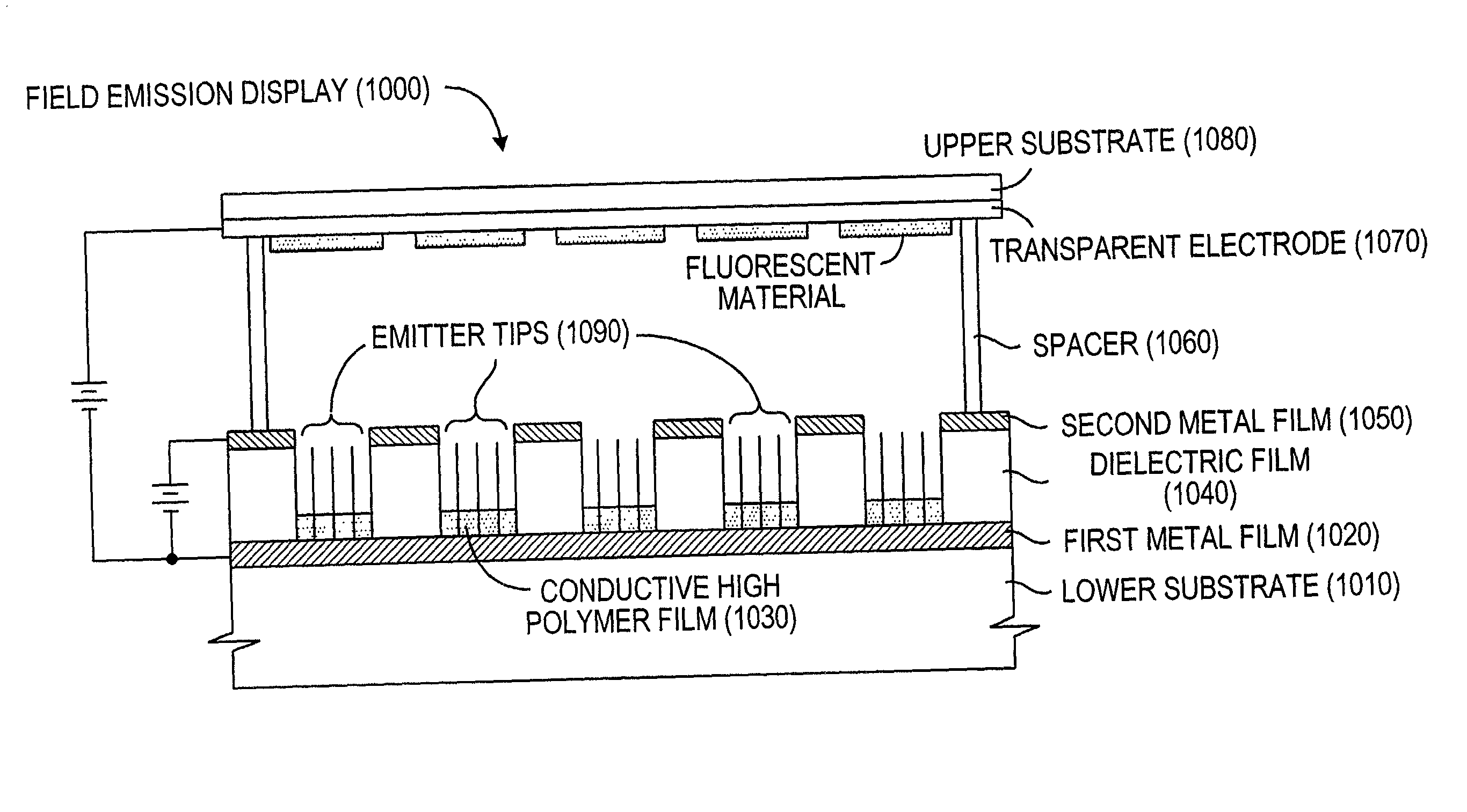
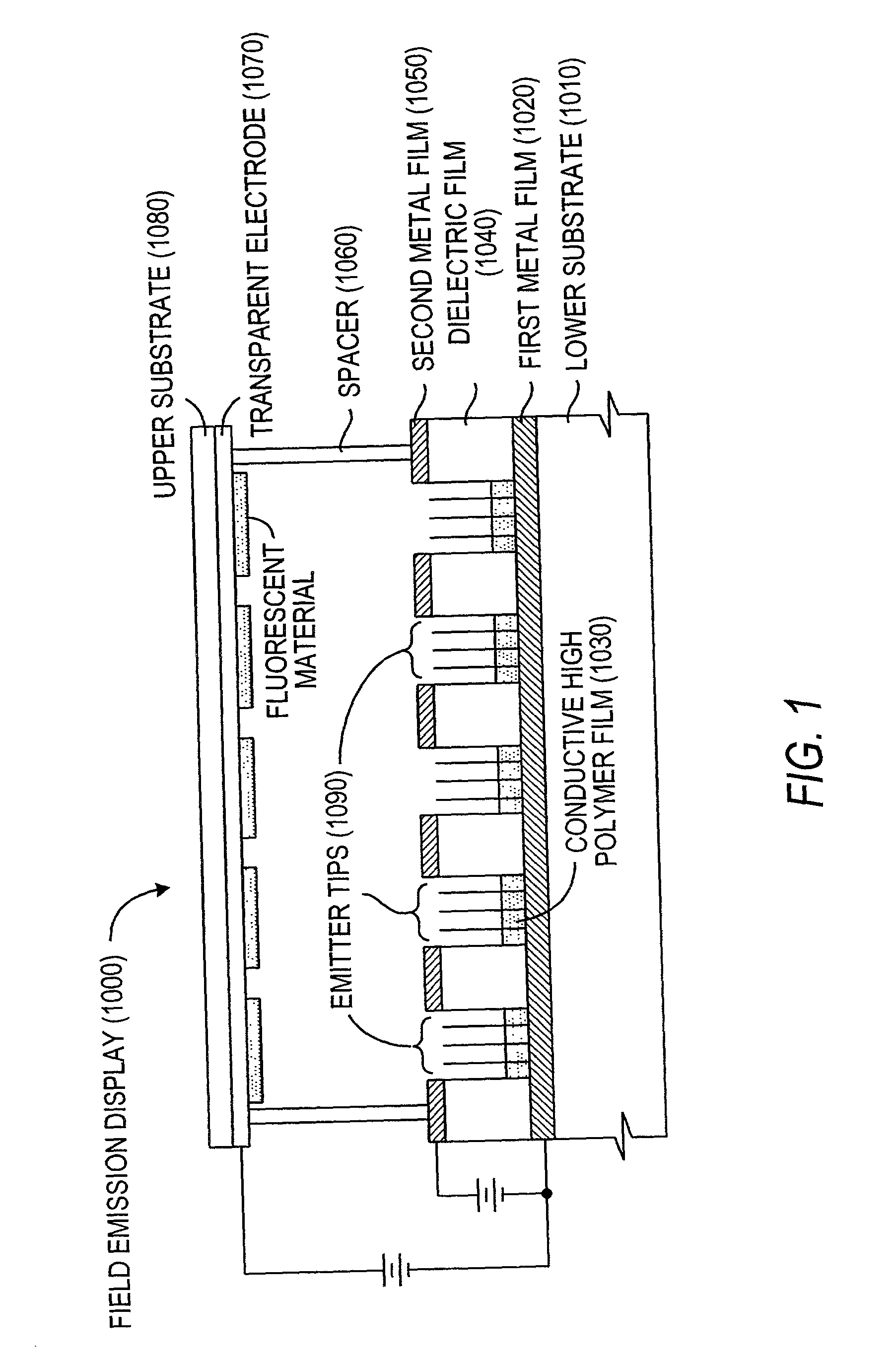
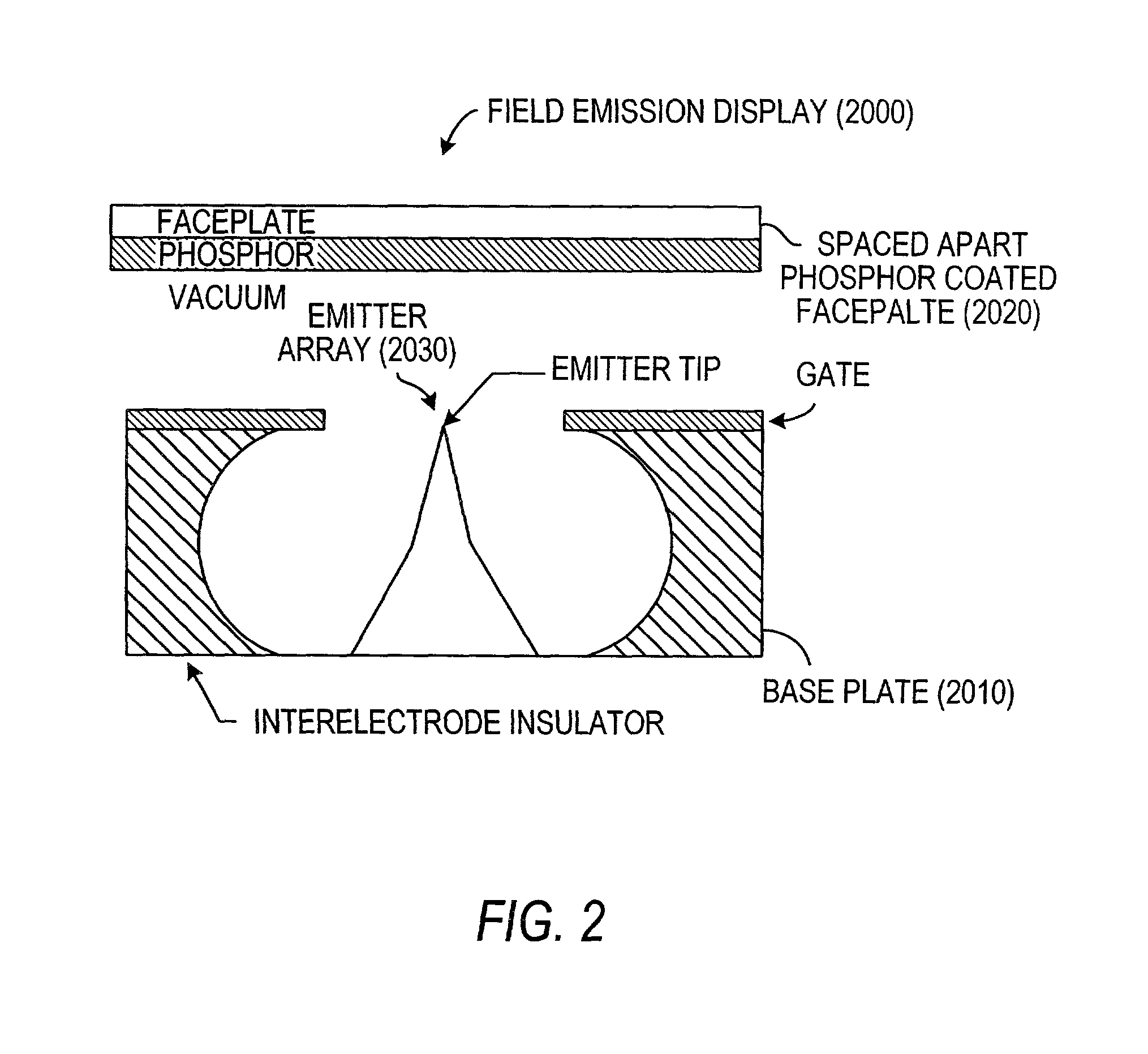
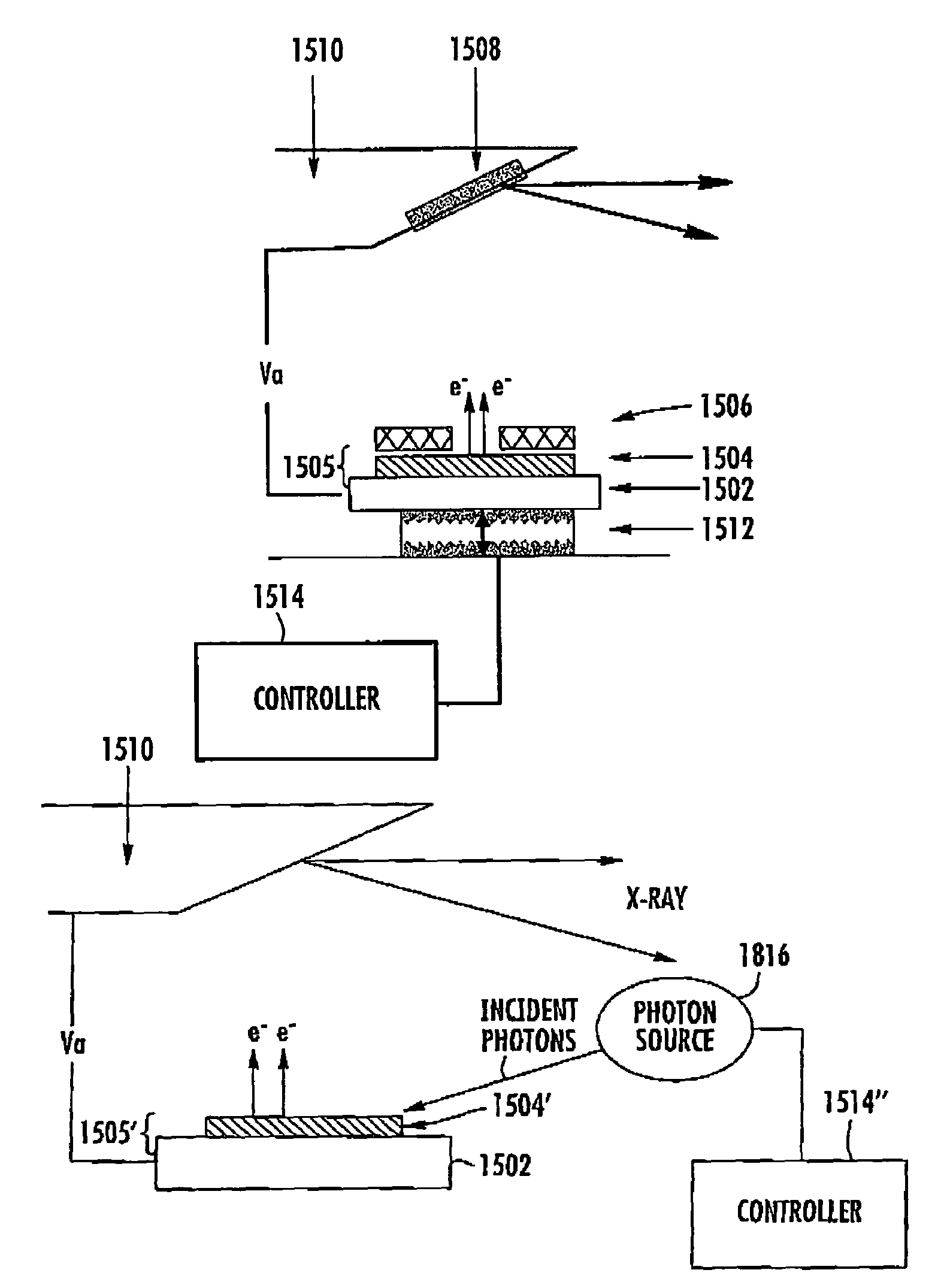
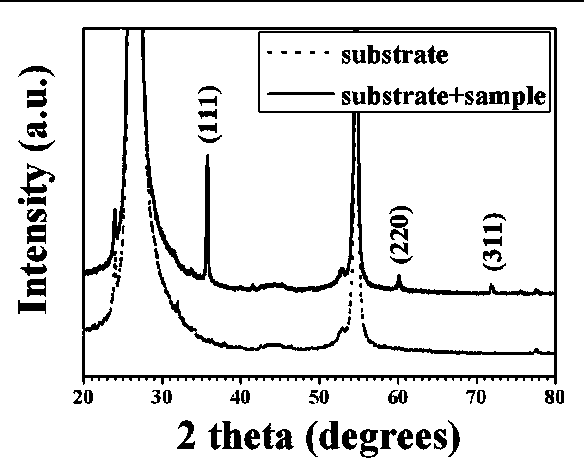
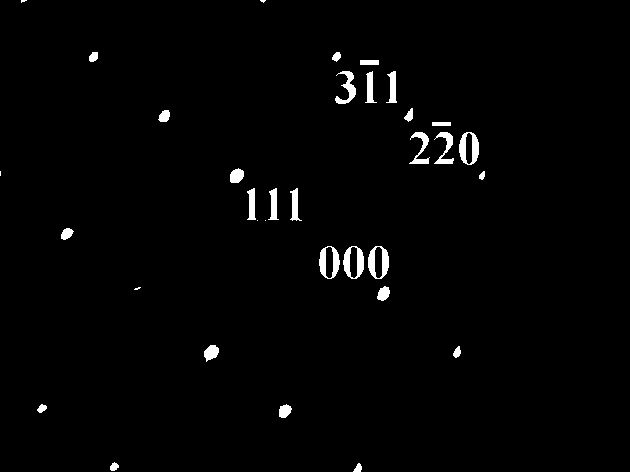Patents
Literature
446 results about "Field emission cathode" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
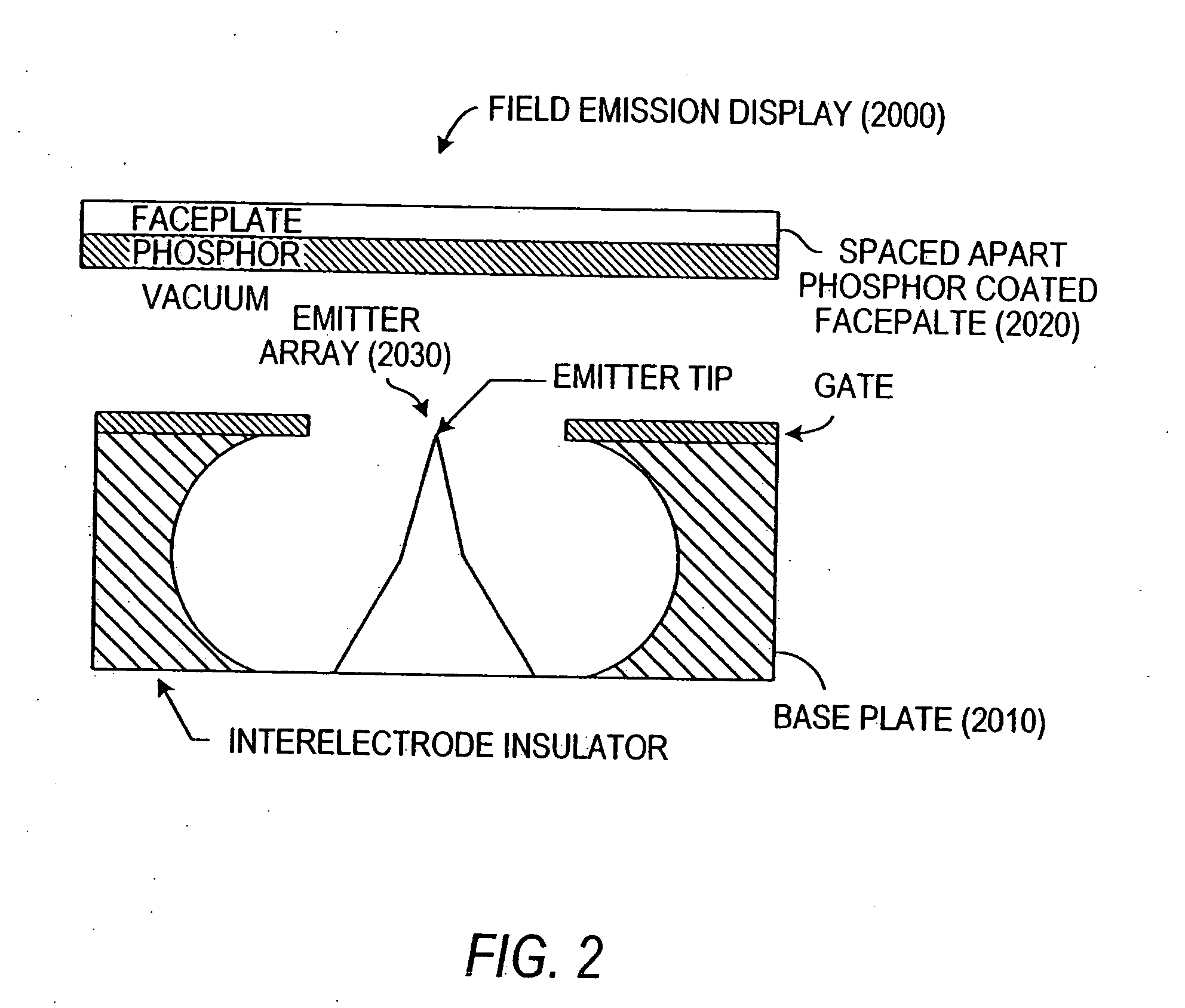
Field emission devices using modified carbon nanotubes
InactiveUS20030090190A1Accelerate emissionsReduce voltageNanostructure manufactureNanoinformaticsField emission deviceModified carbon
The present invention relates to a field emission device comprising an anode and a cathode, wherein said cathode includes carbon nanotubes nanotubes which have been subjected to energy, plasma, chemical, or mechanical treatment. The present invention also relates to a field emission cathode comprising carbon nanotubes which have been subject to such treatment. A method for treating the carbon nanotubes and for creating a field emission cathode is also disclosed. A field emission display device containing carbon nanotube which have been subject to such treatment is further disclosed.
Owner:HYPERION CATALYSIS INT
Method and apparatus for controlling electron beam current
InactiveUS7085351B2High emitted electron current densityHigh electron beam currentStatic indicating devicesNanoinformaticsHigh energyX-ray
An x-ray generating device includes a field emission cathode formed at least partially from a nanostructure-containing material having an emitted electron current density of at least 4 A / cm2. High energy conversion efficiency and compact design are achieved due to easy focusing of cold cathode emitted electrons and dramatic reduction of heating at the anode. In addition, by pulsing the field between the cathode and the gate or anode and focusing the electron beams at different anode materials, pulsed x-ray radiation with varying energy can be generated from a single device. Methods and apparatus for independent control of electron emission current and x-ray energy in x-ray tubes are also provided. The independent control can be accomplished by adjusting the distance between the cathode and anode. The independent control can also be accomplished by adjusting the temperature of the cathode. The independent control can also be accomplished by optical excitation of the cathode. The cathode can include field emissive materials such as carbon nanotubes.
Owner:THE UNIV OF NORTH CAROLINA AT CHAPEL HILL
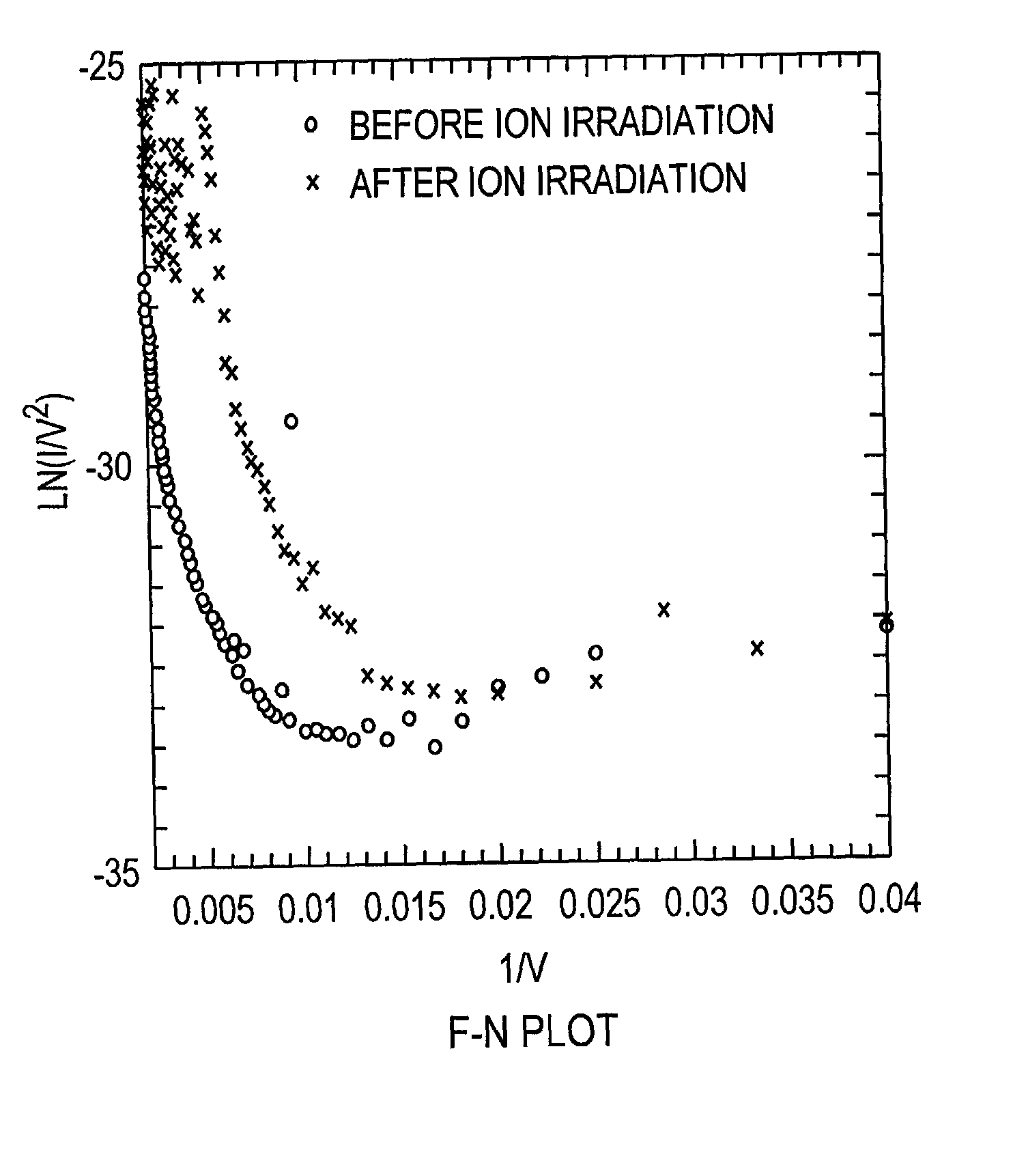
Field emission devices using ion bombarded carbon nanotubes
InactiveUS6911767B2Reduce voltageAccelerate emissionsCathode ray tubes/electron beam tubesNanoinformaticsField emission deviceOxygen
The present invention relates to a field emission device comprising an anode and a cathode, wherein said cathode includes carbon nanotubes which have been treated with an ion beam. The ion beam may be any ions, including gallium, hydrogen, helium, argon, carbon, oxygen, and xenon ions. The present invention also relates to a field emission cathode comprising carbon nanotubes, wherein the nanotubes have been treated with an ion beam. A method for treating the carbon nanotubes and for creating a field emission cathode is also disclosed. A field emission display device containing carbon nanotube which have been treated with an ion beam is further disclosed.
Owner:HYPERION CATALYSIS INT
X-ray generating mechanism using electron field emission cathode
InactiveUS6850595B2High emitted electron current densityHigh electron beam currentX-ray tube electrodesNanoinformaticsElectron currentSoft x ray
An x-ray generating device includes a field emission cathode formed at least partially from a nanostructure-containing material having an emitted electron current density of at least 4 A / cm2. High energy conversion efficiency and compact design are achieved due to easy focusing of cold cathode emitted electrons and dramatic reduction of heating at the anode. In addition, by pulsing the field between the cathode and the gate or anode and focusing the electron beams at different anode materials, pulsed x-ray radiation with varying energy can be generated from a single device.
Owner:THE UNIV OF NORTH CAROLINA AT CHAPEL HILL
Automatically sharp field emission cathodes
InactiveUS6201342B1Clarity is not affectedImprove uniformityThermionic cathodesDischarge tube cold cathodesSingle crystalSelf assembling
Owner:THE UNITED STATES OF AMERICA AS REPRESENTED BY THE SECRETARY OF THE NAVY
Field emission devices using ion bombarded carbon nanotubes
InactiveUS20030044519A1Easy to disassembleReduce voltageCathode ray tubes/electron beam tubesNanoinformaticsField emission deviceOxygen
The present invention relates to a field emission device comprising an anode and a cathode, wherein said cathode includes carbon nanotubes which have been treated with an ion beam. The ion beam may be any ions, including gallium, hydrogen, helium, argon, carbon, oxygen, and xenon ions. The present invention also relates to a field emission cathode comprising carbon nanotubes, wherein the nanotubes have been treated with an ion beam. A method for treating the carbon nanotubes and for creating a field emission cathode is also disclosed. A field emission display device containing carbon nanotube which have been treated with an ion beam is further disclosed.
Owner:HYPERION CATALYSIS INT
Atomically sharp field emission cathodes
InactiveUS6113451AClarity is not affectedImprove uniformityElectric discharge tubesVessels or leading-in conductors manufactureSingle crystalElectron
An electron emitting device characterized by a monocrystalline substrate, a plurality of monocrystalline nanomesas or pillars disposed on the substrate in a spaced relationship and extending generally normally therefrom, monocrystalline self-assembled tips disposed on top of the nanomesas, and essentially atomically sharp apexes on the tips for field emitting electrons. A method for making the emitters is characterized by forming a gate electrode and gate electrode apertures before forming the tips on the nanomesas.
Owner:THE UNITED STATES OF AMERICA AS REPRESENTED BY THE SECRETARY OF THE NAVY
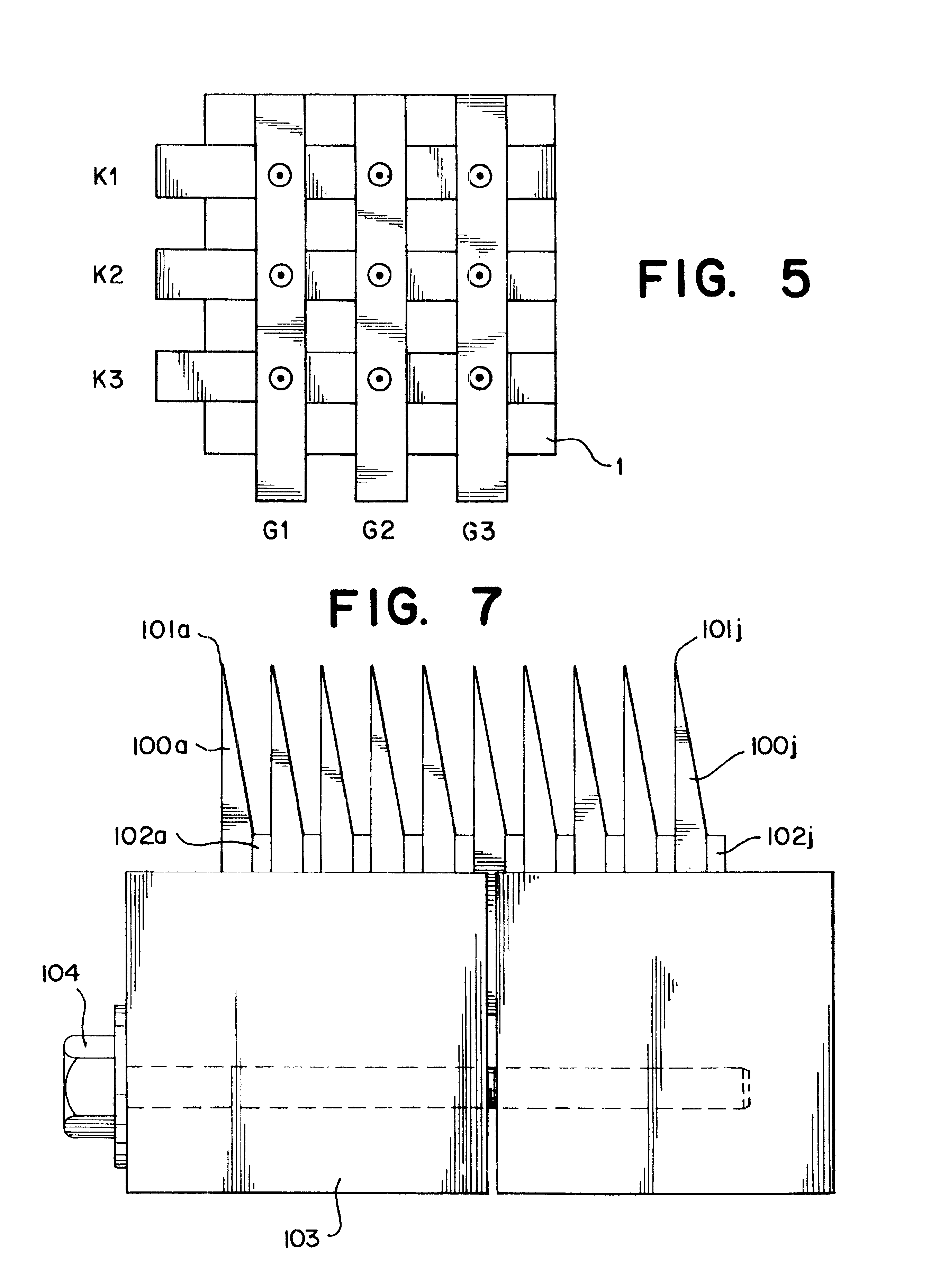
Method for making a carbon nanotube-based field emission cathode device
ActiveUS20050236951A1Improve Field Emission EfficiencyAccelerate emissionsElectric discharge tubesNanoinformaticsCarbon nanotubeSolvent
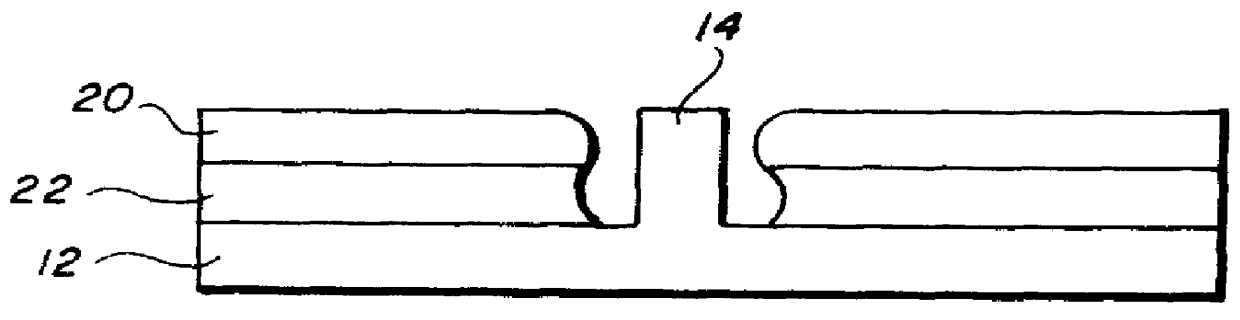
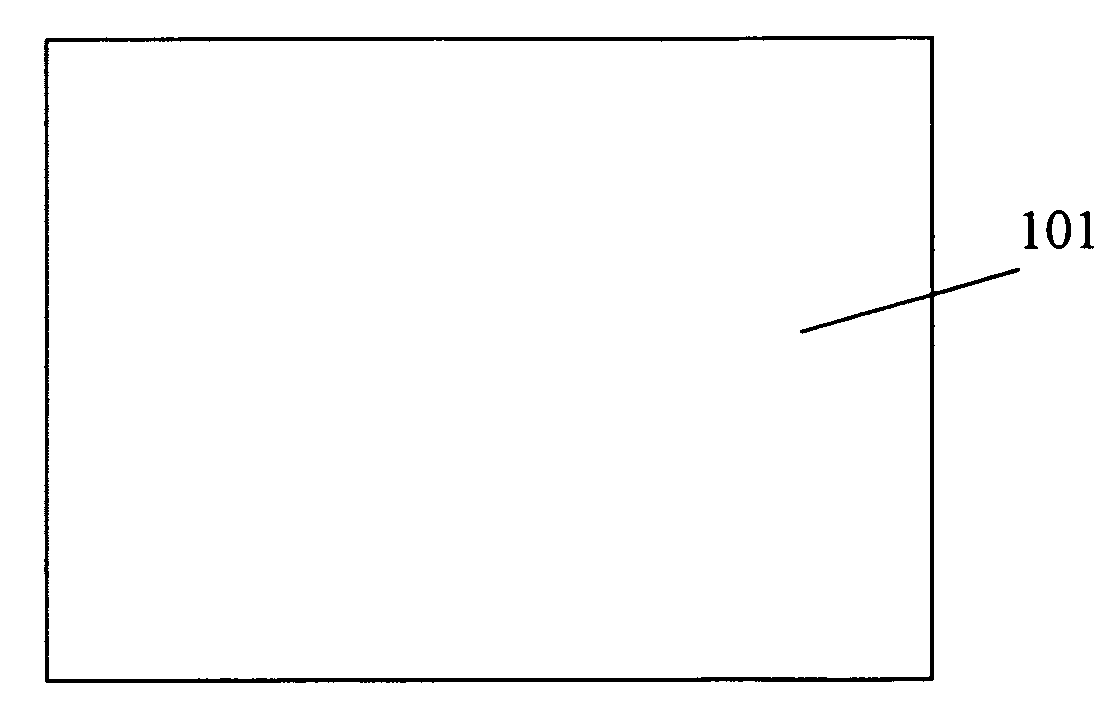
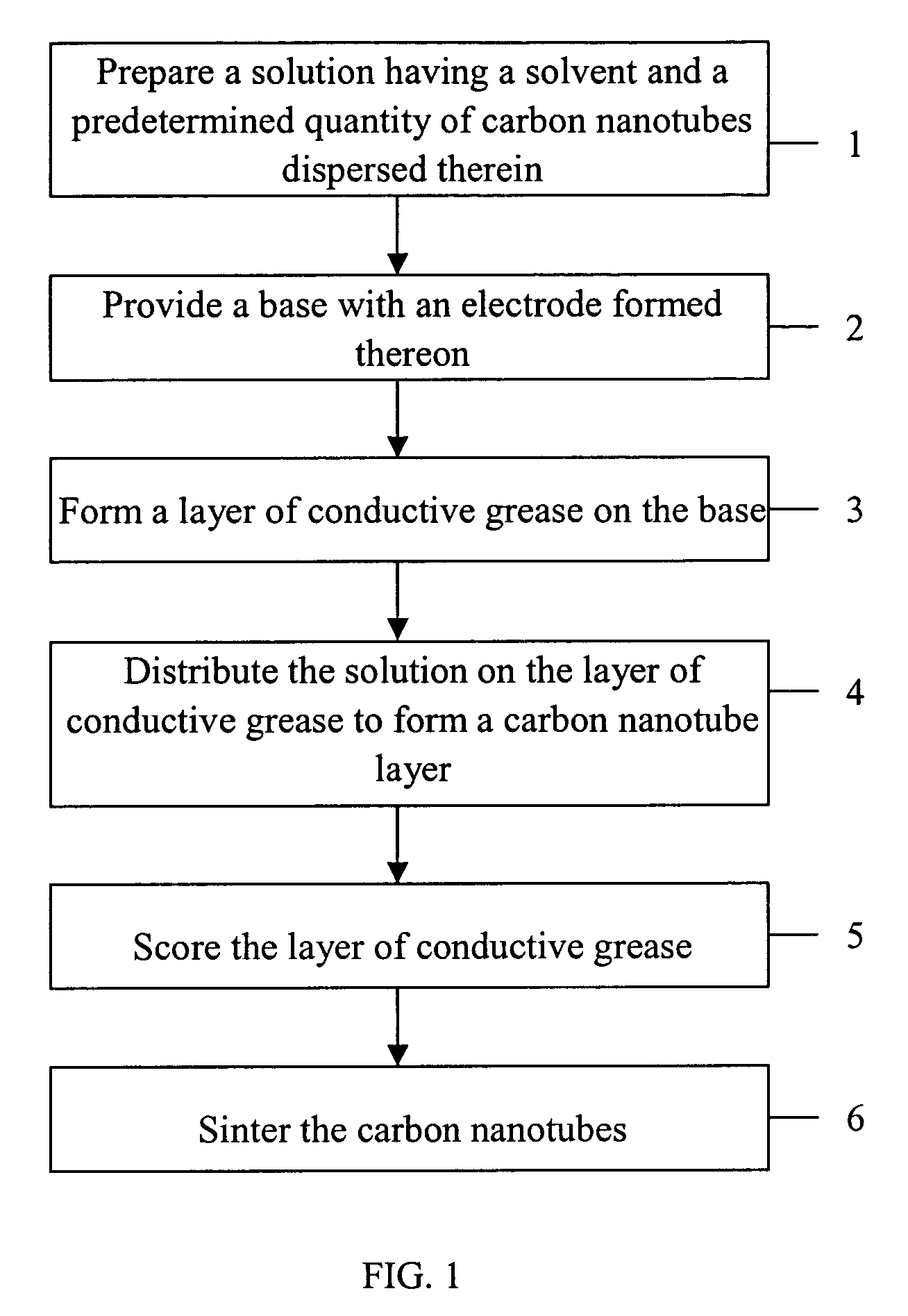
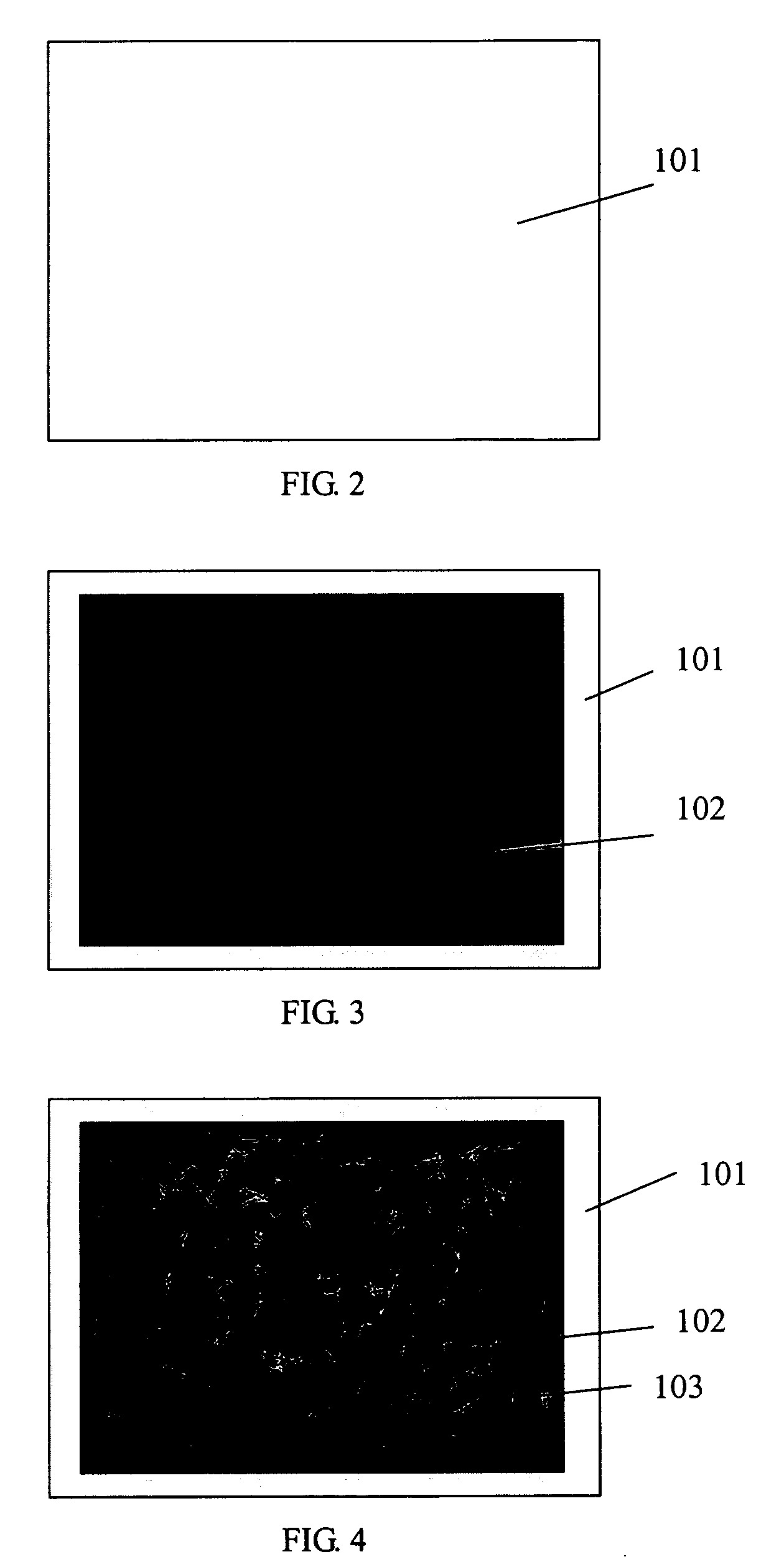
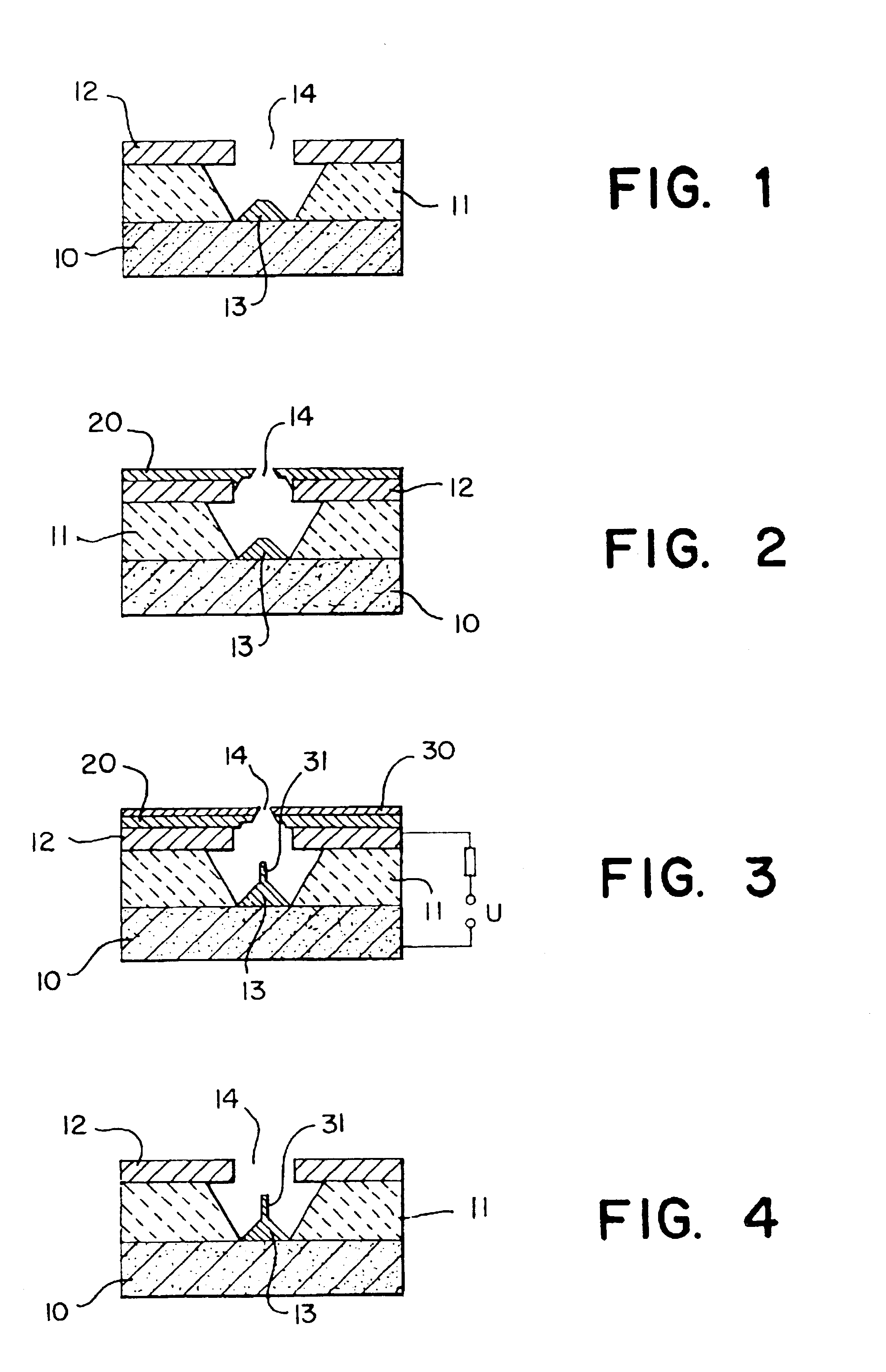
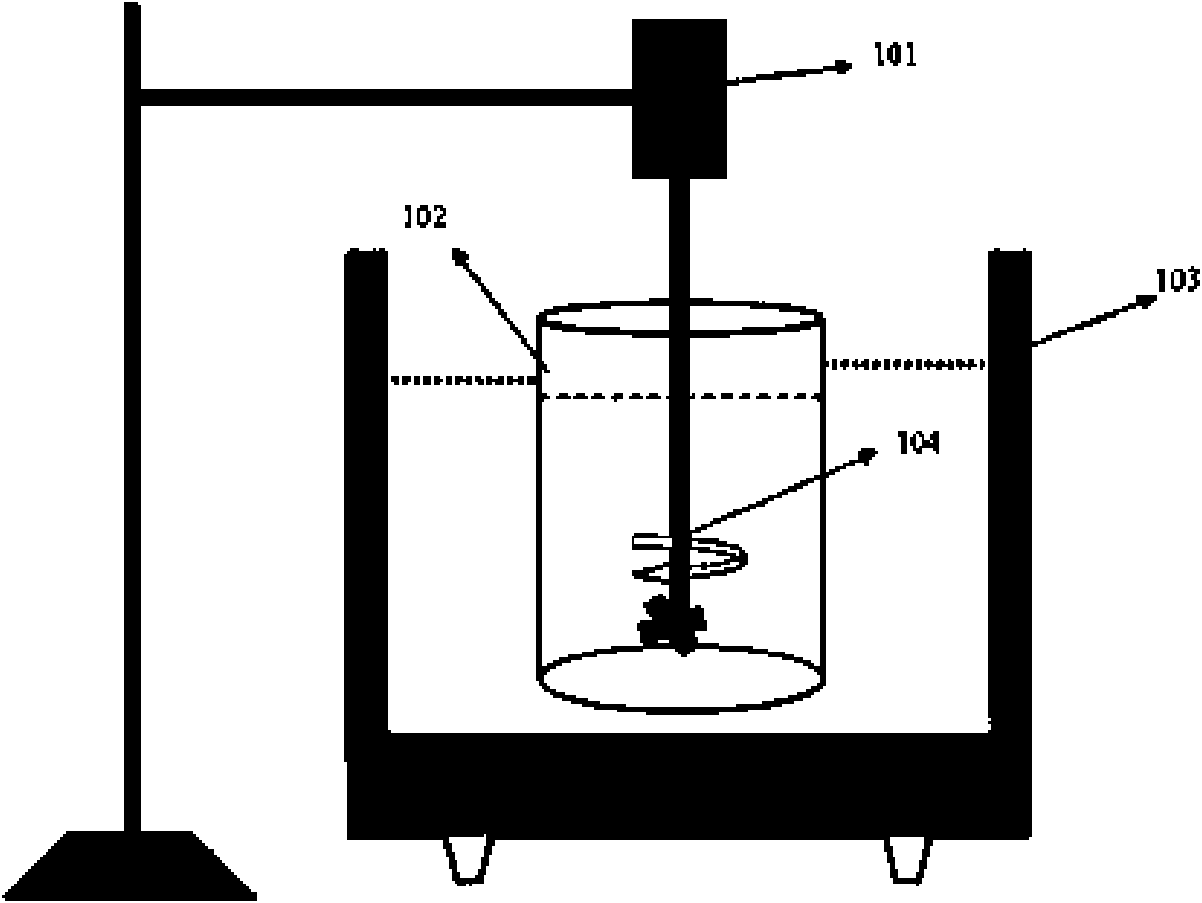
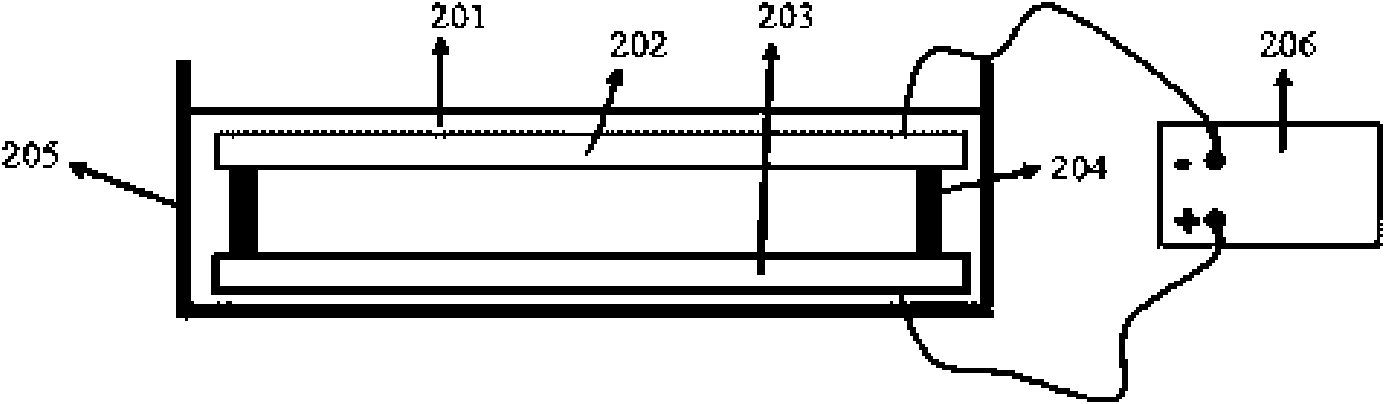
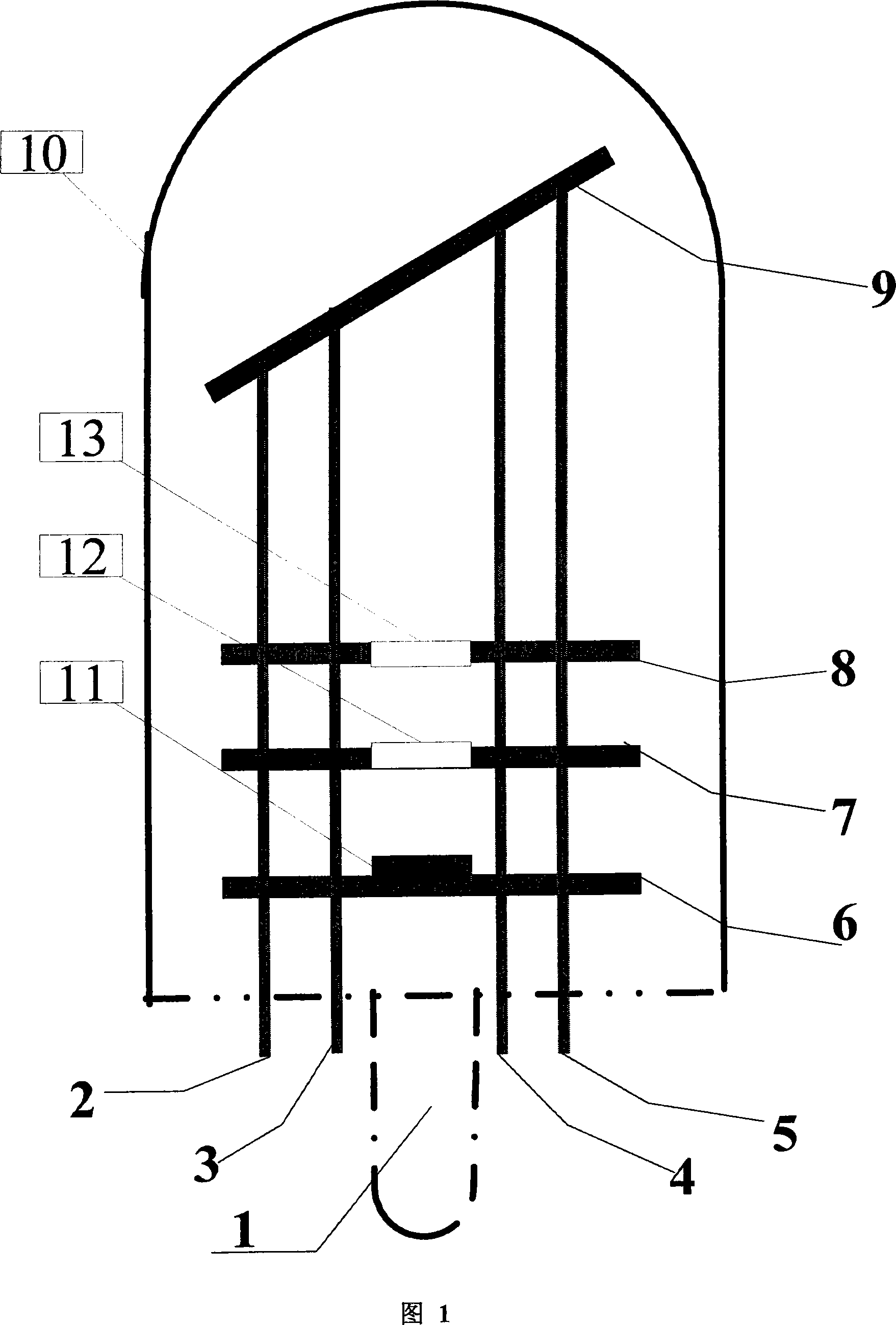
A preferred method for making a carbon nanotube-based field emission cathode device in accordance with the invention includes the following steps: preparing a solution having a solvent and a predetermined quantity of carbon nanotubes dispersed therein; providing a base with an electrode (101) formed thereon; forming a layer of conductive grease (102) on the base; distributing the solution on the layer of conductive grease to form a carbon nanotube layer (103) on the conductive grease; and scoring the layer of conductive grease, for separating first ends of at least some of the carbon nanotubes from the conductive grease for attaining effective carbon nanotube field emission cathode.
Owner:HON HAI PRECISION IND CO LTD +1
Gated fabrication of nanostructure field emission cathode material within a device
InactiveUS6858455B2Electric discharge tubesDecorative surface effectsField emission deviceDielectric
Gated field emission devices and systems and methods for their fabrication are described. A method includes growing a substantially vertically aligned carbon nanostructure, the substantially vertically aligned carbon nanostructure coupled to a substrate; covering at least a portion of the substantially vertically aligned carbon nanostructure with a dielectric; forming a gate, the gate coupled to the dielectric; and releasing the substantially vertically aligned carbon nanostructure by forming an aperture in the gate and removing a portion of the dielectric.
Owner:UT BATTELLE LLC
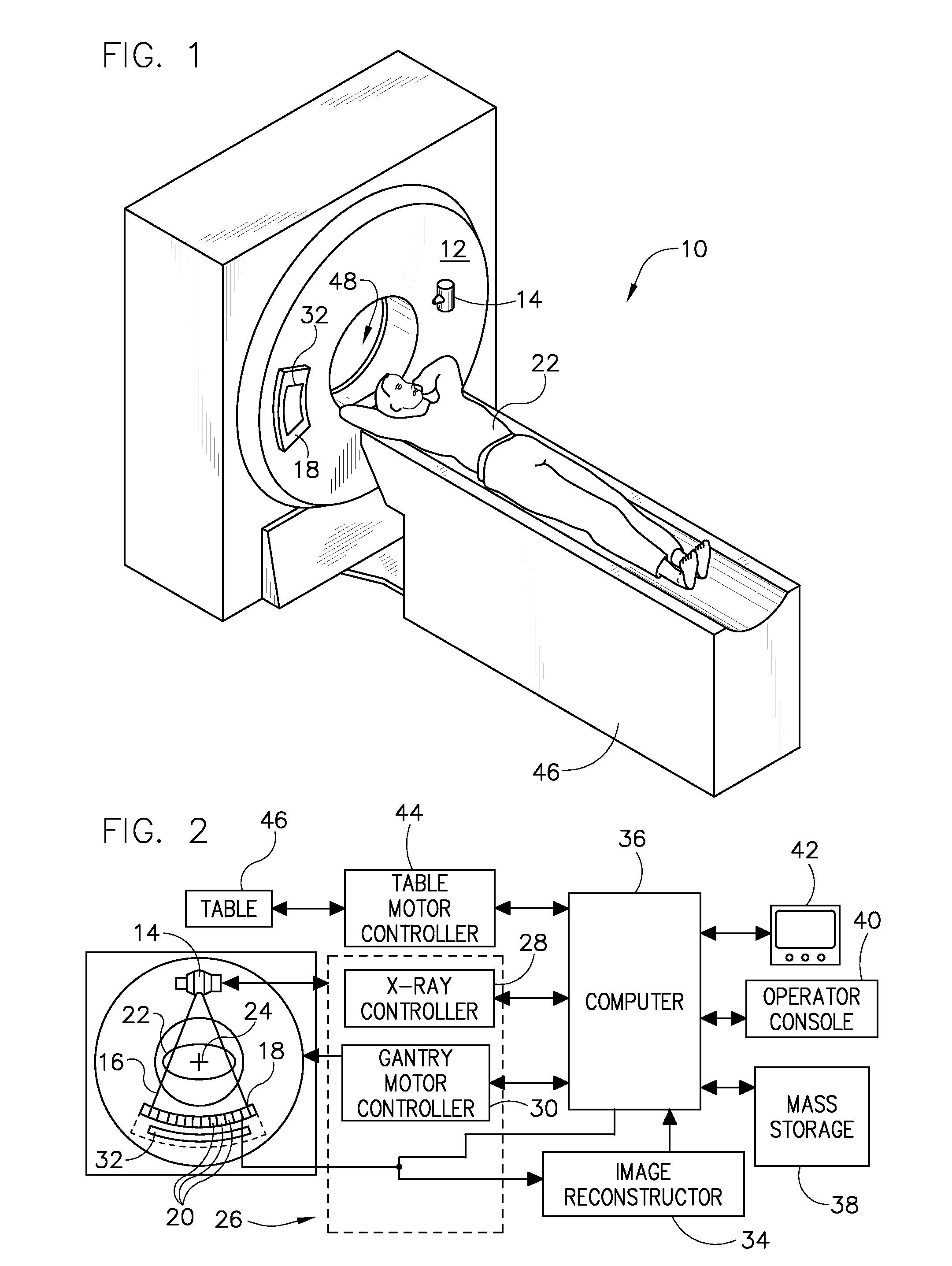
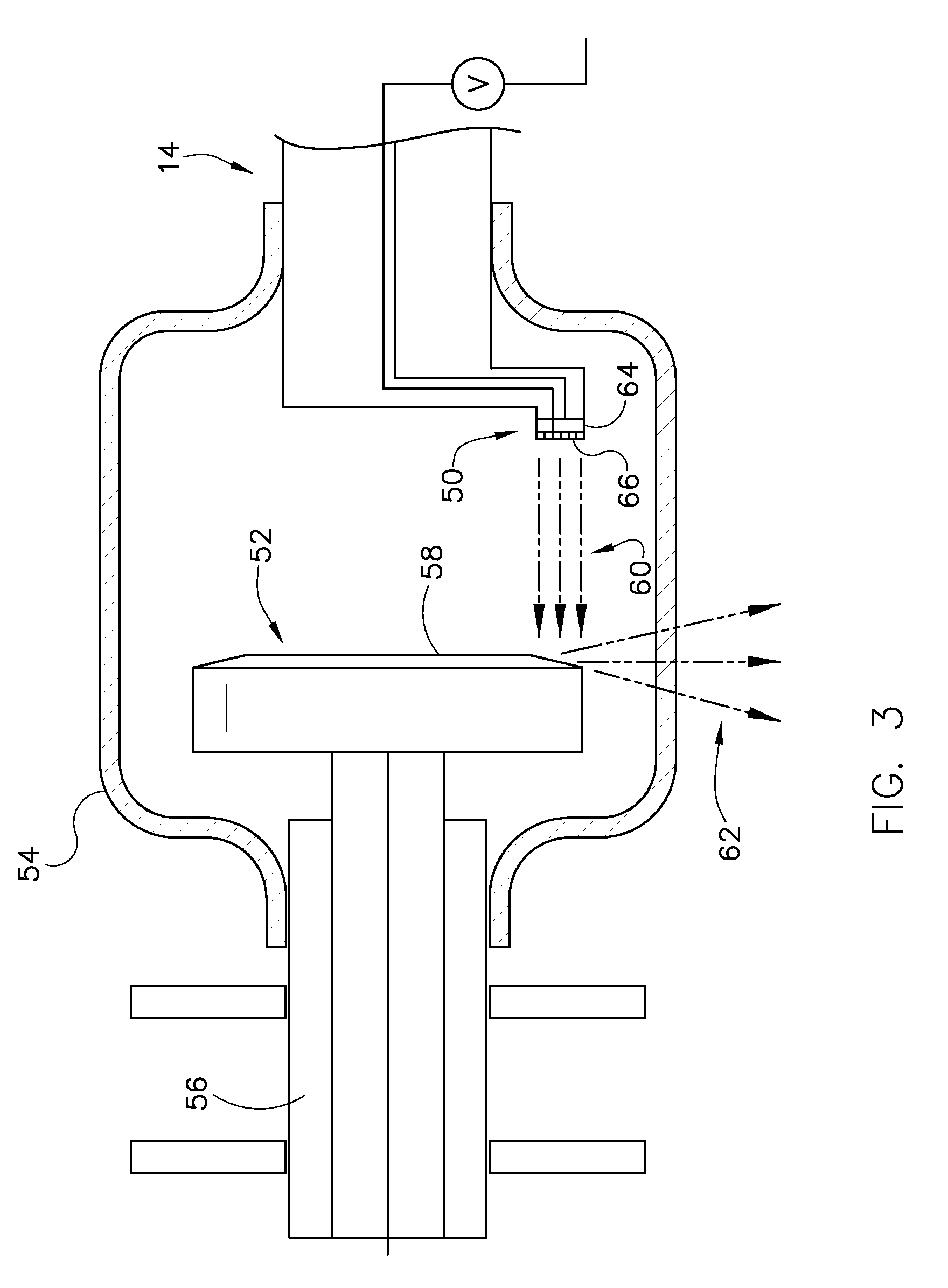
Mobile computed tomography (CT) scanner and operation method thereof
InactiveCN102697517AExtended service lifeReduce operating costsComputerised tomographsTomographyCt scannersImaging quality
The invention discloses a mobile computed tomography (CT) scanner. The mobile CT scanner comprises a bottom plate platform, a machine frame, a rotary plate, an X-ray emitting source, and a detector and data acquisition system. The bottom plate platform is provided with a linear guide rail; and one end of the machine frame is provided with a guide rail sliding block which is slidably connected with the linear guide rail, and the other end of the machine frame is connected with the rotary plate. The rotary plate can rotate relative to the machine frame. The X-ray emitting source and the detector and data acquisition system are arranged on the rotary plate and are respectively positioned at two ends of the same diameter of the rotary plate. The X-ray emitting source comprises a grid controlled carbon nano tube-based field emission cathode X-ray tube. The invention also provides an operation method for the mobile CT scanner. The mobile CT scanner is simple in structure, low in radiation dosage, and high in imaging quality, and has two purposes.
Owner:SUZHOU INST OF BIOMEDICAL ENG & TECH
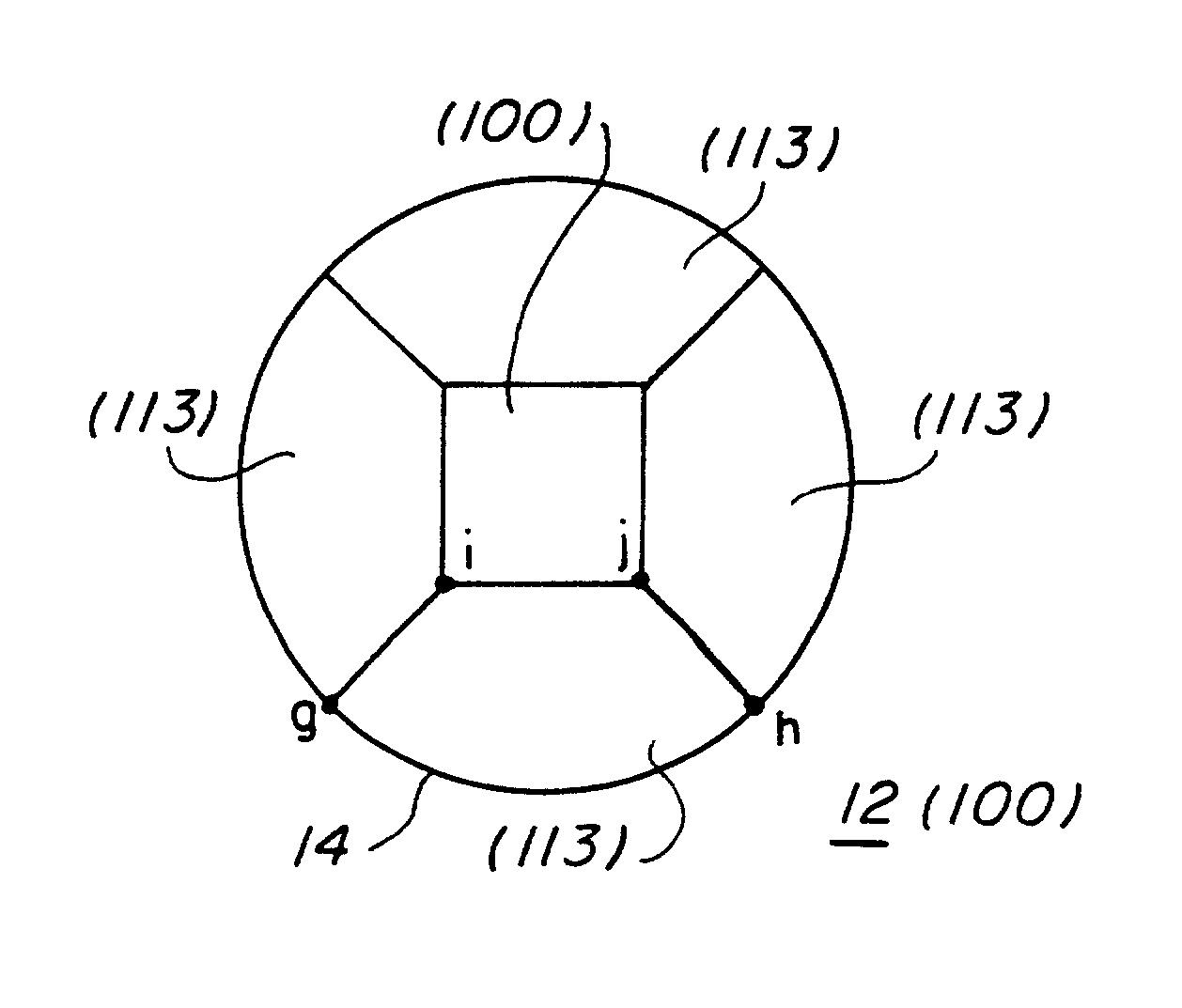
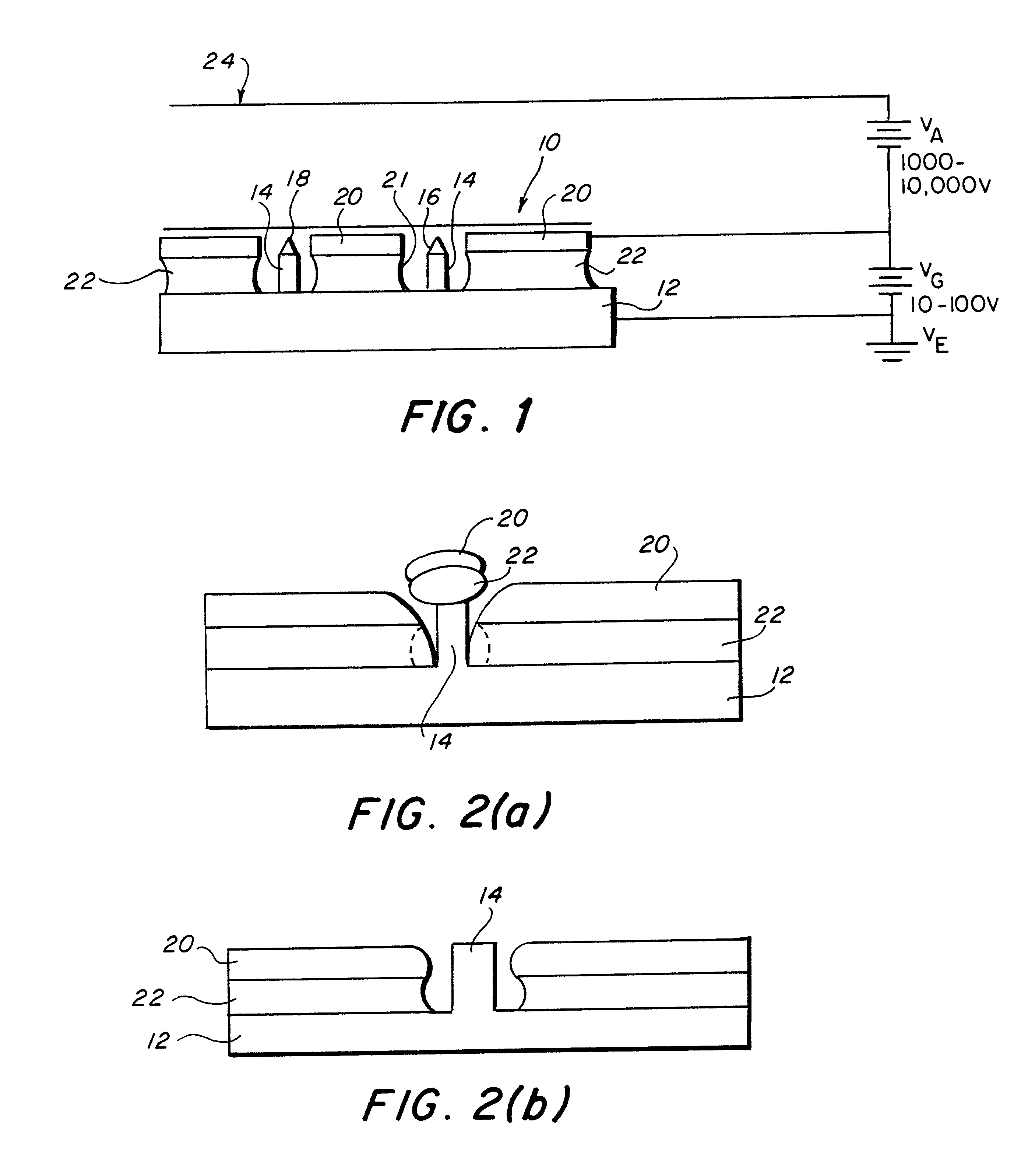
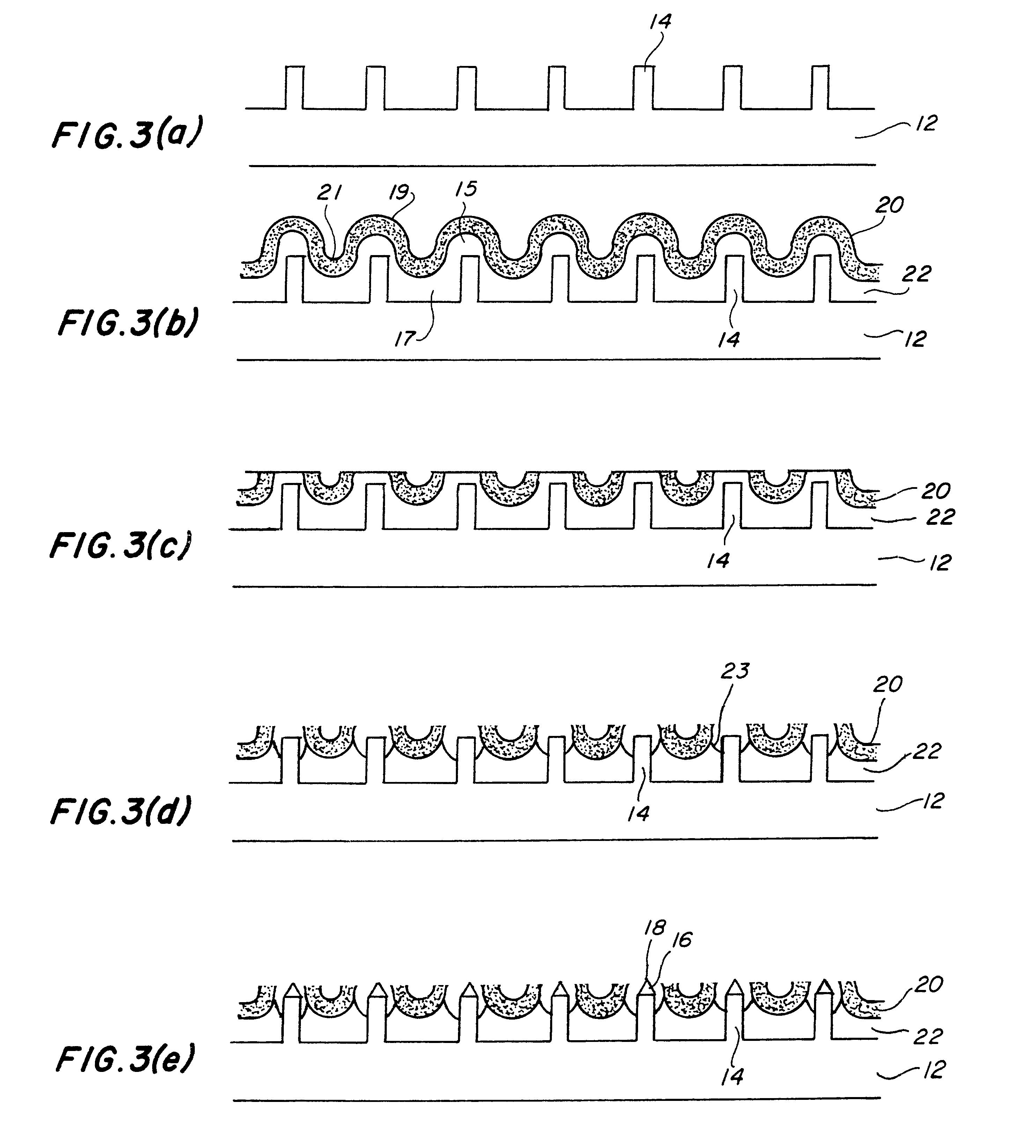
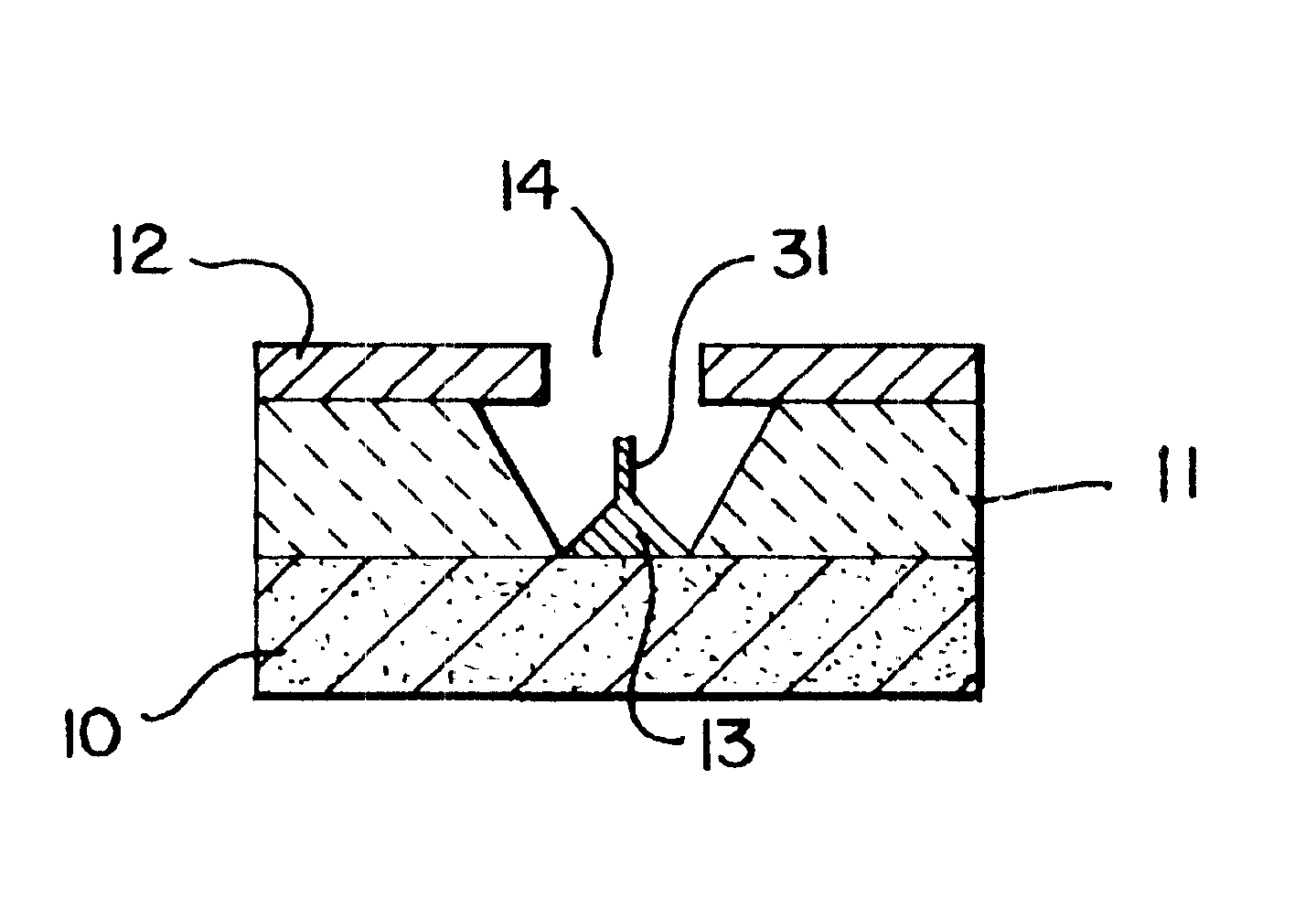
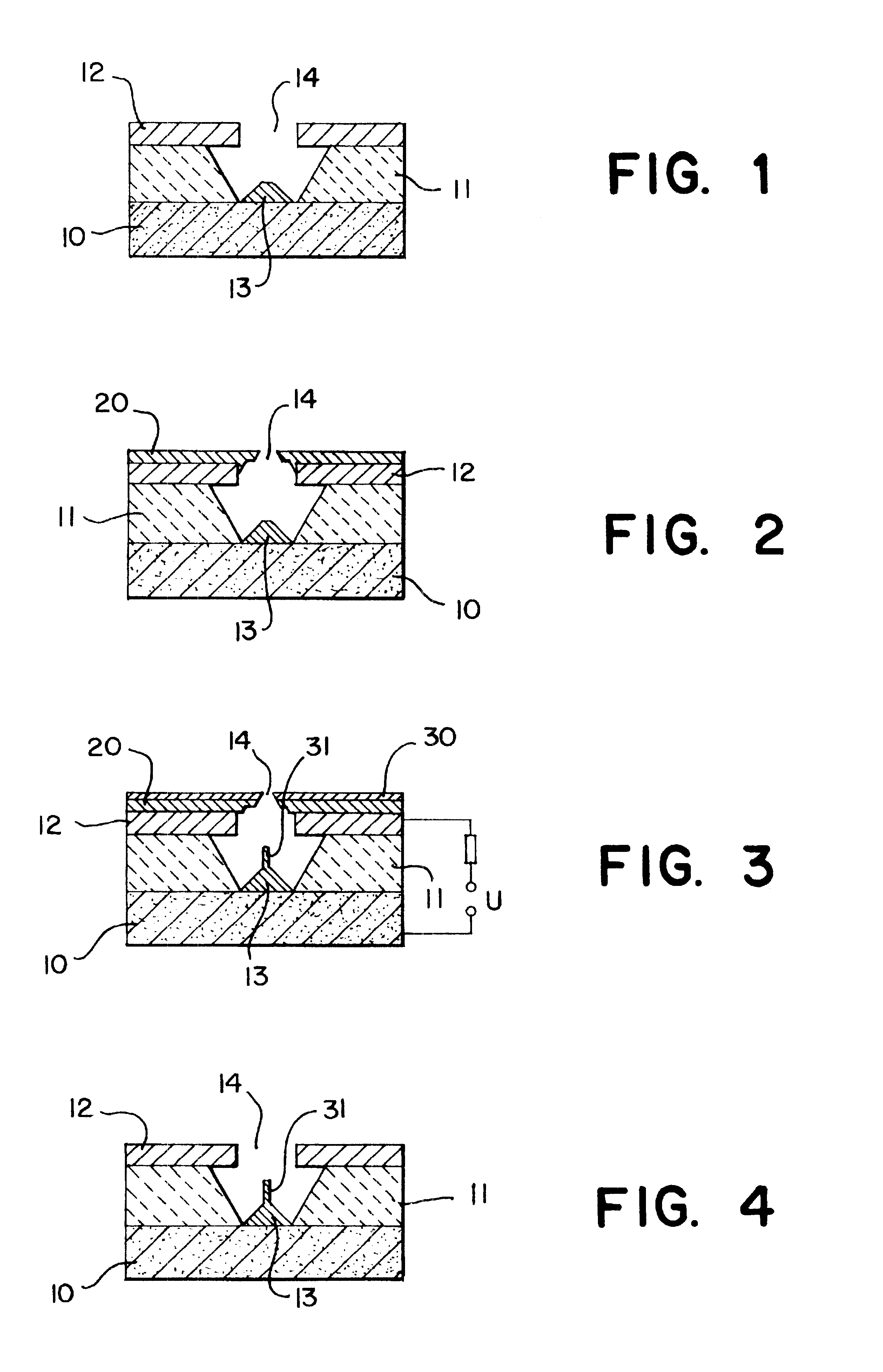
Field emission cathode having an electrically conducting material shaped of a narrow rod or knife edge
InactiveUSRE38223E1Improve emission qualityLong lastingNanoinformaticsThermionic cathodesConfocalConductive materials
A field emission cathode device consisting of an electrically conducting material and with a narrow, rod-shaped geometry or a knife edge, to achieve a high amplification of the electric field strength is characterized in that the electron-emitting part of the field emission cathode at least partly has preferred cylindrical host molecules and / or compounds with host compounds and / or cylindrical atomic networks, possibly with end caps with diameters measuring in the nanometer range.
Owner:KEESMANN TILL
Method and apparatus for controlling electron beam current
An x-ray generating device includes a field emission cathode formed at least partially from a nanostructure-containing material having an emitted electron current density of at least 4 A / cm2. High energy conversion efficiency and compact design are achieved due to easy focusing of cold cathode emitted electrons and dramatic reduction of heating at the anode. In addition, by pulsing the field between the cathode and the gate or anode and focusing the electron beams at different anode materials, pulsed x-ray radiation with varying energy can be generated from a single device. Methods and apparatus for independent control of electron emission current and x-ray energy in x-ray tubes are also provided. The independent control can be accomplished by adjusting the distance between the cathode and anode. The independent control can also be accomplished by adjusting the temperature of the cathode. The independent control can also be accomplished by optical excitation of the cathode. The cathode can include field emissive materials such as carbon nanotubes.
Owner:THE UNIV OF NORTH CAROLINA AT CHAPEL HILL
Electron injection nanostructured semiconductor material anode electroluminescence method and device
ActiveUS20110297846A1Lower operating temperatureAccelerate emissionsElectroluminescent light sourcesPhotometryPhoton emissionSemiconductor materials
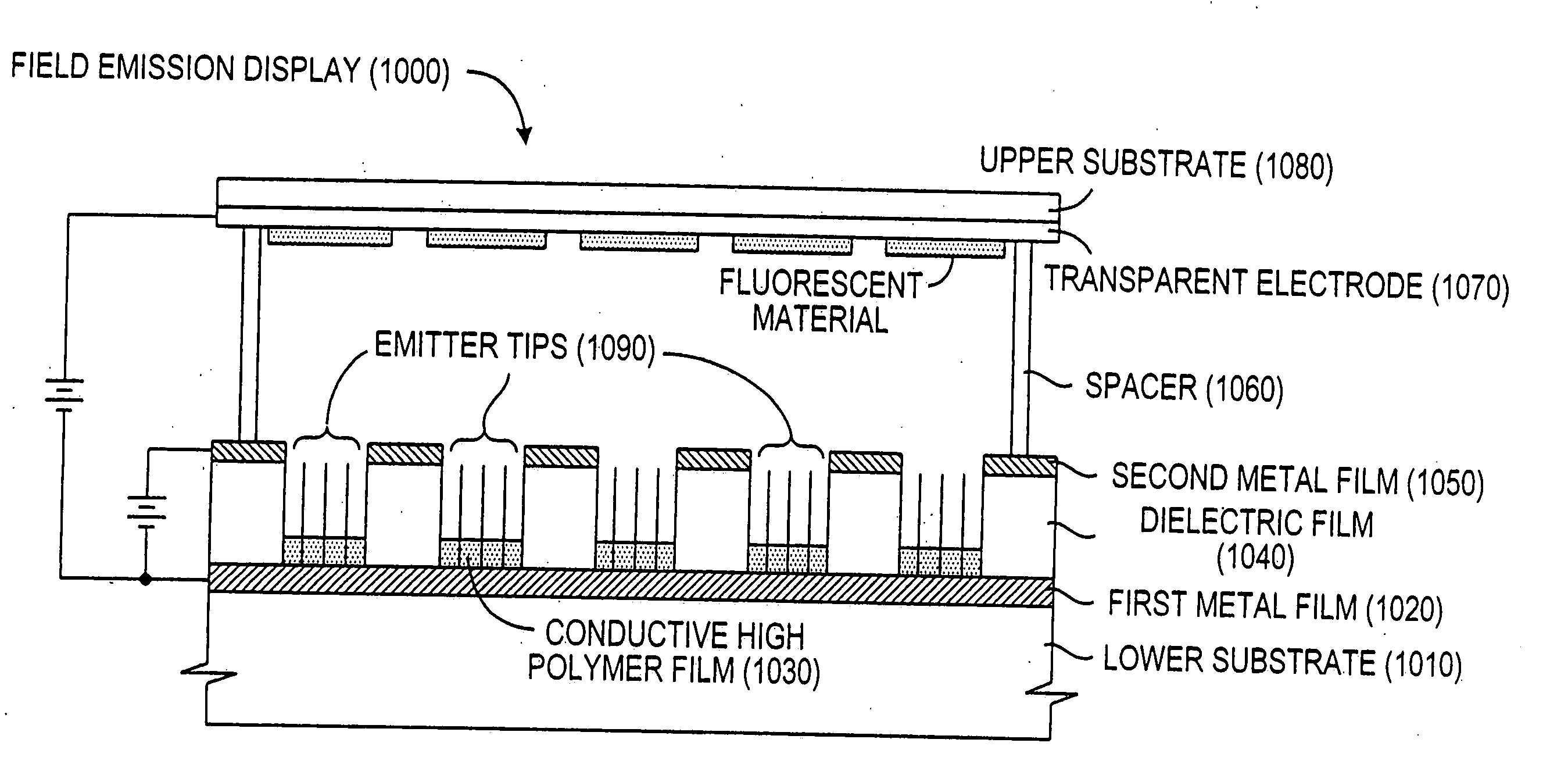
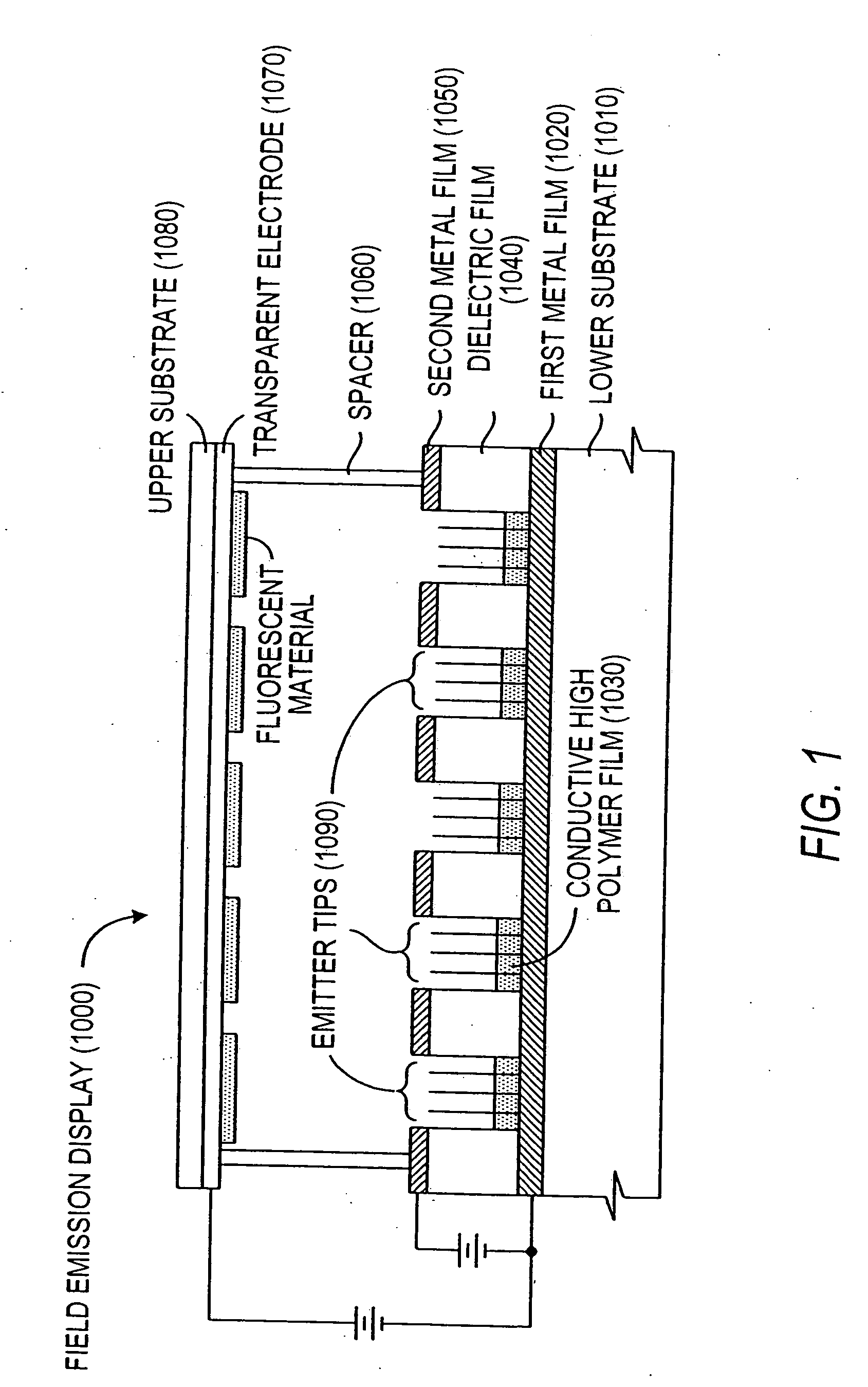
Embodiments of the invention include methods and devices for producing light by injecting electrons from field emission cathode across a gap into nanostructured semiconductor materials, electrons issue from a separate field emitter cathode and are accelerated by a voltage across a gap towards the surface of the nanostructured material that forms part of the anode. At the nanostructure material, the electrons undergo electron-hole (e-h) recombination resulting in electroluminescent (EL) emission. In a preferred embodiment lighting device, a vacuum enclosure houses a field emitter cathode. The vacuum enclosure also houses an anode that is separated by a gap from said cathode and disposed to receive electrons emitted from the cathode. The anode includes semiconductor light emitting nano structures that accept injection of electrons from the cathode and generate photons in response to the injection of electrons. External electrode contacts permit application of a voltage differential across the anode and cathode to stimulate electron emissions from the cathode and resultant photon emissions from the semiconductor light emitting nanostructures of the anode. Embodiments of the invention also include the usage of nanostructured semiconductor materials as phosphors for conventional planar LED and nanowire array light emitting diodes and CFL. For the use in conventional planar LEDs, the nanostructures may take the form of quantum dots, nanotubes, branched tree-like nanostructure, nanoflower, tetrapods, tripods, axial heterostructures nanowires hetero structures.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Field emission cathode
InactiveUSRE38561E1Long life-timeImprove emission qualityDischarge tube luminescnet screensNanoinformaticsConfocalConductive materials
A field emission cathode device consisting of an electrically conducting material and with a narrow, rod-shaped geometry or a knife edge, to achieve a high amplification of the electric field strength is characterized in that the electron-emitting part of the field emission cathode at least partly has preferred cylindrical host molecules and / or compounds with host compounds and / or cylindrical atomic networks, possibly with end caps with diameters measuring in the nanometer range.
Owner:KEESMANN TILL
Field emission devices using modified carbon nanotubes
InactiveUS20050275331A1Reduce voltageAccelerate emissionsNanostructure manufactureNanoinformaticsField emission deviceModified carbon
The present invention relates to a field emission device comprising an anode and a cathode, wherein said cathode includes carbon nanotubes nanotubes which have been subjected to energy, plasma, chemical, or mechanical treatment. The present invention also relates to a field emission cathode comprising carbon nanotubes which have been subject to such treatment. A method for treating the carbon nanotubes and for creating a field emission cathode is also disclosed. A field emission display device containing carbon nanotube which have been subject to such treatment is further disclosed.
Owner:HYPERION CATALYSIS INT
Electron beam apparatus
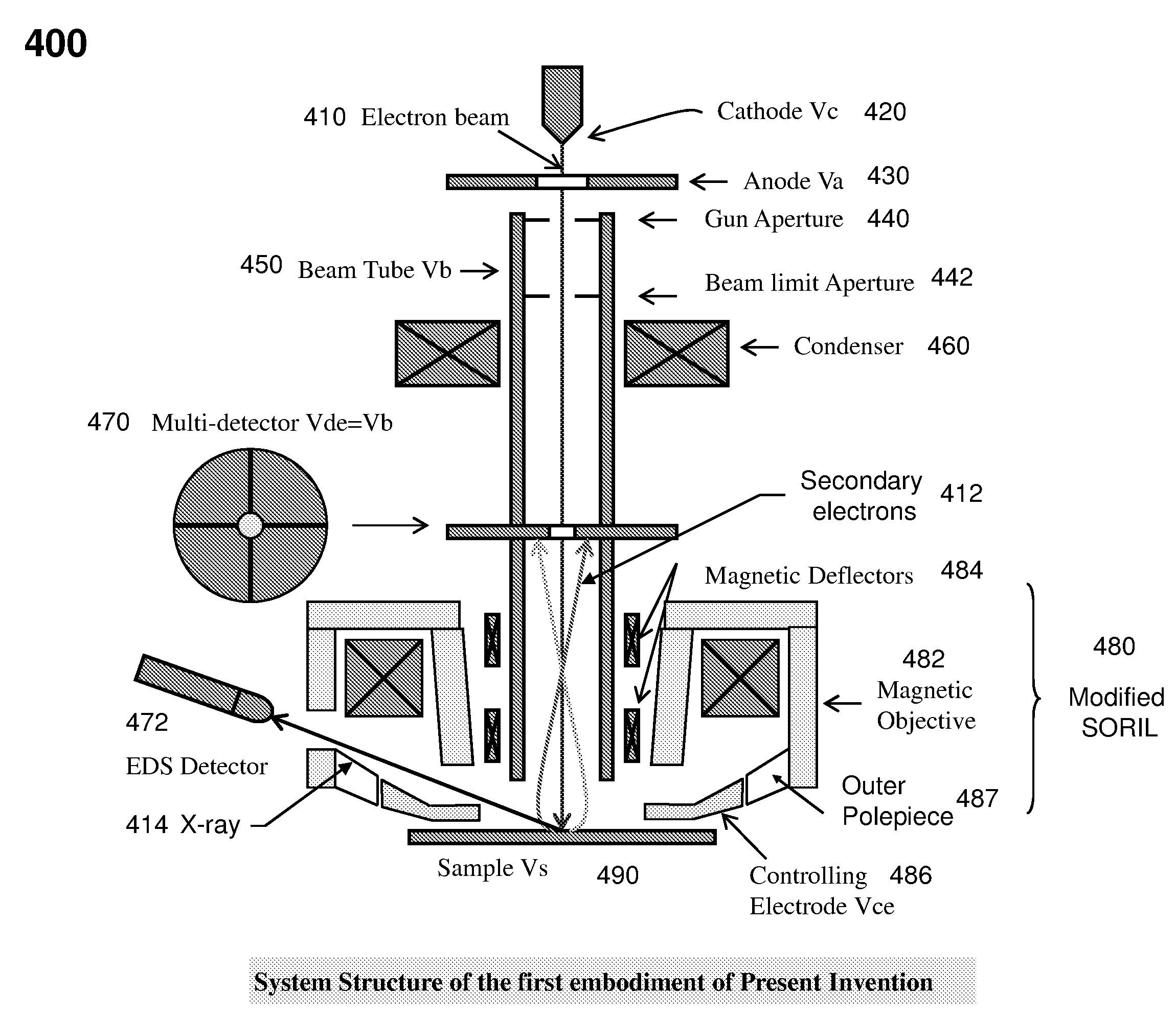
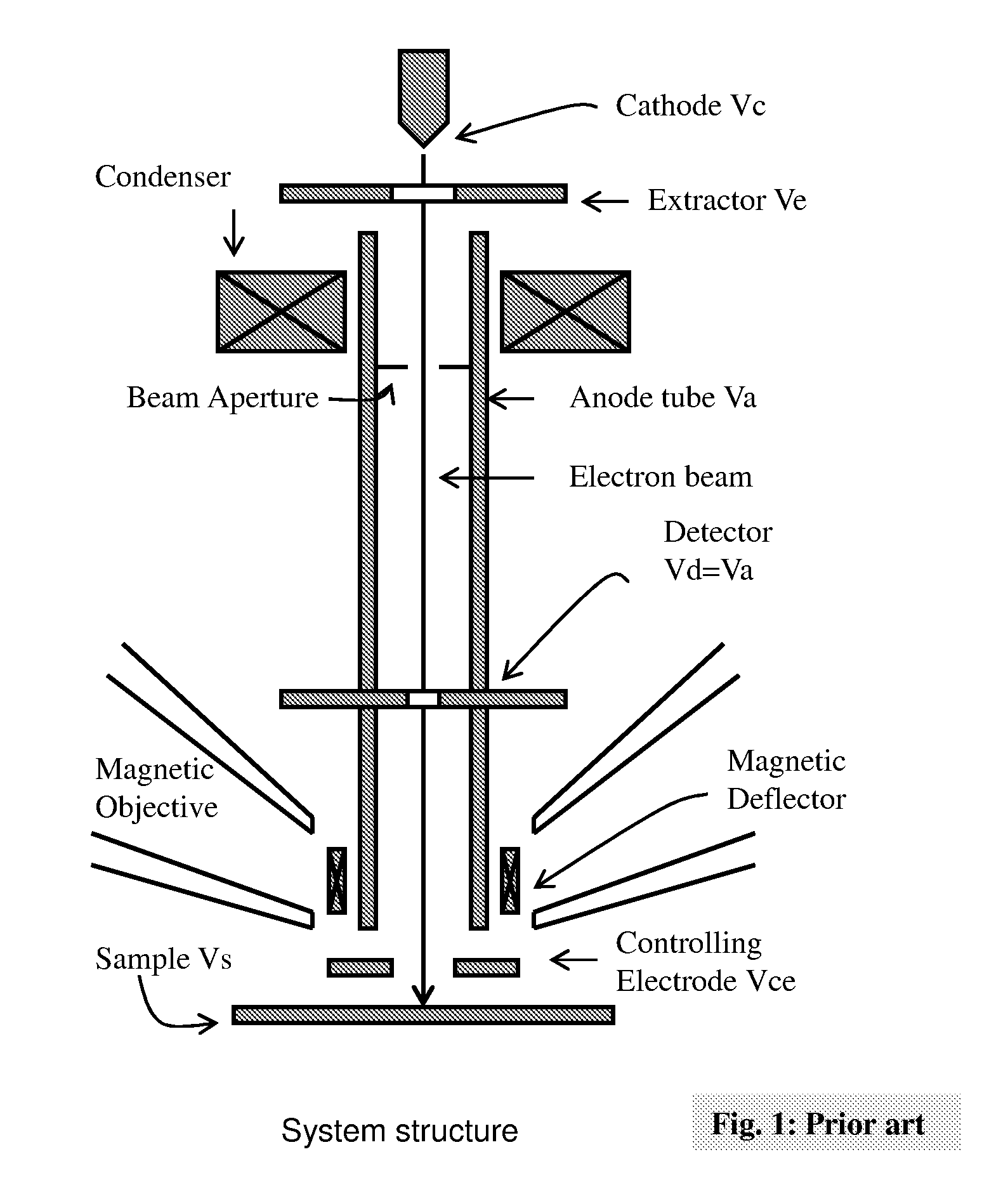
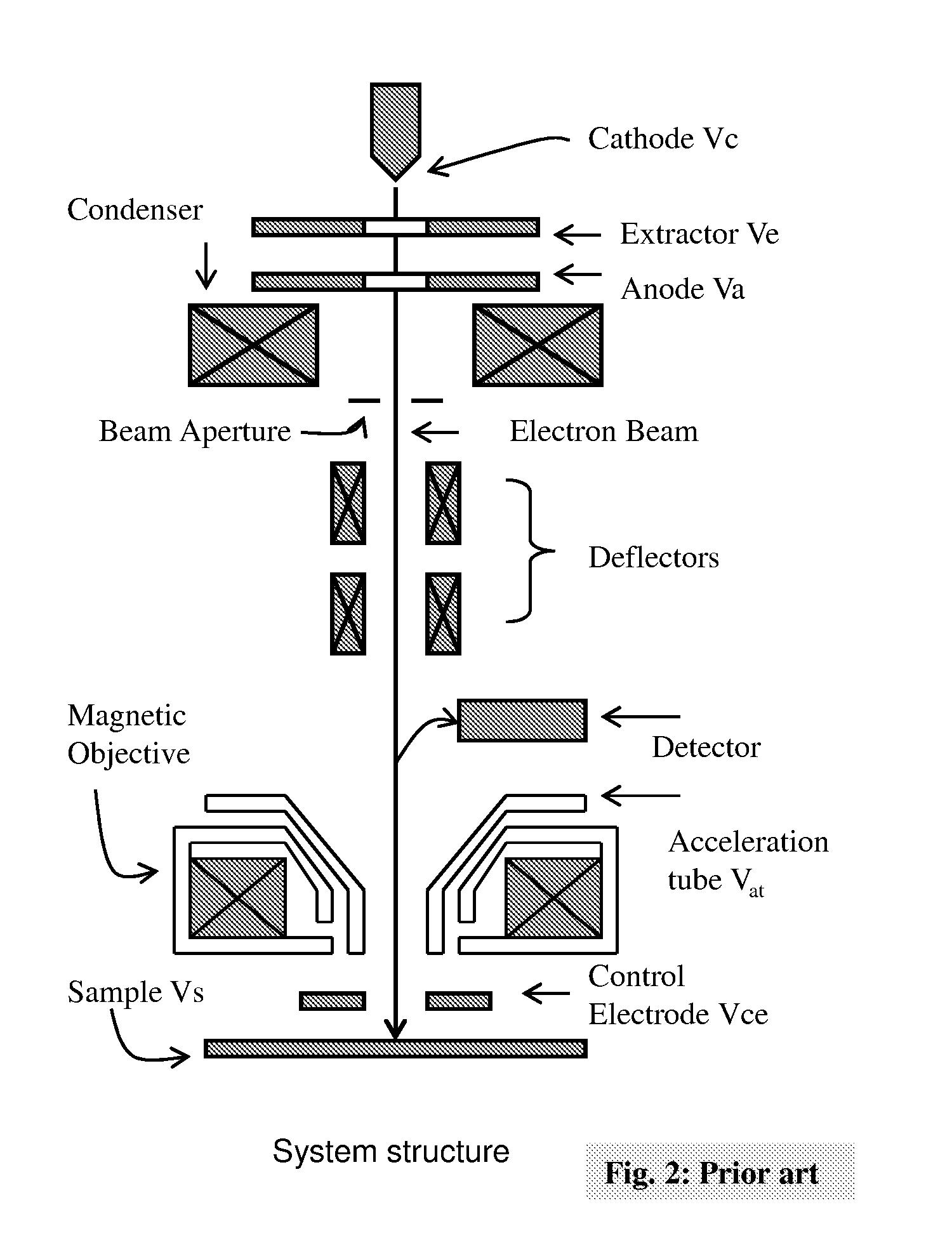
InactiveUS20100102227A1Improve imaging resolutionLarge aberrationThermometer detailsMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationScanning electron microscopeAcceleration voltage
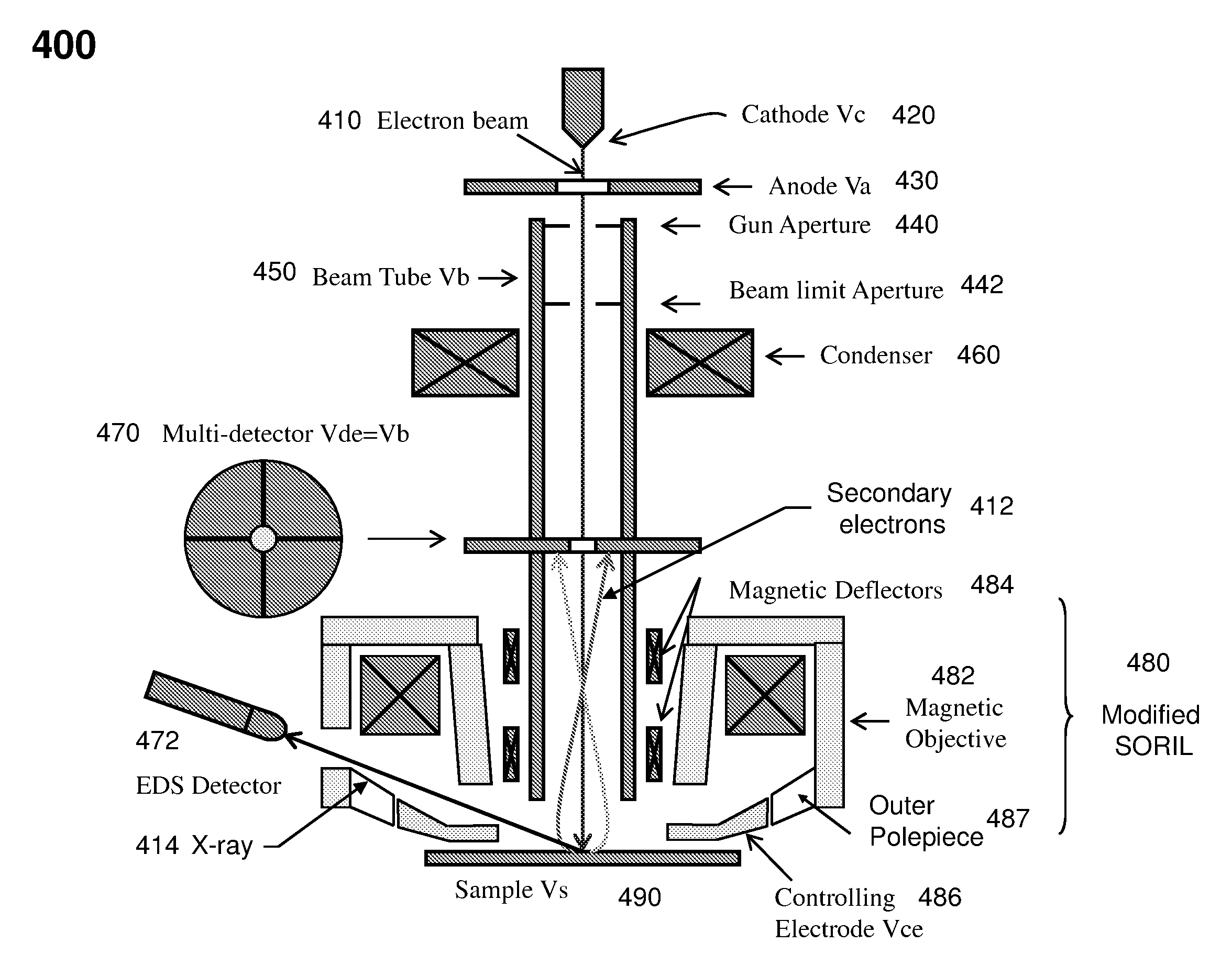
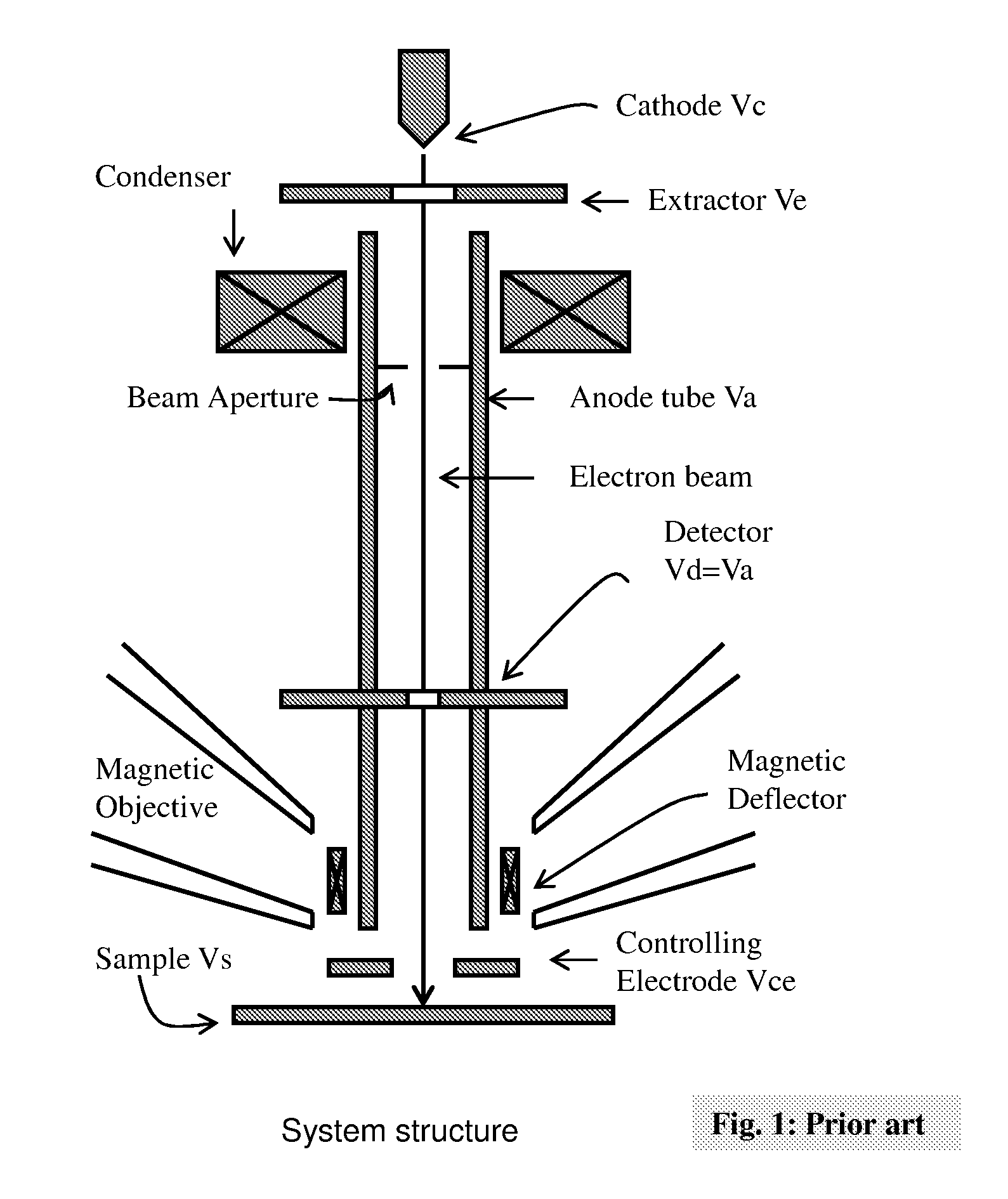
The present invention relates to a charged particle beam apparatus which employs a scanning electron microscope for sample inspection and defect review.The present invent provides solution of improving imaging resolution by utilizing a field emission cathode tip with a large tip radius, applying a large accelerating voltage across ground potential between the cathode and anode, positioning the beam limit aperture before condenser lens, utilizing condenser lens excitation current to optimize image resolution, applying a high tube bias to shorten electron travel time, adopting and modifying SORIL objective lens to ameliorate aberration at large field of view and under electric drifting and reduce the urgency of water cooling objective lens while operating material analysis.The present invent provides solution of improving throughput by utilizing fast scanning ability of SORIL and providing a large voltage difference between sample and detectors.
Owner:ASML NETHERLANDS BV
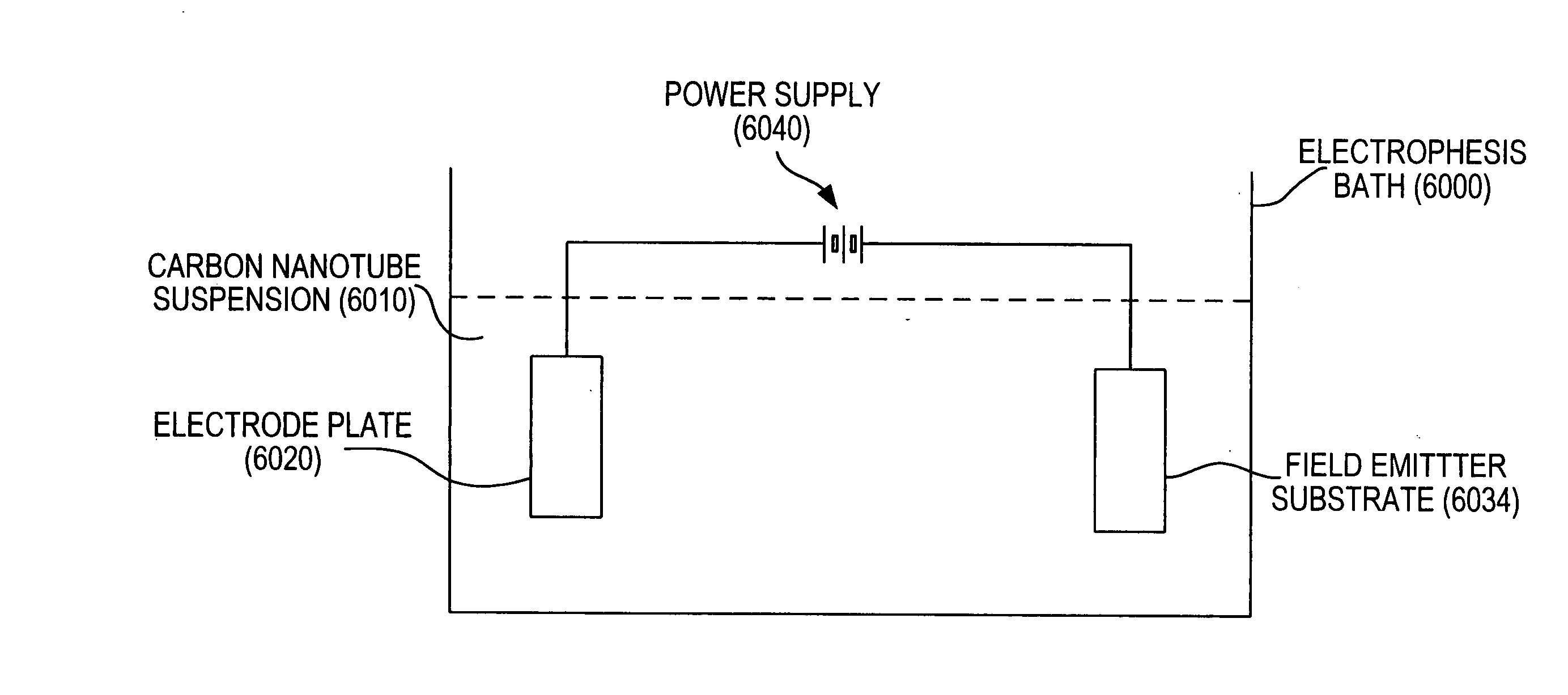
Surface chemical metal plating carbon nanotube field-emission cathode preparation method
ActiveCN101661858AImprove stabilityFacilitates electron conductionCold cathode manufactureState of artChemical plating
The invention provides a surface chemical metal plating carbon nanotube field-emission cathode preparation method, which belongs to a carbon nanotube field emission cathode technology, solves the shortcomings of the existing technology, improves the electronic conduction and emission capabilities of the carbon nanotube and enhances the contact between a carbon nanotube film and a substrate electrode. The preparation method comprises the following steps: the carbon nanotube is processed through purification, cutting, scattering, and then through sensitization and activation, the carbon nanotubesurface forms a noble metal catalytic center; then the carbon nanotube surface forms a metal layer through a chemical plating method, the surface chemical metal plating carbon nanotube is prepared into evenly and stably dispersed carbon nanotube electrophoresis liquid, and finally pulse electrophoresis deposition is used for preparing the cathode of the carbon nanotube. The surface chemical metalplating carbon nanotube has good electronic conduction and emission capabilities, the carbon nanotube field-emission cathode and a substrate electrode can form good attachment, and the invention canrealize large-area, imaging and uniform preparation for the carbon nanotube field-emission cathode.
Owner:FUZHOU UNIV
One-dimensional grid mesh for a high-compression electron gun
ActiveUS7627087B2Minimize degradationLow voltage extractionCathode ray concentrating/focusing/directingElectrode and associated part arrangementsElectronElectric field
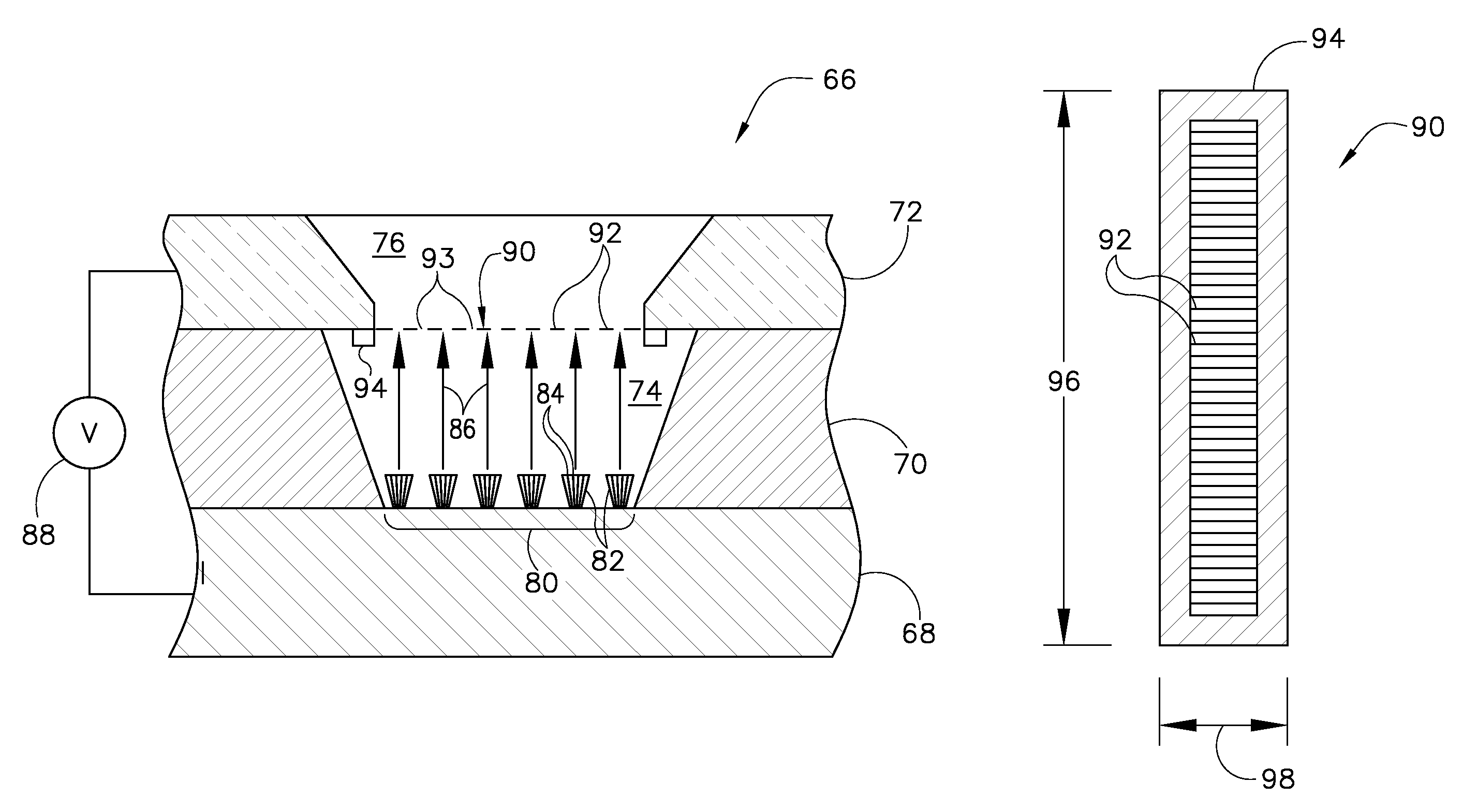
A field emitter electron gun includes at least one field emitter cathode deposited on a substrate layer and configured to generate an electron beam. An extraction plate having an opening therethrough is positioned adjacent to the at least one field emitter cathode and is operated at a voltage so as to extract the electron beam out therefrom. A meshed grid is disposed between each of the at least one field emitter cathodes and the extraction plate. The meshed grid is configured to operate at a voltage so as to enhance an electric field at a surface of the at least one field emitter cathode. The meshed grid is a one-dimensional grid configured to focus the electron beam received from the at least one field emitter cathode into a desired spot size.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
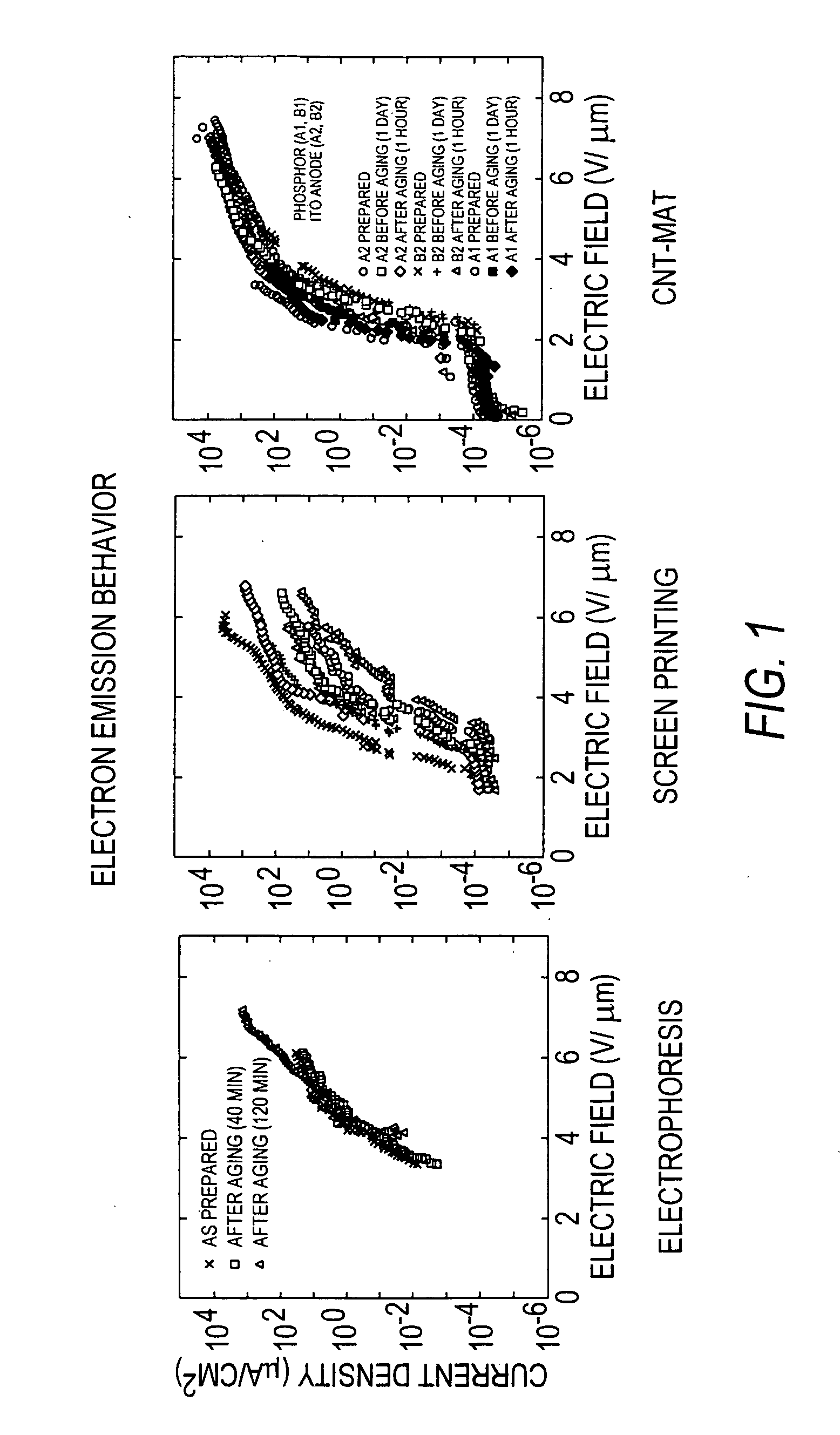
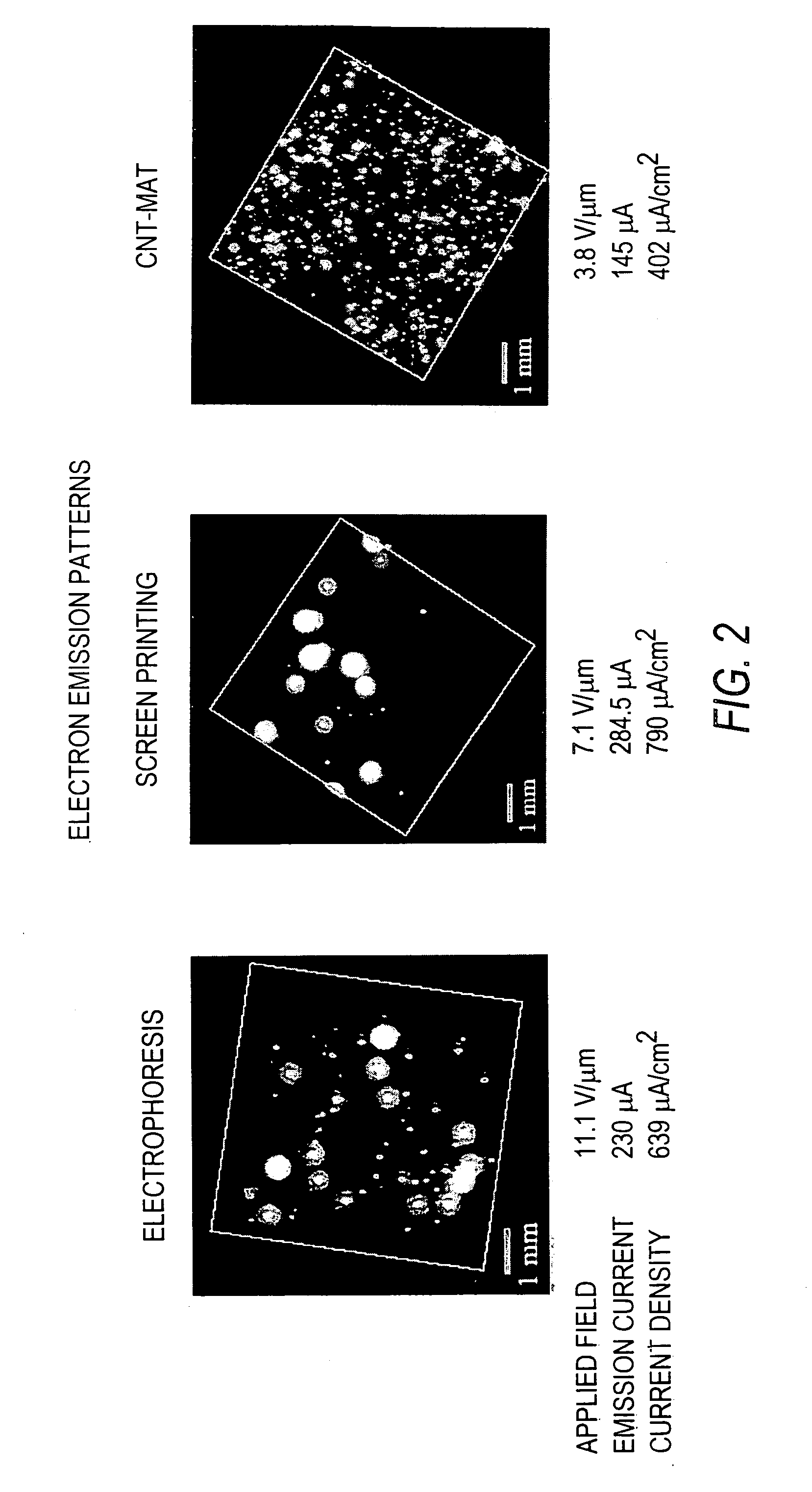
Field emission devices made with laser and/or plasma treated carbon nanotube mats, films or inks
InactiveUS20050156504A1Improve cathode emission current densityLaunch evenlyDischarge tube luminescnet screensElectric discharge tubesField emission deviceFibril
Field emission devices comprising carbon nanotube mats which have been treated with laser or plasma are provided. Mats are formed from carbon nanotubes, also known as carbon fibrils, which are vermicular carbon deposits having diameters of less than about one micron. The carbon nanotube mats are then subjected to laser or plasma treatment. The treated carbon nanotube mat results in improved field emission performance as either a field emission cathode or as part of a field emission device.
Owner:HYPERION CATALYSIS INT
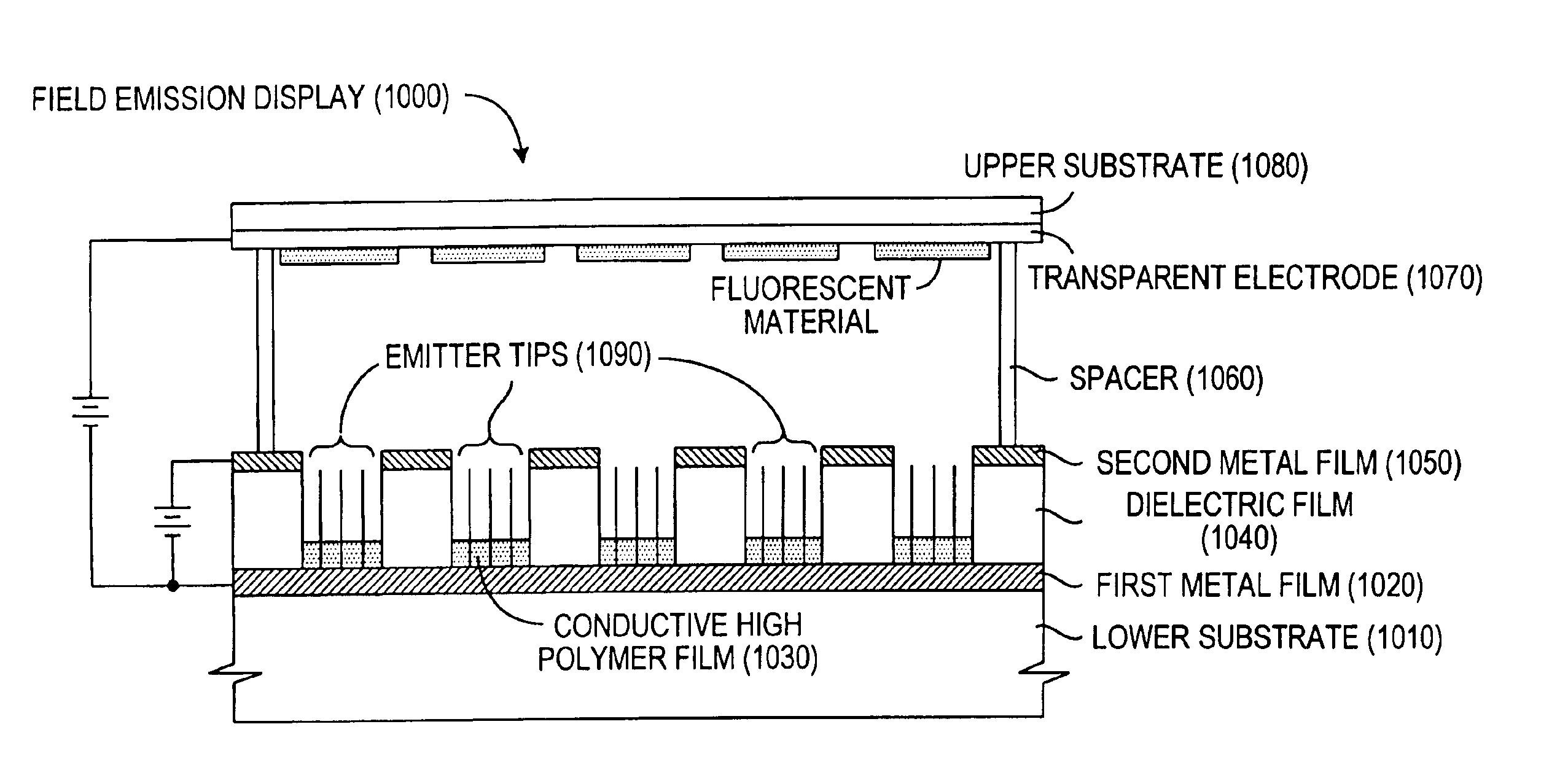
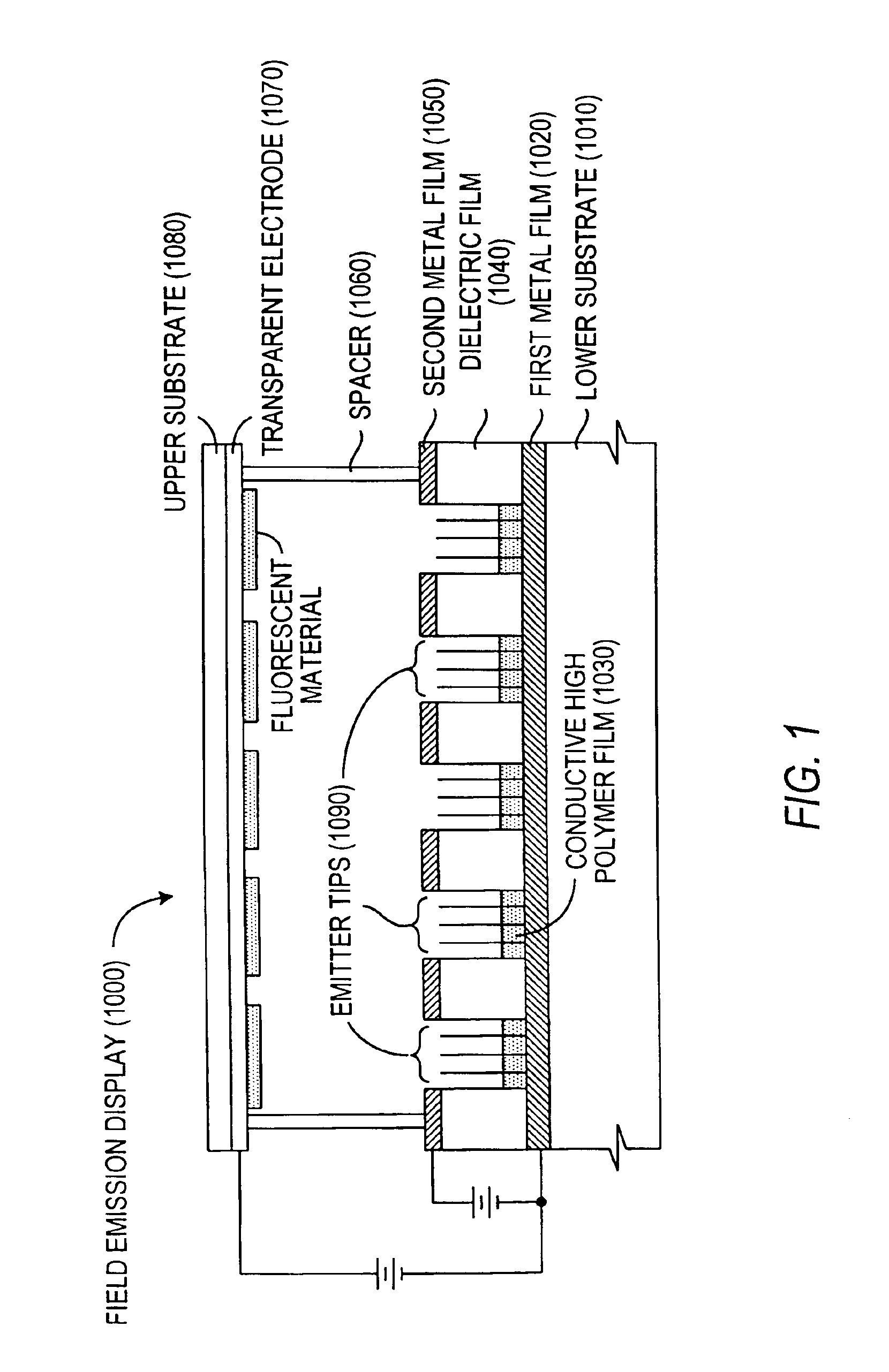
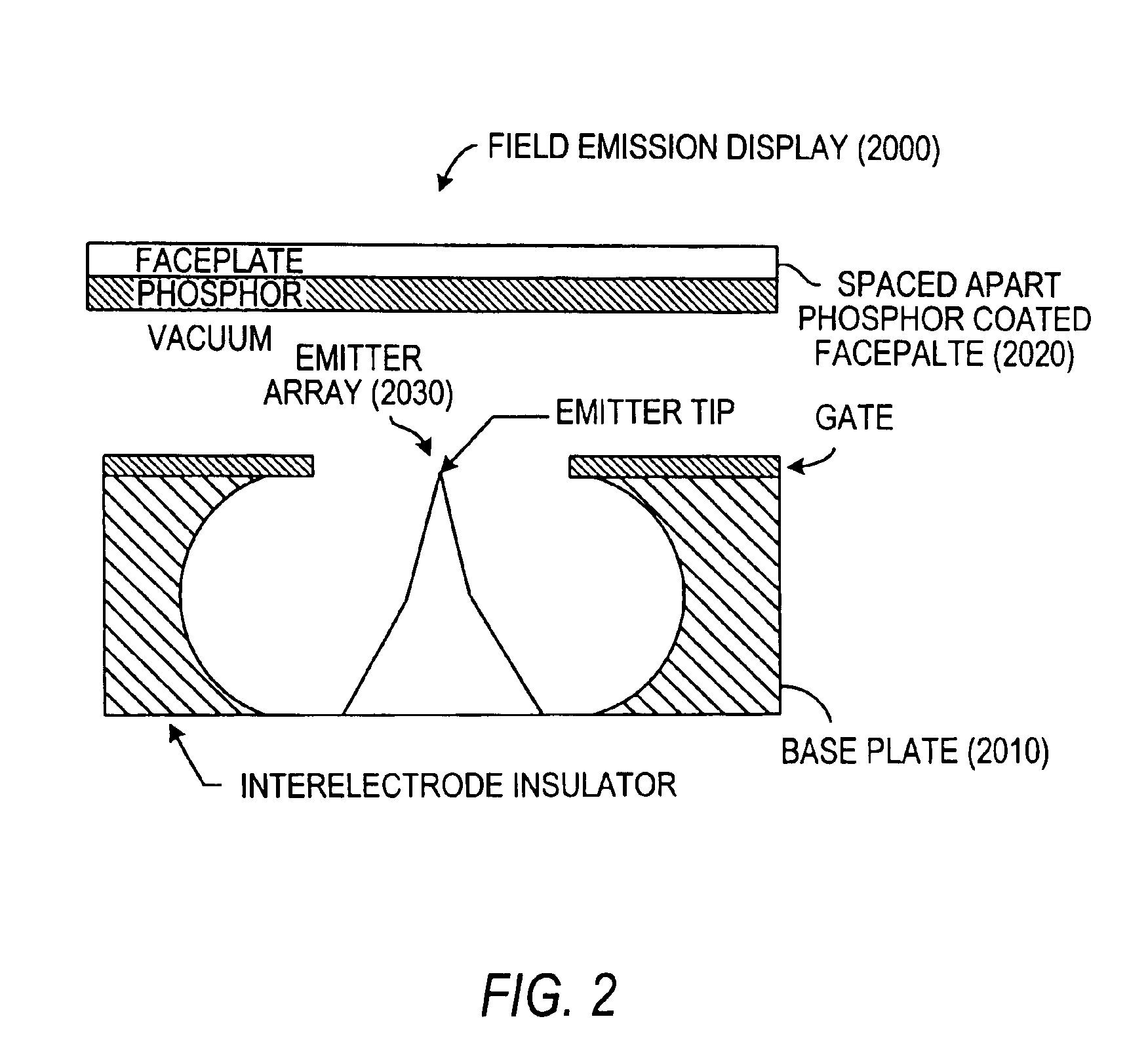
Panel display having adulterated polycrystal silicon field emission cathode array structure and its manufacturing technology
InactiveCN1794408AHighly integratedSimple preparation processImage/pattern display tubesDischarge tube/lamp detailsManufacturing technologyGrating
This invention relates to a panel display with doped-polysilicon field emission cathode array structure and its process technology, in which, the display includes a sealed vacuum cavity composed of a cathode panel, an anode panel and surrounding glasses, anode conduction strips etched on the anode panel and fluorescence powder layer on the conduction strips, a supporting wall and getter attached elements, in which, a doped polysilicon field emission cathode array structure is prepared on the cathode panel to reduce the distance between the cathode and the grating, control the working voltage of the grating and reduce the current of the control grating.
Owner:ZHONGYUAN ENGINEERING COLLEGE
Field emitting cathode and its making process and application
InactiveCN1349240AHigh resolutionSimple structureDischarge tube/lamp detailsCold cathode manufactureDisplay deviceFlat panel display
The invention field emitting cathode is a metal nano wire array which grows on metal base of planar electrode and the metal is same as the base's. The thickness of base is 1 micro m to 0.5 mm, the diameter of nano wire is 20-200 nm, the length is 100 to 500 nm. The producing steps are: to select modular board with nanometer holes according to size requirement of display unit, to make a metal filmelectrode on a surface of the selected modular board by evaporating and electroplating, to electrochemical grow metal nanometer wire array in the nanometer holes of nanometer modular board, to clean and dry the dissolved part or whole modular to expose metal nanometer wires. It can be used to cathode-ray tube and plate display, and has low beginning field strength for field emitting cathode, highcurrent density and low cost.
Owner:PEKING UNIV
High-alloy metals reinforced by diamond-like framework and method for making the same
InactiveUS20060005900A1Improve corrosion resistanceImprove thermal stabilityVacuum evaporation coatingSputtering coatingDiamond-like carbonAlloy
A new class of high-alloy metals is invented. The metals possess an amorphous, nano crystalline, or combined amorphous-nano-crystalline structure and are reinforced, stabilized and hardened with a framework formed by predominantly sp3-bonded carbon, also known-as diamond like carbon. Optionally, other alloying nonmetallic elements selected from the group of Si, B, O, N may additionally stabilize the structure. The disclosed high-alloy metals comprise a metallic matrix which may include iron, nickel, chromium, refractory, and various other metals. These materials are very stable, and do not suffer a structural degradation up to relatively high temperatures. The disclosed high-alloy metals have the properties of high hardness, corrosion and wear resistance, and low friction. They have a wide range of applications as protective coatings on a wide variety of materials in various industries. They may be further applied as magnetic and electronic devices, such as field emission cathodes. Some of these alloys possess high emissivity, and their electrical conductivity may be varied in a relatively wide range.
Owner:DORFMAN BENJAMIN R
Field-emissive cathode X ray tube
InactiveCN101101848ASmall sizeHigh resolutionX-ray tube electrodesX-ray tube vessels/containerCarbon nanotubeX-ray
The invention is concerned with the X-ray tube electron source (cathode) structural design of the field emission cathode X-ray tube, which is the type of source with no heating request. It includes: the field emission cathode sheet (-), the modulation grid sheet (-), the highlights electrode films (-), the extremely high-voltage anode target sheet (-), the electrodes connect each sheets, and the carbon Nano-tube electrode emission layer (-) attaches with the field emission cathode sheet; the modulated voltage of the grid controls the on / off of the X-ray line source, and anode to cathode voltage and the grid voltage controls its strength, highlights voltage controls the emission of the electron beam. The invention is with the miniaturization design, smaller X-ray tube with high resolution.
Owner:SOUTHEAST UNIV
Electron beam apparatus
InactiveUS7960697B2Improve imaging resolutionIncrease intensityThermometer detailsMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationScanning tunneling microscopeScanning electron microscope
The present invention relates to a charged particle beam apparatus which employs a scanning electron microscope for sample inspection and defect review.The present invent provides solution of improving imaging resolution by utilizing a field emission cathode tip with a large tip radius, applying a large accelerating voltage across ground potential between the cathode and anode, positioning the beam limit aperture before condenser lens, utilizing condenser lens excitation current to optimize image resolution, applying a high tube bias to shorten electron travel time, adopting and modifying SORIL objective lens to ameliorate aberration at large field of view and under electric drifting and reduce the urgency of water cooling objective lens while operating material analysis.The present invent provides solution of improving throughput by utilizing fast scanning ability of SORIL and providing a large voltage difference between sample and detectors.
Owner:ASML NETHERLANDS BV
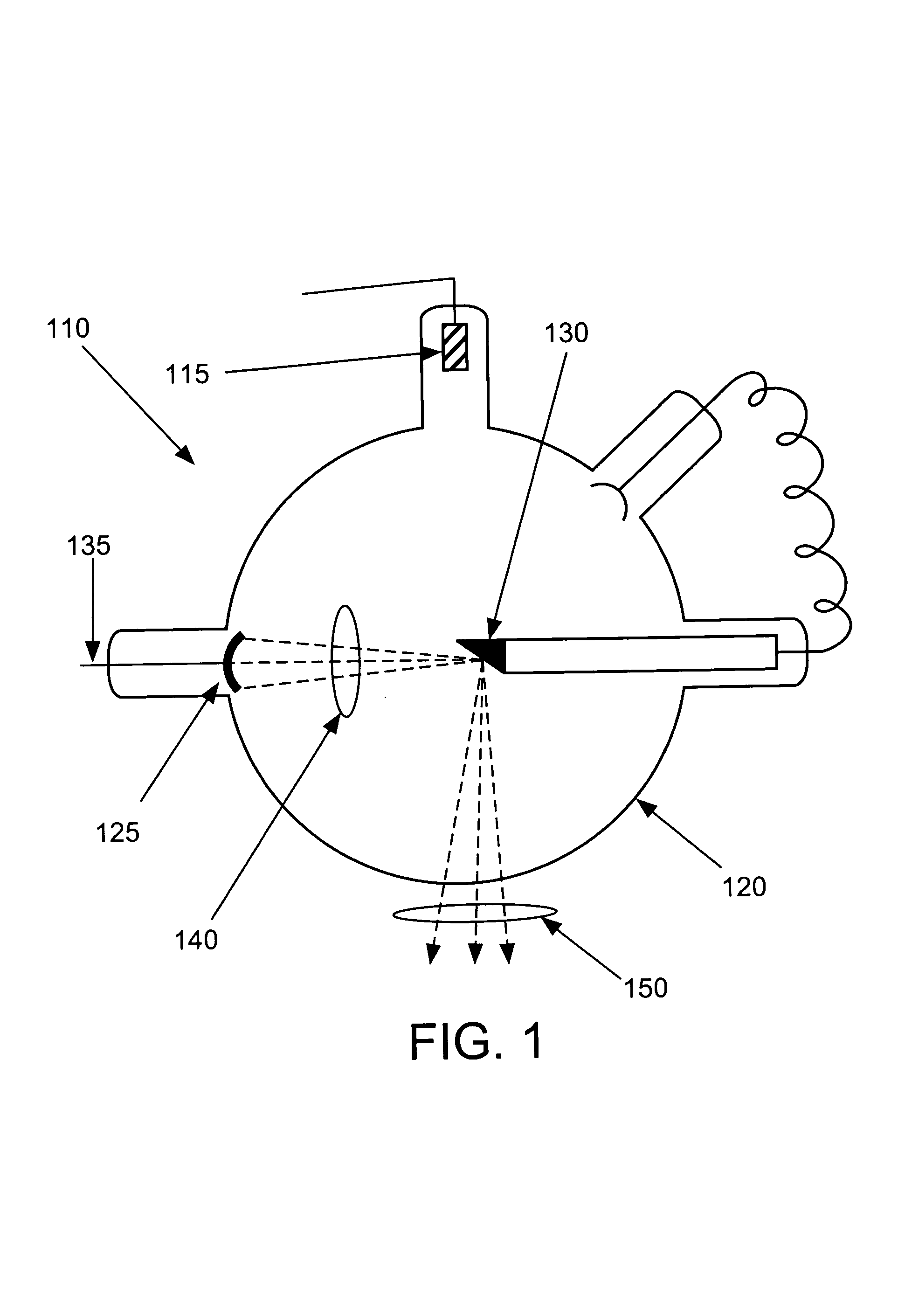
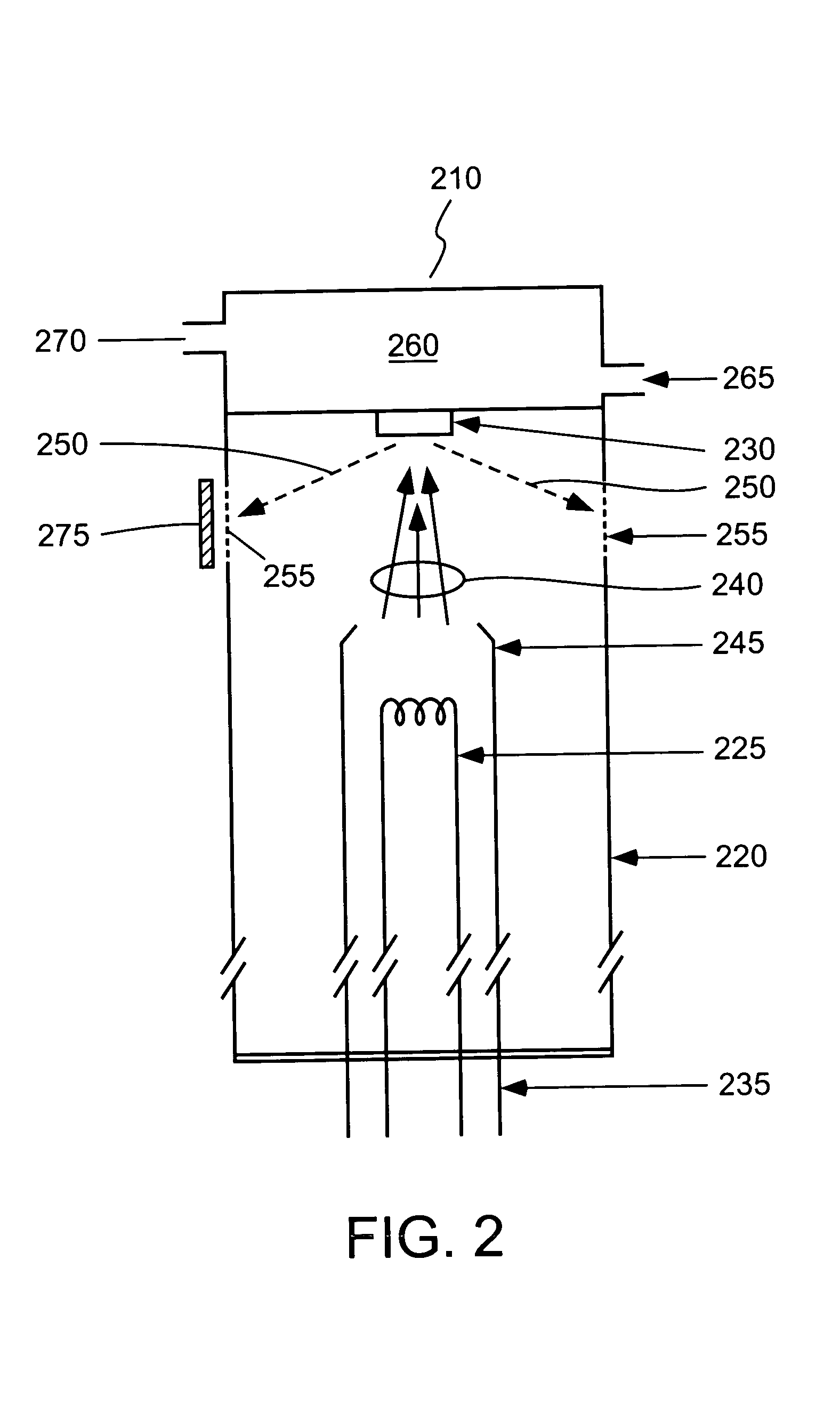
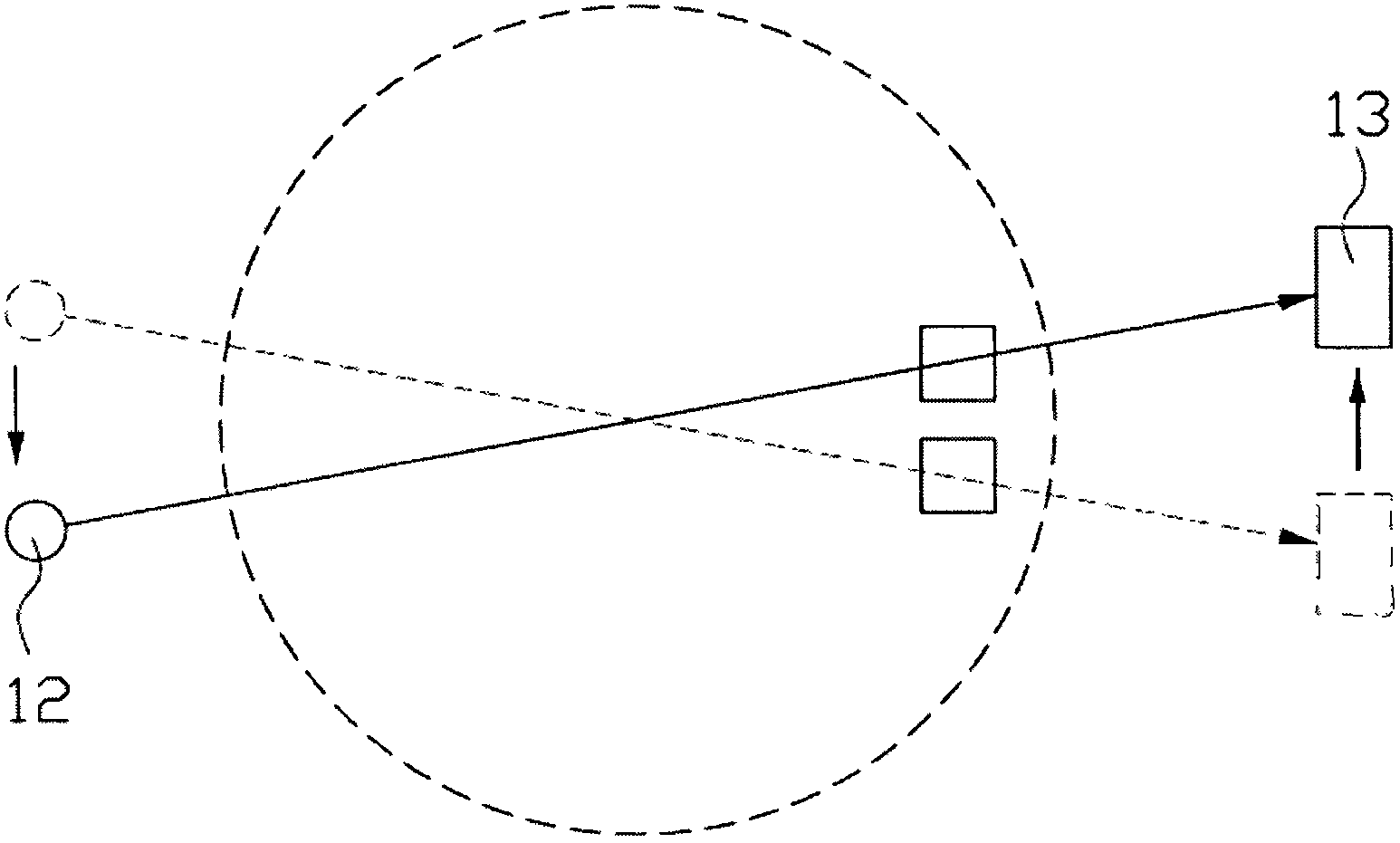
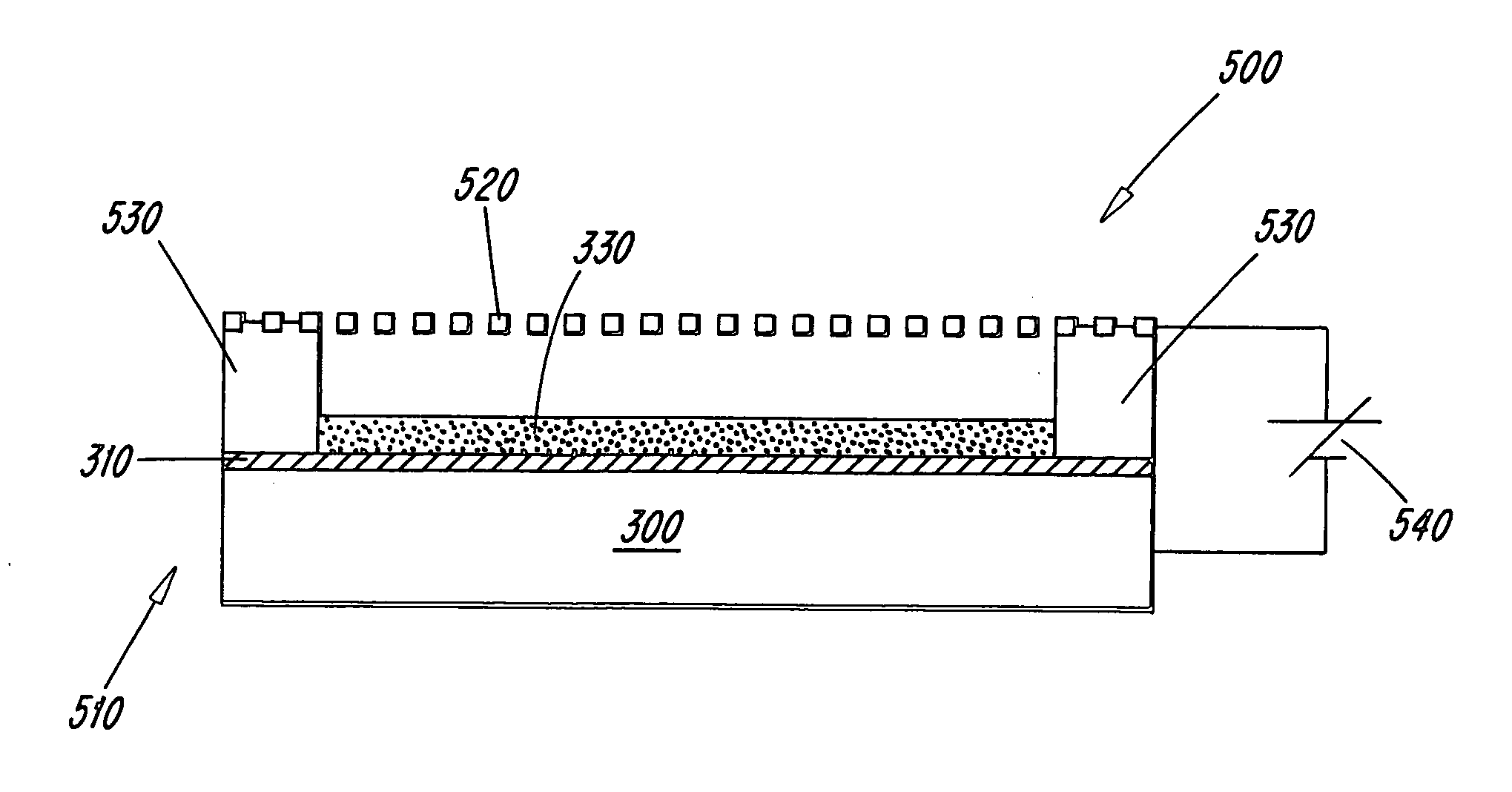
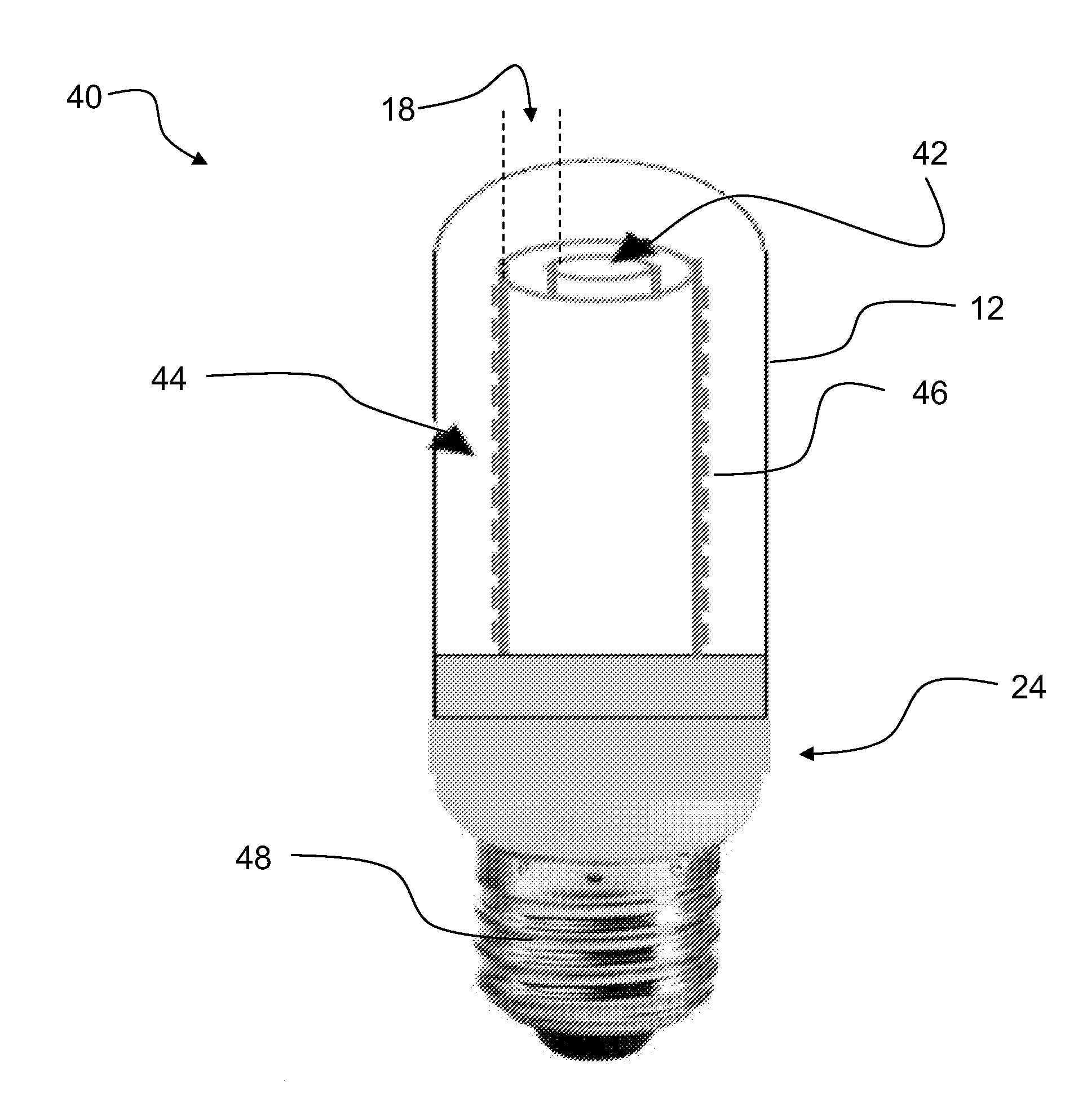
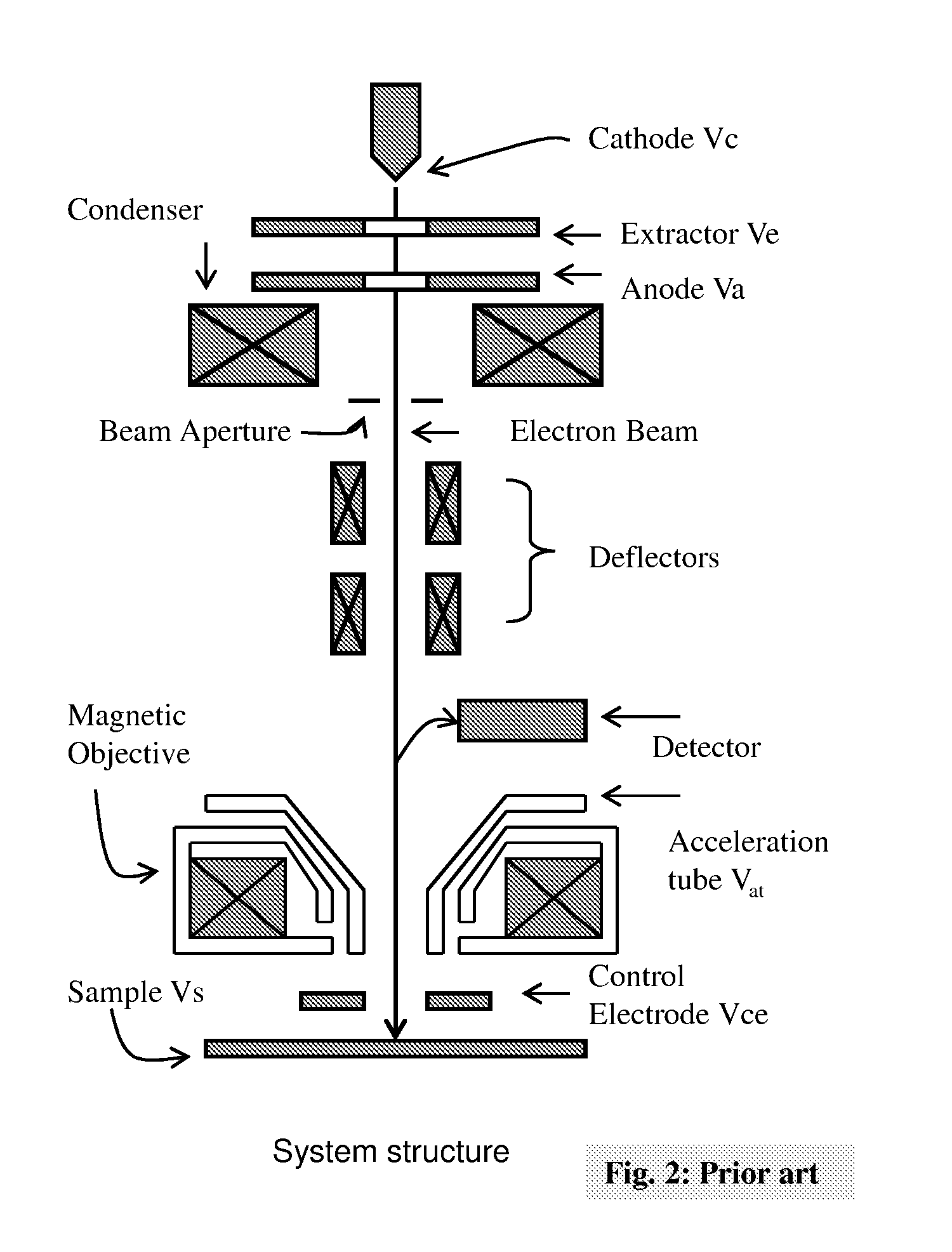
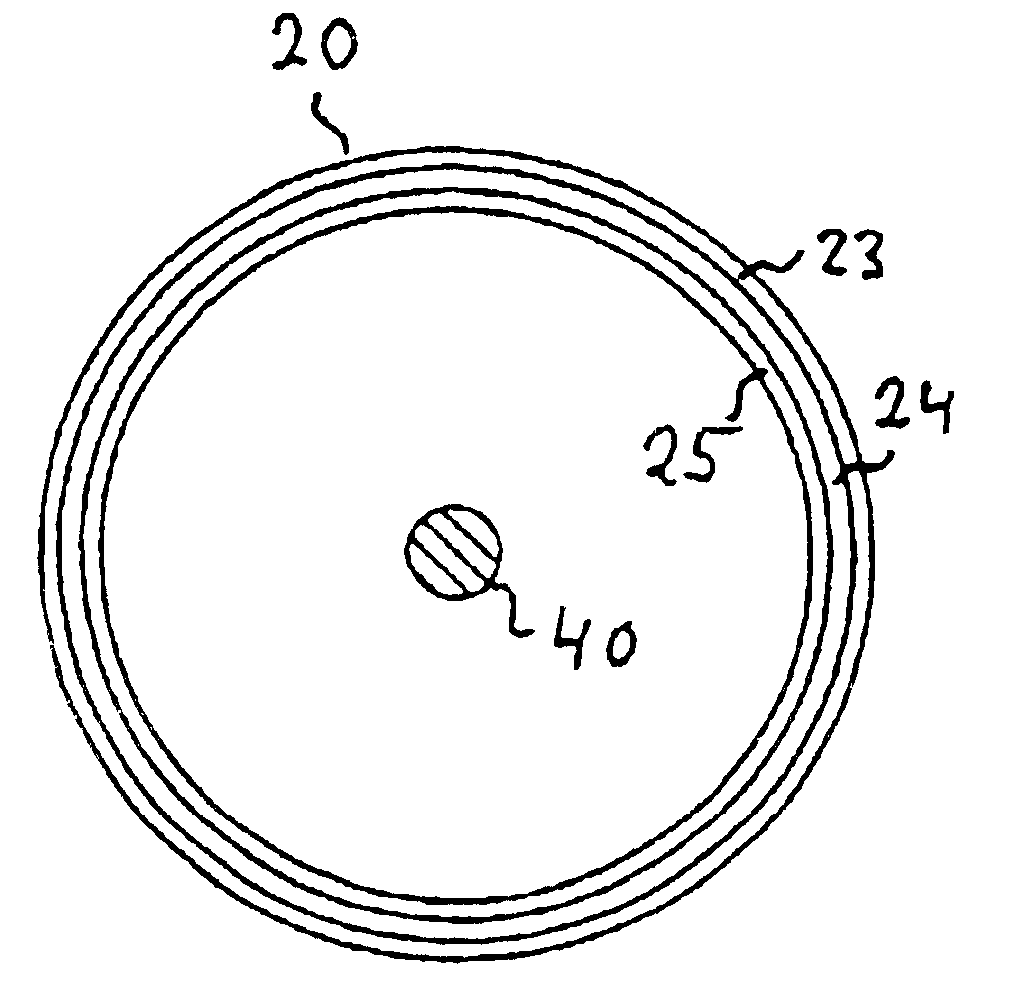
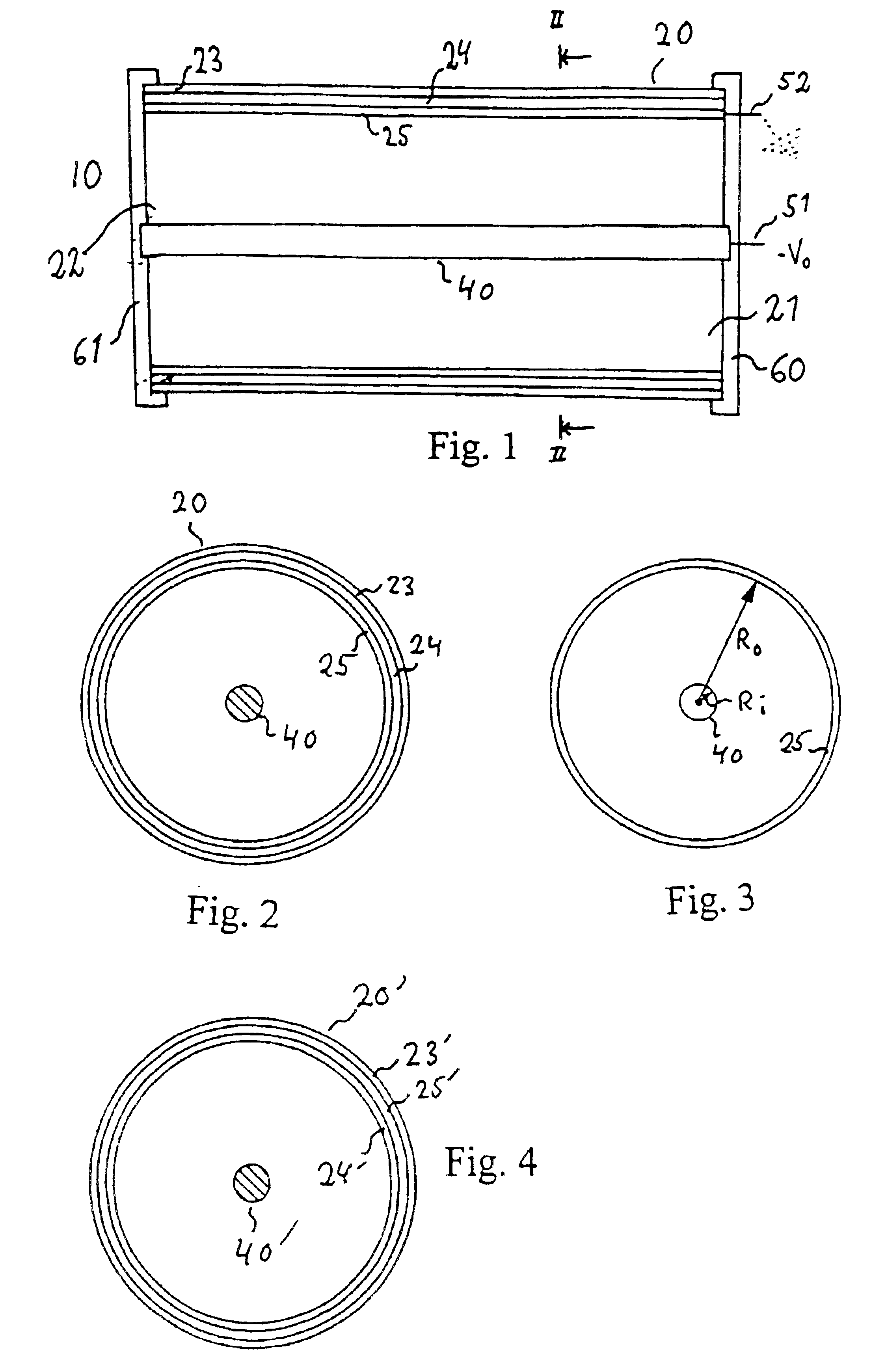
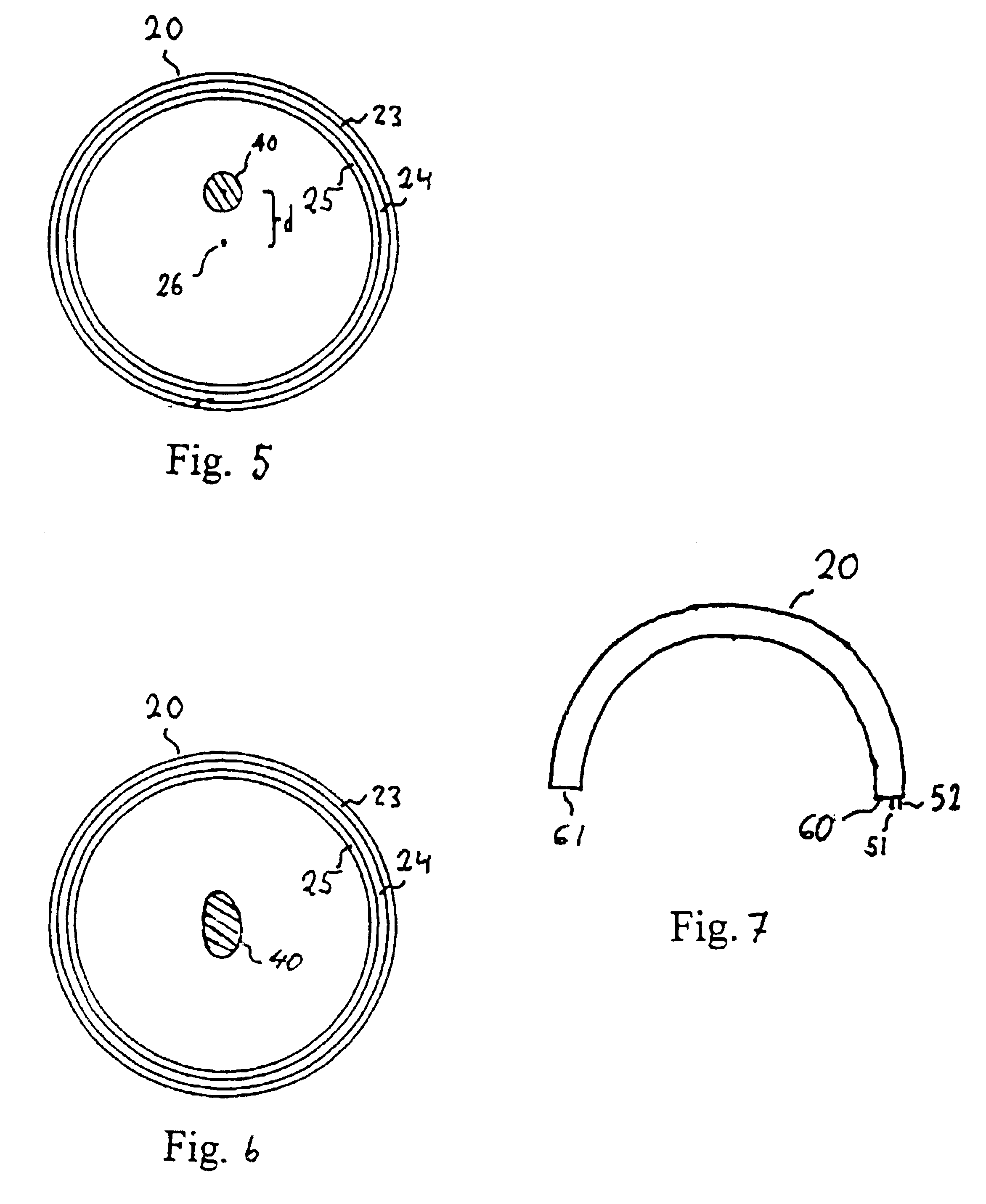
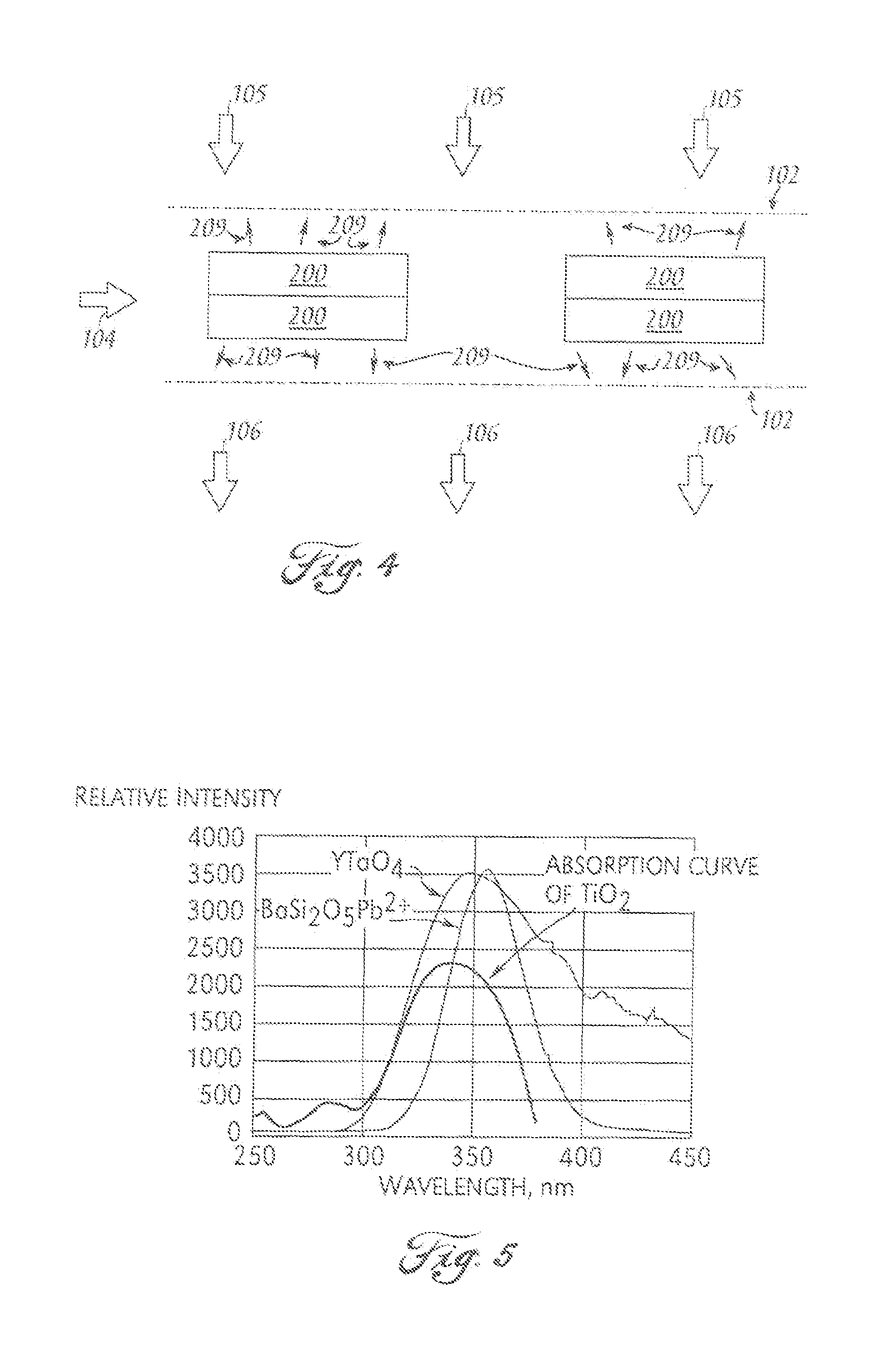
Light source, and a field emission cathode
InactiveUS6873095B1Simple and robust constructionLarge luminous surfaceLamp incadescent bodiesNanoinformaticsEVACUATED CONTAINERPhosphor
The light source, comprises an evacuated container having walls, including an outer glass layer (23) which on at least part thereof is coated on the inside with a layer of phosphor (24) forming a luminescent layer and a conductive layer (25) forming an anode. The phosphor (24) is excited to luminescence by electron bombardment from a field emission cathode (40) located in the interior of the container. The field emission cathode (40) comprises a carrier having a diameter in the mm range. At least a portion of the surface of the carrier is provided with a conductive layer having surface irregularities in the form of tips, having a radial extension being less than about 10 μm. Due to the geometry and the tips, the electric field is concentrated and amplified at the field emission surface.
Owner:NANOLIGHT INT
Field emitting cathode and lighting device
ActiveCN1988108ANice glow effectImprove conversion efficiencyLamp detailsLuminescent screen lampsElectricityEffect light
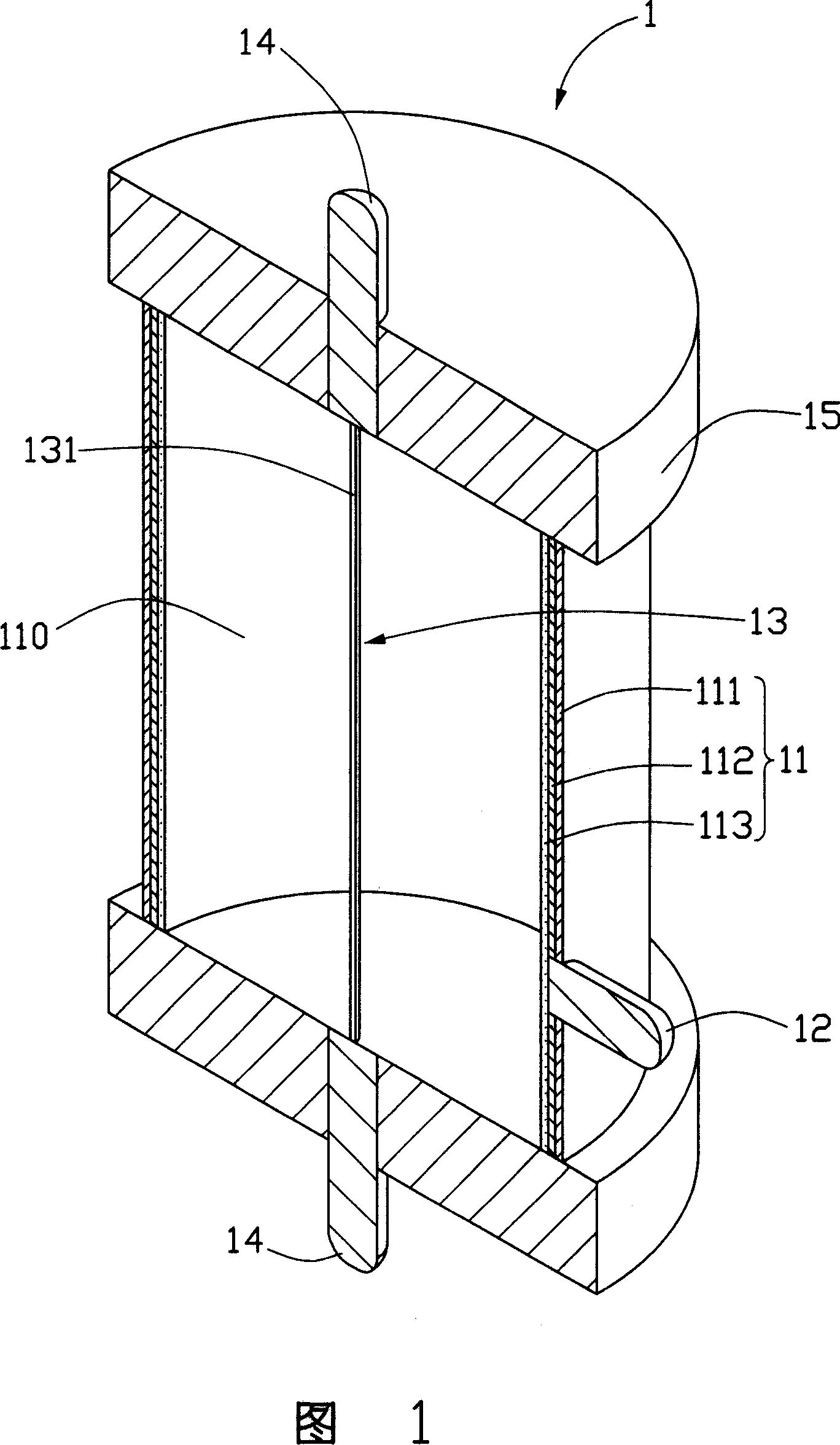
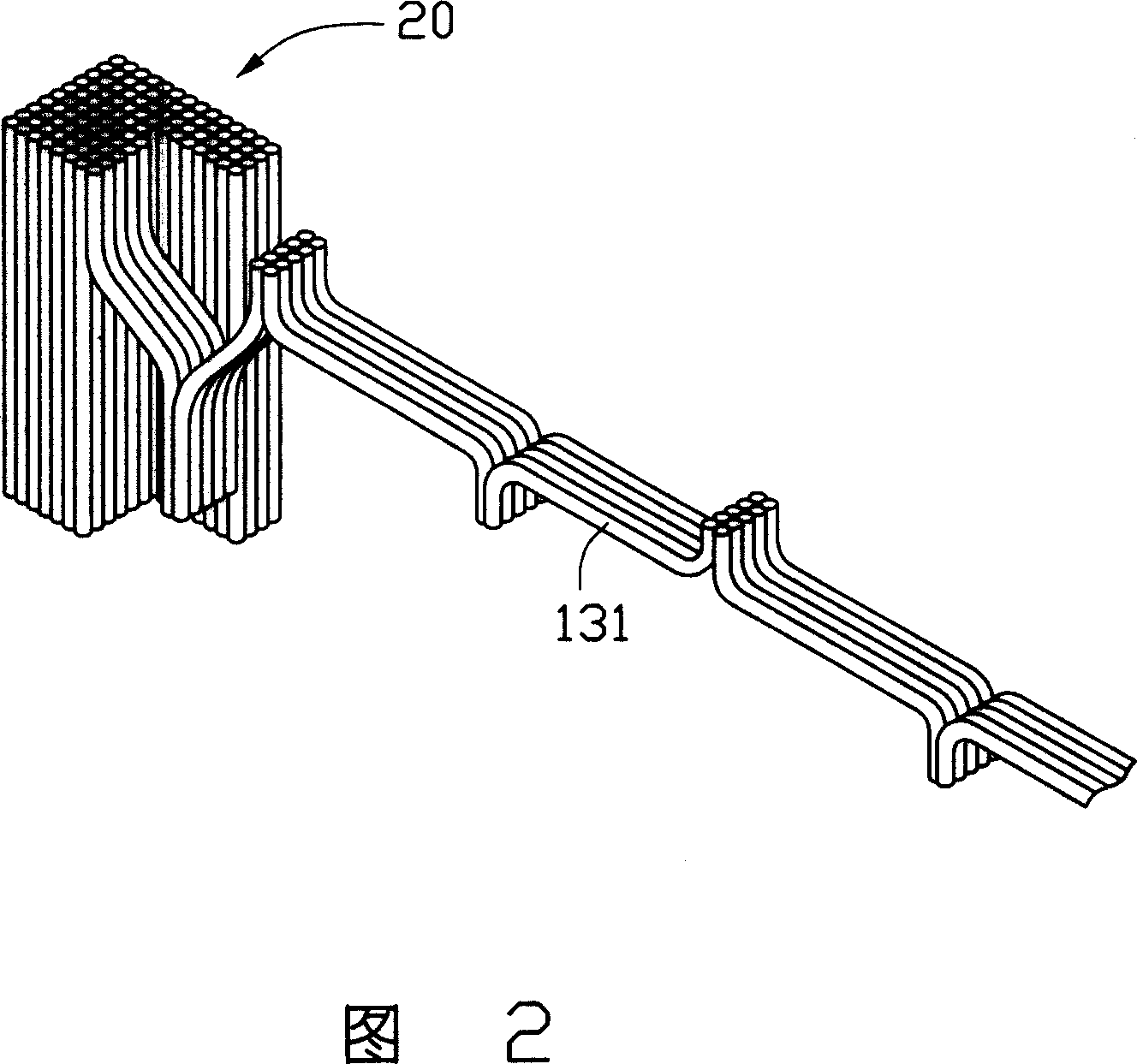
This invention relates to a field emission cathode and a field emission illumination device applying the cathode, in which, the cathode includes carbon nm tube wires pulled out from a carbon nm tube array and is formed by single carbon nm tube wire or multiple wires winded together or by winding single or multiple wires on a metal bar. Said device includes a cathode and an anode opposite to it and the energy conversion passes through a process of electricity-light only.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV +1
Method of synthesizing small-diameter carbon nanotubes with electron field emission properties
ActiveUS7618300B2High emission current densityEasy to prepareSpecific nanostructure formationMaterial nanotechnologyField emission deviceHydrogen
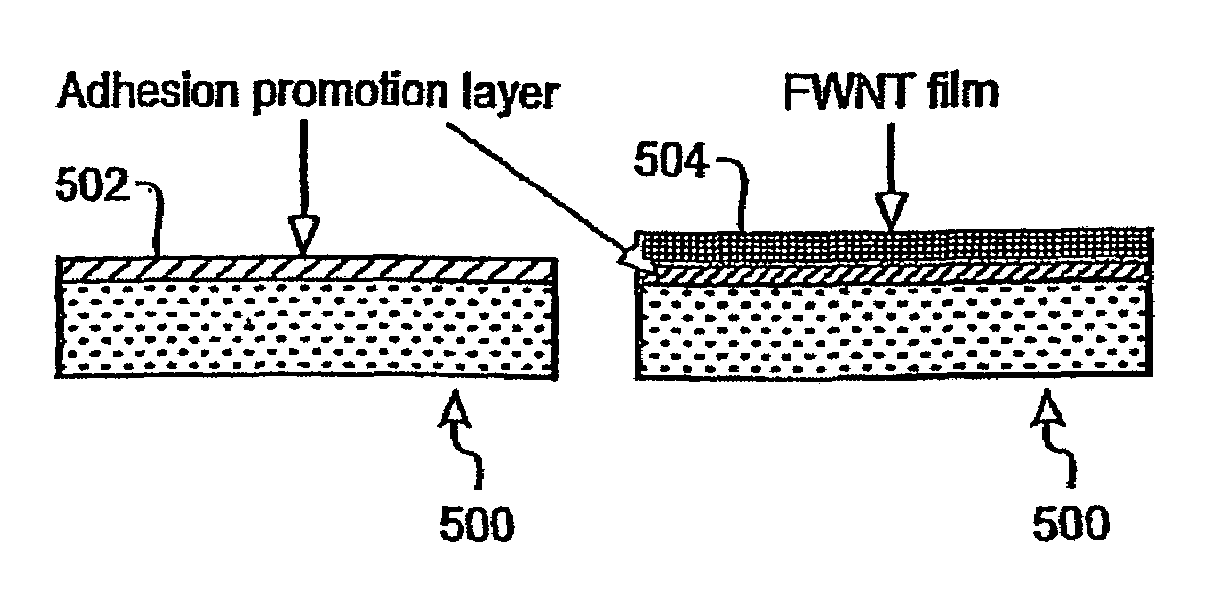
Carbon nanotube material having an outer diameter less than 10 nm and a number of walls less than ten are disclosed. Also disclosed are an electron field emission device including a substrate, an optionally layer of adhesion-promoting layer, and a layer of electron field emission material. The electron field emission material includes a carbon nanotube having a number of concentric graphene shells per tube of from two to ten, an outer diameter from 2 to 8 nm, and a nanotube length greater than 0.1 microns. One method to fabricate carbon nanotubes includes the steps of (a) producing a catalyst containing Fe and Mo supported on MgO powder, (b) using a mixture of hydrogen and carbon containing gas as precursors, and (c) heating the catalyst to a temperature above 950° C. to produce a carbon nanotube. Another method of fabricating an electron field emission cathode includes the steps of (a) synthesizing electron field emission materials containing carbon nanotubes with a number of concentric graphene shells per tube from two to ten, an outer diameter of from 2 to 8 nm, and a length greater than 0.1 microns, (b) dispersing the electron field emission material in a suitable solvent, (c) depositing the electron field emission materials onto a substrate, and (d) annealing the substrate.
Owner:NURAY TECH +1
Photocatalytic process
InactiveUS7300634B2Material nanotechnologyPhysical/chemical process catalystsPhosphorUltraviolet lights
A photocatalytic cleaner for air or water includes a photocatalytic material coating a substrate. An anode, positioned a predetermined distance from the substrate, includes a phosphor that emits ultraviolet light in response to bombardment by electrons from a field emission cathode emitting electrons in response to an electric field. The field emission cathode may be a carbon based field emitter material including incorporating carbon nanotubes.
Owner:APPLIED NANOTECH HLDG
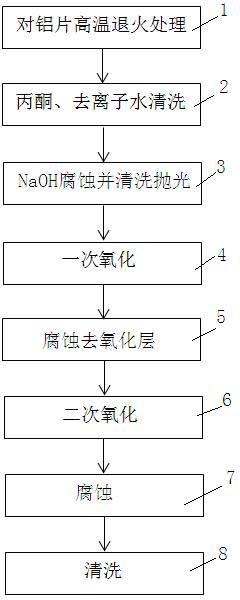
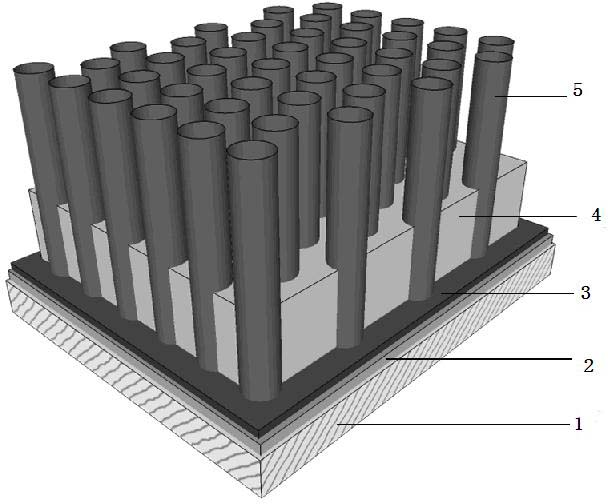
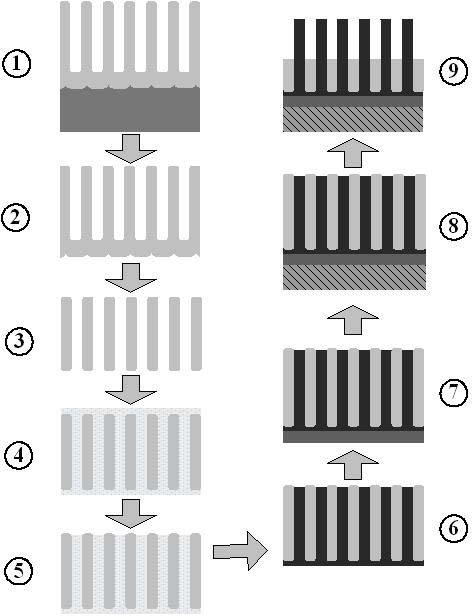
Method for making anodized aluminum template and method for making field emission cathode array material using the template
ActiveCN102262989AArrangement rulesImprove uniformityAnodisationCold cathode manufactureNanoholeCarbonization
The invention relates to a method for manufacturing an anodic aluminum oxide template and a method for manufacturing a field emission cathode array material by using the aluminum oxide template. The anodic aluminum oxide template with a regular appearance and a clean surface is manufactured by adopting a series of surface protection measures; and a field emission vertical nanowire or nanotube array cathode material is manufactured by pouring organic substances, metal organic solution or sol into a nano hole of the aluminum oxide template by a water method, a heat method and the like through processes such as gelation, high temperature carbonization, aluminum oxide template removal and the like. The field emission cathode material manufactured by the method has regular appearance and low starting voltage during field emission performance test; furthermore, the method process is simpler; and manufacturing of large-area field emission materials can be realized easily.
Owner:FUZHOU UNIV
Method for improving emission stability of high-temperature electrons of SiC field emission cathode materials
ActiveCN103928276AAchieve preparationExcellent high temperature electron emission stabilityMaterial nanotechnologyCold cathode manufactureNanowireBall mill
Provided is a method for improving emission stability of high-temperature electrons of SiC field emission cathode materials. The method comprises the following specific steps that 1) heat preservation is carried out on organic precursor polyborosilazane in an atmosphere sintering furnace for 30 min at the temperature of 260 DEG C for thermo crosslinking curing, and then the organic precursor polyborosilazane is smashed through a ball mill; 2) carbon paper is adopted as a substrate, the carbon paper is arranged in 0.05 mol / L Co(NO3)2 ethanol solutions with the purity of 99 percent for immersion treatment, and the carbon paper is taken out and naturally aired for standby application; 3) smashed powder is arranged at the bottom of a graphite crucible, the carbon paper after the immersion treatment is arranged at the top of the graphite crucible, and the powder and the carbon paper are placed in an atmosphere protecting furnace together; 4) the powder is heated to 1550 DEG C from the indoor temperature at the speed of 25 DEG C / min under protection of Ar atmosphere with the purity of 99.9 percent; 5) the temperature is reduced to 1100 DEG C from 1550 DEG C at the speed of 15 DEG C / min; 6) the powder is cooled to the indoor temperature along with the furnace, and in-situ B doped SiC nanowires are manufactured; 7) the SiC nanowires are applied to a field emission cathode for electron emission performance detection and analysis. Through B-site doping, the emission stability of the high-temperature electrons of the SiC field emissioncathode materials is effectively improved.
Owner:NINGBO UNIVERSITY OF TECHNOLOGY
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com