Patents
Literature
1304 results about "Variation of parameters" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
In mathematics, variation of parameters, also known as variation of constants, is a general method to solve inhomogeneous linear ordinary differential equations. For first-order inhomogeneous linear differential equations it is usually possible to find solutions via integrating factors or undetermined coefficients with considerably less effort, although those methods leverage heuristics that involve guessing and don't work for all inhomogeneous linear differential equations.
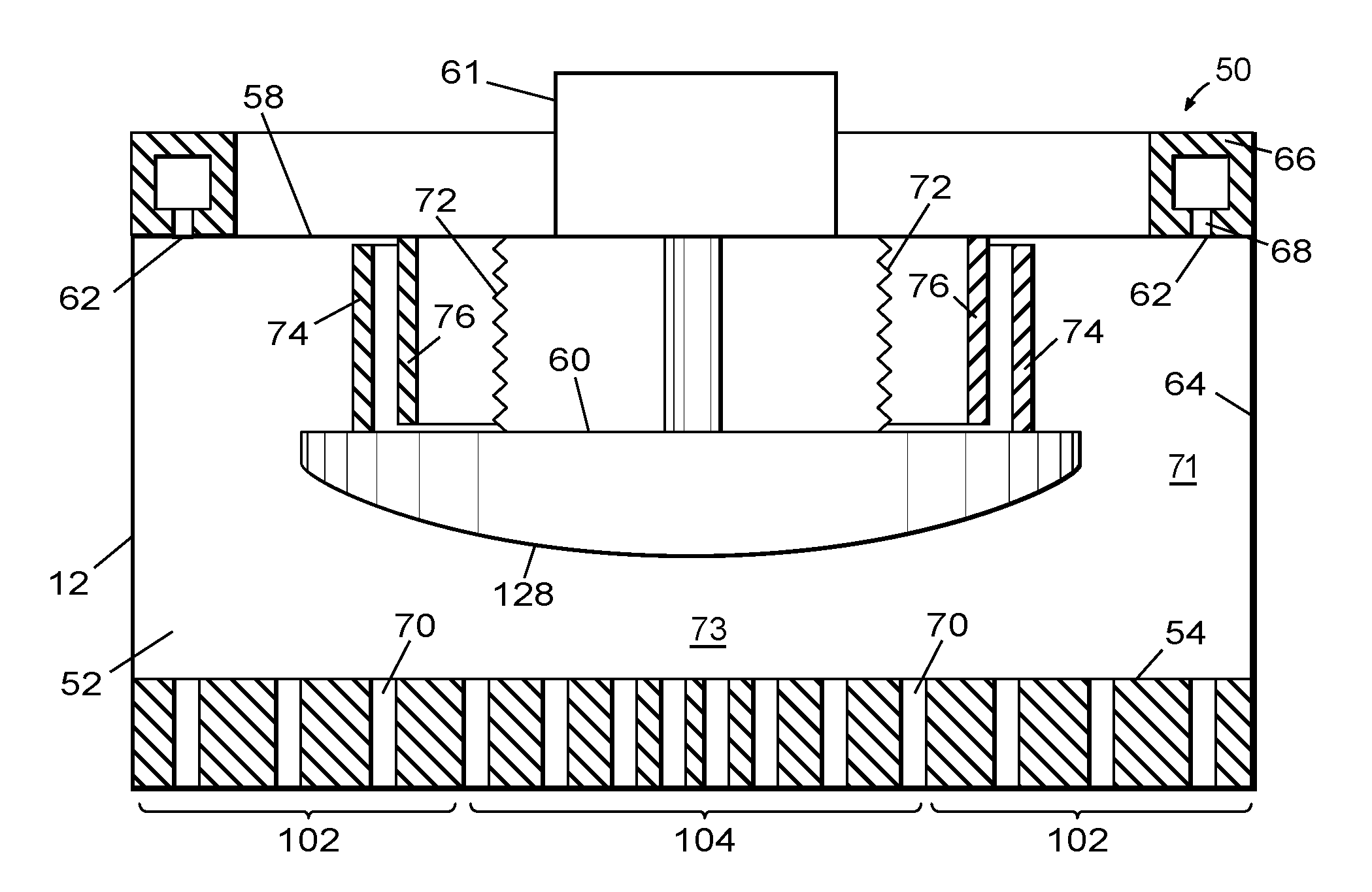
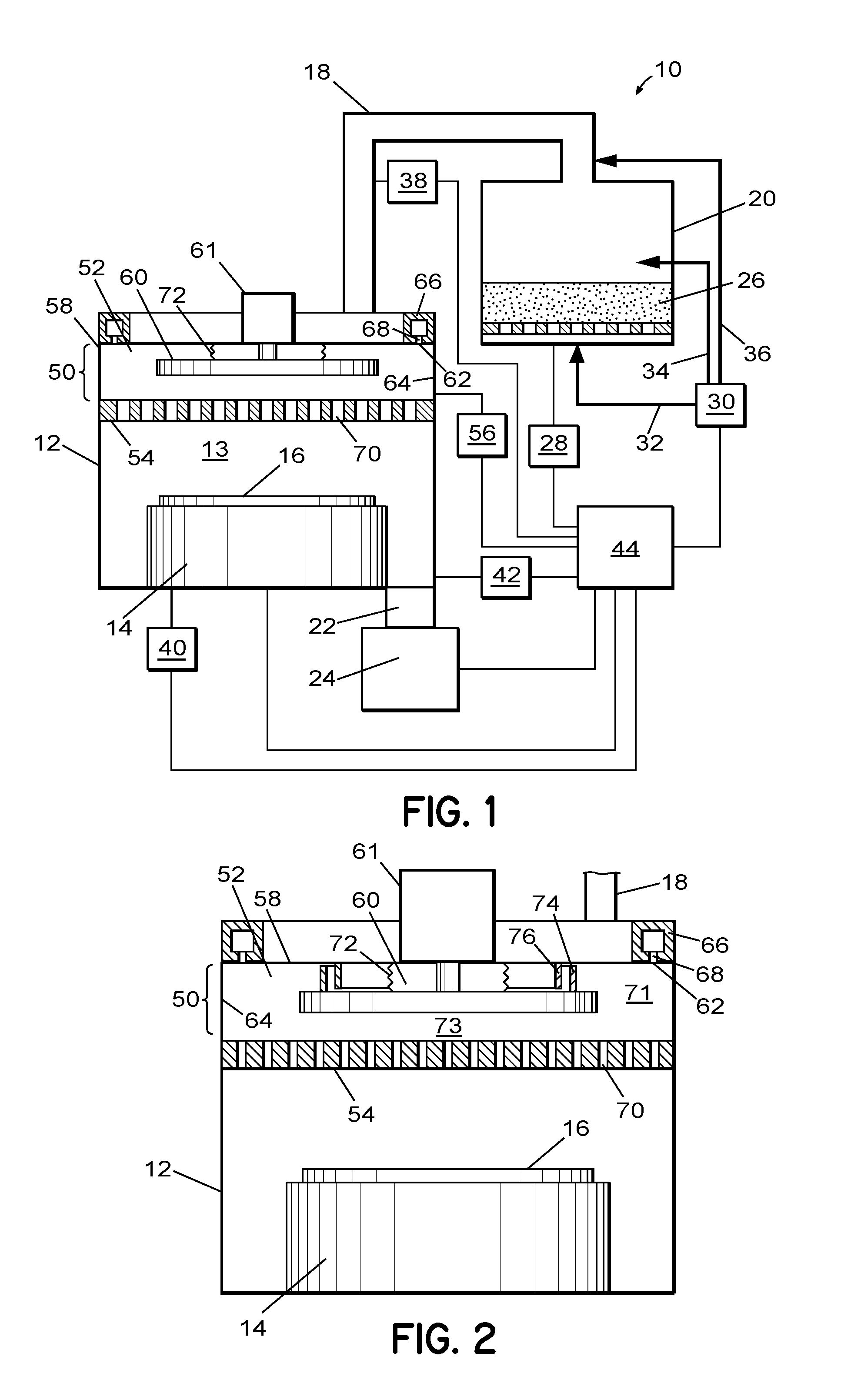
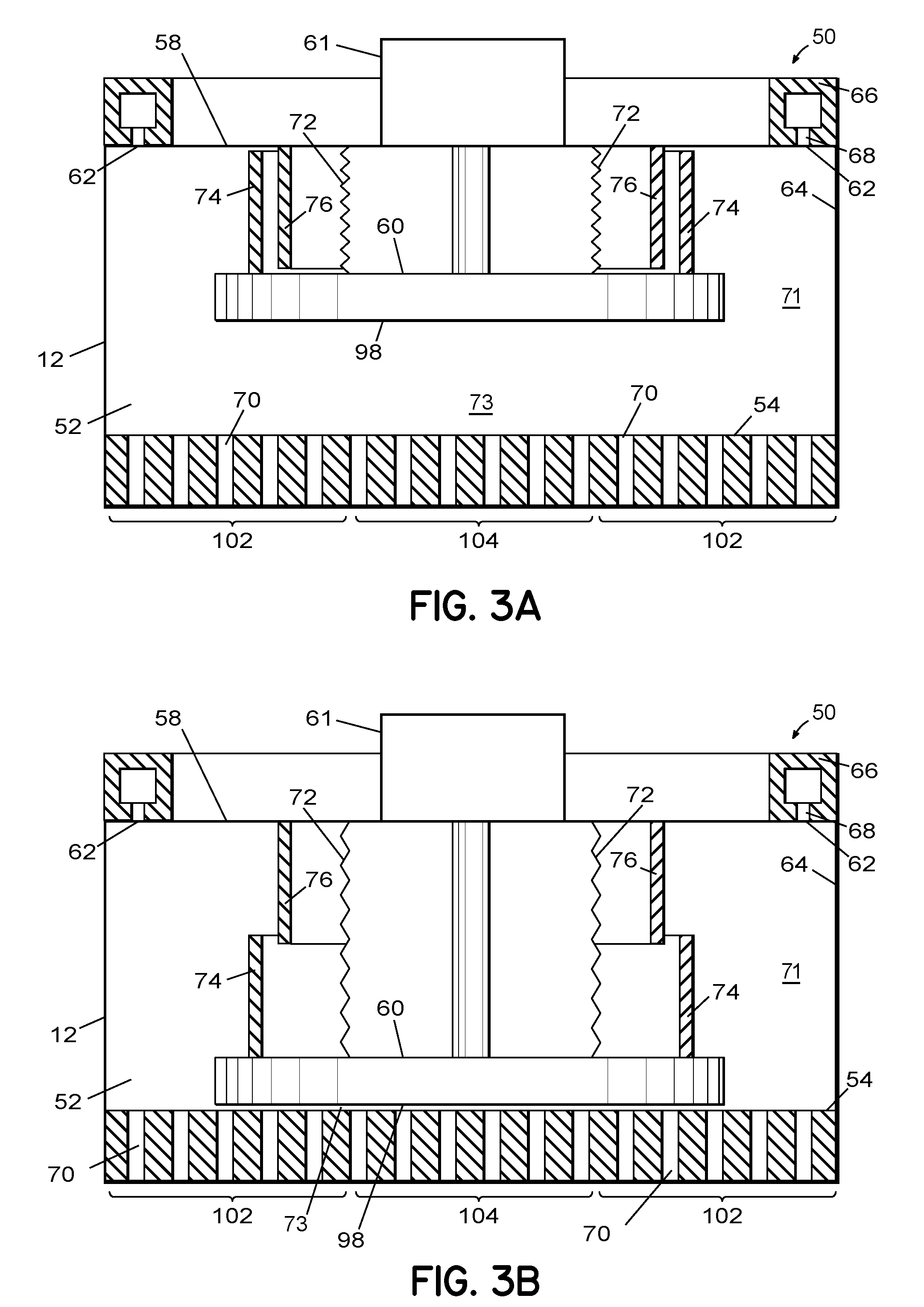
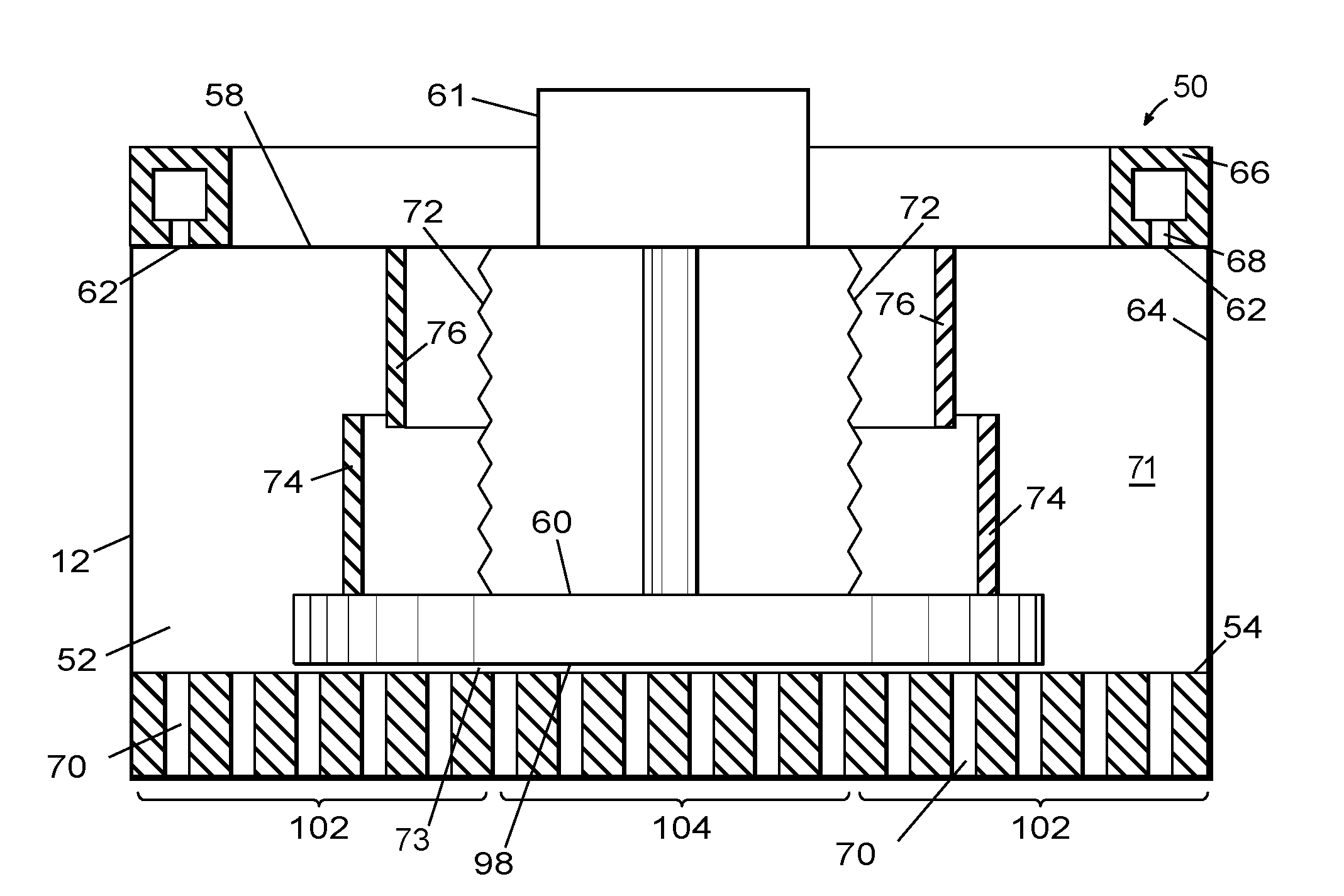
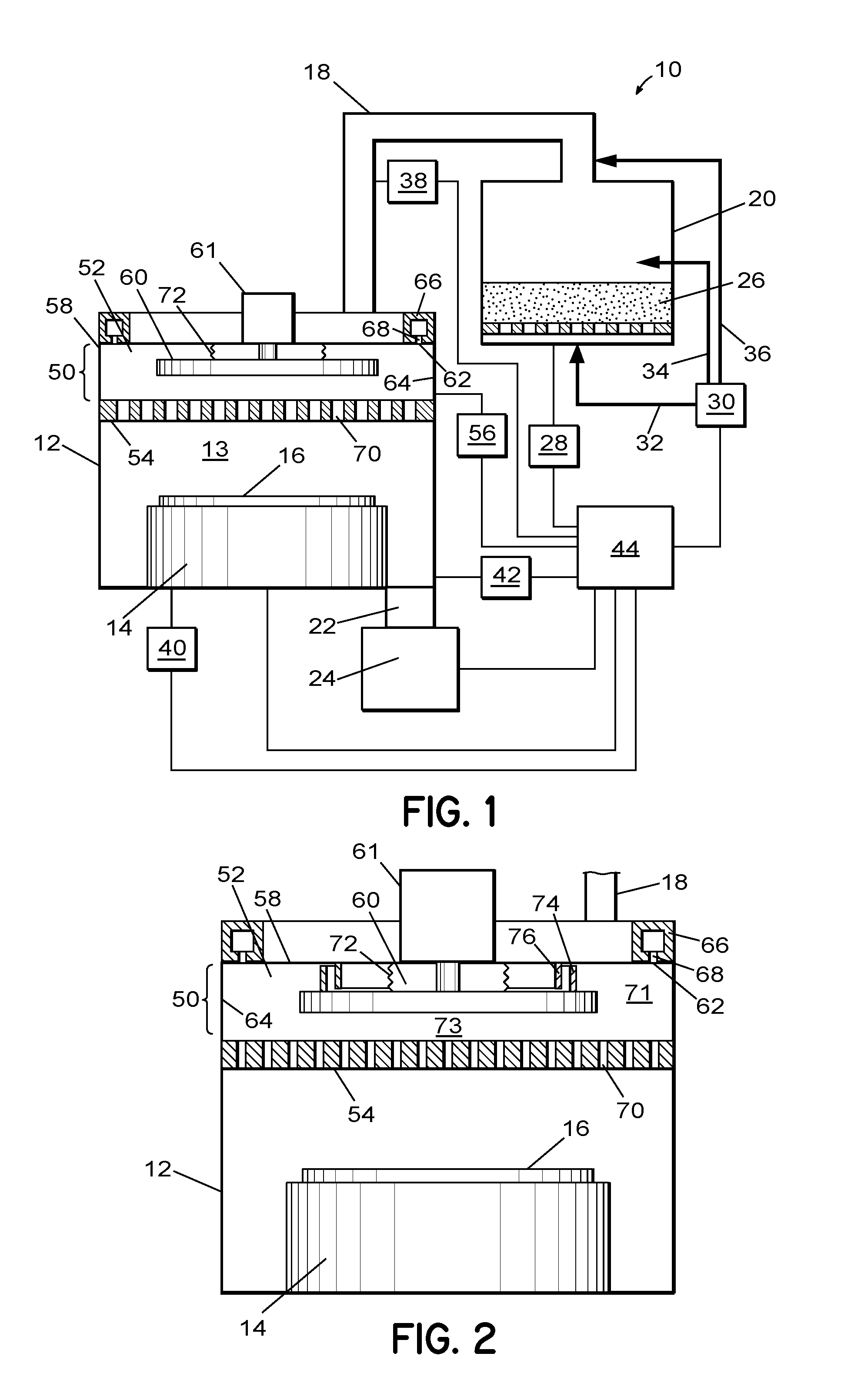
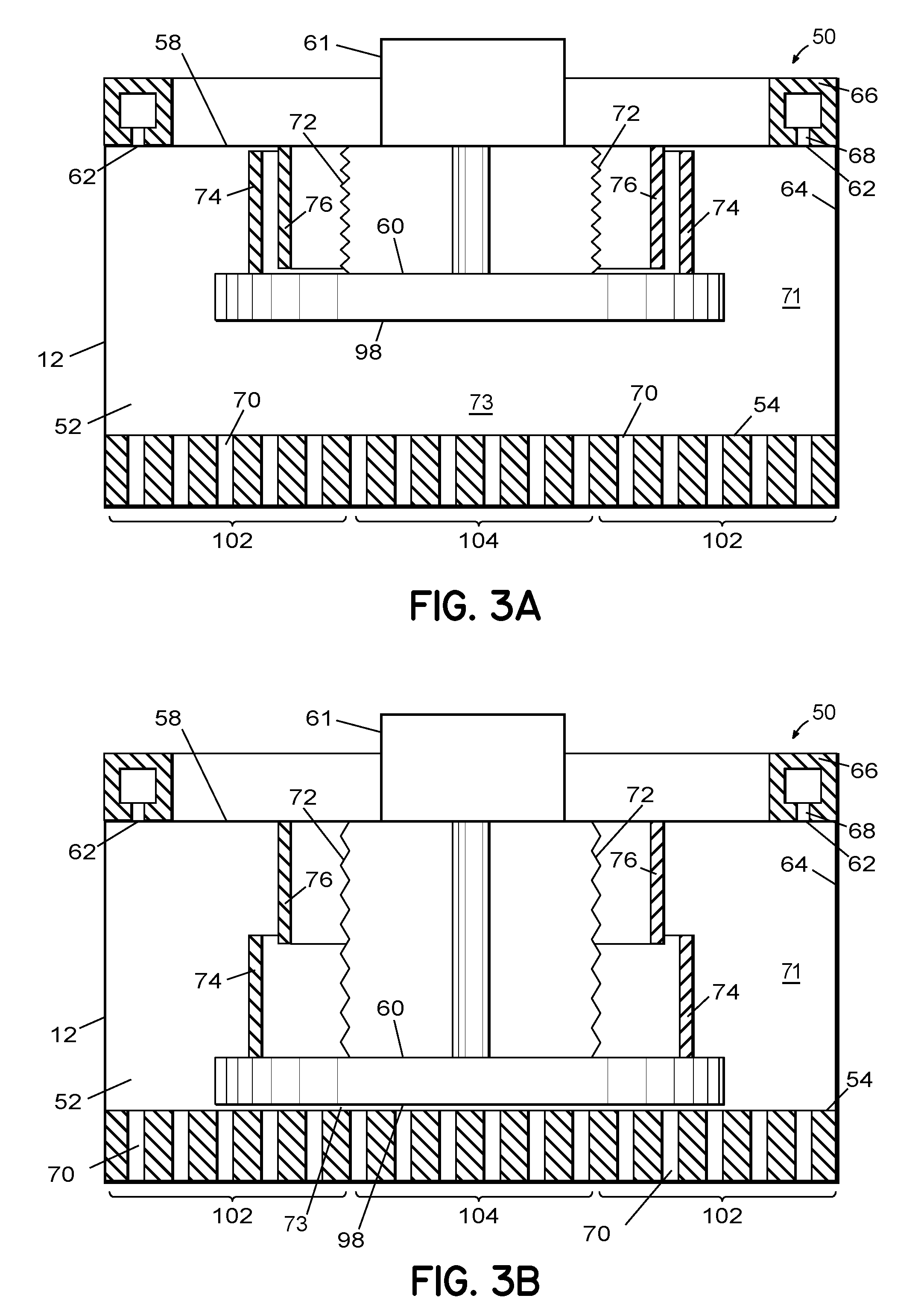
Gas distribution system and method for distributing process gas in a processing system
ActiveUS20090246374A1Semiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingChemical vapor deposition coatingGas phaseDistribution system
An apparatus and related method for distributing process gas in a vapor deposition system is described. The gas distribution system includes a vertically movable piston within its plenum, and the movement of the piston controls the flow rate of process gas through the vapor distribution plate of the gas distribution system. The piston can be used to accommodate changes in processing parameters that affect flow characteristics and to create edge-enhanced, uniform, and center-enhanced profiles of deposited material on a substrate without the need to replace the vapor distribution plate.
Owner:TOKYO ELECTRON LTD
Gas distribution system and method for distributing process gas in a processing system
ActiveUS8252114B2Semiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingChemical vapor deposition coatingGas phaseDistribution system
An apparatus and related method for distributing process gas in a vapor deposition system is described. The gas distribution system includes a vertically movable piston within its plenum, and the movement of the piston controls the flow rate of process gas through the vapor distribution plate of the gas distribution system. The piston can be used to accommodate changes in processing parameters that affect flow characteristics and to create edge-enhanced, uniform, and center-enhanced profiles of deposited material on a substrate without the need to replace the vapor distribution plate.
Owner:TOKYO ELECTRON LTD
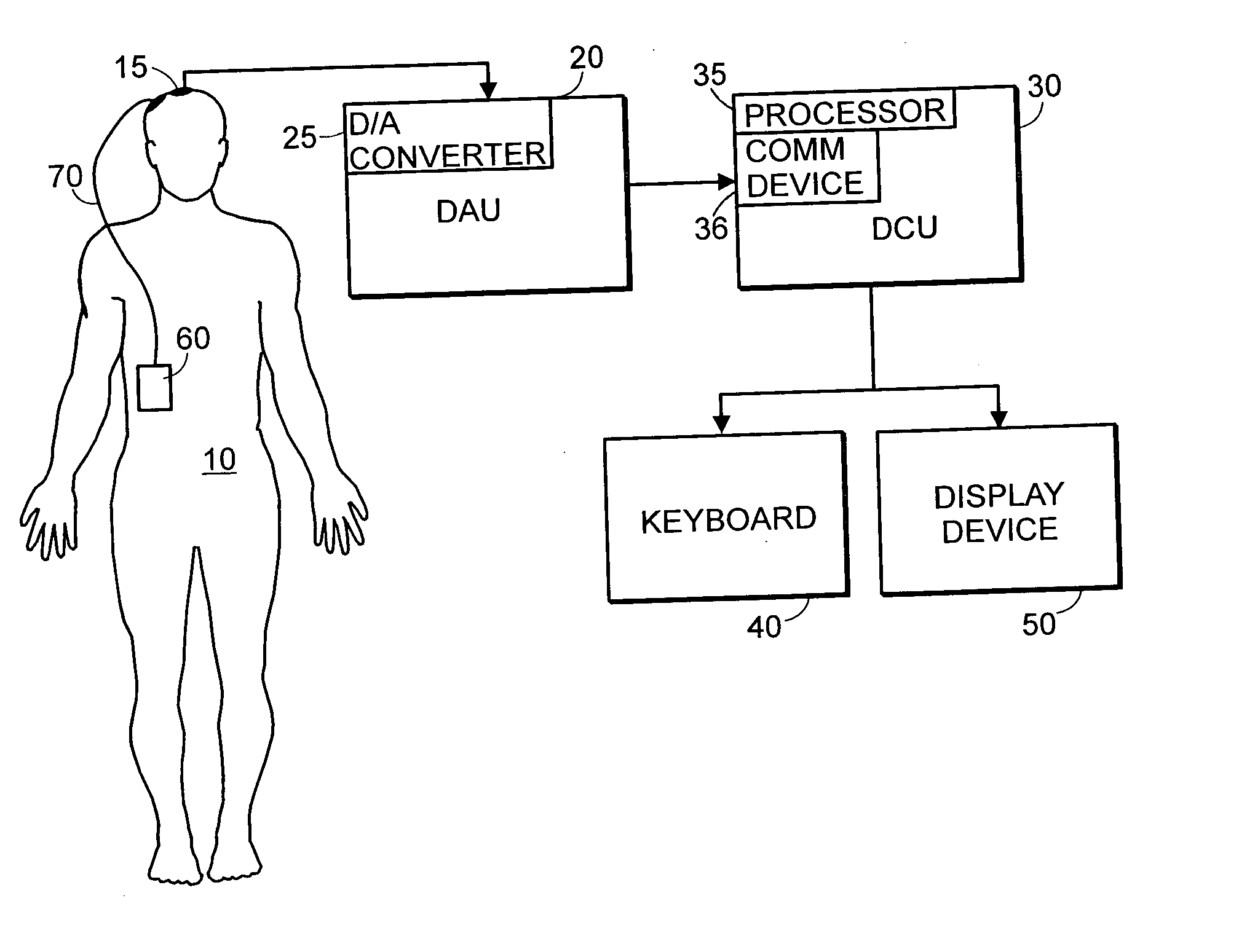
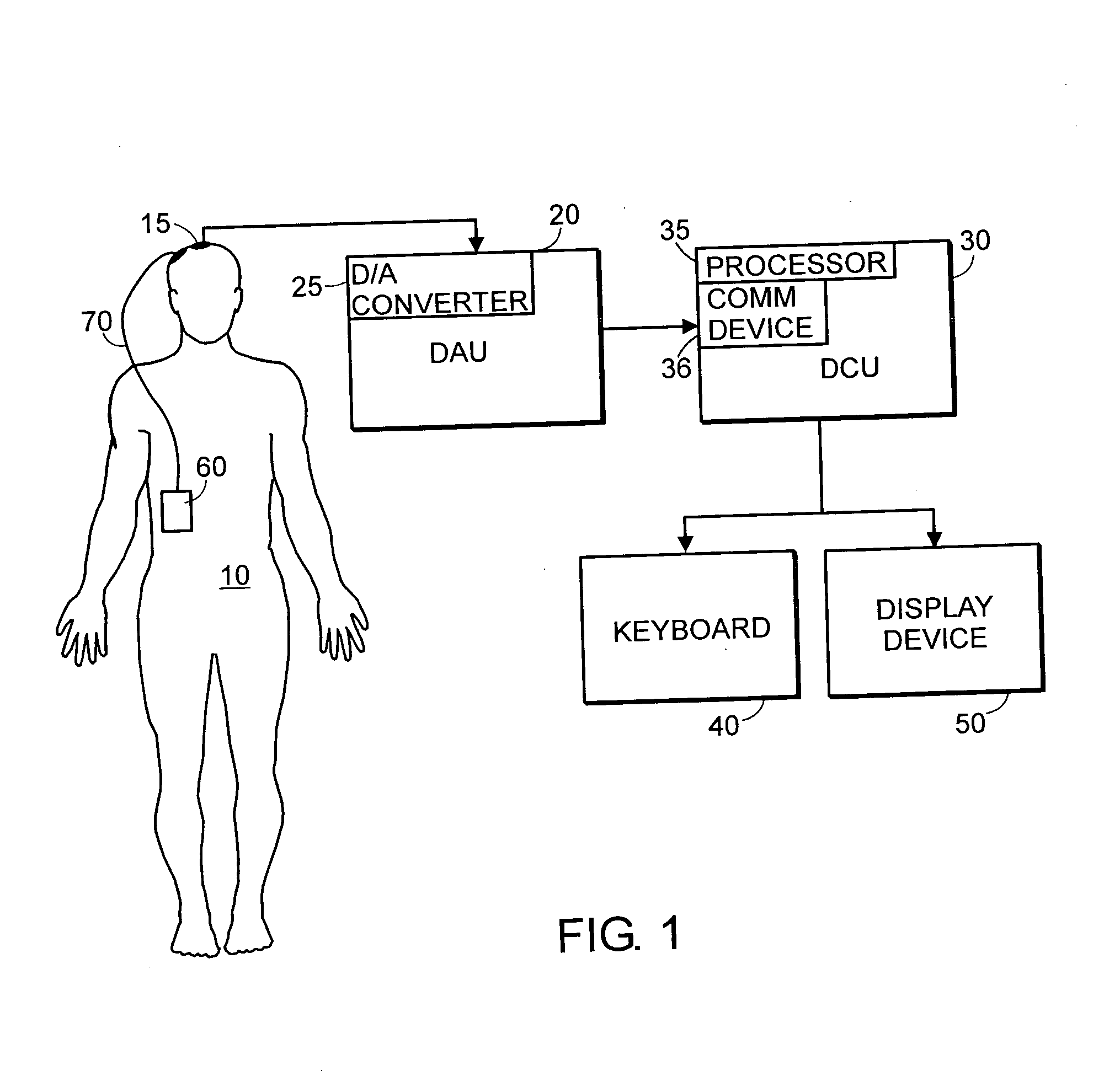
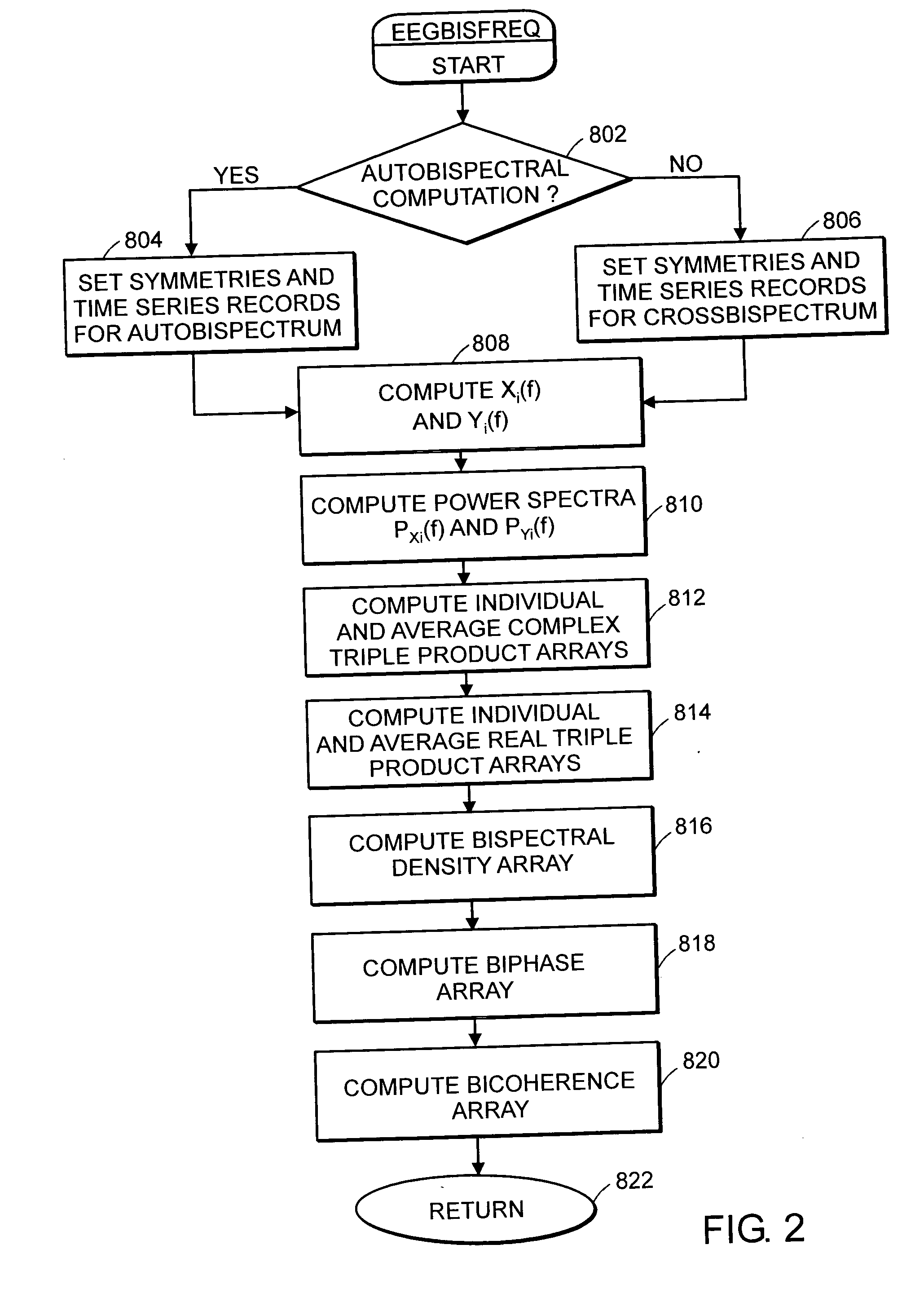
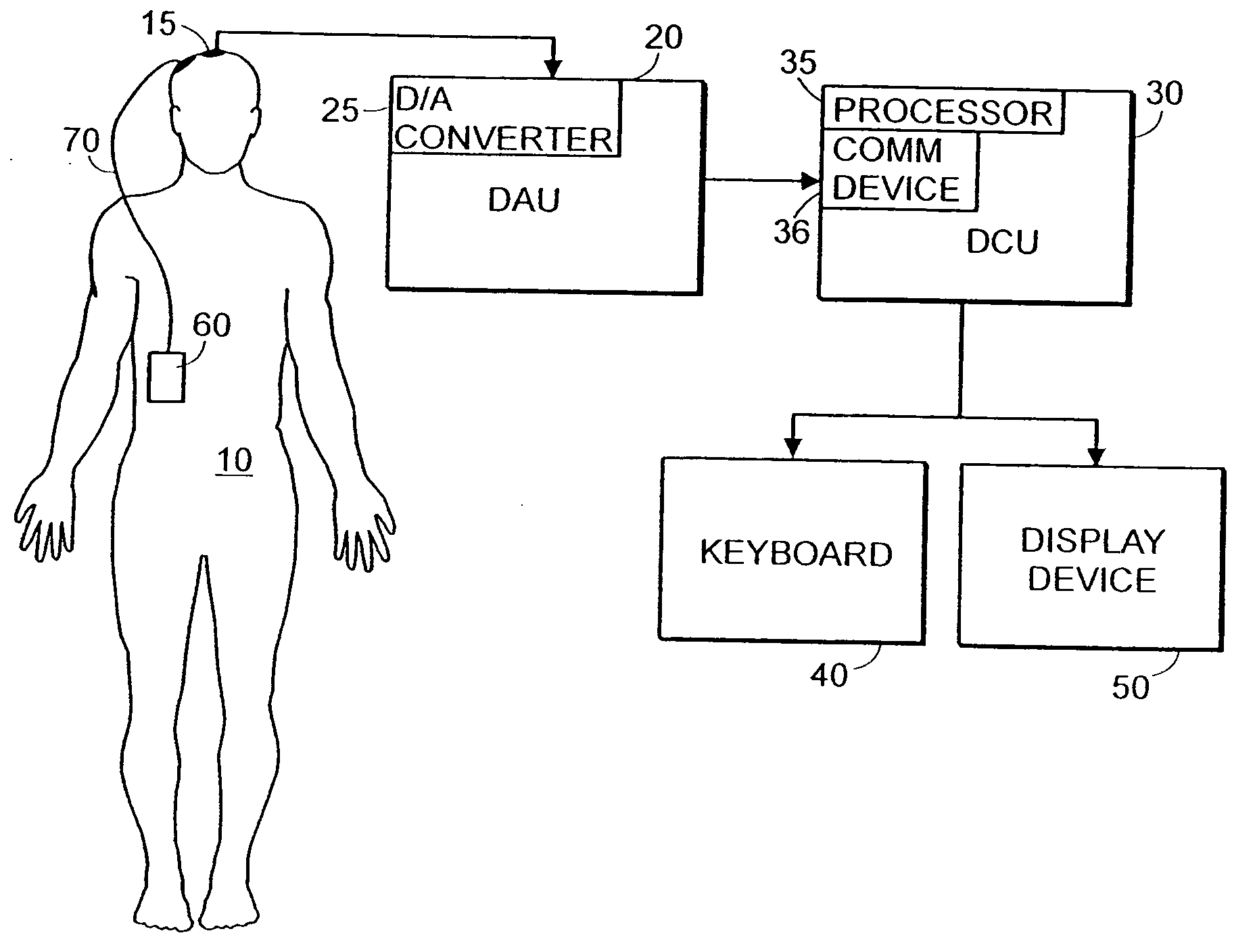
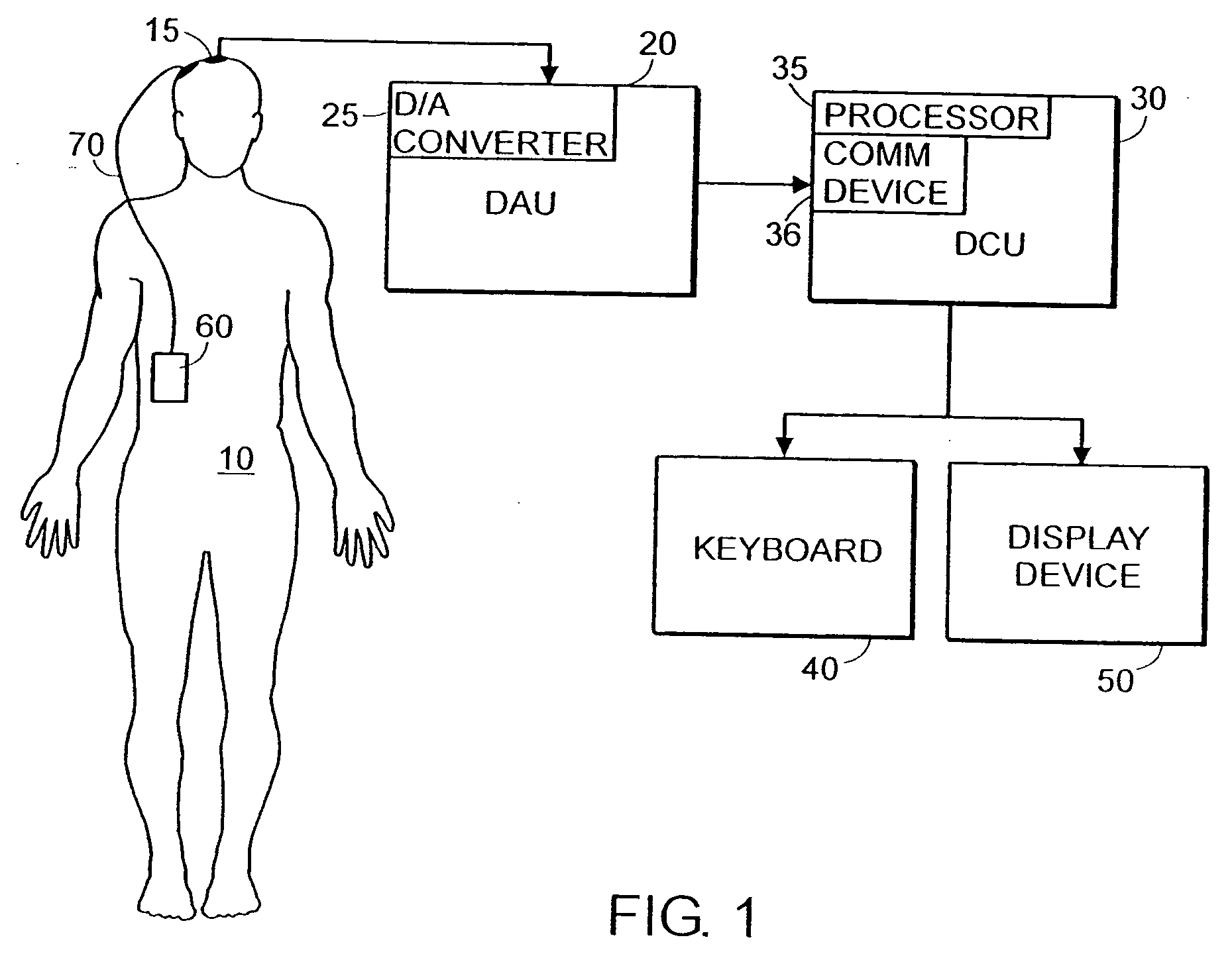
System and method of assessment of the efficacy of treatment of neurological disorders using the electroencephalogram
Disclosed is a system and method of assessing the efficacy of treatment of neurological or psychological disorders. The preferred embodiment uses at least two surface electrodes to acquire EEG signals from the surface of a patient's body, a processor for computing from the EEG signals various features and indices that are representative of the patient's neurological or psychological state. Changes in these parameters may be used to assess the efficacy of treatment and to modify the treatment to optimize the resultant patient state.
Owner:TYCO HEALTHCARE GRP LP
Spectroscopically measured overlay target
InactiveUS7061615B1Adequate fitEasy to measureSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesImage resolutionLine width
An overlay target for spectroscopic measurement includes at least two diffraction gratings, one grating overlying the other. The diffraction gratings may include an asymmetry relative to each other in order to improve resolution of the presence as well as the direction of any mis-registration. For example, the asymmetry between the two diffraction gratings may be a phase offset, a difference in pitch, line width, etc. The overlay target may be spectroscopically measuring, for example, using an optical model and a best fit analysis. Moreover, the overlay target may be optimized by modeling the overlay target and adjusting the variable parameters and calculating the sensitivity of the overlay target to changes in variable parameters.
Owner:ONTO INNOVATION INC
System and method of prediction of response to neurological treatment using the electroencephalogram
Disclosed is a system and method of assessing the efficacy of and predicting response to treatment of neurological or psychological disorders. The preferred embodiment uses at least two surface electrodes to acquire EEG signals from the surface of a patient's body, a processor for computing from the EEG signals various features and indices that are representative of the patient's neurological or psychological state. Pretreatment indices represent a patient's neurological or psychological state and therefore may be used to predict the response to treatment. Changes in these parameters may be used to assess the efficacy of treatment and to modify the treatment to optimize the resultant patient state.
Owner:TYCO HEALTHCARE GRP LP
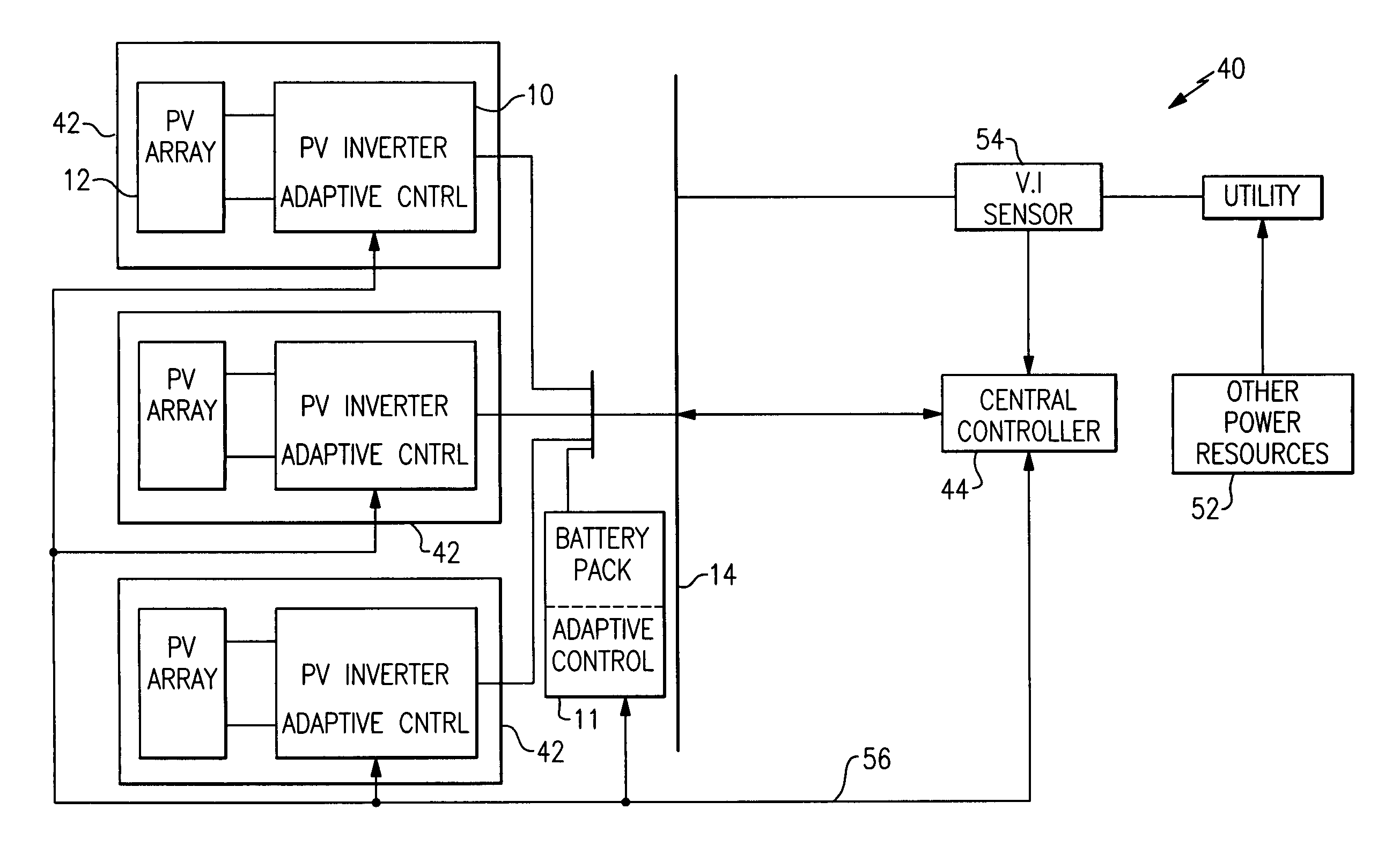
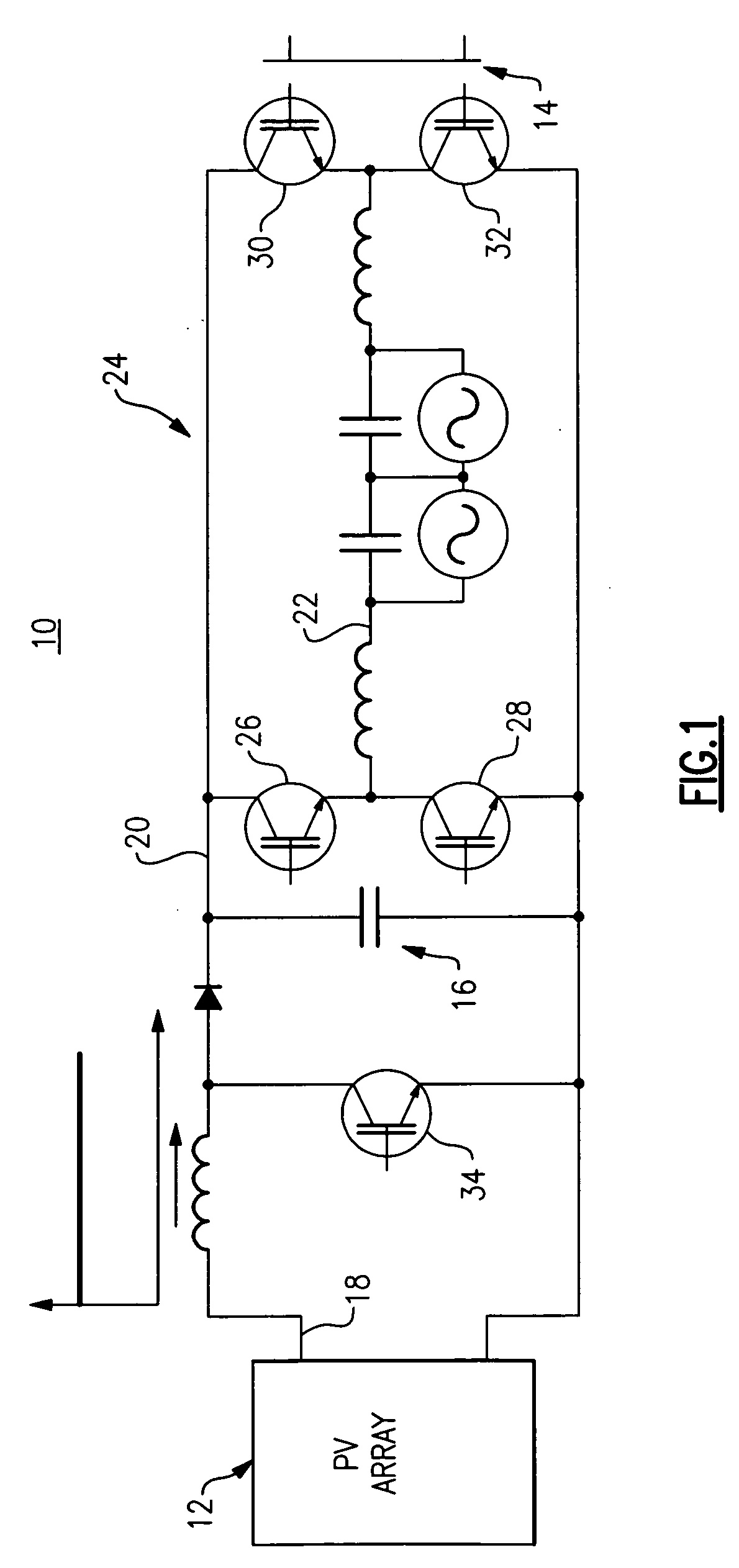
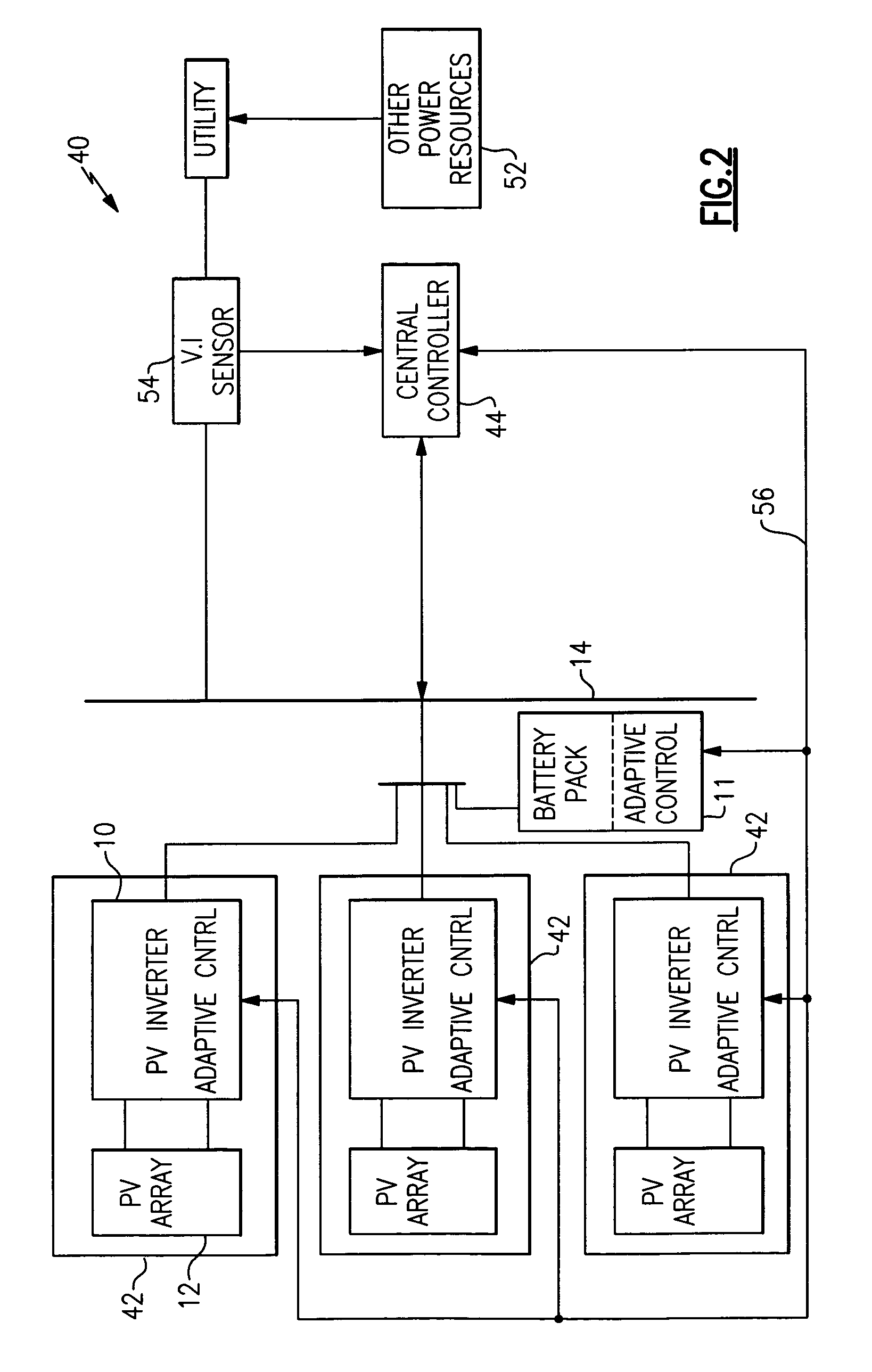
System and method for controlling ramp rate of solar photovoltaic system
A photovoltaic (PV) control system generates a power output rate control signal based on a monitored rate of change of collective power output generated via a plurality of PV subsystems and a desired collective output power change rate for the plurality of PV subsystems and communicates the power output rate control signal to the plurality of PV subsystems to control a rate of change of one or more operating parameters of individual PV subsystems in order to control a rate of change of collective output power of the plurality of solar PV subsystems.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
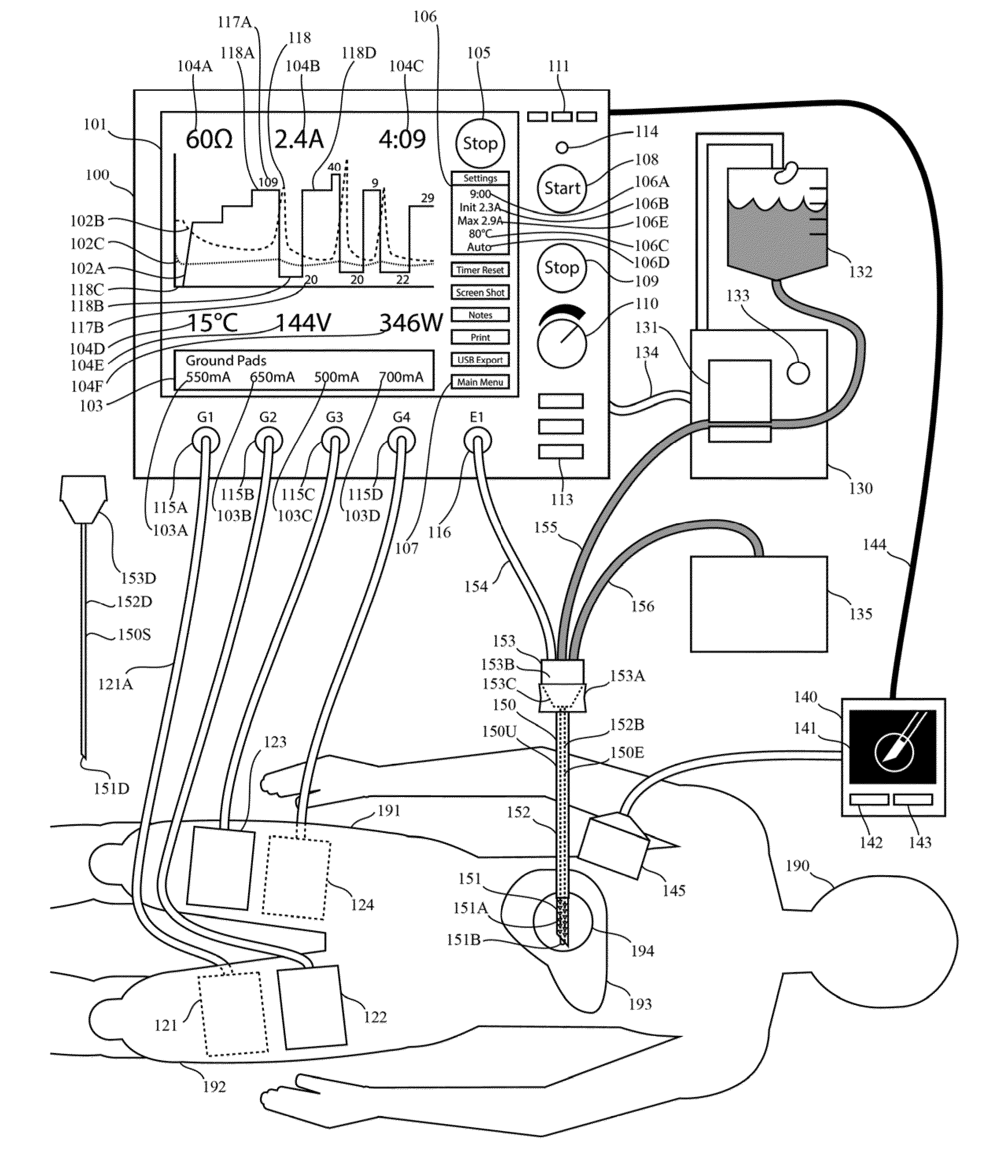
Electrosurgical generator
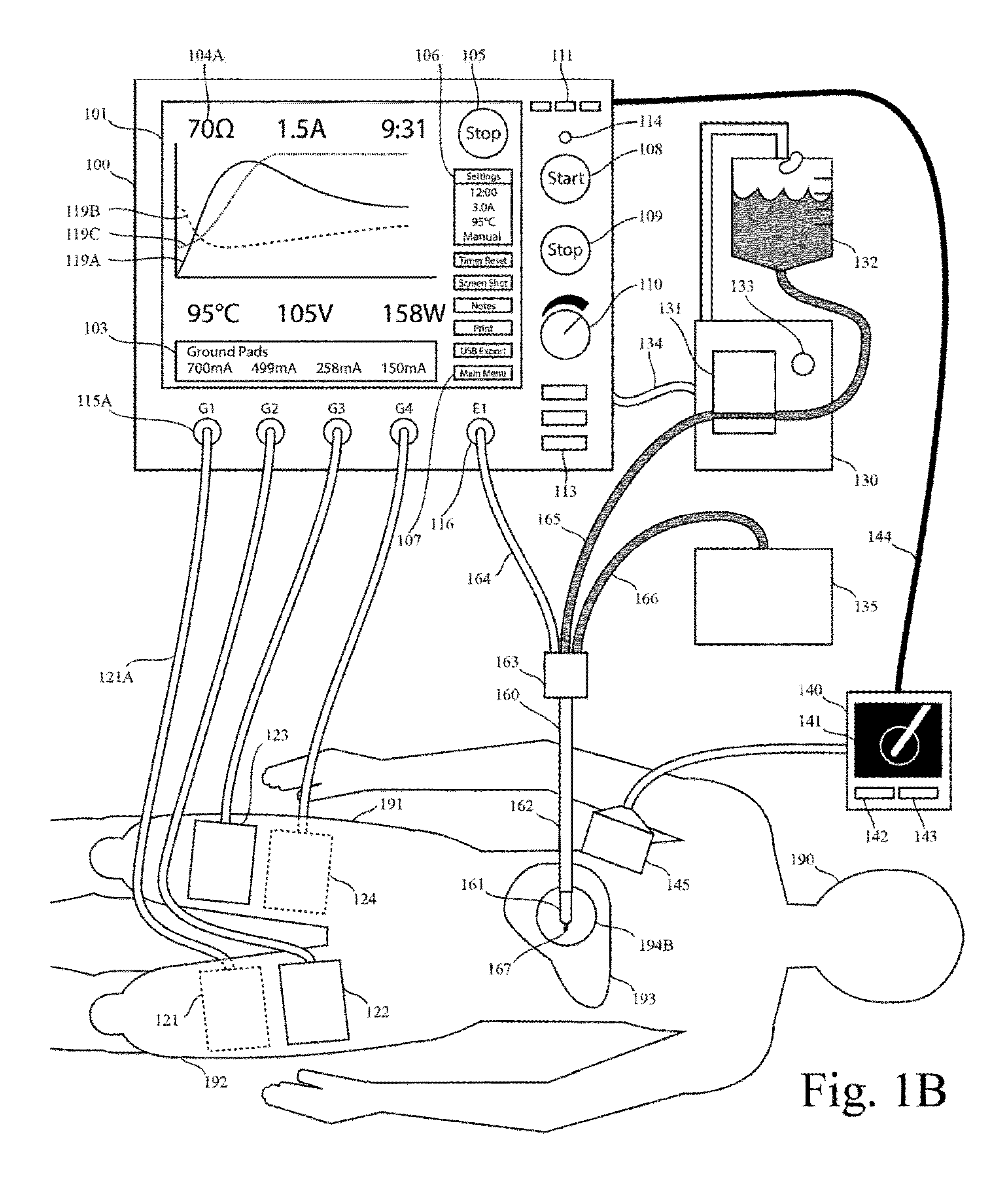
ActiveUS20150320481A1Increase productionRelieve painElectrotherapyDiagnosticsSonificationReturn current
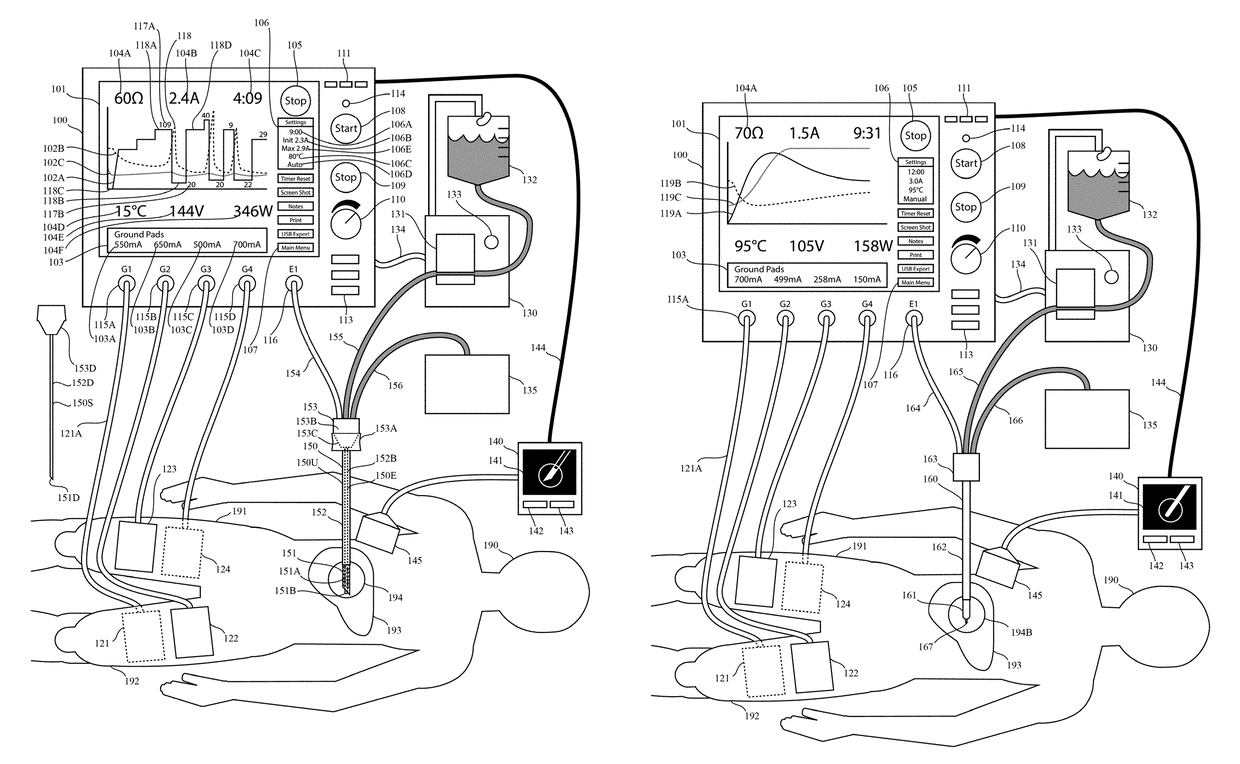
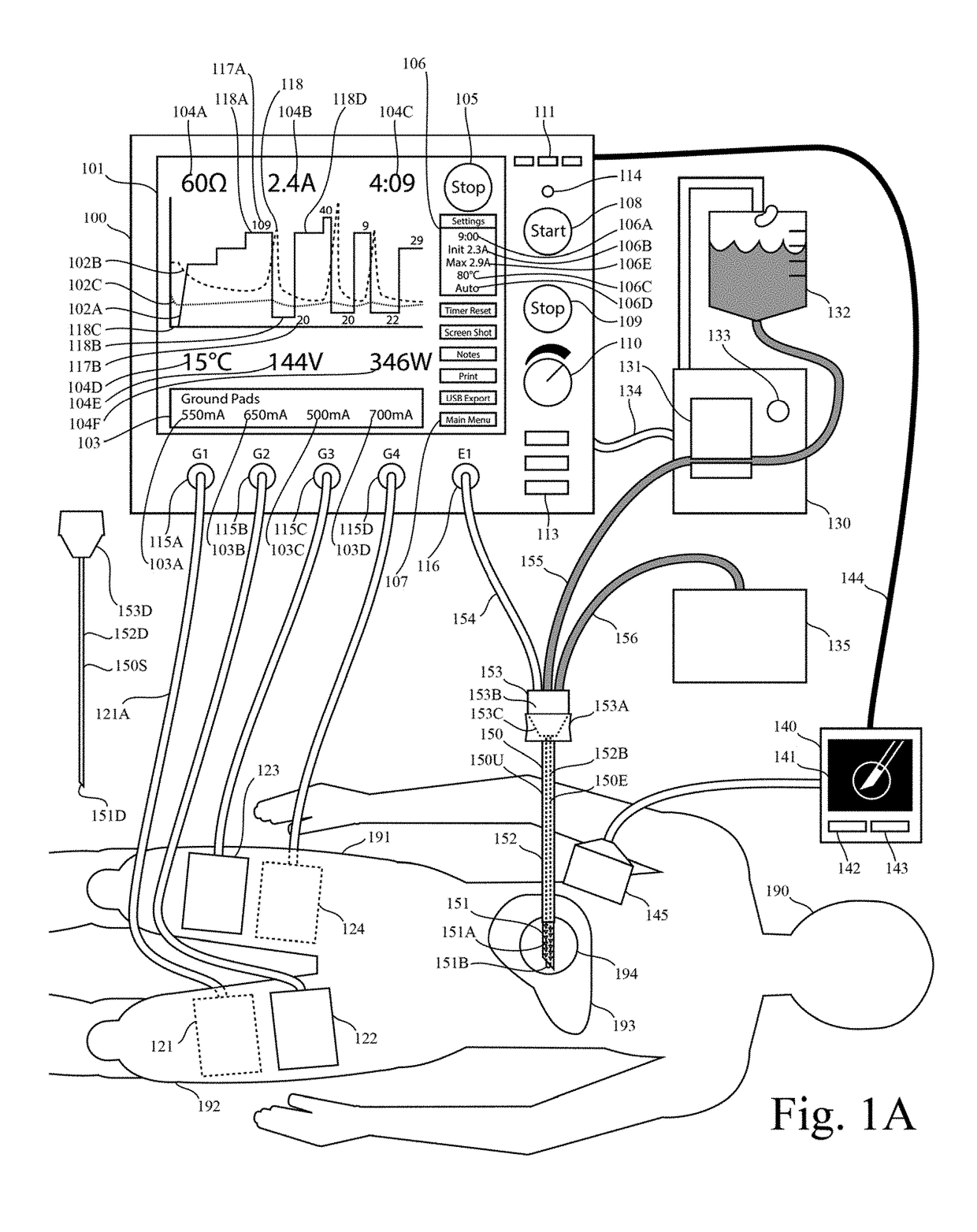
This invention relates to high-frequency ablation of tissue in the body using a cooled high-frequency electrode connected to a high frequency generator including a computer graphic control system and an automatic controller for control the signal output from the generator, and adapted to display on a real time graphic display a measured parameter related to the ablation process and visually monitor the variation of the parameter of the signal output that is controlled by the controller during the ablation process. In one example, one or more measured parameters are displayed simultaneously to visually interpret the relation of their variation and values. In one example, the displayed one or more parameters can be taken from the list of measured voltage, current, power, impedance, electrode temperature, and tissue temperature related to the ablation process. The graphic display gives the clinician an instantaneous and intuitive feeling for the dynamics and stability of the ablation process for safety and control. This invention relates to monitoring and controlling multiple ground pads to optimally carry return currents during high-frequency tissue ablation, and to prevent of ground-pad skin burns. This invention relates to the use of ultrasound imaging intraoperatively during a tissue ablation procedure. This invention relates to the use of nerve stimulation and blocking during a tissue ablation procedure.
Owner:COSMAN INTRUMENTS LLC
Power converter in a utility interactive system
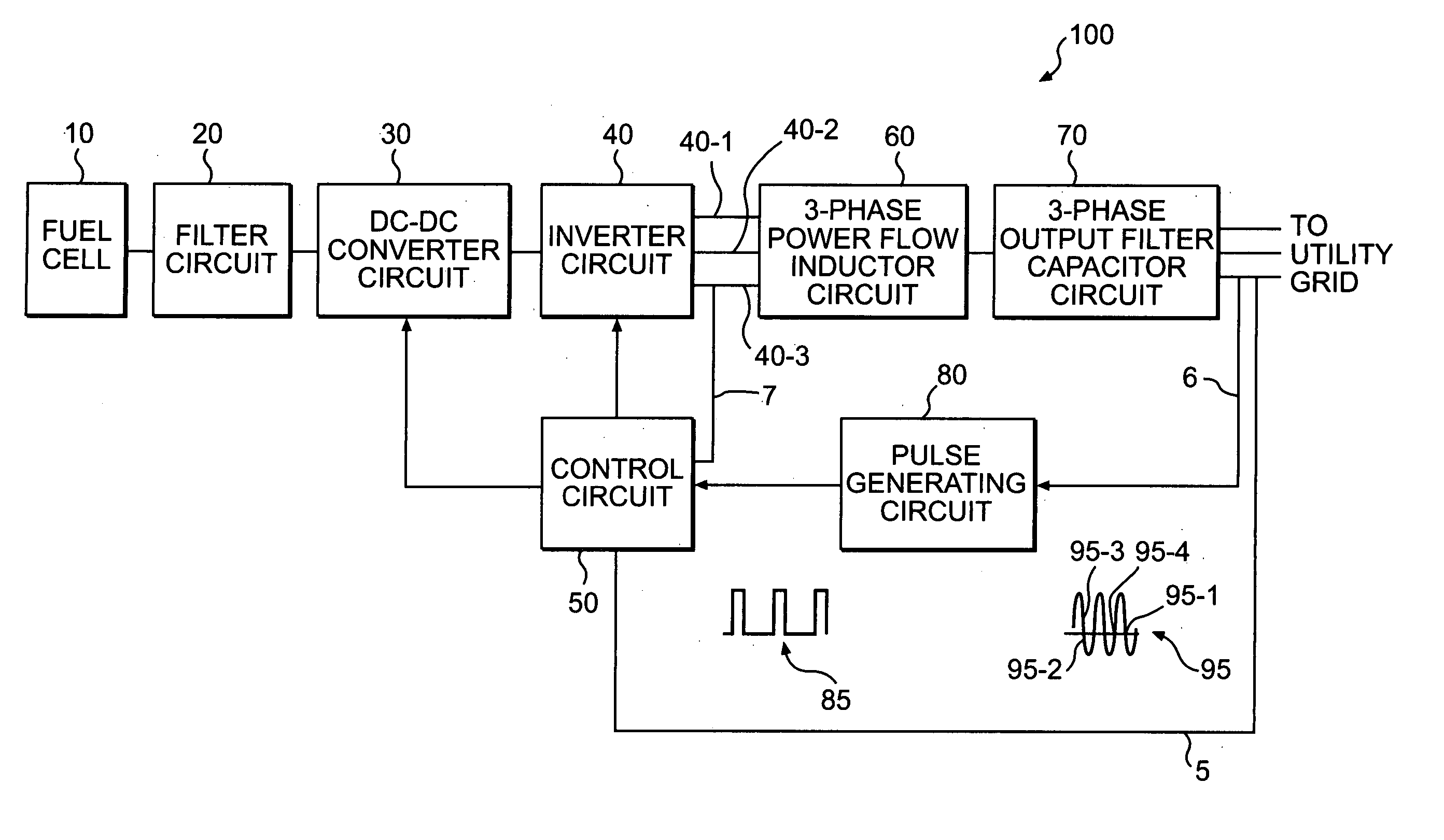
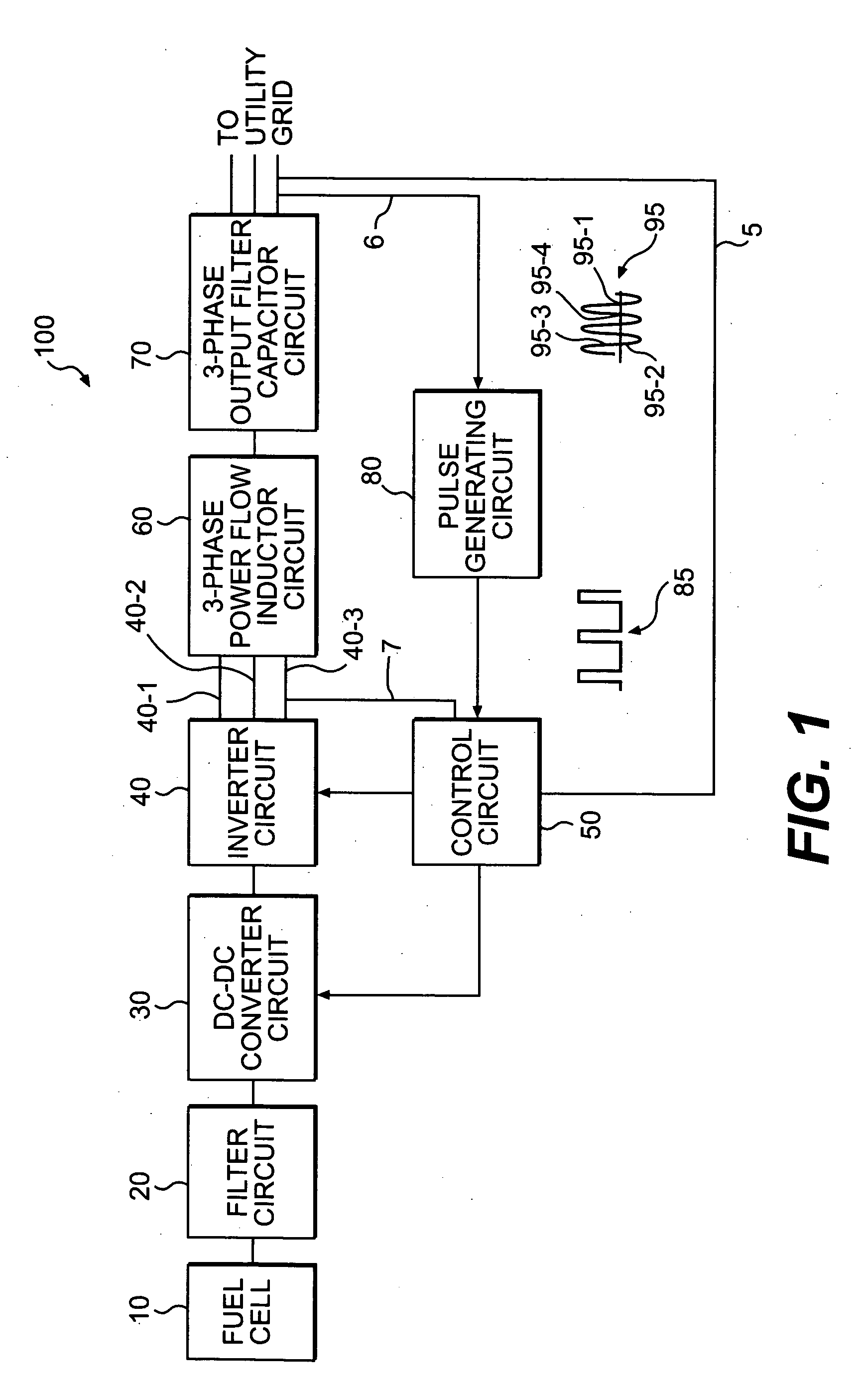
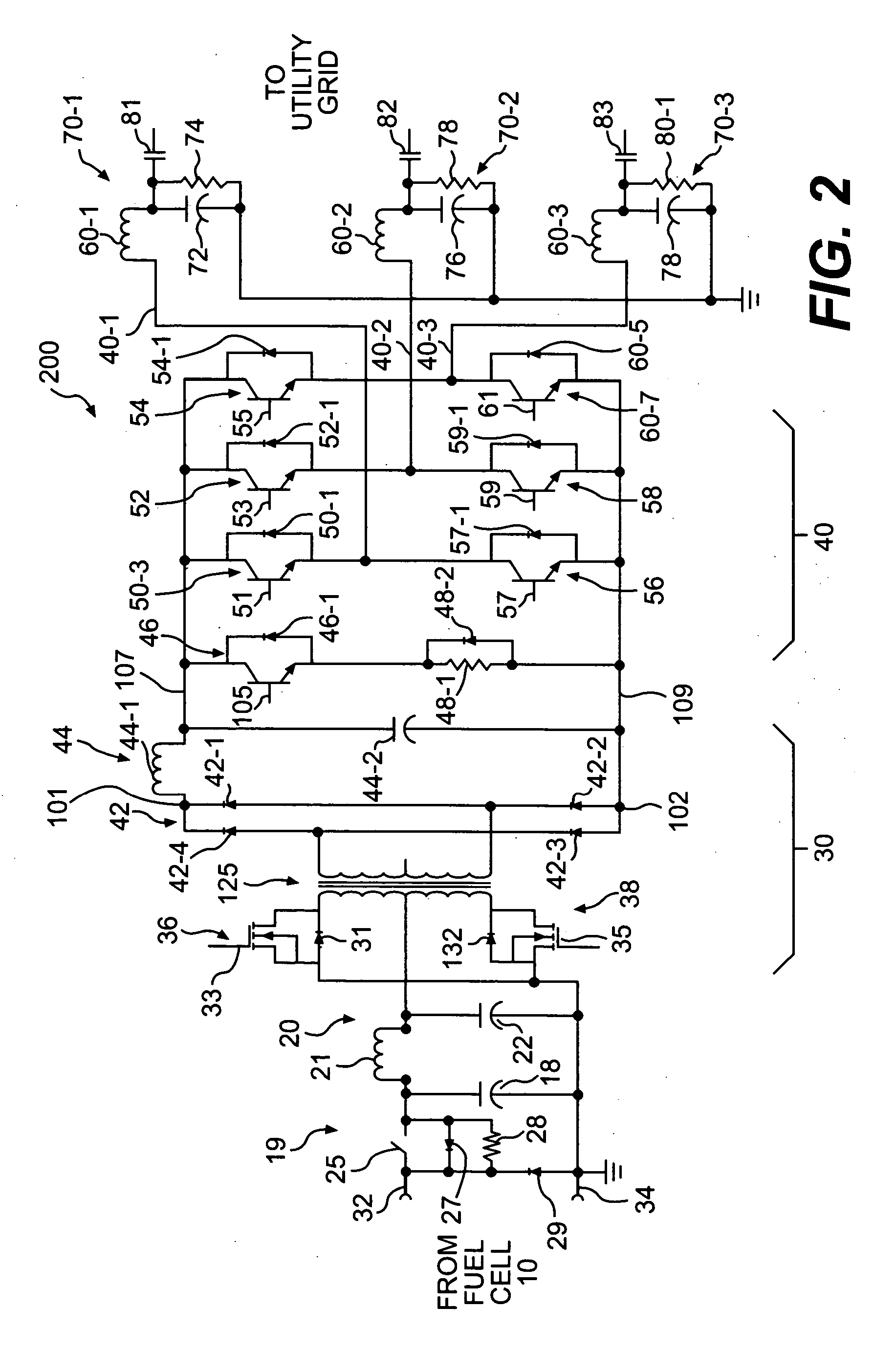
ActiveUS20060034106A1Adjustable levelConversion with intermediate conversion to dcDc-dc conversionFuel cellsControl signal
Consistent with an aspect of the present disclosure, a backup fuel cell, for example, is coupled to a utility power grid, through a power conversion circuit. The power conversion circuit may include an inverter circuit, pulse generating circuit and control circuit. The inverter circuit is configured to receive a DC signal and output a first AC signal, and the pulse generating circuit generates a pulse signal in response to a change in a parameter associated with a second utility generated AC signal. The control circuit is coupled to the inverter circuit, and is configured to receive the pulse signal. In addition, the control circuit supplies a control signal to the inverter circuit to adjust a parameter associated with the first AC signal in response to the pulse.
Owner:CATERPILLAR INC
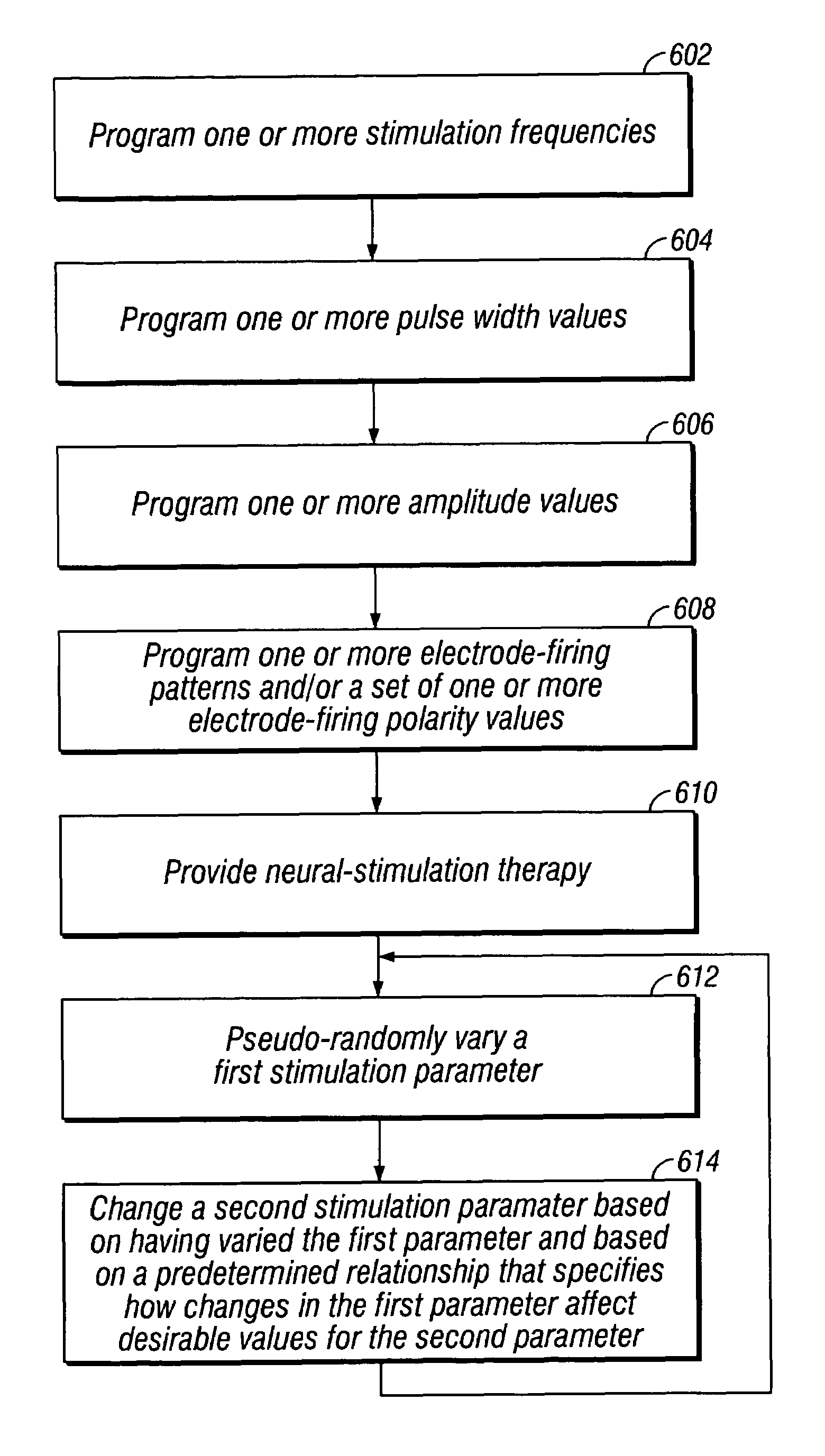
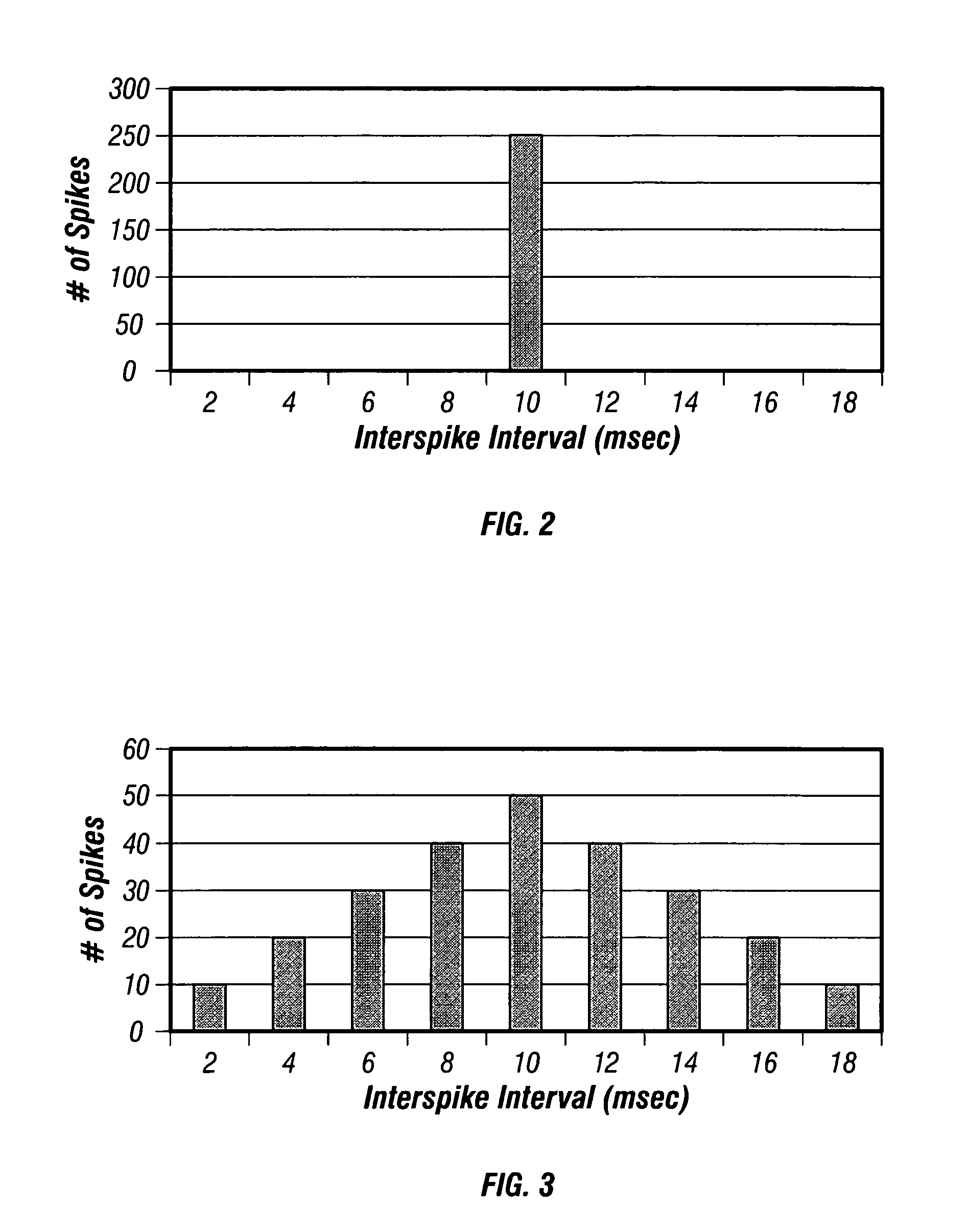
Variation of neural-stimulation parameters
InactiveUS7050856B2Reduce lossesOvercomes shortcomingInternal electrodesExternal electrodesSide effectMedicine
Techniques for varying stimulus parameters used in neural stimulation to improve therapy efficacy, minimize energy consumption, minimize undesired side effects, and minimize loss of therapeutic effectiveness due to physiologic tolerance to stimulation. Neural stimulation is provided having a stimulation amplitude, a stimulation frequency, a stimulation pulse duration, an electrode-firing pattern, and a set of electrode-firing-polarity conditions. At least one of the stimulation parameters is pseudo-randomly varied. A second stimulation parameter is changed based upon having pseudo-randomly varied the first stimulation parameter and based upon a predetermined relationship specifying how changes in the first parameter affect desirable values for the second parameter.
Owner:MEDTRONIC INC
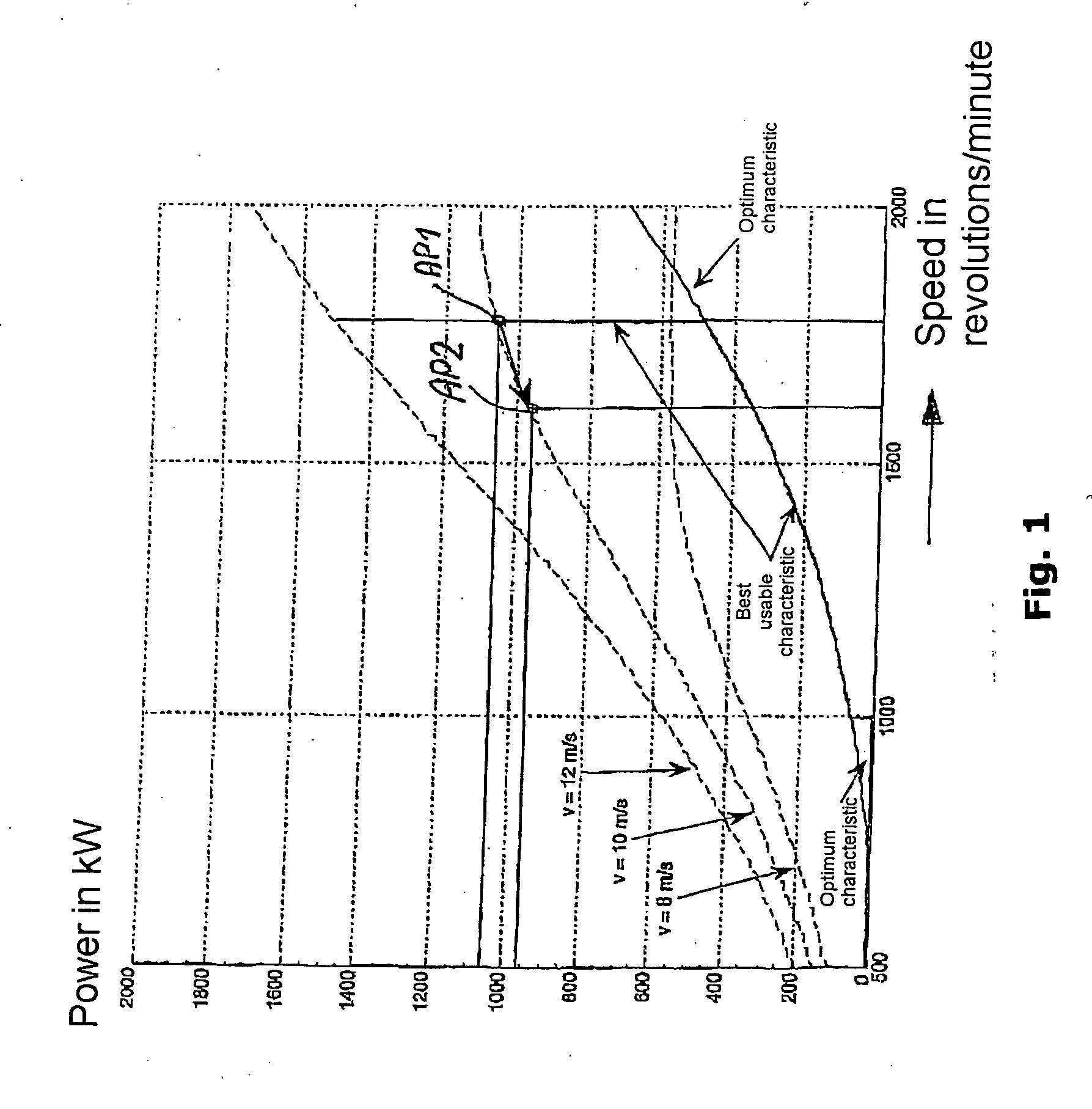
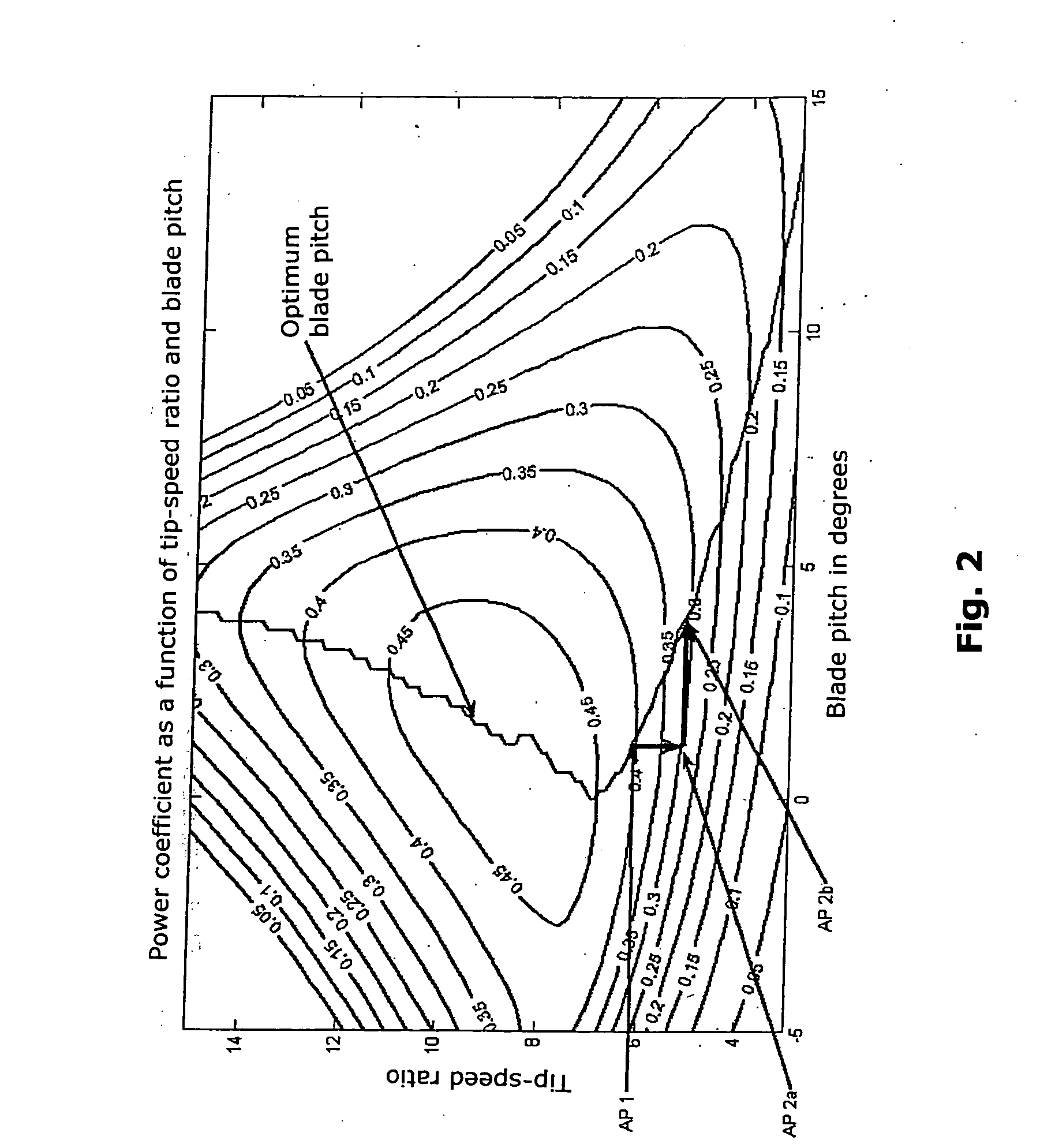
Method for operating or controlling a wind turbine and method for providing primary control power by means of wind turbines
ActiveUS20070085343A1Reduce yield lossImprove power transmissionWind motor controlSingle network parallel feeding arrangementsElectric forcePower station
A method for operating at least one wind turbine with a rotor and an electric generator coupled to the rotor for delivering electrical power into an energy distribution system with the aid of a control device ensures that the wind turbine operates within its operating range. The wind turbine is controlled in response to the change of a system operating parameter and for a period of time, in such a manner that a higher power is fed into the system than belongs to the operating range of the steady-state operation. The same conditions also apply to a method for providing control power or primary control power for an electric energy generator and distributor system to which a multiplicity of power stations including wind turbines is connected, and to a wind turbine.
Owner:SIEMENS GAMESA RENEWABLE ENERGY SERVICE GMBH
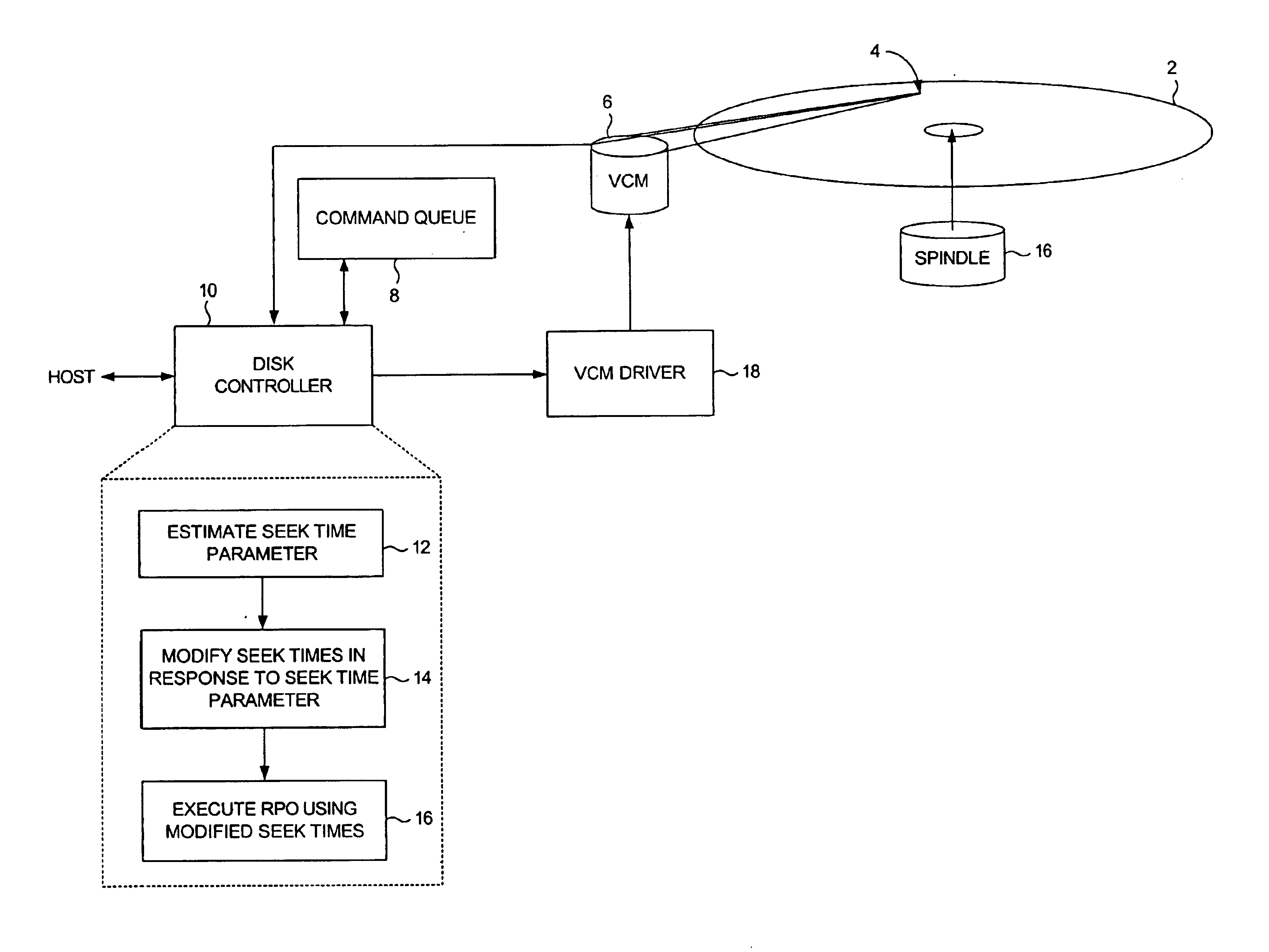
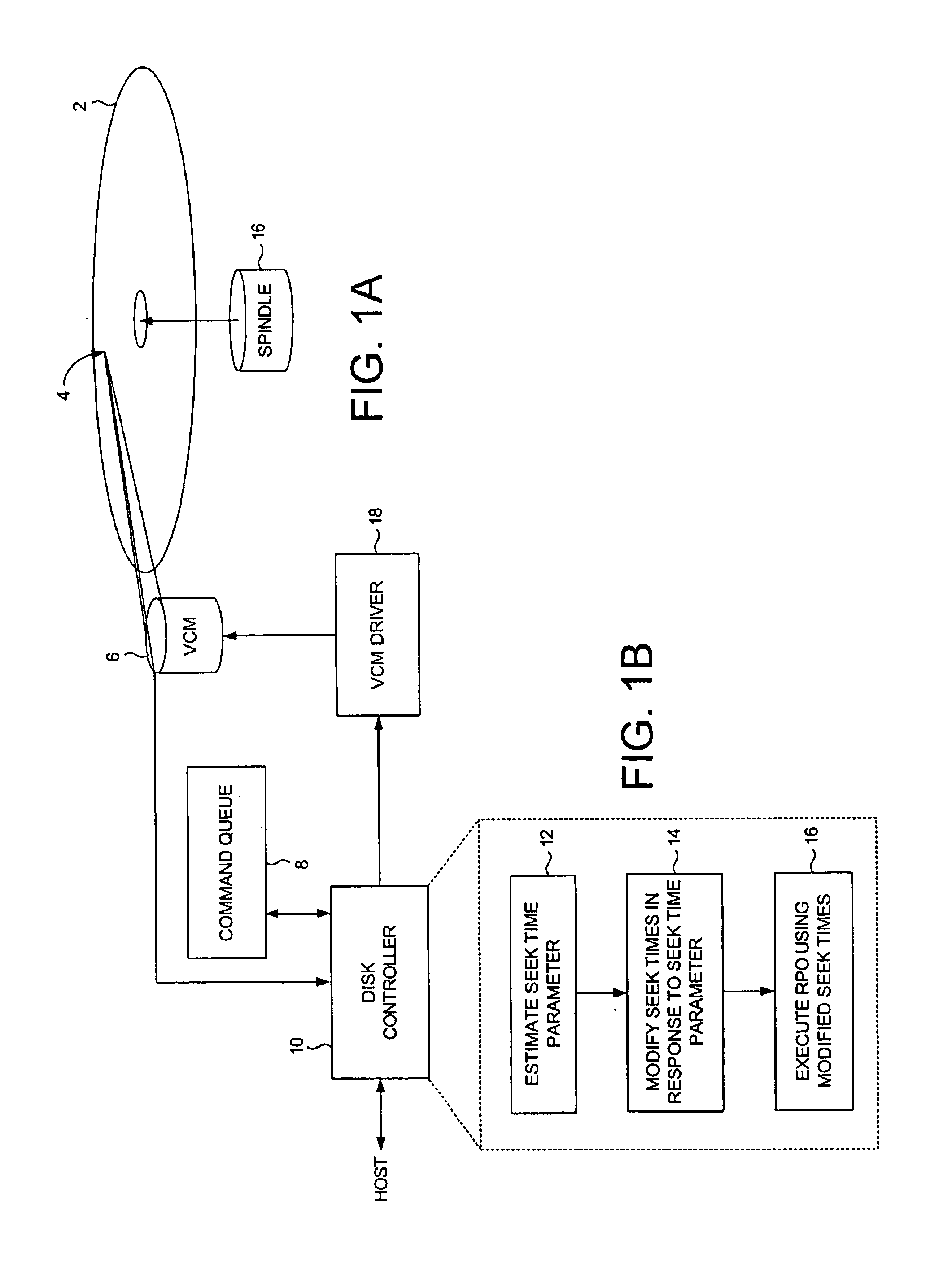
Disk drive modifying estimated seek times for a rotational position optimization algorithm based on change in estimated seek time parameter
A disk drive is disclosed comprising a disk, a head, and a voice coil motor (VCM) for actuating the head over the disk. The disk drive executes a rotational position optimization (RPO) algorithm to select a next command to execute relative to an estimated seek time computed for each command in a command queue. A seek time parameter is estimated and a seek time delta computed in response to the estimated seek time parameter. The seek time delta is added to a nominal estimated seek time to generate a modified estimated seek time for each command in the command queue, thereby optimizing the RPO algorithm.
Owner:WESTERN DIGITAL TECH INC
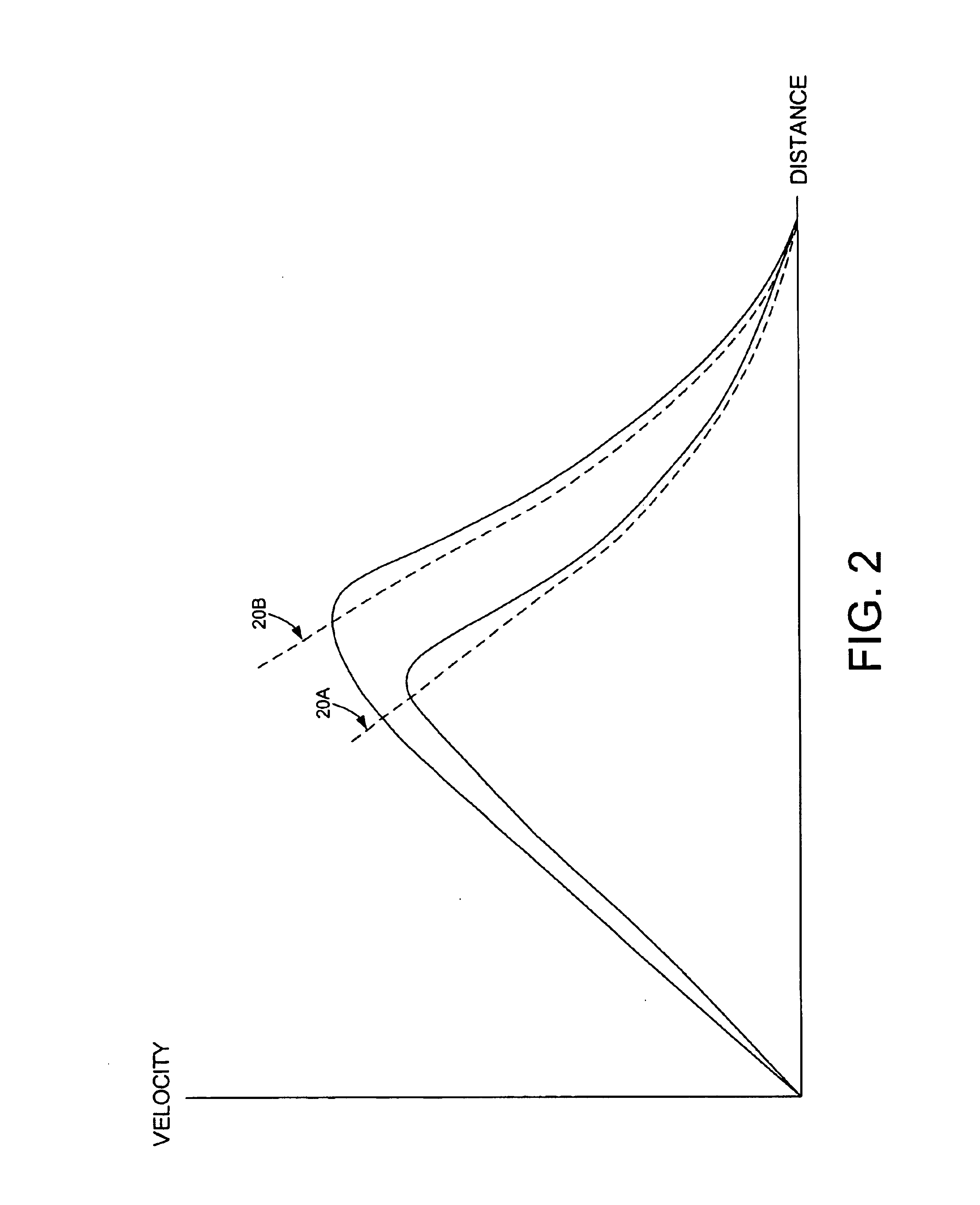
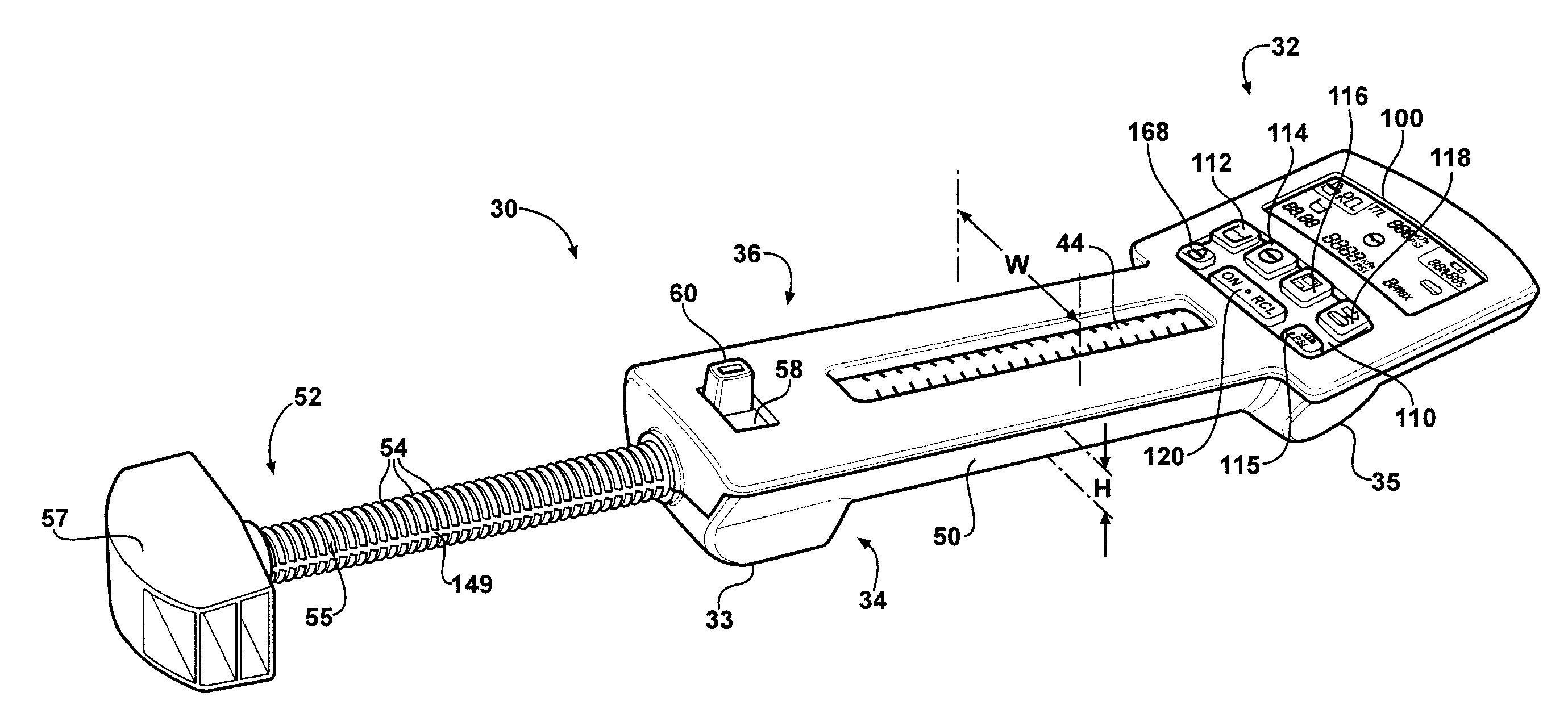
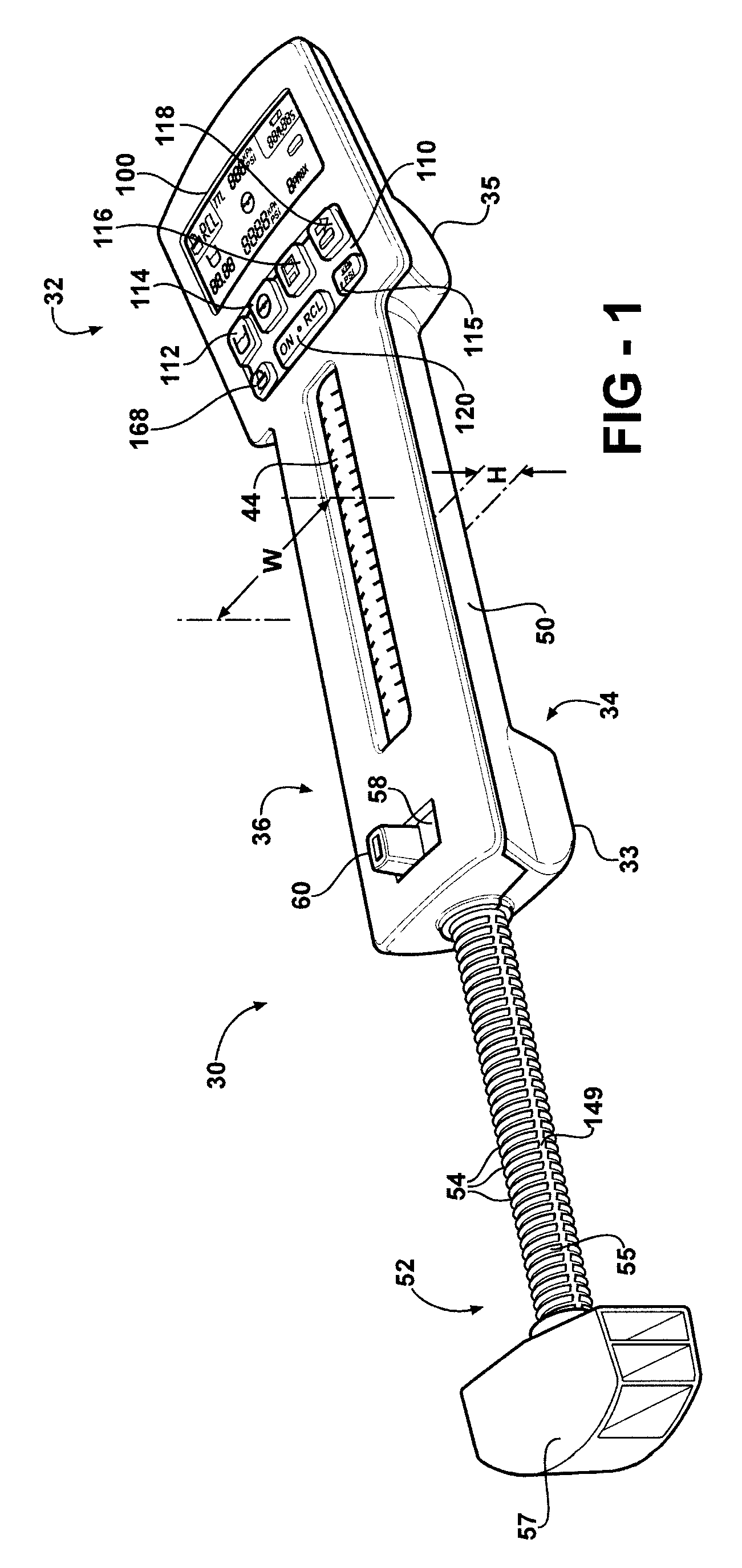
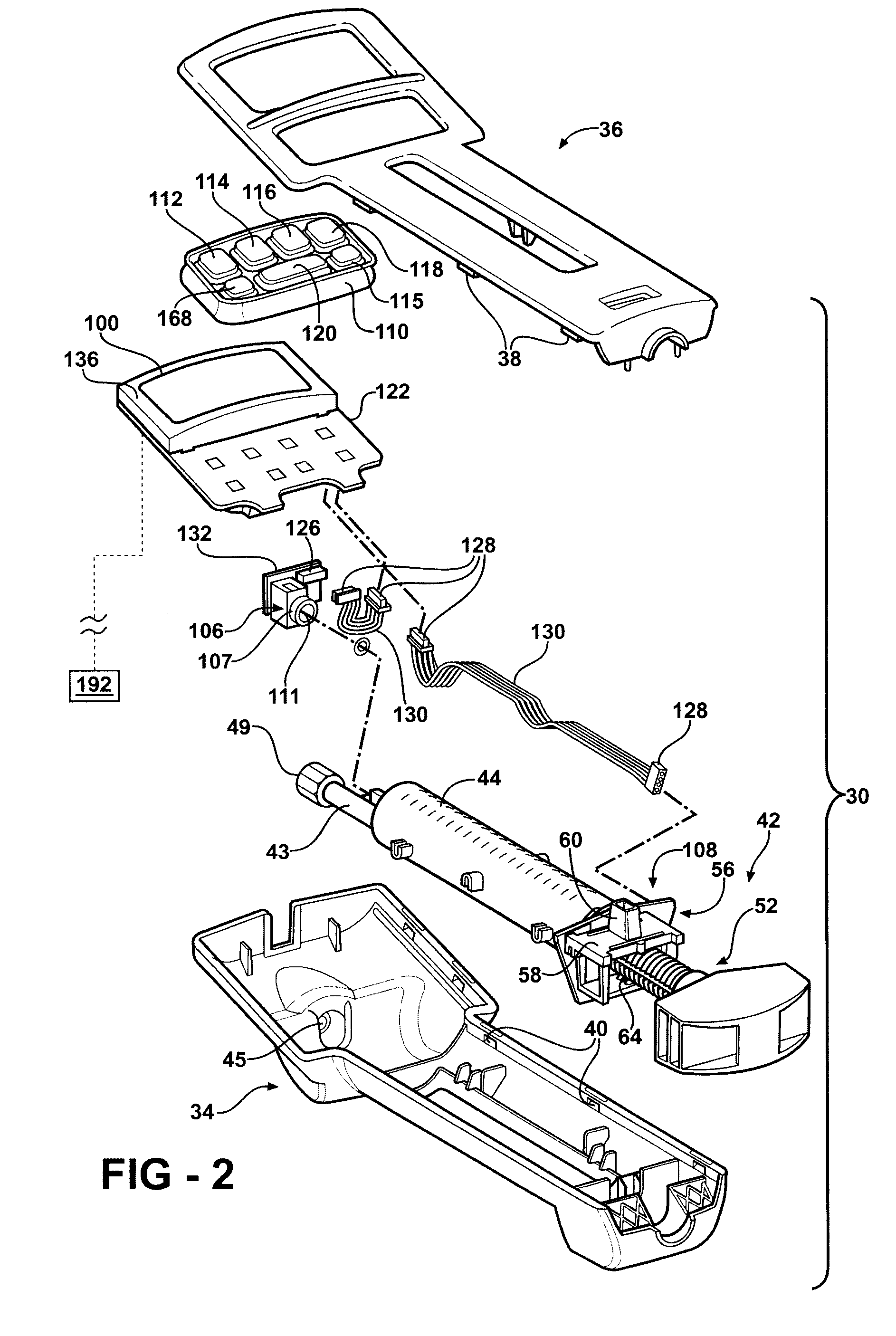
Hand-held fluid delivery device with sensors to determine fluid pressure and volume of fluid delivered to intervertebral discs during discography
ActiveUS20070112299A1Easy to operateContinuous monitoringPerson identificationMedical devicesHand heldSTERILE FIELD
A fluid delivery device is provided for delivering fluid to a target site such as an intervertebral disc during discography. The fluid delivery device includes pressure and volume sensors to determine the pressure and the volume of the fluid delivered to the intervertebral disc. The fluid delivery device is hand-held during use and includes a syringe assembly having a plunger with threads that enables controlled discharge of the fluid from the fluid delivery device by rotating the plunger in a housing of the fluid delivery device. The fluid delivery device may also include a communication module to wirelessly transfer data to an external device outside of a sterile field, while the fluid delivery device is in the sterile field. The fluid delivery device may also include a physiological sensor to monitor involuntary pain responses based on changing physiological parameters such as increases in body temperature or blood pressure.
Owner:STRYKER CORP
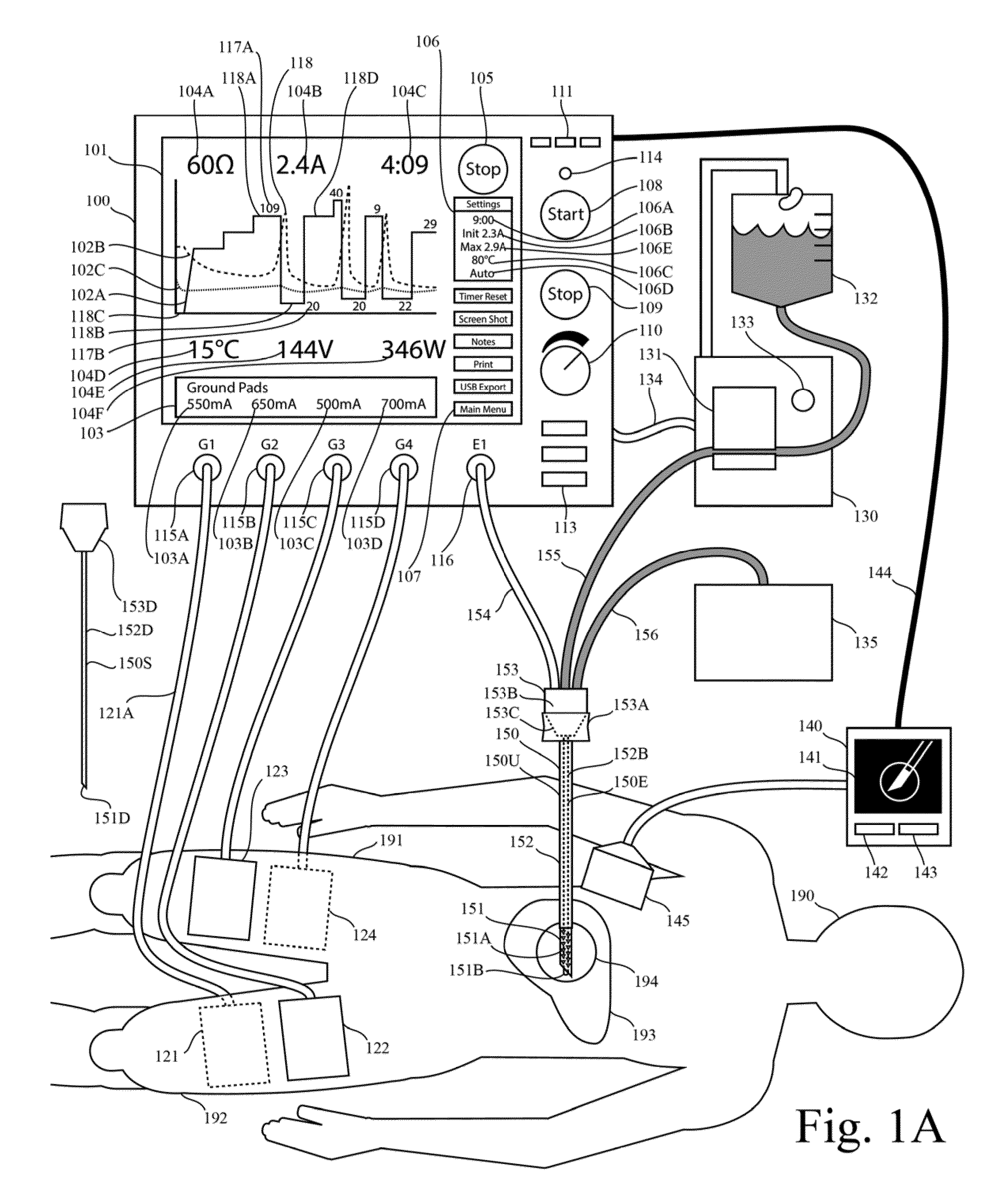
Electrosurgical generator
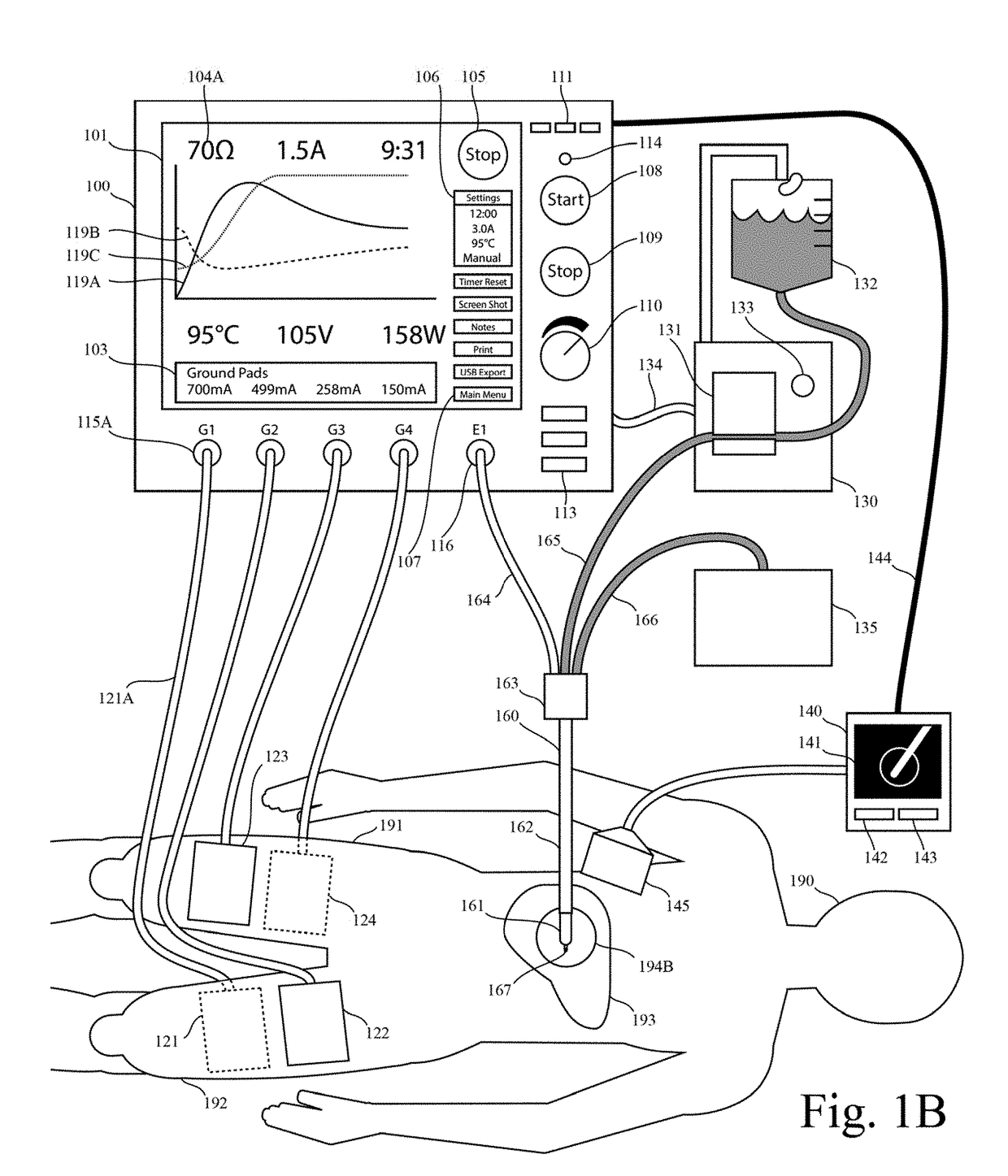
This invention relates to high-frequency ablation of tissue in the body using a cooled high-frequency electrode connected to a high frequency generator including a computer graphic control system and an automatic controller for control the signal output from the generator, and adapted to display on a real time graphic display a measured parameter related to the ablation process and visually monitor the variation of the parameter of the signal output that is controlled by the controller during the ablation process. In one example, one or more measured parameters are displayed simultaneously to visually interpret the relation of their variation and values. In one example, the displayed one or more parameters can be taken from the list of measured voltage, current, power, impedance, electrode temperature, and tissue temperature related to the ablation process. The graphic display gives the clinician an instantaneous and intuitive feeling for the dynamics and stability of the ablation process for safety and control. This invention relates to monitoring and controlling multiple ground pads to optimally carry return currents during high-frequency tissue ablation, and to prevent of ground-pad skin burns. This invention relates to the use of ultrasound imaging intraoperatively during a tissue ablation procedure. This invention relates to the use of nerve stimulation and blocking during a tissue ablation procedure.
Owner:COSMAN INTRUMENTS LLC
Implantable wireless sensor for in vivo pressure measurement
A sensor suitable for in vivo implantation has a capacitive circuit and a three-dimensional inductor coil connected to the capacitive circuit to form an LC circuit. The LC circuit is hermetically encapsulated within an electrically insulating housing. An electrical characteristic of the LC circuit is responsive to a change in an environmental parameter.
Owner:ST JUDE MEDICAL LUXEMBOURG HLDG II S A R L SJM LUX II
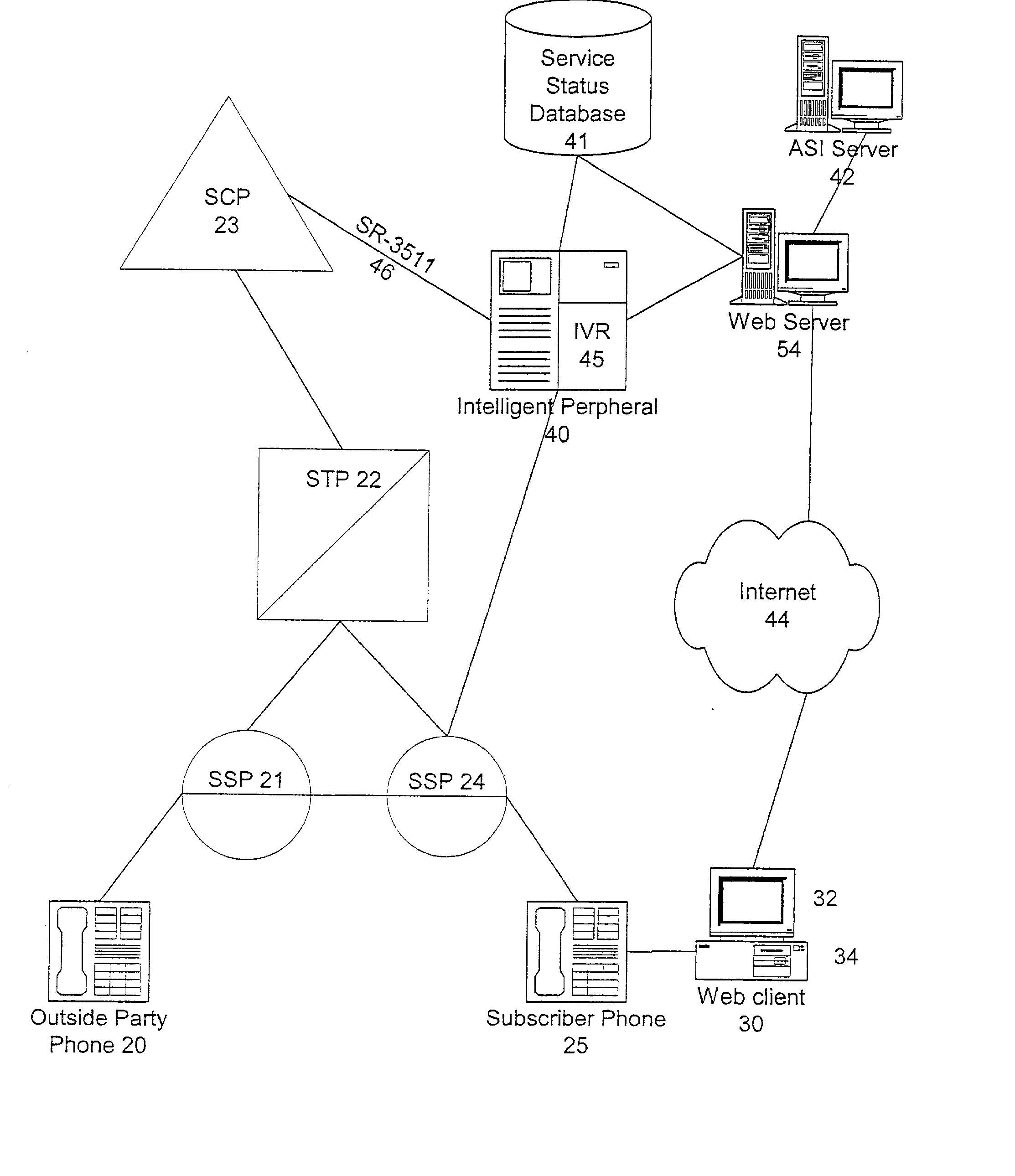
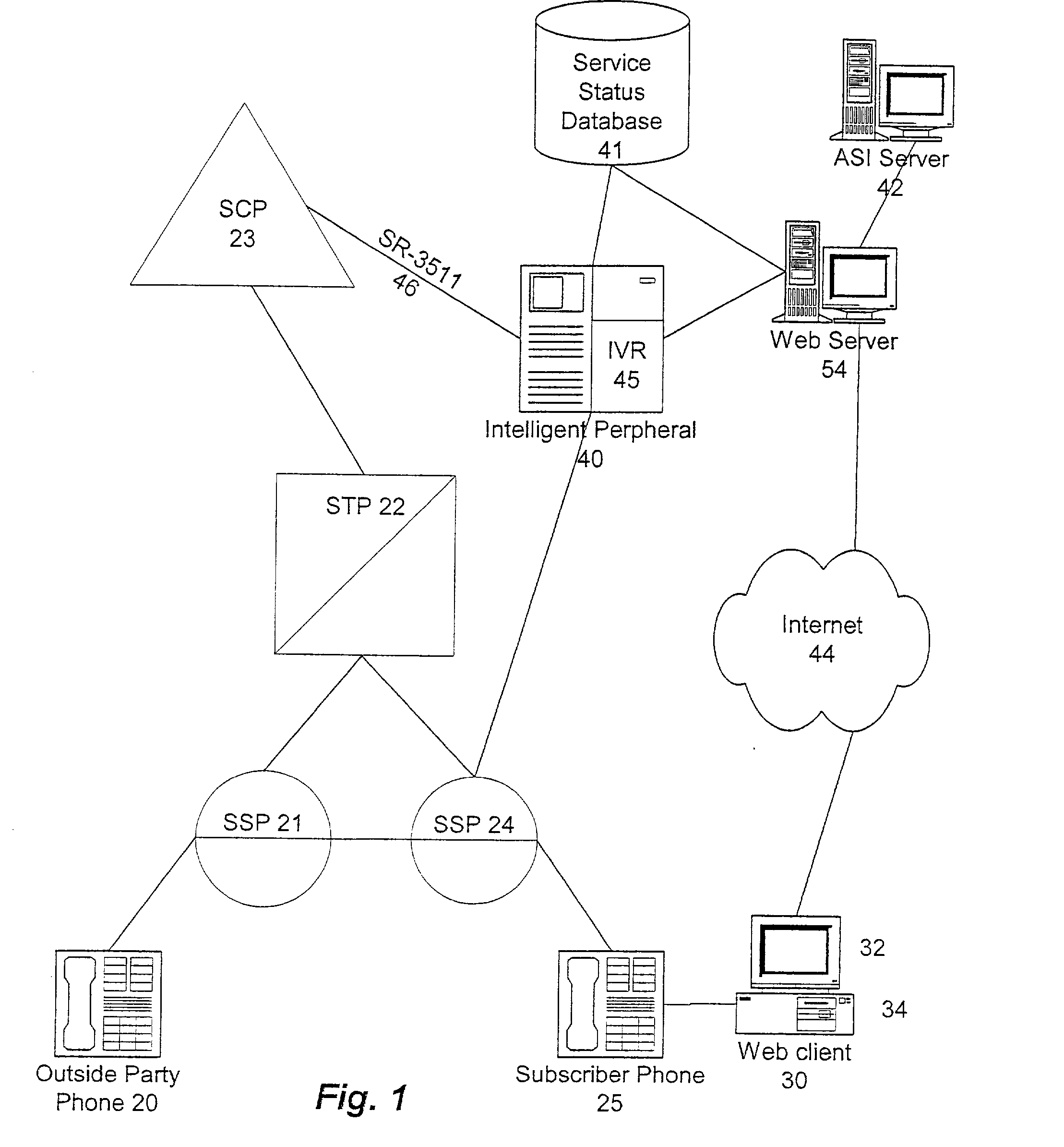
Voice enhancing for advance intelligent network services
InactiveUS20020168055A1Avoid disturbanceIntelligent networksTelephone data network interconnectionsIntelligent NetworkSpeech identification
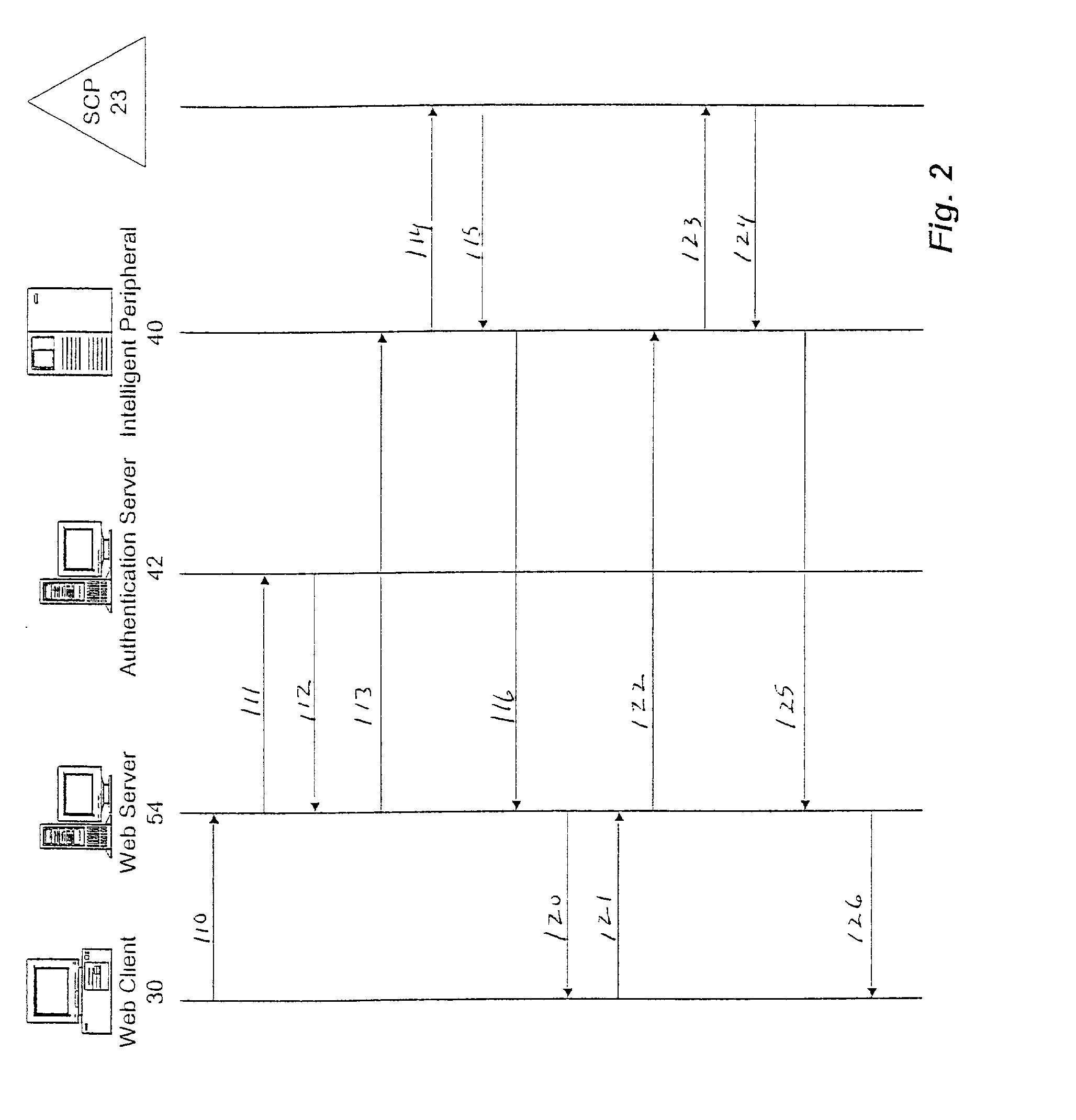
A service includes verbally editing at least one parameter of a subscriber's advanced intelligent network (AIN) service using speech recognition functionality of an intelligent peripheral. A call is received from the subscriber at a switch, including a dialed number for editing the AIN service. A connection is established with the intelligent peripheral in response to the dialed number. Call service data, including the parameter, is retrieved from a database. The intelligent peripheral plays a voice announcement identifying the parameter to the subscriber, receives a voice instruction from the subscriber in response to the voice announcement and translates the voice instruction into digital command data relating to a change to the parameter. The digital command data and the change to the parameter are stored in the database for near real-time implementation. The intelligent peripheral and the database are likewise accessible by the subscriber through a packet switched data network.
Owner:NUANCE COMM INC
Evoked response variability as an indicator of autonomic tone and surrogate for patient condition
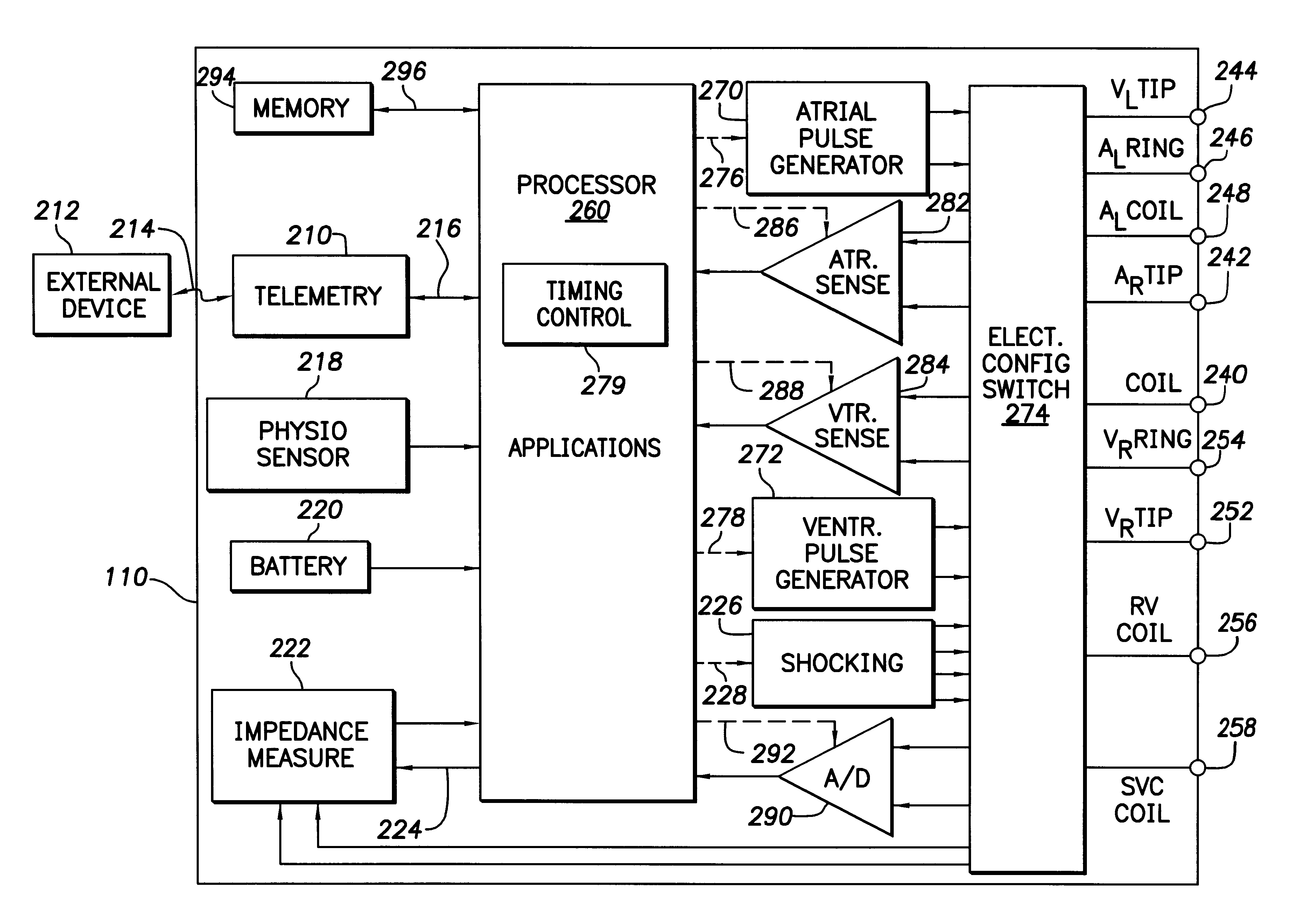
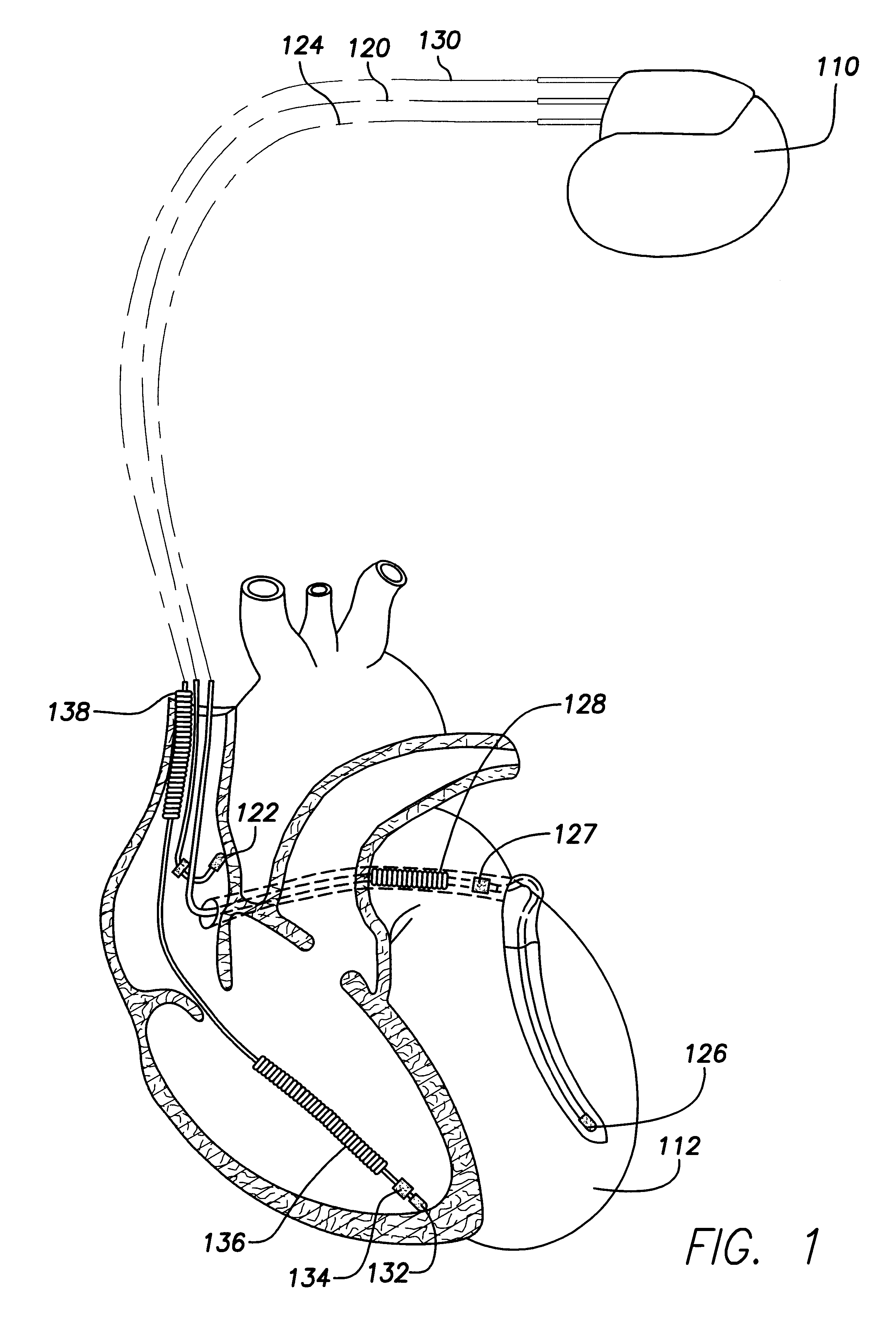
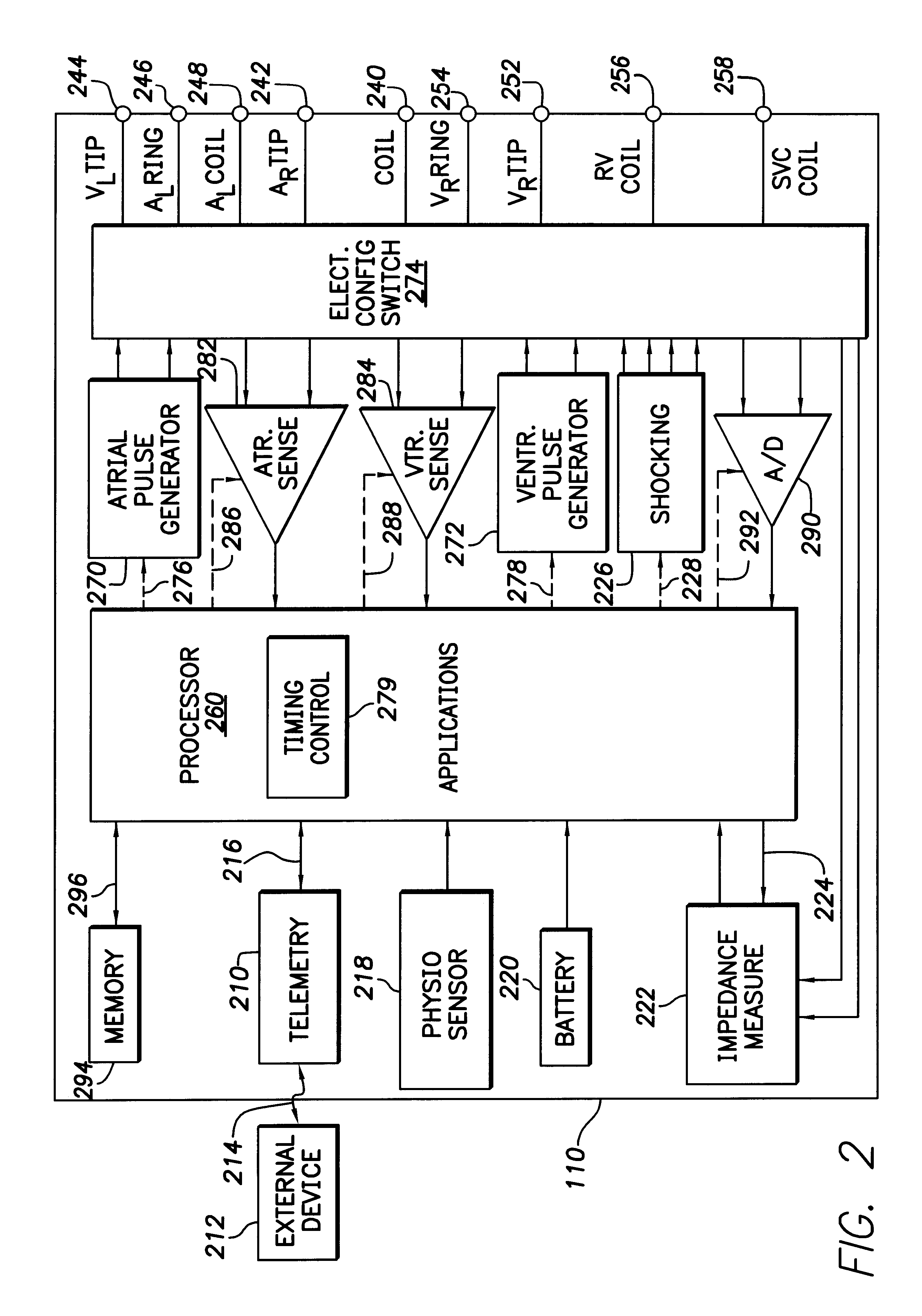
Modern implantable cardiac stimulation devices include processing and data storage capabilities that may be exploited to track myocardial condition and autonomic tone. Implantable devices have a capability to measure and store electrogram information over a period of time in a relatively large capacity memory, with advances in technology allowing increases in memory size. The evoked response varies in amplitude and morphology with changes in autonomic tone, ventricular filling, paced rate, and other parameters. The implantable cardiac device can be configured to sense and accurately quantify the evoked response, derive parameters from the quantified evoked response, store the parameters over long time periods, and derive variability statistics from the parameters to assist in tracking the patient's condition over time, and guiding the patient's therapy.
Owner:PACESETTER INC
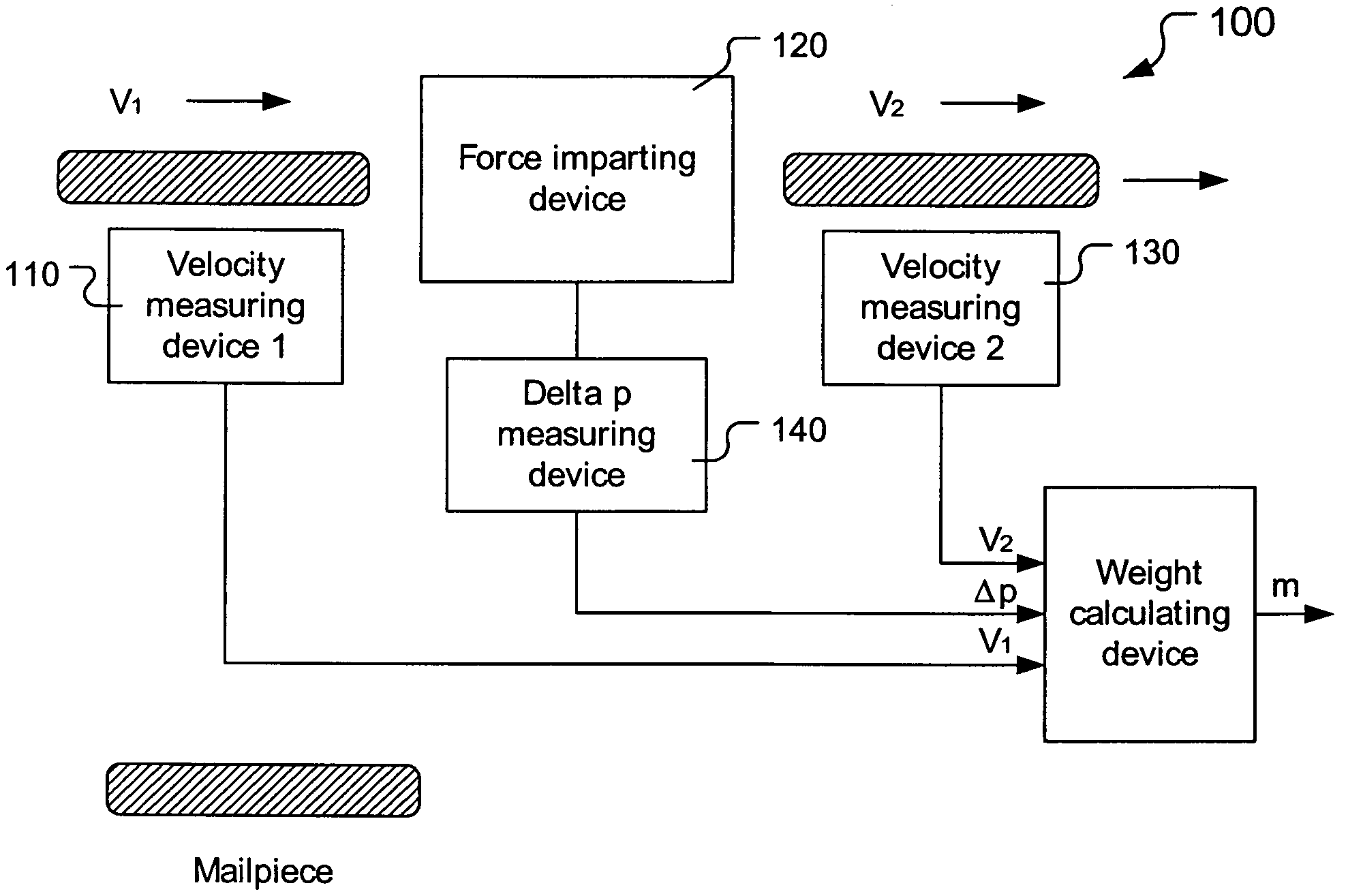
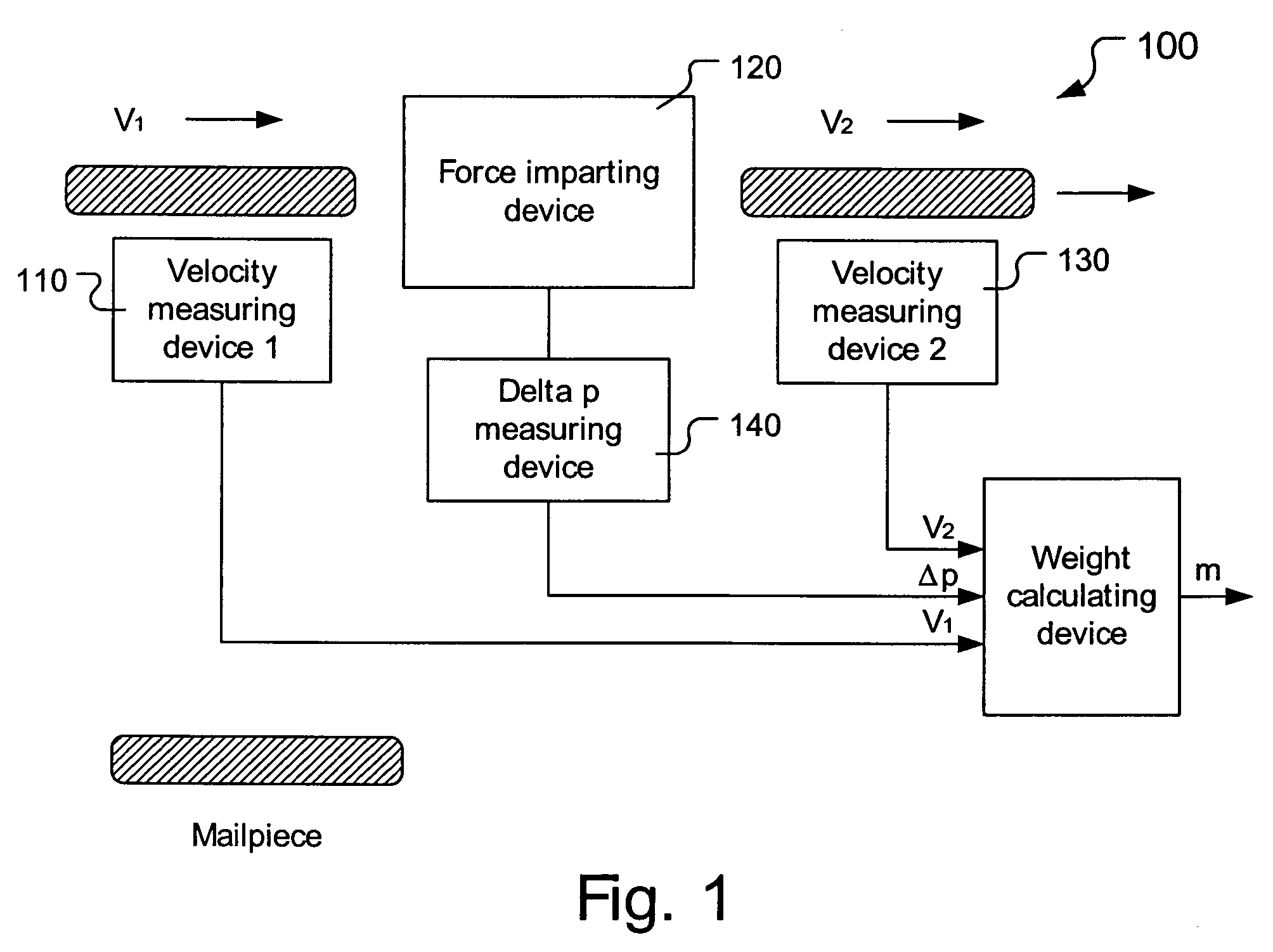
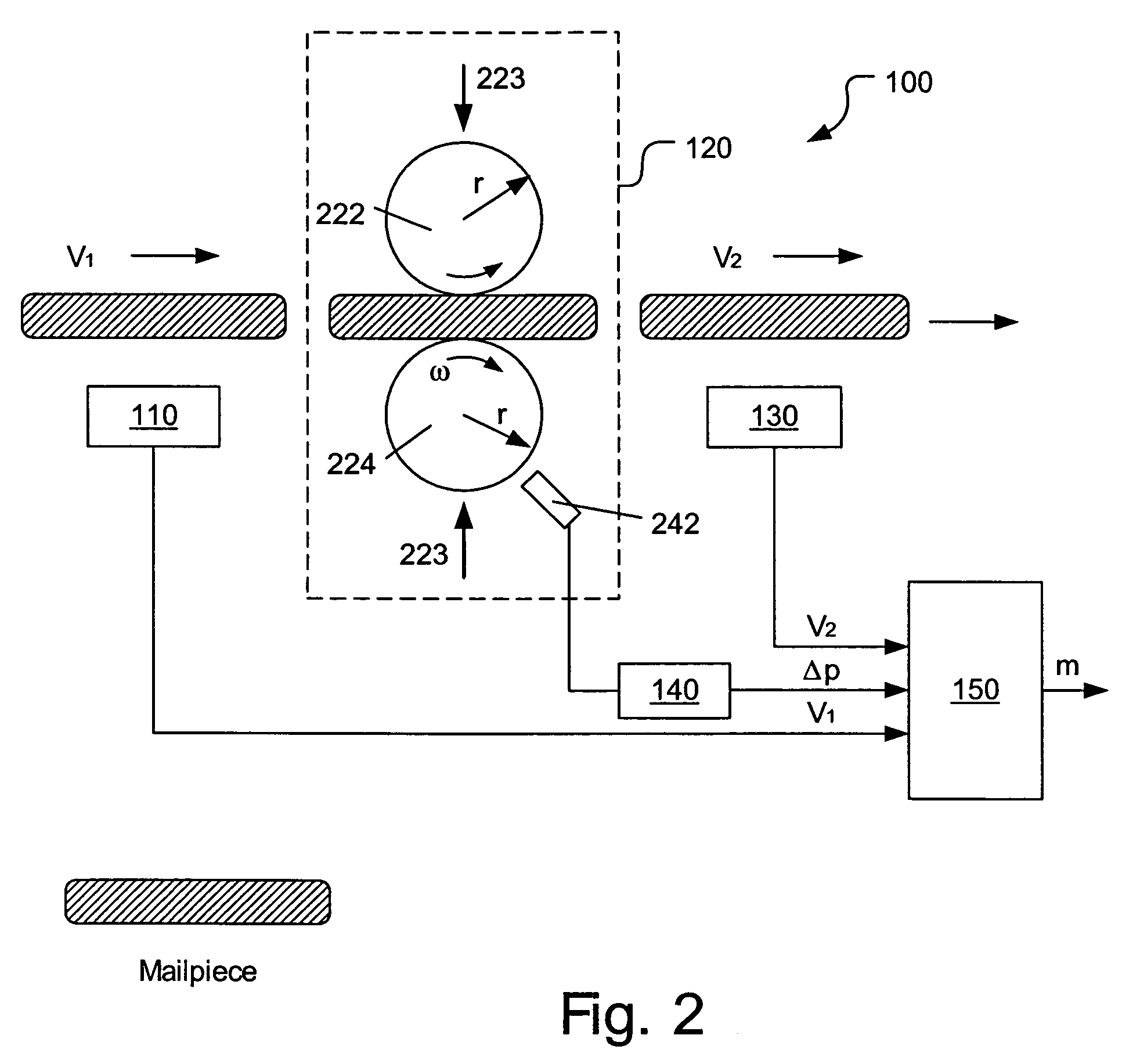
Method and apparatus for determining weight of moving mailpieces
The invention pertains to a mailpiece weight measuring apparatus for use with a high speed automatic mailpiece processing system. The weight measuring apparatus measures the inertial mass of the mailpiece as the weight equivalent. The apparatus includes a device for determining a first velocity of a mailpiece, a device for imparting a force to the mailpiece in a direction co-linear with the first velocity so that the mailpiece exits said force impacting device at a second velocity, a device for determining the second velocity of the mailpiece, a device for determining a change in a parameter proportional to the force imparted on the mailpiece, and a device for determining the weight of the mailpiece based upon the determined first velocity, second velocity and change in the parameter.
Owner:DMT SOLUTIONS GLOBAL CORP
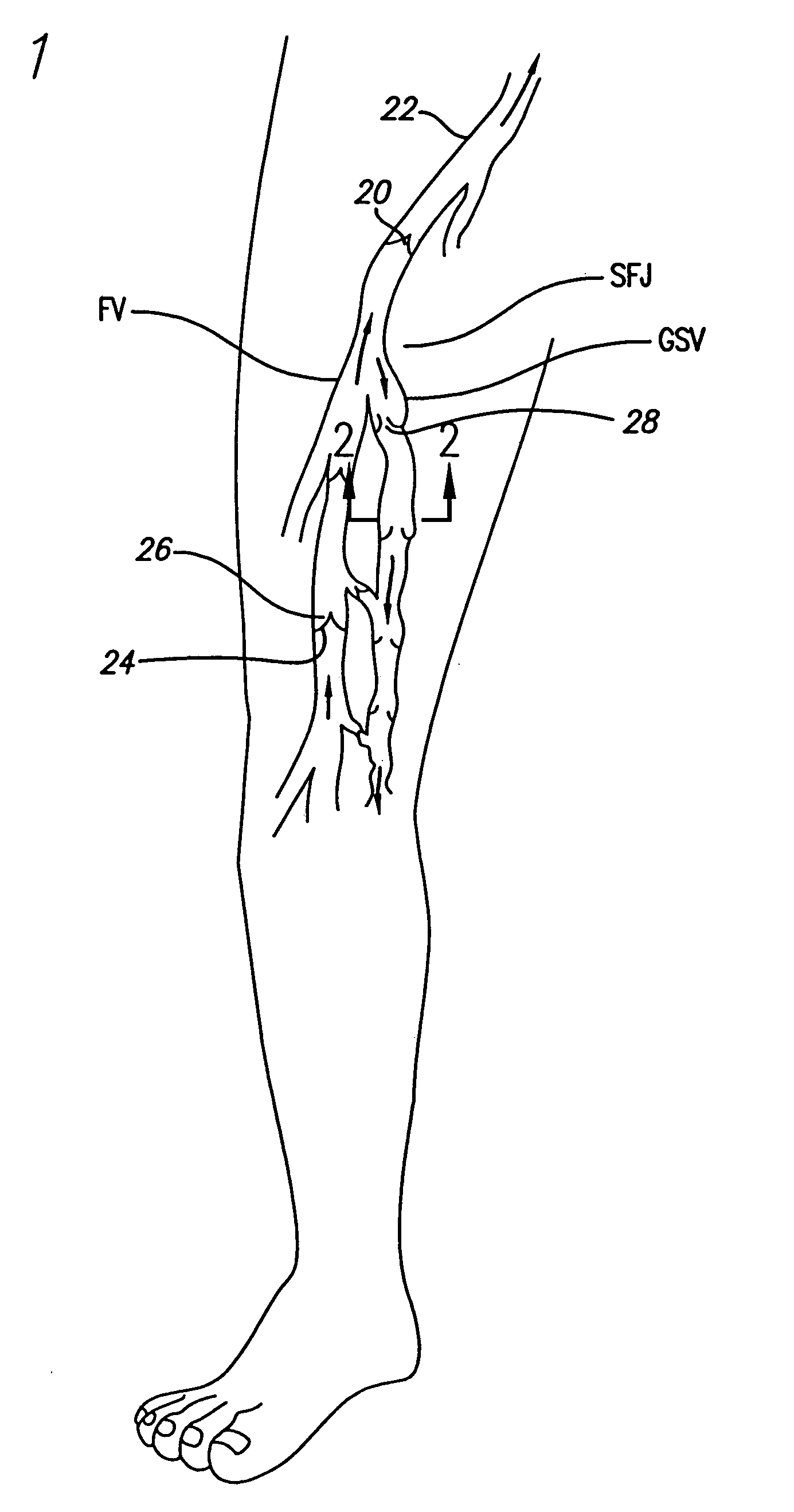
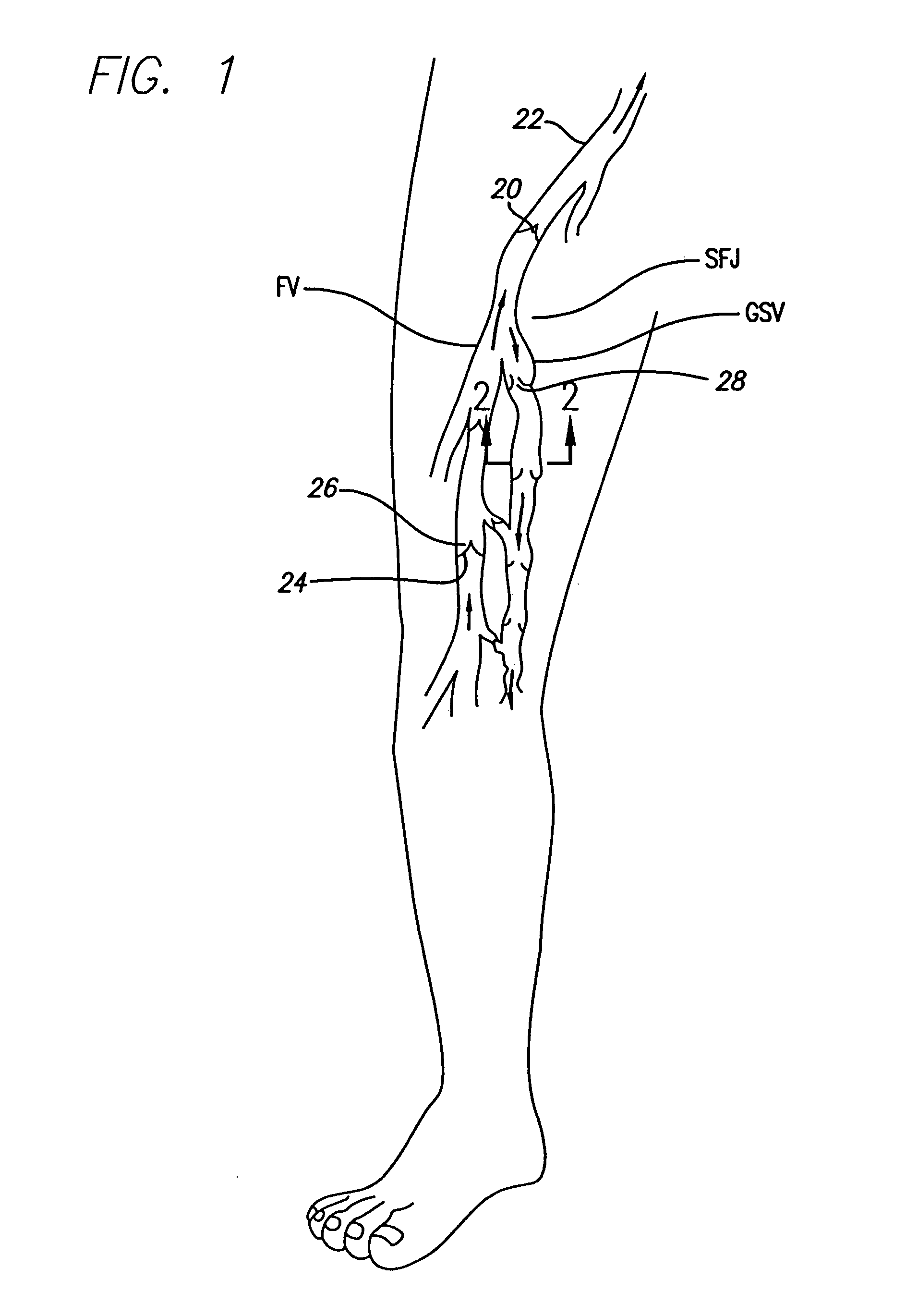
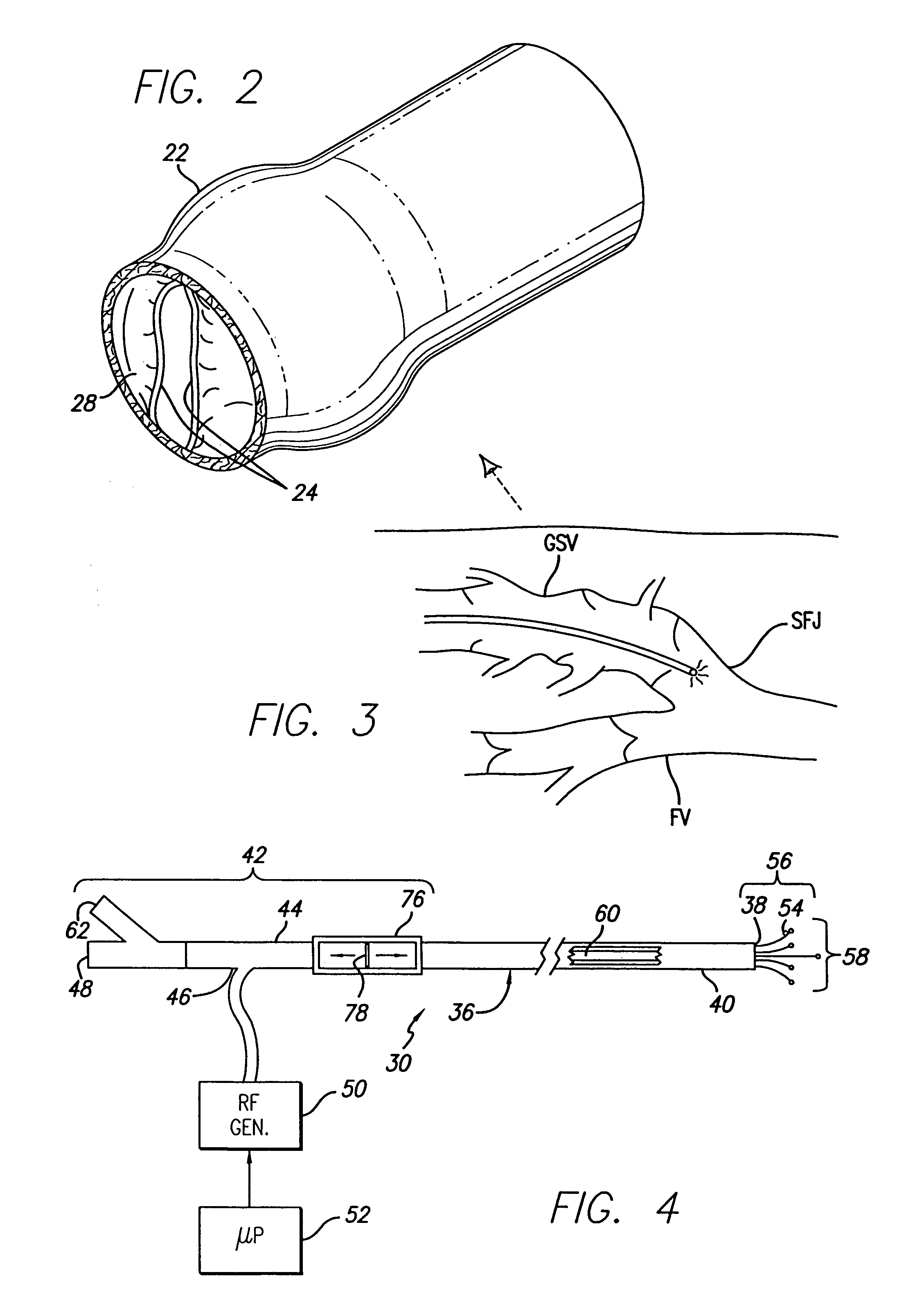
Method and apparatus for positioning a catheter relative to an anatomical junction
An electrode catheter is introduced into a vein or other hollow anatomical structure, and is positioned at a treatment site within the structure. The end of the catheter is positioned near a junction formed in the structure. This junction can be the sapheno-femoral junction. The position of the catheter near the junction is determined based on a signal from a device associated with the catheter within the structure. A fiber optic filament which emits light is used with the catheter or a guide wire over which the catheter is advanced. The light is visible externally from the patient. The light dims and may no longer externally visible at the sapheno-femoral junction where the catheter moves past the deep fascia and toward the deep venous system. The position of the catheter can be determined based on this external observation. The position of the catheter can also be determined based on measured parameters such as temperature or flow rate within the structure, and the measured changes in one or more of these parameters as the catheter nears the junction. The hollow anatomical structure can be compressed for this procedure. The position of the catheter can also be determined mechanically by including a hook-shaped tip on the catheter or guide wire which would physically engage the junction.
Owner:TYCO HEALTHCARE GRP LP
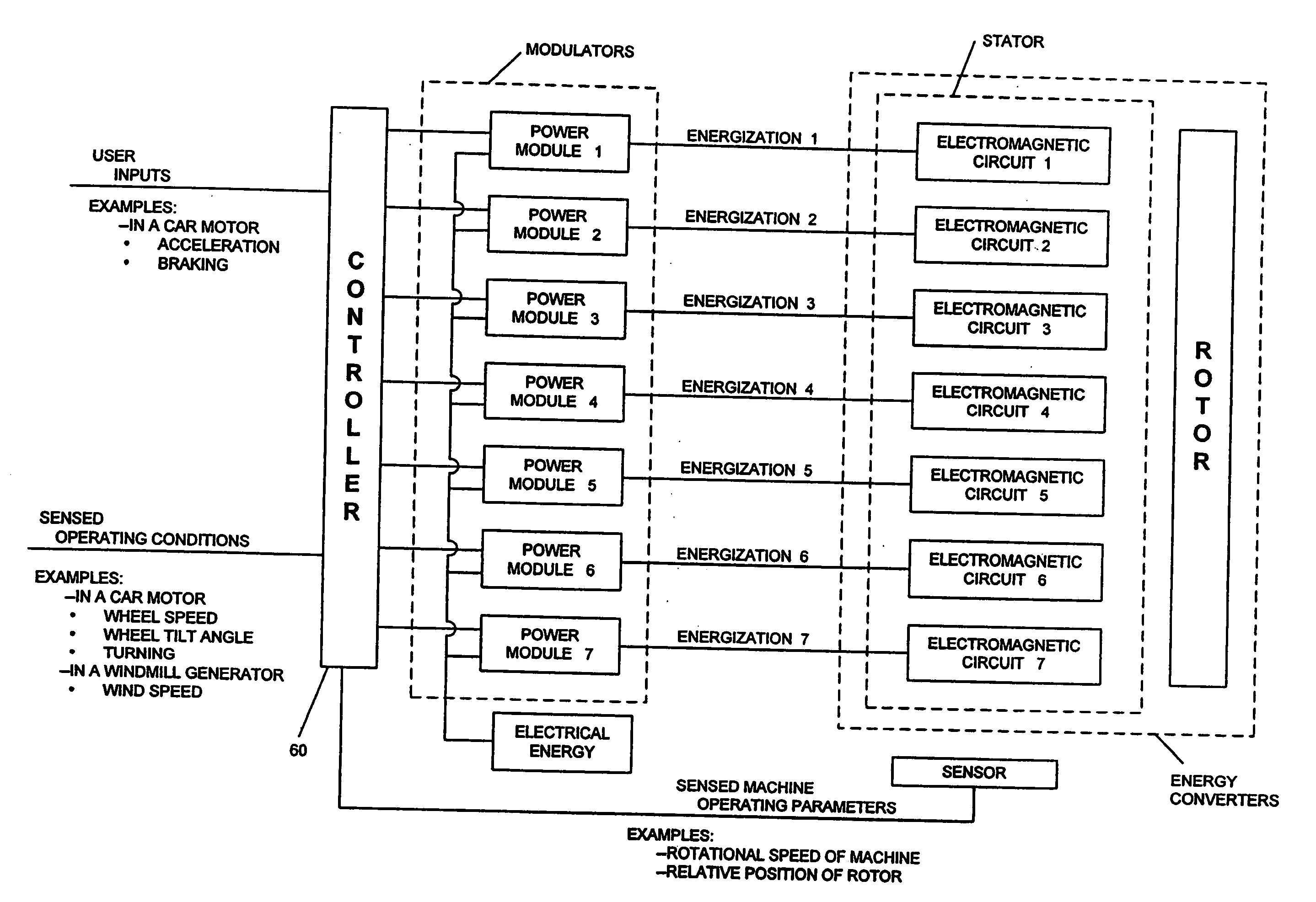
Adaptive electric motors and generators providing improved performance and efficiency
InactiveUS20050184689A1Induced currentLow reliabilityMagnetic circuitVehicular energy storageElectric vehicleHigher Power
An adaptive architecture for electric motors, generators and other electric machines. An adaptive electric machine provides optimal performance by dynamically adapting its controls to changes in user inputs, machine operating conditions and machine operating parameters. Isolating the machine's electromagnetic circuits allows effective control of more independent machine parameters, enabling greater freedom to optimize and providing adaptive motors and generators that are cheaper, smaller, lighter, more powerful, and more efficient than conventional designs. An electric vehicle with in-wheel adaptive motors enables delivery of higher power with lower unsprung mass, giving better torque-density. The motor control system can adapt to the vehicle's operating conditions, including starting, accelerating, turning, braking, and cruising at high speeds, thereby consistently providing higher efficiency. A wind powered adaptive generator can adapt to changing wind conditions, consistently providing optimal performance. An adaptive architecture may improve performance in a wide variety of electric machine applications, particularly those requiring optimal efficiency over a range of operating conditions.
Owner:BLUWAV SYST LLC
Method for operating or controlling a wind turbine and method for providing primary control power by means of wind turbines
ActiveUS7528496B2Improve power transmissionHigh yieldWind motor controlSingle network parallel feeding arrangementsEngineeringDistributor
A method for operating at least one wind turbine with a rotor and an electric generator coupled to the rotor for delivering electrical power into an energy distribution system with the aid of a control device ensures that the wind turbine operates within its operating range. The wind turbine is controlled in response to the change of a system operating parameter and for a period of time, in such a manner that a higher power is fed into the system than belongs to the operating range of the steady-state operation. The same conditions also apply to a method for providing control power or primary control power for an electric energy generator and distributor system to which a multiplicity of power stations including wind turbines is connected, and to a wind turbine.
Owner:SIEMENS GAMESA RENEWABLE ENERGY SERVICE GMBH
Physiological parameter measurement mechanism
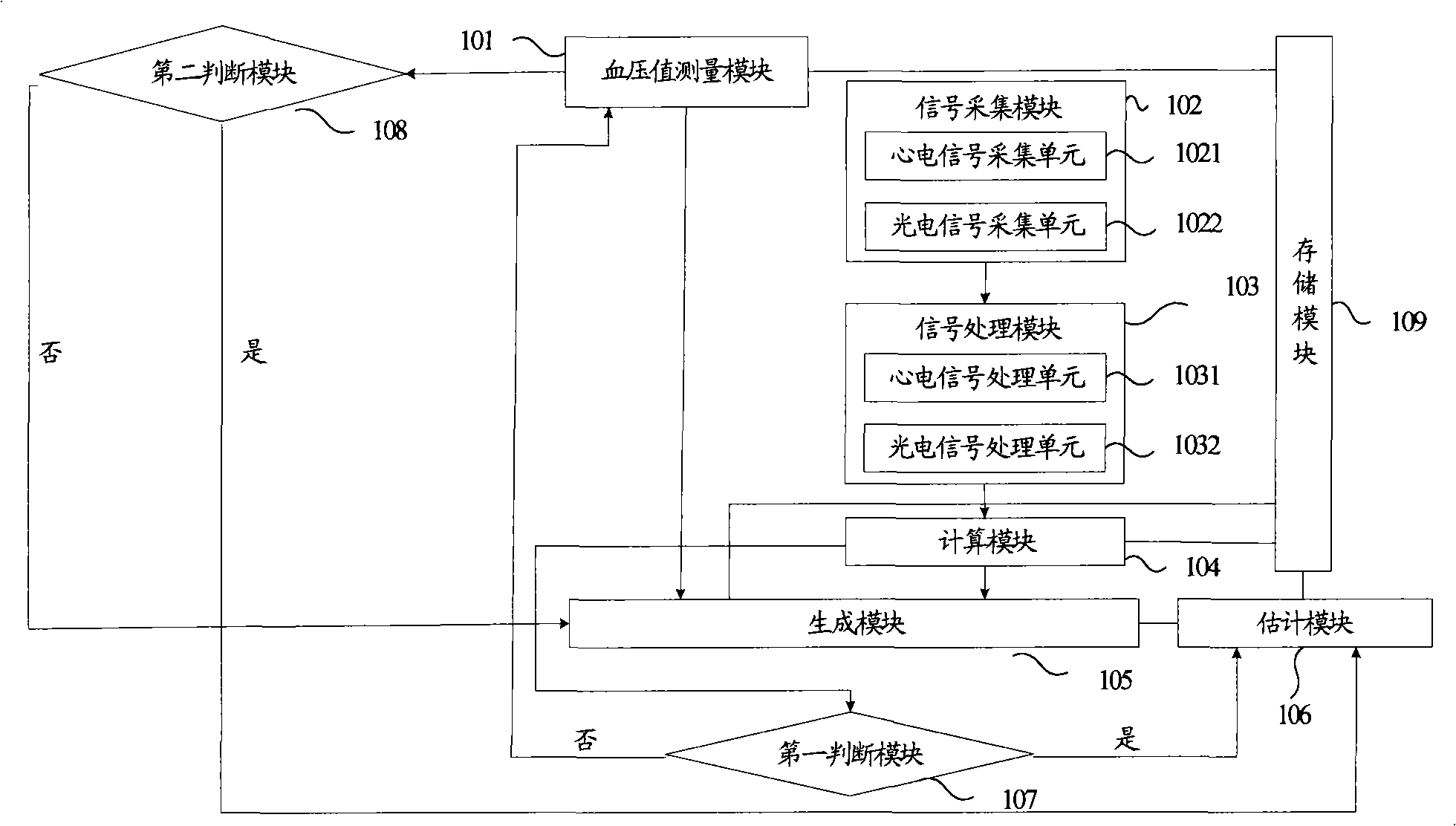
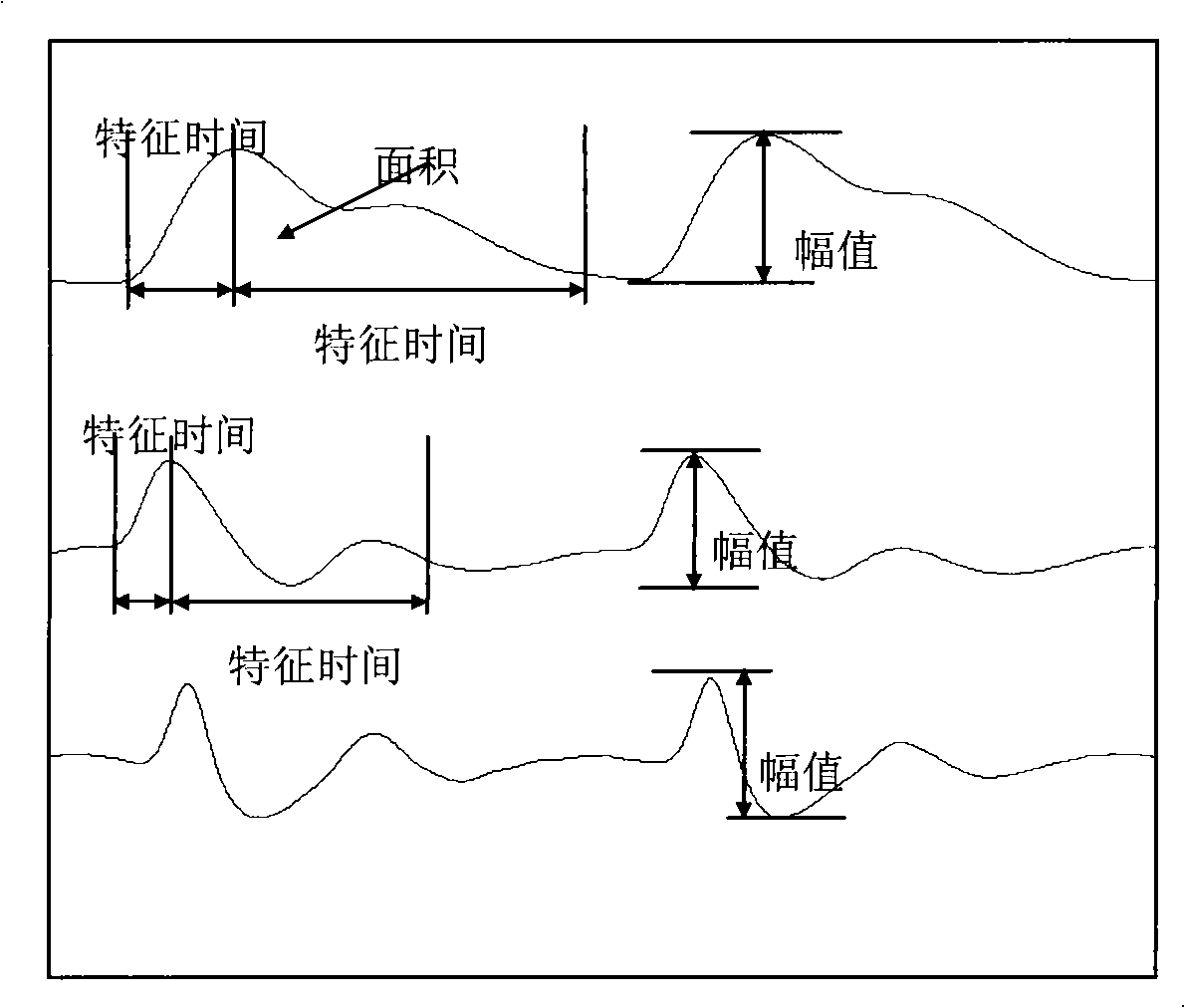
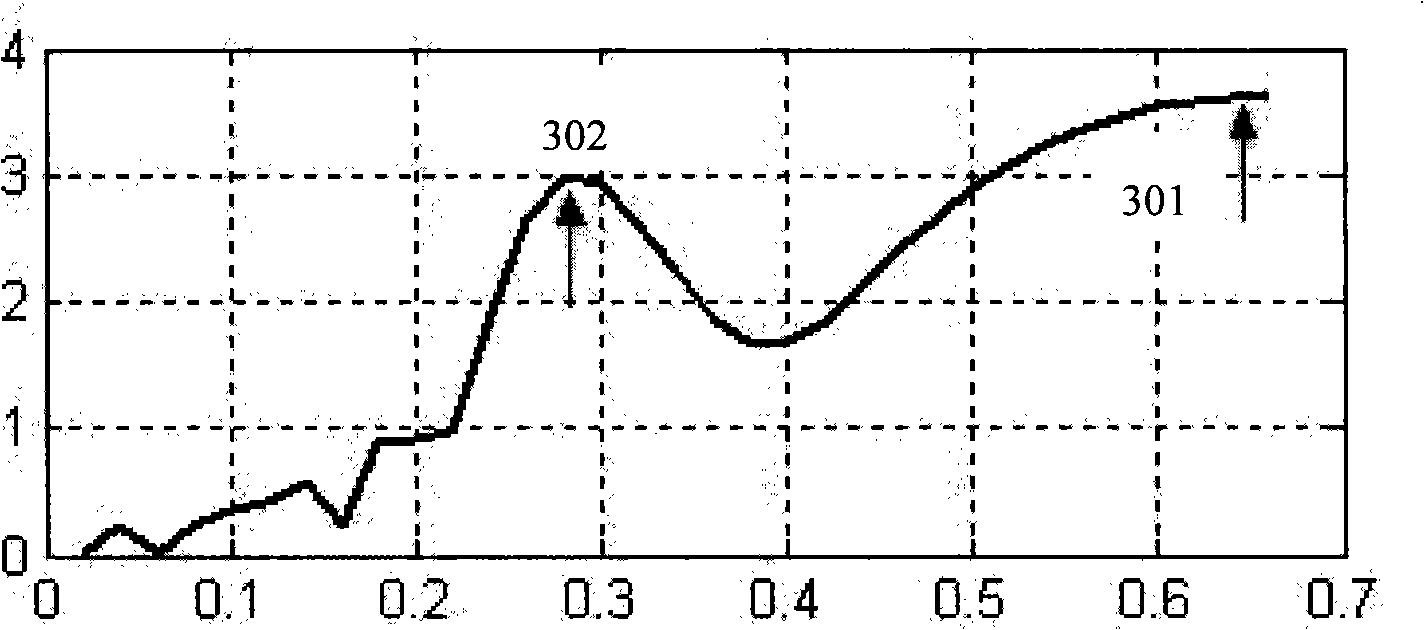
InactiveCN101327121AImprove accuracyReduce the impactCatheterSpecial data processing applicationsContinuous measurementBlood pressure
The present invention discloses a physical parameter measuring device. The present invention comprises a first judging module, the first judging module is used to judge whether the changes of the pulse wave characteristic value are in line with the set conditions, if yes, a prediction module is triggered to calculate the blood pressure prediction value, and if no, a blood pressure value measuring module is triggered to regain the reference blood pressure value; a second judging module, the second judging module is used to judge whether the regained reference blood pressure value is within the prediction range, if yes, the prediction module is triggered to calculate the blood pressure prediction value, and if no, a generating module is triggered to regenerate the blood pressure prediction rules. The present invention can make continuous synchronous measurement of the physical parameters which reflect the function of the cardiovascular system and adopts a continuous synchronous calibrating mechanism particularly for blood pressure measurement, thus not only reducing the impact of the changes of other physical parameters on the relationship between the pulse wave characteristic value and the blood pressure, but also automatically starting the measurement of the reference blood pressure value in the continuous measuring process so as to ensure more accurate continuous measurement.
Owner:THE CHINESE UNIVERSITY OF HONG KONG
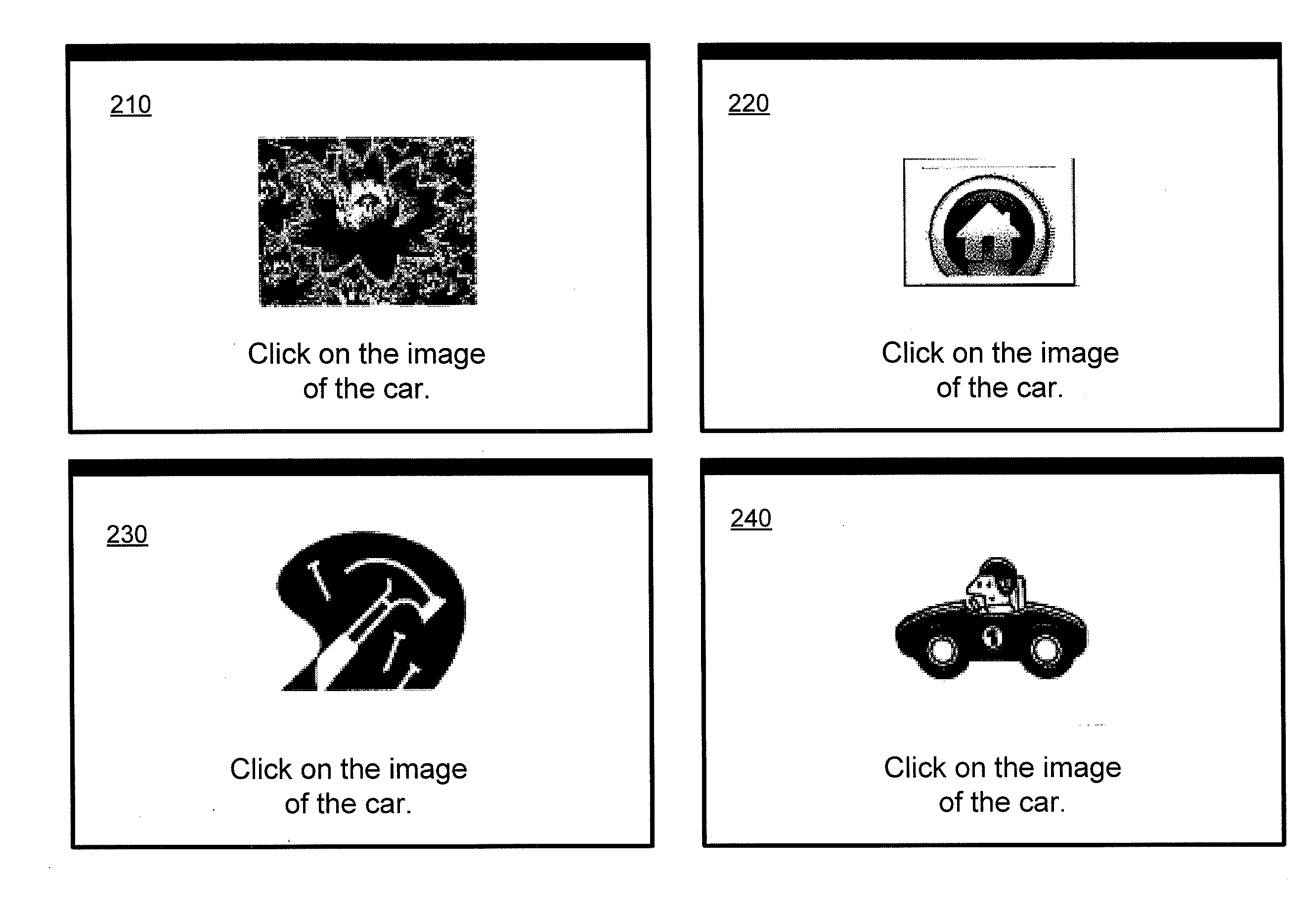
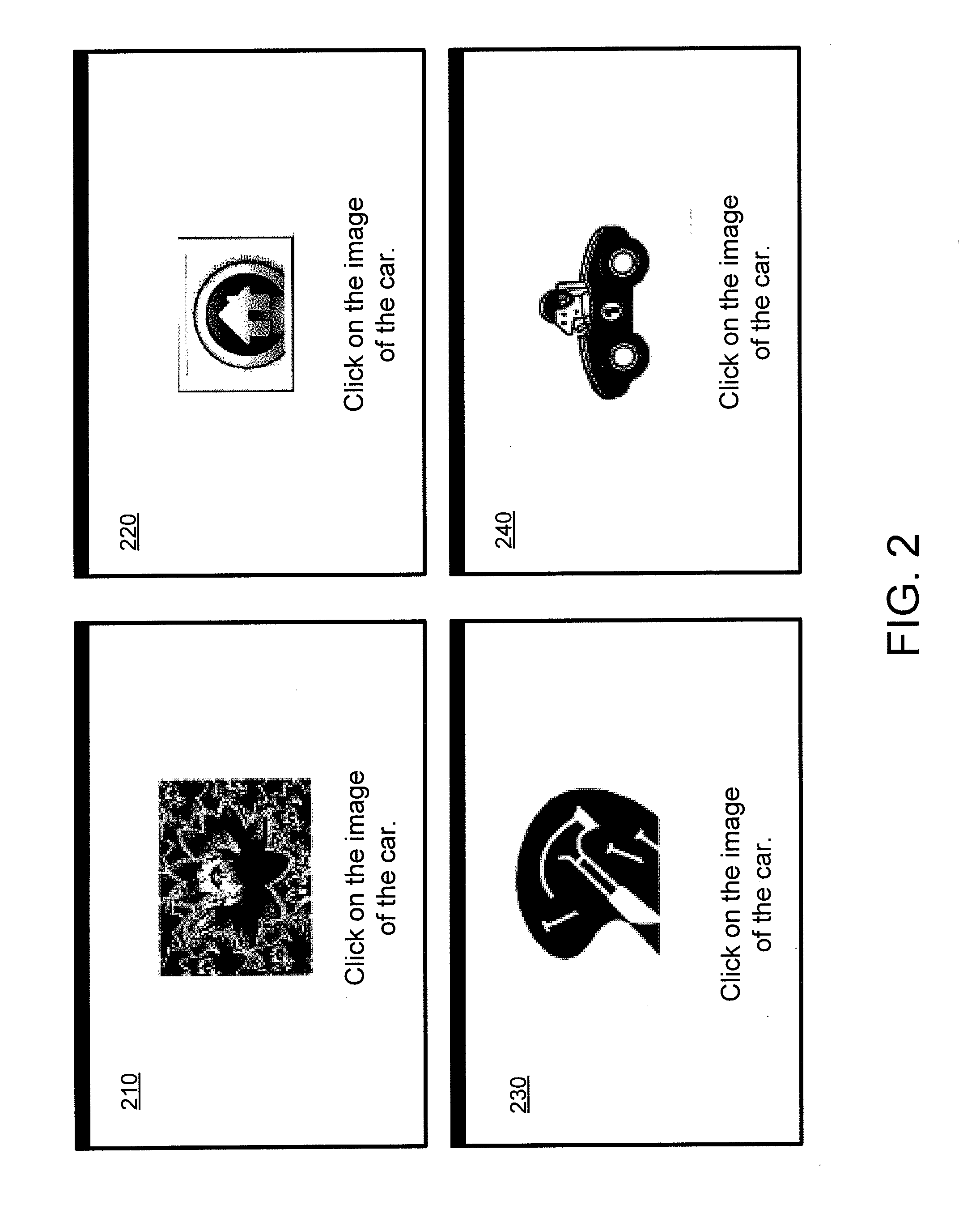
Automated test to tell computers and humans apart
ActiveUS20100325706A1Raise the possibilityEasy to distinguishDigital data processing detailsUser identity/authority verificationHuman–computer interactionVariation of parameters
Techniques for verifying a user is human as opposed to a machine are provided. A series of images may be presented to the user sequentially along with a challenge question that instructs the user to select the image that is responsive to the challenge question. If the user selects the correct image, there likelihood that the user is a human as opposed to a machine is greatly increased. Techniques for varying certain parameters associated with display of images and challenge question are also provided. The variations in these parameters may further help distinguish human users from machines.
Owner:VISA INT SERVICE ASSOC
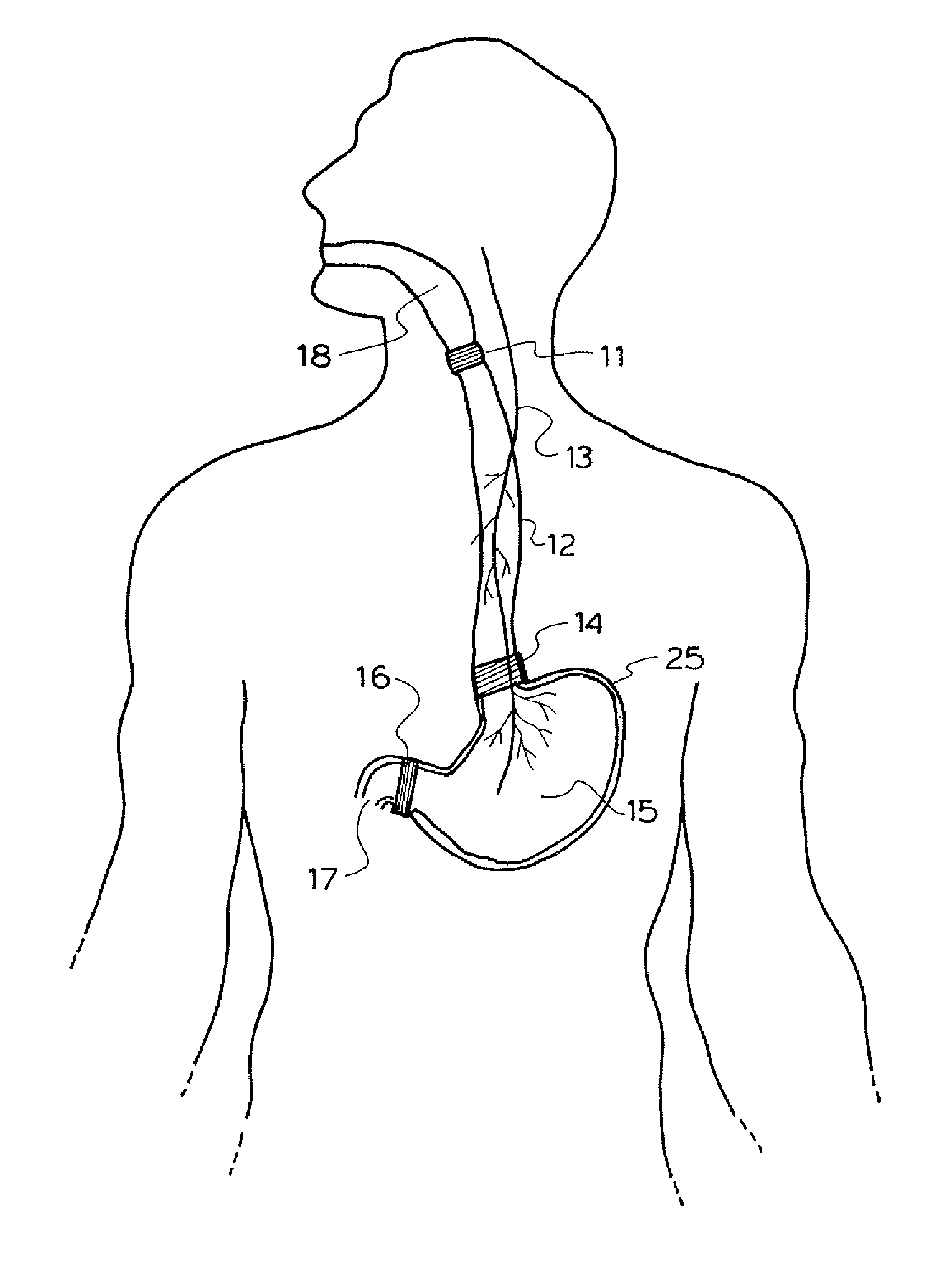
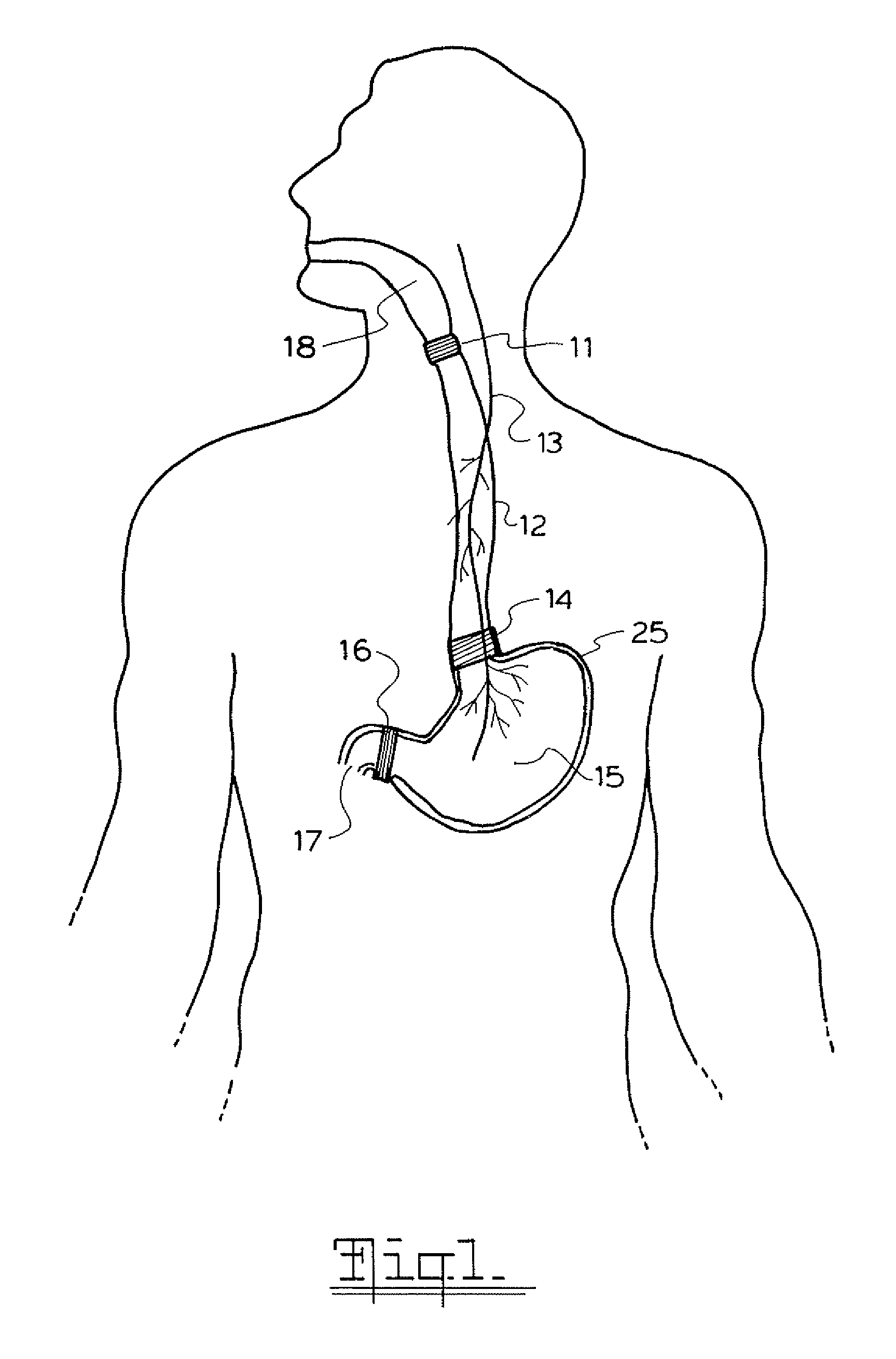
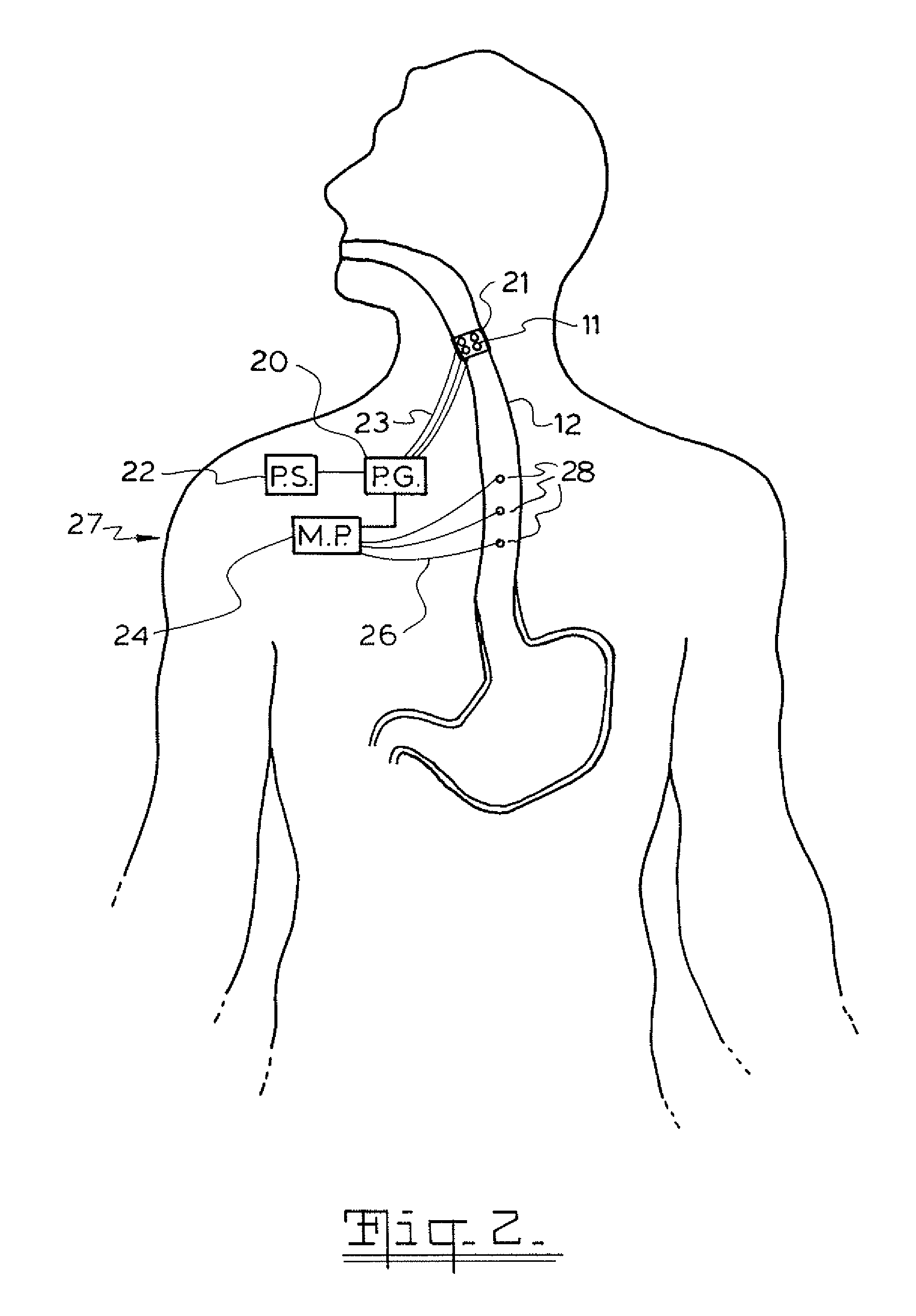
Method and apparatus for treatment of the gastrointestinal tract
InactiveUS7738961B2Increasing UES, esophageal or LES sphincter toneReduce delaysElectrotherapyArtificial respirationUpper esophageal sphincterSmall intestine
A method and device for electrically stimulating one or more structures in the gastrointestinal tract as described. The one or more structures are preferably selected from the upper esophageal sphincter, the esophagus and gastric fundus. The method may involve the step of arranging a plurality of stimulating electrodes adjacent one or more structures which may further include the lower esophageal sphincter, the stomach, the pyloric sphincter, the small intestine, the colon and the vagus. The method and device may further include sensing electrodes to detect change in one or more physiological parameters in the gastrointestinal tract and modulate the stimulating electrodes in response to the change. The device comprises a pulse generator, a power source, a plurality of stimulating electrode set, one or more sensing electrodes and means for varying activity of the stimulating electrodes in response to change detected in the gastrointestinal tract. The method and device may be used to treat obesity and / or GERD.
Owner:PARAS HLDG LLC +1
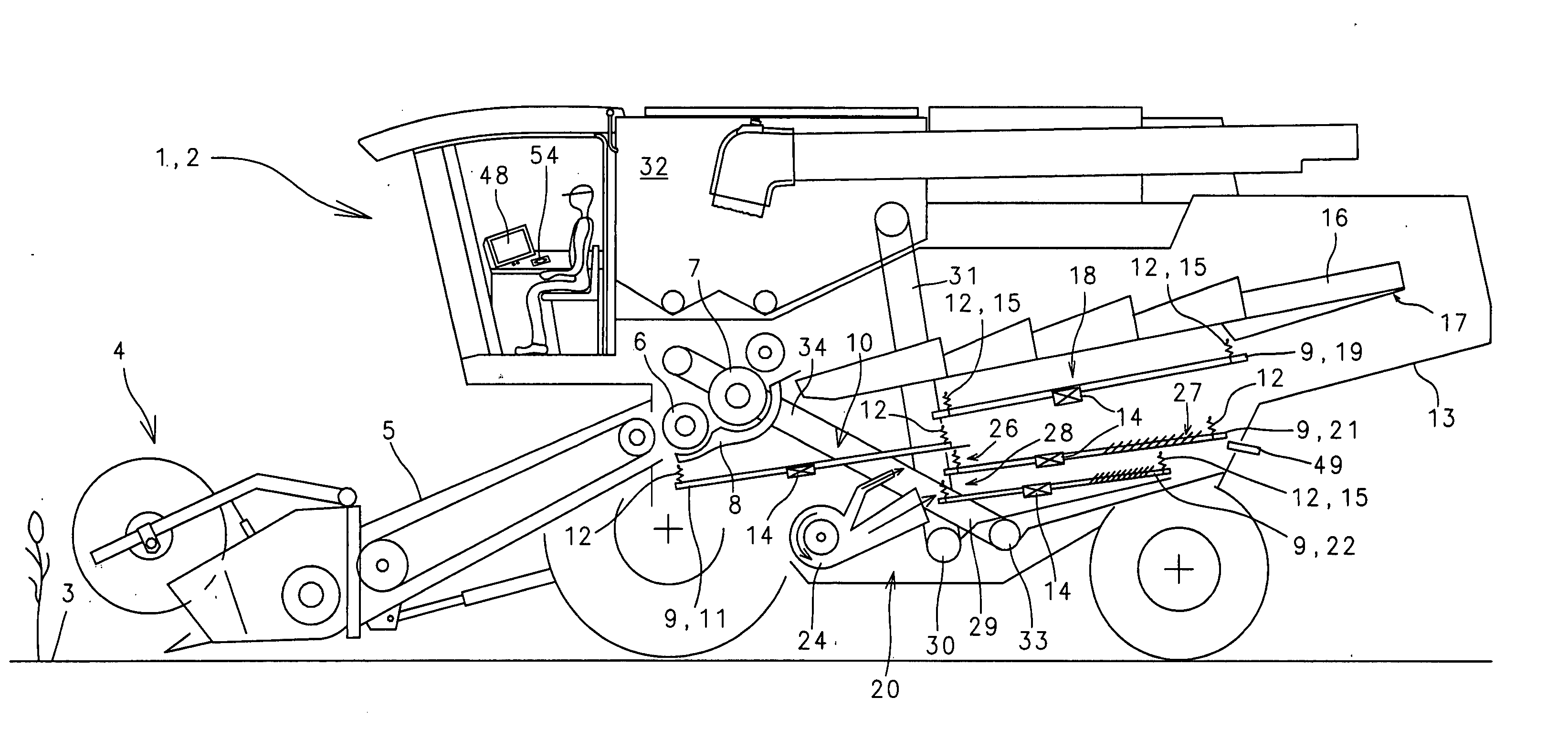
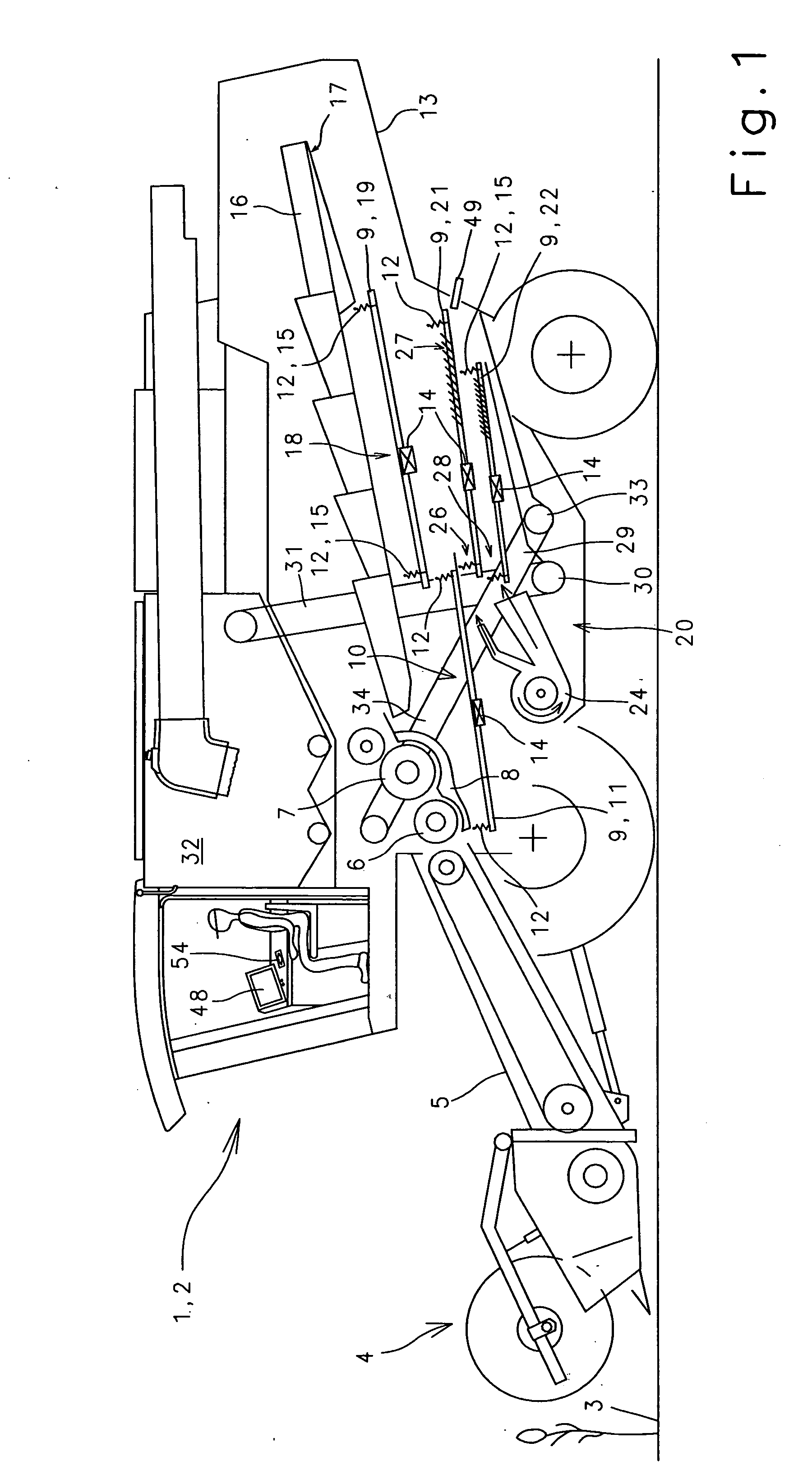
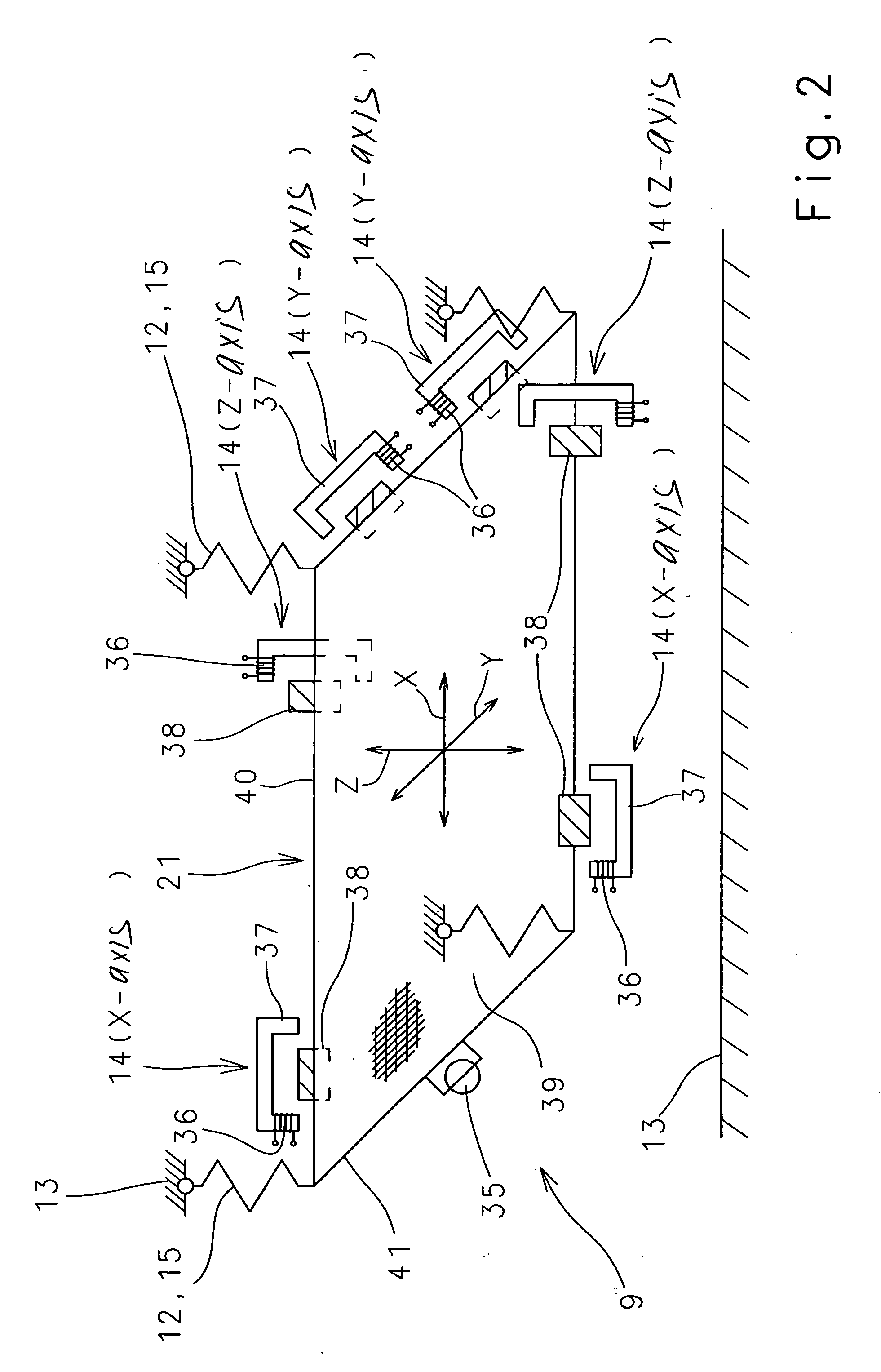
Drive system for a crop conveying device
InactiveUS20060229119A1Simple functional geometryFunction increaseSievingScreeningEngineeringVariation of parameters
In a method and a device for driving a crop conveying unit composed substantially of at least one pan with at least one sieve the pen and receive are hung in an oscillation-facilitating manner in a machine housing, at least one oscillation-reducing drive unit is provided, drive unit is formed by a linearly-oscillation unit, and the drive unit is controlled via a change in a parameter selected from the group consisting of frequency, stroke, and both.
Owner:CLAAS SELBSTFAHRENDE ERNTEMASCHINEN GMBH
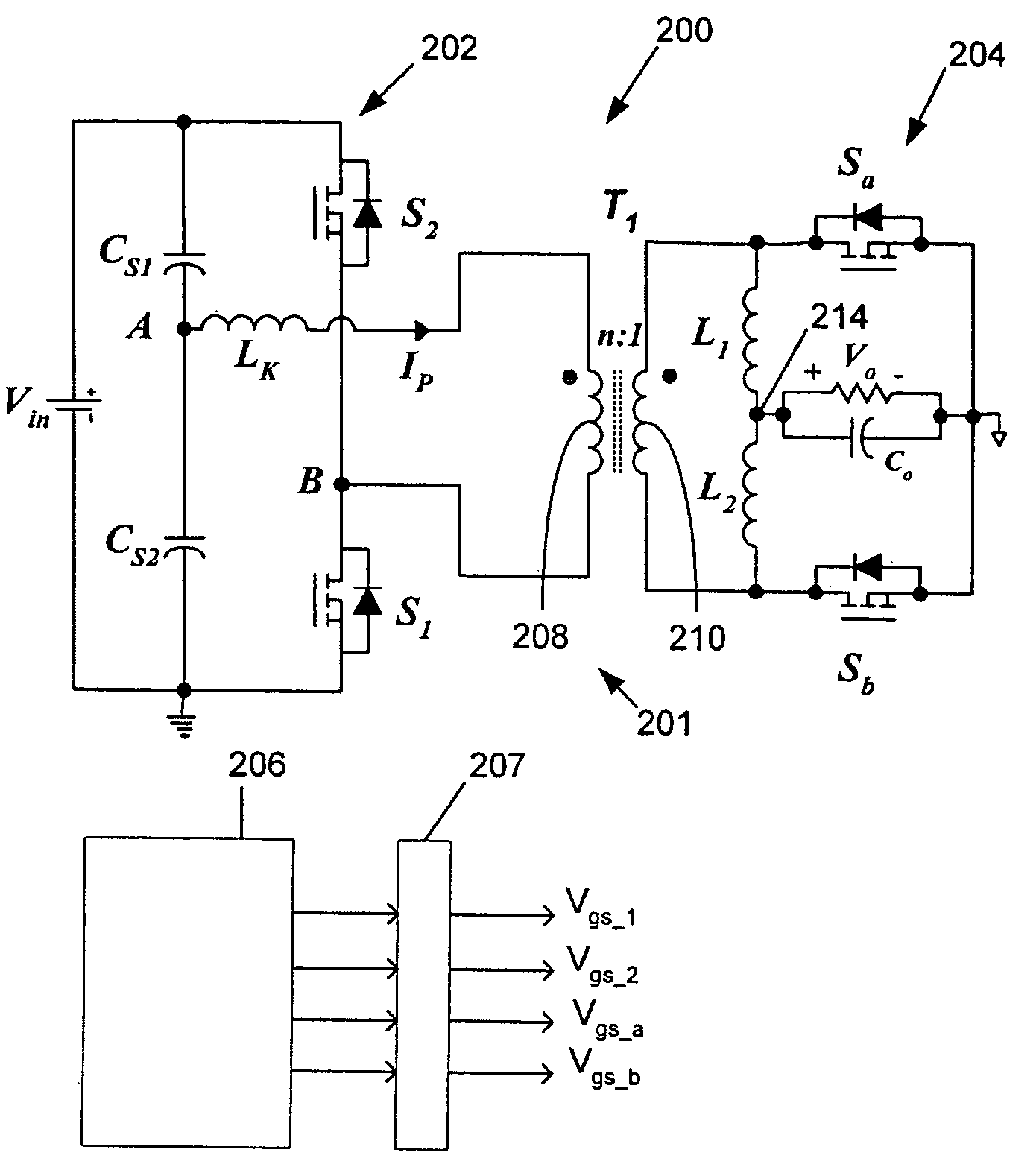
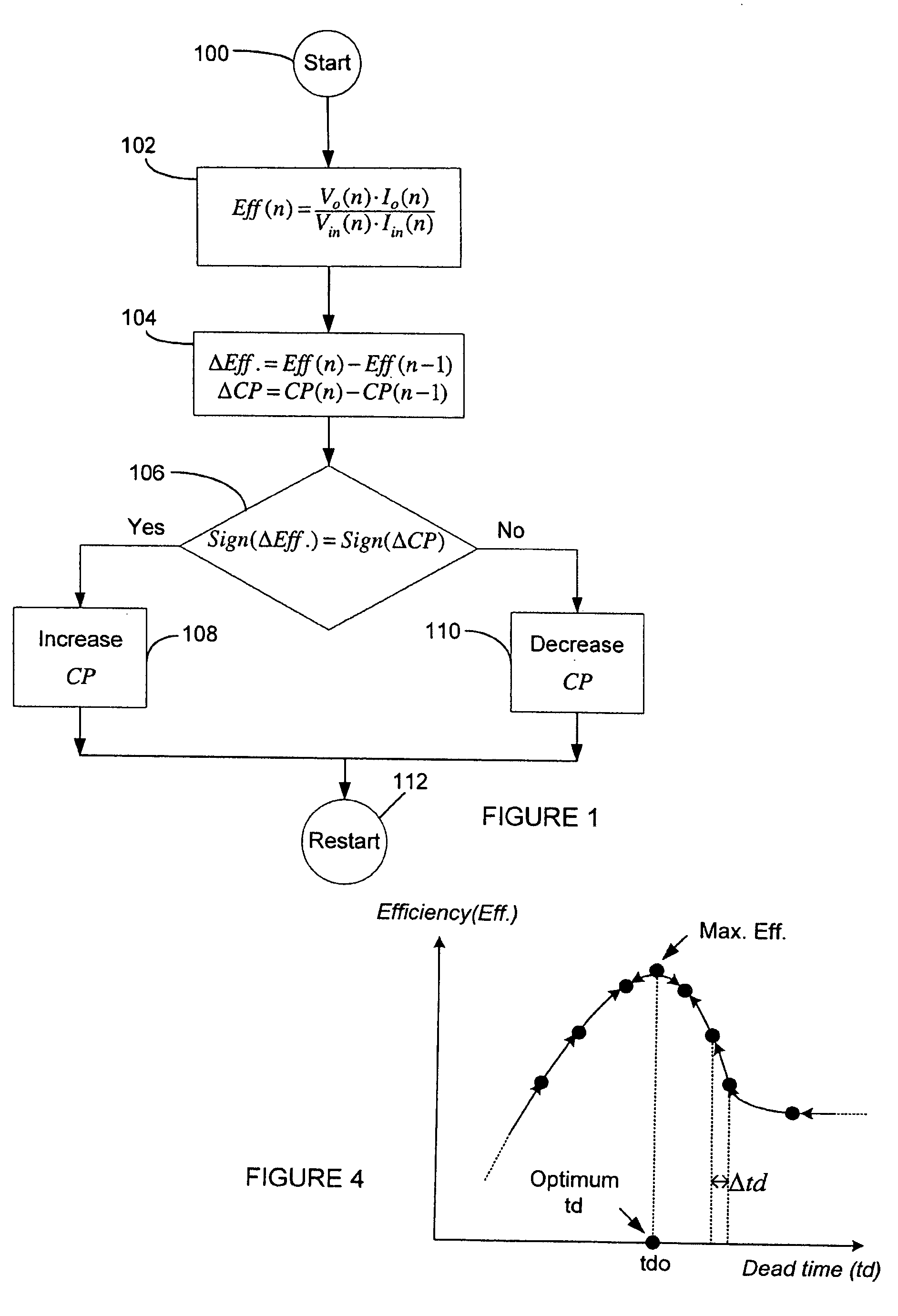
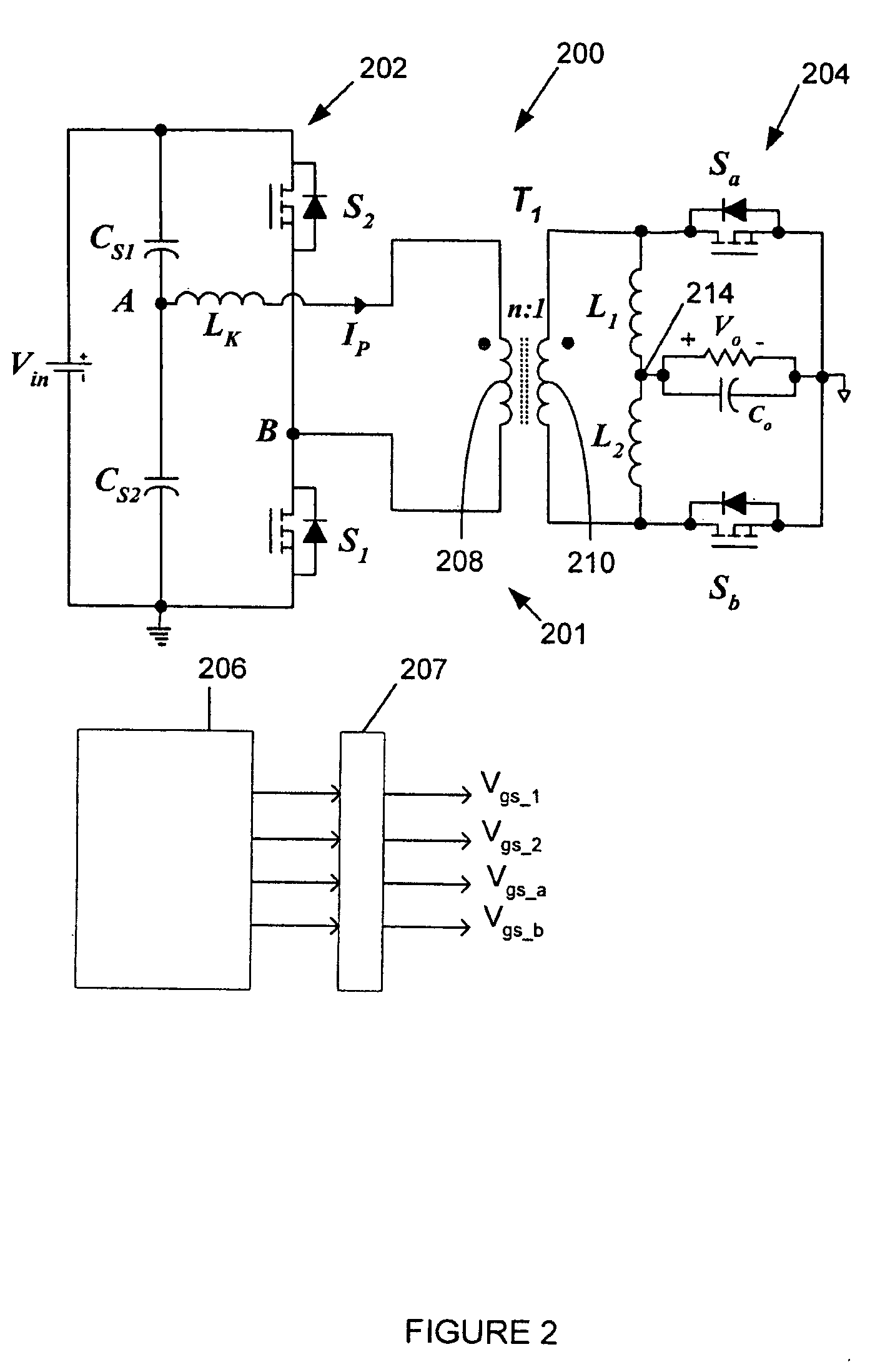
Dynamic optimization of efficiency using dead time and FET drive control
A power converter uses a control method to optimize efficiency by dynamically optimizing a controlled parameter. A change in efficiency of the converter after changing at least one controlled parameter is determined. The direction of change in efficiency of the converter is compared to a direction of the change in the controlled parameter. The controlled parameter is changed in a positive direction when the direction in the change in the efficiency of the converter and the direction of the change in the controlled parameter are the same and changed in a negative direction when the direction in the change in the efficiency of the converter and the direction of the change in the controlled parameter are opposite. The controlled parameters may include dead time between turn-on and turn-off and between turn-off and turn-on of the primary and corresponding secondary side switches of the controller, drive voltage(s) for the switches, and intermediate bus voltages.
Owner:ASTEC INT LTD
System and method for locating fluid leaks at a drape of a reduced pressure delivery system
A system and method for performing tissue therapy may include applying a reduced pressure to a tissue site of a patient. A fluid parameter associated with applying a reduced pressureto the tissue site may be sensed. An audible fluid leak location sound may be generated in response to sensing the fluid parameter. The audible fluid leak location sound may be altered in response to sensing that the fluid parameter changes. By altering the audible fluid leak location sound in response to sensing a change of the fluid parameter, a clinician may detect location of a fluid leak at the drape by applying force to the drape. The force applied to the drape may be a clinician pressing a finger onto an edge of the drape.
Owner:SOLVENTUM INTPROP CO
Detection of reduced defibrillation pad contact
A system and method of detecting a loss of electrical contact between a pair of electrodes that are electrically coupled to skin of a subject. The method includes monitoring parameters of a transthoracic impedance between the pair of electrodes in at least one of a low frequency regime and a high frequency regime, detecting an occurrence of chest compressions based on a signal indicative of chest compressions, establishing baseline levels of the parameters in at least one of the low and high frequency regimes, detecting whether changes in at least one parameter exceeds the baseline level by a threshold, determining that at least one electrode of the pair of electrodes is losing electrical contact with the skin responsive to the at least one parameter exceeding the baseline level by the threshold, and issuing an alert in response to a determination that the at least one electrode is losing electrical contact.
Owner:ZOLL MEDICAL CORPORATION
Parameter evaluation system
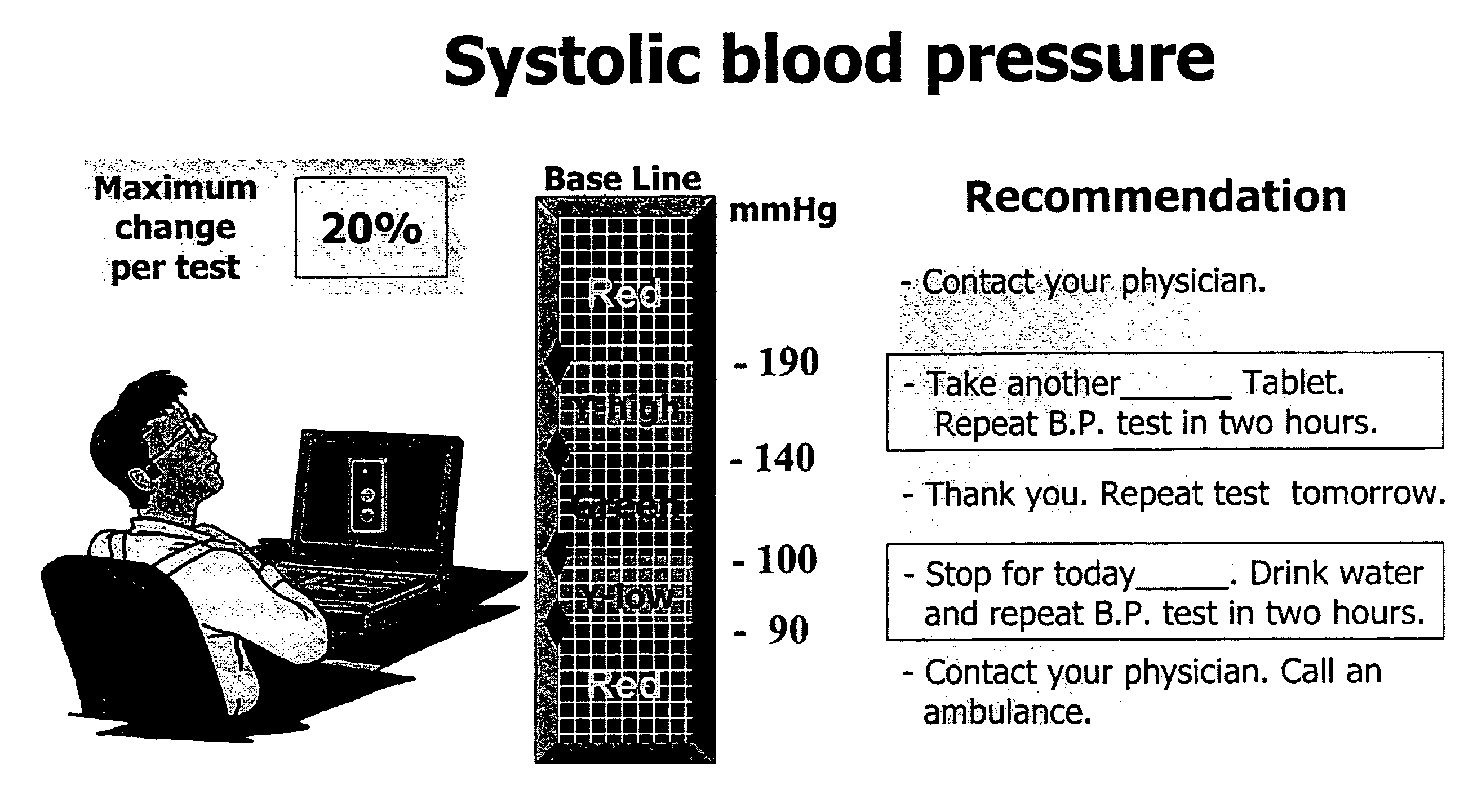
A parameter evaluation system comprising a boundary input device for setting boundaries in a variation range of one or more parameters, thereby to define regions within said variation range, a label input device for associating labels with said regions, a rule input device for setting rules to associate at least one of a plurality of output recommendations with each of said regions and with combinations thereof and an output device to present a user with an output recommendation associated with a region or combination thereof corresponding to at least one measured parameter input to said system. The input device is a parameter value region selection and categorization input device for setting boundaries in the variation range of the parameter, defining regions therebetween and categorizing the regions. The device comprises a visual representation of the variation range as a linear continuum, a continuum divider for visually dividing the continuum at user selectable points therealong, the points corresponding to values of the parameter, thereby to define regions therebetween and a category definer for defining categories for association with the regions. The device has an application in a patient monitoring kit under remote supervision of a physician.
Owner:F POSZAT HU
Methods and devices for non-invasive cerebral and systemic cooling
ActiveUS20100211140A1Minimize neurologic deficitMaximize coolingTracheal tubesHalogenated hydrocarbon active ingredientsNasal cavityWhole body
A method for providing and adjusting cerebral cooling in response to changes in a physiological parameter. A spray having a boiling point between 38-300° C. is delivered to the surface of a patient's nasal cavities. The spray causes cooling by direct heat transfer through the nasopharynx and hematogenous cooling through the carotids and the Circle of Willis. A physiological parameter, such as cerebral temperature, changes in cerebral blood flow or brain oxygenation is monitored. The delivery rate of the spray is adjusted in response to the physiological parameter.
Owner:BRAINCOOL +1
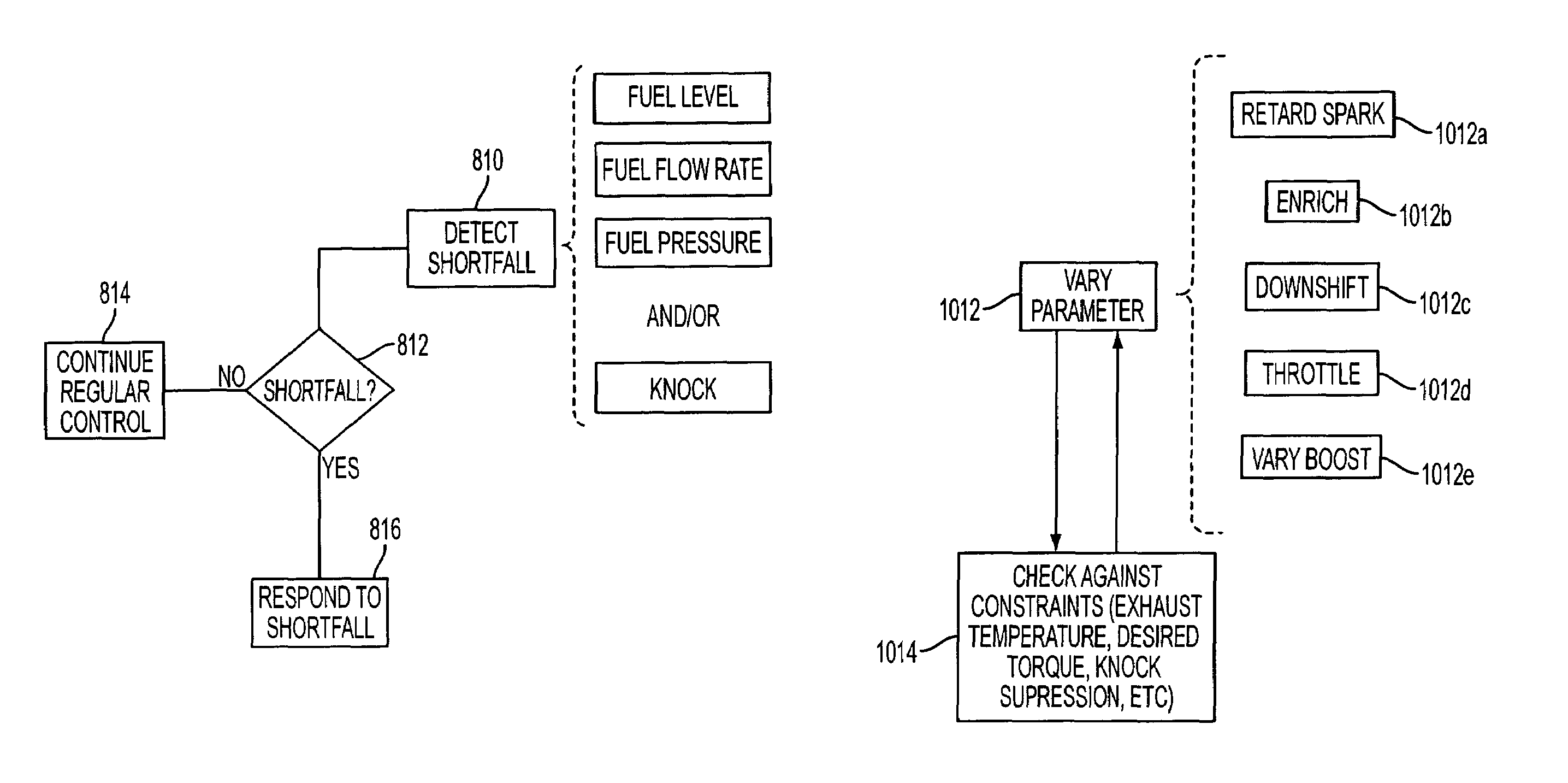
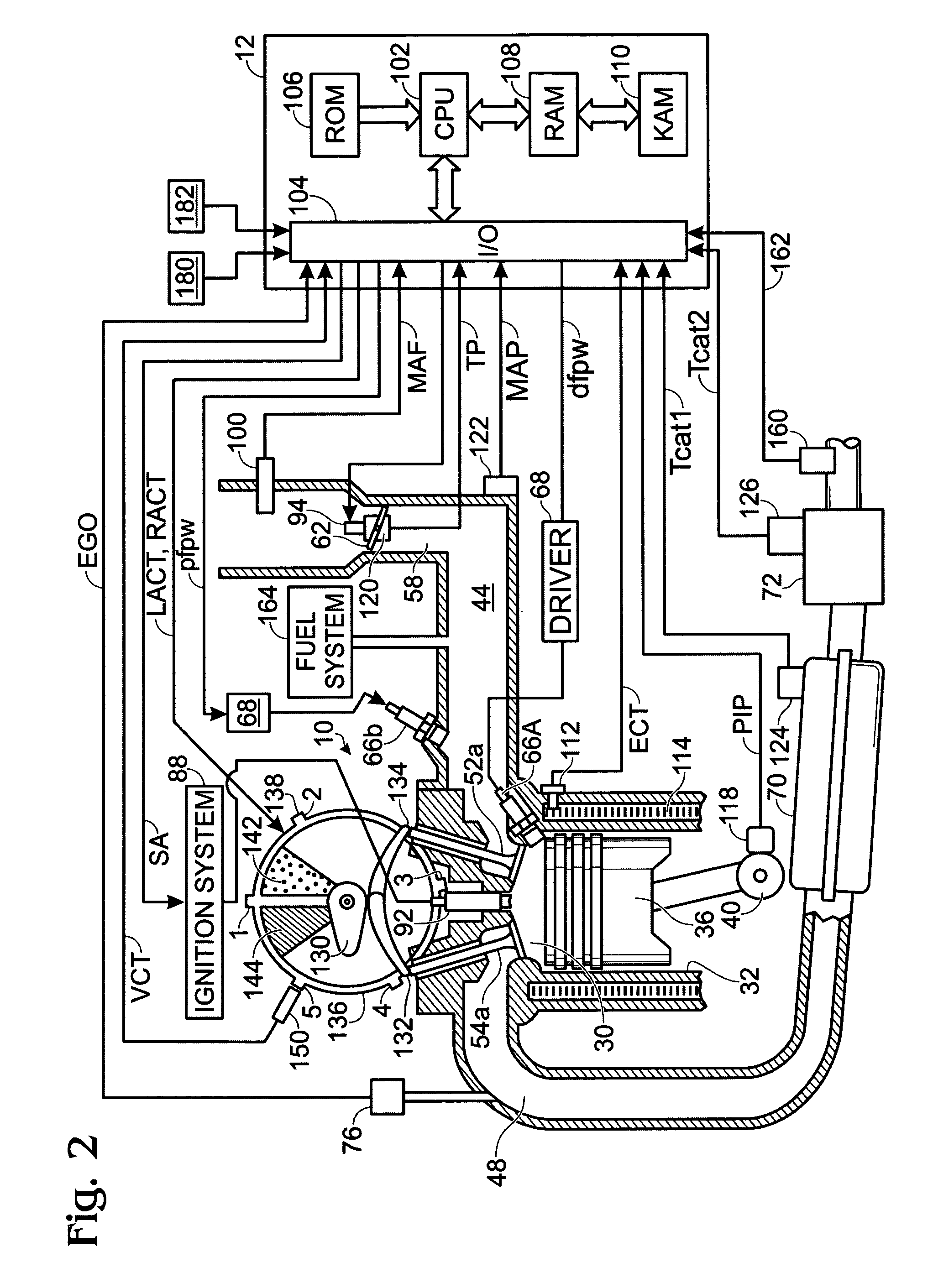
Control strategy for engine employng multiple injection types
ActiveUS7581528B2Electrical controlInternal combustion piston enginesMultiple injectionVariation of parameters
A system for an engine, comprising a cylinder, a first injection subsystem for injecting a first substance into the cylinder, a second injection subsystem for injecting a second substance into the cylinder, and an electronic engine controller configured to control a plurality of operating parameters of the engine, where the electronic engine controller is configured to cause variation of at least one of the operating parameters in response to a shortfall condition of the second injection subsystem.
Owner:FORD GLOBAL TECH LLC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com