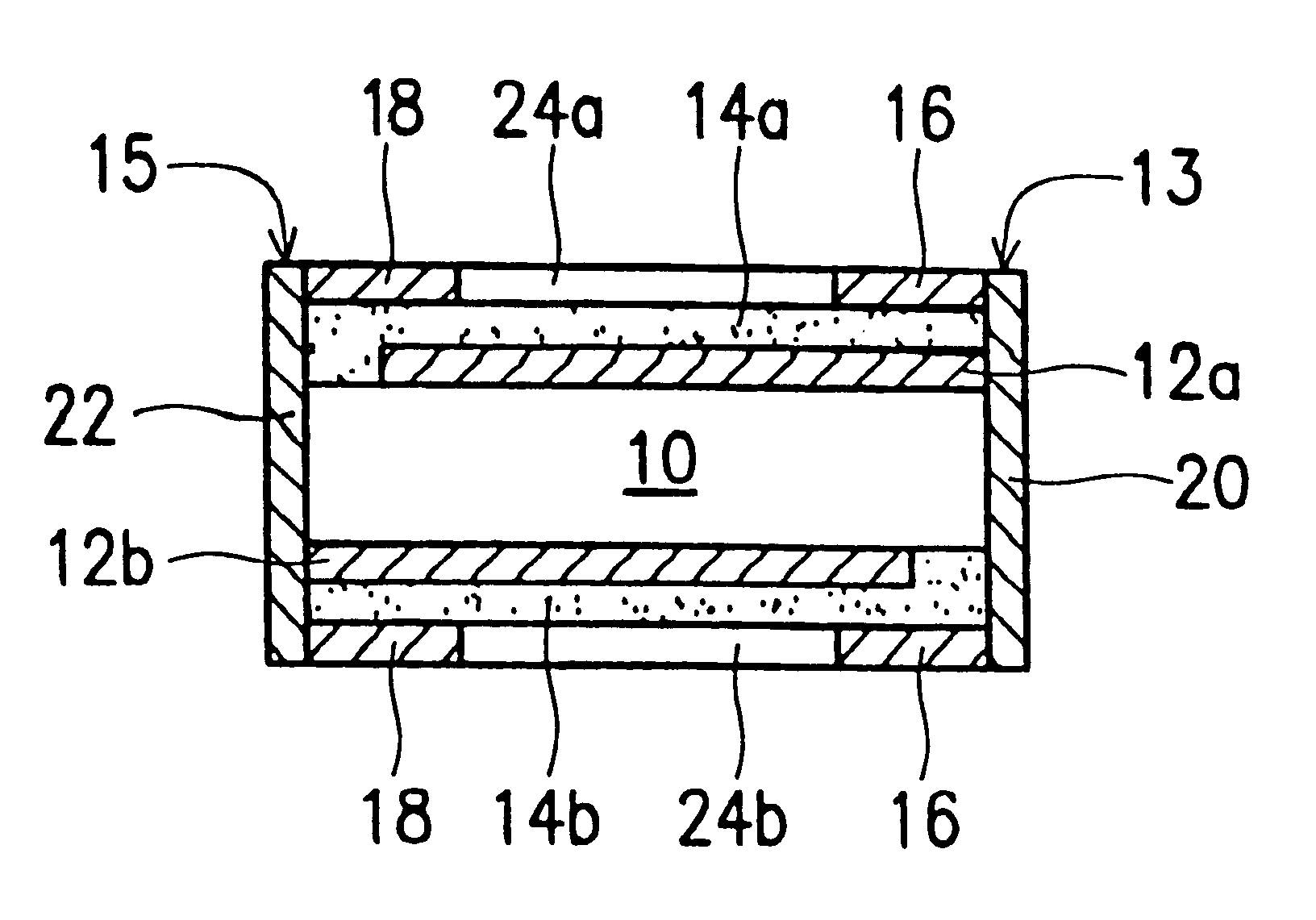
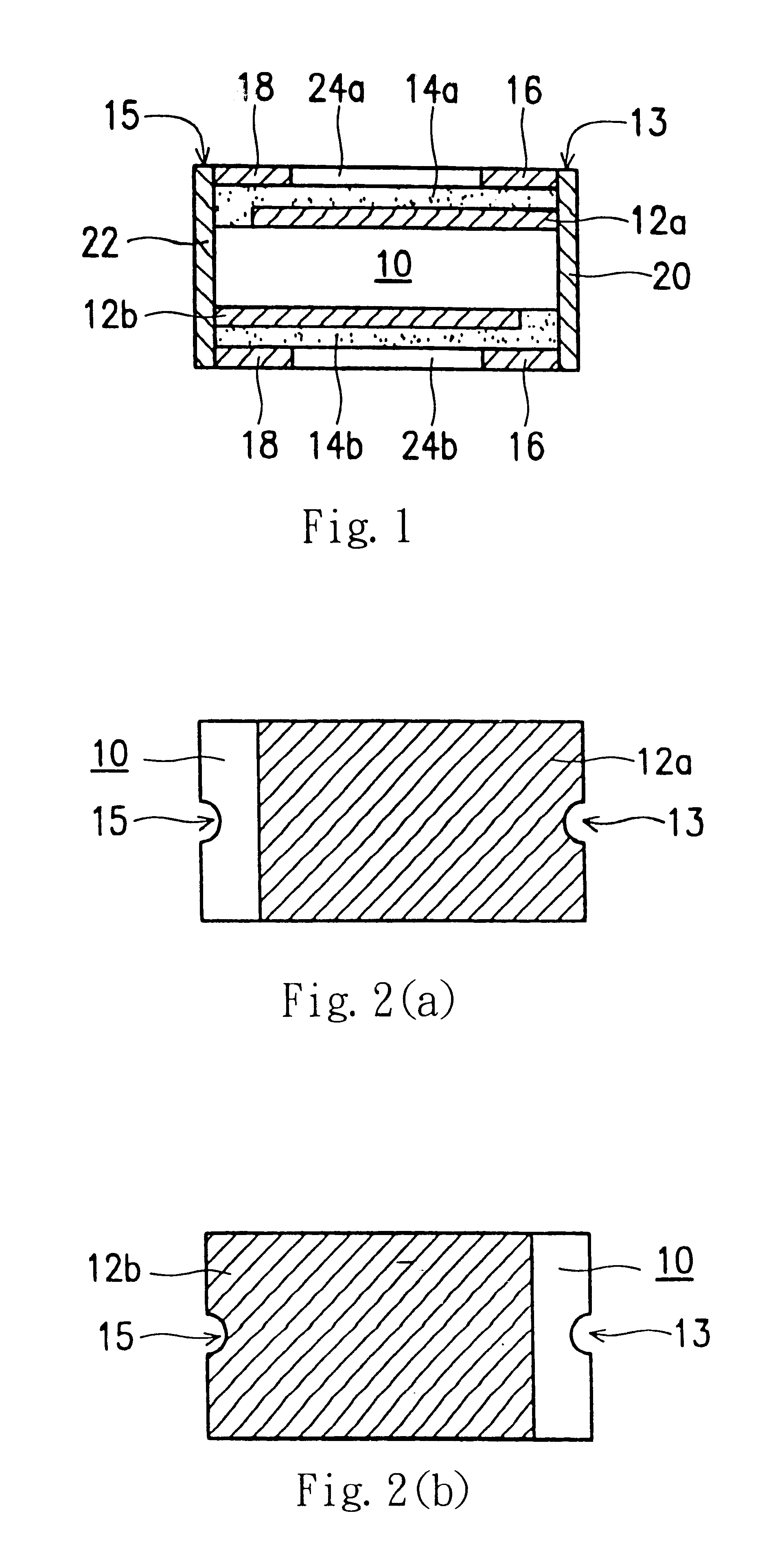
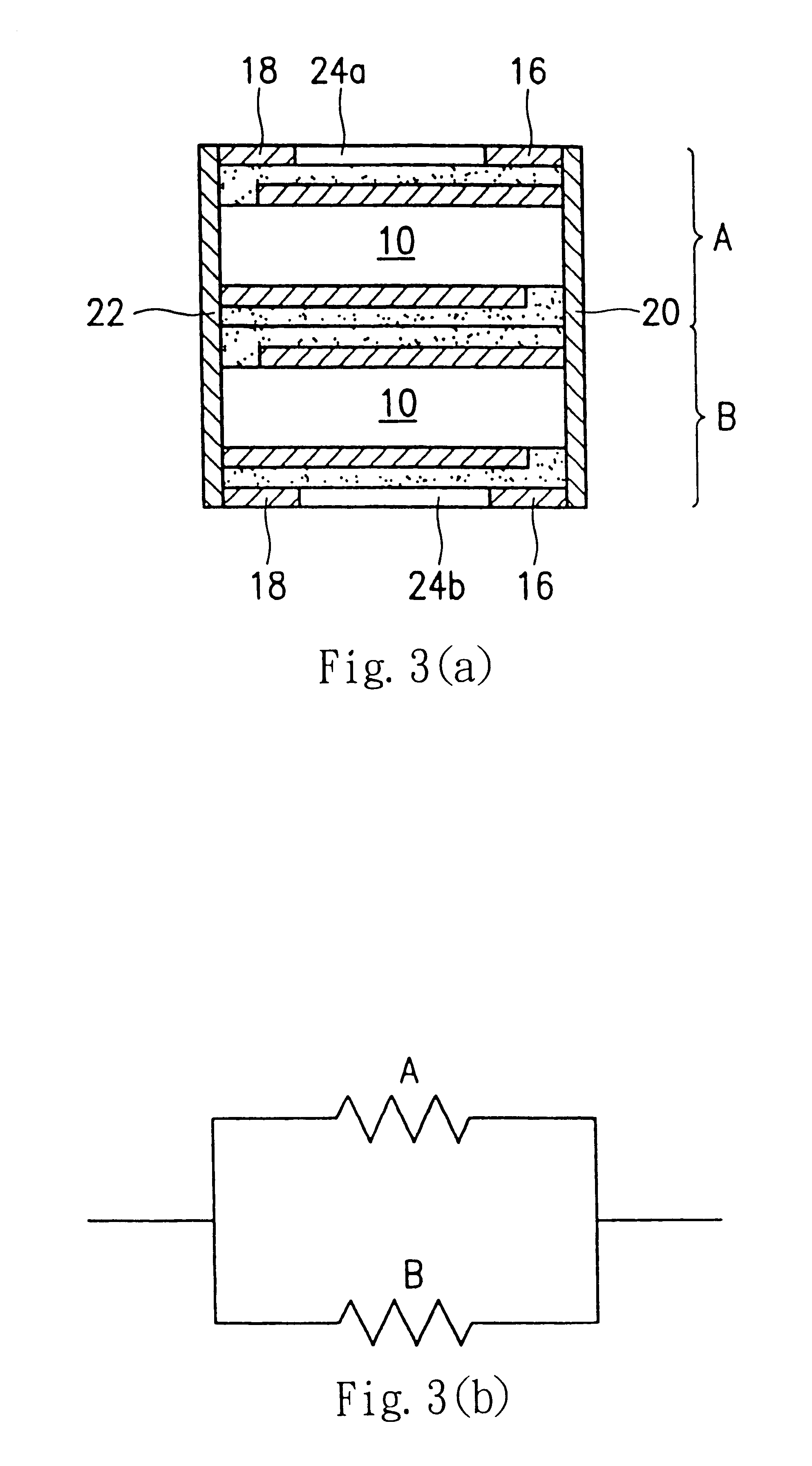
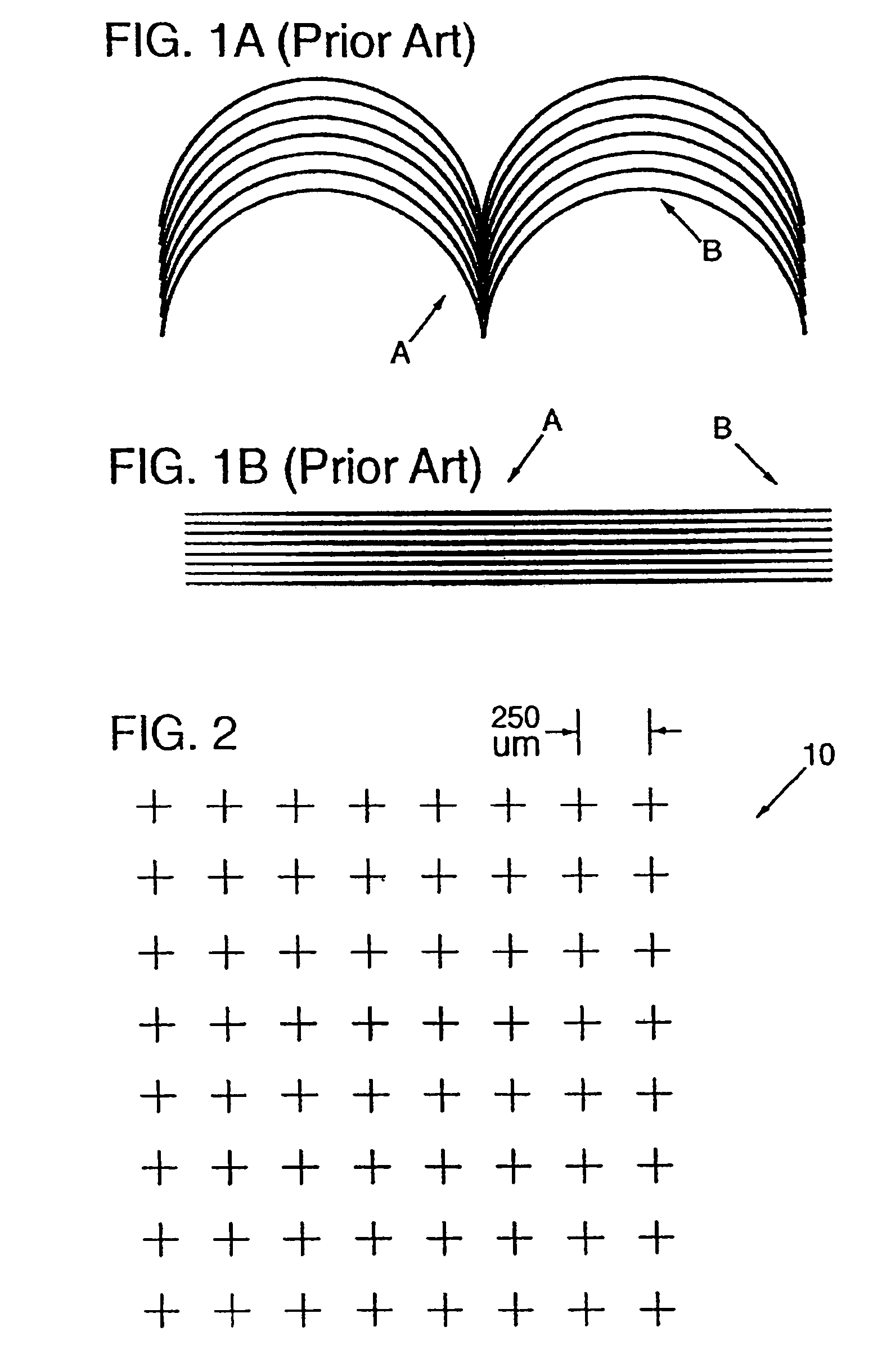
Patents
Literature
4497 results about "Line width" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
The linewidth (or line width) of a laser, e.g. a single-frequency laser, is the width (typically the full width at half-maximum, FWHM) of its optical spectrum . More precisely, it is the width of the power spectral density of the emitted electric field in terms of frequency, wavenumber or wavelength. Similarly,...
Semiconductor device, electronic device, and method of manufacturing semiconductor device
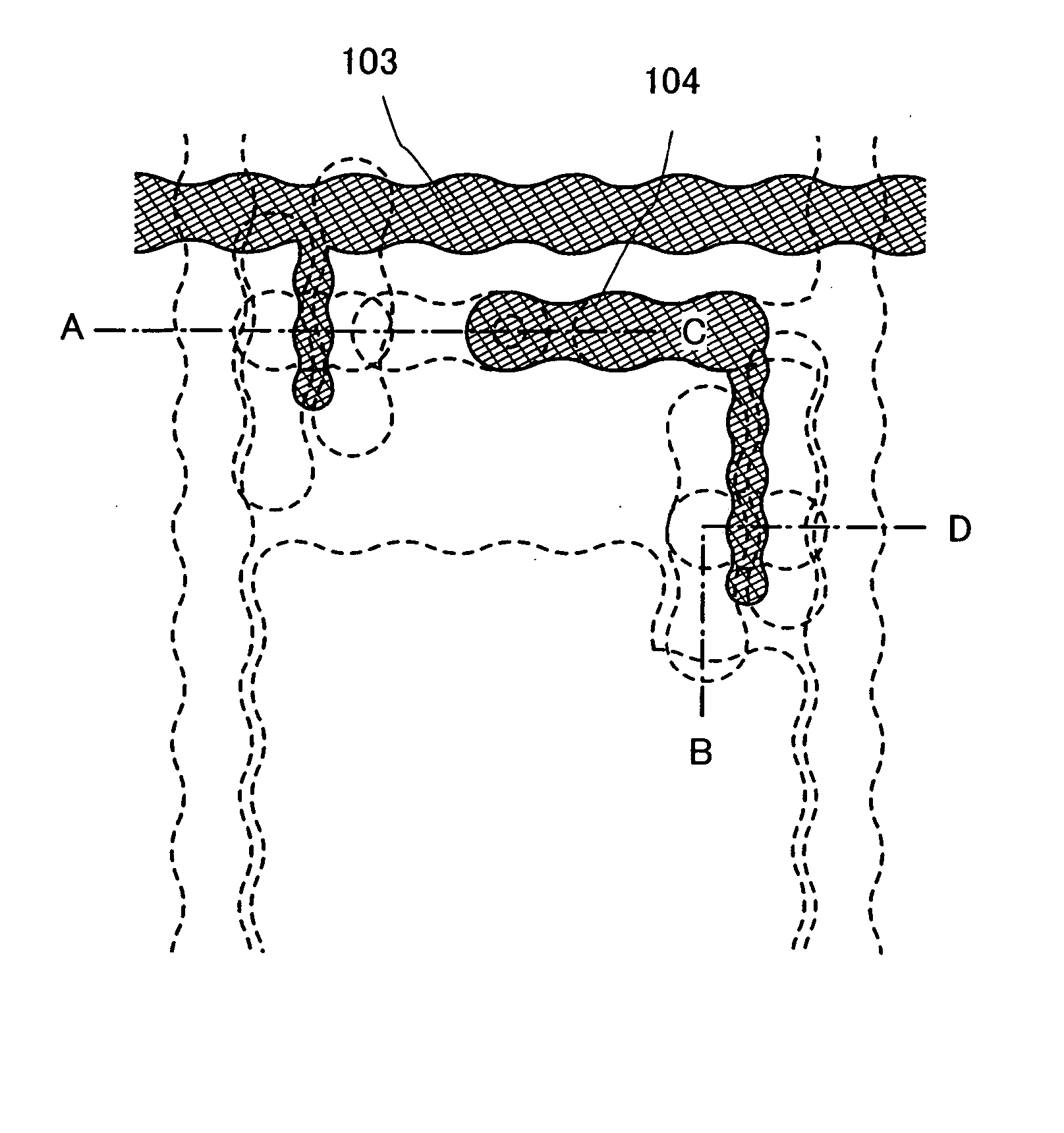
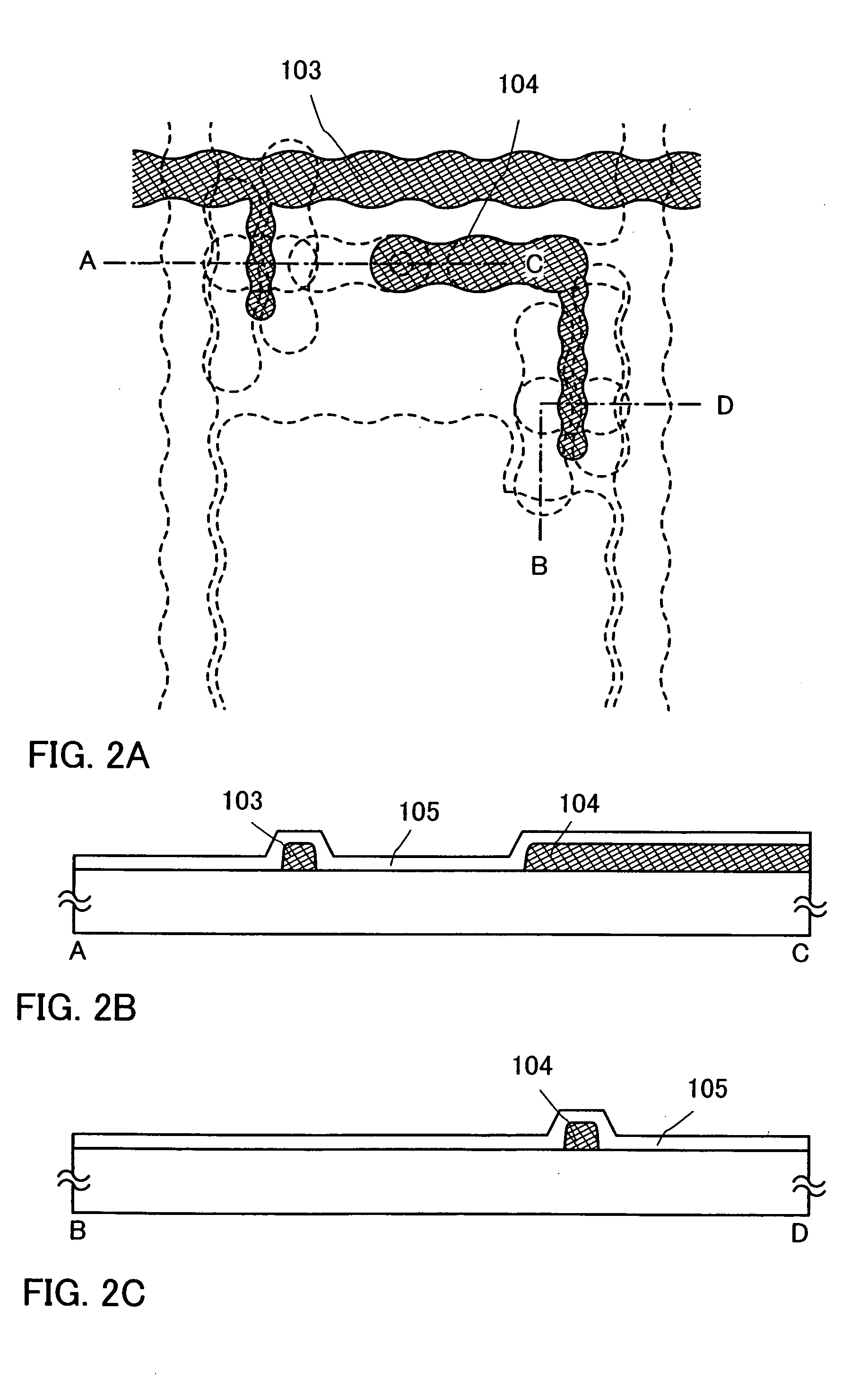
InactiveUS20060170111A1Stable formationImprove performanceSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesDevice materialShortest distance
Conductive layers having knots are adjacently formed with uniform distance therebetween. Droplets of the conductive layers are discharged to stagger centers of the droplets in a length direction of wirings so that the centers of the discharged droplets are not on the same line in a line width direction between the adjacent conductive layers. Since the centers of the droplets are staggered, parts of the conductive layers each having a widest line width (the widest width of knot) are not connected to each other, and the conductive layers can be formed adjacently with a shorter distance therebetween.
Owner:SEMICON ENERGY LAB CO LTD
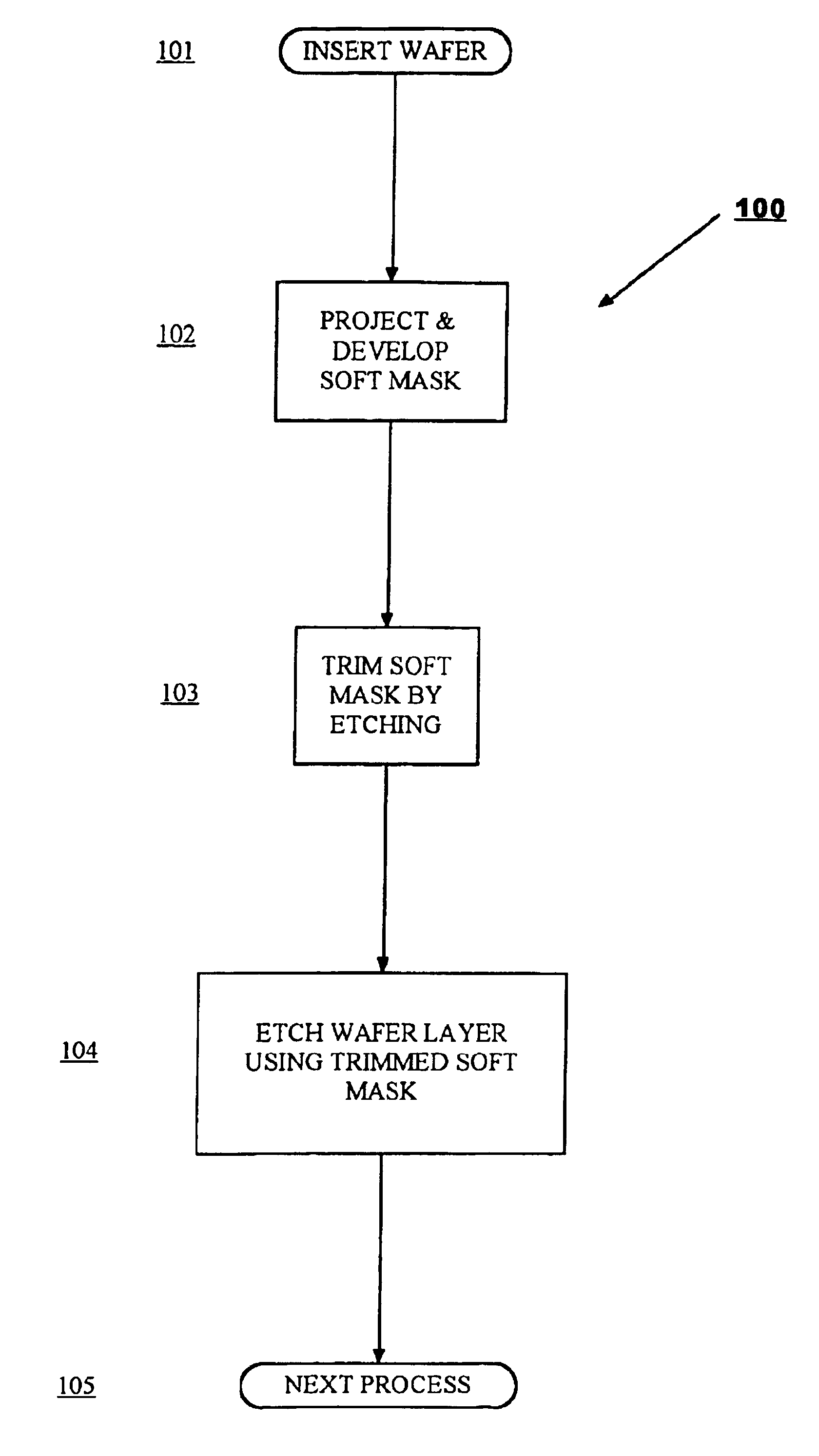
Gate linewidth tailoring and critical dimension control for sub-100 nm devices using plasma etching
InactiveUS6864041B2Tight tolerance variationMinimal variationVacuum gauge using ionisation effectsDecorative surface effectsImage resolutionLine width
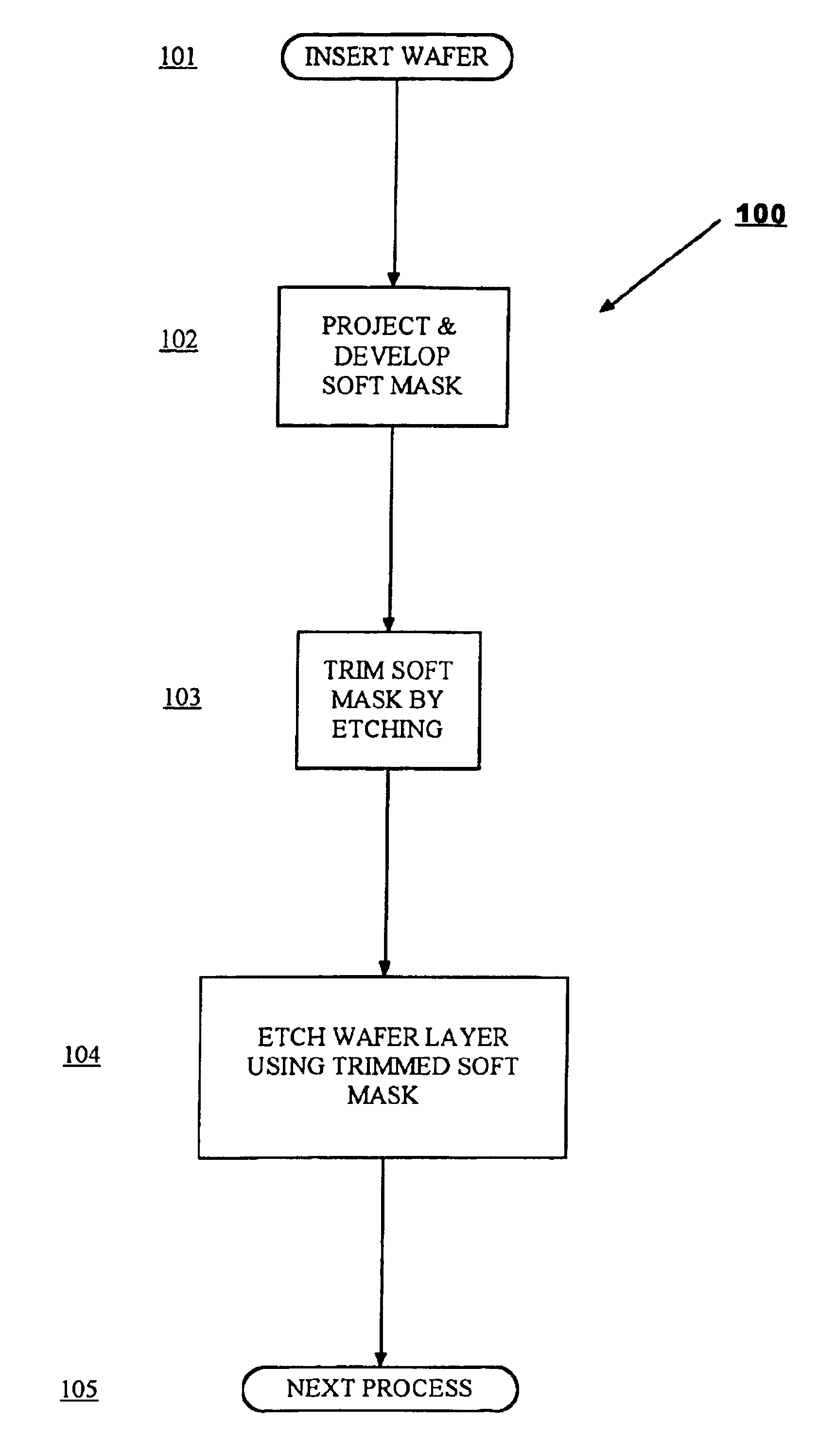
A method of fabricating an electronic chip on a wafer in which a first mask at a predetermined lower resolution is developed on the wafer and then etched under a first set of conditions for a predetermined period to achieve a mask that is below the resolution limit of current lithography. The etched mask is then used as a hard mask for etching material on a lower layer.
Owner:INT BUSINESS MASCH CORP
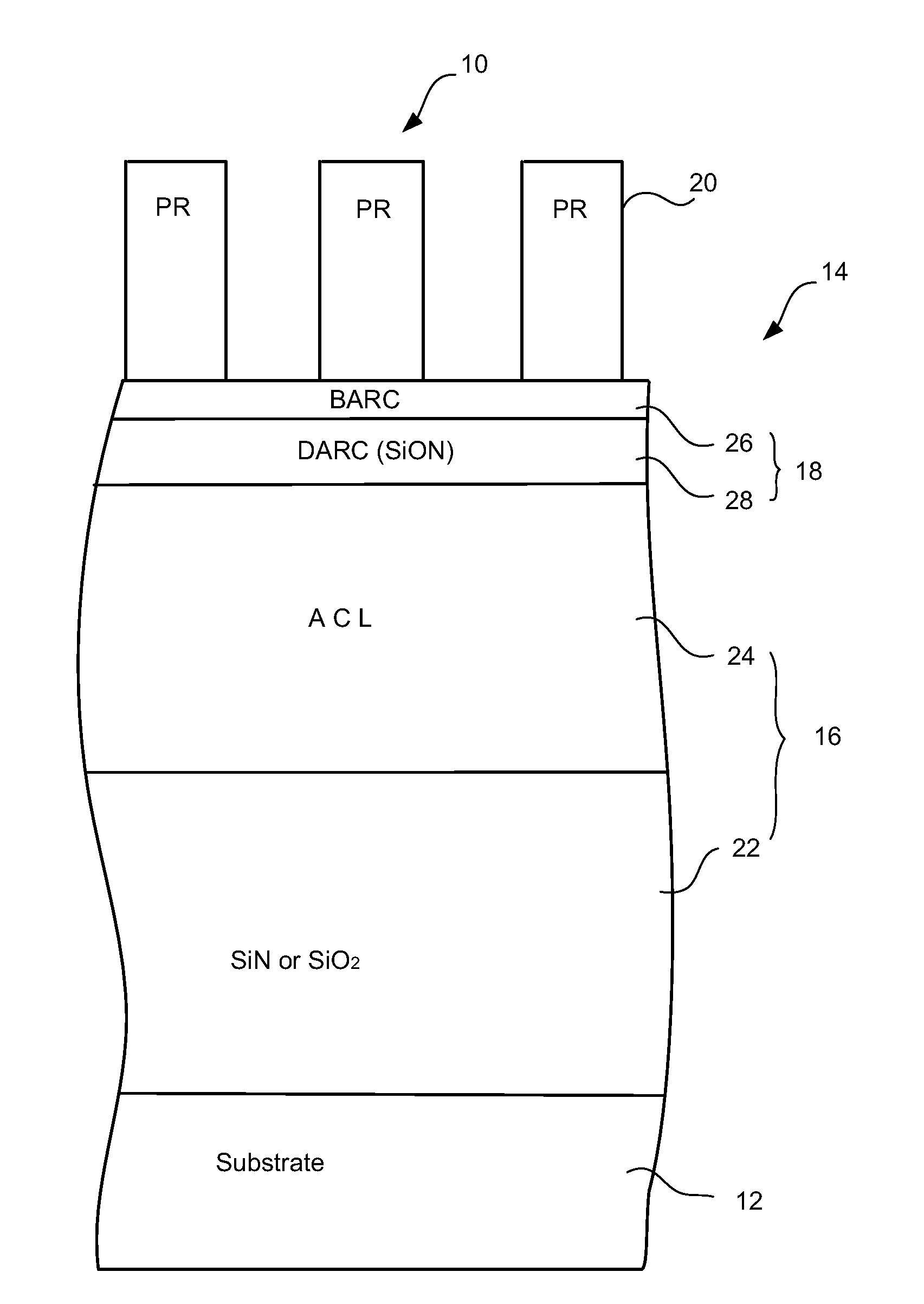
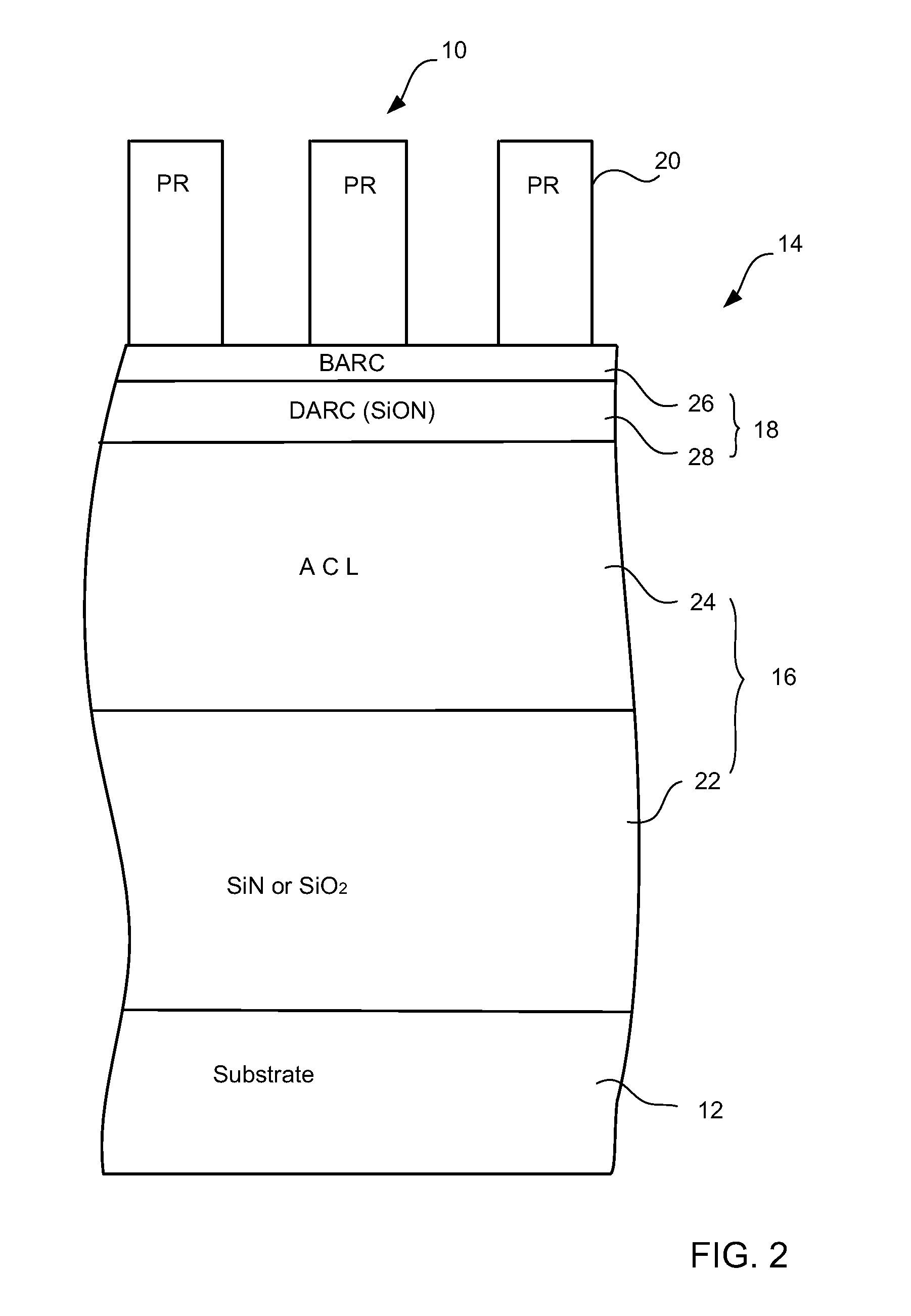
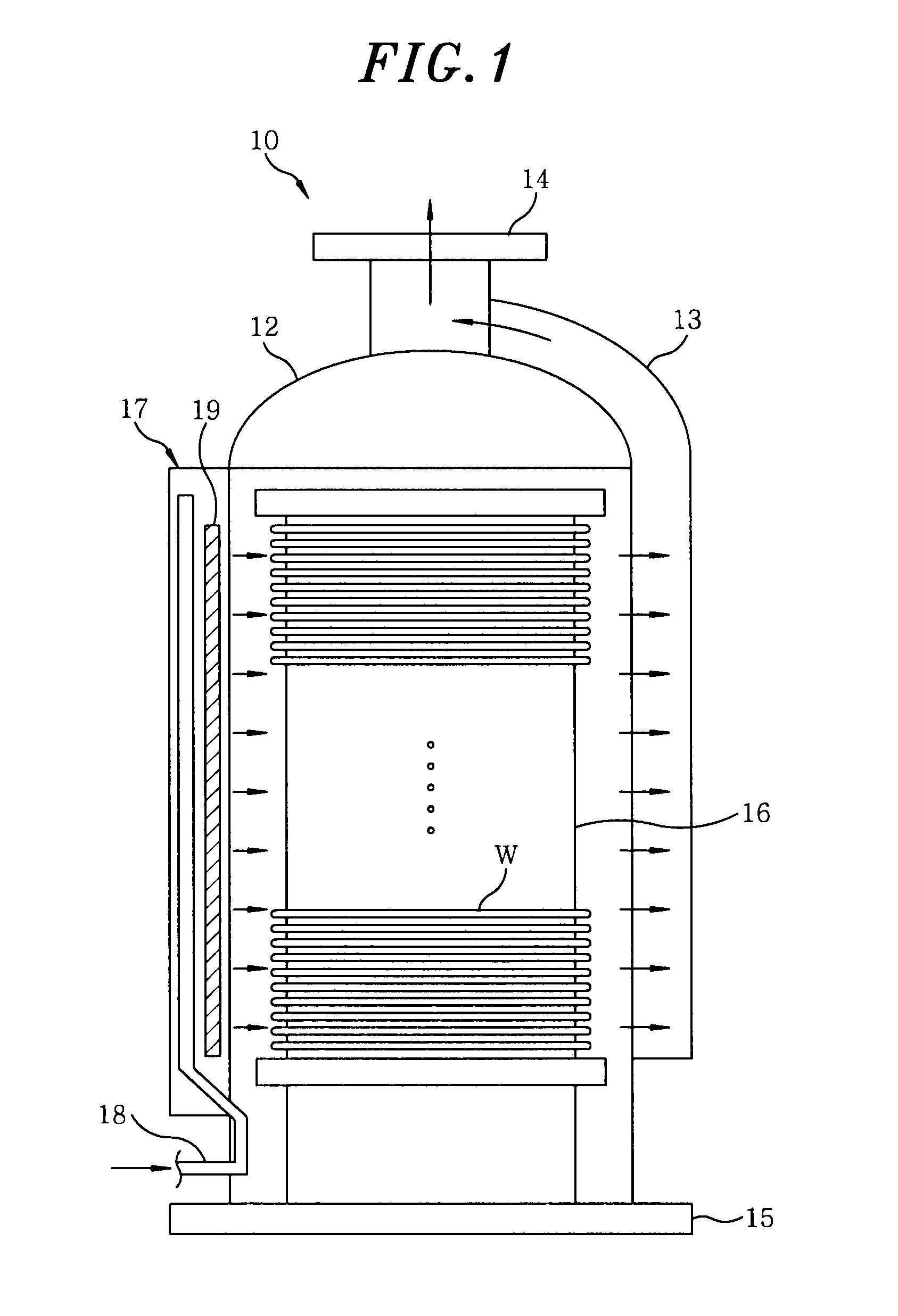
Methods and apparatus for controlling photoresist line width roughness
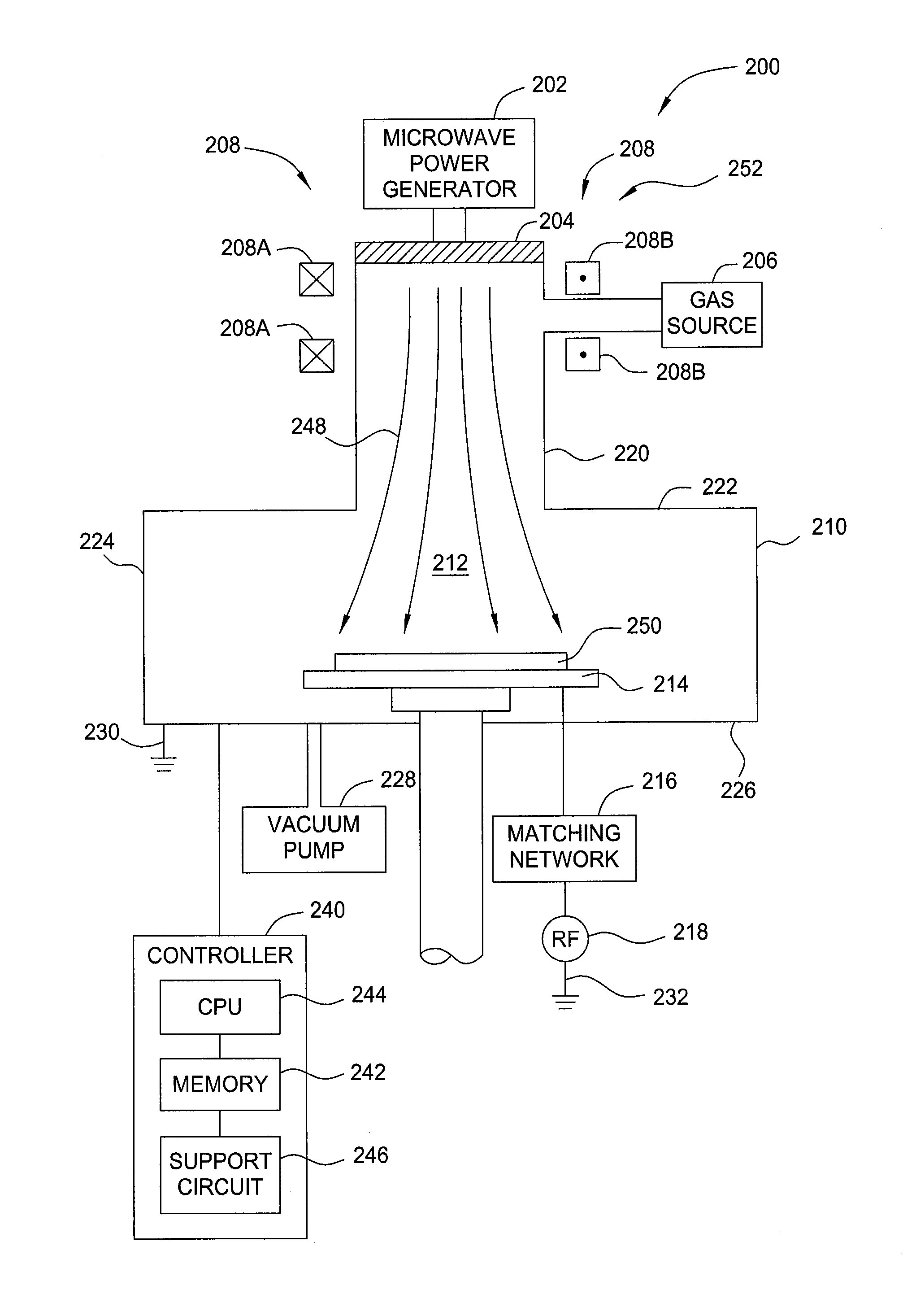
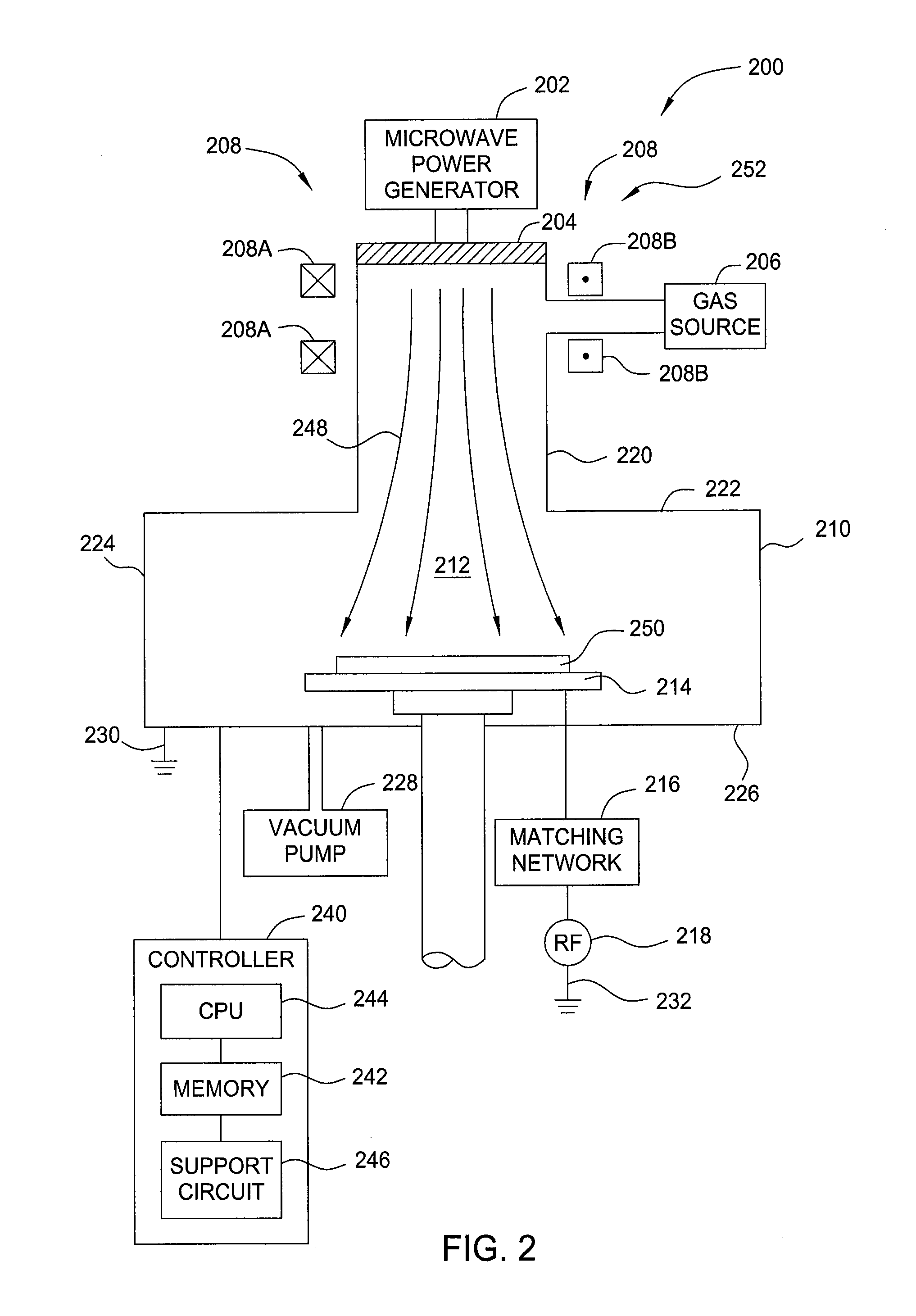
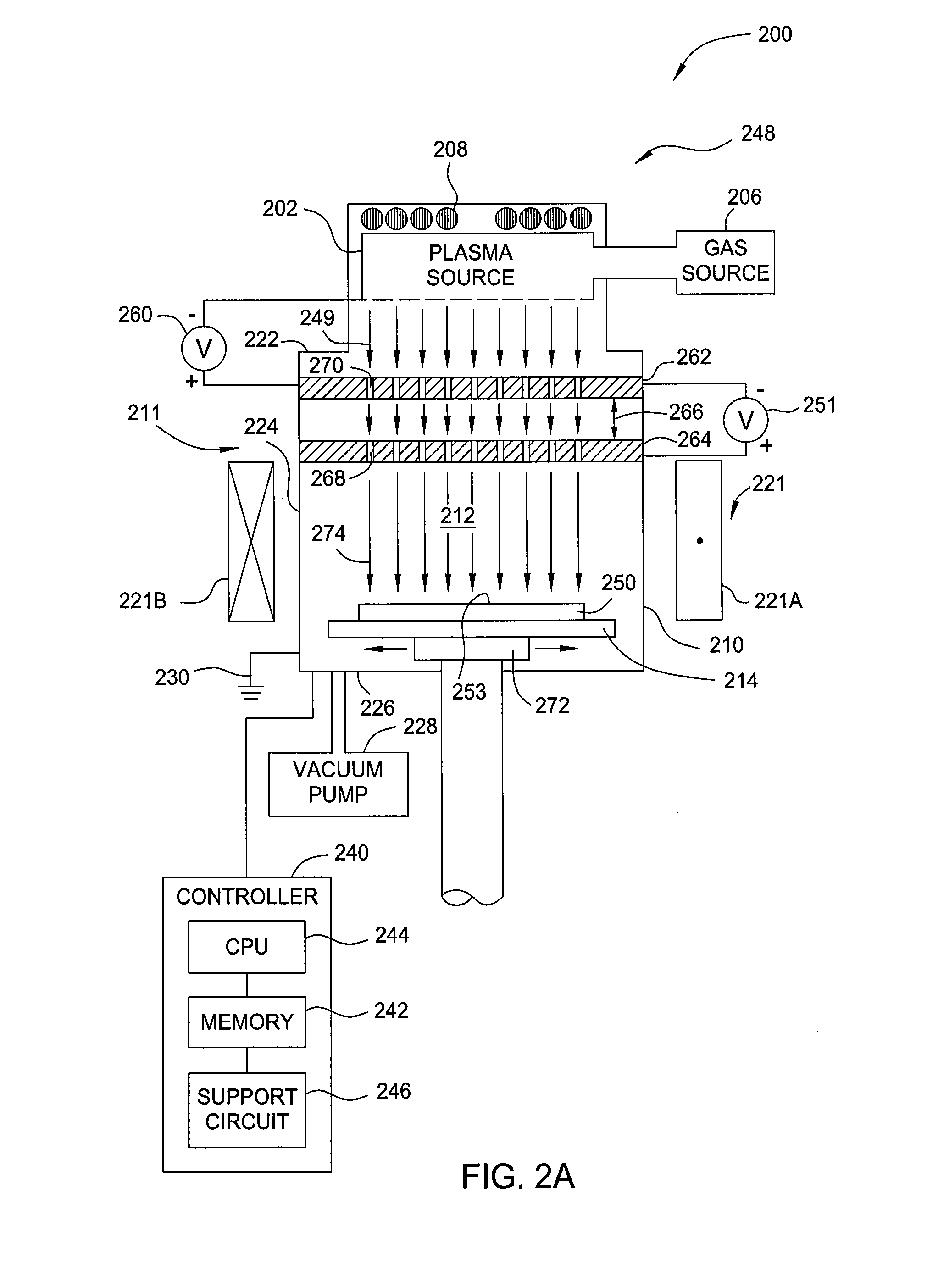
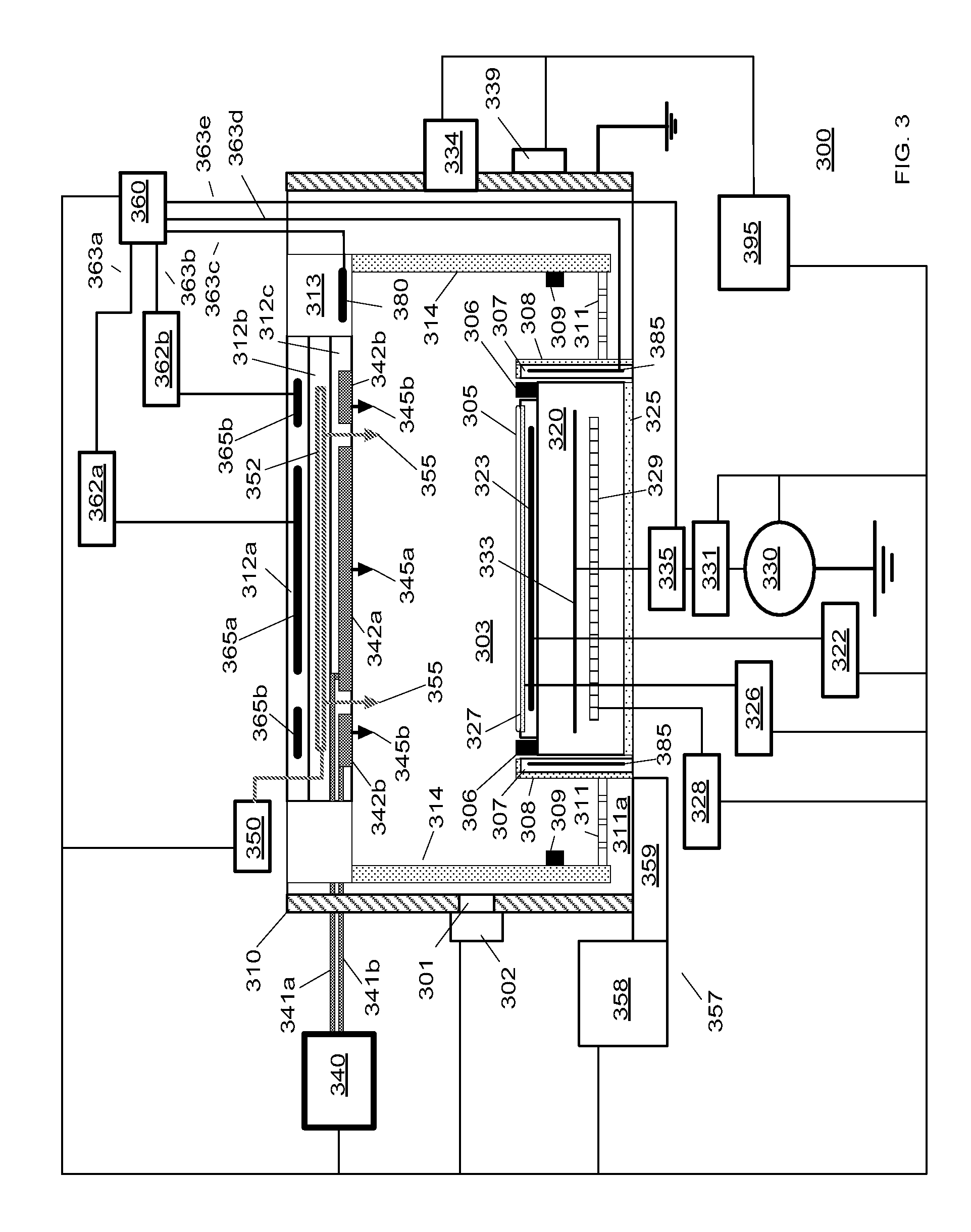
The present invention provides methods and an apparatus for controlling and modifying line width roughness (LWR) of a photoresist layer. In one embodiment, an apparatus for controlling a line width roughness of a photoresist layer disposed on a substrate includes a chamber body having a top wall, side wall and a bottom wall defining an interior processing region, a microwave power generator coupled to the to the chamber body through a waveguild, and one or more coils or magnets disposed around an outer circumference of the chamber body adjacent to the waveguide, and a gas source coupled to the waveguide through a gas delivery passageway.
Owner:APPLIED MATERIALS INC
Method for reducing line width roughness with plasma pre-etch treatment on photoresist
InactiveUS20110117749A1Reduce line width roughnessElectric discharge tubesDecorative surface effectsEtchingLine width
A method for reducing line width roughness (LWR) of a feature in an etch layer below a patterned photoresist mask having mask features is provided. The method includes (a) non-etching plasma pre-etch treatment of the photoresist mask, and (b) etching of a feature in the etch layer through the pre-treated photoresist mask using an etching gas. The non-etching plasma pre-etch treatment includes (a1) providing a treatment gas containing H2 and COS, (a2) forming a plasma from the treatment gas, and (a3) stopping the treatment gas.
Owner:LAM RES CORP
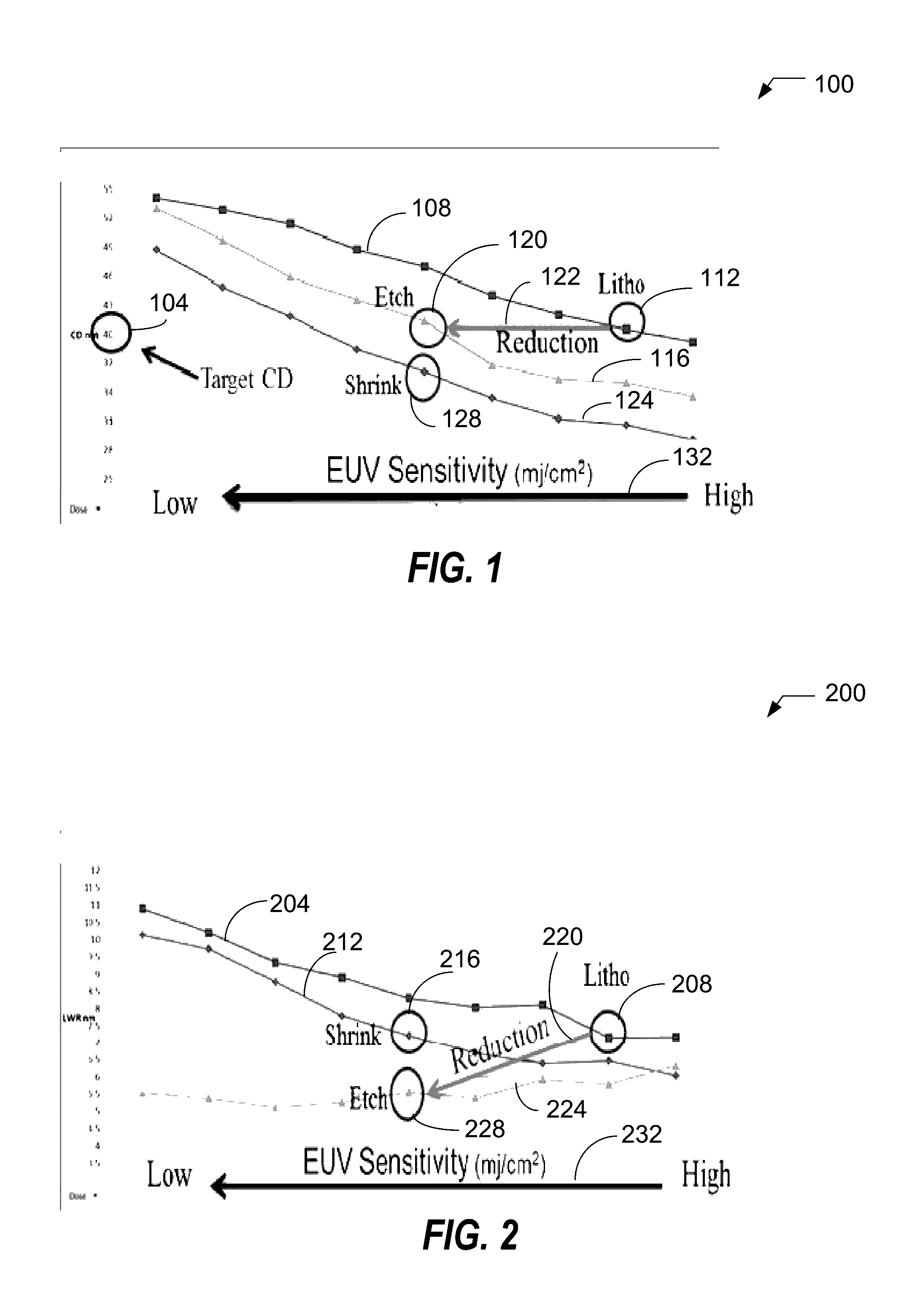
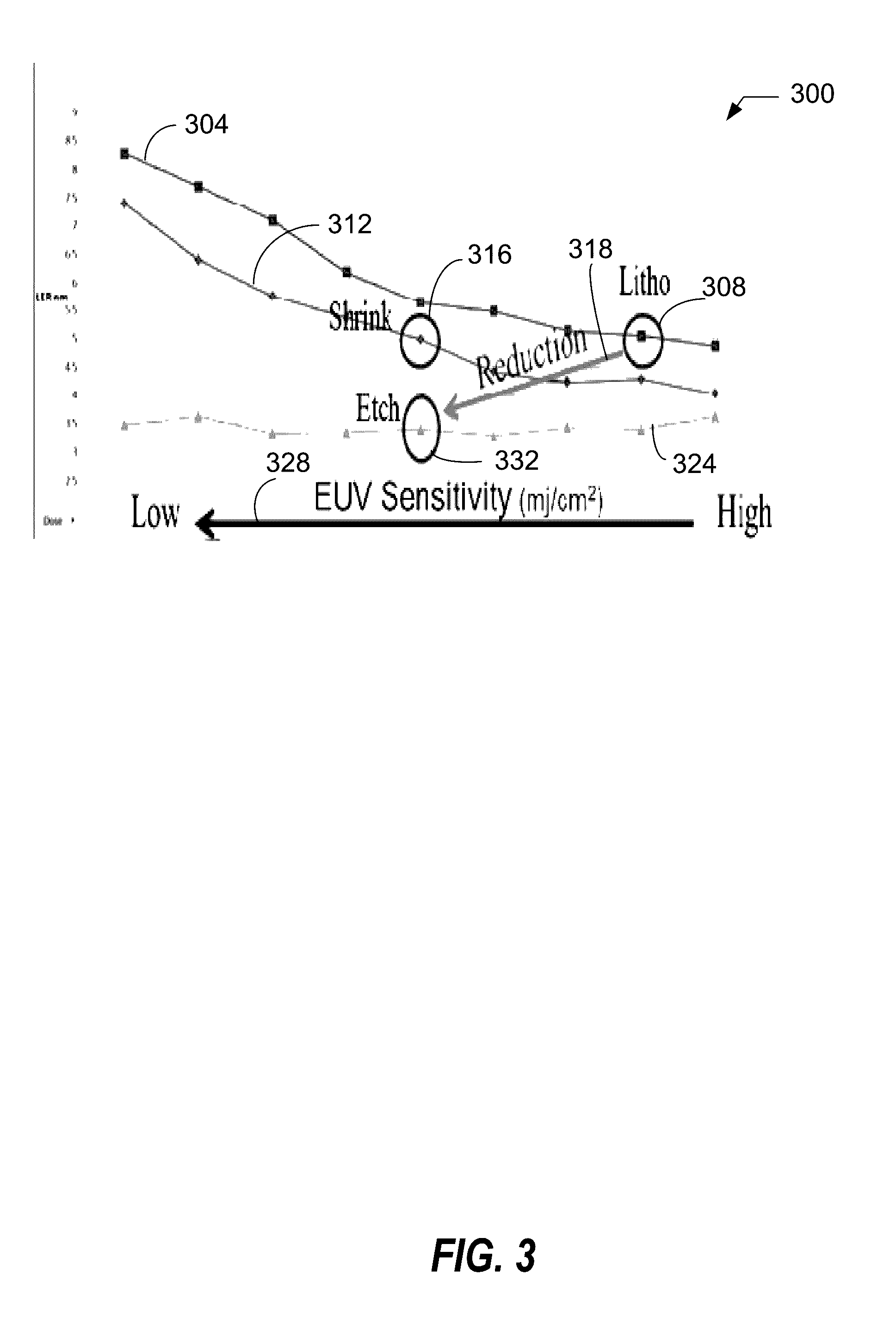
Extreme ultra-violet sensitivity reduction using shrink and growth method
ActiveUS20160334709A1Substrate throughput can be increasedImprove throughputPhotomechanical exposure apparatusPhotosensitive material processingCooking & bakingLine width
Provided is a method for patterning a substrate, comprising: forming a layer of radiation-sensitive material on a substrate; preparing a pattern in the layer of radiation-sensitive material using a lithographic process, the pattern being characterized by a critical dimension (CD) and a roughness; following the preparing the pattern, performing a CD shrink process to reduce the CD to a reduced CD; and performing a growth process to grow the reduced CD to a target CD. Roughness includes a line edge roughness (LER), a line width roughness (LWR), or both LER and LWR. Performing the CD shrink process comprises: coating the pattern with a hard mask, the coating generating a hard mask coated resist; baking the hard mask coated resist in a temperature range for a time period, the baking generating a baked coated resist; and developing the baked coated resist in deionized water.
Owner:TOKYO ELECTRON LTD
Substrate processing method
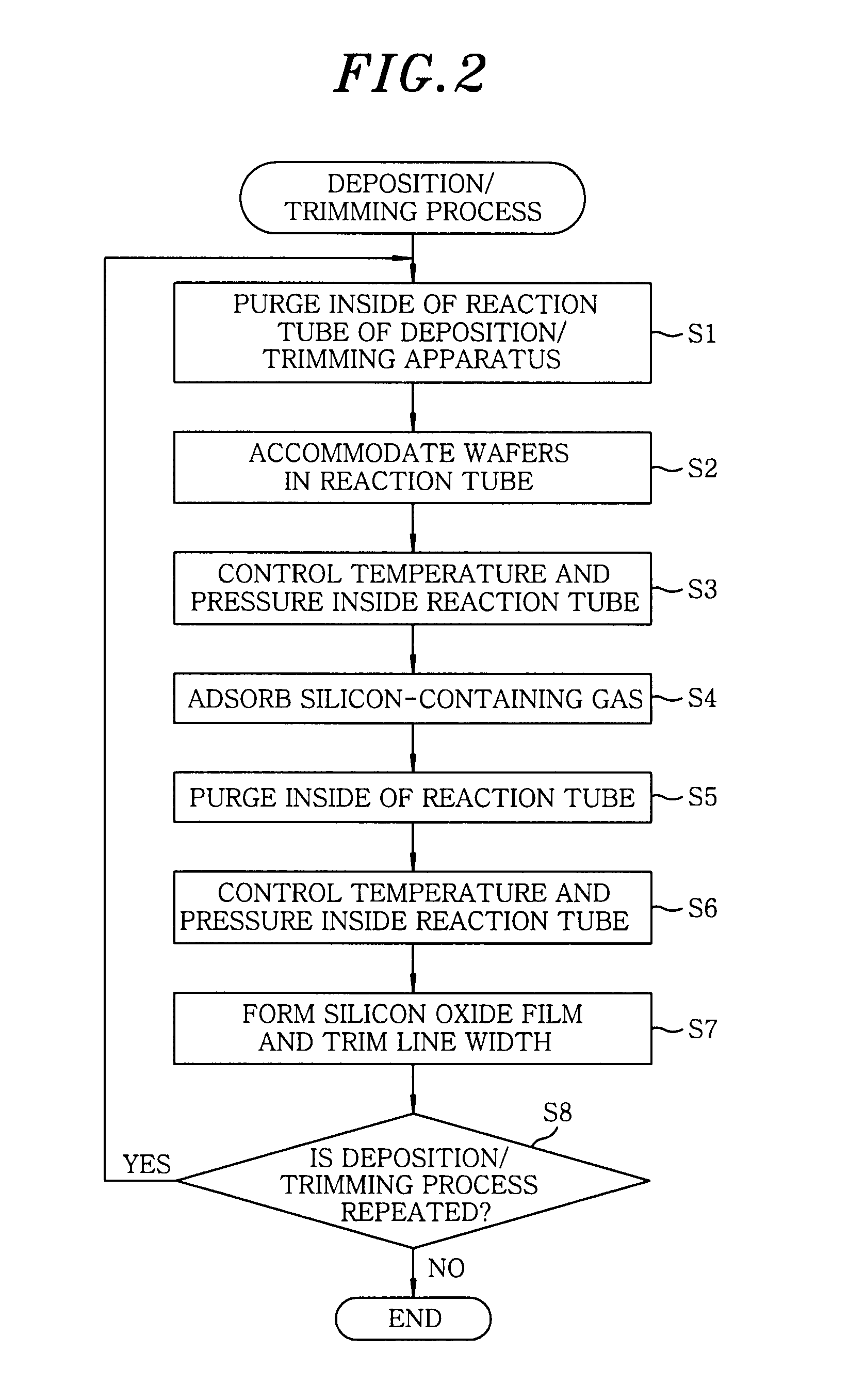
ActiveUS20100233885A1Electric discharge tubesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingOrganic filmLine width
A method for processing a substrate including a processing target layer and an organic film, include: a deposition / trimming process of forming a reinforcement film on a surface of the organic film and, at the same time, trimming a line width of a line portion of the organic film constituting an opening pattern. The deposition / trimming process includes an adsorption process for allowing a silicon-containing gas to be adsorbed onto the surface of the organic film and an oxidation process in which the line width of the organic film is trimmed while the adsorbed silicon-containing gas is converted into a silicon oxide film. A monovalent aminosilane is employed as the silicon-containing gas.
Owner:TOKYO ELECTRON LTD
Methods and apparatus for controlling photoresist line width roughness with enhanced electron spin control
InactiveUS20120318773A1Easy to moveLiquid surface applicatorsElectric discharge tubesPhotoresistLine width
The present invention provides methods and an apparatus for controlling and modifying line width roughness (LWR) of a photoresist layer with enhanced electron spinning control. In one embodiment, an apparatus for controlling a line width roughness of a photoresist layer disposed on a substrate includes a processing chamber having a chamber body having a top wall, side wall and a bottom wall defining an interior processing region, a support pedestal disposed in the interior processing region of the processing chamber, and a plasma generator source disposed in the processing chamber operable to provide predominantly an electron beam source to the interior processing region.
Owner:APPLIED MATERIALS INC
Method for improving optical proximity correction
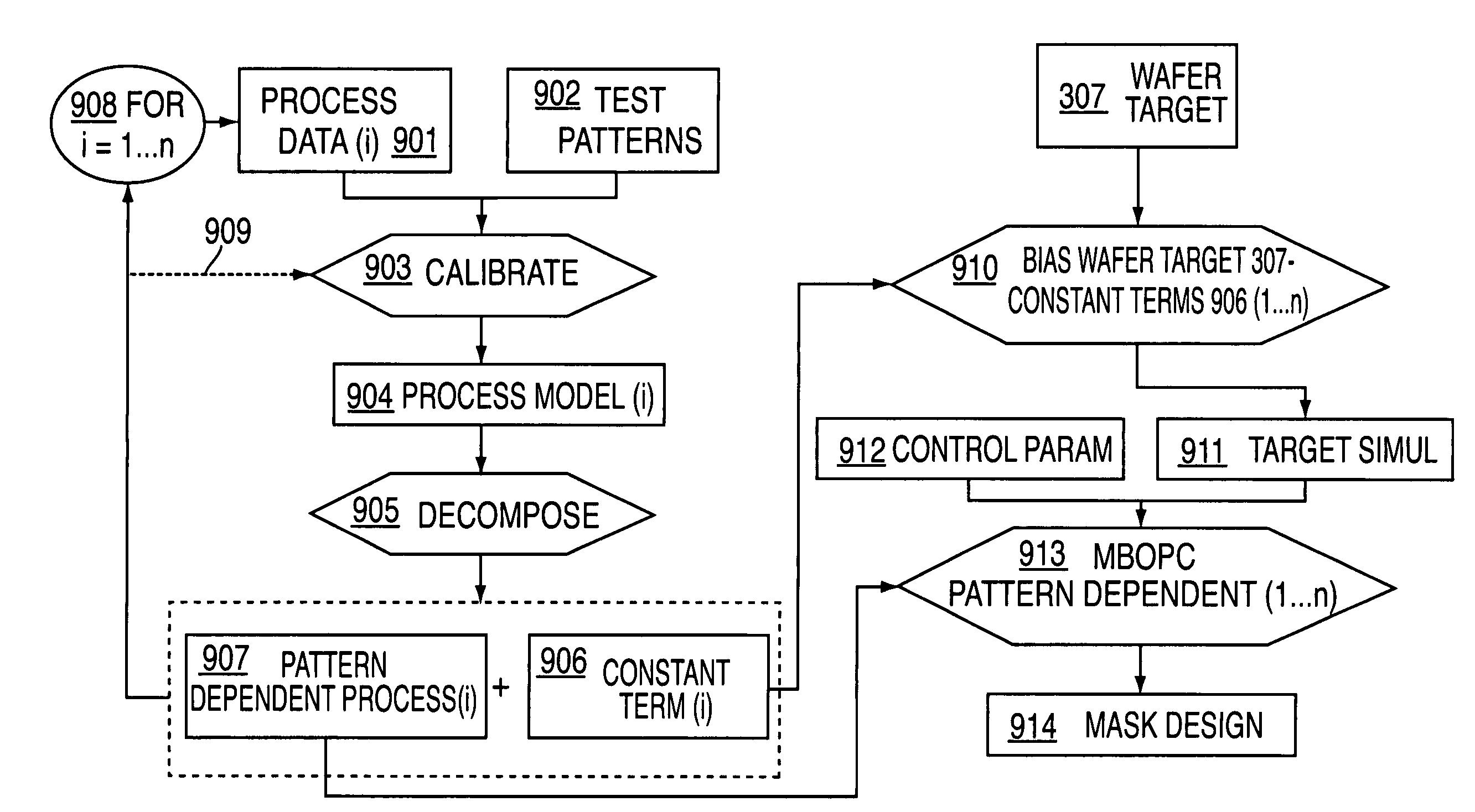
ActiveUS7350183B2Improve variationDefect minimizationPhotomechanical apparatusOriginals for photomechanical treatmentLine widthComputer science
Owner:GLOBALFOUNDRIES U S INC
Spectroscopically measured overlay target
InactiveUS7061615B1Adequate fitEasy to measureSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesImage resolutionLine width
An overlay target for spectroscopic measurement includes at least two diffraction gratings, one grating overlying the other. The diffraction gratings may include an asymmetry relative to each other in order to improve resolution of the presence as well as the direction of any mis-registration. For example, the asymmetry between the two diffraction gratings may be a phase offset, a difference in pitch, line width, etc. The overlay target may be spectroscopically measuring, for example, using an optical model and a best fit analysis. Moreover, the overlay target may be optimized by modeling the overlay target and adjusting the variable parameters and calculating the sensitivity of the overlay target to changes in variable parameters.
Owner:ONTO INNOVATION INC
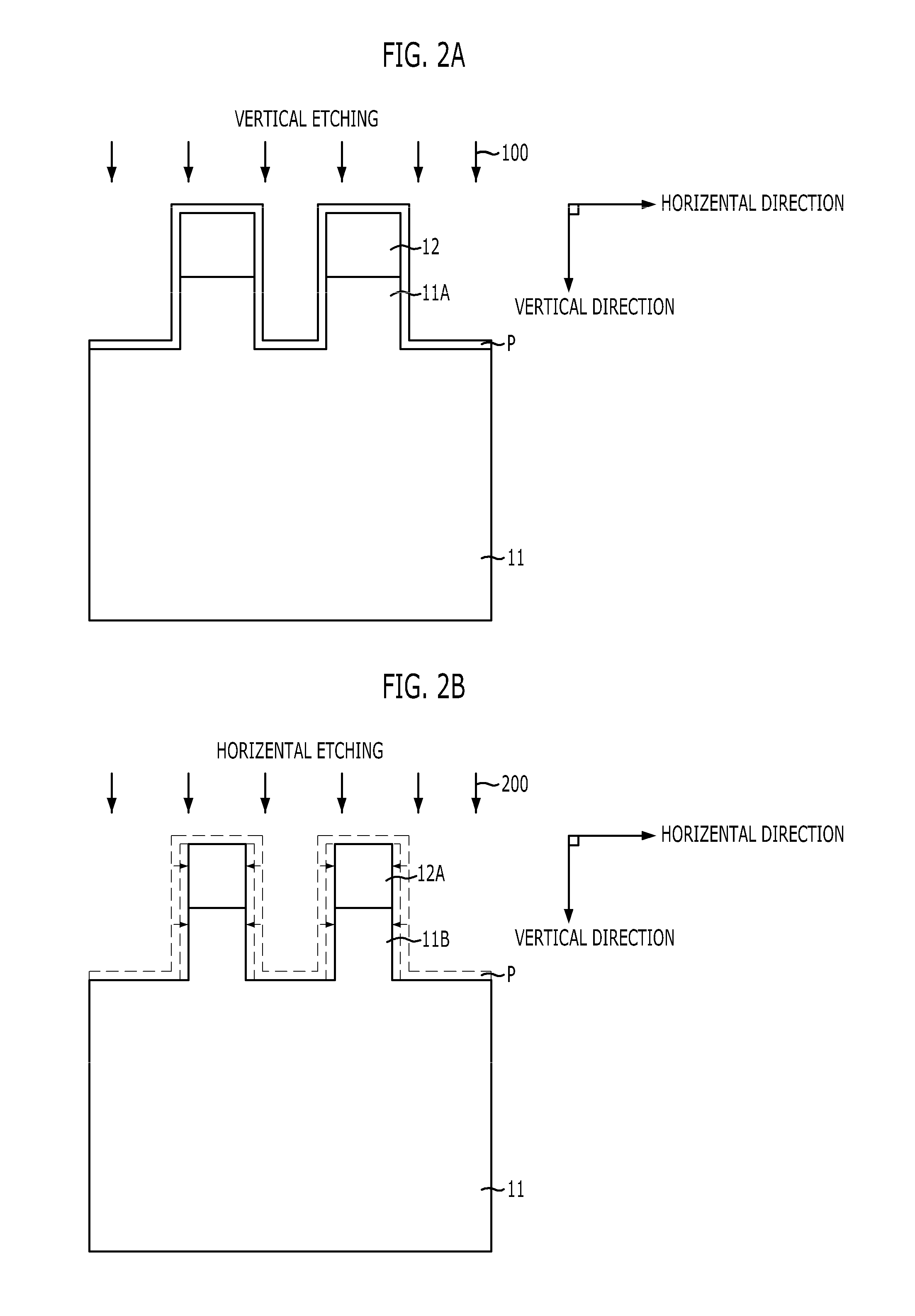
Method for forming active pillar of vertical channel transistor
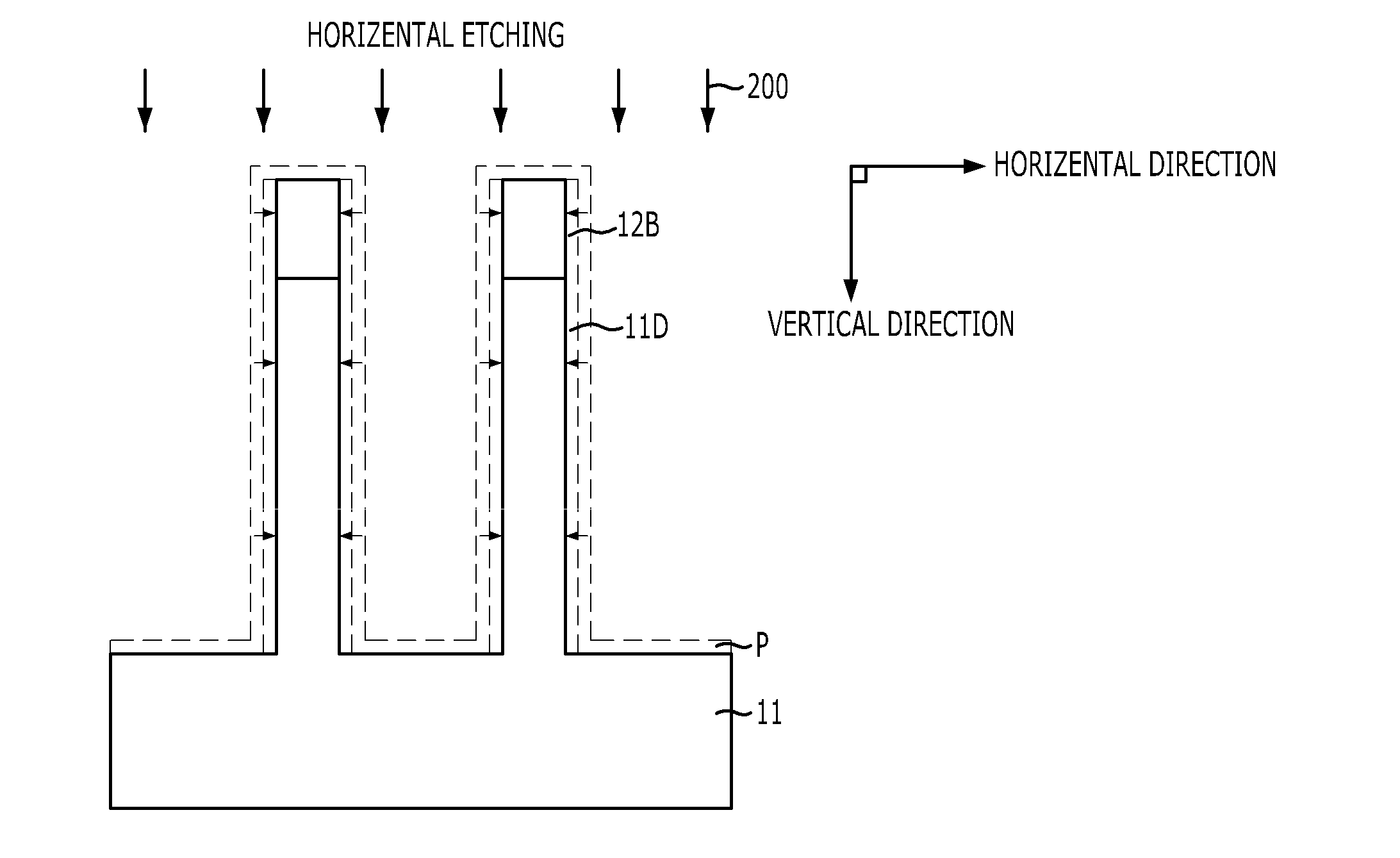
ActiveUS20100055917A1Reduce horizontal widthOvercome limitationsSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSemiconductor devicesEtchingLine width
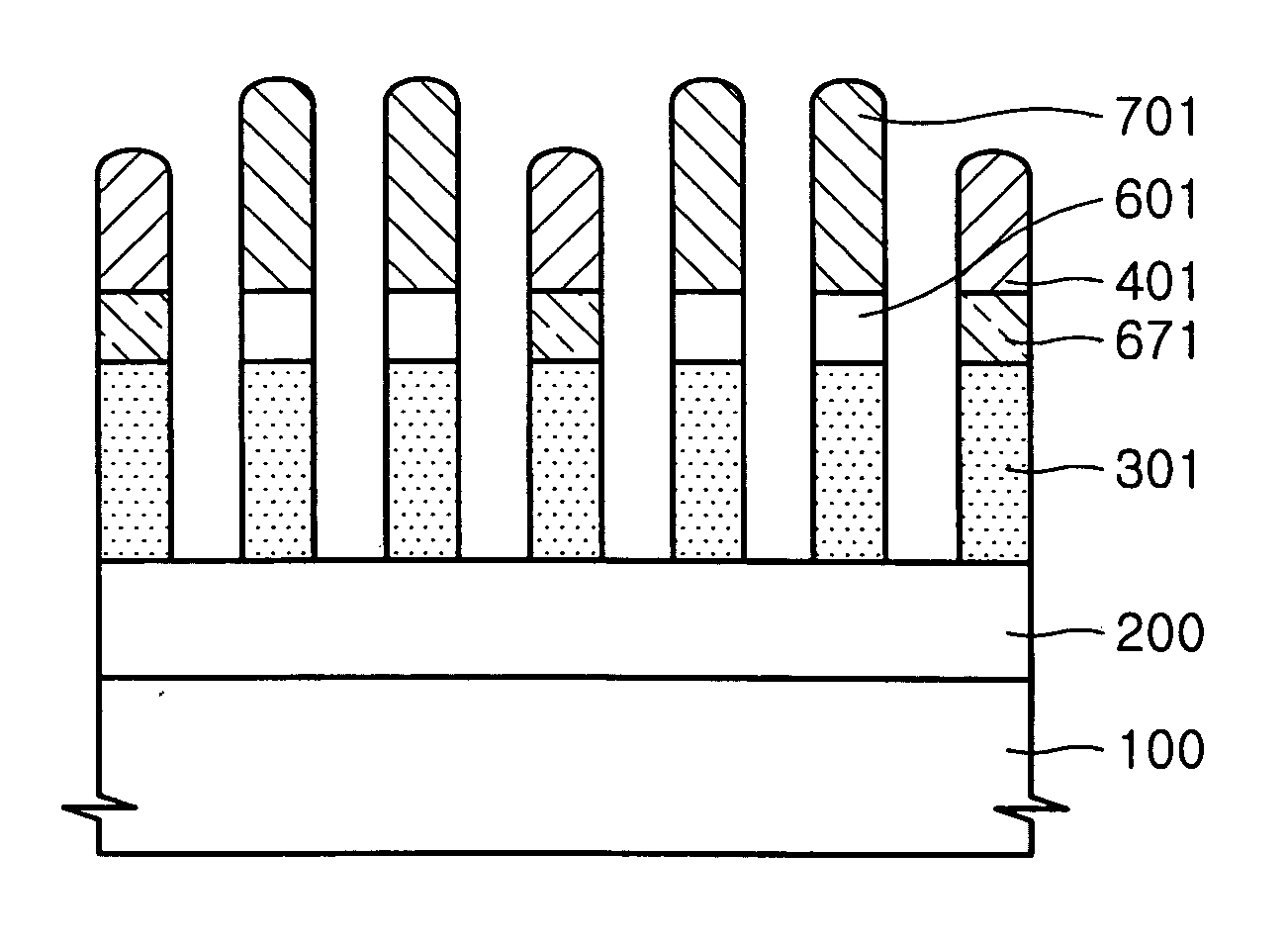
A method for forming an active pillar of a vertical channel transistor includes forming a hard mask pattern on a substrate, etching vertically the substrate using the hard mask pattern as an etch barrier to form an active pillar, and etching horizontally to remove by-product remaining on the exposed substrate, the hard mask pattern and the active pillar and at the same time to reduce line width of the hard mask pattern and the active pillar, wherein a unit cycle in which the vertical etching and the horizontal etching are each performed subsequently once, respectively, is performed repeatedly at least two times or more. According to the present invention, an active pillar having vertical profiles on its sidewalls and having height and line width (or diameter) required in a highly integrated vertical channel transistor can be provided.
Owner:SK HYNIX INC
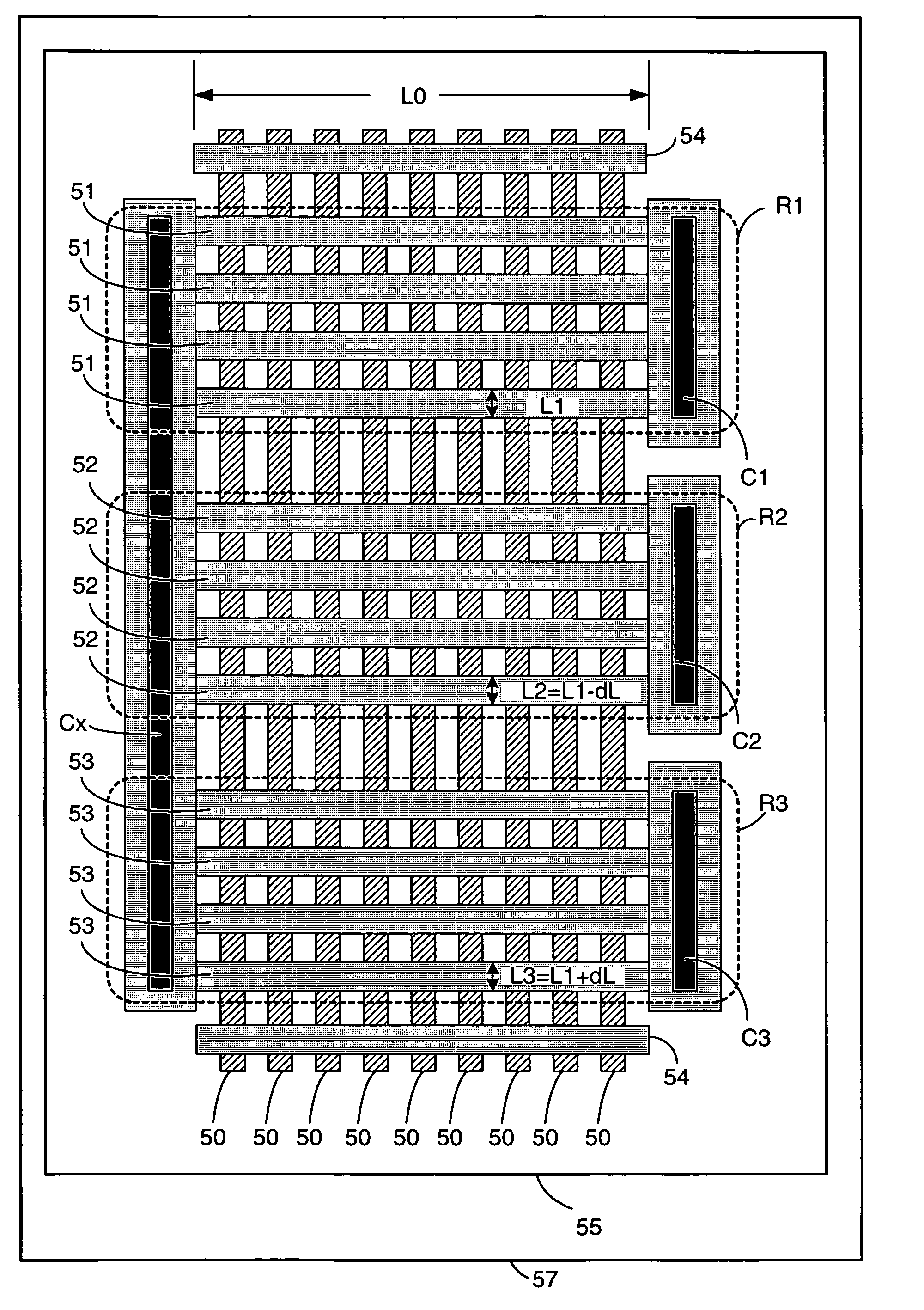
Polysilicon conductor width measurement for 3-dimensional FETs
InactiveUS7227183B2Sure easyImprove accuracyTransistorSemiconductor/solid-state device testing/measurementElectrical resistance and conductanceElectrical conductor
An apparatus and method is disclosed for determining polysilicon conductor width for 3-dimensional field effect transistors (FinFETs). Two or more resistors are constructed using a topology in which polysilicon conductors are formed over a plurality of silicon “fins”. A first resistor has a first line width. A second resistor has a second line width. The second line width is slightly different than the first line width. Advantageously, the first line width is equal to the nominal design width used to make FET gates in the particular semiconductor technology. Resistance measurements of the resistors and subsequent calculations using the resistance measurements are used to determine the actual polysilicon conductor width produced by the semiconductor process. A composite test structure not only allows calculation of the polysilicon conductor width, but provides proof that differences in the widths used in the calculations do not introduce objectionable etching characteristics of the polysilicon conductors.
Owner:IBM CORP
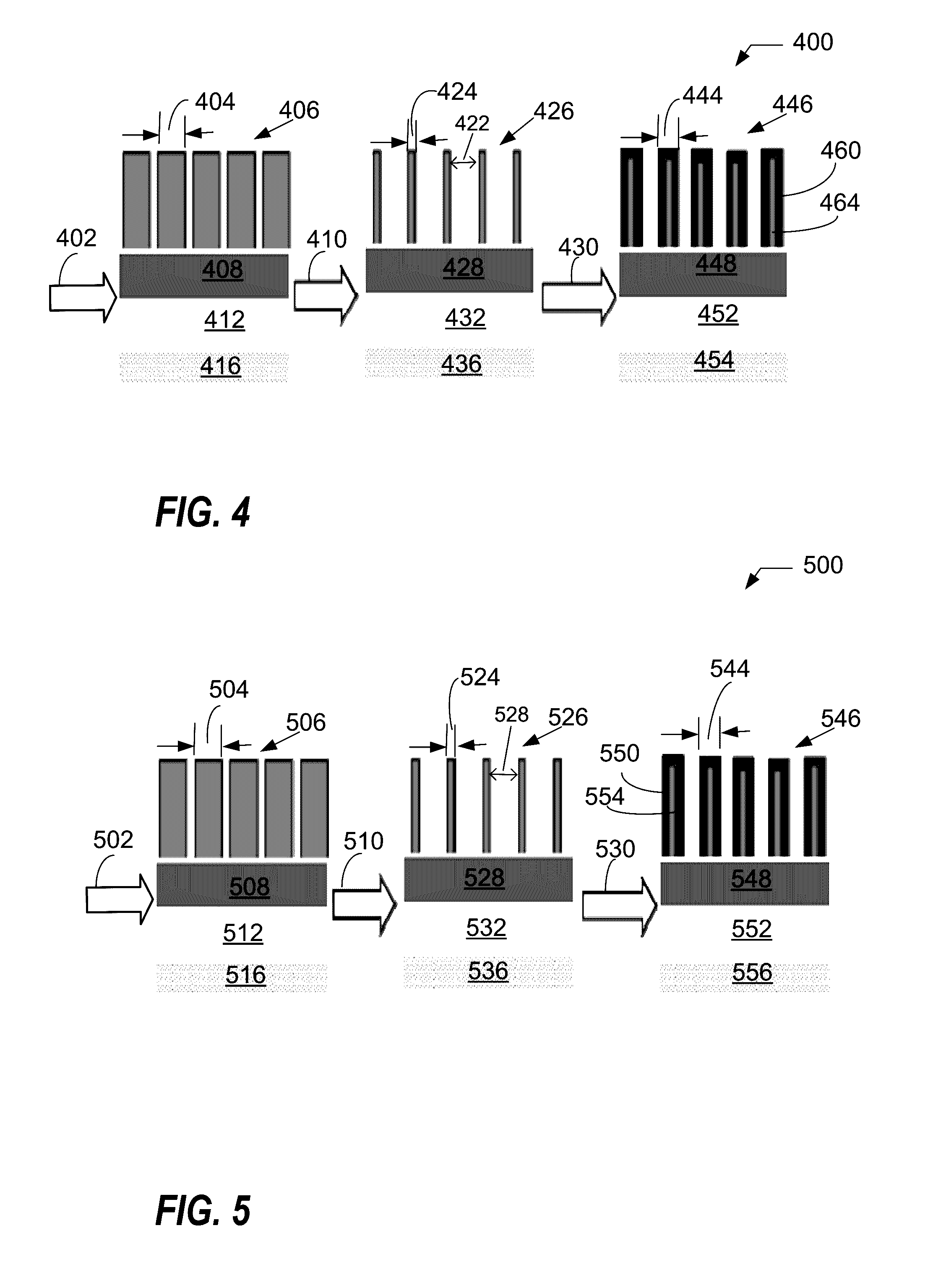
Method of forming a pattern in a semiconductor device and method of forming a gate using the same
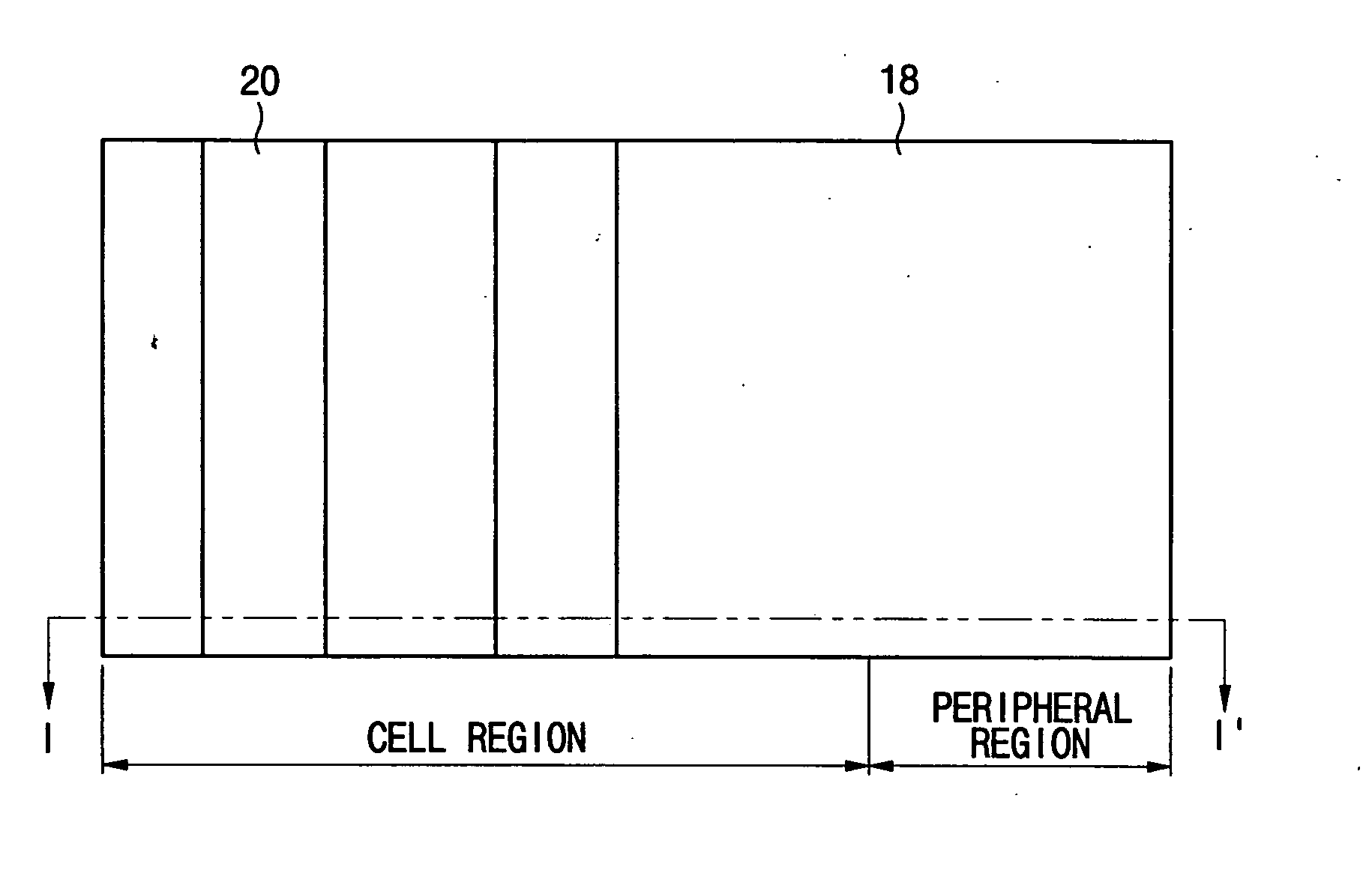
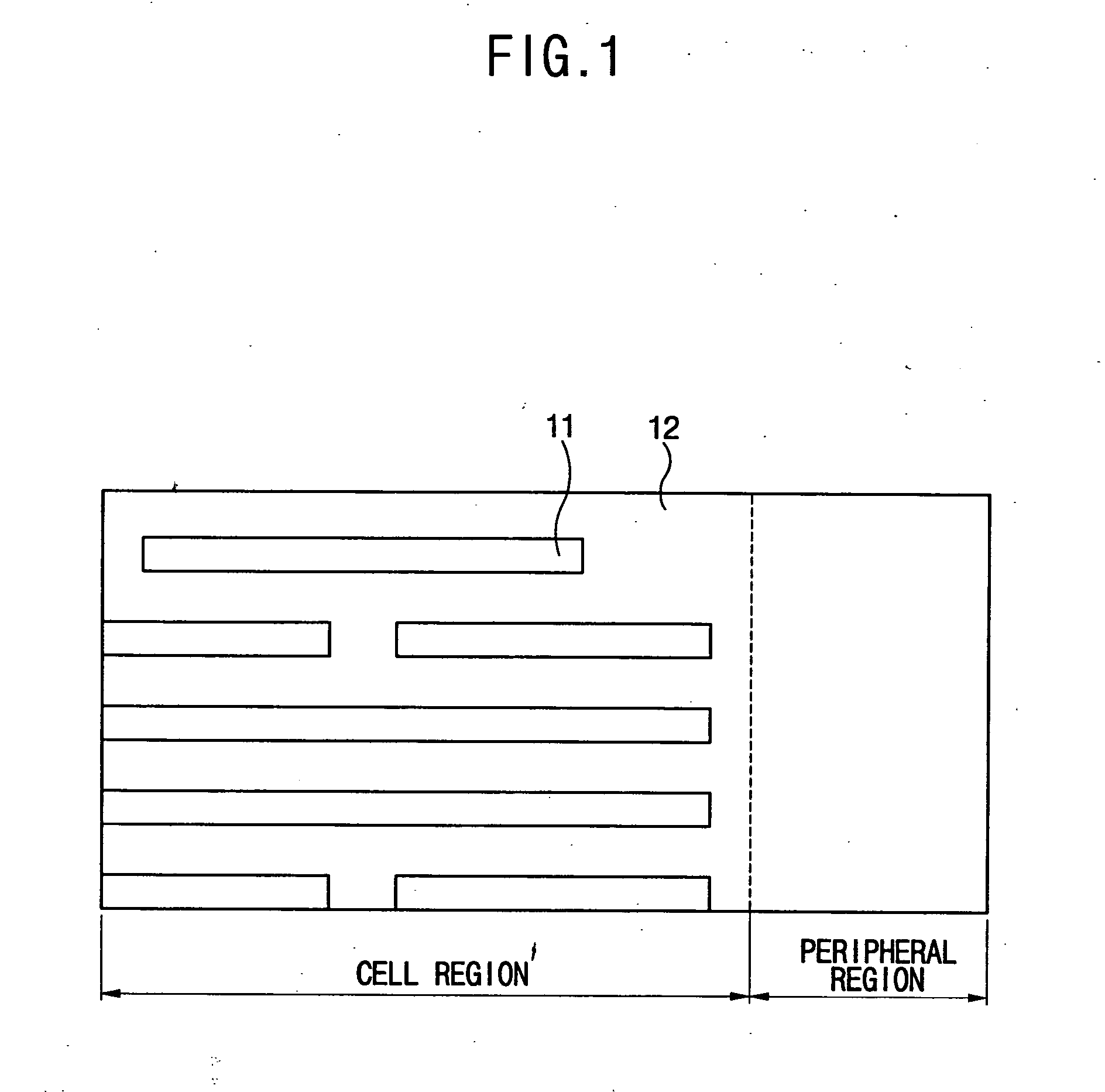
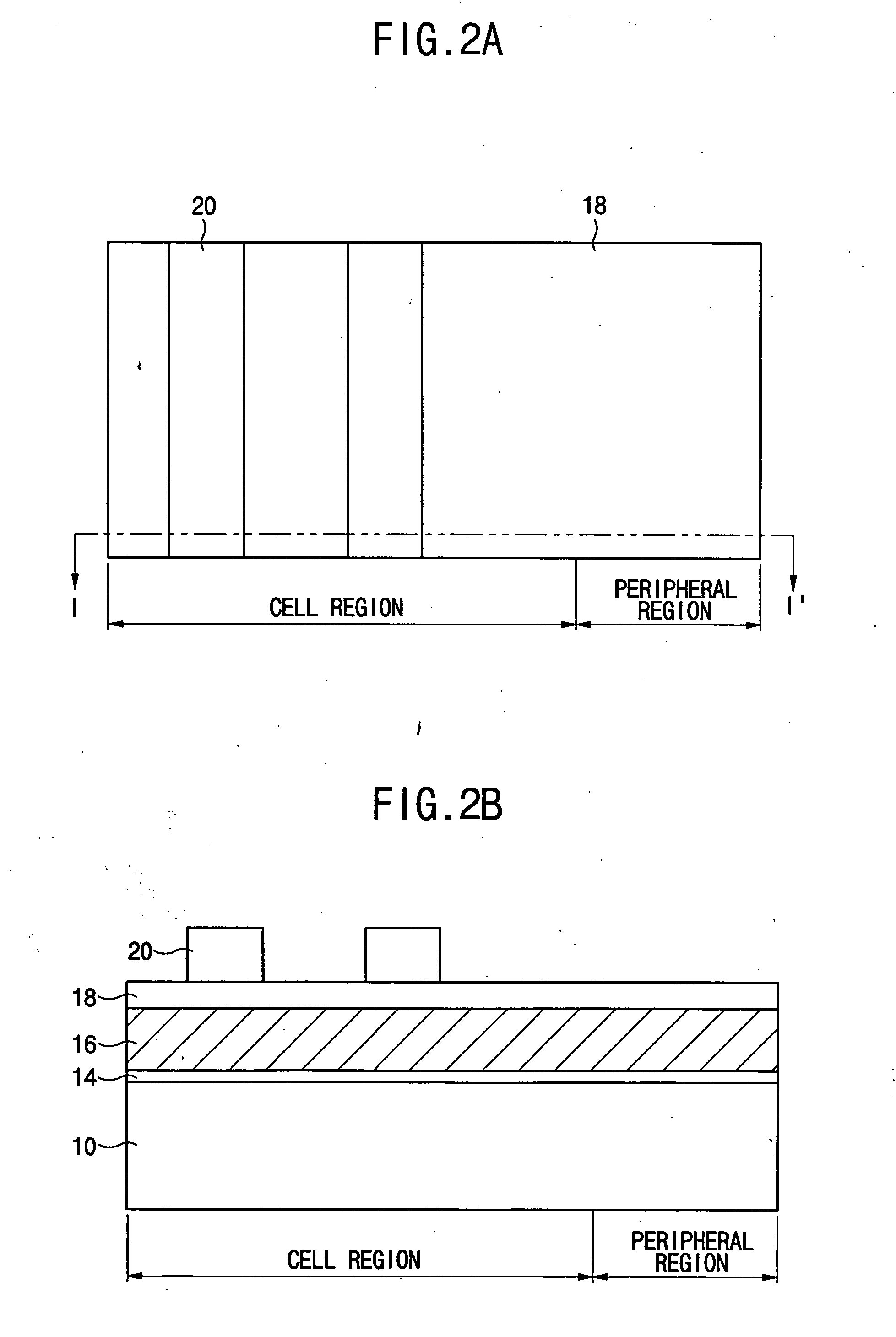
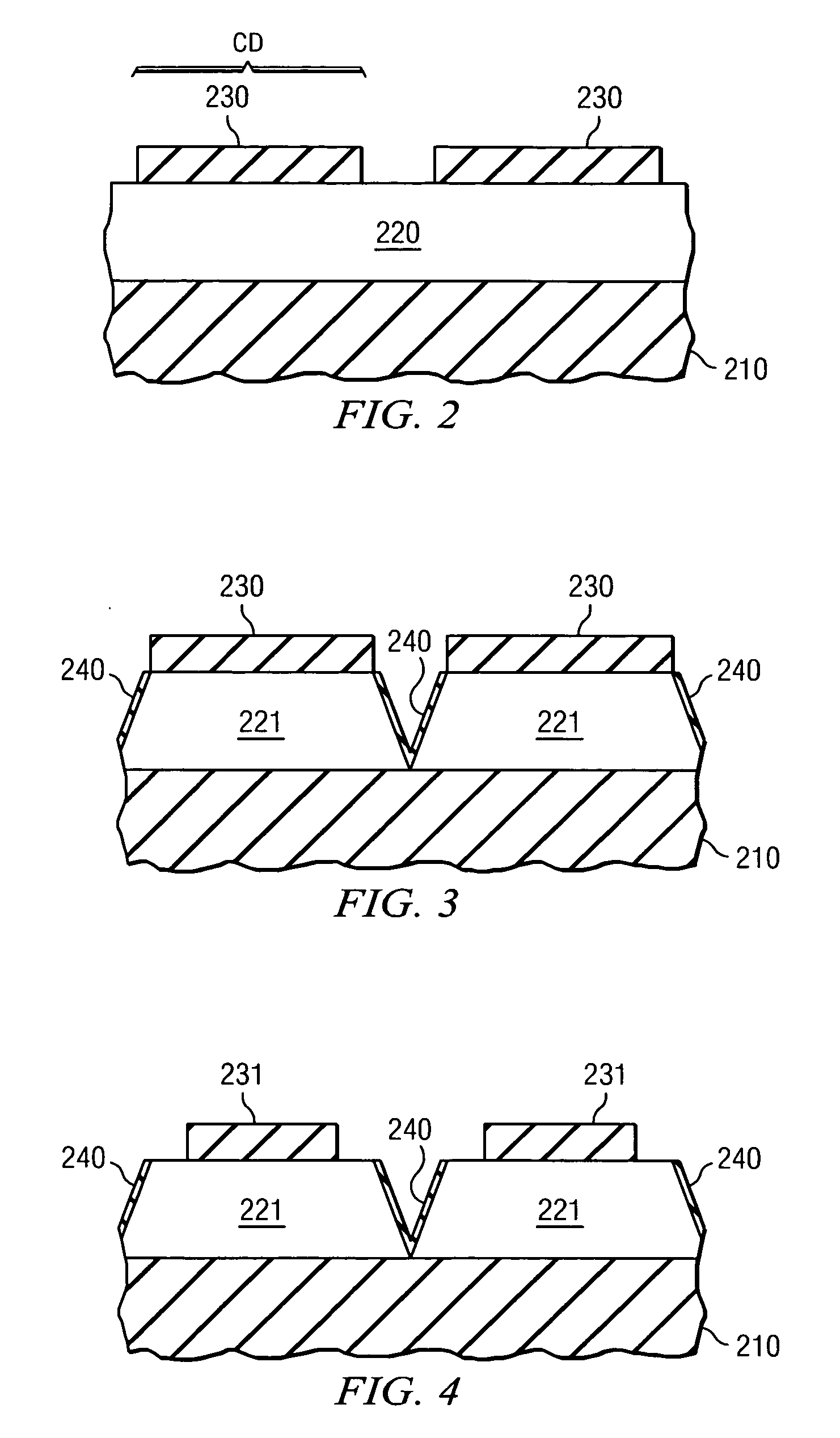
InactiveUS20050142497A1Small line widthLine width variationPhotomechanical apparatusSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingDevice materialCell region
A method of forming a pattern in a semiconductor device is described. A substrate divided into cell and peripheral regions is provided, and an object layer is formed on a substrate. A buffer pattern is formed on the object layer in the cell region along a first direction. A spacer is formed along a sidewall of the buffer pattern in the cell region, and a hard mask layer remains on the object layer in the peripheral region. The buffer layer is removed, and the spacer is separated along a second direction different from the first direction, thereby forming a cell hard mask pattern. A peripheral hard mask pattern is formed in the peripheral region. A minute pattern is formed using the cell and peripheral hard mask patterns in the substrate. Therefore, a line width variation or an edge line roughness due to the photolithography process is minimized.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
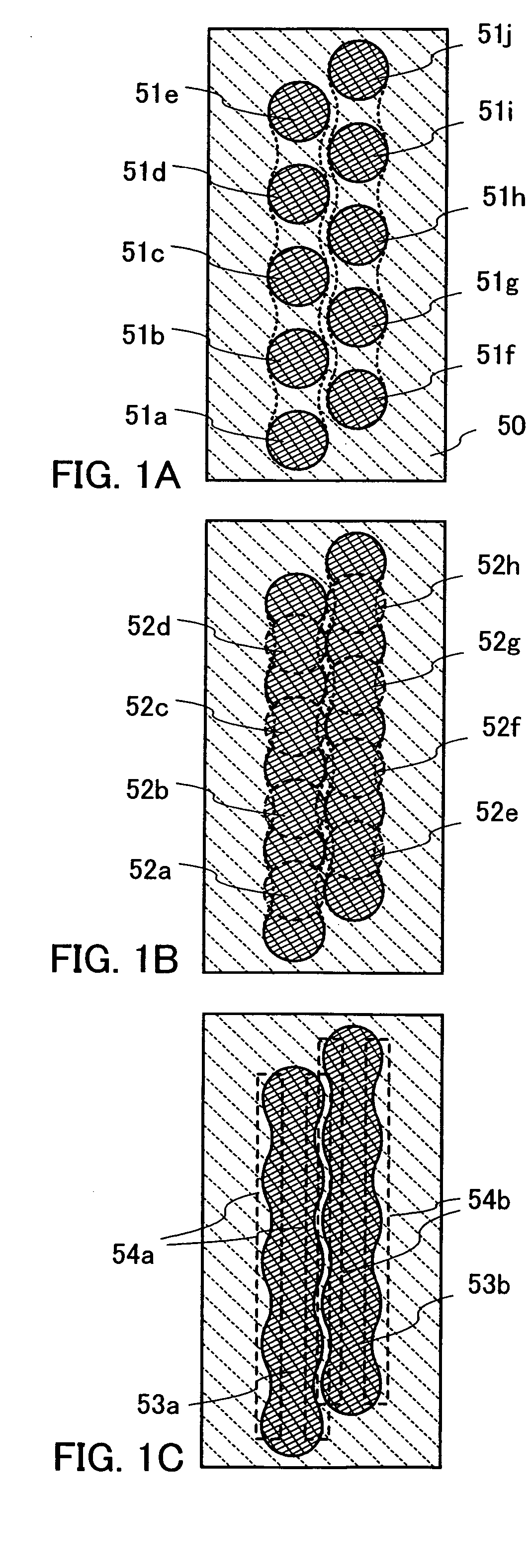
Apparatus and methods for forming film pattern
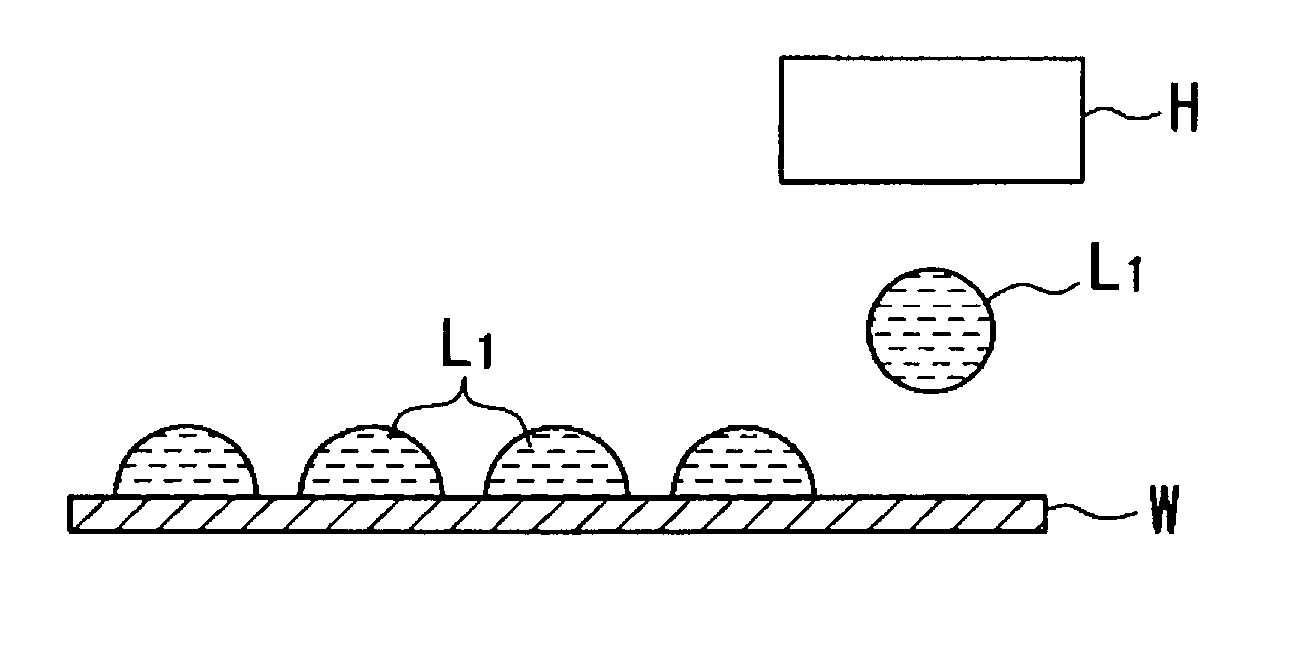
The invention provides a method for forming a film pattern, in which a method for forming a film pattern by the ink-jet method is improved, an increase in film thickness is achieved efficiently with simple steps, a requirement for a decrease in line width is met and, in addition, problems such as breaks and short circuits are not brought about when a conductive film is made. The method can include a first discharging step, wherein droplets are discharged in the whole film formation region with a pitch larger than the diameter of the droplet after being hit onto the substrate. In the second discharging step, droplets are discharged at positions in the whole film formation region different from the discharge positions in the first discharging step with the same pitch as that in the first discharging step. In the third discharging step, droplets are discharged in the whole film formation region with a pitch smaller than the pitch in the first discharging step. The substrate is treated beforehand in order to have the contact angle of 60 degrees or more with respect to the droplets.
Owner:SEIKO EPSON CORP
Pitch multiplication process
ActiveUS7208379B2Solid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingLine widthOptoelectronics
Owner:TEXAS INSTR INC
Method of forming small pitch pattern using double spacers
ActiveUS20060240361A1Semiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingAuxillary members of forms/shuttering/falseworksLine widthEngineering
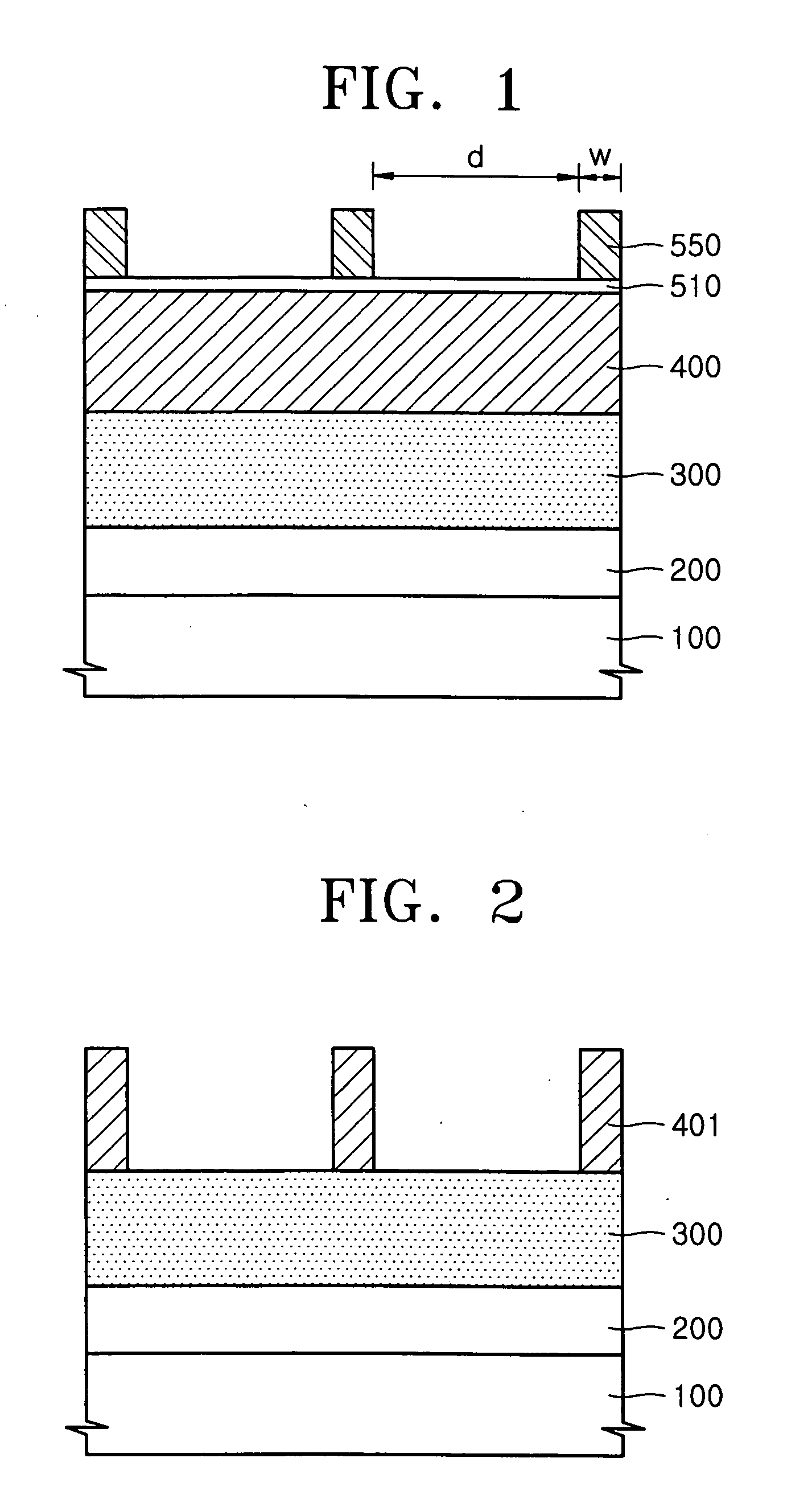
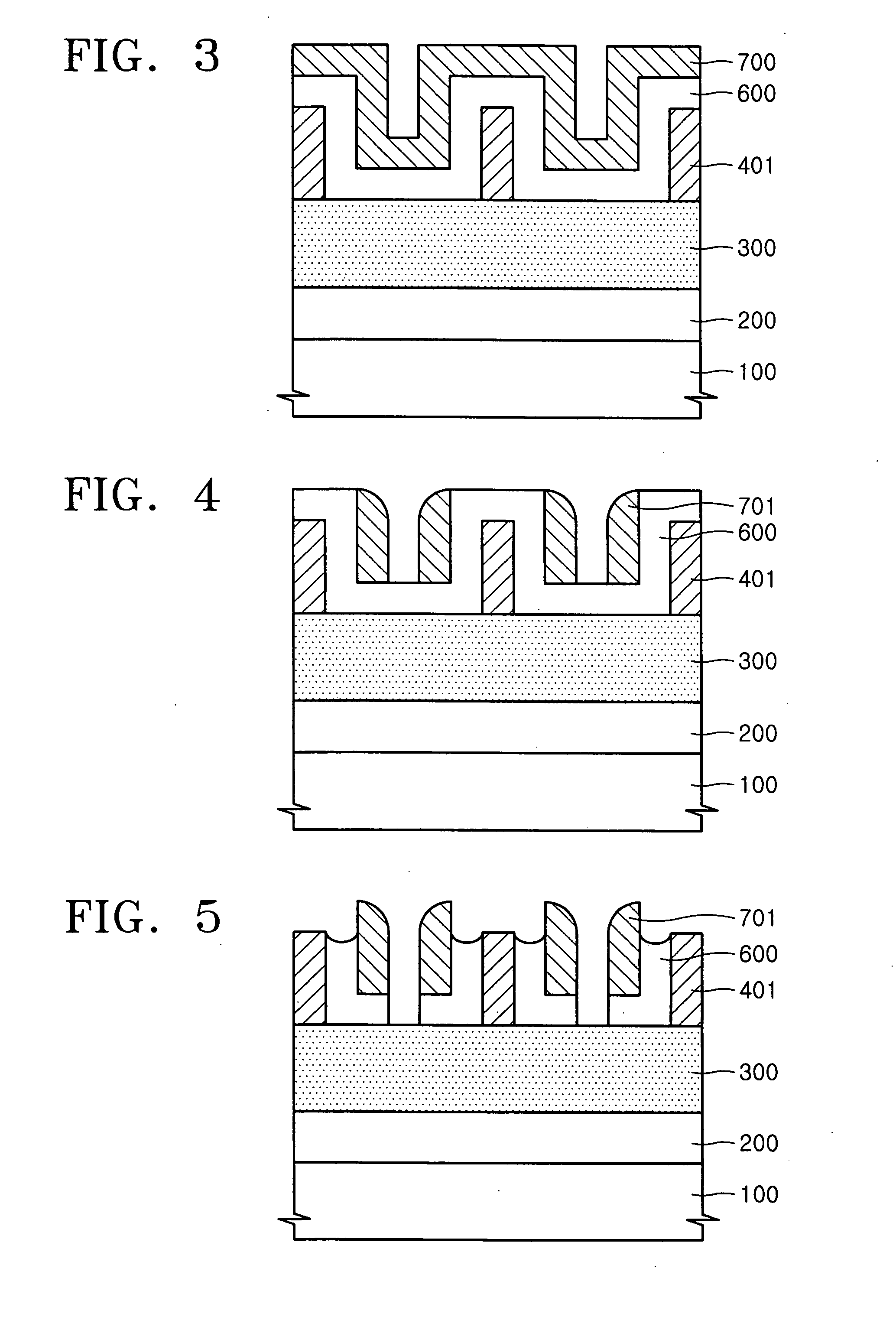
A method of forming a small pitch pattern using double spacers is provided. A material layer and first hard masks are used and characterized by a line pattern having a smaller line width than a separation distance between adjacent mask elements. A first spacer layer covering sidewall portions of the first hard mask and a second spacer layer are formed, and spacer-etched, thereby forming a spacer pattern-shaped second hard mask on sidewall portions of the first hard mask. A portion of the second spacer layer between the first hard mask and the second hard mask is selectively removed. The material layer is selectively etched using the first and second hard masks as etch masks, thereby forming the small pitch pattern.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Pattern forming method and semiconductor device manufacturing method
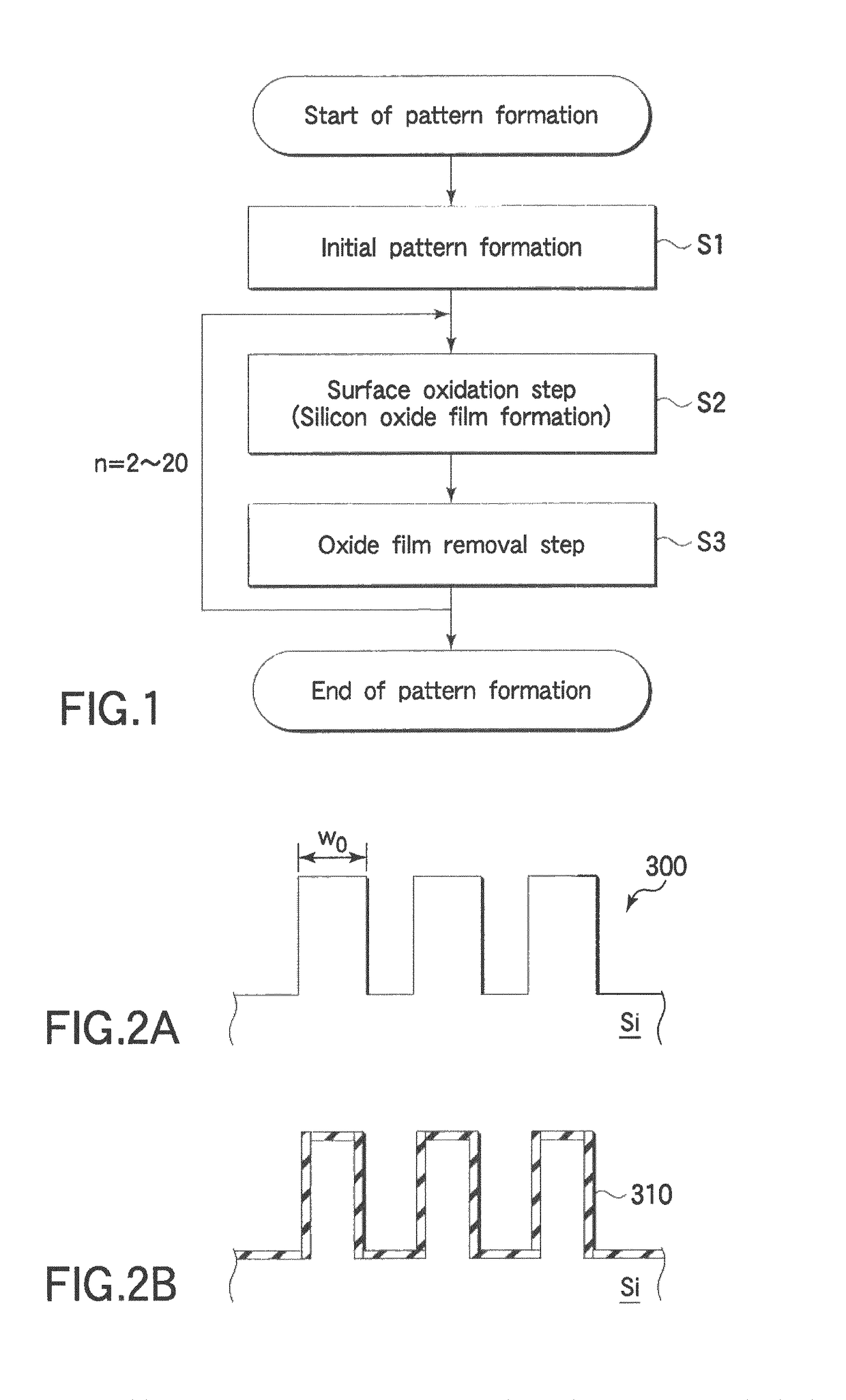
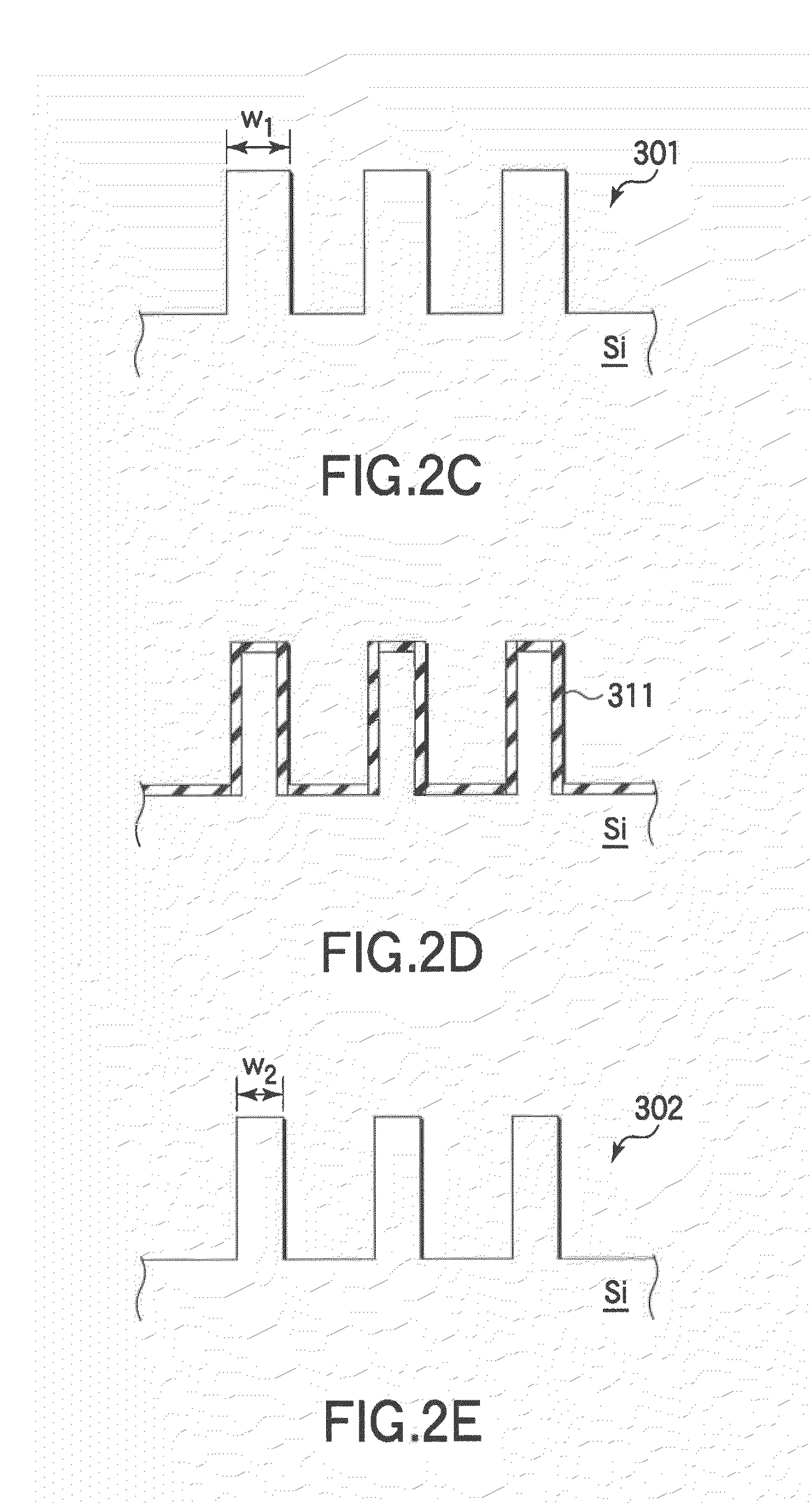
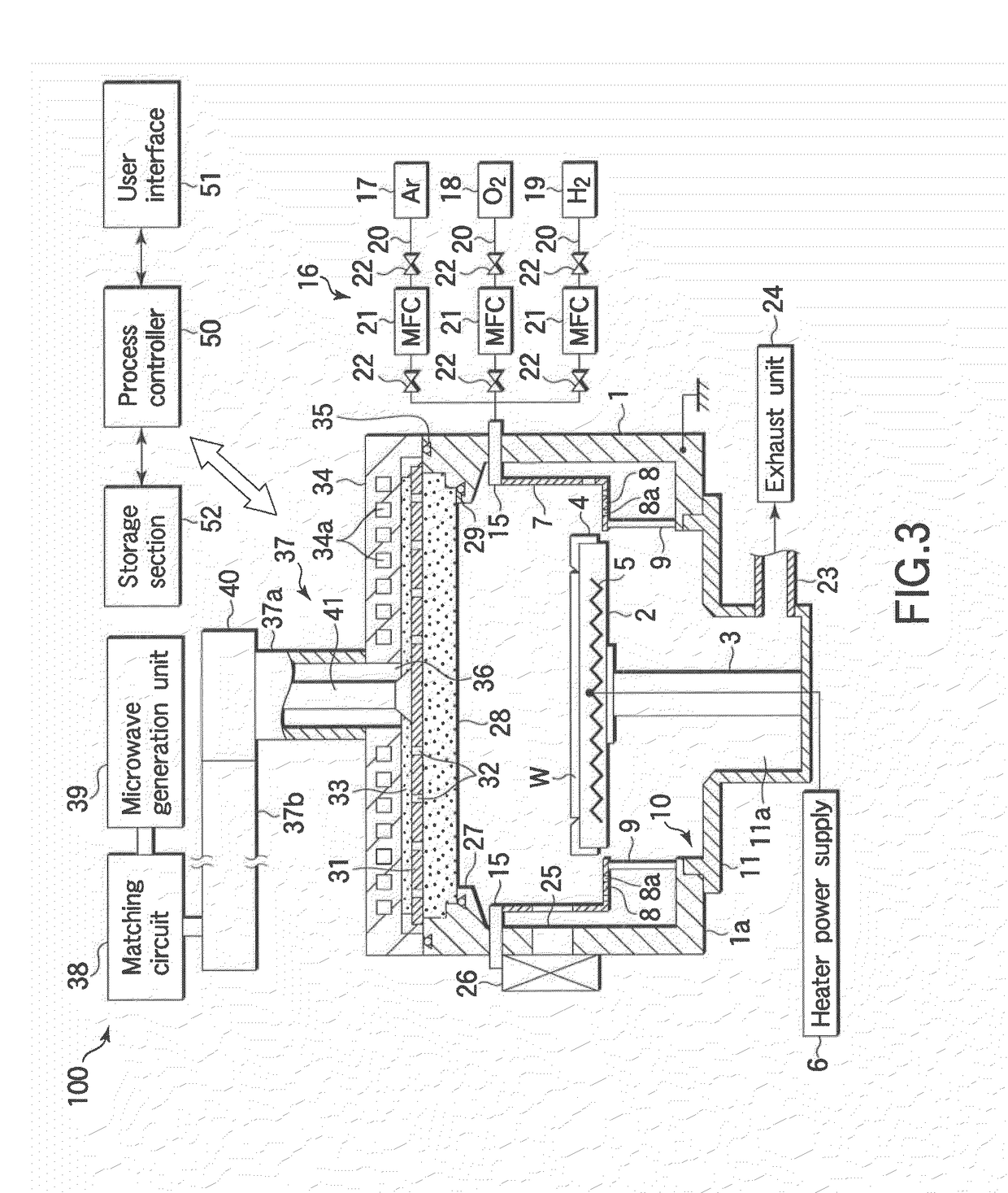
ActiveUS8119530B2Not easy to damageImprove film qualitySemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSemiconductor devicesLine widthSilicon oxide
A pattern forming method includes preparing a target object including silicon with an initial pattern formed thereon and having a first line width; performing a plasma oxidation process on the silicon surface inside a process chamber of a plasma processing apparatus and thereby forming a silicon oxide film on a surface of the initial pattern; and removing the silicon oxide film. The pattern forming method is arranged to repeatedly perform formation of the silicon oxide film and removal of the silicon oxide film so as to form an objective pattern having a second line width finer than the first line width on the target object.
Owner:NAGOYA UNIVERSITY +1
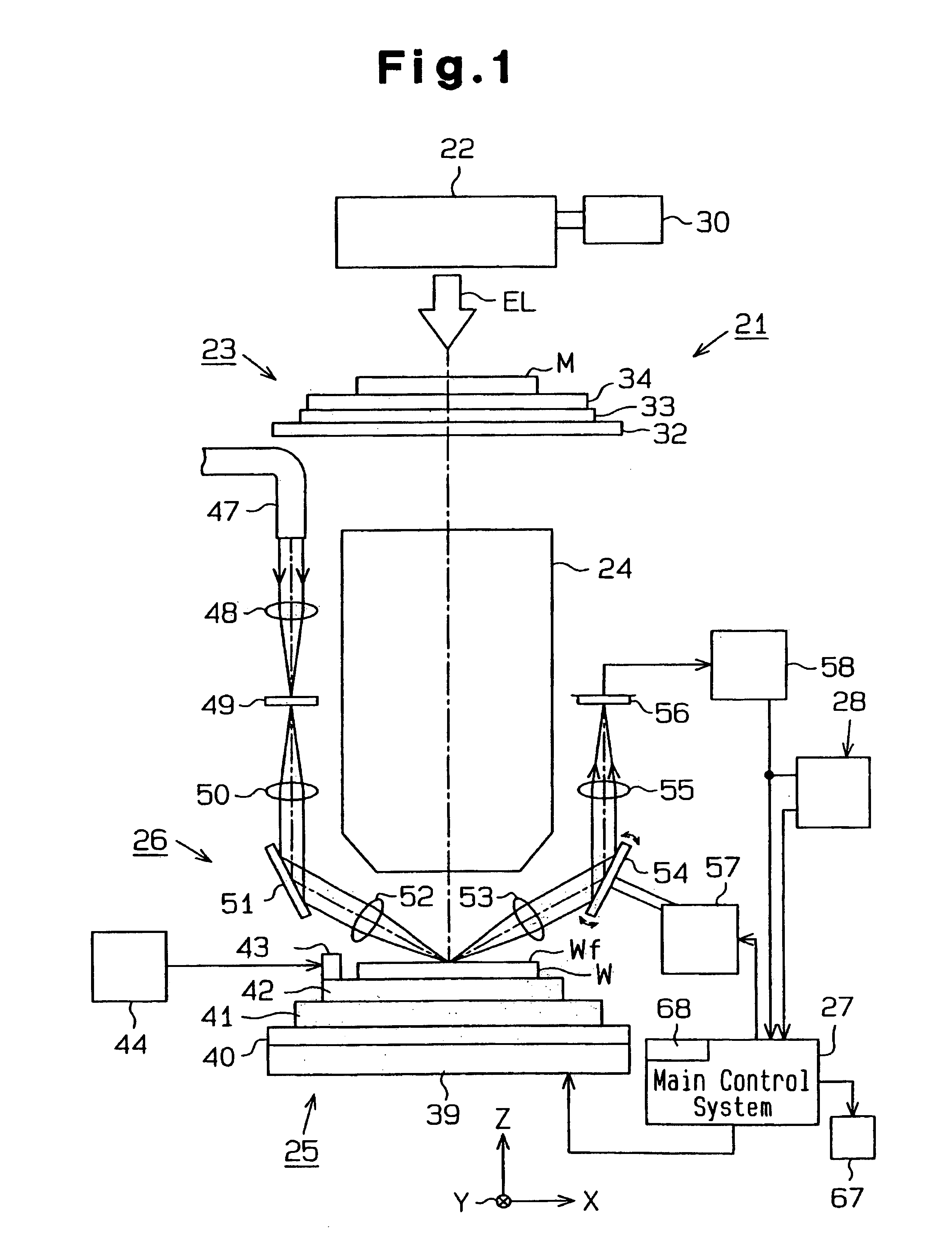
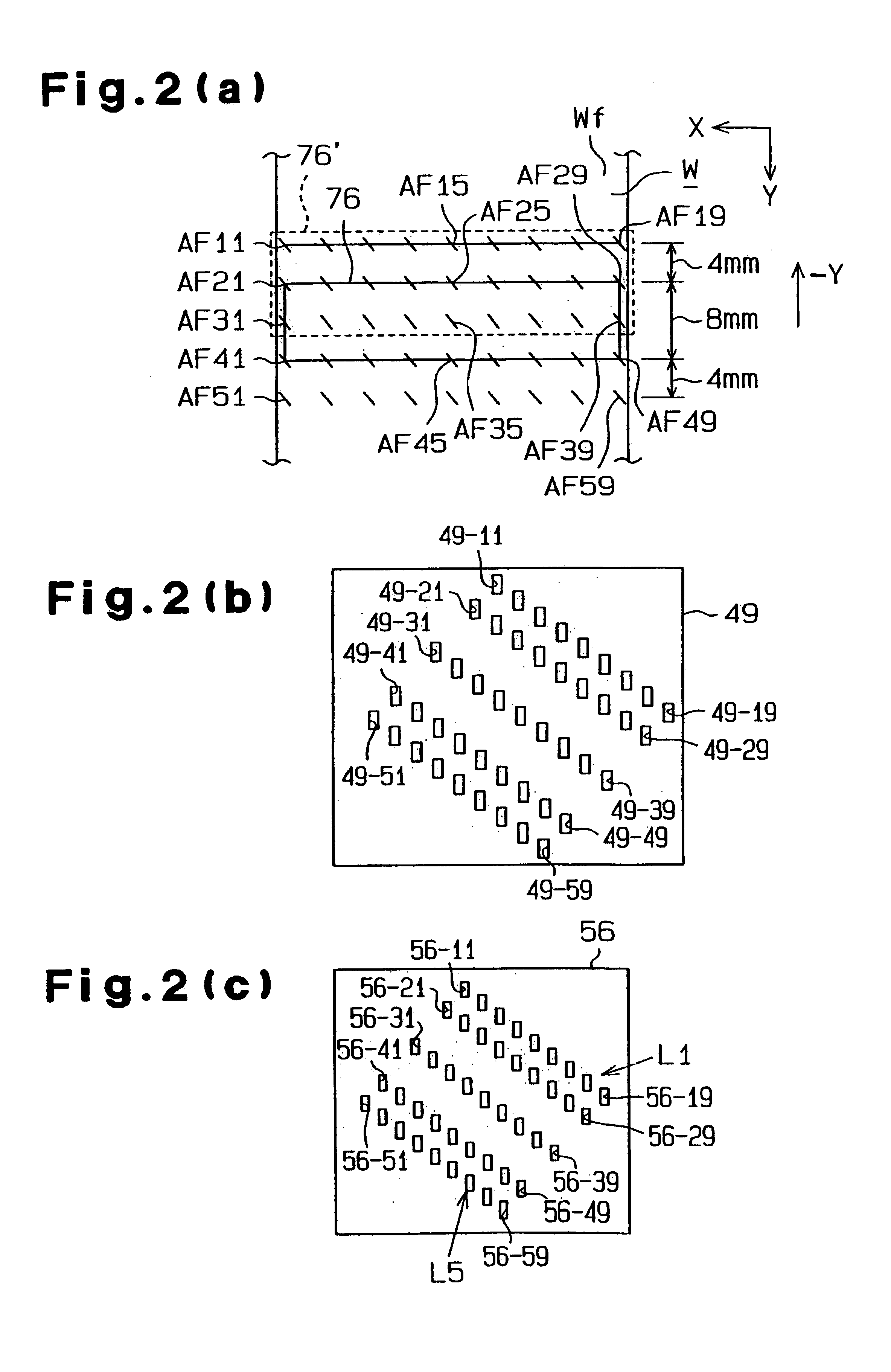
Scanning exposure apparatus
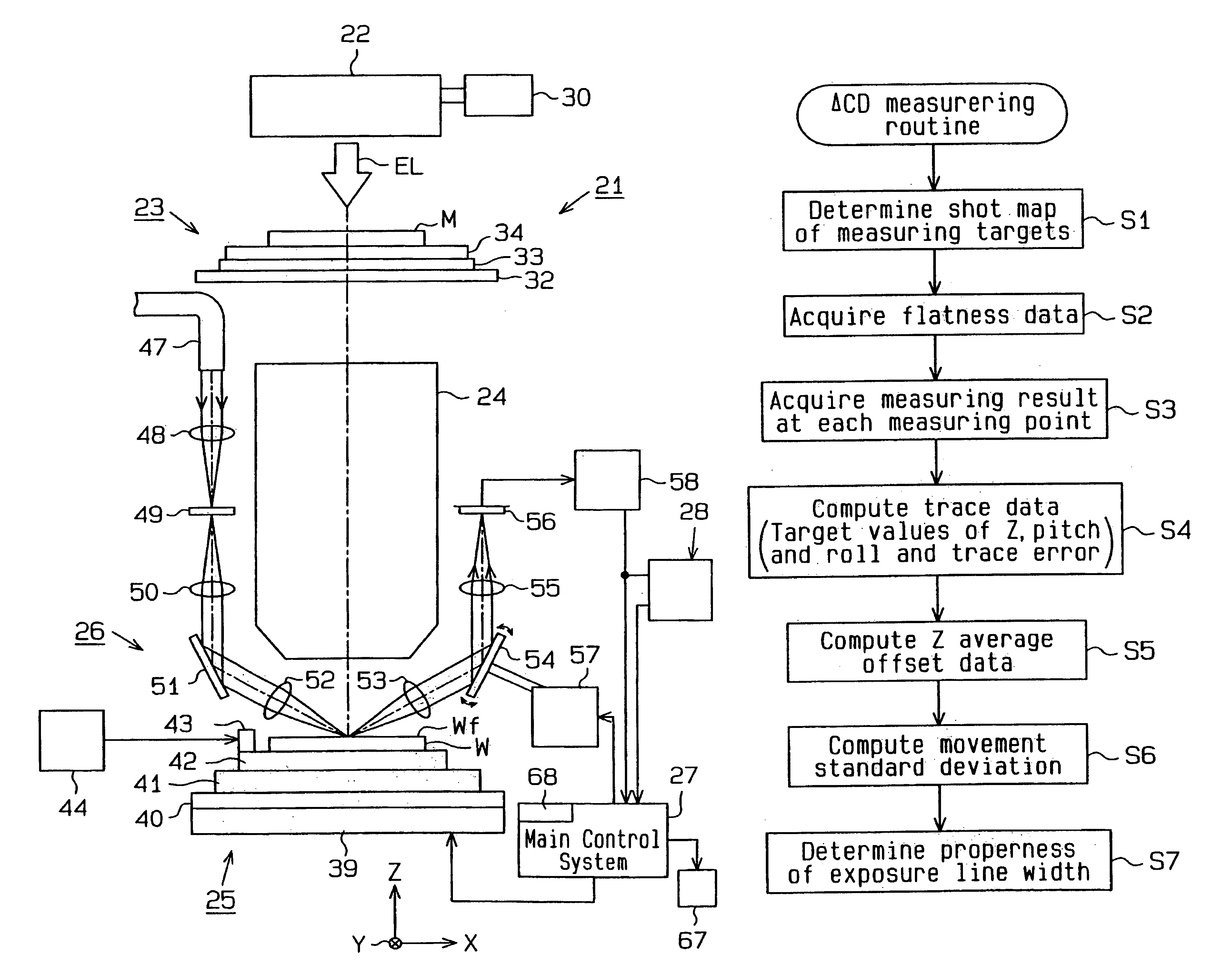
InactiveUS6992751B2Quick analysisUsing optical meansPhotomechanical exposure apparatusLine widthBiomedical engineering
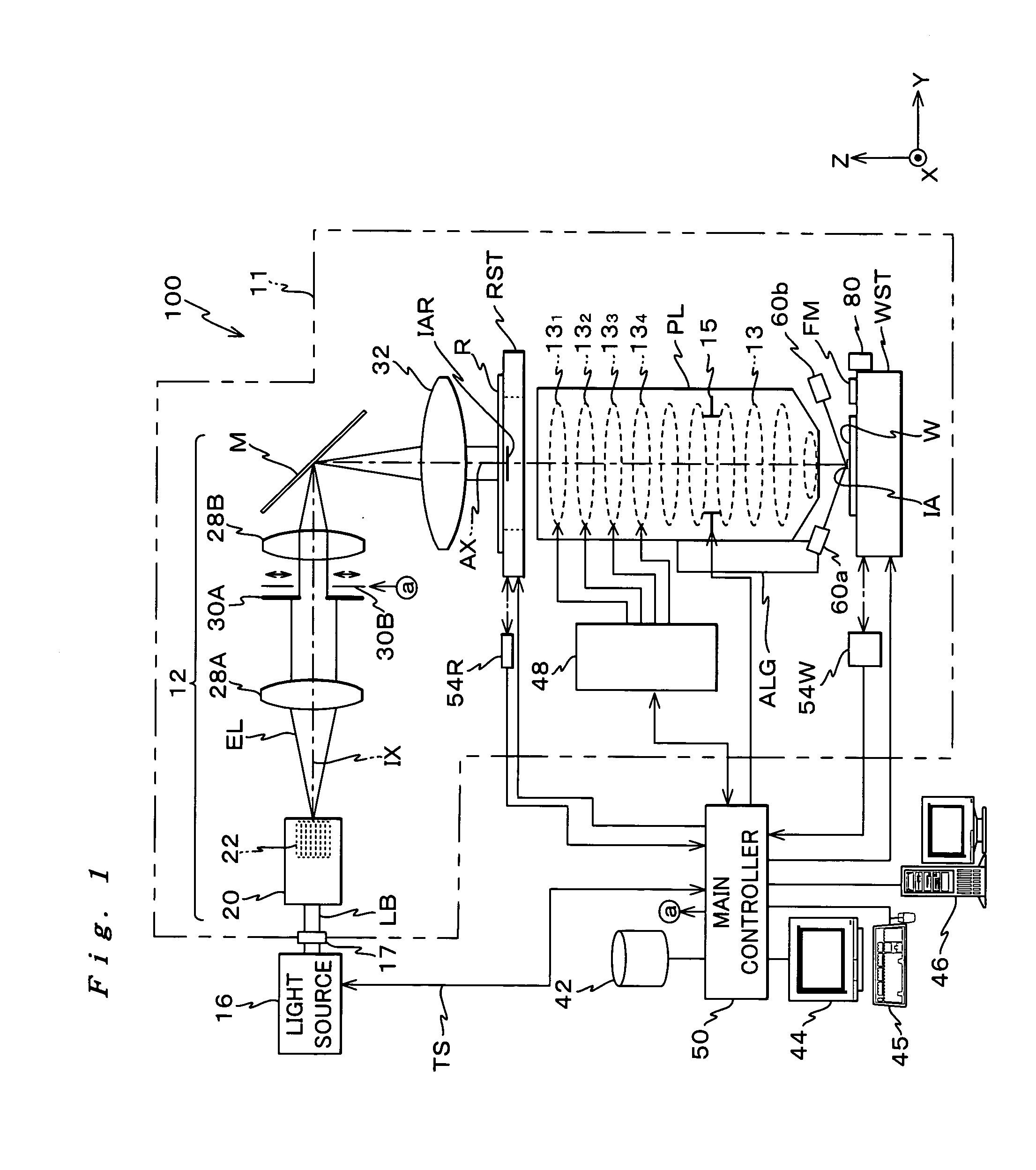
A scanning exposure apparatus which promptly analyzes a cause for a variation in exposure line width. The scanning exposure apparatus includes a mask stage on which a mask is placed, a wafer stage on which a wafer is placed, a focusing mechanism which detects surface position information of the wafer and adjustment means which adjusts the surface position of the wafer. Control means acquires pose information of the wafer adjusted by the adjustment means at the time of exposure and stores the pose information in a memory in association with preacquired surface shape information of an exposure area. A state in which the exposed surface of the wafer has been exposed with respect to exposure light is known from the pose information and the surface shape information.
Owner:NIKON CORP
Apparatus and Method for Improving Photoresist Properties
InactiveUS20100081285A1Harden radiation-sensitive materialsRemove roughnessSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingPhotosensitive material processingLine widthEngineering
The invention can provide apparatus and methods of processing a substrate in real-time using subsystems and processing sequences created to improve the etch resistance of photoresist materials. In addition, the improved photoresist layer can be used to more accurately control gate and / or spacer critical dimensions (CDs), to control gate and / or spacer CD uniformity, and to eliminate line edge roughness (LER) and line width roughness (LWR).
Owner:TOKYO ELECTRON LTD
Apparatus, methods and precision spray processes for direct write and maskless mesoscale material deposition
InactiveUS20040197493A1Reduce package sizeElectric discharge heatingVacuum evaporation coatingOptoelectronicsBiological materials
Apparatuses and processes for maskless deposition of electronic and biological materials. The process is capable of direct deposition of features with linewidths varying from the micron range up to a fraction of a millimeter, and may be used to deposit features on substrates with damage thresholds near 100° C. Deposition and subsequent processing may be carried out under ambient conditions, eliminating the need for a vacuum atmosphere. The process may also be performed in an inert gas environment. Deposition of and subsequent laser post processing produces linewidths as low as 1 micron, with sub-micron edge definition. The apparatus nozzle has a large working distance-the orifice to substrate distance may be several millimeters-and direct write onto non-planar surfaces is possible. This invention is also of combinations of precision spray processes with in-flight laser treatment in order to produce direct write electronic components, and additionally lines of conductive, inductive, and resistive materials. This development has the potential to change the approach to electronics packaging in that components can be directly produced on small structures, thus removing the need for printed circuit boards.
Owner:OPTOMEC DESIGN CO
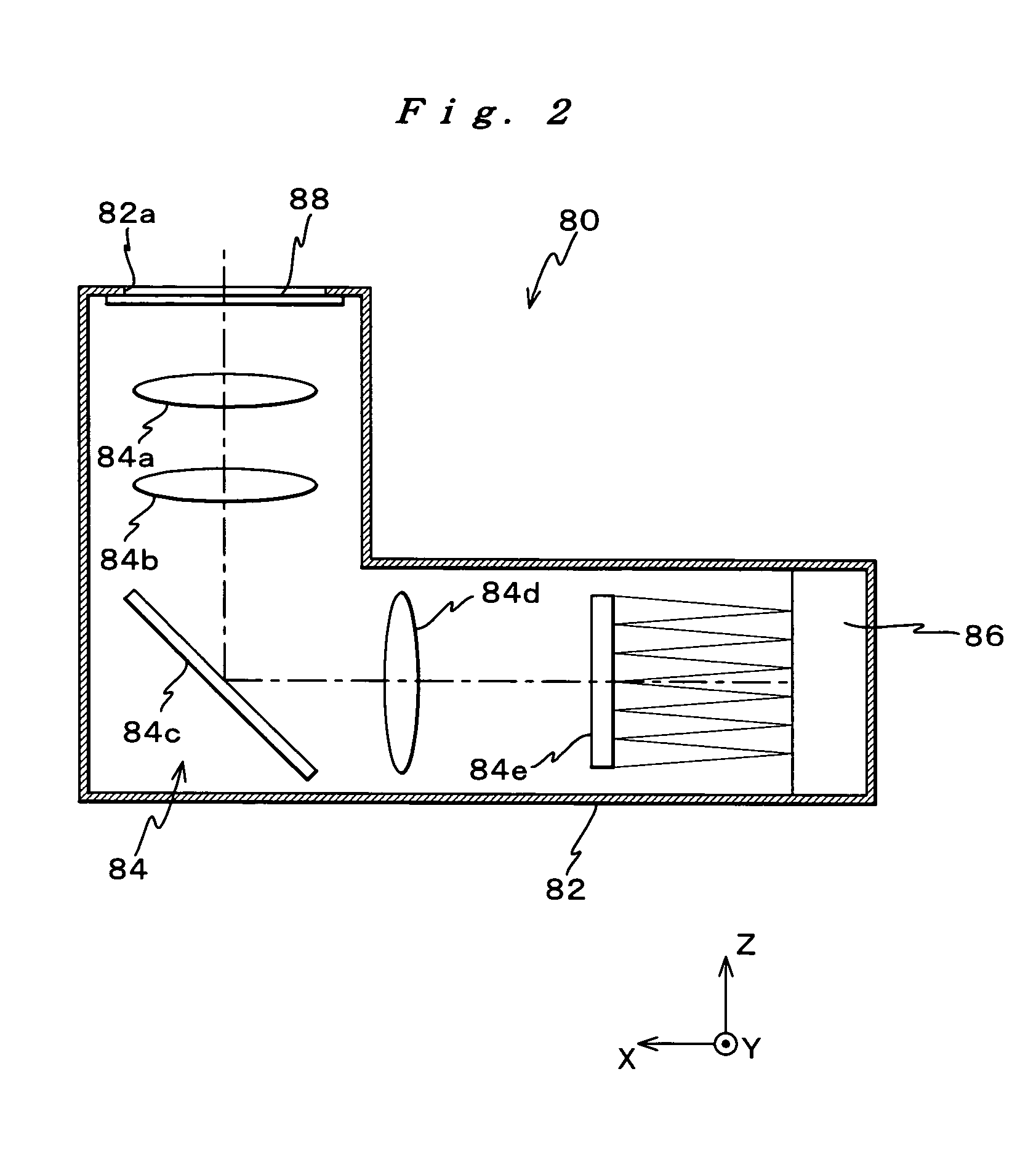
Differential confocal scanning detection method with high spatial resolution
InactiveCN1527026AImprove axial resolutionImprove horizontal resolutionUsing optical meansLine widthHigh spatial resolution
The present invention belongs to the field of fine surface structure measuring technology, and relates to one kind of differential confocal scanning detection method with high spatial resolution. Differential confocal microscopic double receiving light path configuration and double detector subtraction form the differential confocal signal in measuring the workpiece. Optical super-resolution confocal microscopic detection method is adopted to raise the transverse resolution, and differential confocal microscopic detection method is adopted to raise the longitudinal resolution, so as to reach differential confocal scanning detection of high spatial resolution. The method can meet the requirements in high spatial resolution, high precision and great measurement range, and is especially suitable for the measurement of fine surface 3D structure, miniature steps, miniature grooves, line width, surface appearance, etc.
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH
Projection optical system adjustment method, prediction method, evaluation method, adjustment method, exposure method and exposure apparatus, program, and device manufacturing method
InactiveUS20050024612A1Improve accuracyPrediction is simplePhotomechanical exposure apparatusMicrolithography exposure apparatusResistLine width
Wavefront aberration of a projection optical system is measured and information on the wavefront aberration is obtained (step 102). Furthermore, a pattern of a reticle is transferred onto a wafer via a projection optical system (steps 104 to 108). Then, the waver on which the pattern is transferred is developed, and line width measurement is performed on the resist image formed on the wafer and line width difference of images of a first line pattern extending in a predetermined direction and a second line pattern that is orthogonal to the first line pattern is measured (steps 112 to 118). And, according to a value of the 12th term of the Zernike polynomial, which is an expansion of the wavefront aberration, and the line width difference, the projection optical system is adjusted so that magnitude of the 9th term (a low order spherical aberration term) is controlled (steps 120 to 124).
Owner:NIKON CORP
Phase-shifting mask for equal line/space dense line patterns
A phase-shifting mask suited for equal line / space, small pitched, dense line pattern is disclosed. The phase-shifting mask includes a transparent substrate, a partially shielded mesa line pattern of first phase formed on the substrate, and a 100% clear recessed line pattern of second phase etched into the substrate and is disposed right next to the partially shielded mesa line pattern. The partially shielded mesa line pattern has a plurality of alternating 45-degree, oblique areas and 100% transmittance clear regions of the first phase. The partially shielded mesa line pattern and the clear recessed line pattern have the same line width. The light that passes through the clear regions of the first phase and the light that passes through the clear recessed line pattern of second phase have a phase difference of 180 degree.
Owner:NAN YA TECH
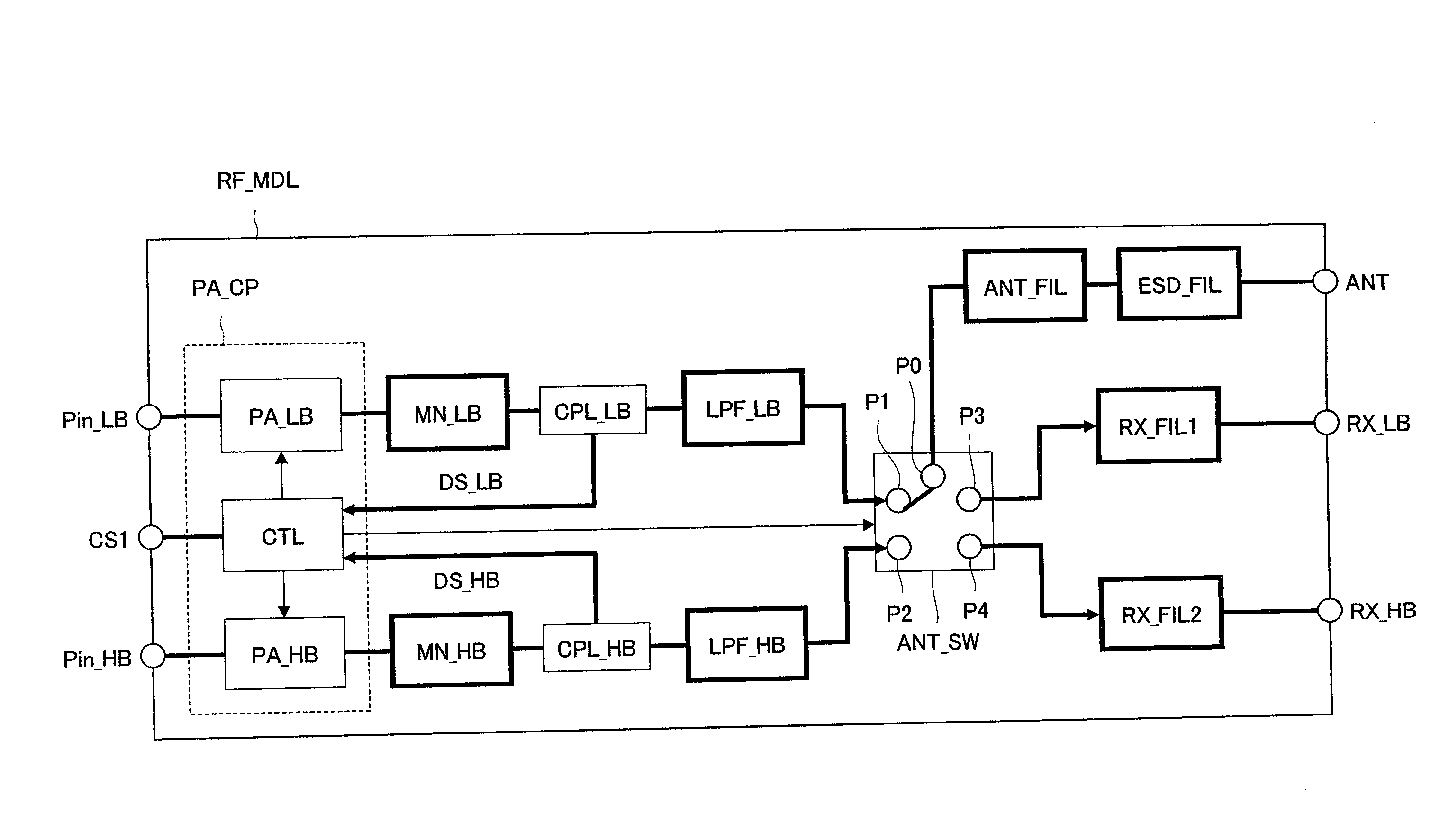
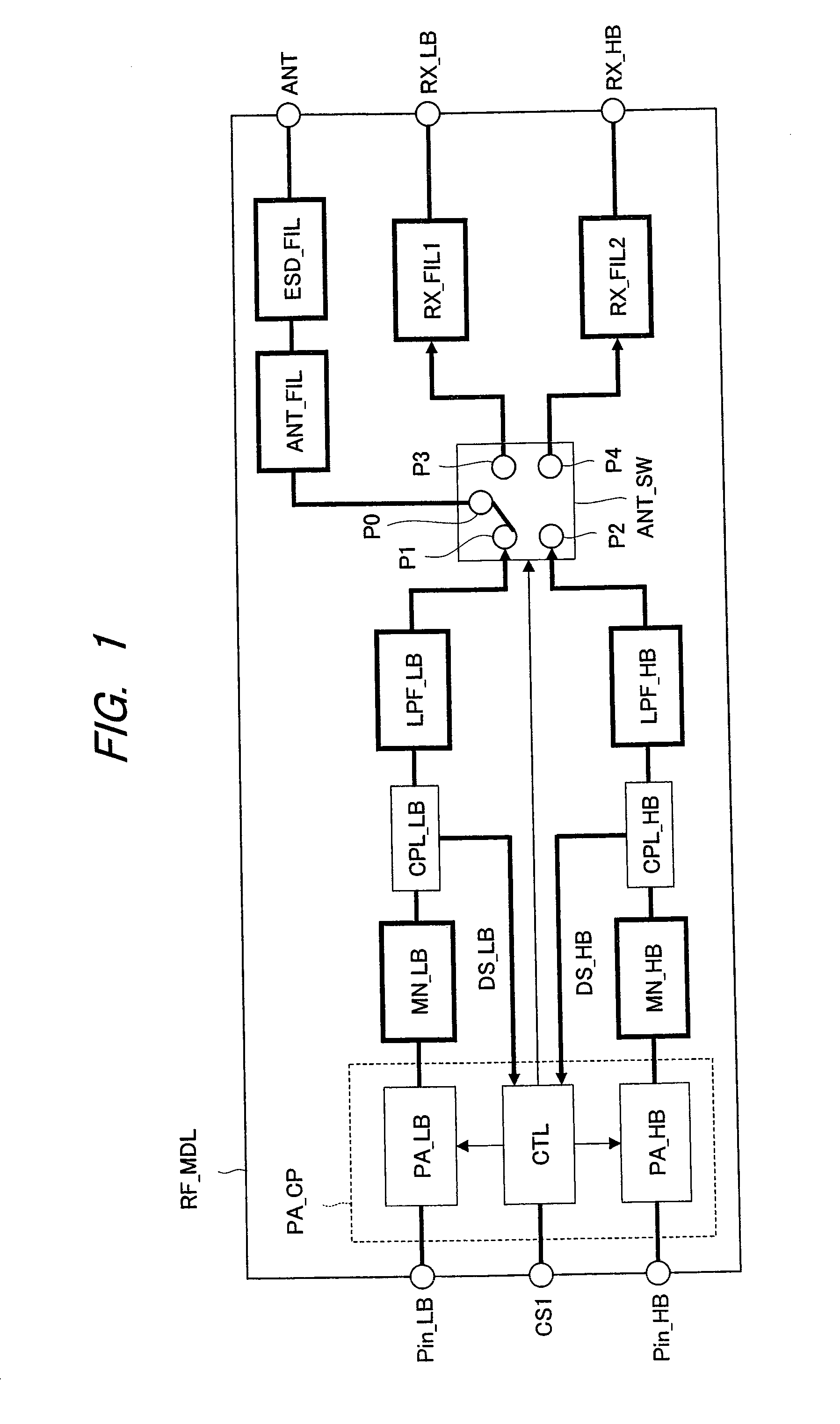
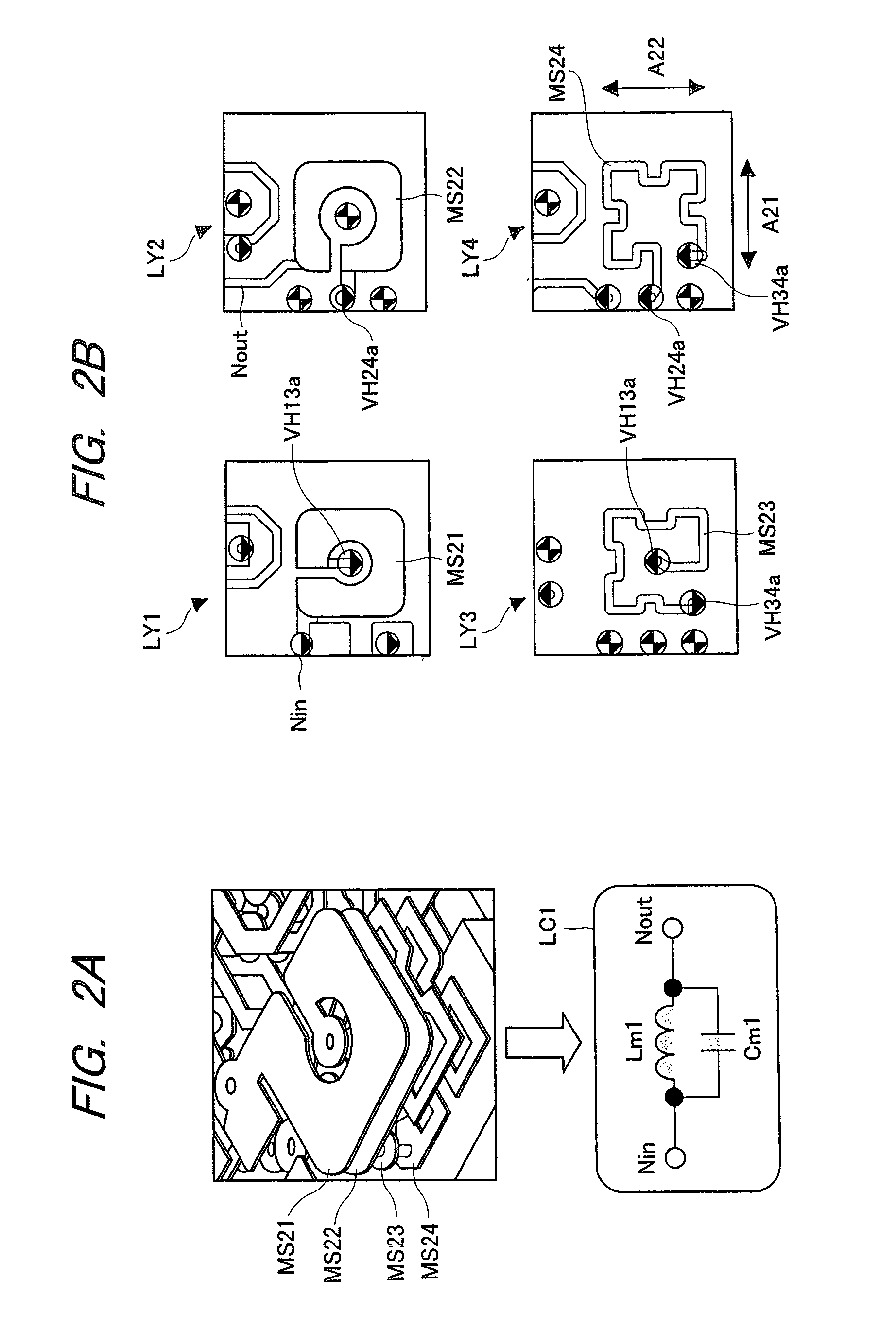
Electronic device and RF module
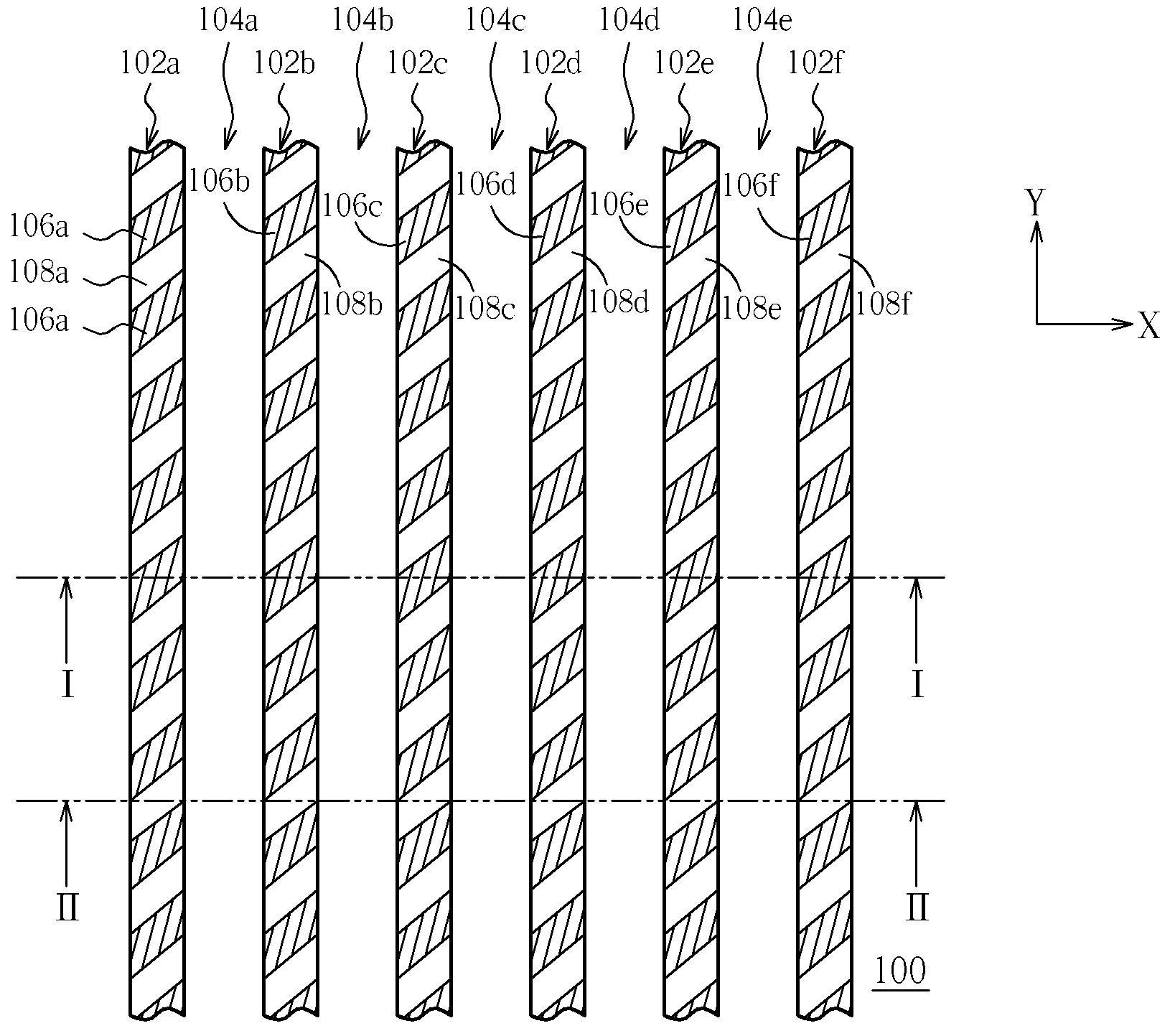
InactiveUS20080136559A1Reduce signal reflectionInhibit deteriorationMultiple-port networksPrinted circuit aspectsCapacitanceLine width
A parallel resonant circuit is realized by stacking first to fourth wiring patterns each having at least an inductance element. One of the adjacent first and second wiring patterns is set to a signal input node and the other thereof is set to a signal output node. Then, the signal input node is connected to the signal output node via inductance elements of the first wiring pattern, third wiring pattern, fourth wiring pattern and second wiring pattern in order. By adjacently forming wiring layers of the signal input and output nodes, a capacitance value between the input and output nodes is increased compared to that when they are separated. Also, by increasing the line width of the first and second wiring patterns, the capacitance value can be further increased. Therefore, it is possible to achieve a large capacitance value in a small area and downsizing of the electronic device.
Owner:RENESAS ELECTRONICS CORP
Surface mountable over-current protecting device
InactiveUS6377467B1Easy to installGood dimensional stabilityResistor terminals/electrodesNegative temperature coefficient thermistorsElectrical resistance and conductancePlanar electrode
The present invention relates to a novel thermal-sensitive resistive apparatus, such as PTC and NTC, which allocates planar electrode films on the top and bottom surfaces of a prior art thermal-sensitive resistive apparatus, such as a PTC apparatus, to laminate with an outer electrode layer. A plurality of interconnection vias are electroplated with conductive material to connect to any plane. It is convenient to surface mount the apparatus of the present invention on a printed circuit board. The present invention can largely increase the dimensional stability of components and overcome the disadvantage that thermal diffusion of the prior are surface mounted resistive apparatus is affected easily by line width and environments.
Owner:POLYTRONICS TECH
Electro-optically tunable external cavity mirror for a narrow linewidth semiconductor laser
InactiveUS6041071AImprove efficiencyLaser optical resonator constructionOptical resonator shape and constructionLine widthErbium lasers
An external cavity mirror for use in a semiconductor laser, the external cavity mirror comprising a waveguide formed on a substrate of highly electro-optic material, and including electrically-operated means for determining the reflectance attributes of the external cavity mirror.
Owner:CORETEK INC +2
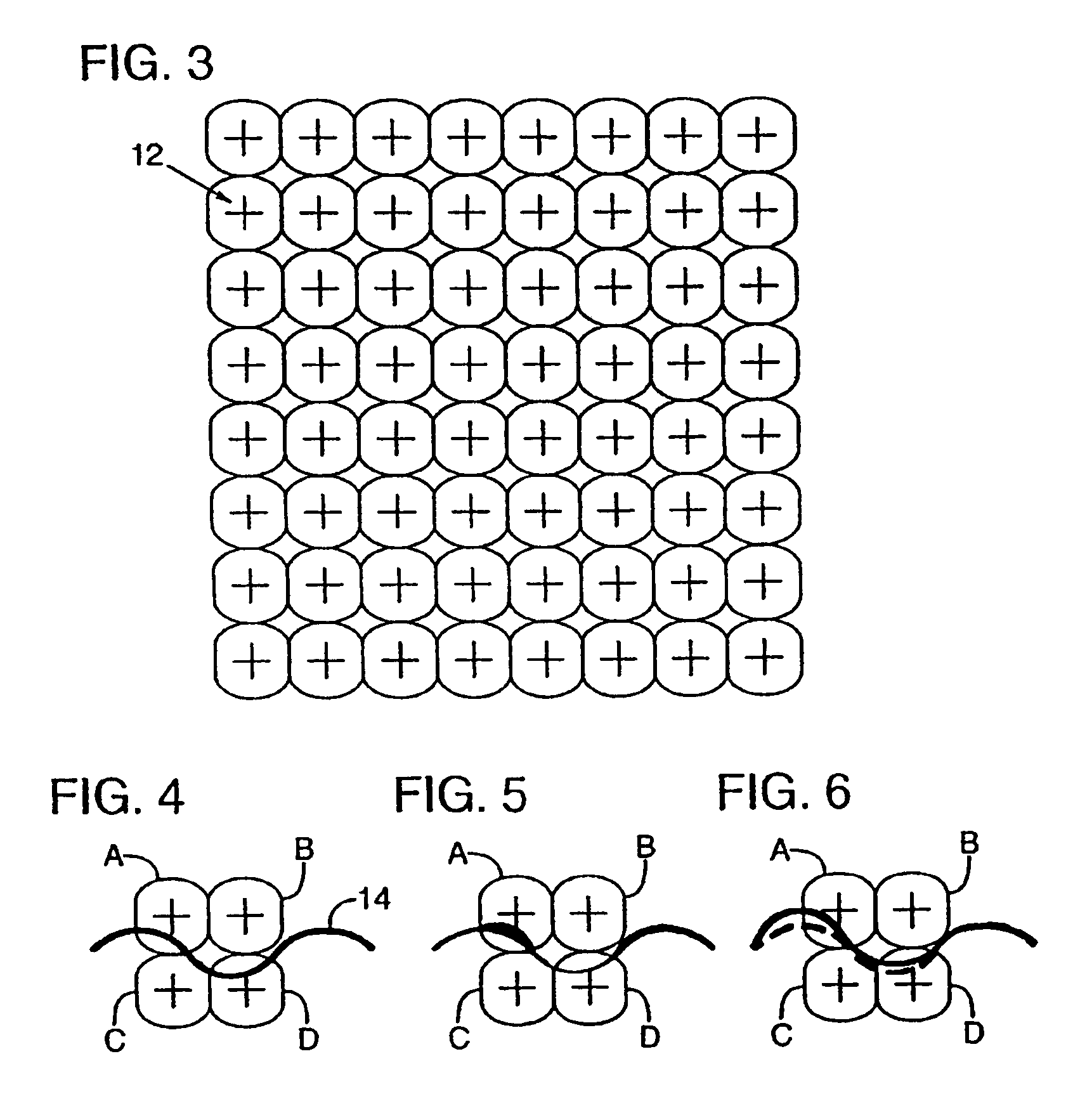
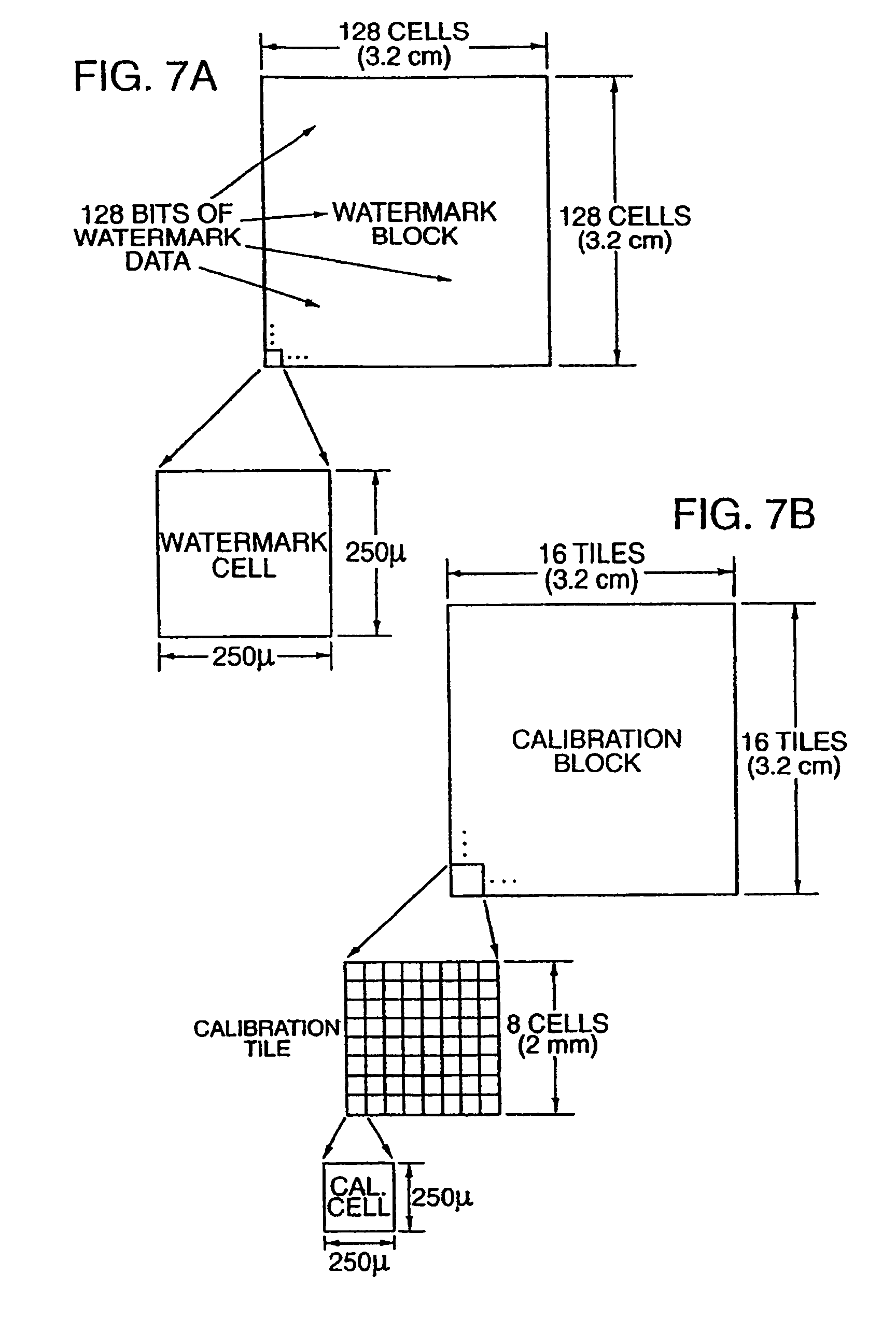
Secure documents with hidden signals, and related methods and systems
InactiveUS7555139B2Character and pattern recognitionSecret communicationPattern recognitionLine width
A security document comprising artwork including a security pattern, characterized in that the security pattern has the form of a line structure in which lines width or line spacing is adjusted to carry predefined data. The artwork is generated by the modifying at least one color of at least a part of the artwork to embed the security pattern in the artwork. Methods for detecting the security pattern include use of a frequency domain structure to detect the security pattern despite rotation and scaling of the document, use of signal tiling to improve signal detection, and use of statistical analyses to verify detection of the security pattern.
Owner:DIGIMARC CORP
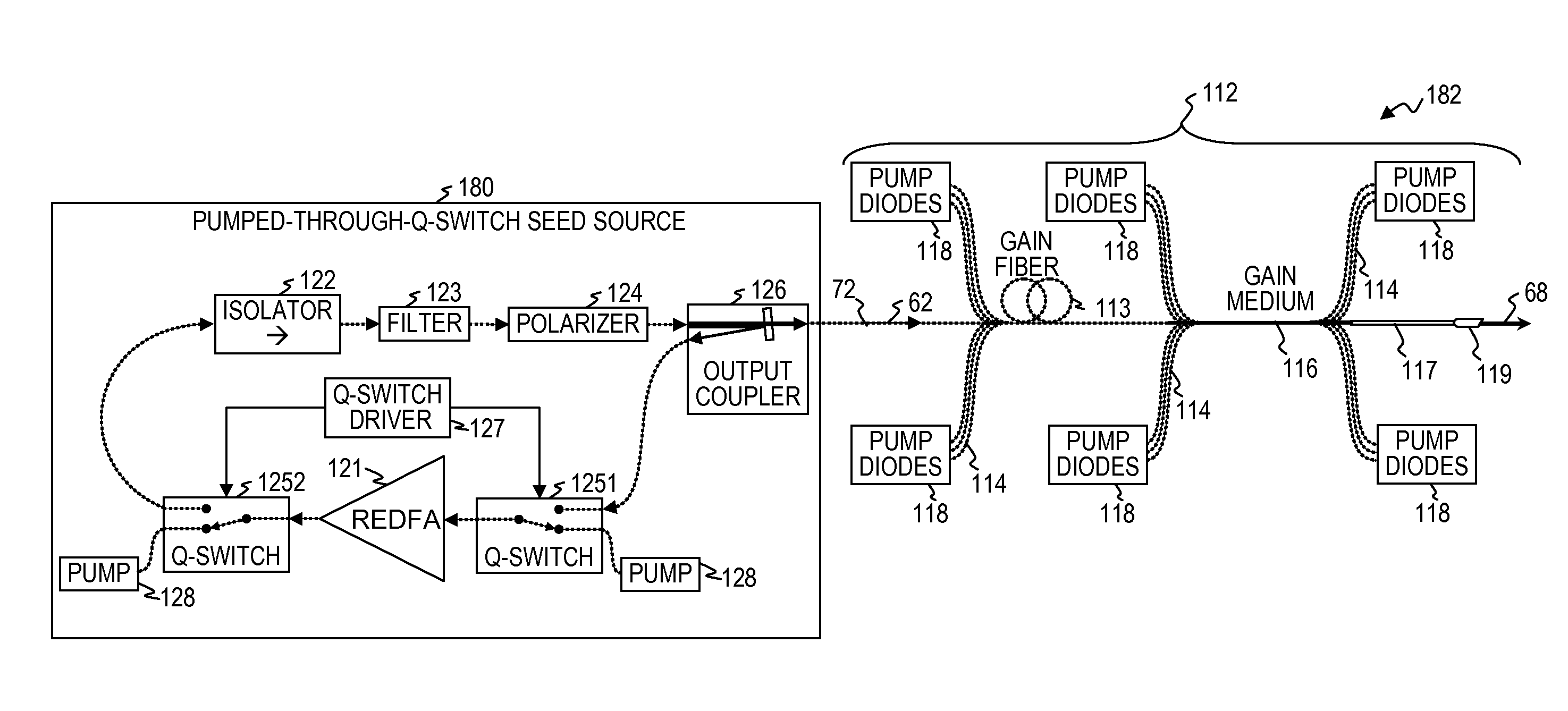
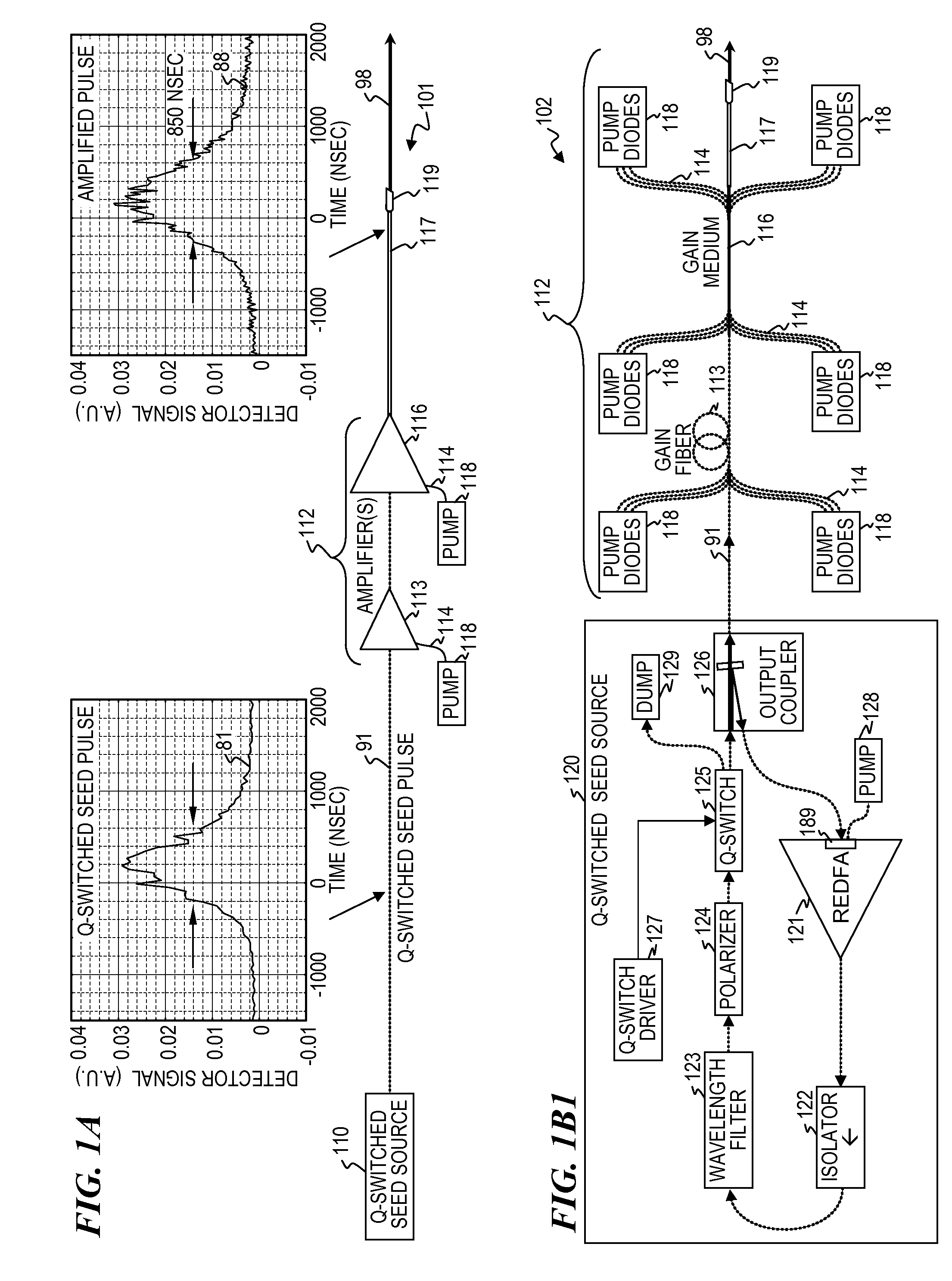
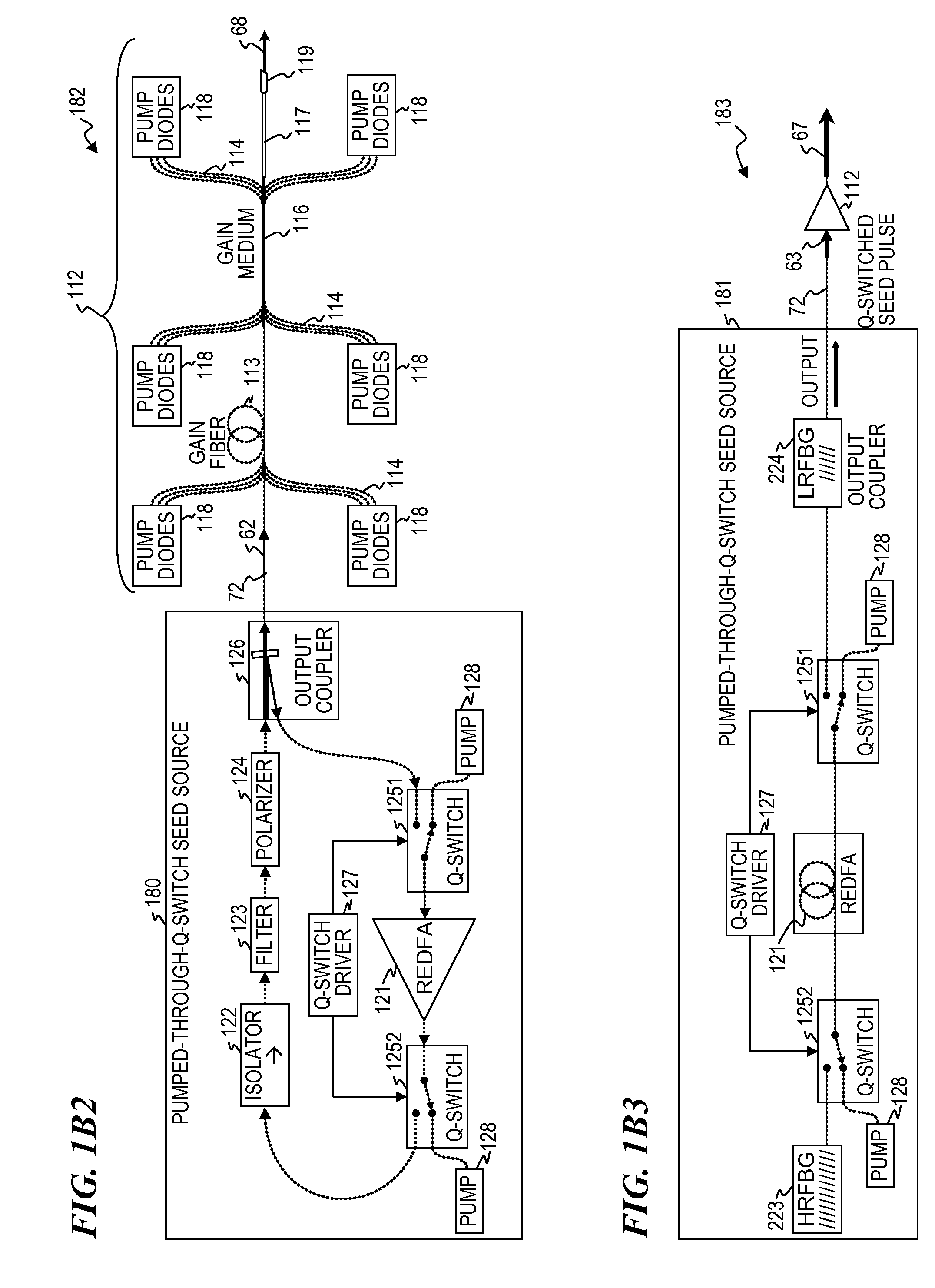
Q-switched oscillator seed-source for MOPA laser illuminator method and apparatus
ActiveUS8934509B2Wide dynamicAccelerate buildingLaser using scattering effectsLaser optical resonator constructionFrequency spectrumLine width
An apparatus, method and system that uses a Q-switched laser or a Q-seed source for a seed pulse signal having a controlled high-dynamic-range amplitude that avoids and / or compensates for pulse steepening in high-gain optical-fiber and / or optical-rod amplification of optical pulses. Optionally, the optical output is used for LIDAR or illumination purposes (e.g., for image acquisition). In some embodiments, well-controlled pulse shapes are obtained having a wide dynamic range, long duration, and not-too-narrow linewidth. In some embodiments, upon the opening of a Q-switch in an optical cavity having a gain medium, the amplification builds relatively slowly, wherein each round trip through the gain medium increases the amplitude of the optical pulse. Other embodiments use quasi-Q-switch devices or a plurality of amplitude modulators to obtain Q-seed pulses. These configurations provide optical pulses having wide dynamic ranges that ameliorate problems of pulse steepening, non-linear spectral broadening and the like in very-high-power MOPA devices.
Owner:LOCKHEED MARTIN CORP
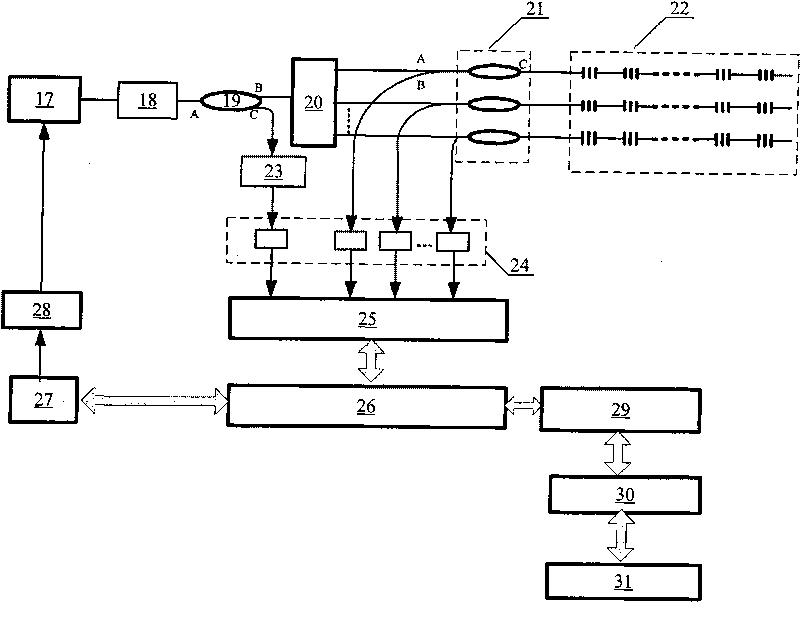
Multi-channel fiber Bragg grating (FBG) demodulator
InactiveCN101718942AImprove signal-to-noise ratioReduce usageAbsorption/flicker/reflection spectroscopyLight demodulationGratingLine width
The invention discloses a multi-channel fiber Bragg grating (FBG) demodulator, which adopts a scanning fiber laser as a light source. The scanning fiber laser is on the basis of a micro-mechanical structural filter with temperature control, and belongs to a narrow-linewidth and high-coherent light source which is calibrated accurately. The calibration is implemented by a thermostable FP etalon with a wavelength label. A gain matching fiber amplifier amplifies the power of the output of a laser and achieves the power flatness of scanning laser spectroscopy. A fiber Bragg grating reflected signal enters a data acquiring and processing system after passing through a photoelectric detector and an AD converter processing module. A data acquiring and processing and peak detection system is implemented by adopting an FPGA-based all-digital scheme, and simultaneously utilizes a synchronous signal of a direct numerical frequency synthesis module to obtain a control voltage of the micro-mechanical structural filter. By combining with other equipment, the scanning fiber laser, the etalon and the FPGA realize the multichannel, high-precision, high-stability, high-repeatability, and serial-parallel structure detection of a grating sensor network signal.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
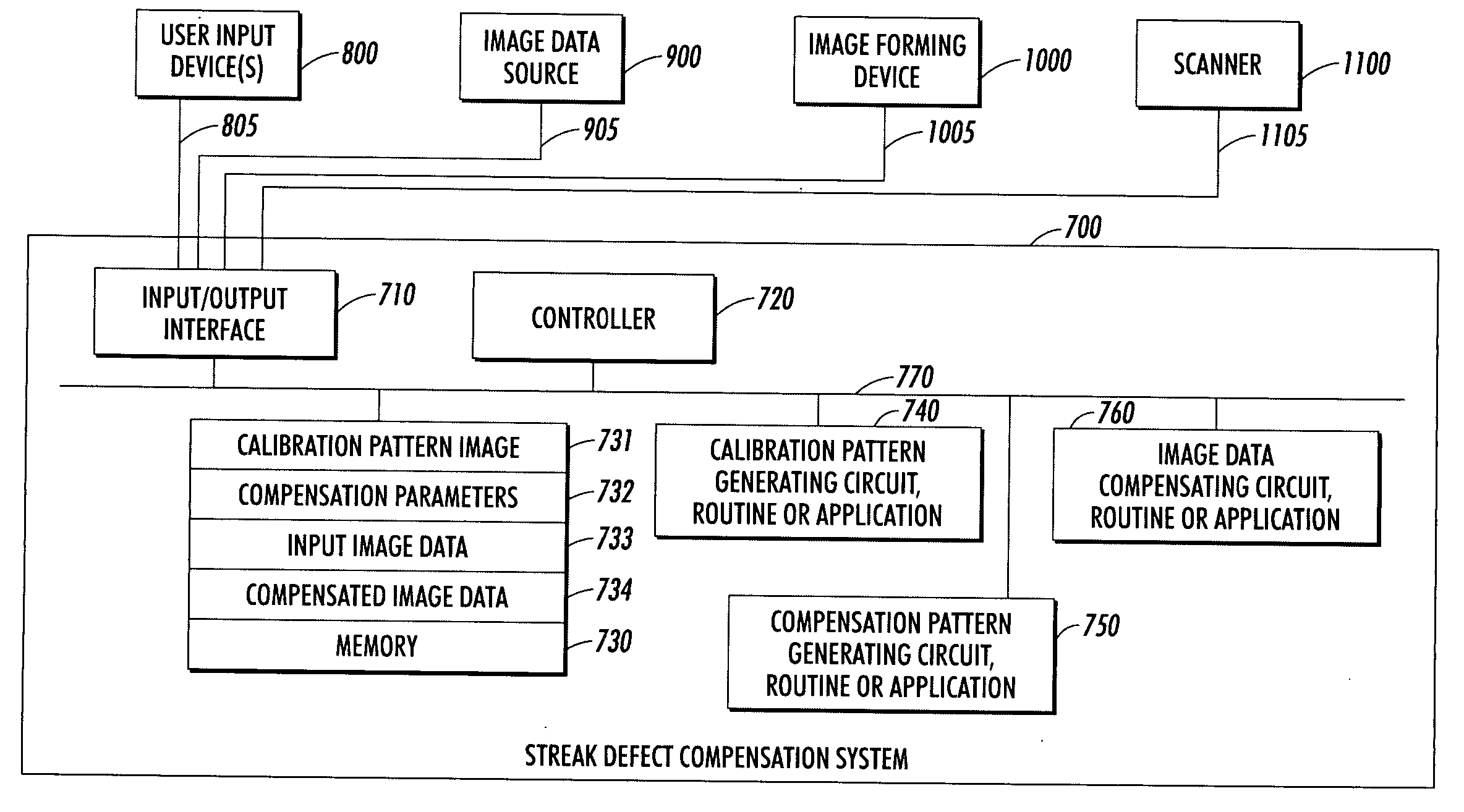
Systems and methods for compensating for streaks in images
ActiveUS20050099446A1Reduce the impact of noiseReduce impactImage enhancementDigitally marking record carriersTone reproductionGray level
Defects in an image forming system may give rise to visible streaks, or one-dimensional defects in an image that run parallel to the process direction. One known method for compensating for streaks introduces a separate tone reproduction curve for each pixel column in the process direction. A compensation pattern according to this invention has a plurality of halftone regions that are lead by, trained by, and separated by rows of fiducial marks. The fiducial marks allow the printer pixel grid and a scanning pixel grid to be correlated. The gray level in each pixel column of each gray level portion is measured and analyzed to produce a local tone reproduction curve for each pixel column and associated line width. The local tone reproduction curves are then used to compensate for the streak defect when printing.
Owner:XEROX CORP
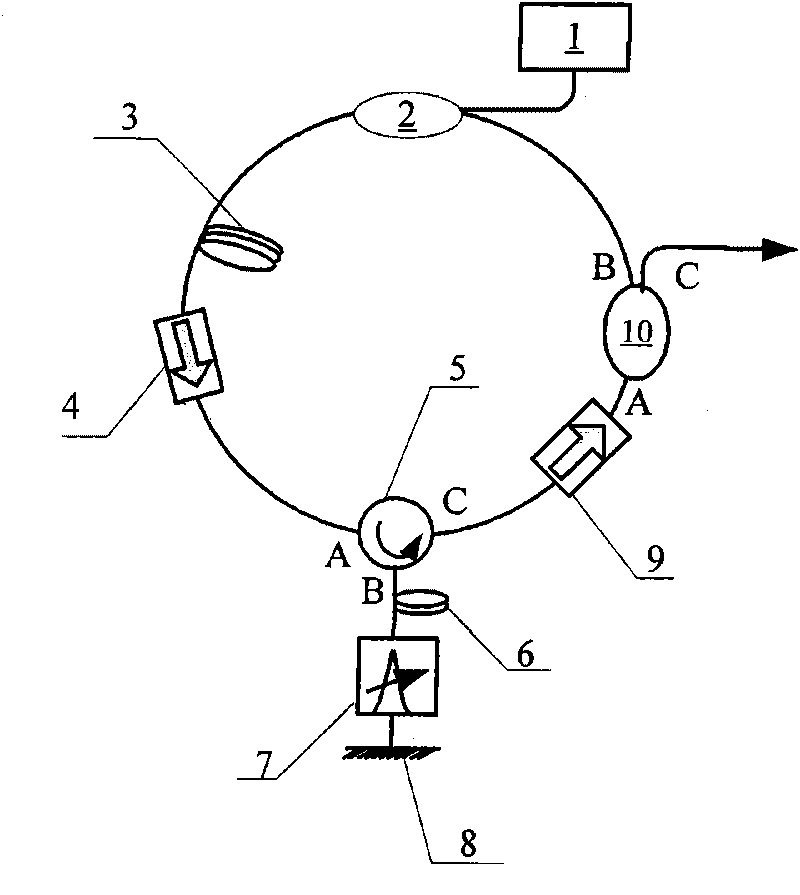
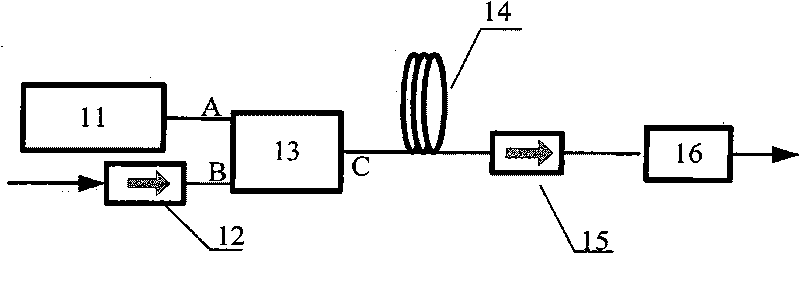
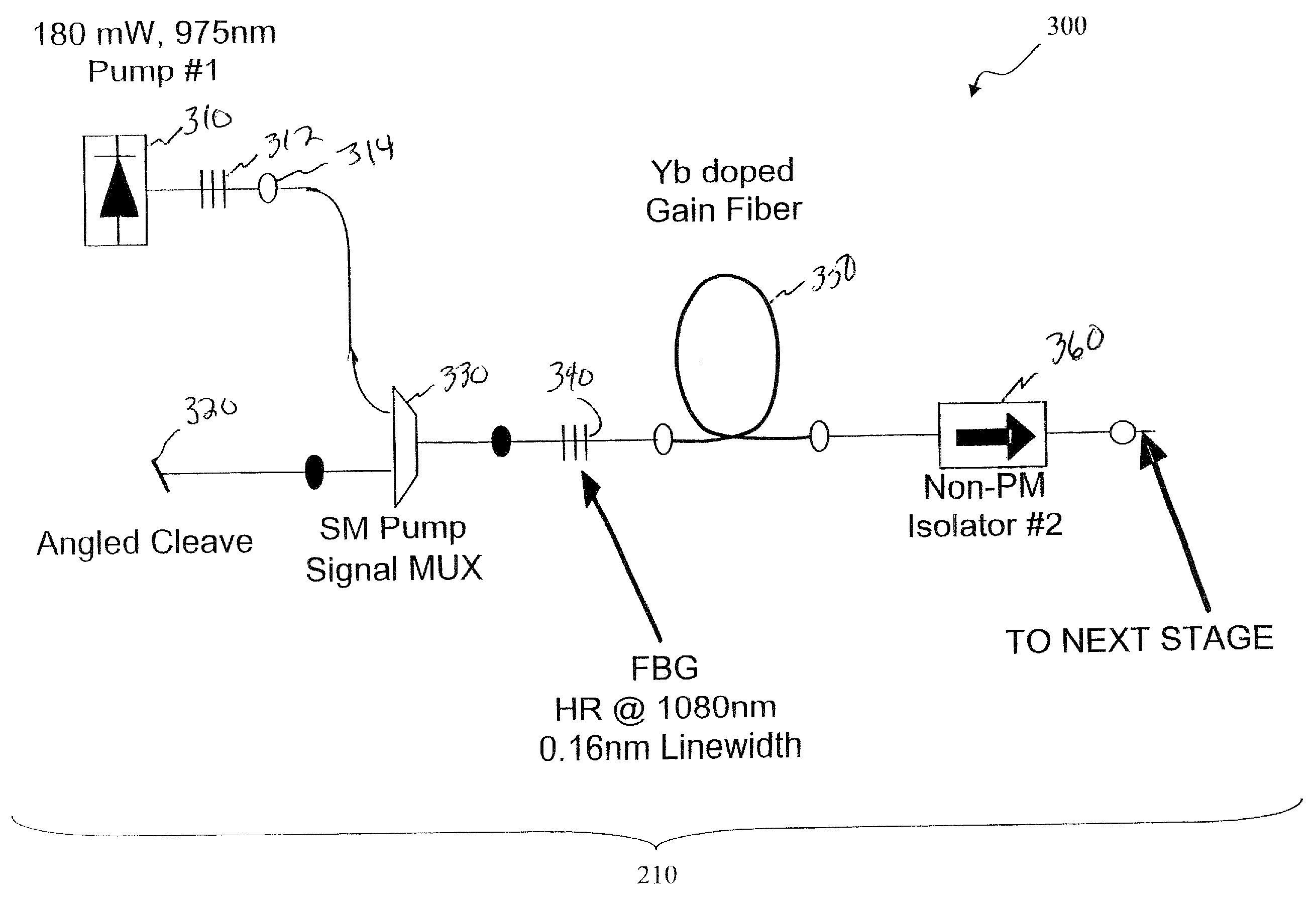
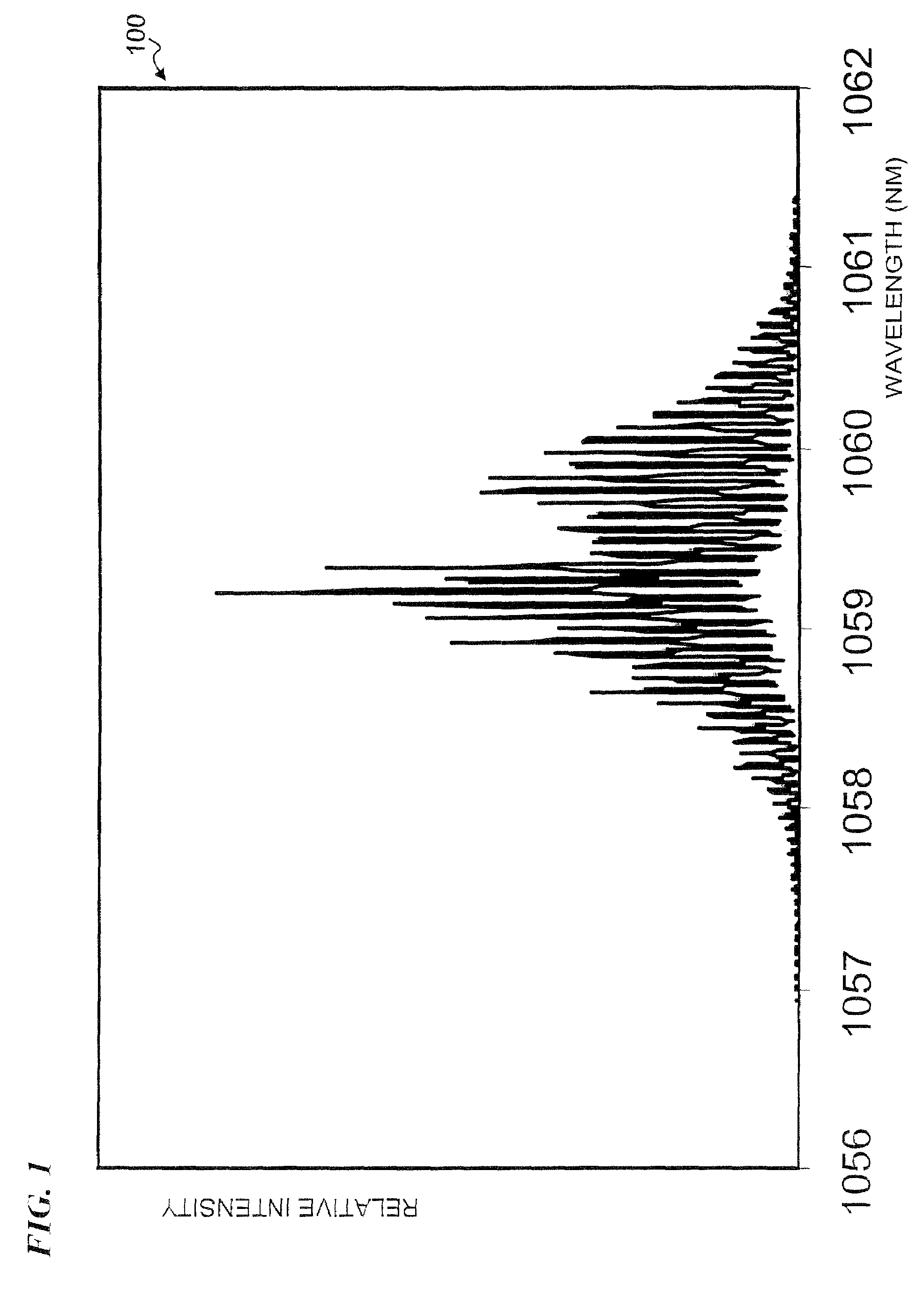
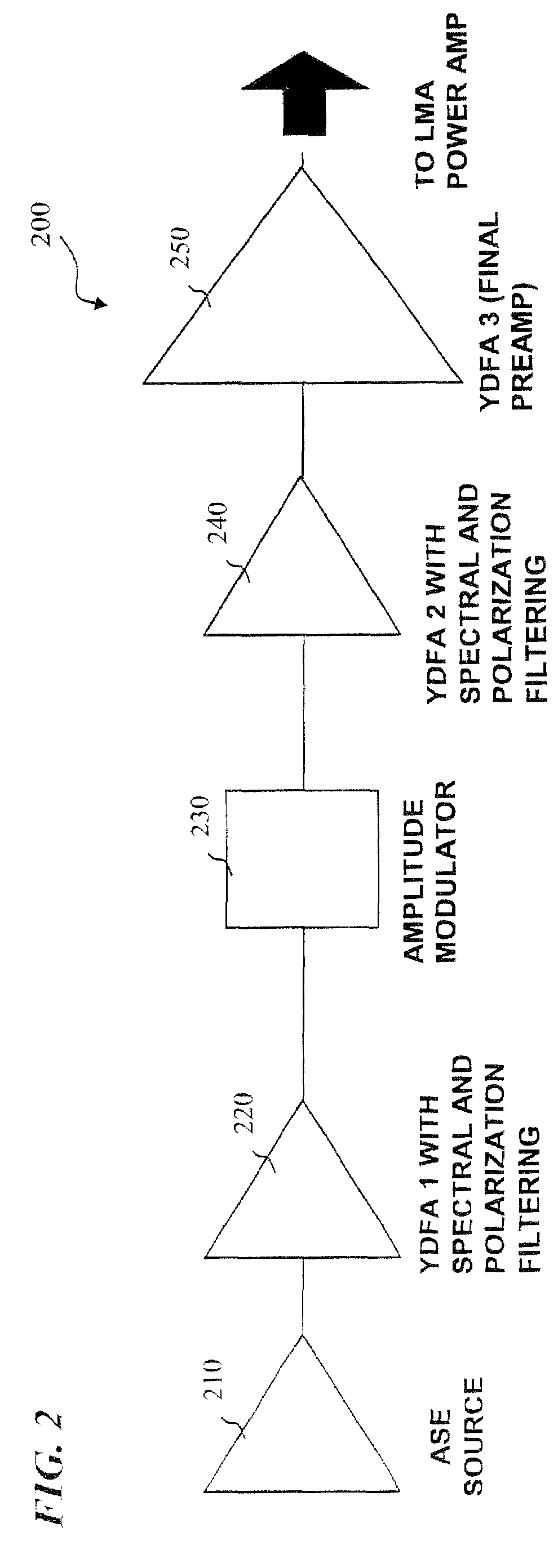
Apparatus and method for generating controlled-linewidth laser-seed-signals for high-powered fiber-laser amplifier systems
Apparatus and method for generating controlled-linewidth laser-seed-signals for high-powered fiber-laser amplifier systems. In some embodiments, the natural chirp (frequency change of laser light over a short start-up time) of a DBR laser diode when driven by pulsed current is used to broaden the linewidth of the laser output, while adjusting the peak current and / or the pulse duration to obtain the desired linewidth.
Owner:LOCKHEED MARTIN CORP
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com