Patents
Literature
246 results about "Electron current" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Electron Current: Normally, Flow of electron or flow of charge is called current. Two types of current are normally employed is electric circuit one is Conventional current and another one is Electron current. The flow of electrons from source negative terminal to positive terminal is termed as electron current.
Field emission electron source
InactiveUS6057637AStable and reproducible current-voltage characteristicStraightforward and commercially feasibleElectric discharge tubesLayered productsElectron currentElectron source
A novel field emitter material, field emission electron source, and commercially feasible fabrication method is described. The inventive field emission electron source produces reliable electron currents of up to 400 mA / cm2 at 200 volts. The emitter is robust and the current it produces is not sensitive to variability of vacuum or the distance between the emitter tip and the cathode. The novel emitter has a sharp turn-on near 100 volts.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Organic devices, organic electroluminescent devices, organic solar cells, organic FET structures and production method of organic devices
ActiveUS20050098207A1TransistorDischarge tube luminescnet screensElectronic transmissionOrganic solar cell
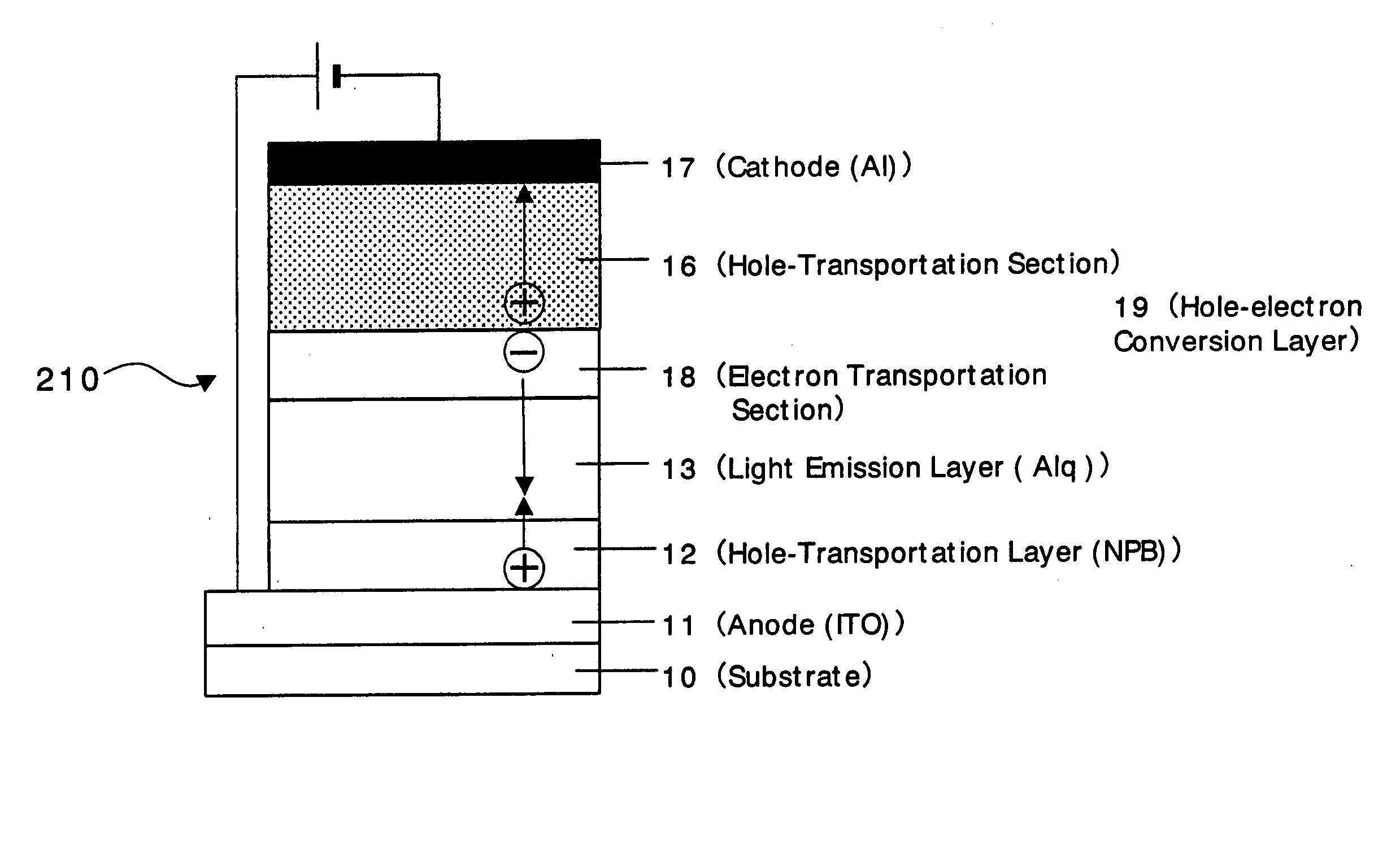
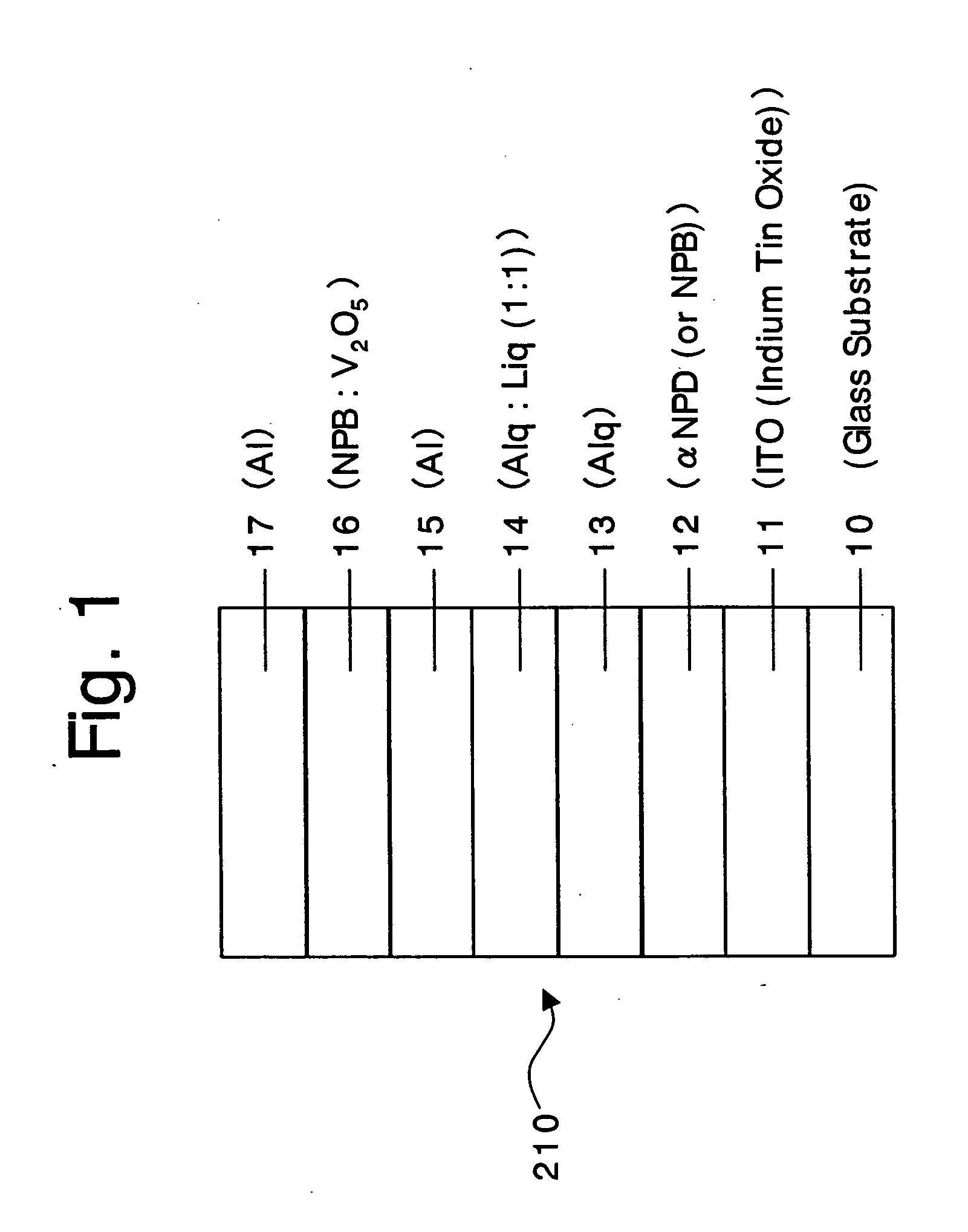
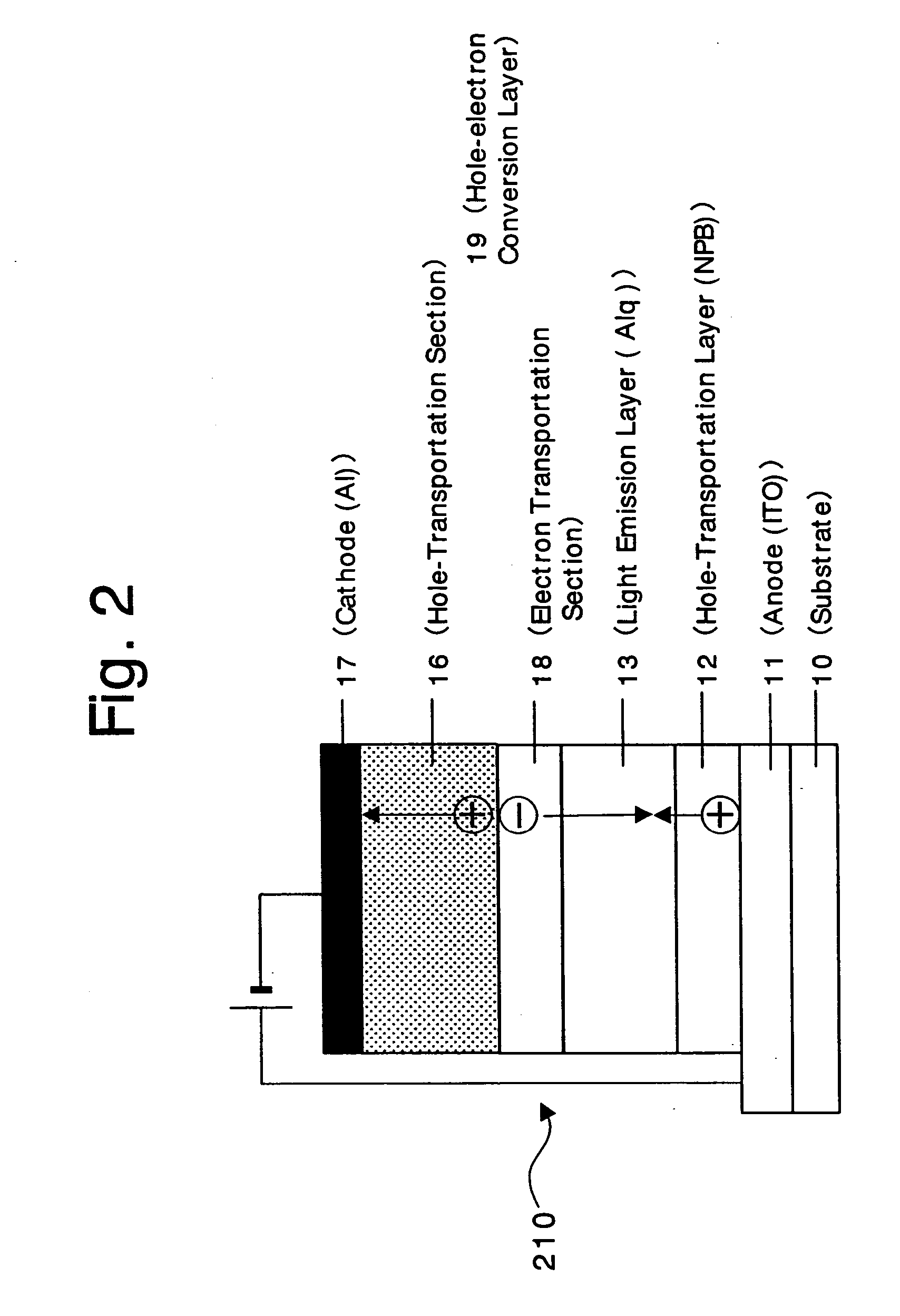
An organic device has a hole current-electron current conversion layer which comprises a laminate of an electron transportation section and a hole transportation section. The electron transportation section includes a charge transfer complex formed upon an oxidation-reduction reaction between a reduced low work function metal and an electron-accepting organic compound, the reduced metal being produced upon an in-situ thermal reduction reaction caused upon contact, through lamination or mixing by co-deposition, of an organic metal complex compound or an inorganic compound containing at least one metal ion selected from ions of low work function metals having a work function of not more than 4.0 eV, and a thermally reducible metal capable of reducing a metal ion contained in the organic metal complex compound or the inorganic compound in vacuum to the corresponding metal state, and the electron transportation section having the electron-accepting organic compound in the state of radical anions. The hole transportation section includes an organic compound having an ionization potential of less than 5.7 eV and an electron-donating property and an inorganic or organic substance capable of forming a charge transfer complex upon its oxidation-reduction reaction with the organic compound, the organic compound and the inorganic or organic substance being contacted through lamination or mixing, and the electron-donating organic compound is in the state of radical cations.
Owner:MITSUBISHI HEAVY IND LTD +1
Plasma etching device
InactiveUS8114245B2Lower impedanceLiquid surface applicatorsElectric discharge tubesElectron currentElectricity
A plasma etching device which has an auxiliary electrode enabling realization of a uniform plasma density of generated plasma on the surface of a base and which enables uniform etching with respect to the base without depending upon pressure and without rotating a magnetic field applying means. The plasma etching device has magnetic field applying means which has two parallel plate electrodes I and II and RF power applying means, with the base set on the electrode I, and which is horizontal and unidirectional with respect to the surface of the base where plasma etching is carried out. In this plasma etching device, an auxiliary electrode is provided at least on the upstream side of the base in a flow of electron current generated by the magnetic field applying means. The auxiliary electrode includes a local electrode arranged on the side facing the electrode II and means for adjusting impedance provided at a part of the local electrode to be electrically connected with the electrode I.
Owner:OHMI TADAHIRO +1
Method and apparatus for controlling electron beam current
InactiveUS7085351B2High emitted electron current densityHigh electron beam currentStatic indicating devicesNanoinformaticsHigh energyX-ray
An x-ray generating device includes a field emission cathode formed at least partially from a nanostructure-containing material having an emitted electron current density of at least 4 A / cm2. High energy conversion efficiency and compact design are achieved due to easy focusing of cold cathode emitted electrons and dramatic reduction of heating at the anode. In addition, by pulsing the field between the cathode and the gate or anode and focusing the electron beams at different anode materials, pulsed x-ray radiation with varying energy can be generated from a single device. Methods and apparatus for independent control of electron emission current and x-ray energy in x-ray tubes are also provided. The independent control can be accomplished by adjusting the distance between the cathode and anode. The independent control can also be accomplished by adjusting the temperature of the cathode. The independent control can also be accomplished by optical excitation of the cathode. The cathode can include field emissive materials such as carbon nanotubes.
Owner:THE UNIV OF NORTH CAROLINA AT CHAPEL HILL
X-ray generating mechanism using electron field emission cathode
InactiveUS6850595B2High emitted electron current densityHigh electron beam currentX-ray tube electrodesNanoinformaticsElectron currentSoft x ray
An x-ray generating device includes a field emission cathode formed at least partially from a nanostructure-containing material having an emitted electron current density of at least 4 A / cm2. High energy conversion efficiency and compact design are achieved due to easy focusing of cold cathode emitted electrons and dramatic reduction of heating at the anode. In addition, by pulsing the field between the cathode and the gate or anode and focusing the electron beams at different anode materials, pulsed x-ray radiation with varying energy can be generated from a single device.
Owner:THE UNIV OF NORTH CAROLINA AT CHAPEL HILL
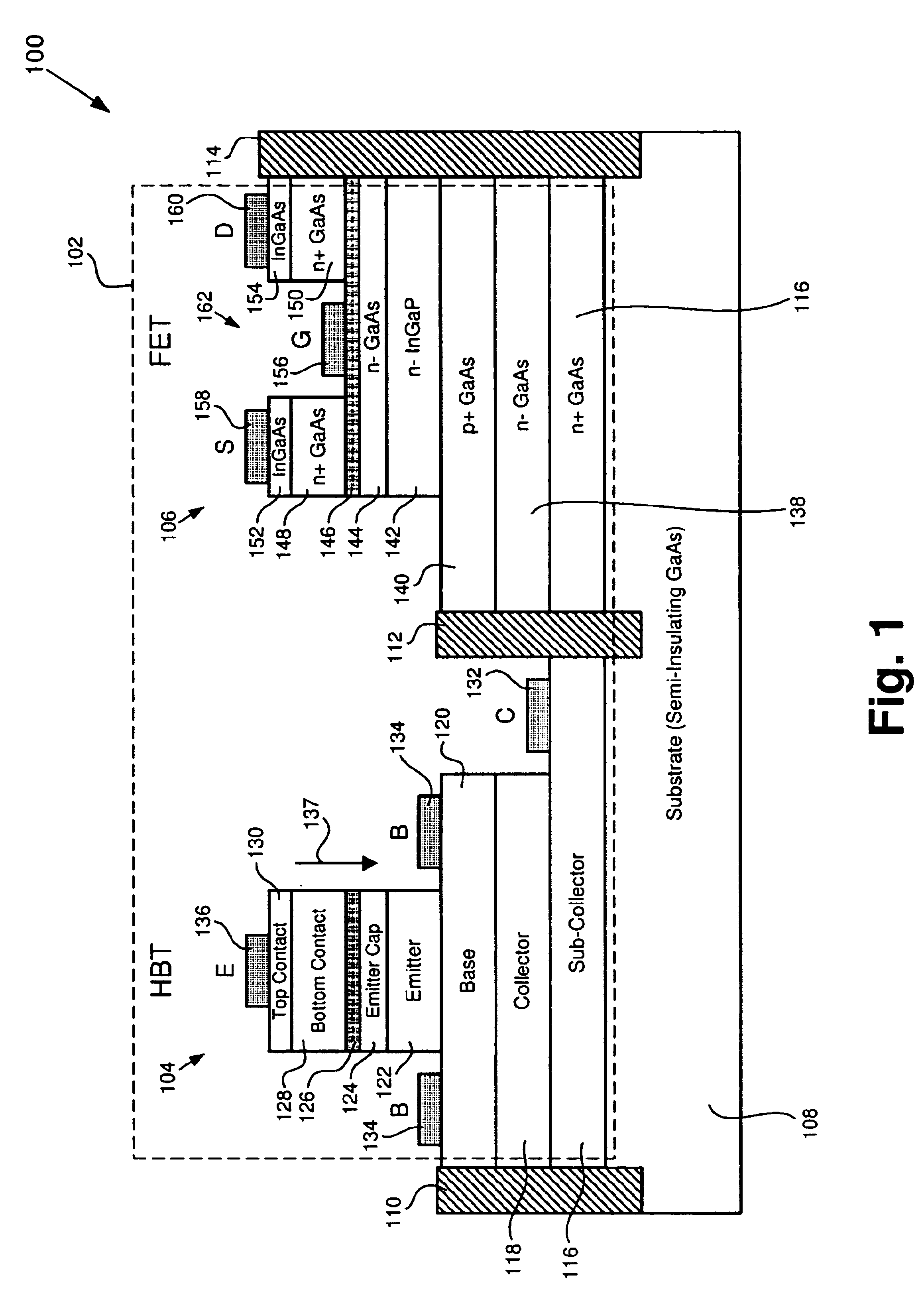
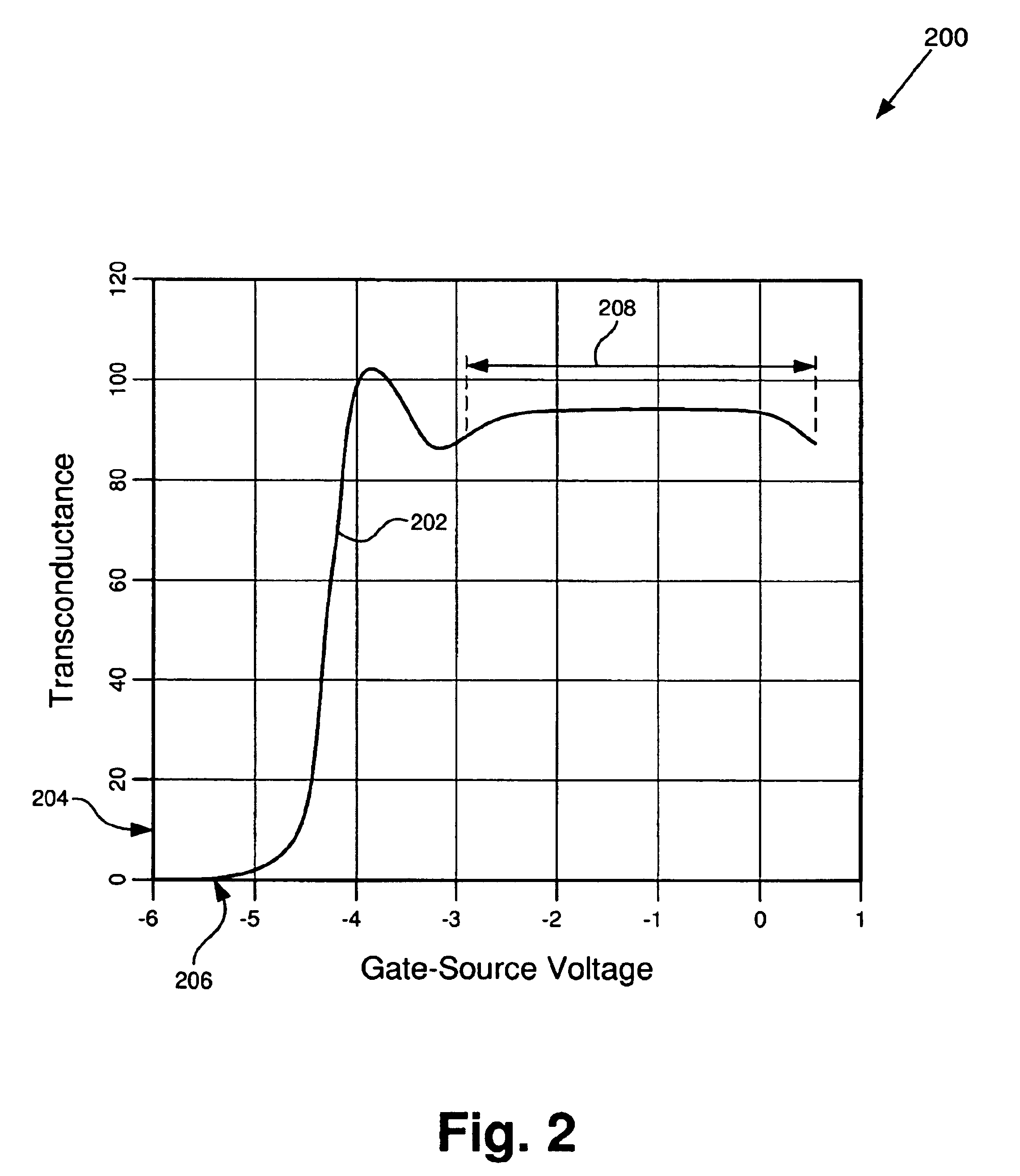
BiFET including a FET having increased linearity and manufacturability
According to one exemplary embodiment, a BiFET situated on a substrate comprises an emitter layer segment situated over the substrate, where the emitter layer segment comprises a semiconductor of a first type. The HBT further comprises a first segment of an etch stop layer, where the first segment of the etch stop layer comprises InGaP. The BiFET further comprises a FET situated over the substrate, where the FET comprises source and drain regions, where a second segment of the etch stop layer is situated under the source and drain regions, and where the second segment of the etch stop layer comprises InGaP. The FET further comprises a semiconductor layer of a second type situated under the second segment of the etch stop layer. The etch stop layer increases linearity of the FET and does not degrade electron current flow in the HBT.
Owner:SKYWORKS SOLUTIONS INC
System for alternately pulsing energy of accelerated electrons bombarding a conversion target
InactiveUS7130371B2Laser detailsCathode ray concentrating/focusing/directingElectron currentPulse energy
A RF linear electron accelerator system for generating a beam of accelerated electrons bunched in pulses having different energy spectra from pulse to pulse. The system is operable to generate a beam of high energy X-rays from such beam of accelerated electrons, using a conversion target, with pulses of the X-ray beam having energy spectra which are different from X-ray pulse to X-ray pulse. Preferably, the pulses of the electron beam have energy spectra which alternate from pulse to pulse and, correspondingly, the pulses of the X-ray beam have energy spectra which alternate from pulse to pulse. Also preferably, the current of electrons injected into the system's accelerating section and the frequency of the pulse RF power supplied to the accelerating section are changed in a synchronized manner to generate the electron beam. The system is employable in an inspection system for discriminating materials present in containers by atomic numbers.
Owner:SCANTECHIBS IP HLDG
High resolution detection for time-of-flight mass spectrometers
InactiveUS6870156B2High resolutionInhibit transferSpectrometer detectorsTime-of-flight spectrometersEngineeringMass analyzer
The invention covers a method for detecting ions in high resolution time-of-flight mass spectrometers which operate with secondary electron multiplier multichannel plates and in which many single spectra are acquired and added to produce a sum spectrum. The invention involves (a) using an analog digital converter (ADC) for converting electron currents from secondary electron multipliers, instead of a time-to-digital converter (TDC) which was previously used for highest possible signal resolution, (b) performing a separate rapid peak recognition procedure for the ion signals of each spectrum by a fast calculation method, thereby collecting flight time and intensity value pairs for the ion peaks, and (c) constructing a time-of-flight / intensity histogram, which is further processed as a composite time-of-flight spectrum. The invention retains the significantly higher measurement dynamics of an ADC and achieves the improved resolution capability of a TDC, but without showing the latter's known signal distortion due to dead times.
Owner:BRUKER DALTONIK GMBH & CO KG
Ion-assisted magnetron deposition
InactiveUS6454910B1Easy to operateFree from damageCellsElectric discharge tubesElectron currentIon beam
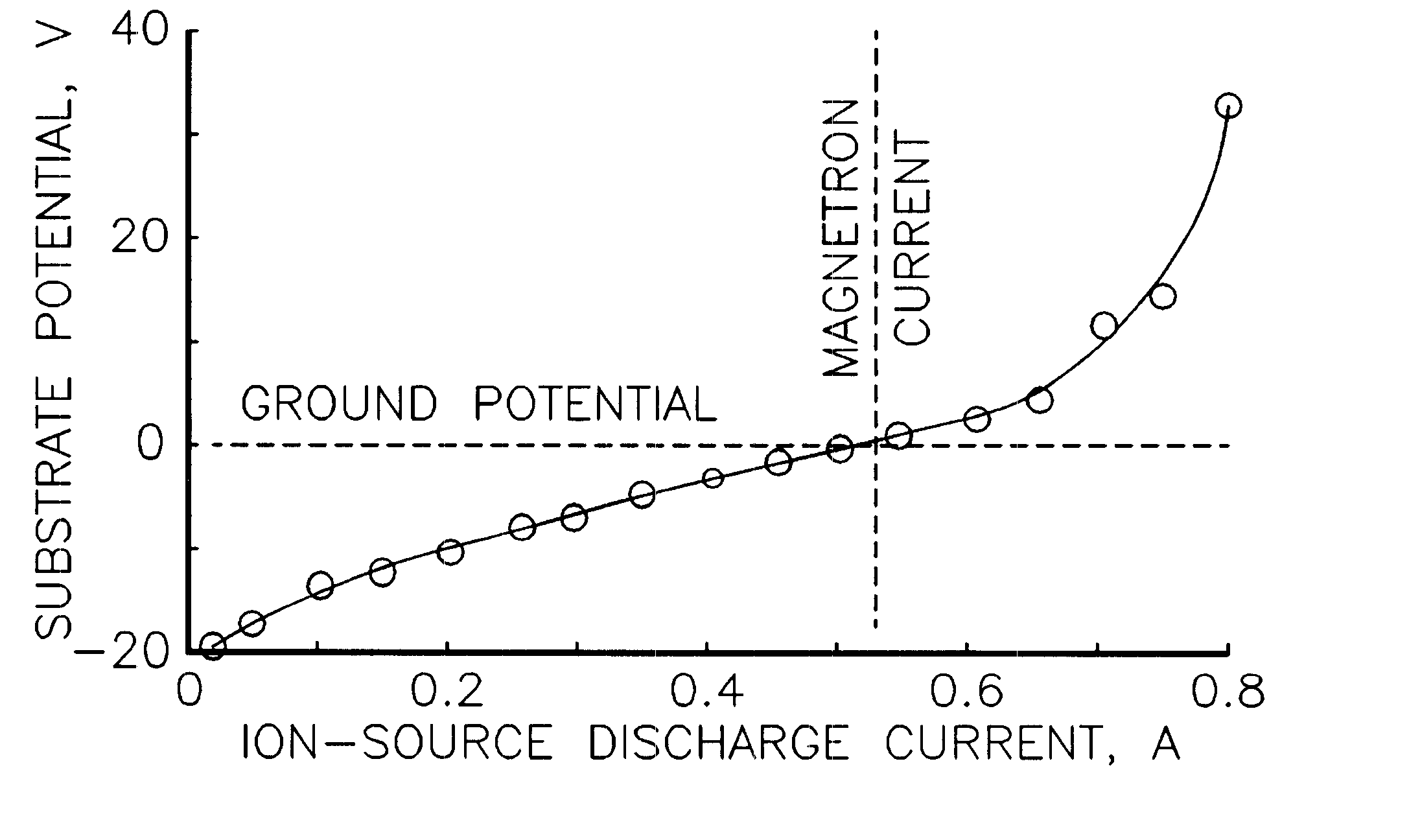
In accordance with an embodiment of the present invention, apparatus for ion-assisted magnetron deposition takes a form that includes a magnetron, a deposition substrate displaced from the magnetron, and an ion source also displaced from the magnetron and located so that the ion beam from the ion source is directed at the deposition substrate. The ion source is operated without an electron-emitting cathode-neutralizer, the electron current for this function being provided by electrons from the magnetron. In one specific embodiment, the ion source is operated so that the potential of the deposition substrate is maintained close to that of a common ground for the magnetron and the ion source. In another embodiment, the ion source is of the Hall-current type and the discharge current of the ion source is approximately equal in magnitude to the current of the magnetron discharge.
Owner:KAUFMAN & ROBINSON
Method and apparatus for controlling electron beam current
An x-ray generating device includes a field emission cathode formed at least partially from a nanostructure-containing material having an emitted electron current density of at least 4 A / cm2. High energy conversion efficiency and compact design are achieved due to easy focusing of cold cathode emitted electrons and dramatic reduction of heating at the anode. In addition, by pulsing the field between the cathode and the gate or anode and focusing the electron beams at different anode materials, pulsed x-ray radiation with varying energy can be generated from a single device. Methods and apparatus for independent control of electron emission current and x-ray energy in x-ray tubes are also provided. The independent control can be accomplished by adjusting the distance between the cathode and anode. The independent control can also be accomplished by adjusting the temperature of the cathode. The independent control can also be accomplished by optical excitation of the cathode. The cathode can include field emissive materials such as carbon nanotubes.
Owner:THE UNIV OF NORTH CAROLINA AT CHAPEL HILL
Magneto-luminescent transducer
InactiveUS20050007323A1Without burdenFacilitate emission of lightNanotechStatic indicating devicesMagnetic storageDisplay device
Owner:PRESIDENT & FELLOWS OF HARVARD COLLEGE
Magnetic field for small closed-drift ion source
InactiveUS6456011B1Reduce flux densityMinimize gas flowMaterial analysis by optical meansElectric arc lampsElectron currentPole piece
In one embodiment of a compact closed-drift ion source, an ionizable gas is introduced into a annular discharge region. An anode is at one end of this region and an electron-emitting cathode is near the opposite and open end. A magnetic circuit extends from an inner pole piece to an outer pole piece, with both pole pieces near the open end. The electron current in the discharge region interacts with the magnetic field therein to generate and accelerate ions out of the open end. A permeable enclosure surrounds the anode end of the discharge region. Adjacent elements of the permeable enclosure, the inner pole piece, and any intermediate permeable elements are in close proximity, one to the next. A magnetizing means is located only between the outer pole piece and the permeable enclosure.
Owner:KAUFMAN & ROBINSON
Powerful glow discharge excilamp
A powerful glow discharge lamp comprising two coaxial tubes, the outer tube being optically transparent, with a cathode and anode placed at opposite ends of the tubes, the space between the tubes being filled with working gas. The electrodes are made as cylindrical tumblers placed in line to one other in such a way that one end of the cathode is inserted into the inner tube, one end of the anode coaxially covers the end of the outer tube, the inner tube penetrating and extending through the anode. The increased electrodes' surface area increases glow discharge electron current and, correspondingly, average radiation power of discharge plasma. The inner tube contains at least one cooling liquid tube placed along the axis of the inner tube along the entire lamp length to provide cathode cooling. The anode has a circumferential heat extracting radiator which removes heat from the anode. The invention is related to lighting engineering and can be applied for realization of photostimulated processes under the action of powerful radiation in required spectral range.
Owner:THE UNITED STATES AS REPRESENTED BY THE DEPARTMENT OF ENERGY
Multilayer transparent electricity conductive film and manufacture method
InactiveCN101609729AImprove conductivityHigh optical transmittanceConductive layers on insulating-supportsVacuum evaporation coatingDisplay devicePeak value
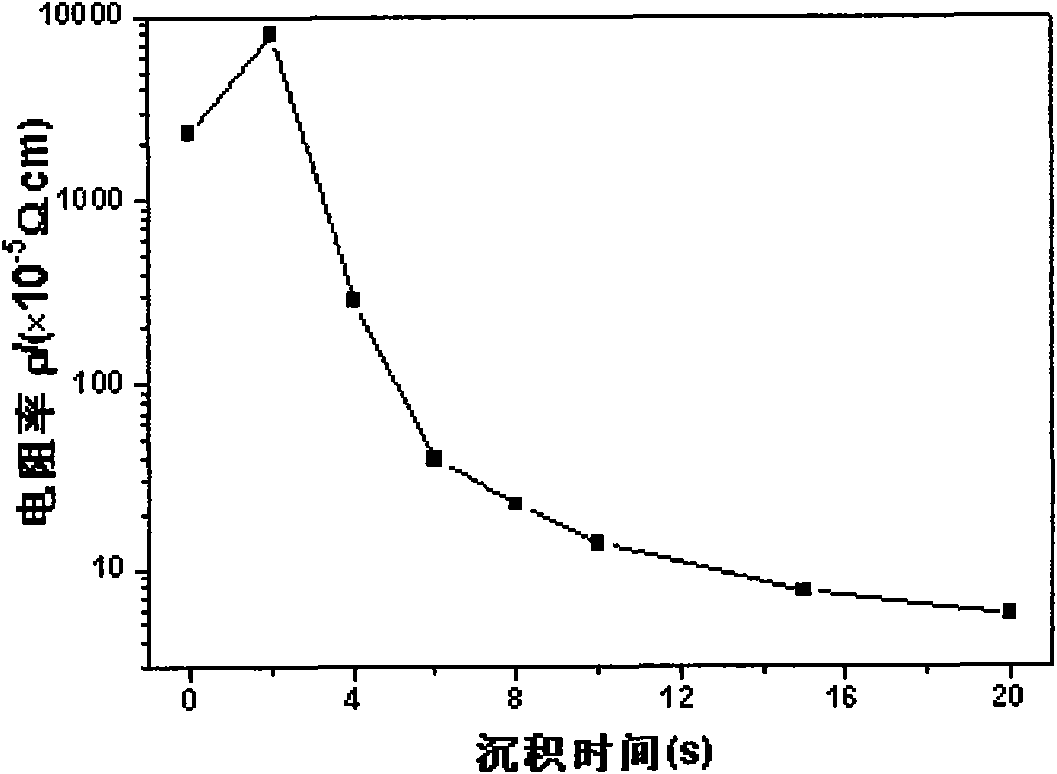
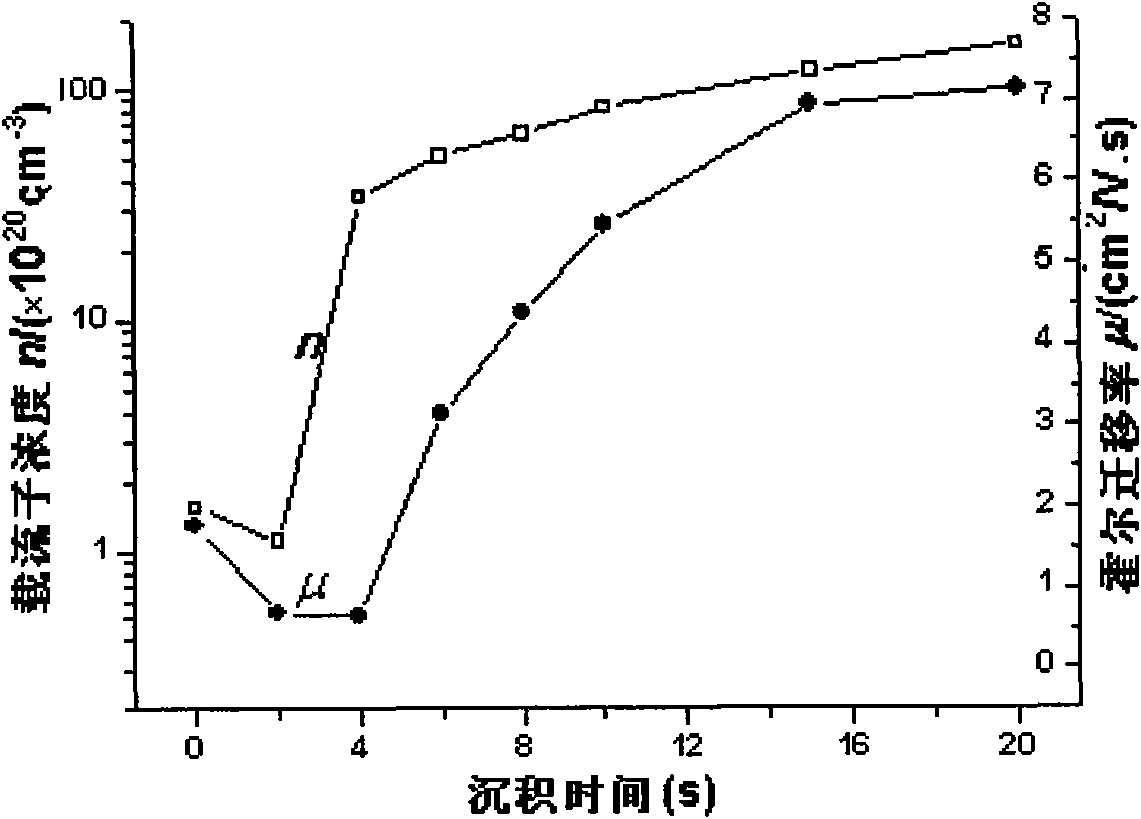
The invention provides a multilayer transparent electricity conductive film, comprising a substrate, n layers of metal Cu layers and m layers of ZnO layers. The n layers of metal Cu layers and the m layers of ZnO layers are alternately deposited on the substrate, wherein n is more than and equal to 1, and m is more than and equal to 1. The film is manufactured by a magnetic control sputtering method. The multilayer transparent electricity conductive film is characterized in that: the average transmittance of a visible light area is more than 70%, peak value transmittance is larger than 80%, the concentration of electron current carrier is not less than 5*10cm, and electric resistivity is not larger than 3*10 Omega. cm. The multilayer film obtained by the invention is manufactured under room temperature; the photoelectric property of the film is greatly improved relatively to a ZnO: Ca monolayer film; and the multilayer film can be used for photoelectric devices such as solar battery, flat-panel display, and the like, and the structure of a sunshade type infrared reflecting film.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
X-ray generation using secondary emission electron source
InactiveUS20080187093A1Harsh operating environmentEasy to operateMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationRadiation/particle handlingElectron currentSecondary emission
A method and apparatus are provided for generating high frequency electromagnetic energy using a secondary emission electron source. An x-ray source is therefore provided having a primary electron emitter, a secondary emission member, and an anode. The primary electron emitter provides a primary electron current directed to the secondary emission member. The secondary emission member then generates a secondary electron current which causes x-ray generation when impinging upon the anode.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
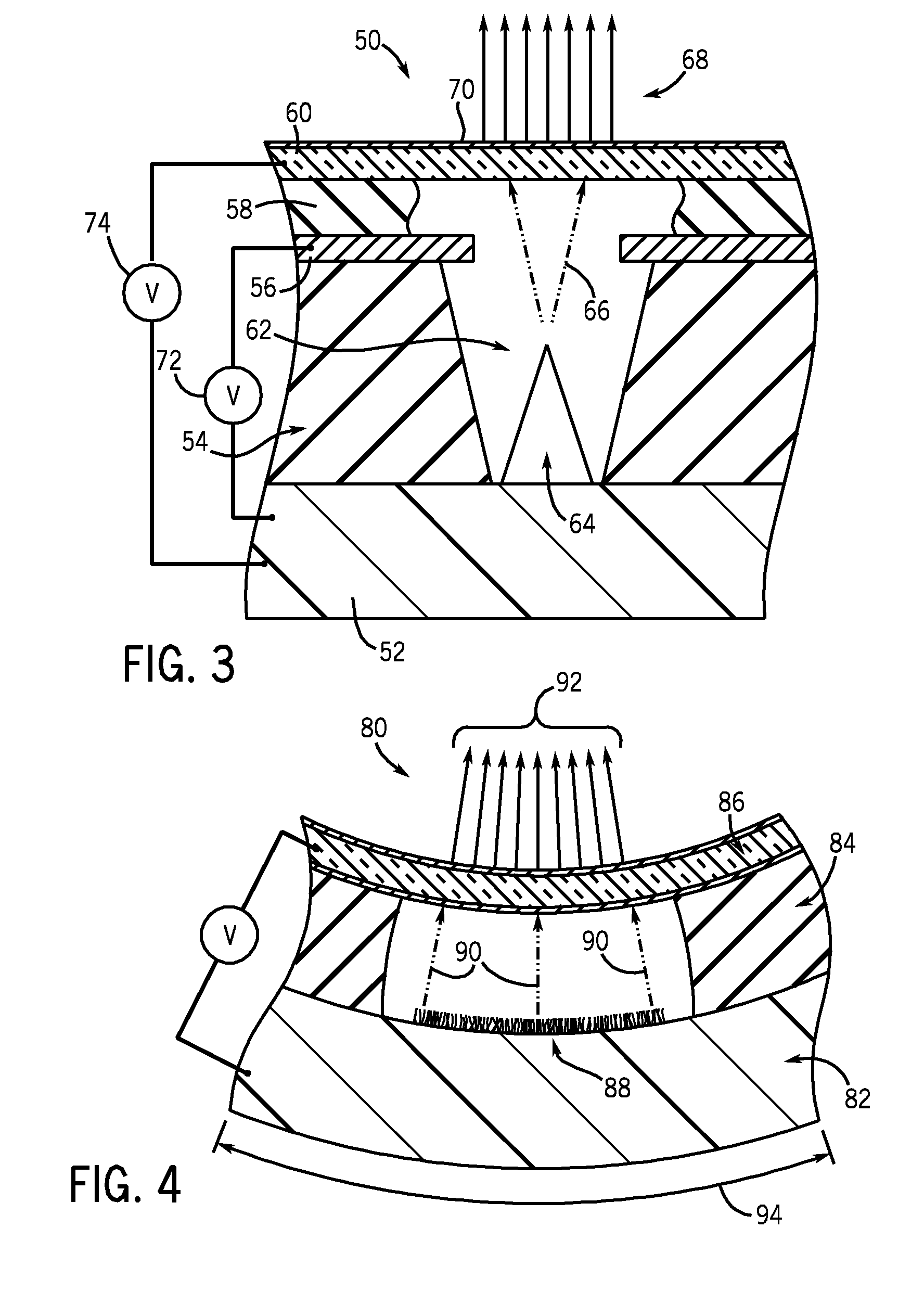
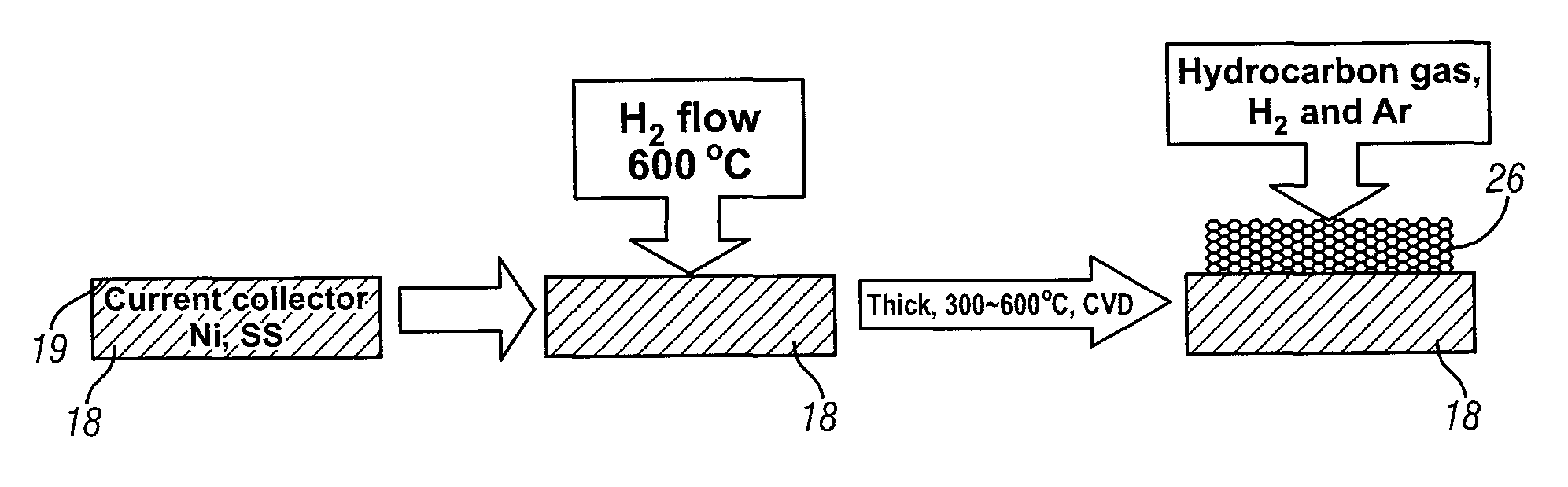
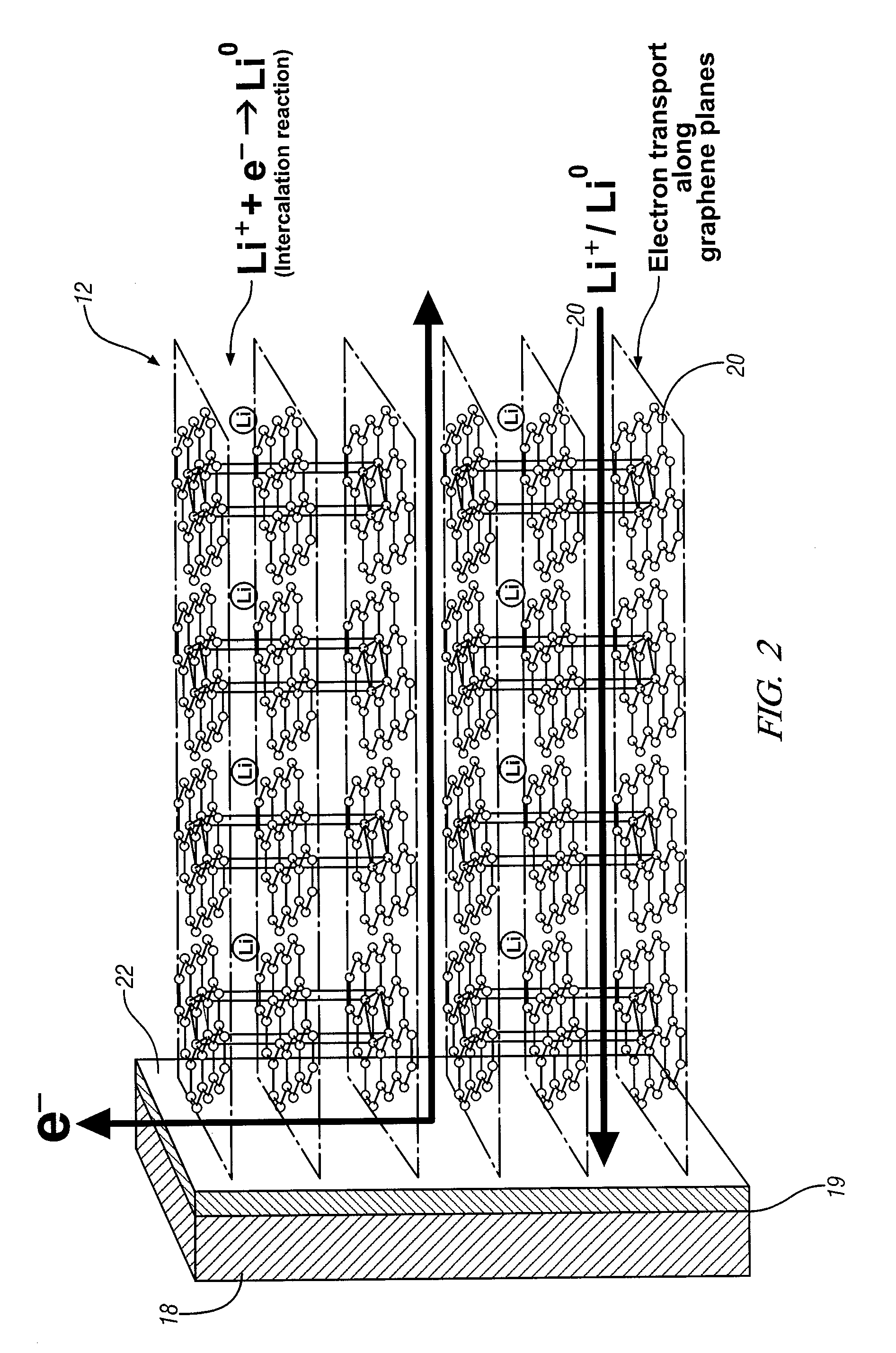
Intercalation electrode based on ordered graphene planes
ActiveUS9356281B2Efficient transportImprove volumetric efficiencySilver accumulatorsPolycrystalline material growthElectron currentGas phase
An intercalation electrode includes an electron current collector and graphene planes deposited normal to the surface of the current collector substrate. The graphene planes are deposited on the current collector substrate from a carbon-precursor gas using, for example, chemical vapor deposition. In an embodiment of an anode for a lithium-ion battery, the graphene planes are intercalated with lithium atoms. A lithium-ion battery may include this anode, a cathode, and a non-aqueous electrolyte. In repeated charging and discharging of the anode, lithium atoms and ions are readily transported between the graphene planes of the anode and the electrolyte.
Owner:GM GLOBAL TECH OPERATIONS LLC
Magnetic field for small closed-drift ion source
InactiveUS20020145389A1Easy to useCompact and efficient and economicalElectric arc lampsMachines/enginesElectron currentElectron flow
Owner:KAUFMAN & ROBINSON
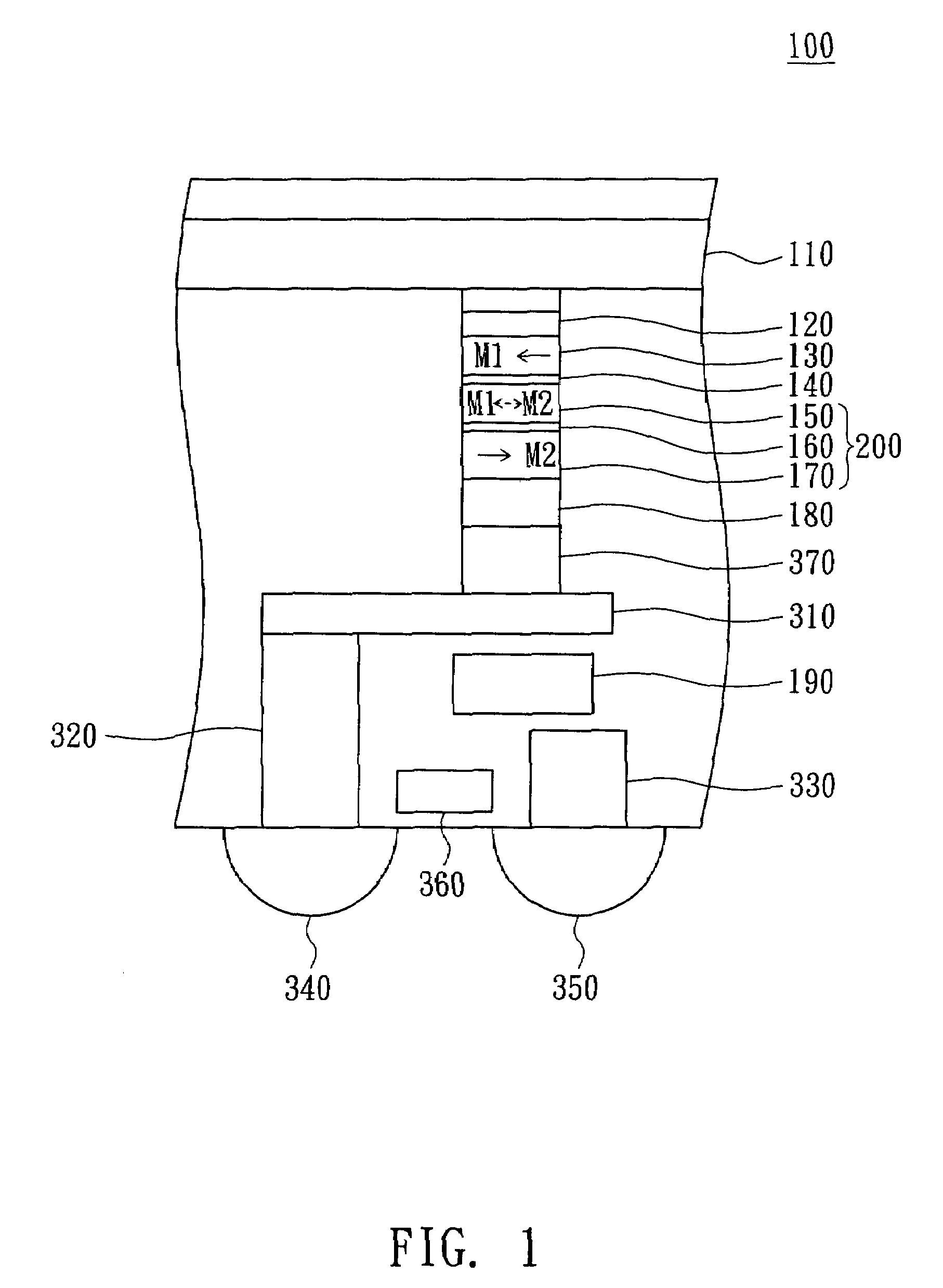
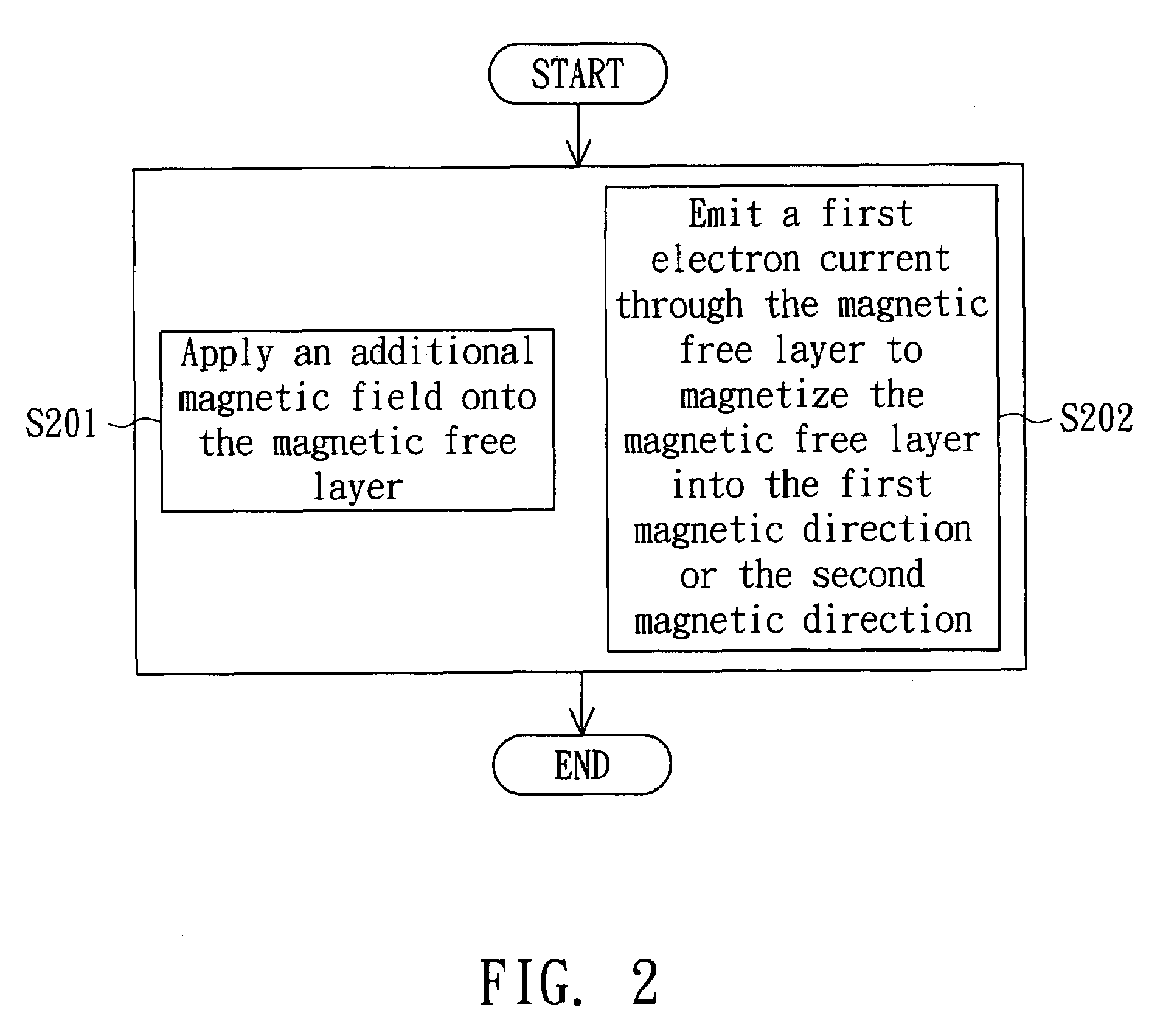
Programming method of magnetic random access memory
ActiveUS7508702B2Reduce power consumptionAvoiding electronicDigital storageElectron currentStatic random-access memory
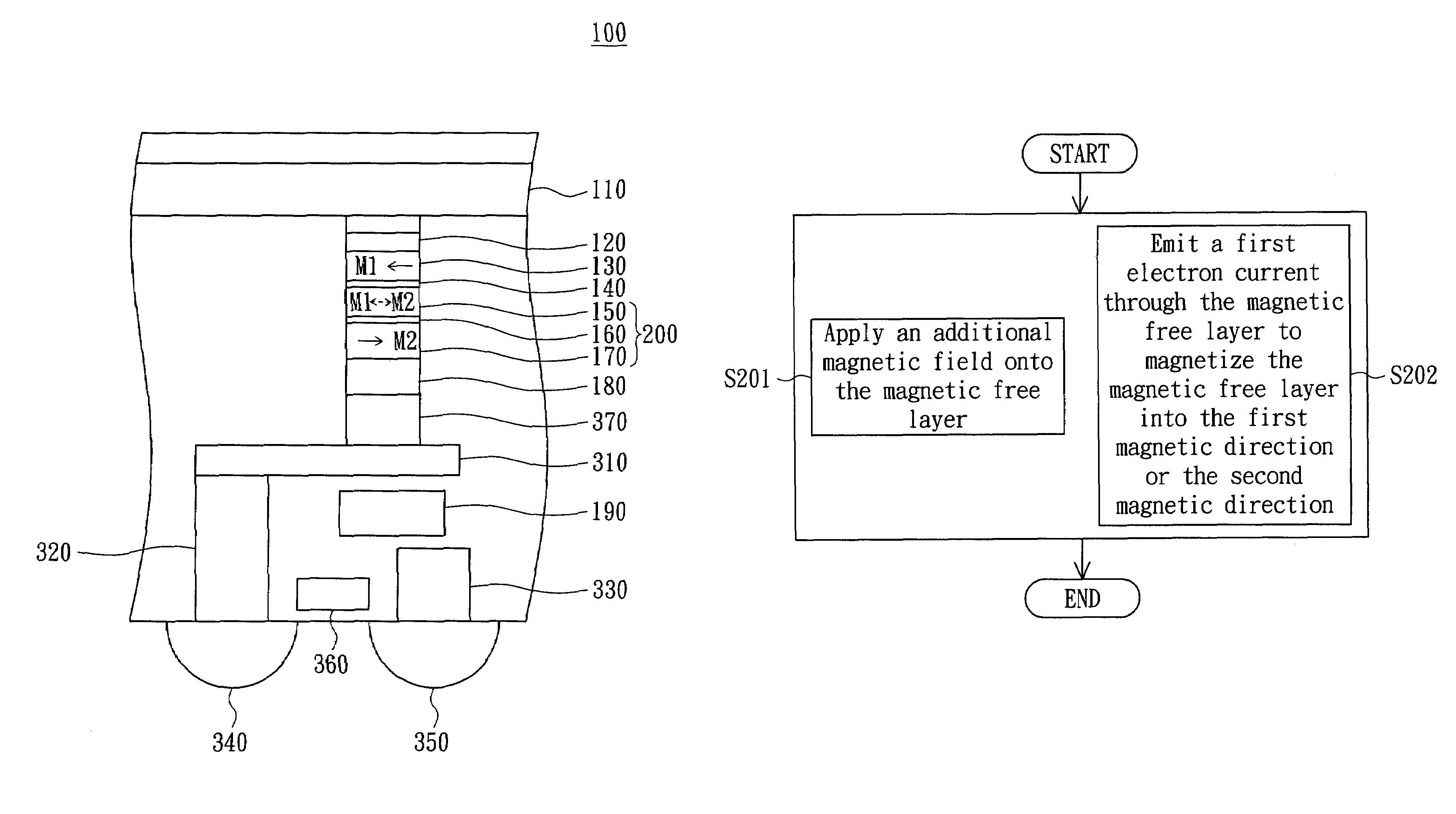
A programming method of a magnetic random access memory (MRAM) is provided. The magnetic random access memory includes a first magnetic pinned layer, a second magnetic pinned layer and a magnetic free layer. The first magnetic pinned layer is pinned at a first magnetic direction. The second magnetic pinned layer is pinned at a second magnetic direction. The magnetic free layer is magnetized into the first magnetic direction or the second magnetic direction. The programming method includes the following the steps. In the step (a), an additional magnetic field is applied onto the magnetic free layer. In the step (b), a first electron current is emitted through the magnetic free layer to magnetize the magnetic free layer into the first magnetic direction or the second magnetic direction.
Owner:MACRONIX INT CO LTD
Photodetector utilizing a HEMTstructure
The present invention relates to MSM photodetectors based on the high electron mobility transistor (HEMT) structure. More specifically, the present invention relates to MSM photodetectors based on the high electron mobility transistor (HEMT) structure that use a barrier layer of the HEMT structure as a Schottky barrier layer of the photodetector and use the channel layer of the HEMT structure as an absorption layer of the photodetector by doping the bottom part of the channel layer with a p-type dopant. Modification of the HEMT structure for the MSM photodetector can enhance electron current and suppress hole current, resulting in an impulse photocurrent response having a narrow pulse width. The present invention comprises an undoped buffer layer grown on the semi-insulating substrate, a p-doped channel layer that is used as an absorption layer grown on the said buffer layer, an undoped channel layer that is used as an absorption layer grown on the said channel layer, an undoped barrier layer that is composed of a material having a larger band gap energy than the said channel layers grown on the said undoped channel layer, a heavily n-type delta-doped barrier layer that is composed of a material having a larger band gap energy than the said channel layers grown on the said undoped barrier layer, and an undoped barrier layer that is composed of a material having a larger band gap energy than the said channel layers grown on the said heavily n-type delta-doped barrier layer.
Owner:GWANGJU INST OF SCI & TECH
Electrostatic propulsion engine with neutralizing ion source
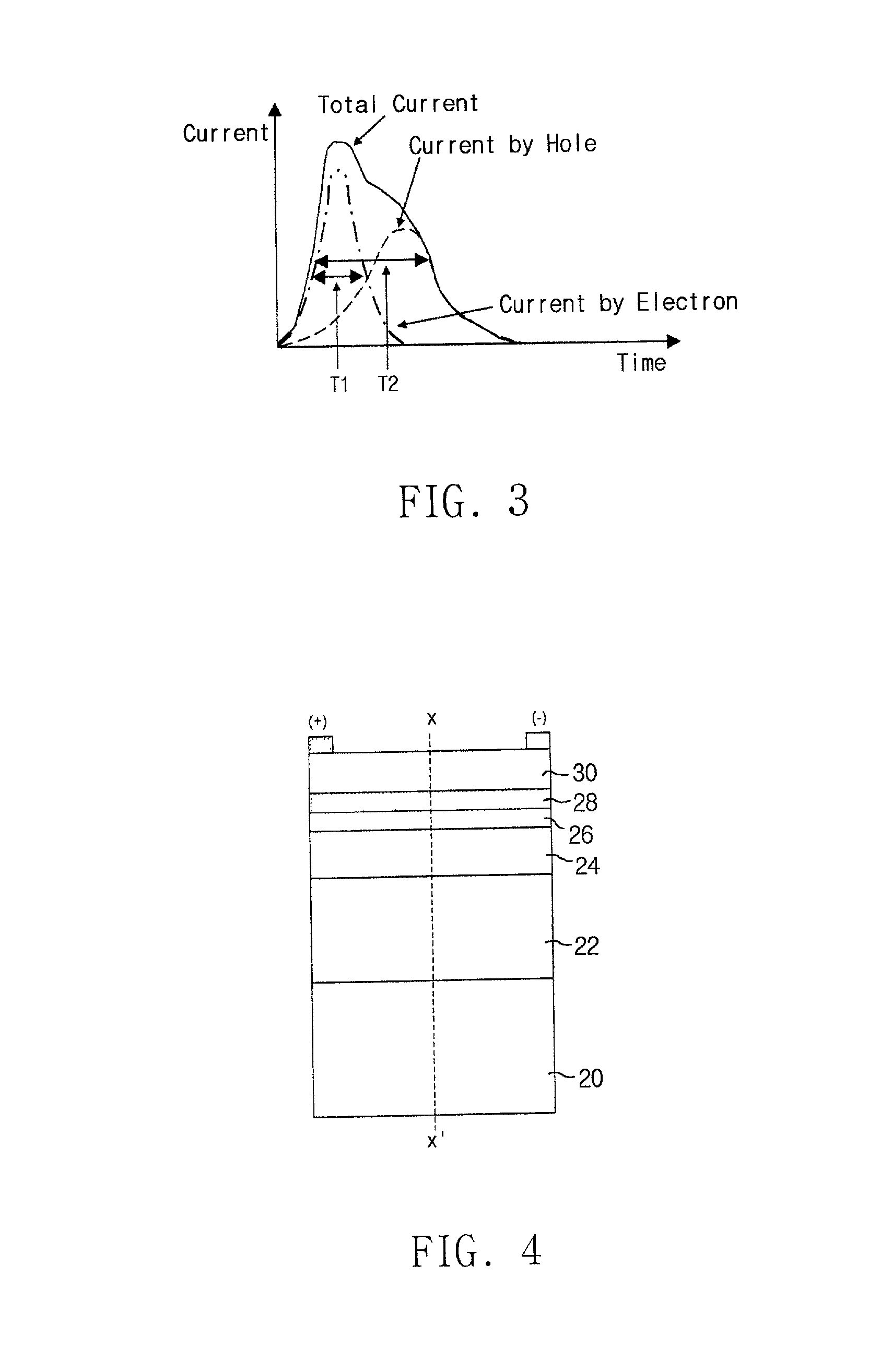
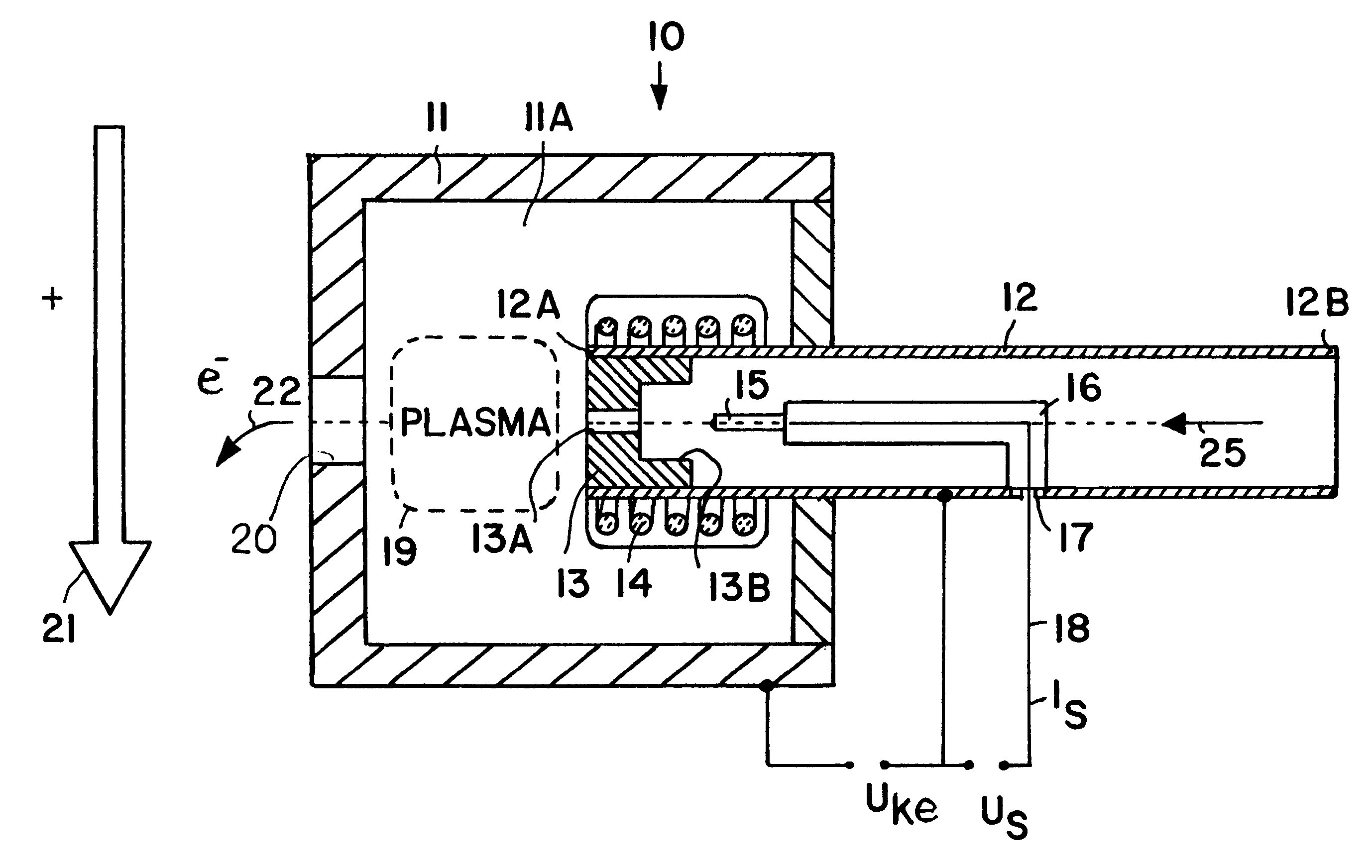
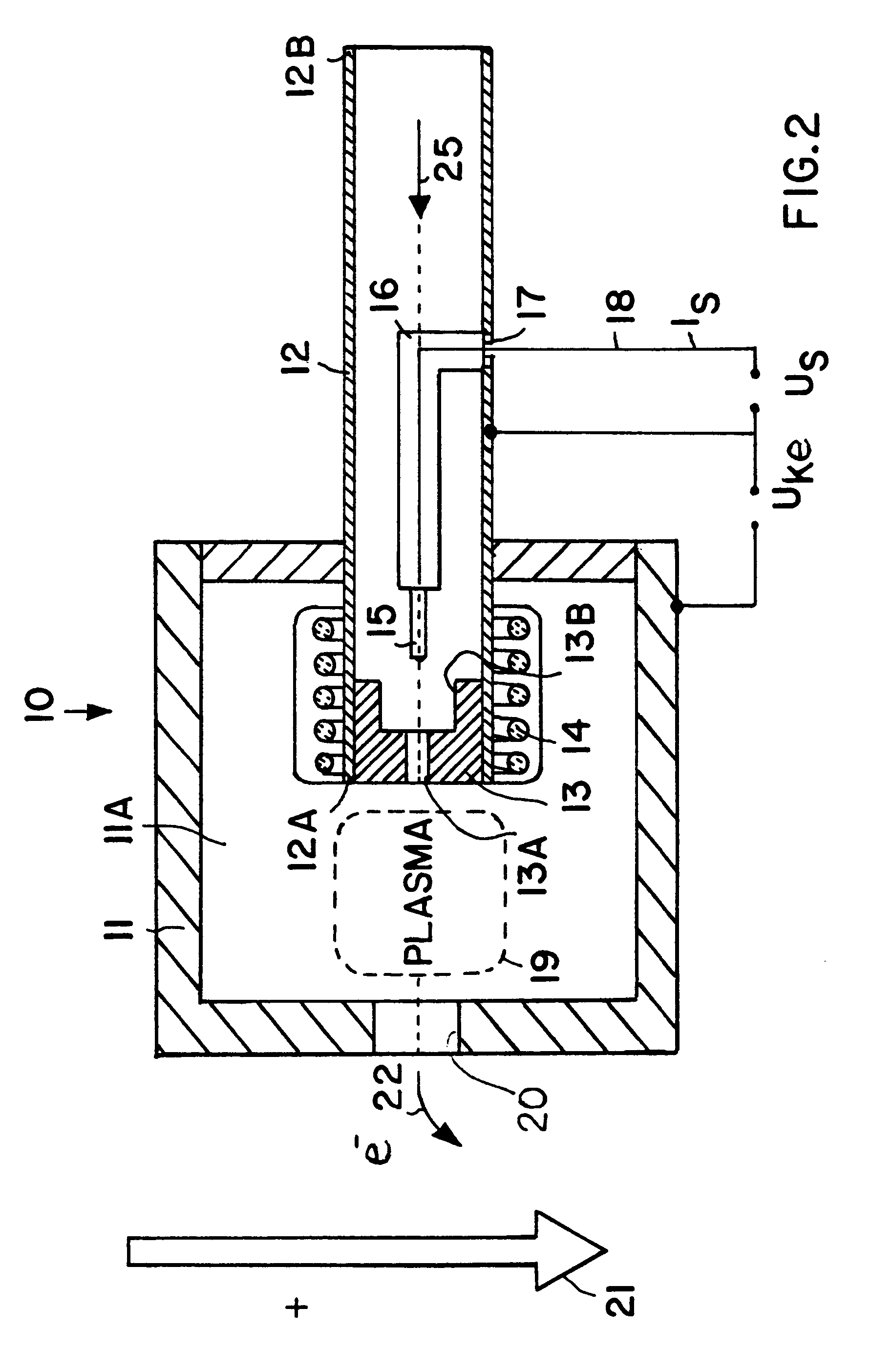
InactiveUS6195980B1Weaken energyLower average currentMachines/enginesUsing plasmaEngineeringAuxiliary electrode
An electrostatic ion propulsion engine for satellites and spacecraft is equipped with an electron source for neutralizing the propellant gas ion beam or jet emitted by the engine. The electron source includes an anode housing, a hollow cathode tube with gas flowing therethrough, a cathode element at the outlet end of the cathode tube within the interior space of the anode housing, and a pin- or rod-shaped auxiliary electrode arranged along the lengthwise axis in the hollow cathode tube. An ignition pulse is applied to the auxiliary electrode relative to the cathode tube, which causes a pulse discharge in the cathode tube, and in turn ignites the gas discharge between the anode and the cathode which generates the electron current.
Owner:DAMELERKLESLER AVIATION
Self-respiration type fuel battery membrane electrode and method for producing the same
InactiveCN101159333ALower resistanceImprove performanceCell electrodesSolid electrolyte fuel cellsEngineeringContact resistance
The invention discloses a membrane electrode of air-breathing fuel cells and a fabrication method thereof, relating to the membrane electrodes of air-breathing fuel cells and the fabrication method. The invention resolves the problem that the contact resistance of the electron current collection mode of the prior film electrode is large, which is harmful to electric pile integration. In the membrane electrode in the invention, a porous metal reticular current collector (5) is longitudinally provided inside a cathode catalyst layer (3), and a proton exchange membrane (1), an anode catalyst layer (2), the cathode catalyst layer (3), an anode diffusion layer (4), the porous metal reticular current collector (5) and a cathode diffusion layer (6) are solidified by hot pressing into a unity. The fabrication method includes that: 1. fabricating the anode diffusion layer; 2. fabricating the cathode diffusion layer; 3. integrating the porous metal reticular current collector with the cathode catalyst layer; 4. fabricating the anode catalyst layer; 5. fabricating the cathode catalyst layer; 6. the membrane electrode is formed by hot pressing. The invention uses the internal current collection mode, allowing the air-breathing fuel cells to reduce the resistance of membrane electrodes and enhancing the performance of membrane electrodes.
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH
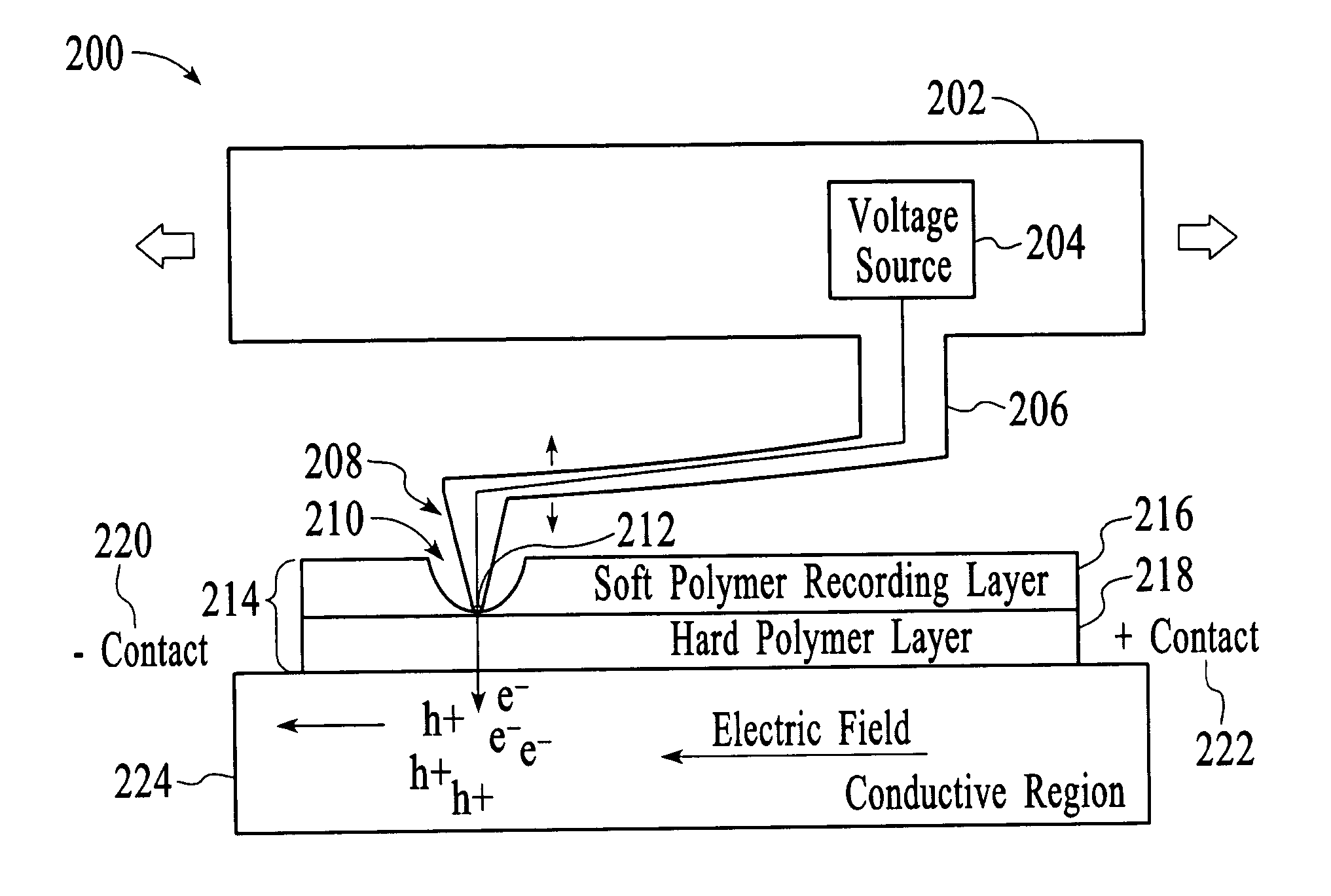
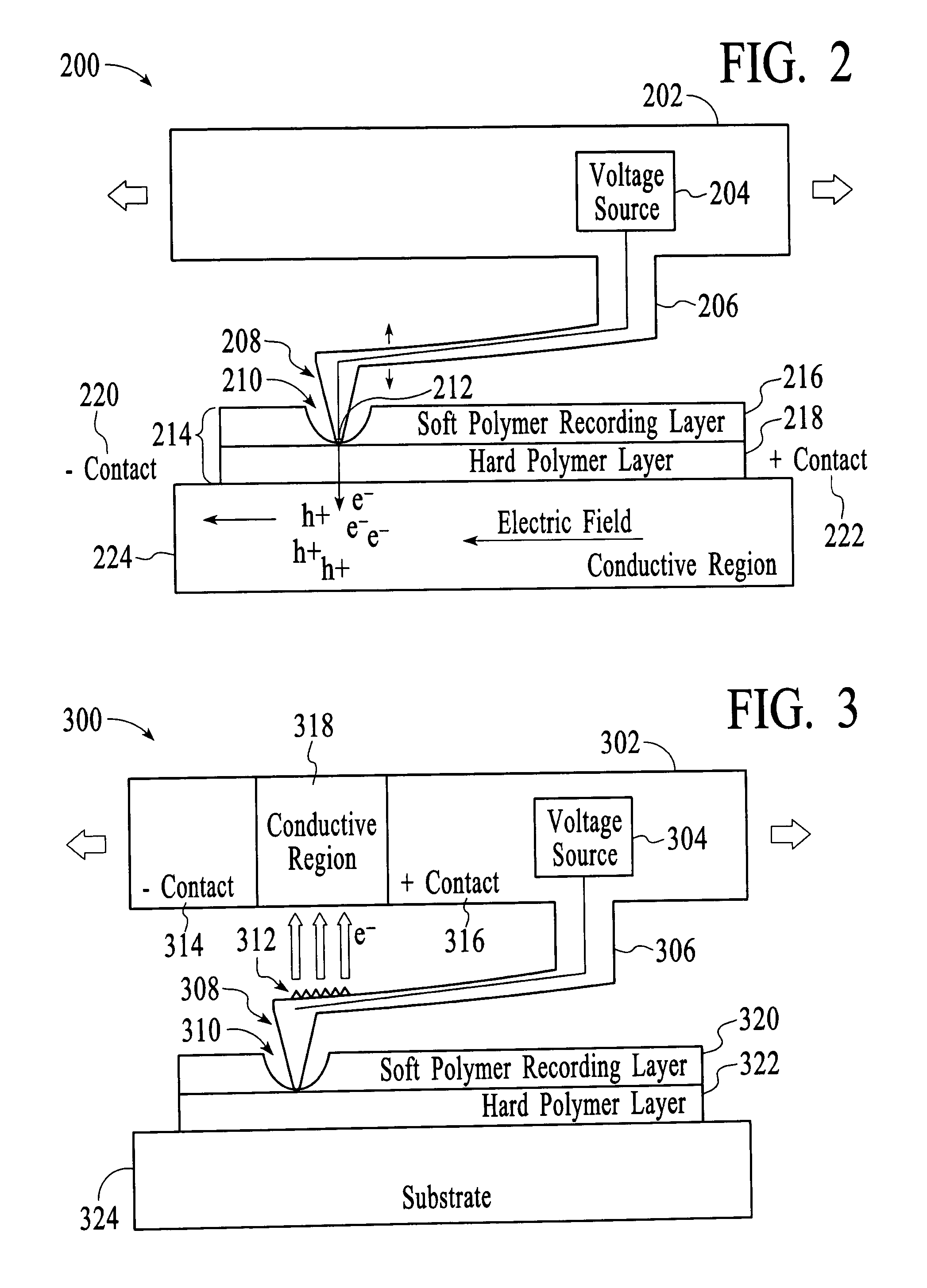
Data storage device and a method of reading data in a data storage device
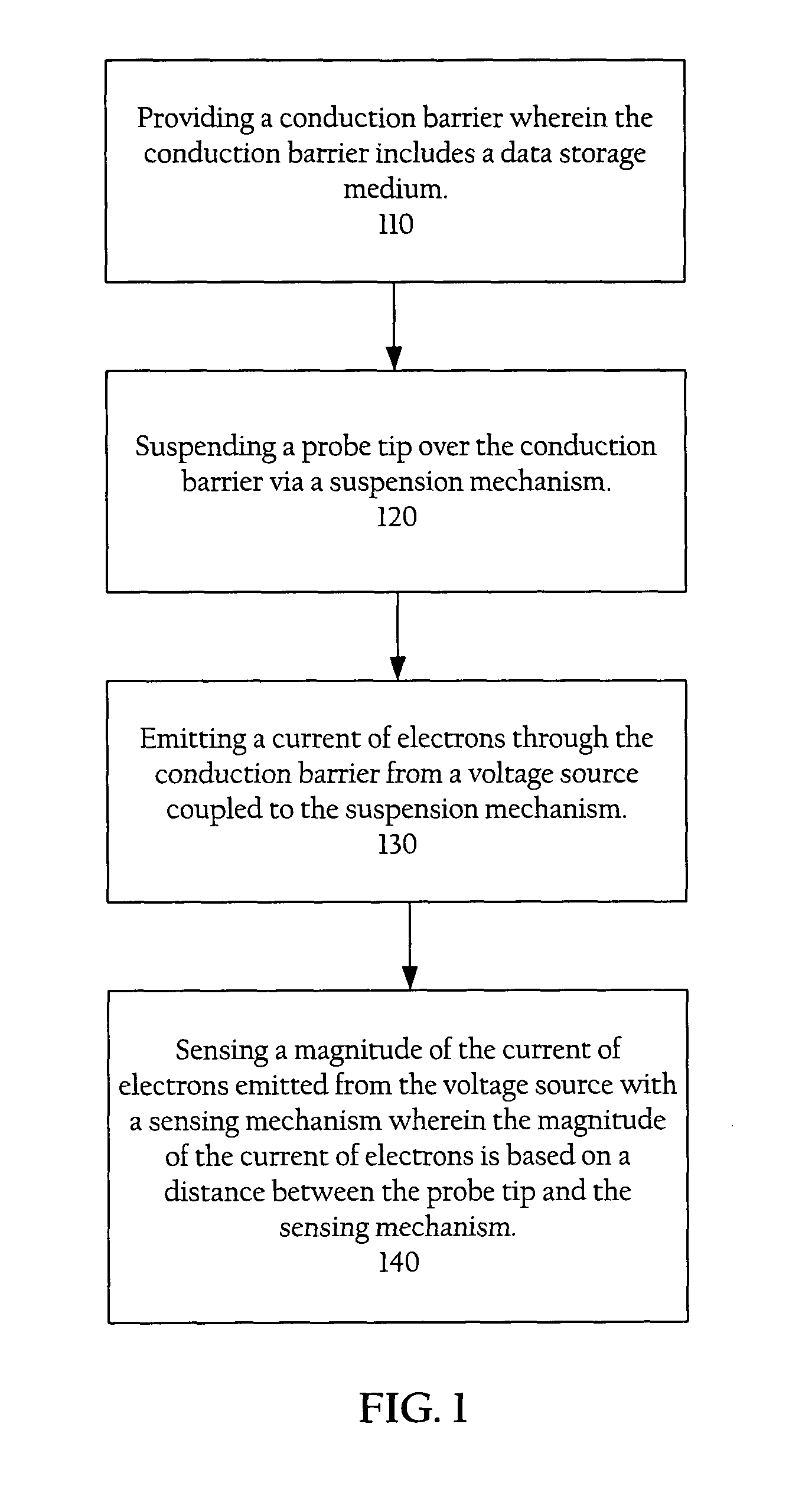
The present invention includes a method and apparatus for storing data. Accordingly, a first aspect of the present invention is a data storage device. The data storage device includes a conduction barrier, a probe tip mounted on a suspension mechanism, a voltage source coupled to the suspension mechanism for emitting a current of electrons through the conduction barrier, a sensing mechanism for sensing a magnitude of the emitted current wherein the magnitude of the current of electrons emitted through the conduction barrier is based on a distance between the probe tip and the sensing mechanism.
Owner:HEWLETT PACKARD DEV CO LP
Electrochromic panel and control device
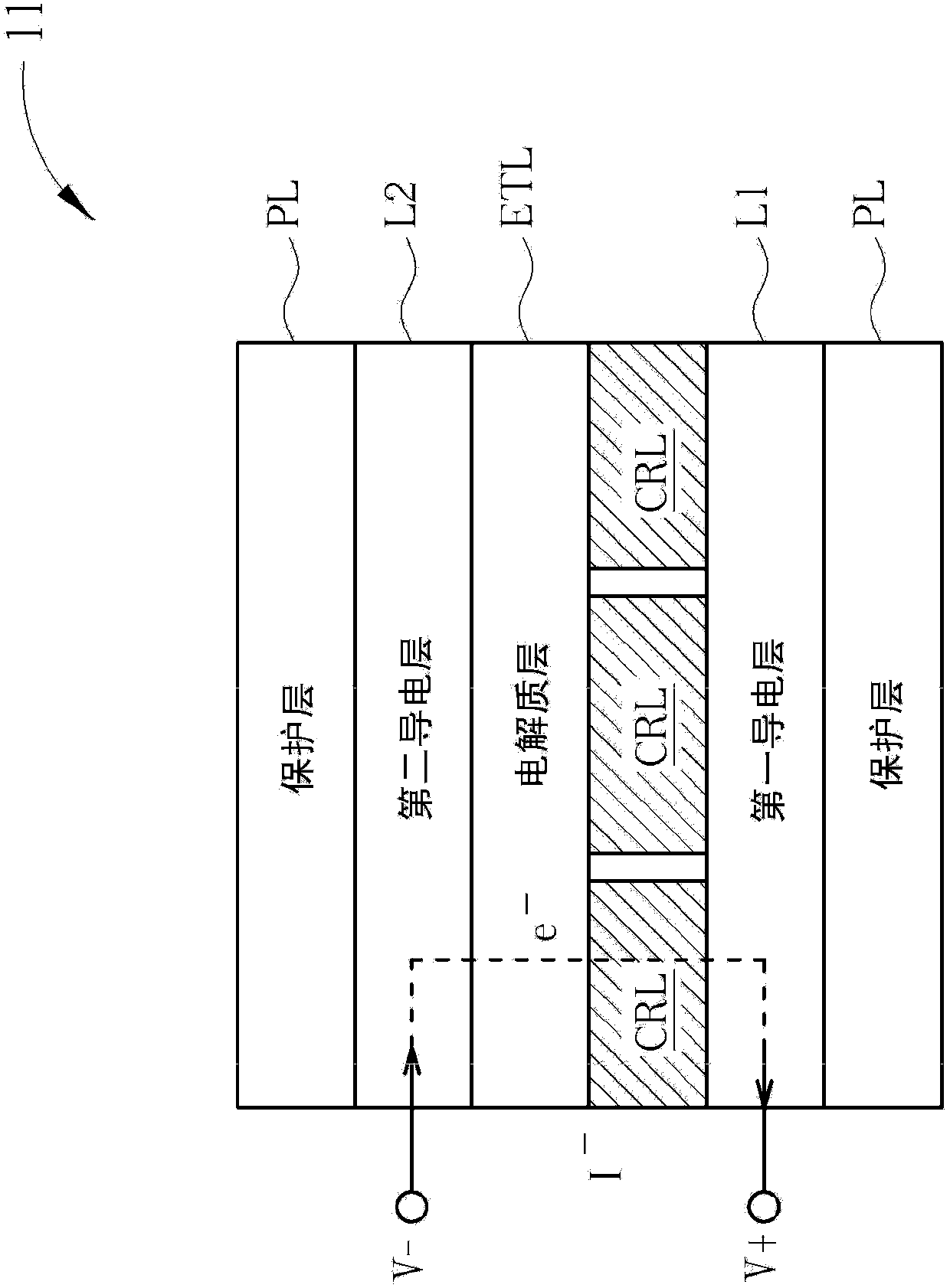
ActiveCN103676391AAdd fun to using electronicsAdd funStatic indicating devicesDigital data processing detailsElectron currentRedox
The present invention discloses an electrochromic panel and a control device. The electrochromic panel includes a first conduction layer for receiving a positive drive voltage, a second conduction layer for receiving a negative drive voltage, an electrolyte layer disposed on the second conduction layer, and a coloration layer having a pattern and disposed between the electrolyte layer and the first conduction layer, wherein an electron current generated by the negative drive voltage flows from the second conduction layer, the electrolyte layer, the coloration layer to the first conduction layer, such that the coloration layer performs a reduction-oxidation reaction and the pattern of the coloration layer changes from transparent to a non-transparent color. The electrochromic panel of the present invention can display key pattern thereof by changing from transparent to non-transparent color, thereby increasing a usage convenience and entertainment of an electronic product.
Owner:WISTRON CORP
Surface plasmon polariton-enhanced photoelectric detector based on MIM (Metal Injection Molding) structure
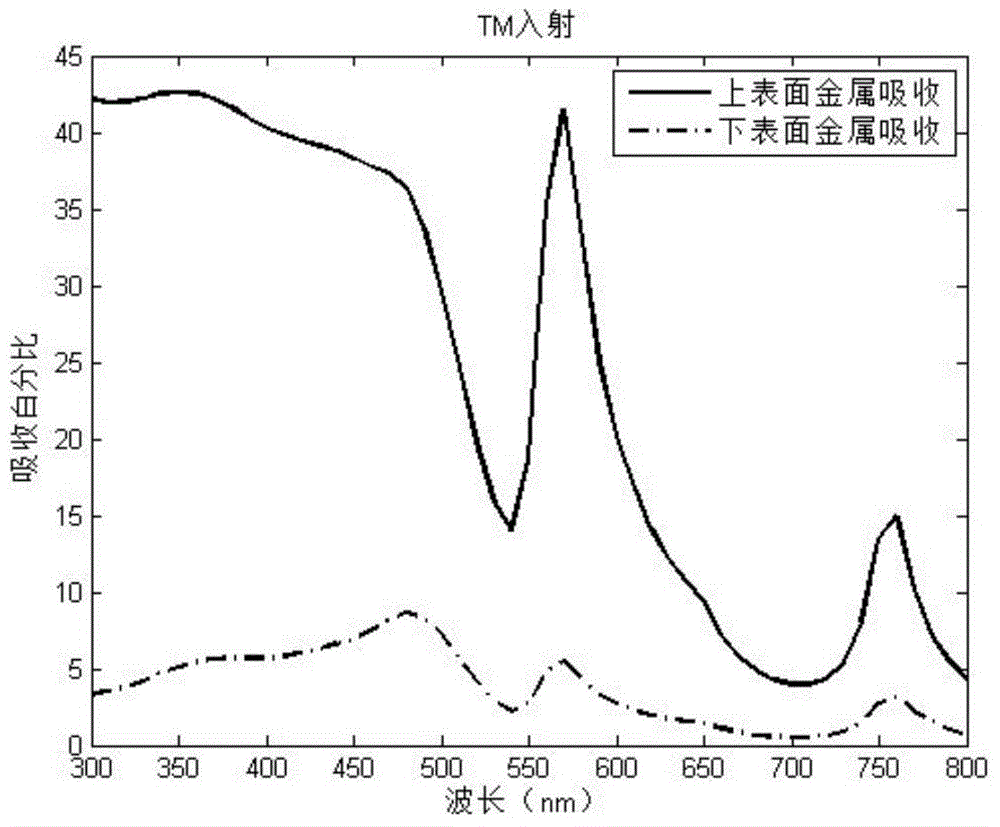
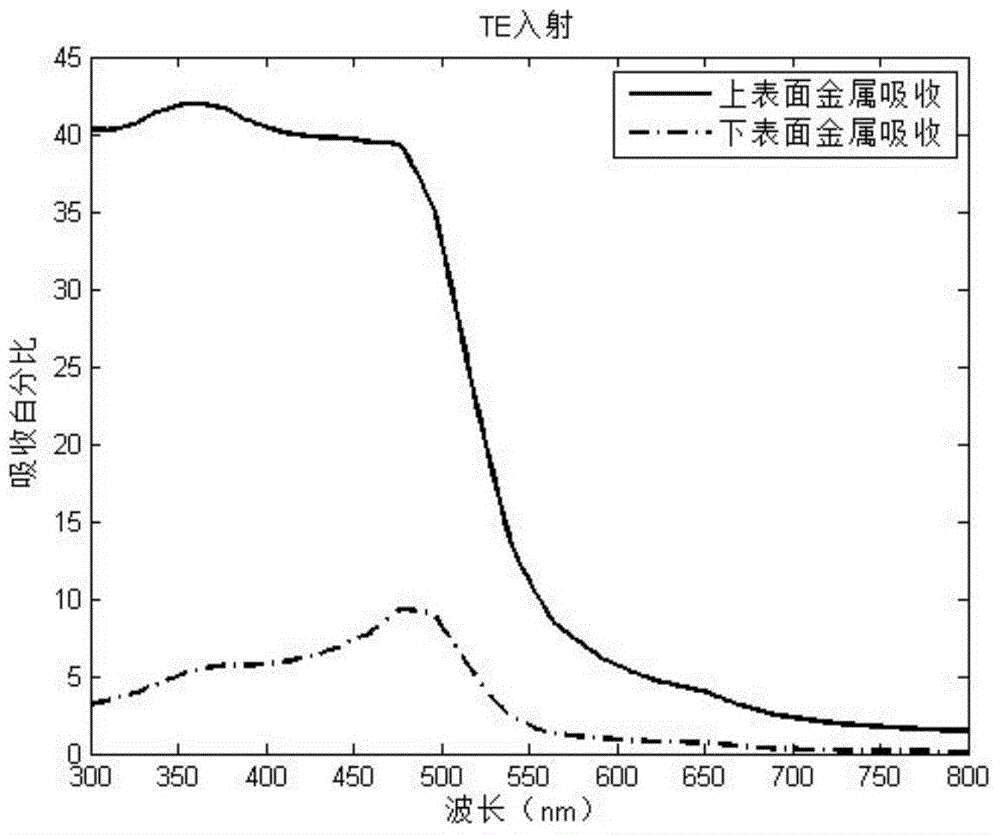
InactiveCN104064620ALess consumablesThe angle of incidence is not requiredSemiconductor devicesSpectral responseTrapping
The invention discloses a surface plasmon polariton-enhanced photoelectric detector based on an MIM (Metal Injection Molding) structure. The photoelectric detector comprises a substrate, and is characterized in that a lower metal film layer, a lower dielectric isolating layer, an upper metal film layer, an upper dielectric isolating layer and a metal grating layer are formed in sequence on the substrate from top to bottom. The surface plasmon polariton-enhanced photoelectric detector further comprises an upper metal film layer electrode lead, a lower metal film layer electrode lead, and a detector output port which is connected to the upper and lower metal film layers respectively. In the design, the local light trapping effect of a grating layer is achieved through the metal optical grating layer serving as a core, and an electron current tunneling effect is caused by remarkable difference between the light absorption of the upper and lower metal film layers. The photoelectric detector has the characteristics of small size (nanoscale), small number of consumables, simple structure, easiness in machining, wide spectral response, large detection angle and the like.
Owner:SUZHOU UNIV
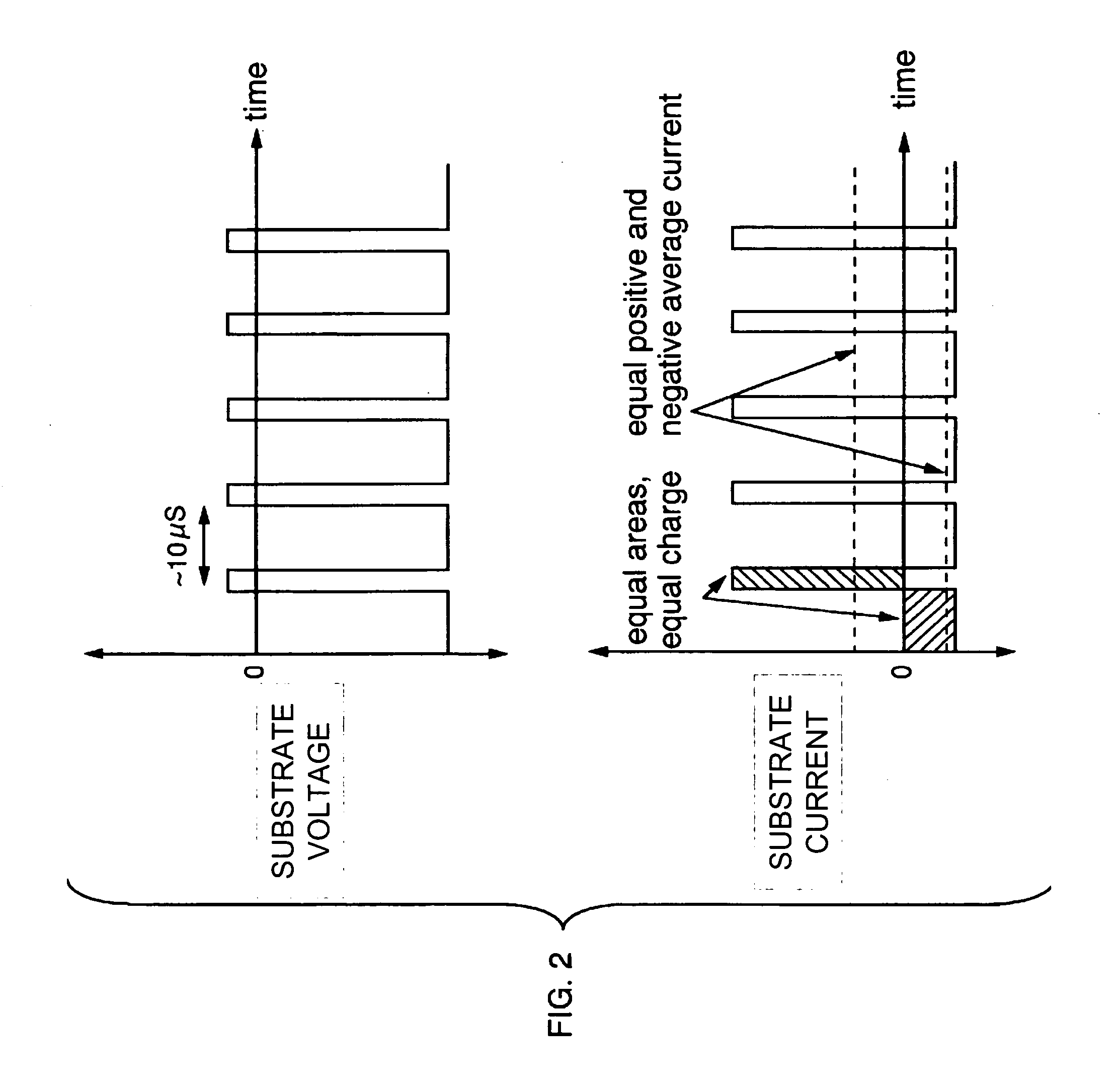
System and method for performing sputter etching using independent ion and electron sources and a substrate biased with an a-symmetric bi-polar DC pulse signal
A system and method for performing sputter etching includes an ion source that generates an ion current that is directed at a substrate and an electron source that generates an electron current directed at the substrate. Biasing circuitry biases the substrate with an a-symmetric bi-polar DC voltage pulse signal. The biasing circuitry is formed from a positive voltage source with respect to ground, a negative voltage source with respect to ground and a high frequency switch. At least one current sensor, coupled to the biasing circuitry, monitors a positive current and a negative current from the substrate during one or more cycles of the a-symmetric bi-polar DC voltage pulse signal. A control system, coupled to the at least one current sensor, varies the ion current independently from the electron current. The ion and electron sources create a continuous plasma that is proximate the substrate and the biasing circuitry causes the substrate to alternatively attract ions and electrons from the plasma. The ions attracted from the plasma sputter etch the substrate. The electrons attracted from the plasma neutralize accumulated charge on the substrate.
Owner:4WAVE
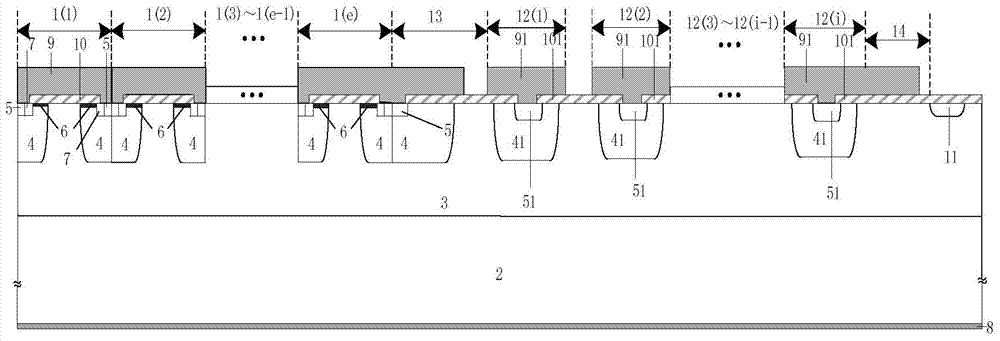
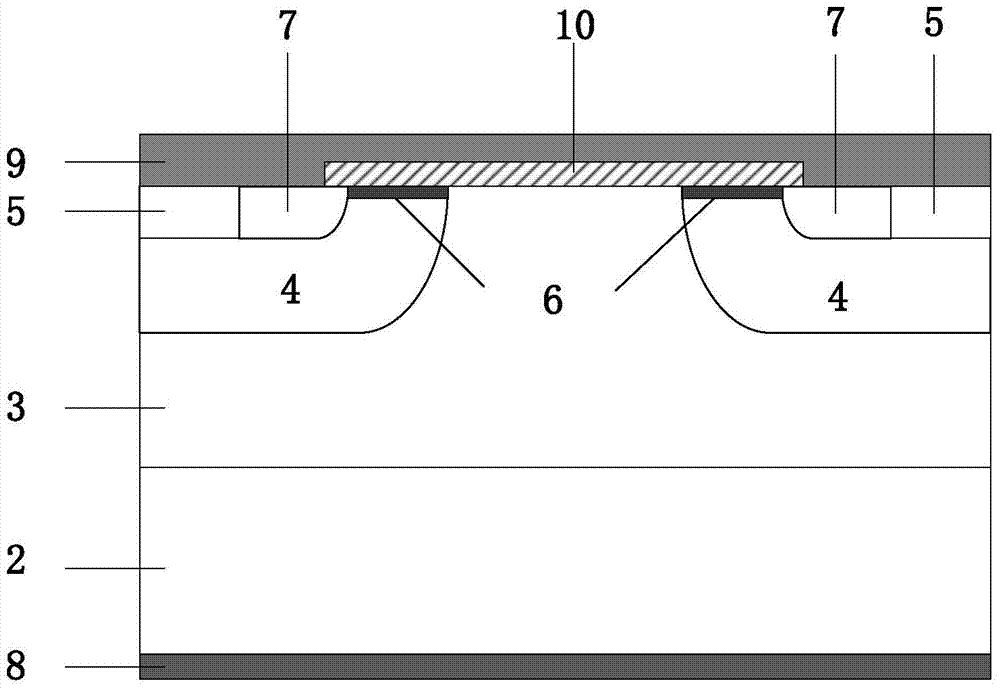
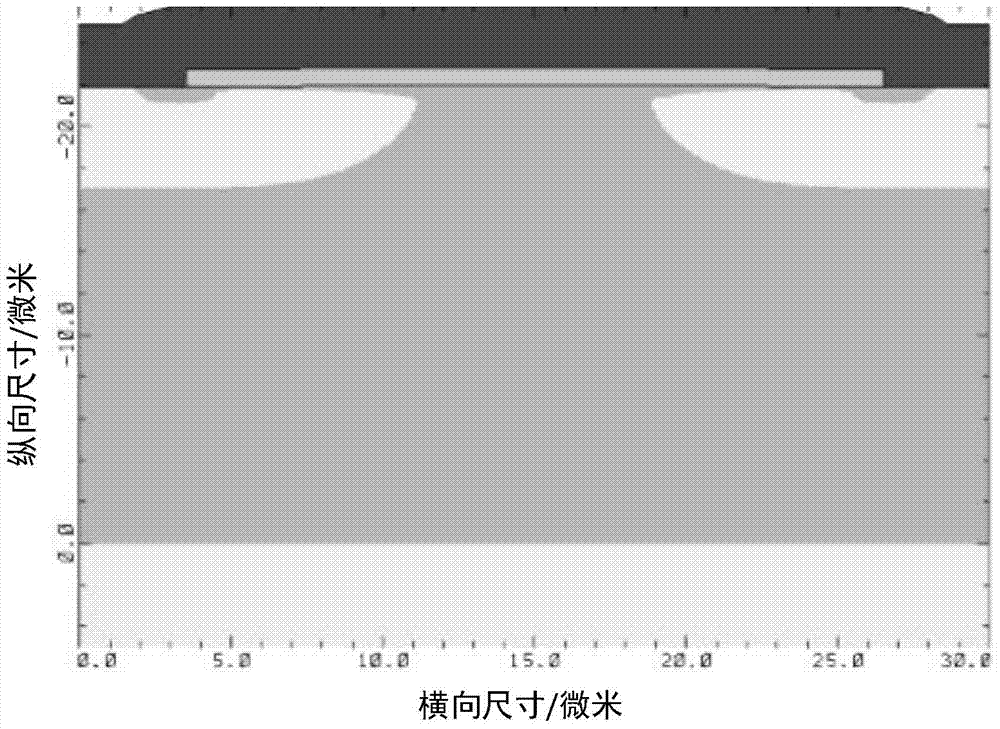
Vertical constant-current diode and manufacturing method thereof
ActiveCN104779303AIncrease current densityFaster pinch offSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSemiconductor devicesElectron currentEngineering
The invention discloses a vertical constant-current diode and a manufacturing method thereof, and belongs to the technical field of semiconductors. The vertical constant-current diode comprises a cellular structure and a terminal structure connected in sequence, wherein the cellular structure comprises a plurality of cells same in structure and connected in sequence; the terminal structure comprises a cut-off ring and a plurality of field limiting rings connected in sequence. The constant-current diode adopts a P-type doped semiconductor material opposite to an epitaxial layer in doping type as a substrate, and a P-type light-doped substrate injects holes to an N-type light-doped epitaxial layer, so that the constant-current diode has two carrier currents, namely hole current and electron current, and the current density of a device is increased; moreover, substrates with different doping types assist in depletion of a channel, accelerate pinching-off of a JFET (junction field-effect transistor) region channel and enable pinch-off voltage to be lower than 4 V.
Owner:UNIV OF ELECTRONICS SCI & TECH OF CHINA
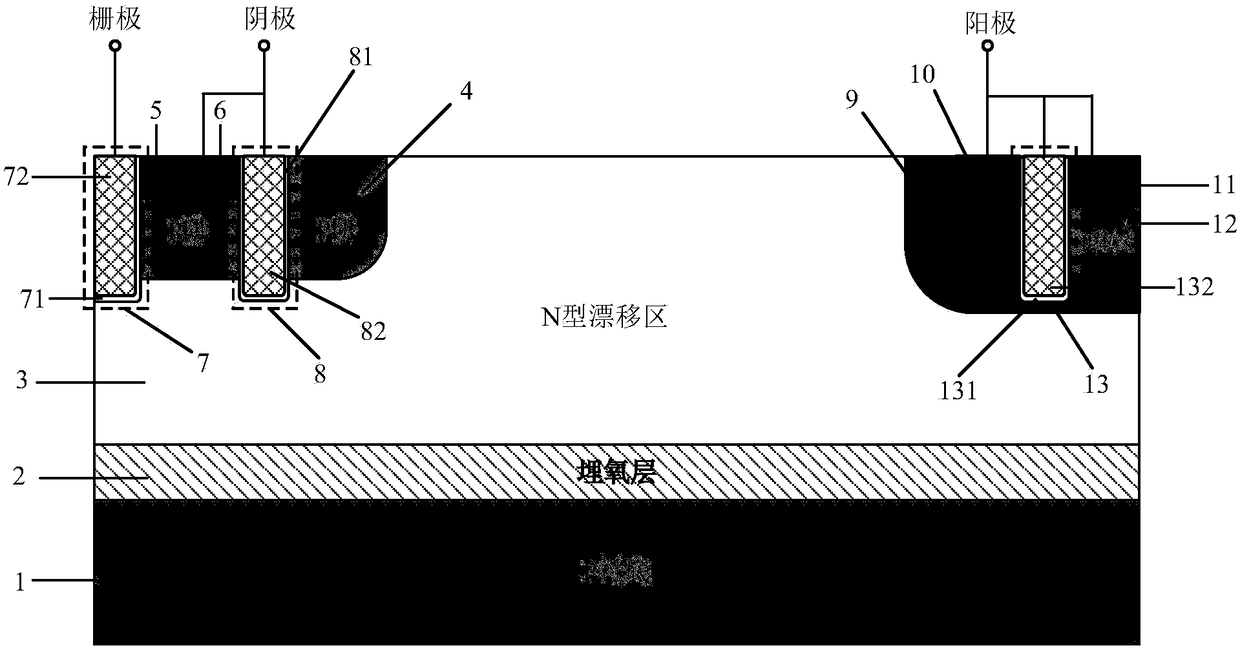
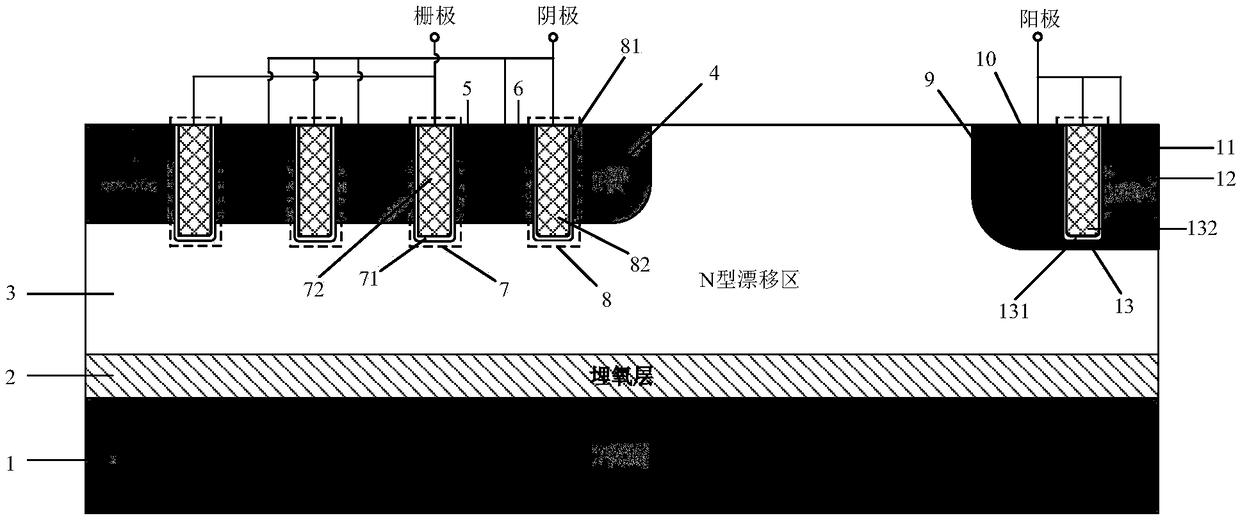
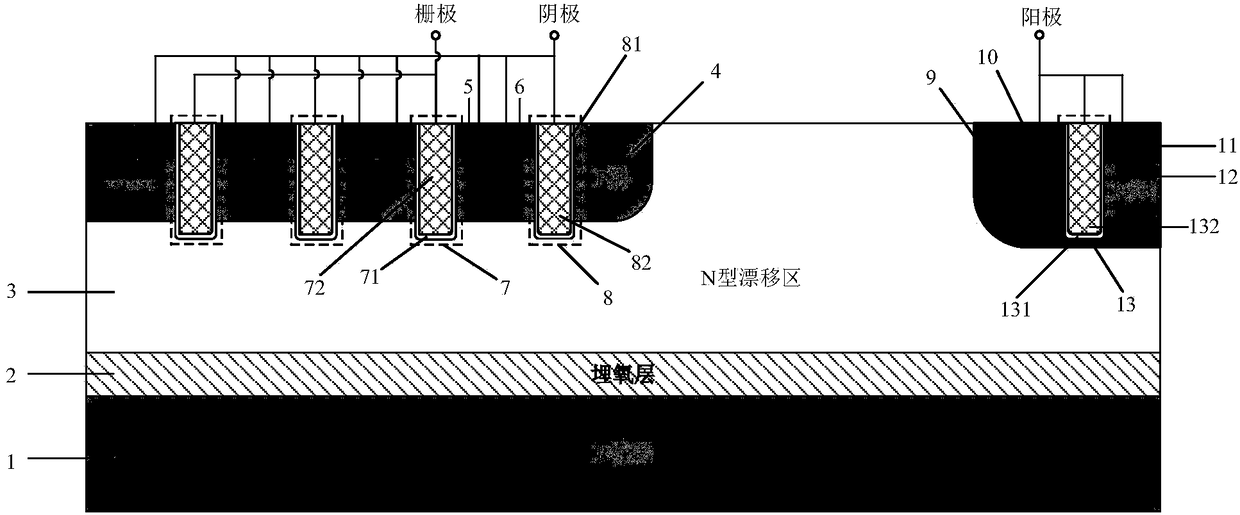
Grooved gate short circuit anode SOI LIGBT
The invention belongs to the technical field of power semiconductors and relates to a grooved gate short circuit anode SOI LIGBT. In comparison with the traditional short circuit anode LIGBT, anode grooves connected to anode potential are introduced at an anode end, and a P body area is introduced right below an N+ anode area; and grooved gates and cathode grooves connected with a cathode are introduced in a cathode area. When the device is turned off, the anode groove is connected to high potential, an NMOS in the anode area is started automatically, extraction of electrons stored in a driftarea is quickened, and the turn-off time and the turn-off energy loss are reduced; when the device is in a high-voltage high-current state, the cathode groove forms a hole bypass, and happening of latch-up effects is suppressed; when the device is conducted, under blocking of an electronic barrier in the P body area, electron current in the drift region is not easy to be collected by the N+ anode,voltage reentry effects are eliminated, and as the grooved gate structures of the cathode are in parallel connection, the channel density is increased and the conduction voltage drop is reduced. Thegrooved gate short circuit anode SOI LIGBT has the beneficial effects that in comparison with the traditional short circuit anode LIGBT, a voltage reentry phenomenon is eliminated under a smaller transverse cell size, and the conduction voltage drop is lower.
Owner:UNIV OF ELECTRONICS SCI & TECH OF CHINA
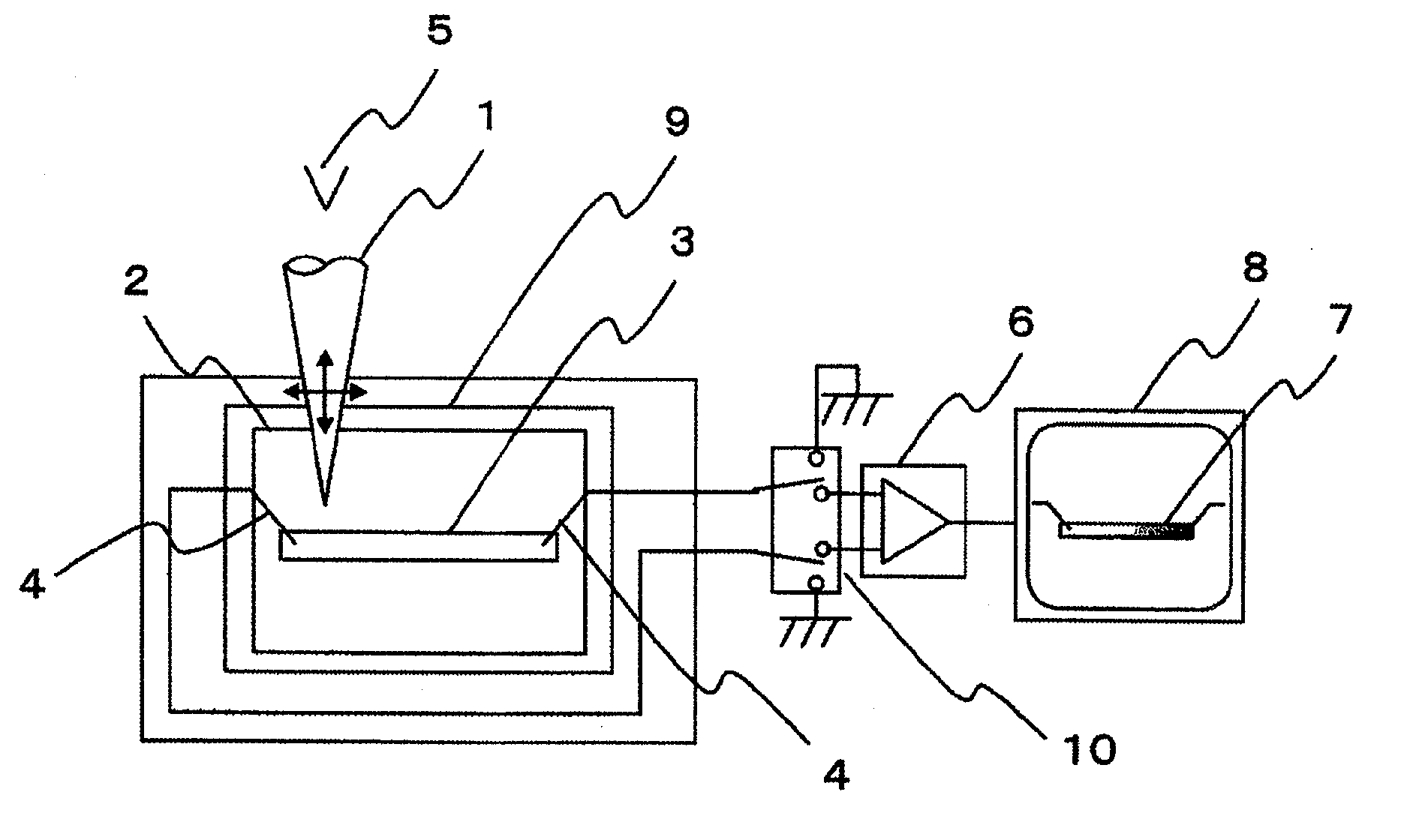
Sample inspection apparatus
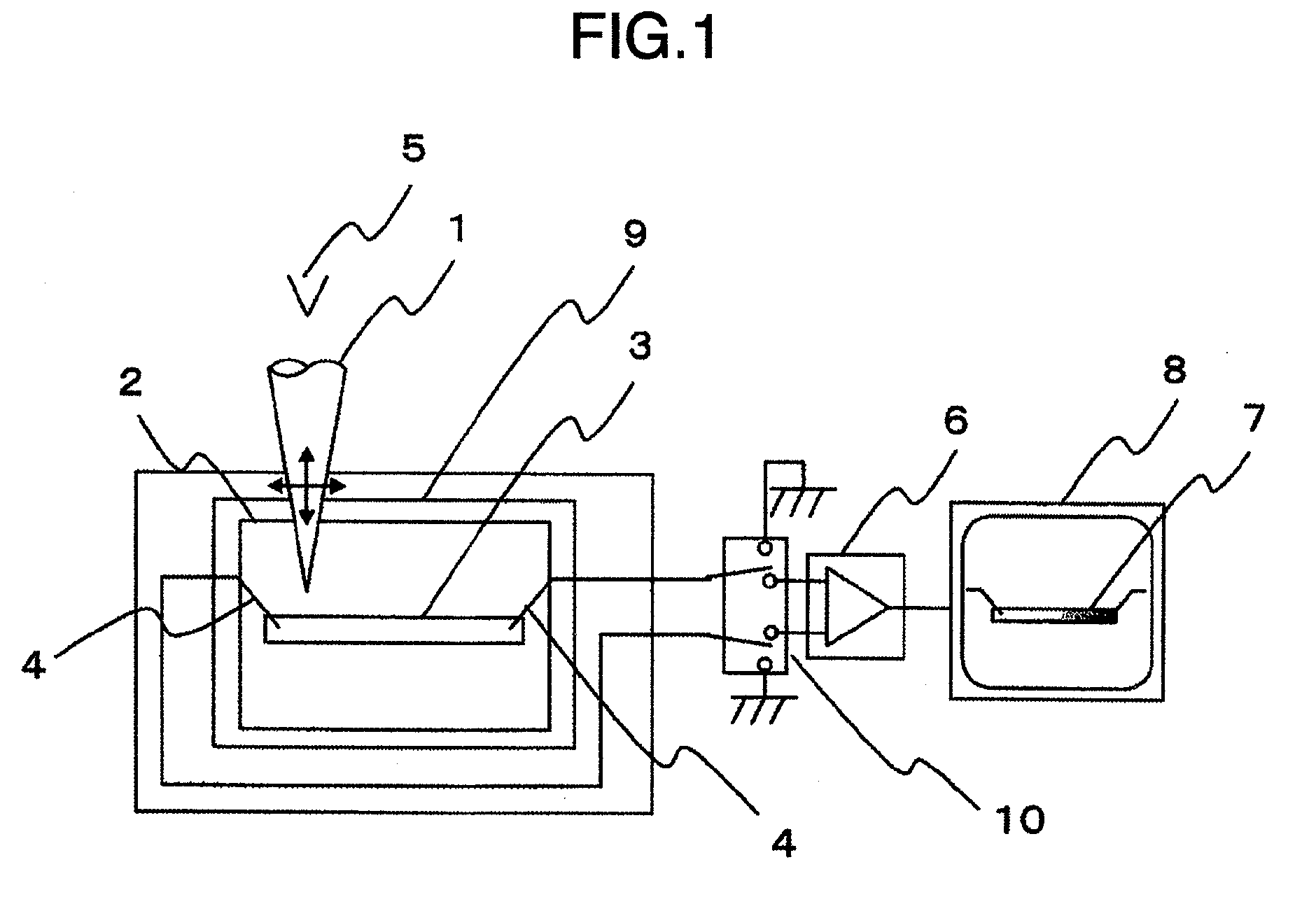
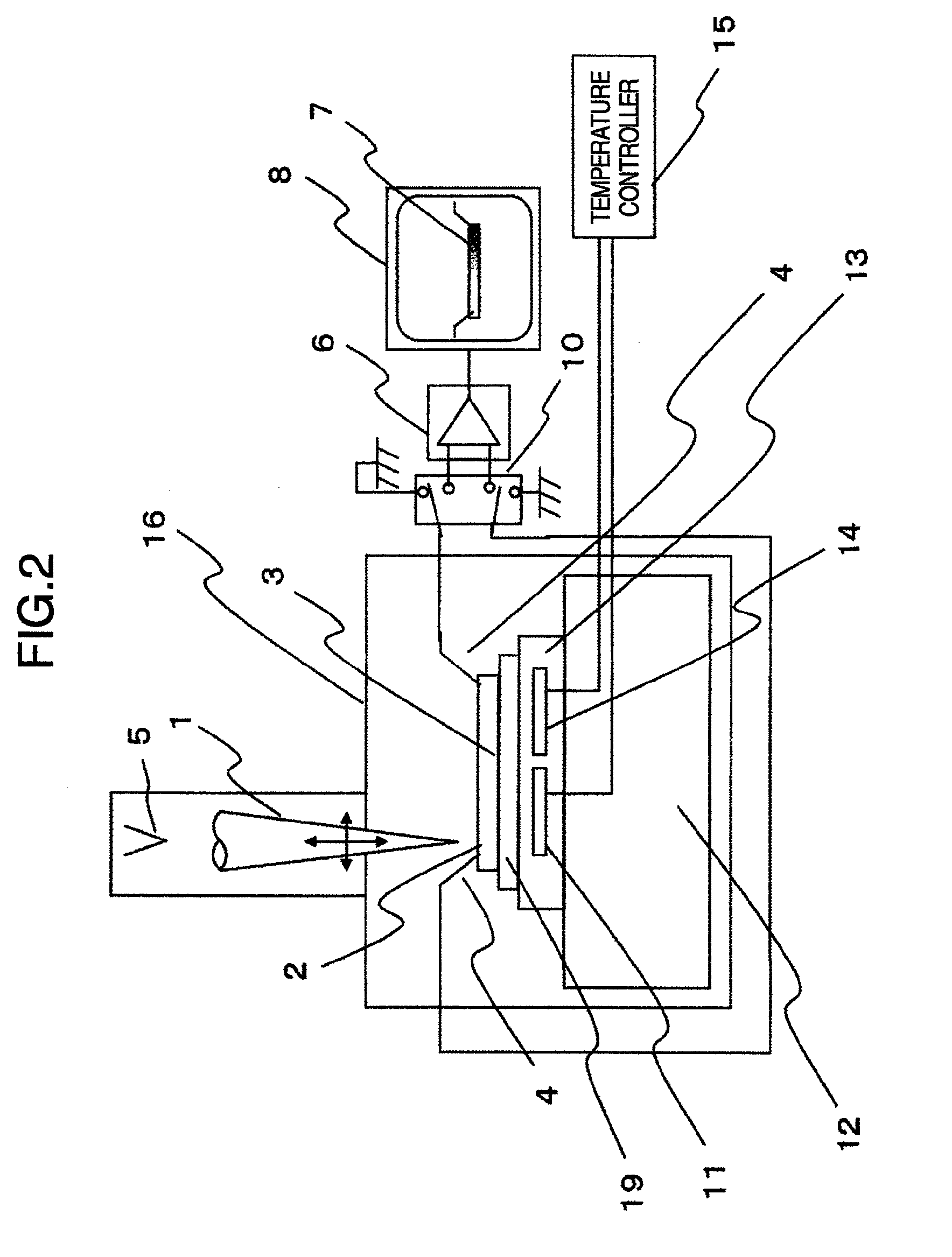
ActiveUS20090250610A1High voltagePotential differenceMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationElectric discharge tubesElectron currentImaging processing
A sample inspection apparatus in which a fault in a semiconductor sample can be measured and analyzed efficiently. A plurality of probes are brought into contact with the sample. The sample is irradiated with an electron beam while a current flowing through the probes is measured. Signals from at least two probes are supplied to an image processing unit so as to form an absorbed electron current image. A difference between images obtained in accordance with a temperature change of the sample is obtained. A faulty point is identified from the difference between the images.
Owner:HITACHI HIGH-TECH CORP
Hall thruster with double magnetic screens
ActiveCN111219306AAvoid discharge thermal instabilityInhibit currentMachines/enginesUsing plasmaElectron currentEngineering
The invention discloses a Hall thruster with double magnetic screens, and belongs to the technical field of Hall thrusters. The Hall thruster solves the problems that in an existing Hall thruster channel, due to the fact that electrons and the wall face interact frequently, energy deposition of the wall face is caused, and heat instability and energy loss are caused. According to the Hall thruster, an additional magnetic screen is additionally arranged on a traditional Hall thruster to form a double-magnetic-screen structure, the double magnetic screens are used for carrying out secondary short circuit on a magnetic field close to the wall face, and therefore magnetic lines of force are guided not to penetrate through the channel and an anode any more, the energy deposition problem of theelectrons on the wall face is reduced, and the electron current is controlled. The double magnetic screens are used for solving the energy deposition problem of the electrons in the channel on the wall face, and the problems of discharge heat instability of the thruster and performance loss caused by energy loss are avoided. Meanwhile, the electron current is restrained, and the current utilization rate is increased. In addition, the thickness of the additional magnetic screen and insulation between an inner magnetic screen and the anode are guaranteed, the robustness and the service life of the additional magnetic screen are guaranteed, and the Hall thruster can effectively work for a long time.
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH
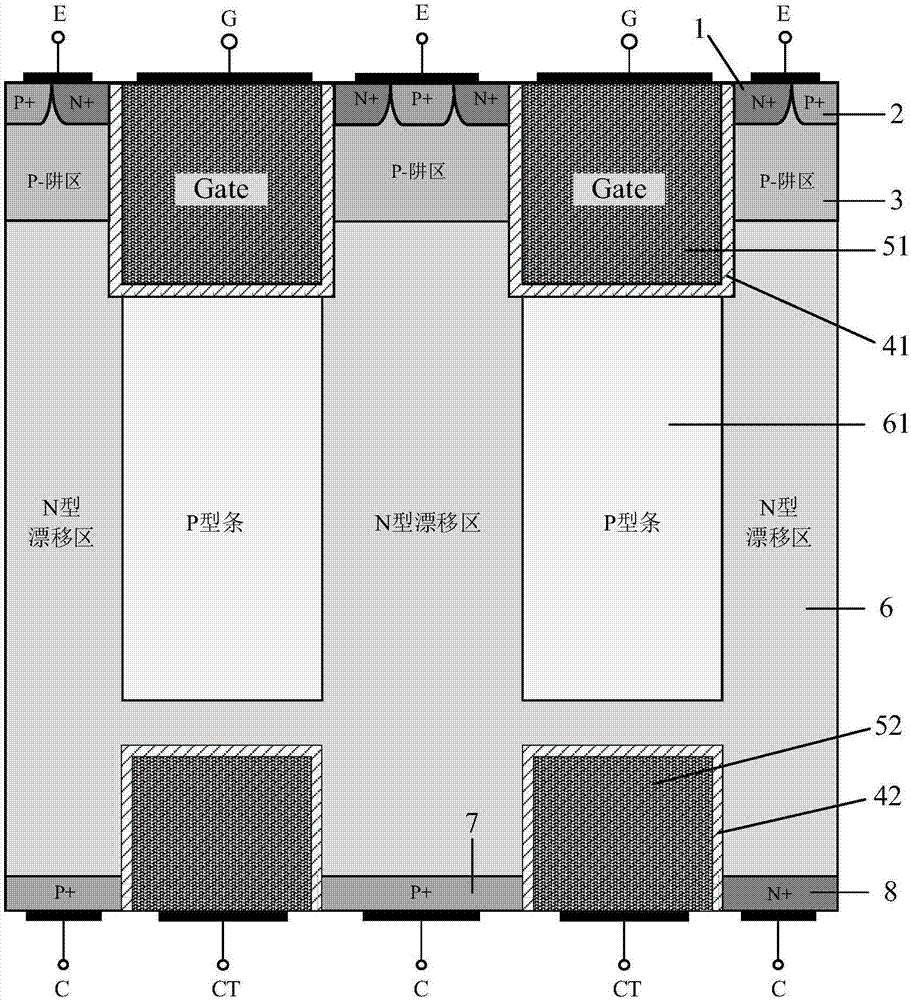
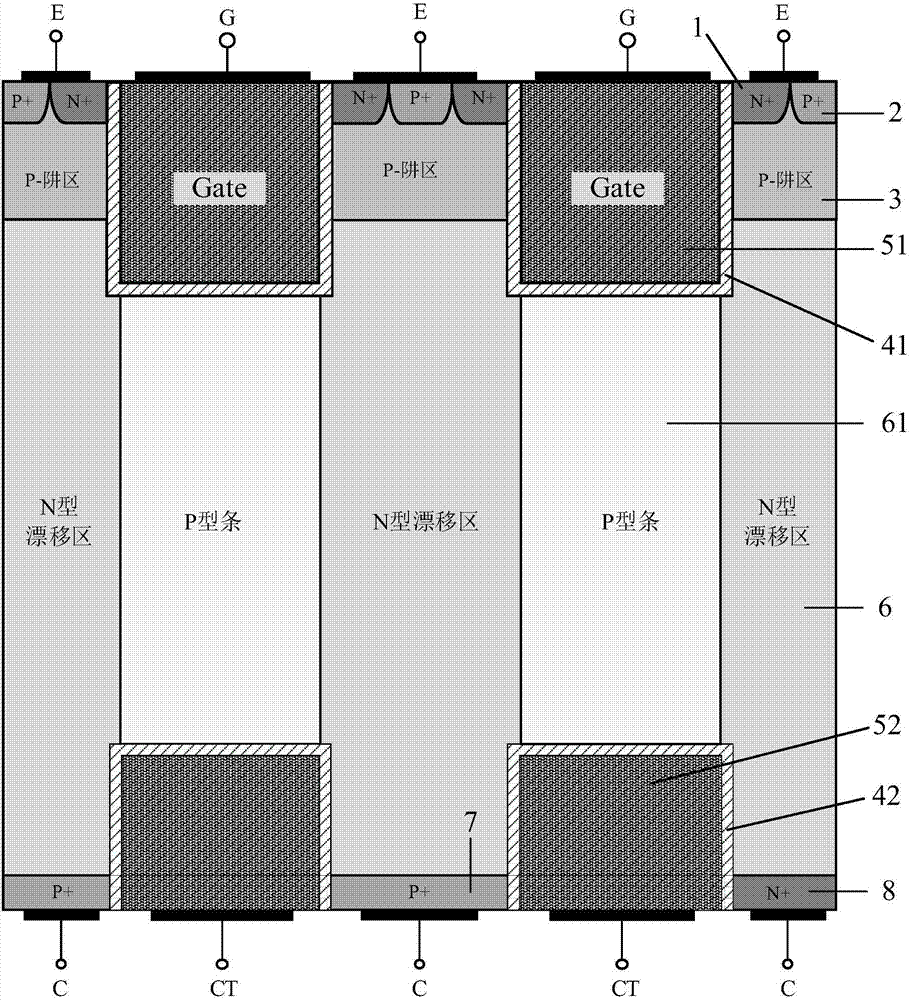
Superjunction reverse conducting-insulated gate bipolar transistor (IGBT) with collector groove
InactiveCN107464842AIncreased shutdown speedEliminate the snapback effectSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSemiconductor devicesHigh pressureSmall cell
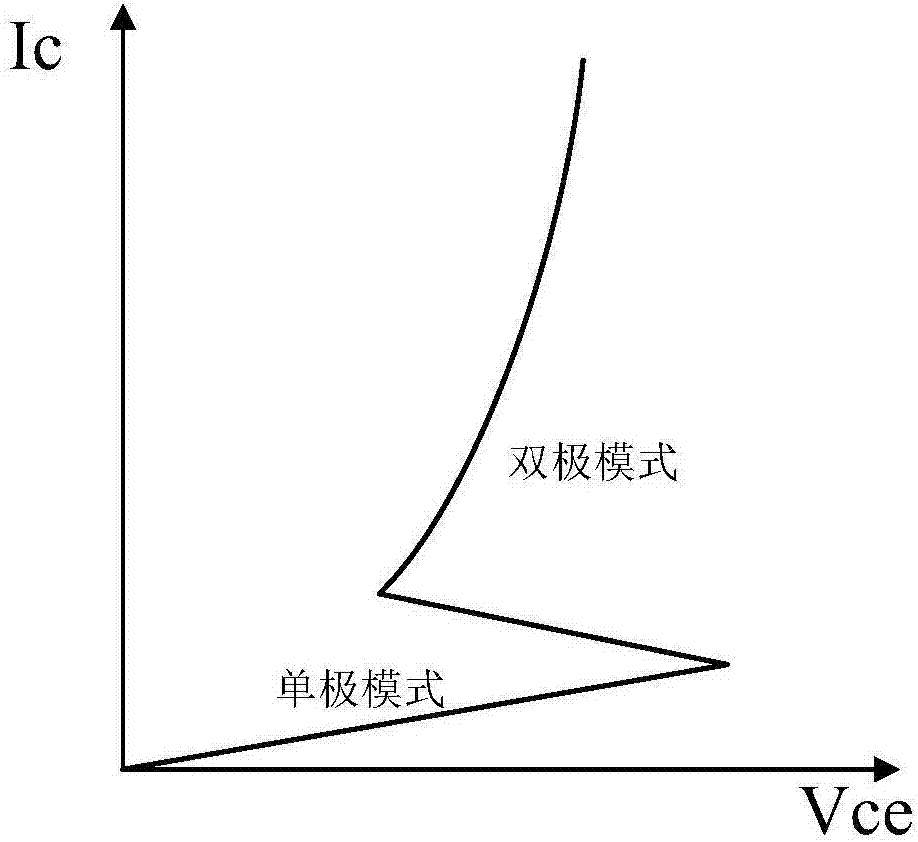
The invention belongs to the technical field of a power semiconductor, and particularly relates to a superjunction reverse conducting-insulated gate bipolar transistor (IGBT) with a collector groove. Compared with a traditional superjunction RC-IGBT structure, the superjunction RC-IGBT has the advantages that a collector groove structure is mainly introduced to a bottom current collection region, an N drift region at the bottom of the collector groove can be consumed by P-type strips when a new device is positively conducted and does not enter a bipolar mode, so that an electron current path is occupied, the effective electron concentration is reduced, the electron current distribution resistance around the current collection region is increased, and a snapback effect of the device can be eliminated by the new device under relatively small cell size; and when the new device is switched off, the collector structure has an effect equivalent to a buffer layer, and the device can be enabled to bear high pressure. The superjunction RC-IGBT has the beneficial effects that compared with the traditional superjunction RC-IGBT structure, the snapback effect can be eliminated under smaller cell size, meanwhile, the superjunction RC-IGBT has faster switch-off speed, and the current distribution is more uniform in a reverse diode mode.
Owner:UNIV OF ELECTRONICS SCI & TECH OF CHINA
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com