Patents
Literature
128 results about "Hcci combustion" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
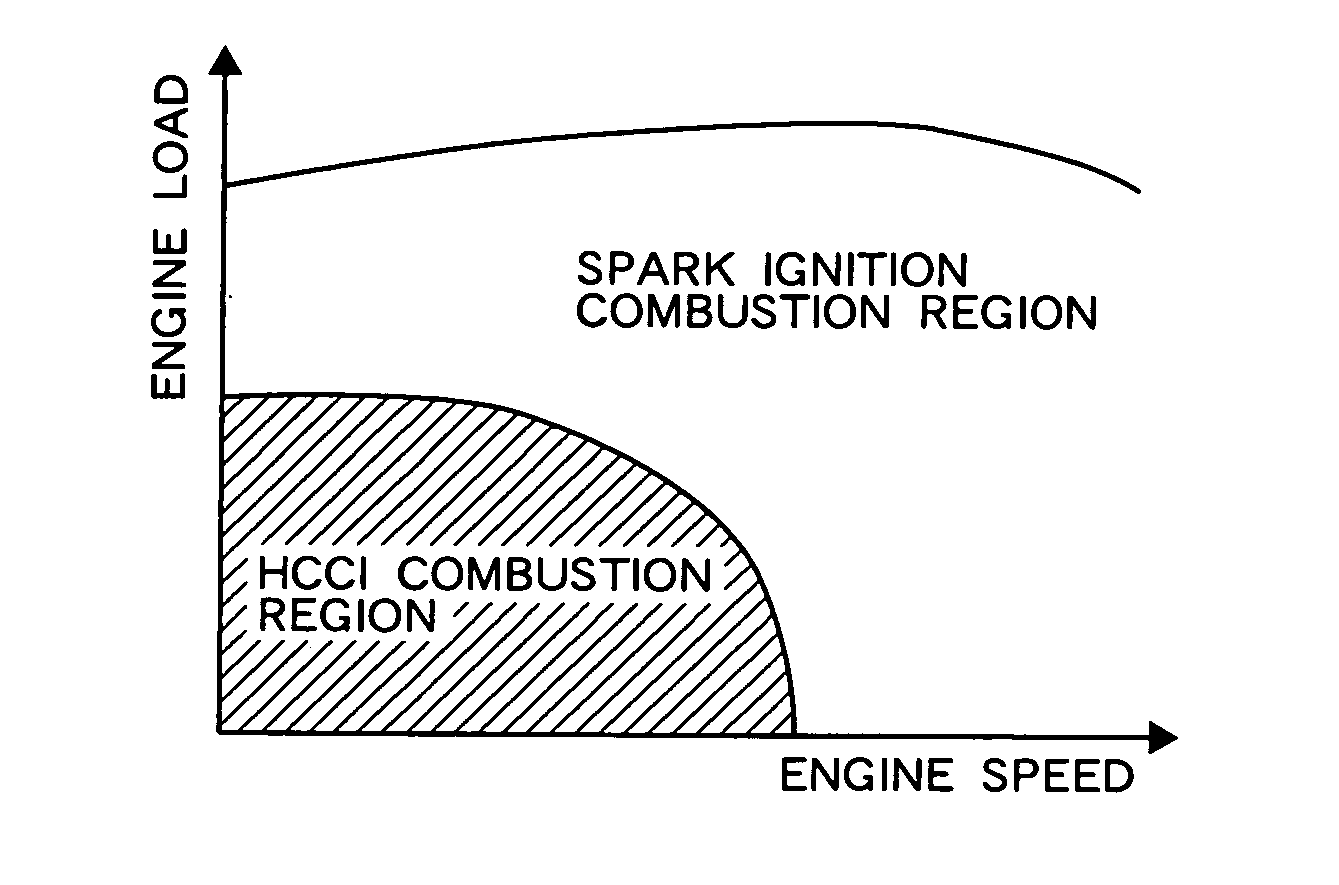
HCCI is the ultimate combustion method for achieving both CO2 reduction and clean exhaust using auto-ignition of gasoline, as in a diesel engine. The system features lower-temperature combustion compared to ordinary gasoline engines, resulting in nearly no NOx emissions.
Multi-fuel compression ignition engine
InactiveUS7036482B2Improve performanceMaximizing intensityElectrical controlInternal combustion piston enginesHcci combustionCombustion chamber
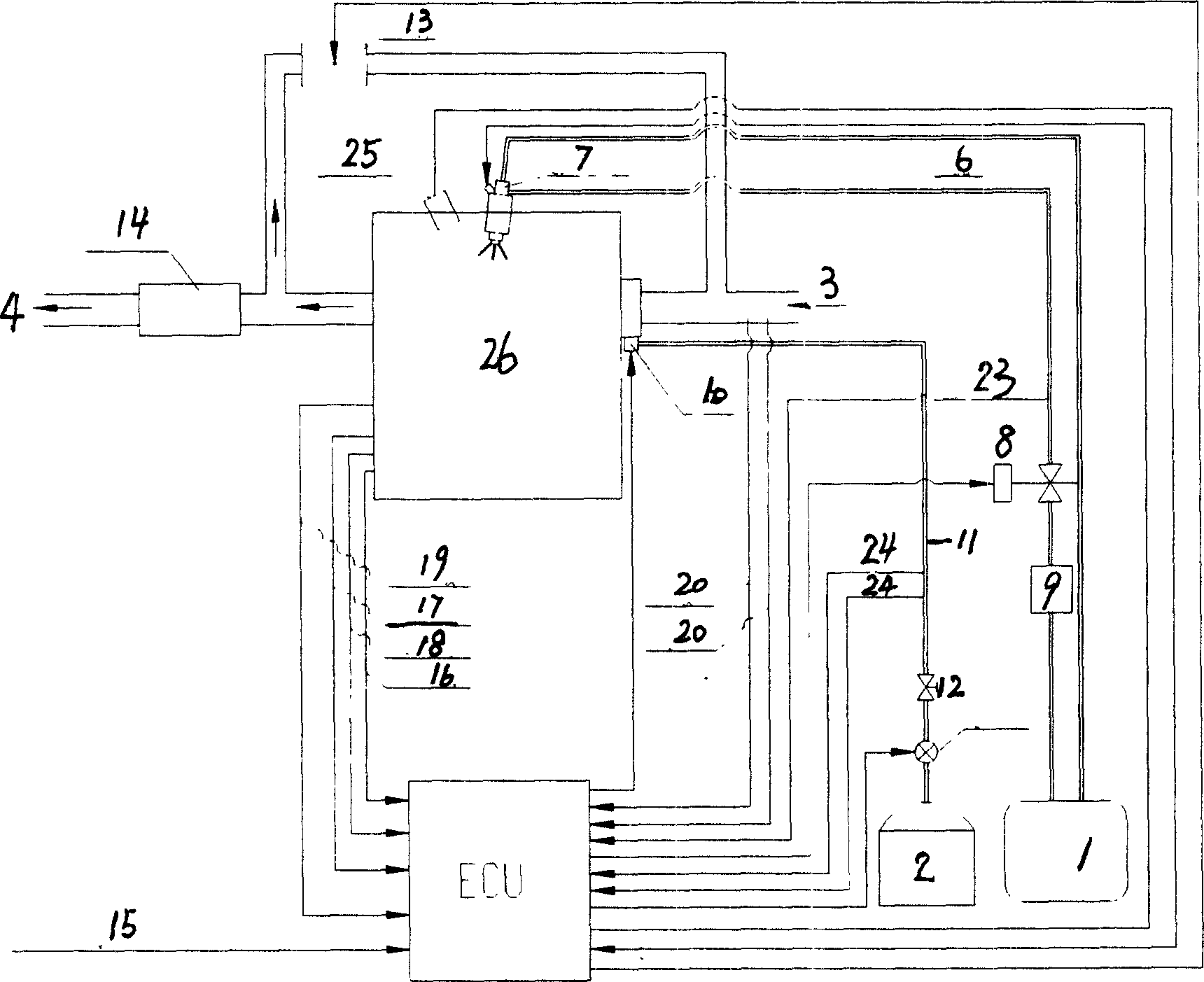
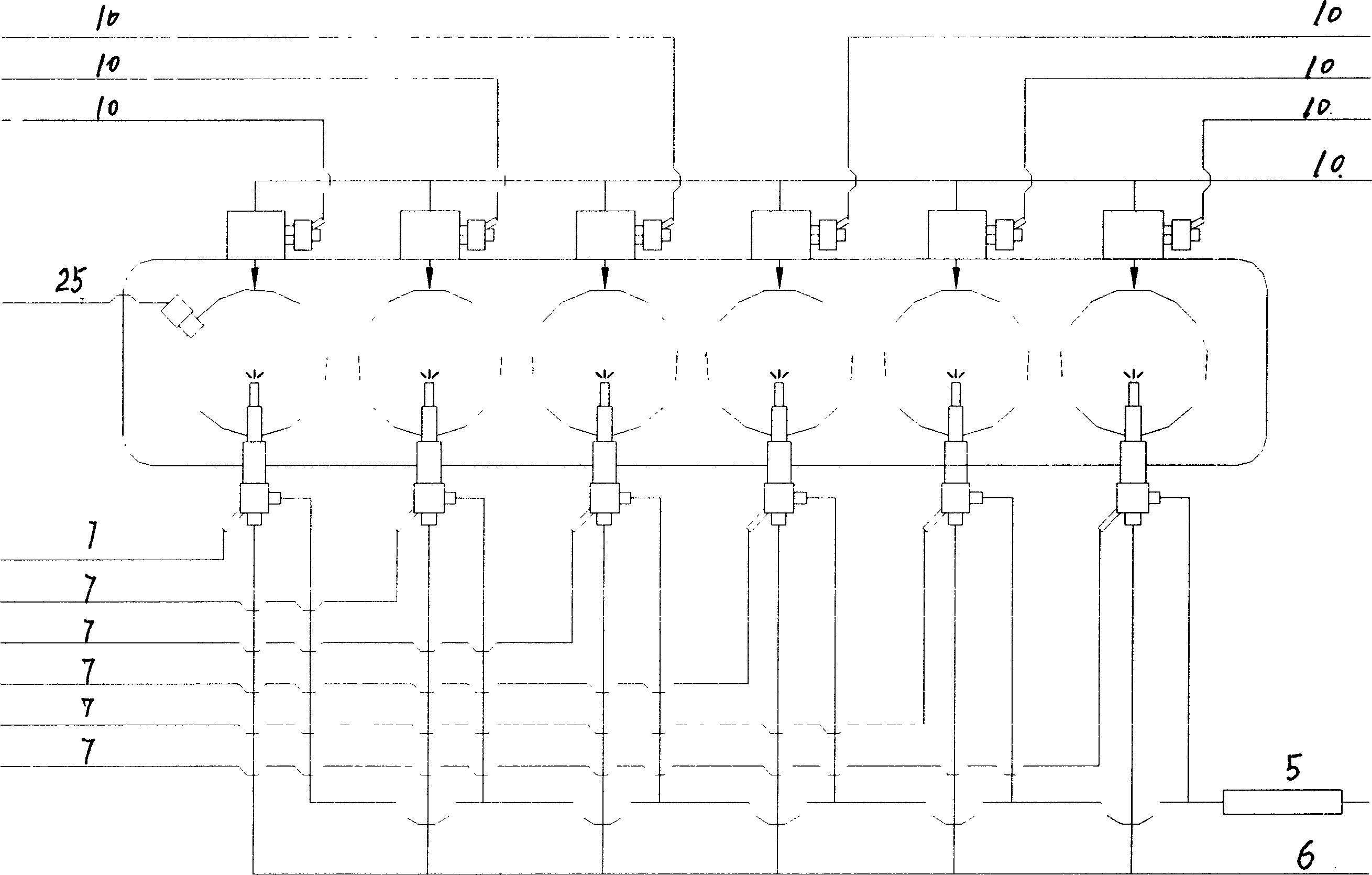
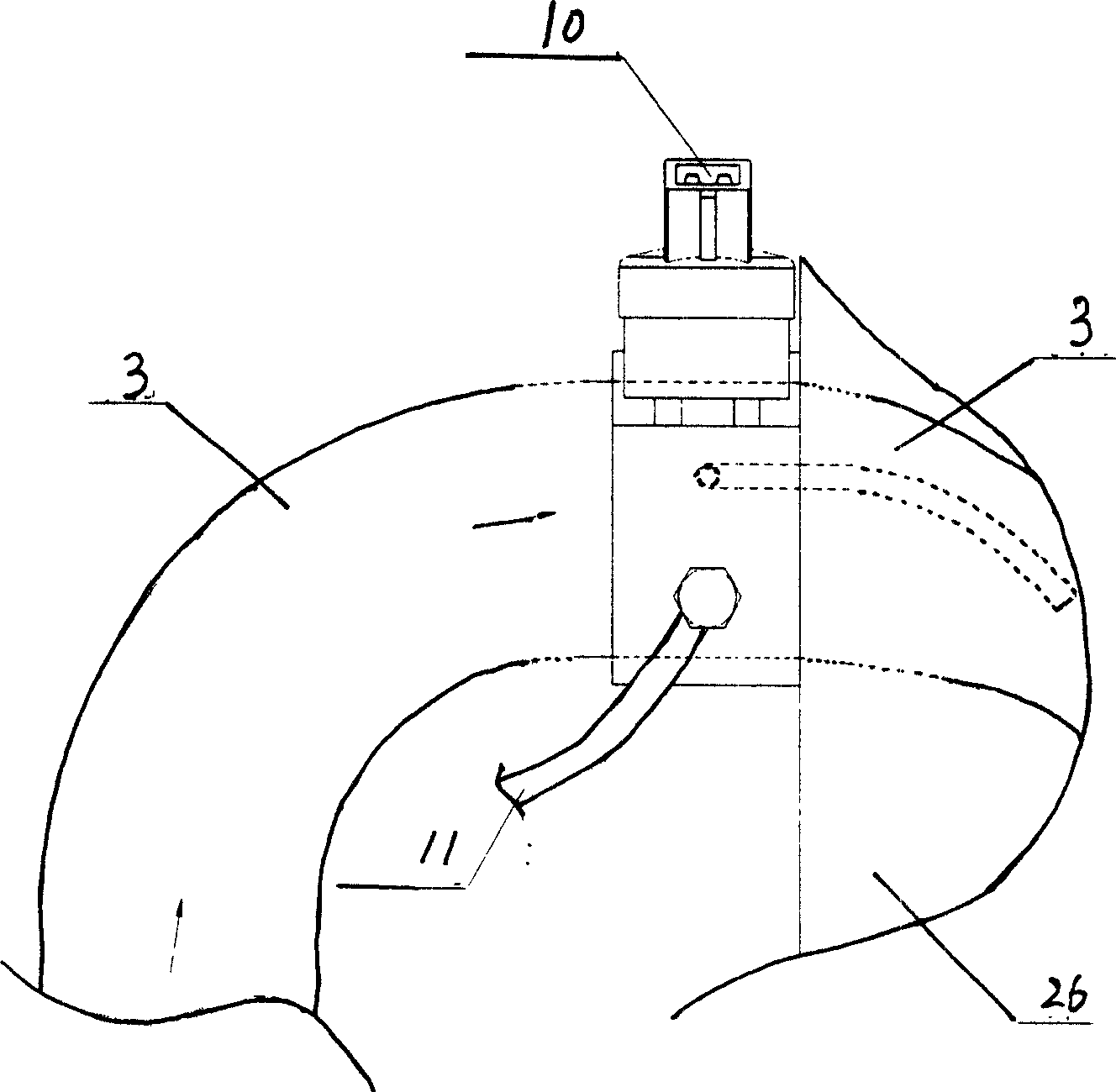
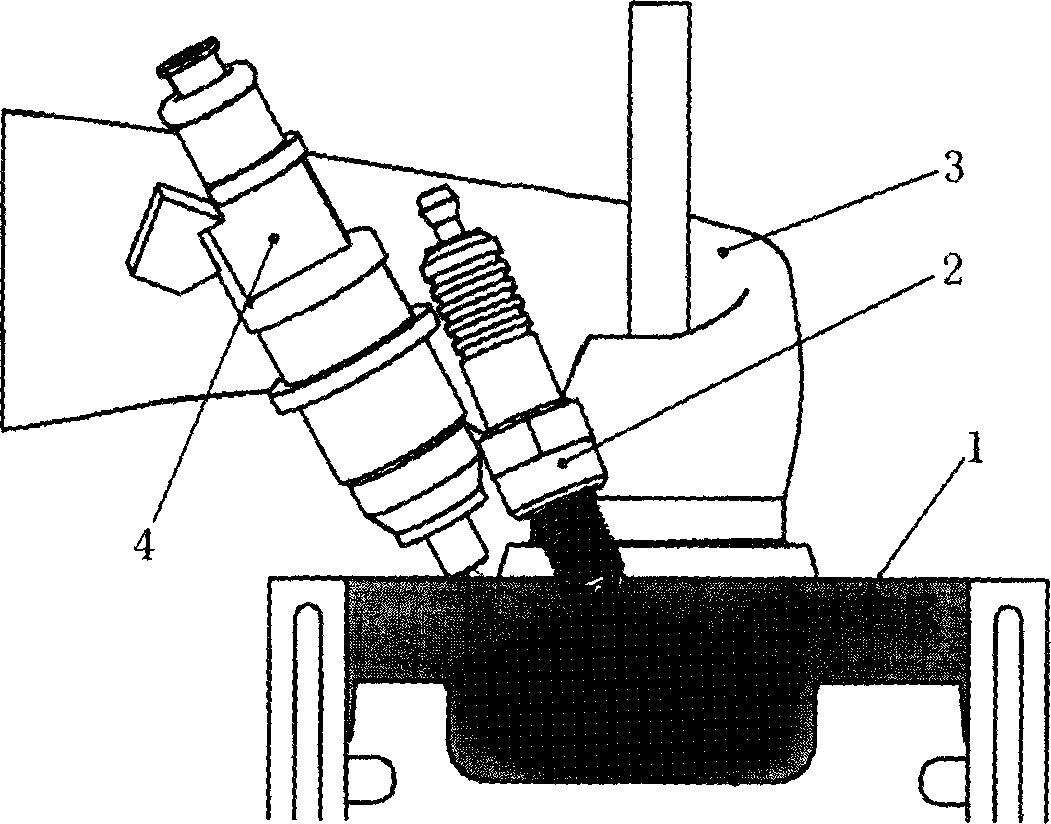
A liquid primary fuel is ignited by HCCI with the assistance of the early injection of a liquid pilot fuel. Pilot fuel injection and / or ignition are preferably controlled so as to permit the injected pilot fuel to become thoroughly distributed through and mixed with the primary fuel / air charge in the combustion chamber and vaporized prior to ignition. Pilot fuel having a lower autoignition temperature will be ignited by compression ignition, followed by the ignition of the homogeneous mixture of the primary fuel and air. HCCI combustion of the primary fuel is facilitated by 1) selection of the properties of the primary and pilot fuels and 2) obtaining a homogenous mixture of primary fuel and air by injecting primary fuel into the engine's intake air stream in the form of finely atomized droplets having a mean diameter in the micron range.
Owner:CLEAN AIR POWER
Spark timing and control during transitions between spark ignited combustion and homogenous charge compression ignition
InactiveUS20090229562A1Electrical controlInternal combustion piston enginesHcci combustionControl system
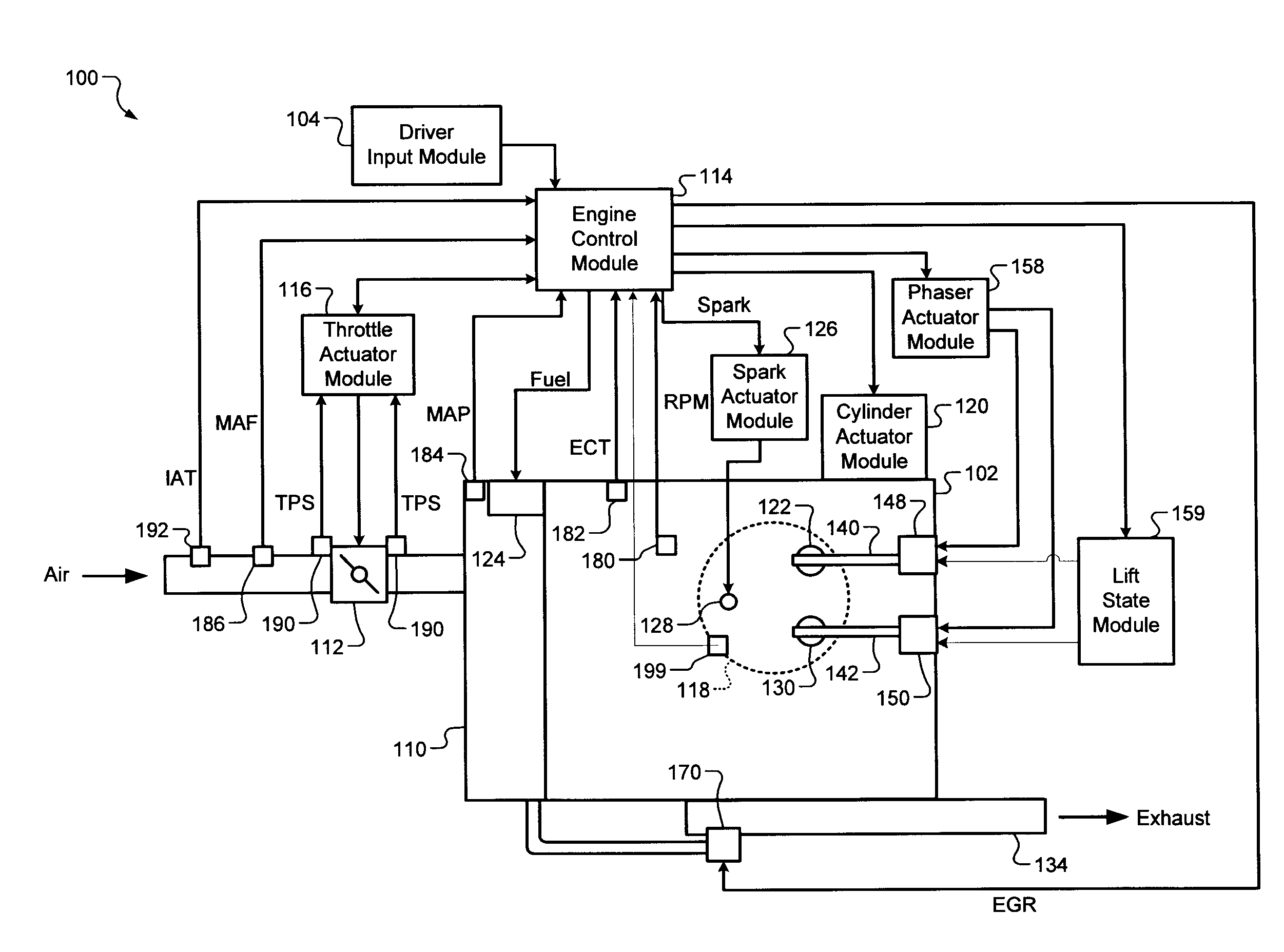
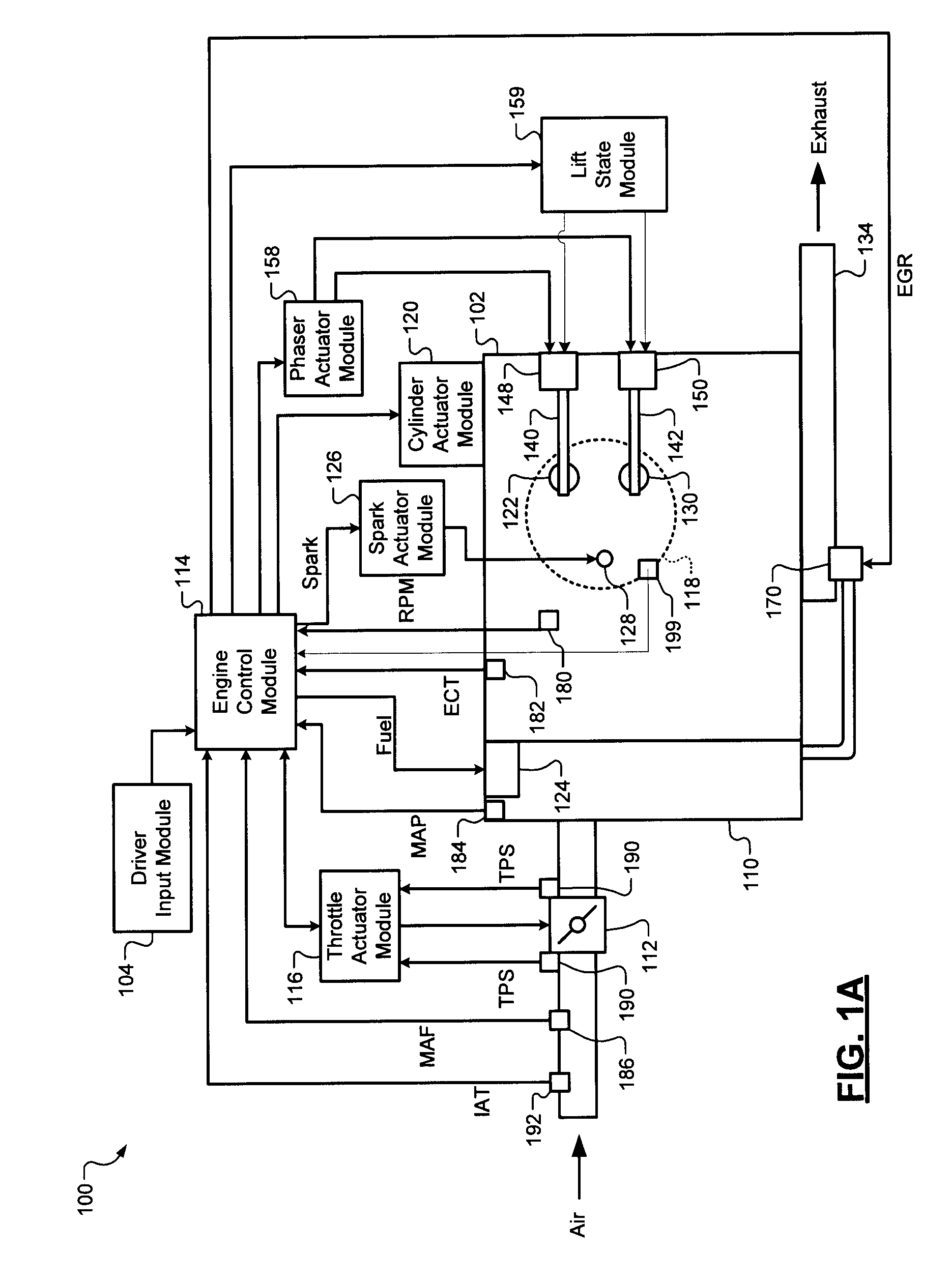
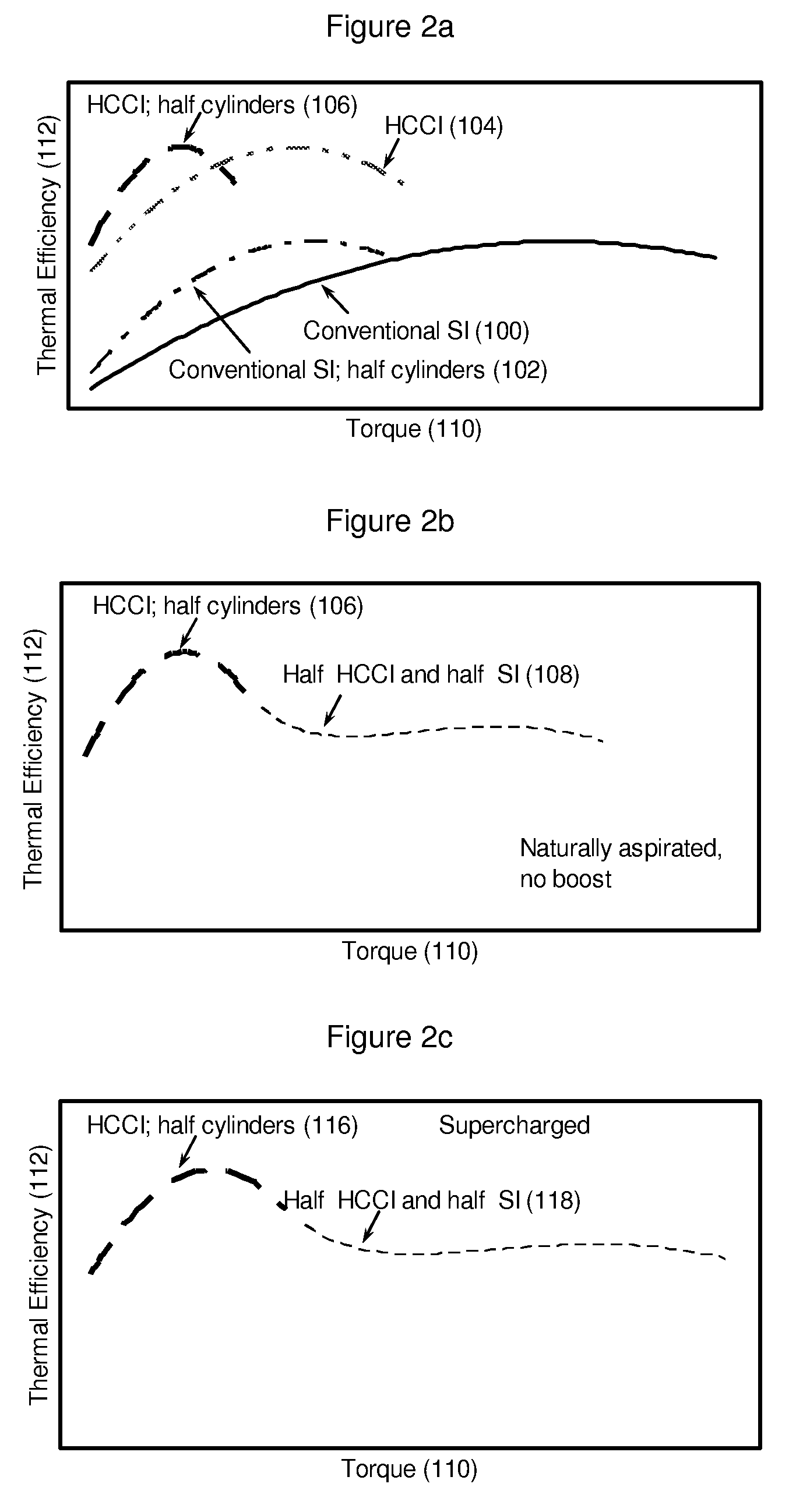
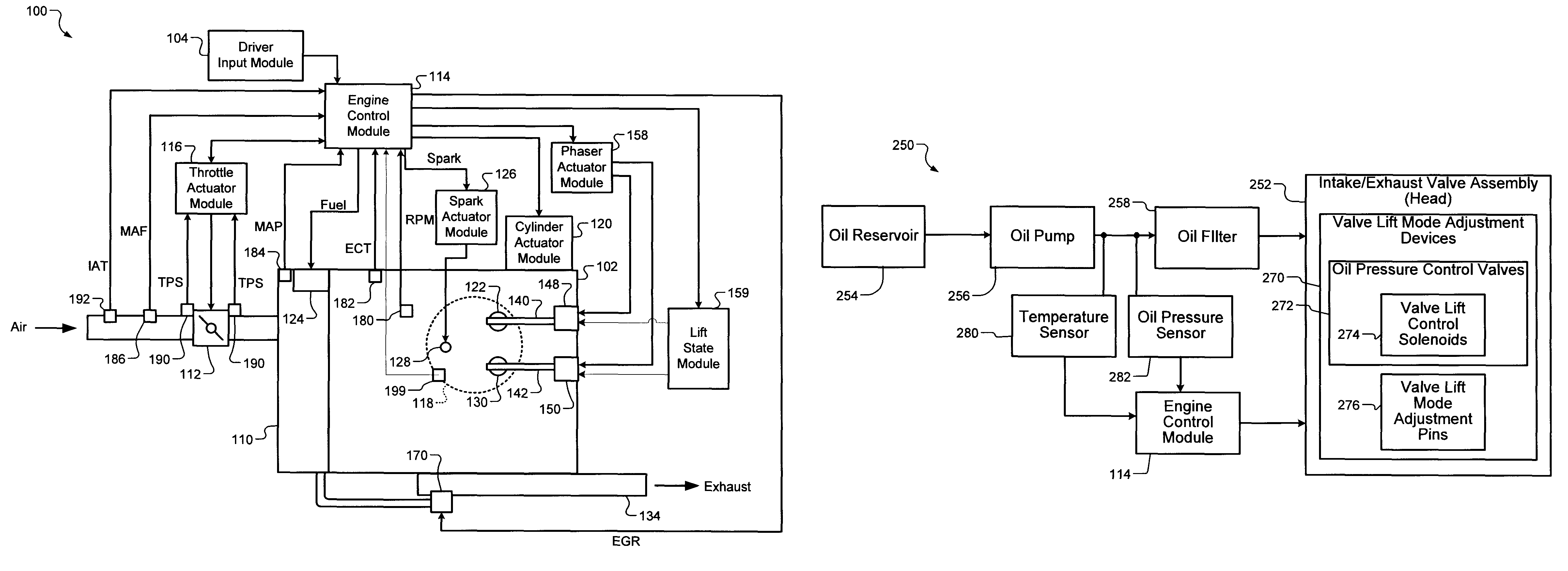
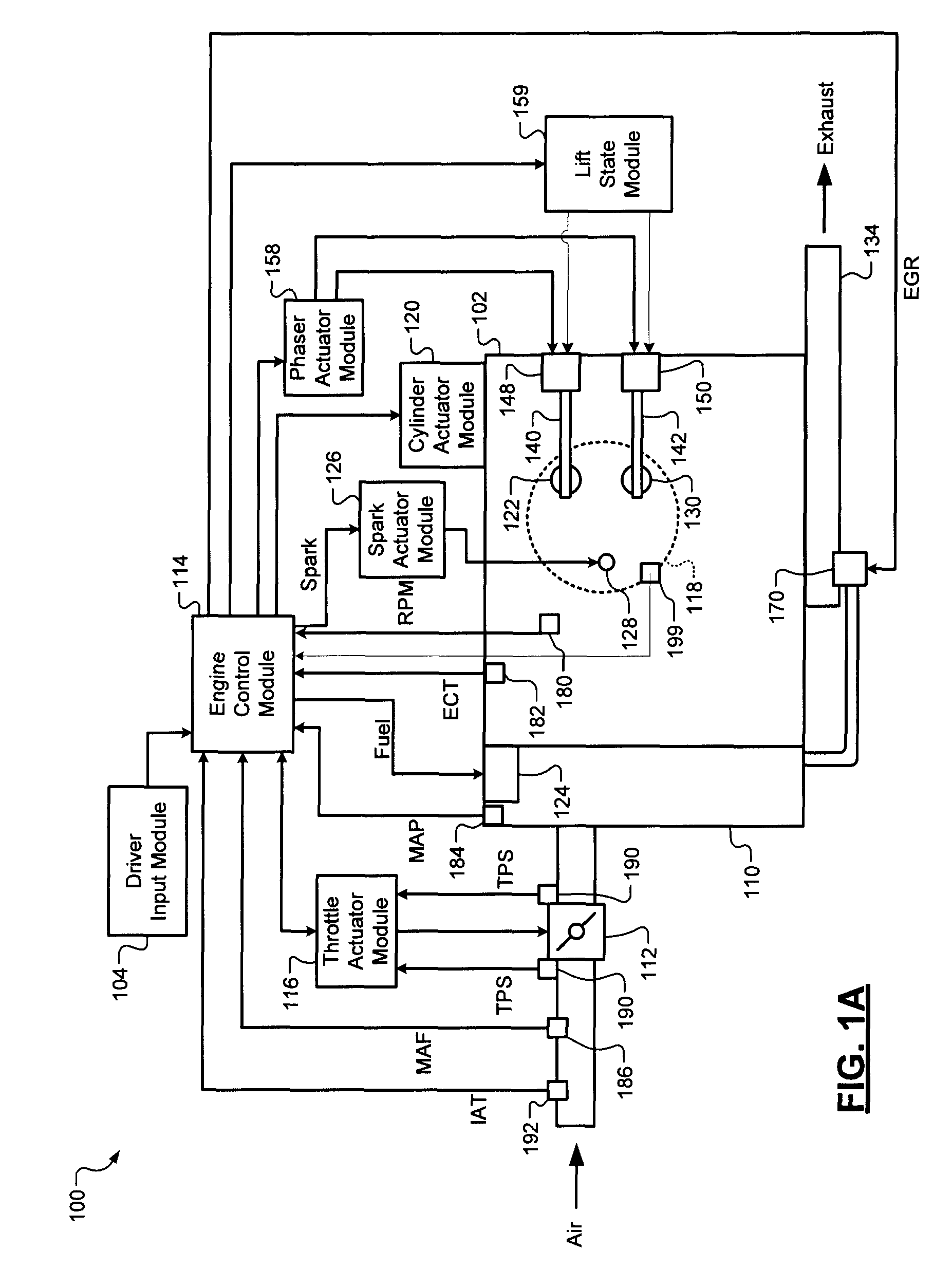
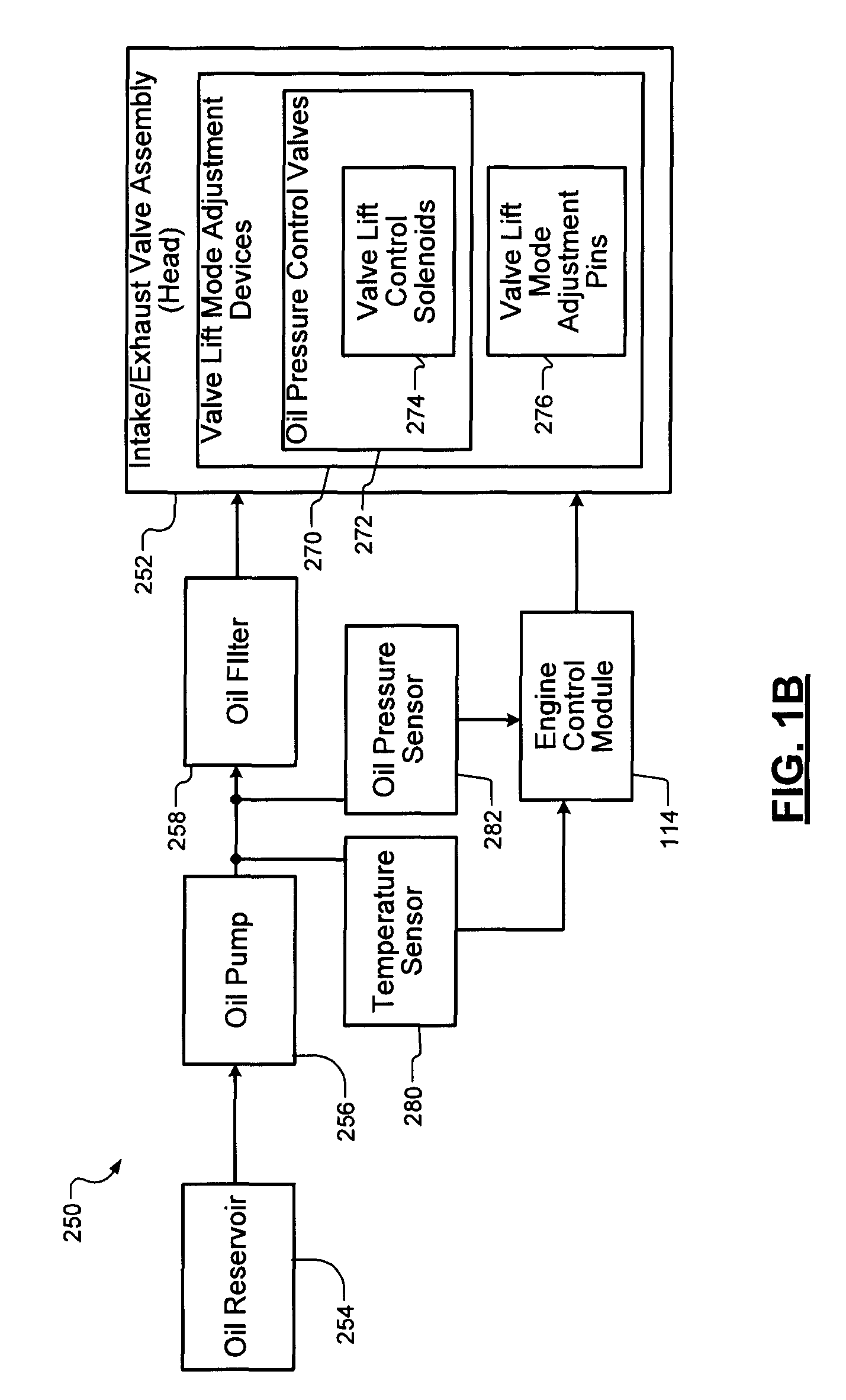
A control system for an engine comprises an air per cylinder (APC) generating module that generates measured and desired APC values. A combustion transition module selectively transitions the engine from spark ignition (SI) combustion to homogeneous charge compression ignition (HCCI) combustion and from HCCI combustion to SI combustion. A spark control module selectively retards spark during the transitions based on a ratio of the measured APC value and the desired APC value. Alternately, spark retard can be based on measured and desired engine torque representing values (ETRVs).
Owner:GM GLOBAL TECH OPERATIONS LLC
Method and system of transient control for homogeneous charge compression ignition (HCCI) engines
InactiveUS20100031924A1Reduce computing loadRobust engine controlElectrical controlInternal combustion piston enginesApplying knowledgeHcci combustion
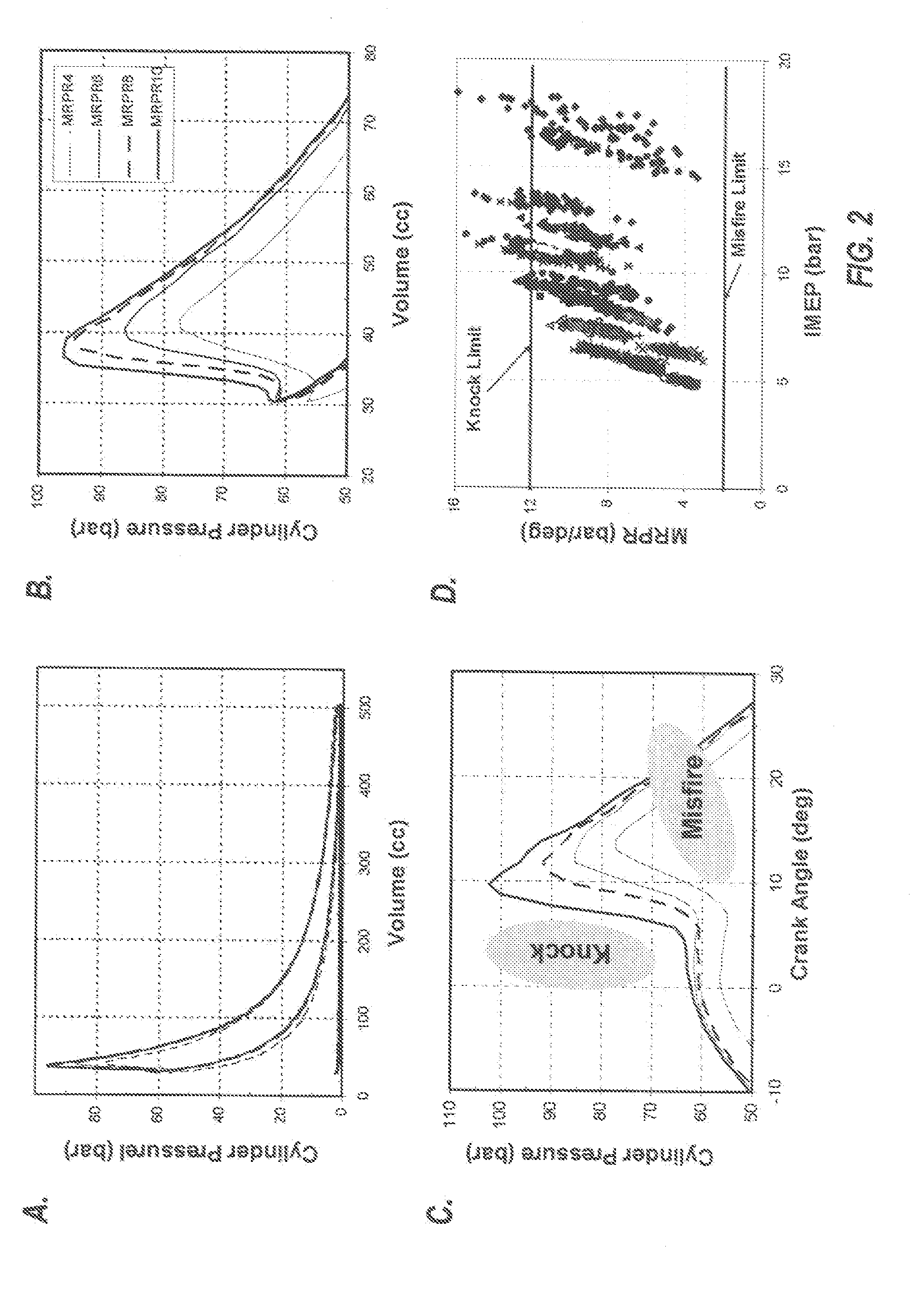
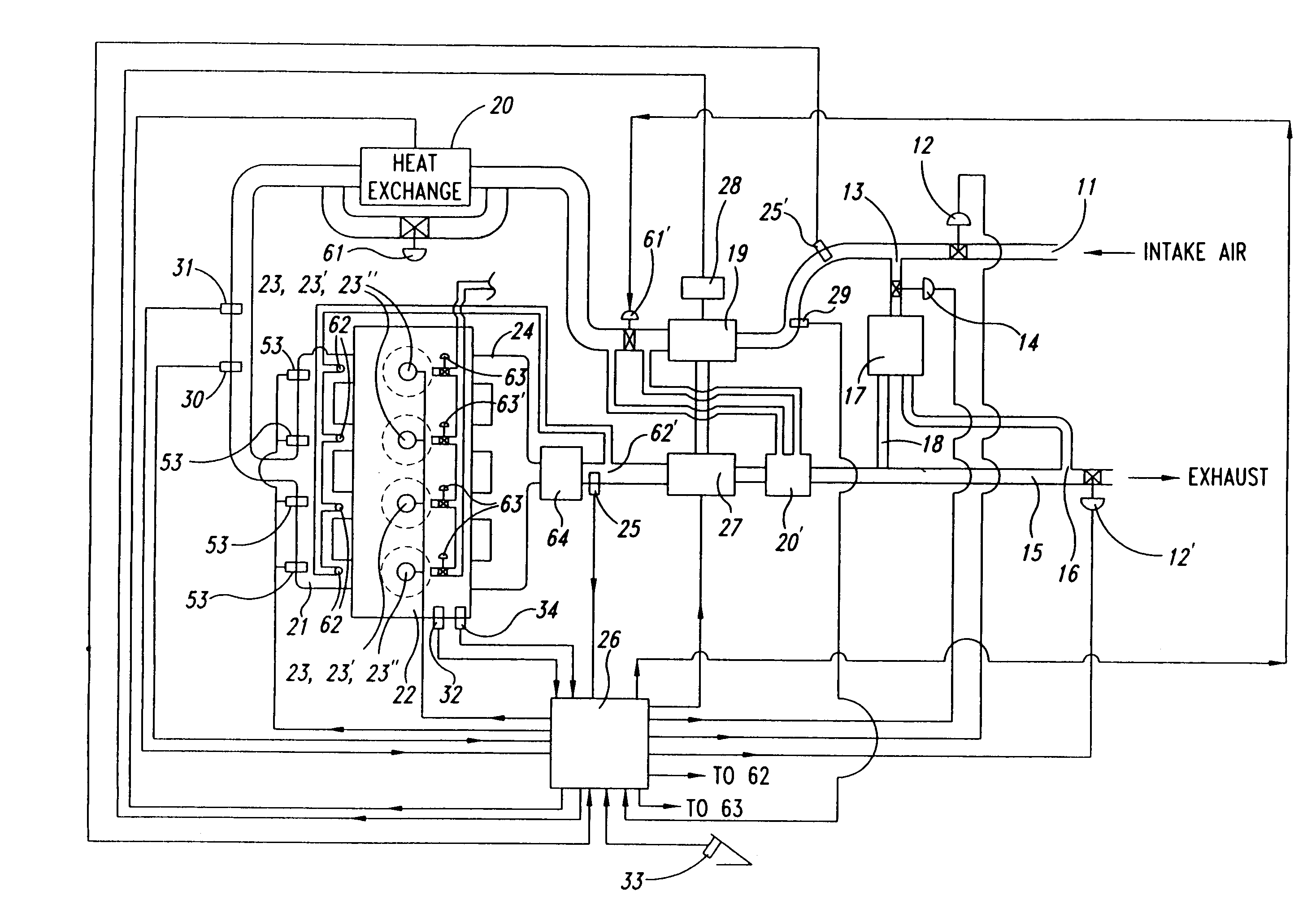
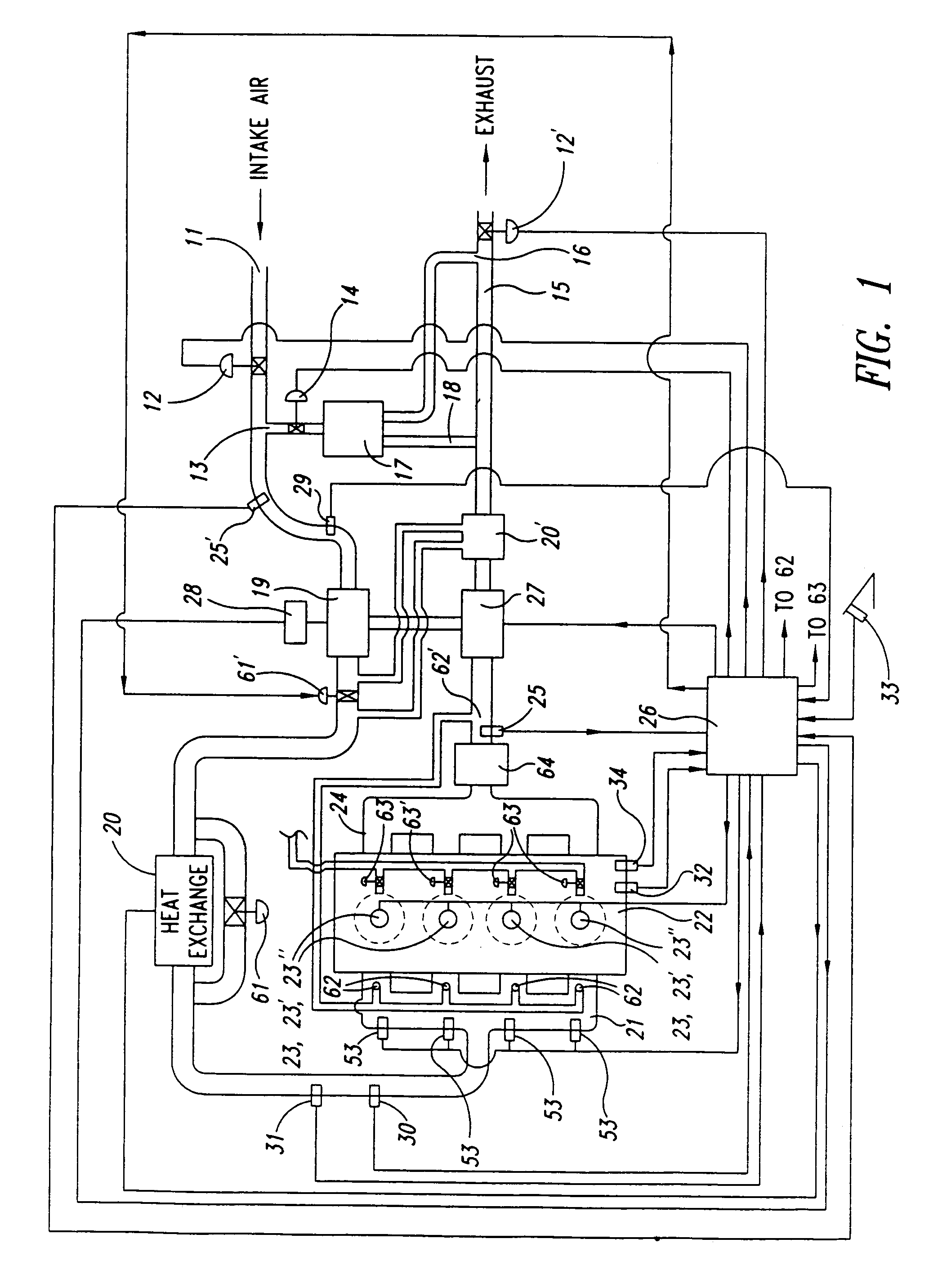
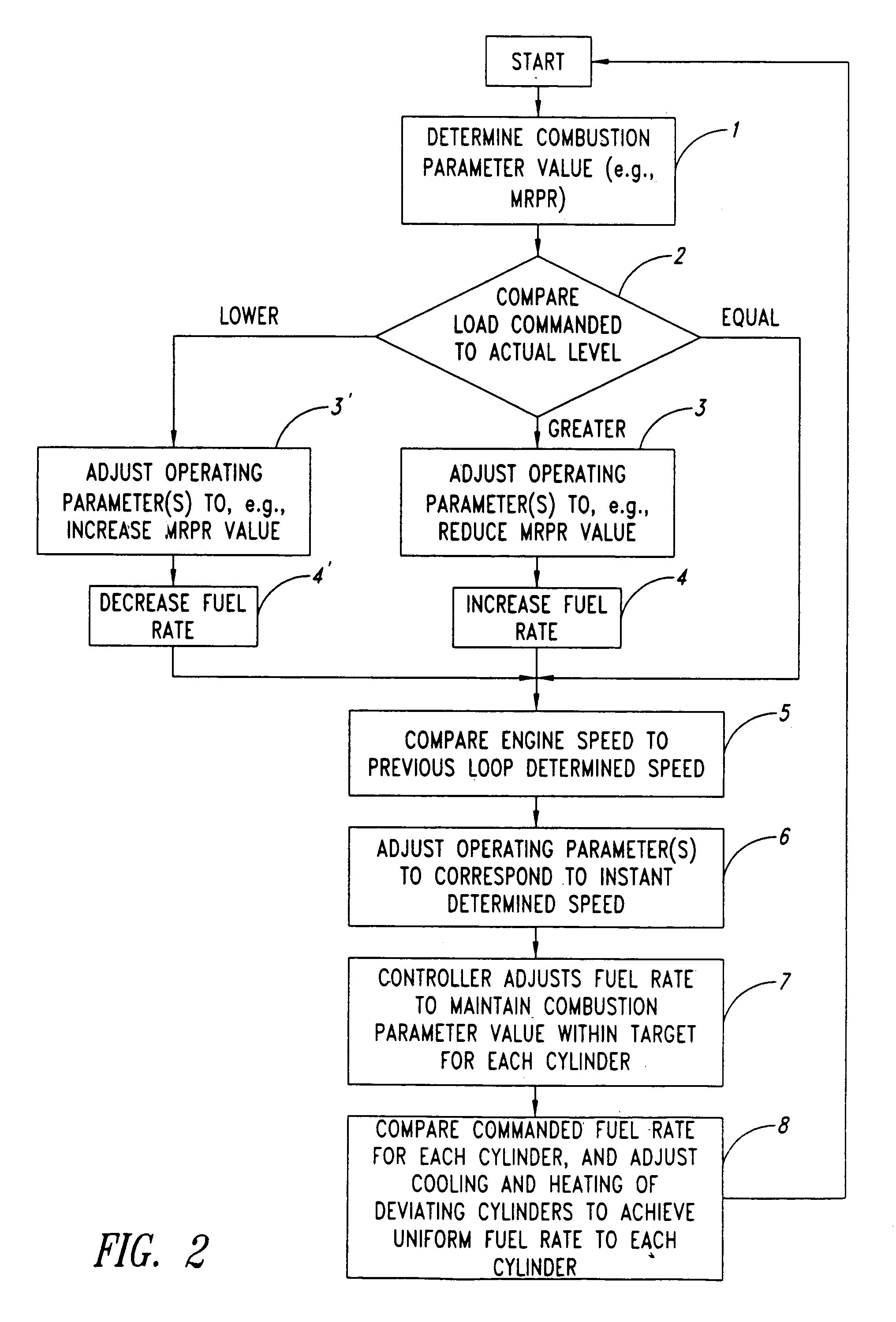
A HCCI engine with a model reference adaptive feedback control system maintains stable HCCI combustion during speed / load transitions by: (1) estimating the maximum rate of pressure rise (MRPR), for each cycle, from an extra-cylinder sensor metric, such as a crankshaft dynamics or knock sensor metric, via statistical vector-to-vector correlation; (2) periodically self-tuning the vector-to-vector correlation; (3) applying knowledge base models to guide cycle-to-cycle adjustments of fuel quantity and other engine parameters, to maintain a target MRPR value.
Owner:U S ENVIRONMENTAL PROTECTION AGENCY UNITED STATES OF AMERICA AS REPRESENTED BY THE
Controller for compression ignition engine
InactiveUS20070215095A1Increase blockingInhibit deteriorationElectrical controlNon-fuel substance addition to fuelHcci combustionControl theory
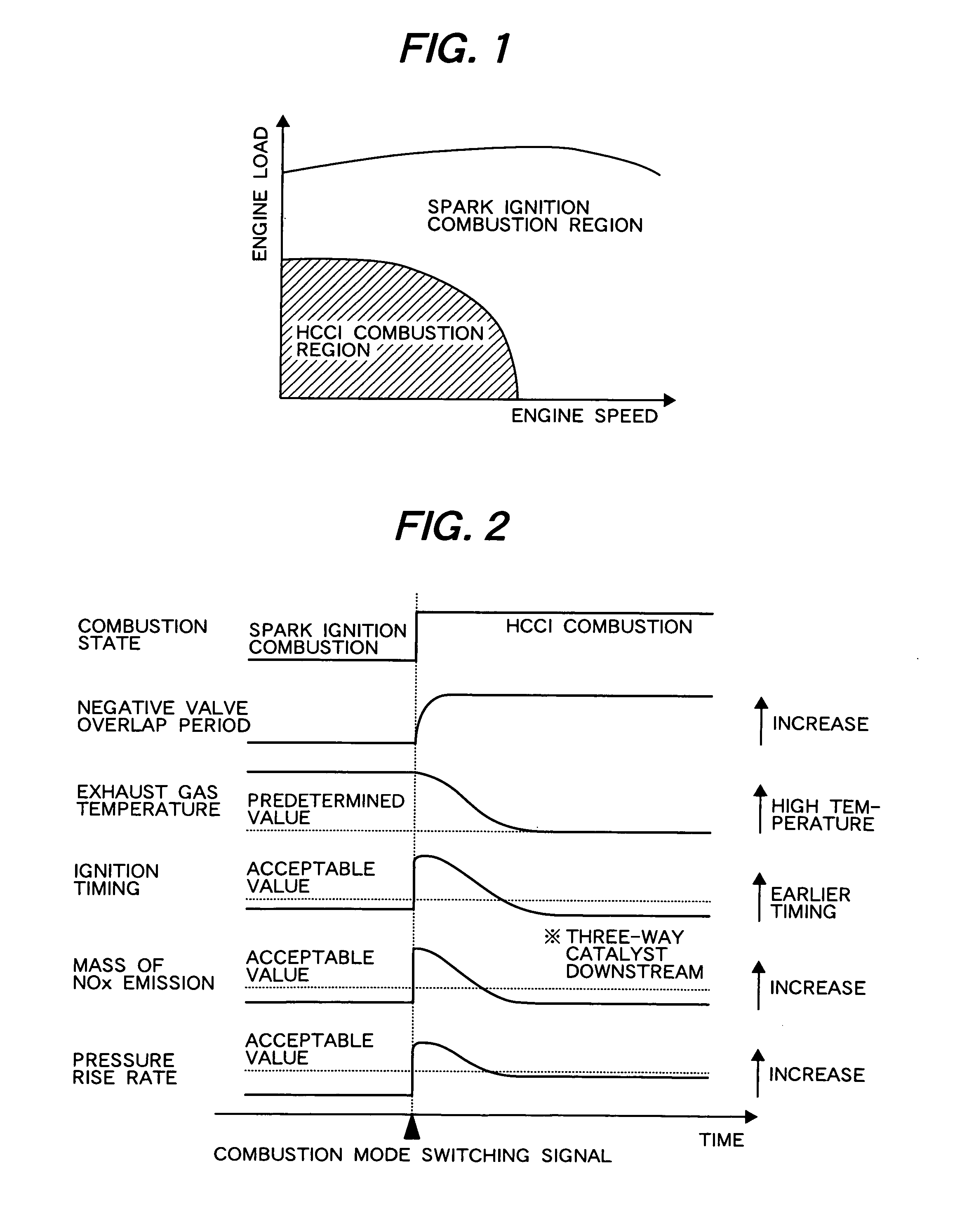
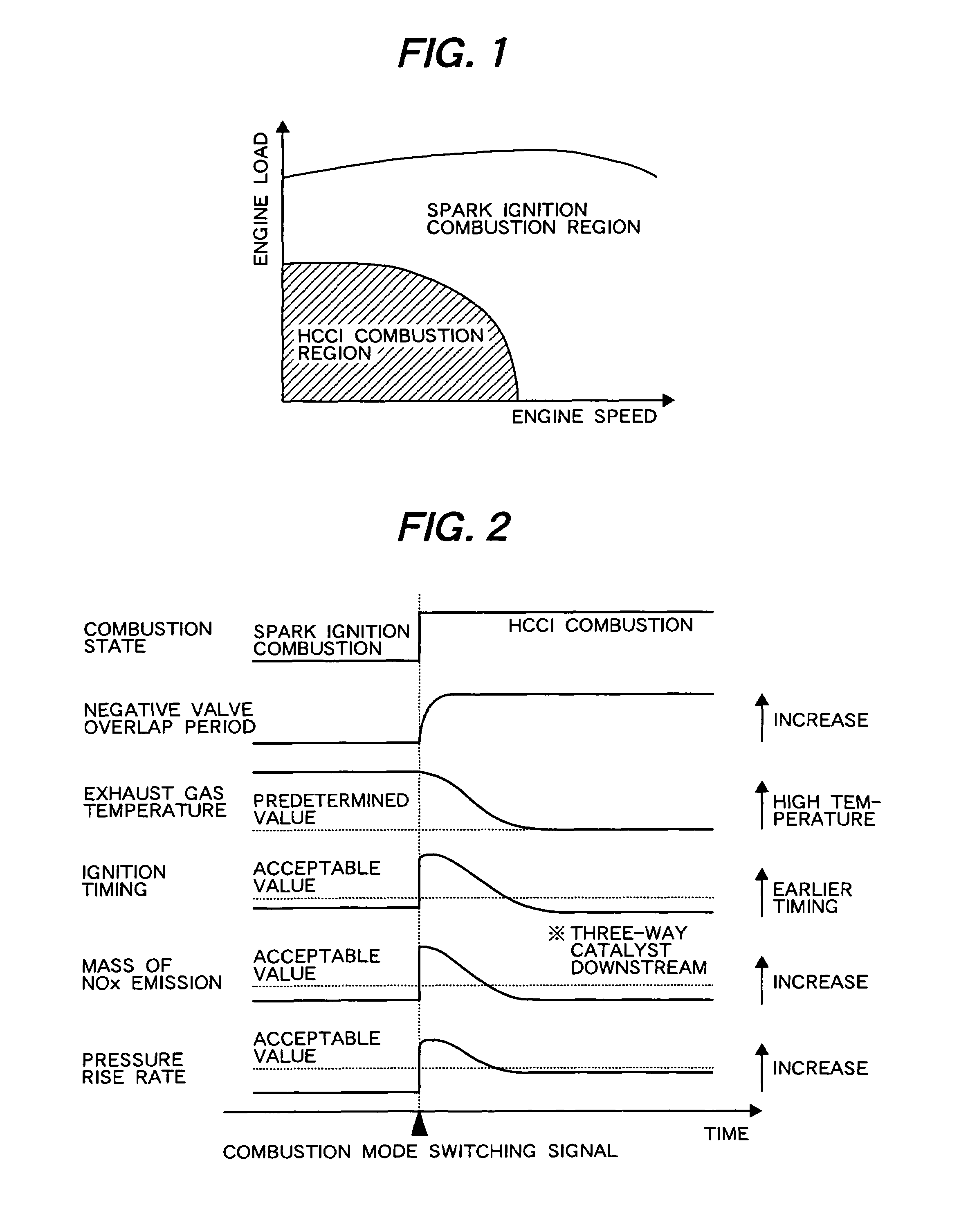
The controller includes combustion mode switching means for decreasing an exhaust gas temperature in the spark ignition combustion immediately before the combustion mode switching based on an estimated exhaust gas temperature immediately before the combustion mode switching, or for decreasing an EGR amount in the HCCI combustion immediately after the combustion mode switching.
Owner:HITACHI LTD
Control strategy for expanding diesel HCCI combustion range by lowering intake manifold temperature
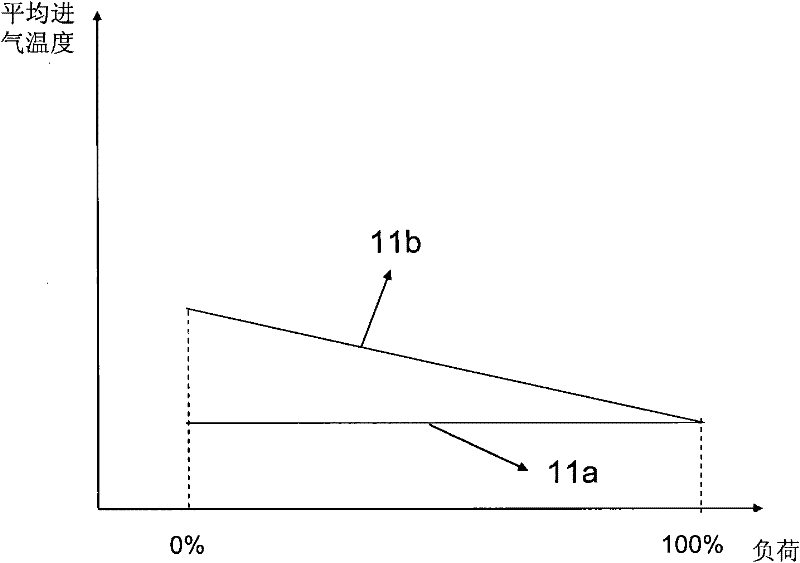
ActiveUS20060200297A1Large loading rangeWide speed rangeElectrical controlInternal combustion piston enginesHcci combustionLow load
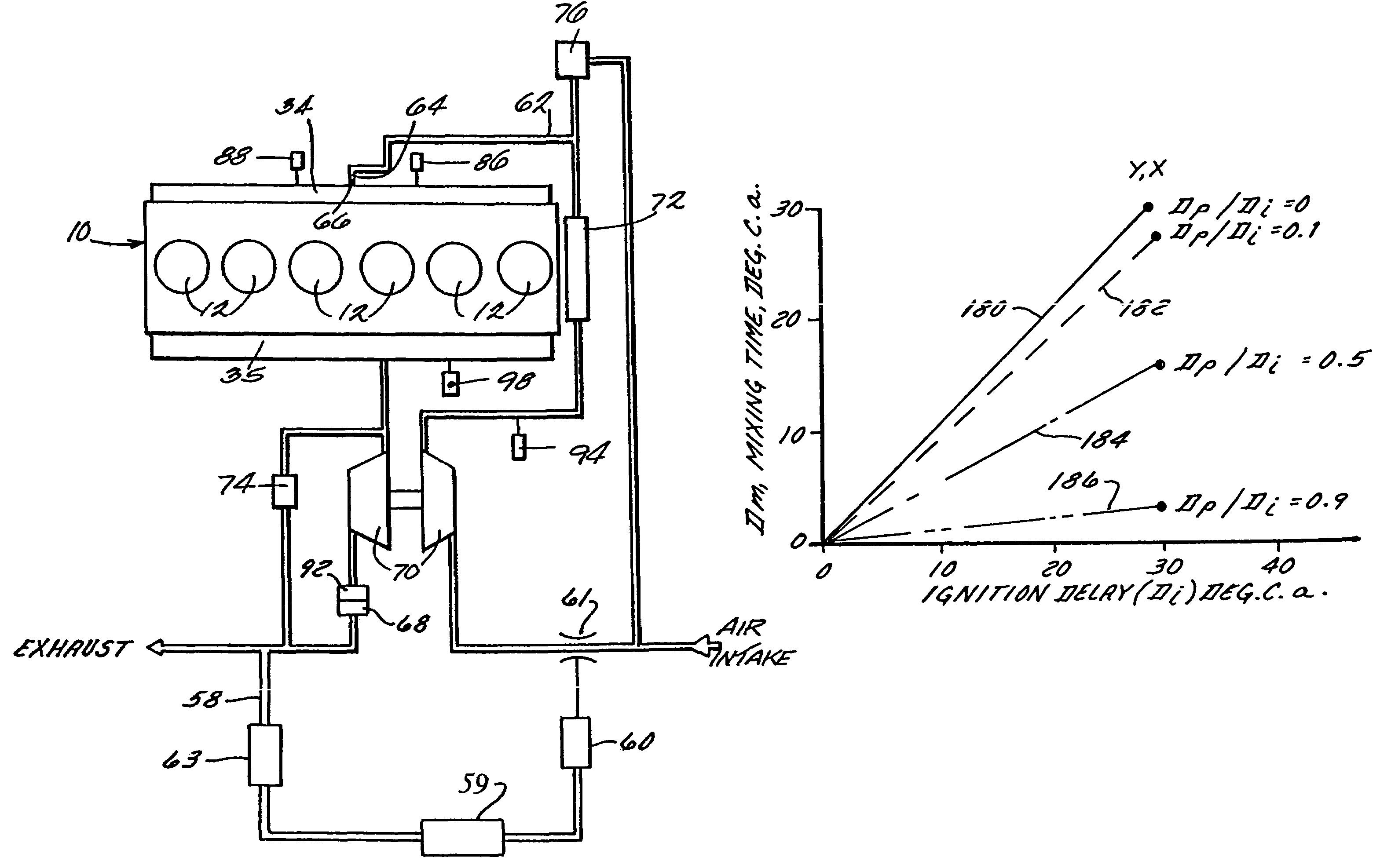
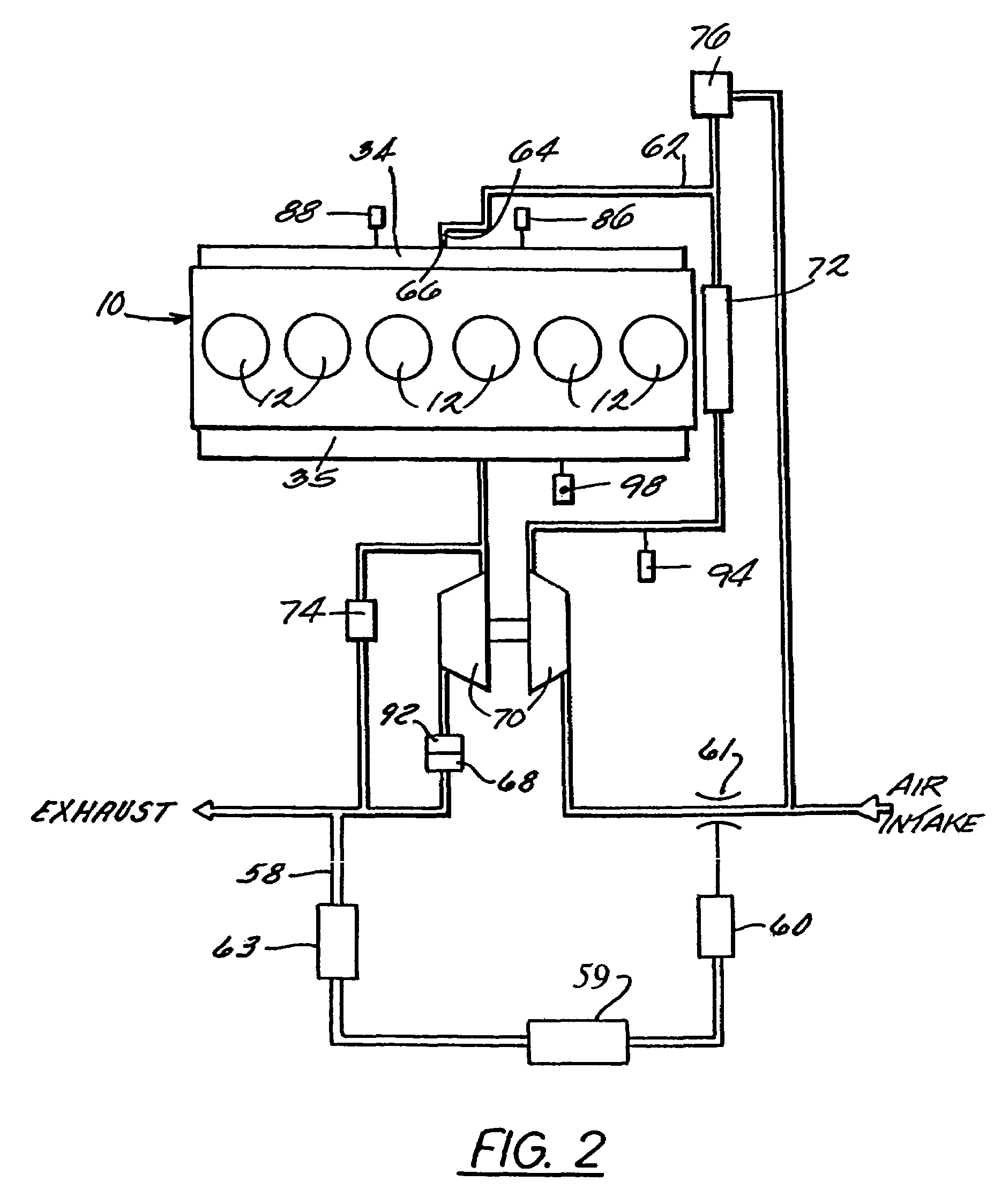
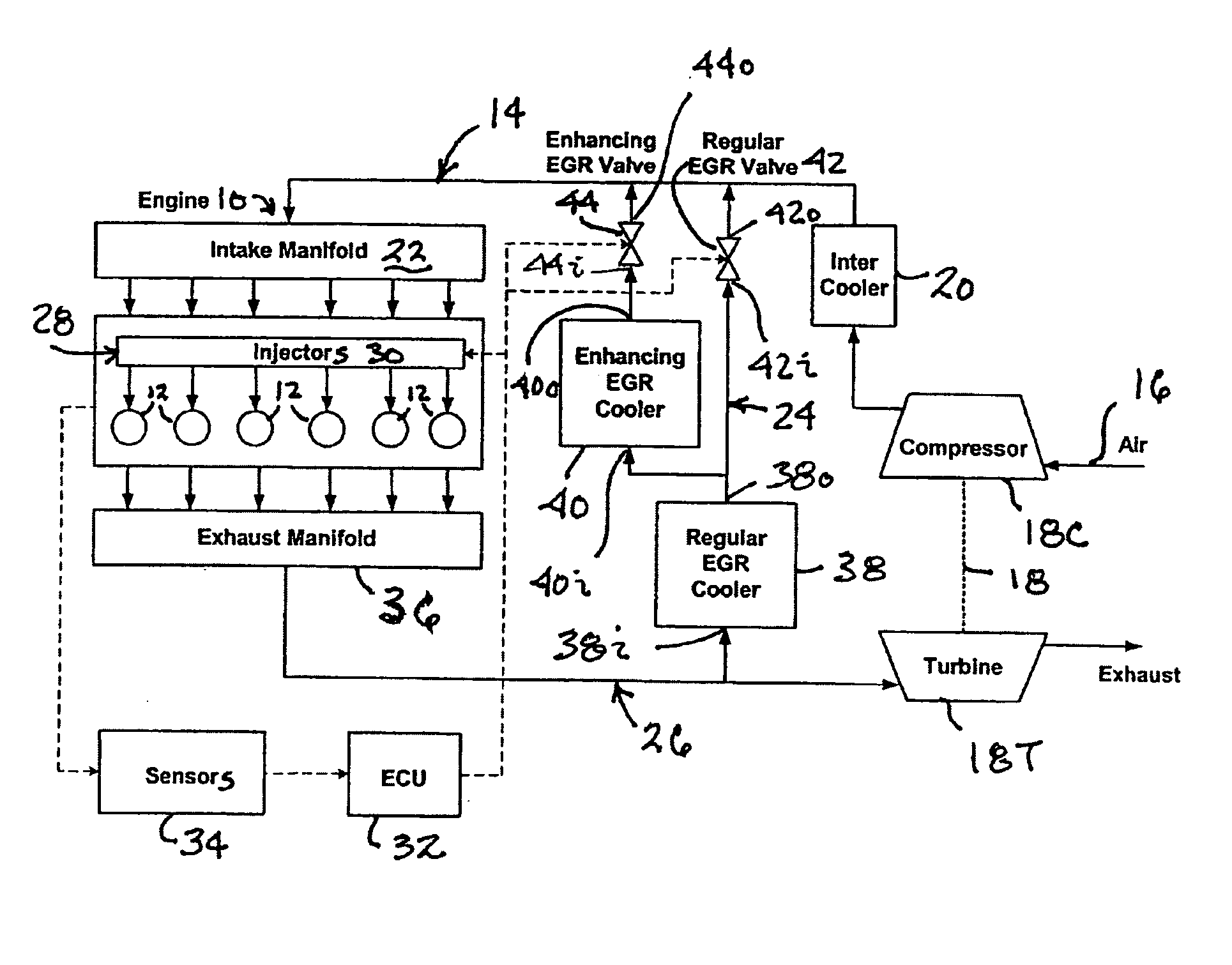
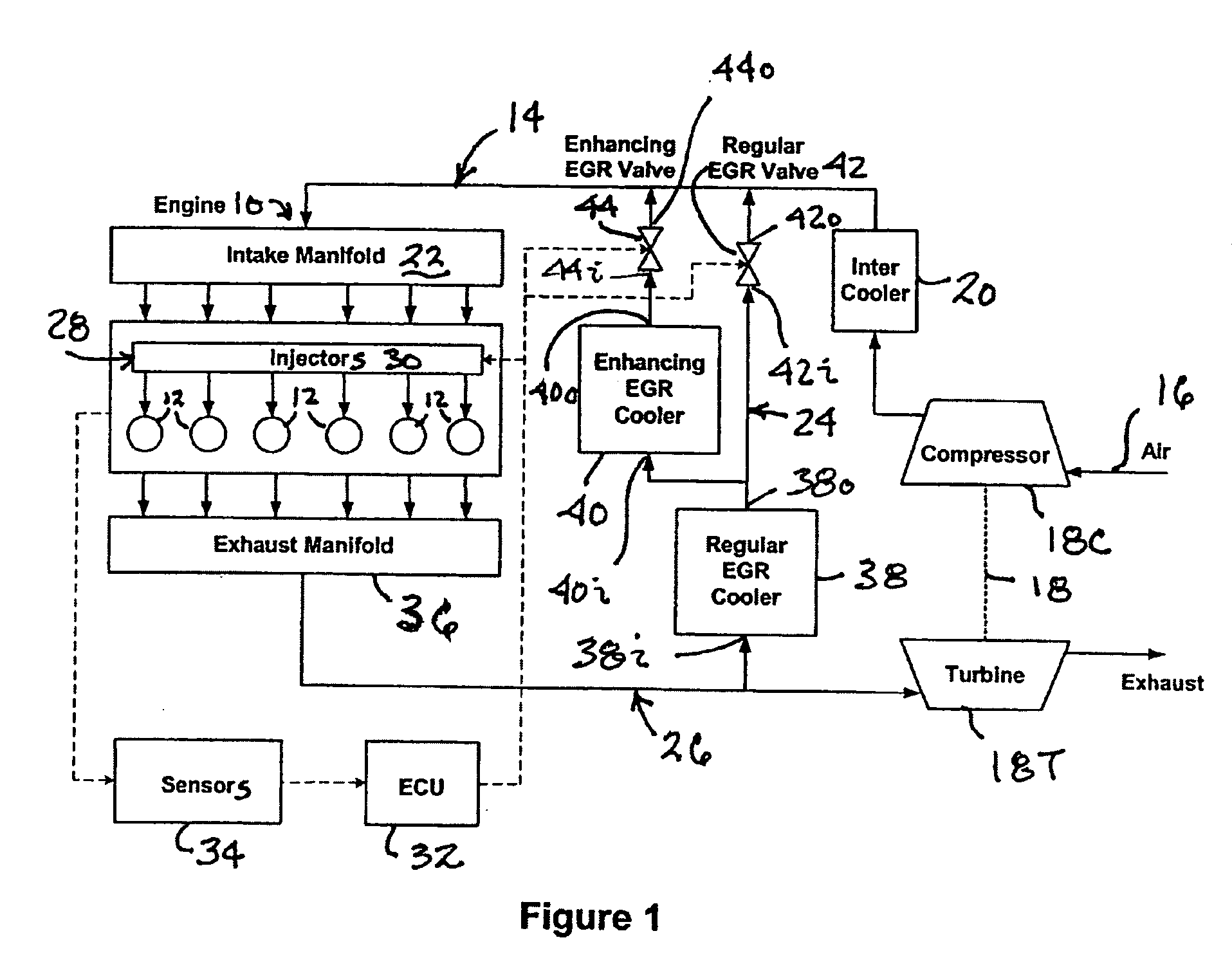
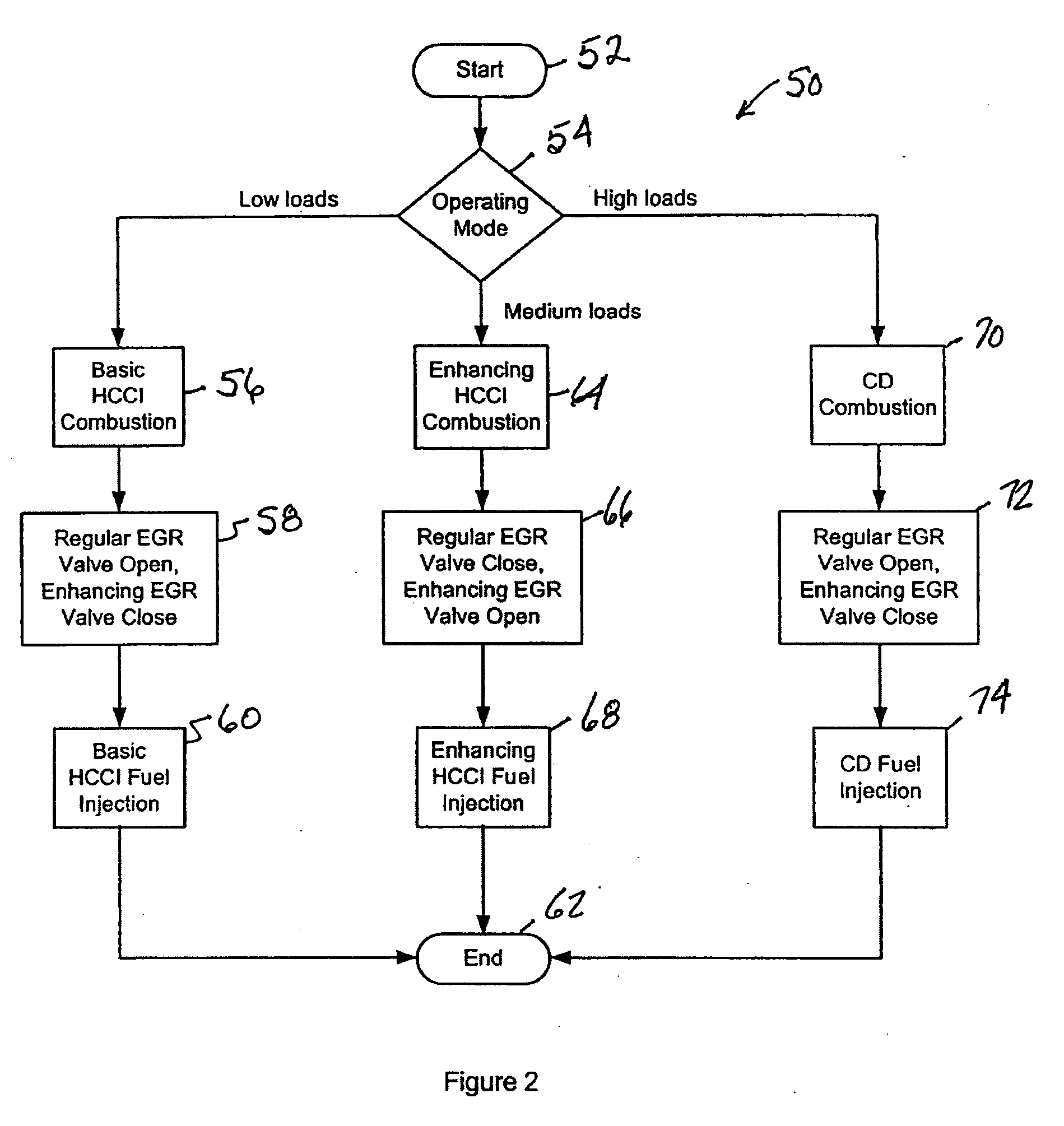
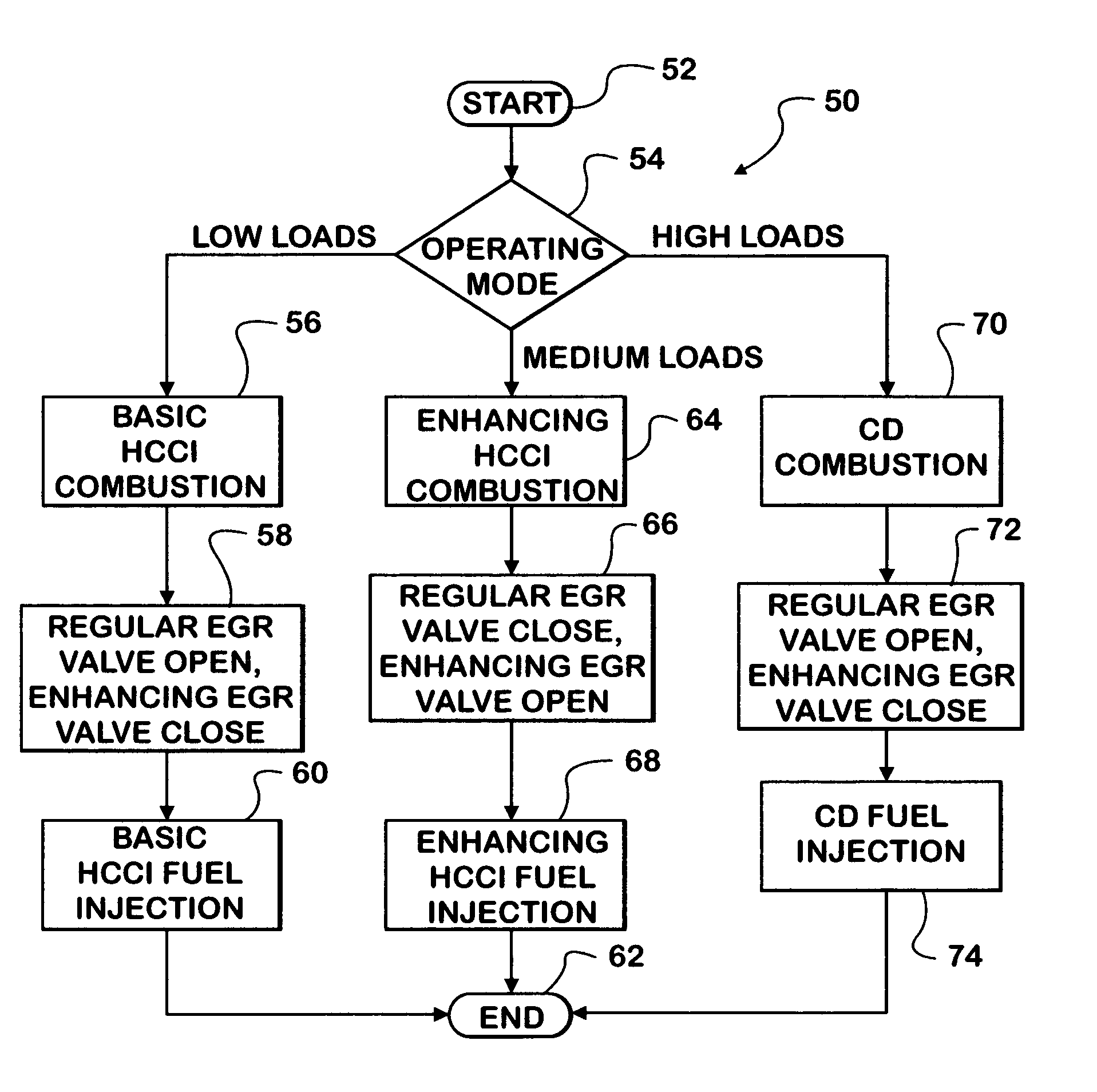
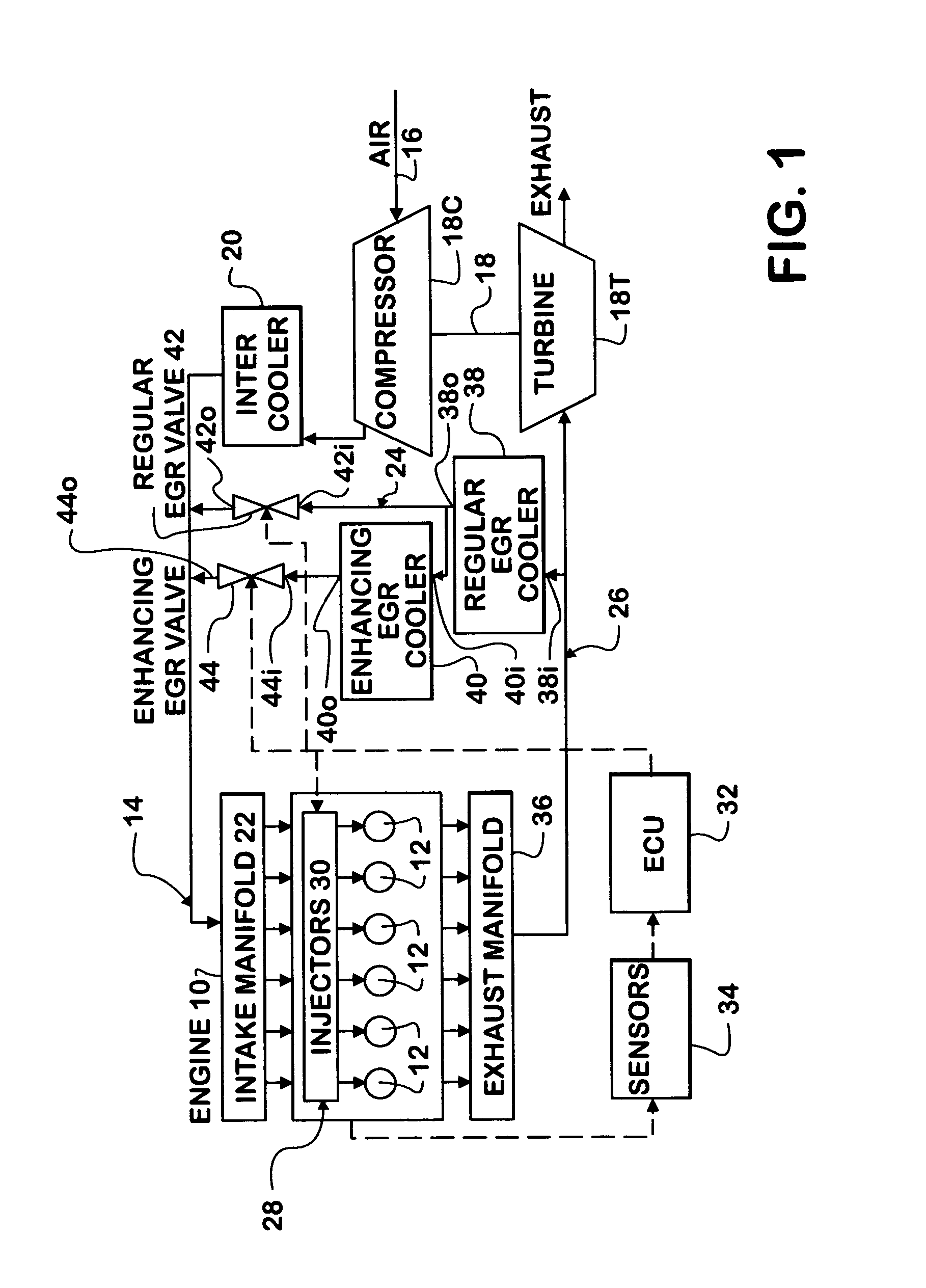
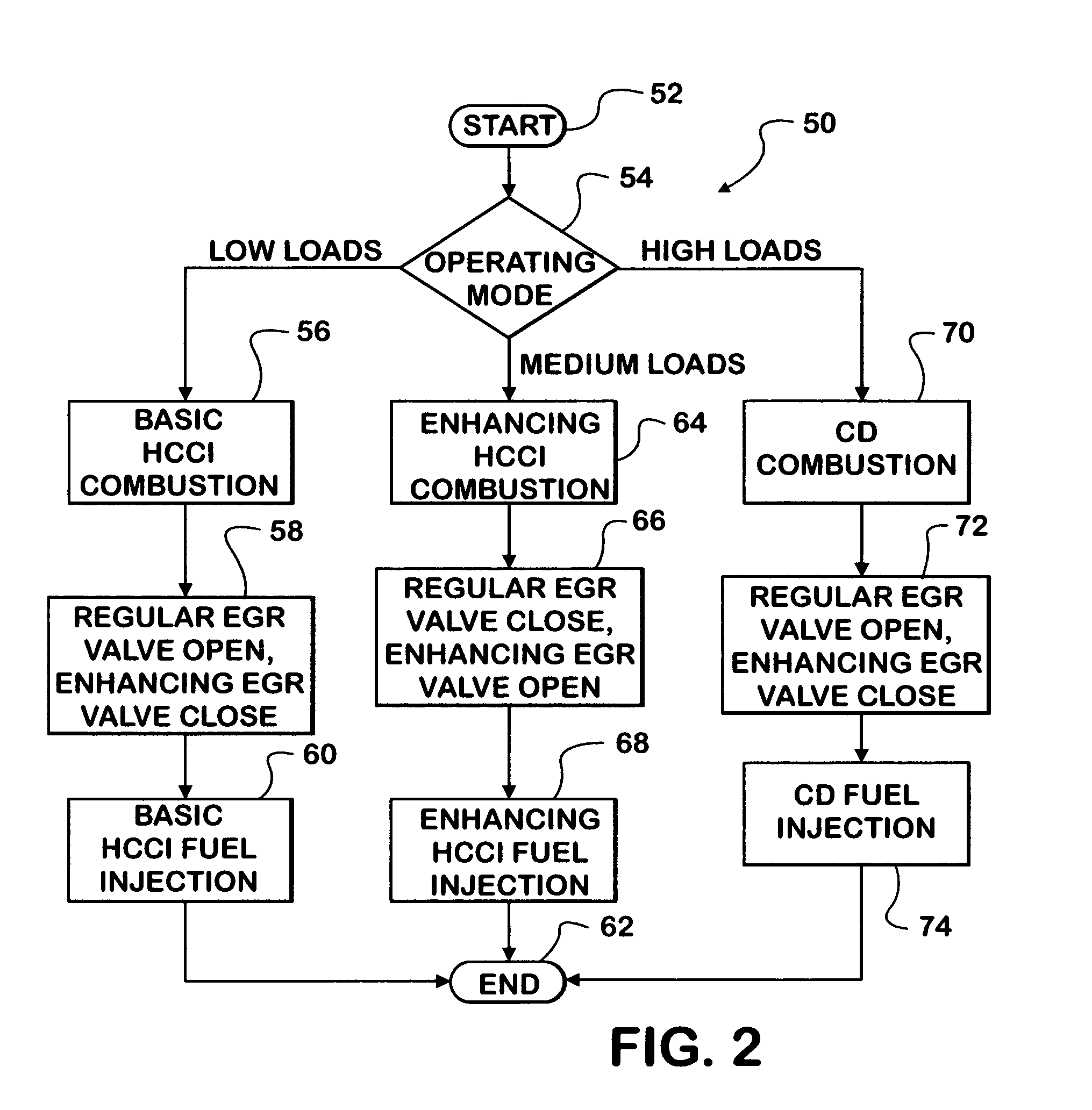
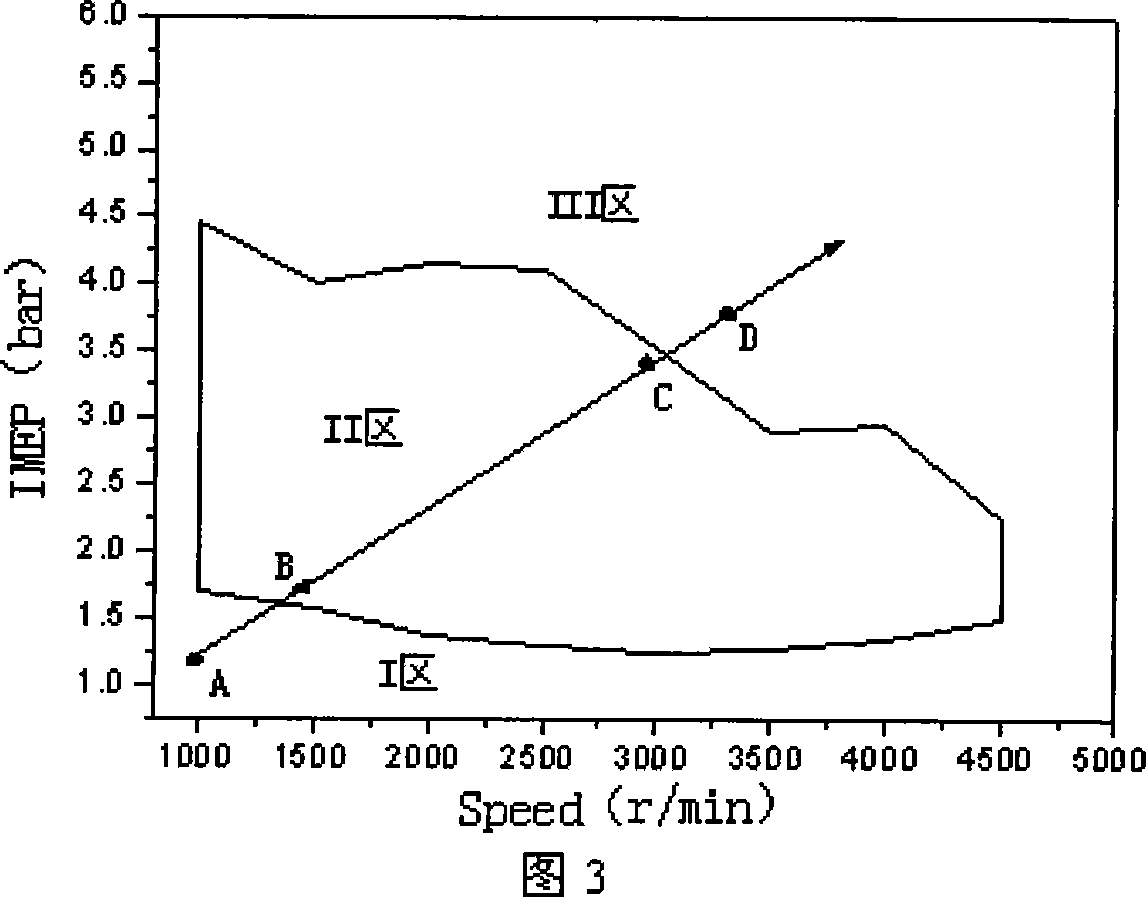
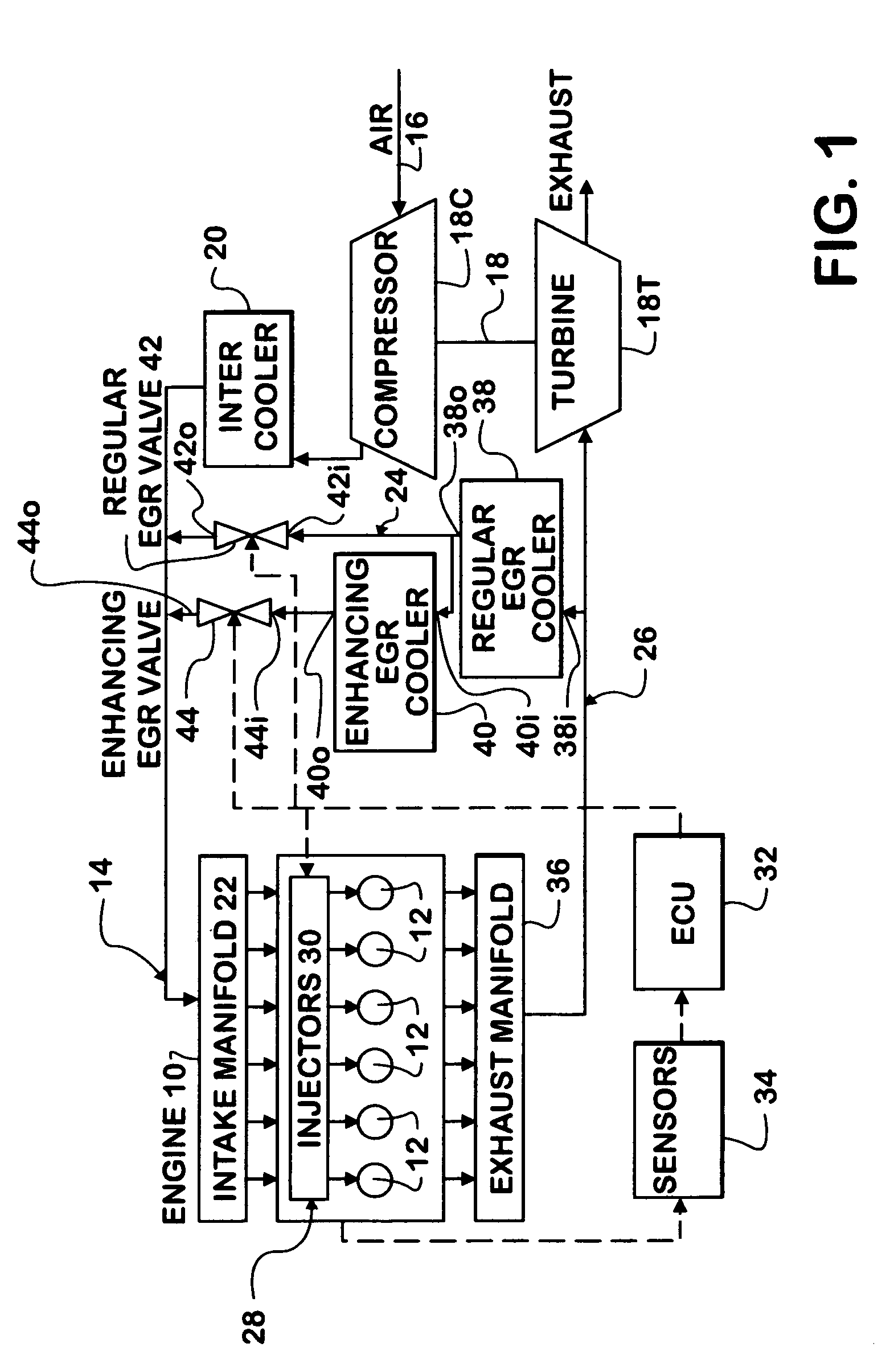
An engine (10, 100) utilizes “regular EGR cooling” when operating in HCCI mode within a low load range and “enhanced EGR cooling” that allows the engine to continue to operate in HCCI mode when engine load increases beyond the low load range. When engine load increases to a high load range, the combustion mode changes over to conventional diesel combustion, and exhaust gas recirculation reverts to “regular EGR cooling”. In a first embodiment, cooling is provided by two heat exchangers, one being a regular EGR cooler always used when cooling is needed and the other, an enhancing EGR cooler that is selectively used. In a second embodiment, cooling is also provided by two heat exchangers, one being an EGR cooler through which liquid coolant always flows when cooling is needed, and the other being a radiator used selectively to cool the liquid coolant before it enters the EGR cooler.
Owner:INT ENGINE INTPROP CO LLC +1
Control strategy for expanding diesel HCCI combustion range by lowering intake manifold temperature
ActiveUS7017561B1Large loading rangeWide speed rangeNon-fuel substance addition to fuelInternal combustion piston enginesHcci combustionLow load
Owner:INT ENGINE INTPROP CO LLC
Controller for compression ignition engine
InactiveUS7367310B2Inhibit deteriorationQuality improvementElectrical controlInternal combustion piston enginesHcci combustionControl theory
The controller includes combustion mode switching means for decreasing an exhaust gas temperature in the spark ignition combustion immediately before the combustion mode switching based on an estimated exhaust gas temperature immediately before the combustion mode switching, or for decreasing an EGR amount in the HCCI combustion immediately after the combustion mode switching.
Owner:HITACHI LTD
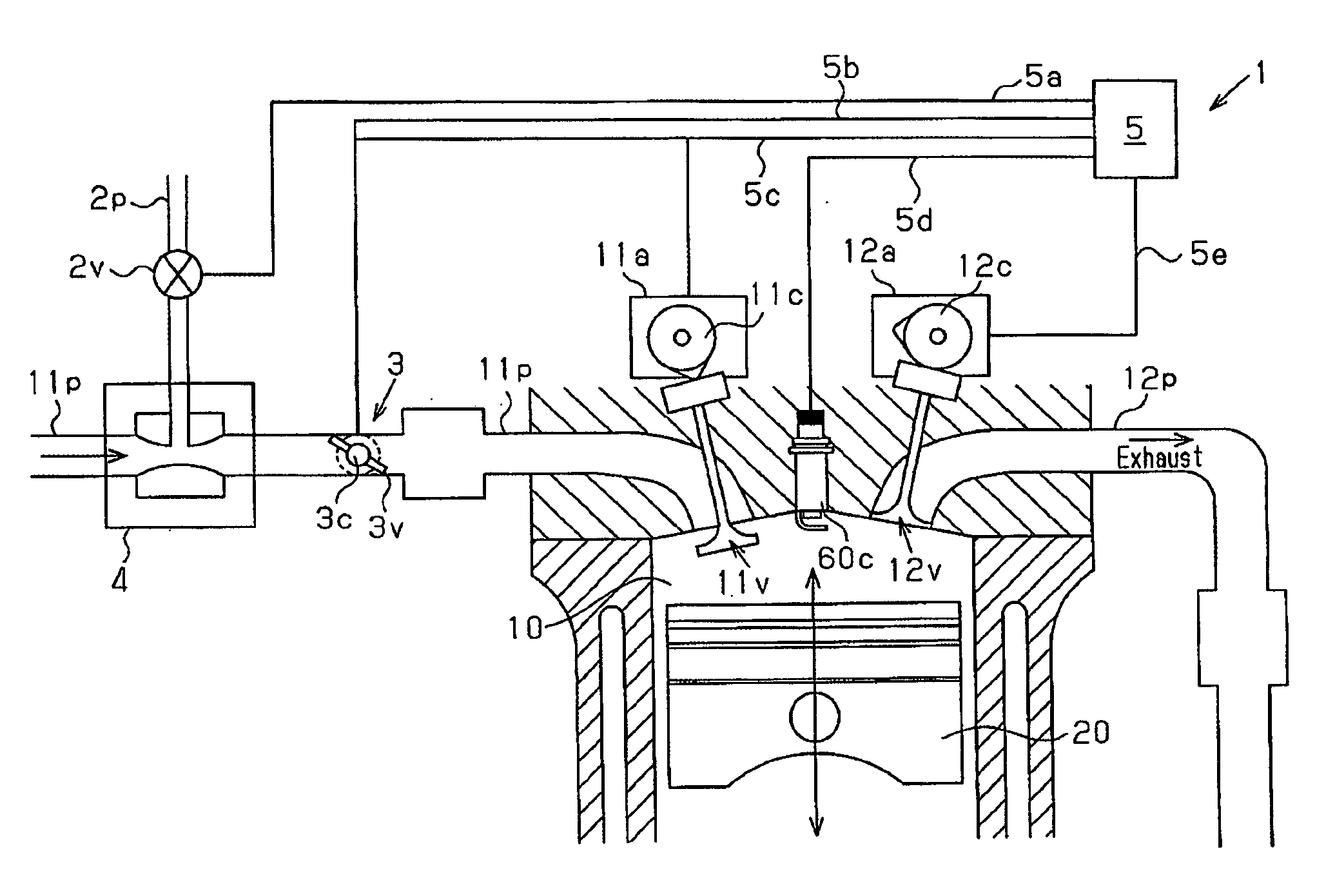
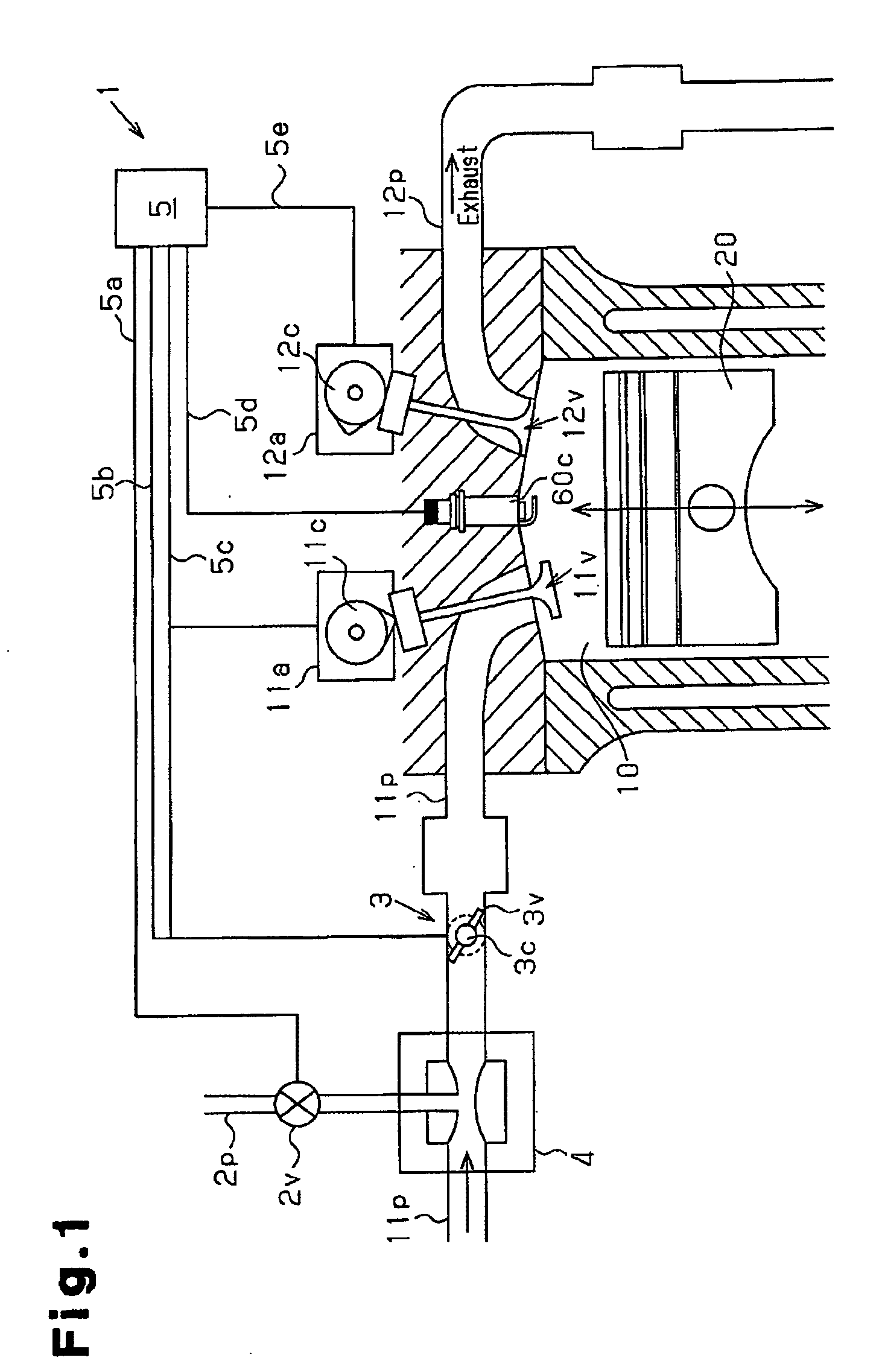
Engine and method for controlling homogenous charge compression ignition combustion in a diesel engine
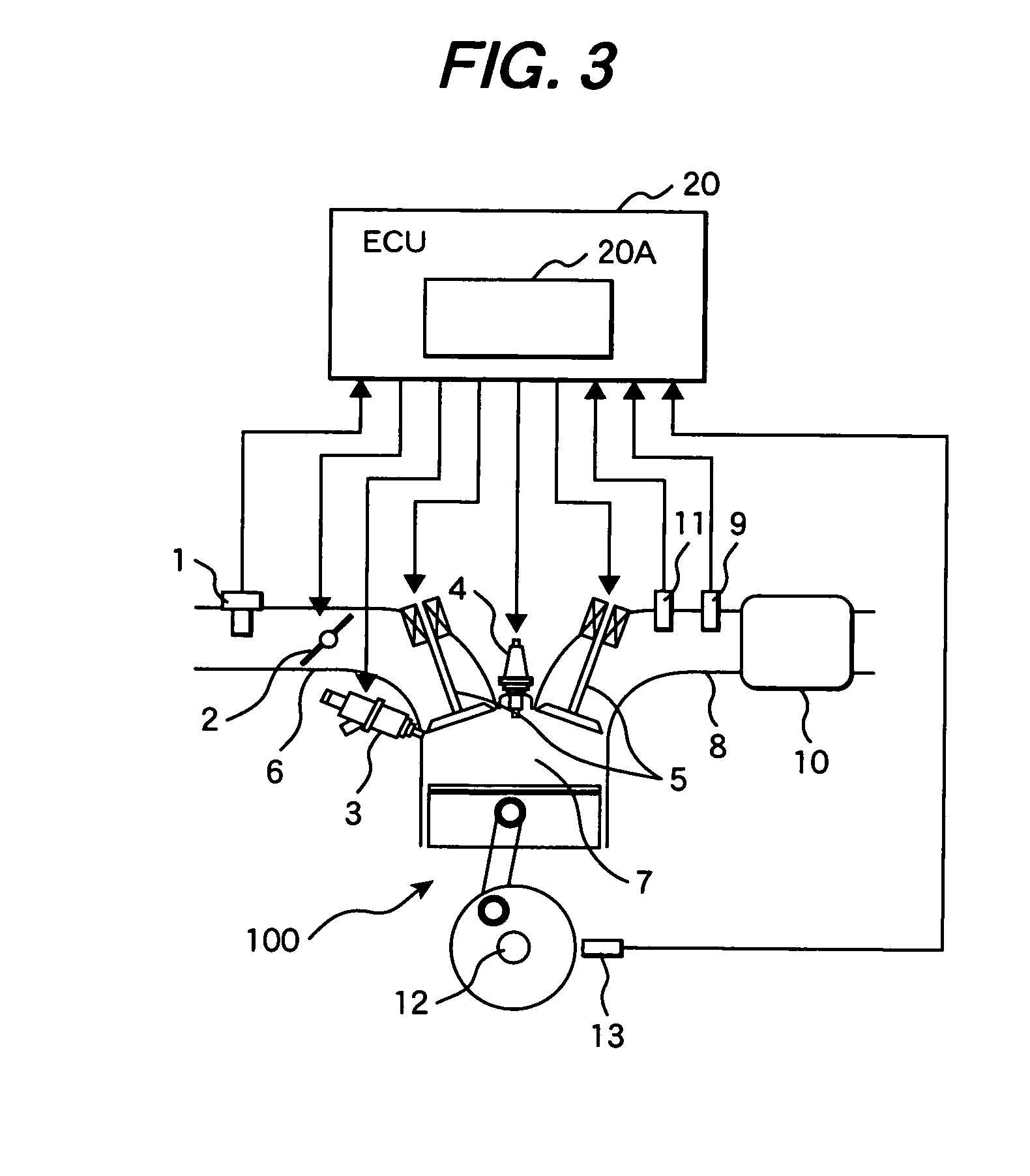
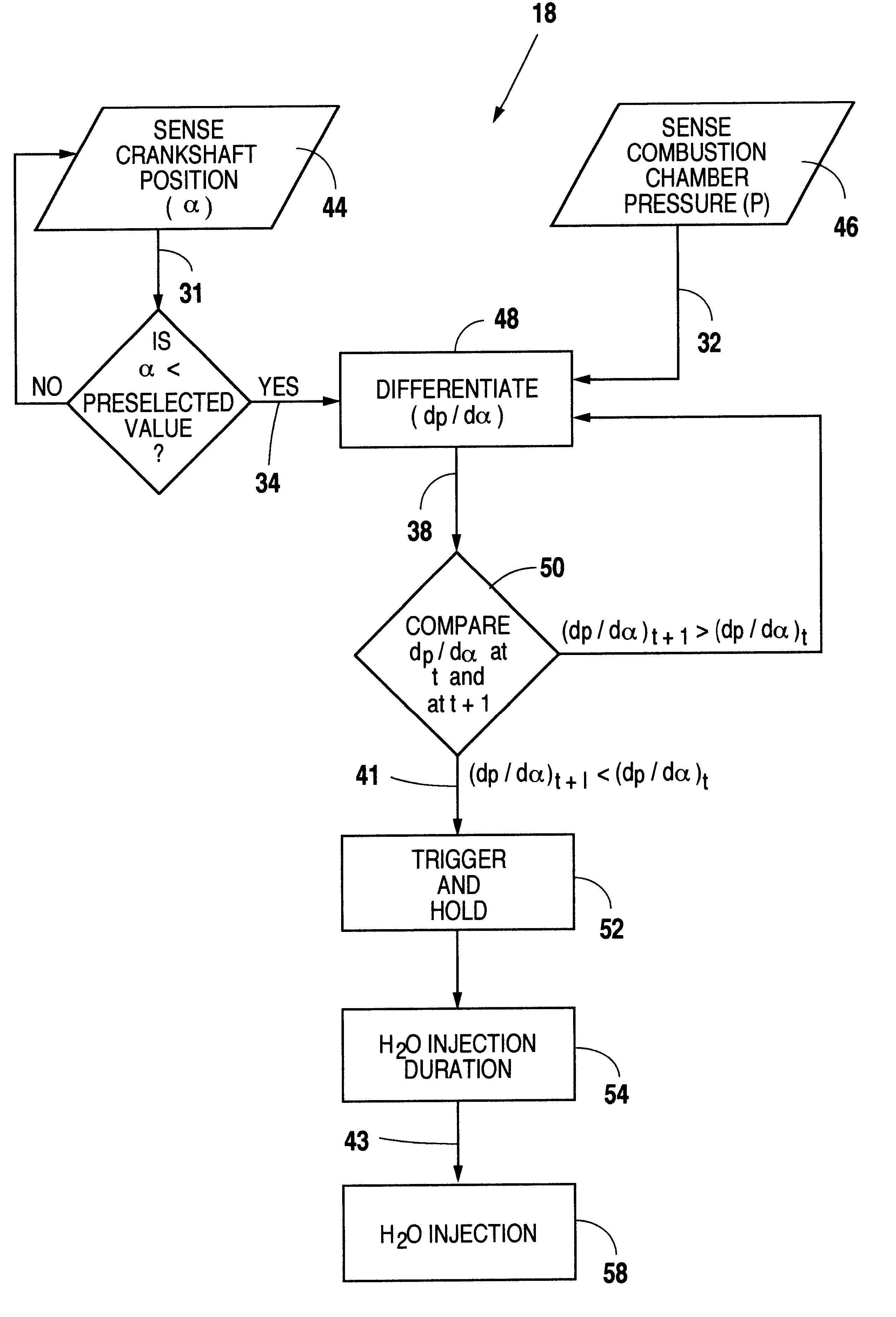
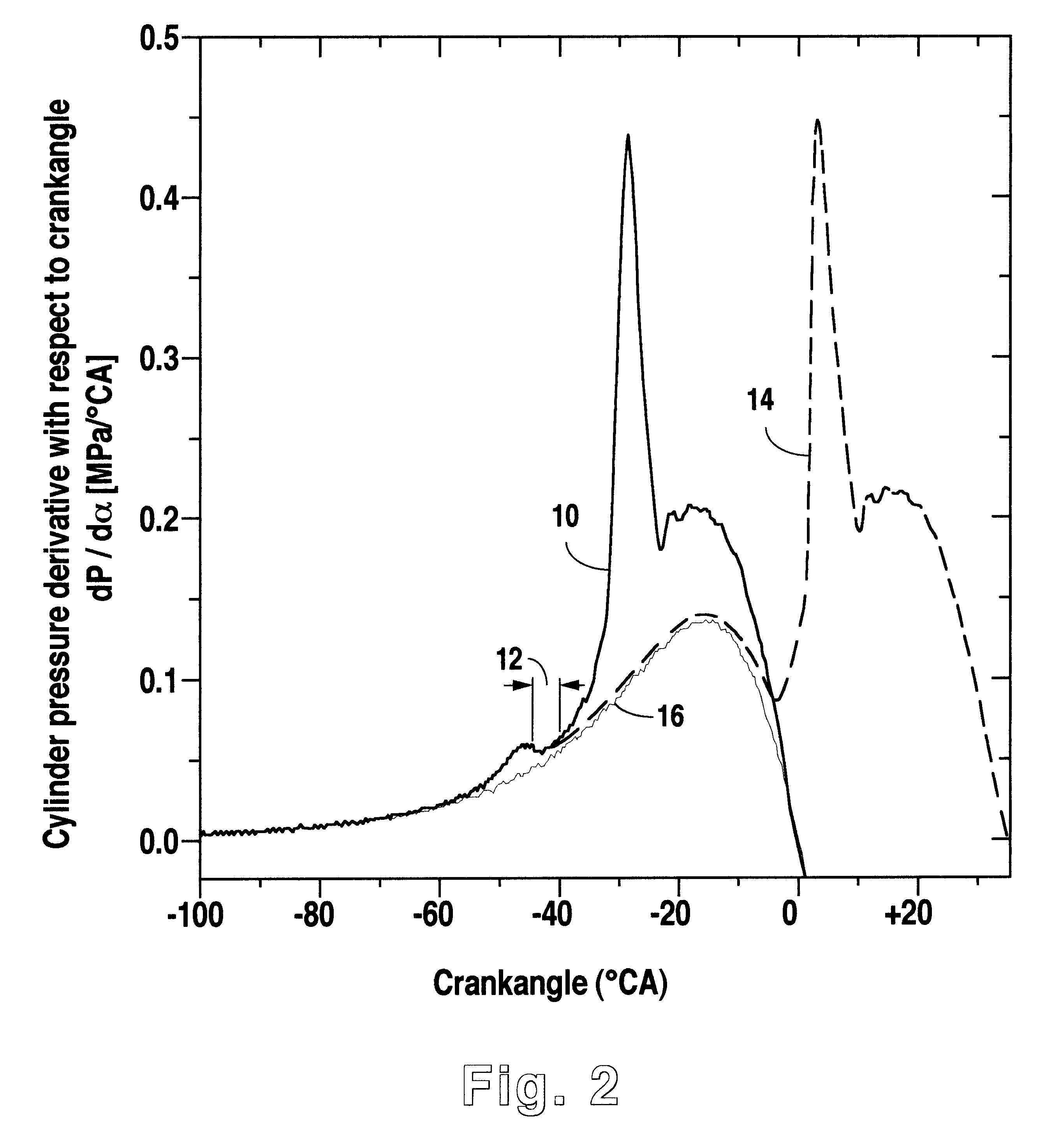
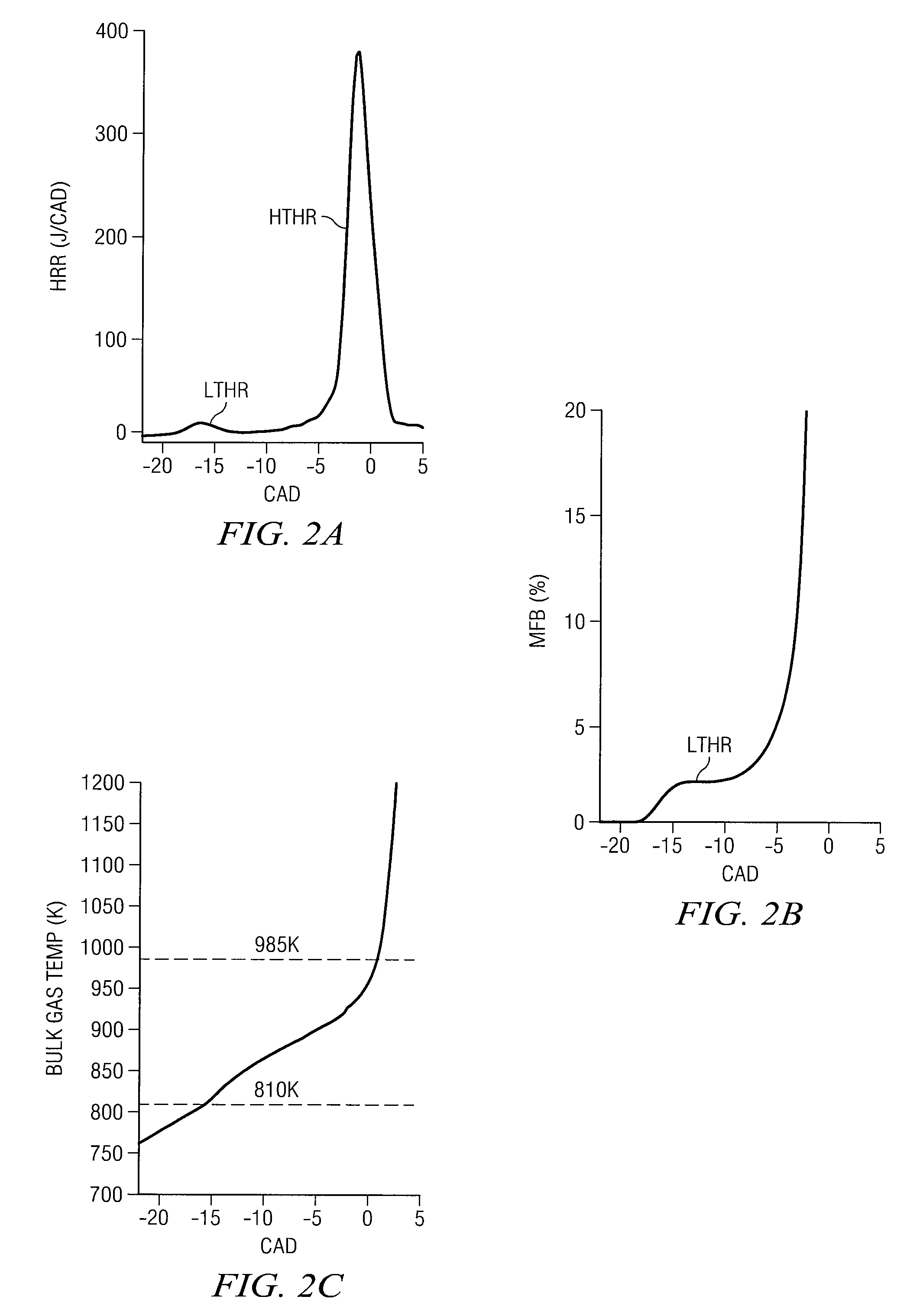
An operating characteristic representative of a first stage reaction in HCCI combustion is sensed and used as a control event for injecting water into the combustion chamber to delay the start of combustion of the primary HCCI reaction.
Owner:SOUTHWEST RES INST
Methods of operation for controlled temperature combustion engines using gasoline-like fuel, particularly multicylinder homogenous charge compression ignition (HCCI) engines
InactiveUS7025042B2Stable and efficient and low emissionElectrical controlNon-fuel substance addition to fuelPressure riseHcci combustion
Owner:ENVIRONMENTAL PROTECTION AGENCY US
Control system of HCCI/SI double-mode harmonization press-combustion engine and method therefor
ActiveCN101070791AImprove fuel economyImprove robustnessElectrical controlMachines/enginesThree levelMicrocontroller
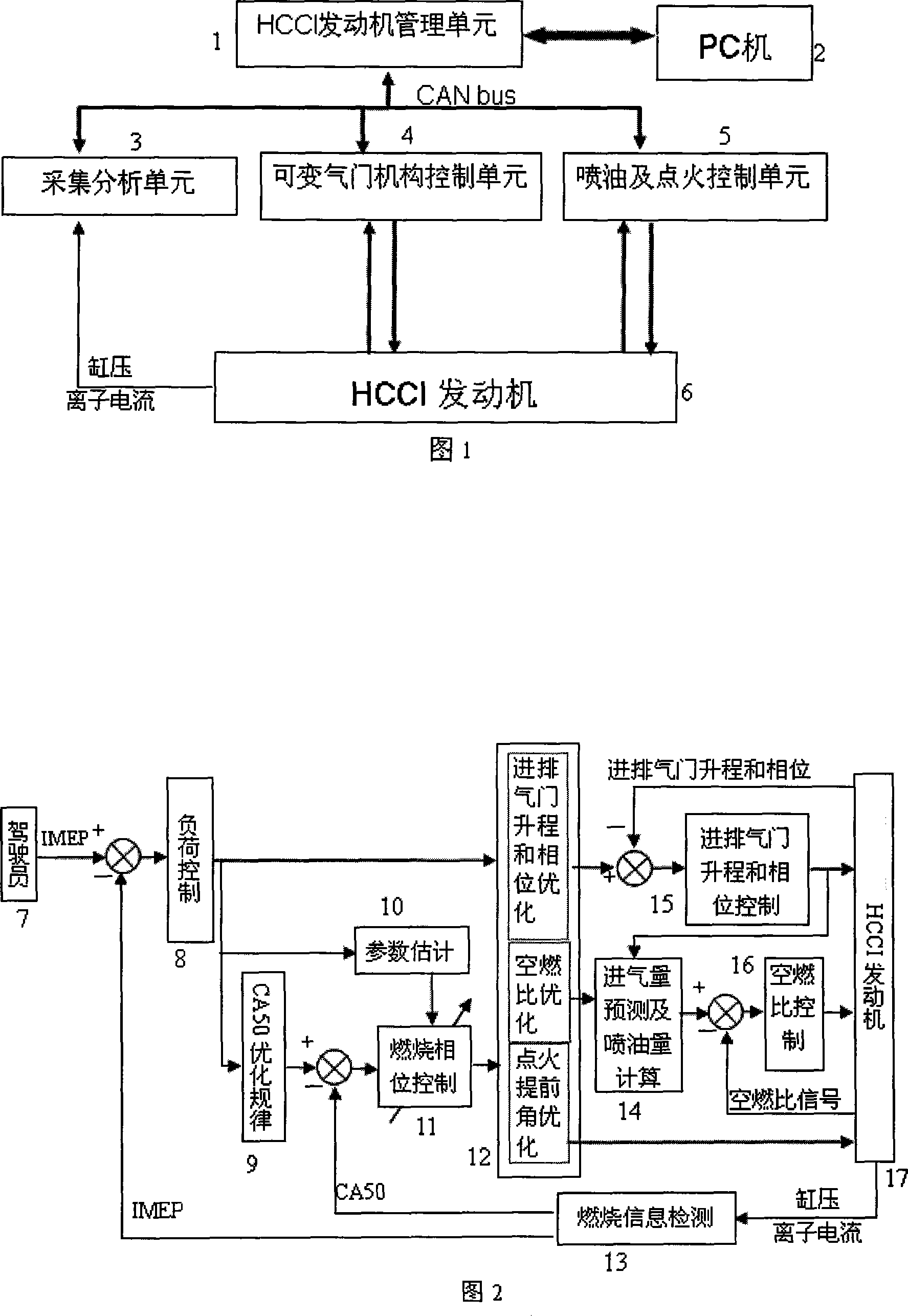
This invention relates to HCCI / SI dual-mode engine control systems and control methods. Based on SCM and CAN Bus, HCCI / SI dual-mode engine distributing control systems includes engine management unit, the fuel injection control unit ignition, valve train control unit and combustion information collection and analysis modules. HCCI / SI dual-mode HCCI engine control method uses a hierarchical closed-loop management strategies, dividing control of the whole engine into load control, combustion control and the control of phase three levels, which have adopted corresponding closure central control. The present invention considers the engine load control as the main line, by controlling the combustion phase to ensure the stability of HCCI combustion. The invention controls each loop separately, streamlining its coupling relations. The idea of closed-loop hierarchical control is not only of clear, easy to implement, but also especially helps improve the robustness of the control system.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV
Control strategy for expanding diesel HCCI combustion range by lowering intake manifold temperature
ActiveUS7171957B2Less undesirableCompromise performanceElectrical controlInternal combustion piston enginesHcci combustionLow load
An engine (10, 100) utilizes “regular EGR cooling” when operating in HCCI mode within a low load range and “enhanced EGR cooling” that allows the engine to continue to operate in HCCI mode when engine load increases beyond the low load range. When engine load increases to a high load range, the combustion mode changes over to conventional diesel combustion, and exhaust gas recirculation reverts to “regular EGR cooling”. In a first embodiment, cooling is provided by two heat exchangers, one being a regular EGR cooler always used when cooling is needed and the other, an enhancing EGR cooler that is selectively used. In a second embodiment, cooling is also provided by two heat exchangers, one being an EGR cooler through which liquid coolant always flows when cooling is needed, and the other being a radiator used selectively to cool the liquid coolant before it enters the EGR cooler.
Owner:INT ENGINE INTPROP CO LLC +1
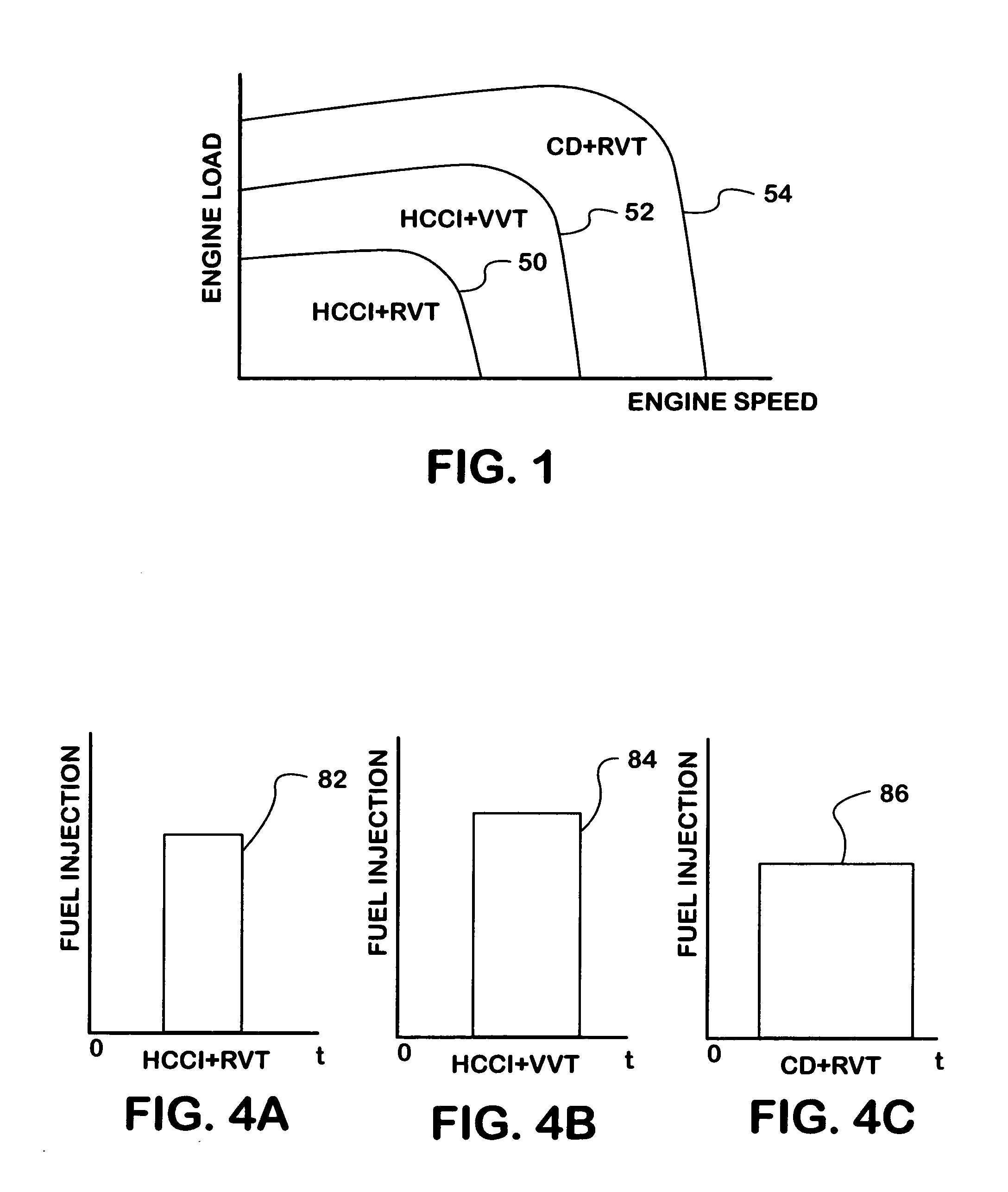
Strategy for fueling a diesel engine by selective use of fueling maps to provide HCCI+RVT, HCCI+VVT, and CD+RVT combustion modes
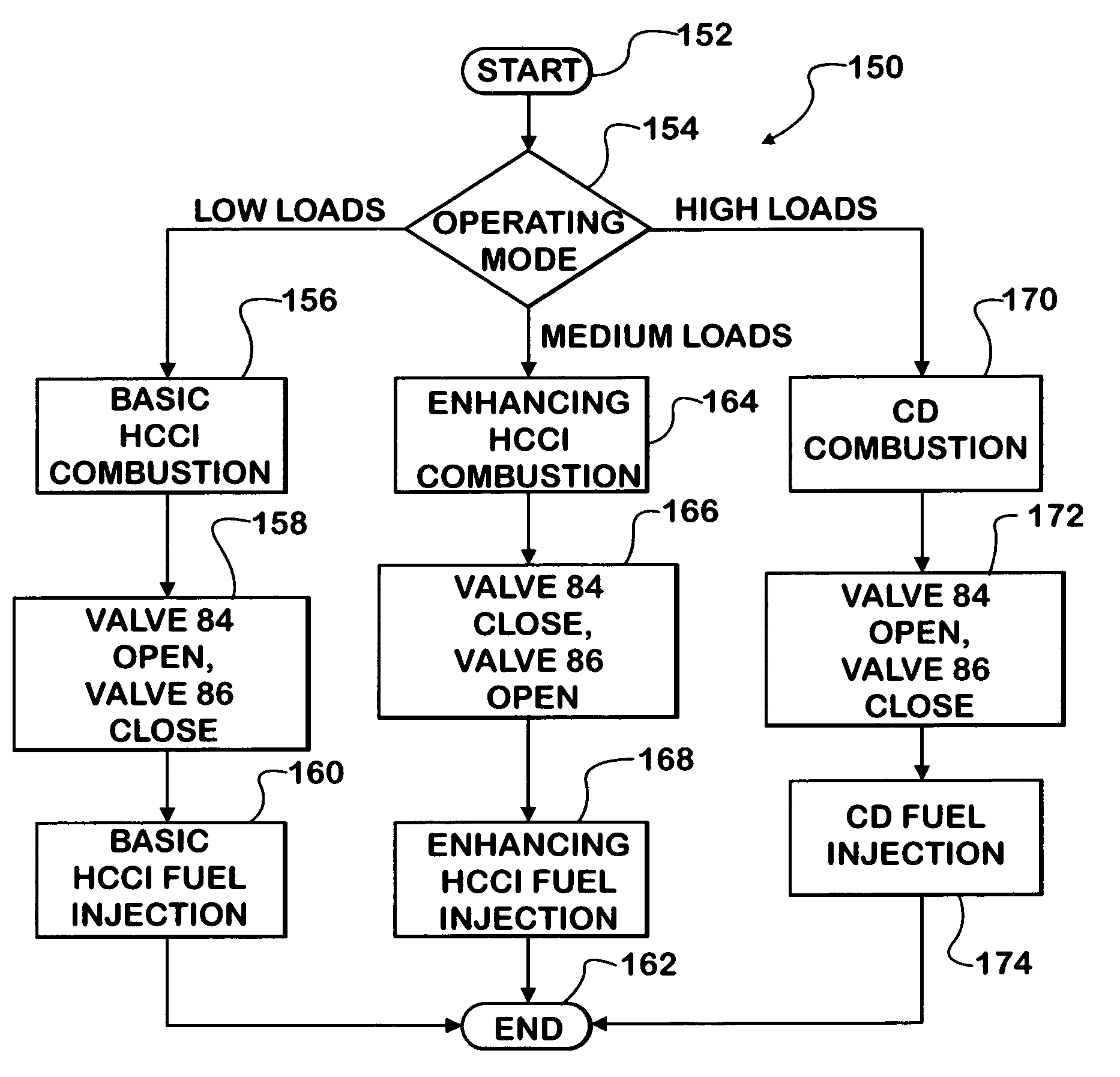
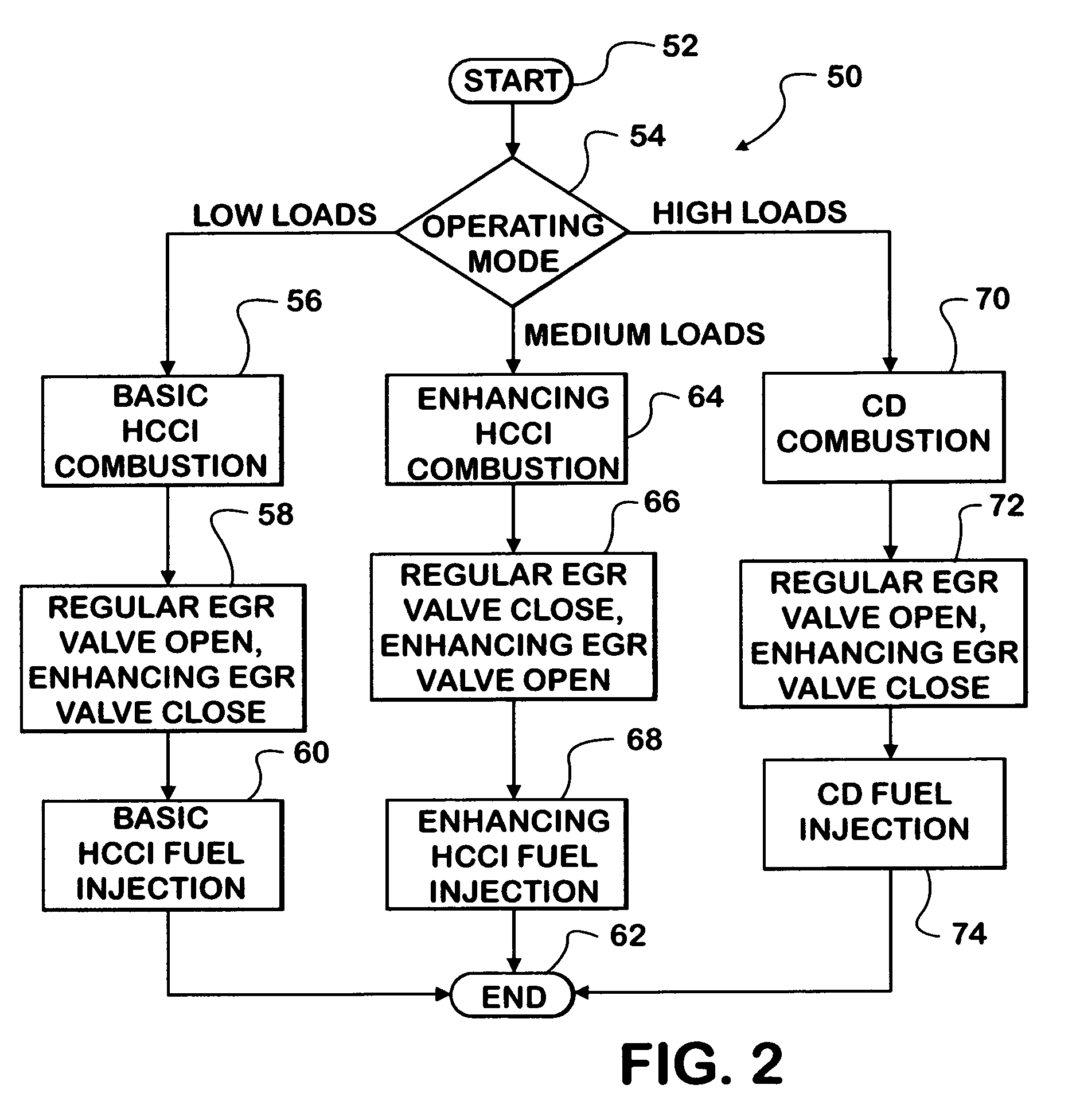
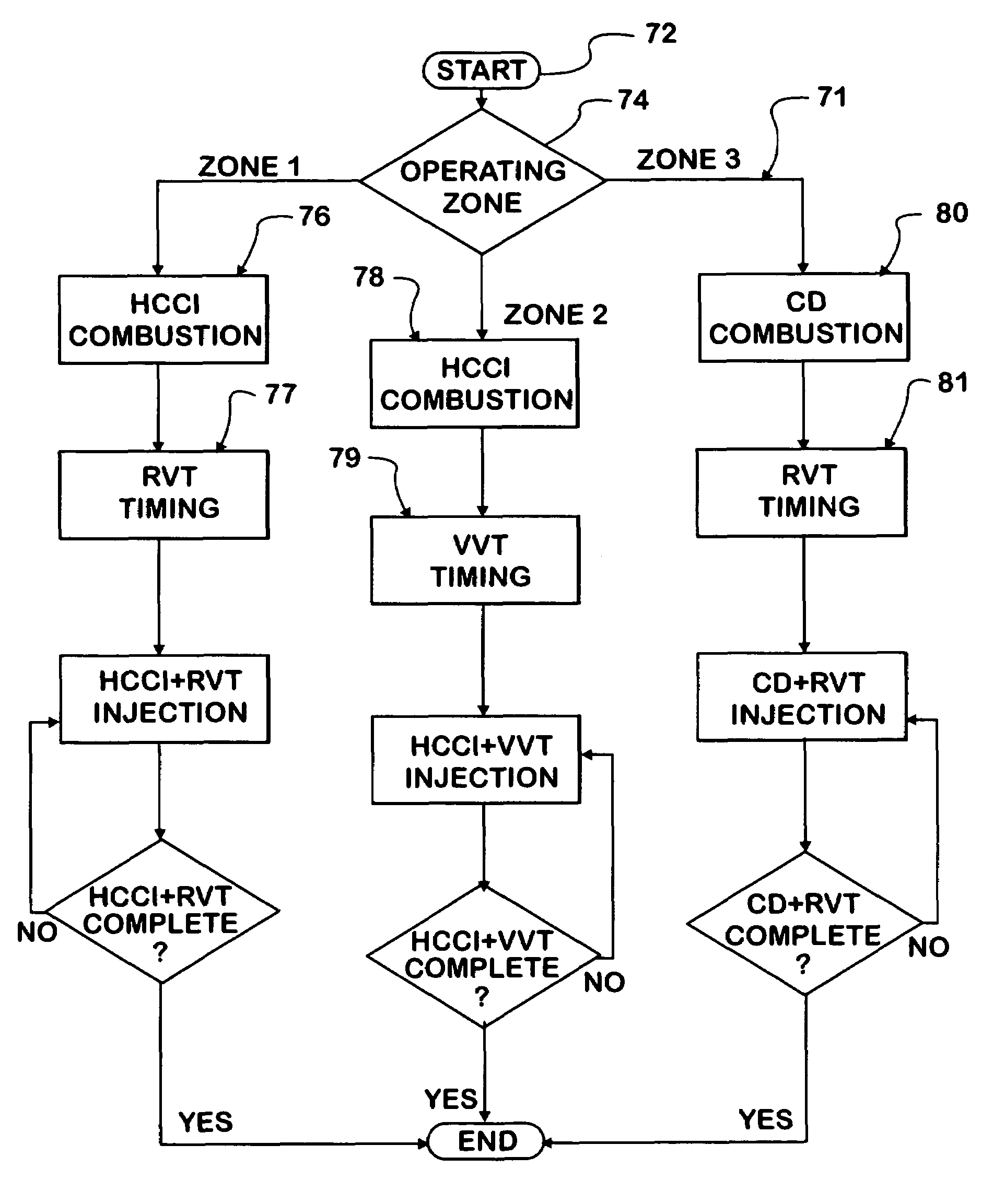
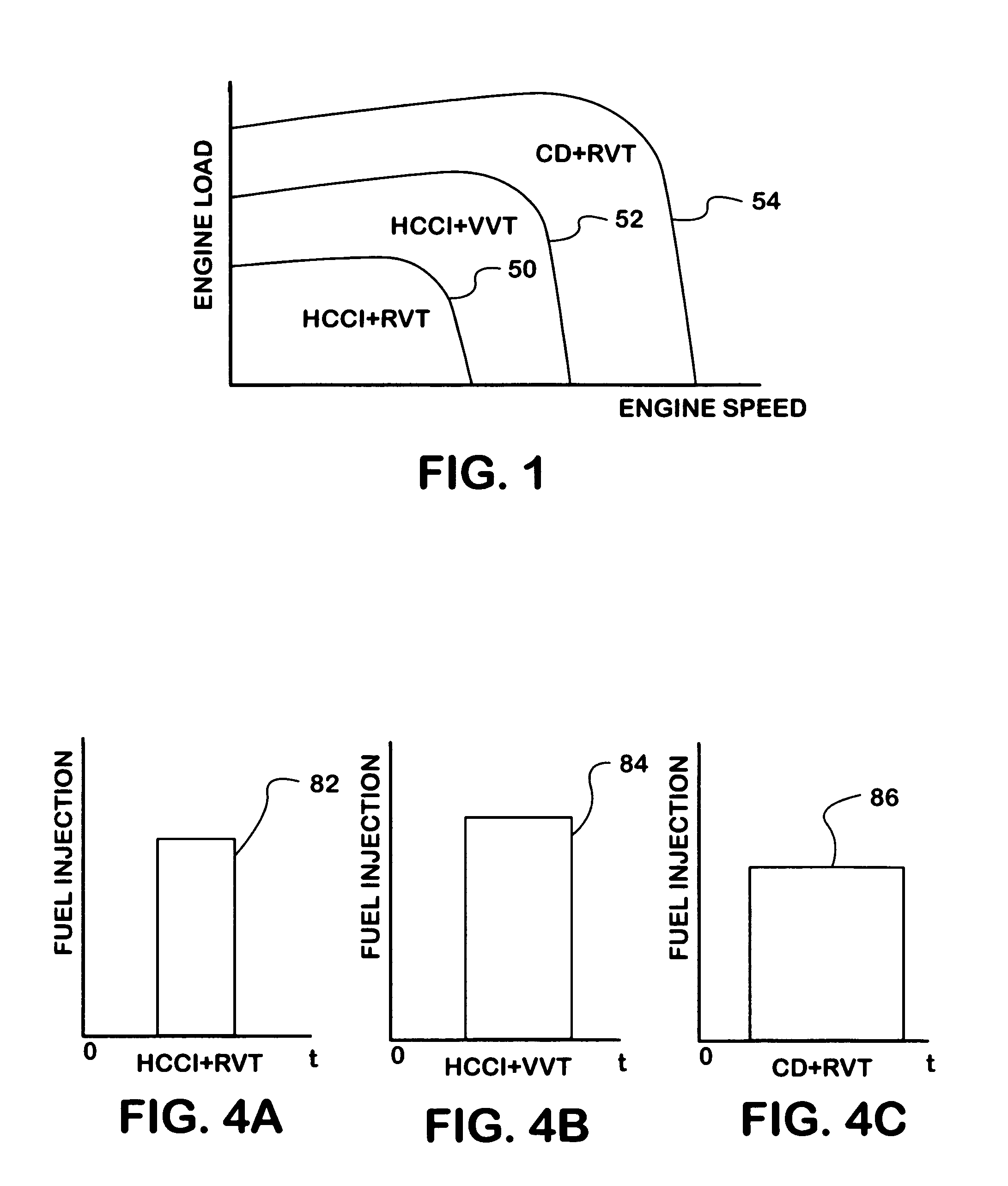
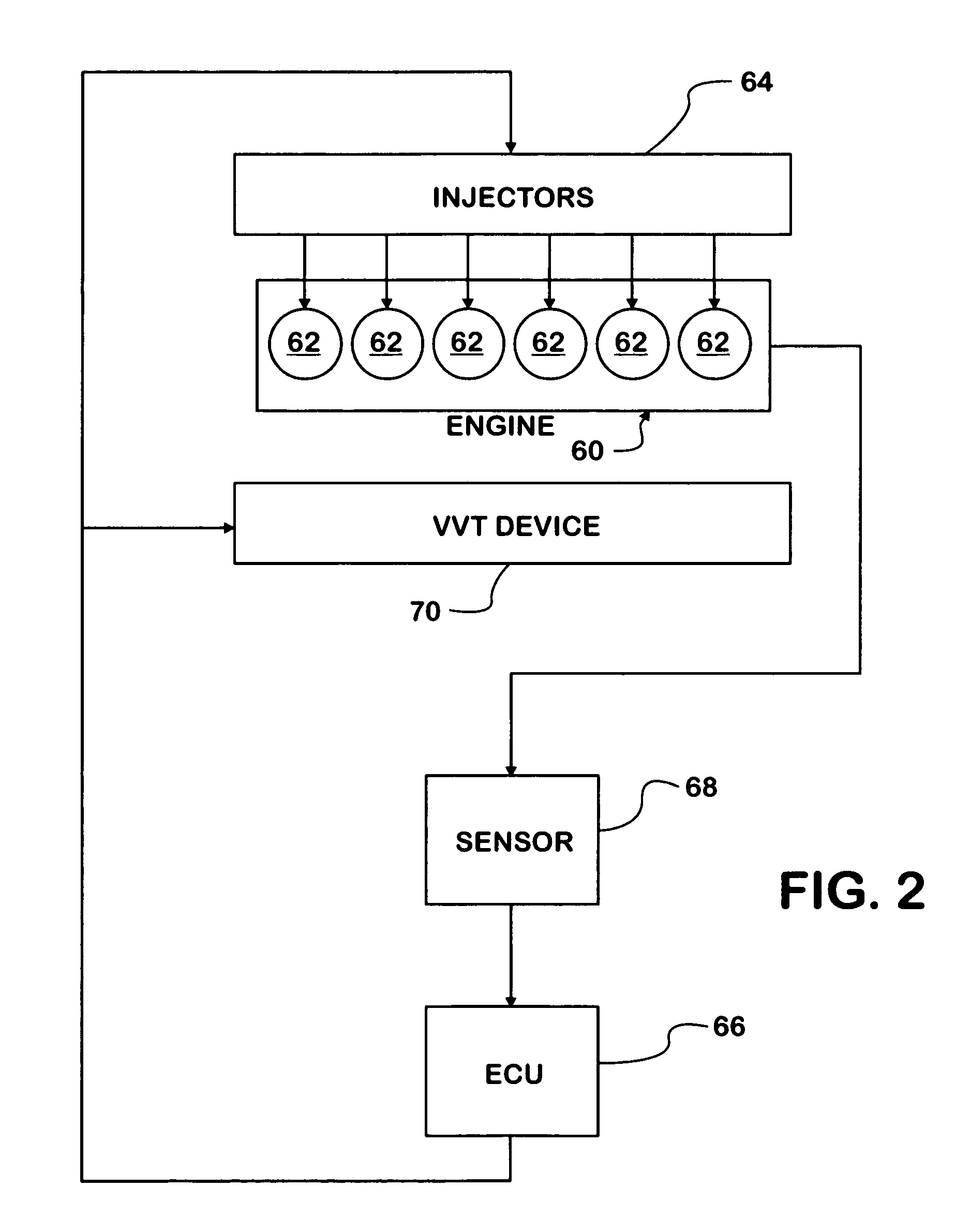
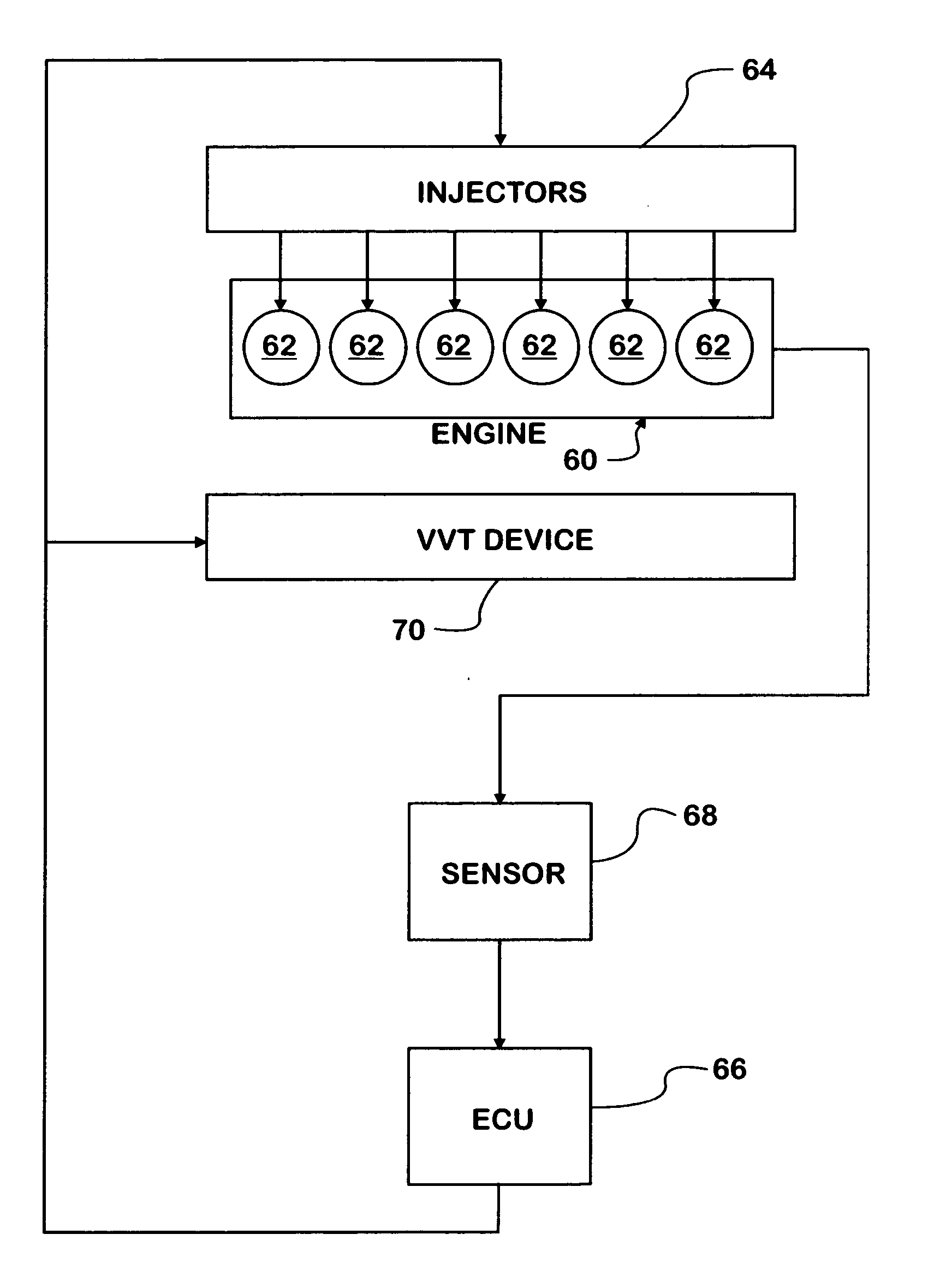
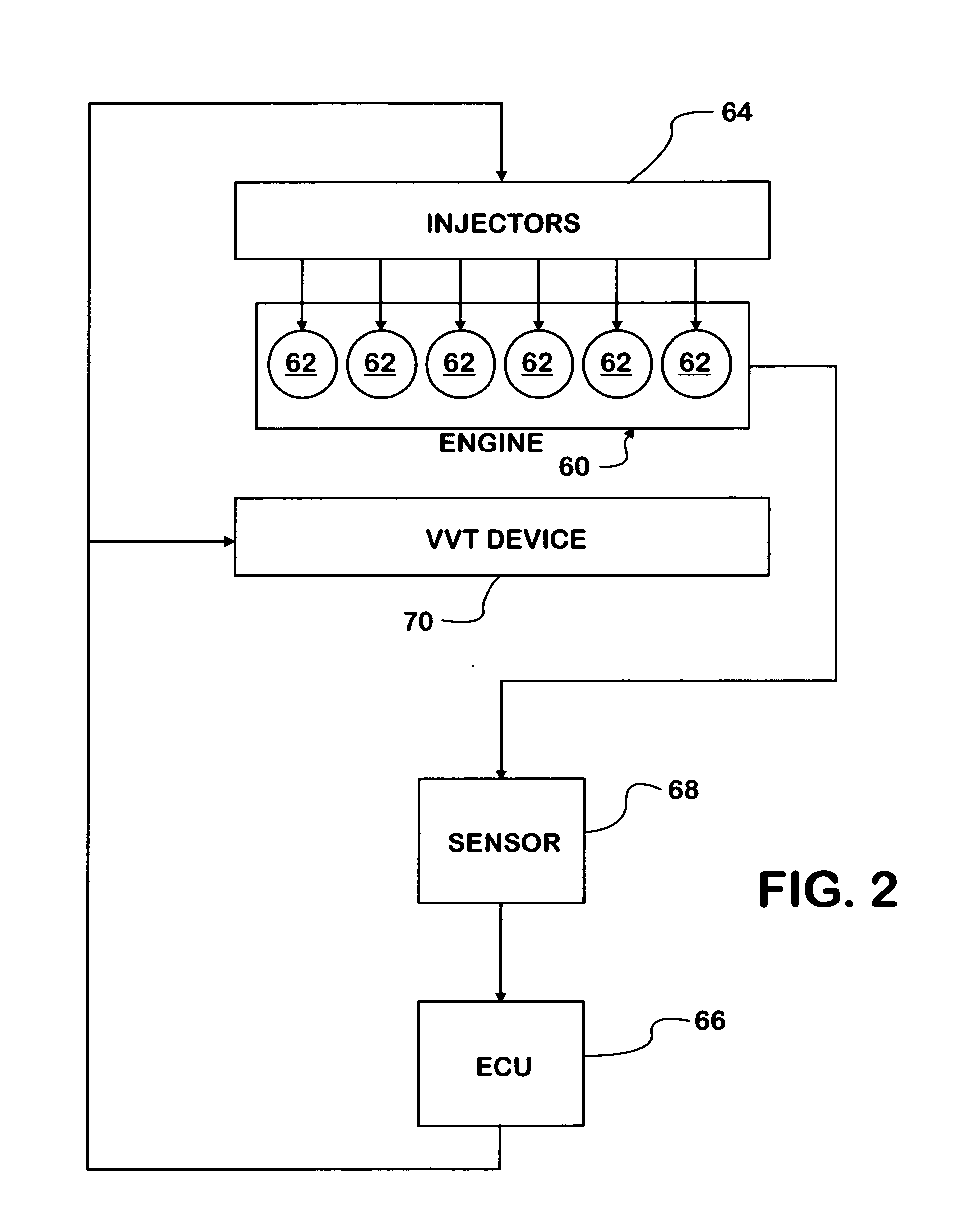
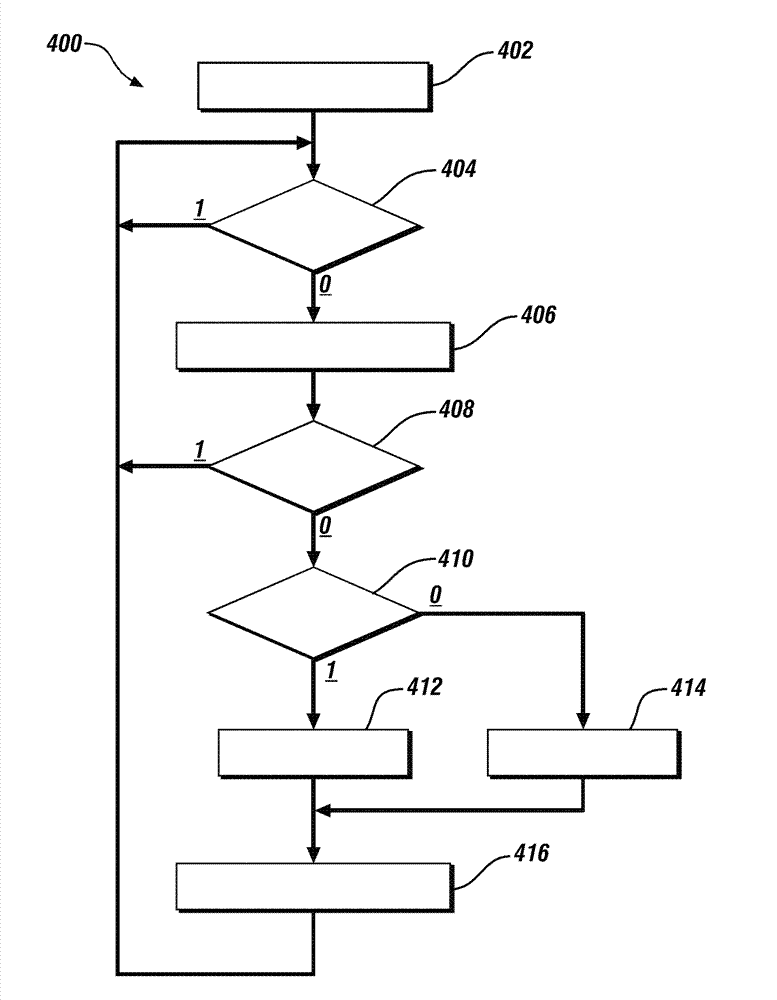
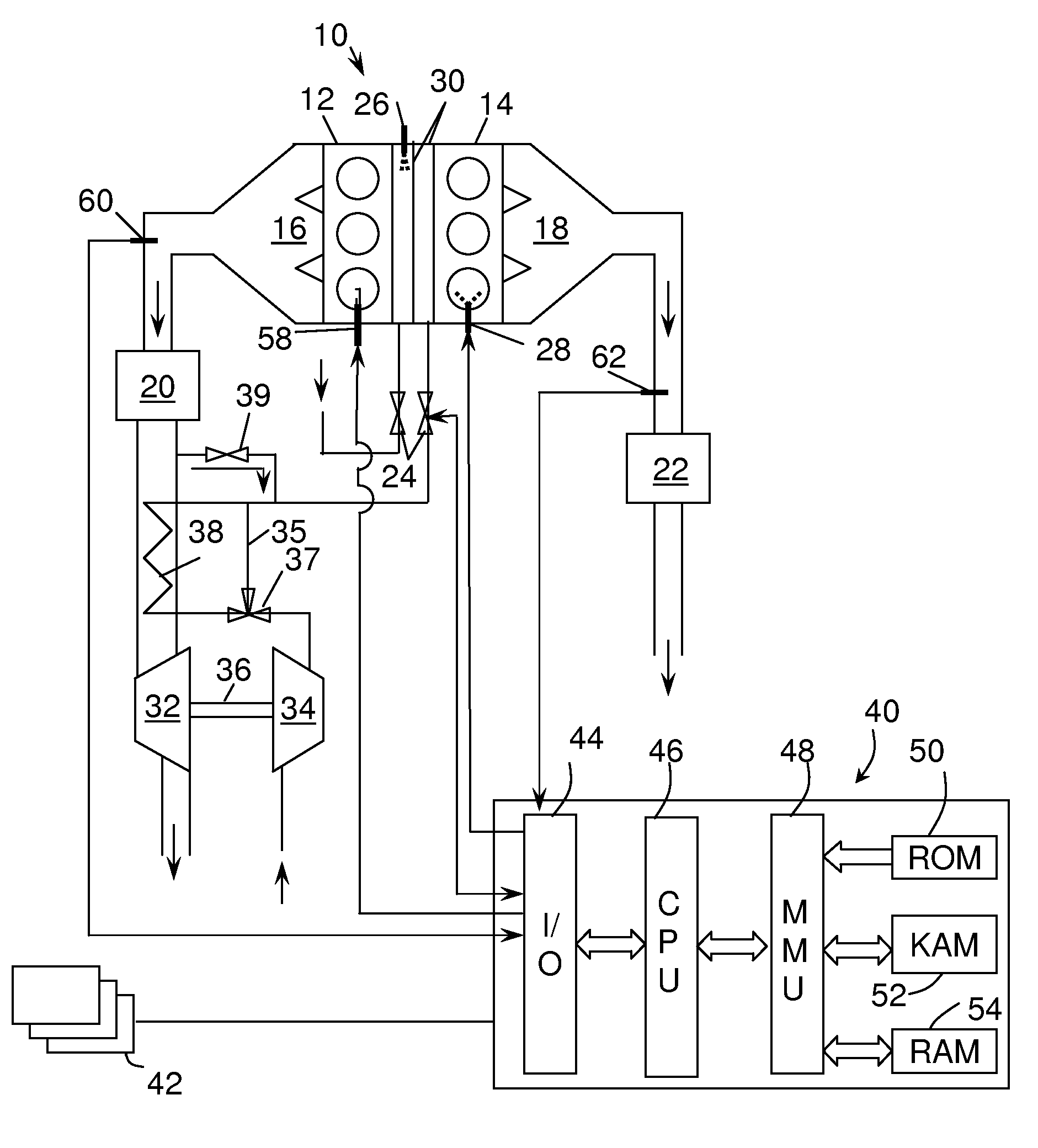
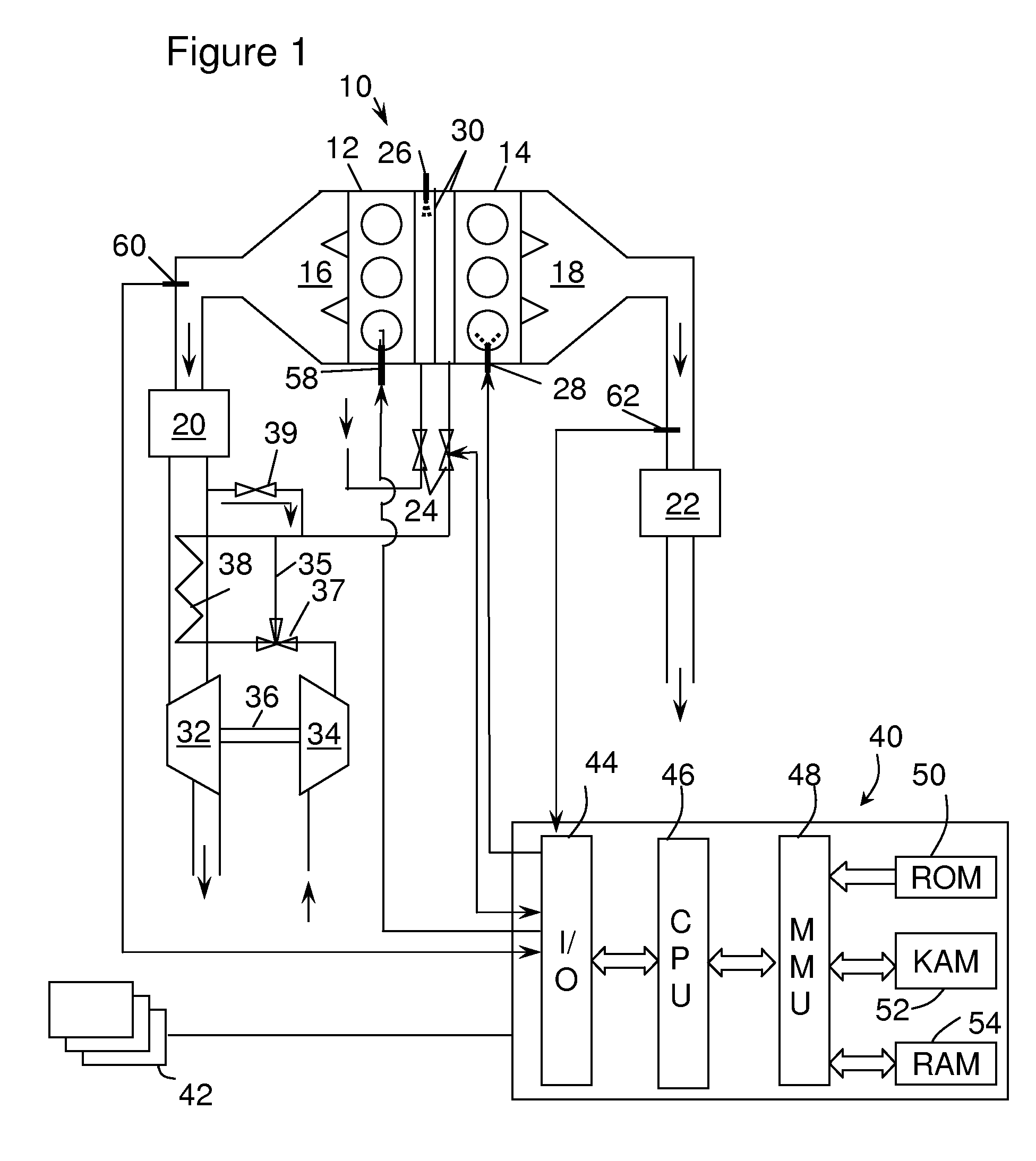
A compression ignition engine (60) has a control system (66) for processing data, one or more combustion chambers (62), and fuel injectors (64) for injecting fuel into the chambers. The control system controls fueling using a result of the processing of certain data, such as engine speed and engine load, to select one of three fueling modes (HCCI+RVT, HCCI+VVT, CD+RVT) for operating the engine. When the result of the processing selects the HCCI+RVT mode, intake valves operate with regular valve timing (RVT), and the engine is fueled to cause homogeneous-charge compression-ignition (HCCI) combustion. When the result of the processing selects the HCCI+VVT mode, intake valve timing is changed relative to RVT, and the engine is fueled to cause HCCI combustion. When the result of the processing selects the CD+RVT mode, the intake valves operate with RVT, and the engine is fueled to cause CD combustion.
Owner:INT ENGINE INTPROP CO LLC
Strategy for fueling a diesel engine by selective use of fueling maps to provide HCCI+RVT, HCCI+IVC, HCCI+IVC+EVC, and CDcombustion modes
InactiveUS20050288846A1Easy to useReduce generationAnalogue computers for vehiclesElectrical controlHcci combustionExhaust valve
A compression ignition engine (60) has a control system (66) for processing data, one or more combustion chambers (62), and fuel injectors (64) for injecting fuel into the chambers. The control system controls fueling by processing engine speed and load, to select one of four fueling modes (HCCI+RVT, HCCI+IVC, HCCI+IVC+EVC, and CD+RVT) for operating the engine (FIG. 5). When HCCI+RVT mode is selected, intake valves operate with regular valve timing (RVT), and the engine is fueled to cause homogeneous-charge compression-ignition (HCCI) combustion. When HCCI+IVC mode or HCCI+IVC+EVC mode is selected, intake valve timing is changed relative to RVT, and the engine is fueled to cause HCCI combustion. When the processing selects the CD+RVT mode, the intake valves operate with RVT, and the engine is fueled to cause CD combustion. In HCCI+IVC+EVC mode, exhaust valve closing is retarded relative to its timing in HCCI+IVC mode to reduce cylinder pressure and temperature.
Owner:INT ENGINE INTPROP CO LLC
Energy-saving ultra low emission dual-mode homogeneous compression-ignition engine based on fully variable valve mechanism
ActiveCN101016868AWith vehicle conditionsRealize switchingElectrical controlInternal combustion piston enginesHcci combustionDual mode
The invention discloses an energy-saving ultra-low discharge dual-mode uniform engine, based on variable-throttle device, wherein a cylinder cover is a variable-throttle cylinder cover arranged with two throttle strike continuous changers and a variable-throttle phase device whose frame is arranged with a chain tooth around and connected with a crank of the engine via chain. The inventive engine can completely utilize the high-effect energy-saving ultra-low discharge character of uniform HCCI burning mode to switch between spark burning SI and HCCI burning mode according to working conditions, to save energy and ultra-low discharge. And the variable-throttle device can realize the control on different burning modes, and switch between two modes.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV
Operating strategy for hcci combustion during engine warm-up
InactiveUS20100241341A1Analogue computers for vehiclesElectrical controlHcci combustionAutomotive engineering
An engine operating in a spark-assisted homogeneous charge compression ignition mode during warm-up cycle is controlled using settings determined by interpolating between cold engine temperature settings fully warmed-up engine temperature settings.
Owner:GM GLOBAL TECH OPERATIONS LLC
Model-based decoupling and disturbance-rejection control method for homogeneous charge compression ignition (HCCI)
ActiveCN103195599AReduce workloadReduce dependenceElectrical controlMachines/enginesHcci combustionActive disturbance rejection control
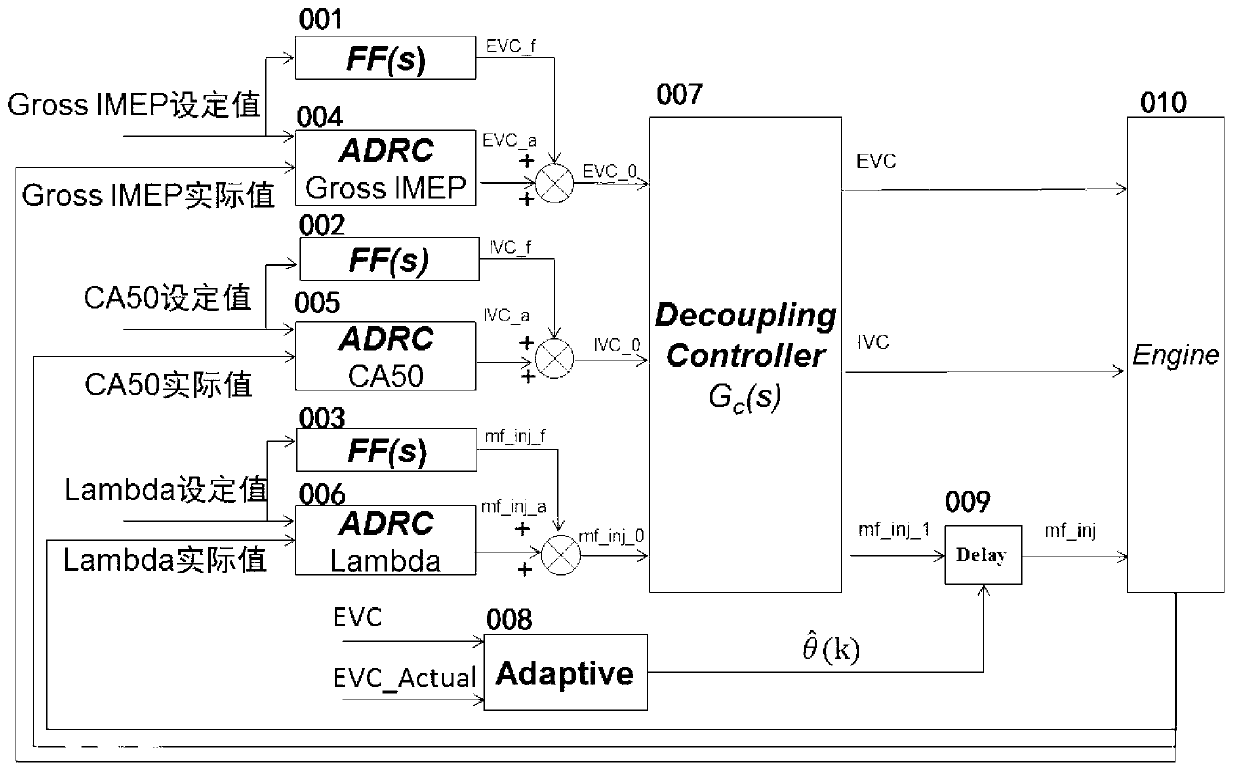
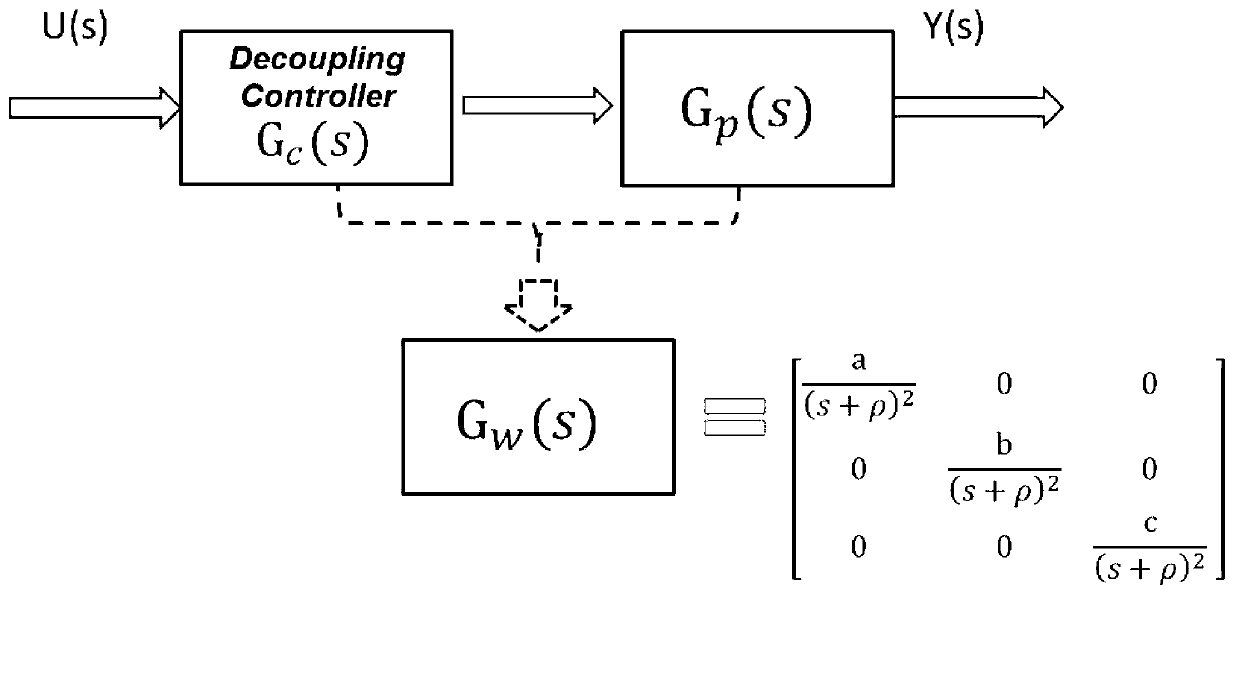
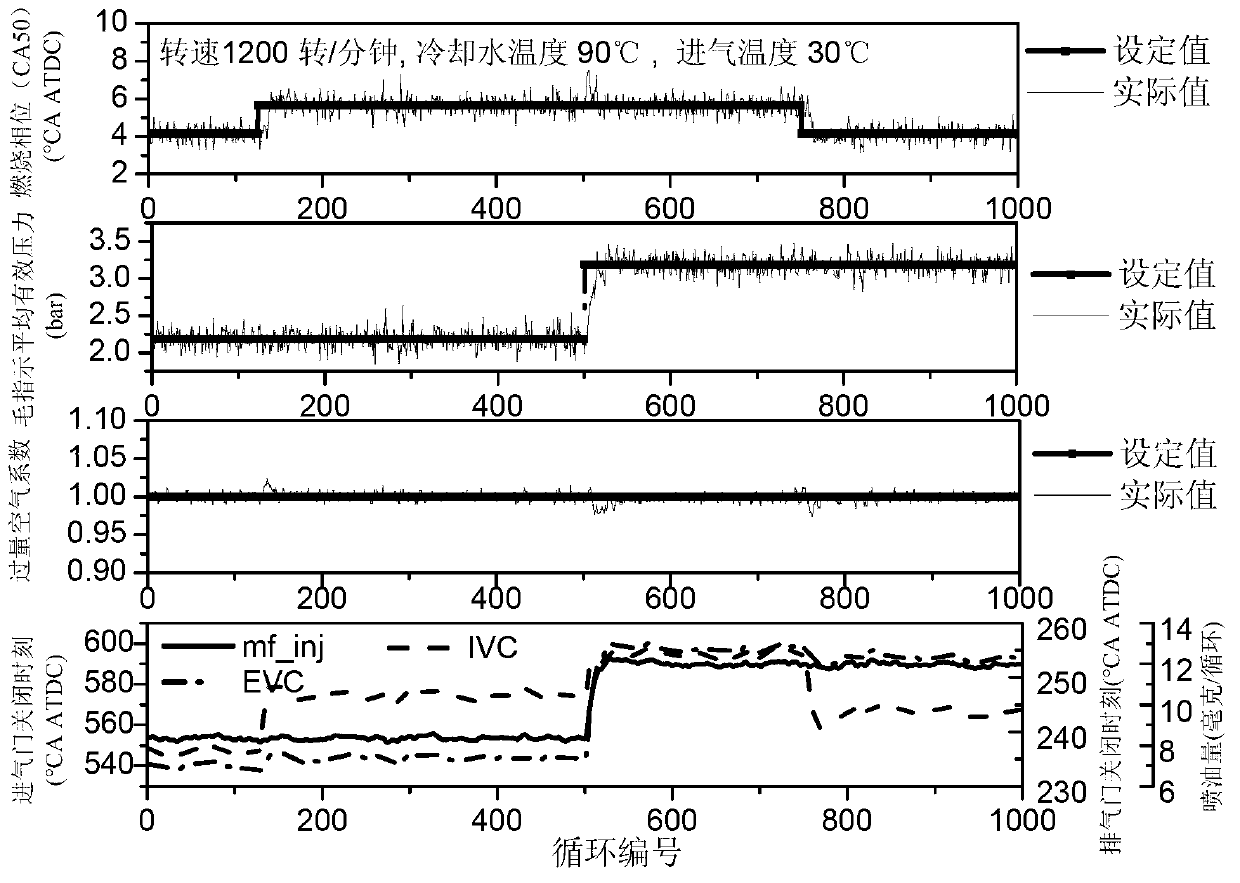
The invention discloses a model-based decoupling and disturbance-rejection control method for HCCI. The method comprises model-based decoupling control, active disturbance rejection control (ADRC), feed-forward control and self-adaptation compensation control for valve mechanism action delay. The method comprises the steps of designing a decoupling compensator on the basis of a control model of the HCCI, and converting an HCCI system into a plurality of independent single-input single-output (SISO) systems; conducting inversion on transfer functions of all SISO systems to obtain a feed-forward controller; designing ADRC controllers for all SISO systems respectively, and observing and compensating deviations of the model and random disturbance of the outside in real time; and estimating the action delay of a valve mechanism in real time, actively delaying an oil injection action, and obtaining the response speed which is the same as that of the valve mechanism. By the aid of the method, the modeling burden of the HCCI control model and the standard workload of controller parameters can be reduced greatly, the robustness for engine working condition variations is high, and the ignition process control is stable.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV
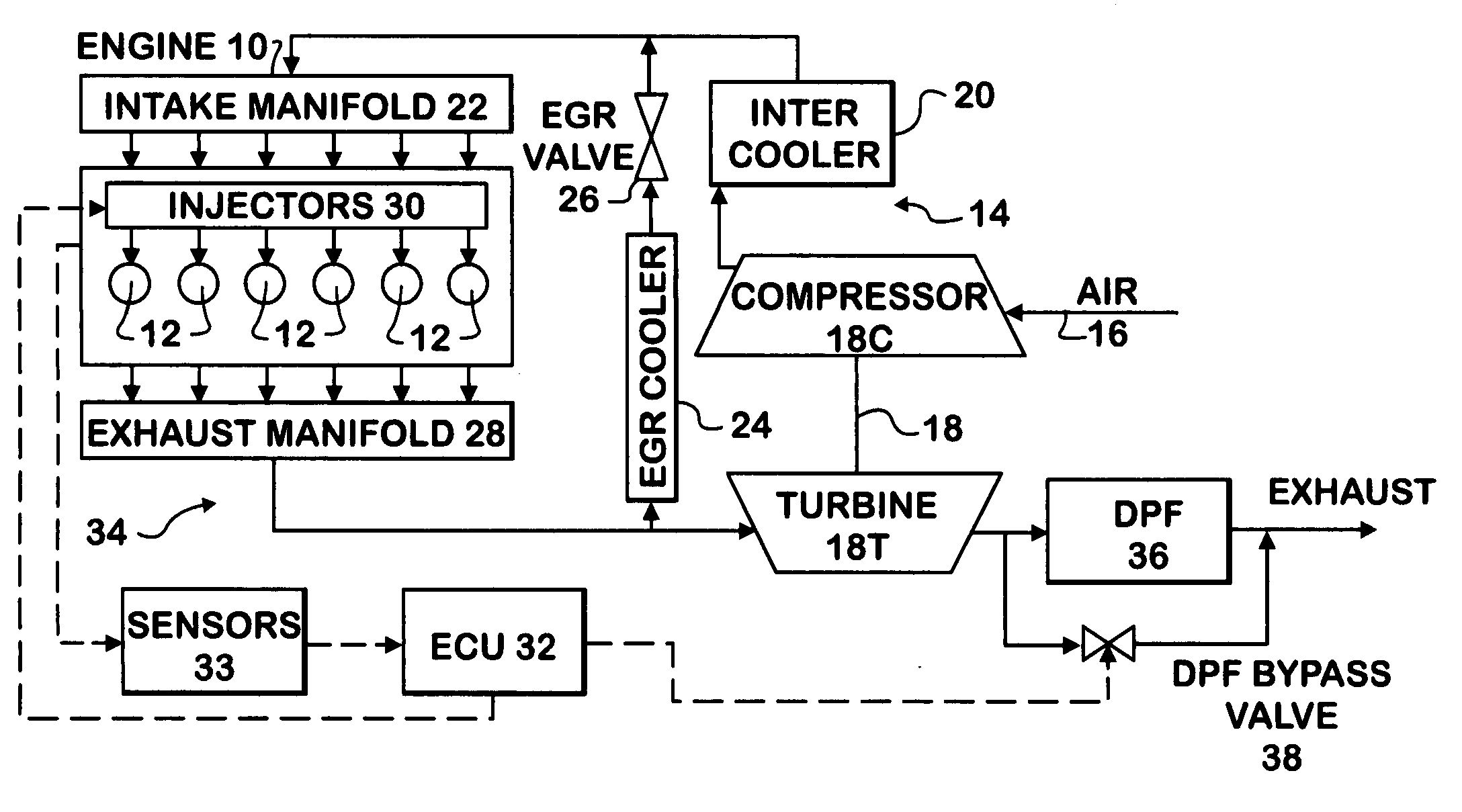
Strategy for selectively bypassing a DPF in a hybrid HCCI combustion engine
ActiveUS20060185353A1Improve operationMinimize disruptionElectrical controlInternal combustion piston enginesHcci combustionDiesel combustion
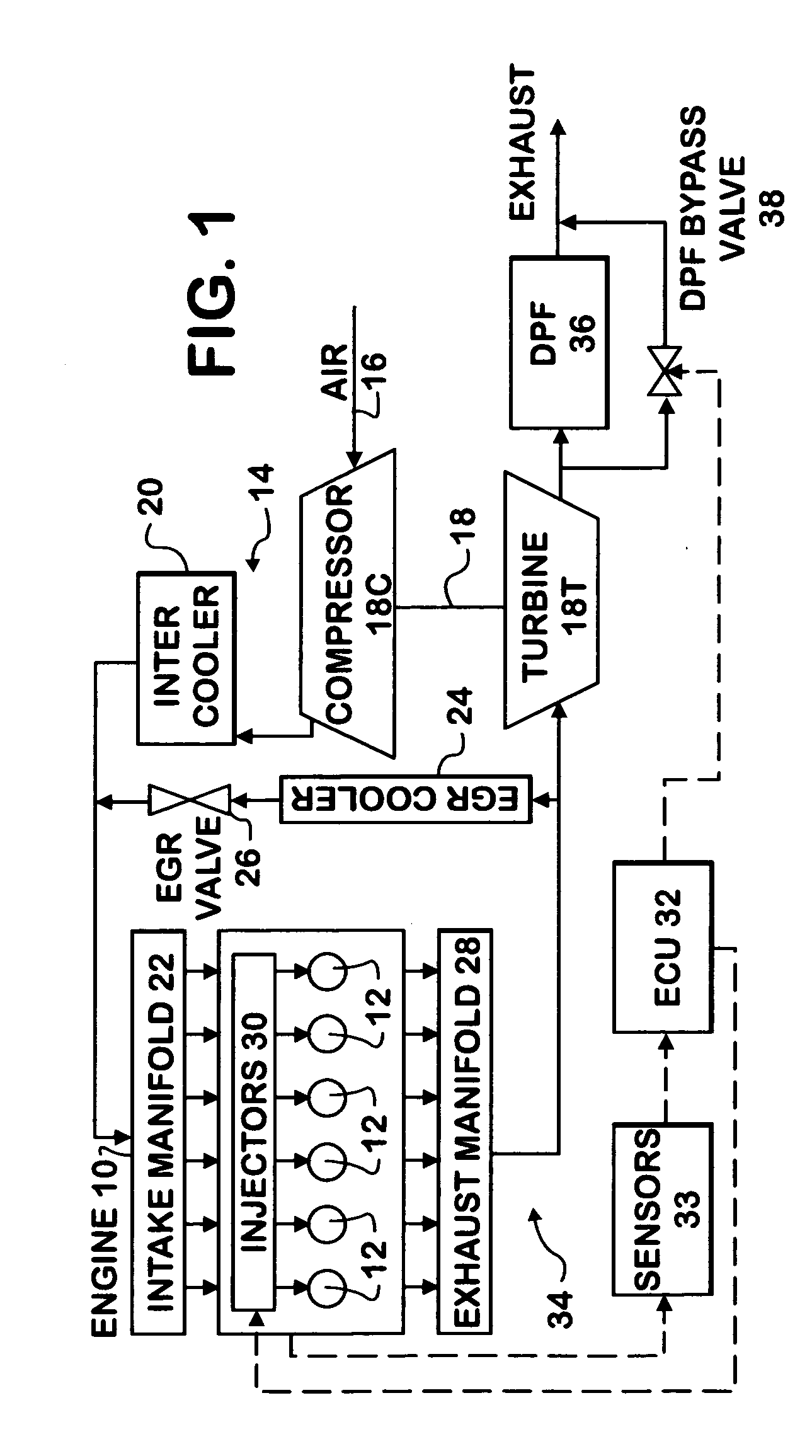
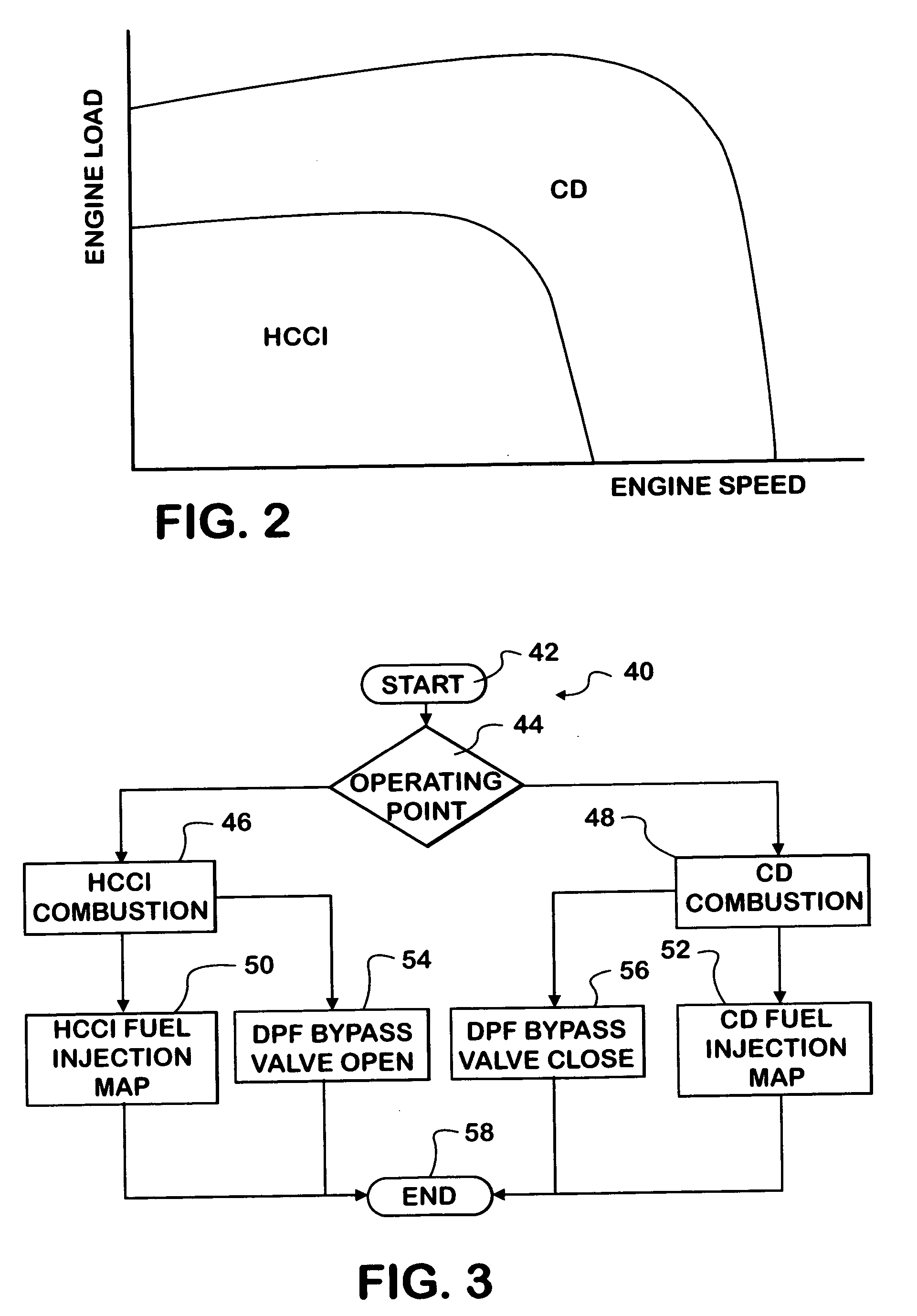
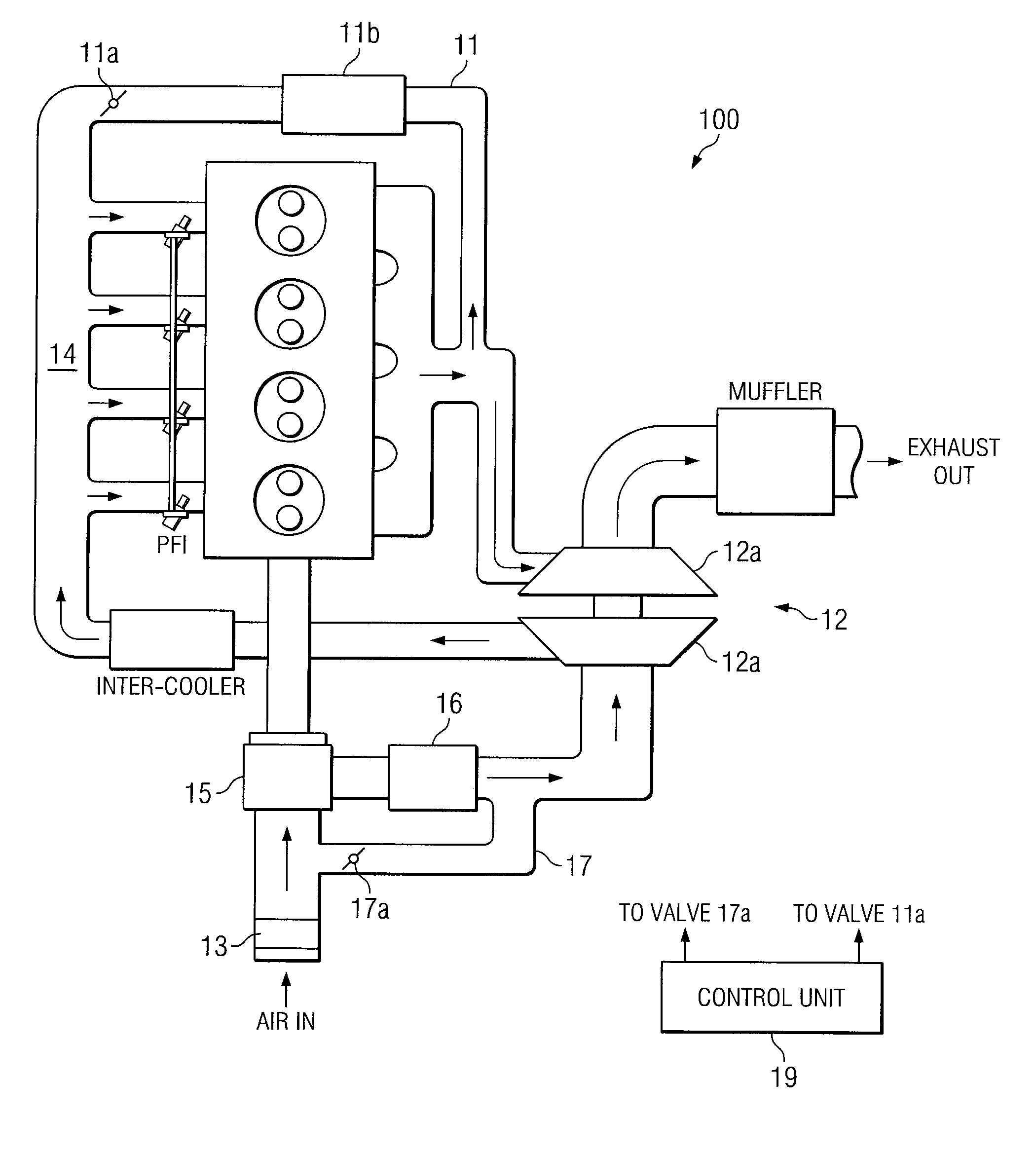
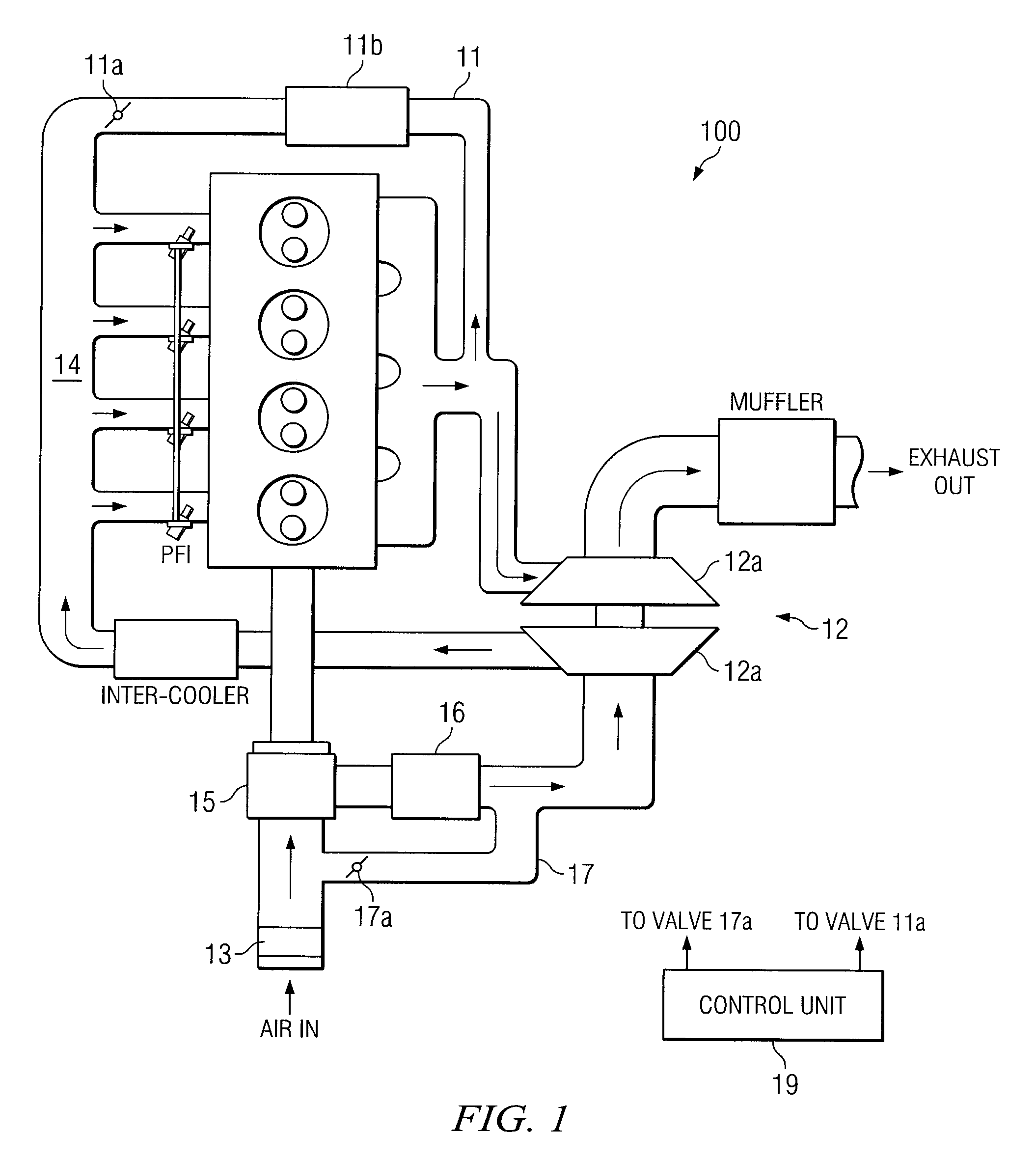
In a conventional diesel combustion mode, one or more cylinders (12) of an engine (10) is or are fueled to cause conventional diesel combustion in each such cylinder. The resulting exhaust gas is treated by a diesel particulate filter (36) in an exhaust system (34) before exiting the exhaust system. In an alternative diesel combustion mode, such as HCCI, one or more cylinders of the engine are fueled to create in each such cylinder an in-cylinder fuel-air charge that ignites by auto-ignition as the charge is increasingly compressed. Also a bypass valve (38) is opened so that the resulting exhaust gas bypasses the DPF as the exhaust gas passes through the exhaust system.
Owner:INT ENGINE INTPROP CO LLC
Hybrid combustion in a diesel engine
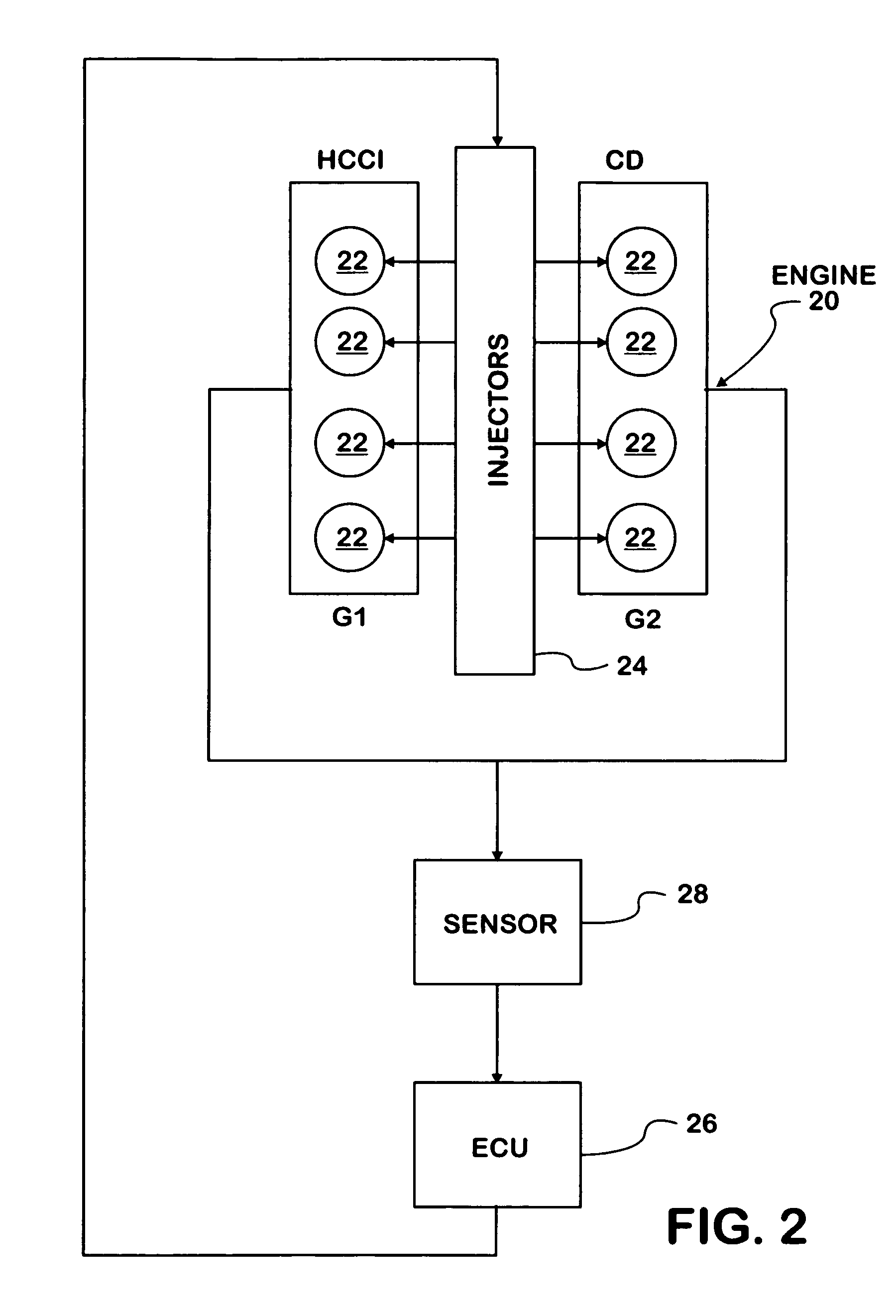
ActiveUS7461627B2Increase rangeElectrical controlInternal combustion piston enginesHcci combustionCombustion chamber
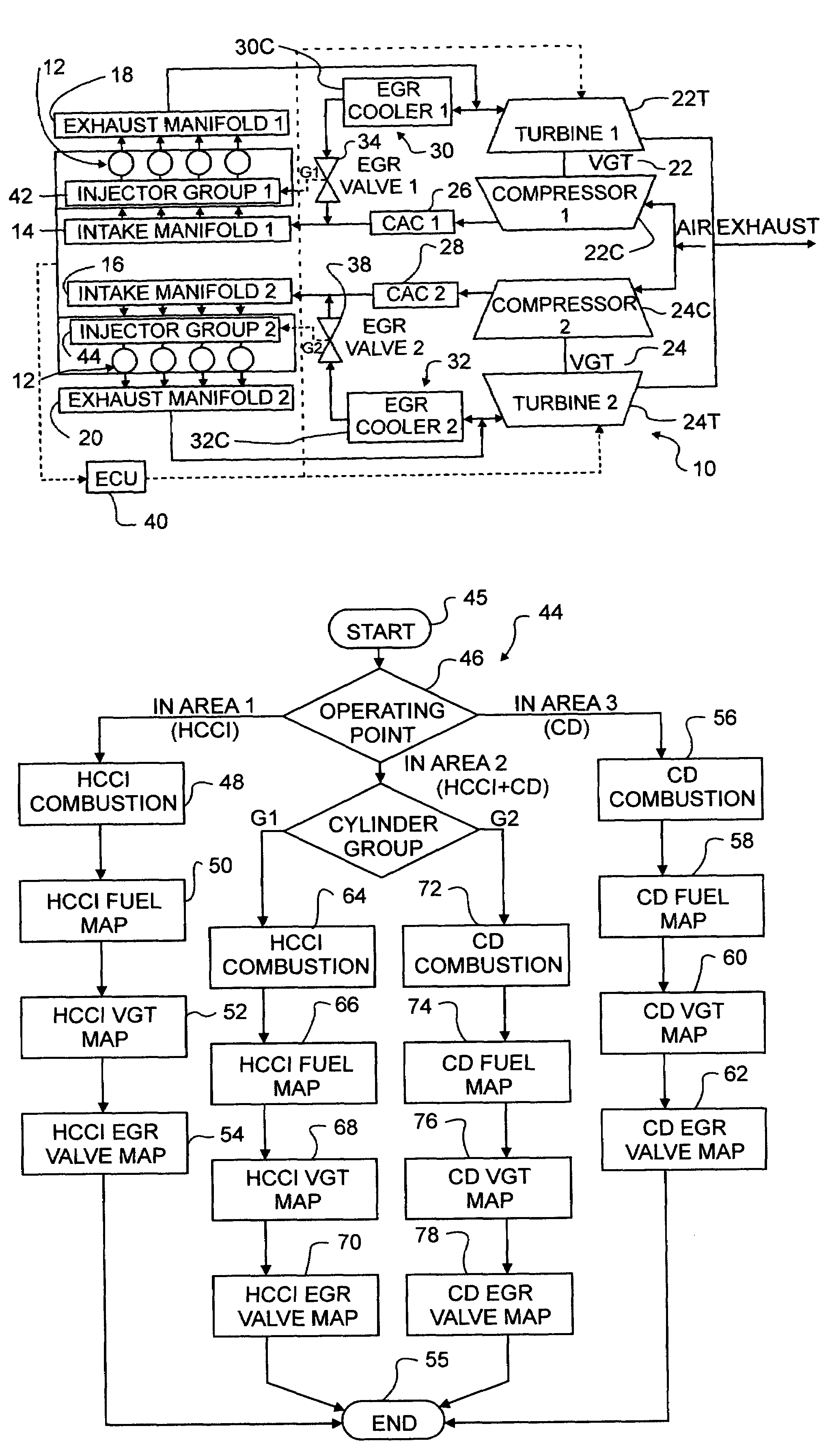
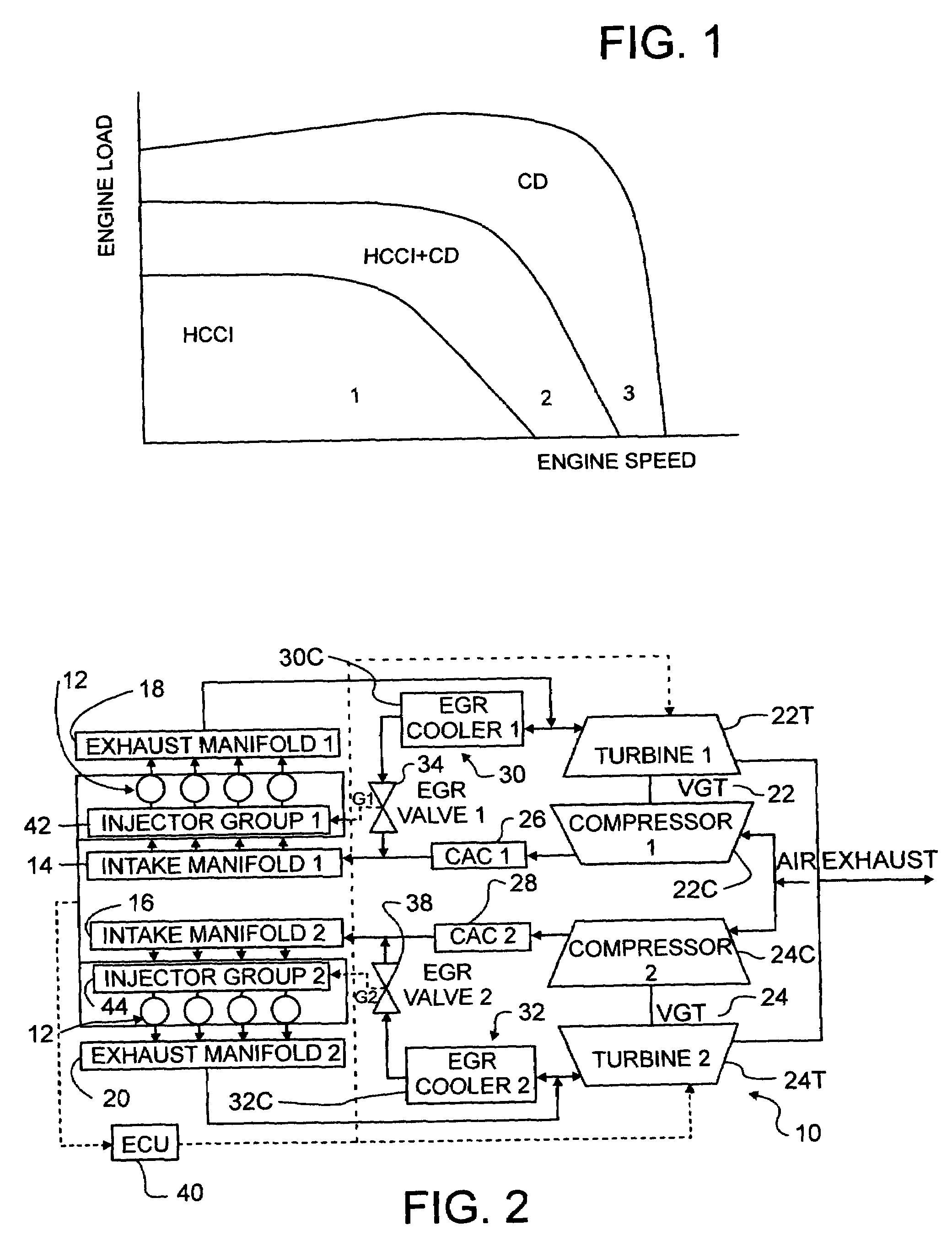
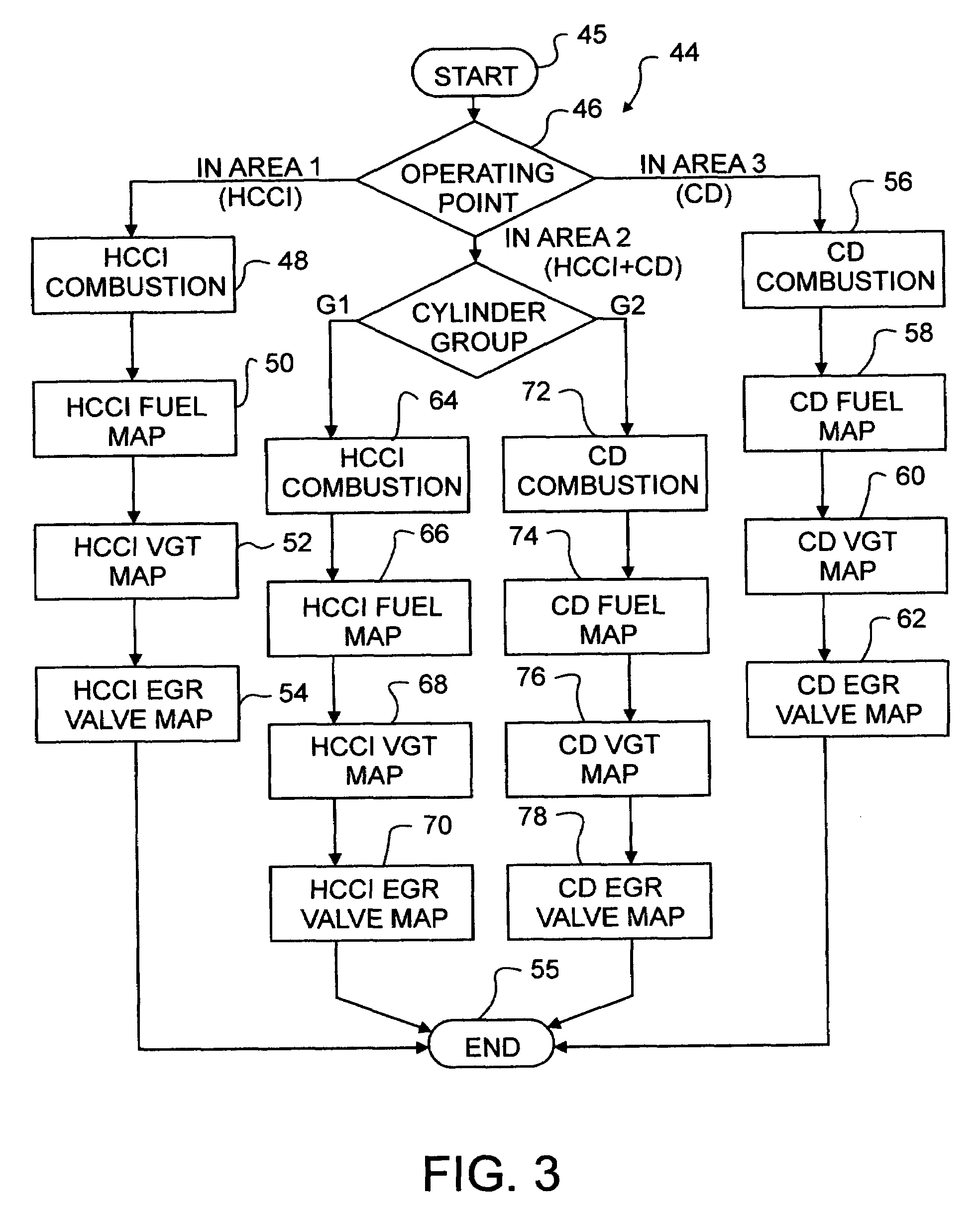
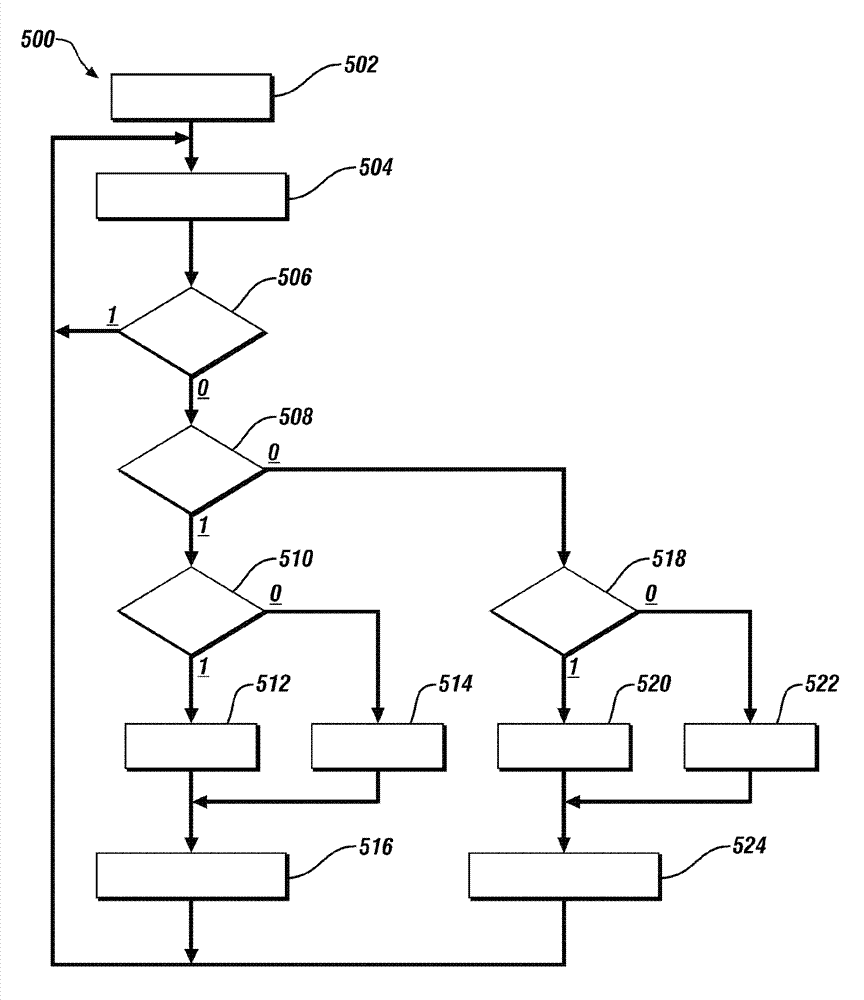
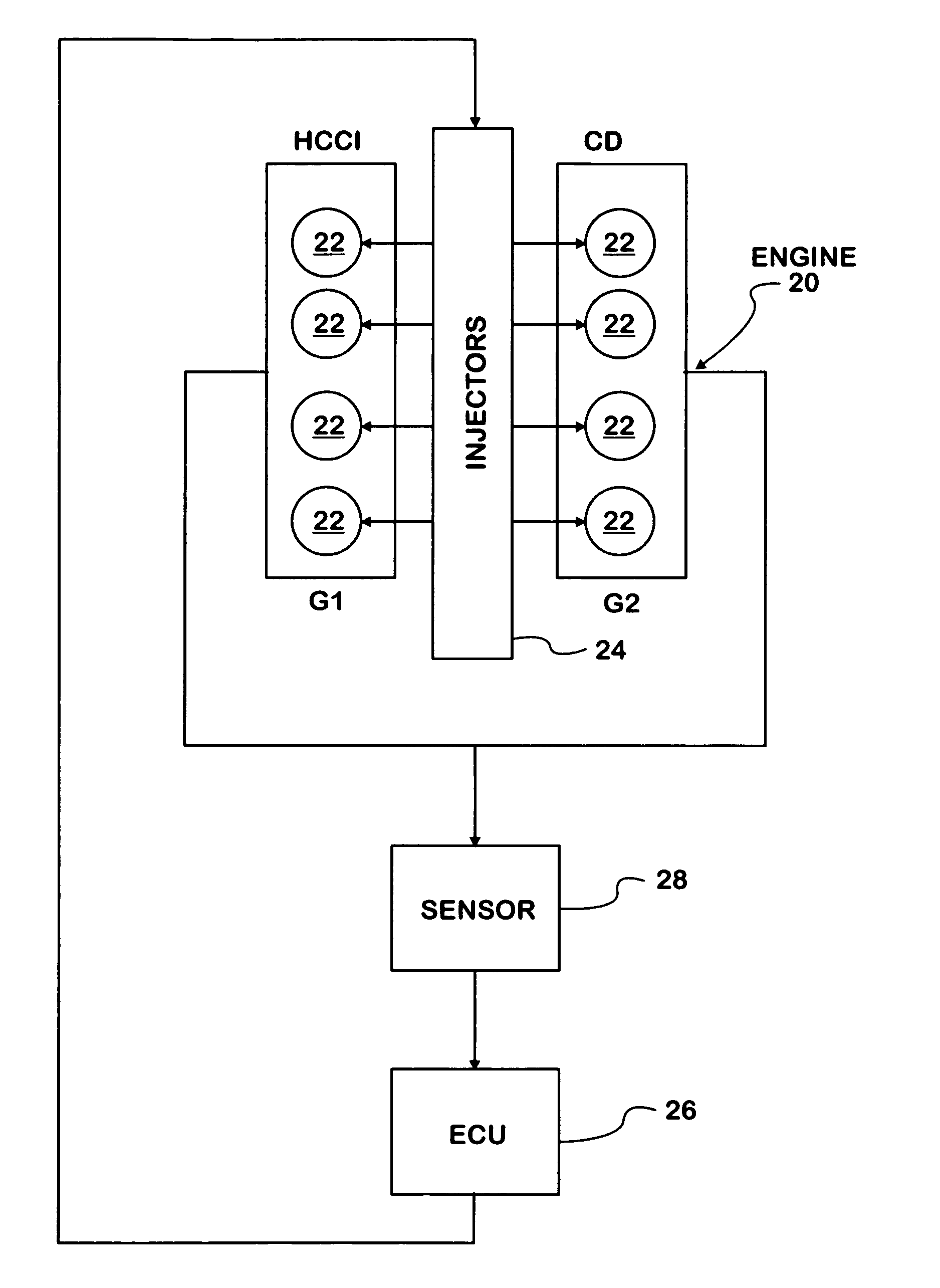
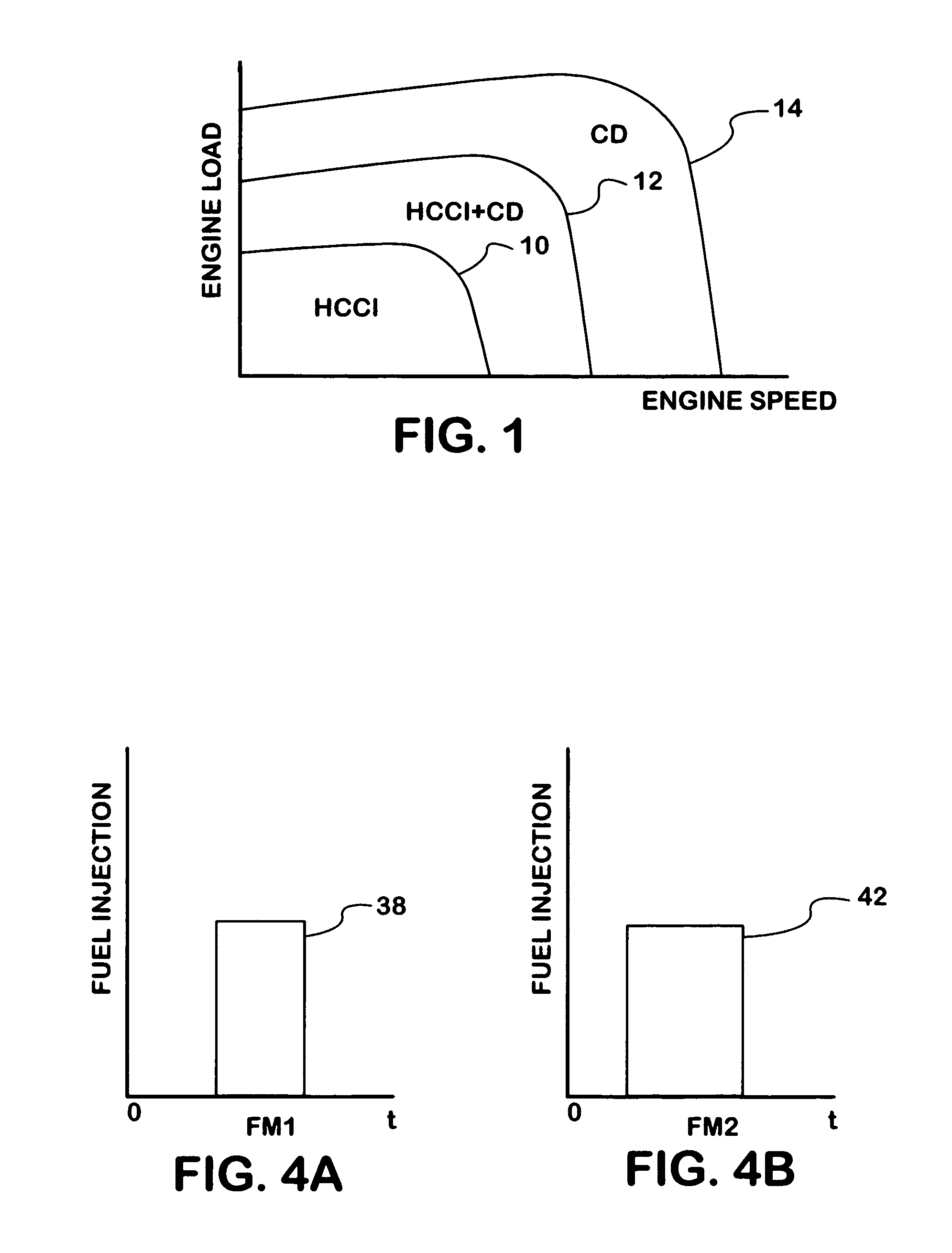
A compression ignition engine (10) has a control system (40), one or more combustion chambers (12), and fuel injectors (42, 44) for injecting fuel into the combustion chambers. The control system controls fueling using a result of the processing of engine speed and engine load to select a particular domain for engine operation (HCCI, HCCI+CD, or CD, —FIG. 1). When the processing selects HCCI, the engine is fueled to cause alternative diesel combustion (such as HCCI) in all combustion chambers. When the processing selects CD, all combustion chambers are fueled for conventional diesel combustion. When the processing selects HCCI+CD, a first group of combustion chambers are fueled for HCCI combustion and a second group for CD combustion. Each group (G1, G2) has its own EGR valve (34, 38) and turbocharger (22, 24).
Owner:INT ENGINE INTPROP CO LLC
Hcci combustion timing control with decoupled control of in-cylinder air/egr mass and oxygen concentration
ActiveUS20090178405A1Easy to controlConsiderable combustion noiseElectrical controlNon-fuel substance addition to fuelPressure riseHcci combustion
A method of controlling homogenous charge compression ignition (HCCI) combustion timing and pressure rise rate. A constant volume air pump, such as a supercharger, is equipped to provide a variable amount of fresh air to a turbocharger. The also turbocharger drives a high pressure exhaust gas recirculation (EGR) loop. The fresh air intake and the EGR ratio are independently controlled. This combination of hardware allows for good control of combustion timing by providing for EGR variations without undue effect from varying oxygen concentration. Additionally, by adjusting the EGR ratio, the pressure rise rate during combustion can be controlled to reduce combustion noise.
Owner:SOUTHWEST RES INST
Double-fuel homogeneous compression ignition/quasi-homogeneous compression compound combustion system
InactiveCN1580531AAchieve emissionsRealize sequential spontaneous combustionElectrical controlMachines/enginesCombustion systemHcci combustion
A double fuel homogeneous compression ignition / quasi-homogeneous compression ignition combustion system is composed of a diesel tank, a gas tank, a high pressure common track spray device, a gas channel spray device, cooled waste gas recycle device and an electronic control unit, among which, the diesel tank and the gas tank are connected with the engine via the high pressure spray device and gas recycle device is connected with the inlet and discharge tubes of the engine, the input of the engie work state output by the engine and the output is connected with the common track spray device, gas channel device and the cooled waste gas recycle device.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV
Methodology to compensate the effect of humidity and altitude on hcci combustion
InactiveCN102889148AElectrical controlNon-fuel substance addition to fuelHcci combustionOperation mode
A method for controlling combustion in a spark-ignition direct-injection internal combustion engine includes monitoring an engine operating mode and an ambient parameter, determining a deviation of the ambient parameter relative to a nominal ambient parameter, determining a nominal desired engine operation parameter based on engine speed and load, determining and adjusted desired engine operation parameter based on the nominal desired engine operation parameter and said deviation of the ambient parameter, and controlling the engine based on the engine operating mode and one of the nominal desired engine operation parameter and adjusted desired engine operation parameter.
Owner:GM GLOBAL TECH OPERATIONS LLC
Strategy for fueling a diesel engine by selective use of fueling maps to provide HCCI, HCCI+CD, and CD combustion modes
InactiveUS20050284441A1Easy to useReducing generation of undesired constituentElectrical controlInternal combustion piston enginesHcci combustionControl system
A compression ignition engine (20) has a control system (26) for processing data, one or more combustion chambers (22), and fuel injectors (24) for injecting fuel into the chambers. The control system controls fueling using a result of the processing of certain data, such as engine speed and engine load, to select one of three fueling modes (HCCI, HCCI+CD, CD) for operating the engine. When the result of the processing selects the HCCI mode, the engine is fueled to cause homogeneous-charge compression-ignition (HCCI) combustion in all combustion chambers. When the result of the processing selects the HCCI+CD mode, the engine is fueled to cause HCCI combustion in some chambers and CD (conventional diesel) combustion in the remaining chambers. When the result of the processing selects the CD mode, the engine is fueled to cause CD combustion in all chambers.
Owner:INT ENGINE INTPROP CO LLC
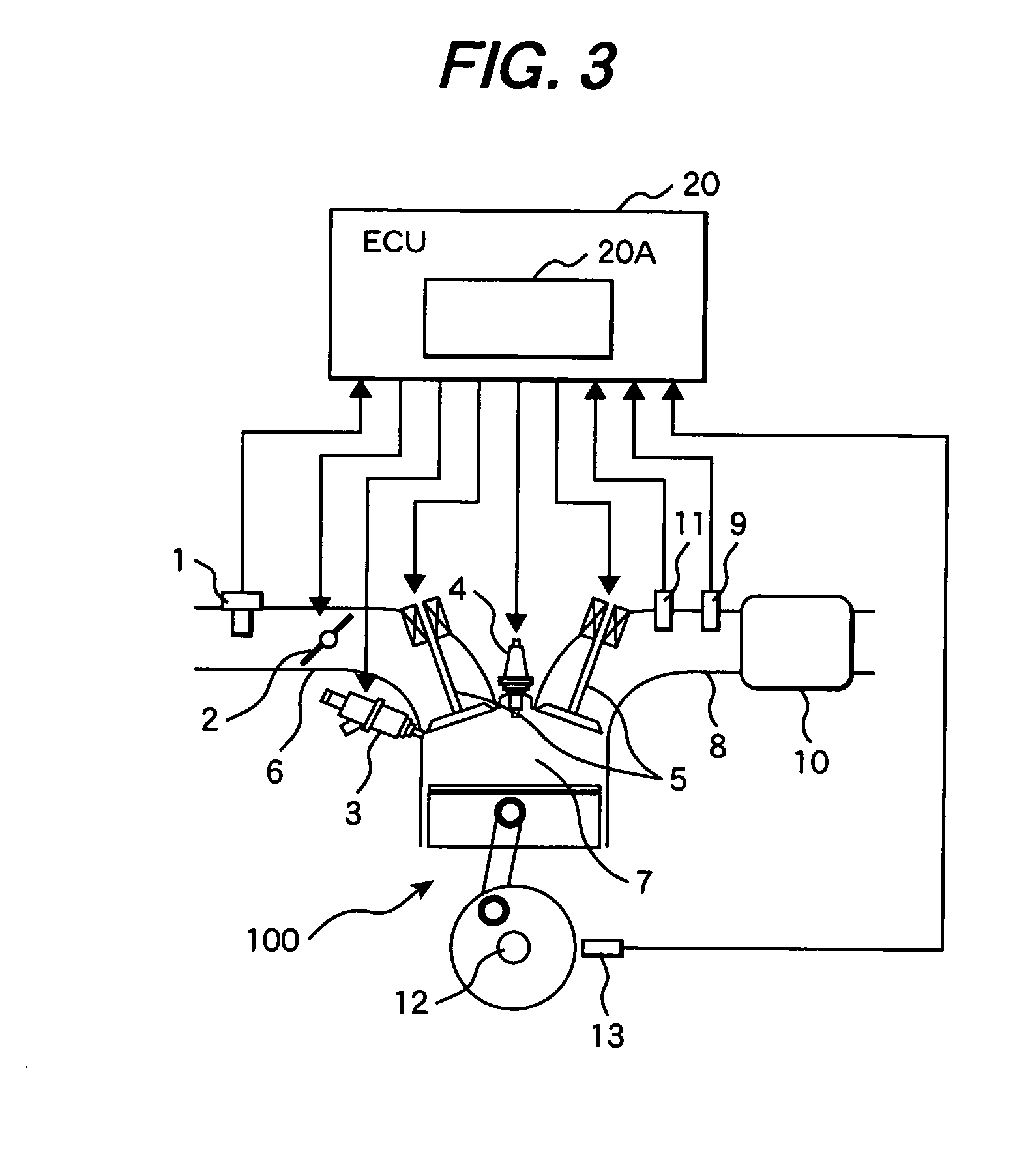
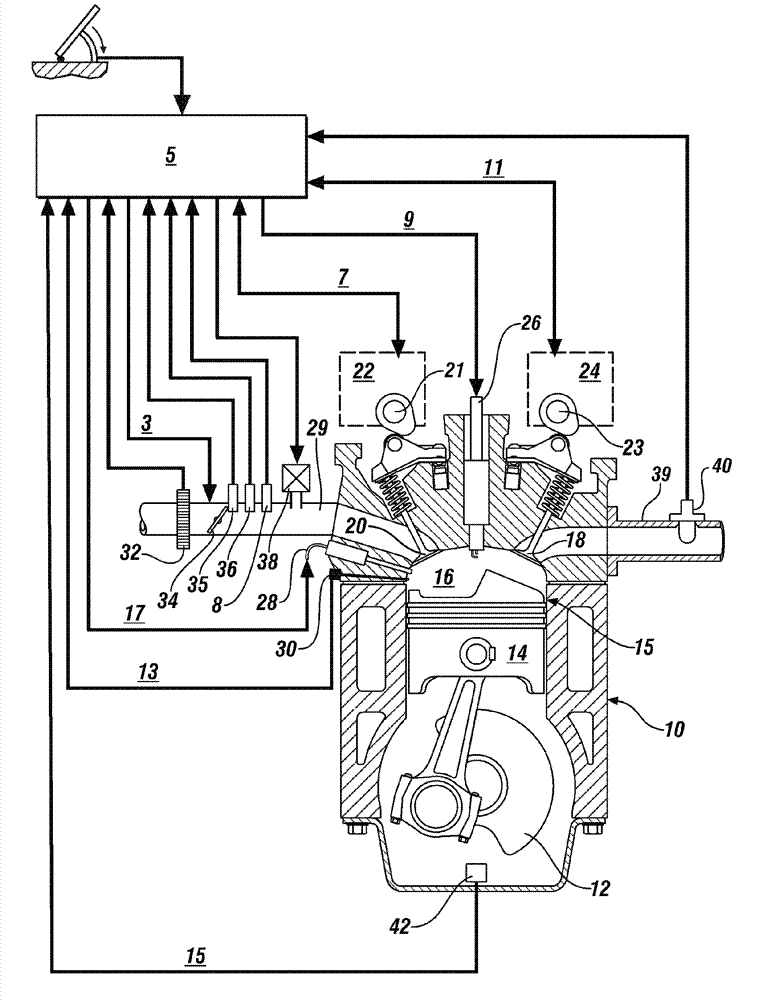
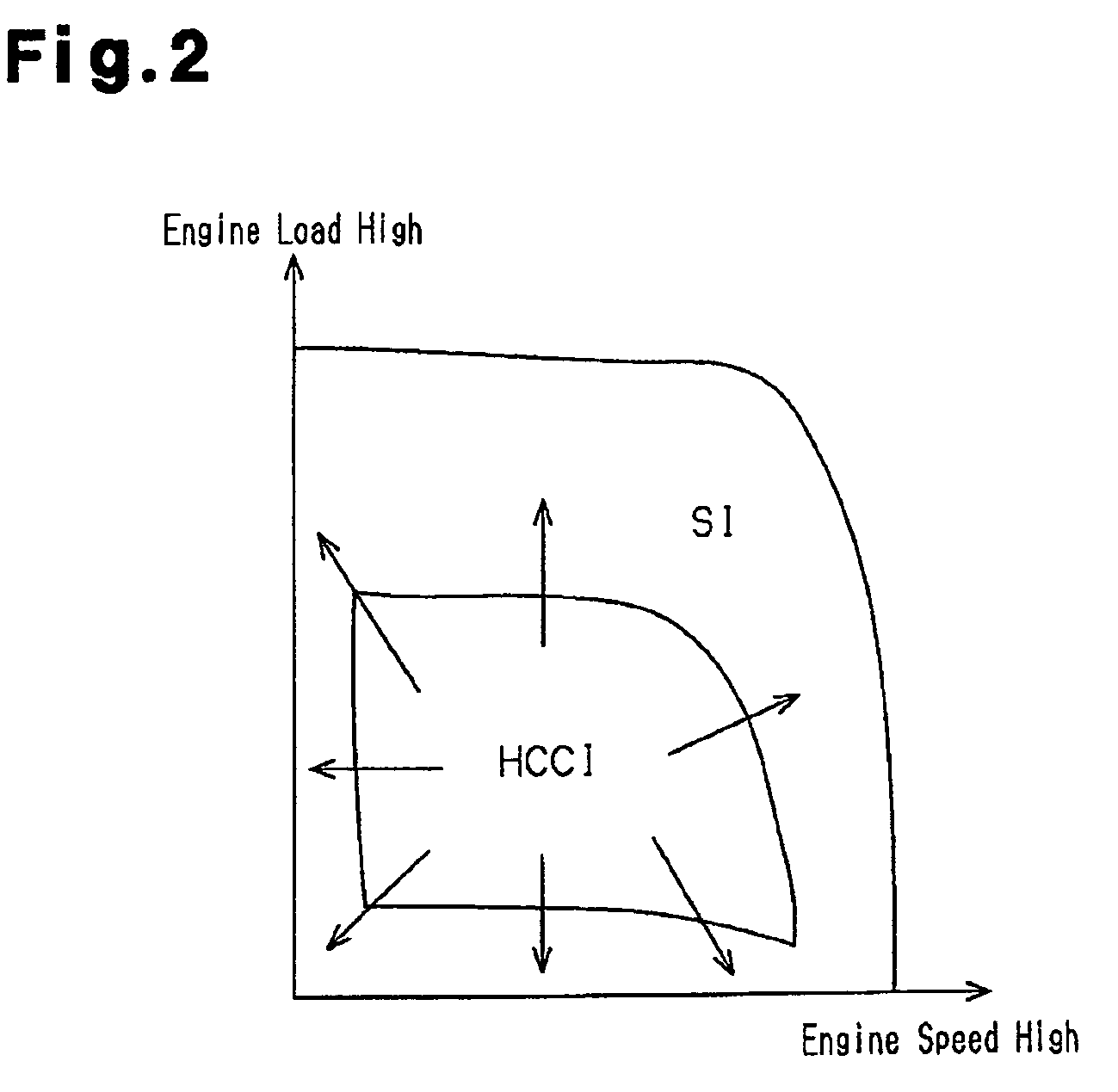
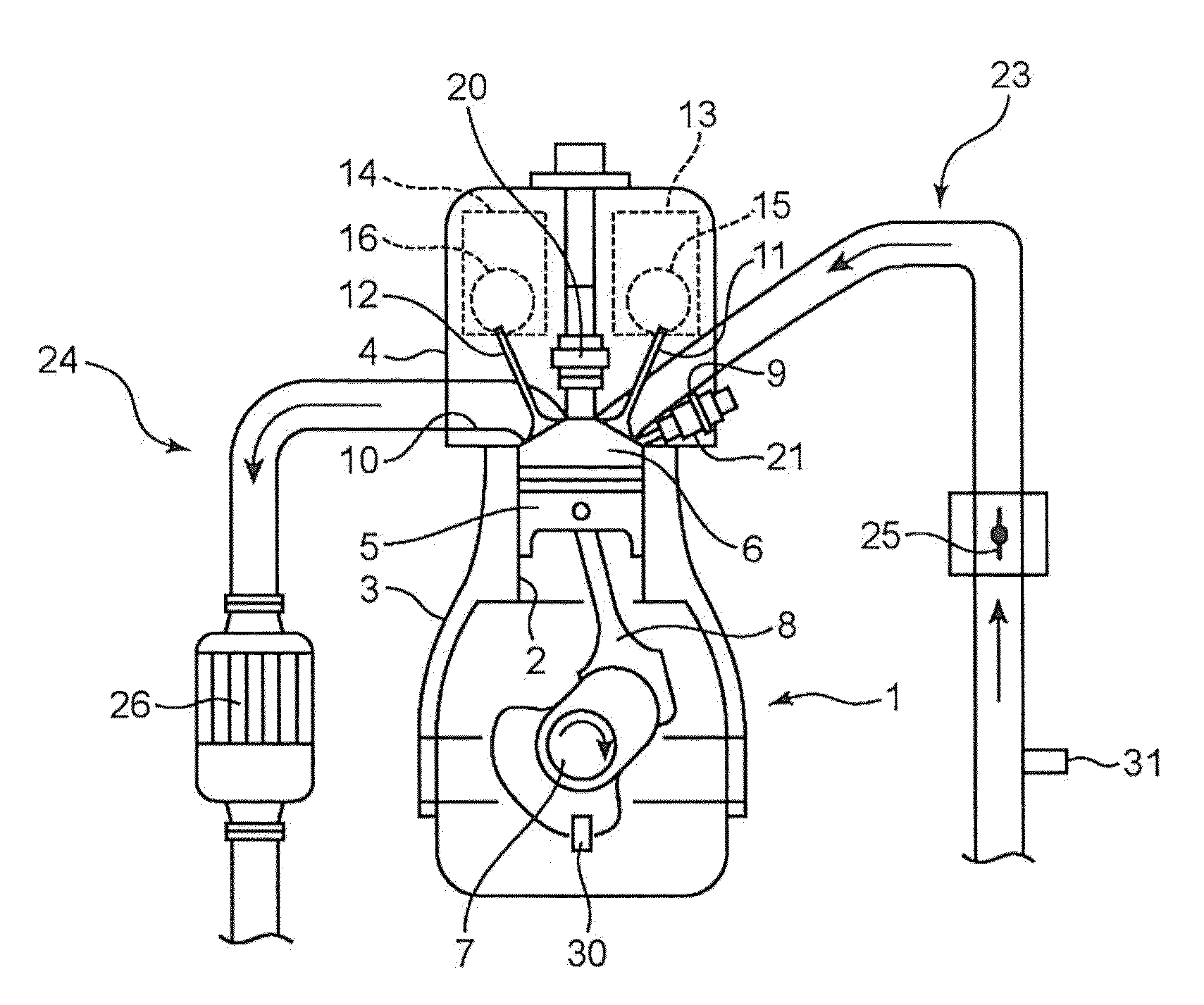
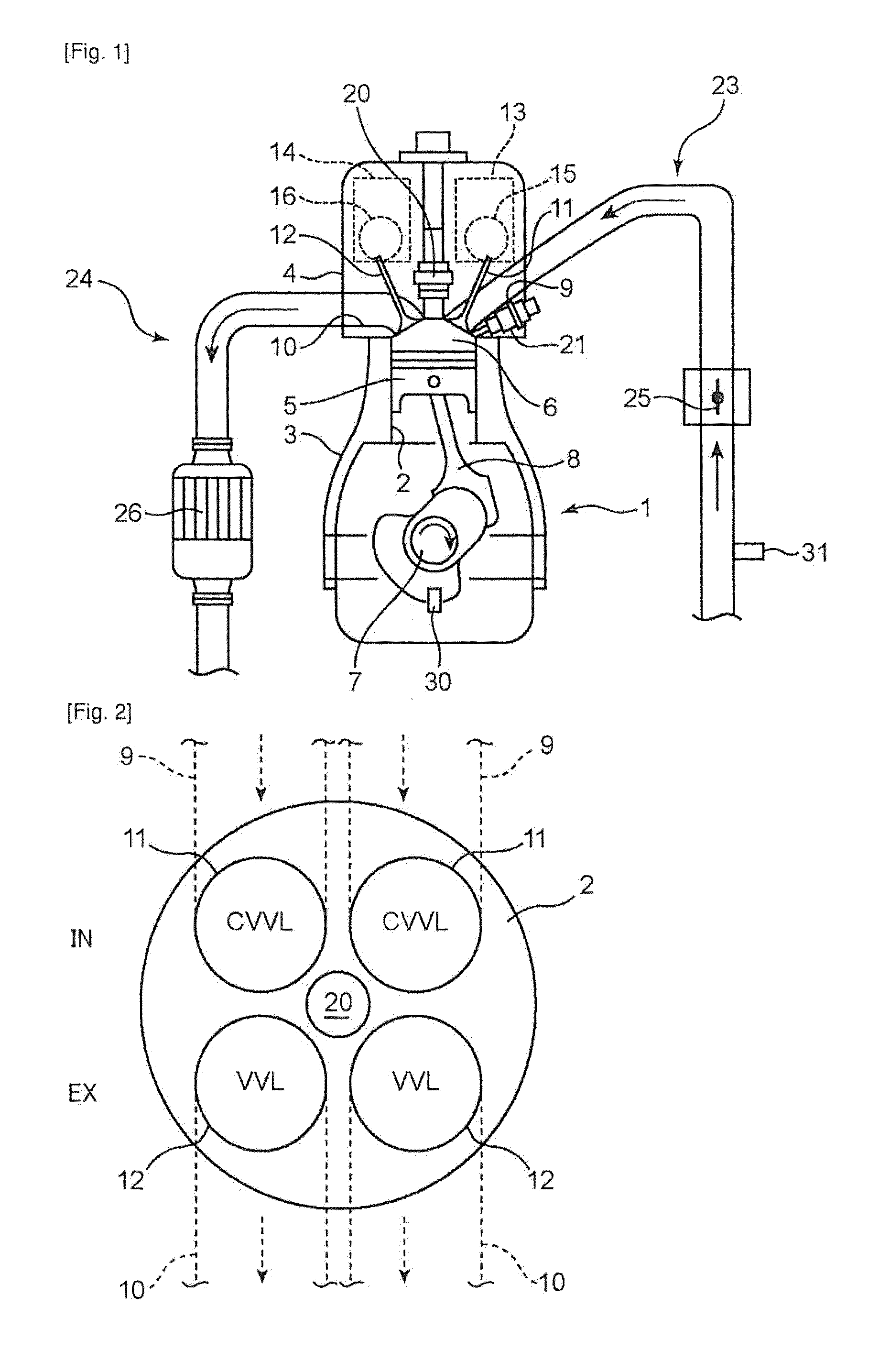
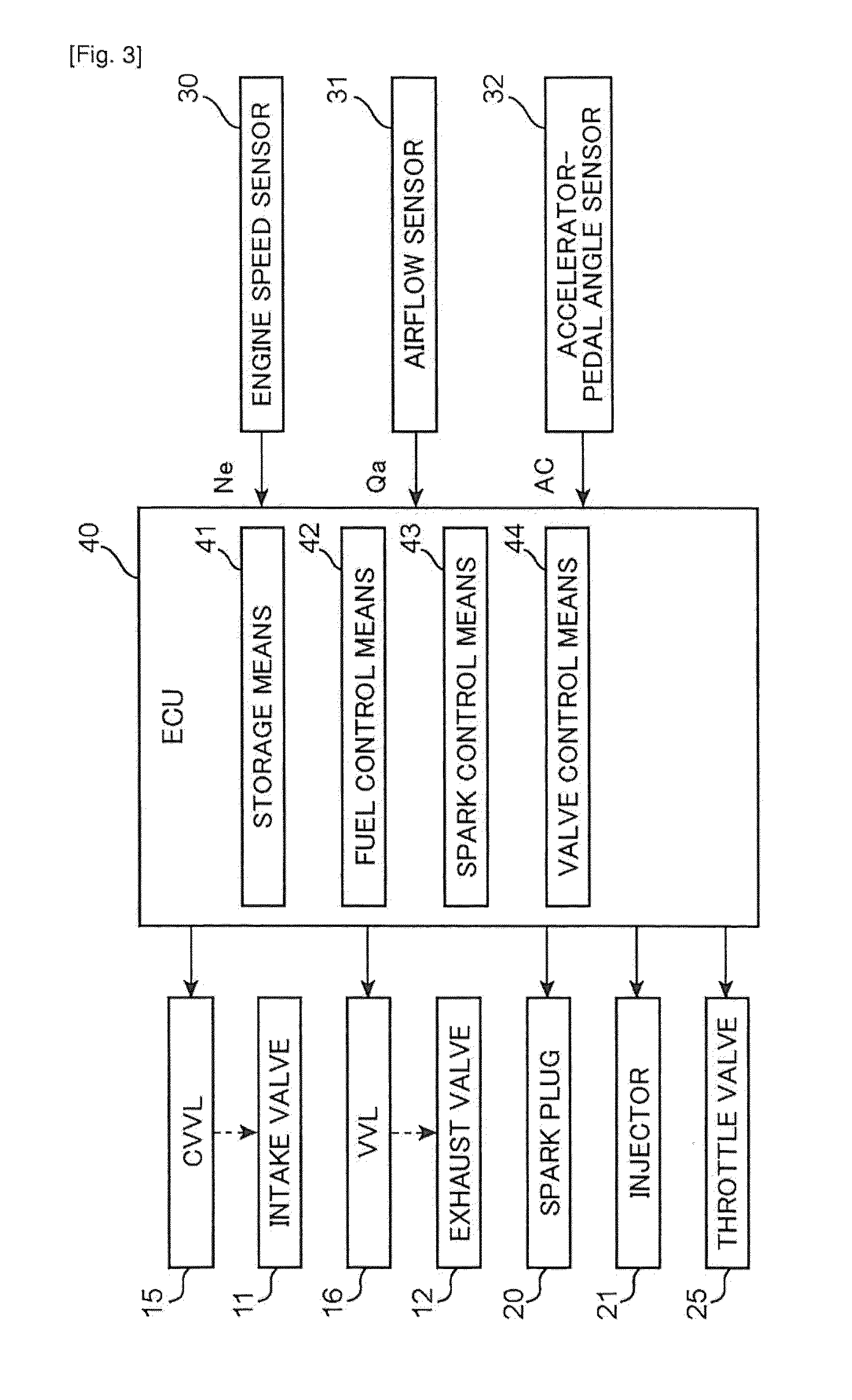
Homogenous charge compression ignition engine and controlling method of the engine
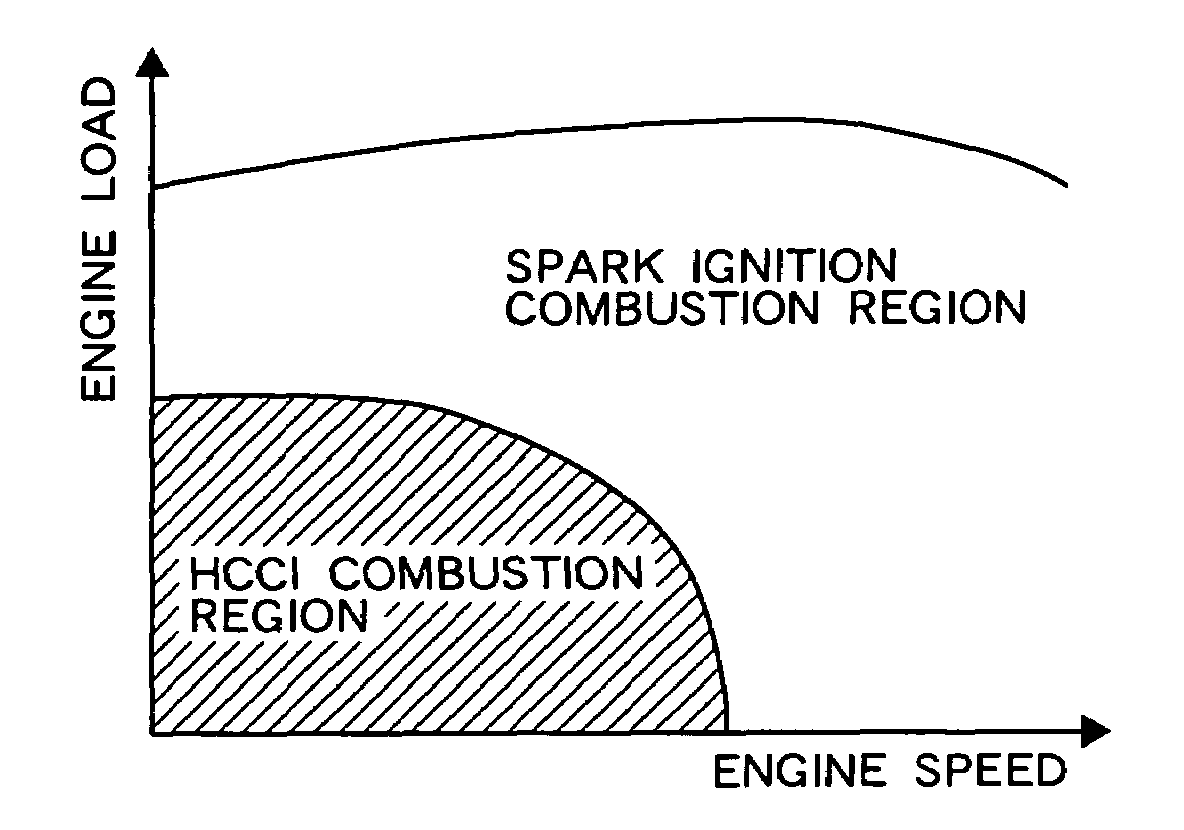
An ECU switches a combustion mode of an HCCI engine from HCCI combustion to spark ignition combustion. The ECU executes the following operations a) and b) before switching an intake lift amount from a first intake lift amount to a second intake lift amount:a): switching an exhaust lift amount from a first exhaust lift amount to a second exhaust lift amount while ensuring an internal EGR amount, andb): delaying a closing timing of an exhaust valve so as to reduce the internal EGR amount after switching the exhaust lift amount from the first exhaust lift amount to the second exhaust lift amount.
Owner:TOYOTA IND CORP
Method of controlling charge compression Ignition of direct spray type gasoline engine homogeneous
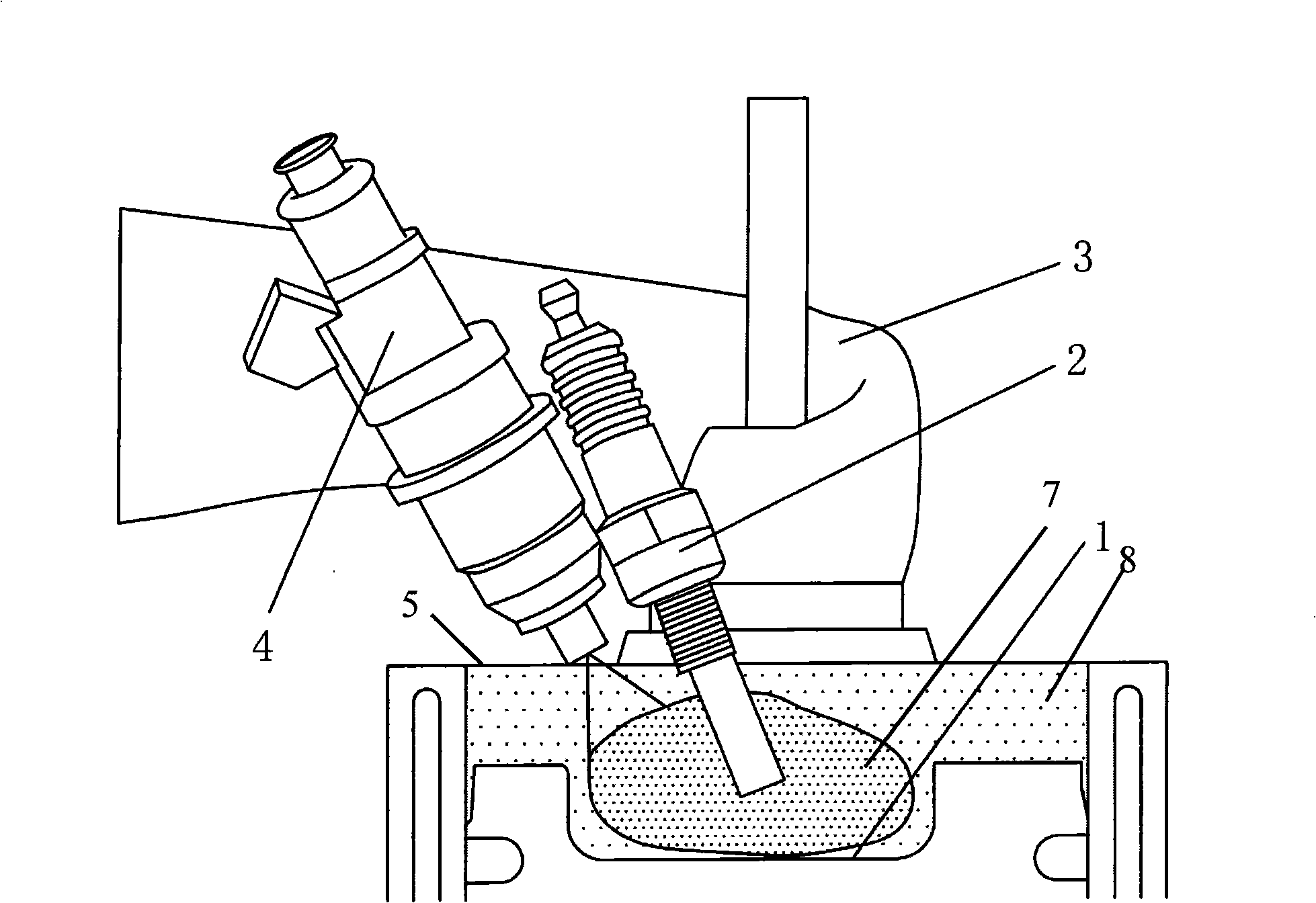
InactiveCN1603592AImprove reliabilityExpand the range of combustion operating conditionsElectrical controlInternal combustion piston enginesSpontaneous combustionHcci combustion
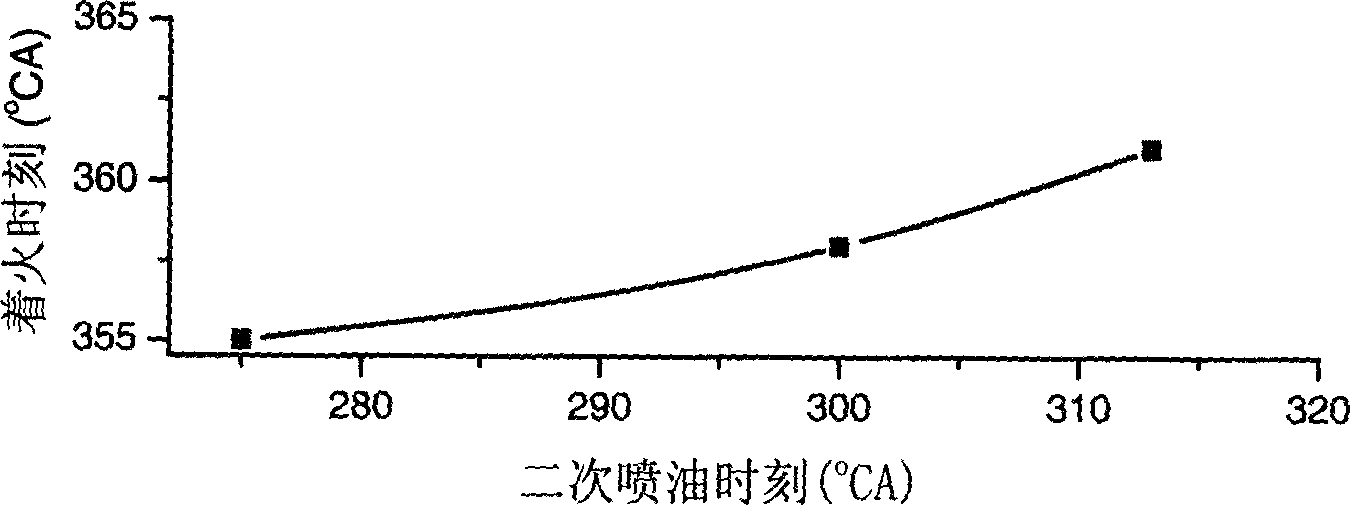
With two time sprays controls straight spurts executes the gasoline engine to reduce fire burning the method, this method through carries on in the cylinder two time fuel injection, forms the thick thin different lamination mixture air, first causes rich mixture kcarburettork the spontaneous combustion fire. Adjusts the time and the proportion which two time blows may control the lamination carburetion the time and the density, thus may adjust and control the HCCI burning the fire time and the reduction catches fire; At the same time, because has formed district order burning, thus may control, accurate. Indicated on the real engine experiment that, this method may enhance gasoline engine HCCI the burning stability, example NOx discharges is 0~230ppm, the comparatively same compound under gasoline engine reduces NOx to discharge above 95%, the non- carbon smoke discharges, the fuel oil consumption rate achieves the diesel engine level.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
Dual combustion mode engine
InactiveUS7255095B1Efficient HCCI combustionTemperature controlPower operated startersElectrical controlHcci combustionCombustion
In an engine in which a first portion of engine cylinders operate in HCCI combustion mode only and a second portion of engine cylinders operate in SI combustion mode only, two EGR ducts and valves are provided: a first EGR duct adapted to provide flow from an exhaust of HCCI engine cylinders to an intake of HCCI cylinders; a first EGR valve disposed in the first EGR duct; a second EGR duct adapted to provide flow from an exhaust of SI cylinders to an intake of HCCI cylinders via a first EGR valve; and a second EGR valve disposed in the second EGR duct. By adjusting the EGR valves, the intake temperature to HCCI cylinders is controlled. During cold start, the second EGR valve is opened to pull SI exhaust through HCCI cylinders for the purpose of preheating HCCI cylinders.
Owner:FORD GLOBAL TECH LLC
Spark timing and control during transitions between spark ignited combustion and homogenous charge compression ignition
InactiveUS7975668B2Electrical controlInternal combustion piston enginesHcci combustionControl system
A control system for an engine comprises an air per cylinder (APC) generating module that generates measured and desired APC values. A combustion transition module selectively transitions the engine from spark ignition (SI) combustion to homogeneous charge compression ignition (HCCI) combustion and from HCCI combustion to SI combustion. A spark control module selectively retards spark during the transitions based on a ratio of the measured APC value and the desired APC value. Alternately, spark retard can be based on measured and desired engine torque representing values (ETRVs).
Owner:GM GLOBAL TECH OPERATIONS LLC
Engine control system
ActiveUS20130019828A1Wide load rangeAddressing Insufficient ControlValve arrangementsElectrical controlHcci combustionCombustion
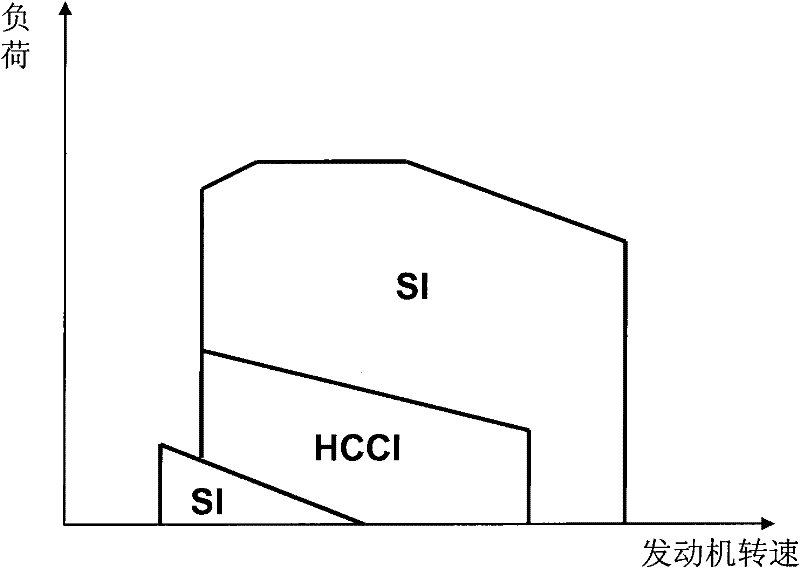
Disclosed is an engine control system which is designed to allow homogeneous-charge compression ignition combustion to be performed in an HCCI region (R) defined as an engine operating region including at least a partial-load range of an engine. In a low load zone (R1) of the HCCI region (R), a lift amount of an intake valve (11) is set to a first predetermined value, and an exhaust valve (12) is allowed to start being opened during an intake stroke at a given timing later than an opening timing of the intake valve (11). Further, in the medium load zone of the HCCI region, the lift amount of the intake valve (11) is gradually increased up to a second predetermined value greater than the first predetermined value, along with an increase in an engine load. The engine control system is capable of adequately controlling an amount of burned gas to be introduced into a cylinder, depending on the engine load to allow the HCCI combustion to be adequately performed in a wider engine load range.
Owner:MAZDA MOTOR CORP
Device and method for expanding compression-ignition type gasoline engine load range
InactiveCN101338693AReduced pressure rise rateExtended high load rangeElectrical controlInternal combustion piston enginesHcci combustionCombustion chamber
The present invention relates to a device expanding the load range of a compression ignition gasoline engine and a method thereof. The device comprises a cylinder which is respectively connected with an air inlet channel and an exhaust channel by a vale, a piston which moves up and down in the cylinder and is provided with a drop pit at the top, an electric heater plug with a heating end extended into the drop pit when the piston runs to an upper stop point, and an oil atomizer with a nozzle opposite to the drop pit when the piston runs to the upper stop point. The method has the steps as follows: the oil atomizer sprays oil respectively during an air intake stroke and a compression stroke to form delaminated mixed gas in dense and thin areas; the electric heater plug heats the mixed gas in the cylinder to form heat delamination; the area with dense gas and high temperature in the drop pit of a combustion chamber fires firstly and ignites other areas to fire accordingly. The present invention controls the dense and the thin areas to fire successively, so as to reduce the pressure increase rate in the cylinder, ensure the reliable firing and achieve the purpose of developing HCCI combustion executable high and low charge ranges at the same time.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
Gas inlet and outlet system for homogeneous charge compression ignition (HCCI) engine, gas inlet control method and engine
ActiveCN102444507AAvoid difficultiesImprove emission performanceExhaust apparatusSilencing apparatusHcci combustionCombustion
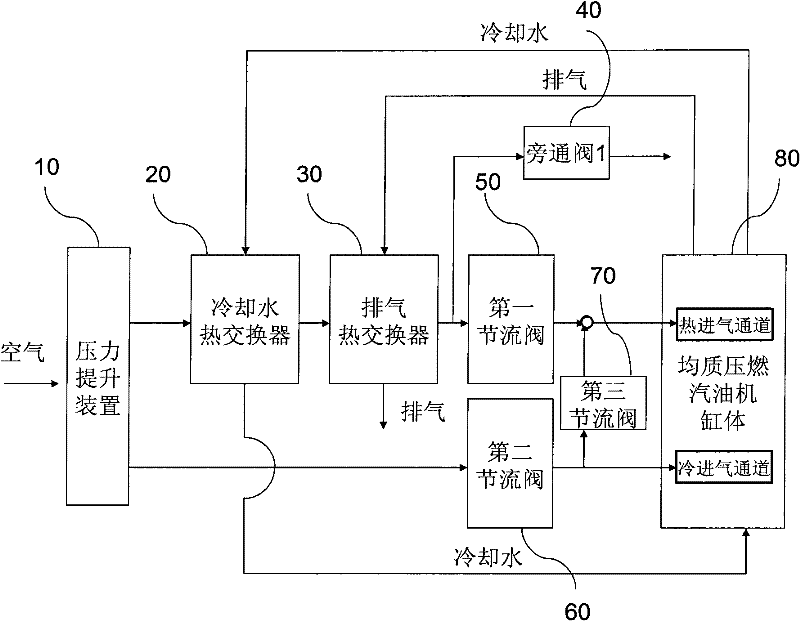
The invention provides a gas inlet and outlet system for a homogeneous charge compression ignition (HCCI) engine, a gas inlet control method and an engine, belonging to the technical field of power assemblies. The gas inlet and outlet system comprises a first gas channel and a second gas channel, wherein the first gas channel is provided with a first heat exchanger and a second heat exchanger for heating gas, and a first throttling valve; the second gas channel is provided with a second throttling valve; and the first throttling valve and the second throttling valve are adjusted and controlled to adjust the gas flow ratio of the first gas channel and the second gas channel, so that optimized working performance can be realized for the HCCI engine under the working condition of a spark ignition (SI) combustion mode, in particular the cold engine startup working condition and the working condition of a normal HCCI combustion mode respectively.
Owner:SAIC MOTOR
HCCI (homogeneous charge compression ignition) engine fire detecting and controlling method
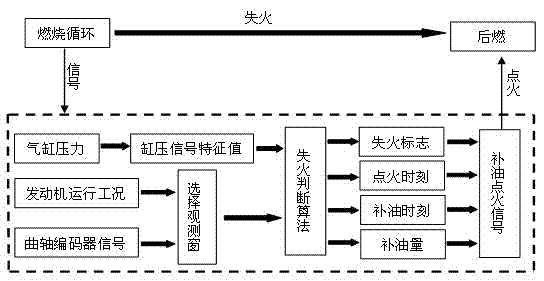
ActiveCN102817738AEliminate misfiresReduce cycle-to-cycle fluctuationsInternal-combustion engine testingElectrical controlHcci combustionTop dead center
An HCCI (homogeneous charge compression ignition) engine fire detecting and controlling method includes that a crank angle signal and a cylinder pressure signal are acquired in each working cycle of an HCCI engine, a pressure observation window with a compression top dead center is arranged, the integral value of the cylinder pressure signal in the pressure observation window is compared with a fire pressure threshold value at a finishing point of the pressure observation window, when the integral value is smaller than or equal to the fire pressure threshold value, an ECU (electronic control unit) sequentially transmits an oil recharging signal and an ignition signal to an oil injector and an ignition coil, and mixed gas in a fire cylinder is ignited in an expansion stroke. The HCCI engine fire detecting and controlling method has the advantages of simplicity, reliability, high control precision and the like, inter-circulation fluctuation of the HCCI engine can be reduced effectively, stability of combustion of a small load is improved, a running range of an HCCI combustion mode is expanded, fuel economy is improved, and HC (hydrocarbon compound) emission caused by fire is reduced.
Owner:GREAT WALL MOTOR CO LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com