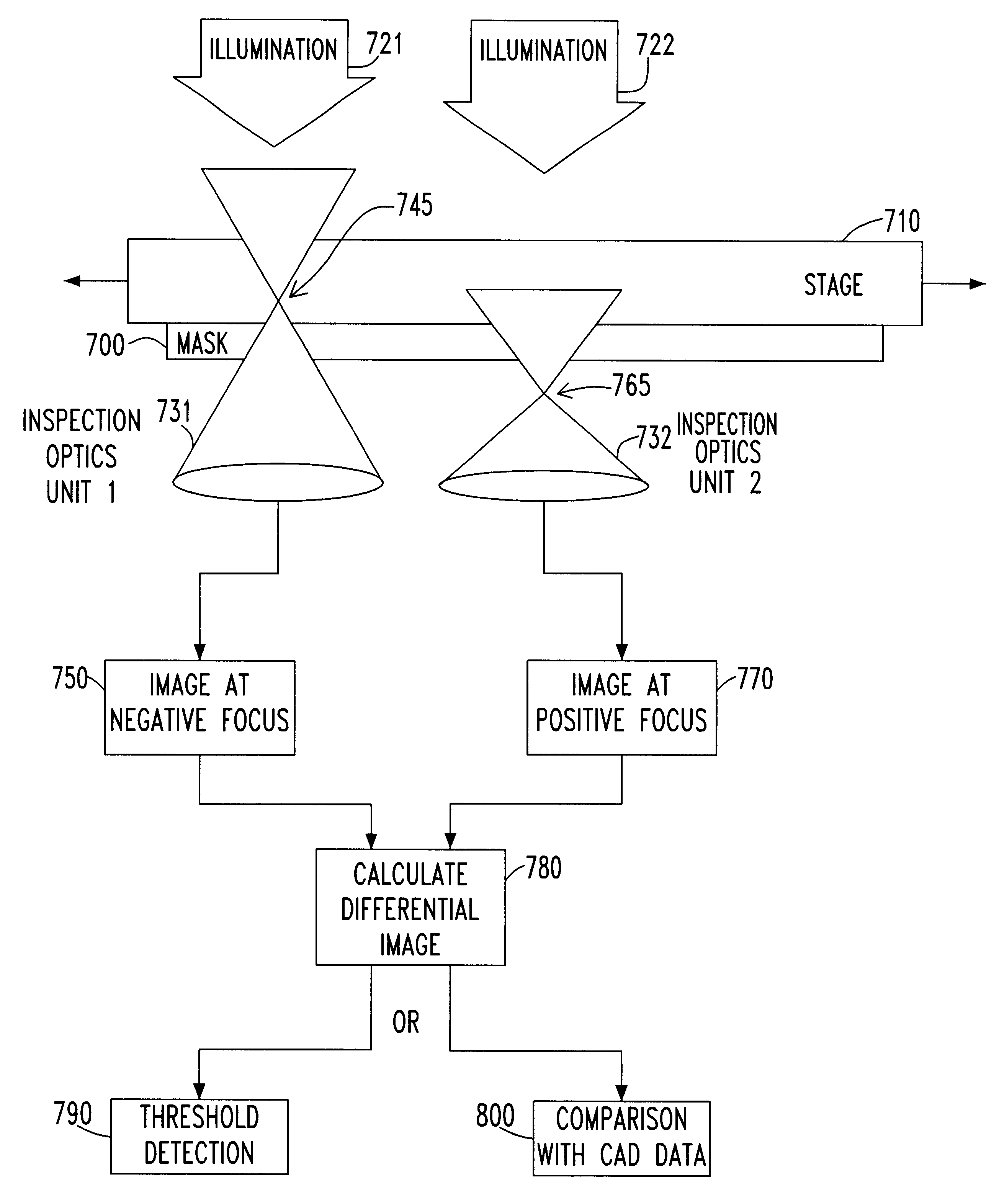
Detection of phase defects on photomasks by differential imaging
InactiveUS6327033B1Optically investigating flaws/contaminationUsing optical meansImage InspectionImaging processing
A method for detecting phase features or phase defects on photomasks for optical lithography is described. The asymmetric imaging behavior through focus of defects or features with a phase other than 0° or 180° is used to distinguish them from other features on the mask. The mask is inspected at equally spaced positions about an optimum focus in both positive and negative directions. The images are subtracted from one another to produce a differential image of the mask. While opaque features as well as transmitting features at 0° and 180° behave identically at positive and negative defocus, thus leading to a zero-valued differential image, the focus asymmetry of phase defects and features produces a non-zero differential image from which these phase defects and features can be located. By comparing the locations on the mask for which a non-zero differential image is obtained with the designed data for the mask, the phase defects can be sorted from the phase features and the absence of phase features can be detected. Additional image processing can be applied to verify the integrity of the phase features. The differential image inspection technique can be implemented on existing optical inspection tools by employing a two-pass inspection performed at positive and negative defocus in sequence. In addition, a new apparatus with parallel inspection optics is described for inspecting the mask at positive and negative focus simultaneously.
Owner:IBM CORP
Image inspection device
InactiveUS7076086B2Simplify of output imageEasy to checkImage enhancementDigitally marking record carriersImage InspectionImaging processing
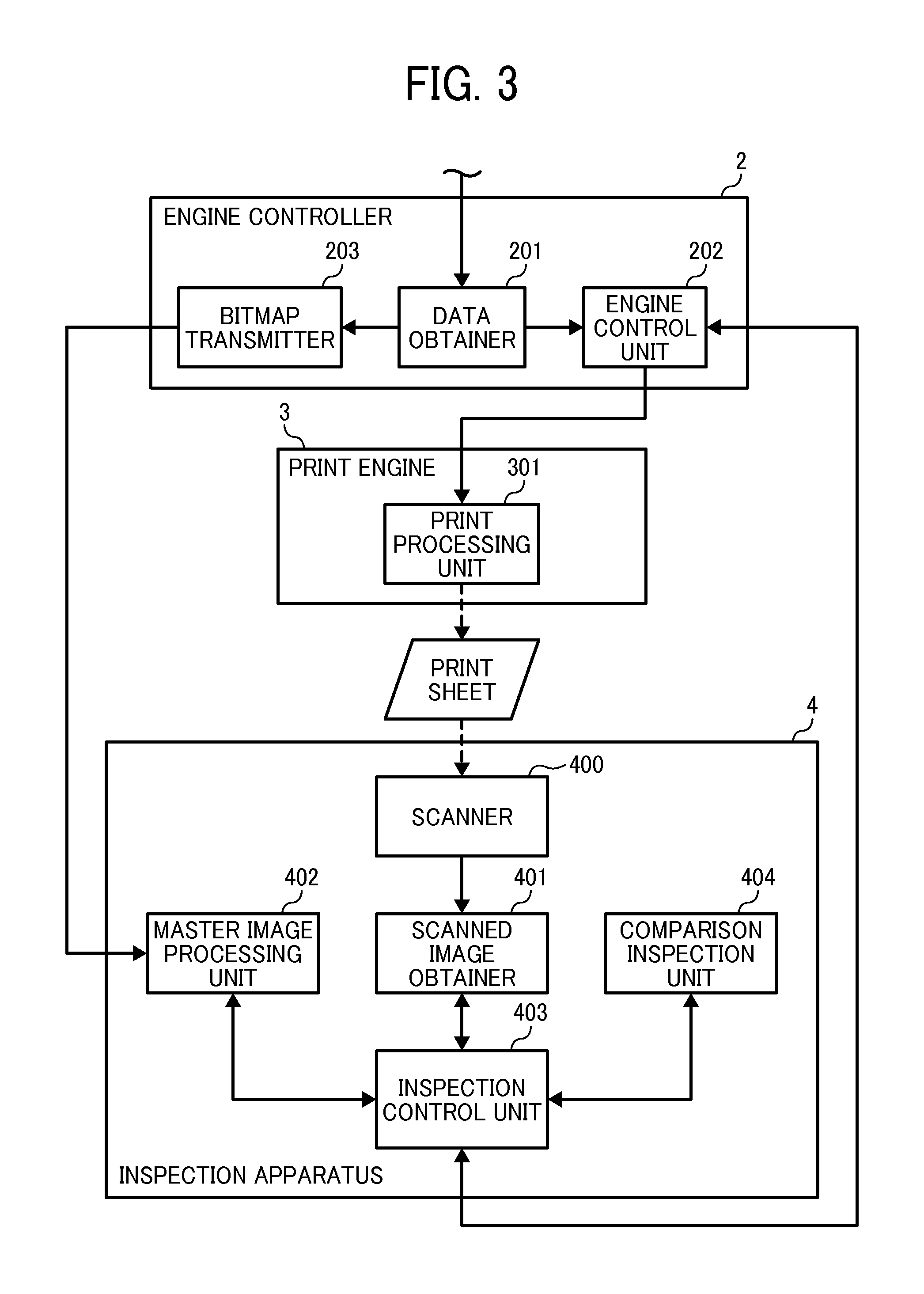
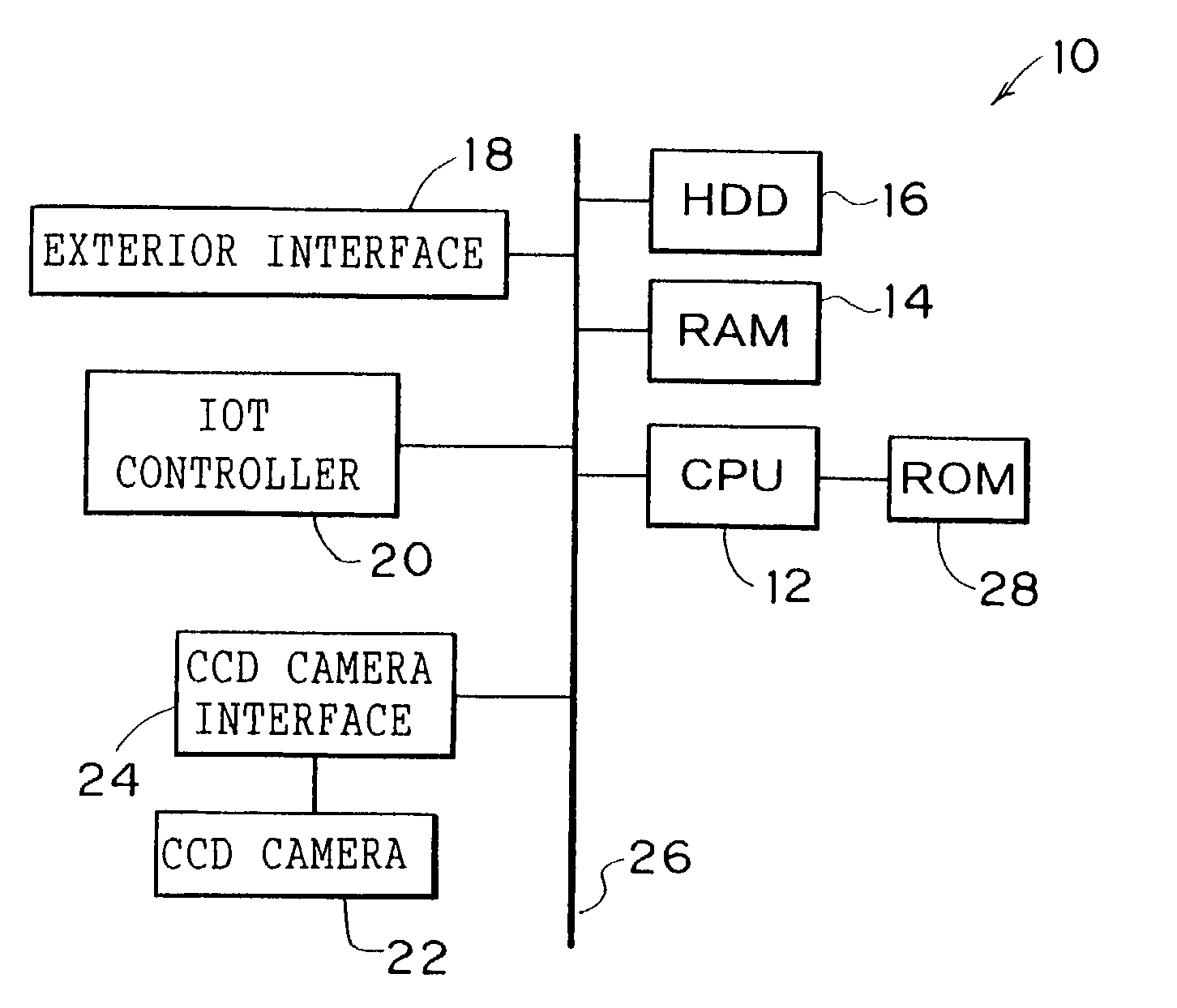
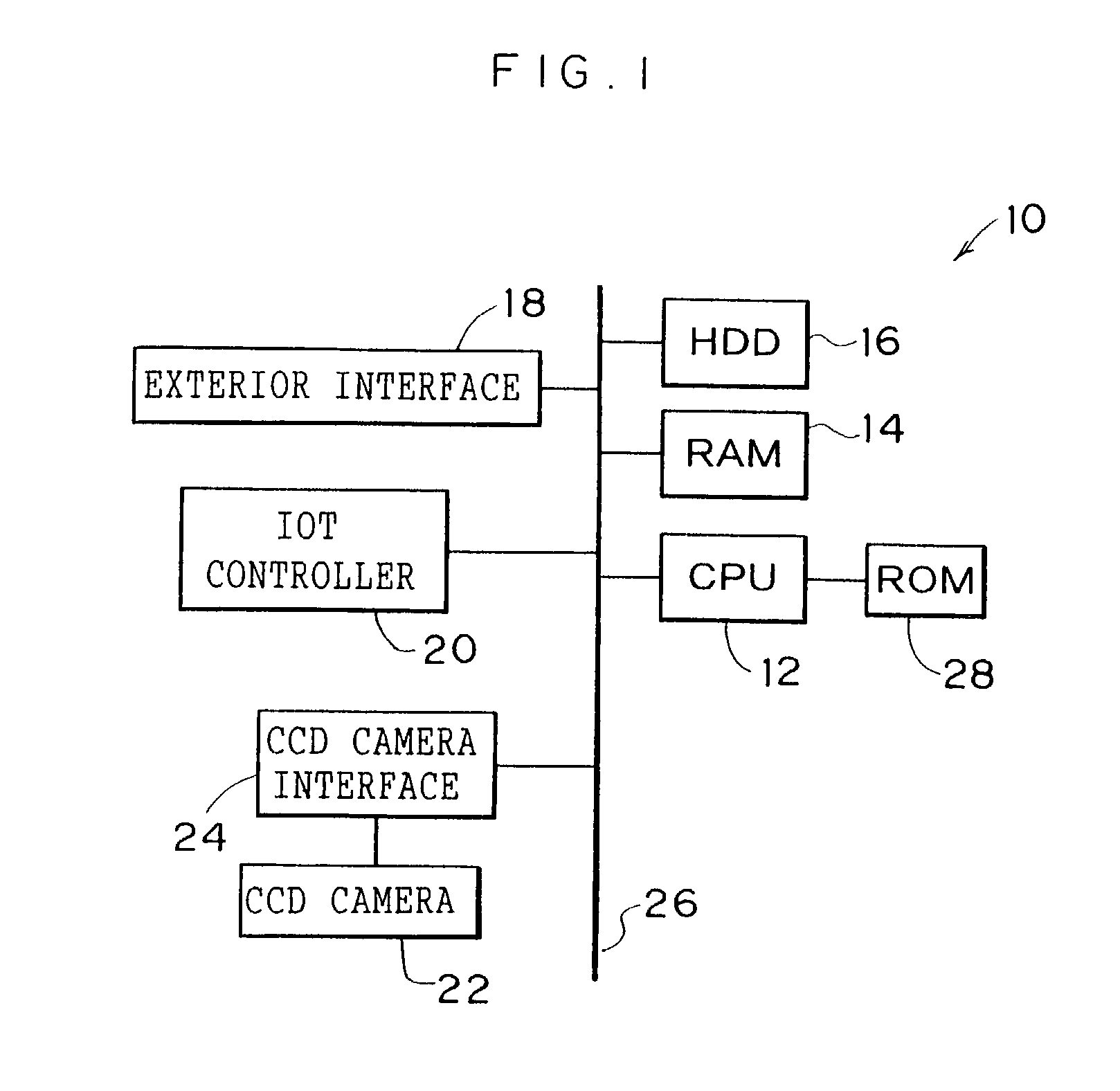
An image inspection device to automate and simplify inspection of an output image. A paper discharge tray of a printer is a different color from paper. A CCD camera is disposed above a paper discharge portion of the printer, at which paper is discharged, and can capture the whole upper face of the paper discharge tray. When, directly after a state in which there is no paper on the paper discharge tray, a print job is received and a first print-processed sheet is outputted to the paper discharge tray, a CPU controls the CCD camera to capture the paper discharge tray in this state. Captured image data including the paper is acquired, corrections are applied to the captured image data and to original image data by image processing, and image characteristics thereof are made substantially the same. Thereafter, the outputted image is inspected by comparison of the two data sets.
Owner:FUJIFILM BUSINESS INNOVATION CORP
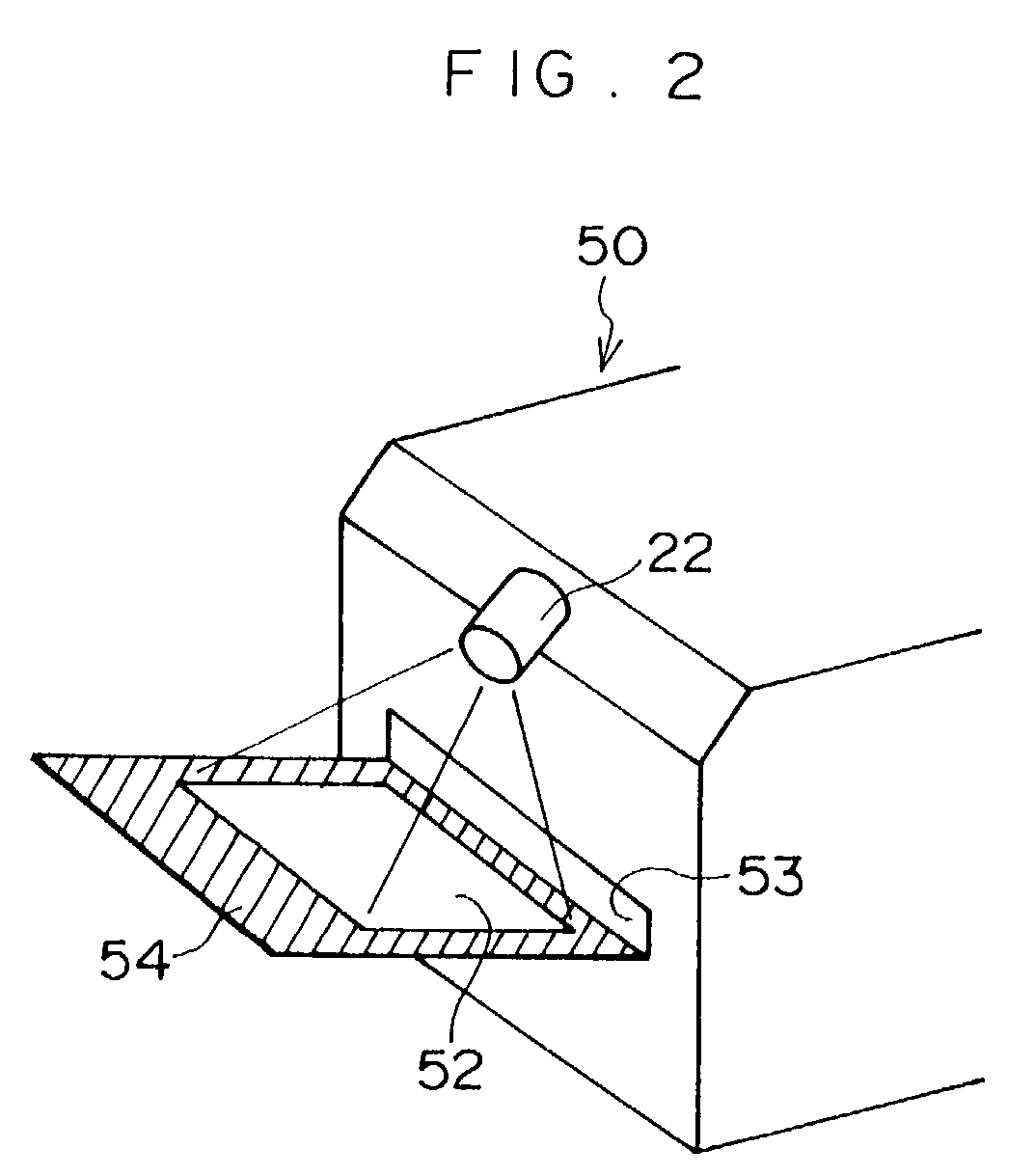
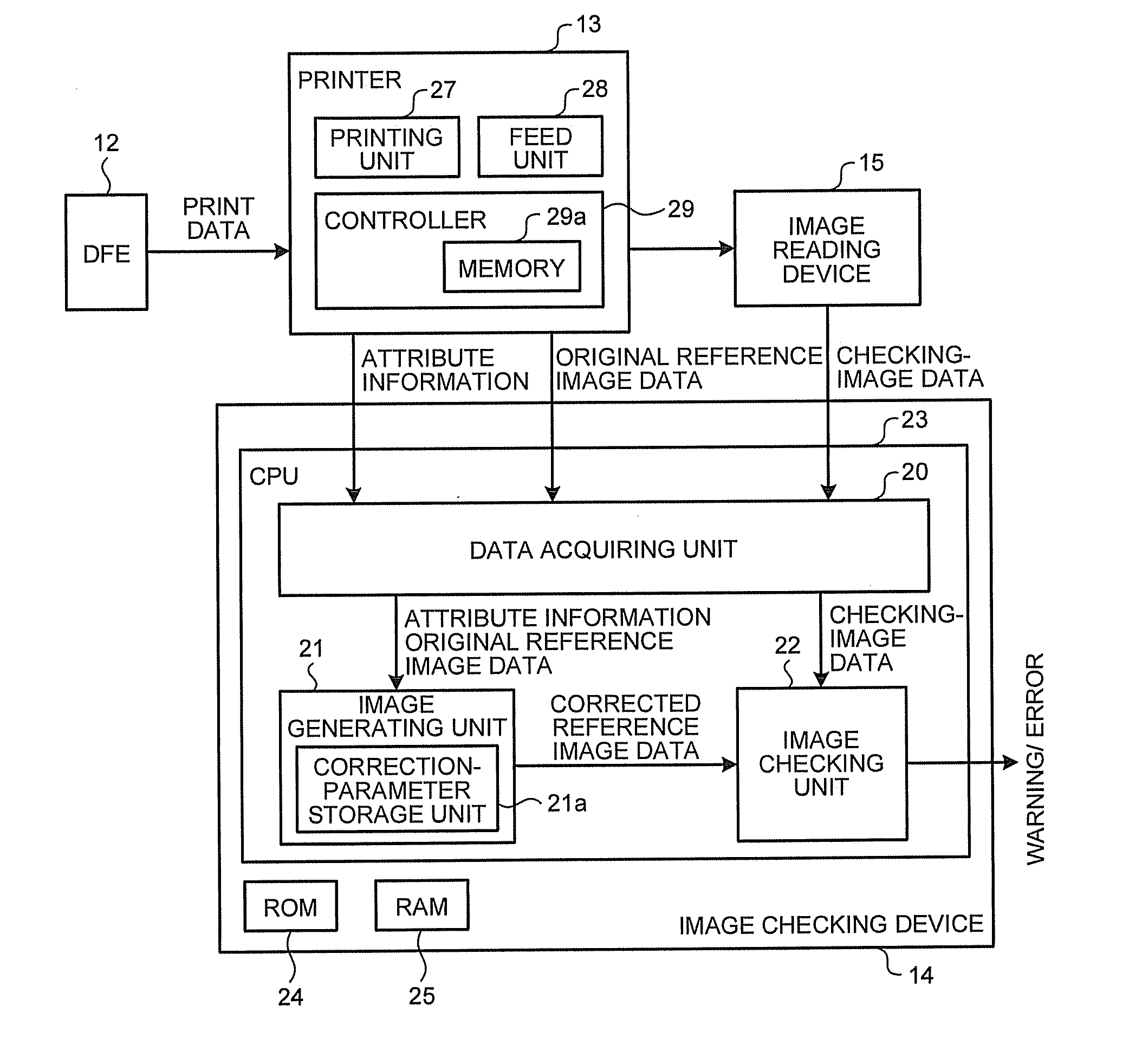
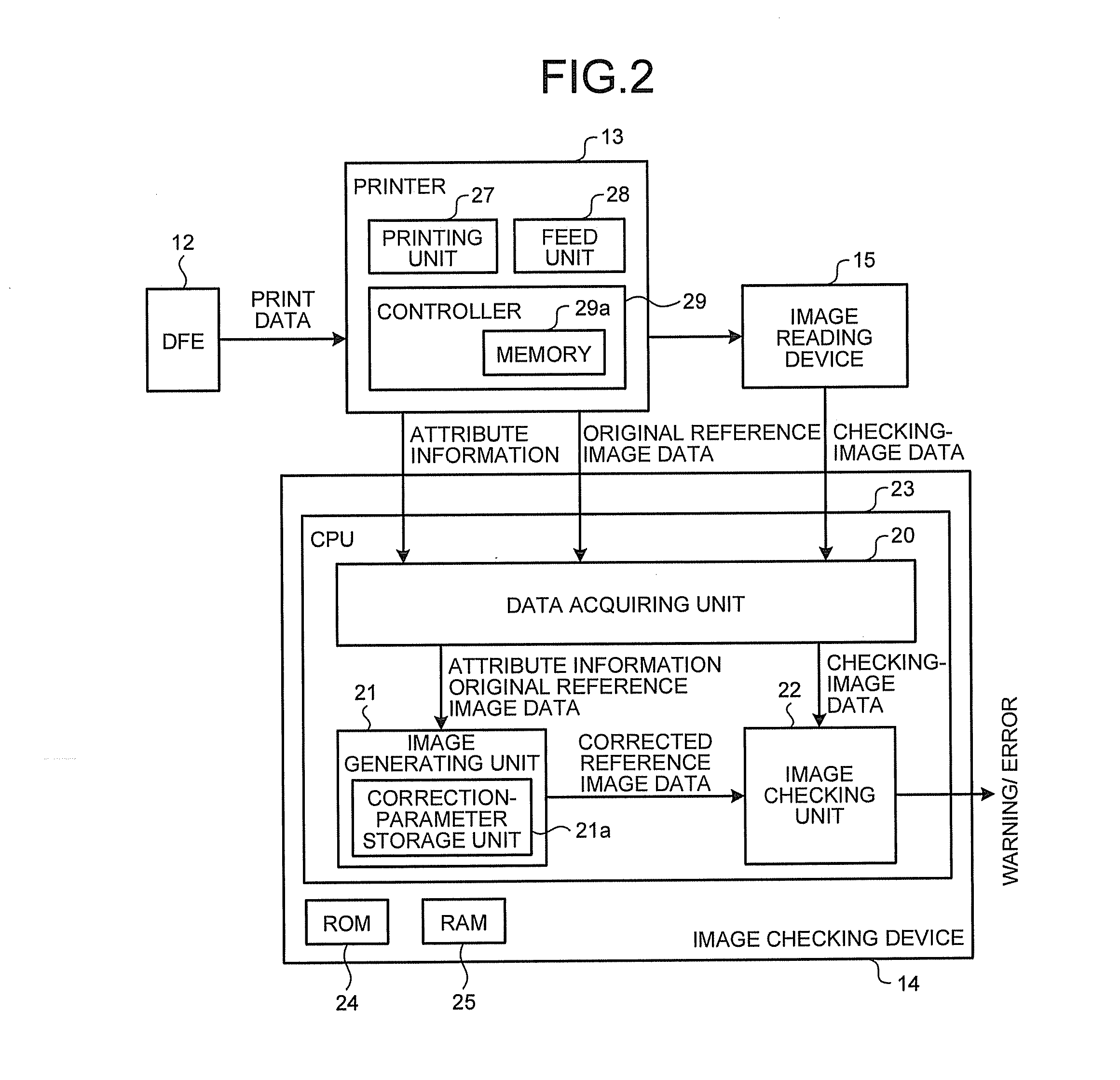
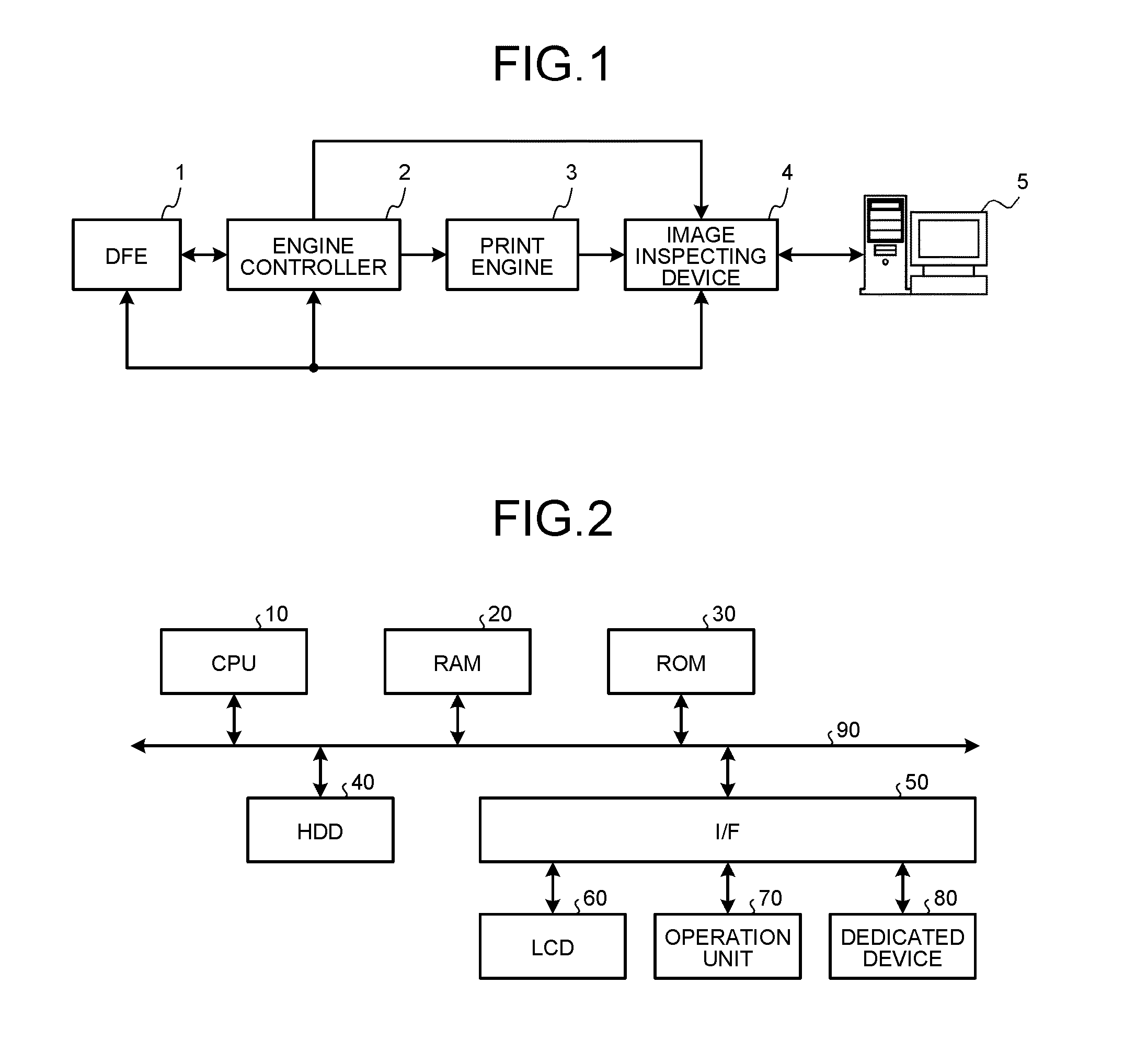
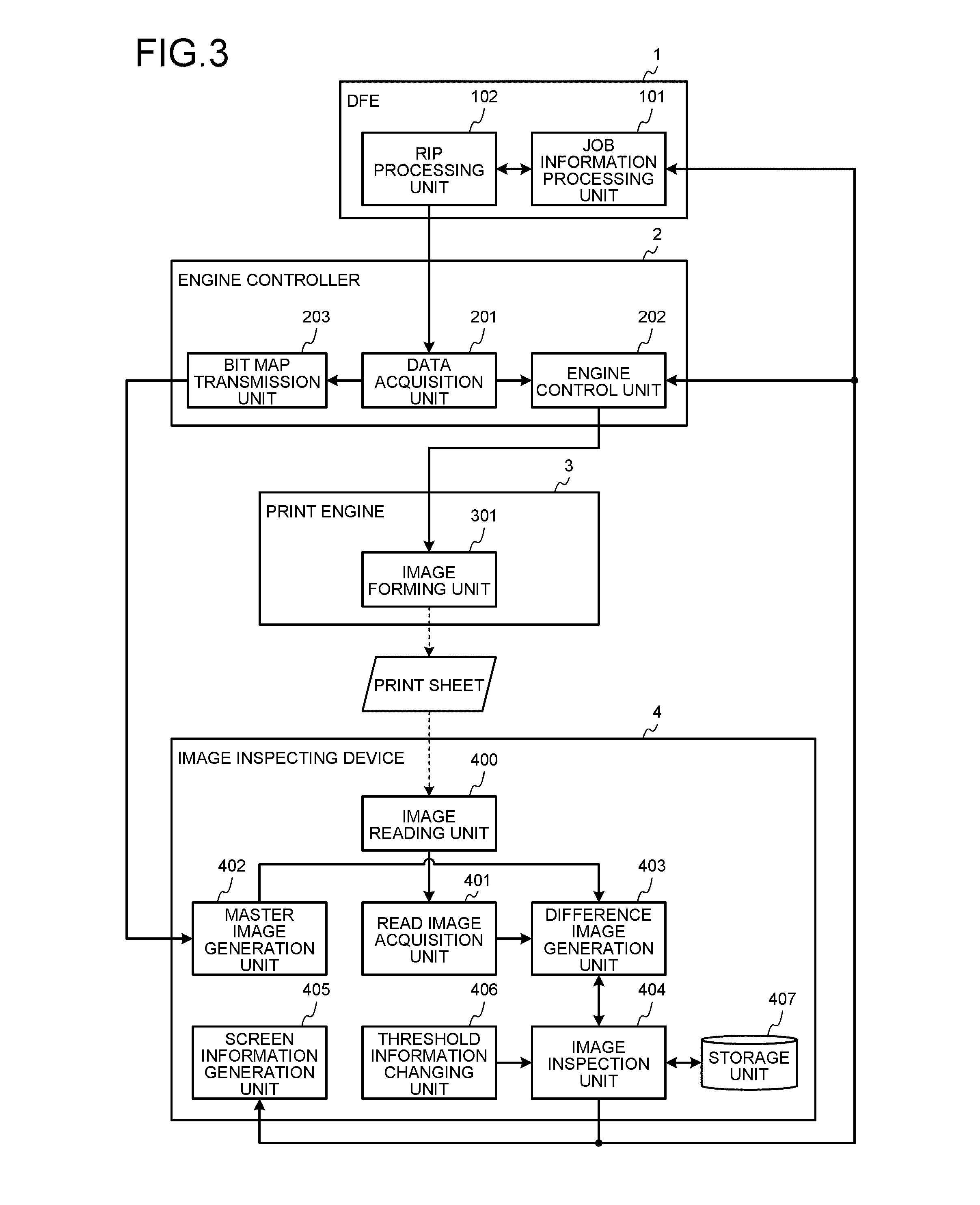
Image Checking Device, Printing System, Image Checking Method, And Computer Program Product.
ActiveUS20120147397A1Solve problemsDigitally marking record carriersDigital computer detailsImage InspectionImage formation
An image checking device checks a printed image printed out on a printing medium. The image checking device includes a data acquiring unit that acquires checking-image data, original reference image data input to an image forming device, and, from an attribute-information storage unit of the image forming device, attribute information about a printing medium; a correction-parameter storage unit that stores therein a correction parameter corresponding to the attribute information; an image generating unit that reads, from the correction-parameter storage unit, a correction parameter corresponding to the attribute information, corrects the original reference image data by using the correction parameter, and generates corrected reference image data; and an image checking unit that compares the checking-image data with the corrected reference image data by using a pre-set value to determine the degree of matching between the checking-image data and the corrected reference image data, thereby performing image checking on the printed image.
Owner:RICOH KK
Method for diagnosing disease from tongue image
A digital image processing method for a centralized multi-mode medical tongue image inspection system, comprising the steps of: forming at least one service unit (300) for performing tongue record (220) construction; forming a processing unit (320) for tongue record inspection (308); and providing communication links (330) between the service units and the processing unit.
Owner:CARESTREAM HEALTH INC
Distributed architecture for mammographic image acquisition and processing
InactiveUS7406150B2Easy to useHigh patient throughputOrgan movement/changes detectionPatient positioning for diagnosticsImage InspectionDICOM
A distributed architecture allows for decoupling of mammographic image acquisition and review, thereby enabling more efficient use of resources and enhanced processing. In one embodiment, the system (100) includes a number of image acquisition stations (102) and a number of image review stations (110) all associated with a central server (104). The server (104) is operative to access an image repository (106), a patient information data base (108) and a number of DICOM tools (112). The invention allows for more efficient and / or more convenient use of the image acquisition equipment and image processing stations. Moreover, the distributed architecture including the central image repository provides certain processing and analysis advantages. The invention also provides certain processing and workflow enhancements that allow for a more full realization of potential digital mammography advantages.
Owner:HOLOGIC INC
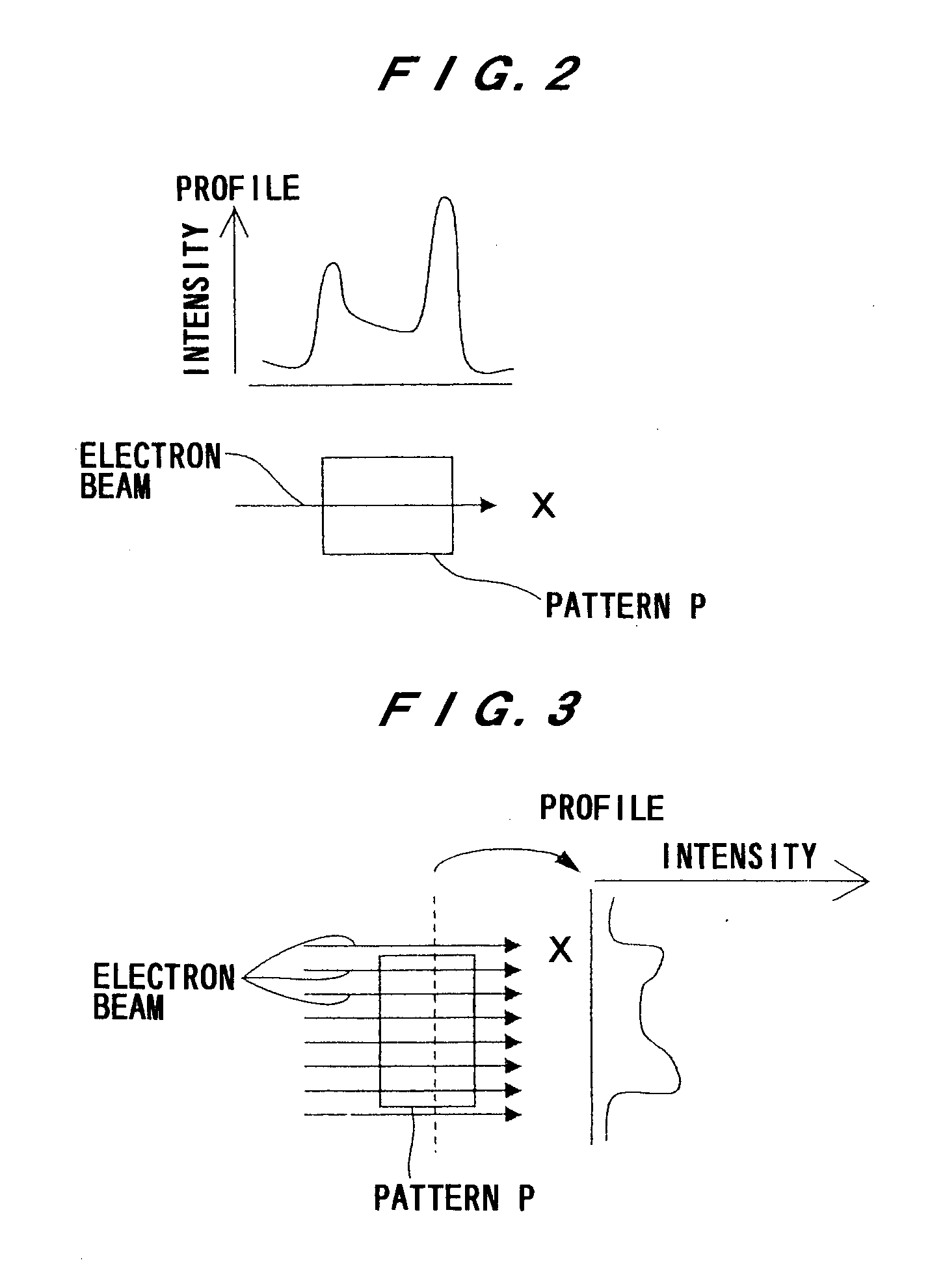
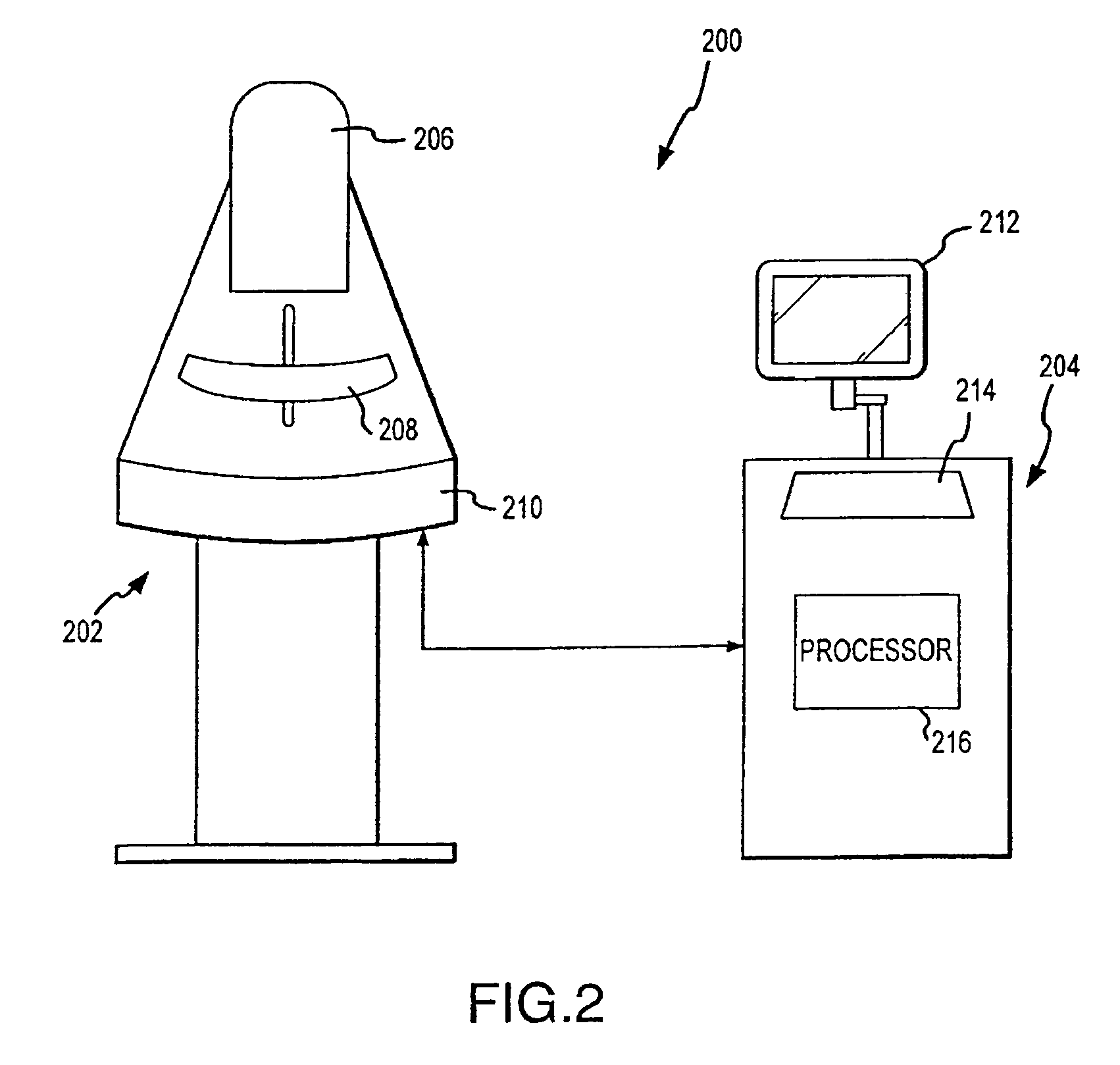
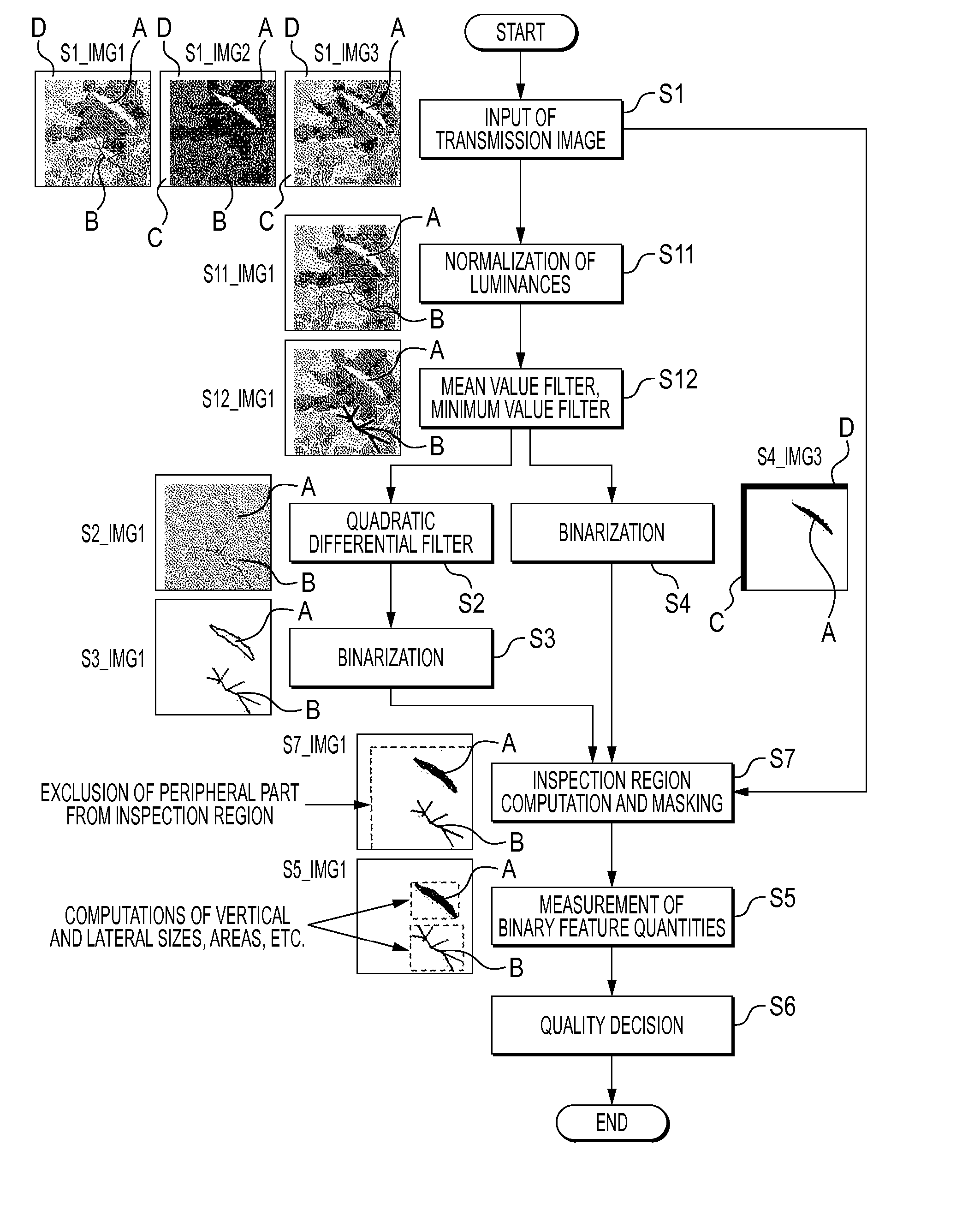
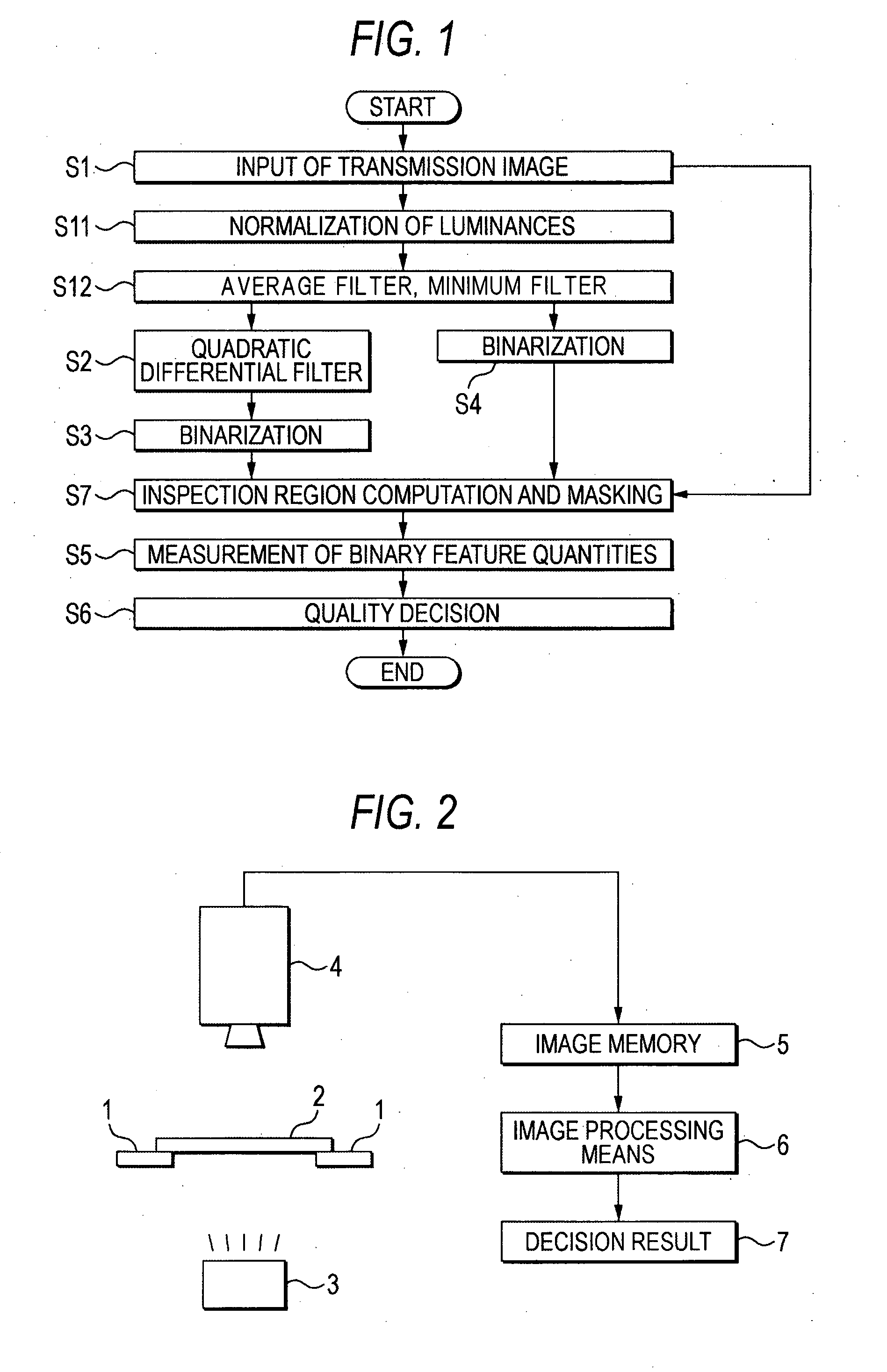
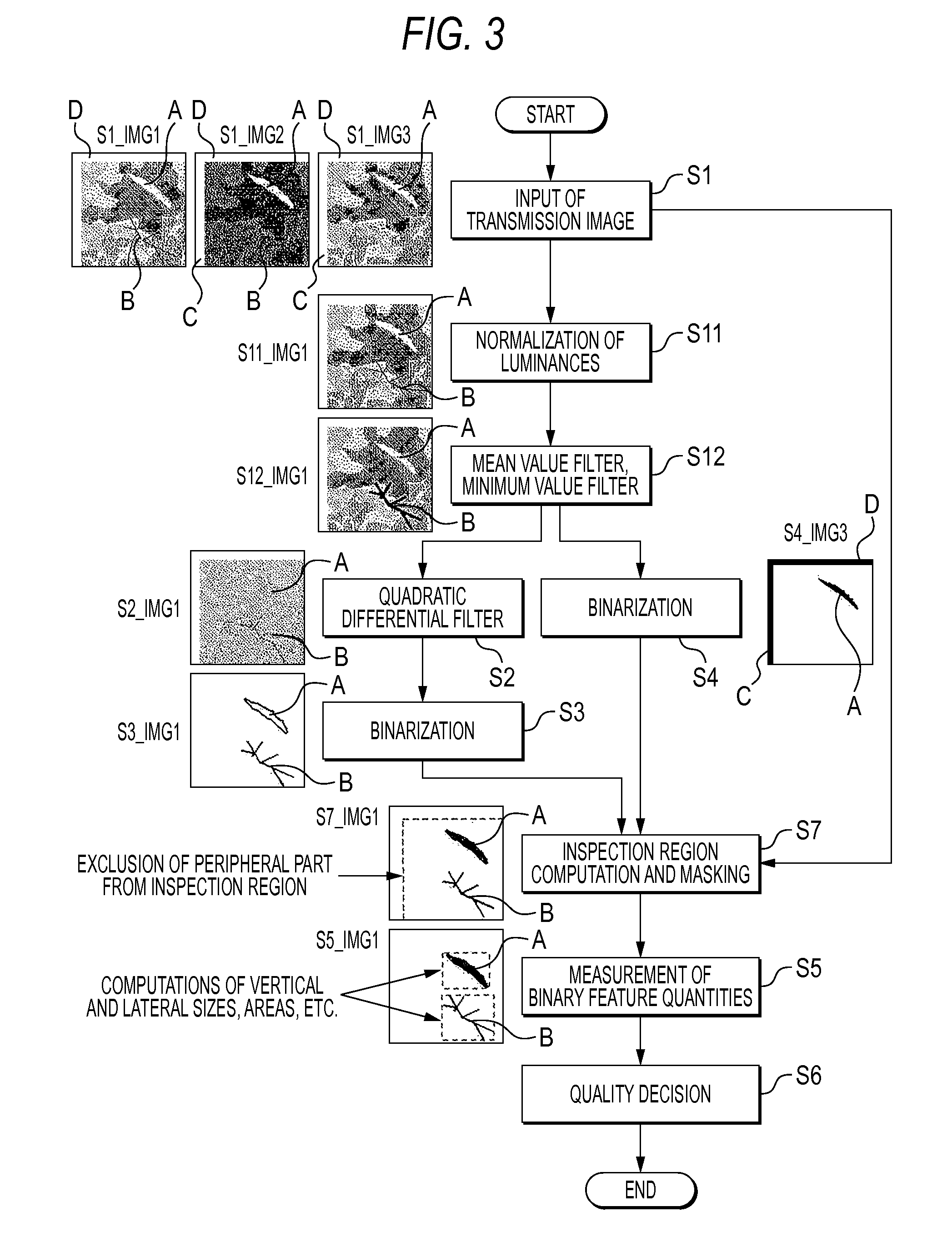
Image inspection method and image inspection apparatus employing the same
The method comprises a first step (S1 in FIG. 1) of obtaining a transmission image, a second step (S2) of applying a quadratic differential filter to the transmission image, thereby to emphasize a part of large luminance change as a quadratic differential filter image, a third step (S3) of binarizing the quadratic differential filter image with a predetermined threshold value, and then storing the resulting binarized image, a fourth step (S4) of binarizing the transmission image with another predetermined threshold value, and then storing the resulting binarized image, a fifth step (S5) of performing the measurement of binary feature quantities for the binarized image stored at the third step (S3) and the binarized image stored at the fourth step (S4), and a sixth step (S6) of deciding the quality of the object to-be-inspected from the binary feature quantities.
Owner:MITSUBISHI ELECTRIC CORP
Apparatus, system, and method of inspecting image, and recording medium storing image inspection control program
ActiveUS20130250370A1Improve accuracySimple configurationCharacter and pattern recognitionPictoral communicationImage InspectionRecording media
An apparatus, system, method, and non-transitory recording medium storing an image inspection control program, each of which is capable of inspecting a printed image are provided. While generating an inspection image to be used for inspecting a read image obtained by reading the printed image, attribute data indicating, for each pixel in the inspection image, whether the pixel belongs to drawing data in the inspection image is generated. The attribute data is used to process inspection of the read image based on comparison between the read image and the inspection image.
Owner:RICOH KK
Image inspecting device, image forming system, and computer program product
InactiveUS20150269719A1Solve problemsImage enhancementImage analysisPattern recognitionImage Inspection
Owner:RICOH KK
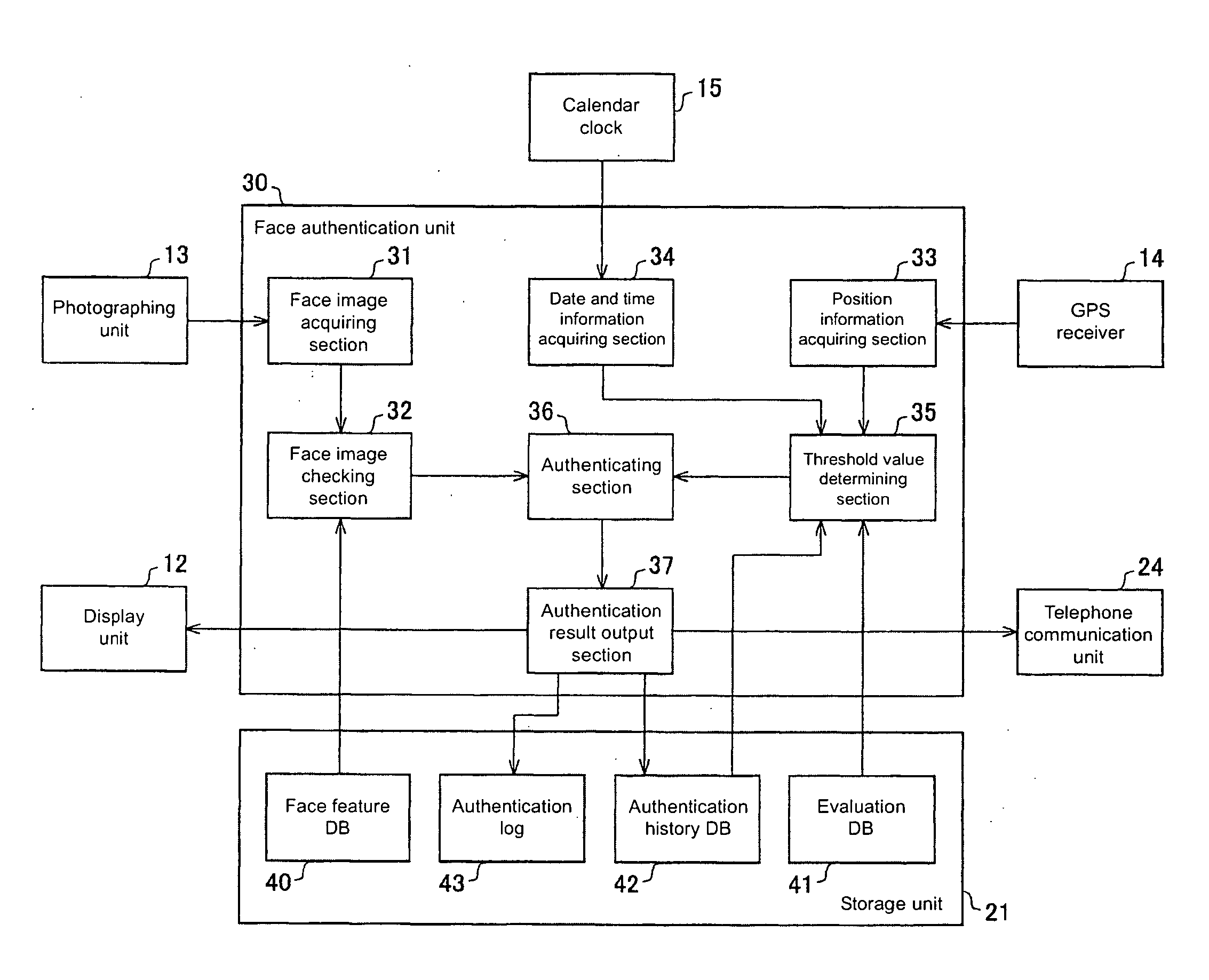
Authentication device and method of controlling the same, electronic equipment Equipped with authentication device, authentication device control program and recording medium recorded with program
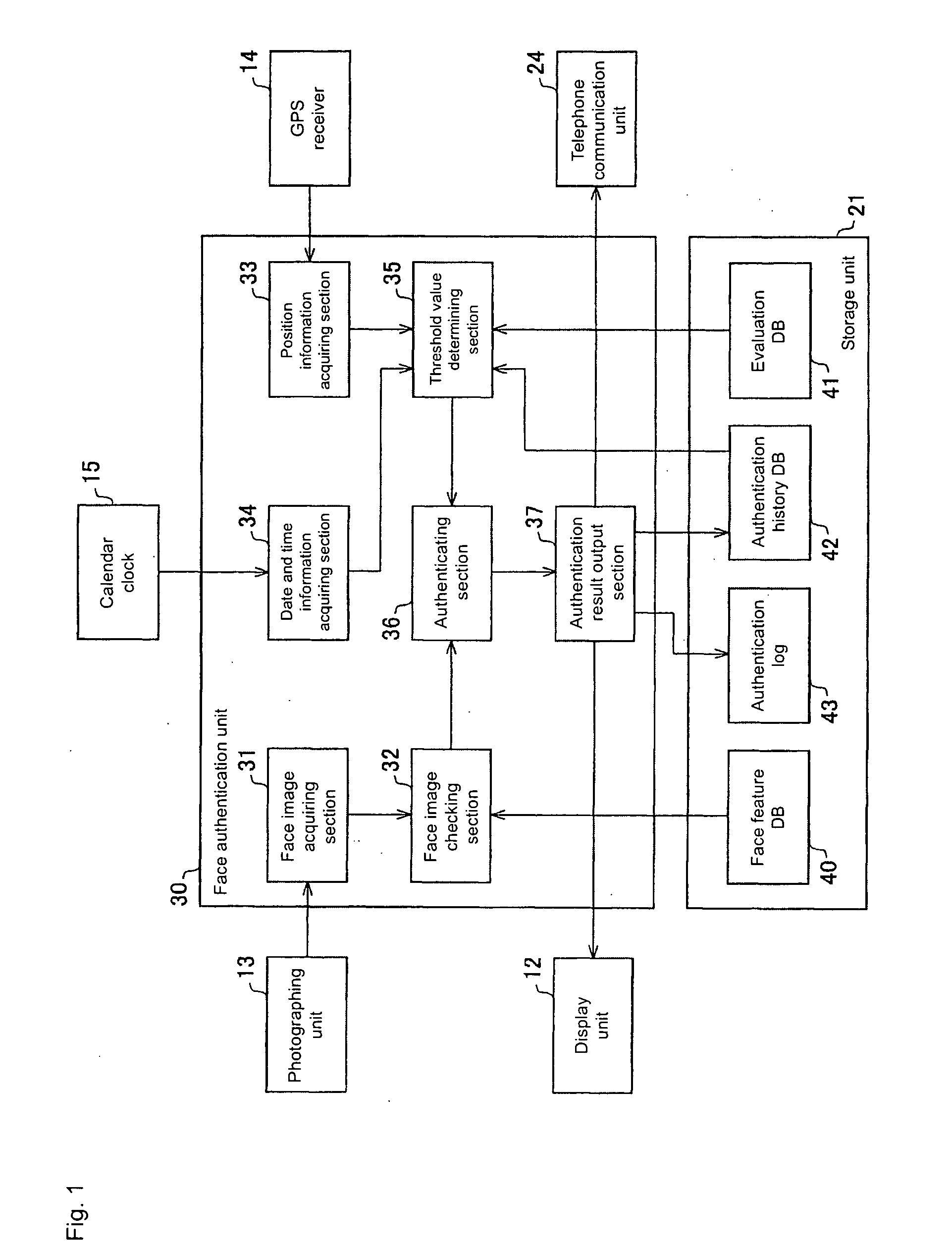
InactiveUS20070288748A1Effectively preventing spoofingMaintain convenienceUser identity/authority verificationInternal/peripheral component protectionImage InspectionGps receiver
The present invention aims to effectively prevent spoofing in authentication and maintain convenience of the user. In a face authentication unit of the portable telephone, the face image checking part checks the face image of the person to be authenticated, which is acquired by a face image acquiring part through a photographing unit, with face feature information contained in a face feature DB of the storage unit and calculates the matching degree. A threshold value determining section determines the threshold value by searching the evaluation DB based on the position information of the own device acquired by the position information acquiring section through the GPS receiver. An authenticating section compares the matching degree calculated by the face image checking section and the threshold value determined by the threshold value determining section, and determines success and failure of the face authentication.
Owner:ORMON CORP
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com