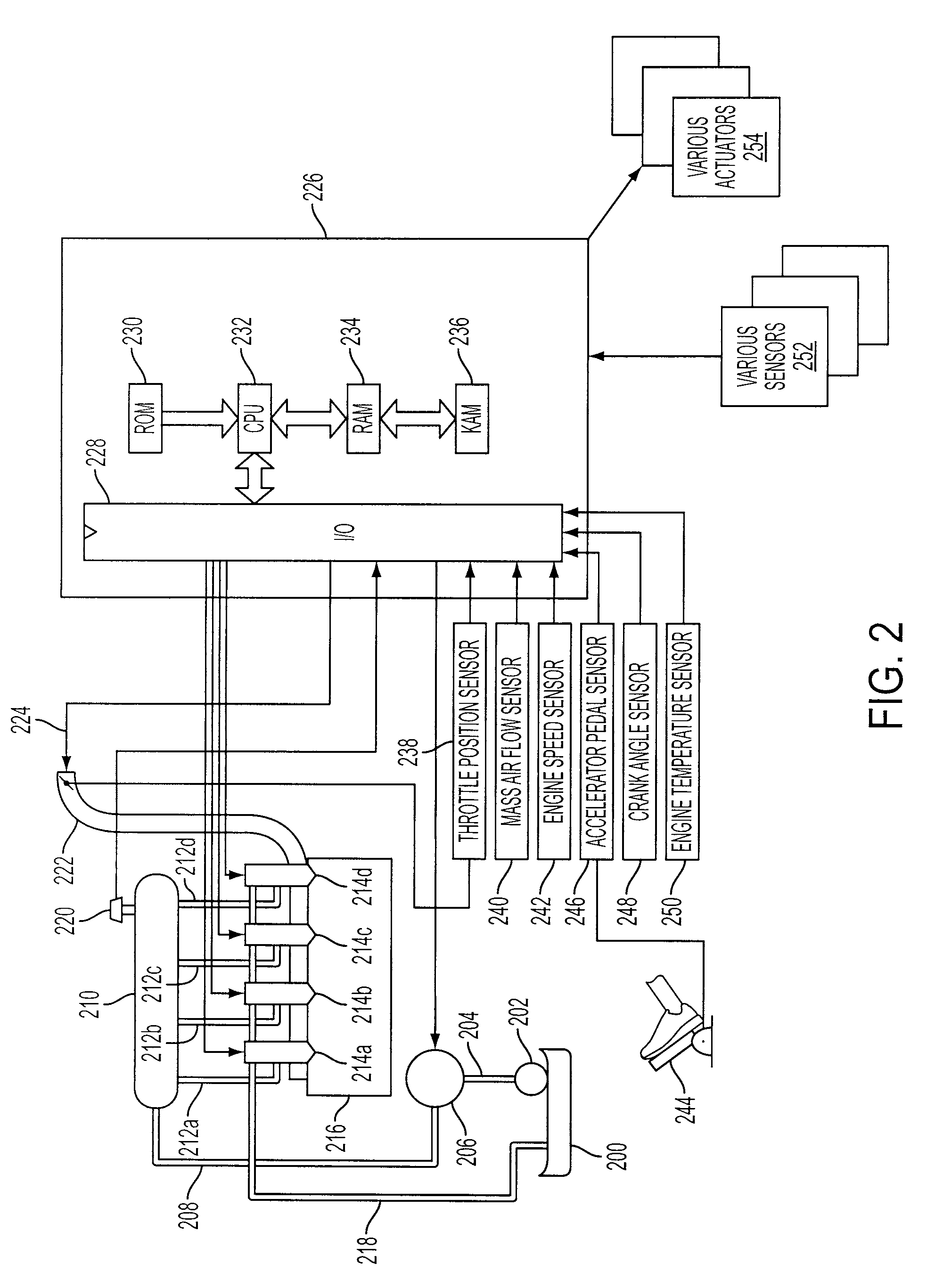
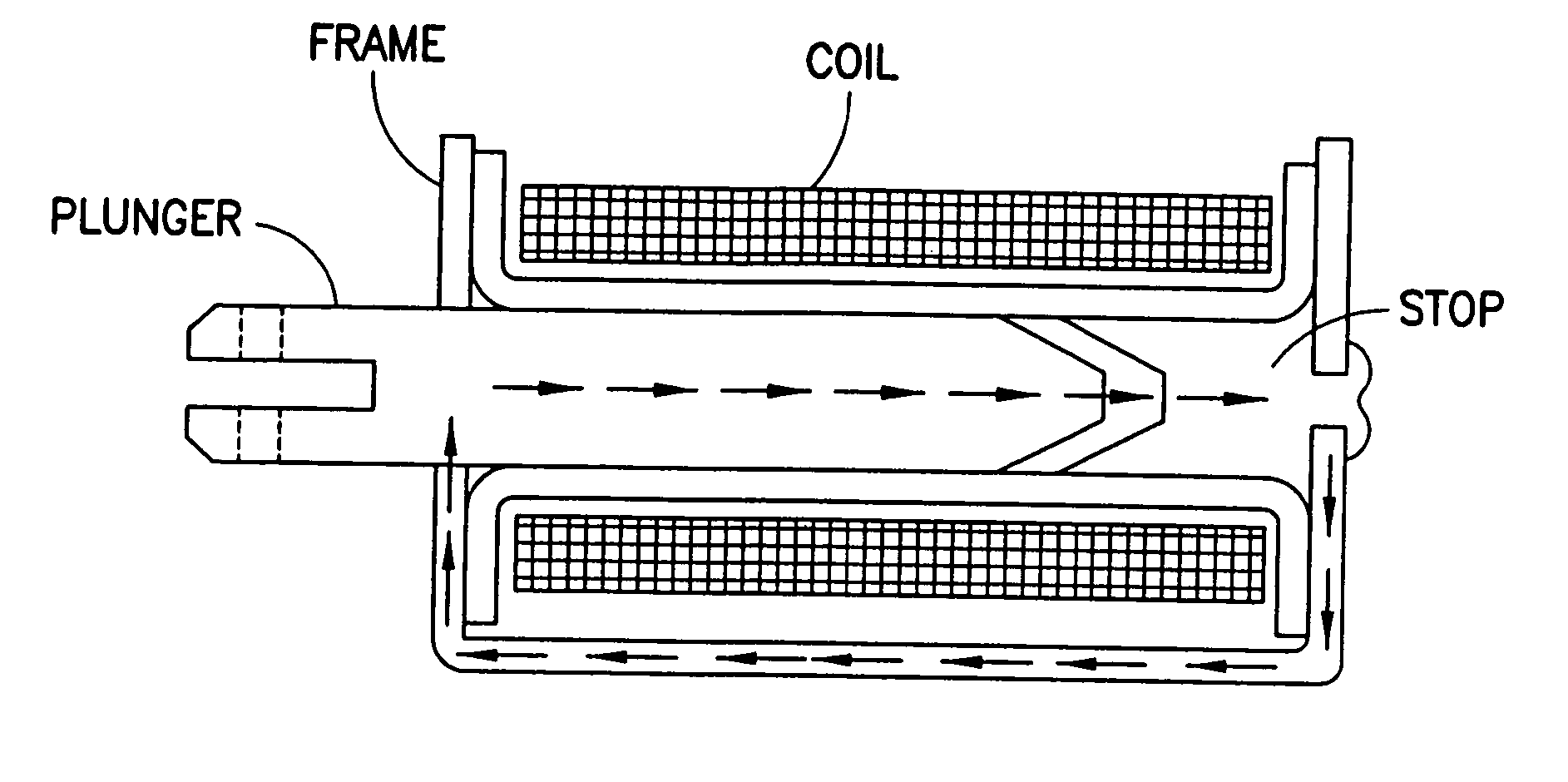
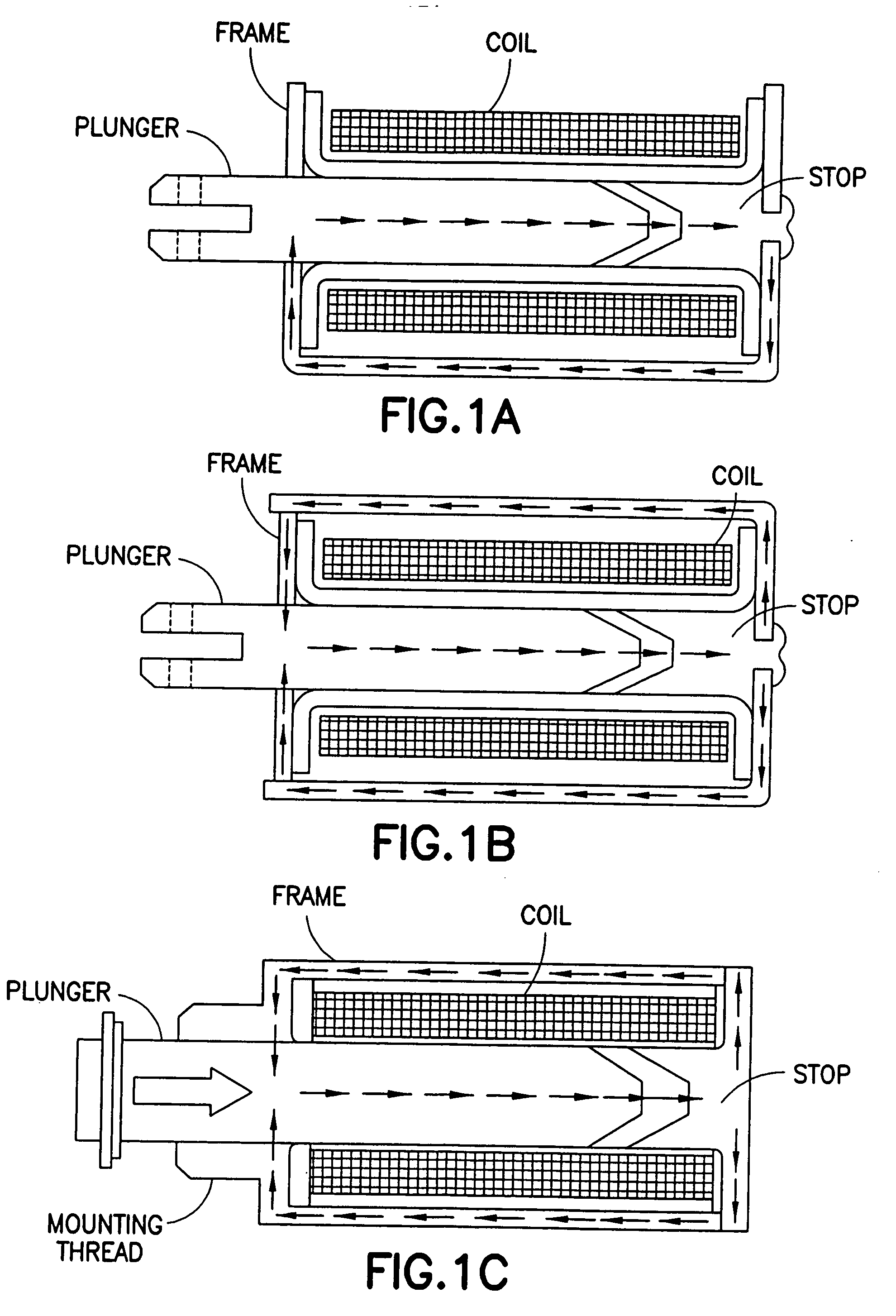
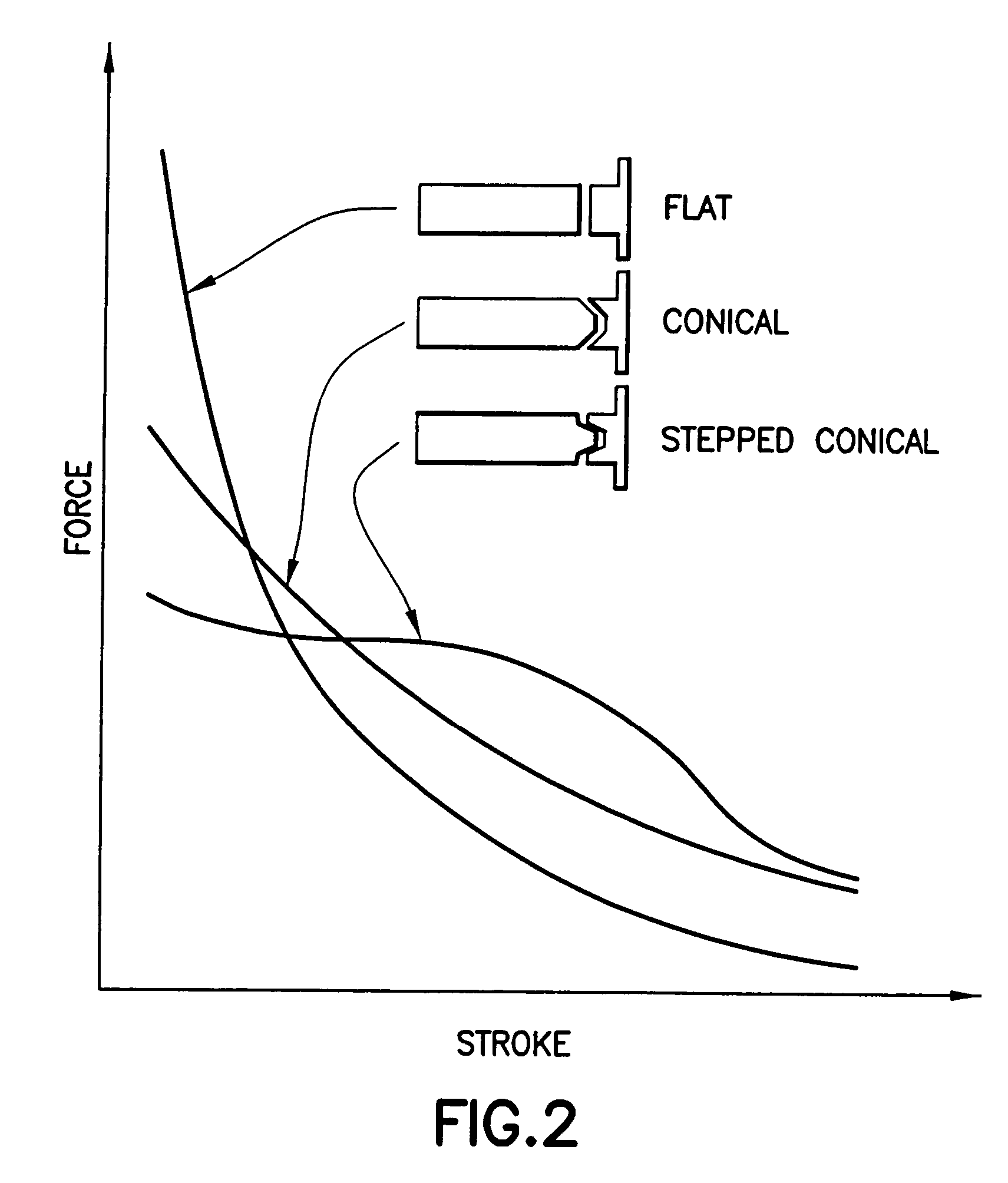
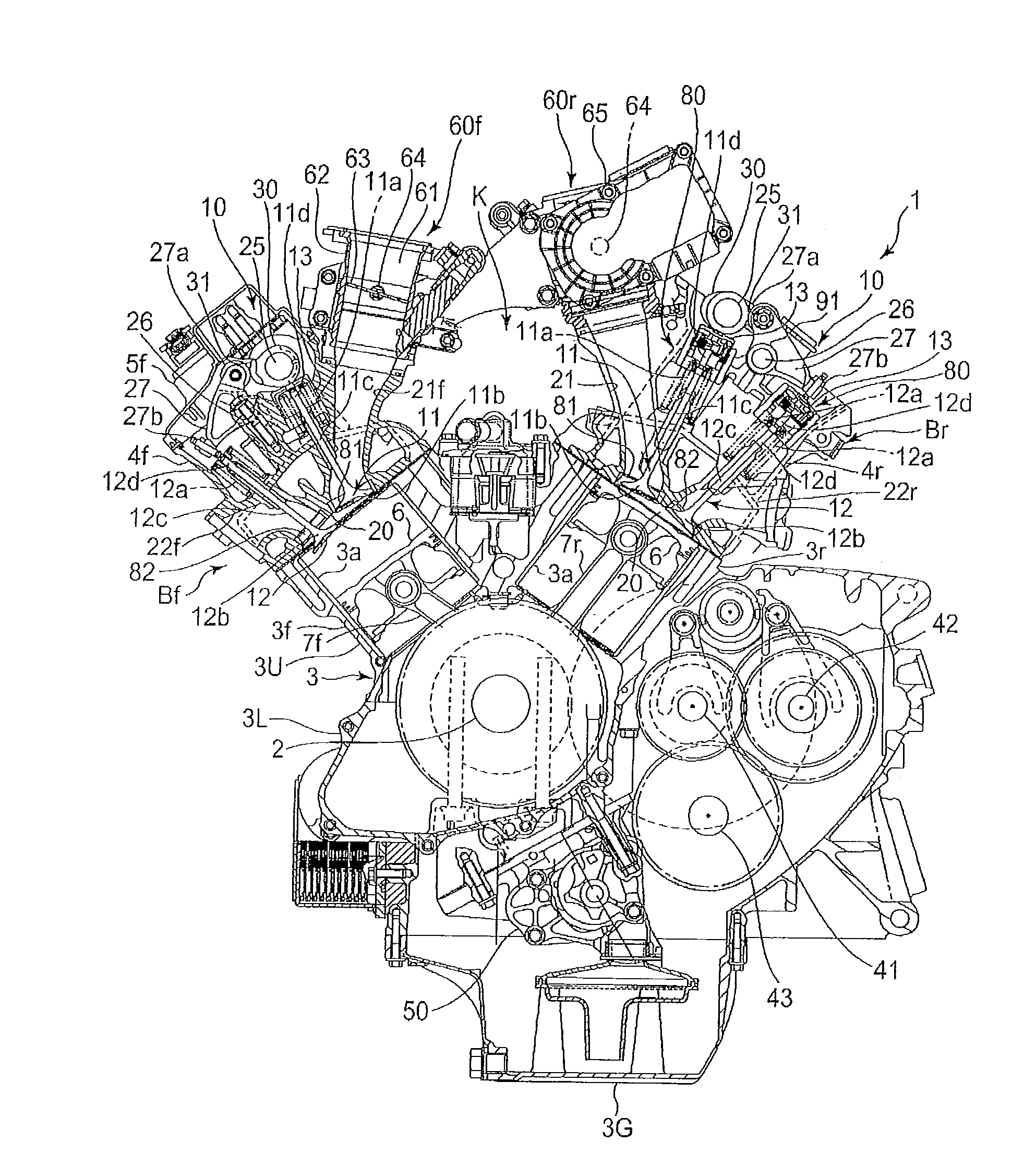
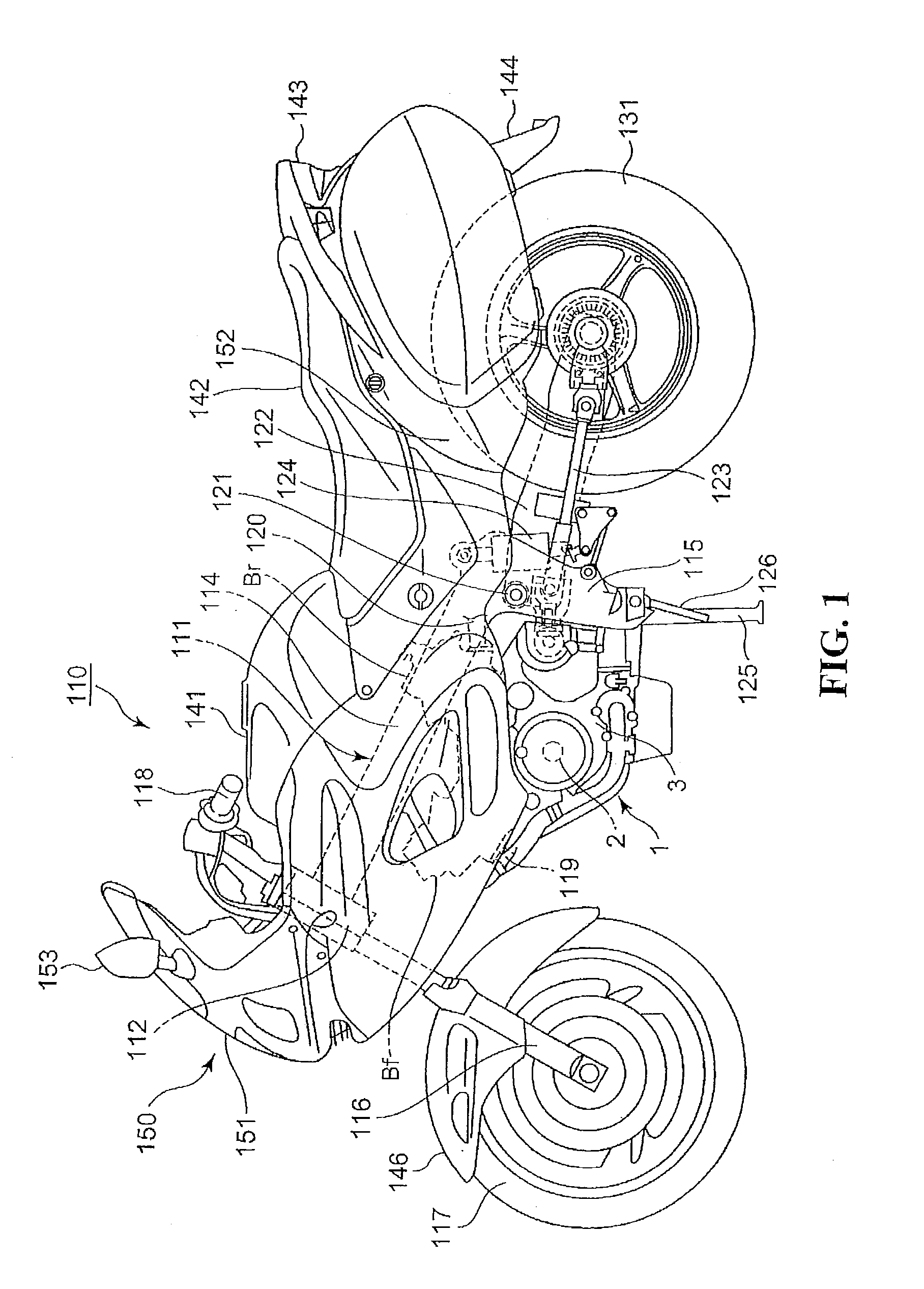
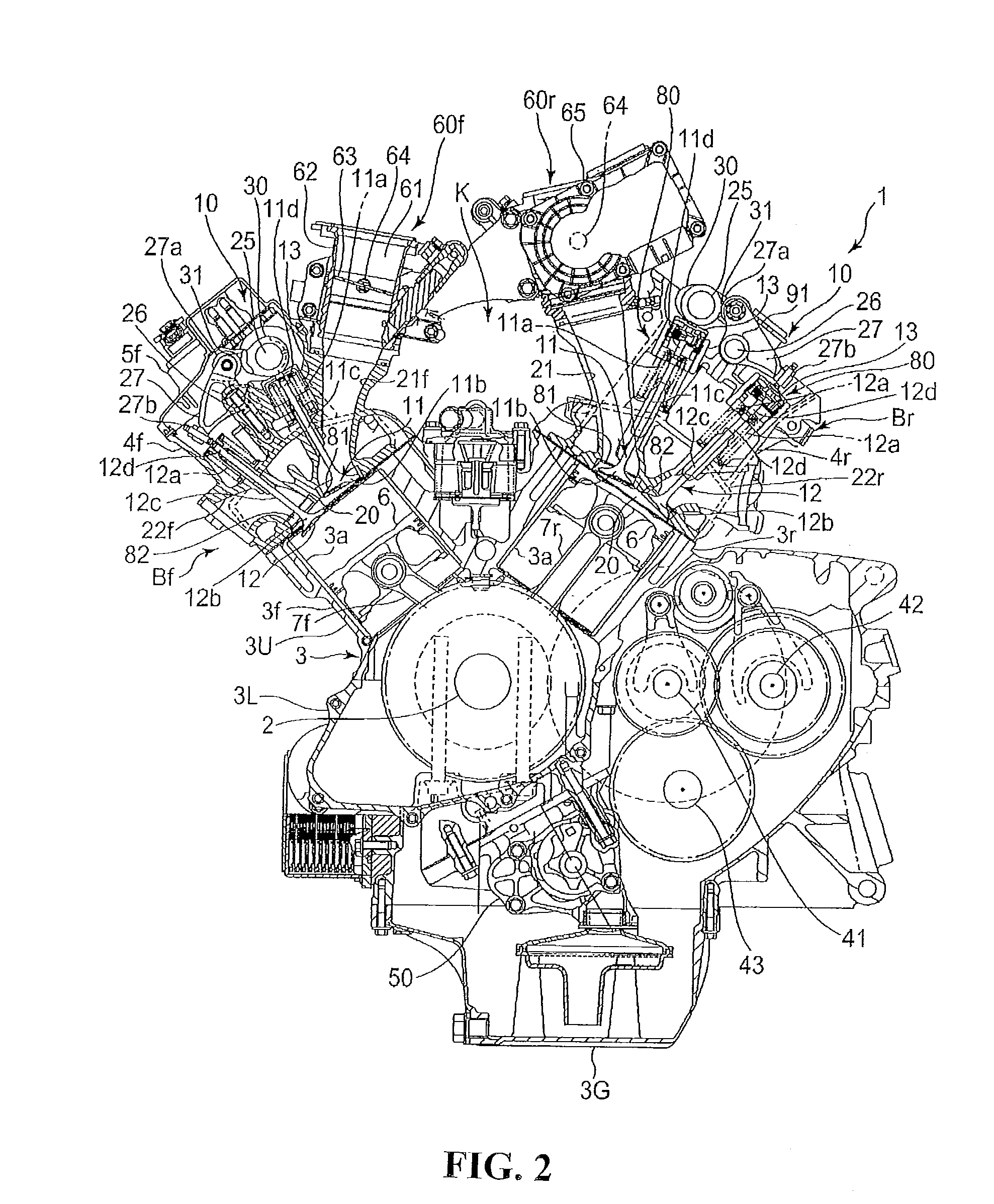
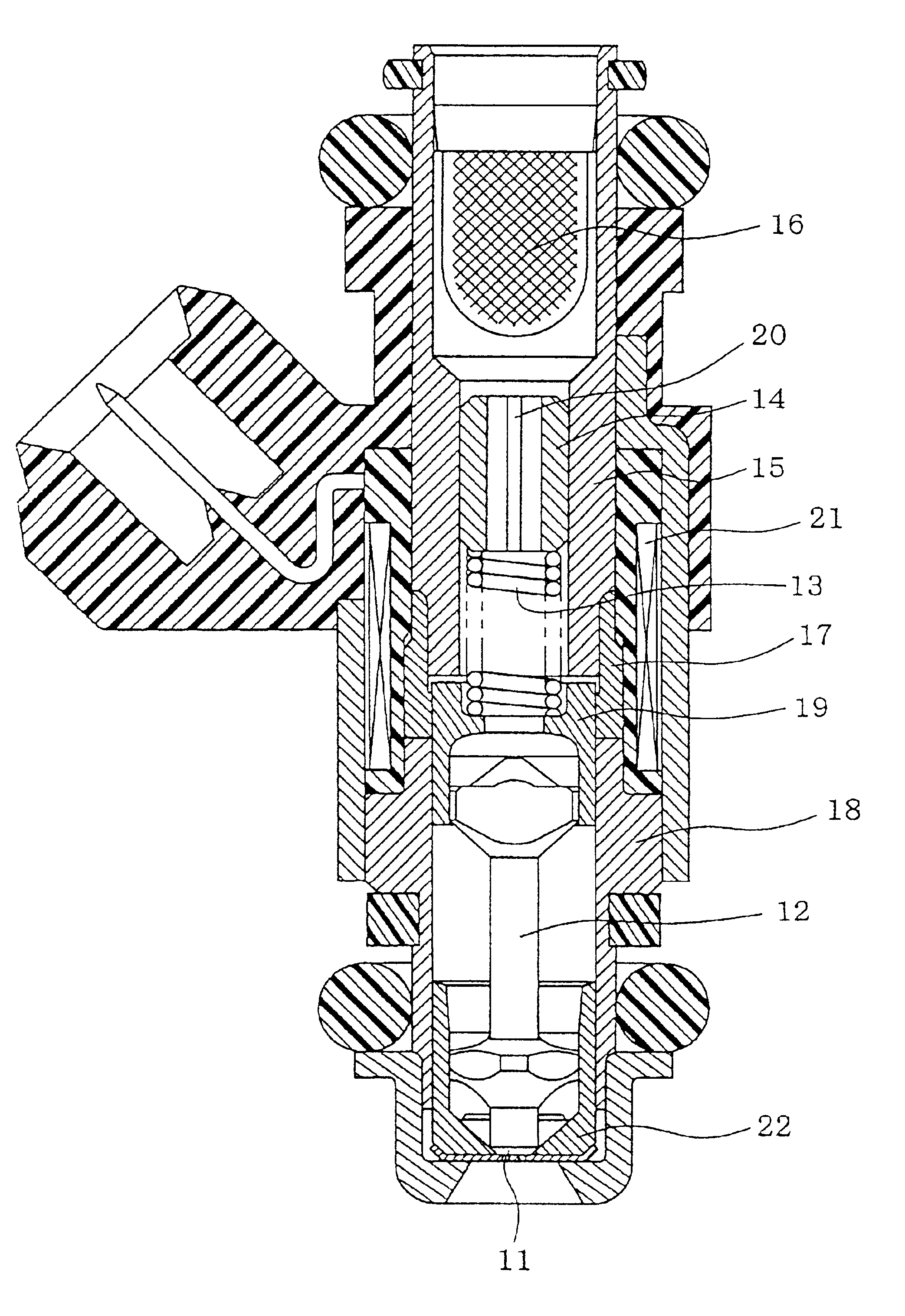
Patents
Literature
901results about "Fuel-injection pumps" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
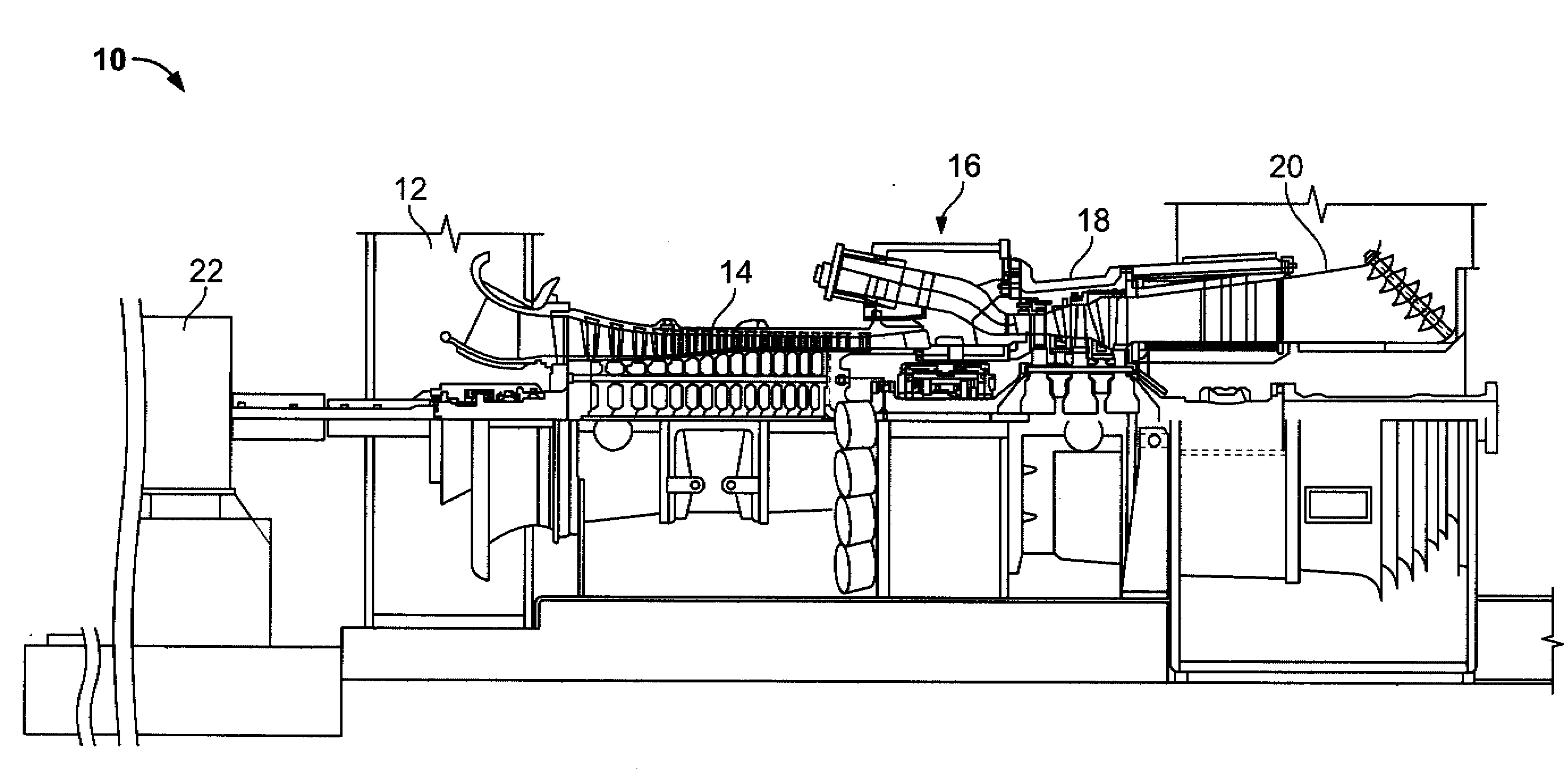
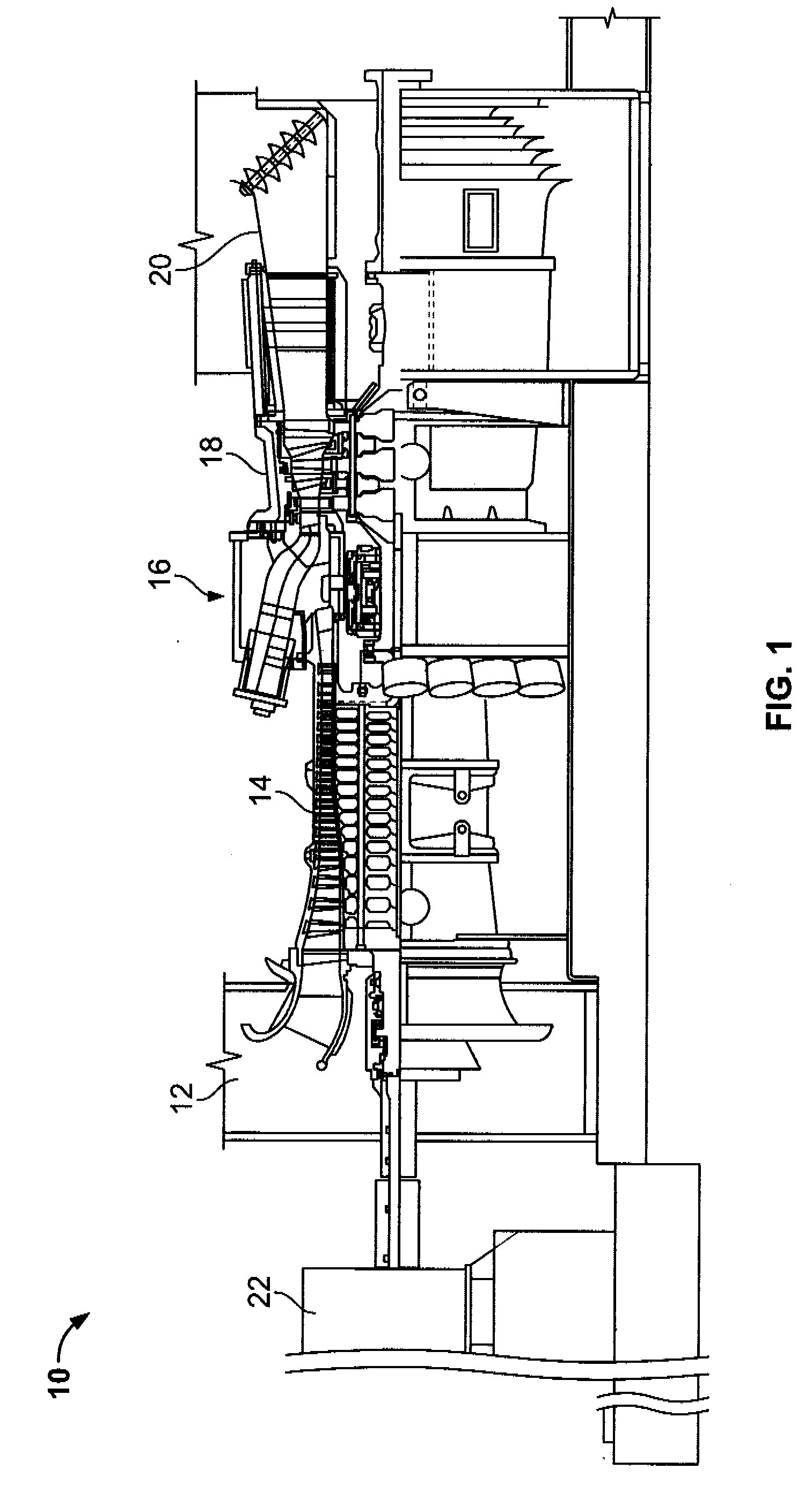
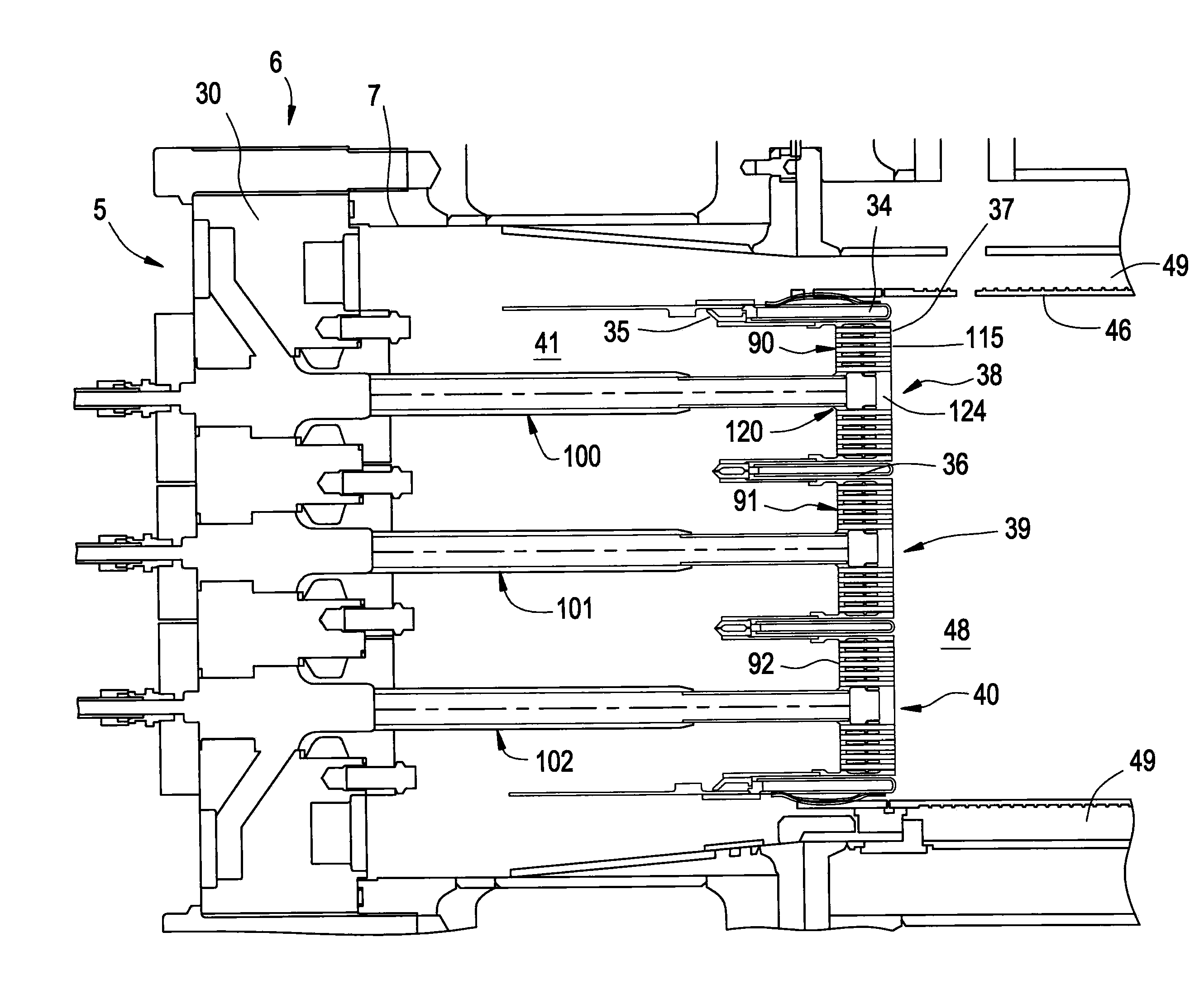
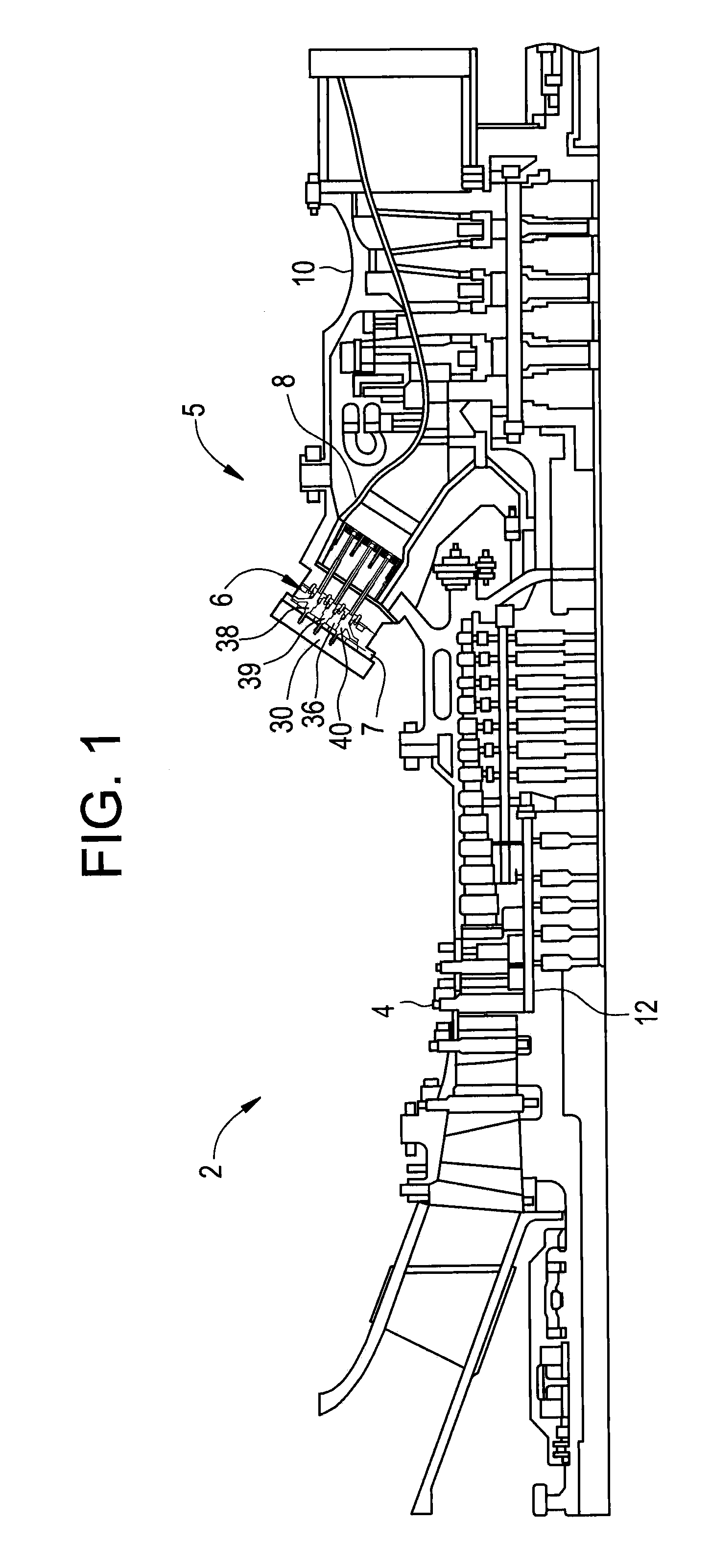
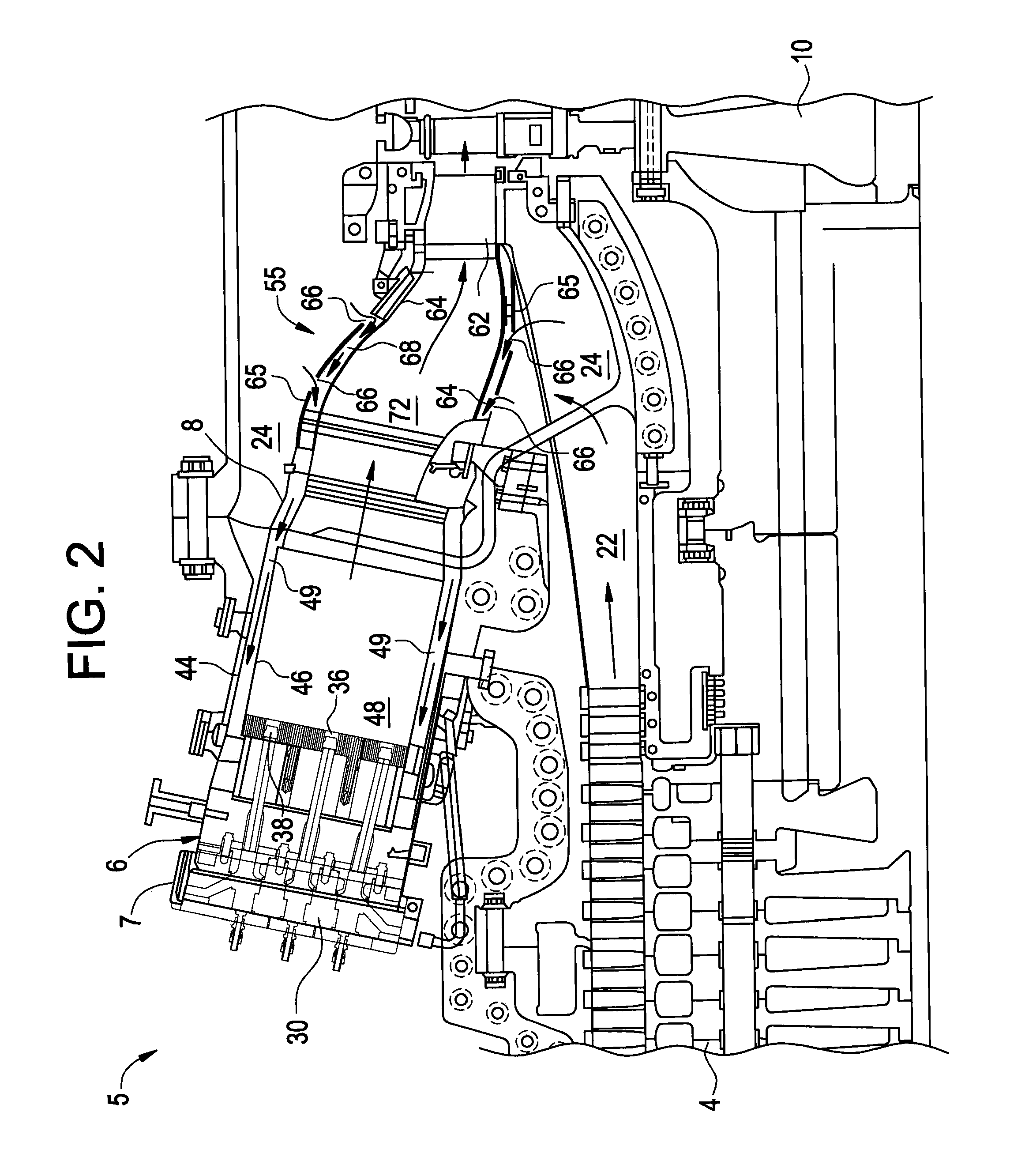
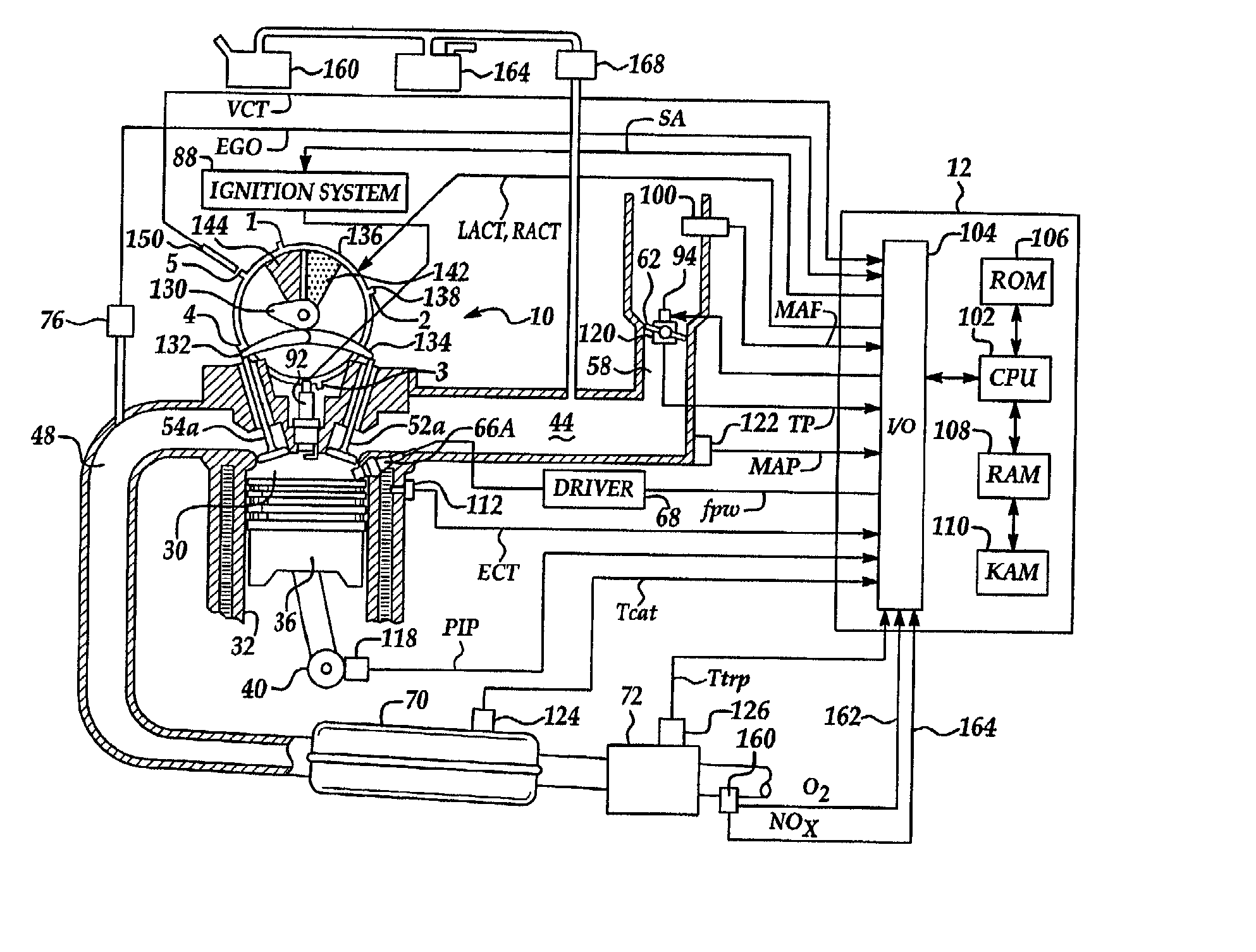
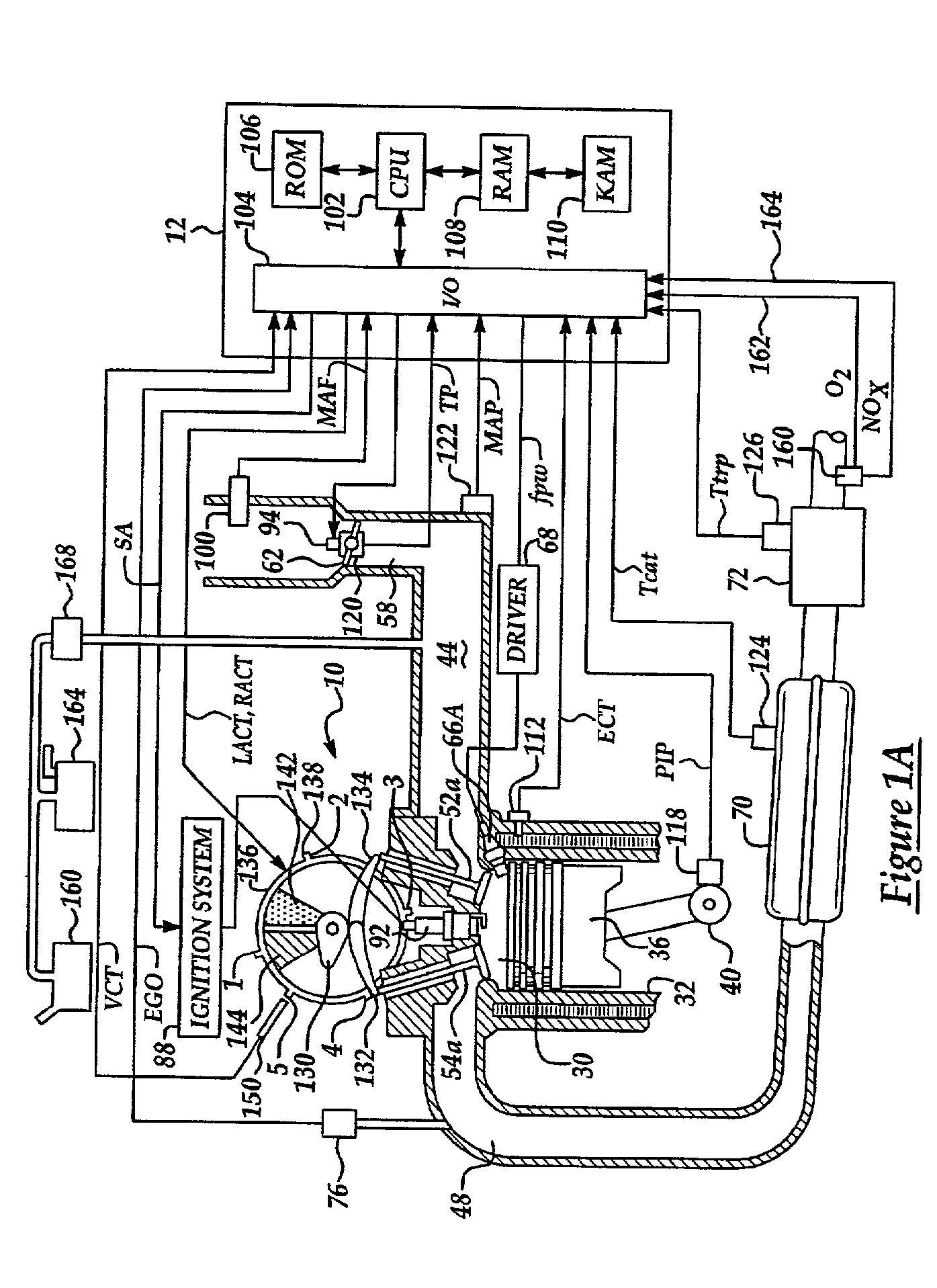
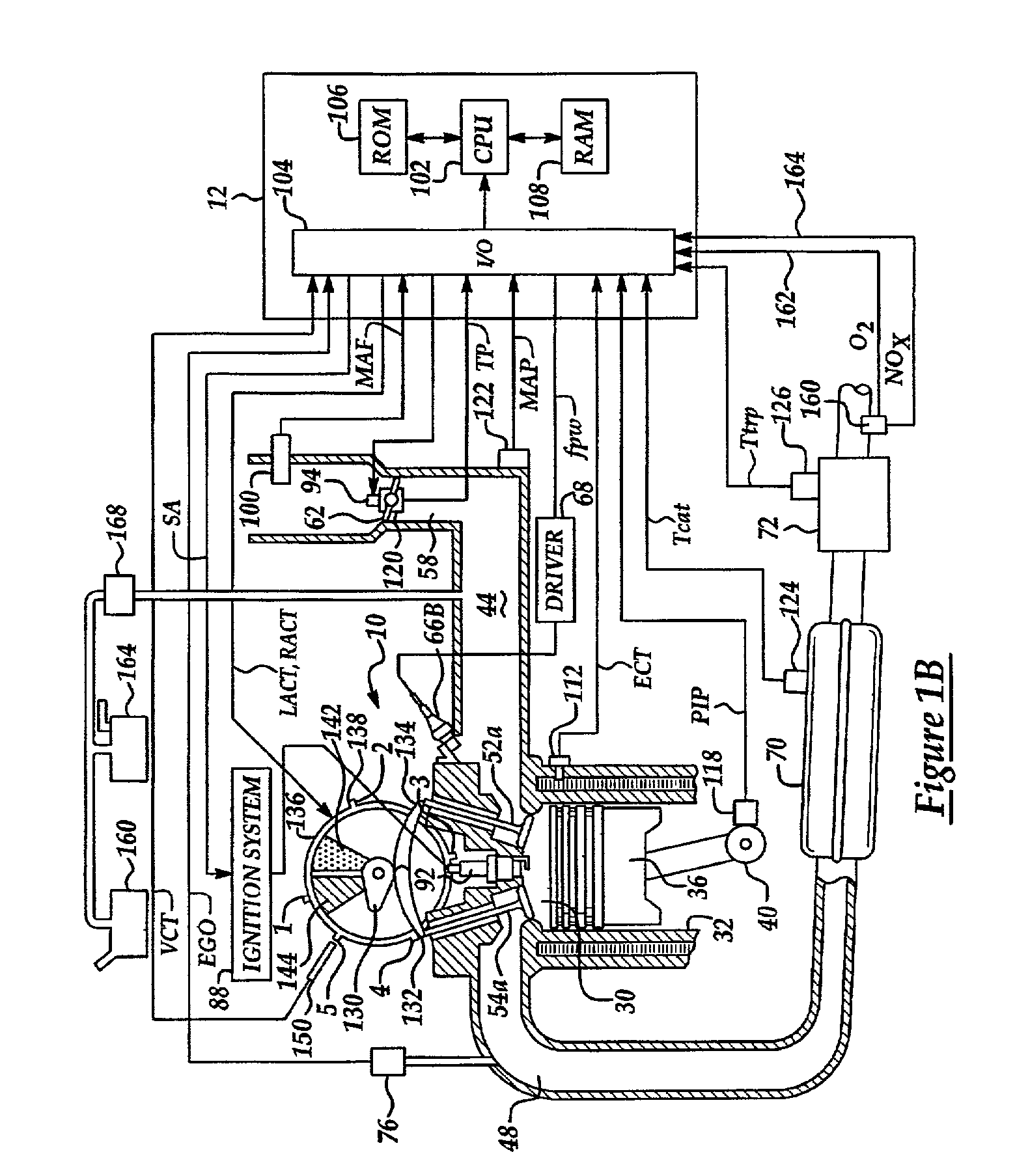
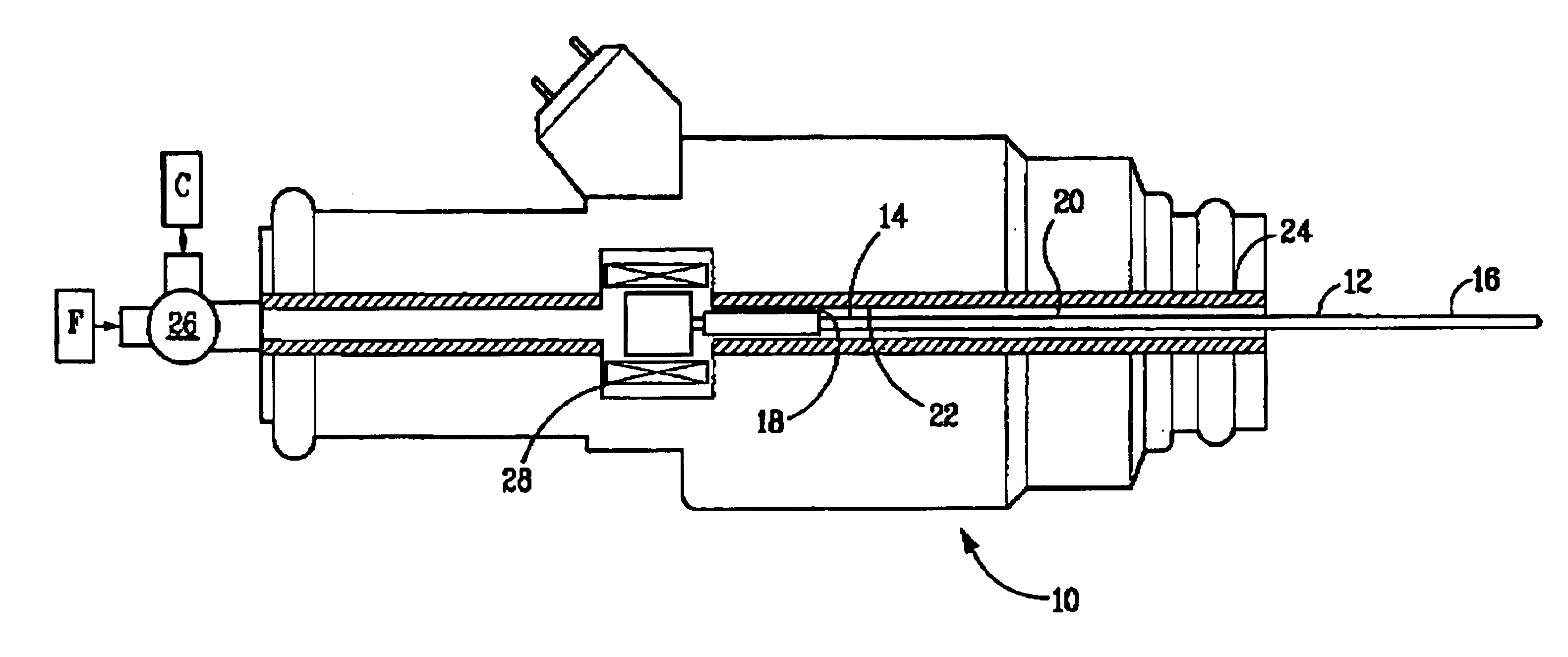
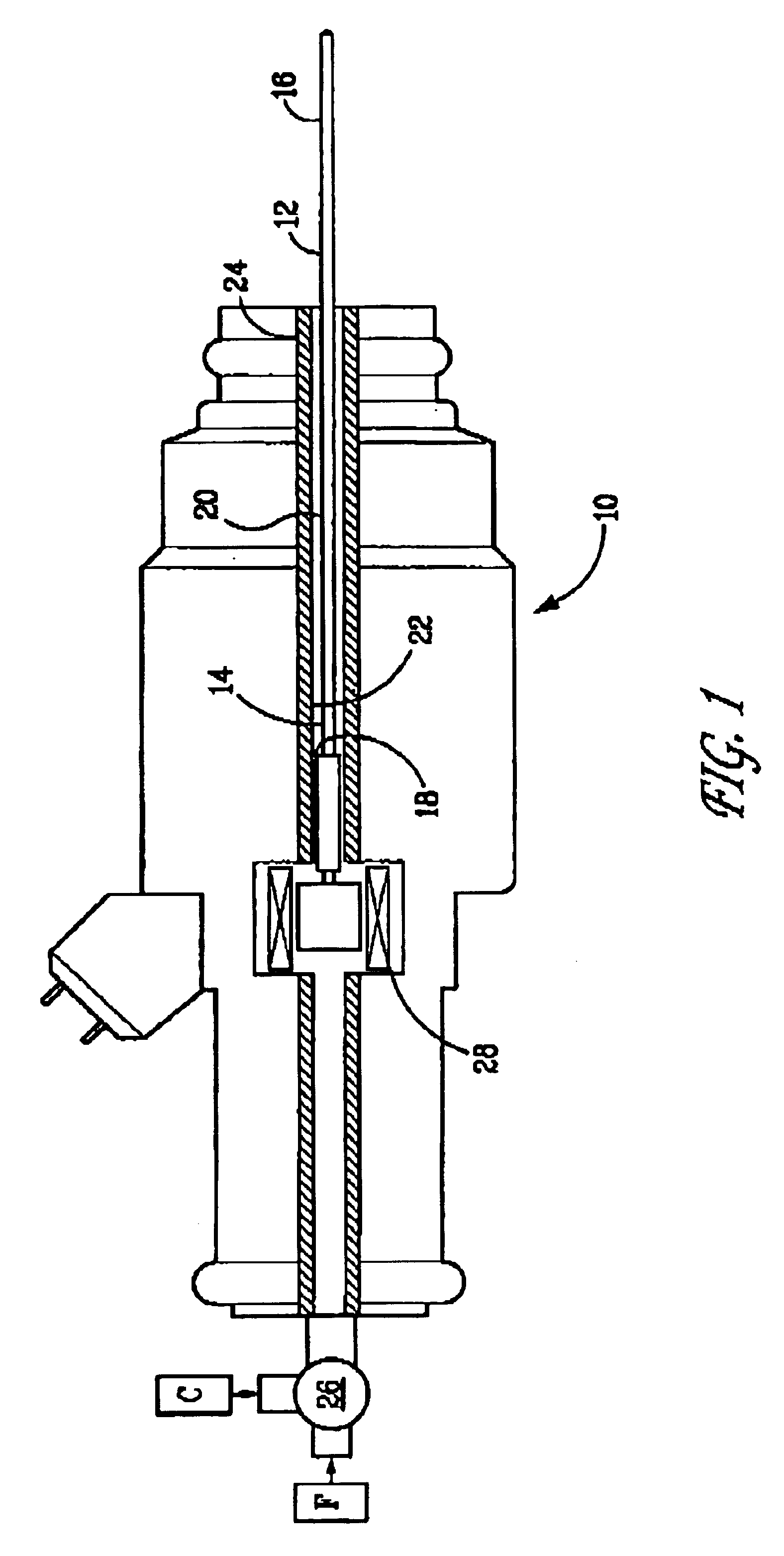
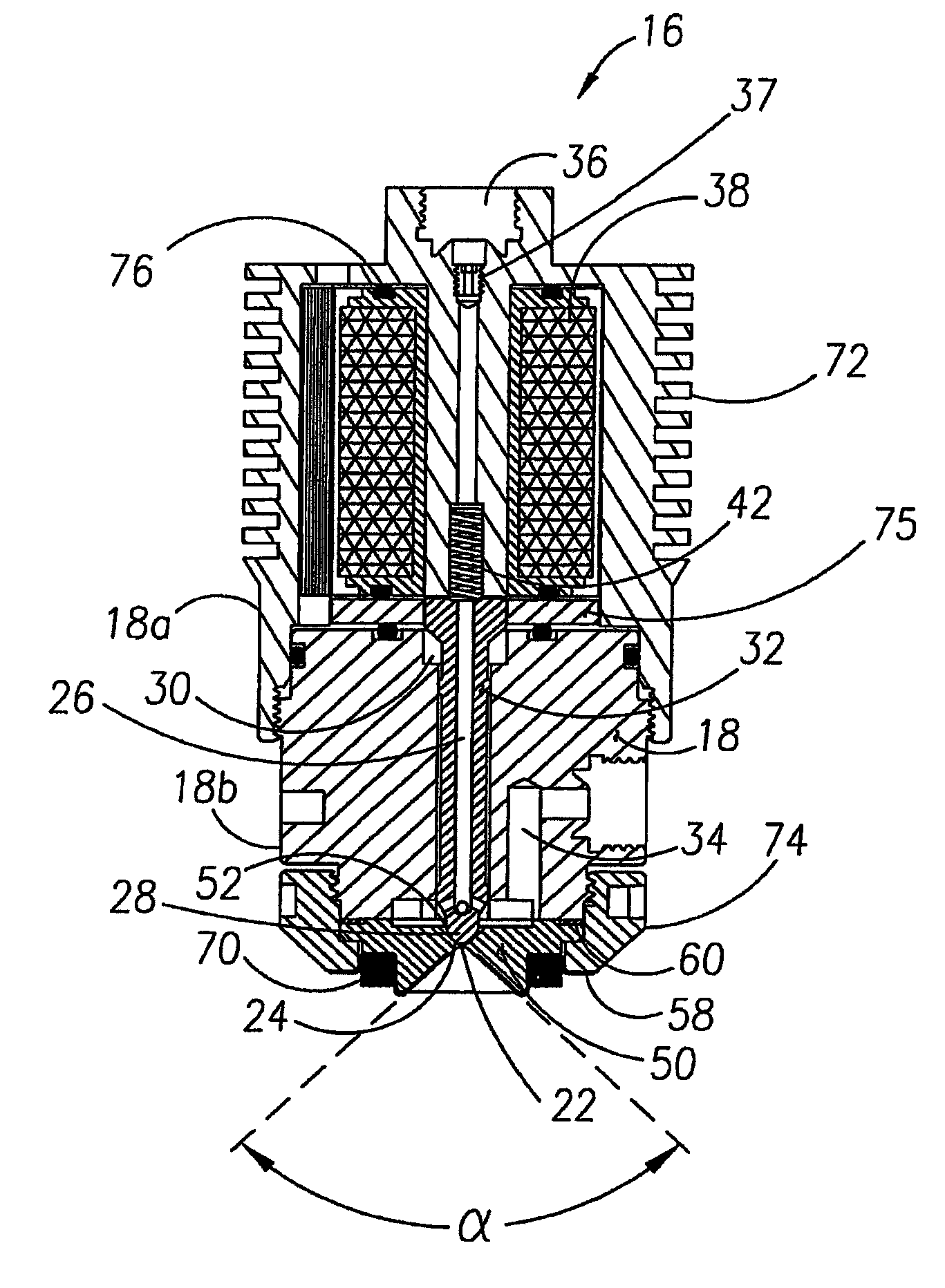
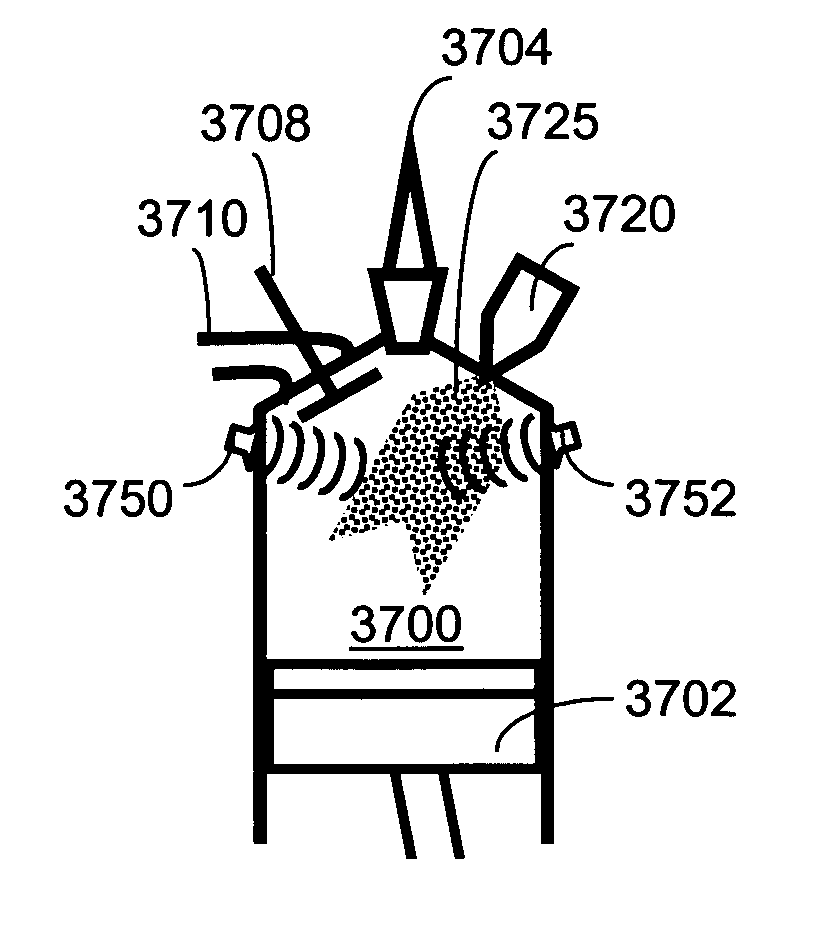
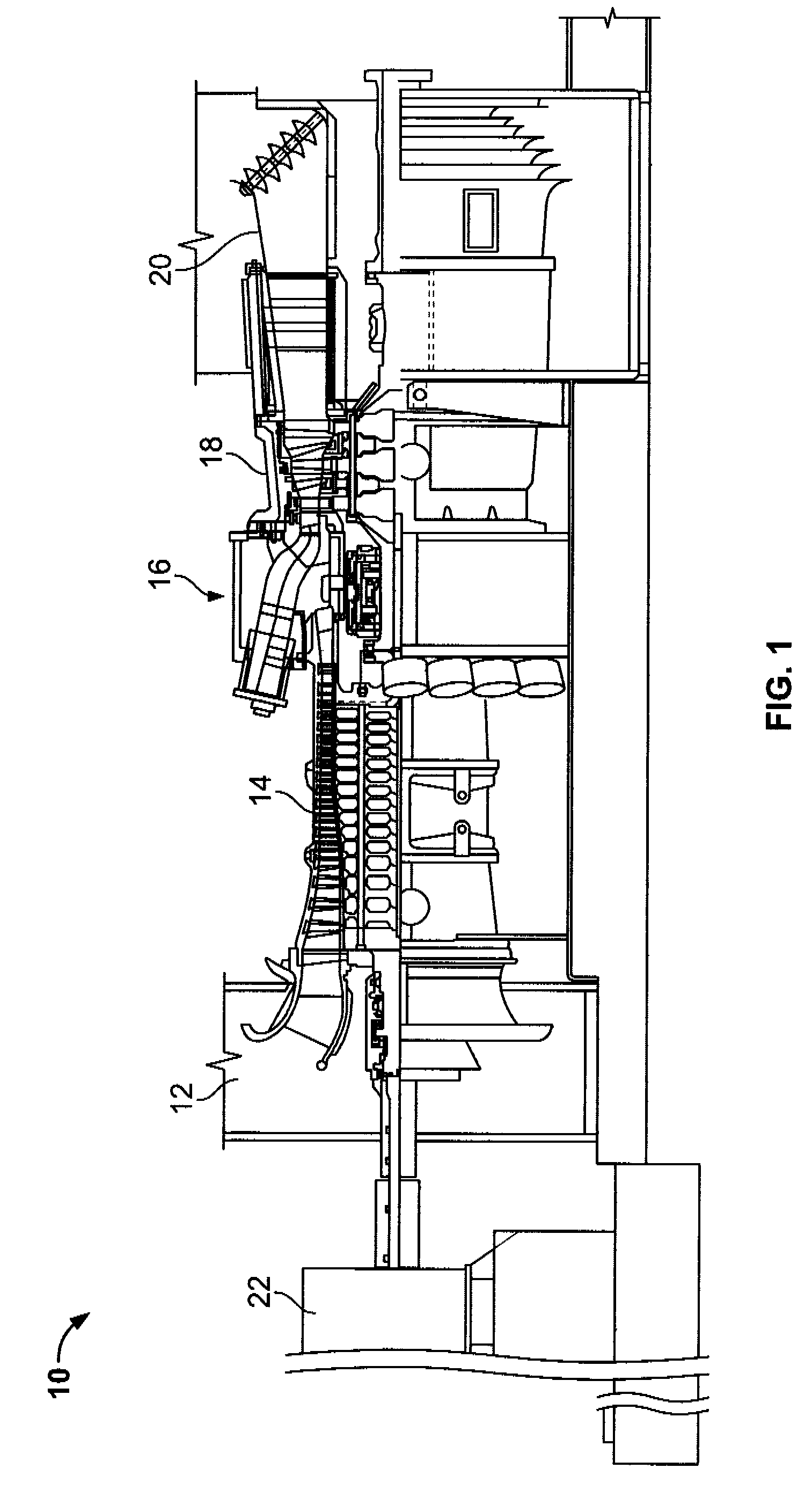
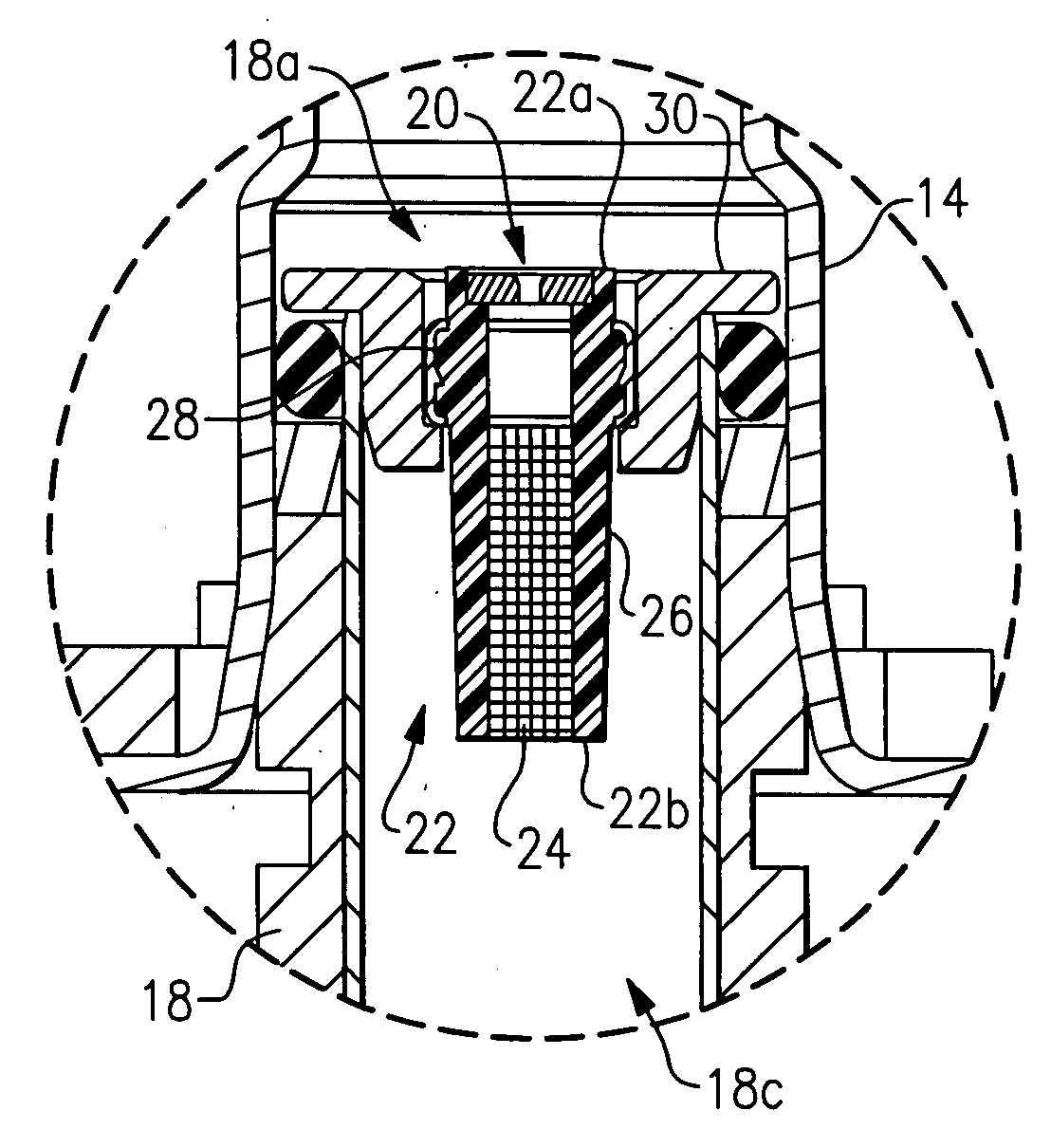
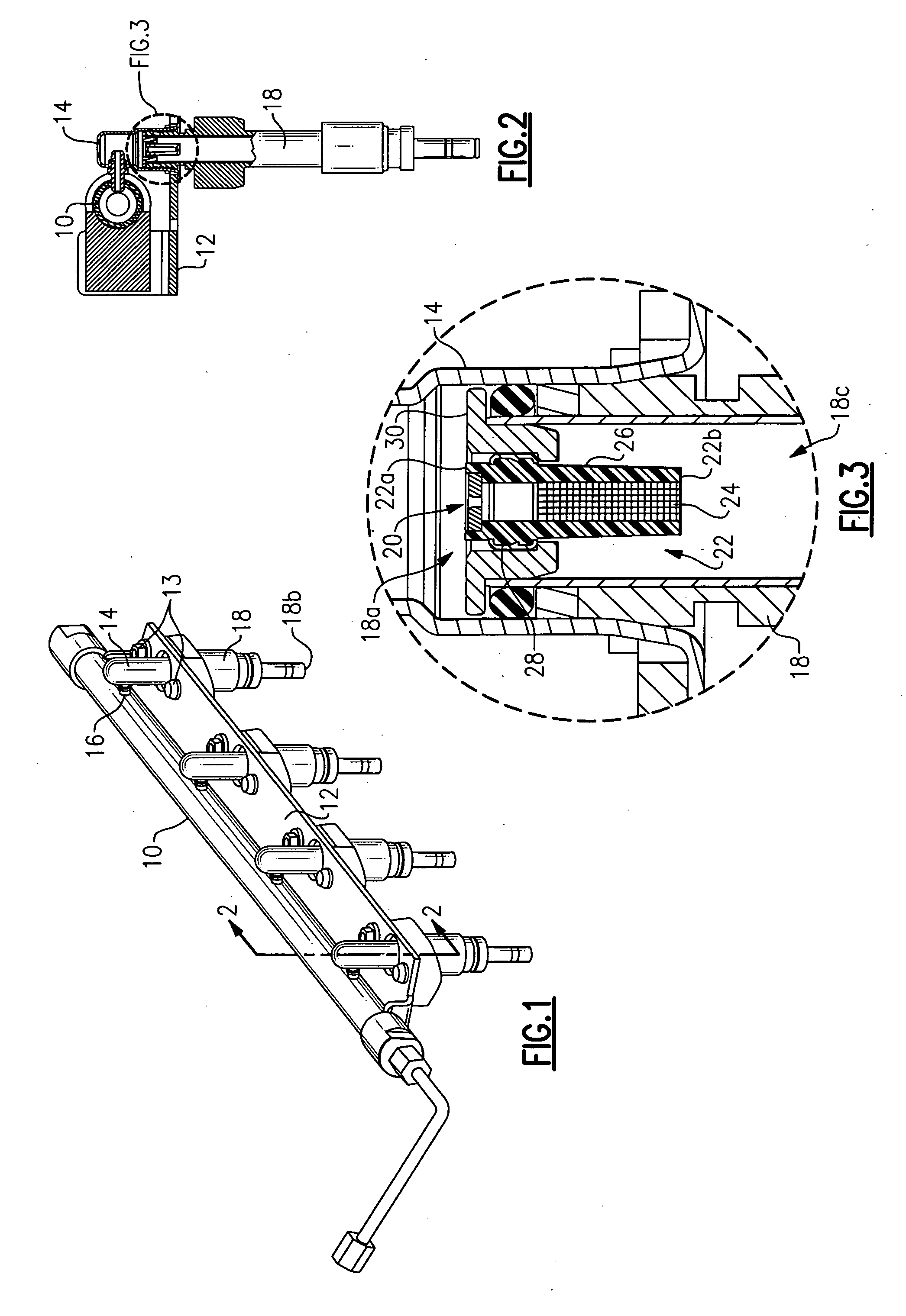
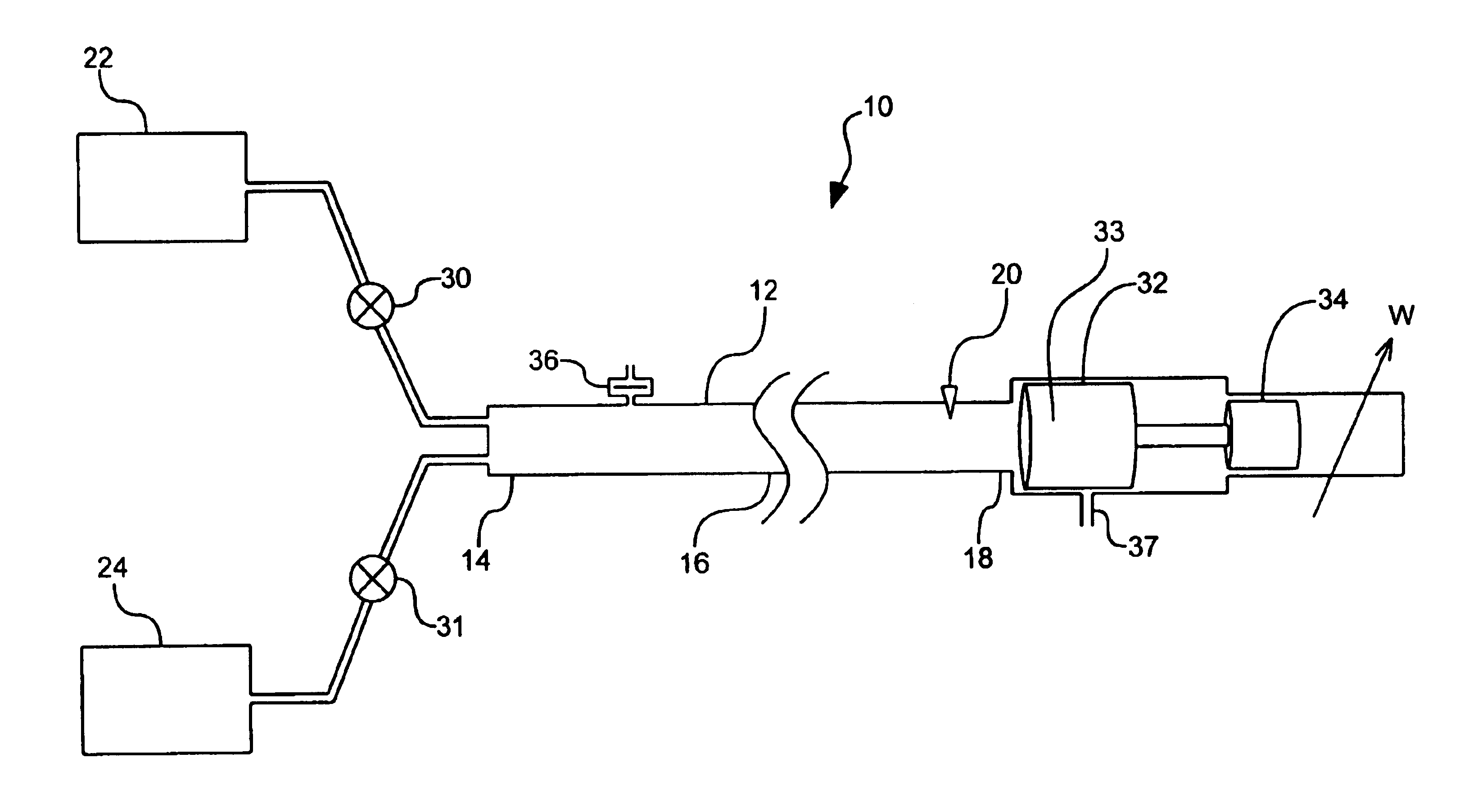
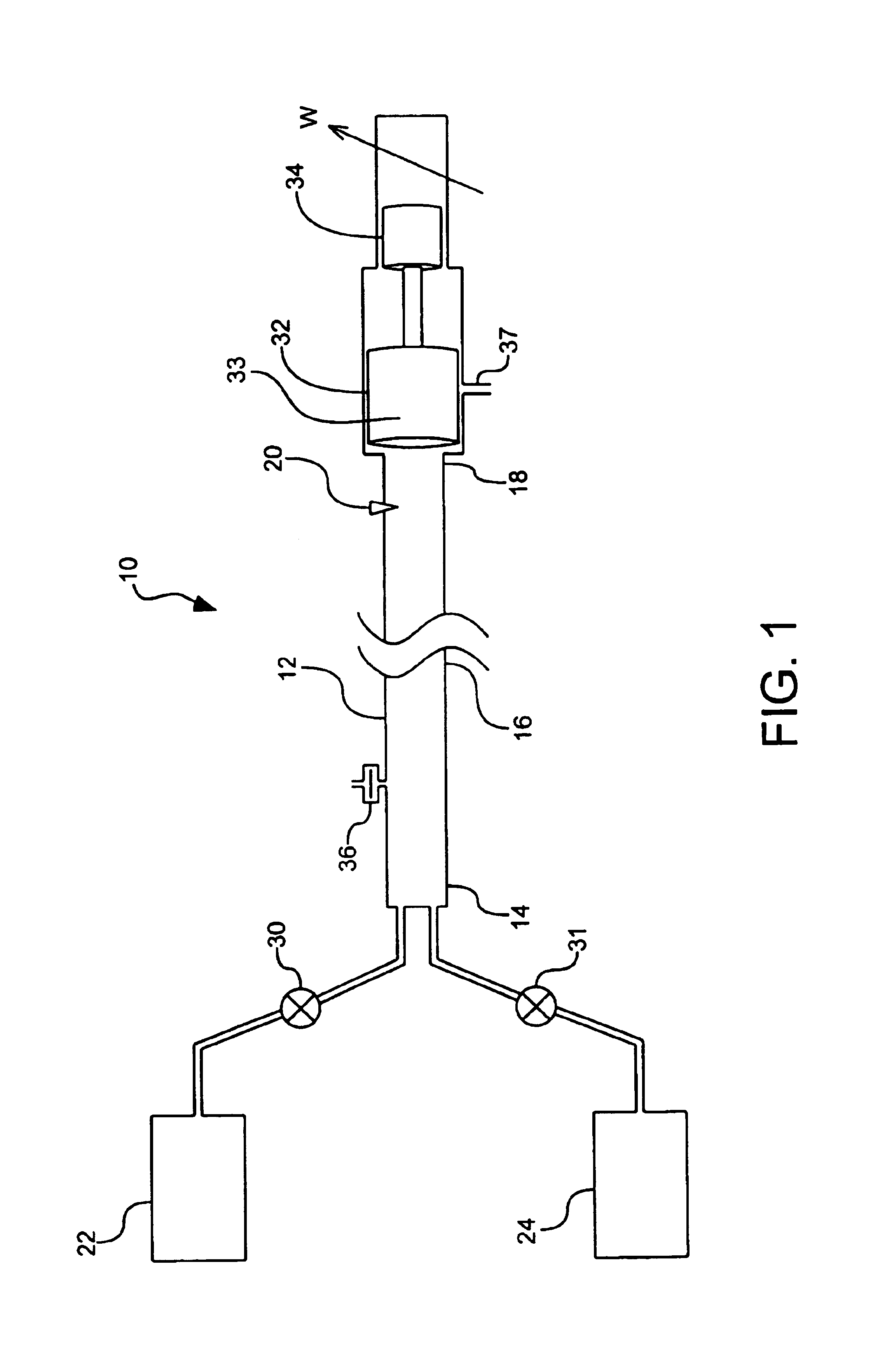
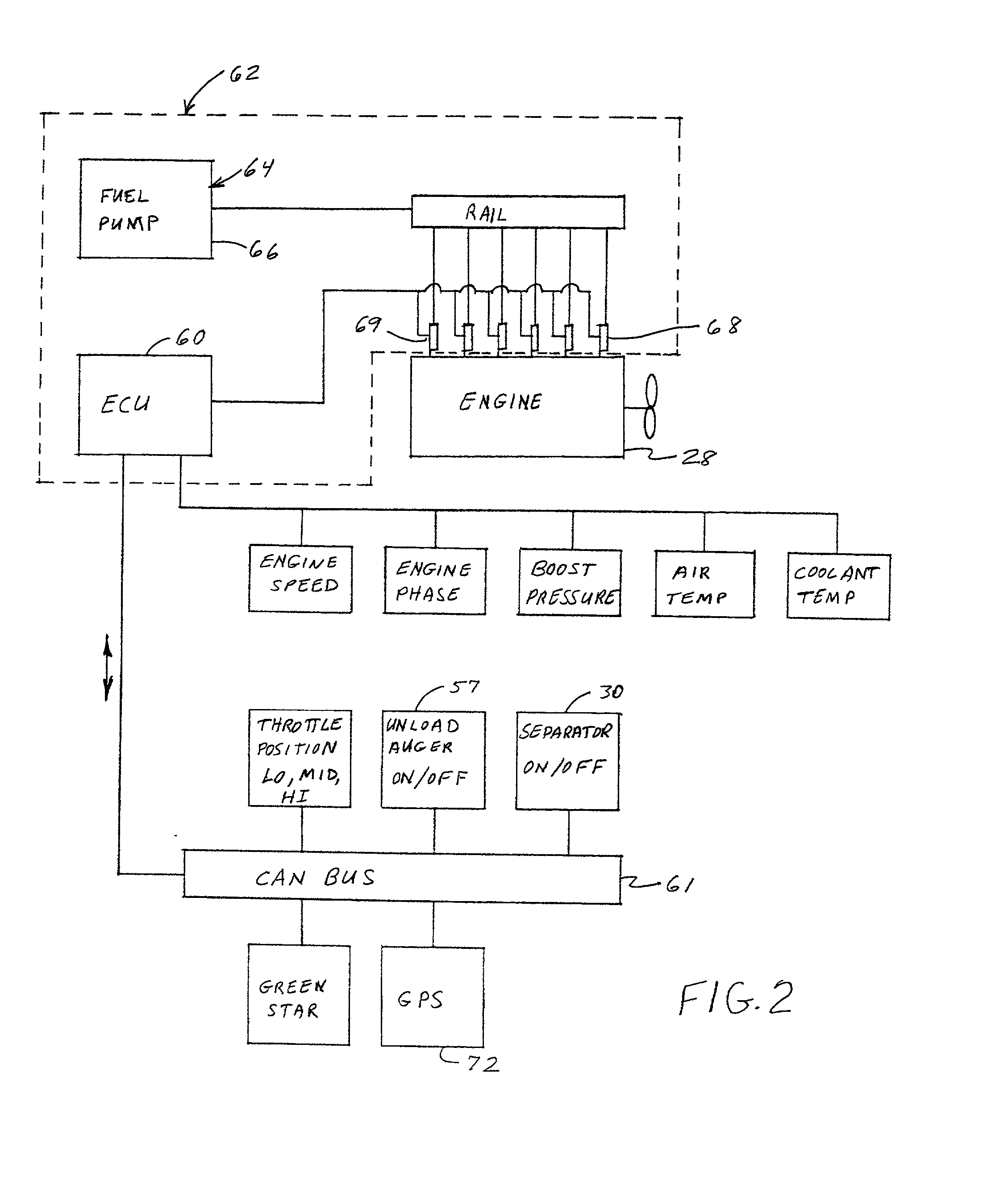
METHODS AND SYSTEMS TO FACILITATE REDUCING NOx EMISSIONS IN COMBUSTION SYSTEMS
A method for assembling a gas turbine combustor system is provided. The method includes providing a combustion liner including a center axis, an outer wall, a first end, and a second end. The outer wall is orientated substantially parallel to the center axis. The method also includes coupling a transition piece to the liner second end. The transition piece includes an outer wall. The method further includes coupling a plurality of lean-direct injectors along at least one of the liner outer wall and the transition piece outer wall such that the injectors are spaced axially apart along the wall.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
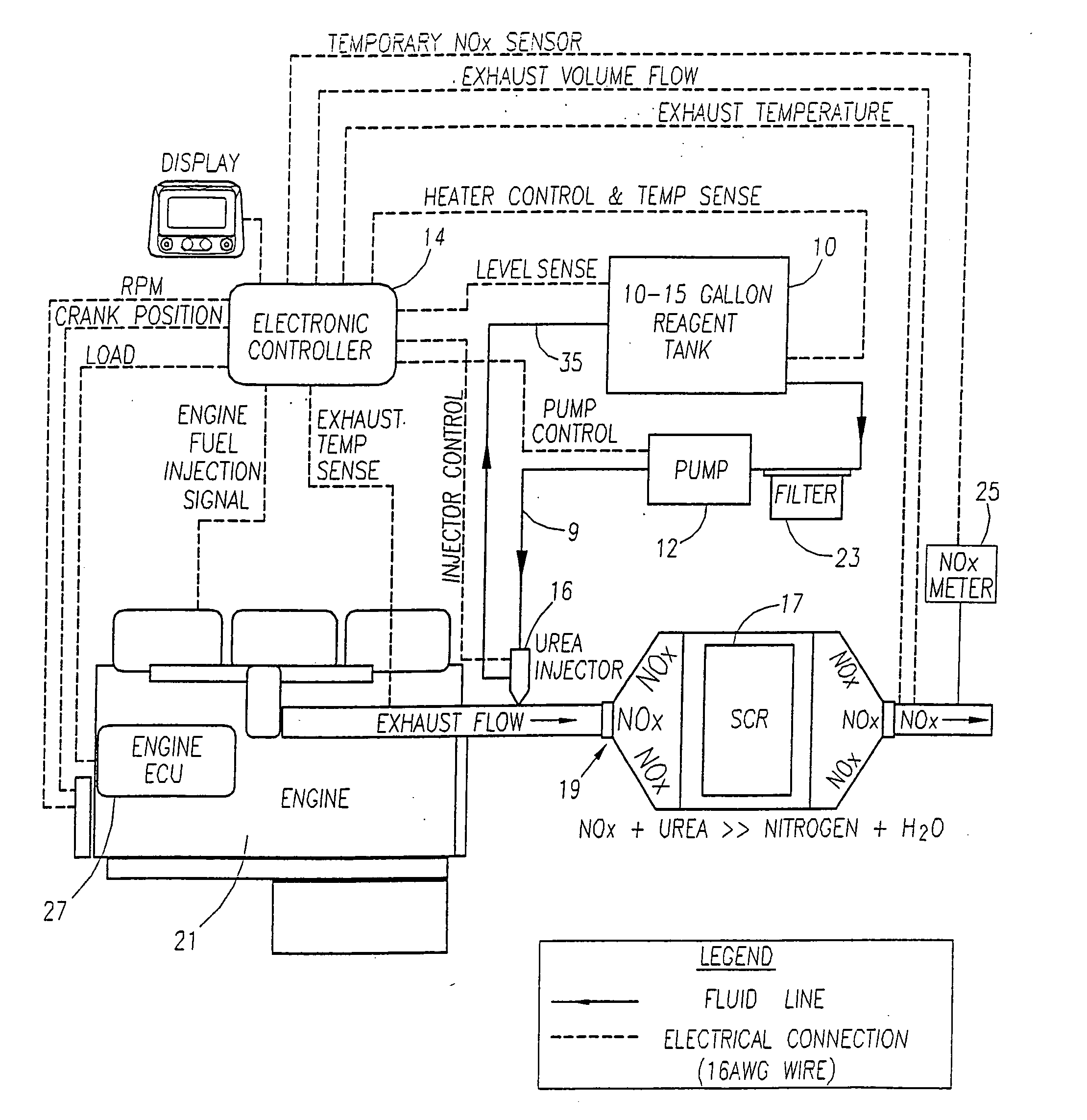
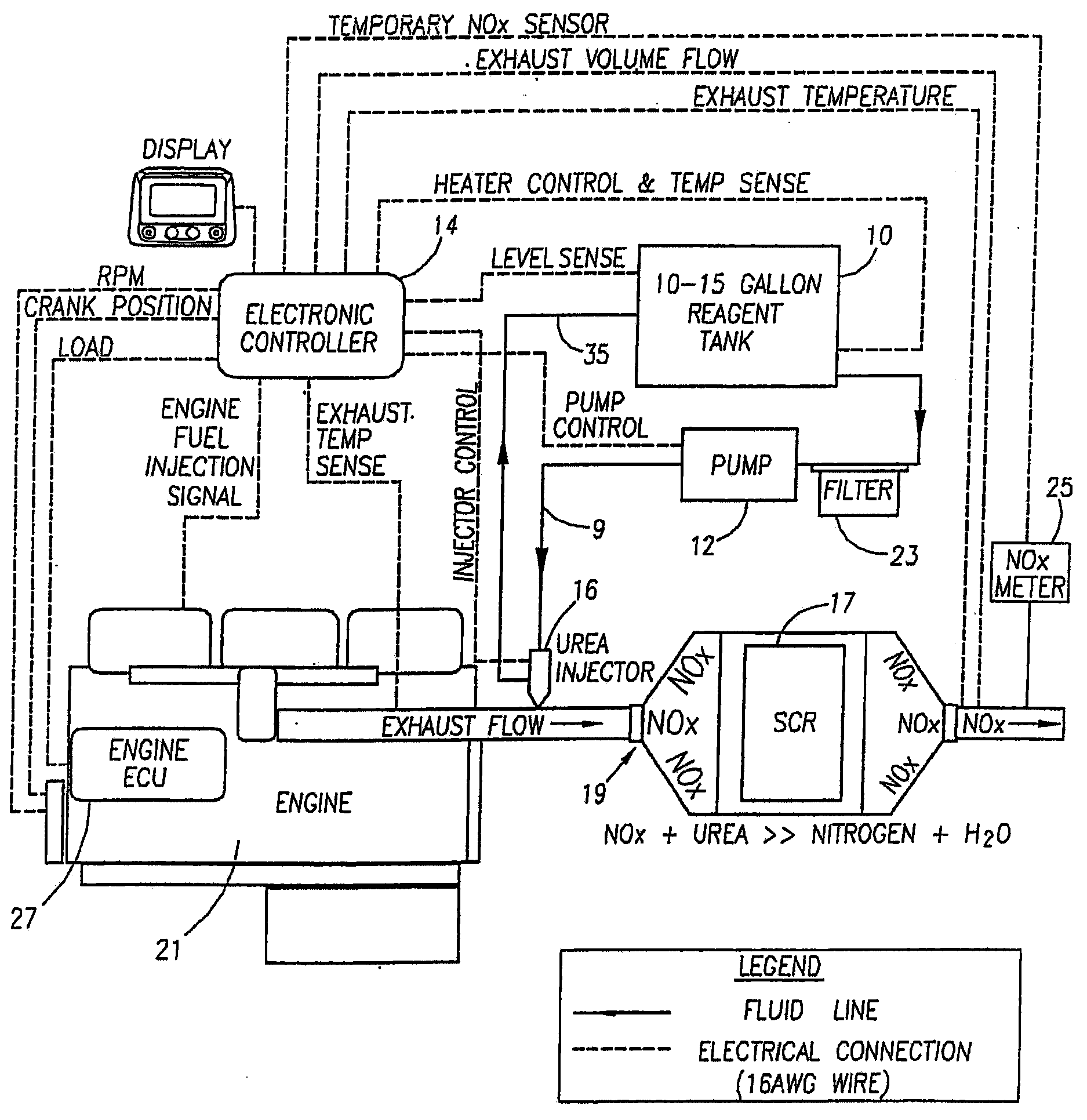
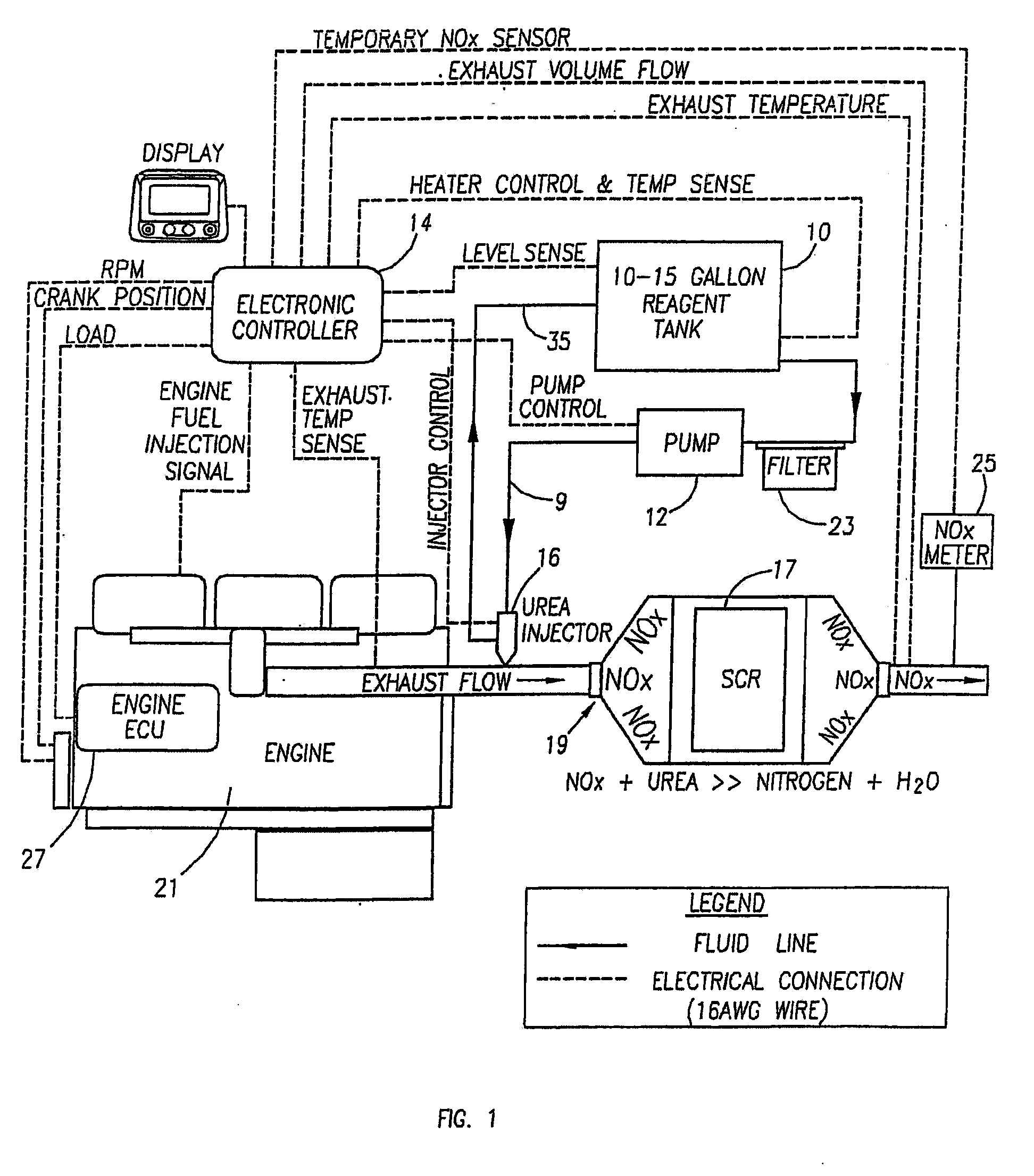
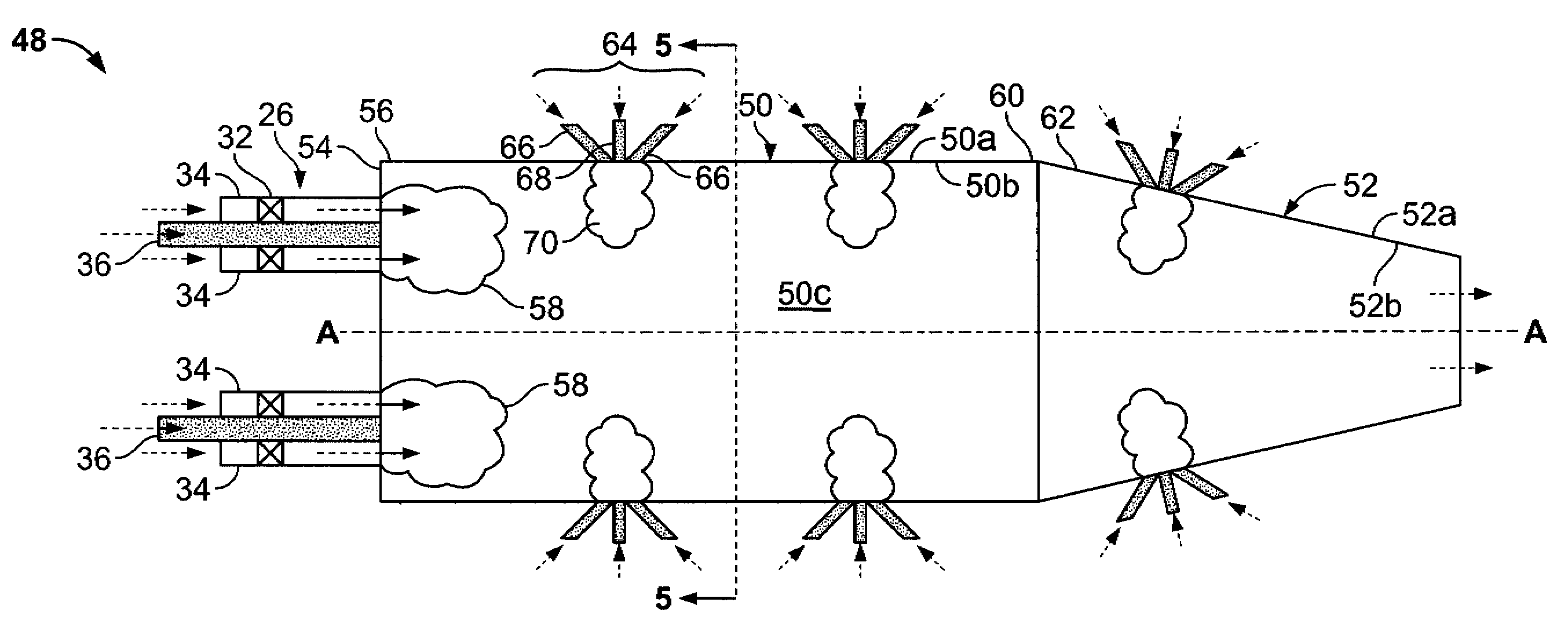
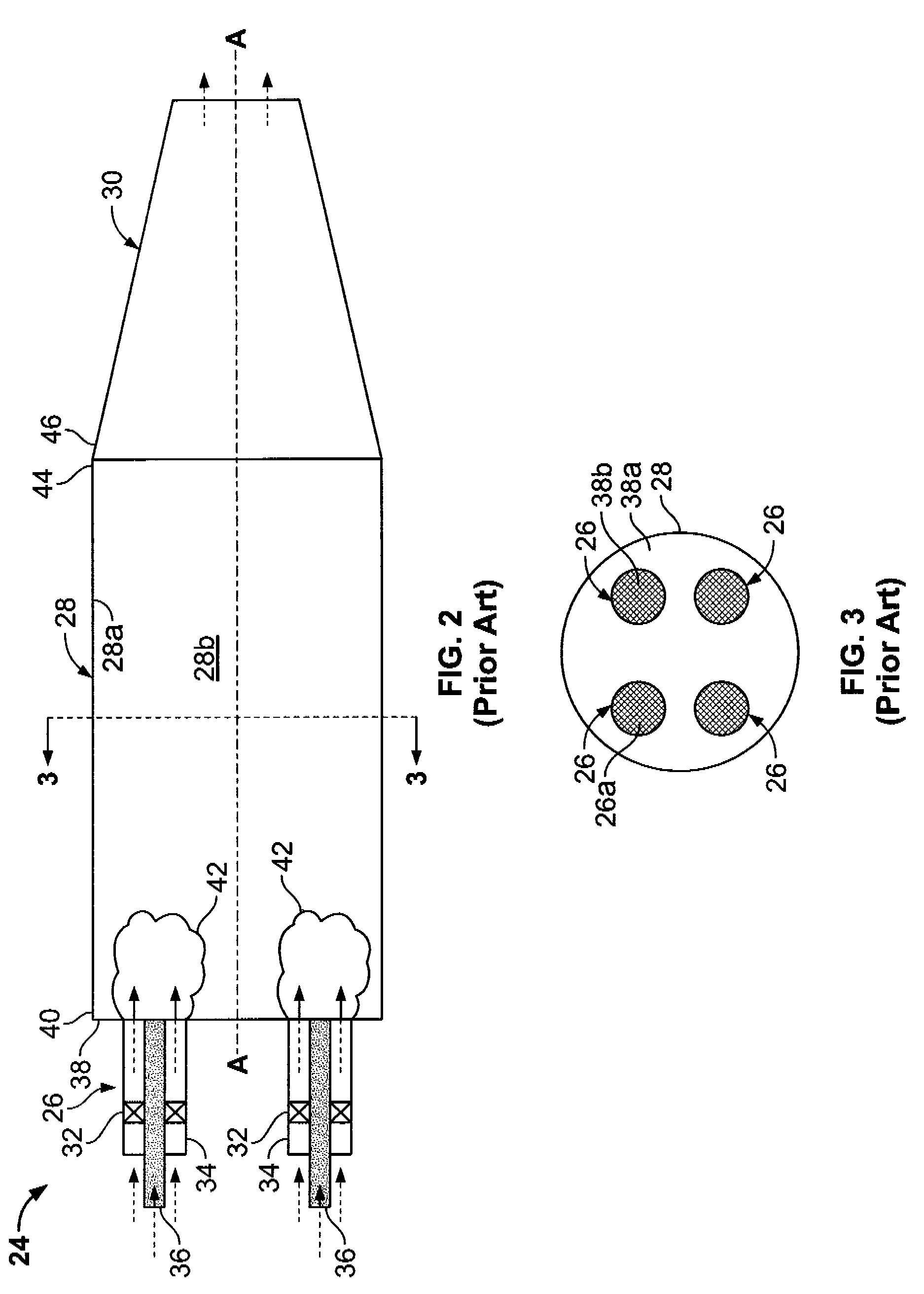
Methods and apparatus for injecting atomized fluid
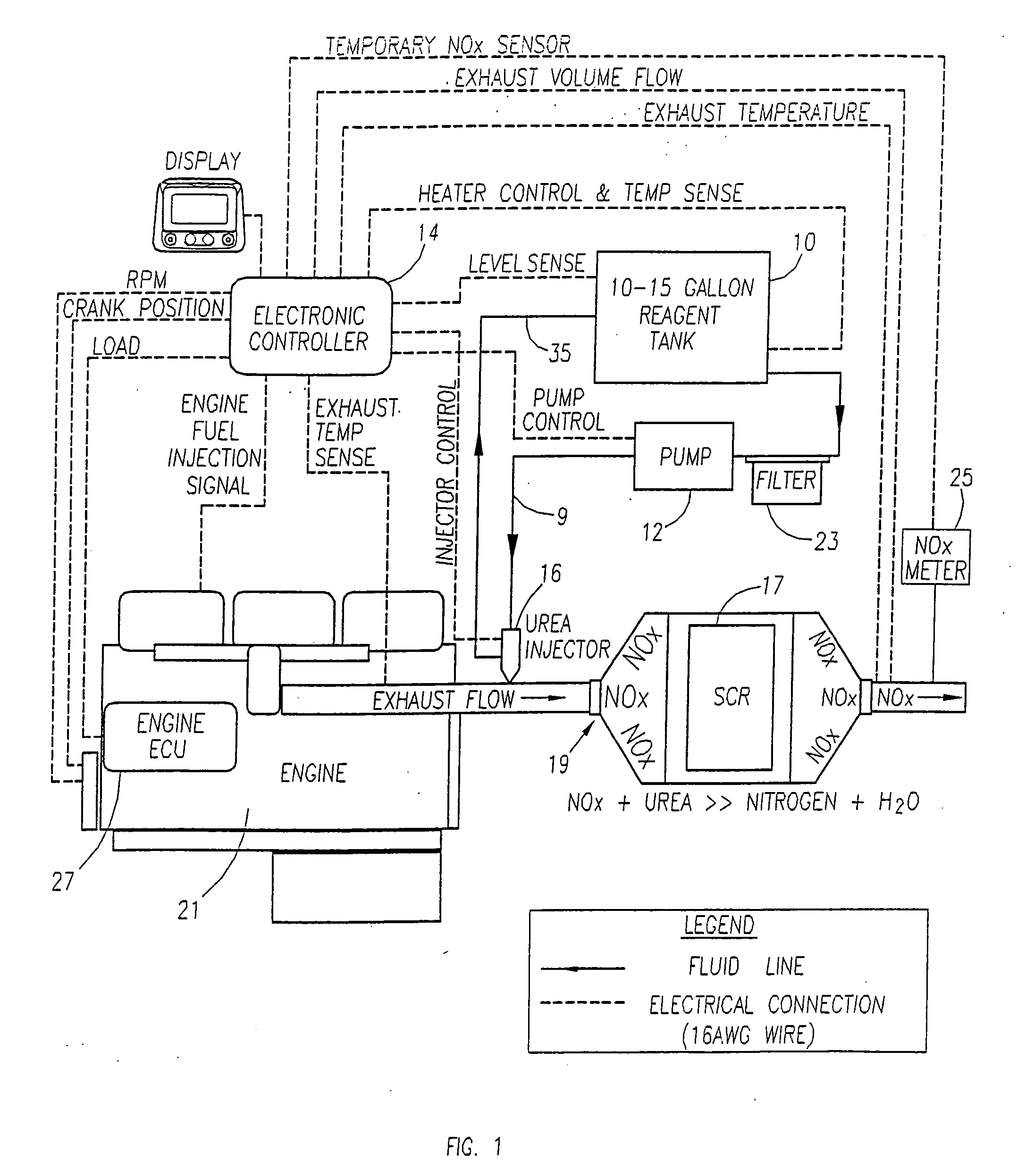
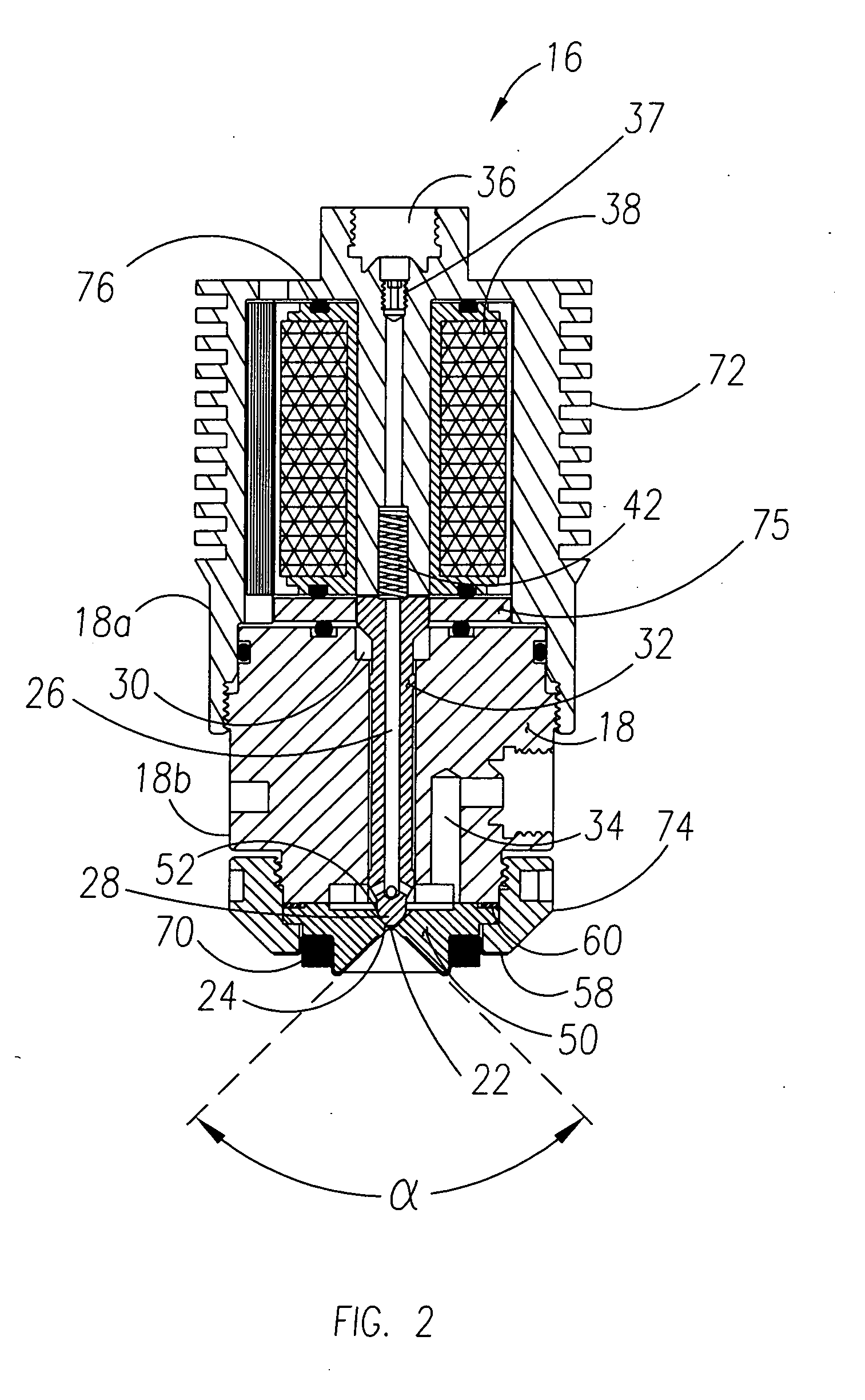
ActiveUS20050235632A1Reduce oxide of nitrogen (NOx) emissionImprove performanceInternal combustion piston enginesExhaust apparatusDiesel engineNOx
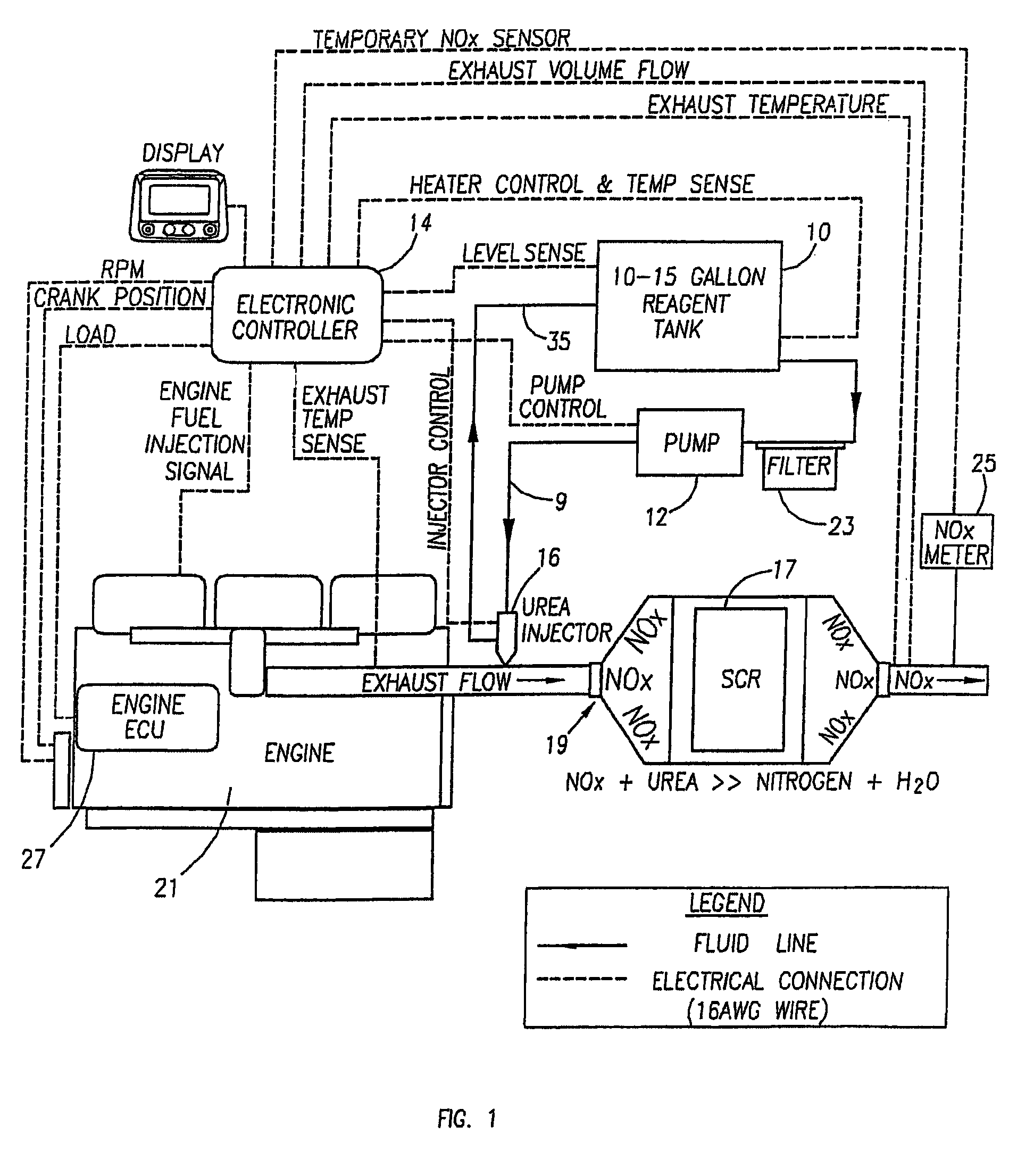
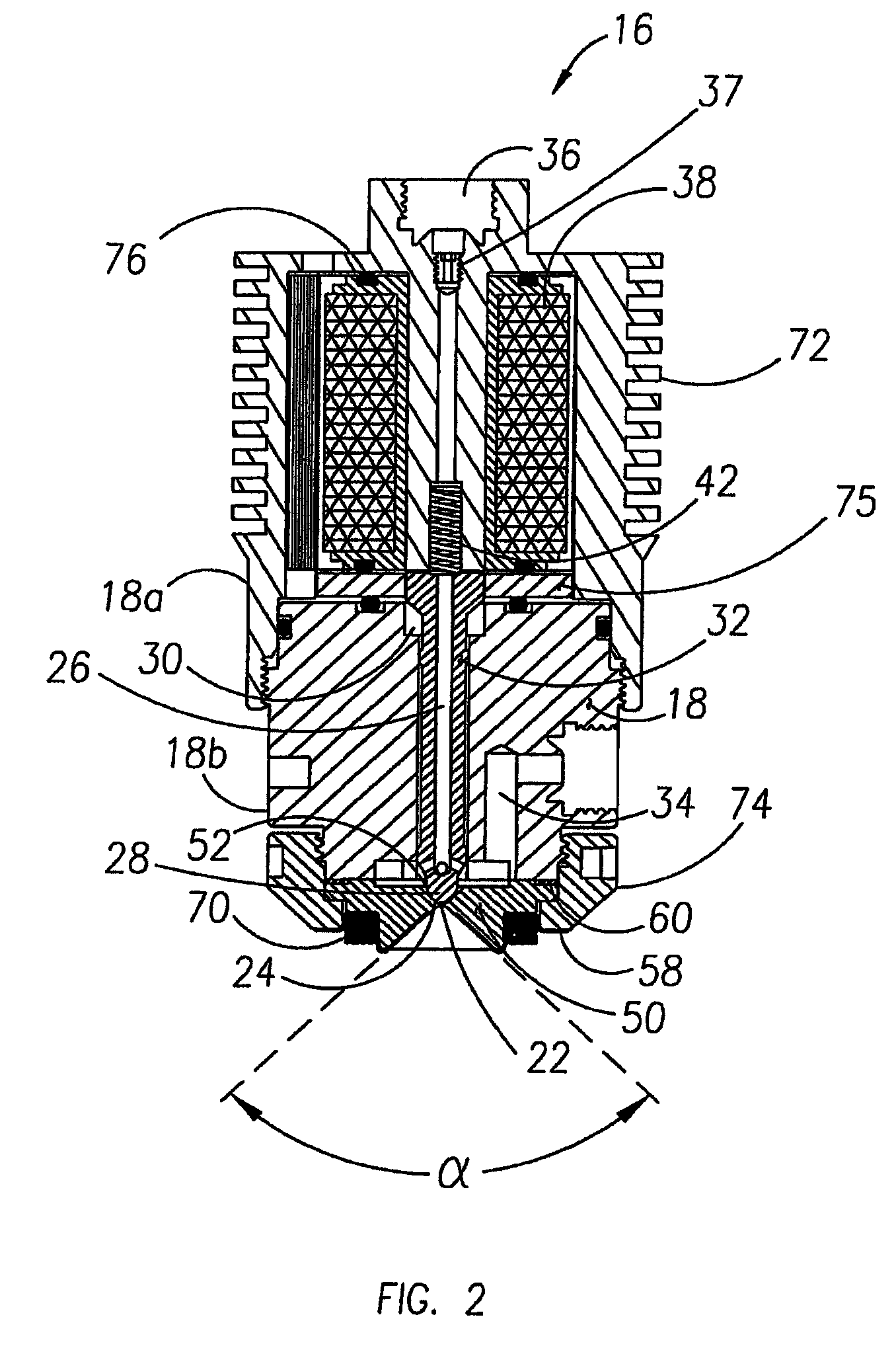
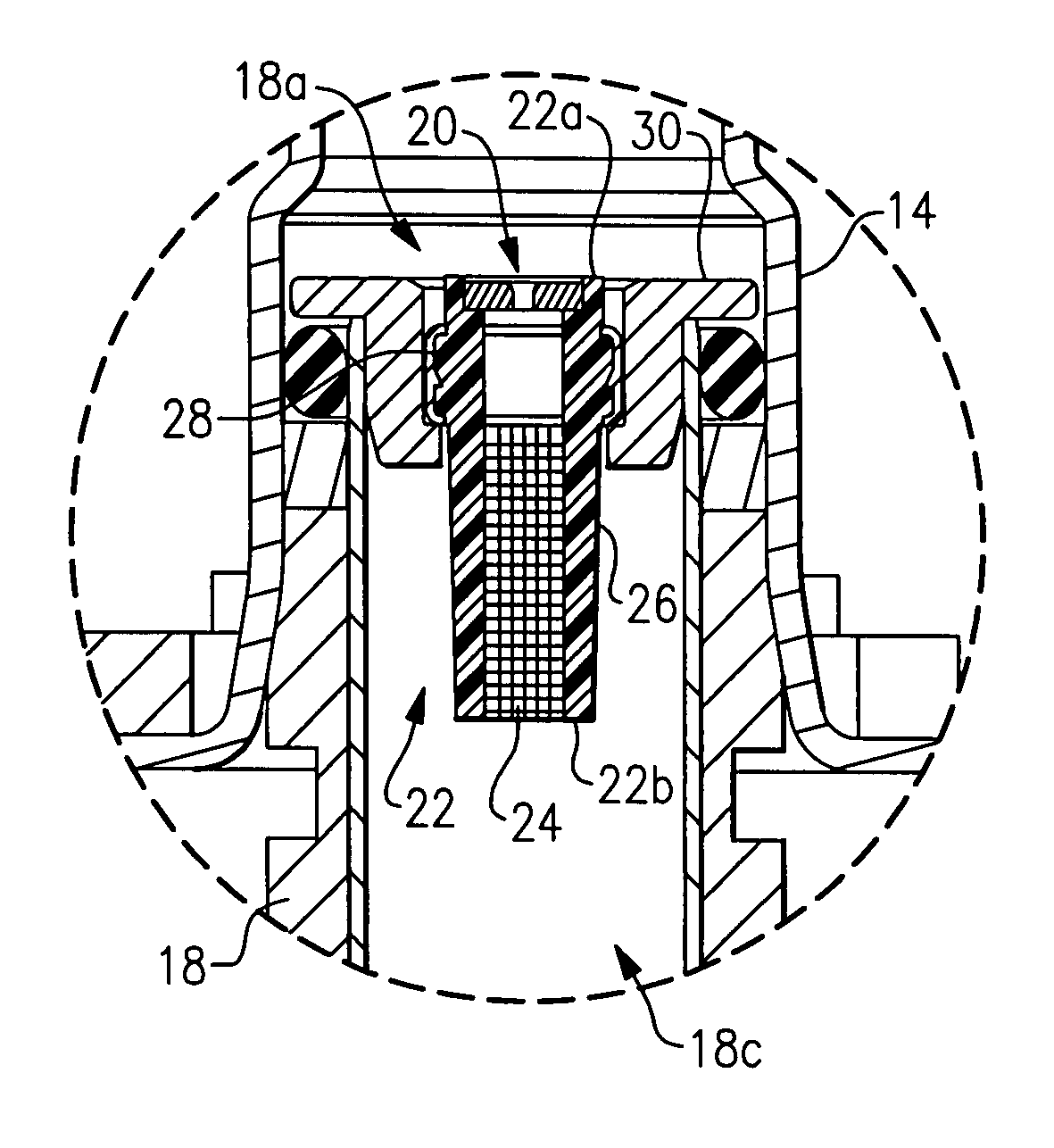
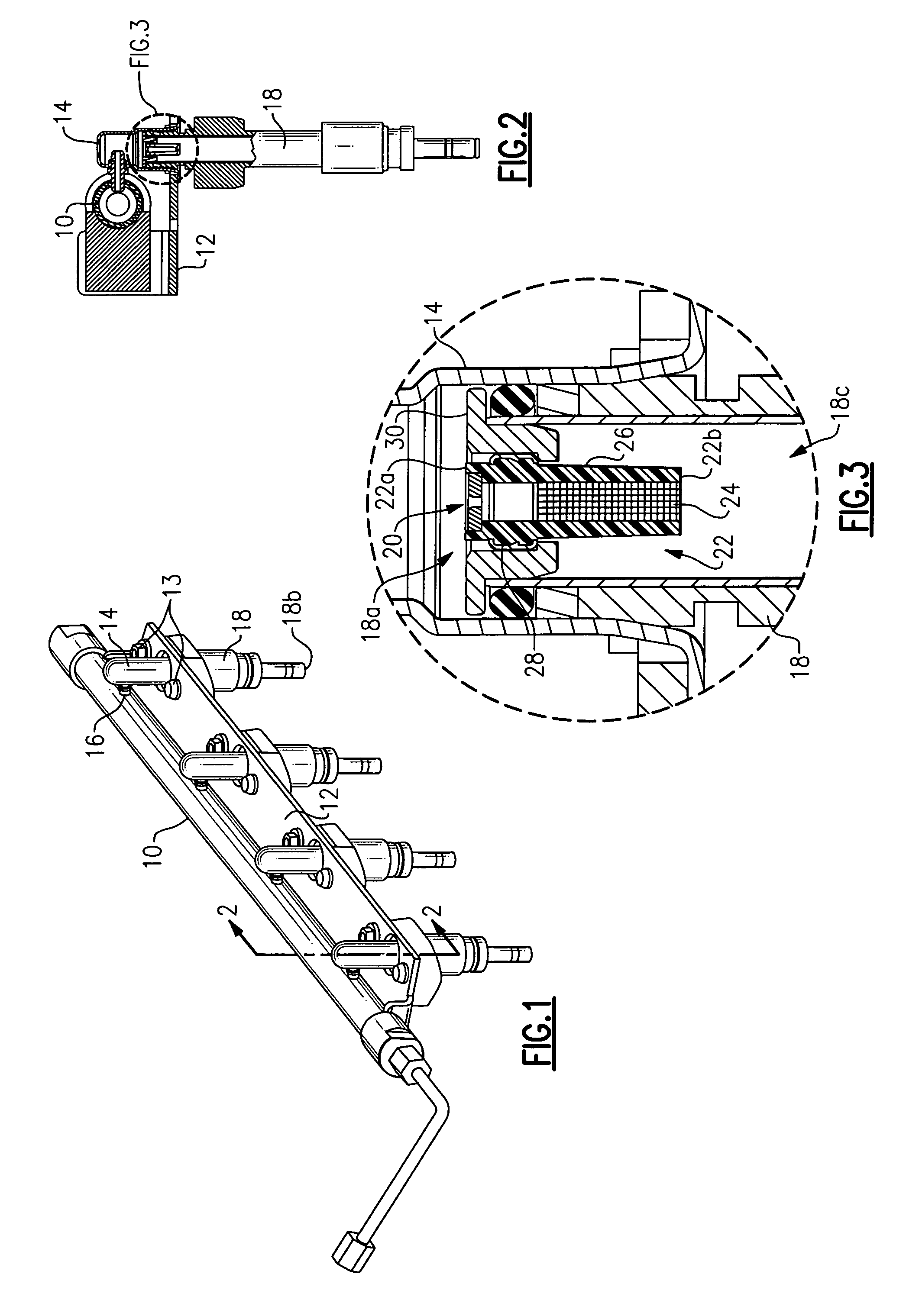
The present invention provides methods and apparatus for injecting fluid, such as an aqueous urea solution, into an exhaust stream in order to reduce oxides of nitrogen (NOx) emissions from diesel engine exhaust The present invention uses mechanical spill return atomization techniques to produce droplets approximately 50 μm SMD (Sauter mean diameter) or smaller. This size range is appropriate to allow urea to react into ammonia within the residence time associated with an on-road diesel engine. This effect is achieved through the use of a whirl plate having a plurality of whirl slots surrounding an exit orifice of the injector, which produce a high velocity rotating flow in the whirl chamber. When the rotating flow of fluid is passed through the exit orifice into an exhaust stream, atomization occurs from a combination of centrifugal force and shearing of the fluid by air as it jets into the exhaust stream.
Owner:TENNECO AUTOMOTIVE OPERATING CO INC
Bundled multi-tube nozzle for a turbomachine
ActiveUS20100186413A1Turbine/propulsion fuel supply systemsContinuous combustion chamberCombustorEngineering
A turbomachine includes a compressor, a combustor operatively connected to the compressor, an end cover mounted to the combustor, and an injection nozzle assembly operatively connected to the combustor. The injection nozzle assembly includes a cap member having a first surface that extends to a second surface. The cap member further includes a plurality of openings. A plurality of bundled mini-tube assemblies are detachably mounted in the plurality of openings in the cap member. Each of the plurality of bundled mini-tube assemblies includes a main body section having a first end section and a second end section. A fluid plenum is arranged within the main body section. A plurality of tubes extend between the first and second end sections. Each of the plurality of tubes is fluidly connected to the fluid plenum.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Multi-fuel compression ignition engine
InactiveUS7036482B2Improve performanceMaximizing intensityElectrical controlInternal combustion piston enginesHcci combustionCombustion chamber
A liquid primary fuel is ignited by HCCI with the assistance of the early injection of a liquid pilot fuel. Pilot fuel injection and / or ignition are preferably controlled so as to permit the injected pilot fuel to become thoroughly distributed through and mixed with the primary fuel / air charge in the combustion chamber and vaporized prior to ignition. Pilot fuel having a lower autoignition temperature will be ignited by compression ignition, followed by the ignition of the homogeneous mixture of the primary fuel and air. HCCI combustion of the primary fuel is facilitated by 1) selection of the properties of the primary and pilot fuels and 2) obtaining a homogenous mixture of primary fuel and air by injecting primary fuel into the engine's intake air stream in the form of finely atomized droplets having a mean diameter in the micron range.
Owner:CLEAN AIR POWER
Method for split ignition timing for idle speed control of an engine
InactiveUS20030221664A1High load conditionMore ignition timingAnalogue computers for vehiclesElectrical controlTemperature controlAdaptive learning
A method is disclosed for controlling operation of an engine coupled to an exhaust treatment catalyst. Under predetermined conditions, such as after an engine cold start, the method operates an engine with a first group of cylinders having a first ignition timing, and a second group of cylinders having a second ignition timing more retarded than the first group. In addition, the engine control method also provides the following features in combination with the above-described split air / lean mode: idle speed control, sensor diagnostics, air / fuel ratio control, adaptive learning, fuel vapor purging, catalyst temperature estimation, default operation, and exhaust gas and emission control device temperature control. In addition, the engine control method also can change to combusting all cylinders at substantially the same ignition timing under preselected operating conditions such as fuel vapor purging, manifold vacuum control, and purging of stored oxidants in an emission control device.
Owner:FORD GLOBAL TECH LLC
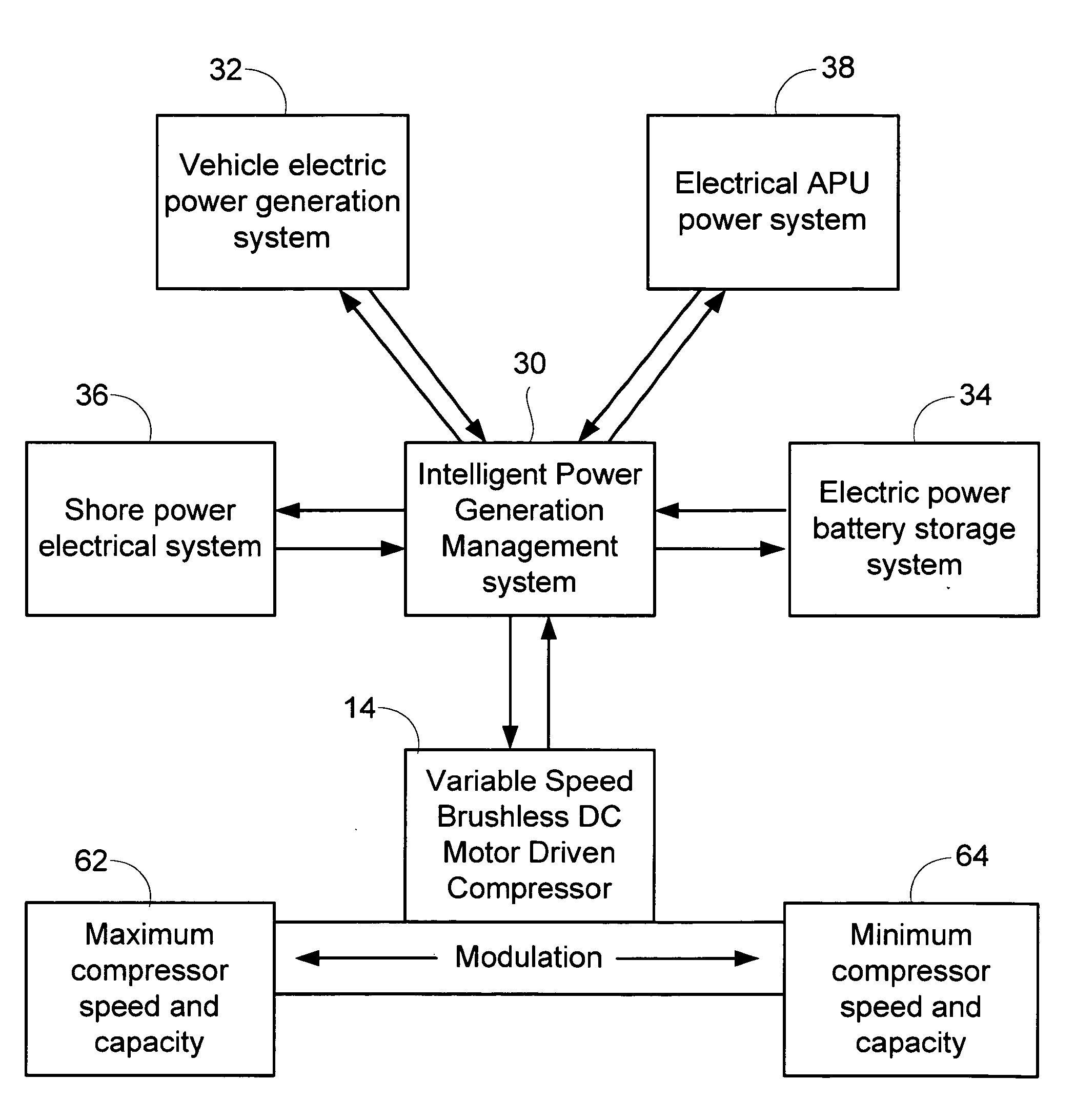
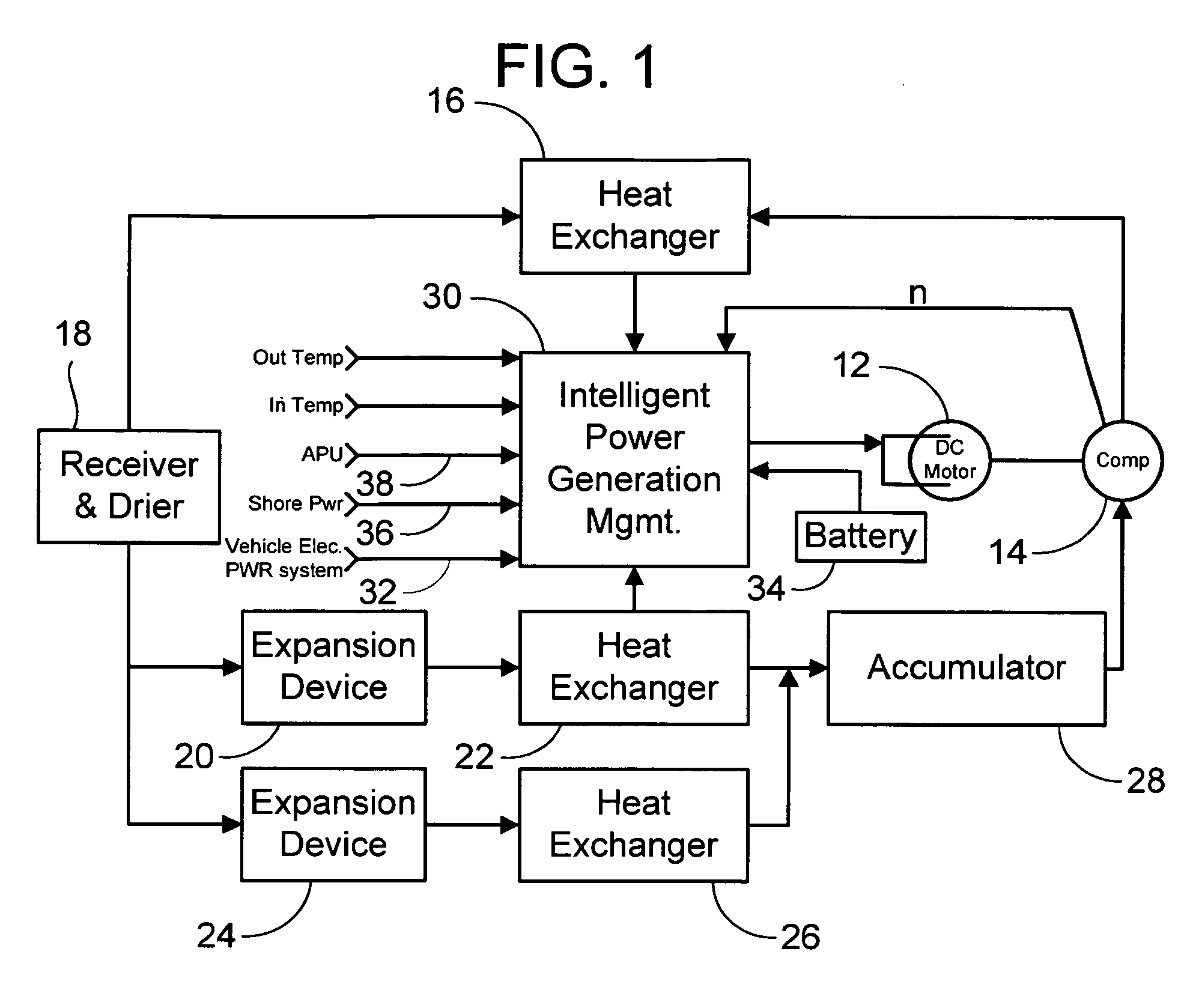
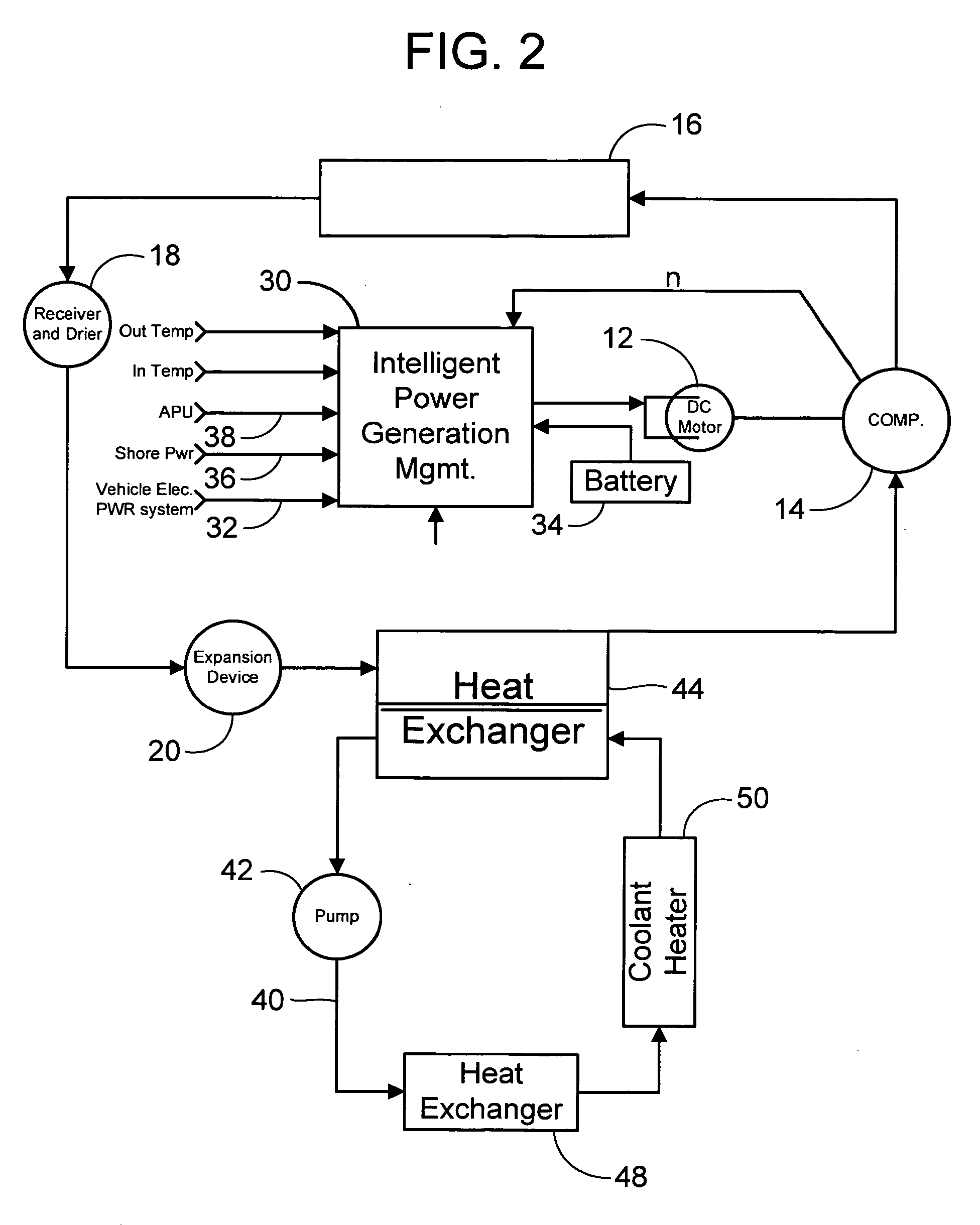
Vehicle air conditioning and heating system providing engine on and engine off operation
InactiveUS20050161211A1Solve insufficient capacityAccurate lifeAir-treating devicesCompression machines with non-reversible cycleMotor driveAir conditioning
An air conditioning system for use in an over-the-road or off road vehicle is provided that allows operation during both engine on and engine off conditions. The system utilizes a variable speed, motor driven compressor controlled by an intelligent power generation management controller. This controller selects from one of the available sources of power on the vehicle to drive the compressor, and modulates the compressor speed and capacity based on operational parameters and source availability and depletion. The controller may also operate a coolant or air heater to provide heating to the interior compartments.
Owner:BERGSTROM INC
Method and apparatus for injecting atomized fluids
ActiveUS20090179087A1Emission reductionImprove performanceInternal combustion piston enginesExhaust apparatusEngineeringCentrifugal force
Methods and apparatus for injecting reagent, such as an aqueous urea solution, into an exhaust stream in order to reduce emissions from an engine exhaust. The present teachings can use a whirl plate having a plurality of whirl slots surrounding an exit orifice of an injector, which produce a high velocity rotating flow in the whirl chamber. When the rotating flow of reagent is passed through the exit orifice into an exhaust stream, atomization occurs from a combination of centrifugal force and shearing of the reagent by air as it jets into the exhaust stream.
Owner:TENNECO AUTOMOTIVE OPERATING CO INC
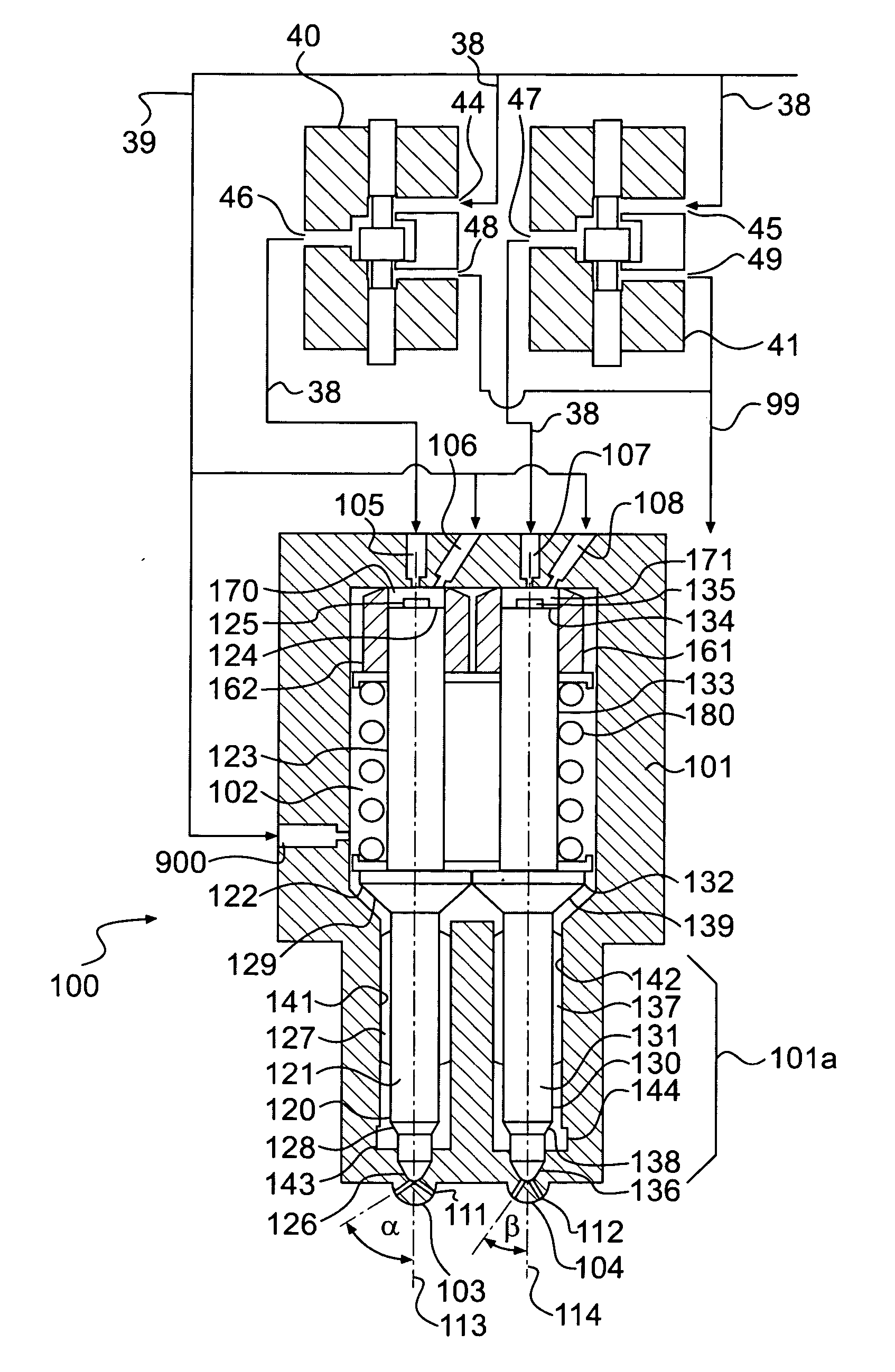
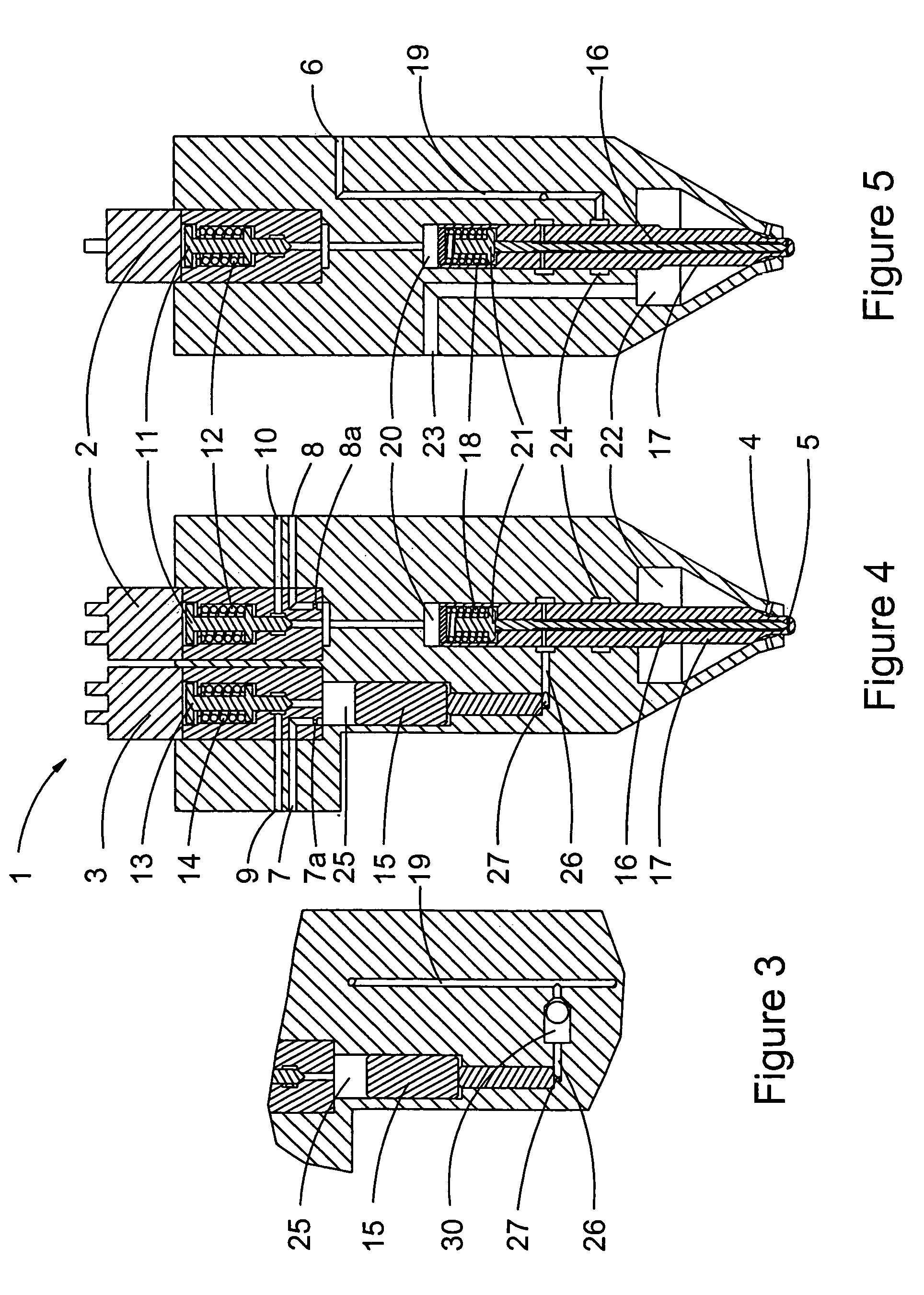
Twin needle valve dual mode injector
A fuel injector having an injector body defining a hollow interior configured to receive pressurized fuel, a first nozzle configured for providing a first fuel spray pattern, and a second nozzle configured for providing a second fuel spray pattern different from the first fuel spray pattern. The first and second nozzles may be configured to inject fuel supplied from a common source into a combustion space. The fuel injector may further include first and second needle valve members corresponding to the first and second nozzles, respectively. The first and second needle valve members may be positioned within the hollow interior of the injector body, with the second needle valve member being spaced from, but adjacent to the first needle valve member.
Owner:CATERPILLAR INC
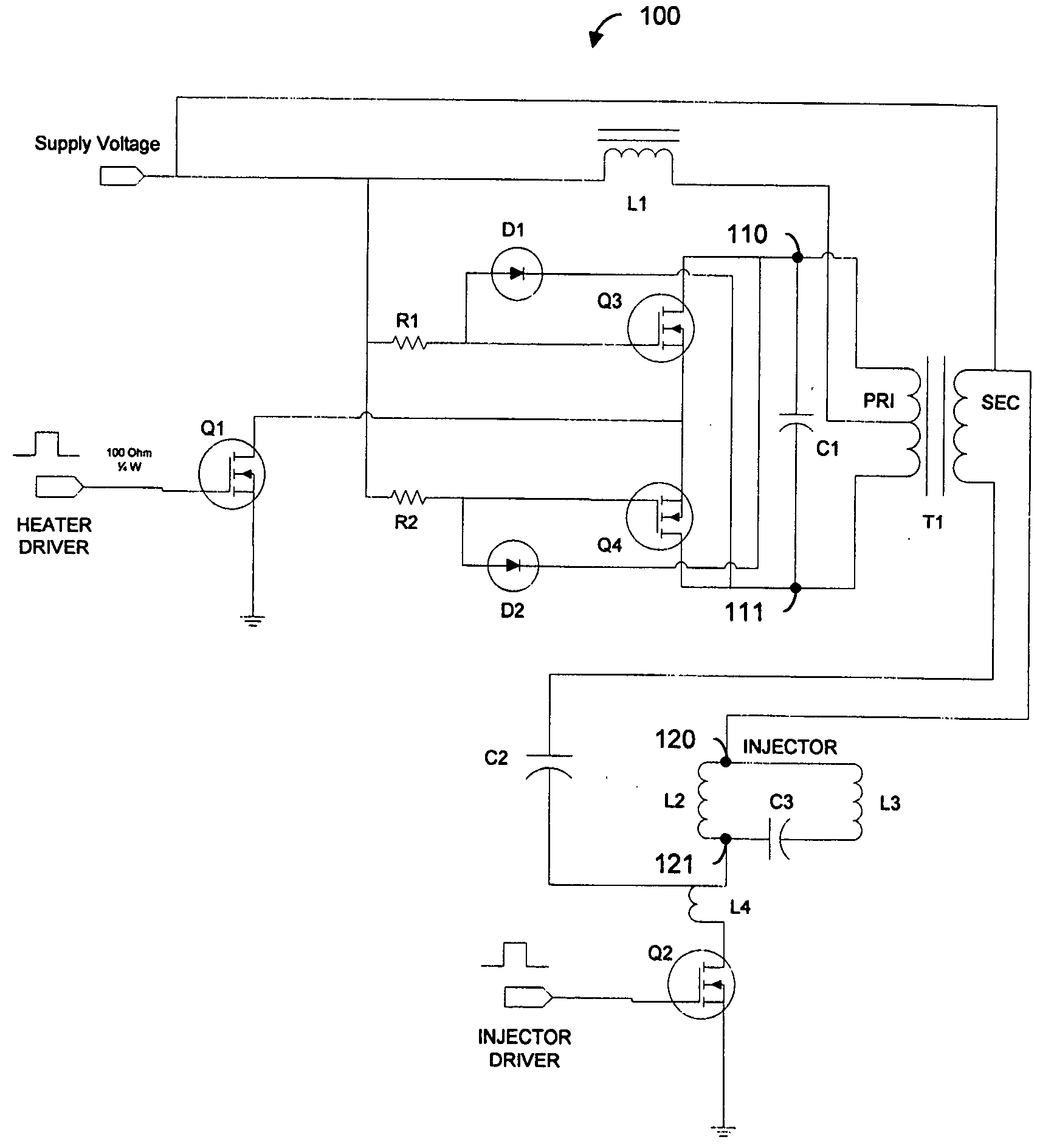
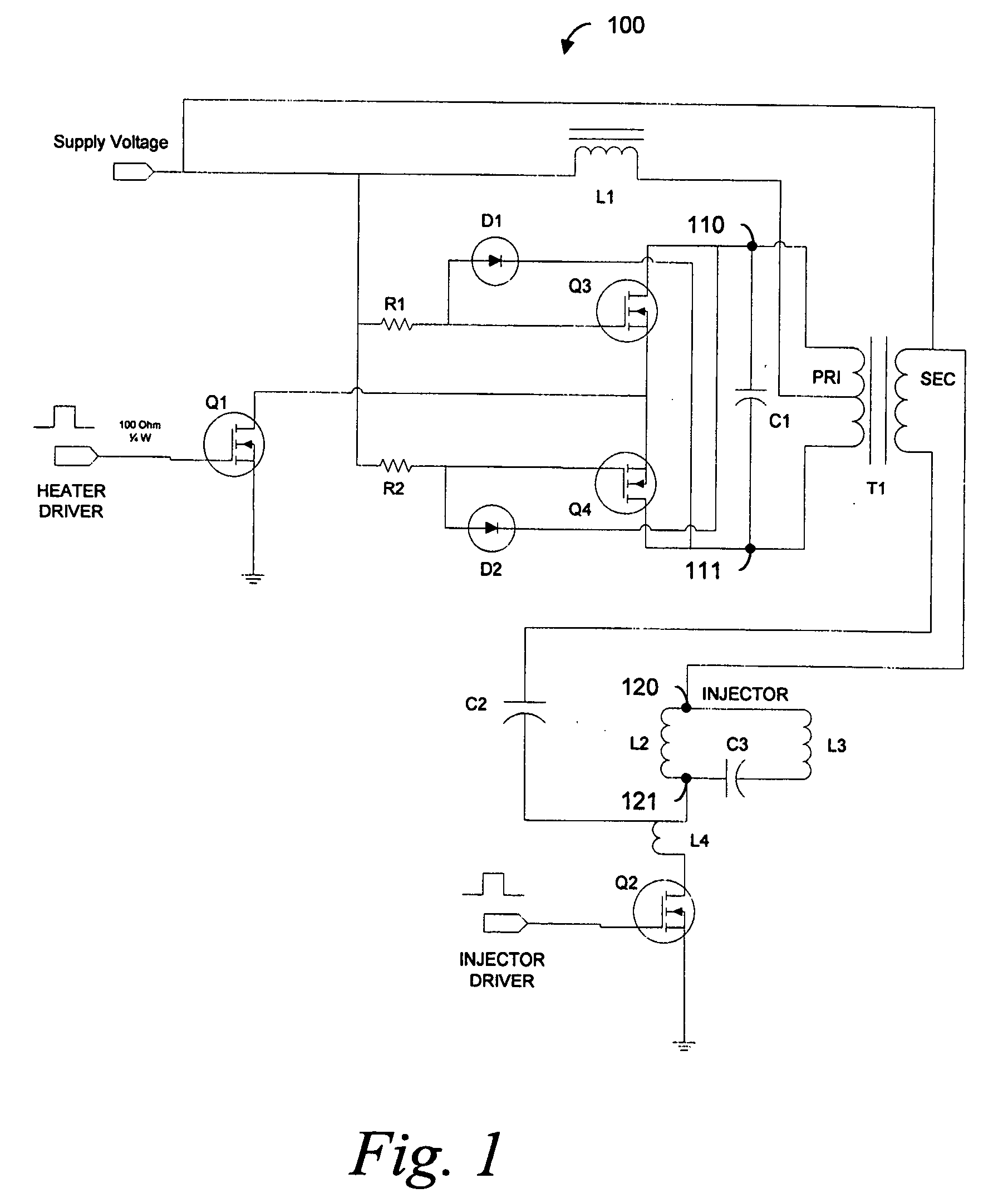
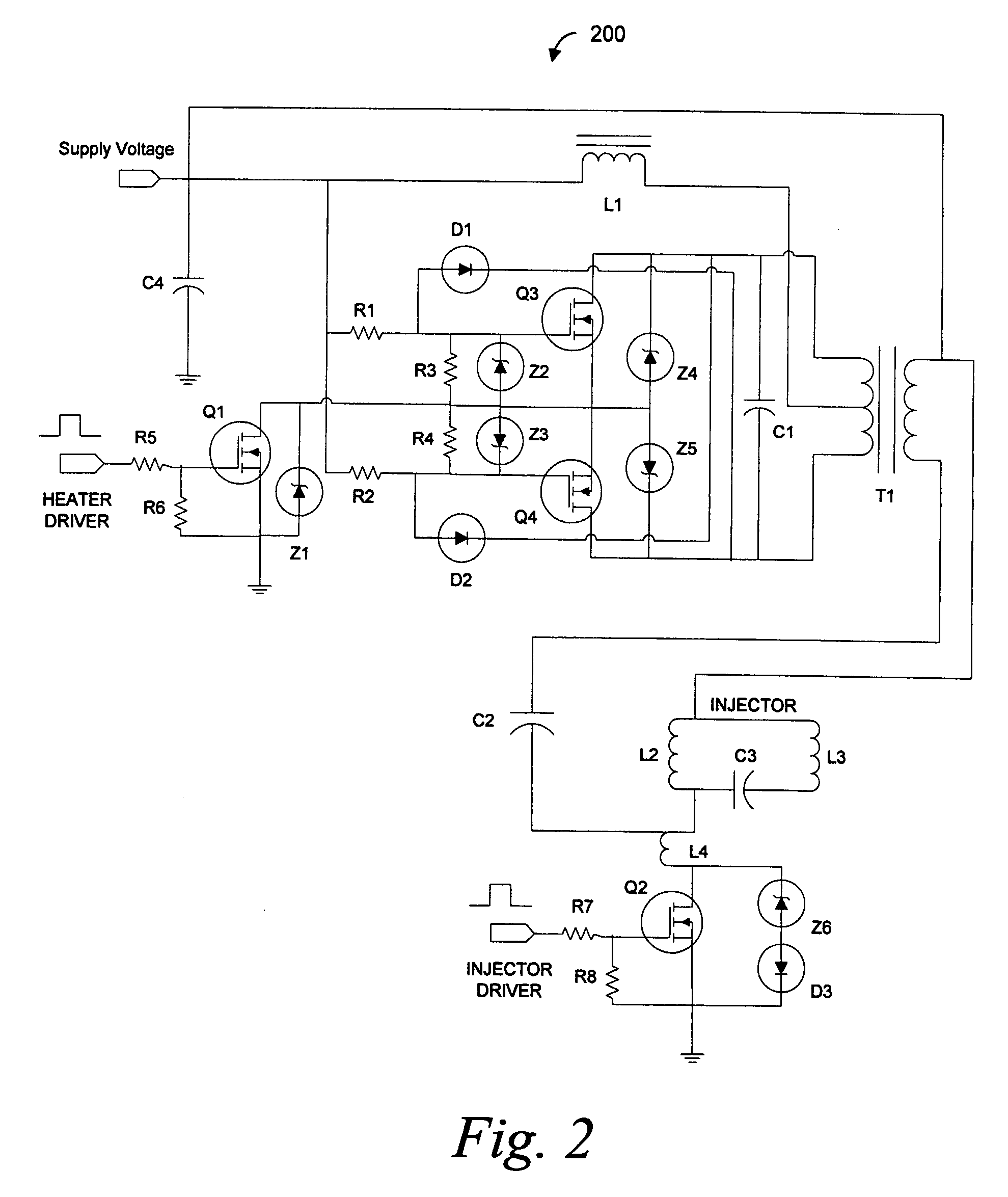
Constant current zero-voltage switching induction heater driver for variable spray injection
An electronic high frequency induction heater driver, for a variable spray fuel injection system, uses a zero-voltage switching oscillator that is impedance coupled to an imbedded multiple function signal separator and integrated with a conventionally implemented electronic fuel injector driver. The induction heater driver, upon receipt of a turn-on signal, multiplies a supply voltage through a self-oscillating series resonance, and couples the high frequency energy to a high pass filter such that the useful energy is utilized in an appropriate loss component so that fuel inside a fuel component is heated to a desired temperature.
Owner:VITESCO TECH USA LLC
Dual fuel injection valve and method of operating a dual fuel injection valve
InactiveUS7124959B2Increase pressureReduce pressureInternal combustion piston enginesFuel supply apparatusBiomedical engineeringFuel injection
A dual fuel injection valve separately and independently injects two different fuels and comprises a dual needle assembly with a hollow open-ended outer needle and an inner needle disposed within the hollow interior. A cap cooperates with the outer needle to cover the open end, and the outer needle and the cap together comprise the inner valve body. The outer and inner needles are each movable independently from each other between respective open and closed positions. A spring disposed between the cap and the inner needle contributes to biasing the inner needle in the closed position. The cap can be joined to the outer needle, whereby the cap can provide a limit to the movement of the inner needle. In another embodiment the cap can be detached from the outer body, allowing the spring to space the cap away from the outer needle, assisting with biasing the outer needle closed.
Owner:WESTPORT FUEL SYST CANADA INC
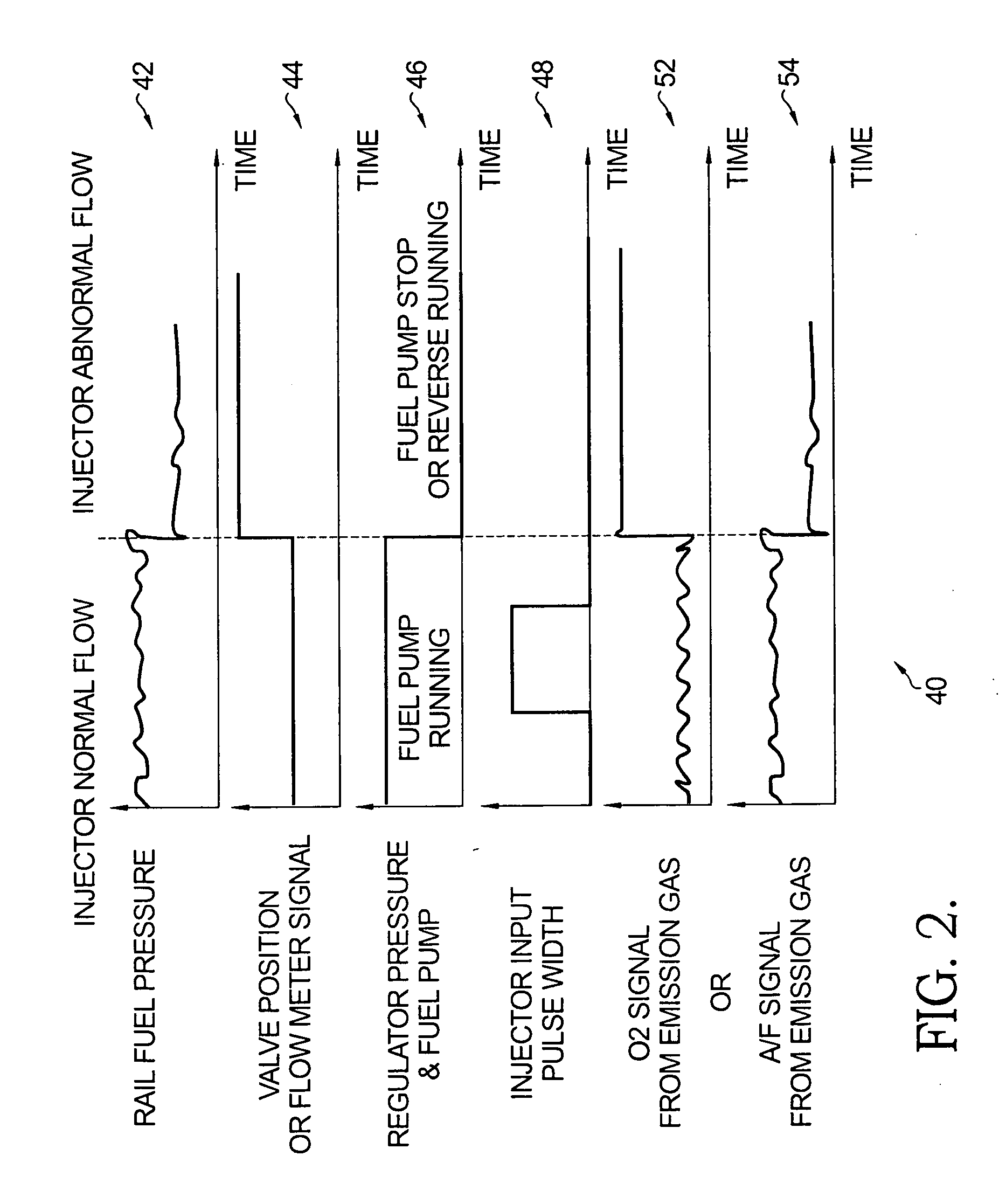
Method of detecting and compensating for injector variability with a direct injection system
ActiveUS7717088B2Improve pressure resistanceReduce temperature sensitivityElectrical controlInternal combustion piston enginesPressure decreaseEngineering
A method for controlling fuel injection of a direct injection fuel system, the fuel system having a fuel pump, the method comprising: variably operating the fuel pump to maintain a fuel pressure at a selected pressure, temporarily increasing pump operation to increase pressure sufficiently above said selected pressure and then reducing pump operation; during at least a fuel injection subsequent to the reduction in pump operation, correlating pressure decrease to injector operation, and adjusting fuel injection operation based on the correlation.
Owner:FORD GLOBAL TECH LLC
Systems and methods for operating an electromagnetic actuator
InactiveUS20050279867A1Electrical controlInternal combustion piston enginesElectromagnetic actuatorElectrical and Electronics engineering
One embodiment of the present invention relates to a method for constructing a circuit for controlling an electromagnetic actuator. Another embodiment of the present invention relates to a method for designing a circuit for controlling an electromagnetic actuator.
Owner:COMBUSTION DYNAMICS
Apparatus and method for preparing and delivering fuel
InactiveUS6871792B2Increase power consumptionOvercome problemsBurnersLiquid surface applicatorsElectrical resistance and conductanceFluid control
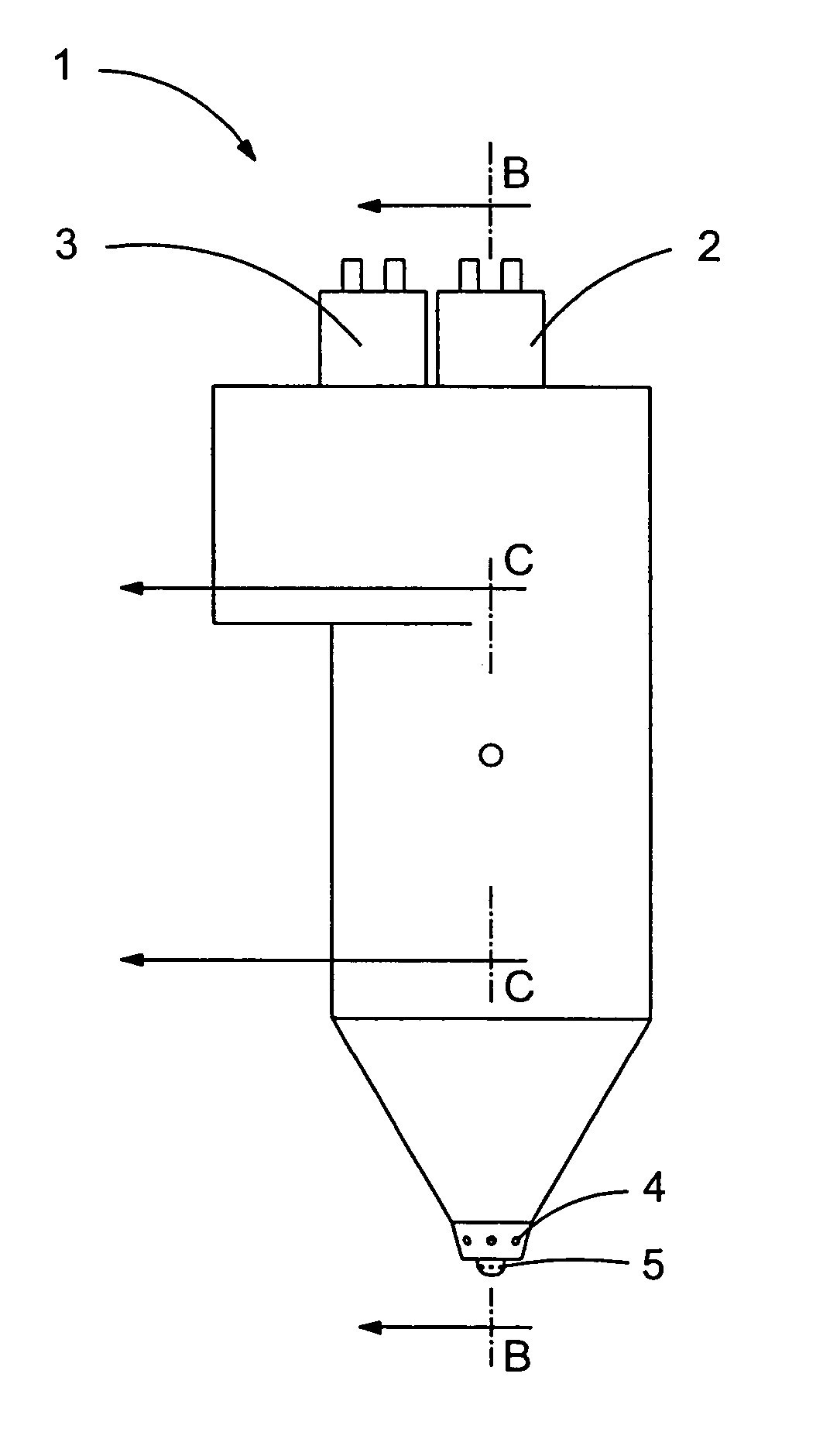
A method and apparatus for vaporizing liquid fuel. The apparatus includes at least one capillary flow passage, the at least one capillary flow passage having an inlet end and an outlet end; a fluid control valve for placing the inlet end of the at least one capillary flow passage in fluid communication with the liquid fuel source and introducing the liquid fuel in a substantially liquid state; a heat source arranged along the at least one capillary flow passage, the heat source operable to heat the liquid fuel in the at least one capillary flow passage to a level sufficient to change at least a portion thereof from the liquid state to a vapor state and deliver a stream of substantially vaporized fuel from the outlet end of the at least one capillary flow passage; and means for cleaning deposits formed during operation of the apparatus. The flow passage can be a capillary tube heated by a resistance heater or a section of a tube heated by passing electrical energy therethrough. The liquid fuel can be supplied to the flow passage at any desired pressure depending on the required mass flow rate for the application. The vaporized fuel can be mixed with air to form an aerosol having a mean droplet size of 25 μm or less to minimize ignition energy of the fuel-air mixture, promote fuel flow in an air stream, and combust the liquid fuel efficiently and cleanly.
Owner:PHILIP MORRIS USA INC
Method and apparatus for injecting atomized fluids
ActiveUS8047452B2Emission reductionImprove performanceInternal combustion piston enginesExhaust apparatusEngineeringCentrifugal force
Methods and apparatus for injecting reagent, such as an aqueous urea solution, into an exhaust stream in order to reduce emissions from an engine exhaust. The present teachings can use a whirl plate having a plurality of whirl slots surrounding an exit orifice of an injector, which produce a high velocity rotating flow in the whirl chamber. When the rotating flow of reagent is passed through the exit orifice into an exhaust stream, atomization occurs from a combination of centrifugal force and shearing of the reagent by air as it jets into the exhaust stream.
Owner:TENNECO AUTOMOTIVE OPERATING CO INC
Injector fuel filter with built-in orifice for flow restriction
ActiveUS7617991B2Reduce pressure pulsationReduce or eliminate pressure pulsations through the fuel injectorSedimentation separationMachines/enginesFuel filterEngineering
Owner:DELPHI TECH IP LTD
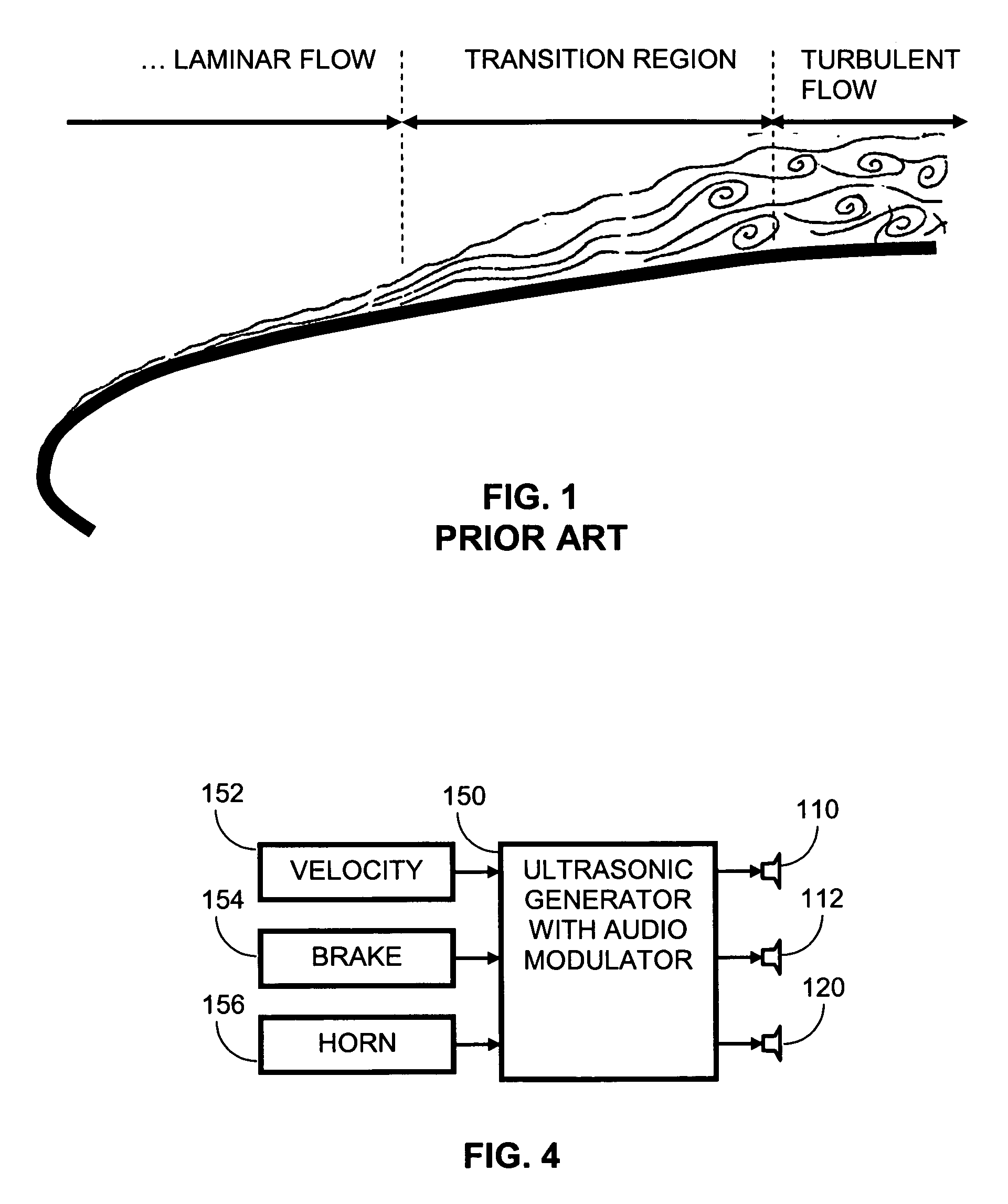
Active drag and thrust modulation system and methods
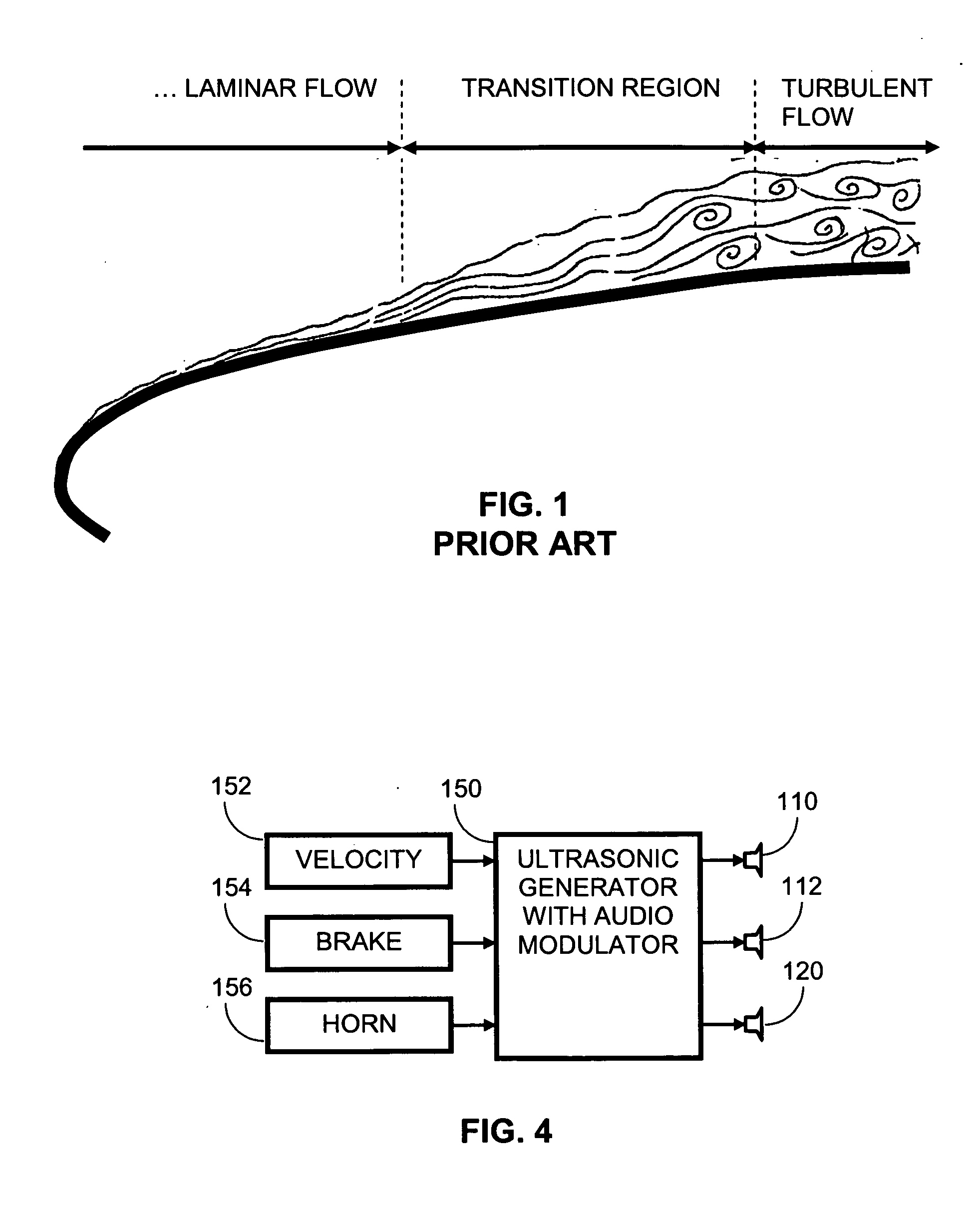
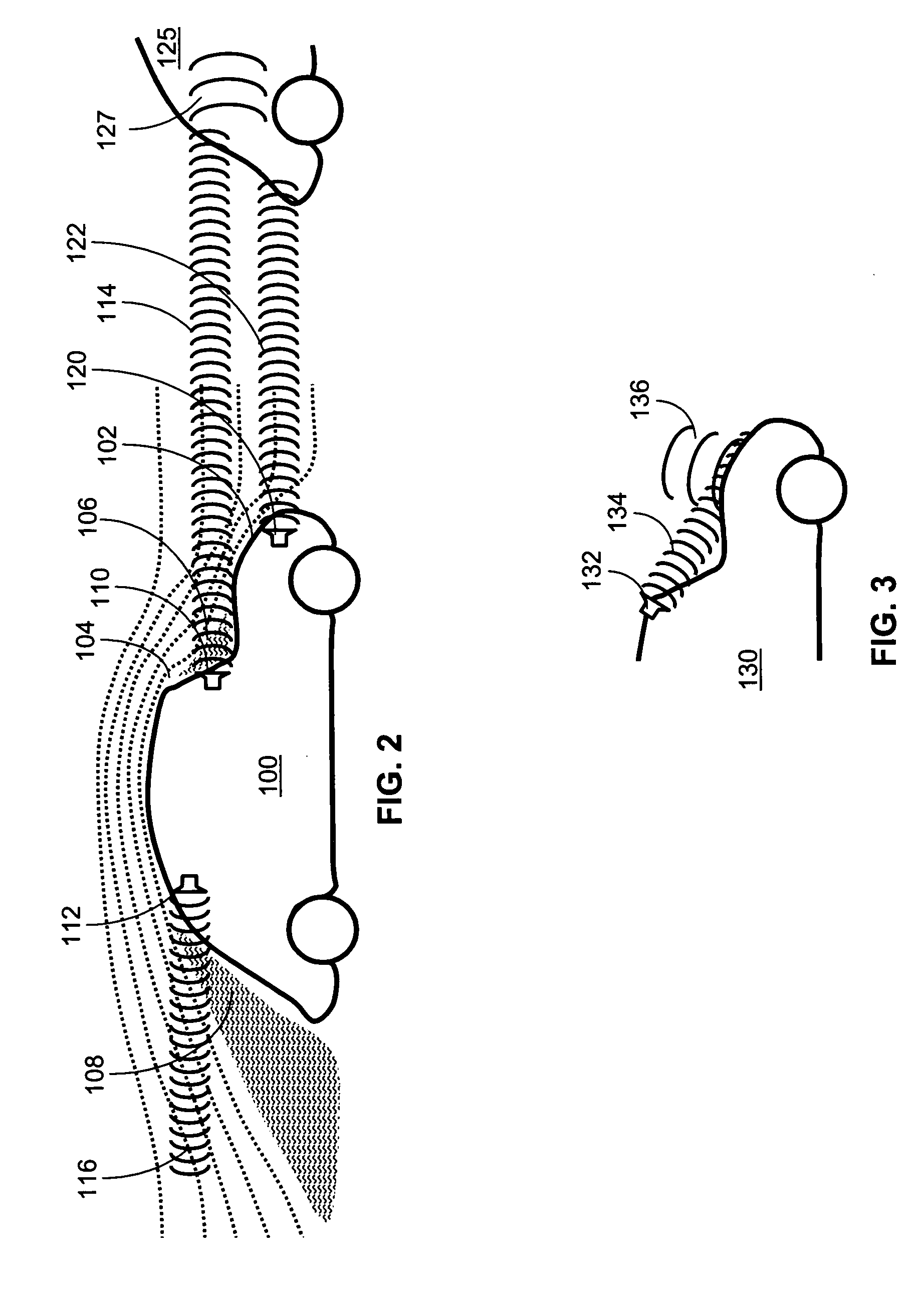
InactiveUS20050257776A1Good fuel atomizationPromote atomizationTyre partsInternal combustion piston enginesLeading edgeCombustion
A vehicle traveling through an environmental media such as air experiences drag. The drag is actively modulated by energy beams which may either increase or decrease the drag. The energy beams may provide either a chemical, acoustic or electromagnetic energy at a transition region between turbulent and laminar flows or at the leading edge of a laminar flow or in the direction of a crosswind in order to facilitate the respective increase or decrease in drag. If the vehicle is a sailing ship, areas of the sails are selectively roughened or widened to enhance the thrust derived from the wind. Furthermore, the keel or hull of the sailing ship may be modified to improve the hydrodynamic characteristics of the sailing ship. If the vehicle is an automobile, the tires or road surface may be selectively heated to improve the traction of the automobile. Furthermore, the energy beams may be used to facilitate atomization of the air / fuel mixture prior to combustion in an internal combustion engine thereby improving the thrust of provided to the vehicle. Energy beams may be used to generate virtual extensions of a vehicle to enhance traveling efficiency.
Owner:P TECH
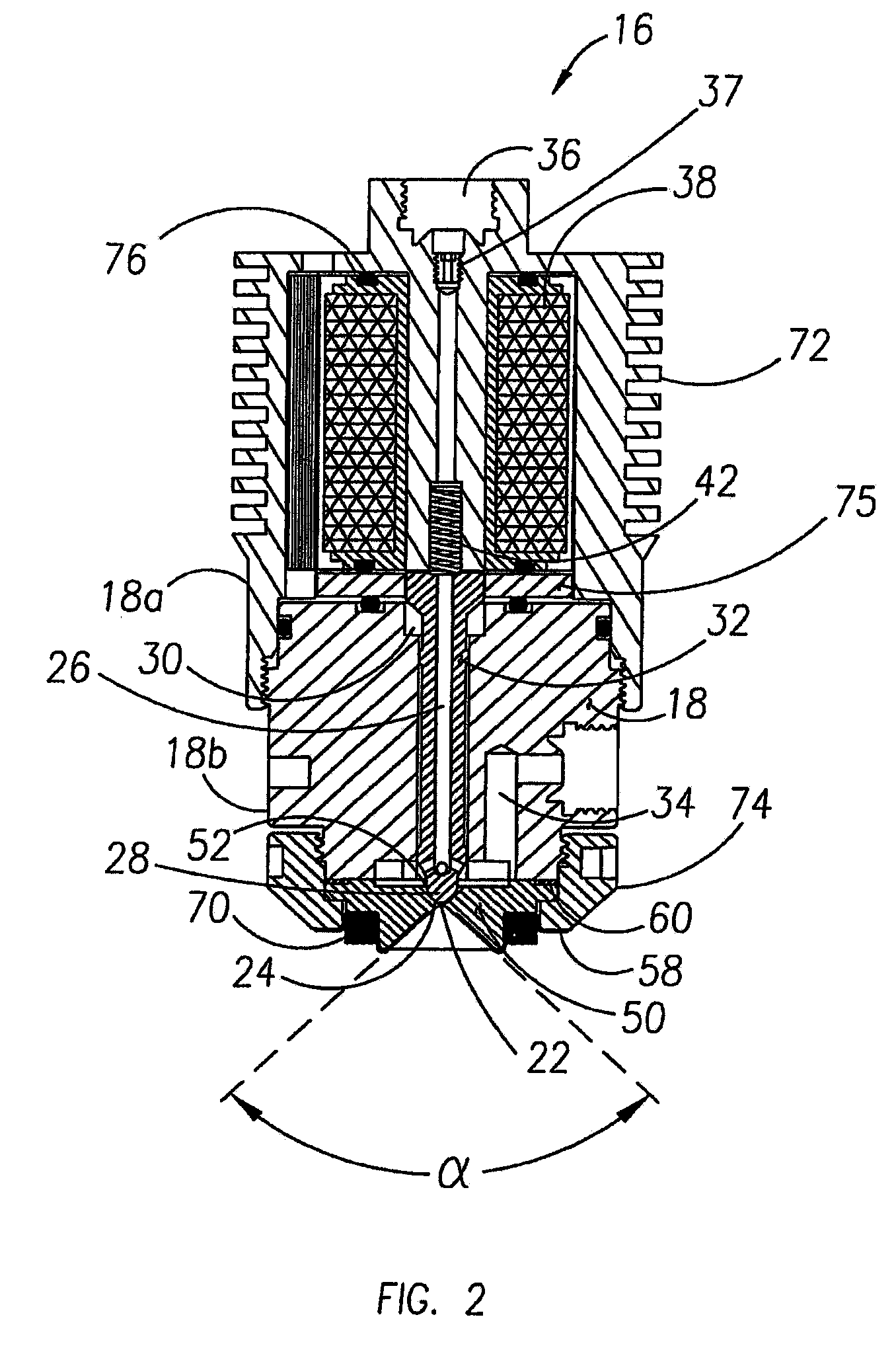
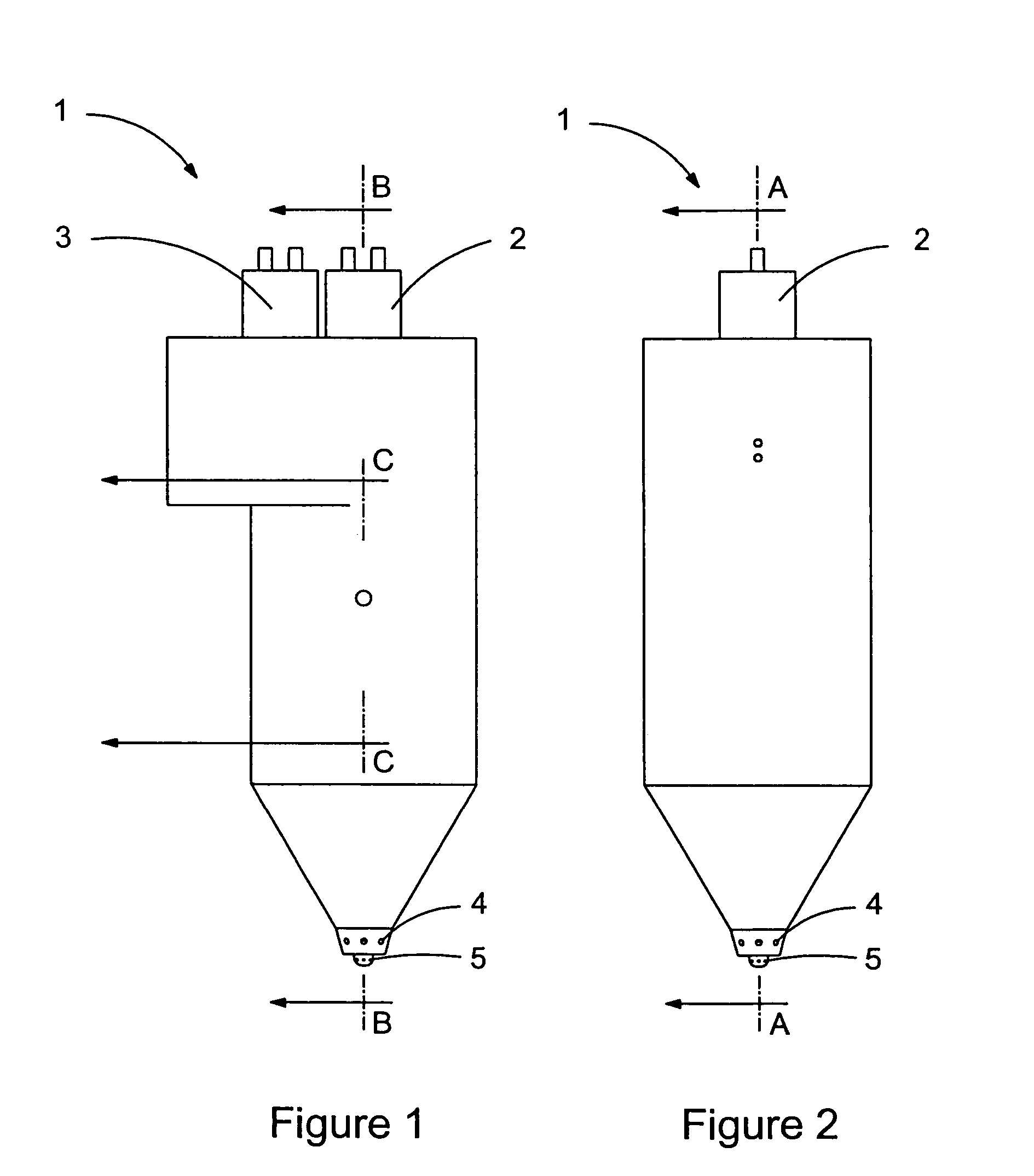
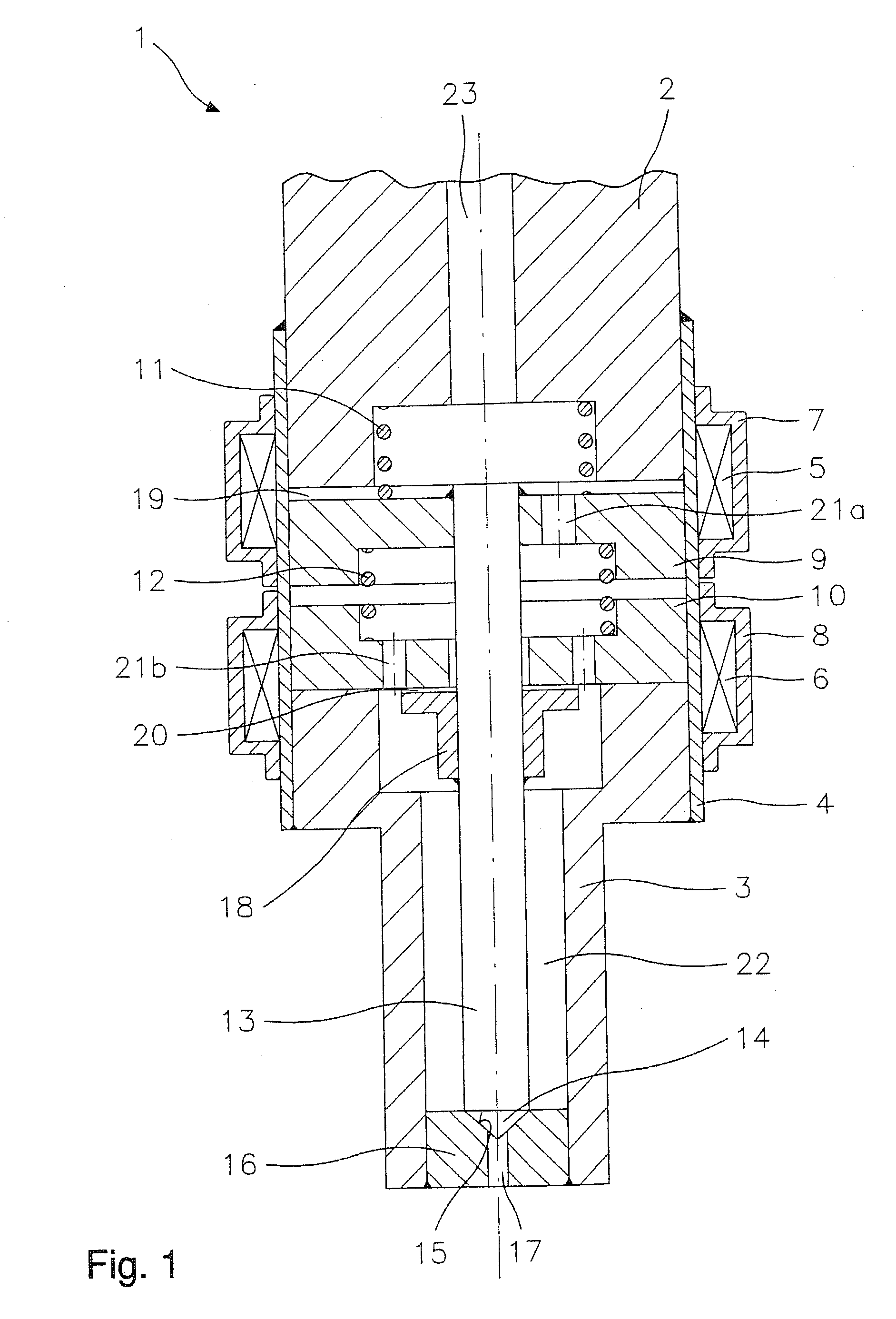
Methods and systems to facilitate reducing NOx emissions in combustion systems
A method for assembling a gas turbine combustor system is provided. The method includes providing a combustion liner including a center axis, an outer wall, a first end, and a second end. The outer wall is orientated substantially parallel to the center axis. The method also includes coupling a transition piece to the liner second end. The transition piece includes an outer wall. The method further includes coupling a plurality of lean-direct injectors along at least one of the liner outer wall and the transition piece outer wall such that the injectors are spaced axially apart along the wall.
Owner:GE INFRASTRUCTURE TECH INT LLC
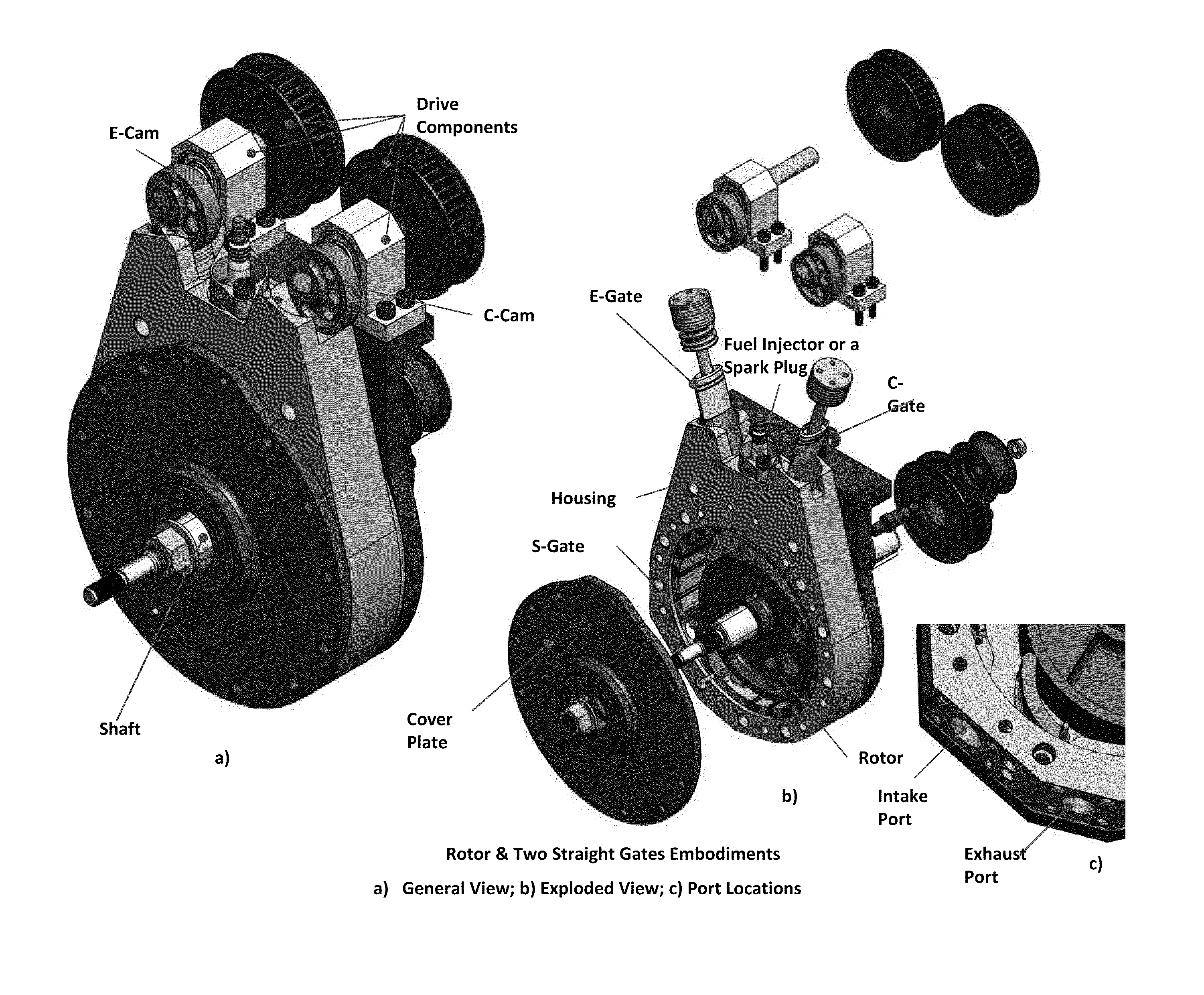
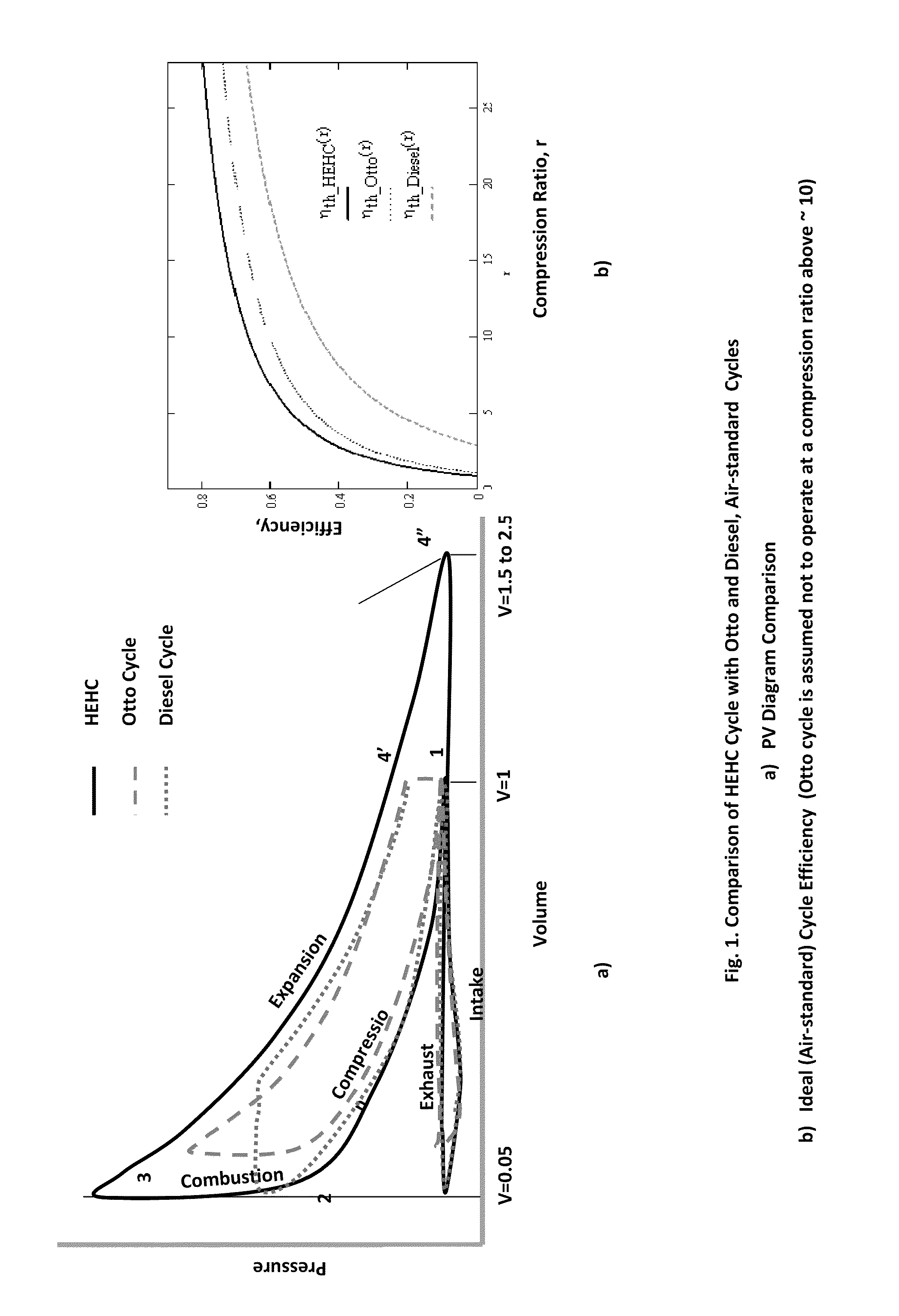
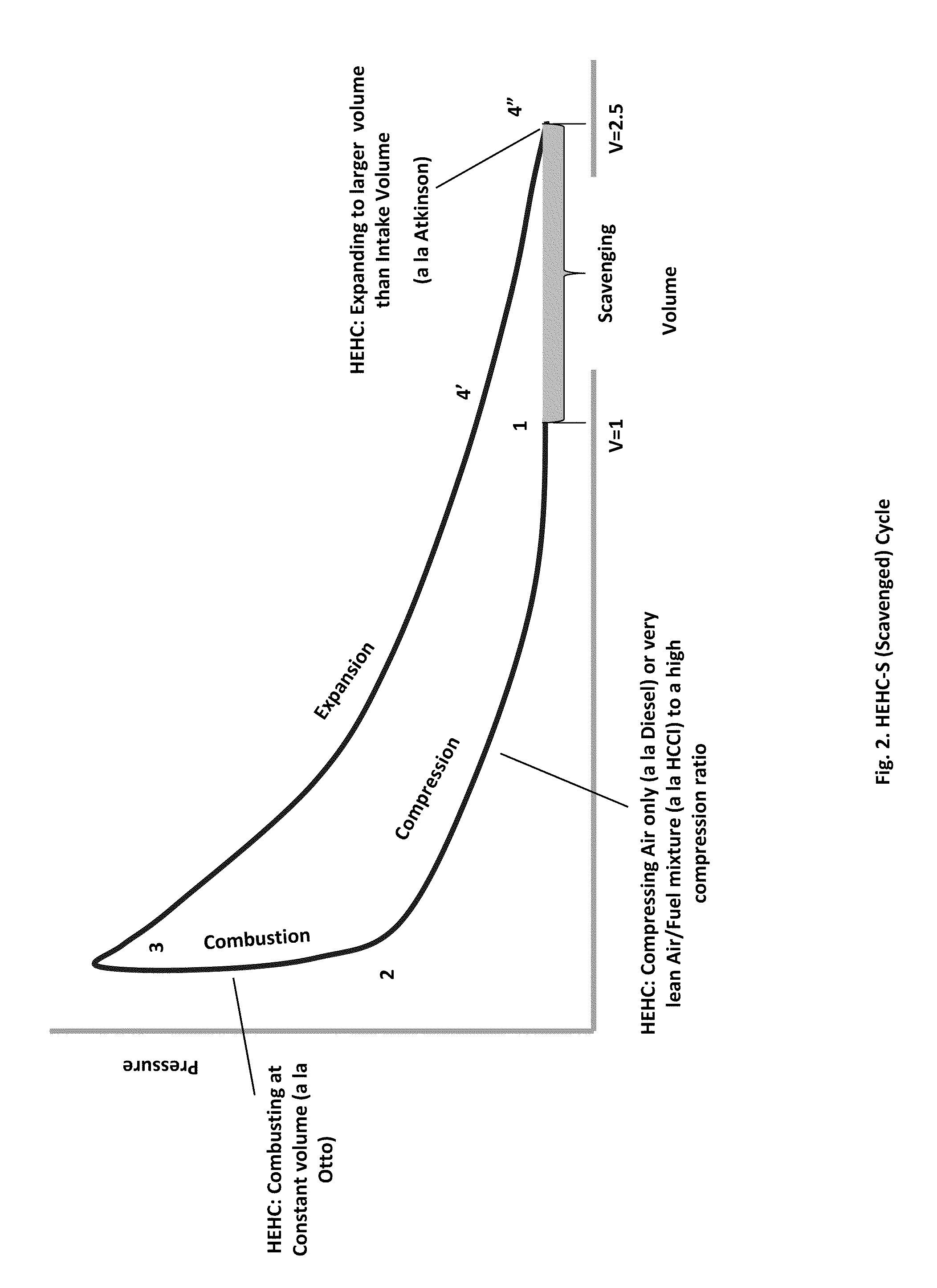
Isochoric Heat Addition Engines and Methods
ActiveUS20110023814A1Improve sealingReduce tangential flow of fluidInternal combustion piston enginesFuel-injection pumpsProcess engineeringHigh-efficiency hybrid cycle
Engines and methods execute a high efficiency hybrid cycle, which is implemented in a volume within an engine. The cycle includes isochoric heat addition and over-expansion of the volume within the engine, wherein the volume is reduced in a compression portion of the cycle from a first quantity to a second quantity, the volume is held substantially constant at the second quantity during a heat addition portion of the cycle, and the volume is increased in an expansion portion of the cycle to a third quantity, the third quantity being larger than the first quantity.
Owner:LIQUIDPISTON INC
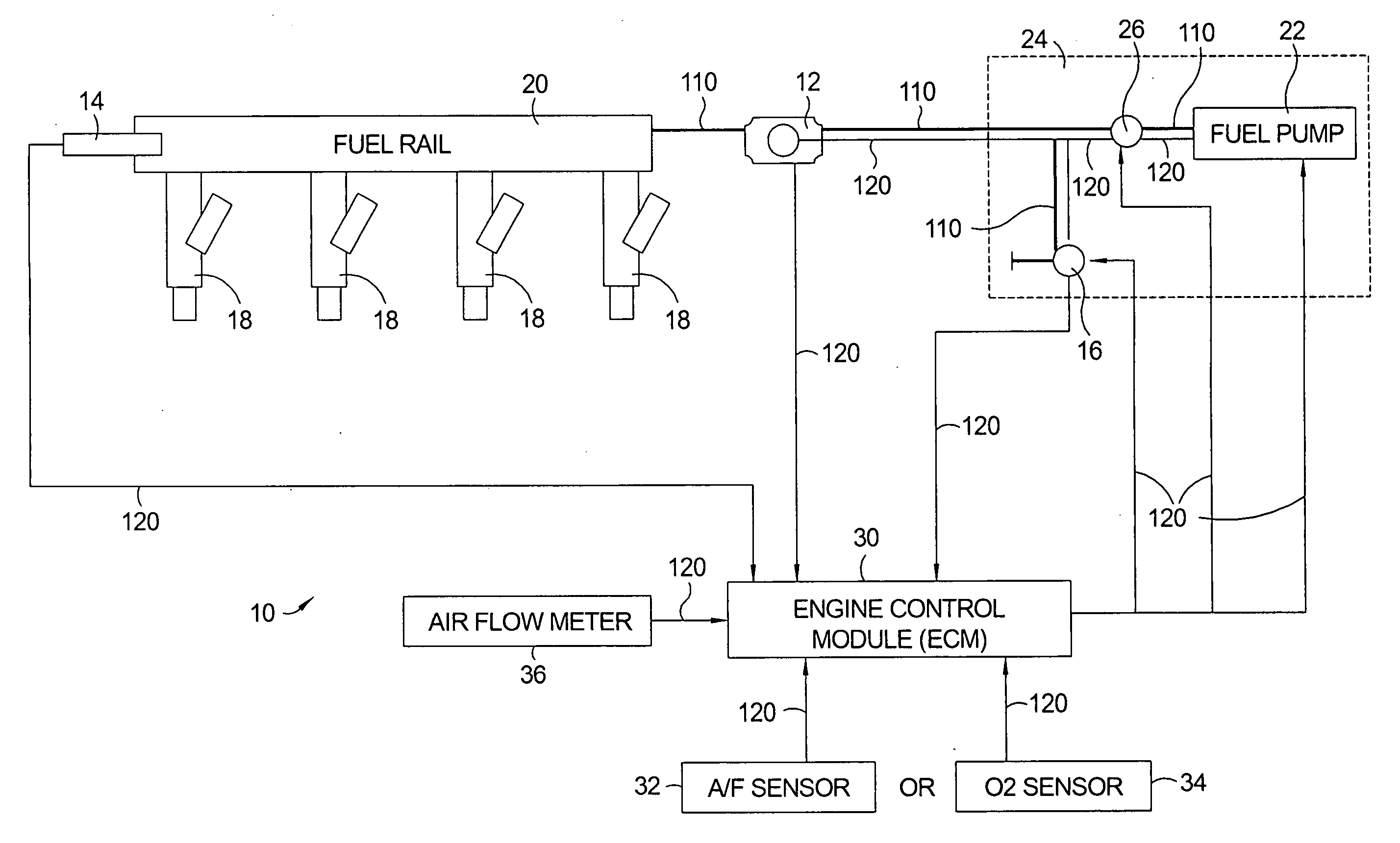
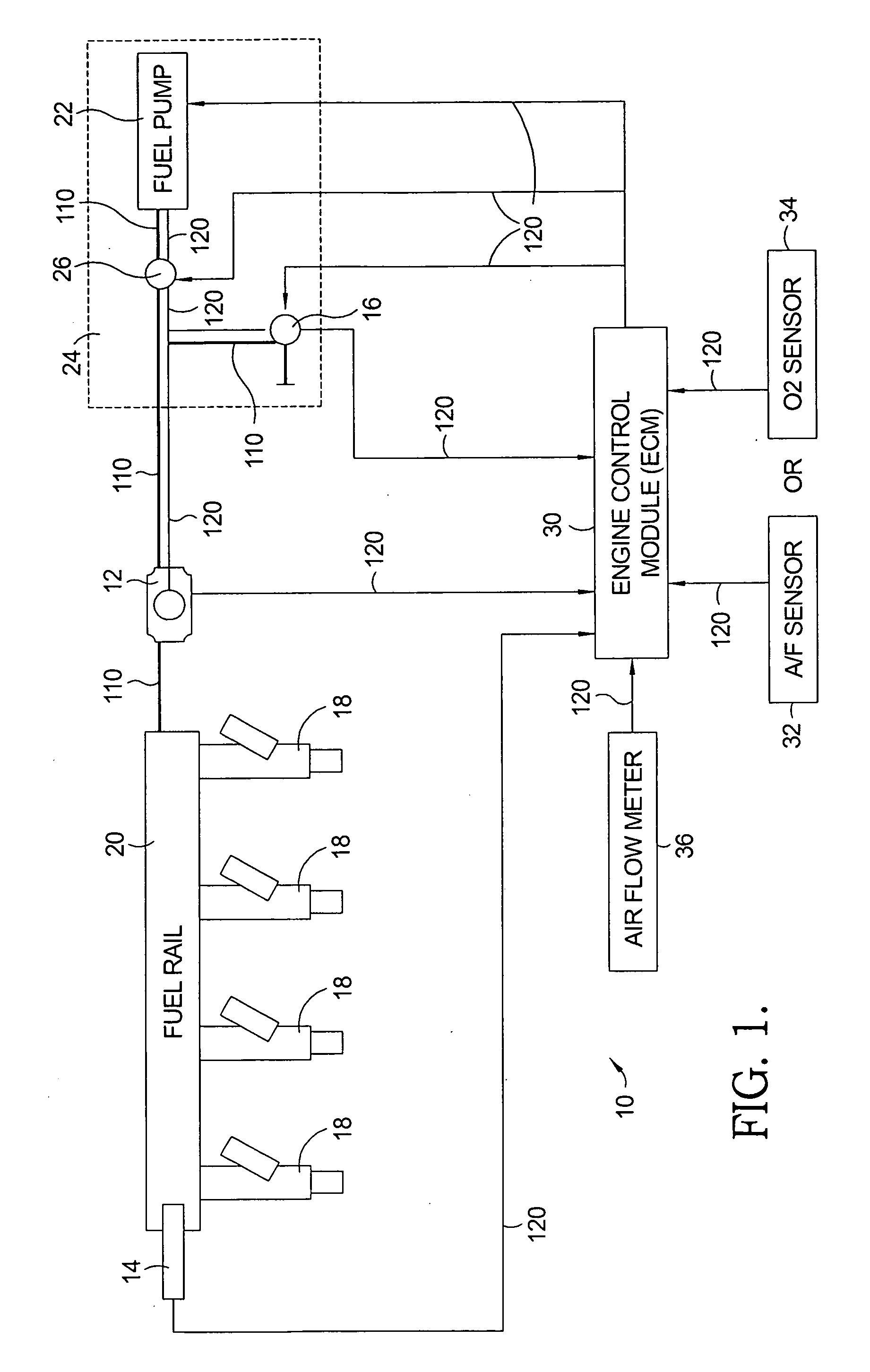
Flow sensing fuel system
InactiveUS20090250038A1Prevent fuel leakagePrevent leakageAnalogue computers for vehiclesElectrical controlGasoline direct injectionPort fuel injection
A flow sensing fuel system for multiple port fuel injection gasoline engines, gasoline direct injection engines, or common rail diesel engines include a flow monitoring device positioned in a fuel flow passage between a fuel pump and a fuel rail, a fuel pressure sensor in fluid communication with said fuel rail, and a controllable pressure regulator closing to a fuel tank. By integrating flow monitoring device, fuel pressure sensor, and controllable pressure regulator in existing fuel systems, a flow sensing fuel system is provided that protects the engine and limits the fuel leaking into the environment in case of a stuck open condition or sealing problem of one or more injectors or in case of a leak in the fuel rail assembly. The flow sensing fuel system enables monitoring the fuel flow during engine start-up, during engine operation, and after engine shut down.
Owner:DELPHI TECH INC
Injector fuel filter with built-in orifice for flow restriction
ActiveUS20070227984A1Reduce pressure pulsationReduce or eliminate pressure pulsations through the fuel injectorSedimentation separationMachines/enginesEngineeringFuel filter
Owner:DELPHI TECH IP LTD
Active drag and thrust modulation system and methods
InactiveUS6978767B2Good fuel atomizationPromote atomizationTyre partsInternal combustion piston enginesLeading edgeCombustion
A vehicle traveling through an environmental media such as air experiences drag. The drag is actively modulated by energy beams which may either increase or decrease the drag. The energy beams may provide either a chemical, acoustic or electromagnetic energy at a transition region between turbulent and laminar flows or at the leading edge of a laminar flow or in the direction of a crosswind in order to facilitate the respective increase or decrease in drag. If the vehicle is a sailing ship, areas of the sails are selectively roughened or widened to enhance the thrust derived from the wind. Furthermore, the keel or hull of the sailing ship may be modified to improve the hydrodynamic characteristics of the sailing ship. If the vehicle is an automobile, the tires or road surface may be selectively heated to improve the traction of the automobile. Furthermore, the energy beams may be used to facilitate atomization of the air / fuel mixture prior to combustion in an internal combustion engine thereby improving the thrust of provided to the vehicle. Energy beams may be used to generate virtual extensions of a vehicle to enhance traveling efficiency.
Owner:P TECH
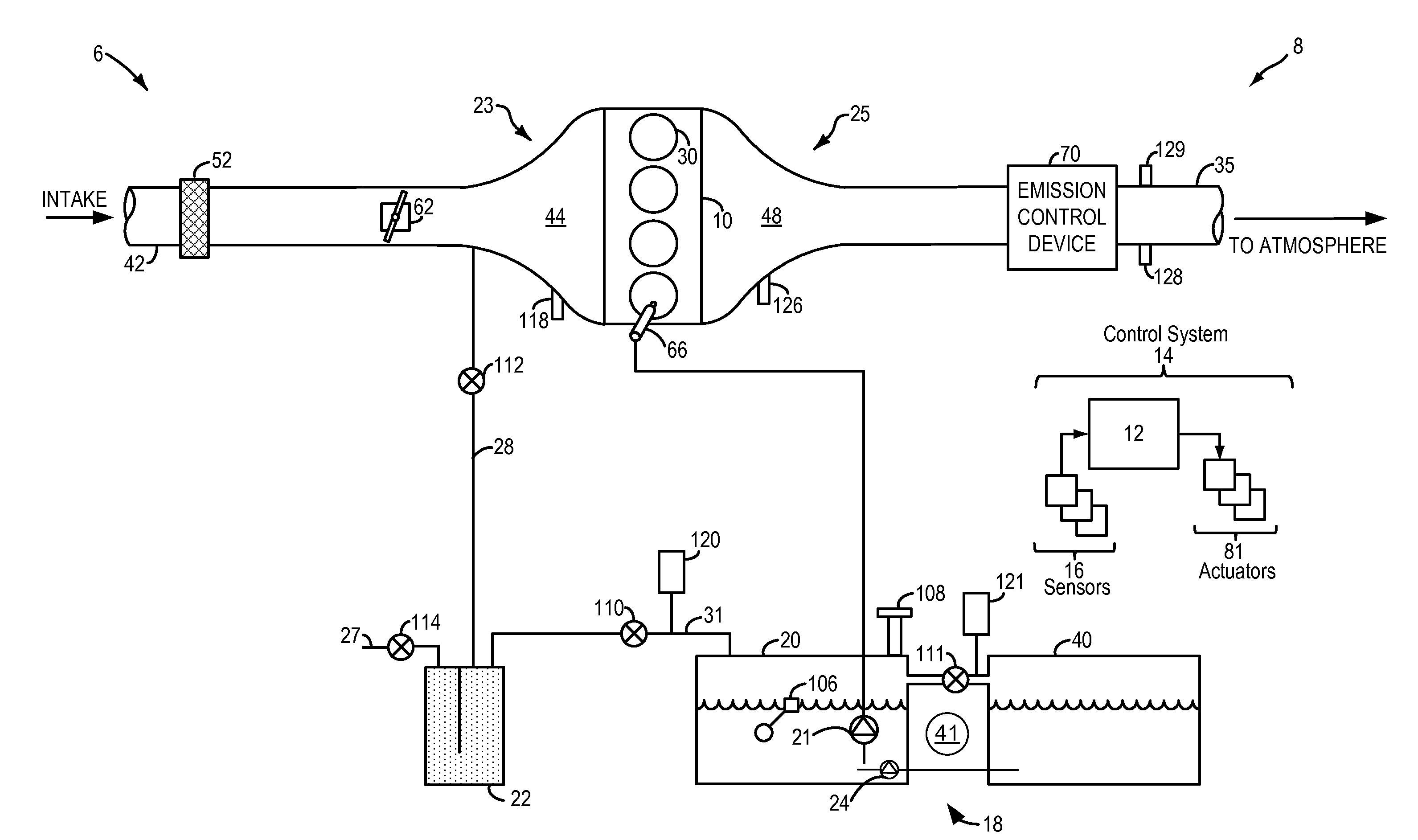
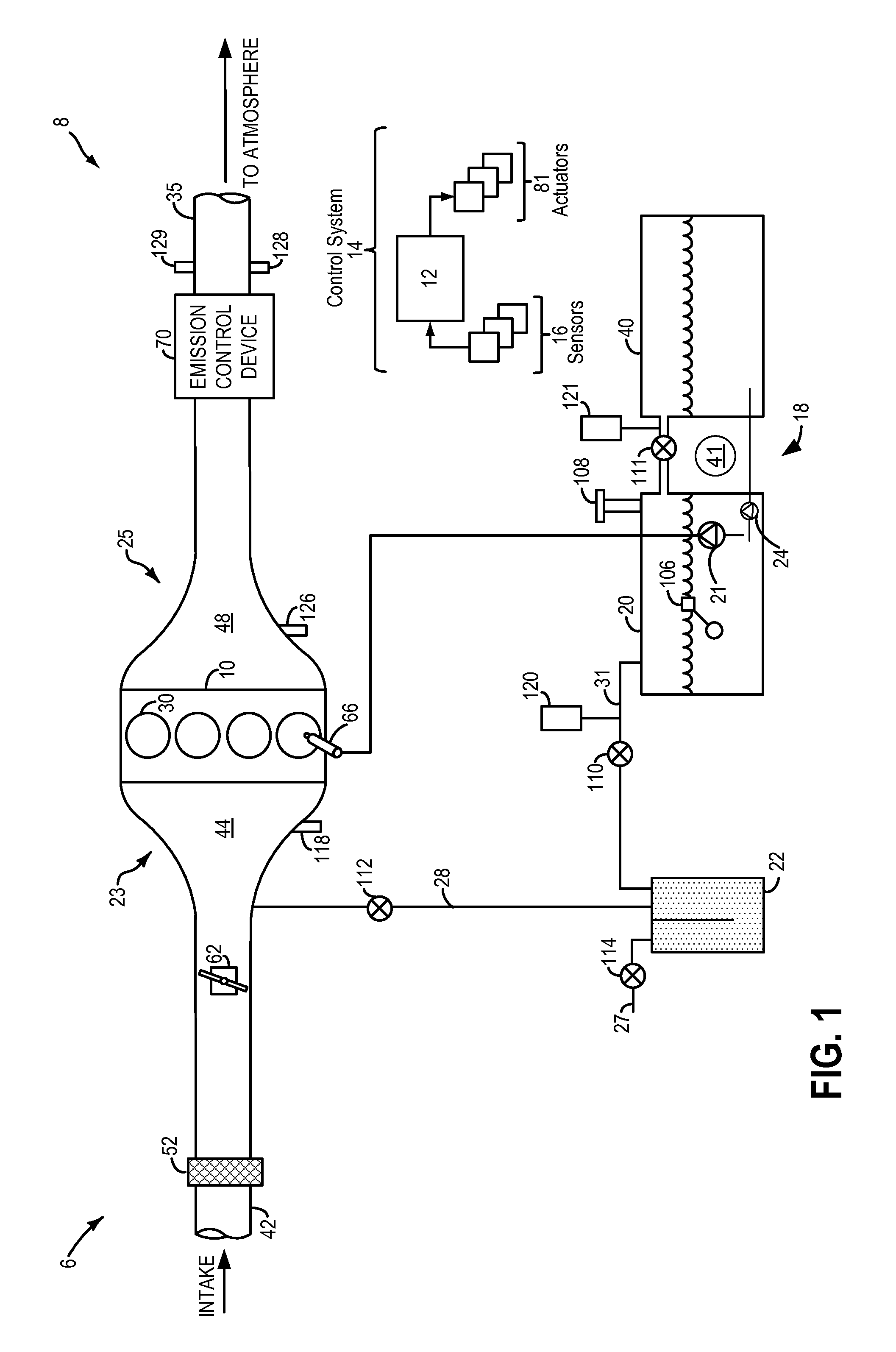
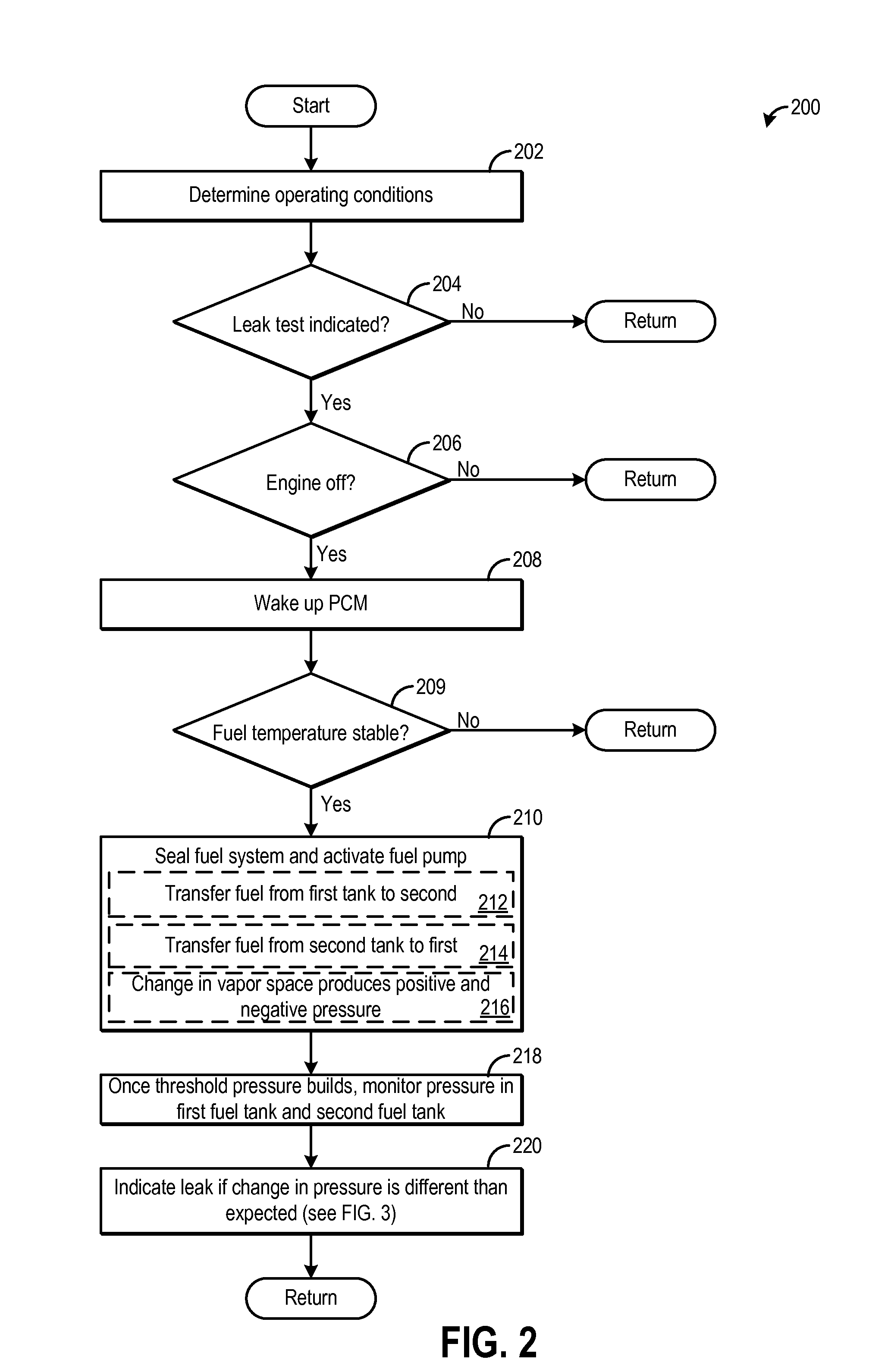
Fuel system degradation test using two fuel tanks
ActiveUS20140107906A1Saving engine packaging spaceImprove engine efficiencyHybrid vehiclesAnalogue computers for vehiclesSystem pressureFuel tank
Embodiments for monitoring fuel system degradation are provided. In one example, a method for a vehicle comprises evacuating fuel from a first fuel tank to a second fuel tank, and indicating fuel system degradation in response to a change in fuel system pressure following the evacuation of fuel. In this way, fuel system degradation may be indicated without use of a separate pressure building device.
Owner:FORD GLOBAL TECH LLC
Controllable combustion method and device
InactiveUS6938588B2High bandwidthFast energy extractionPulsating combustionFuel-injection pumpsCombustionEngineering
A method and device for controllably combusting combustible material, including a combustion device comprising an elongate combustion tube having an inlet section including an inlet for combustible material, an ignition section, including an igniter displaced along a length of the tube from the inlet section to ignite the combustible material, and at least one energy extraction device operatively coupled to the combustion tube and configured to extract energy from combustion of the combustible mixture.
Owner:SARCOS LC
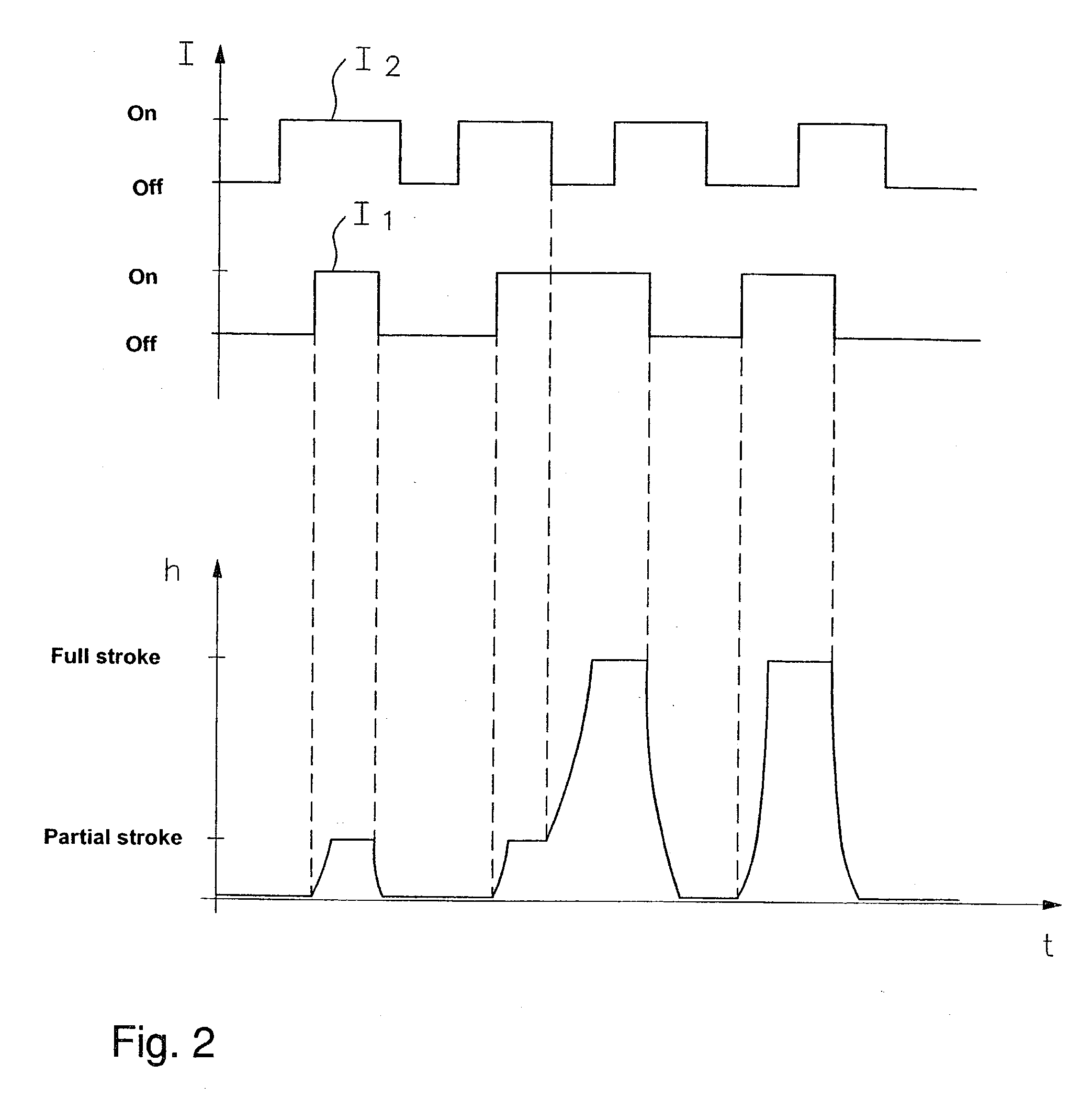
Fuel injection valve and a method for operating the same
InactiveUS20030127531A1High closing dynamicsShort closing timeOperating means/releasing devices for valvesInternal combustion piston enginesCombustionEngineering
A fuel injector (1), especially an injector for fuel injection systems of internal combustion engines, includes a first solenoid coil (5), which cooperates with the first armature (9), a valve needle (13) in a force-locking connection with the first armature (9) for actuating a valve-closure member (14), which together with a valve seat surface (15) forms a sealing seat, and a second solenoid coil (6). In this context, the first armature (9) is acted upon in a closing direction by a first resetting spring (11). A second armature (10) cooperates with the second solenoid coil (6) such that, when the first solenoid coil (5) and the second solenoid coil (6) are supplied with current, a limit stop body (18) that is connected with the valve needle (13) strikes against the second armature (10).
Owner:ROBERT BOSCH GMBH
Electronic control unit
InactiveUS7189918B2Simple structureImprove ventilation efficiencySubstation/switching arrangement detailsCasings/cabinets/drawers detailsElectronic control unitElectronic circuit
An Electronic Control Unit which houses electronic circuit for controlling various devices of vehicles in a sealing case is characterized in that the case has a ventilation hole to communicate an interior and an exterior of the case, the ventilation hole comprises a filter for preventing from entering contaminants from the outside, and a sectional area of the ventilation hole is gradually enlarged toward the interior of the case.
Owner:NSK LTD +1
Hydraulic cylinder
InactiveUS20050268608A1Prevent escapeIncrease the effective sectionRotary clutchesFluid actuated clutchesHydraulic cylinderEngineering
A hydraulic cylinder includes a housing having a fluid connection for connecting to a hydraulic system and an after-running connection for connecting to a fluid after-running vessel, and a piston which is axially displaceable in the housing to define a variable pressure space having a gas collecting portion, the piston being fixed against rotation in the housing and having at least one after-running groove which is oriented substantially toward the gas collecting portion. A primary seal arranged in the housing and receiving the piston therethrough is bridged by the after-running groove when the piston is in an extended end position, whereby the gas collecting portion of the pressure space communicates with the after-running connection when the piston is in the extended end position.
Owner:ZF FRIEDRICHSHAFEN AG
Internal combustion engine including valve deactivation mechanism
InactiveUS20110239987A1Analogue computers for vehiclesElectrical controlExhaust valveExternal combustion engine
An internal combustion engine which includes a valve deactivation mechanism for reducing an output power shock upon changing of the cylinder number. In an internal combustion engine which includes a valve deactivation mechanism driven by a slide pin which is driven by hydraulic pressure, response delay time after a signal is sent to oil control valves until an intake valve and an exhaust valve are activated or deactivated is used to form a control map in response to control parameters, and the valve deactivation mechanism is controlled based on the control map.
Owner:HONDA MOTOR CO LTD
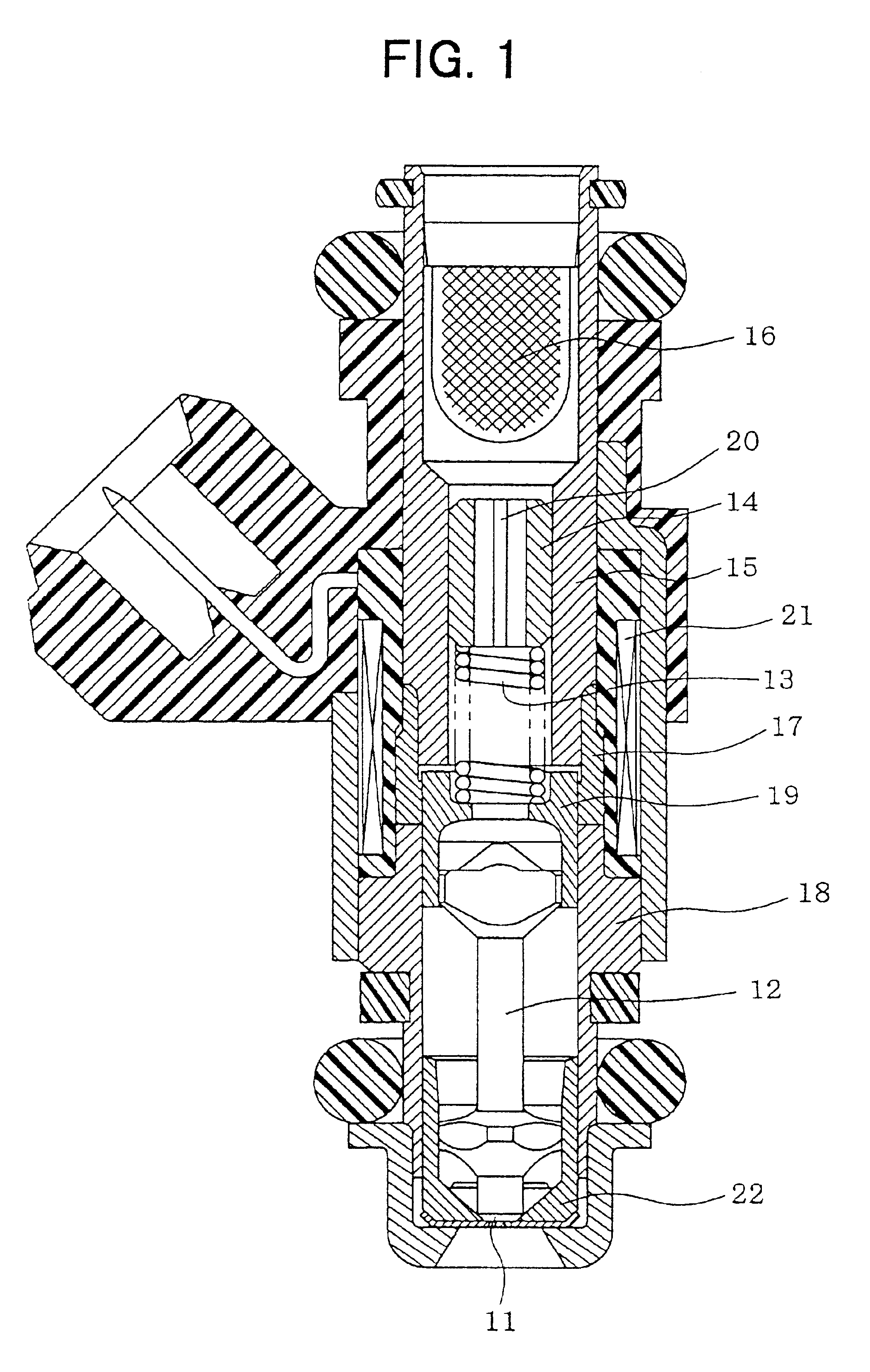
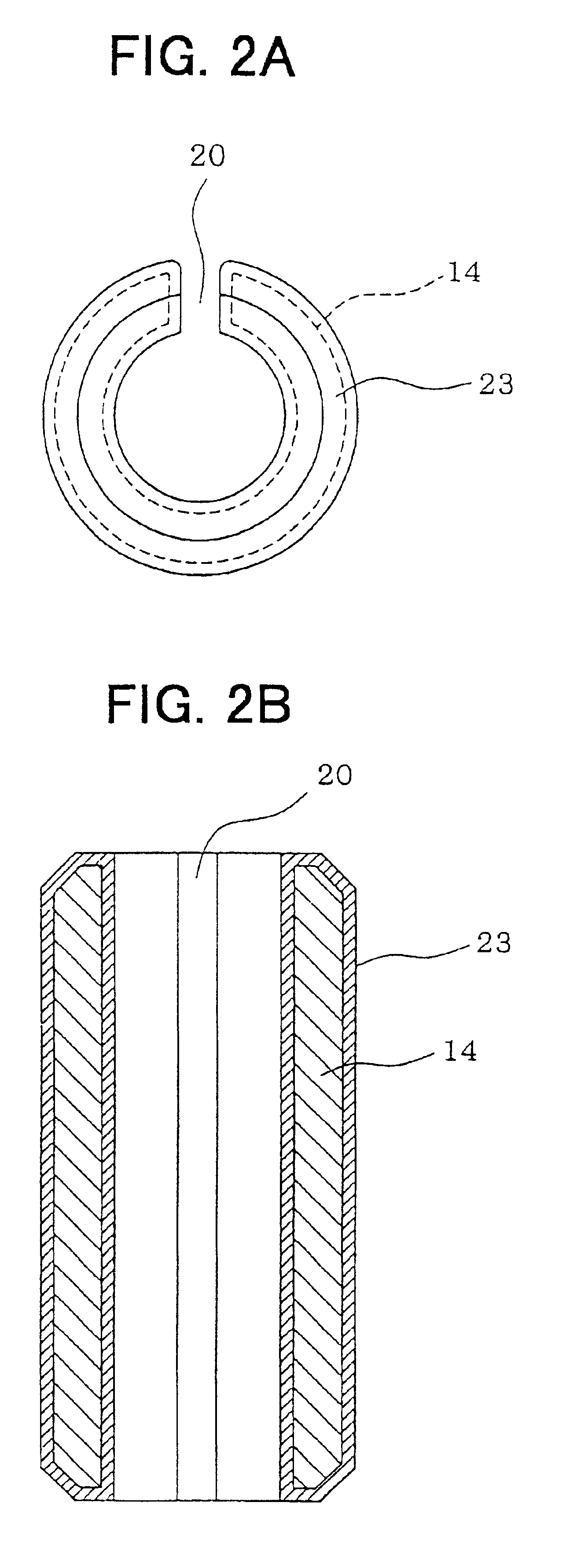
Adjustment pipe for fuel injection valve, and press-fitting structure and press-fitting method for the same
InactiveUS6834667B2Control deformationEasy to adjustVolume/mass flow measurementPipe elementsSpring forceEngineering
In a fuel injection valve, an adjustment pipe made of stainless steel and for adjusting a compression amount of a spring biasing a valve member is press-fitted into a cylindrical housing made of stainless steel, and a fuel injection amount is adjusted by adjusting a spring force of the spring in accordance with a press-fitted amount of the adjustment pipe. The adjustment pipe is immersed in an oxalic acid solution so that an oxalate film is formed thereon before being press-fitted into the cylindrical housing. Therefore, the oxalate film prevents a direct press-contact between an outer peripheral surface of the adjustment pipe and an inner peripheral surface of the cylindrical housing.
Owner:DENSO CORP
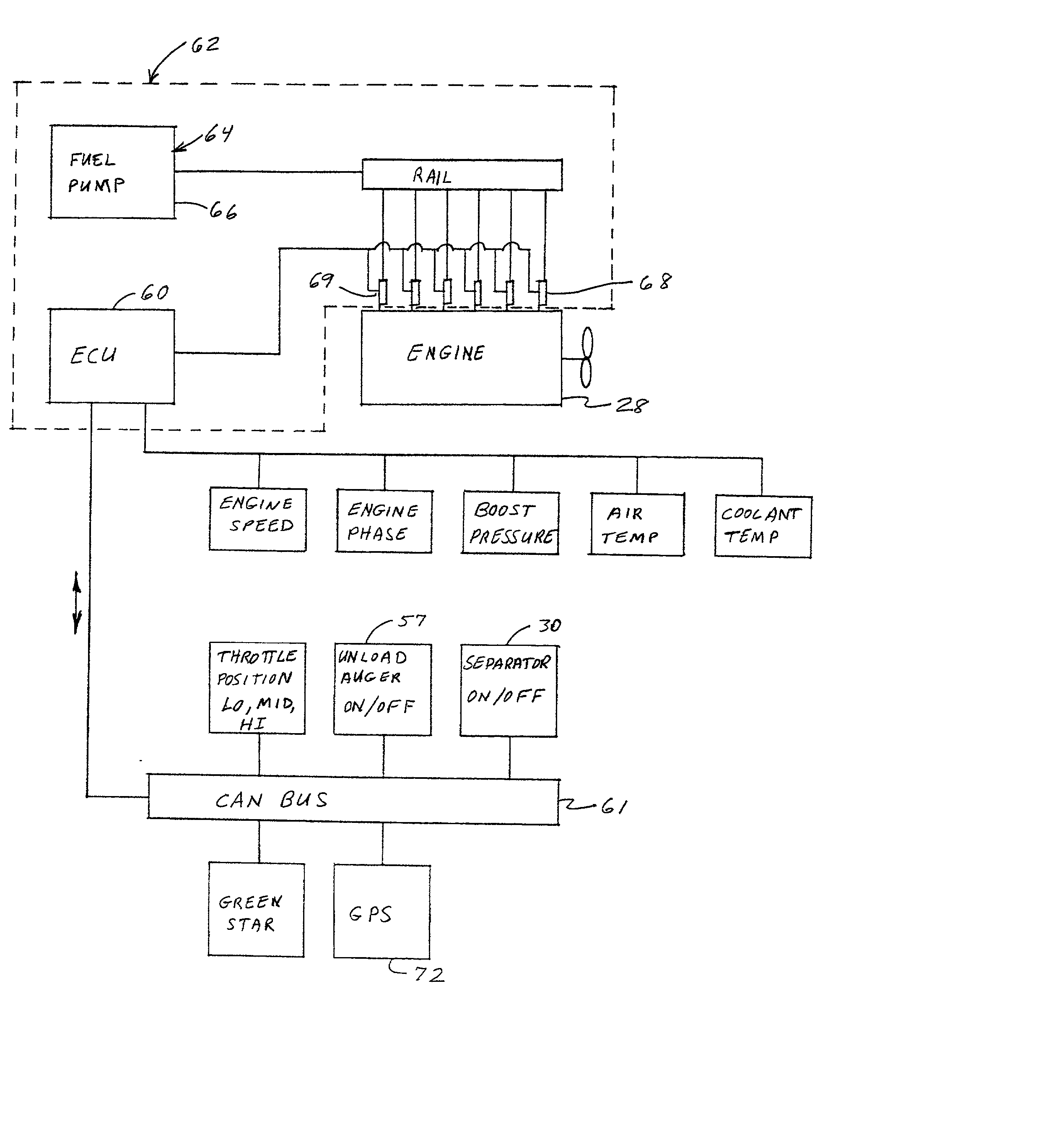
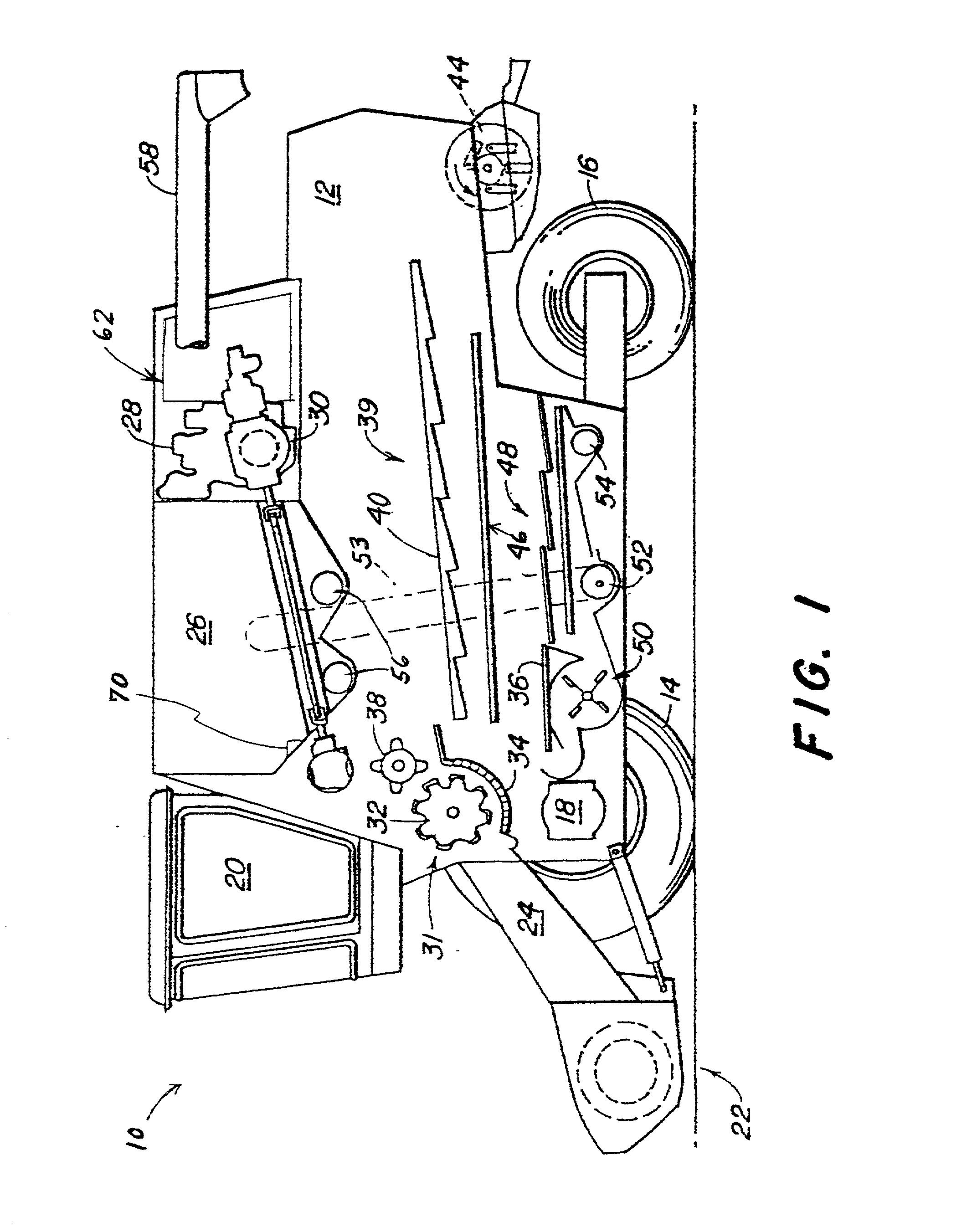
Vehicle engine control
An engine control unit, and method of use, uses a power curve or algorithm to pro-actively adjust fuel flow rate to an engine, optionally in combination with a reactive power curve or algorithm, thereby to adjust engine power, in anticipation of changes in loads being imposed on the engine, as well as to respond to engine speed changes. The ECU has a power curve or algorithm stored in memory which responds to certain predetermined operating conditions other than sensed engine speed, by providing a sequence of pro-active change inputs, at predetermined rates of change, in rate of delivery of fuel to the engine combustion chambers, independent of engine speed change, thereby to produce pro-active incremental changes in power output of the engine. Such pro-active incremental power changes are effected in anticipation of changes in load demand on the engine, and correspond generally with expected incrementally progressive changes in load demand on the engine. In preferred embodiments, the power curve or algorithm includes a first upwardly sloping line representing small increment increases in engine power, a second step change increase in engine power, a third downwardly sloping line representing small incremental decreases in engine power, and a fourth relatively greater magnitude step change decrease in engine power. The pro-active change input signals can be combined with reactive change input signals to make respective combination change input signals which take into consideration a variety of operating parameters, including engine speed changes.
Owner:DEERE & CO
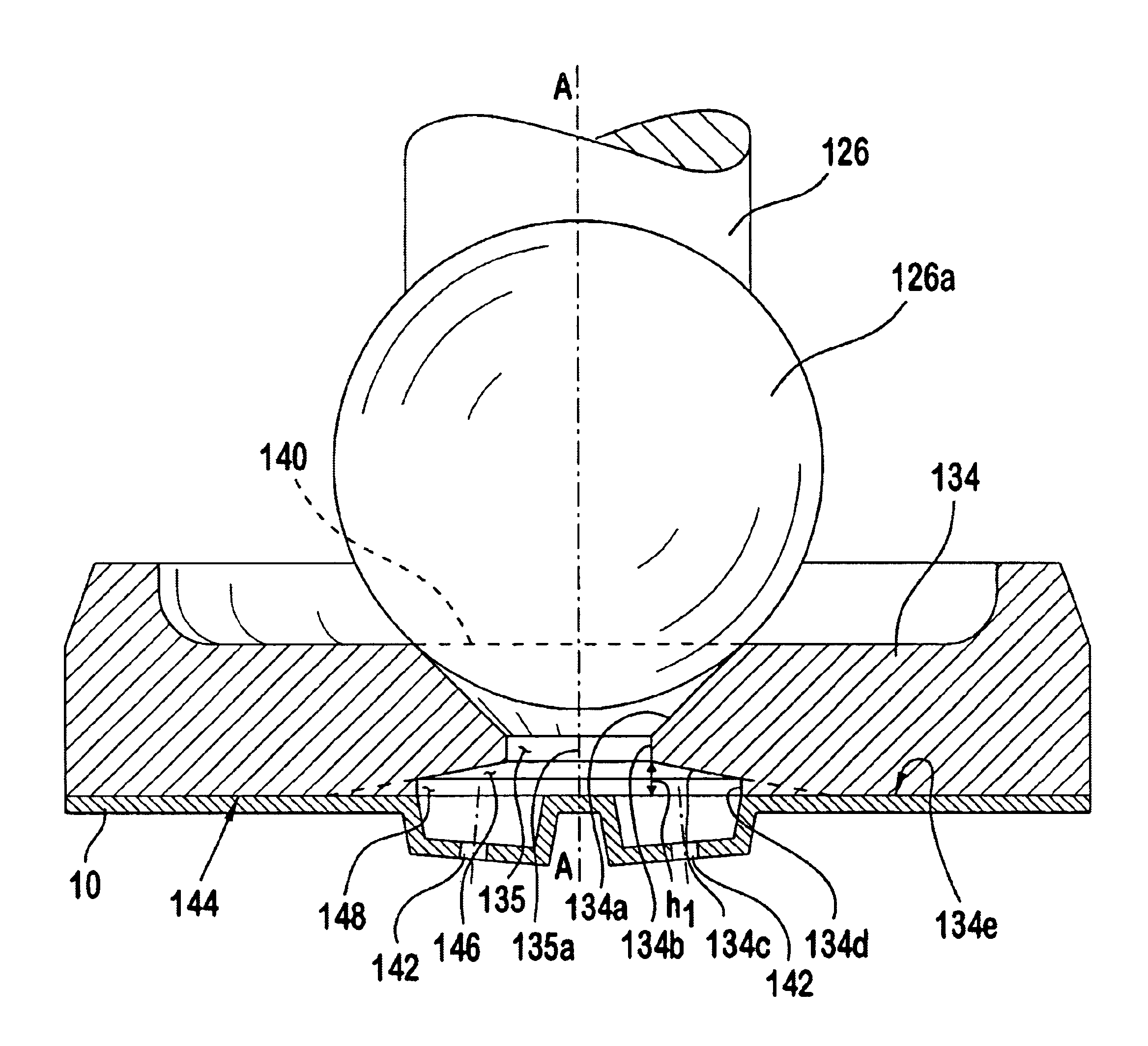
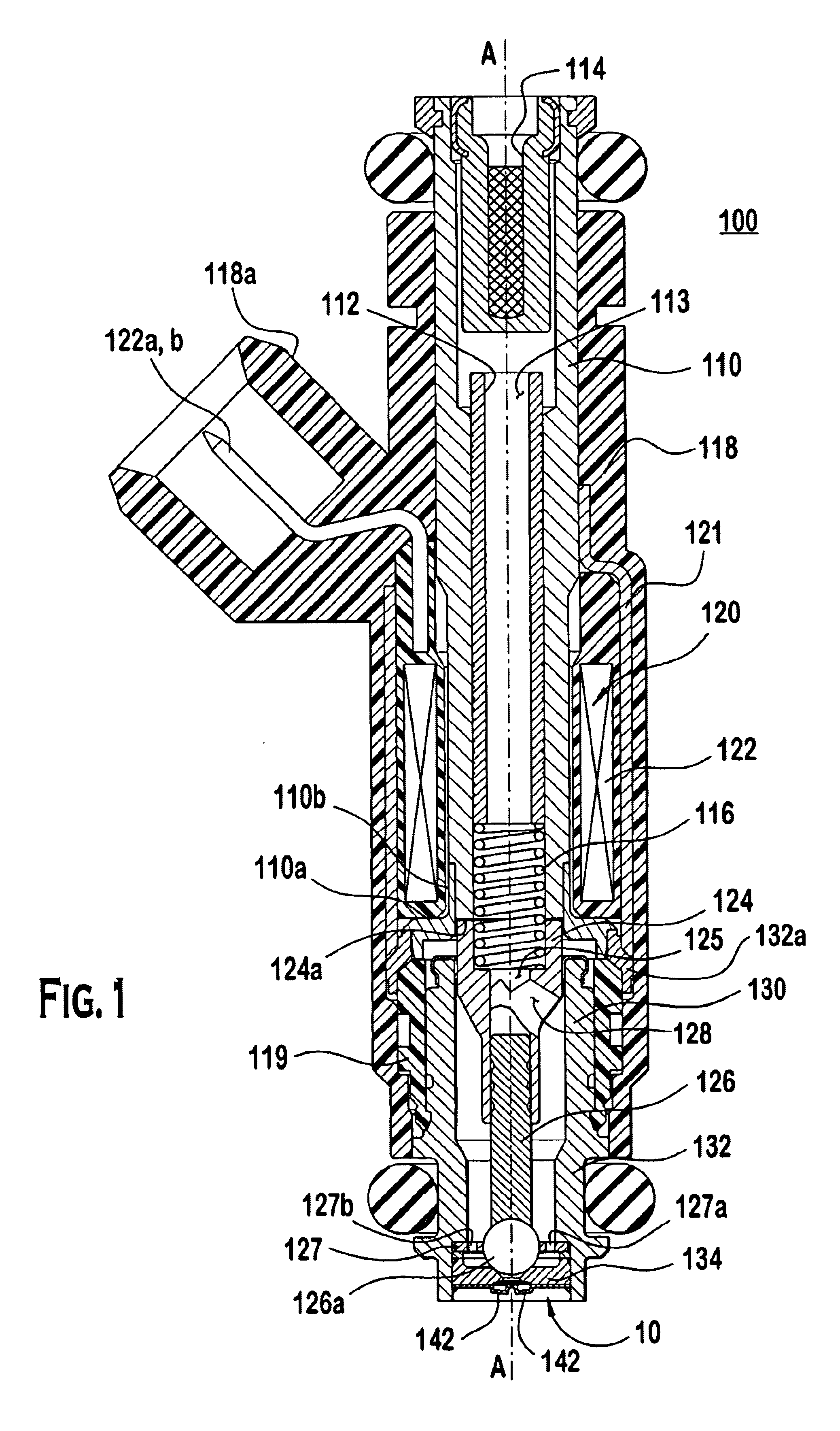
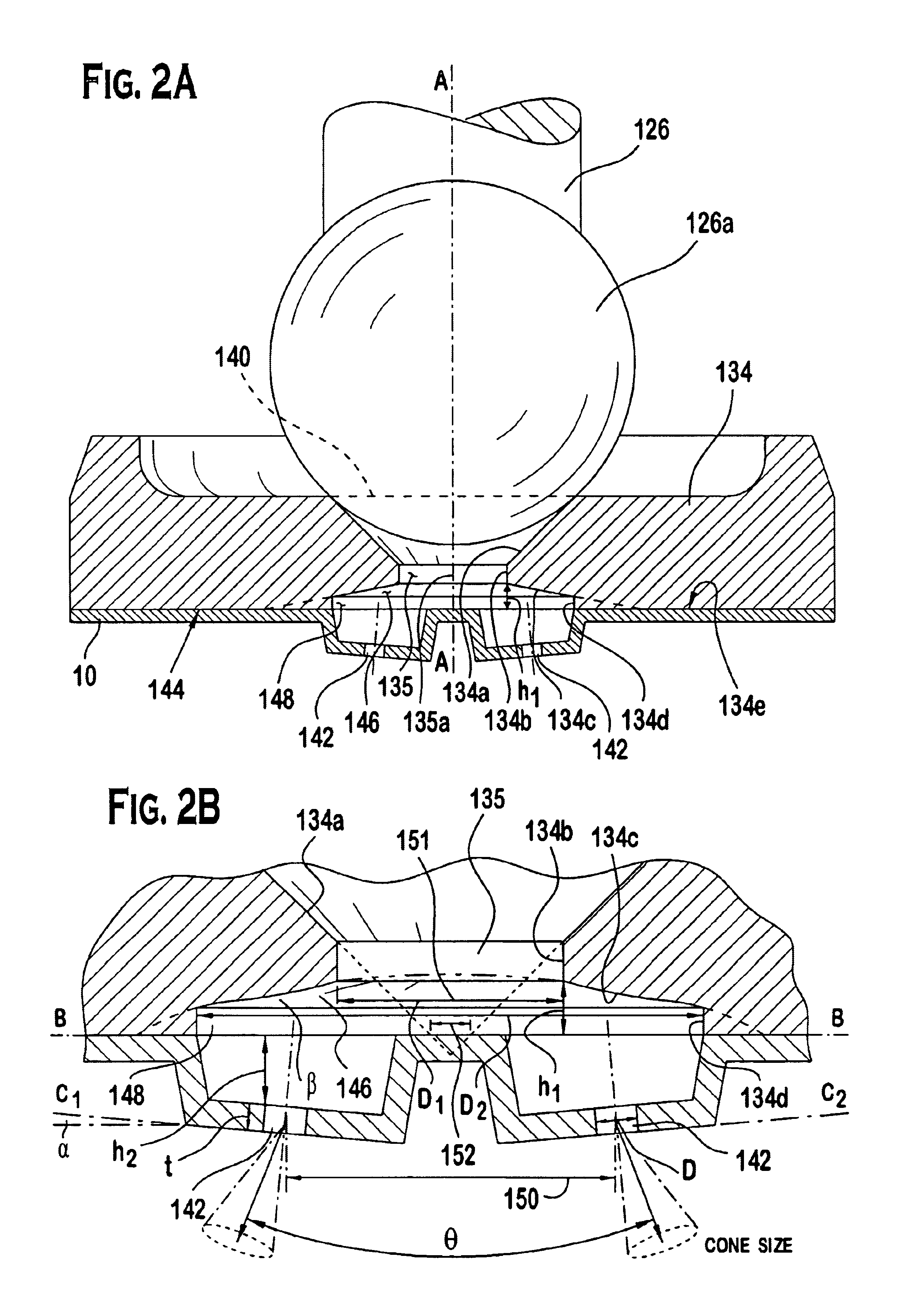
Spray pattern control with non-angled orifices formed on a generally planar metering disc and reoriented on subsequently dimpled fuel injection metering disc
A fuel injector that includes a housing, a seat, a metering disc and a closure member. The metering orifices can be located on a first virtual circle greater than a second virtual circle as defined by a projection of a sealing surface converging at a virtual apex projected on the metering disc. The metering disc can be dimpled to increase the spray angle. Various parameters can be utilized to achieve a desired cone size and spray angle. A method of controlling spray targeting of a fuel injector is also described.
Owner:VITESCO TECH USA LLC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com