Patents
Literature
205results about How to "Increased shutdown speed" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
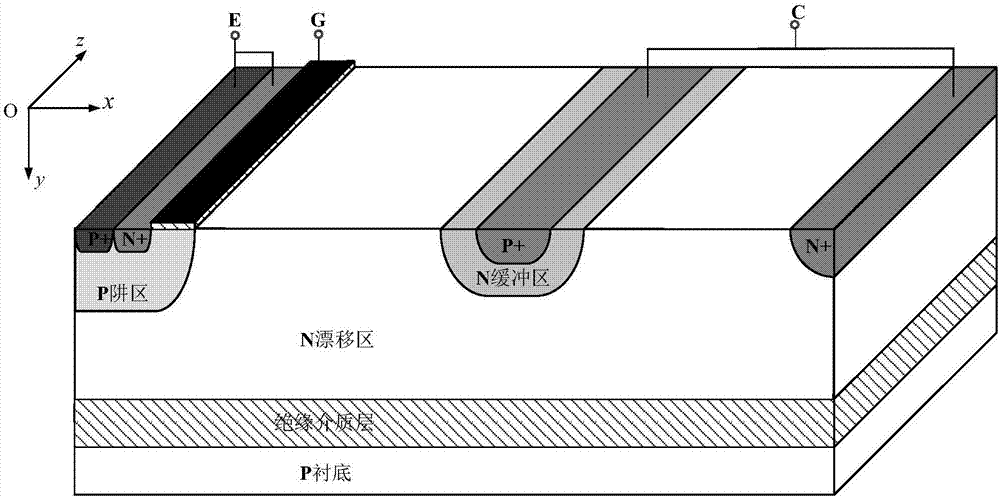
Heterojunction carbon nano-tube field effect transistor and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN106356405AGuaranteed driving abilityGuaranteed speedSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSemiconductor devicesHeterojunctionCarbon nano tube field effect transistor
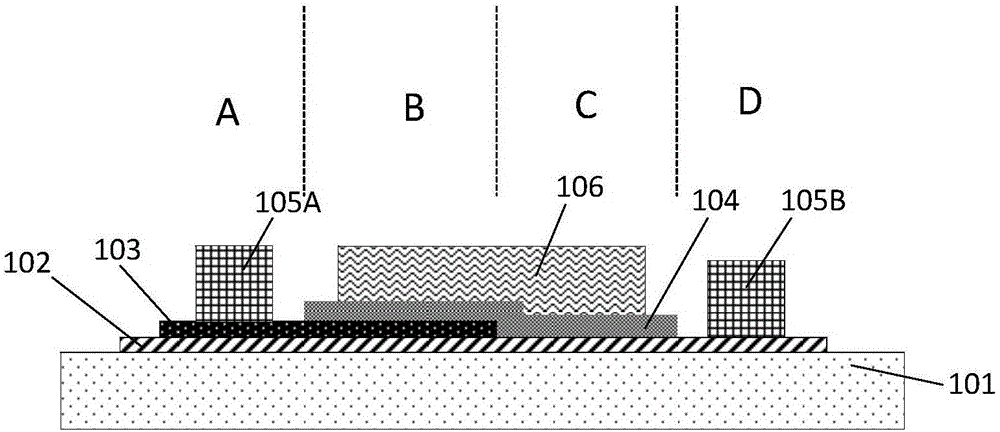
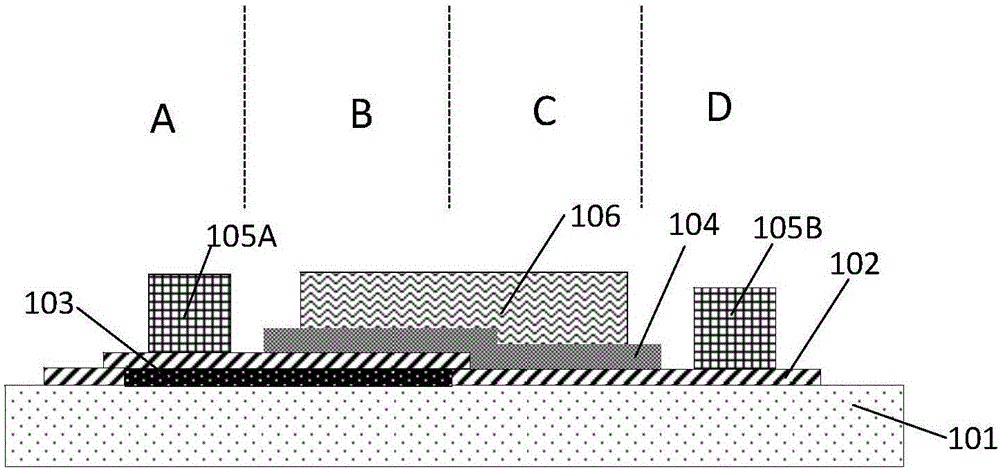
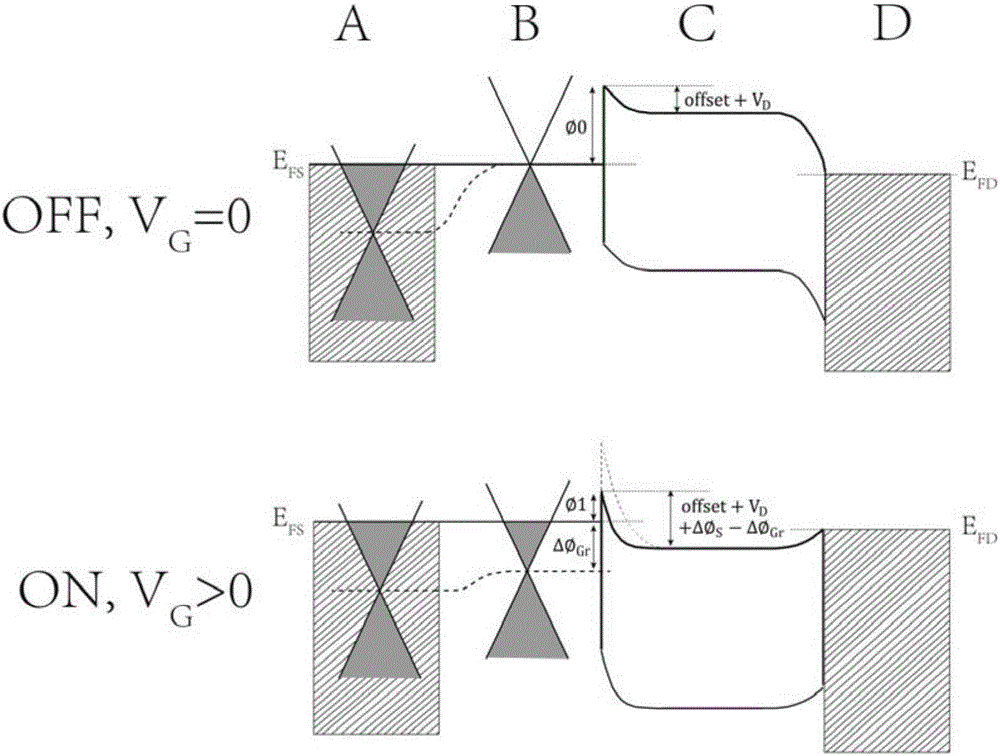
The invention provides a heterojunction carbon nano-tube field effect transistor of which a subthreshold swing is smaller than 60 millivolt / magnitude in the room temperature and a preparation method thereof. The device uses the semiconductor carbon nano-tube as the active layer, the heterojunction formed by the graphene layer and the semiconductor carbon nano-tube is used as the source end of the device, the gate medium and the gate electrode modulate the carbon nano-tube channel and the graphene / carbon nano-tube junction at the same time, so that the turn-off of the transistor is accelerated by using the character that the graphene / carbon nano-tube junction barrier is modulated by the gate voltage. The transistor can control the polarity through the selection of the source-drain metal, namely the metal of high power function is used as the source-drain electrode for realizing the p-type field effect transistor, and the metal of low power function is used as the source-drain electrode for realizing the n-type field effect transistor.
Owner:BEIJING HUA TAN YUAN XIN ELECTRONICS TECH CO LTD
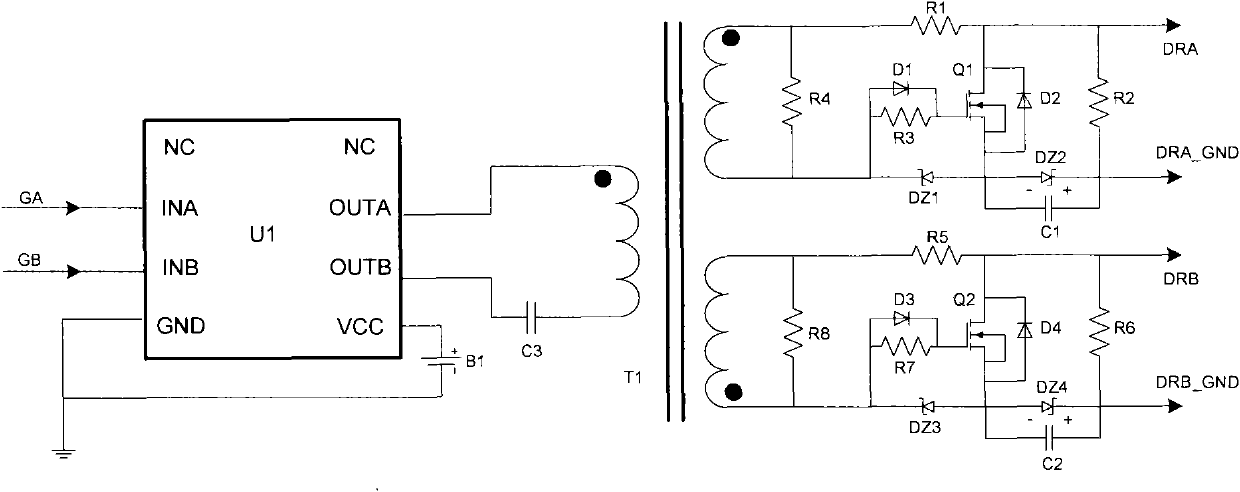
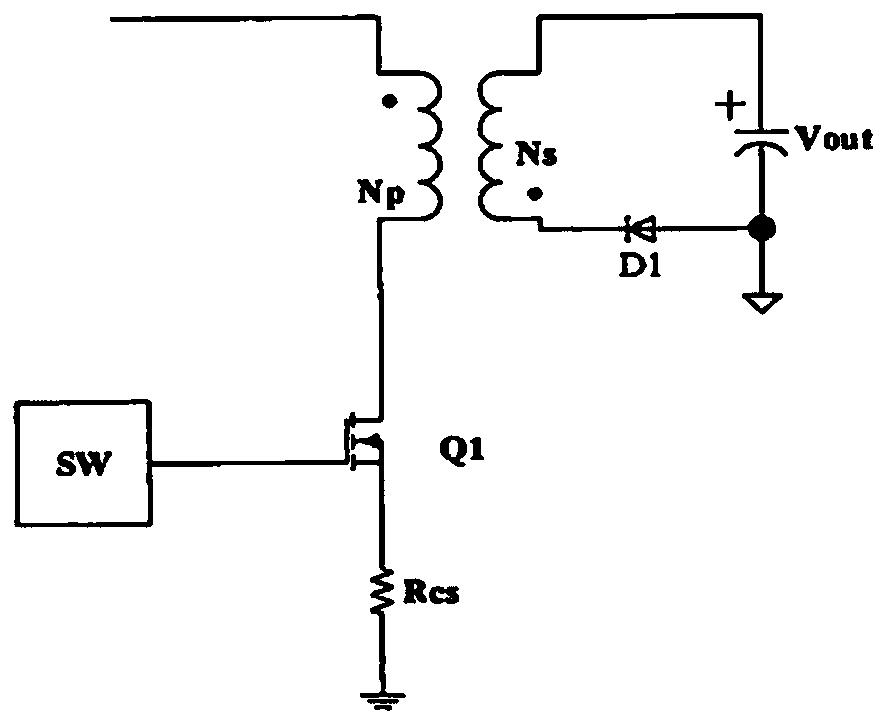
Isolated drive circuit of DC converter
ActiveCN101771335ASimple topologyImprove reliabilityPower conversion systemsHemt circuitsEngineering
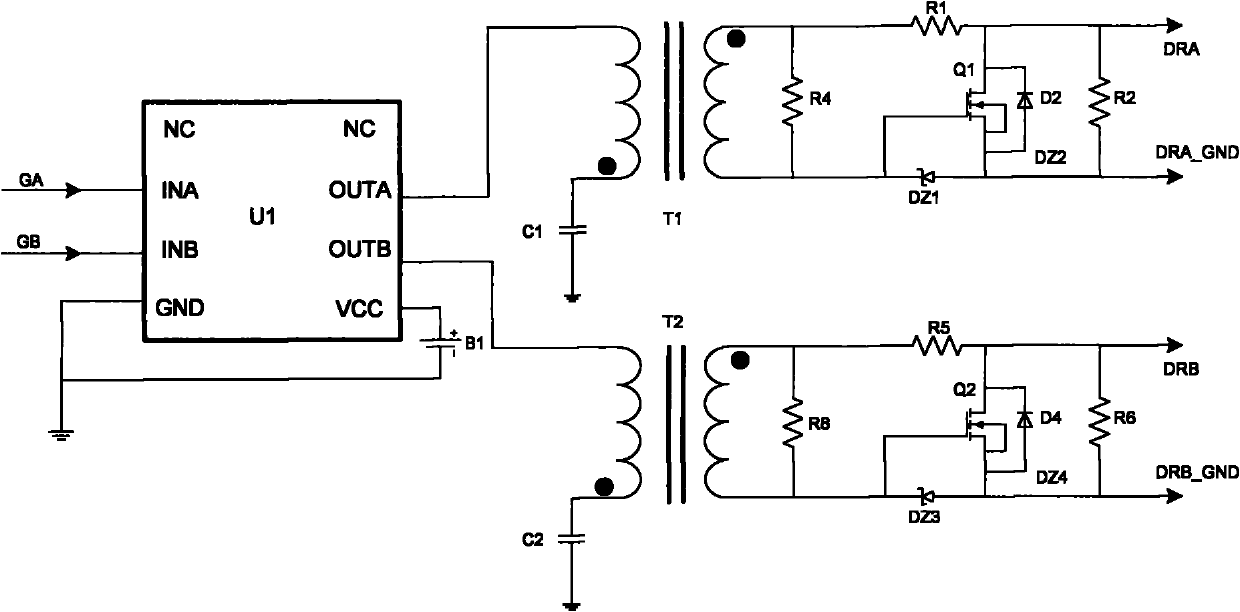
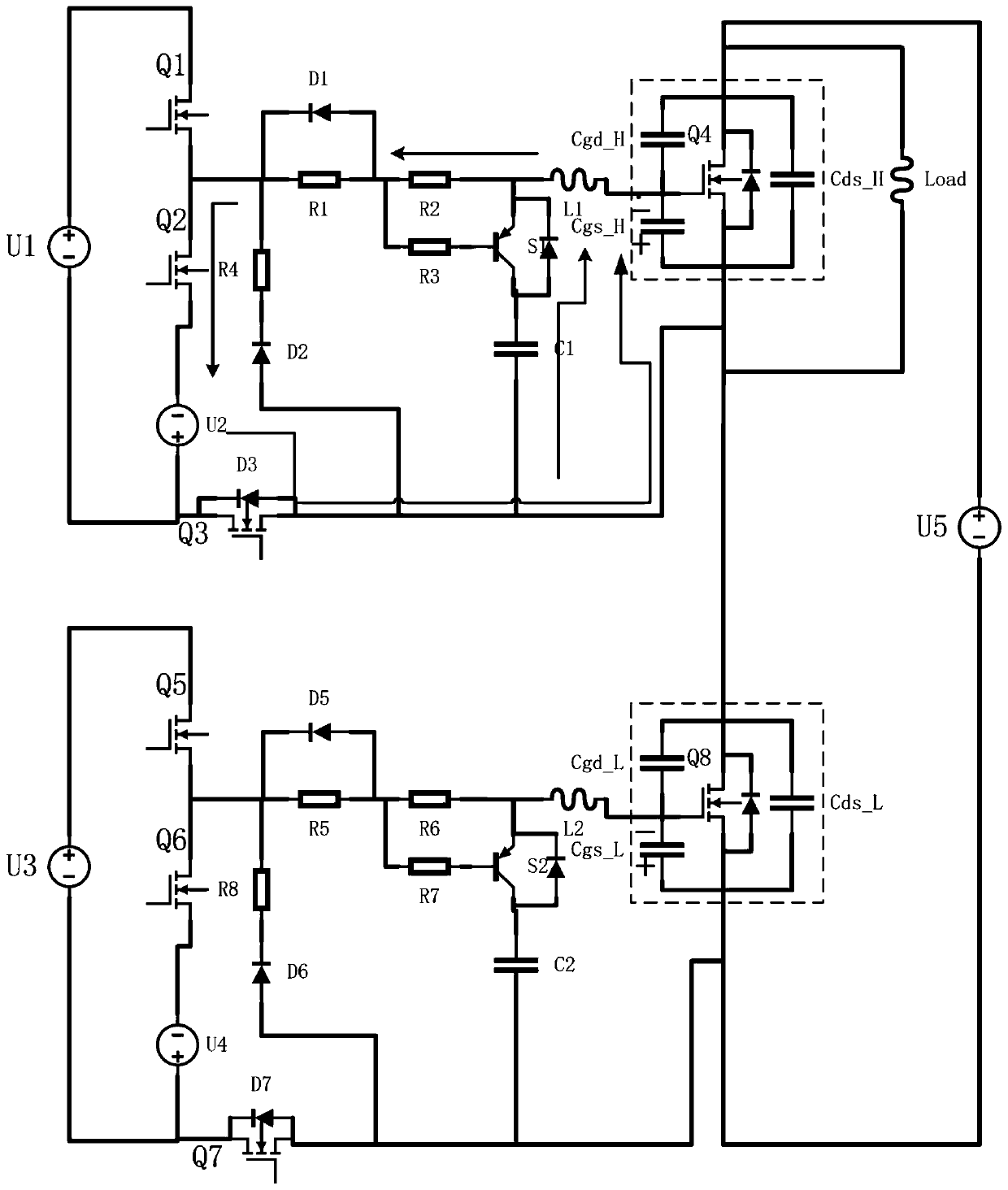
The invention discloses an isolated drive circuit of a DC converter, which relates to technical field of circuit drive. The isolated drive circuit of the DC converter comprises: an isolated transformer, a primary winding, a primary winding drive circuit, a first secondary winding and a second secondary winding whose same name ends are opposite, and a first switch pipe and a second switch pipe; the different name end of the first secondary winding is connected with source electrode of the first switch pipe, the same name end is connected with the drain electrode of the first switch pipe through a first resistance, the different name end of the first secondary winding is connected with the grid electrode of the first switch pipe through a first diode; the different name end of the first secondary winding is connected with the anode of the first diode; the same name end of the second secondary winding is connected with the source electrode of the second switch pipe, the different name end is connected with the drain electrode of the second switch pipe through a second resistance, the same name end of the second secondary winding is connected with the grid electrode of the second switch pipe through a second diode; the same name end of the second secondary winding is connected with the anode of the second diode. The whole circuit has simple topology, high reliability, can be used for many occasions flexibly.
Owner:BEIJING SUPLET +1
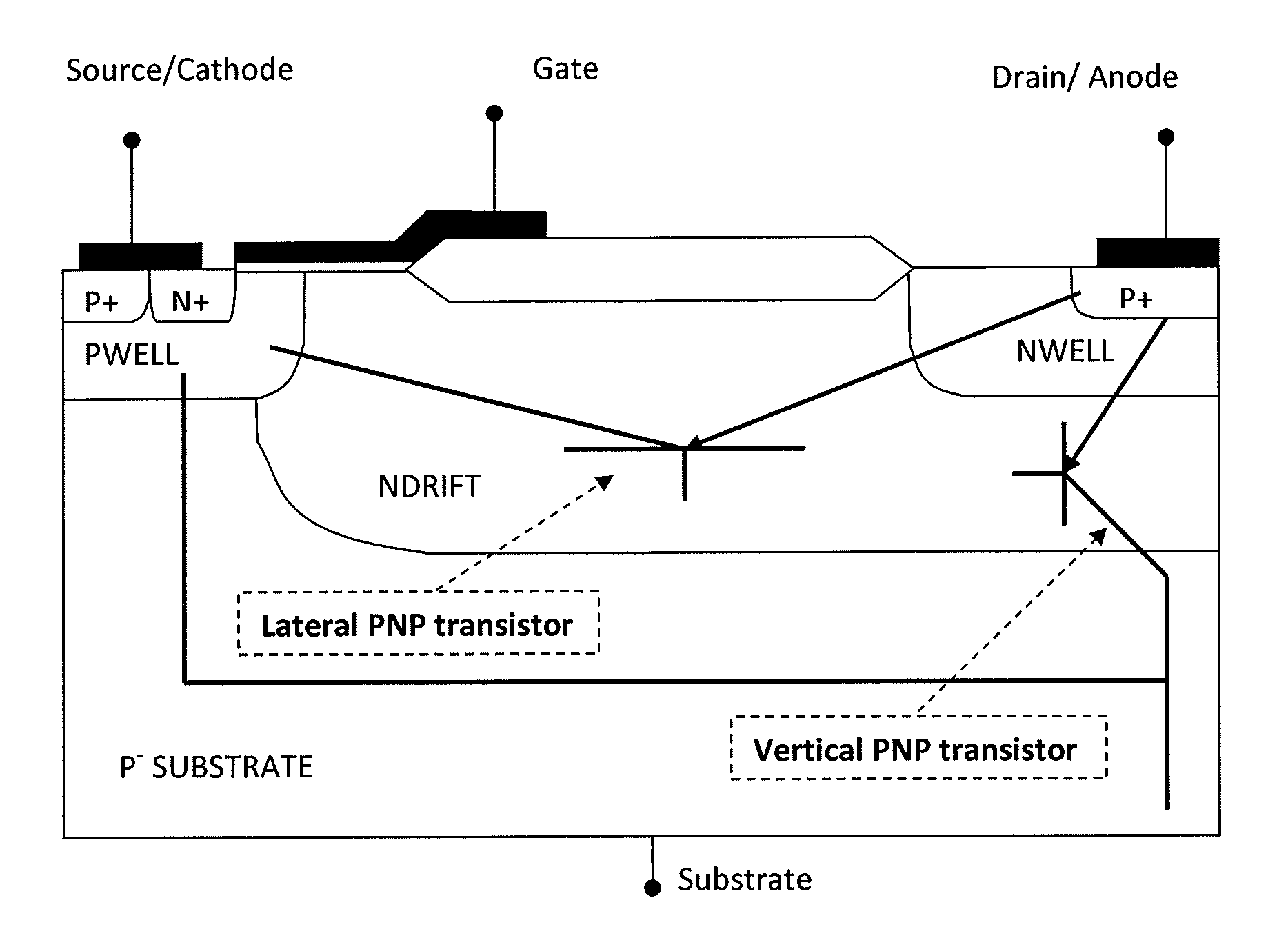
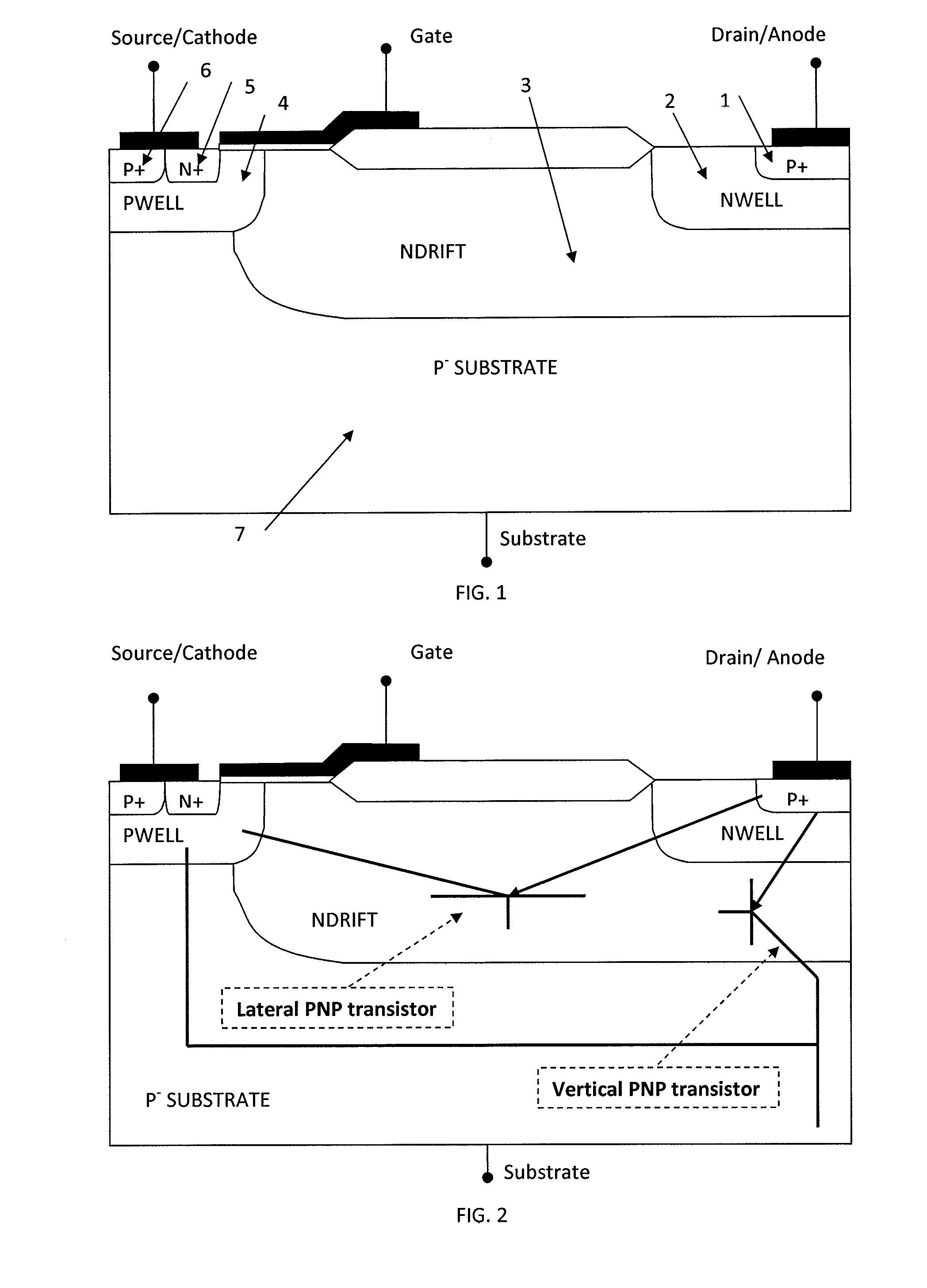
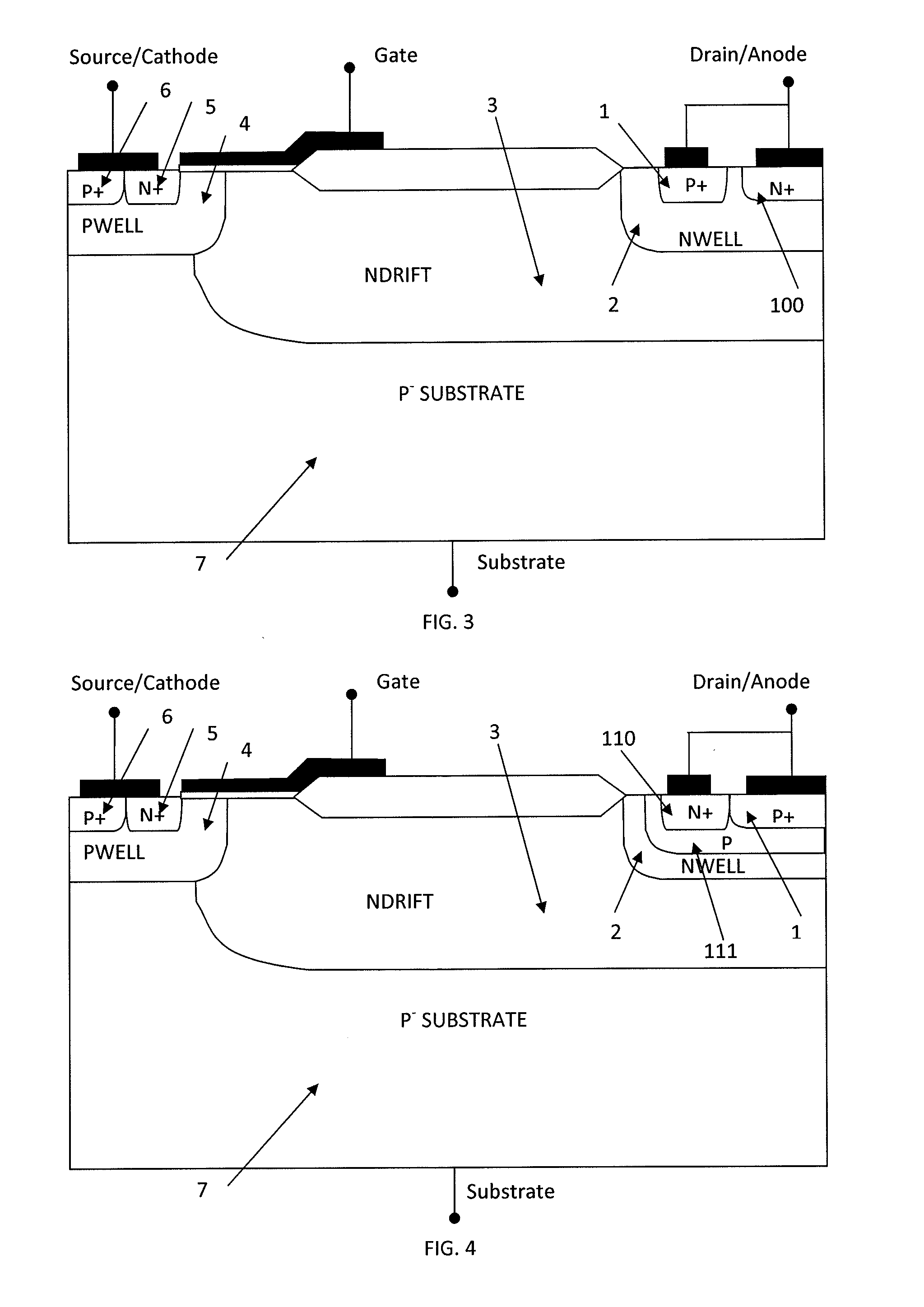
Lateral power semiconductor transistors
ActiveUS20150008481A1Increase the doping concentrationIncrease concentrationTransistorSolid-state devicesFloating electrodeSemiconductor
The invention generally relates to a lateral power semiconductor transistor for example in integrated circuits. In particular the invention relates to Lateral Insulated Gate Bipolar Transistors or other lateral bipolar devices such as PIN diodes. The invention also generally relates to a method of increasing switching speed of a lateral bipolar power semiconductor transistor. There is provided a lateral bipolar power semiconductor transistor comprising a first floating semiconductor region of the first conductivity type located laterally spaced to an anode / drain region and a second floating semiconductor region of the second conductivity type located laterally adjacent the first floating semiconductor region, and a floating electrode placed above and in direct contact to the first and second floating semiconductor regions.
Owner:CAMBRIDGE MICROELECTRONICS LTD
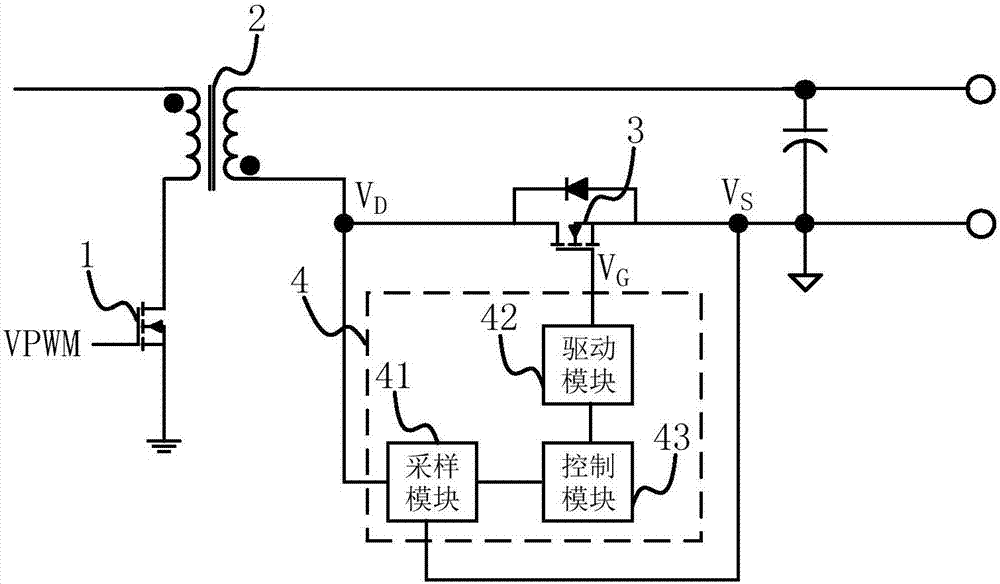
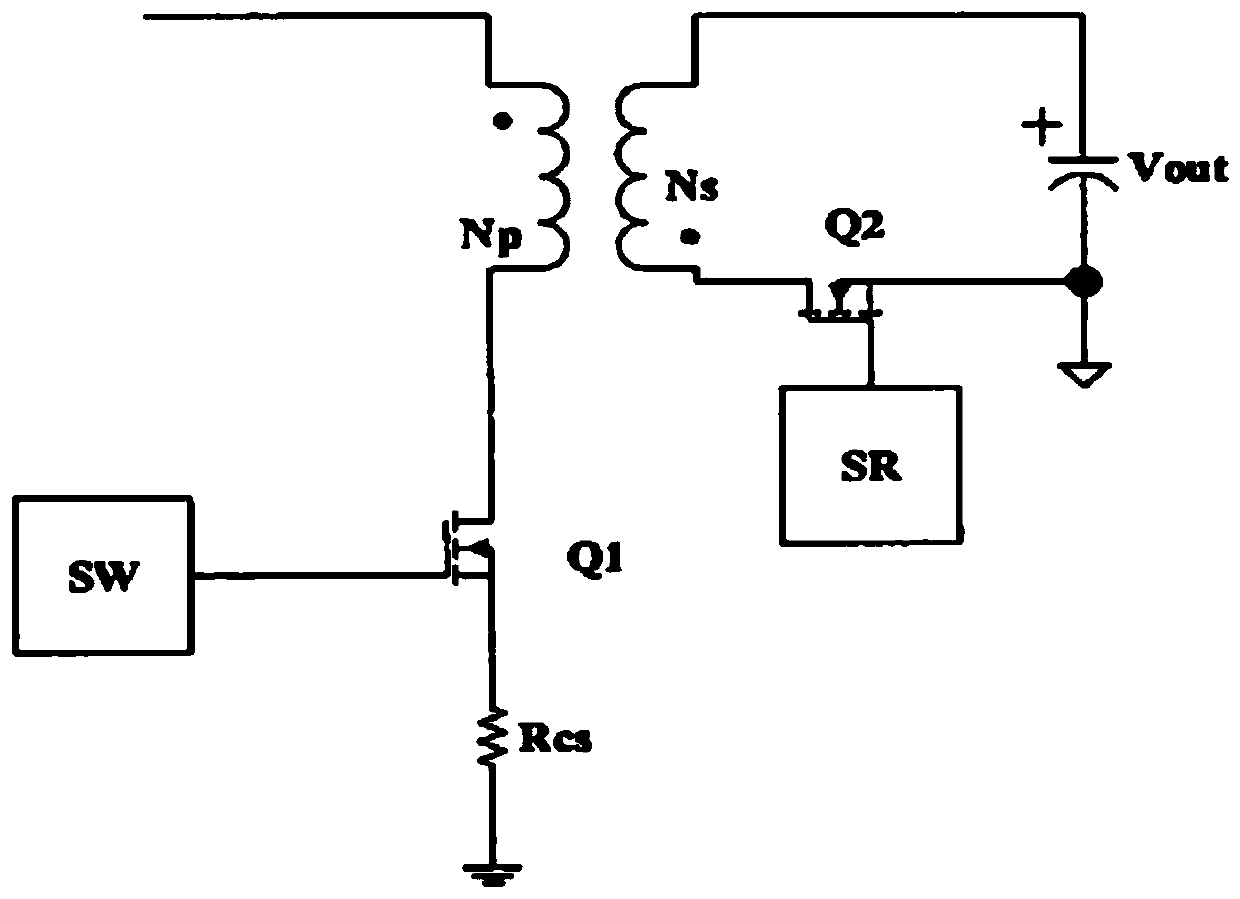
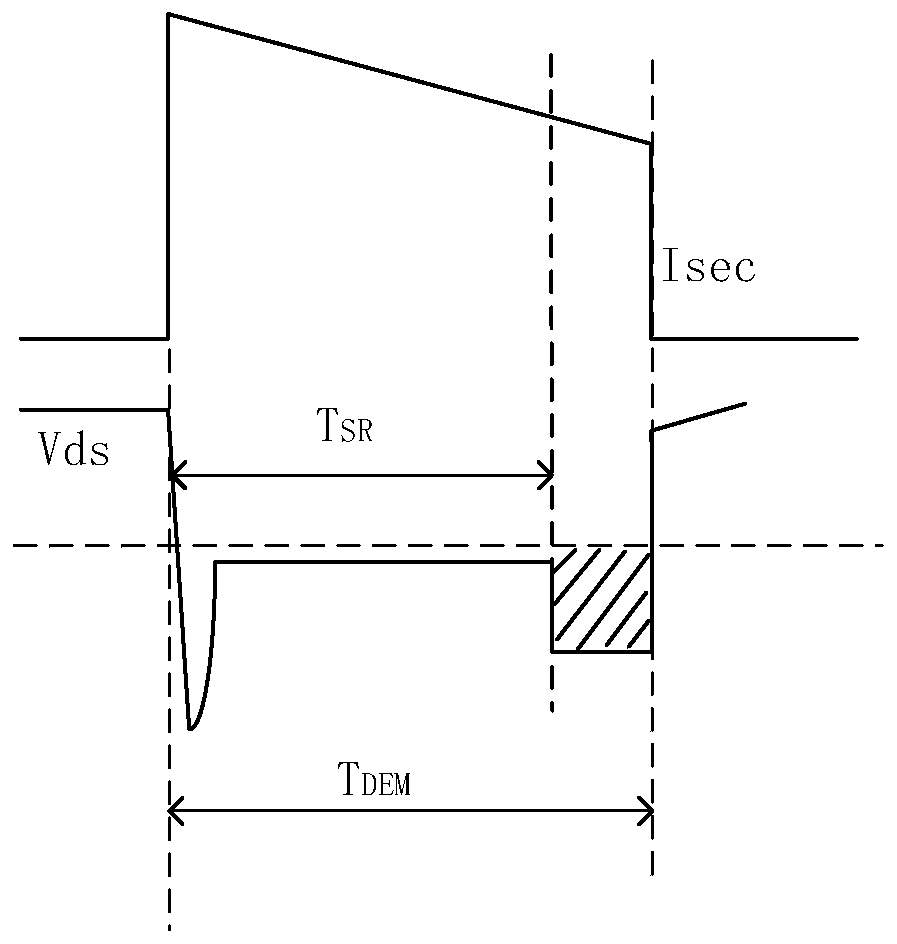
Synchronous rectification controller and synchronous rectification control method
ActiveCN107968569AReduce lossImprove efficiencyEfficient power electronics conversionDc-dc conversionOxide semiconductorThreshold voltage
The invention discloses a synchronous rectification controller and a synchronous rectification control method. The controller comprises a sampling module, a driving module and a control module, wherein the sampling module is used for sampling a source voltage and a drain voltage of a synchronous rectification metal-oxide-semiconductor (MOS) tube and acquiring a voltage difference value between thesource voltage and the drain voltage, the driving module is used for adjusting a grid voltage of the tube, and the control module is used for comparing the voltage difference value, a first thresholdvalue and a second threshold value, controlling the driving module to adjust the grid voltage of the tube to maximum output voltage when the voltage difference value is smaller than the first threshold value, controlling the driving module to adjust the grid voltage of the tube to change between 0 and the maximum output voltage when the voltage difference value is larger than the first thresholdvalue and smaller than the second threshold value so that the voltage difference value is adjusted to be equal to the first threshold value, and controlling the driving module to adjust the grid voltage of the tube to 0 when the voltage difference value is larger than the second threshold value. By the controller, the switch-on and switch-off speed of the synchronous rectification MOS tube can beincreased, so that the efficiency is obviously improved, and the loss is obviously reduced.
Owner:成都启臣微电子股份有限公司
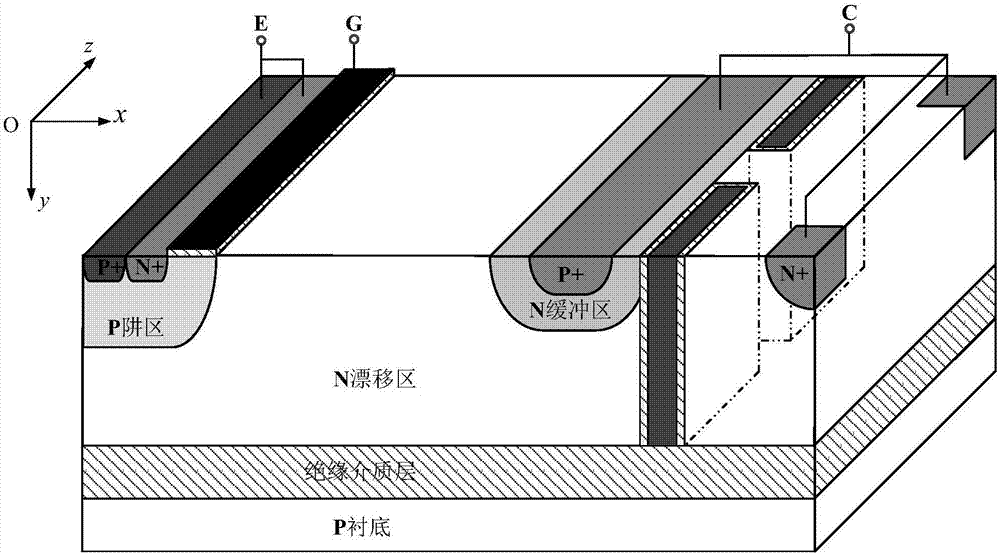
Lateral insulated gate bipolar transistor
ActiveCN107170815AImprove breakdown voltageFast shutdown speedSolid-state devicesSemiconductor devicesInsulated-gate bipolar transistorCapacitance
The invention belongs to the technical field of a semiconductor power device, and specifically relates to a lateral insulated gate bipolar transistor. On the basis of a conventional positive electrode short circuit LIGBT structure, an isolation dielectric groove is formed in one end of a collector in a device drift region; an integrated PMOS structure is formed at the other end of the isolation dielectric groove, and the integrated PMOS structure is connected with a positive electrode short circuit N+ region in series; and meanwhile, an integrated capacitive structure is introduced between the gate of the integrated PMOS structure and the emitter of the LIGBT device. By virtue of a self-biasing effect formed by the integrated PMOS structure and the capacitor, the lateral insulated gate bipolar transistor has the same working condition as the conventional LIGBT and the same conduction voltage drop, without causing a negative impedance phenomenon in the conduction process, in the conduction state; in a blocking state, the lateral insulated gate bipolar transistor has higher breakdown voltage; and meanwhile, in the switching-off process, the lateral insulated gate bipolar transistor has higher switching-off speed and lower switching-off loss.
Owner:UNIV OF ELECTRONIC SCI & TECH OF CHINA
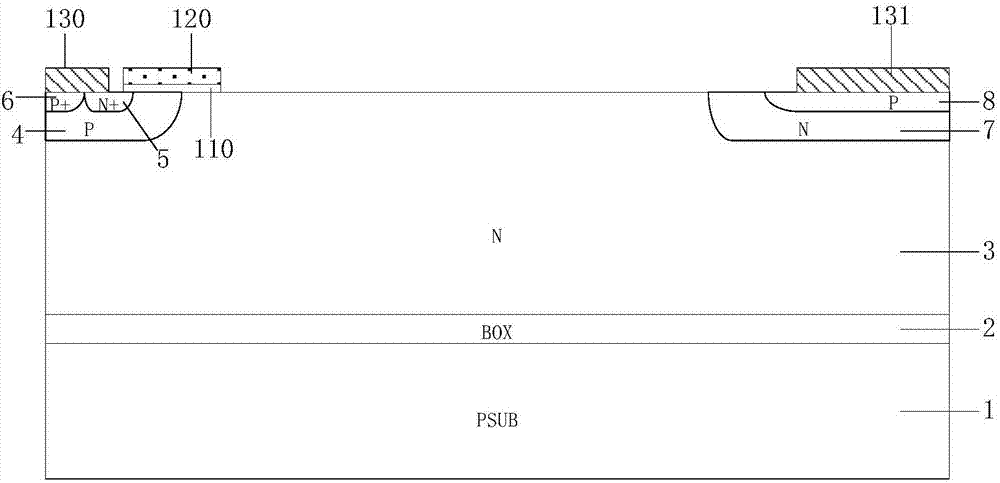
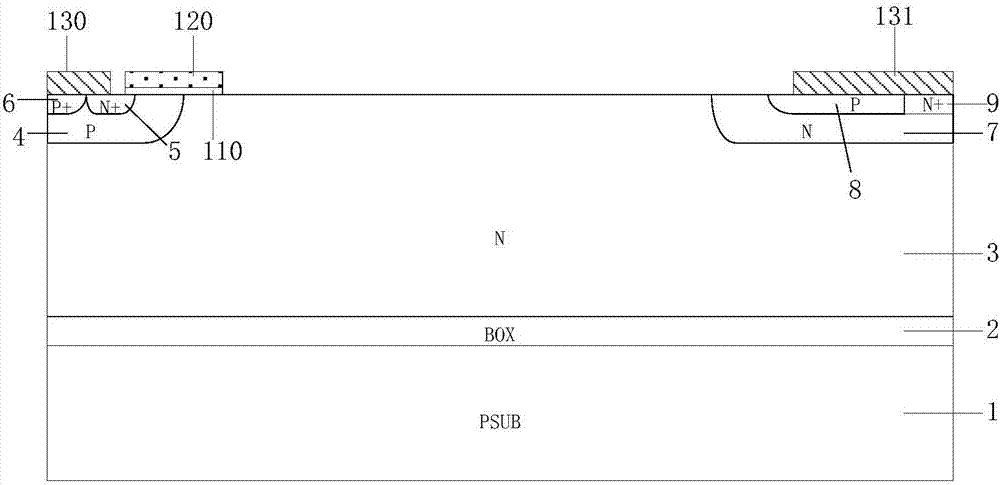
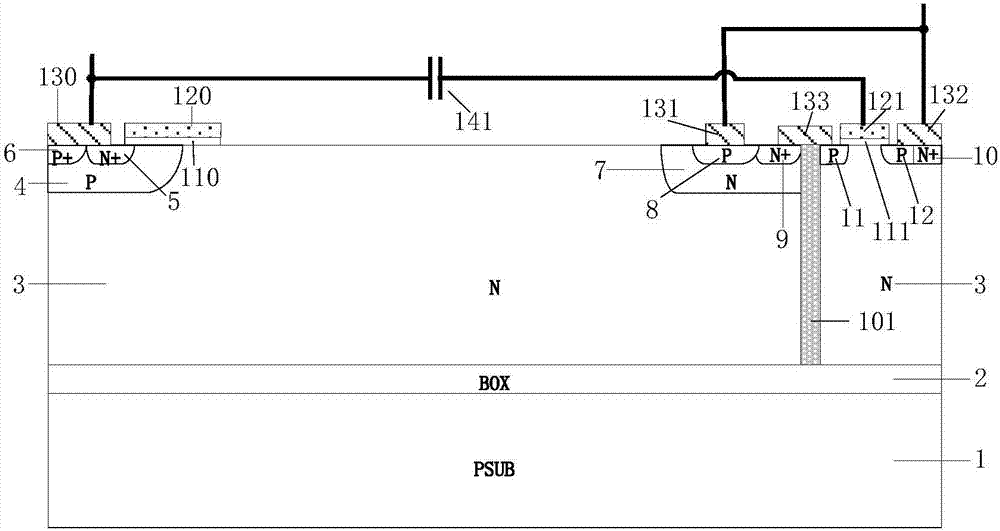
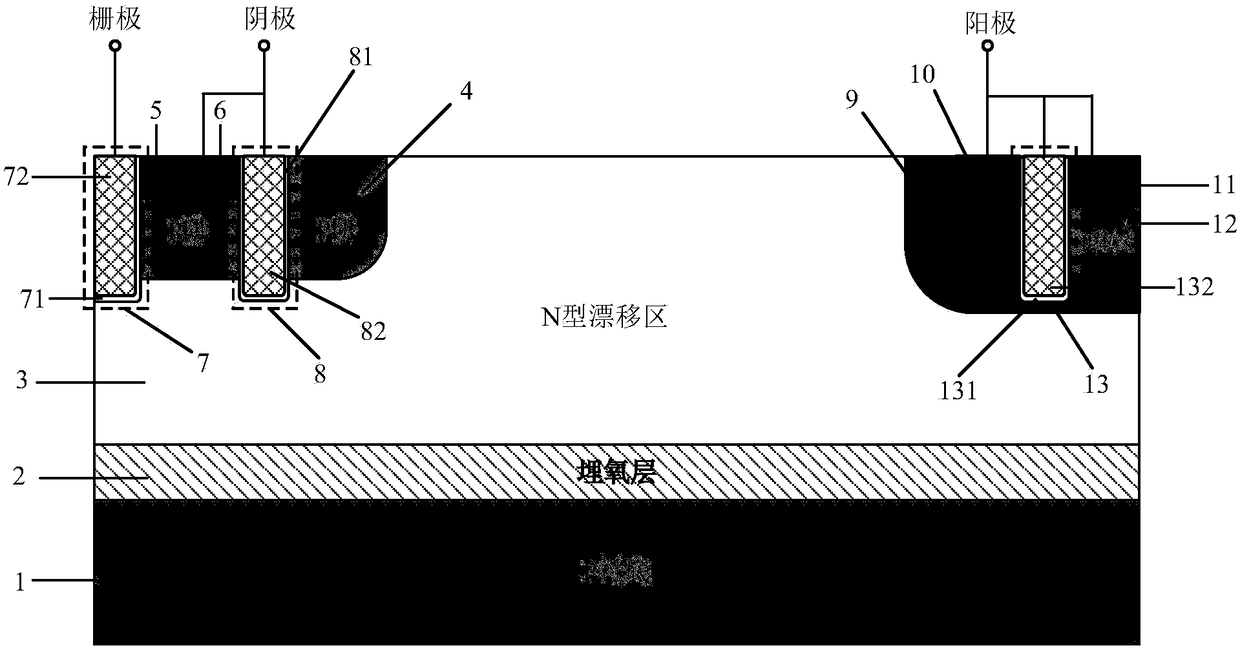
Grooved gate short circuit anode SOI LIGBT
The invention belongs to the technical field of power semiconductors and relates to a grooved gate short circuit anode SOI LIGBT. In comparison with the traditional short circuit anode LIGBT, anode grooves connected to anode potential are introduced at an anode end, and a P body area is introduced right below an N+ anode area; and grooved gates and cathode grooves connected with a cathode are introduced in a cathode area. When the device is turned off, the anode groove is connected to high potential, an NMOS in the anode area is started automatically, extraction of electrons stored in a driftarea is quickened, and the turn-off time and the turn-off energy loss are reduced; when the device is in a high-voltage high-current state, the cathode groove forms a hole bypass, and happening of latch-up effects is suppressed; when the device is conducted, under blocking of an electronic barrier in the P body area, electron current in the drift region is not easy to be collected by the N+ anode,voltage reentry effects are eliminated, and as the grooved gate structures of the cathode are in parallel connection, the channel density is increased and the conduction voltage drop is reduced. Thegrooved gate short circuit anode SOI LIGBT has the beneficial effects that in comparison with the traditional short circuit anode LIGBT, a voltage reentry phenomenon is eliminated under a smaller transverse cell size, and the conduction voltage drop is lower.
Owner:UNIV OF ELECTRONICS SCI & TECH OF CHINA
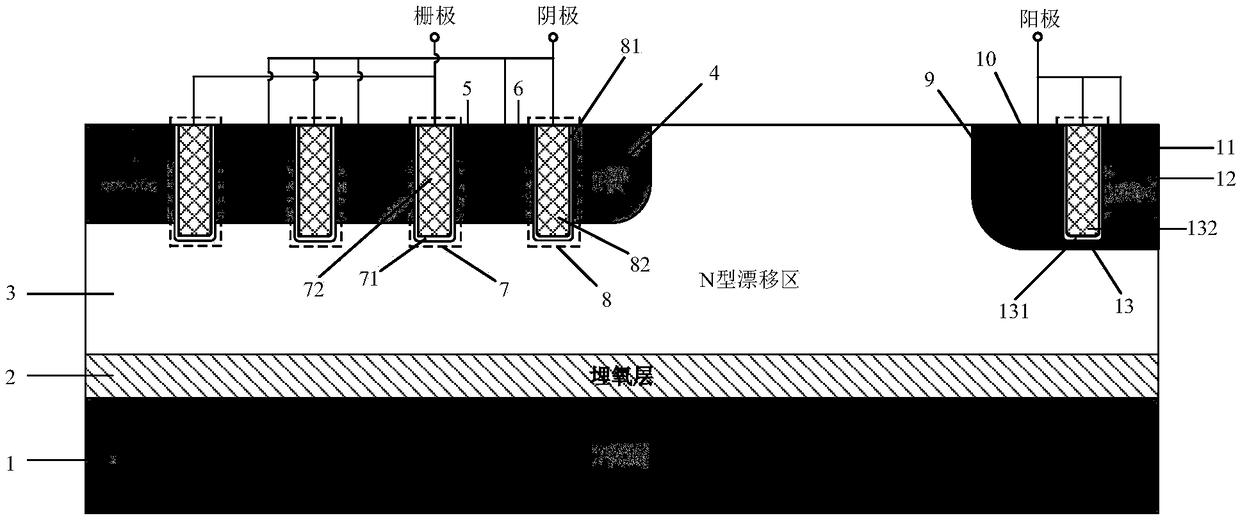
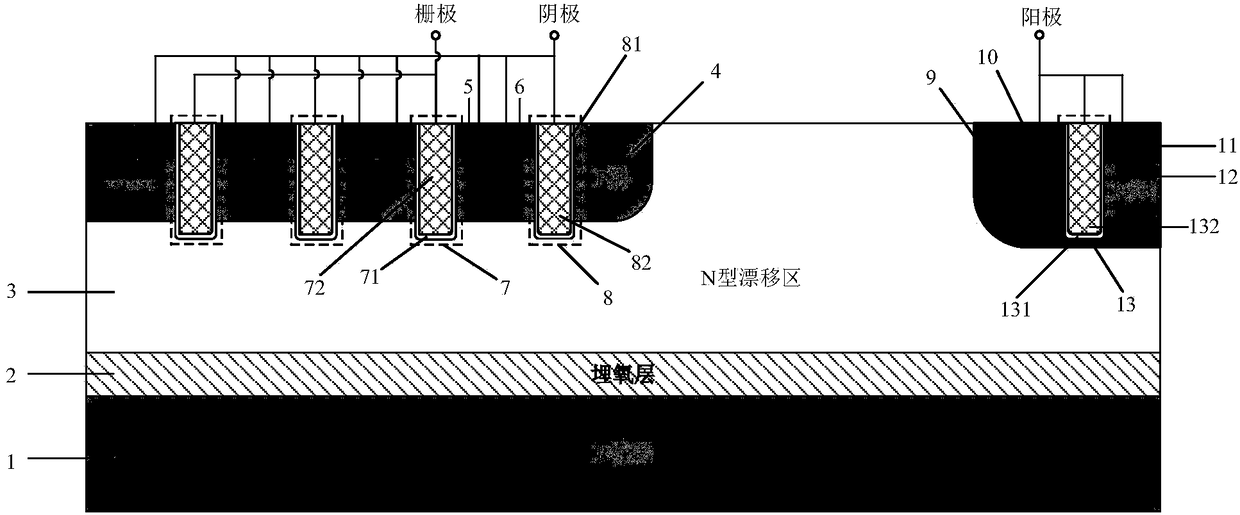
Superjunction reverse conducting-insulated gate bipolar transistor (IGBT) with collector groove
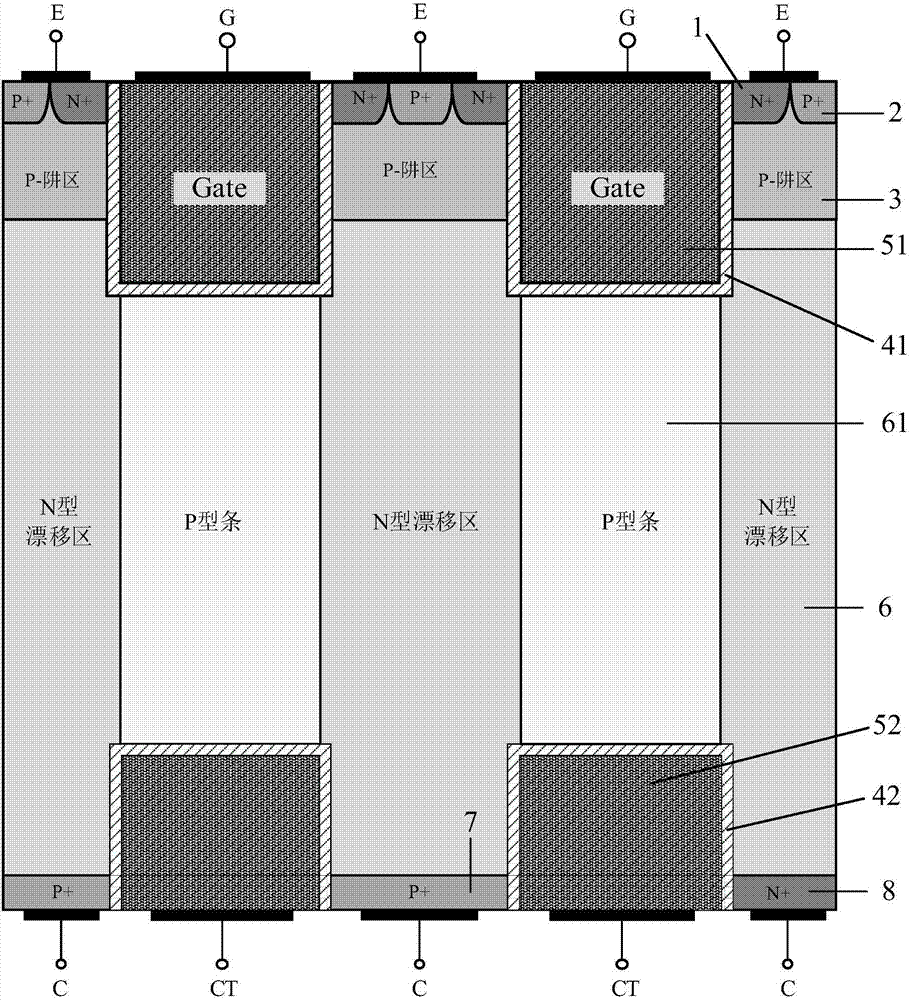
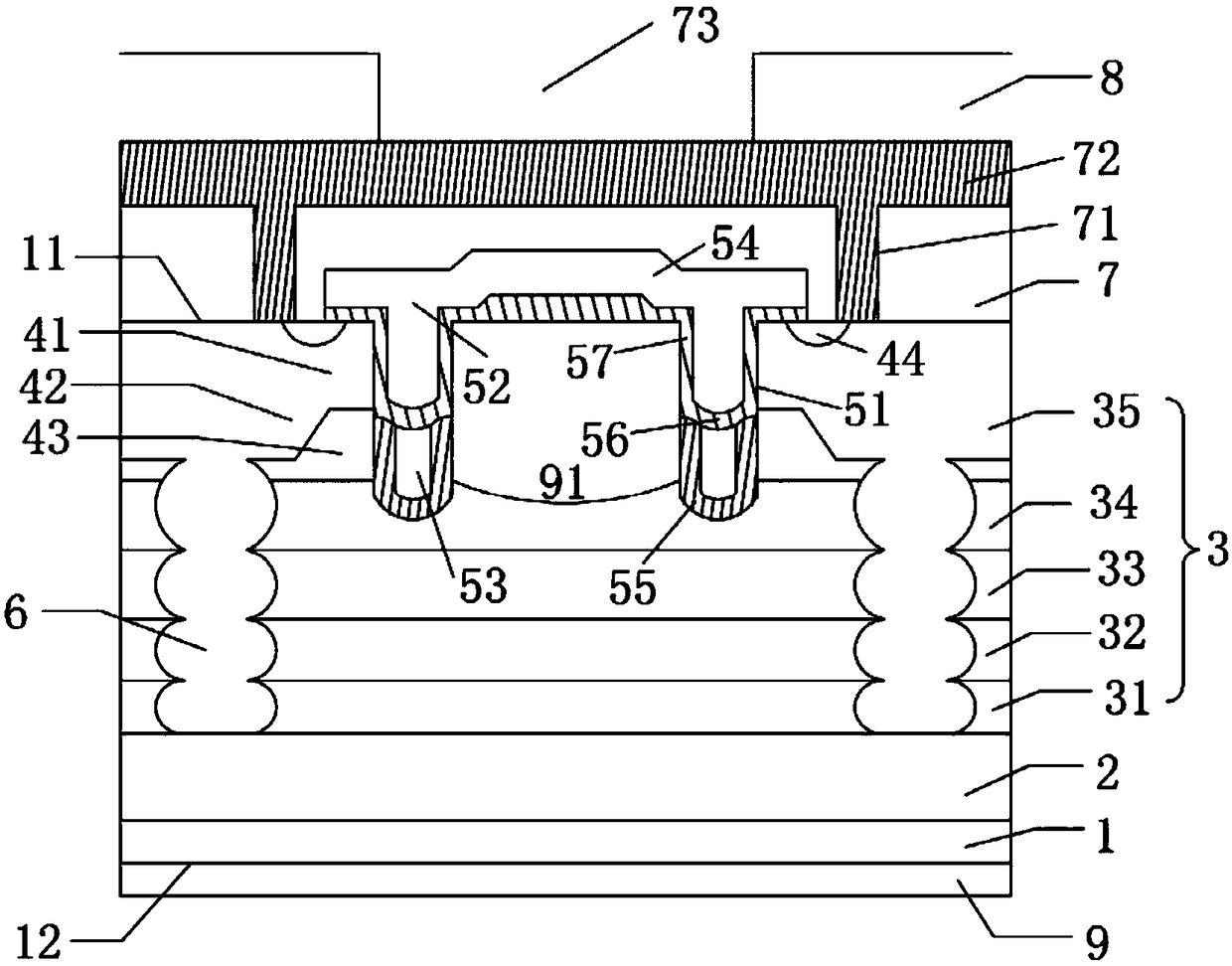
InactiveCN107464842AIncreased shutdown speedEliminate the snapback effectSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSemiconductor devicesHigh pressureSmall cell
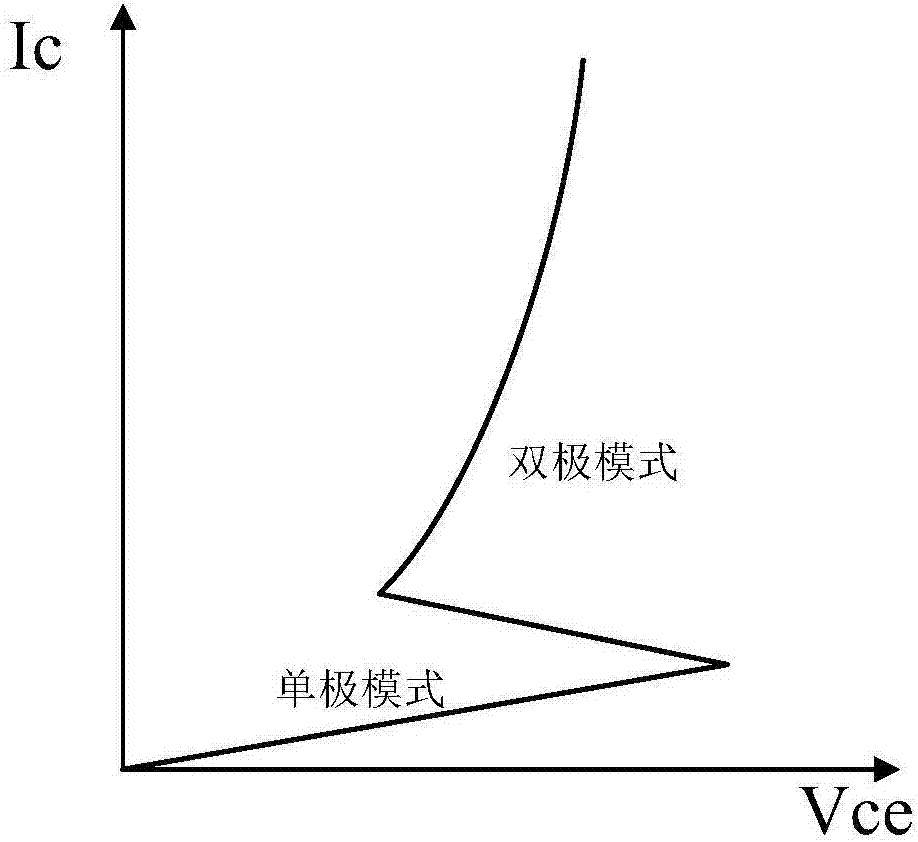
The invention belongs to the technical field of a power semiconductor, and particularly relates to a superjunction reverse conducting-insulated gate bipolar transistor (IGBT) with a collector groove. Compared with a traditional superjunction RC-IGBT structure, the superjunction RC-IGBT has the advantages that a collector groove structure is mainly introduced to a bottom current collection region, an N drift region at the bottom of the collector groove can be consumed by P-type strips when a new device is positively conducted and does not enter a bipolar mode, so that an electron current path is occupied, the effective electron concentration is reduced, the electron current distribution resistance around the current collection region is increased, and a snapback effect of the device can be eliminated by the new device under relatively small cell size; and when the new device is switched off, the collector structure has an effect equivalent to a buffer layer, and the device can be enabled to bear high pressure. The superjunction RC-IGBT has the beneficial effects that compared with the traditional superjunction RC-IGBT structure, the snapback effect can be eliminated under smaller cell size, meanwhile, the superjunction RC-IGBT has faster switch-off speed, and the current distribution is more uniform in a reverse diode mode.
Owner:UNIV OF ELECTRONICS SCI & TECH OF CHINA
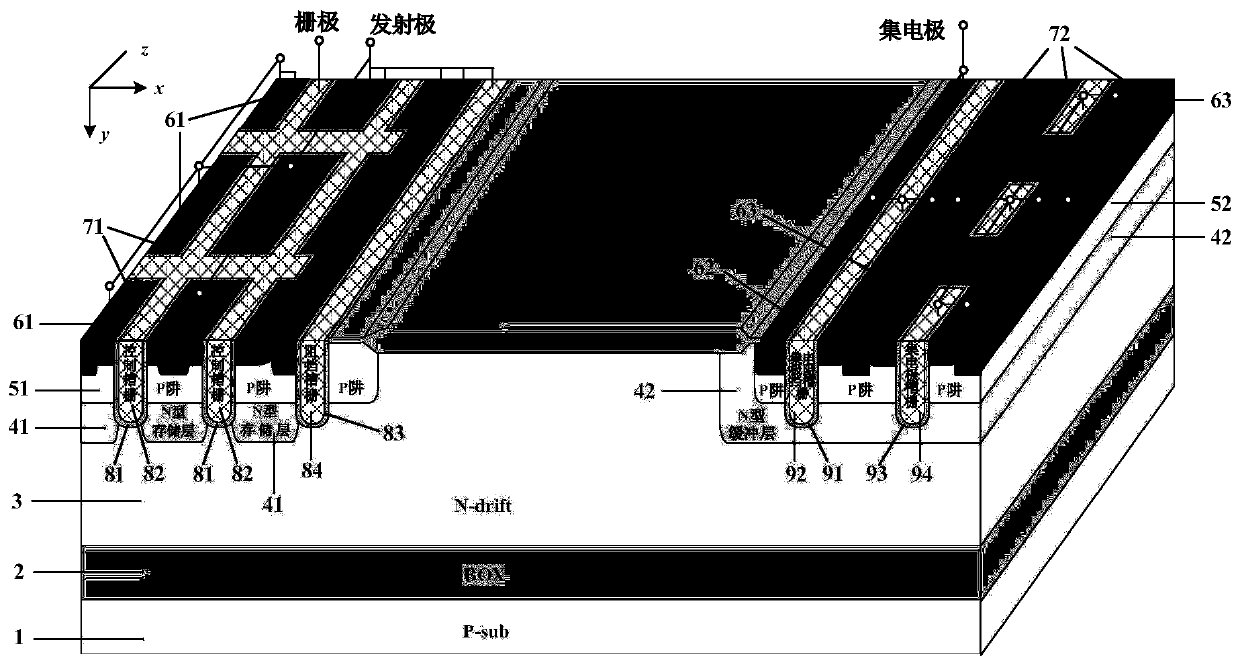
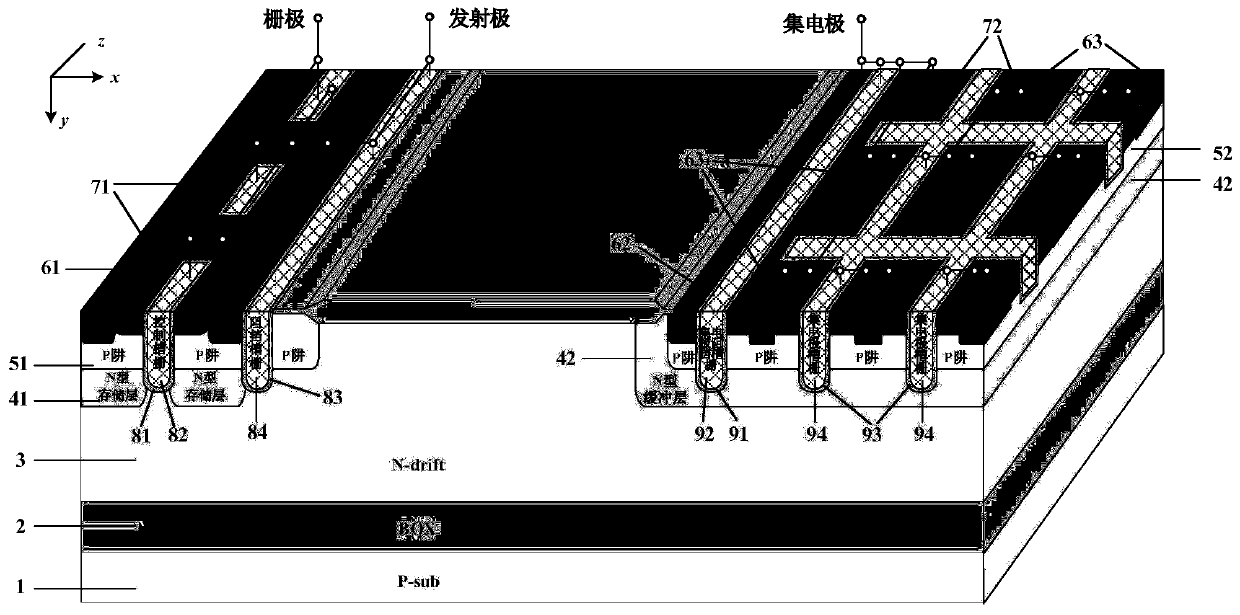
A superjunction IGBT with a shielded gate and a manufacturing method thereof
PendingCN109037312AReduce lossLow resistivitySemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSemiconductor devicesCapacitanceCell region
The invention discloses a superjunction IGBT with a shield gate and a manufacturing method thereof. The superjunction IGBT comprises a semiconductor substrate, a cell region and a terminal protectionarea. The semiconductor substrate comprises a second conductivity type collector region, a first conductivity type field termination layer and at least one first conductivity type epitaxial layer. Thecell region comprises a plurality of cells connected in parallel with each other, which includes a plurality of cell trenches and a gate conductive polysilicon and a shield gate filled in the cell trenches, A seventh oxide layer is arranged on both sides and sidewalls of the notch of the cell trench opposite to the gate conductive polysilicon, a fifth oxide layer is arranged between the gate conductive polysilicon and the shield gate, and a fourth oxide layer is arranged on the bottom and sidewalls of the cell trench opposite to the shield gate. A P-pillar is also provided in the first conductivity type epitaxial layer, one end of the P-pillar is connected to the second conductivity type well layer, and the other end extends toward the first conductivity type field termination layer. Theinvention adopts the shielding gate structure, reduces the Miller capacitance, thereby reducing the switching loss.
Owner:无锡市乾野微纳科技有限公司
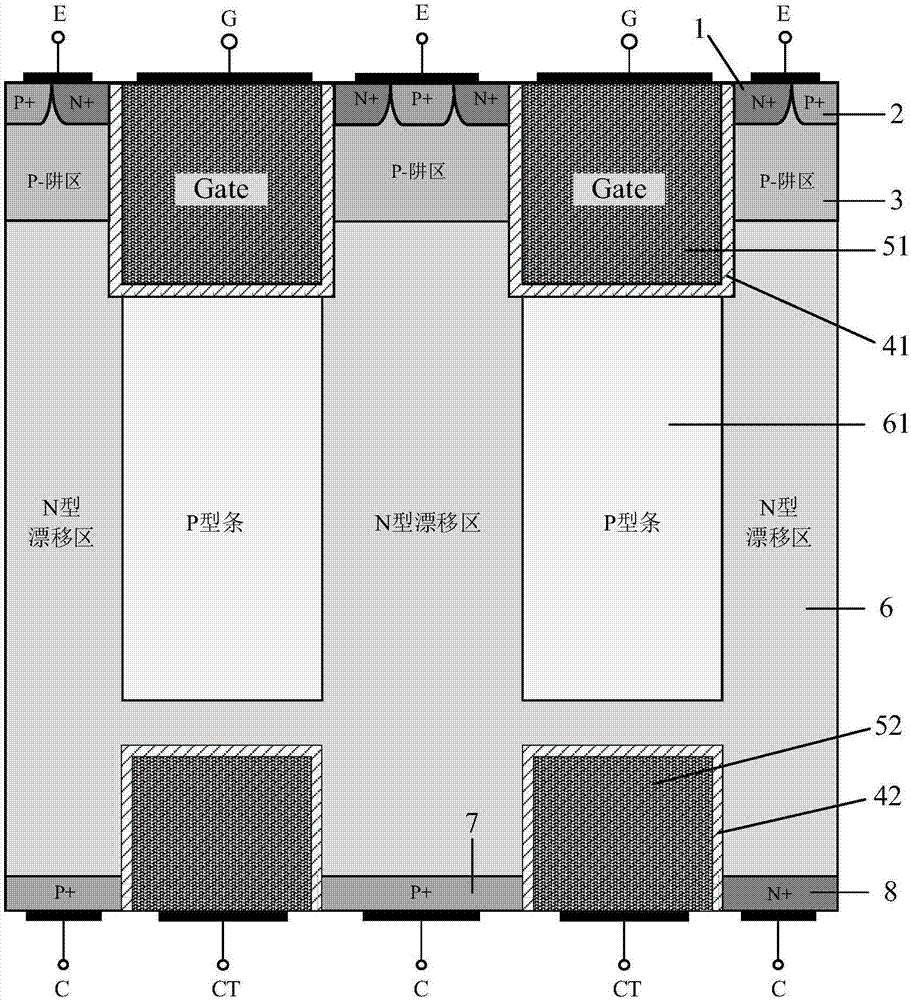
Carrier-stored trench gate bipolar transistor
InactiveCN102800691AImprove pressure resistanceIncreased shutdown speedSemiconductor devicesPower semiconductor devicePeak value
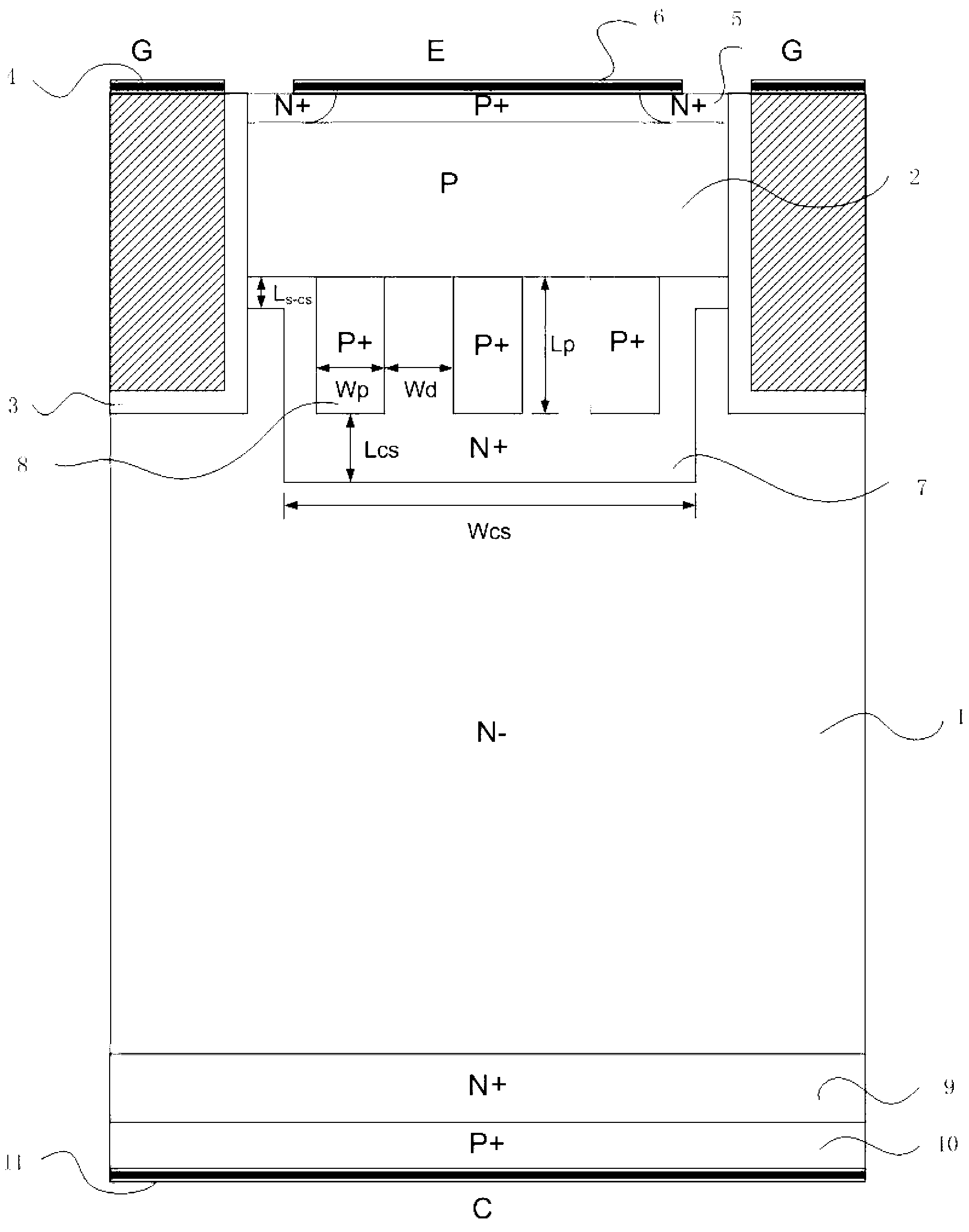
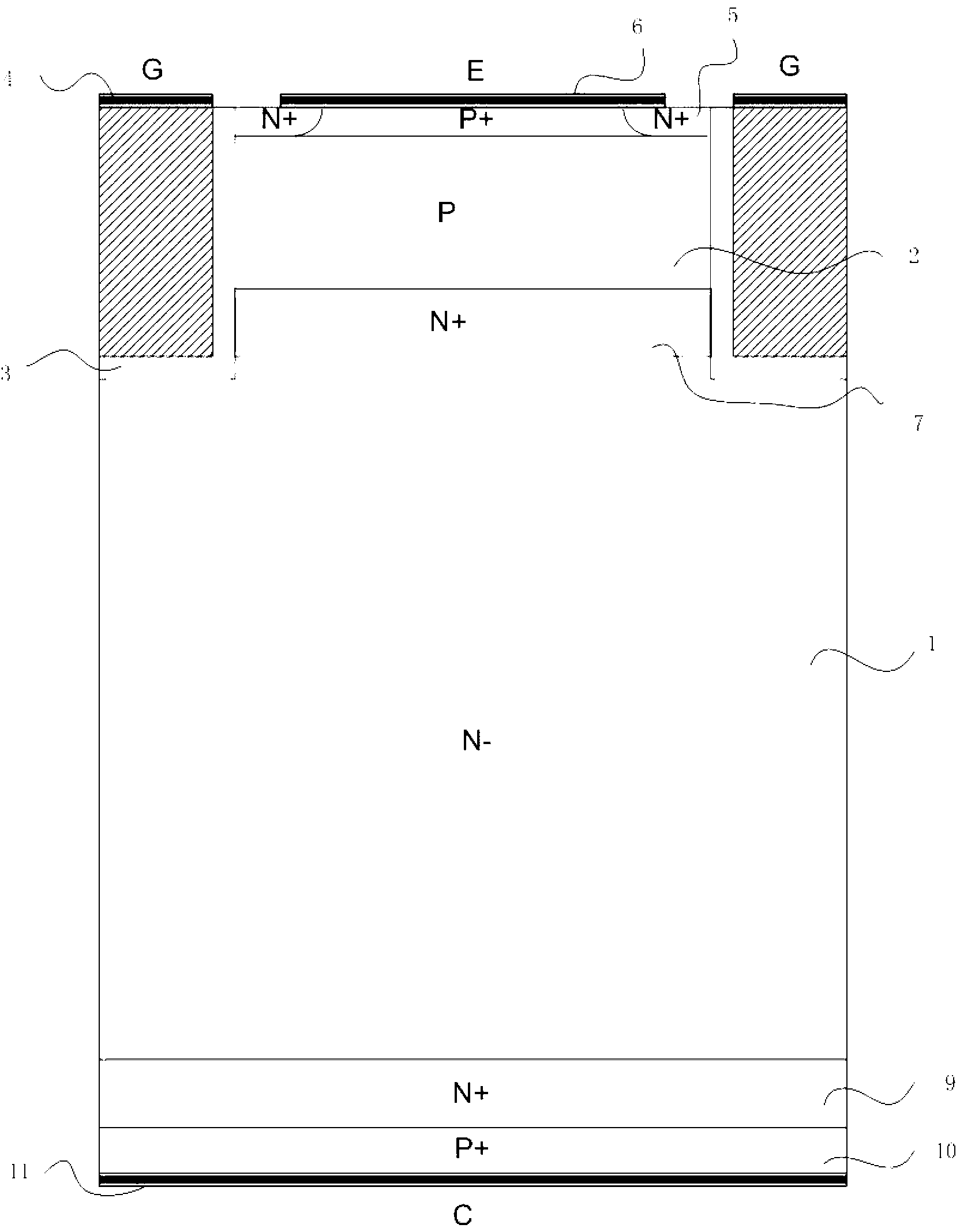
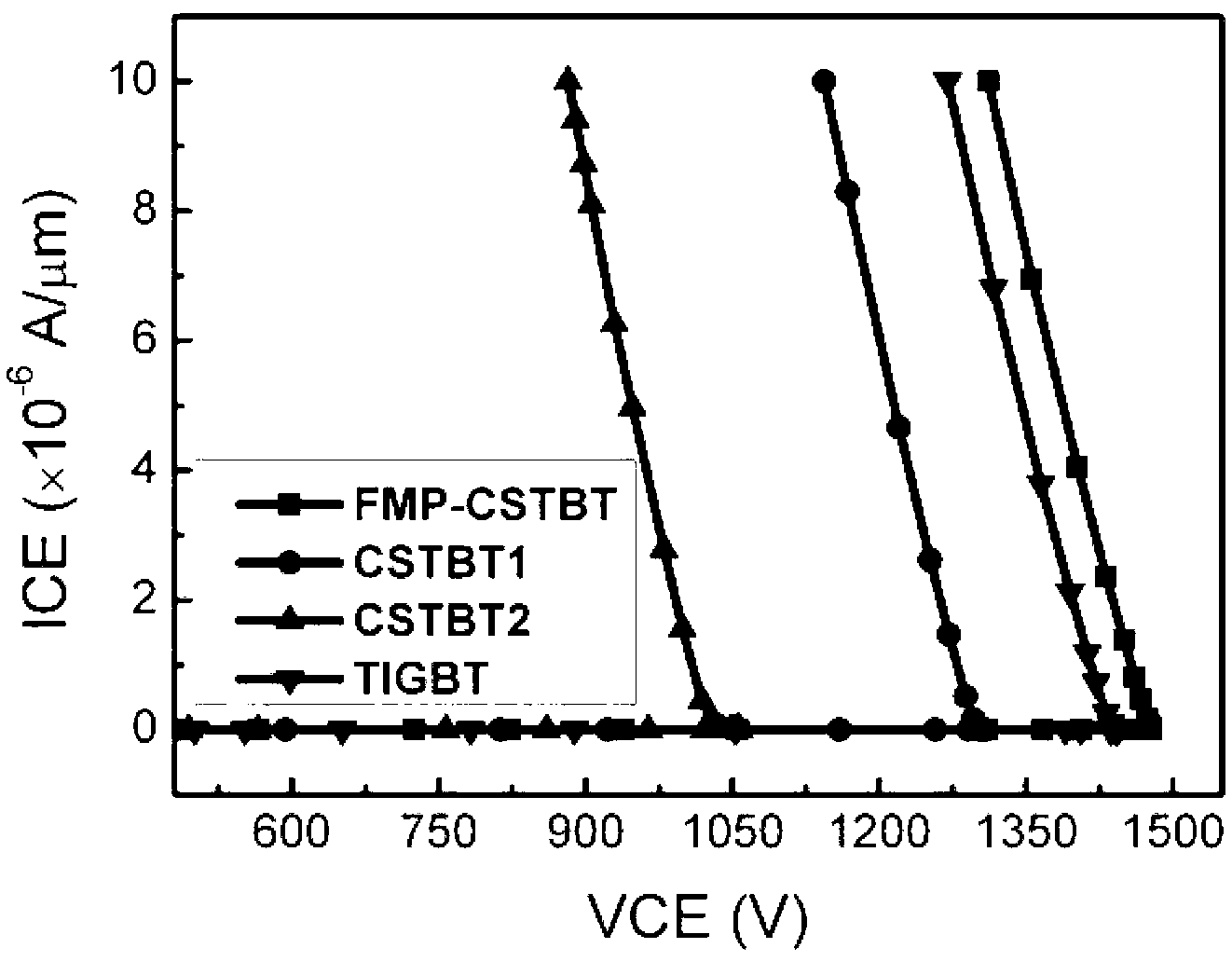
The invention provides a carrier-stored trench gate bipolar transistor (FMP-CSTBT), and belongs to the technical field of power semiconductor devices. According to the carrier-stored trench gate bipolar transistor, a plurality of P+ strips are inserted into an N+ carrier stored layer under a P type base area of a common CSTBT, wherein the top surface of a P+ strip 8 is in contact with a P type base area 2, and while the bottom surfaces are in contact with an N- layer 1; and the length direction of the P+ strip 8 is parallel to the width direction of the whole device. The P+ strips are partially depleted to generate negative depletion charges when the device is subject to pressure resistance, so that an electric field close to the edge of a trench gate can be modulated, the radius of curvature of the potential in the edge of the trench gate can be reduced, and as a result, the peak value of the electric field is transferred to a PN node of the base area, therefore, the device is prevented form being punctured in advance, and the reverse pressure resistance and the stability of the device can be effectively improved. The P type strips without being completely depleted provide additional extracting channels for conveying fewer carriers, so as to accelerate the extraction, shorten the turn-off time and reduce the turn-off loss.
Owner:UNIV OF ELECTRONICS SCI & TECH OF CHINA +1
High-power-density single-phase cascaded H-bridge rectifier, control method and control system
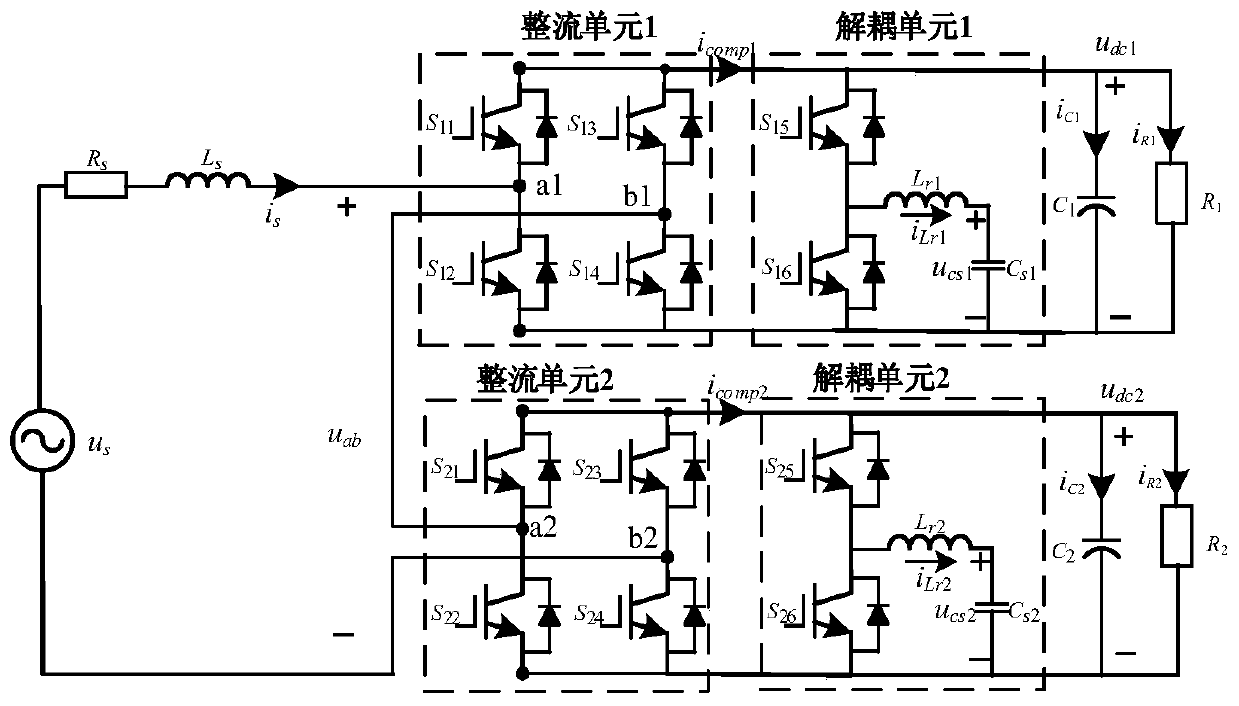
ActiveCN110380626AReduce voltageEasy to controlAc-dc conversion without reversalDc-dc conversionCapacitanceControl system
The invention provides a high-power-density single-phase cascaded H-bridge rectifier, a control method and a control method. The high-power-density single-phase cascaded H-bridge rectifier comprises an AC network side filter inductor and at least two cascaded power conversion units, wherein each power conversion unit comprises an H-bridge power unit, a decoupling unit and a DC side equivalent loadwhich are connected in parallel; wherein each decoupling unit is an independent buck type active power decoupling loop, and the decoupling units are used for buffering secondary ripple power so as toreduce the capacity of a DC bus capacitor.
Owner:SHANDONG UNIV
High-frequency high-voltage high-power power supply for electrostatic dust removal
InactiveCN102097956AImprove stabilityImprove control characteristicsAc-dc conversion without reversalDc-dc conversionCapacitanceFull bridge
The invention discloses a high-frequency high-voltage high-power power supply for electrostatic dust removal, which mainly comprises a three-phase power-frequency power supply, a rectification part, an inverter part, a resonant circuit, a high-frequency transformer, a high-voltage rectifier bridge, a load and a control module. The rectification part consists of a thyristor rectification module capable of rectifying the power-frequency electric energy output by the three-phase power supply into direct current, and a filter capacitor; the back of the rectification part is connected with the inverter part consisting of a high-frequency full-bridge Insulated Gate Bipolar Transistor (IGBT) inverter capable of inverting the direct current into high-frequency square wave; the resonant circuit consisting of a series inductor Lr, a series capacitor Cr and a parallel capacitor Cp and supplying power to the post-stage circuit in a resonant manner is connected behind the inverter part. By the invention, the deficiency of the conventional electrostatic dust removing power supply can be compensated, the dust removing effect is improved, and the utilization ratio of electric energy can be increased.
Owner:ZHEJIANG ELECTRIC POWER DESIGN INST +1
High-power MOSFET driving circuit
InactiveCN103715871AImprove driving abilityImprove work efficiencyPower conversion systemsEngineeringPower MOSFET
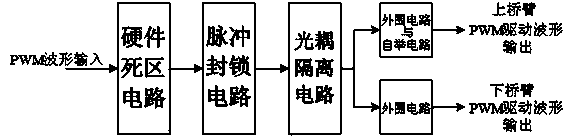
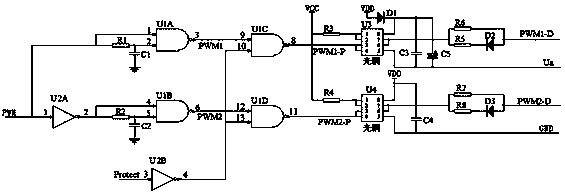
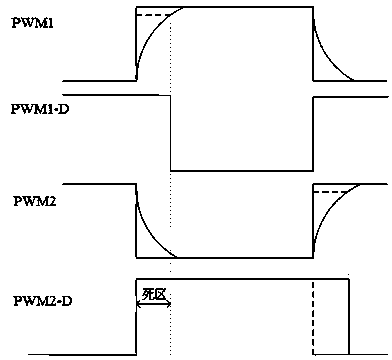
The invention relates to a high-power MOSFET driving circuit. PWM input signals pass through a hardware deadzone circuit, a pulse blocking circuit, an optical coupling isolation circuit and a peripheral circuit in sequence to generate the gate drive signals of the Mosfet of an upper bridge arm and the Mosfet of a lower bridge arm, the hardware deadzone circuit generates hardware deadzone time, the pulse blocking circuit is used for blocking pulse signals when a protection state occurs, the hardware deadzone circuit, the optical coupling isolation circuit, the peripheral circuit and a bootstrap circuit are combined to form the high-power MOSFET driving circuit used for driving the high-power Mosfets, and the measure of additionally installing the bootstrap circuit is taken to prevent the Mosfet gate-to-source voltage of the upper bridge arm from floating. The turn-on and turn-off speed of the Mosfets is improved, and therefore the turn-on and turn-off losses of the Mosfets are reduced. A blocking and judging circuit is used for blocking drive of hardware, and therefore the Mosfets are protected, the driving capacity of the driving circuit is improved, the work efficiency of the circuit is improved, and therefore cost is lowered.
Owner:UNIV OF SHANGHAI FOR SCI & TECH
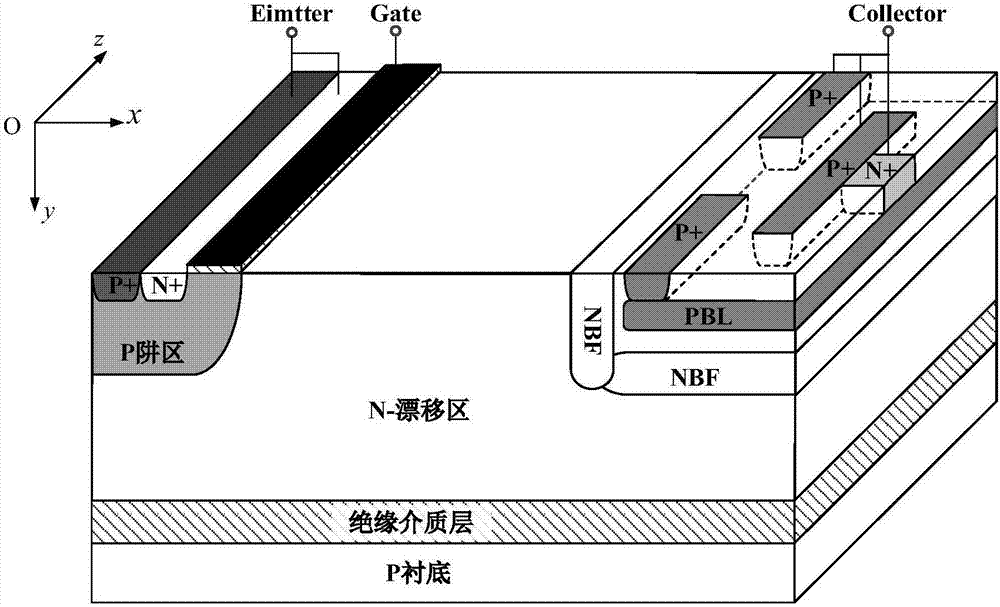
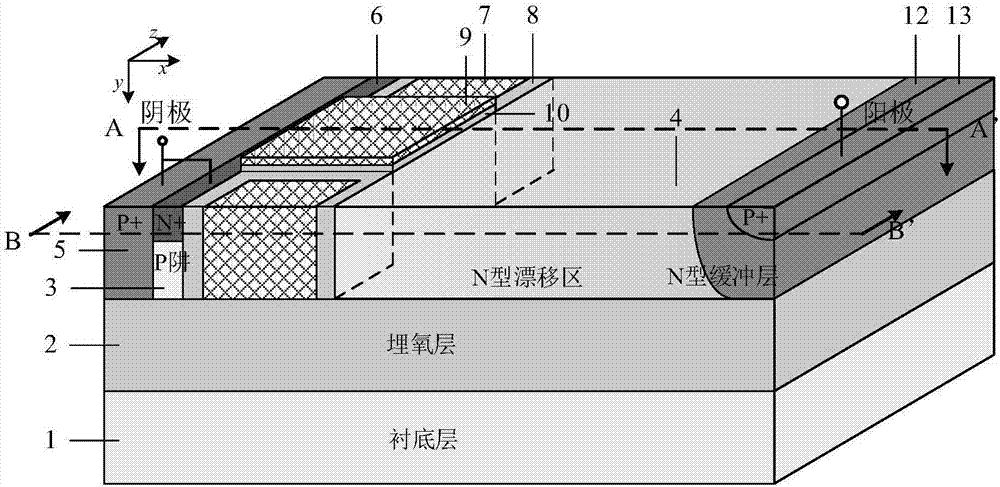
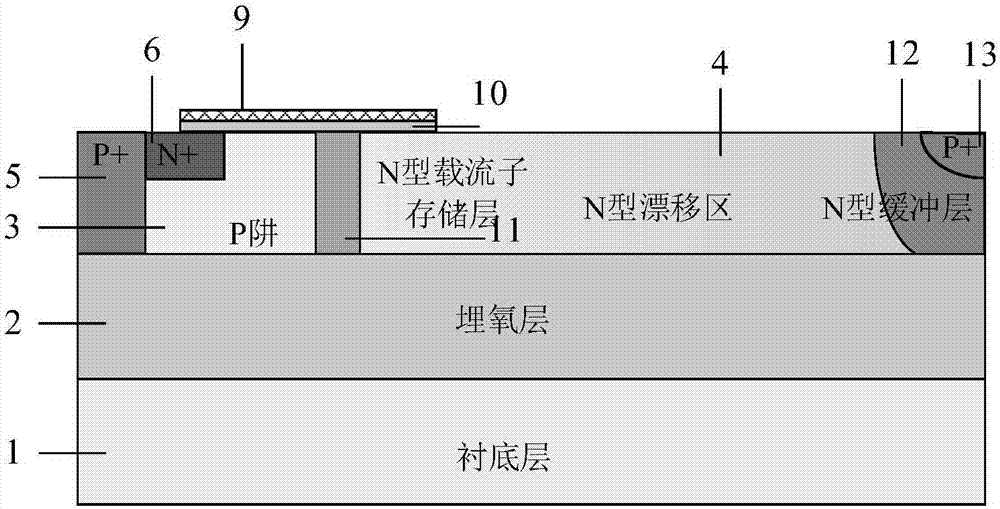
Self-adaptive SOI LIGBT device
ActiveCN111816699AIncreased shutdown speedImprove short circuit resistanceSemiconductor devicesZener diodeVoltage drop
The invention belongs to the technical field of power semiconductors, and particularly relates to a self-adaptive SOI LIGBT device. Compared with a traditional structure, the self-adaptive NMOS structure is introduced into the collector electrode end, and a Zener diode structure is introduced into the emitter electrode end. During forward conduction, the NMOS channel at the collector end is closed, an electron extraction path at the collector end is blocked to eliminate the voltage turn-back effect, and at the moment, the Zener diode is reversely biased but is not broken down, and holes storedin the drift region cannot be extracted, so that the new device can obtain low forward conduction voltage drop. In the turn-off process, along with rise of collector voltage, the collector NMOS channel is adaptively opened to form the electron extraction path, the Zener diode is reversely broken down and conducted to extract an emitter end hole, and the NMOS channel and the Zener diode accelerateturn off of the device to reduce the turn-off loss; and in a short-circuit state, the Zener diode is reversely broken down and conducted, so that the saturation current density can be reduced to improve the short-circuit resistance. Therefore, the device has smaller conduction voltage drop and turn-off loss, and a wider safety working area.
Owner:UNIV OF ELECTRONIC SCI & TECH OF CHINA
SOI LIGBT with controllable collector trough
ActiveCN107342321AImprove hole injection efficiencyEliminate the snapback phenomenonSemiconductor devicesHigh densityVoltage drop
The invention belongs to the technical field of power semiconductors, and specifically relates to an SOI LIGBT with a controllable collector trough. Compared with a conventional structure, the LIGBT mainly introduces a controllable collector trough structure to a collector end and introduces a plurality of trough grid structures to the collector. During the forwarding conduction, the bias voltage of a trough collector relative to the collector is negative, and a side wall of the collector trough forms a high-density P-type reflection layer so as to increase the hole implantation. The segmented trough grid structures serve as the blocking layers of hole extraction. Therefore, the increase of the hole / electron concentration in a drift region facilitates the obtaining of a lower forwarding conduction voltage drop. Meanwhile, because an N+ collector region is located on the upper surface of a P+ collector region and does not make contact with an N-type drift region, a new device does not has a voltage turning-back effect. The beneficial effects of the invention are that the LIGBT, compared with a conventional short-circuit anode-LIGBT structure, is higher in switching-off speed and lower in forwarding conduction voltage drop, and does not have the voltage turning-back effect.
Owner:UNIV OF ELECTRONICS SCI & TECH OF CHINA +1
Synchronous rectification control circuit, isolated power supply conversion circuit and control method
PendingCN110896283APrecise shutdownIncreased shutdown speedEfficient power electronics conversionAc-dc conversionHemt circuitsDriver circuit
The invention discloses a synchronous rectification control circuit, an isolated power supply conversion circuit and a control method, the synchronous rectification control circuit can be coupled witha synchronous rectification transistor and can send a control signal to the synchronous rectification transistor; the synchronous rectification control circuit comprises a comparison circuit, a drivecircuit, a signal adjusting circuit and a conduction voltage drop adjusting circuit. The input end of the comparison circuit is respectively coupled with the synchronous rectification transistor andat least one reference signal, and the output end of the comparison circuit is respectively coupled with the drive circuit and the signal conditioning circuit; the output end of the drive circuit is coupled with the synchronous rectification transistor and used for sending a control signal to the synchronous rectification transistor according to the signal output by the comparison circuit; the output end of the signal adjusting circuit is coupled with the comparison circuit and used for adjusting a set reference signal in the at least one reference signal according to the signal output by thecomparison circuit. According to the invention, accurate turn-off of the synchronous rectification transistor can be realized, the turn-off speed can be improved, and the reliability of the circuit isimproved.
Owner:杭州必易微电子有限公司
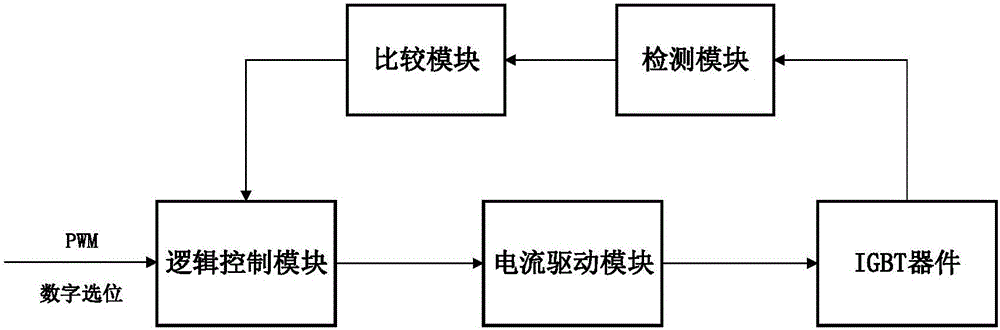
IGBT device drive circuit and method capable of reducing turn-off loss
InactiveCN106505839AReduced shutdown power lossGuaranteed to workEfficient power electronics conversionPower conversion systemsVoltage overshootFeedback circuits
The invention discloses an IGBT device drive circuit and method capable of reducing the turn-off loss. The circuit comprises a detection module, a current drive module, a comparison module and a logic control module, wherein an input end of the logic control module is used for connecting external pulse width modulation signal and digital bit selection signal; a feedback end of the logic control module is connected with an output end of the comparison module; the input end of the current drive module is connected with the output end of the logic control module; the output end of the current drive module is used for being connected to a control end of an IGBT device; the input end of the detection module is used for being connected with the output end of the IGBT device; and the output end of the detection module is connected to the input end of the comparison module. According to the IGBT device drive circuit and method, the turn-off power loss of the IGBT device can be reduced; the device is prevented from being burnt by current and voltage overshoots caused by turn-off; meanwhile, output voltage and current of the drive circuit can be accurately controlled; the turn-off speed is increased while the turn-off overshoot voltage of the IGBT is not increased; the signal delay is relatively small; and the condition that a feedback circuit of the drive module normally works within short turn-off time of the IGBT device can be ensured.
Owner:HUAZHONG UNIV OF SCI & TECH
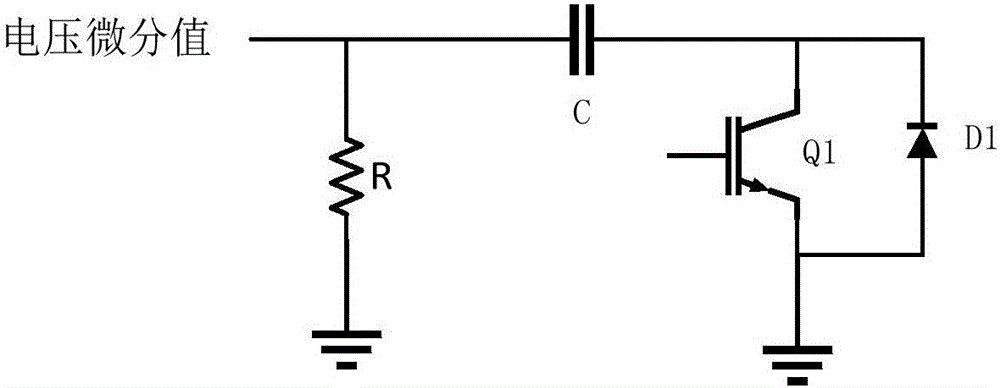
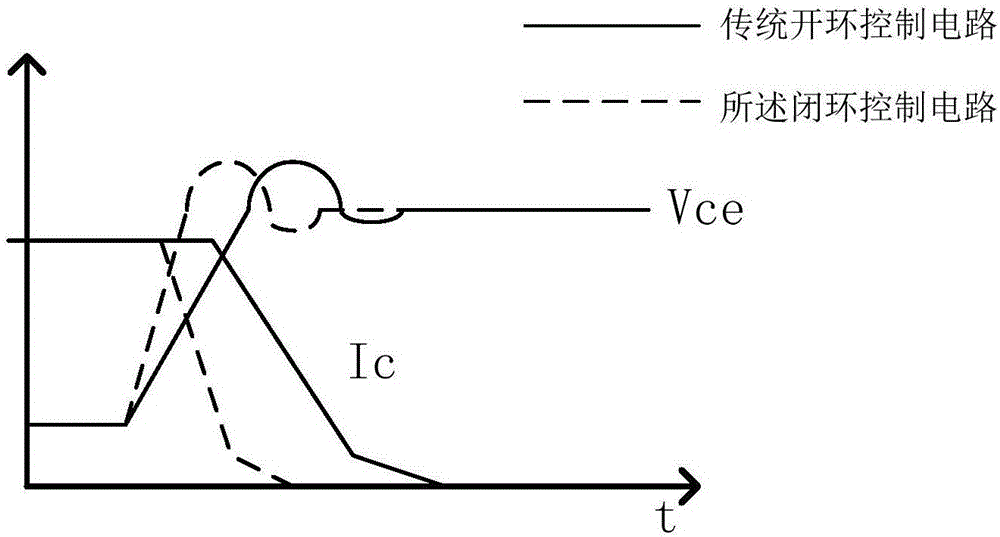
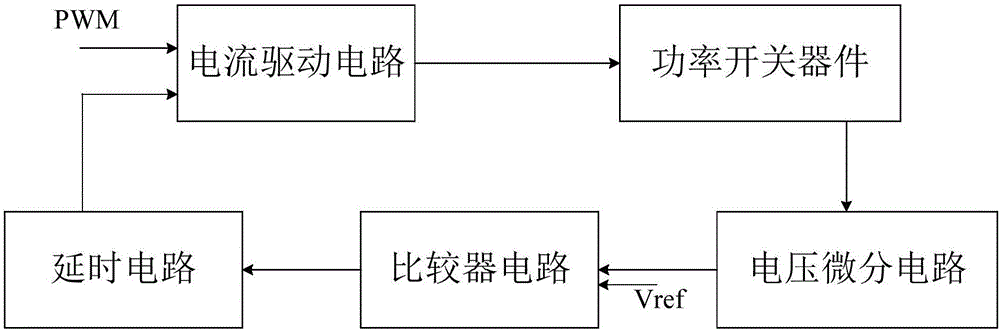
Closed-loop control circuit for power switching device and method
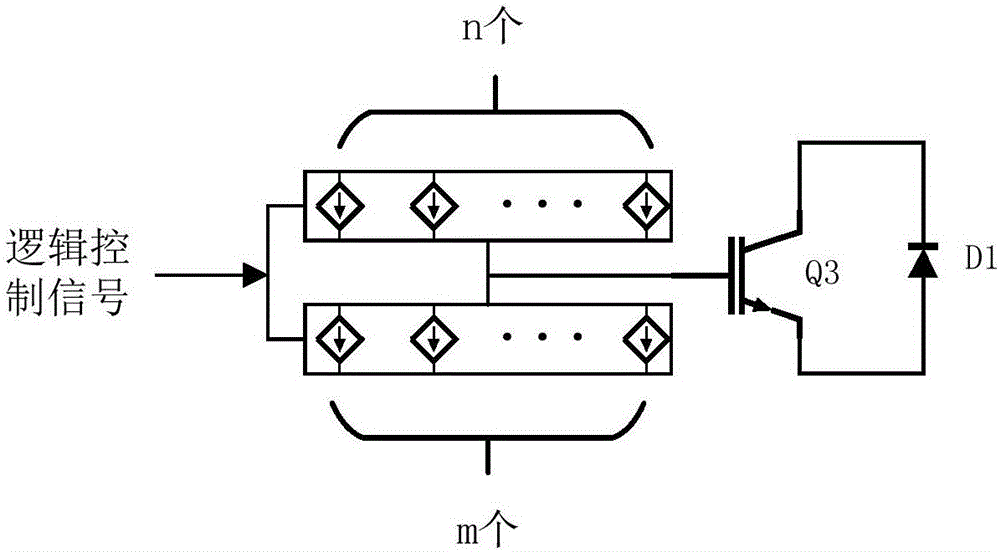
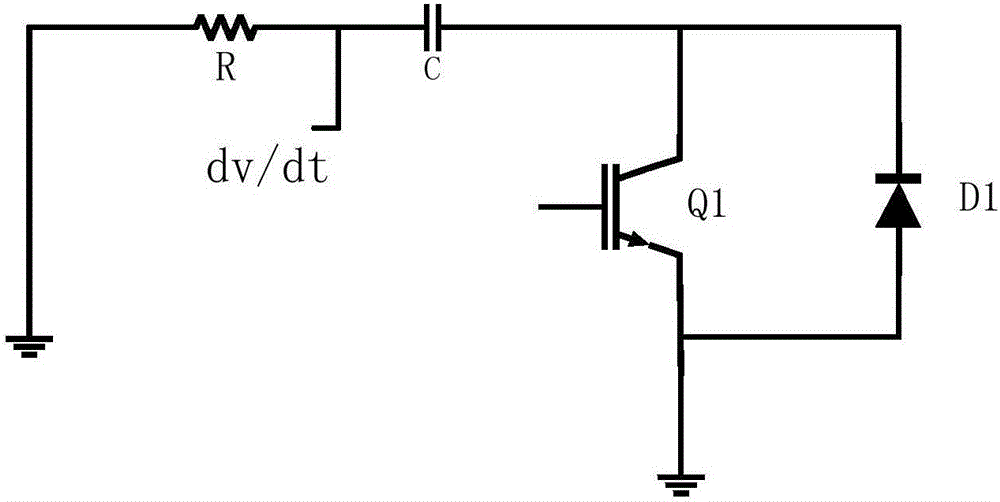
InactiveCN106571794AReduce gate drive currentIncreased shutdown speedElectronic switchingComparators circuitsDifferential circuits
The invention discloses a closed-loop control circuit for a power switching device and a method. The closed-loop control circuit comprises a voltage differential circuit, a comparator circuit, a delay circuit and a current driving circuit, wherein the first input end of the comparator circuit is connected with the output end of the voltage differential circuit; the second input end of the comparator circuit is used for being connected with reference voltage; the input end of the delay circuit is connected with the output end of the comparator circuit; the first input end of the current driving circuit is connected with the output end of the delay circuit; the second input end of the current driving circuit receives PWM signals; and the output end of the current driving circuit is connected with the control end of the power switching device. A voltage change rate dv / dt signal is detected through the differential circuit, when the dv / dt signal is larger than the reference voltage, the current driving circuit is controlled, instantaneous current is provided, gate driving current is reduced, and the voltage overshoot is maintained to be unchanged basically. The driving circuit can be accurately controlled to output voltage and current, the turn-off speed is quickened, and the turn-off loss is reduced.
Owner:HUAZHONG UNIV OF SCI & TECH
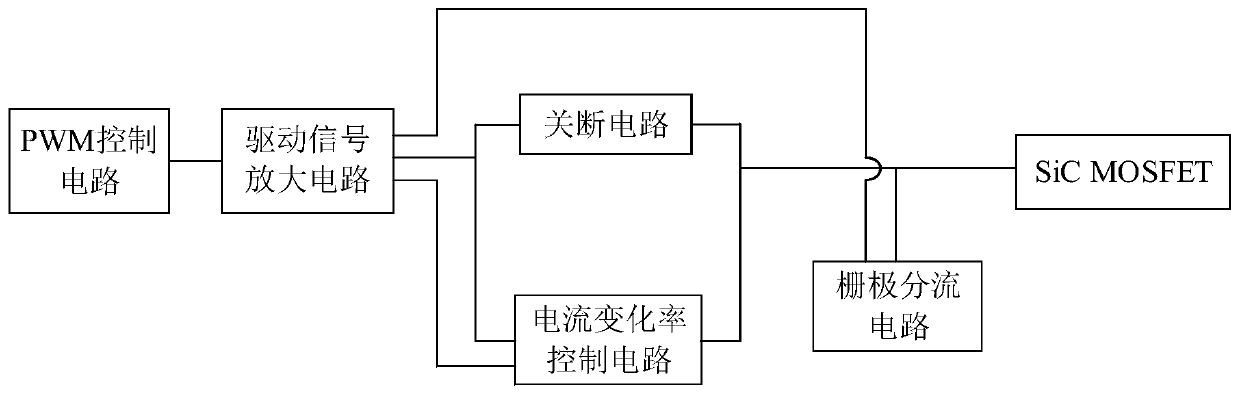
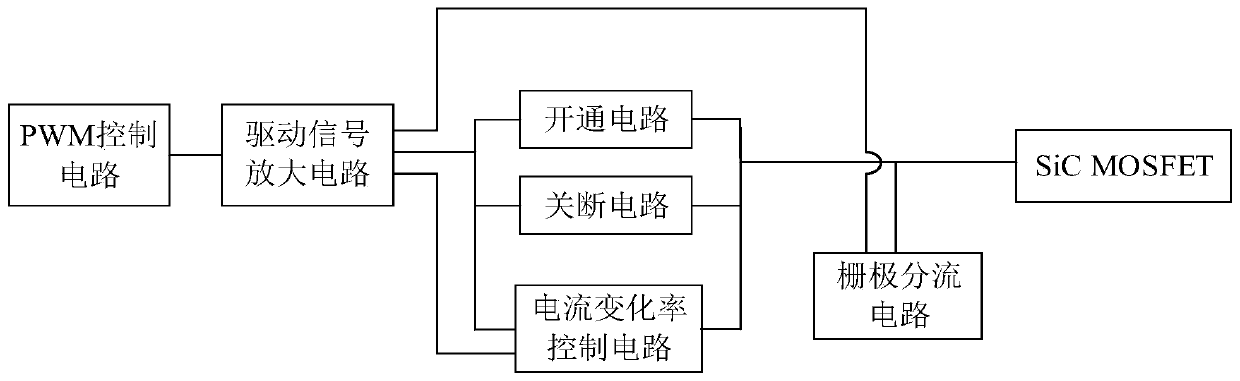
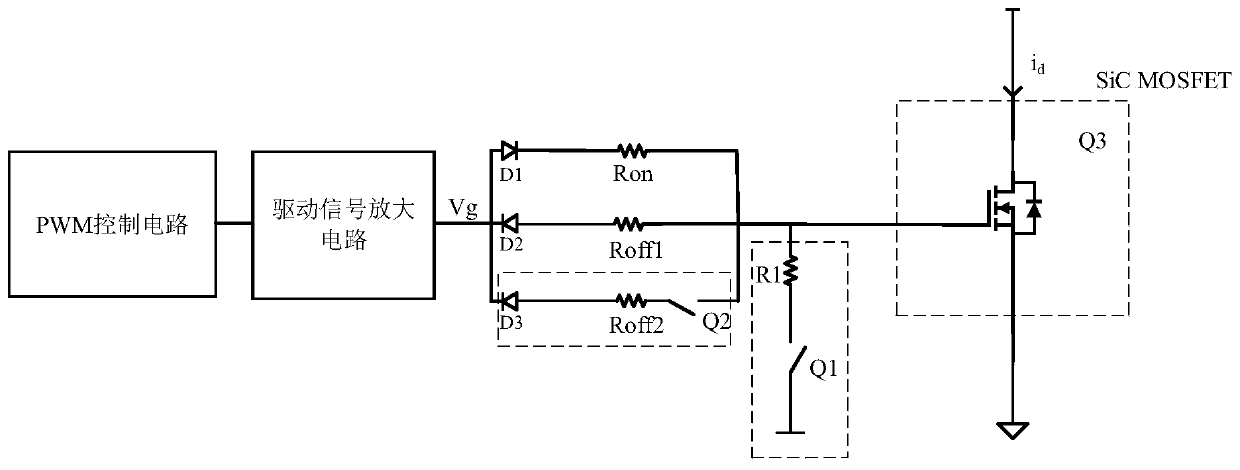
Drive circuit of silicon carbide semiconductor field effect transistor
InactiveCN110112893AIncreased shutdown speedReduce the rate of change of leakage currentEfficient power electronics conversionPower conversion systemsMOSFETLow voltage
The invention discloses a drive circuit of a silicon carbide semiconductor field effect transistor. The drive circuit comprises a PWM control circuit, a drive signal amplification circuit, a turn-offcircuit, a gate shunt circuit and a current change rate control circuit, wherein the gate shunt circuit is switched on when the turn-off circuit works to perform shunt of the gate current of a SiC MOSFET (Metal-Oxide-Semiconductor Field-Effect Transistor) and accelerate the switch-off of the SiC MOSFET; the SiC MOSFET is switched off when the drain-source voltage of the SiC MOSFET is increased toa preset value; the current change rate control circuit is switched off when the drain-source voltage of the SiC MOSFET is increased to the preset value to reduce the leakage current change rate. Thegate shunt circuit is arranged to perform shunt of the gate output current in the SiC MOSFET switch-off process and speed up the decreasing speed of the gate-source voltage so as to improve the switch-off speed of the SiC MOSFET; and besides, in the switch-off process of the SiC MOSFET, the switch-off of the current change rate control circuit reduces the leakage current change rate so as to reduce the voltage peak when the SiC MOSFET is switched off, the two circuits cooperatively act to achieve the voltage reduction speed and the low-voltage peak of the high gate-source voltage and ensure the safety operation of the SiC MOSFET.
Owner:HUAZHONG UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Transverse insulated gate bipolar transistor
InactiveCN107068744AThere is no negative resistance phenomenonImprove breakdown voltageTransistorSolid-state devicesPower flowCharge carrier
The invention belongs to the semiconductor power device technology field, and particularly relates to a transverse insulated gate bipolar transistor. In the invention, a poly-diode is formed on a surface of a drift region of a member and a PMOS and a Zener diode are formed in proximity to a collector; in a blocking state, under an action of charges and a field plate which are supplied through depleting the drift area in a reverse bias state of a polycrystalline diode on the surface of the member, voltage resistance higher than that that of a traditional structure is obtained while a doping concentration of the drift region of the member; in a process of switching off the member, a voltage change of a collector and a self-bias effect formed by a surface polycrystalline diode and a zener diode make PMOS near the collector automatically start and conduct and accelerate carrier extraction in an LIGBT so as to improve switching off speed of the member; in a conductive state, the PMOS around the collector is in a switching off state and an access of electronic current is cut off. As a result, the transverse insulated gate bipolar transistor has higher breakthrough voltage, and, in the process of switching off, has faster switching off speed and switching off loss.
Owner:UNIV OF ELECTRONICS SCI & TECH OF CHINA
Under-voltage protection circuit
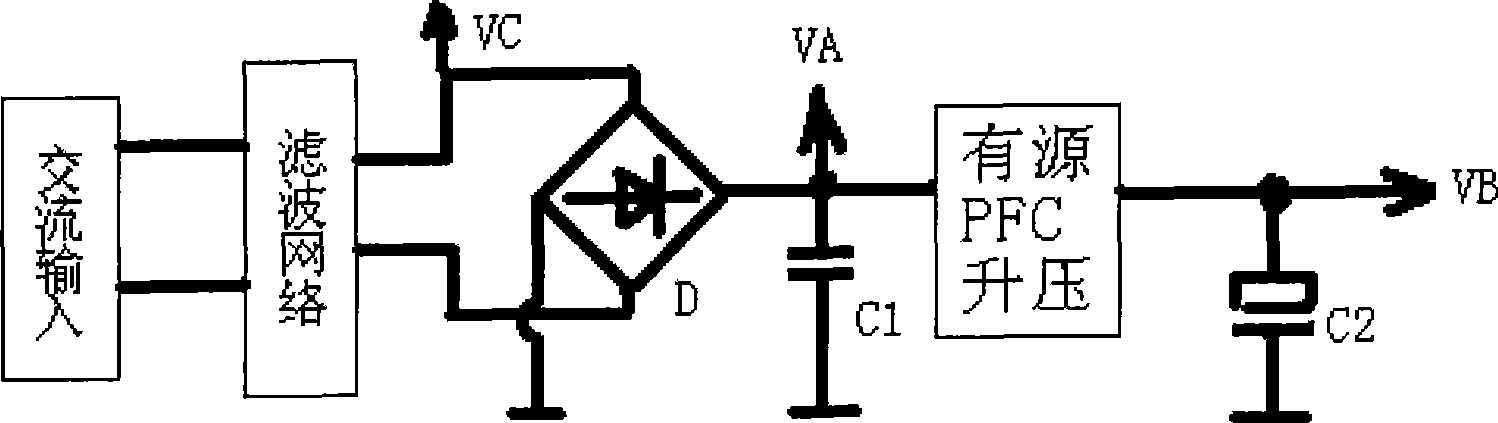
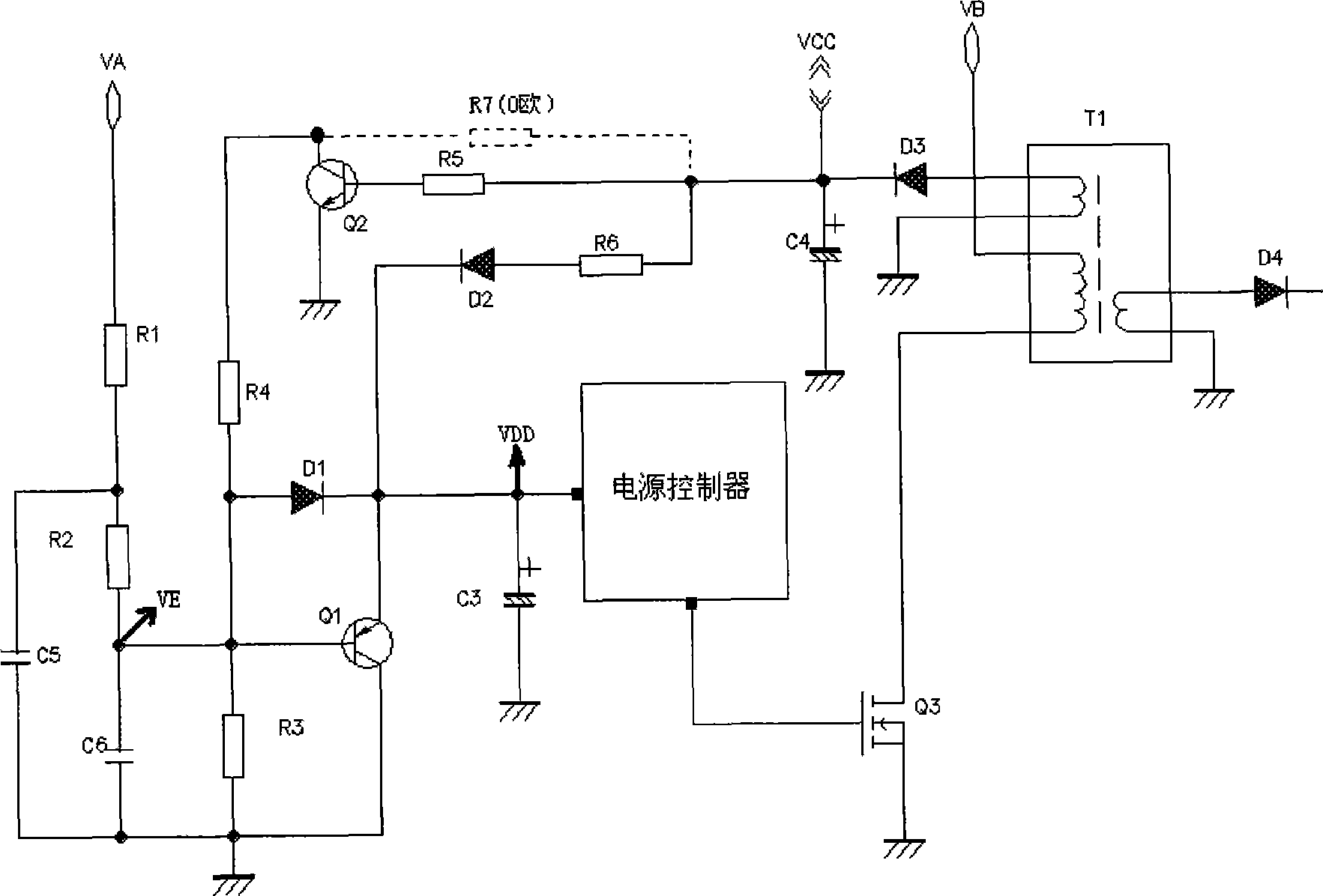
ActiveCN101471556ALow costThe circuit is simple and reliableArrangements responsive to undervoltageActive power factor correctionHysteresis
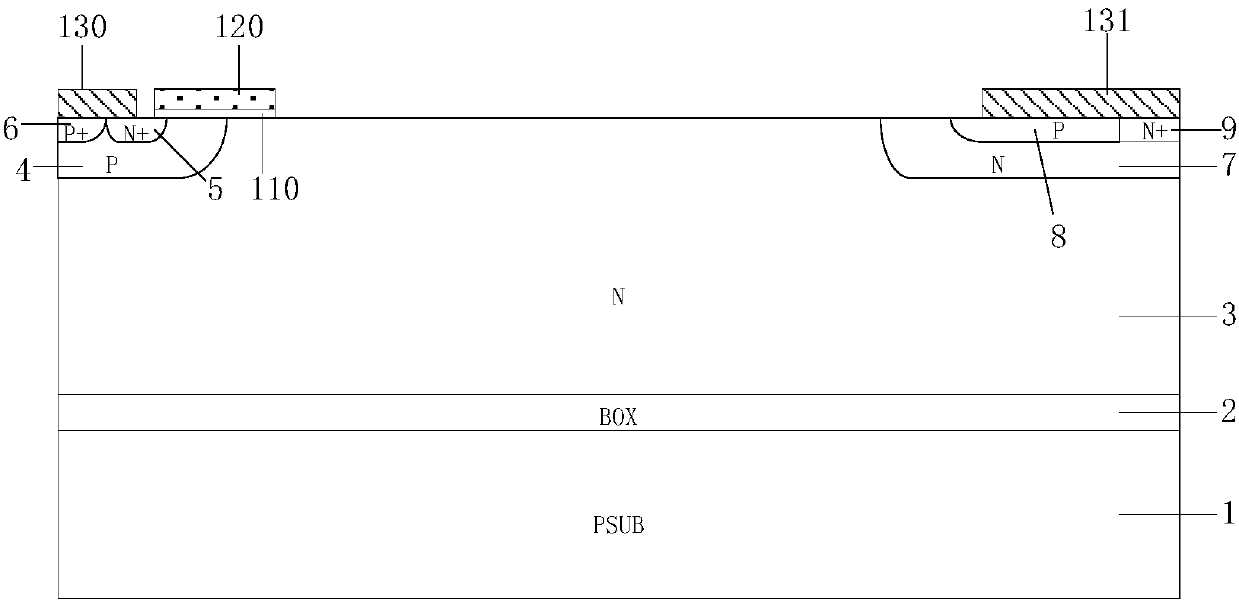
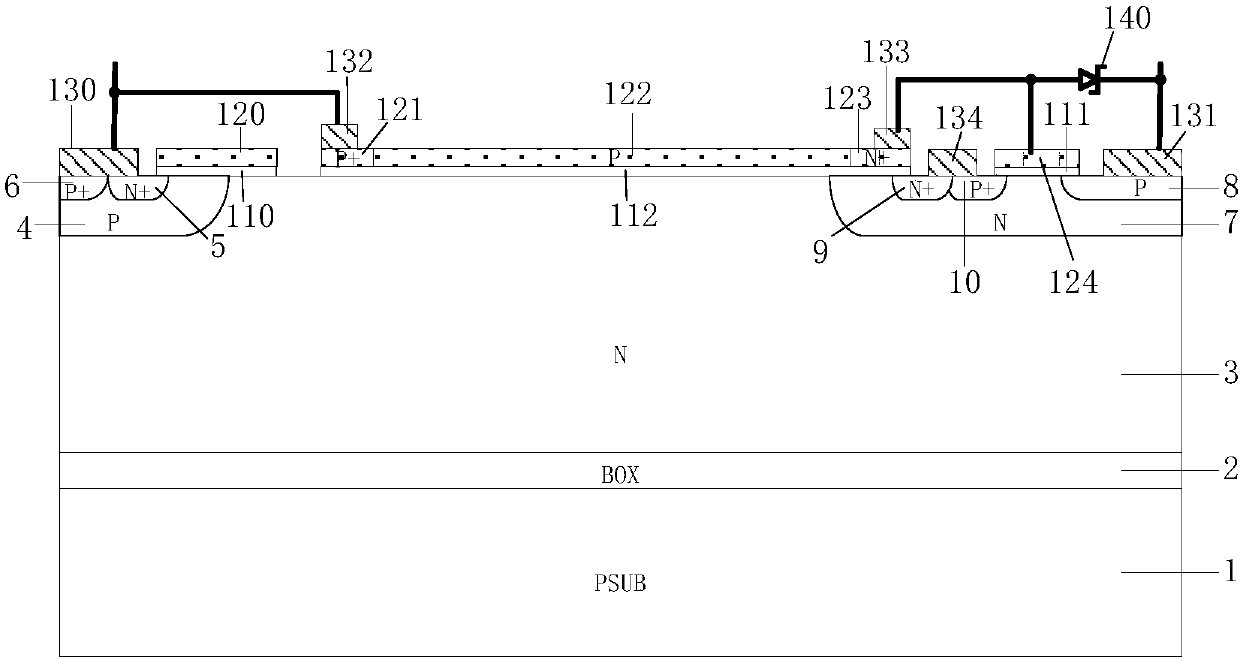
The invention provides an under-voltage protection circuit used for protecting a power supply of an electric appliance when an external input voltage is too low. The electric appliance comprises a filter network, a bridge rectifier unit, an active power factor correction boost module, and a power supply controller. The under-voltage protection circuit is characterized in that the circuit is connected between an output terminal of the bridge rectifier unit and an input terminal of the power supply controller; and when the output voltage of the under-voltage protection circuit is lower than the turn-off threshold voltage of the power supply controller, the power supply controller stops working, and the power supply of the electric appliance is cut off. The technical proposal has lower cost and simple and reliable circuit, solves the problem that the hysteresis amount of the power supply controller in the prior art can not meet the demands in practical application, and improves the turn-off speed of the power supply.
Owner:SHENZHEN TCL NEW-TECH CO LTD
Synchronous rectification control circuit, method and flyback switch circuit
ActiveUS10505442B2Improve system reliabilityIncreased shutdown speedMultiple input and output pulse circuitsEfficient power electronics conversionVoltage regulationEngineering
The present invention provides a synchronous rectification control circuit, a method and a flyback switching circuit. A drive circuit outputs a drive signal to control the turn-on and turn-off of a synchronous rectification transistor; a threshold comparison circuit controls the drive circuit to output a pull-up drive signal to turn on the synchronous rectification transistor when a drain-source voltage is lower than a preset low threshold voltage and controls the drive circuit to output a pull-down drive signal to turn off the synchronous rectification transistor when the drain-source voltage is higher than or equal to a preset high threshold voltage; a voltage regulation control circuit controls the drive circuit to output a drive signal for pulling up a voltage of the drive signal to a preset pull-up voltage high value when the drain-source voltage is lower than a preset voltage regulation reference value.
Owner:JOULWATT TECH INC LTD
Current enhanced type lateral insulated gate bipolar transistor
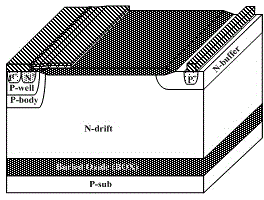
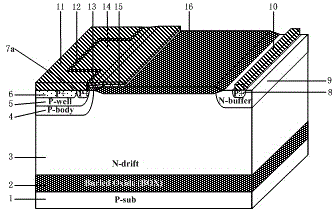
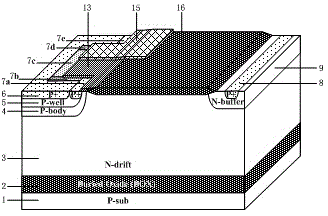
ActiveCN104916674AStrong on-current capabilityImprove the conduction current capabilitySemiconductor devicesHigh current densityParasitic bipolar transistor
A current enhanced type lateral insulated gate bipolar transistor improves current density and the turn-off speed on the premise that a latching ability is maintained to be unchanged. The semiconductor is provided with buried oxide disposed on a P-type substrate and an N-drift region disposed on the buried oxide, a P-body region and an N-buffer region are disposed on the N-drift region, a P-type collecting electrode region is disposed in the N-buffer region, an anode metal is connected to the P-type collecting electrode region, a field oxide layer is disposed on the N-drift region, a P-well region is disposed in the P-body region, a P-type emitting electrode region and an emitting electrode region are disposed in the P-well region, the inner-side boundaries of the four regions, i.e., the P-body region, the P-well region, the P-type emitting electrode region and the emitting electrode region are synchronously recessed inwardly to form a square groove, the emitting electrode region surrounding the groove is successively defined as a first P-type emitting electrode region, second, third and fourth N-type emitting electrode regions and a fifth P-type emitting electrode region, the N-drift region protrudes outwardly and fills the square groove, a surface of the P-body region is provided with a gate oxide layer, a surface of the gate oxide layer is provided with a polysilicon layer, and a gate metal is connected to the polysilicon layer.
Owner:SOUTHEAST UNIV +1
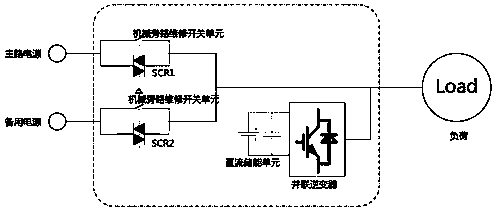
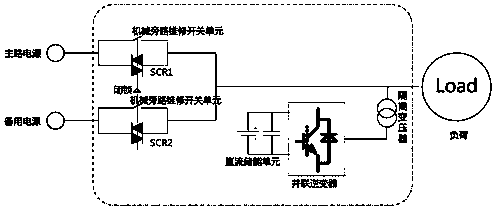
Apparatus and method for low-cost control of voltage sag and short-term interruption of power grid
ActiveCN109119990ARapid isolation of voltage faultsIncreased shutdown speedAc network load balancingChannel powerEconomic benefits
The invention discloses an apparatus and method for the low-cost control of voltage sag and short-term interruption of a power grid. The method employs a double-channel power supply for solving a problem of the quick mutual switching of load power supply reliability and employs the advantages of the conventional DVR, and combines the two sides, so the apparatus can solve a problem of voltage sag and energy quality which commonly exist in the power grid, effectively guarantees the power utilization reliability of a sensitive load, solves problems that the energy storage element in a conventional voltage sag compensation device is expensive and difficult to maintain, can reduce the energy consumption, can save the installation space, can reduce the operation cost of the apparatus, and is very good in economic benefits.
Owner:NANJING HEXI ELECTRIC CO LTD
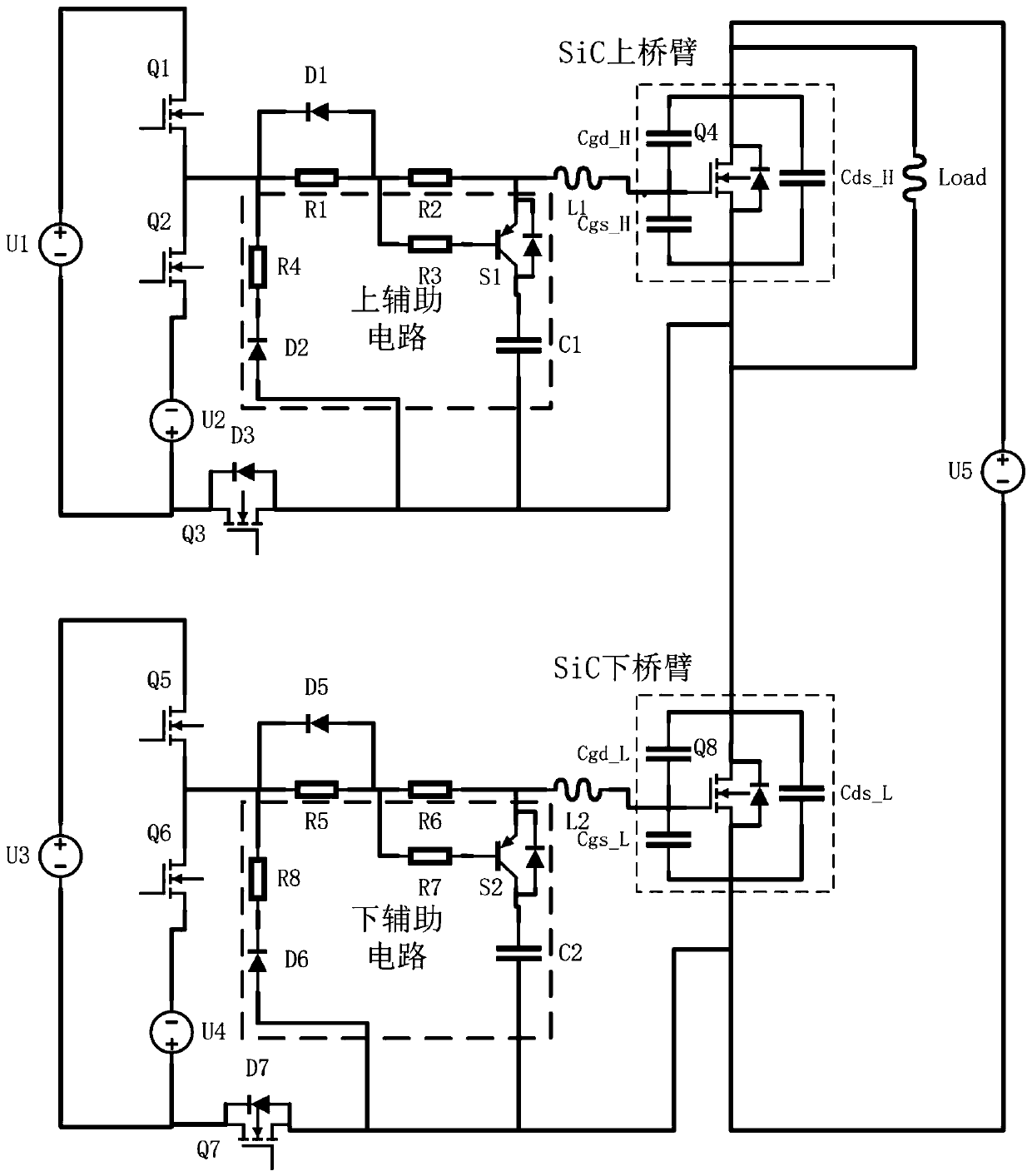
SiC power tube driving circuit with active crosstalk suppression function and control method
ActiveCN111464005ALower impedanceReduced risk of negative pressure breakdownEfficient power electronics conversionPower conversion systemsDriver circuitHemt circuits
The invention discloses a SiC power tube driving circuit with an active crosstalk suppression function. The driving circuit comprises a basic driving circuit and an auxiliary circuit, wherein the basic driving circuit comprises an amplifying circuit, R1, R2 and D1, one end of the R1 is connected with the amplifying circuit, the other end of R1 is connected with one end of the R2, the other end ofthe R2 is connected with a grid electrode of a power tube, a positive electrode of the D1 is connected with the other end of the R1, a negative electrode of the D1 is connected with one end of the R1,the auxiliary circuit comprises R3, R4, C1, S1, D2 and Q3, an emitter of the S1 is connected with the other end of the R2, one end of the R3 is connected with the other end of the R1, the other end of the R3 is connected with a base of the S1, two ends of the C1 are respectively connected with a collector of the S1 and a source of the power tube, an anode of the D2 is connected with a source of the Q3, the cathode is connected with one end of the R4, the other end of the R4 is connected with one end of the R1, a drain of the Q3 is connected with the amplifying circuit, and the source is connected with a source of the power tube. The driving circuit has advantages of simple structure, simple overall structure, low cost, easy control, crosstalk suppression and the like.
Owner:HUNAN UNIV
Lateral insulated gate bipolar transistor
InactiveCN107170816AReduce conduction voltage dropReduced turn-off lossTransistorSolid-state devicesEtchingZener diode
The invention belongs to the technical field of a semiconductor power device, and specifically relates to a lateral insulated gate bipolar transistor. On the basis of a conventional lateral insulated gate bipolar transistor structure, trench etching is performed in the surface of a device in a channel length direction to form a three-dimensional structure and to form the lateral insulated gate bipolar transistor with the three-dimensional structure; and meanwhile, a polycrystal diode is formed on the surface of a three-dimensional drift region of the device, and a three-dimensional PMOS and a zener diode are integrated close to a collector. The lateral insulated gate bipolar transistor has a lower forward conduction voltage drop compared with the conventional LIGBT, without causing a negative impedance phenomenon in the conduction process; and meanwhile, the lateral insulated gate bipolar transistor has higher device breakdown voltage, higher switching-off speed and lower switching-off loss.
Owner:UNIV OF ELECTRONICS SCI & TECH OF CHINA
Insulated gate bipolar transistor (IGBT) driving push-pull circuit
InactiveCN102739211AIncrease charging currentIncrease discharge currentElectronic switchingCharge currentPower flow
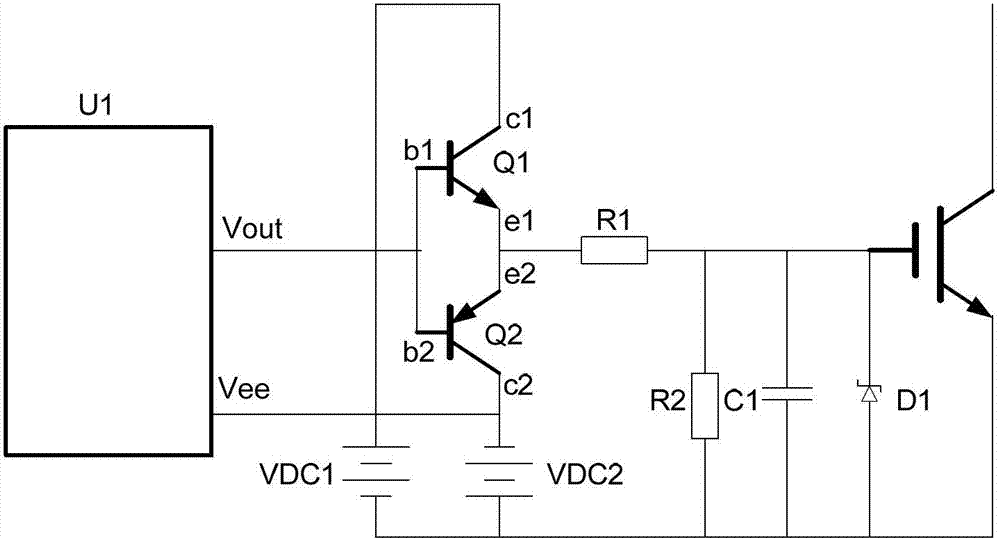
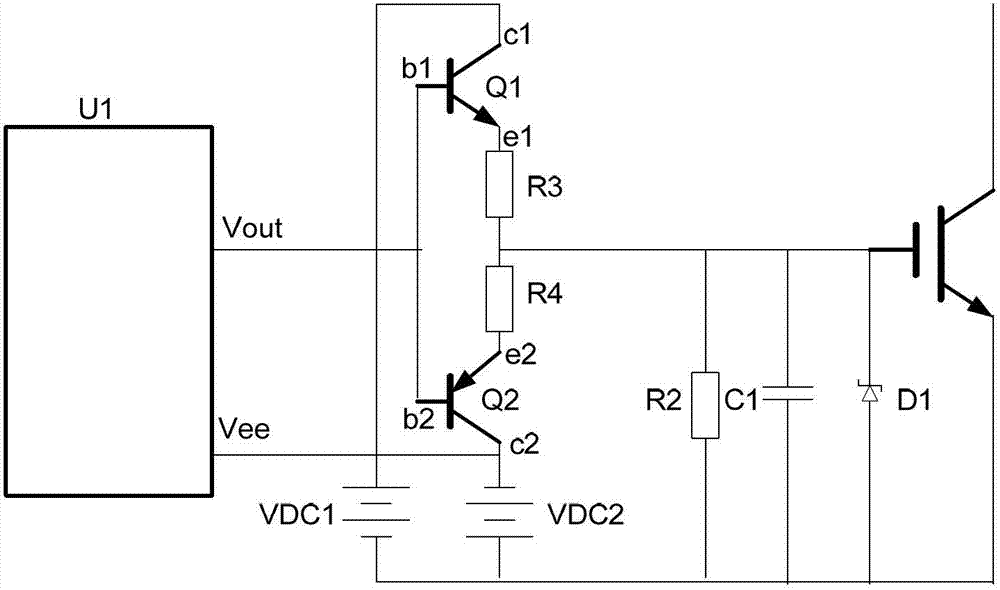
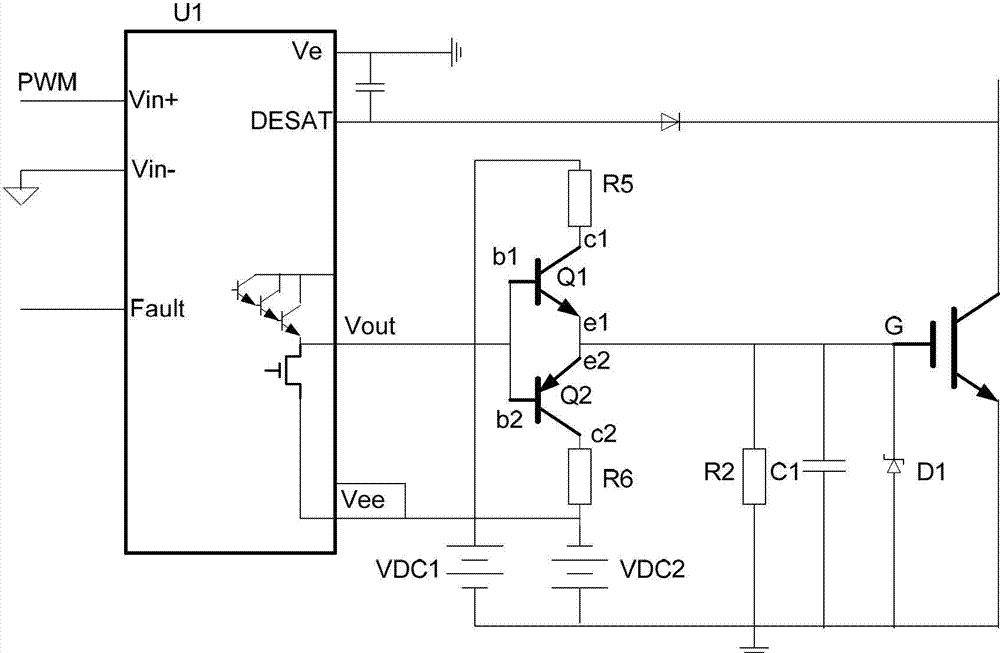
The invention discloses an insulated gate bipolar transistor (IGBT) driving push-pull circuit, which mainly comprises an NPN triode (Q1), a PNP triode (Q2), a charging resistor (R5) and a discharging resistor (R6), wherein one end of the charging resistor (R5) is connected to an anode of an input power supply (VDC1), and the other end of the charging resistor (R5) is connected to a collector (c1) of the NPN triode (Q1); an emitter (e1) of the NPN triode (Q1) and an emitter (e2) of the PNP triode (Q2) are connected to form a point and connected with a gate (G) of an IGBT; the emitter (e2) of the PNP triode (Q2) is connected with one end of the discharging resistor (R6); and the other end of the discharging resistor (R6) is connected with the ground of a power supply (VDC2). By adoption of a push-pull circuit structure, in the turn-on moment of the IGBT, the NPN triode works in a saturation area, charging current is improved, and the loss of the NPN triode is reduced; and in the turn-off moment of the IGBT, the PNP triode works in the saturation area, discharging current is improved, and the loss of the PNP triode is reduced.
Owner:INST OF ELECTRICAL ENG CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
High-speed and low-loss multi-trench gate high-voltage power device
ActiveCN110504308AImprove injection efficiencyImproves latch-up resistanceSemiconductor devicesChannel densityCharge carrier
The invention belongs to the technical field of power semiconductors and particularly relates to a high-speed and low-loss multi-trench gate high-voltage power device. Compared with a traditional structure, the structure of the high-speed and low-loss multi-trench gate high-voltage power device has the advantage that a plurality of trench gate structures are introduced into an emitter terminal anda collector terminal. Channels in side walls of trench gates at the collector terminal are turned off and a connection path of an N+ collector region and an N-type buffer layer is blocked during forward conduction, so that the voltage foldback effect can be eliminated. A trench gate structure at the emitter terminal can increase the channel density to reduce the resistance of a channel region, and a barrier trench gate and a carrier storage layer can effectively improve the carrier concentration of a drift region, so that the novel device can obtain lower forward conduction voltage drop. In the turn-off process, the channels in the side walls of the trench gates at the collector terminal are opened along with voltage rise of a collector, so that the N+ collector region communicates with the N-type buffer layer to form a rapid electron extraction path and turn-off of the device is accelerated to reduce the turn-off loss. Therefore, the high-speed and low-loss multi-trench gate high-voltage power device has lower forward conduction voltage drop and smaller turn-off loss and does not have the voltage foldback effect.
Owner:UNIV OF ELECTRONICS SCI & TECH OF CHINA +1
Thin SOI LIGBT device with carrier storage layer
ActiveCN107482058AReduce forward voltage dropReduced turn-off lossSemiconductor devicesHigh densityCharge carrier
The invention belongs to the technical field of power semiconductors, and specifically relates to a thin SOI LIGBT device with a carrier storage layer. The device is mainly characterized in that the device employs two trench gates and one plane gate structure, and the carrier storage layer is introduced between the two trench gates and below a plane gate. During forwarding conduction, the side walls of the trench gates block a hole loop, thereby achieving an effect of injection enhancement, and reducing the forwarding conduction voltage drop of a device. Meanwhile, the N-type carrier storage layer plays a role in hole blocking, promotes the electrons to be injected into a drift region, improves the electric conduction modulation effect, and further reduces the forwarding conduction voltage drop. During forwarding blocking, the trench gates play a role in using up the carrier storage layer, and enable the device to maintain a high withstand voltage under the high density of the storage layer. The beneficial effects of the invention are that the device, compared with a conventional LIGBT structure, is lower in forwarding conduction voltage drop, is higher in switching-off speed, and is lower in switching-off loss.
Owner:UNIV OF ELECTRONICS SCI & TECH OF CHINA +1
Power device soft switching-off circuit
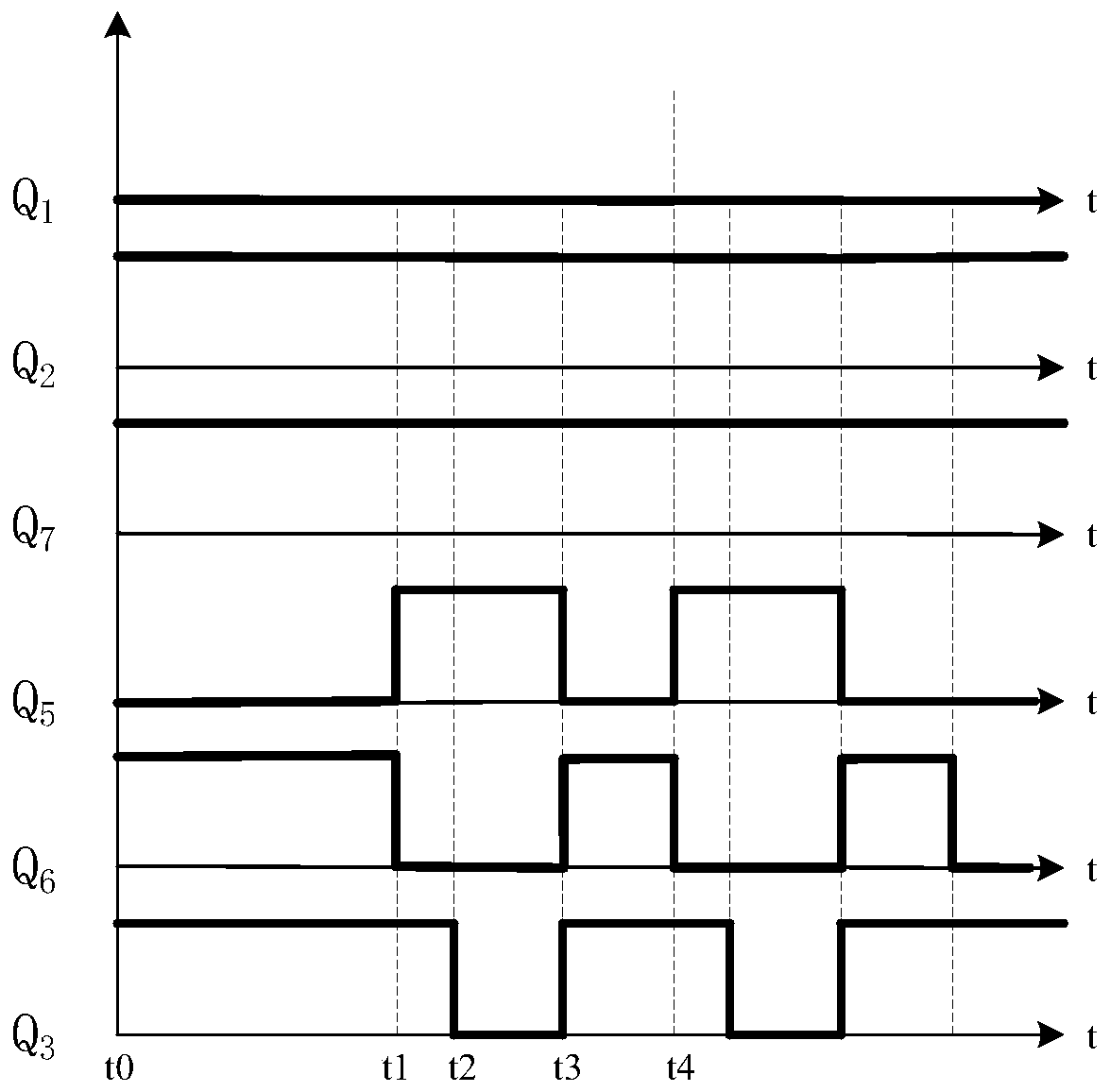
The invention discloses a power device soft switching-off circuit comprising a load electronic component Load, an input voltage and a lead inductor arranged in the same series circuit of a power device. The power device is connected to power device withstand voltage, driving voltage and the gate capacitor of the power device. A driving circuit is disposed on a circuit where the power device is connected with the driving voltage in series. The power device soft switching-off circuit processes a switching-off process in segments. The switching-off speed is increased at the phase t1-t2 and the phase t2-t3, and is slowed down at the phase t3-t4. The switching-off speed is increased at the phase t2-t3 in order to reduce the loss of the switching-off phase, and is slowed down at the phase t3-t4in order to reduce the induced voltage caused by switching-off. The total switching-off time and total switching-off loss are balanced in order to reduce the voltage applied to the power device and reduces the losses and heat generation of the power device.
Owner:河南嘉晨智能控制股份有限公司
Gate voltage bootstrap sampling switch circuit adopting mirror image structure
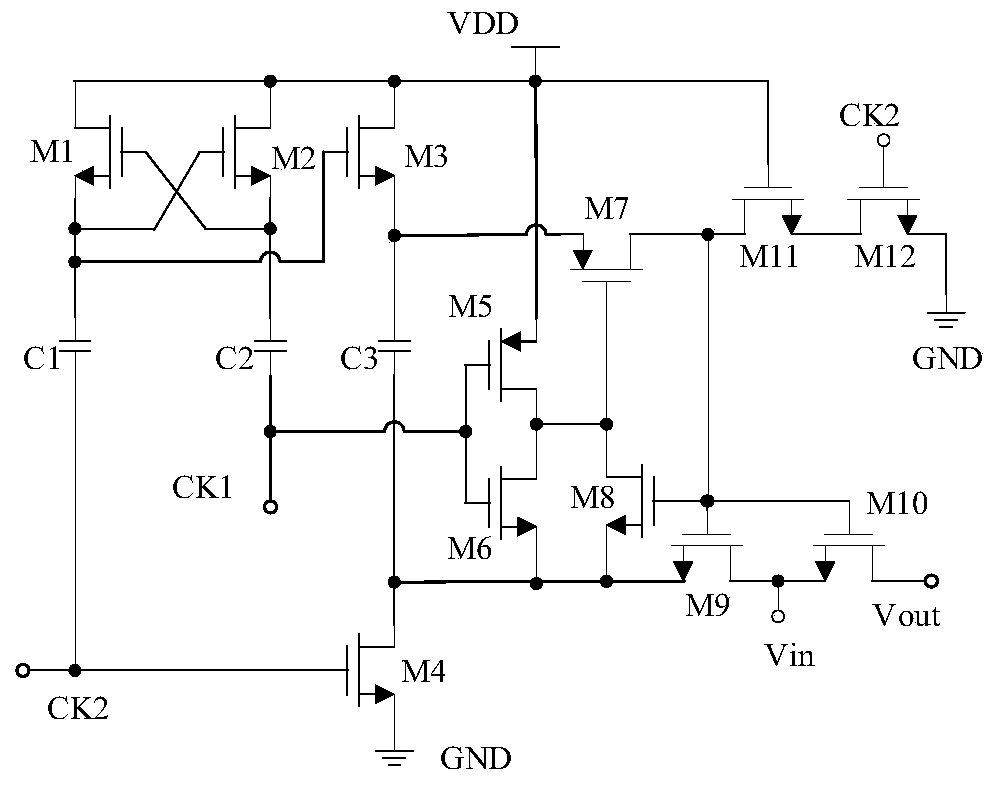
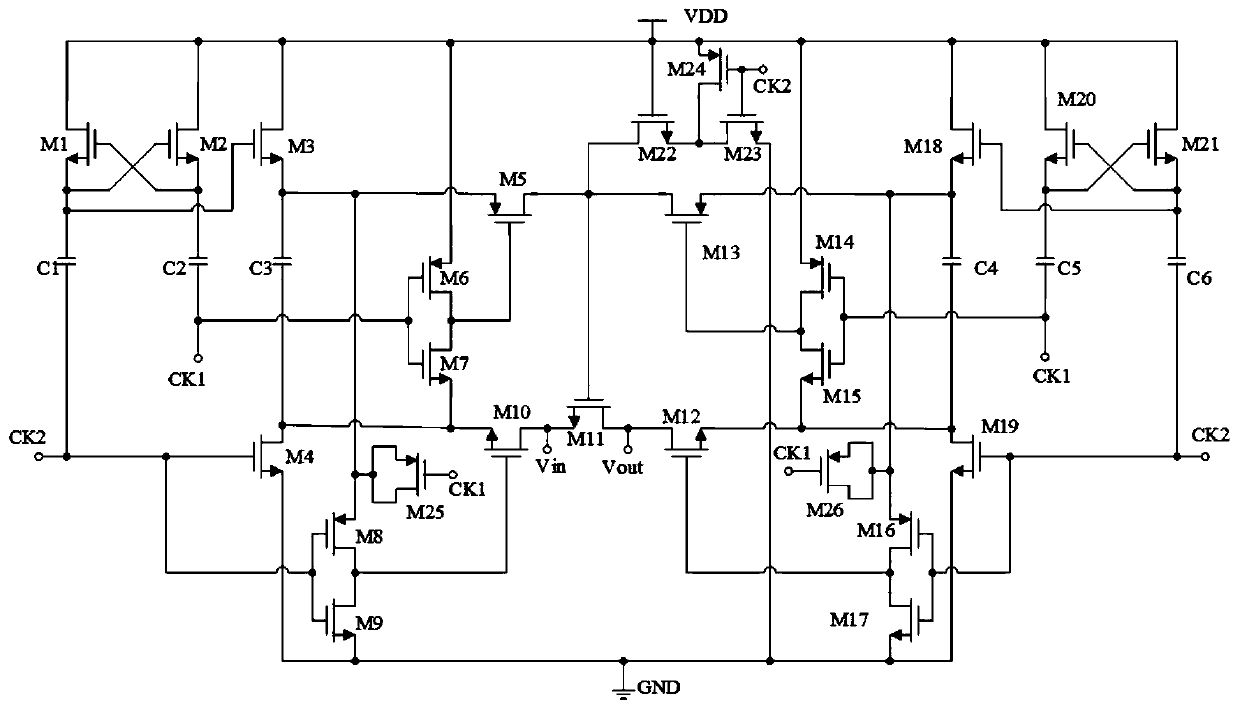
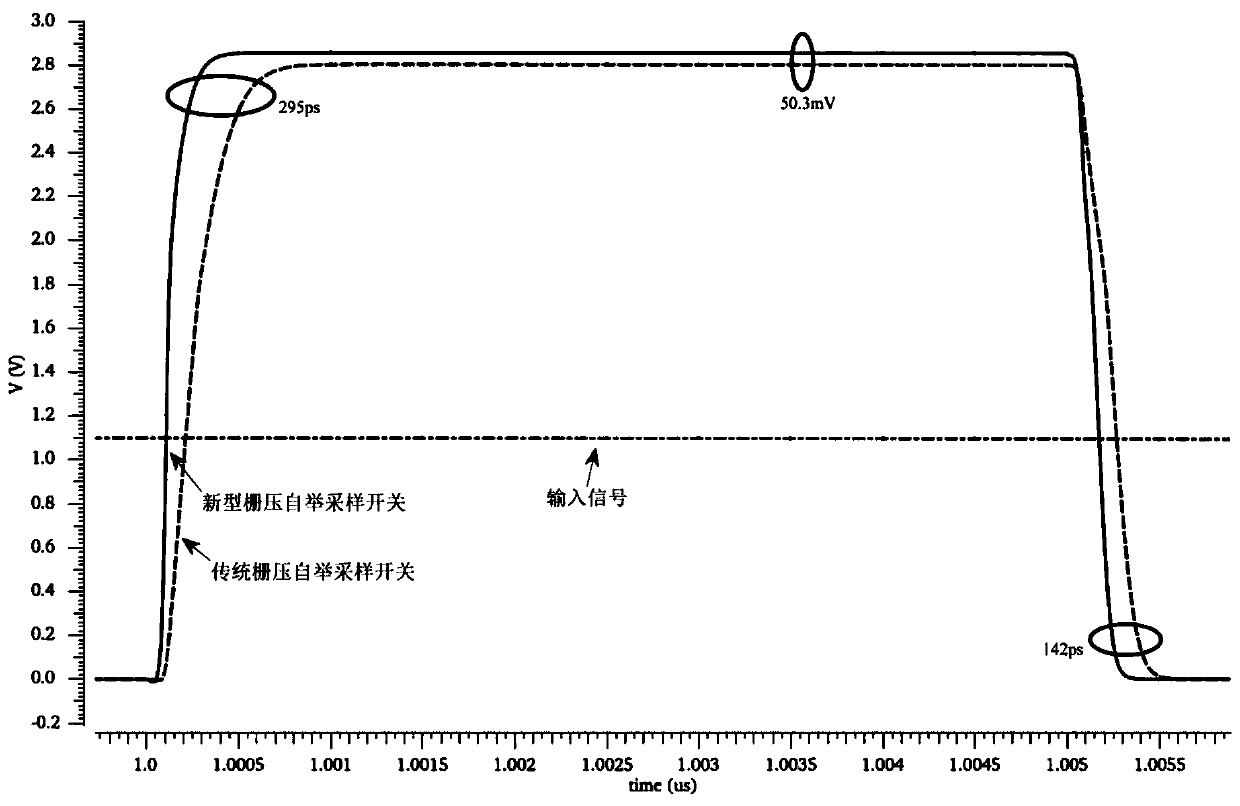
ActiveCN110635791AReduce the impact of sharingReduce parasitic capacitanceTransistorElectronic switchingCharge injectionParasitic capacitance
According to the gate voltage bootstrap sampling switch circuit adopting the mirror image structure, the bootstrap capacitance is increased to two times of that of a traditional circuit by adopting the mirror image structure, and the linearity of a sampling switch is improved; channel charge injection is inhibited by adopting a technology of absorbing channel charges generated by related MOS tubesby a clock-controlled virtual MOS tube; and a structure that the output end of a clock-controlled inverter drives an NMOS tube M10 and an NMOS tube M12 is adopted. The parasitic capacitance of the grid node of the sampling switch tube M11 is reduced; circuit charge sharing is suppressed, and, at the sampling start phase, the NMOS tube M10 and the NMOS tube M12 are respectively conducted with thePMOS tube MOS tube M5 and the PMOS tube M13 at the same time, and the conducted speed of the sampling switch is speeded up; and at the moment from sampling to holding conversion, a circuit composed ofthe PMOS tube M8 and the NMOS tube M9 and a circuit composed of the PMOS tube M16 and the NMOS tube M17 are kept on for a period of time at the same time, and the turn-off speed of the sampling switch is increased. According to the circuit, the linearity and the switching speed of the gate voltage bootstrap sampling switch circuit are effectively improved, so that the overall performance of the gate voltage bootstrap sampling switch circuit is effectively improved.
Owner:CHONGQING UNIV OF POSTS & TELECOMM
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com