Patents
Literature
550results about How to "Increase drive current" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
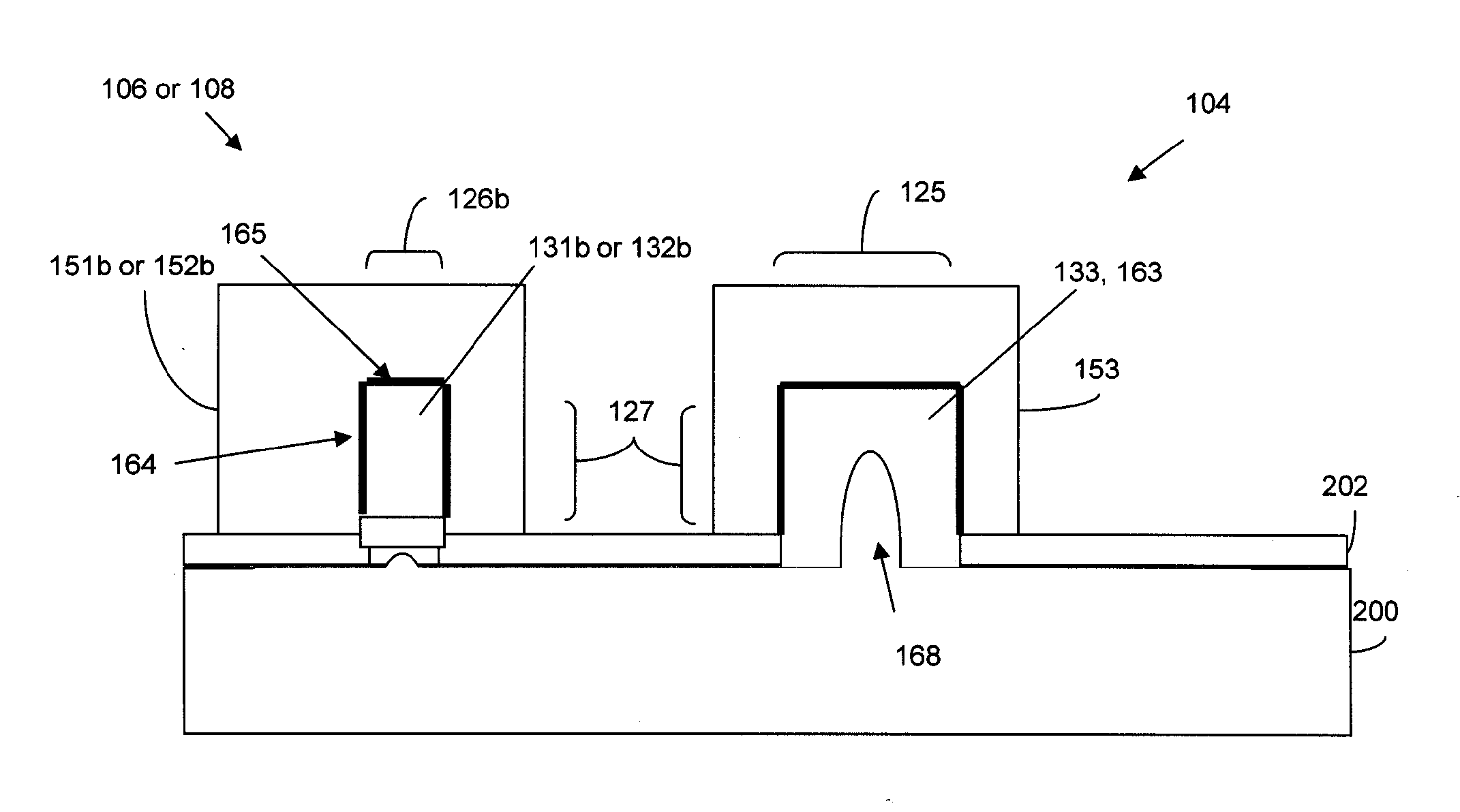
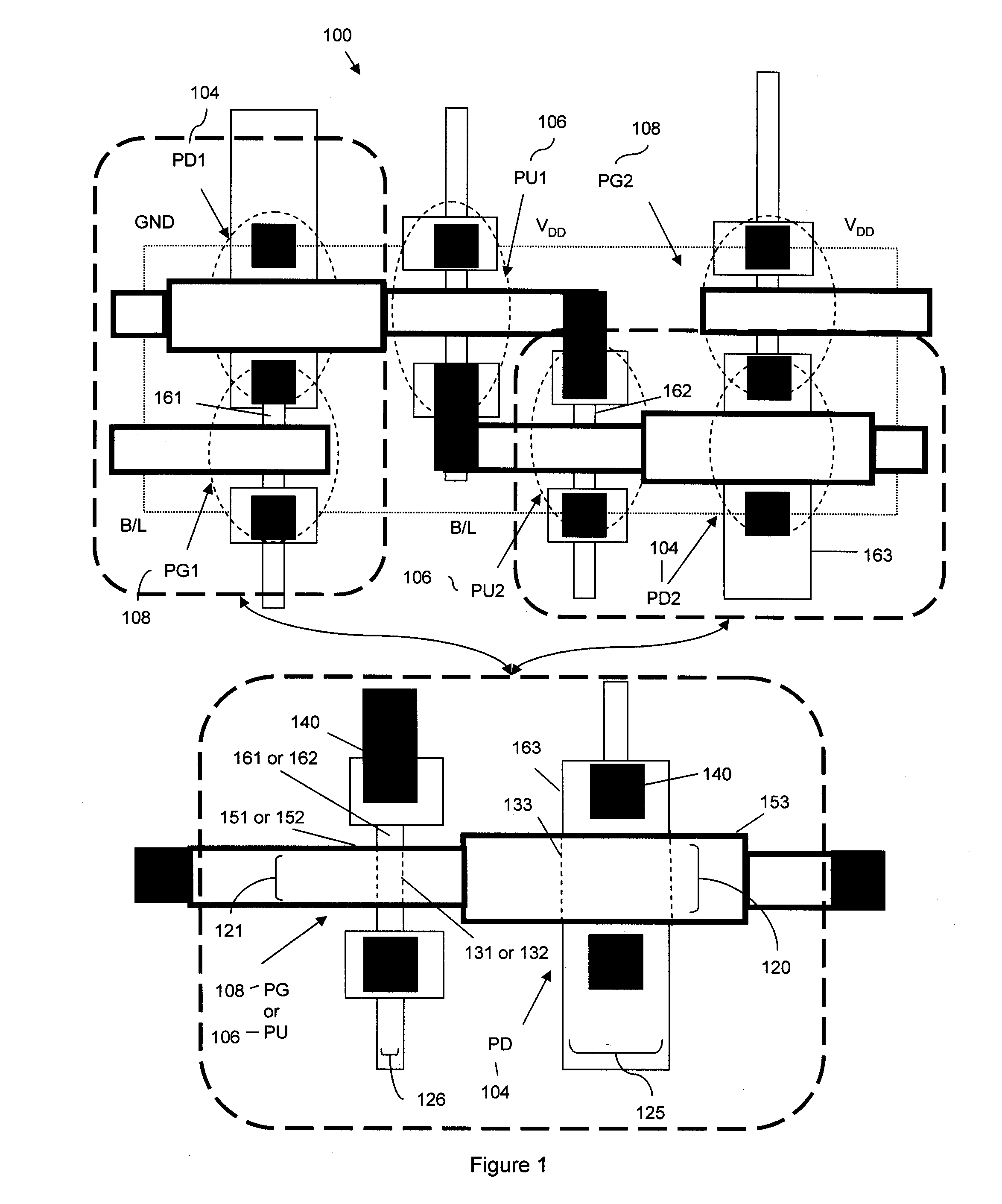
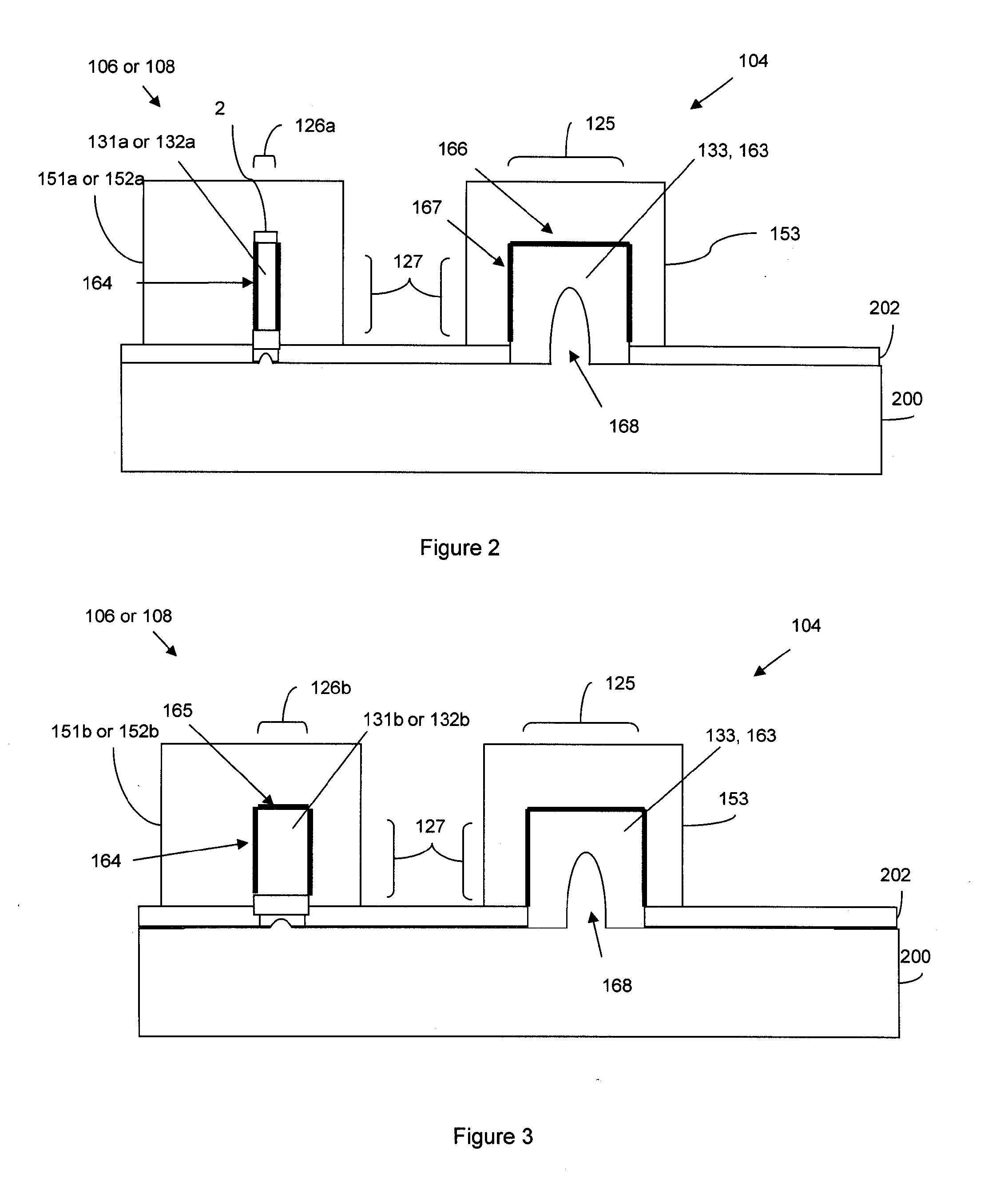
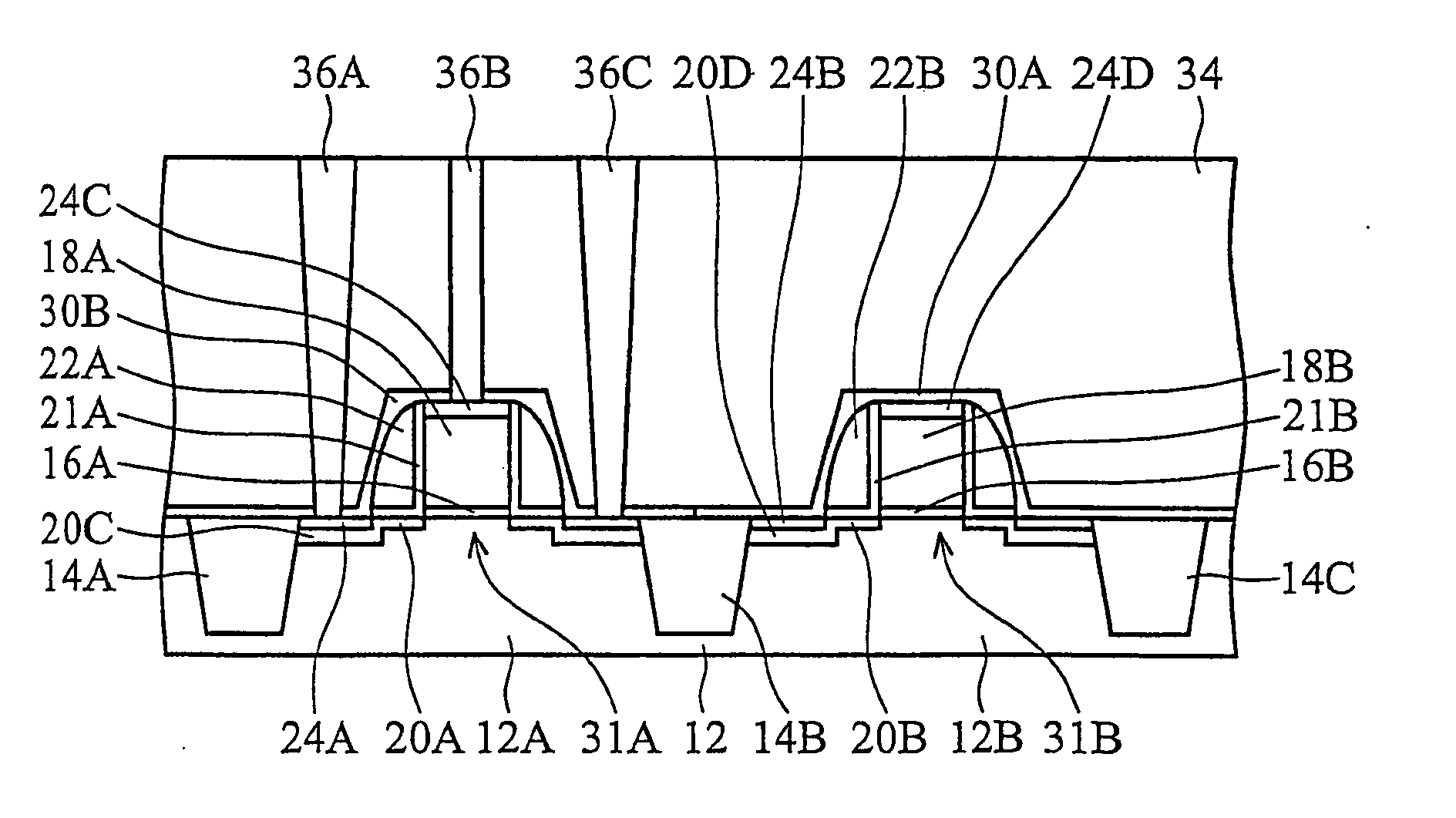
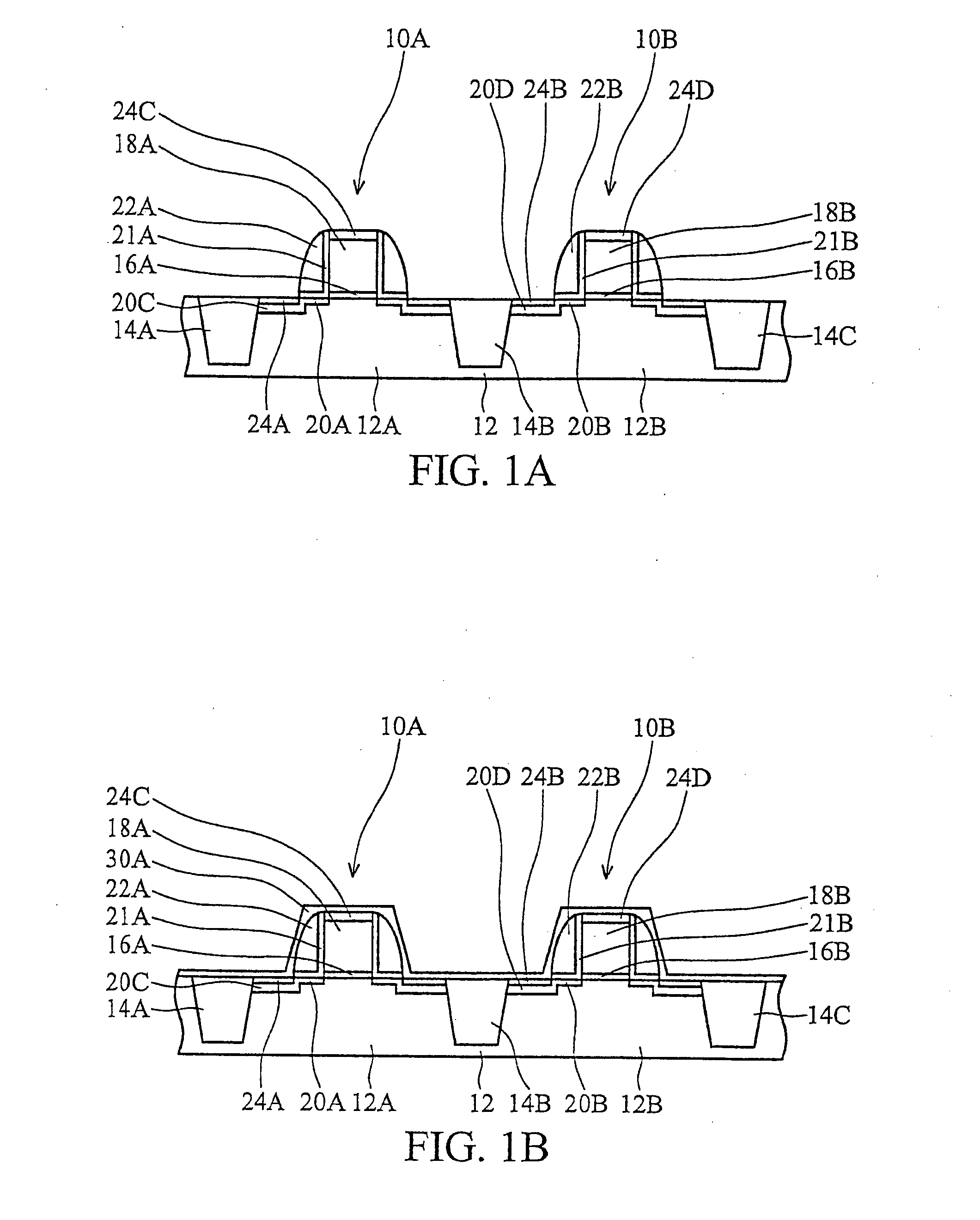
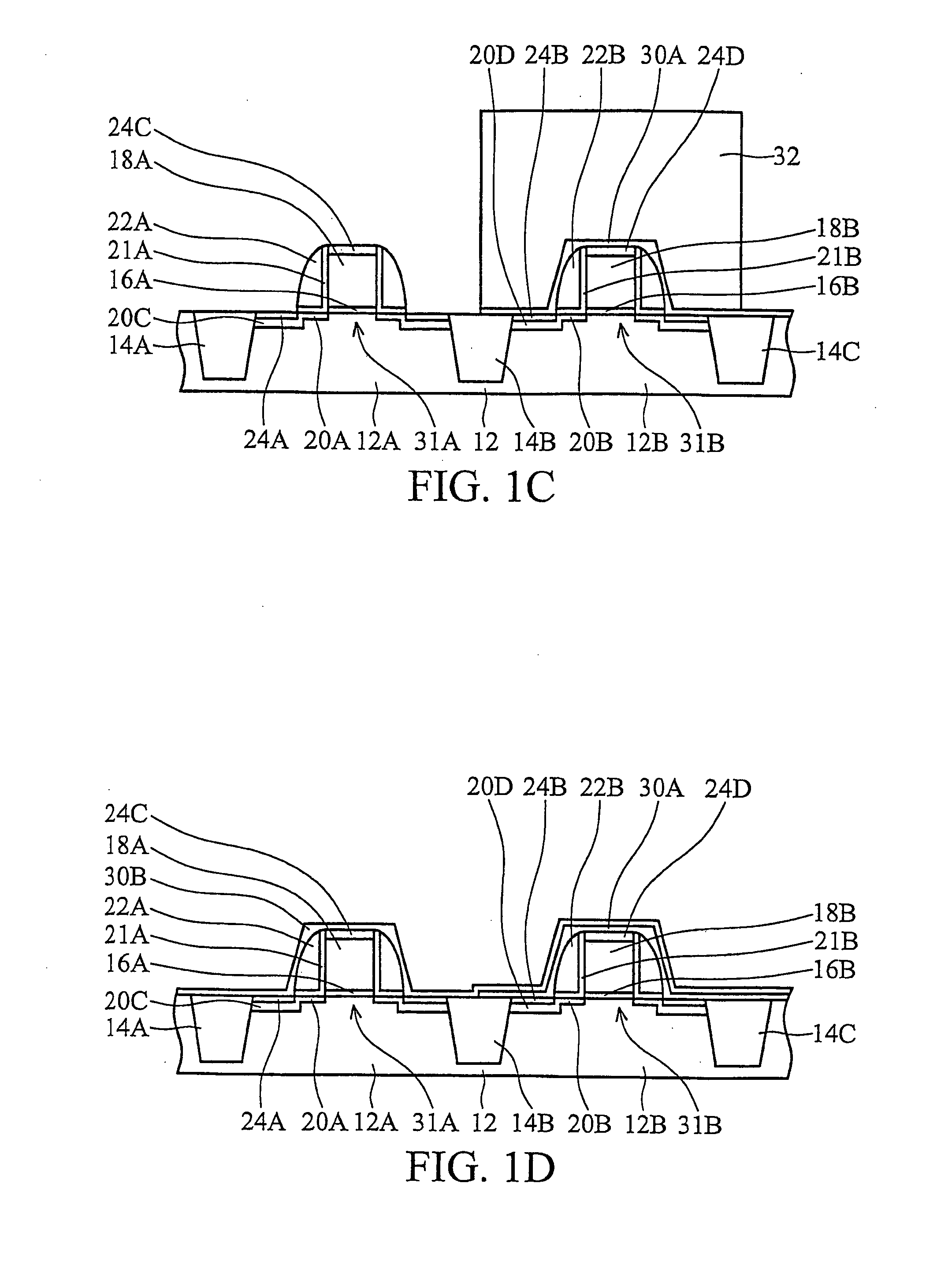
SRAM cell
InactiveUS20070108528A1Increase effective widthImprove carrying capacityTransistorSolid-state devicesDriving currentEngineering
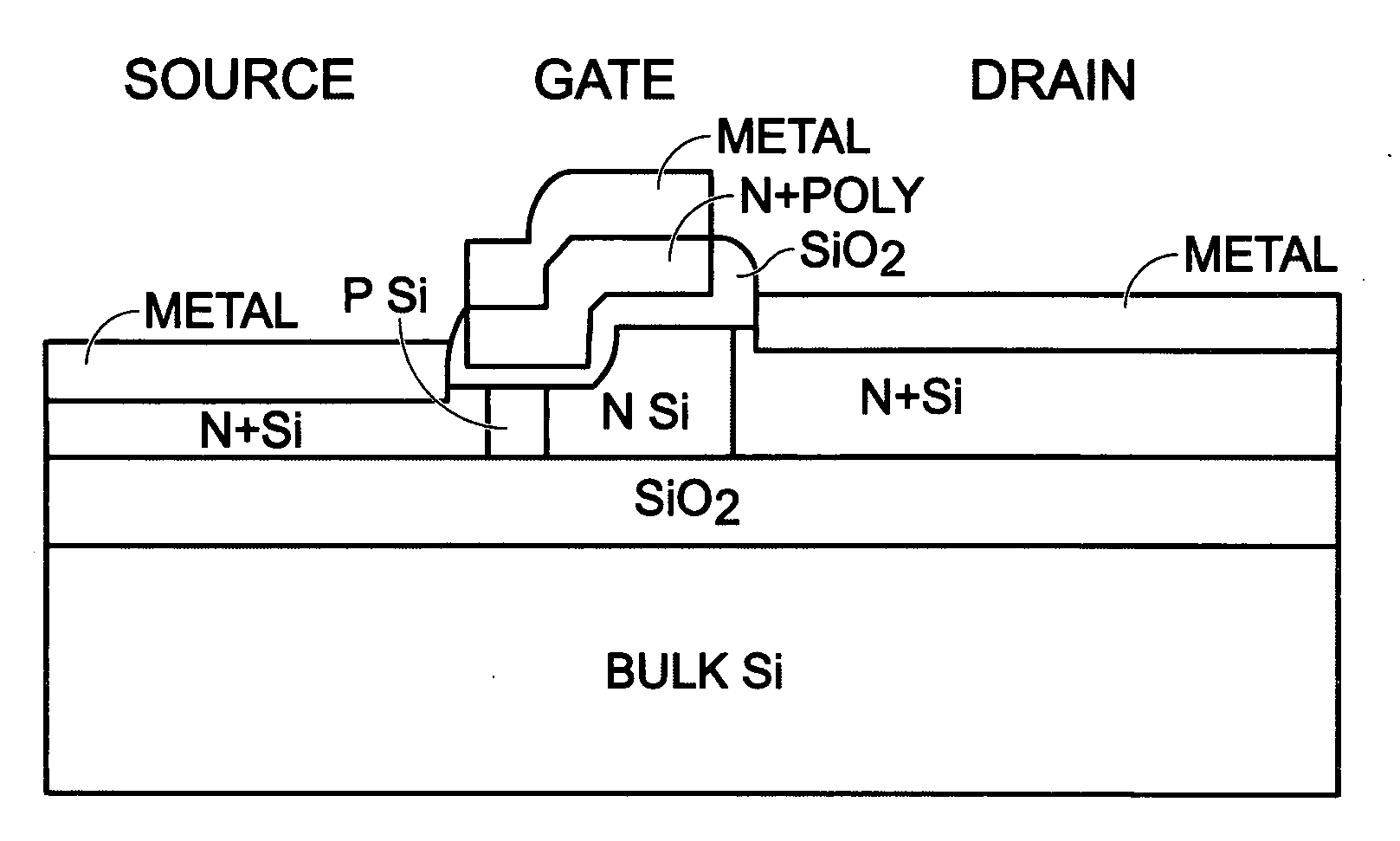
Disclosed is an SRAM cell on an SOI, bulk or HOT wafer with two pass-gate n-FETs, two pull-up p-FETs and two pull-down n-FETs and the associated methods of making the SRAM cell. The pass-gate FETs and pull-down FETs are non-planar fully depleted finFETs or trigate FETs. The pull-down FETs comprise non-planar partially depleted three-gated FETs having a greater channel width and a greater gate length and, thus, a greater drive current relative to the pass-gate and pull-up FETs. Additionally, for optimal electron mobility and hole mobility, respectively, the channels of the n-FETs and p-FETs can comprise semiconductors with different crystalline orientations.
Owner:IBM CORP
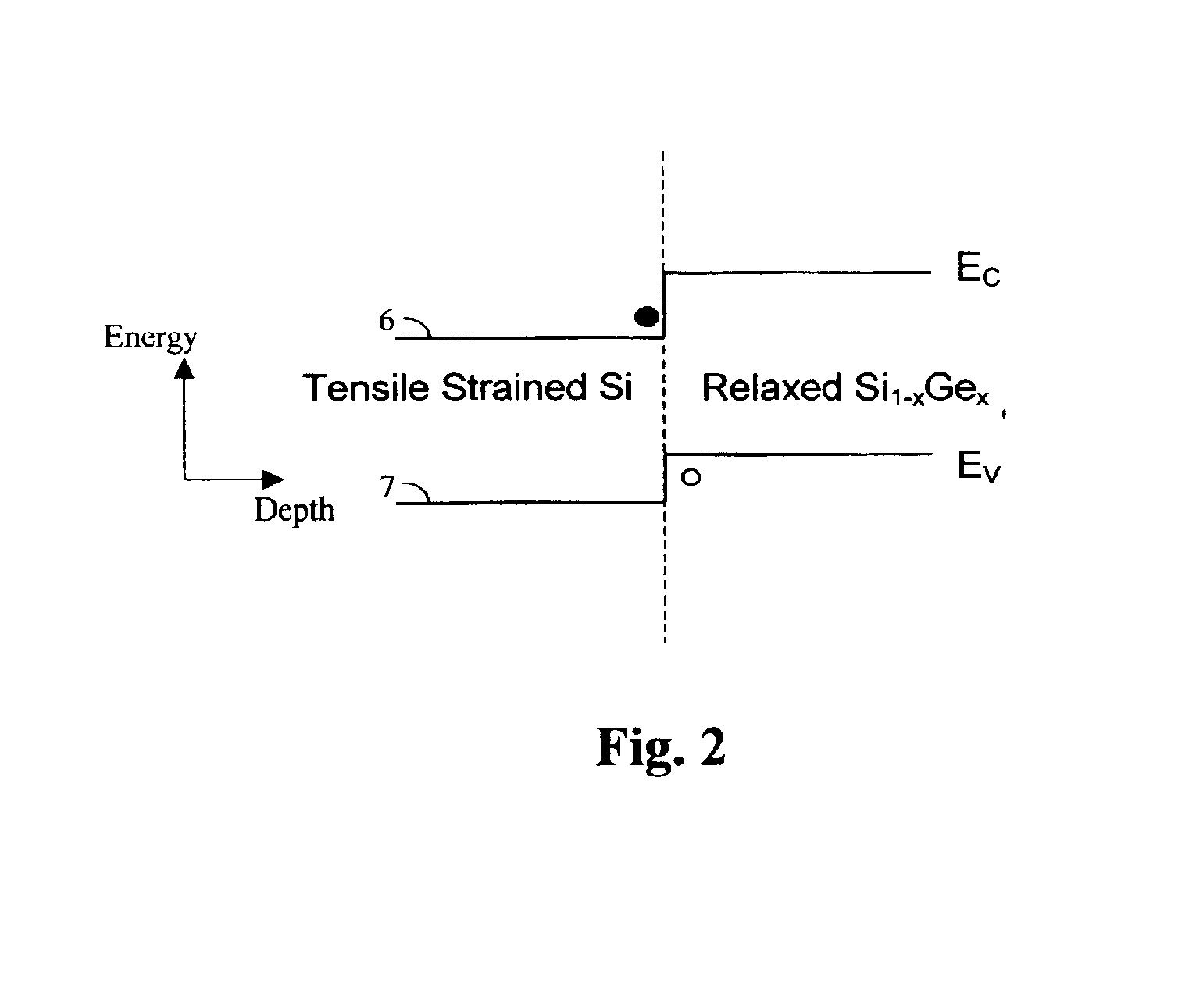
Semiconductor device based on Si-Ge with high stress liner for enhanced channel carrier mobility
ActiveUS20050247926A1Increase drive currentIncrease currentSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSemiconductor devicesDevice materialCharge carrier mobility
The carrier mobility in transistor channel regions of Si—Ge devices is increased by employing a stressed liner. Embodiments include applying a high compressive or tensile stressed film overlying relaxed source / drain regions. Other embodiments include applying a high compressively or high tensilely stressed film, after post silicide spacer removal, over gate electrodes and strained Si source / drain regions of P-channel or N-channel transistors, respectively.
Owner:ADVANCED MICRO DEVICES INC
Ultra scalable high speed heterojunction vertical n-channel MISFETs and methods thereof
ActiveUS7205604B2Superb performanceSuperb scalabilityTransistorDiagnosticsHeterojunctionSemiconductor materials
A method for forming and the structure of a strained vertical channel of a field effect transistor, a field effect transistor and CMOS circuitry is described incorporating a drain, body and source region on a sidewall of a vertical single crystal semiconductor structure wherein a heterojunction is formed between the source and body of the transistor, wherein the source region and channel are independently lattice strained with respect to the body region and wherein the drain region contains a carbon doped region to prevent the diffusion of dopants (boron) into the body. The invention reduces the problem of leakage current from the source region via the heterojunction and lattice strain while independently permitting lattice strain in the channel region for increased mobility via choice of the semiconductor materials.
Owner:GLOBALFOUNDRIES US INC
Semiconductor device based on Si-Ge with high stress liner for enhanced channel carrier mobility
ActiveUS7053400B2Increase currentIncrease drive currentSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSemiconductor devicesCharge carrier mobilityHigh stress
The carrier mobility in transistor channel regions of Si—Ge devices is increased by employing a stressed liner. Embodiments include applying a high compressive or tensile stressed film overlying relaxed source / drain regions. Other embodiments include applying a high compressively or high tensilely stressed film, after post silicide spacer removal, over gate electrodes and strained Si source / drain regions of P-channel or N-channel transistors, respectively.
Owner:ADVANCED MICRO DEVICES INC
Selectively strained MOSFETs to improve drive current
InactiveUS20060024879A1Increase drive currentIntroducing strainSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSemiconductor devicesMOSFETDriving current
A MOSFET device pair with improved drive current and a method for producing the same to selectively introduce strain into a respective N-type and P-type MOSFET device channel region, the method including forming a compressive stressed nitride layer on over the P-type MOSFET device and a tensile stressed nitride layer on the N-type MOSFET device followed by forming a PMD layer having a less compressive or tensile stress.
Owner:TAIWAN SEMICON MFG CO LTD
Method of forming a multi-fin multi-gate field effect transistor with tailored drive current
ActiveUS20090209074A1Tailored drive currentIncrease width of deviceSolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingDriving currentChannel width
Disclosed are embodiments of an improved multi-gated field effect transistor (MUGFET) structure and method of forming the MUGFET structure so that it exhibits a more tailored drive current. Specifically, the MUGFET incorporates multiple semiconductor fins in order to increase effective channel width of the device and, thereby, to increase the drive current of the device. Additionally, the MUGFET incorporates a gate structure having different sections with different physical dimensions relative to the semiconductor fins in order to more finely tune device drive current (i.e., to achieve a specific drive current). Optionally, the MUGFET also incorporates semiconductor fins with differing widths in order to minimize leakage current caused by increases in drive current.
Owner:GLOBALFOUNDRIES US INC
High speed lateral heterojunction MISFETs realized by 2-dimensional bandgap engineering and methods thereof
InactiveUS6927414B2Superb performanceSuperb scalabilityTransistorSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingHeterojunctionCMOS
A method for forming and the structure of a strained lateral channel of a field effect transistor, a field effect transistor and CMOS circuitry is described incorporating a drain, body and source region on a single crystal semiconductor substrate wherein a hetero-junction is formed between the source and body of the transistor, wherein the source region and channel are independently lattice strained with respect the body region. The invention reduces the problem of leakage current from the source region via the hetero-junction and lattice strain while independently permitting lattice strain in the channel region for increased mobility via choice of the semiconductor materials and alloy composition.
Owner:GLOBALFOUNDRIES US INC
Integrated circuit structure
ActiveCN102034866AIncrease drive currentWork function optimizationSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSemiconductor devicesWork functionIntegrated circuit
The invention provides an integrated circuit structure having an n-type fin field effect transistor (FinFET) and a p-type FinFET. The n-type FinFET includes a first germanium fin over a substrate; a first gate dielectric on a top surface and sidewalls of the first germanium fin; and a first gate electrode on the first gate dielectric. The p-type FinFET includes a second germanium fin over the substrate; a second gate dielectric on a top surface and sidewalls of the second germanium fin; and a second gate electrode on the second gate dielectric. The first gate electrode and the second gate electrode are formed of the same material having a work function close to an intrinsic energy level of germanium. The invention can simultaneously reach the requirements for optimizing the work functionsof n-type FinFETs and p-type FinFETs.
Owner:TAIWAN SEMICON MFG CO LTD
Illumination device and method for avoiding flicker
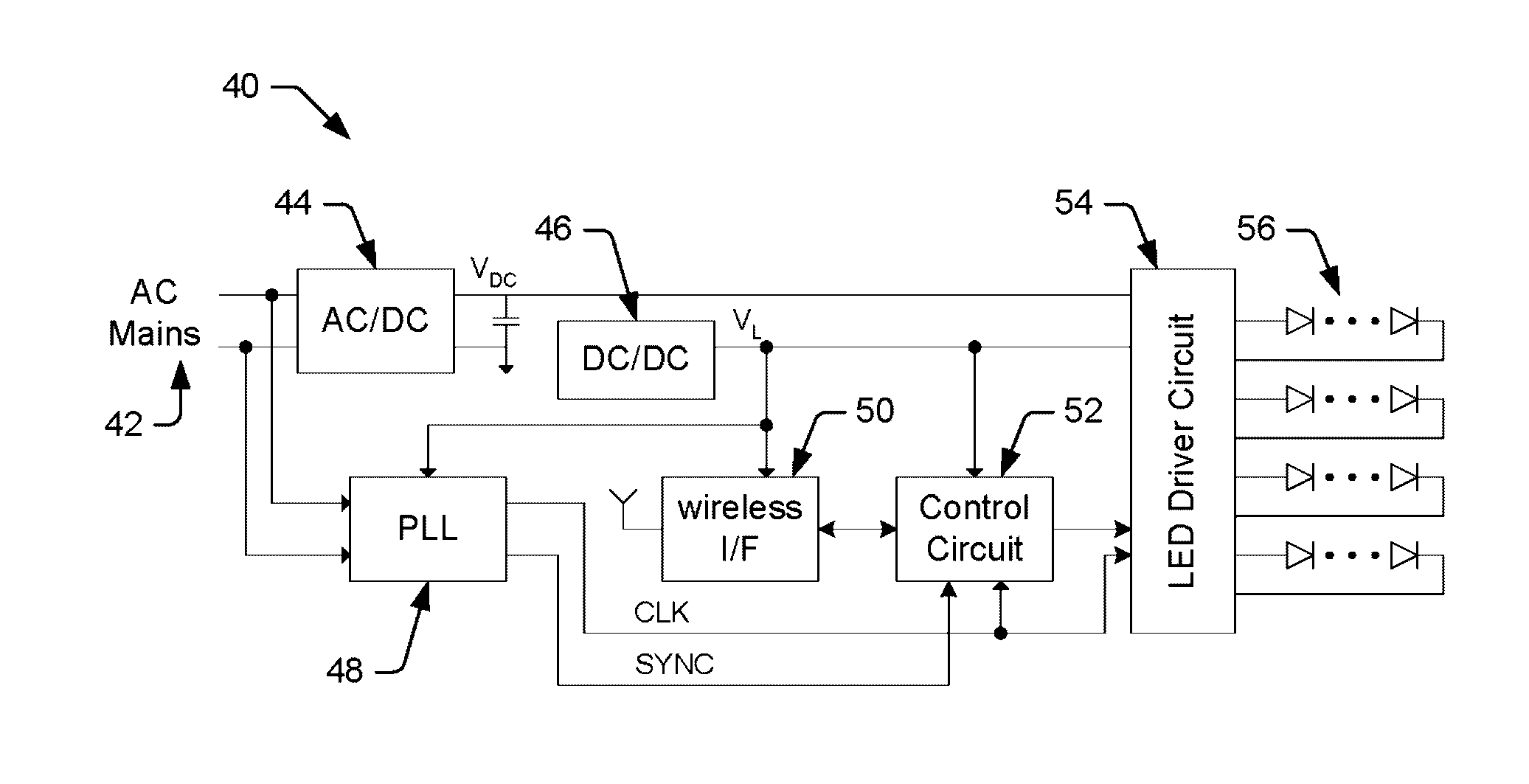
ActiveUS9578724B1Increase drive currentAvoid flickeringElectric light circuit arrangementClose-range type systemsShort durationEngineering
An illumination device comprising a plurality of light emitting diodes (LEDs) and a method for controlling the illumination device while avoiding flicker in the LED output is provided herein. According to one embodiment, the method may include driving the plurality of LEDs substantially continuously with drive currents configured to produce illumination, periodically turning the plurality of LEDs off for short durations of time during a first period to take measurements or communicate optical data, and increasing the drive currents supplied to the plurality of LEDs by a small amount when the LEDs are on during the first period to compensate for lack of illumination when the LEDs are periodically turned off during the first period.
Owner:LUTRON TECH CO LLC
Ultra Scalable High Speed Heterojunction Vertical n-Channel Misfets and Methods Thereof
InactiveUS20070241367A1Superb performanceSuperb scalabilityTransistorSolid-state devicesHeterojunctionSemiconductor materials
A method for forming and the structure of a strained vertical channel of a field effect transistor, a field effect transistor and CMOS circuitry is described incorporating a drain, body and source region on a sidewall of a vertical single crystal semiconductor structure wherein a hetero-junction is formed between the source and body of the transistor, wherein the source region and channel are independently lattice strained with respect to the body region and wherein the drain region contains a carbon doped region to prevent the diffusion of dopants (boron) into the body. The invention reduces the problem of leakage current from the source region via the hetero-junction and lattice strain while independently permitting lattice strain in the channel region for increased mobility via choice of the semiconductor materials.
Owner:GLOBALFOUNDRIES INC
Heterojunction carbon nano-tube field effect transistor and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN106356405AGuaranteed driving abilityGuaranteed speedSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSemiconductor devicesHeterojunctionCarbon nano tube field effect transistor
The invention provides a heterojunction carbon nano-tube field effect transistor of which a subthreshold swing is smaller than 60 millivolt / magnitude in the room temperature and a preparation method thereof. The device uses the semiconductor carbon nano-tube as the active layer, the heterojunction formed by the graphene layer and the semiconductor carbon nano-tube is used as the source end of the device, the gate medium and the gate electrode modulate the carbon nano-tube channel and the graphene / carbon nano-tube junction at the same time, so that the turn-off of the transistor is accelerated by using the character that the graphene / carbon nano-tube junction barrier is modulated by the gate voltage. The transistor can control the polarity through the selection of the source-drain metal, namely the metal of high power function is used as the source-drain electrode for realizing the p-type field effect transistor, and the metal of low power function is used as the source-drain electrode for realizing the n-type field effect transistor.
Owner:BEIJING HUA TAN YUAN XIN ELECTRONICS TECH CO LTD
SRAM cell
InactiveUS7547947B2Increase drive currentEliminate the effects ofTransistorSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsDriving currentEngineering
Disclosed is an SRAM cell on an SOI, bulk or HOT wafer with two pass-gate n-FETs, two pull-up p-FETs and two pull-down n-FETs and the associated methods of making the SRAM cell. The pass-gate FETs and pull-down FETs are non-planar fully depleted finFETs or trigate FETs. The pull-down FETs comprise non-planar partially depleted three-gated FETs having a greater channel width and a greater gate length and, thus, a greater drive current relative to the pass-gate and pull-up FETs. Additionally, for optimal electron mobility and hole mobility, respectively, the channels of the n-FETs and p-FETs can comprise semiconductors with different crystalline orientations.
Owner:INT BUSINESS MASCH CORP
Multi-fin multi-gate field effect transistor with tailored drive current
ActiveUS20090206374A1Tailored drive currentIncrease width of deviceTransistorSolid-state devicesDriving currentField-effect transistor
Disclosed are embodiments of an improved multi-gated field effect transistor (MUGFET) structure and method of forming the MUGFET structure so that it exhibits a more tailored drive current. Specifically, the MUGFET incorporates multiple semiconductor fins in order to increase effective channel width of the device and, thereby, to increase the drive current of the device. Additionally, the MUGFET incorporates a gate structure having different sections with different physical dimensions relative to the semiconductor fins in order to more finely tune device drive current (i.e., to achieve a specific drive current). Optionally, the MUGFET also incorporates semiconductor fins with differing widths in order to minimize leakage current caused by increases in drive current.
Owner:GLOBALFOUNDRIES US INC
Multiple-gate transistors with reverse T-shaped fins
ActiveUS8058692B2Increase drive currentReduce defectsTransistorSolid-state devicesGate dielectricEngineering
A method of forming an integrated circuit structure includes forming a first insulation region and a second insulation region in a semiconductor substrate and facing each other; and forming an epitaxial semiconductor region having a reversed T-shape. The epitaxial semiconductor region includes a horizontal plate including a bottom portion between and adjoining the first insulation region and the second insulation region, and a fin over and adjoining the horizontal plate. The bottom of the horizontal plate contacts the semiconductor substrate. The method further includes forming a gate dielectric on a top surface and at least top portions of sidewalls of the fin; and forming a gate electrode over the gate dielectric.
Owner:TAIWAN SEMICON MFG CO LTD
Laser driver and optical module including same
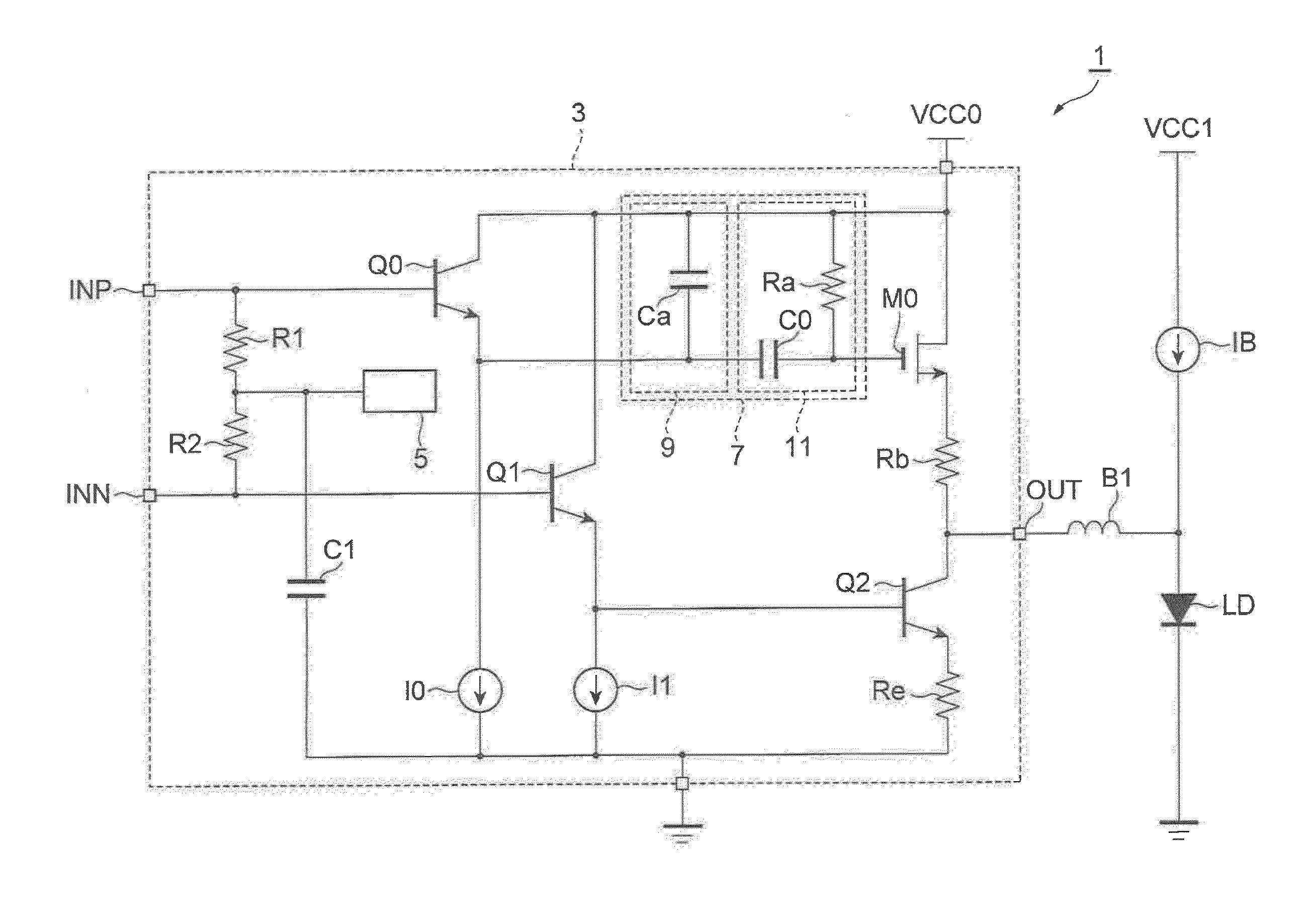
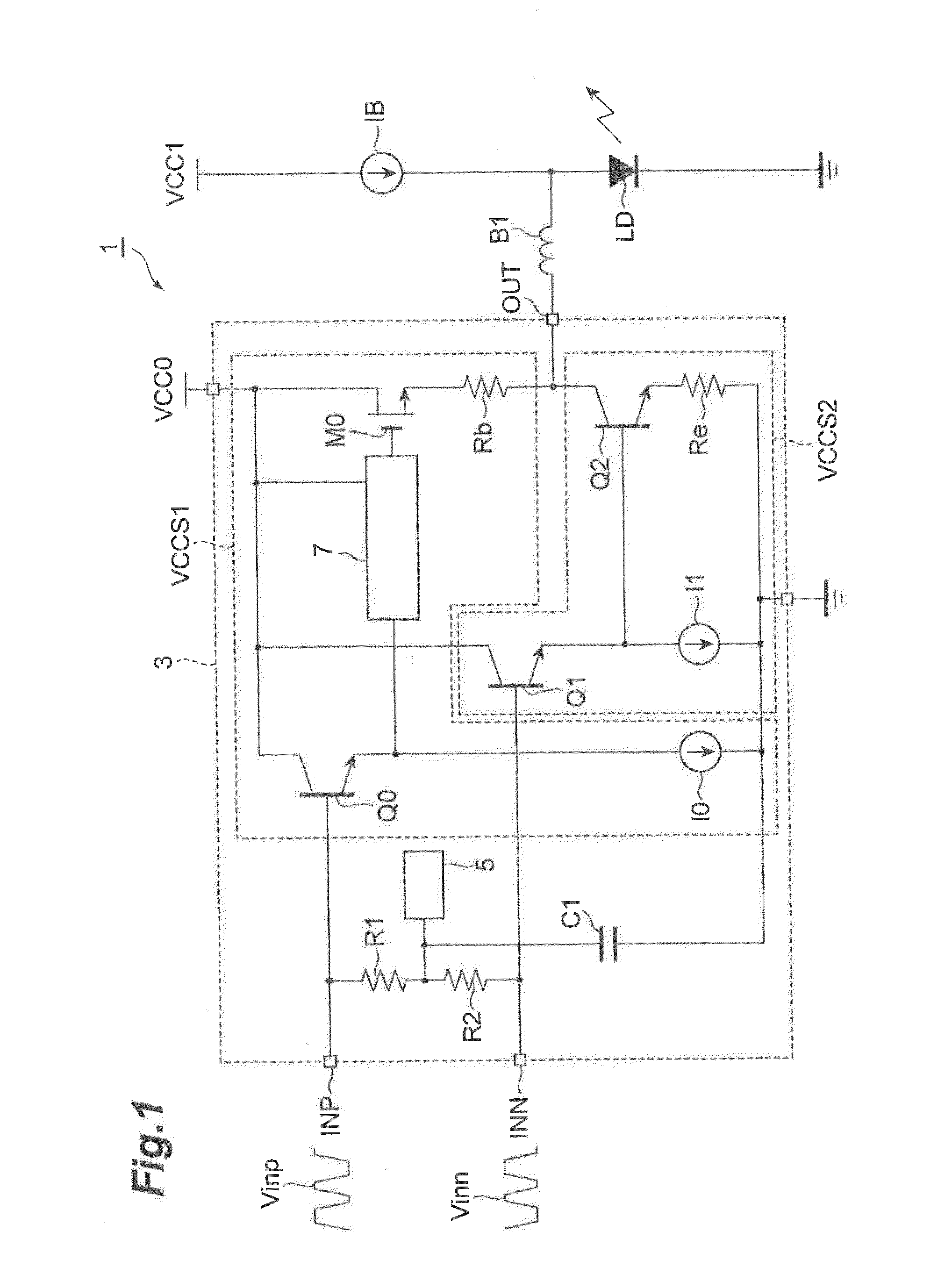
InactiveUS20160013614A1Increase drive currentDecreasing drive currentOptical wave guidanceLaser detailsCurrent sourceLaser diode
A laser driver drives a laser diode by increasing and decreasing a drive current by a differential signal having a pair of positive phase and negative phase components and comprises an upper voltage-controlled current, source increasing the drive current responding to an increase of the positive phase component of the differential signal, a lower voltage-controlled current source for decreasing the drive current responding to an increase of the negative Phase signal of the differential signal, and an output terminal, connected to output terminals of the voltage-controlled current sources, for outputting the drive current. The voltage-controlled current source has a band-pass filter with a gain for the positive phase component set greater in a predetermined frequency region than in a frequency region other than the predetermined frequency region.
Owner:SUMITOMO ELECTRIC IND LTD
Method of forming a multi-fin multi-gate field effect transistor with tailored drive current
ActiveUS8022478B2Increase widthEasy to tuneSolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingDriving currentEngineering
Disclosed are embodiments of an improved multi-gated field effect transistor (MUGFET) structure and method of forming the MUGFET structure so that it exhibits a more tailored drive current. Specifically, the MUGFET incorporates multiple semiconductor fins in order to increase effective channel width of the device and, thereby, to increase the drive current of the device. Additionally, the MUGFET incorporates a gate structure having different sections with different physical dimensions relative to the semiconductor fins in order to more finely tune device drive current (i.e., to achieve a specific drive current). Optionally, the MUGFET also incorporates semiconductor fins with differing widths in order to minimize leakage current caused by increases in drive current.
Owner:GLOBALFOUNDRIES US INC
Electromagnetic valve drive circuit for engine
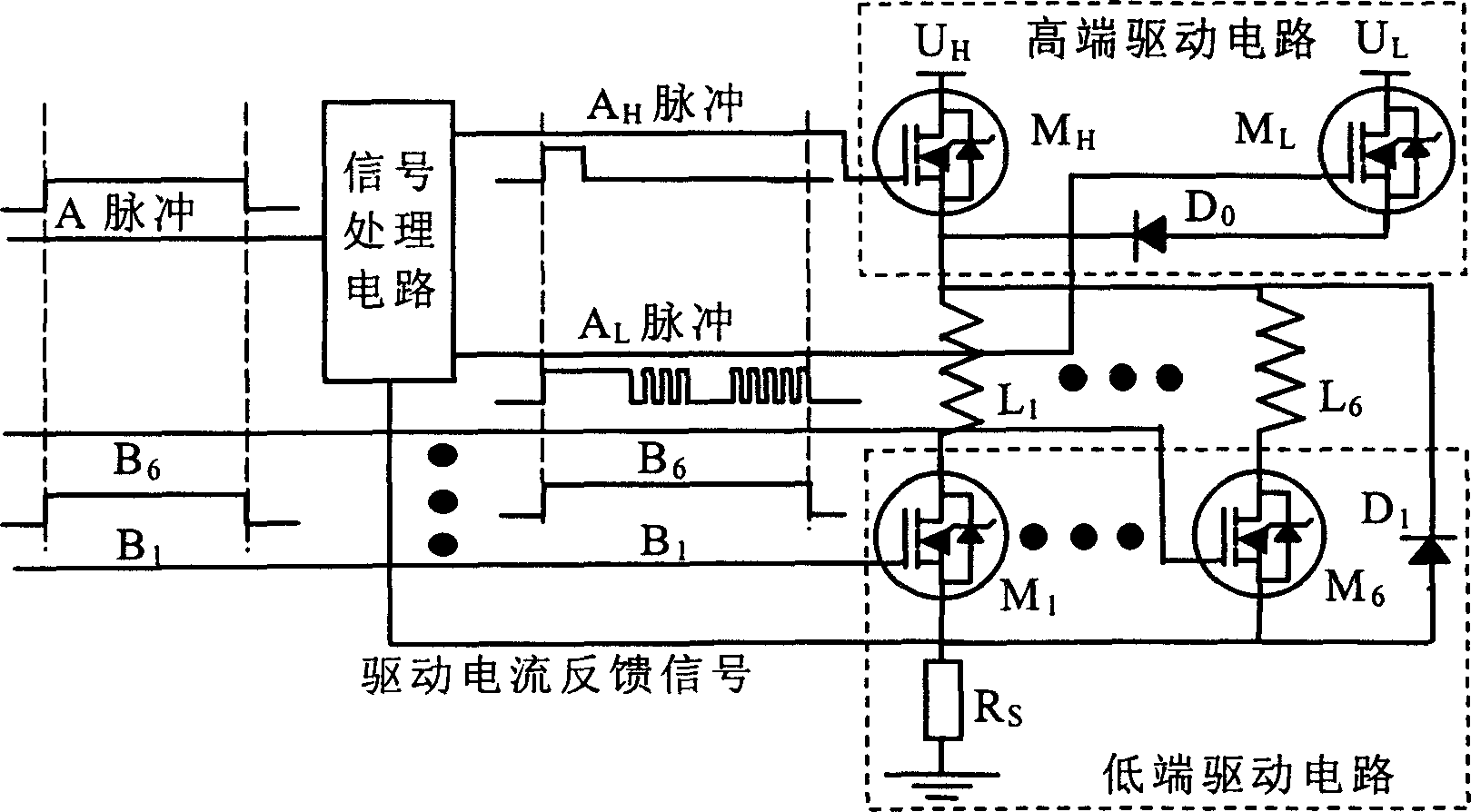
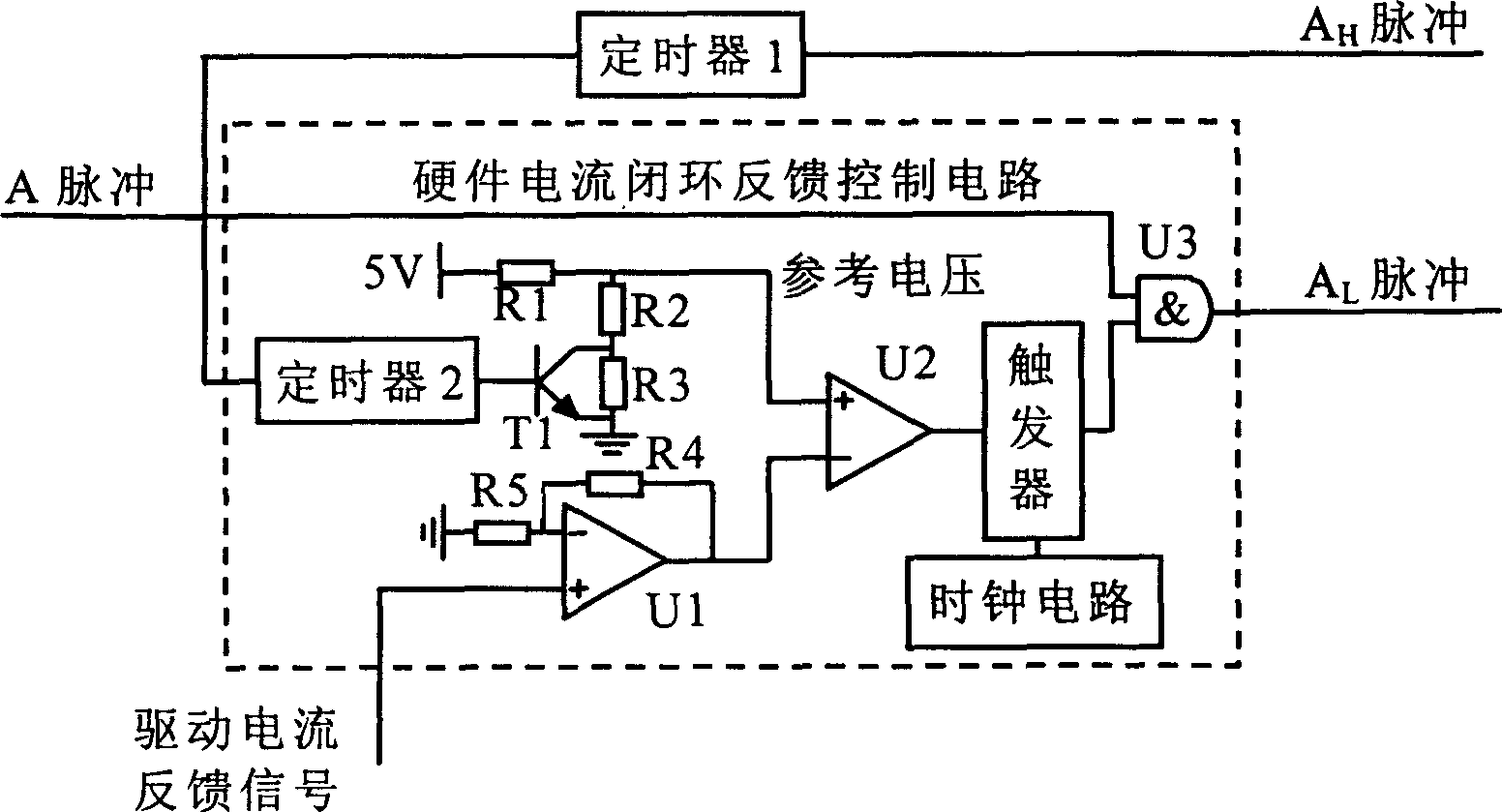
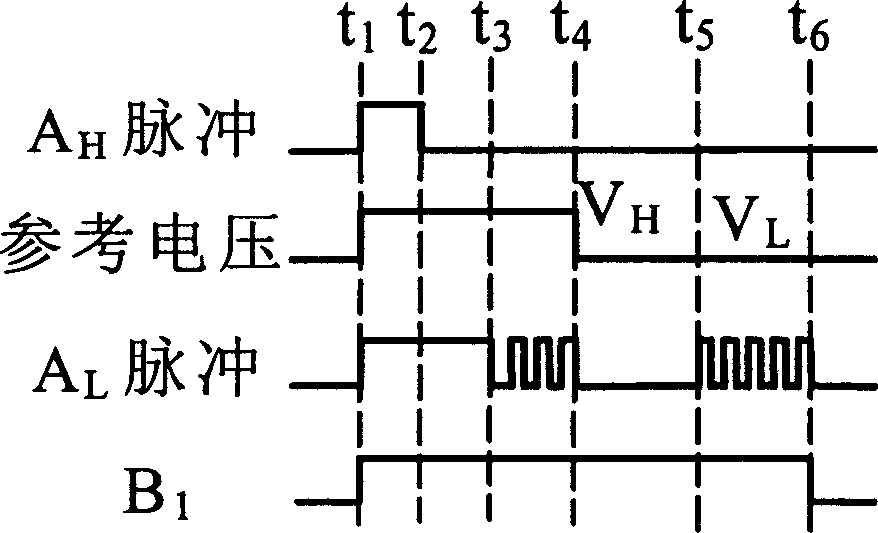
InactiveCN1563691AShorten closing timeIncrease drive currentElectrical controlFuel-injection pumpsElectronic control unitEngineering
The circuit contains a single processing circuit, it receives the control pulse. A from the electronic control unit of the motor and output high voltage driving pulse Ah and low voltage driving pulse Al to higher extreme driving circuit separately and receive the feedback sampling current signal from lower extreme driving circuit, after processing, the low voltage driving pulse Al adjust the higher extreme driving circuit to adjust the driving circuit of the electromagnetic valve. Lower extreme driving circuit receive pulse signal B from electronic control unit of the motor, this pulse signal is same with the control signal A.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
Fin-type tunneling transistor integrated circuit and manufacturing method thereof
InactiveCN101969061AIncrease drive currentFast switching speedTransistorSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingDriving currentSemiconductor
The invention belongs to the technical field of manufacturing of semiconductor integrated circuits, and in particular relates to a fin-type tunneling transistor integrated circuit and a manufacturing method thereof. On the basis of a silicon-on-insulator substrate, a tunneling transistor has a fin-type grid structure, a high-k dielectric is used as a grid dielectric and a low-k dielectric is used as a side wall material. The drive current of the fin-type tunneling transistor integrated circuit is improved, the switching speed of the integrated circuit is increased and the power consumption of a chip is reduced. Further, the invention also discloses the method for manufacturing the fin-type tunneling transistor integrated circuit.
Owner:FUDAN UNIV
III-V group semiconductor MOS field effect transistor with high mobility
InactiveCN102931231AReduce scatterIncrease drive currentSemiconductor devicesControl layerLow voltage
The invention discloses a III-V group MOS (Metal-oxide Semiconductor) field effect transistor with high mobility, which comprises a single-crystal lining, a buffer layer formed on the single-crystal lining, a planar doped layer formed in the buffer layer, a high-mobility channel layer formed on the buffer layer, a doped interface control layer formed on the high-mobility channel layer, a high-doped semiconductor layer formed on the doped interface control layer, a narrow band gap ohm contact layer formed on the high-doped semiconductor layer, and a source-drain metal electrode formed on the narrow band gap ohm contact layer, wherein a grid groove etched to the doped interface control layer is located between two source drain metal electrodes; a high-K grid medium is uniformly covered on the inner surface of the grid groove structure; and a grid metal electrode is formed on the high-K grid medium. The III-V MOS device structure disclosed by the invention not only can lower MOS interface state density, and improve channel mobility, but also can improve channel two-dimensional electron (cavity) gas concentration, and satisfy the application demand of a high-speed lower voltage operation high mobility CMOS technology.
Owner:INST OF MICROELECTRONICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Metal-oxide-semiconductor transistor and manufacturing method thereof
ActiveCN101179028AIncrease drive currentEasy to operateSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSemiconductor devicesSalicideElectrical conductor
The present invention provides a method for fabricating a metal oxide semiconductor transistor. First, a semiconductor substrate is provided, including a gate structure, and the gate structure has a liner layer on two opposite sidewalls. Then, a stress capping layer is formed to cover the semiconductor substrate, the gate structure and the liner layer without spacers. Next, an activation process is performed, and then an etching process is performed on the stress capping layer, so that the stress capping layer becomes a self-aligned metal silicide blocking layer. Then, a self-aligned metal silicide process is performed to form a metal silicide layer in the area not covered with the stress capping layer.
Owner:UNITED MICROELECTRONICS CORP
MOS transistor with stacked nanometer lines and manufacturing method of MOS transistor
InactiveCN104282559AIncrease effective widthIncrease the effective conductive total cross-sectional areaNanoinformaticsSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingDriving currentPower flow
The invention discloses an MOS transistor with stacked nanometer lines and a manufacturing method of the MOS transistor. The MOS transistor comprises toruliform nanometer line stacks, a plurality of grid stacks, a plurality of source and drain regions and a plurality of channel regions, wherein each nanometer line stack is formed by stacking the nanometer lines in the longitudinal direction and extends on a substrate in the first direction; the grid stacks extend in the second direction and cross over the nanometer stacks; the source and drain regions are located on the two sides of each grid stack in the second direction; the channel regions are formed by the nanometer line stacks between the source and drain regions. According to the MOS transistor with the stacked nanometer lines and the manufacturing method of the MOS transistor, the toruliform nanometer line stacks with good quality are formed by means of etching carried out many times and sideward etching and filling of grooves, effective widths of conducting channels are increased at low cost, the total area of effective conductive sections is increased and drive currents are increased.
Owner:INST OF MICROELECTRONICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Tunneling field effect transistor having heterogeneous grid work function and formation method thereof
ActiveCN102169901ASmall subthreshold slopeIncrease drive currentSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSemiconductor devicesDriving currentEngineering
The invention provides a tunneling field effect transistor having heterogeneous grid work function, which comprises a substrate, a channel zone formed in the substrate, a source zone and a drain zone formed at two sides of the channel zone, and a grid stack, wherein the doping type of the source zone is opposite to that of the drain zone; the grid stack comprises a grid dielectric layer and further comprises a first grid electrode and a second grid electrode located on the grid dielectric layer and distributed along the direction from the source zone to the drain zone, and a first side wall and a second side wall located on the grid dielectric layer and respectively formed at a side of the first grid electrode and a side of the second grid electrode; and the first grid electrode and the second grid electrode have different work functions. In the embodiment of the invention, a structure of transverse heterogeneous grid work function is introduced to the tunneling field effect transistor, so the energy zone distribution of the channel zone is adjusted, the sub-threshold gradient of the transistor is substantially decreased, meanwhile, the driving current is greatly improved.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
Ultra small size vertical MOSFET device and method for the manufacture thereof
InactiveUS20040007737A1Increase drive currentIncrease channel widthTransistorNanotechMOSFETHigh concentration
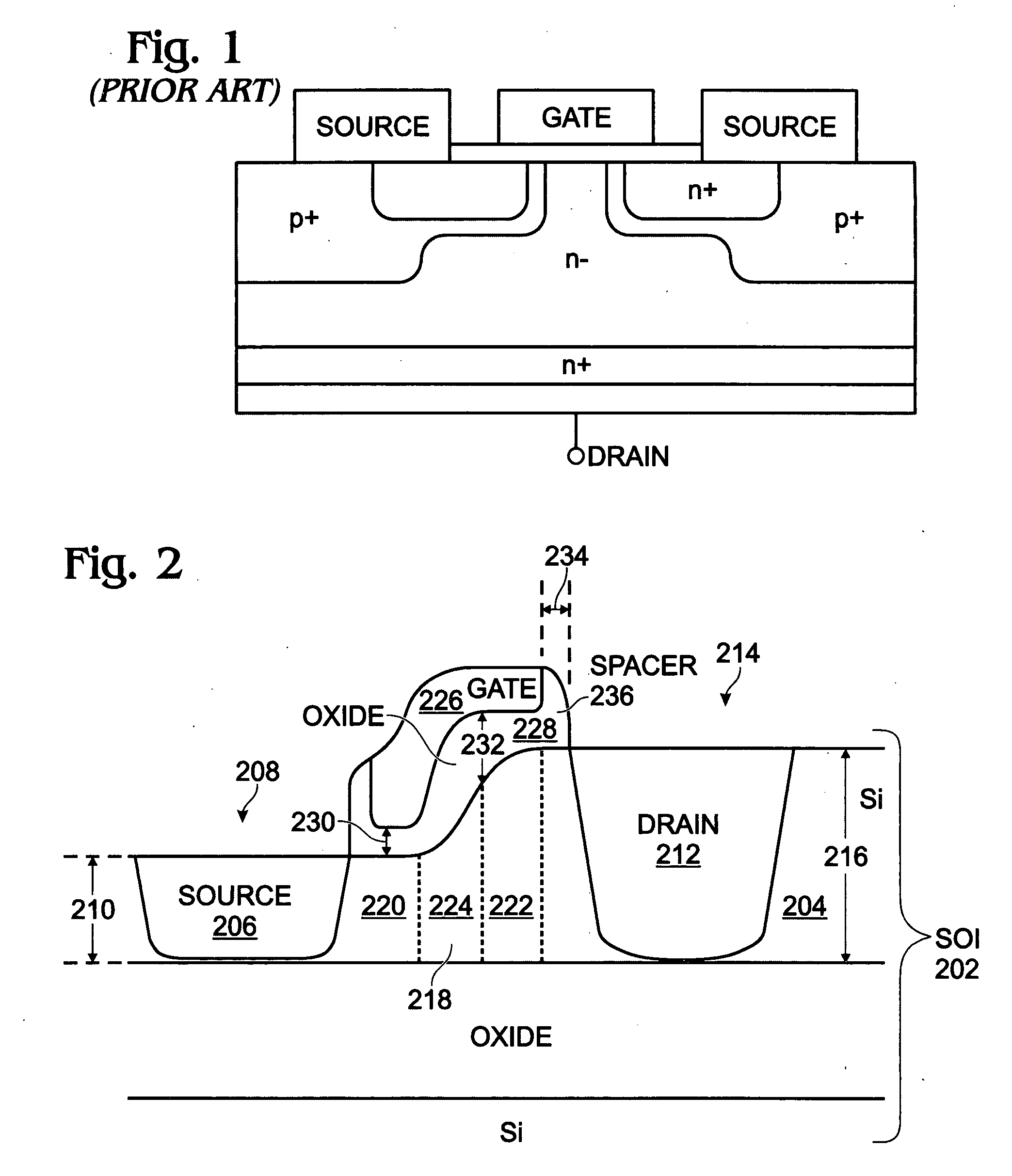
The present invention relates to an ultra small size vertical MOSFET device having a vertical channel and a source / drain structure and a method for the manufacture thereof by using a silicon on insulator (SOI) substrate. To begin with, a first silicon conductive layer is formed by doping an impurity of a high concentration into a first single crystal silicon layer. Thereafter, a second single crystal silicon layer with the impurity of a low concentration and a second silicon conductive layer with the impurity of the high concentration are formed on the first silicon conductive layer. The second single crystal silicon layer and the second silicon conductive layer are vertically patterned into a predetermined configuration. Subsequently, a gate insulating layer is formed on entire surface. Then, an annealing process is carried out to diffuse the impurities in the first silicon conductive layer and the second silicon conductive layer into the second single crystal layer, thereby forming a source contact, a drain contact and a vertical channel. Finally, a gate electrode is formed on side walls of the vertical channel.
Owner:ELECTRONICS & TELECOMM RES INST
Tin compound superlattice barrier semiconductor transistor
ActiveCN103811542AIncrease concentrationReduce dislocation densitySemiconductor devicesDriving currentPower flow
The invention discloses a tin compound superlattice barrier semiconductor transistor, comprising a superlattice barrier layer, wherein the superlattice barrier layer is formed by multi-cycle thin film layers overlapped alternatively, and the thin film layer is composed of tin compound and another doped tin compound. By using the novel compounds of tin and the doping of the tin compounds, a multi-cycle superlattice barrier layer process is formed to obtain low dislocation density, smooth profile of HEMT (High Electron Mobility Transistor), low chip square resistance; the multi-cycle superlattice barrier layer with high conductive performance, high driving current and low MOS (Metal Oxide Semiconductor) interface state density is achieved, and the two-dimensional electron gas concentration or the two-dimensional hole gas concentration in a channel layer is also improved.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA NORMAL UNIVERSITY
IGZO thin film transistor and method for improving electrical property of IGZO thin film transistor
InactiveCN103887344AImprove trap defectsImprove mobilityTransistorSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingElectrical conductorSemiconductor structure
The invention provides an IGZO thin film transistor and a method for improving the electrical property of the IGZO thin film transistor. The method comprises the following steps that a semiconductor structure is provided, the semiconductor structure comprises a substrate, a metal gate is formed on part of the surface of the substrate, and the metal gate and the upper surface of the substrate are respectively covered with a gate oxide layer; an IGZO film layer is manufactured to cover the gate oxide layer, the IGZO film layer is etched to form an active layer and a pixel electrode area, and a source electrode, a drain electrode and a passivation layer are formed above the IGZO film layer in sequence; after the IGZO film layer is etched to form the active layer, the surface of the IGZO film layer is treated through a plasma treatment process. The IGZO film layer is treated through oxygen plasma and UV radiation, the oxygen content of an IGZO film is improved, lattice imperfections between the IGZO film and the gate oxide layer are reduced, meanwhile, impurities and defects on the surface of the IGZO film can be removed, and device performance is improved.
Owner:EVERDISPLAY OPTRONICS (SHANGHAI) CO LTD
Thin silicon-on-insulator double-diffused metal oxide semiconductor transistor
InactiveUS20080290408A1Small parasitic capacitanceIncrease drive currentTransistorSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingDopantSoi substrate
A method is provided for fabricating a silicon (Si)-on-insulator (SOI) double-diffused metal oxide semiconductor transistor (DMOST) with a stepped channel thickness. The method provides a SOI substrate with a Si top layer having a surface. A thinned area of the Si top layer is formed, and a source region is formed in the thinned Si top layer area. The drain region is formed in an un-thinned area of the Si top layer. The channel has a first thickness adjacent the source region with first-type dopant, and a second thickness, greater than the first thickness, adjacent the drain region. The channel also has a sloped thickness between the first and second thicknesses. The second and sloped thicknesses have a second-type dopant, opposite of the first-type dopant. A stepped gate overlies the channel.
Owner:SHARP KK
Fin field effect transistor and forming method thereof
ActiveCN103928327AReduce parasitic capacitanceIncrease capacitanceSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSemiconductor devicesParasitic capacitanceEngineering
The invention discloses a fin field effect transistor and a forming method thereof. The forming method of the fin field effect transistor comprises: providing a semiconductor substrate, the surface of the semiconductor substrate being provided with a projection fin portion and a grid structure which is disposed on the fin portion and covers a part of the top portion and the side wall of the fin portion; forming a first dielectric layer covering the grid structure; forming a second dielectric layer covering the first dielectric layer, the dielectric constant of the second dielectric layer being smaller than the dielectric constant of the first dielectric layer; etching back the second dielectric layer, and forming a second side wall; and etching the first dielectric layer by taking the second side wall as a mask, and forming a first side wall, the first side wall being provided with a horizontal portion and a vertical portion, the part of the fin portion covered by the first side wall constituting a negative covering zone. According to the invention, the parasitic capacitance between the grid structure of the fin field effect transistor and the conductive plug of a source region and a drain region is small.
Owner:SEMICON MFG INT (SHANGHAI) CORP
Tunneling field-effect transistor and manufacturing method thereof
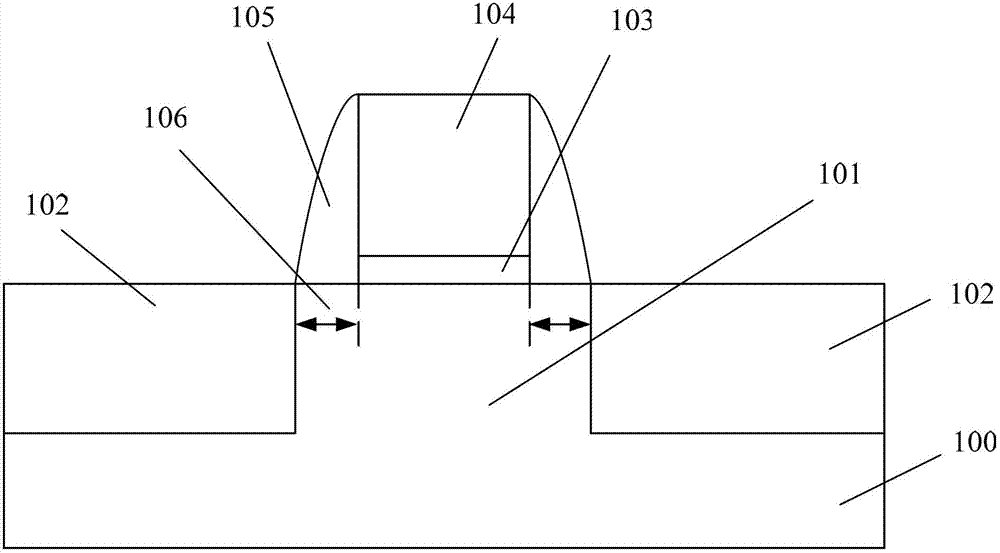
InactiveCN101777580ABig tunnel spaceIncrease drive currentTransistorSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingDriving currentLow leakage
The invention belongs to the technical field of the semiconductor device, and particularly relates to a tunneling field-effect transistor and a manufacturing method thereof. The transistor comprises a source electrode, a drain electrode, a grid electrode and a substrate. The channel of the semiconductor device is indented towards the inside of the substrate, so as to reduce the leakage current and simultaneously drive the current to rise. The invention also discloses a manufacturing method of the semiconductor device. The semiconductor device manufactured by the invention has the advantages of low leakage current, high driving current, high degree of automation and the like. The invention can reduce the static power consumption of the integrated circuit and improve the integrated level thereof.
Owner:FUDAN UNIV
Metal-oxide-semiconductor transistor and method of forming the same
ActiveUS20080099801A1Increase drive currentDeveloping performanceSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSemiconductor devicesSalicideSemiconductor
A method of manufacturing a MOS transistor device. First, a semiconductor substrate having a gate structure is prepared. The gate structure has two sidewalls and a liner on the sidewalls. Subsequently, a stressed cap layer is formed on the semiconductor substrate, and covers the gate structure and the liner. Next, an activating process is performed. Furthermore, the stressed cap layer is etched to be a salicide block. Afterward, a salicide process is performed to form a silicide layer on the regions that are not covered by the stressed cap layer.
Owner:UNITED MICROELECTRONICS CORP
Preparation method of germanium-base schottky transistor
ActiveCN101635262AGood lookingImprove performanceSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingVery large scale integrated circuitsManufacturing technology
The invention discloses a preparation method of a germanium-base schottky transistor, which belongs to the technical field of a manufacturing process of ultra large scale integrated circuits (ULSI). The method comprises the following steps: manufacturing an MOS transistor structure on a germanium-base substrate; depositing a metal thin film; carrying out heat treatment for the first time for quick heat annealing so as to ensure that the metal thin film layer and the germanium layer below the metal thin film layer react to form metal germanide; removing the unreacted metal thin film layer; doping impurities in the germanide layer generated by the reaction; carrying out heat treatment for the second time for annealing so as to ensure that the doped impurities are activated to drive in; and finally forming contact holes and metal connection wires. The method carries out the impurity doping and the activated drive-in annealing after forming the germanide through the first annealing and can effectively regulate and control a barrier height of the contact of a metal semiconductor and also improve the surface appearance of the germanide.
Owner:SEMICONDUCTOR MANUFACTURING INTERNATIONAL (BEIJING) CORP +1
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com