Patents
Literature
666 results about "Saturation level" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
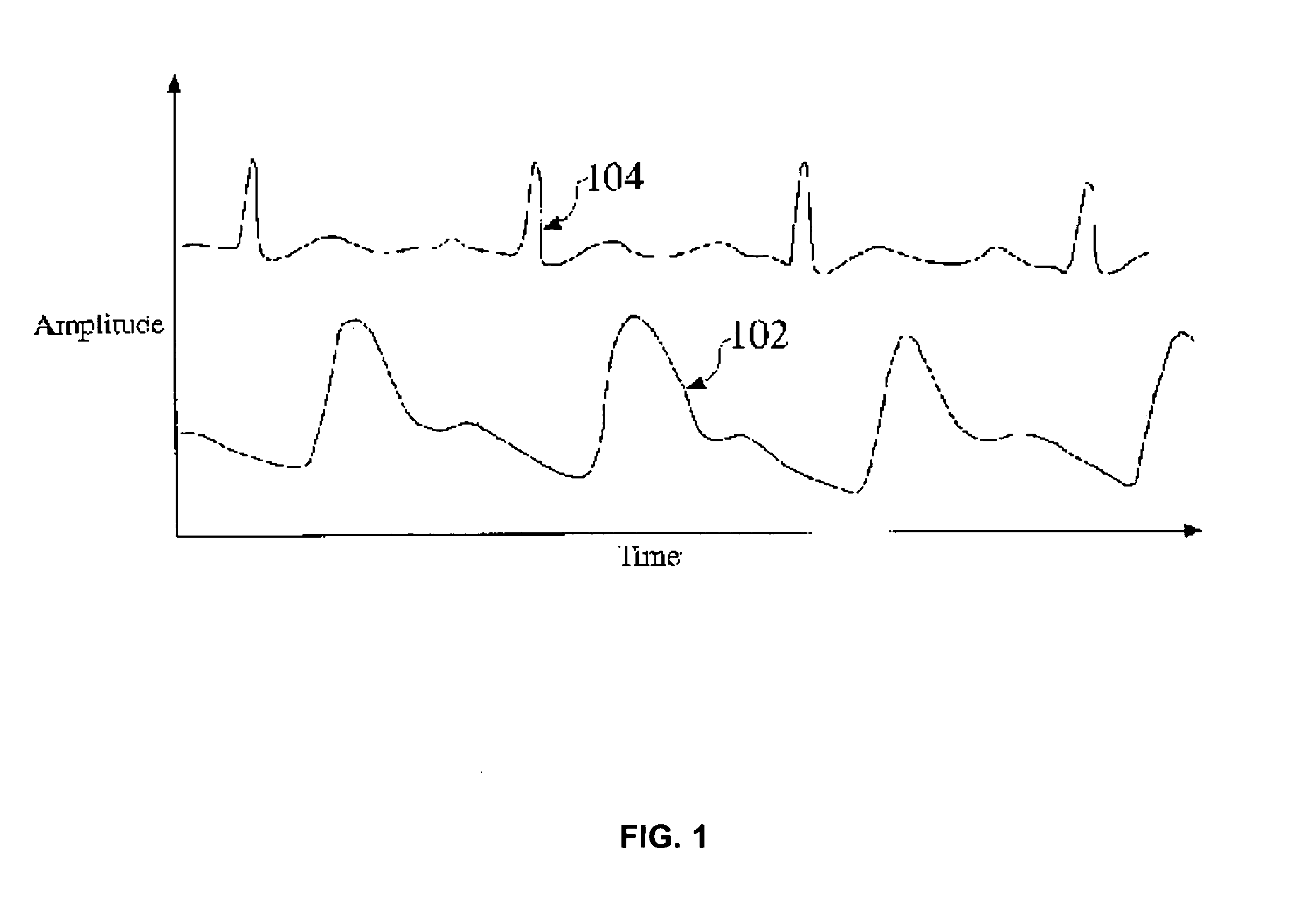
A normal oxygen saturation level is between 95% to 100%. Oxygen levels falling below 90% are typically seen as abnormal, thereby indicating cause for concern. A drop in oxygen saturation levels is known as desaturation and there are many possible causes.
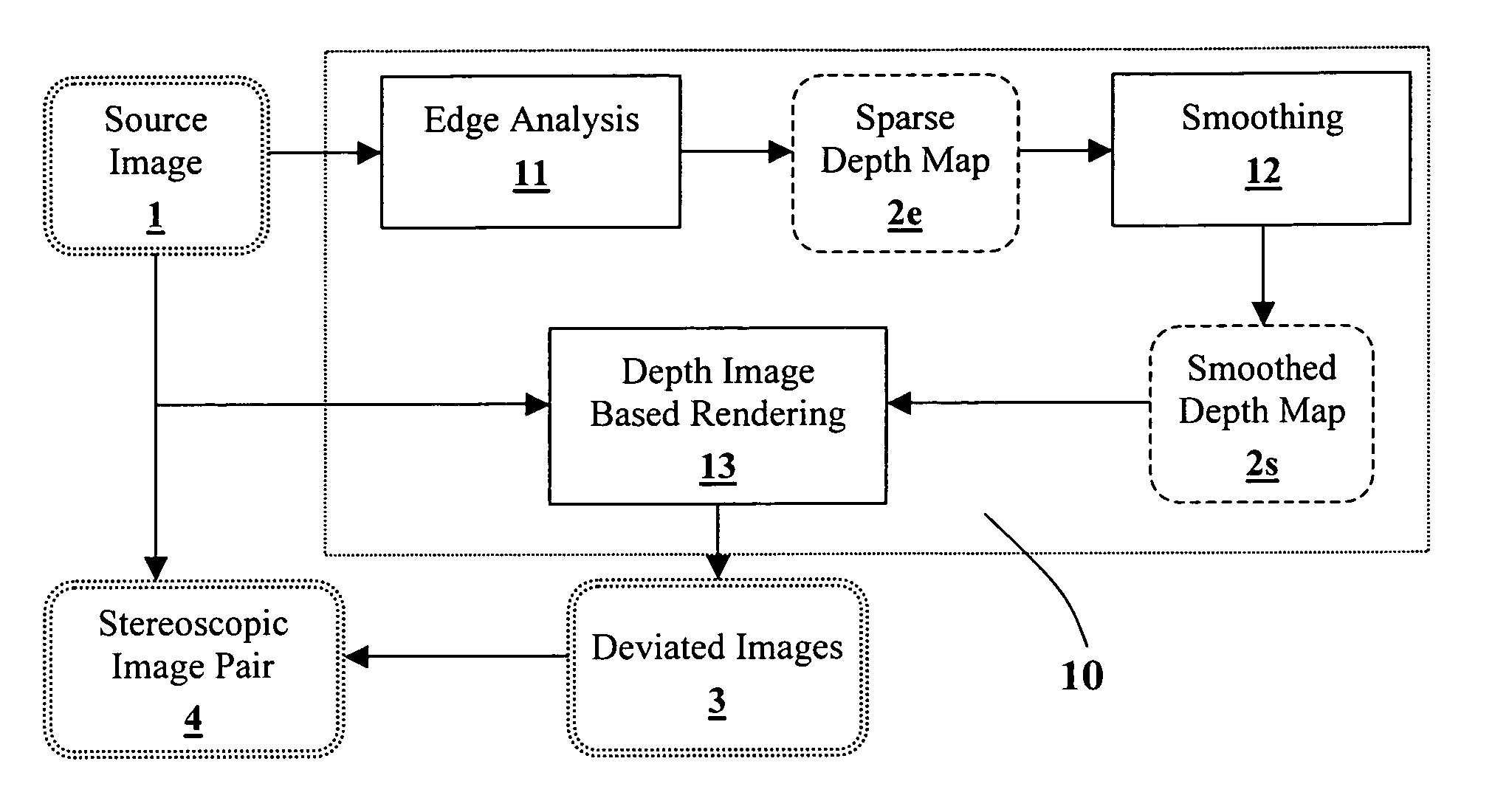
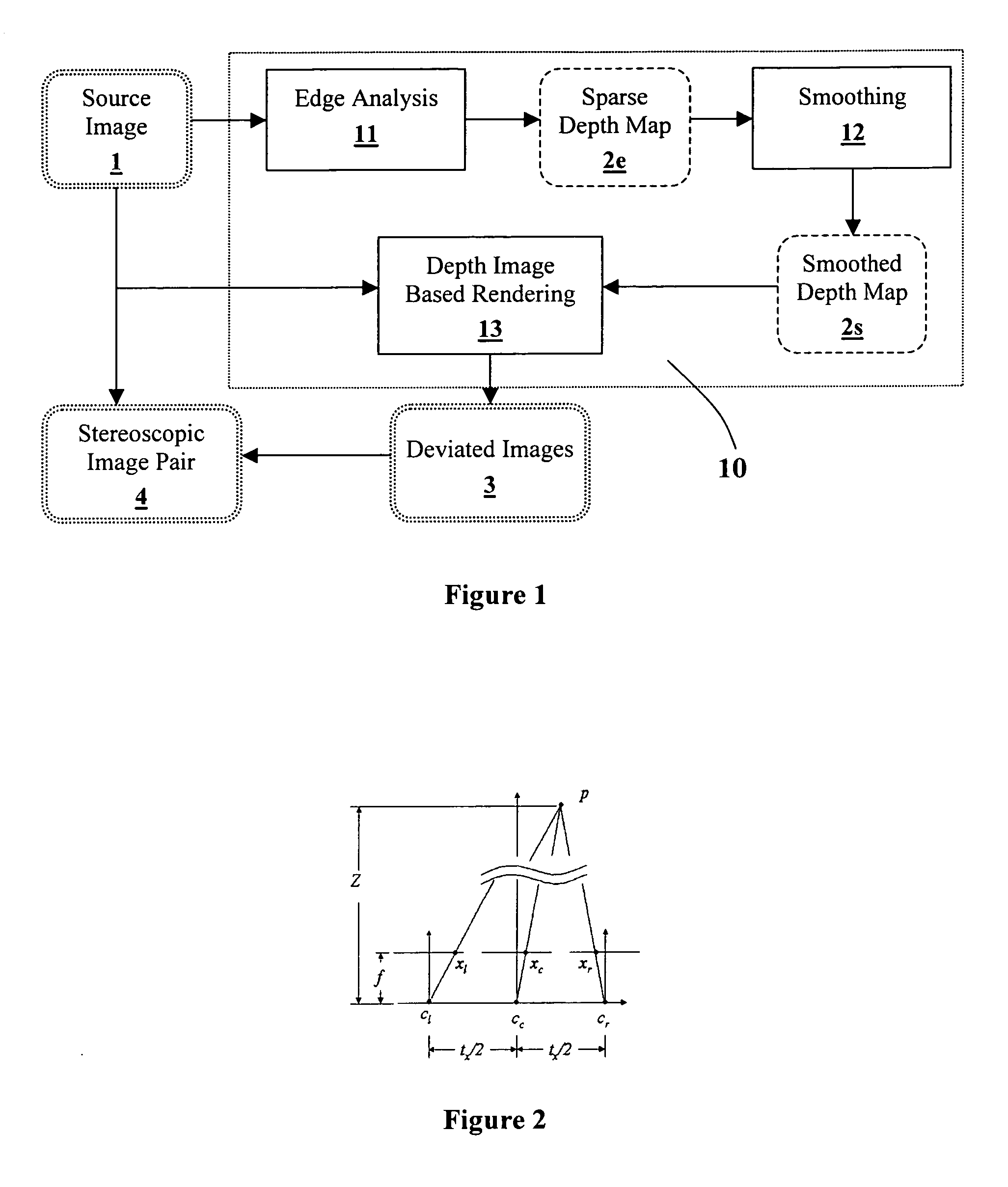
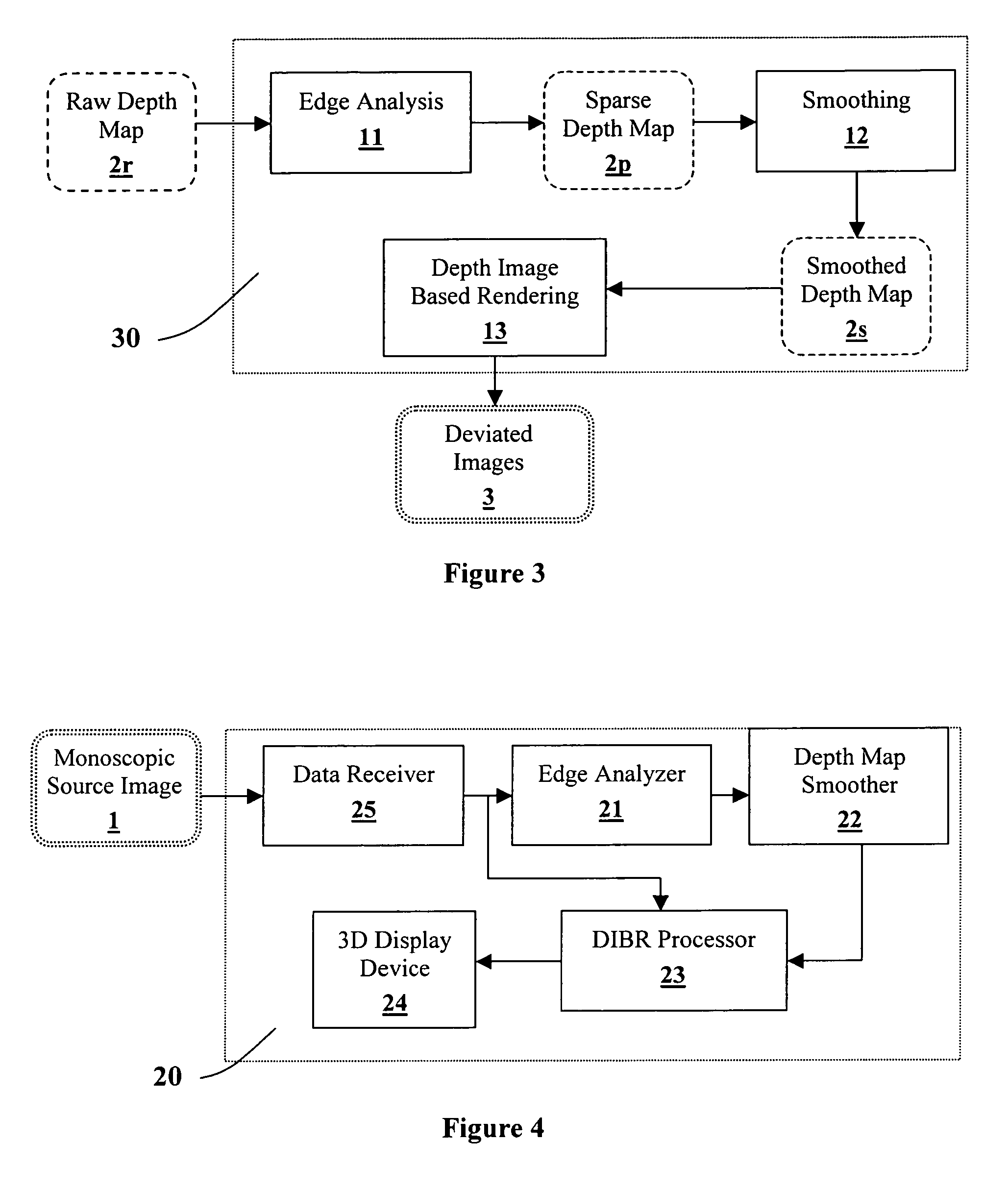
Generating a depth map from a two-dimensional source image for stereoscopic and multiview imaging
InactiveUS20070024614A1Saving in bandwidth requirementIncrease widthImage enhancementImage analysisViewpointsImage pair
Depth maps are generated from a monoscopic source images and asymmetrically smoothed to a near-saturation level. Each depth map contains depth values focused on edges of local regions in the source image. Each edge is defined by a predetermined image parameter having an estimated value exceeding a predefined threshold. The depth values are based on the corresponding estimated values of the image parameter. The depth map is used to process the source image by a depth image based rendering algorithm to create at least one deviated image, which forms with the source image a set of monoscopic images. At least one stereoscopic image pair is selected from such a set for use in generating different viewpoints for multiview and stereoscopic purposes, including still and moving images.
Owner:HER MAJESTY THE QUEEN & RIGHT OF CANADA REPRESENTED BY THE MIN OF IND THROUGH THE COMM RES CENT
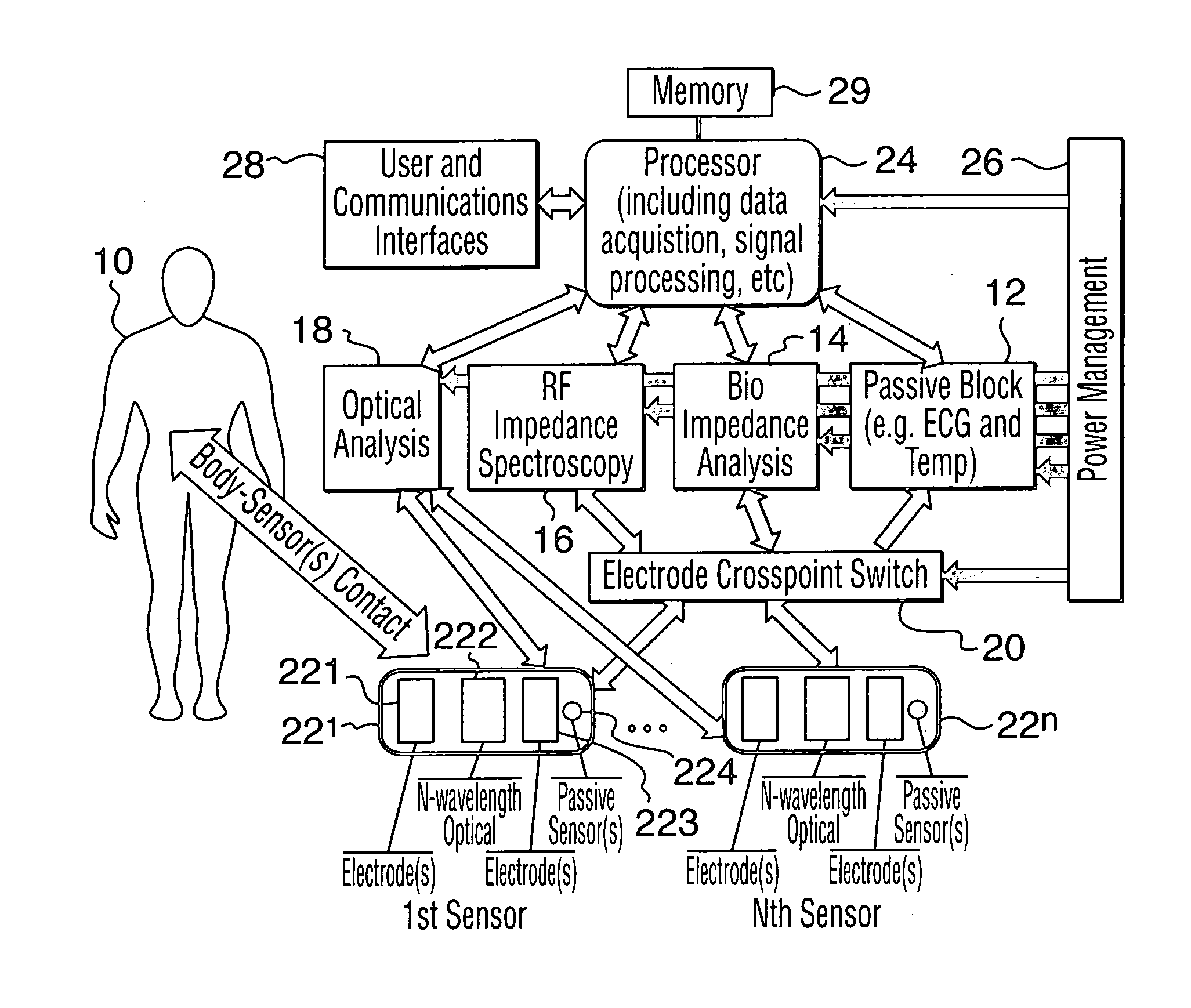
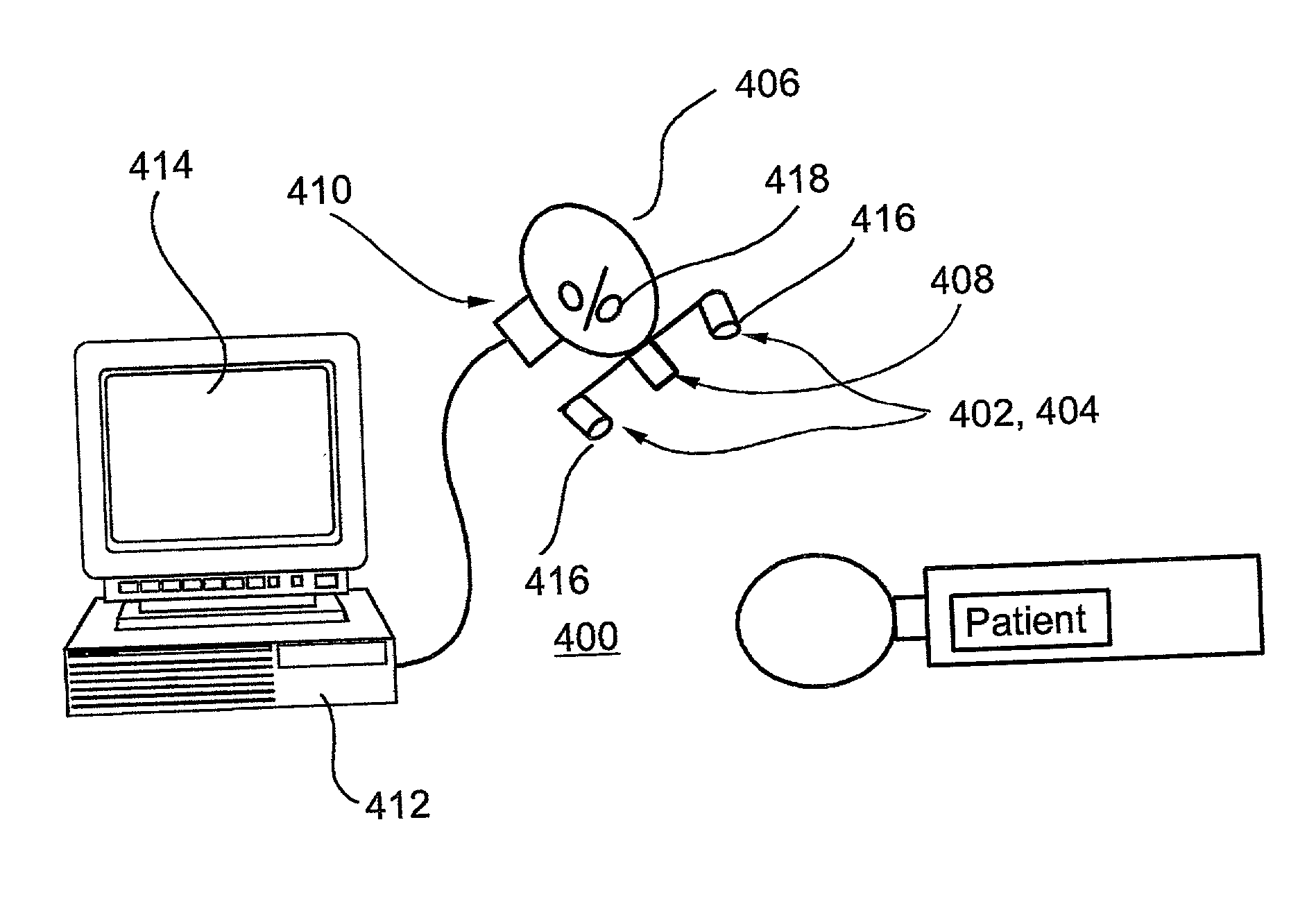
Non-invasive method and apparatus for determining a physiological parameter
InactiveUS20050192488A1Accurate resultAccurately measureElectrotherapyElectrocardiographyLinear algorithmNon invasive
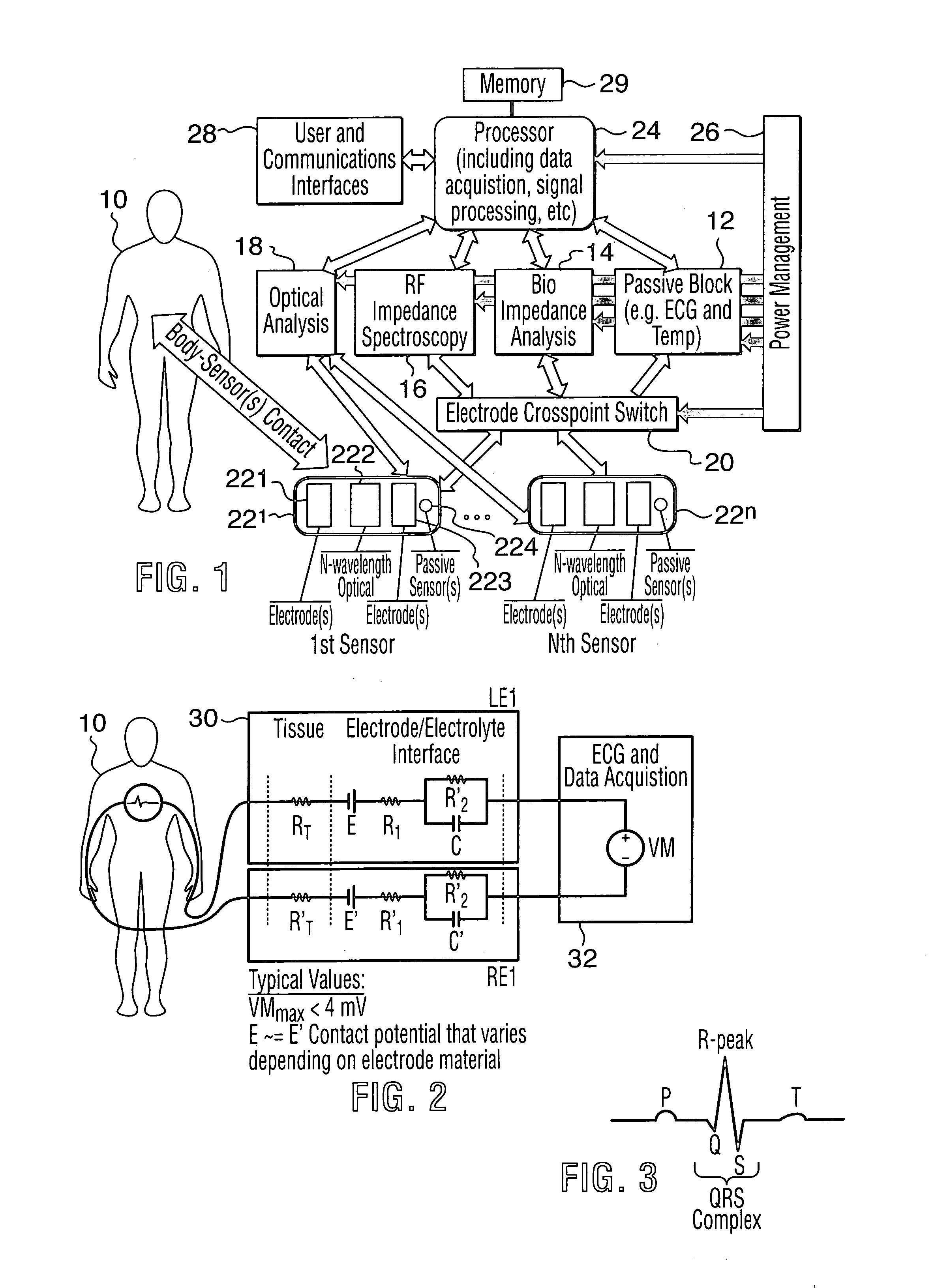
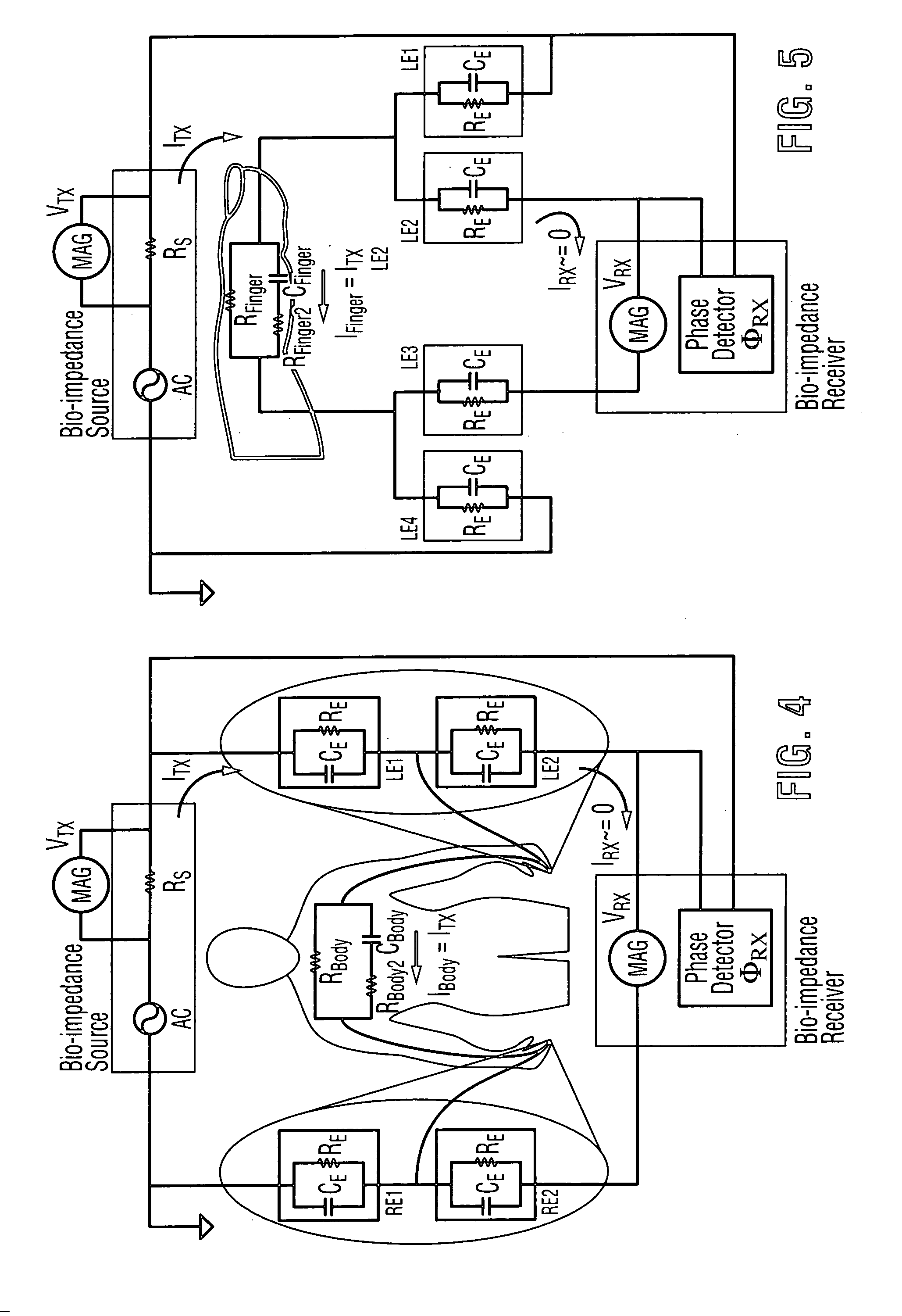
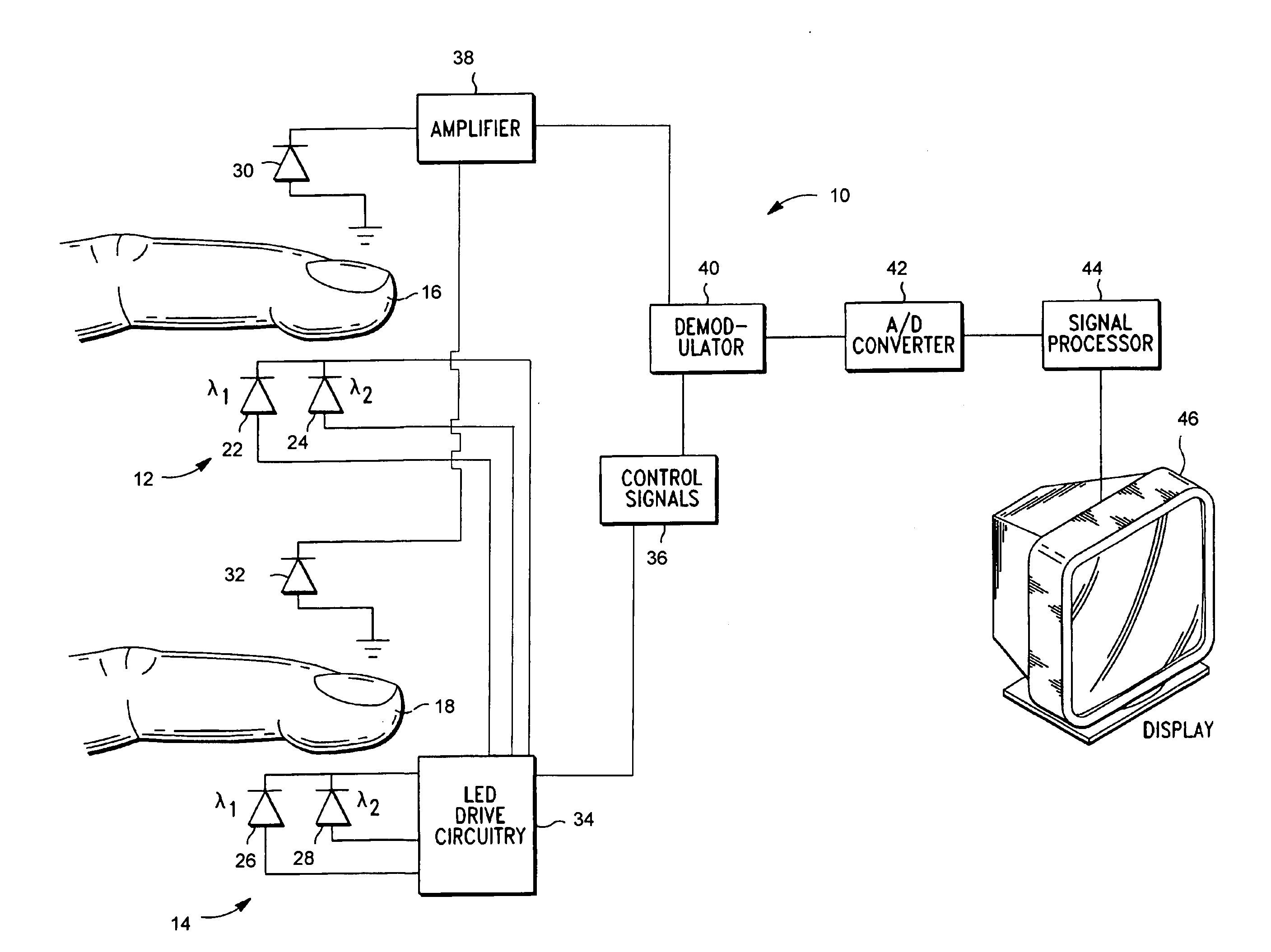
The present invention relates to an apparatus and method for the non-invasive analysis of physiological attributes, such as heart rate, blood pressure, cardiac output, respiratory response, body composition, and blood chemistry analytes including glucose, lactate, hemoglobin, and oxygen saturation. Using a combination of multi-functioning disparate sensors, such as optical and electrical, improvements are made over existing physiological measurement devices and techniques. The special configuration of one or more multi-functional sensors is used to non-invasively measure multi-wavelength optical plus one or more of ECG, Bio-impedance, and RF-impedance spectroscopic data. This information is used to develop self-consistent, non-linear algorithm in order to derive the physiological attributes while compensating for various forms of interfering effects including motion artifacts, sensor attachment variability, device component variability, subject physical and physiology variability, and various interfering physiological attributes.
Owner:BIOPEAK CORP
Method and apparatus for processing signals reflecting physiological characteristics from multiple sensors
InactiveUS20070260132A1Improve accuracyEnhanced signalDiagnostic recording/measuringSensorsMedicineMultiple sensor
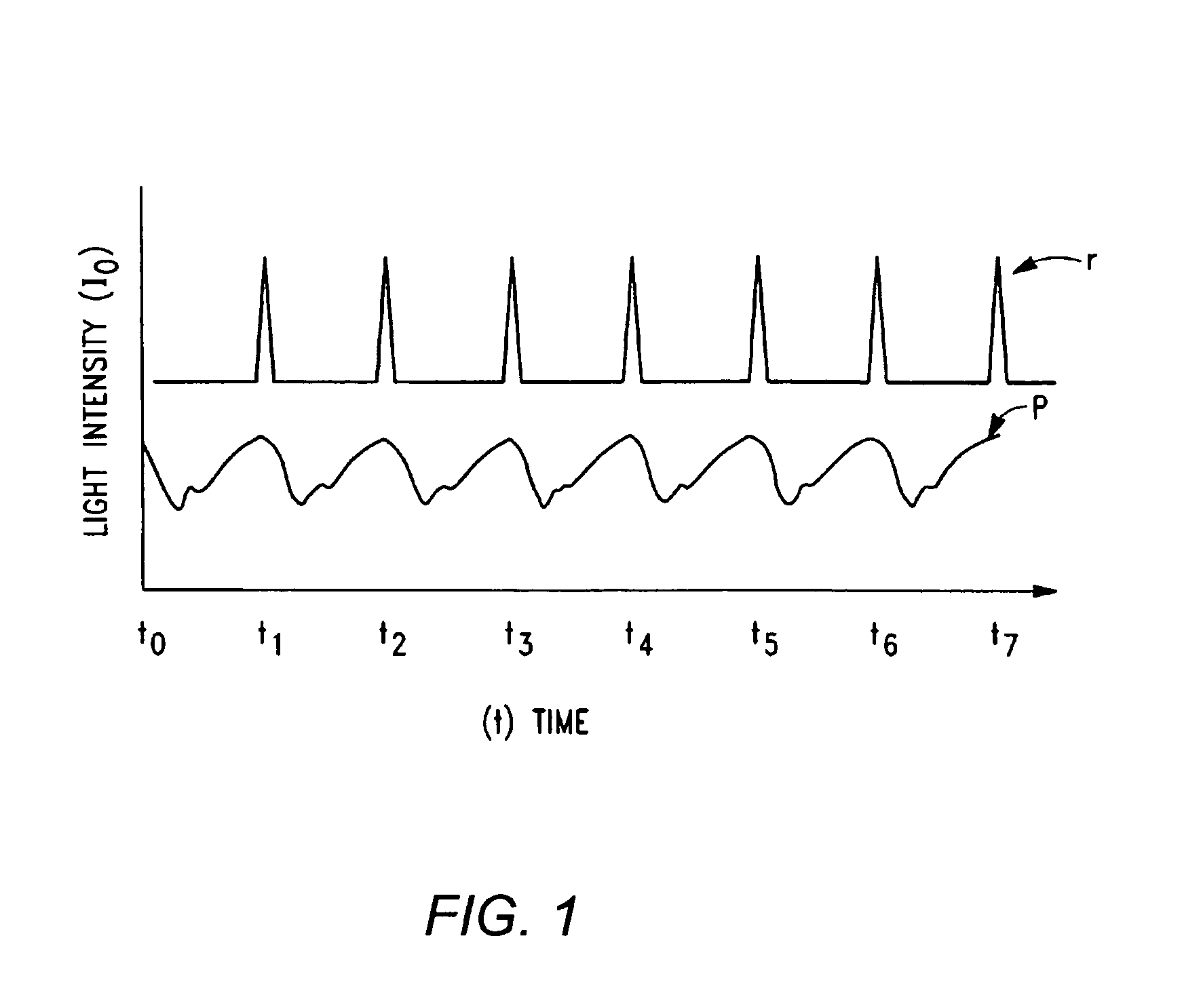
The invention comprises a method and apparatus for processing signals reflecting a physiological characteristic by performing an error minimizing mathematical combination between signals from at least two independent sensors. For example, the intensity of light is detected following tissue absorption at two wavelengths and the signals are corrected. Preferably, corrected intensity signals are derived by orthogonal regression. In one embodiment, the method and apparatus are used to determine arterial oxygen saturation.
Owner:WOOLSTHORPE TECH
Layered absorbent structure
A distinctive absorbent article includes an absorbent core having multiple absorbent layers, wherein the absorbent layers interact in such a manner which preferentially locates absorbed liquid in an appointed, high saturation wicking layer. The localization of the liquid within this wicking layer increases the potential of this layer to move liquid through capillary action due to the higher saturation level and increased amount of liquid available. The intake capability of the absorbent system is maintained or improved over current systems by keeping a second layer of the absorbent system at low saturation levels through as many insults of the product as possible, while providing optimum intake performance through appropriate control of the composite properties. The low saturation in this layer provides void volume for the incoming insult as well, as a high permeability, thus increasing the intake rate of the absorbent system as a whole, but the structure of the low saturation layer is also balanced to provide an appropriately high level of capillary tension to provide enough control of the liquid to stop leakage from occurring. This low saturation layer is used in addition to a surge material and provides intake functionality in addition to that provided by the surge material. In particular aspects of the invention, the body side layer of the absorbent core does not extend over the entire surface of the overall absorbent core, therefore is not used as the high saturation, wicking layer, but as the intake layer. This arrangement also allows the intake layer to be in direct contact with the incoming liquid, therefore allowing for more immediate access and improved intake function.
Owner:KIMBERLY-CLARK WORLDWIDE INC
System and method for functional brain mapping and an oxygen saturation difference map algorithm for effecting same
A method of functional brain mapping of a subject is disclosed. The method is effected by (a) illuminating an exposed cortex of a brain or portion thereof of the subject with incident light; (b) acquiring a reflectance spectrum of each picture element of at least a portion of the exposed cortex of the subject; (c) stimulating the brain of the subject; (d) during or after step (c) acquiring at least one additional reflectance spectrum of each picture element of at least the portion of the exposed cortex of the subject; and (e) generating an image highlighting differences among spectra of the exposed cortex acquired in steps (b) and (d), so as to highlight functional brain regions. Algorithms for calculating oxygen saturation and blood volume maps which can be used to practice the method are also disclosed. Systems for practicing the method are also disclosed.
Owner:APPLIED SPECTRAL IMAGING
Pulse oximetry methods and apparatus for use within an auditory canal
Methods and apparatus for detecting oxygen saturation levels in blood from within an auditory canal of a living being proximal to a tympanic membrane are disclosed. The auditory canal is lined with tissue and includes a proximal bend and a distal bend located between the proximal bend and the tympanic membrane. Oxygen levels are detected by emitting one or more wavelengths of light into a first position on the tissue of the auditory canal in a first region defined by the distal bend and the tympanic membrane. The wavelengths of light are then sensed at a second position on the tissue of the auditory canal in the first region. A blood oxygen saturation level and / or pulse rate is then calculated responsive to intensity information corresponding to the wavelengths of light detected at the second position.
Owner:SARNOFF CORP
Method for spectrophotometric blood oxygenation monitoring
ActiveUS20040024297A1Inhibition effectNon-invasive determinationSensorsColor/spectral properties measurementsBlood oxygenationNon invasive
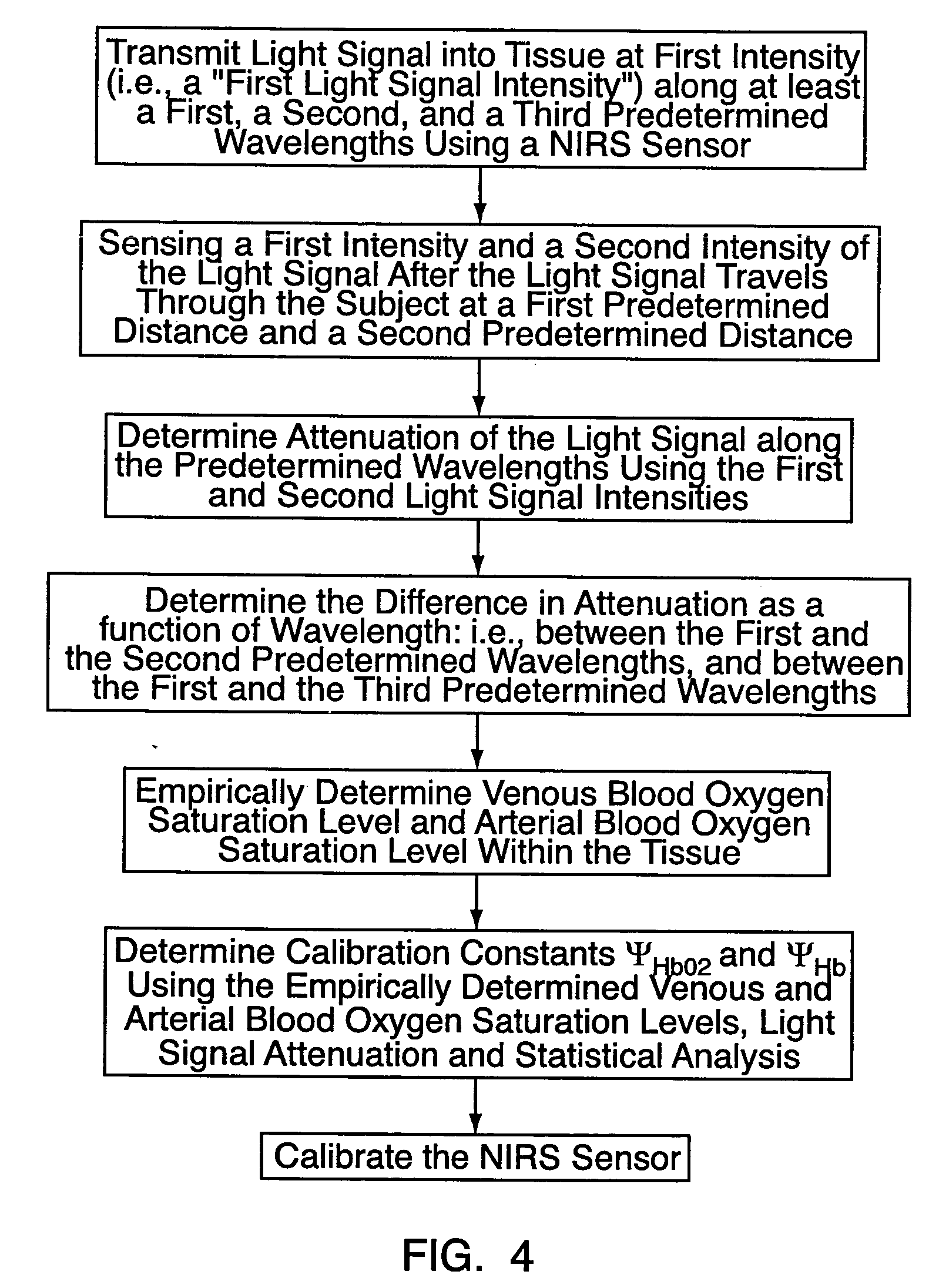
A method and apparatus for non-invasively determining the blood oxygen saturation level within a subject's tissue is provided that utilizes a near infrared spectrophotometric (NIRS) sensor capable of transmitting a light signal into the tissue of a subject and sensing the light signal once it has passed through the transmitting a light signal into the subject's tissue, wherein the transmitted light signal includes a first wavelength, a second wavelength, and a third wavelength; (2) sensing a first intensity and a second intensity of the light signal, along the first, second, and third wavelengths after the light signal travels through the subject at a first and second predetermined distance; (3) determining an attenuation of the light signal for each of the first, second, and third wavelengths using the sensed first intensity and sensed second intensity of the first, second, and third wavelengths; (4) determining a difference in attenuation of the light signal between the first wavelength and the second wavelength, and between the first wavelength and the third wavelength; and (5) determining the blood oxygen saturation level within the subject's tissue using the difference in attenuation between the first wavelength and the second wavelength, and the difference in attenuation between the first wavelength and the third wavelength.
Owner:EDWARDS LIFESCIENCES CORP
Method and apparatus for controlling the flow of data frames through a network switch on a port-by-port basis
InactiveUS6405258B1Effective controlSelectively discontinue transmission of dataError preventionTransmission systemsData streamNetwork switch
Owner:ADVANCED MICRO DEVICES INC
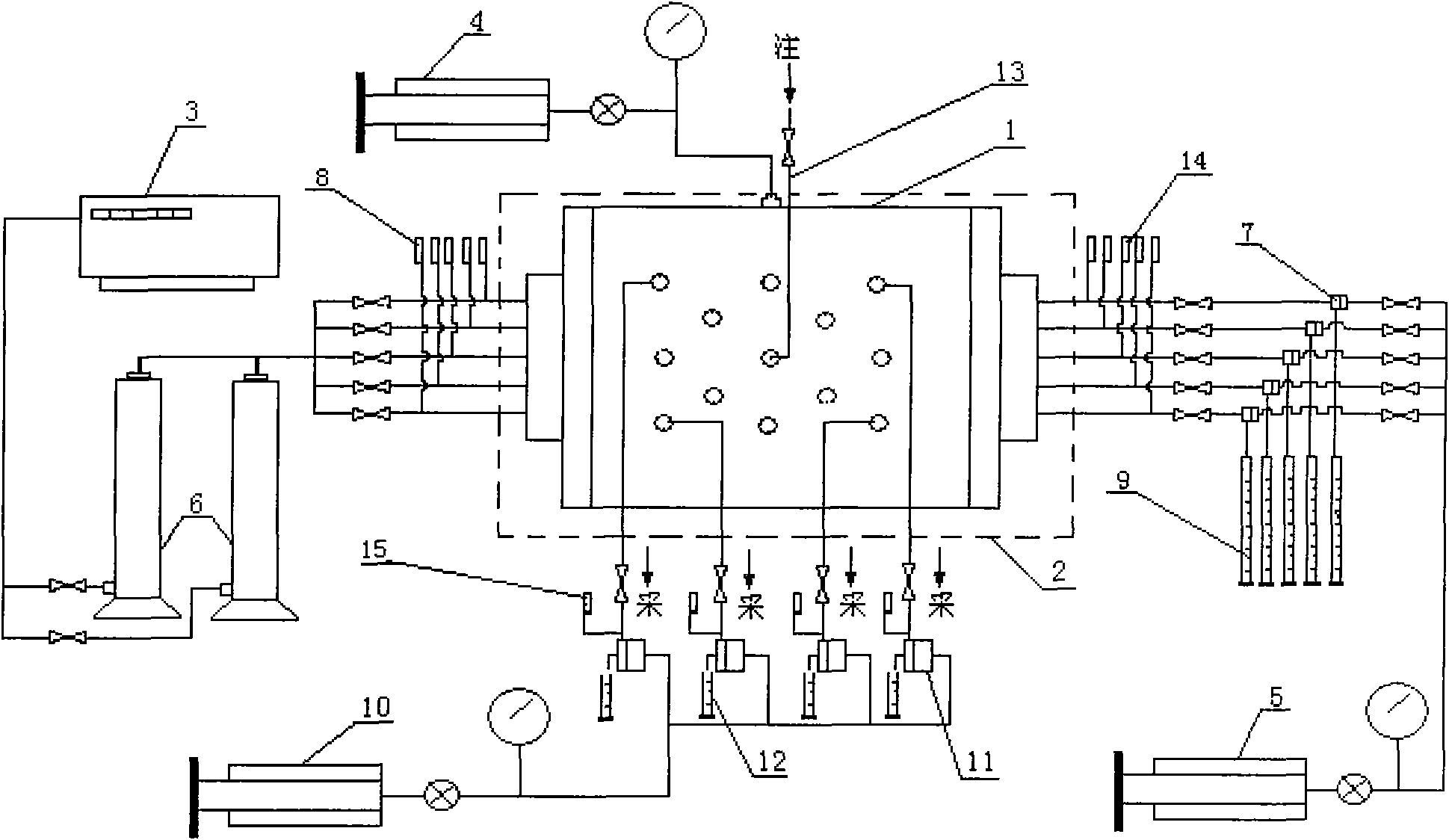
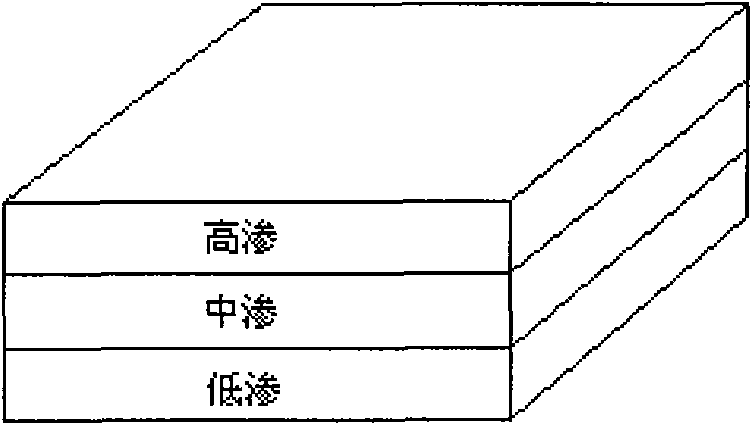
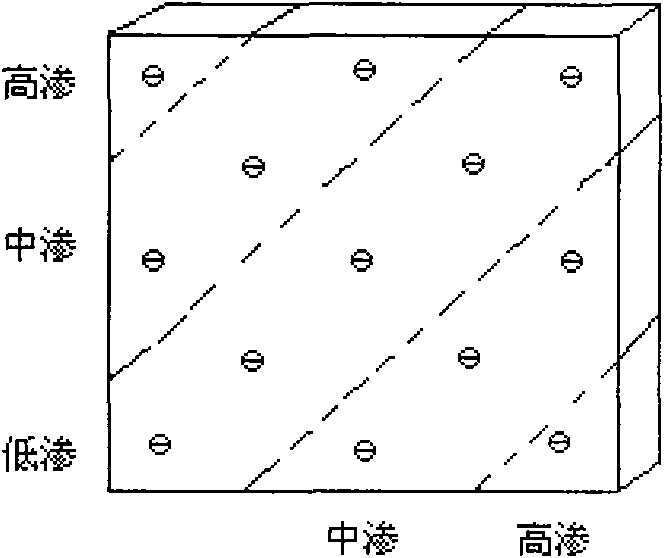
Oil-water displacement efficiency experimental method of longitudinal and planar nonhomogeneous slab models
The invention relates to an oil-water displacement efficiency experimental method of longitudinal and planar nonhomogeneous slab models, which comprises an oil-water displacement efficiency experimental method of a longitudinal nonhomogeneous slab model and an oil-water displacement efficiency experimental method of a planar nonhomogeneous slab model. The experimental method mainly comprises the following steps: 1. applying confining pressure to the core holder of a multilayer slab model, then vacuumizing the multilayer slab model with three layers slab model, injecting simulated formation water to saturate cores, and then heating; 2. injecting simulate formation oil in a piston type container into the core holder of the multilayer slab model, and carrying out water-oil displacement to establish bound water saturation level; and 3. injecting simulate formation water in the piston type container into the core holder of the multilayer slab model, and carrying out water-oil displacement to obtain accumulated displacement oil output and wateryield under different water injection multiples, and thereby, the oil displacement efficiency is obtained. The invention not only can carry out displacement experiment research on the longitudinal nonhomogeneous slab model at high temperature and pressure but also can carry out displacement experiment research of different flooding well networks on the planar nonhomogeneous slab model under high temperature and pressure. The highest pressure reached by the experimental method is 25MPa, and the highest temperature reached by the experimental method is 100 DEG C.
Owner:SOUTHWEST PETROLEUM UNIV
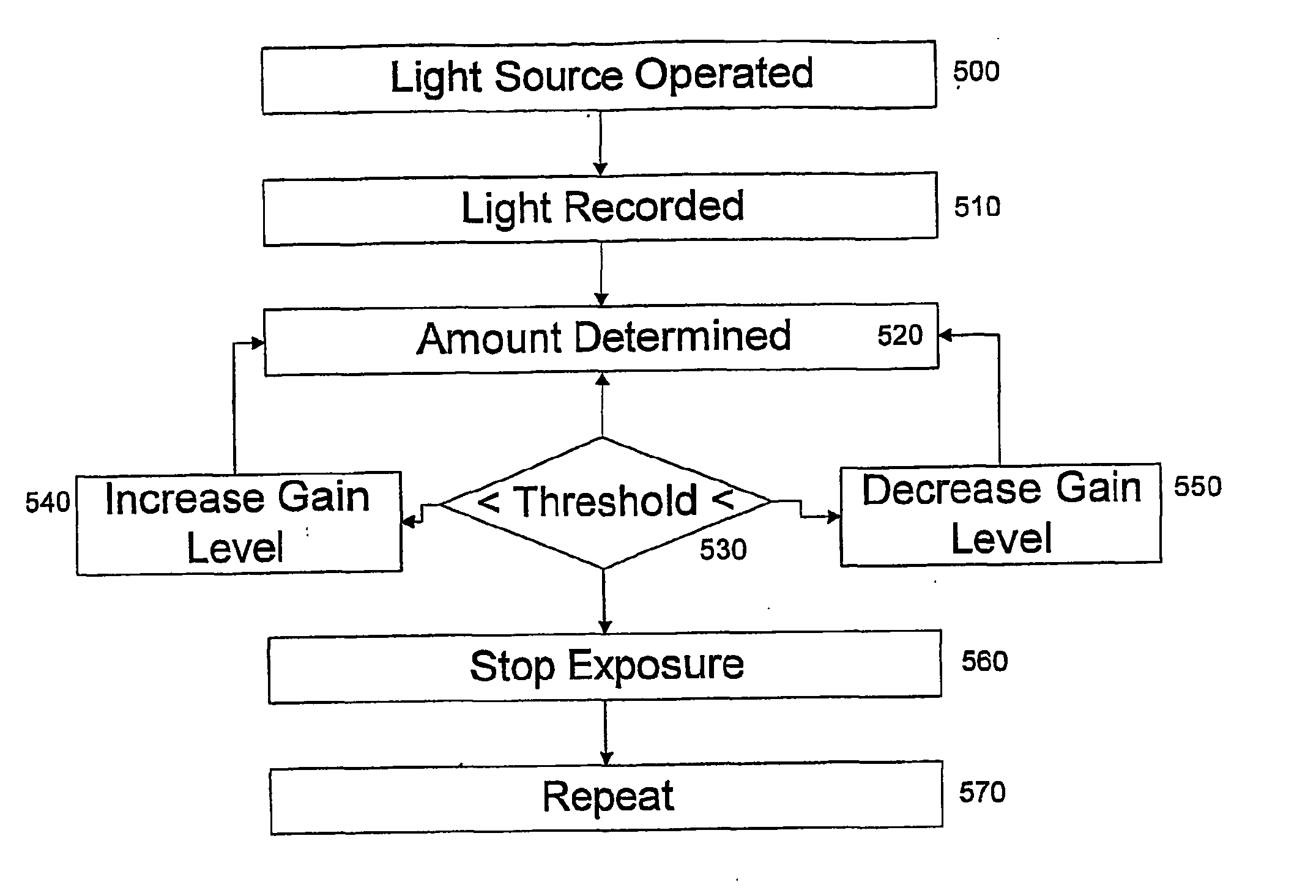
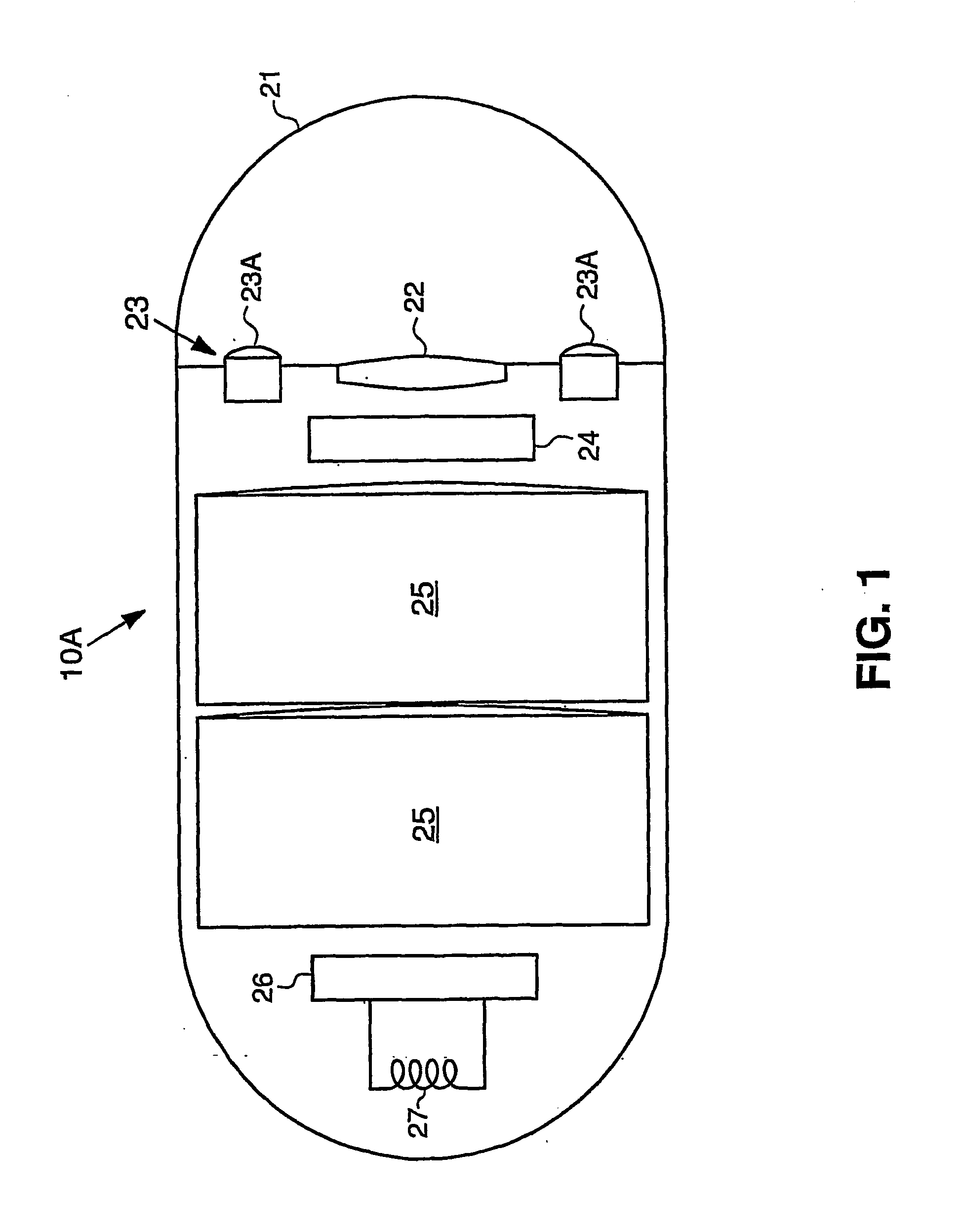
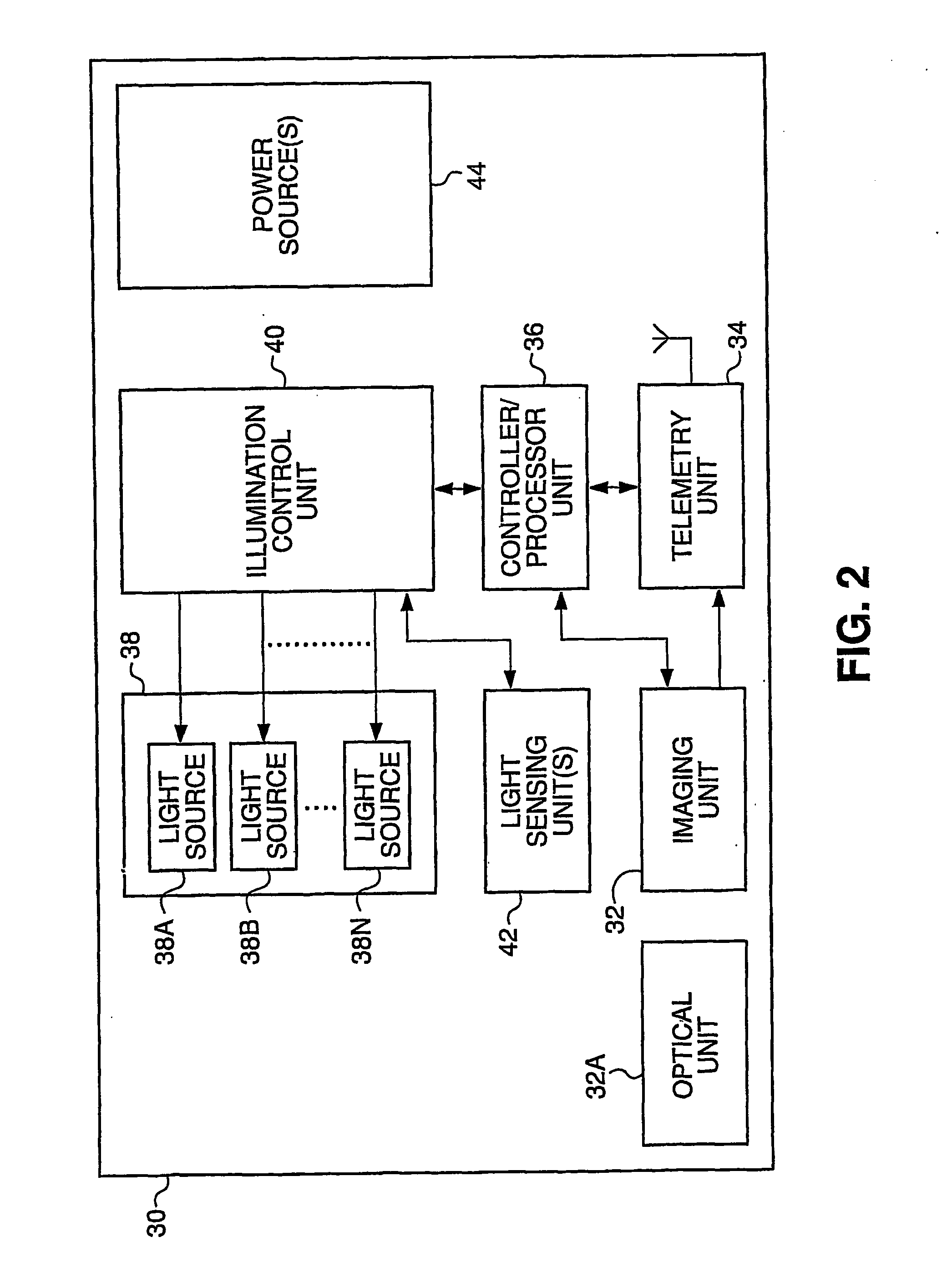
Apparatus and Method for Light Control in an in-Vivo Imaging Device
ActiveUS20070225560A1Efficient illuminationCase blockedGastroscopesSurgeryIn vivoUltimate tensile strength
A device and method for operating an in vivo imaging device (10A) wherein the illumination produced by the device may be varied in intensity and / or duration, and / or the gain level or other parameters may be varied, according to, for example, the amount of illumination produced by the device which is reflected back to the device. In addition, a method is provided for detecting problematic pixels in an imaging device. This method may define and exclude non-functional pixels, based on for example an initial short exposure that enables a threshold saturation level to be reached only for problematic pixels. Moreover, a method is described for determining when an in vivo device enters the body, for example by calculating the progress of a dark frame, based on the light saturation threshold of the dark frame.
Owner:GIVEN IMAGING LTD
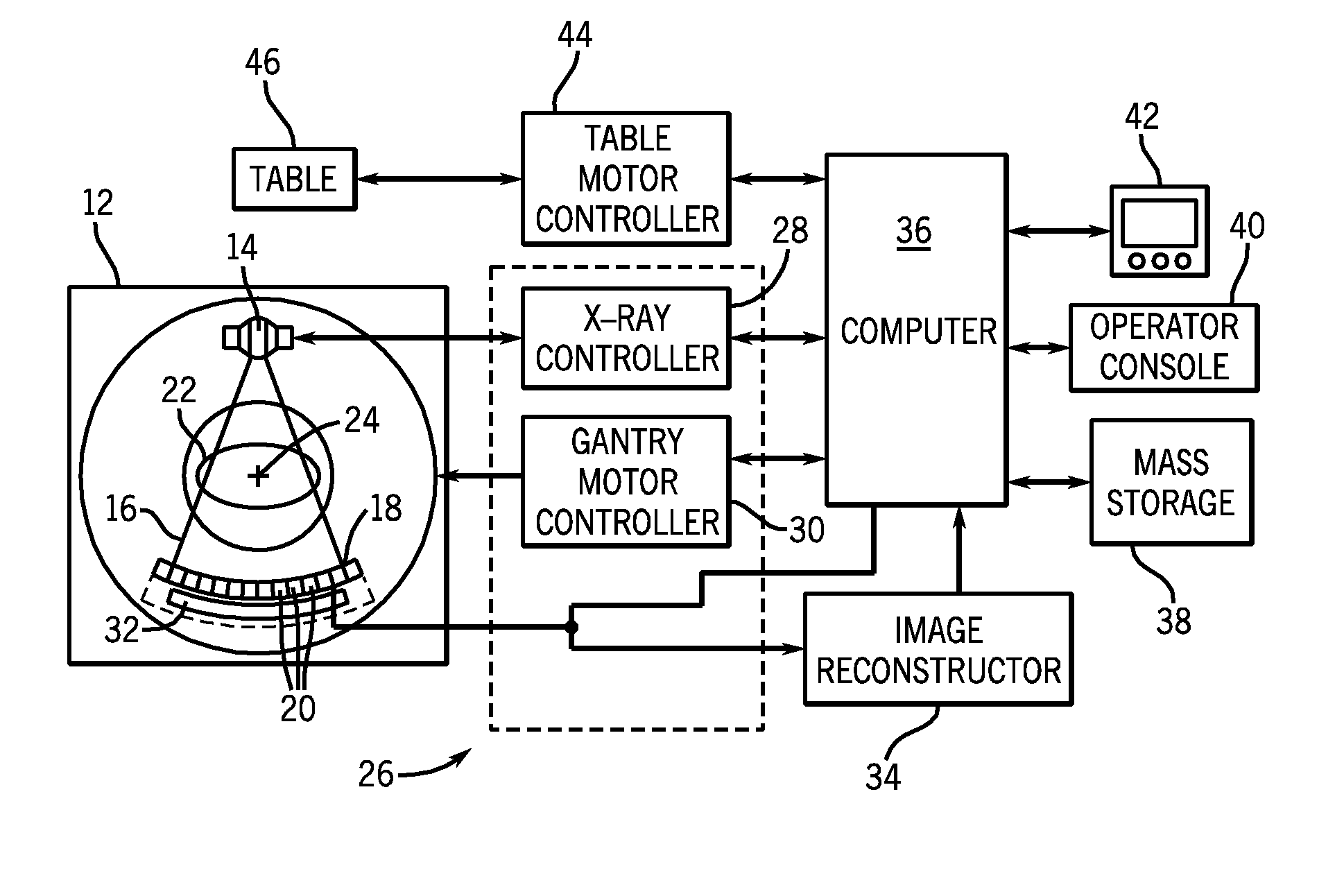
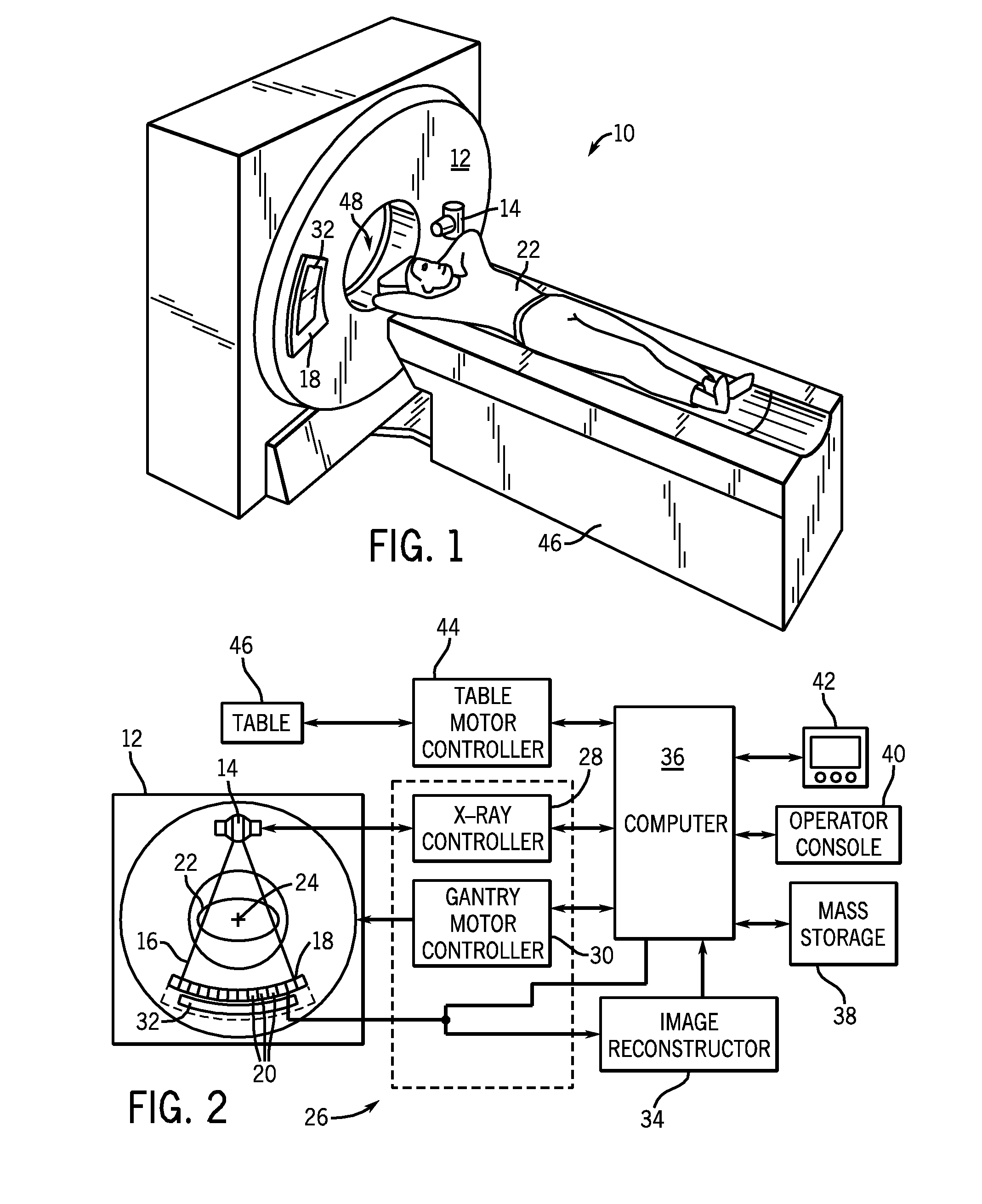
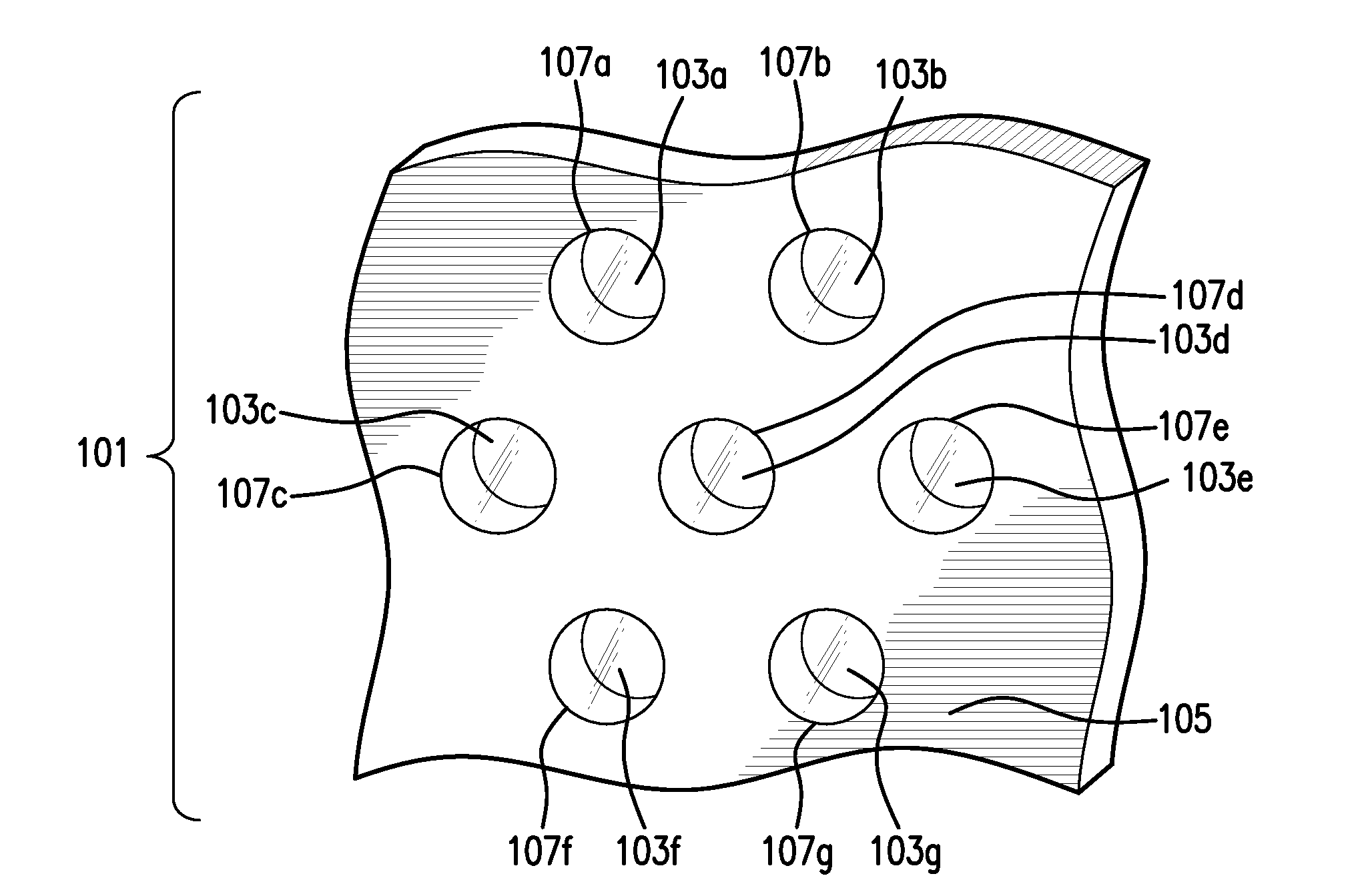
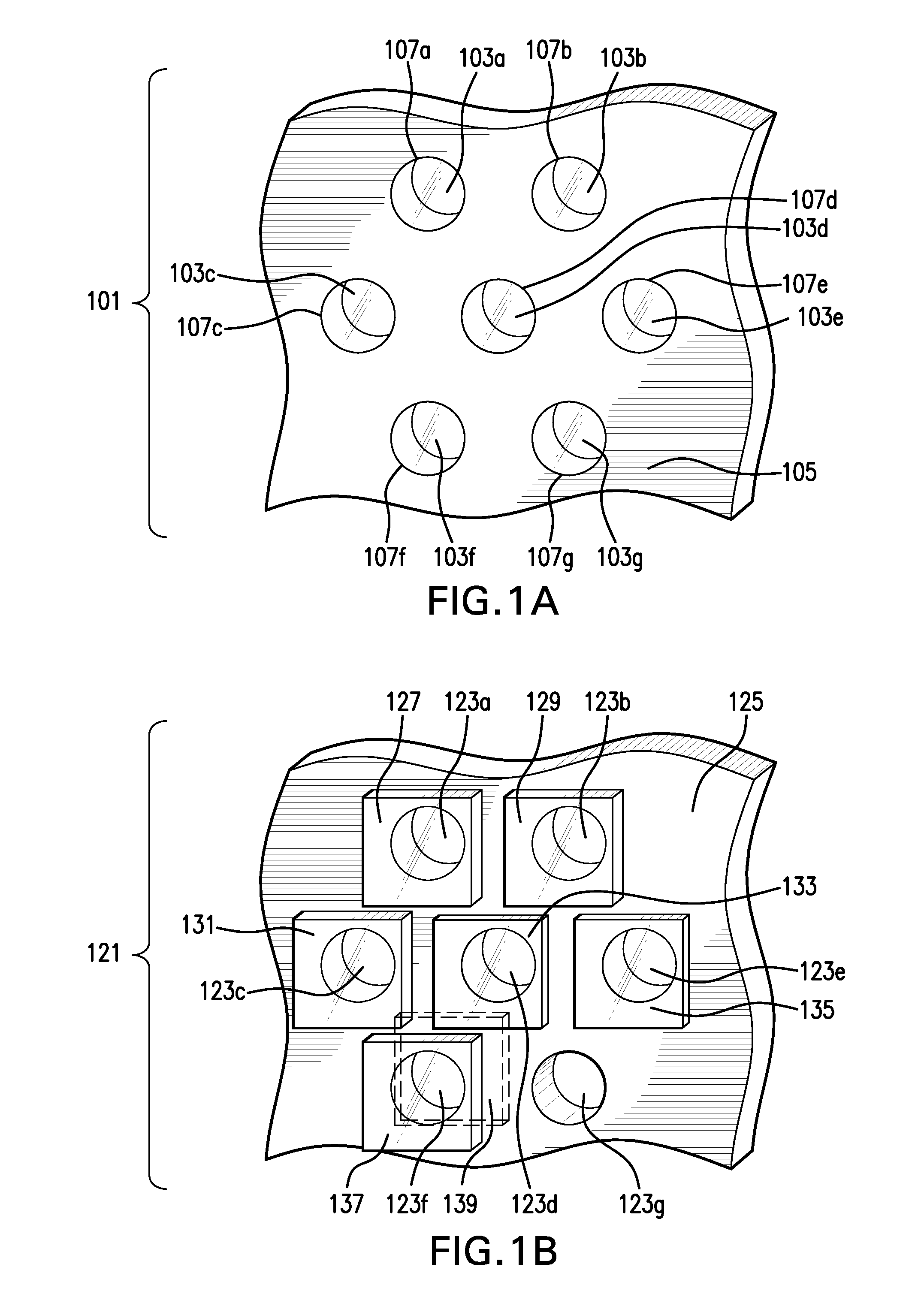
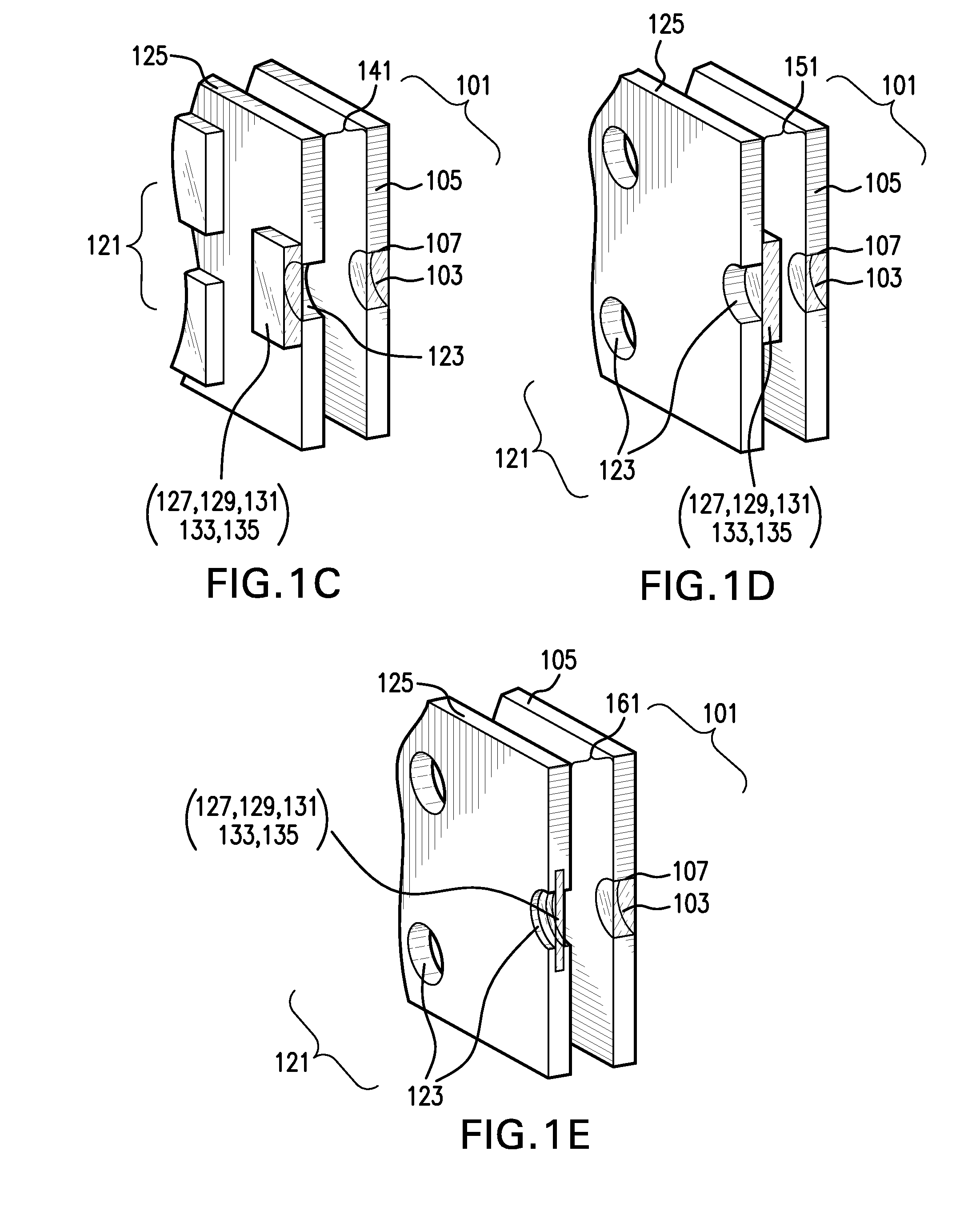
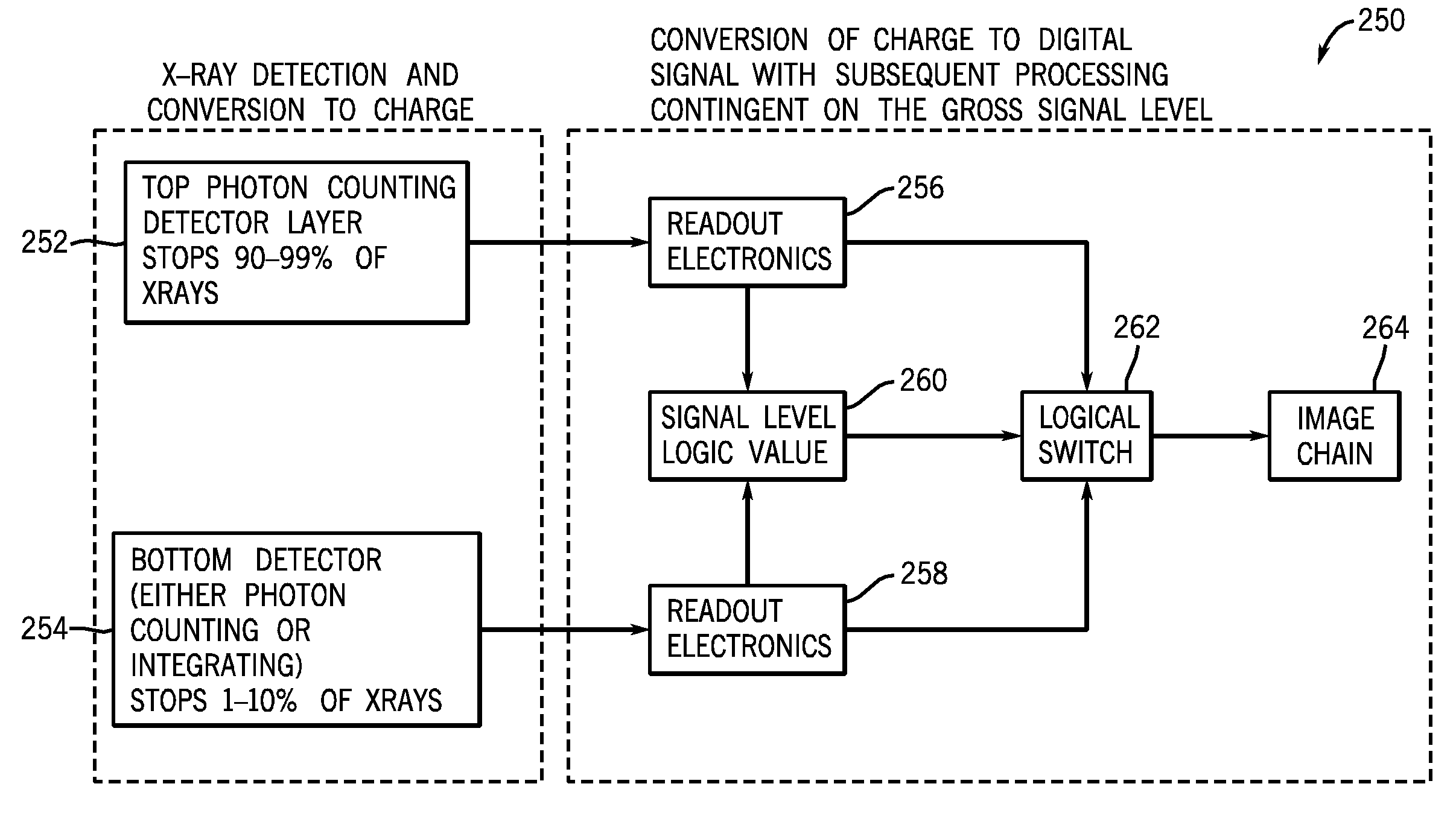
Photon counting x-ray detector with overrange logic control
ActiveUS20070206721A1Reduce the impactImprove visualizationMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationRadiation/particle handlingElectricityX-ray
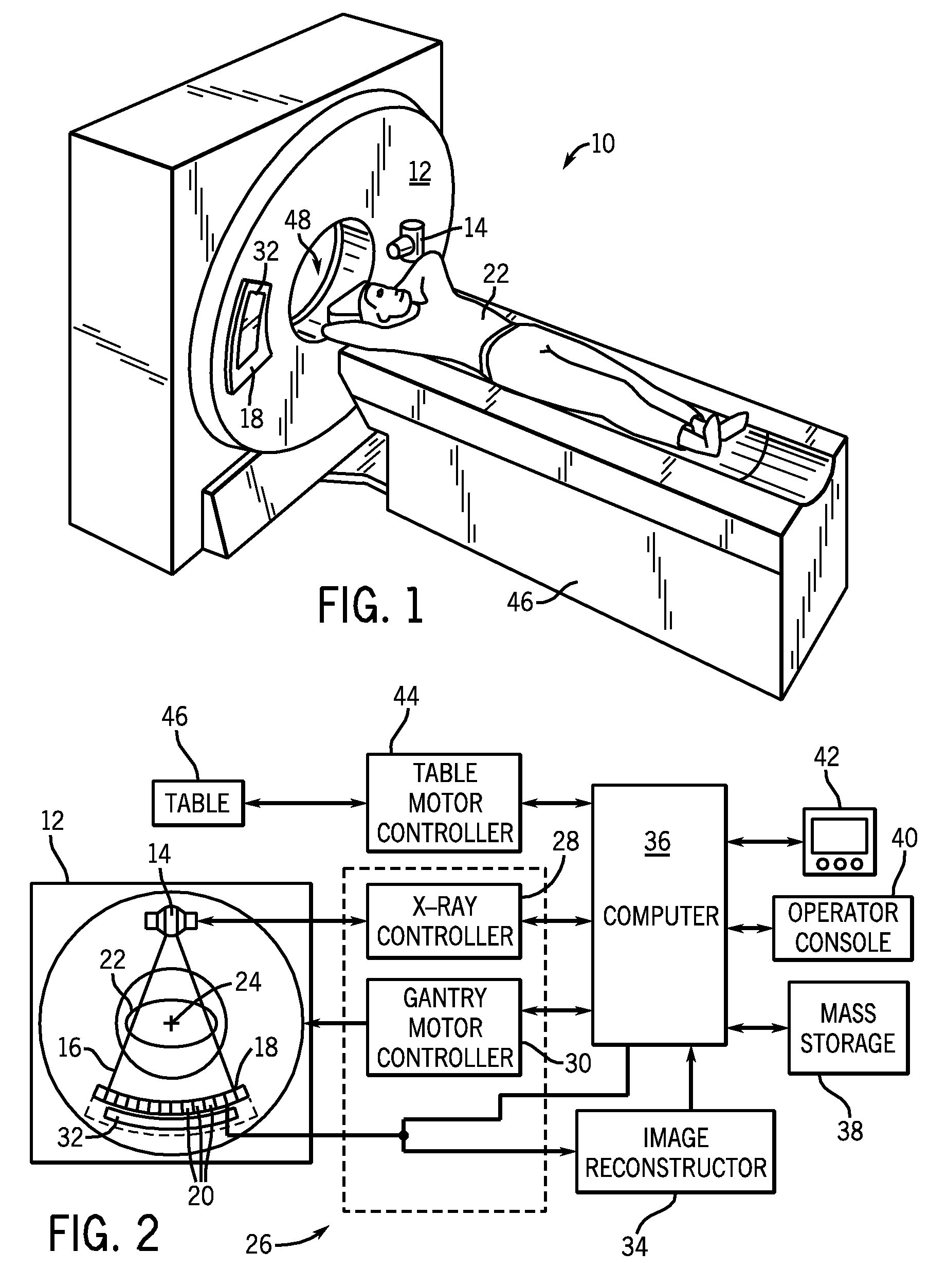
A CT detector includes a first detector configured to convert radiographic energy to electrical signals representative of energy sensitive radiographic data and a second detector configured to convert radiographic energy to electrical signals representative of energy sensitive radiographic data and positioned to receive x-rays that pass through the first detector. A logic controller is electrically connected to the first detector and the second detector and is configured to receive a logic output signal from the second detector indicative of an amount of a saturation level of the first detector, compare the logic output signal to a threshold value, and output, based on the comparison, electrical signals from the first detector, the second detector, or a combination thereof to an image chain.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
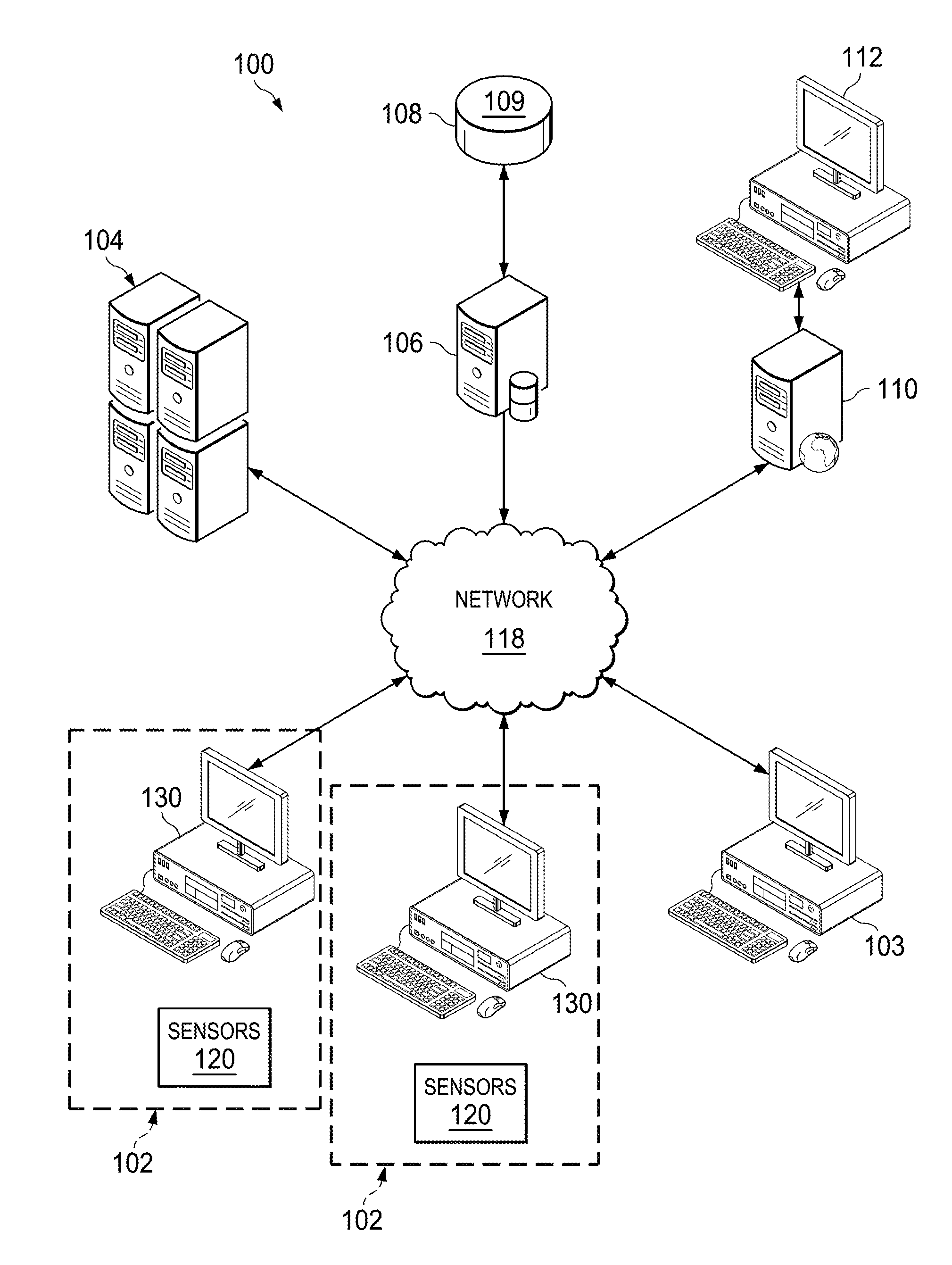
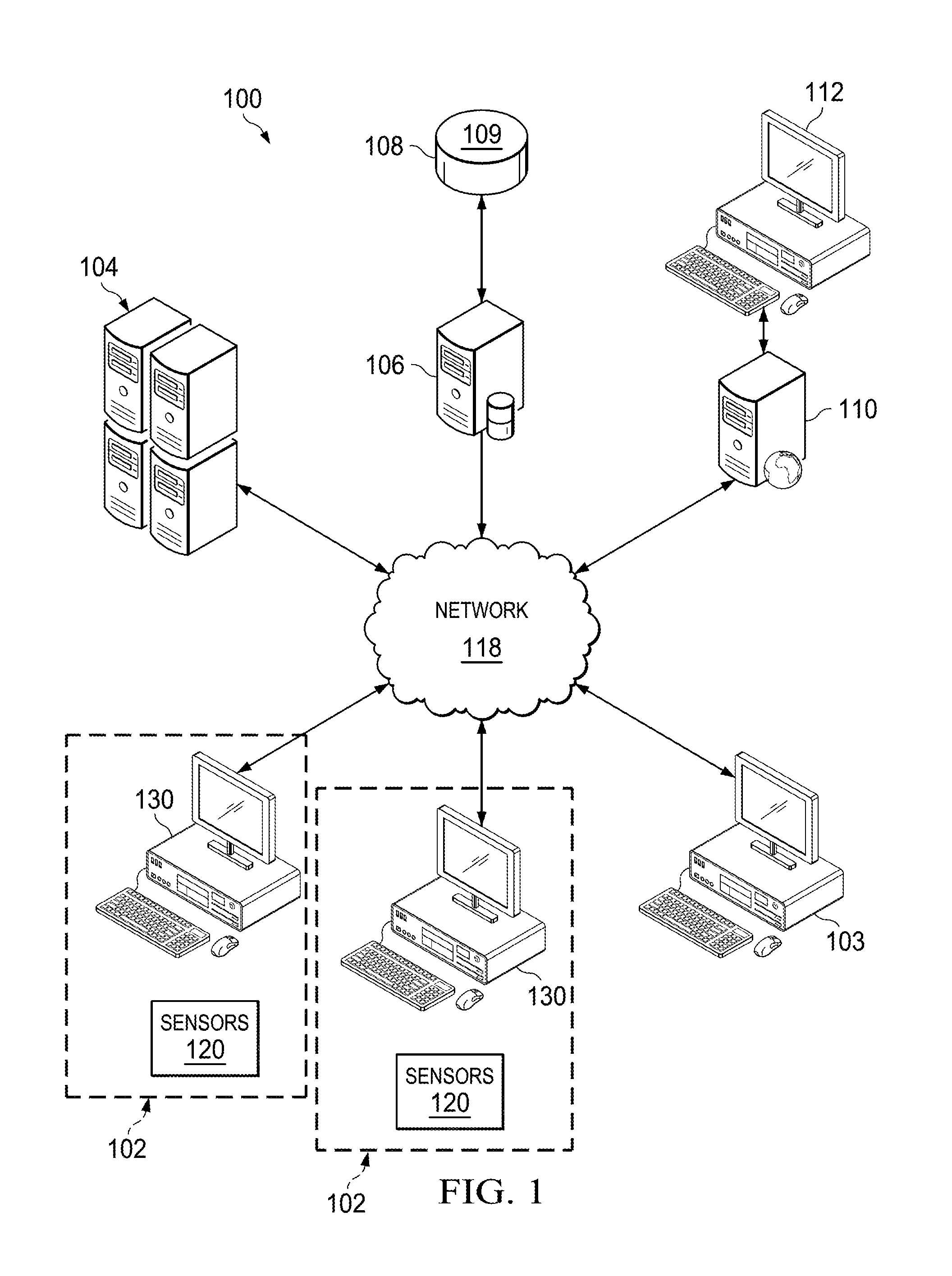
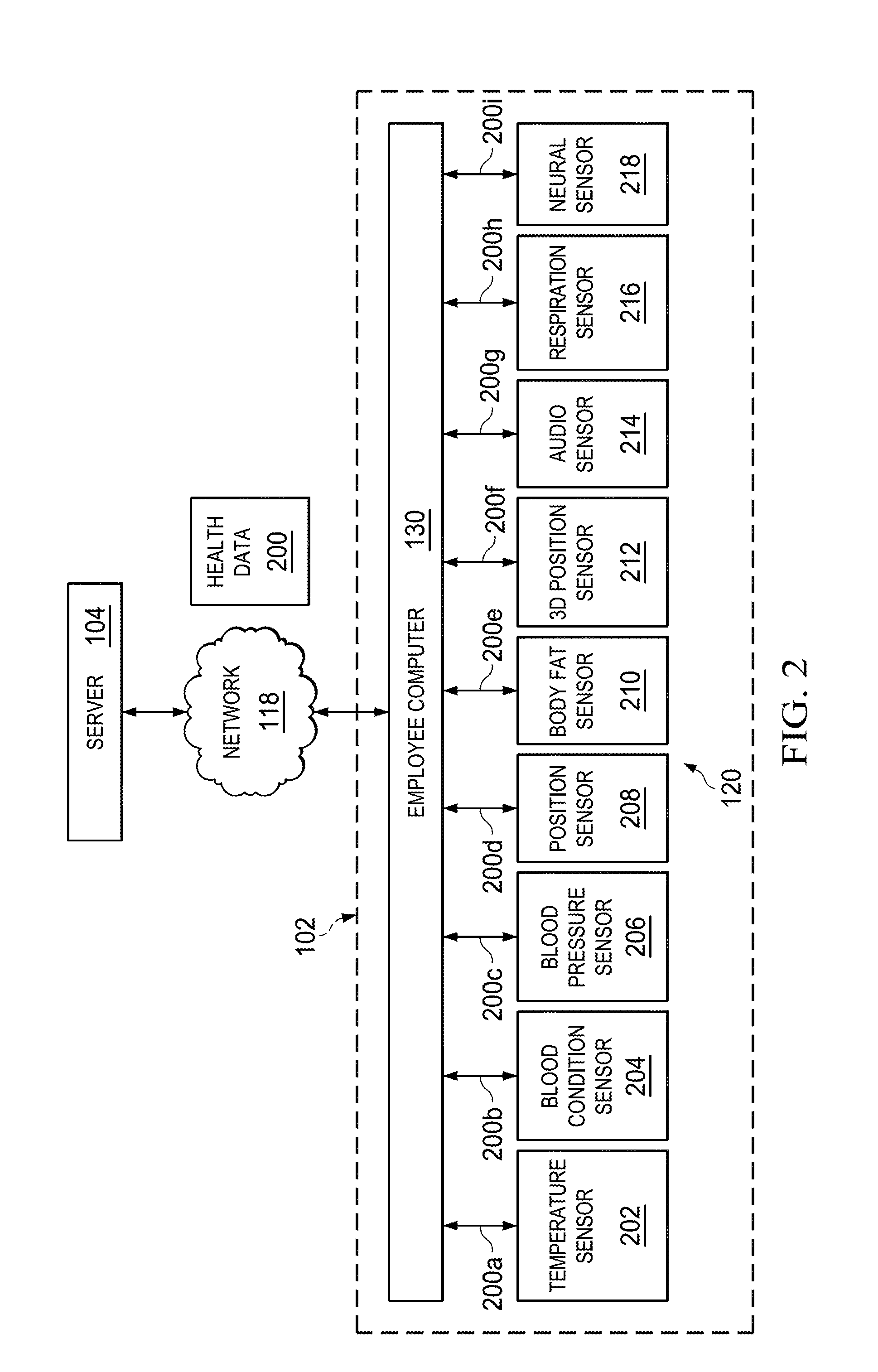
Computer Mouse System and Associated, Computer Medium and Computer-Implemented Methods for Monitoring and Improving Health and Productivity of Employees
ActiveUS20130013327A1Reduce effortQuick identificationElectroencephalographyData processing applicationsBlood pressureWorkstation
Provided are embodiments of systems, computer medium and computer-implemented methods for sensing health characteristics of a user using a computer mouse including, a temperature sensor, a blood condition sensor and a blood pressure sensor. A method for sensing health characteristics of a user using a computer mouse including receiving, from the temperature sensor, temperature data corresponding to a sensed body temperature of the user, receiving, from the blood condition sensor, blood condition data corresponding to a sensed blood saturation level of the user, receiving, from the blood pressure sensor, blood pressure data corresponding to a sensed blood pressure of the user, and transmitting, to the computer workstation, health data corresponding to the temperature data, the blood condition data, and the blood pressure data for use in determining the body temperature, the blood saturation level, and the blood pressure of the user.
Owner:SAUDI ARABIAN OIL CO
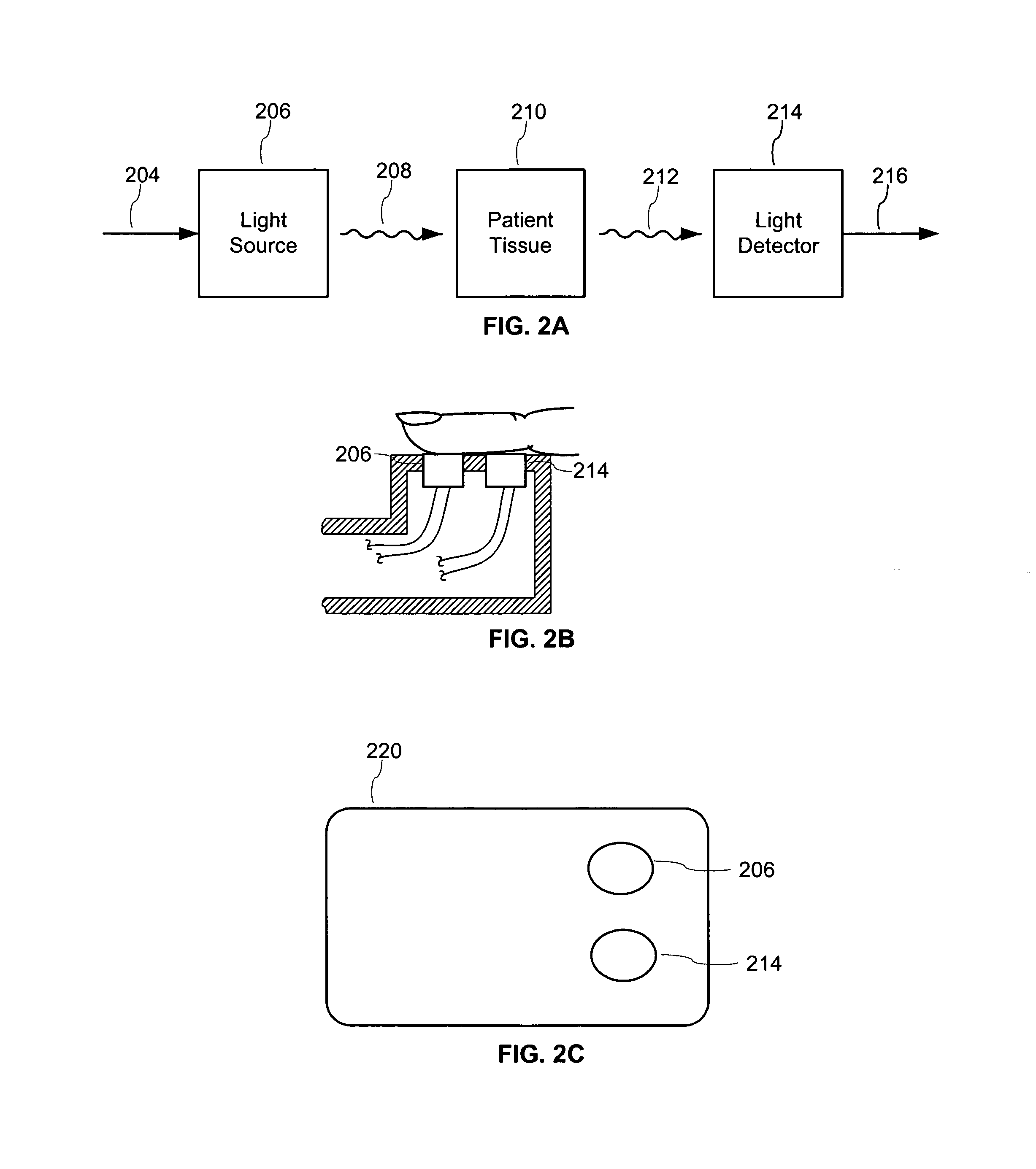
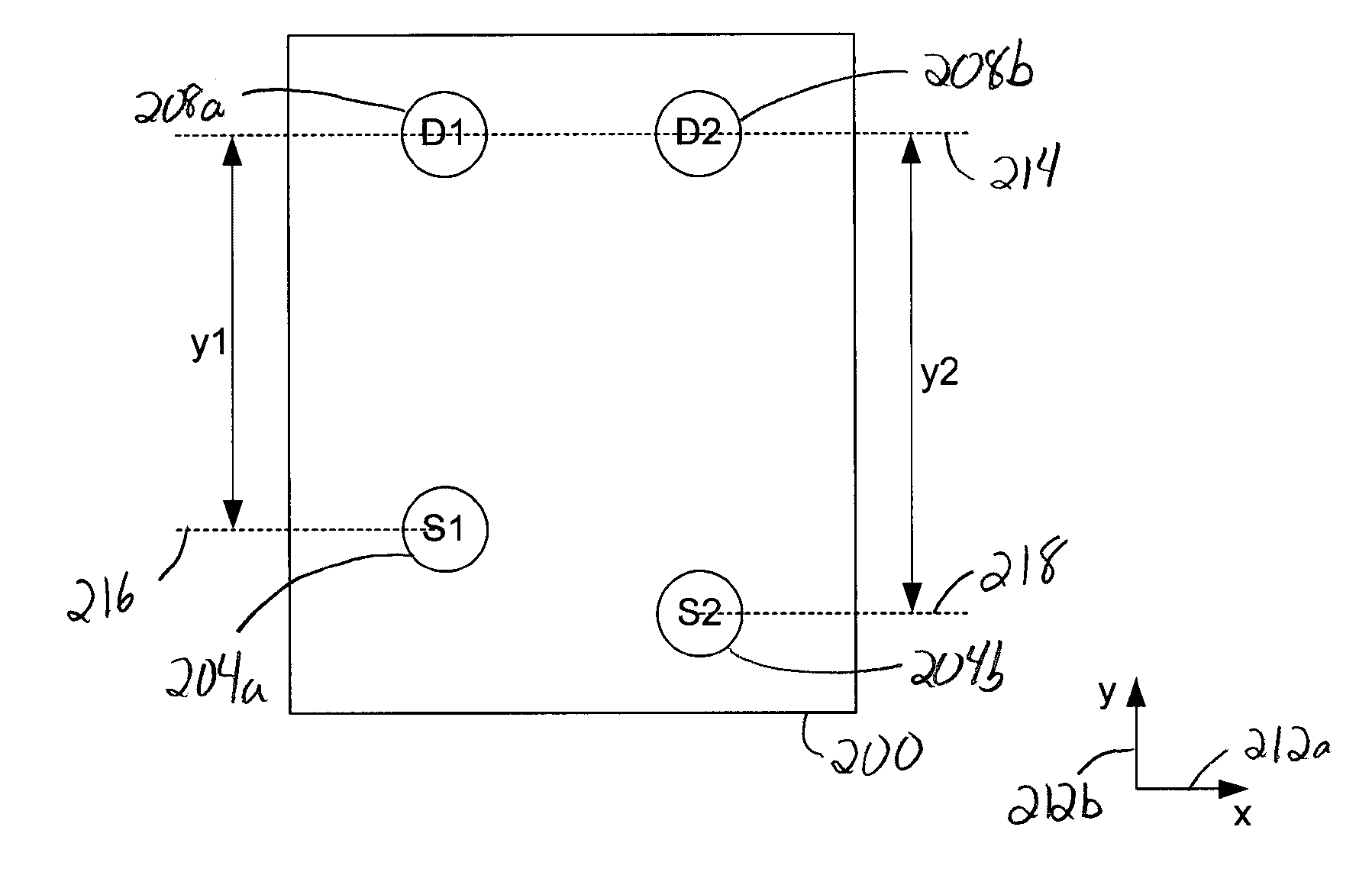
Optical probe for optical imaging system
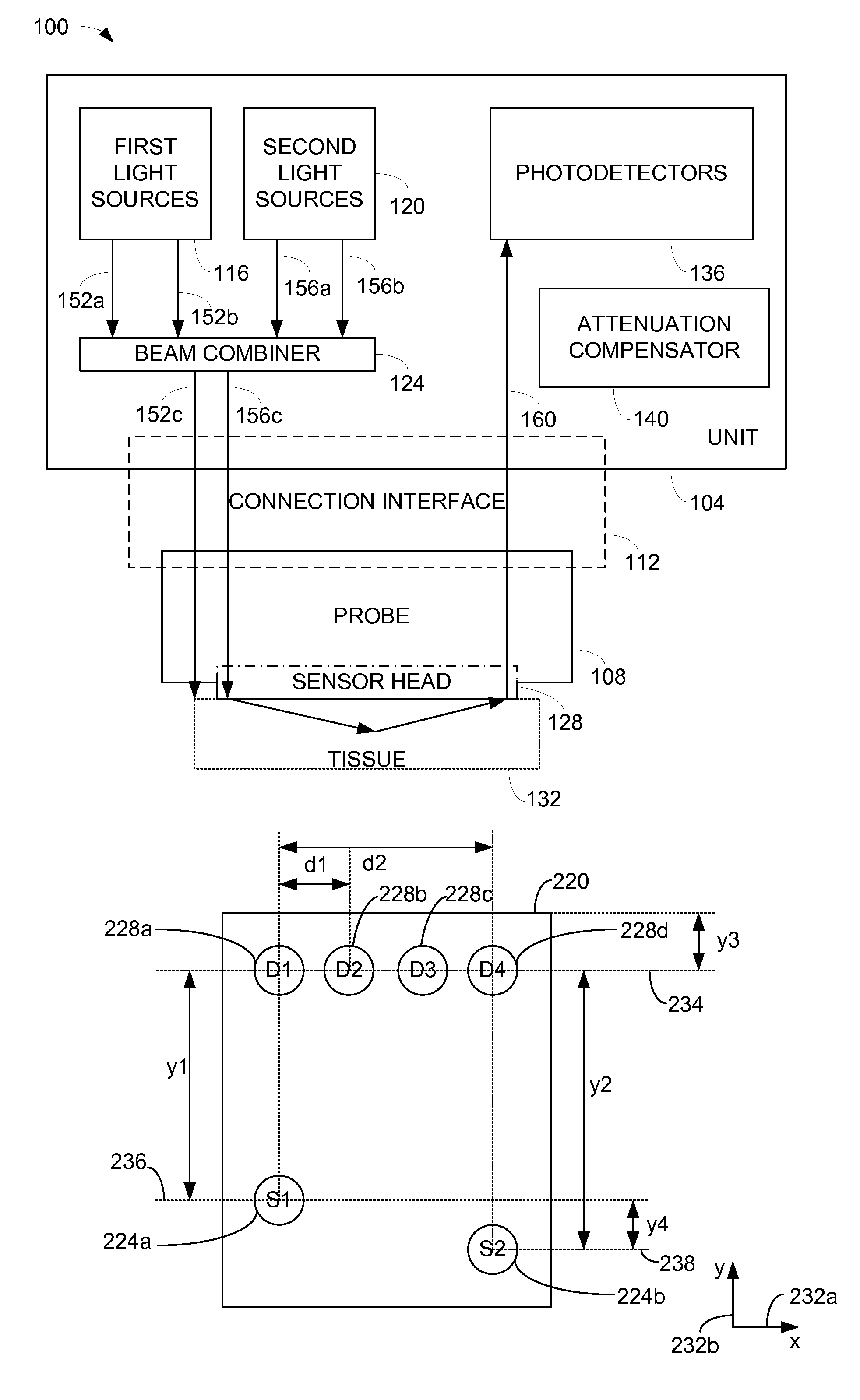
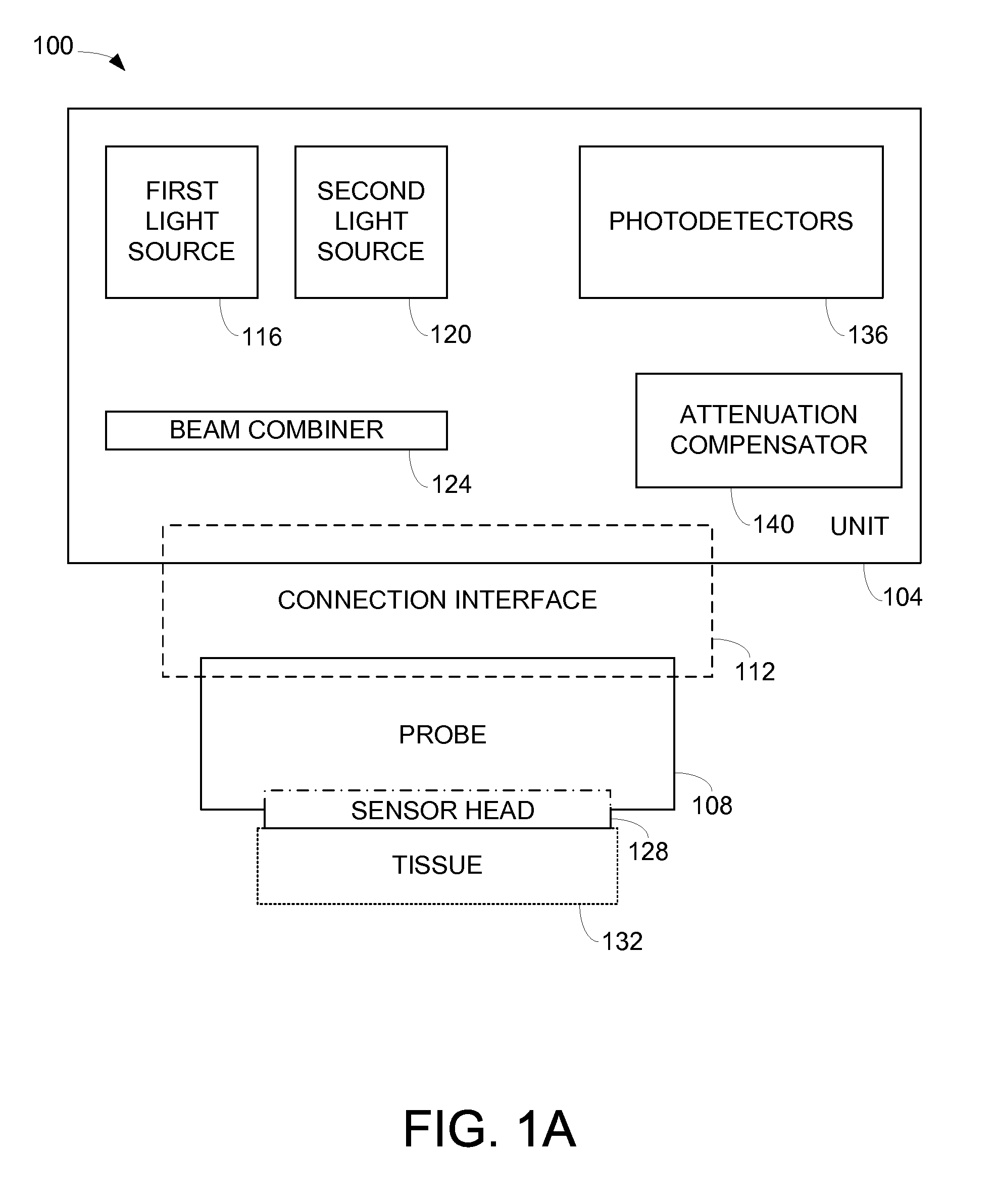
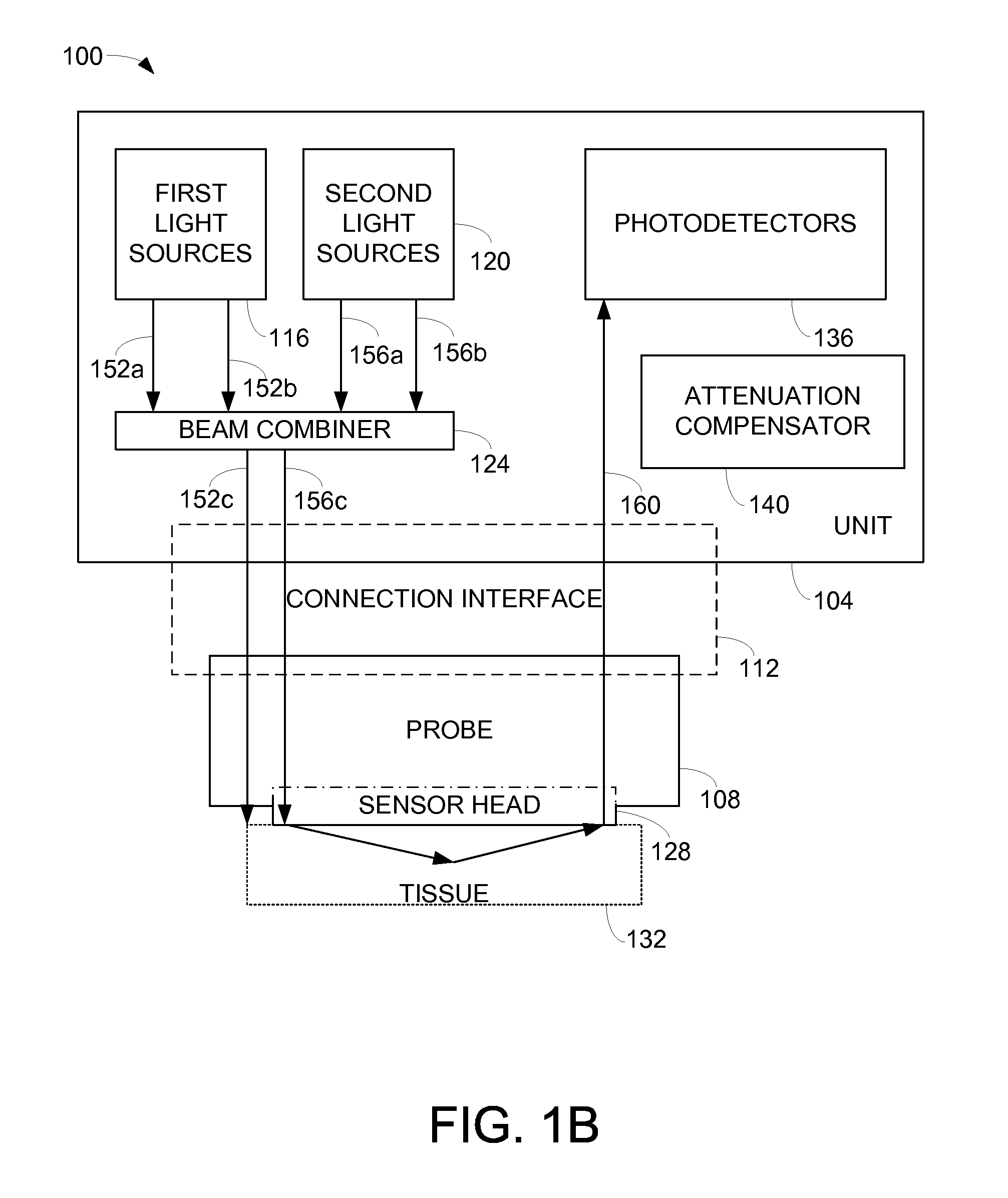
ActiveUS7355688B2Manufacturing toleranceScattering properties measurementsDiagnostic recording/measuringLight beamOxygen saturation
Methods and apparatus for monitoring oxygen saturation levels in tissue are disclosed. According to one aspect of the present invention, a sensor arrangement for use in an optical imaging system includes a first source structure, a second source structure, and a detector arrangement. The first source structure provides a first beam of light and the second source structure provides a second beam of light. The detector arrangement includes detector structures that have centerpoints, and receives the first and second beams of light after the first and second beams of light are reflected off of an external surface. The detector arrangement is arranged to define a first axis that passes through the centerpoint of each detector structure, and a distance from a centerpoint of the first source structure to the first axis is not equal to a distance from a centerpoint of the second source structure to the first axis.
Owner:VIOPTIX
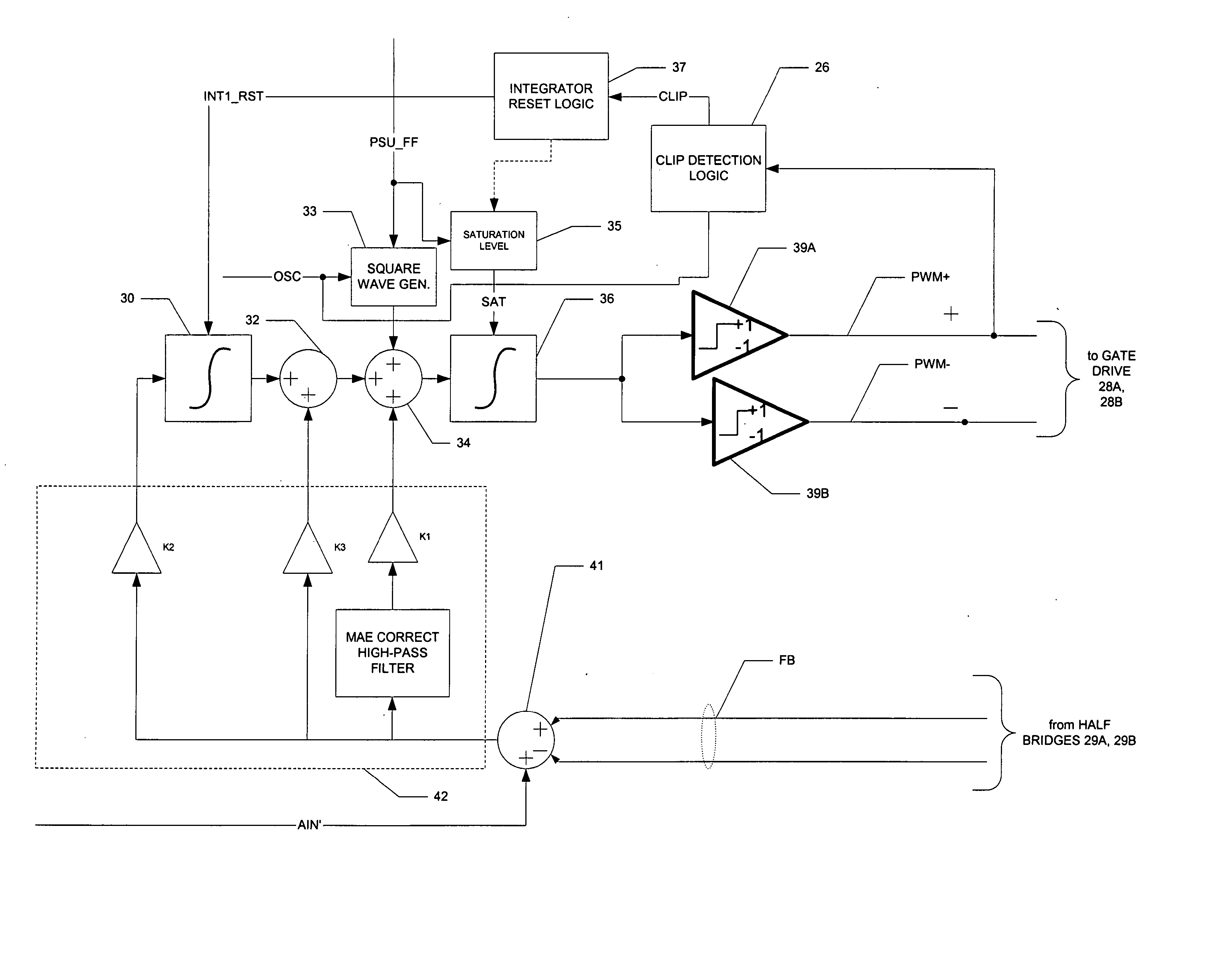
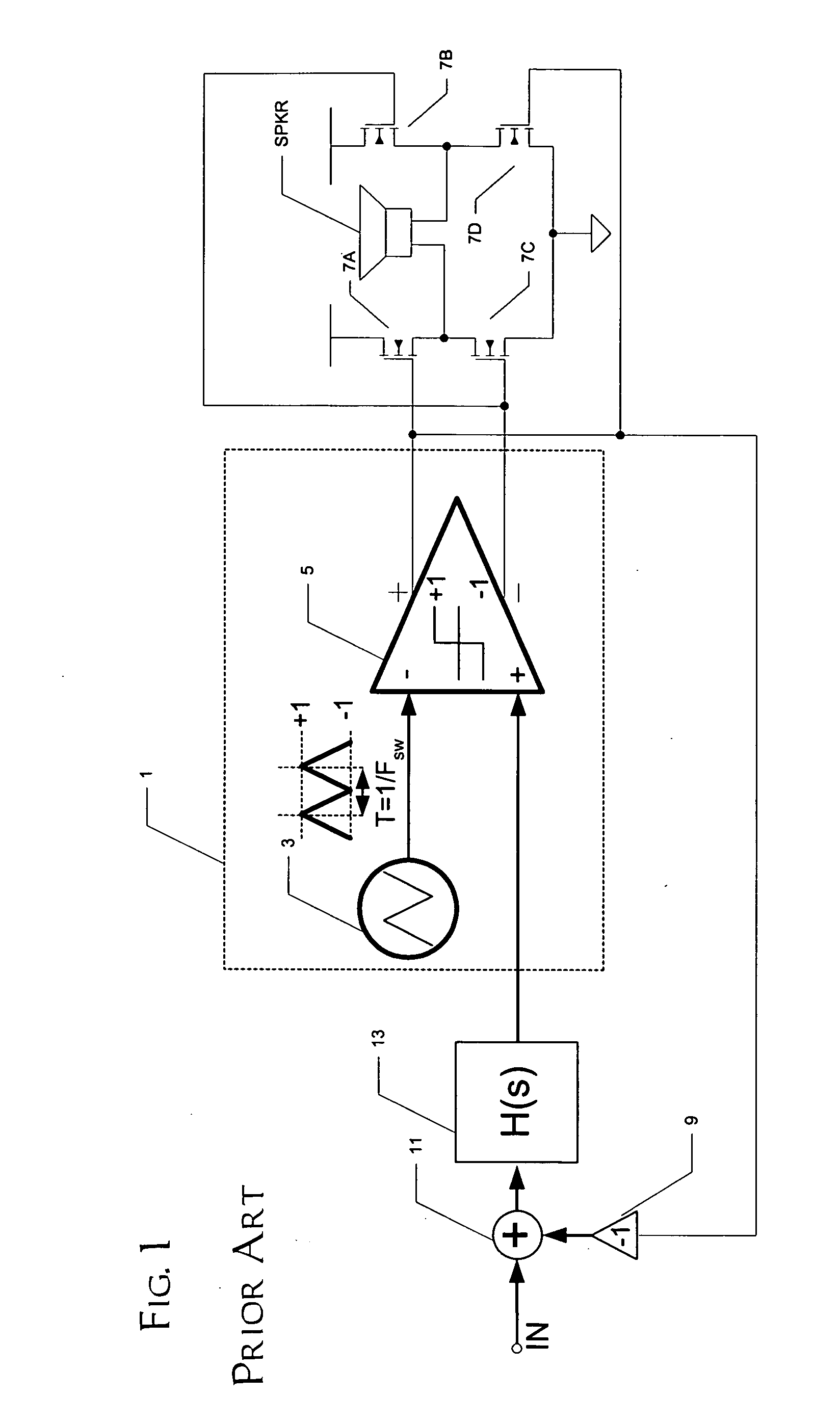
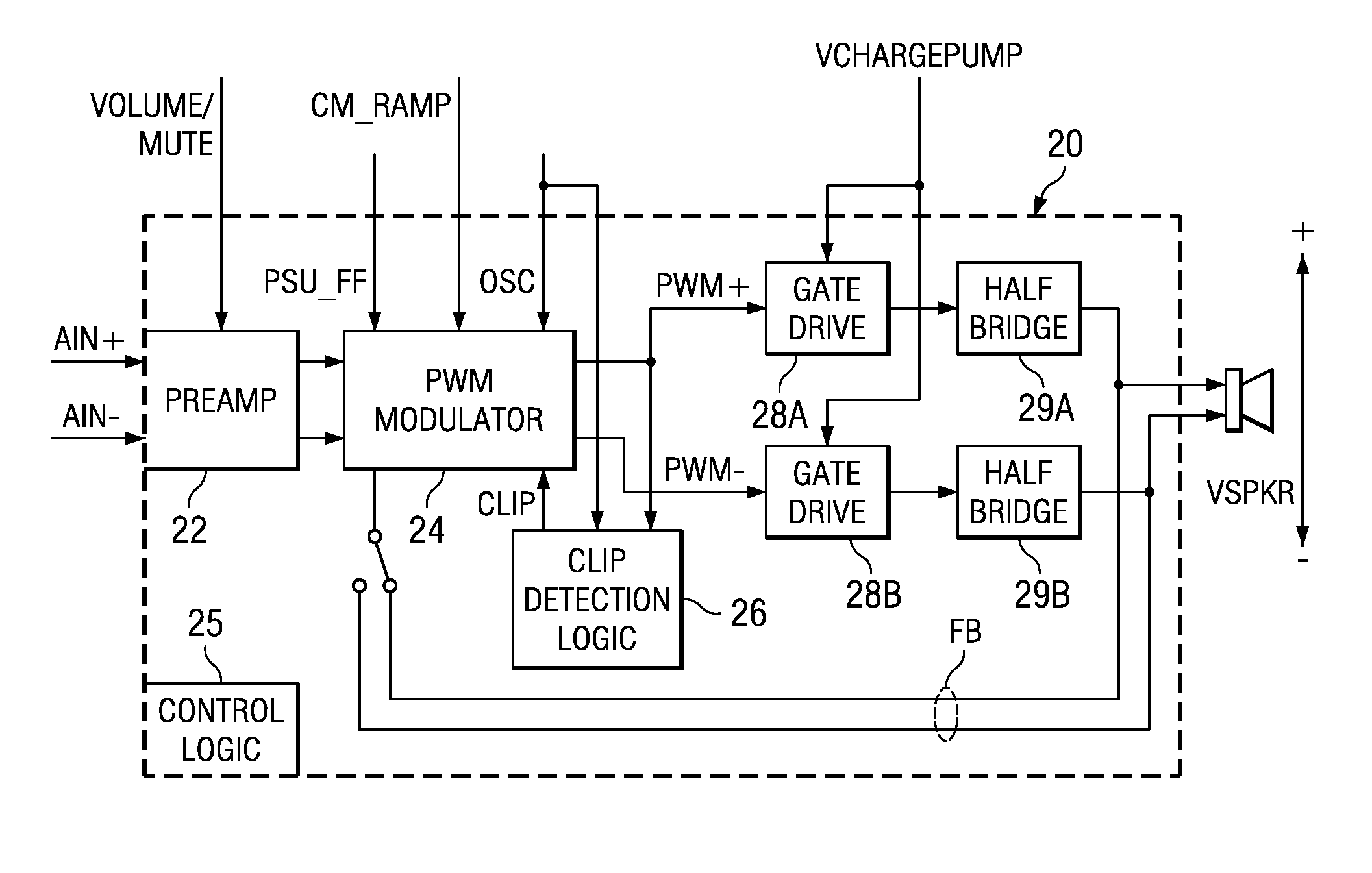
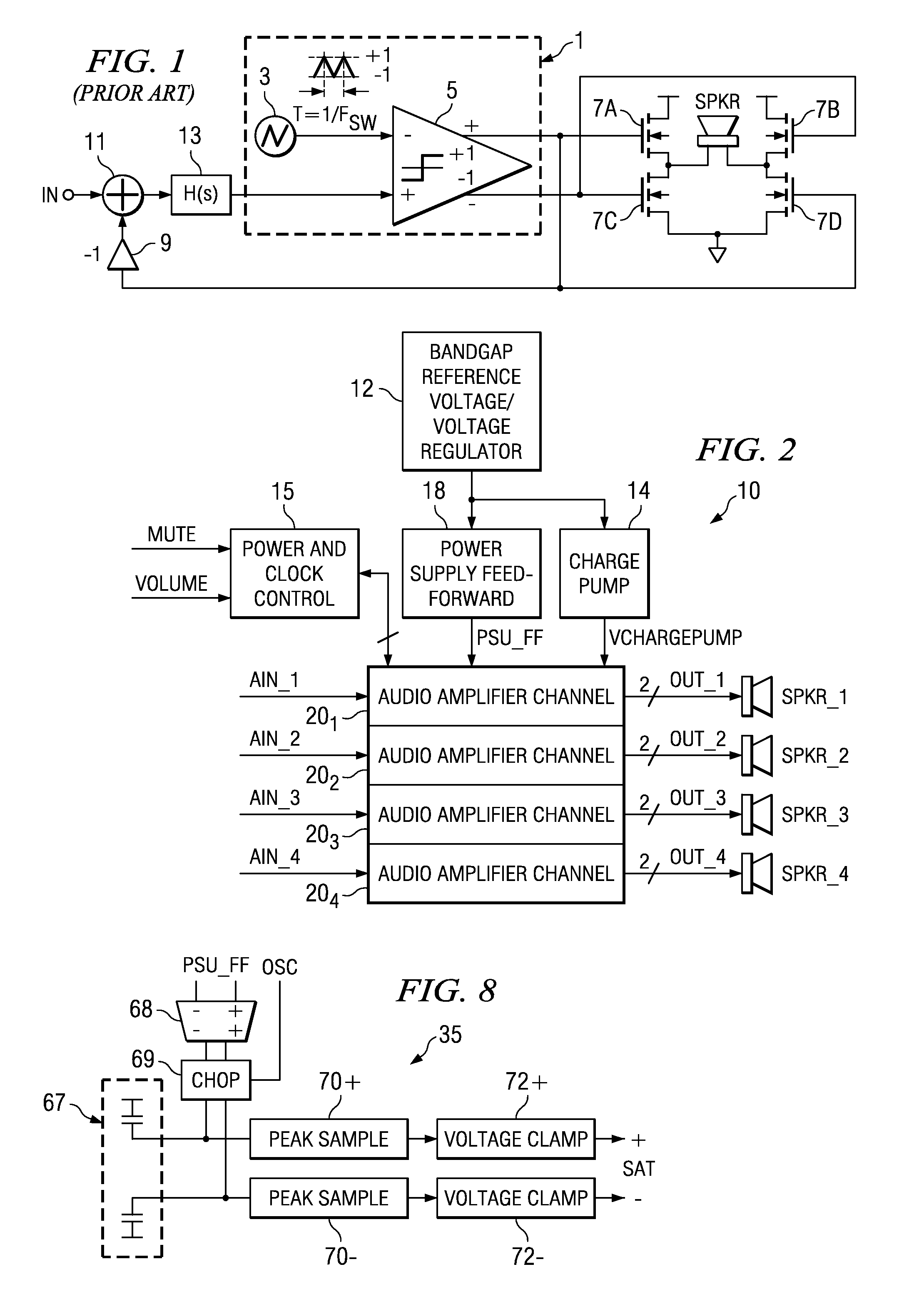
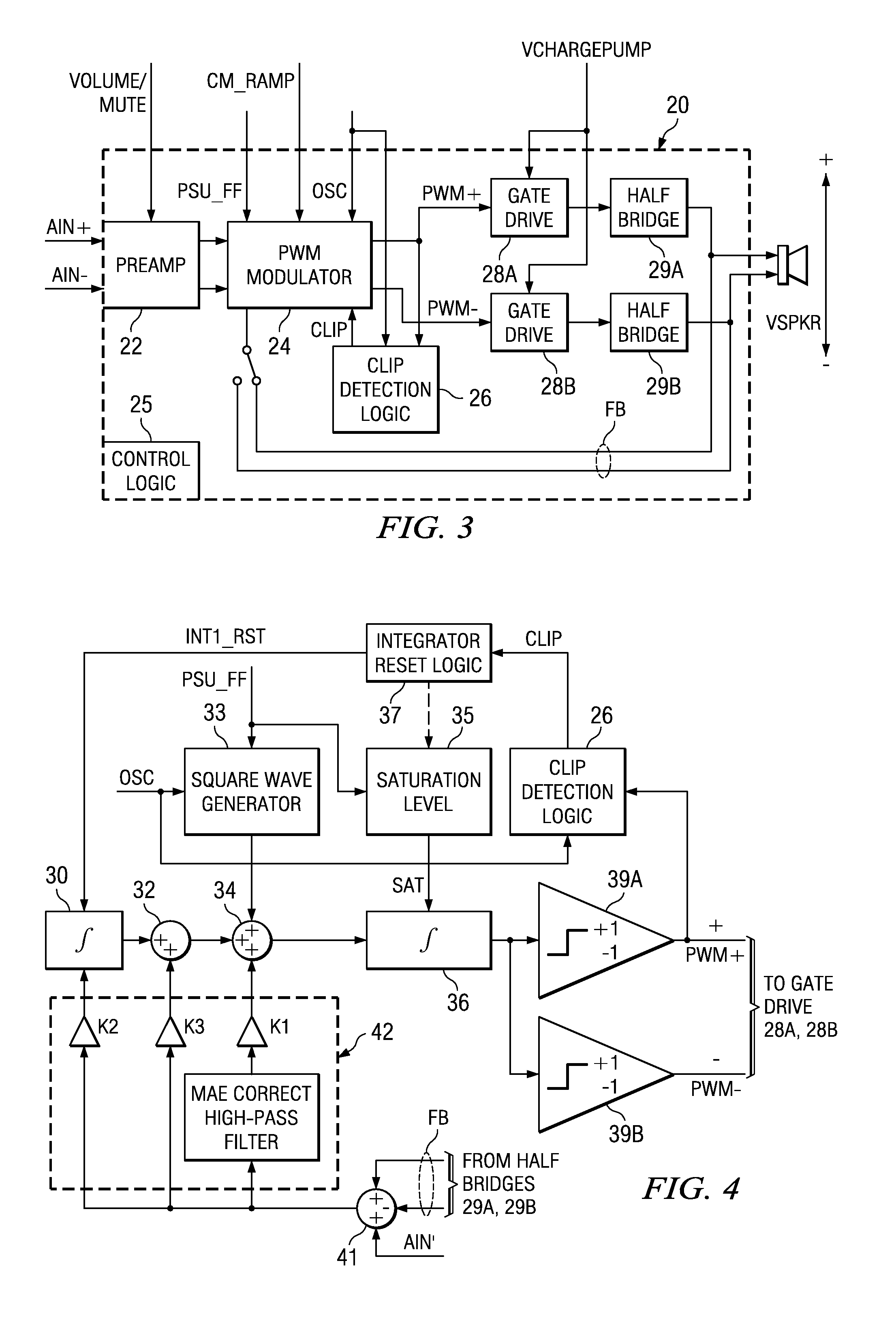
Recovery from clipping events in a class D amplifier
ActiveUS20050083114A1Shorten recovery timeAmplifier combinationsDc amplifiers with modulator-demodulatorLoop filterIntegrator
A class AD audio amplifier system (10) with improved recovery from clipping events is disclosed. The amplifier system (10) includes multiple audio channels (20), each of which can be constructed to include a pulse-width-modulator (PWM) (24). The PWM modulator (24) includes a pair of comparators (39A, 39B; 52+, 52−) that generate complementary PWM output signals based upon the comparison between a filtered difference signal and a reference waveform. Clip detection logic (26) is provided to detect clipping at the output of the channel (20), preferably by detecting successive edges of the reference waveform without an intervening edge of a PWM output signal. In response to detecting clipping, a first integrator (30; 45) is reset to remove residuals and to eliminate the first integrator (30; 45) from the loop filter of the modulator (24). A saturation level circuit (35) applies a clamping voltage, preferably in both clipping and non-clipping situations, to a second integrator (36; 47). As a result, the loop filter is prevented from entering extreme conditions during clipping, which greatly reduces the clipping recovery time.
Owner:TEXAS INSTR INC
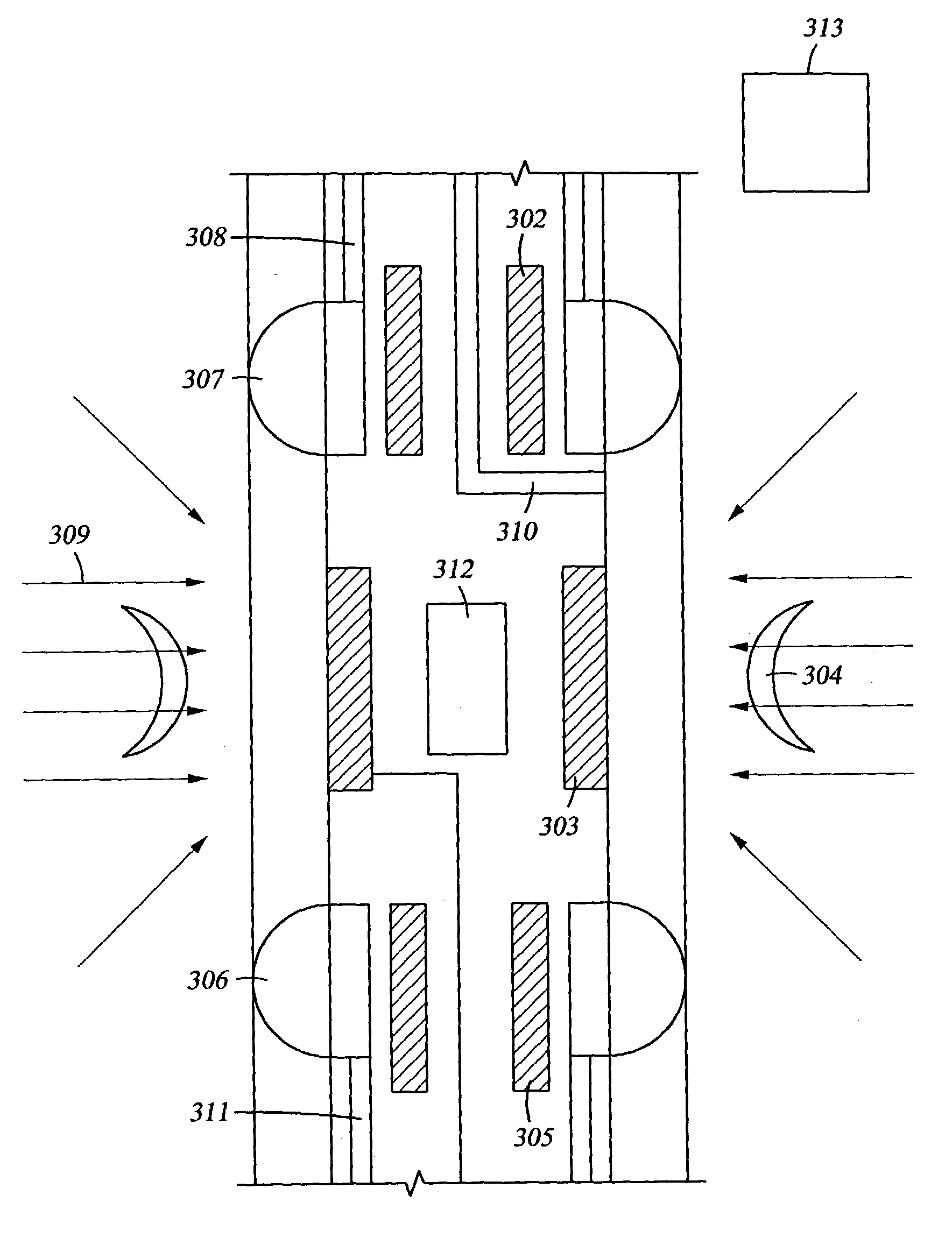
Optical sensor device and image processing unit for measuring chemical concentrations, chemical saturations and biophysical parameters
ActiveUS20090299154A1New riskReduce in quantityImage enhancementImage analysisNutritional deficiencyAntioxidant
Optical sensor devices, image processing devices, methods and computer readable code computer-readable storage media for detecting biophysical parameters, chemical concentrations, chemical saturations, vital signs and physiological information such as a malignant condition are provided. In some embodiments, the optical sensor includes an array of photodetectors, where each photodetector is configured to detect a spectrum of light. In some embodiments, the image processing device receives a live still or video electronic image, or alternatively, the electronic image is provided from an electronic storage media. Exemplary physiological parameters include but are not limited to a pulse rate, a biophysical or physiological property of skin, a cardiovascular property, a property related to an organ such as the liver or the kidneys, and a temperature fluctuation. In some embodiments, the physiological parameter is indicative of a malady including but not limited to an autoimmune disease, a cancer, a nutritional deficiency, a malignant condition of bone marrow, a present of an infectious microbe such as a fungus, a present of hepatitis, and a cardiovascular disorder a pulmonary disorder. Exemplary chemical concentrations include but are not limited to a chemical saturation, a pH level, a pH level in blood vessels such as capillarys or in skin, a glucose level such as a blood glucose level, a urea nitrogen level such as a blood urea nitrogen level, a CO2 level such as a blood CO2 level or a CO2 saturation level, and an oxygen level such as a blood oxygen level or a blood oxygen saturation level. In some embodiments, the biophysical parameter, physiological parameter or chemical concentration is obtained from reflecting light from tissue from a mammalian subject. Alternatively one or more of these parameters are detected from a food item such as food tissue, a consumable beverage such as an alcoholic beverage, a dairy product, wine, a baked good, a fruit and a vegetable. Exemplary parameters related to food items include but are not limited to a parameter indicative of cooking or spoilage, a pH, a concentration of an antioxidant, and a concentration of an anti-inflammatory agent.
Owner:CNOGA HLDG LTD
Image sensor with extended dynamic range
InactiveUS20080211945A1Improve dynamic rangeEfficient captureTelevision system detailsTelevision system scanning detailsComputer scienceImage signal
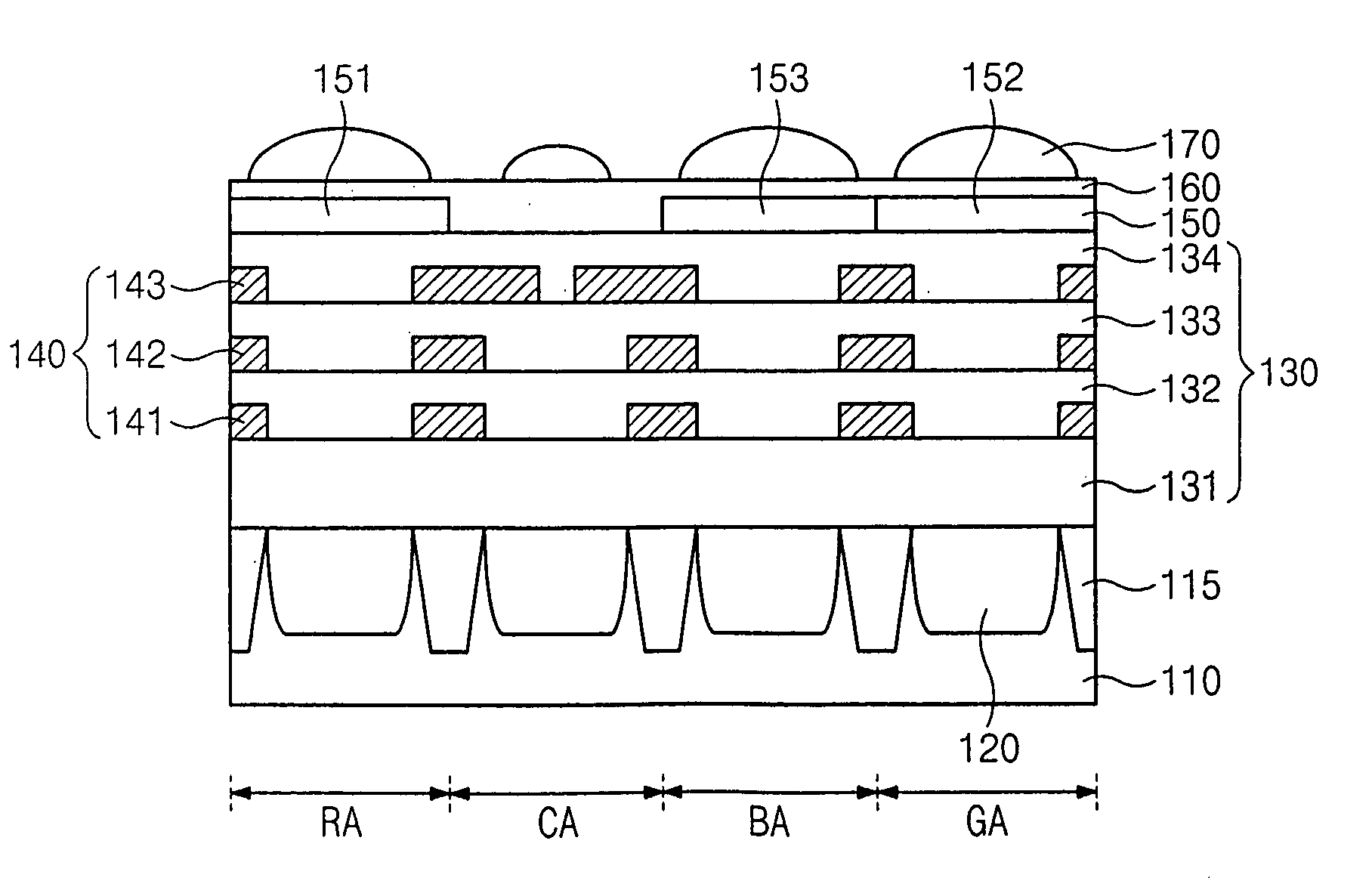
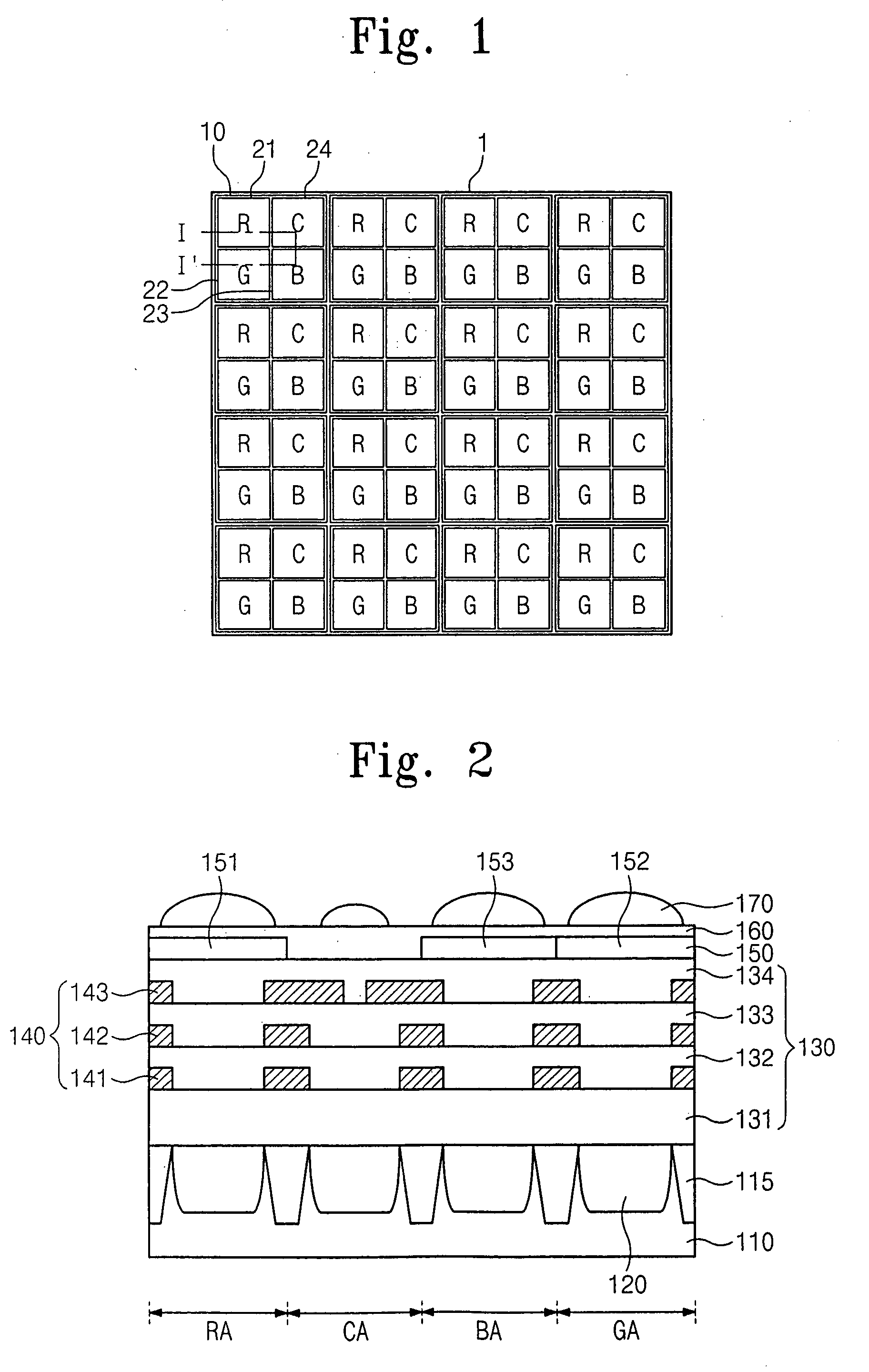
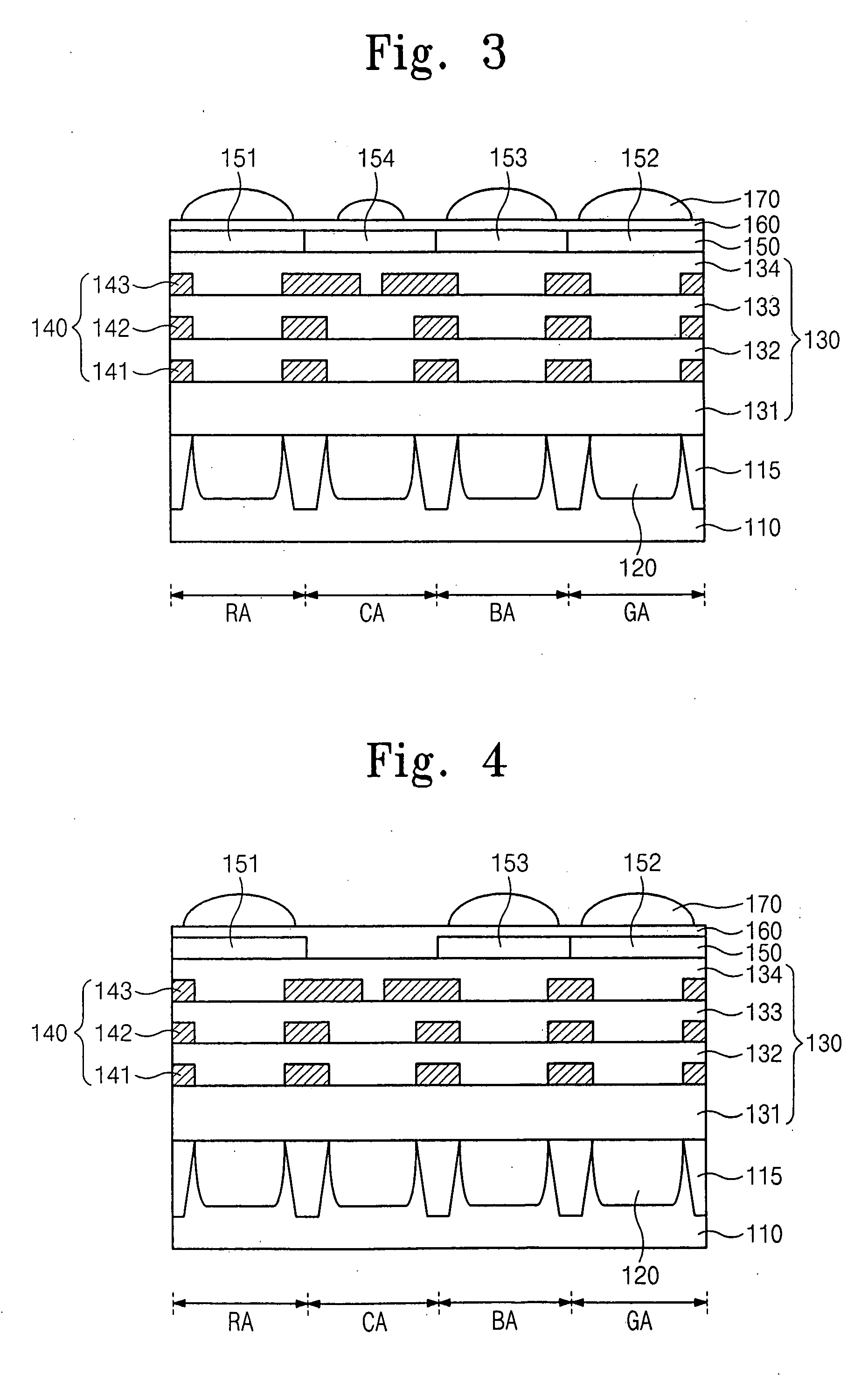
An image sensor includes a first sub-pixel, a second sub-pixel, and an image processor. The first sub-pixel generates a first image signal with a first sensitivity, and the second sub-pixel generates a second image signal with a second sensitivity less than the first sensitivity. The image signal processor adds a change in the second image signal from a saturation level to the first image signal to generate a final image signal when the first sub-pixel is saturated.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
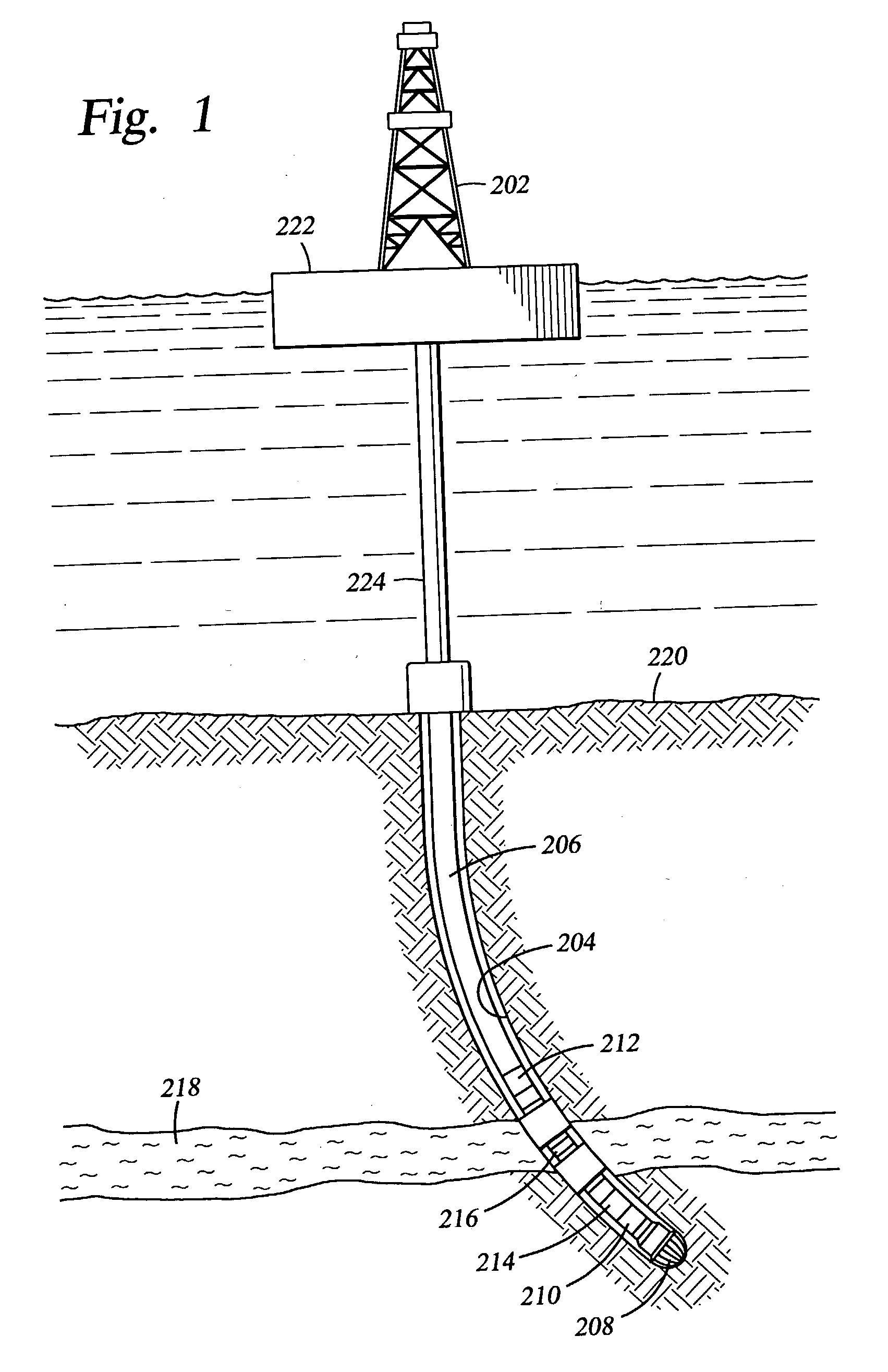
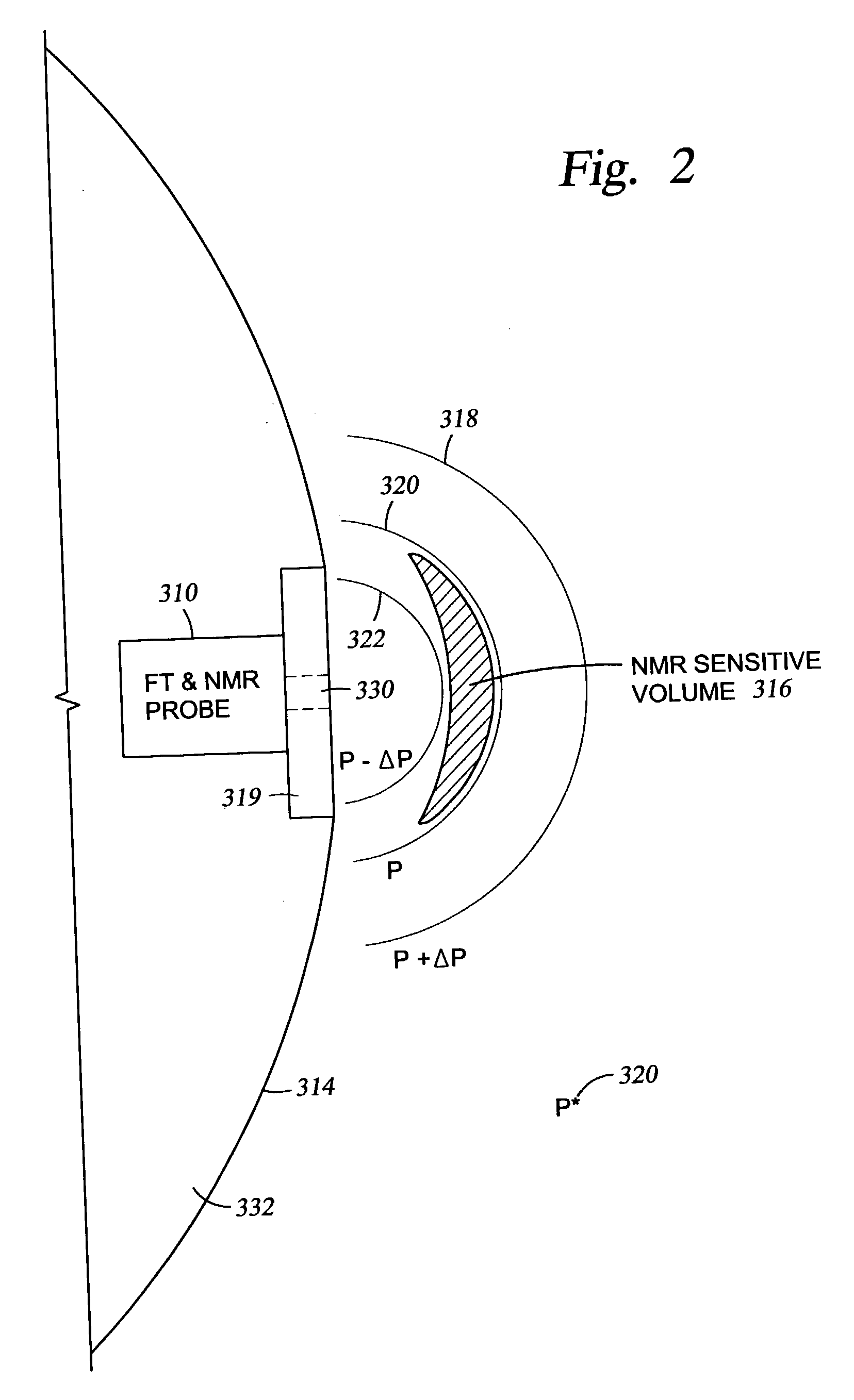
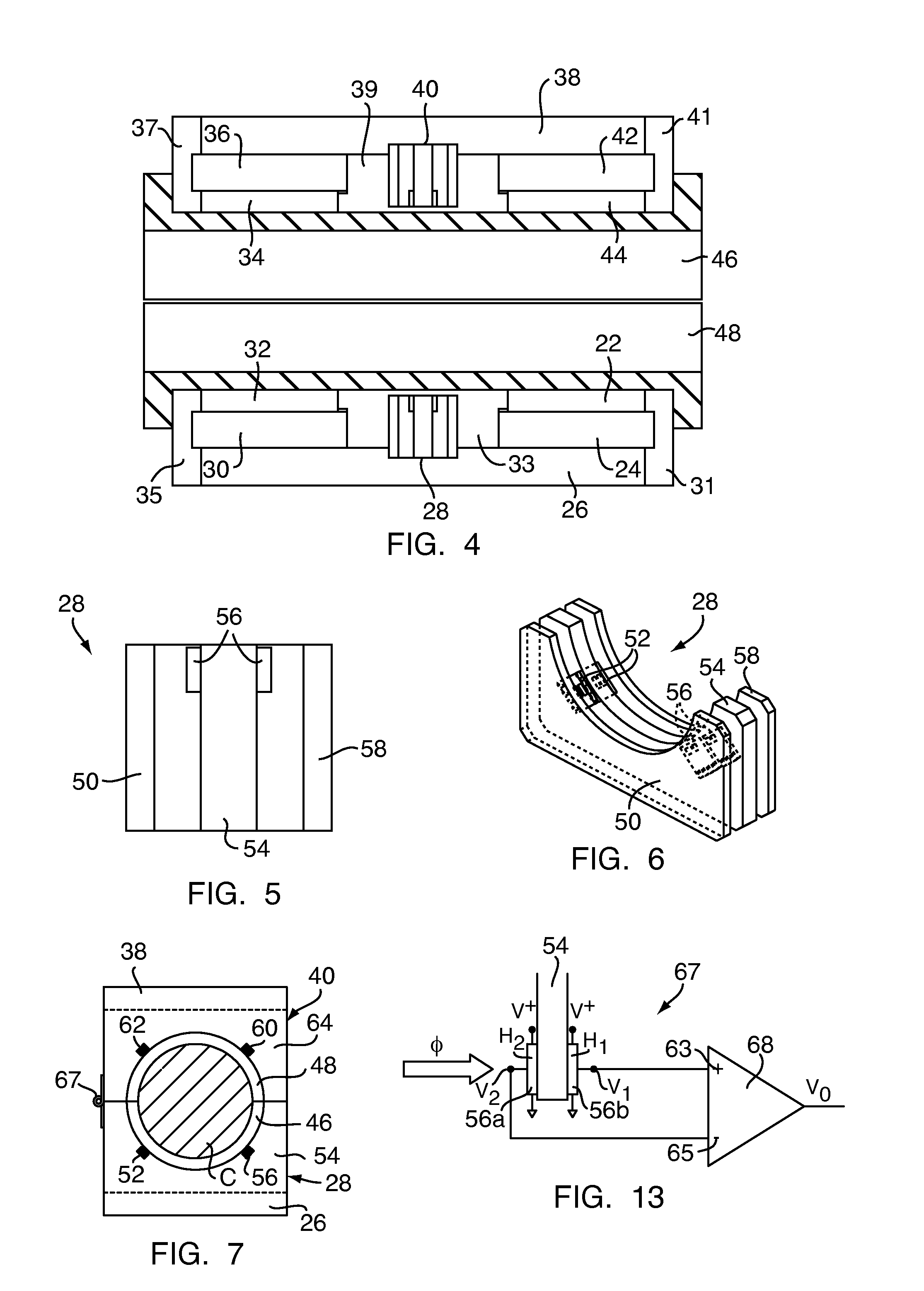
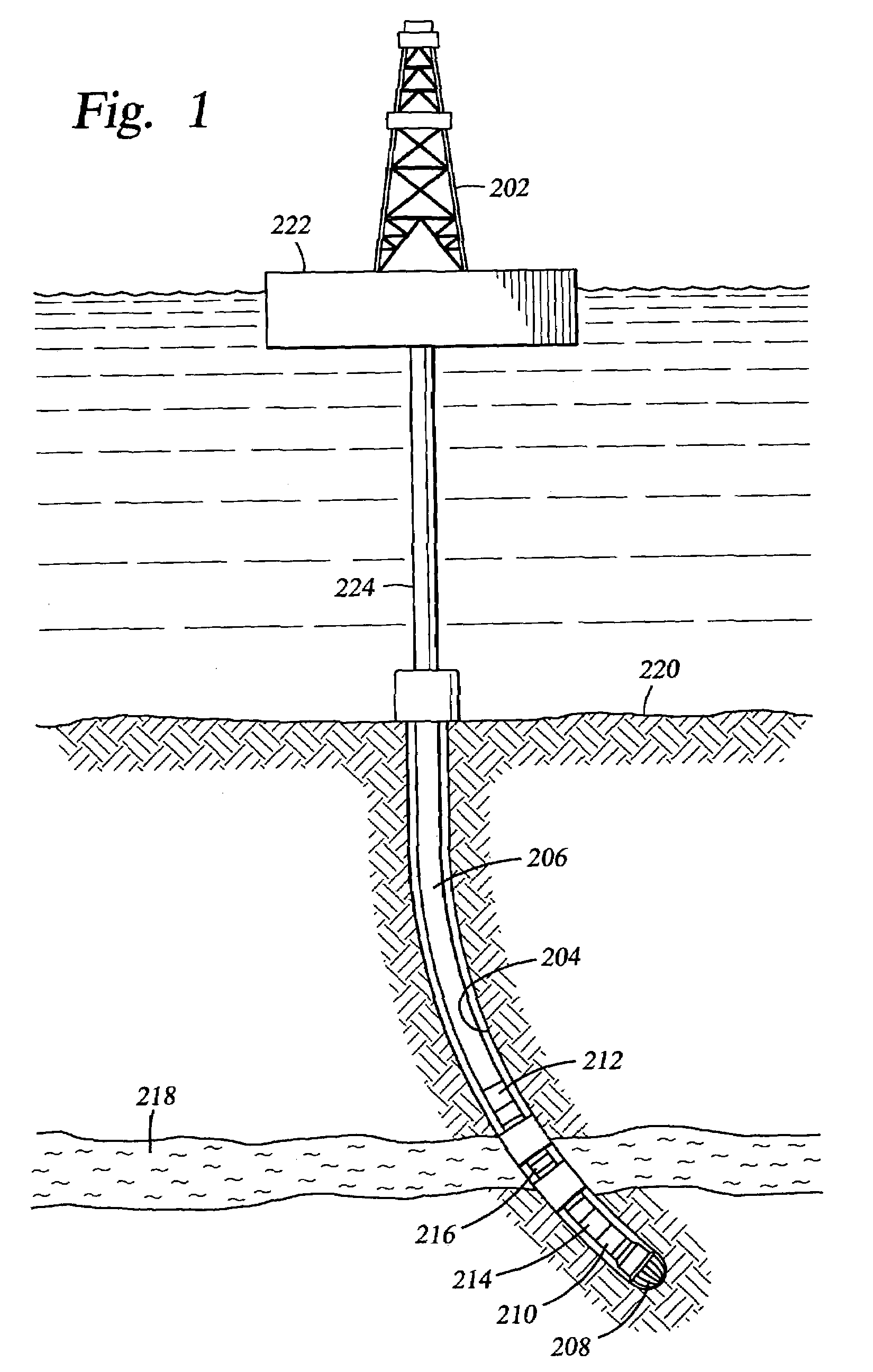
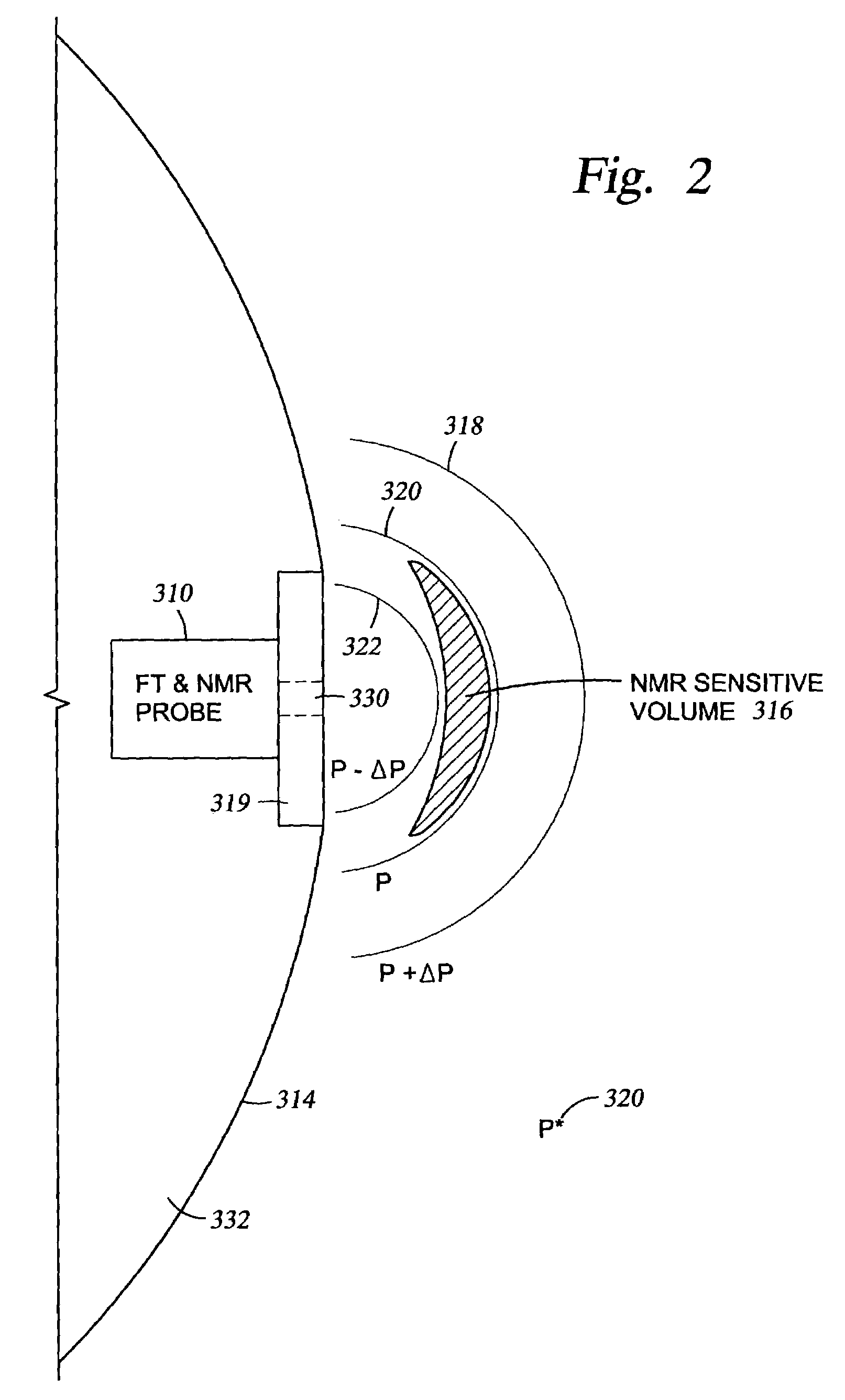
Method and apparatus for combined NMR and formation testing for assessing relative permeability with formation testing and nuclear magnetic resonance testing
InactiveUS20040055745A1Electric/magnetic detection for well-loggingSurveyProduction rateNMR - Nuclear magnetic resonance
Formation testing, resistivity and NMR measurements are used concurrently to determine a relative permeability representative of a formation surrounding the borehole. A method and apparatus is provided for accurate determination of the relative permeability for a formation by measuring saturation levels in a region of interest determined from resistivity or NMR readings versus time during formation draw down pressure testing. The method and apparatus determines and effective permeability over time for various saturation levels to determine the relative permeability for the formation at each saturation level and also enables determination of the efficacy of utilizing completion fluids in the formation to increase formation productivity. The method and apparatus enables more accurate determination of effective permeability and the irreducible saturation level. The method and apparatus also provides for determination of whether a pad is sealed properly against a borehole wall and determines if a probe is clogged.
Owner:BAKER HUGHES INC
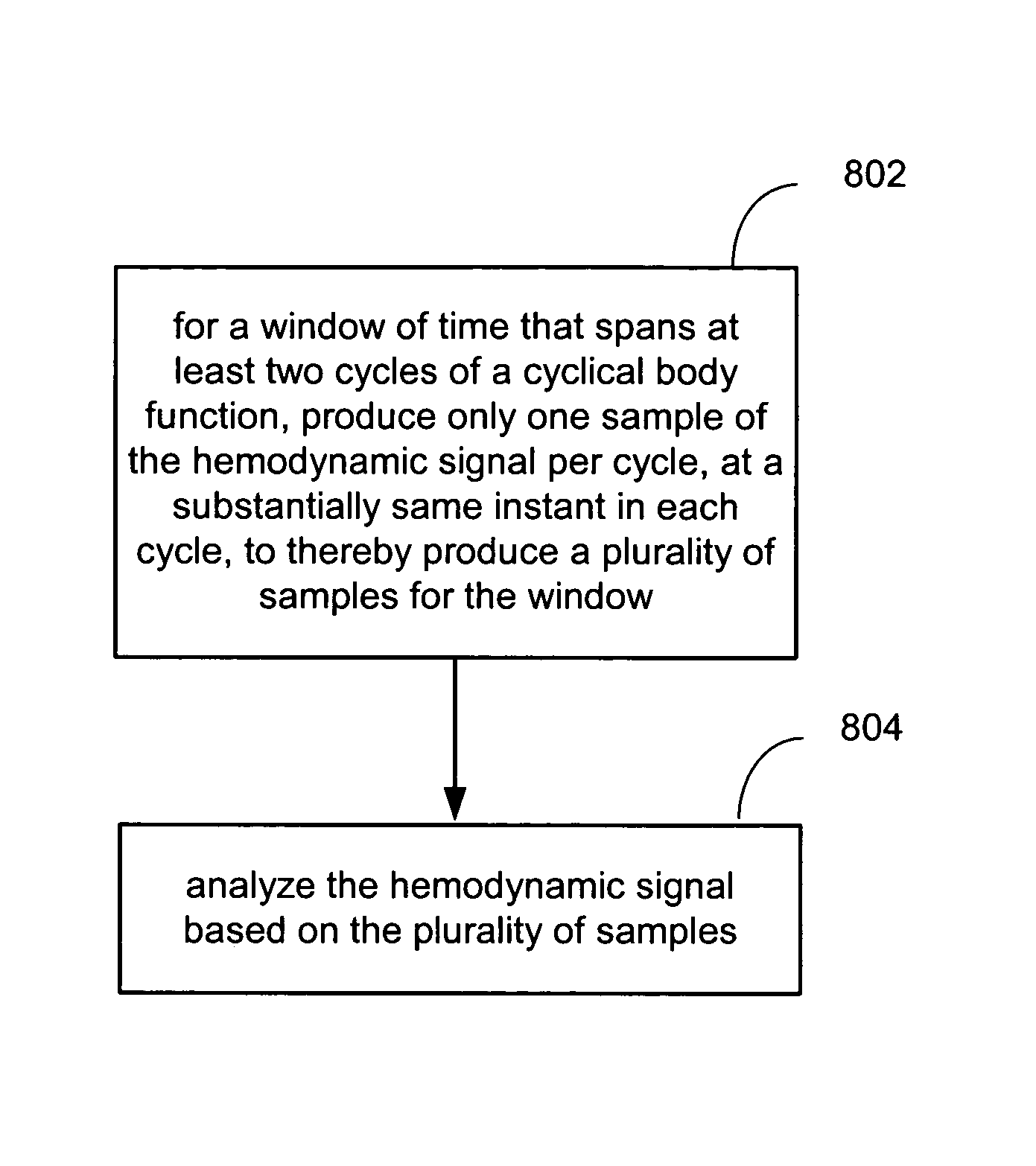
Reducing data acquisition, power and processing for photoplethysmography and other applications
InactiveUS7324848B1Reduce processReduce total powerCatheterHeart stimulatorsHemodynamicsData acquisition
Methods, systems and devices are provided for reducing the amount of data, processing and / or power required to analyze hemodynamic signals such as photoplethysmography (PPG) signals, pressure signals, and impedance signals. Methods, systems and devices are also provided for reducing the amount of processing required to determine blood oxygen (O2) saturation levels.
Owner:PACESETTER INC
Recovery from clipping events in a class D amplifier
ActiveUS7142050B2Shorten recovery timeNegative-feedback-circuit arrangementsAmplifier modifications to raise efficiencyLoop filterAudio power amplifier
A class AD audio amplifier system (10) with improved recovery from clipping events is disclosed. The amplifier system (10) includes multiple audio channels (20), each of which can be constructed to include a pulse-width-modulator (PWM) (24). The PWM modulator (24) includes a pair of comparators (39A, 39B; 52+, 52−) that generate complementary PWM output signals based upon the comparison between a filtered difference signal and a reference waveform. Clip detection logic (26) is provided to detect clipping at the output of the channel (20), preferably by detecting successive edges of the reference waveform without an intervening edge of a PWM output signal. In response to detecting clipping, a first integrator (30; 45) is reset to remove residuals and to eliminate the first integrator (30; 45) from the loop filter of the modulator (24). A saturation level circuit (35) applies a clamping voltage, preferably in both clipping and non-clipping situations, to a second integrator (36; 47). As a result, the loop filter is prevented from entering extreme conditions during clipping, which greatly reduces the clipping recovery time.
Owner:TEXAS INSTR INC
Optical probe for optical imaging system
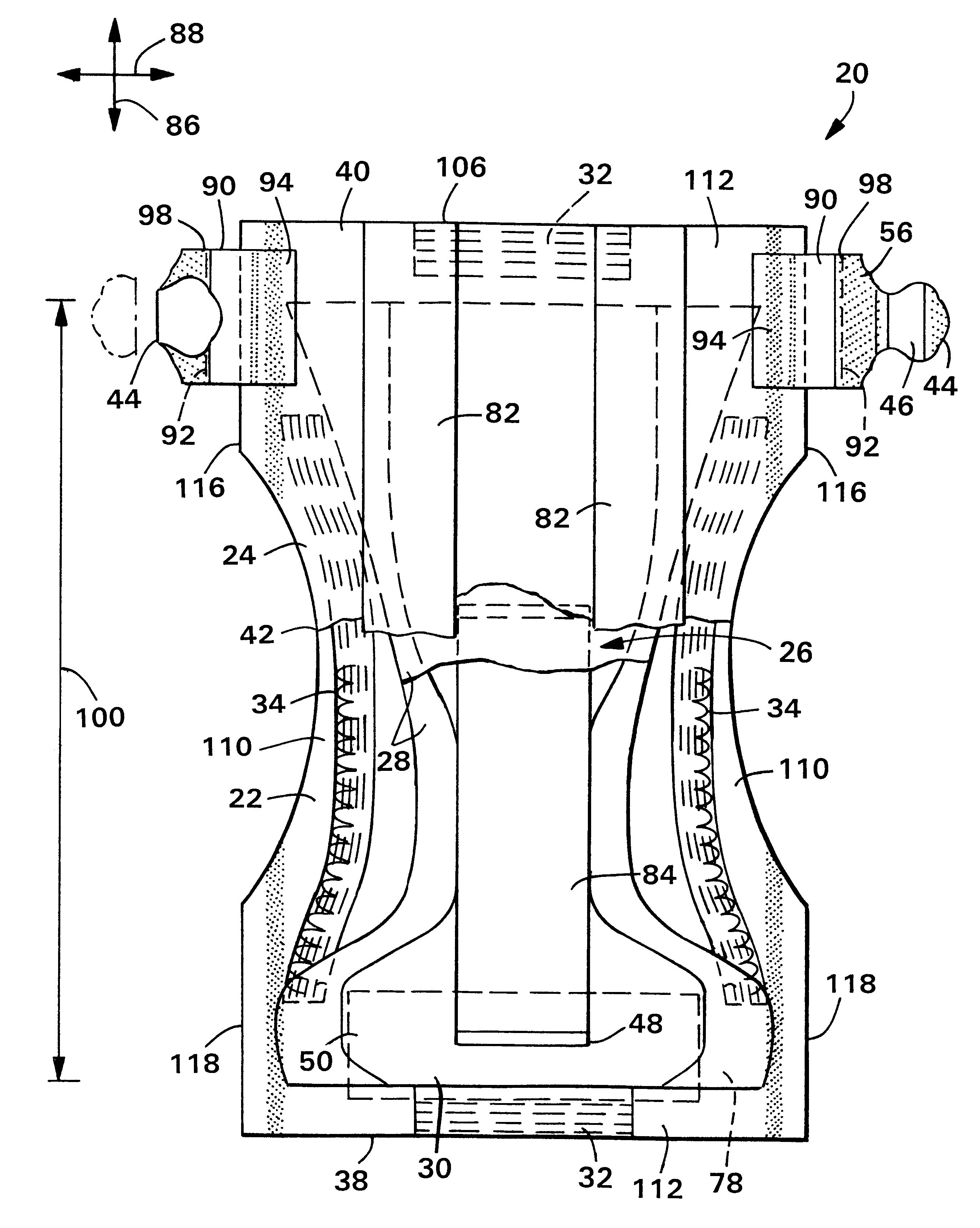
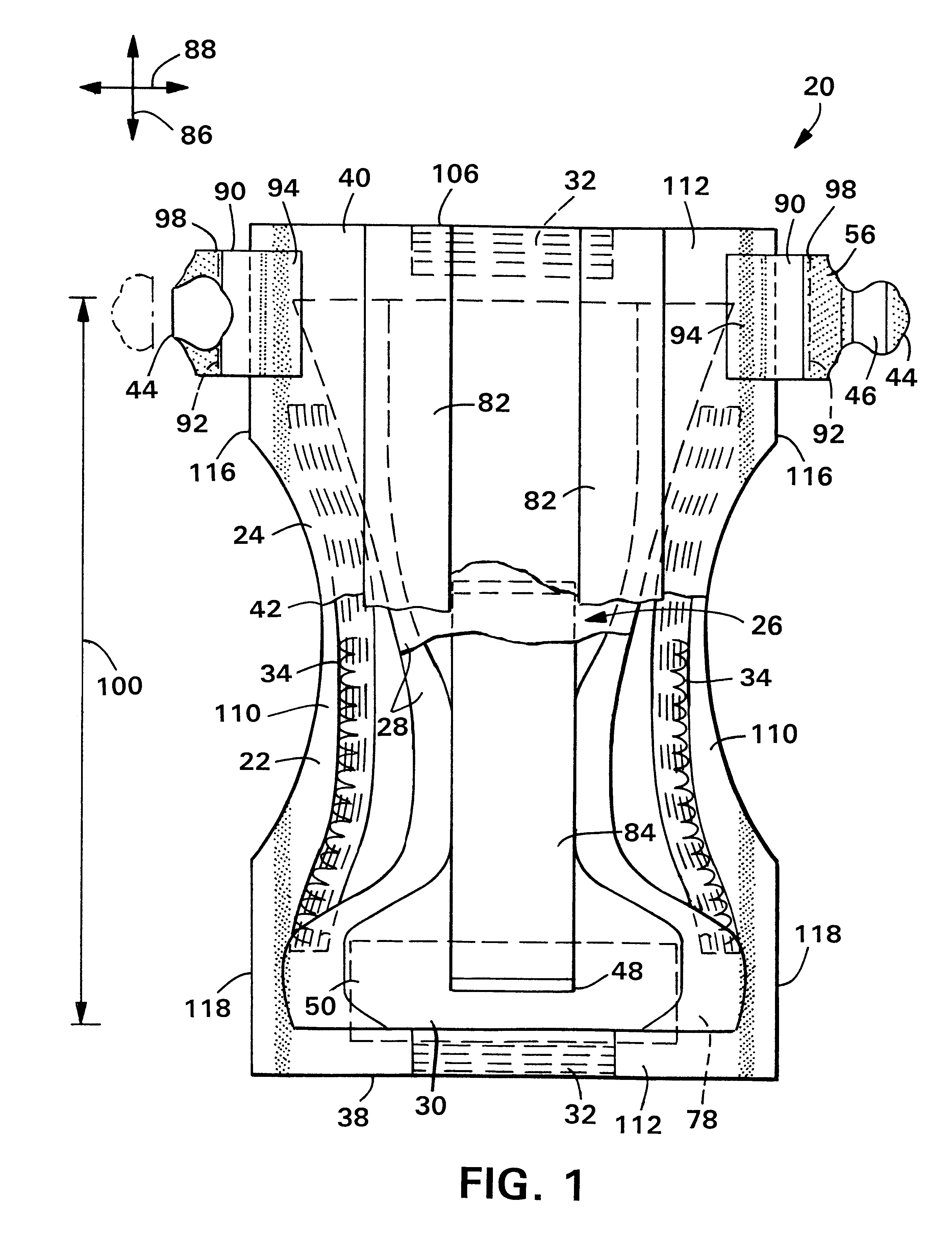
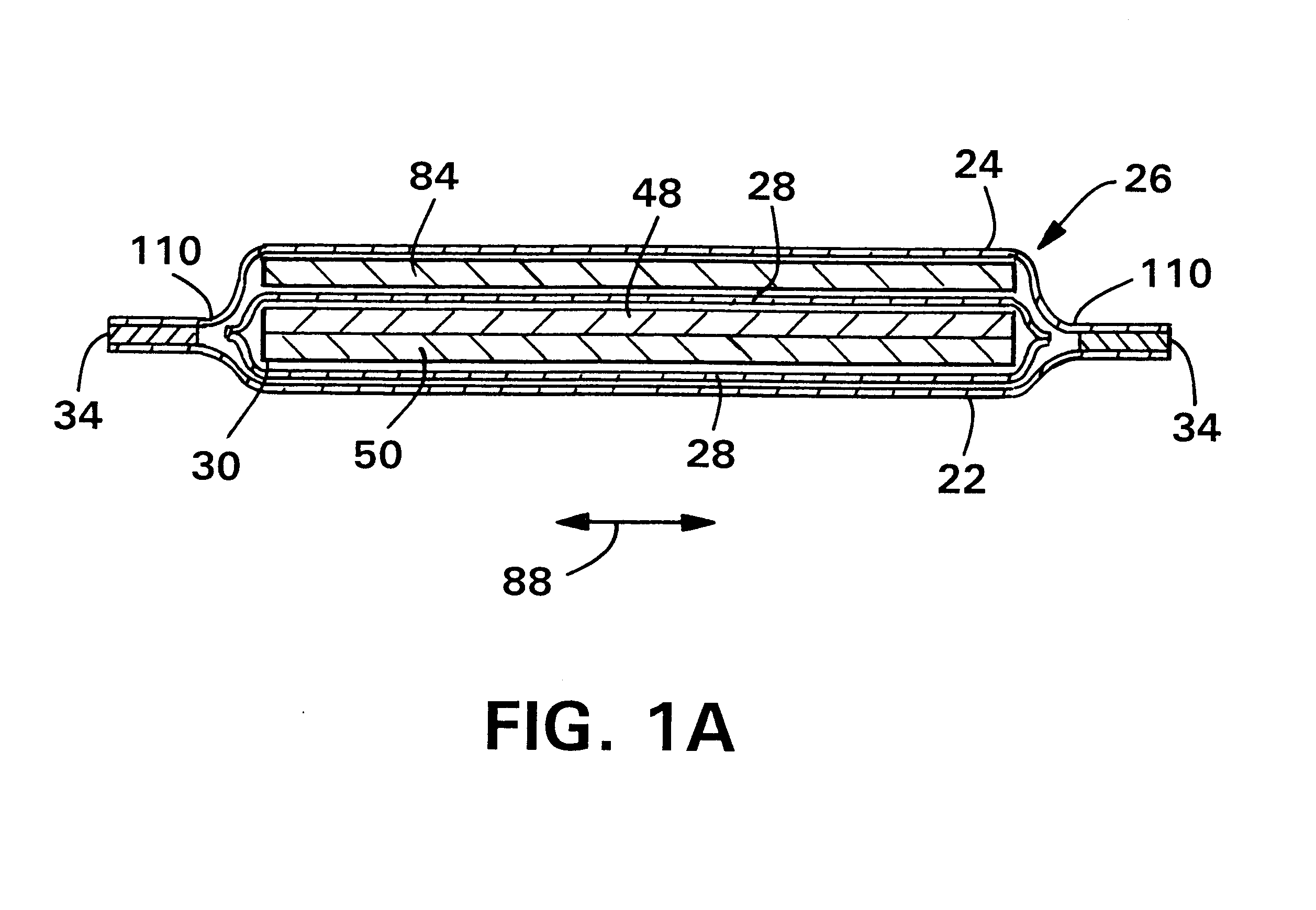
ActiveUS20070055119A1Loosens manufacturing toleranceManufacturing toleranceScattering properties measurementsDiagnostic recording/measuringLight beamSaturation level
Methods and apparatus for monitoring oxygen saturation levels in tissue are disclosed. According to one aspect of the present invention, a sensor arrangement for use in an optical imaging system includes a first source structure, a second source structure, and a detector arrangement. The first source structure provides a first beam of light and the second source structure provides a second beam of light. The detector arrangement includes detector structures that have centerpoints, and receives the first and second beams of light after the first and second beams of light are reflected off of an external surface. The detector arrangement is arranged to define a first axis that passes through the centerpoint of each detector structure, and a distance from a centerpoint of the first source structure to the first axis is not equal to a distance from a centerpoint of the second source structure to the first axis.
Owner:VIOPTIX
Lenslet array for retinal oximetry
The multi-aperture system of the present invention provides a retinal oximetry apparatus for determining the level of oxygen saturation in retinal vessels using a lenslet array comprising at least seven lenses for the simultaneous measurement of reflected light with at least three wavelengths and at least four polarization states. The multi-aperture system of the present invention further provides an apparatus for determining the level of oxygen saturation in retinal vessels using a lenslet array comprising at least ten lenses for the simultaneous measurement of reflected light with at least three wavelengths for oxygen measurement, at least three wavelengths for melanin content, and at least four polarization states. Methods of operating the same are also provided.
Owner:CATHOLIC UNIV OF AMERICA
Photon counting x-ray detector with overrange logic control
ActiveUS7606347B2Reduce impactImprove visualizationMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationRadiation/particle handlingElectricityImaging chain
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Image reinforcement method, image reinforcement device and display device
InactiveCN102779330ASuitable for visual characteristicsAvoid the defect of color lossImage enhancementPictoral communicationDisplay deviceHue
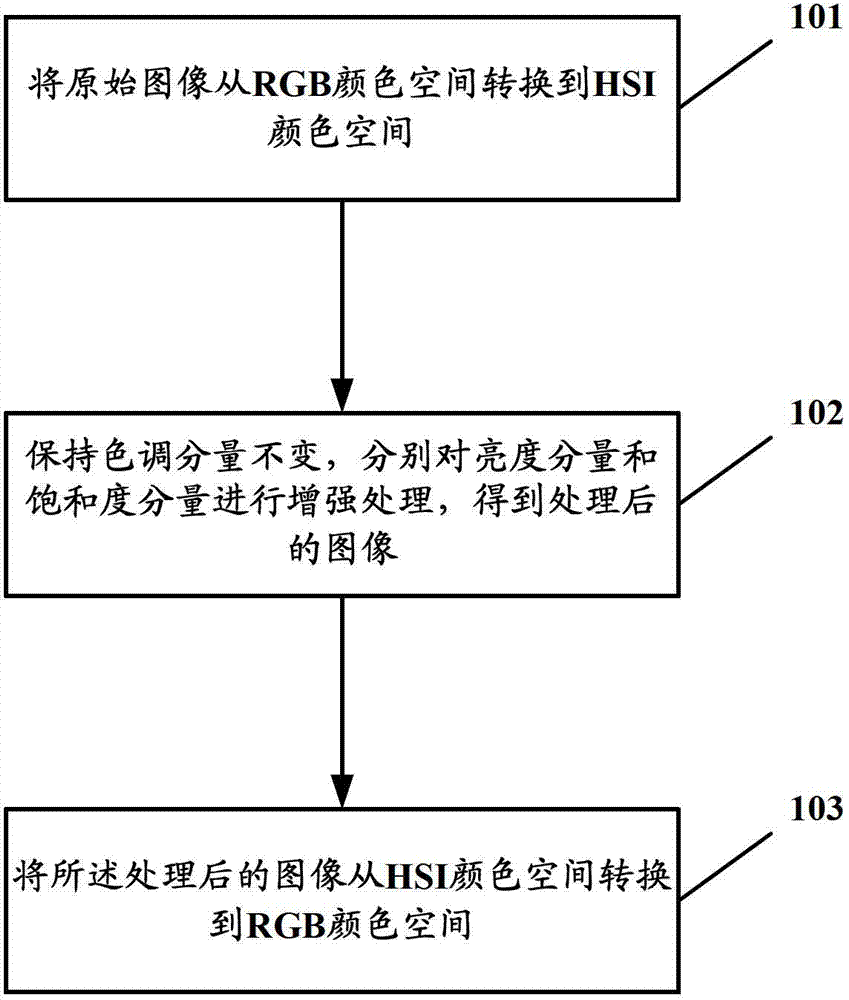
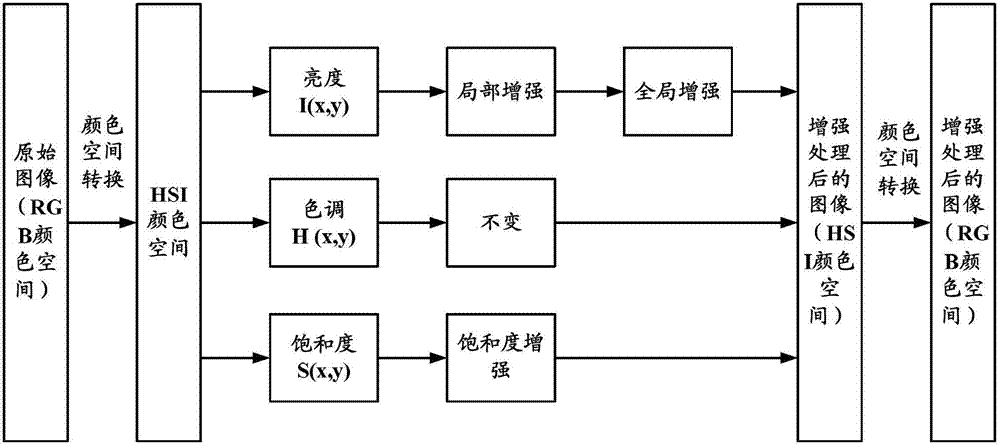
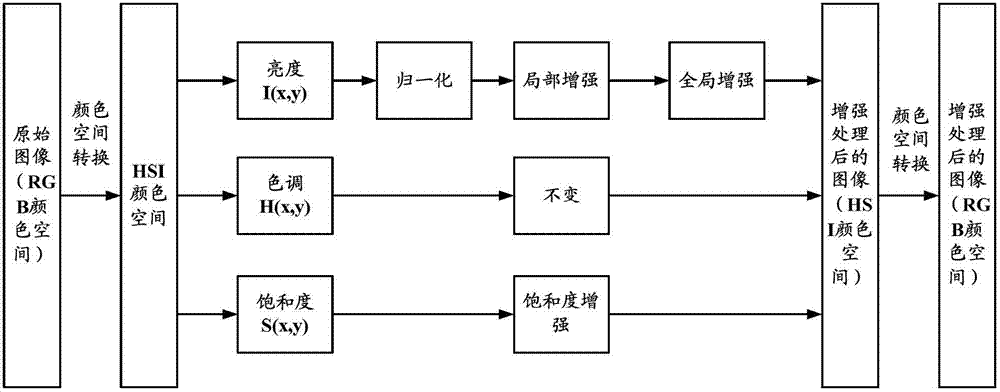
The invention provides an image reinforcement method, an image reinforcement device and a display device. The image reinforcement method comprises the steps of: converting an original image from a RGB (red-green-blue) color space into an HIS (Hue-Saturation-Intensity) color space; maintaining the tone component, and respectively performing reinforcement processing on the brightness component and the saturation level component to obtain a processed image; and converting the processed image from the HIS color space into the RGB color space. The image reinforcement method provided by the invention converts the image from the RGB color space into the HIS color space to perform the reinforcement processing so as to avoid the defect of color loss.
Owner:BOE TECH GRP CO LTD +1
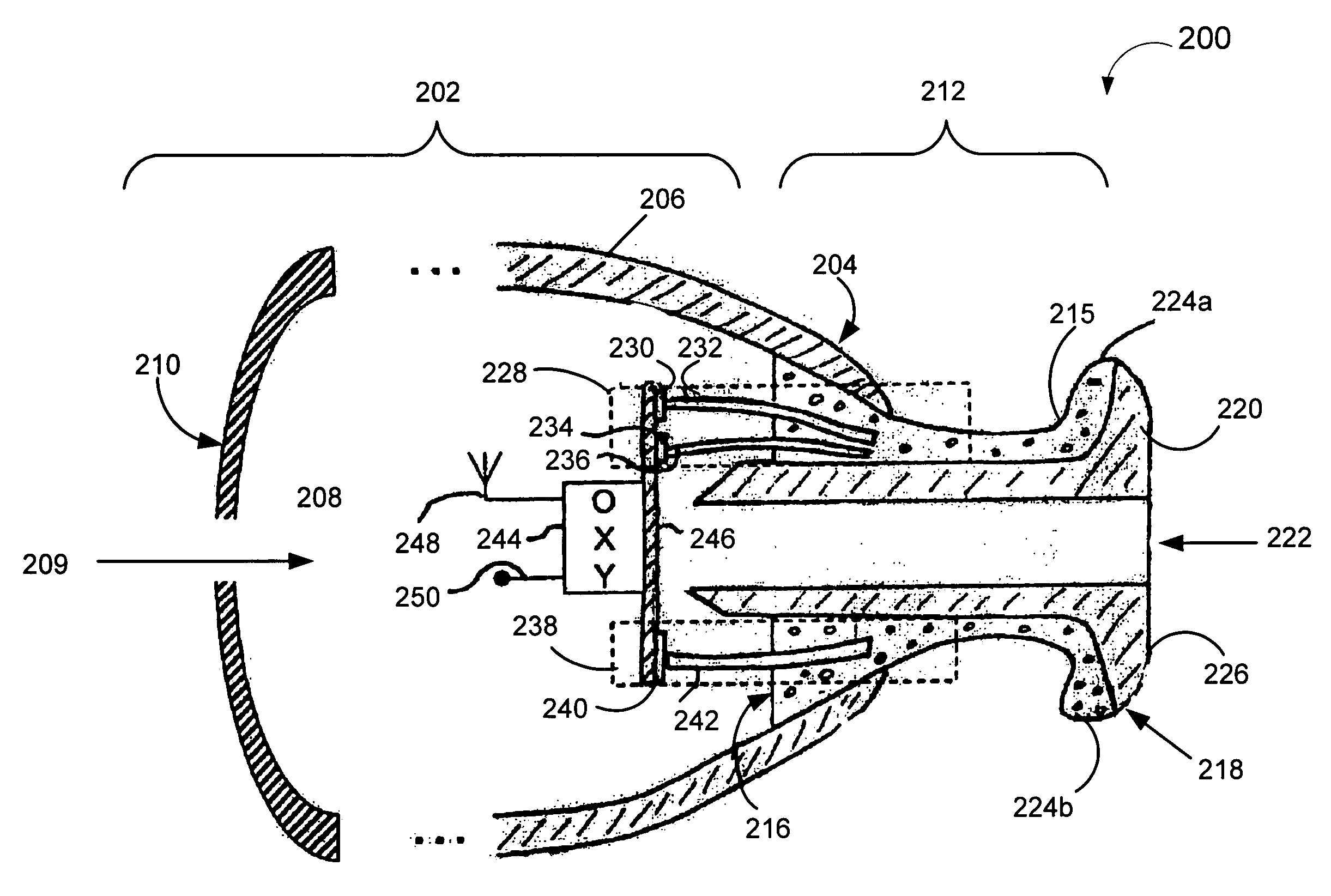
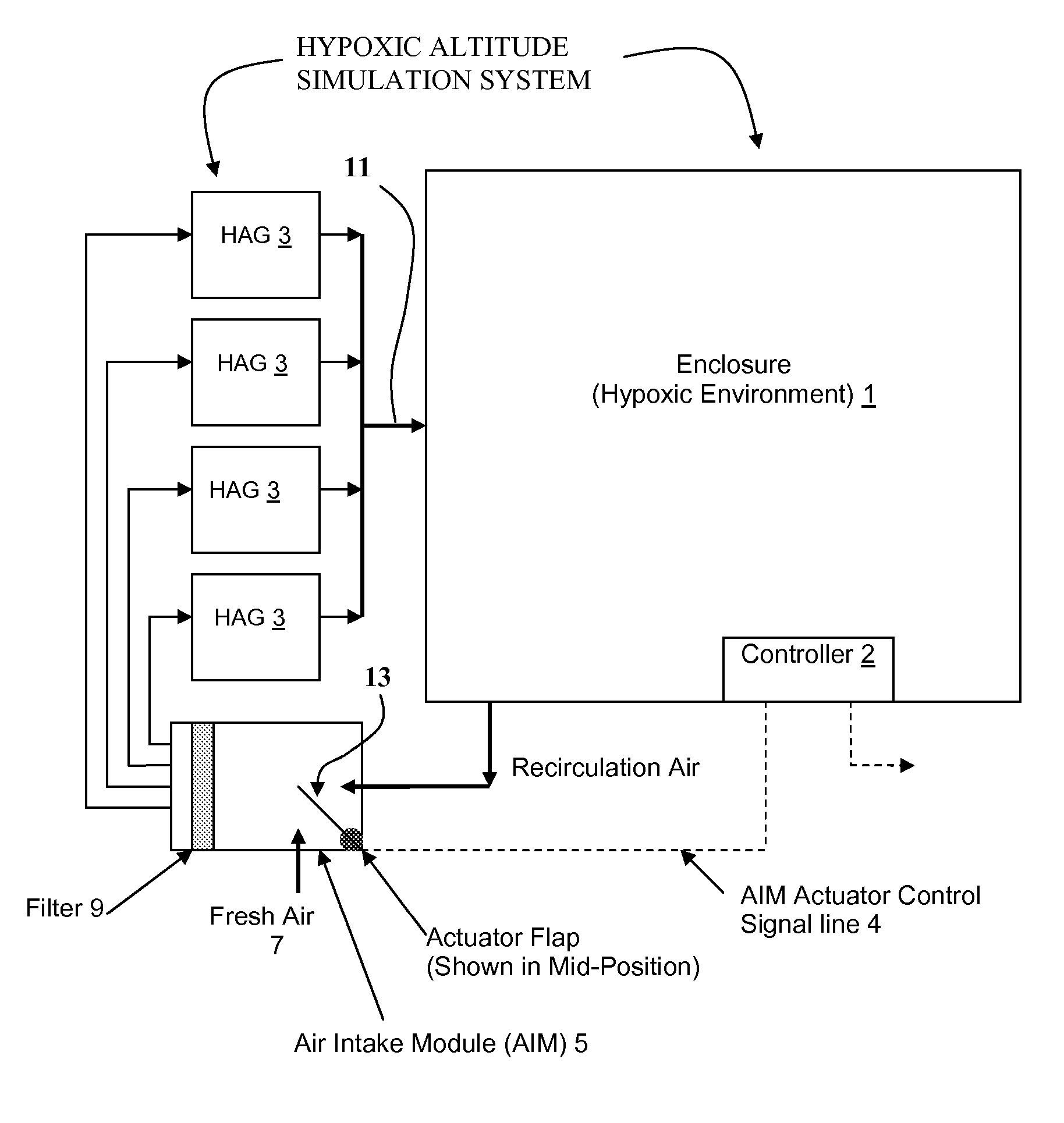
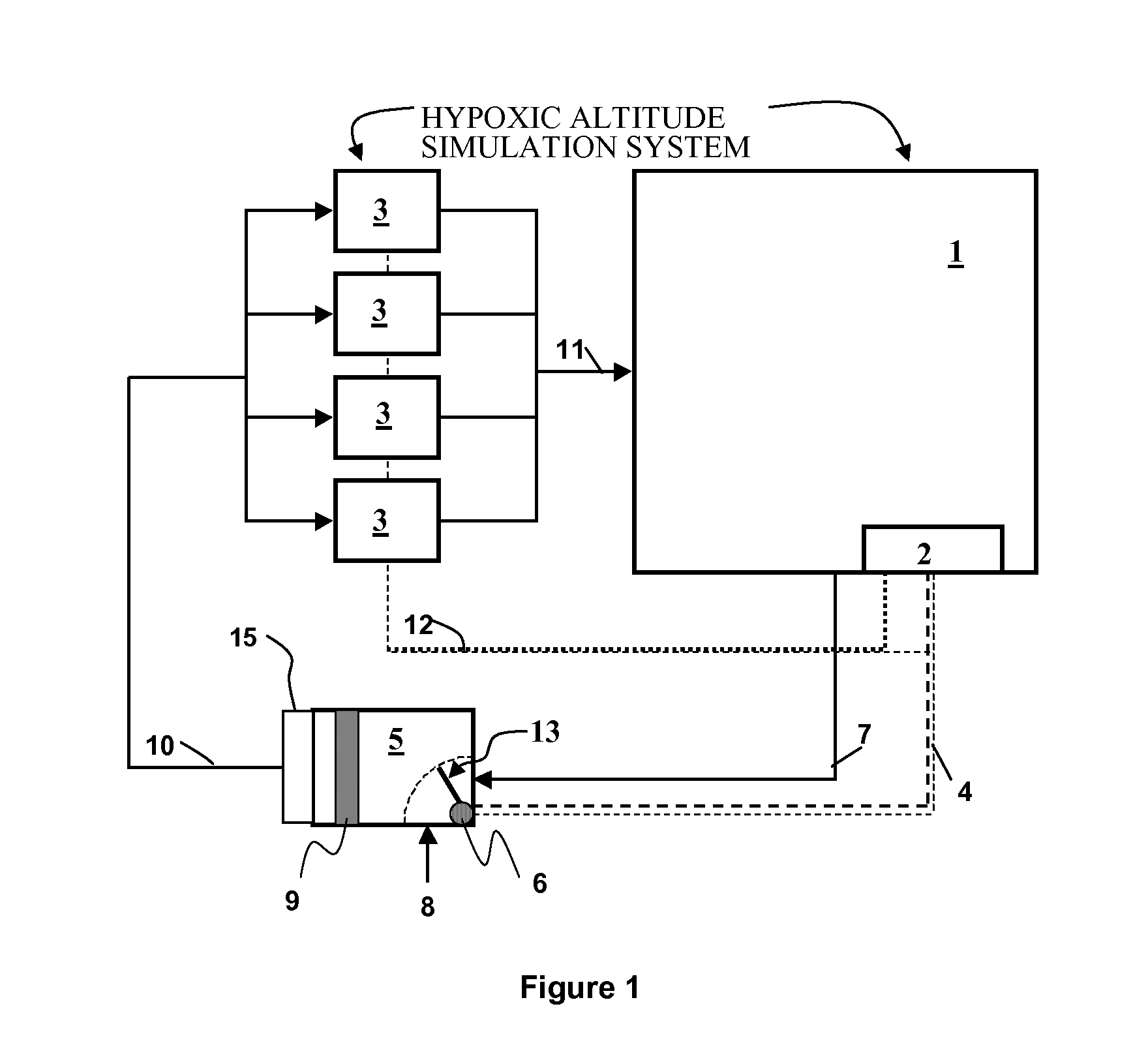
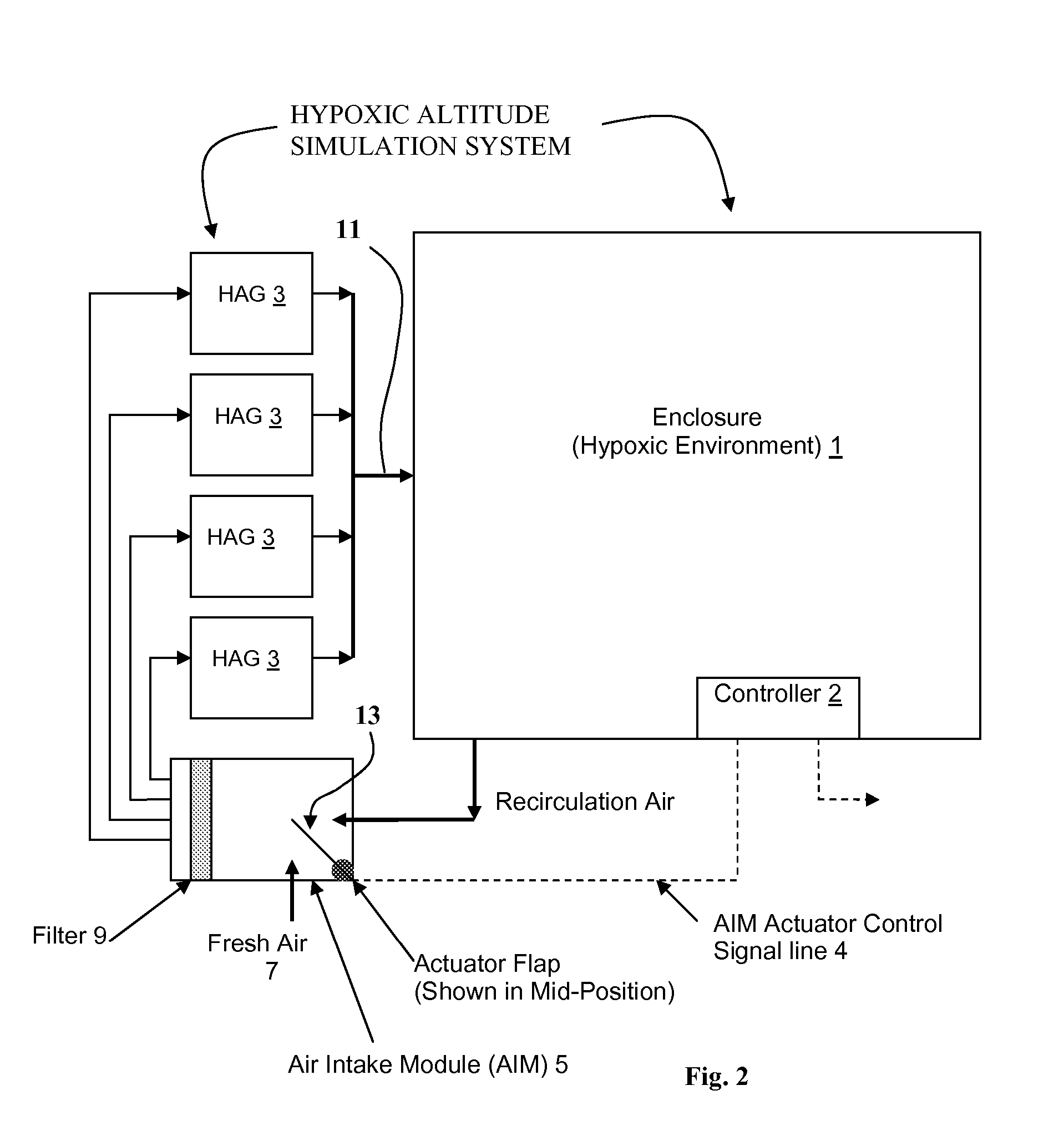
Simulated Altitude Method and Apparatus
InactiveUS20070221225A1Adapt wellQuality controlRespiratorsBreathing protectionSimulated altitudeEngineering
An altitude simulation system is disclosed for simulating an altitude within an enclosure or mask, wherein various improvements are provided, including: (a) a more effective use hypoxpic air generated by the system via recirculating techniques and improvements in air leakage, (b) improvements in determining when a simulated altitude is reached, (c) improvements in controlling hypoxic air generators so that peak electrical power loads are reduced and there are enhanced failsafe features for protecting the health of users, (d) using a pulse oximetry device for measuring oxygen saturation in a user's blood to thereby vary the oxygen content in the air provided to the user.
Owner:COLORADO ALTITUDE TRAINING
Solid-state imaging device and imaging apparatus
ActiveUS20090009635A1Easily affectedHarmful effectTelevision system detailsTelevision system scanning detailsImaging conditionSignal correction
A solid-state imaging device includes a pixel array unit configured by arranging plural unit pixels including charge generating units and output transistors that output processing object signals corresponding to charges generated by the charge generating units, an imaging-condition determining unit that determines whether a large light-amount imaging condition, when an amount of light larger than that of light representing a saturation level is made incident on the charge generating units, is satisfied, and a control unit that performs control, on condition that the imaging-condition determining unit determines that the large light-amount imaging condition is satisfied, to correct an output signal based on processing object signals outputted from the unit pixels such that a harmful effect due to the large light-amount imaging condition is suppressed in the output signal.
Owner:SONY CORP
Pulmonary pulse oximetry method for the measurement of oxygen saturation in the mixed venous blood
InactiveUS20130310669A1Diagnostics using lightMaterial analysis by optical meansVenous bloodPulse oximetry
A method for obtaining diagnostic information relating to the lungs of a subject includes directing into tissue of the lungs of the subject light of a first wavelength and detecting part of the light that has passed primarily through microcirculatory tissue of the lungs and generating a signal which is a function of intensity of the detected light. The signal is then processed to derive a PPG curve for pulmonary microcirculatory arteries. The method is implemented using various locations for a light source and a detector, including various combinations of positioning on the thoracic wall, insertion into the esophagus, and in some cases, insertion of a probe through the thoracic wall to a position adjacent to the pulmonary pleura. Use of two different wavelengths allows derivation of mixed venous blood oxygen saturation.
Owner:JERUSALEM COLLEGE OF TECHNOLOG +1
Magnetic inspection device
ActiveUS20100148766A1Reducing secondary fluxMagnetic field measurement using galvano-magnetic devicesMaterial magnetic variablesNon destructiveMagnetic flux
A magnetic inspection device for nondestructively inspecting elongated objects, such as wire cables, pipes, and the like, for loss of metallic cross-section due to abrasion, corrosion, and external and internal discontinuities, having a magnet for inducing in sections of the object between the stations, magnetic flux at the saturation level. A magnetic flux detector having magnetic sensors positioned between the poles and laterally of the elongated object utilizes shields and flux decompressors to render the flux detector more sensitive to leakage flux caused by discontinuities in the objects.
Owner:NDT TECH LLC
Method and apparatus for combined NMR and formation testing for assessing relative permeability with formation testing and nuclear magnetic resonance testing
InactiveUS7032661B2Electric/magnetic detection for well-loggingSurveyProduction rateNMR - Nuclear magnetic resonance
Formation testing, resistivity and NMR measurements are used concurrently to determine a relative permeability representative of a formation surrounding the borehole. A method and apparatus is provided for accurate determination of the relative permeability for a formation by measuring saturation levels in a region of interest determined from resistivity or NMR readings versus time during formation draw down pressure testing. The method and apparatus determines and effective permeability over time for various saturation levels to determine the relative permeability for the formation at each saturation level and also enables determination of the efficacy of utilizing completion fluids in the formation to increase formation productivity. The method and apparatus enables more accurate determination of effective permeability and the irreducible saturation level. The method and apparatus also provides for determination of whether a pad is sealed properly against a borehole wall and determines if a probe is clogged.
Owner:BAKER HUGHES INC
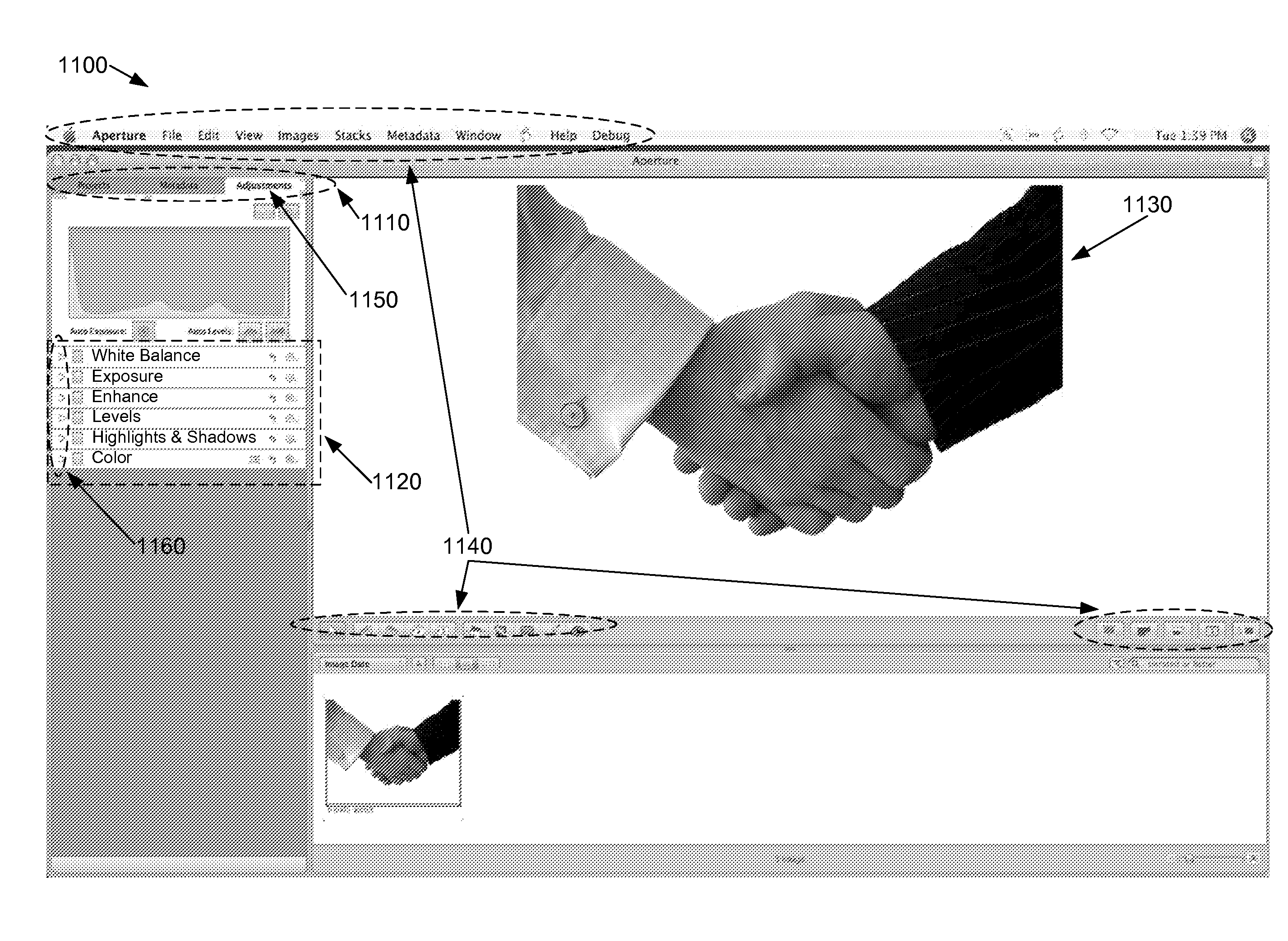
Adjusting color attribute of an image in a non-uniform way
ActiveUS20090201310A1Maintain saturationReduce adjustmentTexturing/coloringCathode-ray tube indicatorsPattern recognitionSaturation level
Some embodiments of the invention provide an image-editing process that non-uniformly adjusts at least one particular color attribute (e.g., saturation level) of pixels in an image. Specifically, the image-editing process of these embodiments uniformly adjusts the particular color attribute of pixels with a first set of values and non-uniformly adjusts the color attribute of pixels with a second set of values. In this manner, some embodiments provide a vibrancy process that non-uniformly adjusts saturation levels of an image in order to preserve saturation levels for skin tones appearing within the image.
Owner:APPLE INC
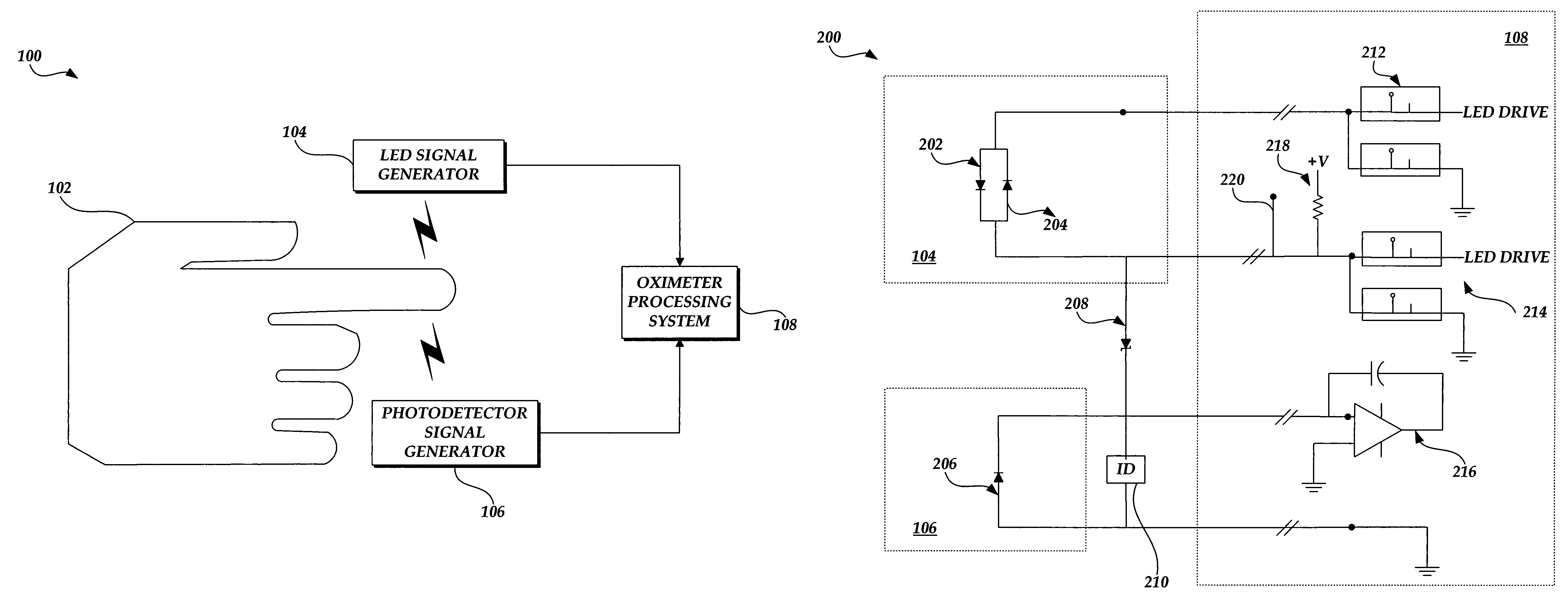
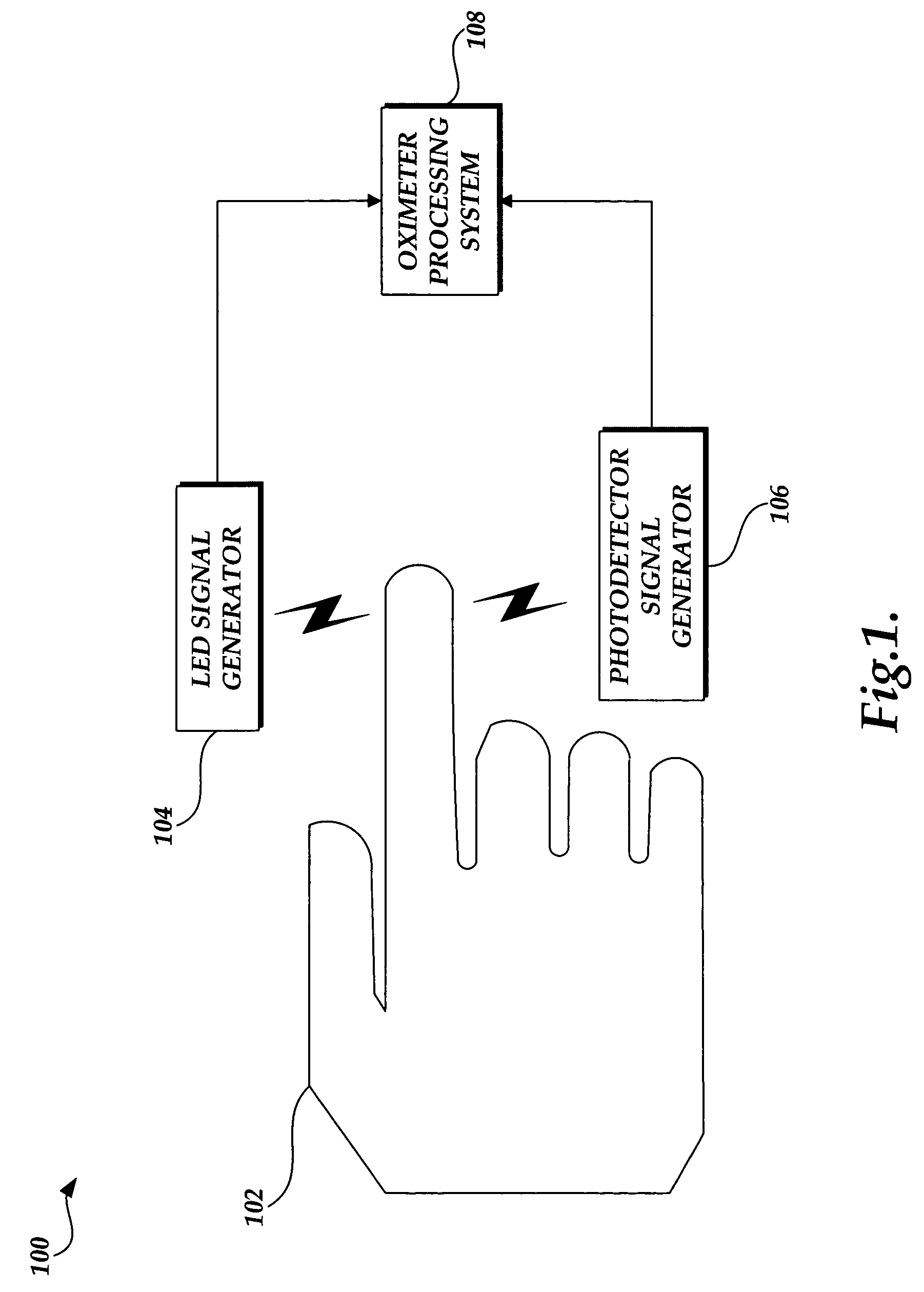
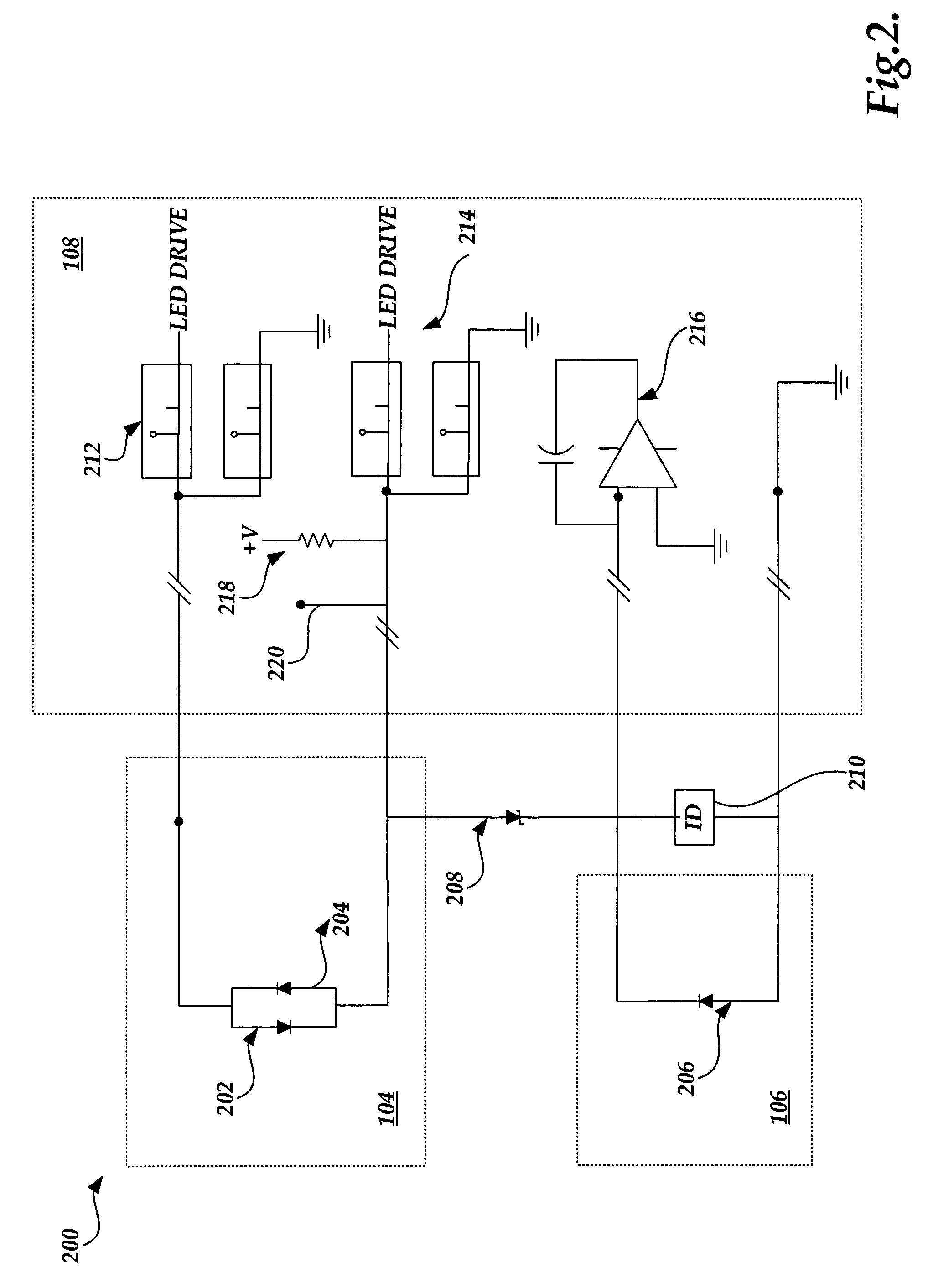
System and method for processing information in a pulse oximeter
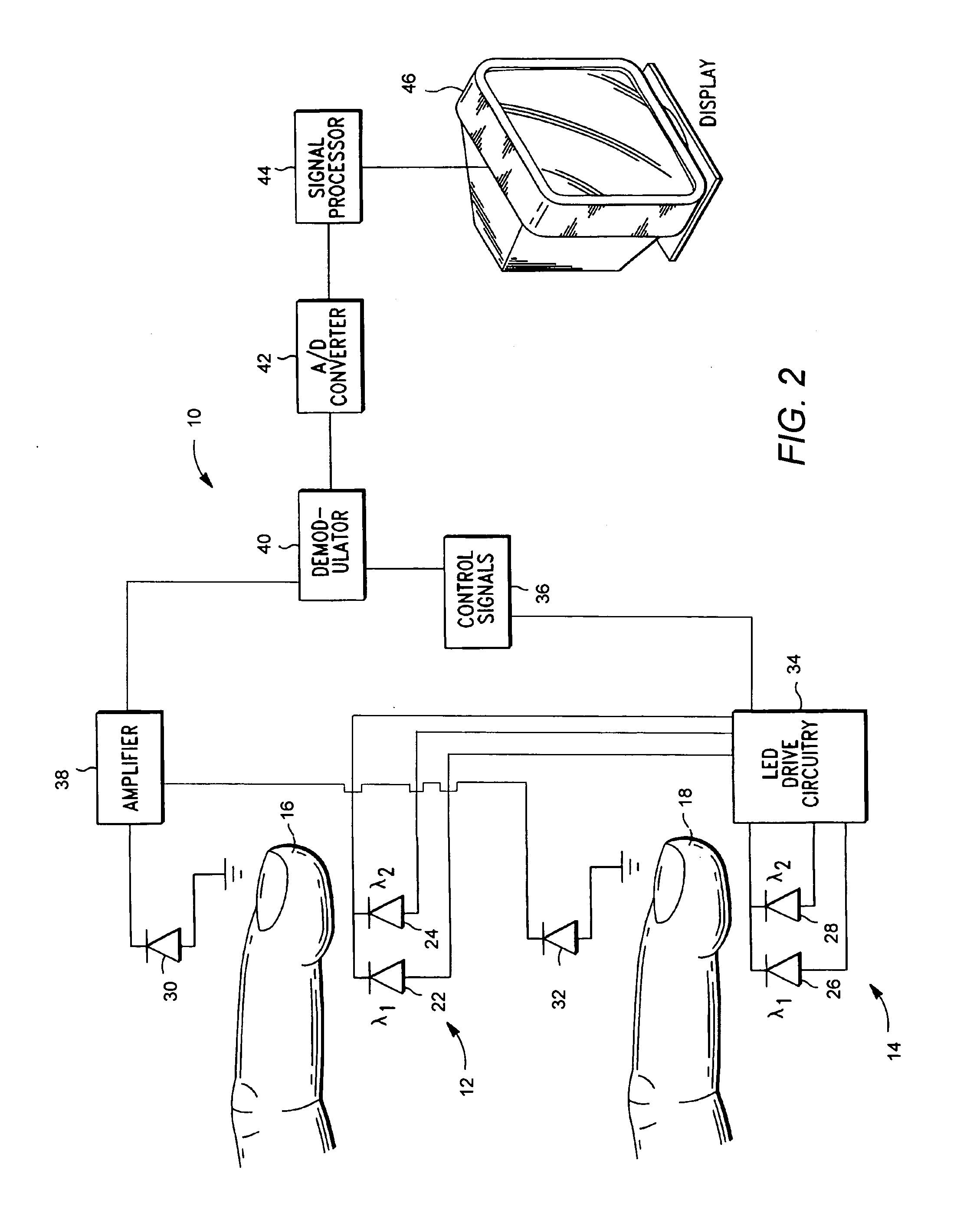
ActiveUS7230688B1High voltage sourceHigh voltageMaterial analysis by optical meansPhotoelectric discharge tubesPhotodetectorPulse oximeters
A pulse oximeter for measuring arterial oxygen saturation levels is provided. The pulse oximeter includes an LED signal generator for transmitting one or more light signals to a testing medium and a photodetector signal generator for processing at least a portion of the light signal generated by the LED signal generator into a photocurrent. The pulse oximeter further includes an integrated information transmission component for transmitting information corresponding to the pulse oximeter and which is integrated with the pulse oximeter without requiring additional wiring. A processing system within the pulse oximeter can generate a voltage to the integrated information transmission component to read the information stored in the component without causing the LED signal generator to generate a signal.
Owner:CADWELL INDS
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com