Patents
Literature
590results about How to "Accurate induction" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
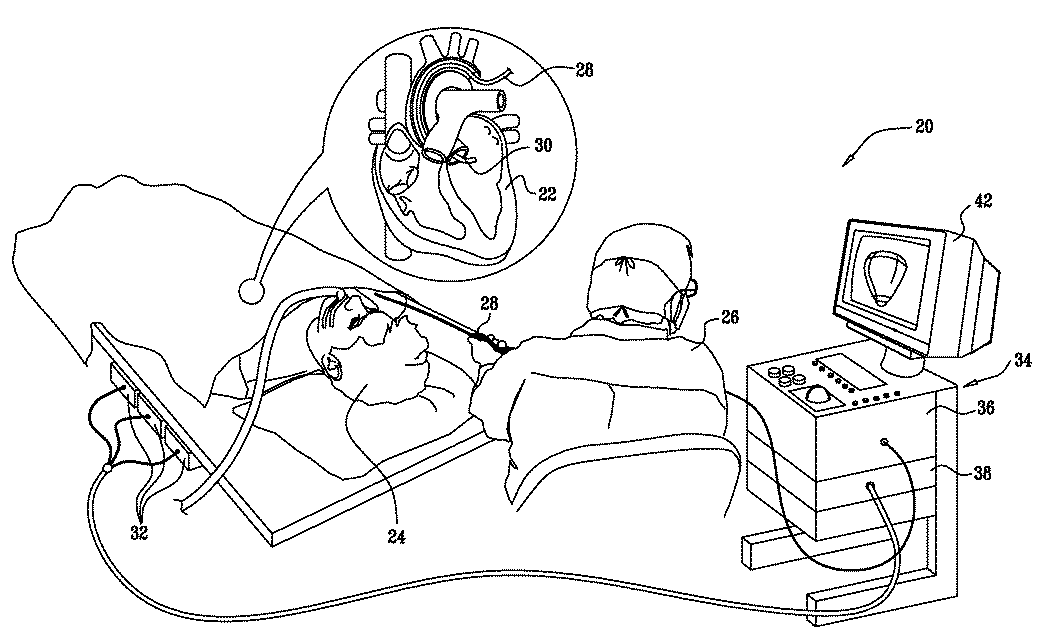
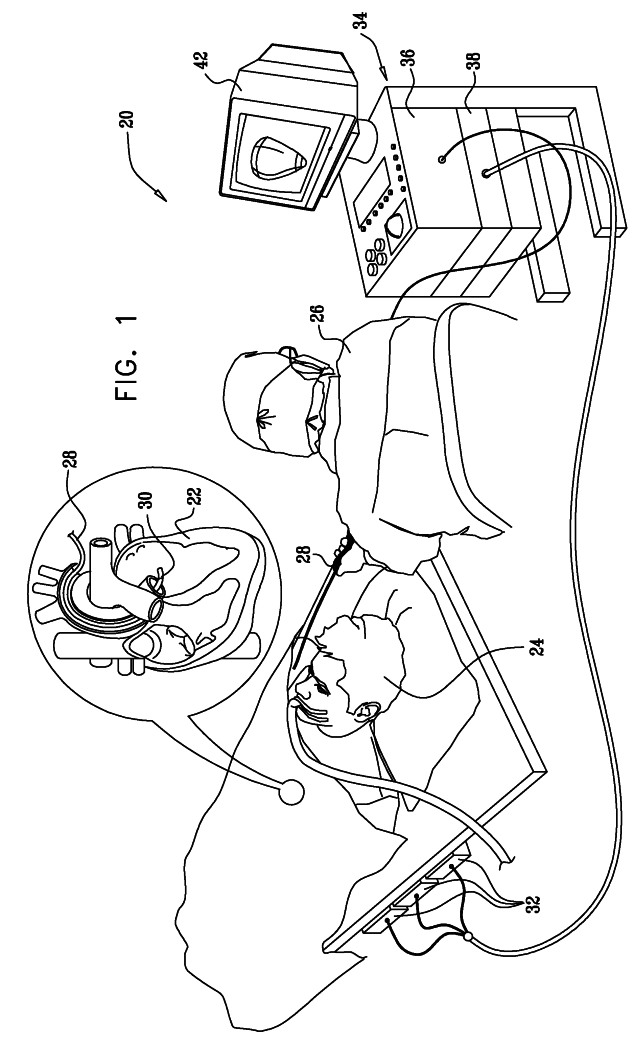
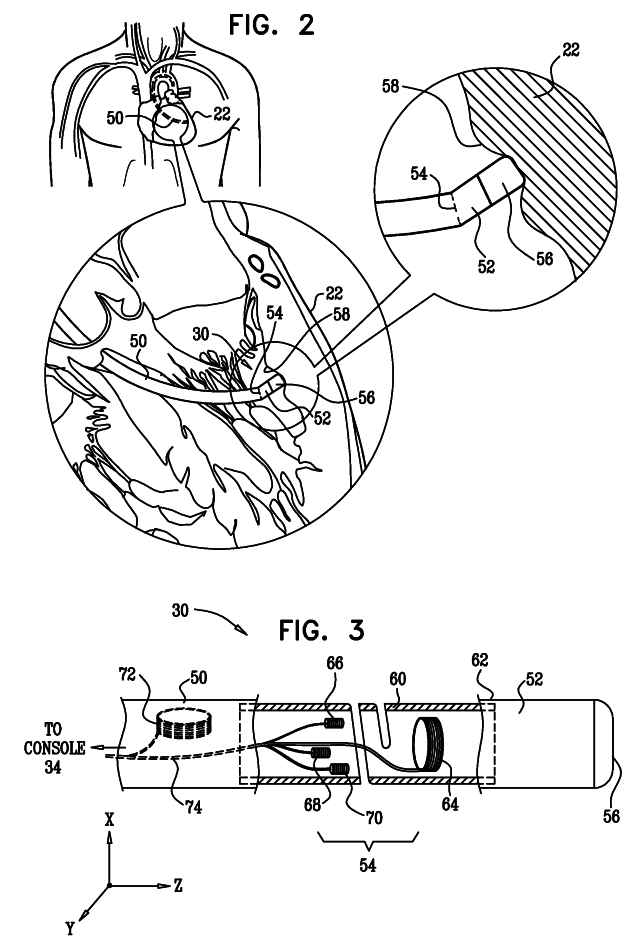
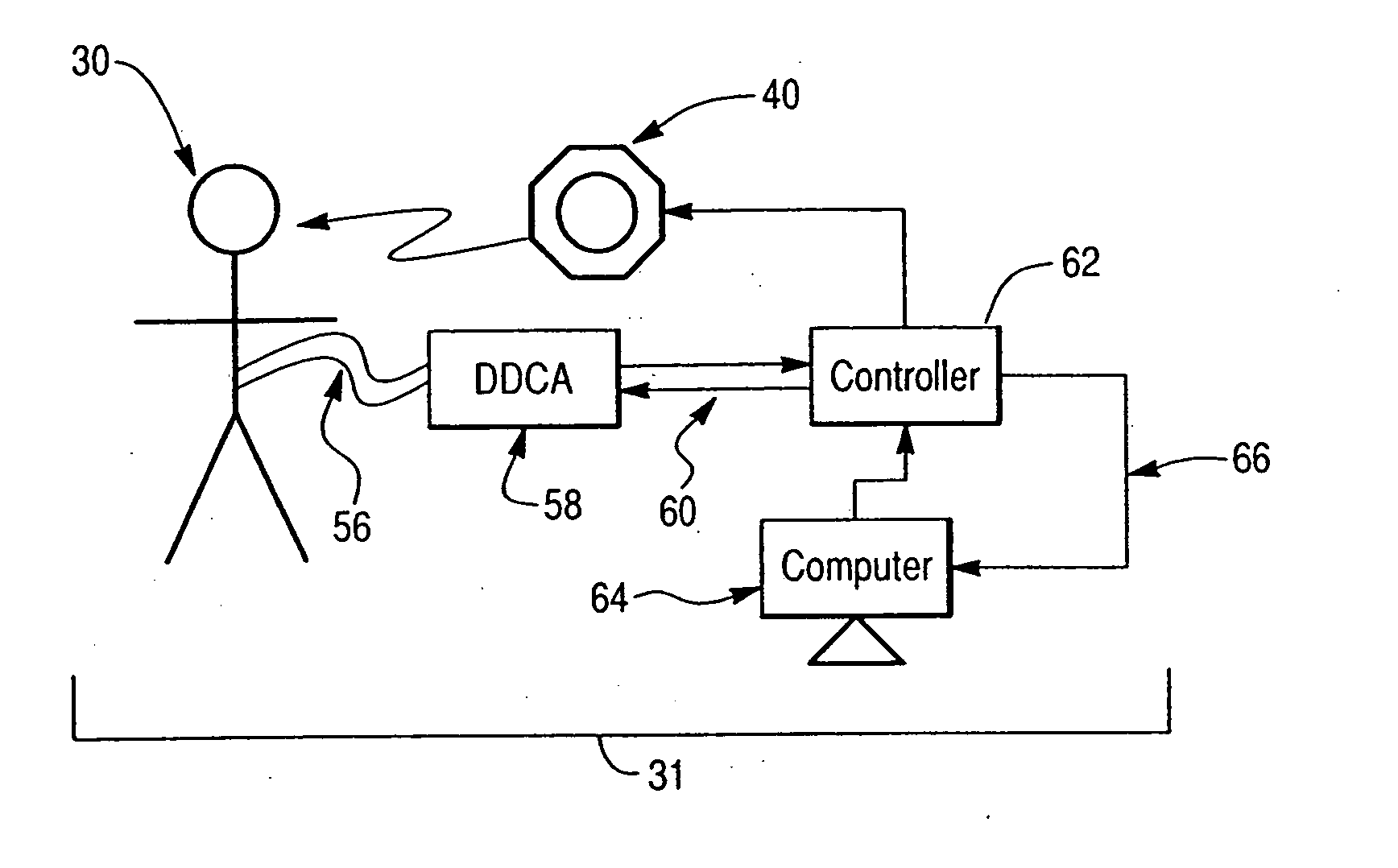
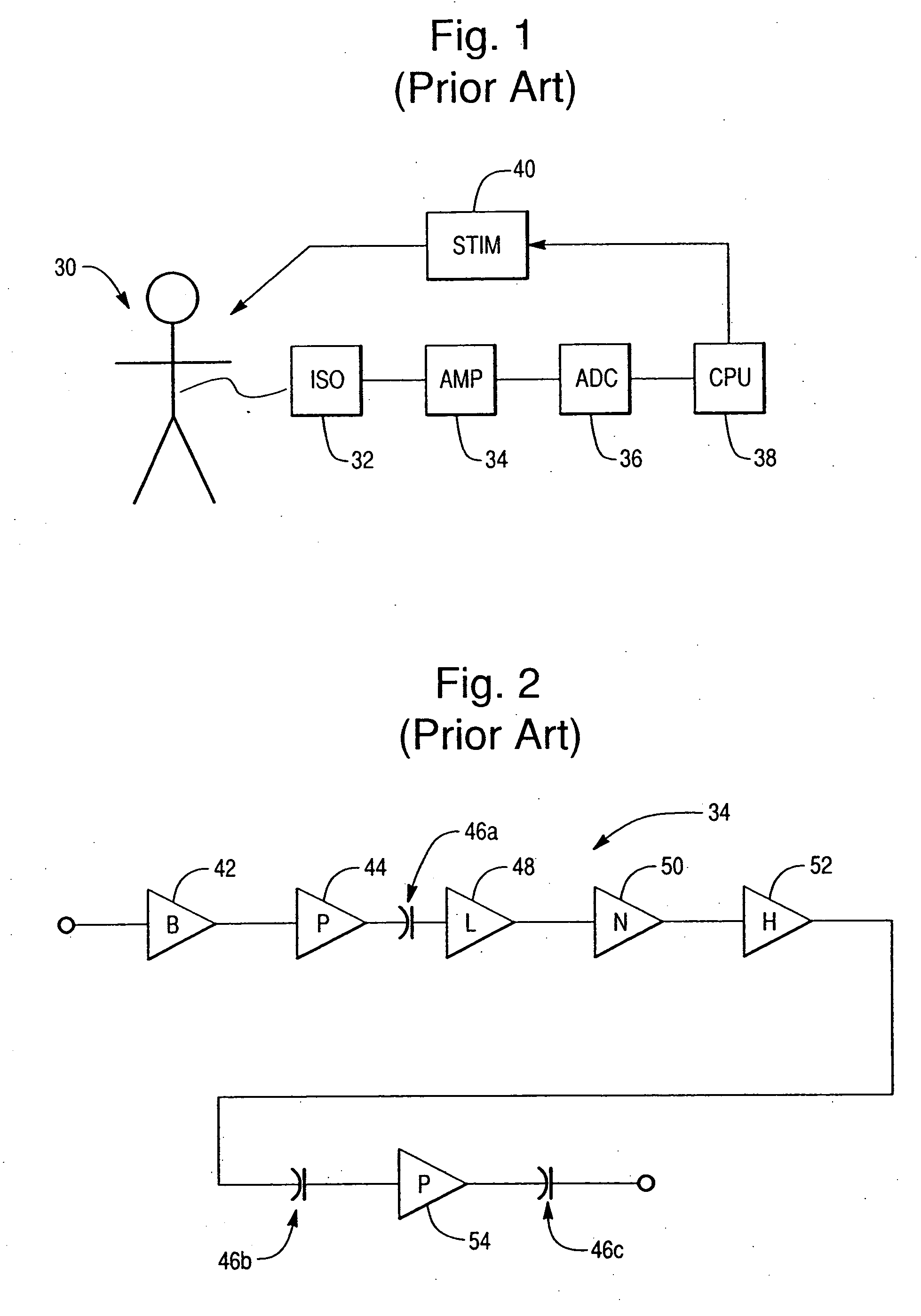
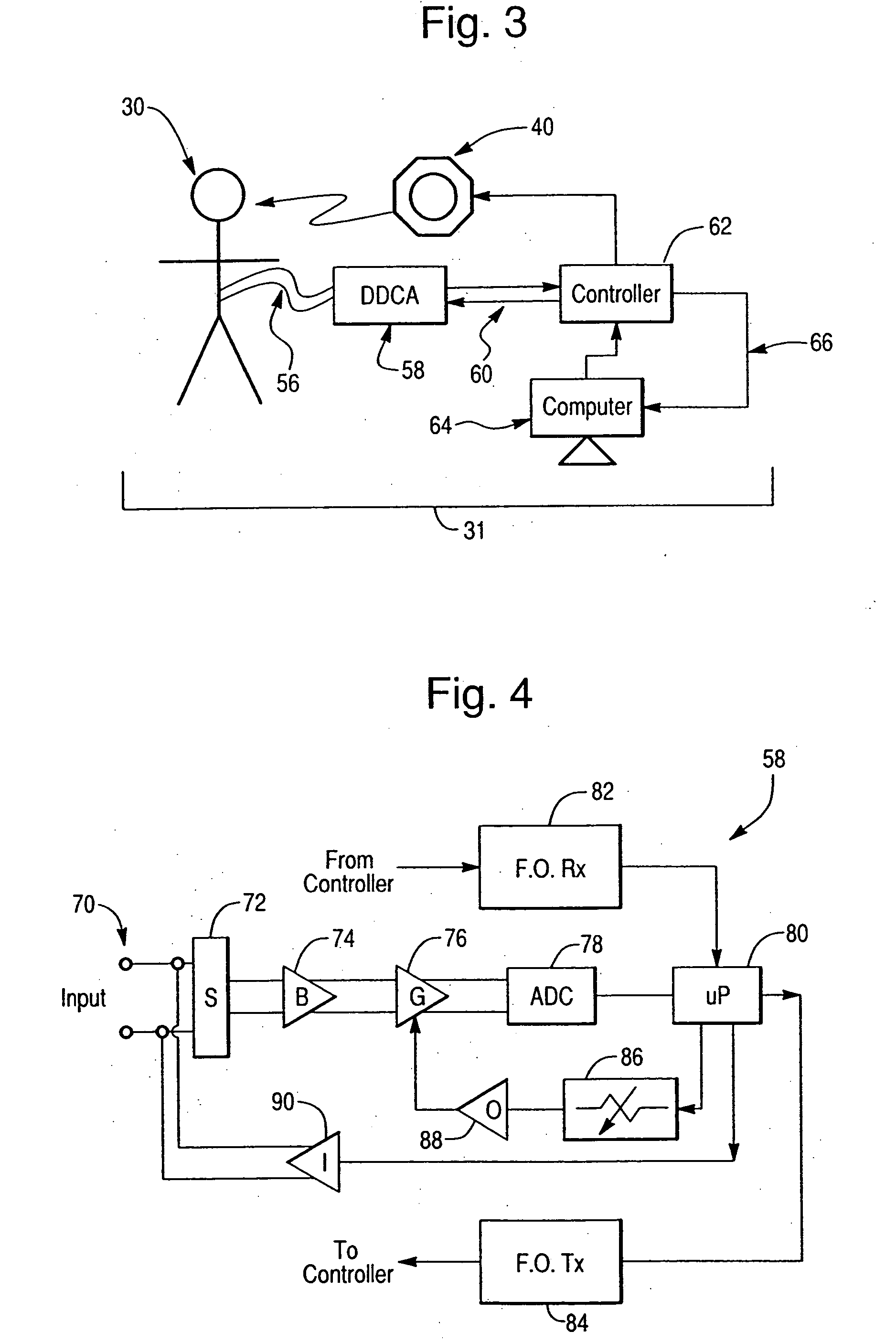
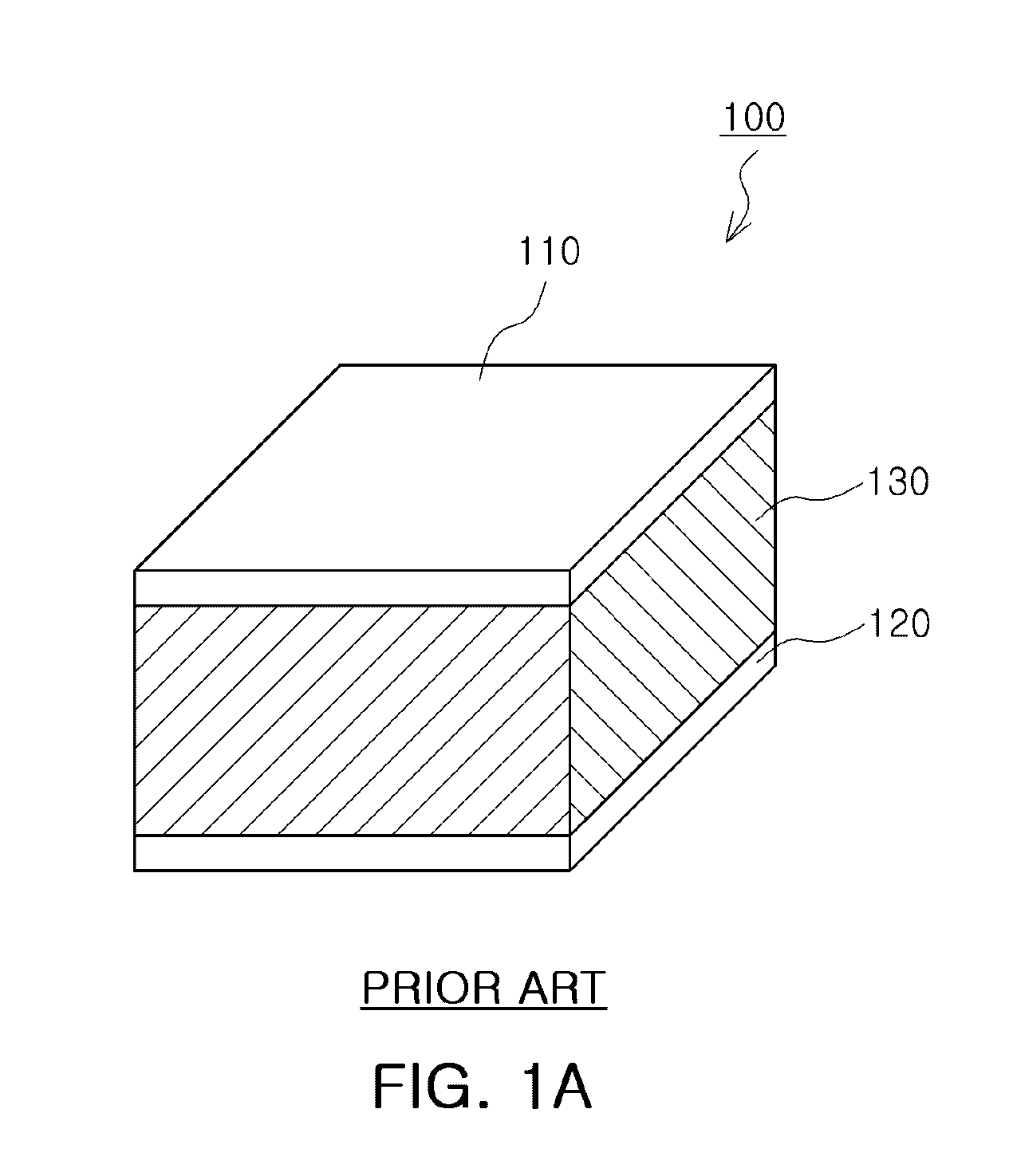
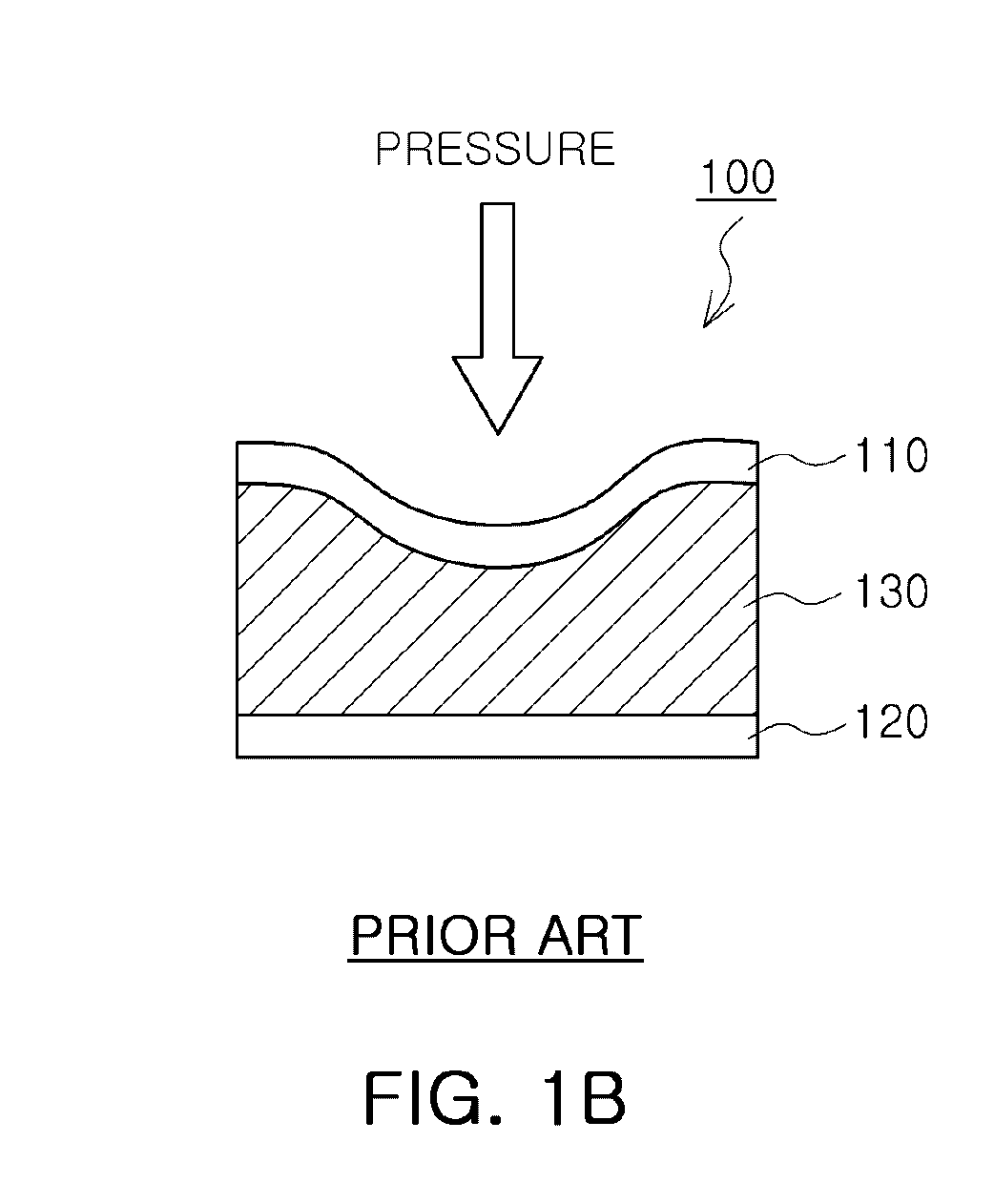
High-sensitivity pressure-sensing probe
ActiveUS20090138007A1Accurate inductionTransvascular endocardial electrodesEndoscopesMagnetic transducersSacroiliac joint
A medical probe includes an insertion tube, having a longitudinal axis and having a distal end. A distal tip is disposed at the distal end of the insertion tube and is configured to be brought into contact with a body tissue. A joint couples the distal tip to the distal end of the insertion tube. A joint sensor, contained within the probe, senses a position of the distal tip relative to the distal end of the insertion tube. The joint sensor includes first and second subassemblies, which are disposed within the probe on opposite, respective sides of the joint and each include one or more magnetic transducers.
Owner:BIOSENSE WEBSTER (ISRAEL) LTD
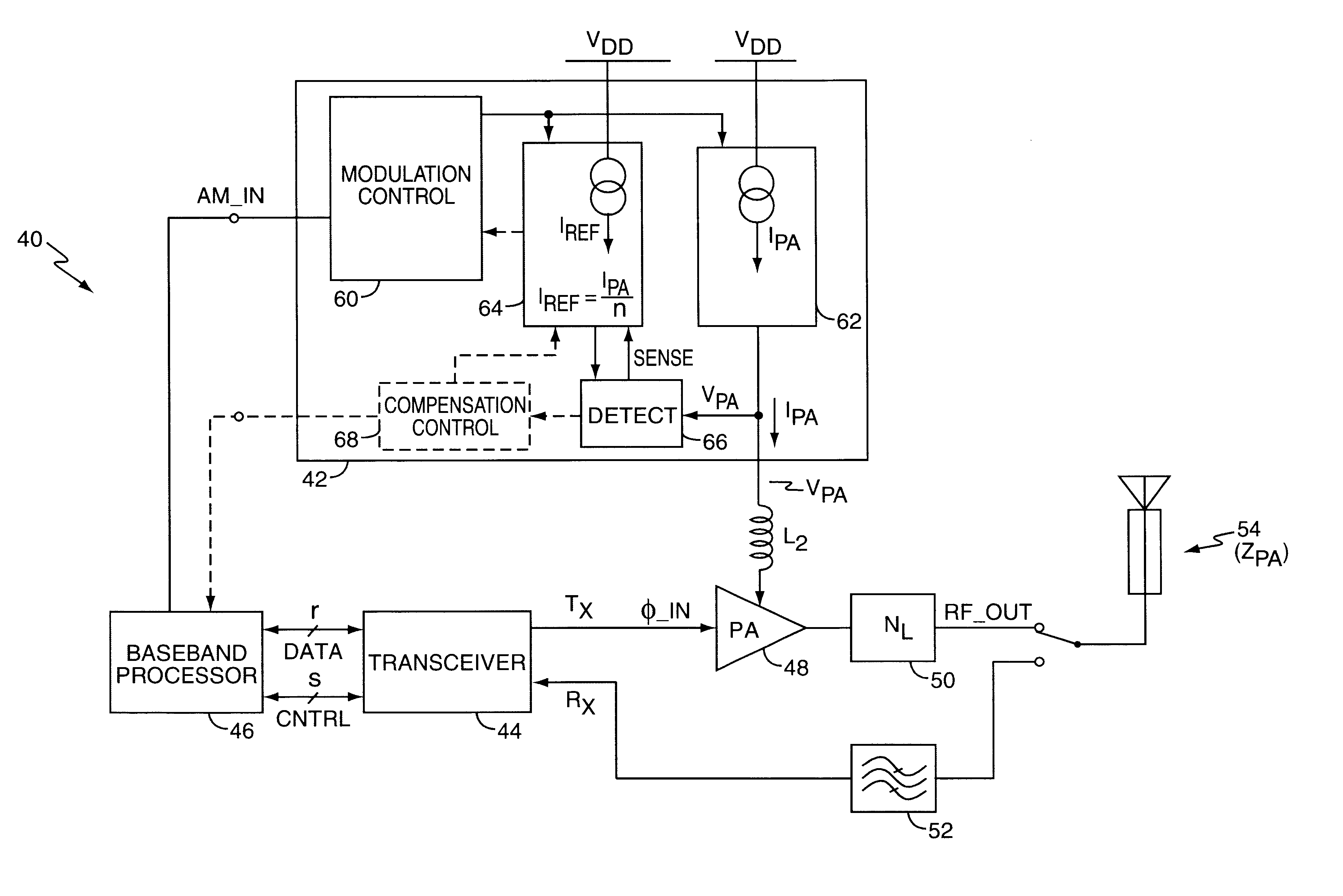
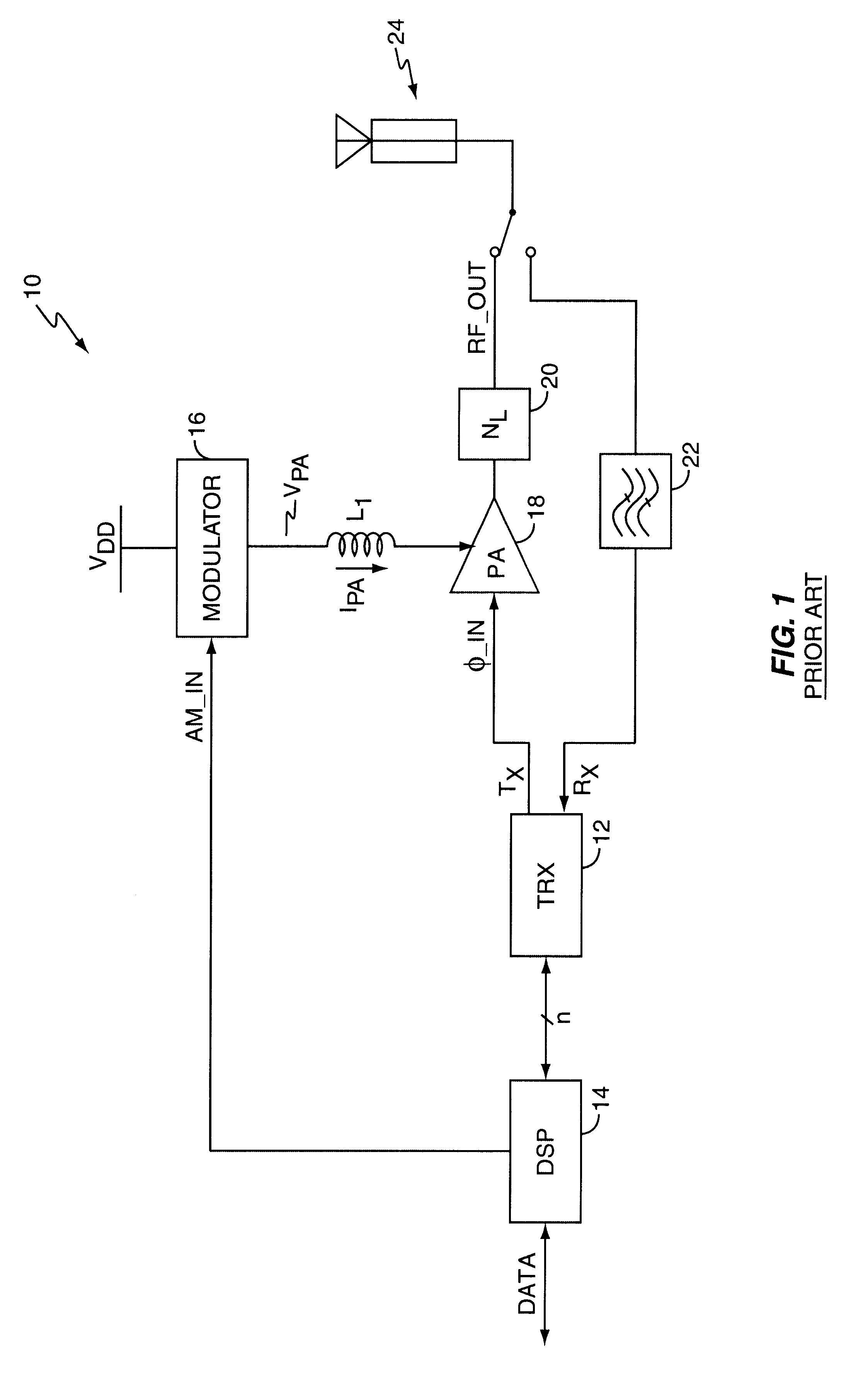
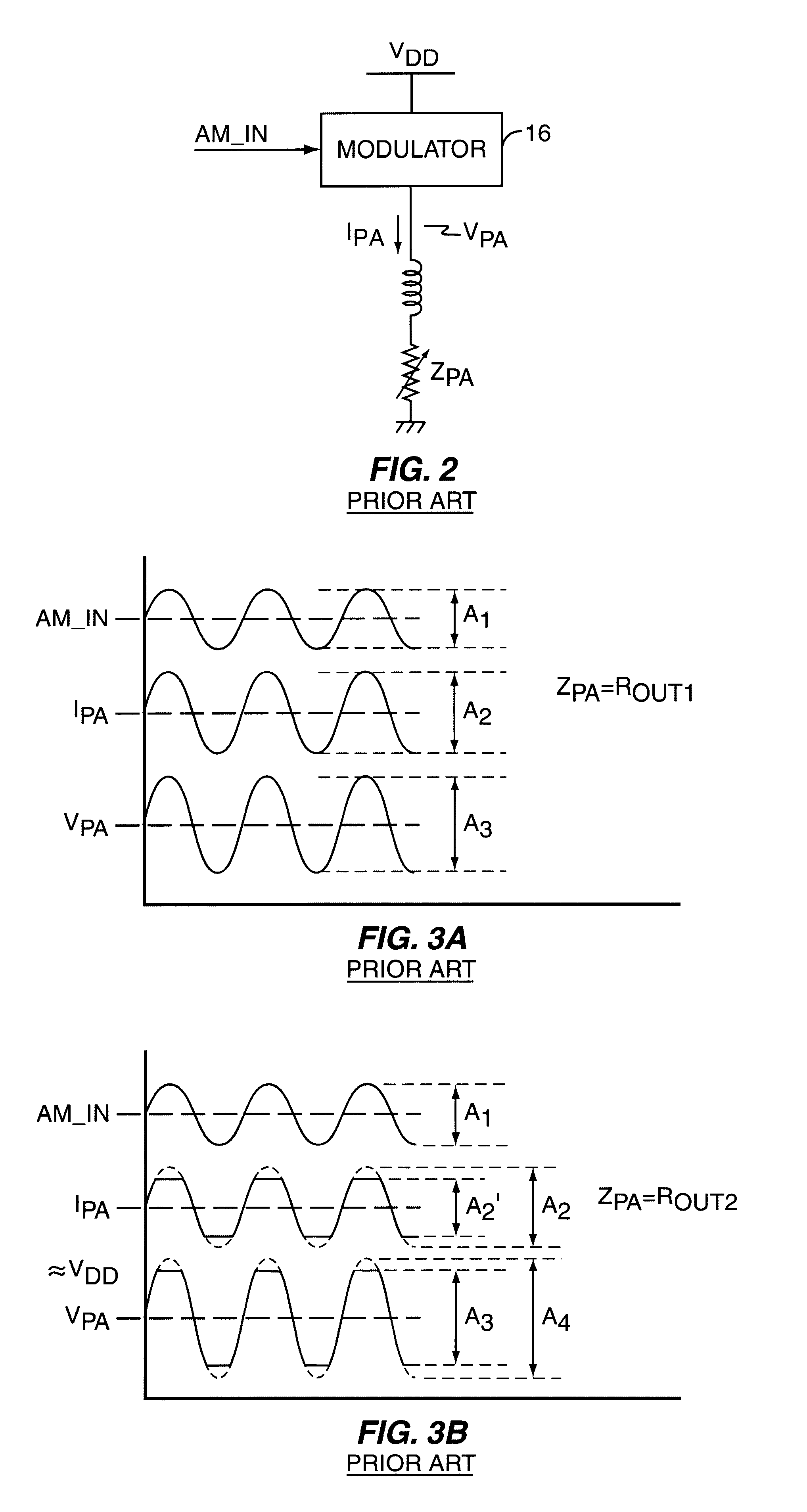
Current modulator with dynamic amplifier impedance compensation
InactiveUS6566944B1Accurately changeAccurate inductionPower amplifiersAmplifier modifications to raise efficiencyRadio frequencyEngineering
An amplitude modulation circuit (modulator) provides modulated supply current, possibly in combination with modulated supply voltage, to a radio frequency (RF) power amplifier (PA), and includes a detection circuit responsive to changes in the ratio of that voltage to the modulated supply current, described herein as its AM modulation impedance. Such impedance (resistance) changes commonly arise from changing coupling characteristics at the RF antenna assembly driven by the PA. A gain control circuit may be associated with the detection circuit, and made responsive thereto, thus allowing adjustment of modulation gain control responsive to changes in PA AM modulation impedance. In one embodiment, this arrangement permits the modulator to hold a fixed modulation gain over changing PA AM modulation impedance, while in other embodiments, modulation gain varies in response to PA impedance changes to avoid signal clipping. Such clipping might otherwise occur where current modulation values in combination with increased PA resistance would result in PA voltages exceeding the supply voltage of the PA.
Owner:ERICSSON INC
Pen type optical mouse device and method of controlling the same
InactiveUS7098894B2Easy to masterAccurate inductionTransmission systemsCathode-ray tube indicatorsComputer scienceOptical mouse
A pen-type optical mouse device indicates a cursor position or inputs writing or a movement of the pen-type optical mouse. An aspect of the pen-type optical mouse is to calculate coordinate values of the mouse device in accordance with a movement of the pen-type optical mouse device. The pen-type optical device includes an image sensor on a side of the interior of a main body of pen-type the mouse device, thereby allowing the pen-type optical mouse device to be slim and easy to hold.
Owner:FINGER SYST
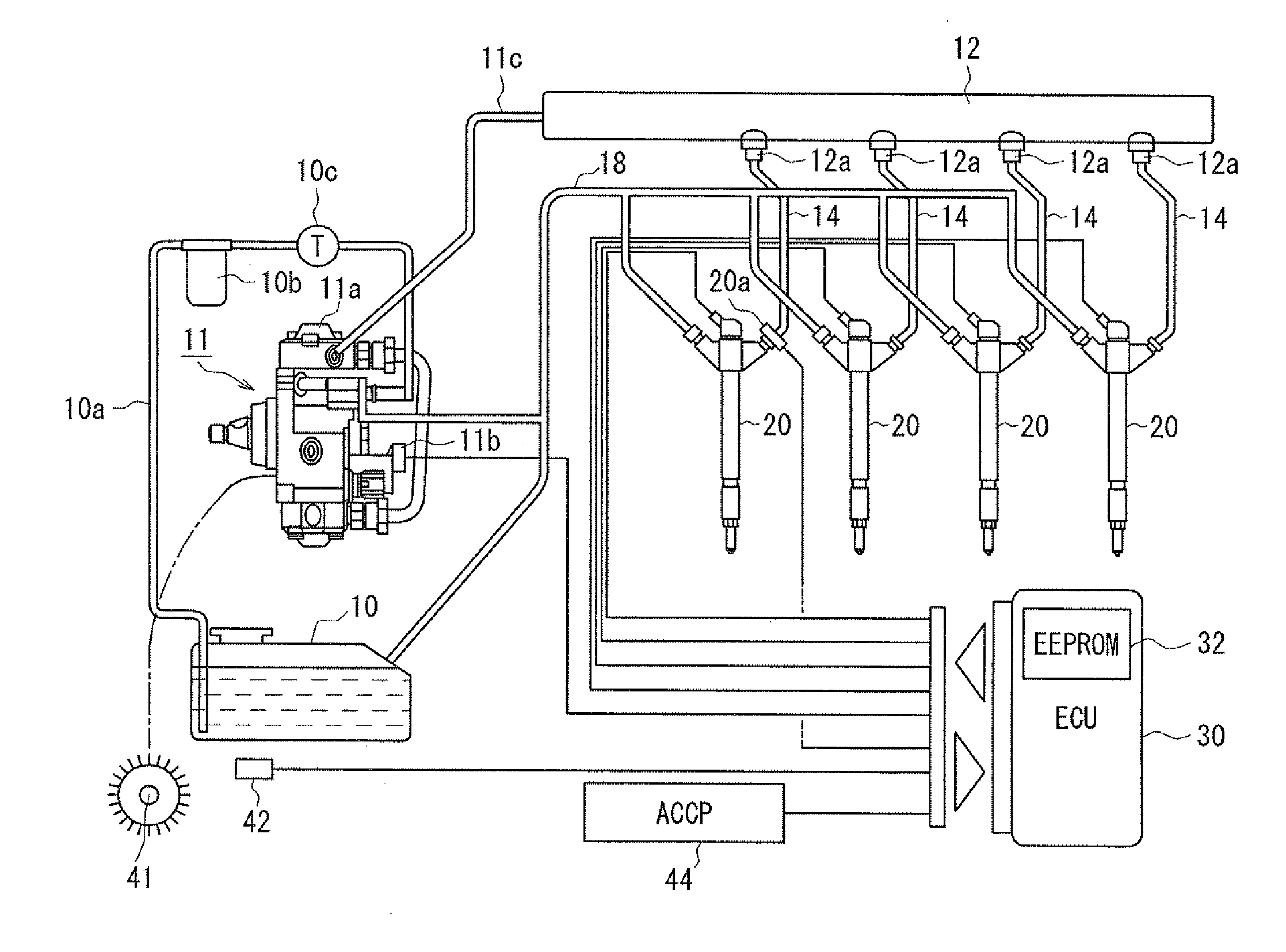
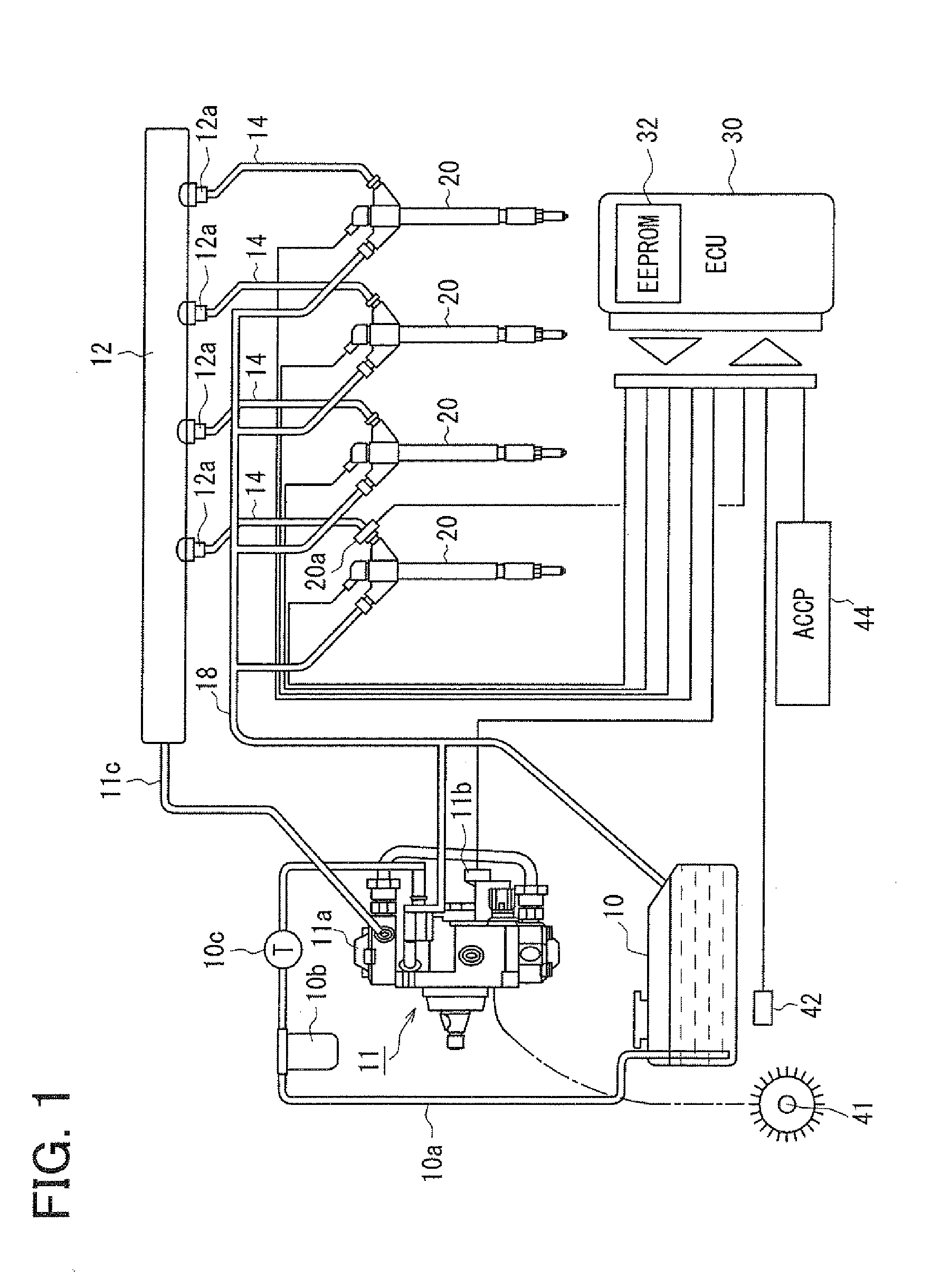
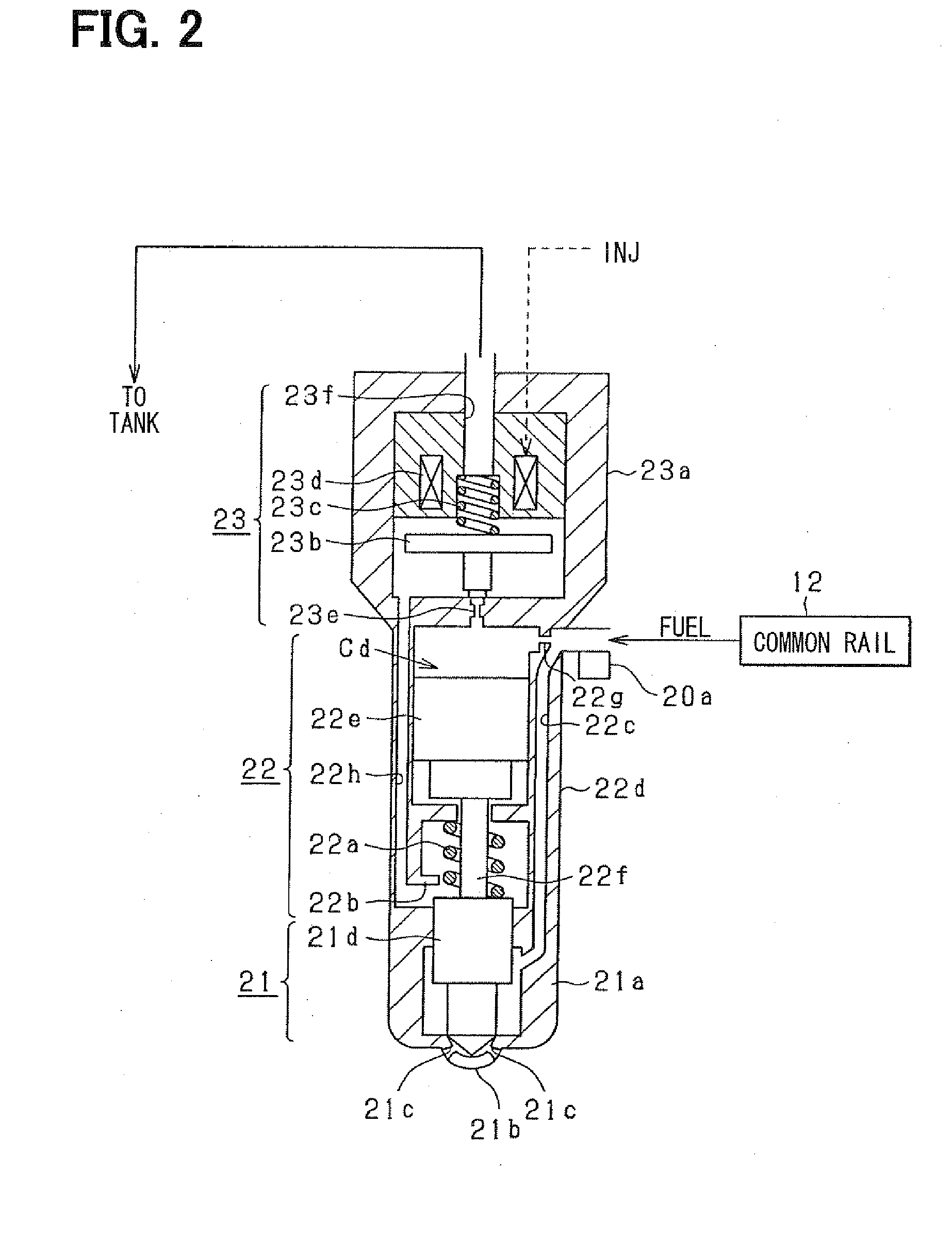
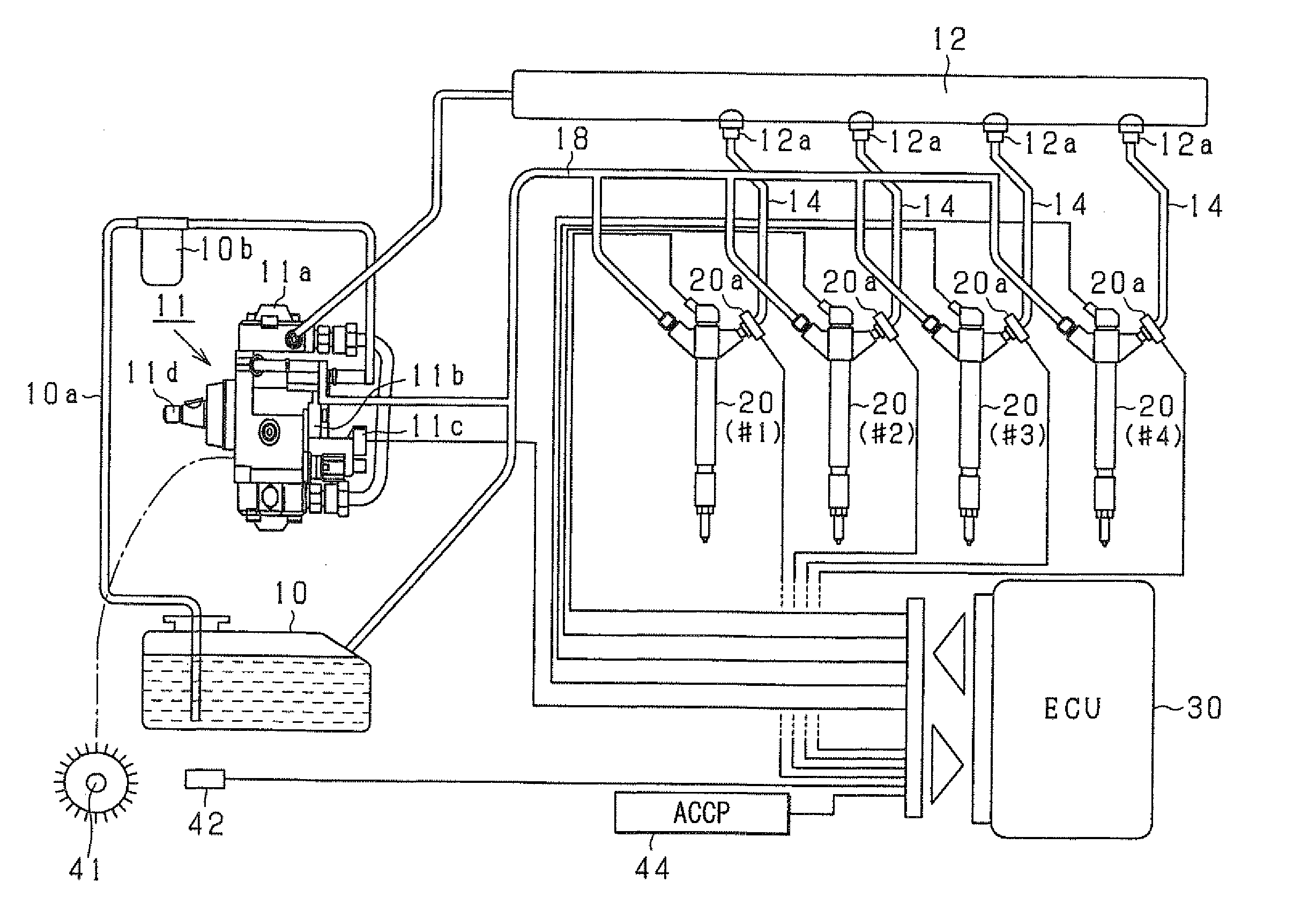
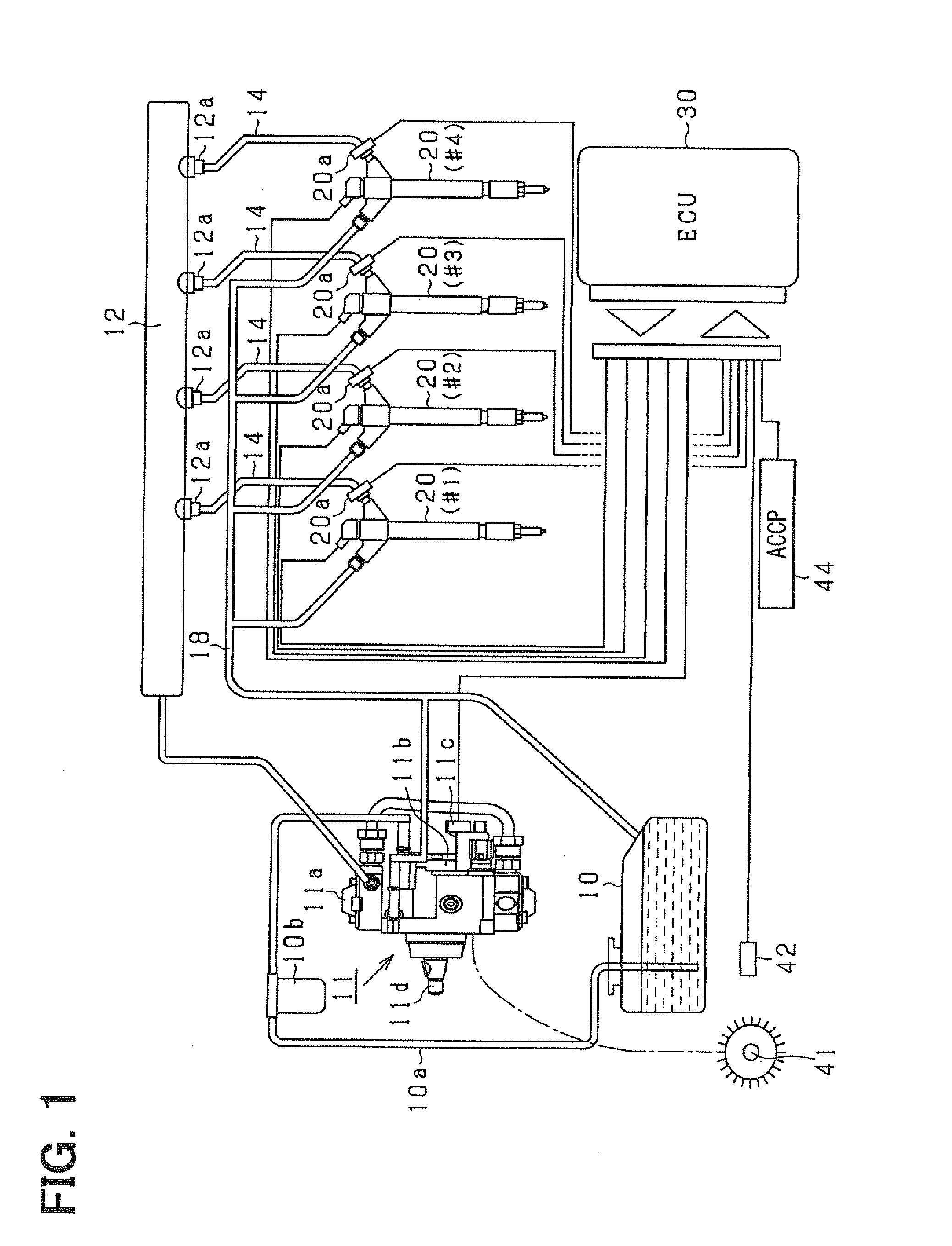
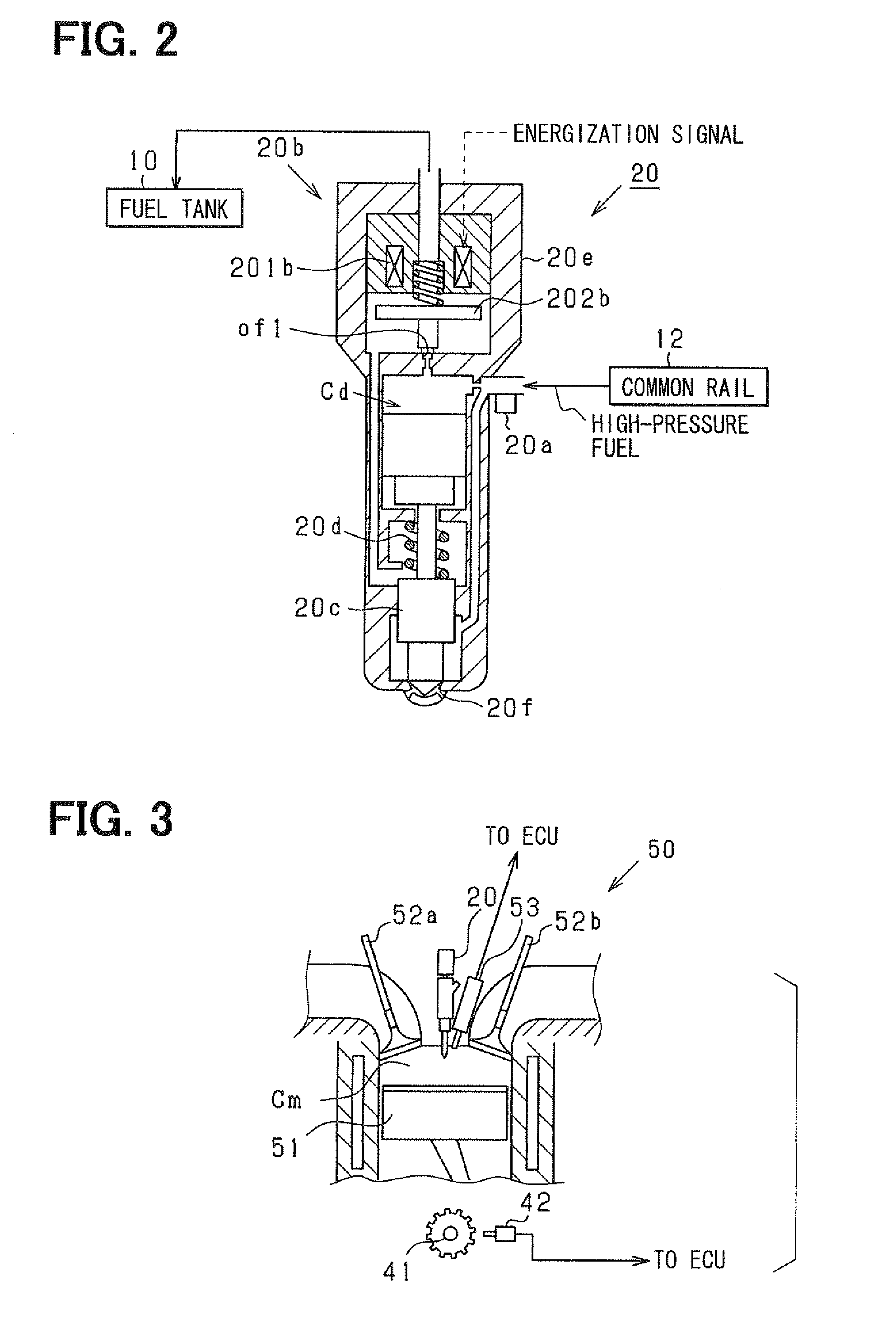
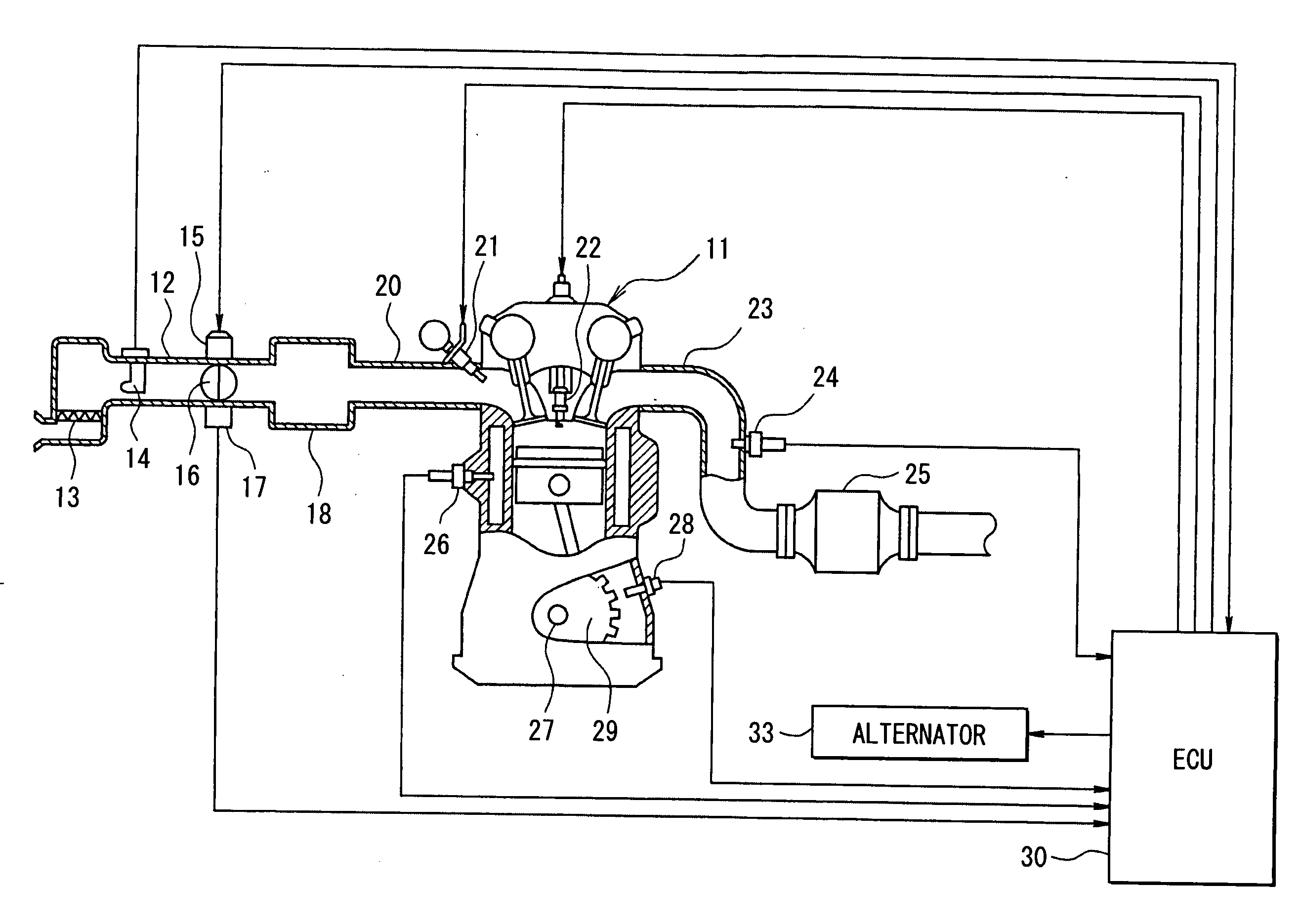
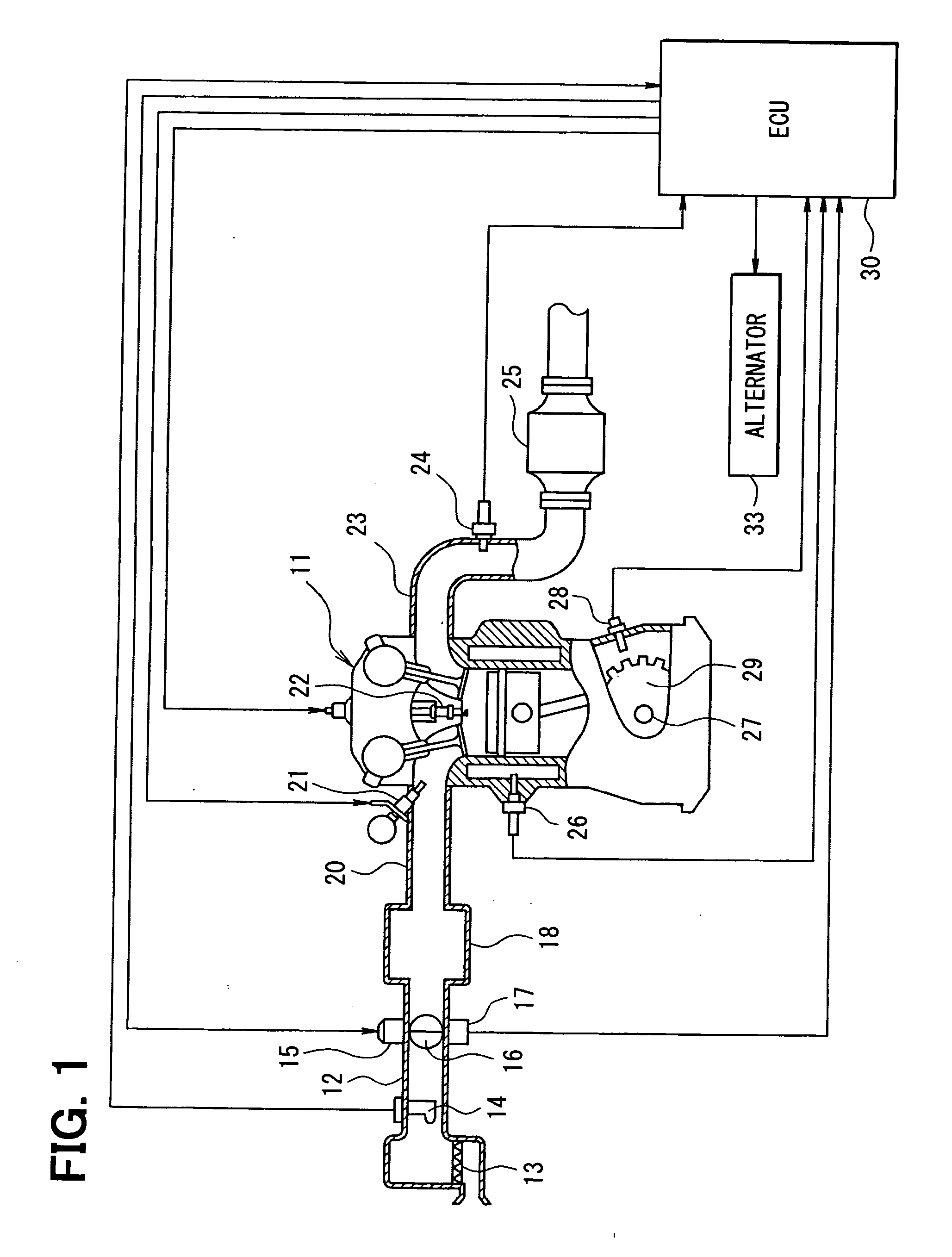
Fuel injection device and adjustment method thereof
ActiveUS20080228374A1Improve accuracyAccurate inductionInternal-combustion engine testingElectrical controlCommon railForce sensor
A fuel injection device (fuel supply system) of a common rail type fuel injection system for an engine includes a pressure sensor disposed in a fuel inlet of an injector for measuring a fuel pressure at a position where the sensor is disposed and an ECU for sensing various kinds of pressure fluctuations associated with the injection including a pressure leak due to an injection operation of the injector and waving characteristics due to actual injection thereof based on sensor outputs from the pressure sensor. The ECU serially obtains the sensor outputs from the pressure sensor at intervals of 20 μsec.
Owner:DENSO CORP
Vehicle periphery monitoring system
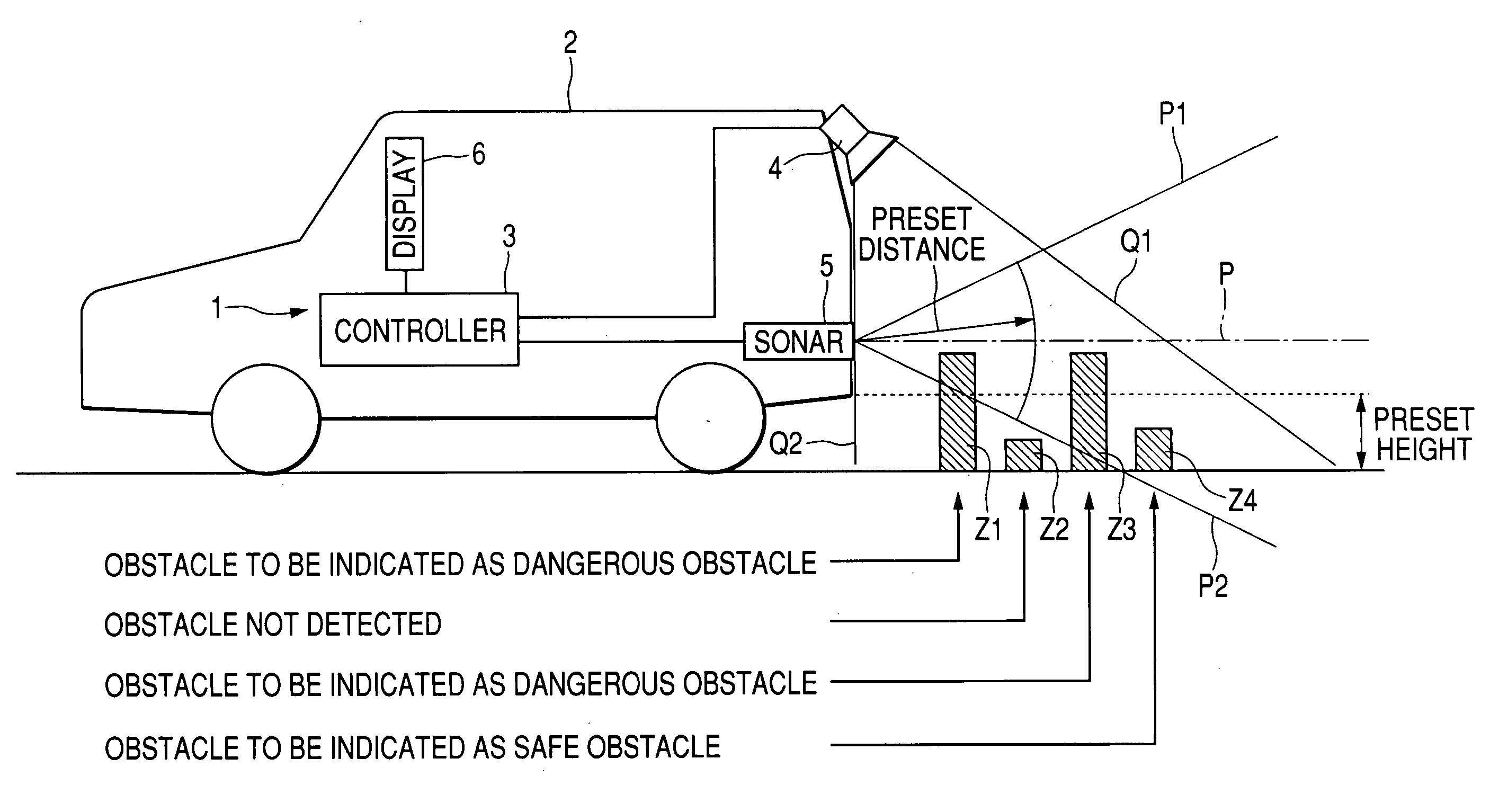
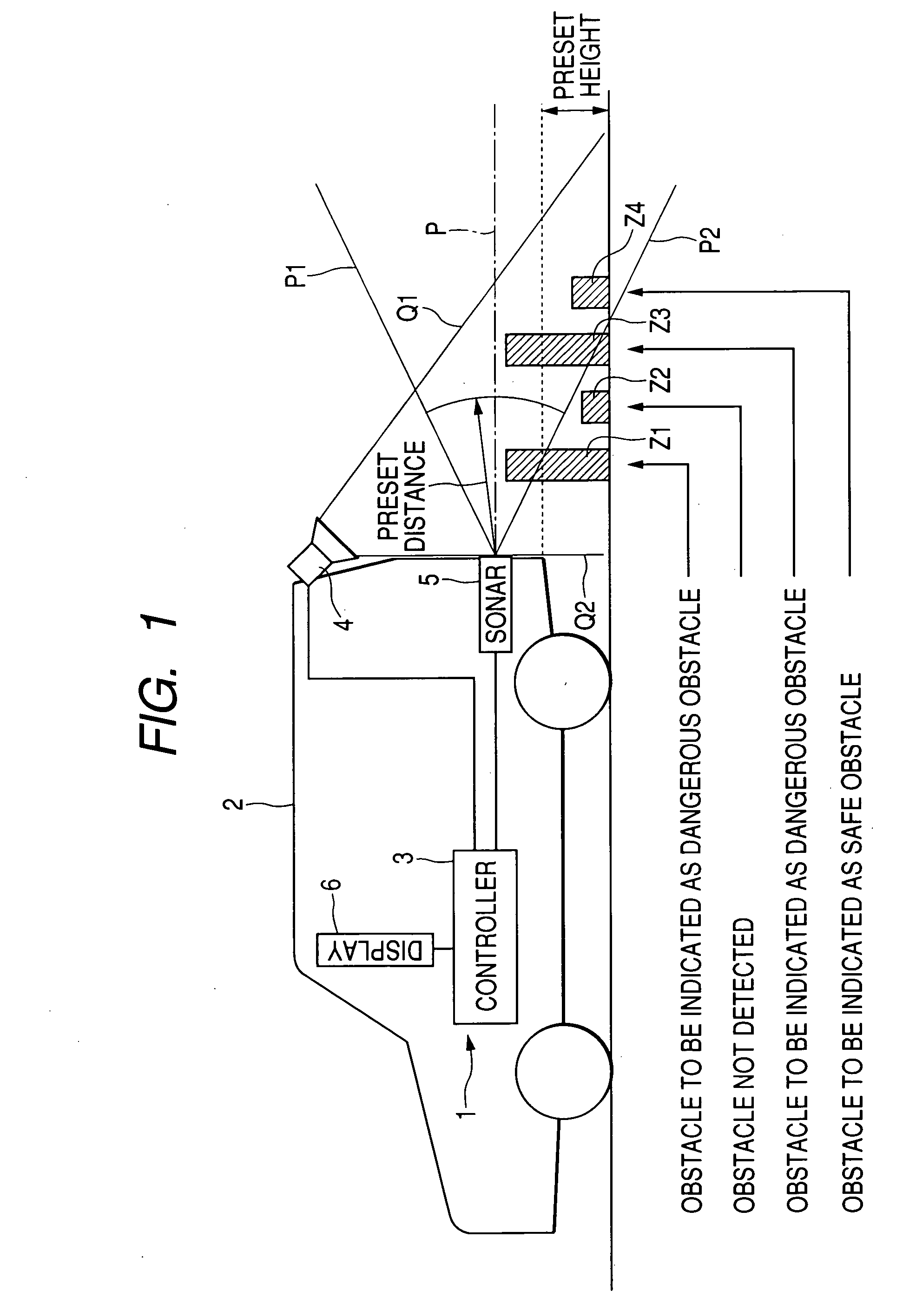
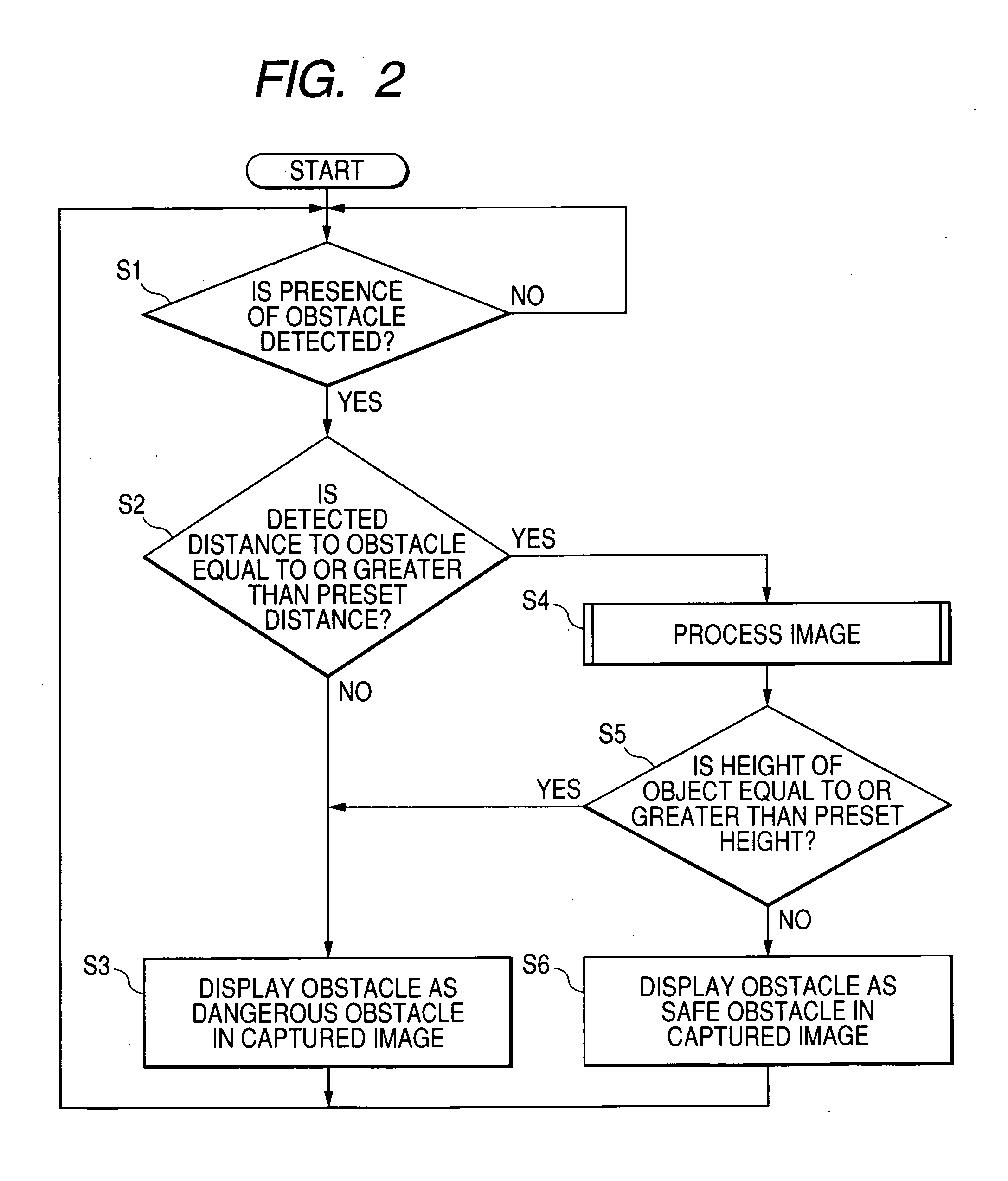
ActiveUS20050231341A1Adequate sense of safetyEasy to handleAnti-collision systemsCharacter and pattern recognitionImaging processingDriver/operator
If the detected distance from a vehicle to a detected obstacle is equal to or greater than a preset distance, then a vehicle periphery monitoring system performs an image processing process on a captured image of the periphery of the vehicle to acquire the height of the vehicle. If the acquired height of the obstacle is less than a preset height, then the obstacle is displayed as a safe obstacle. If the acquired height of the obstacle is equal to or greater than the preset height, then the obstacle is displayed as a dangerous obstacle. The vehicle periphery monitoring system is able to indicate to the vehicle driver whether the detected obstacle is dangerous or safe. The vehicle periphery monitoring system is not required to perform the image processing process on the entire area of the captured image, and does not require a CPU having a high processing capability.
Owner:DENSO CORP
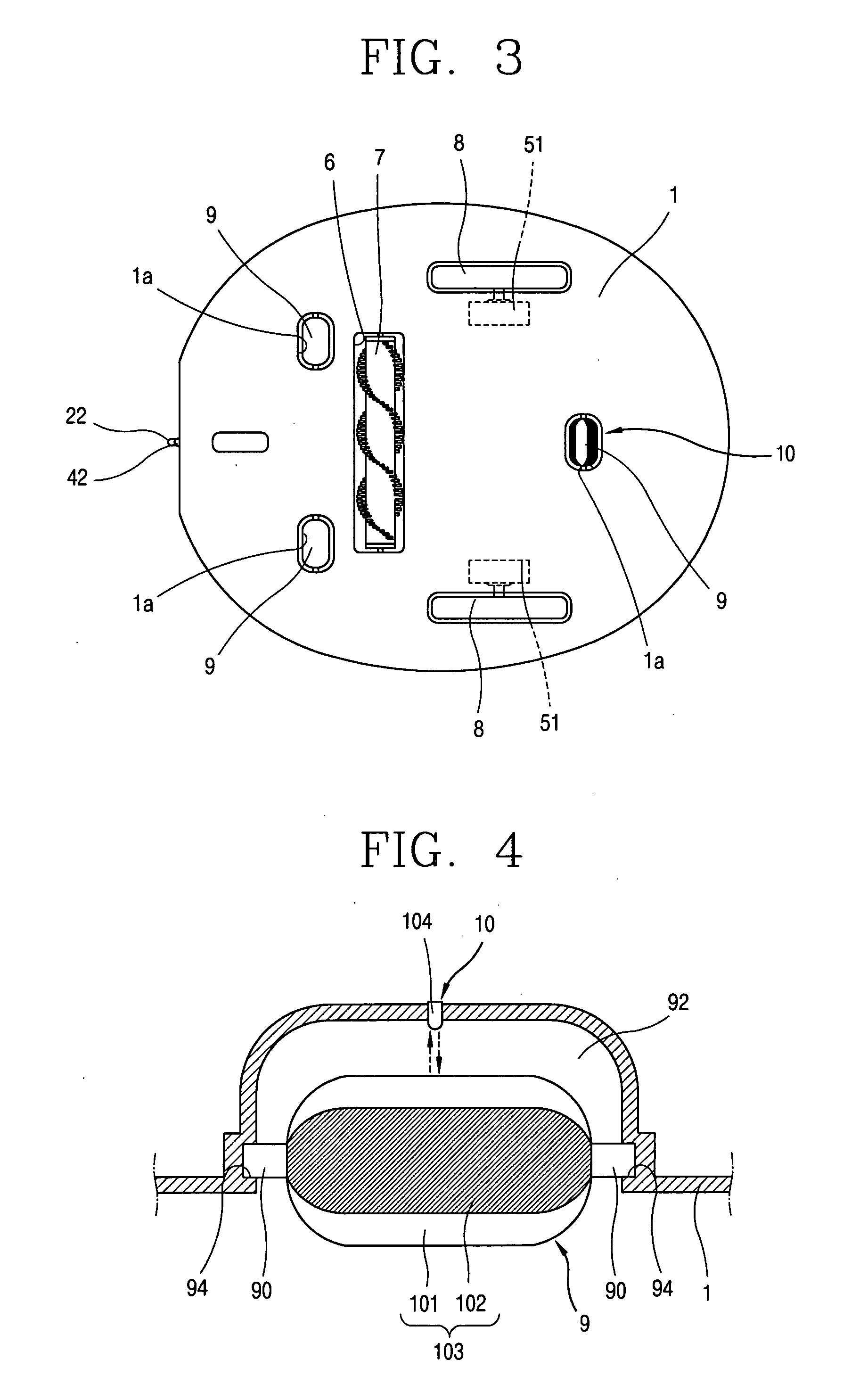
Robot cleaner and operating method thereof
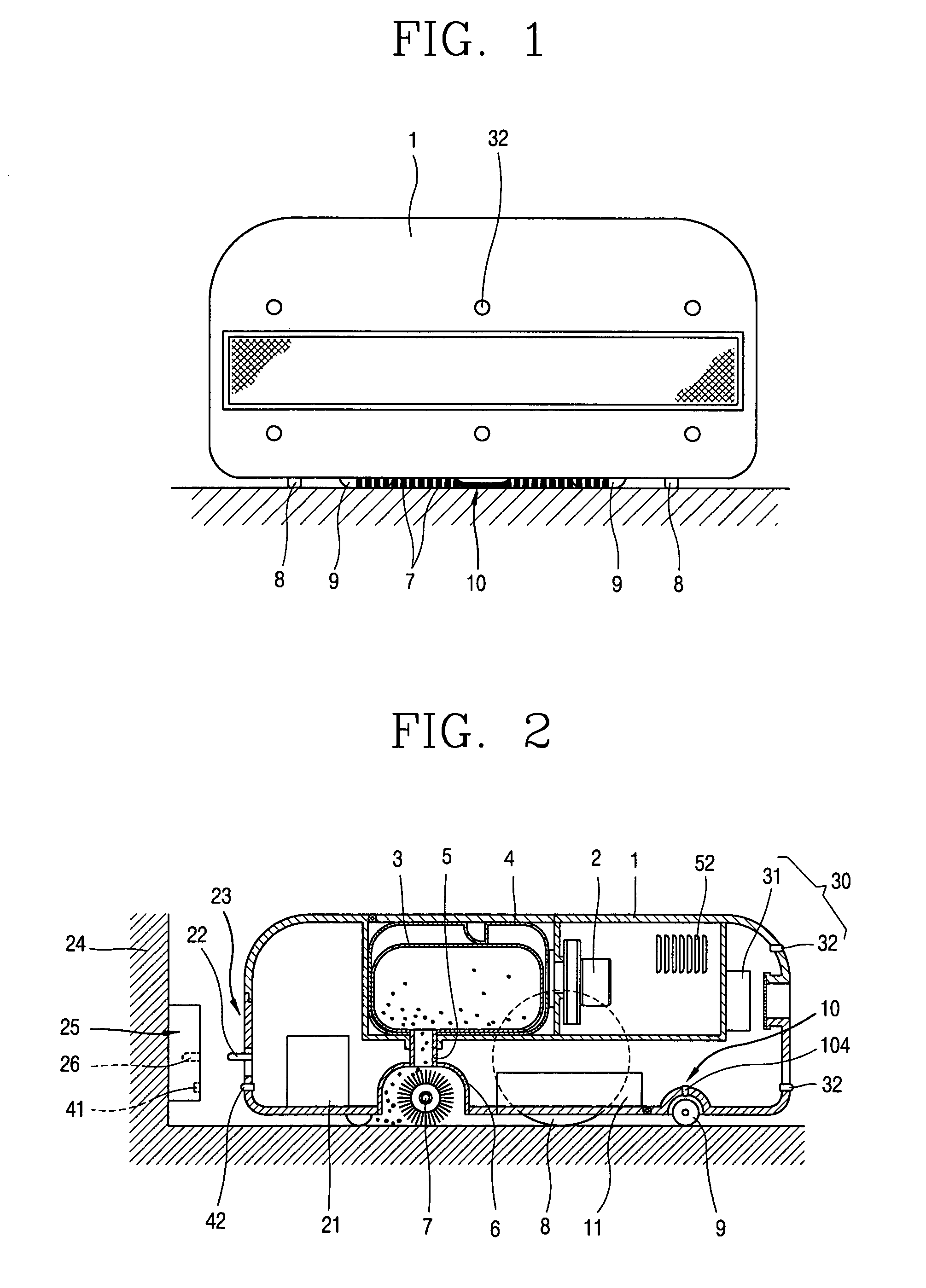
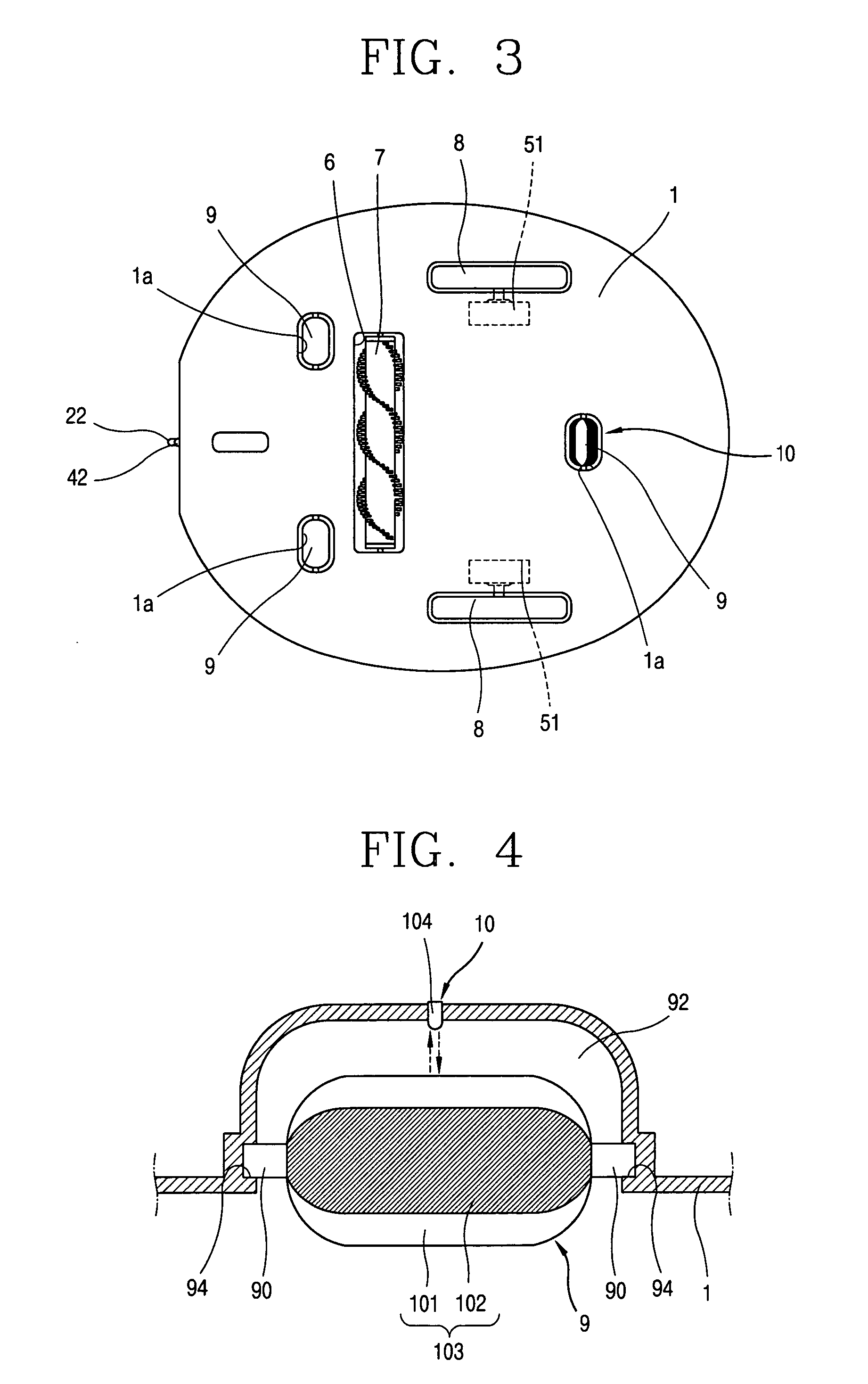
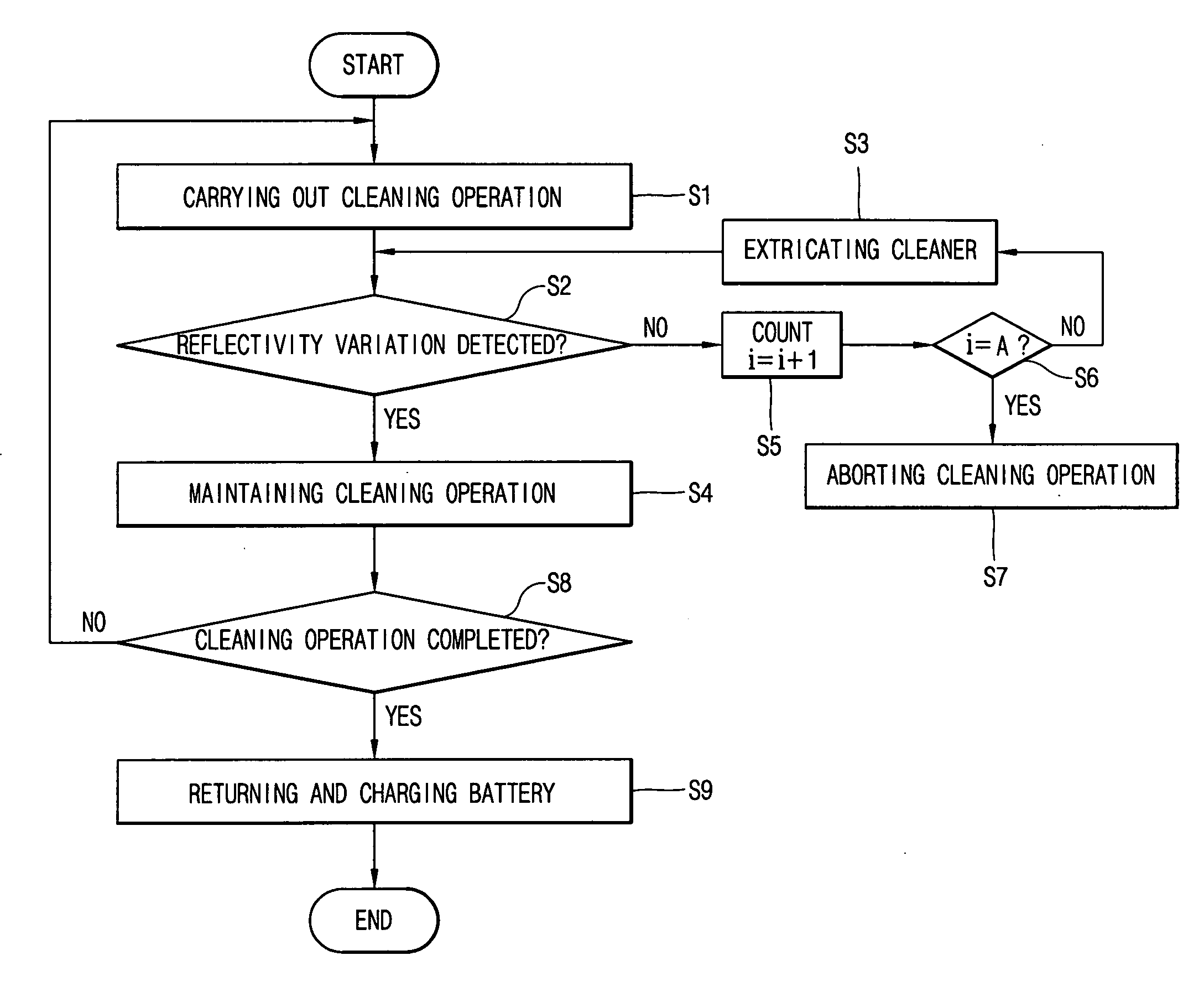
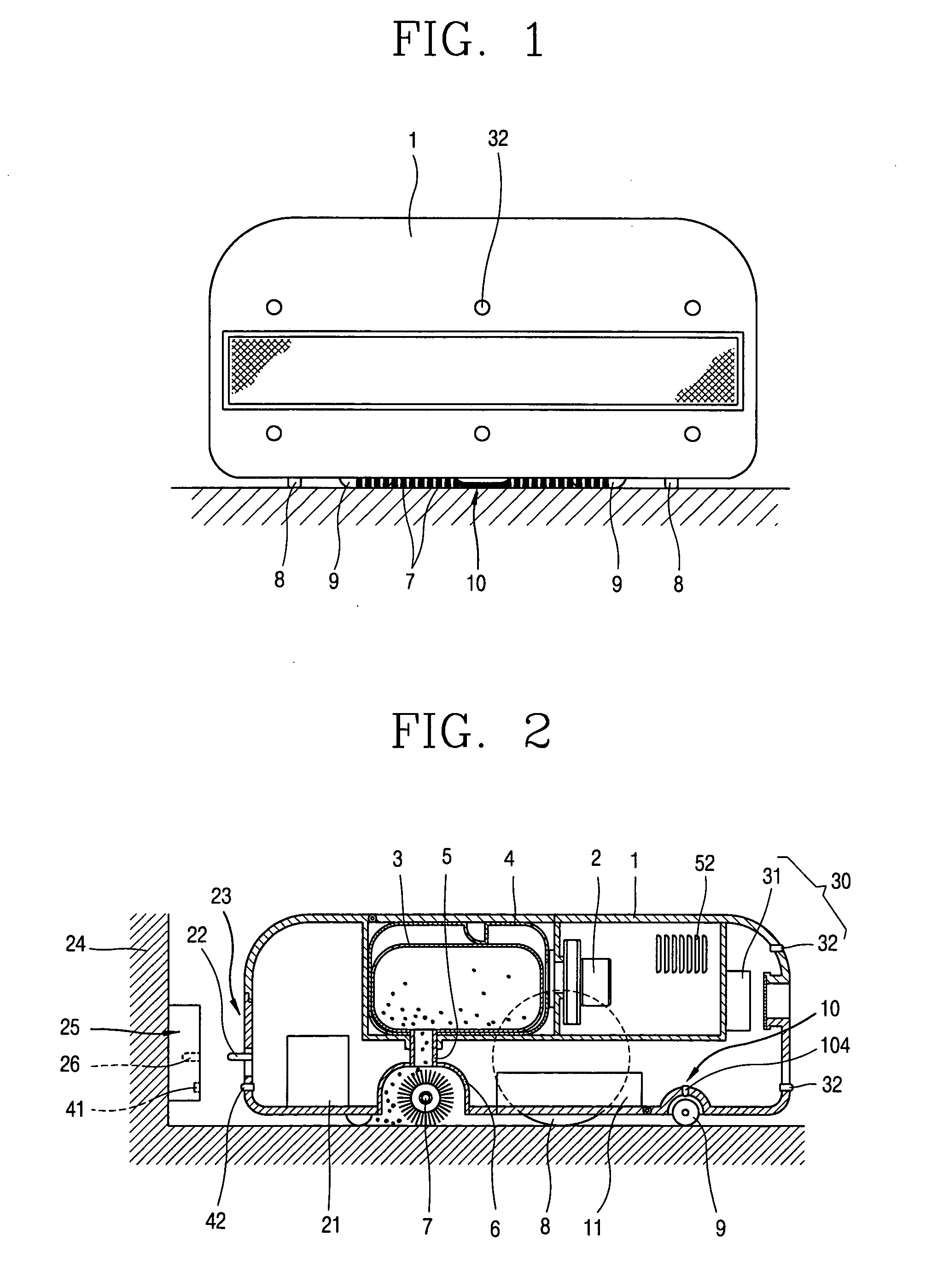
InactiveUS7359766B2Process stabilityAccurate inductionAutomatic obstacle detectionProgramme-controlled manipulatorEngineeringMechanical engineering
A robot cleaner comprises a suction unit installed within a cleaner body, for sucking dirt on a floor; a driving unit for moving the cleaner body; a wheel installed at a bottom of the cleaner body to be contacted with the floor, and rotated by movement of the cleaner body; a detecting unit for detecting whether the wheel is rotated; and a control unit for controlling the driving unit in response to signal from the detecting unit. Accordingly, the robot cleaner can smoothly and continuously carry out a cleaning operation, even when the robot cleaner is abnormally stopped due to an obstacle which is not previously recognized in traveling.
Owner:LG ELECTRONICS INC
Robot cleaner and operating method thereof
InactiveUS20050137749A1Smoothly perform cleaning operationProcess stabilityAutomatic obstacle detectionProgramme-controlled manipulatorEngineeringMechanical engineering
A robot cleaner comprises a suction unit installed within a cleaner body, for sucking dirt on a floor; a driving unit for moving the cleaner body; a wheel installed at a bottom of the cleaner body to be contacted with the floor, and rotated by movement of the cleaner body; a detecting unit for detecting whether the wheel is rotated; and a control unit for controlling the driving unit in response to signal from the detecting unit. Accordingly, the robot cleaner can smoothly and continuously carry out a cleaning operation, even when the robot cleaner is abnormally stopped due to an obstacle which is not previously recognized in traveling.
Owner:LG ELECTRONICS INC
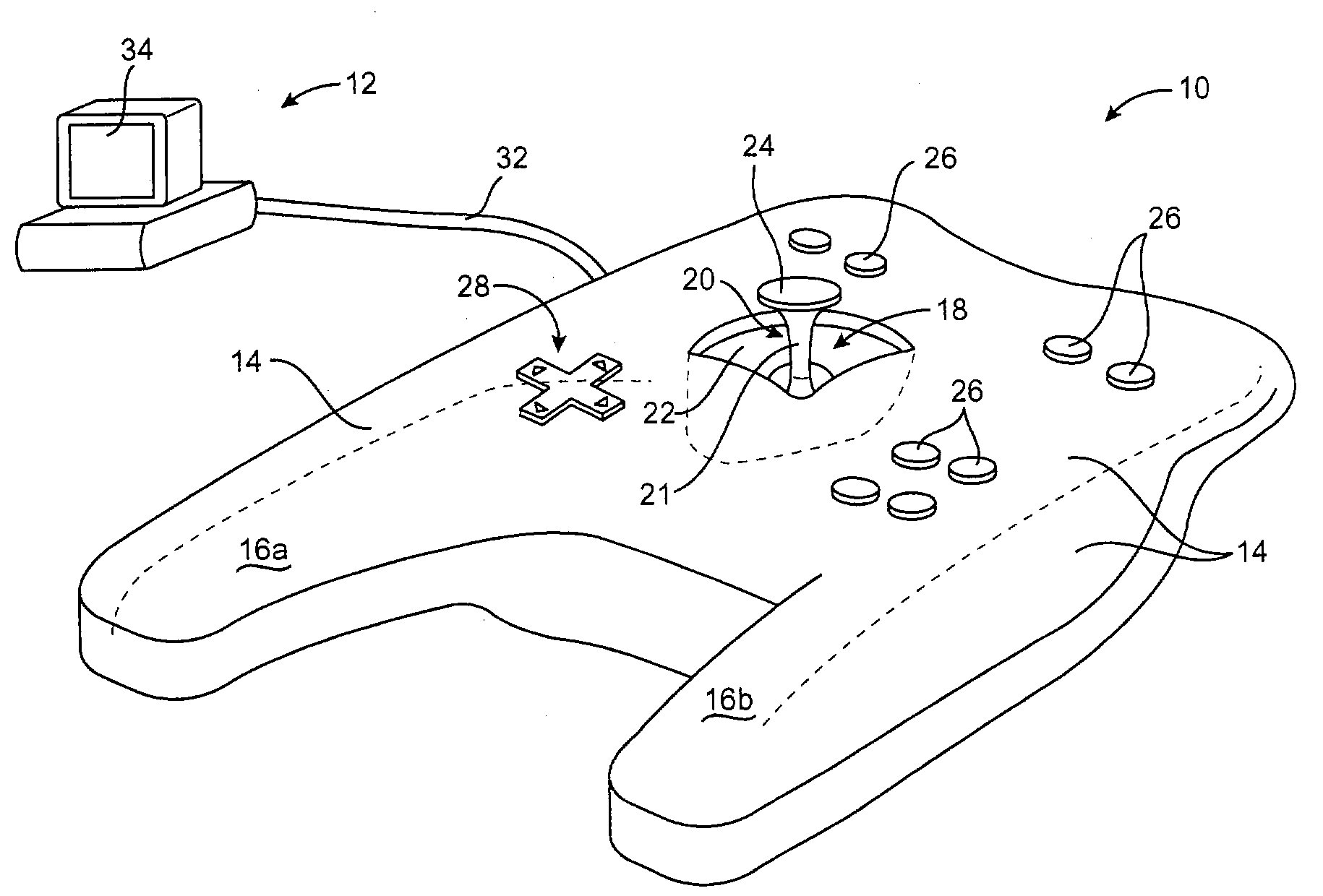
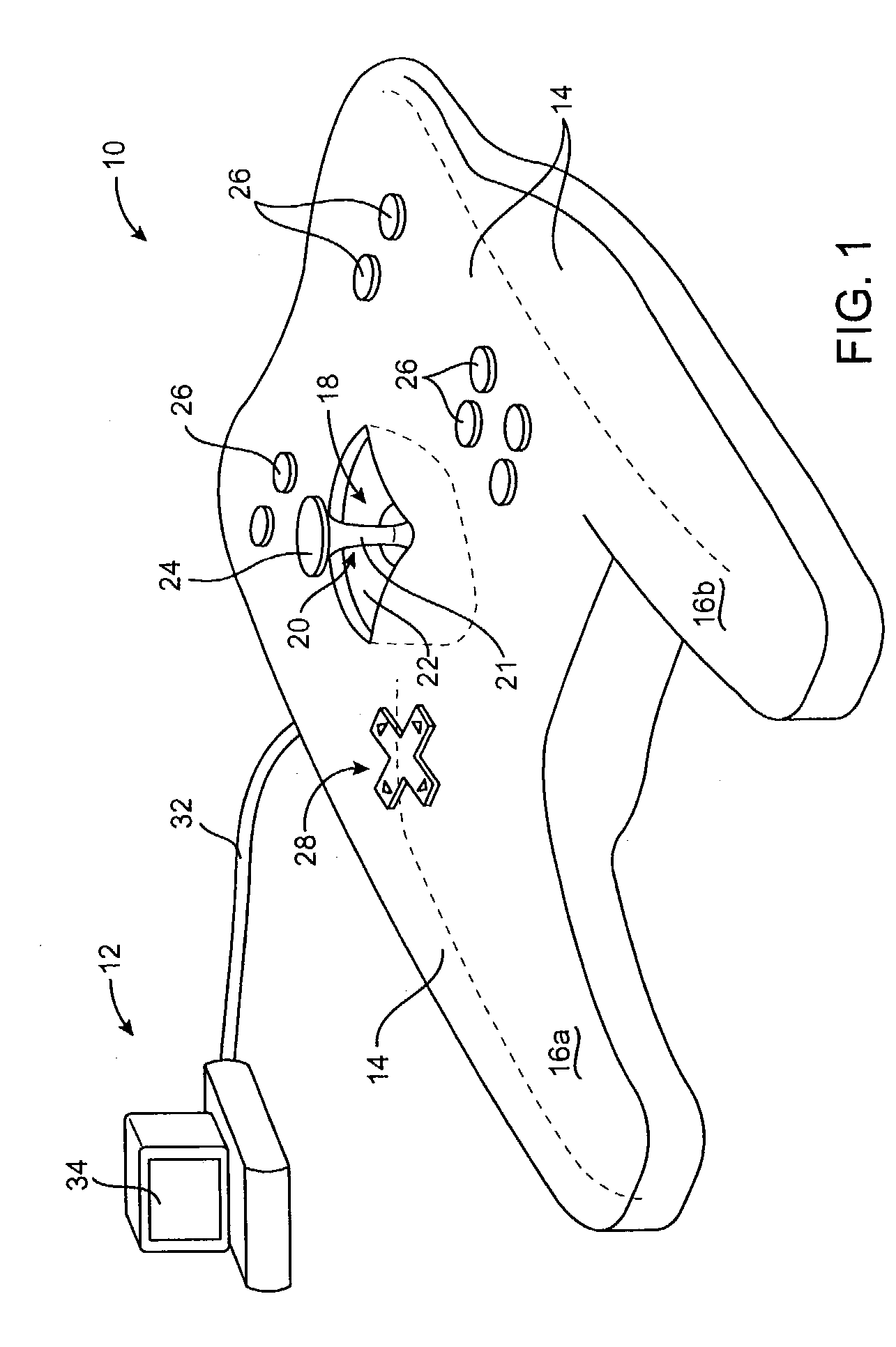
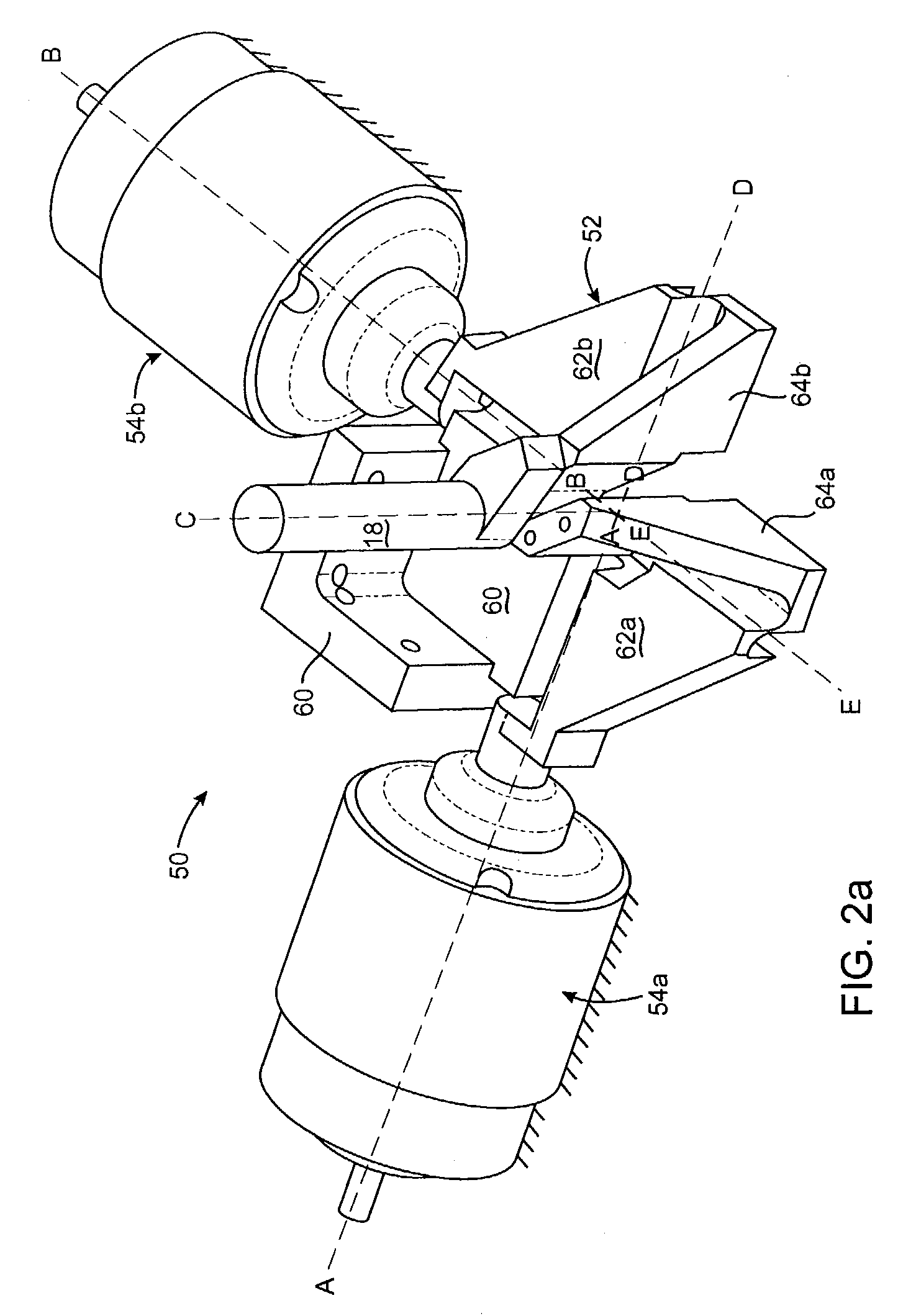
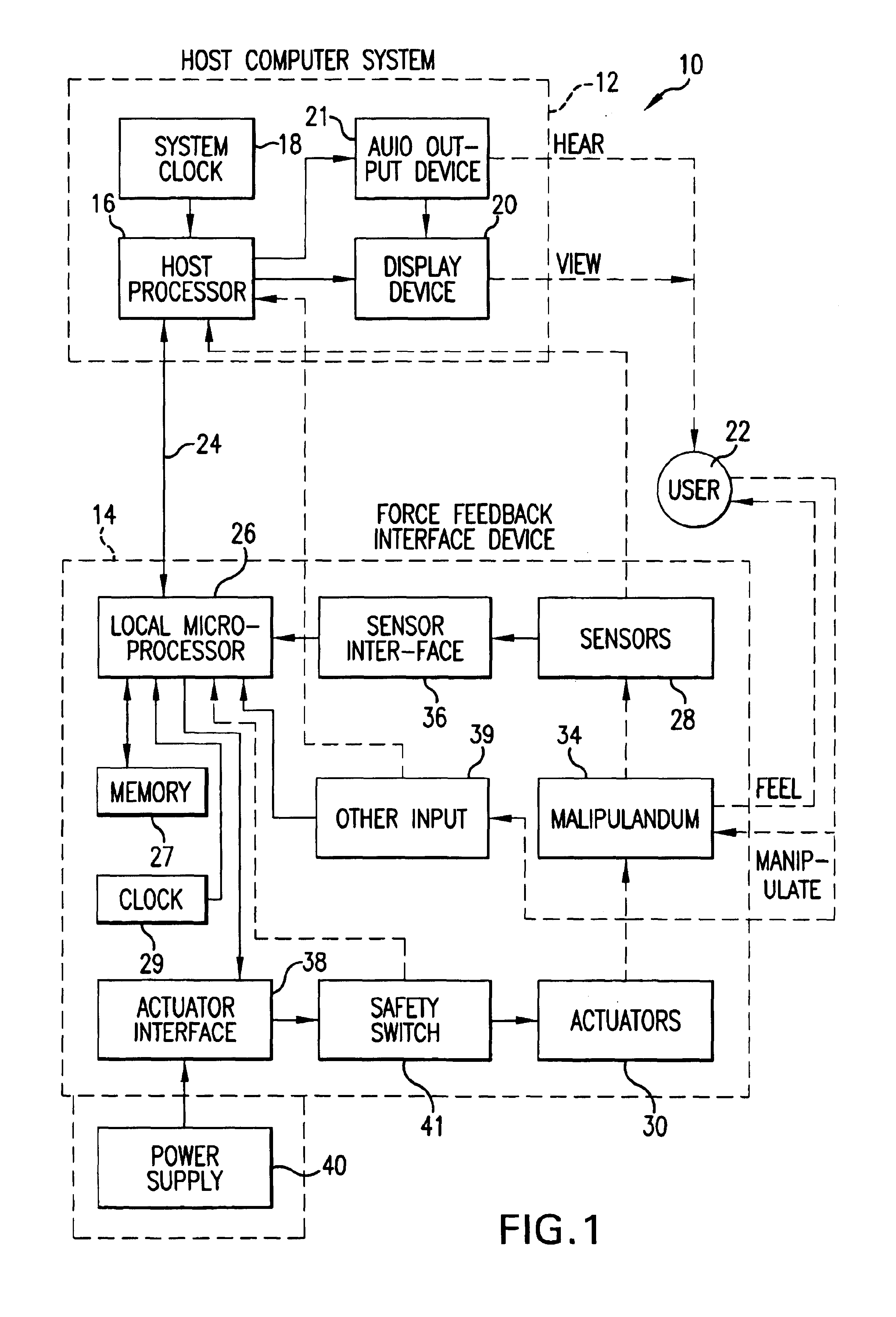
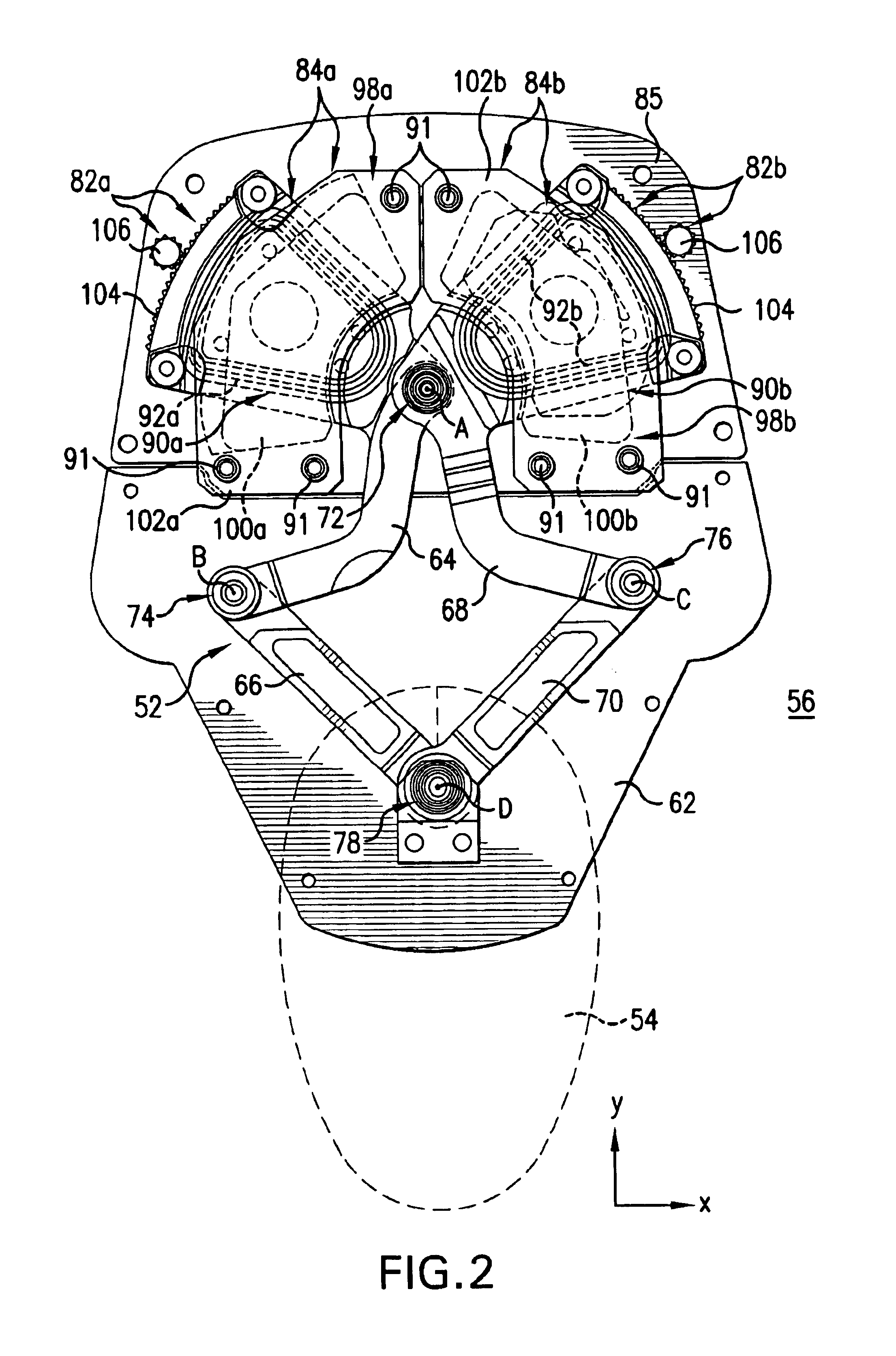
Flexure mechanism for interface device
InactiveUS7193607B2Low costEasy to manufactureInput/output for user-computer interactionManual control with multiple controlled membersCouplingClosed loop
A flexure mechanism for an interface device that interfaces a user with a computer system. An interface device includes a manipulandum physically contacted by the user. A five-bar closed-loop mechanism is coupled to the manipulandum to provide two rotary degrees of freedom to the manipulandum. The mechanism includes members coupled to each other by flexible couplings allowing rotation of the members. In preferred embodiments, four or five of the members are coupled together by flexible couplings that allow bending, thereby forming a unitary piece, where the couplings are oriented along axes of rotation of the mechanism. A senor senses a position of the manipulandum outputs a sensor signal, and in some embodiments actuators are coupled to the mechanism to output a force to the manipulandum in particular degrees of freedom. The manipulandum can be a joystick handle or portion of a sphere, where the device in one embodiment can be a handheld gamepad or similar controller.
Owner:IMMERSION CORPORATION
Sensor system for measuring and monitoring indoor air quality
InactiveUS6941193B2Accurate inductionAccurate measurementMechanical apparatusLighting and heating apparatusIndoor air qualityBuilding under construction
An apparatus for accurately sensing room conditions and positioned in the air stream to the return air plenum. The apparatus is a combination of a temperature and volatile organic compound (VOC) sensor. The sensor module is built into a ceiling grid system with the body of the sensor module extending into the return air plenum. The ceiling grid has a slot fabricated into its face which allows the air stream from the room to flow by the sensors on its way to the plenum. This enables both the temperature and the composition of the air to be monitored at the optimal location. A portable pollution sensor device that measures and monitors leading indicators of indoor air quality and the extent of pollution is used in conjunction with the ceiling grid mounted sensor modules. The portable device documents and benchmarks air quality both in buildings under construction and in existing buildings. The portable device is network-enabled so as to simultaneously transmit the data to various control devices. In addition to its use to monitor areas not otherwise covered by the ceiling grid mounted sensors, the hand-held sensor can be used during building construction to determine the best locations in the ceiling grid system for mounting of the fixed pollution sensors.
Owner:AWI LICENSING
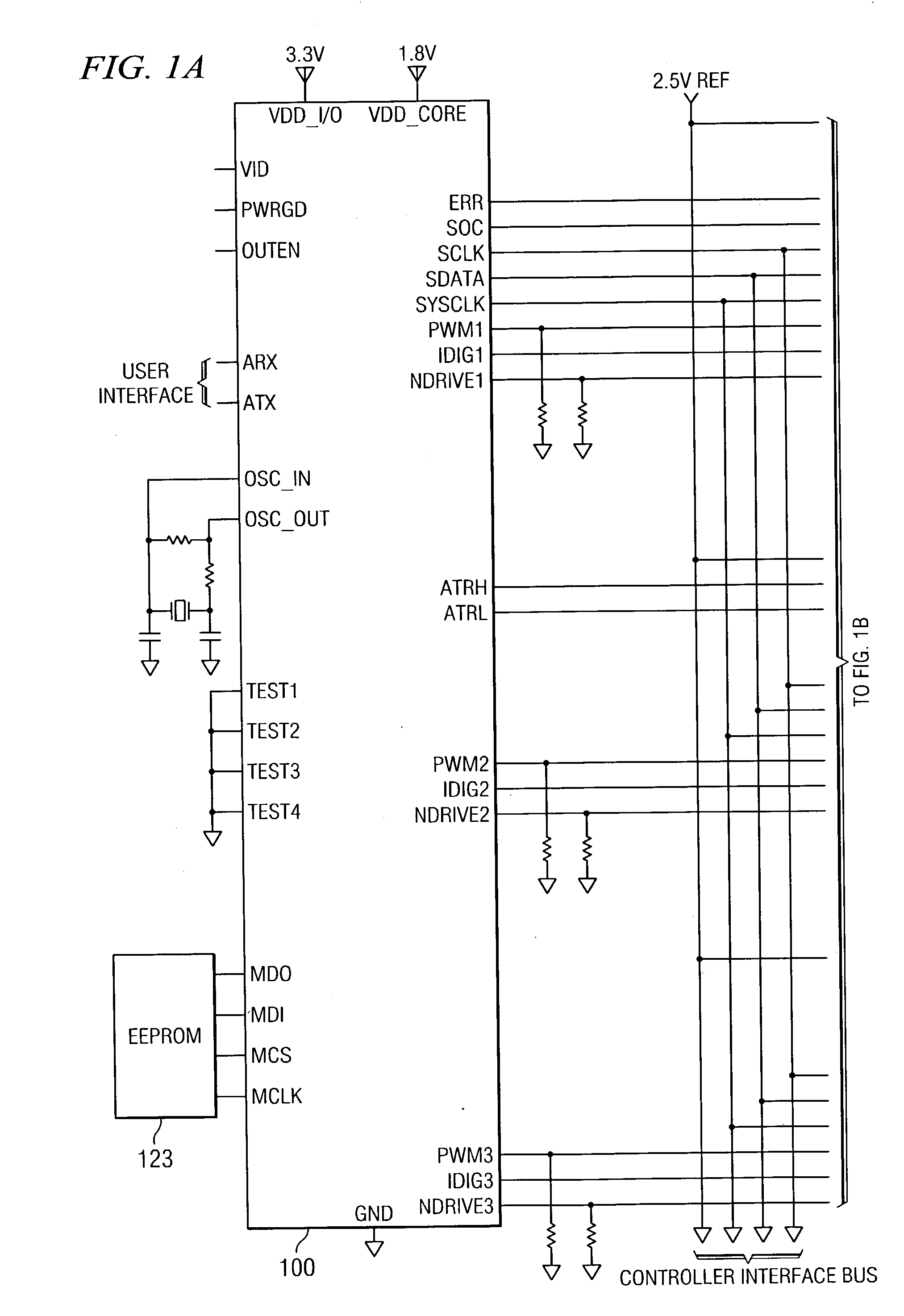
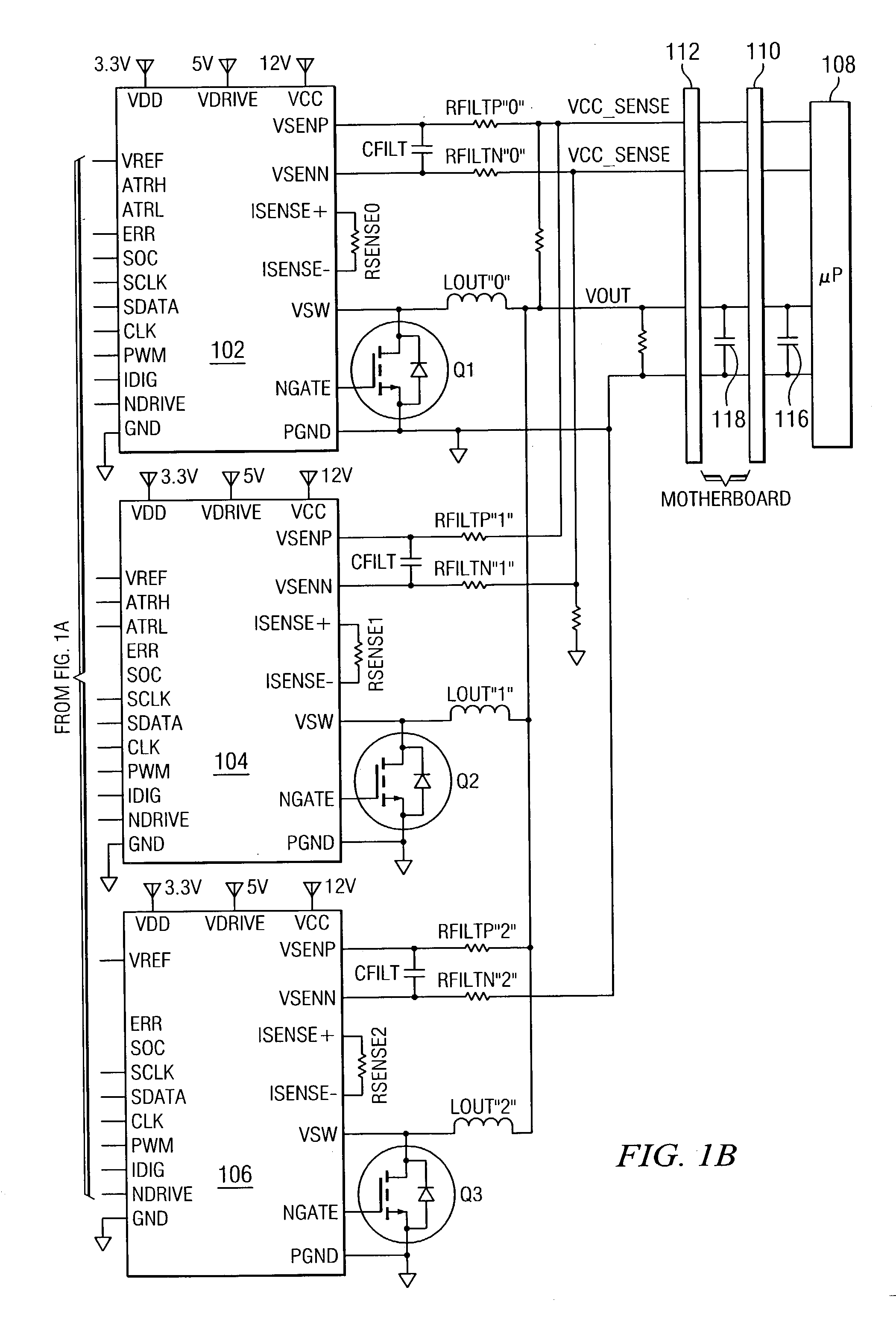
Digitally controlled voltage regulator
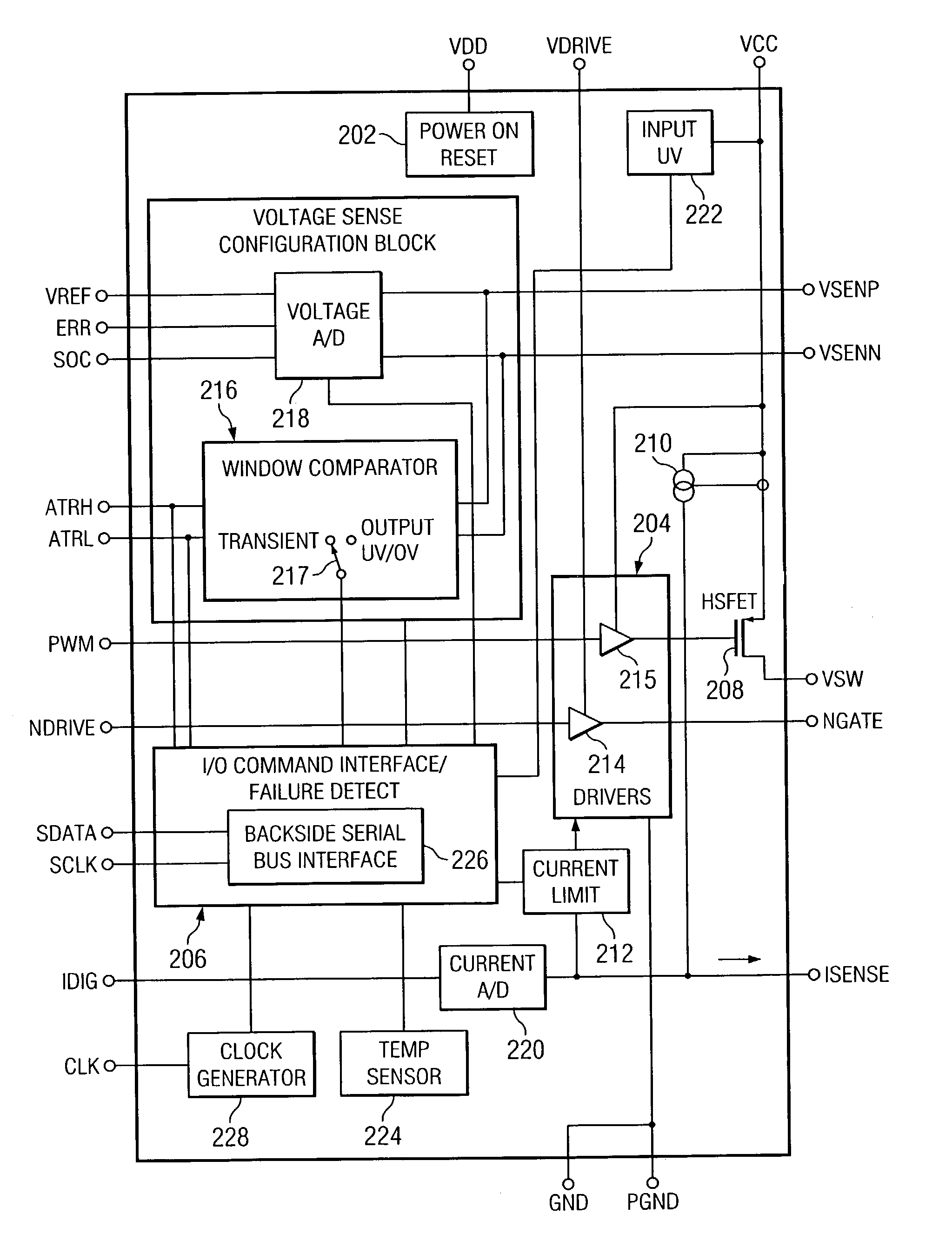
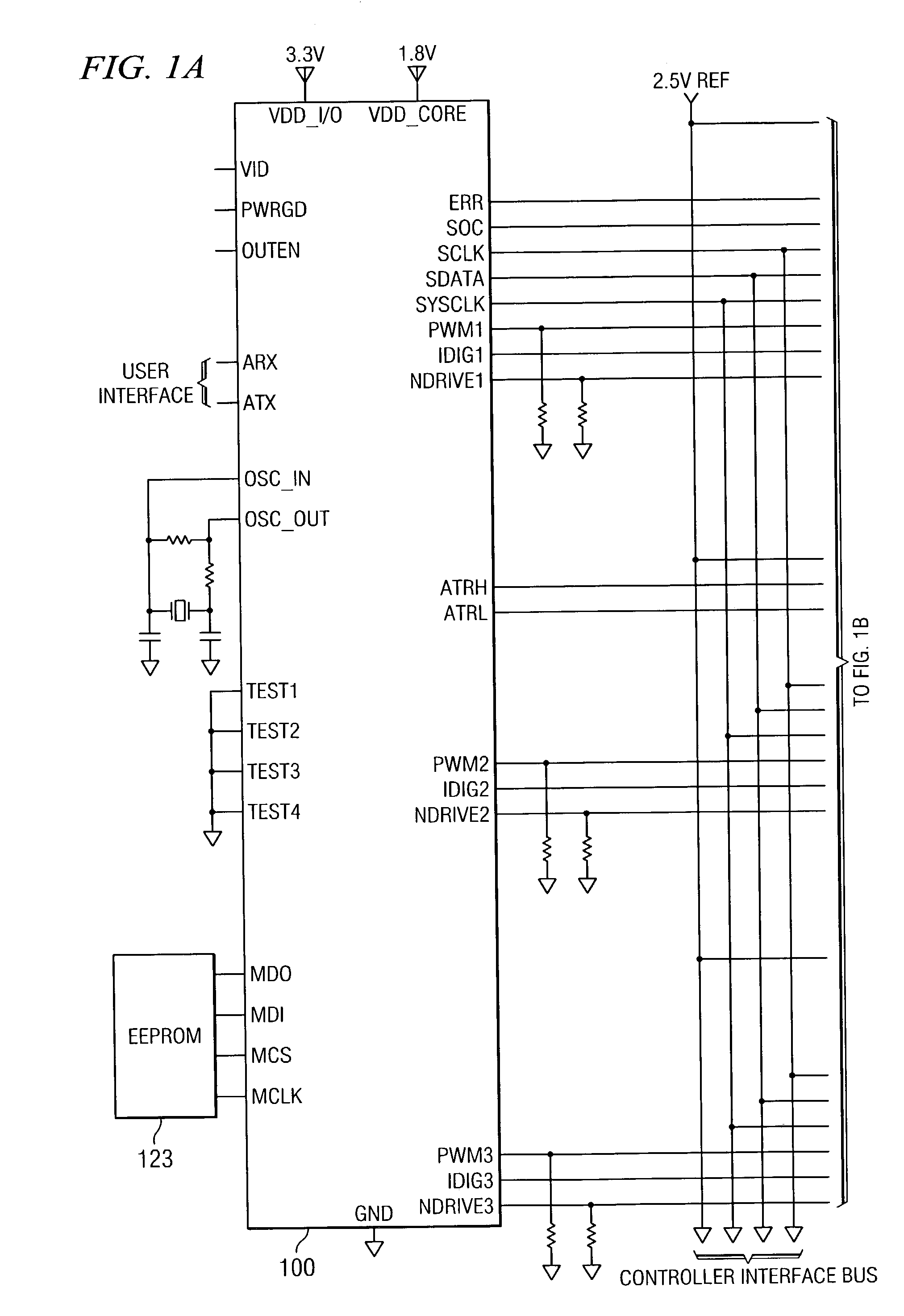
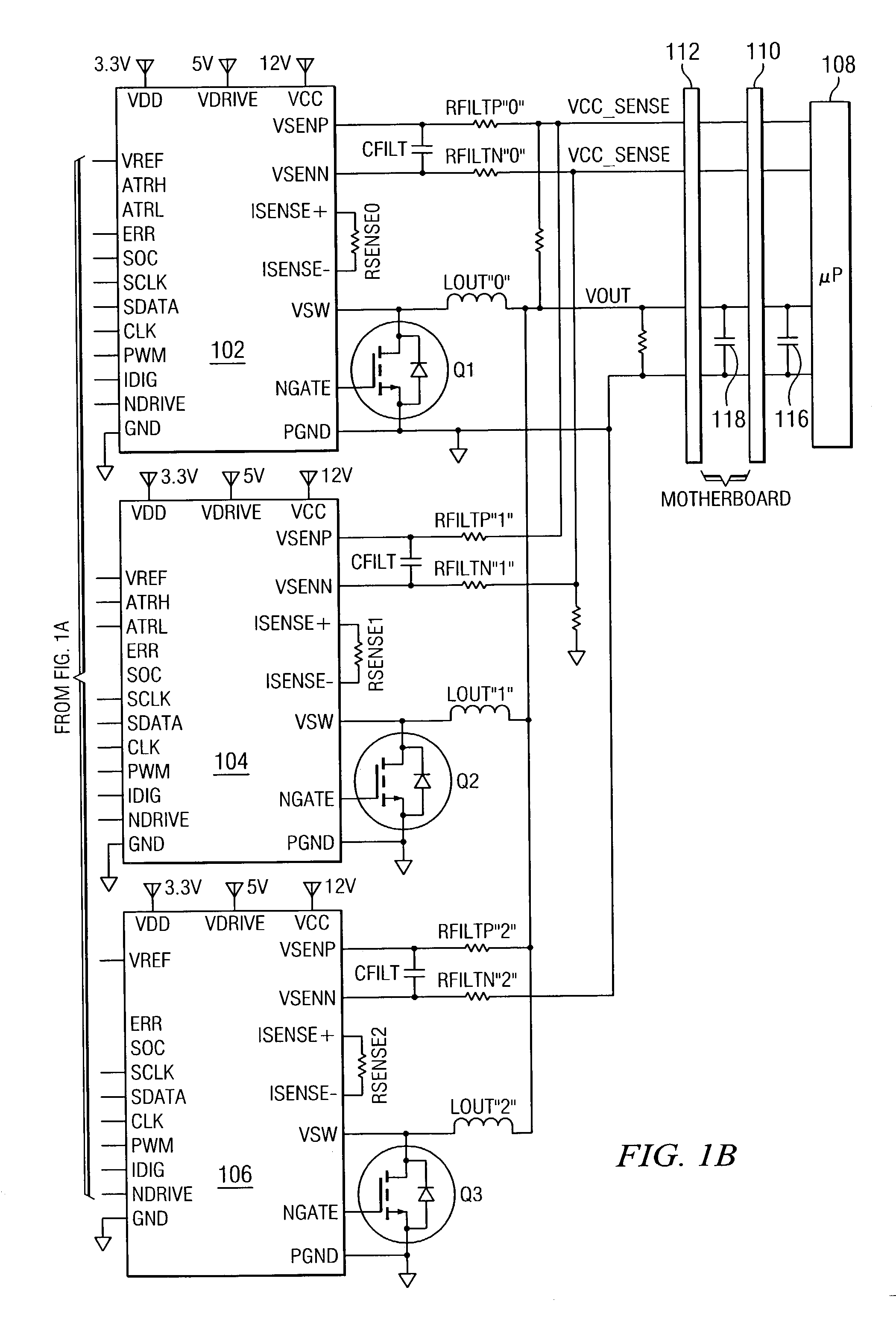
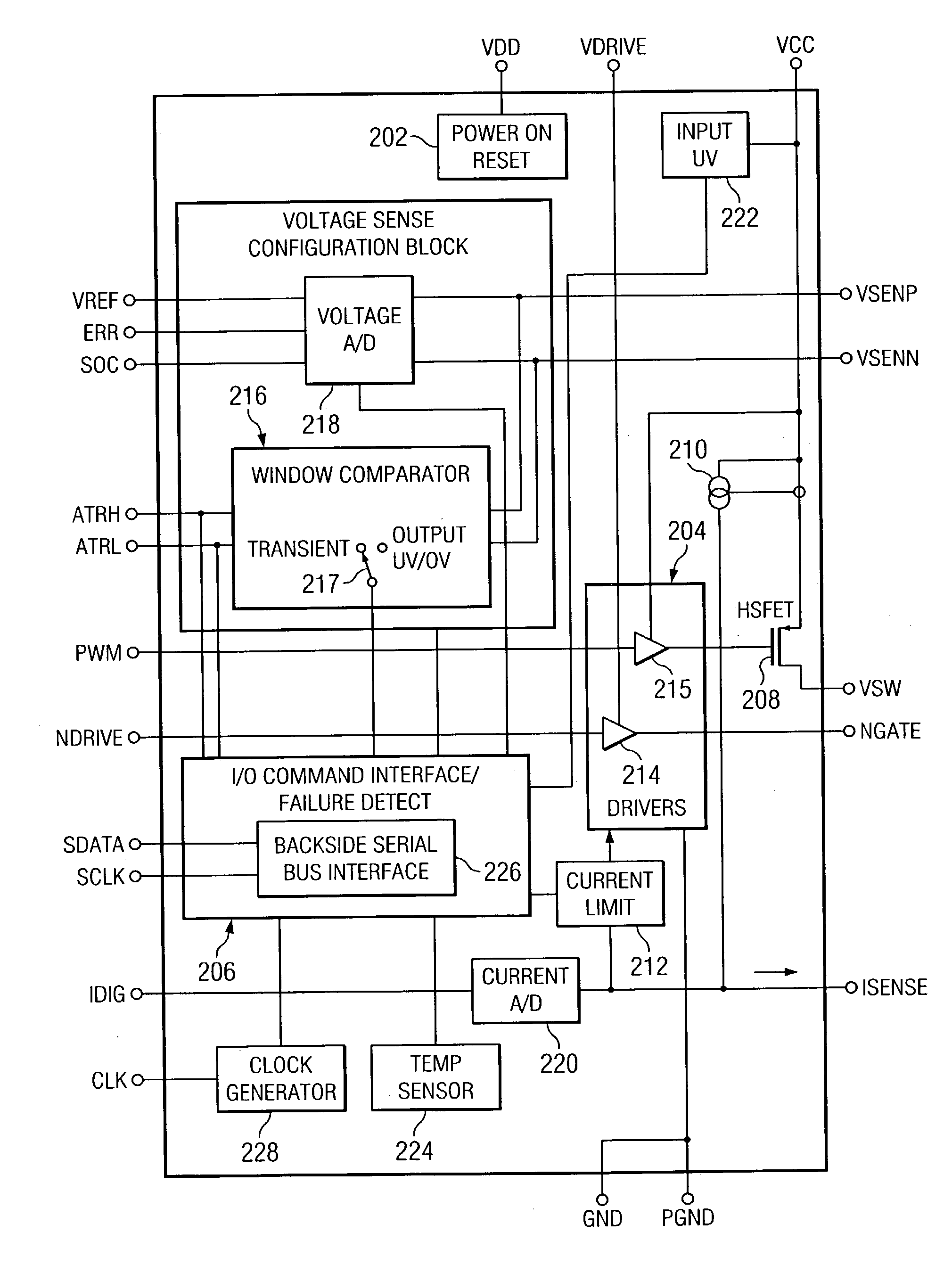
ActiveUS7023672B2Easy to customizePrecise power controlEfficient power electronics conversionDc-dc conversionControl signalOptimal control
Disclosed is a digitally controlled multi-phase voltage regulator system providing regulated power to electronic components that have variable power requirements. Power is supplied by one or more power integrated circuits (IC) each having a high side power switch controlled by pulse width modulated signals and a low side power switch. The power IC senses voltage at the load and has an on-chip current mirror for generating a current that is a ratio of current delivered to the load. The power IC also has current limiting and on-chip temperature sensing components. The voltage and current information is digitized and provided to a control integrated circuit (IC). The control IC receives this digitized information as well as user provided parameters and, in the regulation mode of operation, provides digitized pulse width modulated control signals to the power IC. In an active transient response mode of operation, the control IC provides signals to turn either the high side switches or low side switches ON. Fault detection circuitry identifies over voltage, under voltage, and excessive temperatures. All communications between the control IC and the power IC are digital providing high bandwidth, optimal control frequency response, noise immunity and efficient active transient response.
Owner:INFINEON TECH AUSTRIA AG
Ergonomic Card Delivery Shoe
Owner:LNW GAMING INC
Blender with temperature sensor
ActiveUS20180206677A1Improve temperature sensing accuracyAccurate inductionTransportation and packagingRotary stirring mixersAdditive ingredientEngineering
Owner:VERSUNI HLDG BV
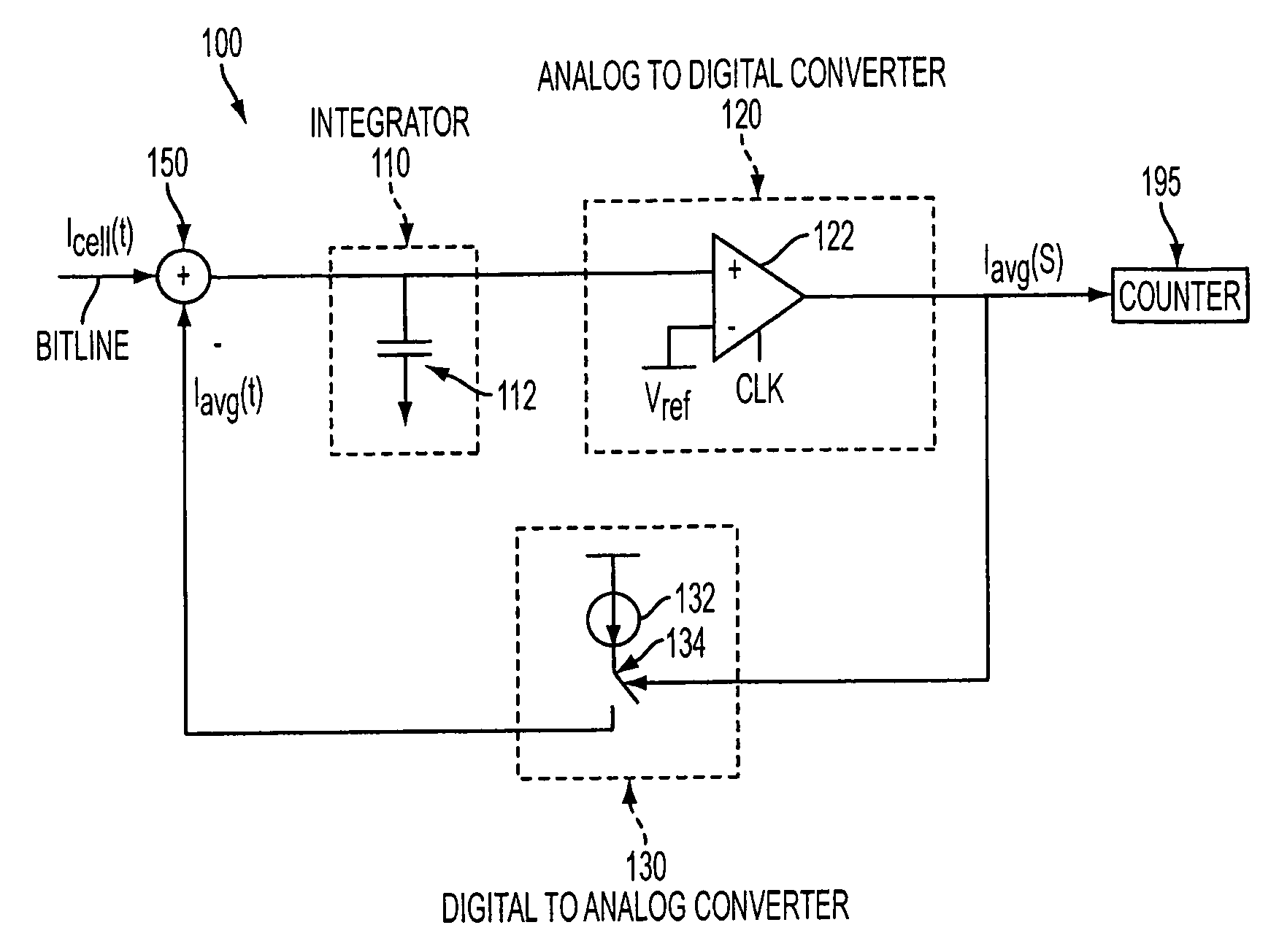
Method and apparatus for sensing flash memory using delta sigma modulation
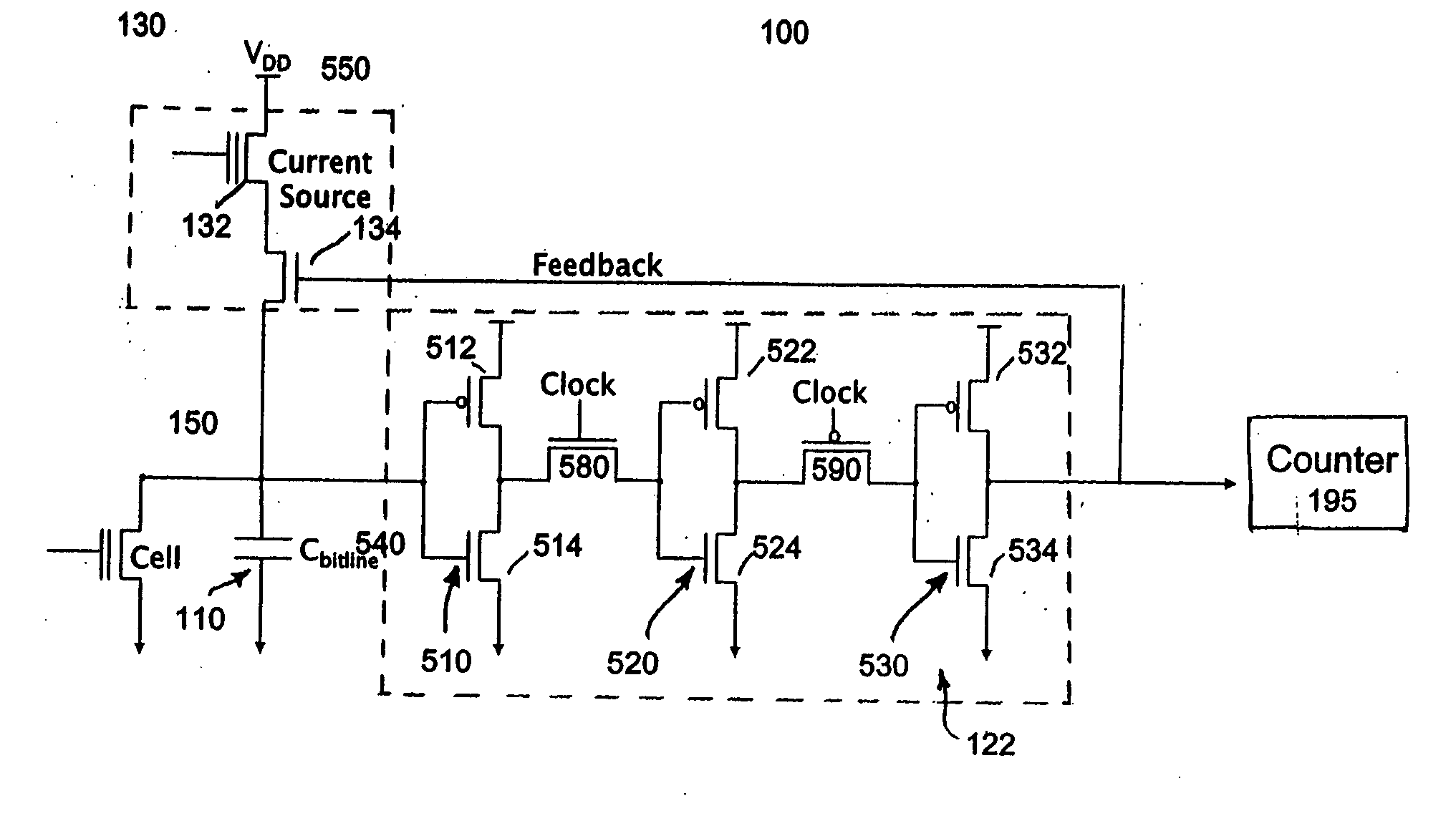
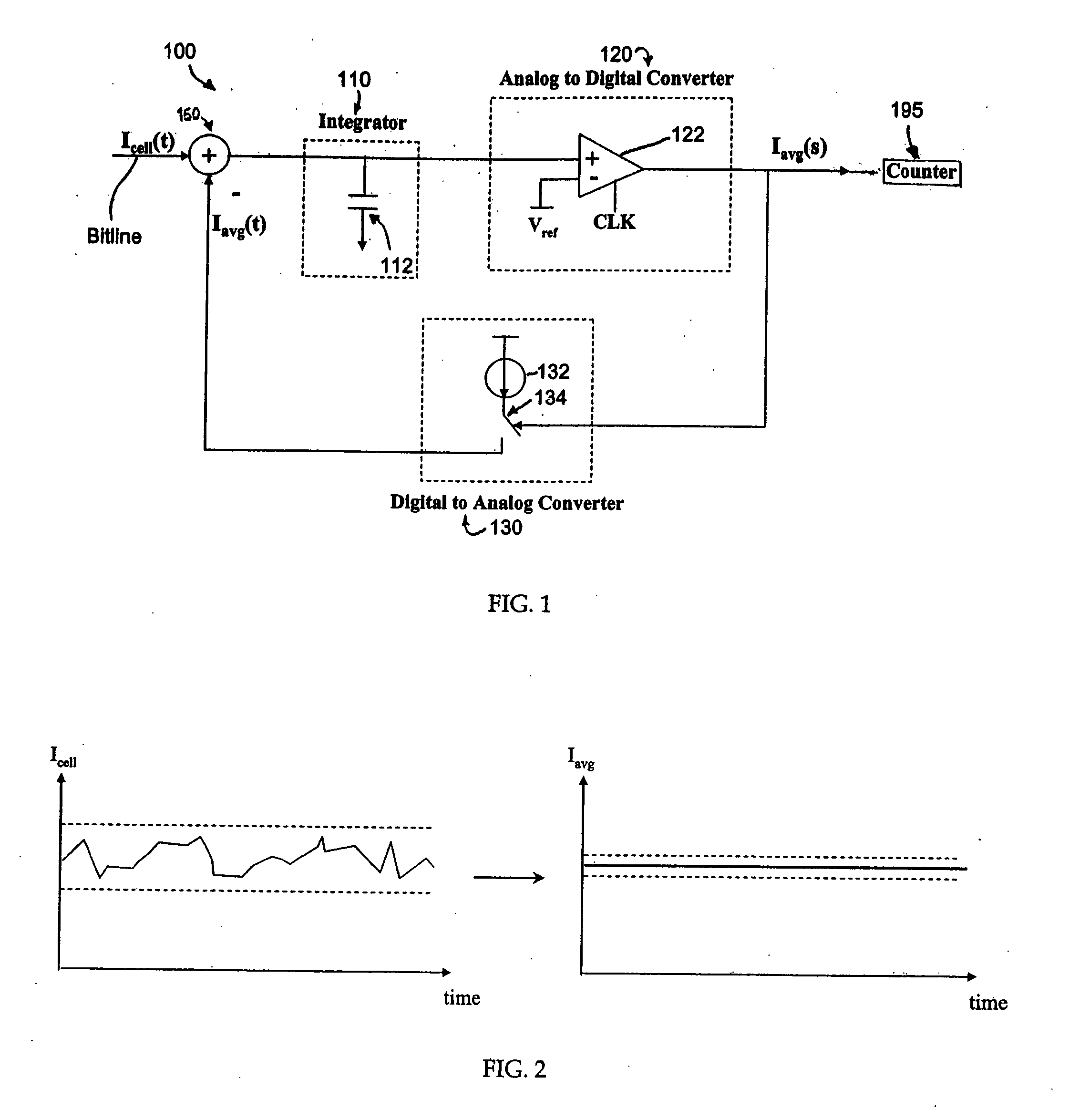
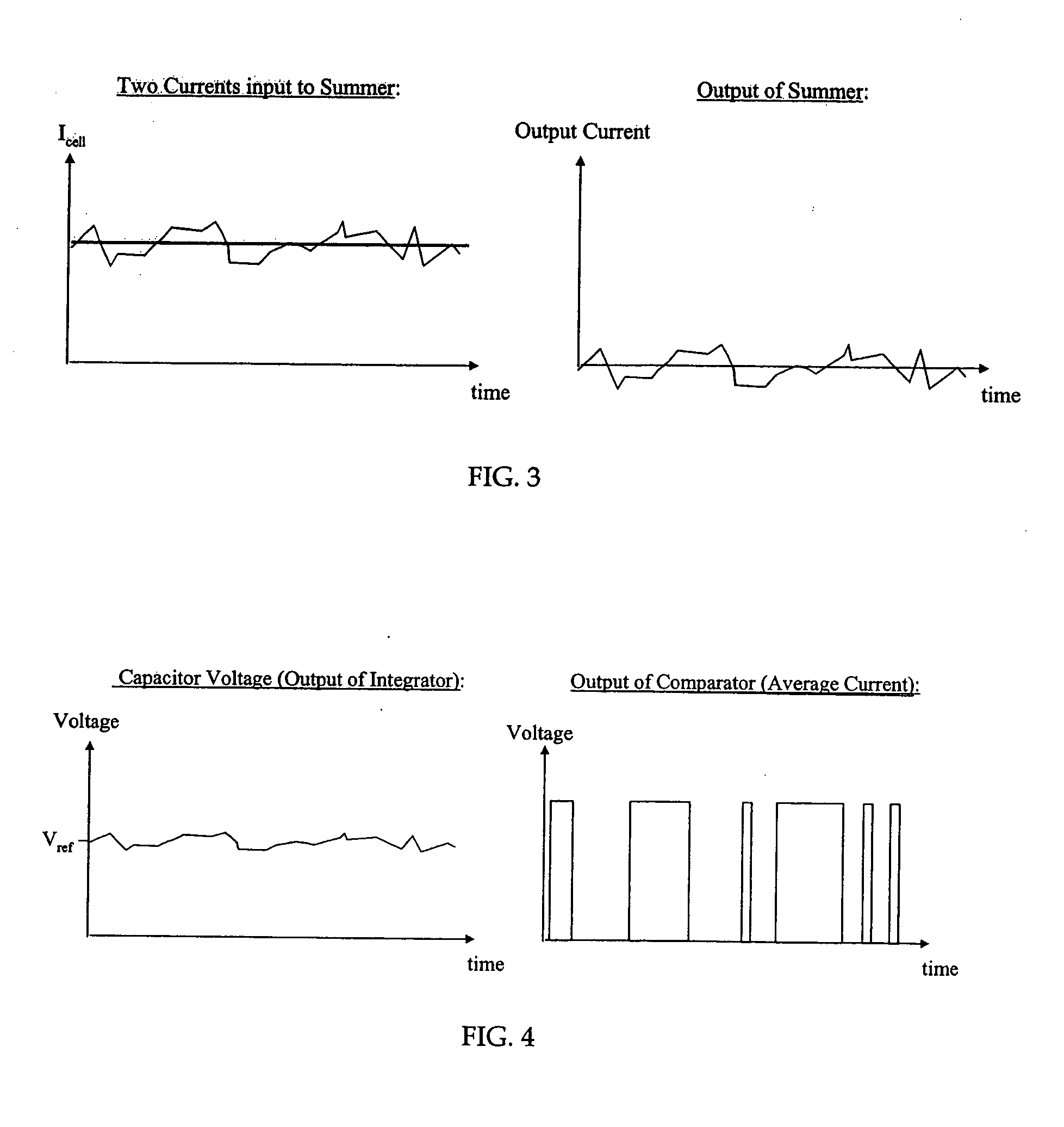
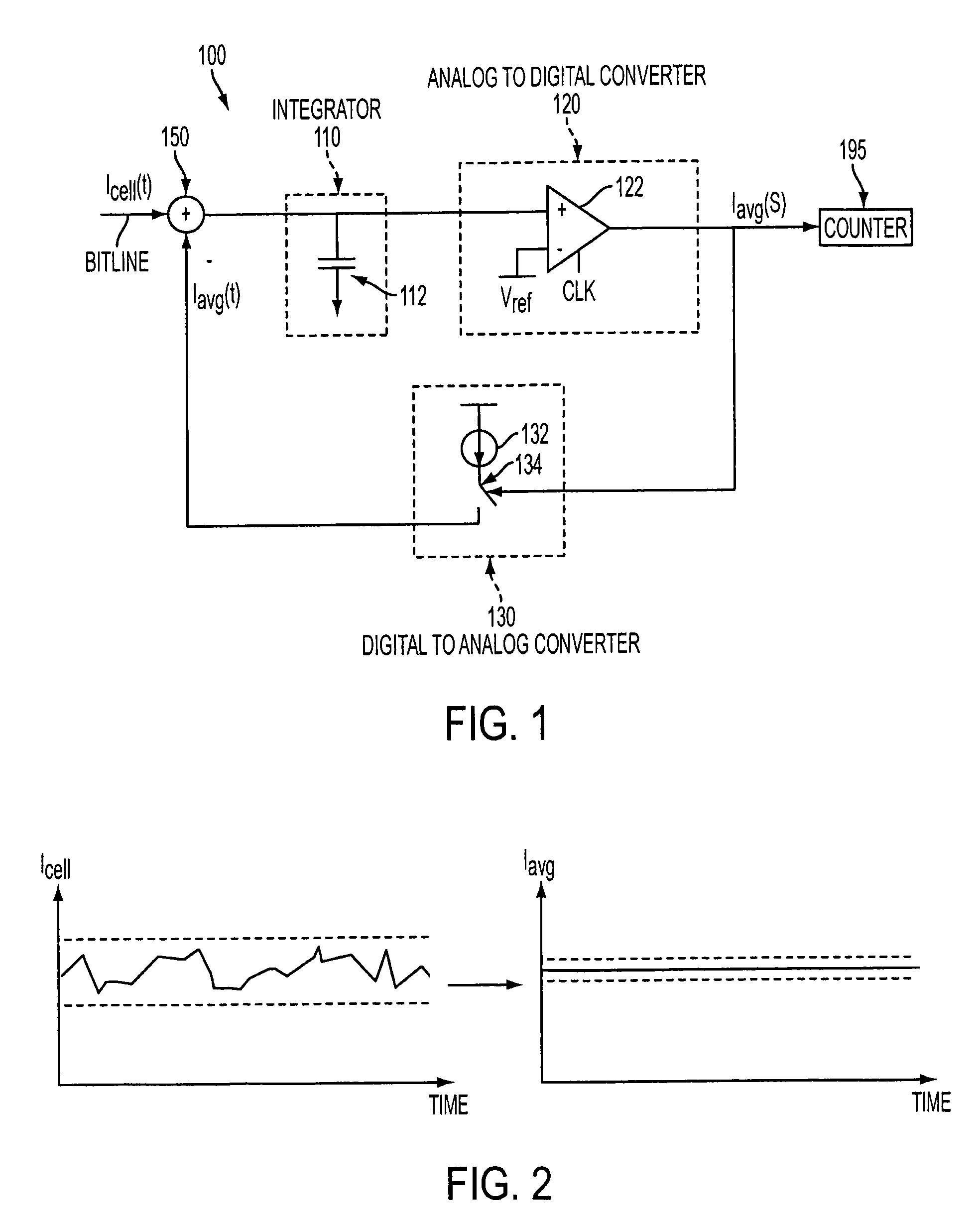
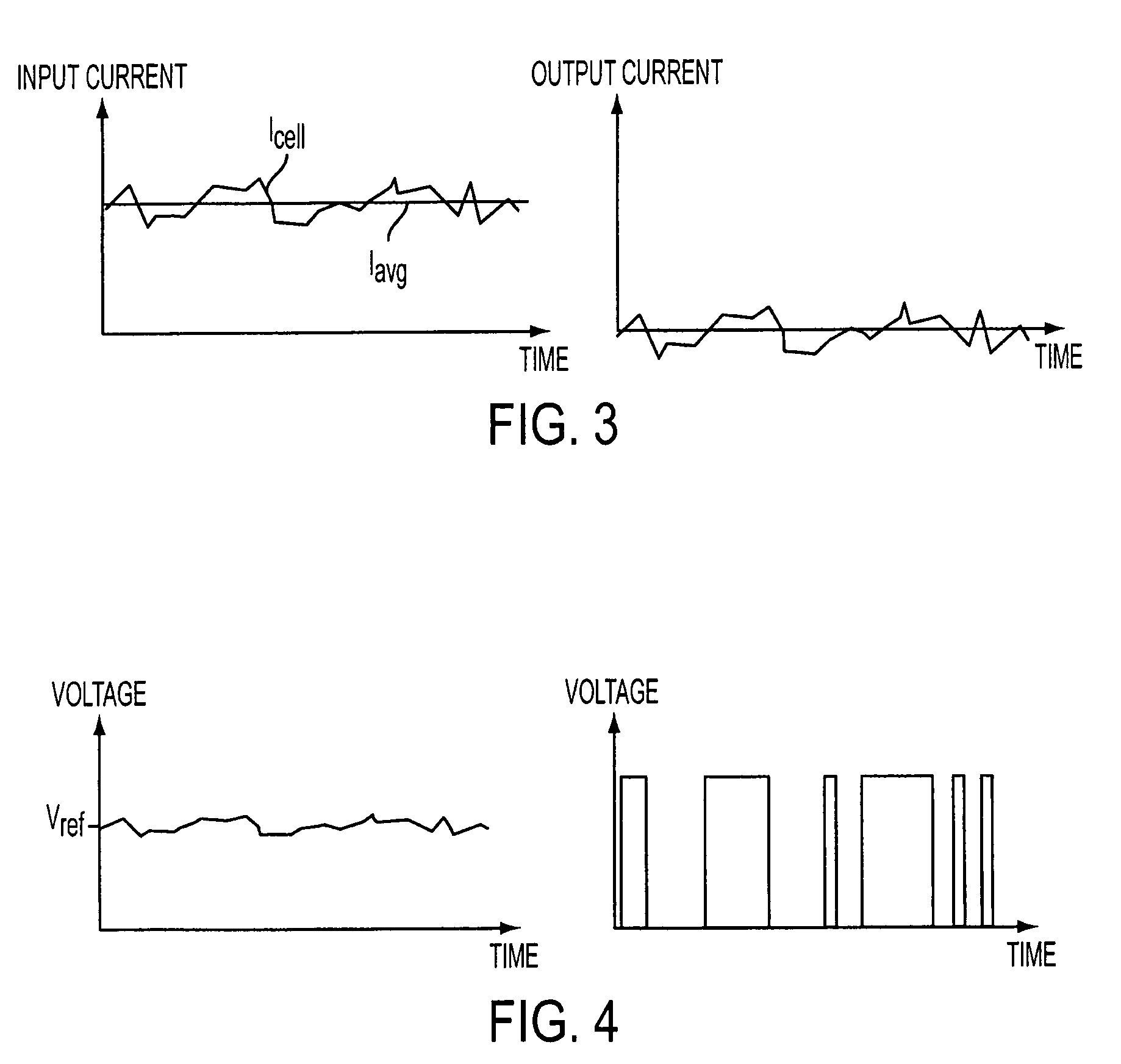
ActiveUS20060250853A1Accurate inductionHigh circuitryRead-only memoriesDigital storageConvertersAverage current
A simple method and device for accurately measuring flash memory cell current. The sensing scheme comprises an integrator, an analog to digital converter, and a digital to analog converter. The method comprises the acts of applying an input current and a feedback output current to a summer, integrating the resulting summer output over time, passing the integrated output to a clocked comparator, outputting a comparator output which controls a feedback circuit that keeps the integrator's voltage at the same level as a reference voltage, and outputting a digital average current to a counter. Delta sigma modulation (averaging) is employed to cancel out noise that would otherwise affect the cell current measurement.
Owner:MICRON TECH INC
Digitally controlled voltage regulator
ActiveUS20040150928A1Easy to customizePrecise power controlEfficient power electronics conversionDc-dc conversionControl signalOptimal control
Disclosed is a digitally controlled multi-phase voltage regulator system providing regulated power to electronic components that have variable power requirements. Power is supplied by one or more power integrated circuits (IC) each having a high side power switch controlled by pulse width modulated signals and a low side power switch. The power IC senses voltage at the load and has an on-chip current mirror for generating a current that is a ratio of current delivered to the load. The power IC also has current limiting and on-chip temperature sensing components. The voltage and current information is digitized and provided to a control integrated circuit (IC). The control IC receives this digitized information as well as user provided parameters and, in the regulation mode of operation, provides digitized pulse width modulated control signals to the power IC. In an active transient response mode of operation, the control IC provides signals to turn either the high side switches or low side switches ON. Fault detection circuitry identifies over voltage, under voltage, and excessive temperatures. All communications between the control IC and the power IC are digital providing high bandwidth, optimal control frequency response, noise immunity and efficient active transient response.
Owner:INFINEON TECH AUSTRIA AG
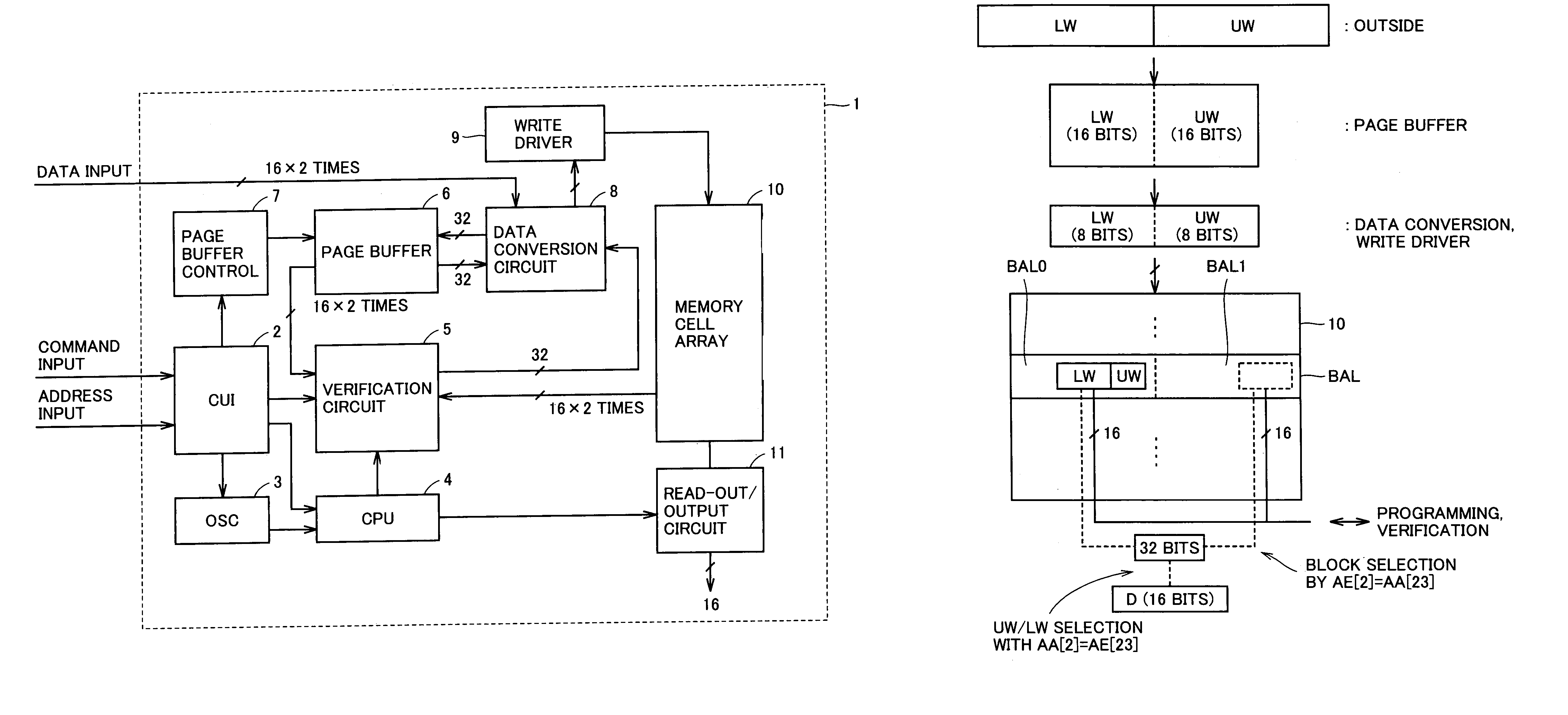
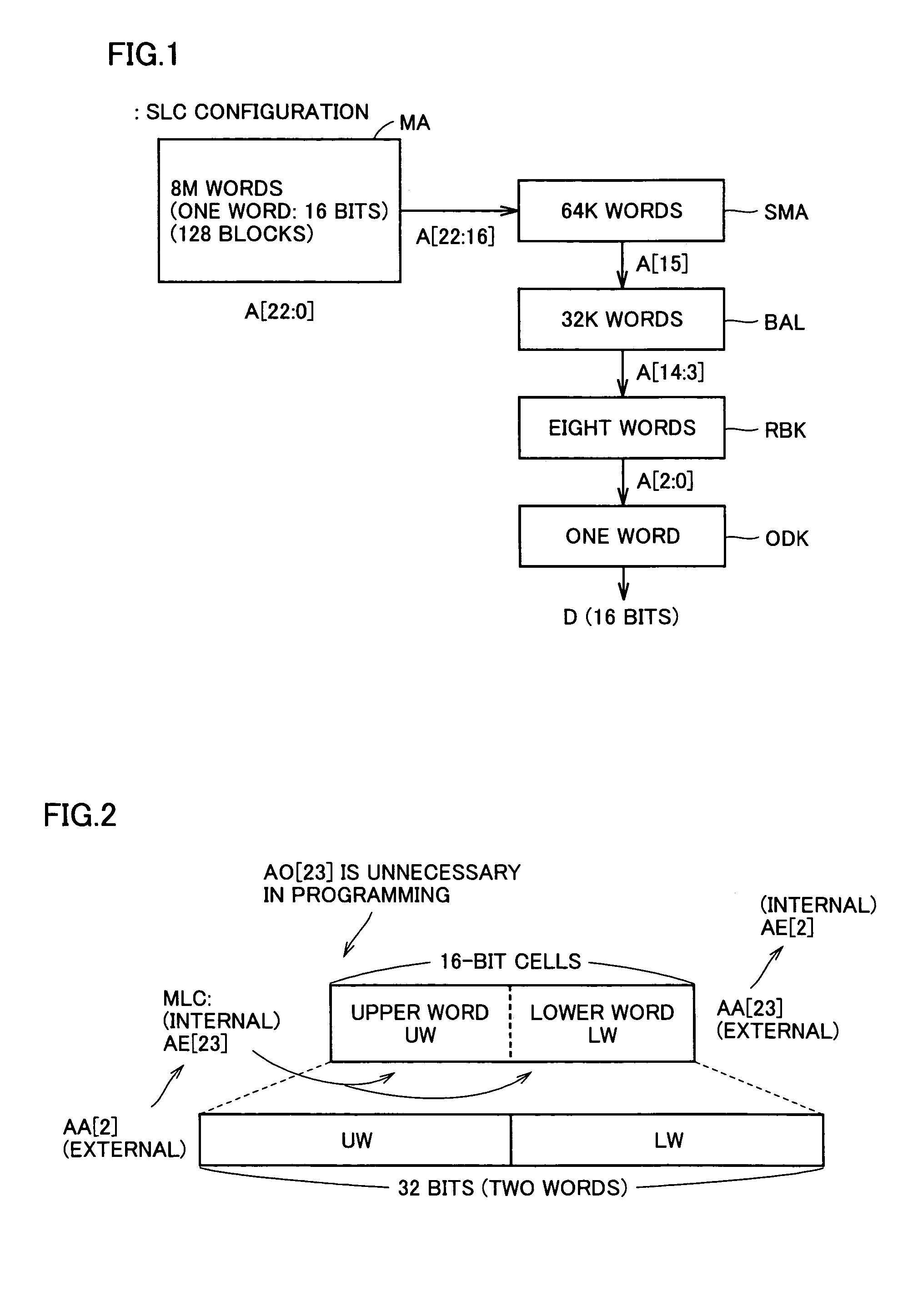
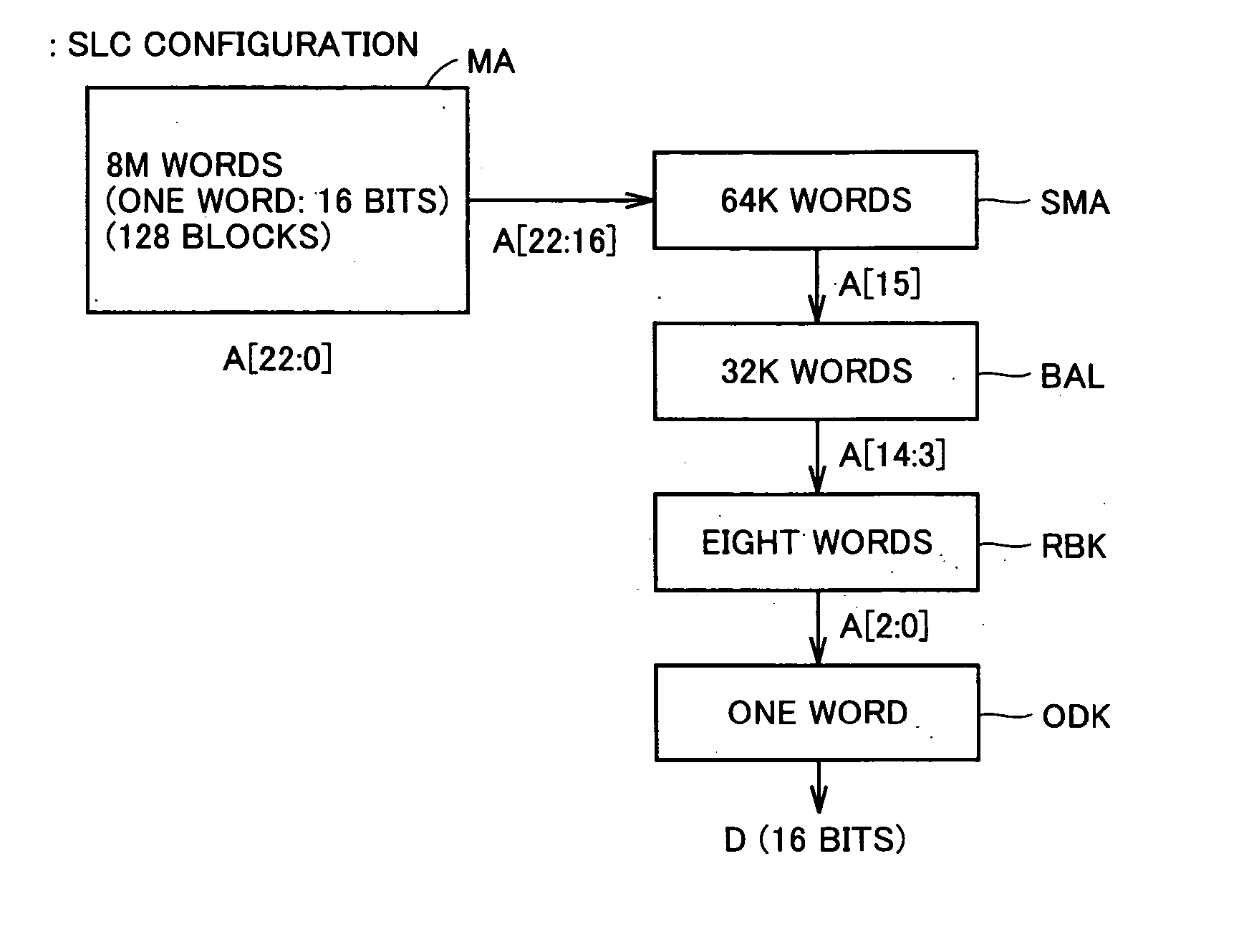
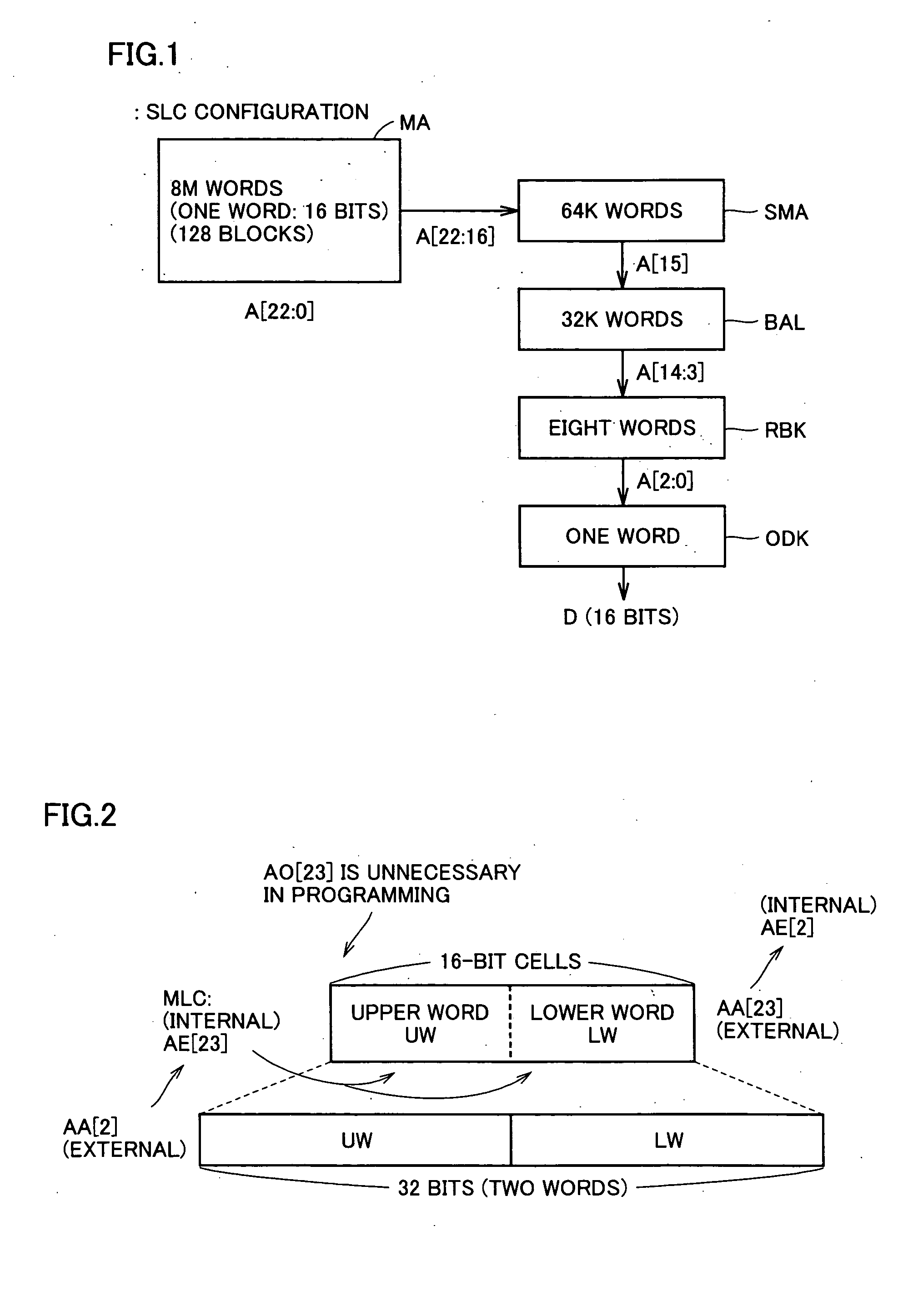
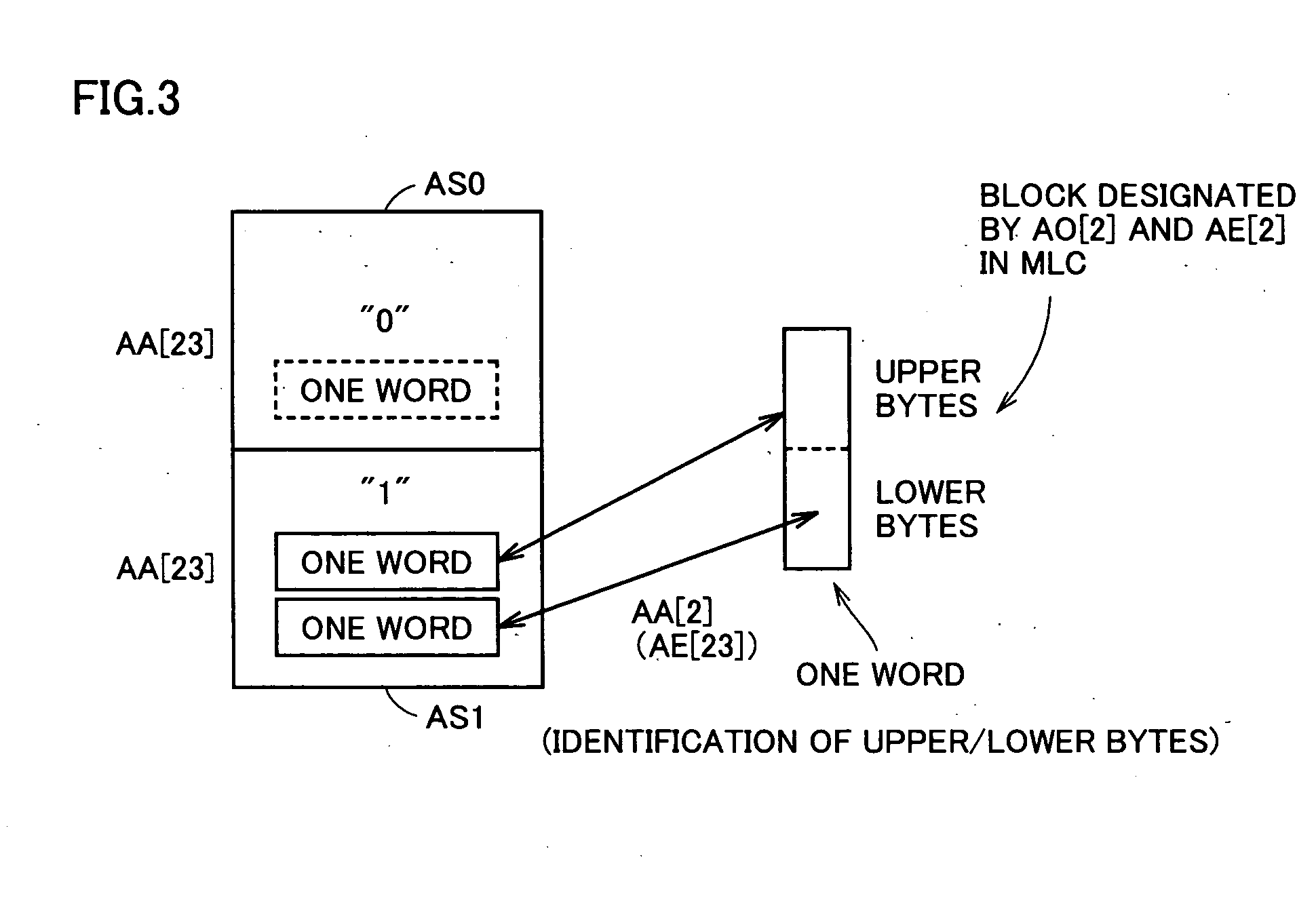
Multi-level nonvolatile semiconductor memory device utilizing a nonvolatile semiconductor memory device for storing binary data
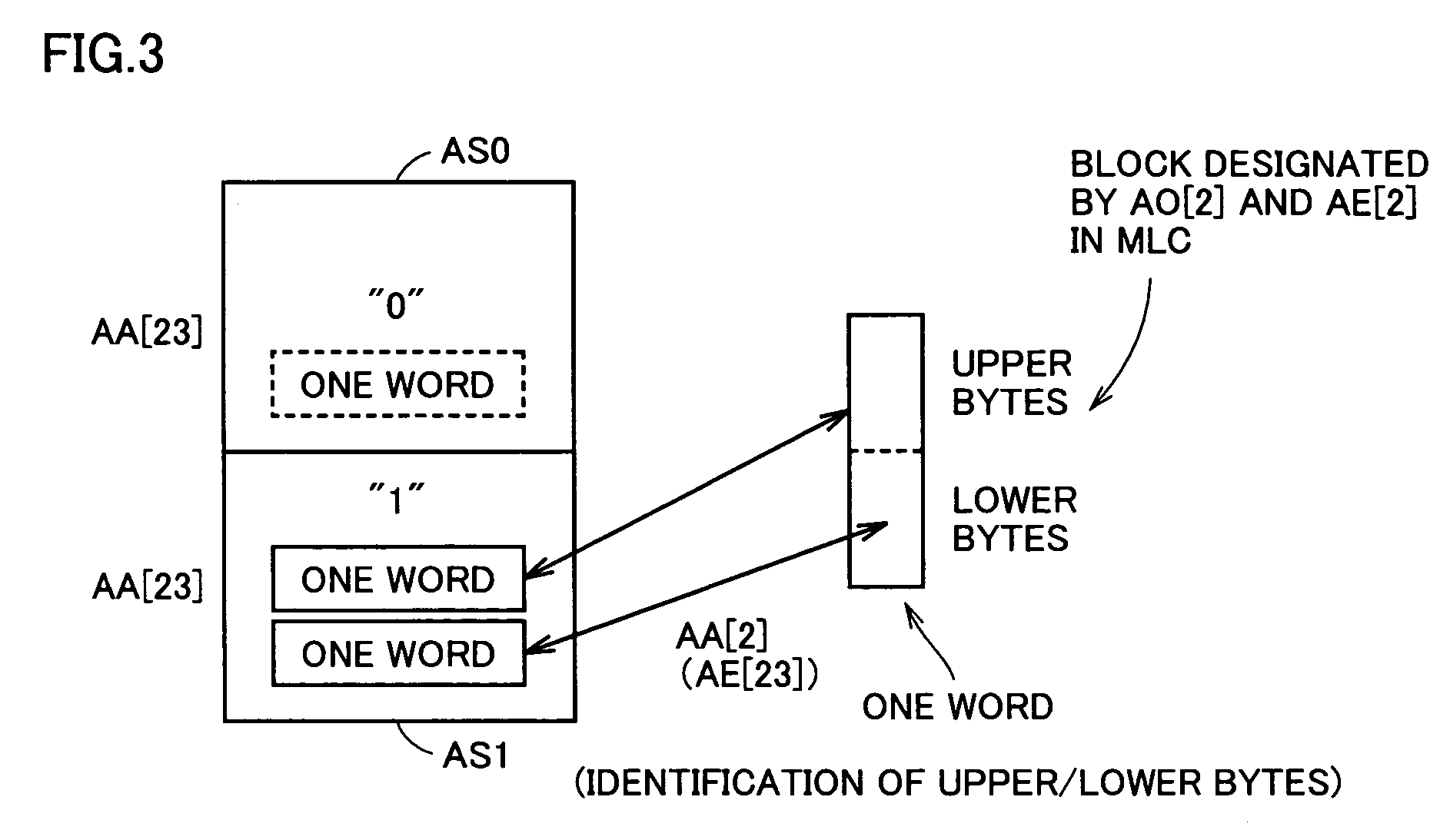
A multi-level semiconductor memory device for storing multi-level data having three or more values is implemented by utilizing a nonvolatile memory device for storing 2-valued data. Identification of successive 16-bit data externally applied is performed with external address bit AA [2], and a storage block is selected with external address bit AA [23]. Upper word data LW and lower word data UW are compressed into byte data of 8 bits, respectively, and stored in a memory cell array.
Owner:RENESAS ELECTRONICS CORP
Systems and Methods of Matching Purchase Requests with Consummated Sales
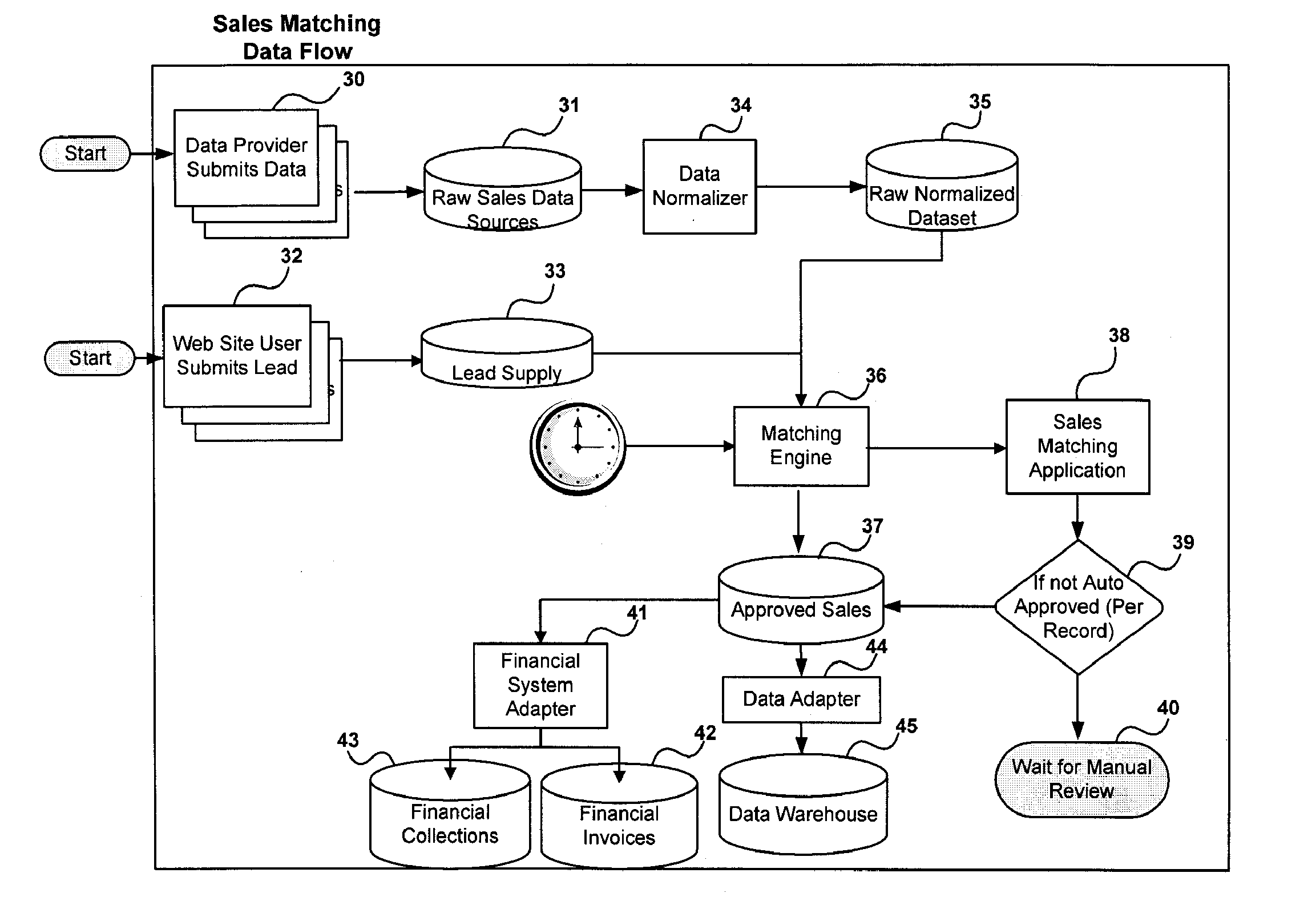
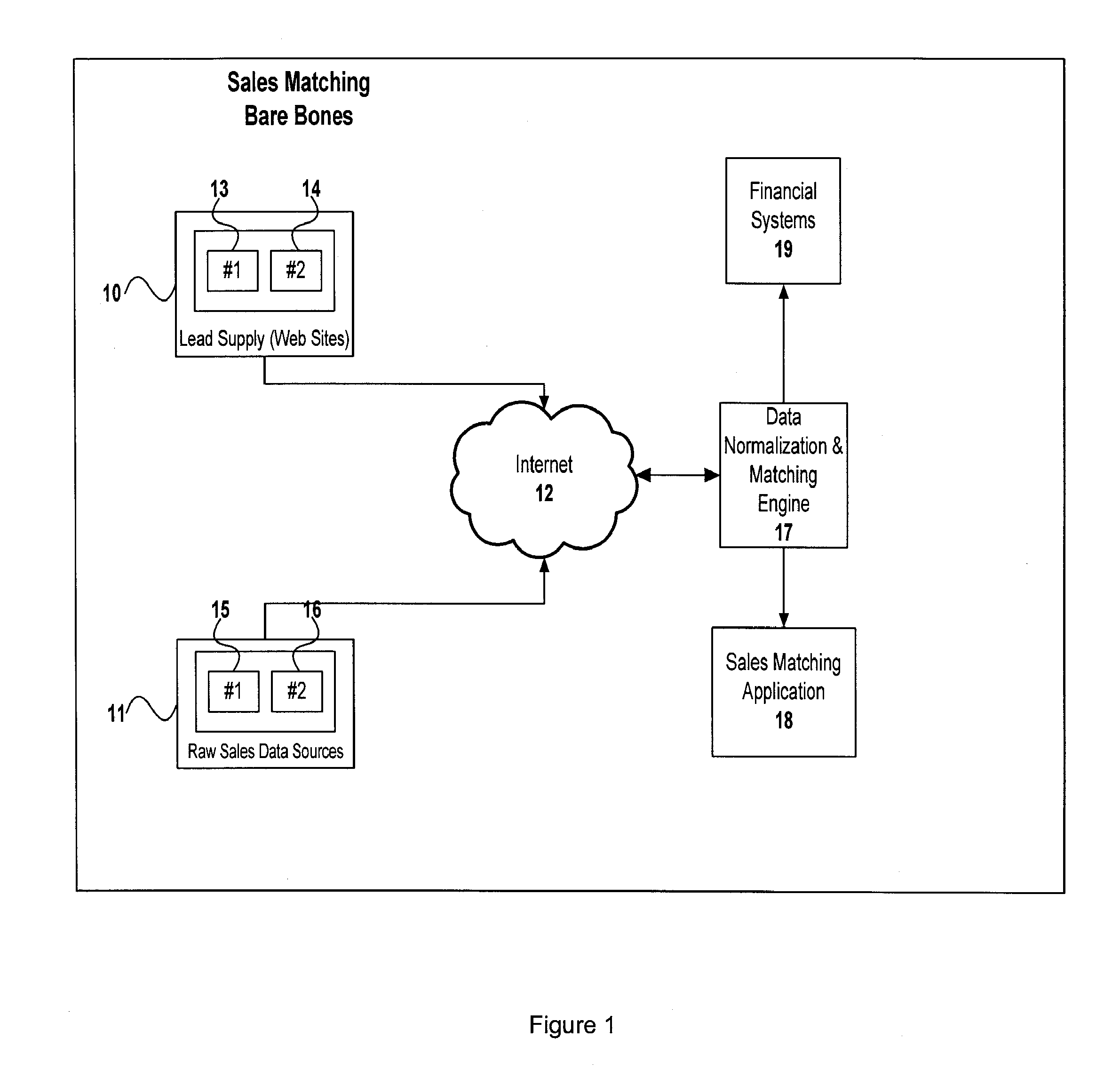
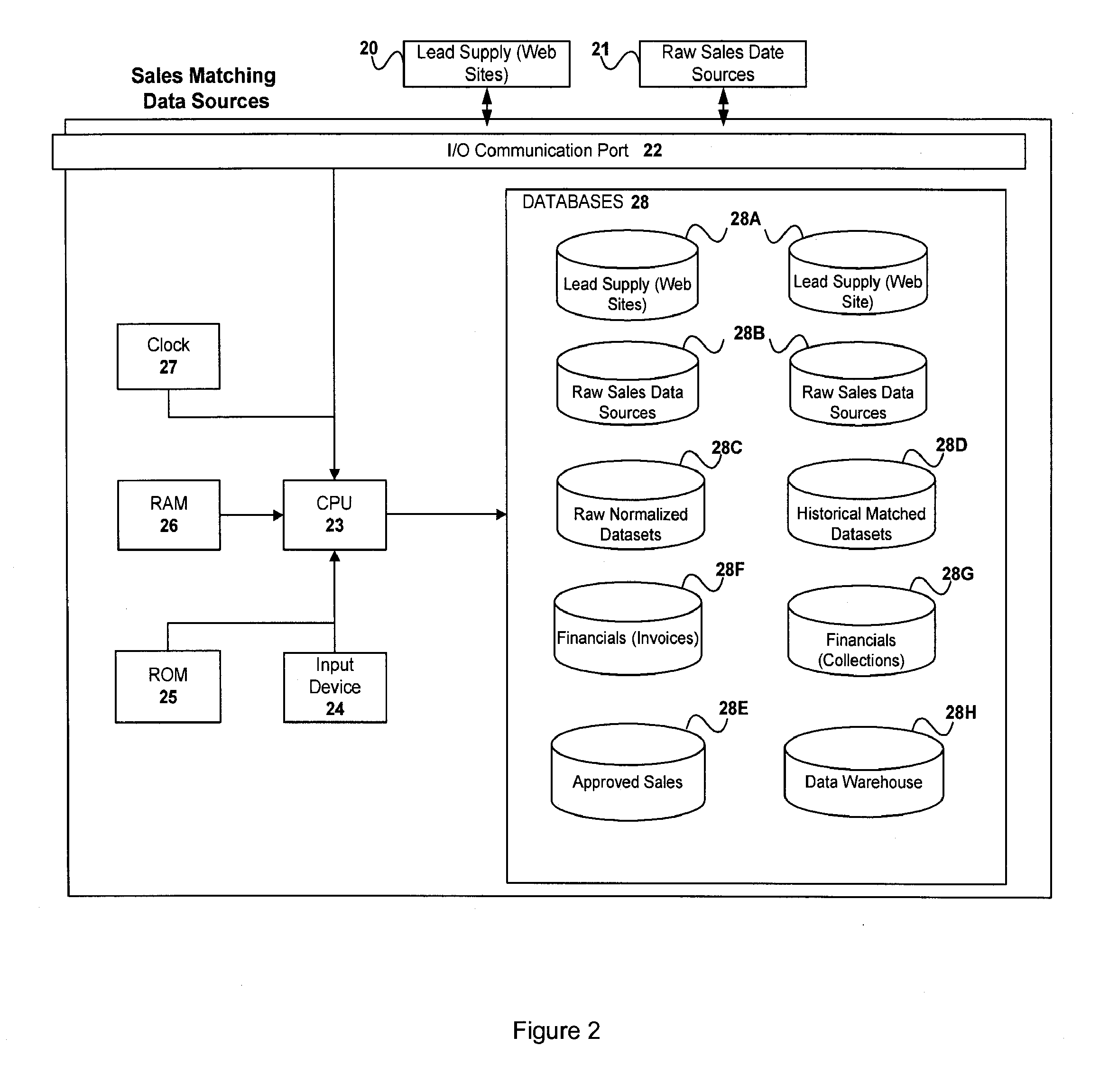
A sales matching system which may match sales of products or services with consummated sales by collecting selected leads from a group of lead suppliers, collecting a plurality of sales records from multiple sales sources, and matching at least some of the sales records to selected leads. The matches may be assigned a matching confidence, and may reach a threshold level of confidence to be considered a matched sale. The system may also generate invoices to selected sellers identifying invoice-able sales for which compensation may be obtained in exchange for providing leads giving rise thereto.
Owner:TRUECAR
Low noise amplifier for electro-physiological signal sensing
InactiveUS20060122529A1Reduce noiseEnhanced response signalElectroencephalographySensorsLow noiseElectrical conductor
Owner:LKC TECH
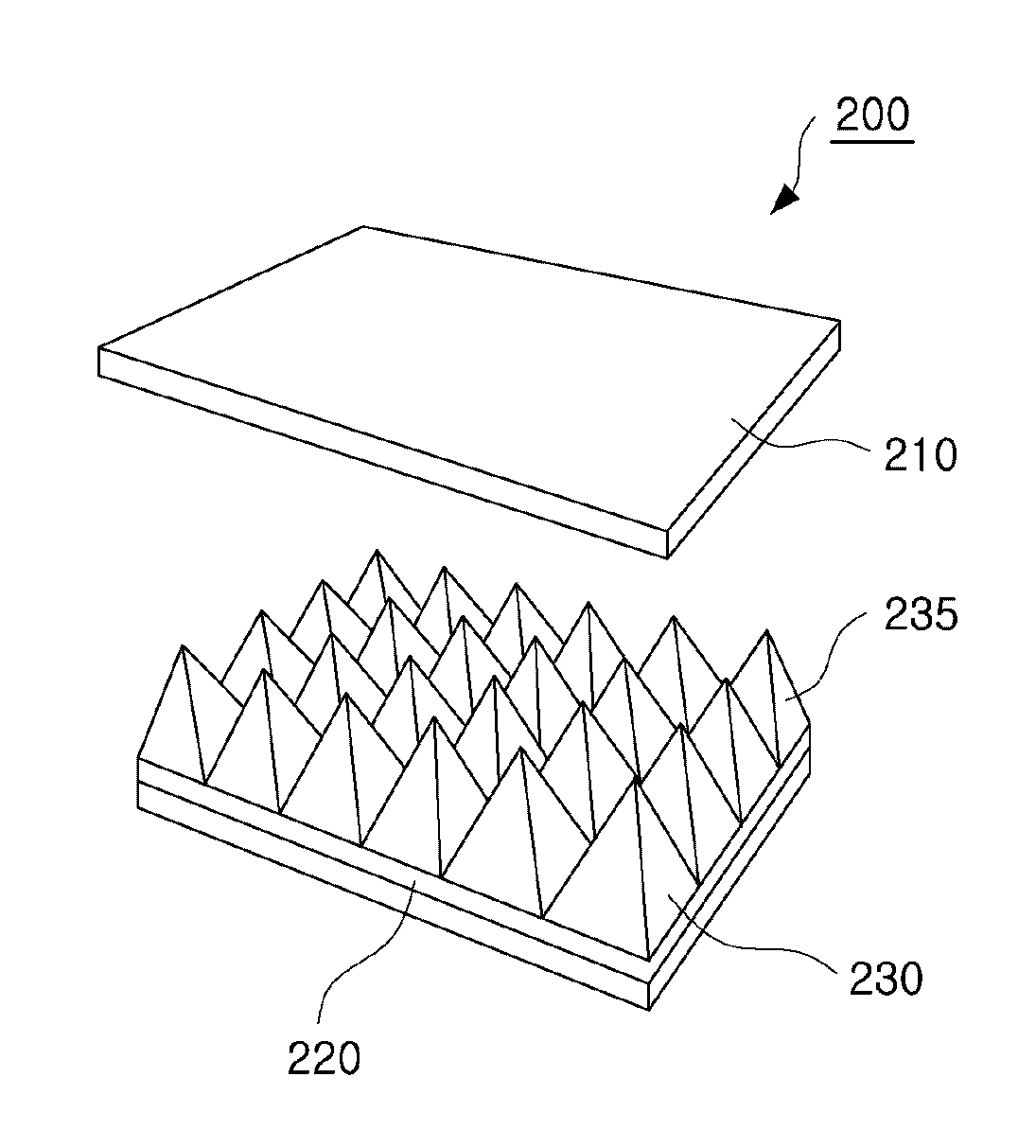
Capacitive pressure sensor and input device including the same
InactiveUS20130047747A1Accurately sensedAccurate inductionForce measurementApparatus for force/torque/work measurementCapacitive pressure sensorInput device
There are provided a pressure sensor and an input device including the same. The pressure sensor includes: a first conductive substrate having flexibility; a second conductive substrate disposed in parallel with the first conductive substrate; and an elastic dielectric layer disposed between the first and second conductive substrates and including a plurality of structures having a pyramidal shape, wherein the structures of the elastic dielectric layer are deformed according to pressure applied to the first conductive substrate to generate a change in capacitance between the first and second conductive substrates. Accordingly, the pressure sensor is capable of efficiently sensing a small amount of pressure.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRO MECHANICS CO LTD
Method of identifying edge swipe gesture and method of opening window control bar using the identifying method
InactiveUS20140375577A1High success rateAccurate inductionInput/output processes for data processingSignal onEdge region
A method of identifying edge swipe gesture has steps of respectively reading sensing signals on an edge area under a hover mode and on a non-edge area under a touch mode; determining if a touch object has appeared on the edge area after determining that the object has appeared on the non-edge area, calculating a displacement of the object moving from the edge area to the non-edge area within a preset time and determining if the displacement exceeds a preset distance, and determining that the movement of the touch is identified as an edge swipe gesture if the displacement meets the condition. Accordingly, the present invention can perform valid touch on the edge area, rendering effective identification of edge swipe gesture and an increased success rate of the identification.
Owner:ELAN MICROELECTRONICS CORPORATION
Touch sensor, liquid crystal display panel having the same and driving method for the same
ActiveUS20100039406A1Accurate inductionCathode-ray tube indicatorsNon-linear opticsCapacitanceLiquid-crystal display
A touch sensor is installed inside a liquid crystal display panel to sense a touch operation and includes a light sensing part including a photodiode, a capacitance sensing part including a liquid crystal capacitor, and a sensing signal output part. The light sensing part generates a control signal corresponding to a variation in the amount of external light when the liquid crystal display panel is touched. The capacitance sensing part varies the control signal based on a variation in the capacitance of the liquid crystal capacitor when the liquid crystal display panel is touched. The sensing signal output part generates a sensing signal in response to the control signal and determines an output timing of the sensing signal.
Owner:SAMSUNG DISPLAY CO LTD
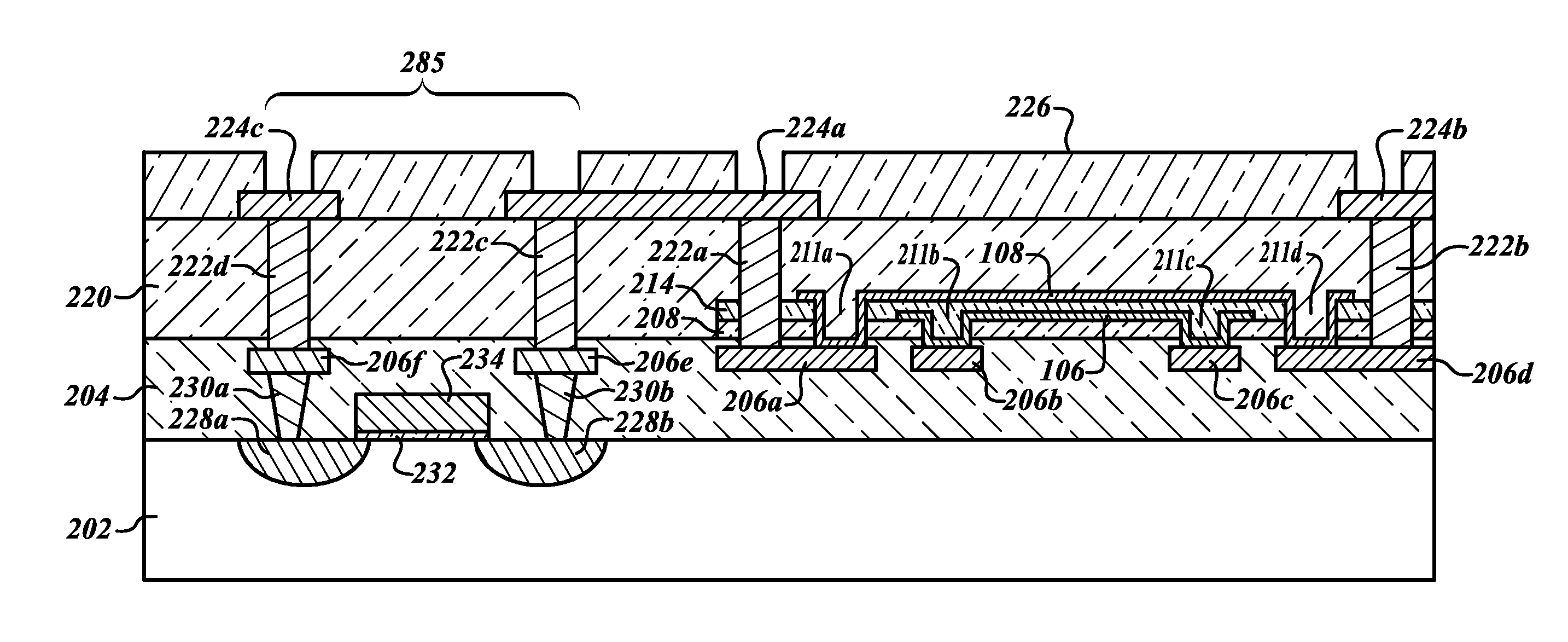
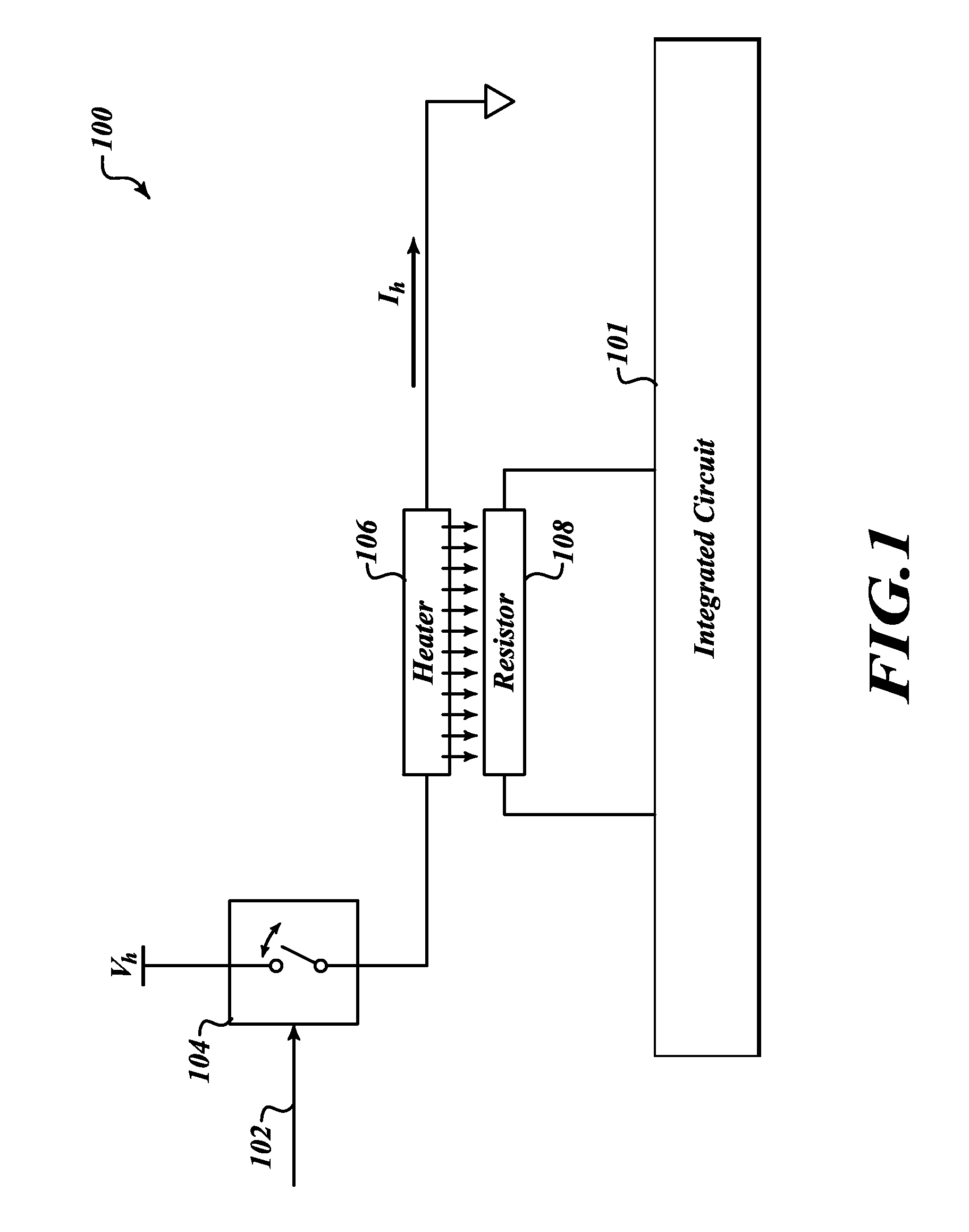
Dual thin film precision resistance trimming
ActiveUS20100073122A1Improve efficiencyIncrease resistanceSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsVacuum evaporation coatingElectrical resistance and conductanceEngineering
A trimmable resistor for use in an integrated circuit is trimmed using a heater. The heater is selectively coupled to a voltage source. The application of voltage to the heater causes the heater temperature to increase and produce heat. The heat permeates through a thermal separator to the trimmable resistor. The resistance of the trimmable resistor is permanently increased or decreased when the temperature of the resistor is increased to a value within a particular range of temperatures.
Owner:STMICROELECTRONICS SRL +1
Semiconductor memory device
A multi-level semiconductor memory device for storing multi-level data having three or more values is implemented by utilizing a nonvolatile memory device for storing 2-valued data. Identification of successive 16-bit data externally applied is performed with external address bit AA [2], and a storage block is selected with external address bit AA [23]. Upper word data LW and lower word data UW are compressed into byte data of 8 bits; respectively, and stored in a memory cell array.
Owner:RENESAS ELECTRONICS CORP
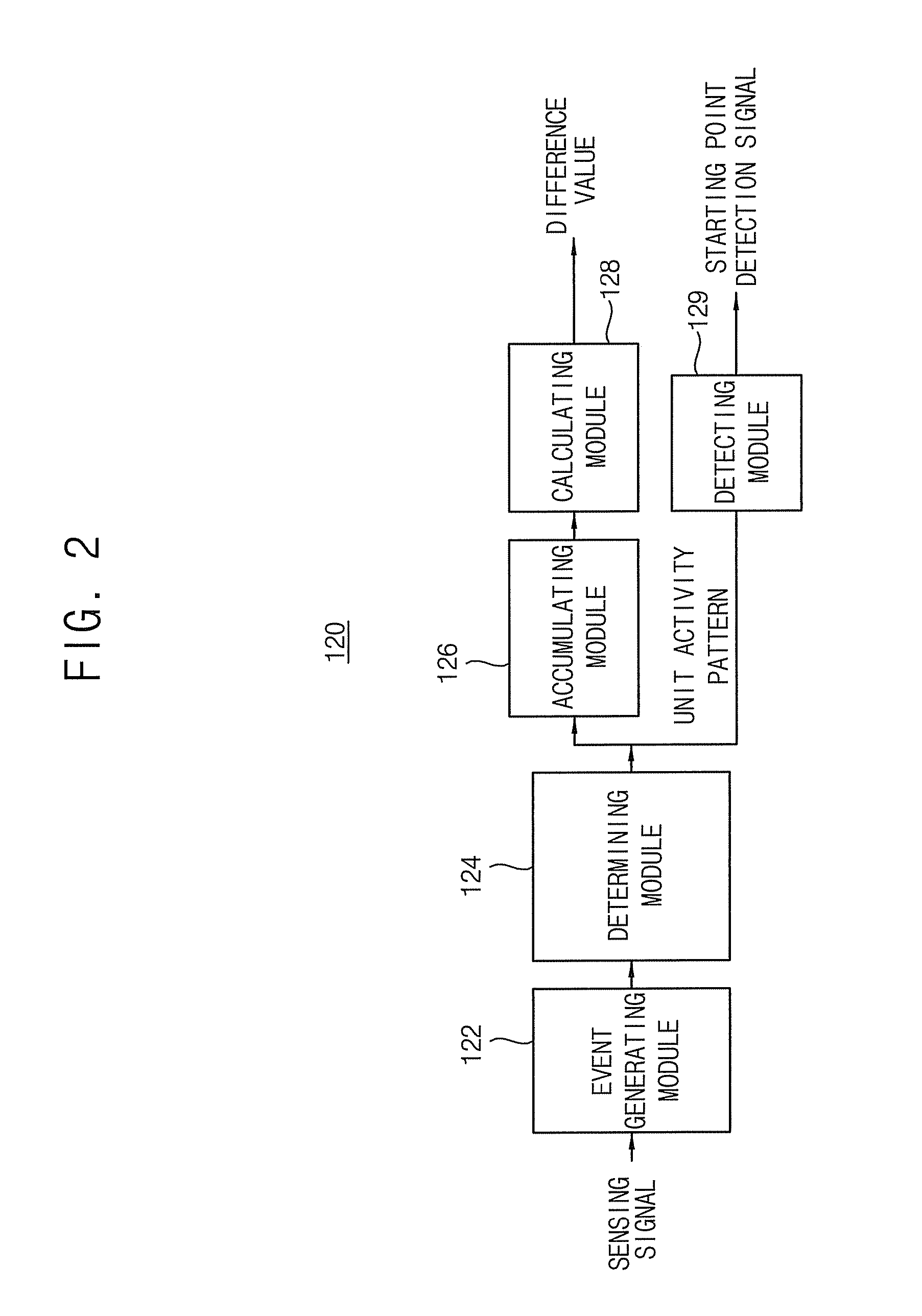
Apparatus and method for correcting life patterns in real time
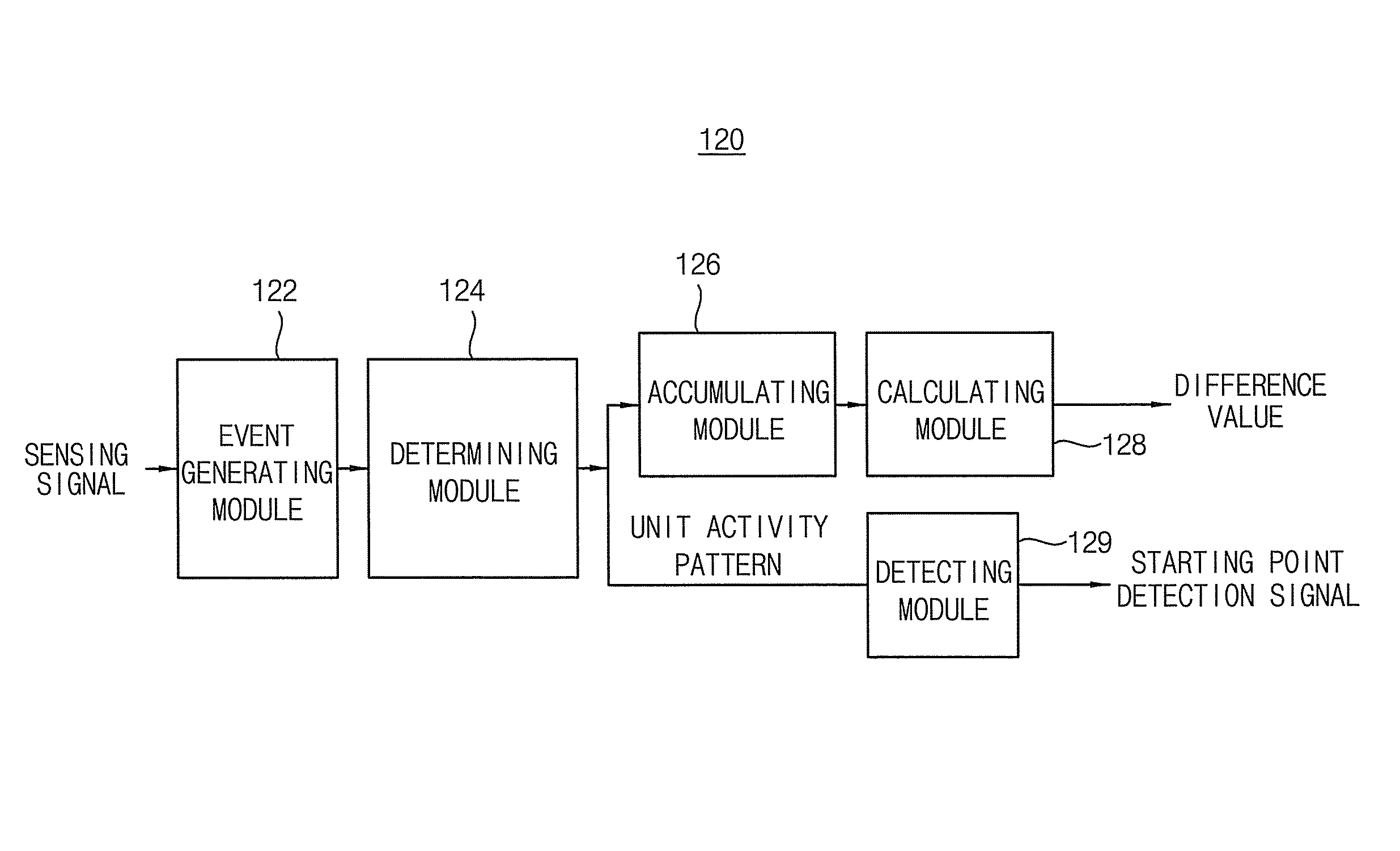
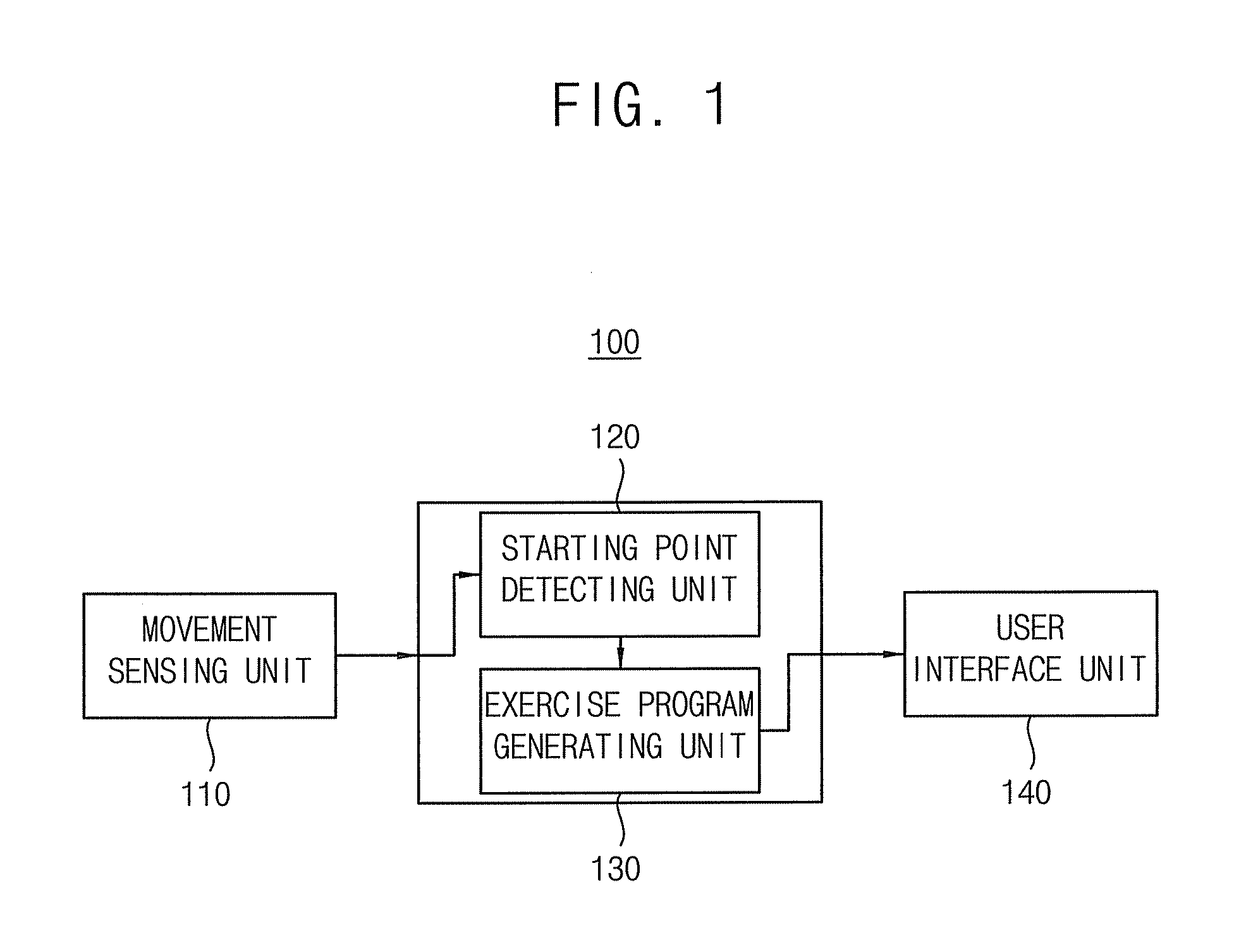
InactiveUS8475339B2Improve adaptabilityReduce inconveniencePhysical therapies and activitiesClubsLife PatternComputer science
A method for correcting life patterns for providing feedback for an exercise program periodically or in real time is disclosed. The method of the present invention detects a starting point of a dynamic activity interval periodically or in real time by sensing movement of a user in daily life, and provides an exercise program for filling a deficient amount of activity compared to a target value in the detected activity interval when the starting point is detected. Therefore, the method of the present invention may simply provide feedback for an amount of activity of a pertinent interval at an actual starting point of the dynamic activity interval, and thus the user may effectively follow the provided exercise program for correcting life patterns.
Owner:XIU SOLUTIONS
Fuel injection characteristic sensing device and fuel injection command correcting device
ActiveUS20090063013A1Compensating for such errorPrecision injectionElectrical controlInternal combustion piston enginesEngineeringPressure sensor
A fuel injection characteristic sensing device obtains an injection characteristic of a target injector (an injector of each cylinder of a multi-cylinder engine) at each time. The device has a program for sequentially sensing fuel pressure at a sensing point corresponding to a fuel pressure sensor, which is provided at a fuel inlet of each injector, based on an output of the fuel pressure sensor. The device has a program for detecting predetermined timings (injection timings such as an injection start timing and an injection end timing) in a series of operations concerning fuel injection of the injector of each cylinder based on the sequentially sensed fuel pressure. Thus, the injection characteristic at each time including a temporal characteristic change can be obtained.
Owner:DENSO CORP
Near-field vector signal enhancement
InactiveUS20080152167A1Improve noiseGood choiceMicrophonesLoudspeakersUltrasound attenuationEnvironmental noise
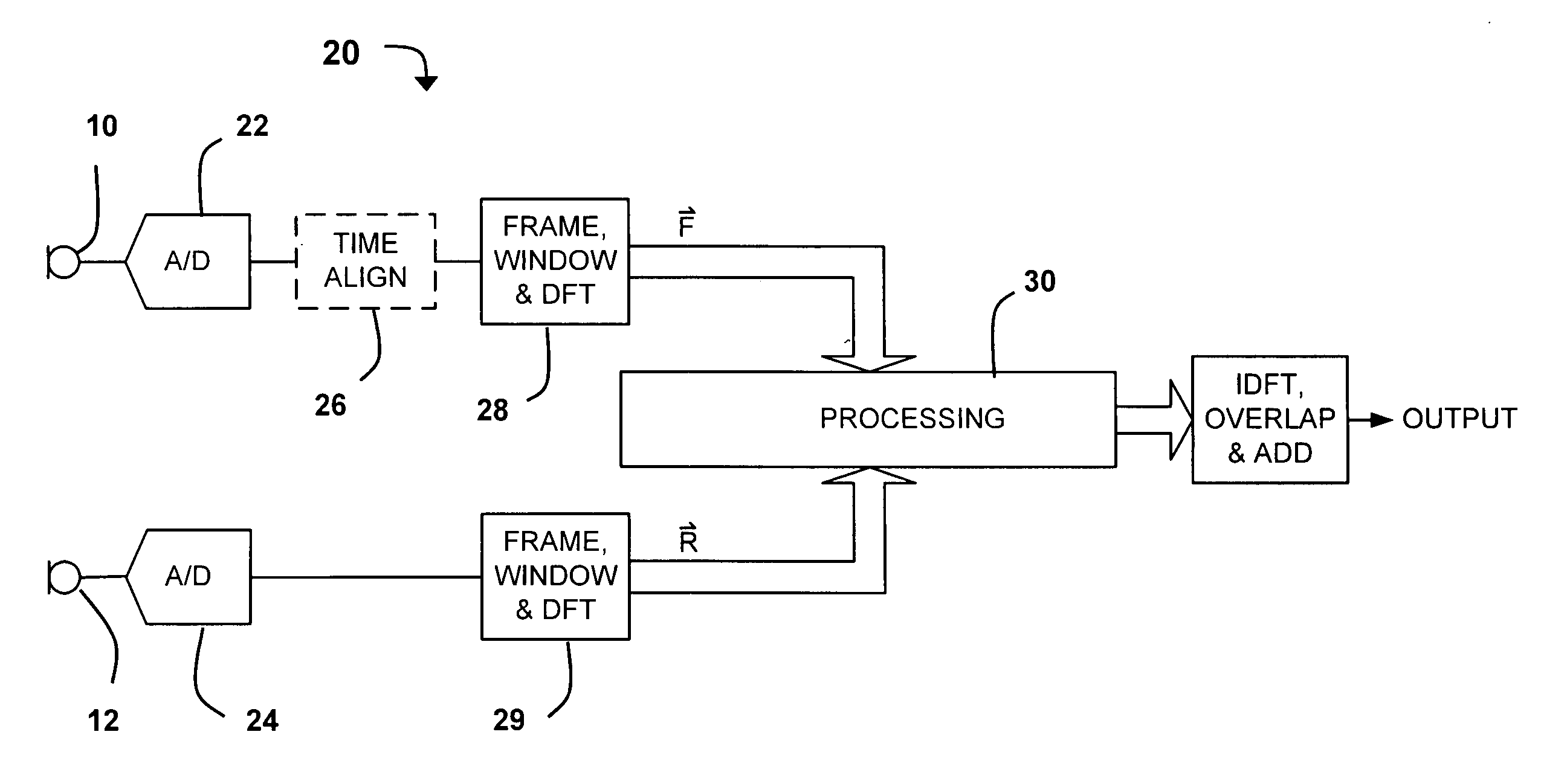
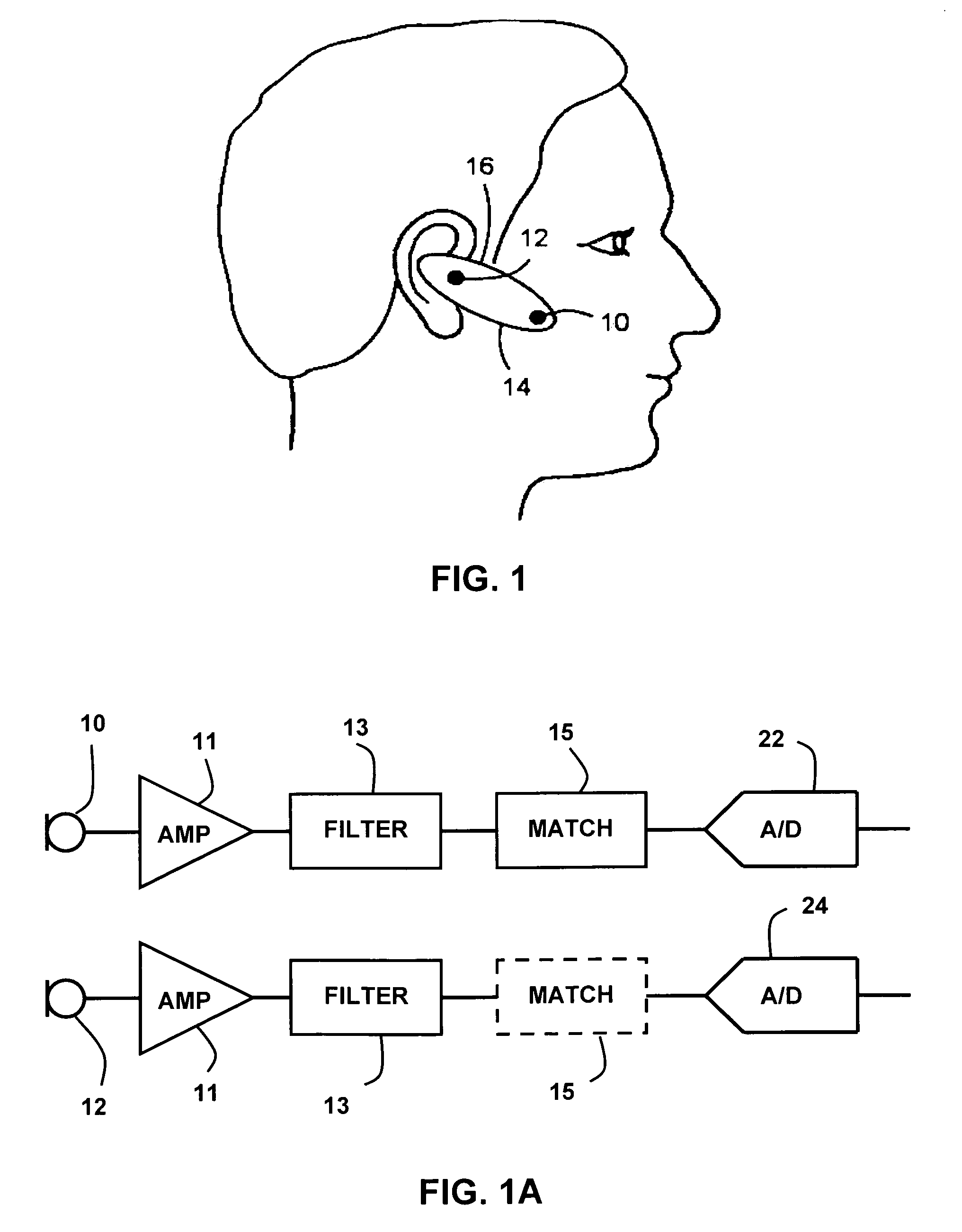
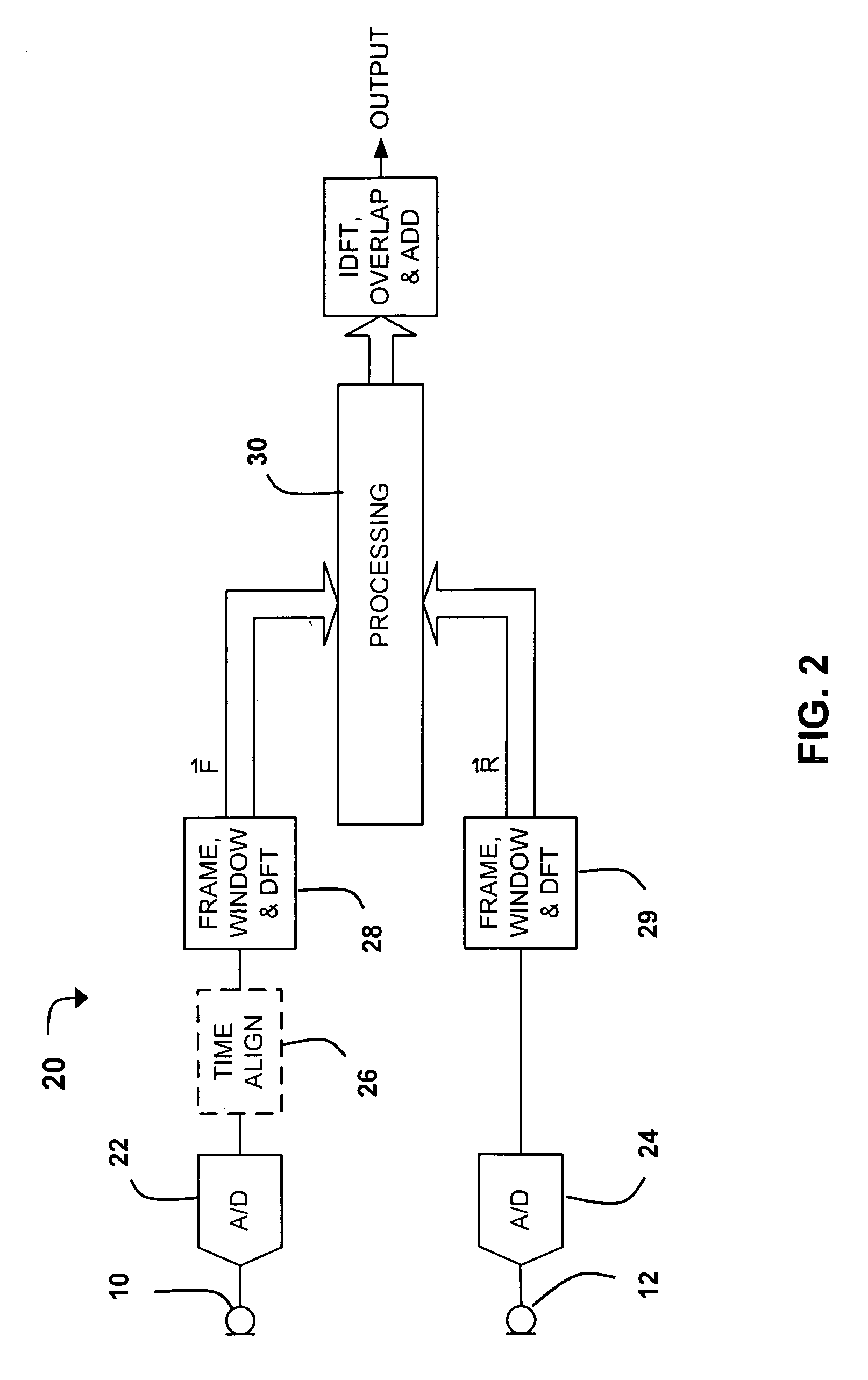
Near-field sensing of wave signals, for example for application in headsets and earsets, is accomplished by placing two or more spaced-apart microphones along a line generally between the headset and the user's mouth. The signals produced at the output of the microphones will disagree in amplitude and time delay for the desired signal—the wearer's voice—but will disagree in a different manner for the ambient noises. Utilization of this difference enables recognizing, and subsequently ignoring, the noise portion of the signals and passing a clean voice signal. A first approach involves a complex vector difference equation applied in the frequency domain that creates a noise-reduced result. A second approach creates an attenuation value that is proportional to the complex vector difference, and applies this attenuation value to the original signal in order to effect a reduction of the noise. The two approaches can be applied separately or combined.
Owner:DOLBY LAB LICENSING CORP
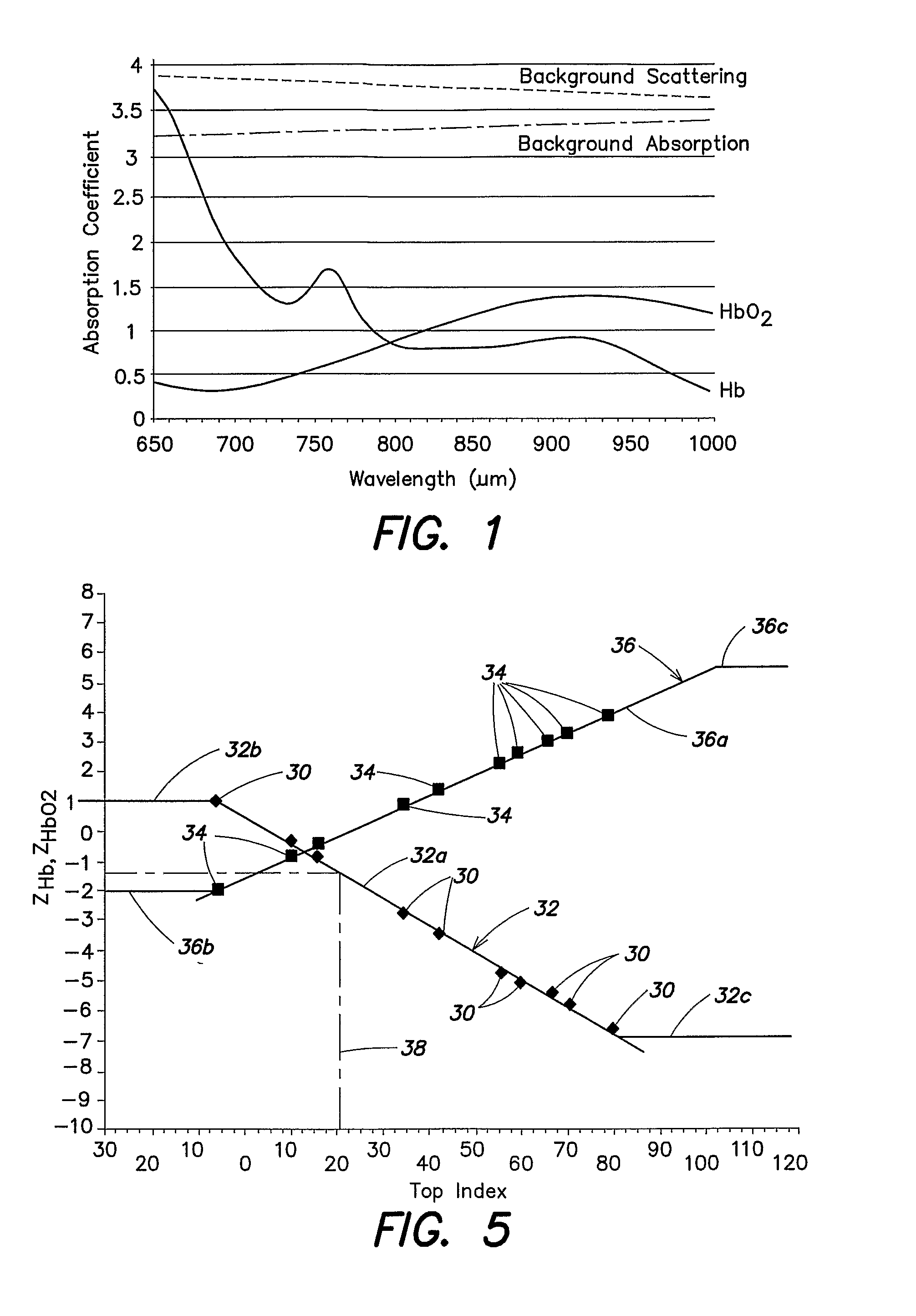
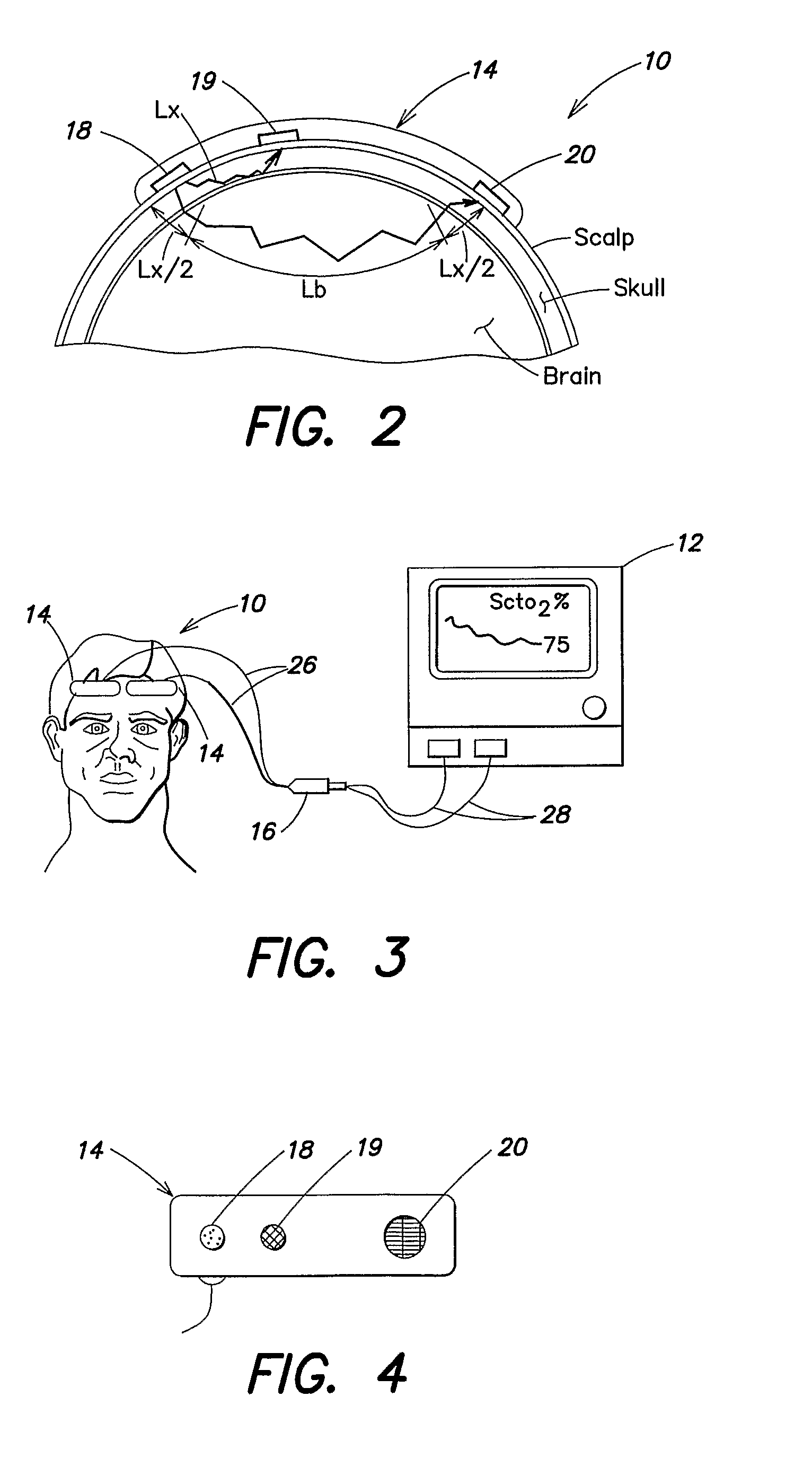
Method for spectrophotometric blood oxygenation monitoring
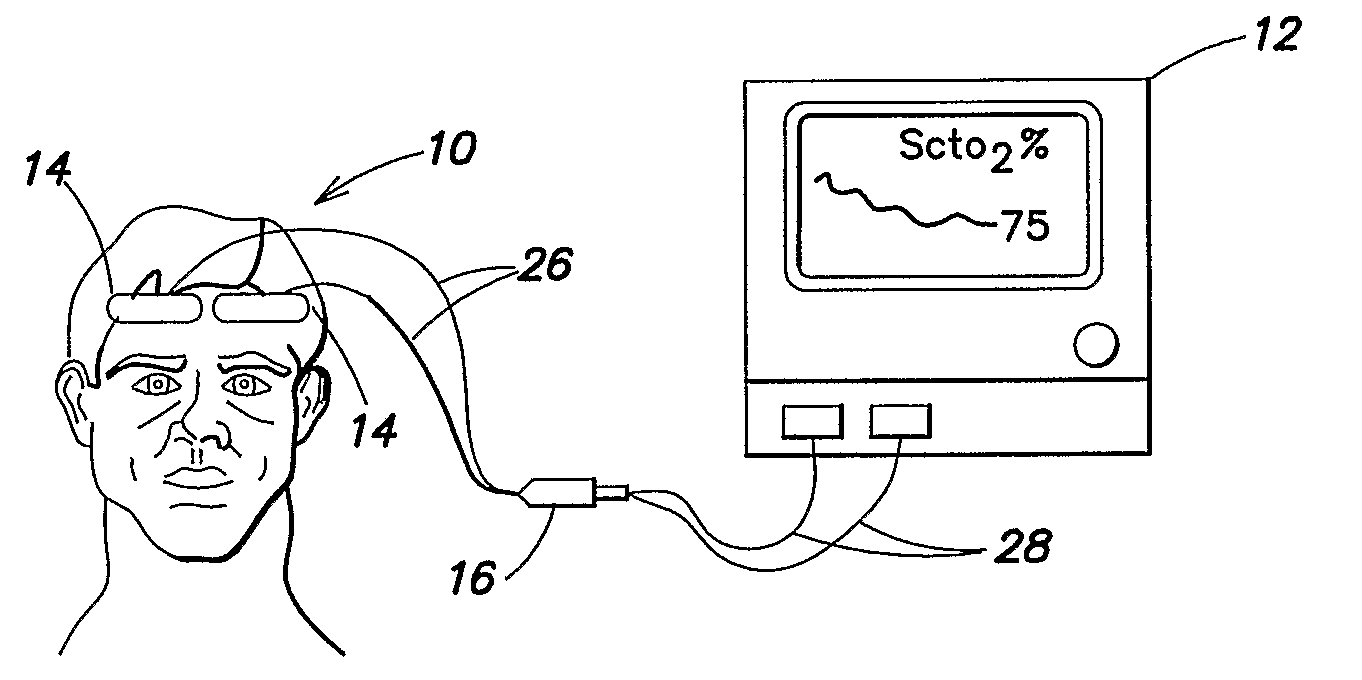
ActiveUS20090281403A1Accurate assessmentImprove accuracyScattering properties measurementsDiagnostic recording/measuringUltrasound attenuationLight sensing
According to the present invention, a method and apparatus for non-invasively determining the blood oxygen saturation level within a subject's tissue is provided. The method comprises the steps of: 1) providing a near infrared spectrophotometric sensor operable to transmit light along a plurality of wavelengths into the subject's tissue; 2) sensing the light transmitted into the subject's tissue using the sensor, and producing signal data representative of the light sensed from the subject's tissue; 3) processing the signal data to account for physical characteristics of the subject; and 4) determining the blood oxygen saturation level within the subject's tissue using a difference in attenuation between the wavelengths. The apparatus includes a sensor having a light source and at least one light detector, which sensor is operably connected to a processor. The sensor is operable to transmit light along a plurality of wavelengths into the subject's tissue, and produce signal data representative of the light sensed from the subject's tissue. The algorithm is operable to process the signal data to account for the physical characteristics of the subject being sensed.
Owner:EDWARDS LIFESCIENCES CORP
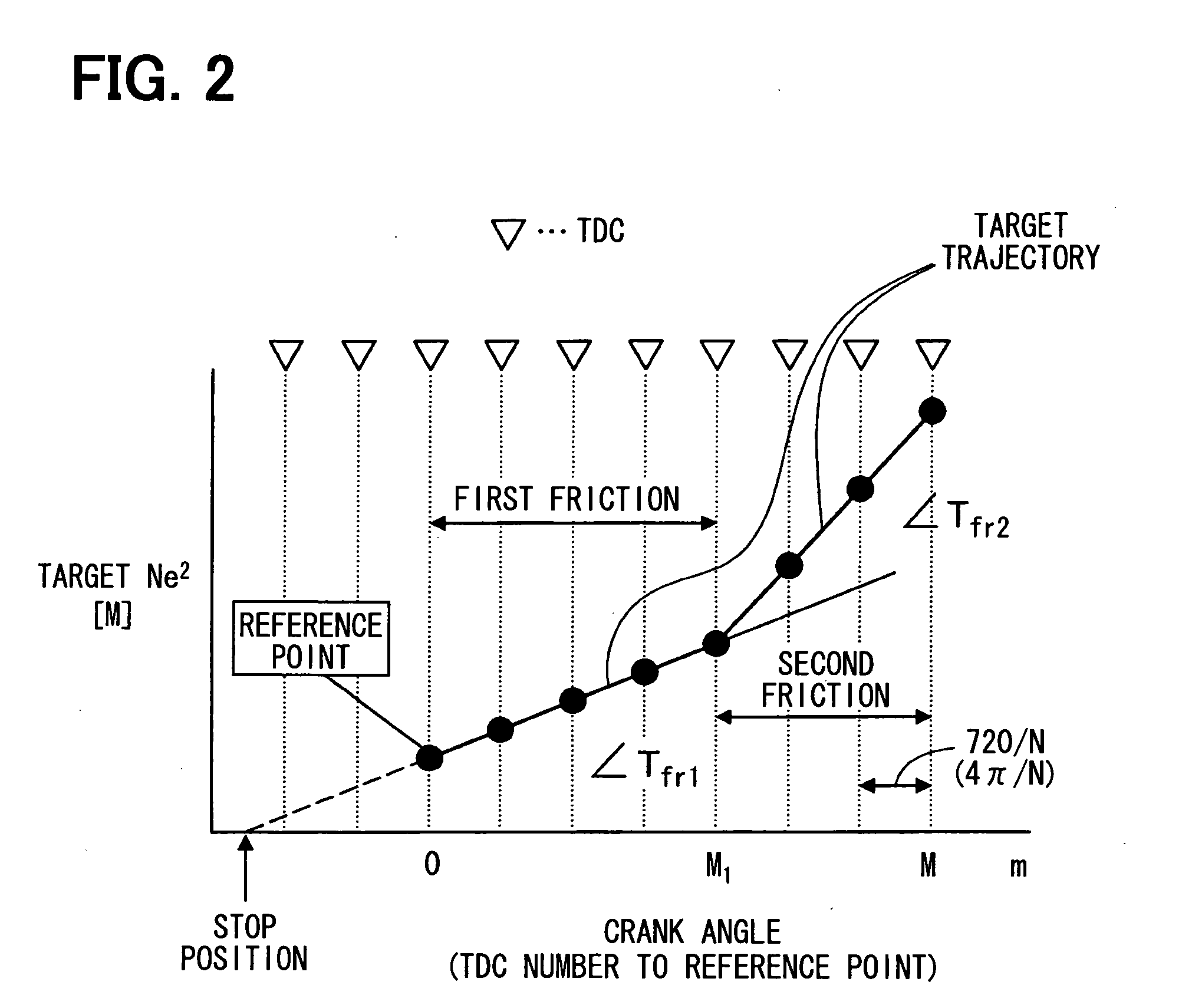
Engine automatic stop-start controller
InactiveUS20100042311A1Accurate inductionAnalogue computers for vehiclesElectrical controlControl theoryFuel supply
A first ignition cylinder that performs ignition first is set based on an engine stop position in automatic start. Existence / nonexistence of a misfire in the first ignition cylinder is determined based on whether a difference ΔNe between engine rotation speed at a predetermined crank angle in an interval from timing immediately before the ignition to timing immediately after the ignition of the first ignition cylinder (e.g., at TDC of first ignition cylinder) and engine rotation speed at a predetermined crank angle before ignition of a second ignition cylinder (e.g., at TDC of second ignition cylinder) is equal to or smaller than a predetermined misfire determination threshold value Nef. When misfire time number of the first ignition cylinder exceeds a predetermined value, fuel supply to the first ignition cylinder is prohibited and the automatic start is started from the second ignition cylinder.
Owner:DENSO CORP
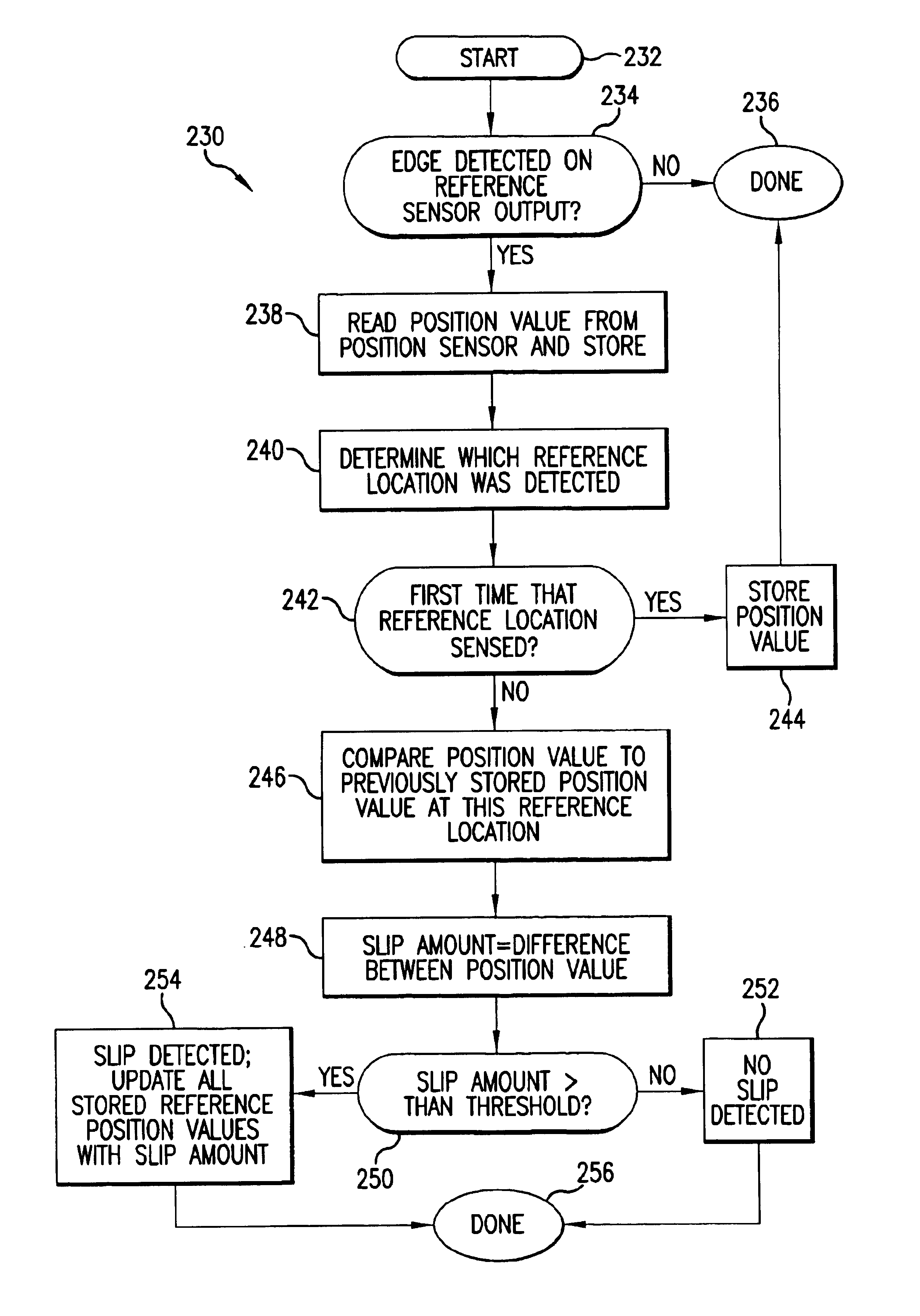
Method and apparatus for compensating for position slip in interface devices
InactiveUS6903721B2Accurate inductionSmooth displayInput/output for user-computer interactionIndoor gamesEmbedded systemObject control
Method and apparatus for compensating for position slip in interface devices that may occur between a manipulandum and a sensor of the device due to a mechanical transmission. A device position delta is determined from a sensed position of a manipulandum of an interface device. It is determined if position slip has occurred caused by a change in position of the manipulandum that was not sensed by a sensor of the interface device, typically caused by a mechanical transmission between sensor and manipulandum. If position slip has occurred, an error in the sensed position caused by the position slip is corrected by adjusting the sensed position to take into account the position slip. The adjusted position delta is used as the position of the manipulandum and the display of objects controlled by the interface device are accordingly compensated.
Owner:IMMERSION CORPORATION
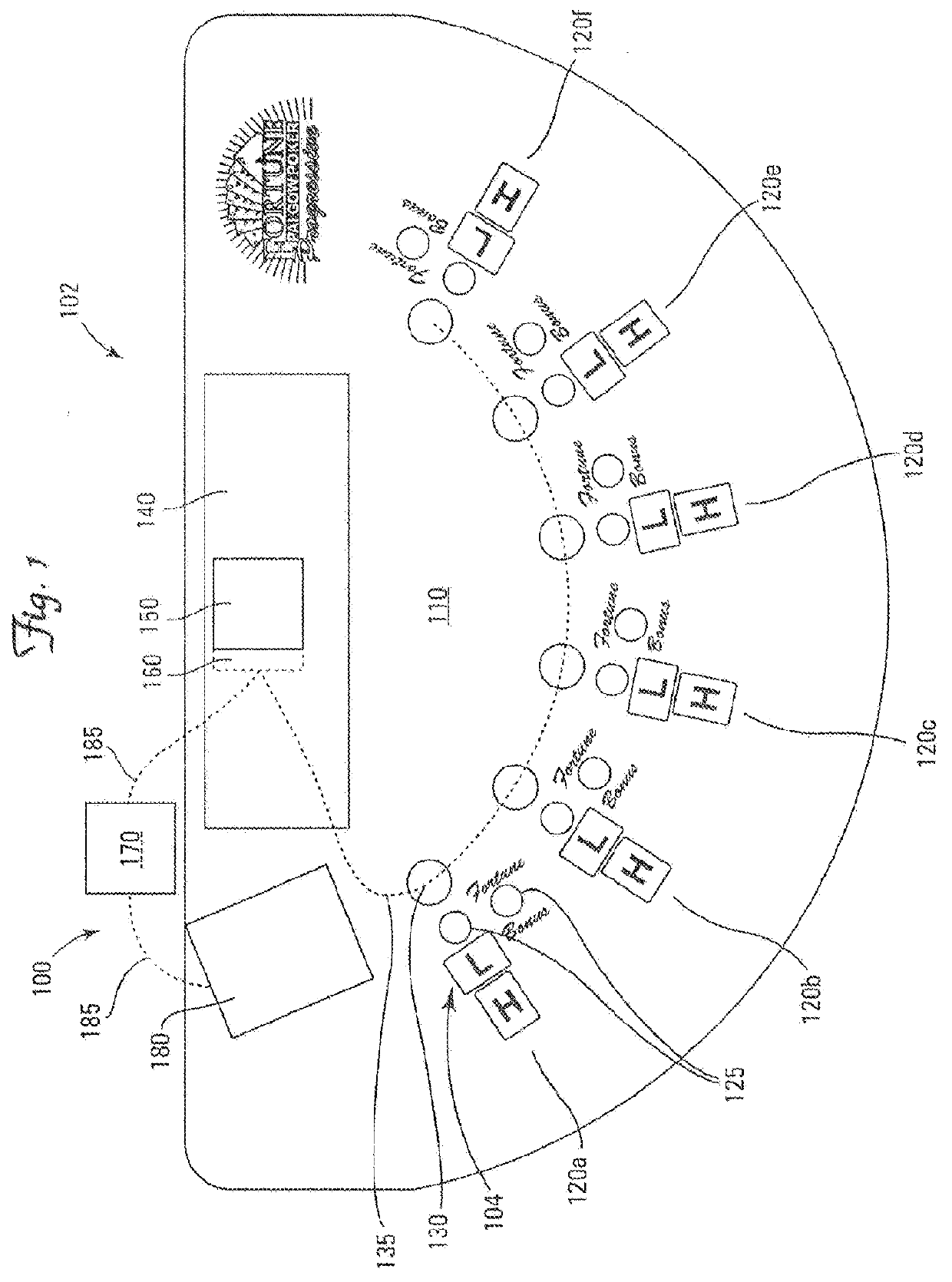
Wager recognition system
ActiveUS20120122559A1Accurate inductionBoard gamesApparatus for meter-controlled dispensingComputer scienceSupport surface
A gaming table apparatus has a gaming table with a gaming table support surface. At least two token sensors are provided which are electrically connected in series to a token sensor controller. The at least two token sensor units are physically restrained by the table support surface. The game controller is in communication with the token sensor controller, wherein the game controller is configured to associate player position data with transmitted wager data received from the token sensor controller.
Owner:LNW GAMING INC
Method and apparatus for sensing flash memory using delta sigma modulation
ActiveUS7366021B2Accurate inductionHigh circuitryRead-only memoriesDigital storageIntegratorAverage current
Owner:MICRON TECH INC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com