Patents
Literature
5414results about "Internal-combustion engine testing" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
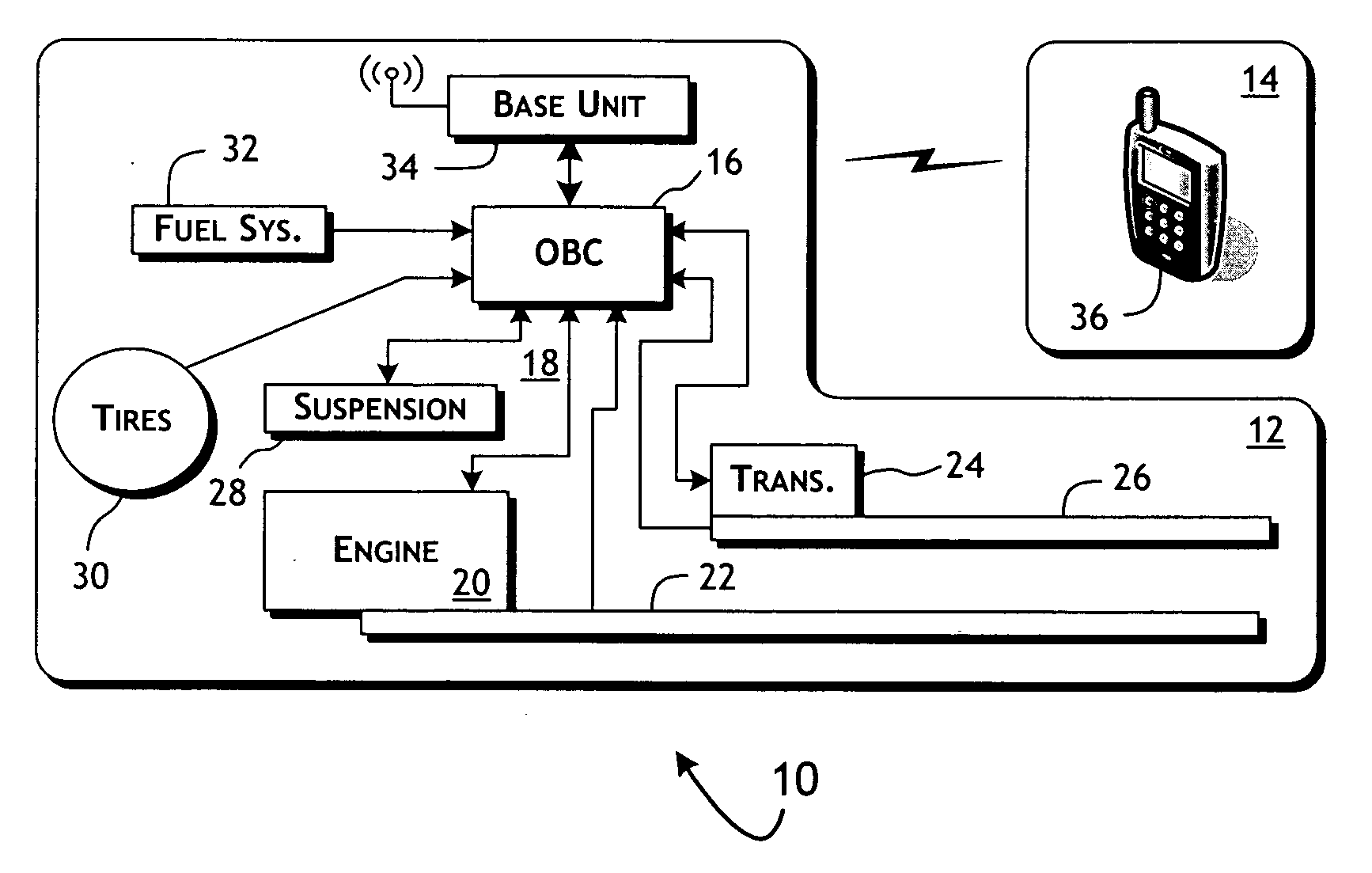
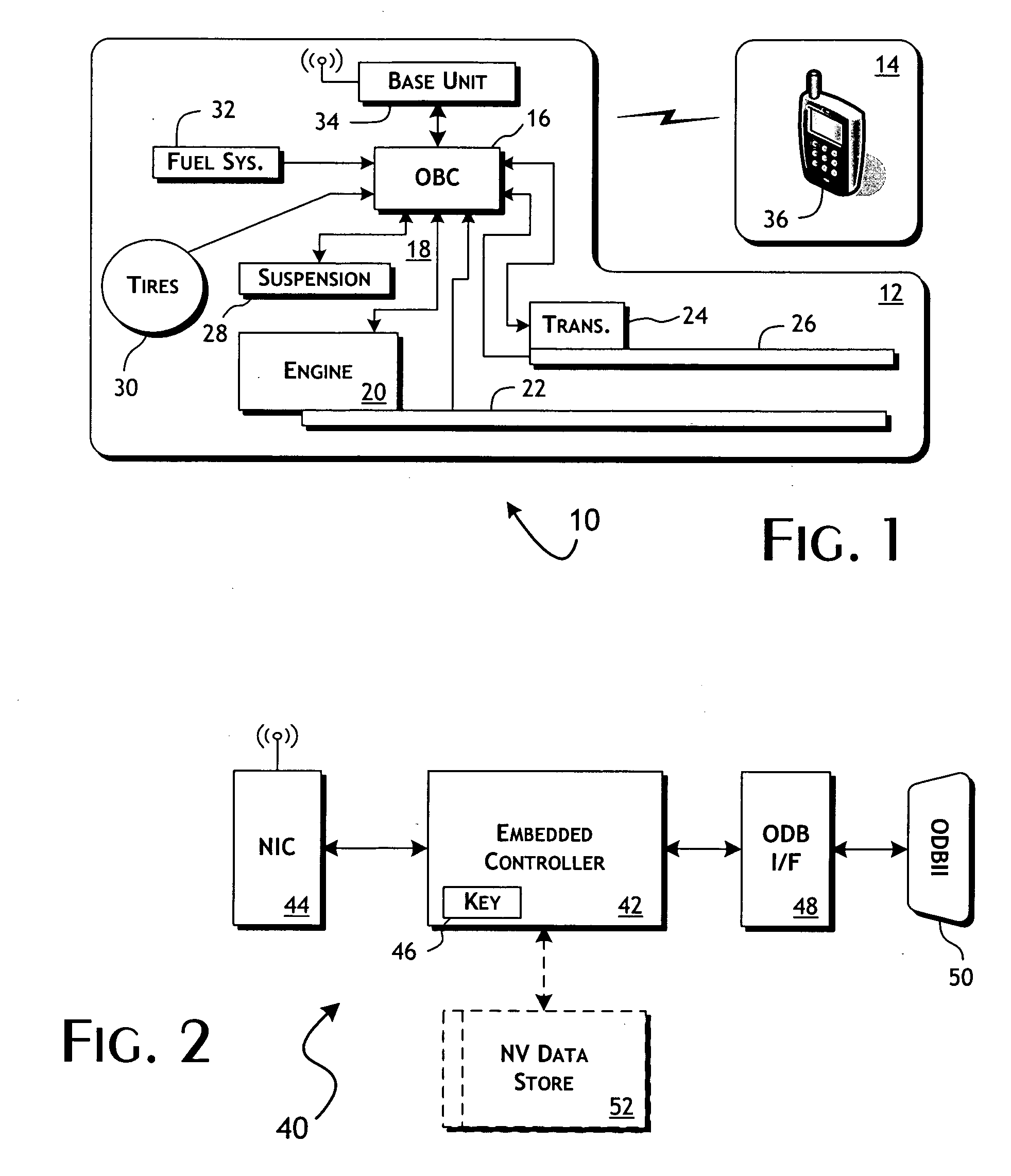
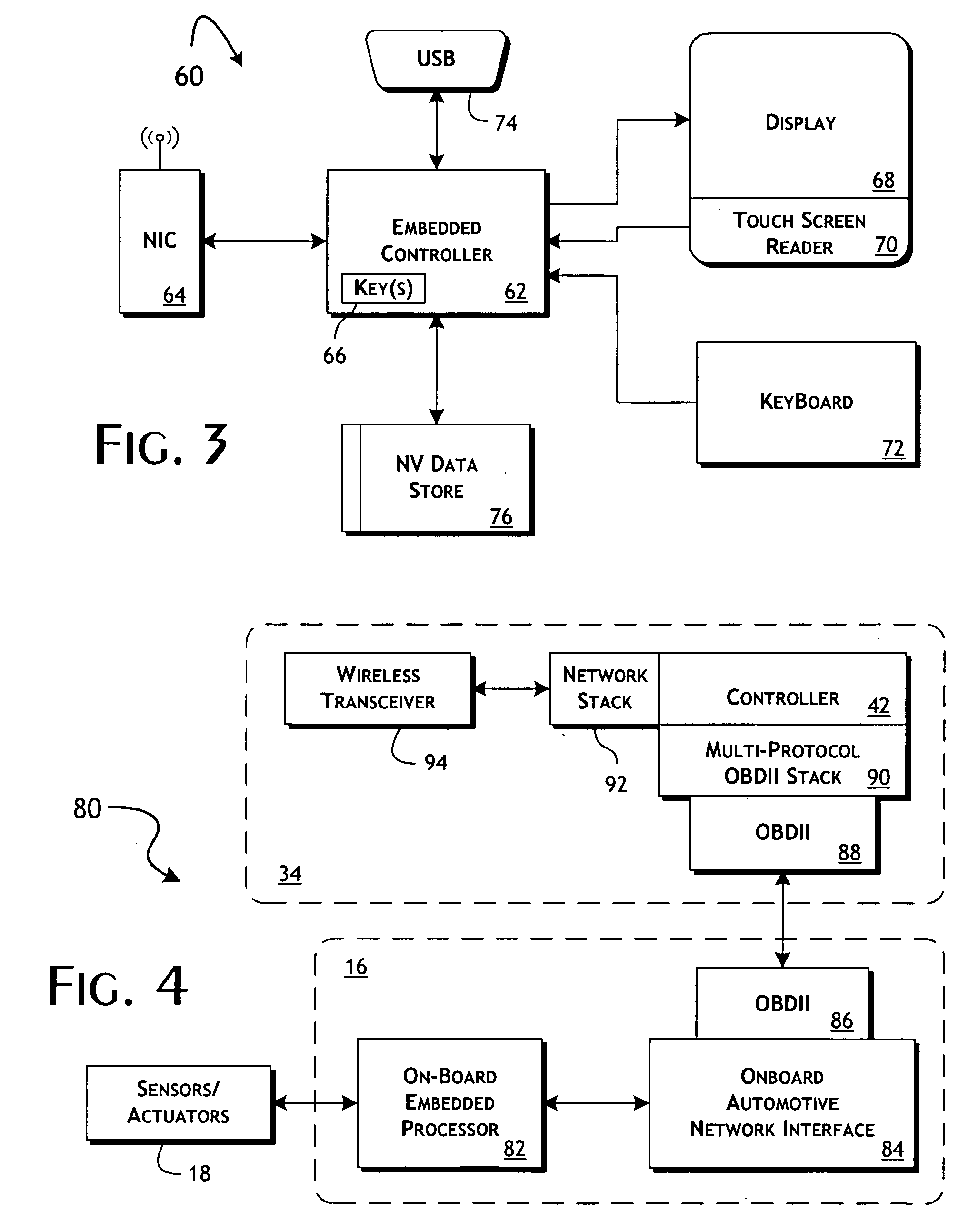
System and methods of performing real-time on-board automotive telemetry analysis and reporting
InactiveUS20060229777A1Readily and safely performedImprove abilitiesVehicle testingInternal-combustion engine testingDiagnostic testControl system
Active diagnosis of current operating and potential fault conditions in the operation of the vehicle is implemented using a diagnostic controller interoperating with an on-board vehicle control system as installed within a vehicle. The diagnostic controller supports autonomous execution of diagnostic tests initiated dependent on the operational state of the vehicle. The control system includes a diagnostics control manager that autonomously selects test routines for execution at defined operational states, including in-service operational states, a monitor, responsive to sensor data retrieved in real-time from the on-board vehicle control system, operative to detect a current instance of the in-service operational state of the vehicle, and a diagnostic test scheduler operative to initiate execution of the diagnostic test routine upon detection of the current instance of the in-service operational state of the vehicle.
Owner:HUDSON MICHAEL D +1
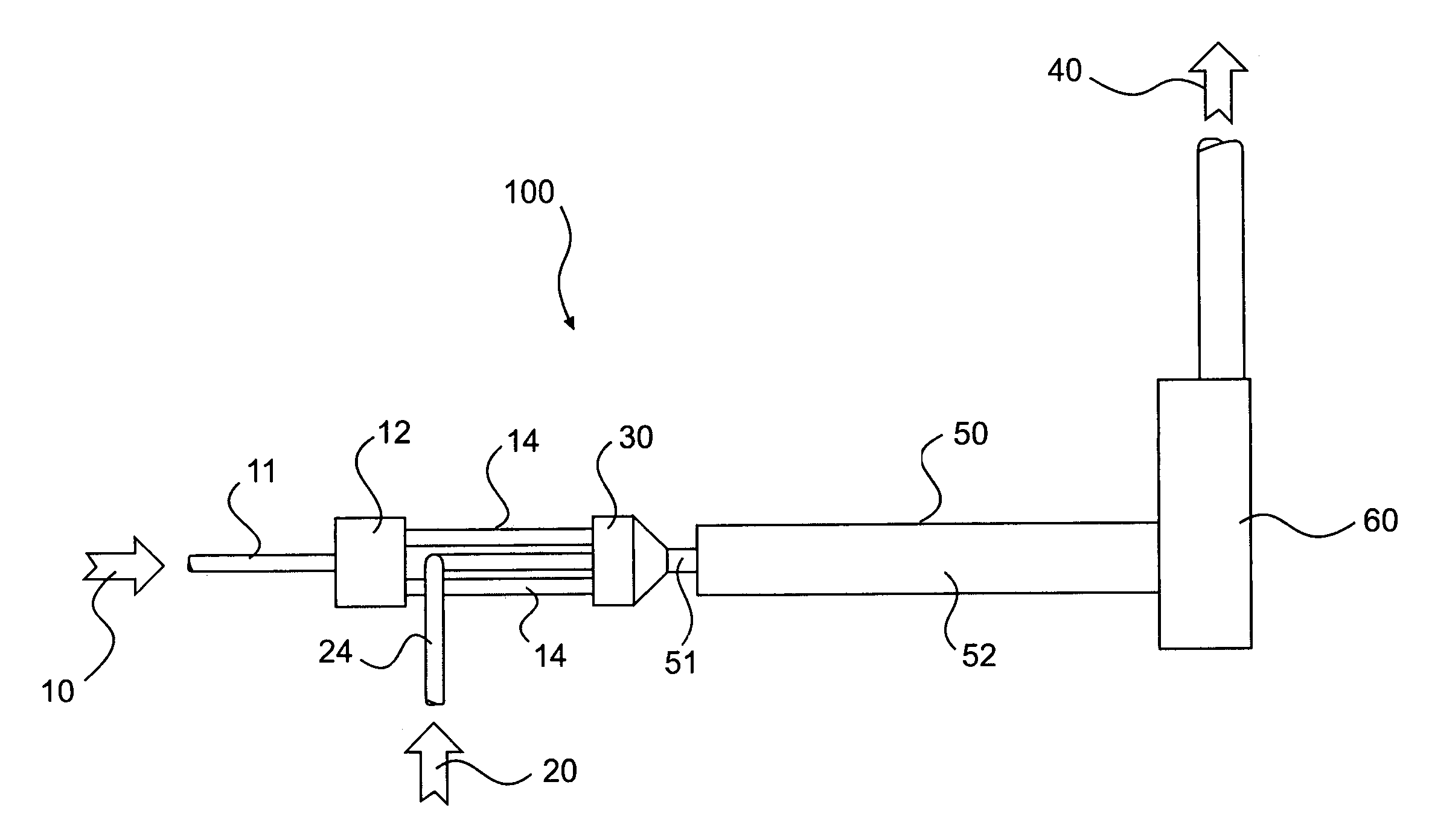
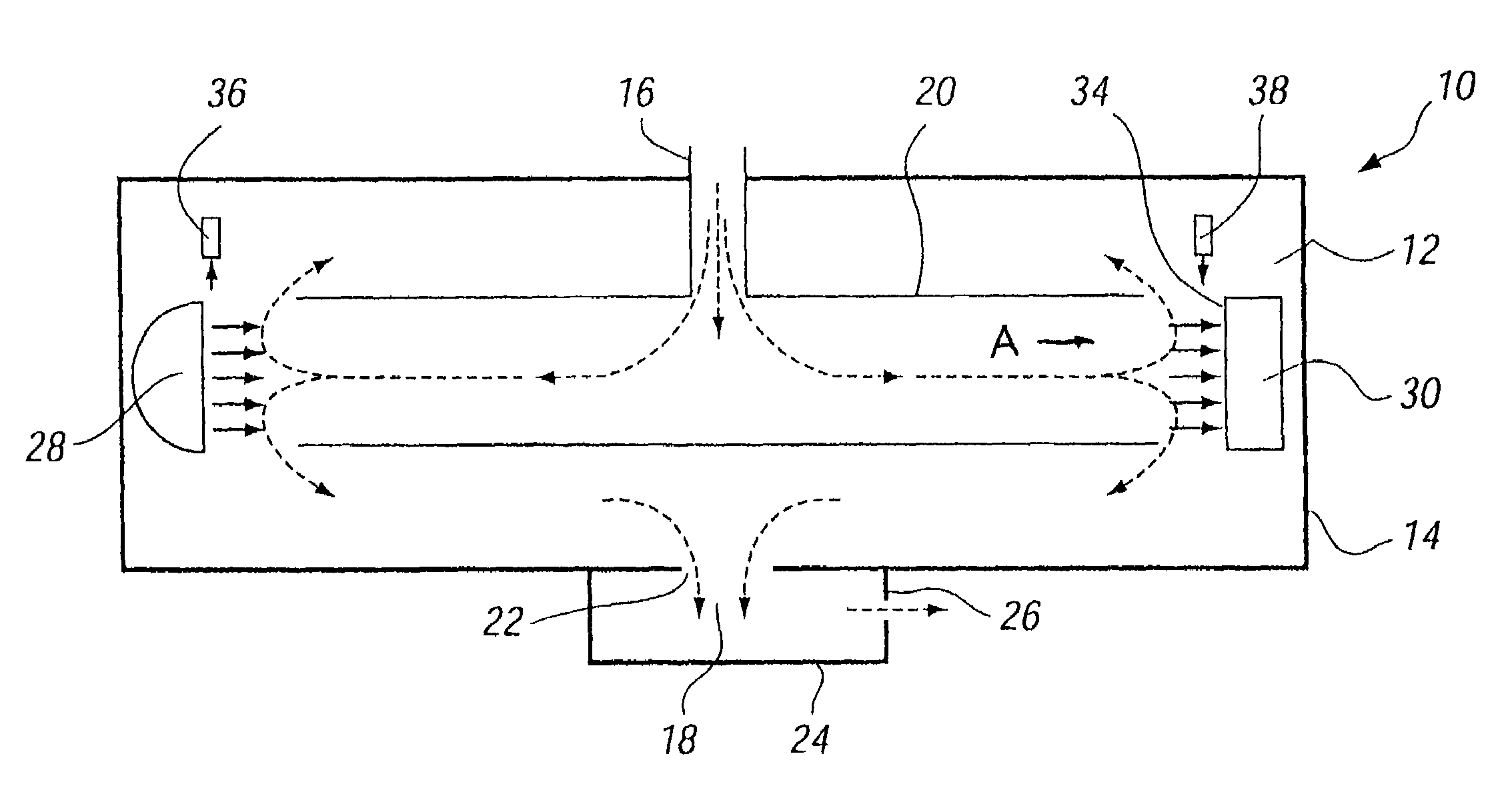
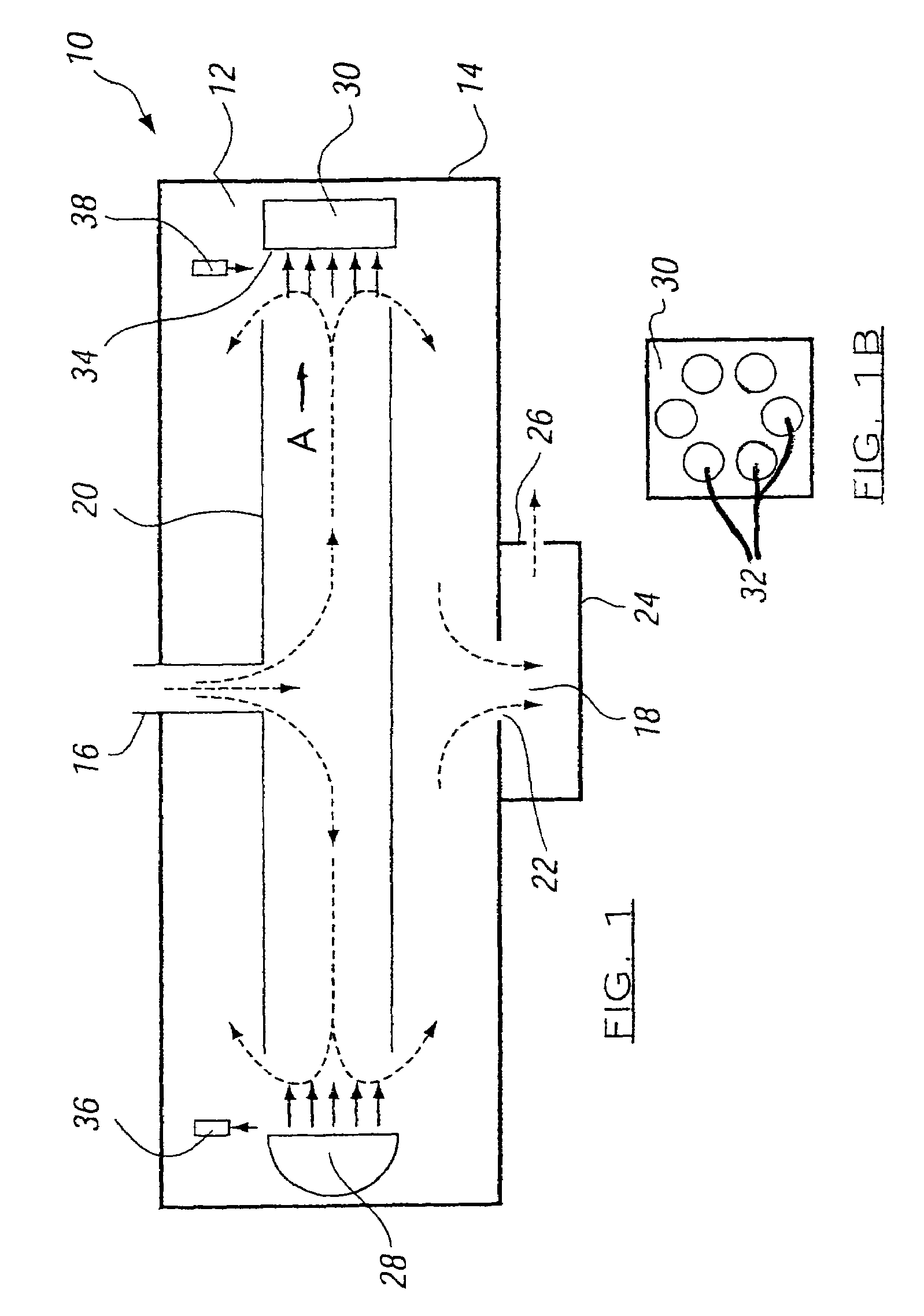
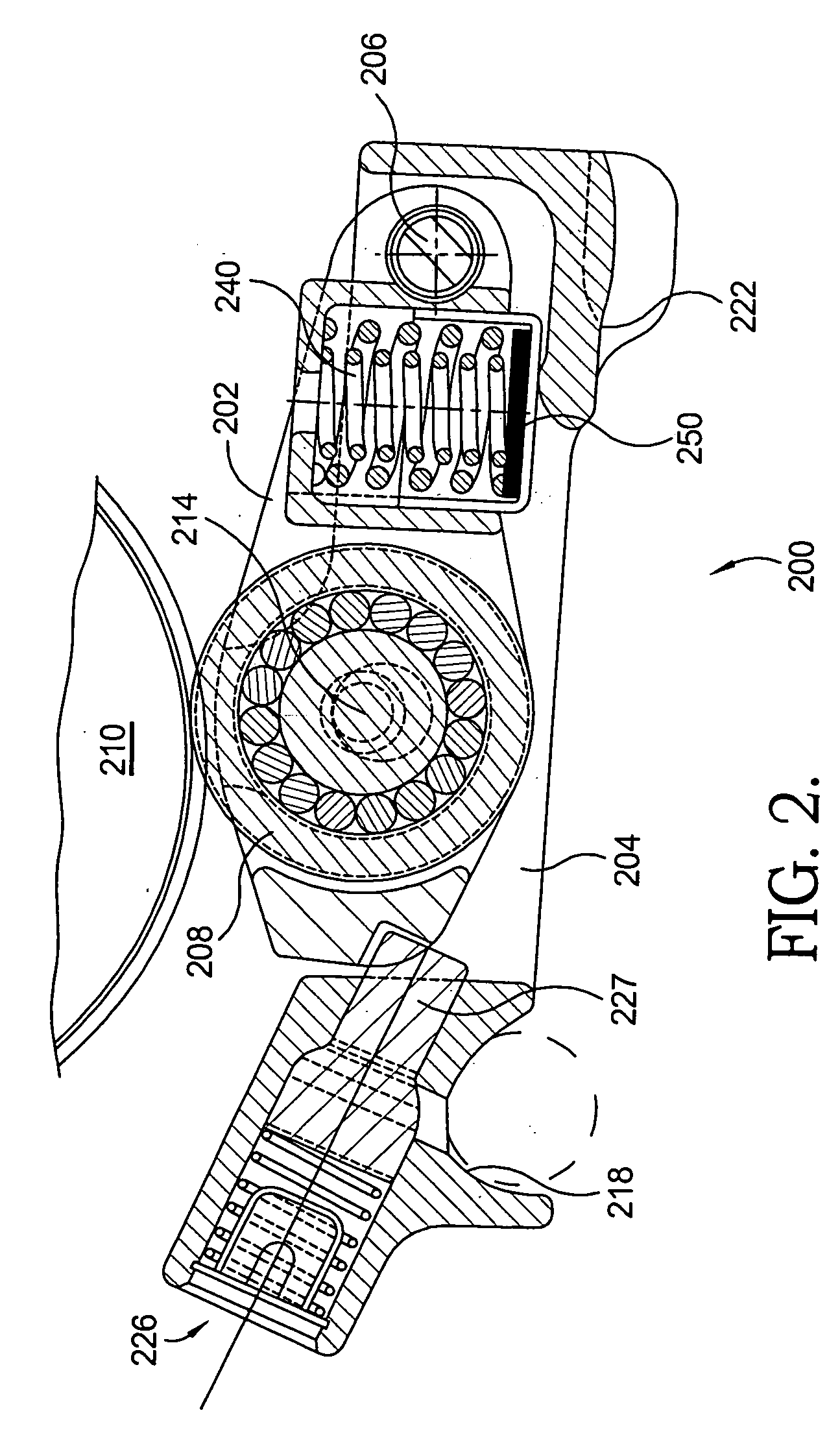
Method and apparatus for mixing gases
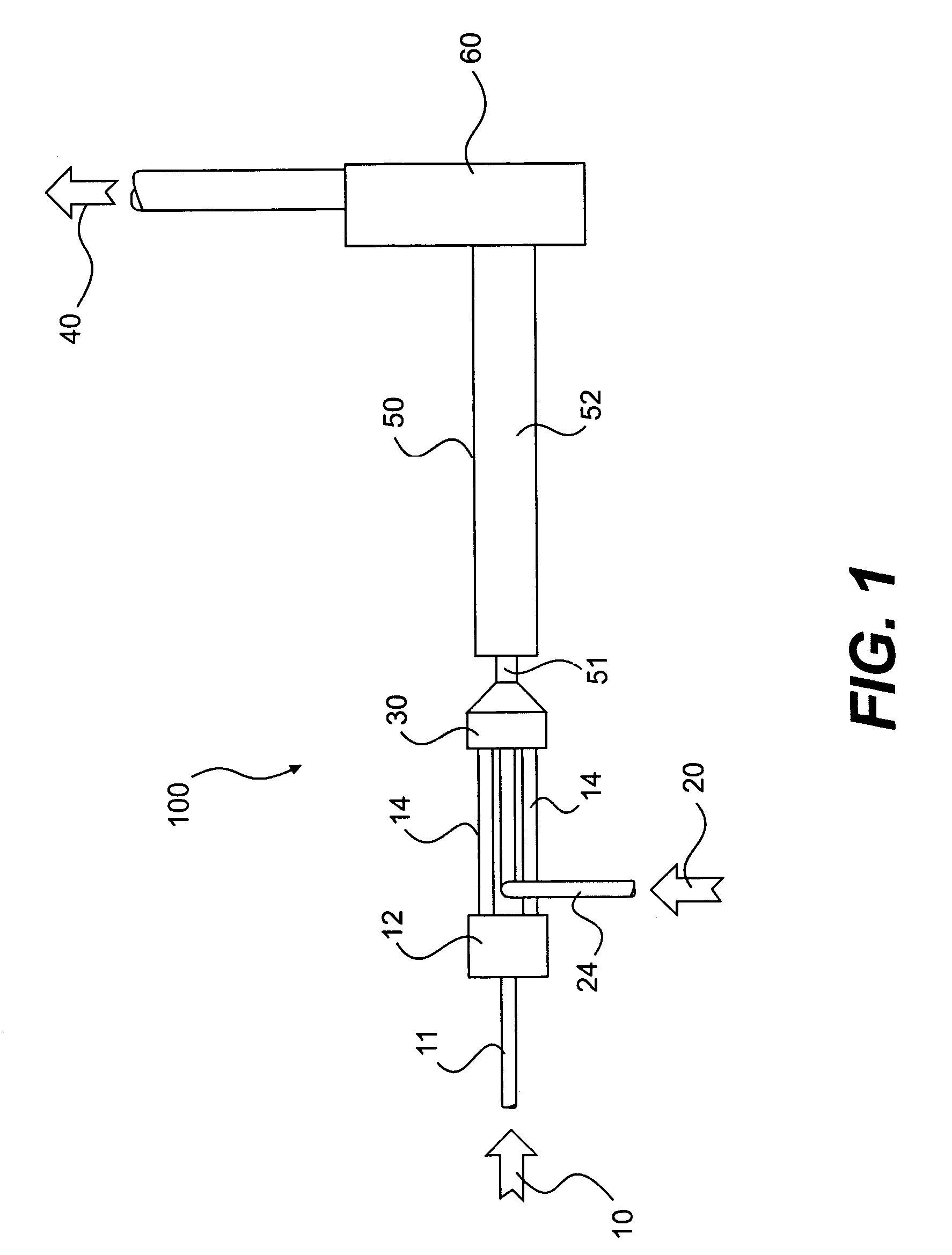
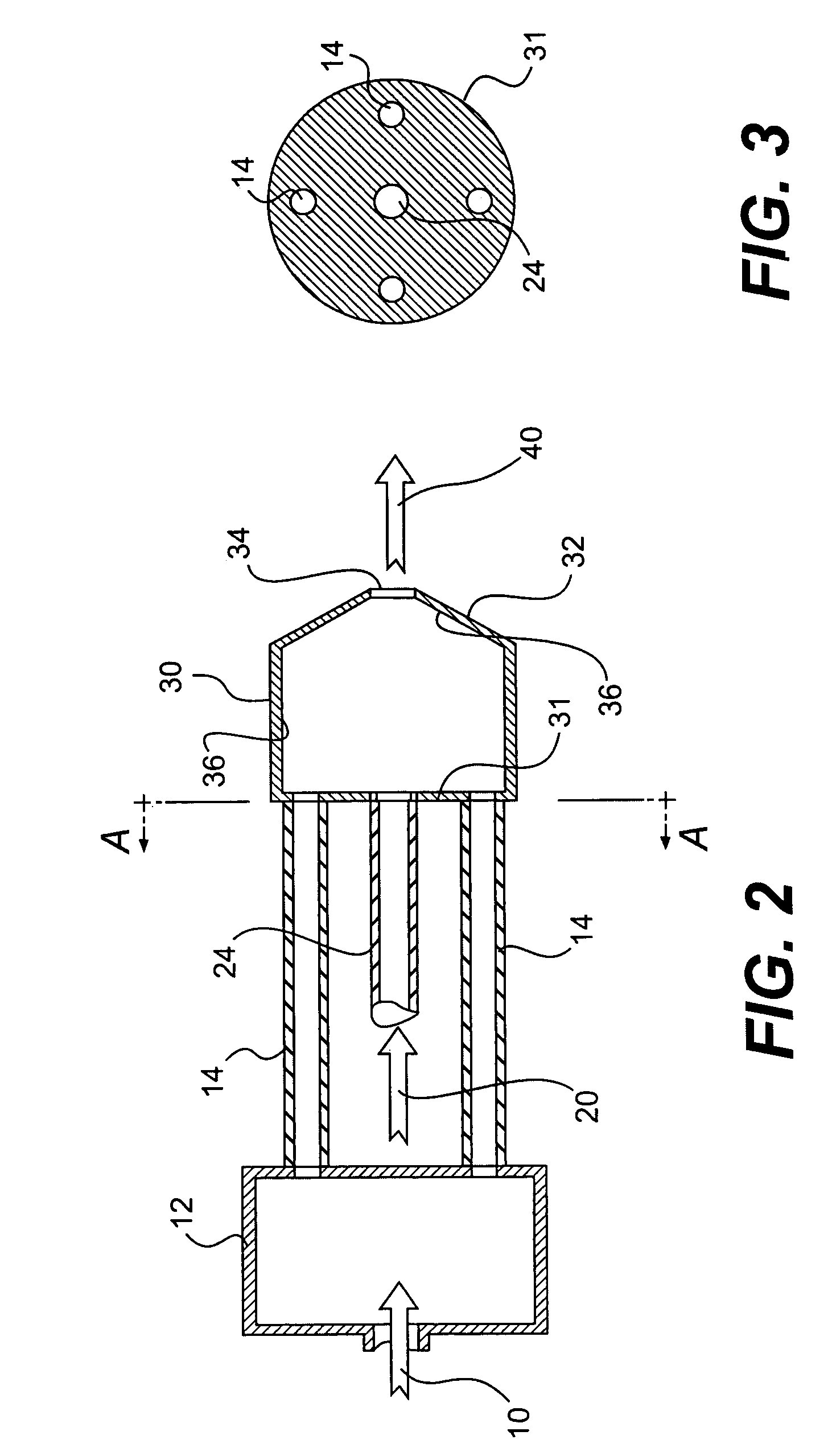
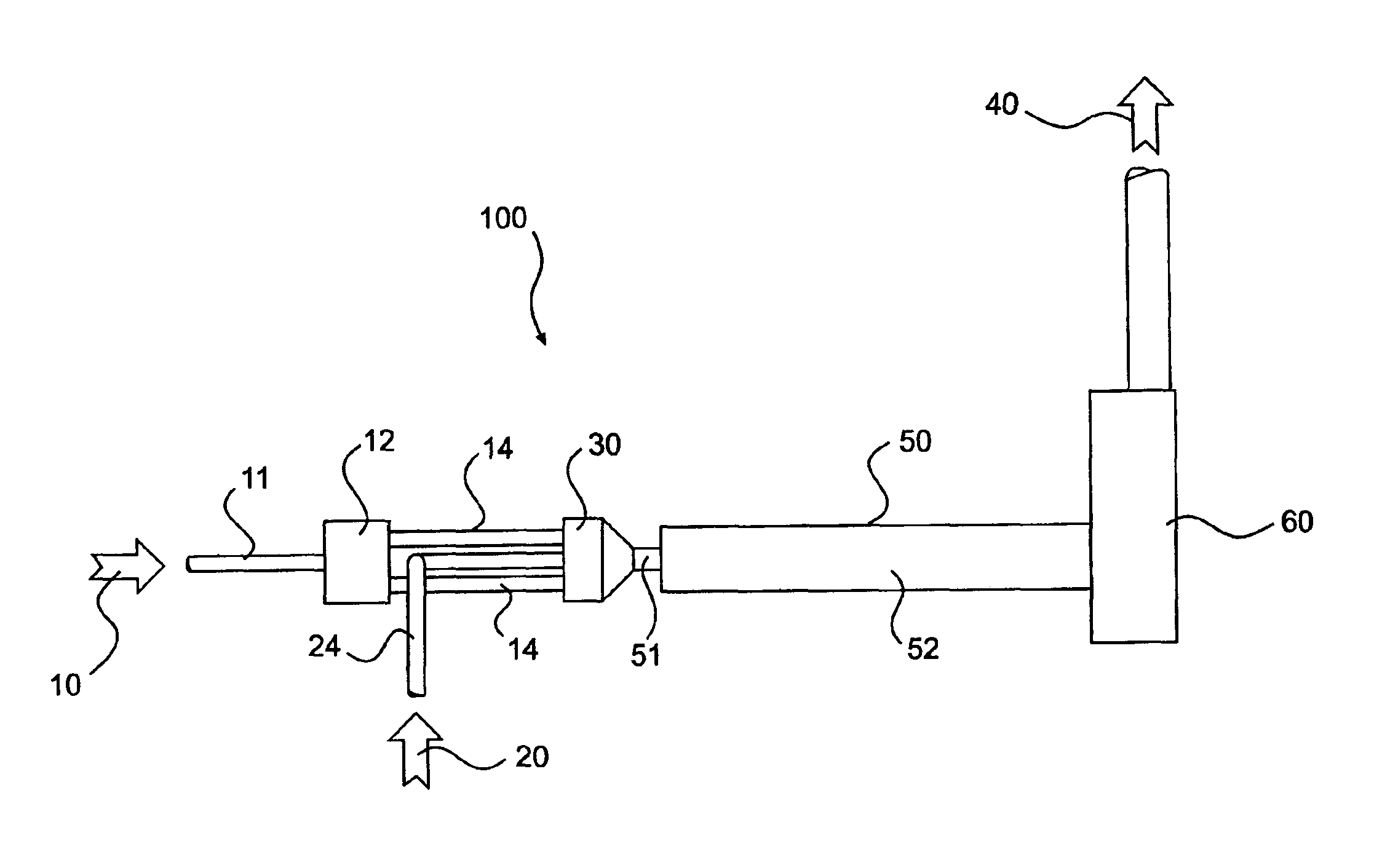
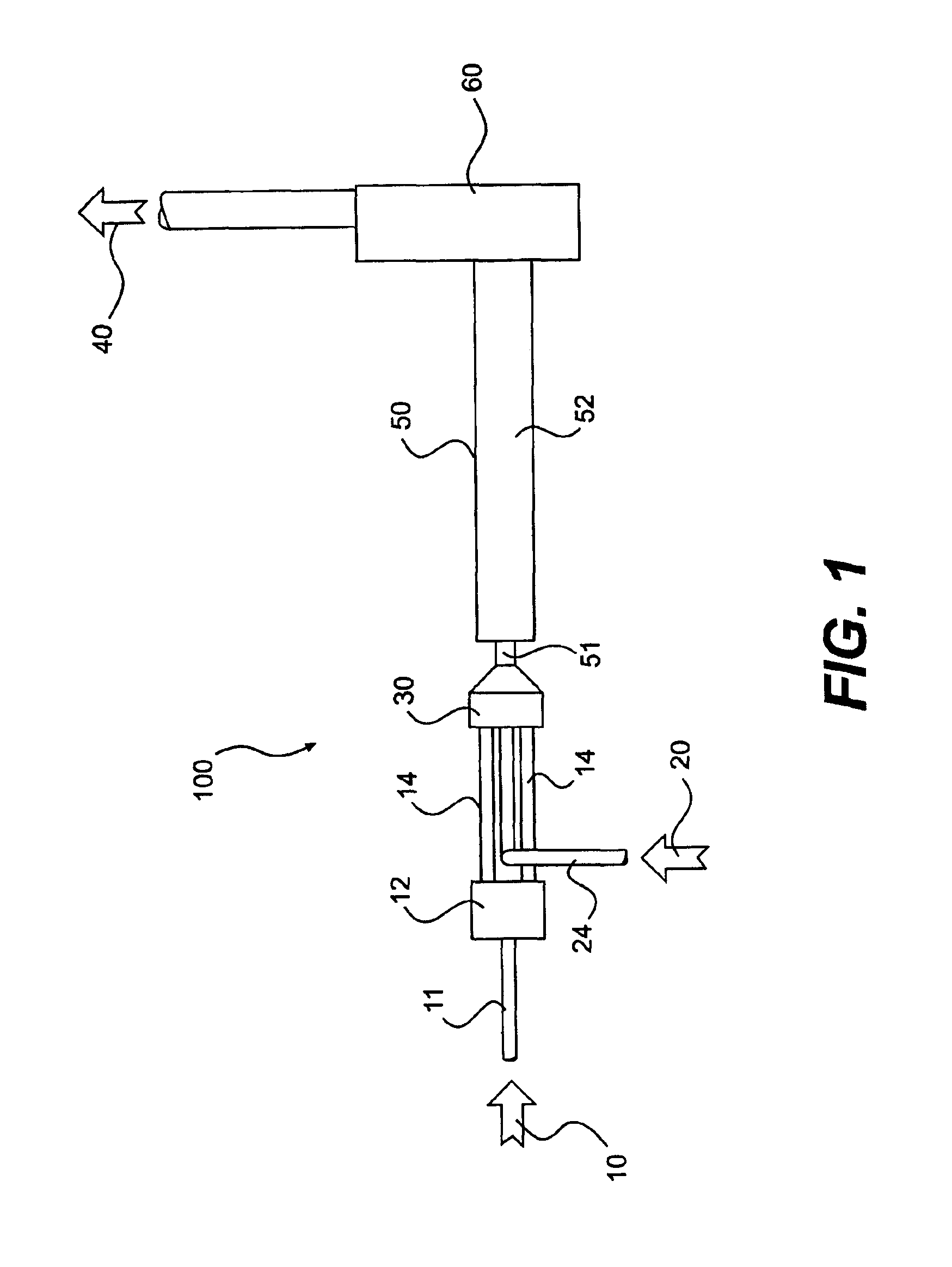
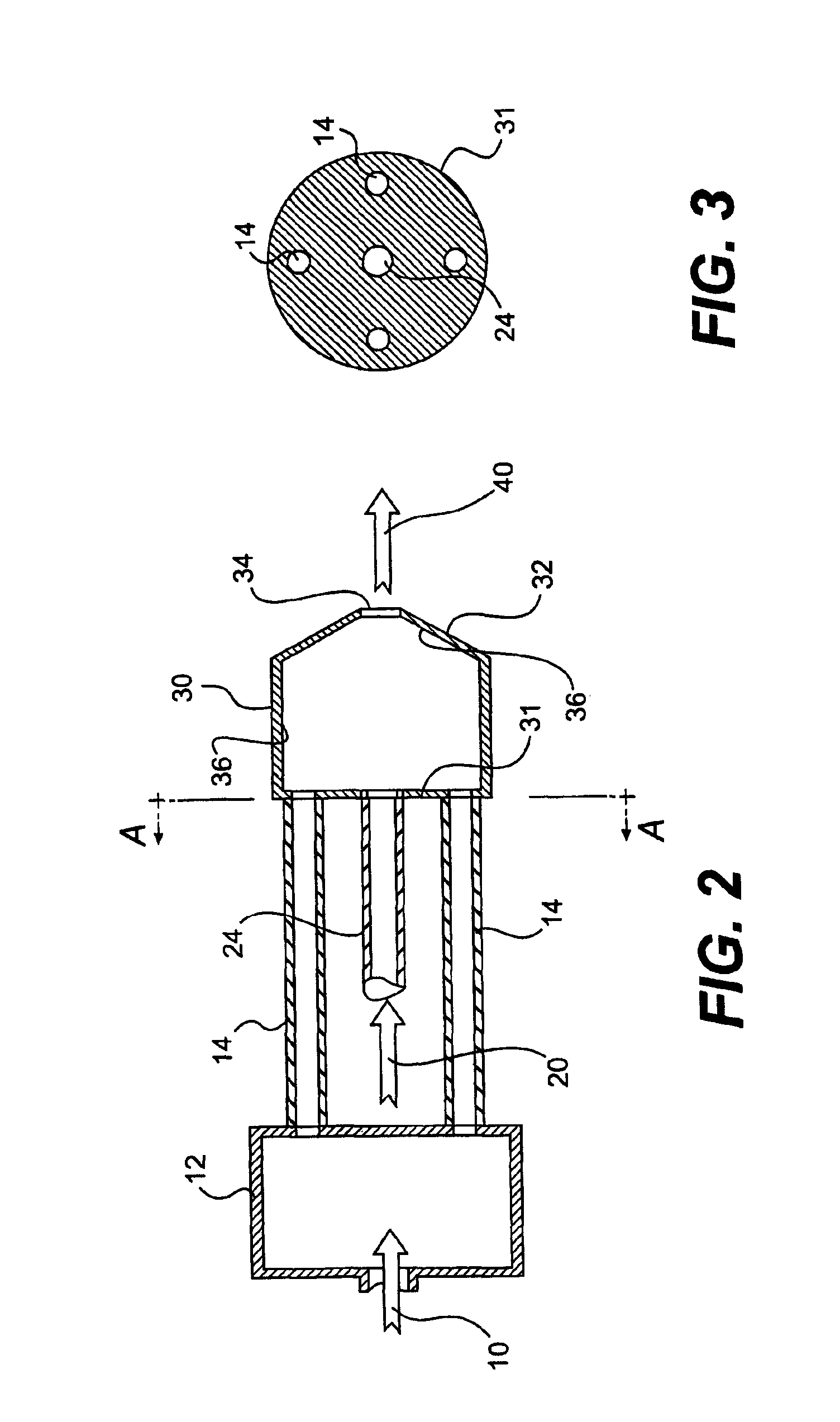
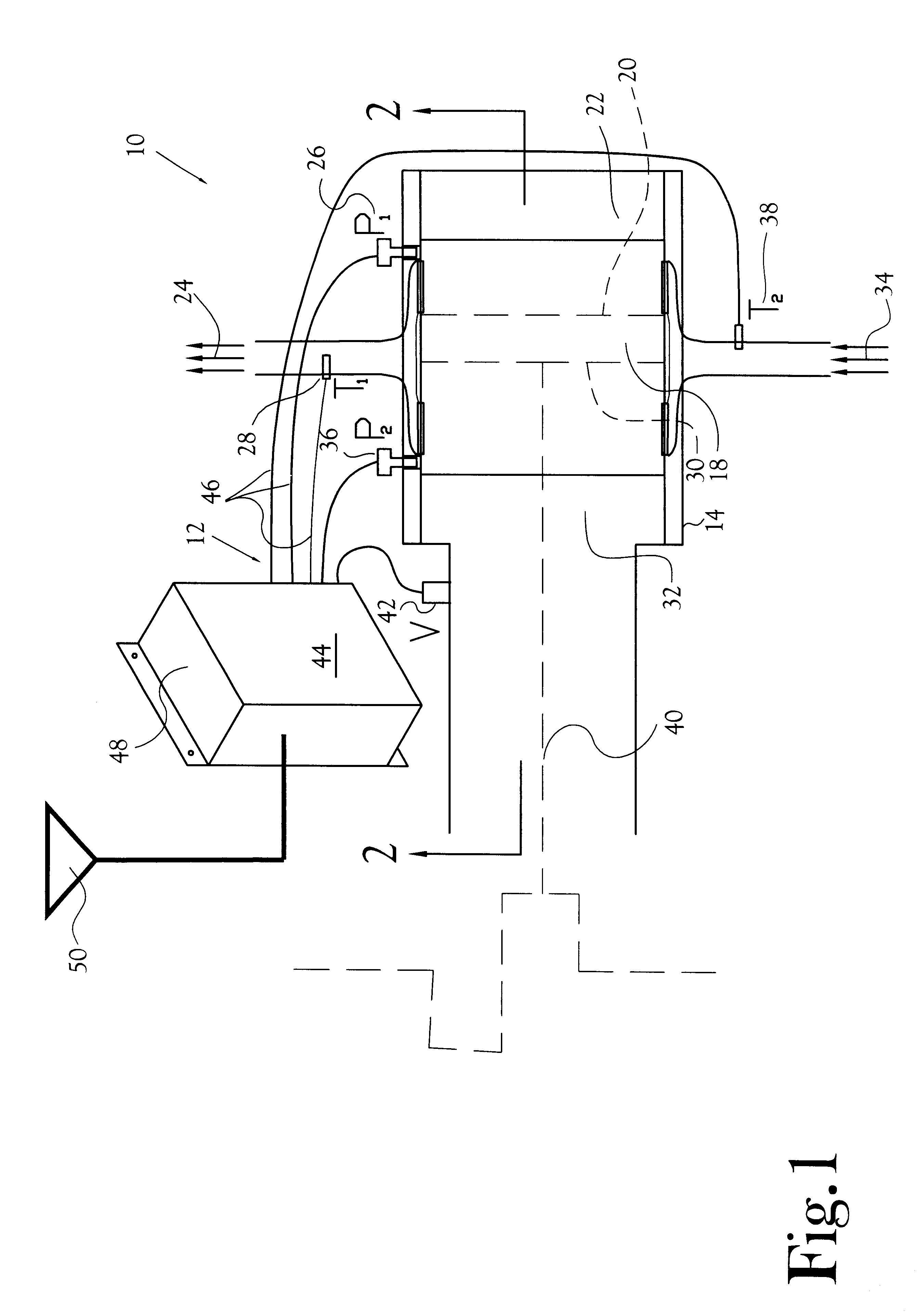
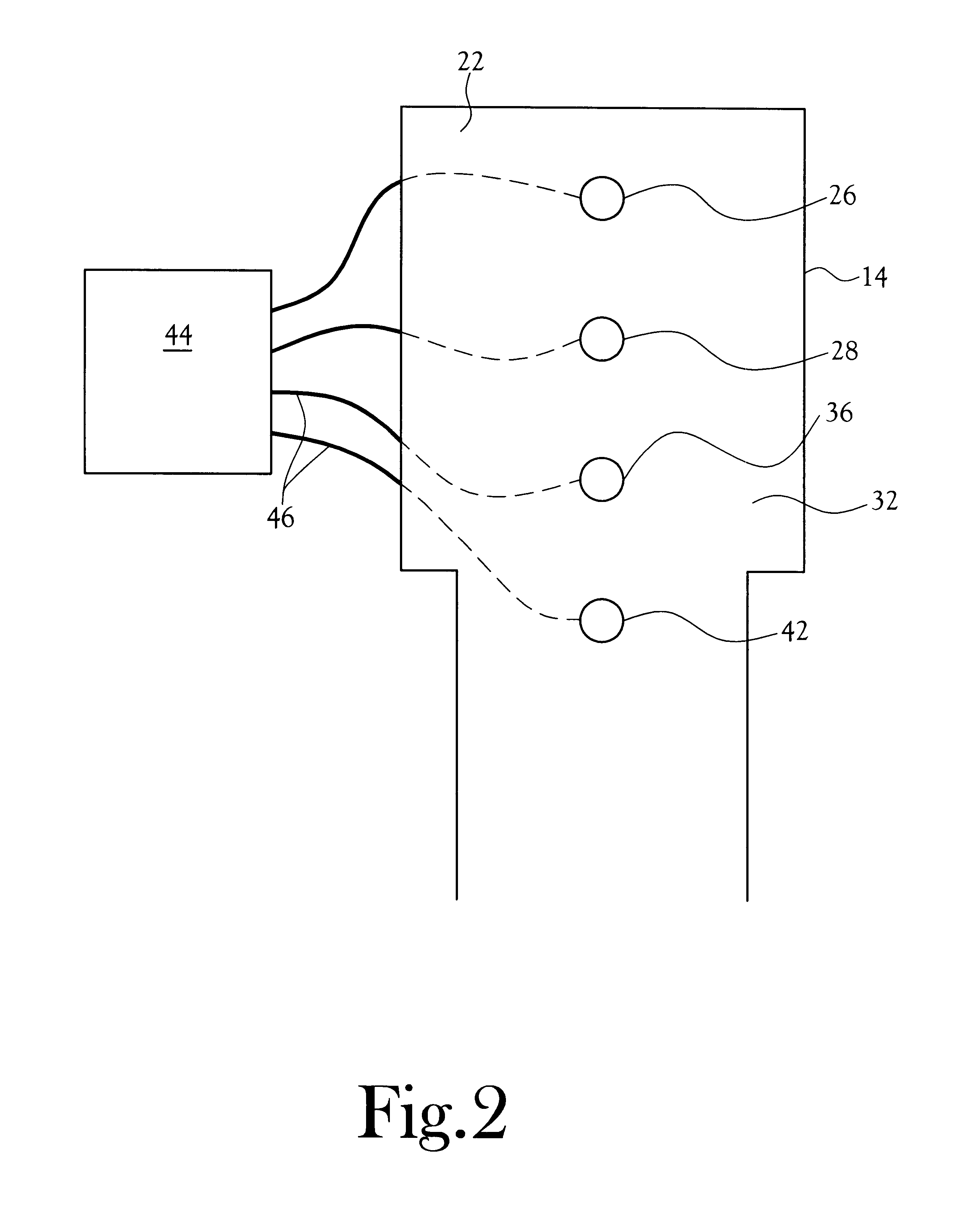
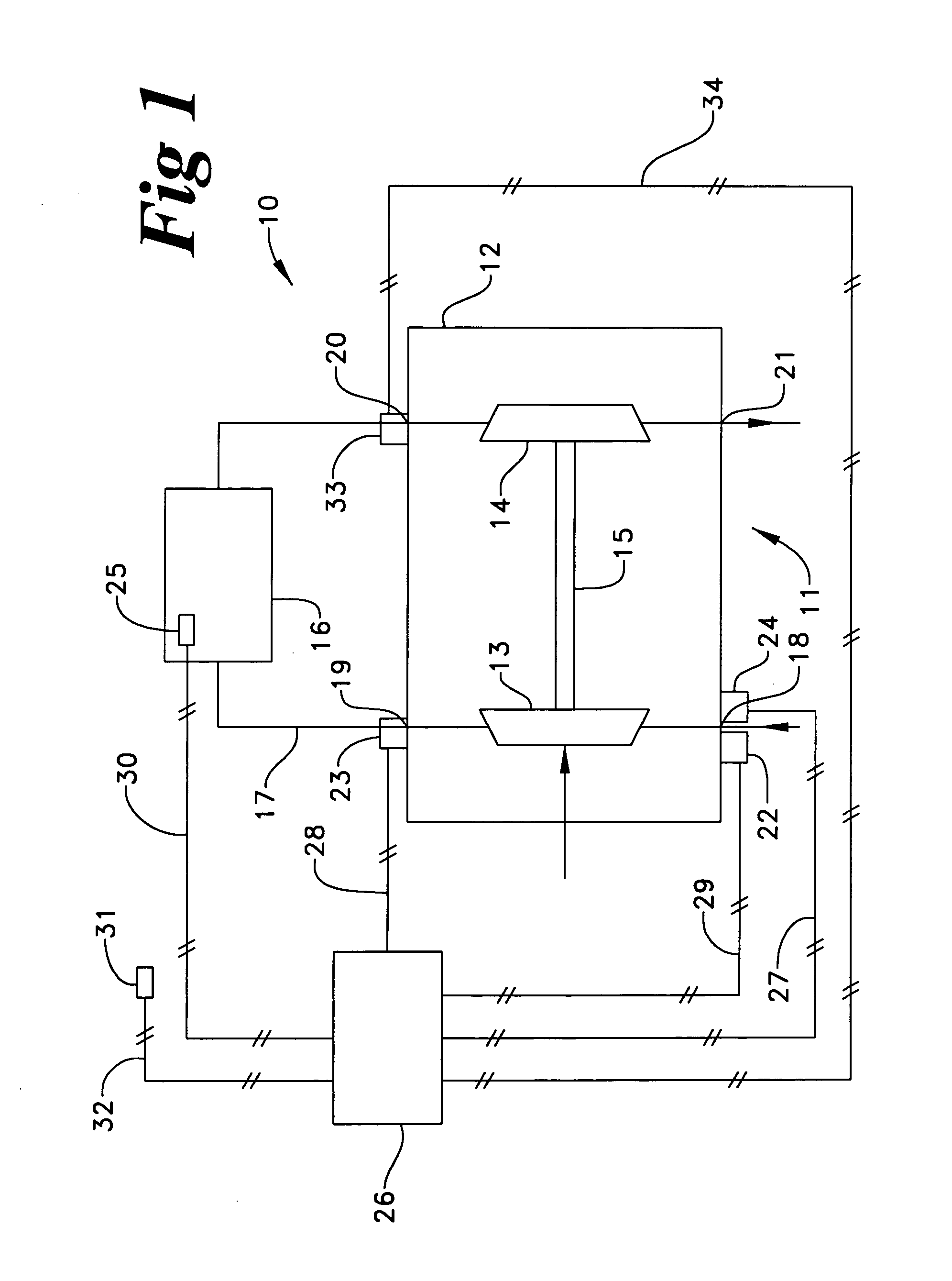
A method and apparatus for mixing a first stream of gas with a second stream of gas is provided. The method includes introducing a first stream of gas into a first stream manifold and directing the first stream from the first stream manifold into a mixing chamber via a plurality of first stream passages flow coupled to the mixing chamber. A second stream of gas is directed into the mixing chamber via at least one second stream passage flow coupled to a first end of the mixing chamber. A combined stream is formed from the first and second streams, gradually converged, and discharged from the mixing chamber through a mixing chamber exit port.
Owner:CATERPILLAR INC
Method and apparatus for mixing gases
A method and apparatus for mixing a first stream of gas with a second stream of gas is provided. The method includes introducing a first stream of gas into a first stream manifold and directing the first stream from the first stream manifold into a mixing chamber via a plurality of first stream passages flow coupled to the mixing chamber. A second stream of gas is directed into the mixing chamber via at least one second stream passage flow coupled to a first end of the mixing chamber. A combined stream is formed from the first and second streams, gradually converged, and discharged from the mixing chamber through a mixing chamber exit port.
Owner:CATERPILLAR INC
Fuel injection device and adjustment method thereof
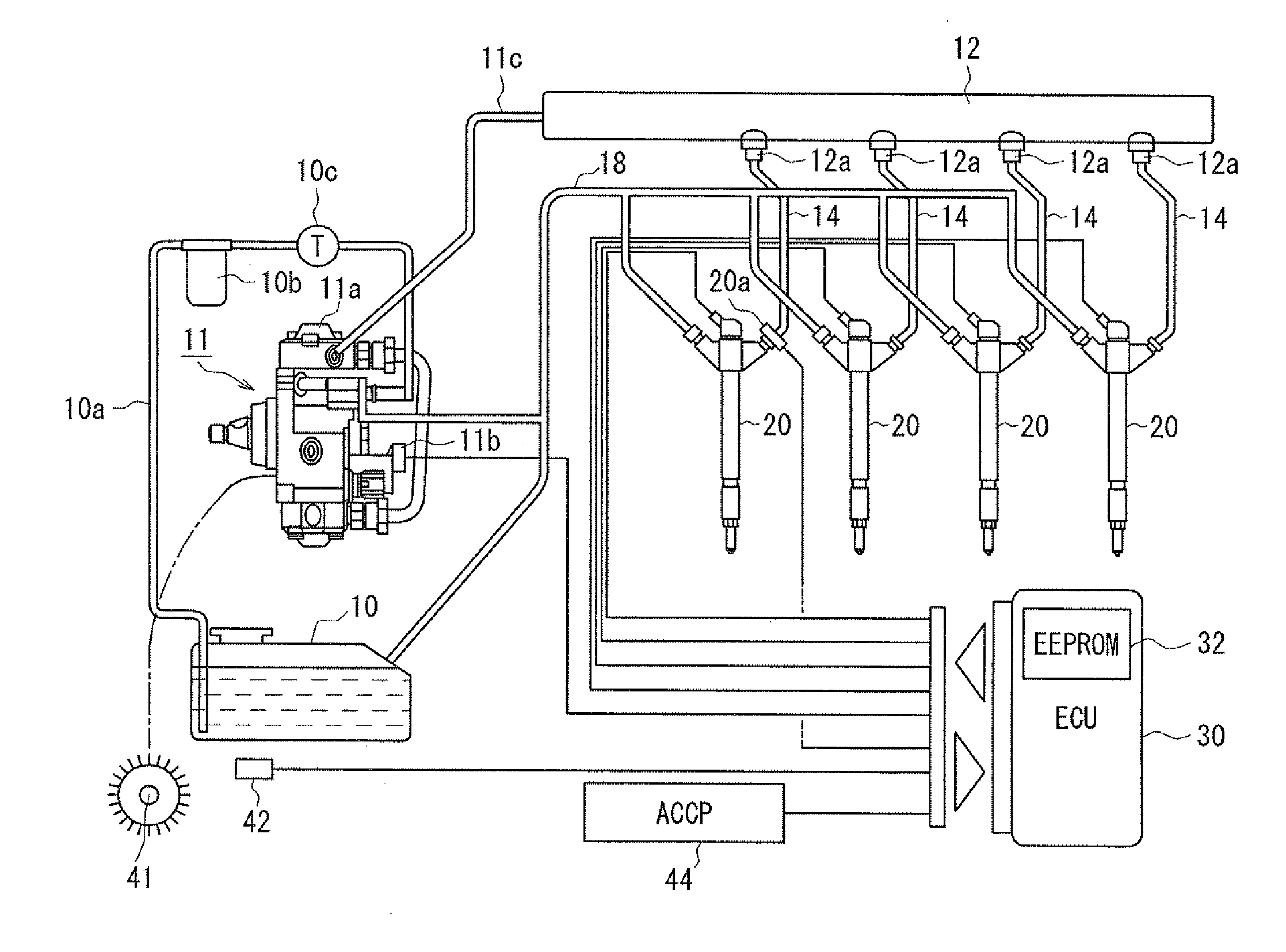
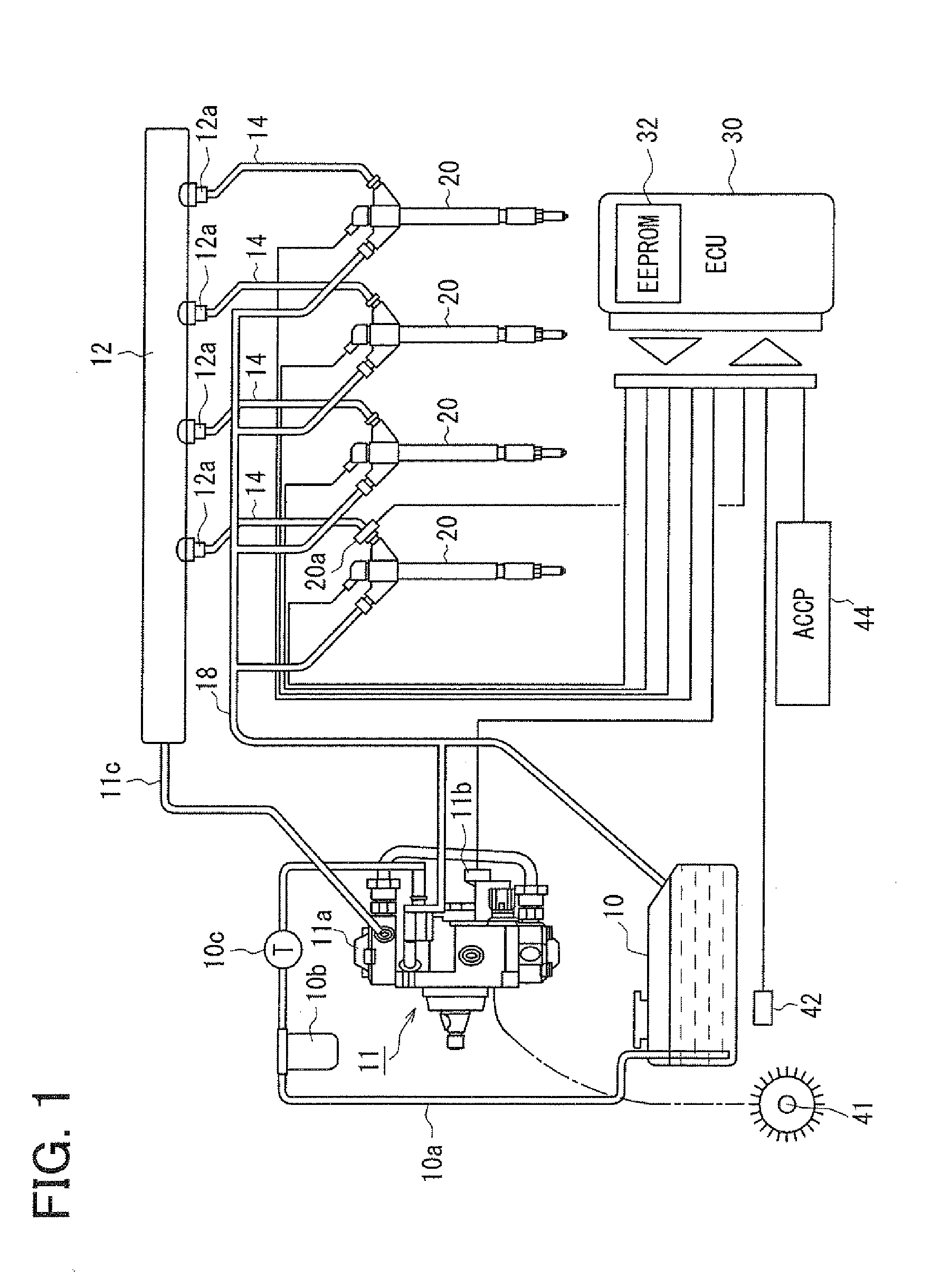
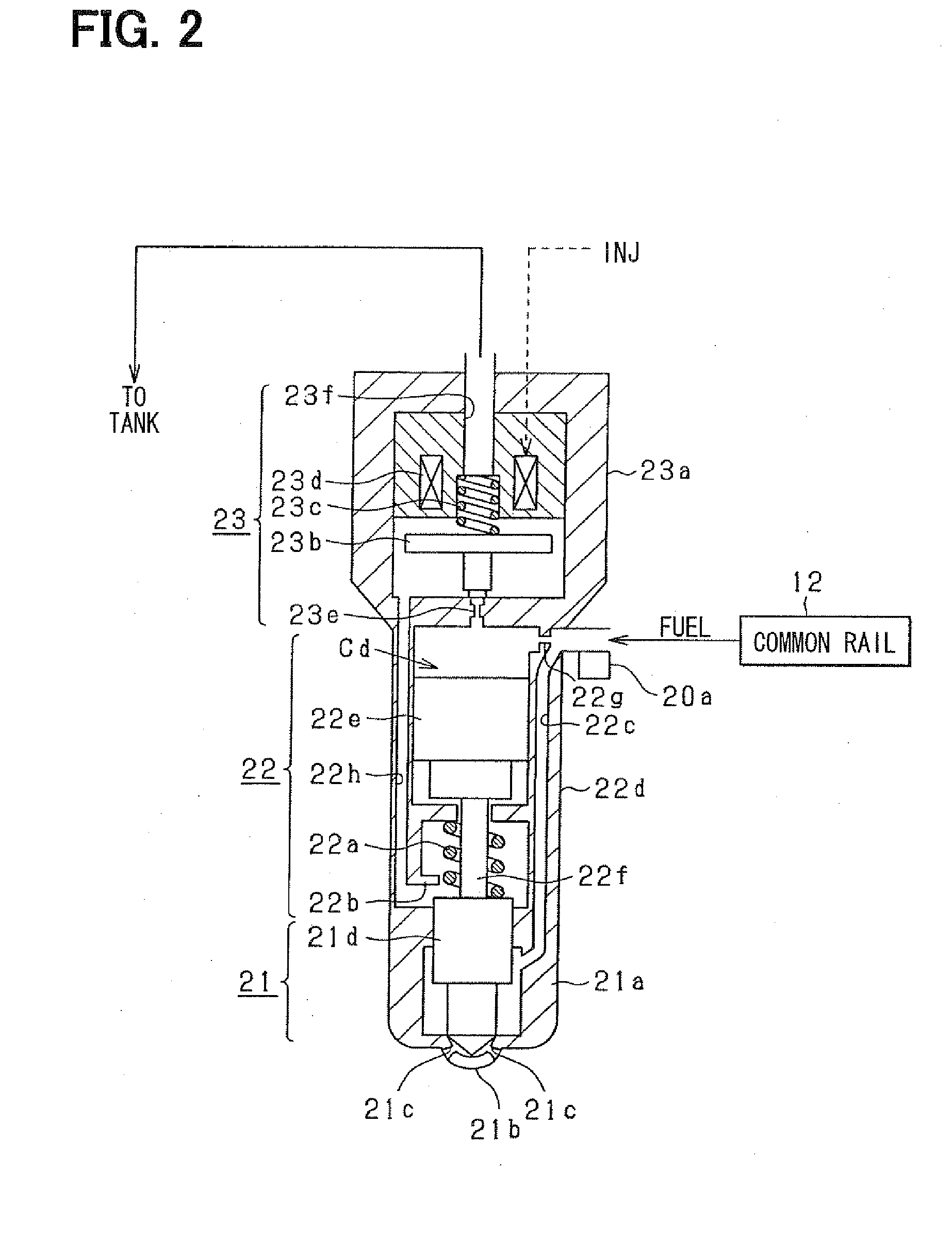
ActiveUS20080228374A1Improve accuracyAccurate inductionInternal-combustion engine testingElectrical controlCommon railForce sensor
A fuel injection device (fuel supply system) of a common rail type fuel injection system for an engine includes a pressure sensor disposed in a fuel inlet of an injector for measuring a fuel pressure at a position where the sensor is disposed and an ECU for sensing various kinds of pressure fluctuations associated with the injection including a pressure leak due to an injection operation of the injector and waving characteristics due to actual injection thereof based on sensor outputs from the pressure sensor. The ECU serially obtains the sensor outputs from the pressure sensor at intervals of 20 μsec.
Owner:DENSO CORP
Flame sensor with dynamic sensitivity adjustment
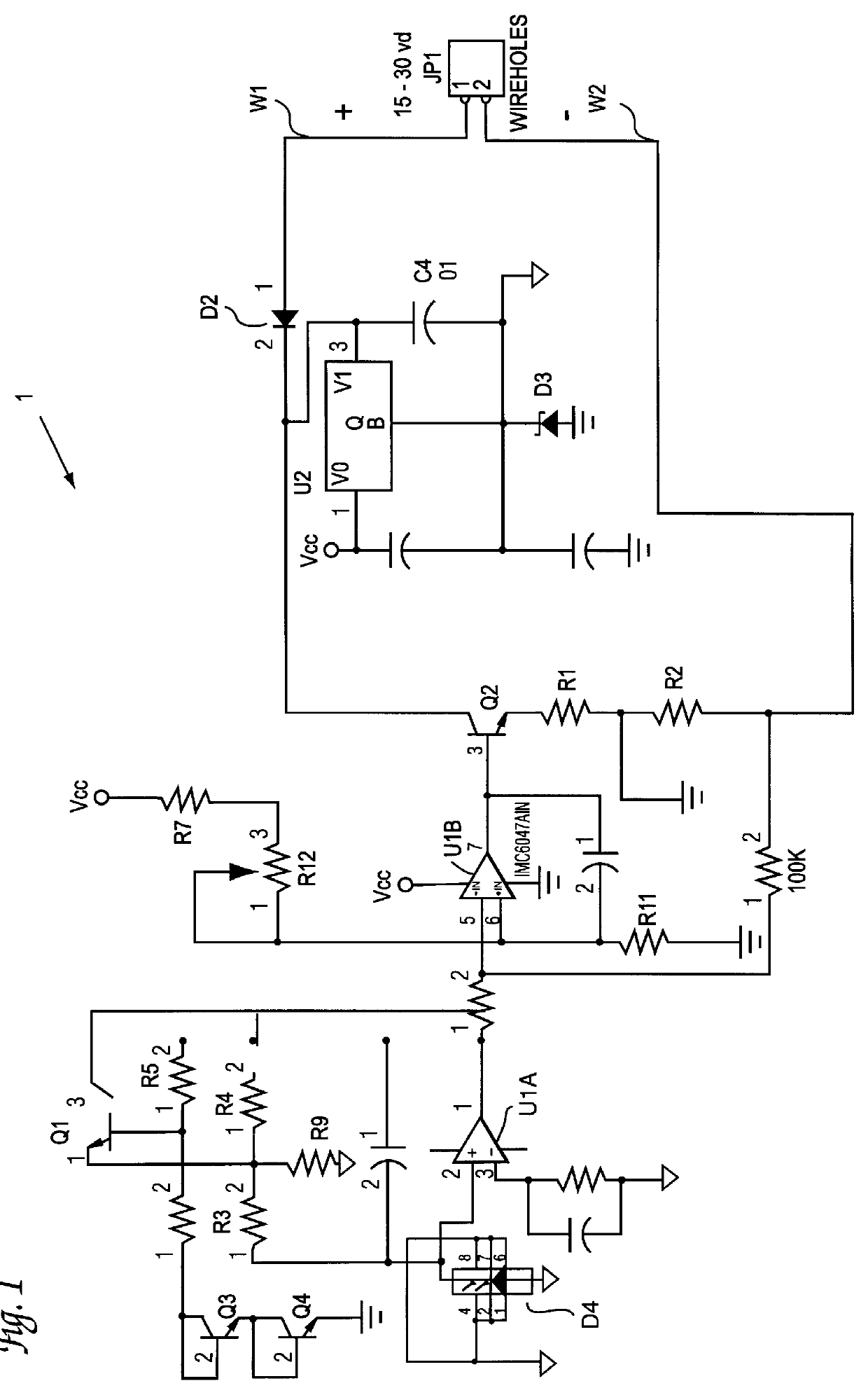
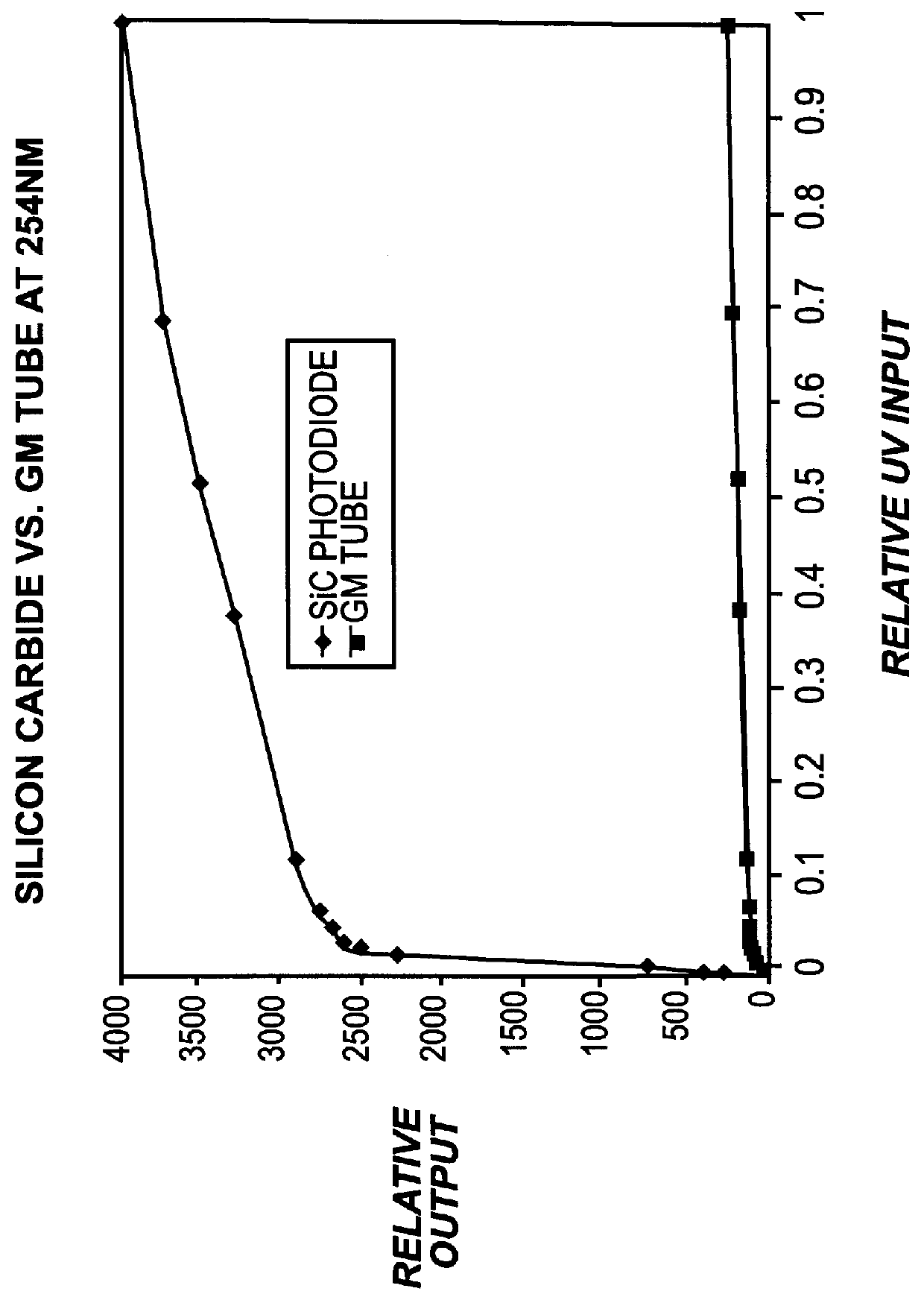
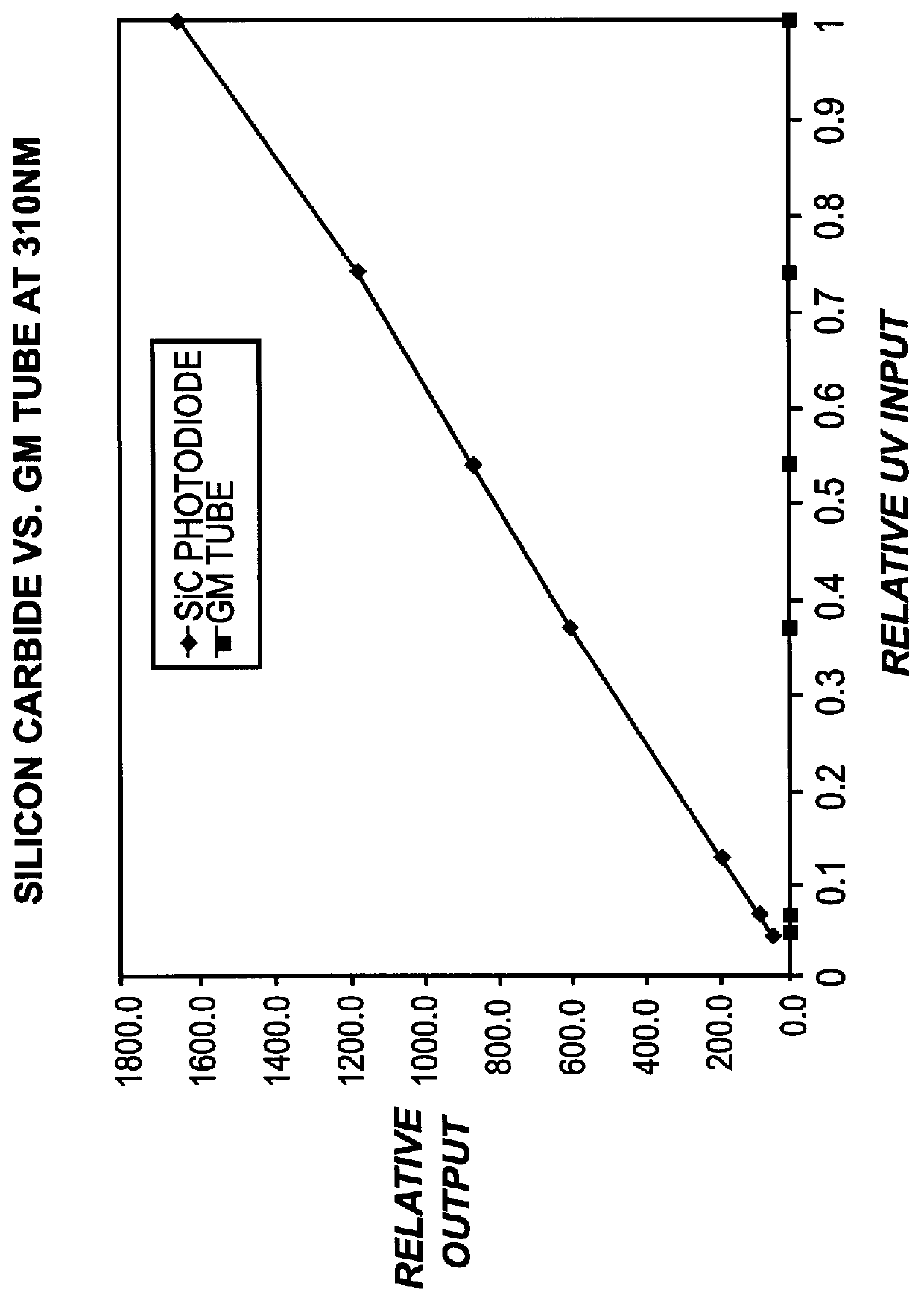
InactiveUS6013919AIncreased ultraviolet sensitivityEliminate needInternal-combustion engine testingContinuous combustion chamberSignal conditioning circuitsUltraviolet lights
The present invention provides a flame sensor having dynamic sensitivity adjustment, wherein the sensitivity of the flame detector can be adjusted by varying the gain of a signal conditioning circuit associated with the flame detector. The flame detector includes a photodiode, such as, for example, a silicon carbide (SiC) photodiode, that, when exposed to electromagnetic radiation having a wavelength in the range of from about 190-400 nanometers, and preferably within the ultraviolet range. The photodiode generates a photocurrent proportional to the ultraviolet light intensity to which it is exposed. The output of the photodiode is processed and amplified by signal conditioning circuitry to produce a signal indicative of the presence of a flame. Moreover, a cutoff wavelength for silicon carbide photodiodes is preferably in the range of about 400 nanometers, which renders the photodiode "blind" to potentially interfering blackbody radiation from the walls of the turbine.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
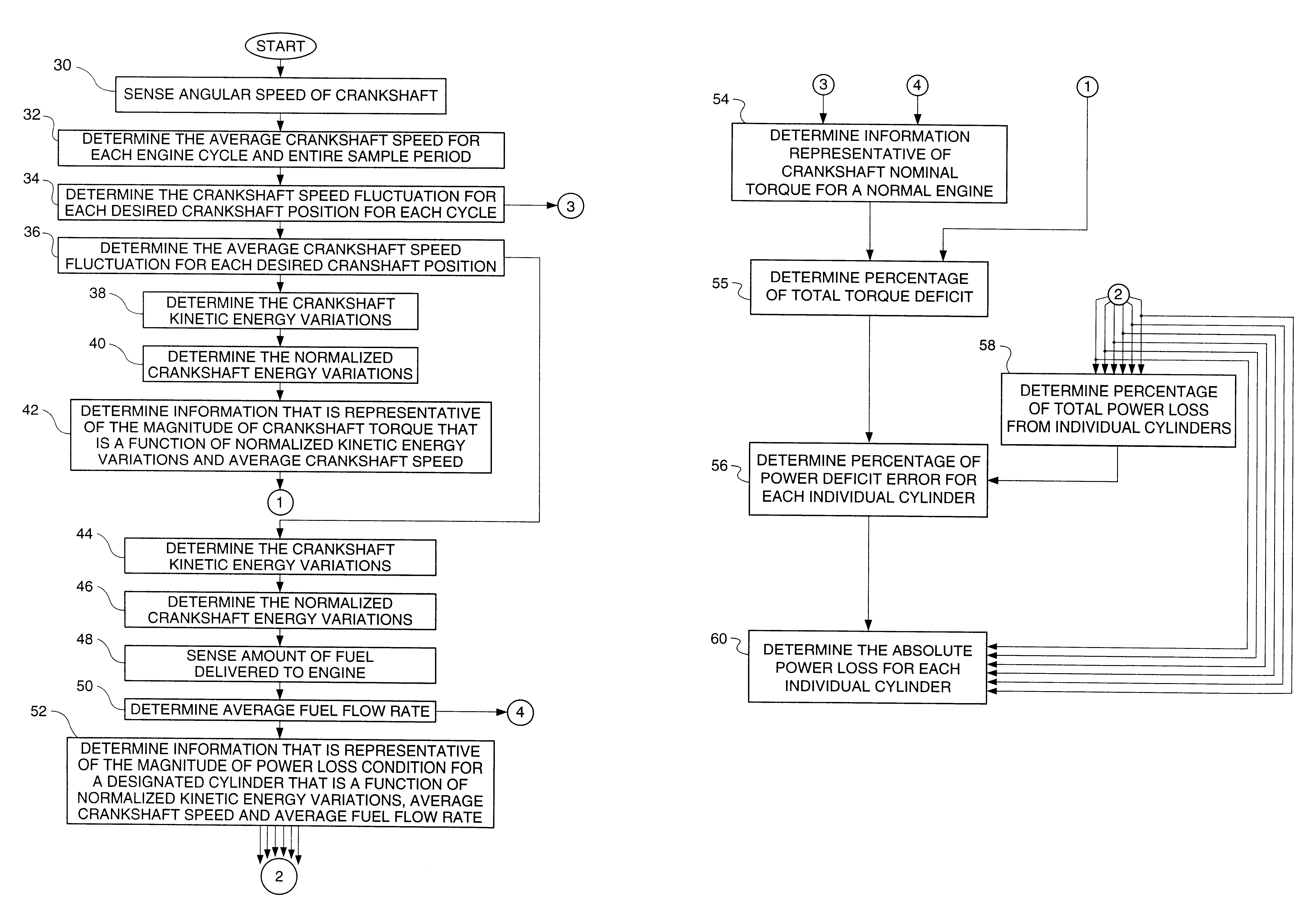
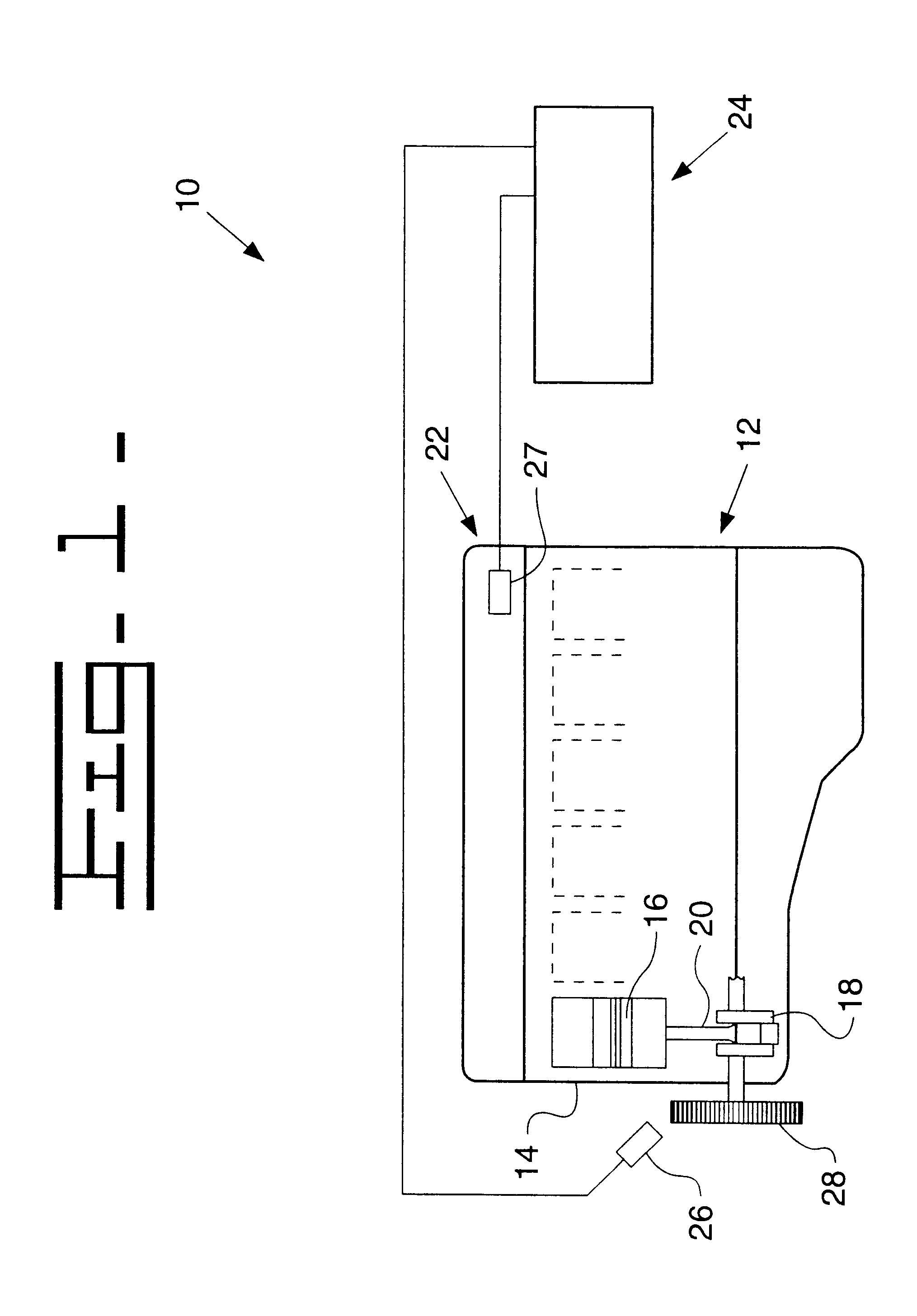
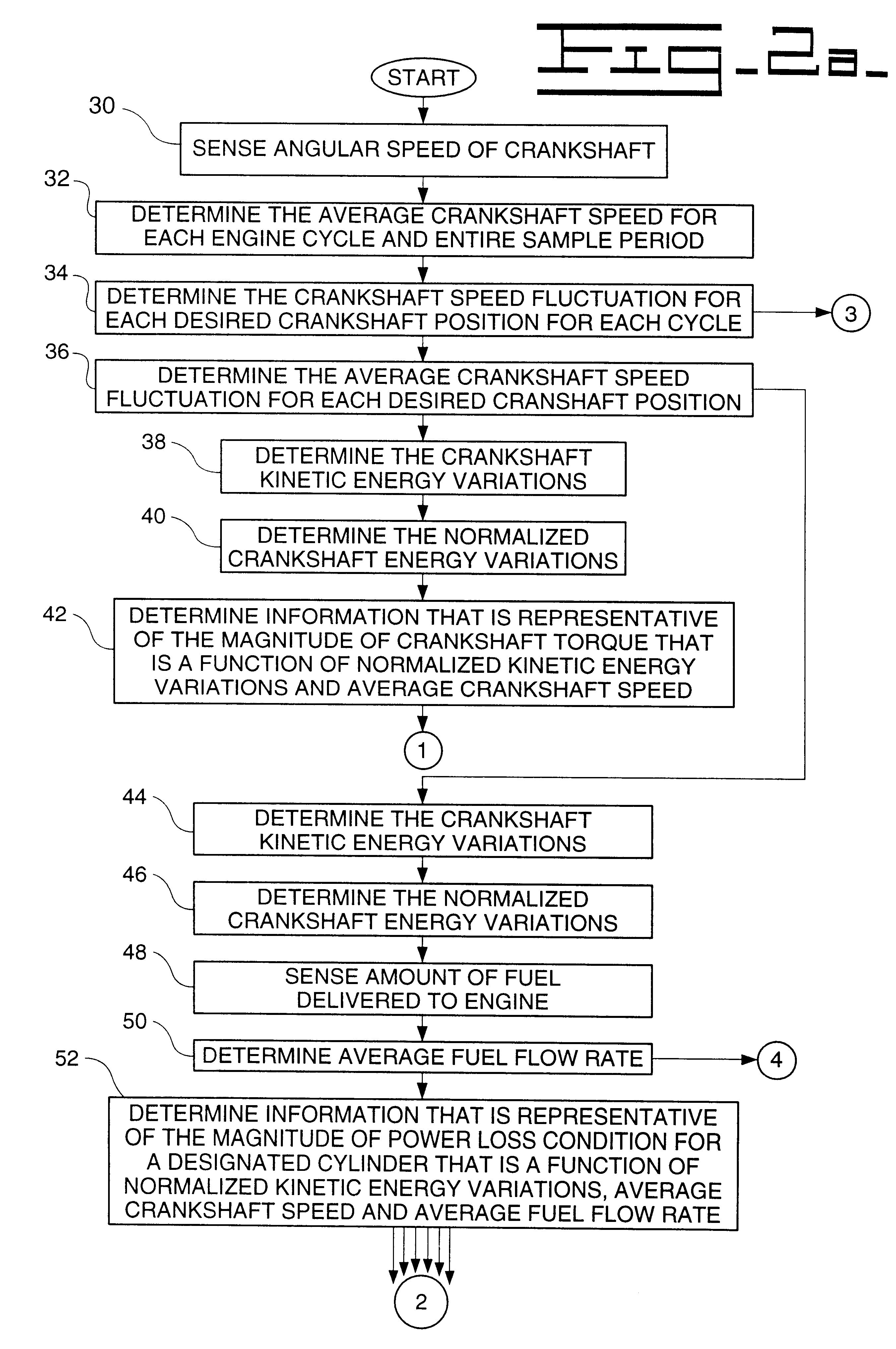
Method and system for determining an absolute power loss condition in an internal combustion engine
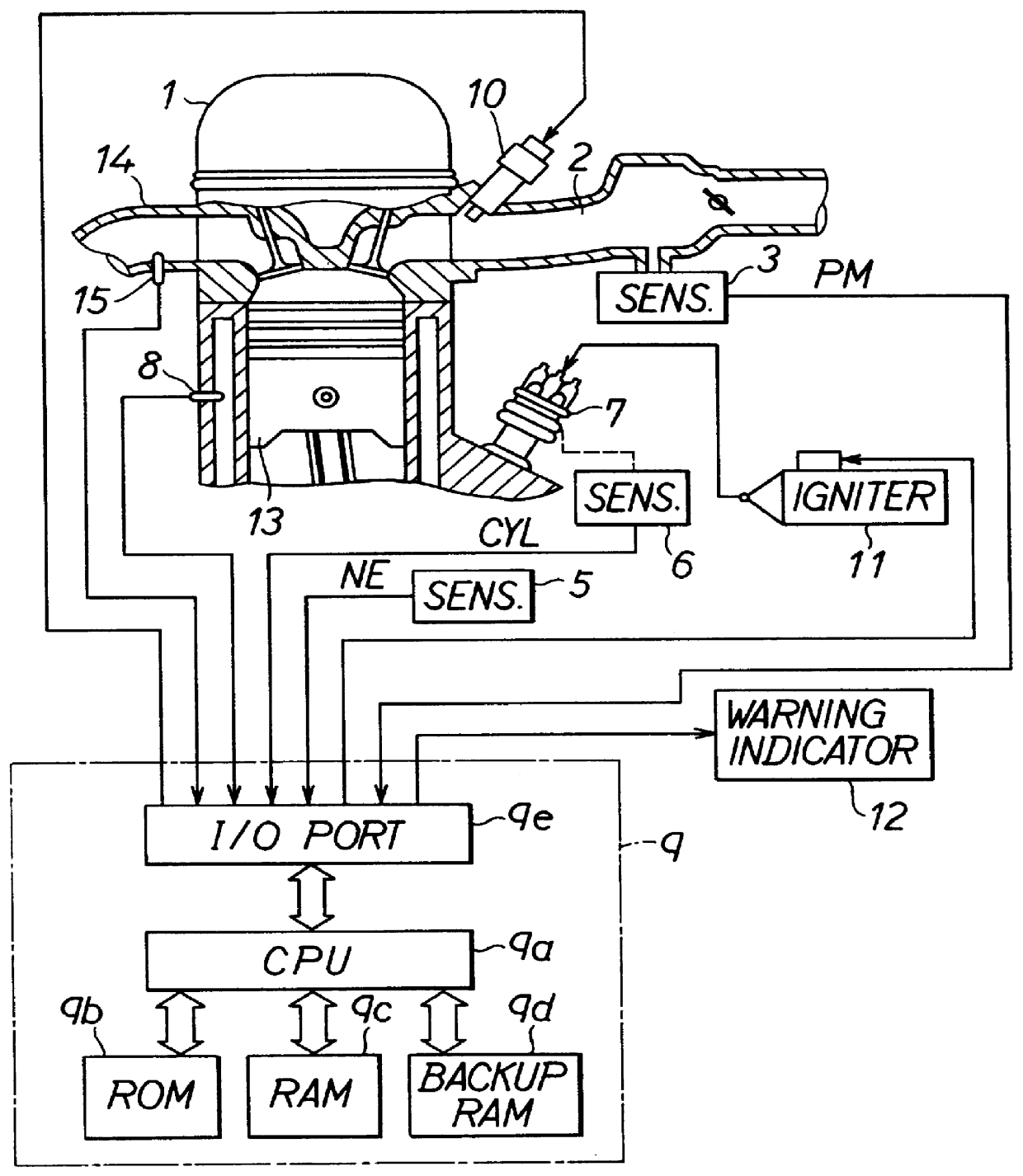
InactiveUS6199007B1Internal-combustion engine testingAnalogue computers for vehiclesInternal combustion engineRotation cycle
A method and system for detecting absolute power loss in a cylinder for a reciprocating internal combustion engine, the internal combustion engine having at least one cylinder and a rotatable crankshaft. This method and system includes sensing rotational crankshaft speed for a number of designated crankshaft rotational positions over a predetermined number of cycles of rotation for each of the crankshaft positions and determining an average crankshaft speed fluctuation for each of the crankshaft positions and determining information representative of crankshaft kinetic energy variations due to each firing event or each firing event and compression event in said cylinder and determining information representative of an average fuel flow rate and determining information representative of power loss for the cylinder as a function of the crankshaft kinetic energy variations due to each firing event, the average crankshaft speed and the average fuel flow rate and responsively producing a representative power loss signal and determining information representative of crankshaft torque as a function of the crankshaft kinetic energy variations due to each firing event and compression event and the average crankshaft speed and responsively producing a representative crankshaft torque signal and determining information representative of absolute power loss for each cylinder.
Owner:CATERPILLAR INC
Apparatus for monitoring engine exhaust
ActiveUS7696501B2Promote absorptionHigh sensitivityInternal-combustion engine testingRadiation pyrometryUltrasound attenuationNitrogen dioxide
An apparatus for monitoring the exhaust of an engine includes a flow-through chamber for receiving exhaust, a source of electromagnetic radiation and a detector. The source provides electromagnetic radiation in a range comprising the infrared, visible and ultraviolet wavelengths. The source and a detector are arranged so that radiation passing through the chamber is incident on the detector. An electronic circuit is connected to the detector to provide a signal indicative of the attenuation of the radiation by particles in the exhaust in the chamber. The detector provides respective measures of radiation which it receives for at least two different wavelengths of the radiation, and the electronic circuit provides corresponding electrical signals indicating the attenuation of the two different wavelengths by particles within the exhaust in the chamber. The wavelengths are selected to be those for which the attenuation caused by nitrogen dioxide in the exhaust is substantially the same.
Owner:HARTRIDGE L
Performing application review validation testing for an engine as installed in an application
InactiveUS20080234919A1Internal-combustion engine testingAnalogue computers for vehiclesApplication softwareValidation testing
A method for performing application review validation testing for an engine as installed in an application, the engine having production sensors and a production electronic control unit (ECU) for controlling the engine using the production sensors, includes running the engine; reading an output of the production sensors with the production ECU during the running of the engine; and determining with the production ECU whether the engine as installed in the application is in compliance with at least one requirement of the application review validation testing based on the output.
Owner:DEERE & CO
Automotive Diagnostic Server
A system and method for an automotive diagnostic server can provide a portable vehicle diagnostic tool to identify a failed vehicle component. It may also provide a remote information device to serve as a connecting intermediary between devices, and to allow remote control of the devices and to provide information to a user. A remote diagnostic device to analyze data and interpret information to aid the user in making, using, maintaining, and fixing a piece of equipment or product may also be included. Web server functionality may be incorporated into the portable vehicle diagnostic tool to allow dissemination of the diagnostic information resulting from the diagnostic testing, and the web server may be accessed by a web browser of the remote information device.
Owner:BOSCH AUTOMOTIVE SERVICE SOLUTIONS
Automated fault diagnosis method and system for engine-compressor sets
InactiveUS7403850B1Improve economic performanceIncrease fuel consumptionInternal-combustion engine testingAutomatic initiationsBaseline dataData acquisition
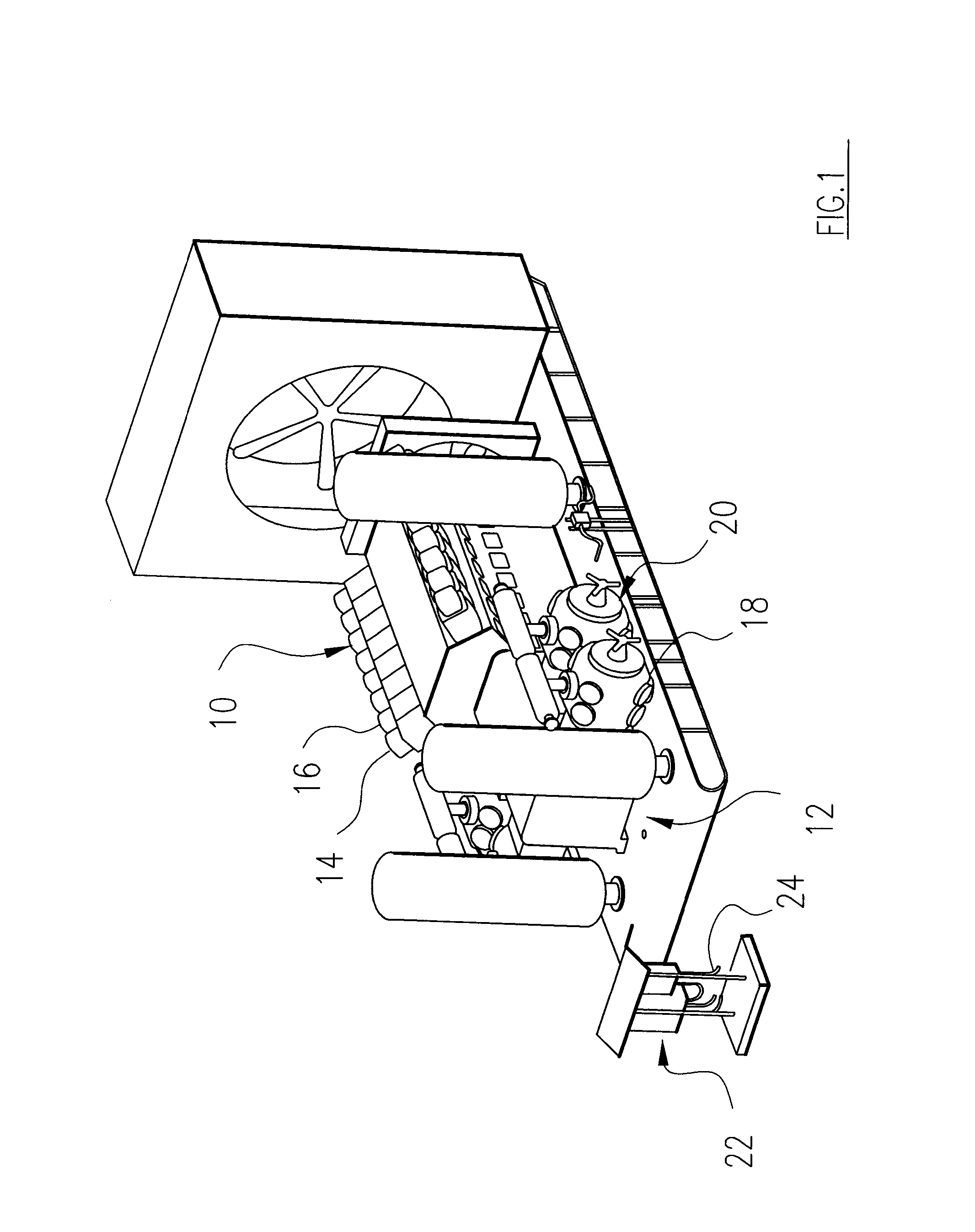
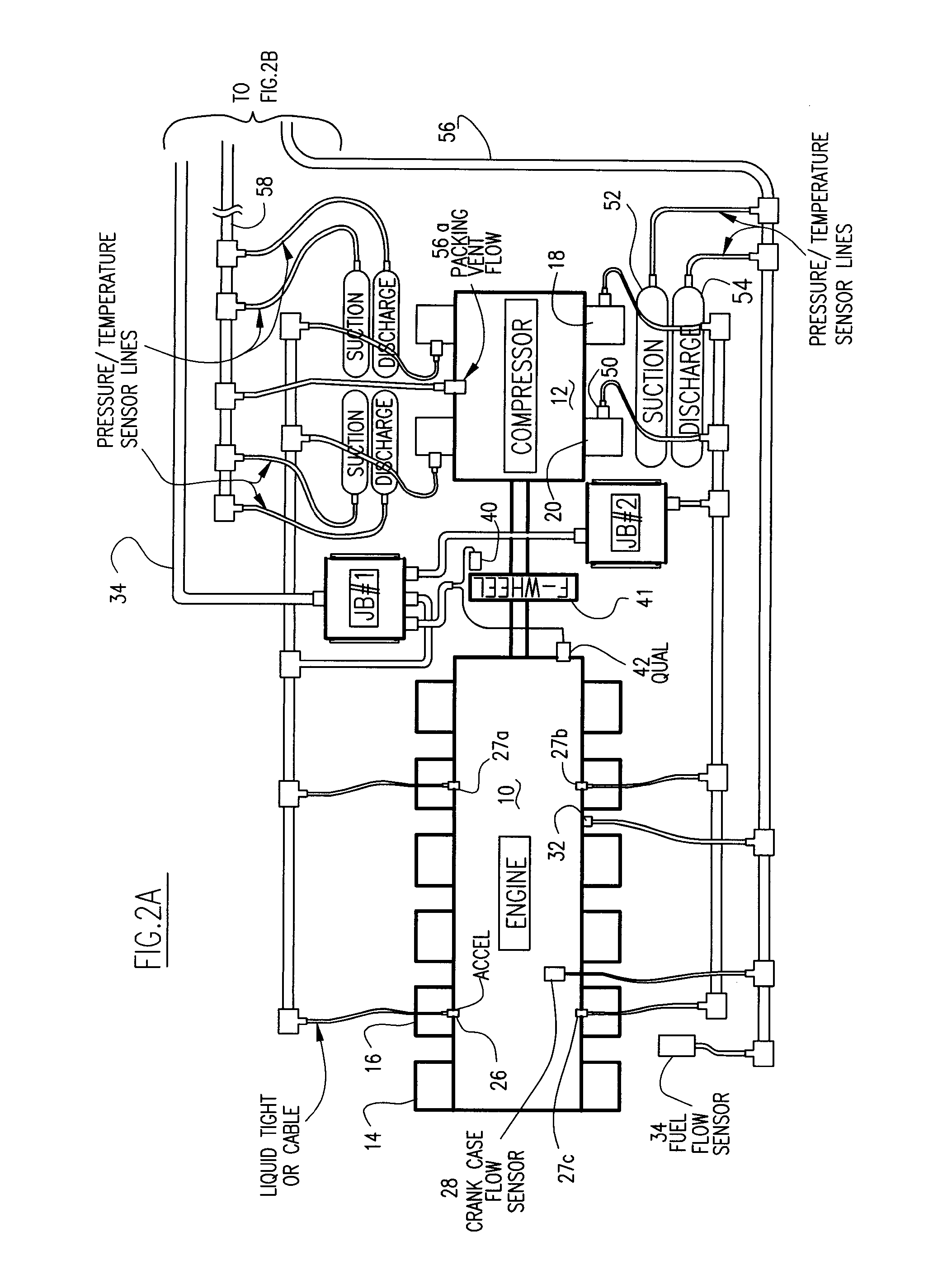
The automated fault diagnostic system operates on engine-compressor sets with one vibration sensor per sub-group of engine cylinders and one sensor per compressor cylinder. Vibration signals linked to crankshaft phase angle windows (“VT”) mark various engine events and compressor events. In data-acquisition-learning mode, VT is stored for each engine and compressor event per operating load condition, statistical process control (SPC) theory identifies alarm threshold bands. Operator input-overrides are permitted. If no baseline data is stored, the system automatically enters the learn mode. To monitor, current VT are obtained and current load condition is matched to the earlier load set and alarms issue linking predetermined engine or compressor event to the over-under VT. Baseline data, SPC analysis, alarms and monitoring are set for crankcase flow, engine cylinder exhaust temperatures, ignition system diagnostic messages. Compressor performance alarms use suction and discharge temperatures and pressures.
Owner:WINDROCK
Failure determination system and method for internal combustion engine and engine control unit
InactiveUS6763707B2Internal-combustion engine testingValve arrangementsExternal combustion engineOxygen
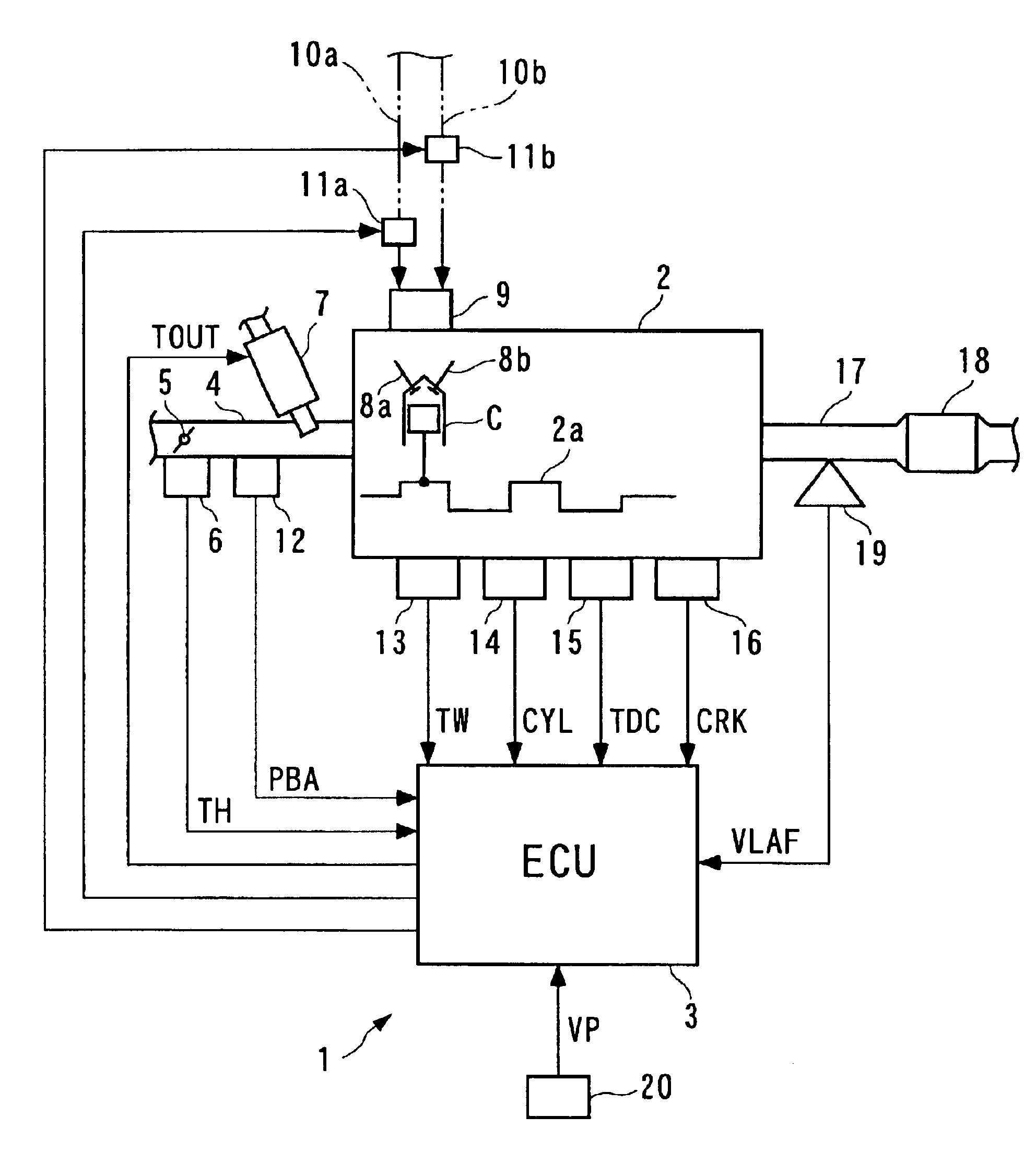
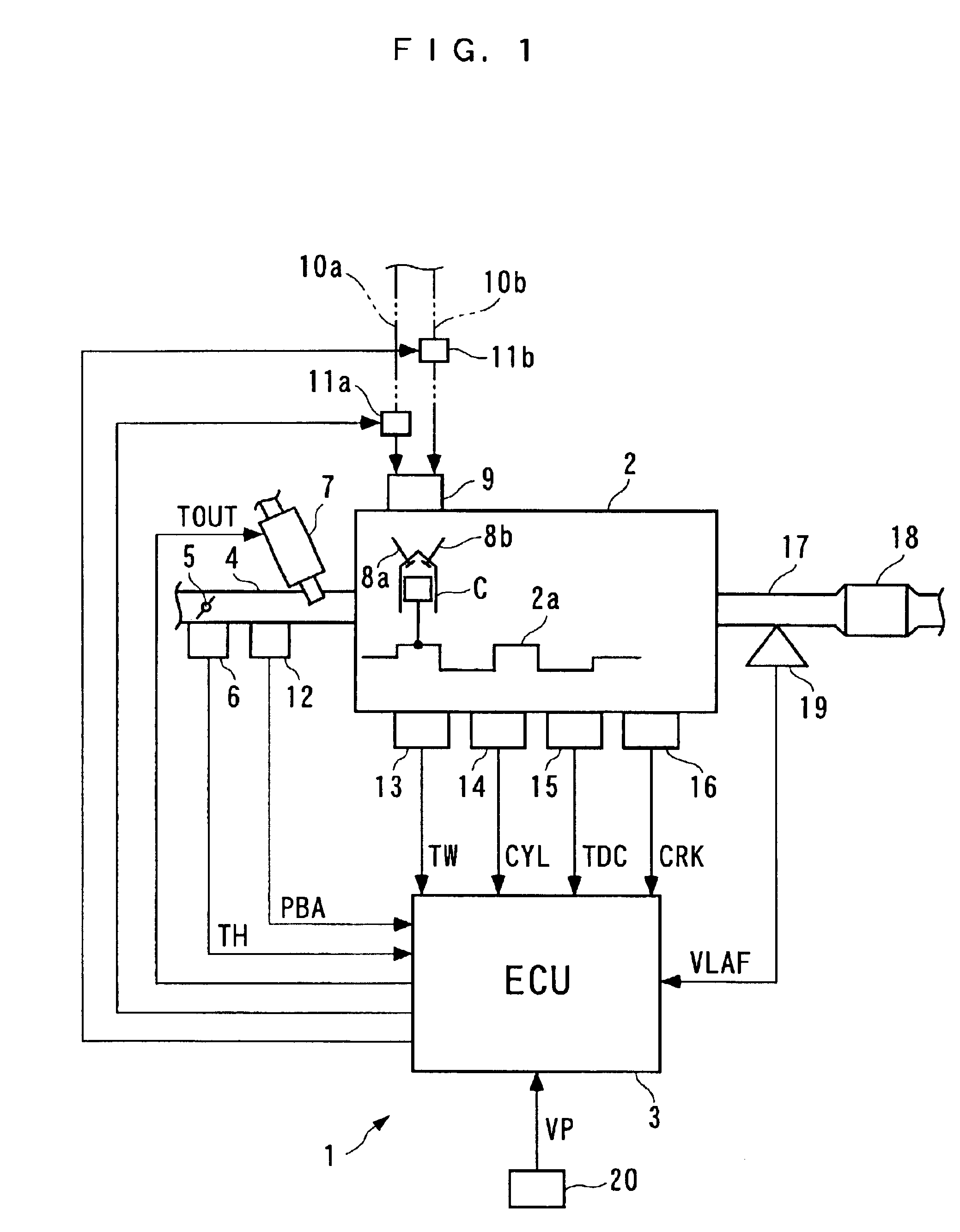
A failure determination system and method for an internal combustion engine and an engine control unit are provided which are capable of properly determining a failure of a variable valve mechanism for inactivating a valve system associated with at least one of cylinders during a predetermined operation of the engine, by discriminating a misfire caused by the failure of the mechanism from a normal misfire. Fuel injection valves inject fuel for each cylinder and oxygen concentration of exhaust gases is detected. A misfire condition is detected on a cylinder-by-cylinder basis. Fuel injection to a misfiring cylinder is stopped. A failure of the mechanism is determined, when a parameter based on the oxygen concentration detection indicates a richer value of an actual air-fuel ratio of the exhaust gases than a predetermined reference value does, under a condition of the fuel injection being stopped.
Owner:HONDA MOTOR CO LTD
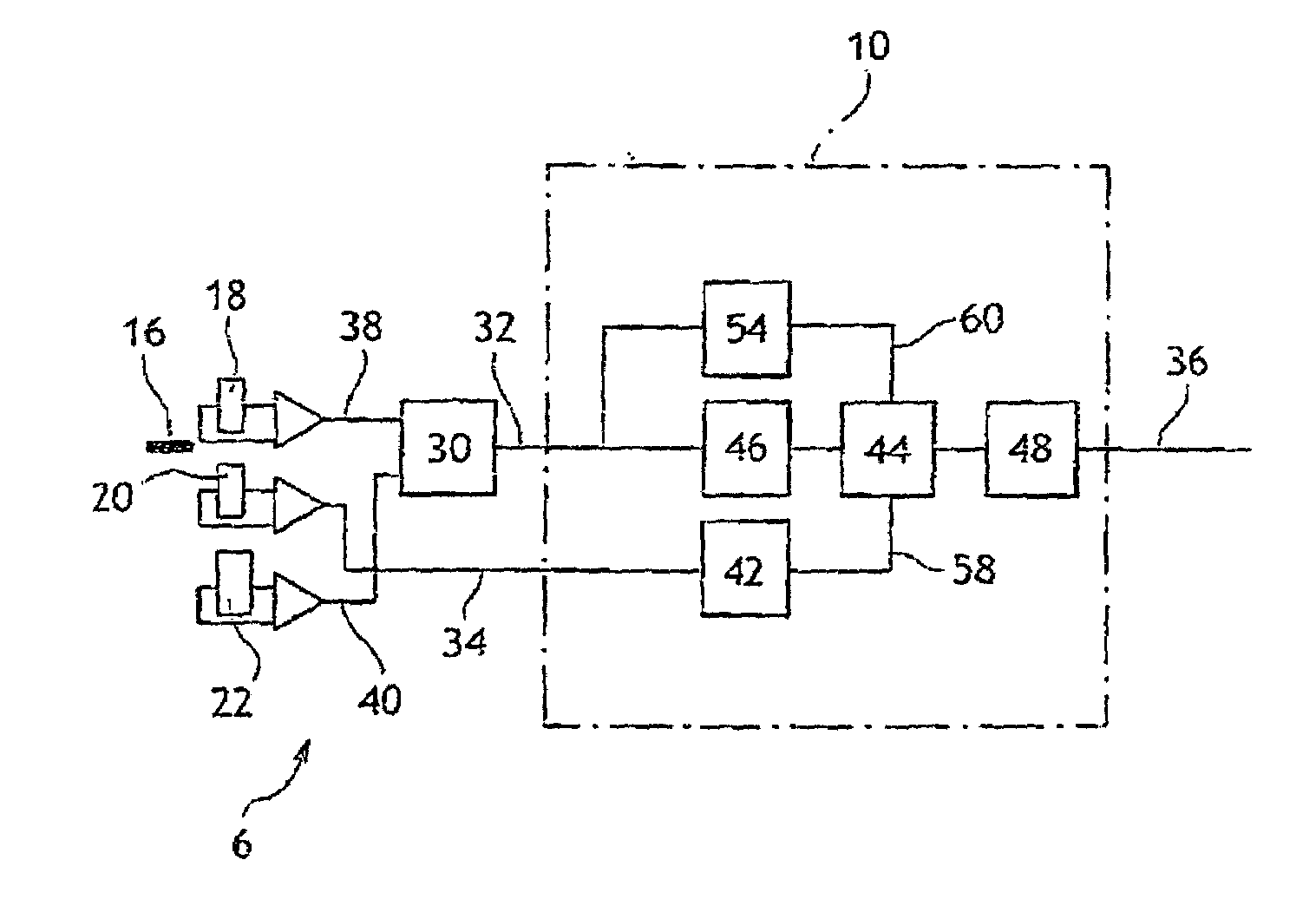
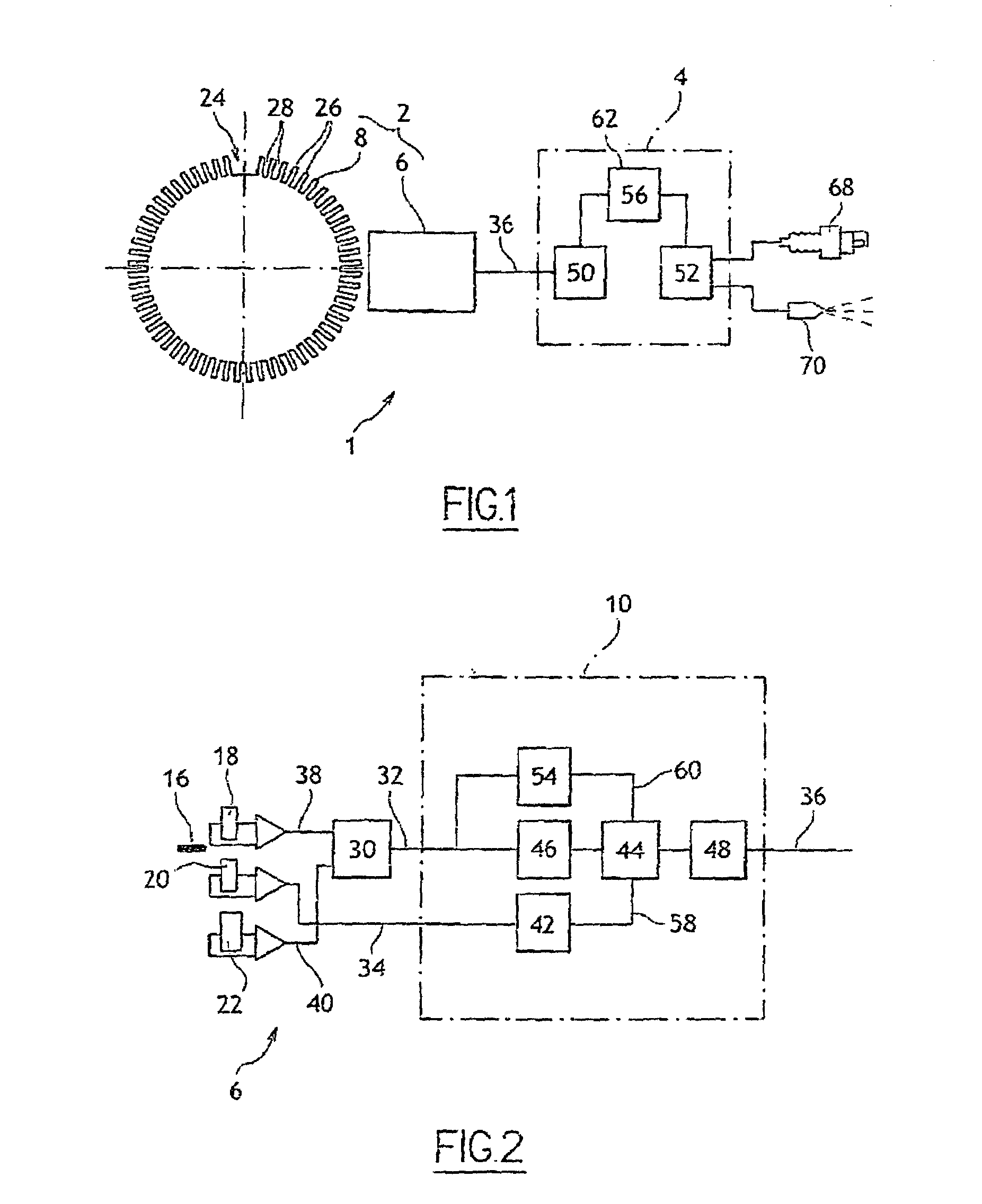
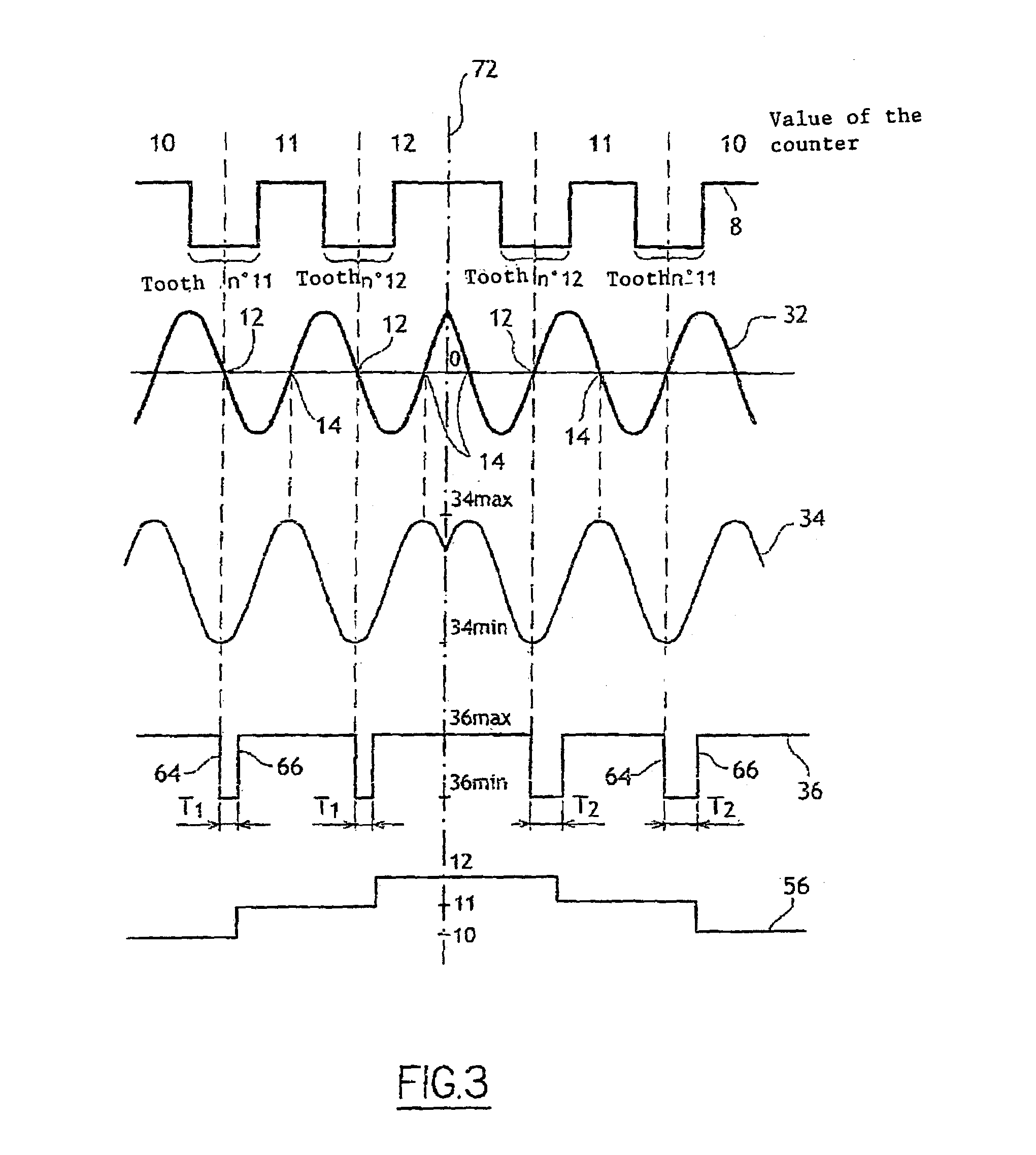
Device and process for determining the position of an engine
InactiveUS7184876B2Low costDrawback can be obviatedInternal-combustion engine testingAnalogue computers for vehiclesPhase shiftedEngineering
Device for determining the position of an engine includes:a sensor that has a rotary part and a fixed part, whereby said fixed part comprises:elements (for generating a first signal based on the position of the rotary part relative to the fixed part),Second elements for generating a second phase-shifted signal relative to the first signal,elements for comparing the value of the second signal to a reference value,elements for detecting at least one characteristic event on the first signal, for generating a third signal of binary type, and for alternating the binary signal from a first value to a second after detection of at least one of the characteristic events if the result of the comparison is positive,engine control elements that include members for detecting the alternations of third signal and a counter.
Owner:SIEMENS VDO AUTOMOTIVE CORP
Integrated automated analysis and repair
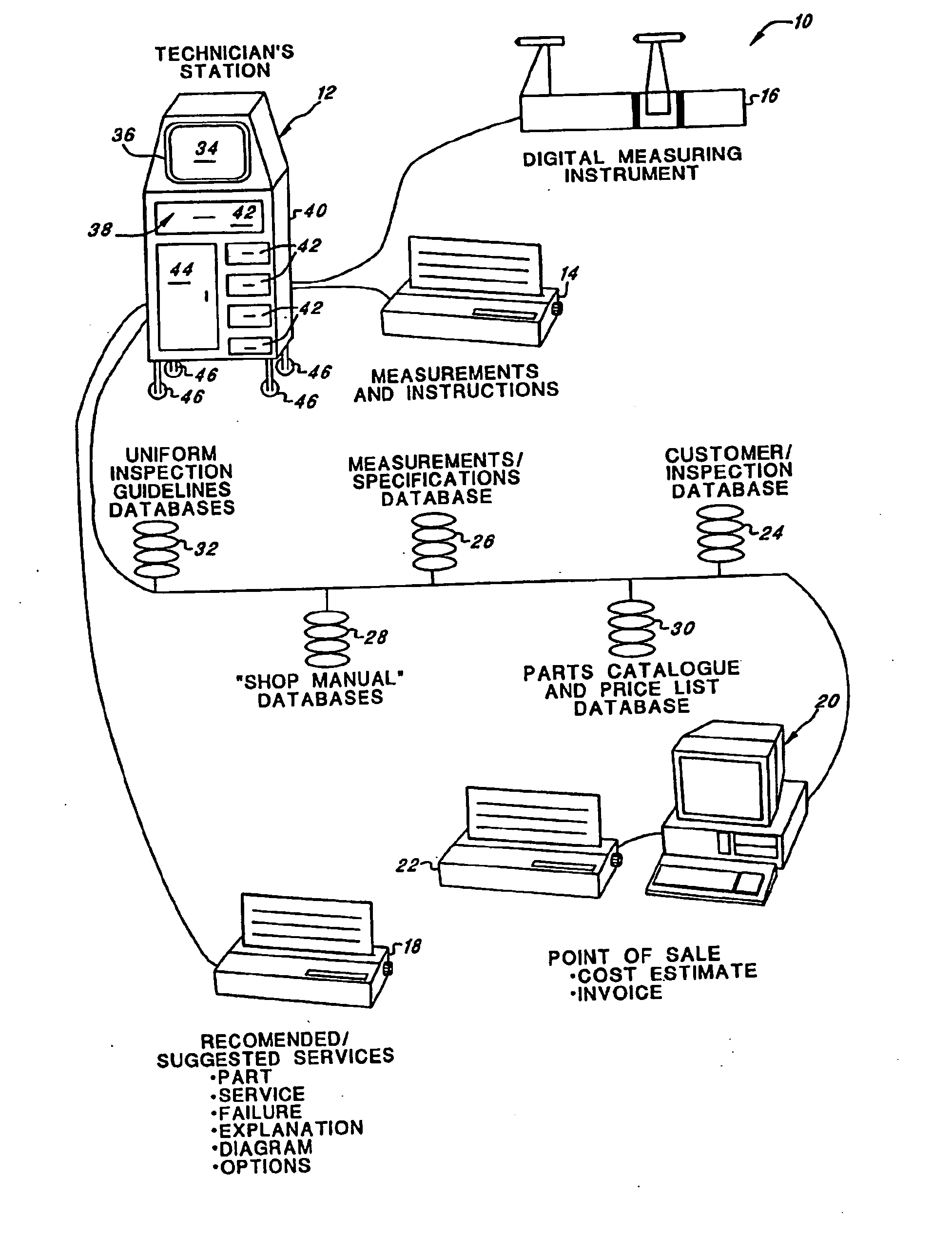
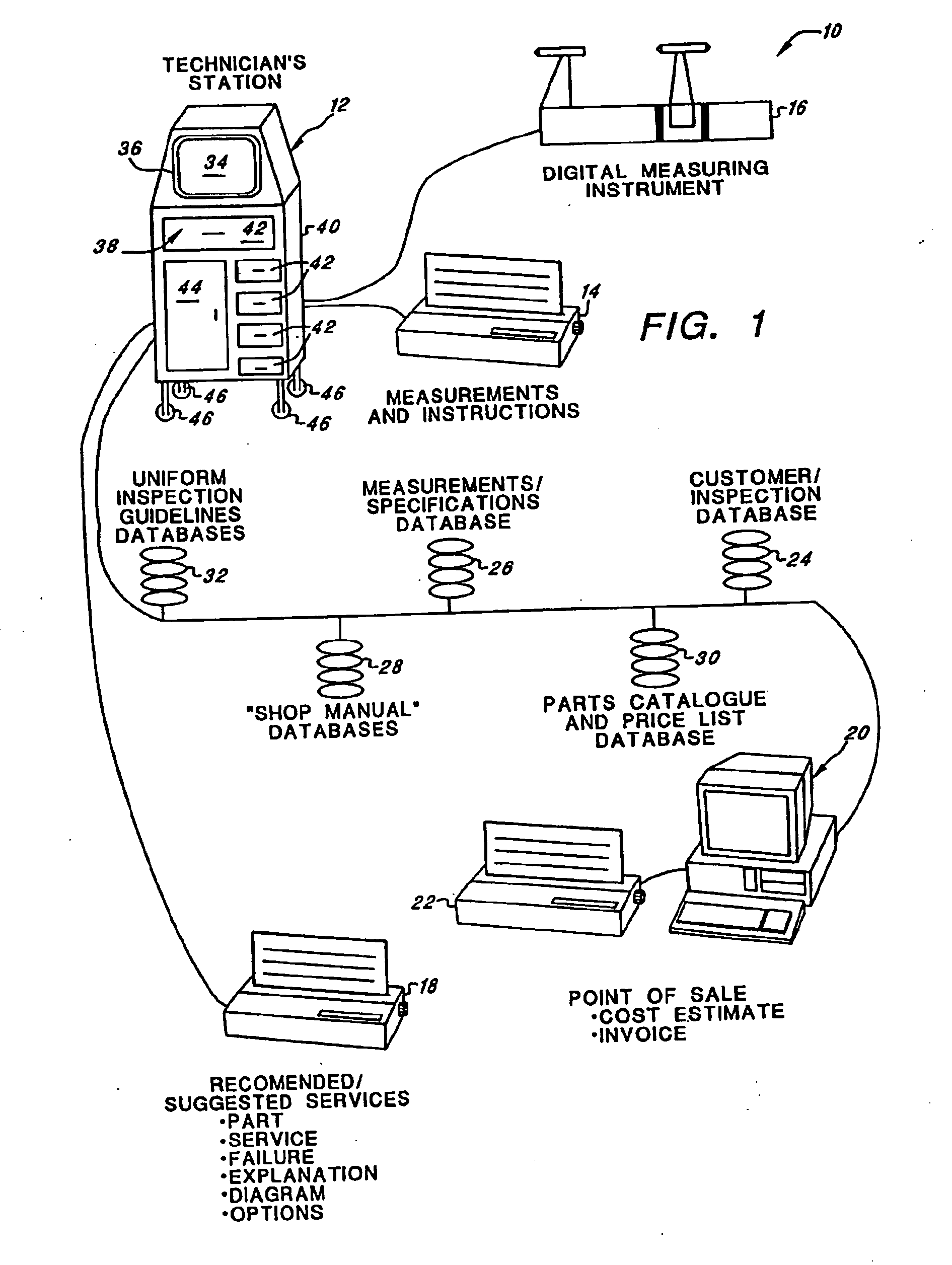
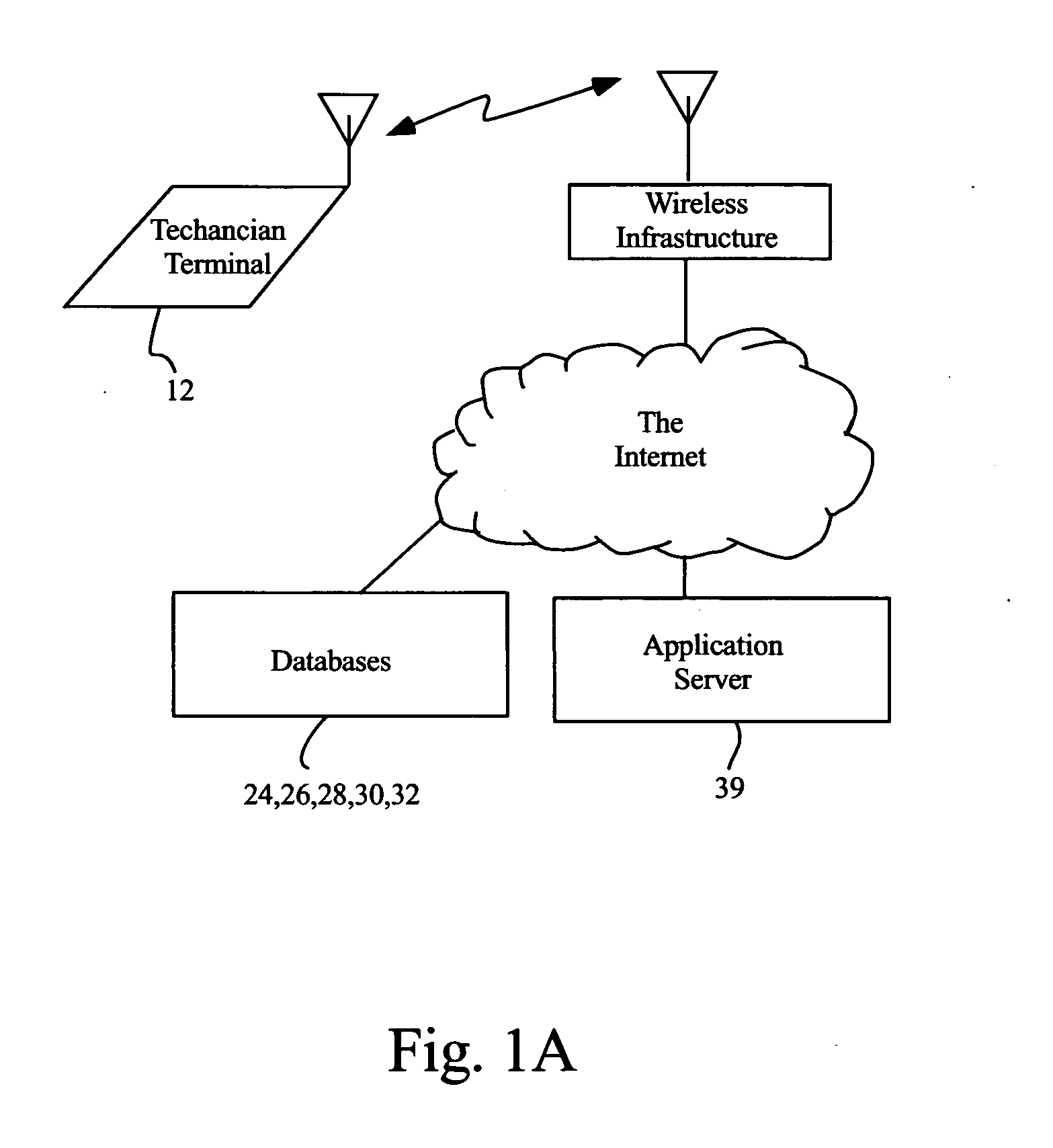
An integrated highly automated analysis system employs a technician terminal for displaying a plurality of inspection screens, and for entering inspection results. The system generates an inspection report after the inspection results have been input. A point-of-sale terminal is coupled to the technician terminal, and the system further generates a cost estimate report in response to the generation of the inspection report and also generates an invoice report. The system includes a plurality of databases, including an inspection guideline database, a specifications database (containing specifications), a customer / inspection database (containing prior inspection records), and a parts catalog database (containing part numbers and part costs).
Owner:CHERRINGTON JOHN K +1
Method of verifying component functionality on egr & air systems
ActiveUS20080148827A1Detect failureVehicle testingInternal-combustion engine testingControl systemElectronic communication
In one aspect, the present invention is directed to a method for operating an electronically controlled internal combustion engine in a vehicle to perform at least one rationality check on at least one sensor to detect impending sensor failure and verify component functionality. The engine is equipped with an engine control system (ECS) having a memory and in electronic communication with various sensors. The sensors transmit data signals to the ECS indicative of associated engine and vehicle component functionality. The method comprises determining a measured operating condition of a first component from sensor data signals indicative of first component functionality, determining a measured operating condition of a second component from sensor data signals indicative of second component functionality, comparing the measured condition of the first component to the measured operating condition of the second component to determine whether sensor readings from the first component are indicative of a component operating within a normal range but indicative of impending sensor or component failure, logging an indication of an impending sensor or component failure as a fault in MPU memory if it occurs for a predetermined period of time and for more than a predetermined number of times and drive cycles, and activating a warning alert to an operator and initiating remedial actions responsive to the indication of impending component or sensor failure. The data logged includes time of fault, type of fault, number of occurrences of the fault, number of drive cycles where the fault occurred and distance traveled with the fault logged.
Owner:DETROIT DIESEL CORP
Diagnostics for two-mode variable valve activation devices
ActiveUS20090228167A1Vehicle testingInternal-combustion engine testingElectricityRadio frequency signal
A method for detecting a low-lift or zero-lift failure mode in a variable valve activation system of an internal combustion engine includes the steps of positioning a piezo-electric element that acts as a radio frequency transmitter relative to a lost motion spring of a two-mode variable valve activation lost motion device, subjecting the piezo-electric element to a compression load when a load from displacement of a lobe of a camshaft acts on the lost motion spring, broadcasting a radio frequency signal each time the piezo-electric element is subjected to the compression load, and evaluating the presence or absence of the broadcasted radio frequency signal in relation to an expected presence or absence of the radio frequency signal. The direct measurement of the mode of each two-mode device is both more reliable and more efficient in the use of engine controller resources compared to currently existing diagnostic methods.
Owner:DELPHI TECH IP LTD
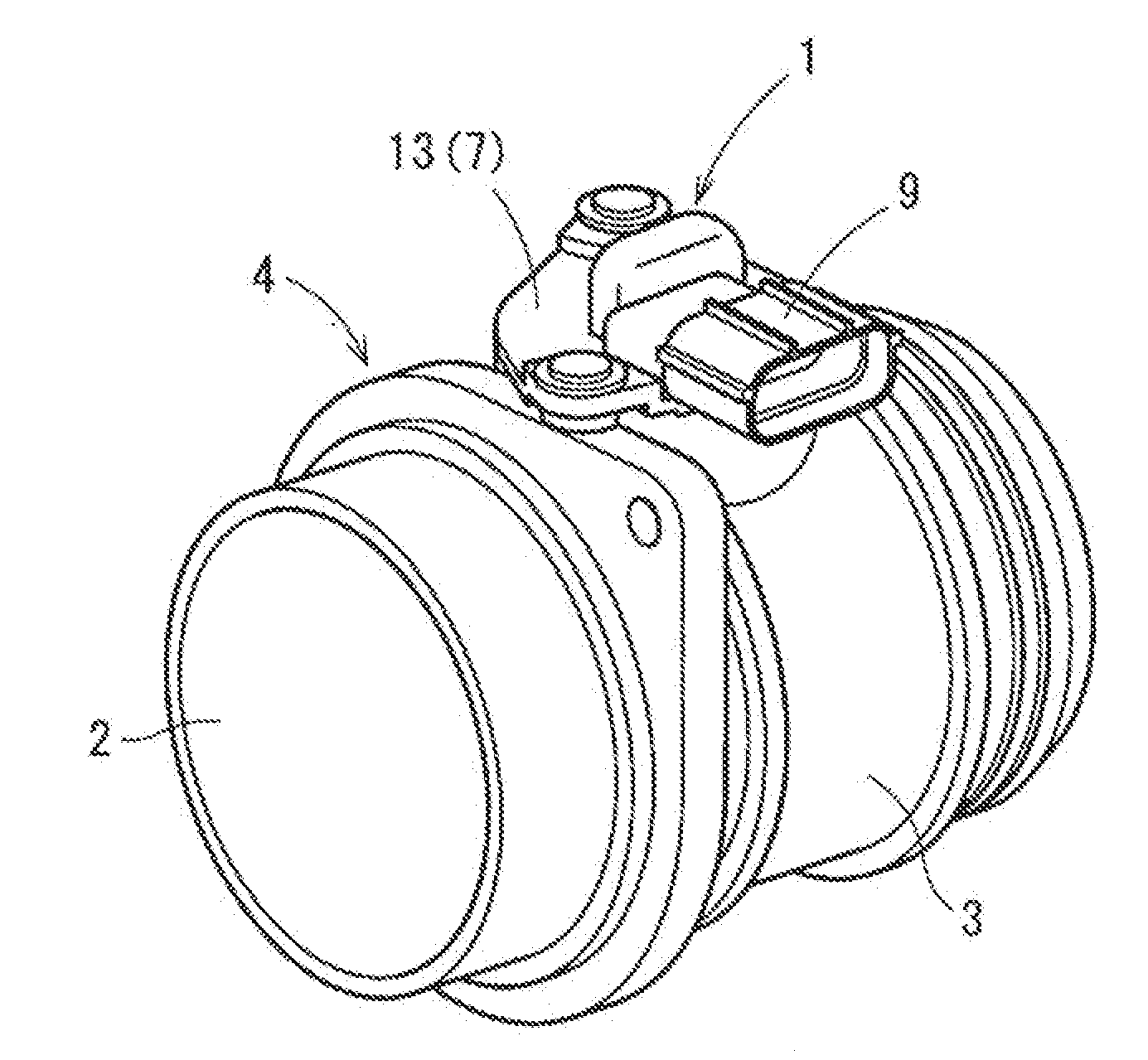
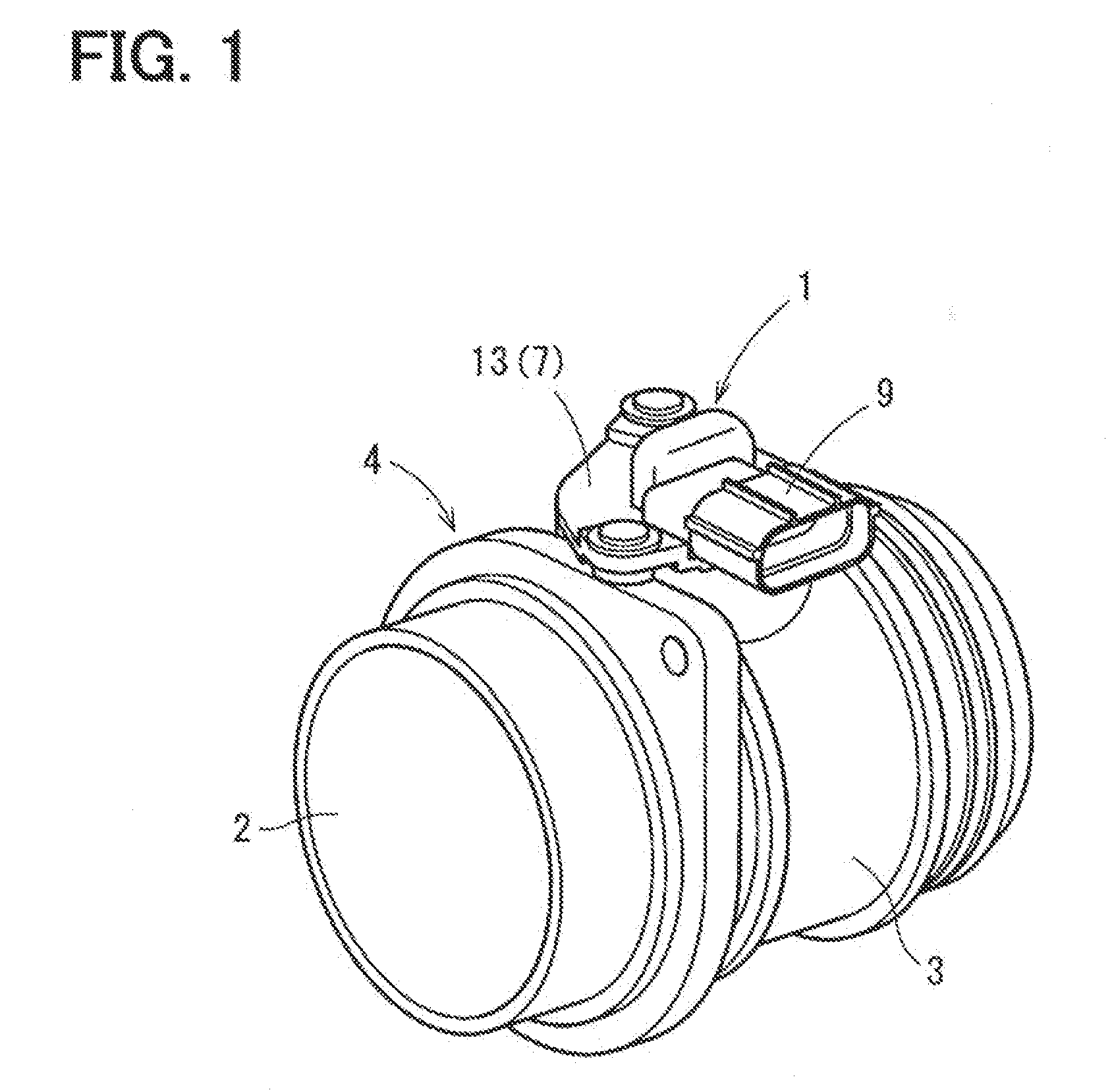
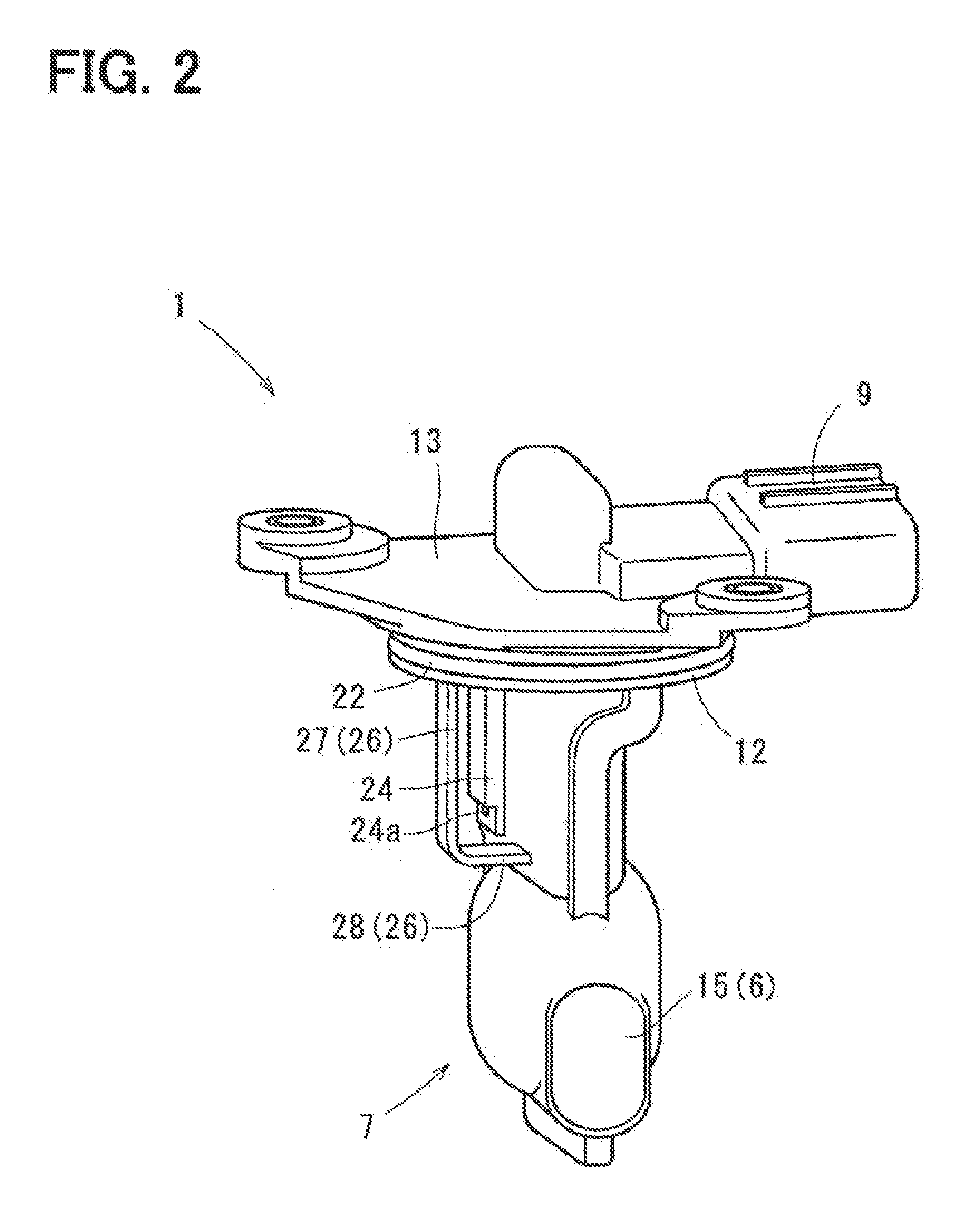
Air flow measuring device
ActiveUS20130036806A1Internal-combustion engine testingVolume/mass flow by thermal effectsFlow transducerMeasurement device
An air flow measuring device includes a housing, flow sensor, and a humidity sensor. The housing defines a bypass flow passage through which intake it passes. A part of intake air is taken into the bypass flow passage to pass through the bypass flow passage. The flow sensor includes a sensing part disposed in the bypass flow passage, and produces a signal which is in accordance with the flow rate of intake air as a result of heat transfer between intake air taken into the bypass flow passage and the sensing part. The humidity sensor includes a sensing part exposed to the intake passage, and projects from an outer wall of the housing into the intake passage. The humidity sensor produces a signal which is in accordance with humidity of intake ail flowing through the intake passage.
Owner:DENSO CORP
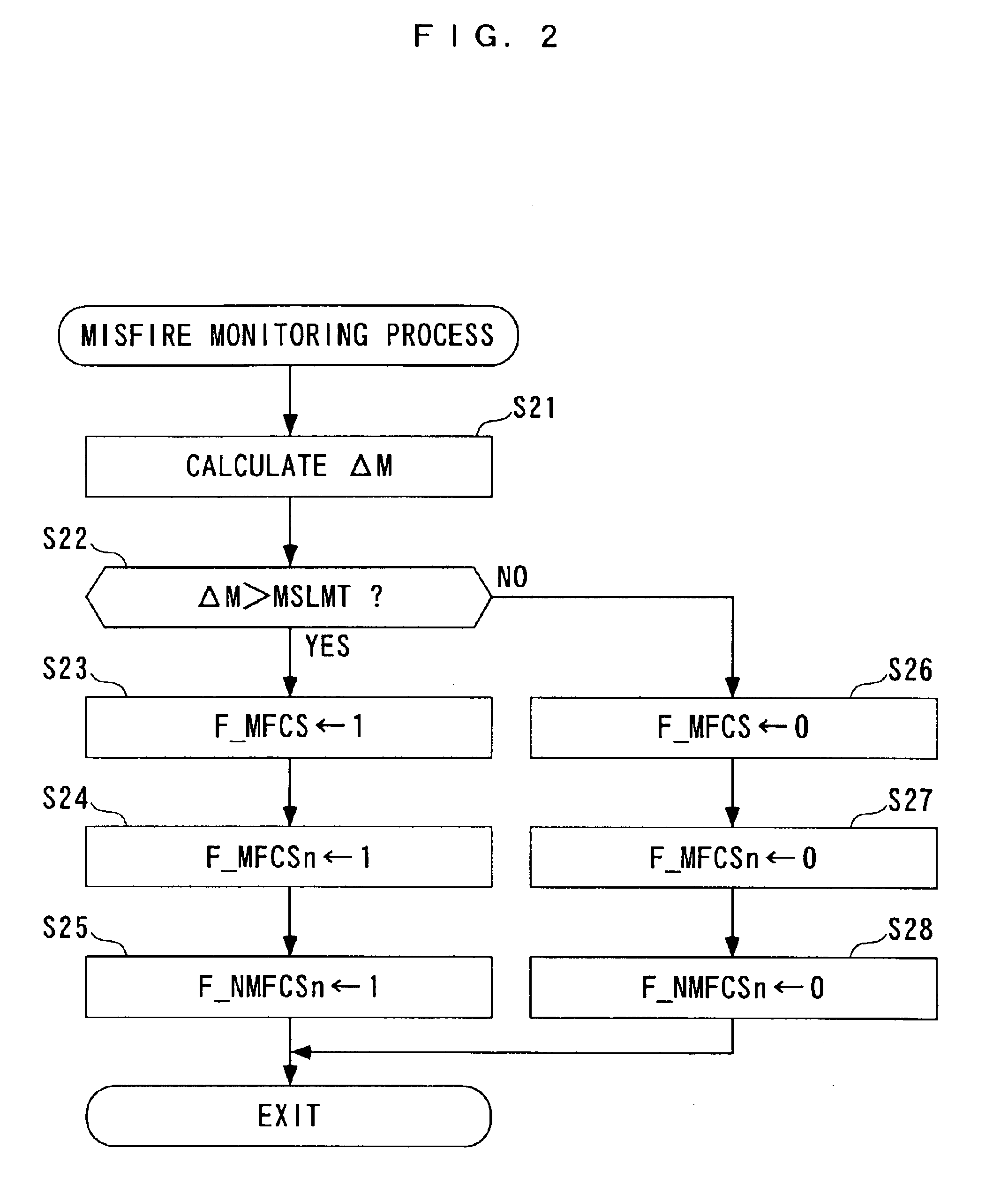
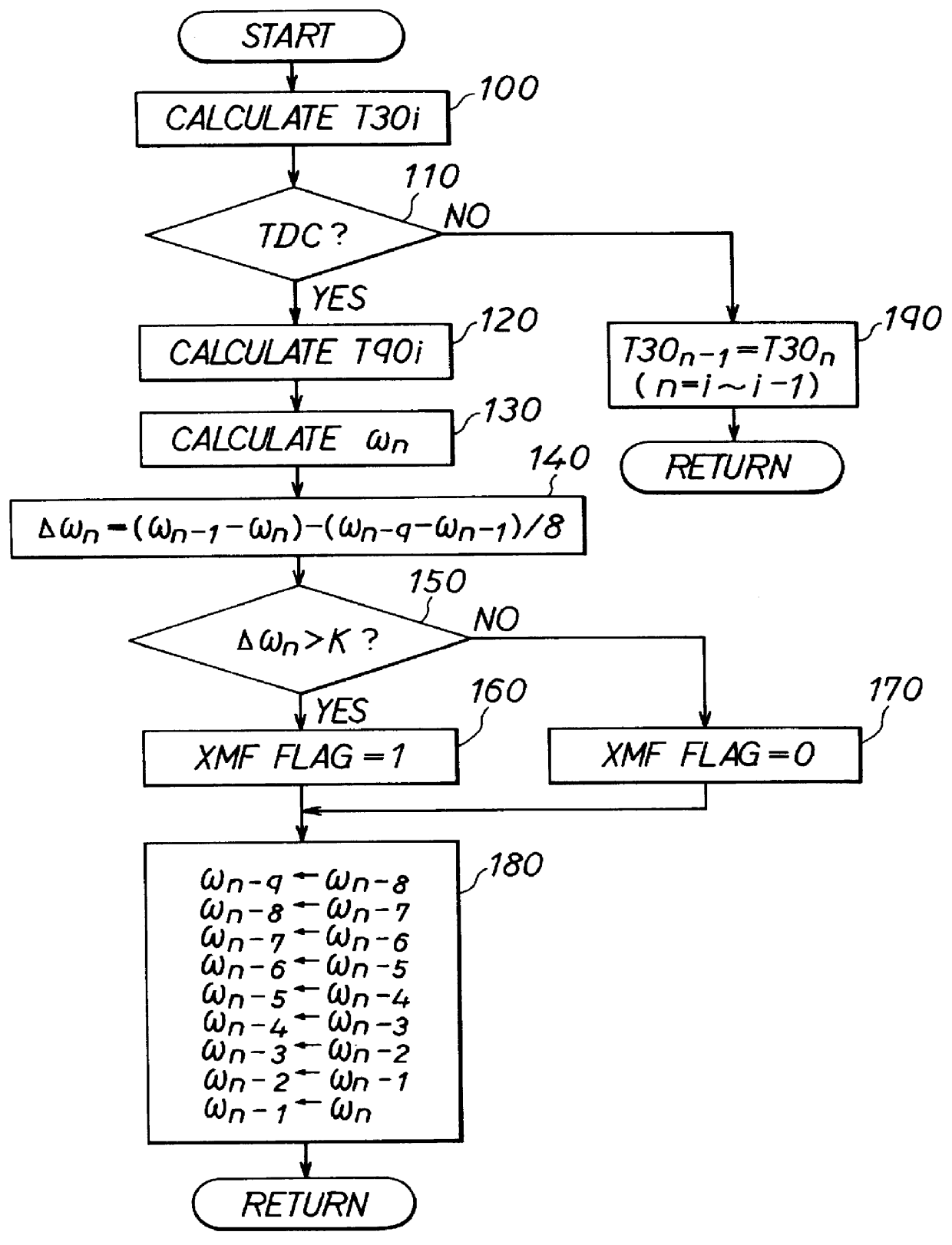
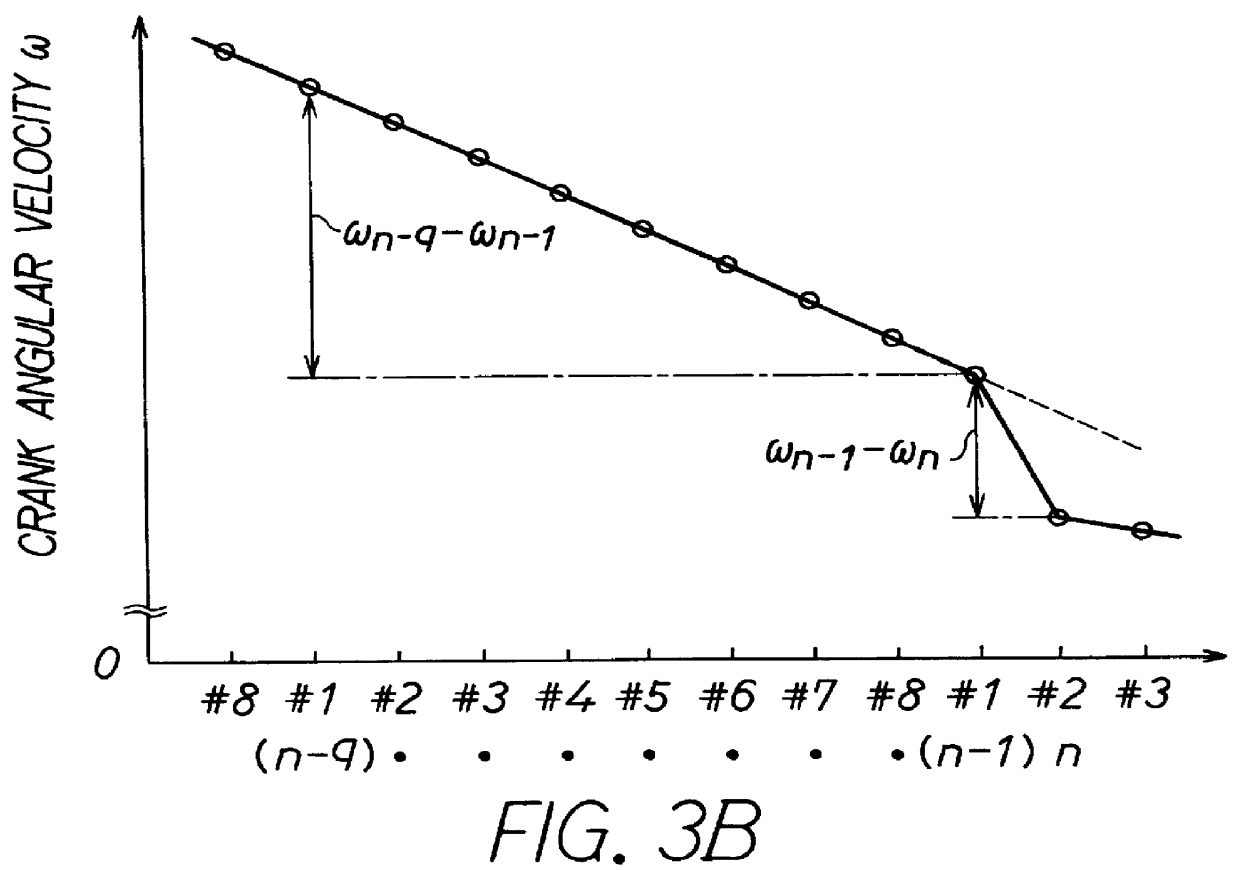
Internal combustion engine misfire detection with engine acceleration and deceleration correction during a repetitive misfire condition
InactiveUS6023651AInternal-combustion engine testingAnalogue computers for vehiclesCombustionInternal combustion engine
To accurately detect patterns of misfires in an internal combustion engine, misfire is detected by calculating angular speed variation responsive to crankshaft rotation and comparing that with a predetermined misfire reference value. The calculated angular speed variation includes a first elementary term showing rotational variation of two different cylinders and a second correction term showing the rotational variation of the same cylinder separated by one combustion cycle. The elementary term shows how much rotational variation is between the cylinder n and the previous cylinder n-1 due to the occurrence of misfire. In contrast, the correction term shows how much error in the rotational variation is caused in same cylinder (e.g., mainly when accelerating or decelerating).
Owner:DENSO CORP
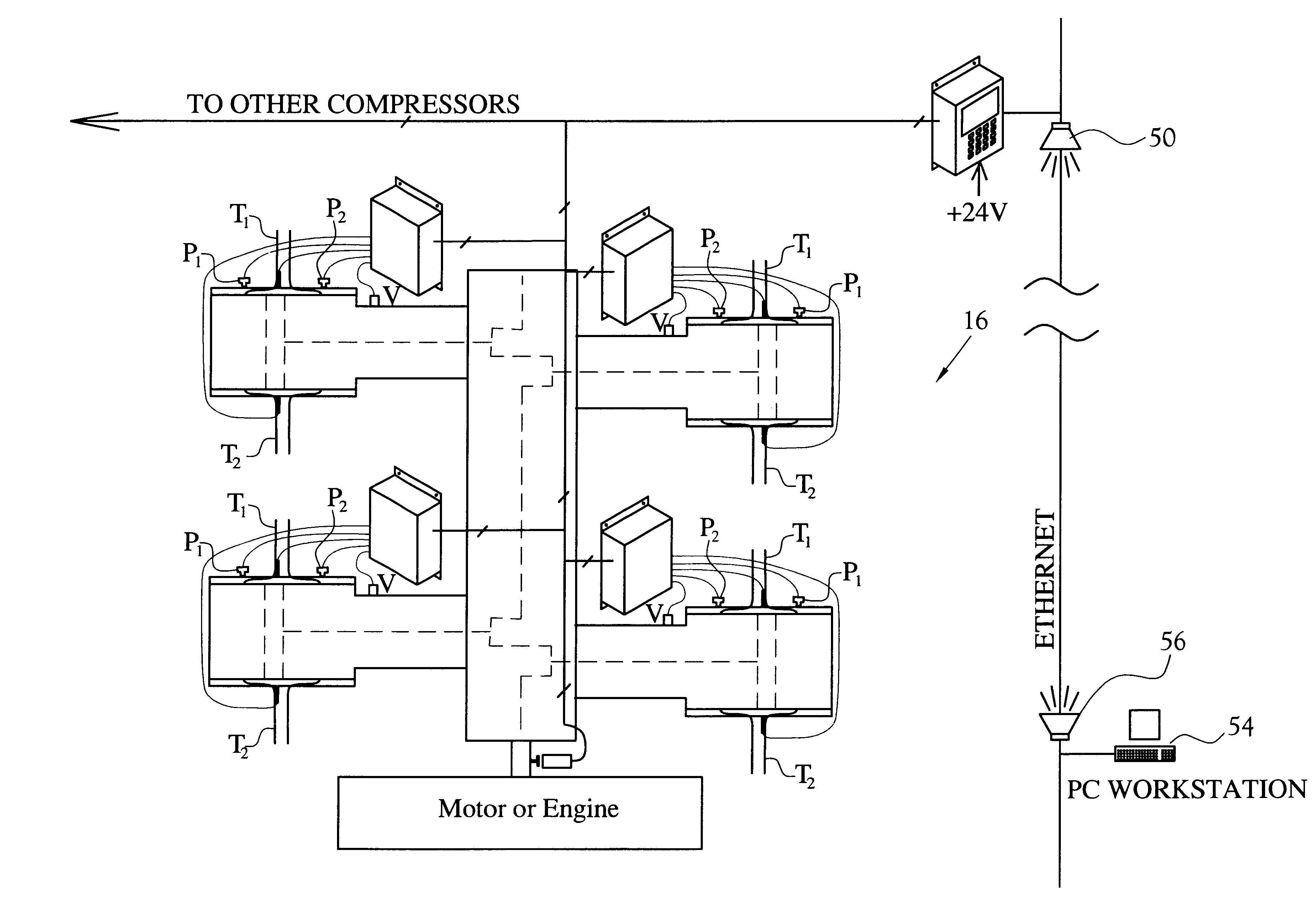
Method and apparatus for continuously monitoring parameters of reciprocating compressor cylinders
InactiveUS6292757B1Continuous monitoringAnalogue computers for vehiclesInternal-combustion engine testingEngineeringVolume Curve
An apparatus and method for continuously monitoring selected parameters of reciprocating compressor cylinders is disclosed, the apparatus includes a plurality of sensors positioned to monitor selected parameters within the cylinder on either side of the piston, with the selected parameters including pressures on each side of the piston for each cycle, temperatures of the gas entering and exiting the cylinder, and vibrations of components such as a piston shaft within the cylinder. A calculator means in close proximity to the cylinder receives the signals from the sensors and analyzes the signals for each cycle of the piston. Output signals proportional to the monitored signals are transmitted to a remotely located computer. The output signals include pressure versus volume curves for each cylinder volume, horsepower consumed by the cylinder, inlet suction and outlet discharge gas temperatures of the gases moved through the cylinder, and compression and tension stress on the piston rod. Computer analyses compare monitored signals to pre-selected ranges of operating parameters to provide alarm signals to alert operators of the performance and mechanical conditions within the monitored reciprocating compressor cylinder. A method of operation for continuously monitoring selected parameters of reciprocating compressor cylinders is also disclosed.
Owner:WINDROCK
Diagnostic system for engine
InactiveUS20010049579A1Increase contactVehicle testingInternal-combustion engine testingInternal combustion engineData storing
A diagnostic system is provided to aid a technician or engineer in diagnosing an internal combustion engine. The diagnostic system comprises an electronic control unit that is operatively coupled to a data storage device and to one or more engine sensors. The electronic control unit is configured to collect data from the one or more engine sensors and to store that data in the data storage device. A computer is selectively coupled to the data storage device. The computer program is configured to display specific sets of data stored in the data storage device in various formats.
Owner:YAMAHA MARINE KK
Fuel composition estimation and control of fuel injection
InactiveUS20090178474A1Analogue computers for vehiclesInternal-combustion engine testingFuel oilEngineering
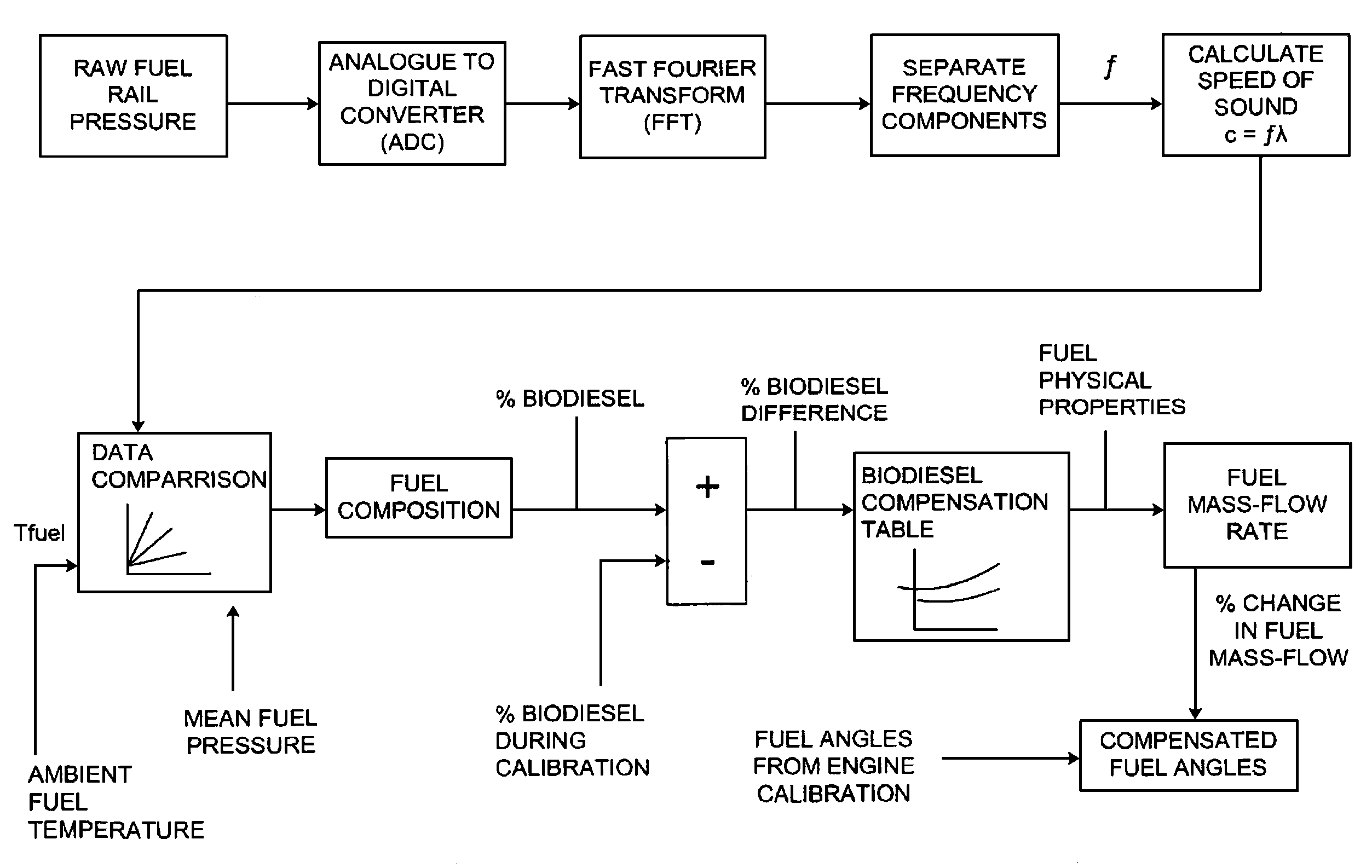
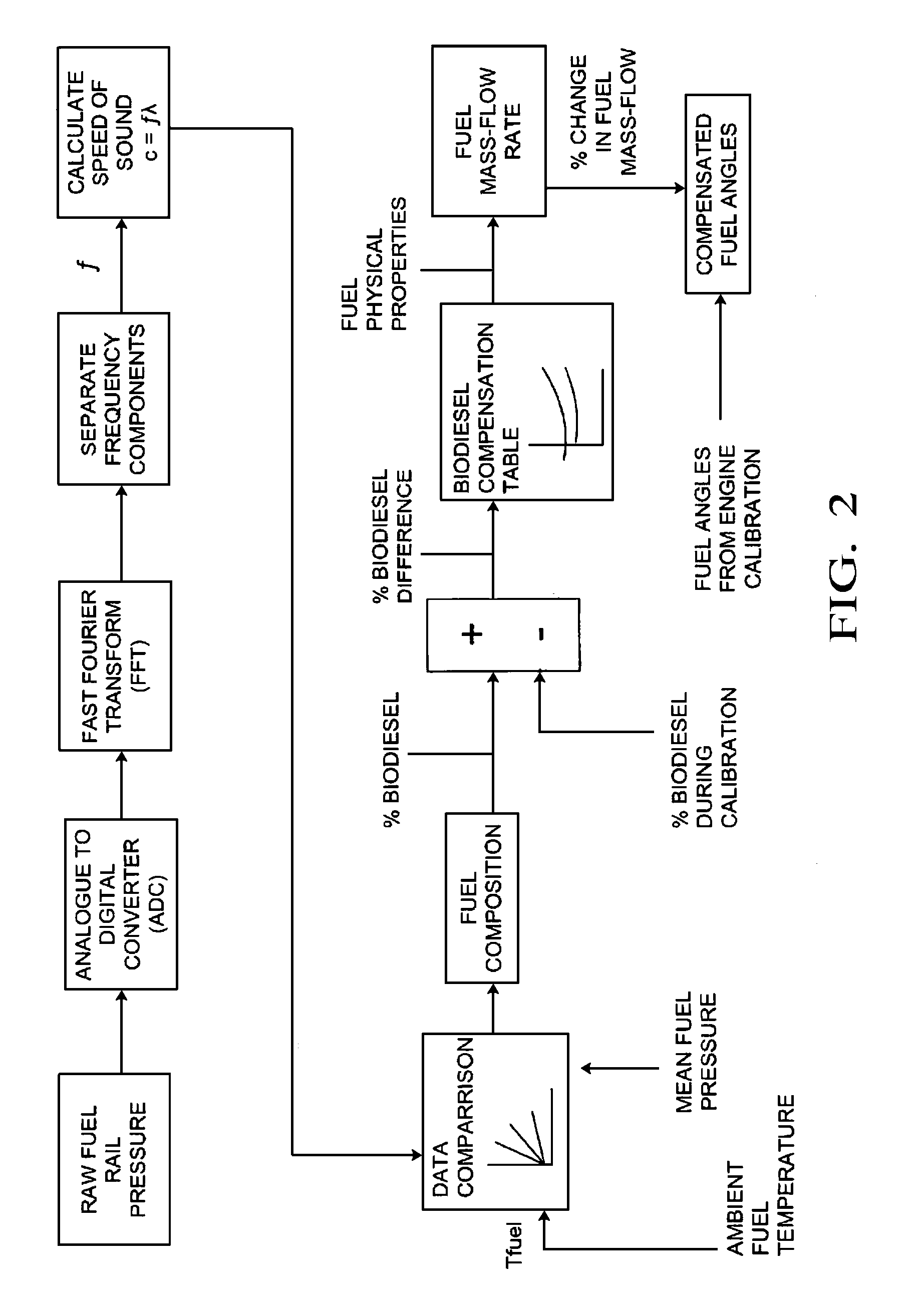
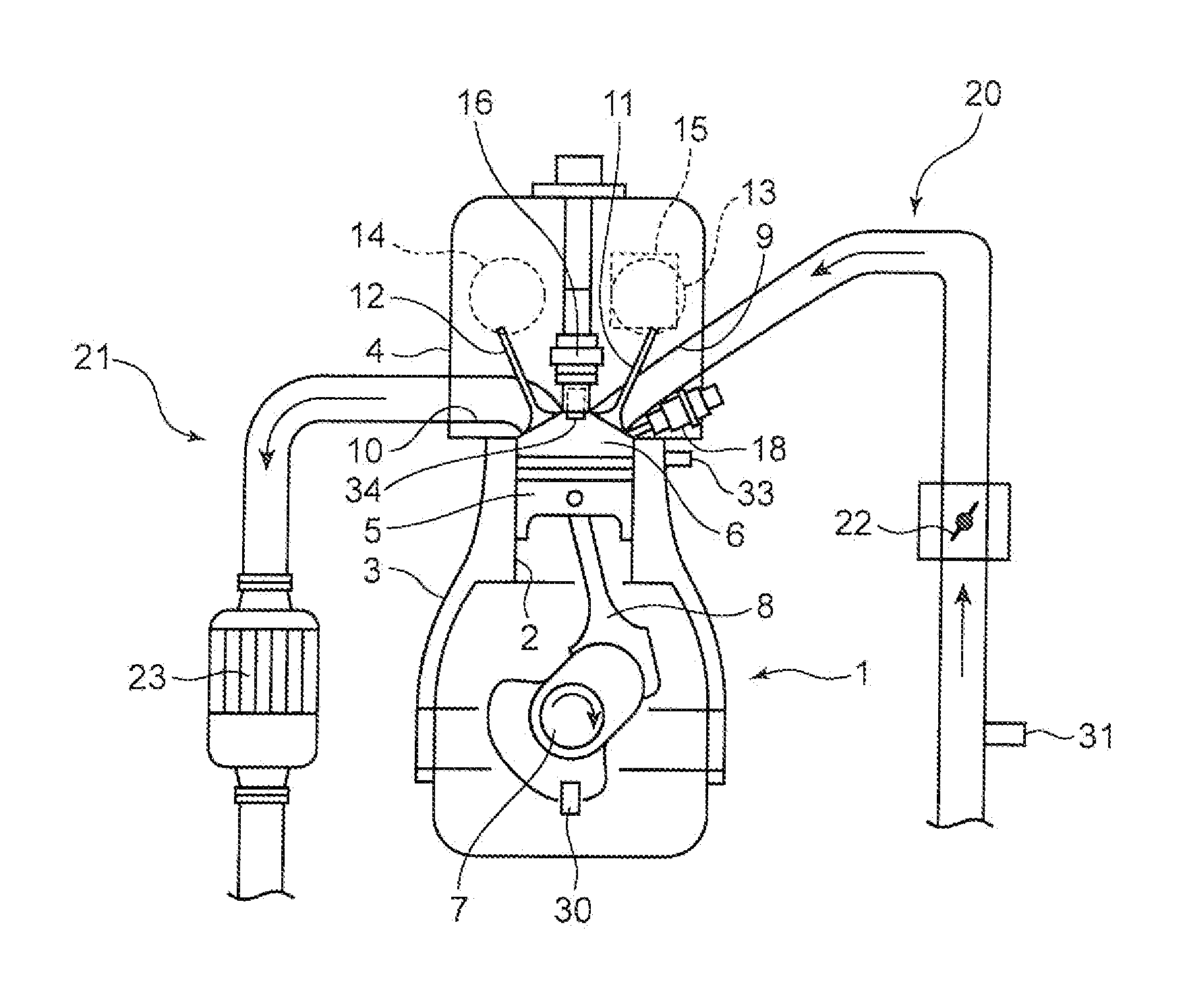
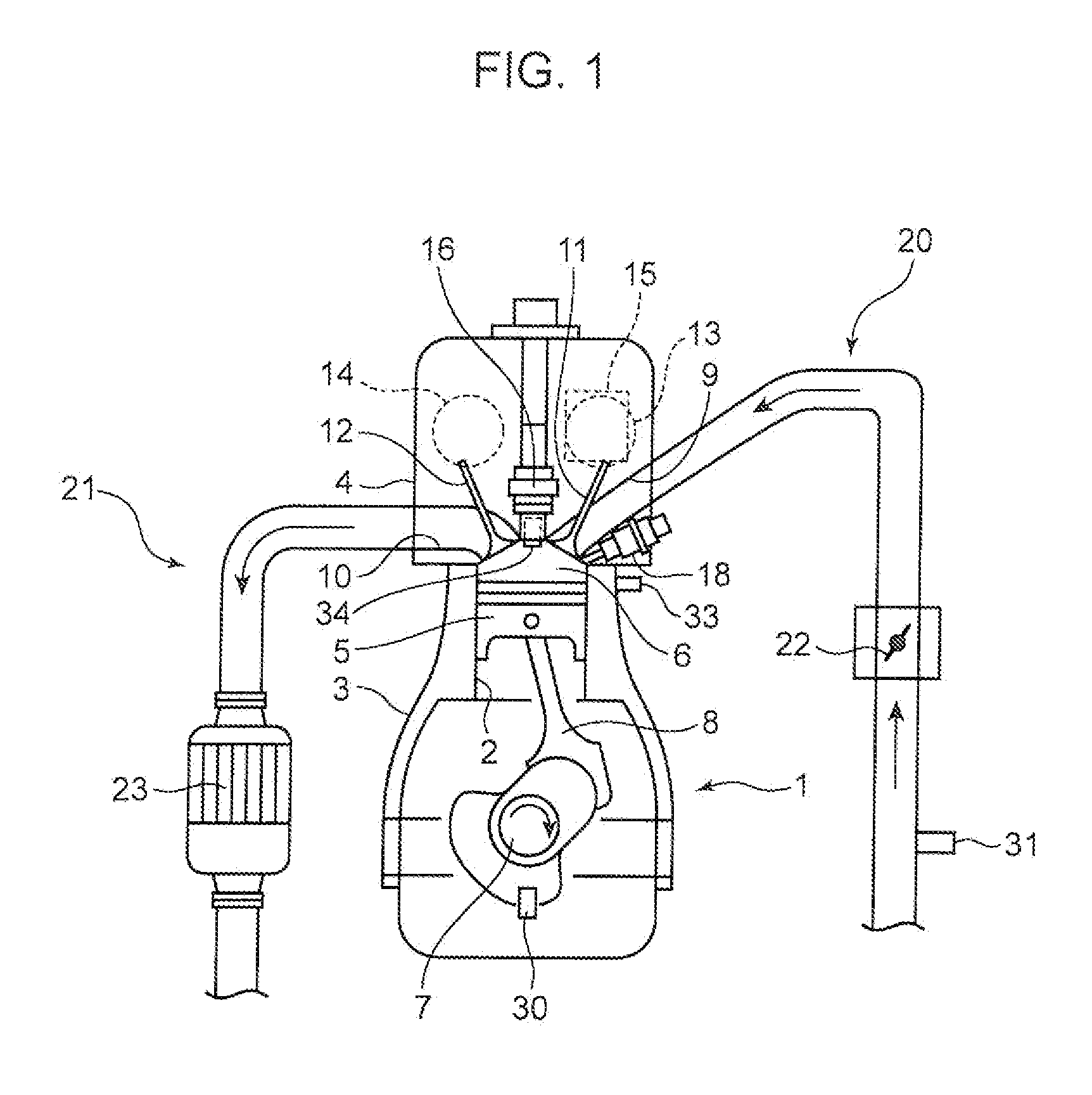
A method for estimating the composition of a fuel within an engine, comprises performing the following steps under ambient conditions: (a′) determining the ambient temperature of the fuel; (a) monitoring the fuel pressure inside a fuel rail of the engine over a period of time; (b) calculating at least one frequency component of the change in fuel pressure; (c) calculating the speed of sound transmission c on the basis of the at least one frequency component; and (d) estimating the composition of the fuel on the basis of the calculated speed of sound transmission at said ambient temperature. Suitably, the speed of sound transmission in the fuel is calculated using the equation: c=fλ, where the wavelength λ of the standing wave with frequency f is 2L, where L is the length of the fuel rail. Also described are methods for estimating the temperature of the fuel at a non-ambient temperature, and determining a fuels physical properties. Methods for controlling a fuel injection system in an engine according to the determined physical properties of the fuel and the resultant fuel injection system are also described.
Owner:DELPHI INT OPERATIONS LUXEMBOURG S A R L
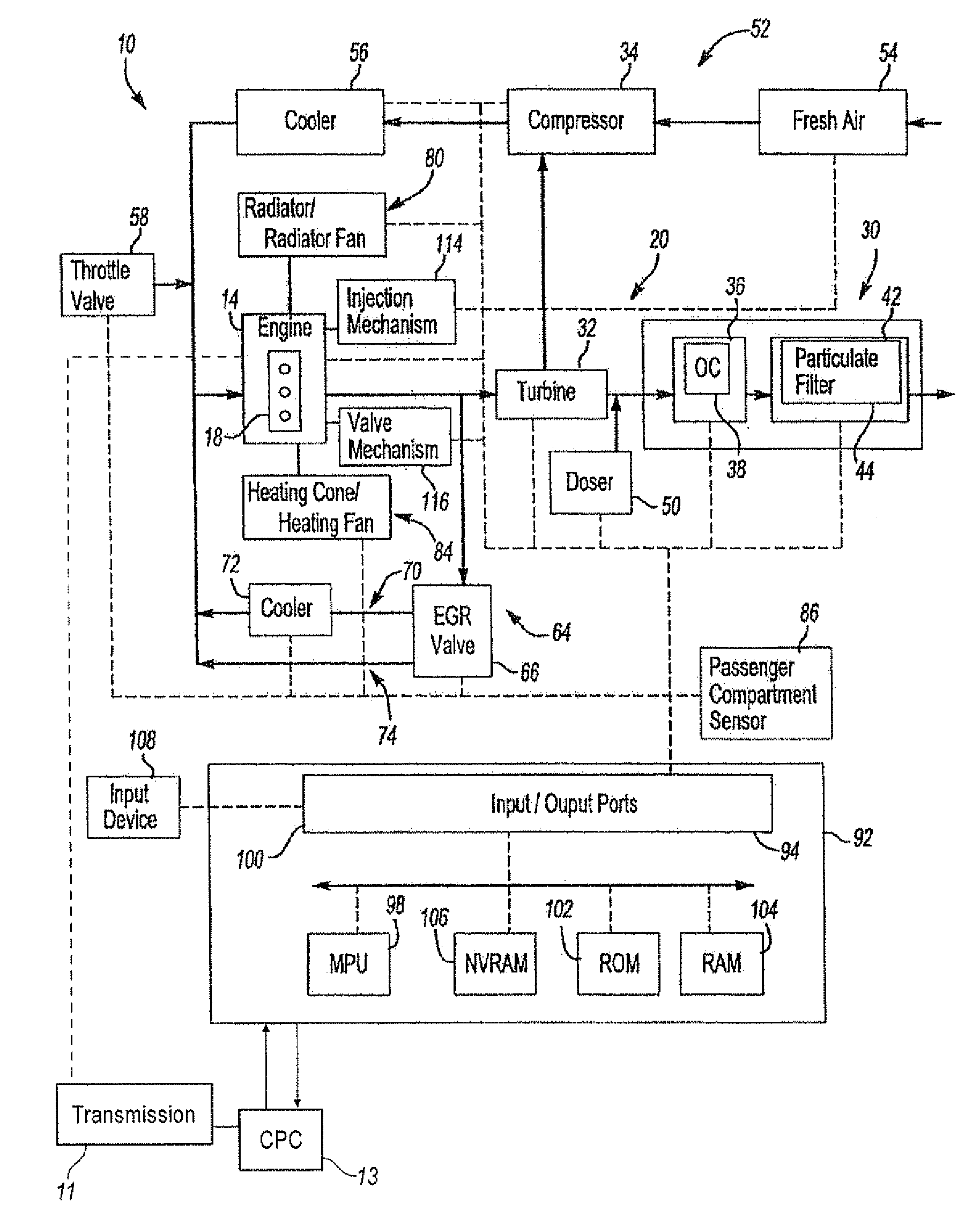
Engine cooling system control
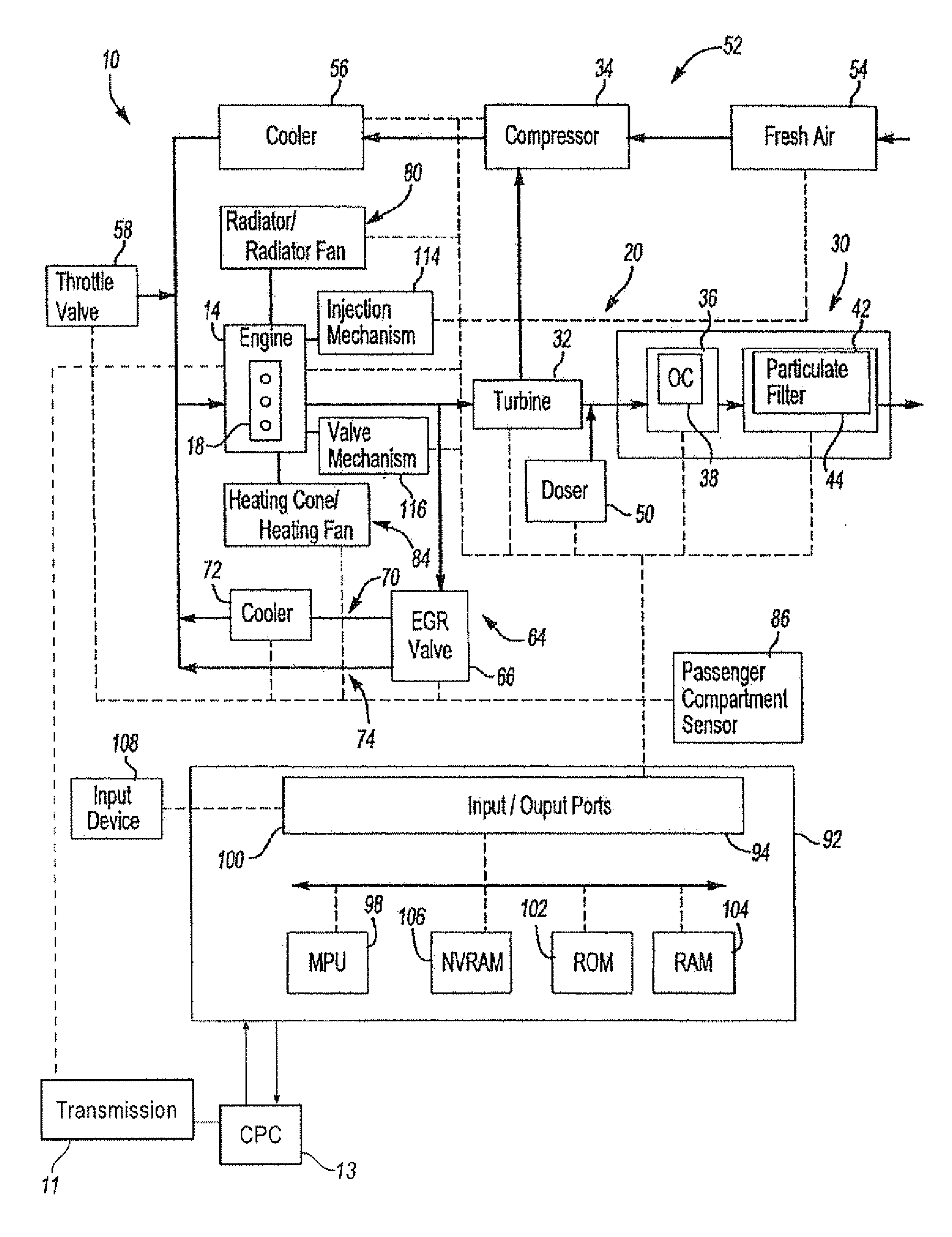
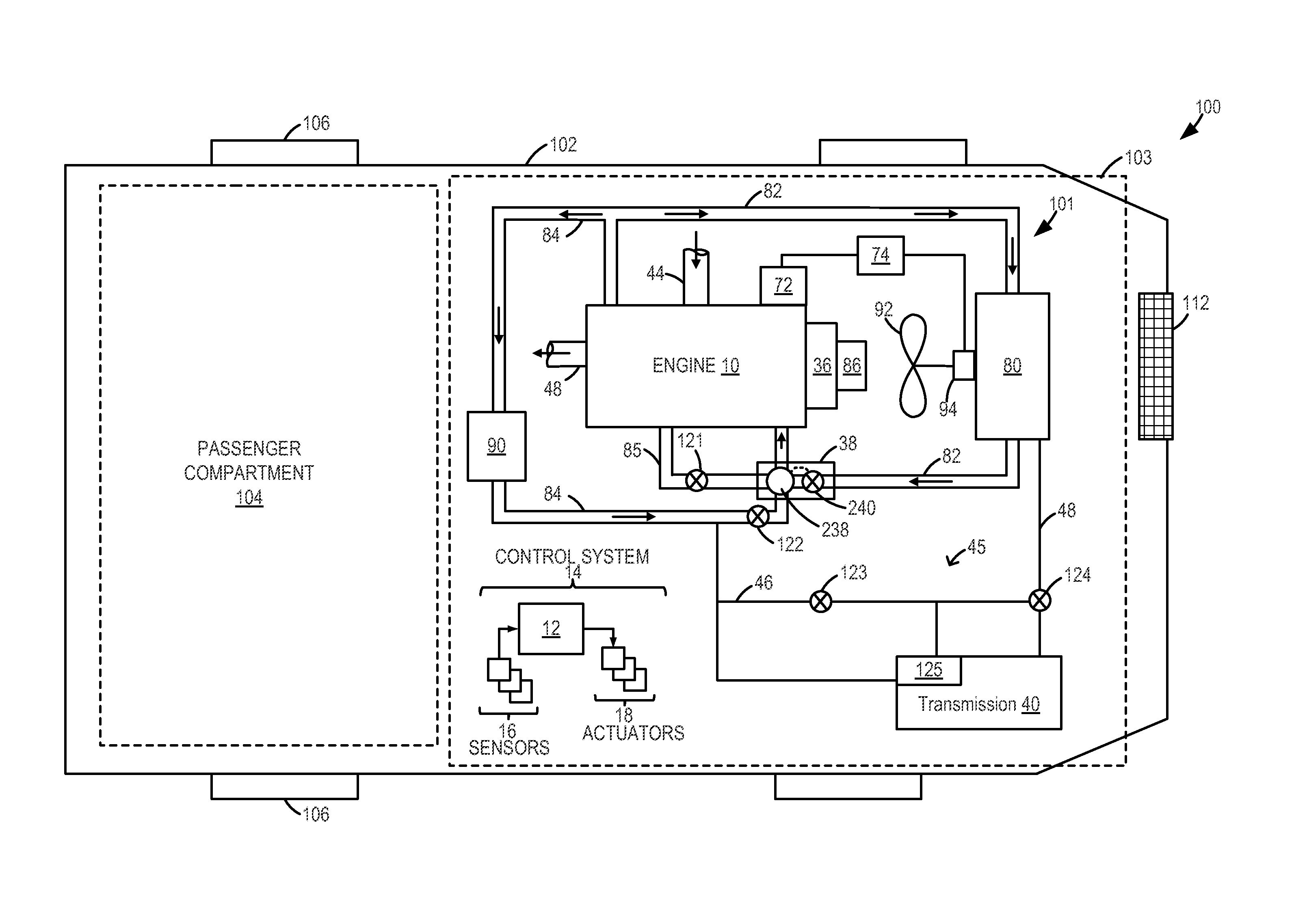
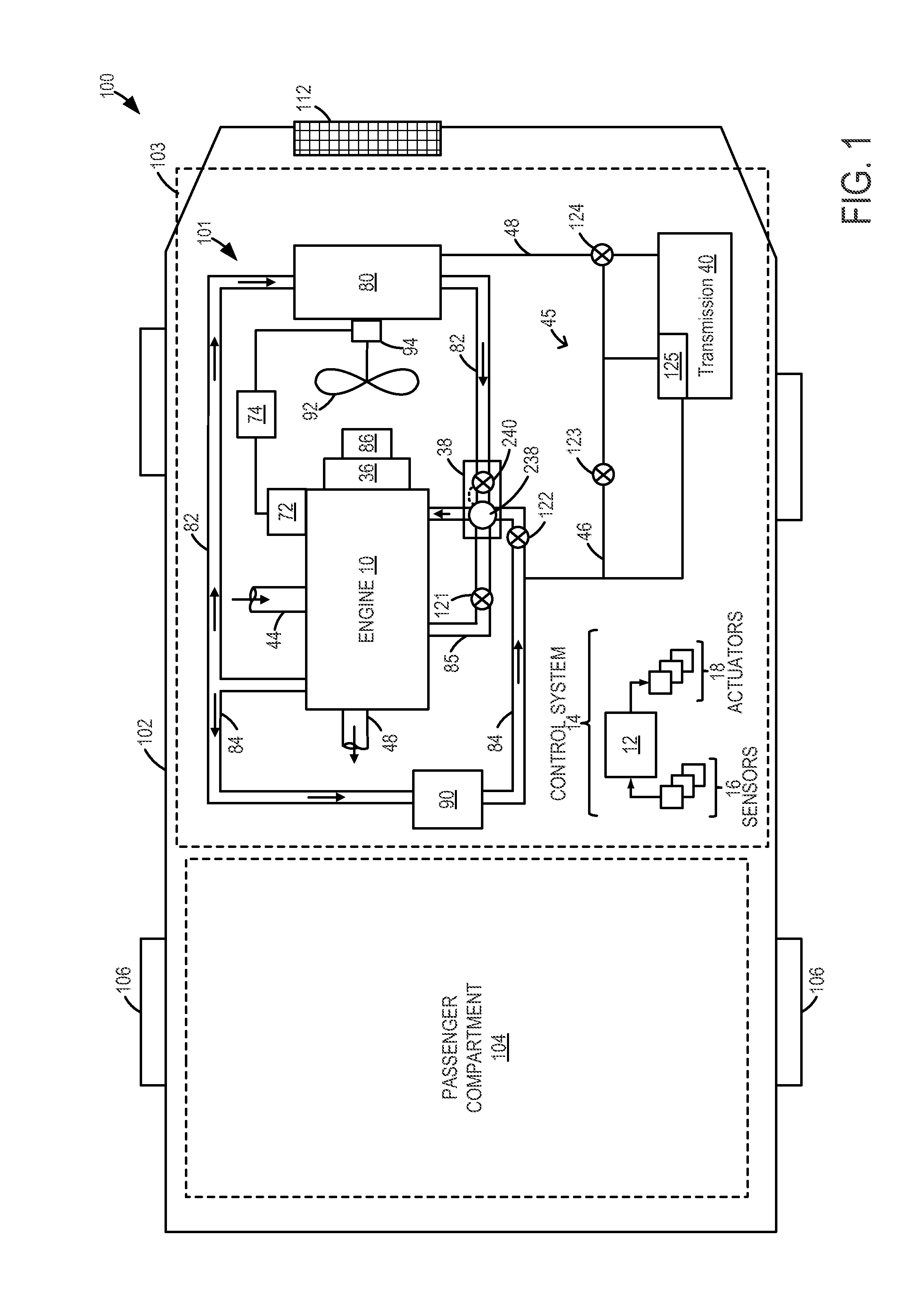
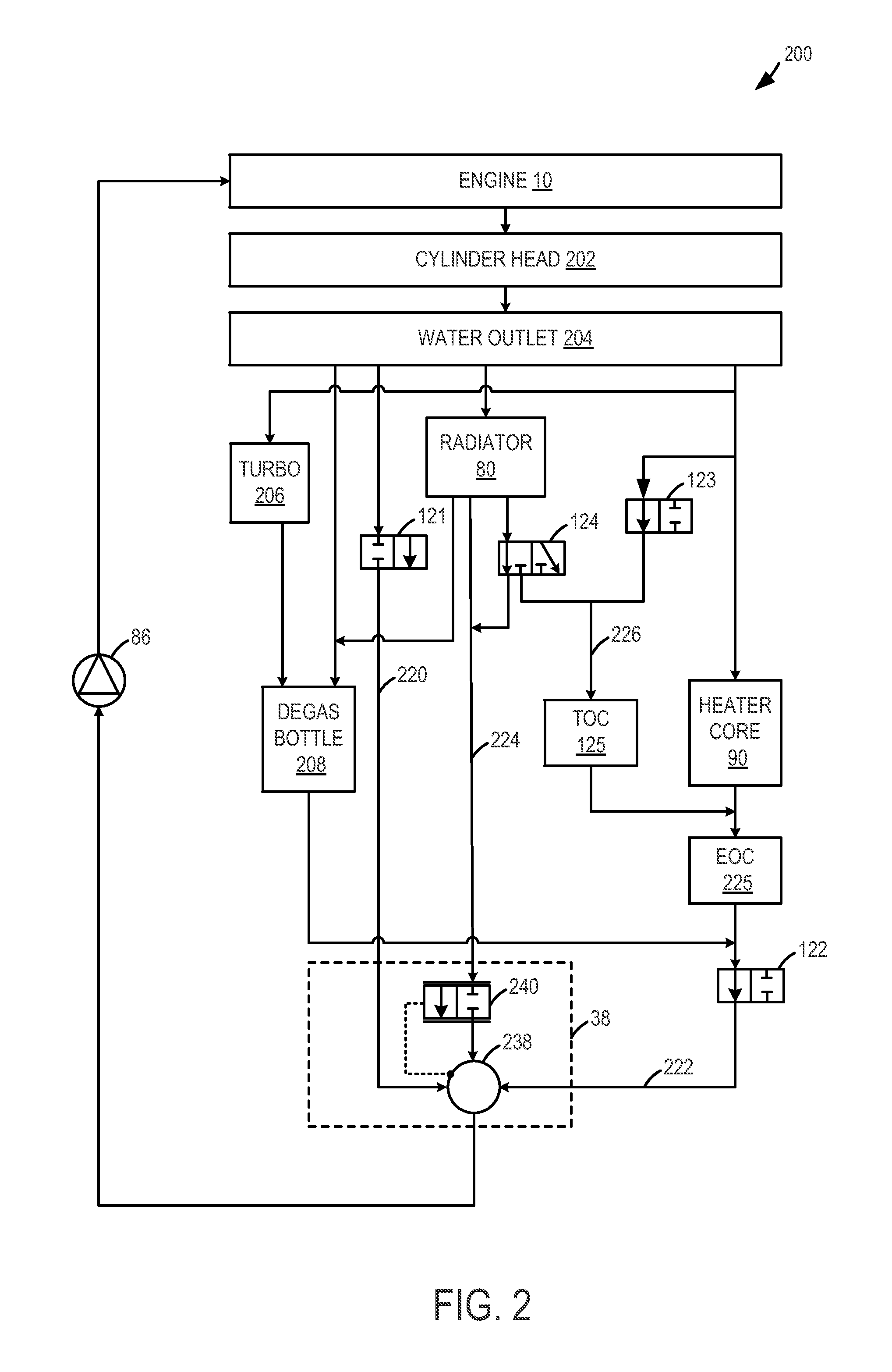
InactiveUS20130255604A1Improve economyInternal-combustion engine testingCoolant flow controlEngineeringCoolant temperature
Methods and systems are provided for diagnosing each of a plurality of engine cooling system components including various valves and grill shutters. Each valve may be individually closed and opened for a specified duration, and corresponding changes in coolant temperature may be monitored. If all the components are functional, the various valves may be adjusted to stagnate coolant at the engine and expedite engine warm-up during a cold-start.
Owner:FORD GLOBAL TECH LLC
Mass air flow measurement device
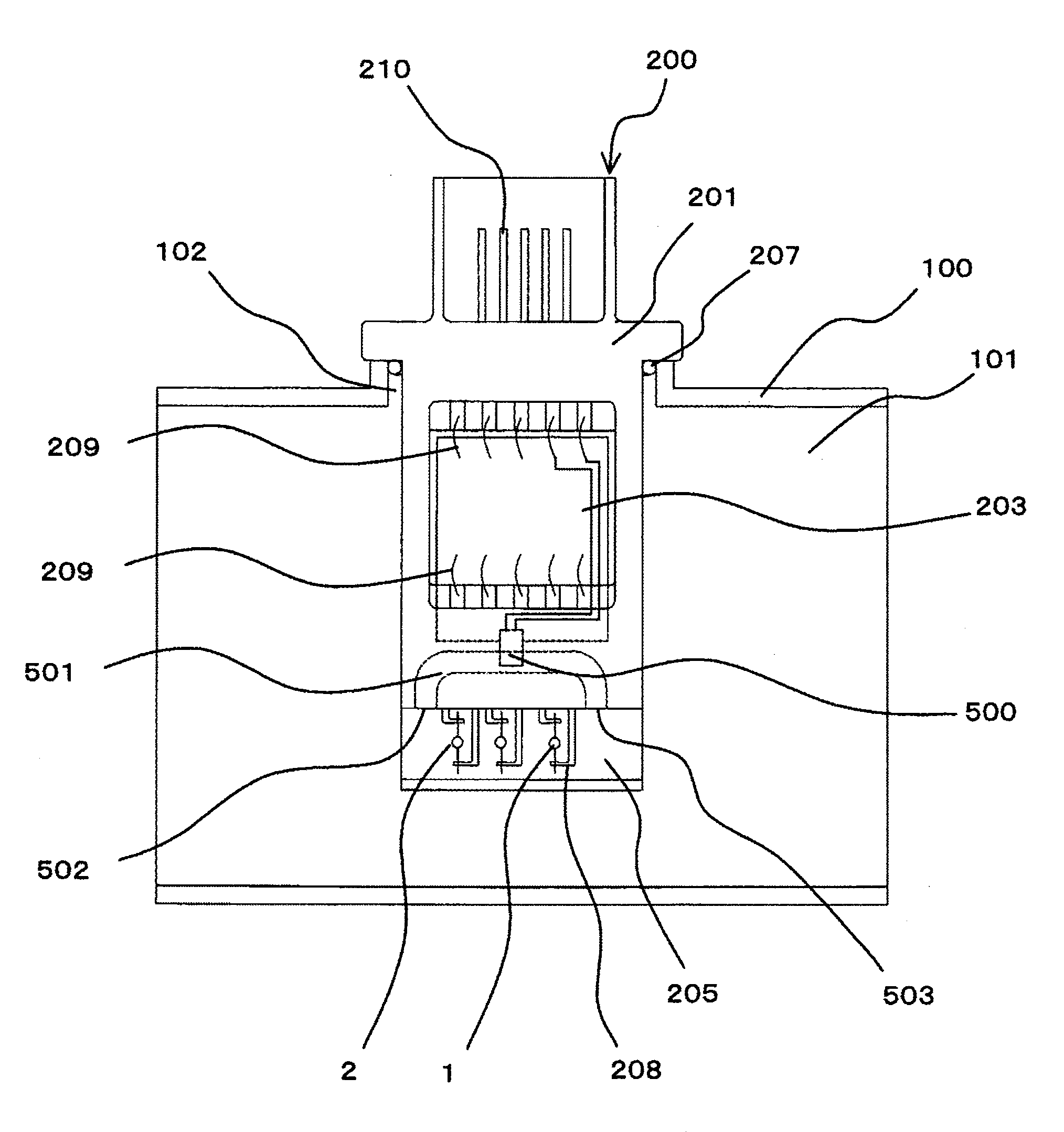
ActiveUS20100031737A1Reduced Possibility of ContaminationReduce amountInternal-combustion engine testingVolume/mass flow by thermal effectsMeasurement devicePressure sense
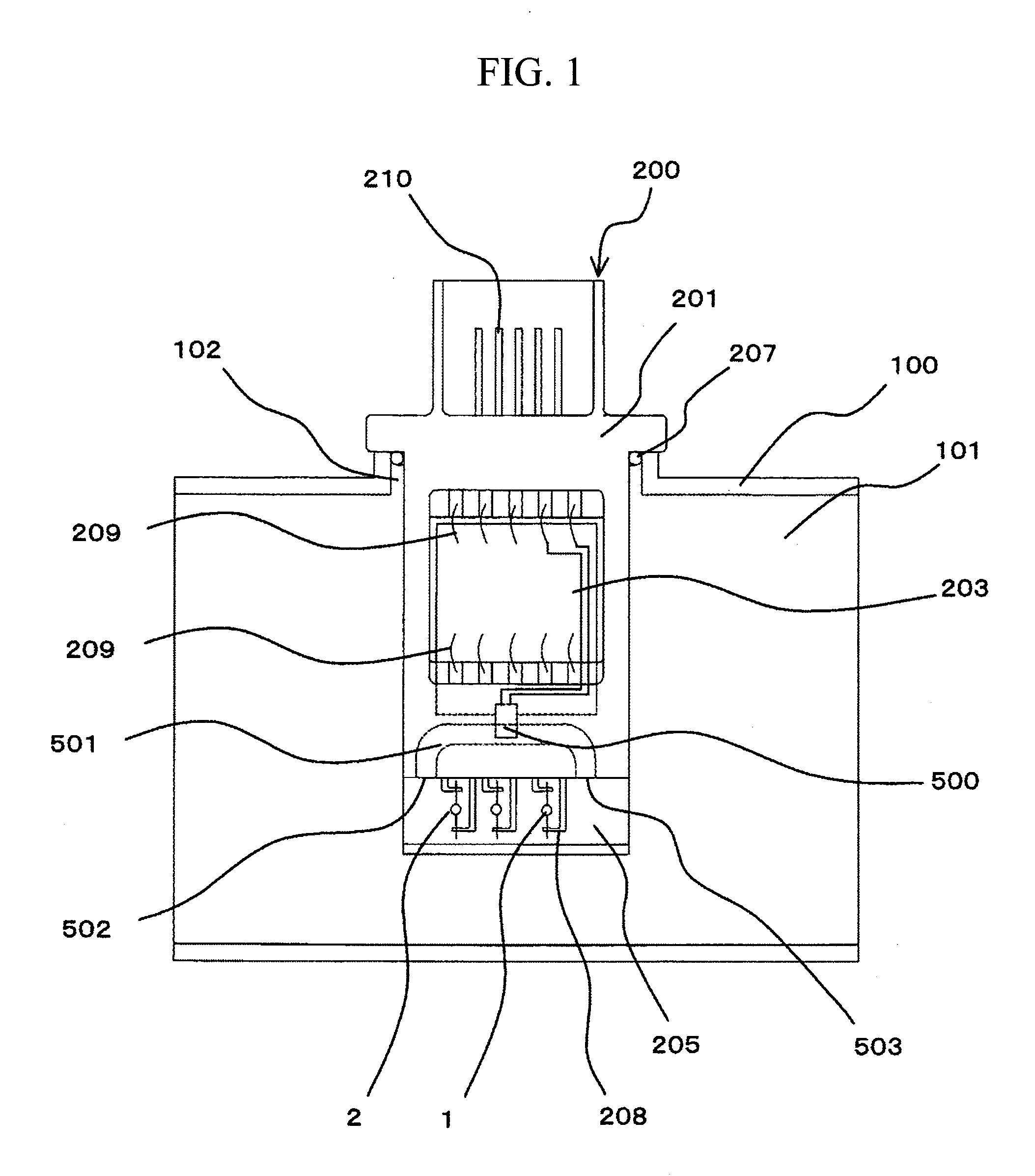
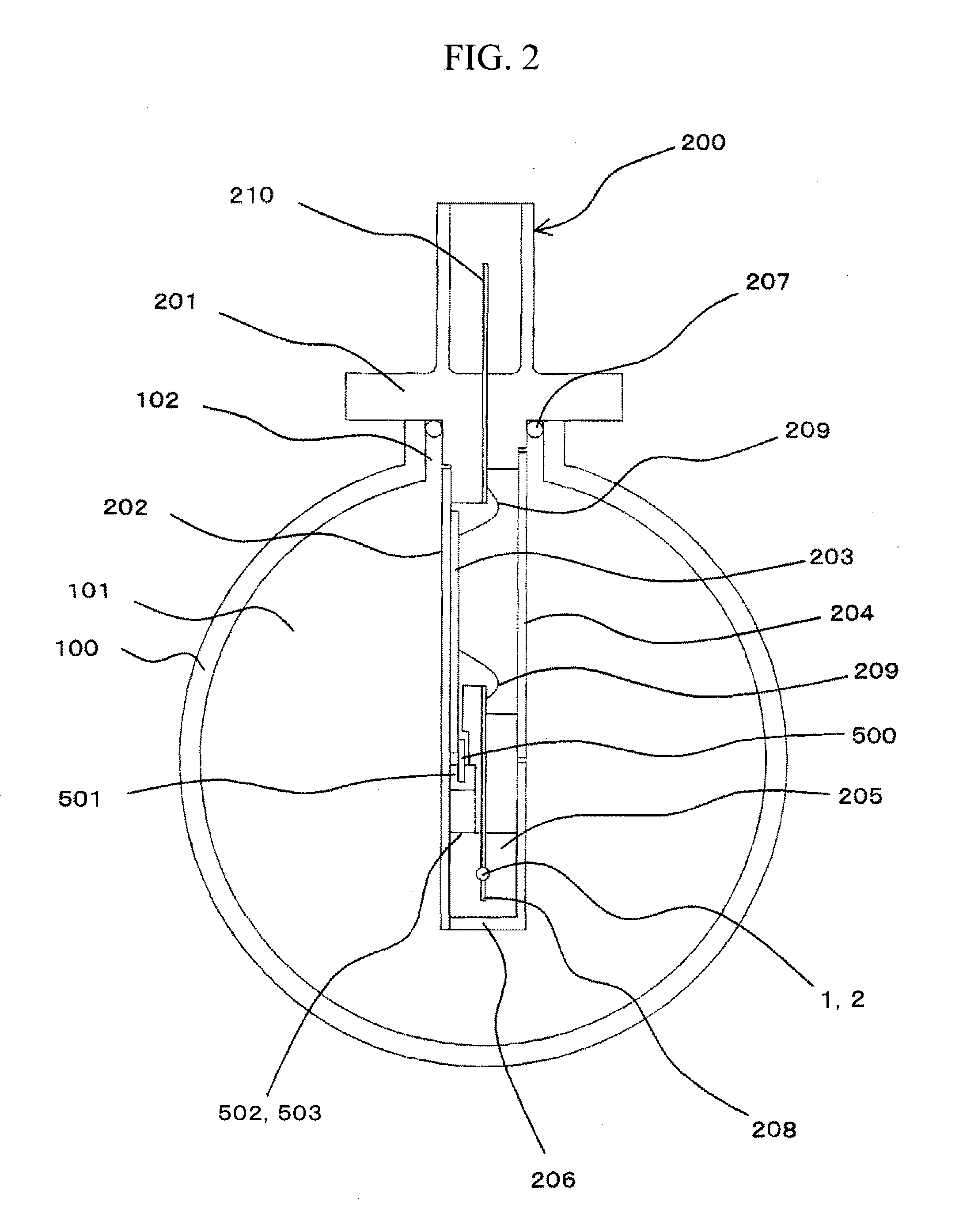
An arrangement of a mass intake air flow measurement device suitable for integrating a humidity sensing device as well as a temperature sensing device and a pressure sensing device is provided. A second bypass passage 501 bypassing a bypass passage 205 is formed and a humidity sensing device 500 is mounted in the second bypass passage 501. A second bypass passage inlet 502 and a second bypass passage outlet 503 formed in a wall surface of the bypass passage 205 are opened parallel to the direction of flow of air flowing in the bypass passage 205.
Owner:HITACHI ASTEMO LTD
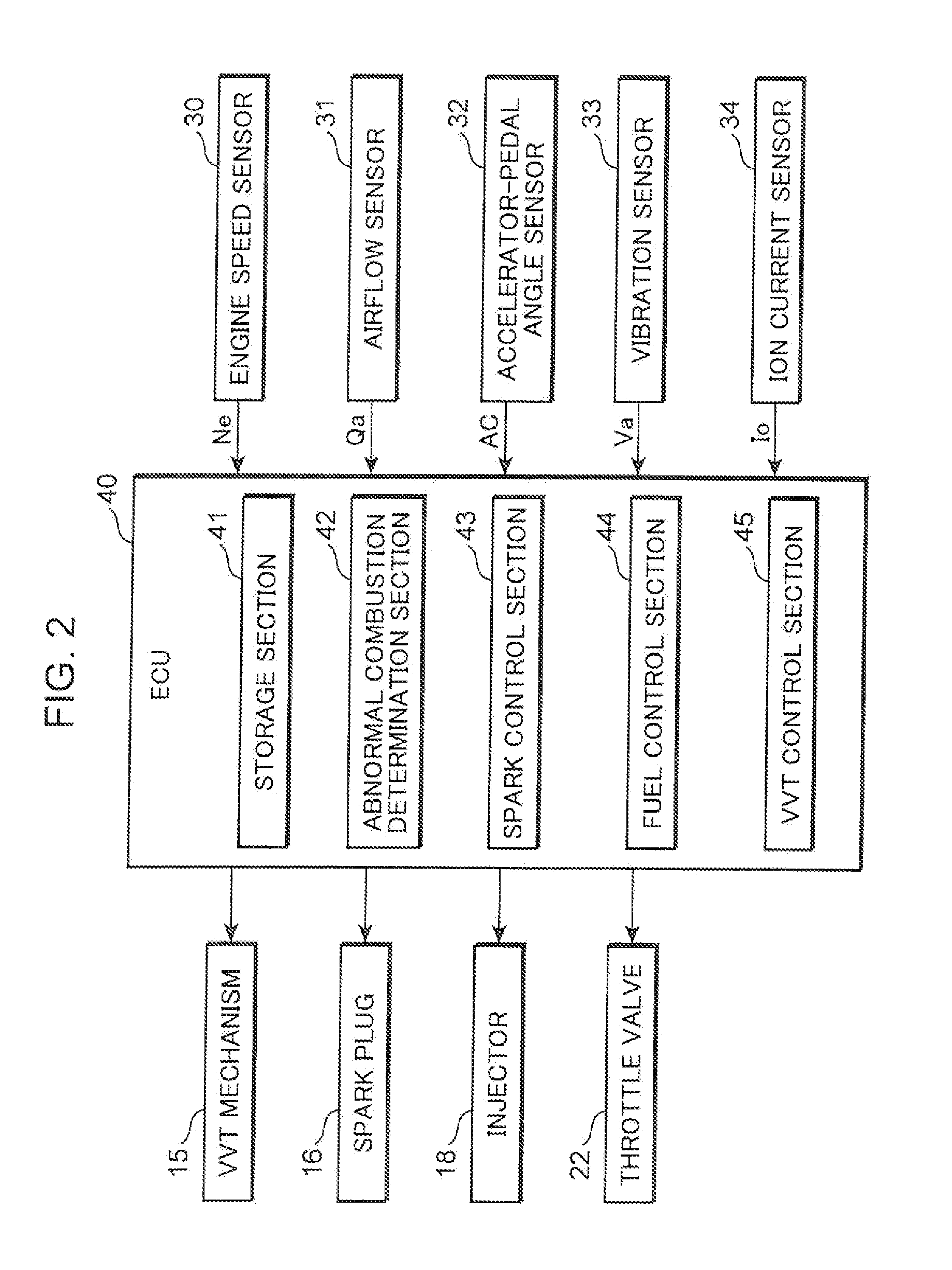
Abnormal combustion detection method for spark-ignition engine, and spark-ignition engine
ActiveUS20110246049A1Enough can be detectedInternal-combustion engine testingAnalogue computers for vehiclesTop dead centerEngineering
When a maximum value of vibration intensity (maximum vibration intensity) (Vmax) acquired from a vibration sensor (33) in a low engine speed / high engine load (operating region (R)) is equal to or greater than a given threshold value (X), a spark timing of a spark plug (16) is shifted from a point set in a normal state on a retard side with respect to a compression top dead center, farther toward the retard side. Then, when a maximum vibration intensity (Vmax2) acquired after the spark timing retard is greater than a maximum vibration intensity (Vmax1) acquired before the spark timing retard, it is determined that preignition occurs. This technique makes it possible to reliably detect preignition using the vibration sensor, while distinguishing the preignition from knocking. An in-cylinder pressure sensor for detecting an in-cylinder pressure of an engine may be used to determine the presence or absence of the preignition, in the same manner.
Owner:MAZDA MOTOR CORP
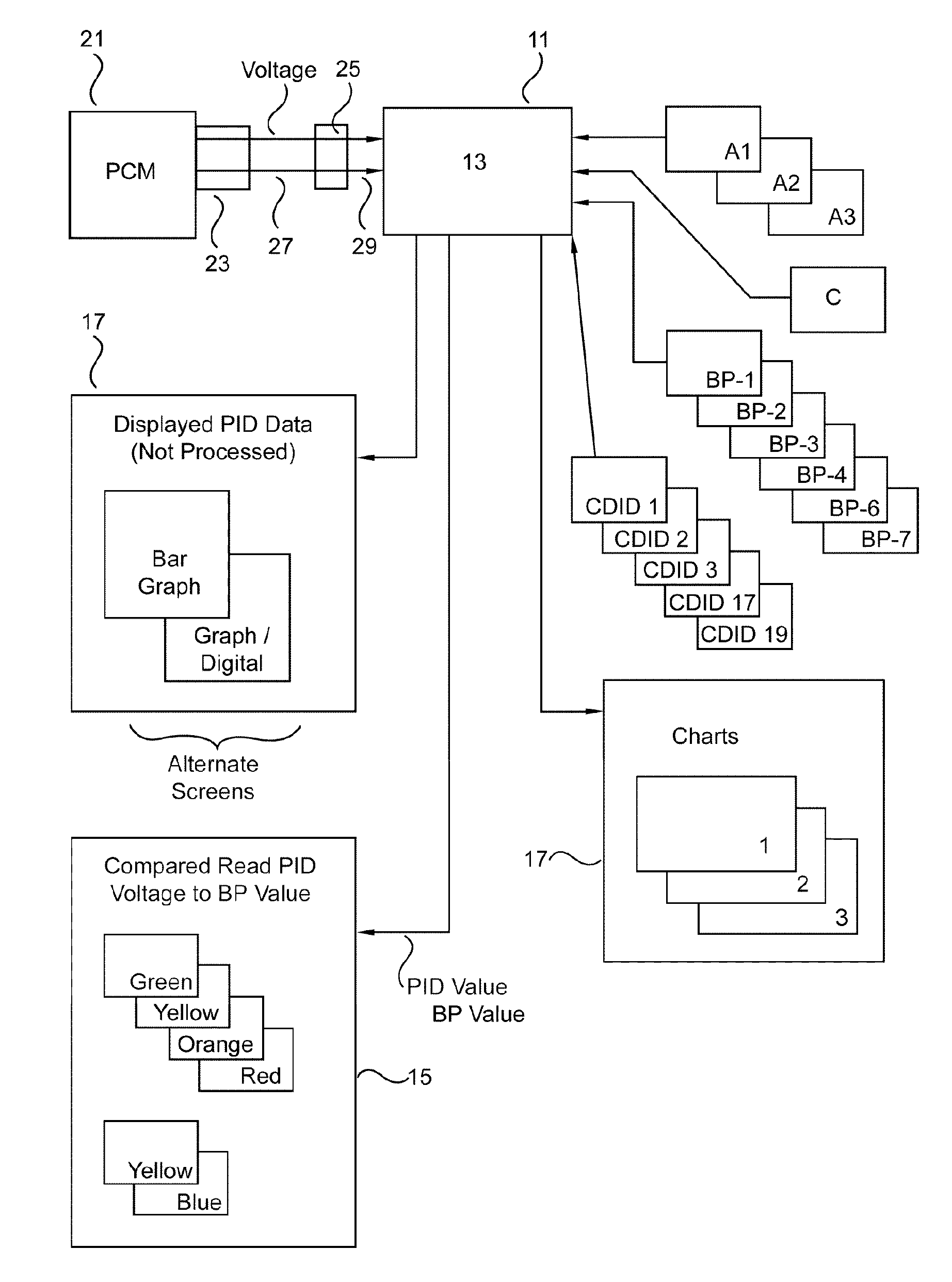
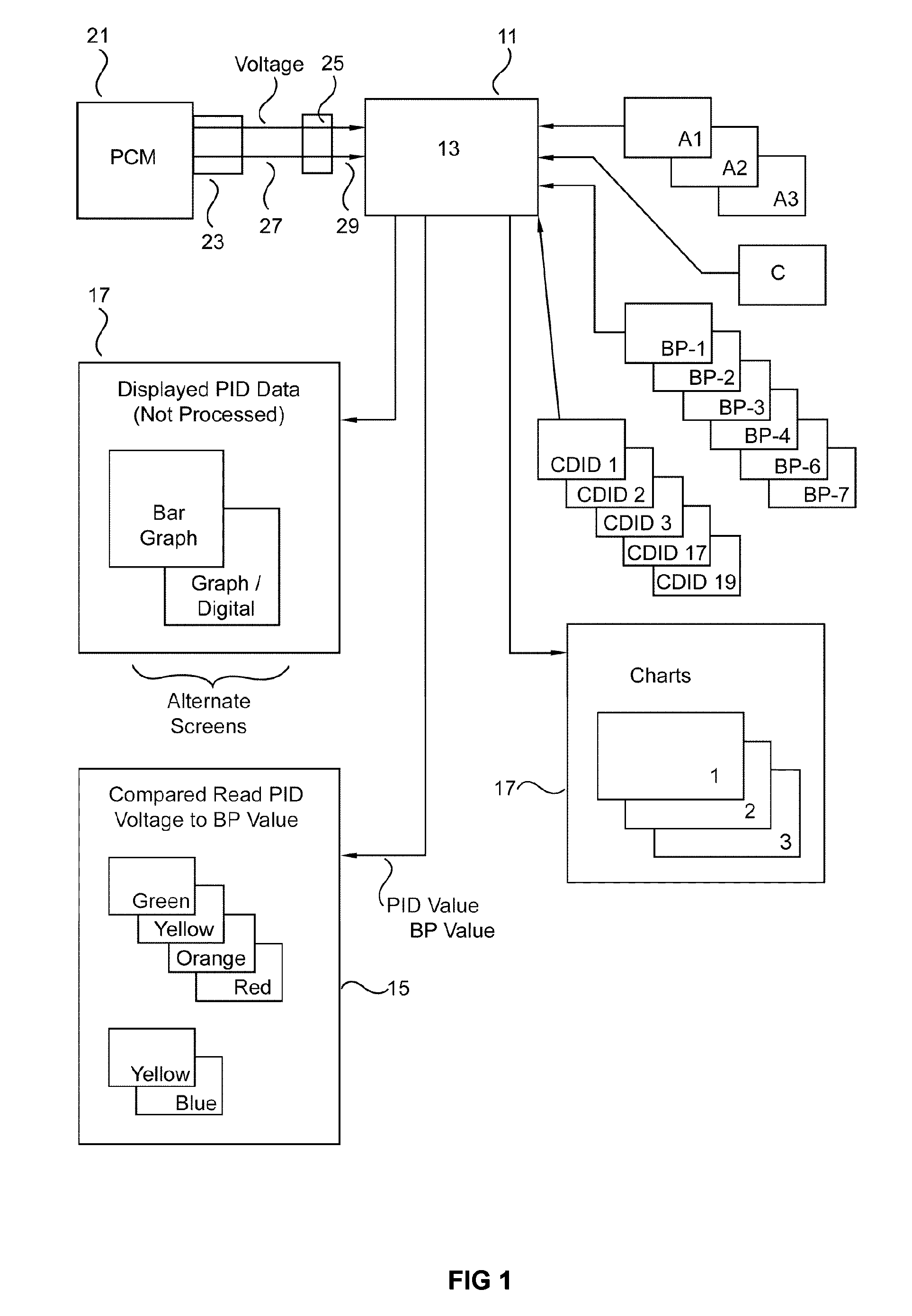
Vehicle diagnostic tool
ActiveUS7953530B1Firmly connectedDiagnose the power plant systems quickly and accuratelyVehicle testingAnalogue computers for vehiclesReal-time dataComputer module
An analysis tool which extracts all the available parameter identifications (i.e. PIDS) from a vehicle's power train control module for diagnostic decisions. This is done by checking these PIDS and other information (e.g., calculated PIDS, Break Points, charts and algorithms) in three states; key on engine off, key on engine cranking, key on engine running. In all three modes the tool is comparing the live data from PIDS and voltage to the other information (e.g, Break Points). If any of this data are outside the programmed values a flag is assigned to the failure or control problem. The relationship between a particular PID and its associated preprogrammed value(s) may be indicated by a light. The depth of the problem (if any) is conveyed by the color of the light. Also included are tests / charts for fuel trim, engine volumetric efficiency, simulated injector, power, catalyst efficiency, and engine coolant range.
Owner:AUTOMOTIVE TEST SOLUTIONS
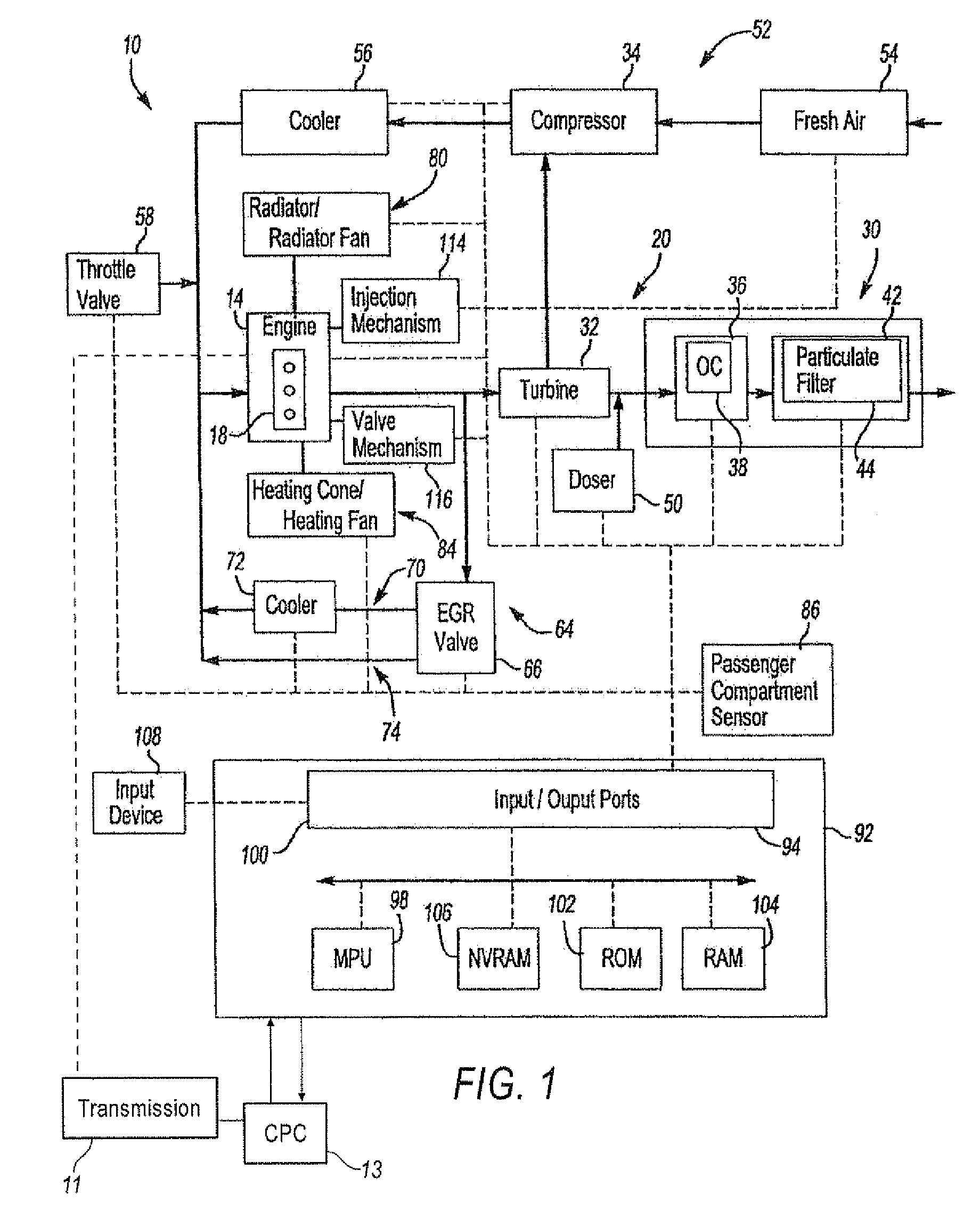
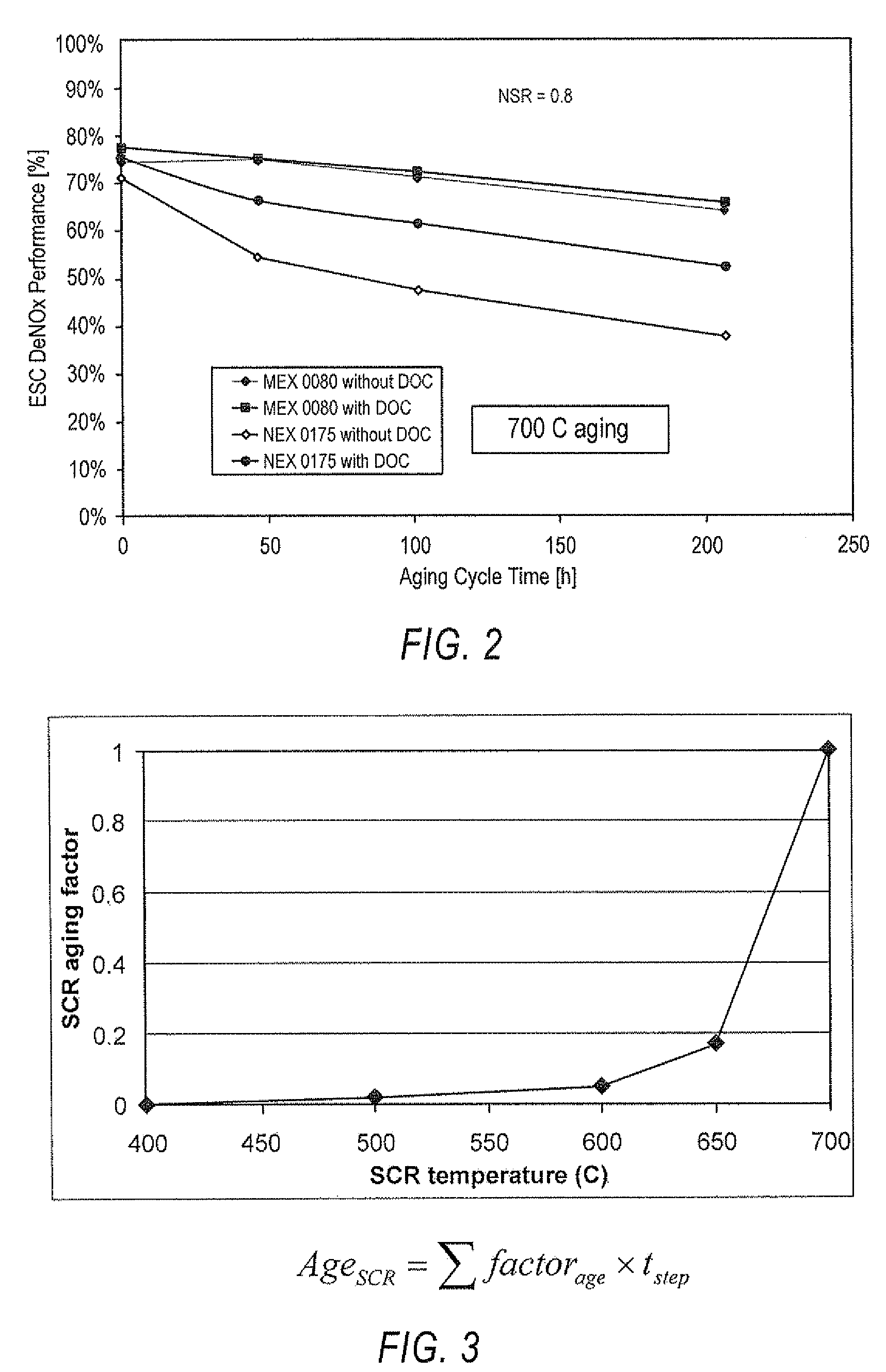
Variable engine out emission control roadmap
InactiveUS20090158706A1Easy to controlEfficiently determinedInternal-combustion engine testingAnalogue computers for vehiclesExternal combustion engineInternal combustion engine
A method for operating an internal combustion engine for variable engine out NOx control talking into account the age of the SCR.
Owner:DETROIT DIESEL CORP
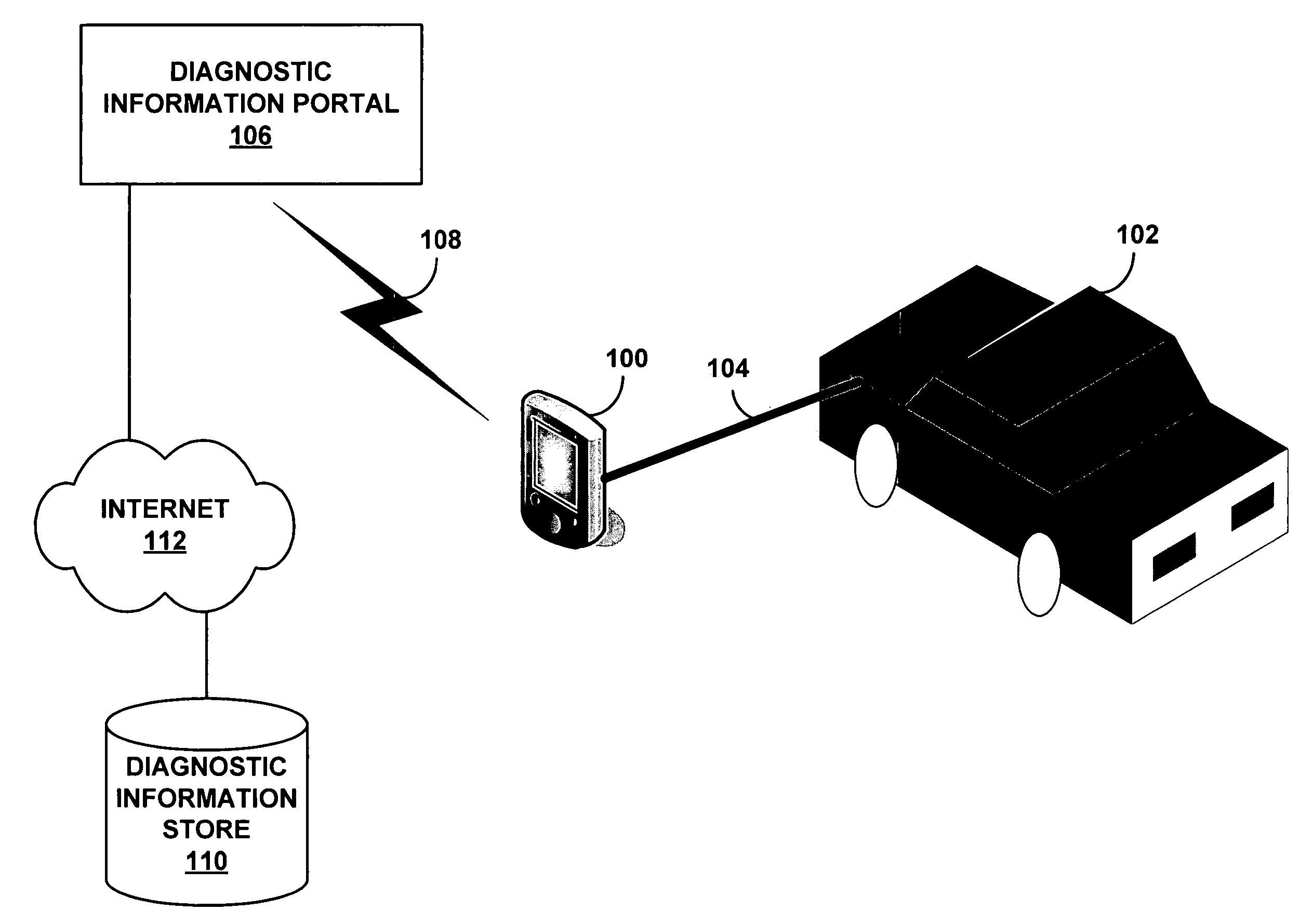
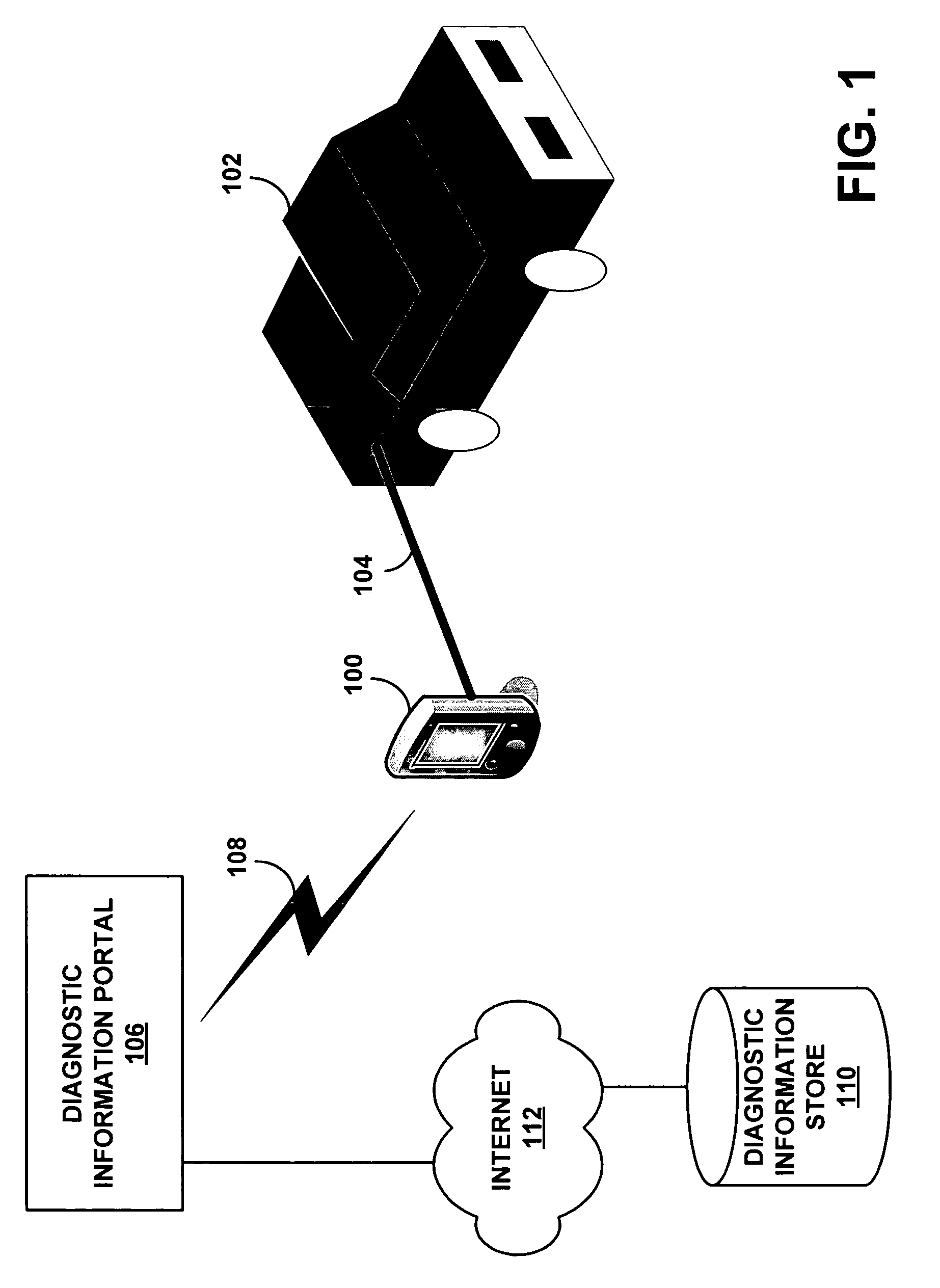
Method and system for enhanced vehicle diagnostics using statistical feedback
InactiveUS20060142907A1Vehicle testingInternal-combustion engine testingDiagnostic programDiagnostic information
A diagnostic information portal can communicate with one or more diagnostic devices used to diagnose problems with vehicles. The diagnostic information portal can receive from the diagnostic devices indications of various problems that have been diagnosed with the vehicles. The information received by the diagnostic information portal can then be used to update one or more information sources (e.g., diagnostic procedures or other information) used to diagnose problems with the vehicles.
Owner:SNAP ON INC
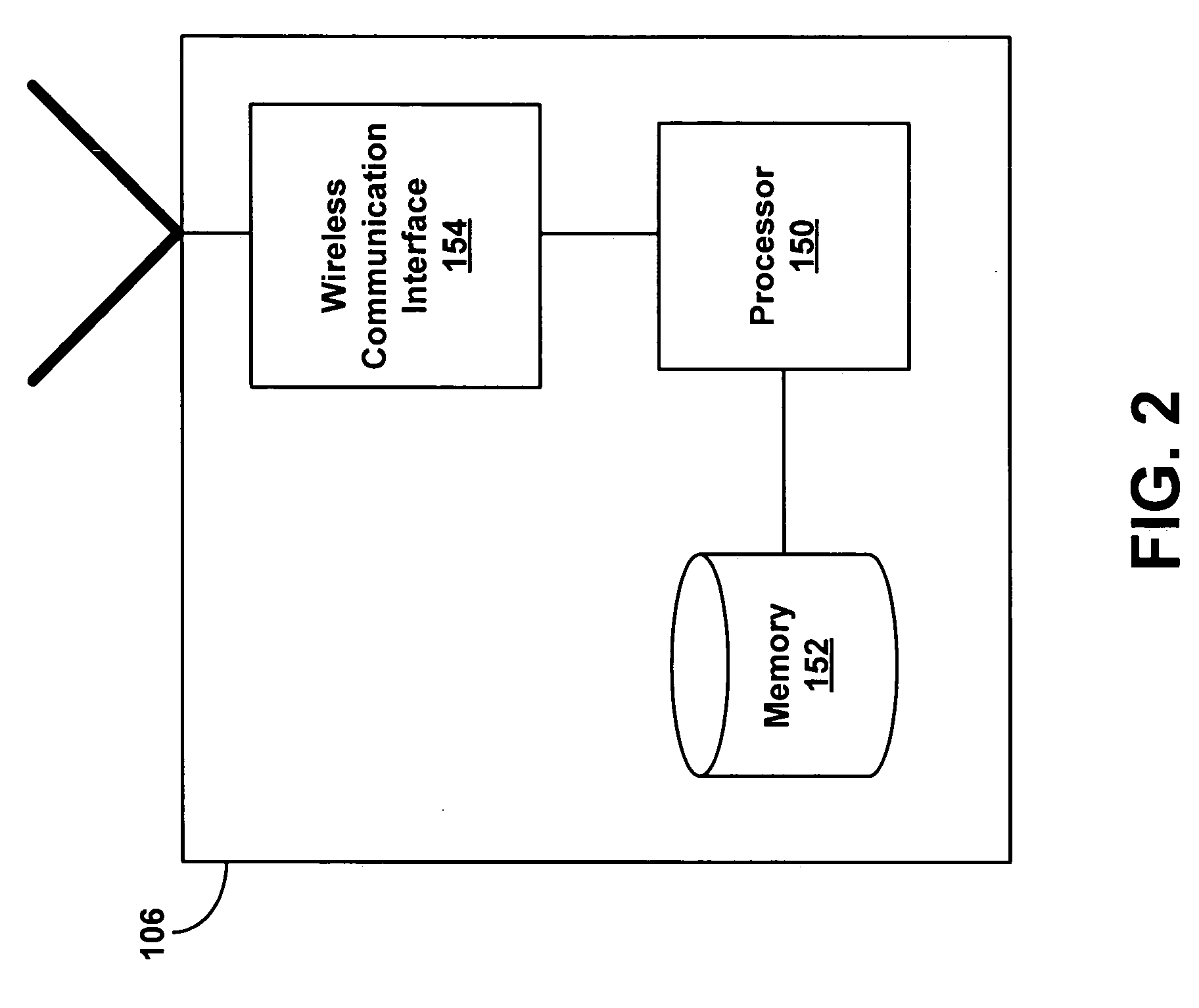
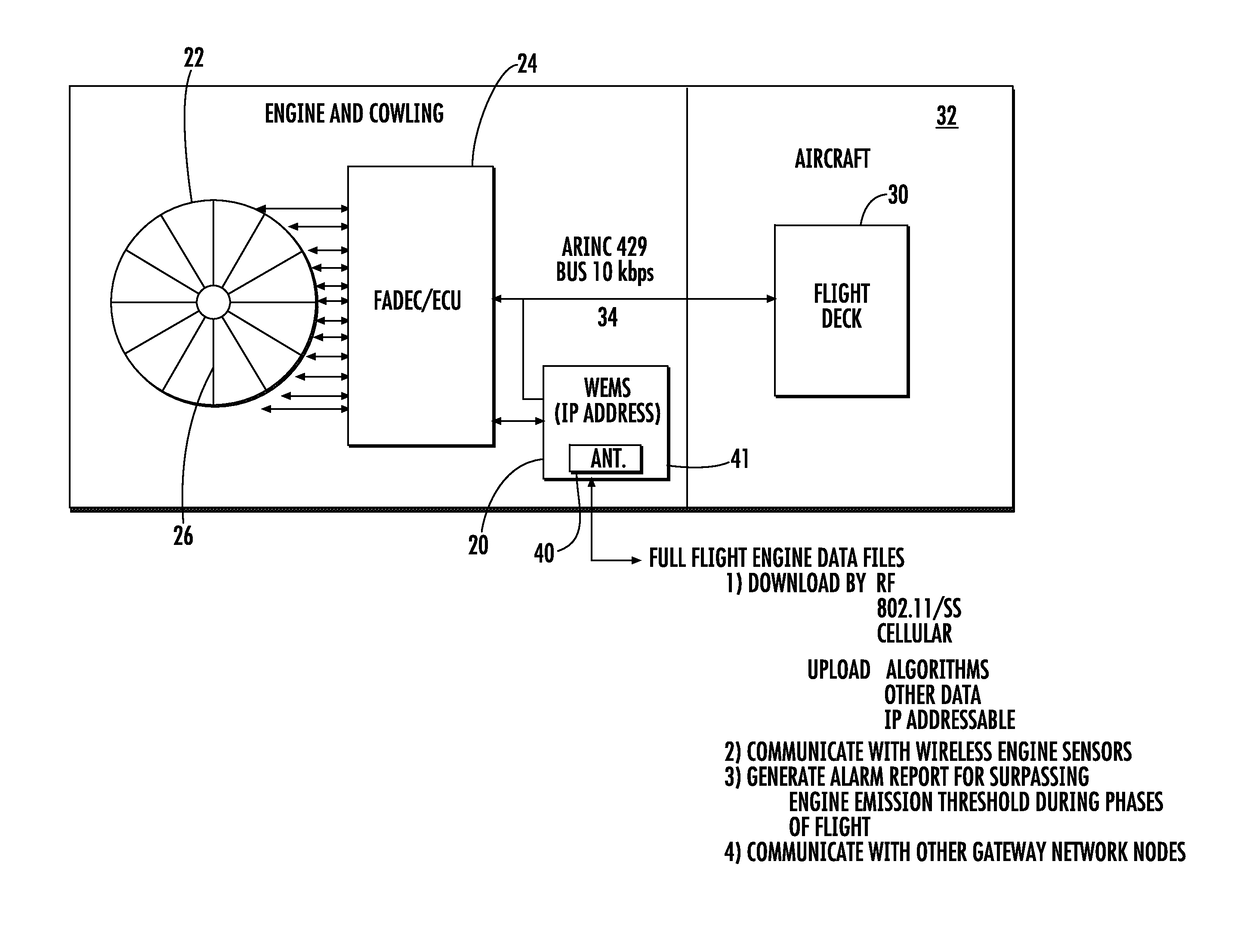
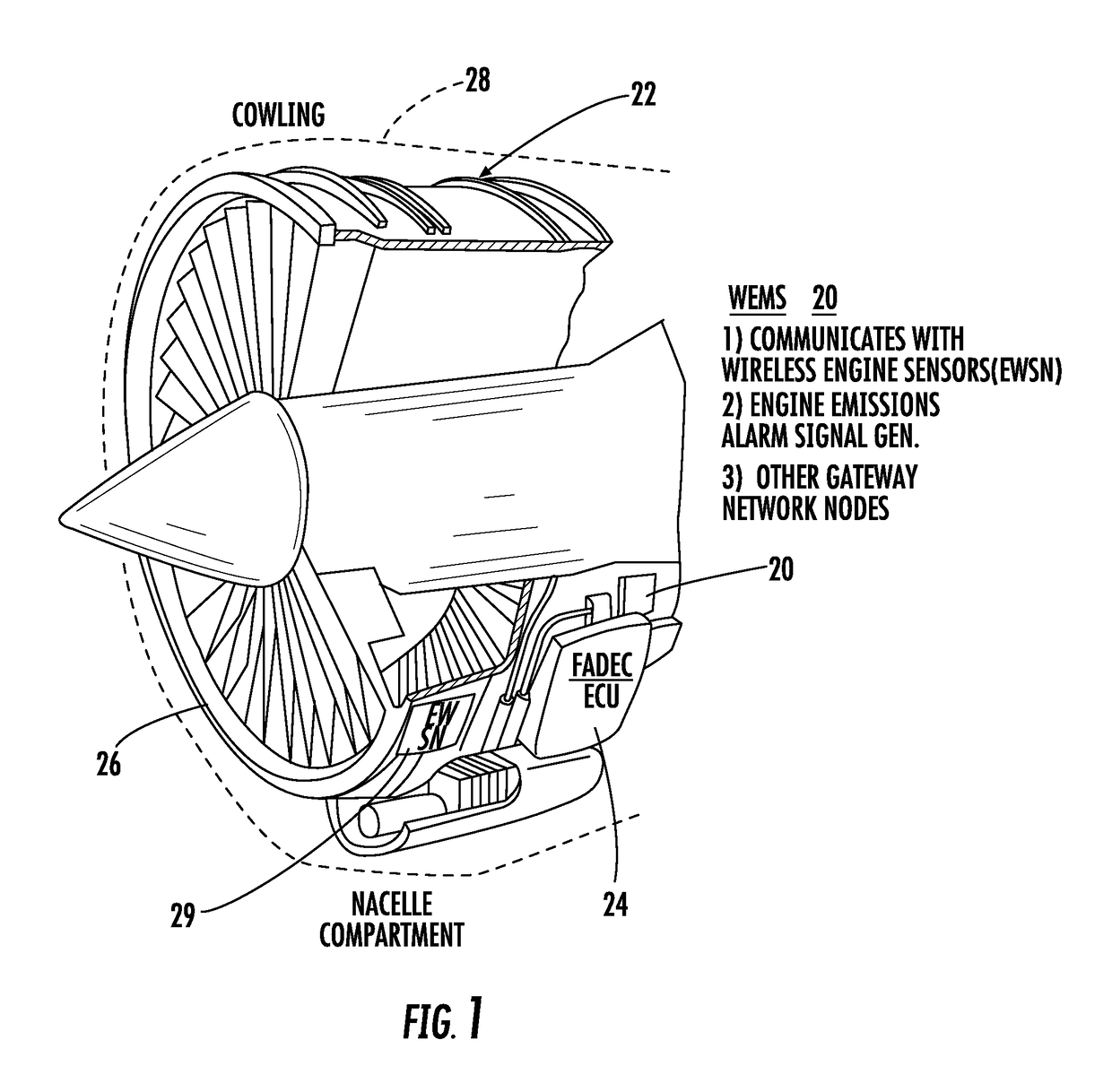
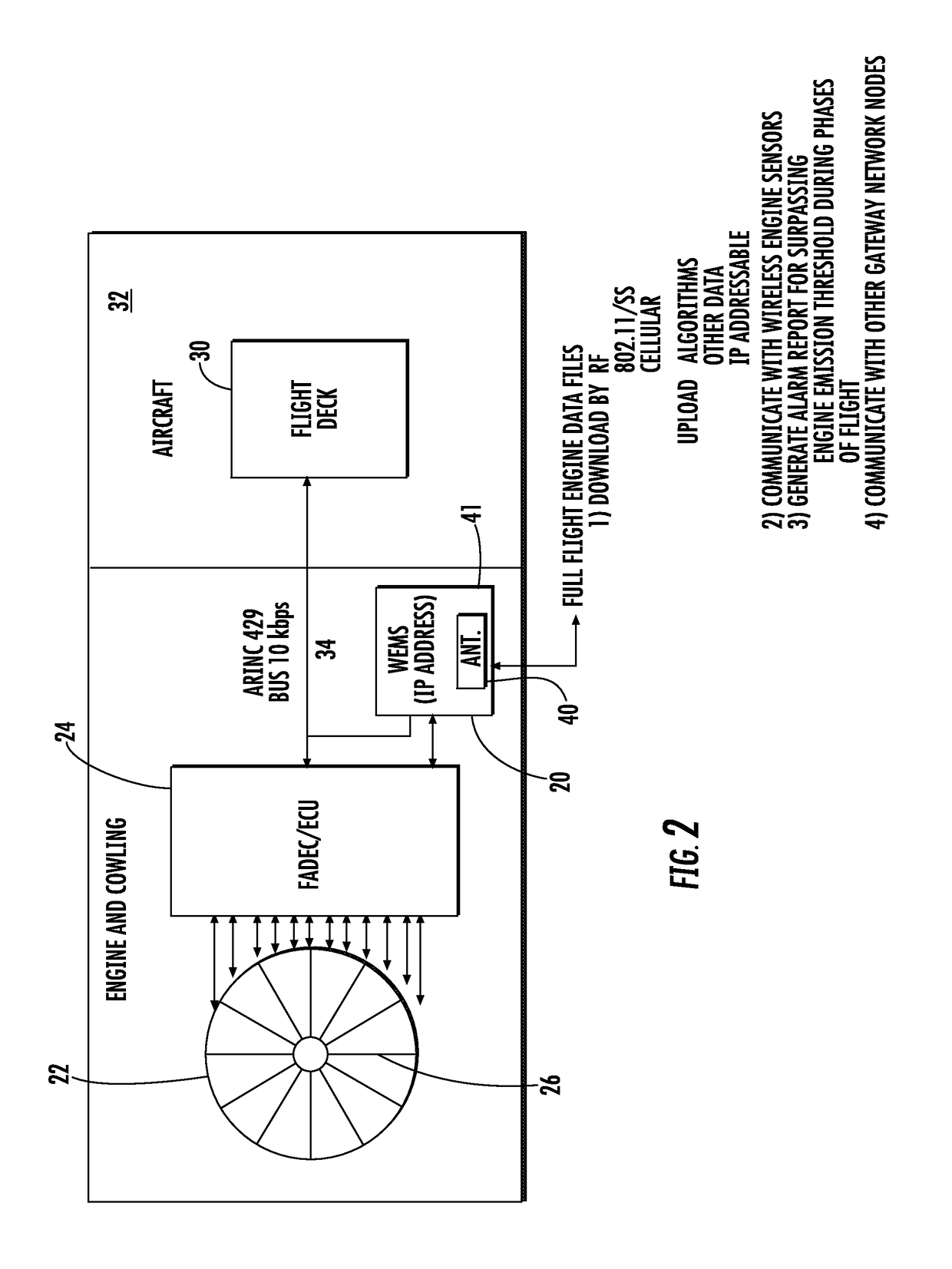
Wireless engine monitoring system for environmental emission control and aircraft networking
ActiveUS20170259942A1Programme controlInternal-combustion engine testingTransceiverWireless transceiver
A wireless engine monitoring system for an aircraft engine includes a housing and wireless transceiver that receives engine data, including engine data relating to environmental engine emissions. A processor processes the engine data and generates an alarm report when the environmental engine emissions exceed a threshold.
Owner:HARRIS CORP
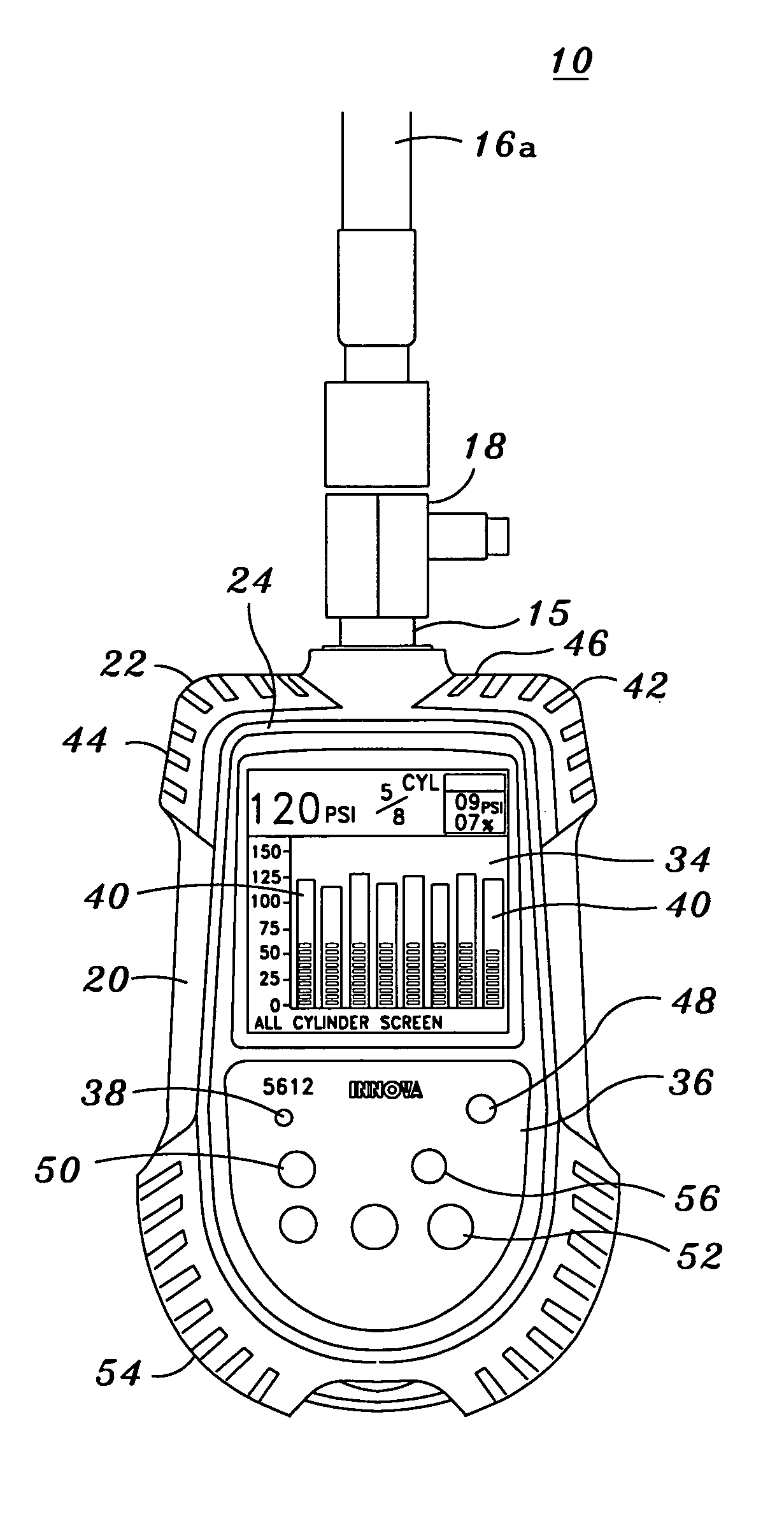
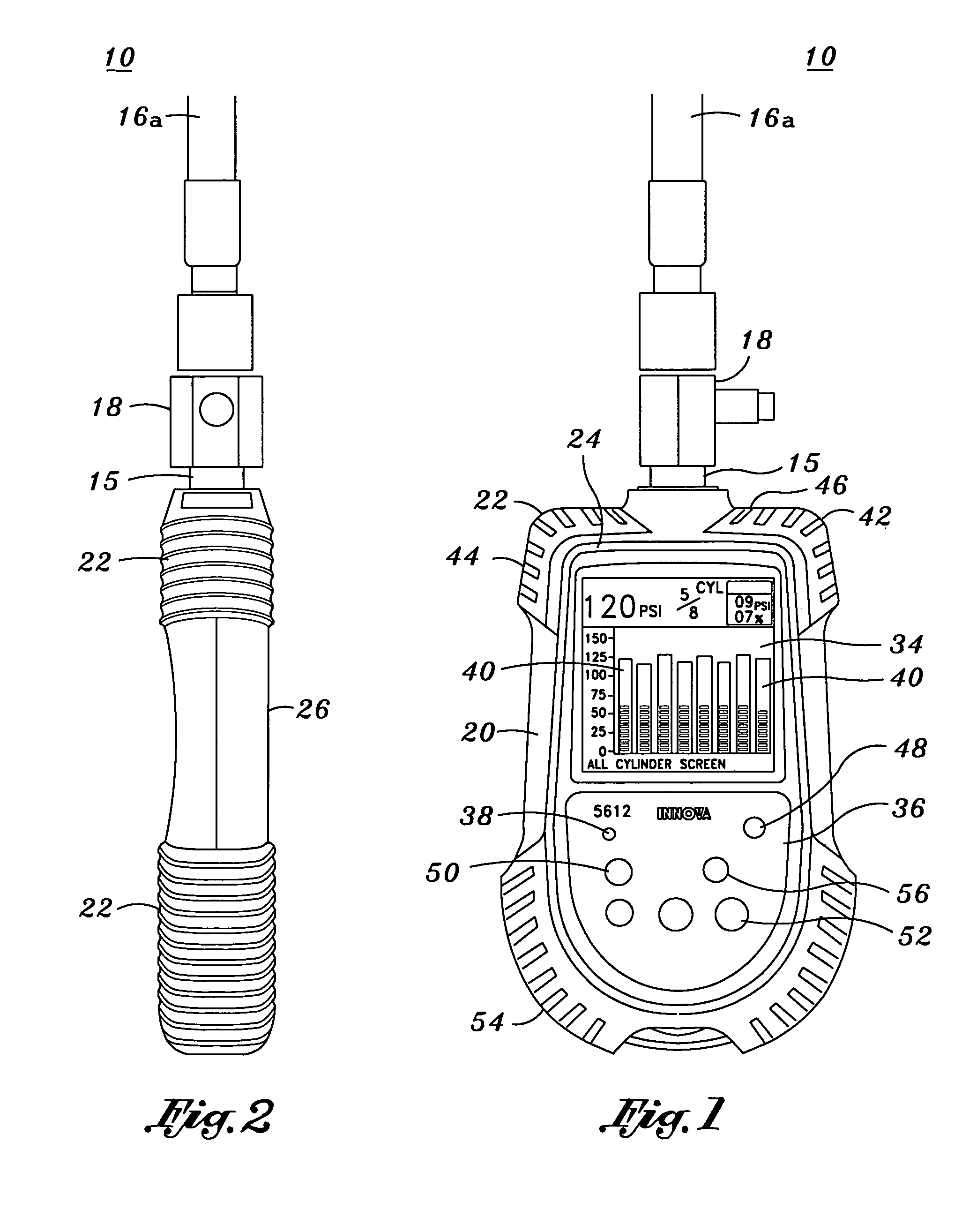
Digital compression gauge
InactiveUS6968733B2Internal-combustion engine testingFluid pressure measurementComparators circuitsDisplay device
There is provided a compression gauge assembly for diagnosing pressure variances of an engine cylinder(s). The gauge assembly comprises a gauge sensor in communication with the engine cylinder(s). The gauge sensor is operative to detect compression stroke pressures within the cylinder(s). A gauge controller is in communication with the gauge sensor. The gauge controller includes a comparator circuit operative to compare detected compression stroke pressures within the cylinder(s) and to derive the pressure variances therebetween. A gauge display is in communication with the gauge controller for displaying the derived pressure variances.
Owner:INNOVA ELECTRONICS
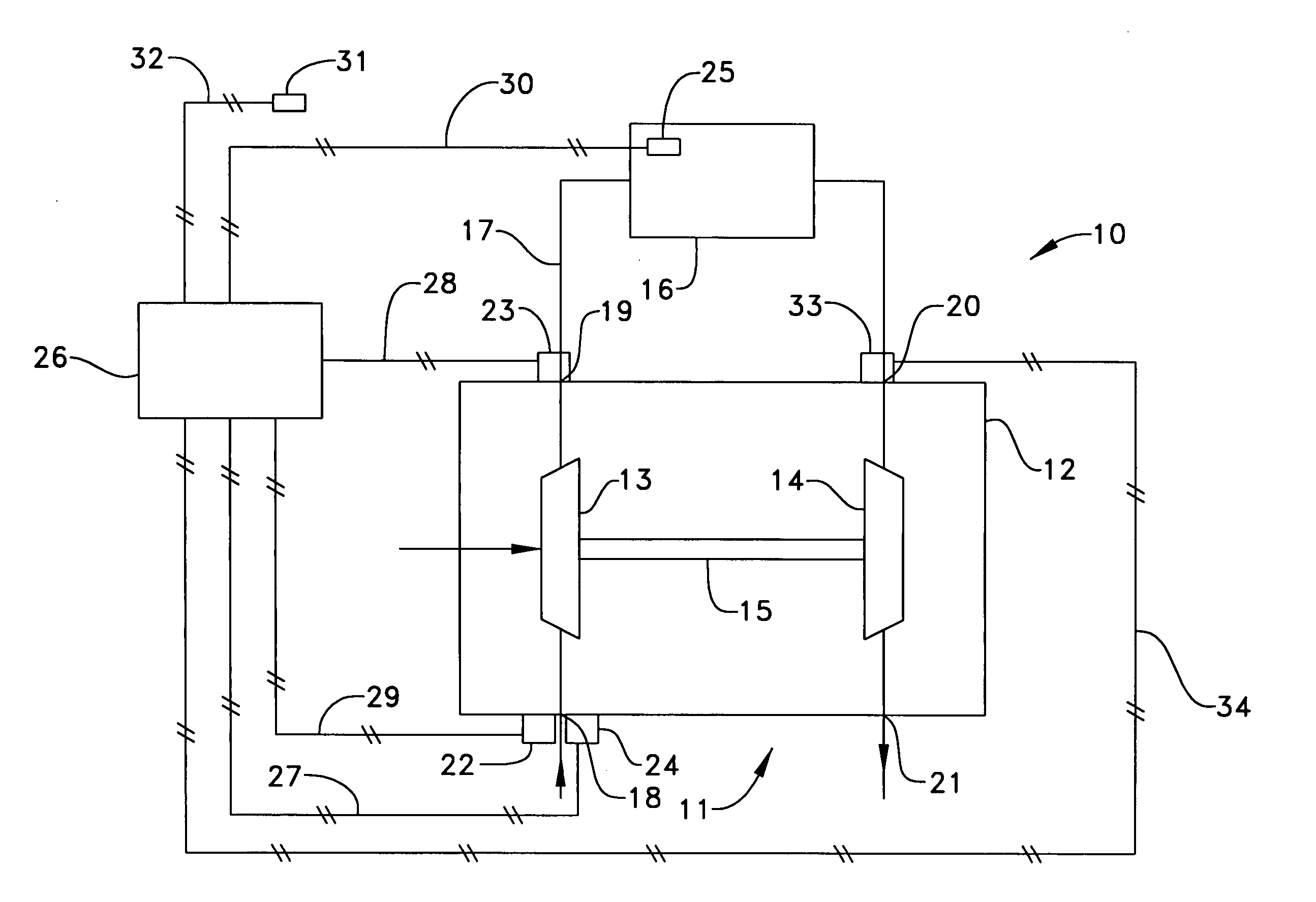
Method and system of determining life of turbocharger
In order to accurately determine a life of a turbocharger, the specific use, herein referred to as a “duty cycle” of the turbocharger, should be monitored. However, in order to directly monitor the duty cycle of the turbocharger, there are additional costs of assembly and installation of a turbocharger rotational speed sensor. The present invention determines a life of a turbocharger by indirectly monitoring the duty cycle of the turbocharger through sensors that generally serve a pre-existing purpose within a vehicle or machine. A compressor inlet pressure sensor and compressor outlet pressure sensor are in communication with an electronic control module that includes a life determining algorithm. The life determining algorithm determines the life of the turbocharger based on a relationship between a sensed compressor inlet pressure and a sensed compressor outlet pressure. By monitoring the relationship between the sensed compressor inlet pressure and the sensed compressor outlet temperature, the fatigue and the creep of at least one component of the turbocharger is monitored.
Owner:CATEPILLAR INC PATENT DEPT
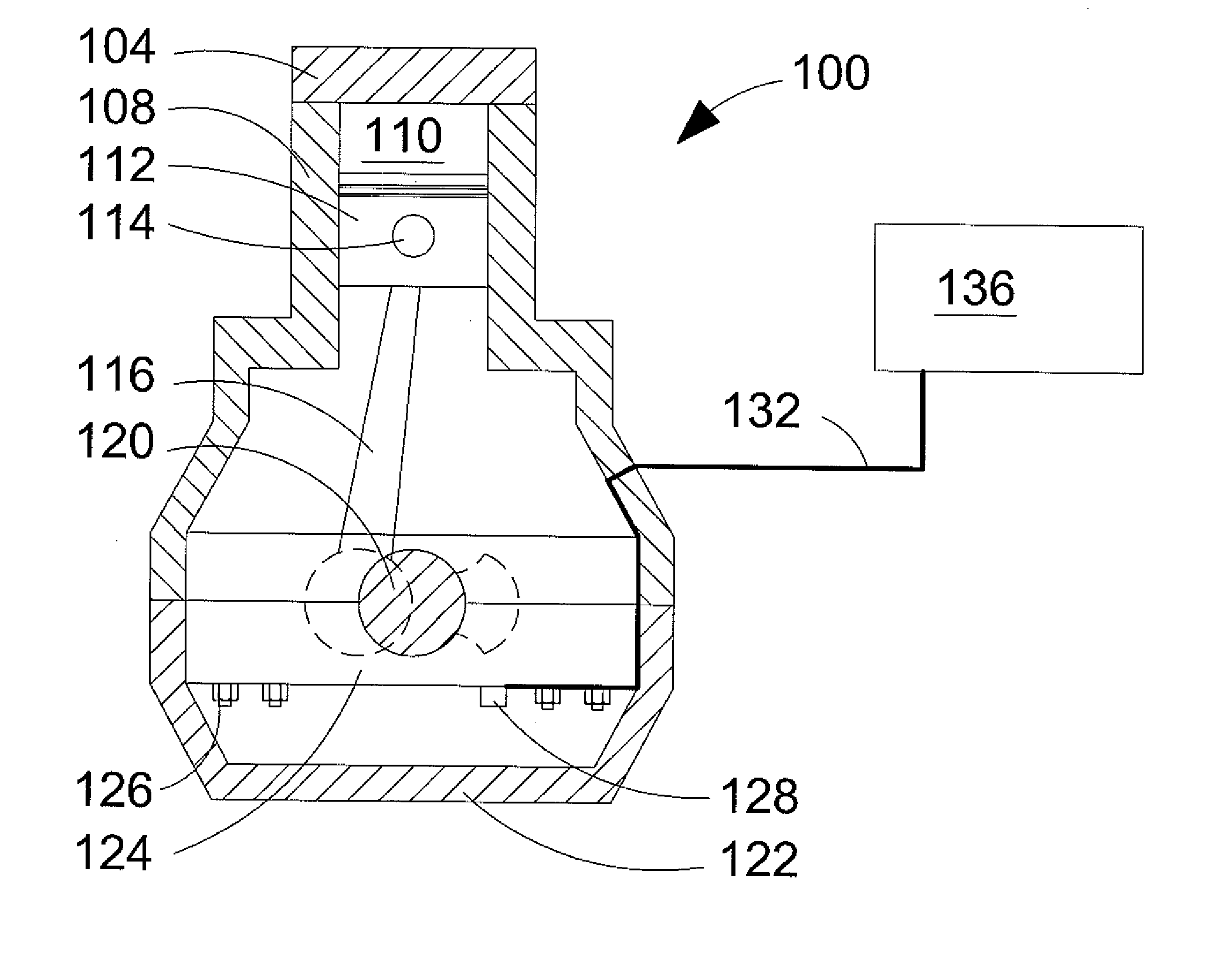
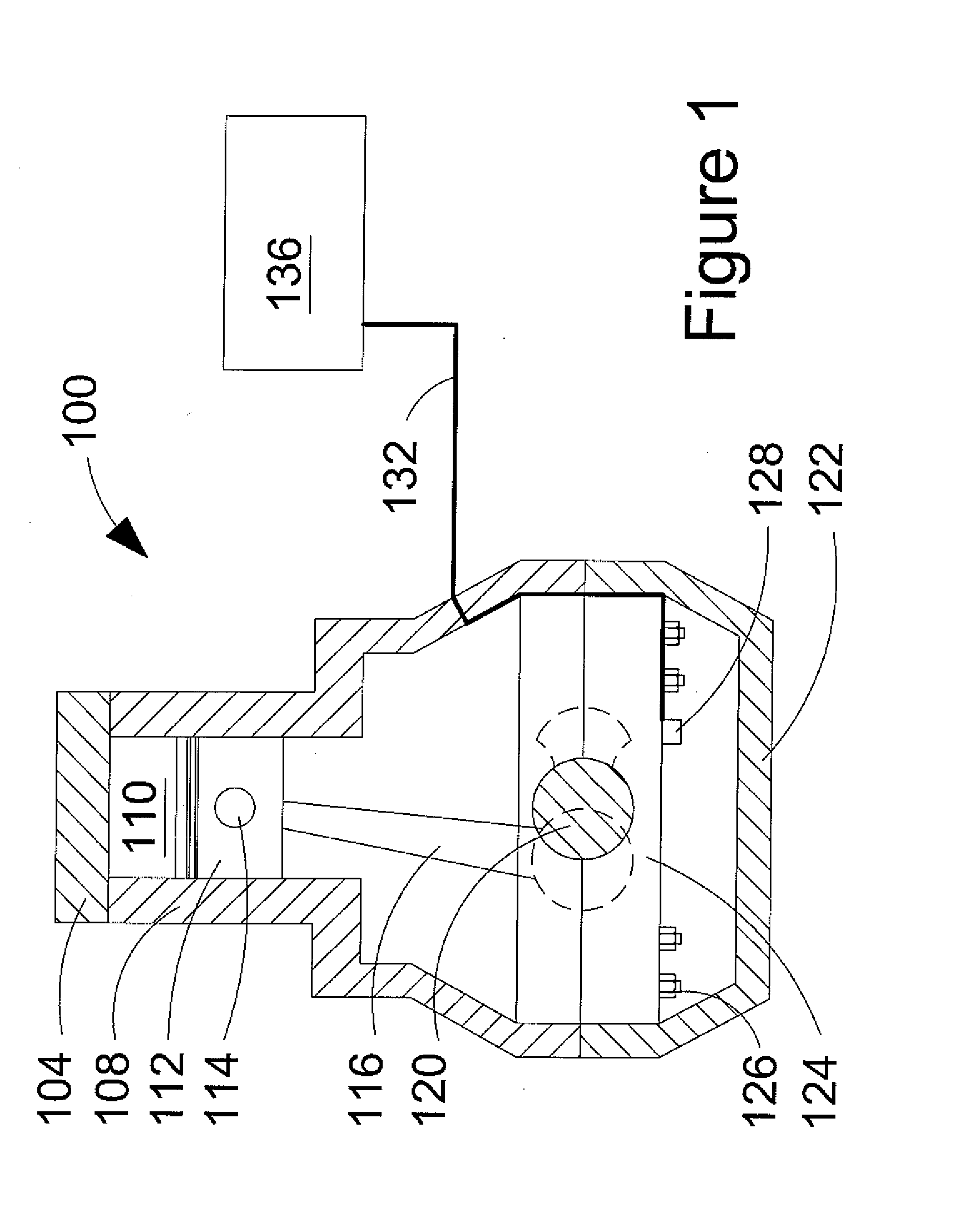
Method of mounting an accelerometer on an internal combustion engine and increasing signal-to-noise ratio
ActiveUS20080035108A1Increases signal output 's signal-to-noise ratioRaise the ratioAnalogue computers for vehiclesInternal-combustion engine testingSignal-to-noise ratio (imaging)Accelerometer
A method of mounting an accelerometer to an internal combustion engine comprises securing the accelerometer to a mating surface on an engine component external to a combustion chamber where the accelerometer can generate a signal output that is characteristic of engine knock, when it occurs, and at least one other combustion behavior inside the combustion chamber during a combustion event. The method further comprises connecting a signal wire at one end to the accelerometer and at an opposite end to a signal processor, and increasing the signal output's signal-to-noise ratio.
Owner:WESTPORT FUEL SYST CANADA INC
Popular searches
Registering/indicating working of vehicles Digital data processing details Testing/monitoring control systems Hardware monitoring Special data processing applications Withdrawing sample devices Mixing gases with gases/vapours Thin material handling Chemical/physical processes Internal combustion piston engines
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com