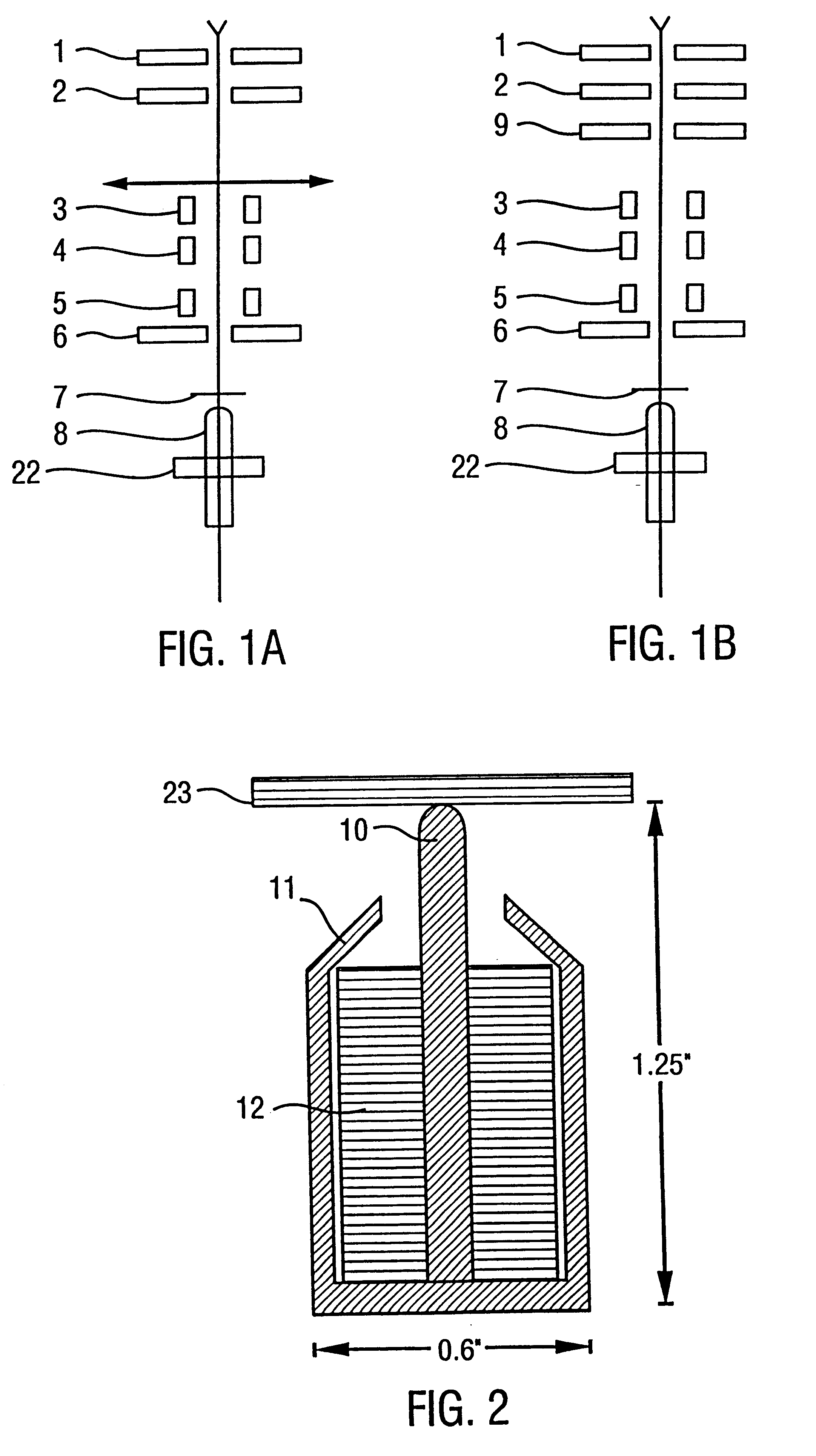
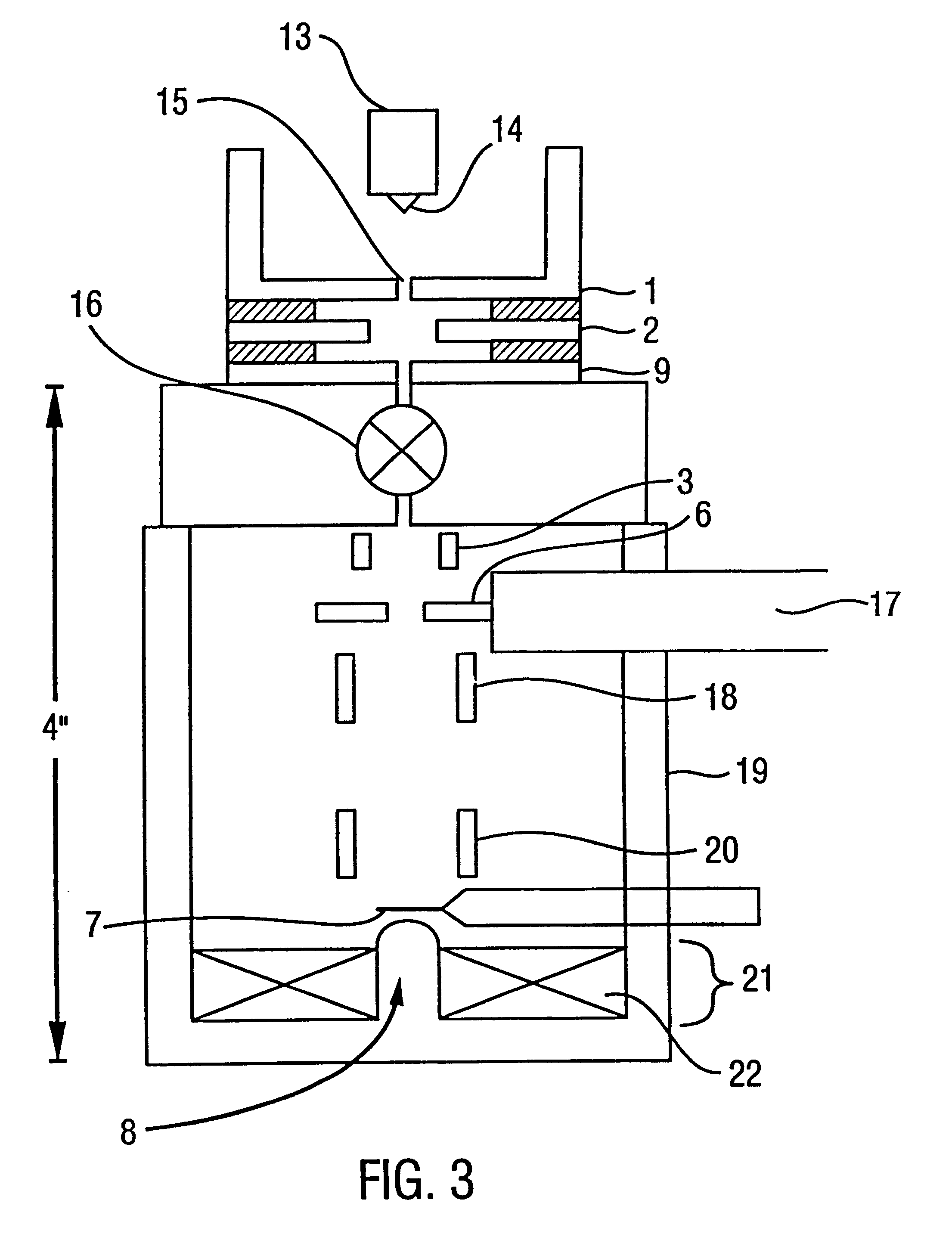
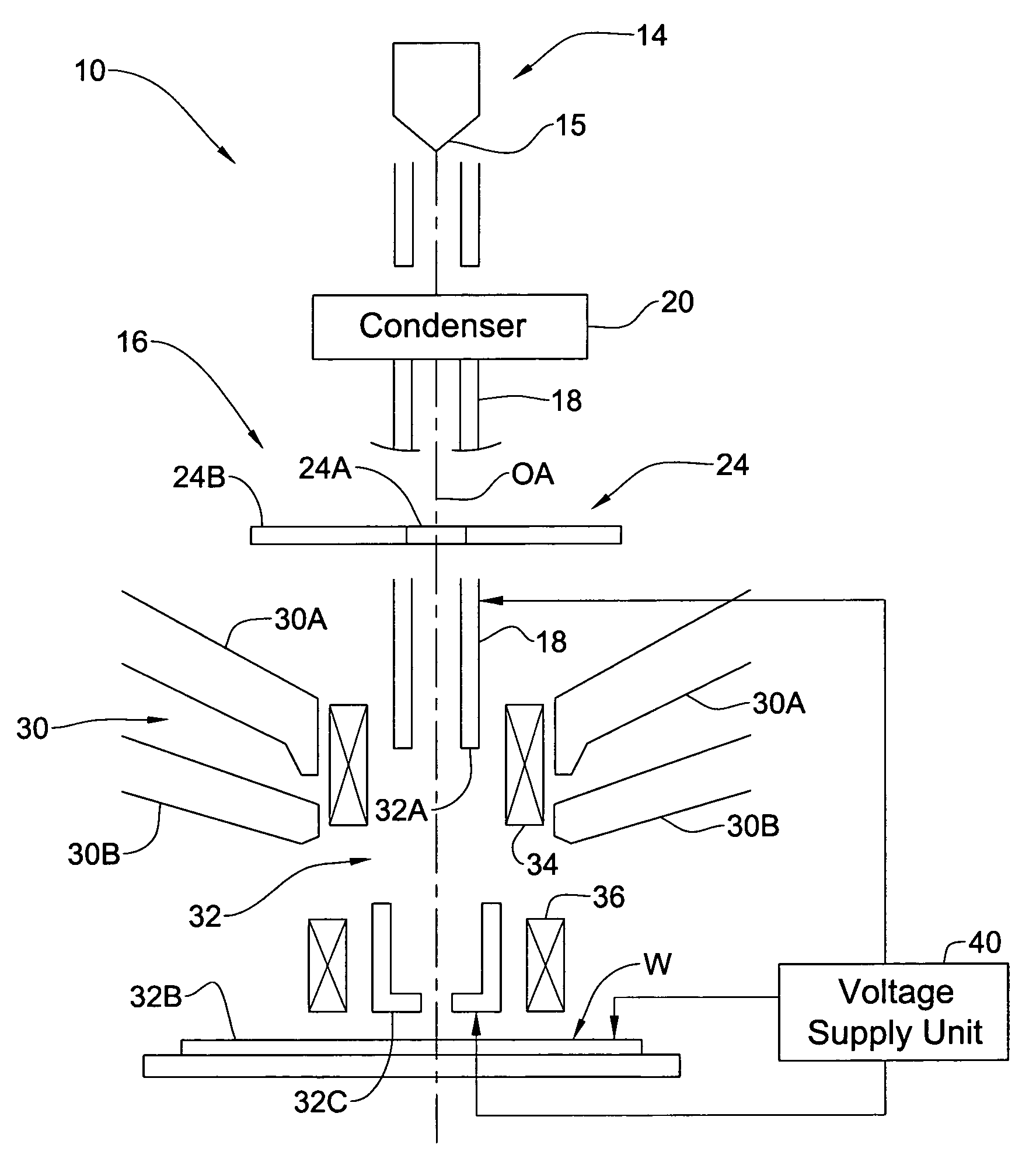
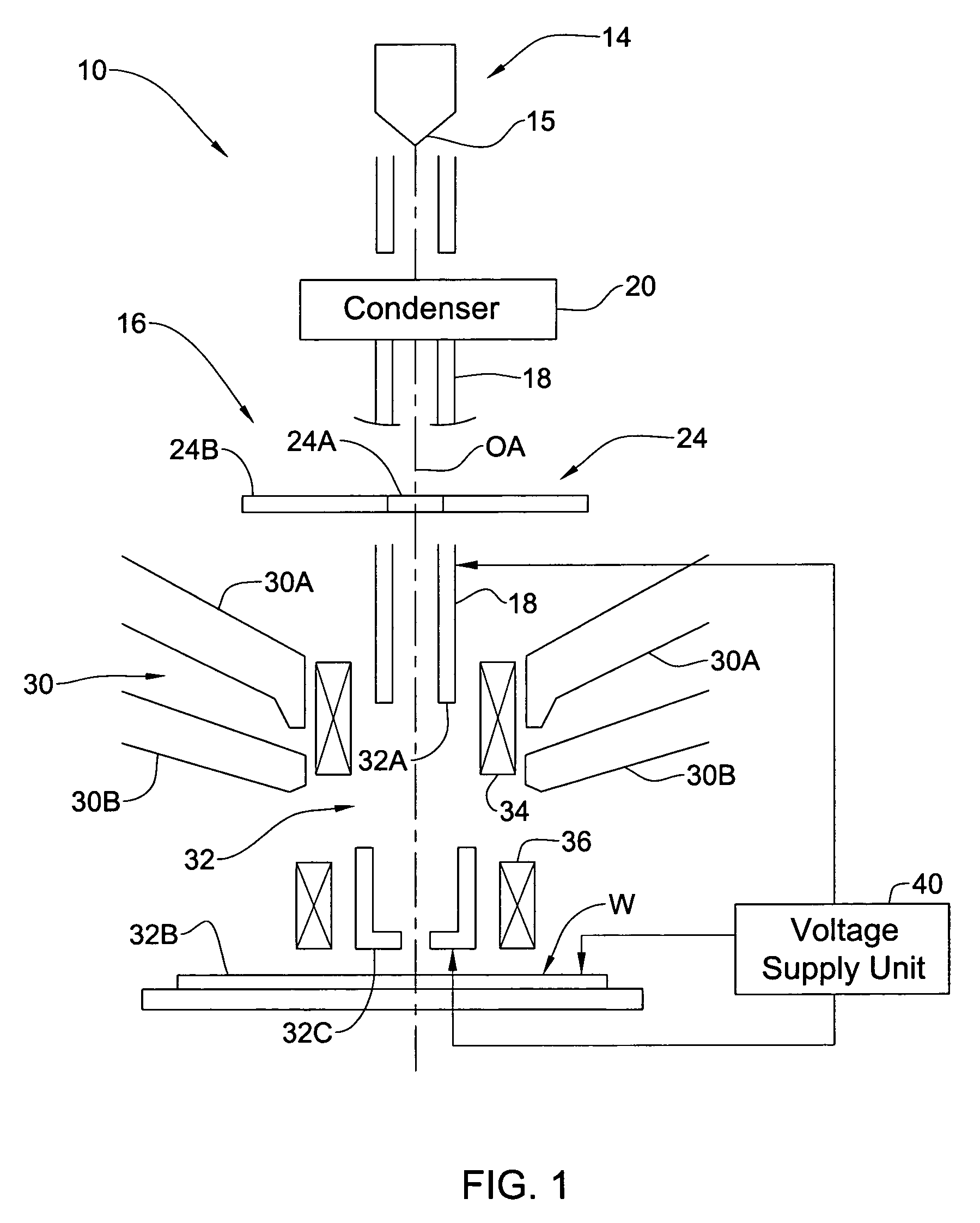
Patents
Literature
452 results about "Acceleration voltage" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
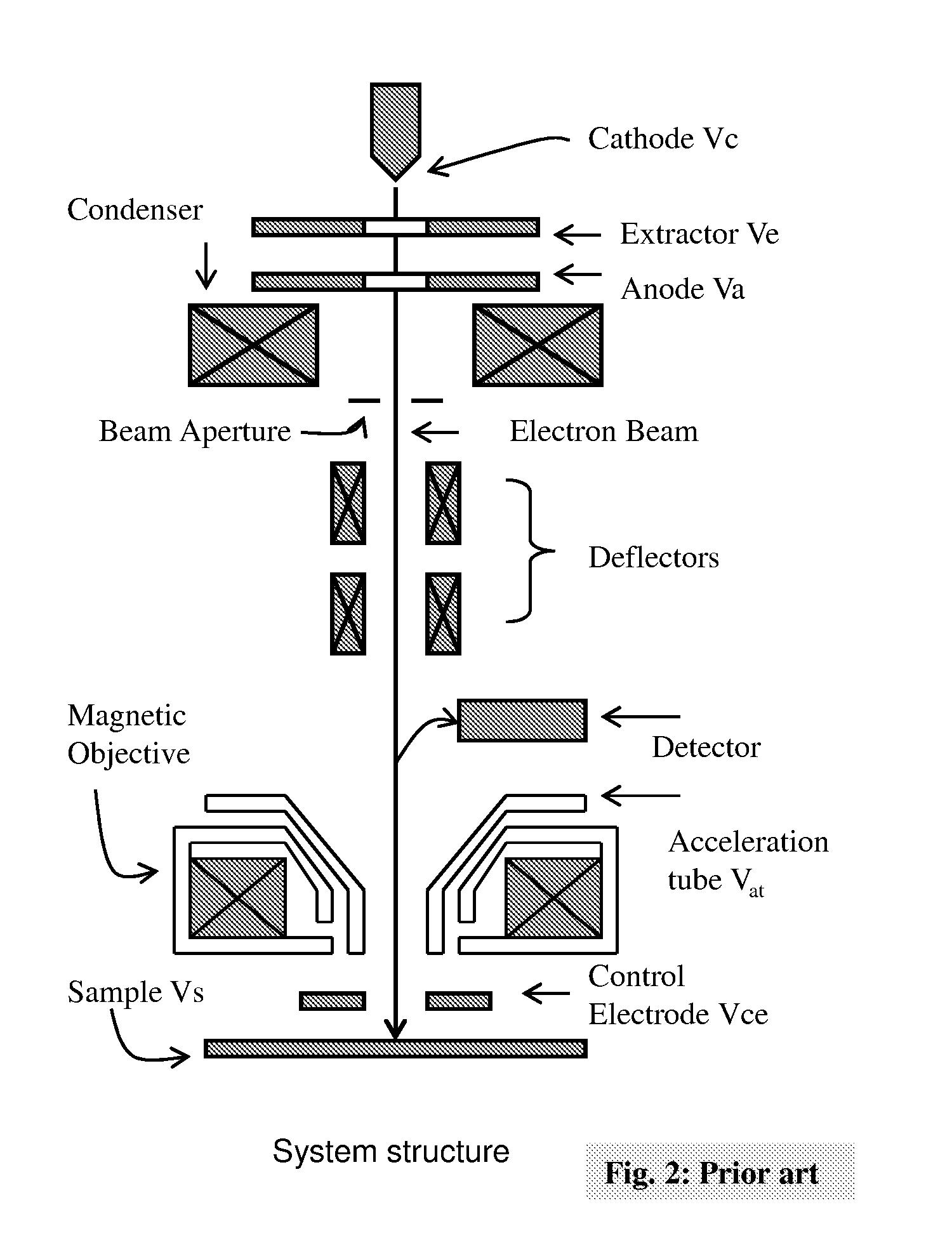
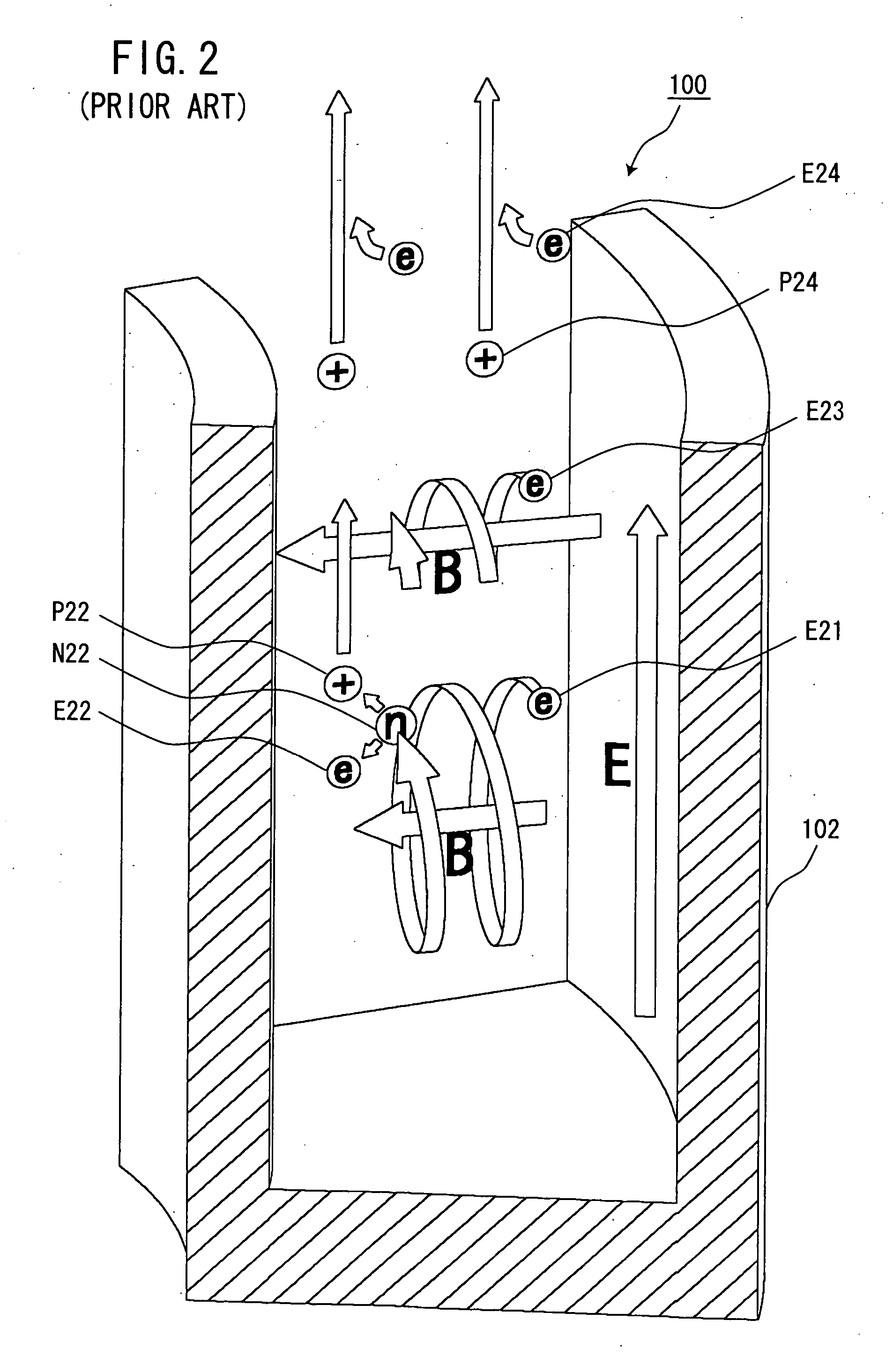
In accelerator physics, the term acceleration voltage means the effective voltage surpassed by a charged particle along a defined straight line. If not specified further, the term is likely to refer to the longitudinal effective acceleration voltage V∥. The acceleration voltage is an important quantity for the design of microwave cavities for particle accelerators. See also shunt impedance. For the special case of an electrostatic field that is surpassed by a particle, the acceleration voltage is directly given by integrating the electric field along its path.
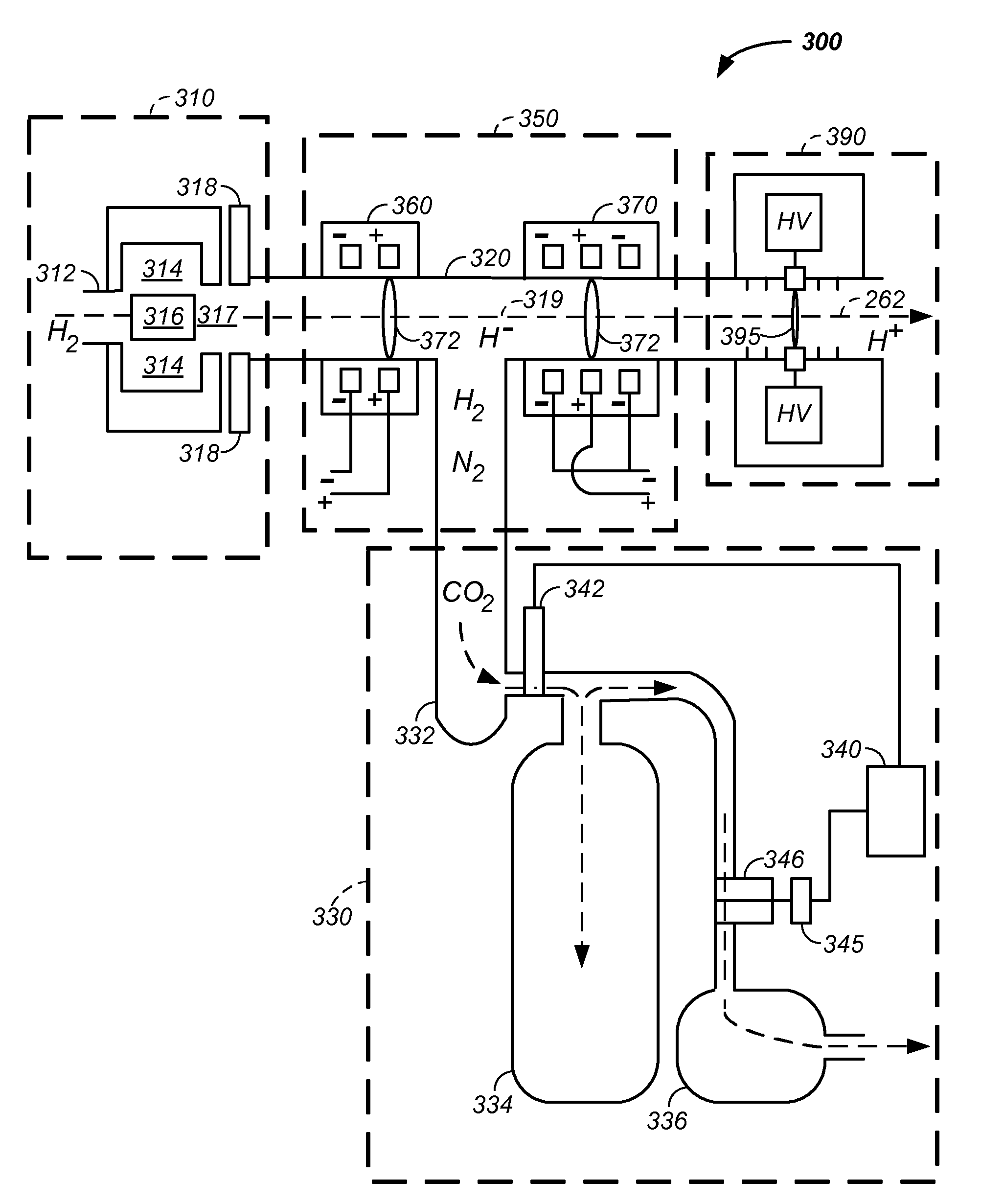
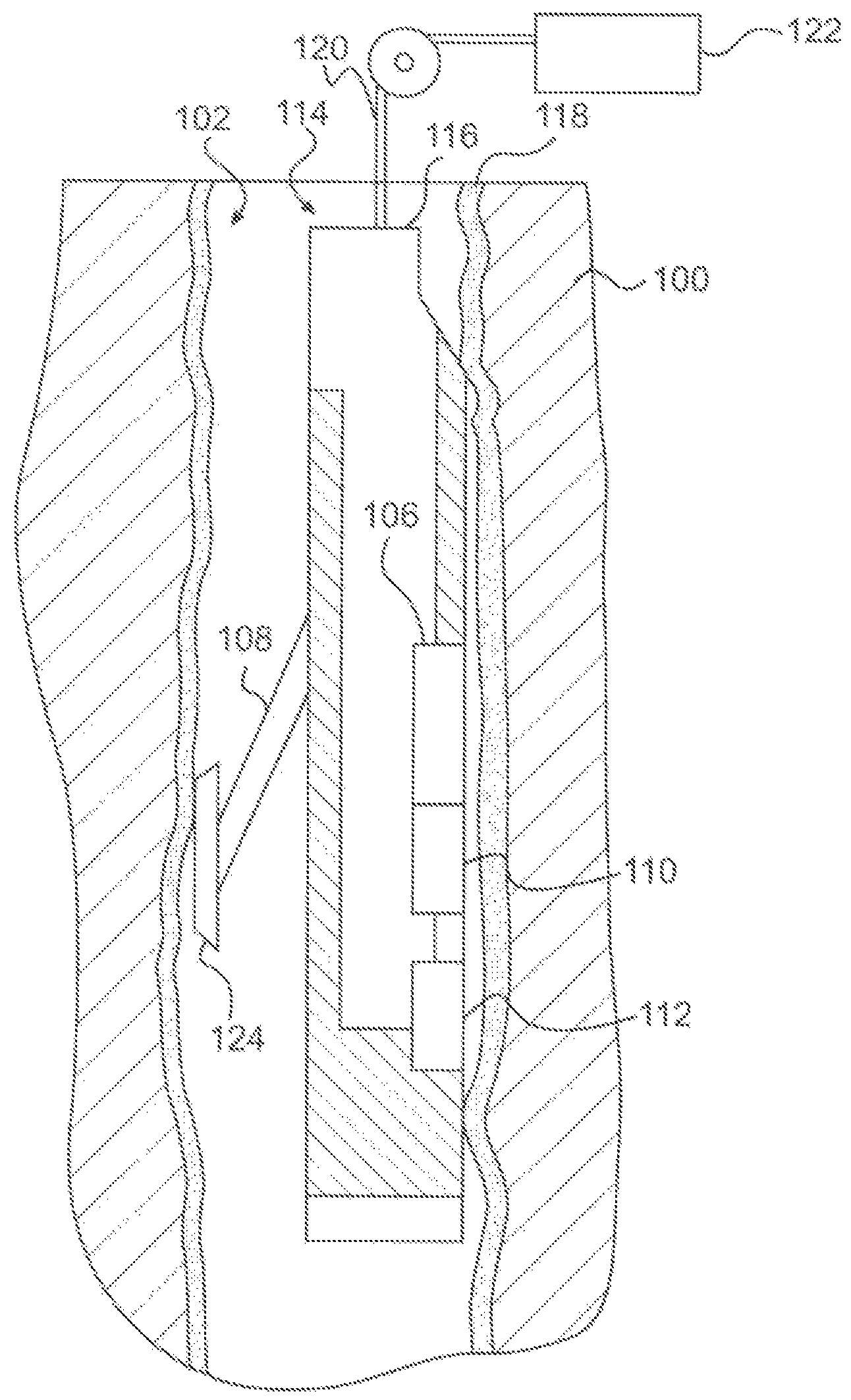
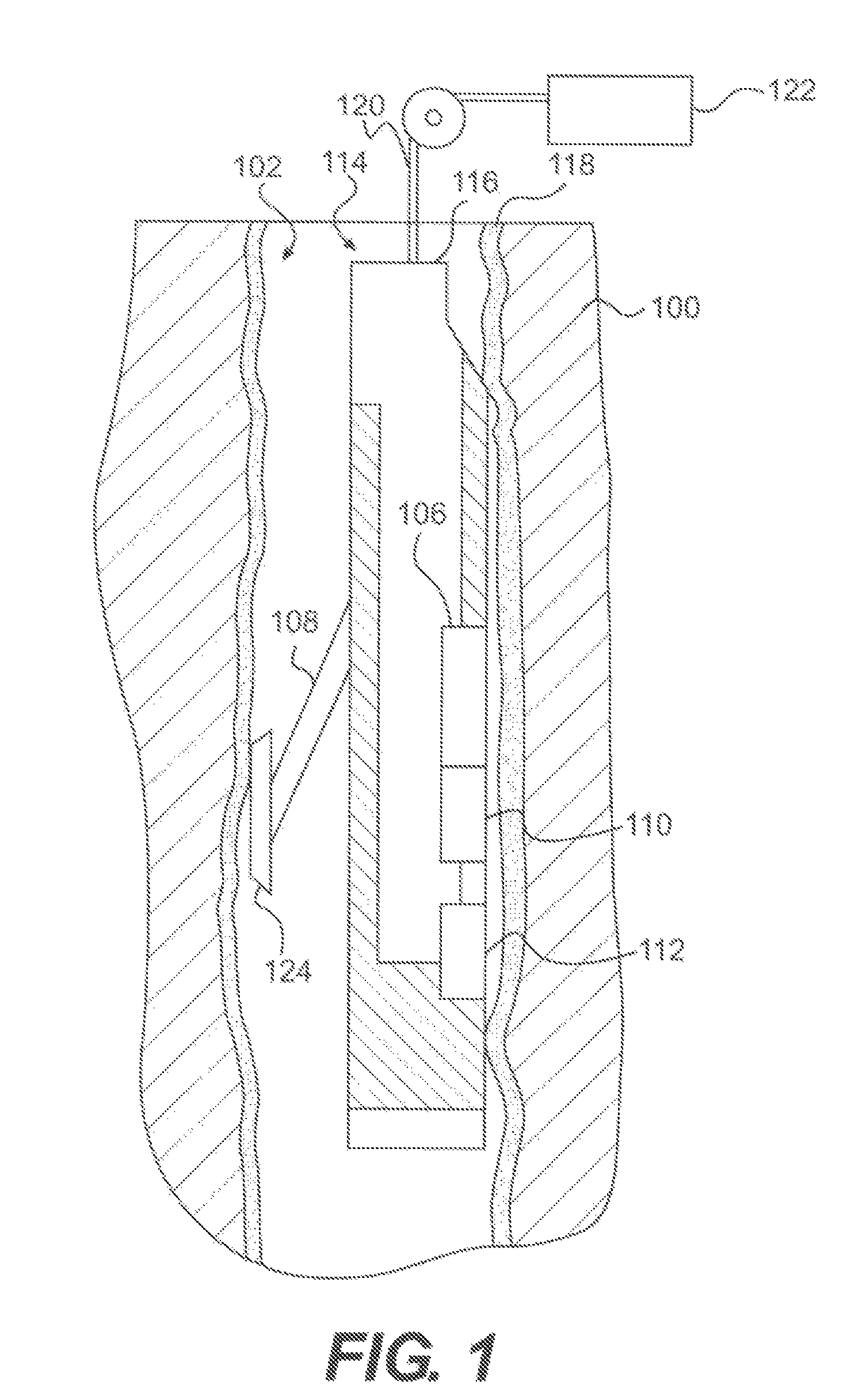
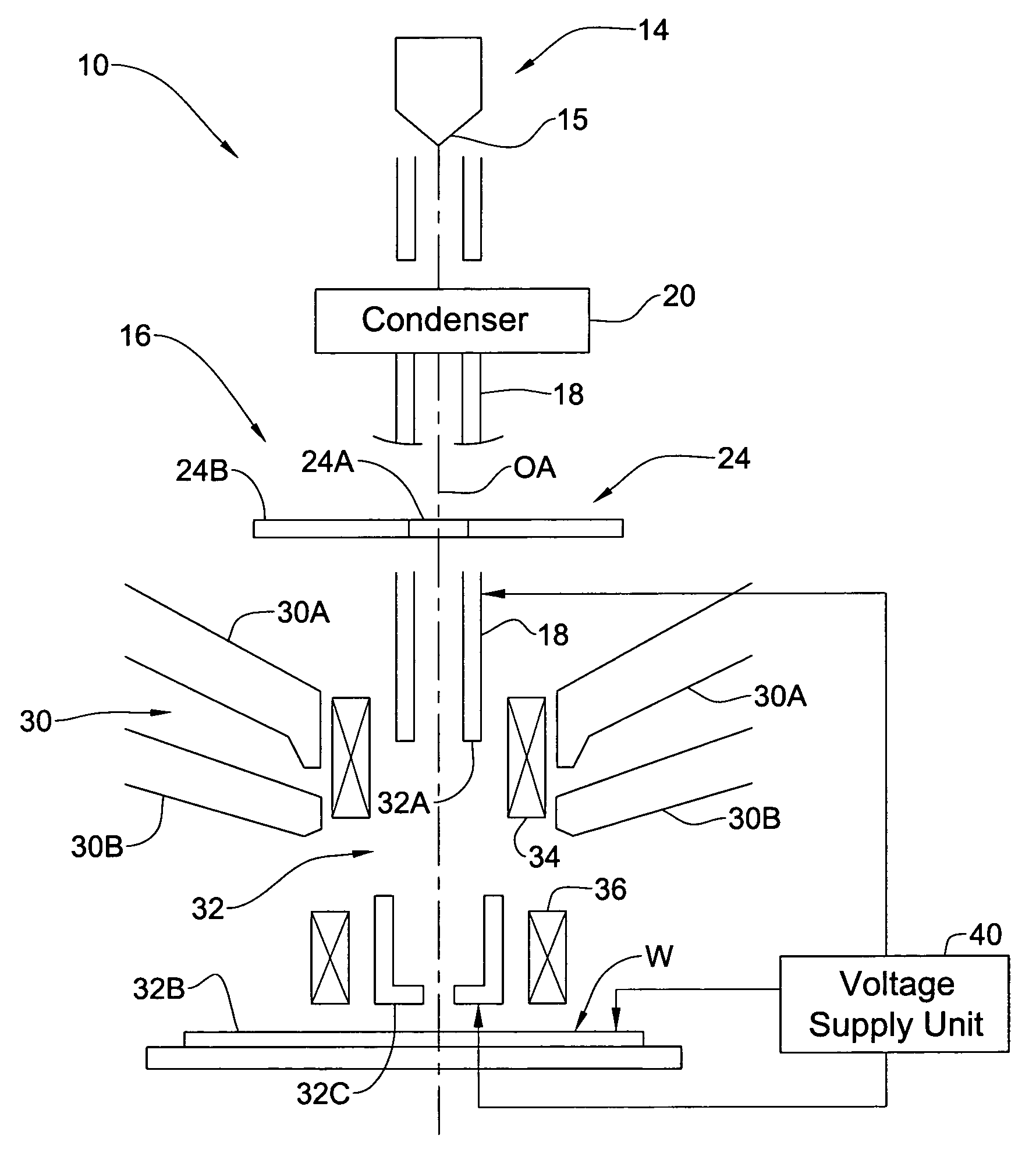
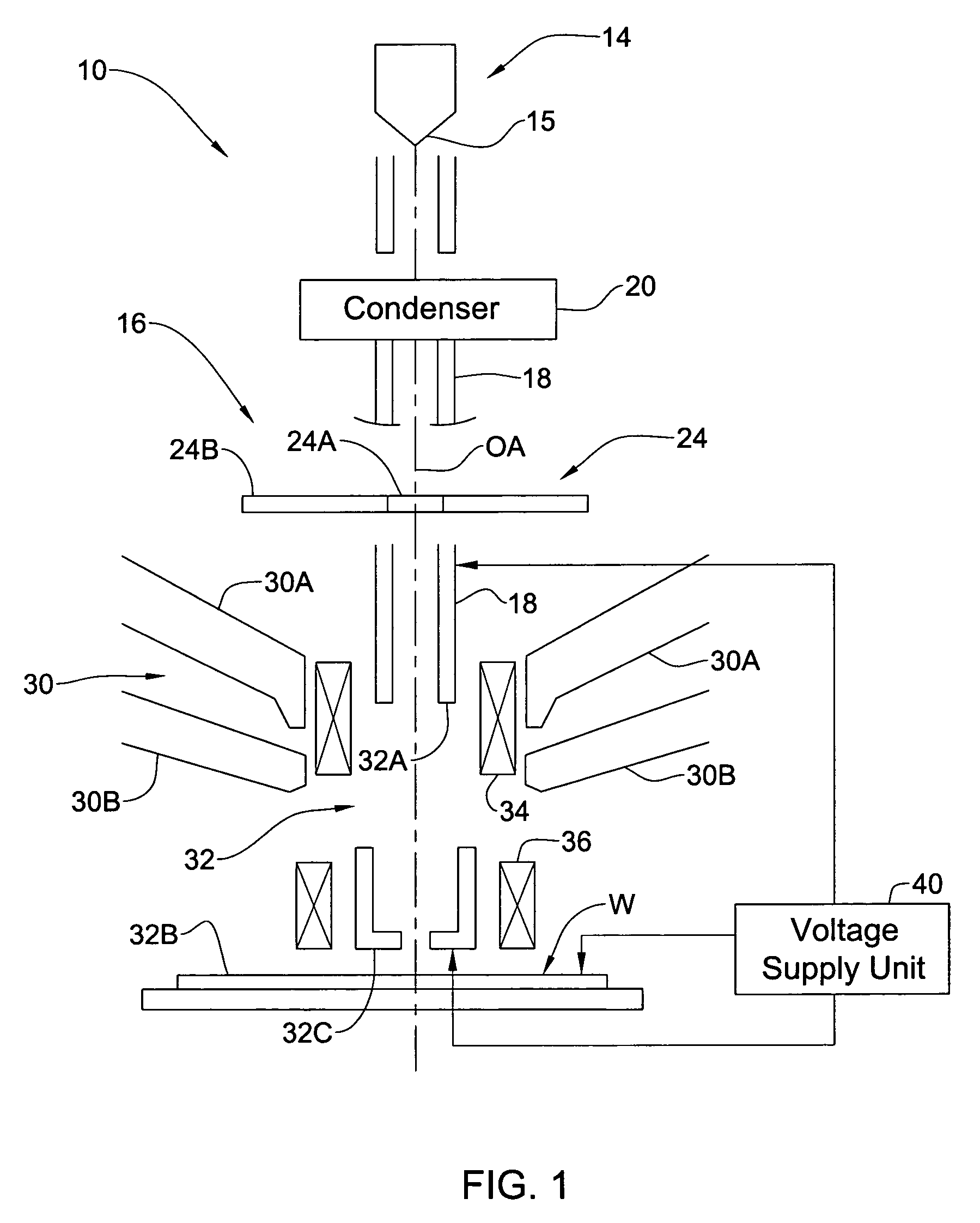
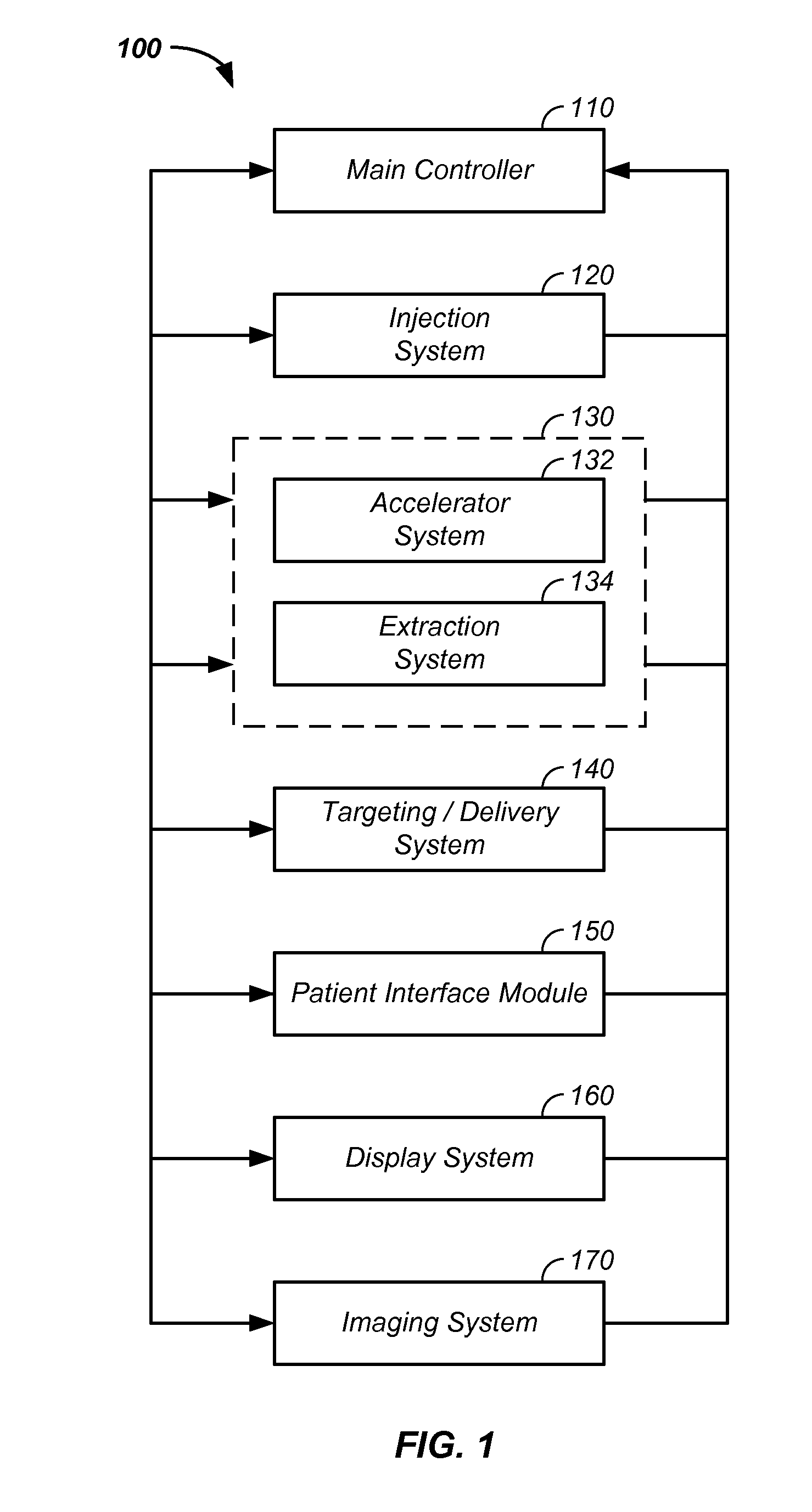
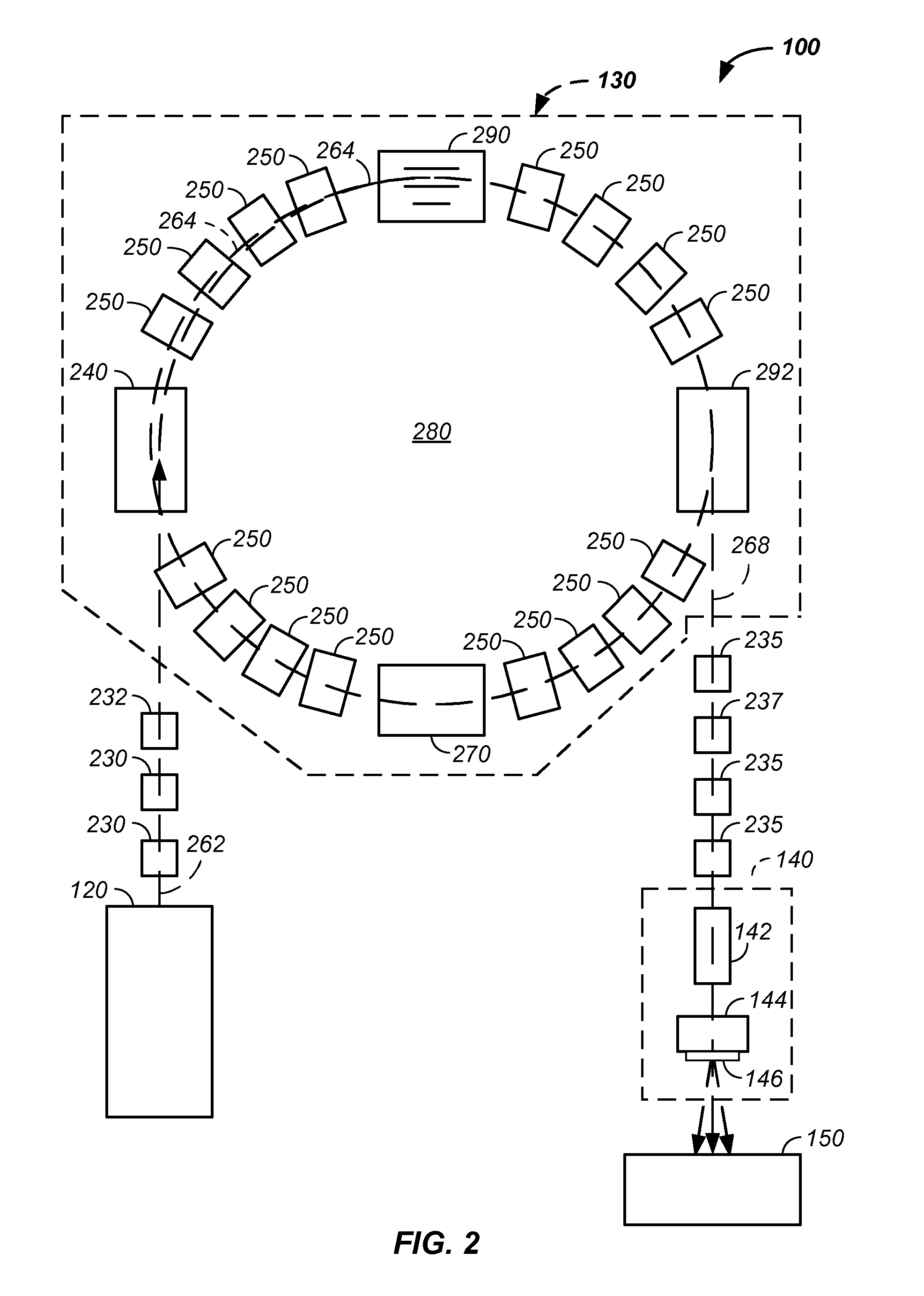
RF accelerator method and apparatus used in conjunction with a charged particle cancer therapy system
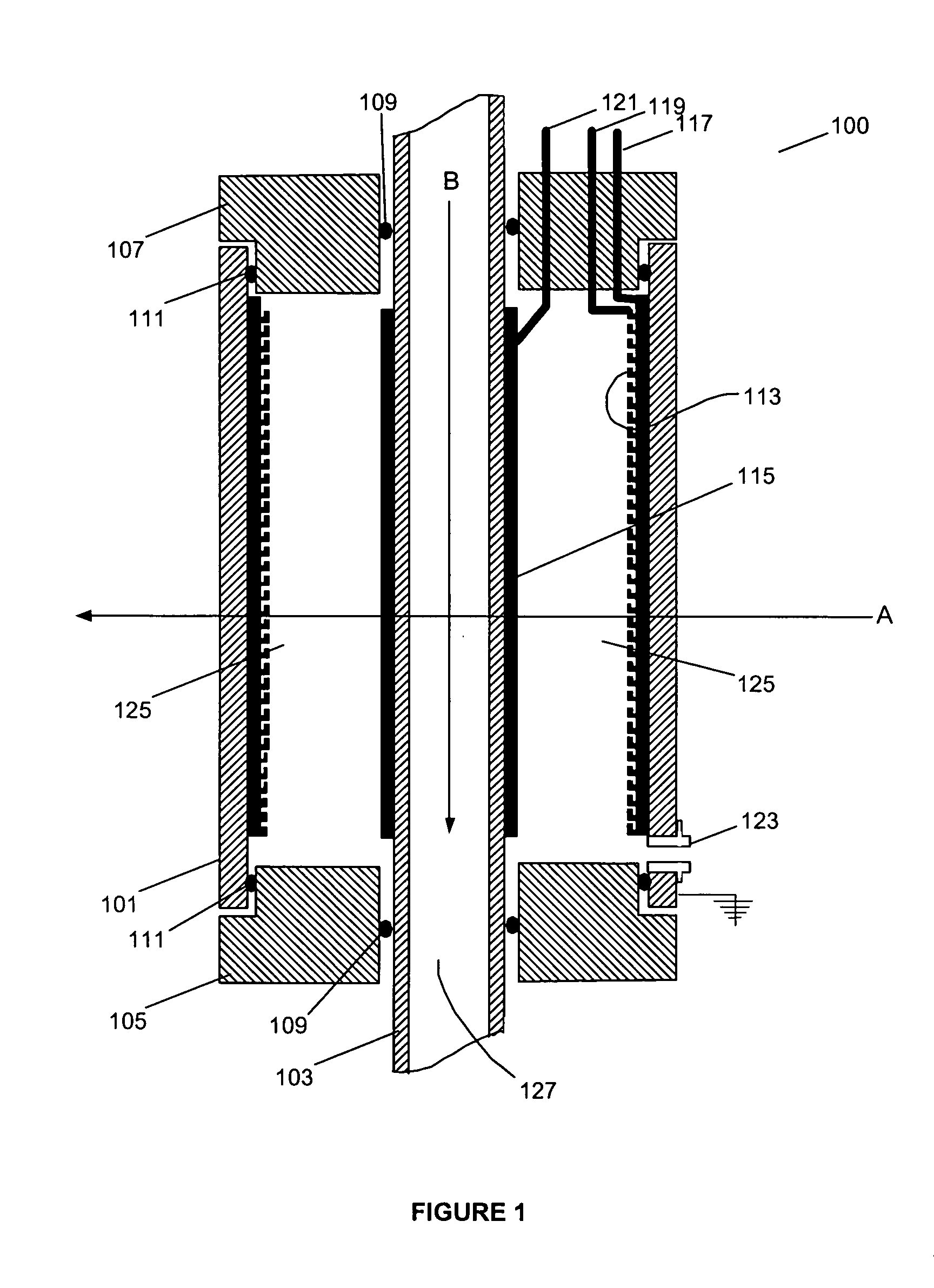
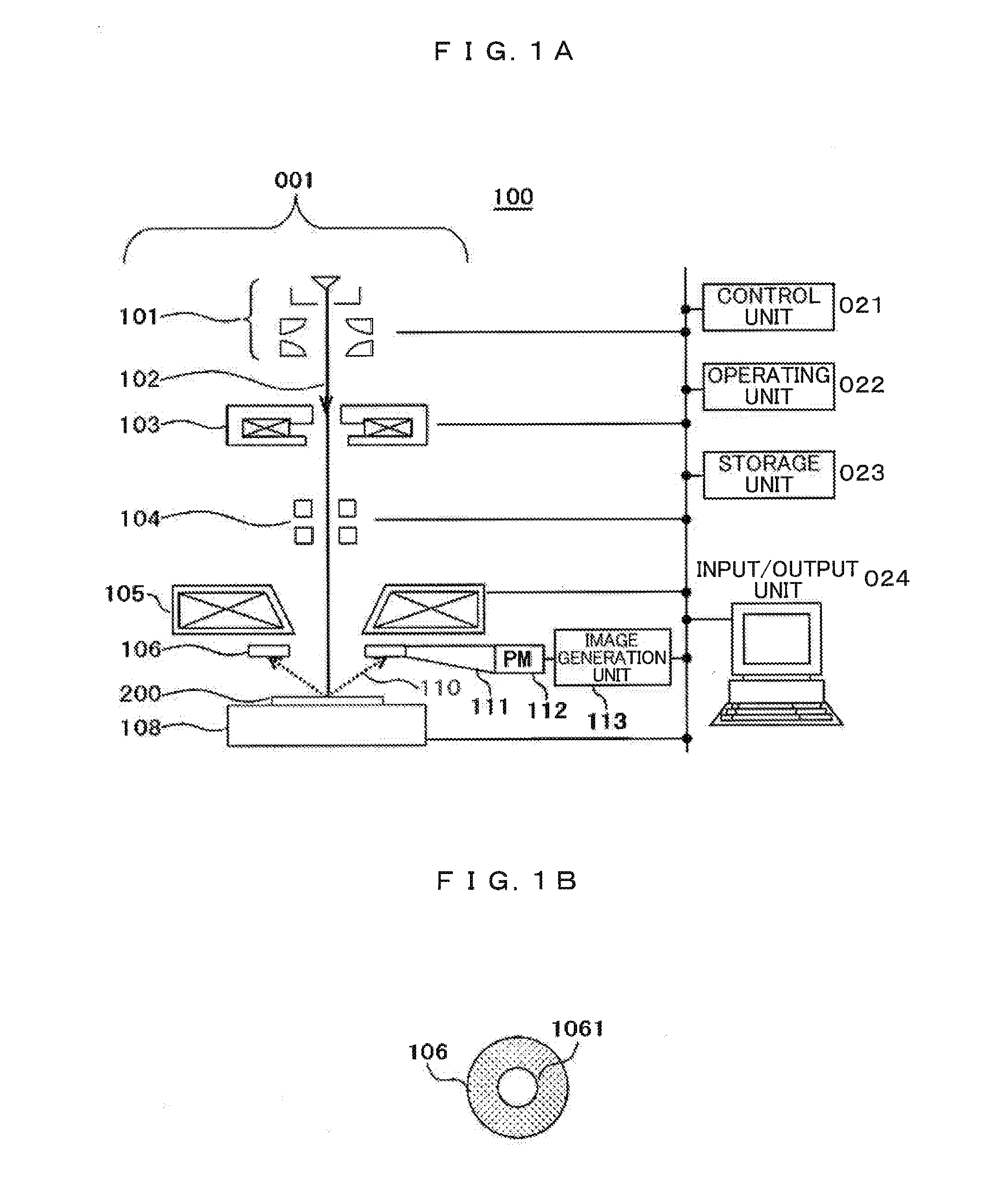
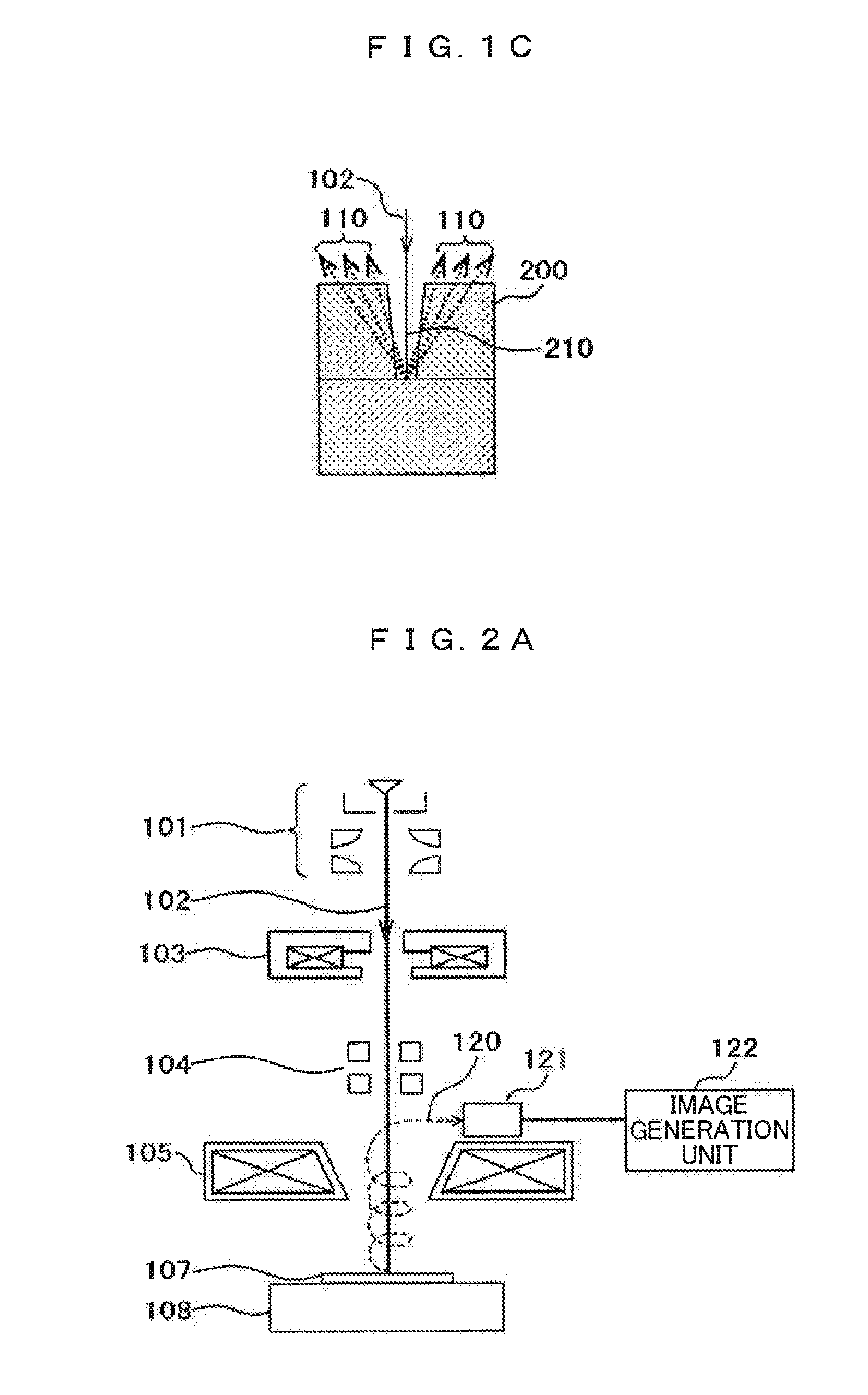
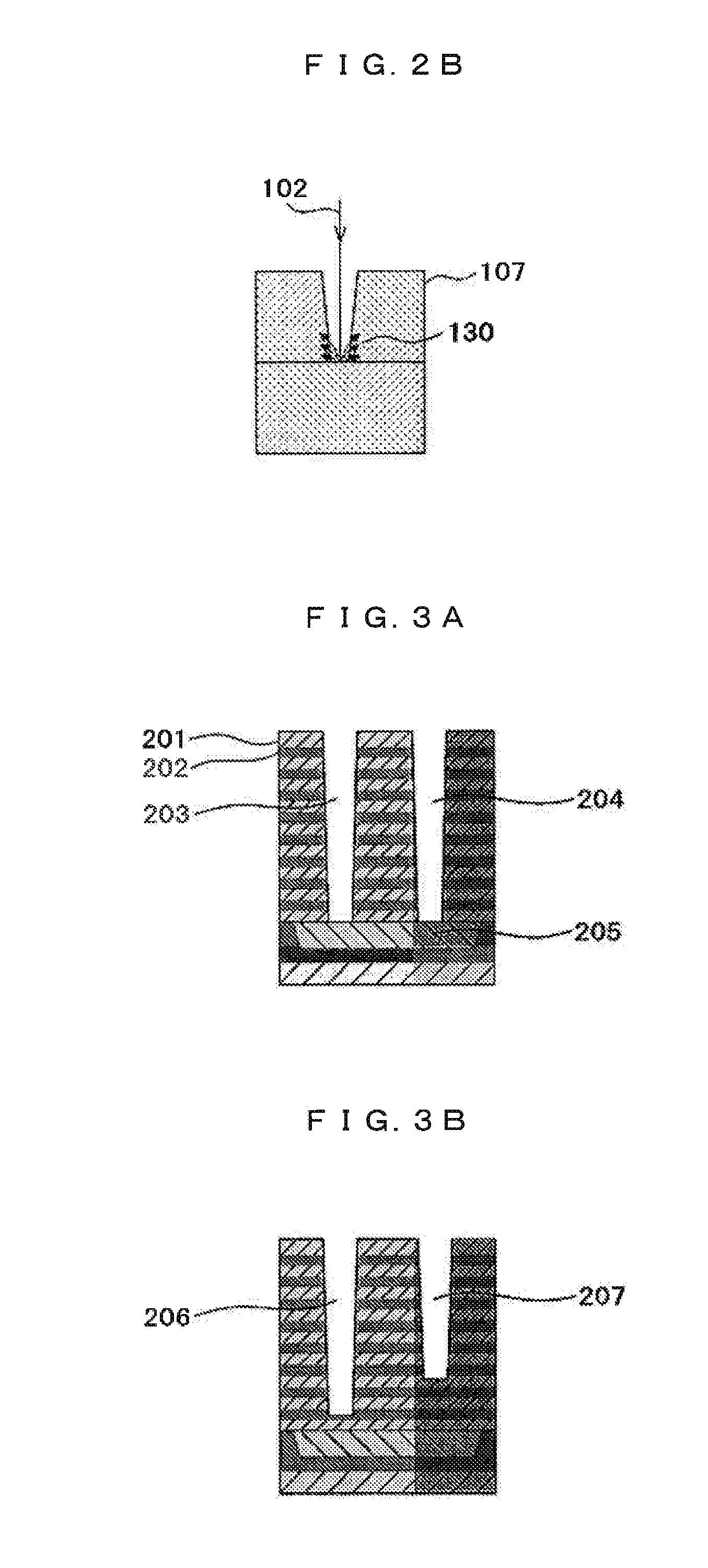
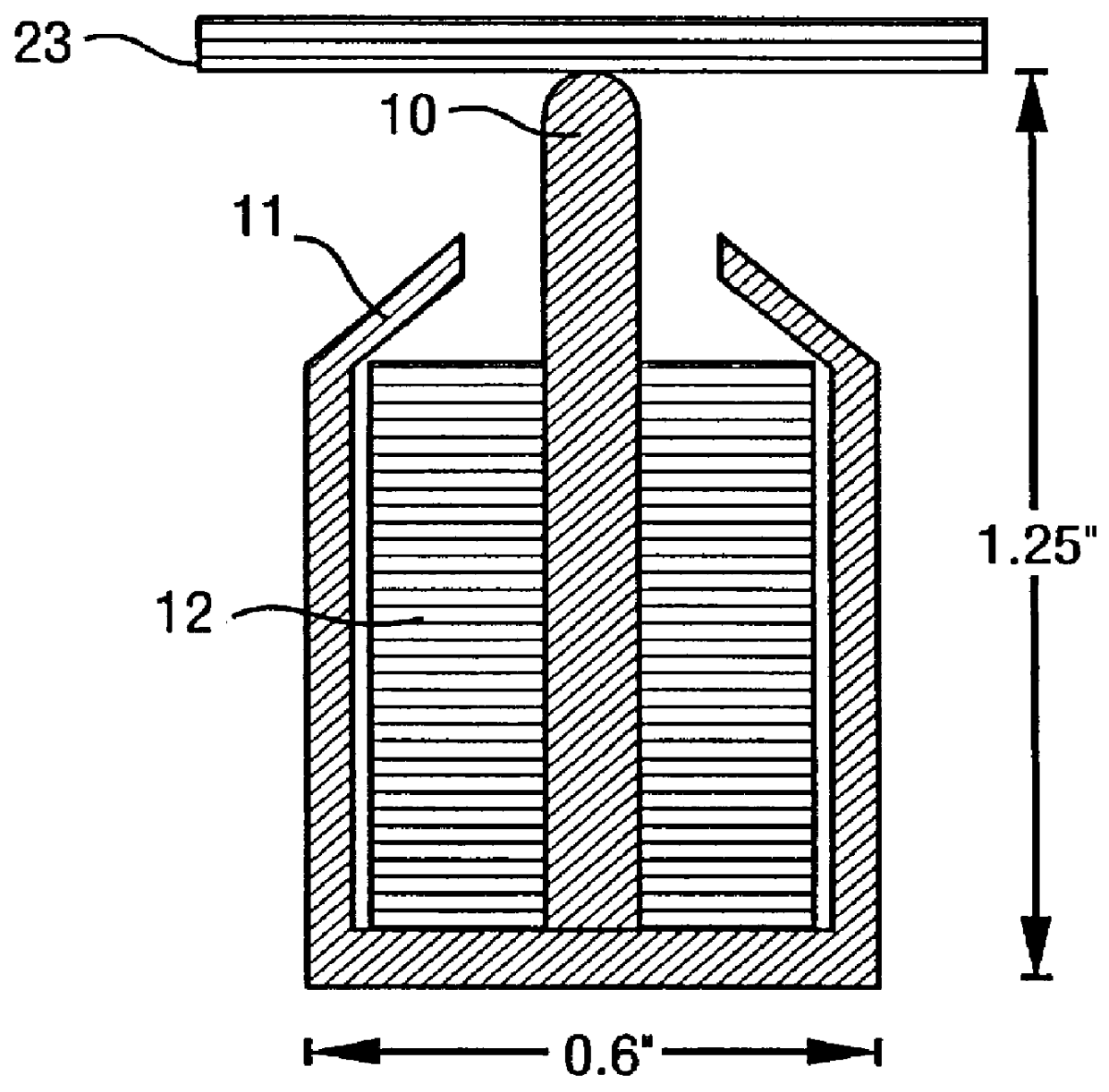
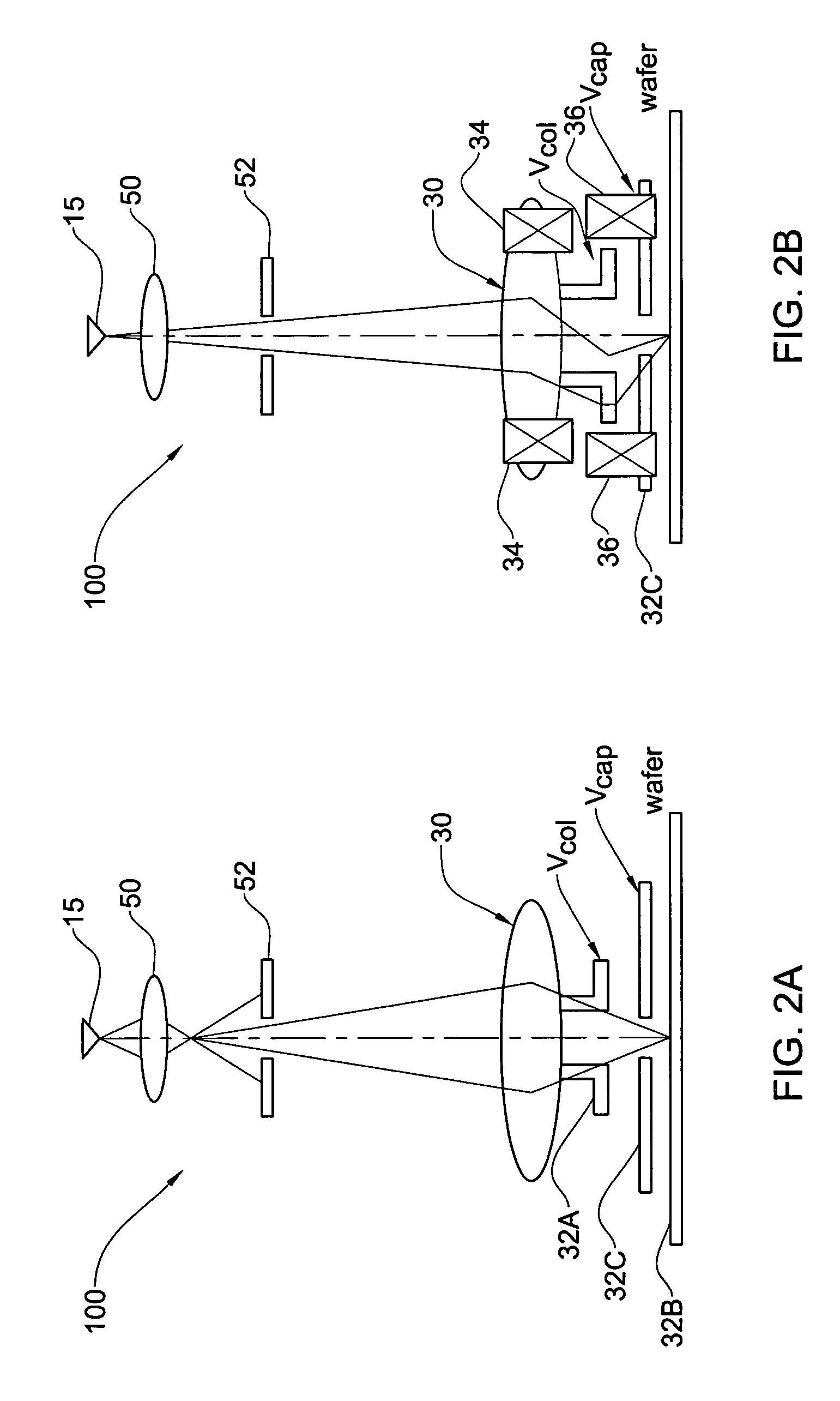
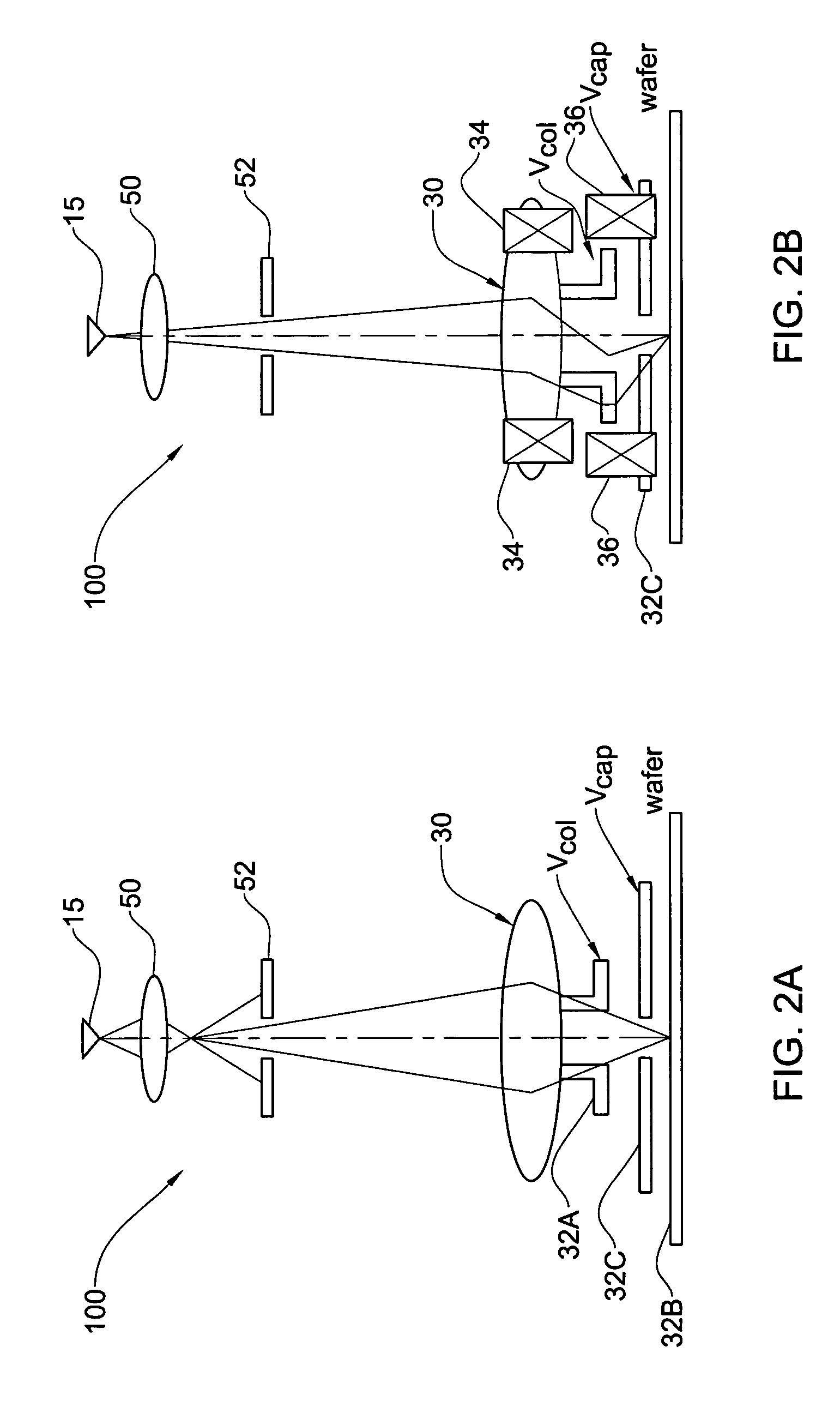
ActiveUS20100060209A1Stability-of-path spectrometersBeam/ray focussing/reflecting arrangementsLow voltageCharged particle radiotherapy
The invention comprises a radio-frequency accelerator method and apparatus used in conjunction with multi-axis charged particle radiation therapy of cancerous tumors. An RF synthesizer provides a low voltage RF signal, that is synchronized to the period of circulation of protons in the proton beam path, to a set of integrated microcircuits, loops, and coils where the coils circumferentially enclose the proton beam path in a synchrotron. The integrated components combine to provide an accelerating voltage to the protons in the proton beam path in a size compressed and price reduced format. The integrated RF-amplifier microcircuit / accelerating coil system is operable from about 1 MHz, for a low energy proton beam, to about 15 MHz, for a high energy proton beam.
Owner:BALAKIN ANDREY VLADIMIROVICH +1
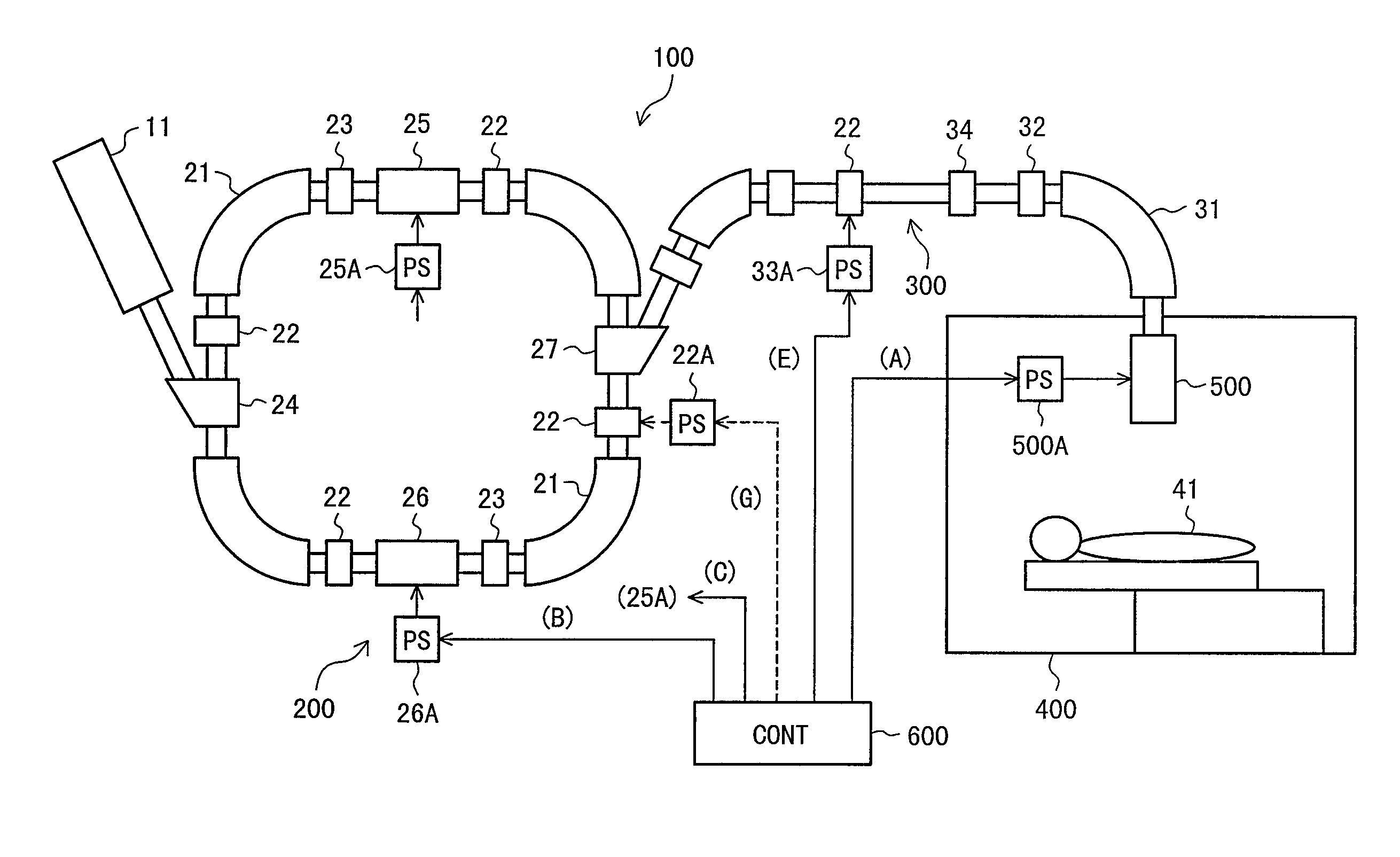
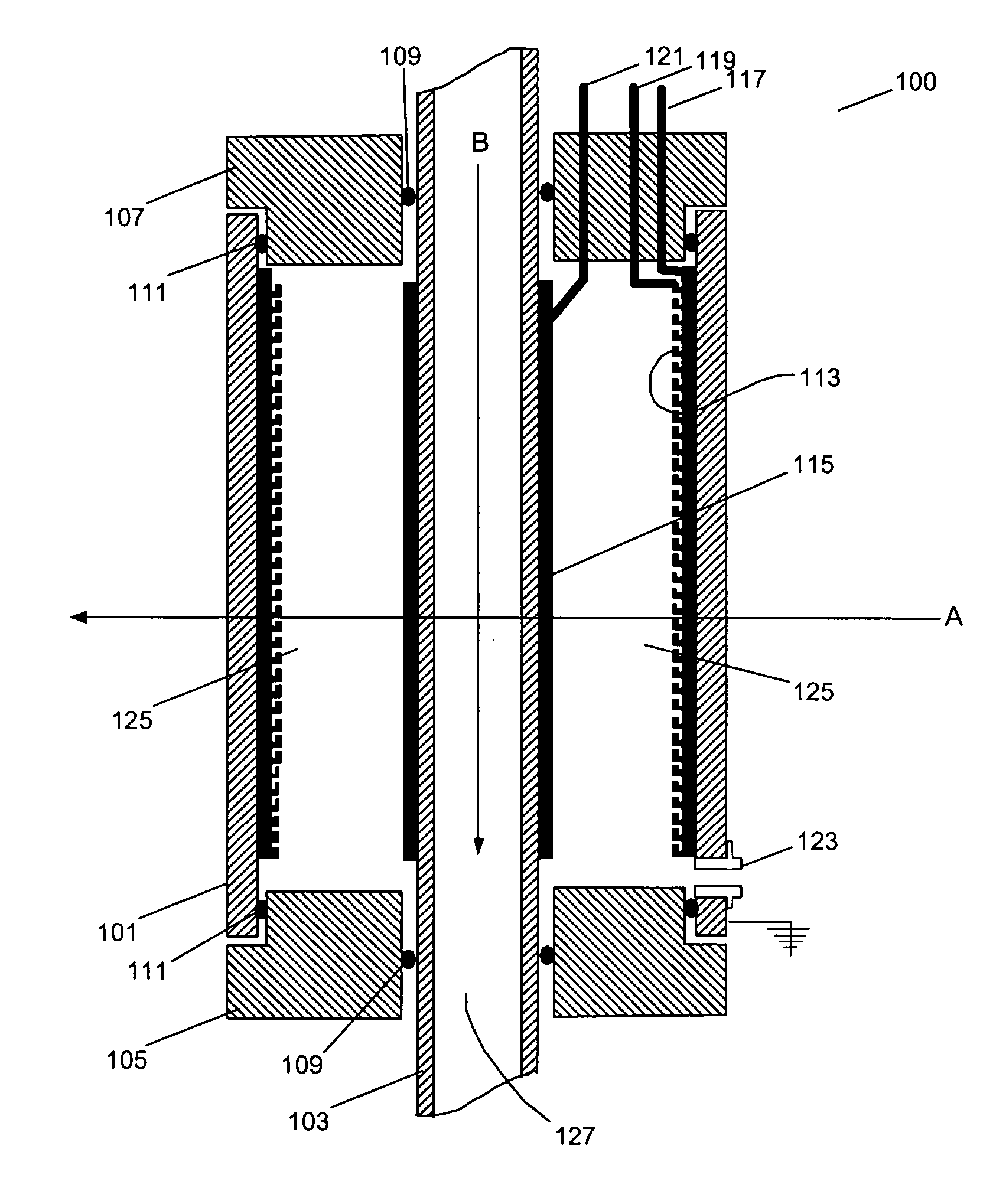
Particle beam therapy system
ActiveUS7772577B2Quality improvementLow costElectrode and associated part arrangementsMaterial analysis by optical meansTransport systemSynchrotron
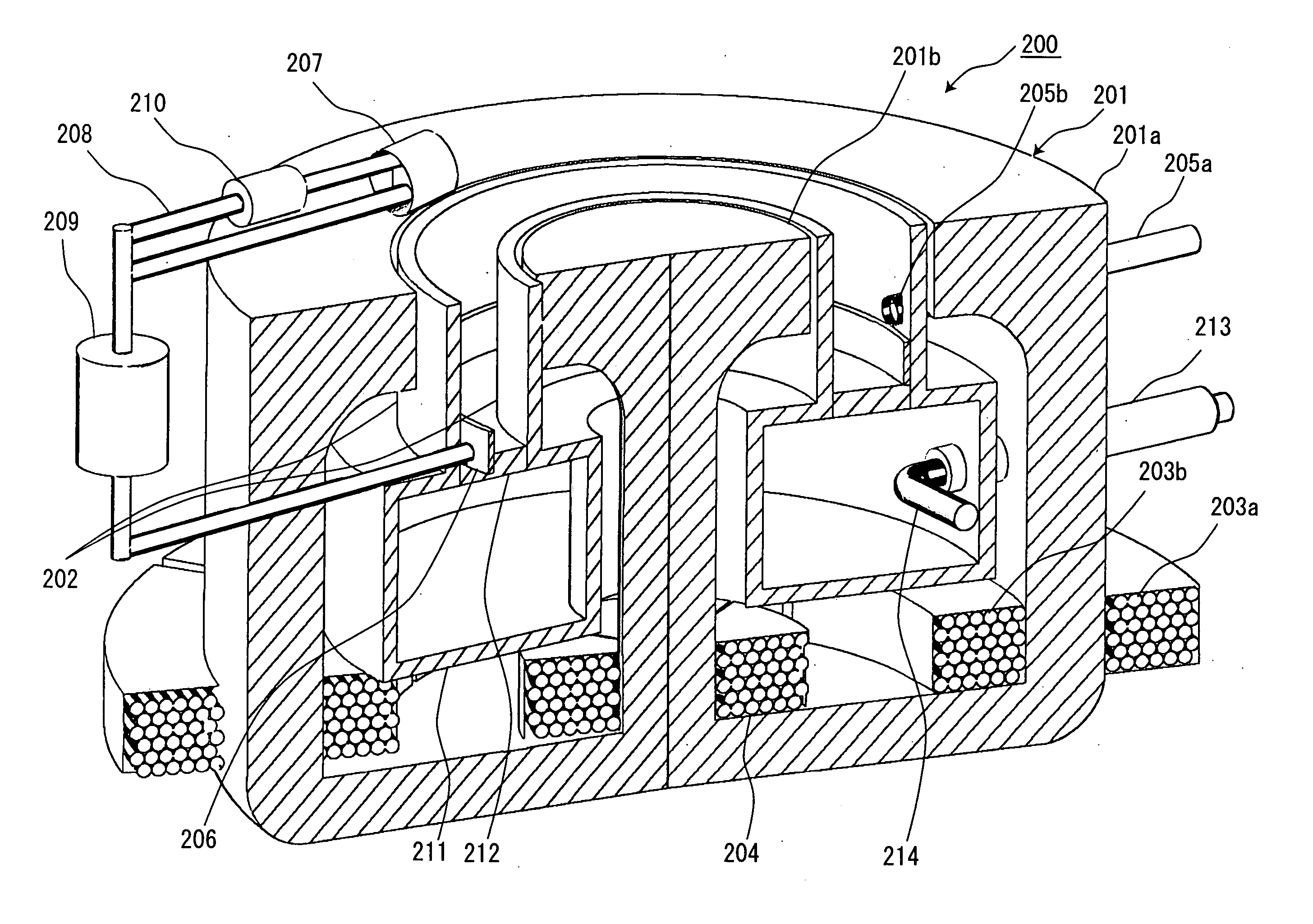
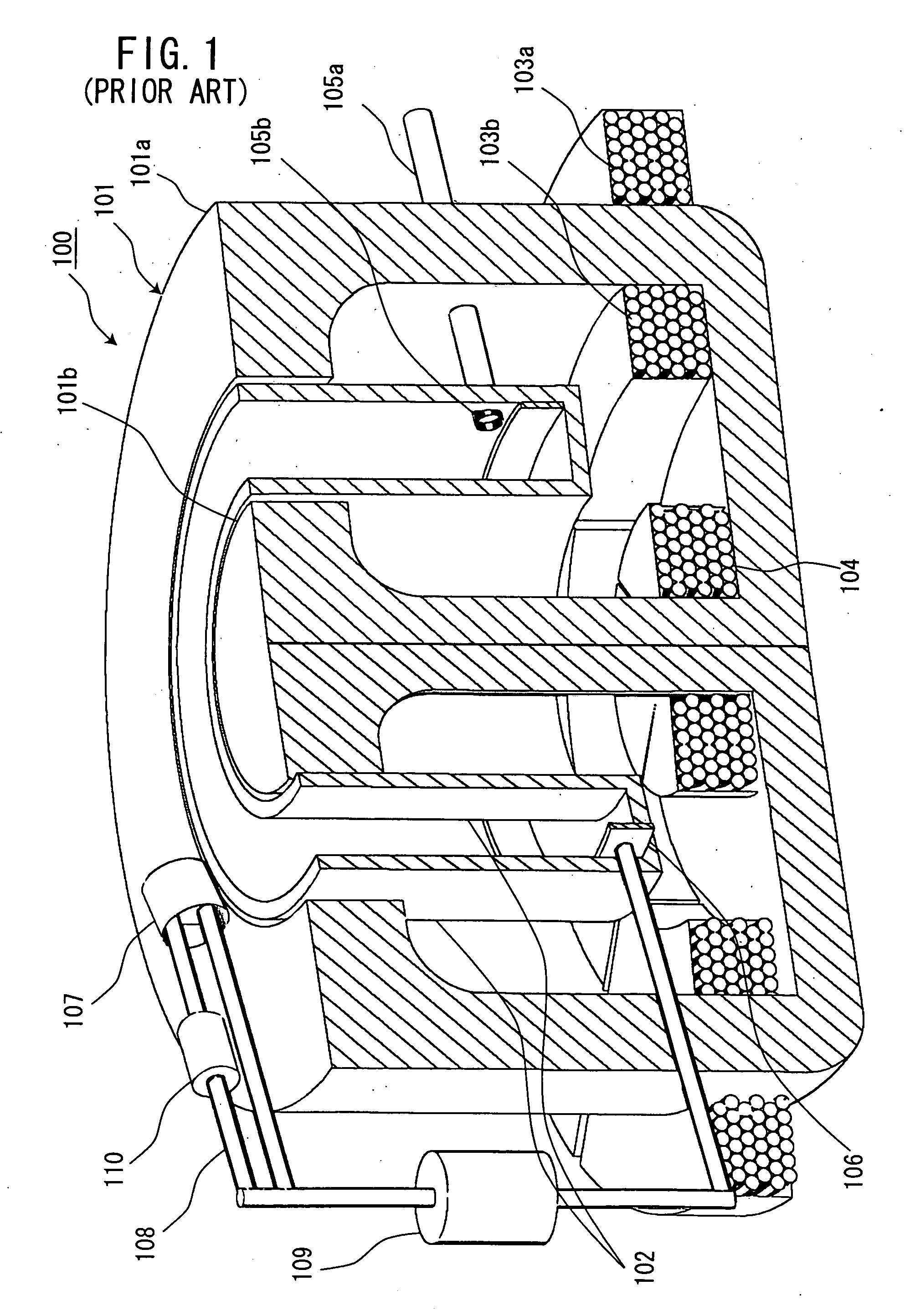
A particle beam therapy system using a spot scanning method includes a synchrotron, a beam transport system, an irradiation system, and a controller. A controller is configured to turn on a radio frequency electromagnetic field to be applied to an extraction system when a charged particle beam is to be supplied to the irradiation system, and turn off the radio frequency electromagnetic field to be applied to the extraction system when the supply of the charged particle beam to the irradiation system is to be blocked by means of an electromagnet provided in the beam transport system or in the synchrotron. The controller is also adapted to turn off a radio frequency acceleration voltage to be applied to an acceleration cavity in synchronization with the turning-off of the radio frequency electromagnetic field to be applied to the extraction device.
Owner:HITACHI LTD
Bio electron microscope and observation method of specimen
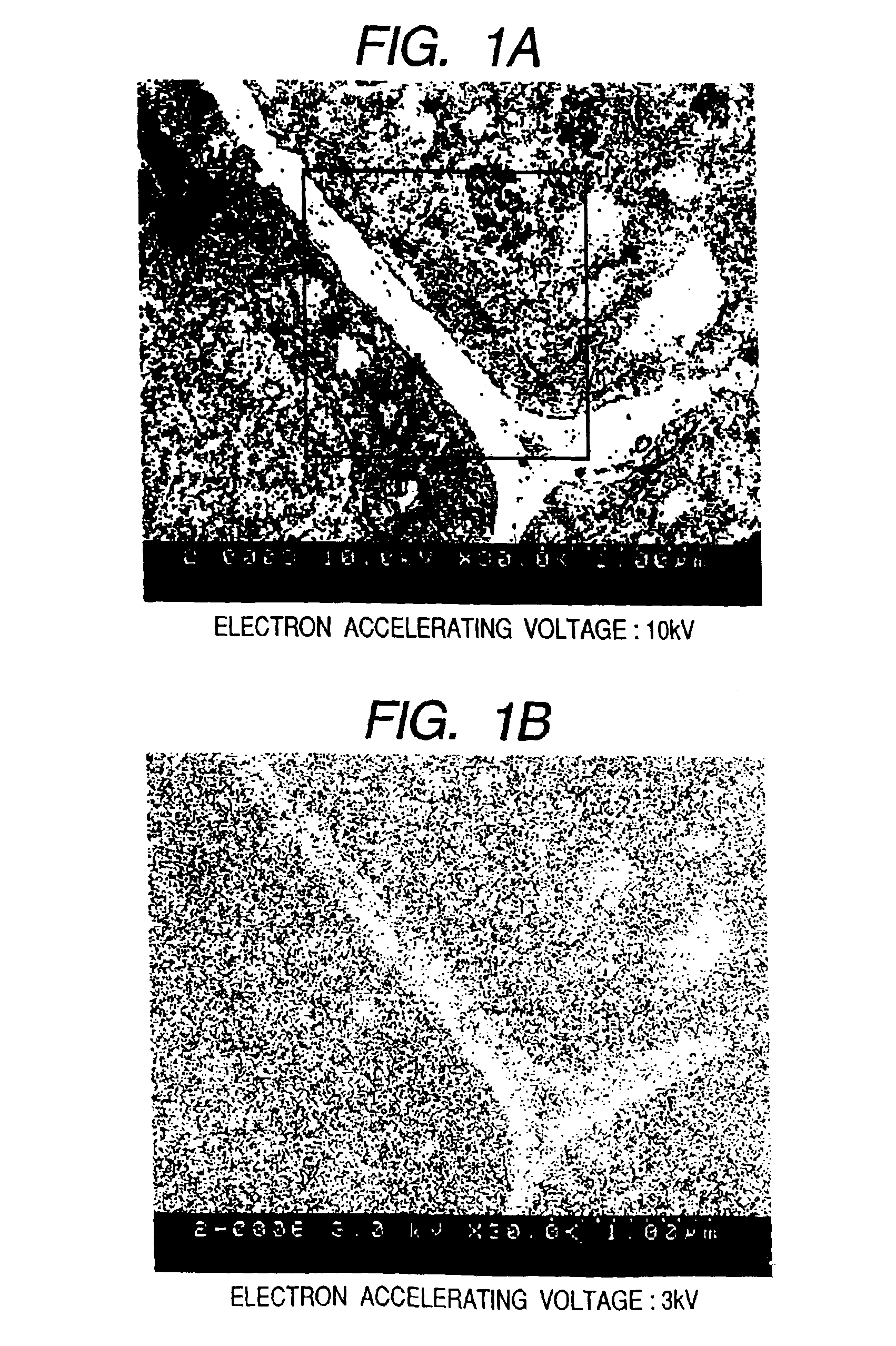
InactiveUS6875984B2Reduce harmHigh-accuracy image analysisEnergy spectrometersPreparing sample for investigationScanning electron microscopeAcceleration voltage
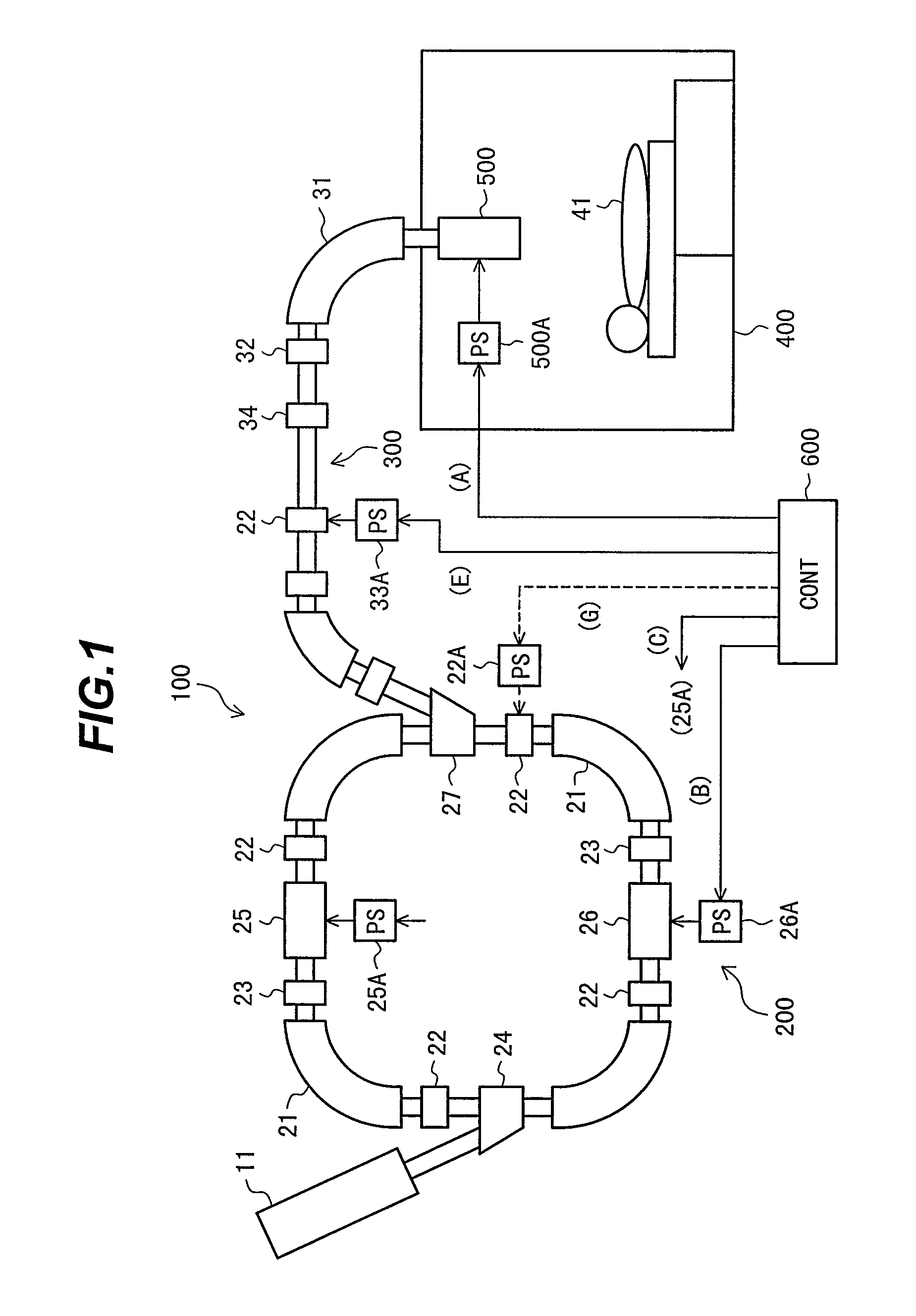
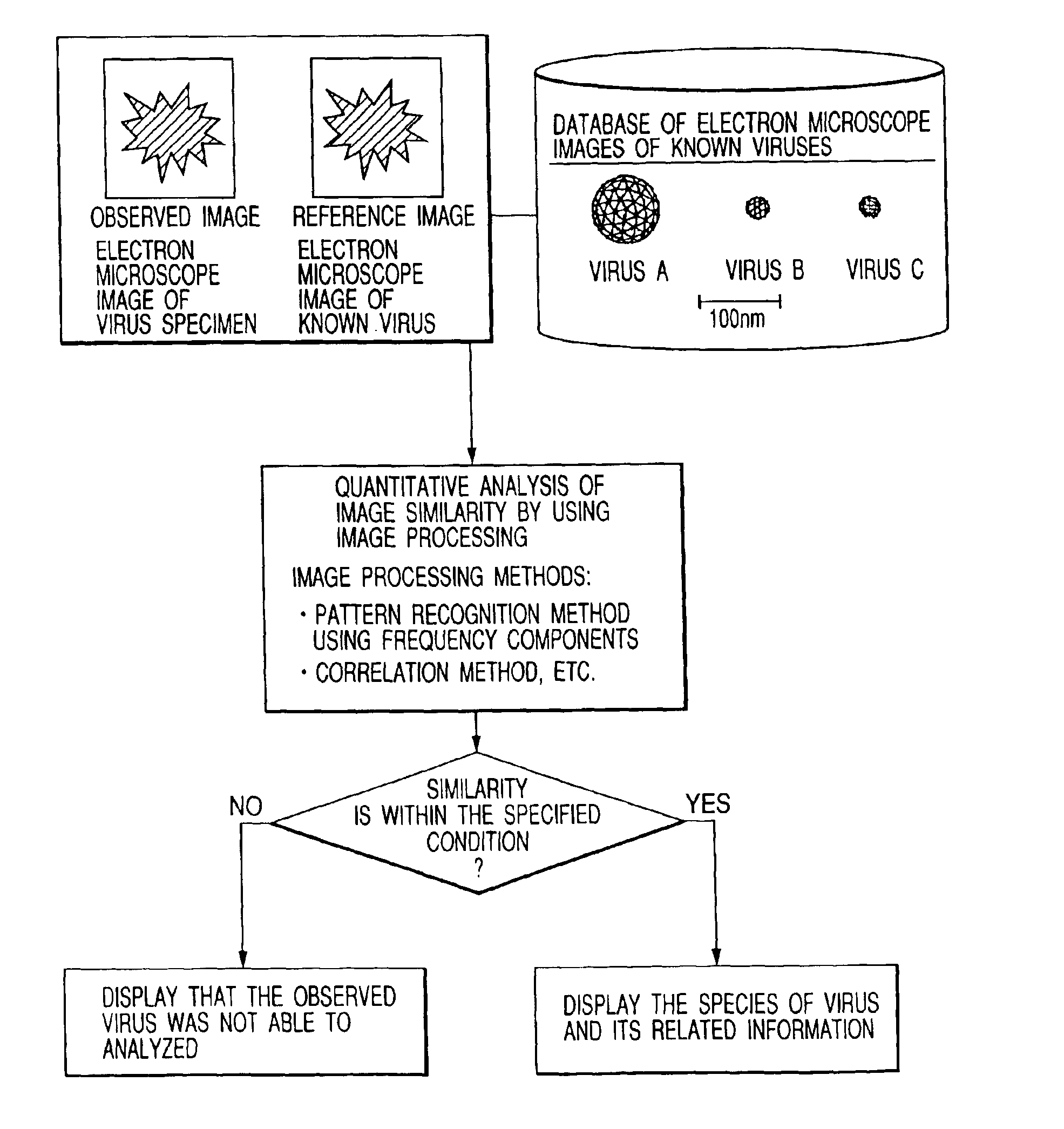
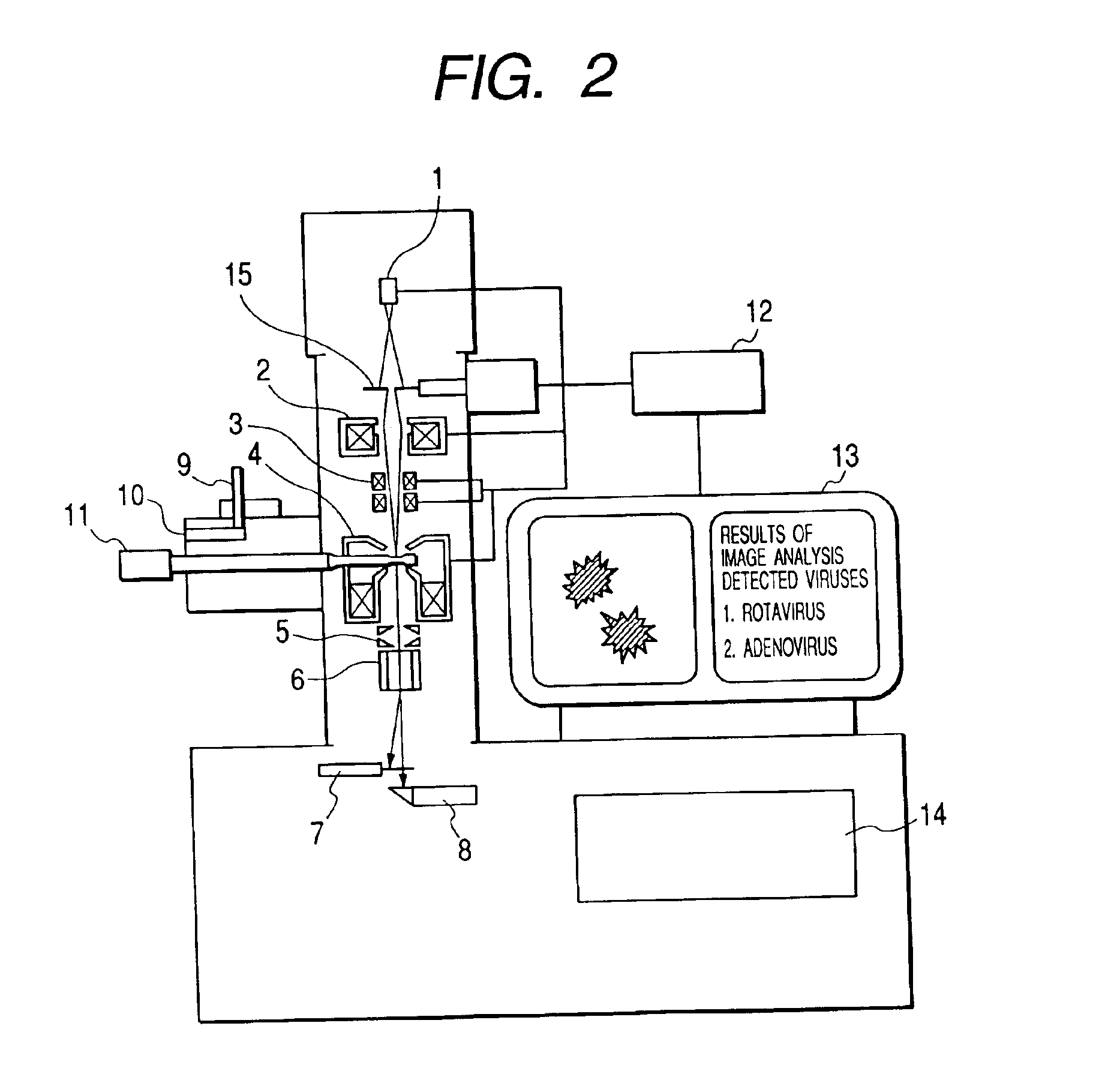
A bio electron microscope and an observation method which can observe a bio specimen by low damage and high contrast to perform high-accuracy image analysis, and conduct high-throughput specimen preparation. 1) A specimen is observed at an accelerating voltage 1.2 to 4.2 times a critical electron accelerating voltage possible to transmit a specimen obtained under predetermined conditions. 2) An electron energy filter of small and simplified construction is provided between the specimen and an electron detector for imaging by the electron beam in a specified energy region of the electron beams transmitting the specimen. 3) Similarity between an observed image such as virus or protein in the specimen and a reference image such as known virus or protein is subjected to quantitative analysis by image processing. 4) A preparation protocol of the bio specimen is made into a chip using an MEMS technique, which is then mounted on a specimen stage part of an electron microscope to conduct specimen introduction, preparation and transfer onto a specimen holder.
Owner:HITACHI HIGH-TECH CORP +1
High voltage x-ray generator and related oil well formation analysis apparatus and method
ActiveUS7564948B2X-ray tube electrodesCathode ray concentrating/focusing/directingSoft x rayAcceleration voltage
Owner:SCHLUMBERGER TECH CORP
X-ray source with nonparallel geometry
InactiveUS20050276382A1Minimize electron electron energyMinimize loss energy lossX-ray tube electrodesX-ray tube vessels/containerSoft x rayX-ray
An improved x-ray generation system produces a converging or diverging radiation pattern particularly suited for substantially cylindrical or spherical treatment devices. In an embodiment, the system comprises a closed or concave outer wall about a closed or concave inner wall. An electron emitter is situated on the inside surface of the outer wall, while a target film is situated on the outside surface of the inner wall. An extraction voltage at the emitter extracts electrons which are accelerated toward the inner wall by an acceleration voltage. Alternately, electron emission may be by thermionic means. Collisions of electrons with the target film causes x-ray emission, a substantial portion of which is directed through the inner wall into the space defined within. In an embodiment, the location of the emitter and target film are reversed, establishing a reflective rather than transmissive mode for convergent patterns and a transmissive mode for divergent patterns.
Owner:CABOT MICROELECTRONICS CORP
Ion source apparatus and cleaning optimized method thereof
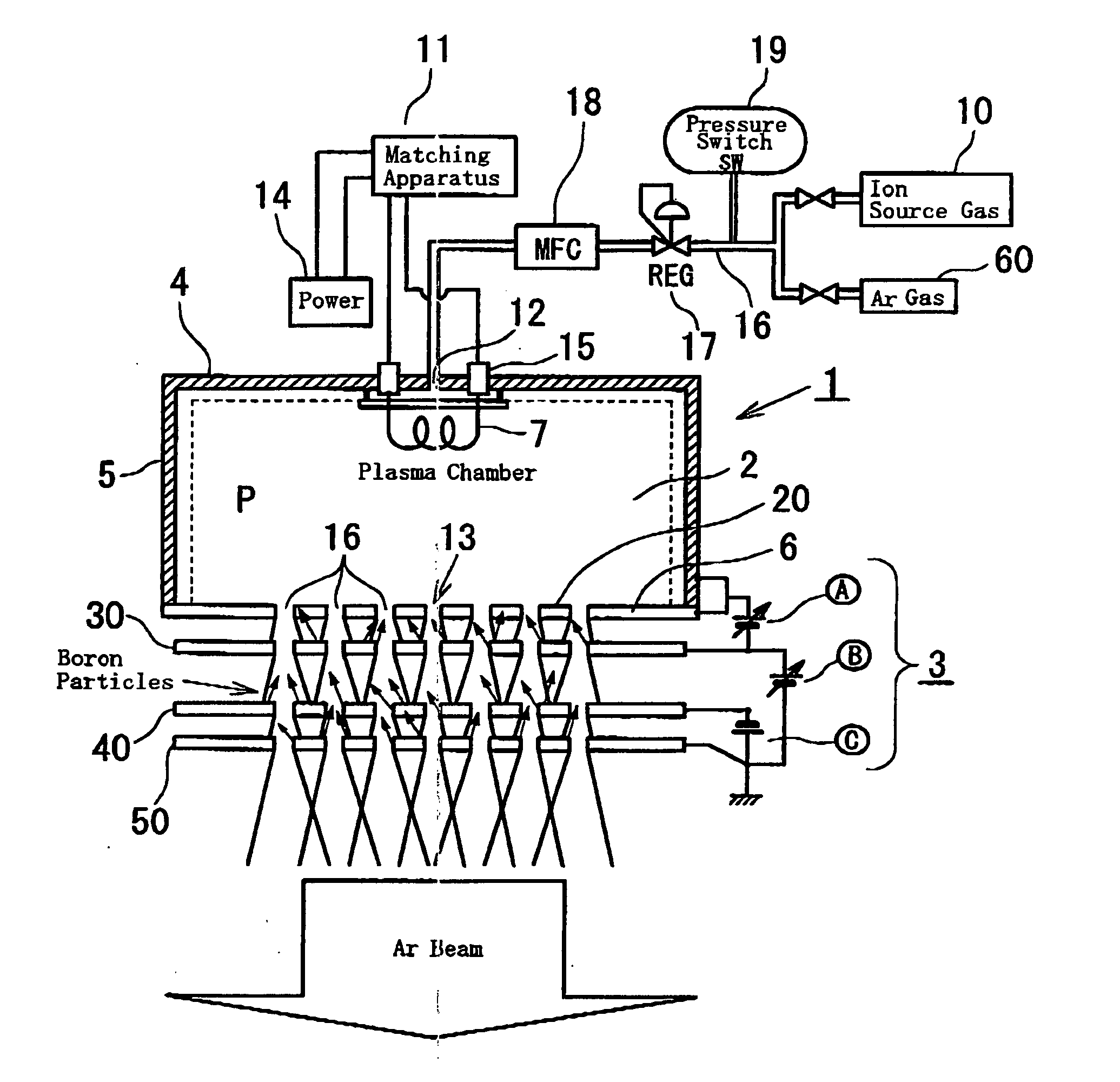
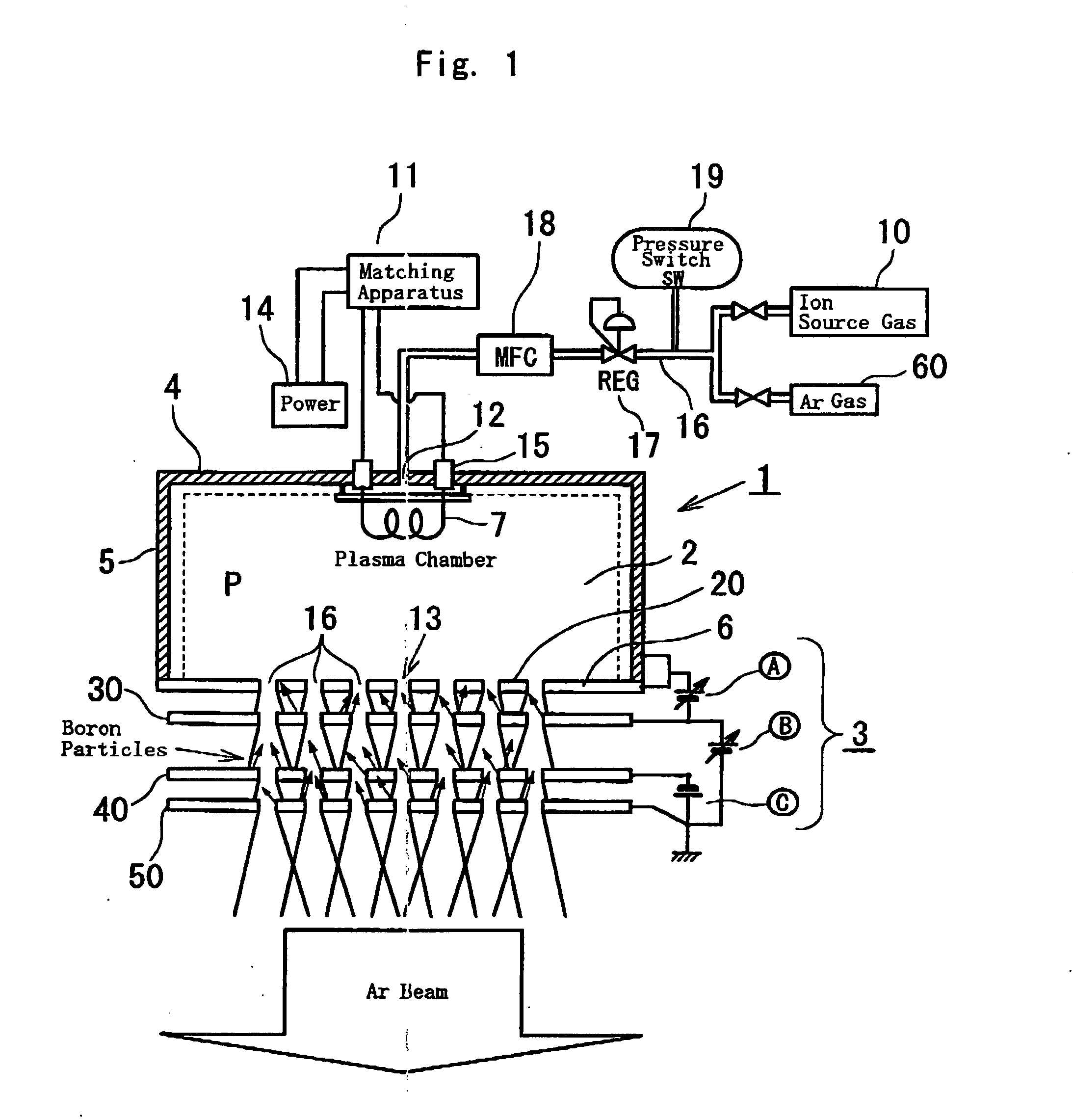
InactiveUS20050016838A1Optimized diameterIncreased durabilityCellsVacuum evaporation coatingNoble gasInsulation layer
An ion source apparatus includes a rare gas supply source supplying rare gas instead of ion source gas to a plasma chamber, means to determine time and timing for cleaning electrodes in consideration of a collecting amount of insulation layers accreting to the electrodes of an extraction electrode system. Based on the above, the ion source apparatus removes the insulation layers by sputtering with ion beam of the rare gas while adjusting extraction or accelerate voltage and supply amount of the rare gas as a setting parameter. Moreover, by adjusting the setting parameter which changes a diameter of ion beam based on the rare gas when the ion beam collides onto each electrode surface of the extraction electrode system, the beam diameter is focused within an effective range in which intension of the sputtering of the insulation layers is maximized thus evenly removing the insulation layers.
Owner:SEN CORP AN SHI & AXCELIS
Magnetic carrier and two-component developer
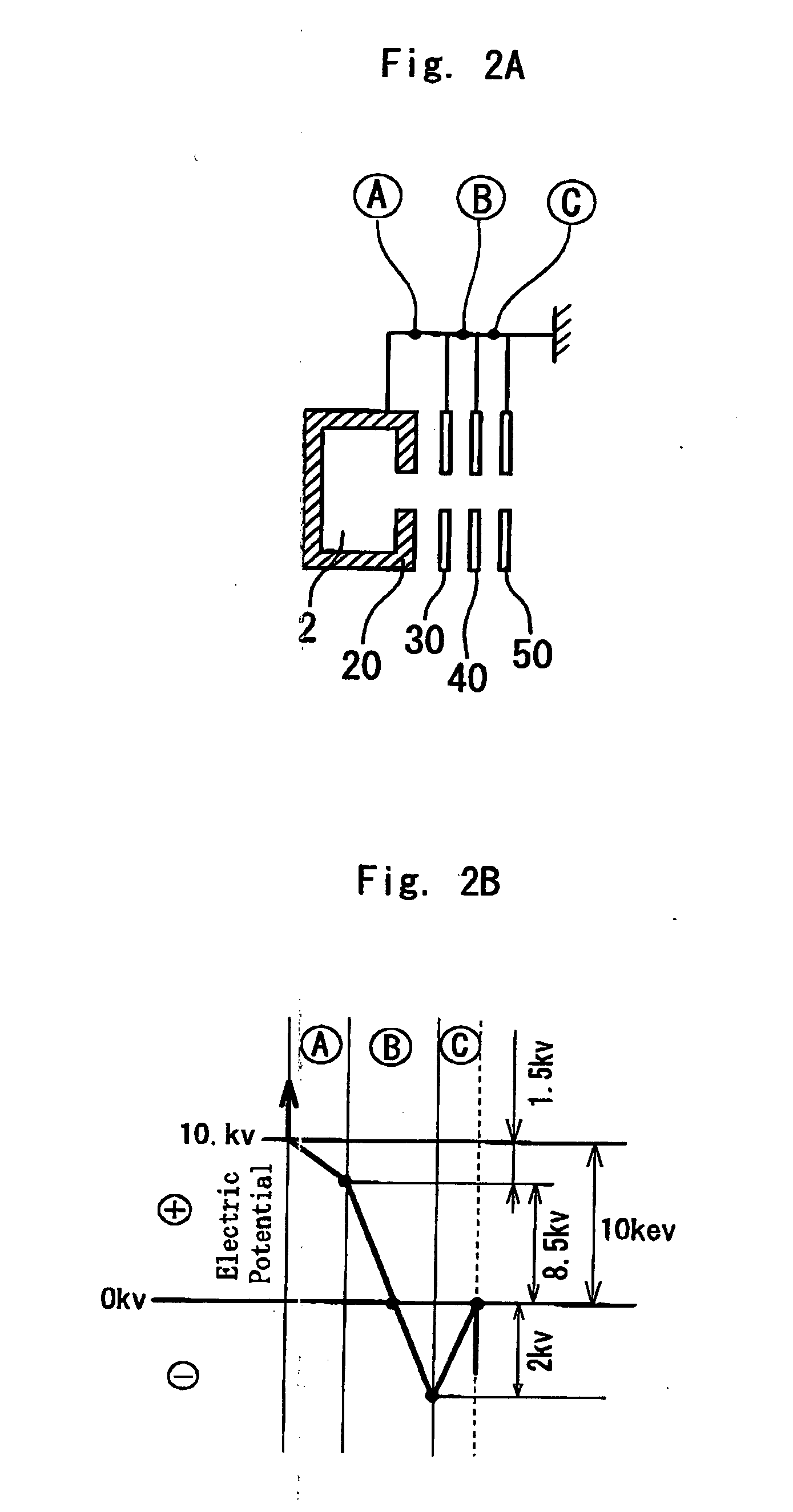
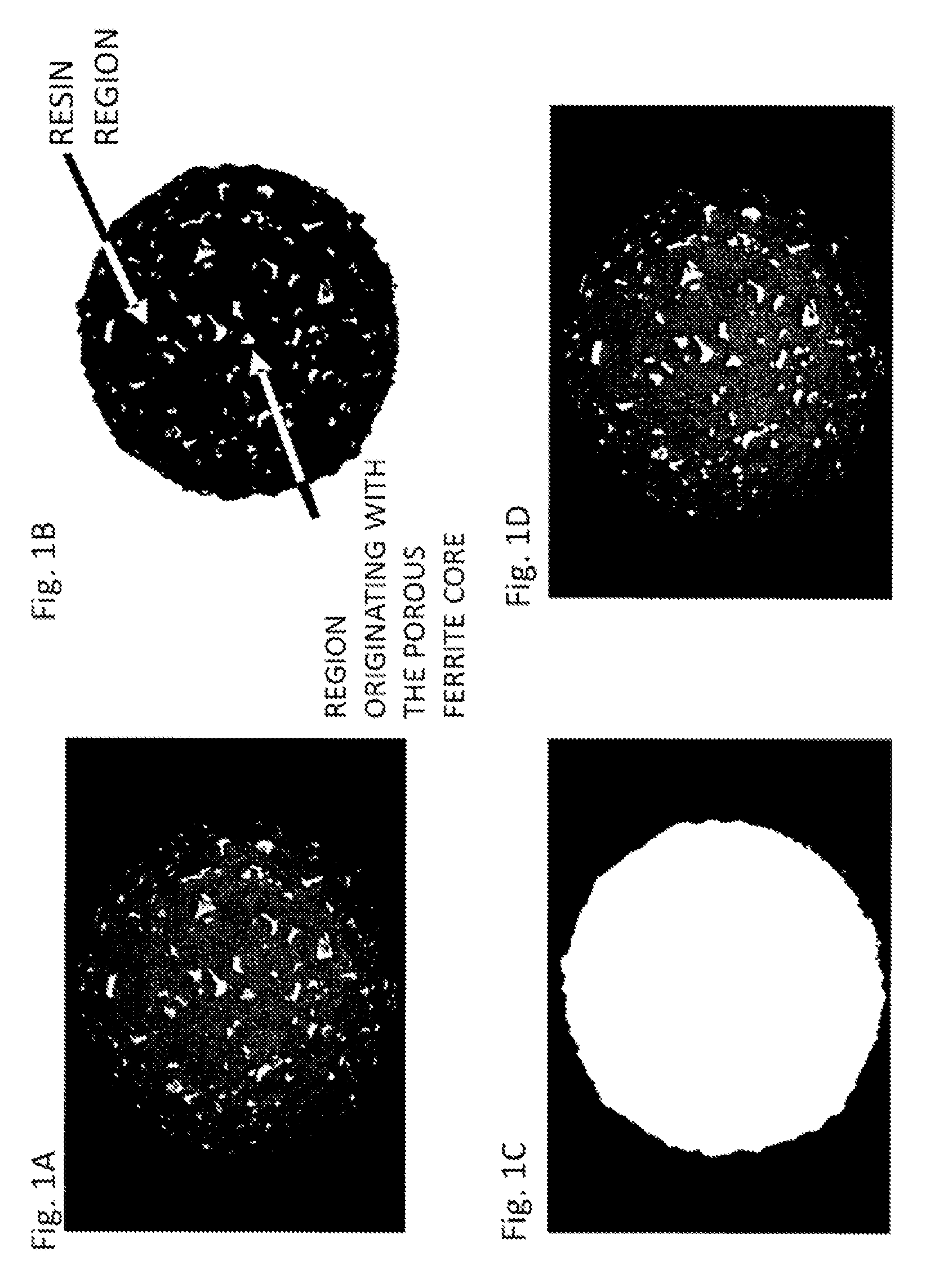
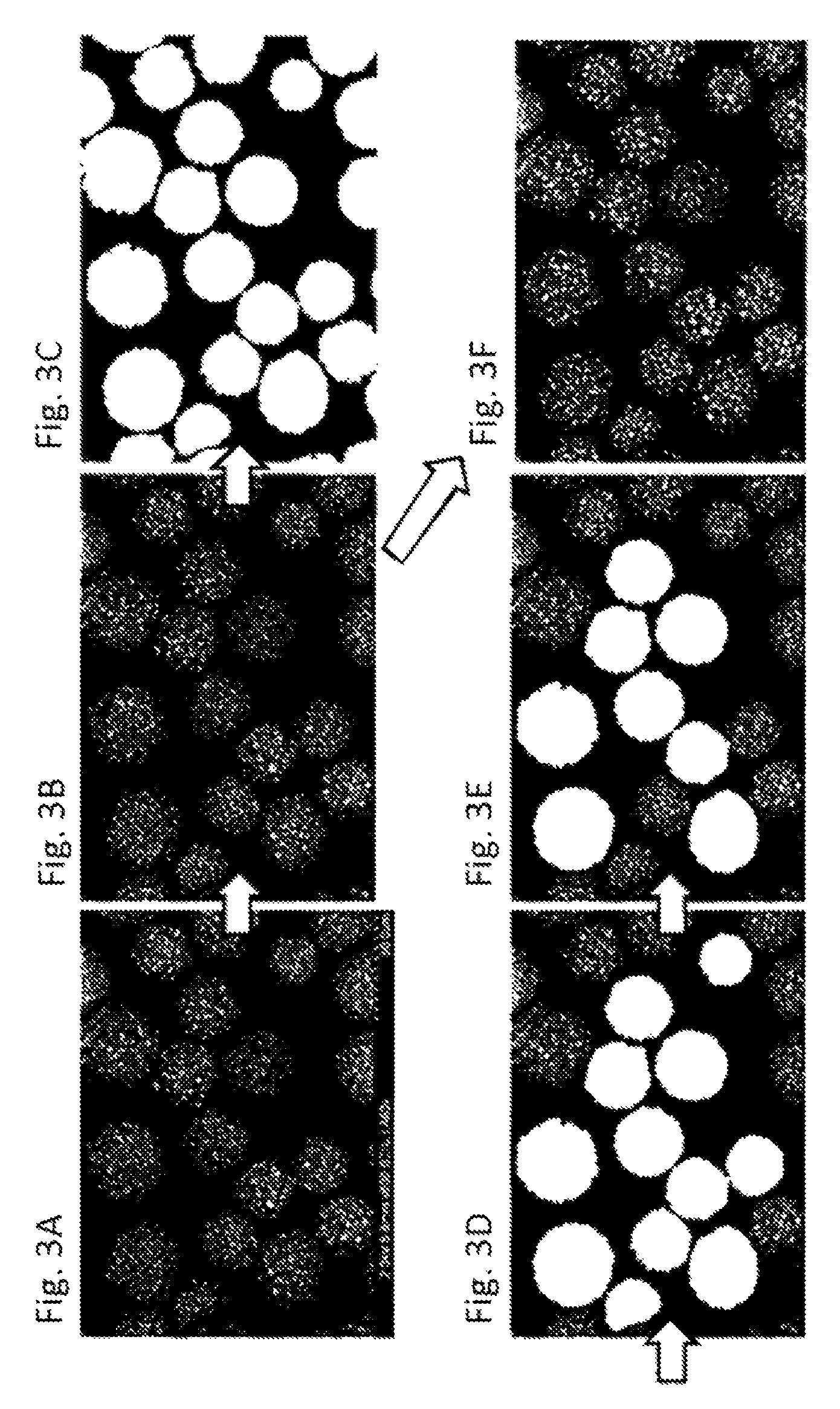
The present invention provides a magnetic carrier that can stably impart charge to a toner on a long term basis and that exhibits an excellent toner separation property and thus exhibits an excellent developing performance. This magnetic carrier is a magnetic carrier in which a vinyl resin coats the surface of a resin-filled core in which a resin is filled in pores of a porous ferrite particle, wherein the resistivity, Mg content, and total content of Sr and Ca oxides of the porous ferrite particle exhibit prescribed values and the magnetic carrier has a total area—in the backscattered electron projection image obtained by observation using a scanning electron microscope at an acceleration voltage of 2.0 kV—for a region originating with the porous ferrite particle of from at least 0.2 area % to not more than 5.0 area % with reference to the projected area of the magnetic carrier.
Owner:CANON KK
Scanning Electron Microscope System, Pattern Measurement Method Using Same, and Scanning Electron Microscope
ActiveUS20160379798A1High aspect ratioMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationSemiconductor/solid-state device testing/measurementElectron microscopeCalibration curve
In order to allow detecting backscattered electrons (BSEs) generated from the bottom of a hole for determining whether a hole with a super high aspect ratio is opened or for inspecting and measuring the ratio of the top diameter to the bottom diameter of a hole, which are typified in 3D-NAND processes of opening a hole, a primary electron beam accelerated at a high accelerating voltage is applied to a sample. Backscattered electrons (BSEs) at a low angle (e.g. a zenith angle of five degrees or more) are detected. Thus, the bottom of a hole is observed using “penetrating BSEs” having been emitted from the bottom of the hole and penetrated the side wall. Using the characteristics in which a penetrating distance is relatively prolonged through a deep hole and the amount of penetrating BSEs is decreased to cause a dark image, a calibration curve expressing the relationship between a hole depth and the brightness is given to measure the hole depth.
Owner:HITACHI HIGH-TECH CORP
Magnetic lens apparatus for use in high-resolution scanning electron microscopes and lithographic processes
InactiveUS6051839AReduce resolutionEasy constructionMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationElectric discharge tubesMagnetic polesScanning electron microscope
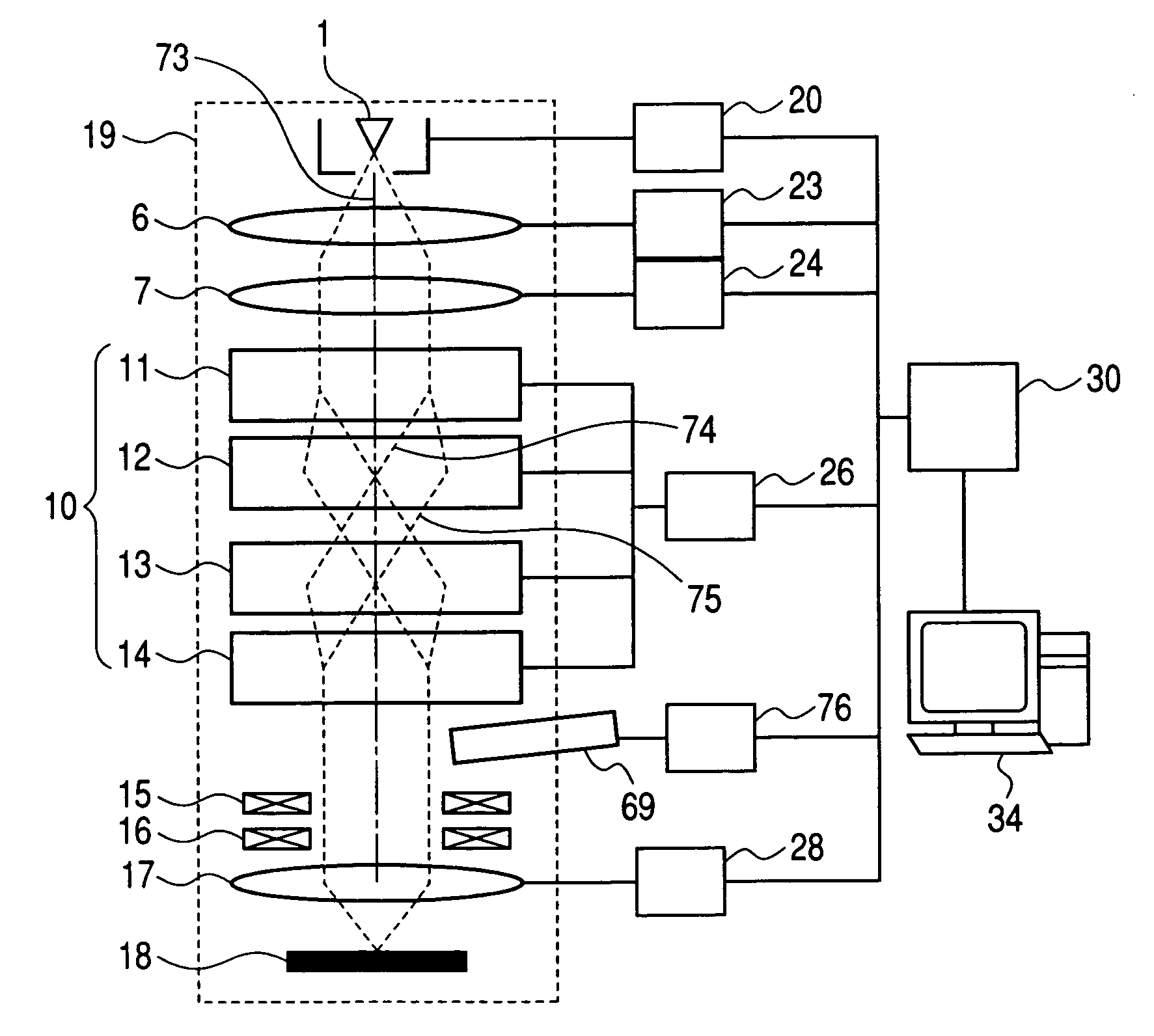
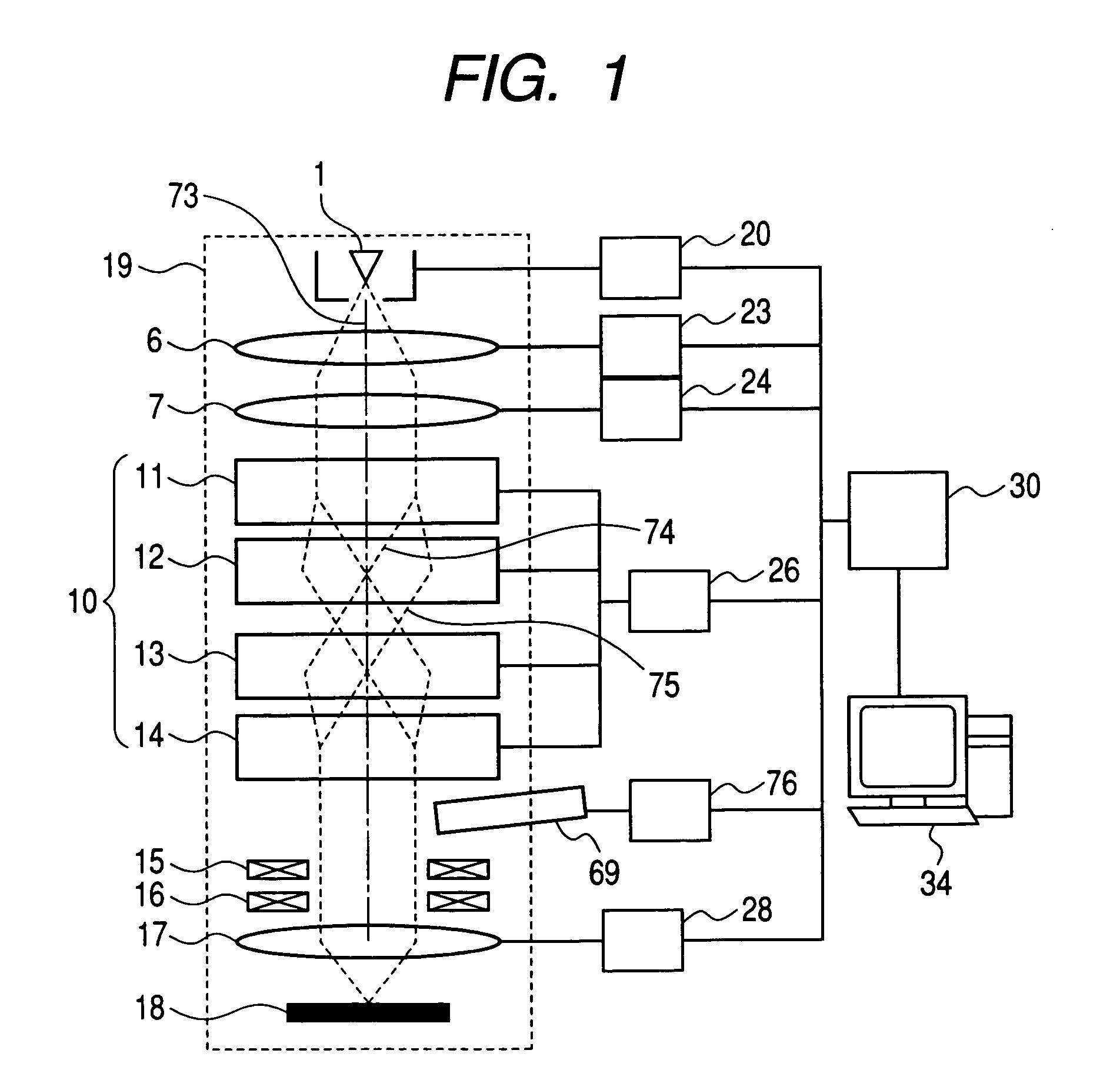
PCT No. PCT / US96 / 09906 Sec. 371 Date Mar. 9, 1998 Sec. 102(e) Date Mar. 9, 1998 PCT Filed Jul. 6, 1996 PCT Pub. No. WO96 / 41362 PCT Pub. Date Dec. 19, 1996Disclosed are lens apparatus in which a beam of charged particlesis brought to a focus by means of a magnetic field, the lens being situated behind the target position. In illustrative embodiments, a lens apparatus is employed in a scanning electron microscopeas the sole lens for high-resolution focusing of an electron beam, and in particular, an electron beam having an accelerating voltage of from about 10 to about 30,000 V. In one embodiment, the lens apparatus comprises an electrically-conducting coil arranged around the axis of the beam and a magnetic pole piece extending along the axis of the beam at least within the space surrounded by the coil. In other embodiments, the lens apparatus comprises a magnetic dipole or virtual magnetic monopole fabricated from a variety of materials, including permanent magnets, superconducting coils, and magnetizable spheres and needles contained within an energy-conducting coil. Multiple-array lens apparatus are also disclosed for simultaneous and / or consecutive imaging of multiple images on single or multiple specimens. The invention further provides apparatus, methods, and devices useful in focusing charged particle beams for lithographic processes.
Owner:ARCH DEVMENT
Electron beam apparatus
InactiveUS20100102227A1Improve imaging resolutionLarge aberrationThermometer detailsMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationScanning electron microscopeAcceleration voltage
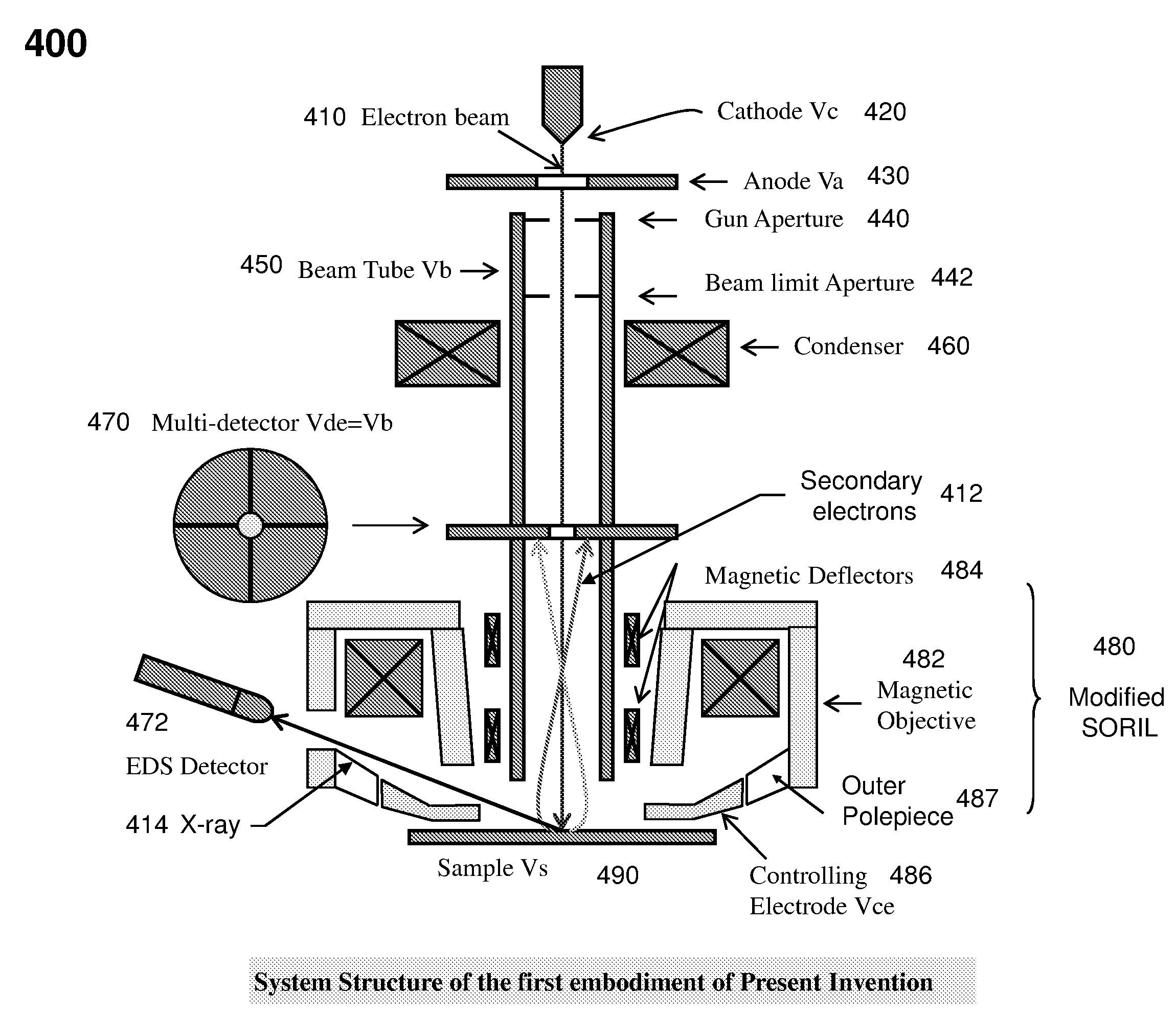
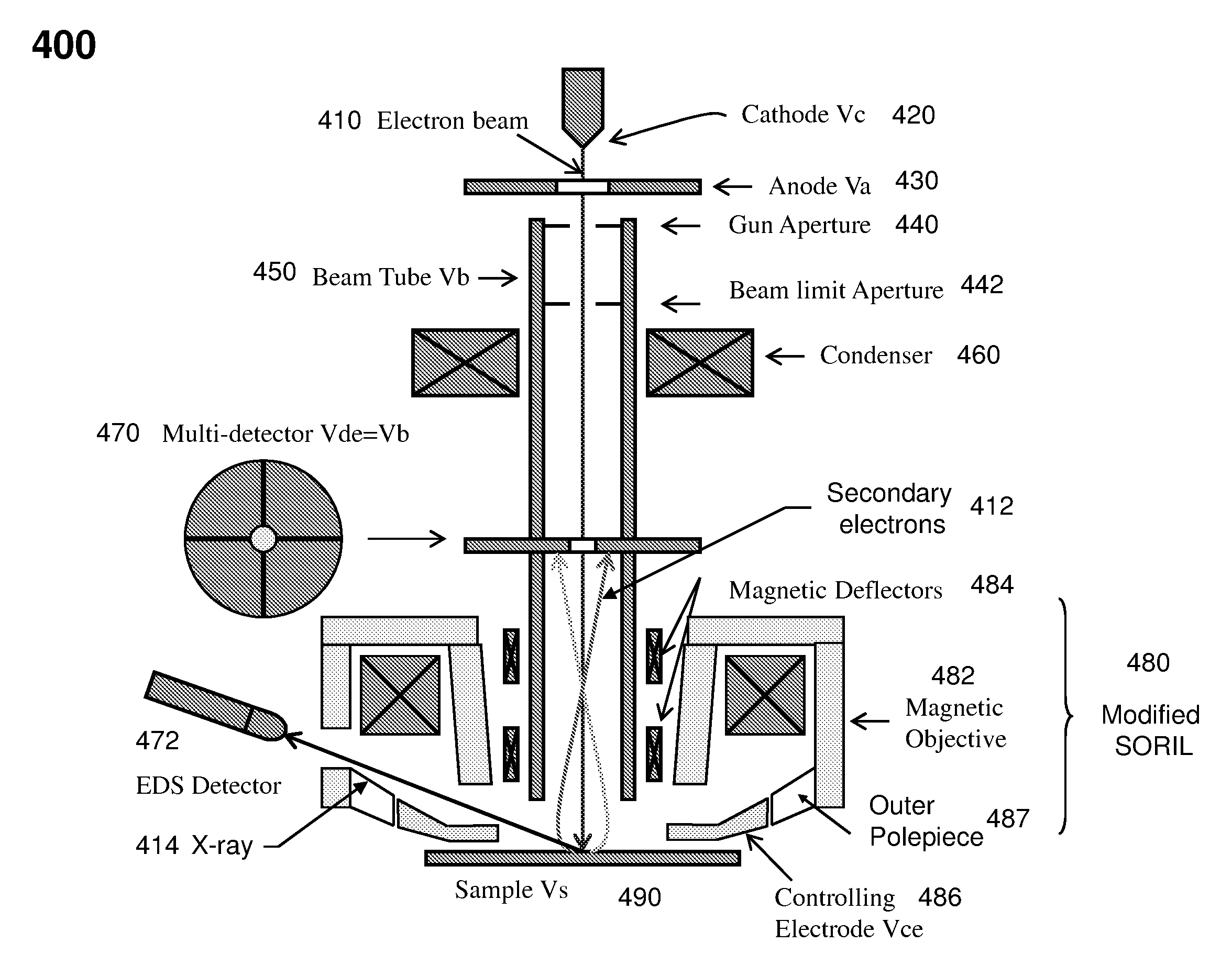
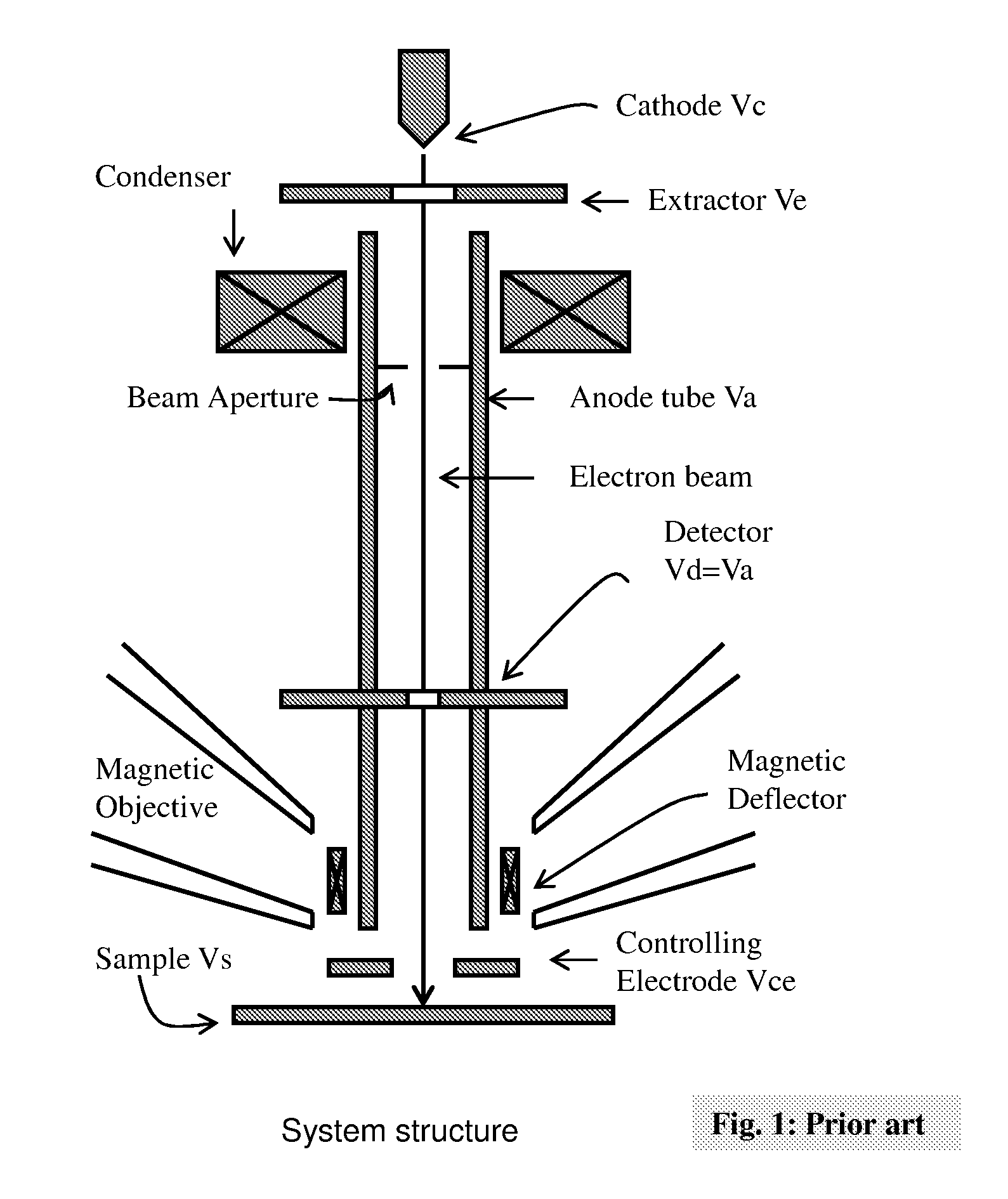
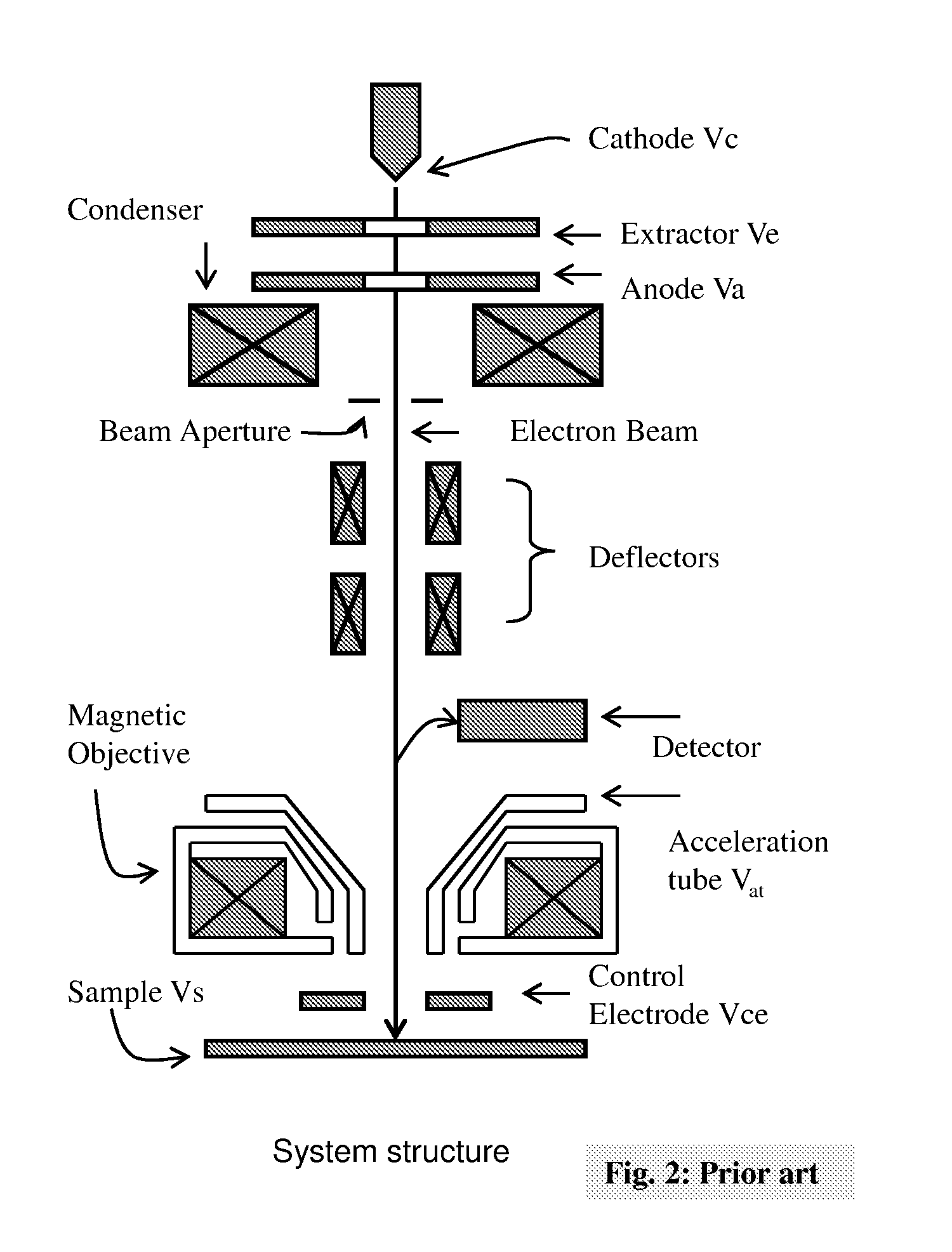
The present invention relates to a charged particle beam apparatus which employs a scanning electron microscope for sample inspection and defect review.The present invent provides solution of improving imaging resolution by utilizing a field emission cathode tip with a large tip radius, applying a large accelerating voltage across ground potential between the cathode and anode, positioning the beam limit aperture before condenser lens, utilizing condenser lens excitation current to optimize image resolution, applying a high tube bias to shorten electron travel time, adopting and modifying SORIL objective lens to ameliorate aberration at large field of view and under electric drifting and reduce the urgency of water cooling objective lens while operating material analysis.The present invent provides solution of improving throughput by utilizing fast scanning ability of SORIL and providing a large voltage difference between sample and detectors.
Owner:ASML NETHERLANDS BV
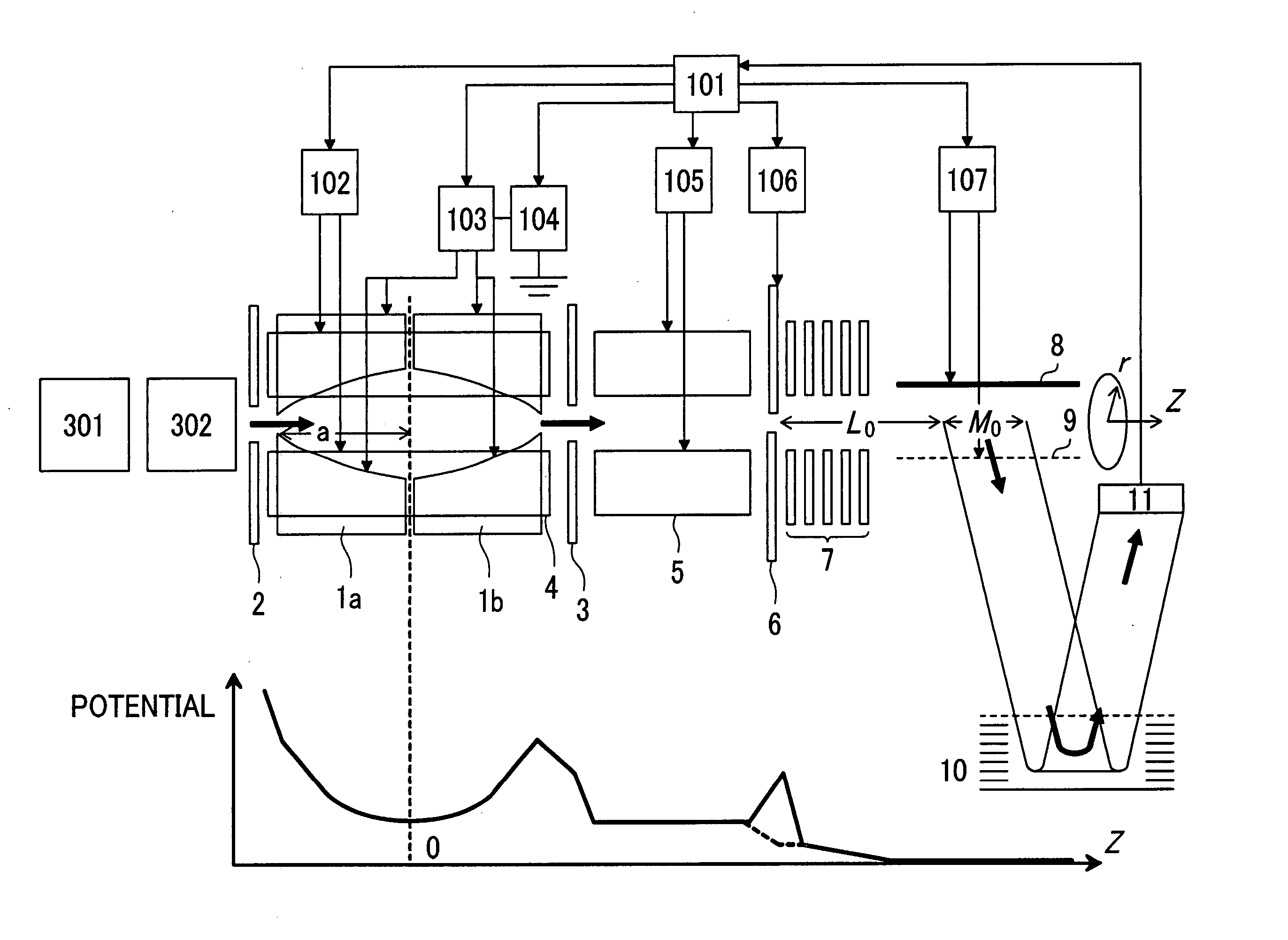
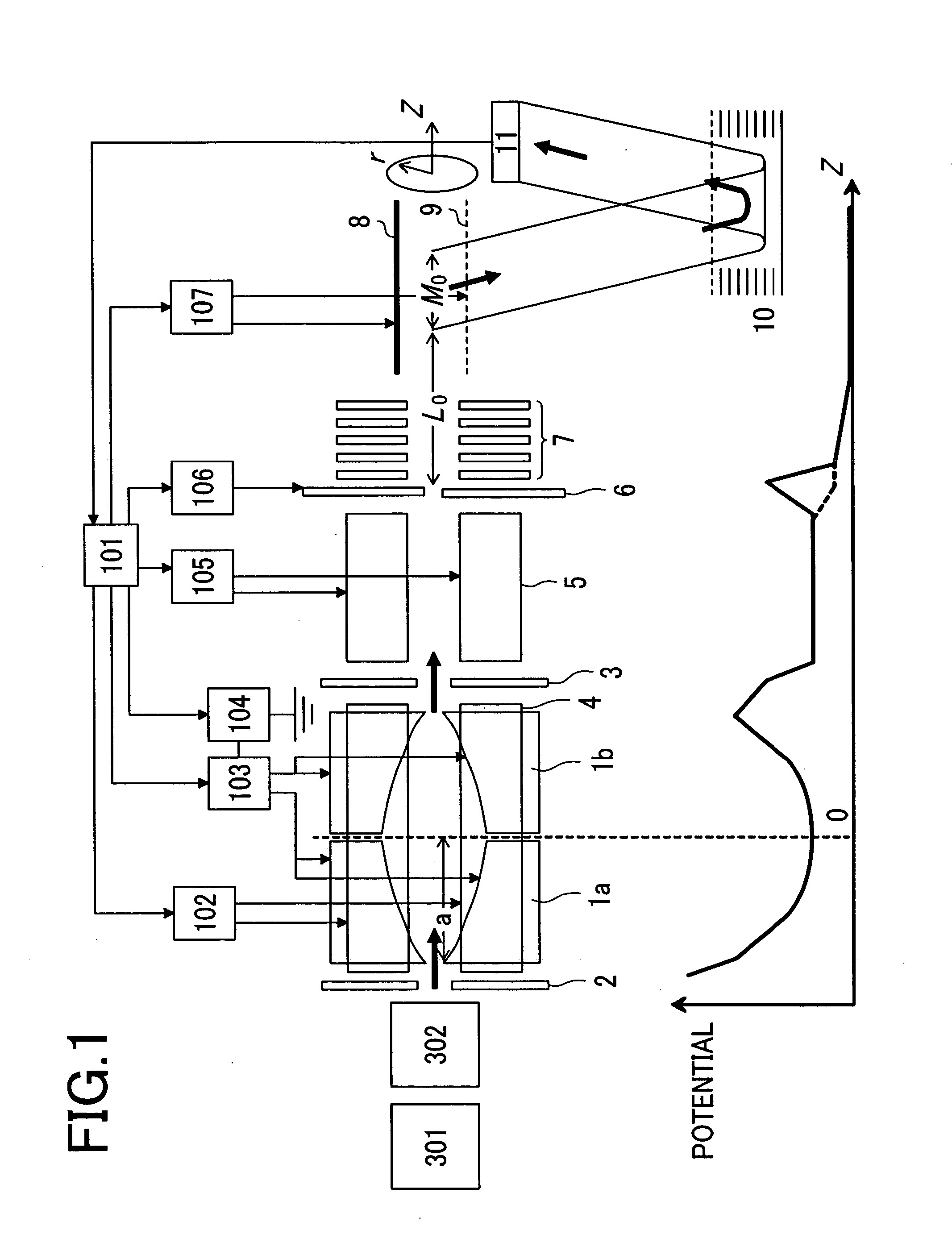
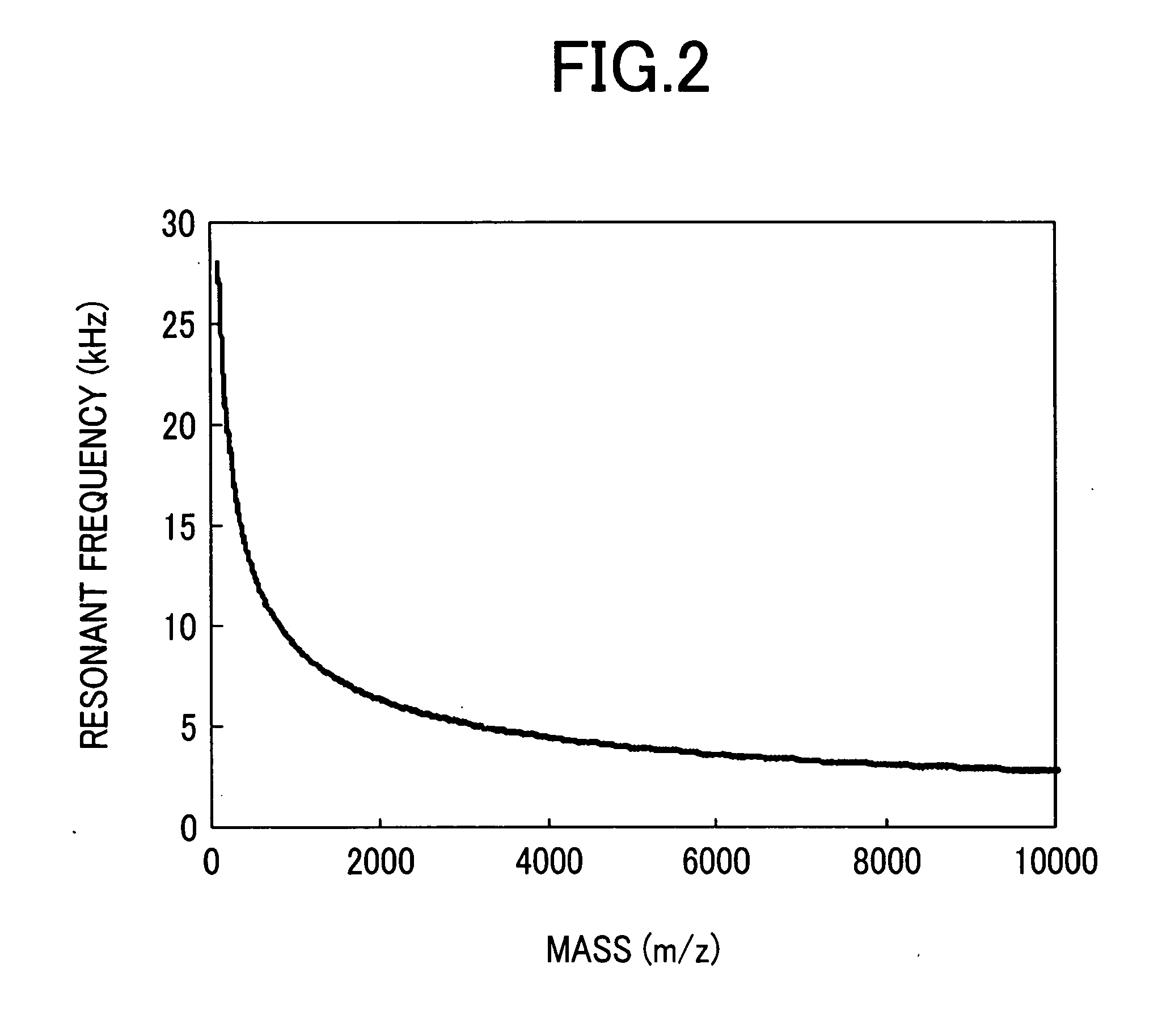
Mass Spectrometer
ActiveUS20050127290A1High sensitivityHigh mass accuracyStability-of-path spectrometersTime-of-flight spectrometersDelayed timeMass analyzer
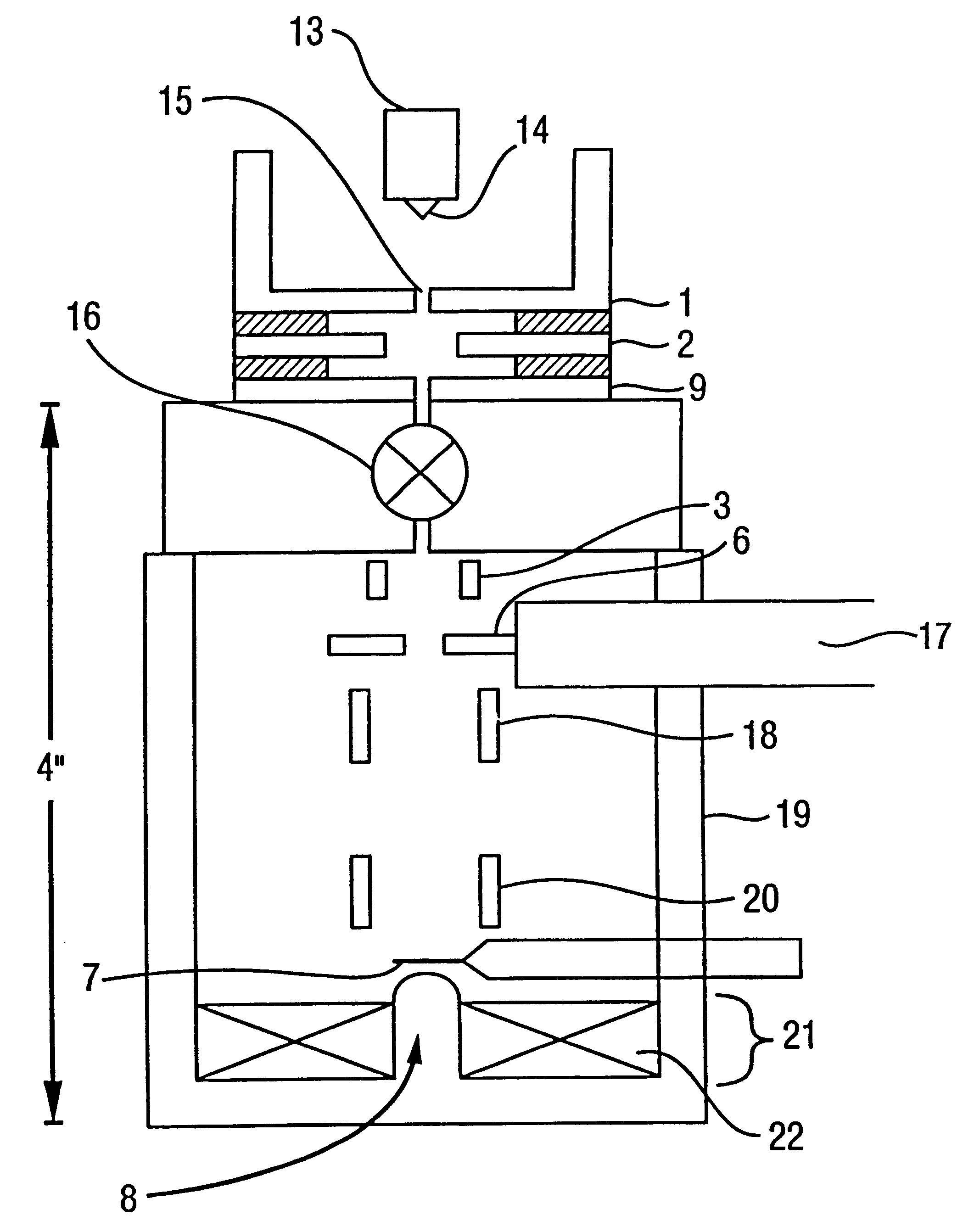
A mass spectrometer capable of analyzing a wide mass range with high sensitivity and high mass accuracy. A mass spectrometer has an ionization source generating ions; an ion transfer optics transferring the ions; a first linear trap accumulating the ions and ejecting the ions in the specific mass range; a second linear trap having an end electrode disposed at the exit end ejecting the ions to change a DC potential gradient relative to a DC potential of the end electrode and trapping the ions ejected from the first linear trap to repeatedly eject them in pulse form; a time-of-flight mass spectrometer accelerating the ions ejected from the second linear trap in the orthogonal direction to detect them; and a controller changing the time duration of the ions in which the ions are ejected from the second linear trap or delay time from the completion of ejection to application of an accelerating voltage of the time-of-flight mass spectrometer according to the mass range of the ions ejected from the first linear trap to the second linear trap.
Owner:HITACHI HIGH-TECH CORP
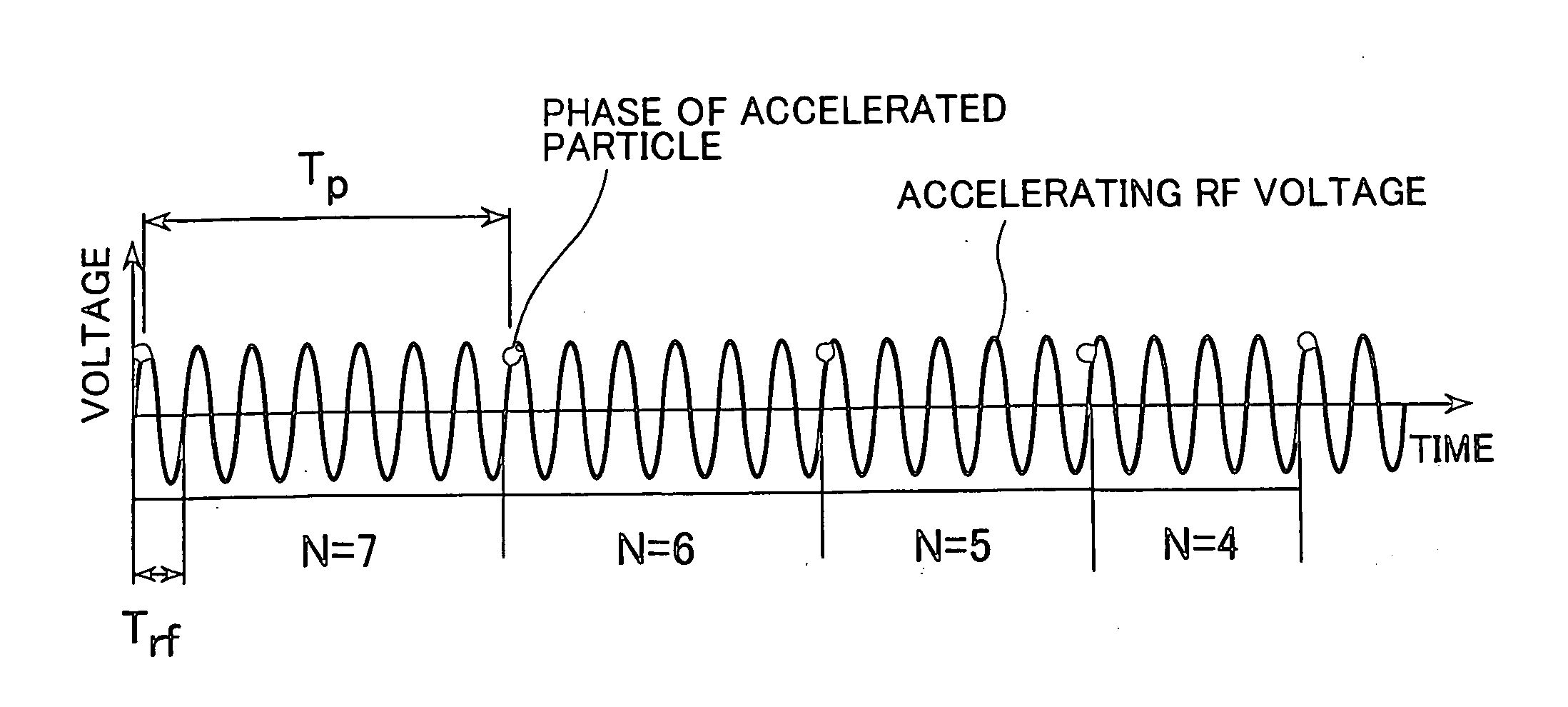
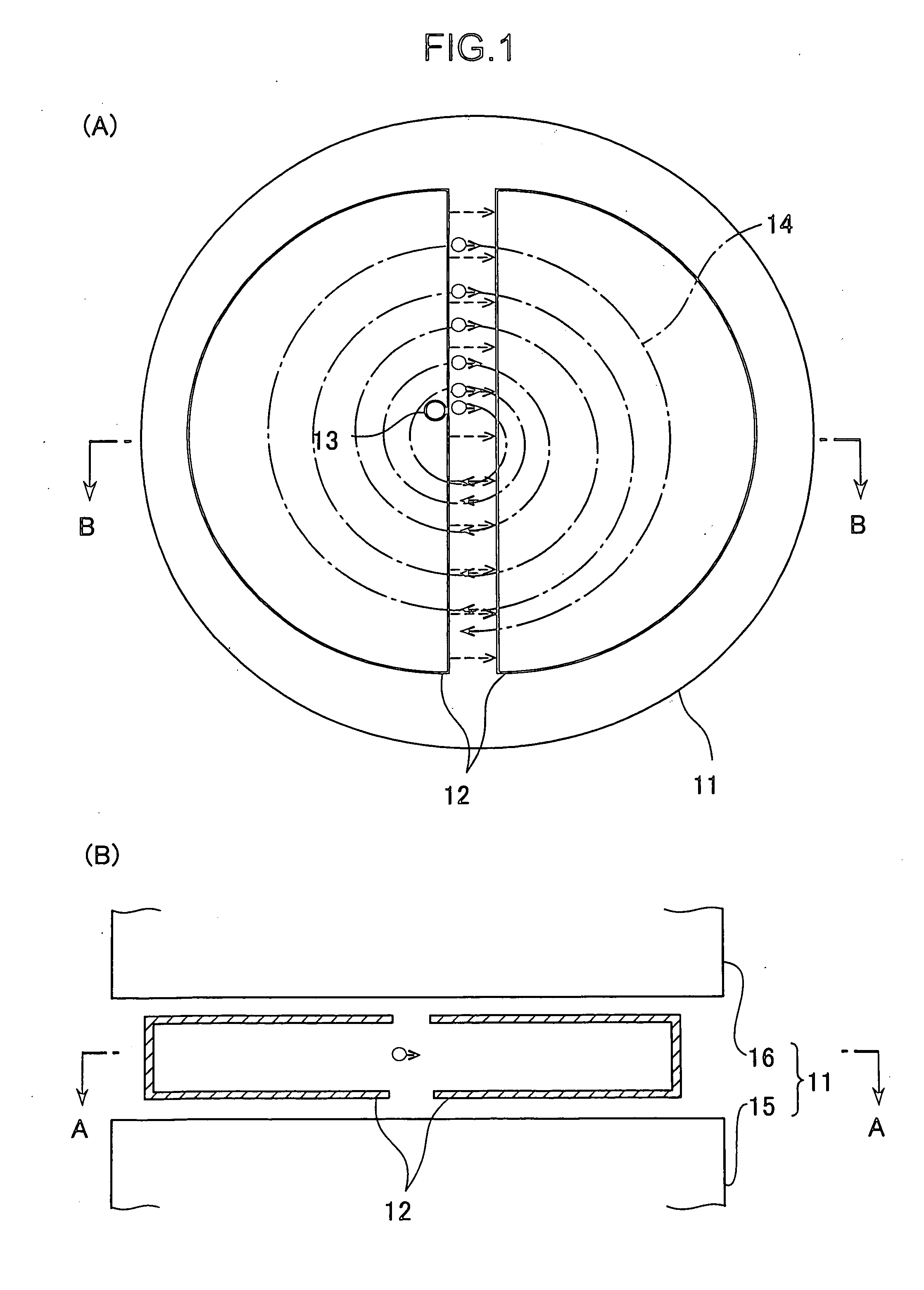
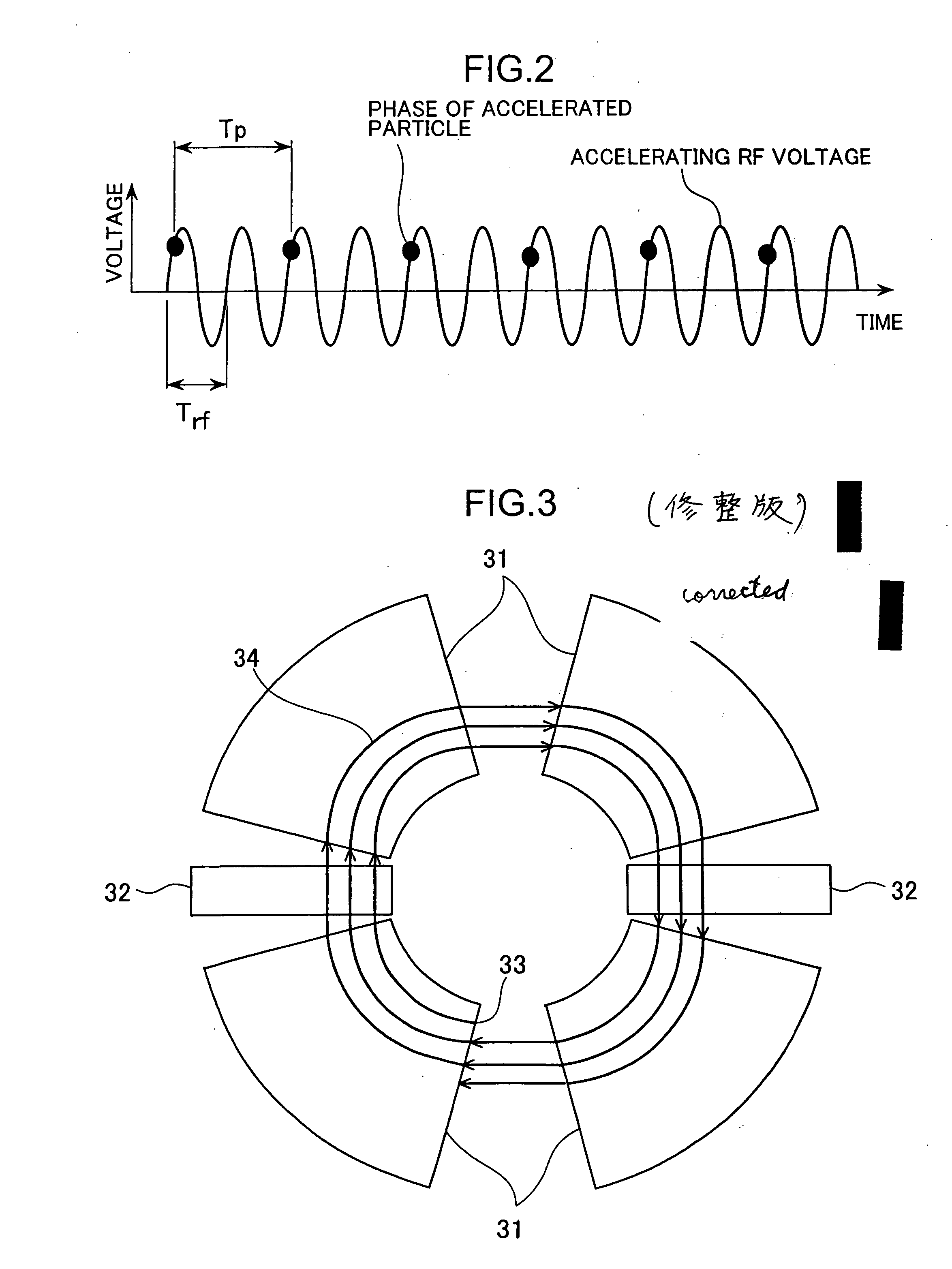
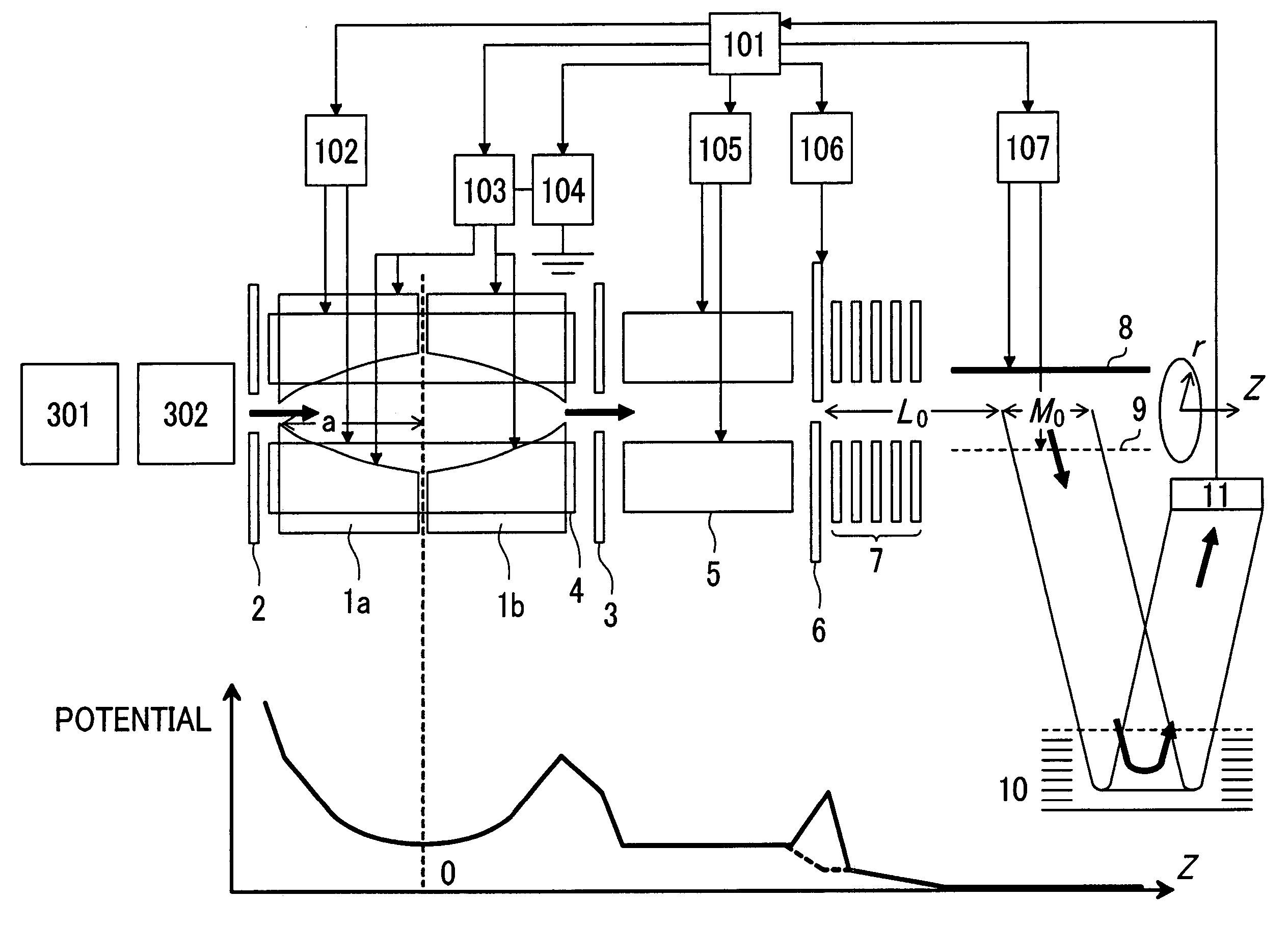
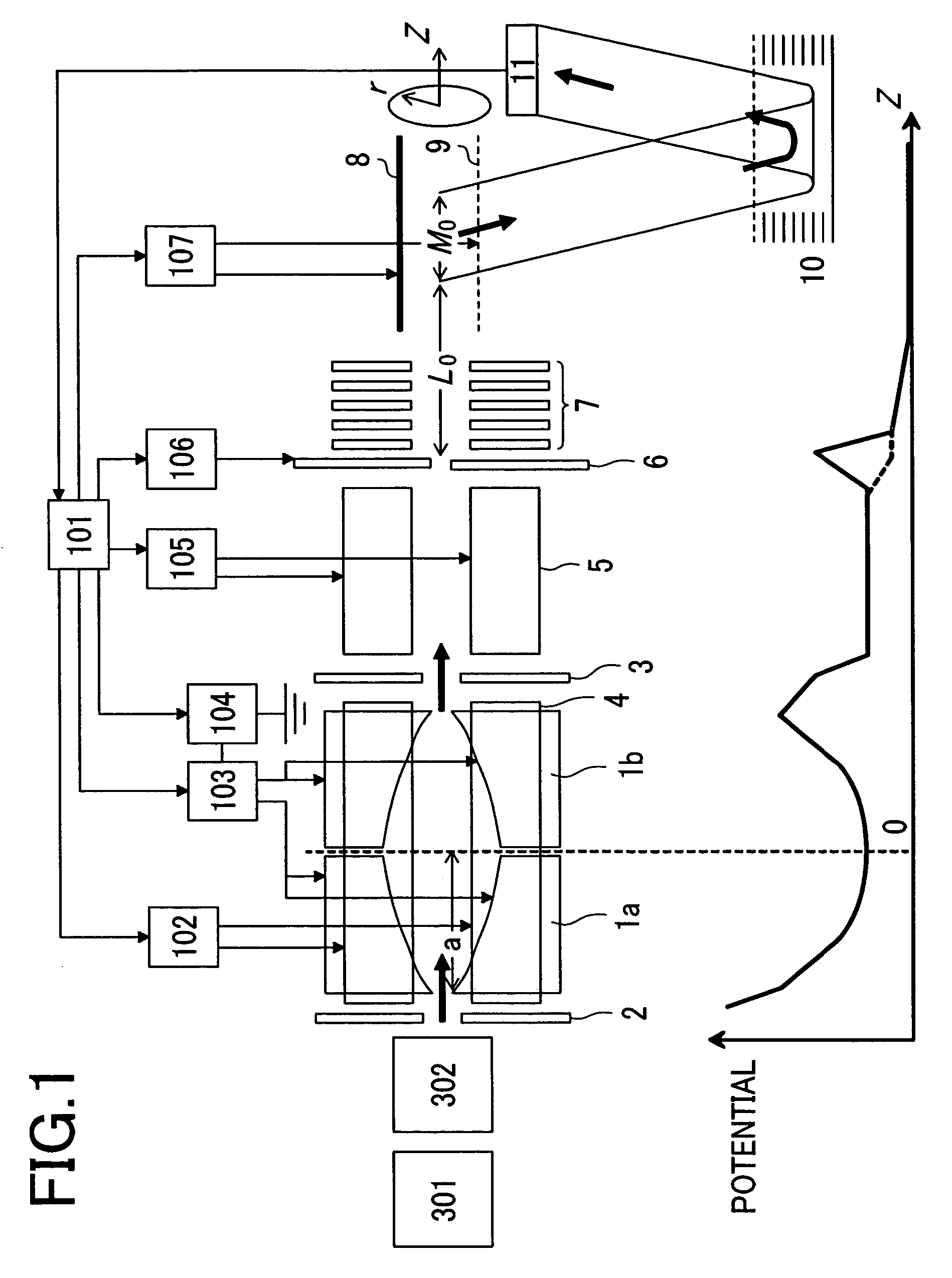
Spiral orbit charged particle accelerator and its acceleration method
InactiveUS20060175991A1High energy gainIncreasing magnet sizeMagnetic resonance acceleratorsKlystronsHarmonicOrbit
According to the present invention, a non-isochronous magnetic field distribution in which the magnetic field increases as the radius increases is formed and a distribution of fixed-frequency accelerating RF voltage is formed, said non-isochronous magnetic field distribution and said distribution of fixed-frequency accelerating RF voltage being formed so that a harmonic number defined as a ratio of the particle revolution period to the period of the accelerating RF voltage decreases in integer for every particle revolution.
Owner:NAT INST OF RADIOLOGICAL SCI
Emission source having carbon nanotube, electron microscope using this emission source, and electron beam drawing device
InactiveUS6930313B2High strengthImprove reliabilityMaterial nanotechnologyNanostructure manufactureCarbonizationCarbon nanotube
A high reliability emission source is constructed to secure the ohmic contact between a carbon nanotube and an electrically conductive base material, so as to ensure sufficient joining strength, and to provide for easy beam shaft adjustment. An electron microscope for realizing high resolution, high brightness, a reduction in sample damage due to a reduction in acceleration voltage, a reduction in cost and compactness, and an electron beam drawing device for realizing high definition, high efficiency, a reduction in cost and compactness in comparison with the conventional device, is achieved by using this high reliability emission source. In the emission source, the carbon nanotube is attached to the tip central portion of the electrically conductive base material through an electrically conductive joining material or an organic material by carbonization-processing the organic material by heat treatment, or by diffusive joining.
Owner:HITACHI LTD
Electrostatic device for correcting chromatic aberration in a particle-optical apparatus
InactiveUS6184975B1Reduce errorsStability-of-path spectrometersBeam/ray focussing/reflecting arrangementsQuadrupole fieldImage resolution
Electron-optical rotationally symmetrical lenses inevitably suffer from chromatic aberration which often determines the resolution limit at low acceleration voltages. This lens defect cannot be eliminated by compensation by means of rotationally symmetrical fields. In order to improve the resolution nevertheless, it has already been proposed to correct the chromatic aberration by means of a corrector (28) provided with two correction elements (34, 40). Each correction element consists of a number of quadrupole fields. Using the known corrector, it has been found that the chromatic magnification error is inadmissibly high. In order to solve this problem, the correction elements in the corrector according to the invention are provided with at least five layers of electrodes (60-a, 60-b, 60-c, 60-d) which produce quadrupole fields. Because of the strong periodicity of the electron paths in the correcting quadrupole fields, the chromatic magnification error is limited sufficiently (or even reduced to zero) so as to allow the use of the corrector for practical purposes.
Owner:FEI CO
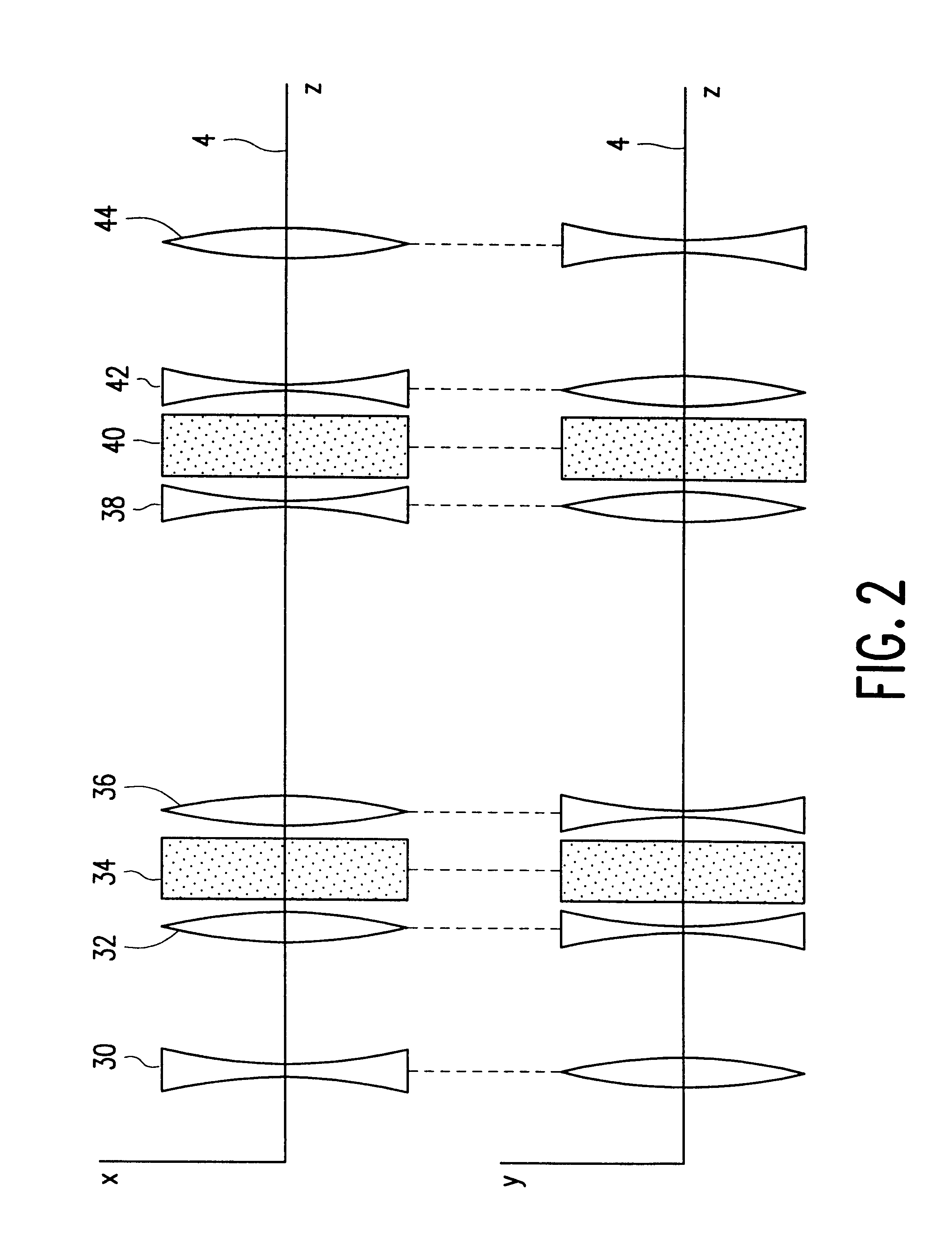
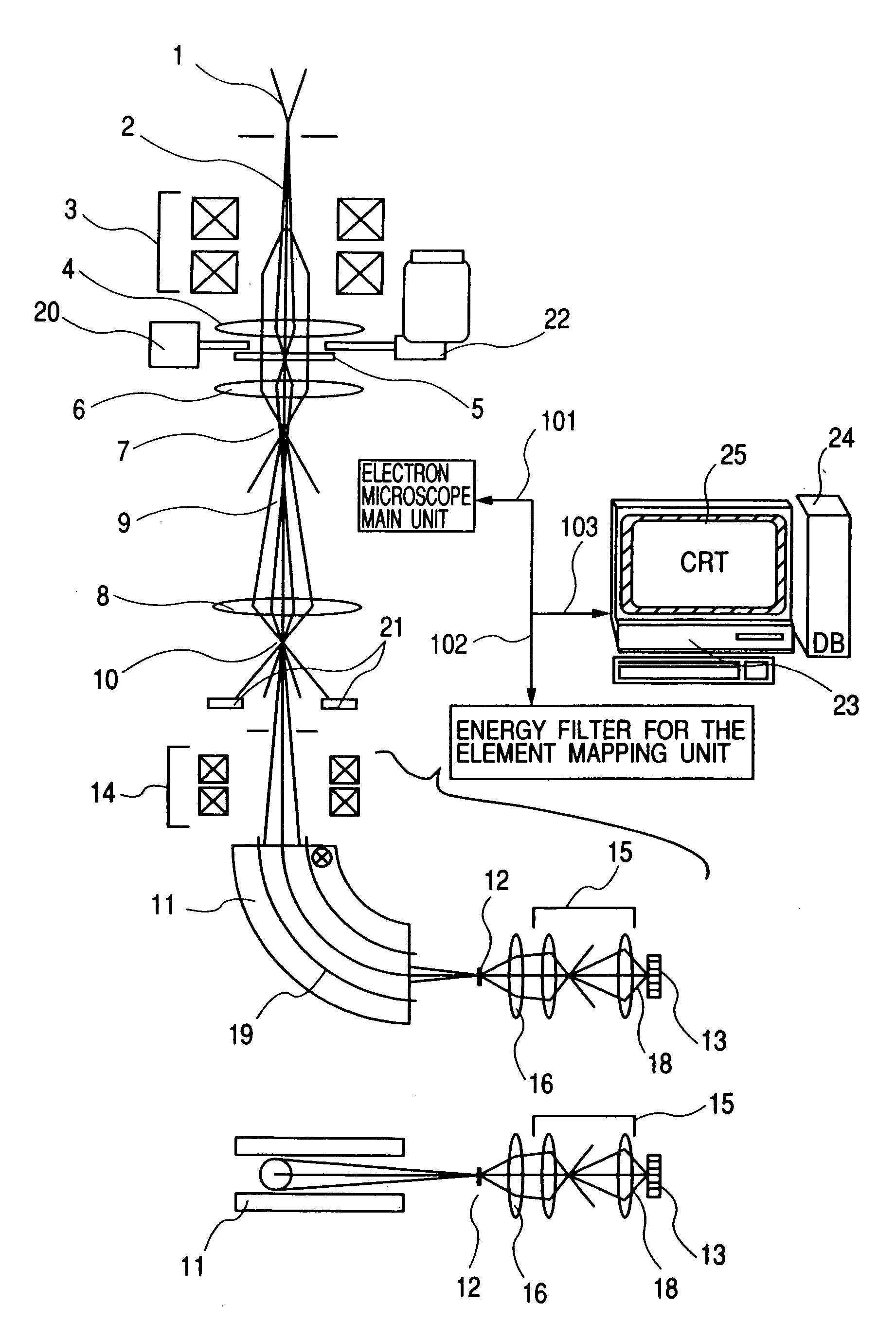
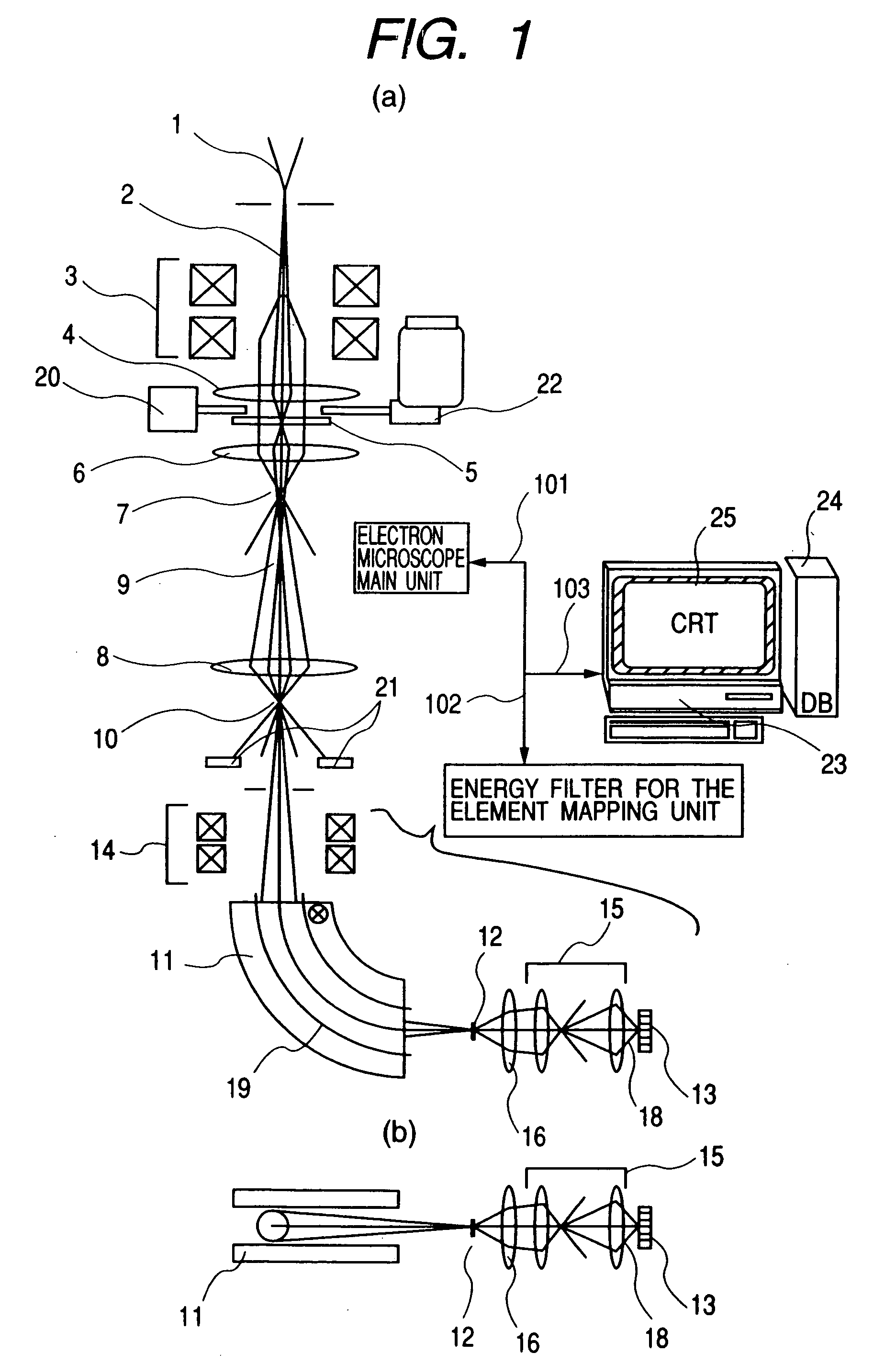
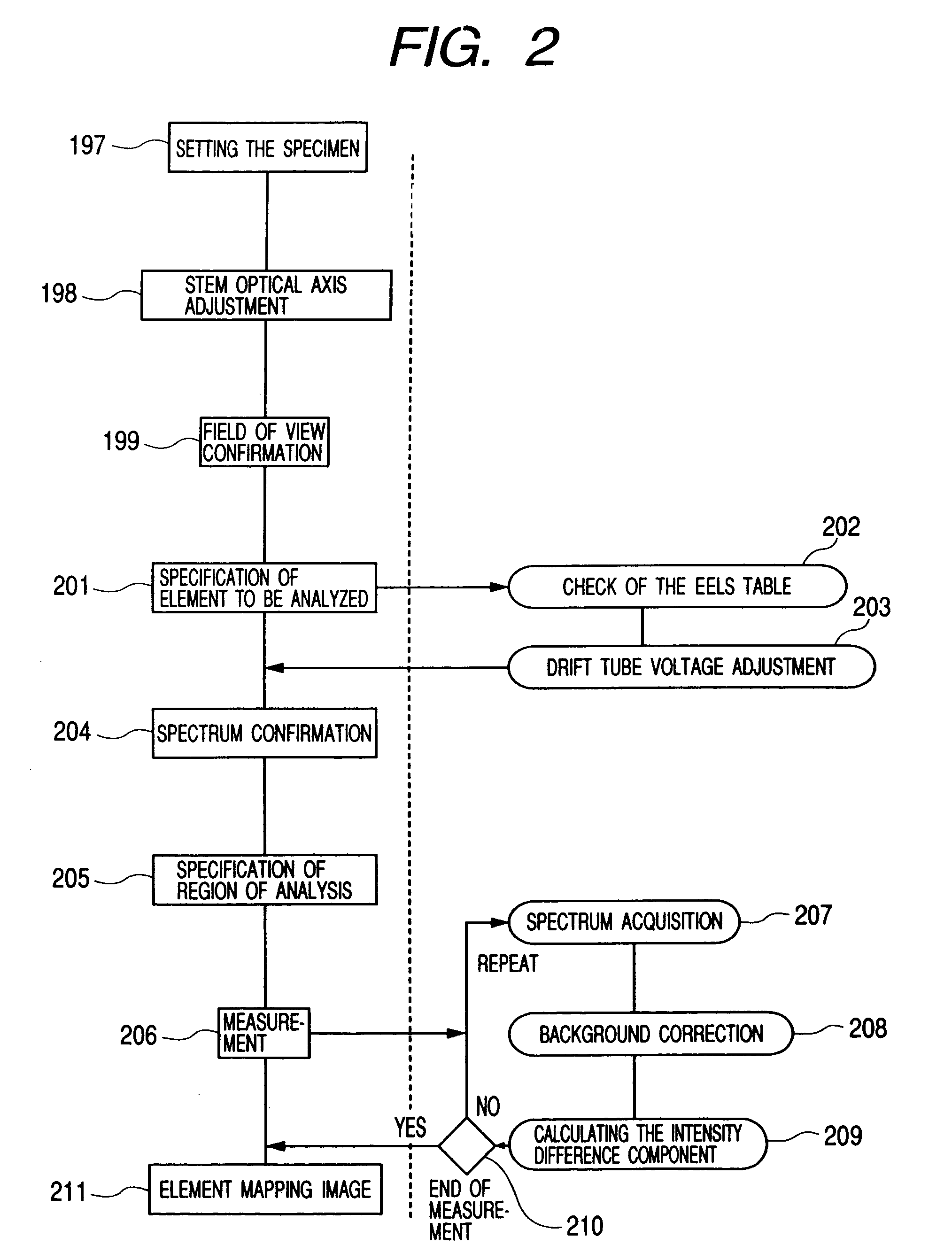
Element mapping unit, scanning transmission electron microscope, and element mapping method
InactiveUS20060011836A1Easy to operateHigh EELS spectrum energy stabilityMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationPhotoelectric discharge tubesConventional transmission electron microscopeFrequency spectrum
There is provided an element mapping unit, scanning transmission electron microscope, and element mapping method that enable to acquire an element mapping image very easily. On the scanning transmission electron microscope, the electron beam transmitted through an object to be analyzed enters into the element mapping unit. The electron beam is analyzed of its energy into spectrum by an electron spectrometer and an electron energy loss spectrum is acquired. Because the acceleration voltage data for each element and window data for 2-window method, 3-window method or contrast tuning method are already stored in a database and accordingly the spectrum measurement is carried out immediately even when an element to be analyzed is changed to another, the operator can confirm a two-dimensional element distribution map immediately. Besides, because every electron beam that enters into an energy filter passes through the object point, aberration strain in the electron spectrometer can be minimized and higher energy stability can be achieved. As a result, drift of the electron energy loss spectrum acquired by analyzing the electron beam into spectrum can be minimized and element distribution with higher accuracy can be acquired.
Owner:HITACHI LTD
Two-stage hall effect plasma accelerator including plasma source driven by high-frequency discharge
Disclosed is a high-frequency discharge plasma generation-based two-stage Hall-effect plasma accelerator, which comprises an annular acceleration channel having a gas inlet port, a high-frequency wave supply section, an anode, a cathode, a neutralizing electron generation portion and a magnetic-field generation means, wherein: gas introduced from the gas inlet port into the annular acceleration channel is ionized by a high-frequency wave supplied from the high-frequency wave supply section, to generate plasma; a positive ion includes in the generated plasma is accelerated by an acceleration voltage applied between the anode and cathode, and ejected outside; and an electron included in the generated plasma is restricted in its movement in the axial direction of the annular acceleration channel by an interaction with a magnetic field. The two-stage Hall-effect plasma accelerator is designed to control a degree of ion acceleration in accordance with the acceleration voltage serving as an acceleration control parameter, and control an amount of plasma generation in accordance with the high-frequency wave output serving as a plasma-generation control parameter. The two-stage Hall-effect plasma accelerator of the present invention can control the ion acceleration and the plasma generation in a highly independent manner.
Owner:JAPAN AEROSPACE EXPLORATION AGENCY
Magnetic lens apparatus for use in high-resolution scanning electron microscopes and lithographic processes
InactiveUS6410923B1Reduce the background by a large factorEasy to adjustThermometer detailsMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationMagnetic polesScanning electron microscope
Disclosed are lens apparatus in which a beam of charged particles is brought to a focus by means of a magnetic field, the lens being situated behind the target position. In illustrative embodiments, a lens apparatus is employed in a scanning electron microscope as the sole lens for high-resolution focusing of an electron beam, and in particular, an electron beam having an accelerating voltage of from about 10 to about 30,000 V. In one embodiment, the lens apparatus comprises an electrically-conducting coil arranged around the axis of the beam and a magnetic pole piece extending along the axis of the beam at least within the space surrounded by the coil. In other embodiments, the lens apparatus comprises a magnetic dipole or virtual magnetic monopole fabricated from a variety of materials, including permanent magnets, superconducting coils, and magnetizable spheres and needles contained within an energy-conducting coil. Multiple-array lens apparatus are also disclosed for simultaneous and / or consecutive imaging of multiple images on single or multiple specimens. The invention further provides apparatus, methods, and devices useful in focusing charged particle beams for lithographic processes.
Owner:ARCH DEVMENT
Charged particle beam column and method of its operation
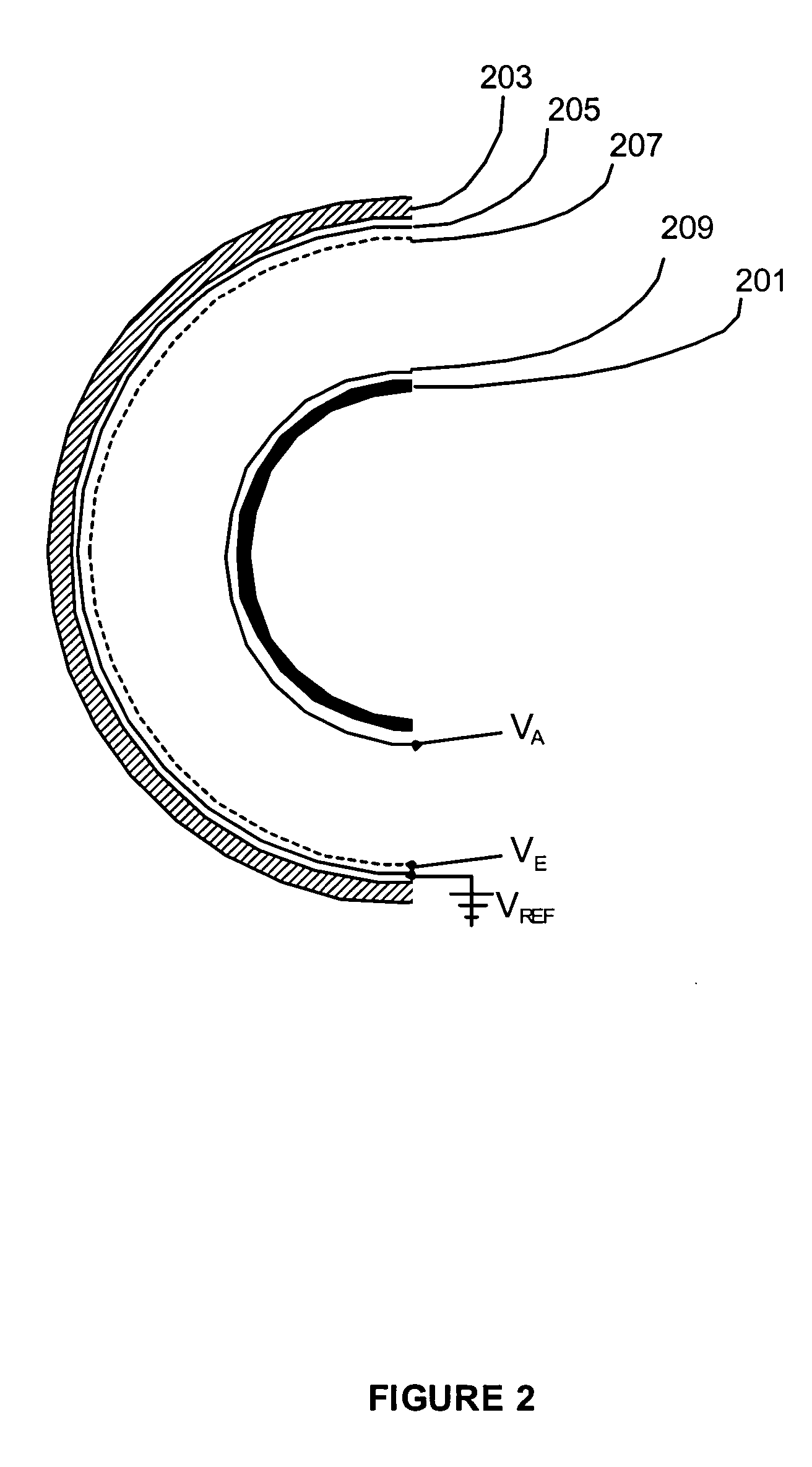
ActiveUS7067807B2Improve imaging resolutionReduce stepsThermometer detailsMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationAcceleration voltageCharged particle beam
A method and system are presented for controlling inspection of a sample with a charged particle beam. A certain given voltage is supplied to an anode of the column to provide a required accelerating voltage for a charged particle beam. A certain negative voltage is supplied to the sample selected so as to provide a desirably high effective voltage of the column at said given voltage of the anode. A certain voltage is supplied an electrode of a lens arrangement located closer to the sample, this voltage being selected to satisfy one of the following conditions: the electrode voltage is either equal to or slightly lower than that of the sample; and the electrode voltage is significantly higher than that of the sample.
Owner:APPL MATERIALS ISRAEL LTD
Charged particle beam column and method of its operation
ActiveUS20060049348A1Increase effective voltageImprove imaging resolutionThermometer detailsMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationAcceleration voltageCharged particle beam
A method and system are presented for controlling inspection of a sample with a charged particle beam. A certain given voltage is supplied to an anode of the column to provide a required accelerating voltage for a charged particle beam. A certain negative voltage is supplied to the sample selected so as to provide a desirably high effective voltage of the column at said given voltage of the anode. A certain voltage is supplied an electrode of a lens arrangement located closer to the sample, this voltage being selected to satisfy one of the following conditions: the electrode voltage is either equal to or slightly lower than that of the sample; and the electrode voltage is significantly higher than that of the sample.
Owner:APPL MATERIALS ISRAEL LTD
Electron beam device and electron beam application device using the same
ActiveUS20110240855A1Broadening energy widthIncrease brightnessMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationElectric arc lampsElectron sourceAcceleration voltage
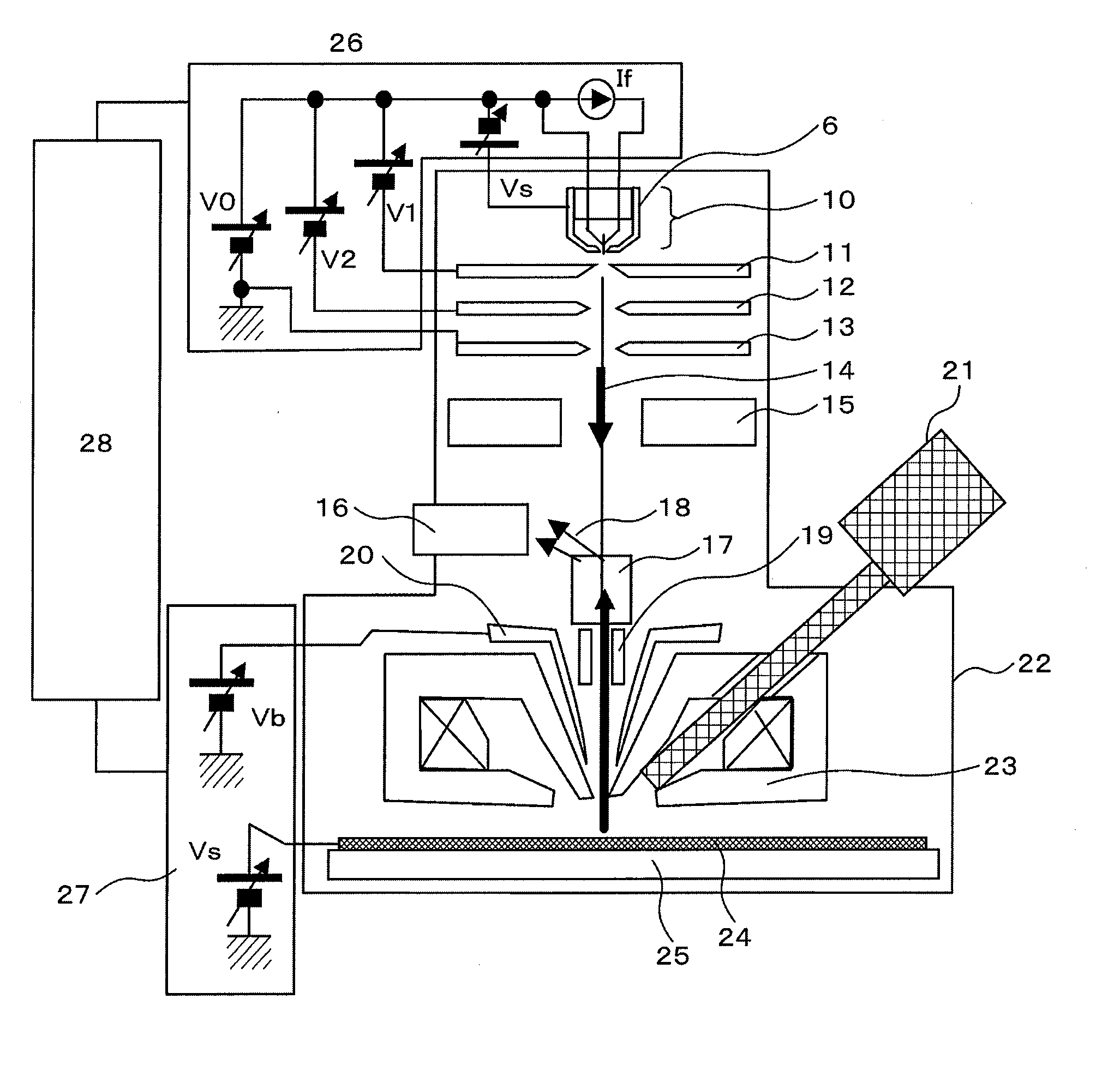
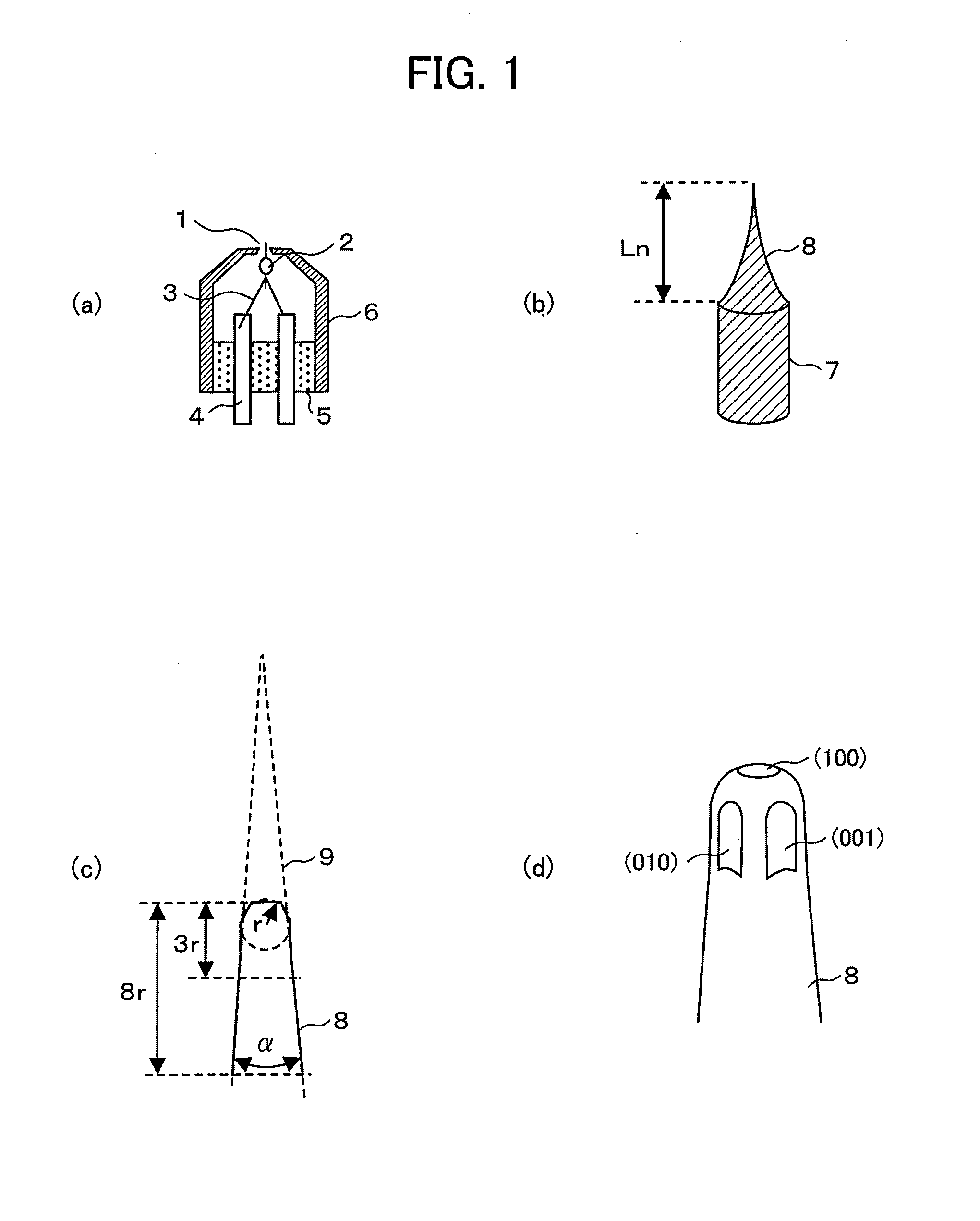
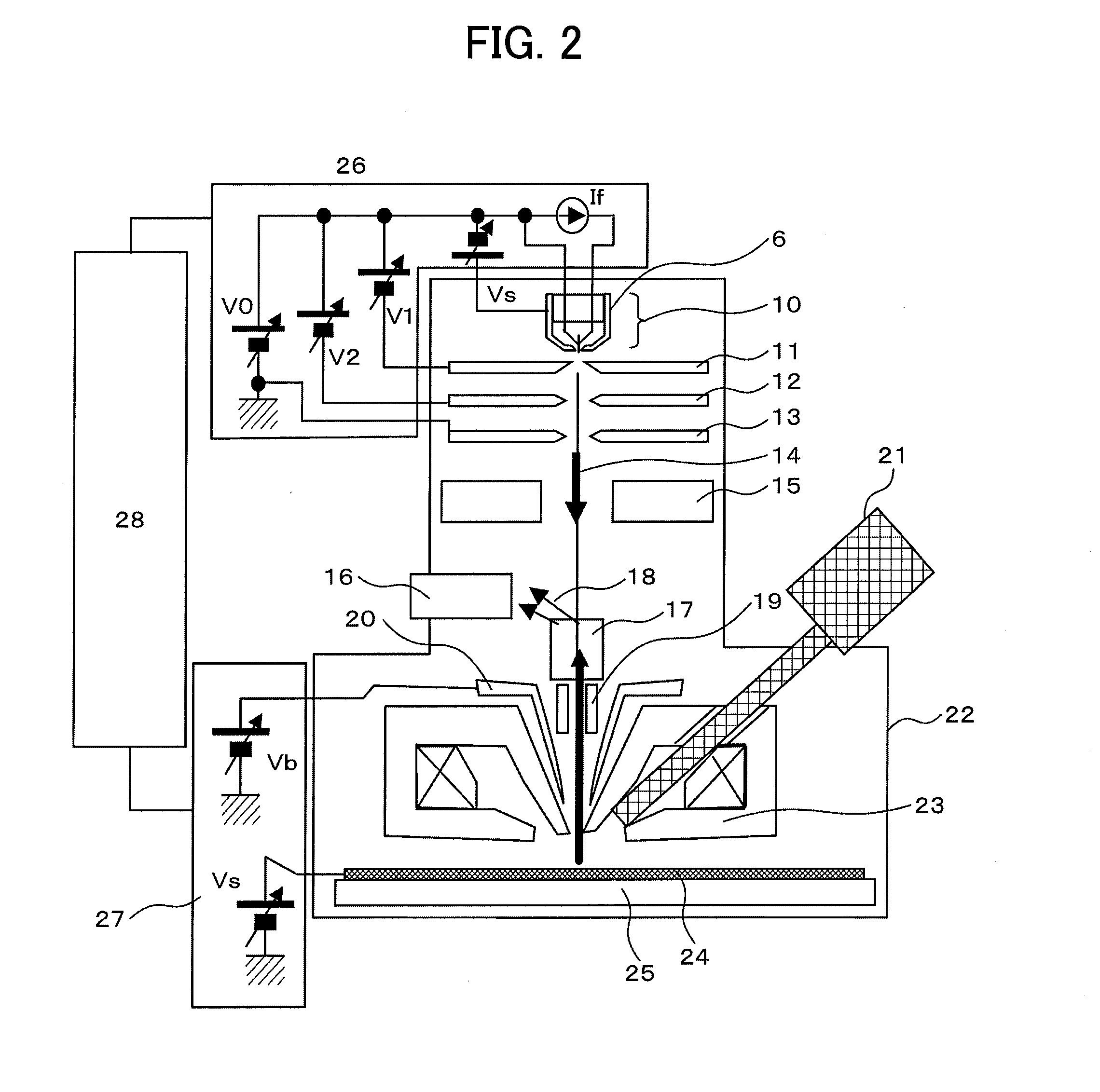
To obtain a SEM capable of both providing high resolution at low acceleration voltage and allowing high-speed elemental distribution measurement, a SE electron source including Zr—O as a diffusion source is shaped so that the radius r of curvature of the tip is more than 0.5 μm and less than 1 μm, and the cone angle α of a conical portion at a portion in the vicinity of the tip at a distance of 3r to 8r from the tip, is more than 5° and less than (8 / r)°. Another SE electron source uses Ba—O and includes a barium diffusion supply means composed of a sintered metal and a barium diffusion source containing barium oxide.
Owner:HITACHI HIGH-TECH CORP
RF accelerator method and apparatus used in conjunction with a charged particle cancer therapy system
ActiveUS8373146B2Stability-of-path spectrometersBeam/ray focussing/reflecting arrangementsParticle radiotherapyNuclear engineering
Owner:BALAKIN ANDREY VLADIMIROVICH +1
Charged particle optical apparatus with aberration corrector
ActiveUS20070181806A1Reduce in quantityImprove stabilityMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationElectric discharge tubesExcitation currentOptical axis
When an accelerating voltage and operating distance are changed, an excitation current and a pole voltage of an aberration corrector must also be changed. Moreover, different multipole voltages or currents must be added individually for each pole in order to superpose multipoles. In view of overcoming the problems explained above, the charged particle optical apparatus of the present invention comprises an excitation device including, to give excitation to form a multipole field to each pole of the multipole lens, electromagnetic type quadrupole of four stages arranged along an optical axis of charged particle beam, electromagnetic type quadrupole of two stages for superposing distribution of voltage similar to distribution of magnetic potential of the electromagnetic type quadrupole of two stages at the center of the electromagnetic type quadrupole of four stages, and electromagnetic type octupole for superposing magnetic potential at least to three multipoles among that of four stages and also comprises a first power supply group for driving the same excitation device and a second power supply group for impressing voltages.
Owner:HITACHI HIGH-TECH CORP
SPAD photodiode covered with a network
ActiveUS9741879B2Solid-state devicesRadiation controlled devicesSemiconductor materialsRefractive index
Owner:COMMISSARIAT A LENERGIE ATOMIQUE ET AUX ENERGIES ALTERNATIVES
Electron beam apparatus
InactiveUS7960697B2Improve imaging resolutionIncrease intensityThermometer detailsMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationScanning tunneling microscopeScanning electron microscope
The present invention relates to a charged particle beam apparatus which employs a scanning electron microscope for sample inspection and defect review.The present invent provides solution of improving imaging resolution by utilizing a field emission cathode tip with a large tip radius, applying a large accelerating voltage across ground potential between the cathode and anode, positioning the beam limit aperture before condenser lens, utilizing condenser lens excitation current to optimize image resolution, applying a high tube bias to shorten electron travel time, adopting and modifying SORIL objective lens to ameliorate aberration at large field of view and under electric drifting and reduce the urgency of water cooling objective lens while operating material analysis.The present invent provides solution of improving throughput by utilizing fast scanning ability of SORIL and providing a large voltage difference between sample and detectors.
Owner:ASML NETHERLANDS BV
Mist spraying apparatus and method, and image forming apparatus
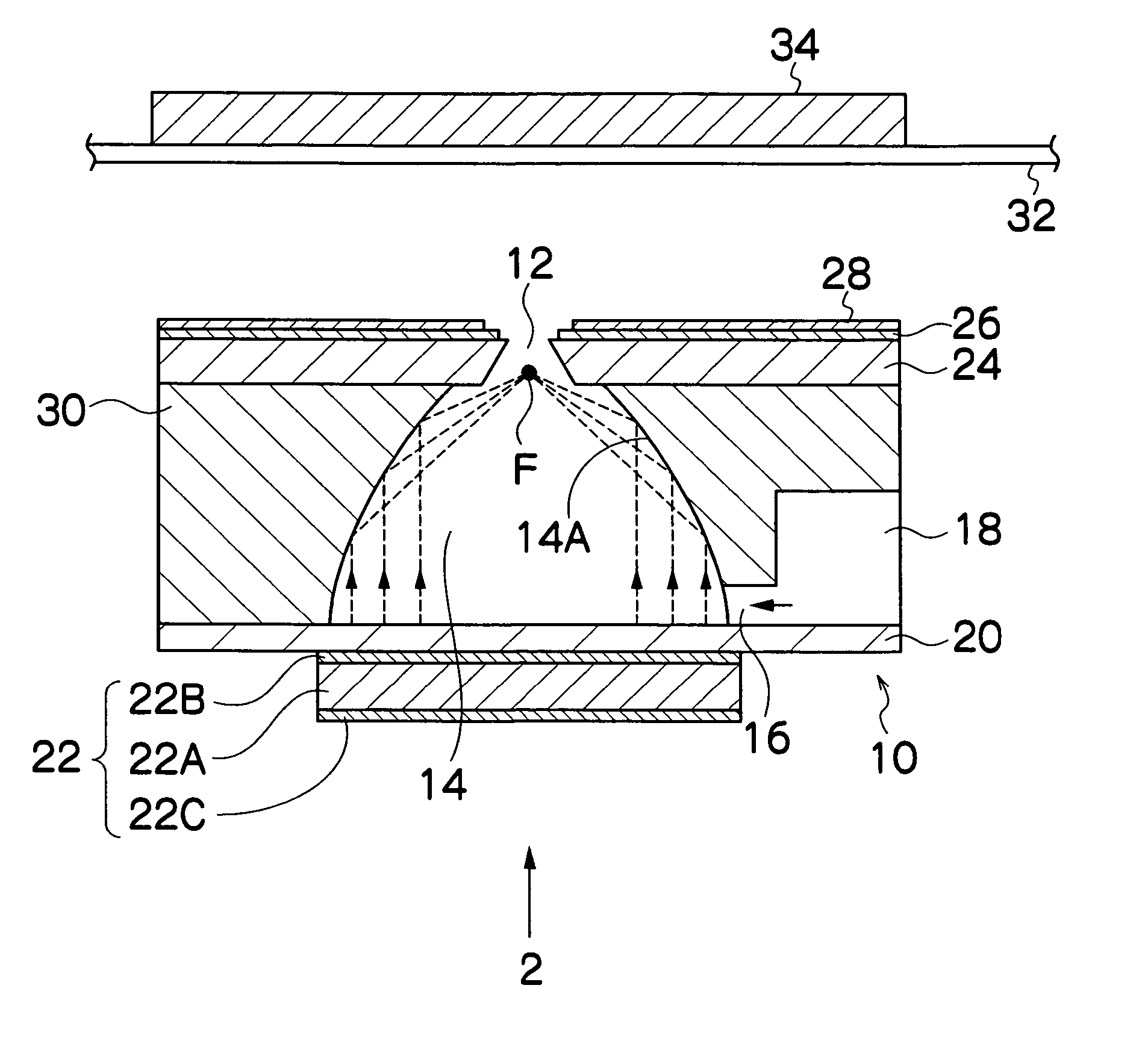
InactiveUS20060209129A1Suppressing amount of chargeImprove the deposition effectPrintingElectricityAcceleration voltage
The mist spraying apparatus comprises: a pressure chamber into which liquid is filled; a charging electrode which is in contact with the liquid and charges the liquid; a vibration generating device which converts the liquid into droplets by applying vibrational energy to the liquid inside the liquid chamber, thereby generating a charged mist; a rear surface electrode which is disposed so as to oppose an ejection surface including an ejection port ejecting the charged mist, and holds an liquid receiving medium onto which the charged mist is deposited from the ejection port; an acceleration electrode which is disposed at a position separated by a prescribed distance in an outward radial direction from an edge of the ejection port, and generates an electric field for acceleration between the acceleration electrode and the opposing rear surface electrode; a charging voltage application device which applies a charging voltage to the charging electrode; and an acceleration voltage application device which applies an acceleration voltage that is higher than the charging voltage to the acceleration electrode, thereby generating, between the acceleration electrode and the rear surface electrode, the electric field for acceleration having an electric field intensity which is greater than an electric field intensity generated between the charging electrode and the rear surface electrode by the voltage applied from the charging voltage application device.
Owner:FUJIFILM CORP
Method for positioning low impedance tiny flaws in comb metal wire structure
InactiveCN102053098ASolve the problem that defects in growth and etching related processes cannot be foundFast positioningScanning probe techniquesMaterial analysis by measuring secondary emissionProduction lineIon beam
The invention discloses a method for positioning low impedance tiny flaws in a comb metal wire structure, comprising the following steps: step one, punching a hole to an earthed terminal by a focused ion beam electron microscope (EMS), and realizing one end of a comb meal wire to be earthed by adopting a focused ion beam electron microscope metallic coating; step two, dividing the comb metal wire into n equal parts, wherein primary voltage contrast detection is performed at each time of dividing, the flaws can be positioned within the halved original area by each voltage contrast, and the flaws can be positioned within the area range of one [n(th) powder]th after evenly dividing for n times, and n is a positive integer; and step three, in the positioned tiny area, adopting an electron microscope for high accelerating voltage scanning to obverse the flaws buried by an insulating film. The method in the invention has high positioning speed and high efficiency, can solve the problem that flaws of some metal growth etching related technologies in semiconductor production lines can not be found out, and can greatly save manpower and use time of the electron microscope for scanning.
Owner:SHANGHAI HUA HONG NEC ELECTRONICS
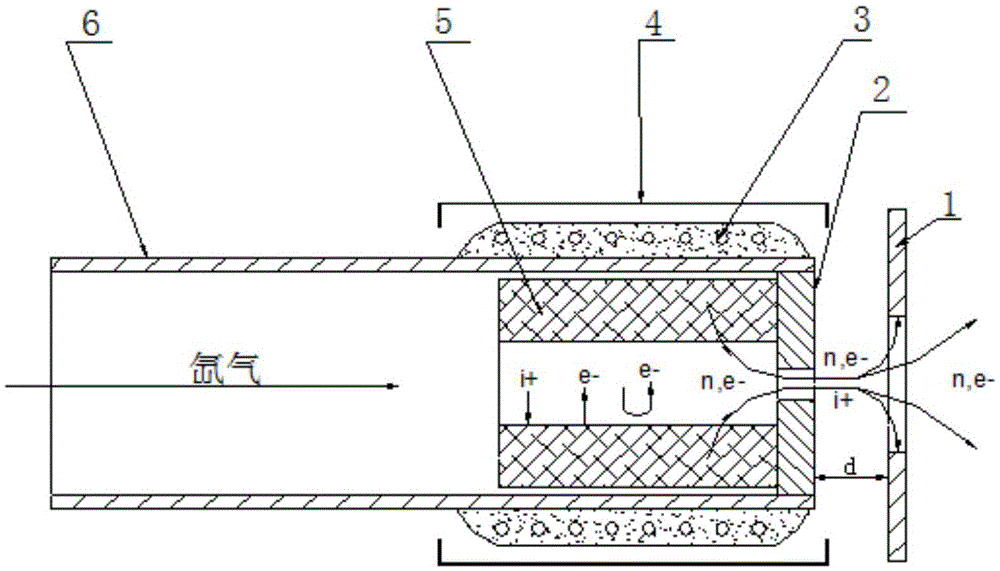
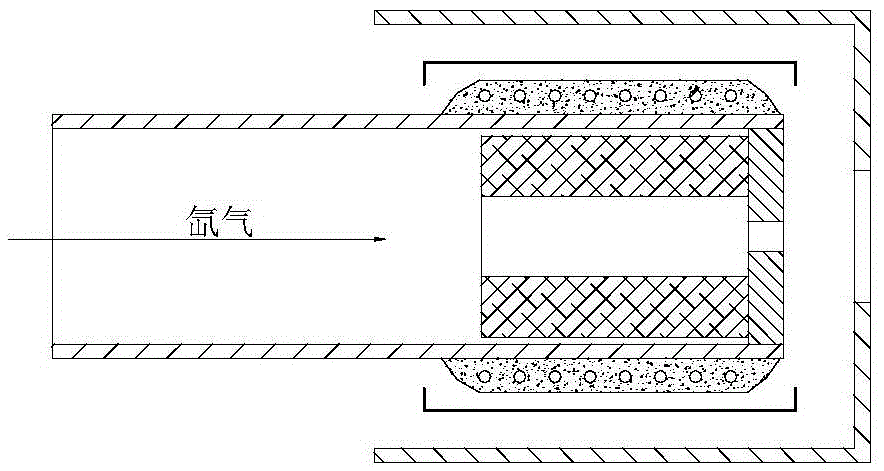
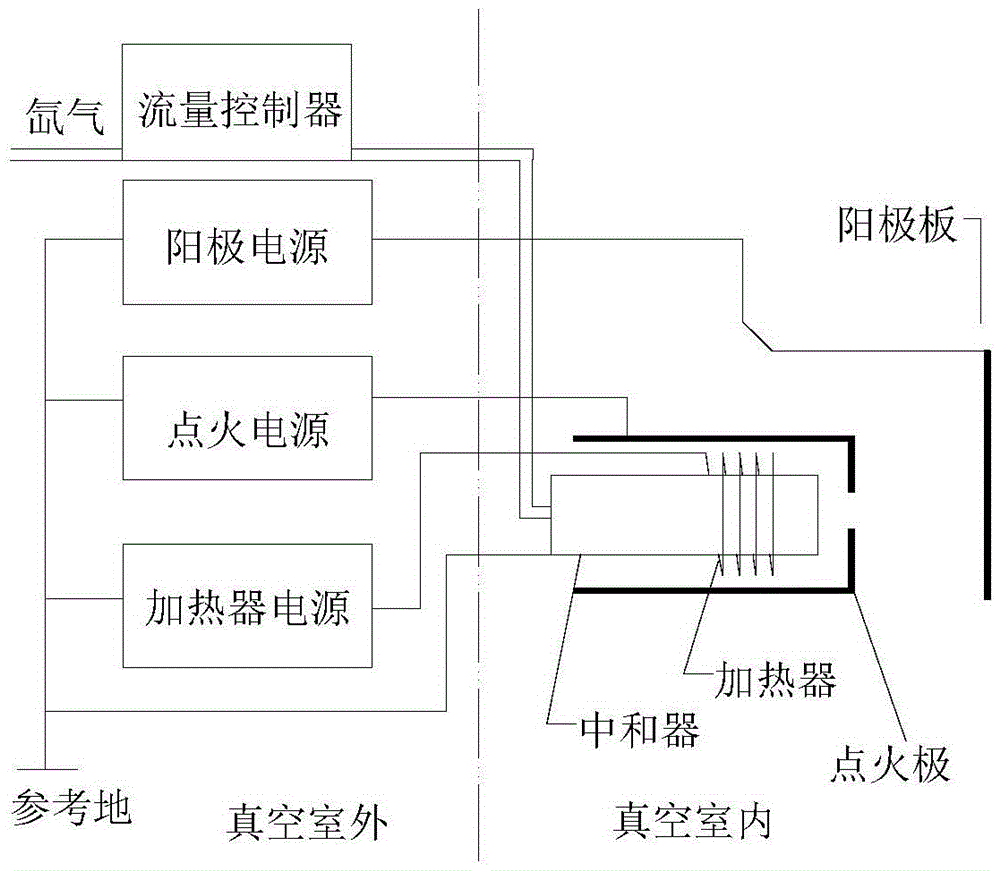
Plume neutralizer of space electric thruster
ActiveCN105626410AAvoid harmful effectsGuaranteed dockingMachines/enginesUsing plasmaGas-discharge lampPower flow
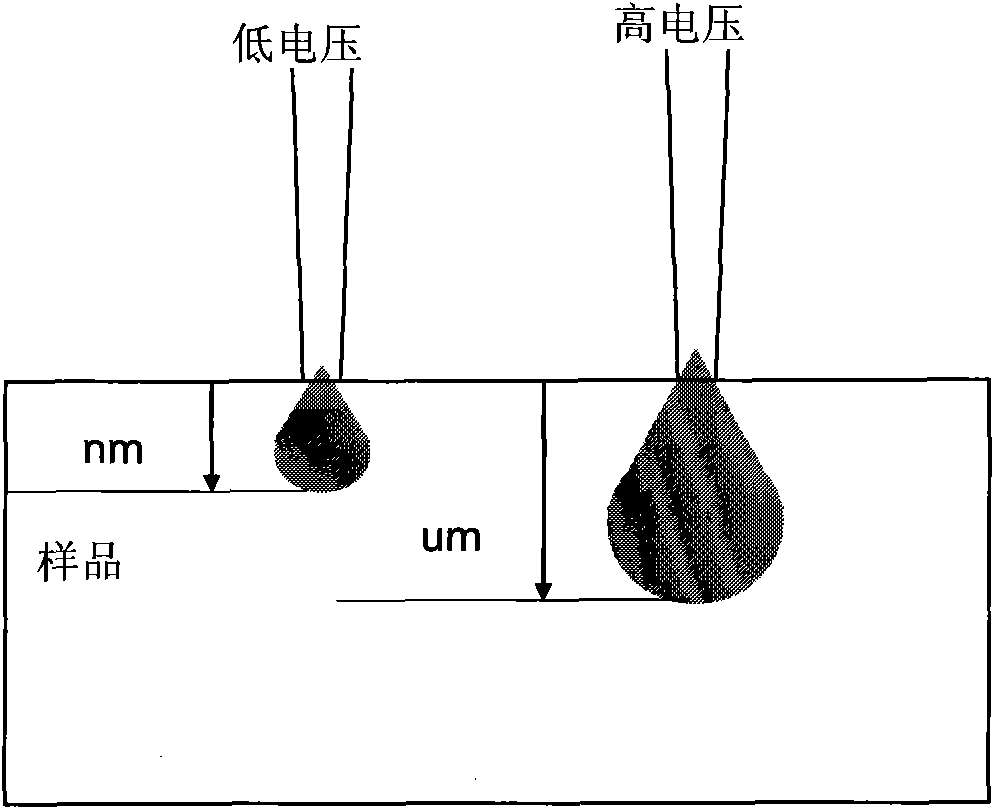
The invention discloses a plume neutralizer of a space electric thruster. The neutralizer comprises an ignition electrode, a top hole plate, a heater, a heat shielding cylinder, an emitting body and a support pipe; the emitting body is mounted in the support pipe; the top hole plate shields out of the emitting body, and is fixedly connected with the support pipe; the heater is mounted out of the support pipe opposite to the emitting body; a heating area covers the whole emitting body; the heater is wrapped with an insulation ceramic layer; the heat shielding cylinder covers the heater, and forms gaps with the heater and the insulation ceramic layer; the ignition electrode is mounted at the downstream of the top hole plate, and forms a gap with a small hole of the top hole plate; and a center hole of the ignition electrode is coaxial with the small hole of the top hole plate. The neutralizer generates a lot of electrons through a hot electron ionized gas discharge mode; continuously emitted electrons are high in density; after the gas discharge is stabilized, the self-heating can be performed to maintain discharge, so that the system power consumption is saved; the equivalent potential is low; the effective acceleration voltage of the thruster is higher; and the specific impulse of the thruster is high.
Owner:SHANGHAI INST OF SPACE PROPULSION
Gray scale all-glass photomasks
InactiveUS20050053844A1Facilitates new designLow costElectric discharge tubesPhotomechanical exposure apparatusThree dimensional microstructureEffect light
A narrowly defined range of zinc silicate glass compositions is found to produce High Energy Beam Sensitive-glass (HEBS-glass) that possesses the essential properties of a true gray level mask which is necessary for the fabrication of general three dimensional microstructures with one optical exposure in a conventional photolithographic process. The essential properties are (1) A mask pattern or image is grainiless even when observed under optical microscope at 1000× or at higher magnifications. (2) The HEBS-glass is insensitive and / or inert to photons in the spectral ranges employed in photolithographic processes, and is also insensitive and / or inert to visible spectral range of light so that a HEBS-glass mask blank and a HEBS-glass mask are permanently stable under room lighting conditions. (3) The HEBS-glass is sufficiently sensitive to electron beam exposure, so that the cost of making a mask using an e-beam writer is affordable for at least certain applications. (4) The e-beam induced optical density is a unique function of, and is a very reproducible function of electron dosages for one or more combinations of the parameters of an e-beam writer. The parameters of e-beam writers include beam acceleration voltage, beam current, beam spot size, addressing grid size and number of retraces. A method of fabricating three-dimensional microstructures using HEBS-glass gray scale photomask for three dimensional profiling of photoresist and reproducing the photoresist replica in the substrate with the existing microfabrication methods normally used for the production of microelectronics is described.
Owner:CANYON MATERIALS
Method and apparatus for enhancing voltage regulator transient response
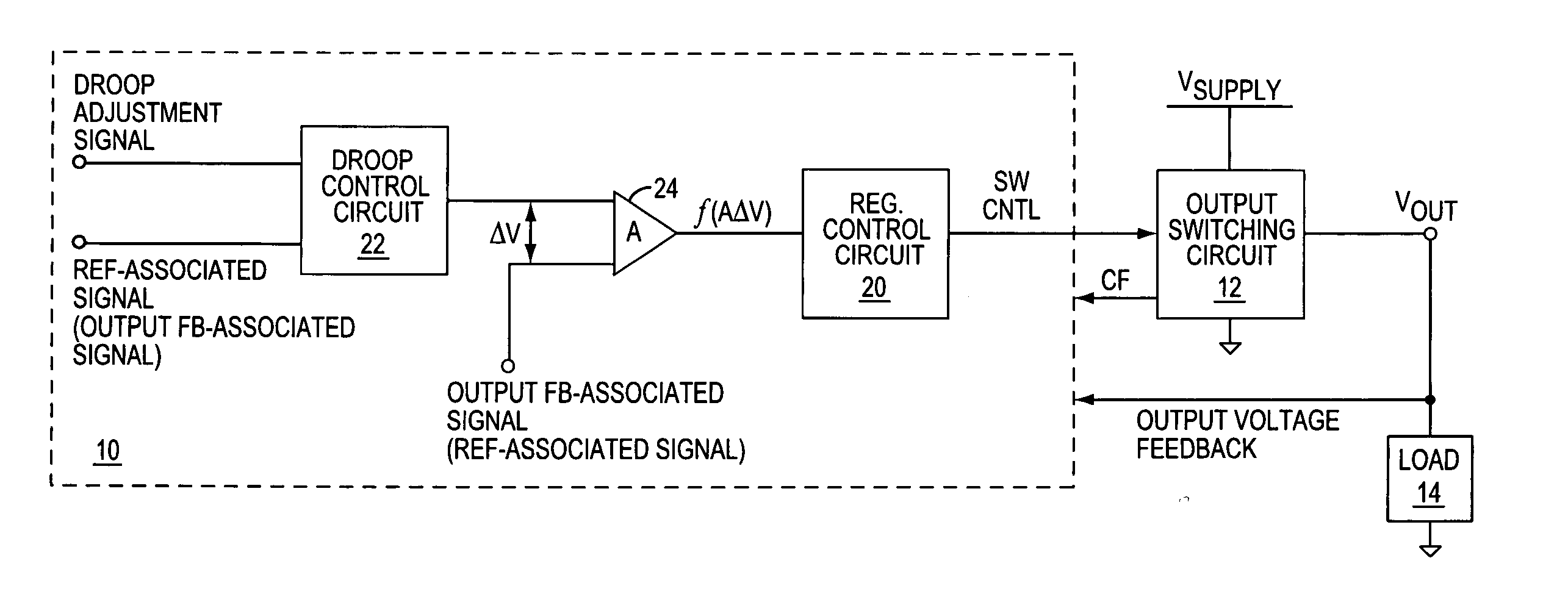
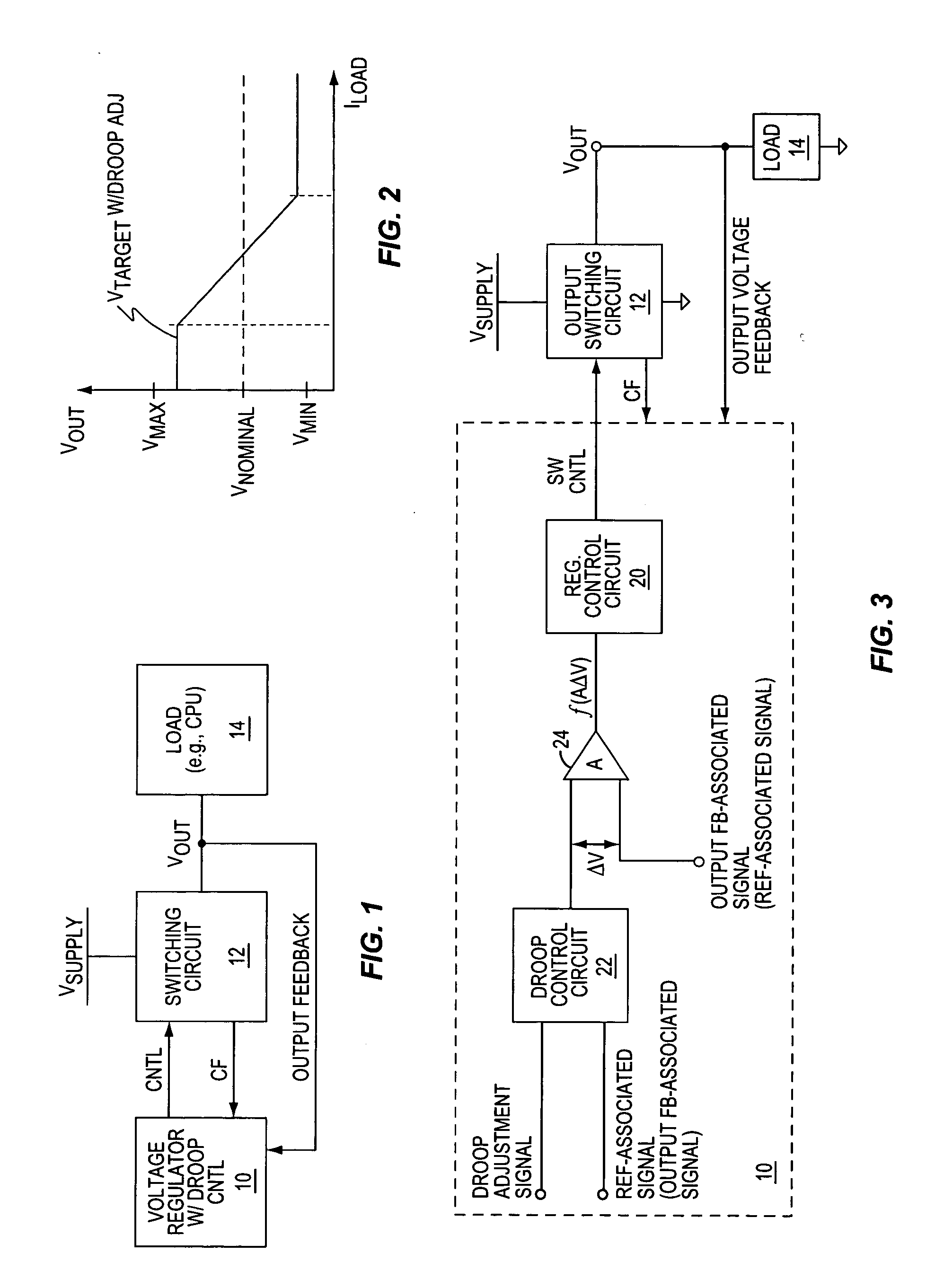
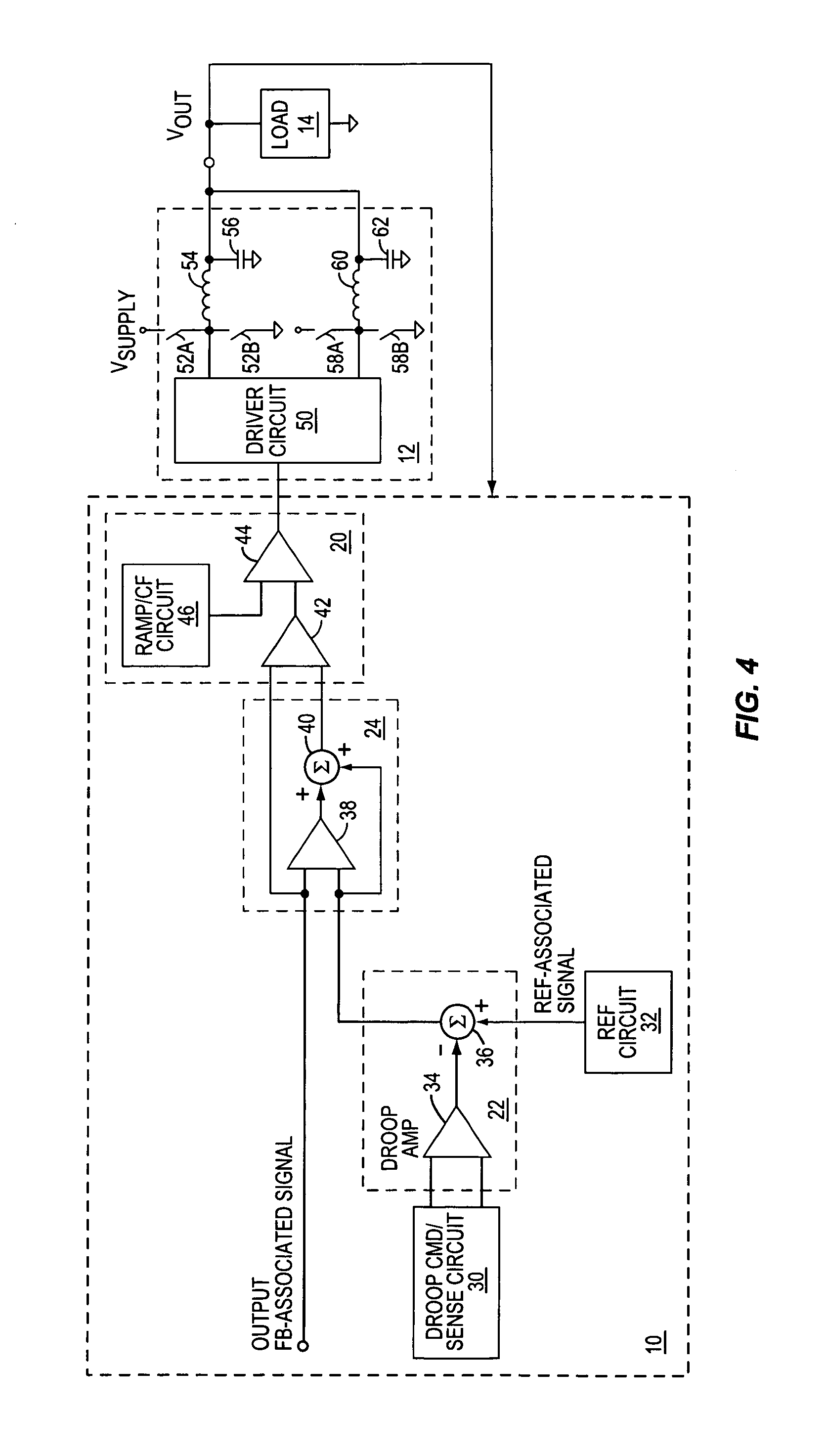
InactiveUS20050194952A1Improve transient responseReduce errorsDc-dc conversionElectric variable regulationAudio power amplifierVoltage regulation
A voltage regulator improves its transient adjustment response by amplifying error in its regulation feedback control path, including any droop-related error. Amplifying the error speeds up the voltage regulator's response to load changes and droop control adjustments by exaggerating the feedback error. Thus, in at least one embodiment, a droop control circuit imparts a droop-related offset between an output feedback signal and a reference signal responsive to a droop adjustment signal, and a response-enhancing amplifier circuit amplifies that offset for input to an error sensing circuit of a regulation control circuit. The gain and frequency response of the response-enhancing amplifier circuit may be set as a function one or more regulation stability criteria, and the response-enhancing method may be adapted to a variety of voltage regulator topologies. Such topologies include, but are not limited to, PWM regulators and hysteretic regulators.
Owner:SEMTECH CORP
Mass spectrometer
ActiveUS7208728B2Wide range of qualityHigh sensitivityStability-of-path spectrometersTime-of-flight spectrometersDelayed timeMass analyzer
A mass spectrometer capable of analyzing a wide mass range with high sensitivity and high mass accuracy. A mass spectrometer has an ionization source generating ions; an ion transfer optics transferring the ions; a first linear trap accumulating the ions and ejecting the ions in the specific mass range; a second linear trap having an end electrode disposed at the exit end ejecting the ions to change a DC potential gradient relative to a DC potential of the end electrode and trapping the ions ejected from the first linear trap to repeatedly eject them in pulse form; a time-of-flight mass spectrometer accelerating the ions ejected from the second linear trap in the orthogonal direction to detect them; and a controller changing the time duration of the ions in which the ions are ejected from the second linear trap or delay time from the completion of ejection to application of an accelerating voltage of the time-of-flight mass spectrometer according to the mass range of the ions ejected from the first linear trap to the second linear trap.
Owner:HITACHI HIGH-TECH CORP
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com