Patents
Literature
83 results about "Mammographic image" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Automated background processing mammographic image data
InactiveUS6891920B1Improve efficiencyQuick displayPatient positioning for diagnosticsCharacter and pattern recognitionRapid accessDigital image
Disclosed is a mammographic imaging system and tools for processing mammographic images to enhance image acquisition and review workflow. The systems and tools enable rapid access to digital image information providing for improved workflow management and identification of images, upon initial review. The system and tools also allow for background processing of image information to reduce workflow delay. Specifically, digital images are processed in the background, i.e., they are automatically processed, free from specific task-orientated direction by a user, using resources that are not otherwise occupied addressing user-directed tasks. Background processing that may be supported includes preprocessing and interim processing. Preprocessing refers to processing of an image that occurs prior to initial review of that image by a physician. Interim processing refers to background processing that occurs during a review session, e.g., in a time period between initial review and a subsequent review of an image.
Owner:HOLOGIC INC
Mastopexy and Breast Reconstruction Prostheses and Method
InactiveUS20080097601A1Easy to handleResistant to biodegradationMammary implantsBandagesMastopexyCell-Extracellular Matrix
Mastopexy and breast reconstruction prostheses and implantation method that allow for radiographic imaging of the breast tissue. The prostheses are arcuate and elongate optionally meshed to conform with breast tissue when implanted. Prostheses are made from naturally occurring extracellular matrix, primarily collagen, that, allows for mammographic imaging without interference as is expected from synthetic materials.
Owner:ORGANOGENESIS
Historical comparison of breast tissue by image processing
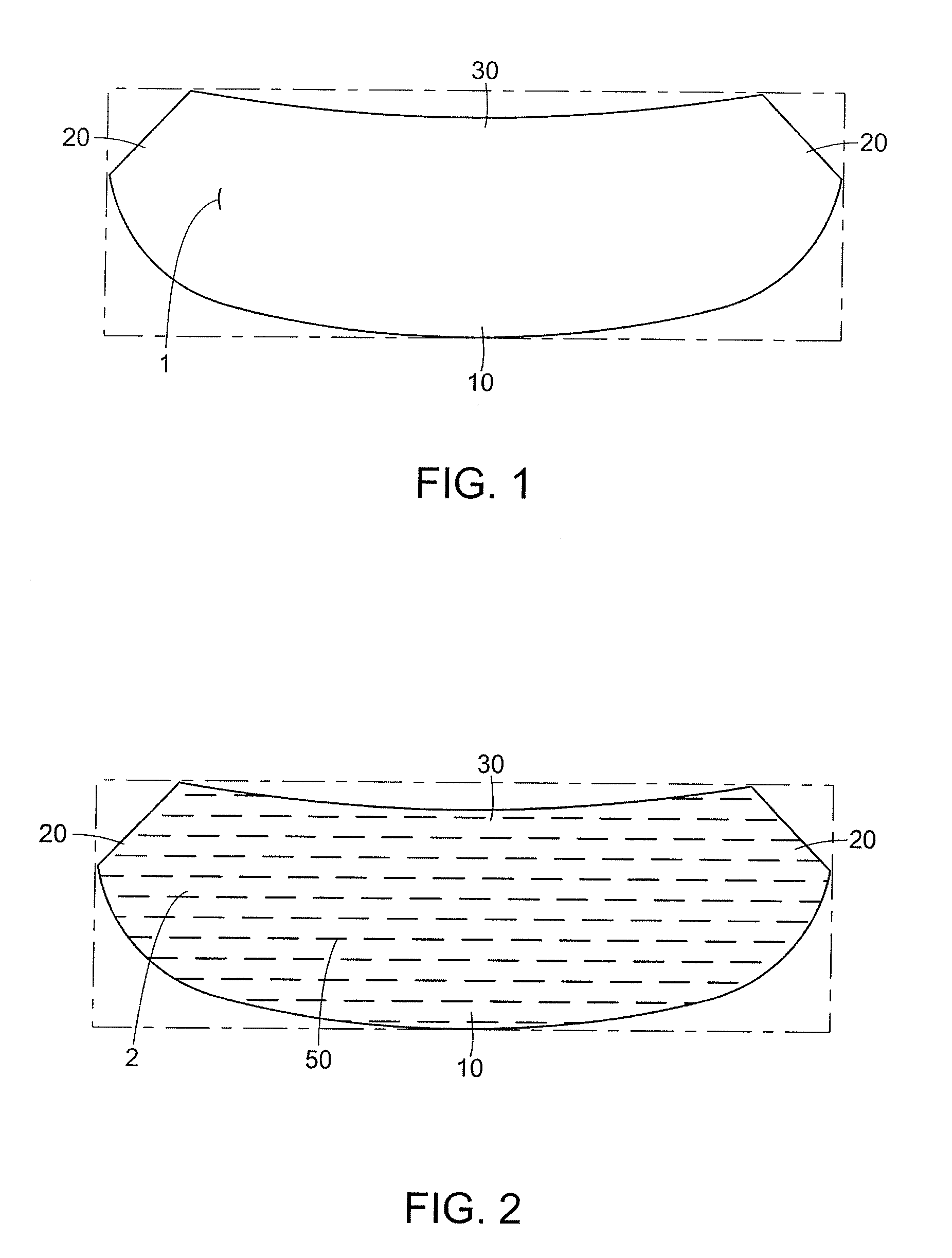
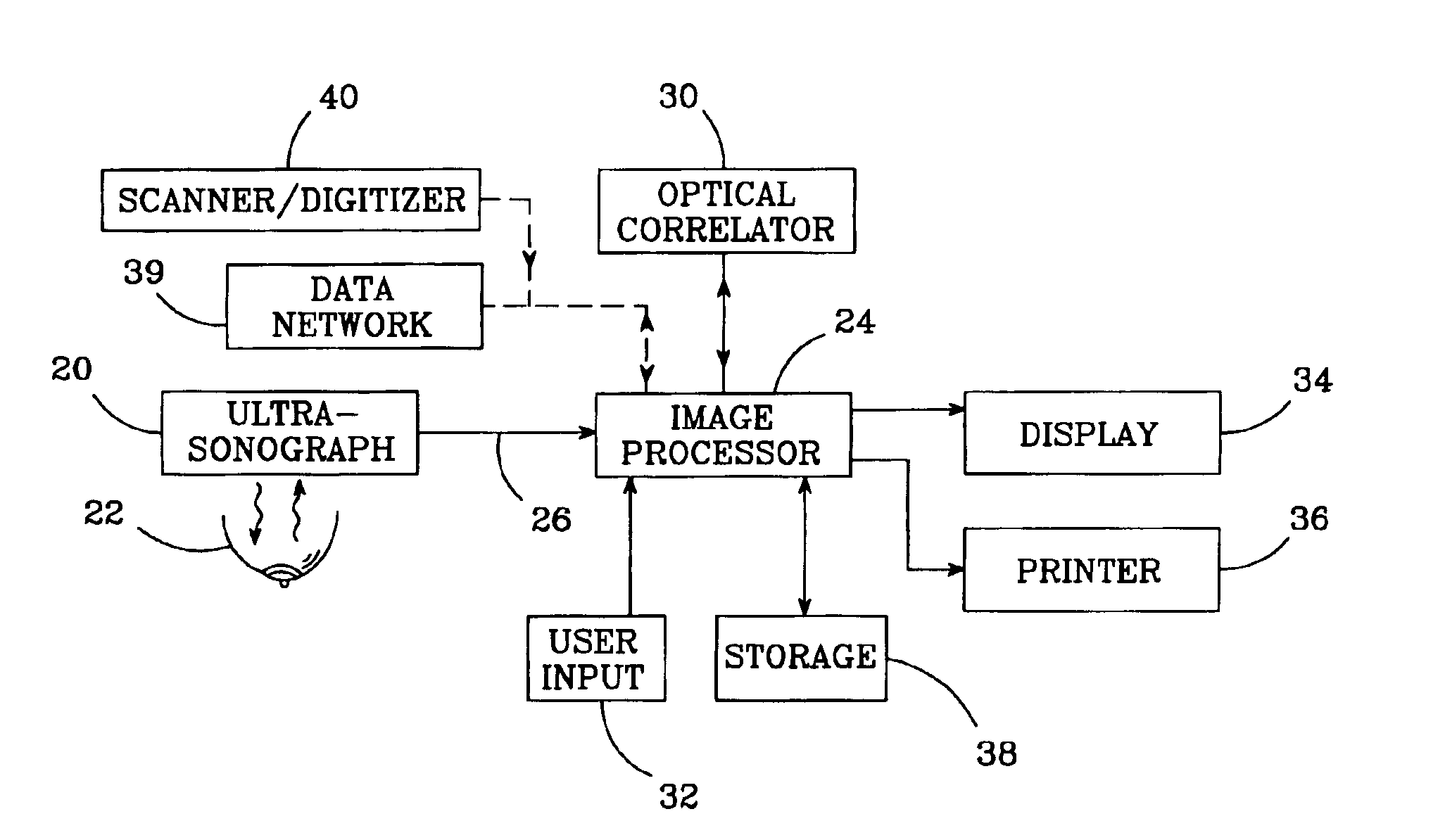
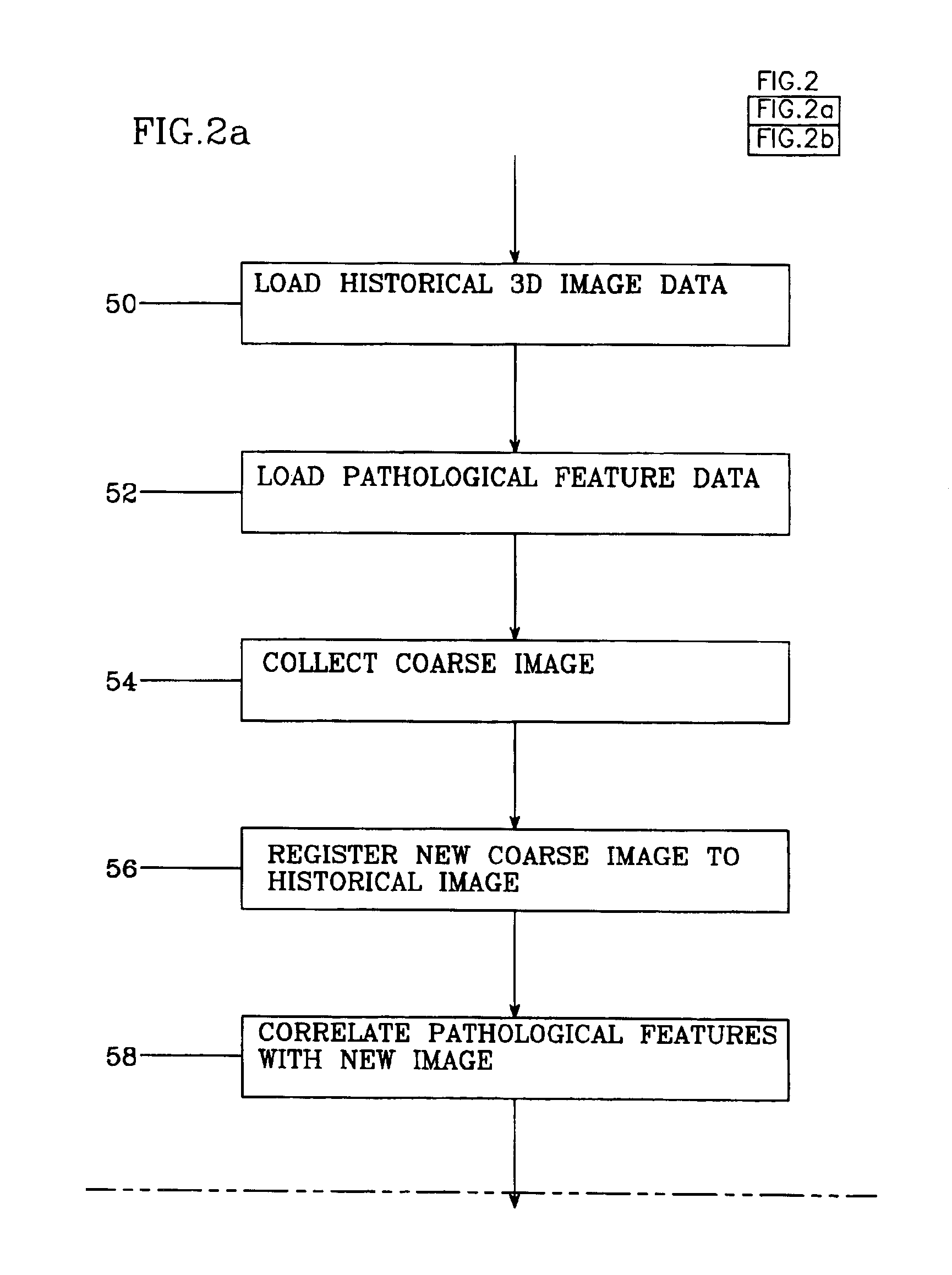
An image processing system and method visually documents and displays changes between historical and later mammographic images, preferably in three dimensions. A composite image is created which visually emphasizes temporal differences between the historical and later images. Preferably three-dimensional, digitized images, displayable in various projections, are stored for archival purposes on computer readable media. An image processor preferably exploits an optical correlator to register the historical and later images accurately and provide correlation values as temporal scalars of the differences. The registered images are then compared, voxel-by-voxel, to detect temporal differences. The composite image is displayed with synthetic colors or other visual clues to emphasize apparent changes (for example, tumor growth or shrinkage).
Owner:LITTON SYST INC +1
Computer Aided Detection Of Abnormalities In Volumetric Breast Ultrasound Scans And User Interface
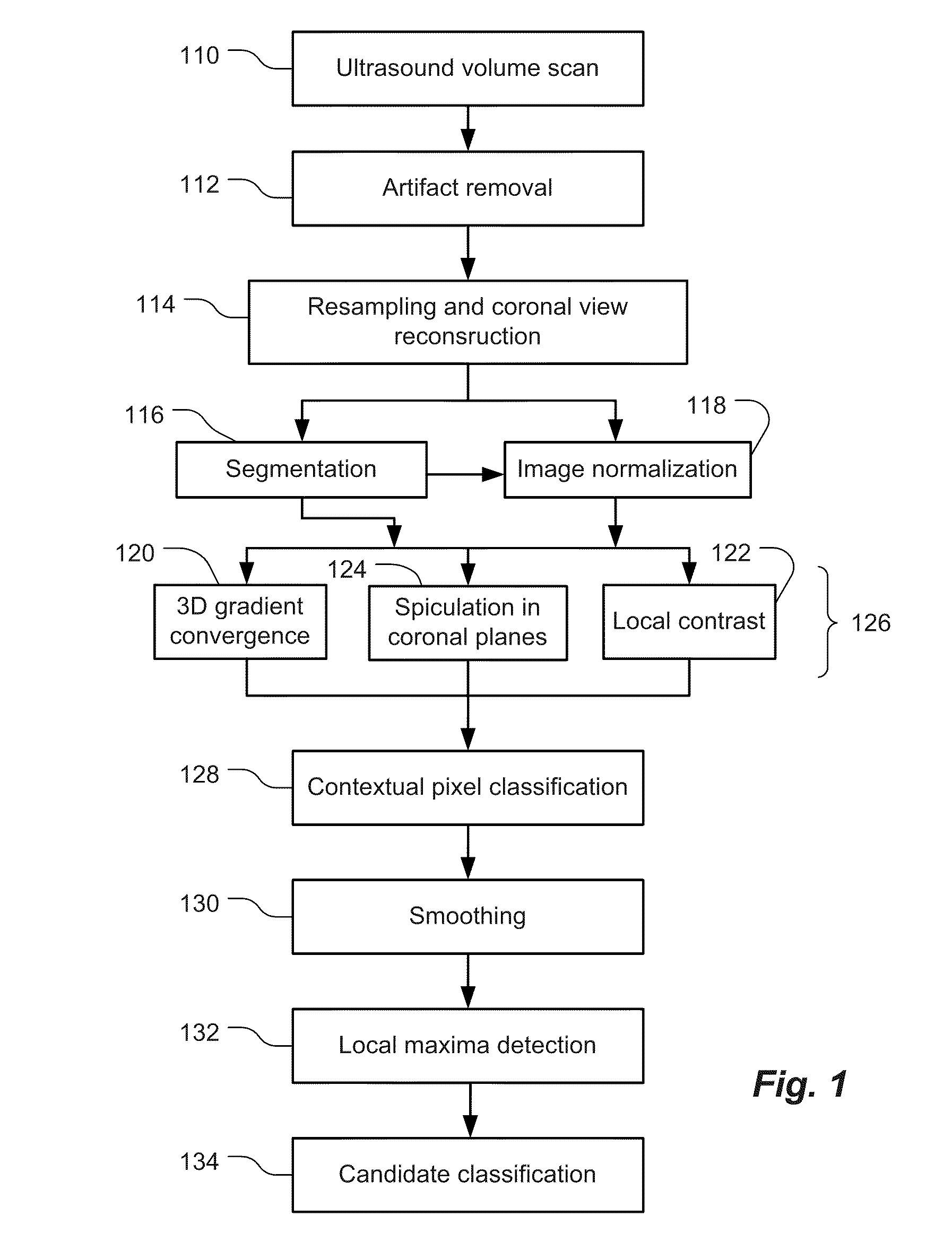
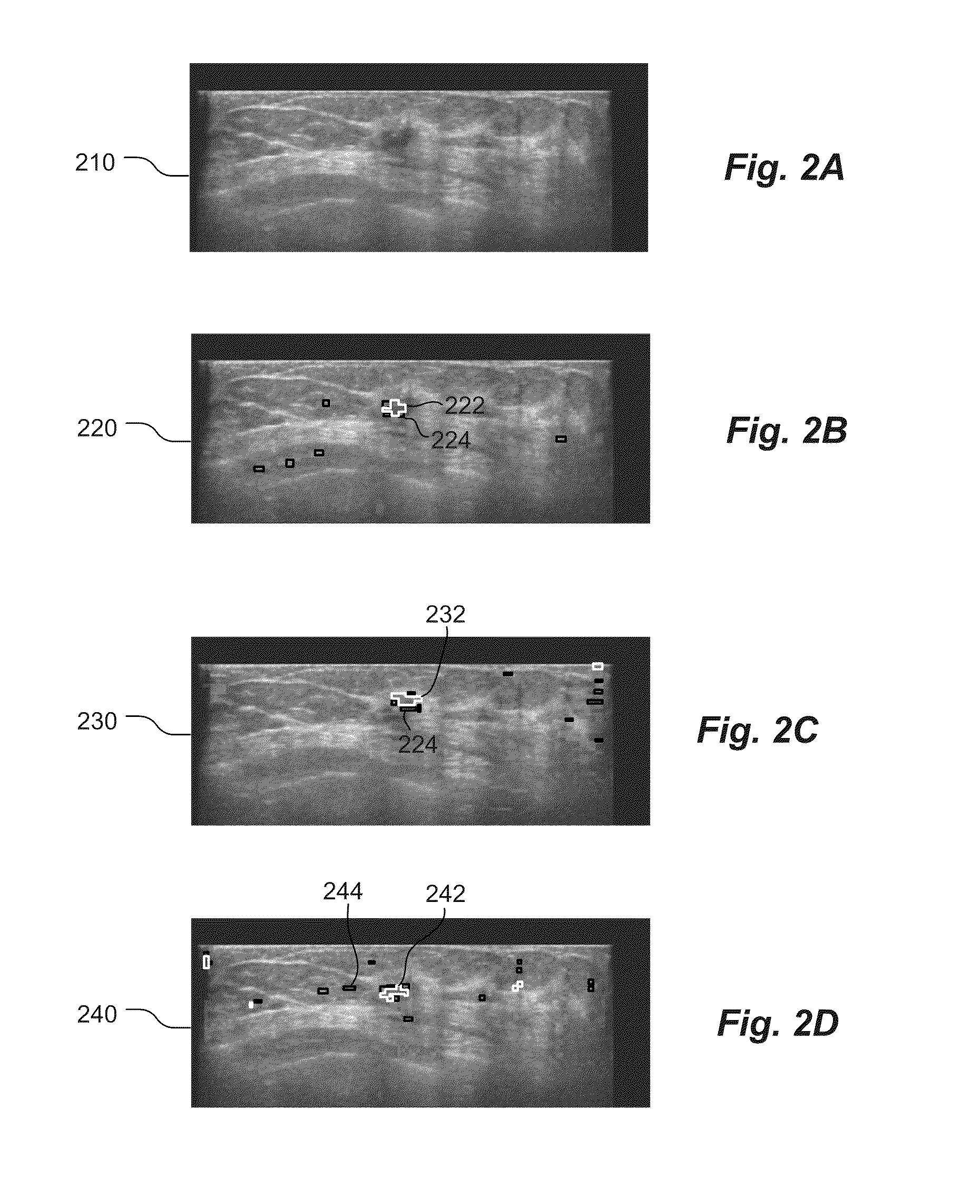
Methods and related systems are described for detection of breast cancer in 3D ultrasound imaging data. Volumetric ultrasound images are obtained by an automated breast ultrasound scanning (ABUS) device. In ABUS images breast cancers appear as dark lesions. When viewed in transversal and sagittal planes, lesions and normal tissue appear similar as in traditional 2D ultrasound. However, architectural distortion and spiculation are frequently seen in the coronal views, and these are strong indicators of the presence of cancer. The described computerized detection (CAD) system combines a dark lesion detector operating in 3D with a detector for spiculation and architectural distortion operating on 2D coronal slices. In this way a sensitive detection method is obtained. Techniques are also described for correlating regions of interest in ultrasound images from different scans such in different scans of the same breast, scans of a patient's right versus left breast, and scans taken at different times. Techniques are also described for correlating regions of interest in ultrasound images and mammography images. Interactive user interfaces are also described for displaying CAD results and for displaying corresponding locations on different images.
Owner:QVIEW MEDICAL
Systems and methods for measurement of objects of interest in medical images
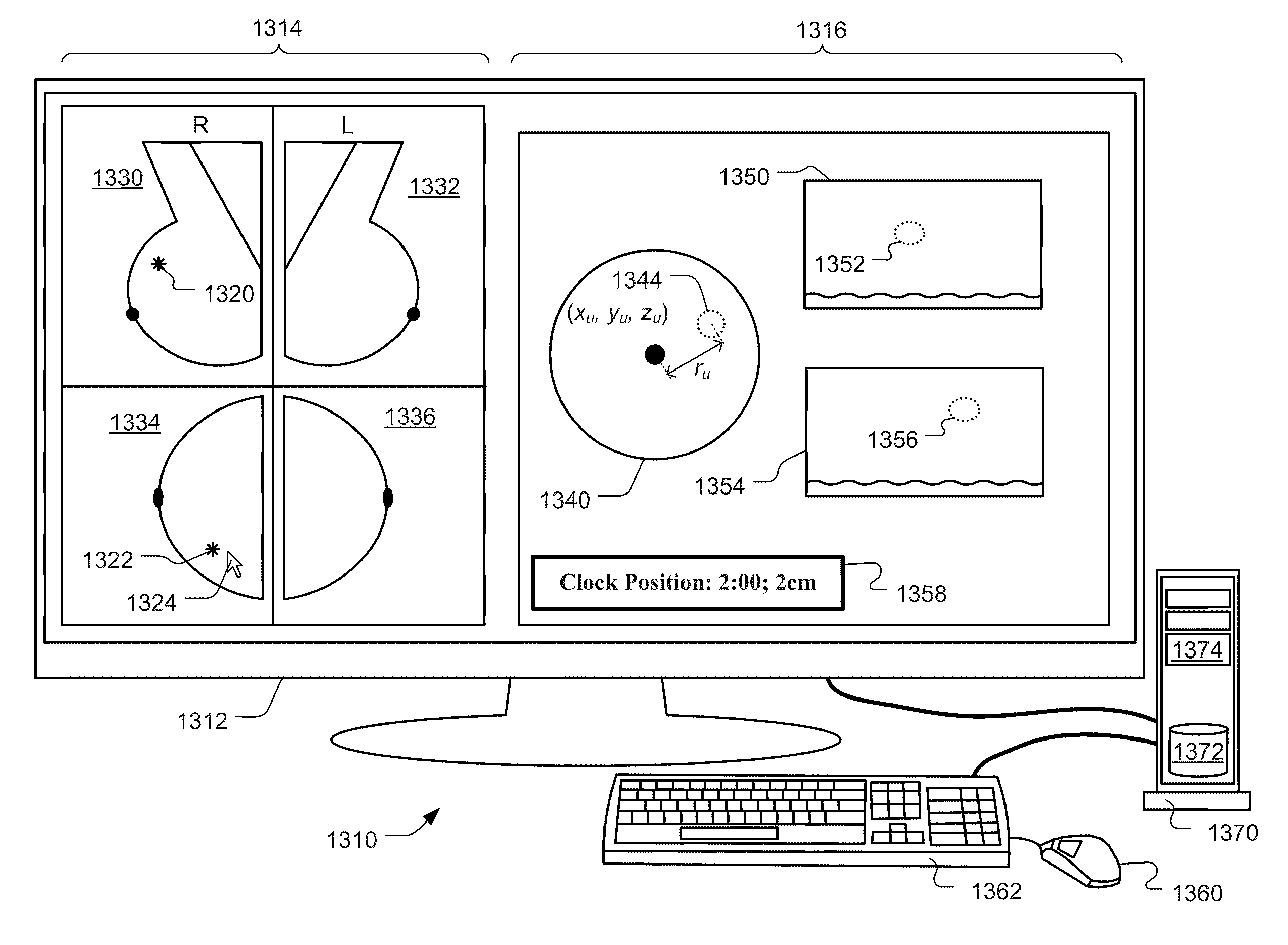
A system and method are provided for the measurement and display of attributes of an object of interest in a medical image. An object of interest is identified, such as a lesion or cluster of lesions in a breast area on a mammography image. At least one attribute of the lesion is then automatically measured, such as the area of the lesion, the width and height of a cluster of lesions, the number of lesions in a cluster, or the distance from one or more lesions to an anatomical feature such as the nipple, skin line or chest wall. The measurements are then displayed to a user, for example by displaying the measurements on the mammography image. Additionally, anatomical zones, such as standard, quadrant and clock zones of the breast area may be determined and displayed on the mammography image or diagram to display the location of the lesion as it corresponds to the zones.
Owner:FUJIFILM CORP
Mastopexy and Breast Reconstruction Prostheses and Method
InactiveUS20120158134A1Easy to handleResistant to biodegradationMammary implantsCell-Extracellular MatrixMastopexy
Mastopexy and breast reconstruction prostheses and implantation method that allow for radiographic imaging of the breast tissue. The prostheses are arcuate and elongate optionally meshed to conform with breast tissue when implanted. Prostheses are made from naturally occurring extracellular matrix, primarily collagen, that, allows for mammographic imaging without interference as is expected from synthetic materials.
Owner:CODORI HURFF JEANNE +1
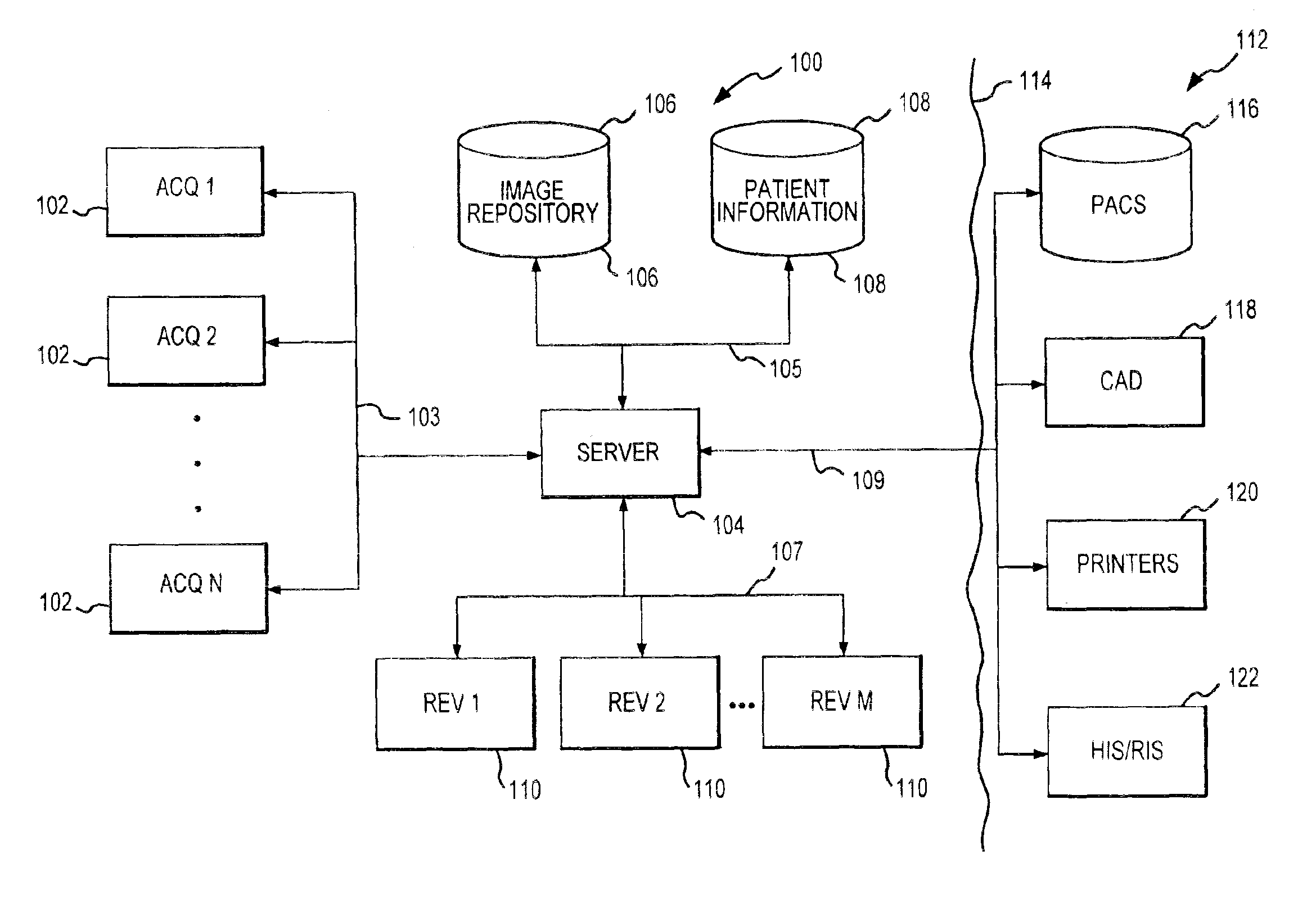
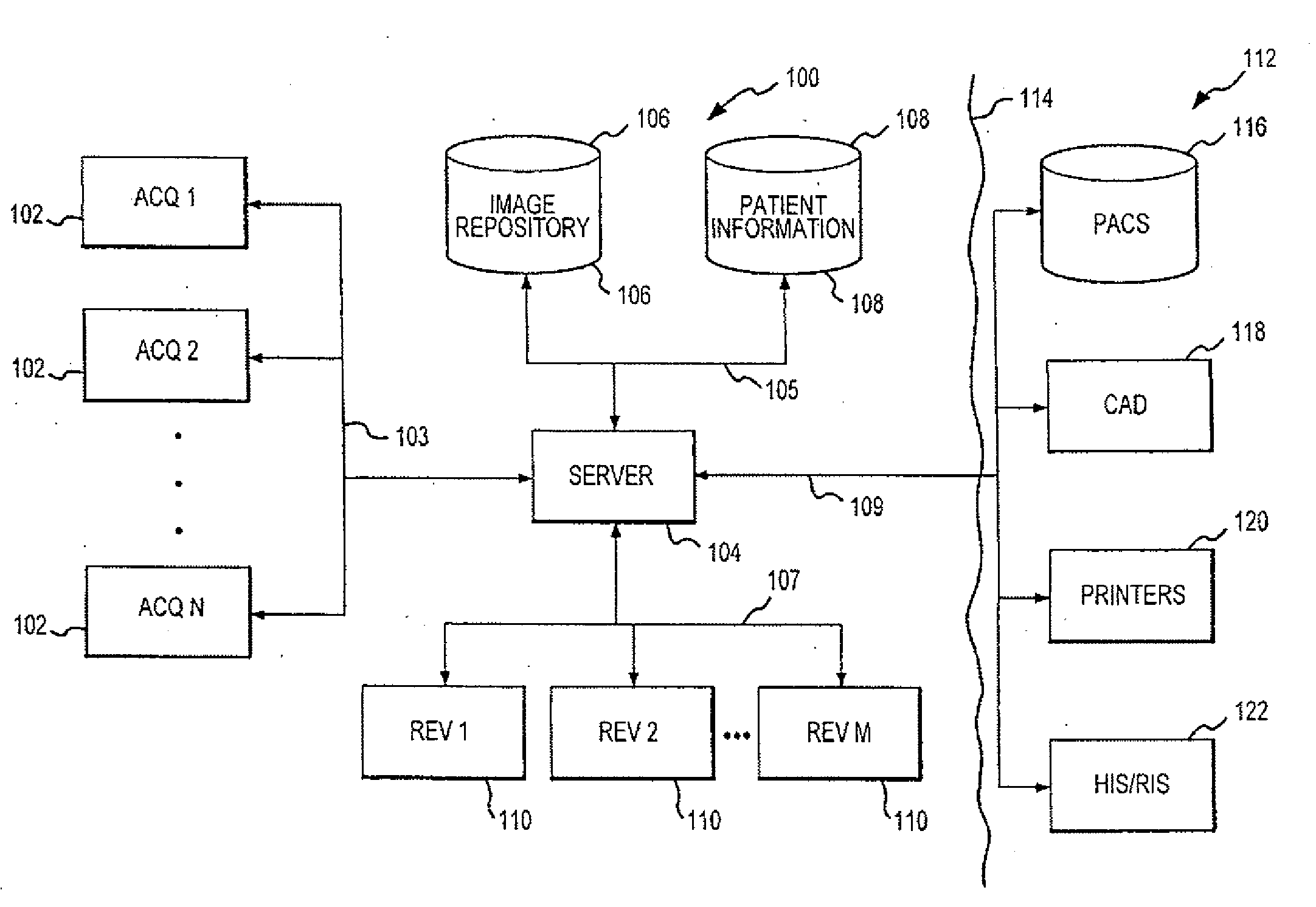
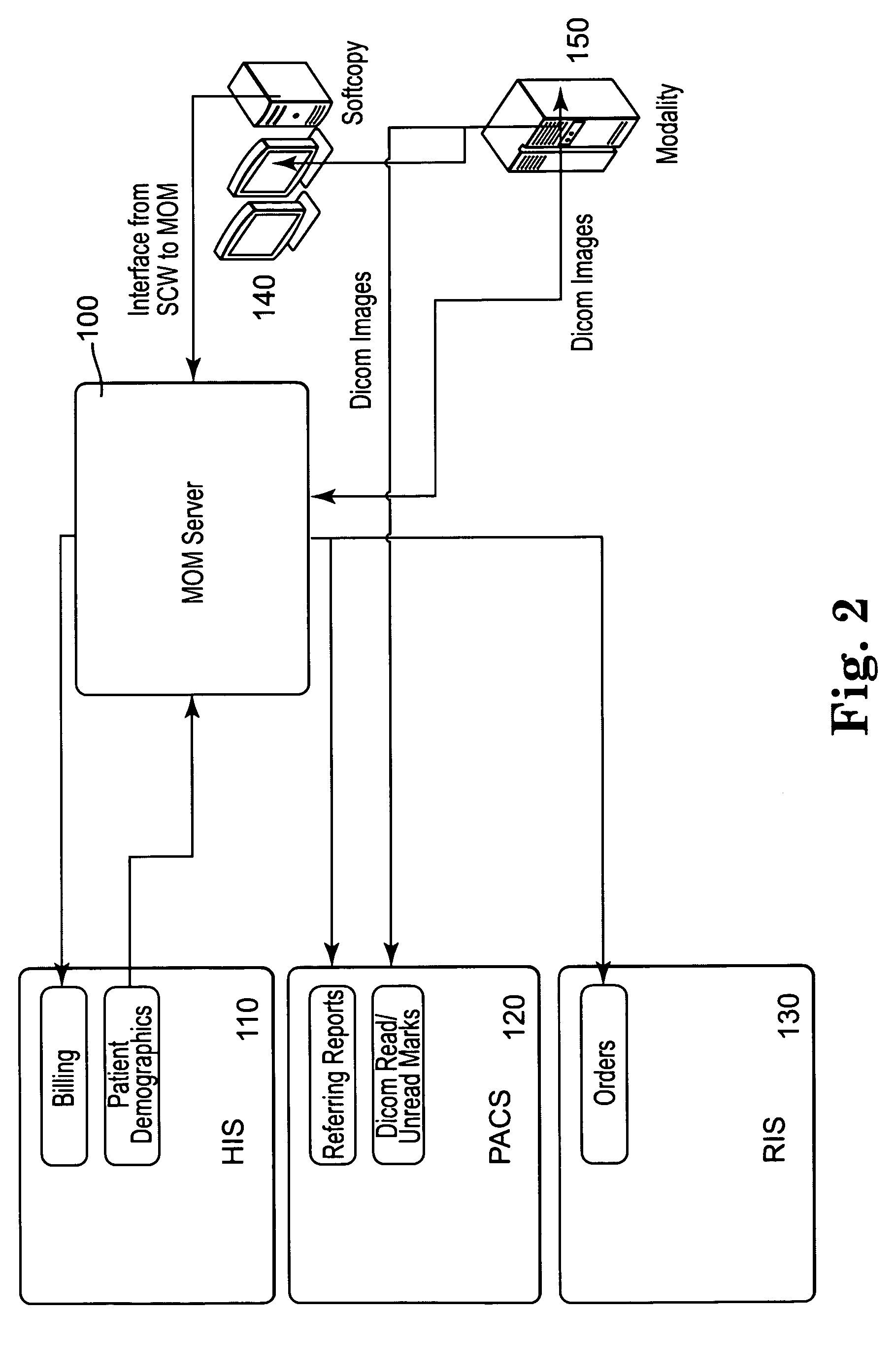
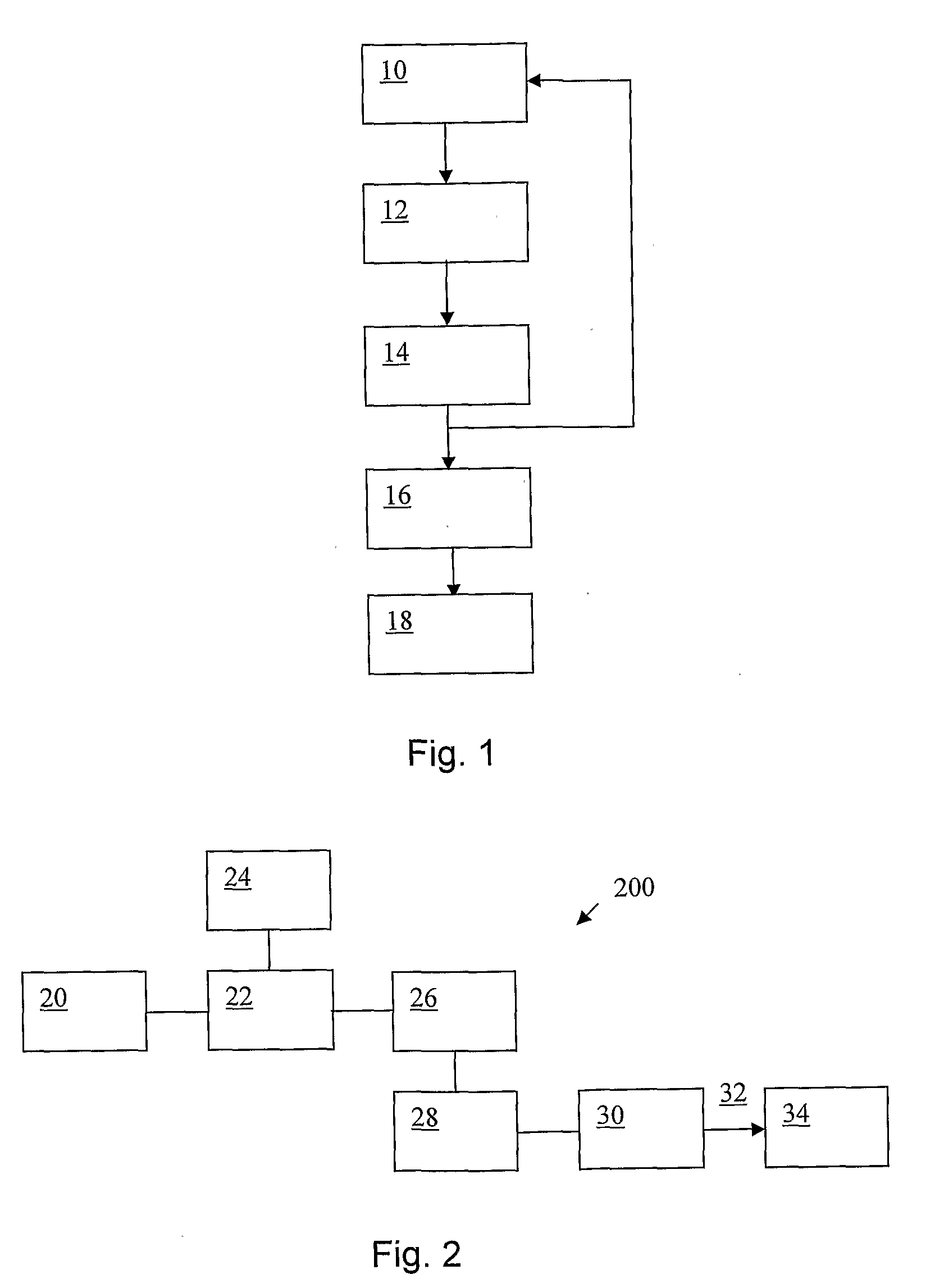
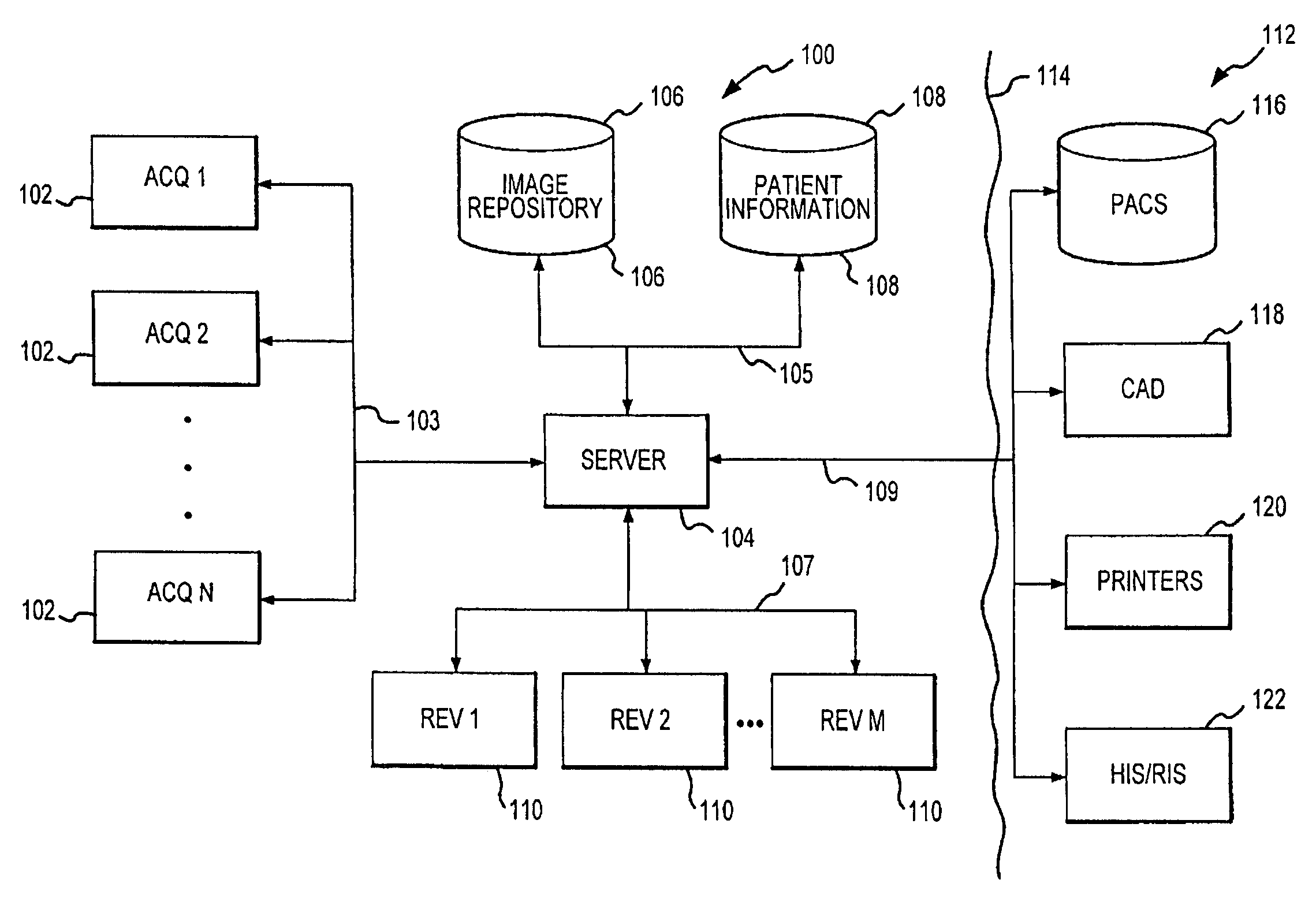
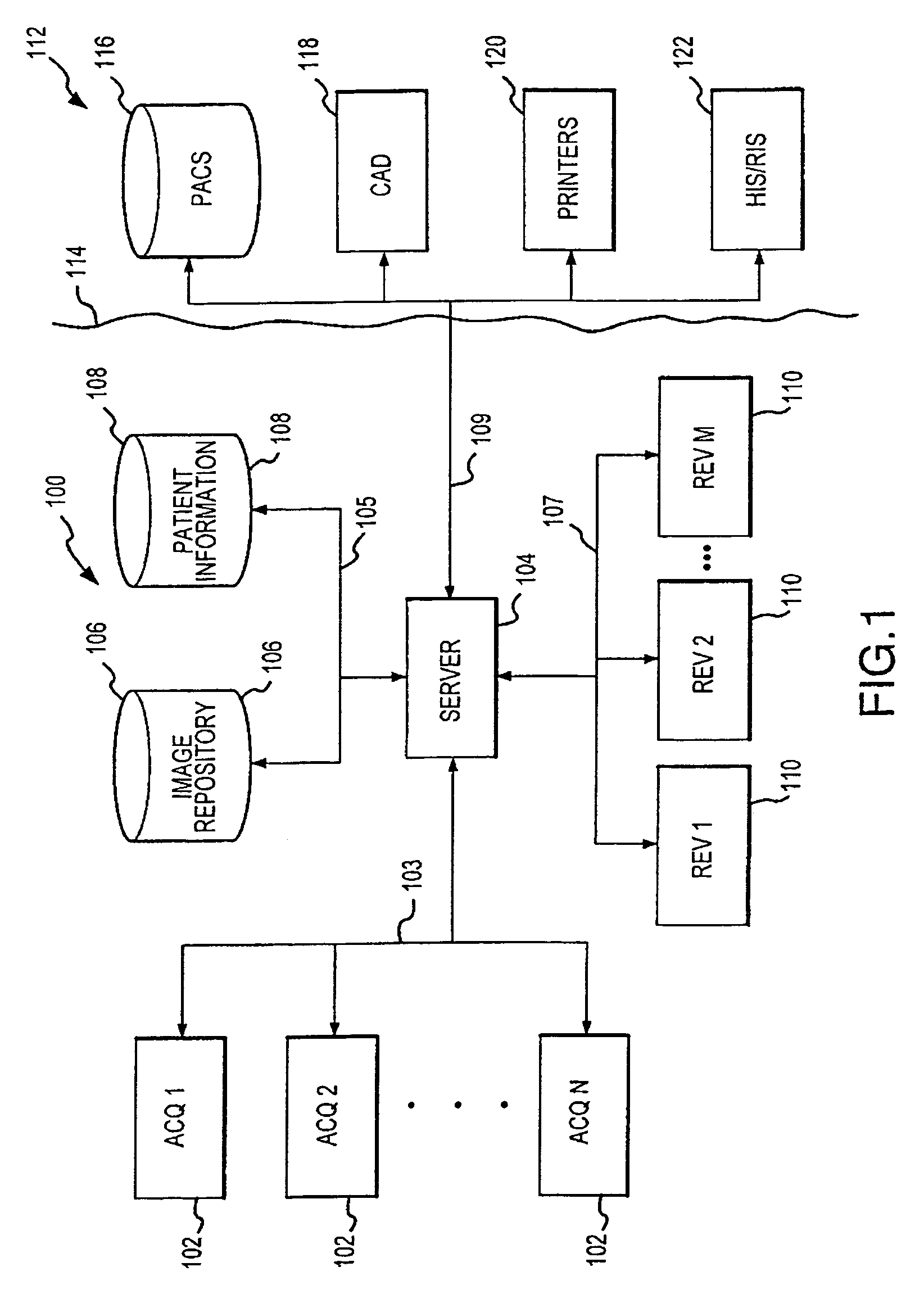
Distributed Architecture for Mammographic Image Acquisition and Processing
InactiveUS20080279439A1Easy to useOrgan movement/changes detectionPatient positioning for diagnosticsImage InspectionDICOM
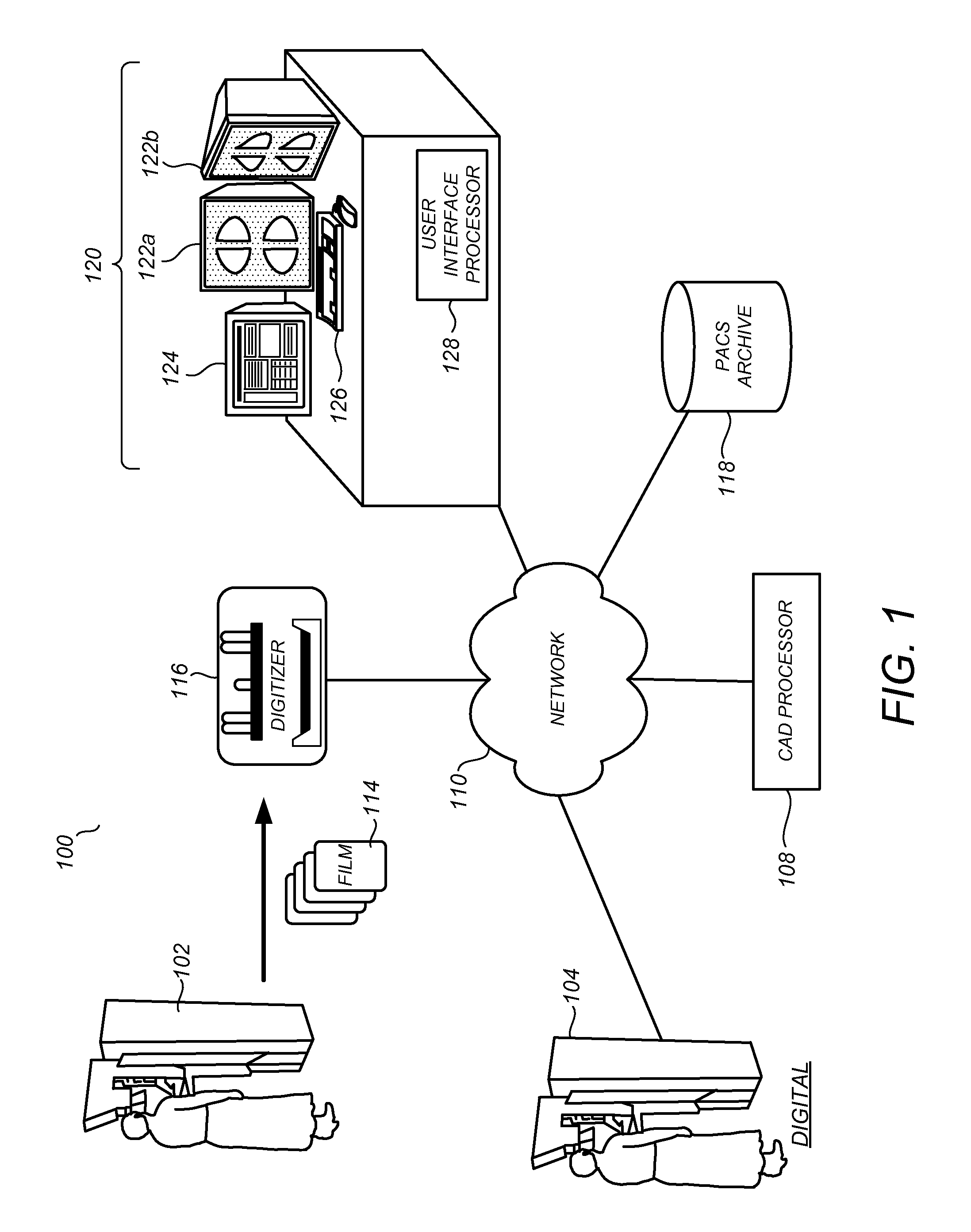
A distributed architecture allows for decoupling of mammographic image acquisition and review, thereby enabling more efficient use of resources and enhanced processing. In one embodiment, the system (100) includes a number of image acquisition stations (102) and a number of image review stations (110) all associated with a central server (104). The server (104) is operative to access an image repository (106), a patient information data base (108) and a number of DICOM tools (112). The invention allows for more efficient and / or more convenient use of the image acquisition equipment and image processing stations. Moreover, the distributed architecture including the central image repository provides certain processing and analysis advantages. The invention also provides certain processing and workflow enhancements that allow for a more full realization of potential digital mammography advantages.
Owner:HOLOGIC INC
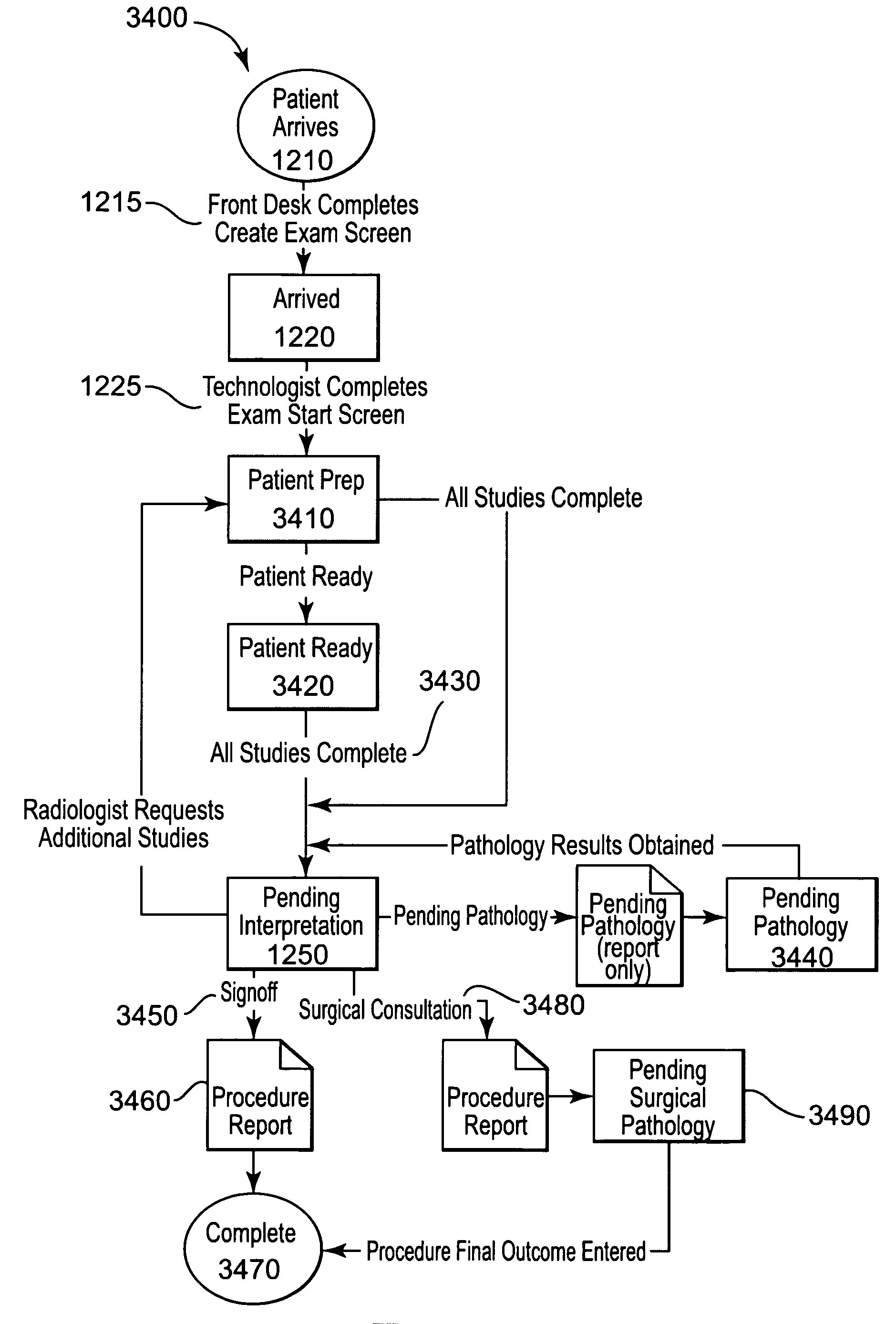
Mammography operational management system and method
InactiveUS20060212317A1Character and pattern recognitionMedical report generationDigital mammographyScreening Examination
In accordance with one embodiment of the present invention, a method in a computer system is provided for managing mammography examination information. The method includes receiving electronically personal information of a patient, such as name, demographic information, and insurance information. Next, digital mammography images of the patient are produced by a modality for a screening examination and / or diagnostic examination, and mammography procedure results data is generated that reflect the results of a procedure examination, such as a biopsy. Then, the personal information, digital images, and procedure data of the user are stored in a database and are logically linked to each other. When a system user, such as a radiologist, is prepared to interpret examination results, the digital images and procedure data of the user are electronically displayed to the user responsive to a user request. At least a first portion of the digital images is electronically retrieved from the database, and at least a second portion of the digital images is retrieved from a Picture Archive and Communications System (PACS). Data from the user representing a medical interpretation of the digital images and procedure data are received, and a medical report based on the medical interpretation is automatically generated responsive to receipt of the interpretation.
Owner:NU DESIGN MEDICAL TECH
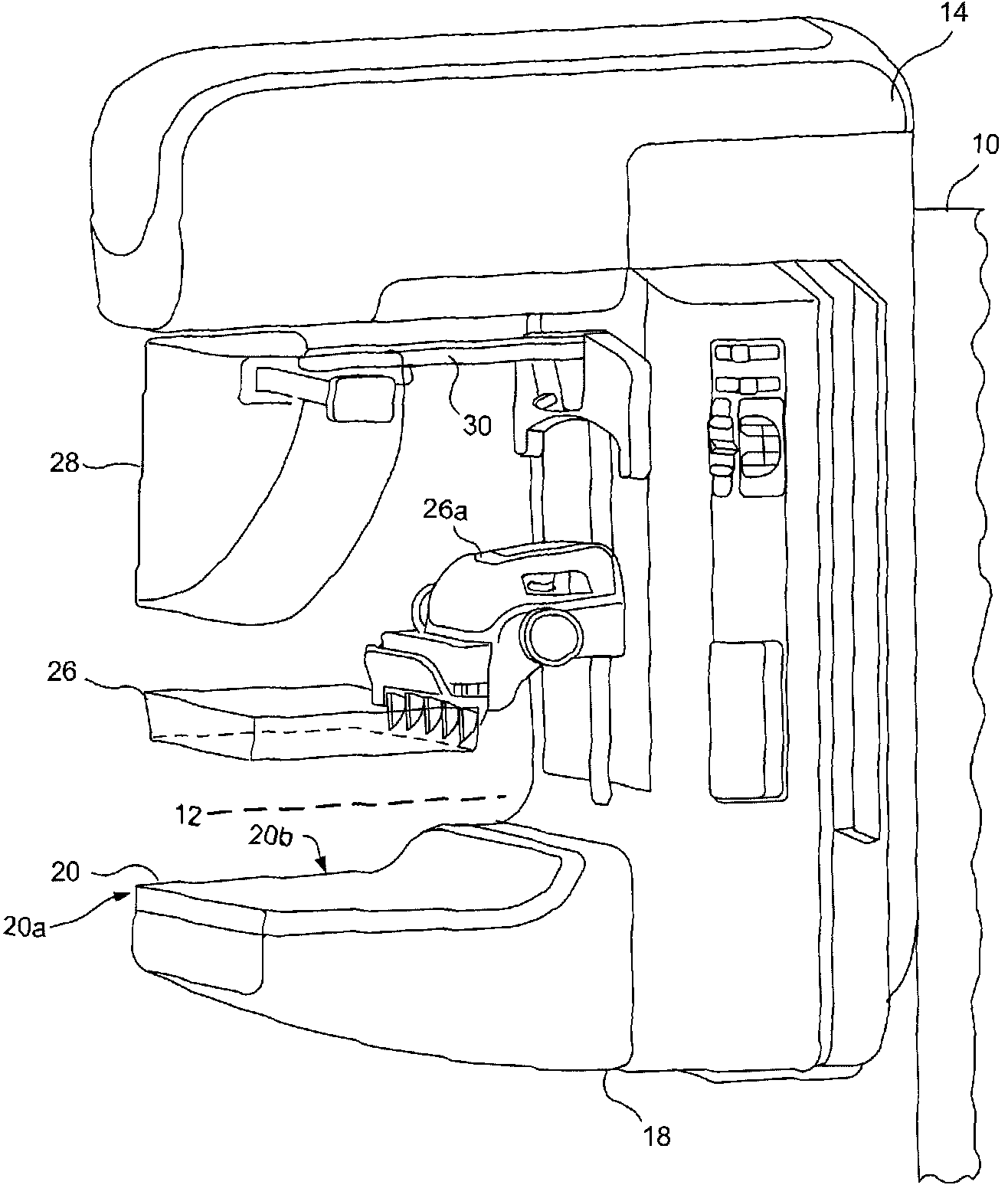
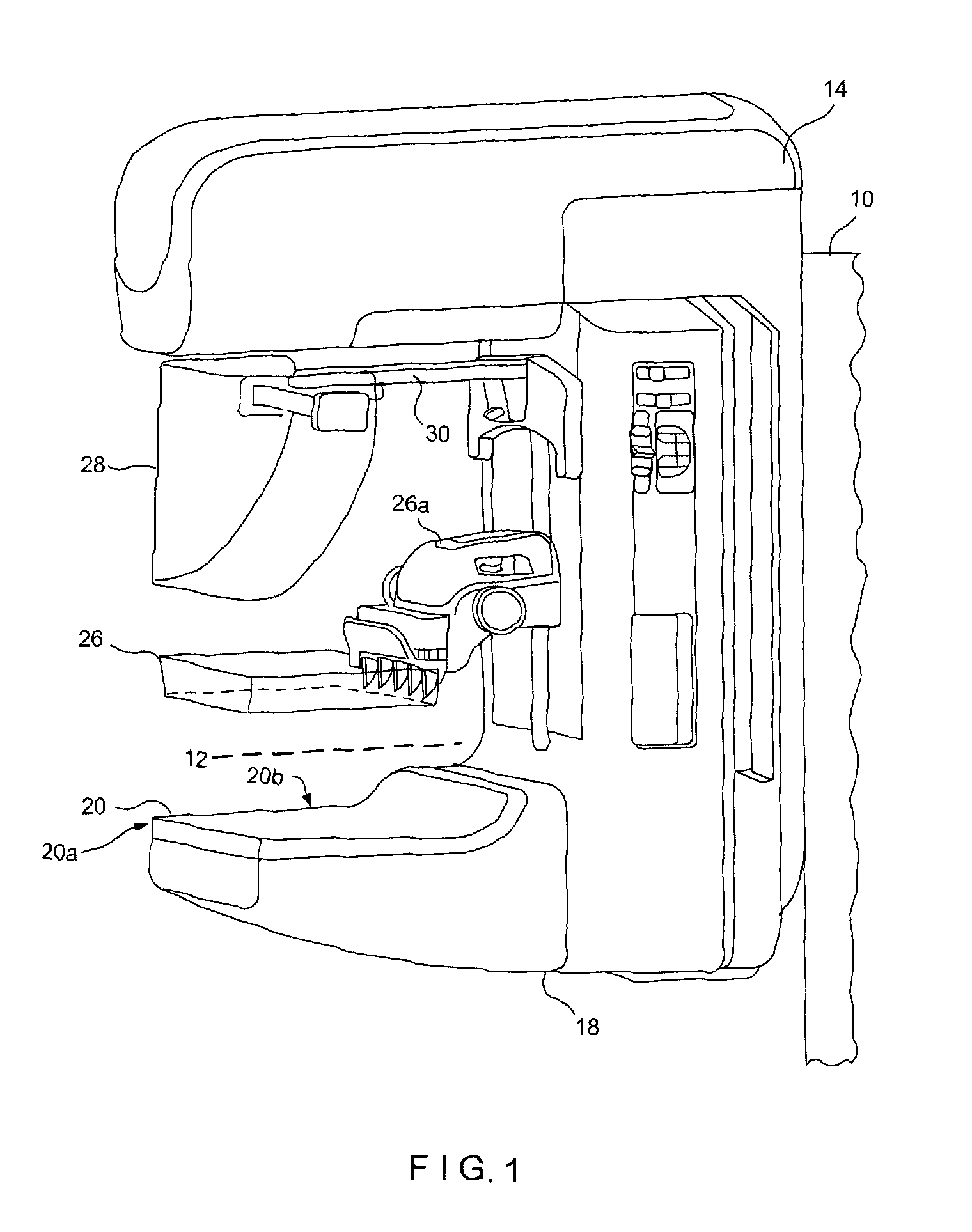
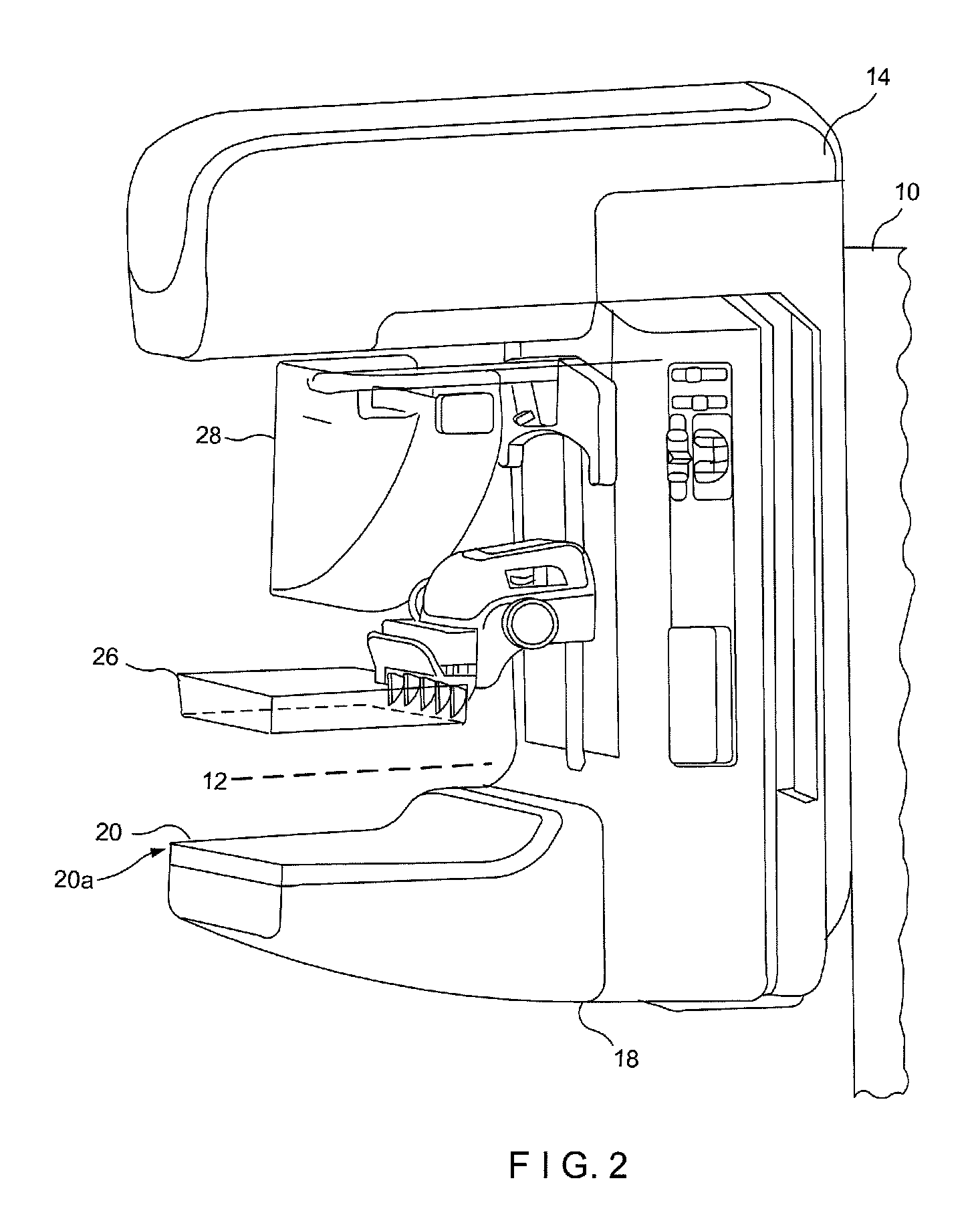
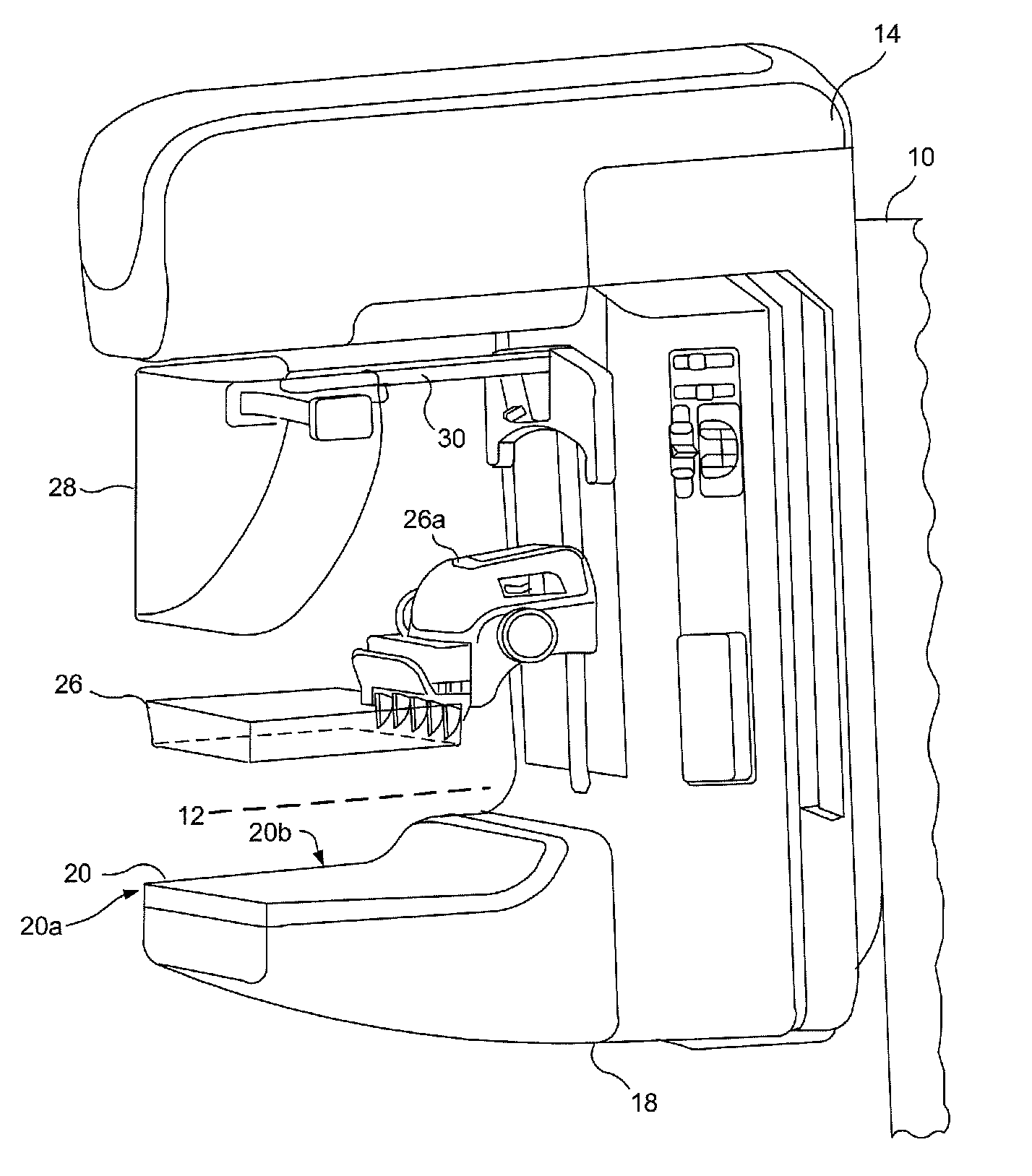
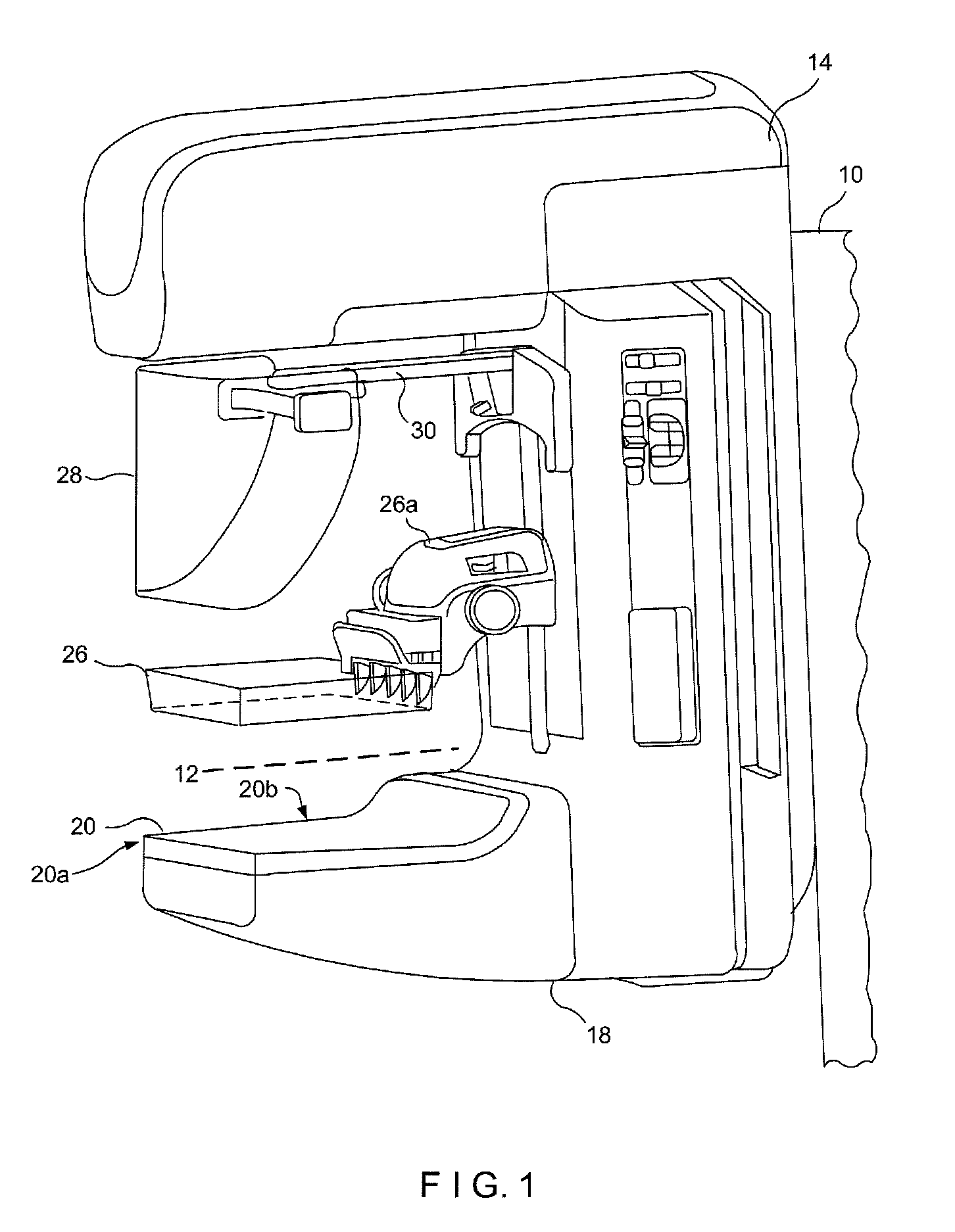
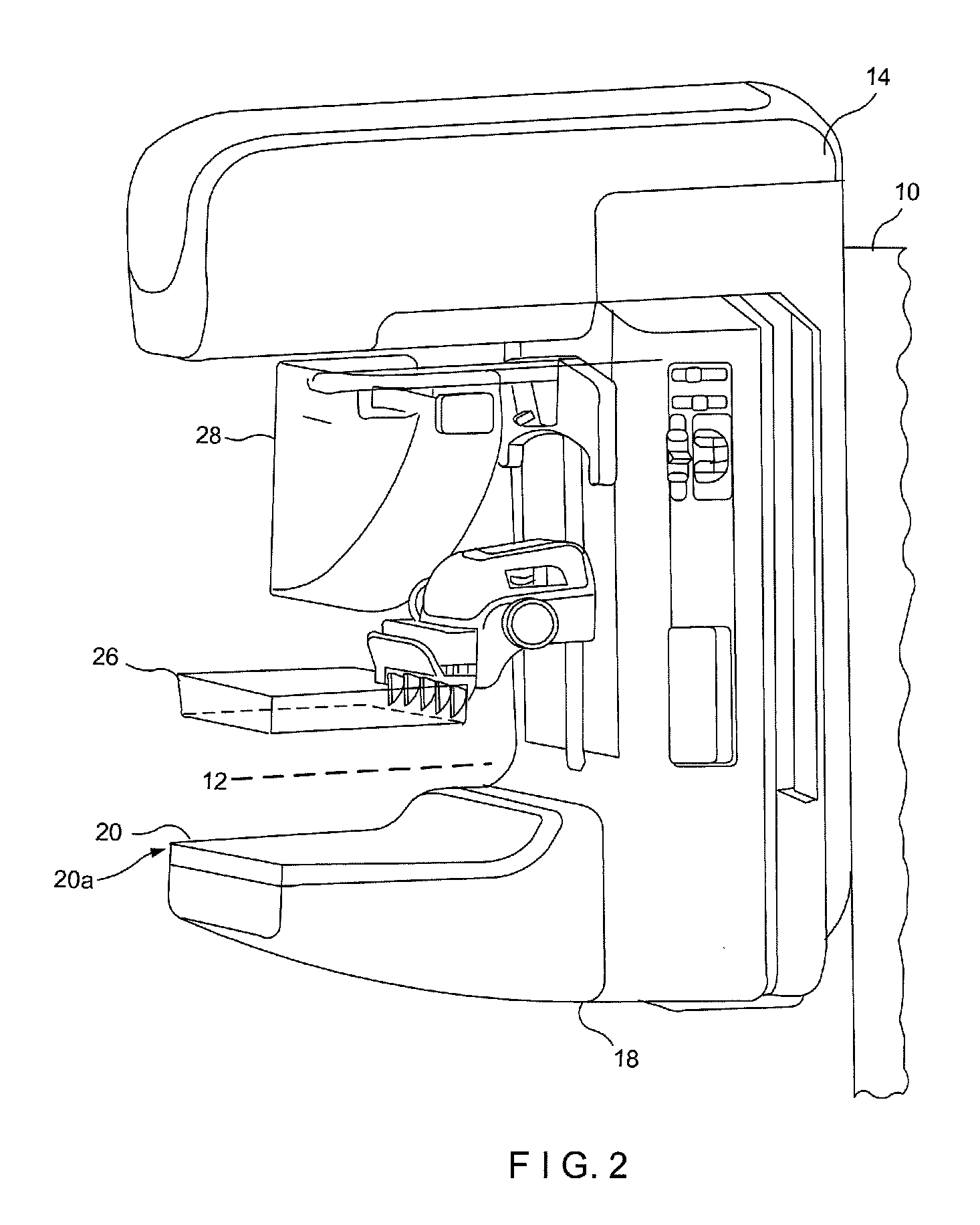
Breast tomosynthesis system with shifting face shield
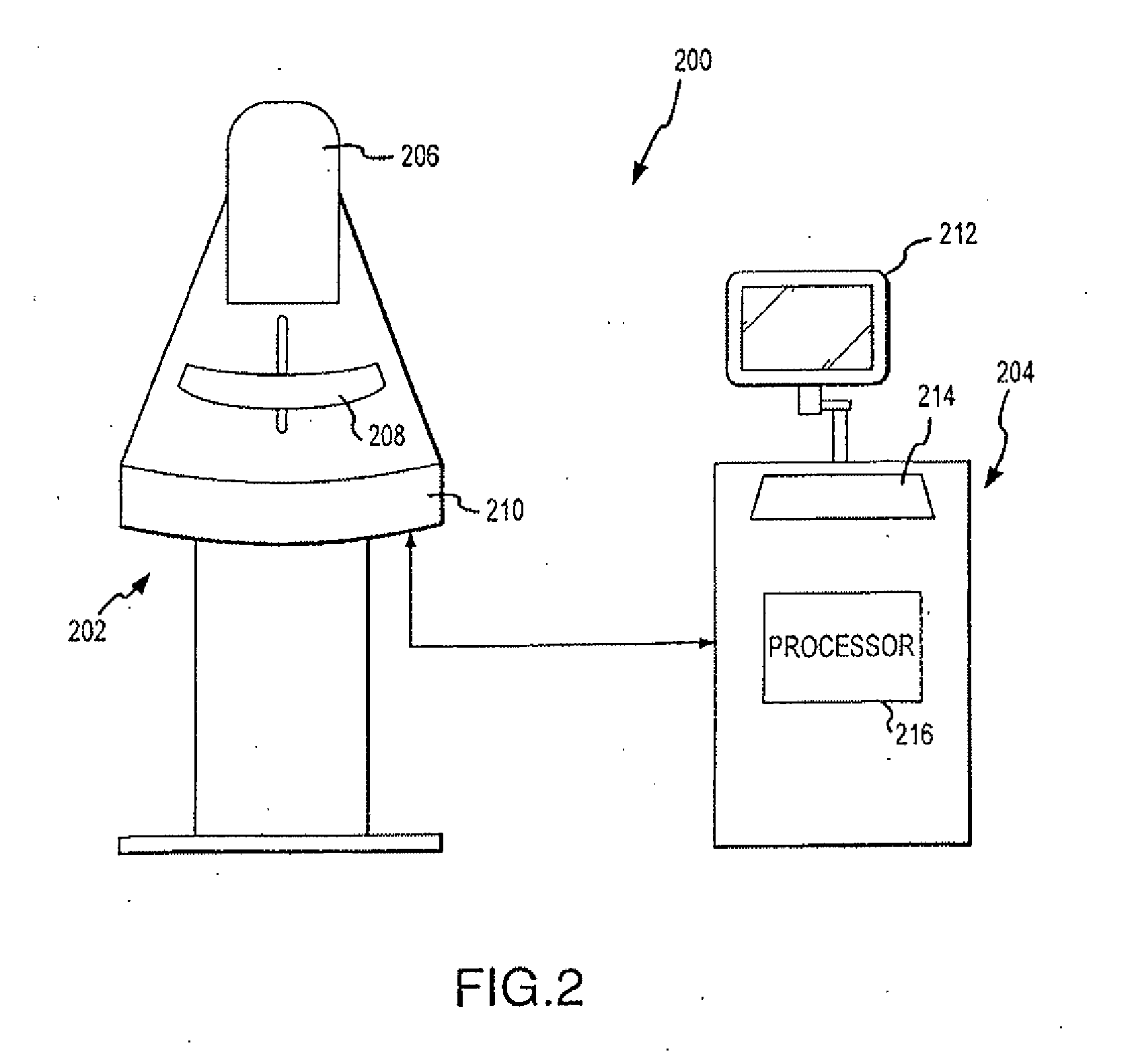
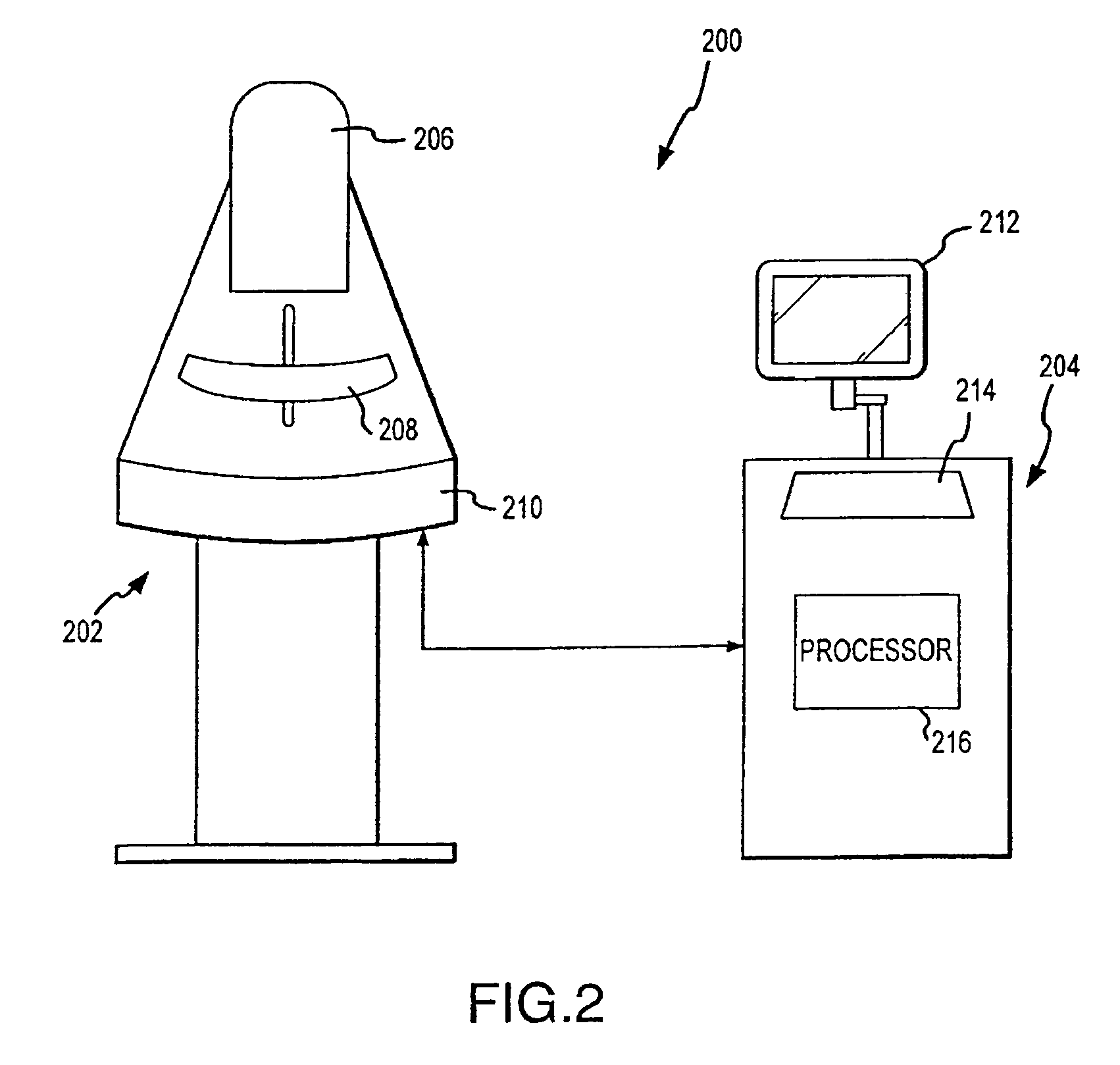
ActiveUS7792245B2Easy to reachProtects patientPatient positioning for diagnosticsX-ray tube vessels/containerTomosynthesisRadiology
Breast imaging using any one of a mammography system, a tomosynthesis system, or a fused system that selectively takes either or both of mammography images and tomosynthesis images, further uses a patient shield that moves closer to and further away from the patient's chest and head, between (1) an access position that facilitates the technologist's access to adjust the patient's breast while the breast is being compressed and (b) a protective position in which the shield helps protect the patient from collision with moving components and from x-ray exposure of tissue other than the tissue that is to be imaged.
Owner:HOLOGIC INC
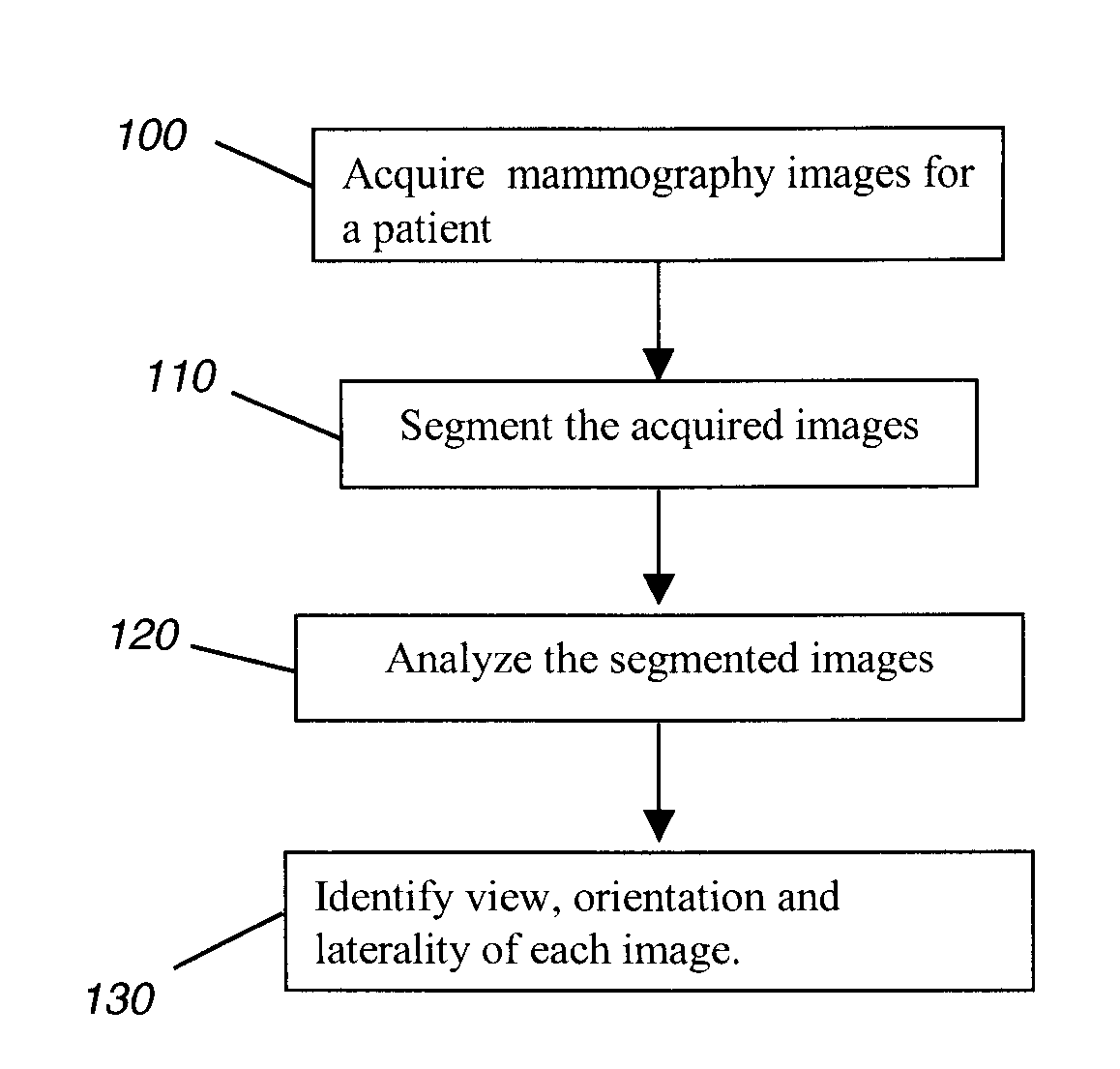
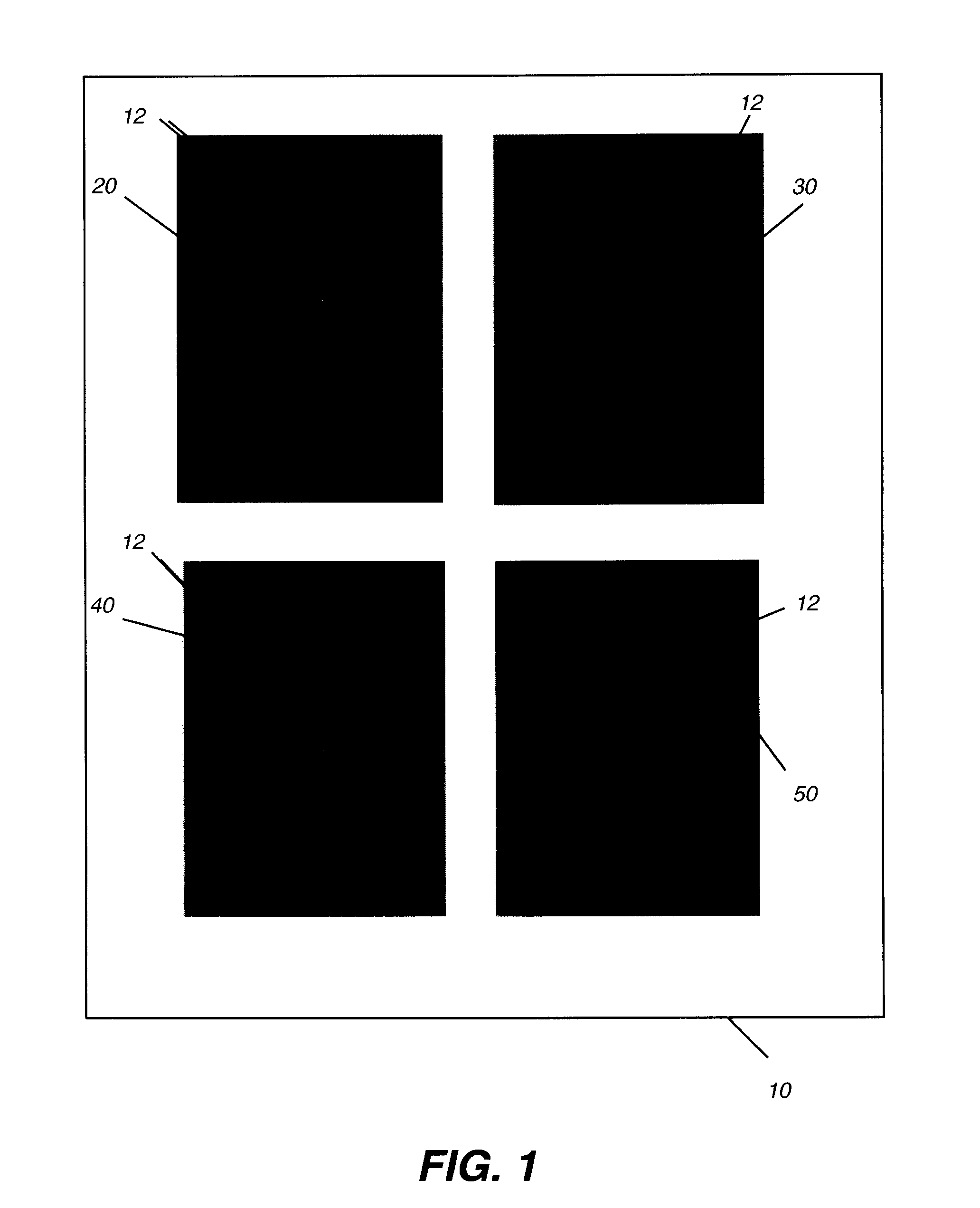
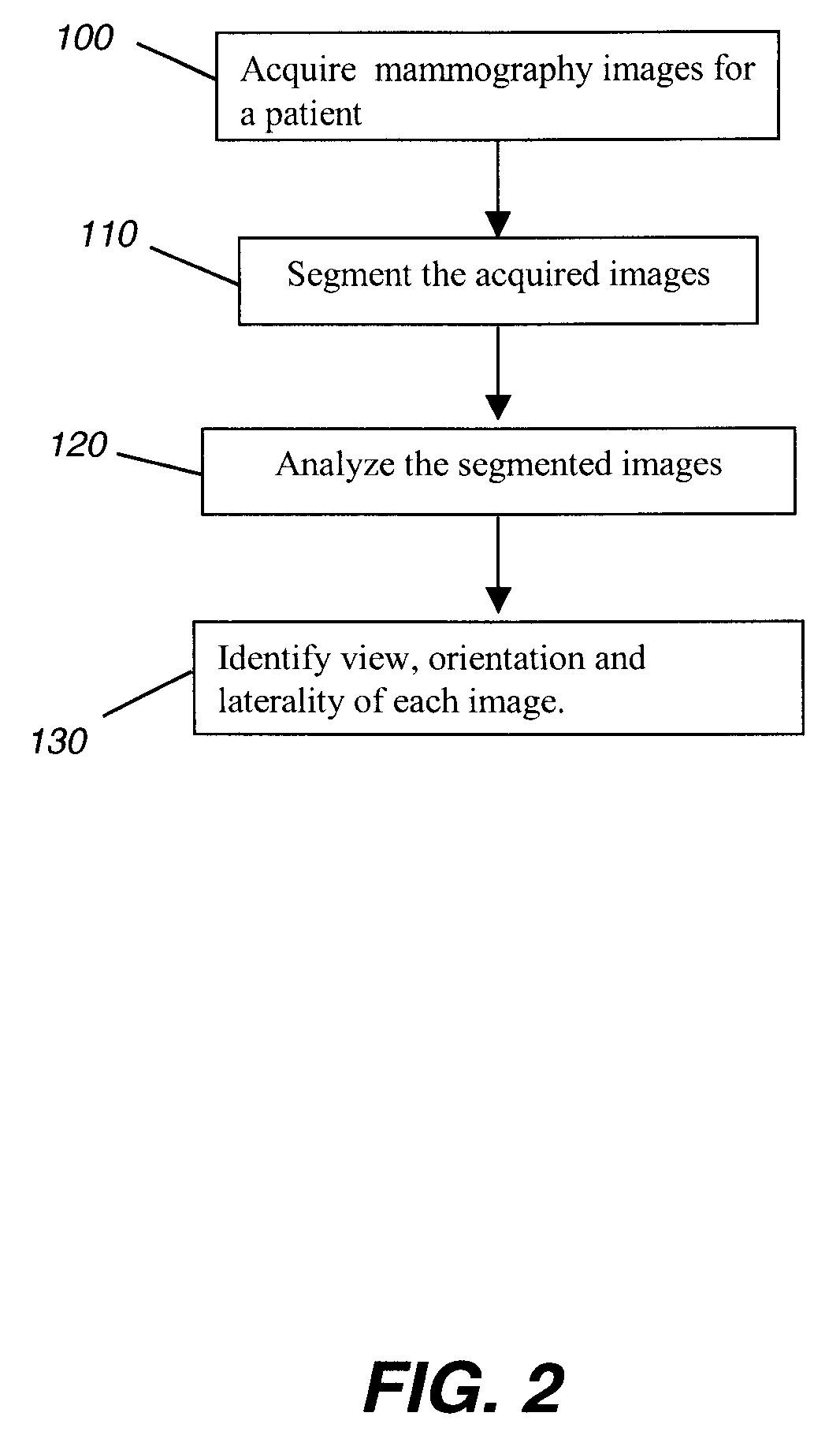
Determining mammographic image view and laterality
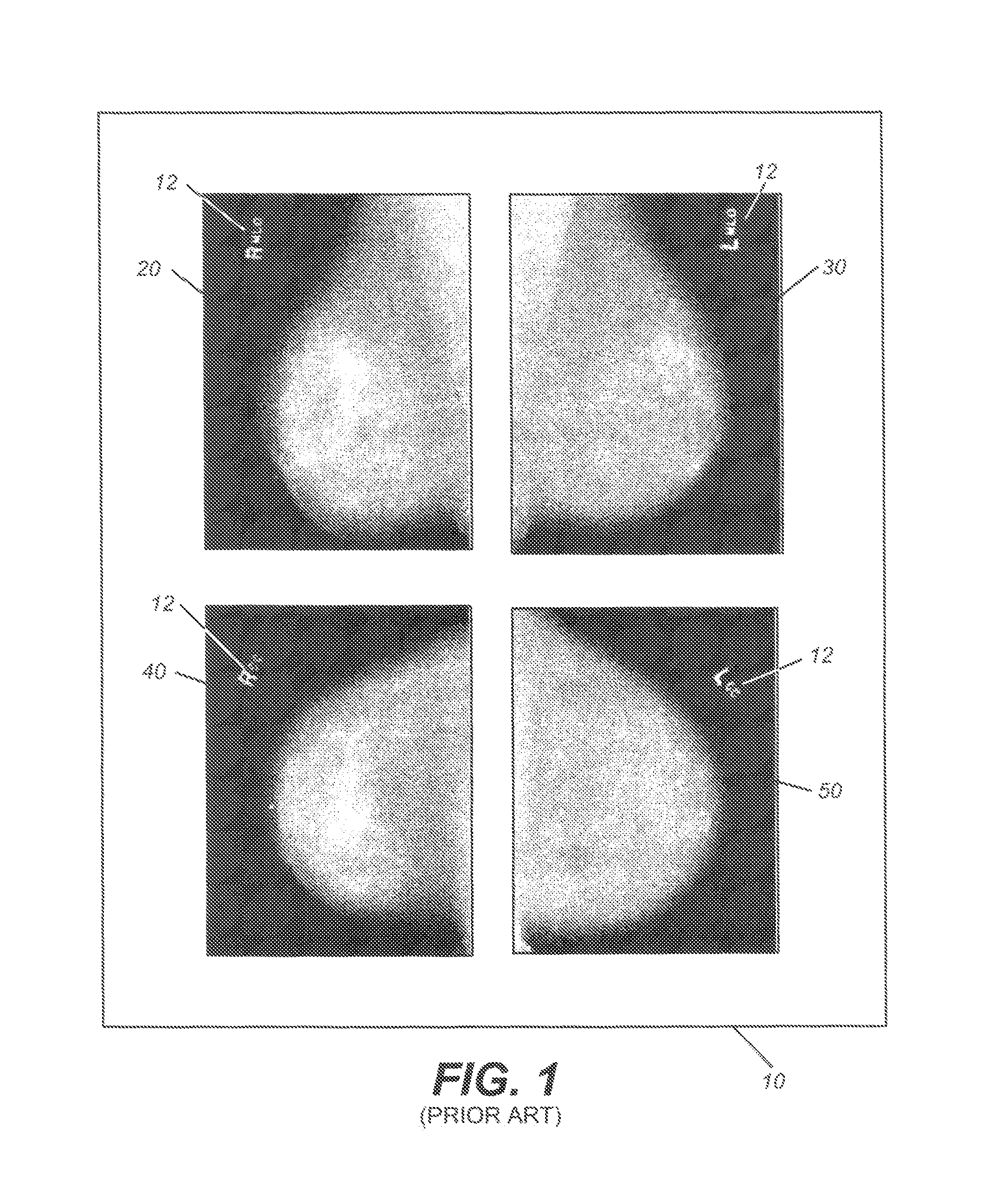
A method for displaying a mammography image. Digital data of the mammography image is obtained. The mammography image is segmented to identify at least a first diagnostically relevant region comprising an image of the breast tissue and a second diagnostically relevant region. A view type is assigned for the image, either cranio-caudal or medio-lateral oblique view, according to a symmetry index calculated from the segmented first diagnostically relevant region. Right or left laterality is assigned to the image according to a laterality feature calculated according to the relative position of at least the second diagnostically relevant region within the image.
Owner:CARESTREAM HEALTH INC
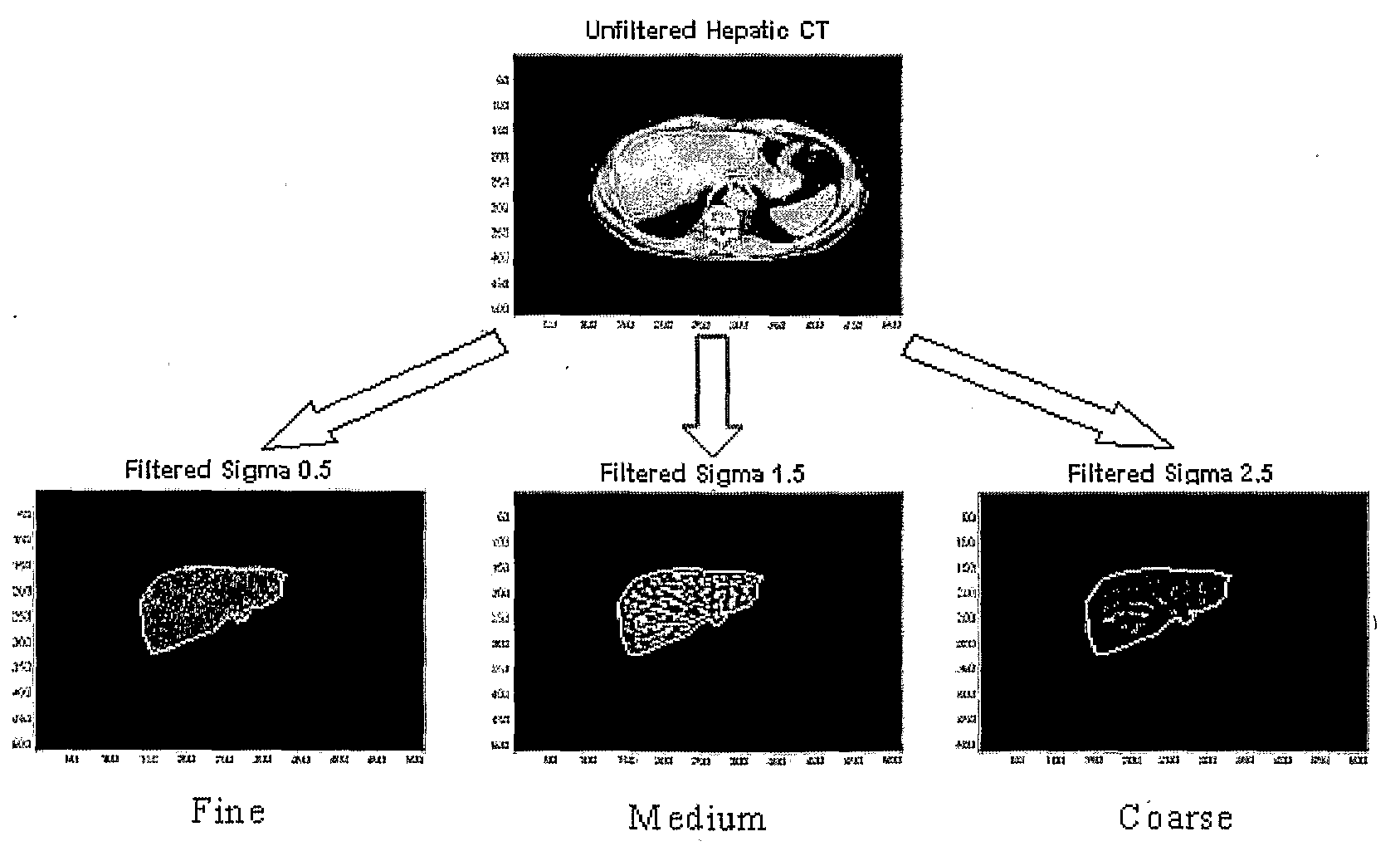
Method, apparatus and computer program for analysing medical image data
InactiveUS20100142775A1Easy to implementEasy to adjustImage enhancementImage analysisTumour metabolismBand-pass filter
Medical image data is analysed to produce a biomarker. The data is filtered with a plurality of band-pass filters each having a different bandwidth. A texture parameter is then determined from the filtered data from each filter and the biomarker is determined as at a ratio of the texture parameters. When the biomarker is obtained from a CT image of a liver, it can be predictive of poor survival, disease extent and liver physiology of a patient following resection of colorectal cancer. When obtained from a mammographic image, the biomarker can be indicative of cancer invasion and receptor status within mammographic abnormalities. When obtained from a CT image of a lung nodule, the biomarker can be predictive of tumour stage (or grading) and tumour metabolism of a patient with non-small cell lung carcinoma (lung cancer). When obtained from an MRI image of the brain, the biomarker can be indicative of schizophrenia and / or other brain disorders.
Owner:TEXRAD
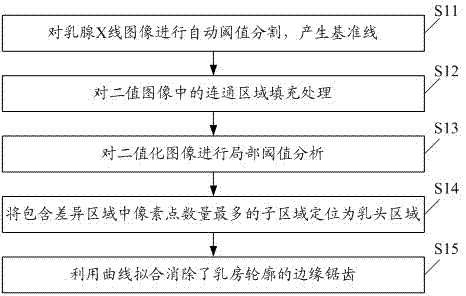
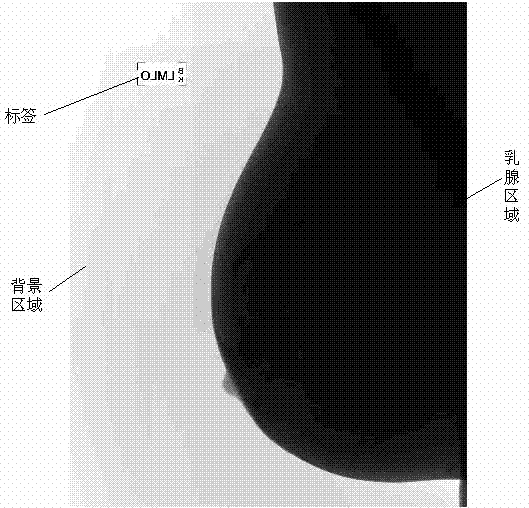
Preprocessing method and preprocessing system used for extracting breast regions in mammographic images
InactiveCN102956035AImprove efficiencyImprove execution performanceImage enhancementImage analysisComputation complexityPretreatment method
The invention discloses a preprocessing method and a preprocessing system used for extracting breast regions in mammographic images. The method includes steps: subjecting the mammographic images to automatic threshold segmentation to obtain binary images; subjecting communicated regions in the binary images to filling processing to remove labels and holes in the mammographic images; dividing the binary images into a plurality of subregions, and binarizing each subregion according to local threshold value to position breast contour regions; subjecting the binary images and the breast contour regions to set 'and' operation, searching number of pixel points in each subregion containing difference in the binary images along a reference line from top to bottom, and positioning the subregion with maximum number of pixel points in regions containing difference to be nipple regions. By overall automatic threshold segmentation and local threshold analysis, the breast regions and the nipple regions in the mammographic images can be accurately positioned, the preprocessing process is low in computation complexity, and execution efficiency is high.
Owner:SHENZHEN LANDWIND IND
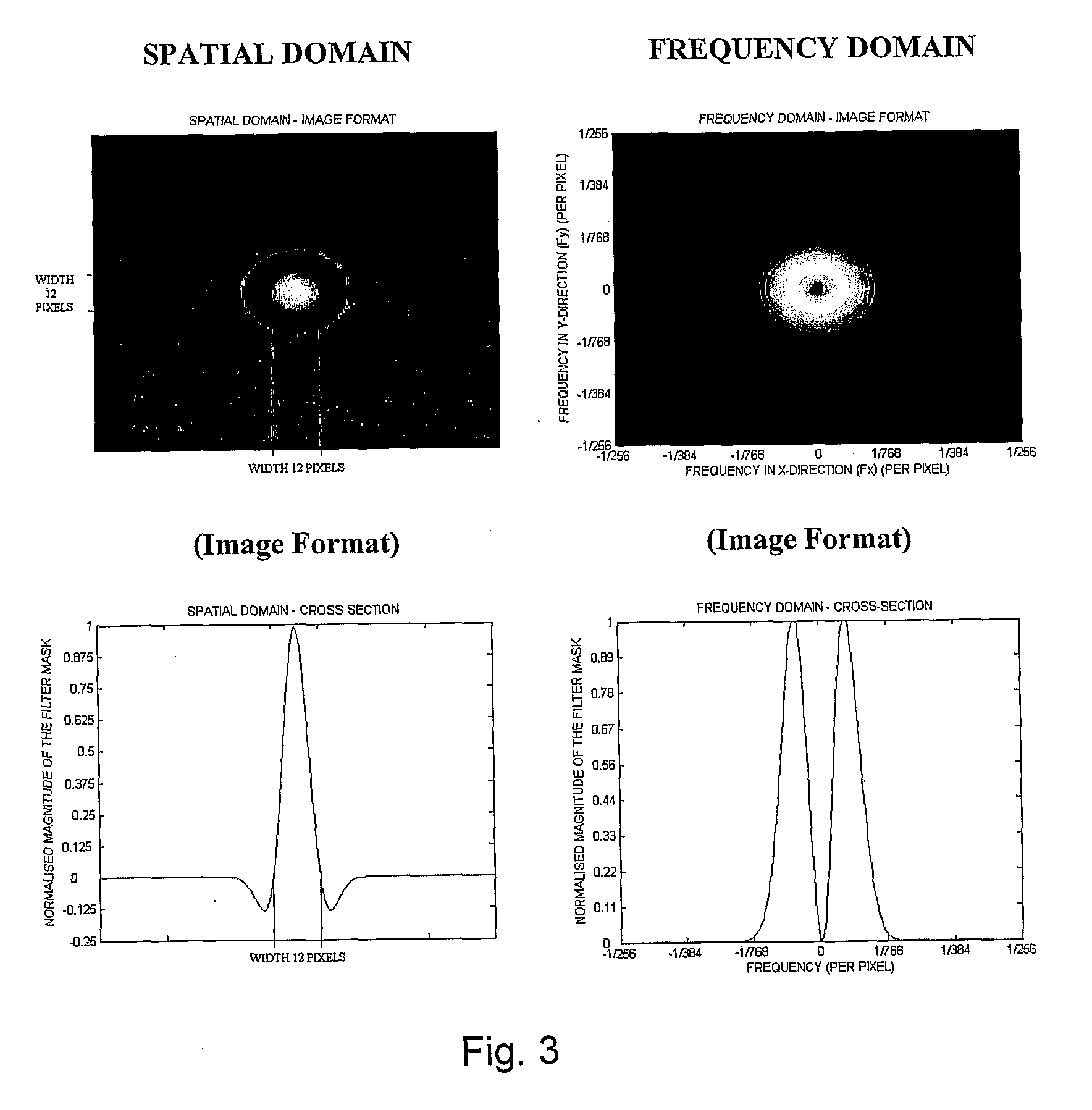
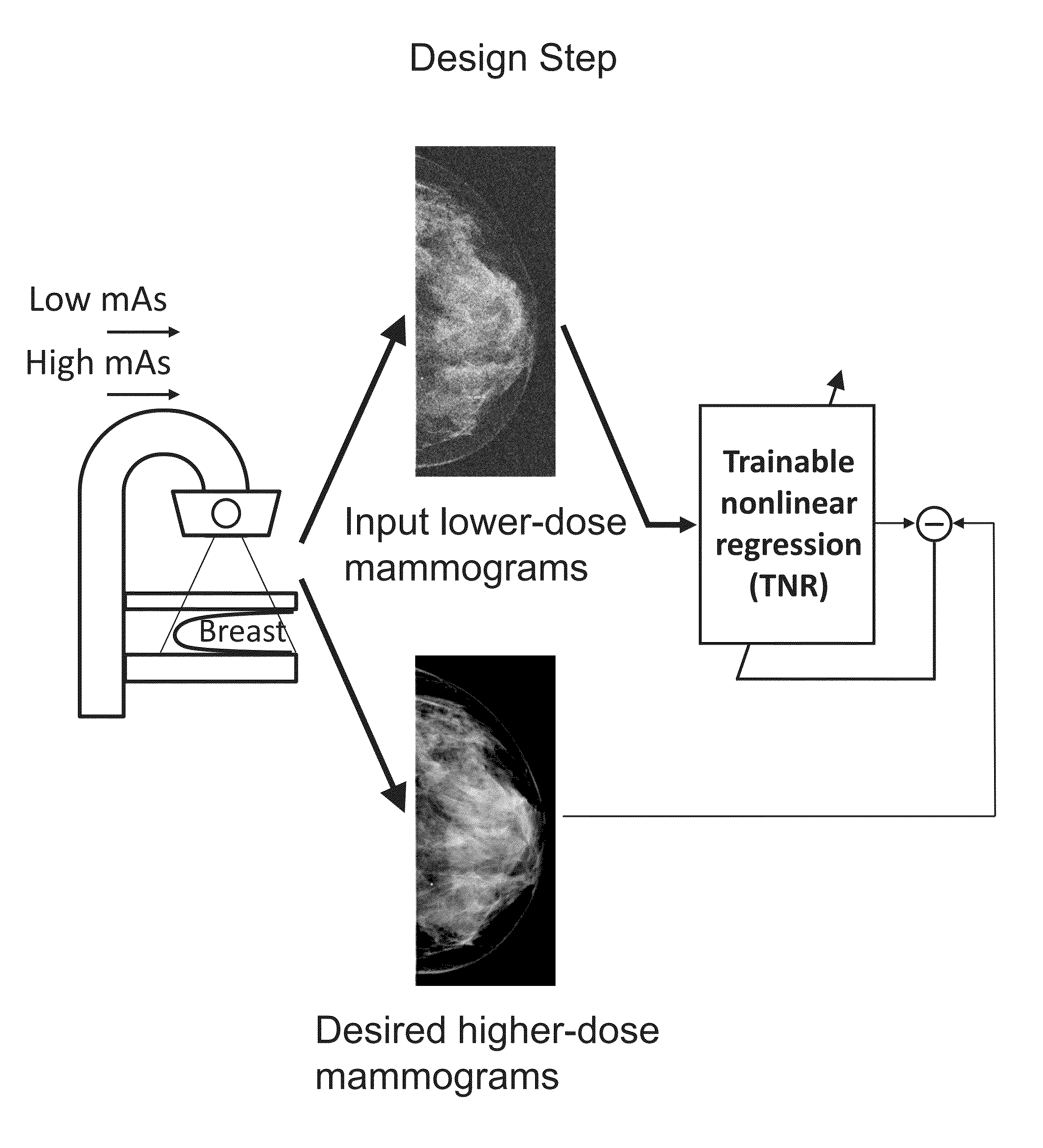
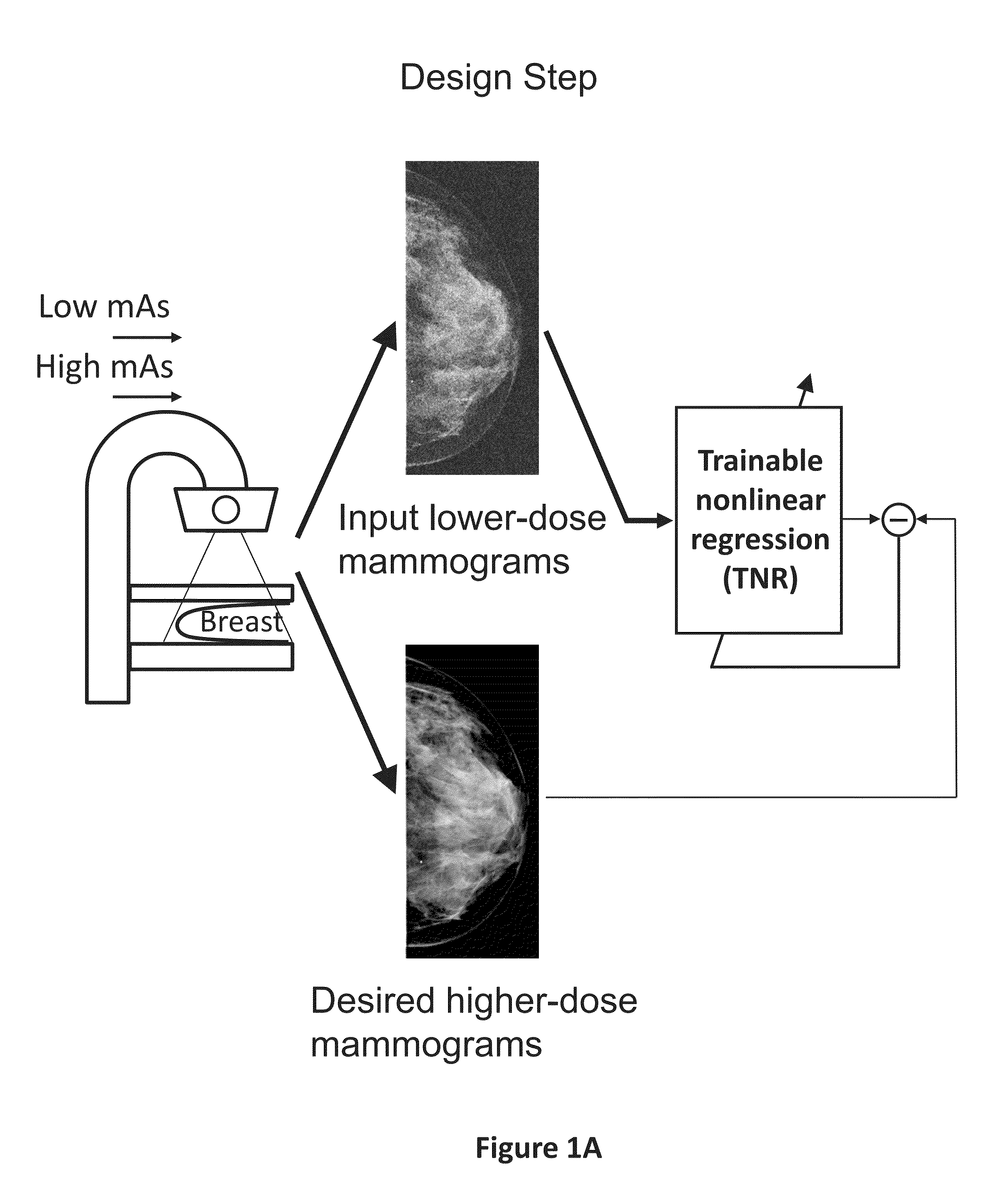
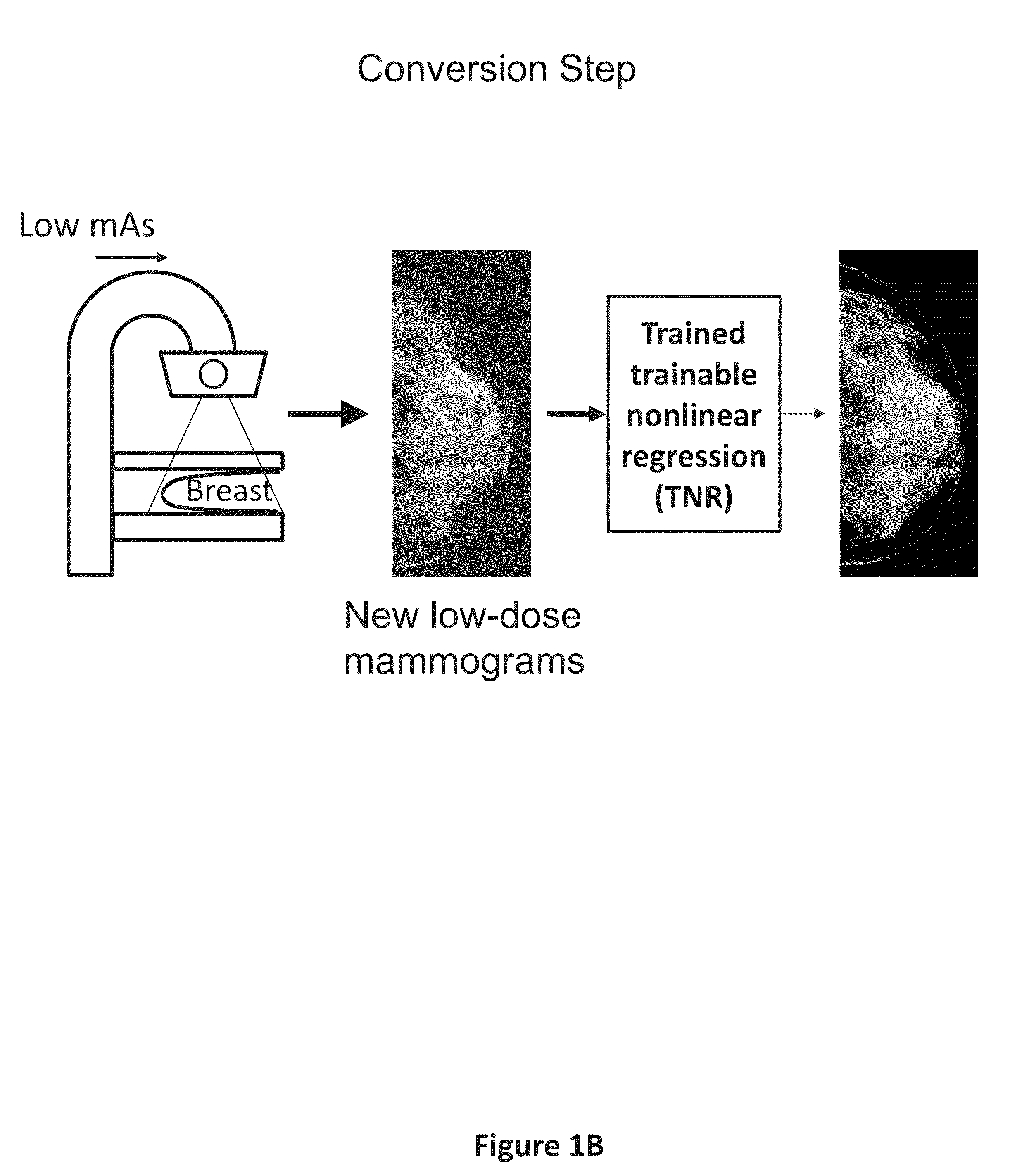
Converting low-dose to higher dose mammographic images through machine-learning processes
ActiveUS20150196265A1Improve image qualityEasy to detectImage enhancementImage analysisImaging qualityX-ray
A method and system for converting low-dose mammographic images with much noise into higher quality, less noise, higher-dose-like mammographic images, using of a trainable nonlinear regression (TNR) model with a patch-input-pixel-output scheme, which can be called a call pixel-based TNR (PTNR). An image patch is extracted from an input mammogram acquired at a reduced x-ray radiation dose (lower-dose), and pixel values in the patch are entered into the PTNR as input. The output of the PTNR is a single pixel that corresponds to a center pixel of the input image patch. The PTNR is trained with matched pairs of mammograms, inputting low-dose mammograms together with corresponding desired standard x-ray radiation dose mammograms (higher-dose), which are ideal images for the output images. Through the training, the PTNR learns to convert low-dose mammograms to high-dose-like mammograms. Once trained, the trained PTNR does not require the higher-dose mammograms anymore. When a new reduced x-ray radiation dose (low dose) mammogram is entered, the trained PTNR would output a pixel value similar to its desired pixel value, in other words, it would output high-dose-like mammograms or “virtual high-dose” mammograms where noise and artifacts due to low radiation dose are substantially reduced, i.e., a higher image quality. With the “virtual high-dose” mammograms, the detectability of lesions and clinically important findings such as masses and microcalcifications can be improved.
Owner:ALARA SYST
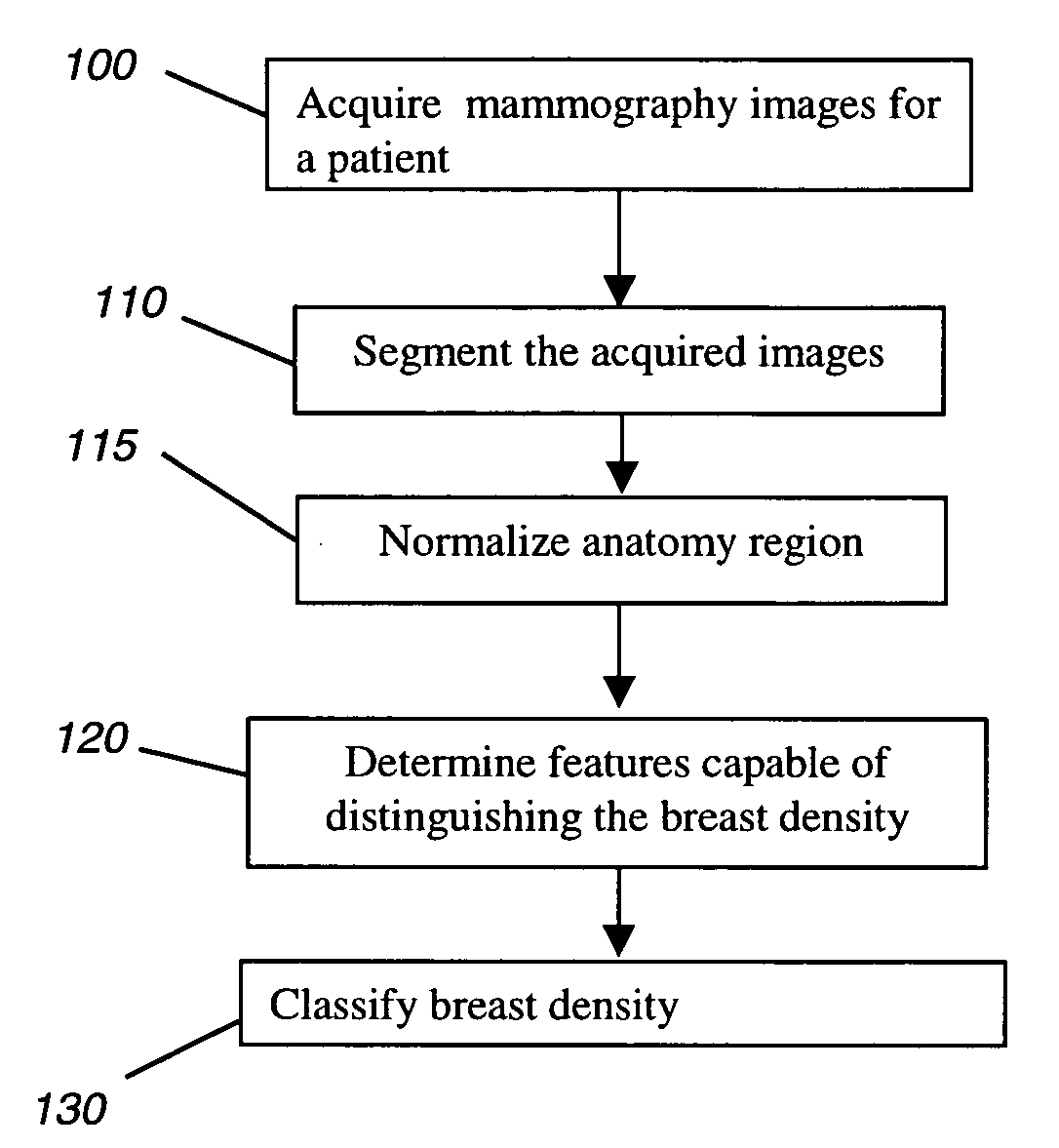
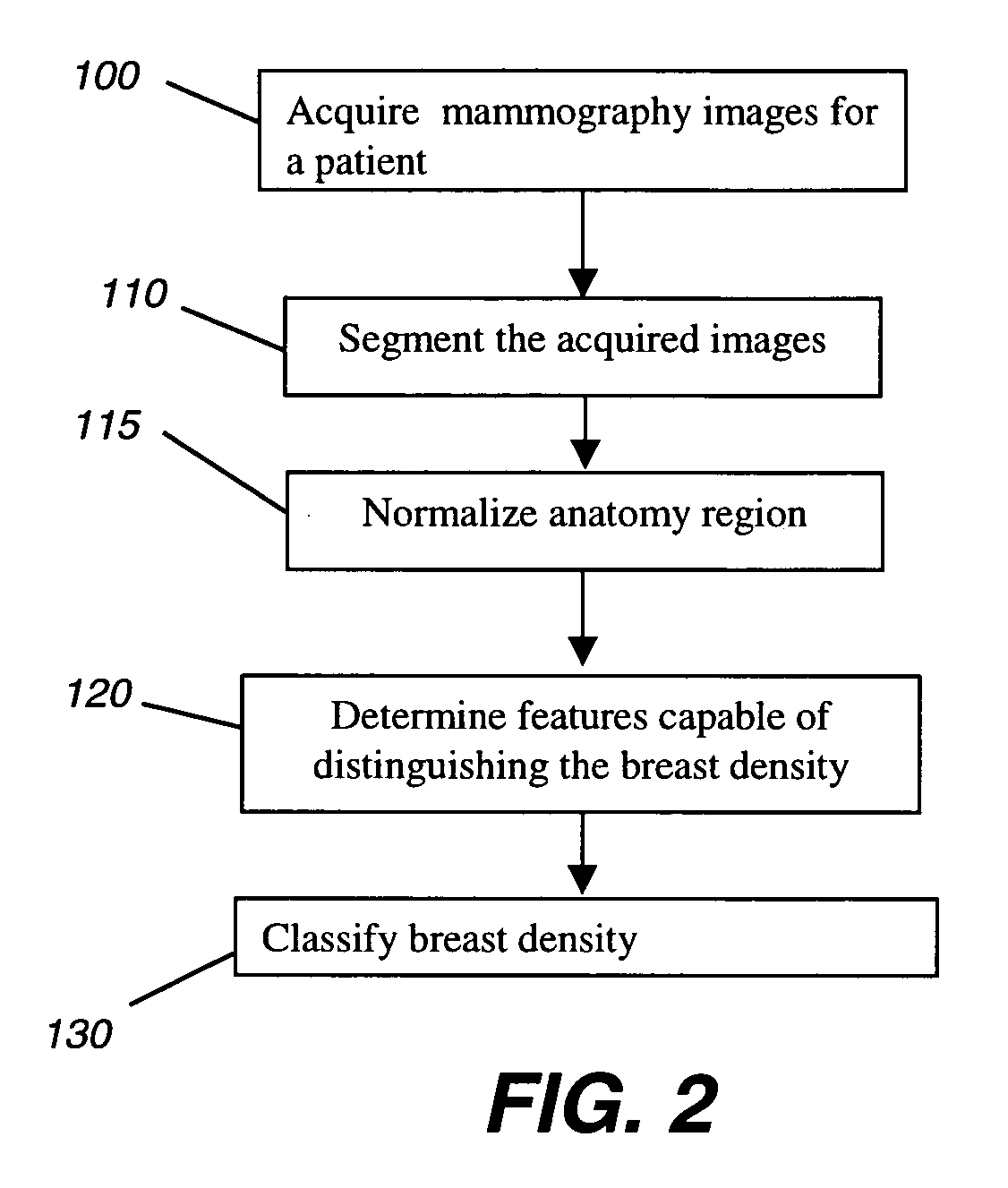
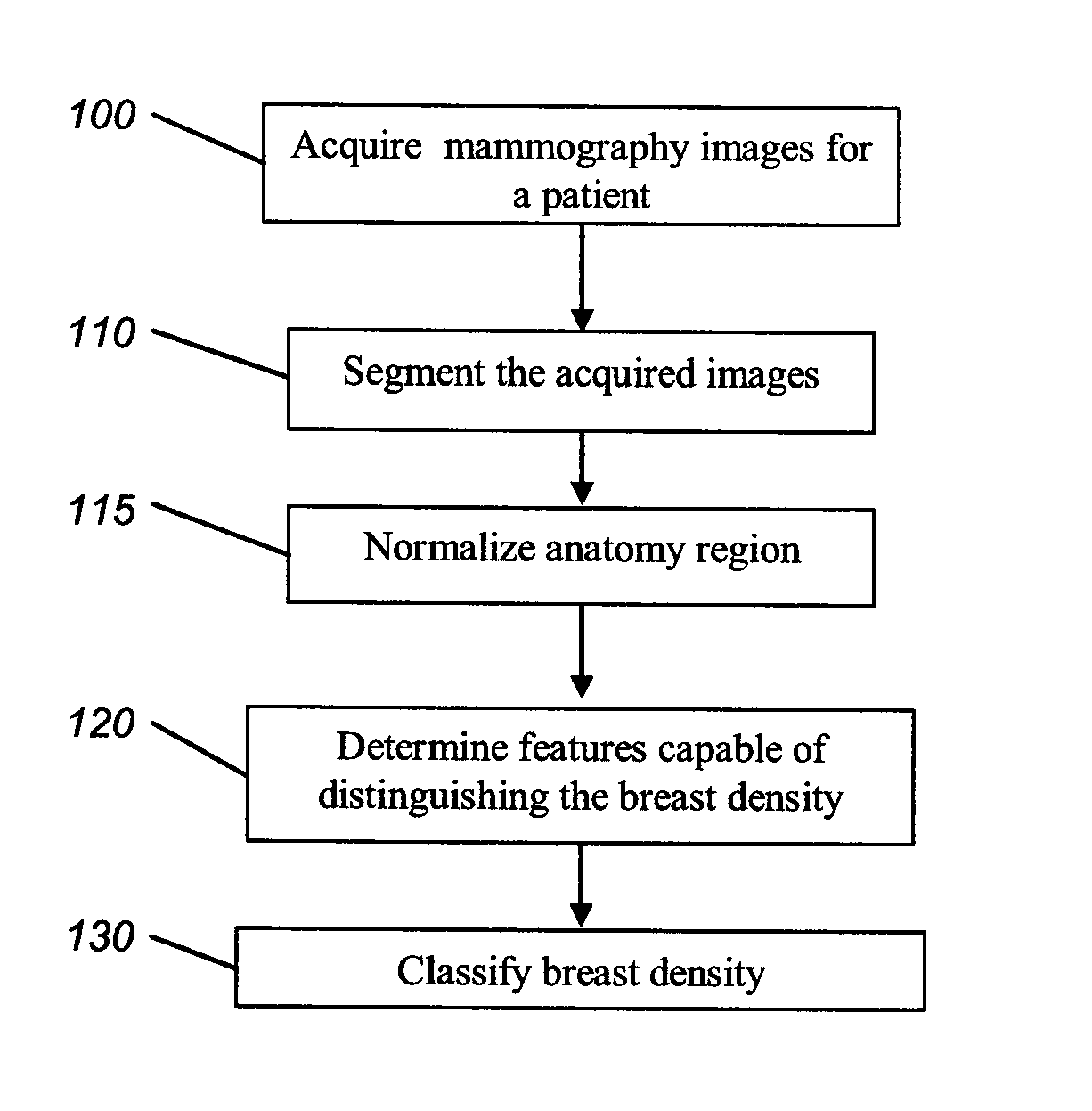
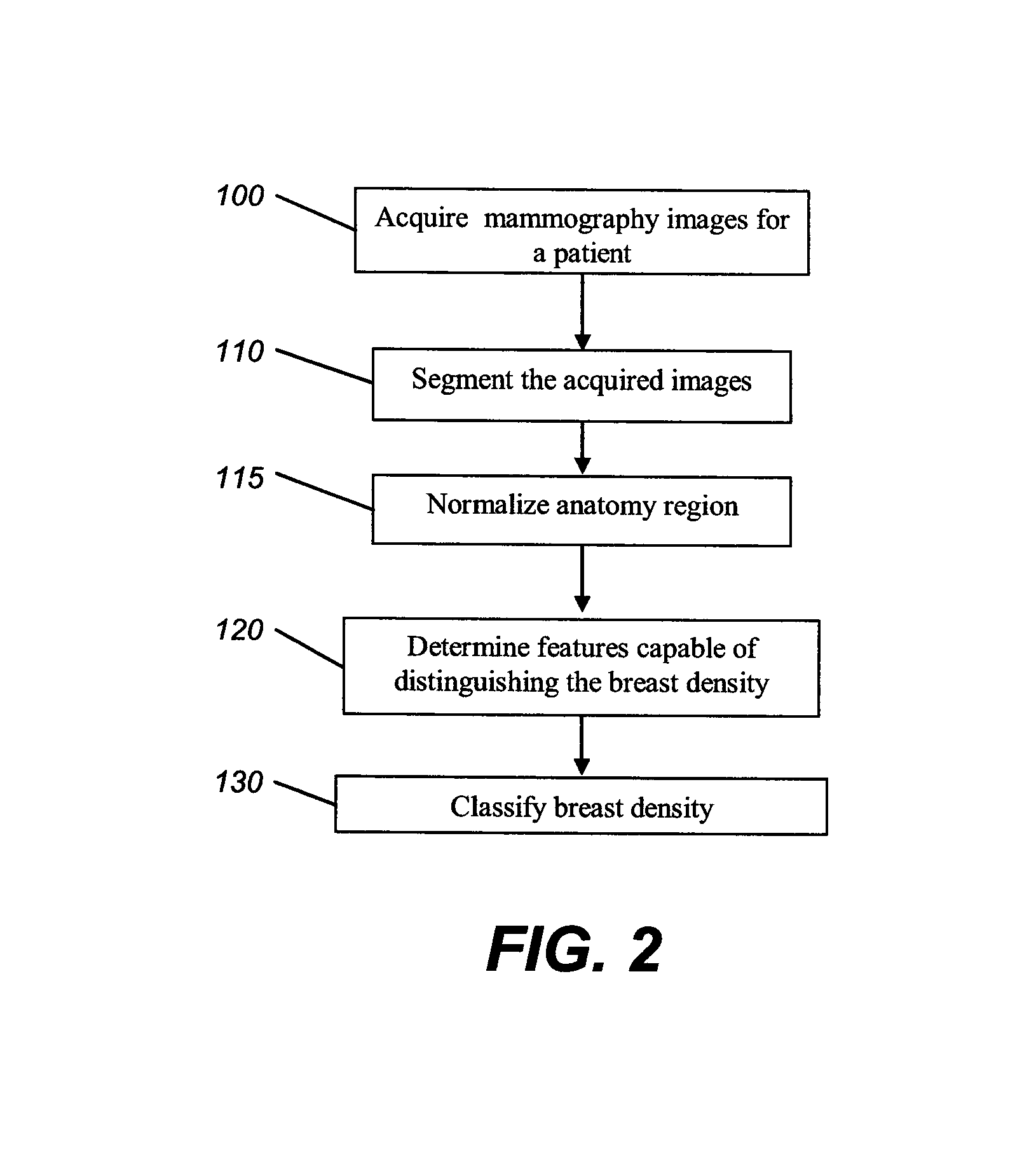
Method for classifying breast tissue density
InactiveUS20080159613A1Assist mammogram imageAssist diagnosisImage enhancementImage analysisTissue densityClassification methods
A method for classifying tissue density of a breast includes obtaining mammography image data and segmenting the mammography image to identify the region representing the breast tissue. A plurality of regions within the breast tissue region are identified for obtaining image features therefrom. A plurality of image features are computed from the identified plurality of regions. The breast tissue density is classified using the computed plurality of image features.
Owner:CARESTREAM HEALTH INC
Breast Tomosynthesis System With Shifting Face Shield
ActiveUS20090323892A1Easy to reachProtects patientPatient positioning for diagnosticsX-ray tube vessels/containerTomosynthesisRadiology
Breast imaging using any one of a mammography system, a tomosynthesis system, or a fused system that selectively takes either or both of mammography images and tomosynthesis images, further uses a patient shield that moves closer to and further away from the patient's chest and head, between (1) an access position that facilitates the technologist's access to adjust the patient's breast while the breast is being compressed and (b) a protective position in which the shield helps protect the patient from collision with moving components and from x-ray exposure of tissue other than the tissue that is to be imaged.
Owner:HOLOGIC INC
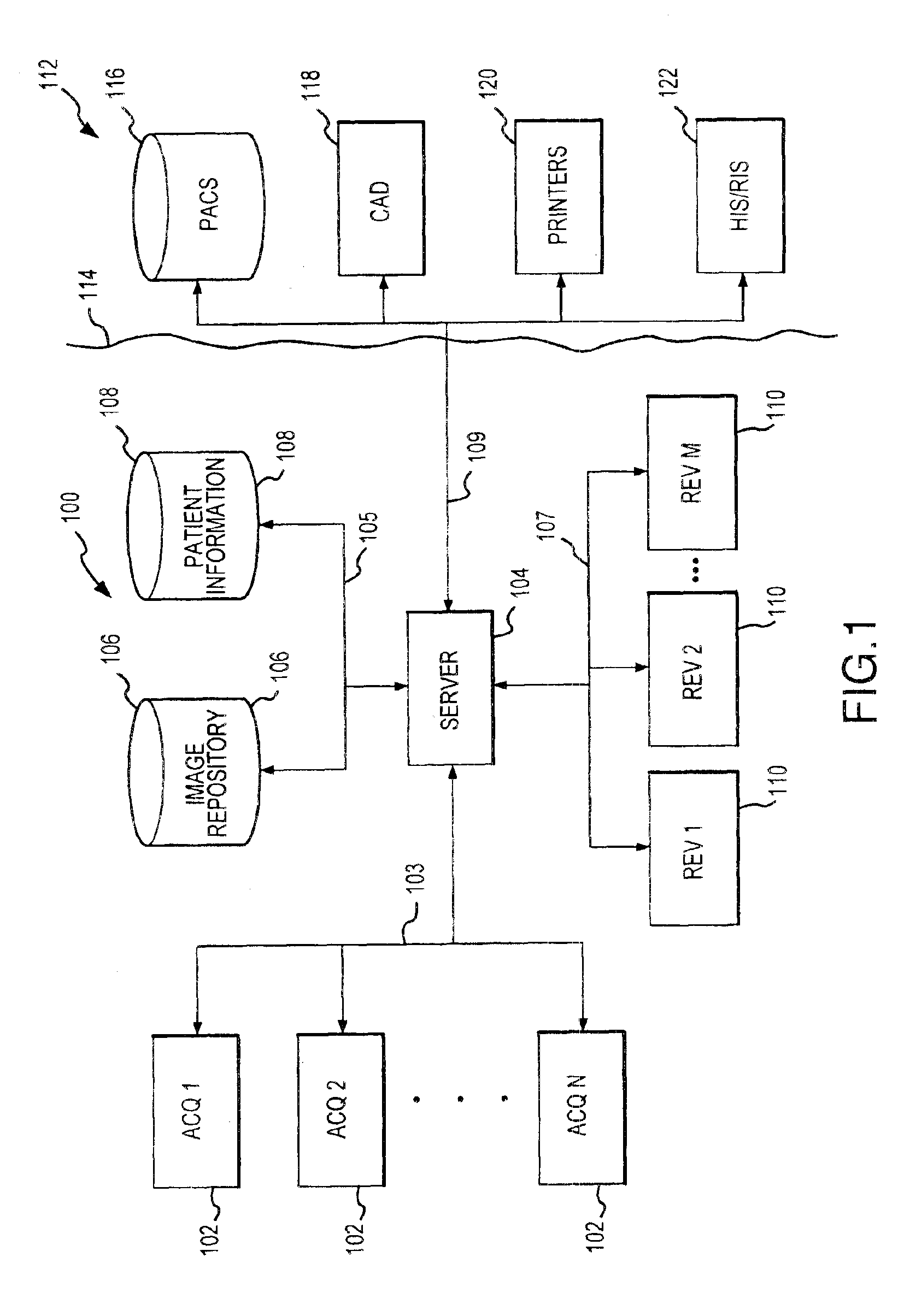
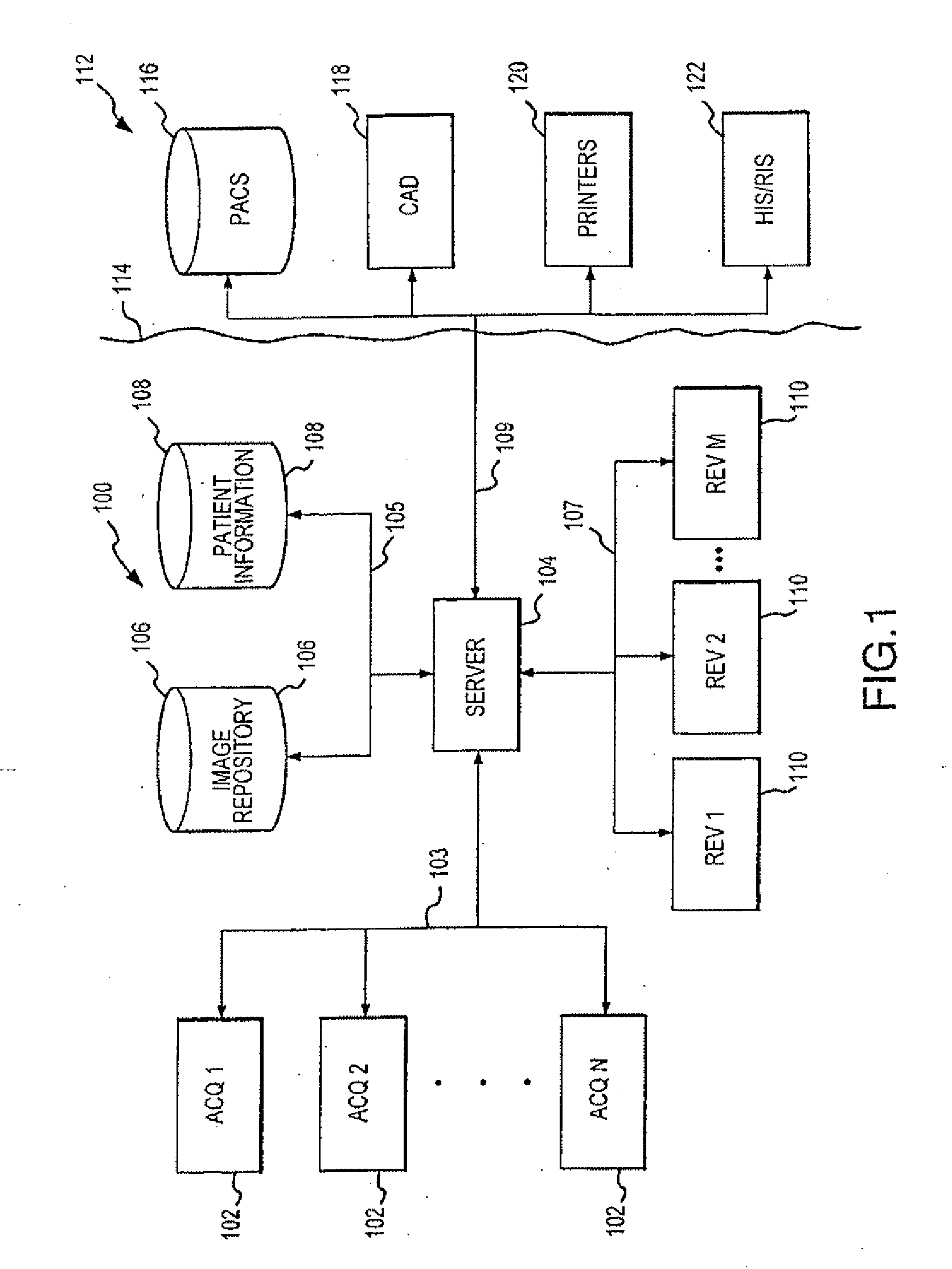
Distributed architecture for mammographic image acquisition and processing
InactiveUS7406150B2Easy to useHigh patient throughputOrgan movement/changes detectionPatient positioning for diagnosticsImage InspectionDICOM
A distributed architecture allows for decoupling of mammographic image acquisition and review, thereby enabling more efficient use of resources and enhanced processing. In one embodiment, the system (100) includes a number of image acquisition stations (102) and a number of image review stations (110) all associated with a central server (104). The server (104) is operative to access an image repository (106), a patient information data base (108) and a number of DICOM tools (112). The invention allows for more efficient and / or more convenient use of the image acquisition equipment and image processing stations. Moreover, the distributed architecture including the central image repository provides certain processing and analysis advantages. The invention also provides certain processing and workflow enhancements that allow for a more full realization of potential digital mammography advantages.
Owner:HOLOGIC INC
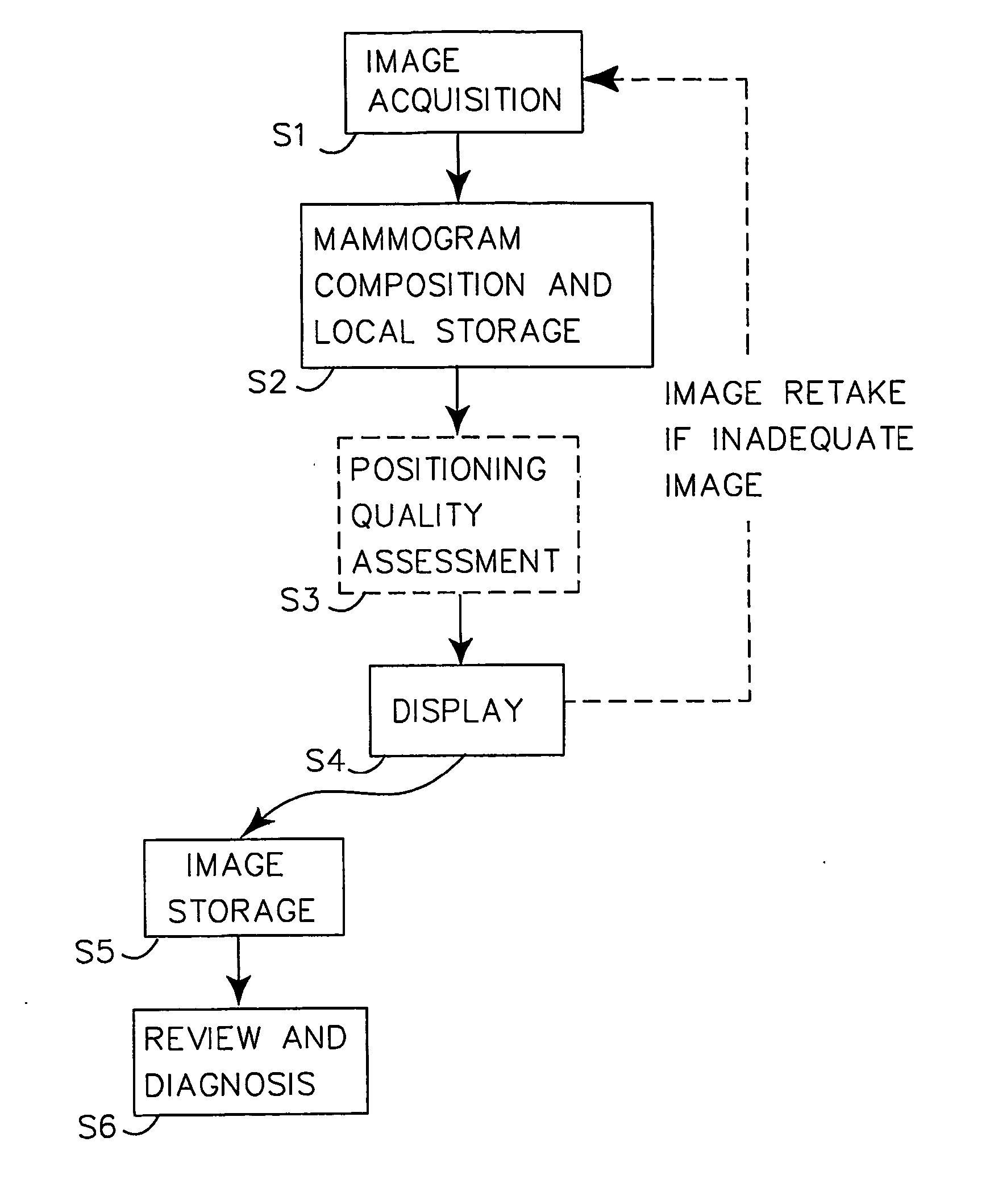
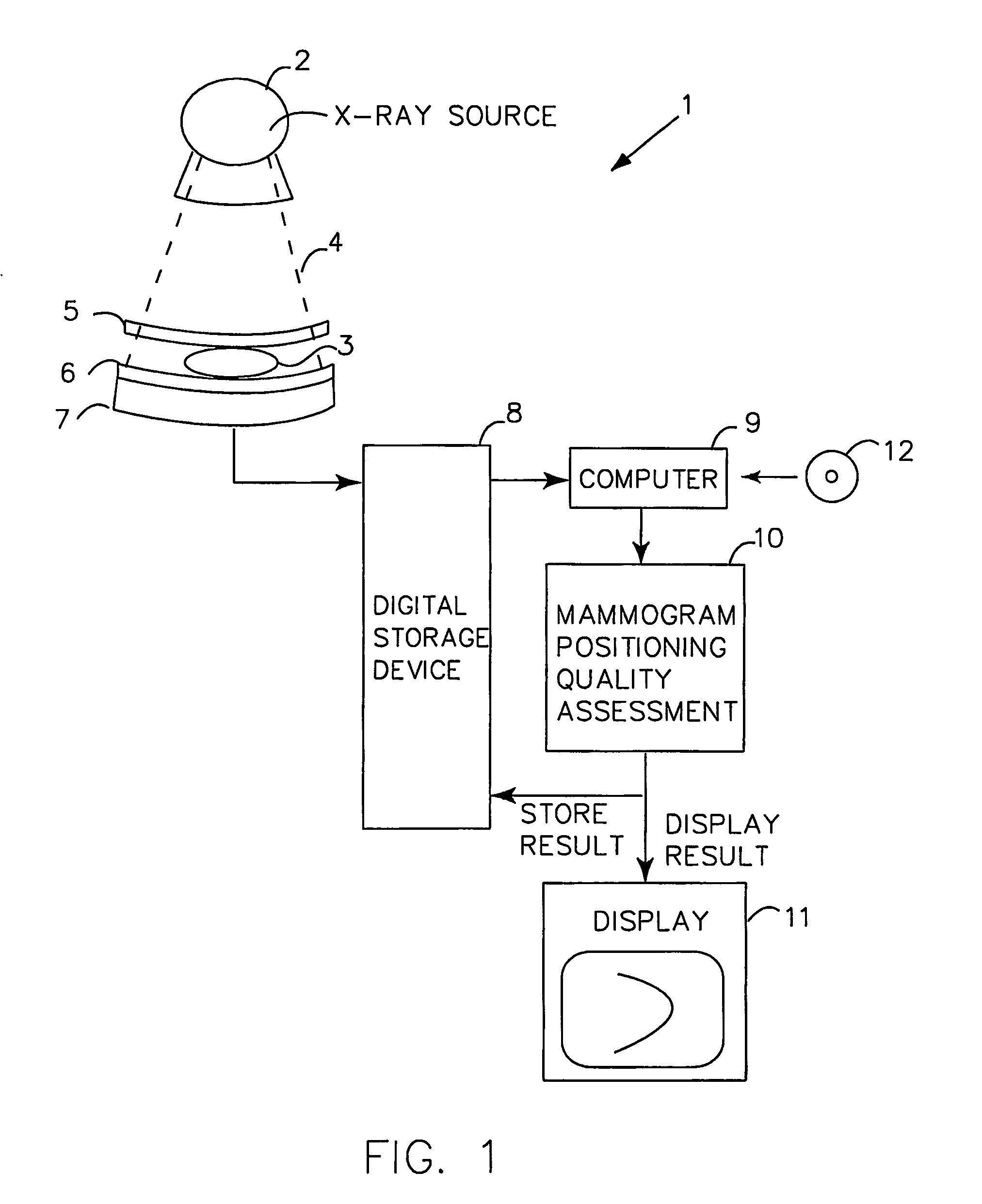
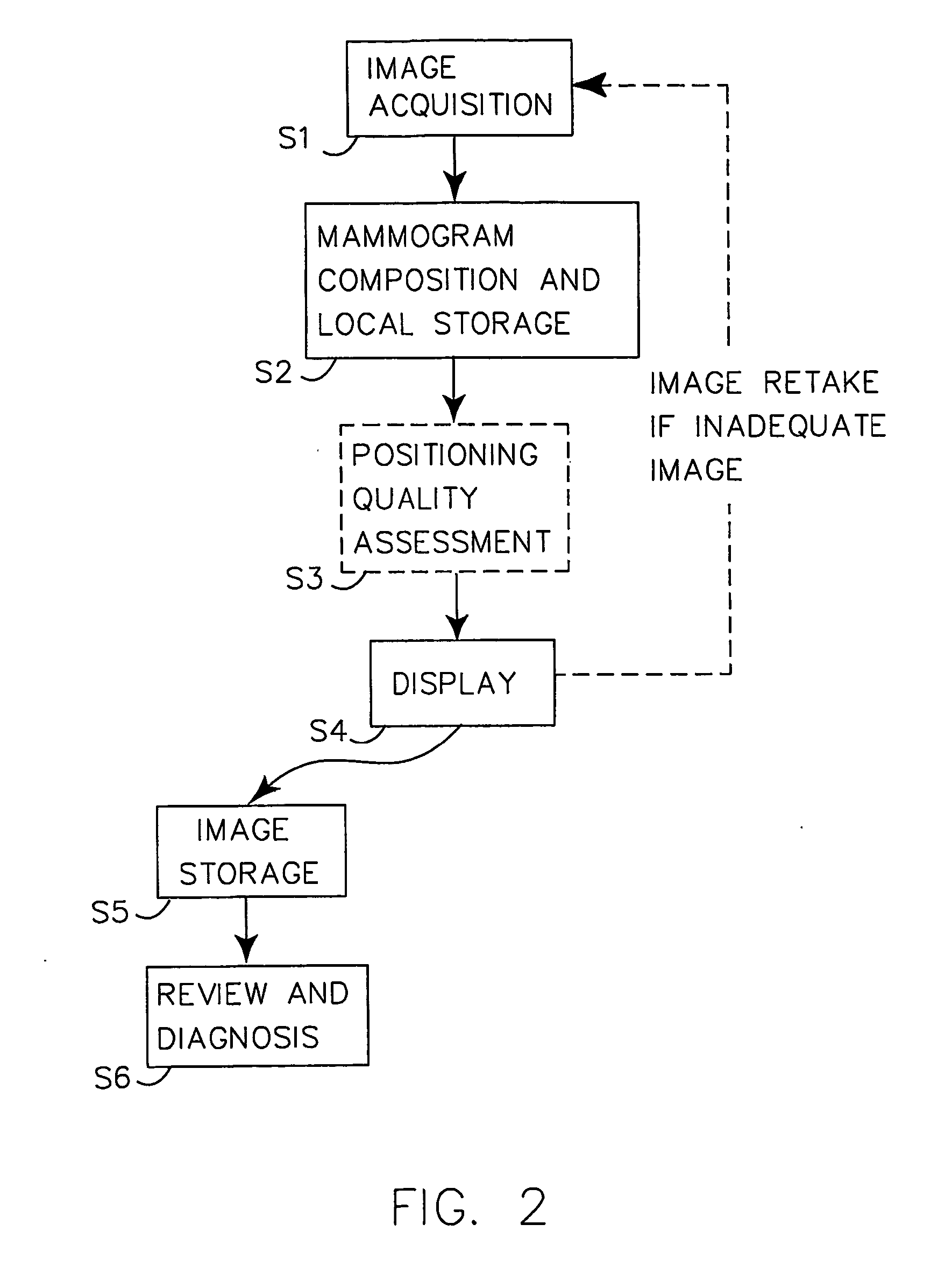
Automatic Positioning Quality Assessment for Digital Mammography
InactiveUS20070248210A1Improve overall mammography processReduce in quantityImage enhancementImage analysisDigital mammographyQuality assessment
The invention presents a way to automatically assess the quality of acquired (S1, S2) digital mammographic images with respect to the image positioning of a patient's breast. The automated digital quality assessment (S3) is executed in real time and preferably notifies (S4) the technologist instantly if the image positioning quality of a mammographic image is inadequate. This makes it possible to retake the image while the patient is still present at the examination facility. The quality assessment notification includes information to the technologist, preferably both visually and statistically of land-mark positioning measurements. Alternatively, the digital quality assessment is accompanied by a computerized decision of whether the mammogram needs to be retaken, requiring a minimum of involvement, if at all, from the technologist. The invention hence provides a set of quality-assured mammographic images that can be stored (S5) and later accessed by a radiologist for review and diagnosis (S6).
Owner:SECTRA IMTEC
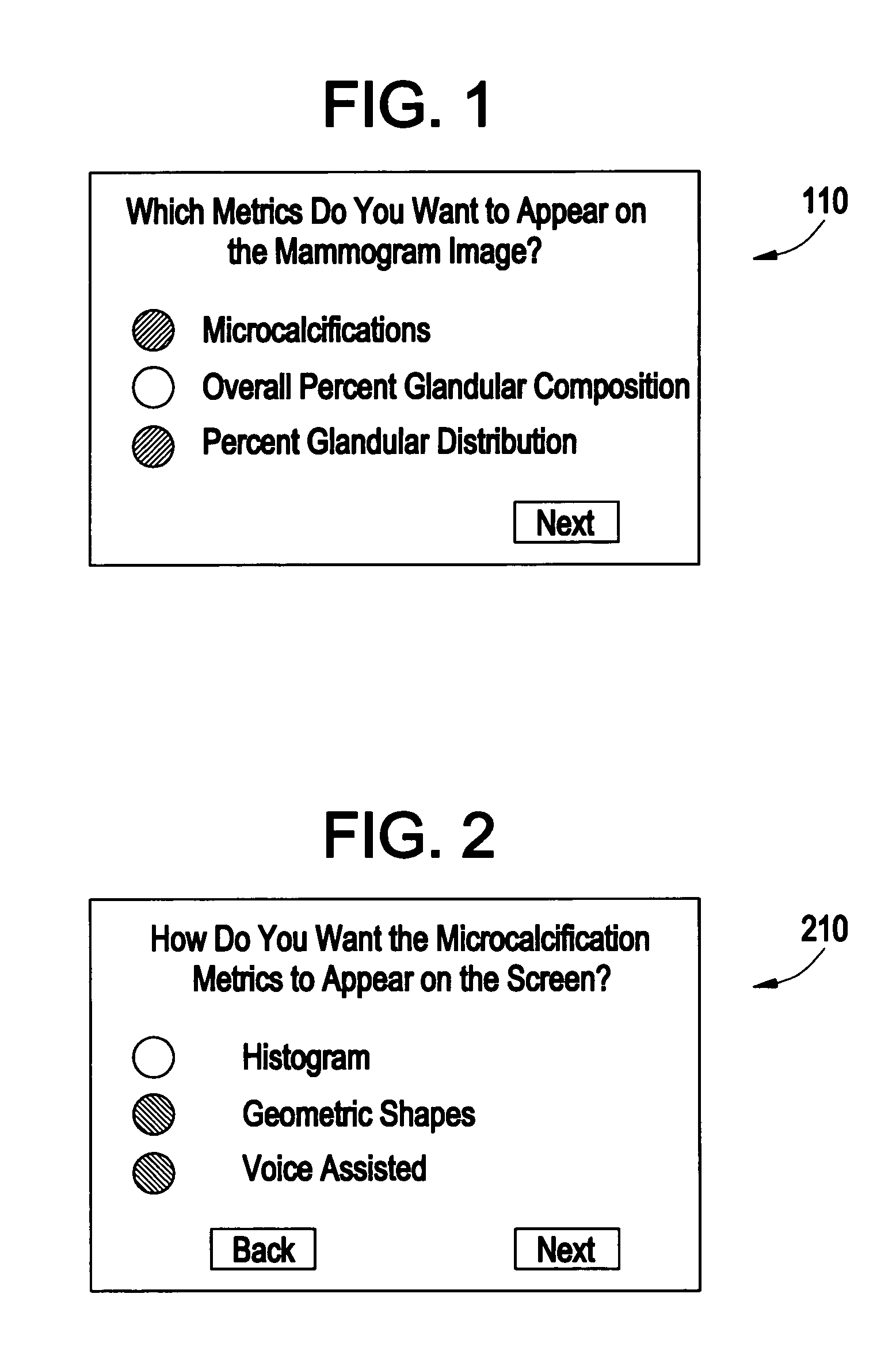
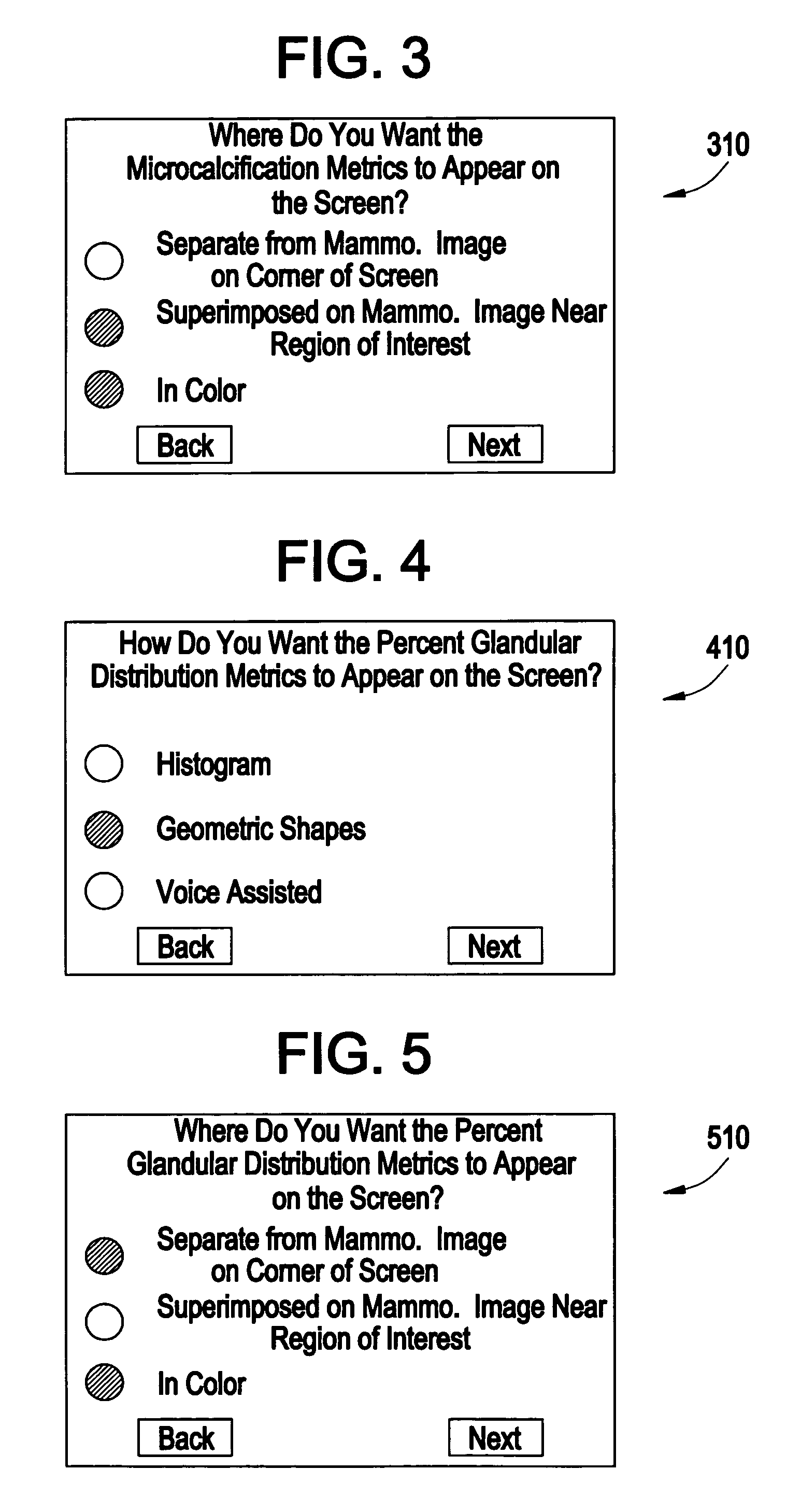
Method and apparatus for providing mammographic image metrics to a clinician
At least one metric for a mammographic image is computed by a workstation, and provided on a workstation display along with the mammographic image. A clinician can select one or more different metrics to be computed for an image, as well as where they are to be shown and the manner in which they are to be shown on the display. Speech (may also be an audible sound which is not speech) may also be used in the workstation to audibly provide metrics information to the clinician.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
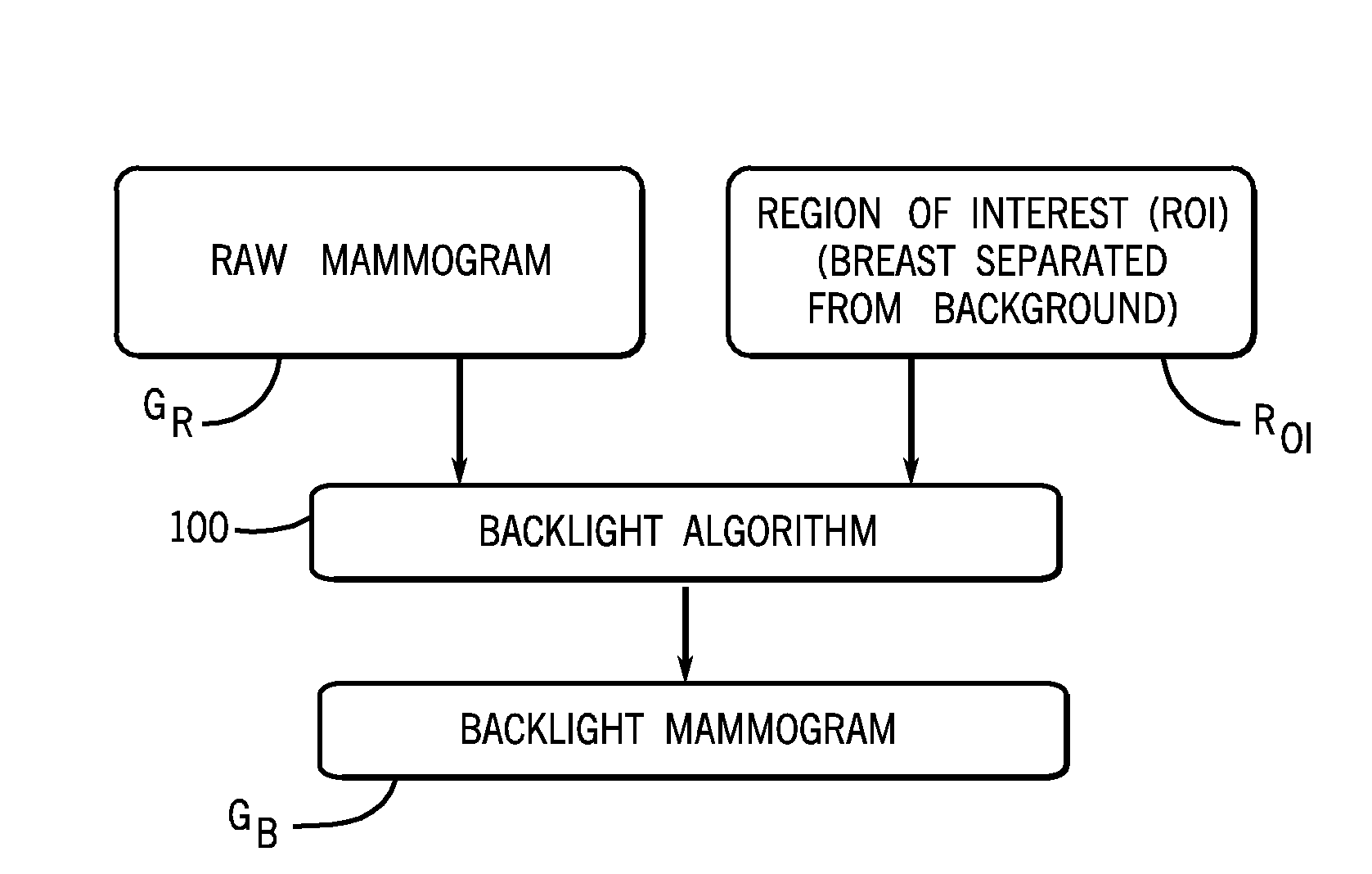
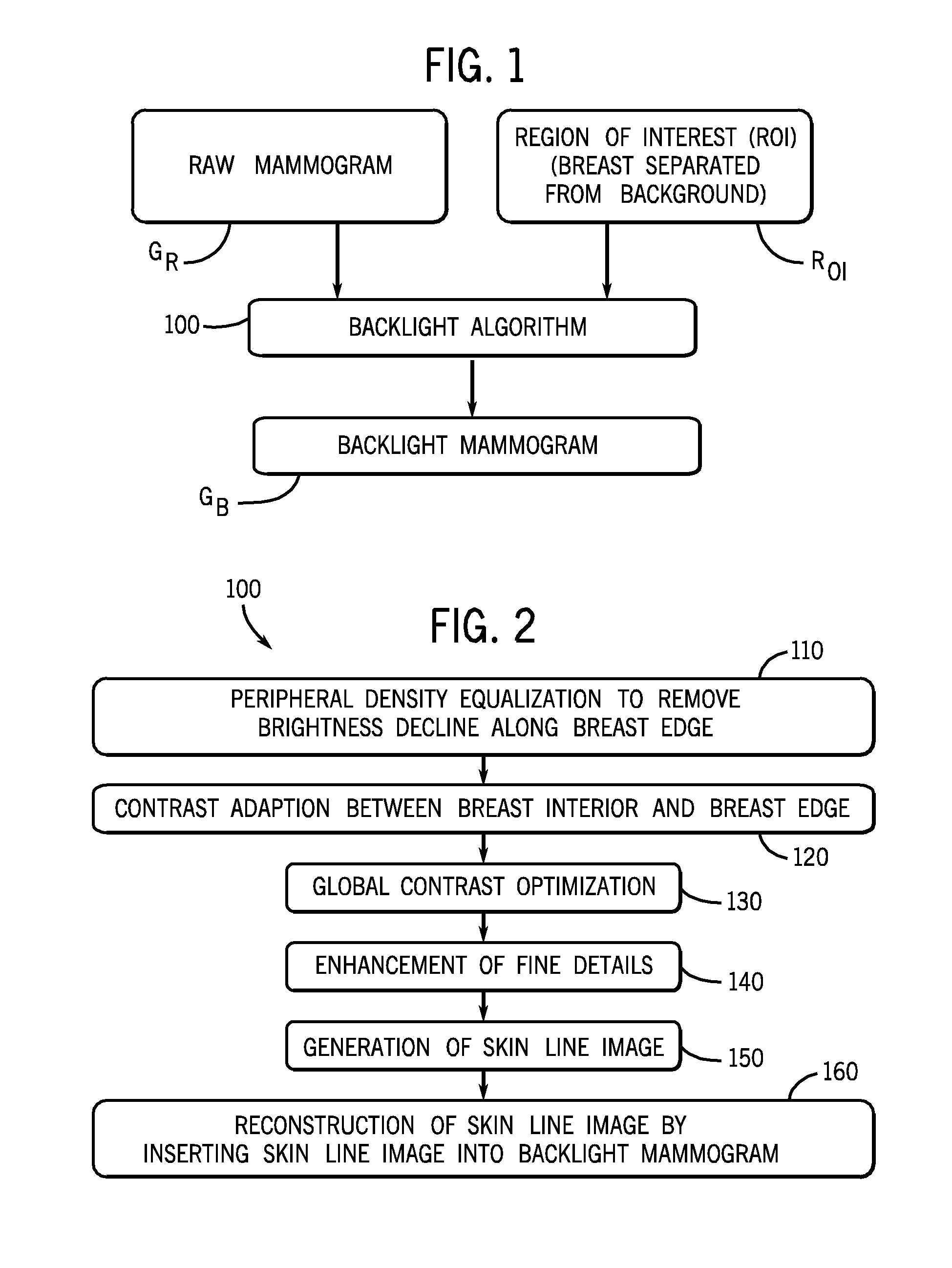
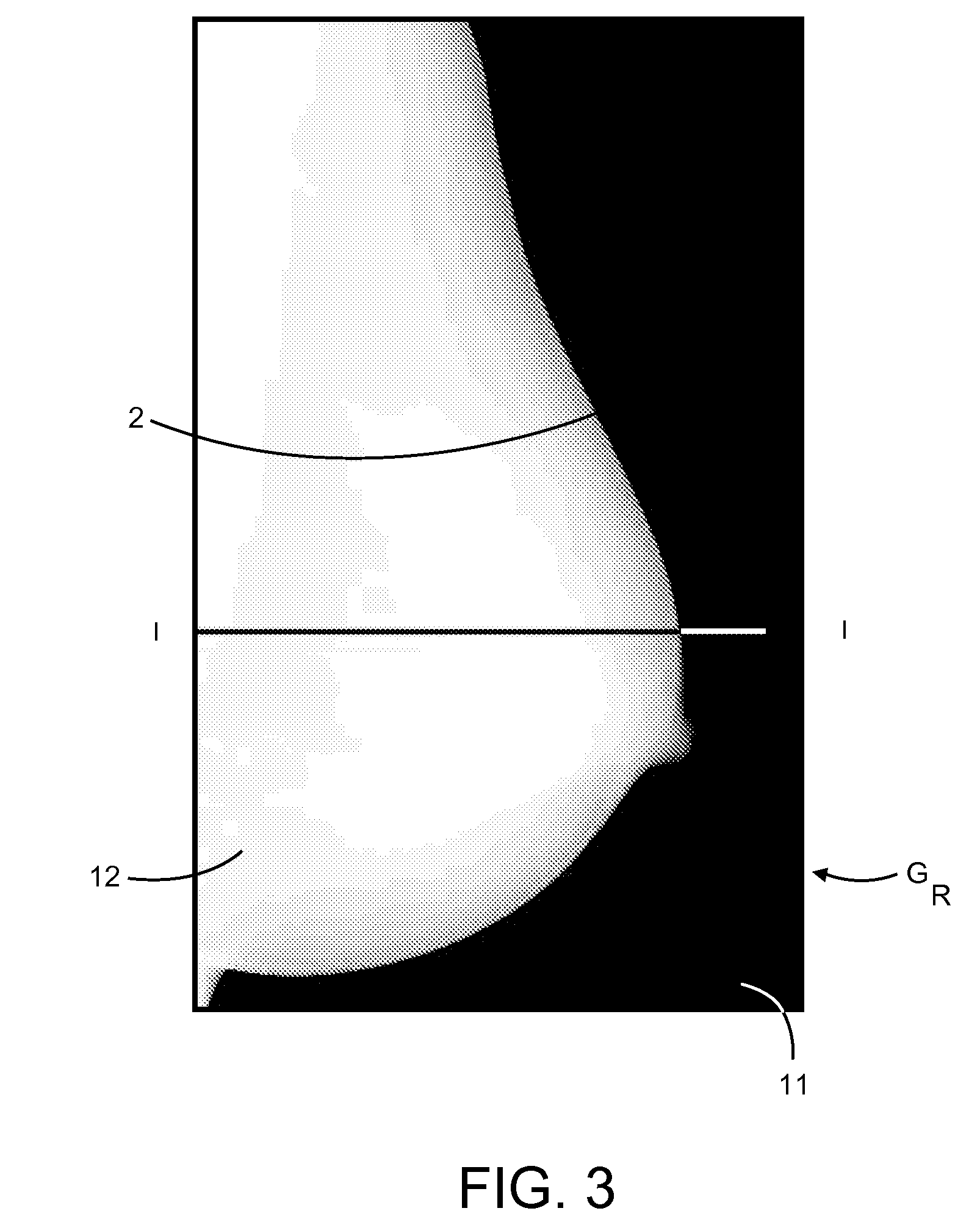
Method and Apparatus for Processing Digital Mammographic Images
ActiveUS20090185733A1Increase contrastImprove visualizationImage enhancementImage analysisLookup tableComputer vision
A method and apparatus for processing digital mammographic images. The method and apparatus providing comparable mammographic images regardless of the imaging device generating the raw mammographic images. The processed mammographic images may be displayed with optimal global and local contrast, enhanced sharpness, and without the need to apply window level settings or data from lookup tables. A second mammographic image is generated out of a processed first mammographic image in such a way that the projected object, the breast, is more perceptible and obvious for a physician or other medical professional reviewing the mammographic image.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
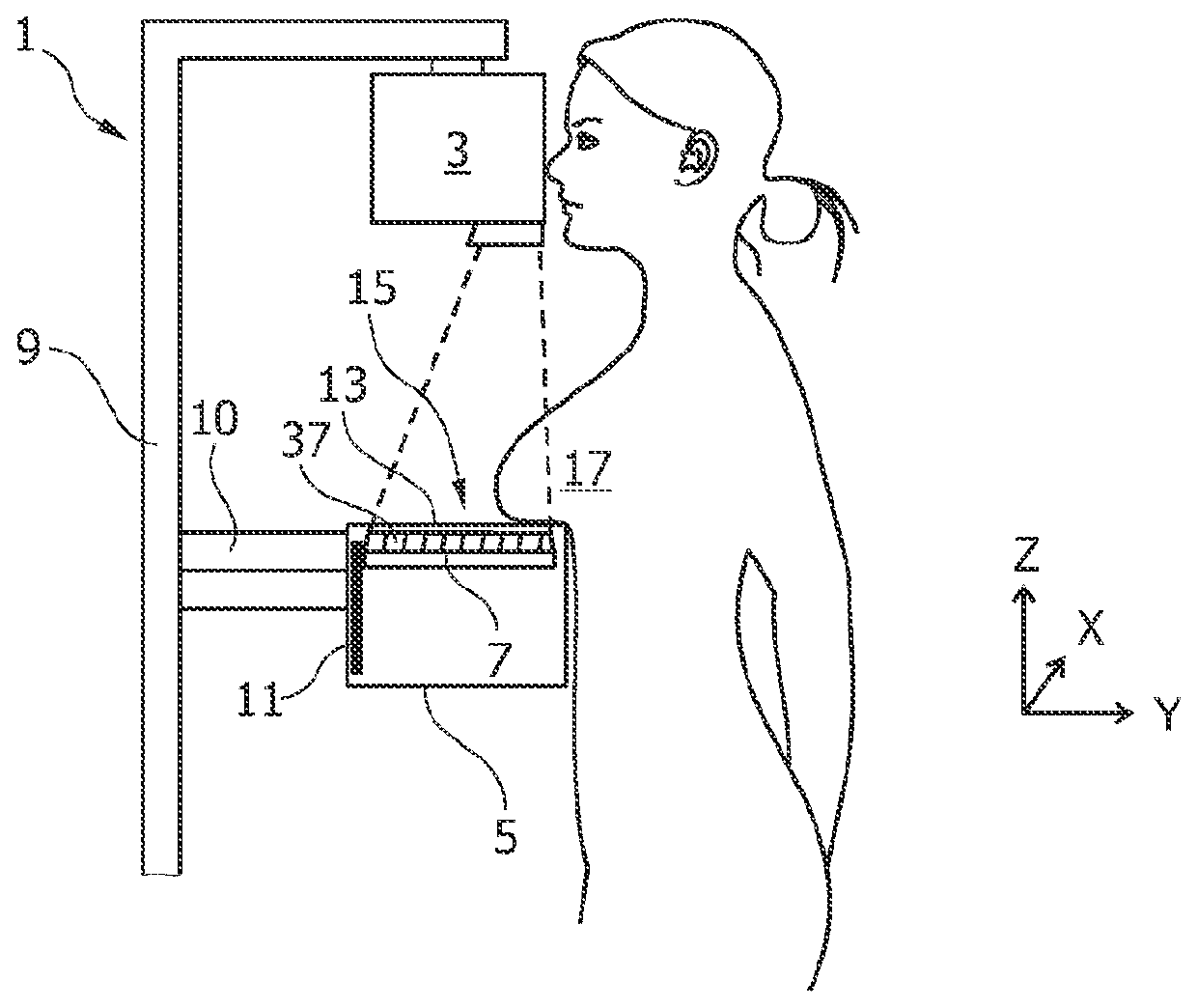
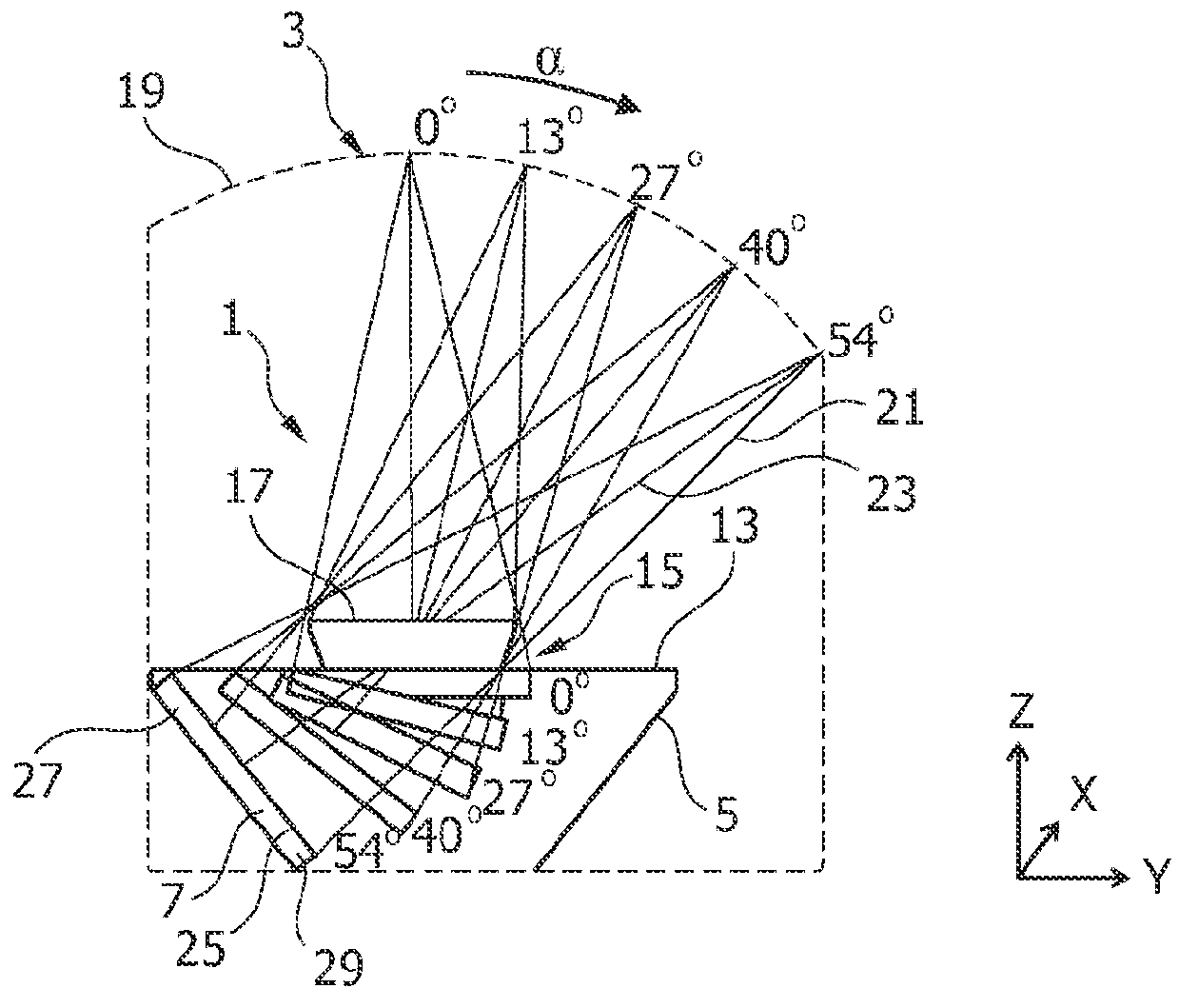
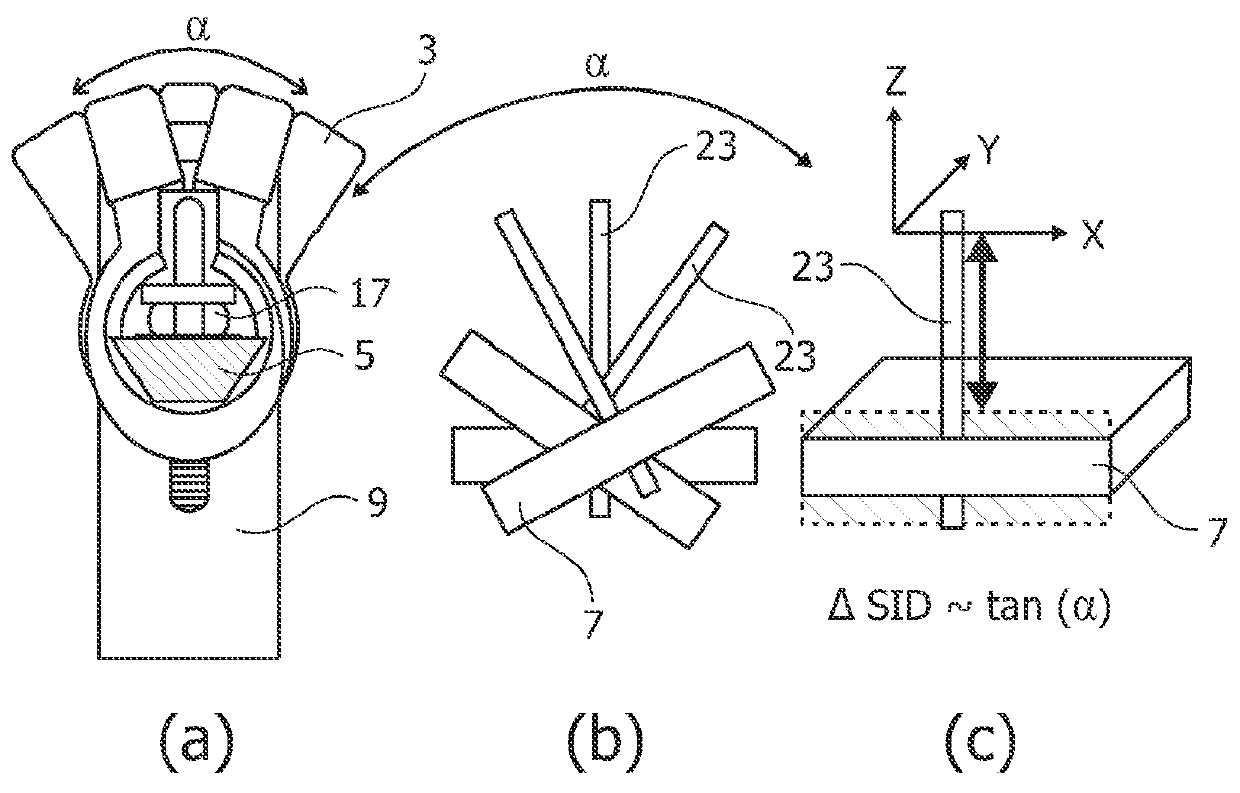
Tomosynthesis mammography system with enlarged field of view
InactiveUS20120224664A1High image resolutionLarge field of viewMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationRadiation/particle handlingTomosynthesisX-ray
A tomosynthesis system for acquiring a three-dimensional image of an object such as a mammography image of a female breast is proposed. The tomosynthesis system (1) comprises an X-ray source (3), an X-ray detector (7), a support arrangement (15) and a moving mechanism (11). The X-ray source (3) and the X-ray detector (7) are adapted for acquiring a plurality of X-ray images while irradiating the object (17) with an X-ray beam (21) from a plurality of tomographic angles α. The moving mechanism (11) is adapted to pivot the X-ray detector (7) in positions such that for each tomographic angle α a detection surface (25) of the X-ray detector (7) is oriented to be substantially perpendicular to the X-ray beam (21). The moving mechanism (11) is adapted to move the X-ray detector (7) in positions such that a distance between the X-ray source (3) and the detector (7) is increased with increasing tomographic angle a thereby enabling that the X-ray detector (7) remains within an enlarged housing (5) during an entire tomographic image acquisition procedure.
Owner:KONINKLIJKE PHILIPS ELECTRONICS NV
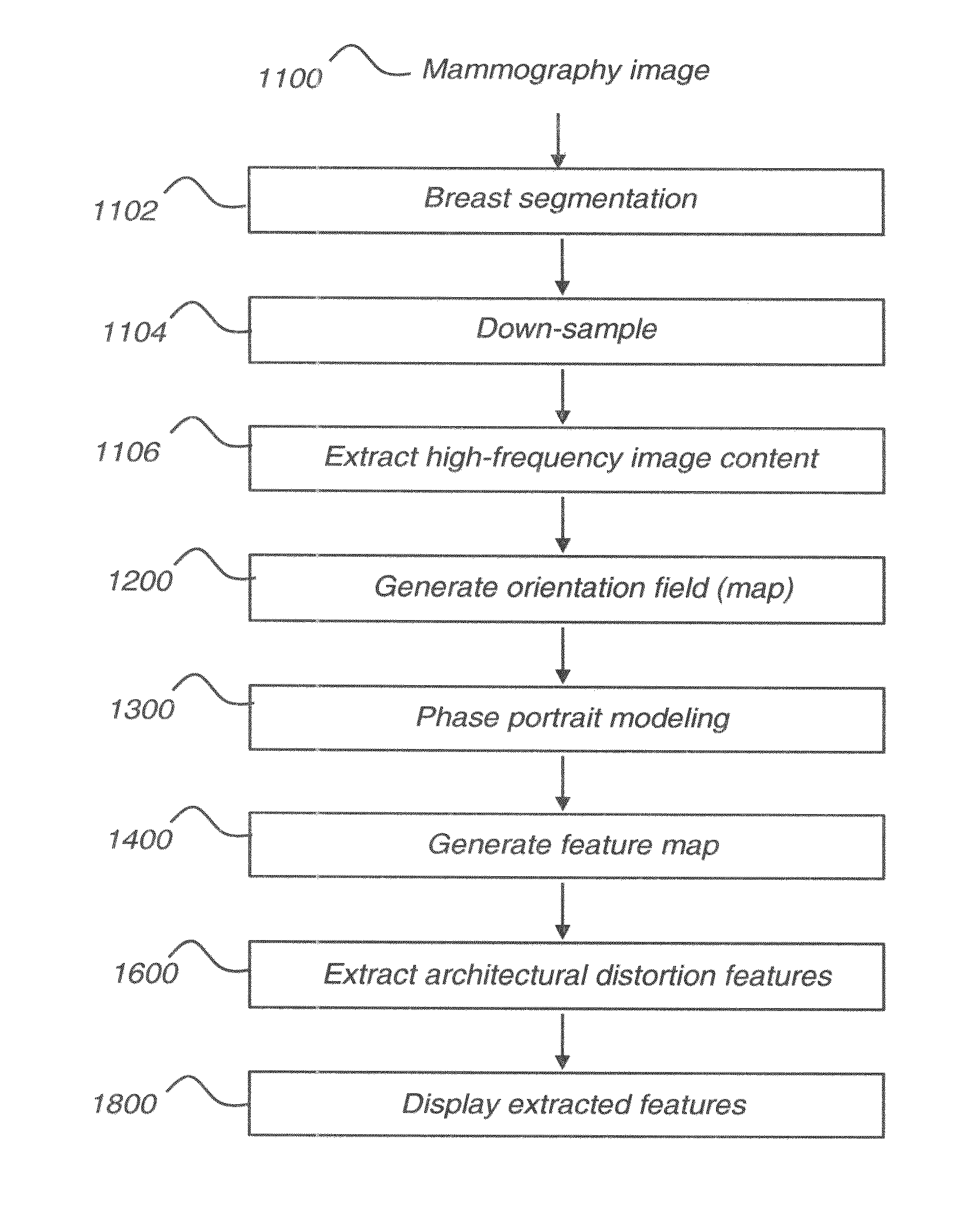
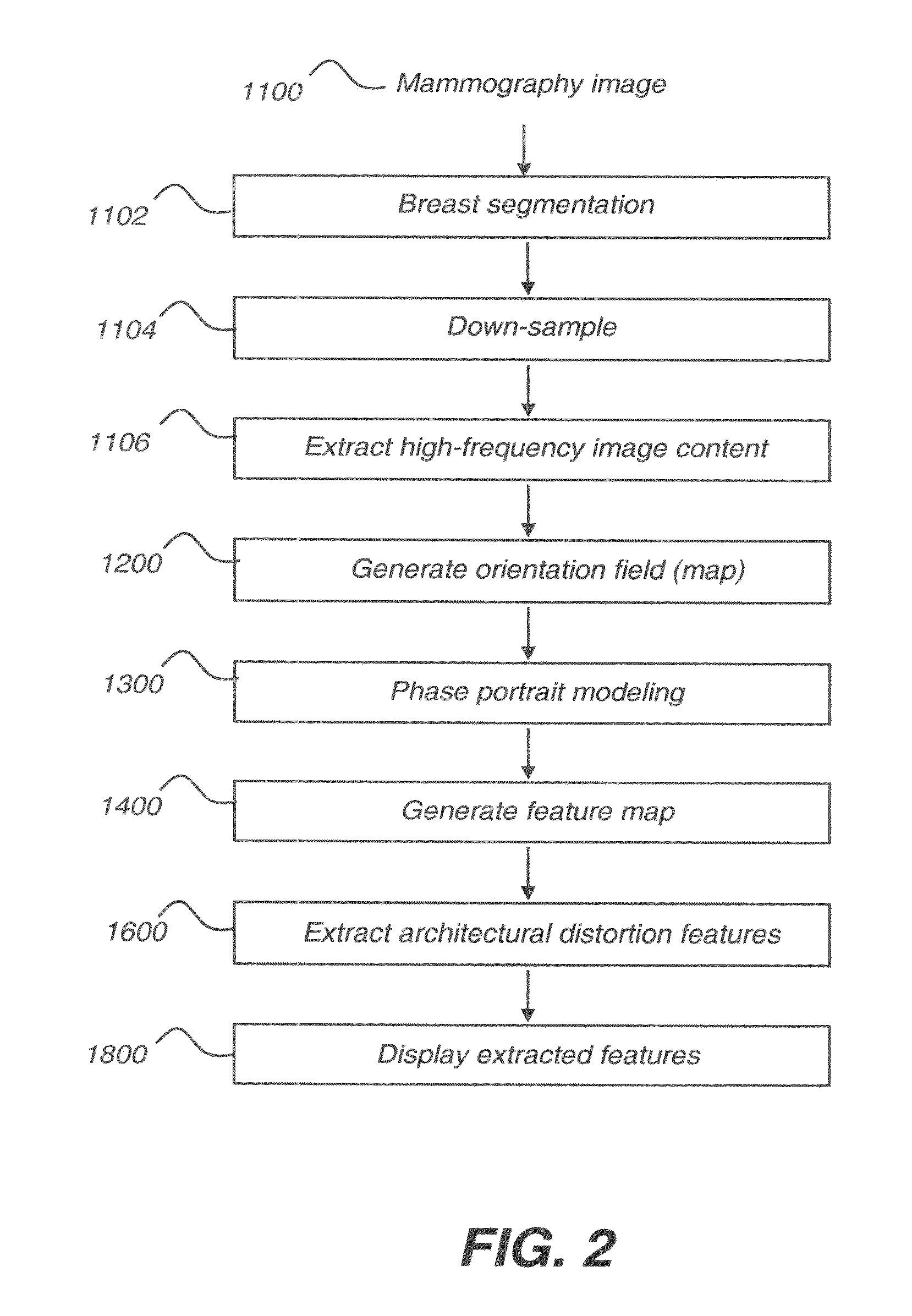
Computer aided detection of architectural distortion in mammography
A method for detecting architectural distortion within mammographic image data. The method identifies breast tissue within the image data, generates an orientation field and a corresponding magnitude field within the identified breast tissue and generates a feature map by processing the orientation field with a phase portrait model at one or more image scales. The method identifies one or more architectural distortion features according to the generated feature map and displays the one or more identified architectural distortion features.
Owner:CARESTREAM HEALTH INC
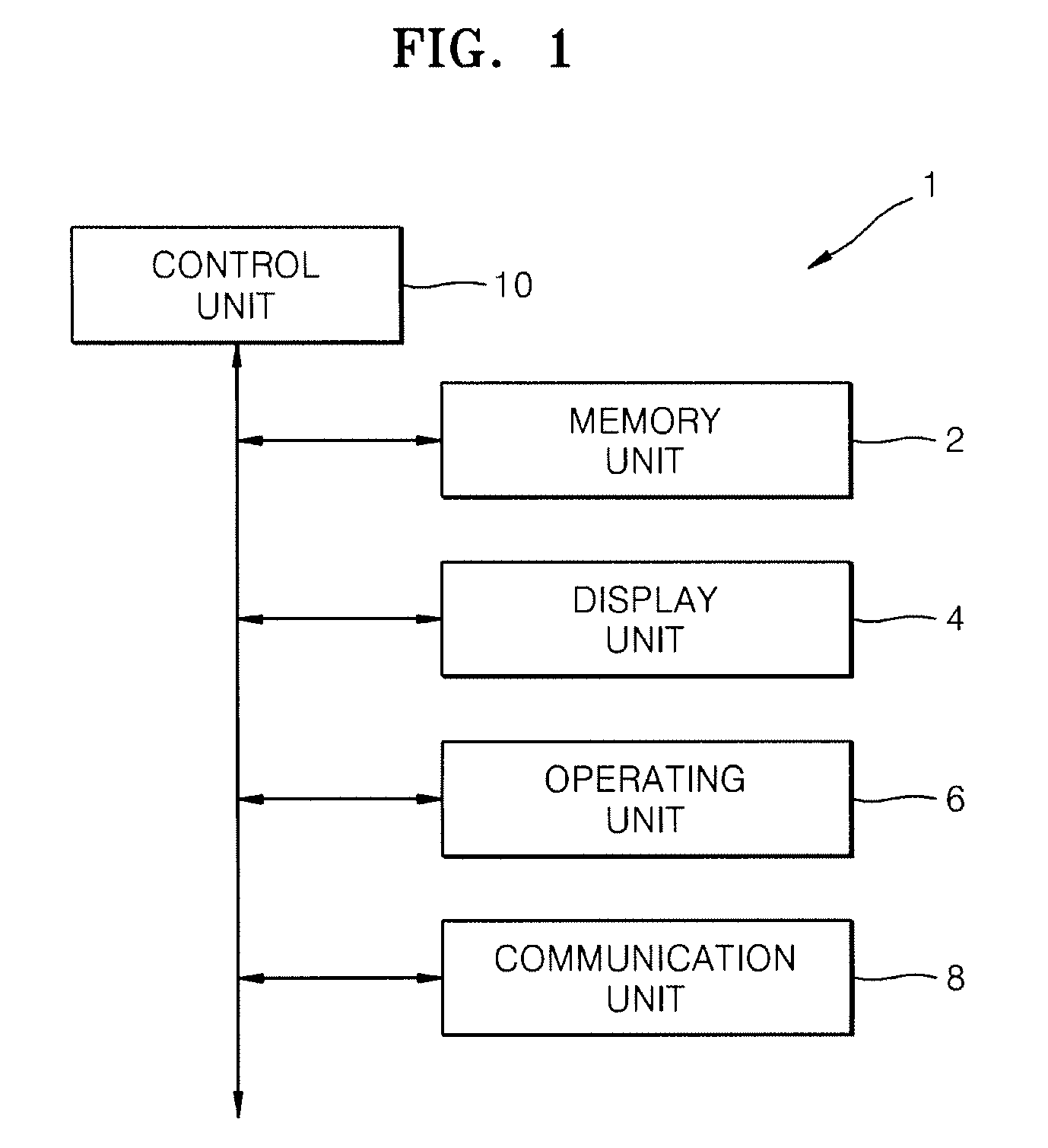
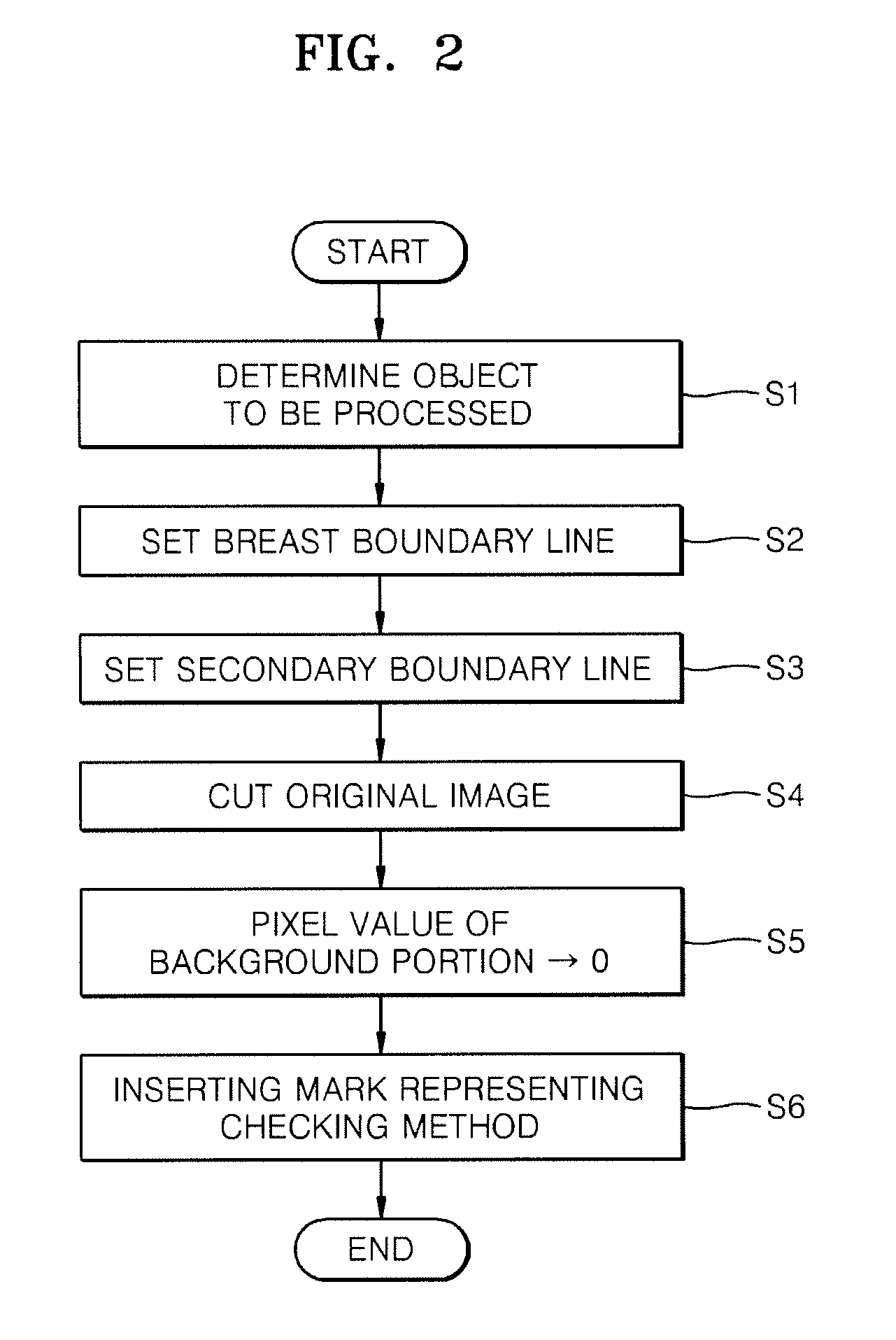
Method, apparatus and program for processing mammographic image
InactiveUS8165380B2Small sizeEnhance the imageImage enhancementImage analysisComputer graphics (images)Control unit
Provided are a method, an apparatus, and a program for processing a mammographic image, whereby the file size of the mammographic image can be remarkably reduced while retaining the original breast portion sufficient for diagnosis. A controlling unit divides an original mammographic image into a breast portion and a background portion based on a predetermined value (whether each pixel value of the original mammographic image is greater or smaller than a predetermined value). It determines the breast boundary line between the breast portion and the background portion (operation S2). It shifts and expands the breast portion upward, downward and forward to result in a secondary boundary line, wherein the breast portion side of the secondary boundary line has a size larger than that of the breast portion (operation S3). In addition, the controlling unit cutting off the background portion of the mammographic image vertically and / or horizontally at the secondary boundary line so that the original breast portion side remains, thereby obtaining the finally processed mammographic image (operation S4). Thus, the controlling unit generates the final image smaller in file size than the original mammographic image.
Owner:HESEL
Adaptive enhancement method based on mammographic image
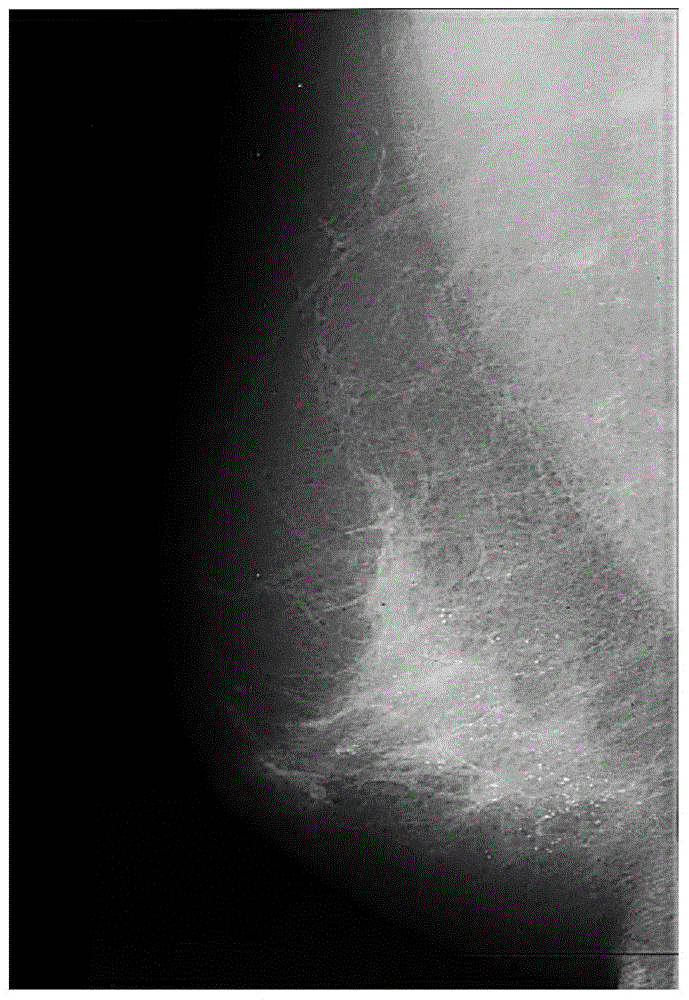
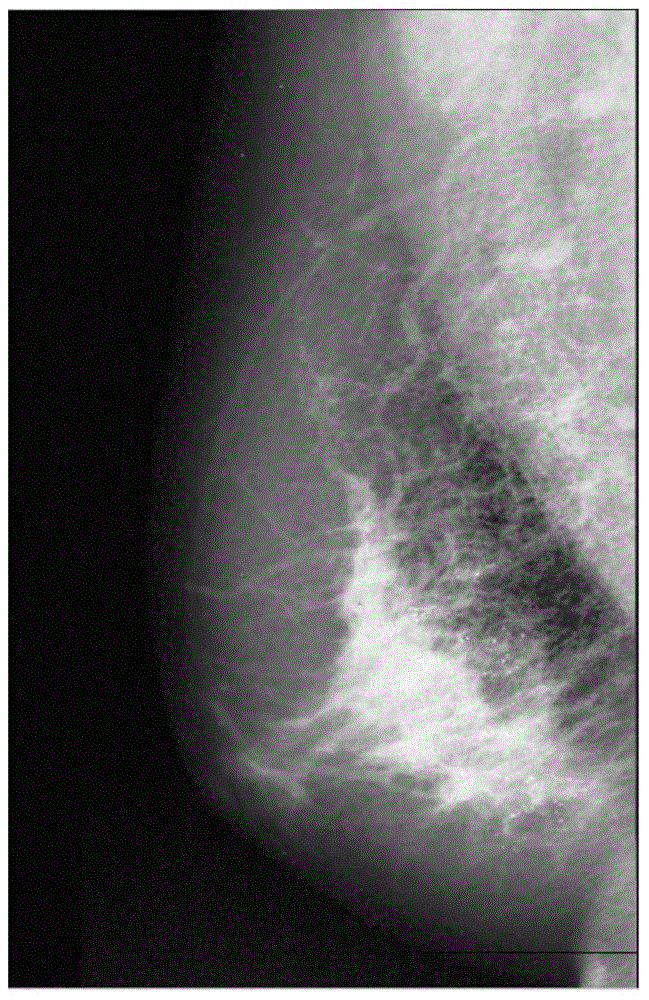
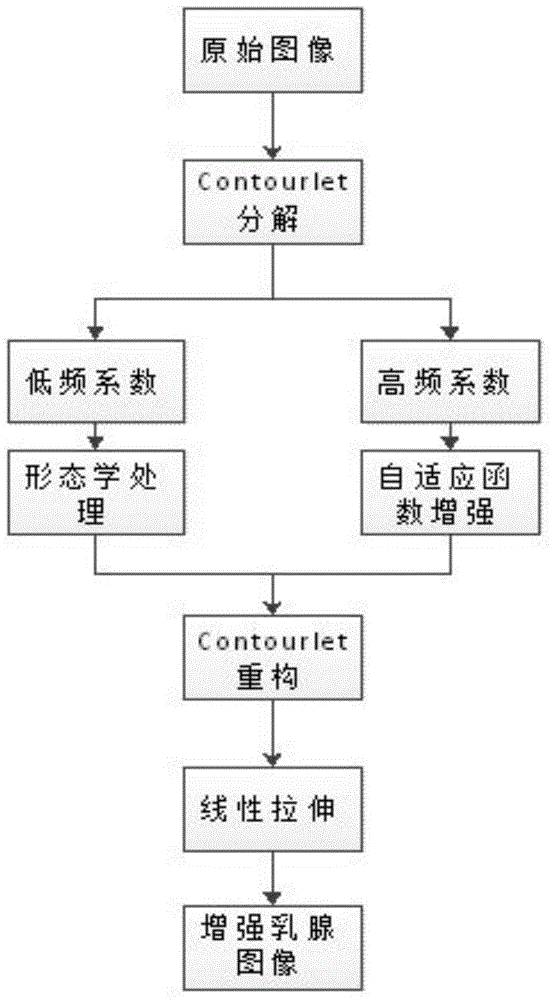
InactiveCN104616255AEnhancement effect is goodAvoid enhancementImage enhancementRadiation diagnosticsImage contrastCalcification
The invention discloses an adaptive enhancement method based on a mammographic image. The method comprises the steps of solving the image by contourlet conversion to obtain high-frequency sub-images in different directions and a low-frequency sub-image; processing the low-frequency sub-image coefficients according to the morphology; enhancing the high-frequency sub-image coefficients in different directions according to the created adaptive enhancement functions; performing contourlet reconstruction for the processed high-frequency coefficient sub-images and the low-frequency coefficient sub-image to obtain the enhanced mammographic image. With the adoption of the method, the weak side edge and calcification points in the images can be enhanced while inhibiting image noise, and therefore, the image contrast ratio can be effectively improved; the enhancement effect is superior to that of the existing counter-peaked mask method and the adaptive histogram equalization method.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF TECH
Method of processing radiological images, and, in particular, mammographic images
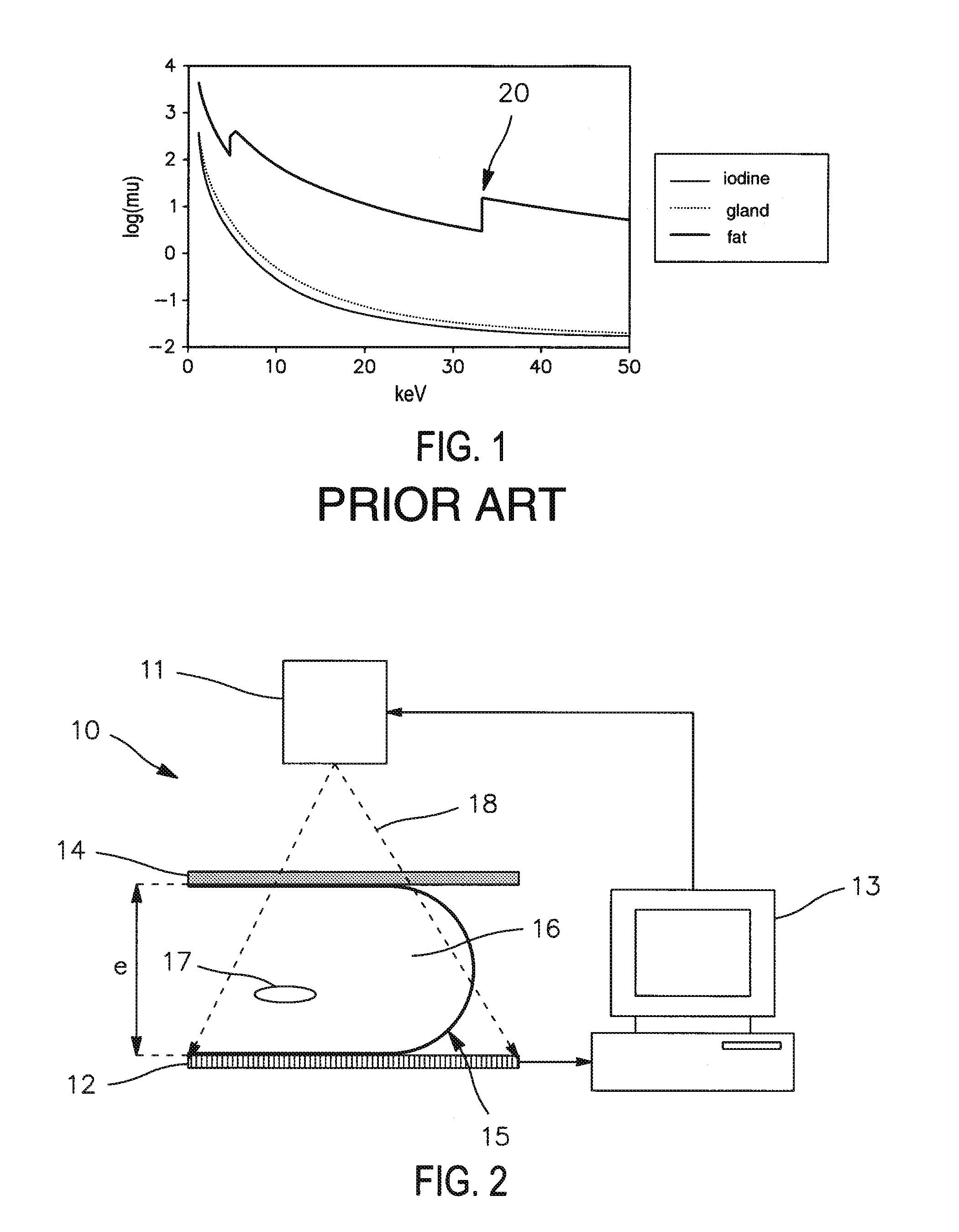
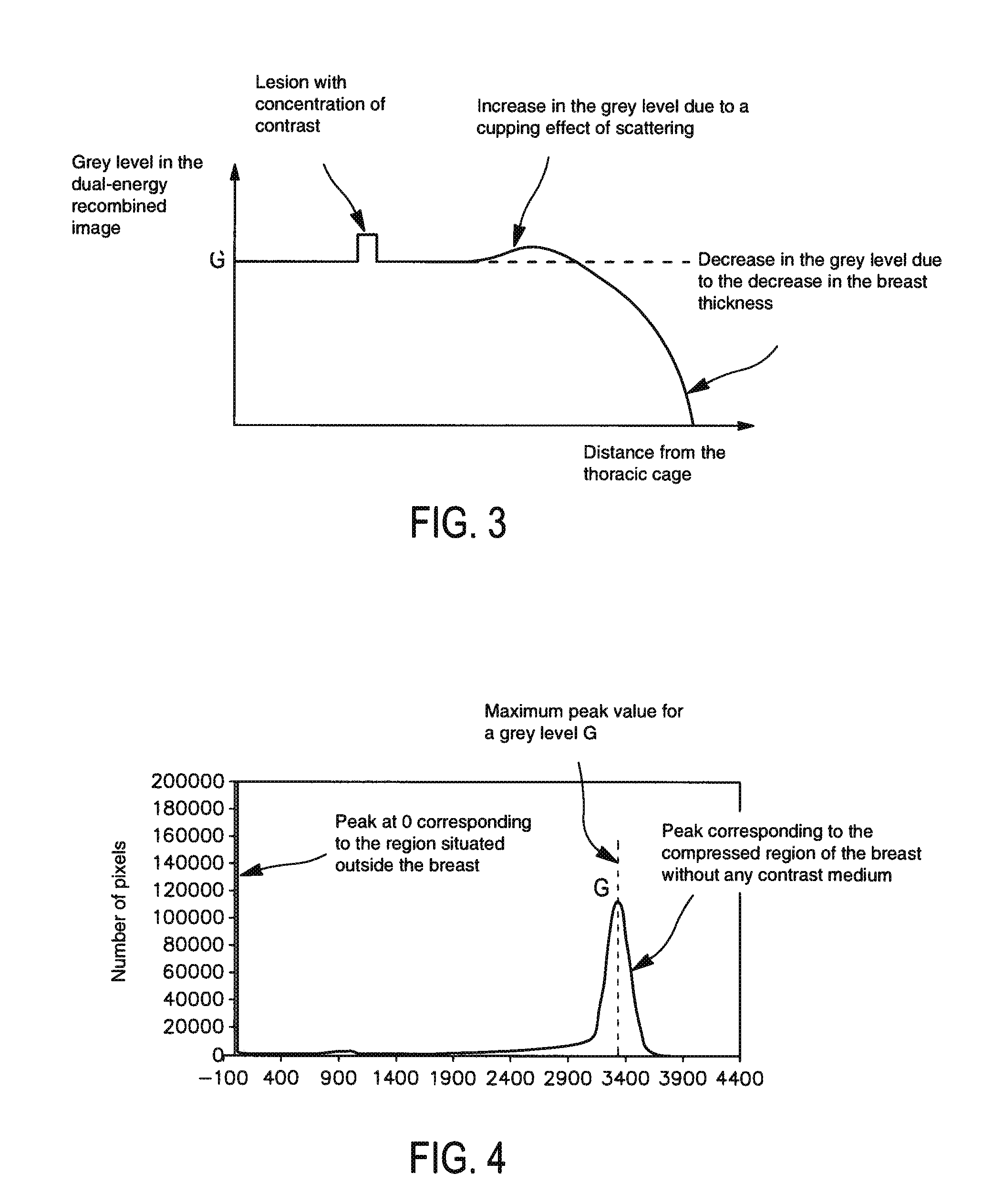
ActiveUS20090304253A1Quality improvementNon-uniform areaImage enhancementPatient positioning for diagnosticsHigh energyGrey level
A method of processing a radiological image of an organ. The method may comprise generating a recombined image (R) from at least one previously acquired low energy image (L) and one high energy image (H) of a portion of the organ. The recombined image comprises a background and one or more areas corresponding to the presence of a contrast medium in the organ. The method may further comprise correcting the recombined image (R) by compensating (C) for the nonuniformities present in the background to obtain a compensated recombined image in which the background has a substantially uniform grey level.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
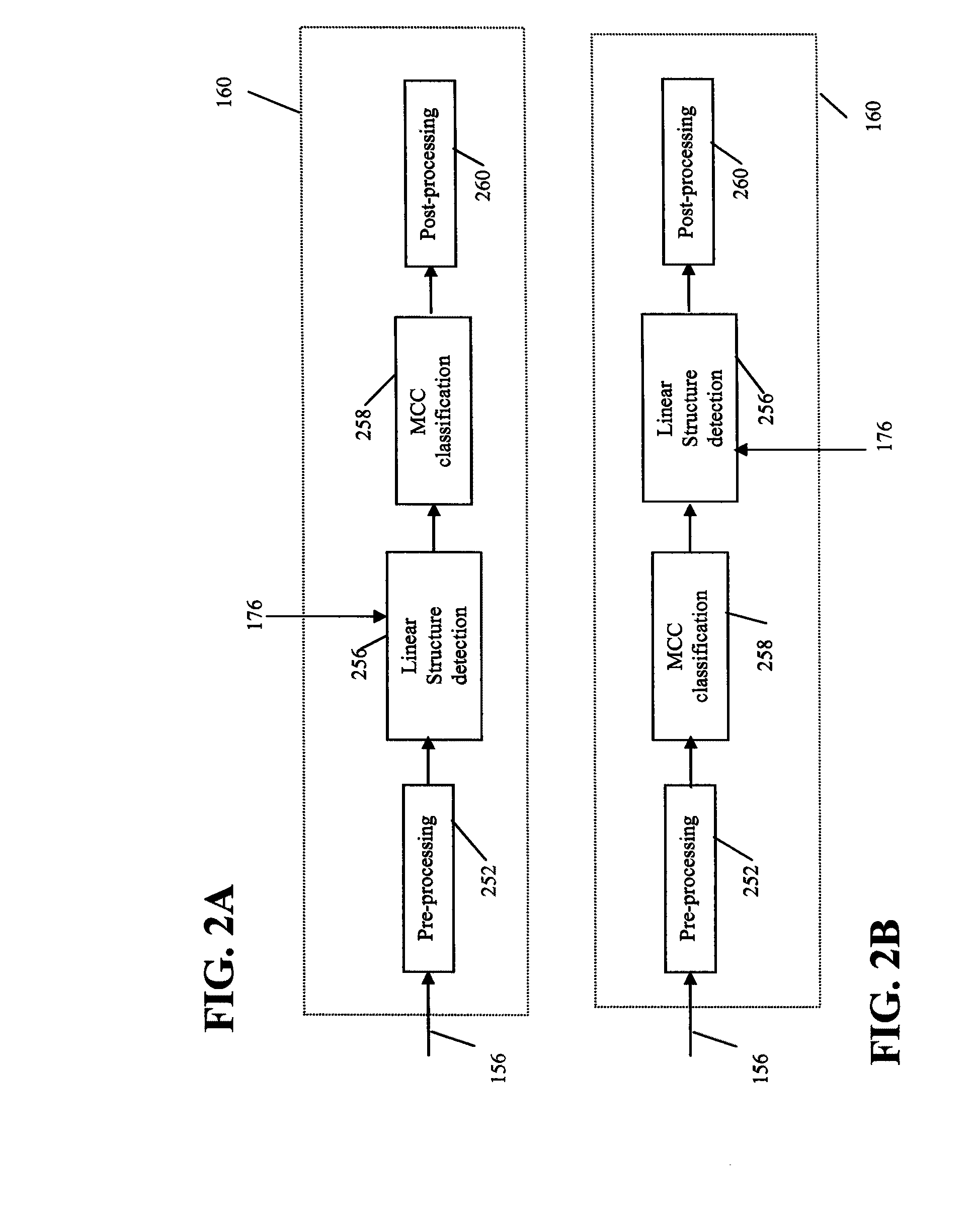
Method for detection of linear structures and microcalcifications in mammographic images
InactiveUS20100104155A1Reducing MCC FPsImage enhancementImage analysisGeometric propertyPattern recognition
A method for linear structure detection in mammographic images, comprising: locating a plurality of microcalcification candidate clusters in digital mammographic images; extracting a region of interest that encloses each of the candidate clusters; processing the region of interest to generate feature points that reveal geometric properties in the region; applying a line detection algorithm to the feature points to produce a line model; and analyzing the line model to determine whether a true linear structure is present in the first region of interest.
Owner:CARESTREAM HEALTH INC
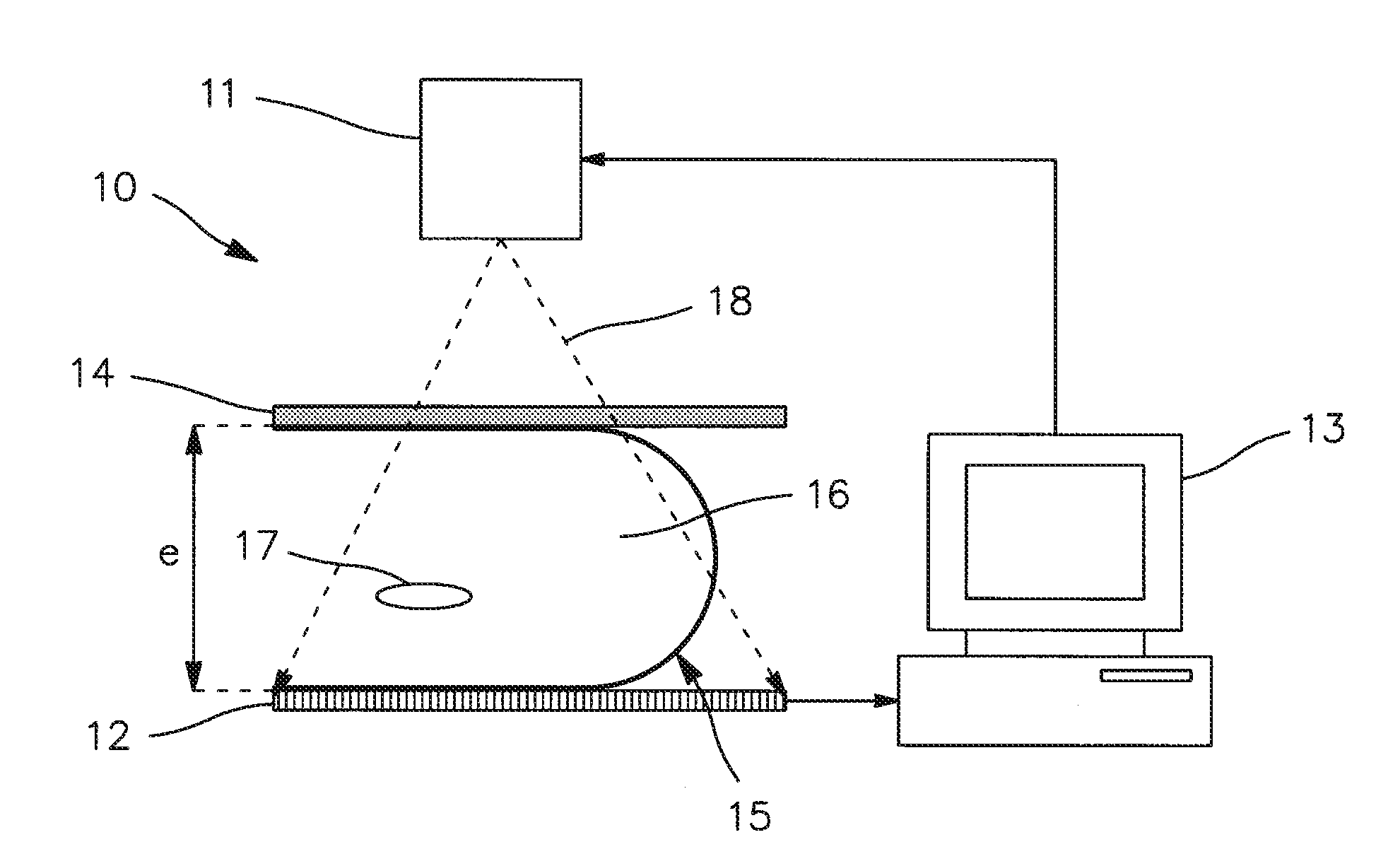
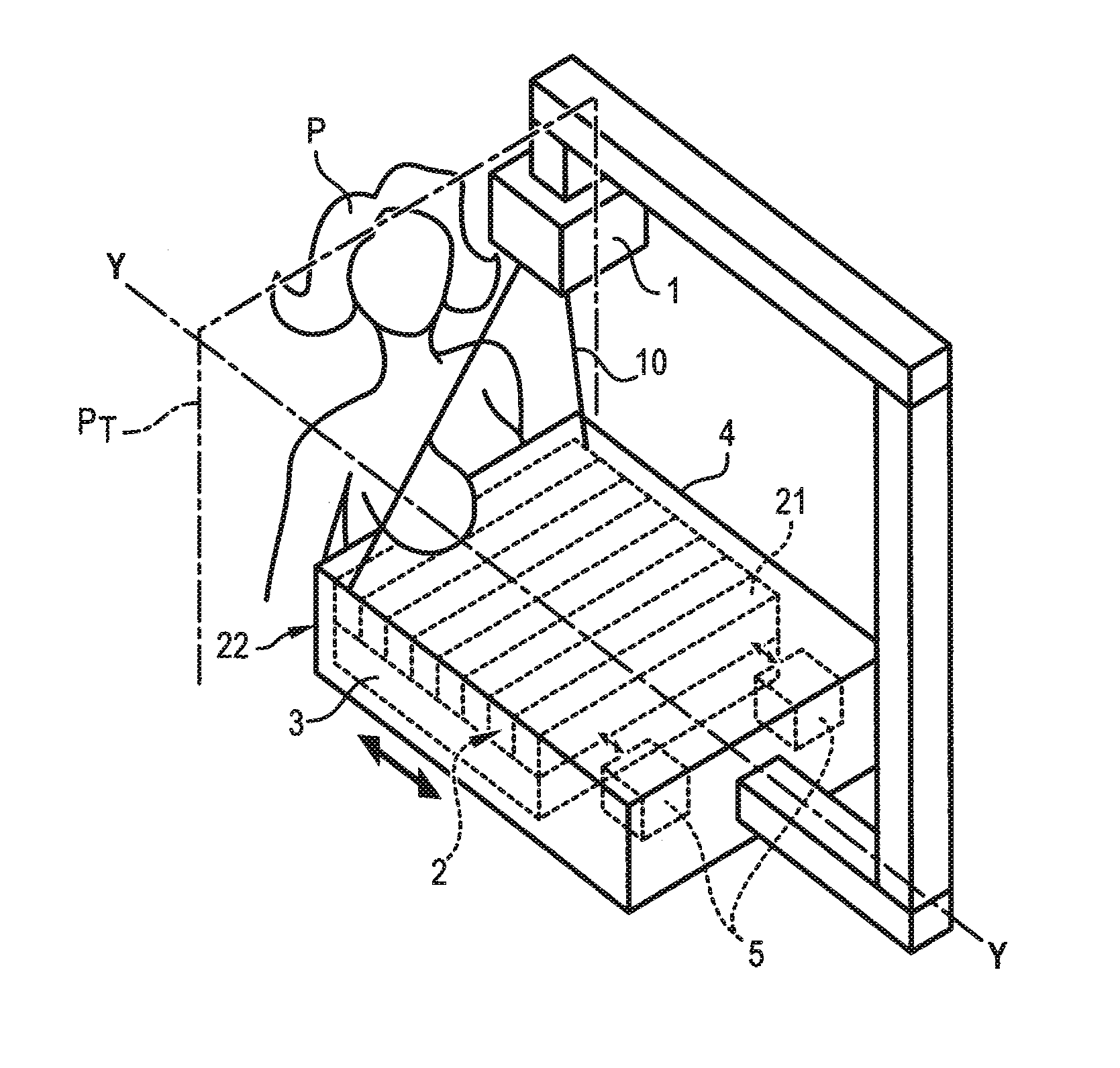
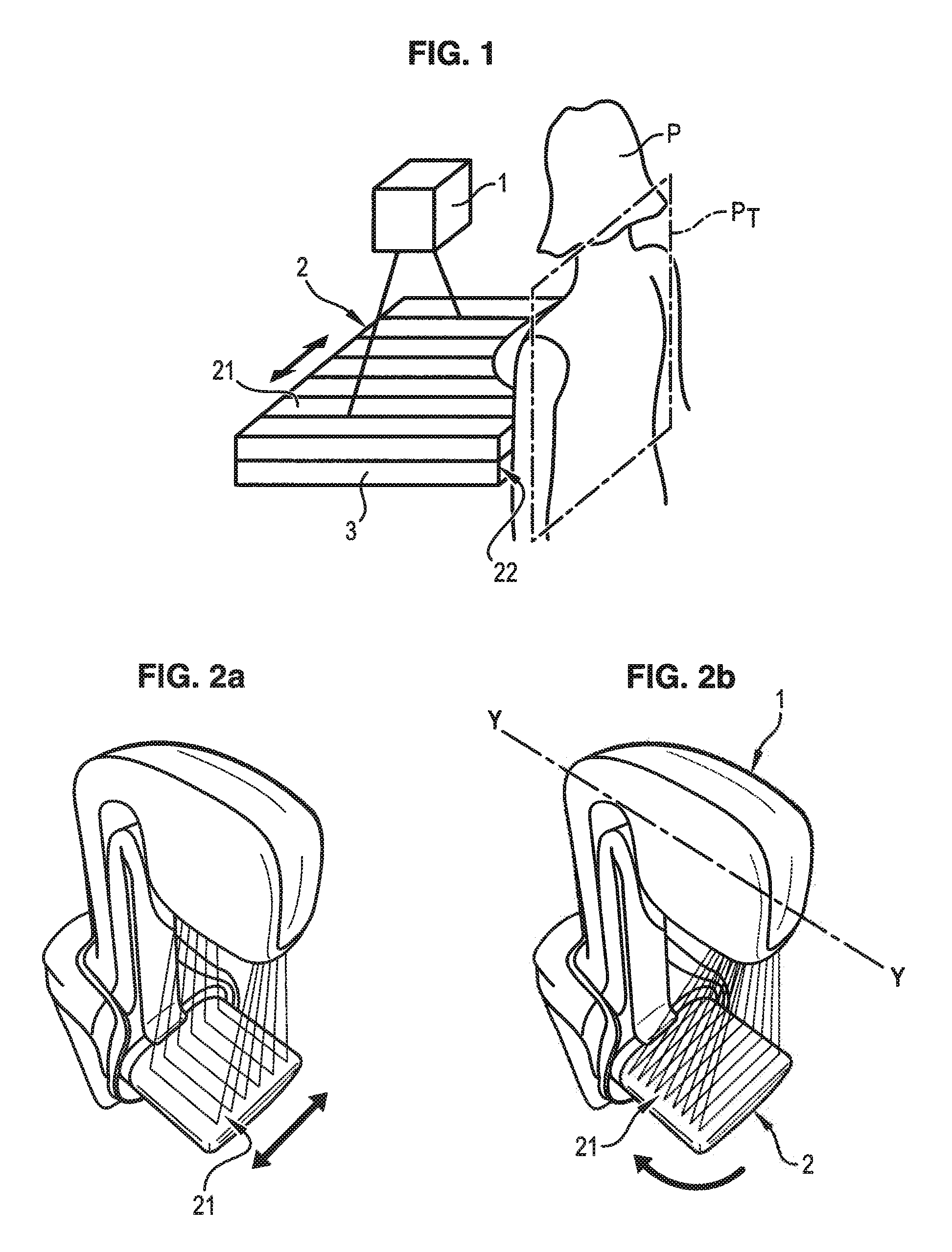
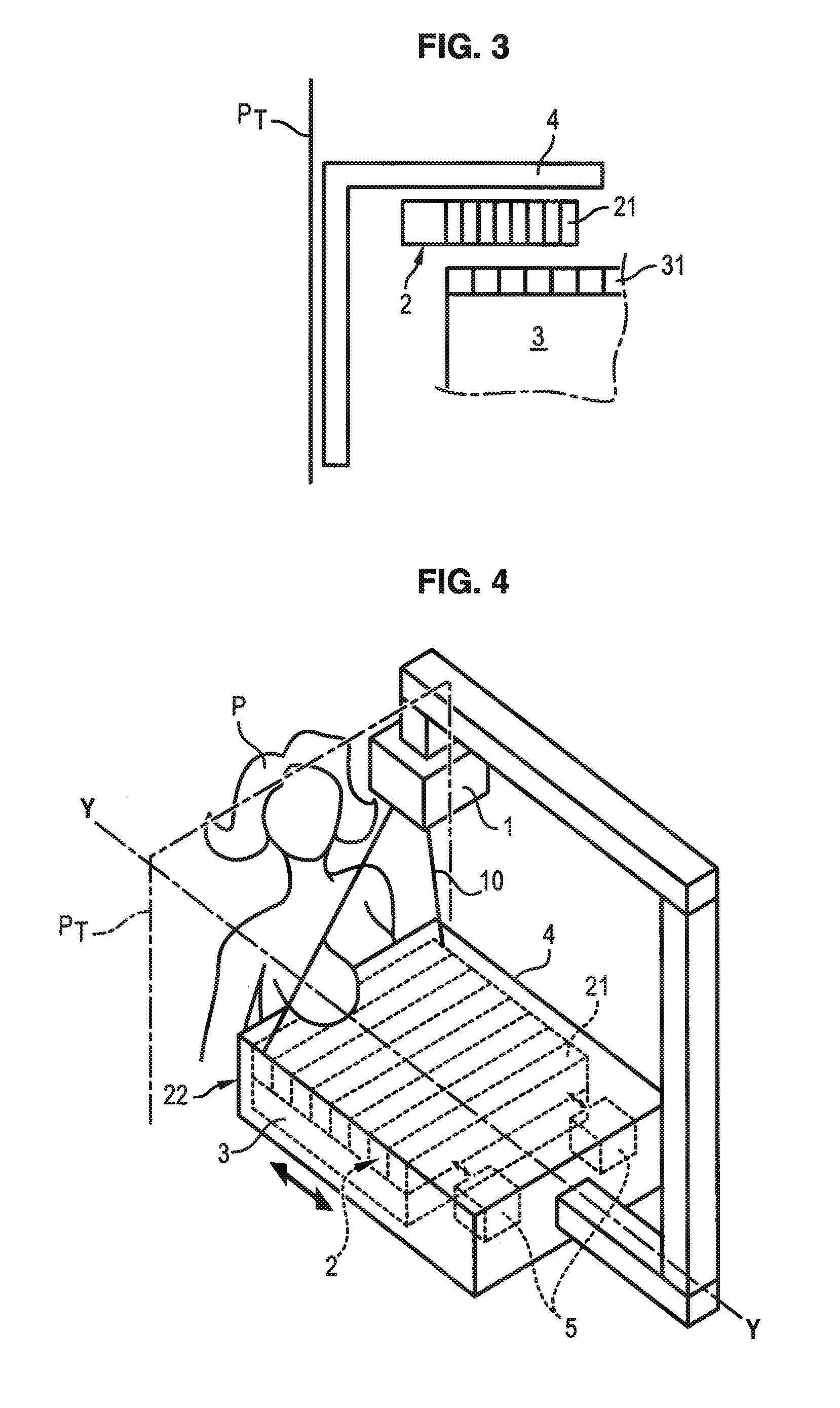
Process and device for deploying an Anti-scattering grid
ActiveUS20120170711A1Eliminate the effects ofEliminates imagePatient positioning for diagnosticsTomographyX ray radiographyPhysics
A process for deploying an anti-scattering grid in a mammograph is provided. The mammograph comprises a radiation source configured to emit radiation for taking mammographic images of a patient, a radiation detector comprising a network of sensors arranged periodically with a first pitch, and an anti-scattering grid arranged between the source and the detector, the anti-scattering grid comprising absorption laminates of radiations arranged parallel to each other and distributed periodically with a second pitch. The process comprises: displacing the anti-scattering grid relative to the detector or displacing the detector relative to the anti-scattering grid during emission of radiation; and adapting the second pitch to the first pitch, wherein displacement is perpendicular to the direction of the laminates of the anti-scattering grid, the laminates being arranged parallel to a side of the anti-scattering grid positioned against the patient.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Method for classifying breast tissue density using computed image features
InactiveUS7903861B2Assist diagnosisAssist imageImage enhancementImage analysisTissue densityRadiology
A method for classifying tissue density of a breast includes obtaining mammography image data and segmenting the mammography image to identify the region representing the breast tissue. A plurality of regions within the breast tissue region are identified for obtaining image features therefrom. A plurality of image features are computed from the identified plurality of regions. The breast tissue density is classified using the computed plurality of image features.
Owner:CARESTREAM HEALTH INC
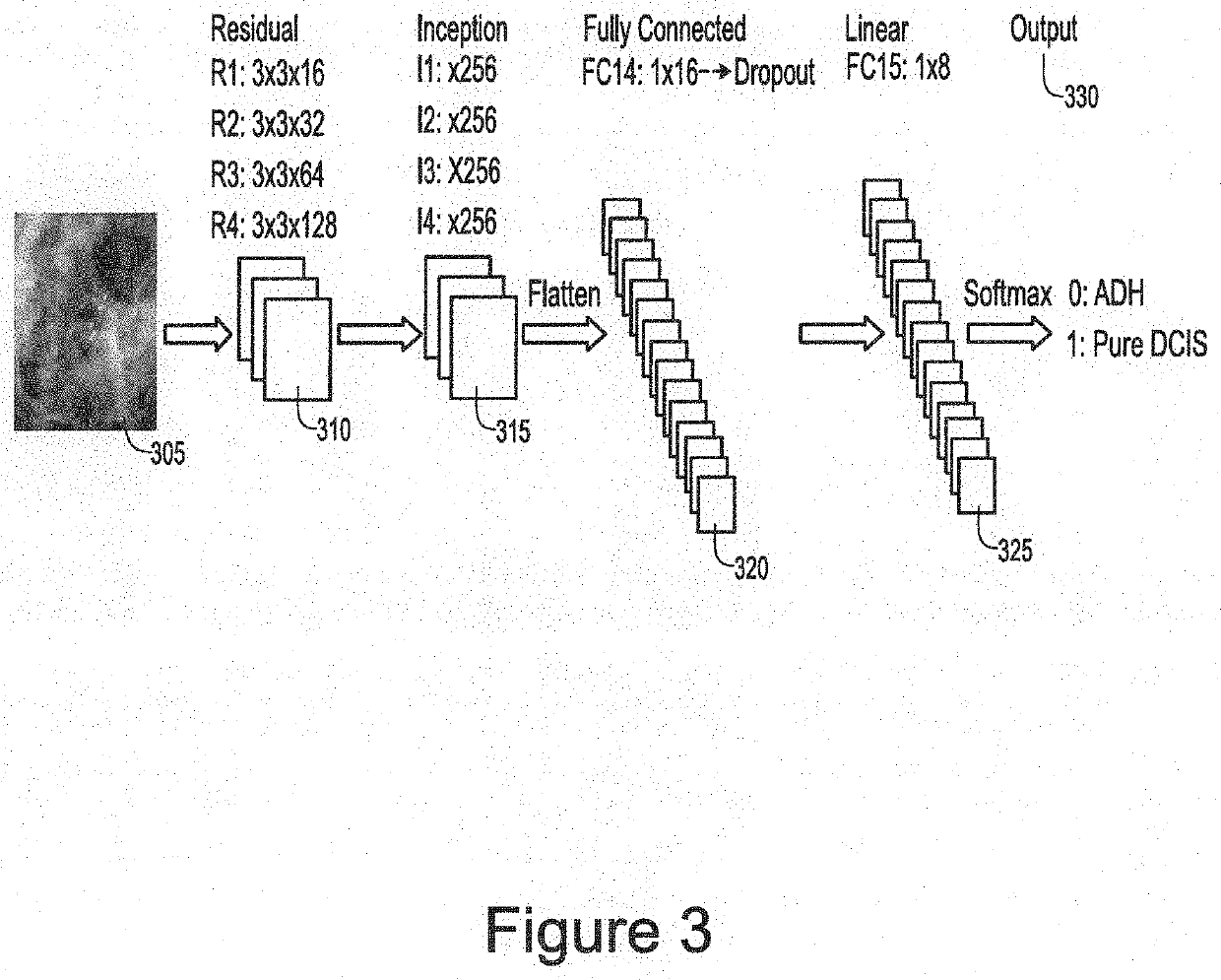
System, method and computer-accessible medium for classifying breast tissue using a convolutional neural network
An exemplary system, method and computer-accessible medium for classifying a breast tissue(s) a patient(s) can include, for example, receiving an image(s) of an internal portion(s) of a breast of the patient(s), and automatically classifying the breast tissue(s) of the breast by applying a neural network(s) to the image(s). The automatic classification can include a classification as to whether the breast tissue(s) is atypical ductal hyperplasia or ductal carcinoma. The automatic classification can include a classification as to whether the breast tissue(s) is a cancerous tissue or a non-cancerous tissue. The image(s) can be a mammographic image or an optical coherence tomography image.
Owner:THE TRUSTEES OF COLUMBIA UNIV IN THE CITY OF NEW YORK
Facilitating Temporal Comparison of Medical Images
InactiveUS20110128289A1Facilitating temporal comparisonFacilitating temporal comparison of breast mammogramsImage enhancementImage analysisDisplay deviceComputer science
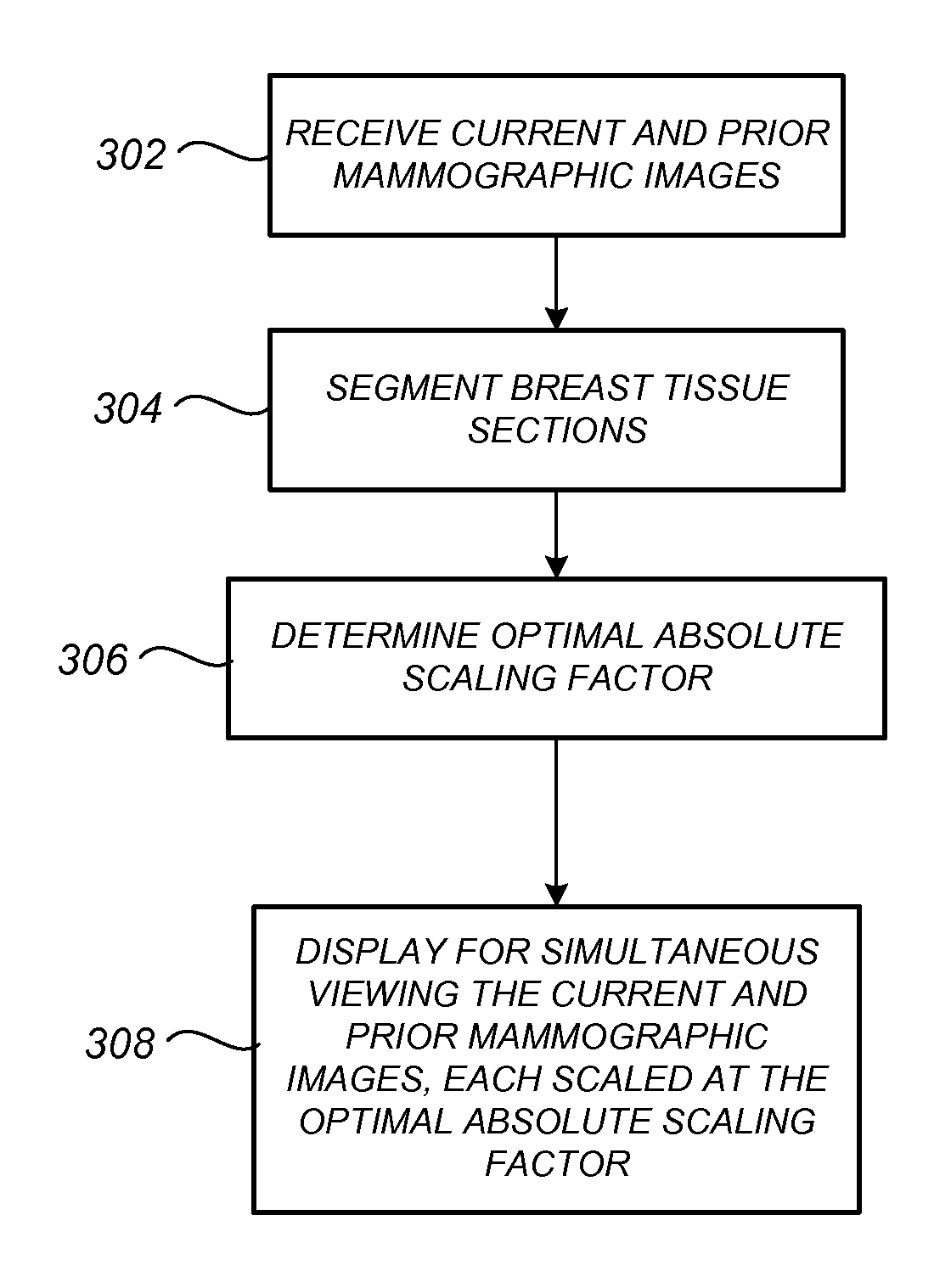
Methods, systems, and computer program products for facilitating temporal comparison of medical images is provided, with one exemplary application being for breast mammograms. In one embodiment, prior and subsequent mammographic images of a breast acquired using at least partially different mammogram acquisition systems are displayed for simultaneous viewing on a same mammogram display at an identical tissue distance per unit display distance without requiring a scale-adjusting viewer input. Also described are other embodiments for optimally scaling, windowing and / or otherwise advantageously processing and / or displaying prior and subsequent mammographic image sets in manners that facilitate temporal comparison therebetween.
Owner:HOLOGIC INC
Linear structure verification in medical applications
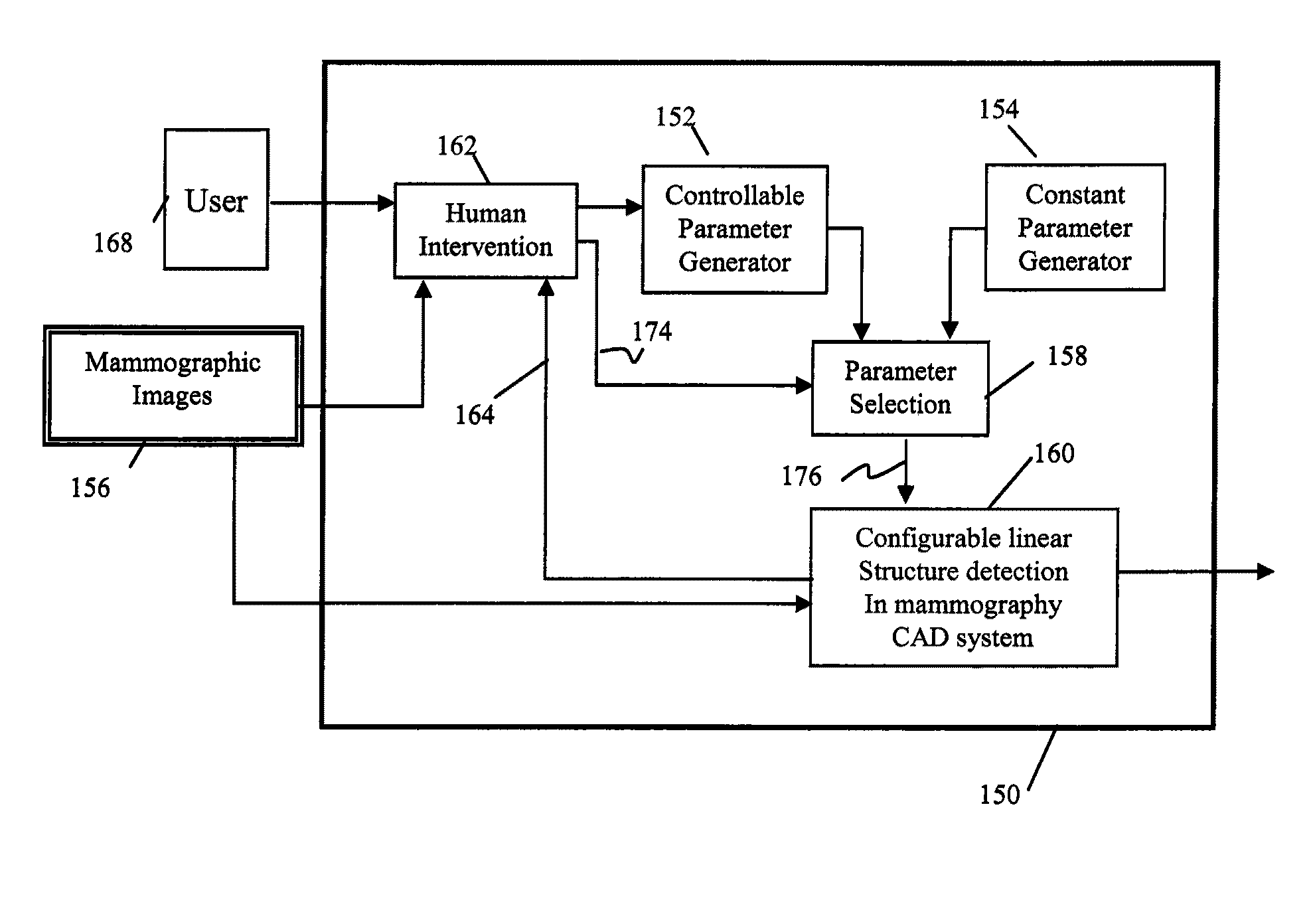
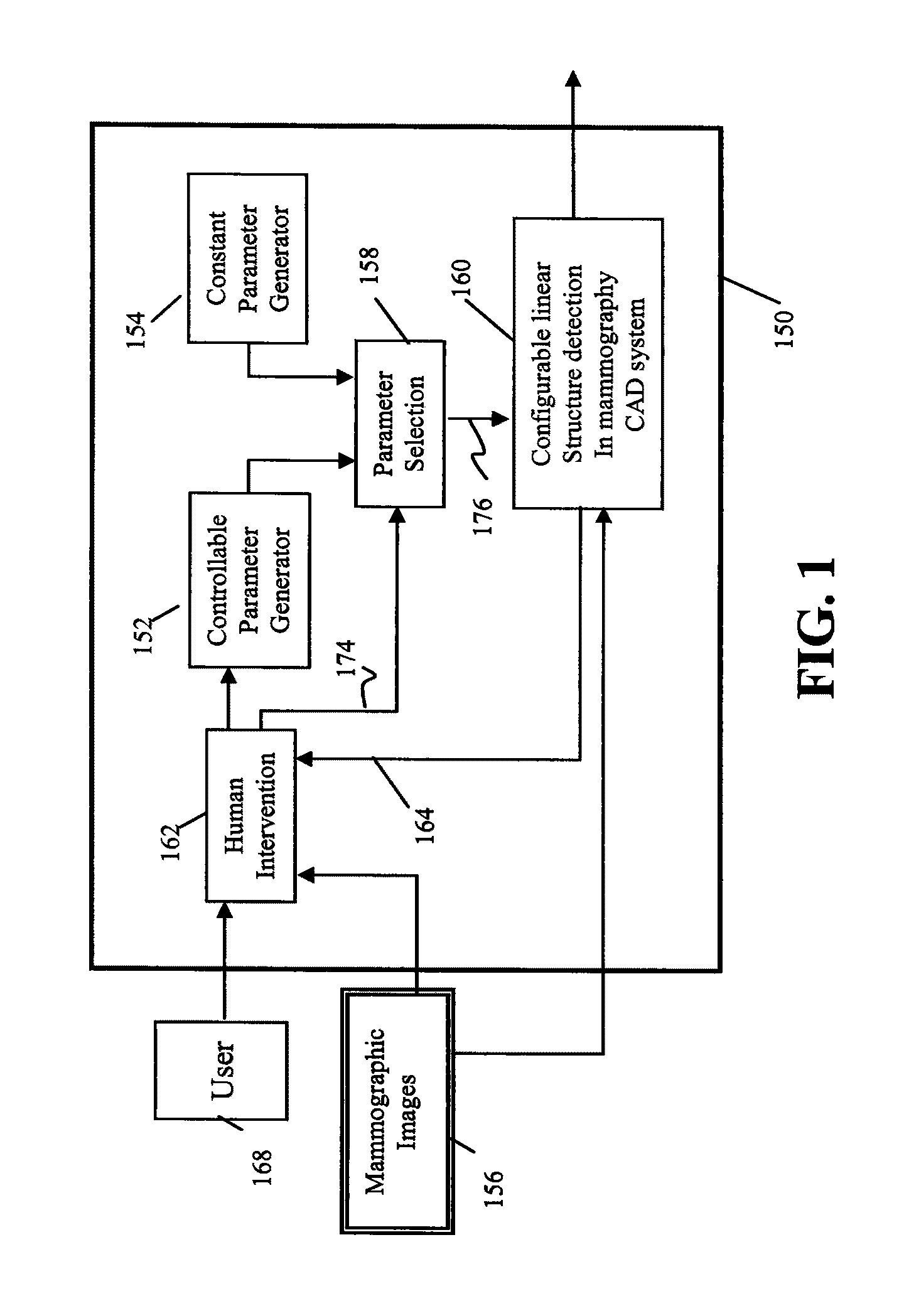
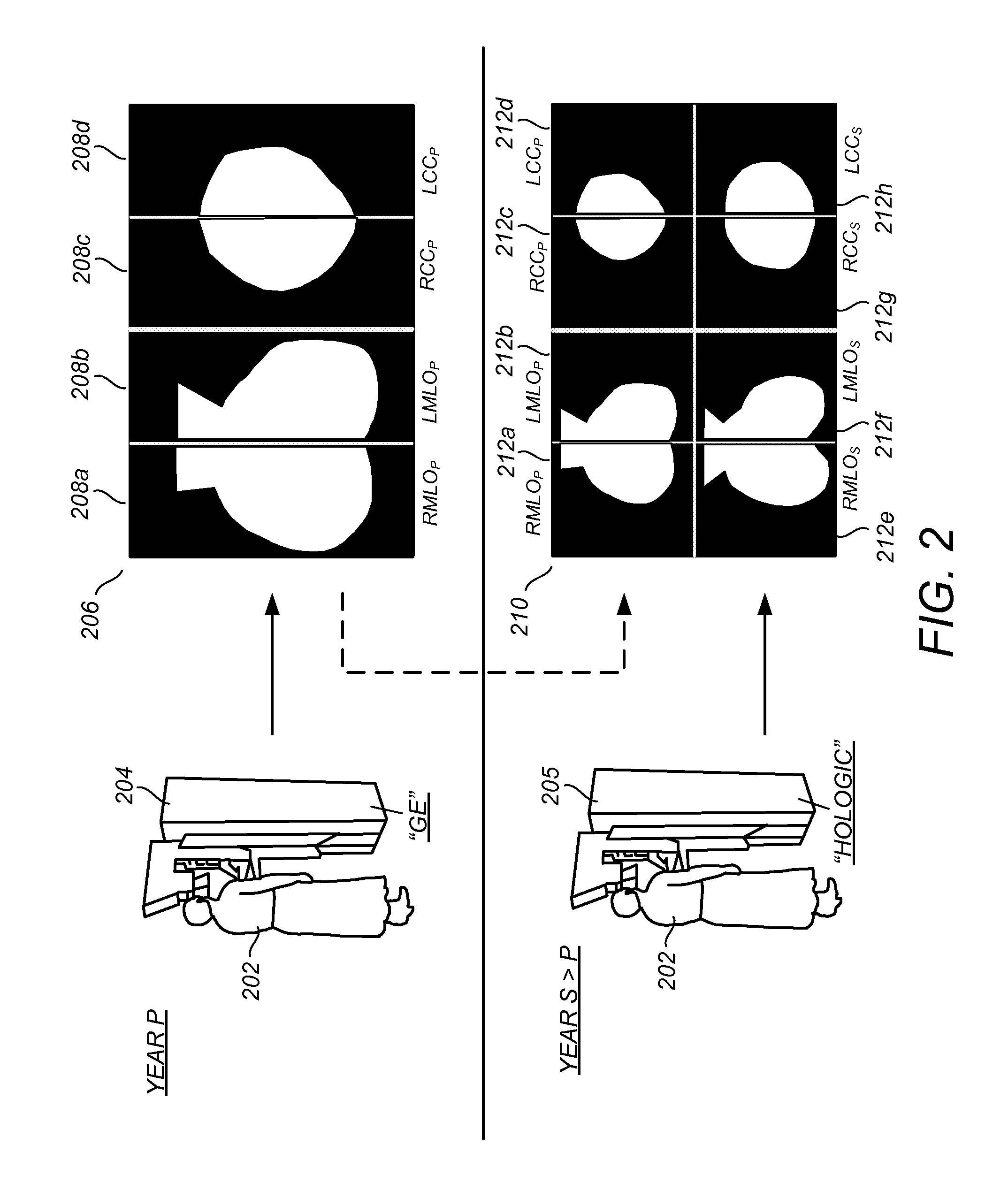
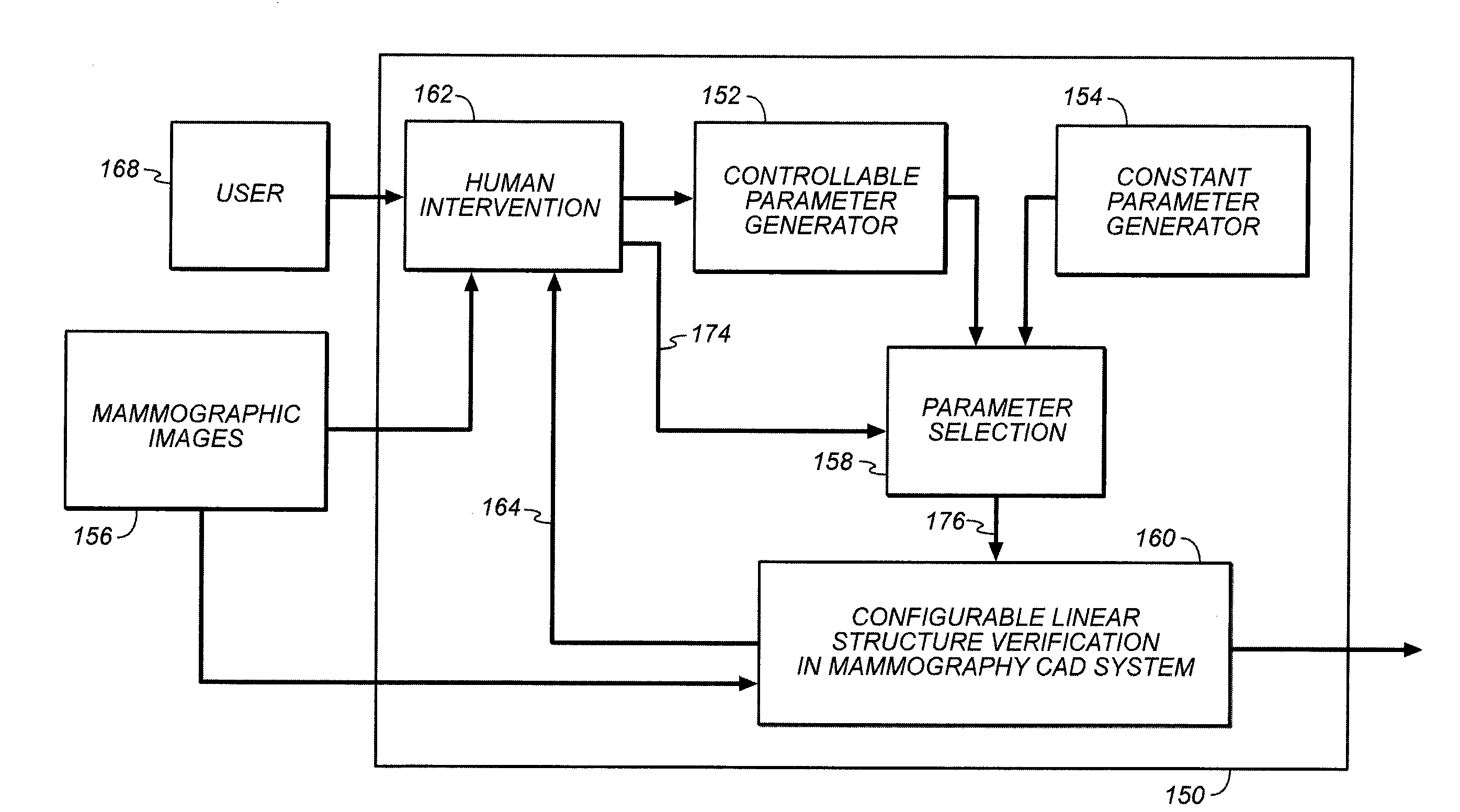
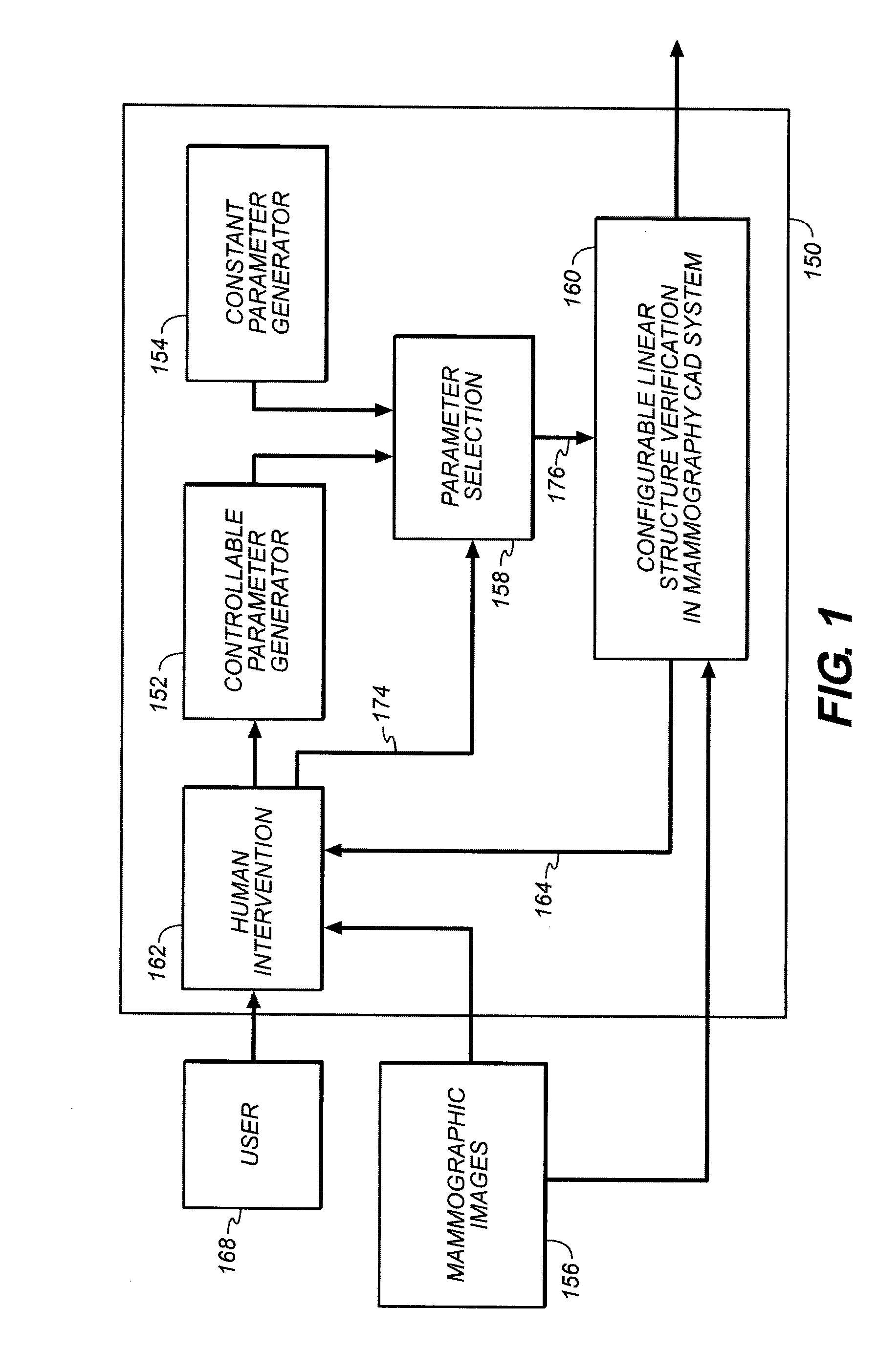
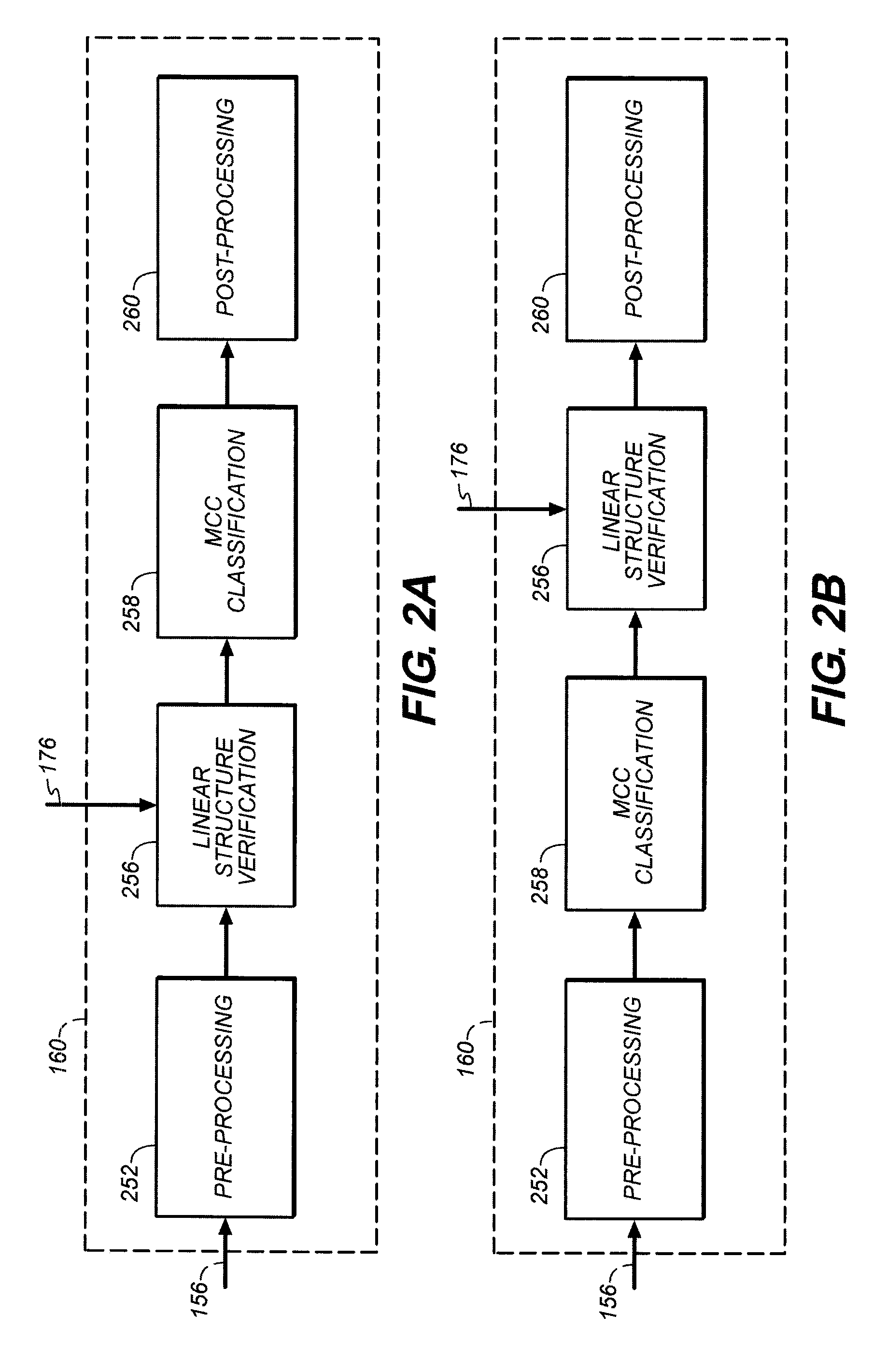
A method is disclosed for verifying linear structures in a digital mammographic image, comprising providing a configurable linear structure verifier in mammography computer assisted diagnosis system; optionally using an microcalcification candidate cluster driven linear structure verification methodology; selecting parameters for the linear structure verifier from a plurality of different parameter generating sources, at least one of which is controllable by human input; configuring the verifier according to selected parameters; and verifying linear structure using cascade rules.
Owner:CARESTREAM HEALTH INC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com