Patents
Literature
891results about "X-ray tube vessels/container" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
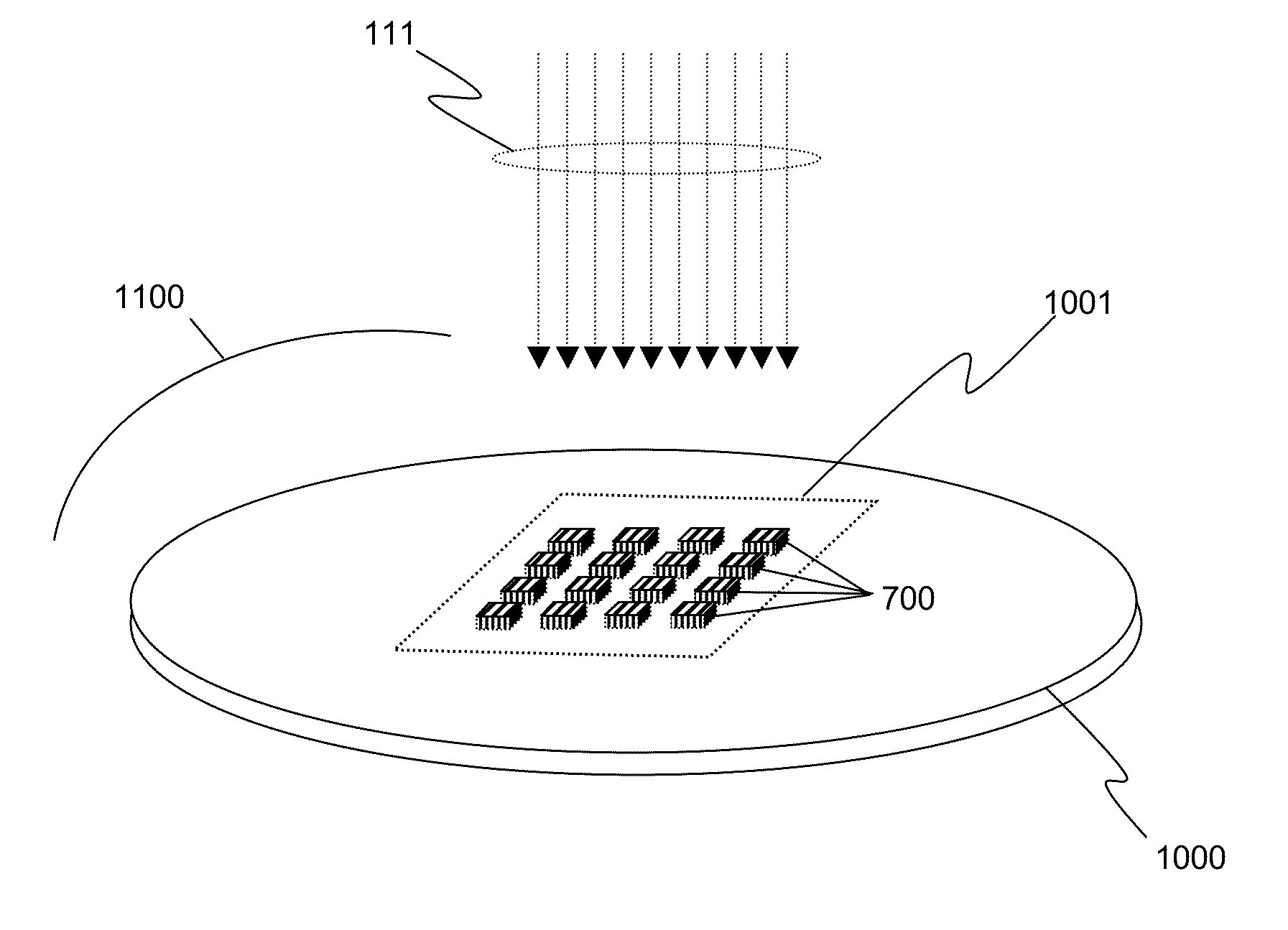
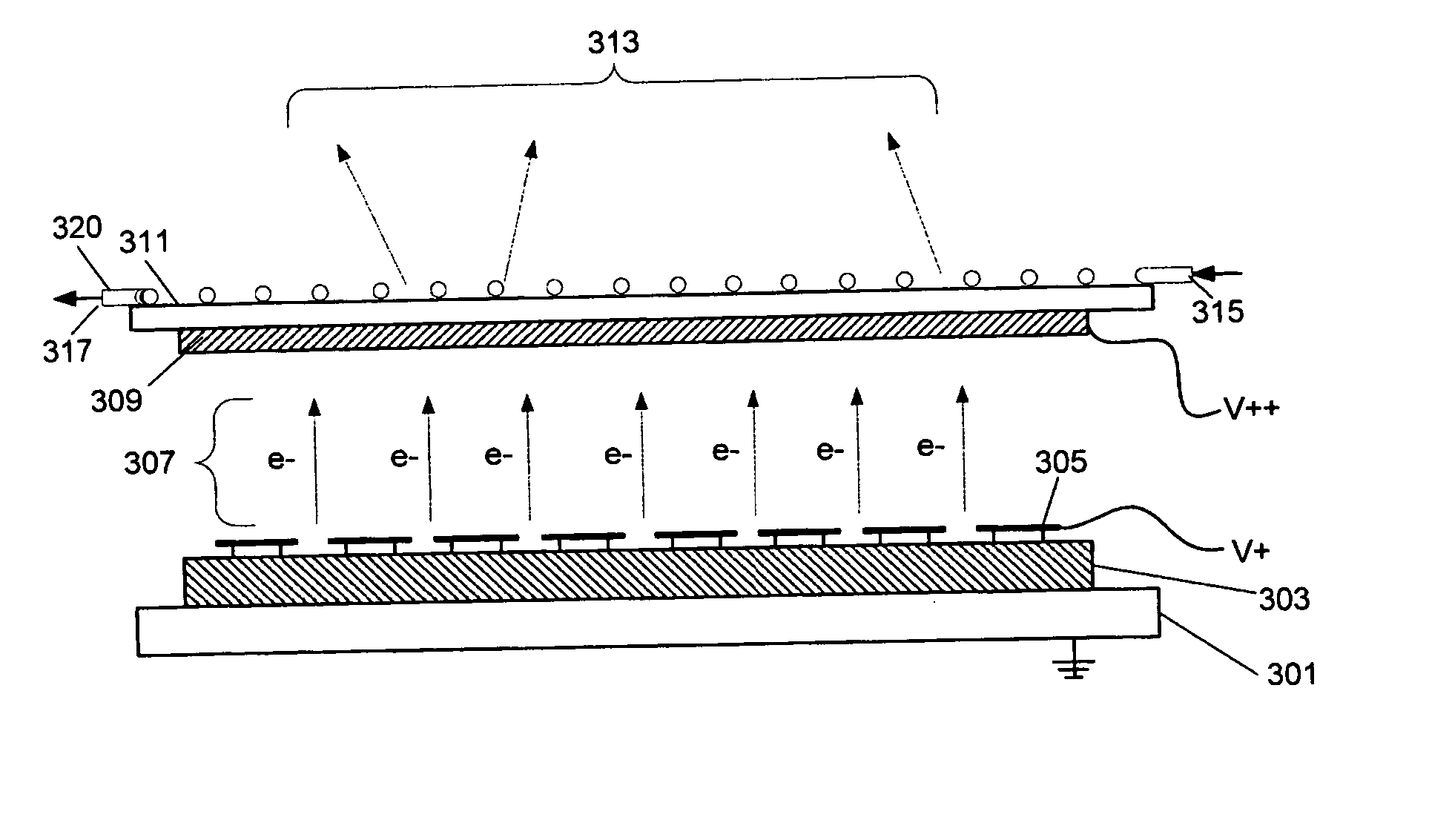
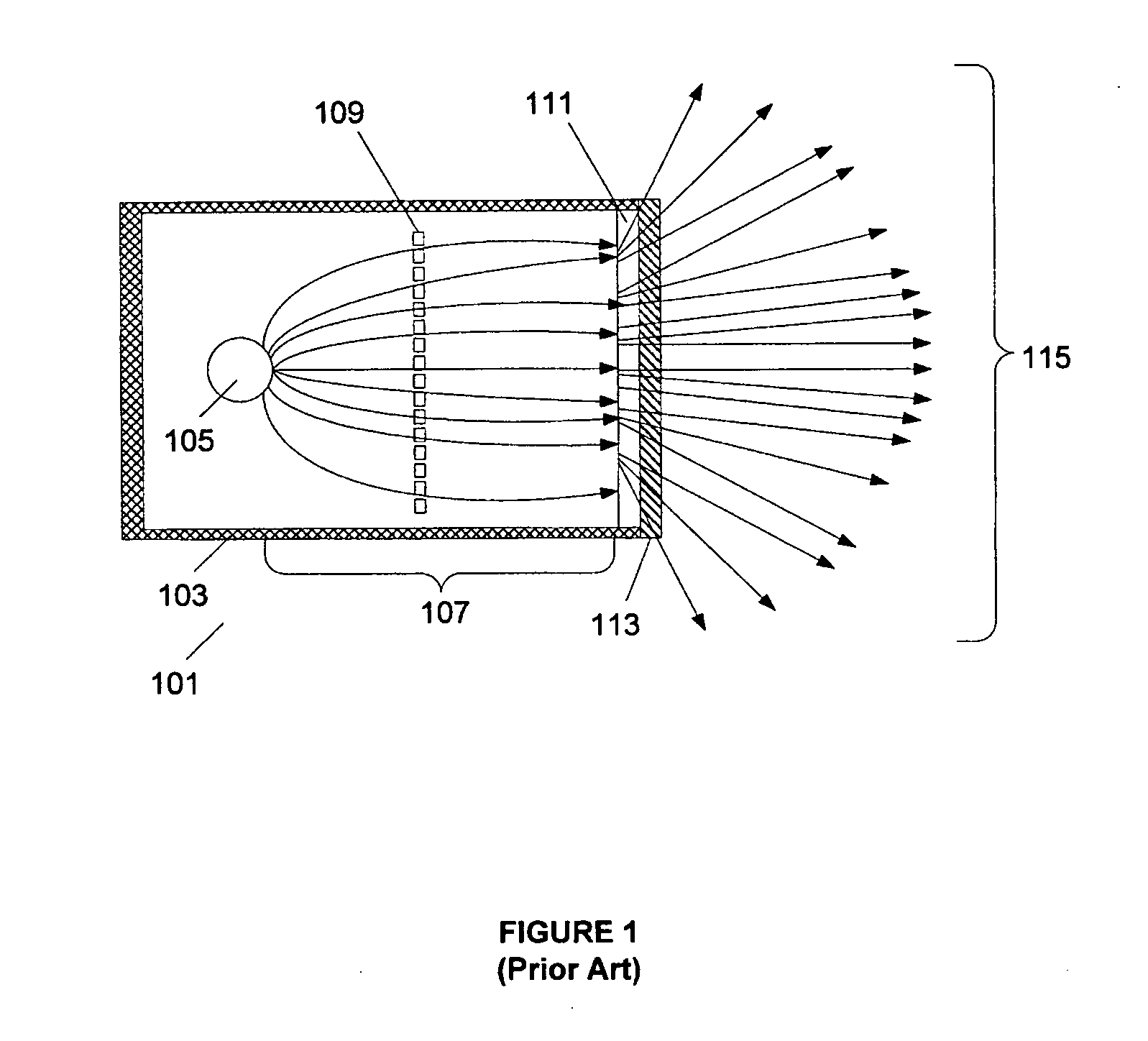
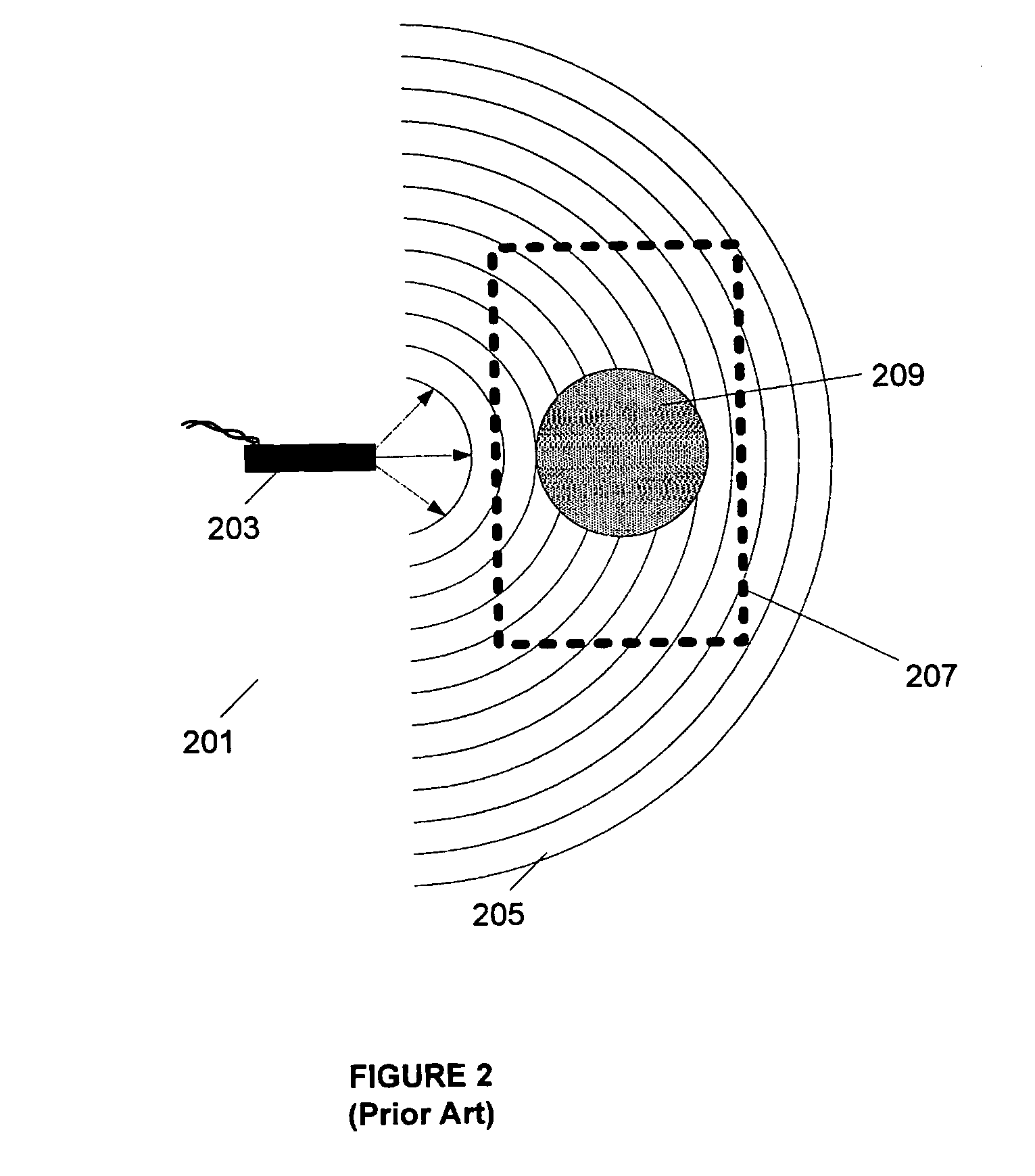
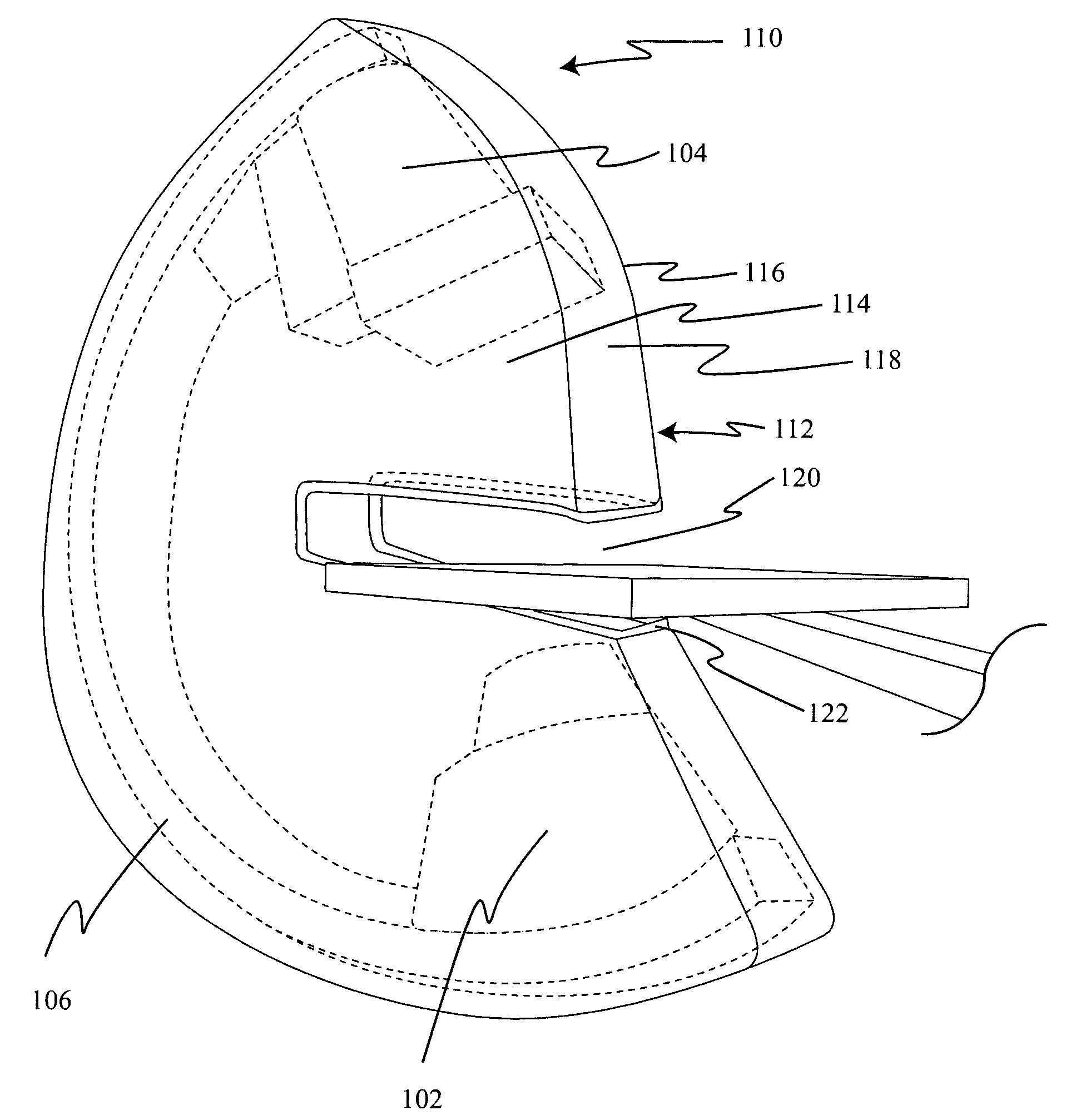
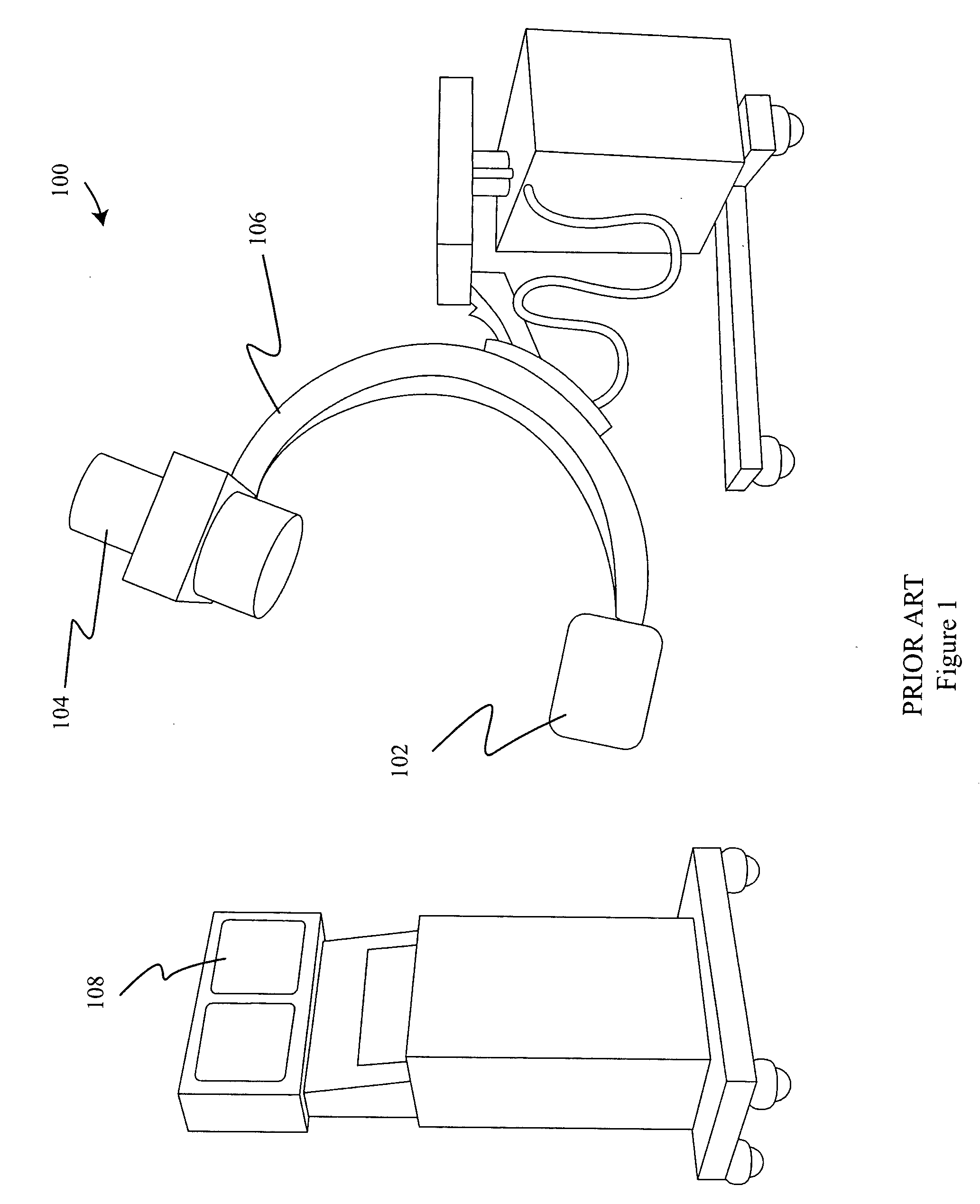
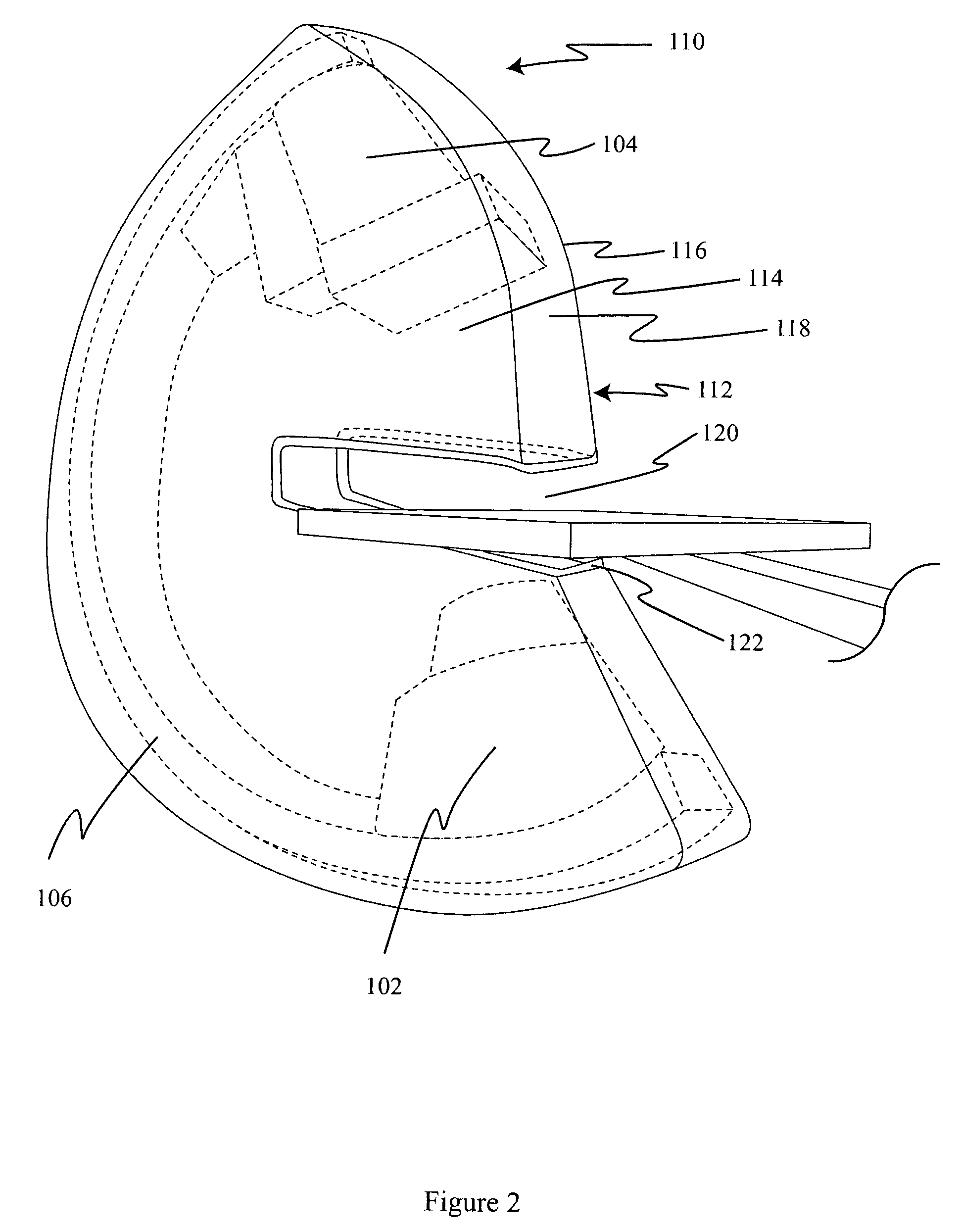
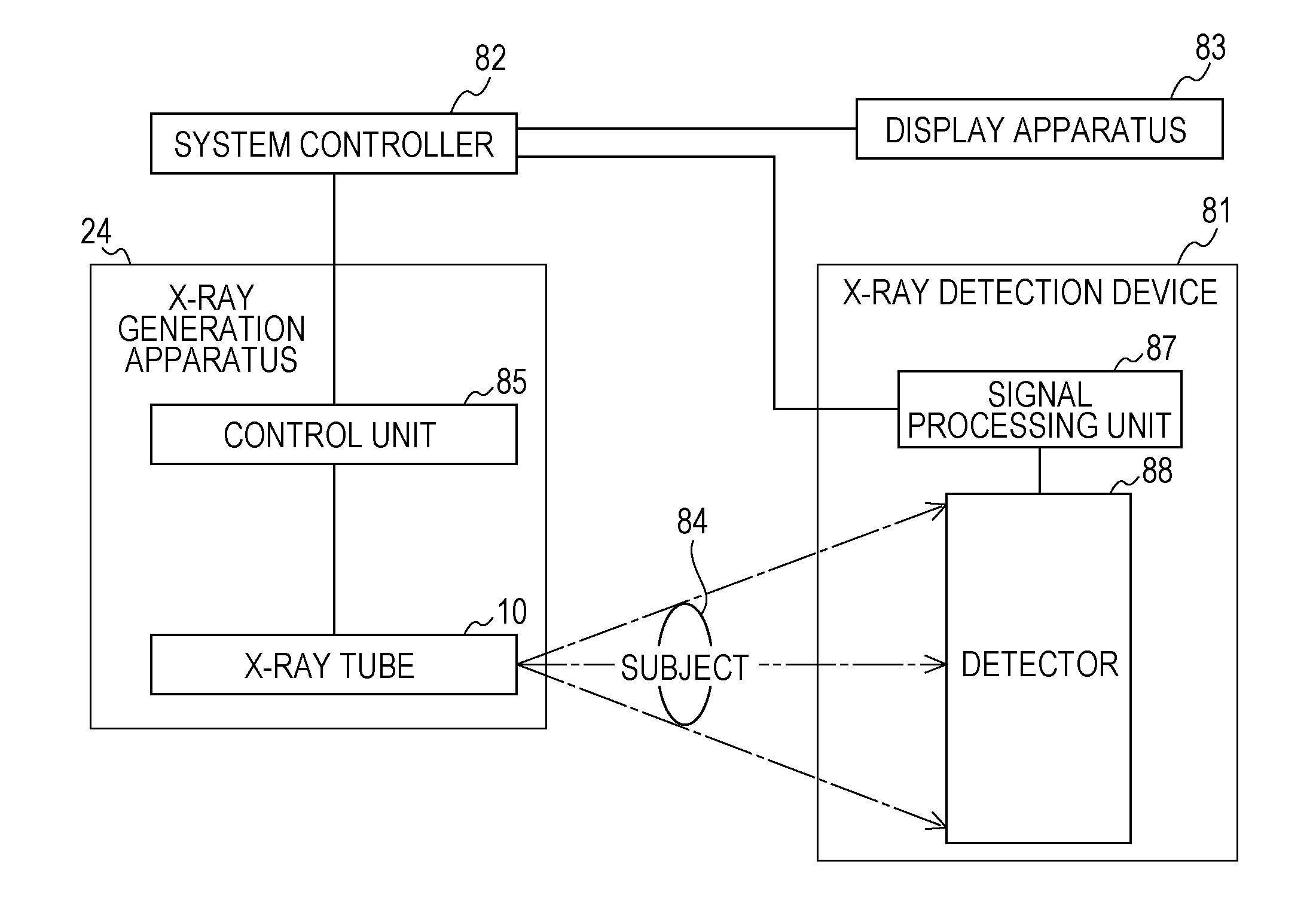
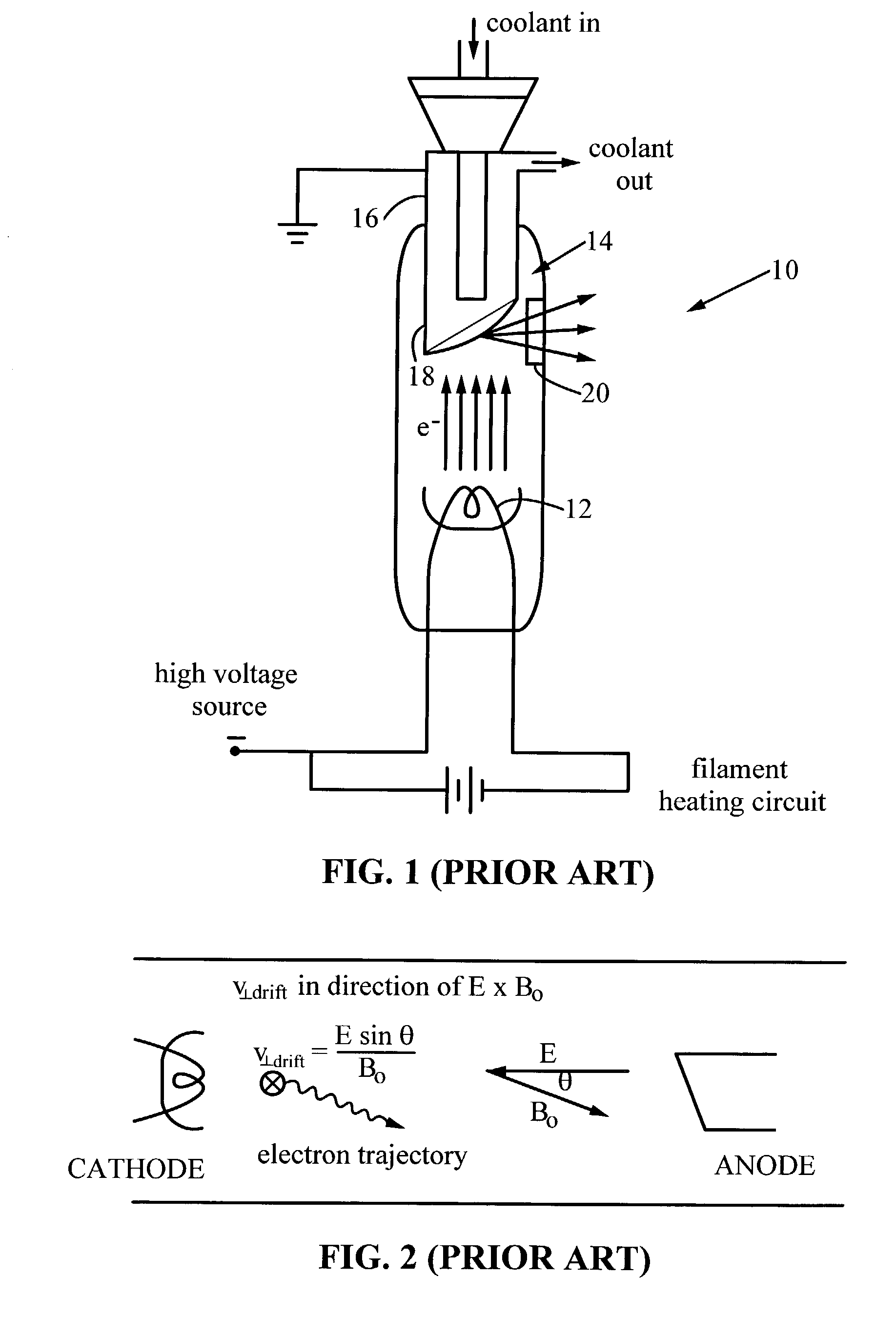
Large-area individually addressable multi-beam x-ray system and method of forming same
A structure to generate x-rays has a plurality of stationary and individually electrically addressable field emissive electron sources with a substrate composed of a field emissive material, such as carbon nanotubes. Electrically switching the field emissive electron sources at a predetermined frequency field emits electrons in a programmable sequence toward an incidence point on a target. The generated x-rays correspond in frequency and in position to that of the field emissive electron source. The large-area target and array or matrix of emitters can image objects from different positions and / or angles without moving the object or the structure and can produce a three dimensional image. The x-ray system is suitable for a variety of applications including industrial inspection / quality control, analytical instrumentation, security systems such as airport security inspection systems, and medical imaging, such as computed tomography.
Owner:THE UNIV OF NORTH CAROLINA AT CHAPEL HILL
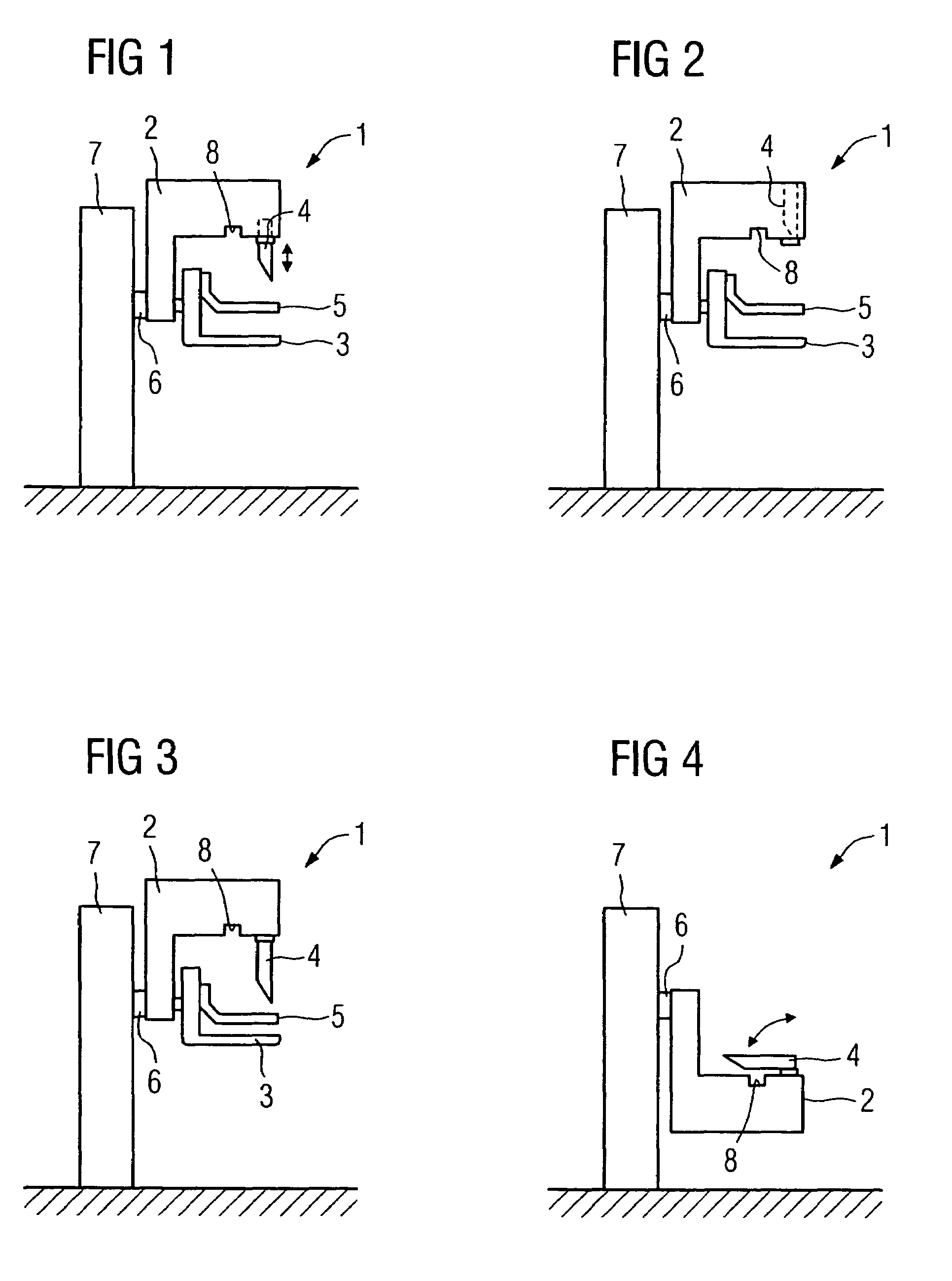
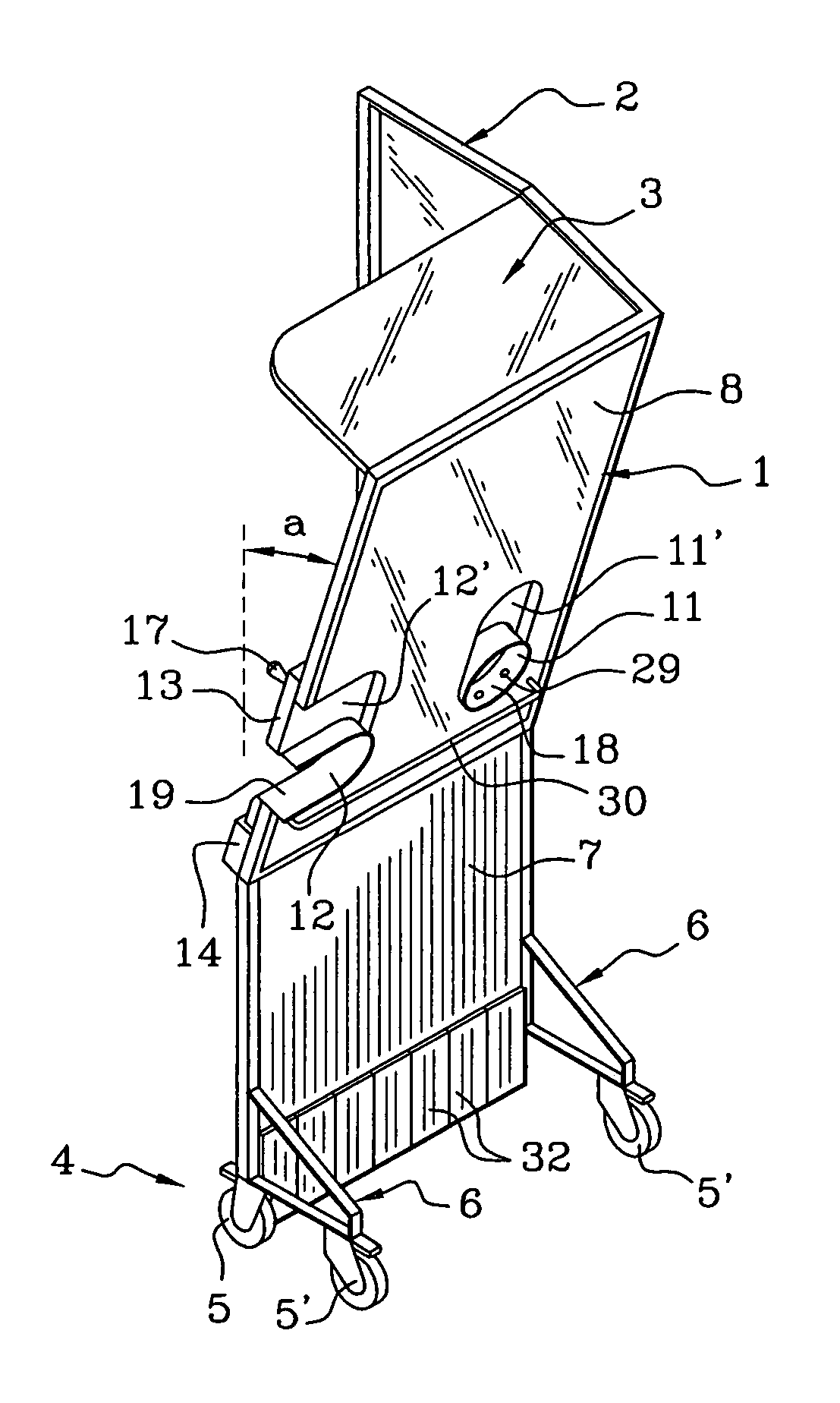
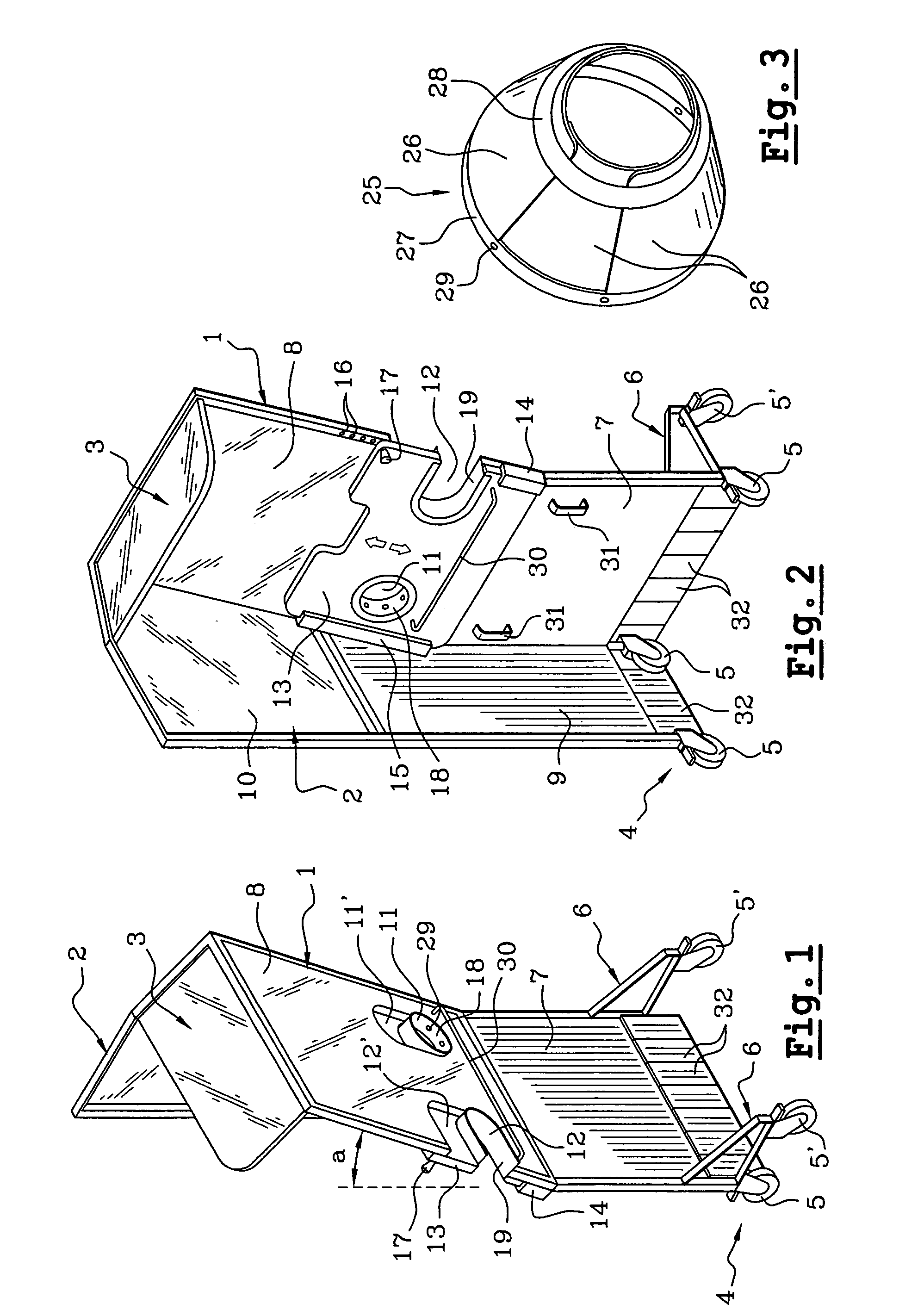
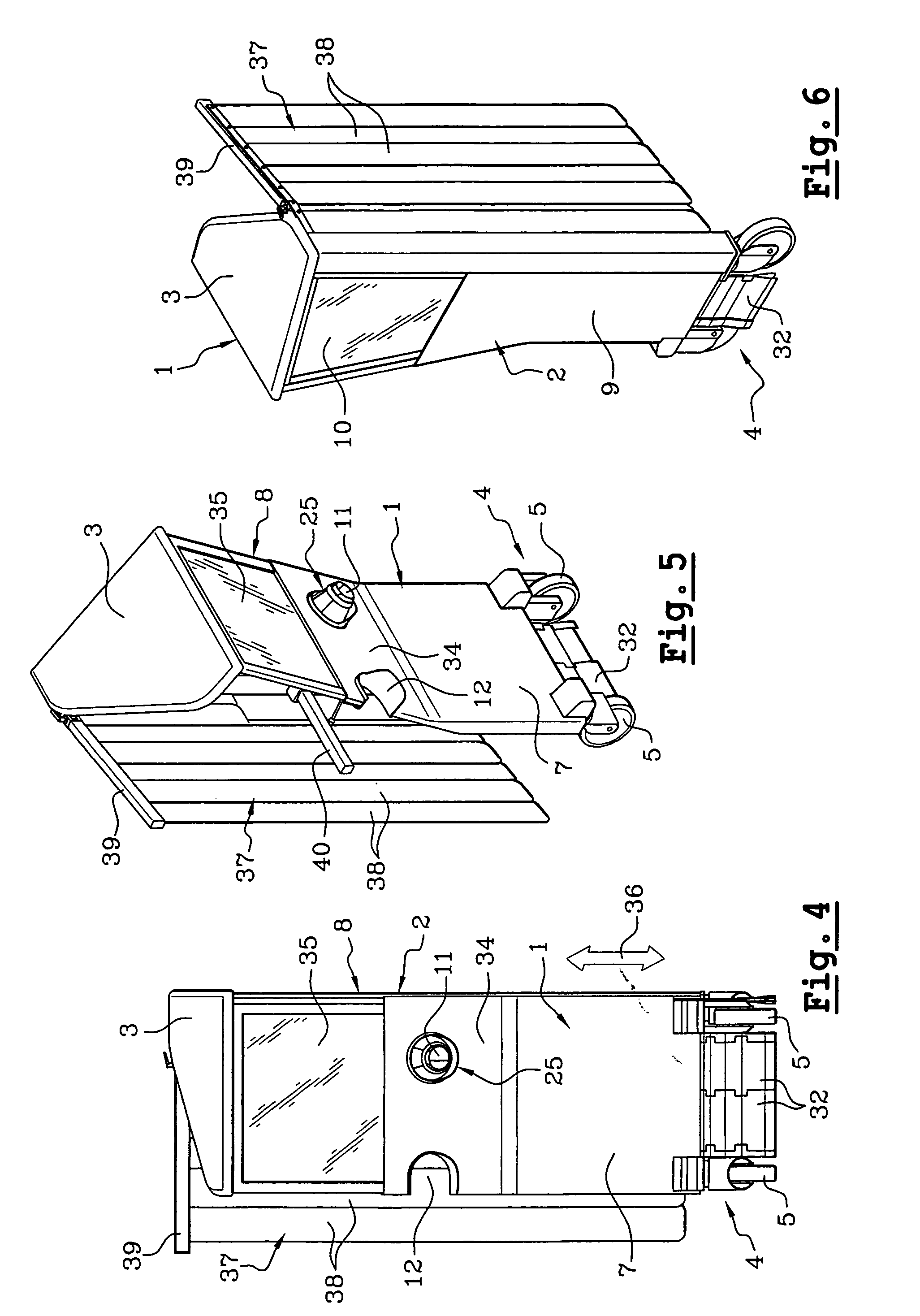
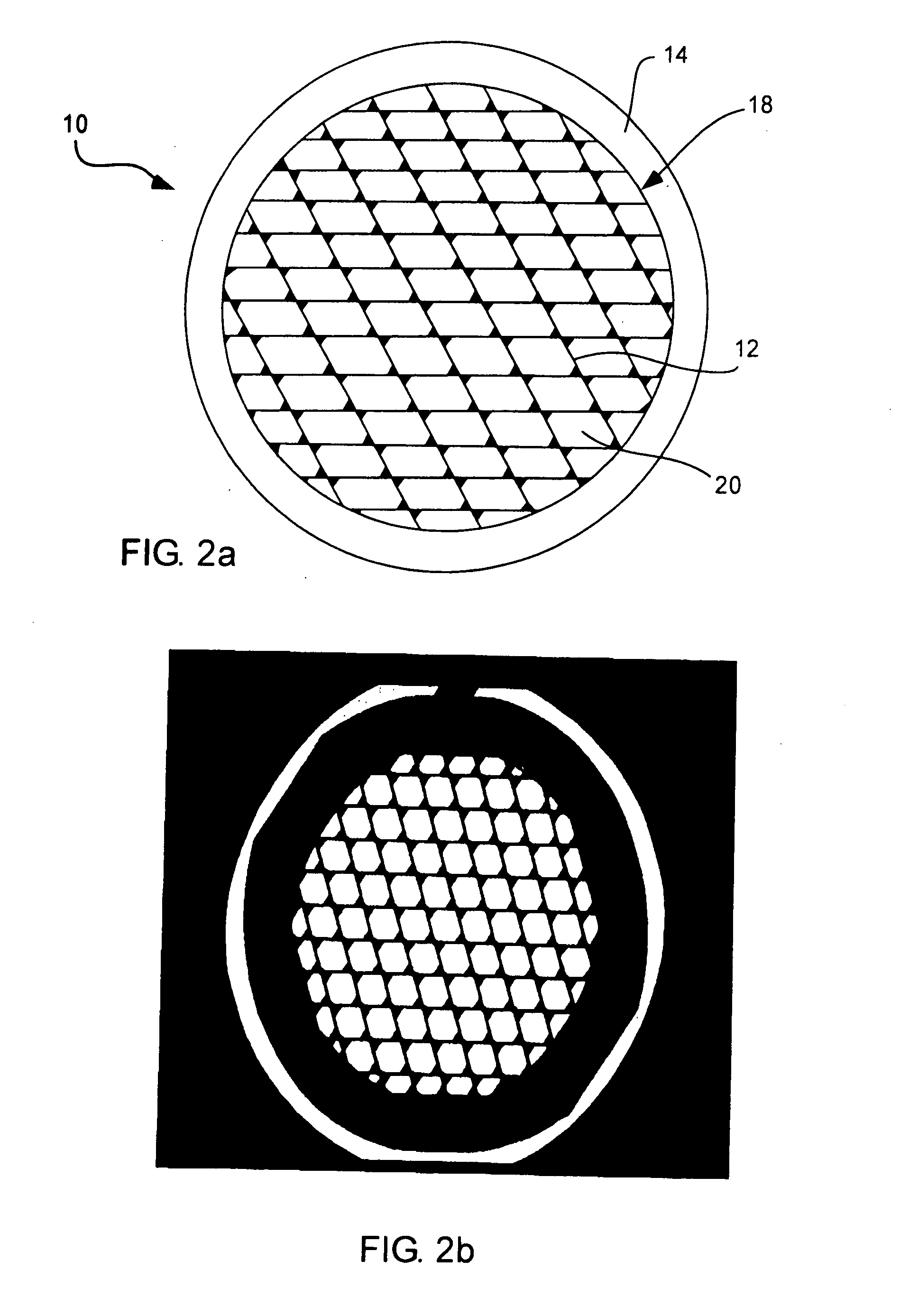
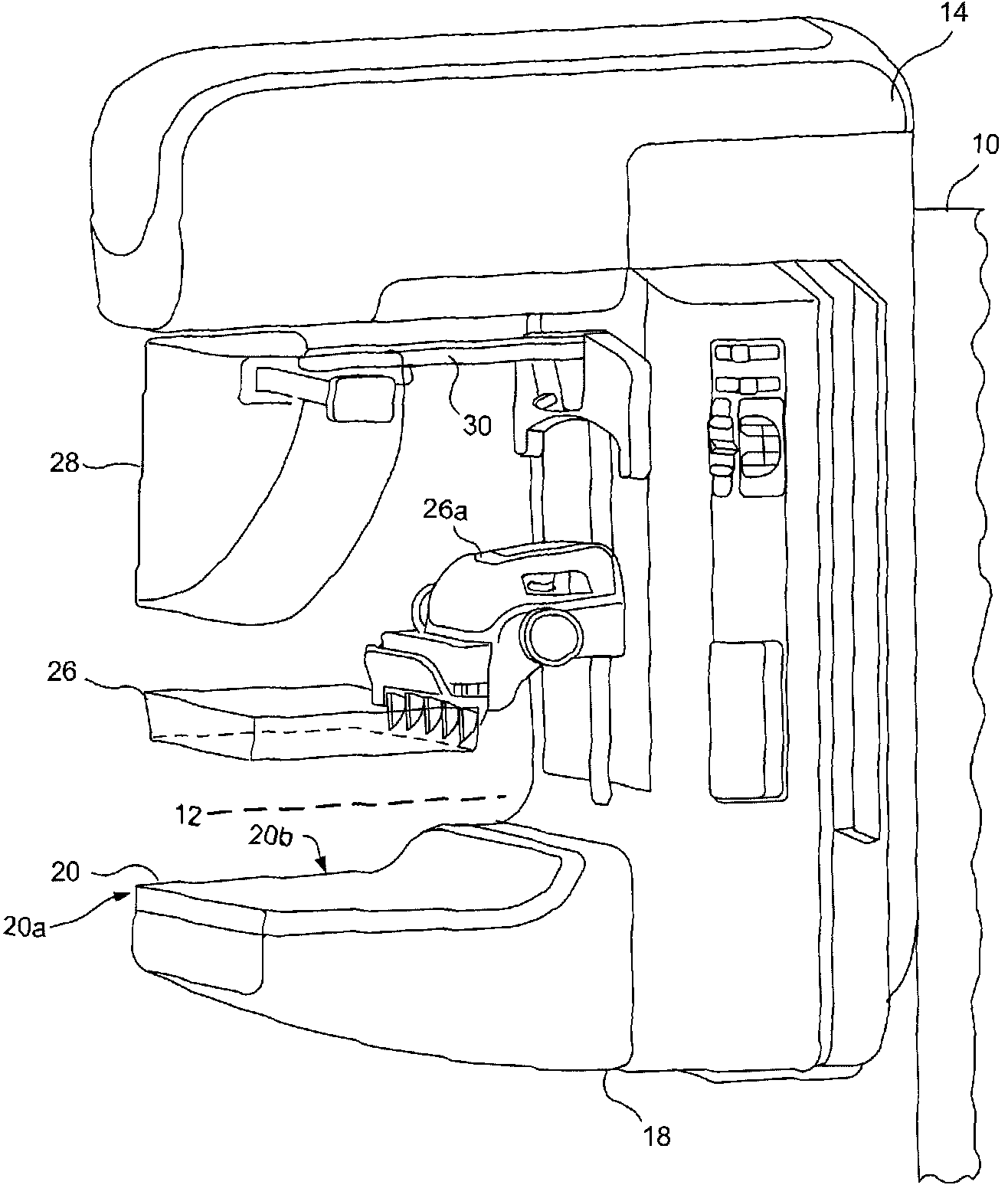
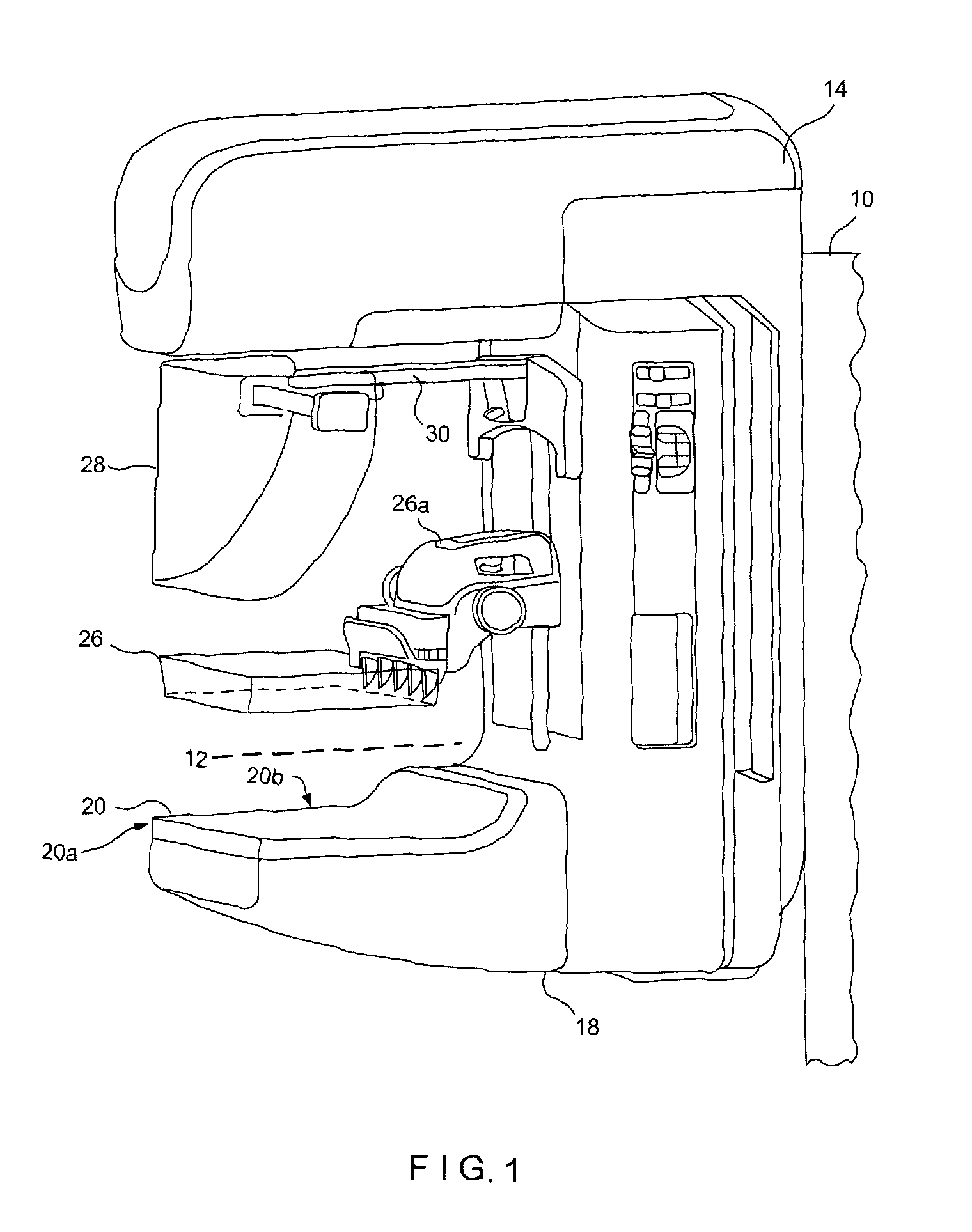
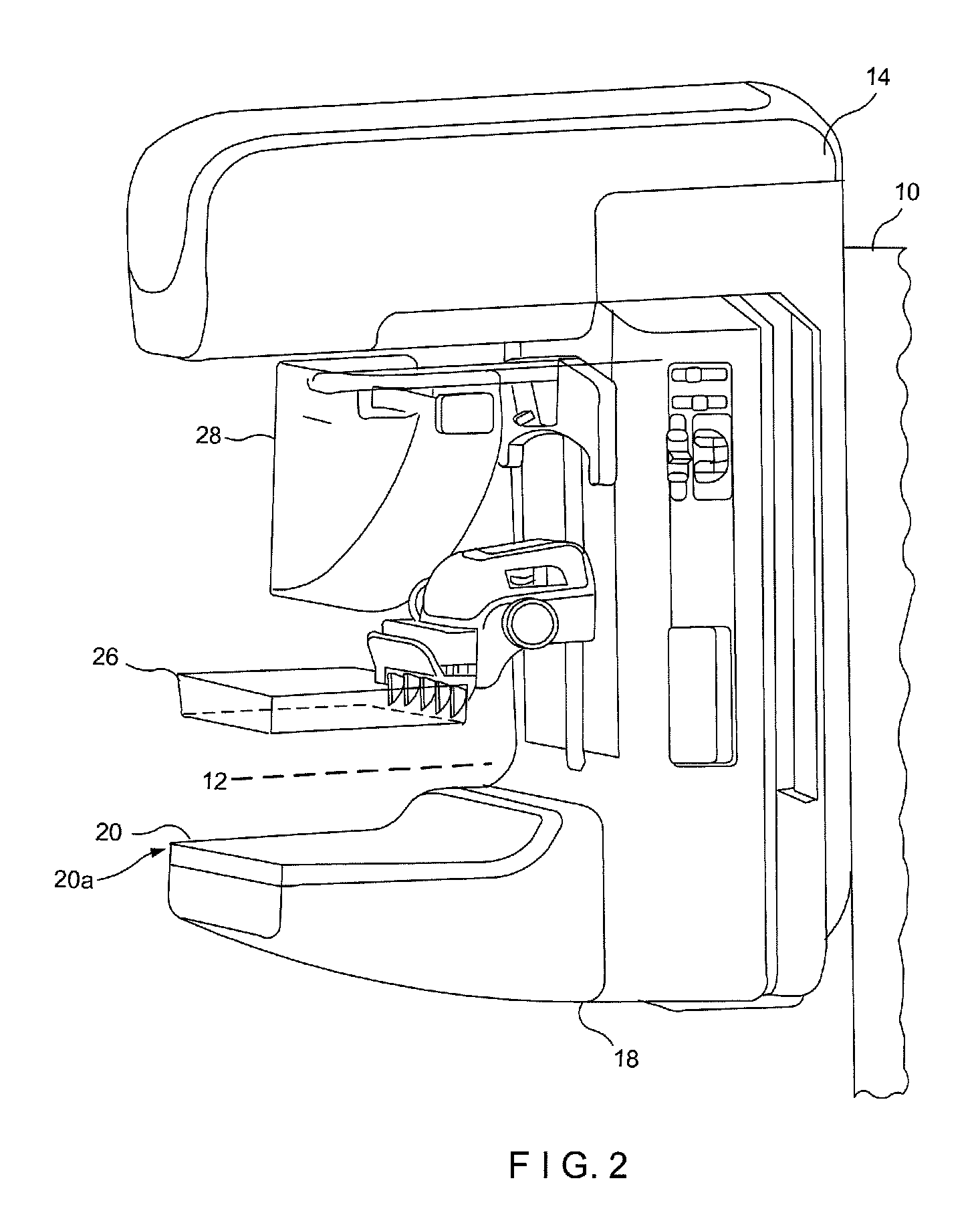
Mammograph system with a face shield
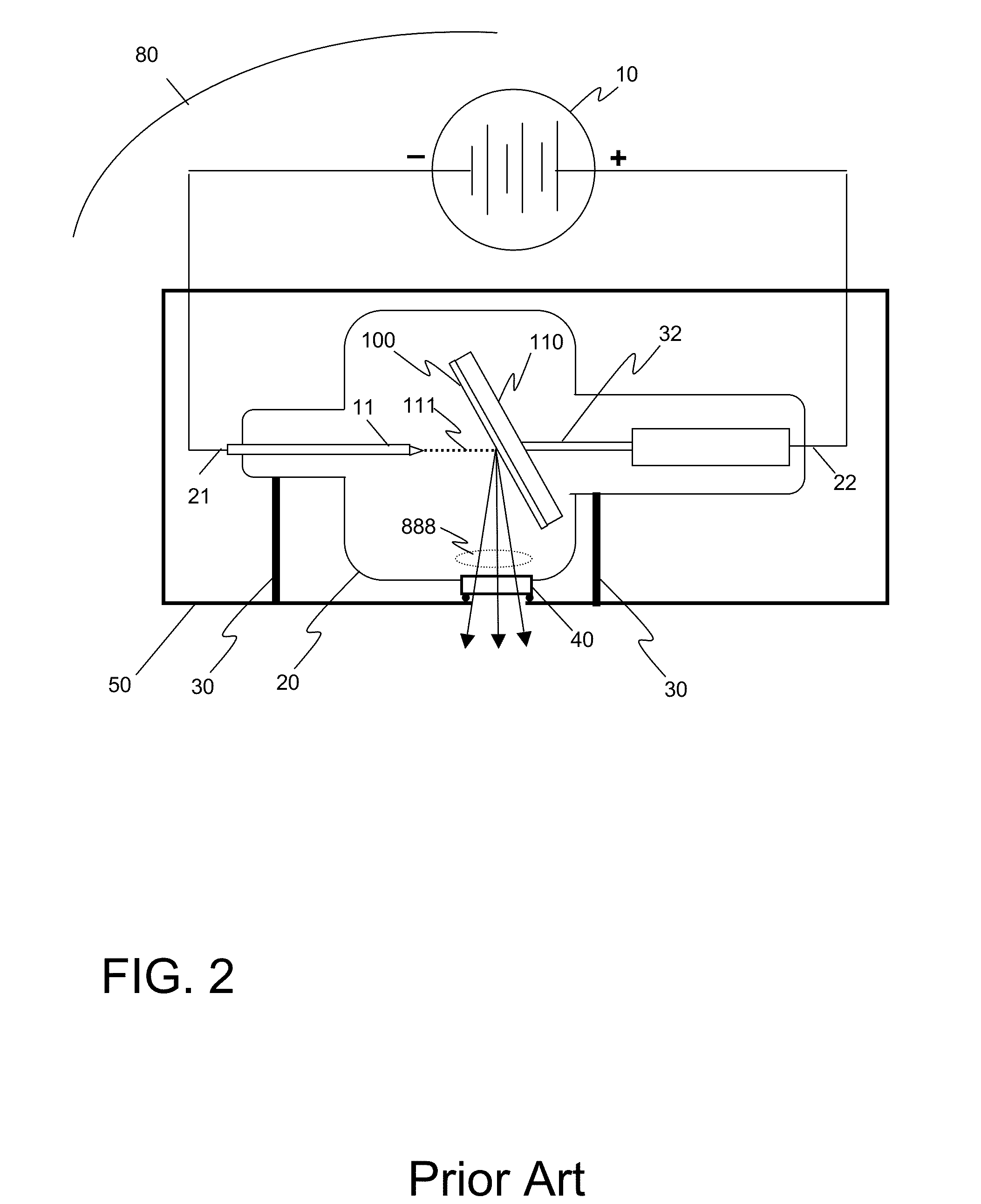
ActiveUS7315607B2Less damageLess fatiguePatient positioning for diagnosticsX-ray tube vessels/containerX-rayEngineering
The present embodiments relate to a mammograph system with a face shield. The mammography system includes an X-ray emitter head; an object table; and a face shield. The face shield is movably supported by the X-ray emitter head and is movable into at least first and second positions. In the first position, the face shield is retracted into the X-ray emitter head. In the second position, at least a portion of the face shield protrudes out of the X-ray emitter head.
Owner:SIEMENS HEALTHCARE GMBH
X-ray protection device
ActiveUS20050078797A1Reduce and eliminate amountAvoid attenuationMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationPatient positioning for diagnosticsX-rayMammography
A shielding arrangement for an x-ray apparatus, preferably for mammography examination is disclosed, and comprises at least an x-ray source, a collimator arrangement and a detector assembly, whereby the collimator is arranged between the x-ray source and the detector assembly and through which x-rays pass. The shielding arrangement, at least partly made of x-ray blocking material and provided for blocking, scattering and / or reflecting x-rays is arranged, at least partly, in a space between the x-ray source and collimator.
Owner:PHILIPS DIGITAL MAMMOGRAPHY SWEDEN
Compact high voltage x-ray source system and method for x-ray inspection applications
ActiveUS20090010393A1Reduce weightSmall sizeX-ray tube coolingX-ray tube vessels/containerX-rayHigh pressure
An x-ray system is disclosed that includes a bipolar x-ray tube. The bipolar x-ray tube includes two insulators that are separated by an intermediate electrode in an embodiment, wherein each insulator forms a portion of an outer wall of a vacuum envelope of the bipolar x-ray tube surrounding at least a portion of a path of an electron beam within the vacuum envelope. In further embodiments, the bipolar x-ray tube includes a first electrode at a positive high voltage potential with respect to a reference potential, a second electrode at a negative high voltage potential with respect to the reference potential, and an x-ray transmissive window that is at the positive high voltage potential.
Owner:NEWTON SCI
X-ray anode and process for its manufacture
InactiveUS6850598B1Improve the heating effectReduce absorptionRadiation/particle handlingX-ray tube electrodesSoft x rayImage resolution
The invention relates to an x-ray anode and a process for its manufacture. The x-ray anode is characterized in that the anode material is embodied as a layer on a diamond window. The x-ray anode is preferably used with x-ray units which require as selective as possible x-radiation production to achieve as high as possible radiation intensity. Use in x-ray microscopes in which a high radiation intensity guarantees the highest resolutions is particularly preferred.
Owner:FRAUNHOFER GESELLSCHAFT ZUR FOERDERUNG DER ANGEWANDTEN FORSCHUNG EV
Integrated X-ray source module
Described is a self-contained, small, lightweight, power-efficient and radiation-shielded module that includes a miniature vacuum X-ray tube emitting X-rays of a controlled intensity and defined spectrum. Feedback control circuits are used to monitor and maintain the beam current and voltage. The X-ray tube, high-voltage power supply, and the resonant converter are encapsulated in a solid high-voltage insulating material. The module can be configured into complex geometries and can be powered by commercially available small, compact, low-voltage batteries.
Owner:NEWTON SCI
X-ray source and fluorescent X-ray analyzing apparatus
InactiveUS20080084966A1Eliminates unwanted noise componentGenerate efficientlyX-ray tube laminated targetsMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationFluorescenceX-ray
The present invention relates to an X-ray source for emitting a characteristic X-ray and a fluorescent X-ray analyzing apparatus using the X-ray source. A secondary target is arranged in superposition on a primary target. An electron beam generated by an electron gun enters the primary target, which passes and emits a continuous X-ray. The secondary target transmits and emits a characteristic X-ray excited by the continuous X-ray emitted from the primary target. The primary target and the secondary target are superposed one on the other, so that the continuous X-ray emitted from the primary target efficiently excites the secondary target thereby to efficiently generate the characteristic X-ray.
Owner:TOSHIBA ELECTRON TUBE & DEVICES
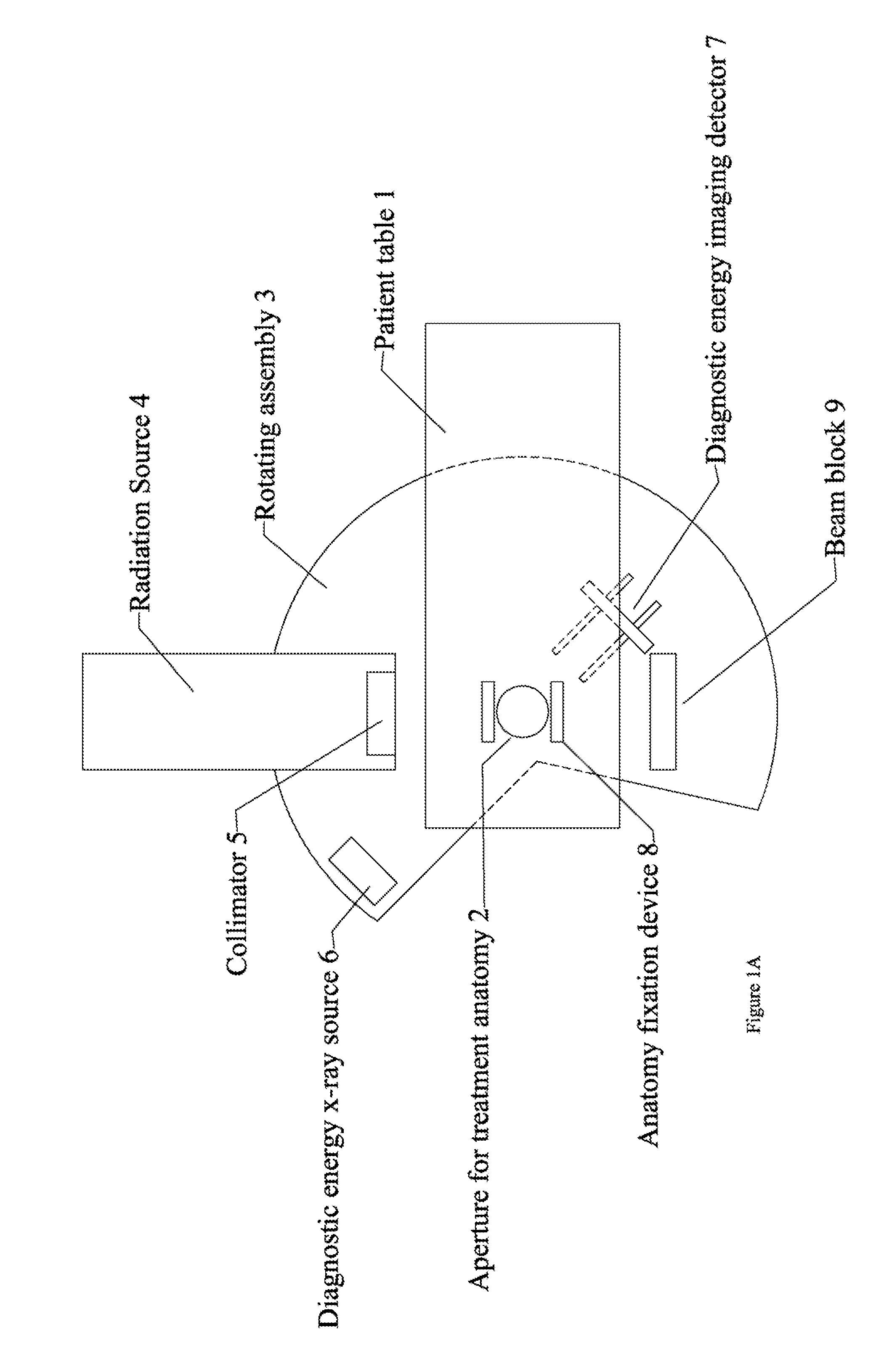
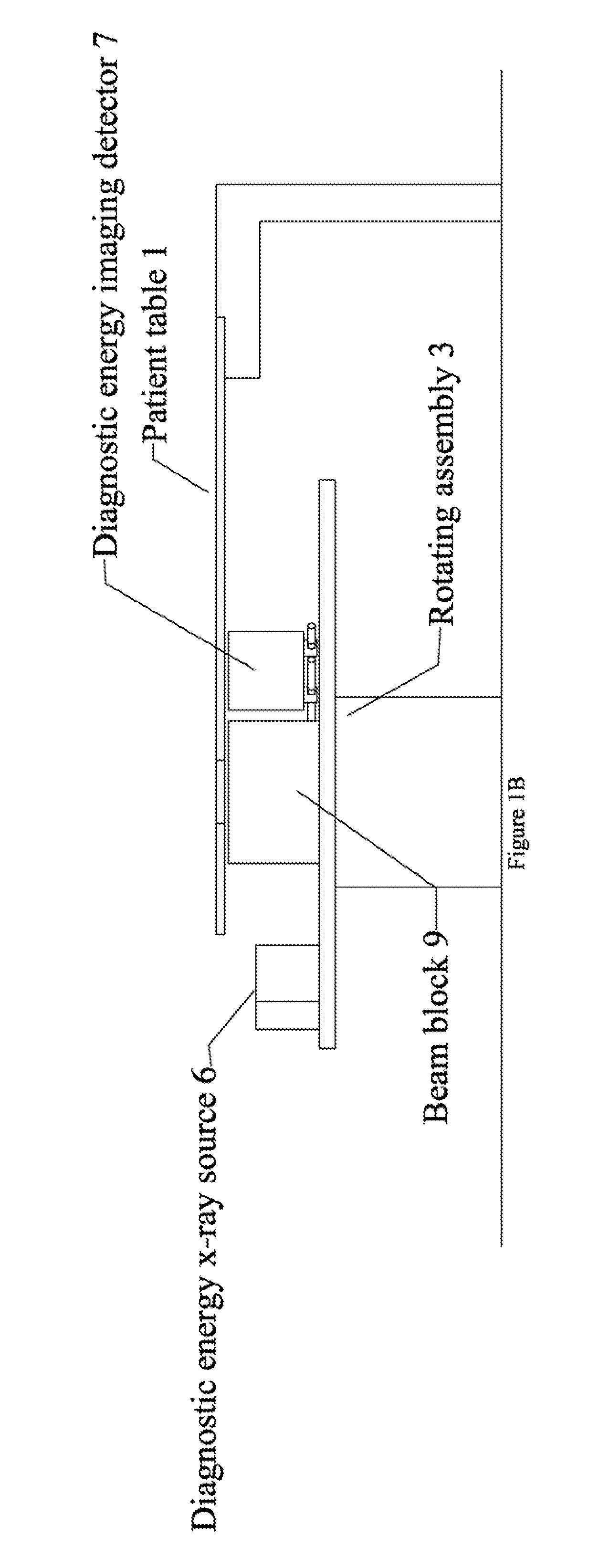
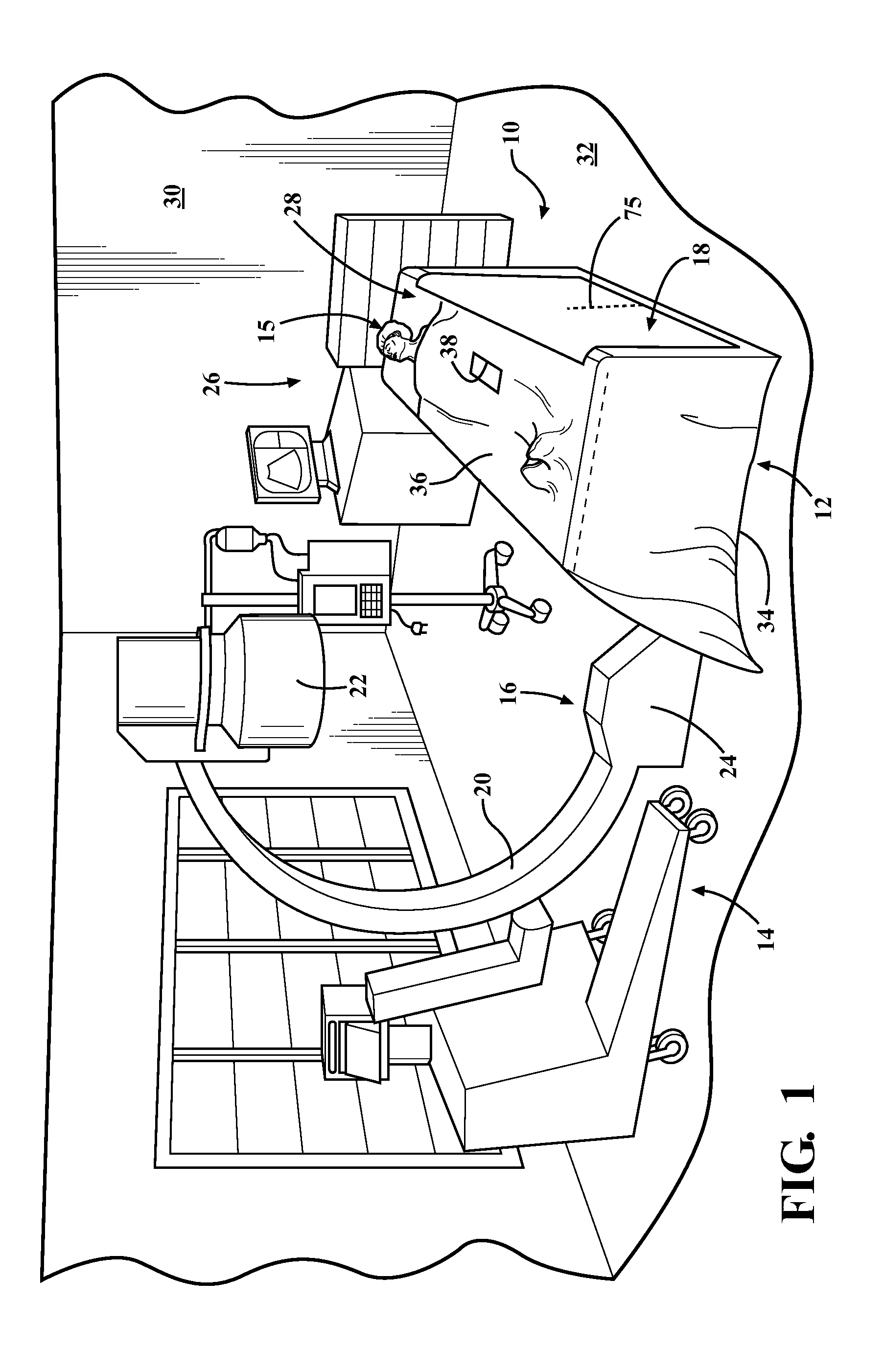
Radiation therapy system for treating breasts and extremities
InactiveUS20070211854A1Maximize separationReduce shielding requirementsPatient positioning for diagnosticsX-ray tube vessels/containerCritical structurePrimary disease
A radiation therapy system optimized for treating extremities such as the breast has unique geometrical features that enable the system to deliver an accurately located prescribed dose to a target volume while eliminating or reducing the collateral dose delivered to the rest of the patient. An optional integral imaging system provides accurate target volume localization for each treatment session. Utilizing the effects of gravity on a prone patient maximizes the separation of a target volume within the breast to adjacent critical structures such as the chest wall, heart and lungs, thereby reducing long term complications not associated with the primary disease. A shielded interface surface between the radiation source and the patient reduces patient dose due to scattered or stray radiation. A shielded enclosure for the radiation sources combined with the shielded interface surface eliminates the need for primary shielding in the room and allows the therapy system to be used in a transportable, mobile facility.
Owner:ORBITAL THERAPY
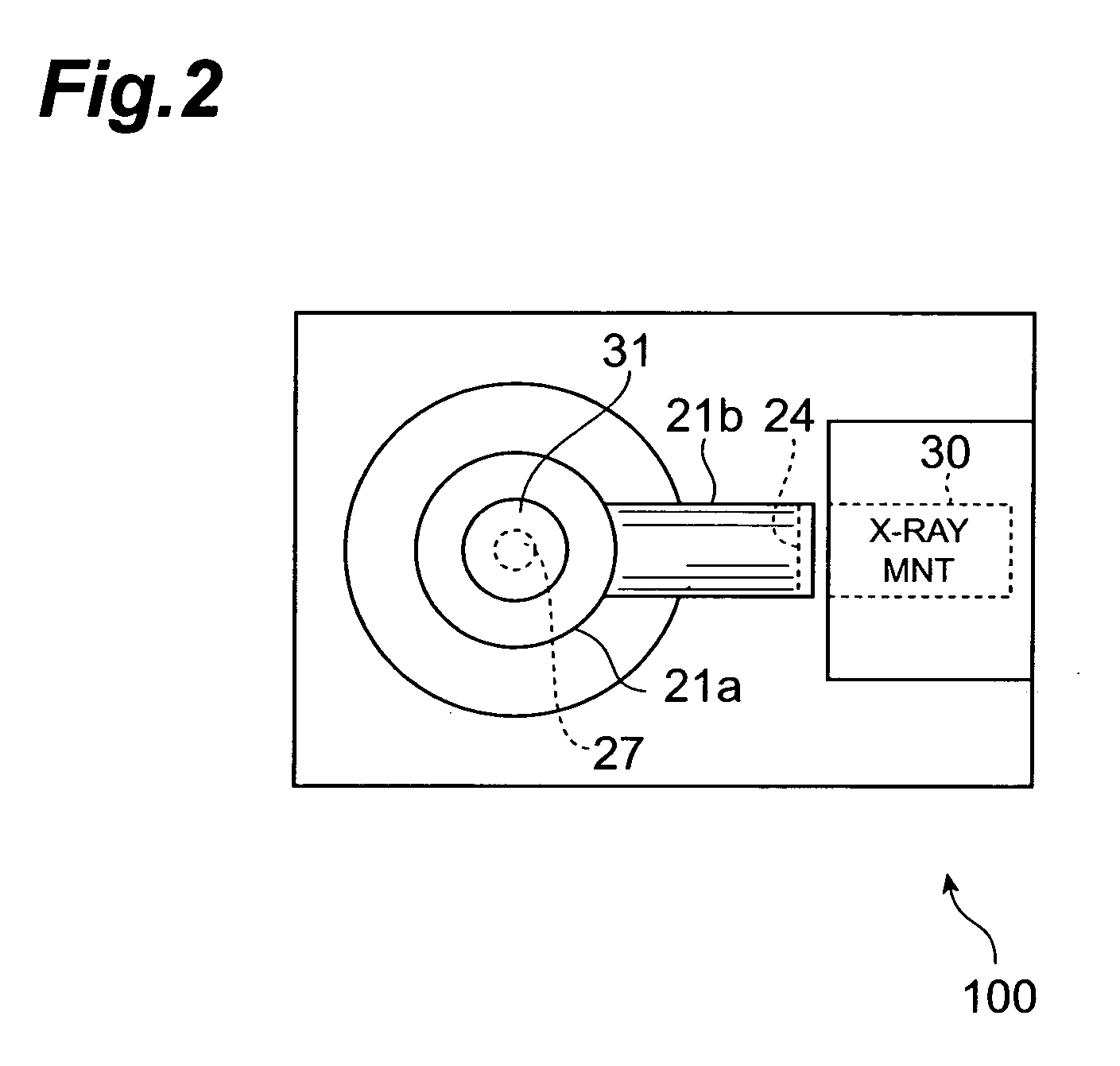
X-ray generator
InactiveUS20050163284A1High strengthImprove precision monitoringX-ray tube electrodesCathode ray concentrating/focusing/directingX ray imageX-ray generator
An X-ray generator of this invention has an X-ray monitor that monitors a state of an X-ray emitted from a target. Hence the state of the X-ray can be monitored in real time to maintain the X-ray in a constant state. The X-ray monitor is positioned off the path on which an X-ray transmitted from a first exit window travels. Hence, when the X-ray is emitted from the first exit window to an object to be inspected, the X-ray monitor does not obstruct the approaching of the object to the first exit window. This makes it possible to acquire X-ray images of high magnification.
Owner:HAMAMATSU PHOTONICS KK
Integrated X-ray source module
Described is a self-contained, small, lightweight, power-efficient and radiation-shielded module that includes a miniature vacuum X-ray tube emitting X-rays of a controlled intensity and defined spectrum. Feedback control circuits are used to monitor and maintain the beam current and voltage. The X-ray tube, high-voltage power supply, and the resonant converter are encapsulated in a solid high-voltage insulating material. The module can be configured into complex geometries and can be powered by commercially available small, compact, low-voltage batteries.
Owner:NEWTON SCI
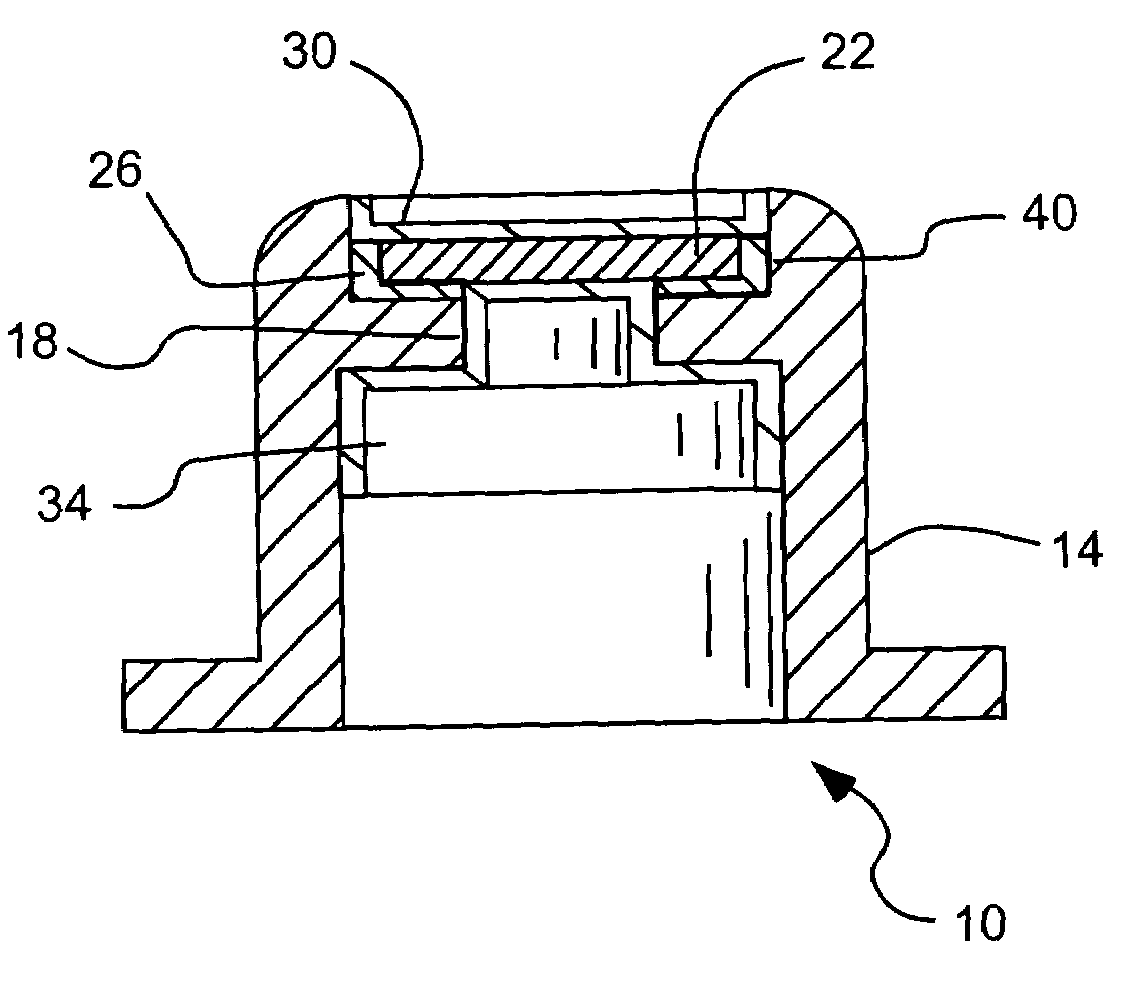
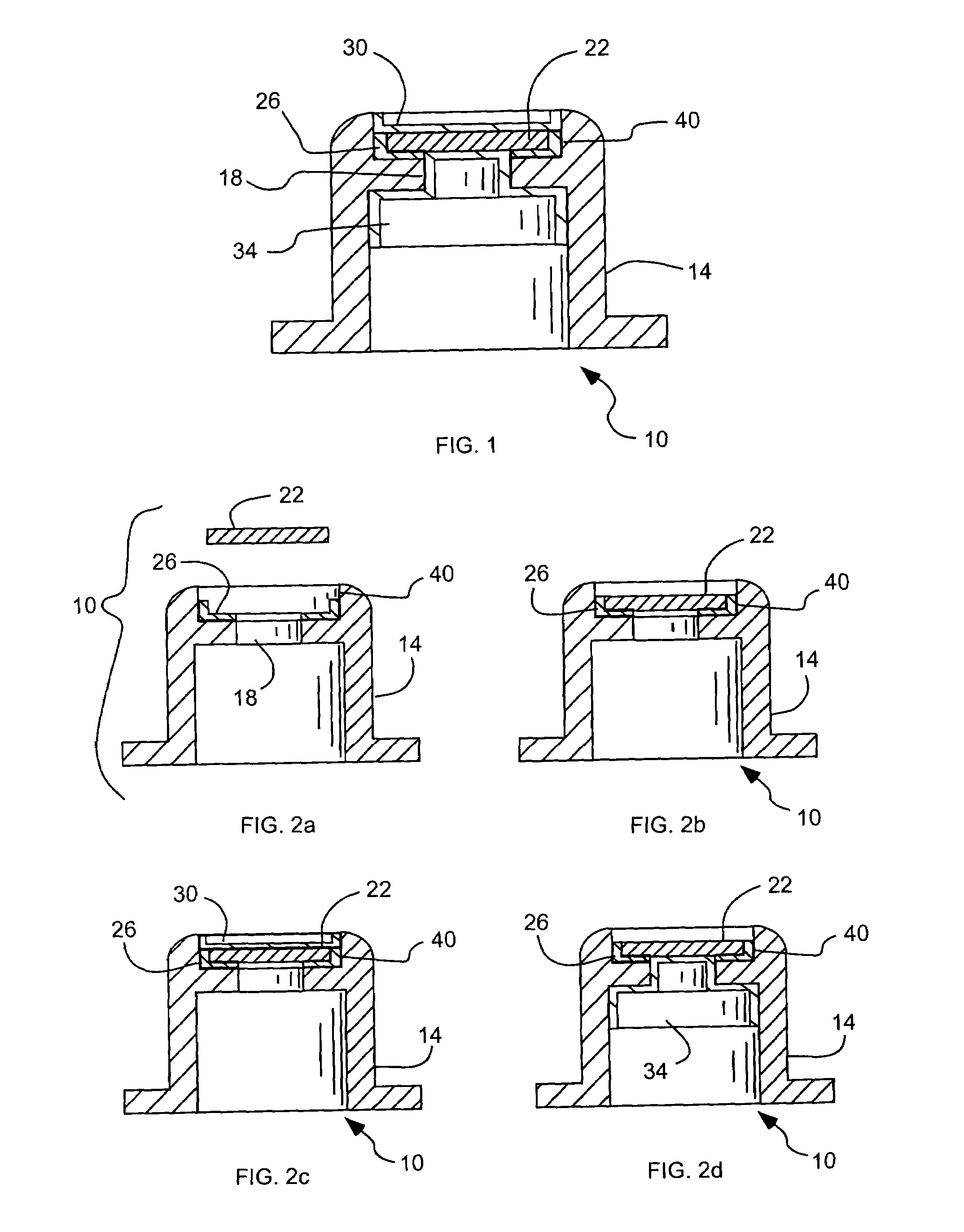
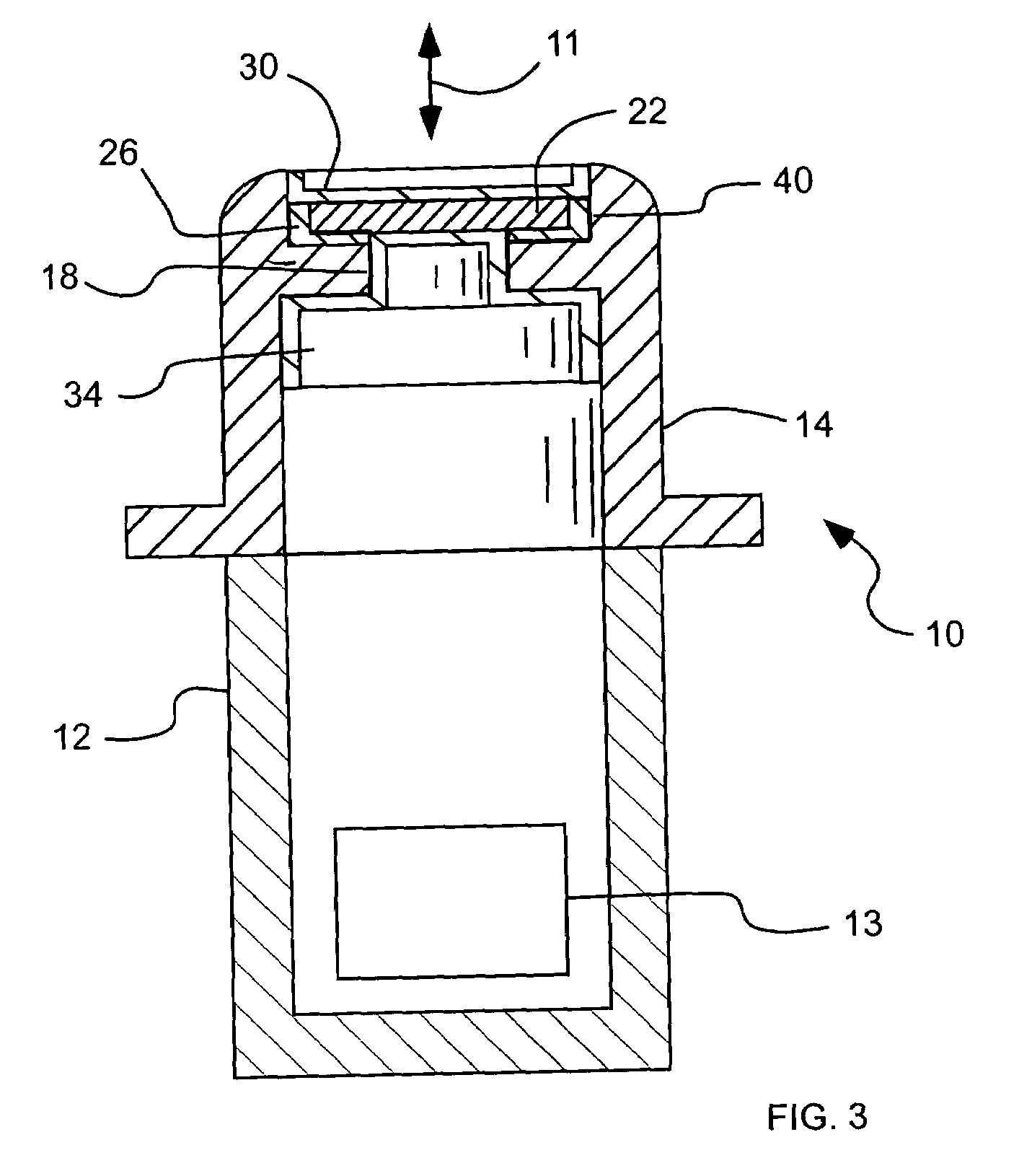
Radiation window and method of manufacture
A radiation window device to transmit radiation as part of an x-ray source or detector includes a support to be subject to a substantial vacuum, and an opening configured to transmit radiation. A film is mounted directly on the support across the opening, and has a material and a thickness selected to transmit soft x-rays. An adhesive directly adheres the film to the support. A coating covers exposed portions of at least one of the evacuated or ambient sides of the film, and covers a portion of the support surrounding the film. The support, film and adhesive form a vacuum tight assembly capable of maintaining the substantial vacuum when one side is subject to the substantial vacuum. In addition, the vacuum tight assembly can withstand a temperature of greater than approximately 250 degrees Celsius.
Owner:MOXTEK INC
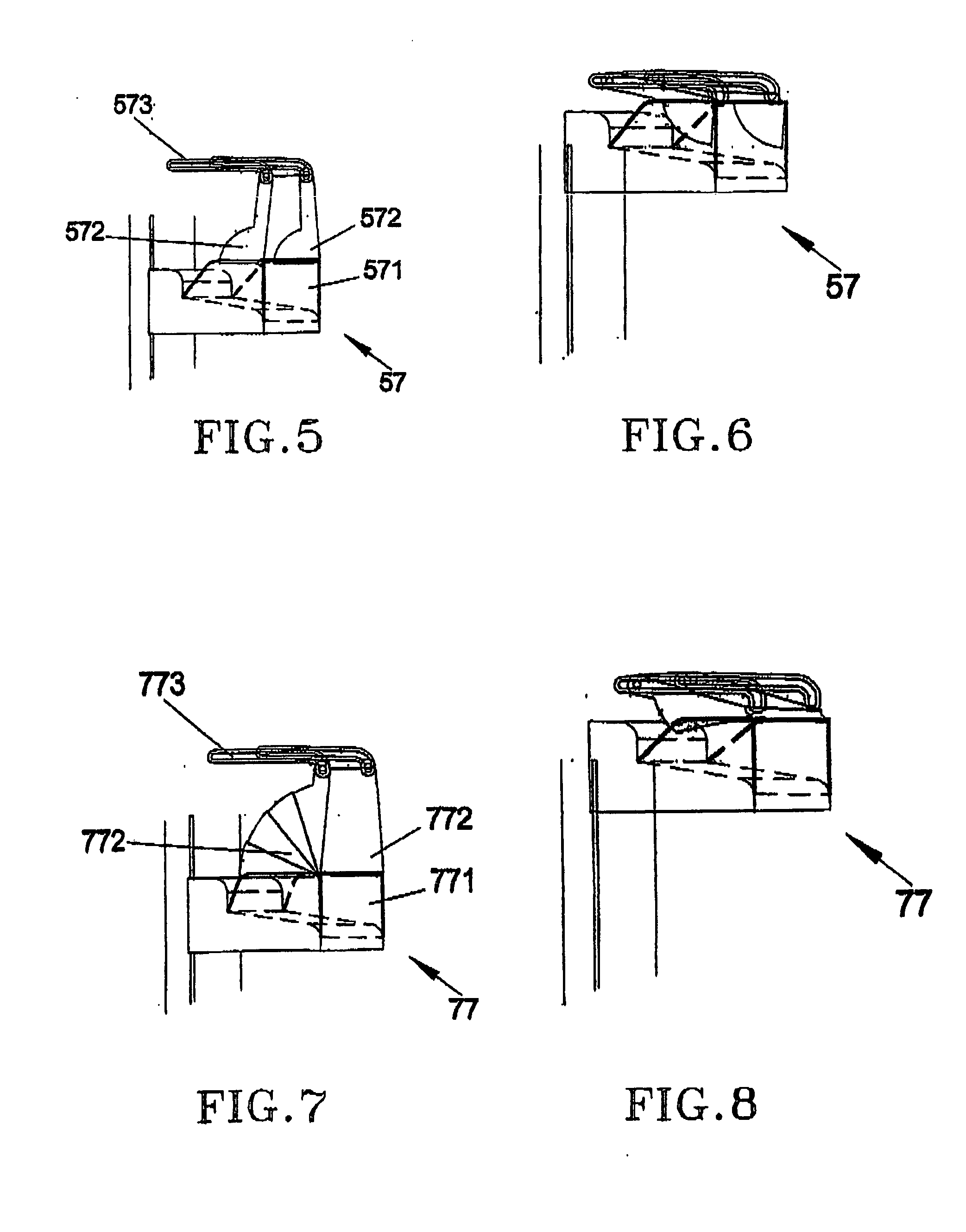
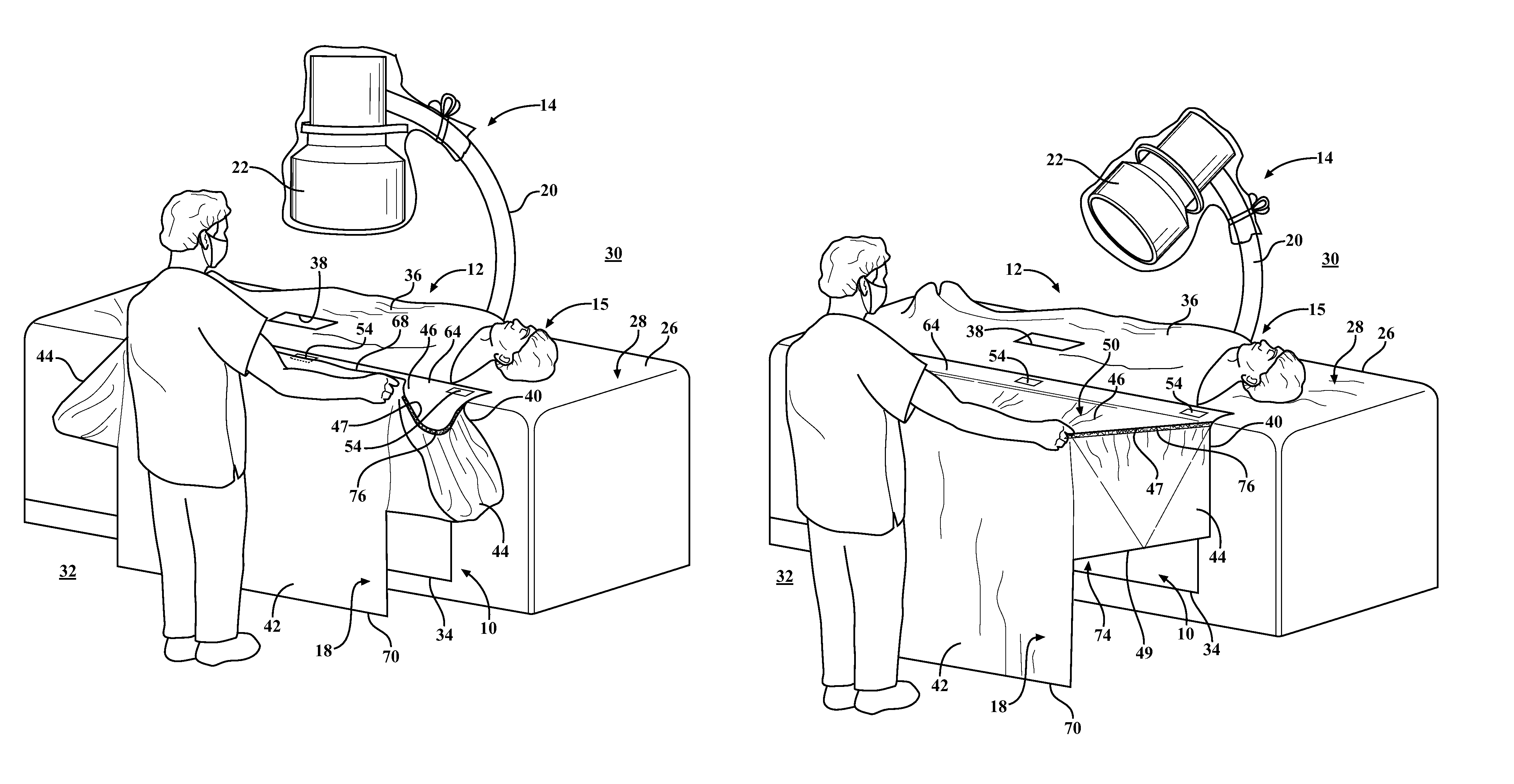
Sterile radiological imaging unit drape and method of providing a sterile surface therewith
A surgical radiological C-arm imaging unit drape configured to provide a sterile outer surface about an end portion of a C-arm imaging unit and method of providing a sterile surface about an end of a C-arm imaging unit is provided. The drape includes a flexible enclosure having an upper wall with a pair of sidewalls and a rear side extending downwardly from the upper wall. The upper wall and the side walls are extendible between expanded and collapsed positions. When in the expanded position, a pocket sized for receipt of the end portion of the imaging unit beneath the upper wall is formed. The upper wall has a sterile outer surface configured to face away from and overlie the end portion of the imaging unit to maintain sterility in a sterile zone above an operating table. When in the collapsed position, the sterile outer surface shielded from external contamination.
Owner:TIDI PROD LLC
X-ray sources using linear accumulation
ActiveUS20150110252A1Heat generationIncrease electron densityCathode ray concentrating/focusing/directingHandling using diffraction/refraction/reflectionHigh energyX-ray
We disclose a compact source for high brightness x-ray generation. The higher brightness is achieved through electron beam bombardment of multiple regions aligned with each other to achieve a linear accumulation of x-rays. This may be achieved by aligning discrete x-ray sources, or through the use of novel x-ray targets that comprise a number of microstructures of x-ray generating materials fabricated in close thermal contact with a substrate with high thermal conductivity. This allows heat to be more efficiently drawn out of the x-ray generating material, and in turn allows bombardment of the x-ray generating material with higher electron density and / or higher energy electrons, leading to greater x-ray brightness.The orientation of the microstructures allows the use of an on-axis collection angle, allowing the accumulation of x-rays from several microstructures to be aligned to appear to have a single origin, also known as “zero-angle” x-ray emission.
Owner:SIGRAY INC
X-ray source and fluorescent X-ray analyzing apparatus
InactiveUS7809113B2Eliminates unwanted noise componentGenerate efficientlyX-ray tube laminated targetsMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationSoft x rayX-ray
Owner:TOSHIBA ELECTRON TUBE & DEVICES
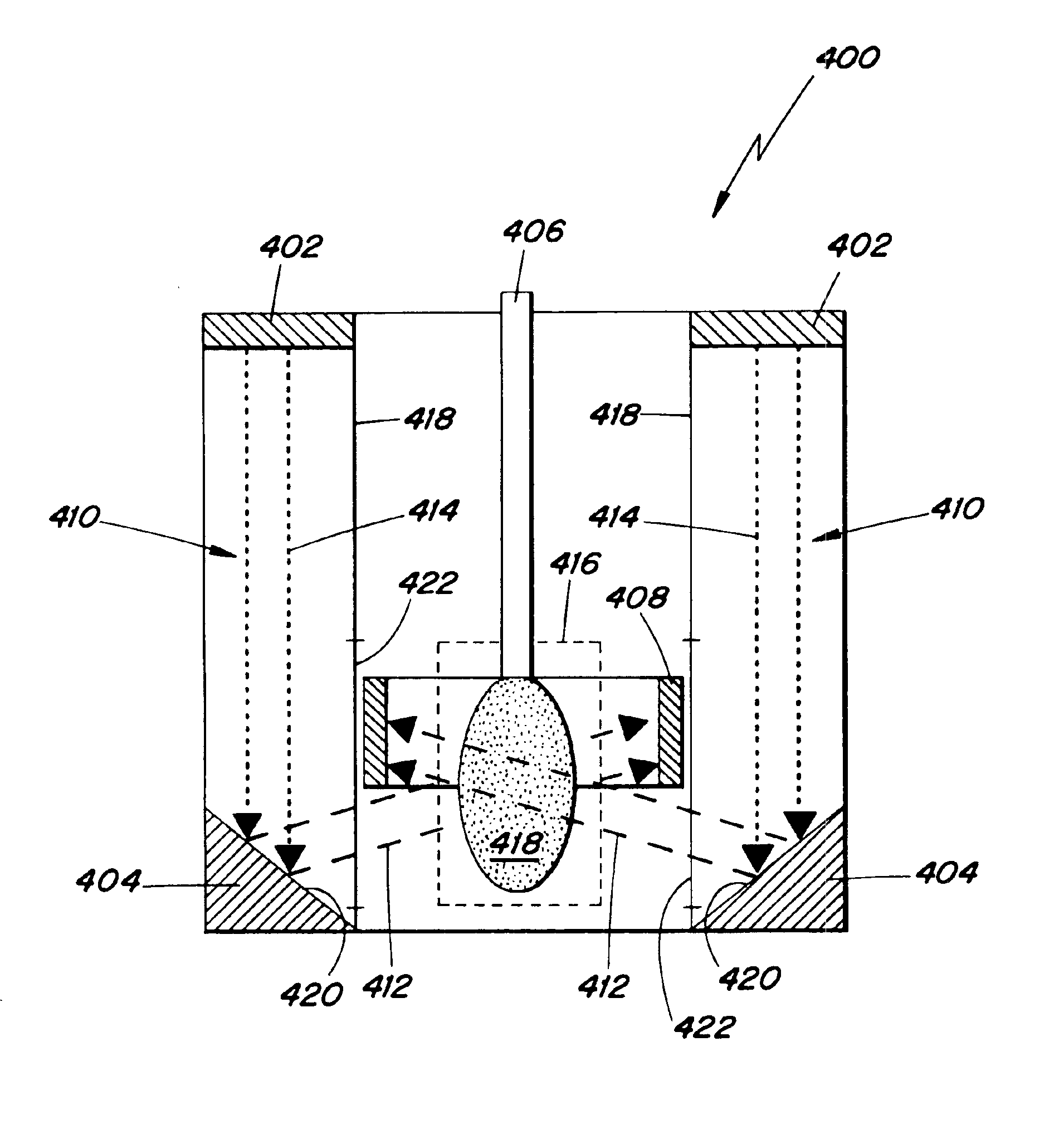
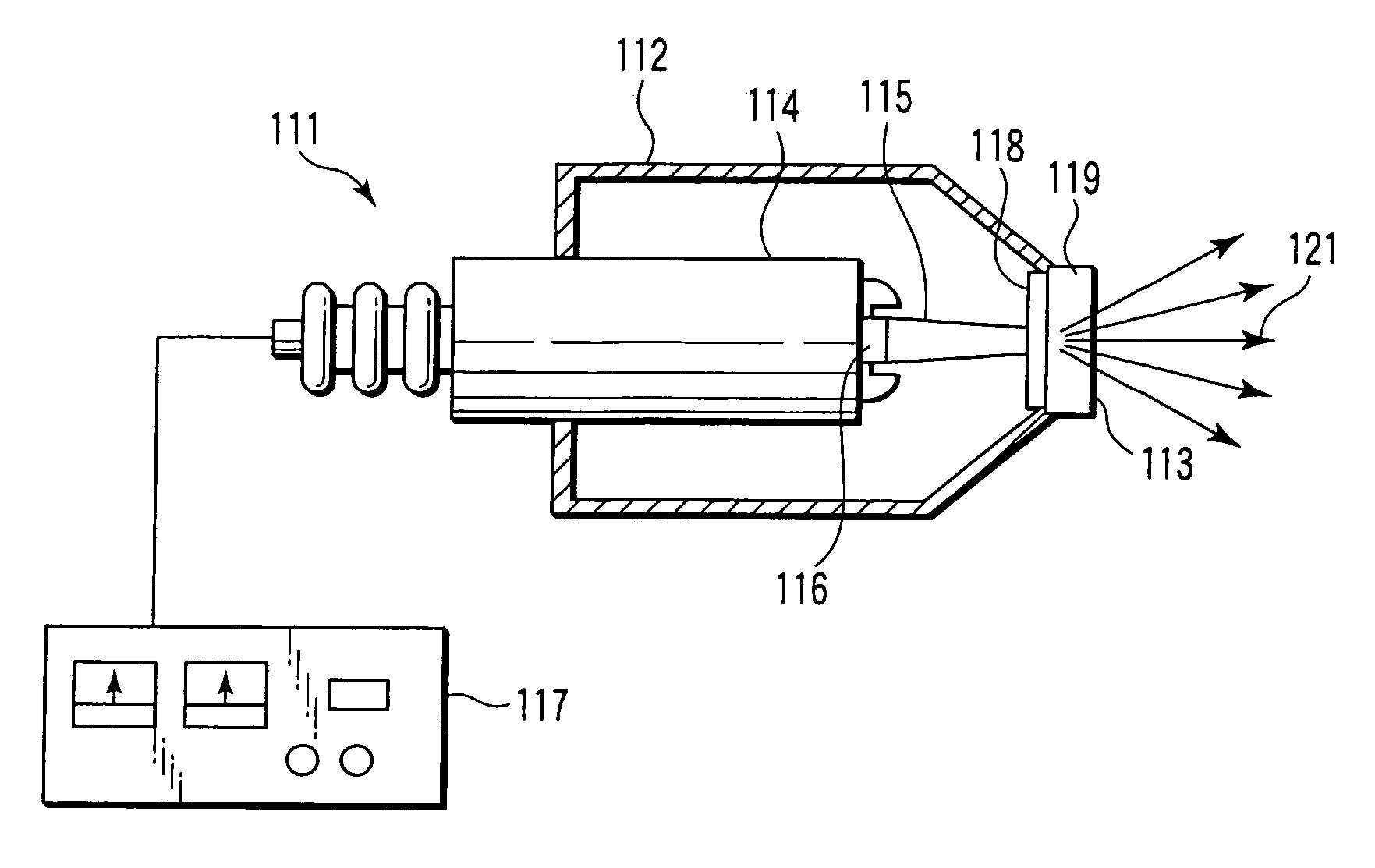
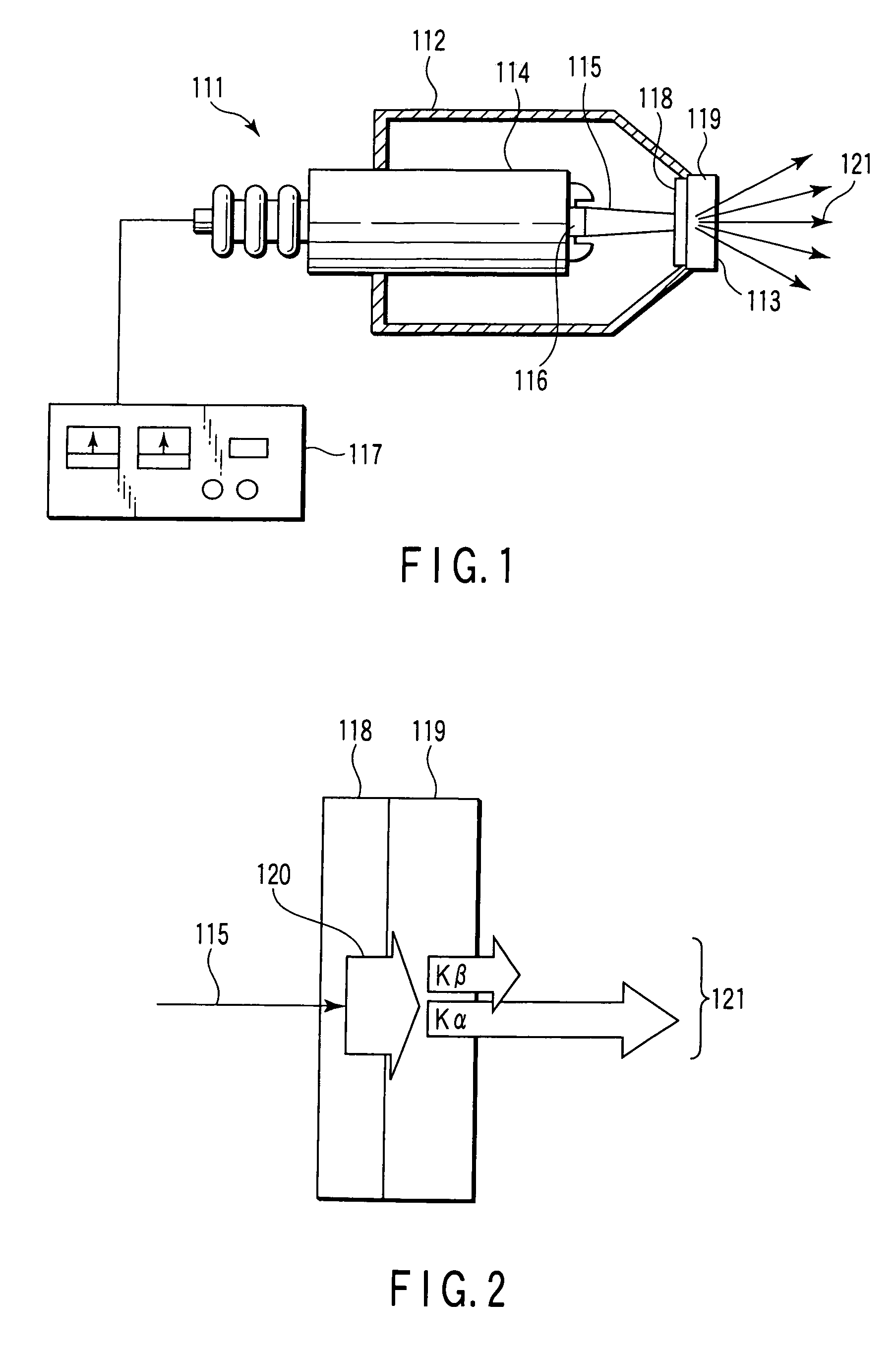
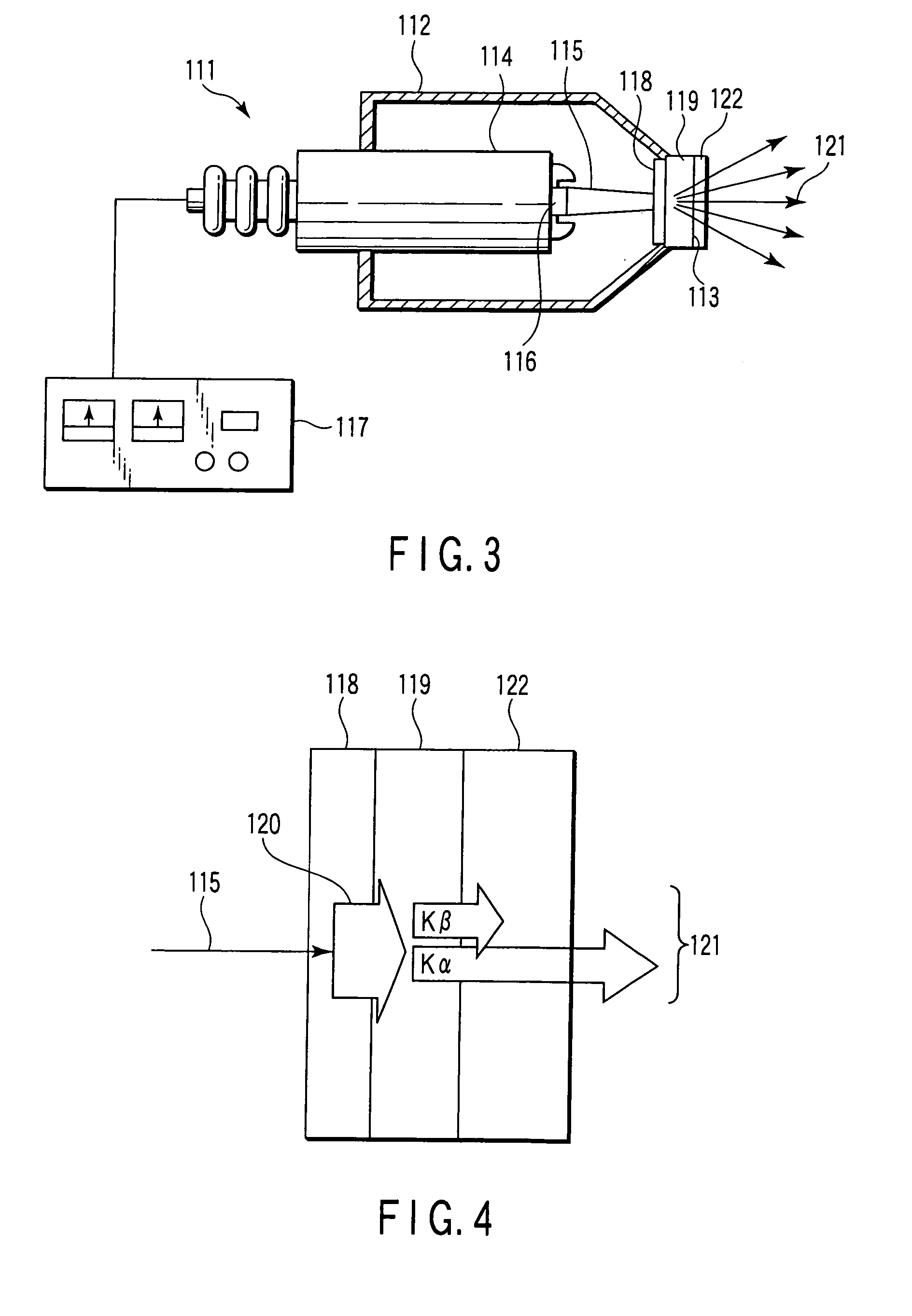
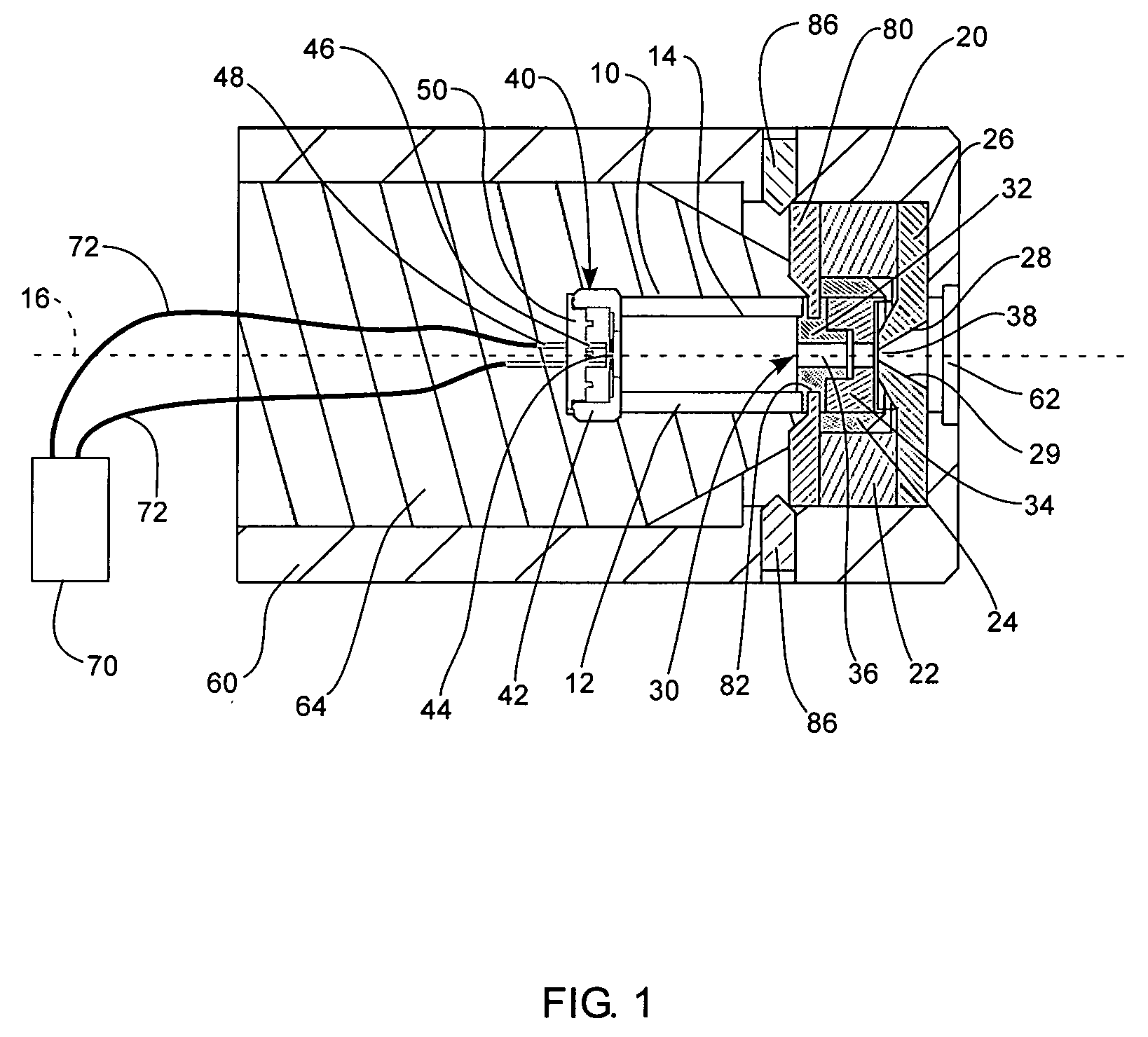
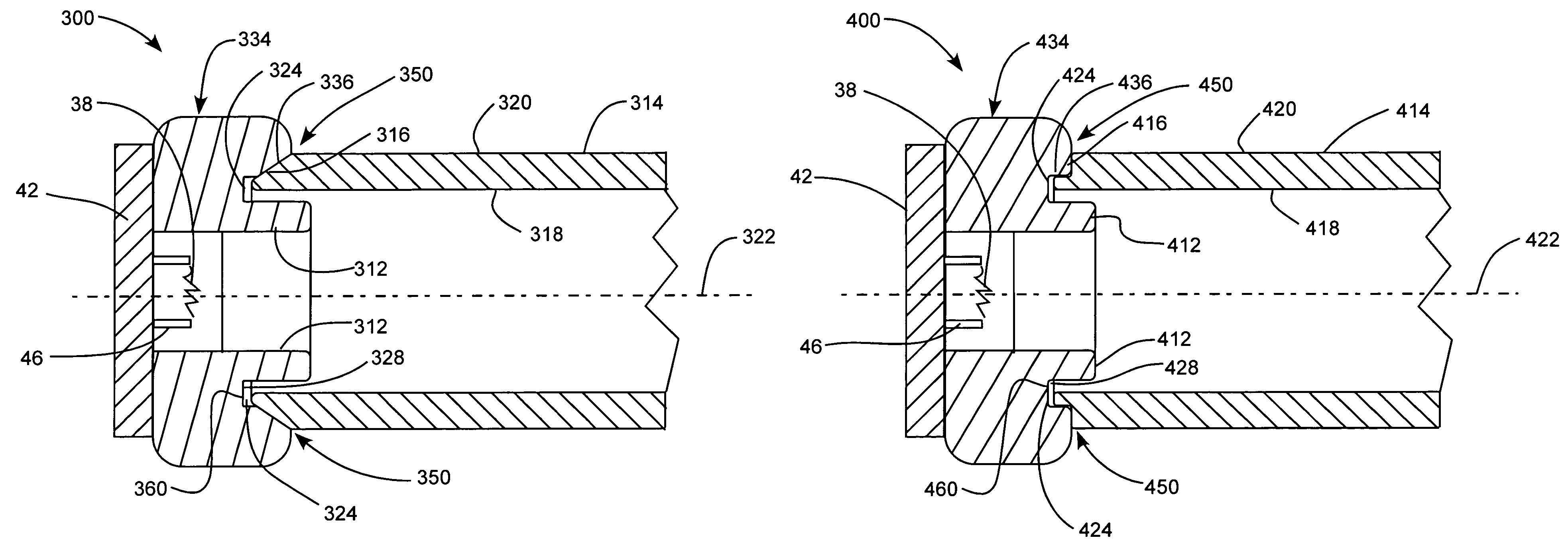
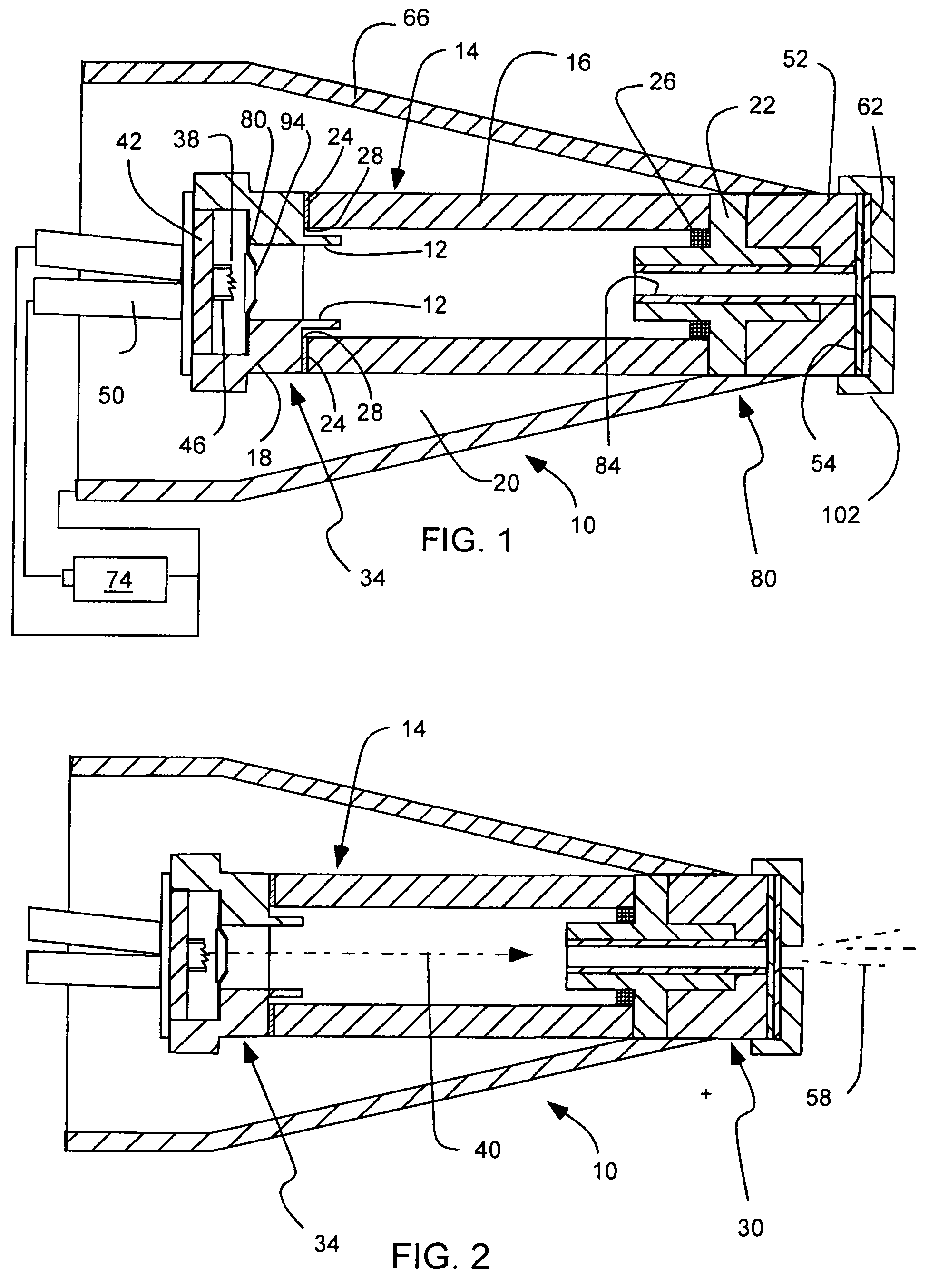
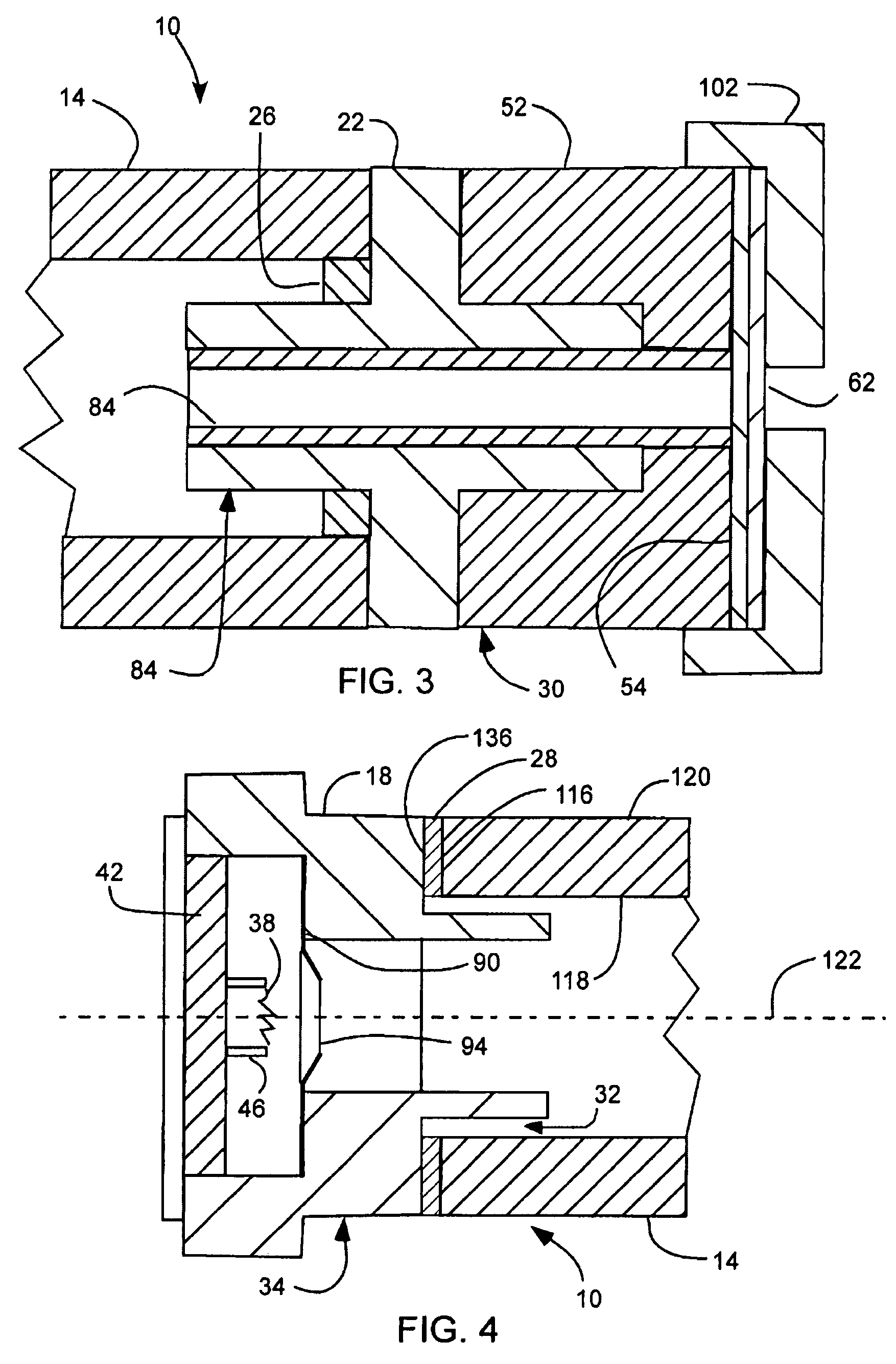
X-ray source with nonparallel geometry
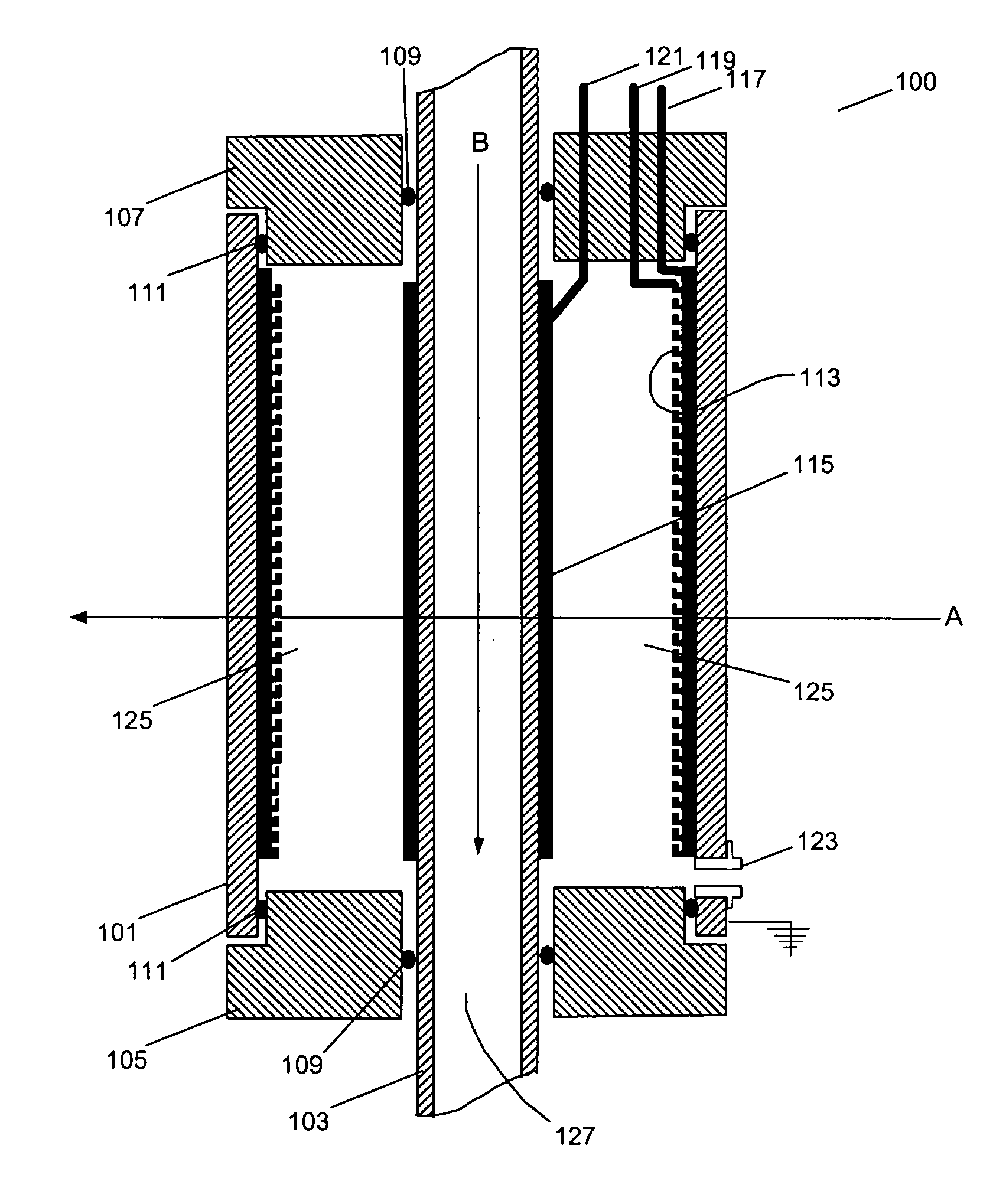
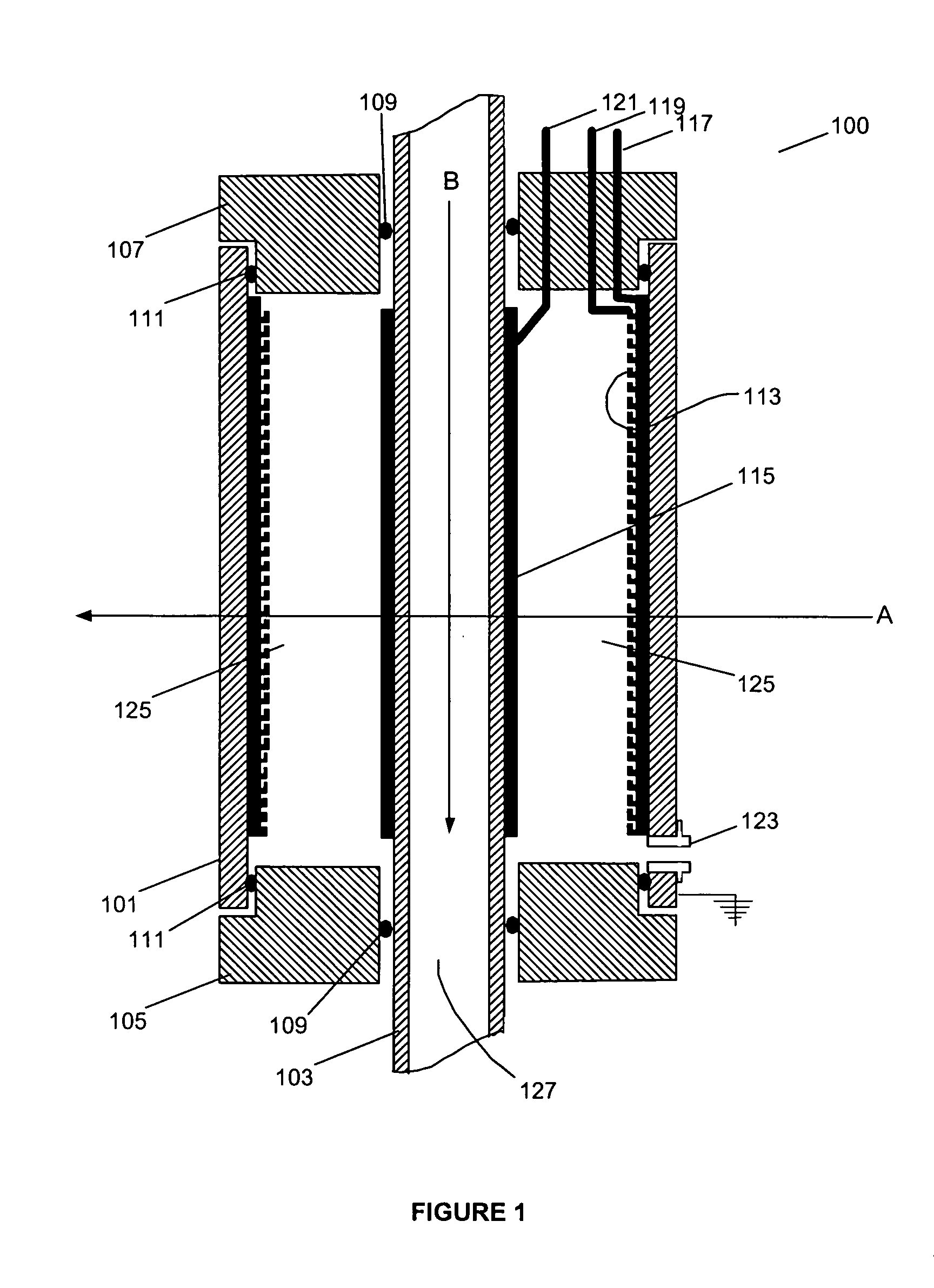
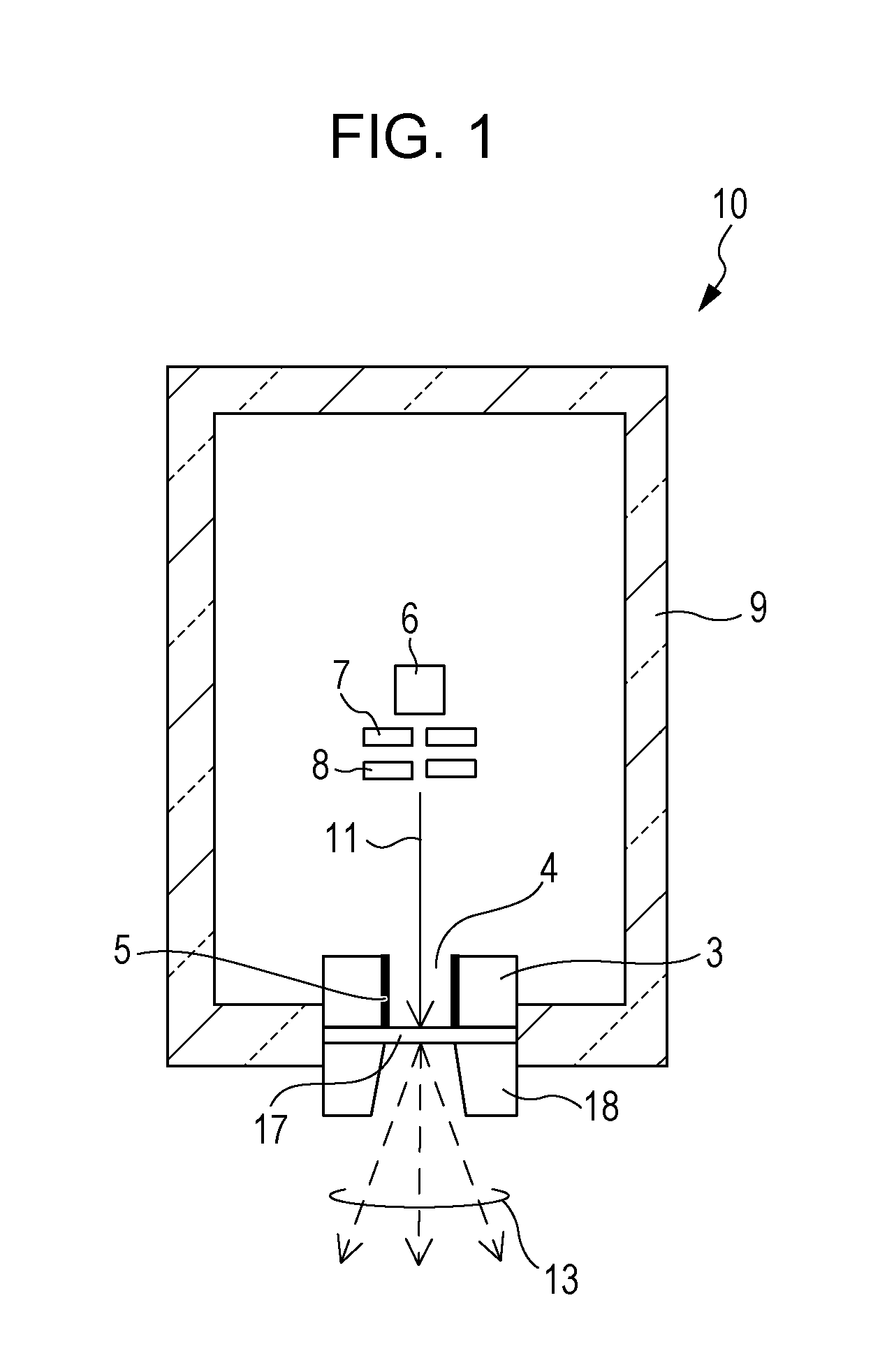
InactiveUS20050276382A1Minimize electron electron energyMinimize loss energy lossX-ray tube electrodesX-ray tube vessels/containerSoft x rayX-ray
An improved x-ray generation system produces a converging or diverging radiation pattern particularly suited for substantially cylindrical or spherical treatment devices. In an embodiment, the system comprises a closed or concave outer wall about a closed or concave inner wall. An electron emitter is situated on the inside surface of the outer wall, while a target film is situated on the outside surface of the inner wall. An extraction voltage at the emitter extracts electrons which are accelerated toward the inner wall by an acceleration voltage. Alternately, electron emission may be by thermionic means. Collisions of electrons with the target film causes x-ray emission, a substantial portion of which is directed through the inner wall into the space defined within. In an embodiment, the location of the emitter and target film are reversed, establishing a reflective rather than transmissive mode for convergent patterns and a transmissive mode for divergent patterns.
Owner:CABOT MICROELECTRONICS CORP
Magnetic head for X-ray source
InactiveUS20070025516A1FocusImprove stabilityCathode ray concentrating/focusing/directingX-ray tube vessels/containerX-rayElectron
An X-ray source includes a magnetic appliance to provide electron beam focusing. The magnetic appliance can provide variably focused and non-focused configurations. The magnetic appliance can include one or more electromagnets and / or permanent magnets. An electric potential difference is applied to an anode and a cathode that are disposed on opposite sides of an evacuated tube. The cathode includes a cathode element to produce electrons that are accelerated towards the anode in response to the electric field between the anode and the cathode. The anode includes a target material to produce x-rays in response to impact of electrons.
Owner:MOXTEK INC
X-ray tube cathode with reduced unintended electrical field emission
ActiveUS7382862B2Easy to controlFocusX-ray tube electrodesCathode ray concentrating/focusing/directingSoft x rayX-ray
An x-ray source has an evacuated tube. An anode is disposed in the tube and includes a material configured to produce x-rays in response to impact of electrons. A cathode is disposed in the tube opposing the anode configured to produce electrons accelerated towards the anode in response to an electric field between the anode and the cathode. A flange extends from the cathode toward the anode, and has a smaller diameter than the evacuated tube. The flange extends closer to the anode than an interface between the cathode and the tube thus forming a reduced-field region between the evacuated tube and the flange.
Owner:MOXTEK INC
Screen for protection against ionising radiation emissions
InactiveUS7112811B2Interesting efficiencyImprove visibilityMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationX-ray tube vessels/containerStructural engineeringRadiation emission
Owner:LEMER PROTECTION ANTI X PAR ABREVIATION SOC LEMER PAX
Decontamination and sterilization system using large area x-ray source
InactiveUS20060049359A1Reduce installationReduce operating costsWater/sewage treatment by irradiationX-ray tube electrodesElectron sourceOperational costs
A novel x-ray treatment system utilizes one or more large area flat panel sources of x-ray radiation directed into a target zone. A target substance within the target zone is irradiated with x-ray radiation from the one or more flat panel sources, reducing the biological effects of a contaminant presence therein. The flat panel source comprises an electron source, an electron accelerator, and an electron target medium. The electron source may emit electrons either via field emission or thermionic emission. The x-ray source may operate in transmissive, reflective, or combined transmissive / reflective mode. The use of large area flat panel x-ray sources in the inventive systems allows for decreased installation and operational costs as well as increased efficiency.
Owner:CABOT MICROELECTRONICS CORP
X-Ray Window with Grid Structure
InactiveUS20080296518A1High strengthReduce manufacturing costRadiation/particle handlingElectrode and associated part arrangementsX-rayHigh intensity
A high strength window for a radiation detection system includes a plurality of intersecting ribs defining a grid having openings therein with tops of the ribs terminate substantially in a common plane. The intersecting ribs are oriented non-perpendicularly with respect to each other and define non-rectangular openings. The window also includes a support frame around a perimeter of the plurality of intersecting ribs, and a film disposed over and spanning the plurality of intersecting ribs and openings. The film is configured to pass radiation therethrough. An associated radiation detection system includes a sensor disposed behind the window. The sensor is configured to detect radiation passing through the high strength window.
Owner:MOXTEK INC
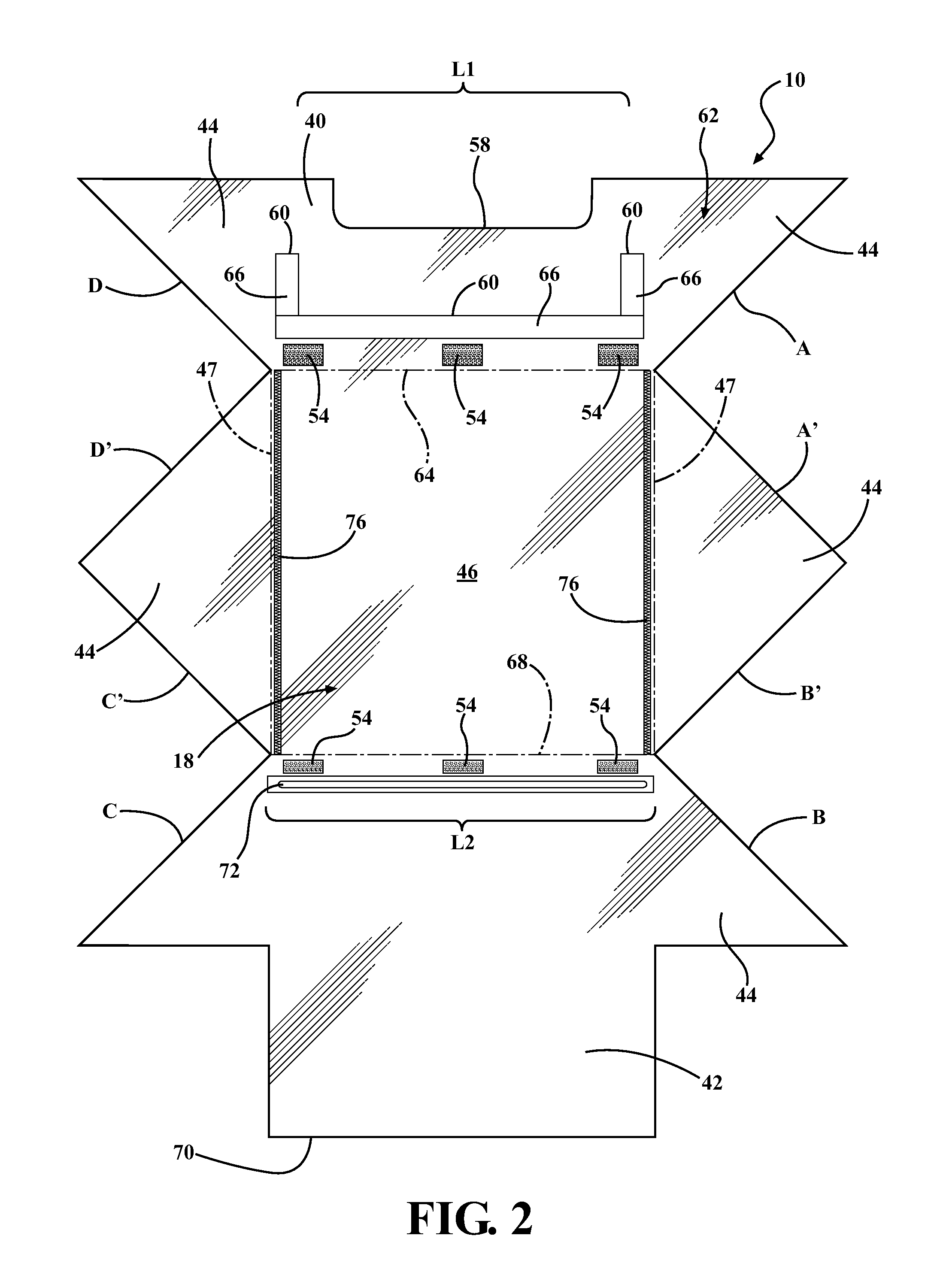
Breast tomosynthesis system with shifting face shield
ActiveUS7792245B2Easy to reachProtects patientPatient positioning for diagnosticsX-ray tube vessels/containerTomosynthesisRadiology
Breast imaging using any one of a mammography system, a tomosynthesis system, or a fused system that selectively takes either or both of mammography images and tomosynthesis images, further uses a patient shield that moves closer to and further away from the patient's chest and head, between (1) an access position that facilitates the technologist's access to adjust the patient's breast while the breast is being compressed and (b) a protective position in which the shield helps protect the patient from collision with moving components and from x-ray exposure of tissue other than the tissue that is to be imaged.
Owner:HOLOGIC INC
Fluoroscopy operator protection device
ActiveUS20090232282A1Patient positioning for diagnosticsX-ray tube vessels/containerX-rayRadiation shield
A radiation protection device attaches to the C-arm of a fluoroscope and shields and collimates the X-ray beam between the X-ray source and the patient and between the patient and the image intensifier. One embodiment has a radiation shield of X-ray opaque material that surrounds the C-arm of the fluoroscopy system, the X-ray source and the image intensifier. A padded slot fits around the patient's body. Another embodiment has conical or cylindrical radiation shields that extend between the X-ray source and the patient and between the patient and the image intensifier. The radiation shields have length adjustments and padded ends to fit the device to the patient. The radiation protection device may be motorized to advance and withdraw the radiation shields. A blanket-like radiation shield covers the patient in the area surrounding where the X-ray beam enters the body.
Owner:RADIACTION
X-ray generation apparatus and x-ray radiographic apparatus
InactiveUS20140369469A1Improve power generation efficiencyX-ray tube electrodesX-ray tube vessels/containerSoft x rayX-ray
In an X-ray generation apparatus of transmission type including an electron passage surrounded by and formed in an electron passage forming member, and generating an X-ray by colliding electrons having passed through the electron passage against a target, wherein the electron passage includes a secondary X-ray generation portion that generates an X-ray with collision of electrons reflected by the target against the secondary X-ray generation portion, the secondary X-ray generation portion and the target are arranged such that the X-ray generated with direct collision of the electrons against the target and the X-ray generated with the collision of the electrons reflected by the target against the secondary X-ray generation portion are both radiated to an outside, and an atomic number of a material of the electron passage forming member is larger than that of the target. X-ray generation efficiency is increased by effectively utilizing the electrons reflected by the target.
Owner:CANON KK
Compact scanned electron-beam x-ray source
ActiveUS20080198970A1Small device sizeAvoid dwell timeRadiation/particle handlingX-ray tube gas controlX-rayLight beam
A compact, reliable scanning electron-beam x-ray source achieves reduced complexity and cost. In particular, the x-ray source includes an electron beam that is propagated parallel to an x-ray target and is swept across the target in response to a moving magnetic cross field. Rather than scanning the beam by deflecting it about a single point, the point of deflection is translated along the target length, dramatically reducing the volume of the device. The magnetic cross field is translated along the target length using either mechanical systems to move permanent magnets, or electrical systems to energize an array of electromagnets.
Owner:L3 TECH INC
Magnetic head for X-ray source
InactiveUS7428298B2FocusImprove stabilityCathode ray concentrating/focusing/directingX-ray tube vessels/containerX-rayElectron
Owner:MOXTEK INC
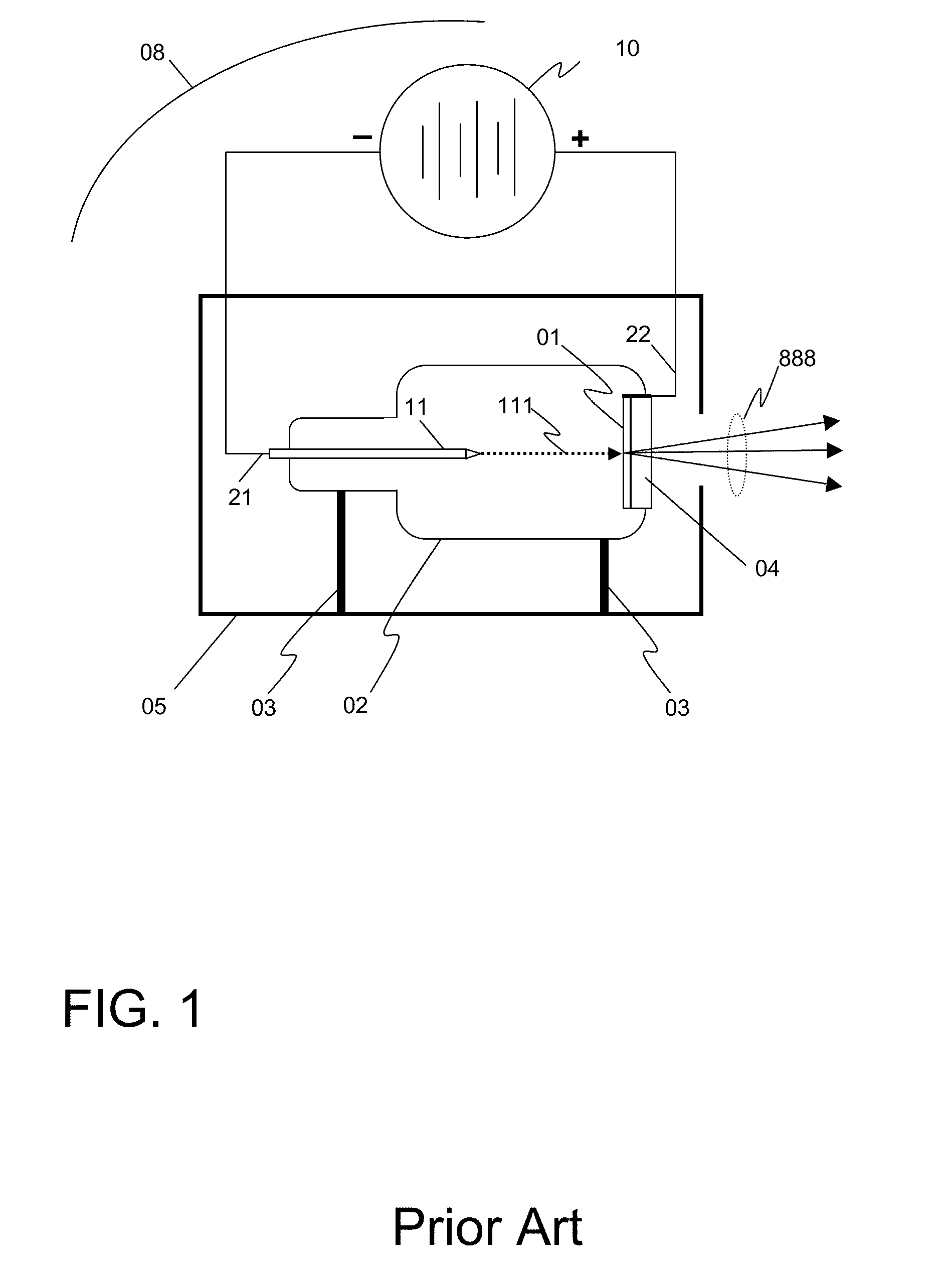
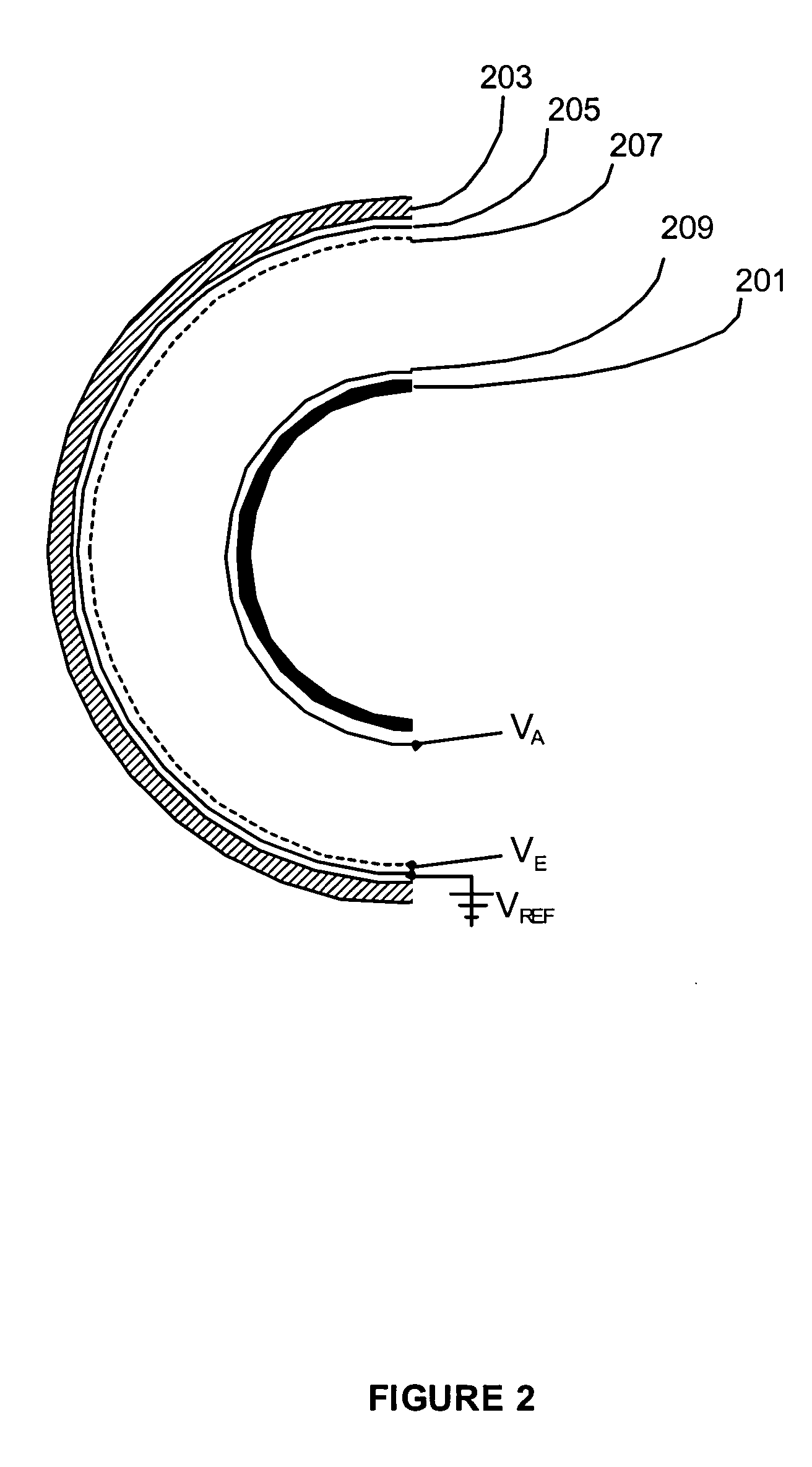
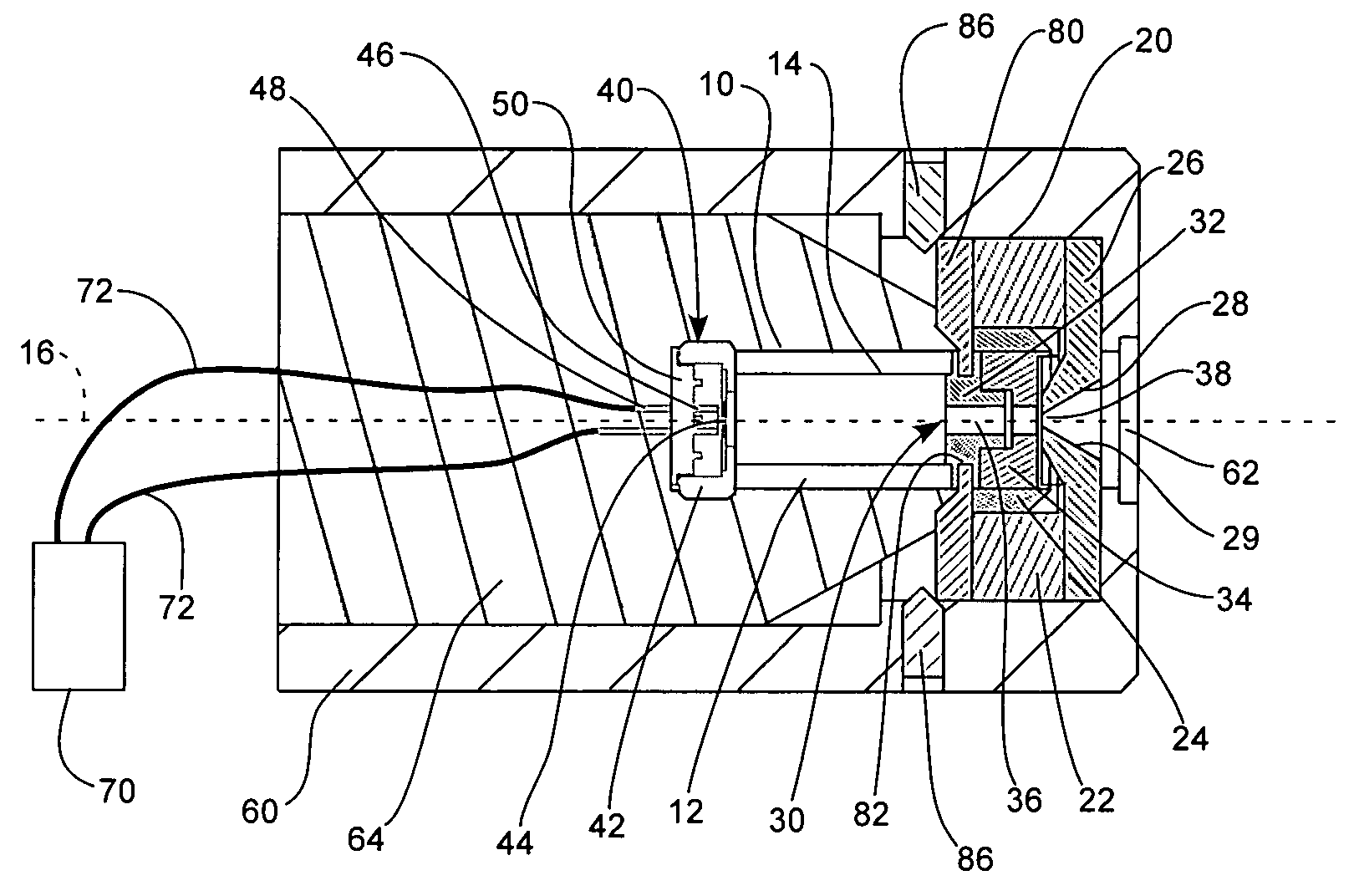
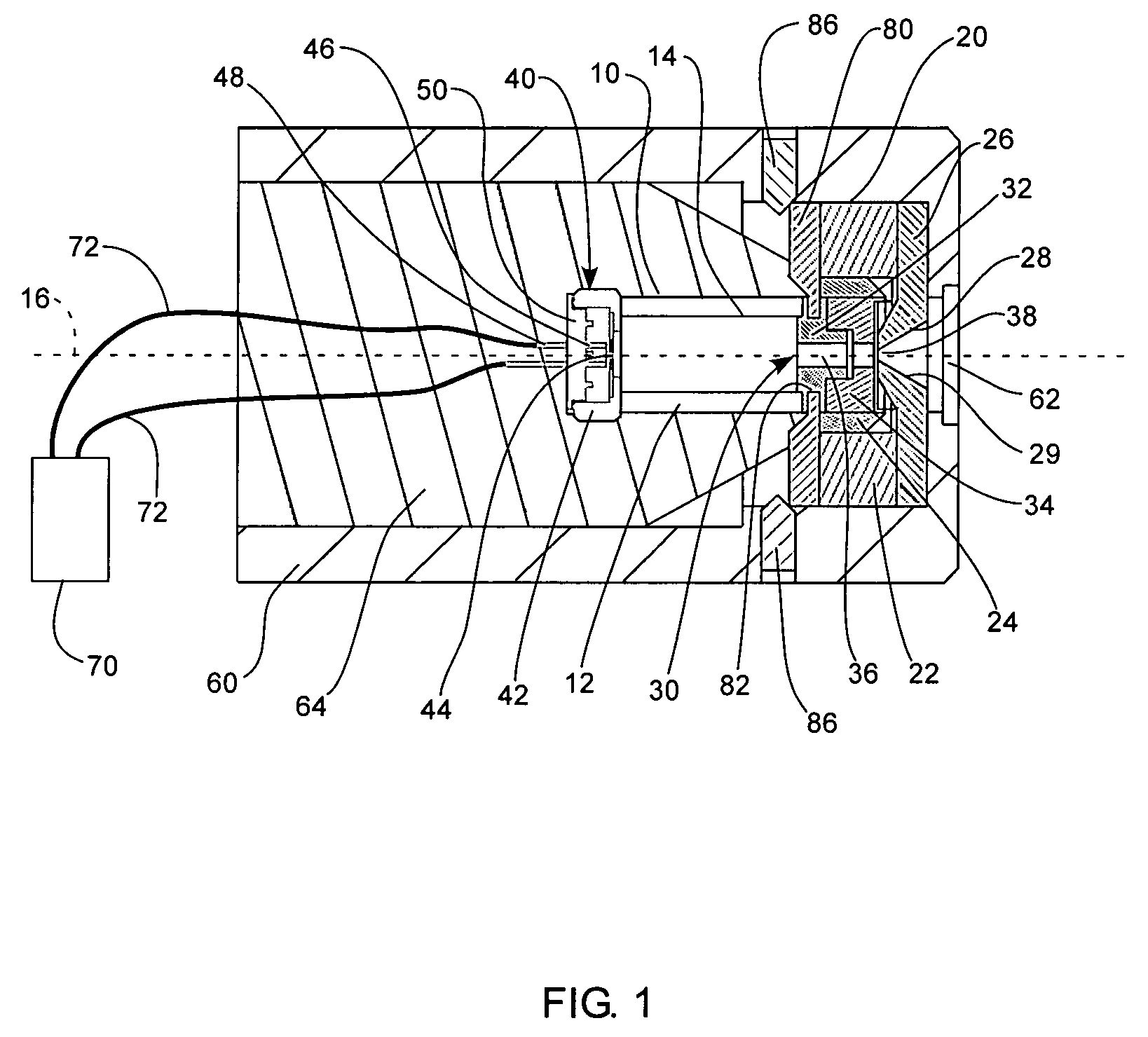
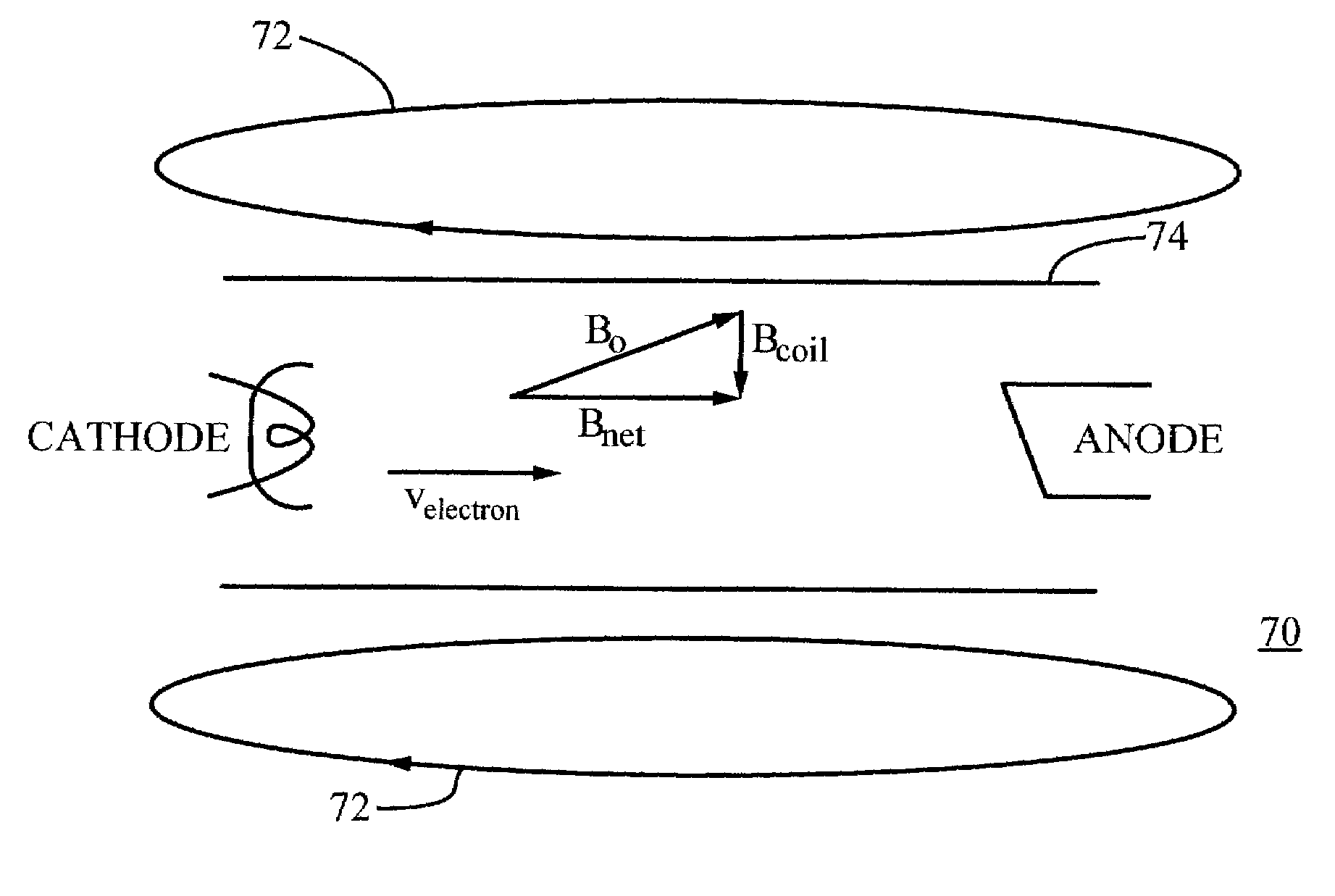
Maintaining the alignment of electric and magnetic fields in an x-ray tube operated in a magnetic field
InactiveUS6976953B1Easy to controlDeflection of the electron beam by the static magnetic field is reduced or eliminatedElectric shock equipmentsMagnetic measurementsLight beamTransverse magnetic field
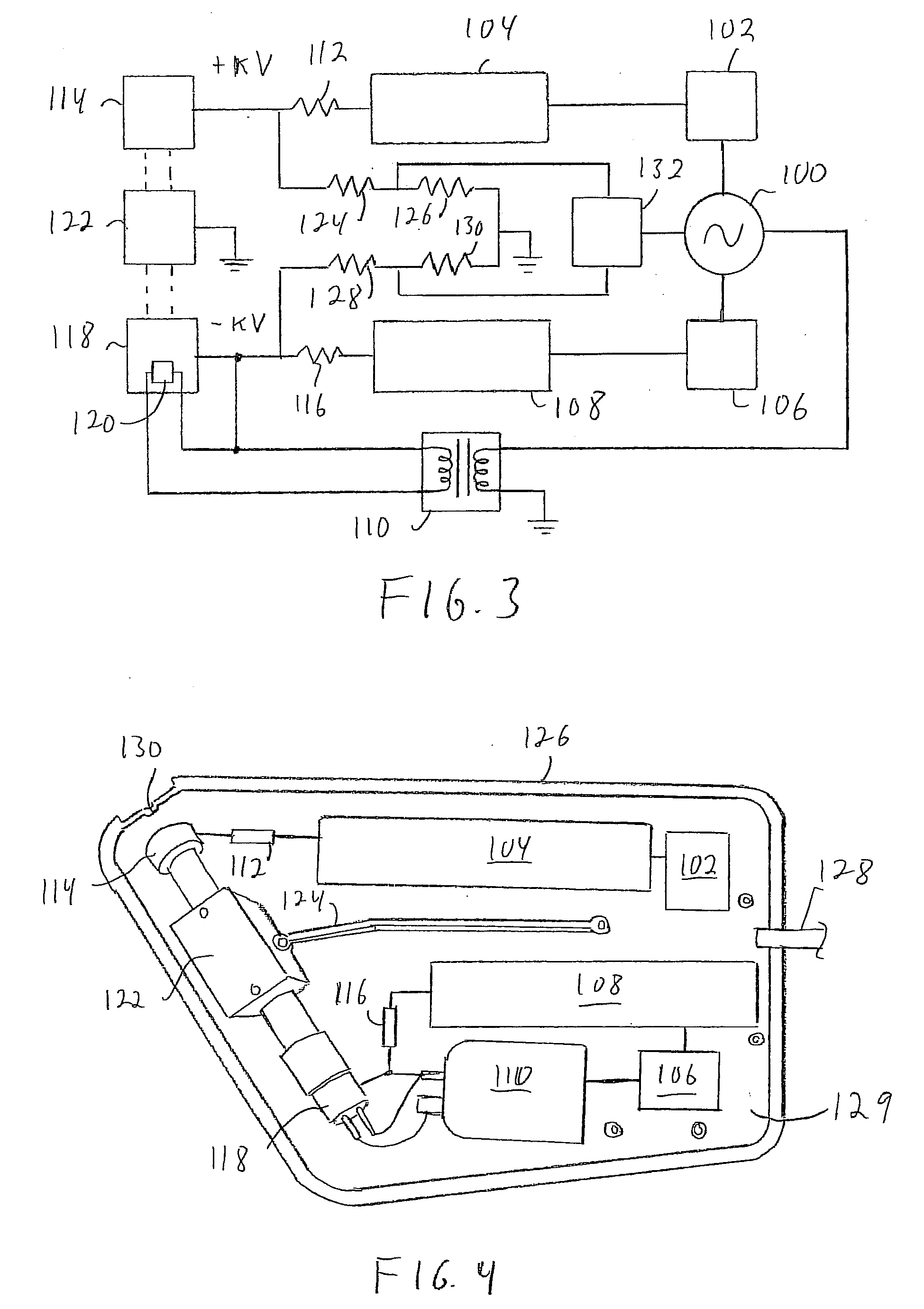
A new technique for maintaining the alignment of electric and magnetic fields in an x-ray tube so the tube can be operated in the presence of a static external magnetic field without being negatively affected thereby. Deflection of the electron beam of the x-ray tube by the high magnetic field is reduced or eliminated by modifying or canceling, at a location near the electron beam, the magnetic field components transverse to the beam. In a preferred embodiment, a set of electromagnet coils are positioned on or near the tube and oriented in a way that when current is applied internal magnetic fields are produced in a direction opposite to the transverse magnetic fields, thereby causing cancellation. In one implementation, one or more sensors are used to detect the transverse magnetic fields. The sensor is positioned near the electron beam, either inside or outside the x-ray tube. The sensor produces a signal dependent on a static magnetic field component transverse to the desired direction of the electron beam. This signal is used to control the amount of current applied to the coils. A controller and a feedback circuit may be included to adjust in real time the amount of current being applied.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE LELAND STANFORD JUNIOR UNIV
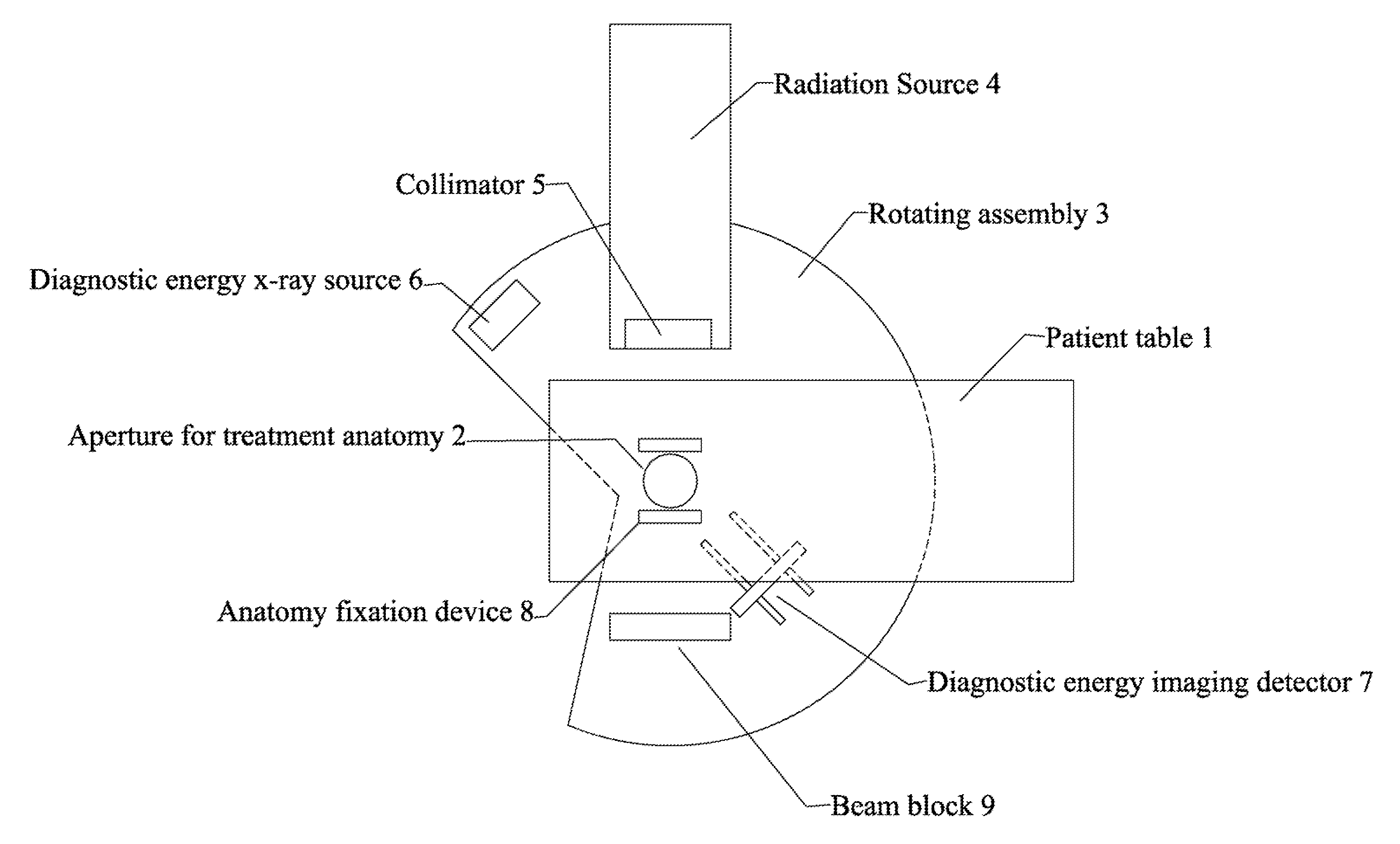
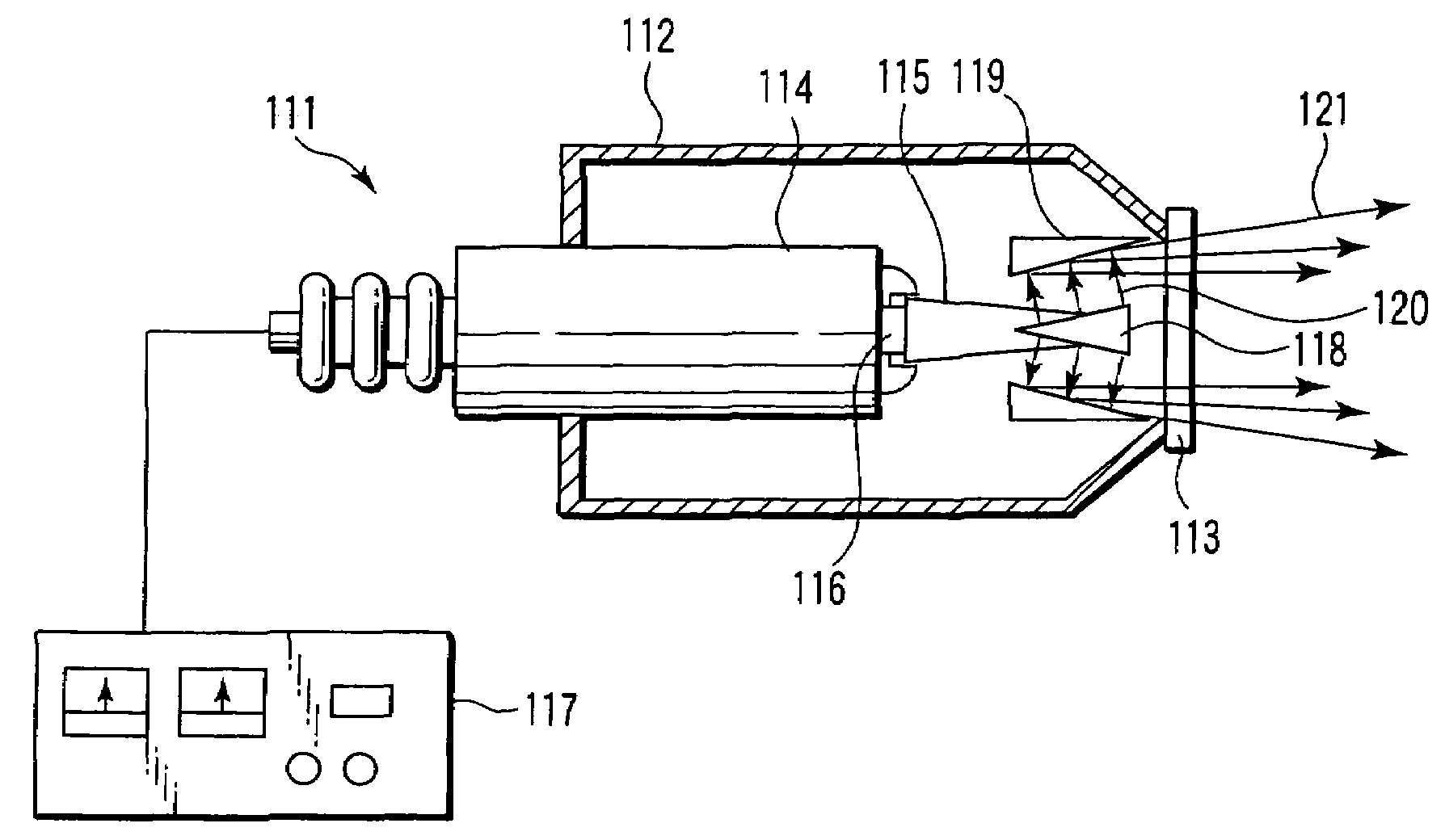
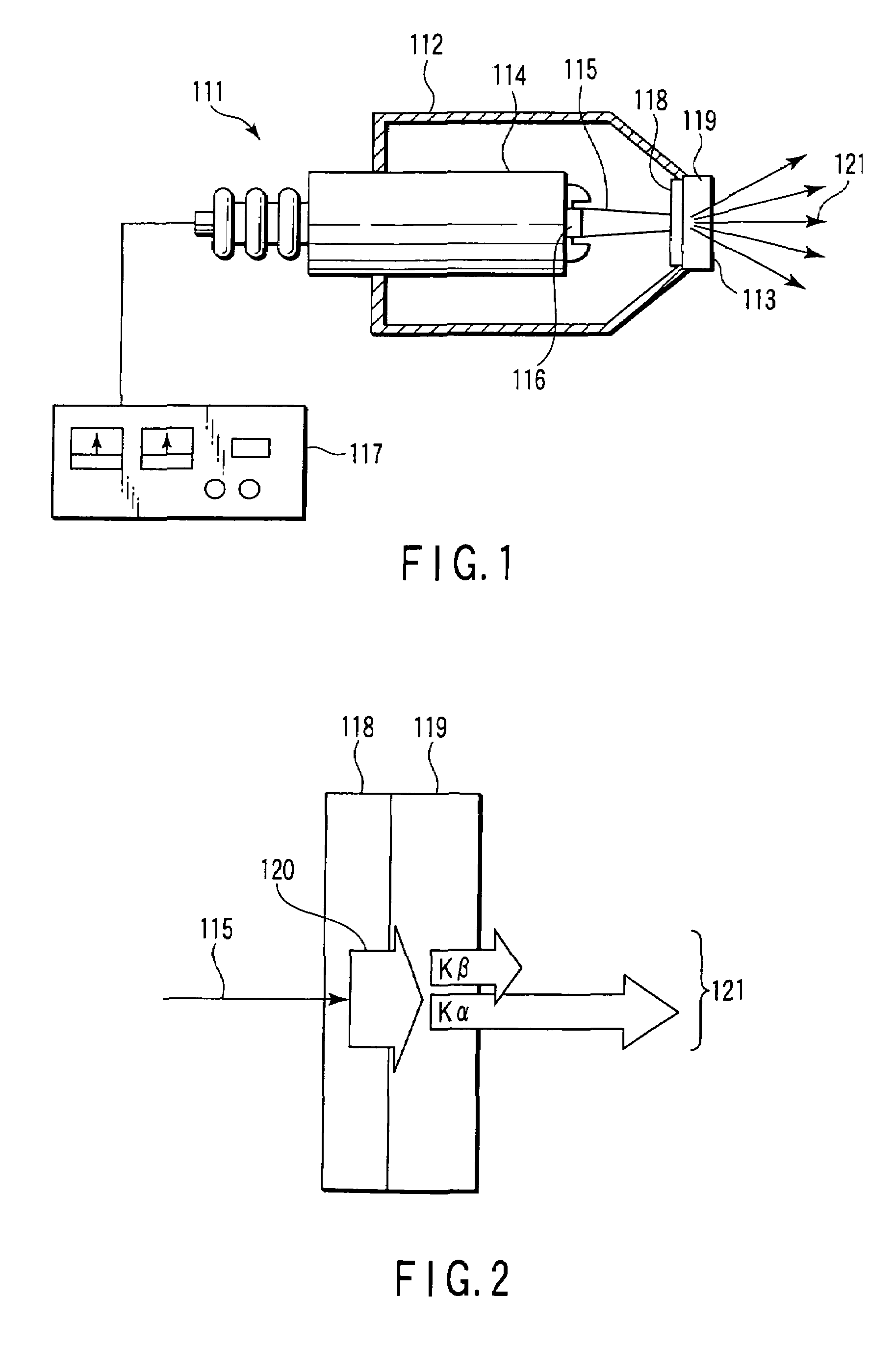
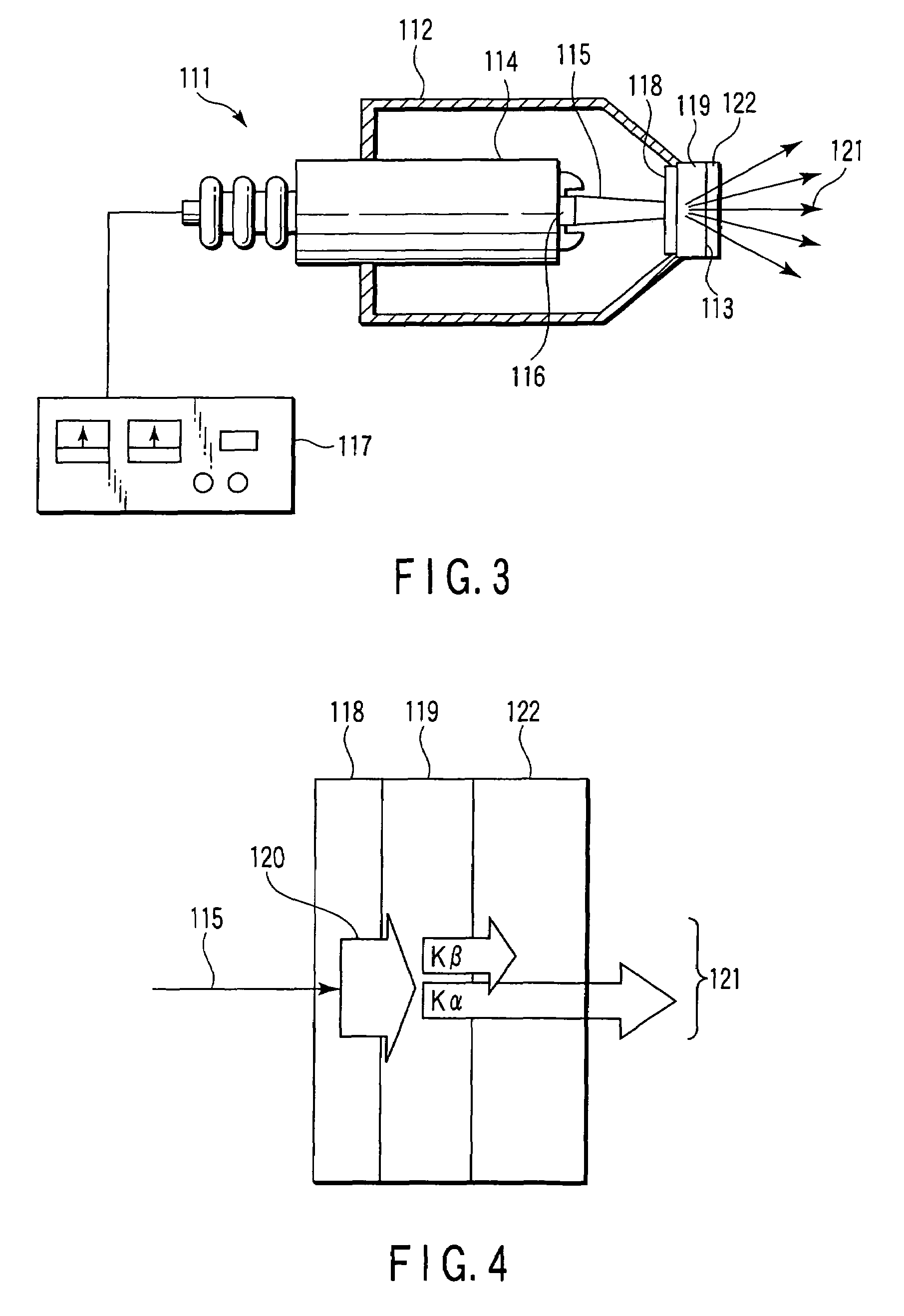
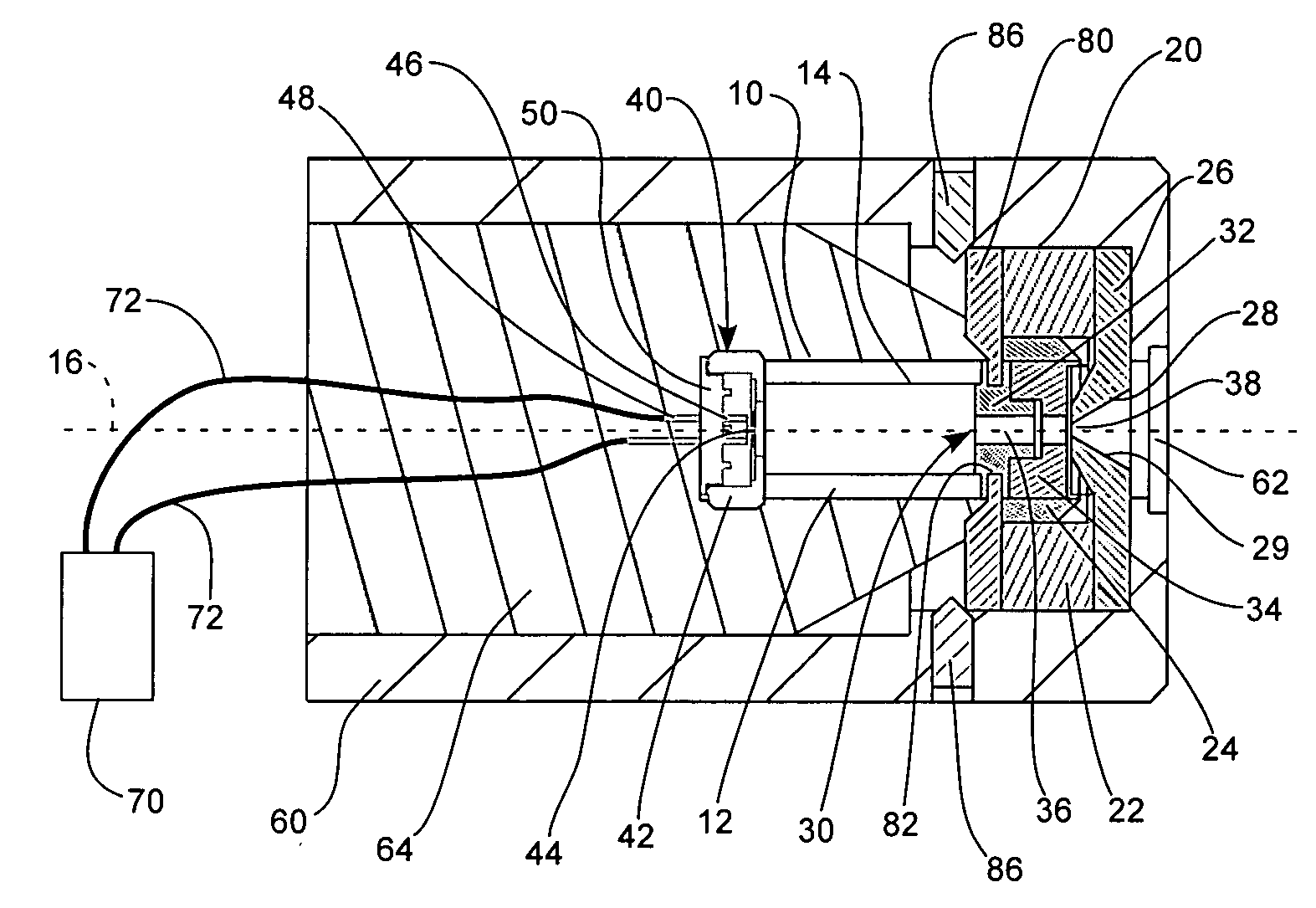
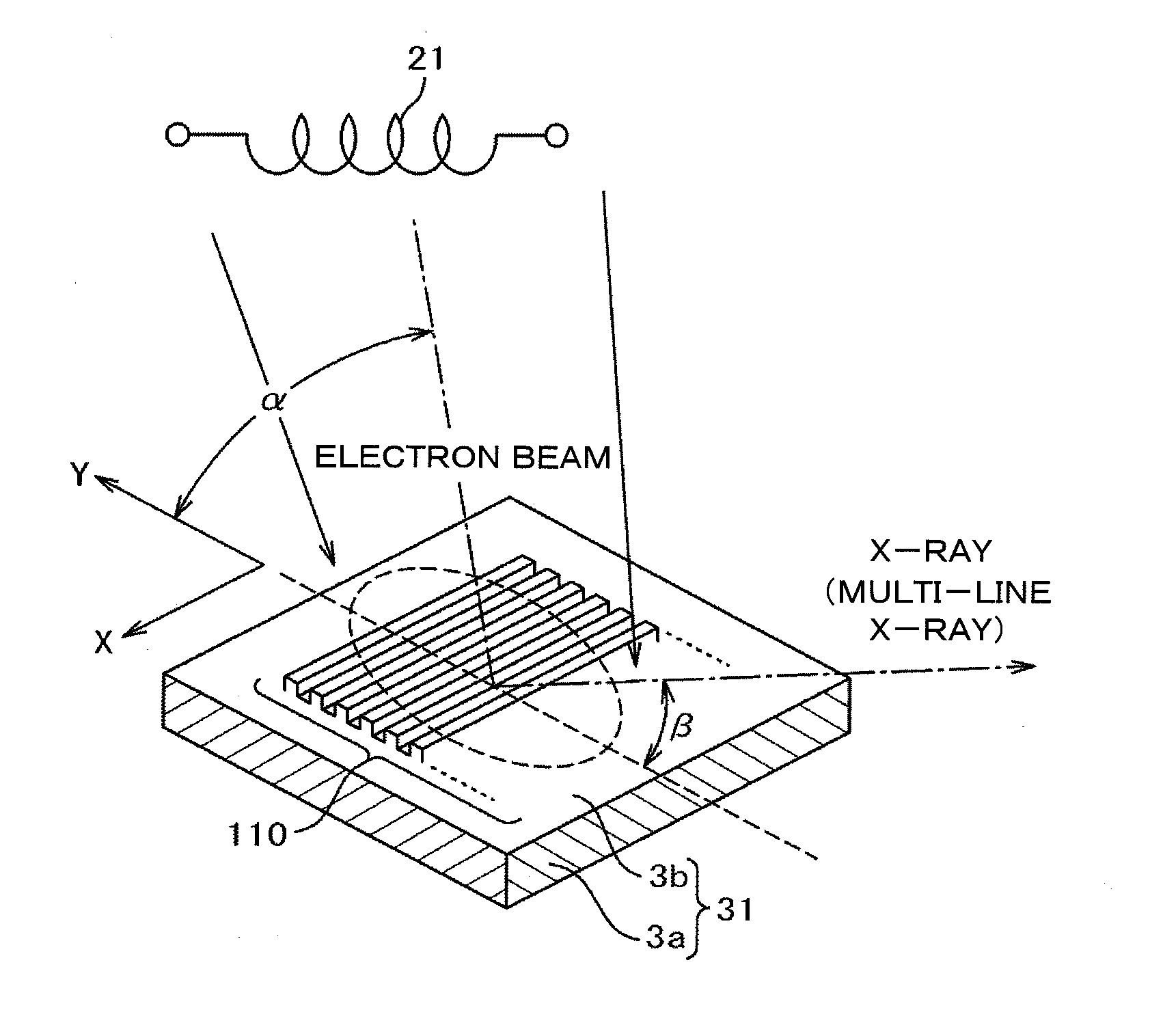
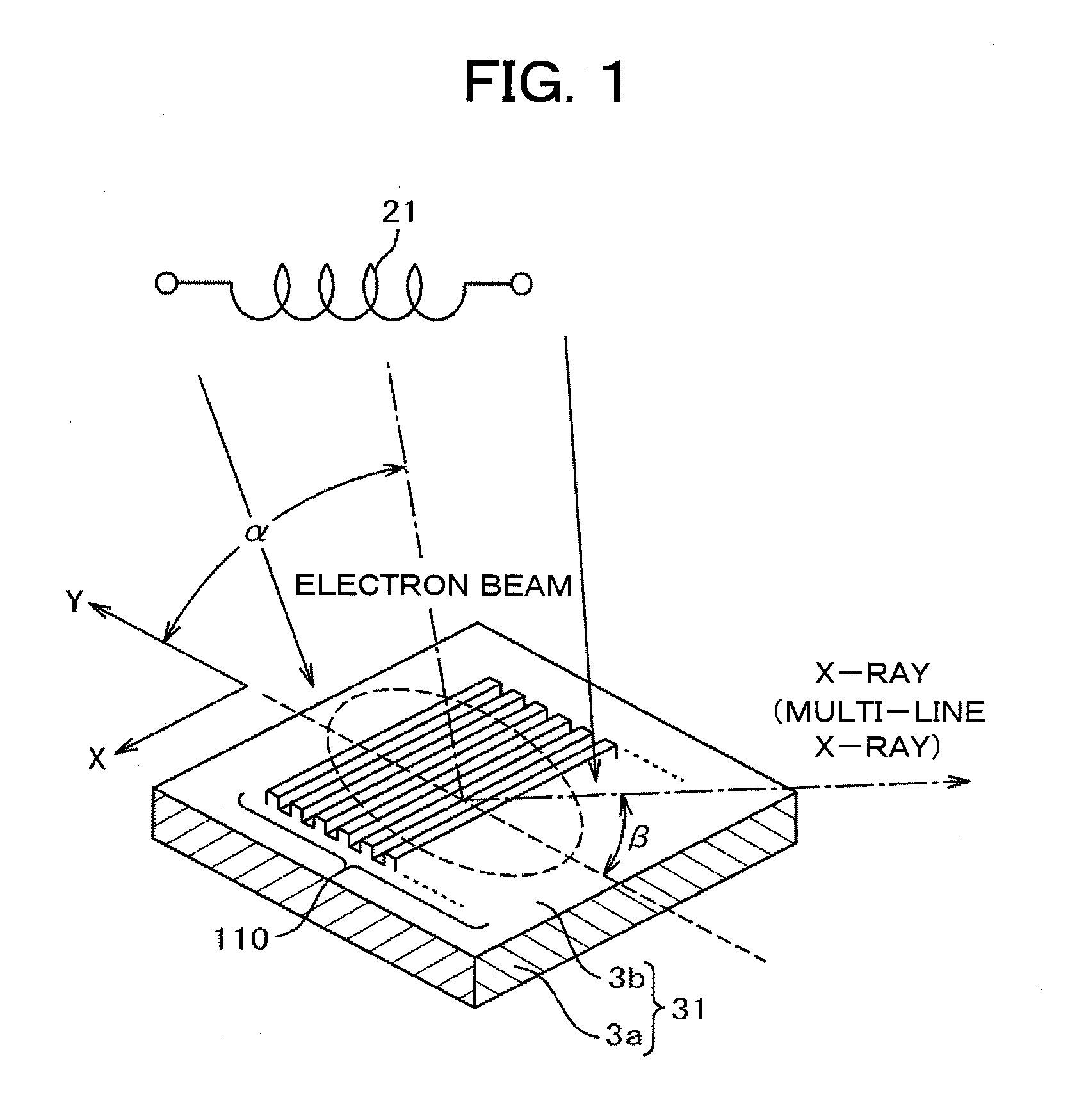
X-ray generating apparatus and inspection apparatus using the same therein
ActiveUS20110235781A1Good effectX-ray tube electrodesX-ray tube vessels/containerElectron sourceX-ray
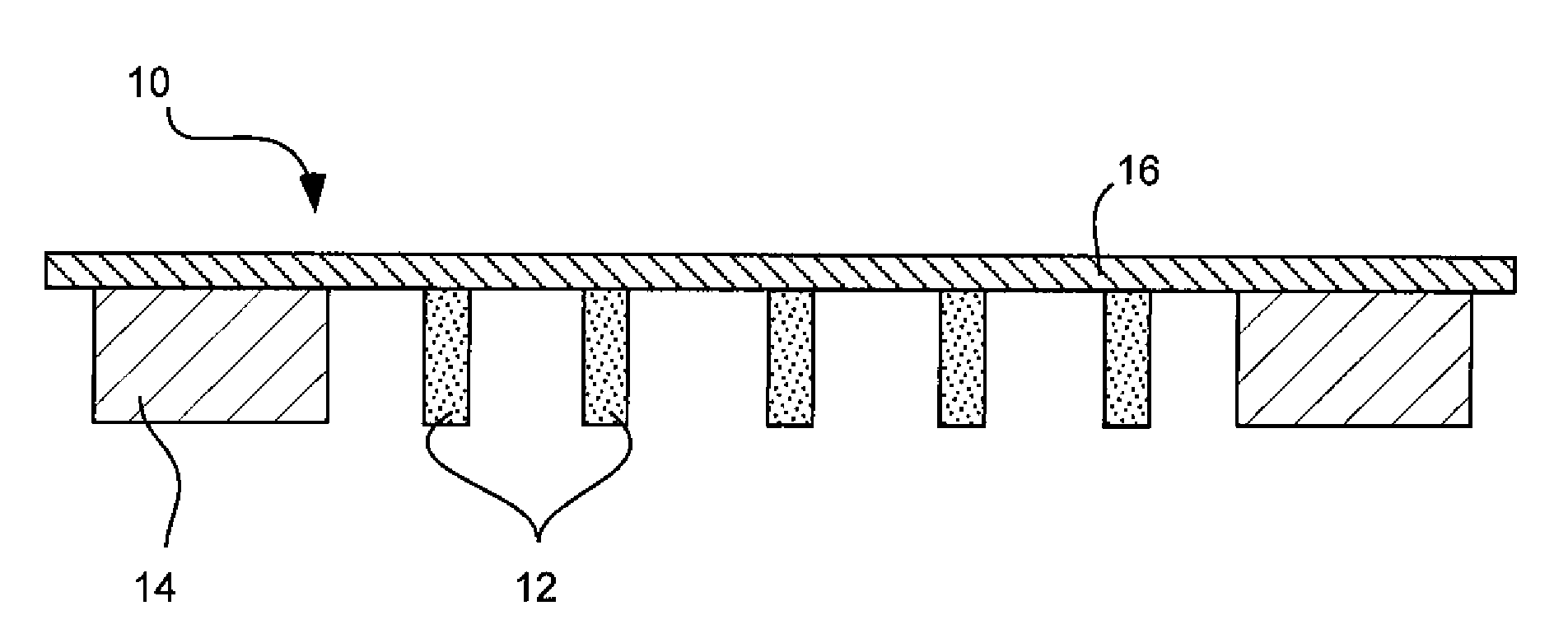
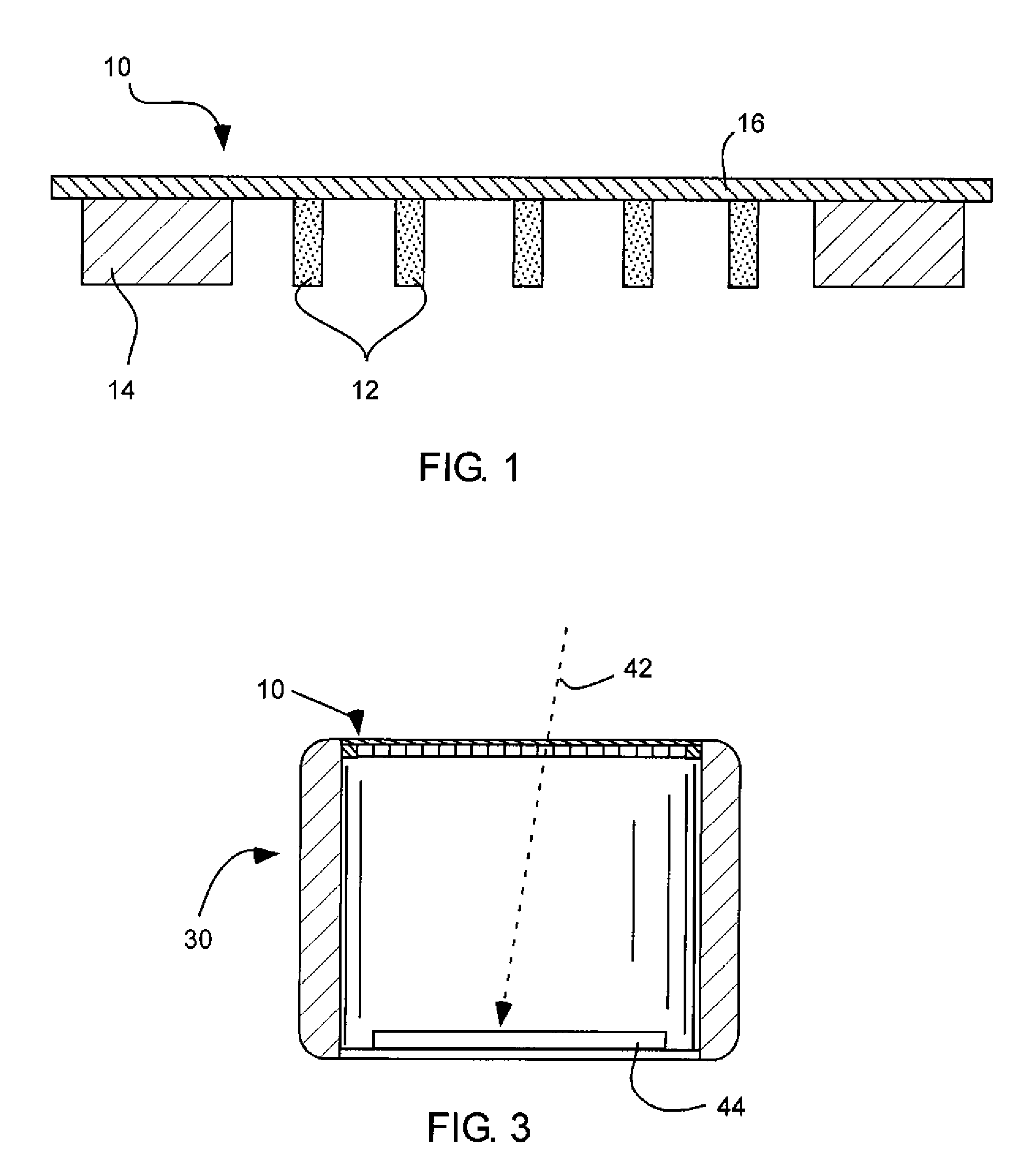
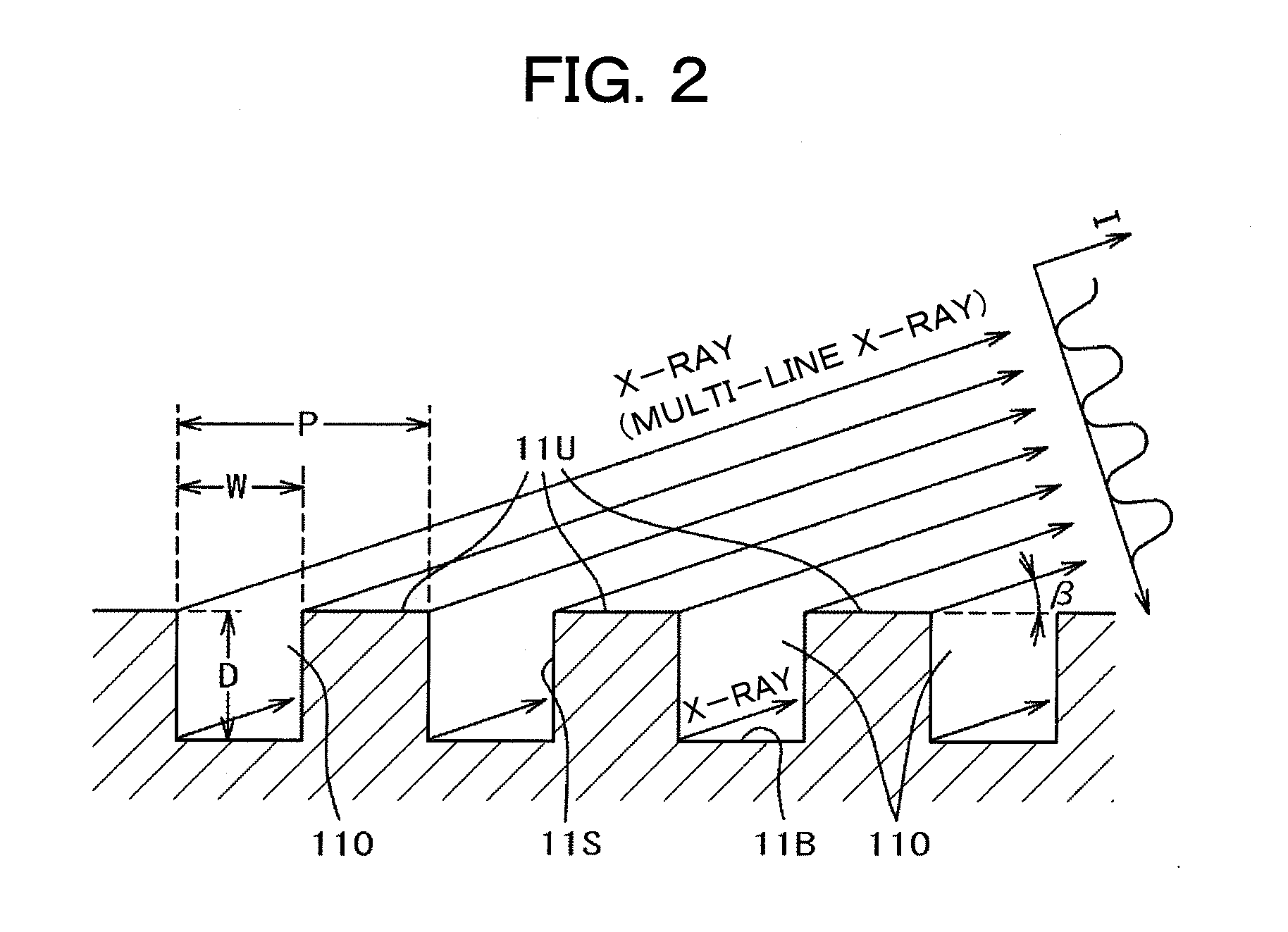
An X-ray generating apparatus is disclosed which includes a tube body having a vacuum interior, an electron source provided within the tube body to generate an electron beam, a target, within the tube body that is irradiated with the electron beam to generate an X-ray, and an X-ray window for taking out the X-ray generated outside of the tube body. A plurality of grooves are formed on a surface of a member building up the target. The grooves each have a fine width and are inclined by a predetermined angle (α), from a direction perpendicular to an elongating direction of the grooves, so that they bridge over the plural numbers of grooves. The X-ray generating apparatus is configured such that a multi-line X-ray generating from the plural numbers of multi-line targets, which are formed between the grooves, emits at a predetermined extraction angle (β), passing through the X-ray window. An inspection apparatus which includes the X-ray generating apparatus is also disclosed.
Owner:RIGAKU CORP
Large surface area x-ray tube window and window cooling plenum
InactiveUS6438208B1Efficiently and effectively removedEnsure adequate heatingRadiation/particle handlingX-ray tube vessels/containerX-rayCoolant
A window and cooling plenum for use with x-ray devices. The x-ray device includes an x-ray tube at least partially immersed in coolant contained within a reservoir. The coolant is continuously circulated through the reservoir by an external cooling unit. The window is brazed into a vacuum enclosure of the x-ray tube and includes a plurality of extended surfaces that are integral with the window. A compensating window is also provided and is disposed substantially proximate to the extended surfaces of the window so that a fluid passageway is defined. The compensating window and window are substantially enclosed within a cooling plenum having fluid inlet and outlet connections in fluid communication with the fluid passageway and the reservoir. A flow of coolant generated by the external cooling unit enters the fluid passageway so that the coolant is able to absorb heat dissipated by the window. Upon exiting the fluid passageway, the coolant returns to the reservoir to repeat the cycle. In addition to facilitating definition of the fluid passageway, the compensating window includes extended surfaces and slots which serve to attenuate differences in the intensity of x-rays emitted through the extended surfaces and slots of the window. By ensuring that the x-rays ultimately emitted from the x-ray device are of substantially uniform intensity, the compensating window serves to maintain the quality of diagnostic images produced by the x-ray device.
Owner:VAREX IMAGING CORP
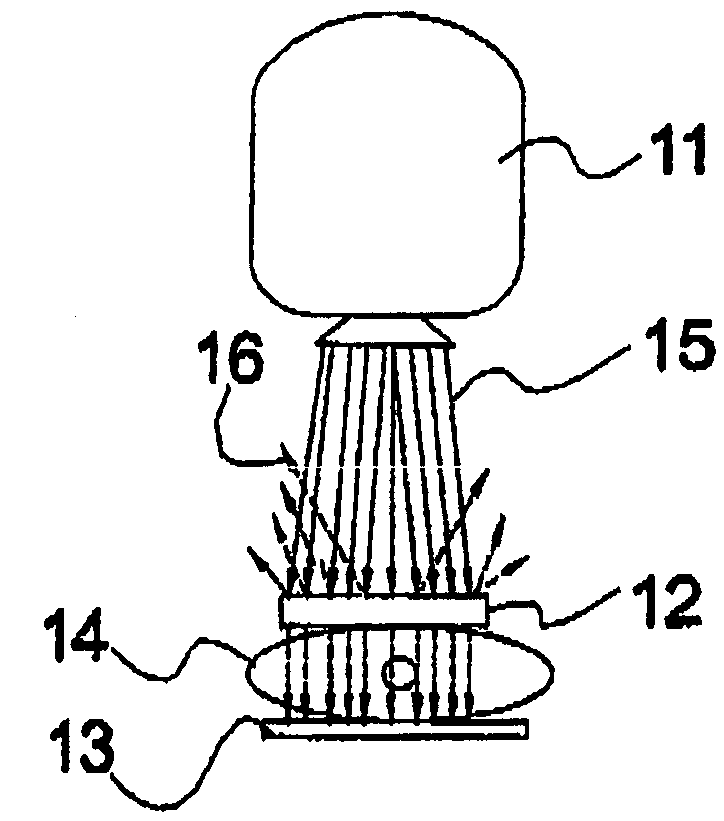
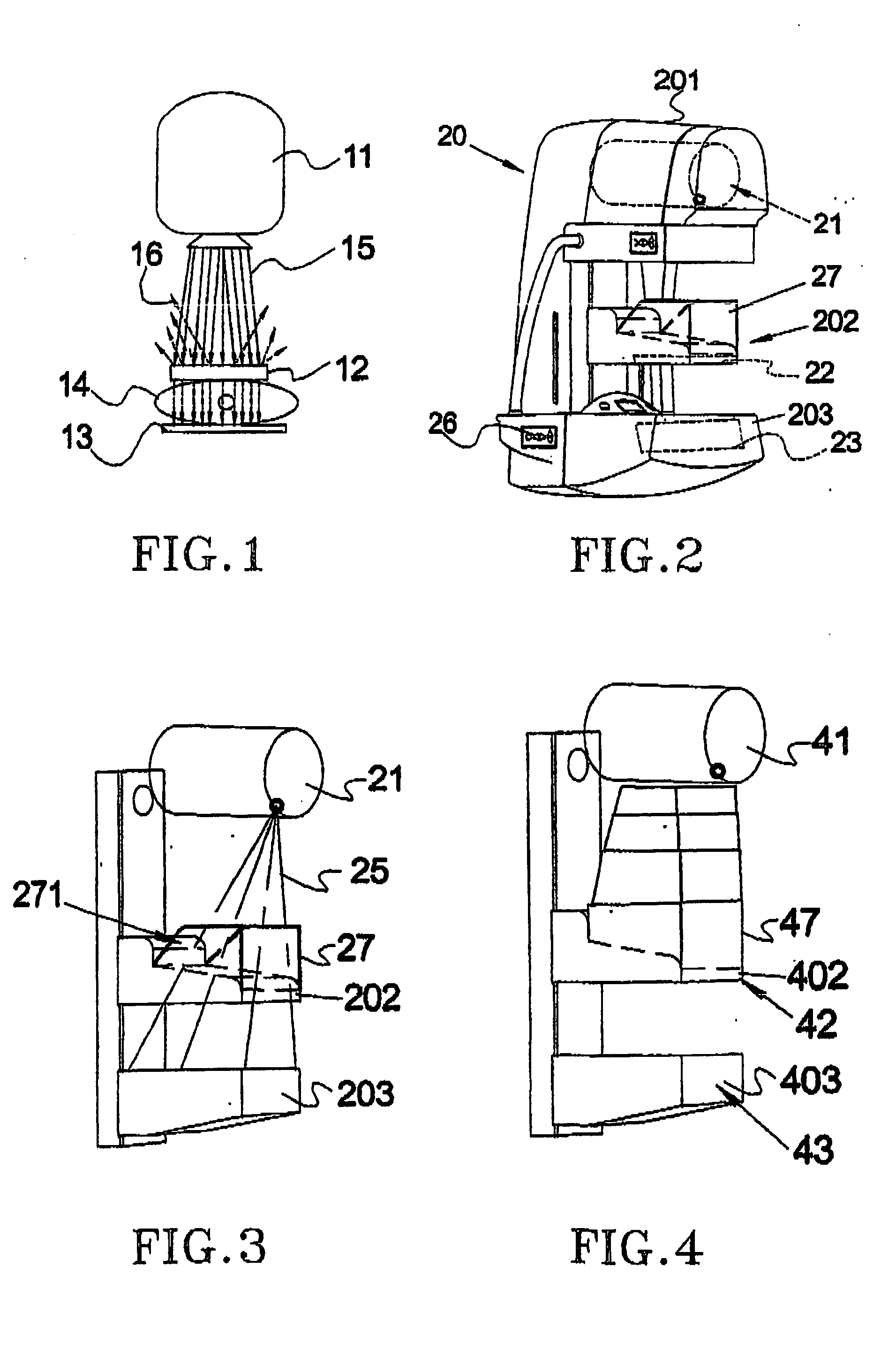
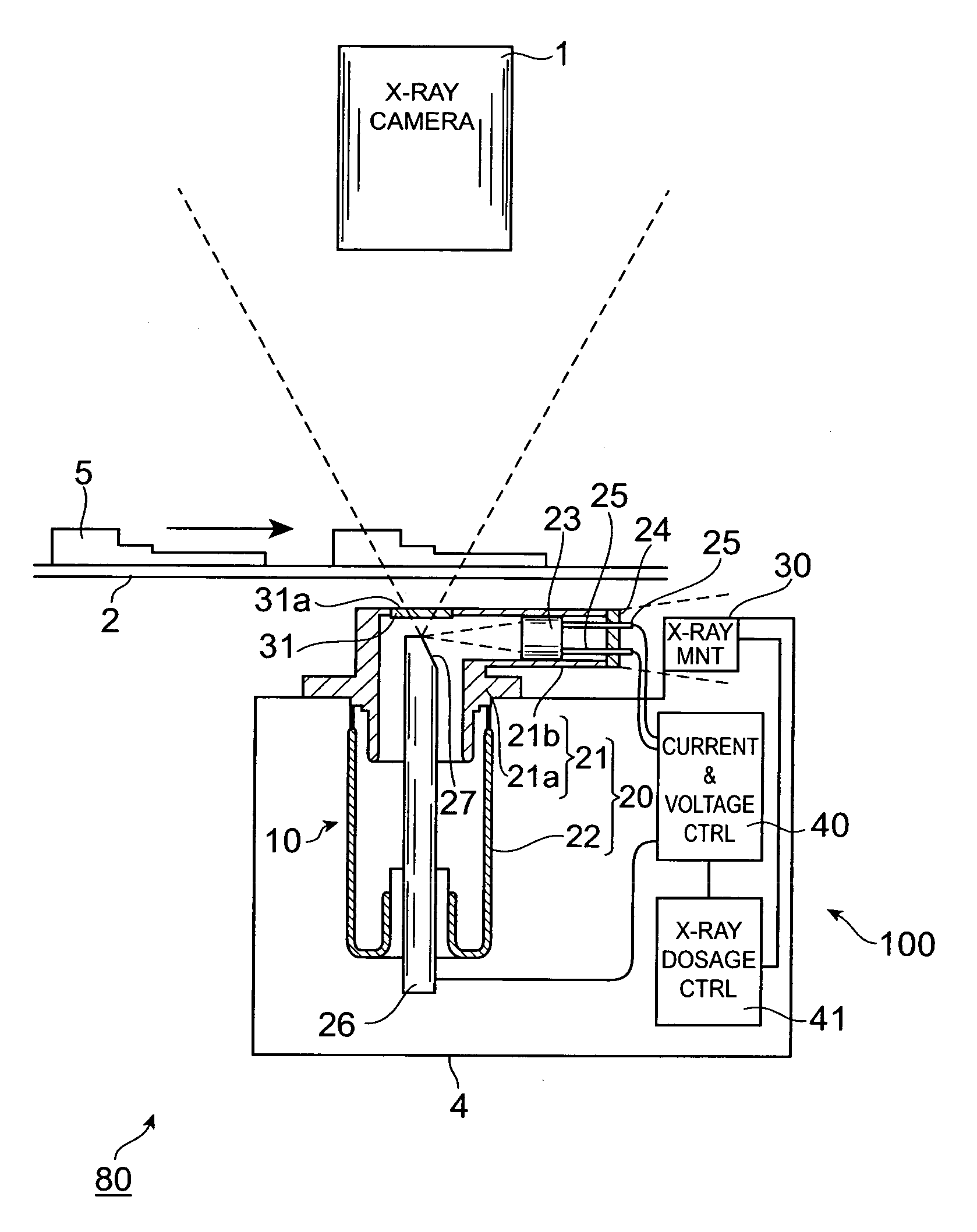
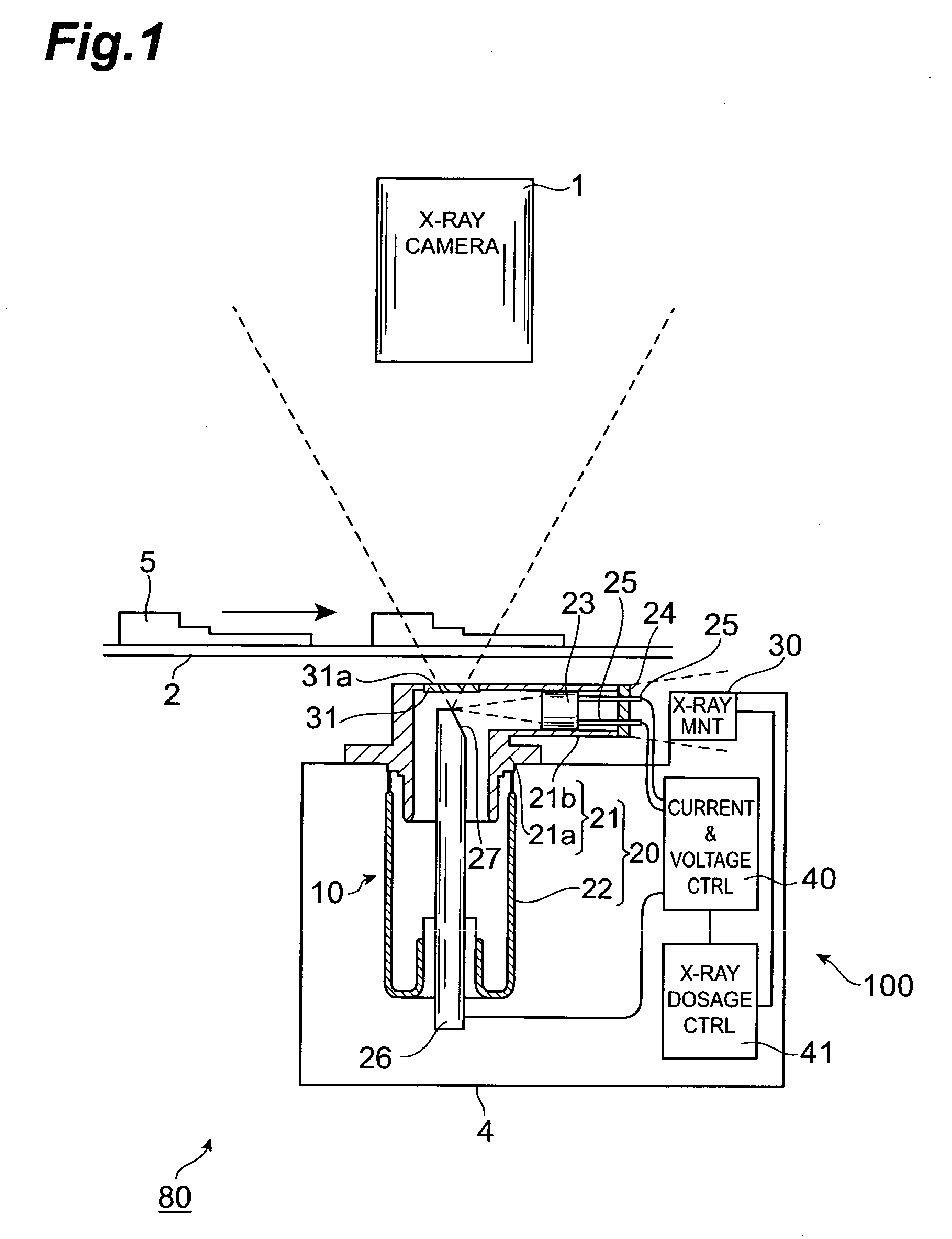
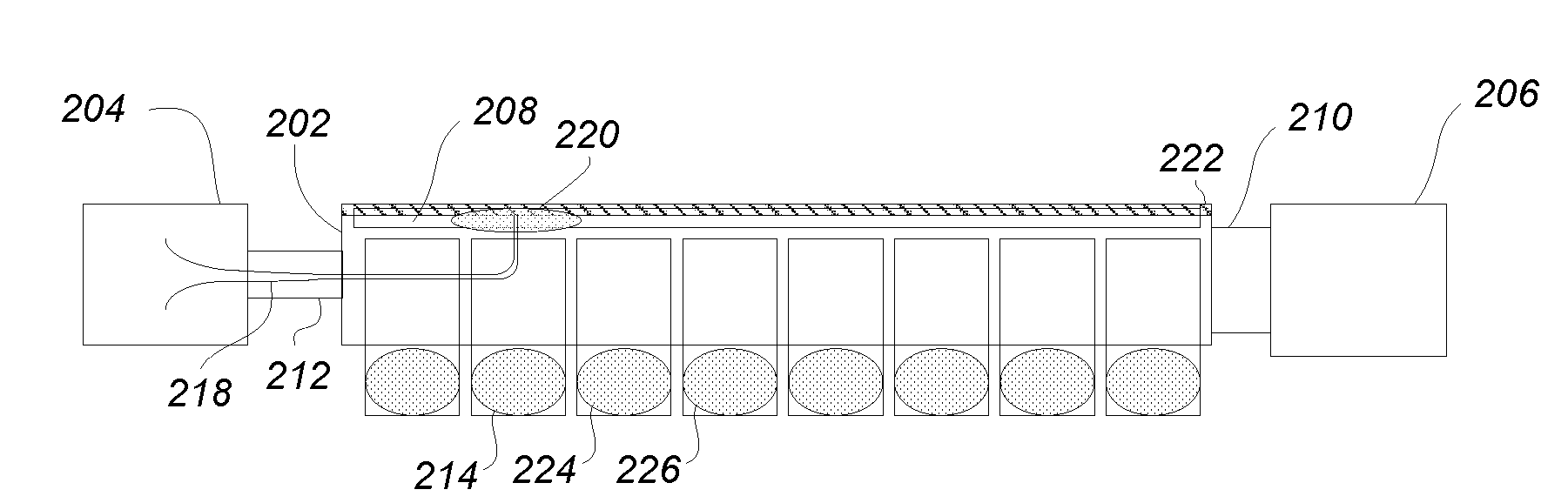
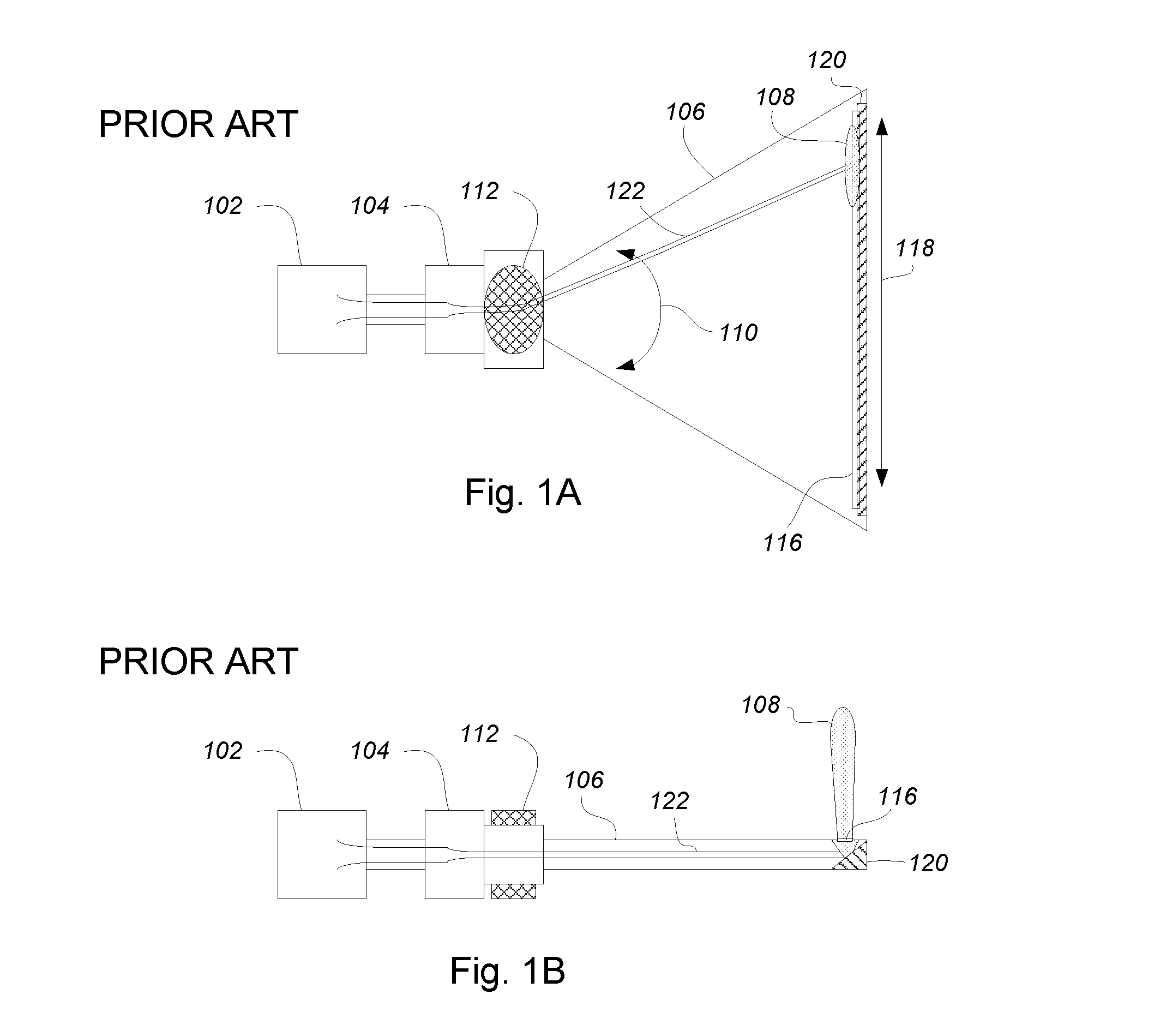
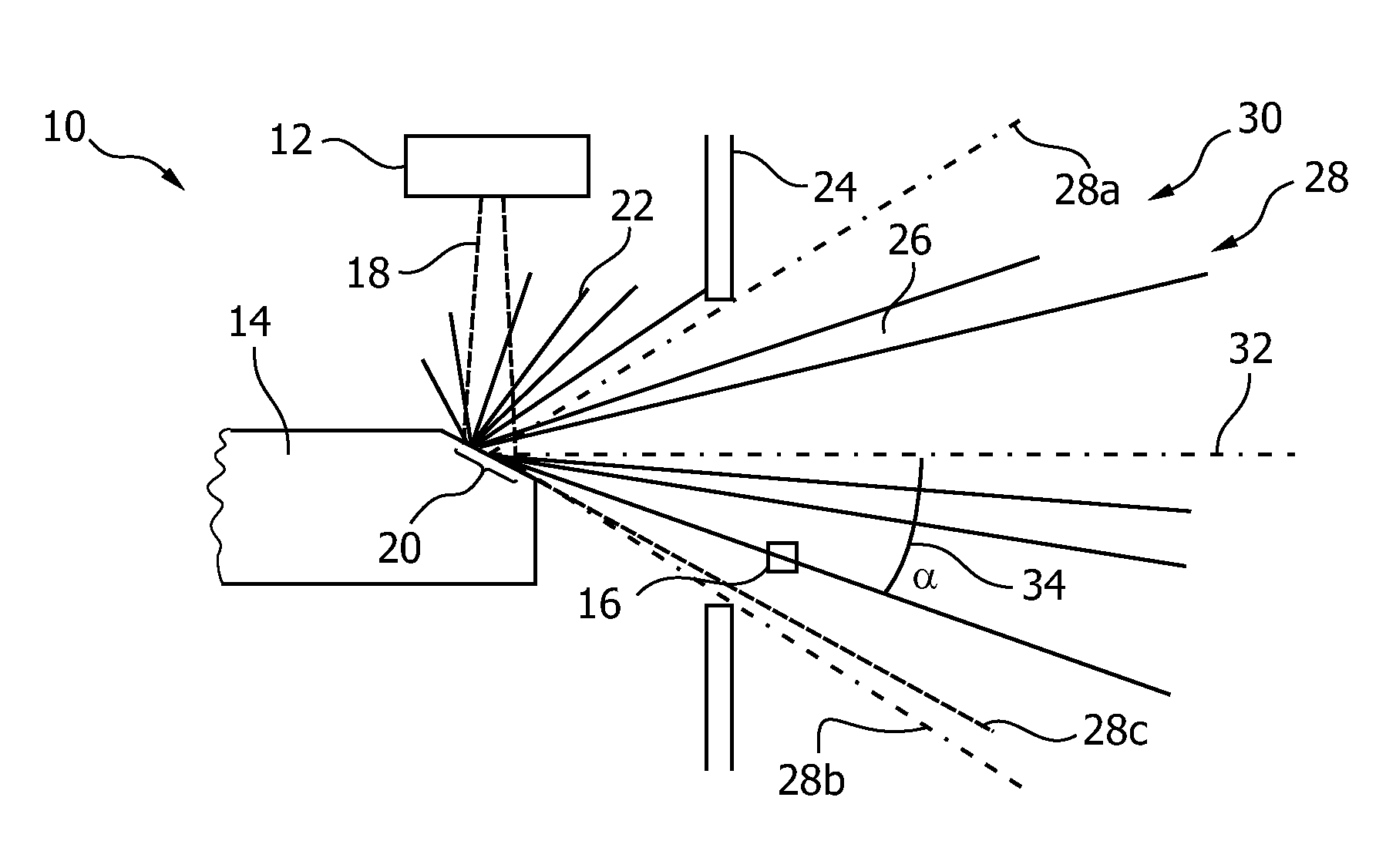
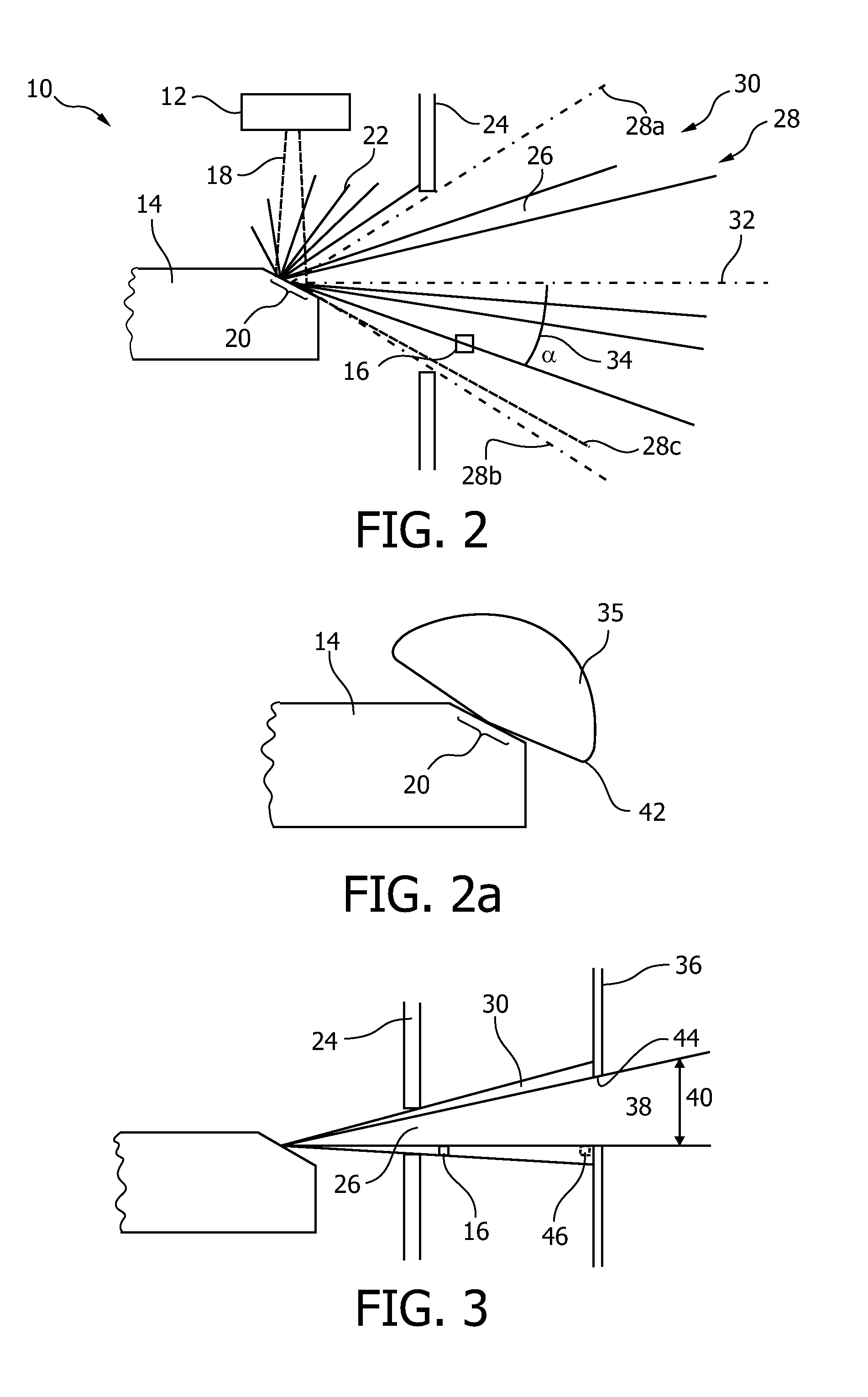
Determining changes in the x-ray emission yield of an x-ray source
The present invention relates to determining changes in the X-ray emission yield of an X-ray tube, in particular determining dose degradation. In order to provide determination of such changes, an X-ray source is provided comprising a cathode, an anode; and at least one X-ray sensor (16). The cathode emits electrons towards the anode and the anode comprises a target area on which the electrons impinge, generating X-ray radiation. An X-ray barrier (24) is provided with an aperture (26) for forming an emitting X-ray beam from the X-ray radiation, wherein the emitting X-ray beam has a beam formation (30) with a central axis. The at least one X-ray sensor is arranged within the beam formation and measures the X-ray intensity for a specific direction of X-ray emission with an angle with respect to the central axis. The at least one X- ray sensor can be positioned inside the beam formation (30), but outside the “actual field of view” (40) as determined by a diaphragm (36).
Owner:KONINKLIJKE PHILIPS ELECTRONICS NV
X-ray sources using linear accumulation
ActiveUS9543109B2Heat generationIncrease electron densityX-ray tube anode coolingX-ray tube electrodesHigh energyX-ray
A compact source for high brightness x-ray generation is disclosed. The higher brightness is achieved through electron beam bombardment of multiple regions aligned with each other to achieve a linear accumulation of x-rays. This may be achieved by aligning discrete x-ray sub-sources, or through the use of x-ray targets that comprise microstructures of x-ray generating materials fabricated in close thermal contact with a substrate with high thermal conductivity. This allows heat to be more efficiently drawn out of the x-ray generating material, and in turn allows bombardment of the x-ray generating material with higher electron density and / or higher energy electrons, leading to greater x-ray brightness. The orientation of the microstructures allows the use of an on-axis collection angle, allowing the accumulation of x-rays from several microstructures to be aligned to appear to have a single origin, also known as “zero-angle” x-ray radiation.
Owner:SIGRAY INC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com