Patents
Literature
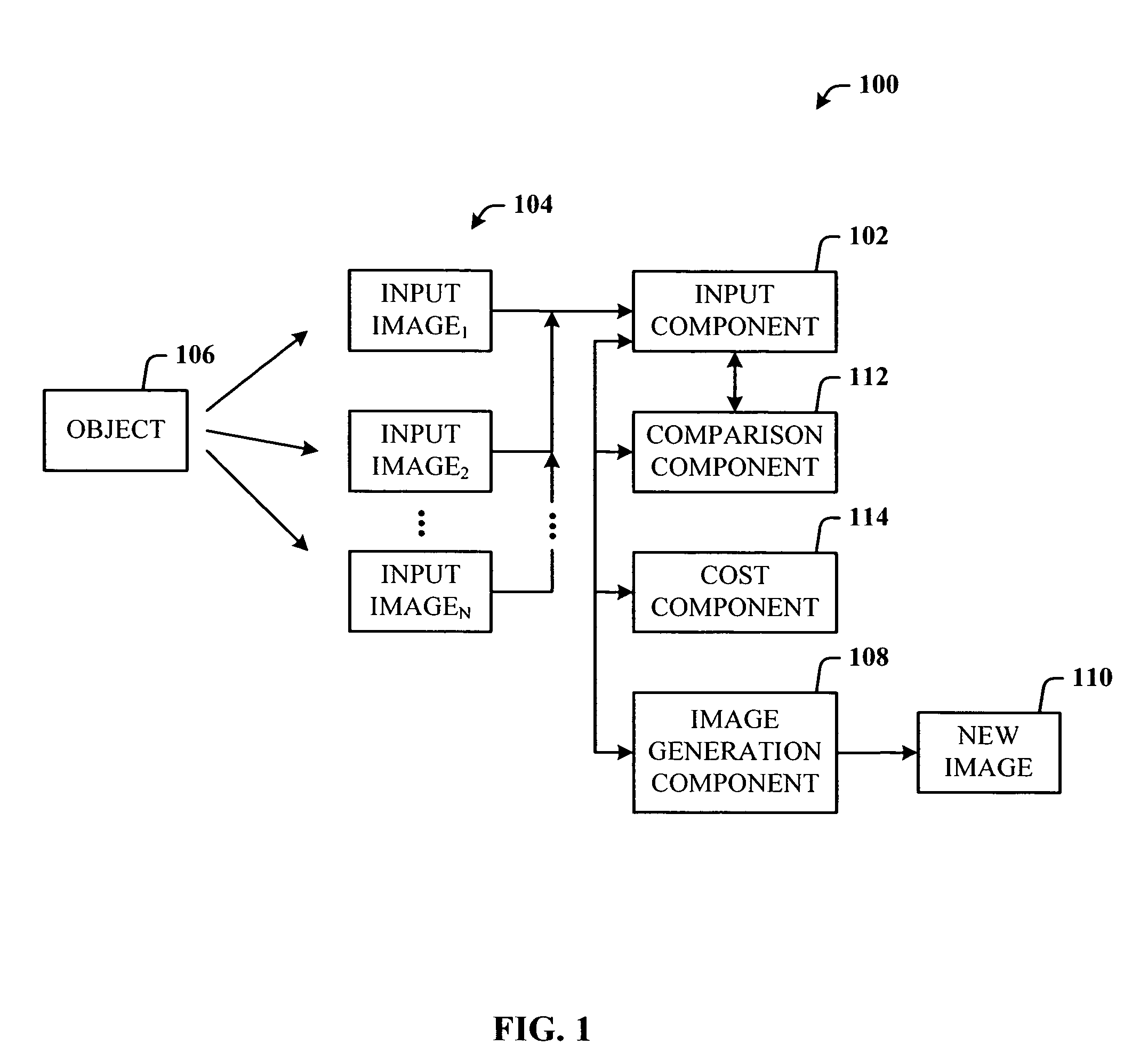
16479 results about "Image pair" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
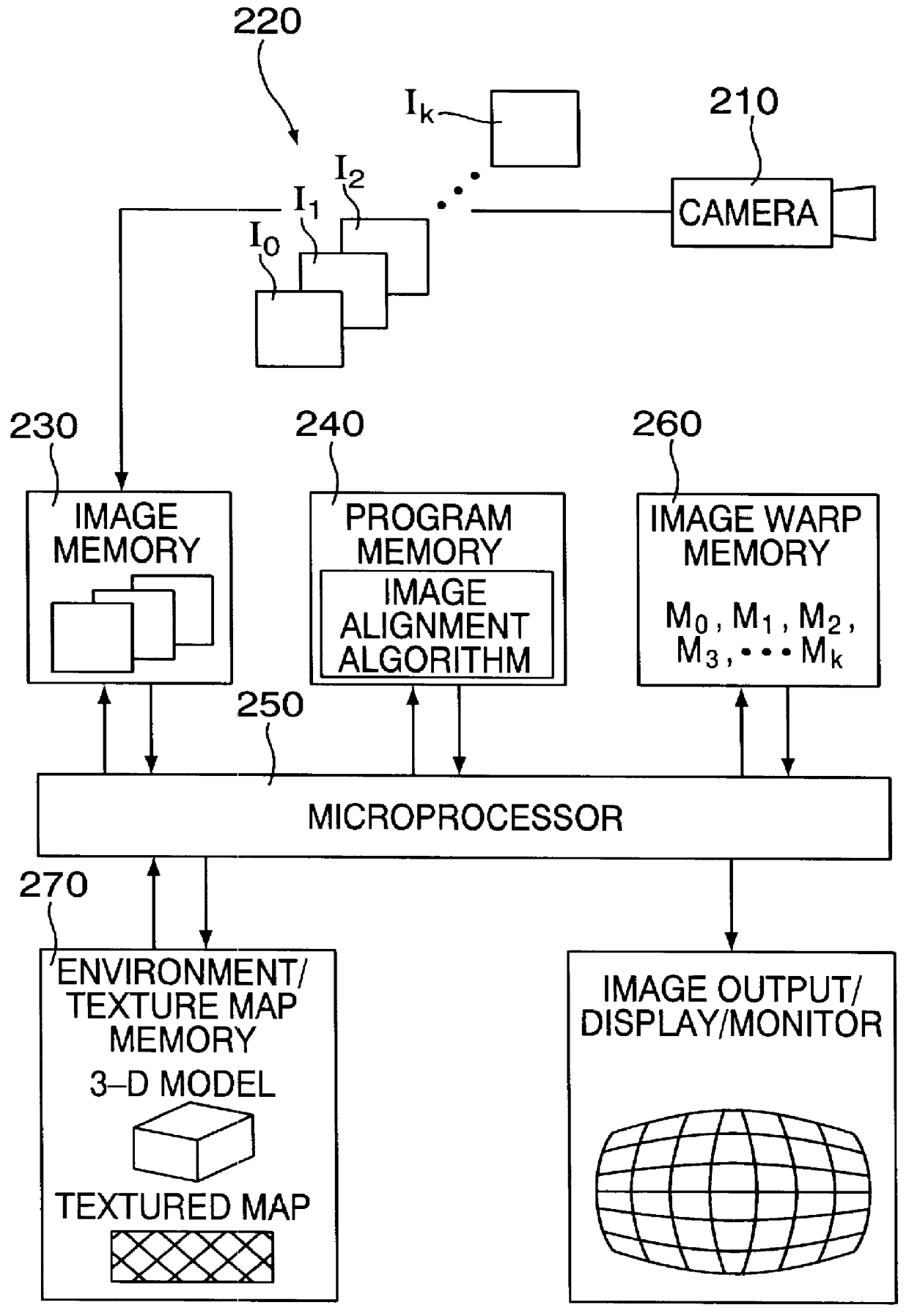
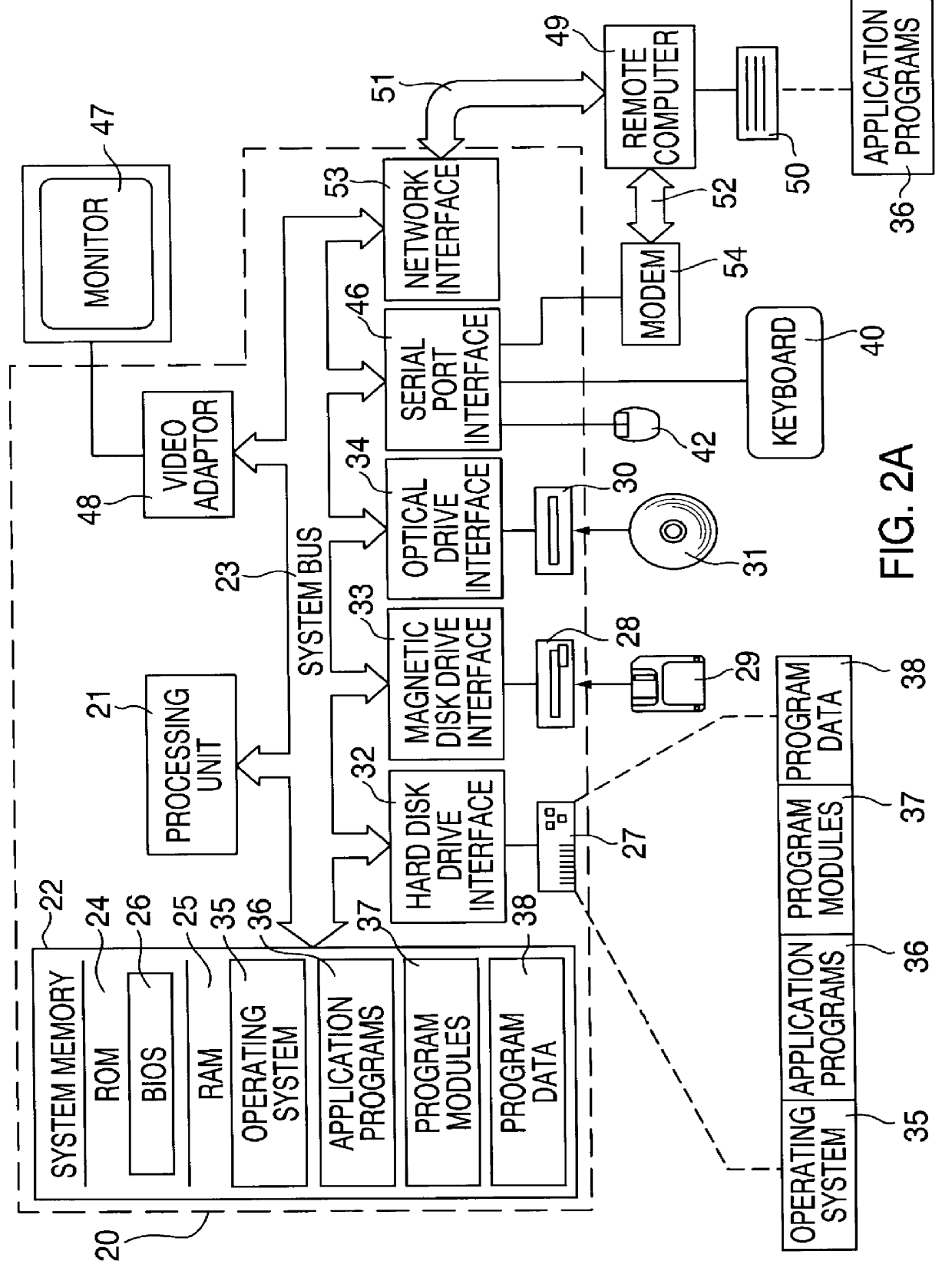
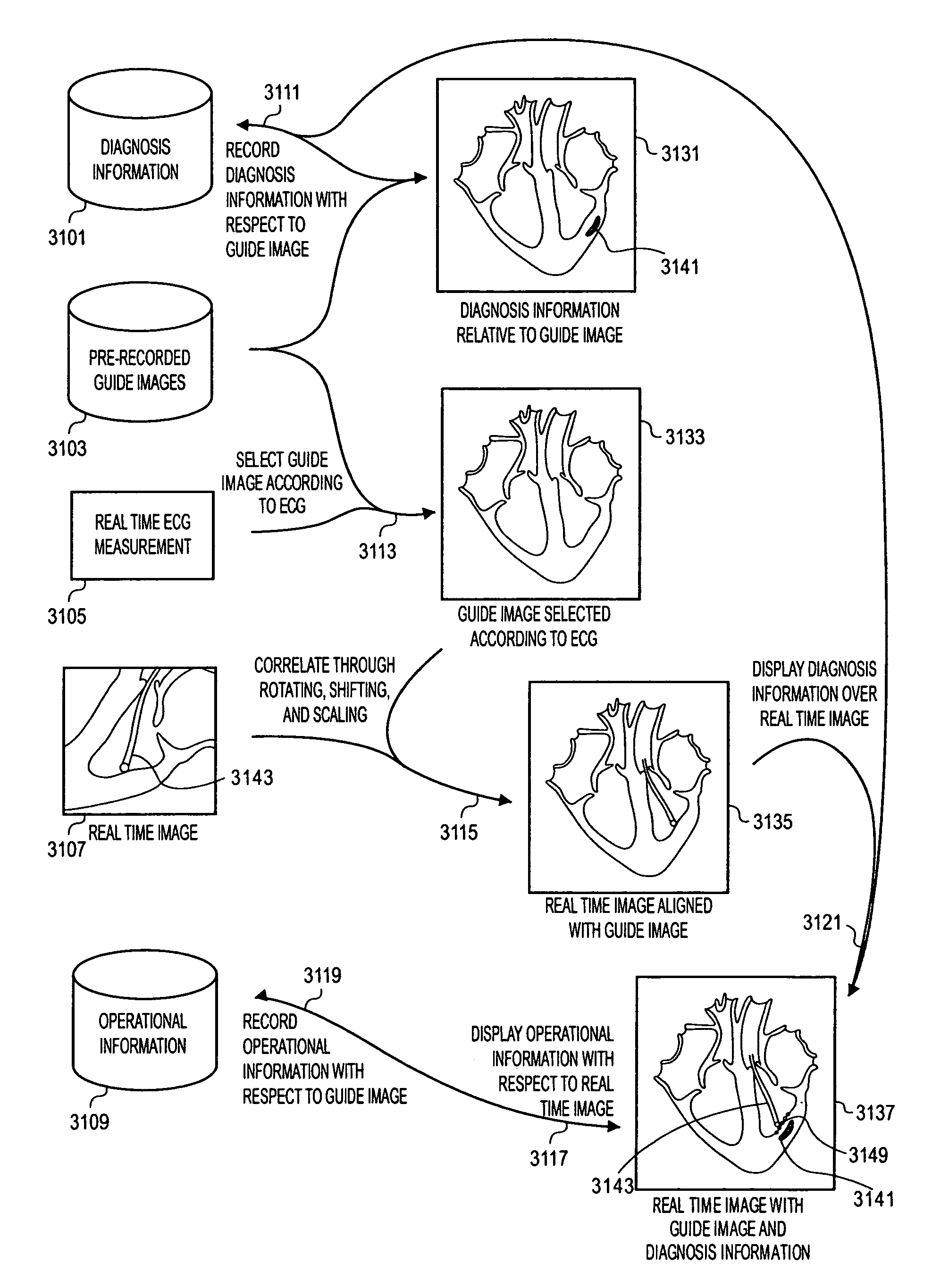
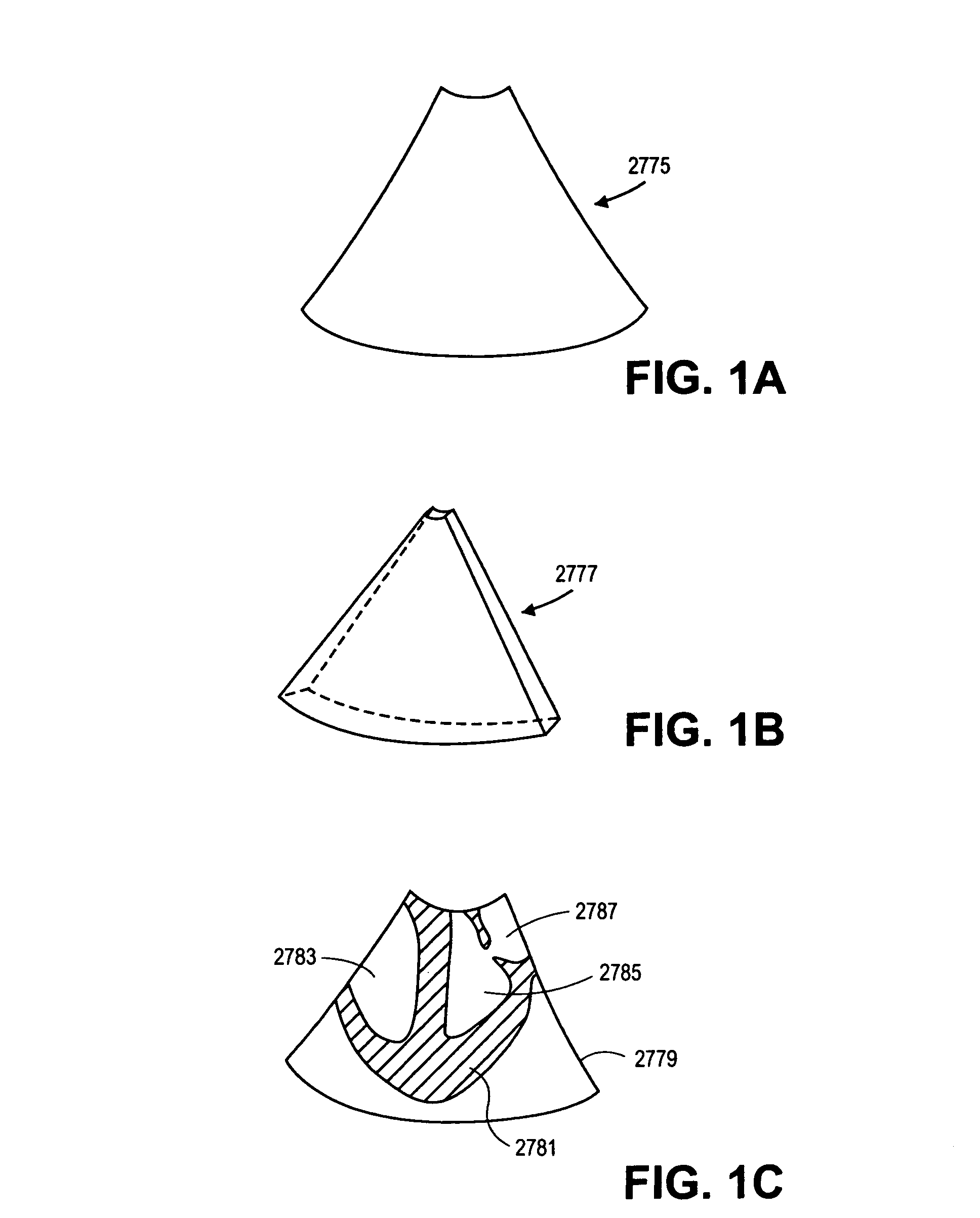
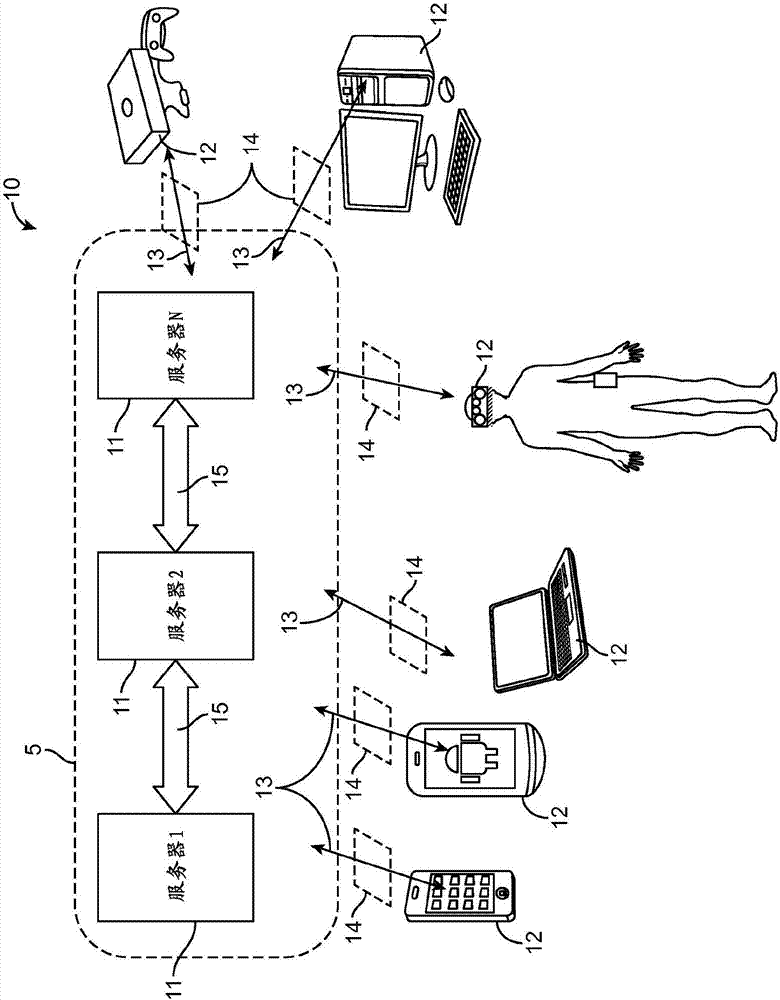
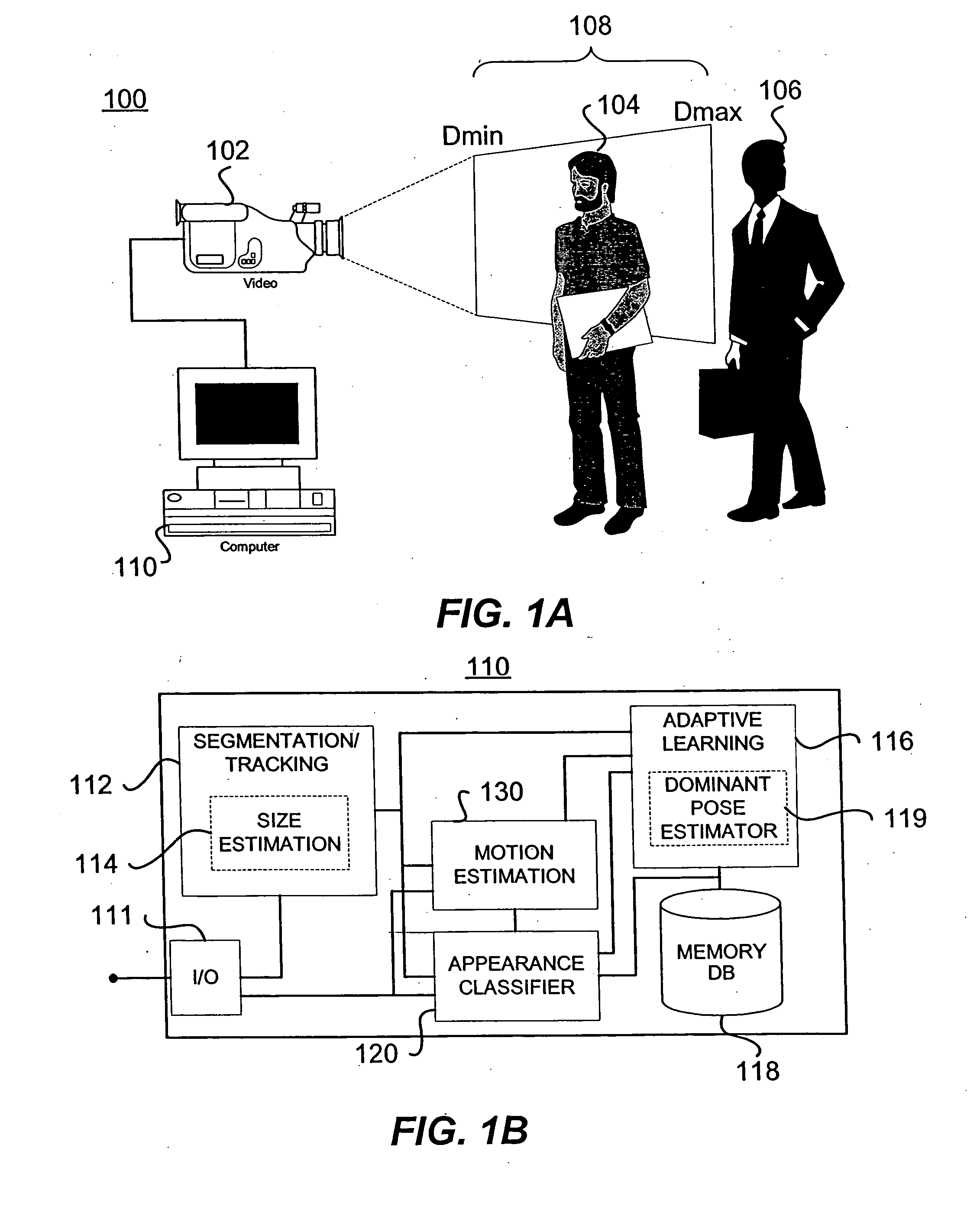
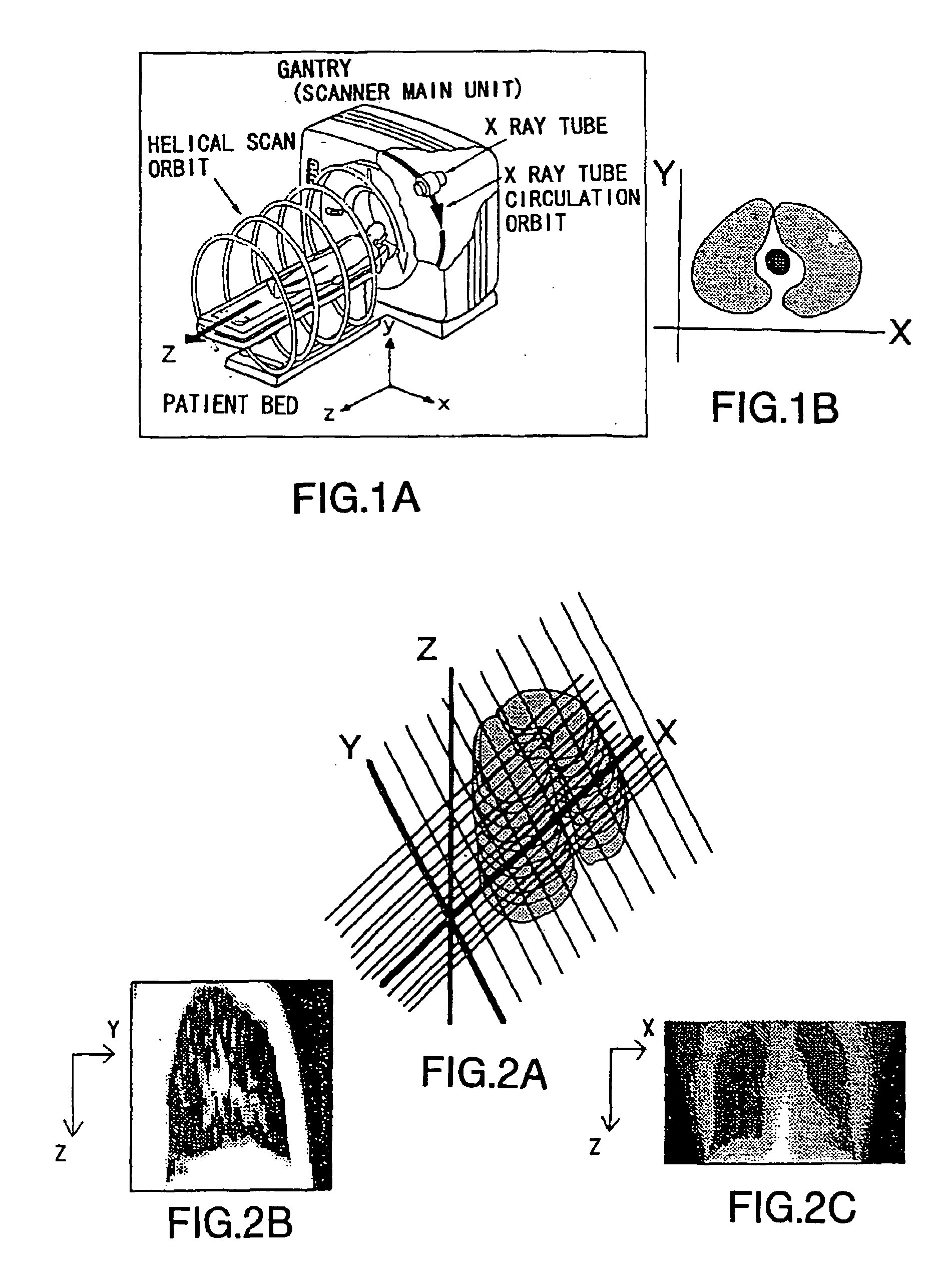
Methods and apparatuses for image guided medical procedures
ActiveUS20070167801A1Reduction of image brightnessEliminate artifactsMedical simulationUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsImage alignmentMedical procedure
Methods and apparatuses for the image guidance and documentation of medical procedures. One embodiment includes combining small field of view images into a recorded image of with a large field of view and aligning the small field of view real time image with the recorded image through correlation of imaging data. A location and orientation determination system may be used to track the imaging system and provide a starting set of image alignment parameters and / or provide change updates to a set of image alignment parameters, which is then further improved through correlating imaging data. The recorded image may be selected according to real time measurement of a cardiac parameter during an image guided cardiac procedure. Image manipulations planned based on the recorded image can be stored and applied to the real time information. The position of the medical device may be determined and recorded through manipulating a cursor in a 3-D image space shown in two non-parallel views.
Owner:ABBOTT CARDIOVASCULAR
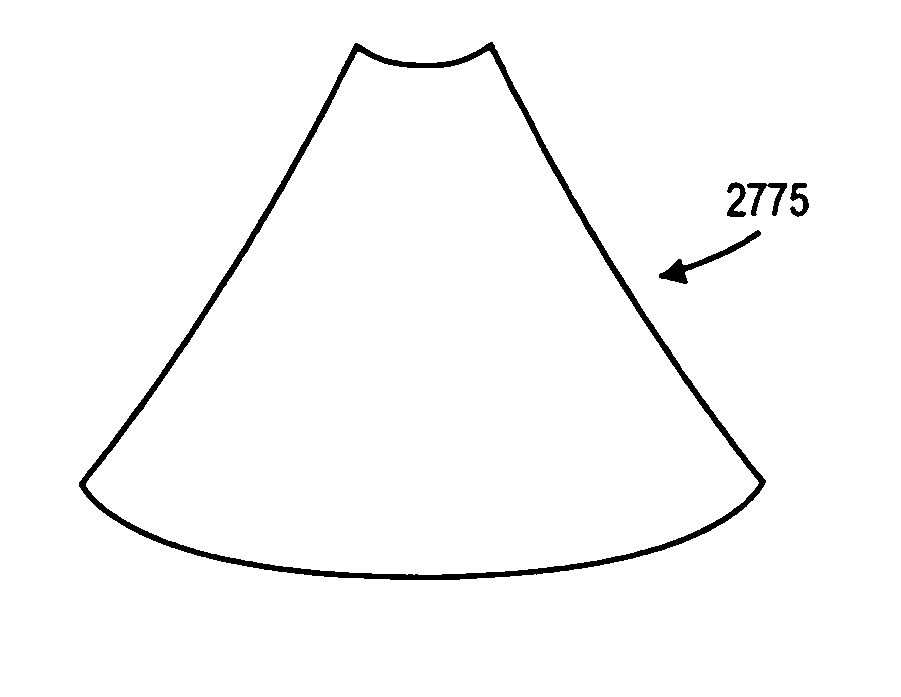
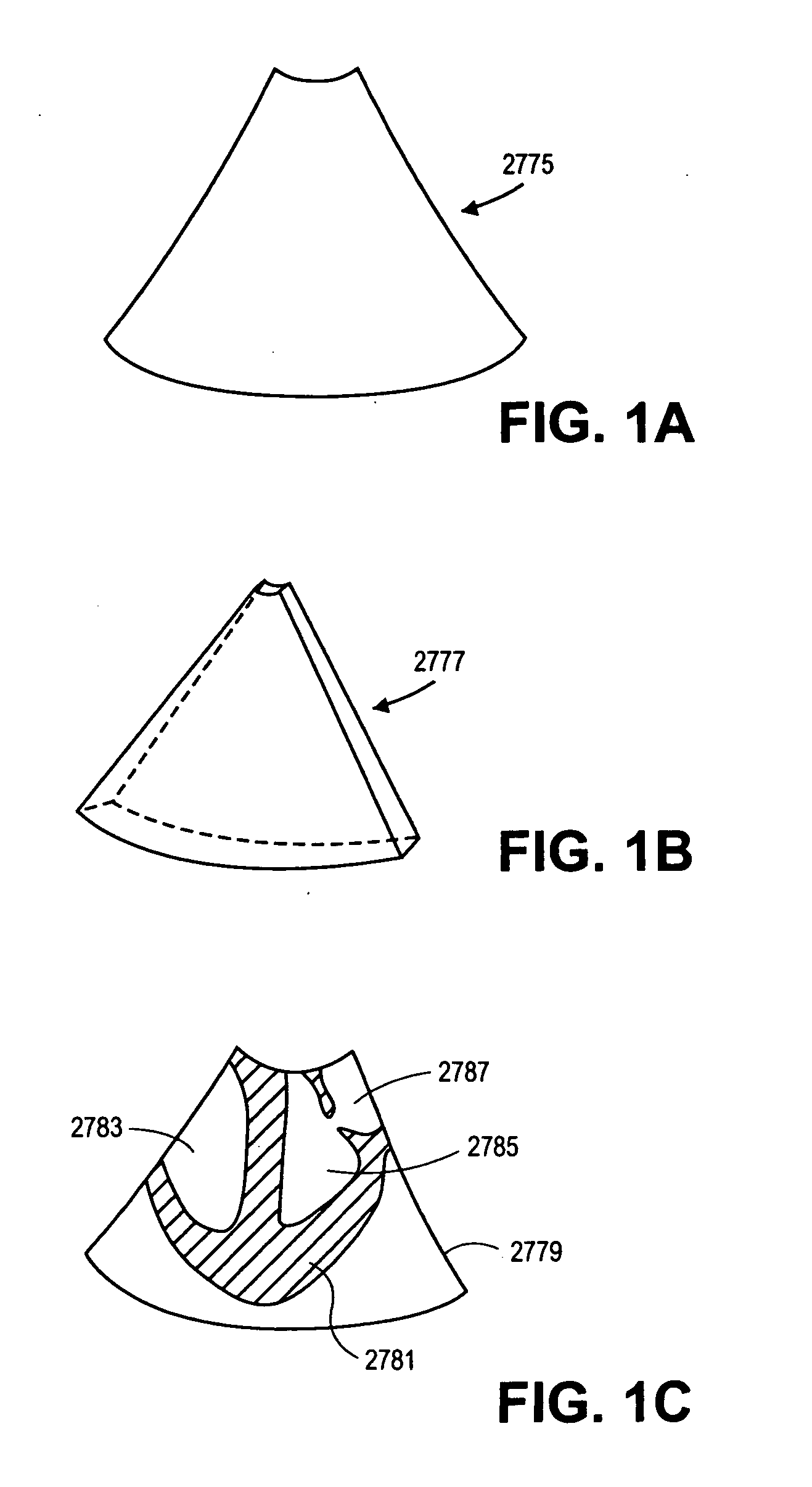
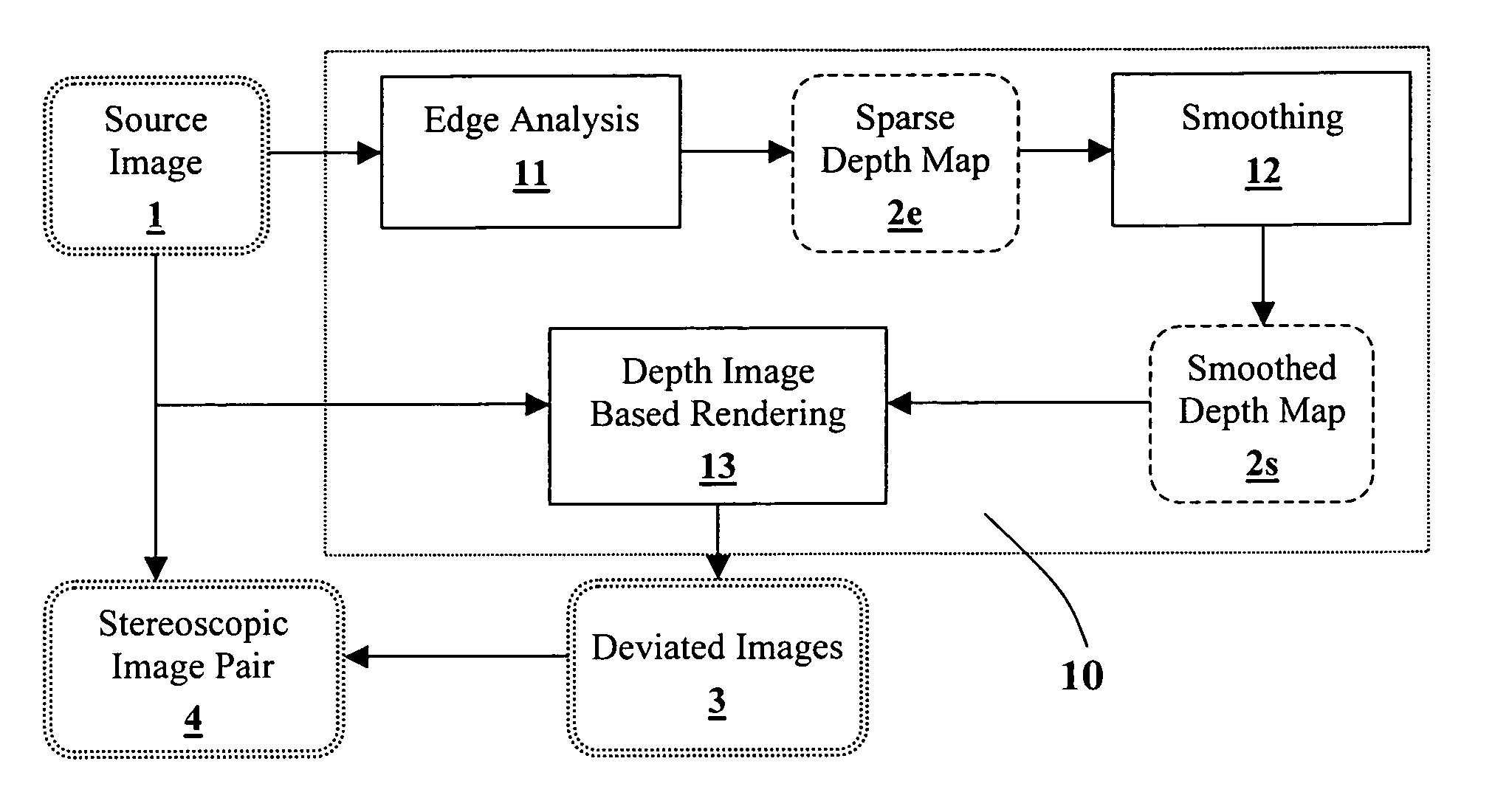
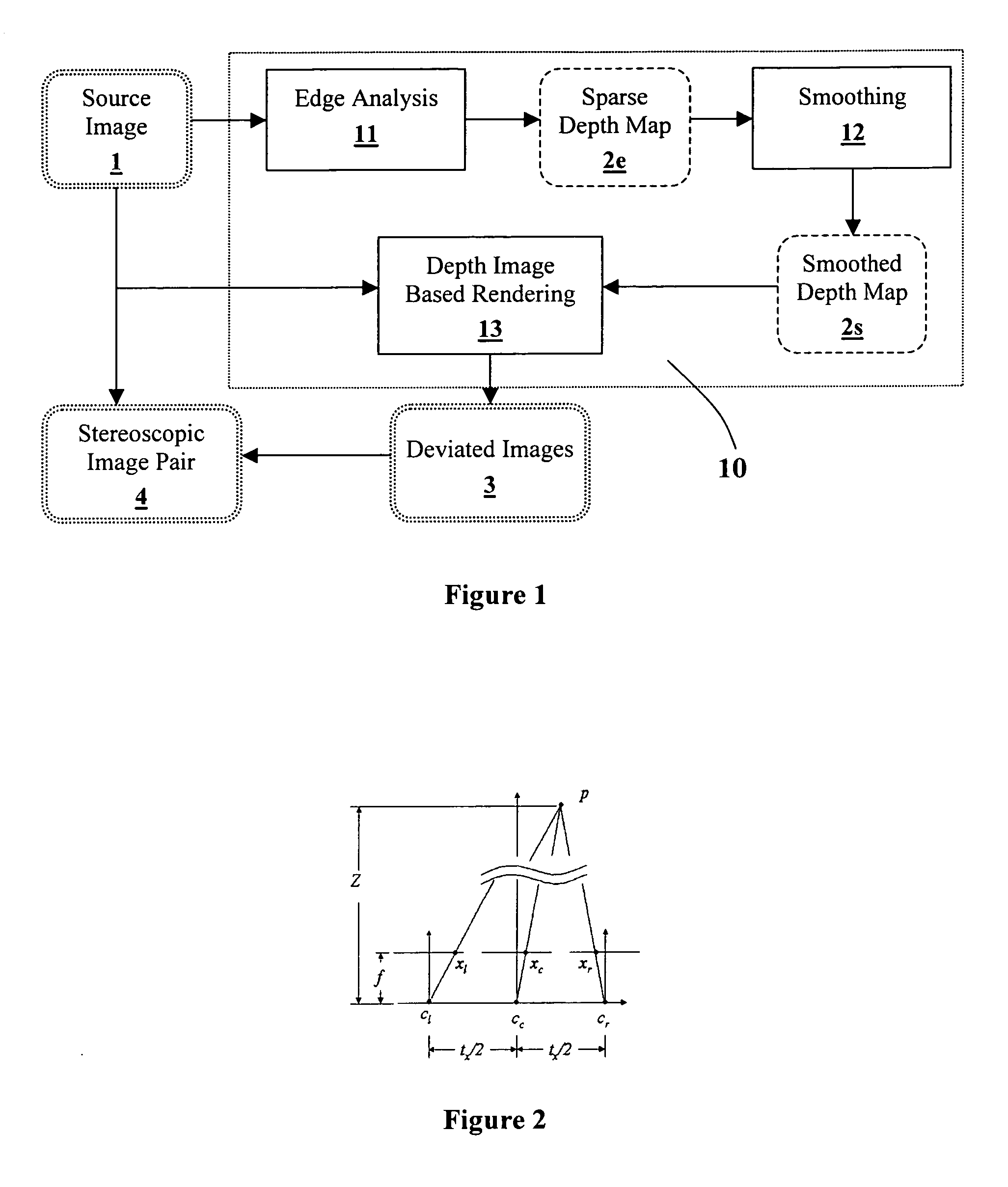
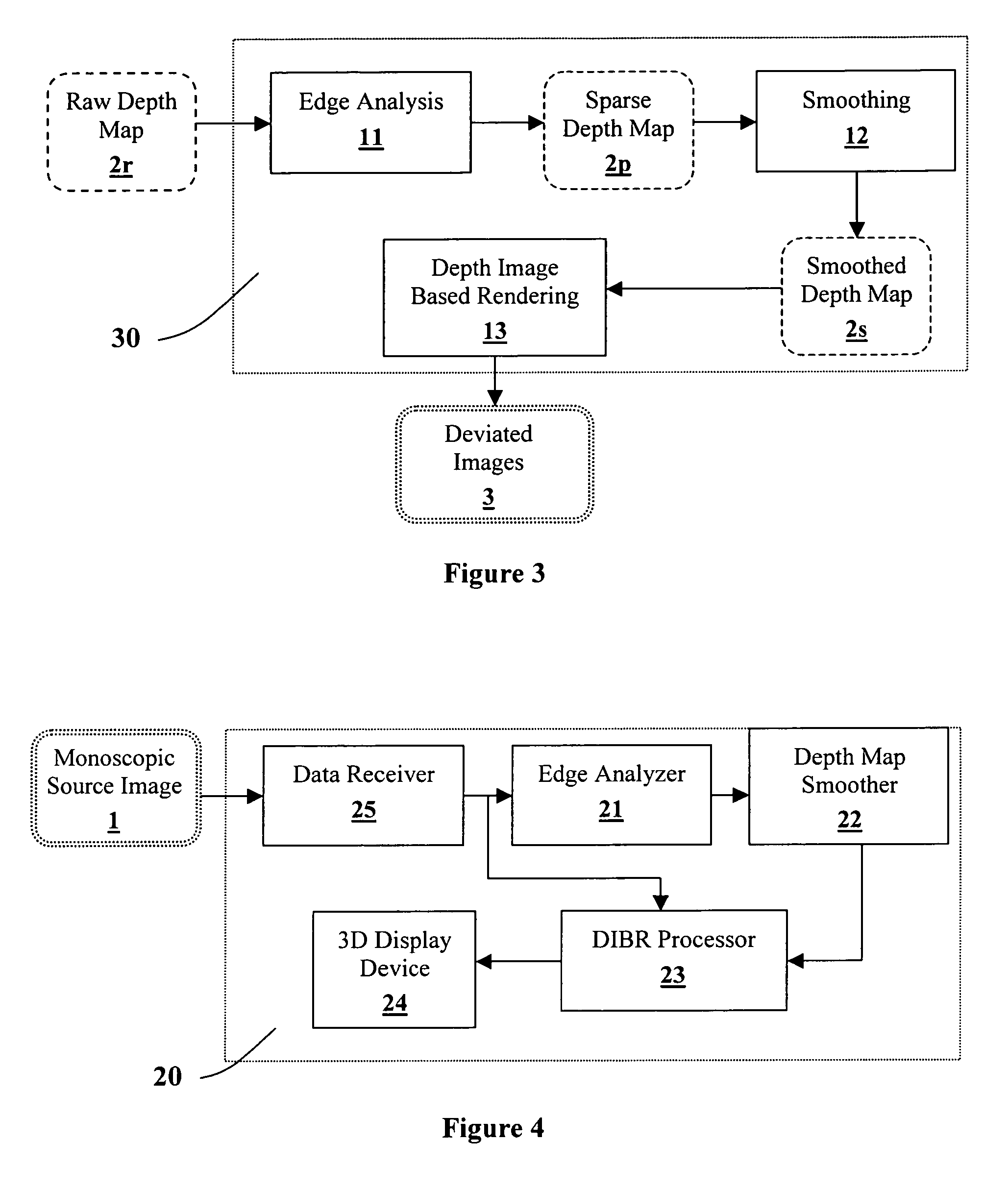
Generating a depth map from a two-dimensional source image for stereoscopic and multiview imaging
InactiveUS20070024614A1Saving in bandwidth requirementIncrease widthImage enhancementImage analysisViewpointsImage pair
Depth maps are generated from a monoscopic source images and asymmetrically smoothed to a near-saturation level. Each depth map contains depth values focused on edges of local regions in the source image. Each edge is defined by a predetermined image parameter having an estimated value exceeding a predefined threshold. The depth values are based on the corresponding estimated values of the image parameter. The depth map is used to process the source image by a depth image based rendering algorithm to create at least one deviated image, which forms with the source image a set of monoscopic images. At least one stereoscopic image pair is selected from such a set for use in generating different viewpoints for multiview and stereoscopic purposes, including still and moving images.
Owner:HER MAJESTY THE QUEEN & RIGHT OF CANADA REPRESENTED BY THE MIN OF IND THROUGH THE COMM RES CENT
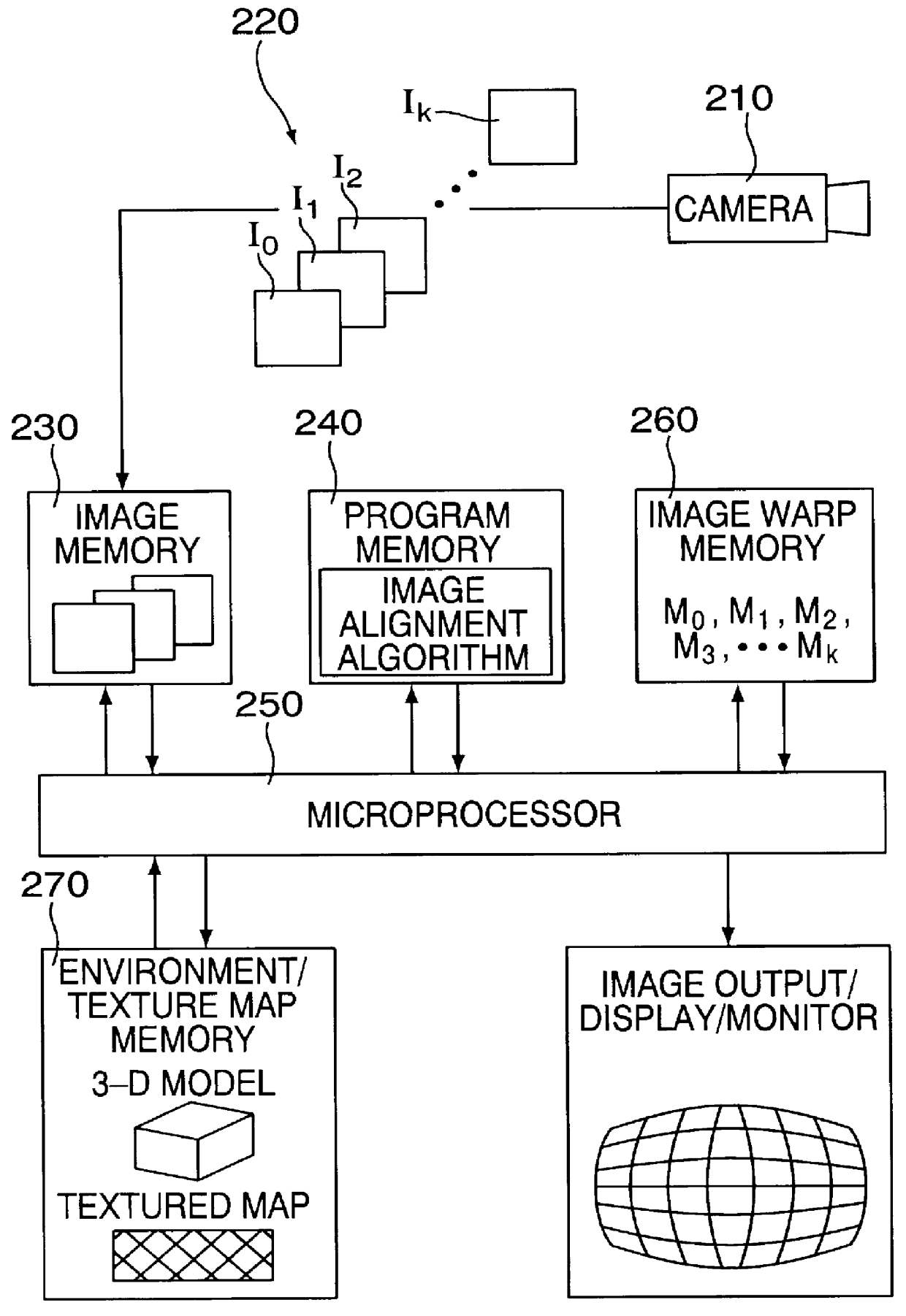
3-dimensional image rotation method and apparatus for producing image mosaics
InactiveUS6157747AQuality improvementEfficient solutionGeometric image transformationCharacter and pattern recognitionPattern recognitionComputer graphics (images)
The invention aligns a set of plural images to construct a mosaic image. At least different pairs of the images overlap partially (or fully), and typically are images captured by a camera looking at the same scene but oriented at different angles from approximately the same location or similar locations. In order to align one of the images with another one of the images, the following steps are carried out: (a) determining a difference error between the one image and the other image; (b) computing an incremental rotation of the one image relative to a 3-dimensional coordinate system through an incremental angle which tends to reduce the difference error; and (c) rotating the one image in accordance with the incremental rotation to produce an incrementally warped version of the one image. As long as the difference error remains significant, the method continues by re-performing the foregoing determining, computing and rotating steps but this time with the incrementally warped version of the one image.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
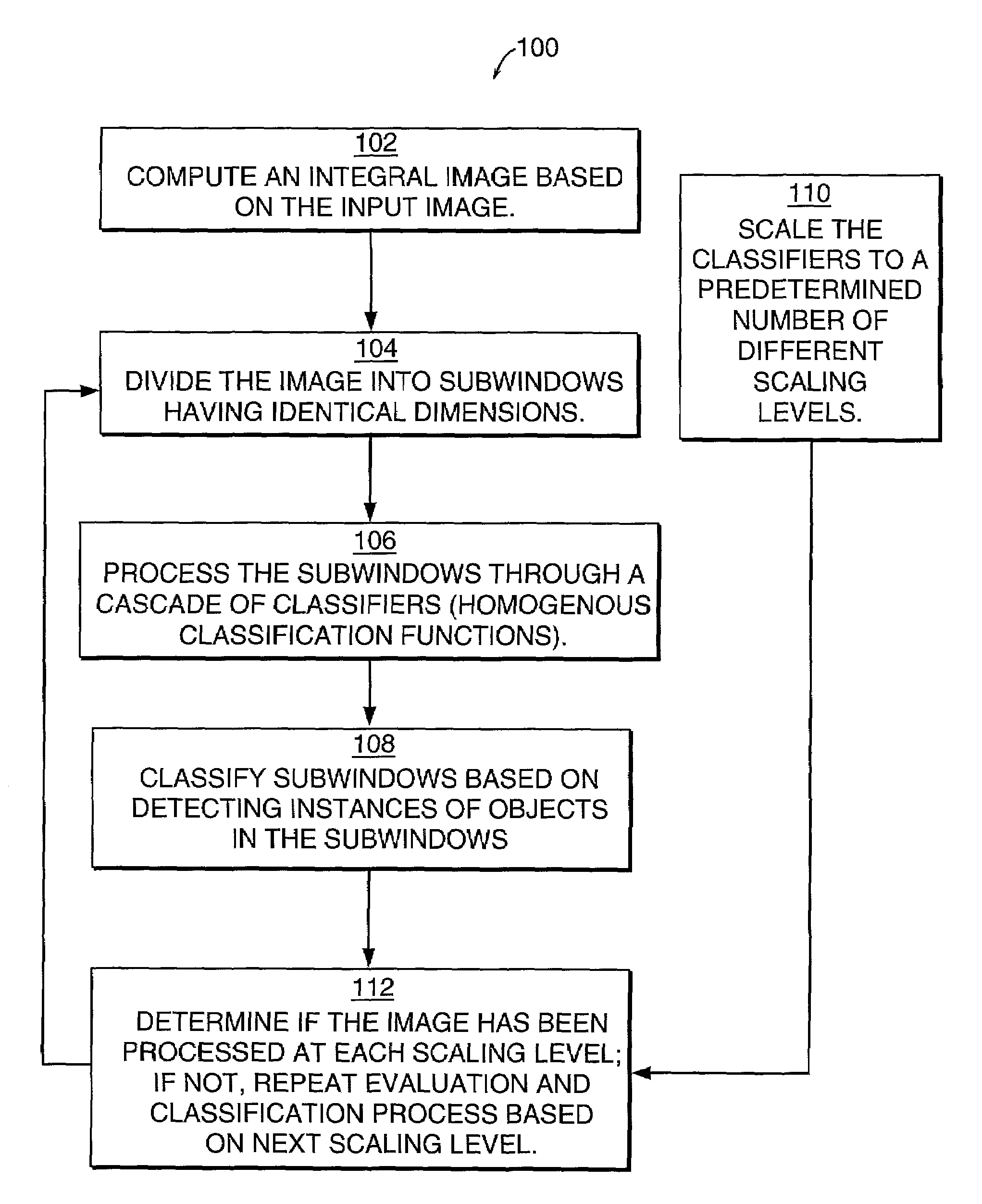
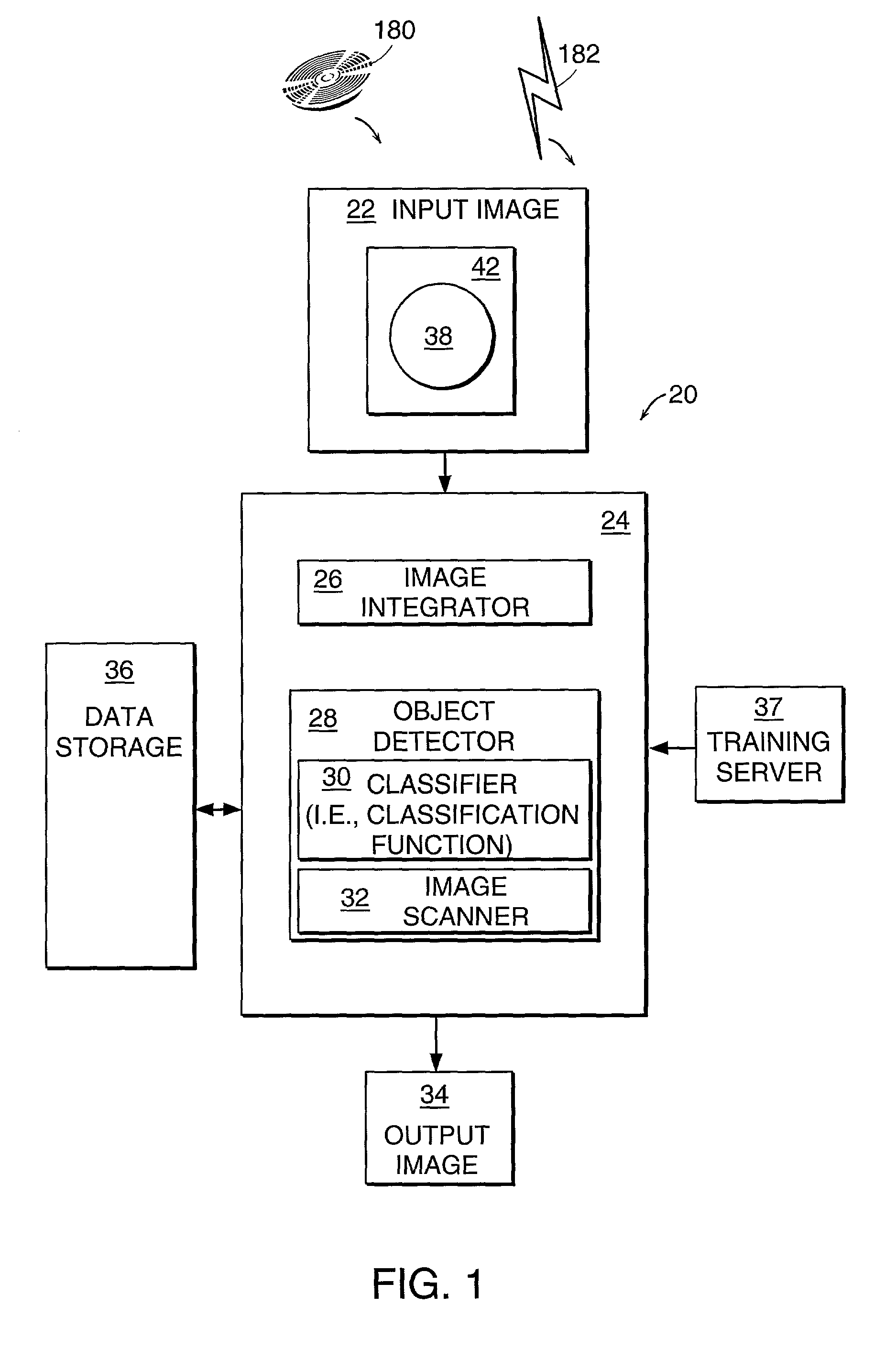
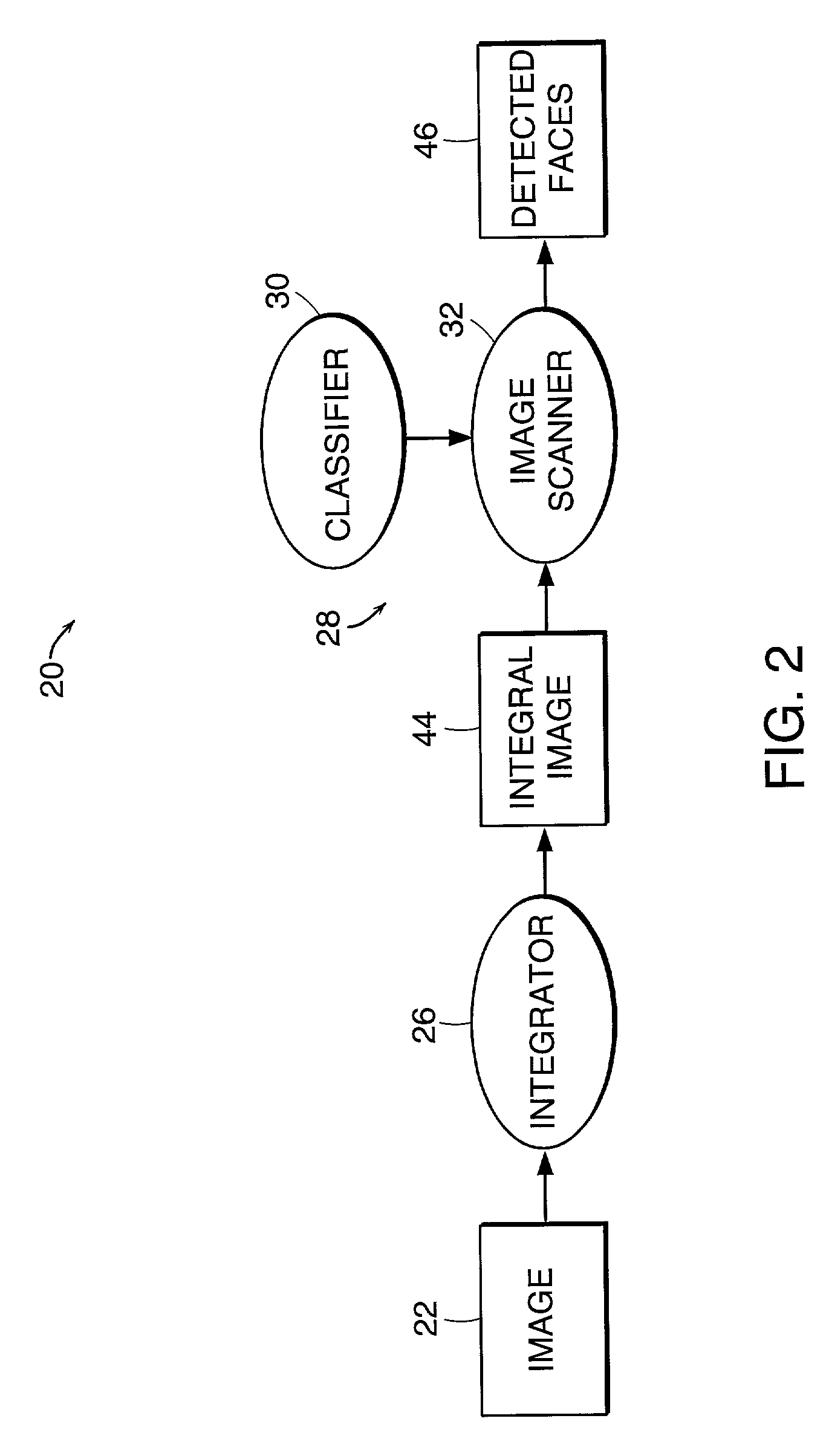
Method and system for object detection in digital images
InactiveUS7099510B2Powerful and efficientComputationally efficientCharacter and pattern recognitionColor television detailsRadiologyDigital image
An object detection system for detecting instances of an object in a digital image includes an image integrator and an object detector, which includes a classifier (classification function) and image scanner. The image integrator receives an input image and calculates an integral image representation of the input image. The image scanner scans the image in same sized subwindows. The object detector uses a cascade of homogenous classification functions or classifiers to classify the subwindows as to whether each subwindow is likely to contain an instance of the object. Each classifier evaluates one or more features of the object to determine the presence of such features in a subwindow that would indicate the likelihood of an instance of the object in the subwindow.
Owner:HEWLETT PACKARD DEV CO LP
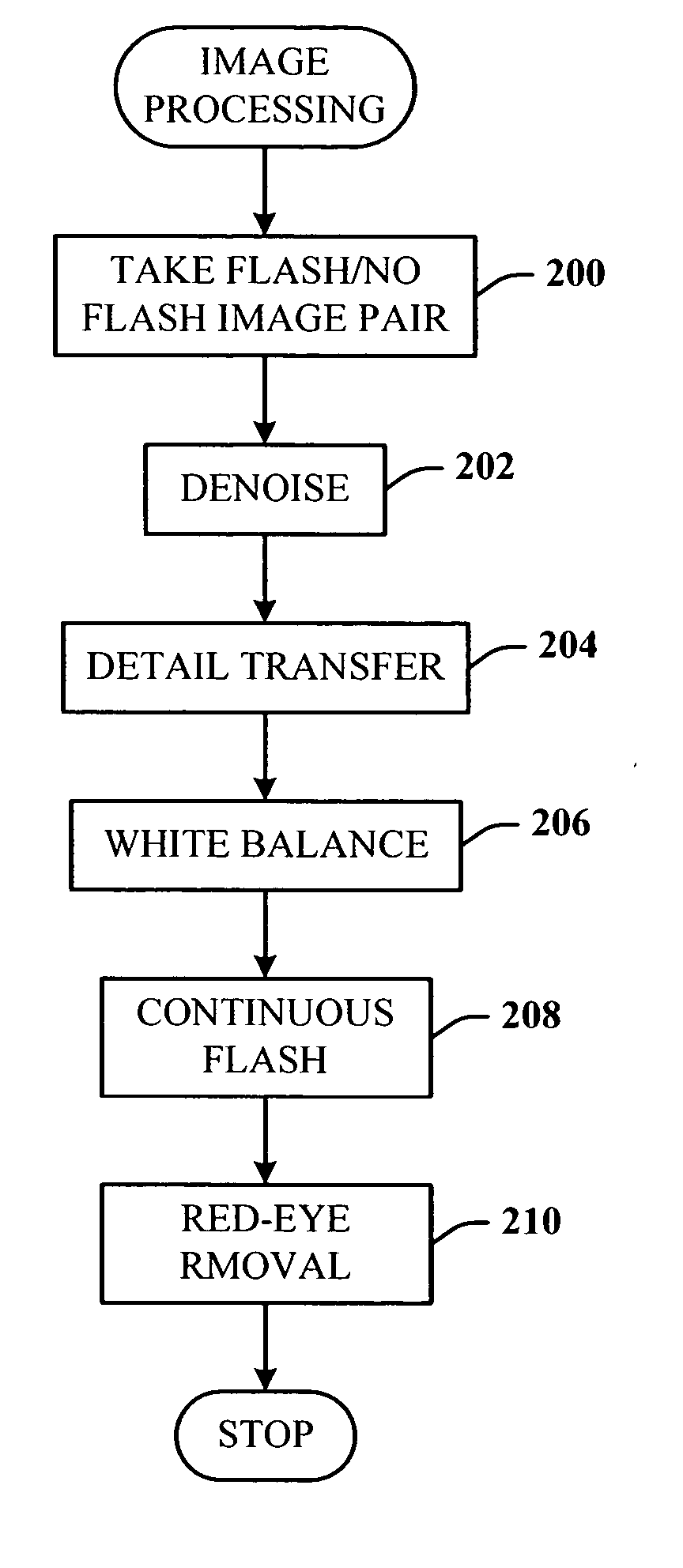
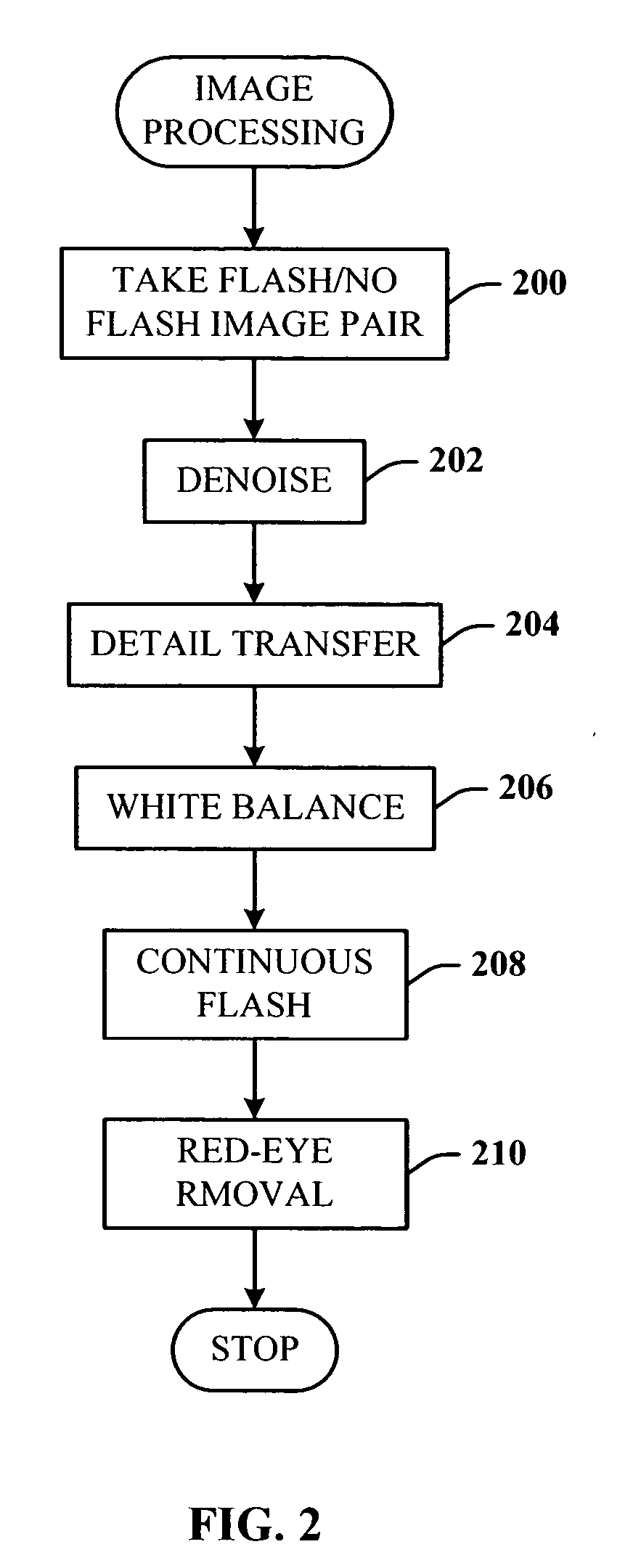
Digital photography with flash/no flash extension
InactiveUS20060008171A1Easy to optimizeTaking imageTelevision system detailsImage enhancementImage pairFlash light
A system and method for improving digital flash photographs. The present invention is a technique that significantly improves low-light imaging by giving the end-user all the advantages of flash photography without producing the jarring look. The invention uses an image pair—one taken with flash the other without—to remove noise from the ambient image, sharpen the ambient image using detail from the flash image, correct for color, and remove red-eye.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
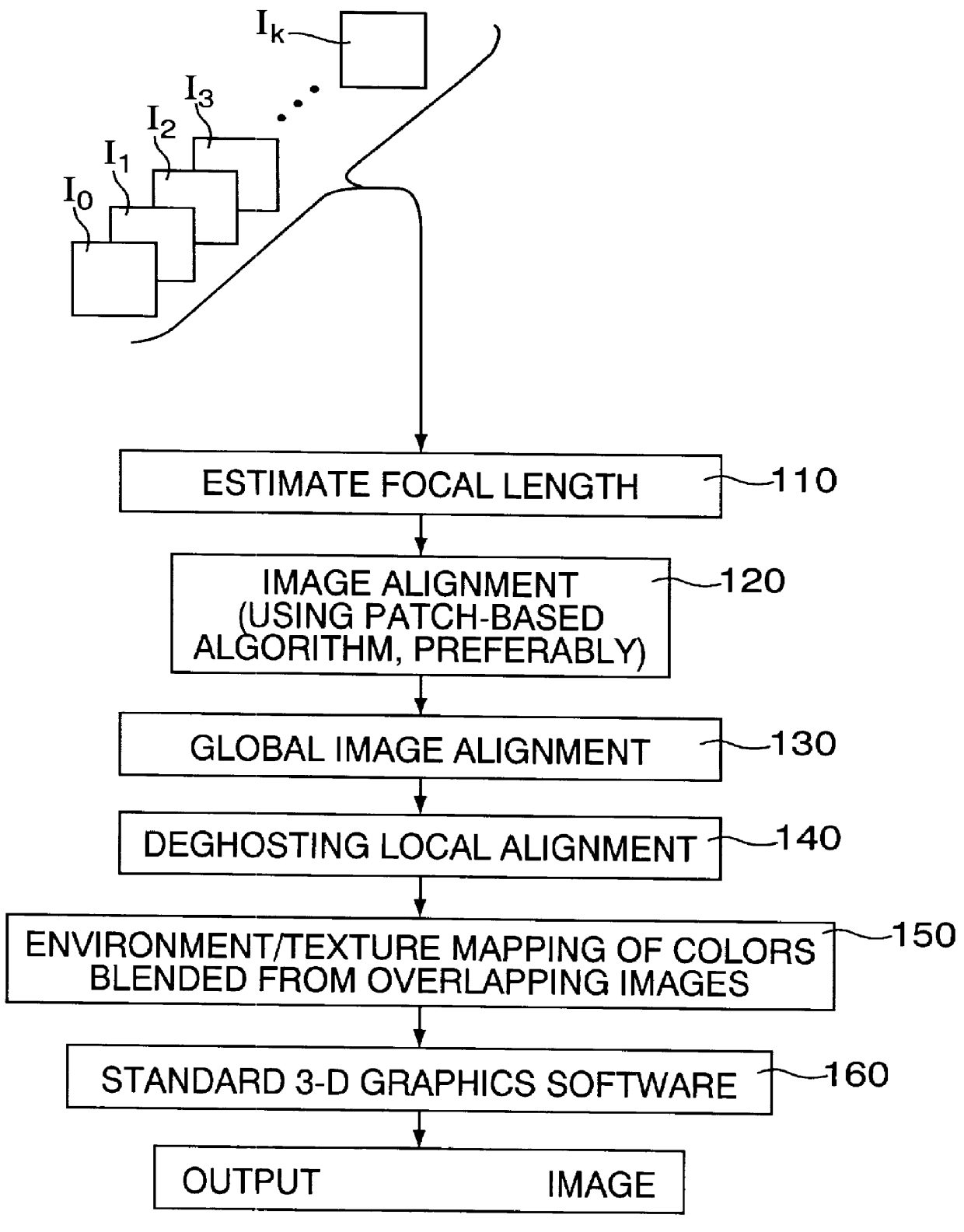
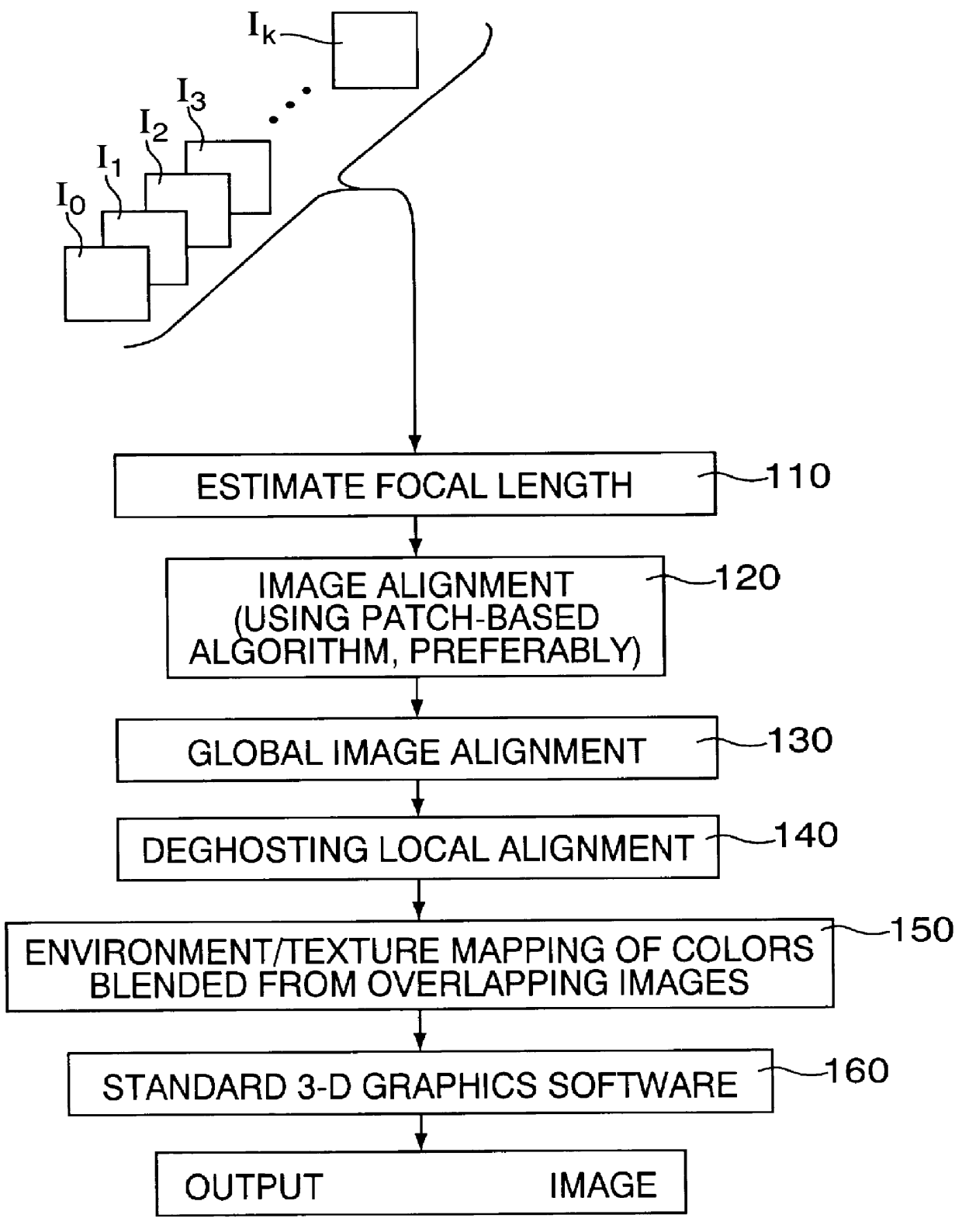
Focal length estimation method and apparatus for construction of panoramic mosaic images
InactiveUS6044181AReduce misregistrationEasy to integrateImage analysisGeometric image transformationEstimation methodsPerspective transformation
The focal length estimation method and apparatus claimed in this application aligns plural overlapping images with one another for constructing an image mosaic. This is accomplished by computing a planar perspective transformation between each overlapping pair of the images, computing from the planar perspective transformation a focal length of each image of the pair, computing from the focal length of each image a focal length transformation, computing a rotational transformation for each of the pair of images whereby a combination of the rotational transformation and the focal length transformation relates the respective image to a three-dimensional coordinate system. Registration errors between the pair of images are reduced by incrementally deforming the rotational transformation of one of the pair of images. The planar perspective transform is a matrix of warp elements, and the focal length is computed as a function of the warp elements, the function being derivable by constraining a first two rows or the first two columns of the matrix to have the same norm and to be orthogonal. The focal length of one image of a pair of images is found by applying the constraint on the matrix columns, while the focal length of the other image of the pair is found by applying the constraint on the matrix rows
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
Methods and apparatuses for image guided medical procedures
ActiveUS8303505B2Uncertainty errorLocation uncertaintyMedical simulationUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsTime informationImaging data
Methods and apparatuses for the image guidance and documentation of medical procedures. One embodiment includes combining small field of view images into a recorded image of with a large field of view and aligning the small field of view real time image with the recorded image through correlation of imaging data. A location and orientation determination system may be used to track the imaging system and provide a starting set of image alignment parameters and / or provide change updates to a set of image alignment parameters, which is then further improved through correlating imaging data. The recorded image may be selected according to real time measurement of a cardiac parameter during an image guided cardiac procedure. Image manipulations planned based on the recorded image can be stored and applied to the real time information. The position of the medical device may be determined and recorded through manipulating a cursor in a 3-D image space shown in two non-parallel views.
Owner:ABBOTT CARDIOVASCULAR
Process for roll-to-roll manufacture of a display by synchronized photolithographic exposure on a substrate web
InactiveUS20020182544A1High aspect ratioWell-defined shapePhoto-taking processesPhotomechanical apparatusDisplay deviceRefractive index
<heading lvl="0">Abstract of Disclosure< / heading> This invention relates to an electrophoretic display or a liquid crystal display and novel processes for its manufacture. The electrophoretic display (EPD) of the present invention comprises microcups of well-defined shape, size and aspect ratio and the microcups are filled with charged pigment particles dispersed in an optically contrasting dielectric solvent. The liquid crystal display (LCD) of this invention comprises well-defined microcups filled with at least a liquid crystal composition having its ordinary refractive index matched to that of the isotropic cup material. A novel roll-to-roll process and apparatus of the invention permits the display manufacture to be carried out continuously by a synchronized photo-lithographic process. The synchronized roll-to-roll process and apparatus permits a pre-patterned photomask, formed as a continuous loop, to be rolled in a synchronized motion in close parallel alignment to a web which has been pre-coated with a radiation sensitive material, so as to maintain image alignment during exposure to a radiation source. The radiation sensitive material may be a radiation curable material, in which the exposed and cured portions form the microcup structure. In an additional process step, the radiation sensitive material may be a positively working photoresist which temporarily seals the microcups. Exposure of a selected subset of the microcups via the photomask image permits selective re-opening, filling and sealing of the microcup subset. Repetition with additional colors permits the continuous assembly of a multicolor EPD or LCD display.
Owner:E INK CALIFORNIA
Methods and systems for creating virtual and augmented reality
Configurations are disclosed for presenting virtual reality and augmented reality experiences to users. The system may comprise an image capturing device to capture one or more images, the one or more images corresponding to a field of the view of a user of a head-mounted augmented reality device, and a processor communicatively coupled to the image capturing device to extract a set of map points from the set of images, to identify a set of sparse points and a set of dense points from the extracted set of map points, and to perform a normalization on the set of map points.
Owner:MAGIC LEAP INC
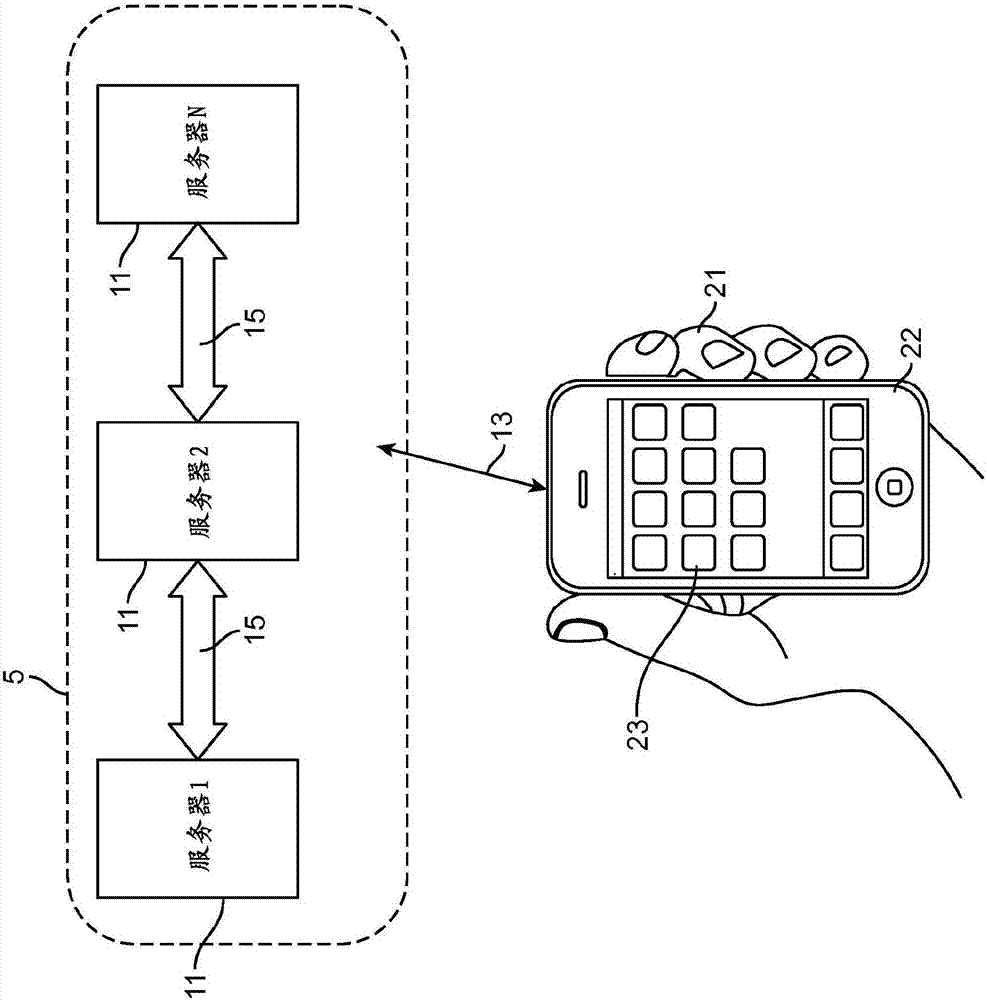
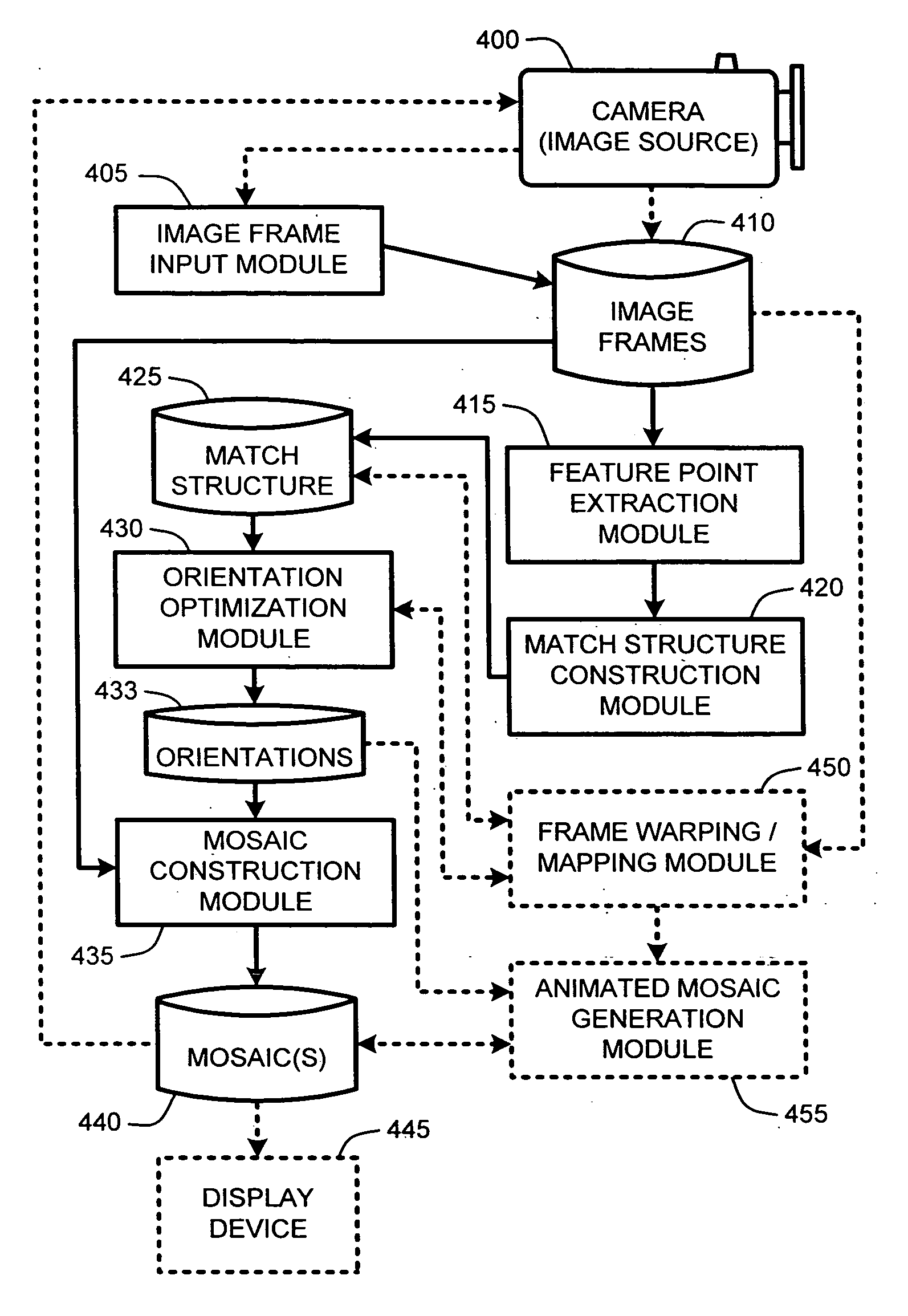
Video registration and image sequence stitching
ActiveUS20070031062A1Reduce computational complexityEasy constructionTelevision system detailsDigital data information retrievalIntermediate imageImage pair
A “Keyframe Stitcher” provides an efficient technique for building mosaic panoramic images by registering or aligning video frames to construct a mosaic panoramic representation. Matching of image pairs is performed by extracting feature points from every image frame and matching those points between image pairs. Further, the Keyframe Stitcher preserves accuracy of image stitching when matching image pairs by utilizing ordering information inherent in the video. The cost of searching for matches between image frames is reduced by identifying “keyframes” based on computed image-to-image overlap. Keyframes are then matched to all other keyframes, but intermediate image frames are only matched to temporally neighboring keyframes and neighboring intermediate frames to construct a “match structure.” Image orientations are then estimated from this match structure and used to construct the mosaic. Matches between image pairs may be compressed to reduce computational overhead by replacing groups of feature points with representative measurements.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
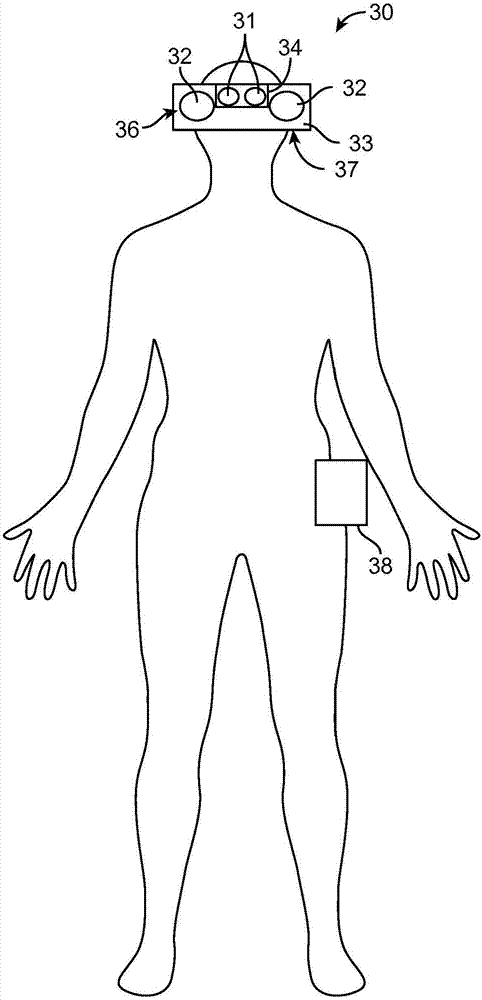
Augmented reality glasses for medical applications and corresponding augmented reality system
Owner:BADIALI GIOVANNI +3
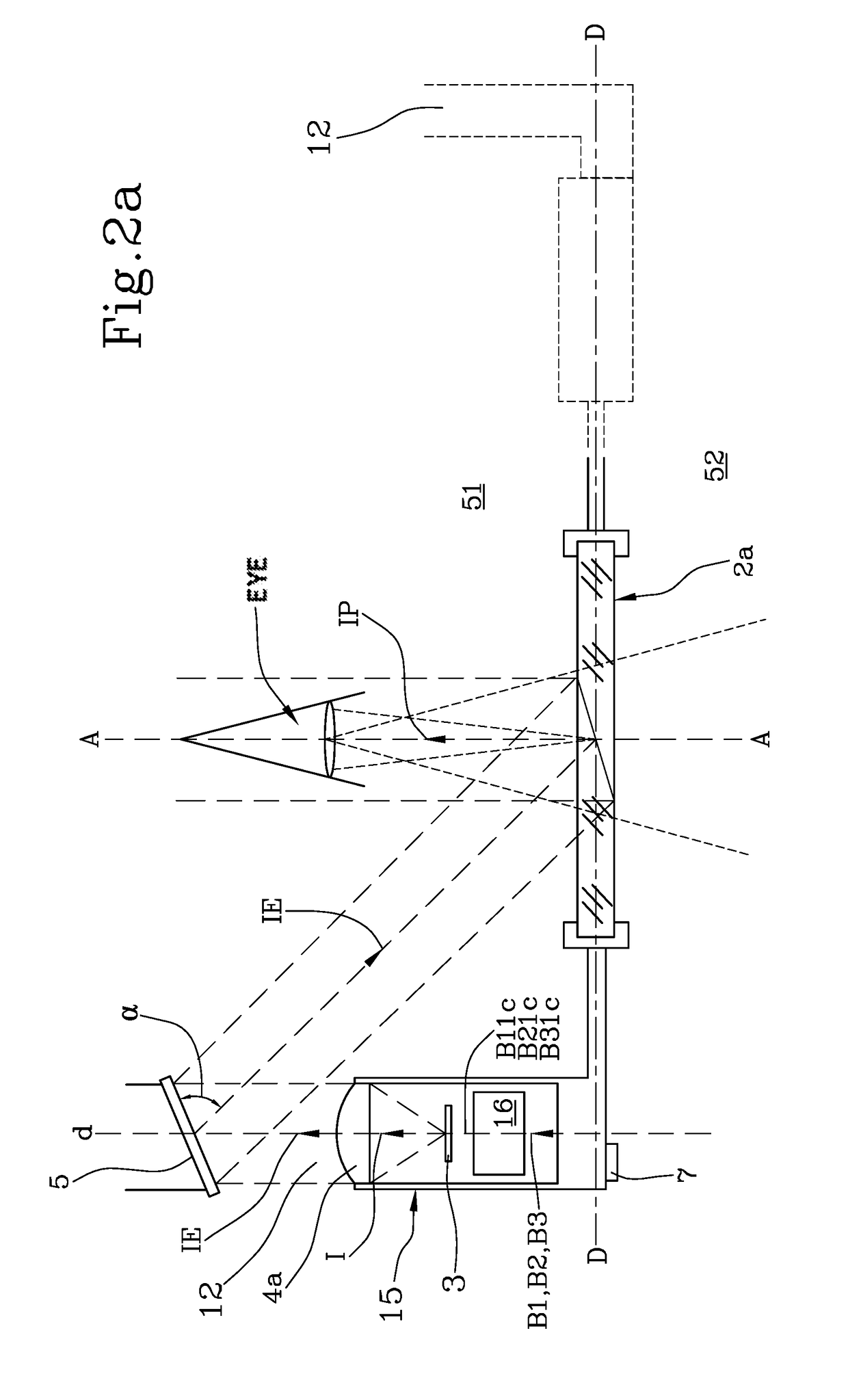
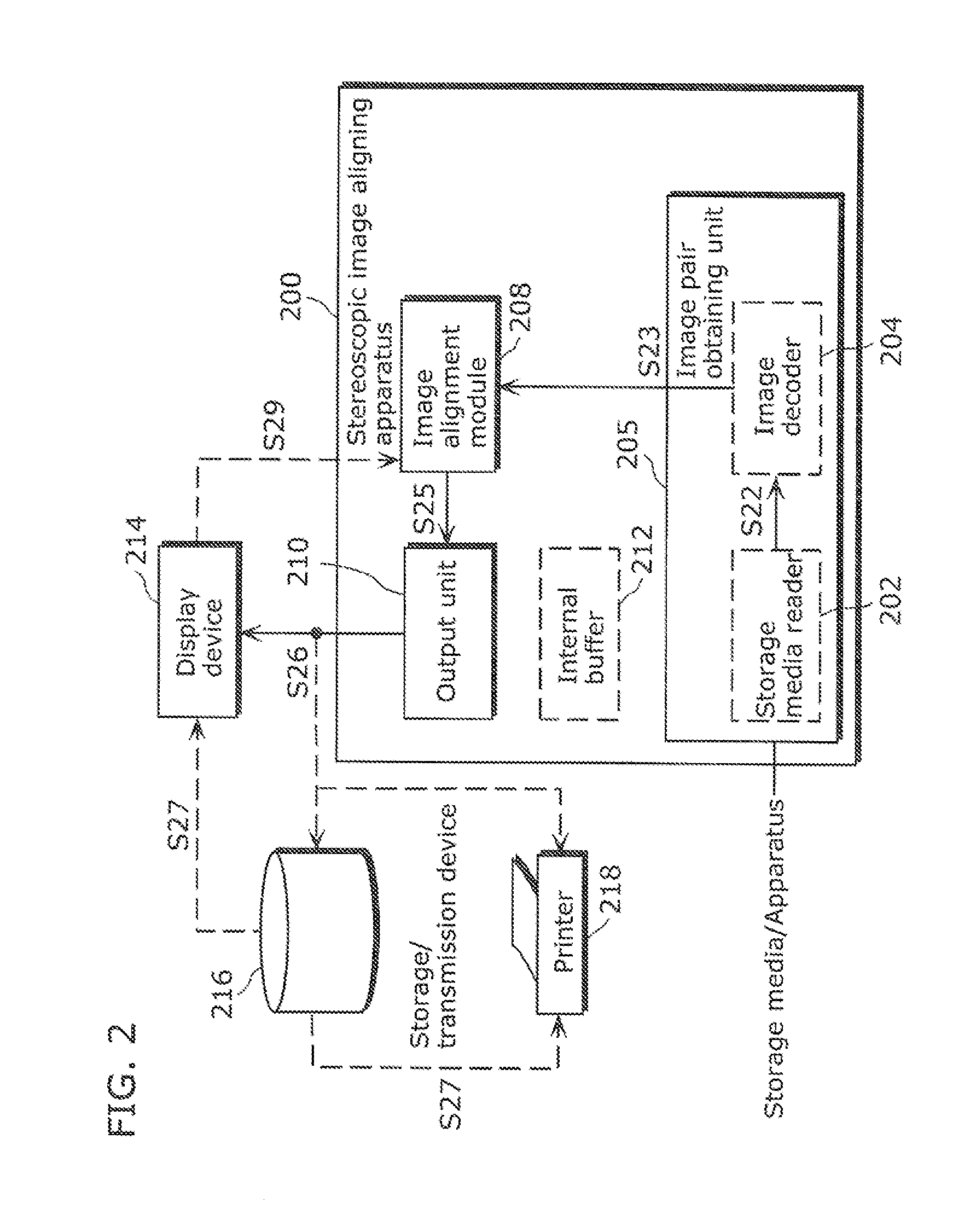
Stereoscopic image aligning apparatus, stereoscopic image aligning method, and program of the same
InactiveUS20120147139A1Short amount of timeFor automatic alignmentStereoscopic photographySteroscopic systemsParallaxImage pair
A stereoscopic image aligning apparatus (200) automatically aligns image pairs for stereoscopic viewing in a shorter amount of time than conventional apparatuses, which is applicable to image pairs captured by a single sensor camera or a variable baseline camera, without relying on camera parameters. The stereoscopic image aligning apparatus (200) includes: an image pair obtaining unit (205) obtaining an image pair including a left-eye image and a right-eye image corresponding to the left-eye image; a corresponding point detecting unit (252) detecting a corresponding point representing a set of a first point included in a first image that is one of the images of the image pair and a second point included in a second image that is the other of the images of the image pair and corresponding to the first point; a first matrix computing unit (254) computing a homography transformation matrix for transforming the first point such that a vertical parallax between the first and second points is smallest and an epipolar constraint is satisfied; a transforming unit (260) transforming the first image using the homography transformation matrix; and an output unit (210) outputting: a third image that is the transformed first image; and the second image.
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
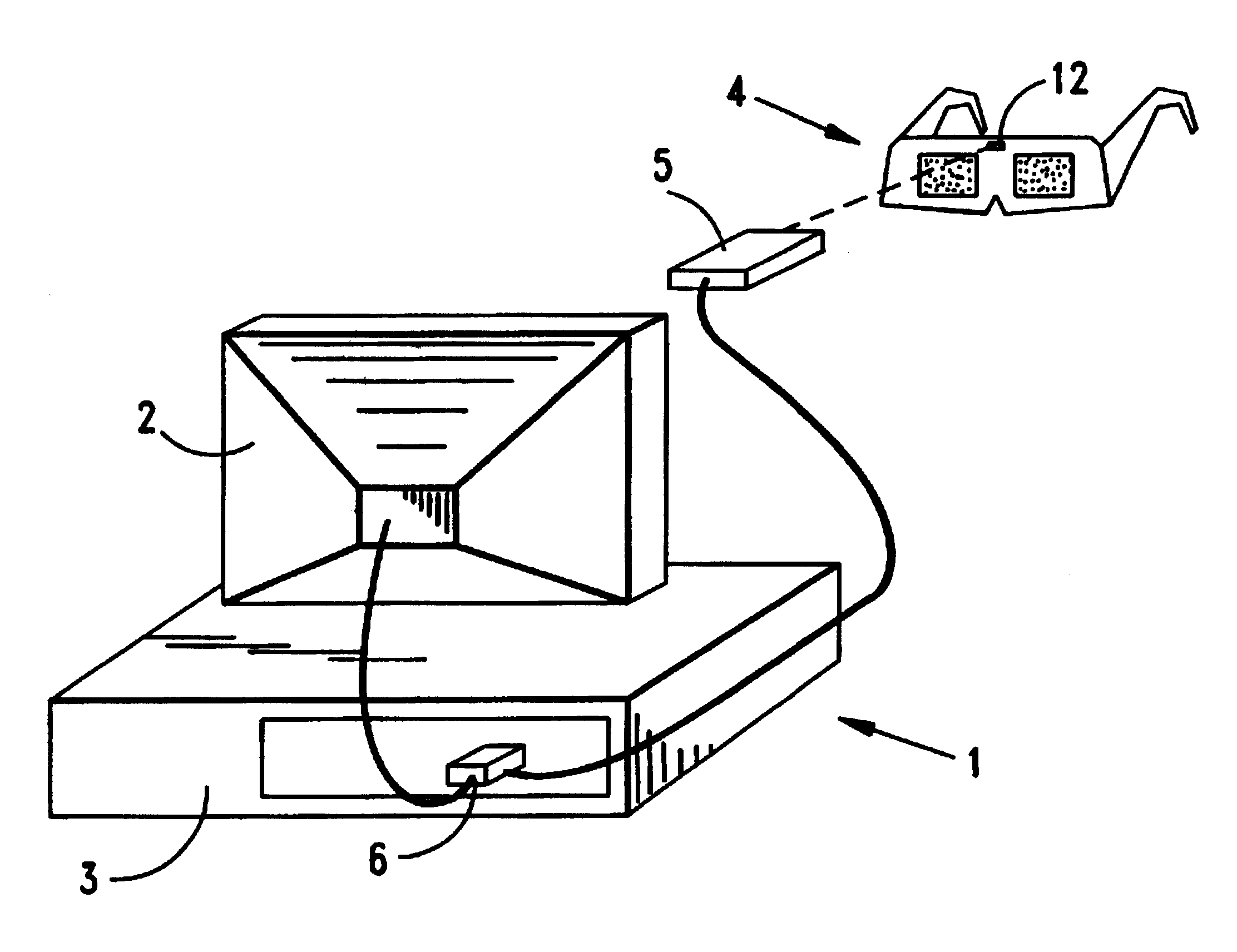
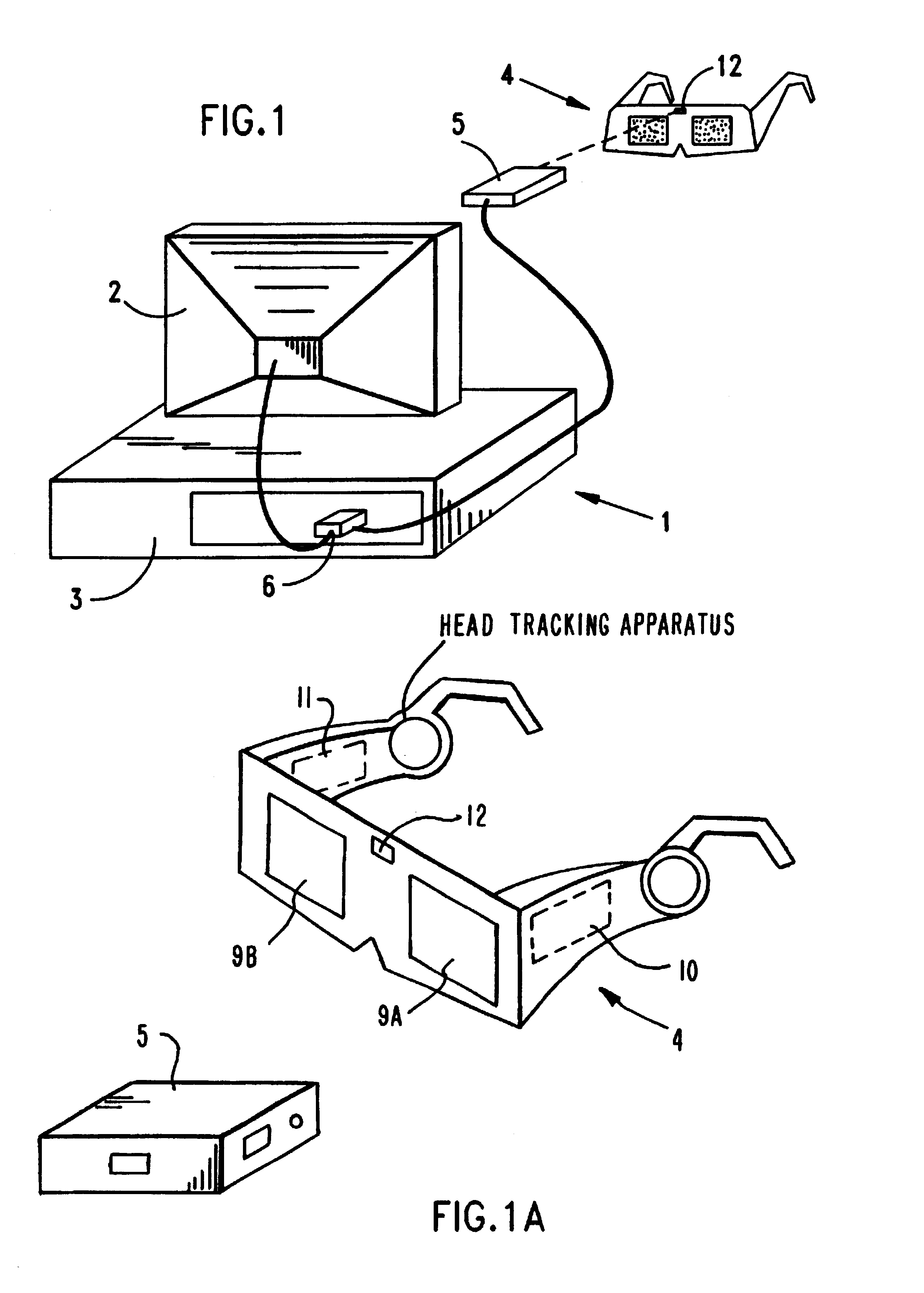
Stereoscopic 3-d viewing system with portable electro-optical viewing glasses and shutter-state control signal transmitter having multiple modes of operation for stereoscopic viewing of 3-d images displayed in different stereoscopic image formats
InactiveUS6456432B1Improve battery lifeExtend battery lifeInput/output for user-computer interactionTelevision system detailsControl signalMultiple modes
The present invention relates to a system and method of viewing pairs of perspective images of 3-D objects (i.e. stereoscopic image pairs) displayed from a CRT display surface in a time-multiplexed or field-sequential manner, and more particularly to a universal method of generating control signals for synchronously changing the optical state of liquid crystal (LC) shutter panels through which the time-multiplexed perspective. images can be sequentially viewed in a substantially flicker-free manner by the left and right eyes of a human viewer, independent of whether the images are displayed on NTSC, PAL, VGA or SVGA styled CRT display devices.
Owner:REVEO
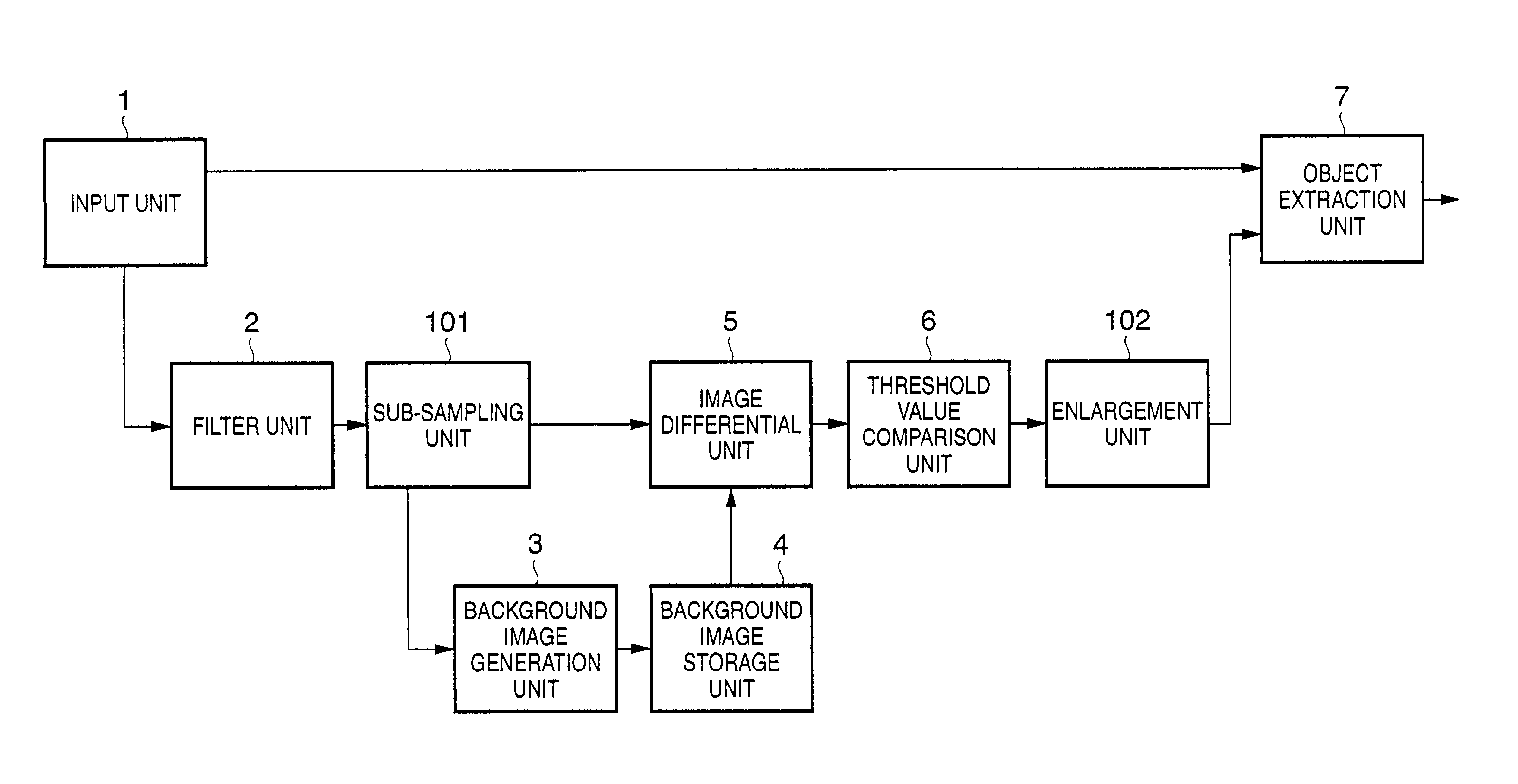
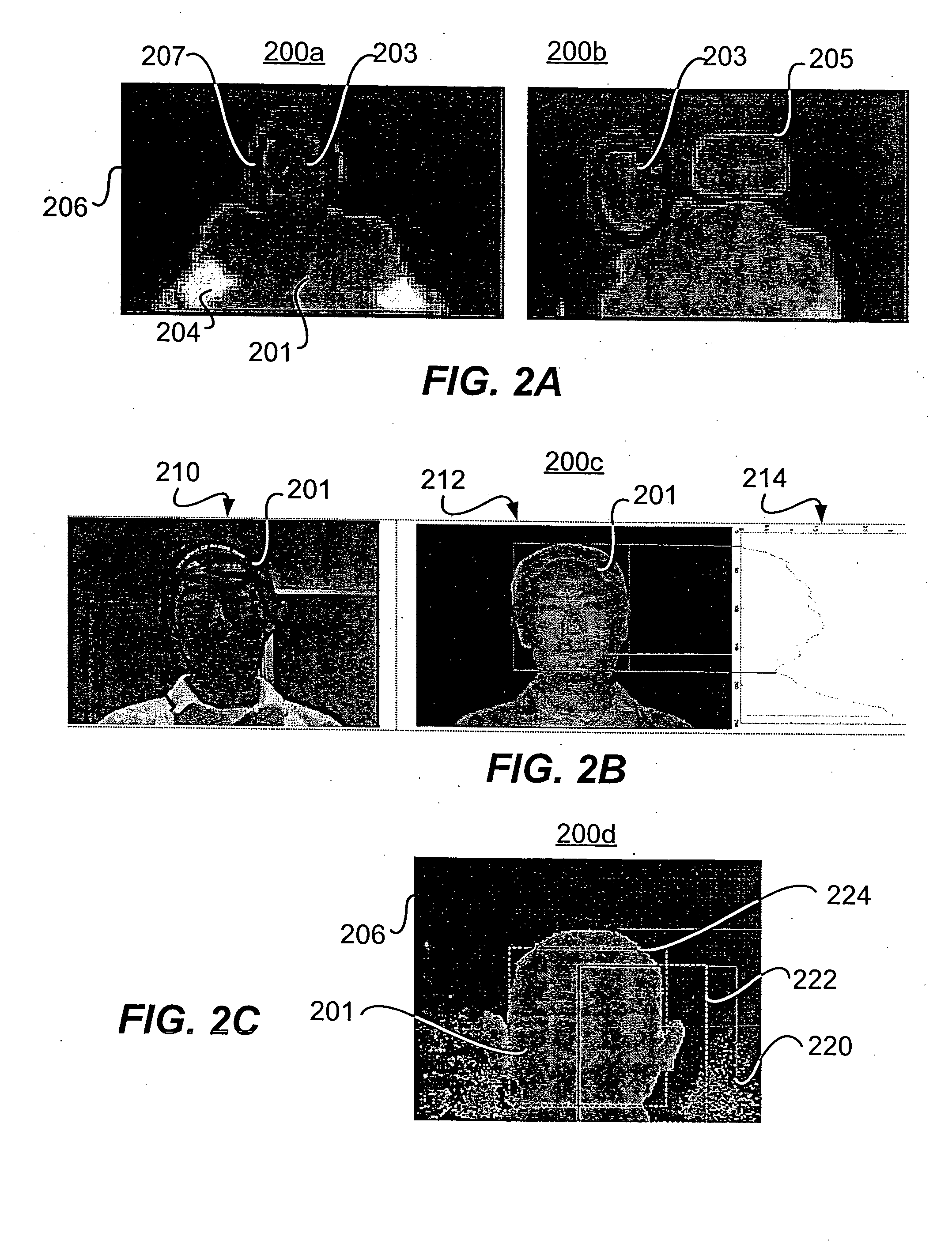
Image processing apparatus and method
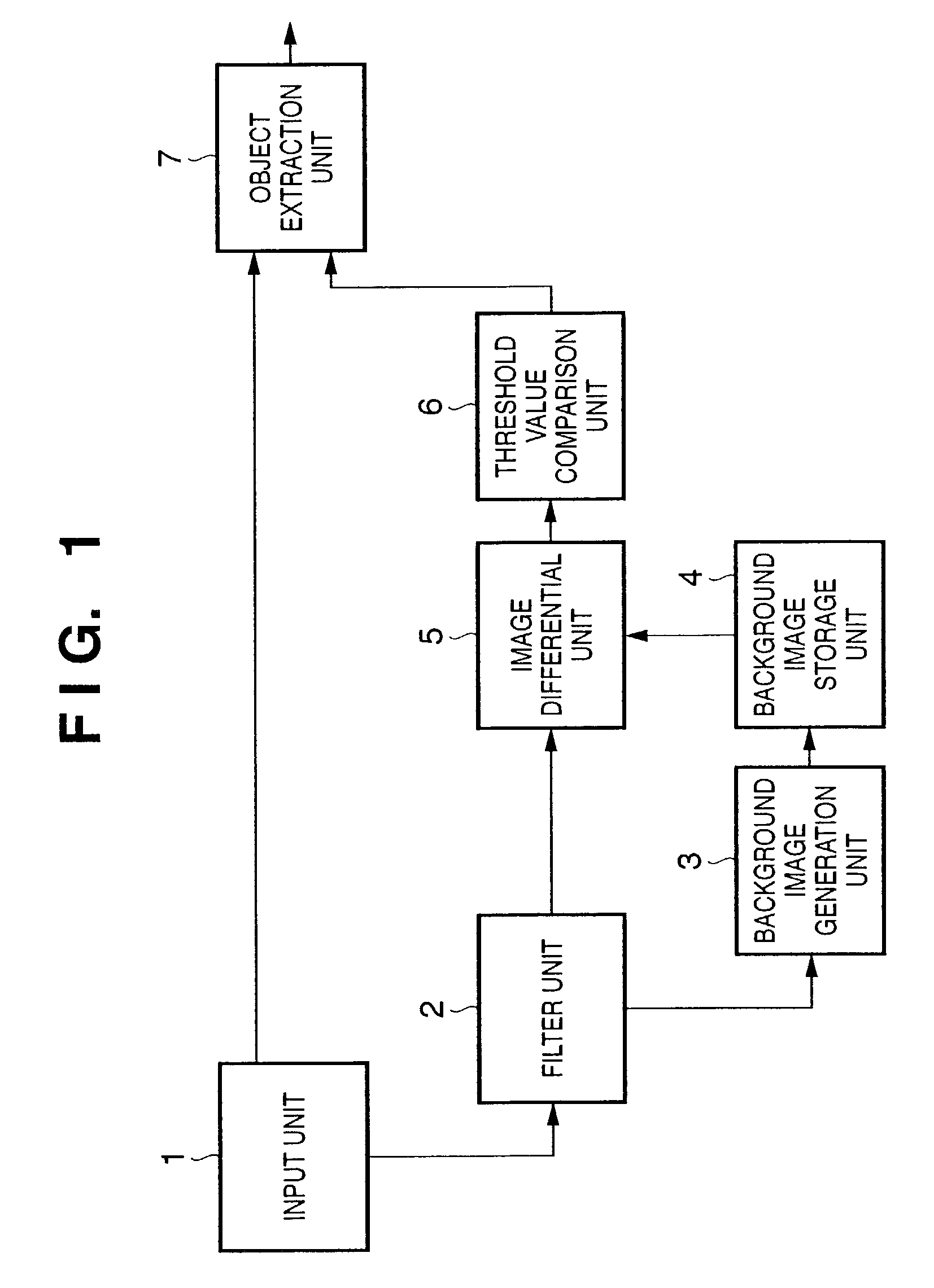
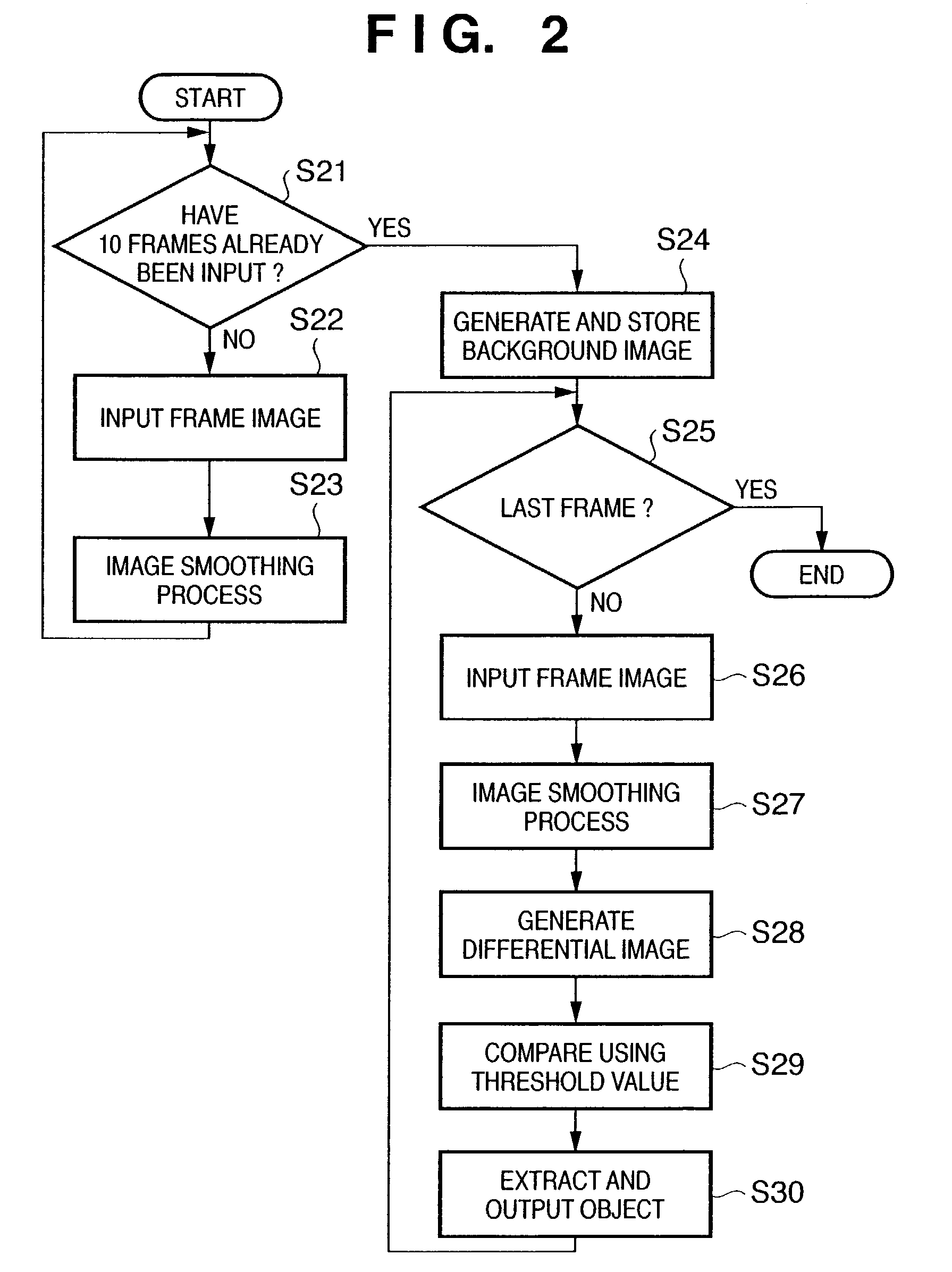
InactiveUS7162101B2Accurate extractionImage enhancementTelevision system detailsImage extractionImaging processing
An image processing apparatus and method, which can appropriately extract an object even when the focus of a camera having an automatic focus adjustment function shifts from the background to the object. To this end, frame images which are sensed by an image sensing unit and are sequential in the time axis direction are input from an input unit. The input frame images are smoothed by a filter unit. A background image generation unit generates an average image of a predetermined number of smoothed frame images as a background image. An image differential unit generates a differential image between the predetermined smoothed frame image and the background image. An object extraction unit extracts an object region where a predetermined object is sensed, on the basis of the differential image.
Owner:CANON KK
Methods and systems for obstacle detection using structured light
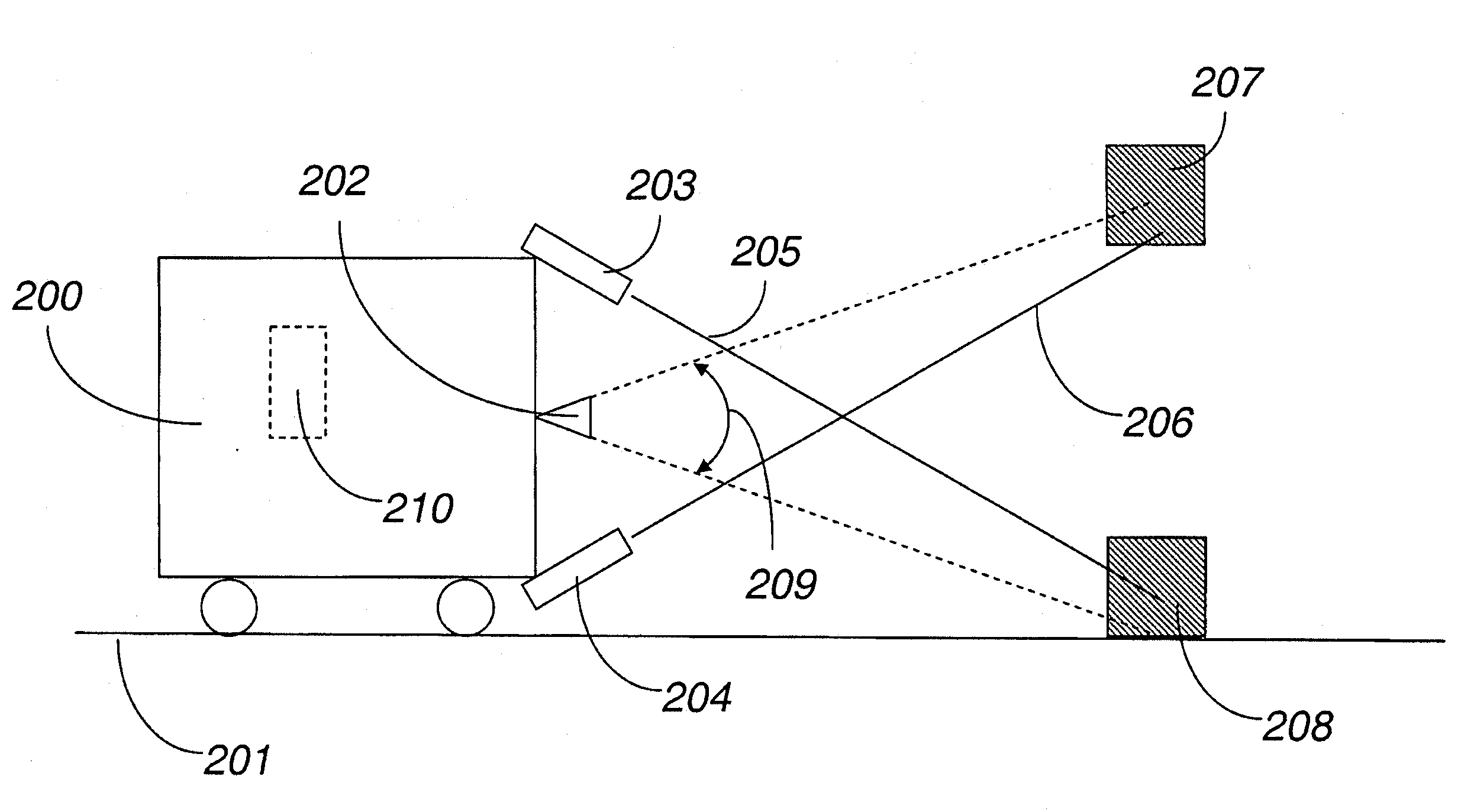
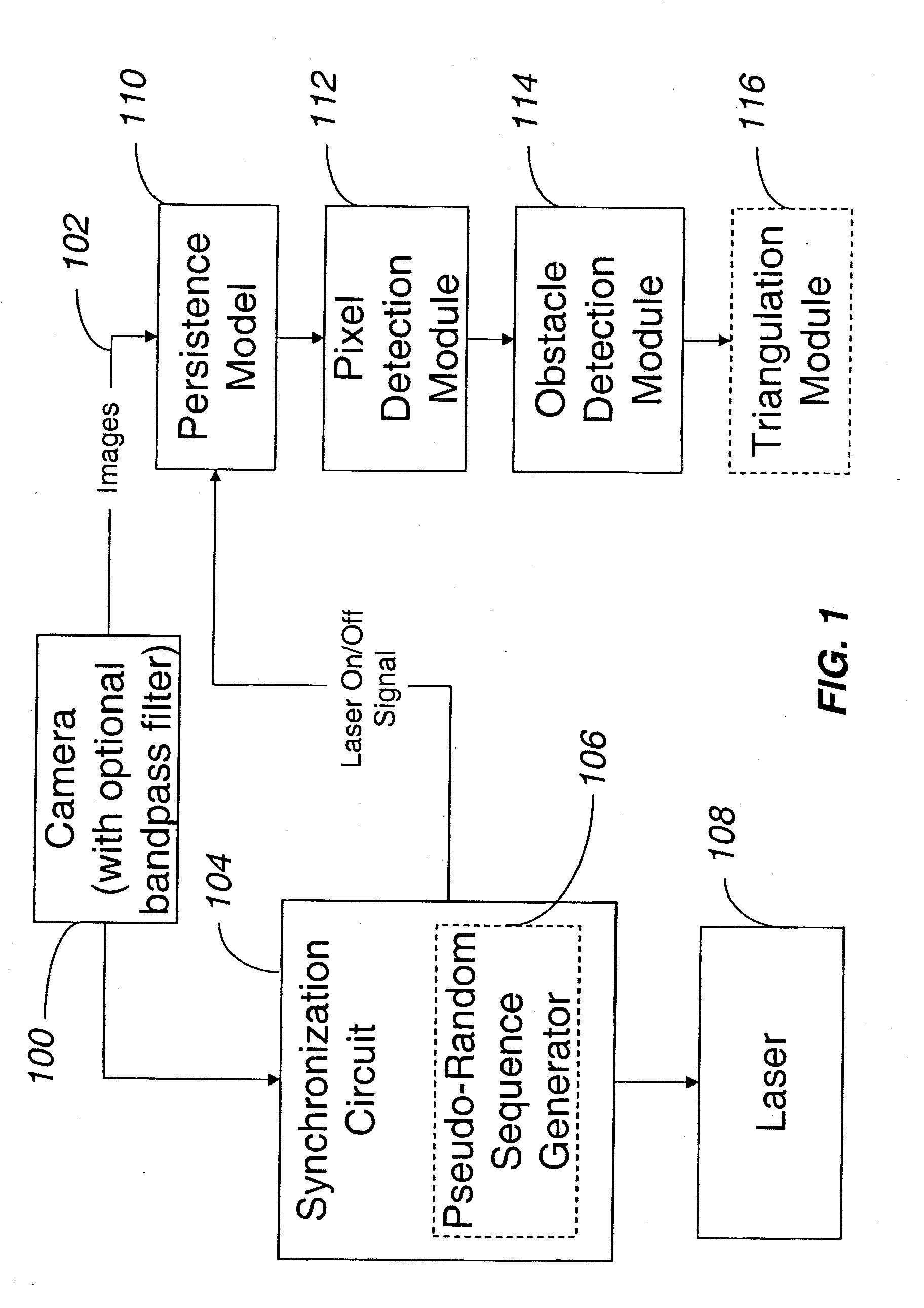
ActiveUS20150168954A1Robust detectionImprove accuracyProgramme controlComputer controlProcessing elementVision sensor
An obstacle detector for a mobile robot while the robot is in motion is disclosed. The detector preferably includes at least one light source configured to project pulsed light in the path of the robot; a visual sensor for capturing a plurality of images of light reflected from the path of the robot; a processing unit configured to extract the reflections from the images; and an obstacle detection unit configured to detect an obstacle in the path of the robot based on the extracted reflections. In the preferred embodiment, the reflections of the projected light are extracted by subtracting pairs of images in which each pair includes a first image captured with the at least one light source on and a second image captured with the at least one light source off, and then combining images of two or more extracted reflections to suppress the background.
Owner:IROBOT CORP
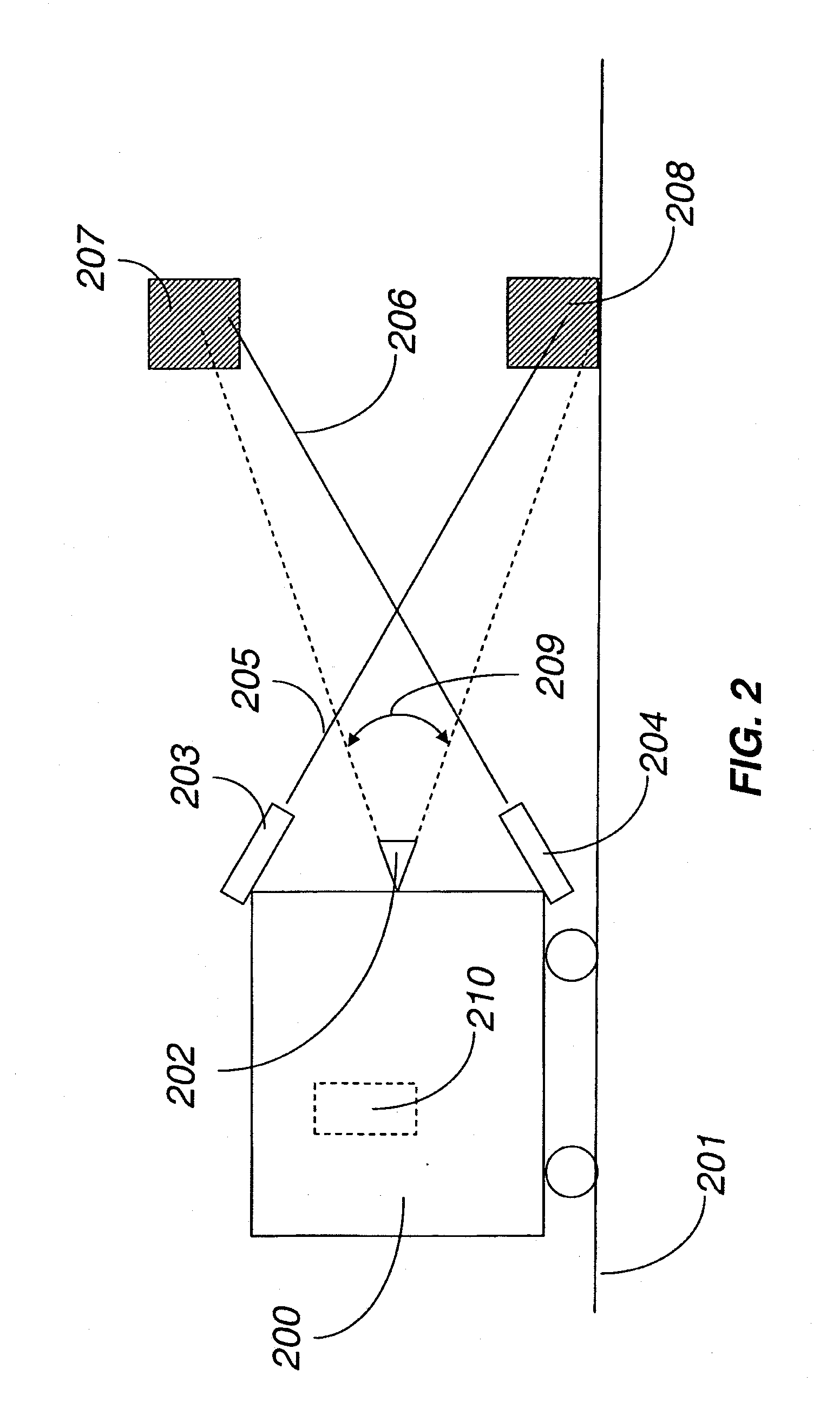
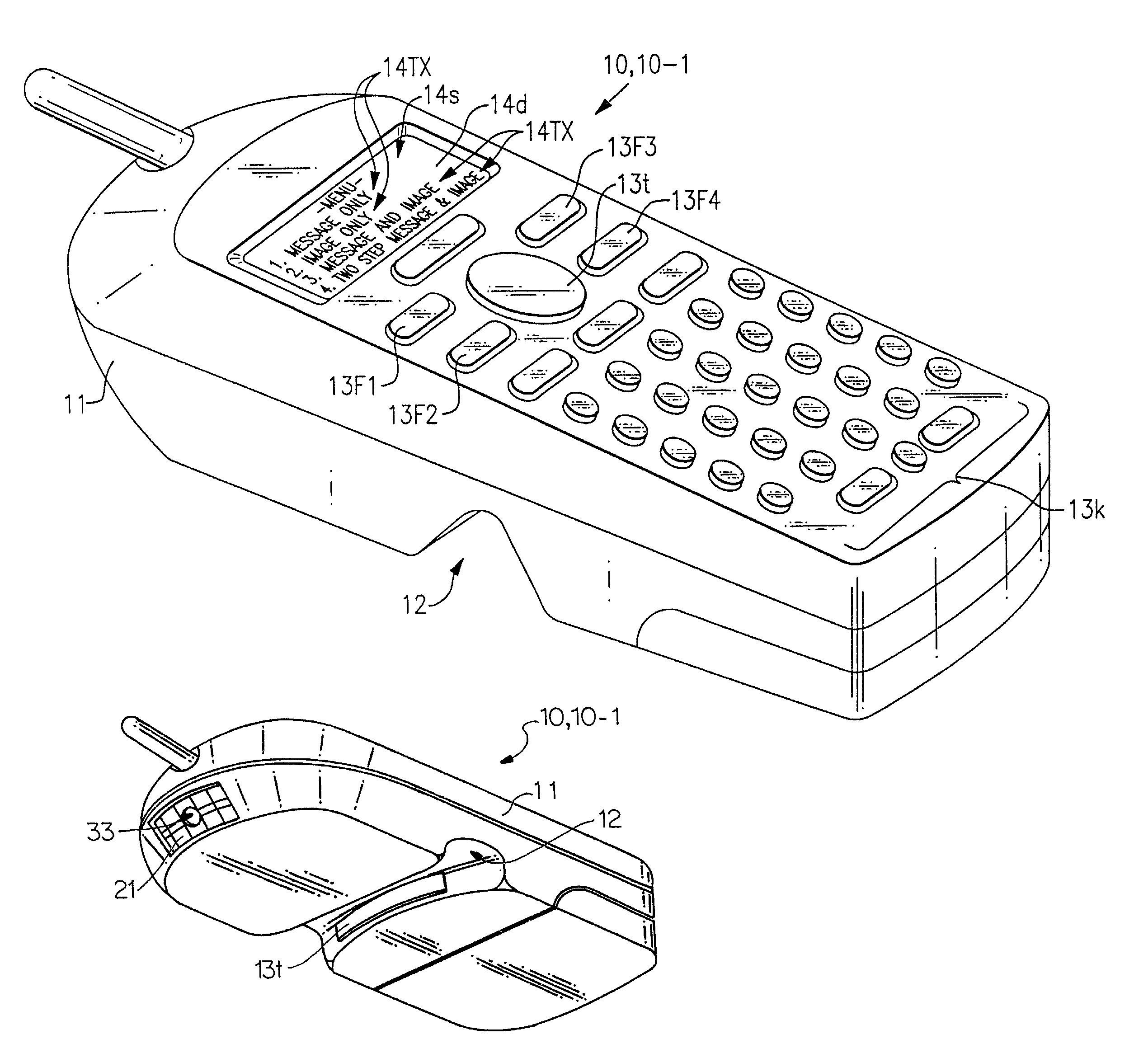
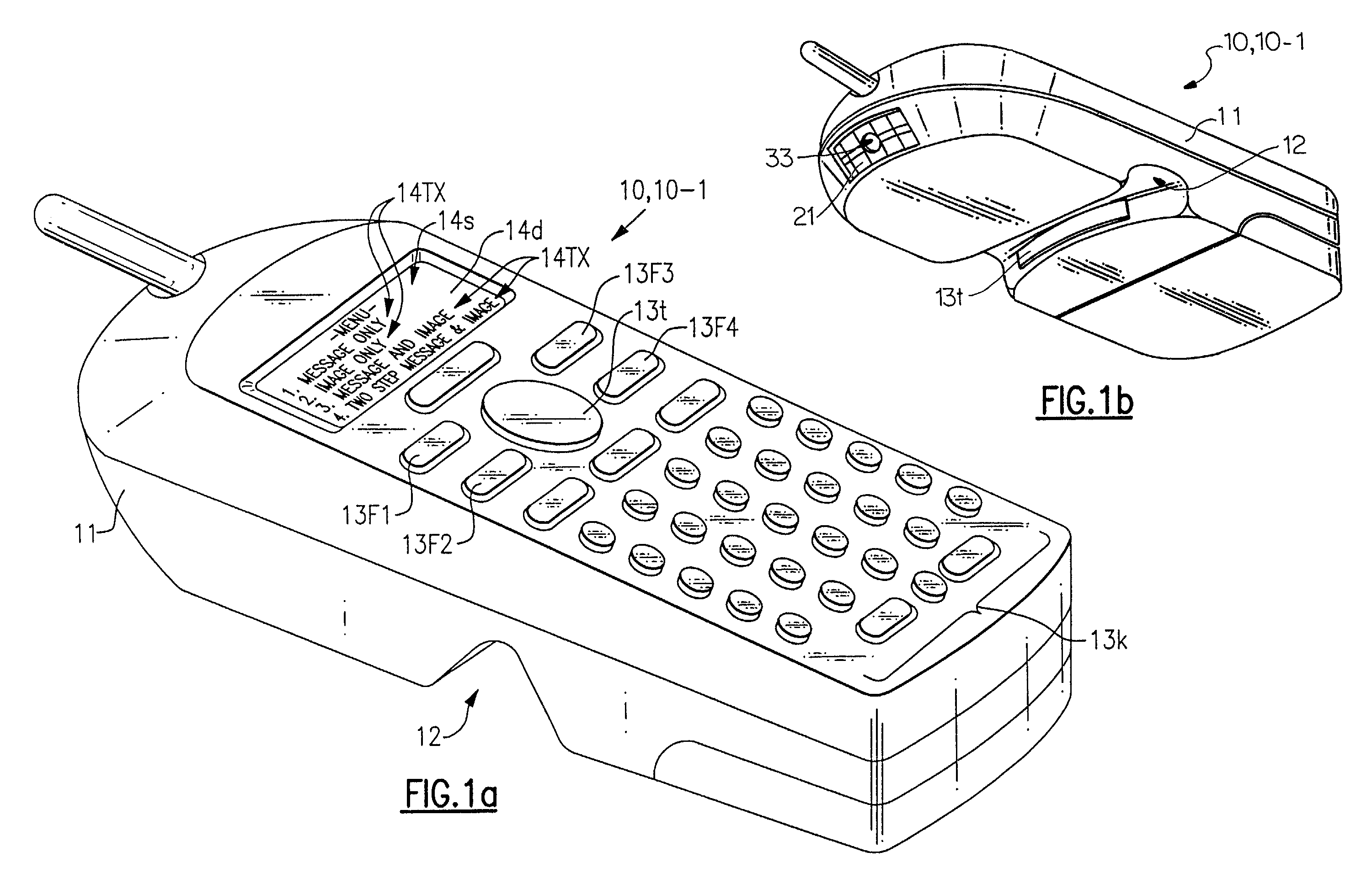
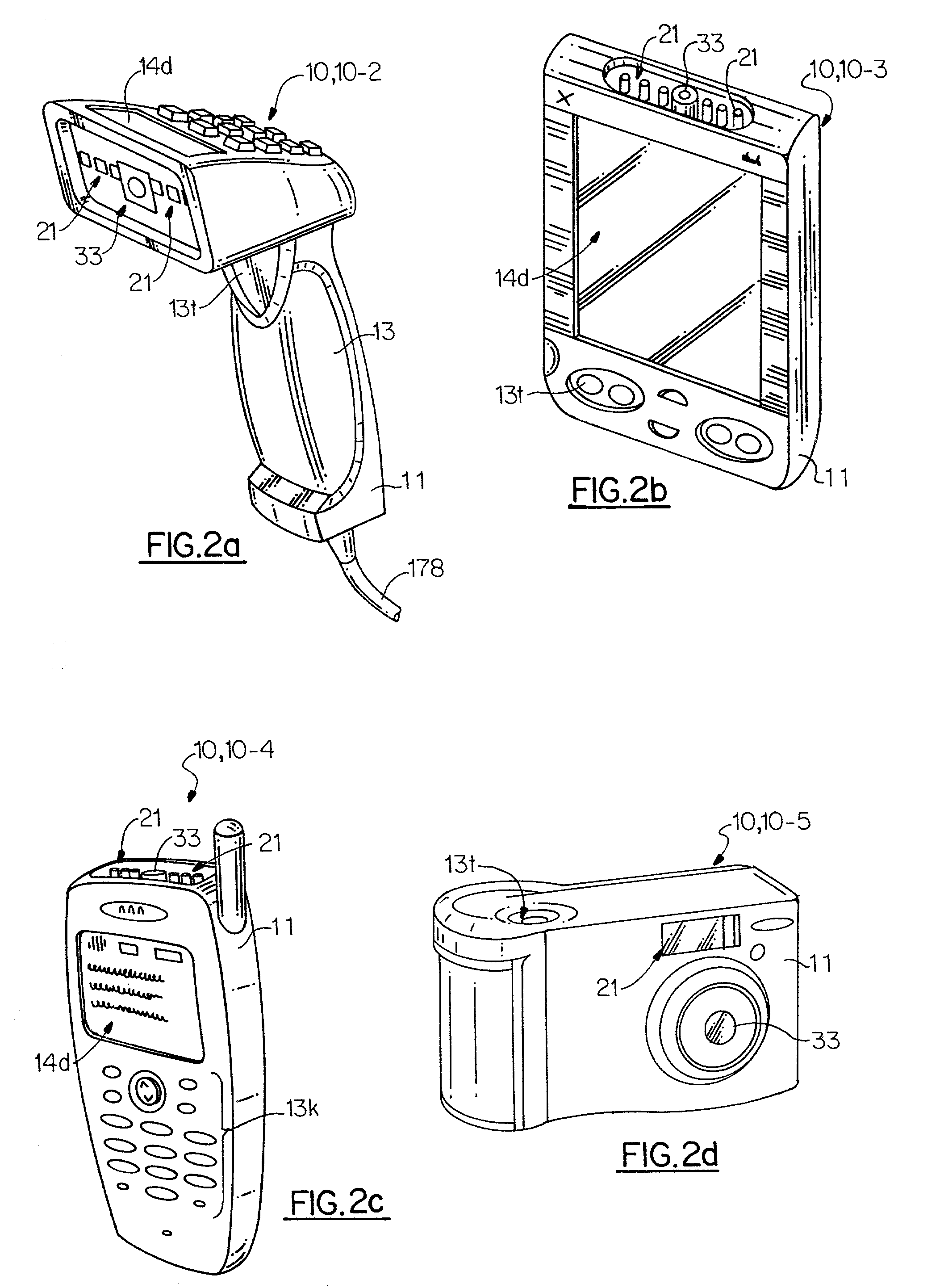
Multimode image capturing and decoding optical reader
InactiveUS7111787B2Easily searchable databaseUseful in detectionVisual representatino by photographic printingCharacter and pattern recognitionComputer hardwareEngineering
The present invention is an imaging device which can be equipped with decode functionality and which can be configured to operate in at least one of four user selected modes. In a first, “message only” mode, the device stores into a designated memory location a decoded-out message corresponding to a decodable indicia. In a second, “image only” mode, the device stores into a designated frame storage memory location an image representation of a scene. In a third, “omage plu message” mode the device stores into a designated frame storage memory location an image representation comprising a representation of a decodable symbol and into the same or other memory location the decoded-out message decoded from the decodable indicia, or data corresponding to the same. In the fourth, “two-step message and image” mode, the device is controlled to capture an image a first time for decoding a decodable indicia and a second time for capturing an image that is associated with the decoded-out message corresponding to the decodable indicia.
Owner:HAND HELD PRODS
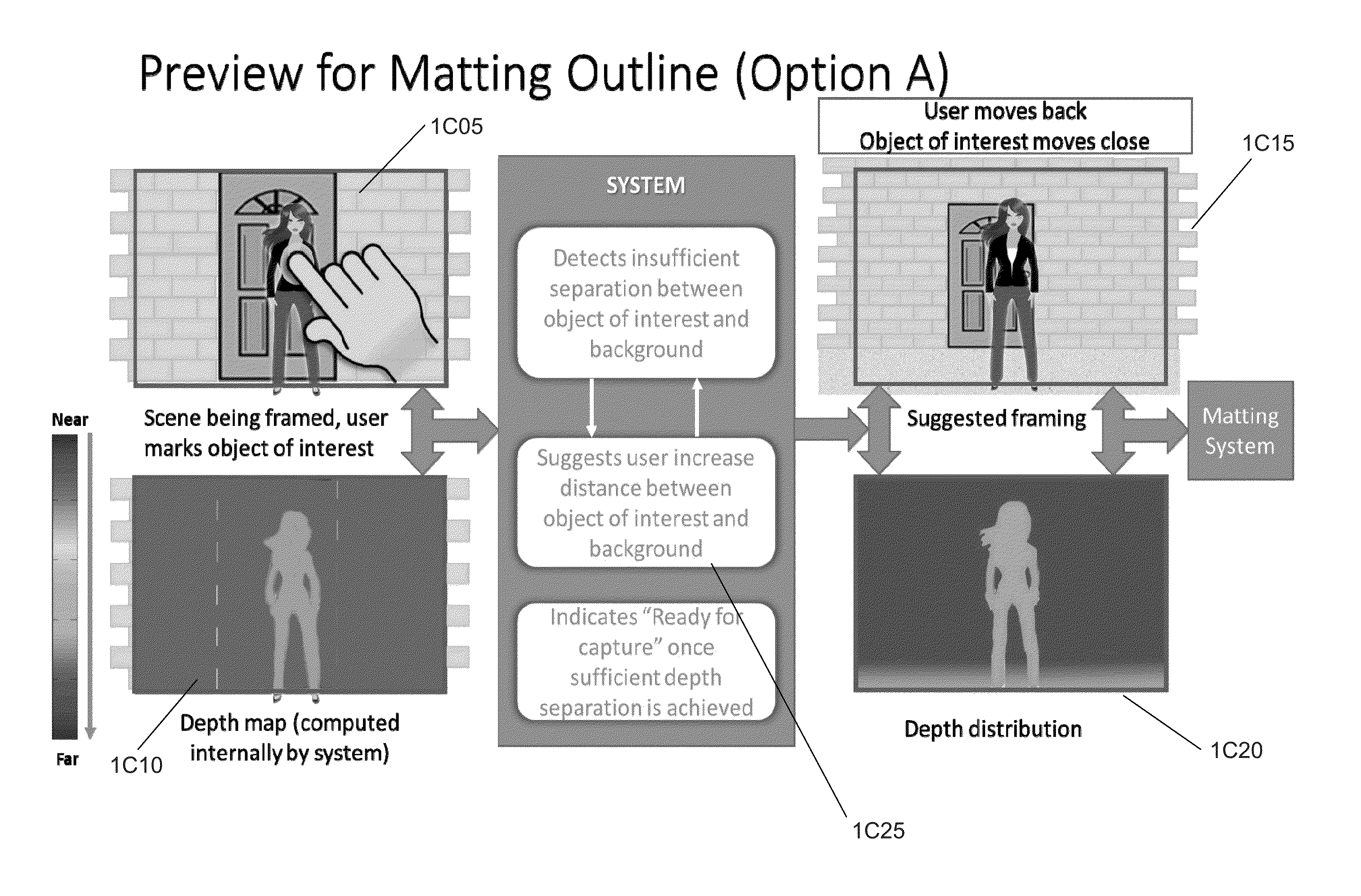
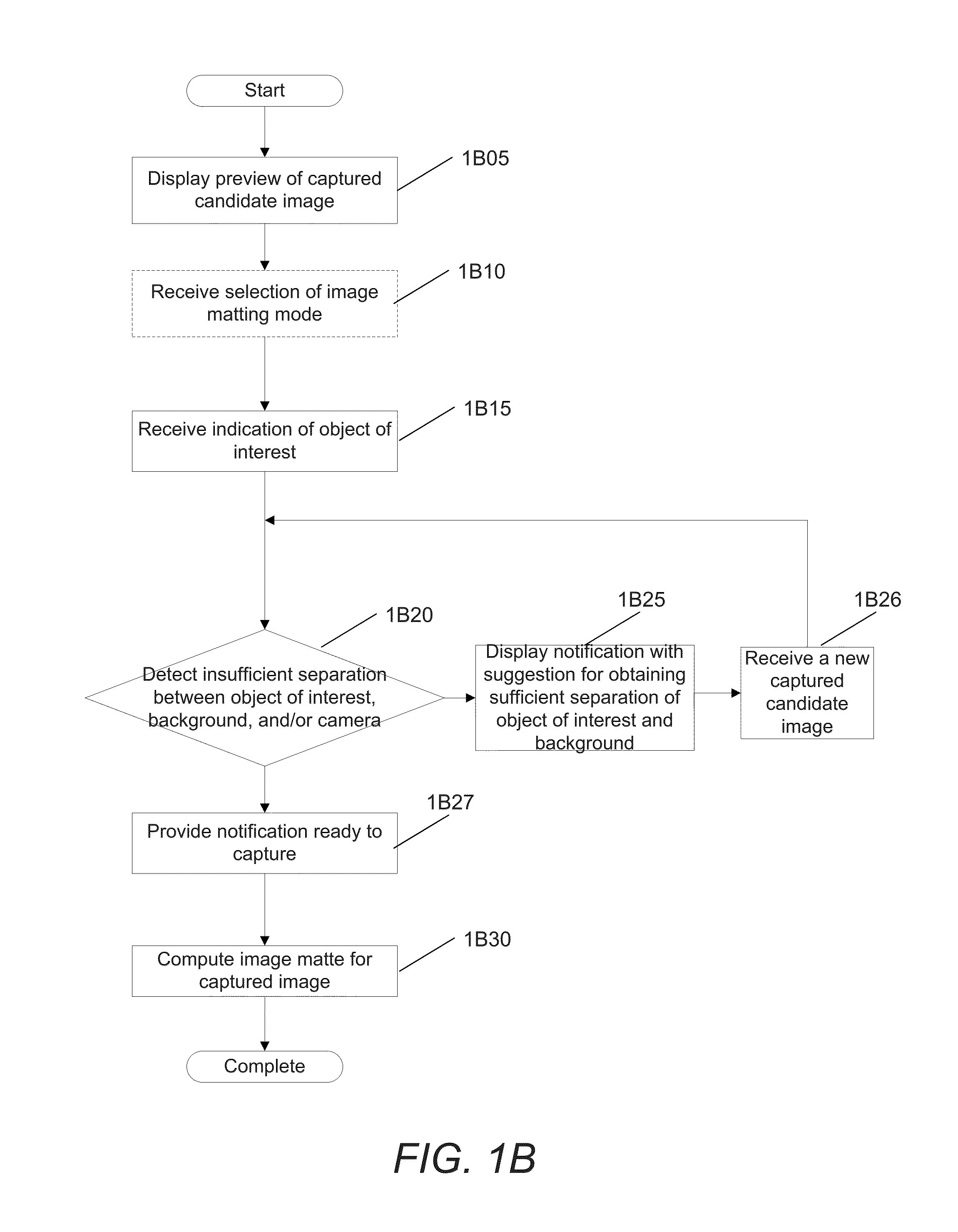
System and methods for depth regularization and semiautomatic interactive matting using rgb-d images
Systems and methods in accordance with embodiments of this invention perform depth regularization and semiautomatic interactive matting using images. In an embodiment of the invention, the image processing pipeline application directs a processor to receive (i) an image (ii) an initial depth map corresponding to the depths of pixels within the image, regularize the initial depth map into a dense depth map using depth values of known pixels to compute depth values of unknown pixels, determine an object of interest to be extracted from the image, generate an initial trimap using the dense depth map and the object of interest to be extracted from the image, and apply color image matting to unknown regions of the initial trimap to generate a matte for image matting.
Owner:FOTONATION LTD
Target orientation estimation using depth sensing
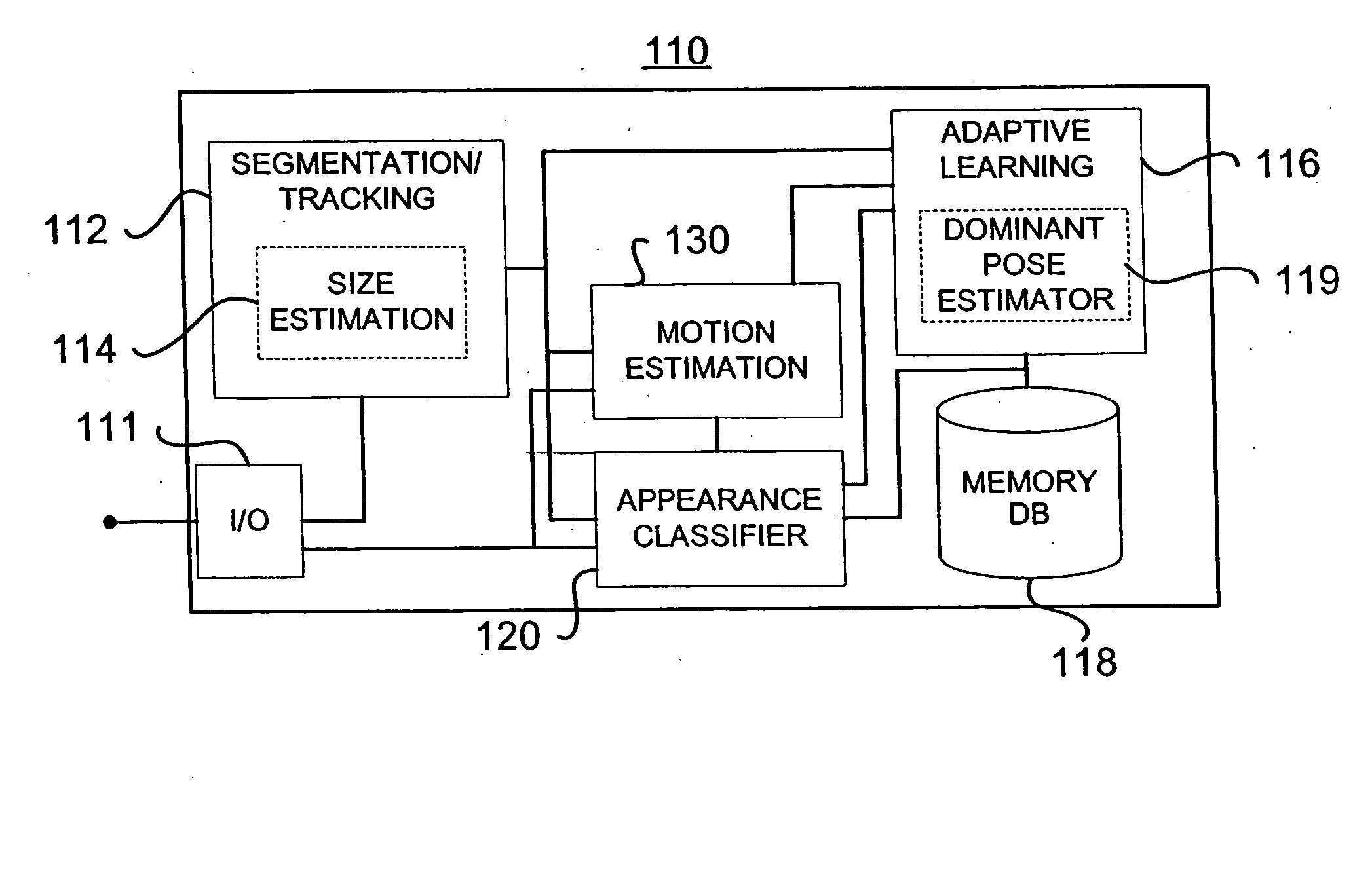
A system for estimating orientation of a target based on real-time video data uses depth data included in the video to determine the estimated orientation. The system includes a time-of-flight camera capable of depth sensing within a depth window. The camera outputs hybrid image data (color and depth). Segmentation is performed to determine the location of the target within the image. Tracking is used to follow the target location from frame to frame. During a training mode, a target-specific training image set is collected with a corresponding orientation associated with each frame. During an estimation mode, a classifier compares new images with the stored training set to determine an estimated orientation. A motion estimation approach uses an accumulated rotation / translation parameter calculation based on optical flow and depth constrains. The parameters are reset to a reference value each time the image corresponds to a dominant orientation.
Owner:HONDA MOTOR CO LTD +1
X-Ray Inspection Trailer
InactiveUS20090257555A1Material analysis by transmitting radiationMaterial analysis using radiation diffractionForward scatterX-ray
An inspection system, and inspection methods, based upon an imaging enclosure characterized by an enclosing body. A source of penetrating radiation and a detector module are concealed entirely within the body of a conveyance such as a trailer. A characterizing value or an image is formed with respect to an inspected object that is disposed entirely outside the conveyance and the characterizing value or image is made available to a remotely disposed operator. Additional detectors may be disposed distally to the inspected object and may detect transmitted, or forward-scattered, penetrating radiation.
Owner:AMERICAN SCI & ENG INC
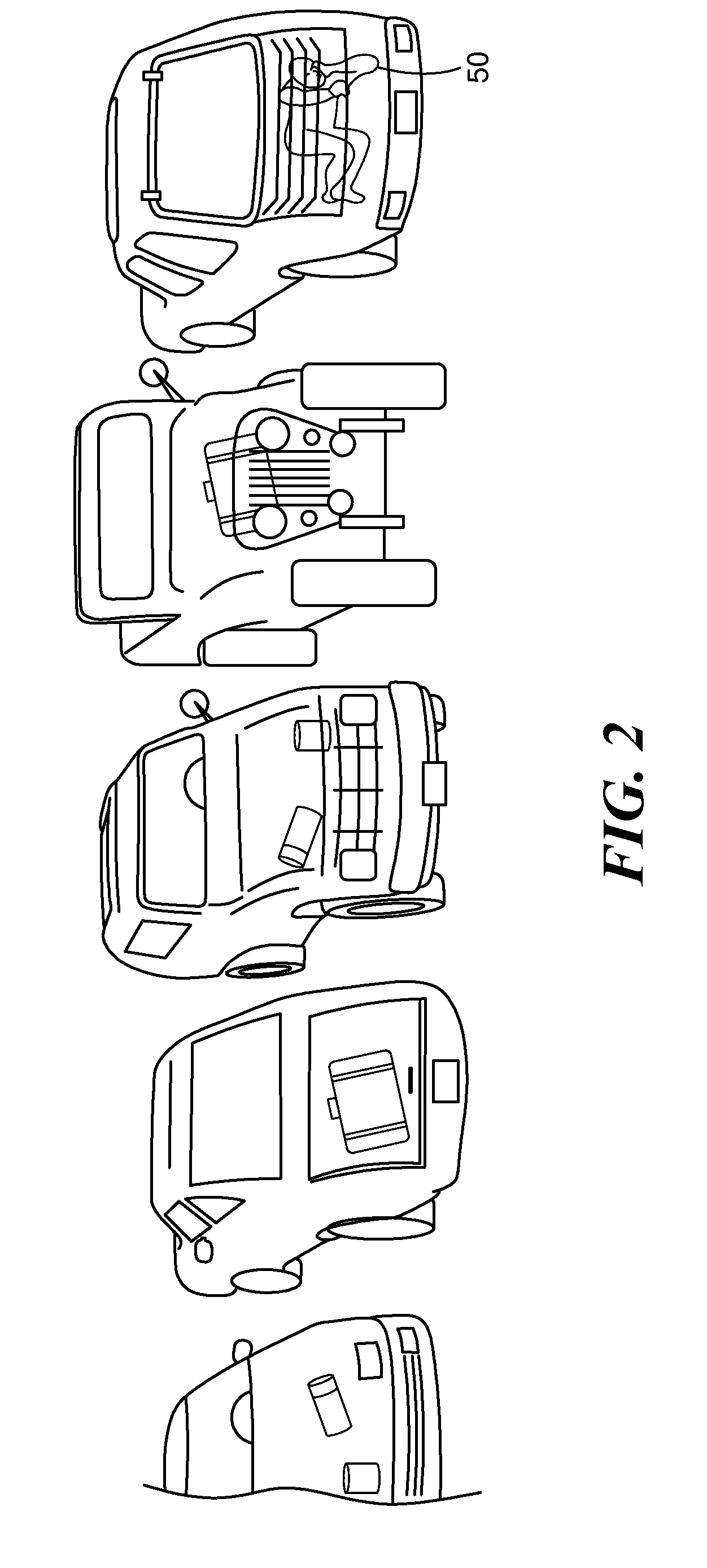
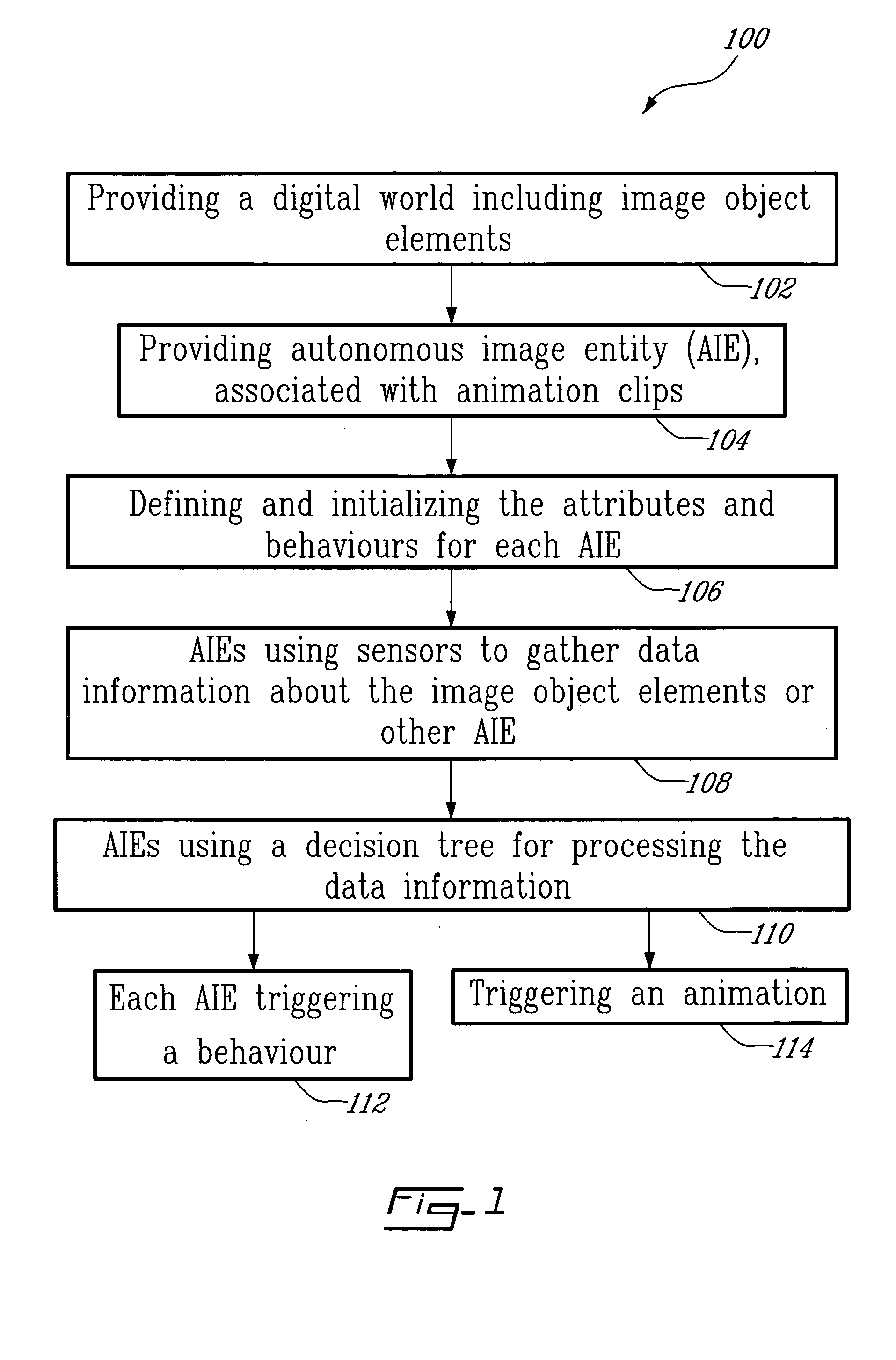
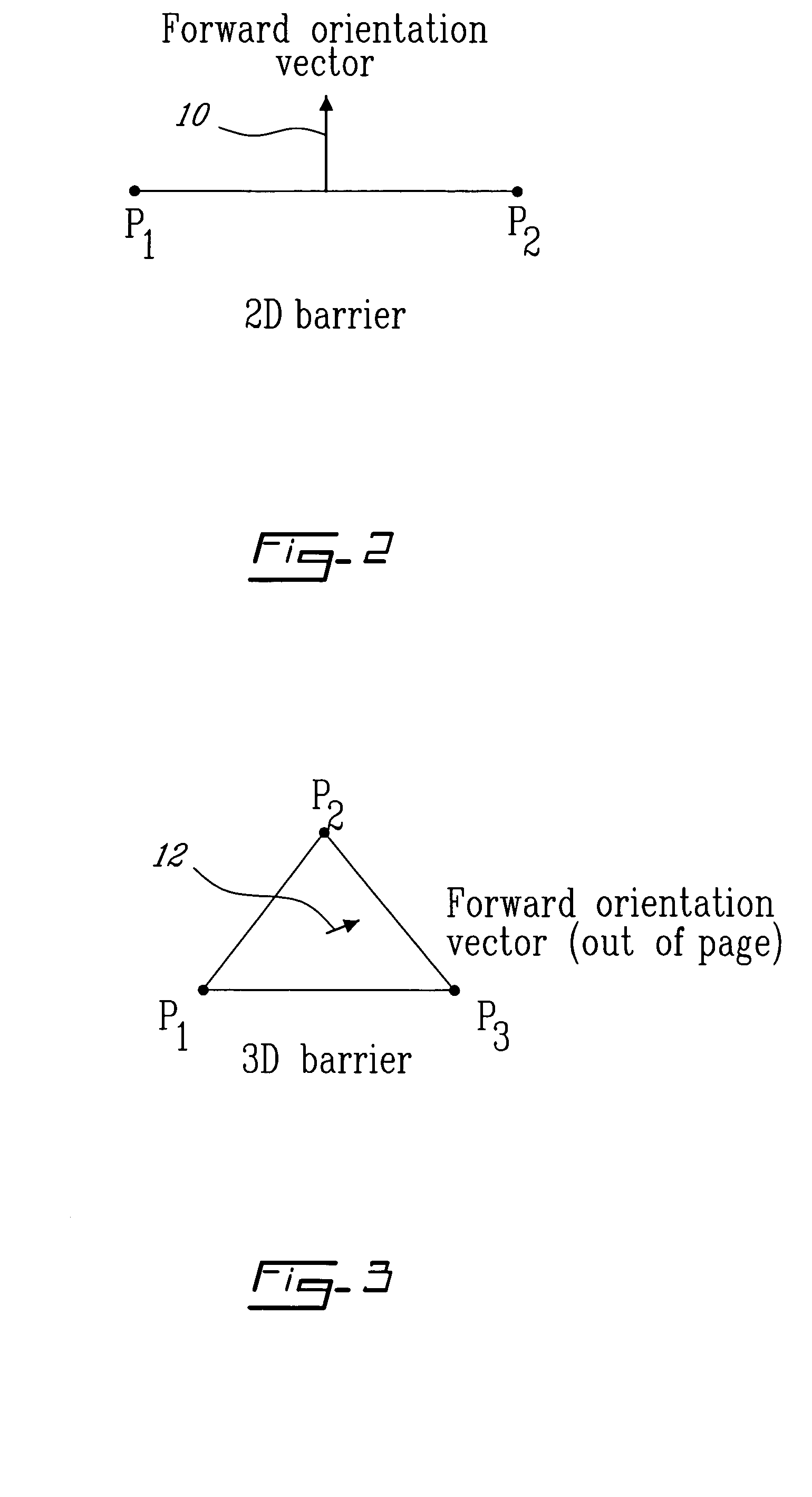
Method and system for on-screen animation of digital objects or characters
The method for on-screen animation includes providing a digital world including image object elements and defining autonomous image entities (AIE). Each AIE may represent a character or an object that is characterized by i) attributes defining the AIE relatively to the image objects elements of the digital world, and ii) behaviours for modifying some of the attributes. Each AIE is associated to animation clips allowing representing the AIE in movement in the digital world. Virtual sensors allow the AIE to gather data information about image object elements or other AIE within the digital world. Decision trees are used for processing the data information resulting in selecting and triggering one of the animation cycle or selecting a new behaviour. A system embodying the above method is also provided. The method and system for on-screen animation of digital entities according to the present invention can be used for creating animation for movies, for video games, and for simulation.
Owner:BGT BIOGRAPHIC TECH
Two dimensional barcodes and mobile terminals
ActiveUS20090307232A1Digital data information retrievalInvestigating moving sheetsTelecommunications networkBarcode
Processing a two dimensional (2D) barcode using a mobile telecommunications terminal having an image scanner includes obtaining a scanned image of the 2D barcode from the image scanner, decoding the image to obtain data, including a web address, and associating an identifier with the decoded web address, such that the identifier is identifiable by a remote proxy server to obtain information relating to the use of the barcode. A browser of the mobile terminal transmits a web page request including the decoded web address and the identifier. The web page request may be identified as originating from a 2D barcode at a server in a mobile telecommunications network. The request is received from a mobile terminal, an inserted identifier is identified in the request, and a record is saved, the record including an identifier of the mobile terminal or a user of the mobile terminal and the web page address.
Owner:VODAFONE GRP PLC
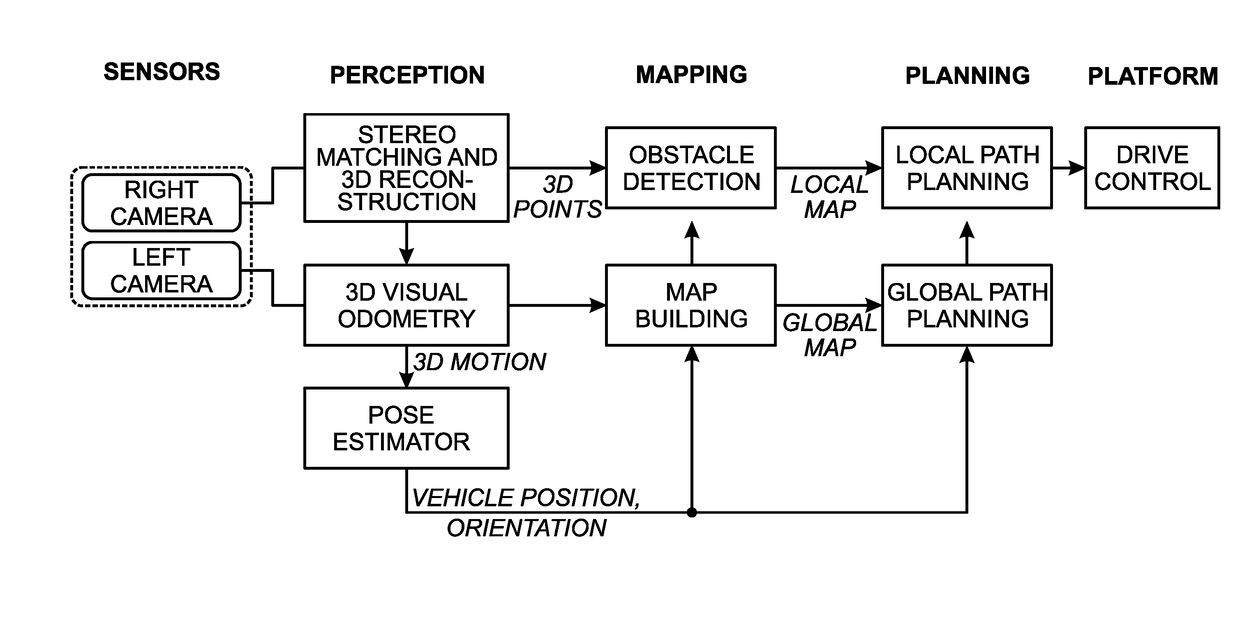
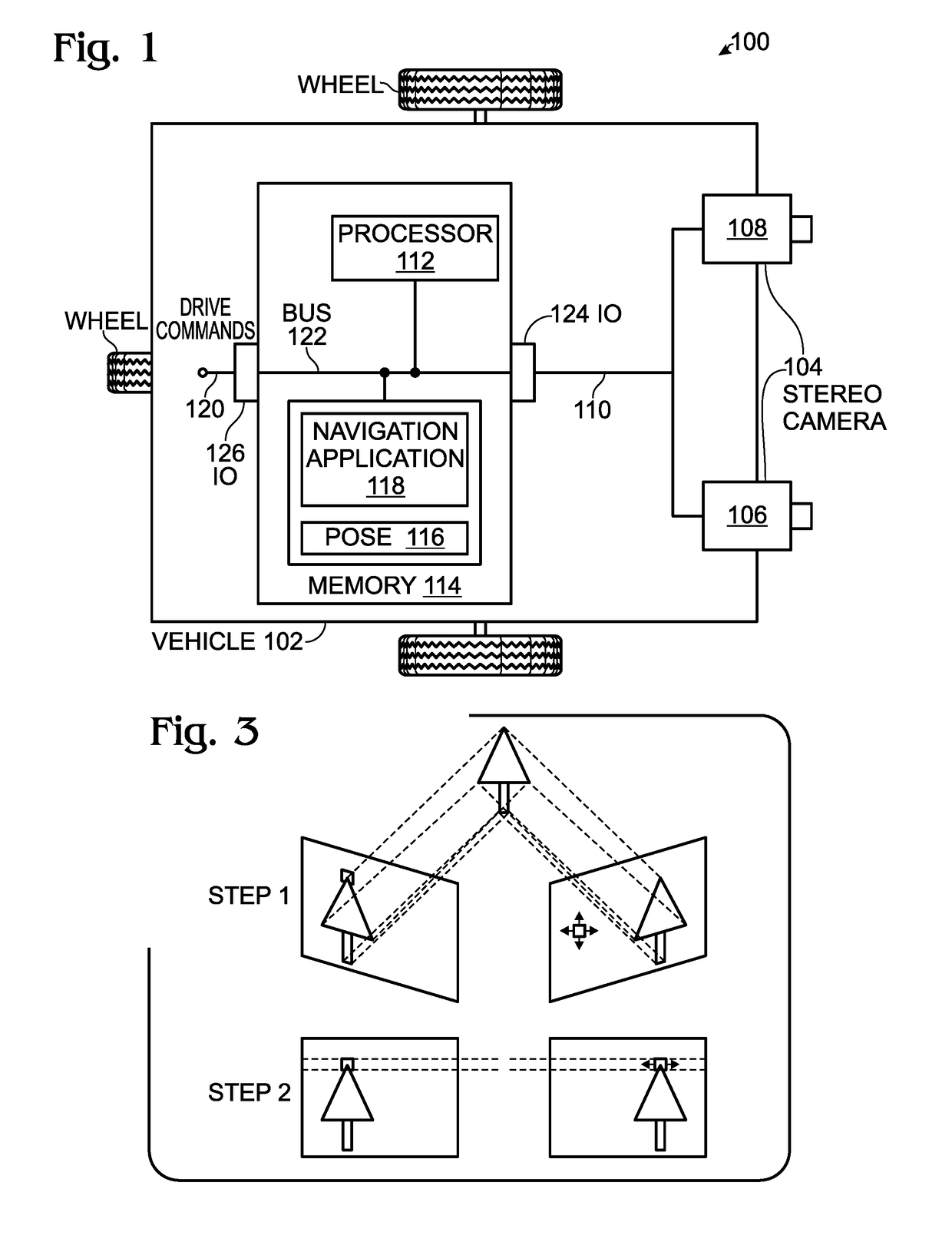
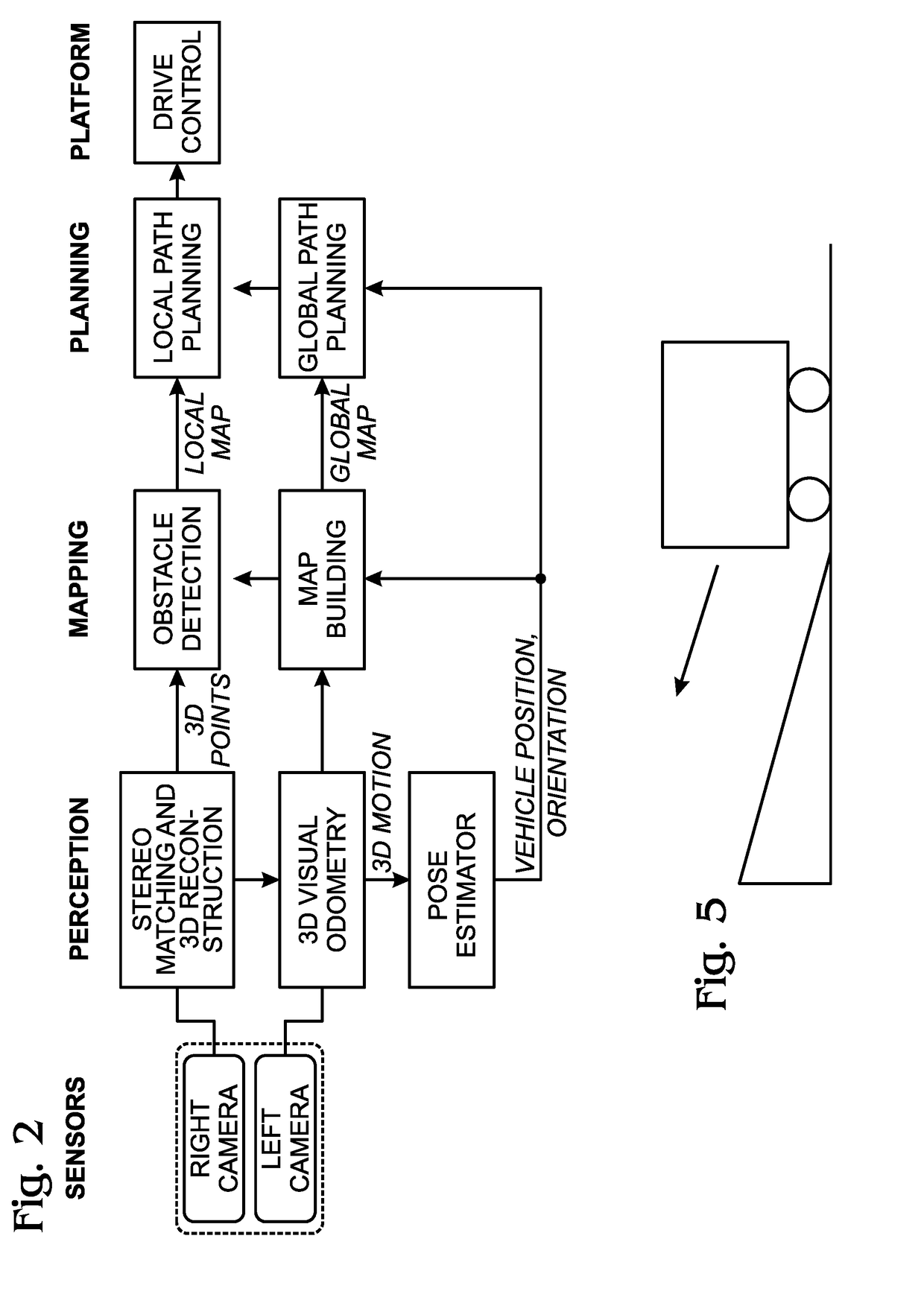
Autonomous Navigation using Visual Odometry
A system and method are provided for autonomously navigating a vehicle. The method captures a sequence of image pairs using a stereo camera. A navigation application stores a vehicle pose (history of vehicle position). The application detects a plurality of matching feature points in a first matching image pair, and determines a plurality of corresponding object points in three-dimensional (3D) space from the first image pair. A plurality of feature points are tracked from the first image pair to a second image pair, and the plurality of corresponding object points in 3D space are determined from the second image pair. From this, a vehicle pose transformation is calculated using the object points from the first and second image pairs. The rotation angle and translation are determined from the vehicle pose transformation. If the rotation angle or translation exceed a minimum threshold, the stored vehicle pose is updated.
Owner:SHARP KK
System and method for spherical stereoscopic photographing
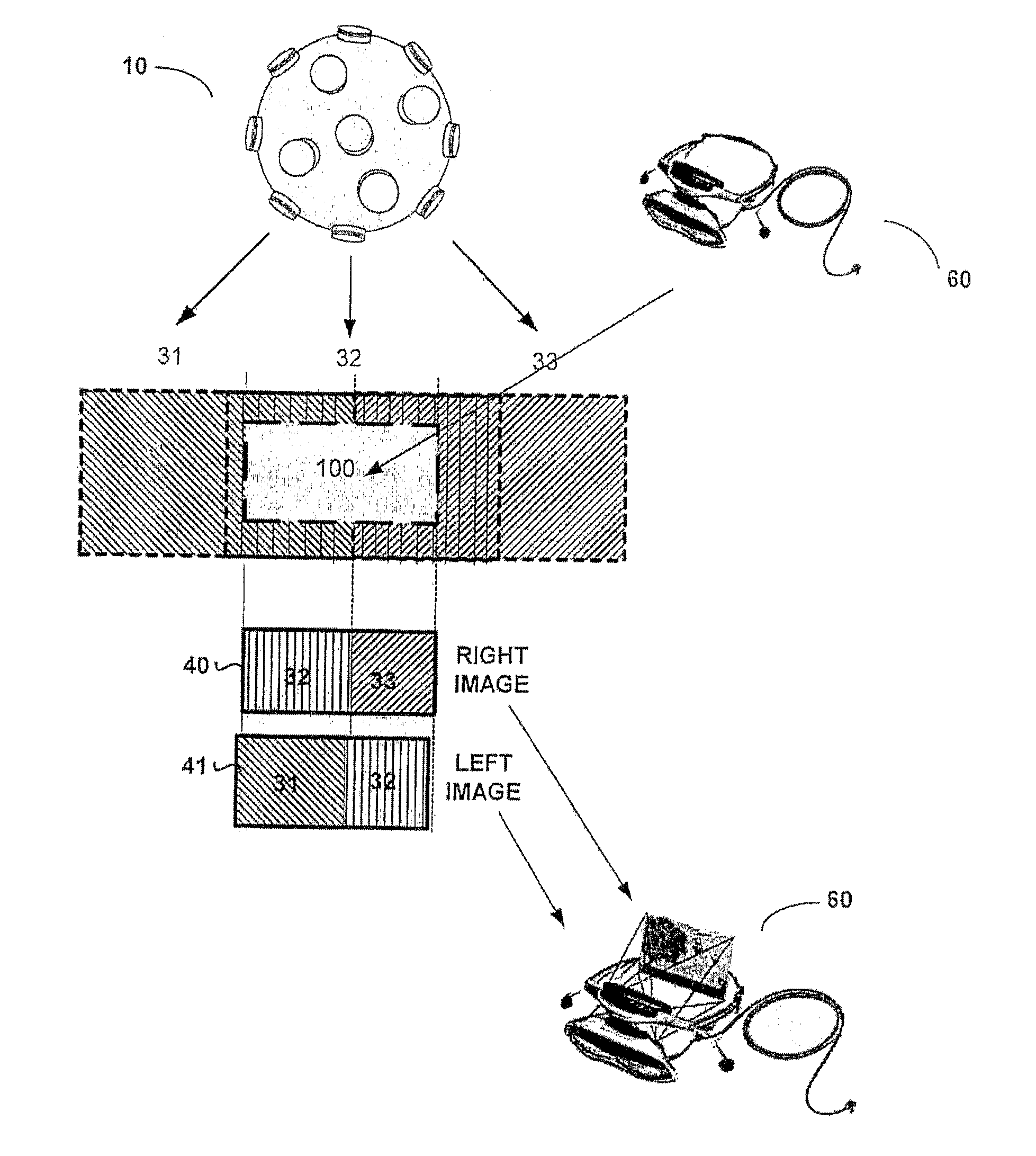
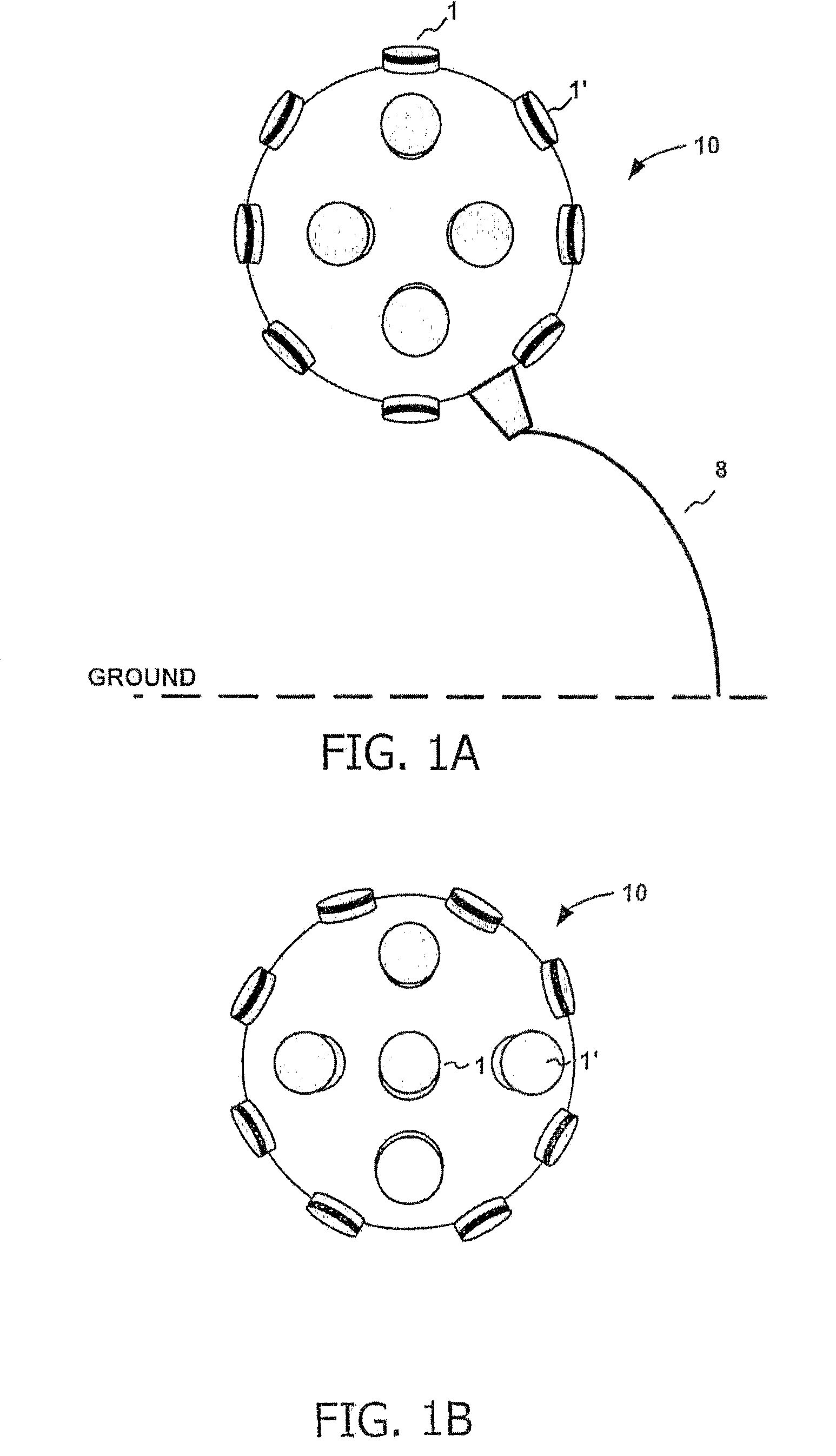
InactiveUS20080316301A1Improve image qualityStereoscopic photographySteroscopic systemsCamera lensStereoscopic depth
The present invention provides a novel imaging system for obtaining full stereoscopic spherical images of the visual environment surrounding a viewer, 360 degrees both horizontally and vertically. Displaying the images obtained by the present system, by means suitable for stereoscopic displaying, gives the viewers the ability to look everywhere around them, as well as up and down, while having stereoscopic depth perception of the displayed images. The system according to the present invention comprises an array of cameras, wherein the lenses of said cameras are situated on a curved surface, pointing out from common centers of said curved surface. The captured images of said system are arranged and processed to create sets of stereoscopic image pairs, wherein one image of each pair is designated for the observer's right eye and the second image for his left eye, thus creating a three dimensional perception.
Owner:MICOY CORP
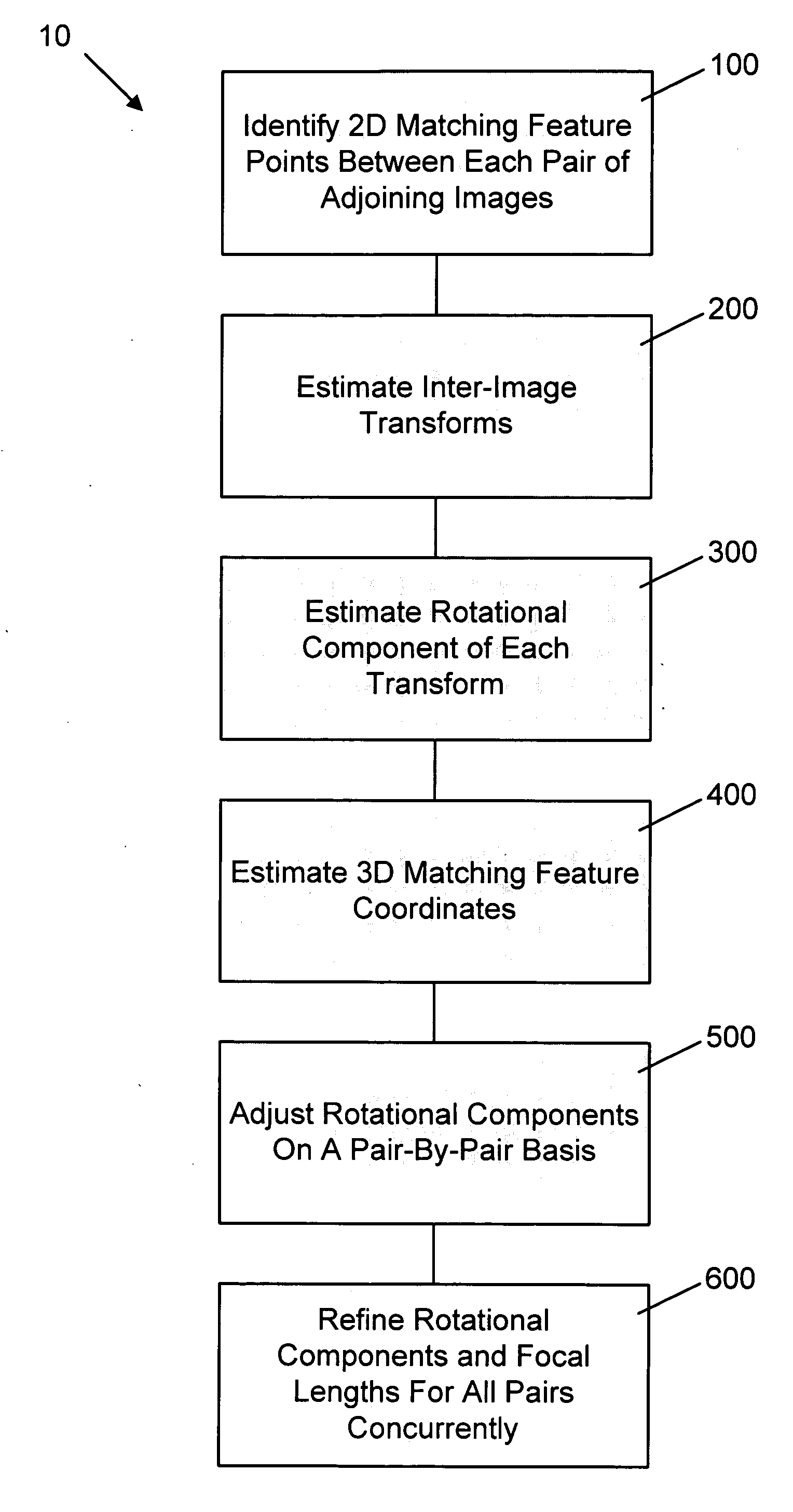
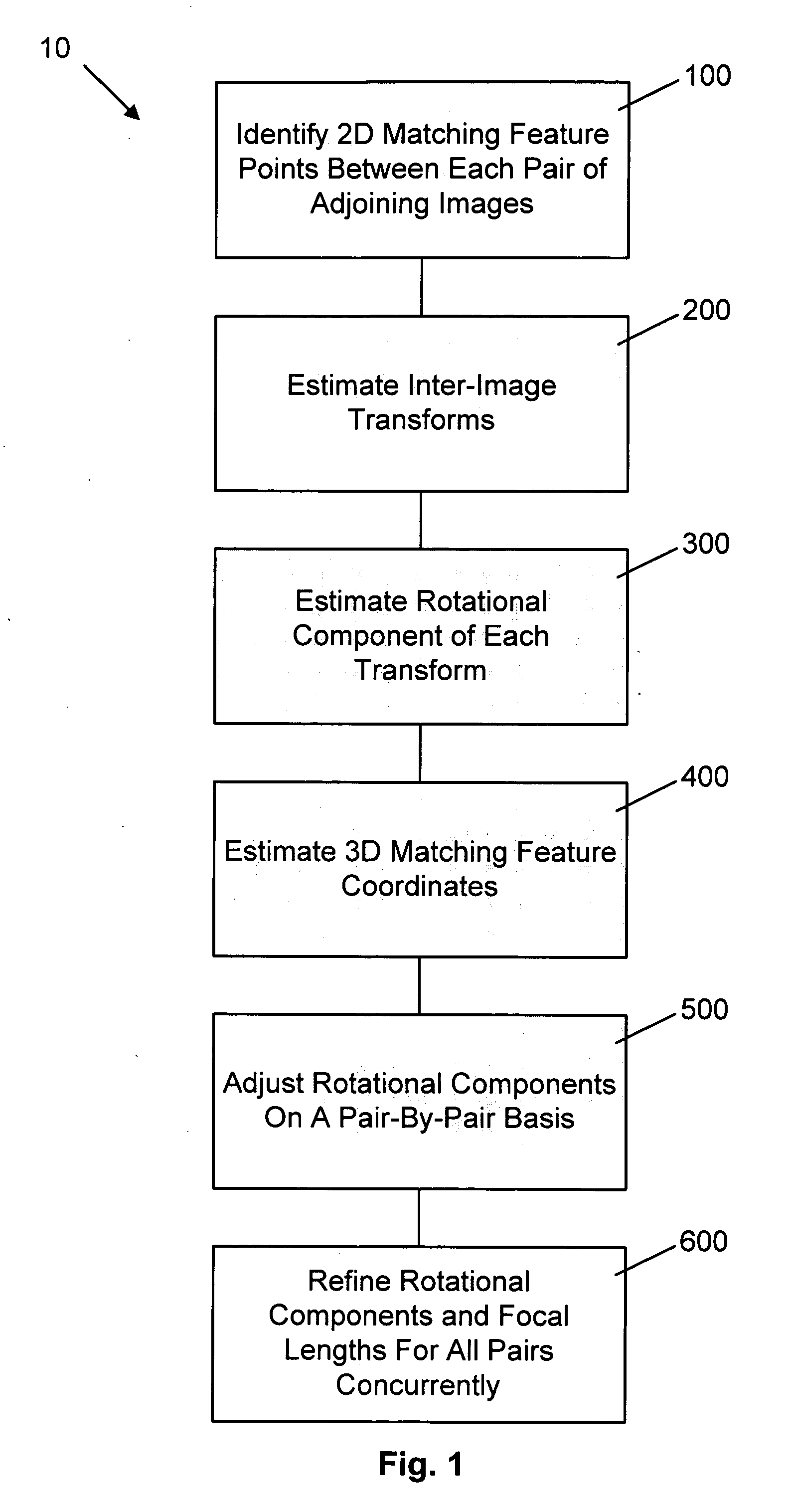
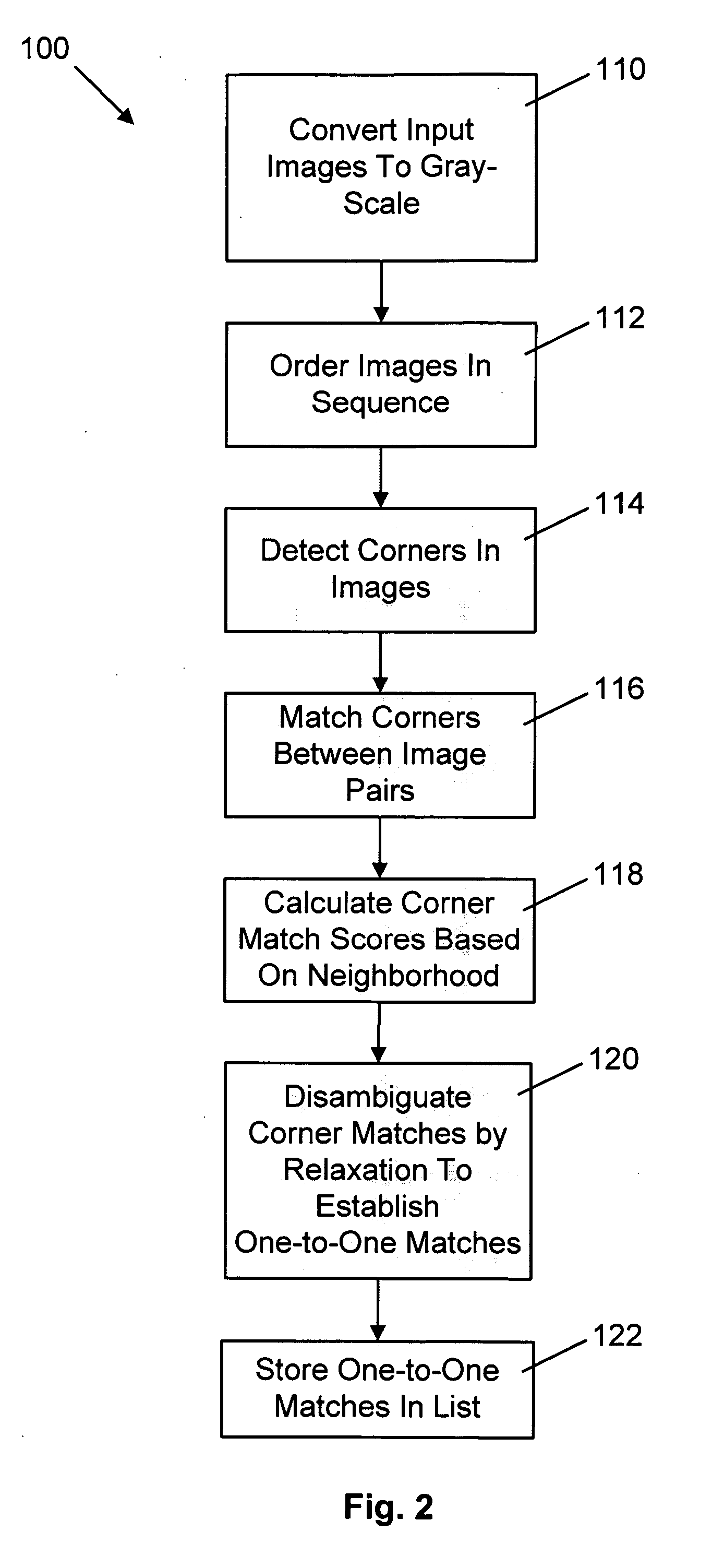
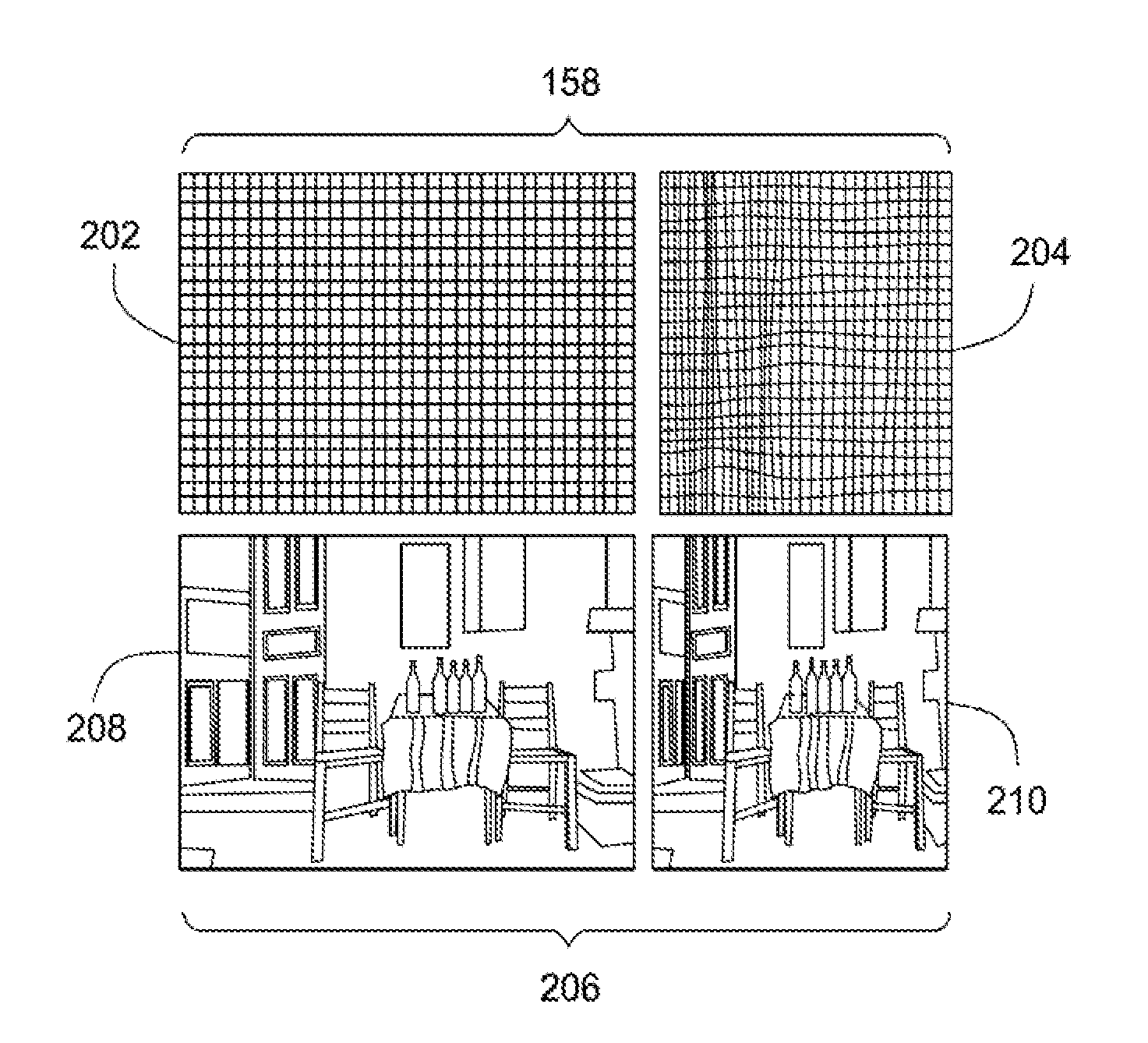
Method for determining camera position from two-dimensional images that form a panorama
InactiveUS20070008312A1Save additional processing resourceShorten the timeImage enhancementImage analysisThree-dimensional spaceGlobal optimization
A method of estimating three-dimensional camera position information from a series of two-dimensional images that form a panorama employs common features in adjoining image pairs in the series to estimate a transform between the images in the pairs. The common features are subsequently employed to adjust an estimated rotational component of each transform by reducing error between coordinates corresponding to the common features in three-dimensional space in image pairs, on a pair-by-pair basis. A global optimization of the position estimation, used for long sequences of images such as 360 degree panoramas, refines the estimates of the rotational and focal length components of the transforms by concurrently reducing error between all 3D common feature coordinates for all adjoining pairs.
Owner:SEIKO EPSON CORP
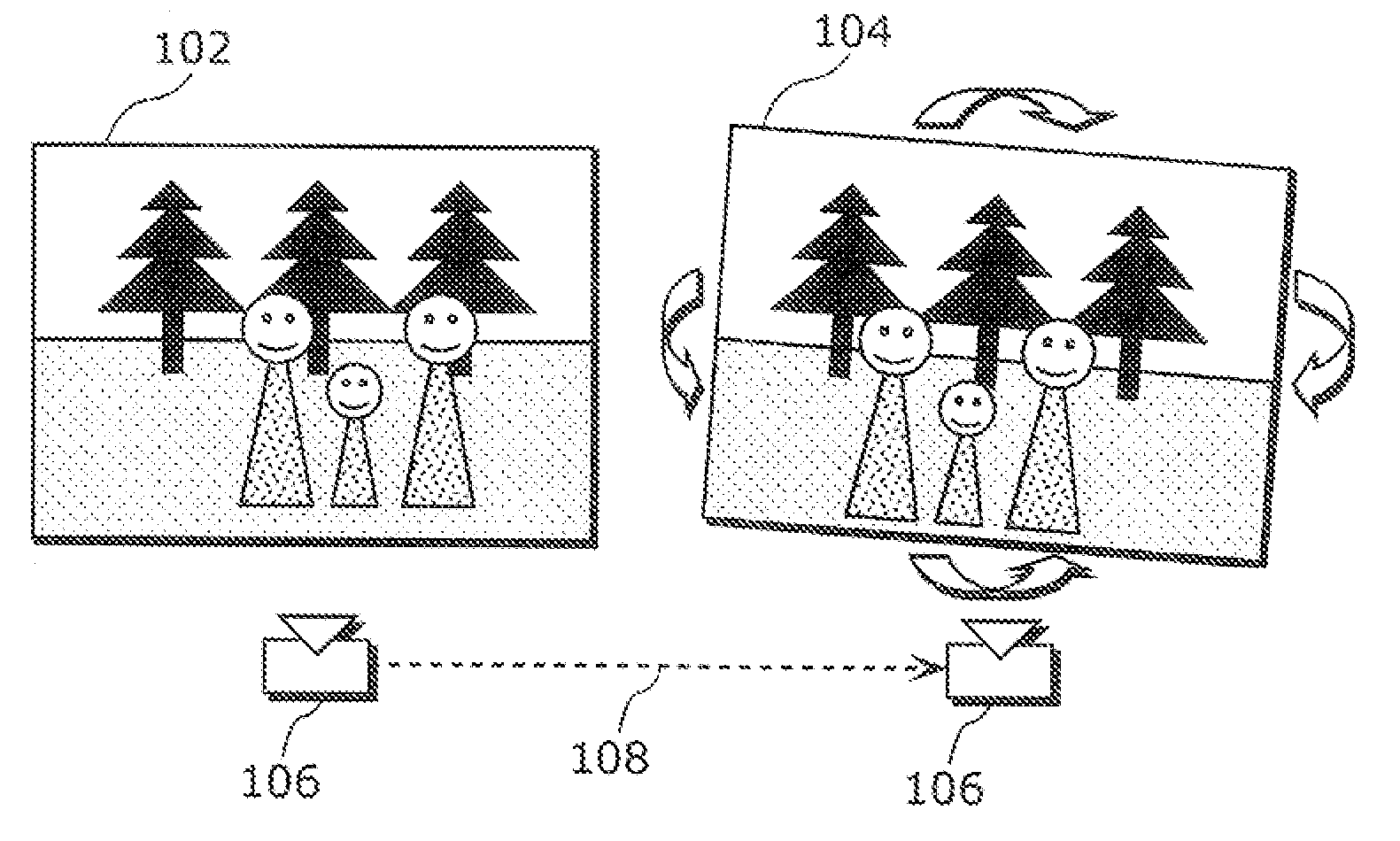
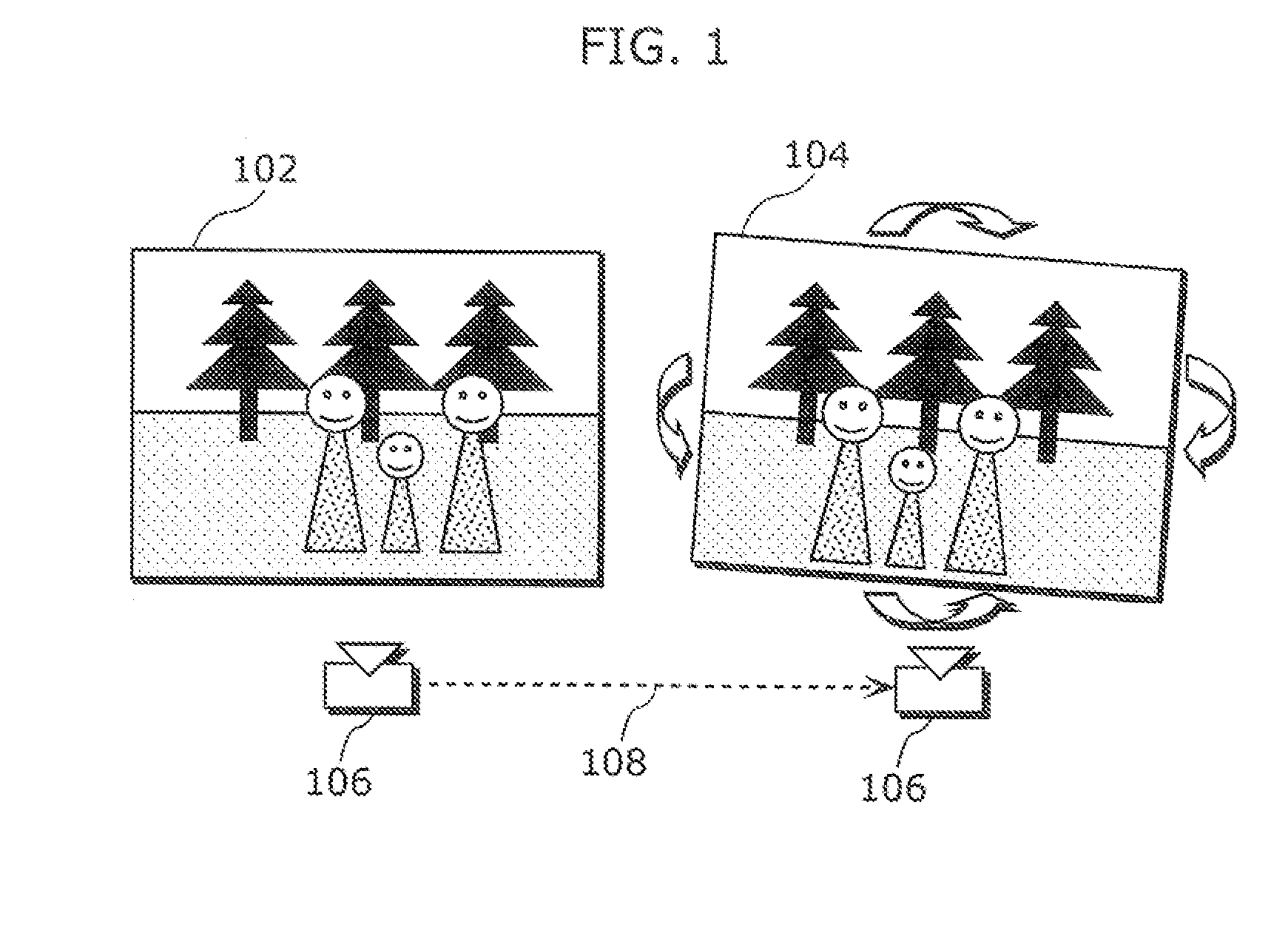
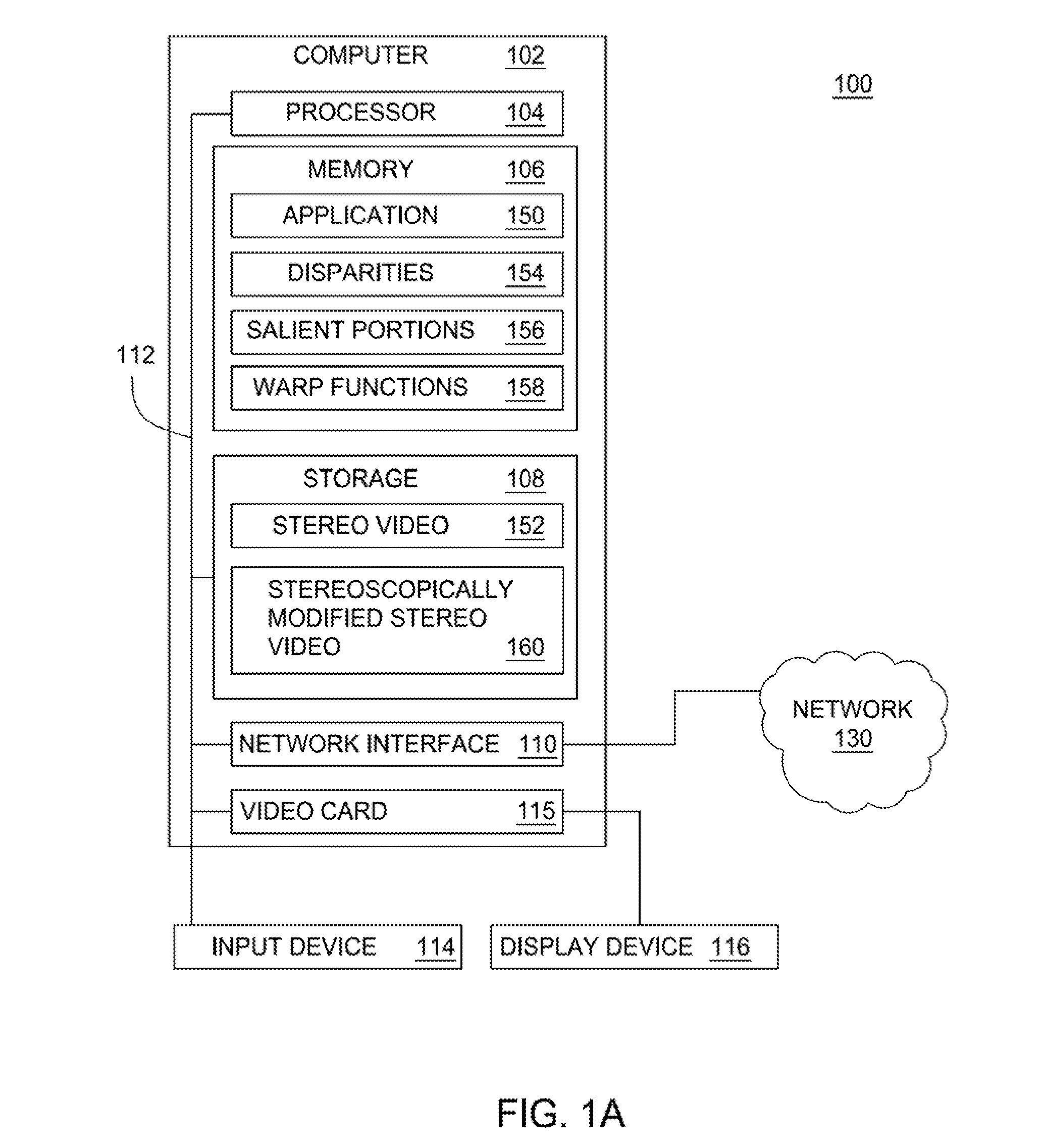
Stereoscopic editing for video production, post-production and display adaptation
Systems, methods and articles of manufacture are disclosed for stereoscopically editing video content. In one embodiment, image pairs of a sequence may be stereoscopically modified by altering at least one image of the image pair. The at least one image may be altered using at least one mapping function. The at least one image may also be altered based on a saliency of the image pair. The at least one image may also be altered based on disparities between the image pair. Advantageously, stereoscopic properties of video content may be edited more conveniently and efficiently.
Owner:DISNEY ENTERPRISES INC
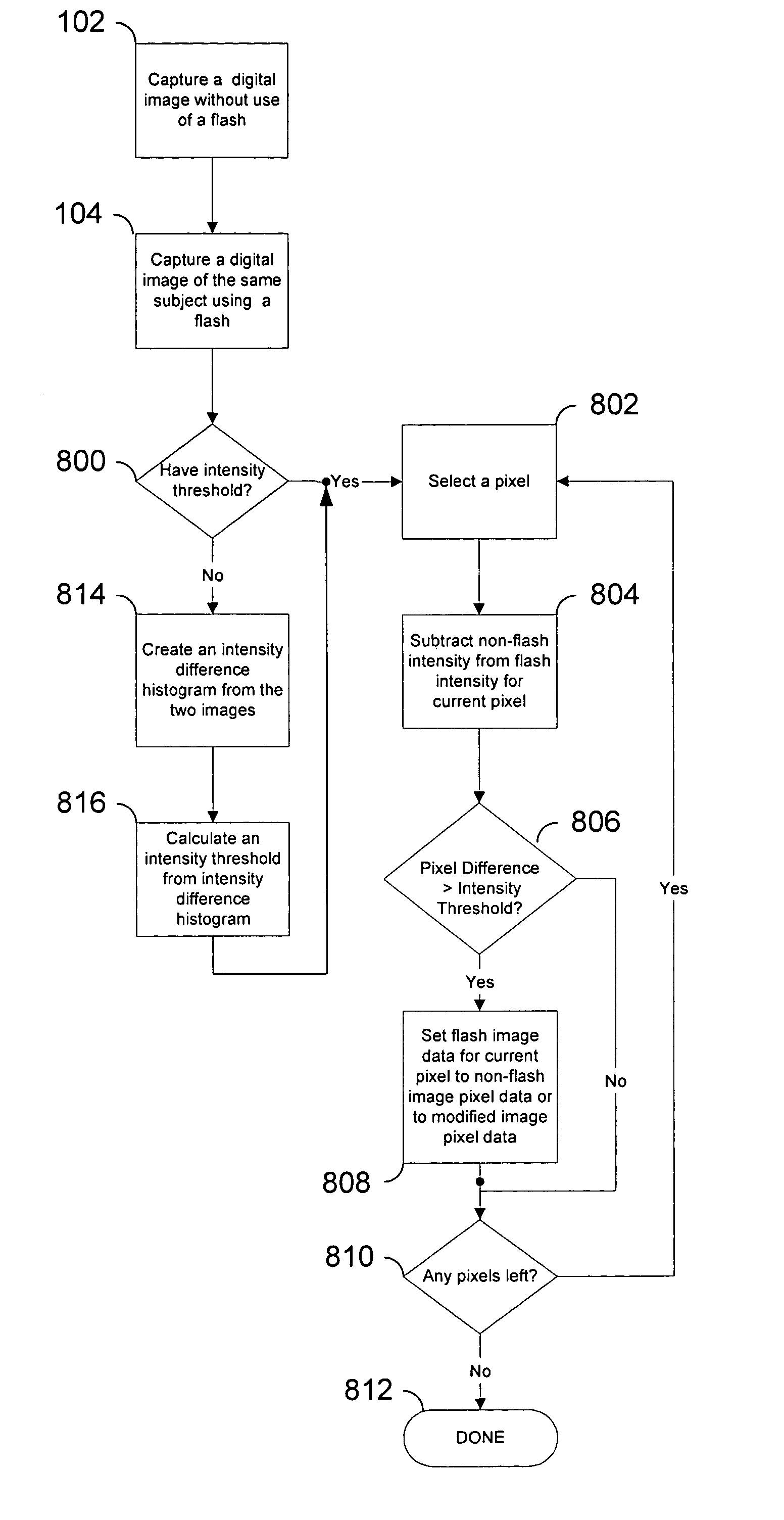
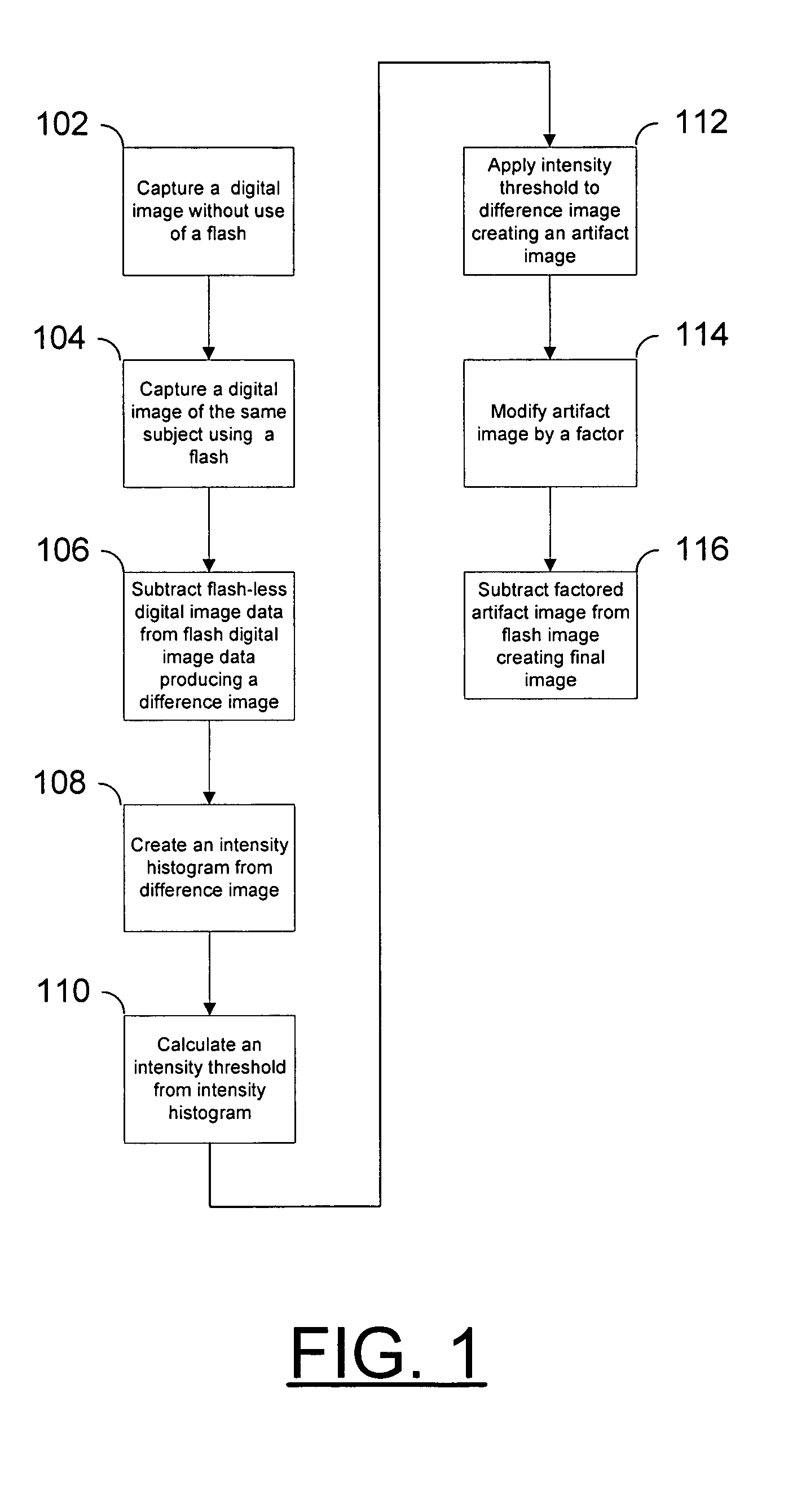
Method and apparatus for the removal of flash artifacts
An image without use of a flash is taken, along with an image using a flash. A difference image is generated by subtracting the flash-less image from the flash image. A threshold is applied to the difference image such that only large differences in intensity remain in the difference image. This artifact image is then subtracted from the flash image, thereby removing flash artifacts such as specular reflections and red-eye. The threshold used may be automatically calculated or may be set by the user. For some applications it may be desirable to set separate thresholds for each dimension of the color space (such as red, green, and blue) used. Once again these separate thresholds may be automatically calculated or may be set by the user.
Owner:APPLE INC
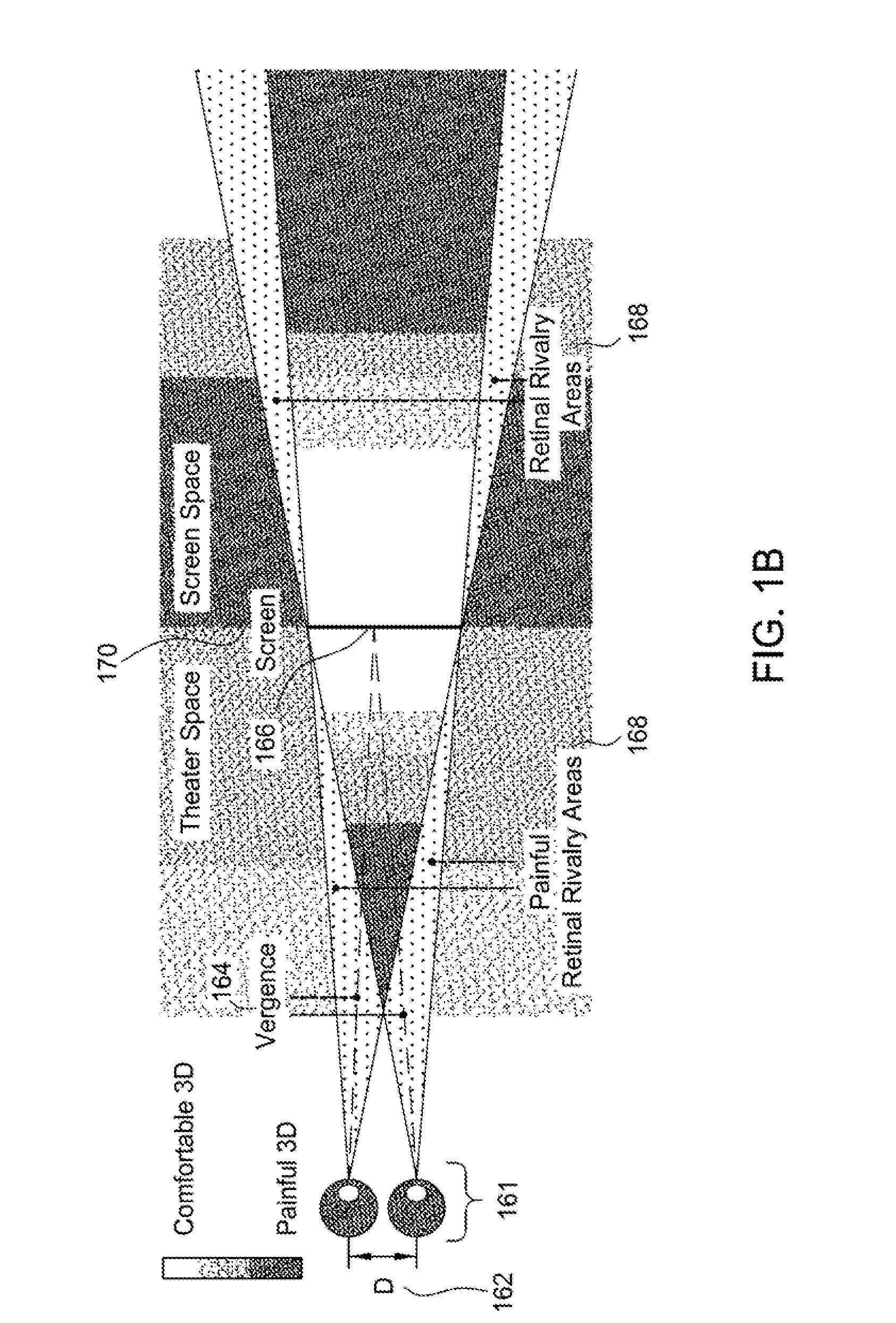
Method for rectifying stereoscopic display systems
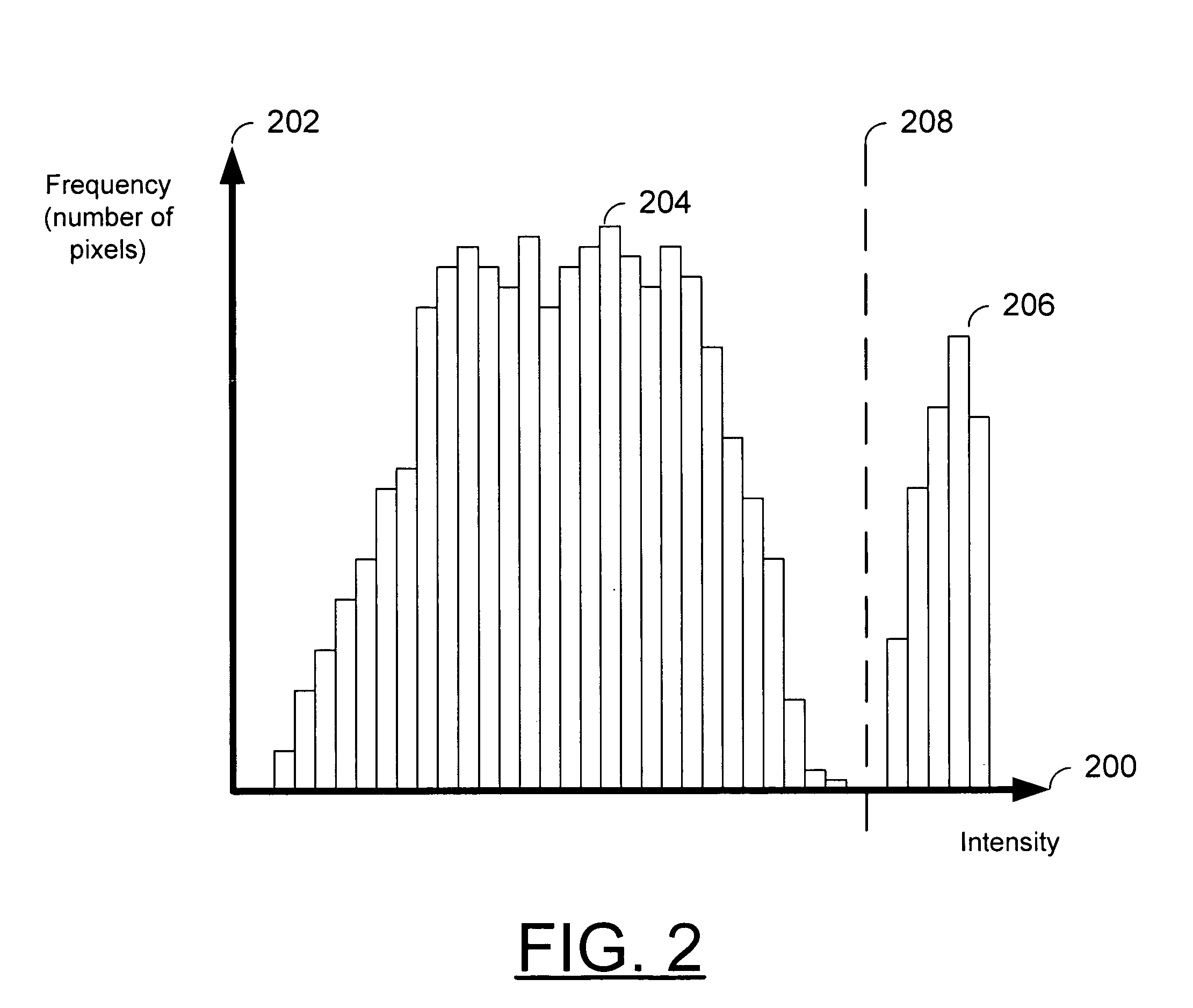
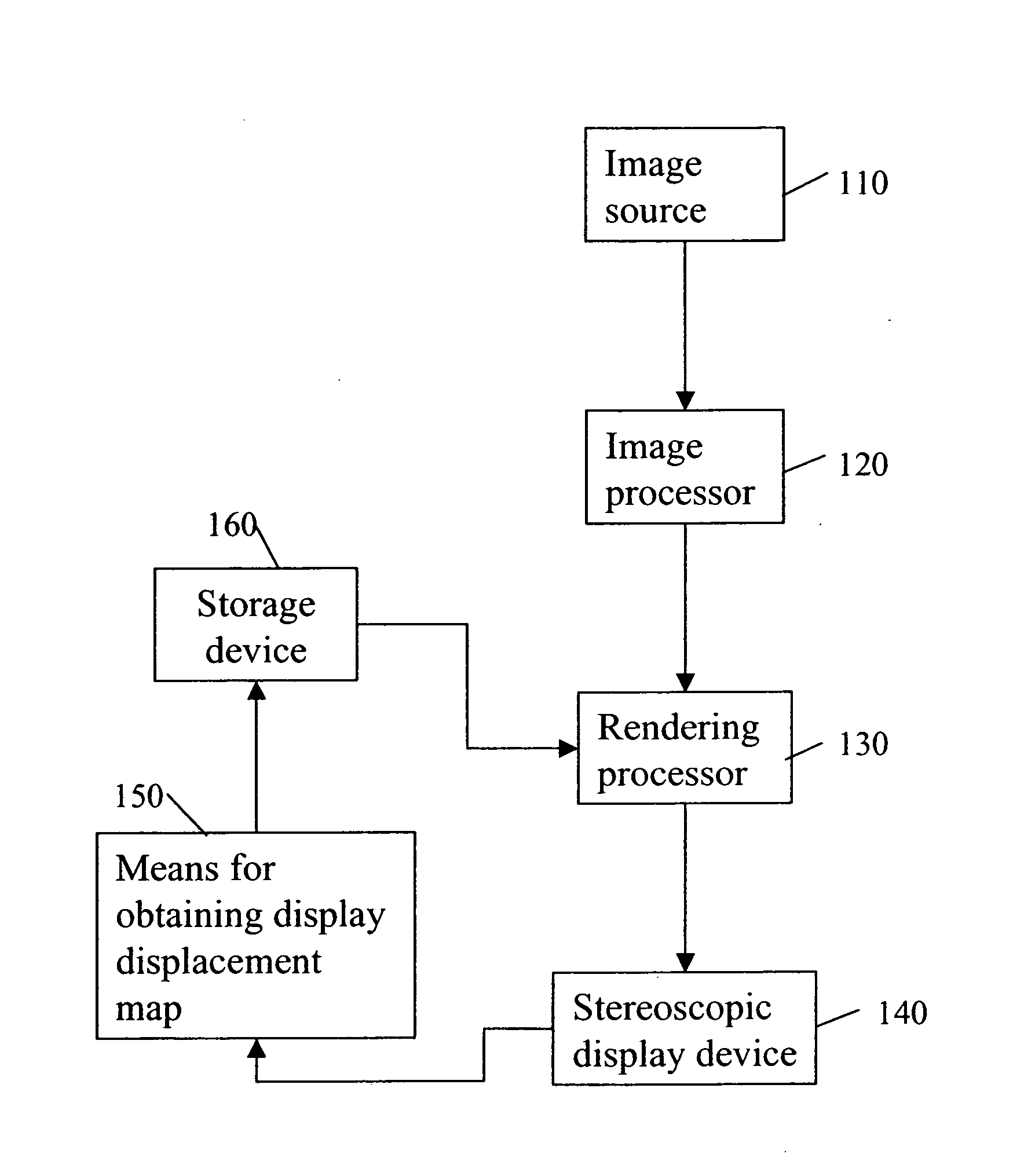
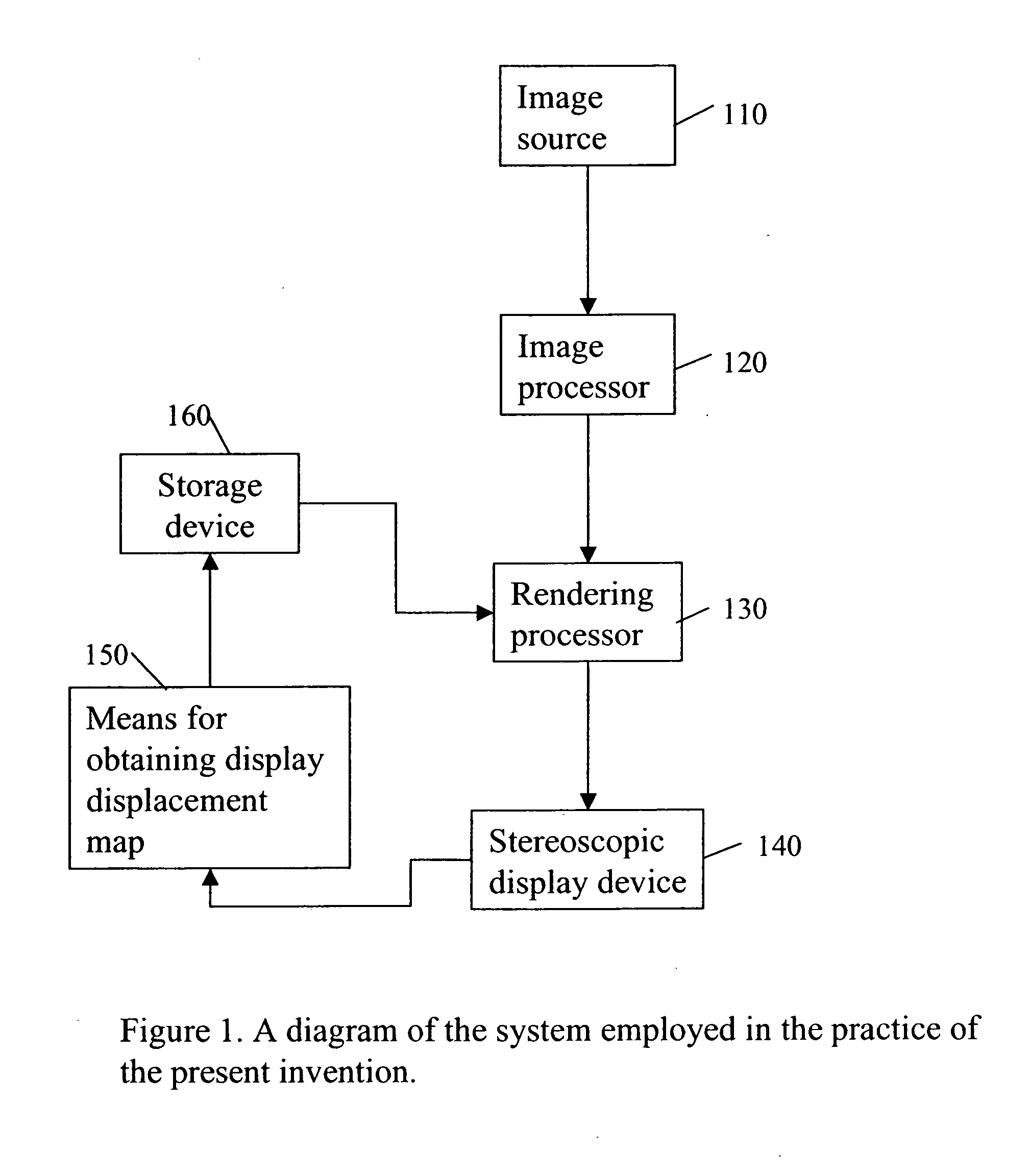
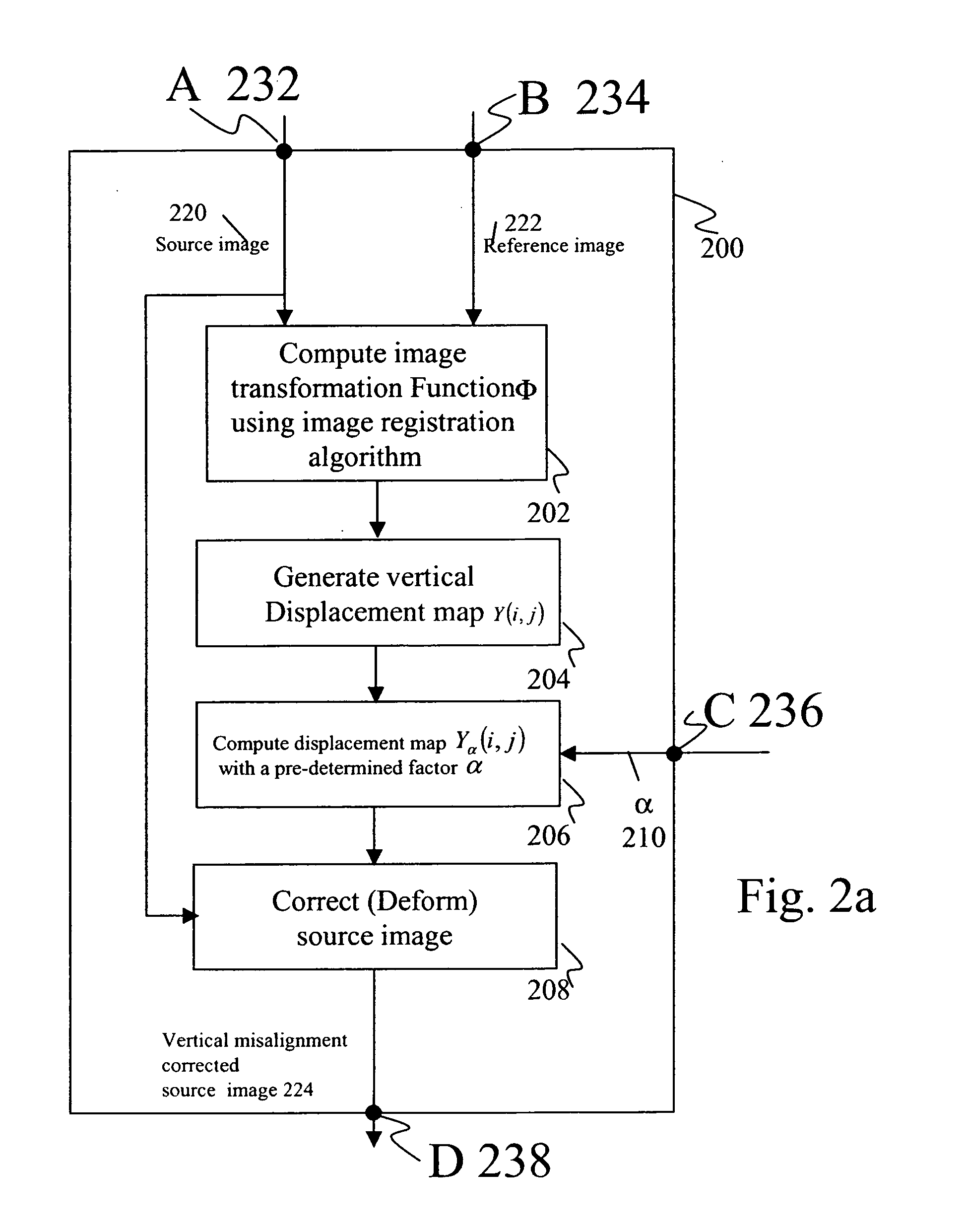
InactiveUS20070165942A1Minimize spatial misalignmentSpace minimizationCharacter and pattern recognitionSteroscopic systemsComputer graphics (images)Image pair
A method for rectifying misalignment in a stereoscopic display system (140) comprises: providing a pair of input images to an image processor (120); creating an image source displacement map for the pair of input images; obtaining a display displacement map (150); and applying the image source displacement map and the display displacement map to the pair of input images to create a rectified stereoscopic image pair.
Owner:EASTMAN KODAK CO
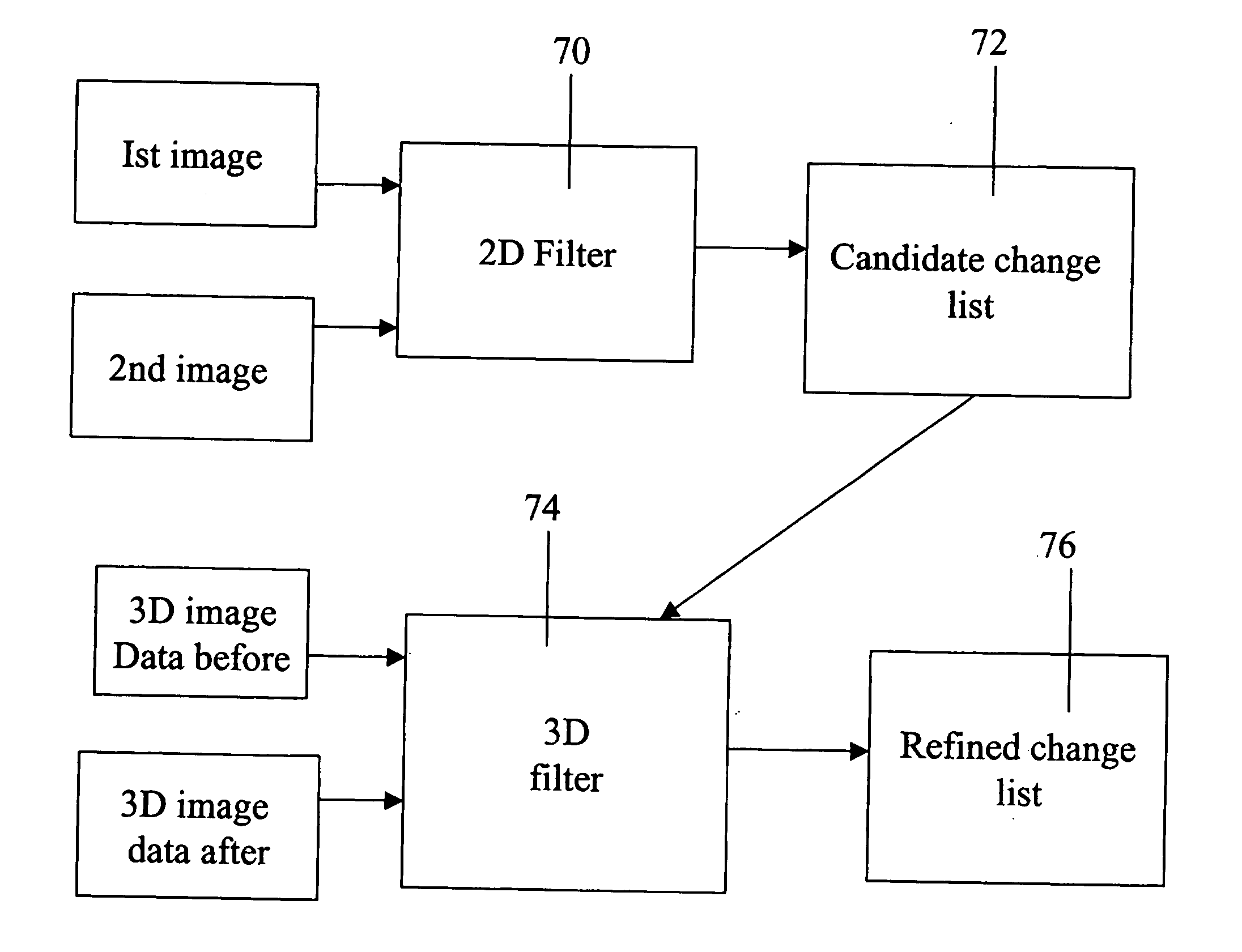
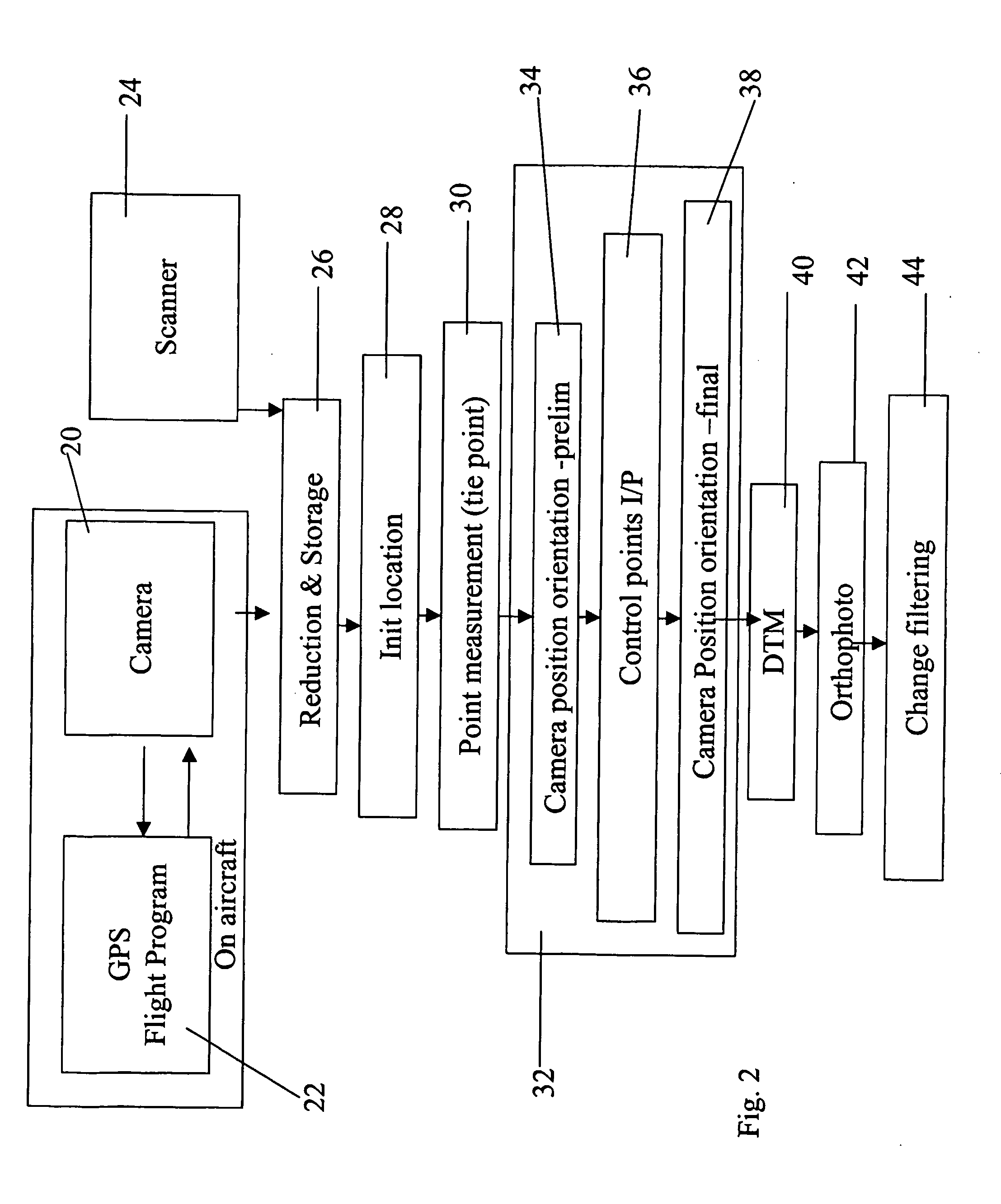
Automatic processing of aerial images
Change detection apparatus for detection of changes between first and second stereoscopic image pairs obtained at different times of a substantially similar view, comprises: a two-dimensional image filter for comparing first and second image pairs to obtain an initial list of change candidates from two-dimensional information in the image pairs, and a three-dimensional image filter for comparing the image pairs at locations of the change candidates using three-dimensional image information. The apparatus retains those change candidates correlating with three-dimensional image change and rejects change candidates not correlating with three-dimensional image change, and produces a refined list of change candidates.
Owner:M A M D DIGITAL DATA PROCESSING SYST +1
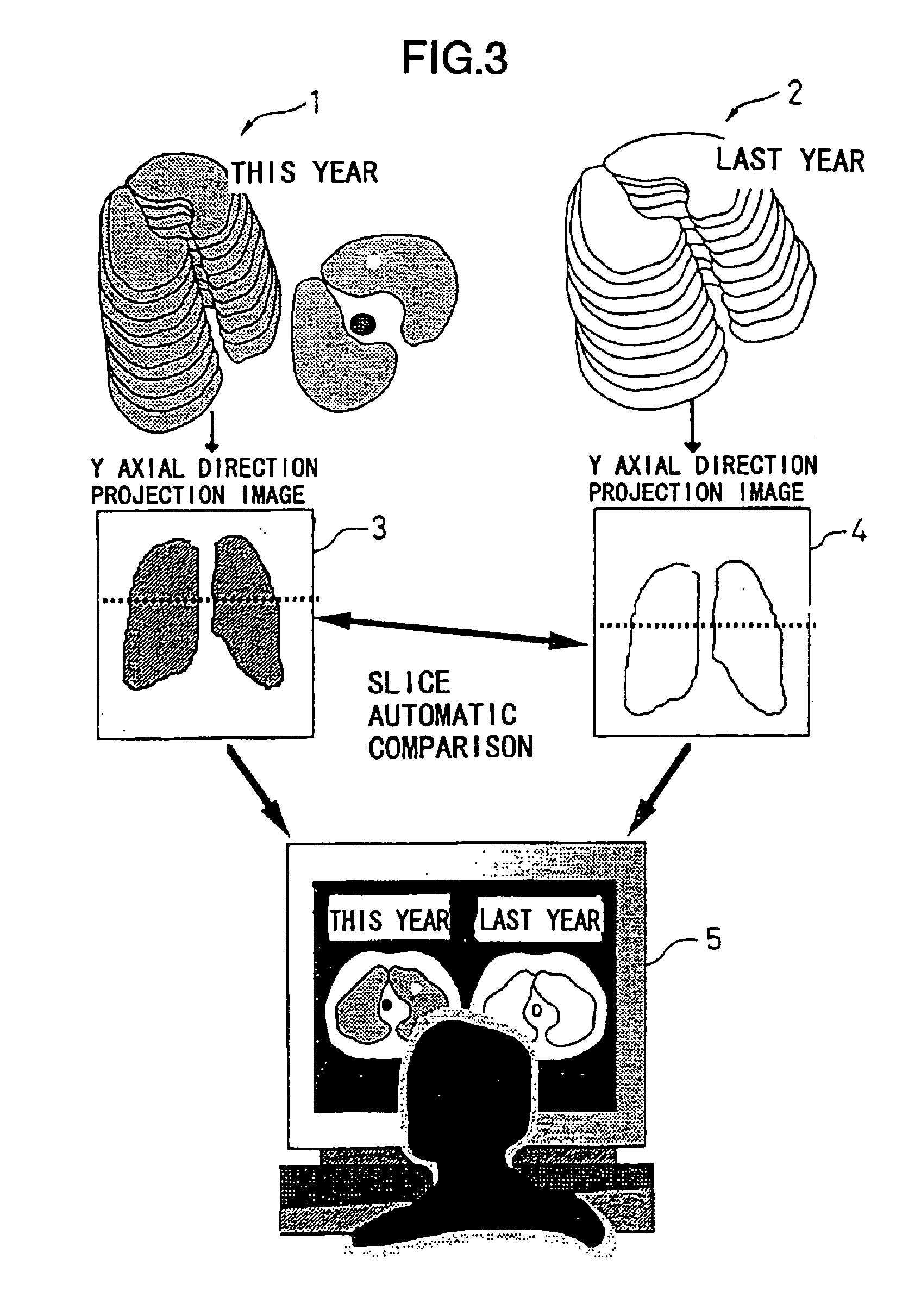
Tomographic image reading method, automatic alignment method, apparatus and computer readable medium
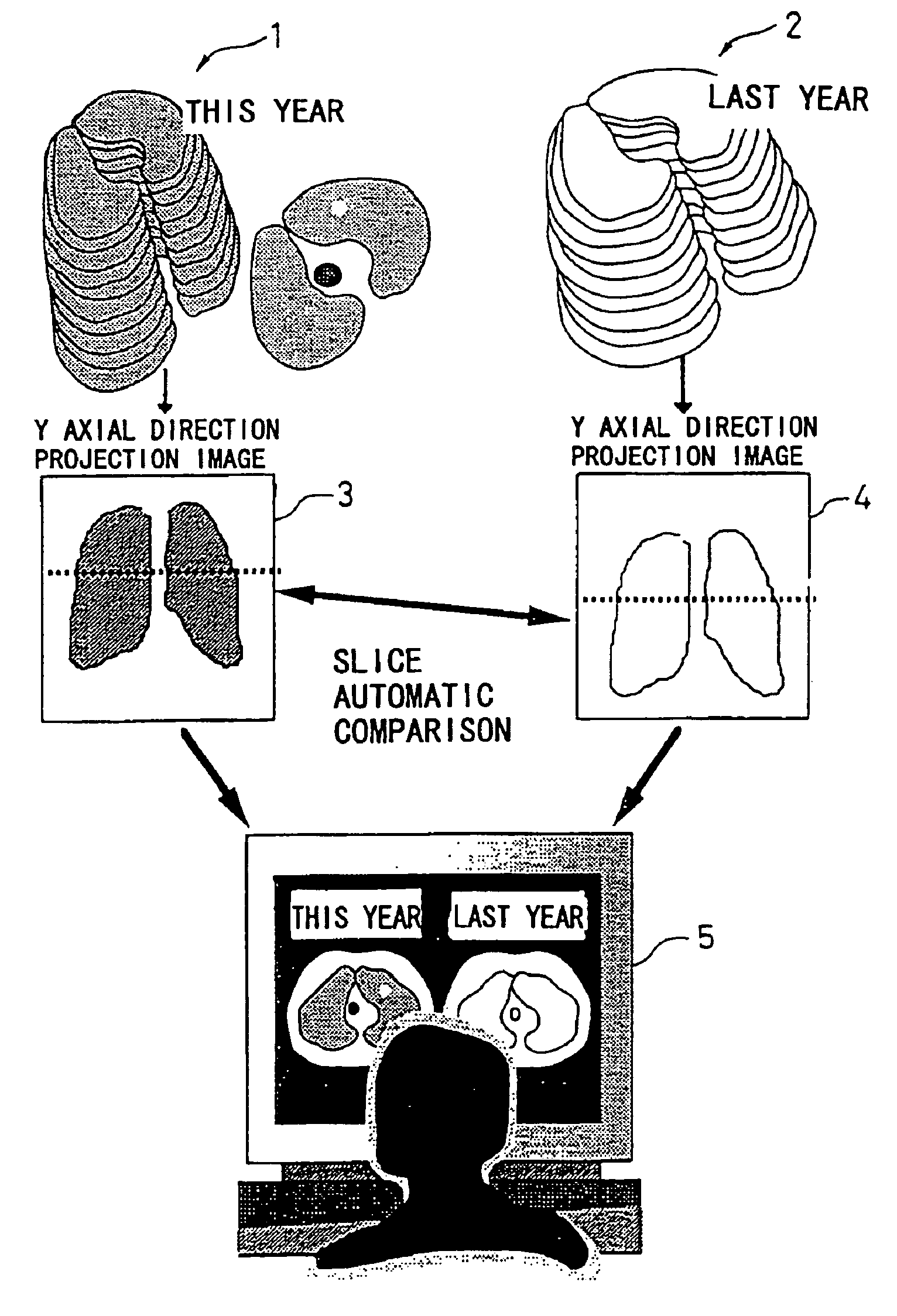
A tomographic image reading method for extracting a comparison image corresponding to a diagnostic image, the diagnostic image being one of first tomographic images, the comparison image being one of second tomographic images, the method including the steps of: inputting the first images and the second images; generating a first projection image from the first images and a second projection image from the second images; measuring shift amount between the first projection image and the second projection image by using a template; correcting the slice position according to the shift amount; and displaying the diagnostic image and the comparison image to a monitor.
Owner:NIPPON TELEGRAPN & TELEPHONE CORP
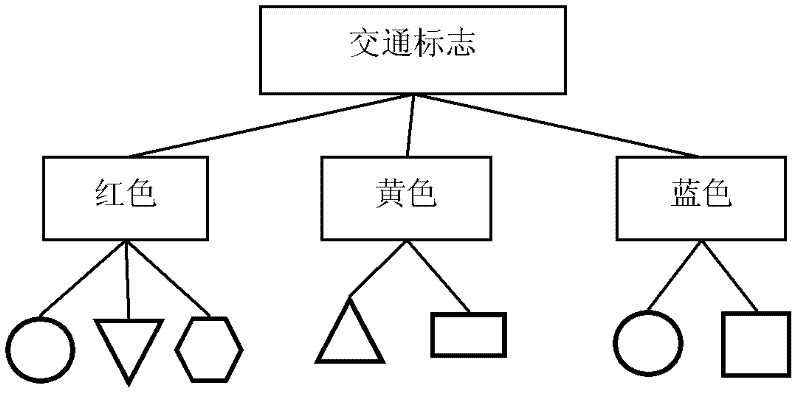
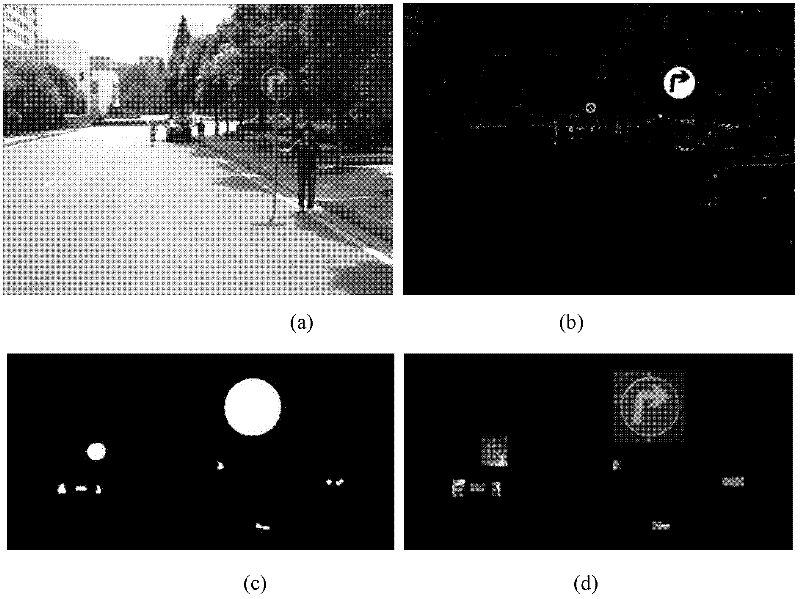
Method for recognizing road traffic sign for unmanned vehicle
InactiveCN102542260AFast extractionFast matchingDetection of traffic movementCharacter and pattern recognitionClassification methodsNear neighbor
The invention discloses a method for recognizing a road traffic sign for an unmanned vehicle, comprising the following steps of: (1) changing the RGB (Red, Green and Blue) pixel value of an image to strengthen a traffic sign feature color region, and cutting the image by using a threshold; (2) carrying out edge detection and connection on a gray level image to reconstruct an interested region; (3) extracting a labeled graph of the interested region as a shape feature of the interested region, classifying the shape of the region by using a nearest neighbor classification method, and removing a non-traffic sign region; and (4) graying and normalizing the image of the interested region of the traffic sign, carrying out dual-tree complex wavelet transform on the image to form a feature vector of the image, reducing the dimension of the feature vector by using a two-dimension independent component analysis method, and sending the feature vector into a support vector machine of a radial basis function to judge the type of the traffic sign of the interested region. By using the method, various types of traffic signs in a running environment of the unmanned vehicle can be stably and efficiently detected and recognized.
Owner:CENT SOUTH UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com