Patents
Literature
2160 results about "High spatial resolution" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
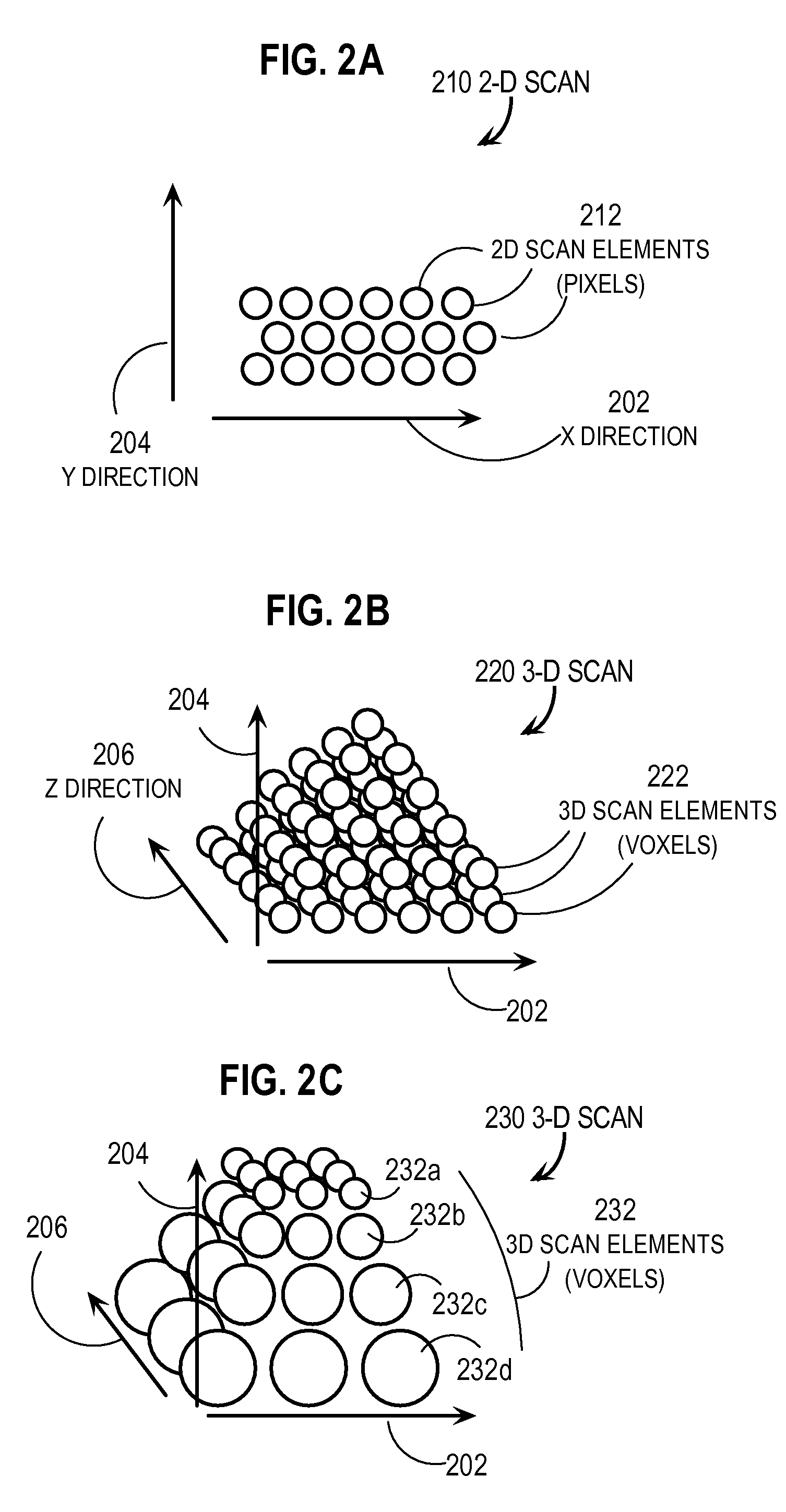
A high spatial resolution is important for one to discriminate between structures that are located within a small proximity to each other.
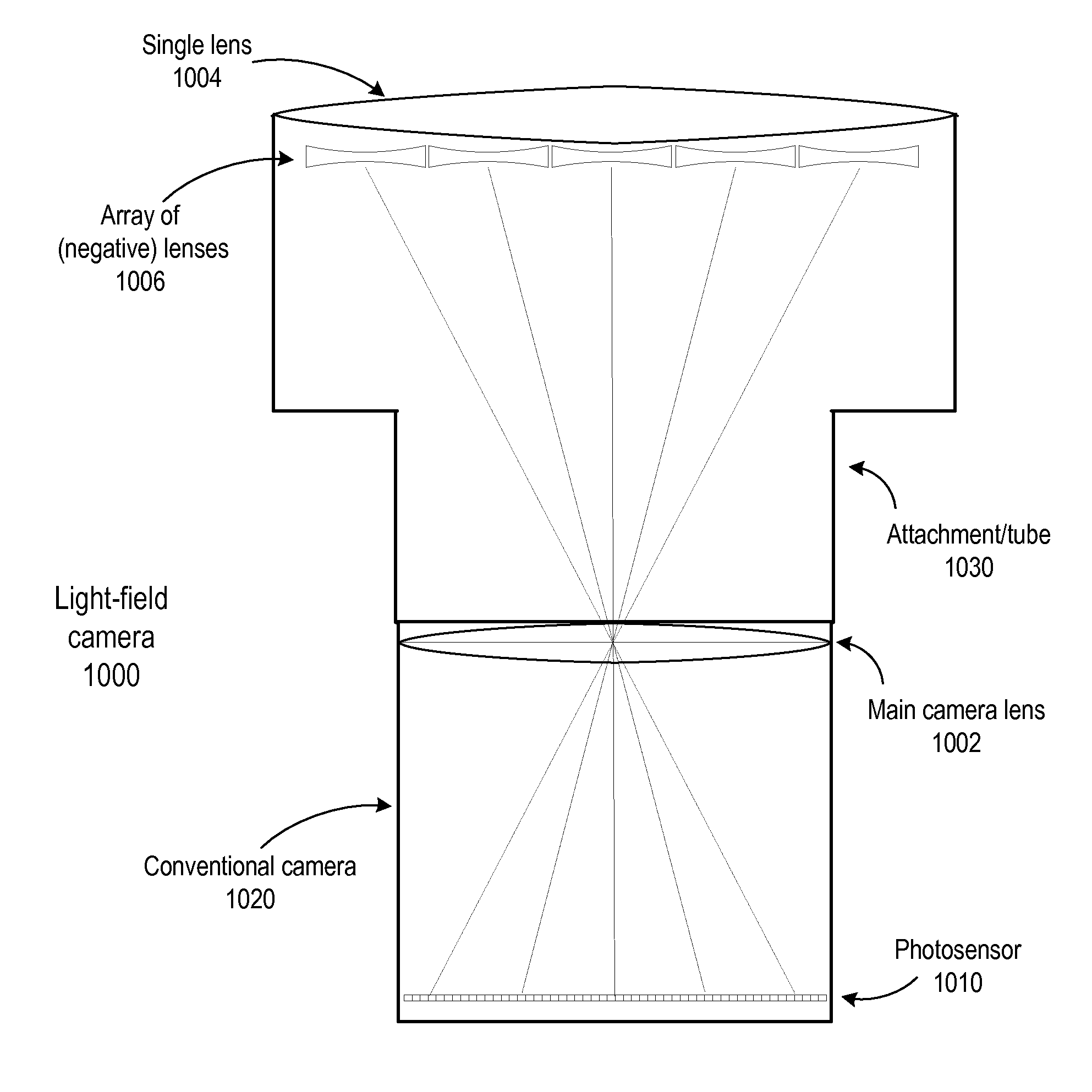
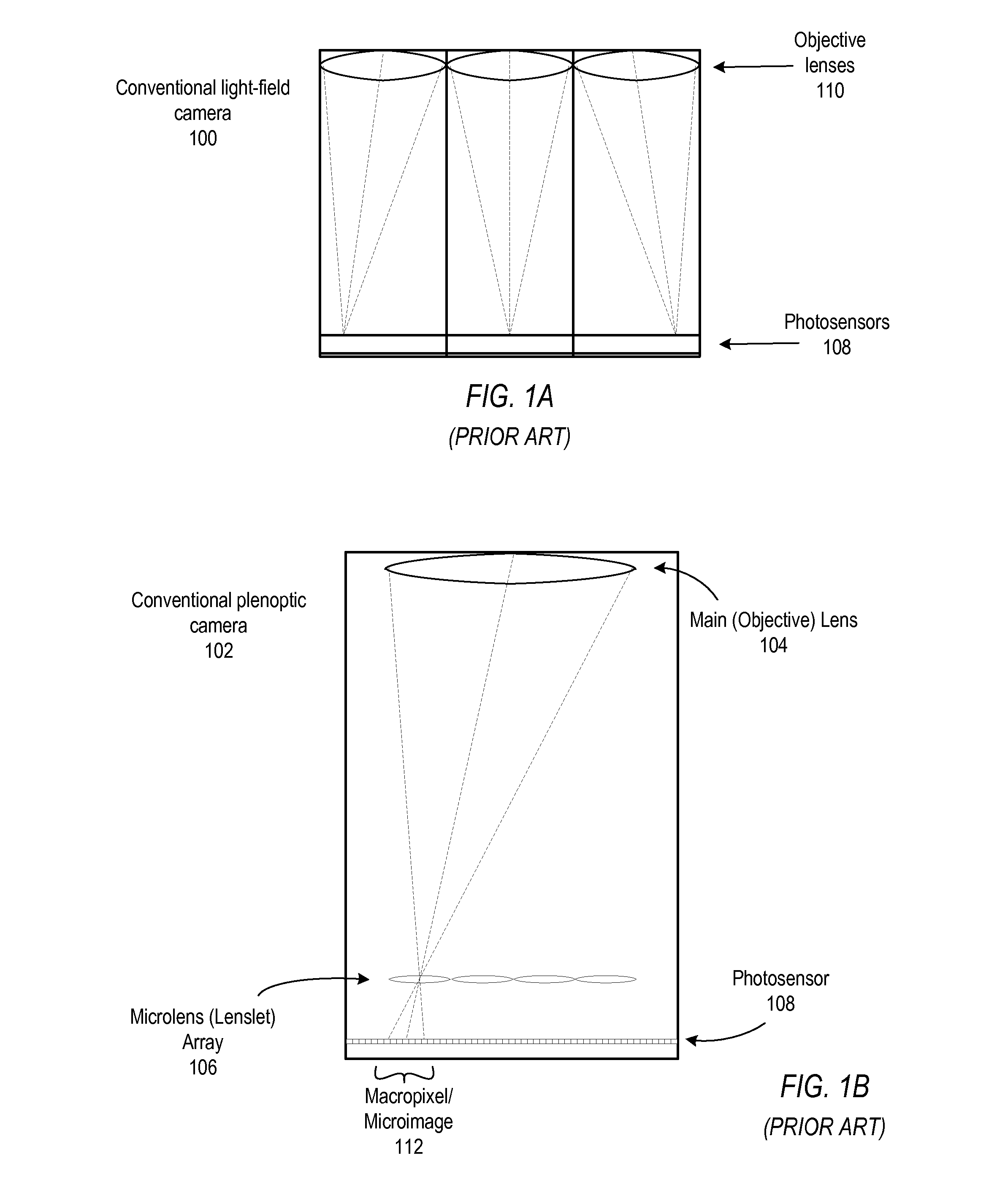
Methods and apparatus for light-field imaging
ActiveUS8290358B1Minimal loss in qualityImprove spatial resolutionStereoscopic photographySteroscopic systemsCamera lensHand held
Methods and apparatus for light-field imaging. Light-field camera designs are described that produce higher spatial resolution than conventional plenoptic camera designs, while trading-off the light-field's angular sampling density. This lower angular resolution may be compensated for by a light-field image processing method that inserts data synthesized by view interpolation of the measured light-field. In one embodiment, a light-field image processing method that performs three-view morphing may be used to interpolate the missing angular samples of radiance. The light-field camera designs may be implemented in hand-held light-field cameras that may capture a light-field with a single exposure. Some of the light-field camera designs are internal to the camera, while others are external to the camera. One light-field camera design includes a single, relatively large lens and an array of negative lenses that are placed in front of (external to) the main lens of a conventional camera.
Owner:ADOBE SYST INC
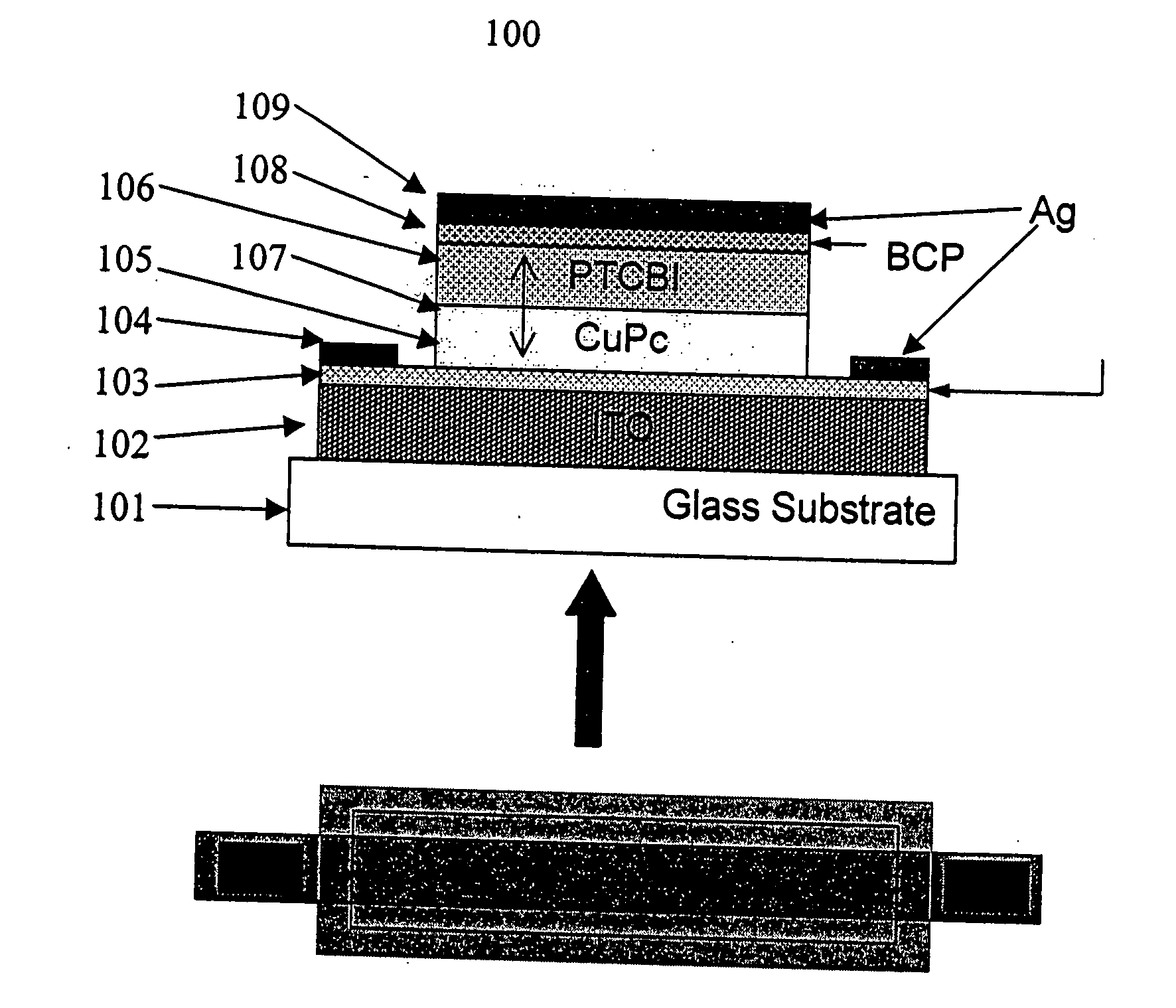
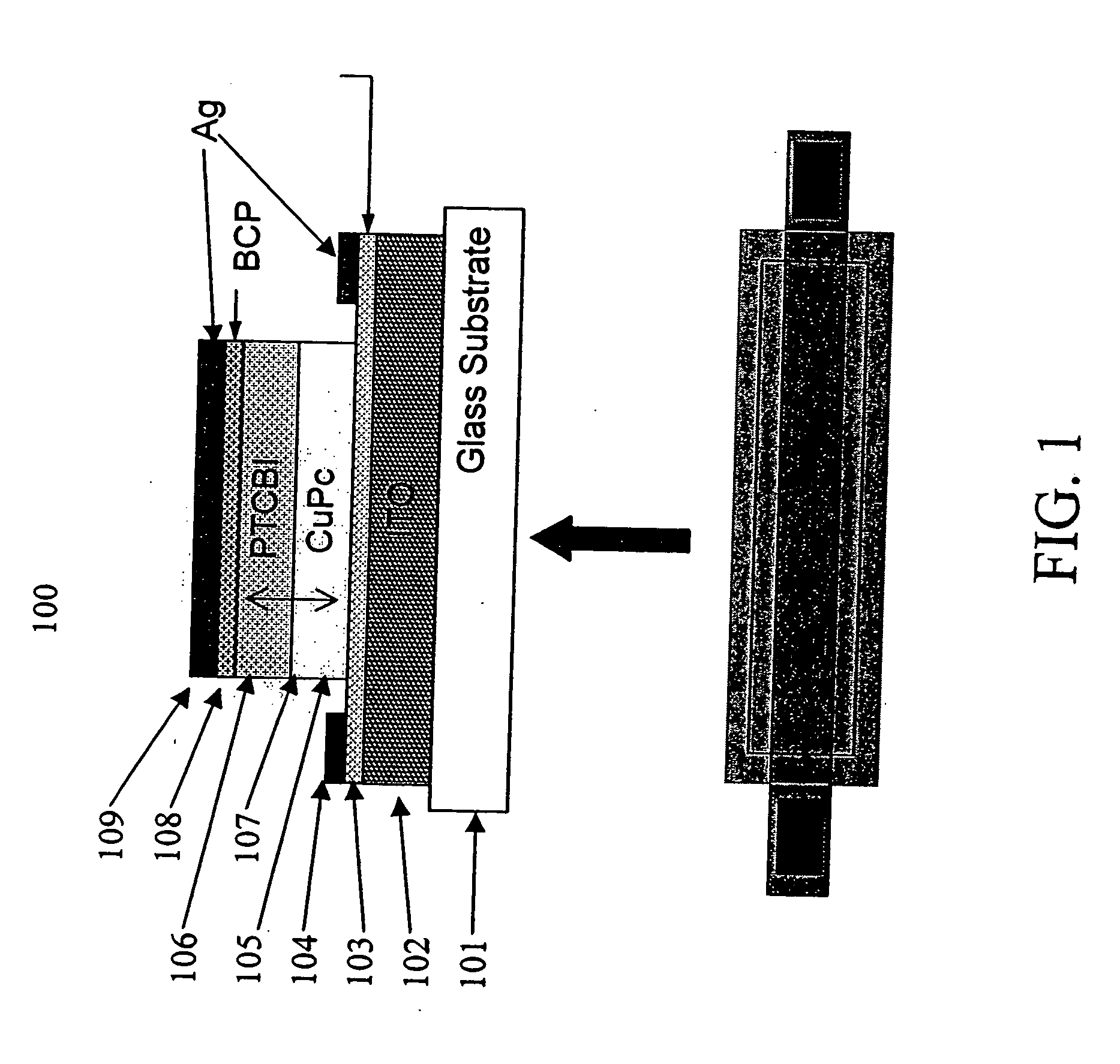
Thin film organic position sensitive detectors
The present invention is directed to organic photosensitive optoelectronic devices and methods of use for determining the position of a light source. Provided is an organic position sensitive detector (OPSD) comprising: a first electrode, which is resistive and may be either an anode or a cathode; a first contact in electrical contact with the first electrode; a second contact in electrical contact with the first electrode; a second electrode disposed near the first electrode; a donor semiconductive organic layer disposed between the first electrode and the second electrode; and an acceptor semiconductive organic layer disposed between the first electrode and the second electrode and adjacent to the donor semiconductive organic layer. A hetero-junction is located between the donor layer and the acceptor layer, and at least one of the donor layer and the acceptor layer is light absorbing. The OPSD has an optical beam spatial resolution of 20 μm and measurements are insensitive to fluctuations in incident light beam intensity and background illumination. The response of the OPSD shows high linearity, low positional error, high spatial resolution, and good beam tracking velocity. The OPSDs exhibited linearities and positional uncertainties of <1%.
Owner:FORREST STEPHEN R +2
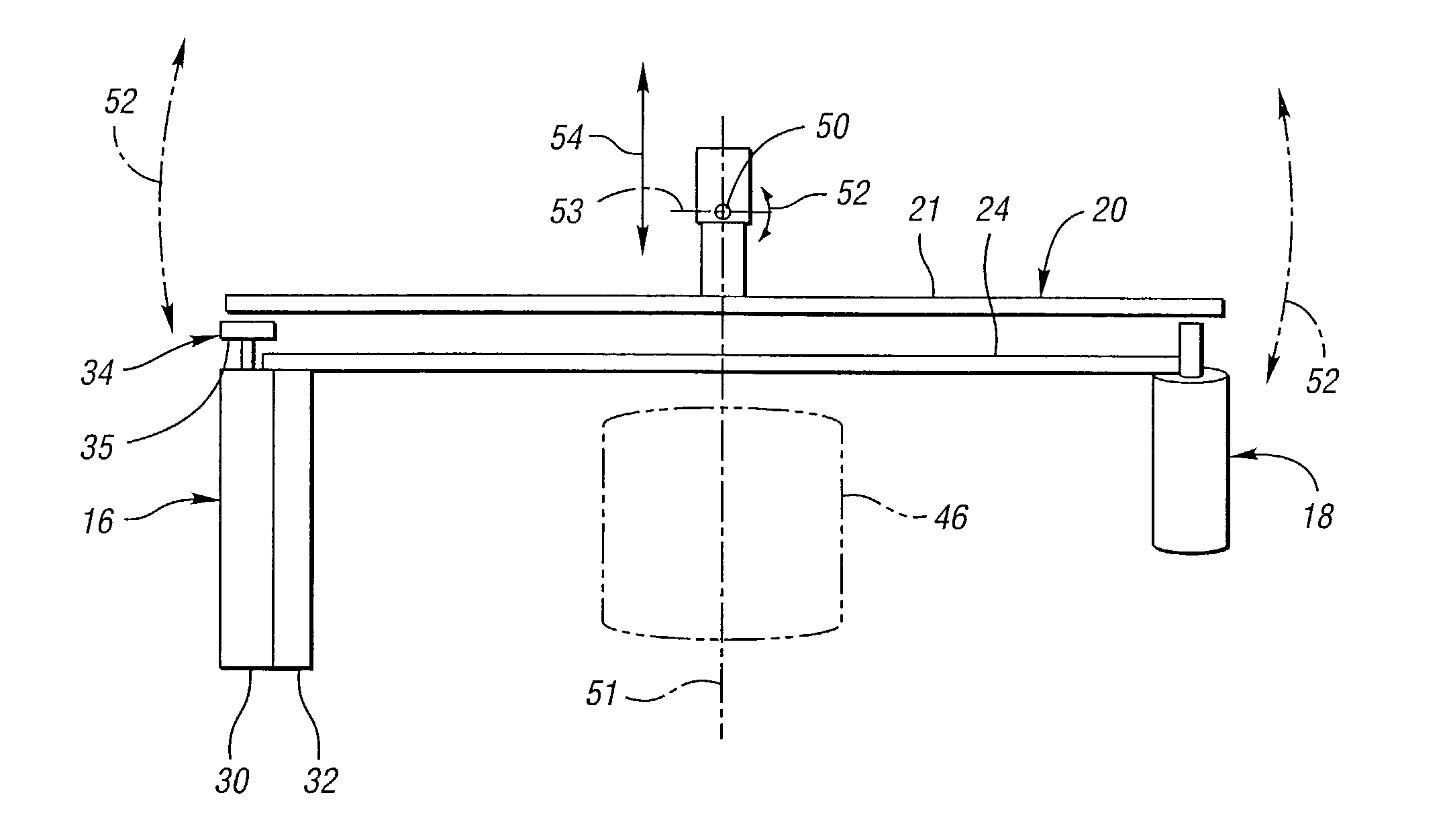
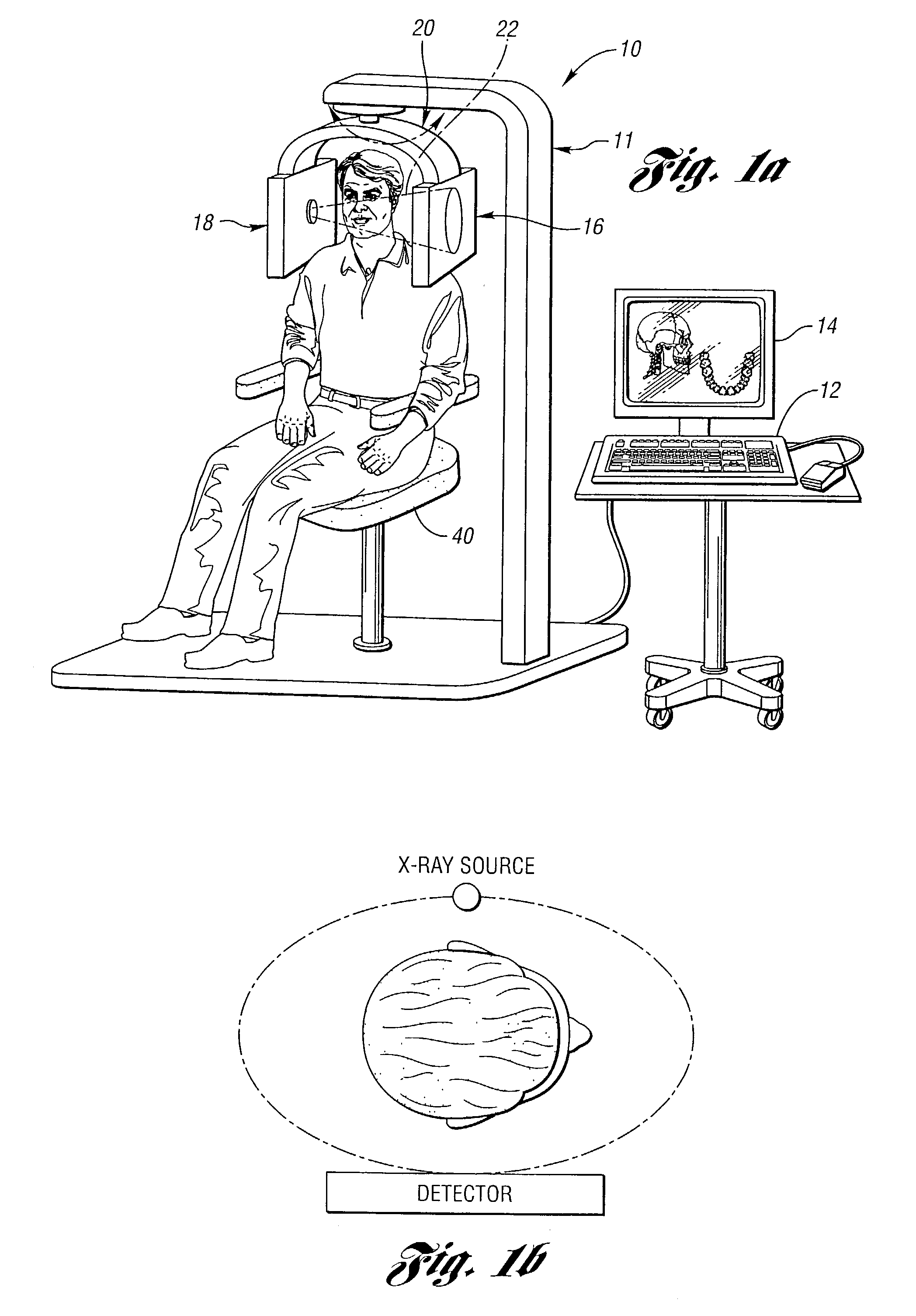
High spatial resolution X-ray computed tomography (CT) system
InactiveUS7099428B2Reduce dispersionMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationRadiation/particle handlingComputed tomographyHigh spatial resolution
A high spatial resolution X-ray computed tomography (CT) system is provided. The system includes a support structure including a gantry mounted to rotate about a vertical axis of rotation. The system further includes a first assembly including an X-ray source mounted on the gantry to rotate therewith for generating a cone X-ray beam and a second assembly including a planar X-ray detector mounted on the gantry to rotate therewith. The detector is spaced from the source on the gantry for enabling a human or other animal body part to be interposed therebetween so as to be scanned by the X-ray beam to obtain a complete CT scan and generating output data representative thereof. The output data is a two-dimensional electronic representation of an area of the detector on which an X-ray beam impinges. A data processor processes the output data to obtain an image of the body part.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF MICHIGAN
Three-dimension imaging lidar
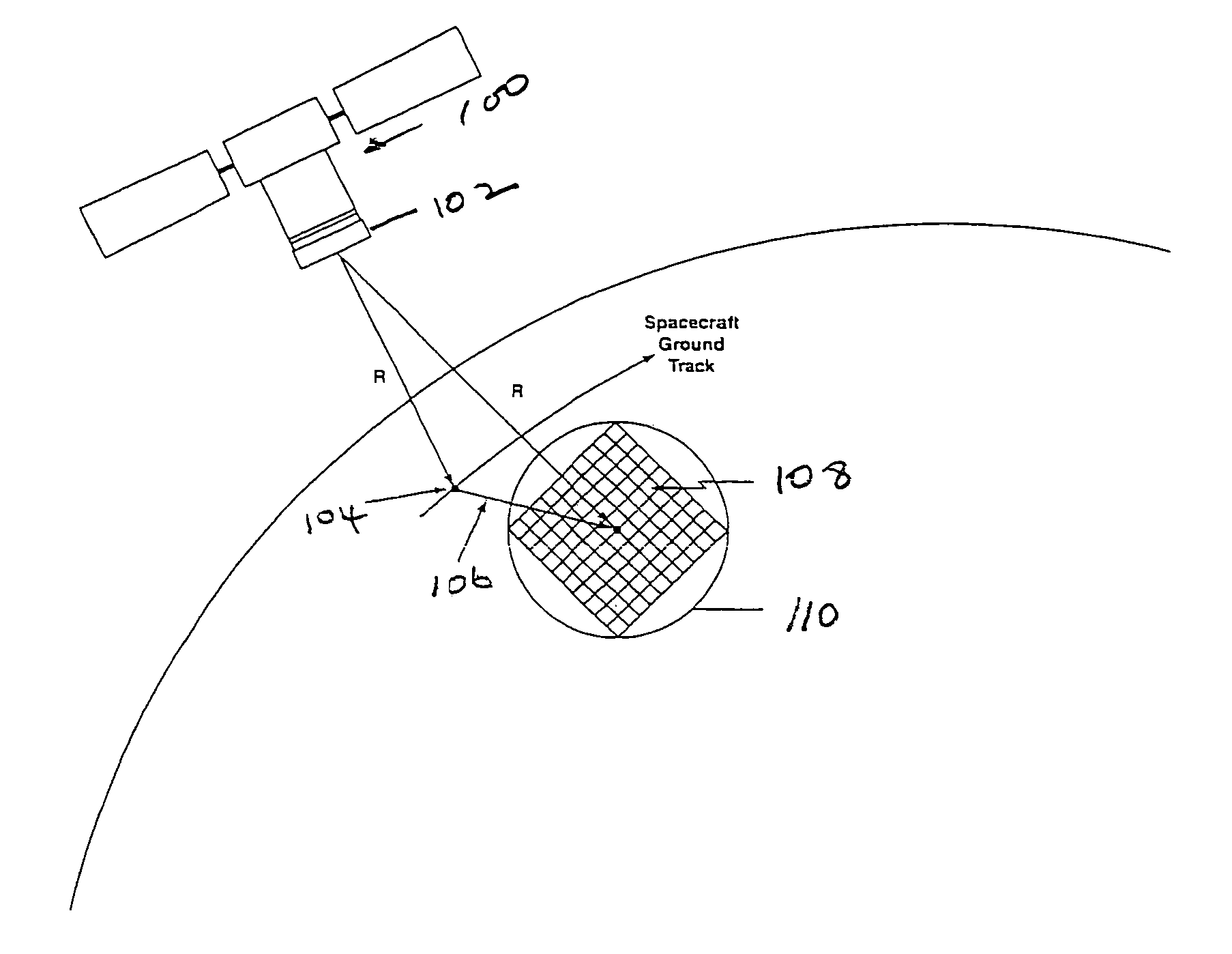
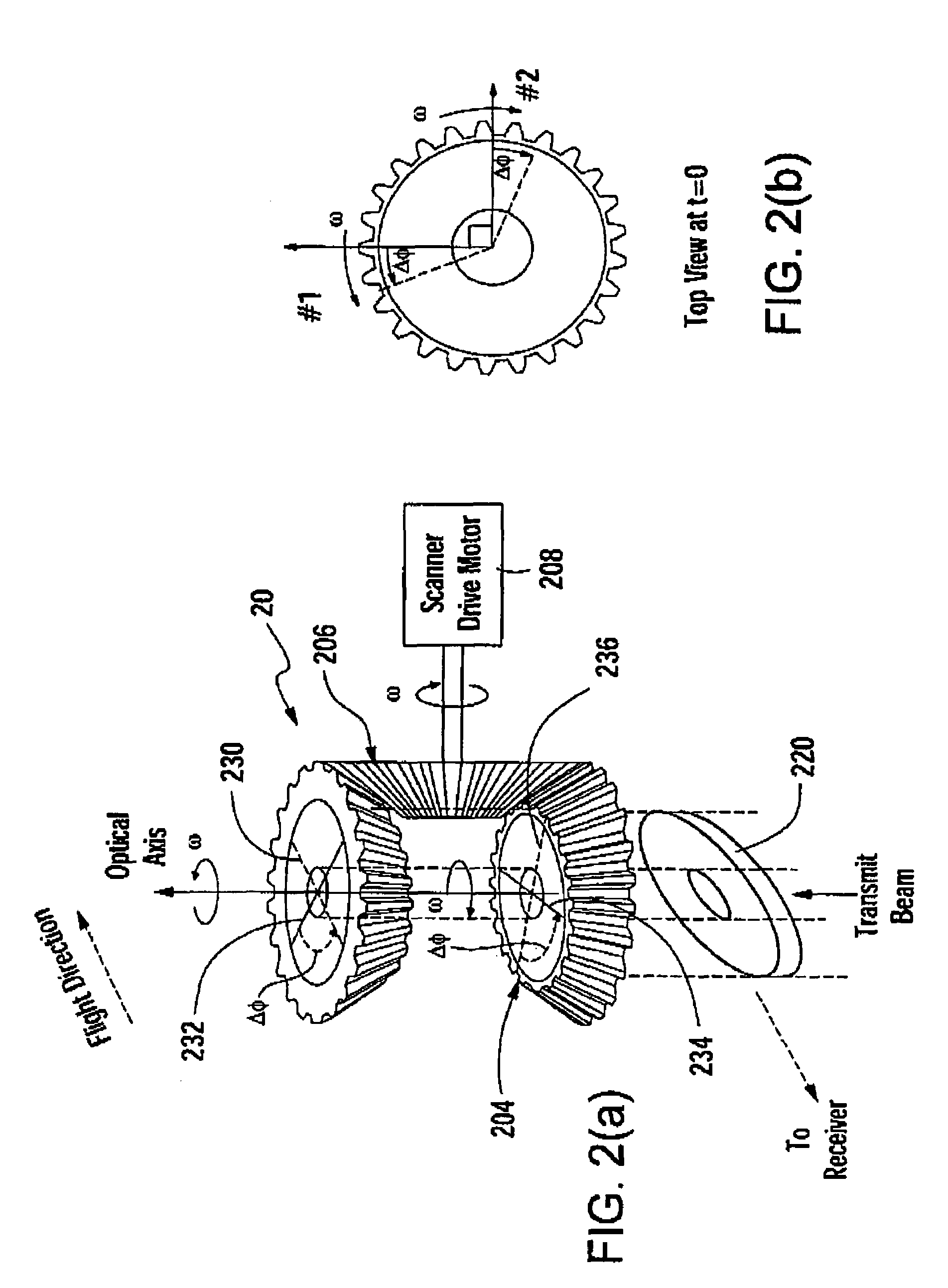
This invention is directed to a 3-dimensional imaging lidar, which utilizes modest power kHz rate lasers, array detectors, photon-counting multi-channel timing receivers, and dual wedge optical scanners with transmitter point-ahead correction to provide contiguous high spatial resolution mapping of surface features including ground, water, man-made objects, vegetation and submerged surfaces from an aircraft or a spacecraft.
Owner:UNITED STATES OF AMERICA AS REPRESENTED BY THE ADMINISTATOR OF THE NAT AERONAUTICS SPACE ADMINISTATION
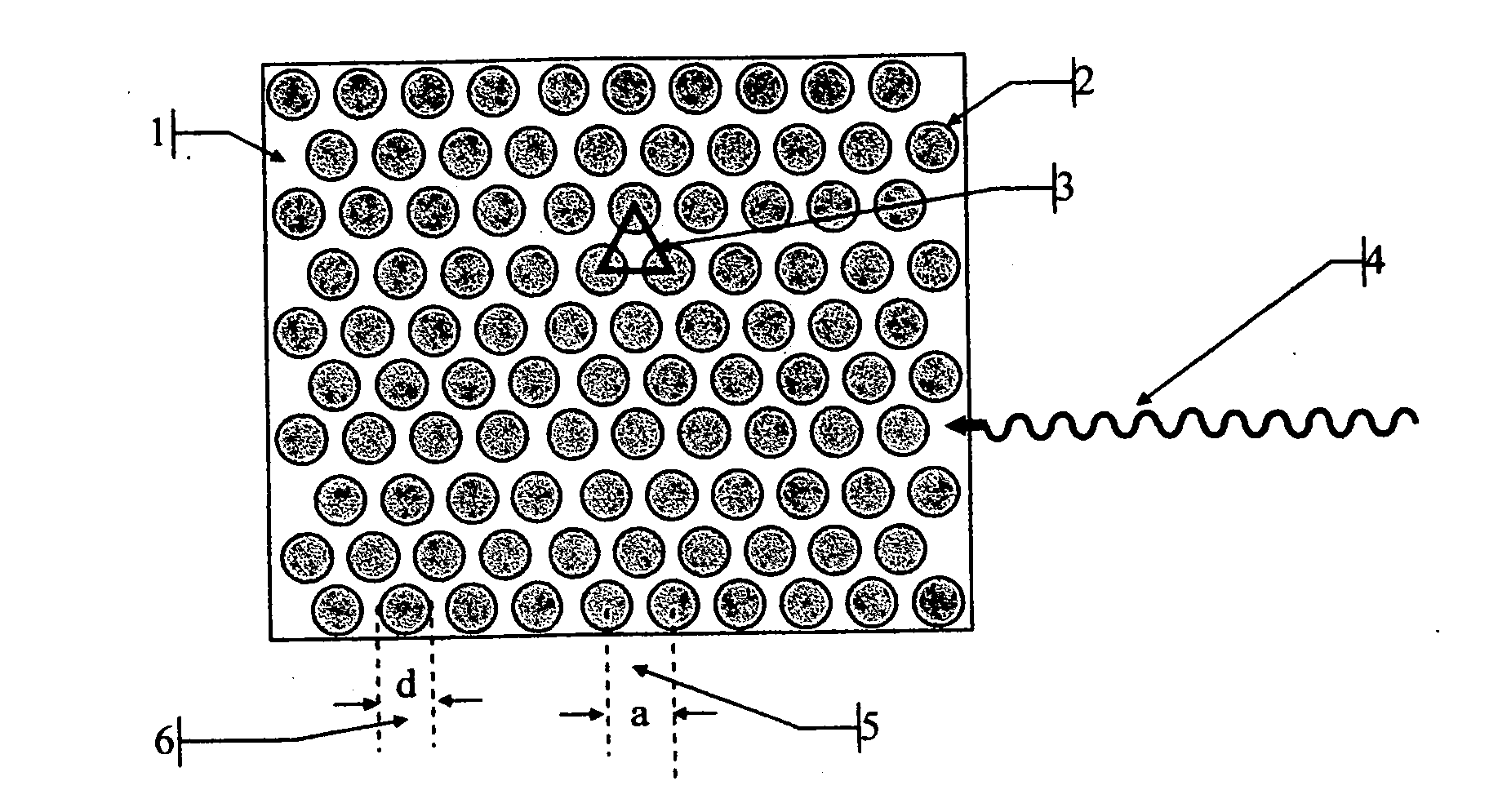
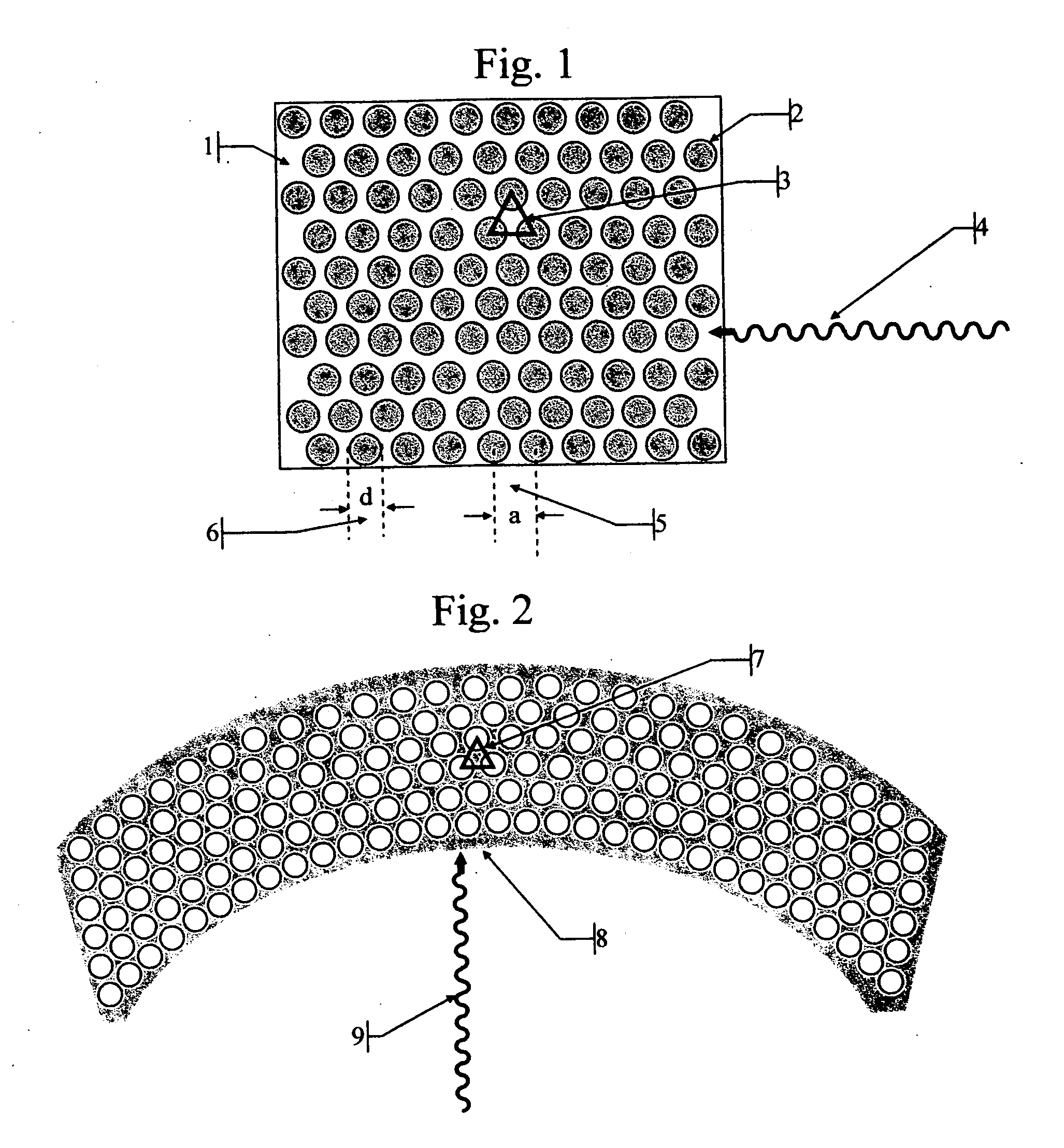
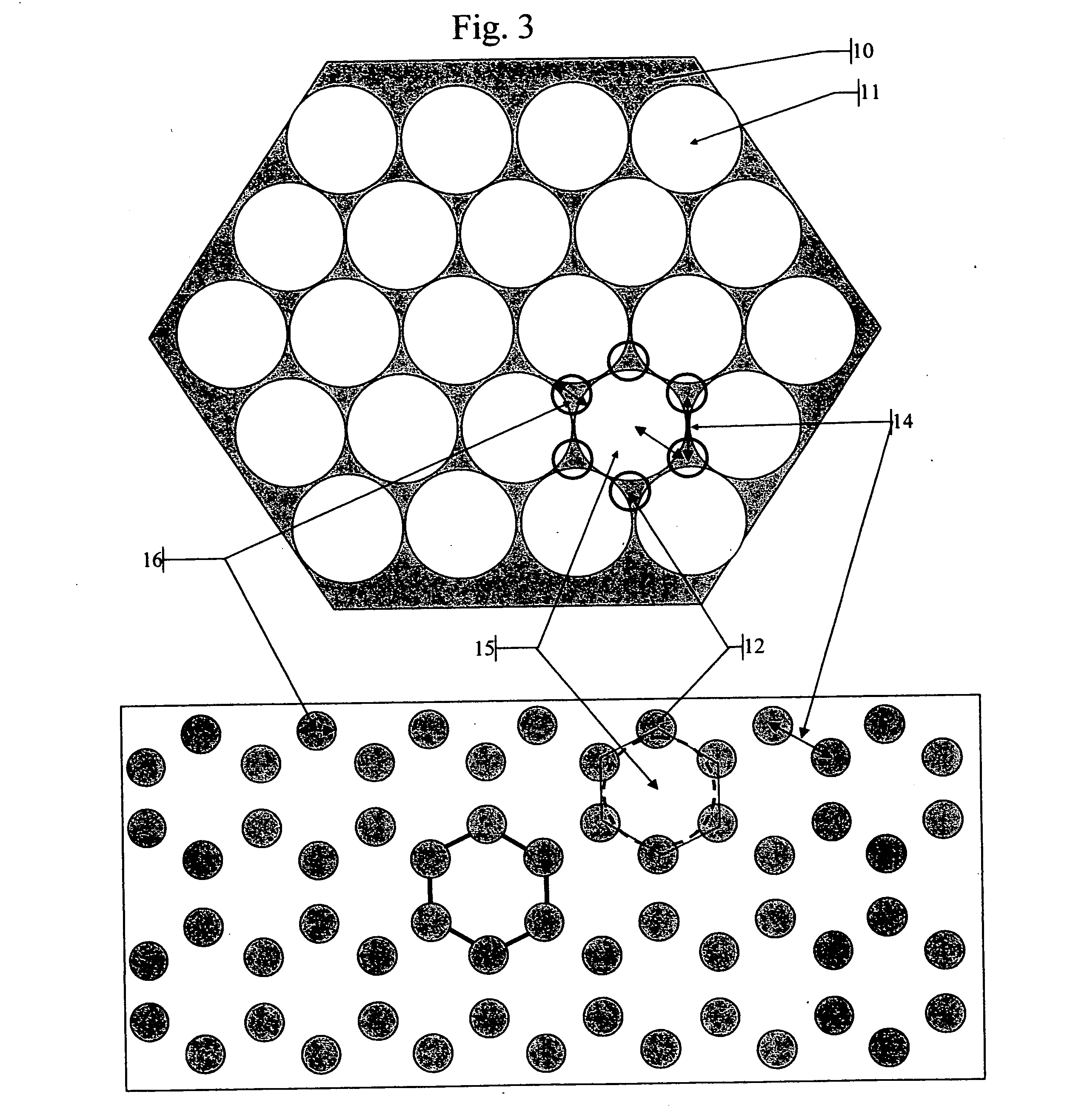
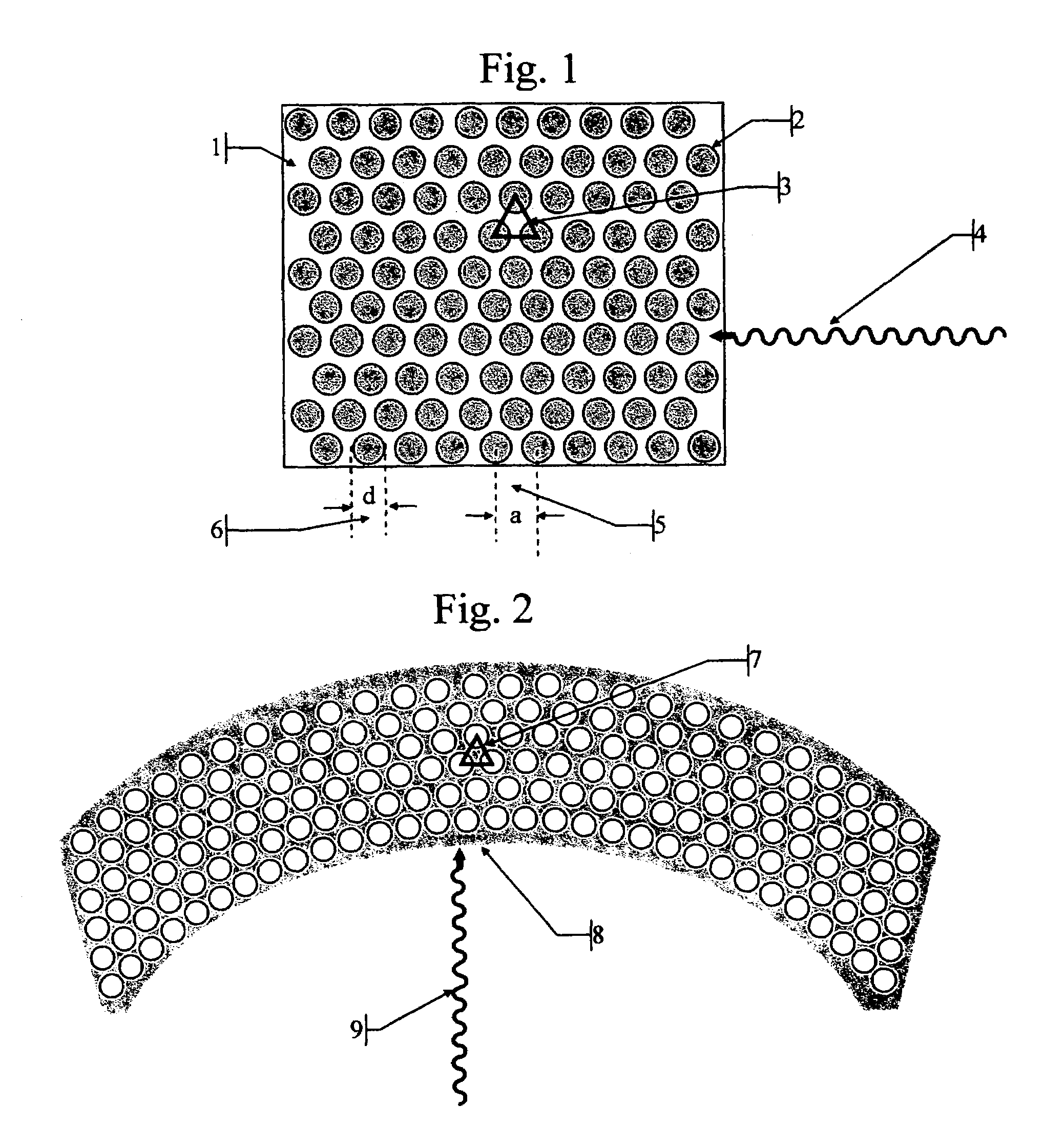
Radiation detectors
InactiveUS20060202125A1Thinner sliceImprove spatial resolutionMaterial analysis by optical meansNanoopticsRecoil electronPhotonic bandgap
The invention consists in structuring scintillation radiation detectors as Photonic Bandgap Crystals or 3D layers of thin filaments, thus enabling extremely high spatial resolutions and achieving virtual voxellation of the radiation detector without physical separating walls. The ability to precisely measure the recoil electron track in a Compton camera enables to assess the directions of the gamma rays hitting the detector and consequently dispensing with collimators that strongly reduce the intensity of radiation detected by gamma cameras. The invention enables great enhancements of the capabilities of gamma cameras, SPECT, PET, CT and DR machines as well as their use in Homeland Security applications. Methods of fabrication of such radiation detectors are decribed.
Owner:SUHAMI AVRAHAM
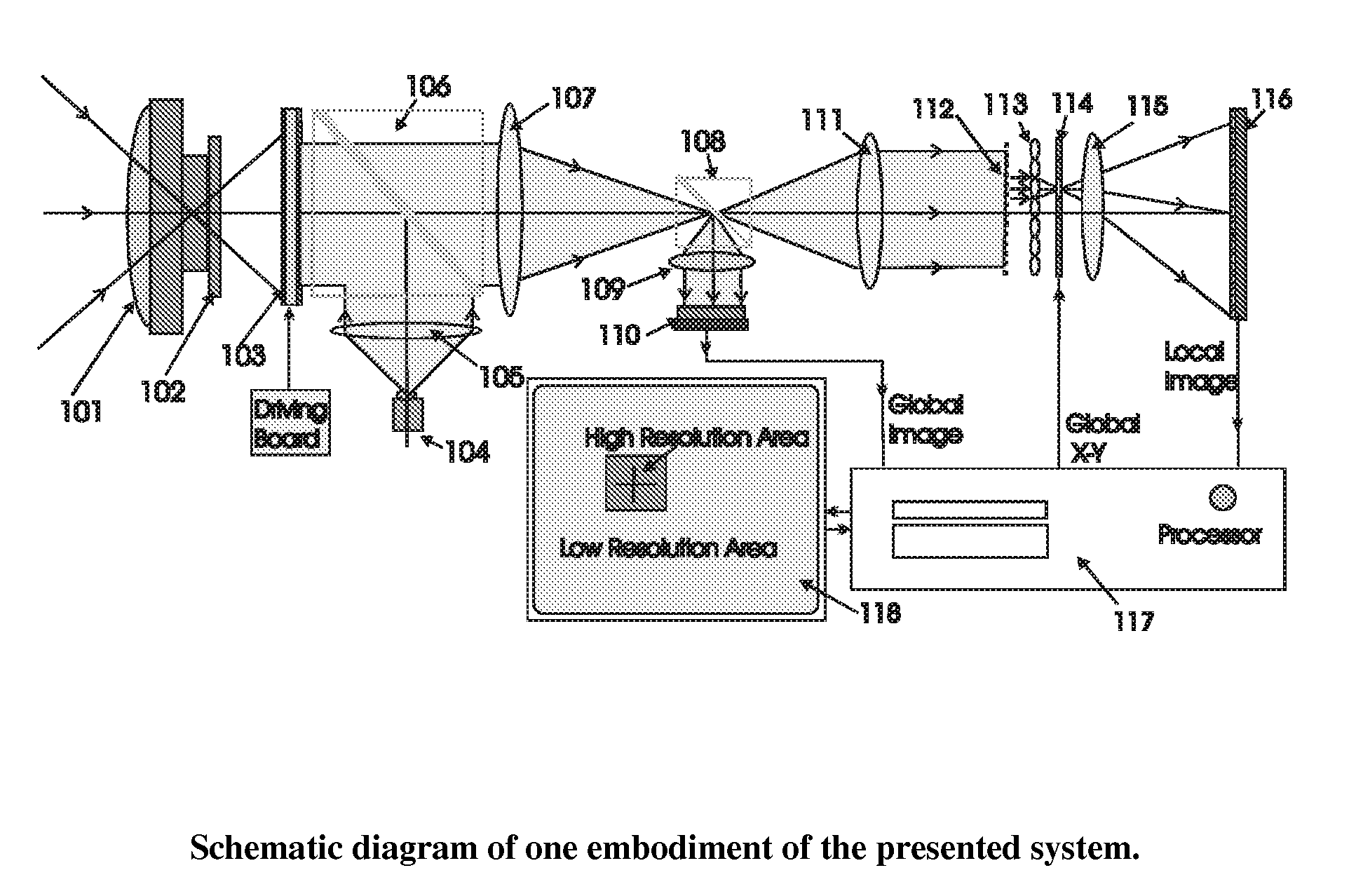
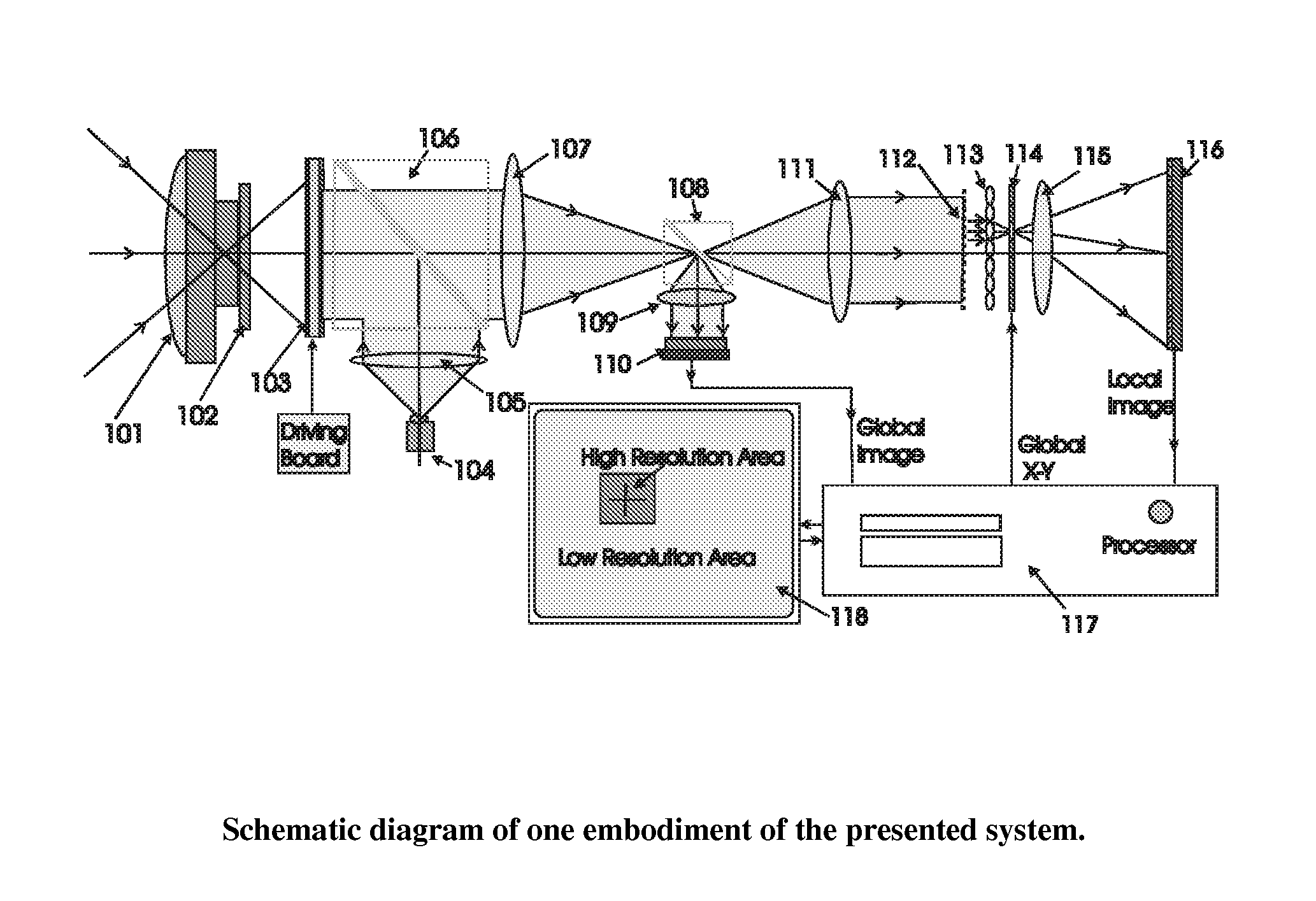
Electro-optical foveated imaging and tracking system
InactiveUS7973834B2Improve spatial resolutionWide field-of-viewTelevision system detailsCharacter and pattern recognitionSensor arrayHigh resolution image
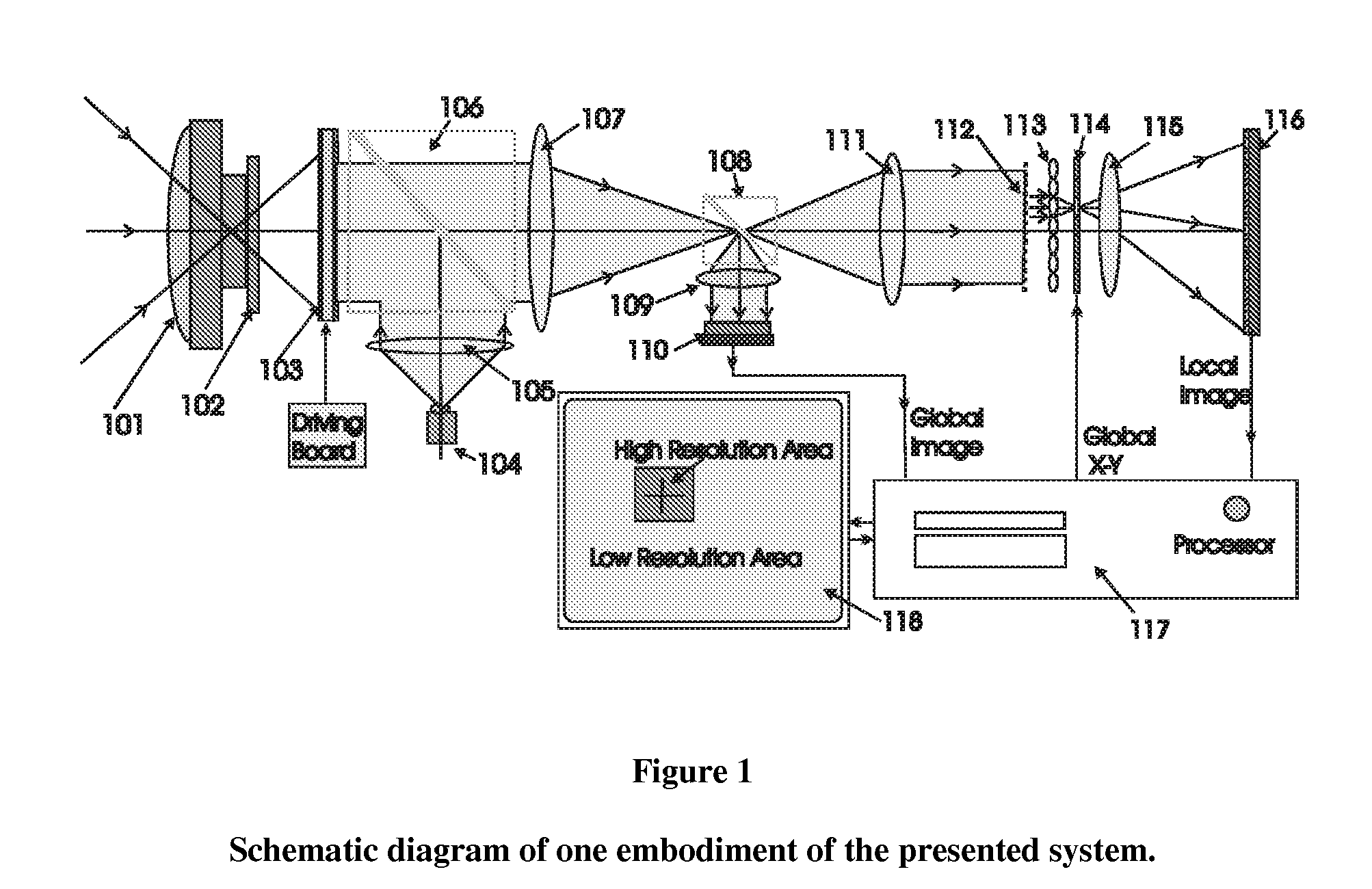
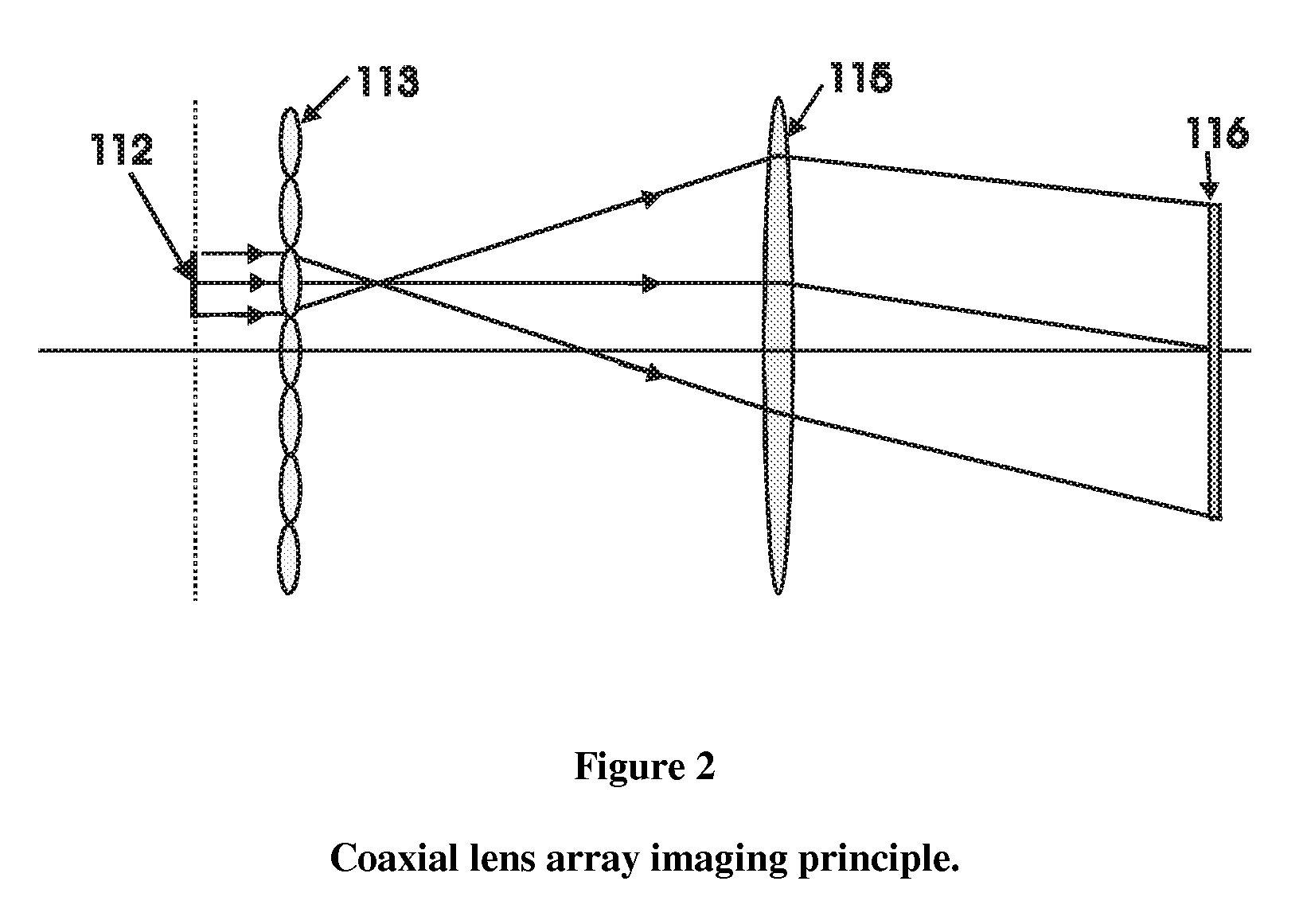
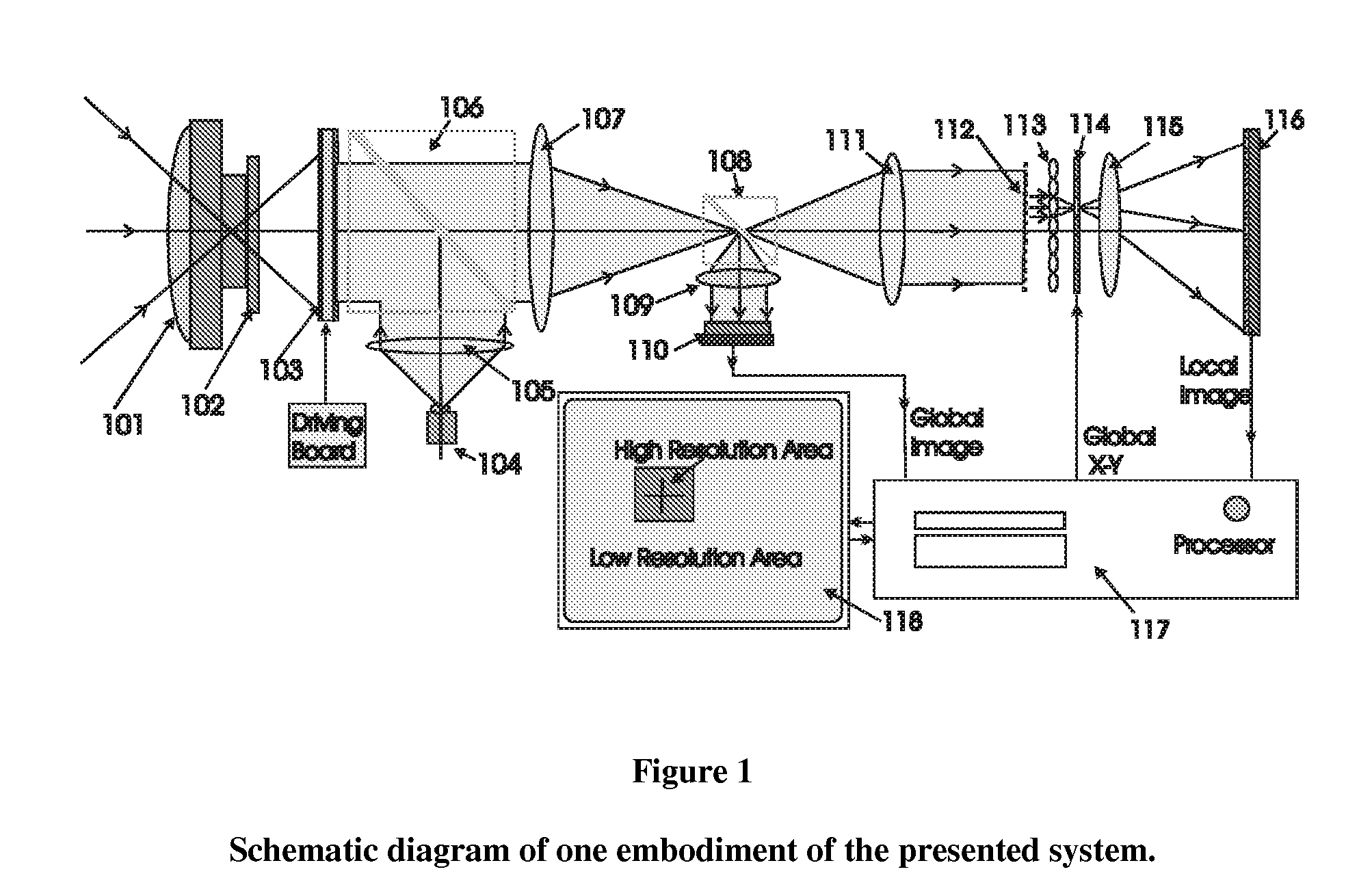
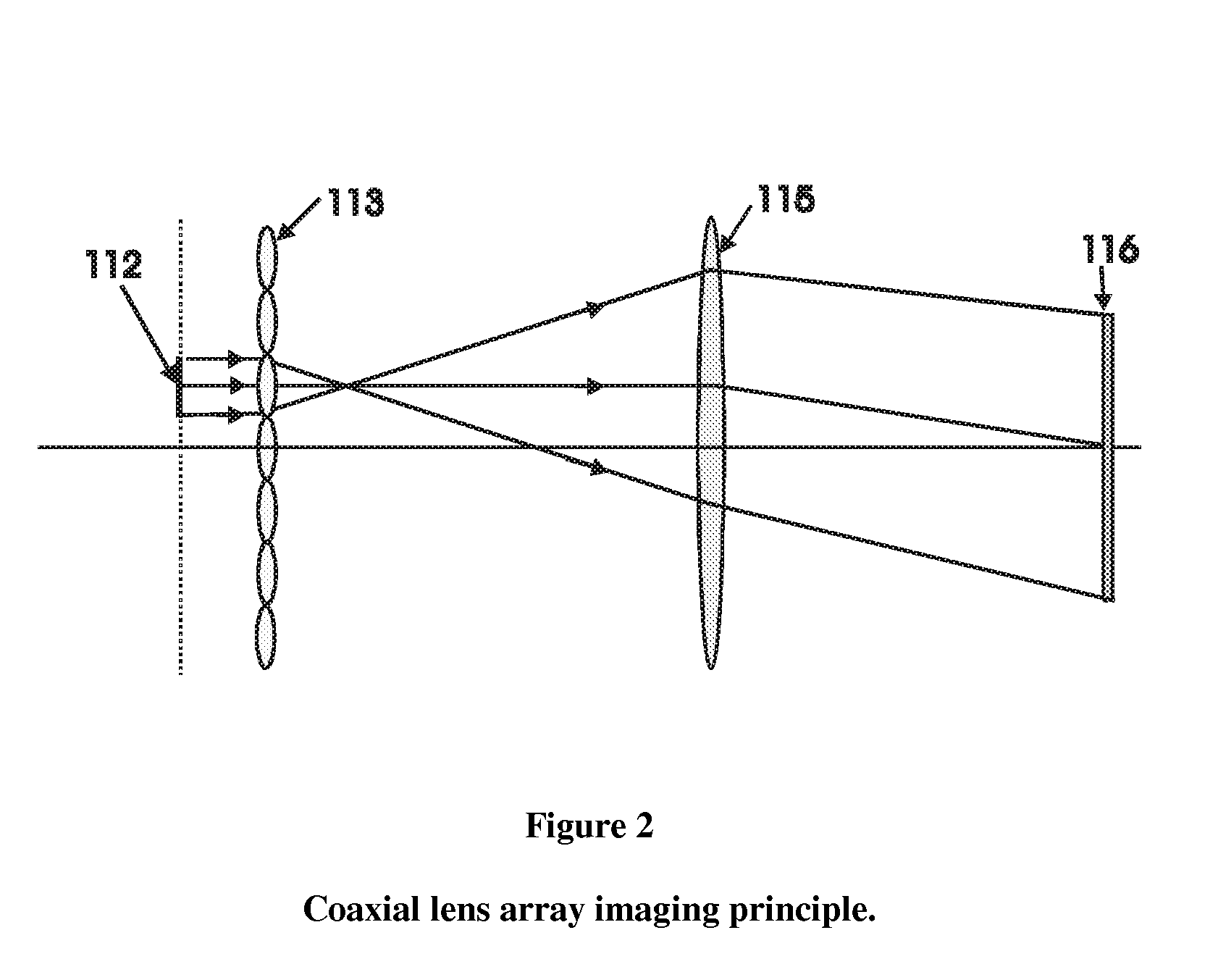
Conventional electro-optical imaging systems can not achieve wide field of view (FOV) and high spatial resolution imaging simultaneously due to format size limitations of image sensor arrays. To implement wide field of regard imaging with high resolution, mechanical scanning mechanisms are typically used. Still, sensor data processing and communication speed is constrained due to large amount of data if large format image sensor arrays are used. This invention describes an electro-optical imaging system that achieves wide FOV global imaging for suspect object detection and local high resolution for object recognition and tracking. It mimics foveated imaging property of human eyes. There is no mechanical scanning for changing the region of interest (ROI). Two relatively small format image sensor arrays are used to respectively acquire global low resolution image and local high resolution image. The ROI is detected and located by analysis of the global image. A lens array along with an electronically addressed switch array and a magnification lens is used to pick out and magnify the local image. The global image and local image are processed by the processor, and can be fused for display. Three embodiments of the invention are described.
Owner:NEW SPAN OPTO TECH
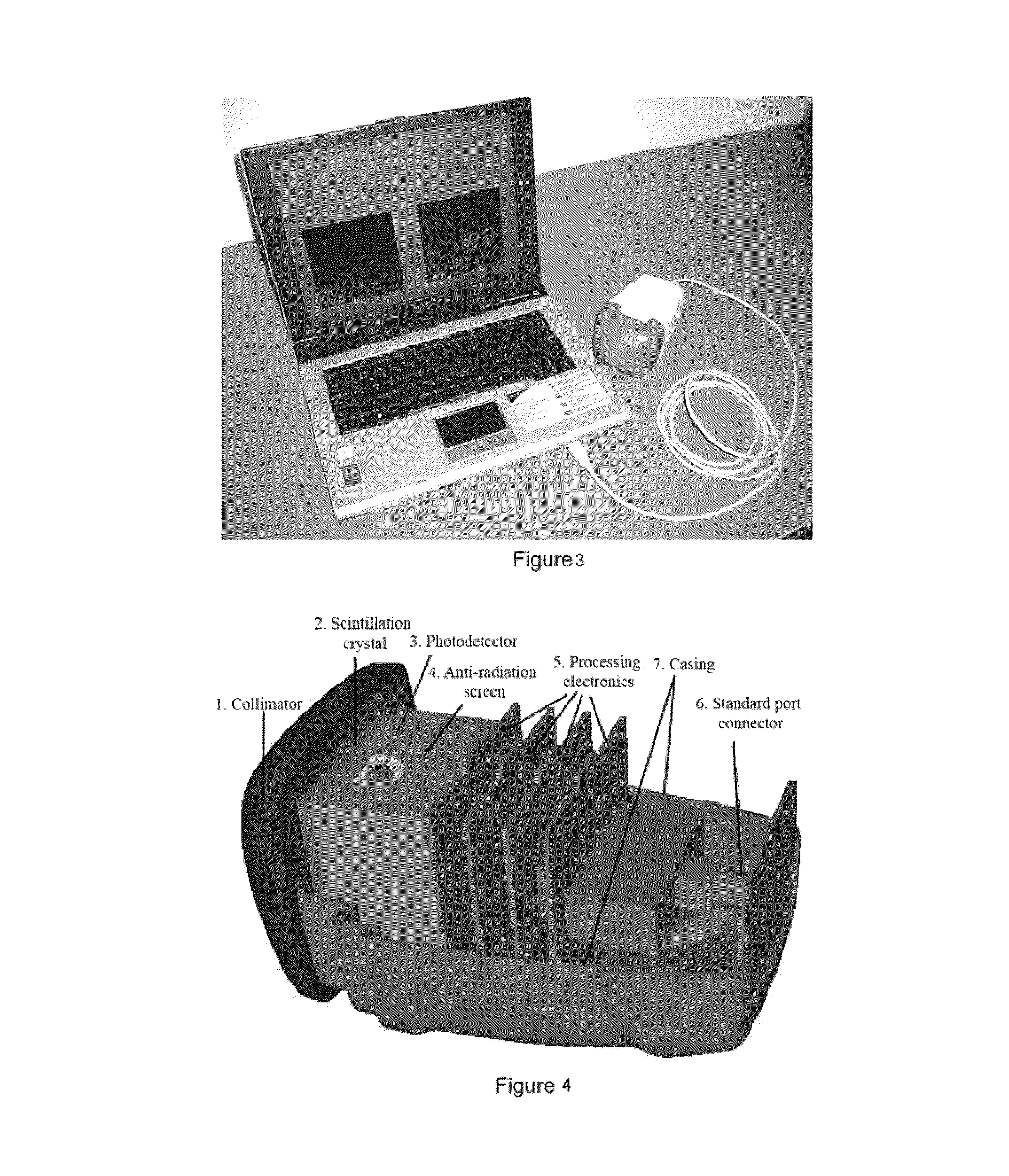
Stand-alone mini gamma camera including a localization system for intrasurgical use
ActiveUS8450694B2Surgical navigation systemsMaterial analysis by optical meansLocalization systemThe Internet
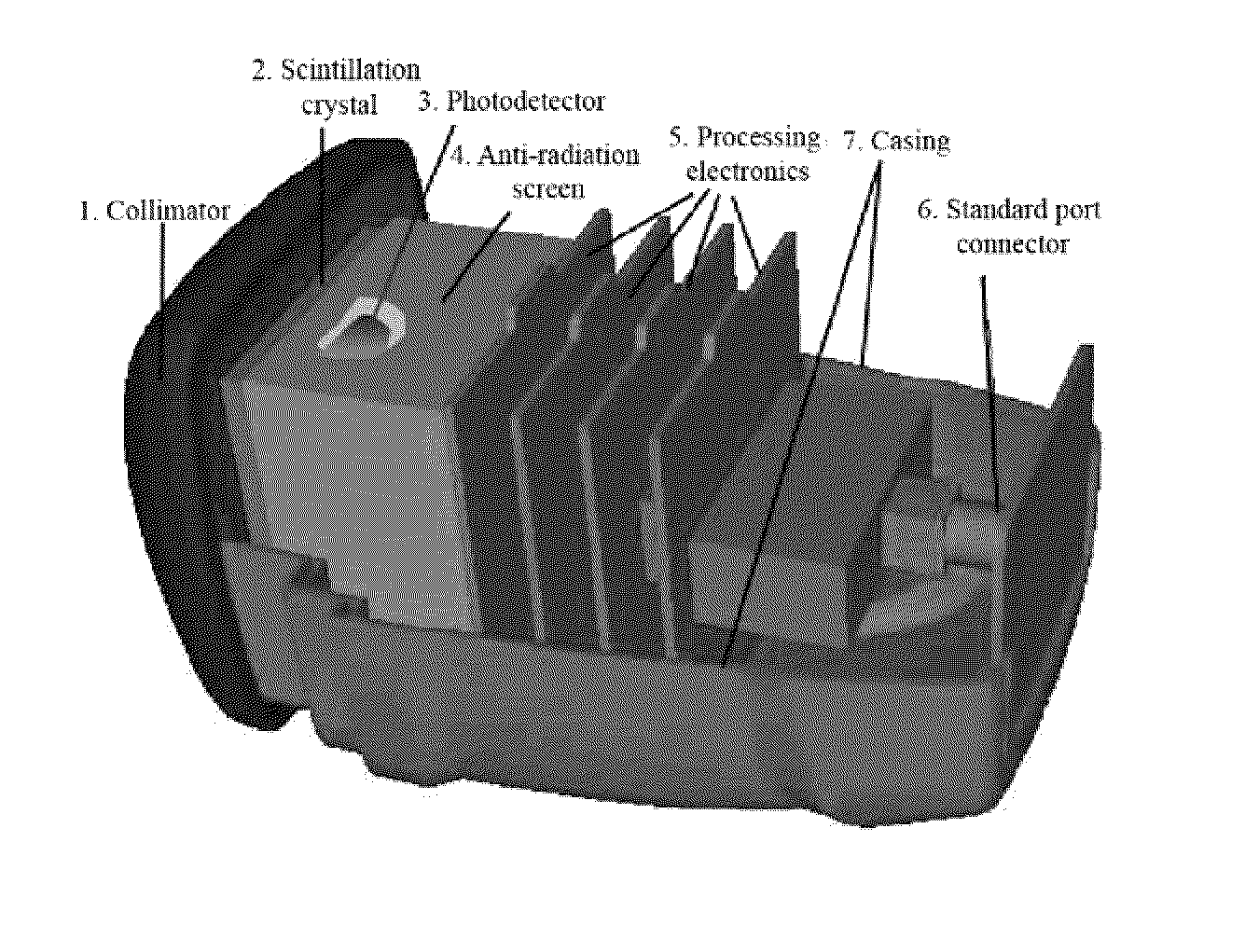
The invention relates to a portable mini gamma camera for intrasurgical use. The inventive camera is based on scintillation crystals and comprises a stand-alone device, i.e. all of the necessary systems have been integrated next to the sensor head and no other system is required. The camera can be hot-swapped to any computer using different types of interface, such as to meet medical grade specifications. The camera can be self-powered, can save energy and enables software and firmware to be updated from the Internet and images to be formed in real time. Any gamma ray detector based on continuous scintillation crystals can be provided with a system for focusing the scintillation light emitted by the gamma ray in order to improve spatial resolution. The invention also relates to novel methods for locating radiation-emitting objects and for measuring physical variables, based on radioactive and laser emission pointers.
Owner:GENERAL EQUIP FOR MEDICAL IMAGING SL +2
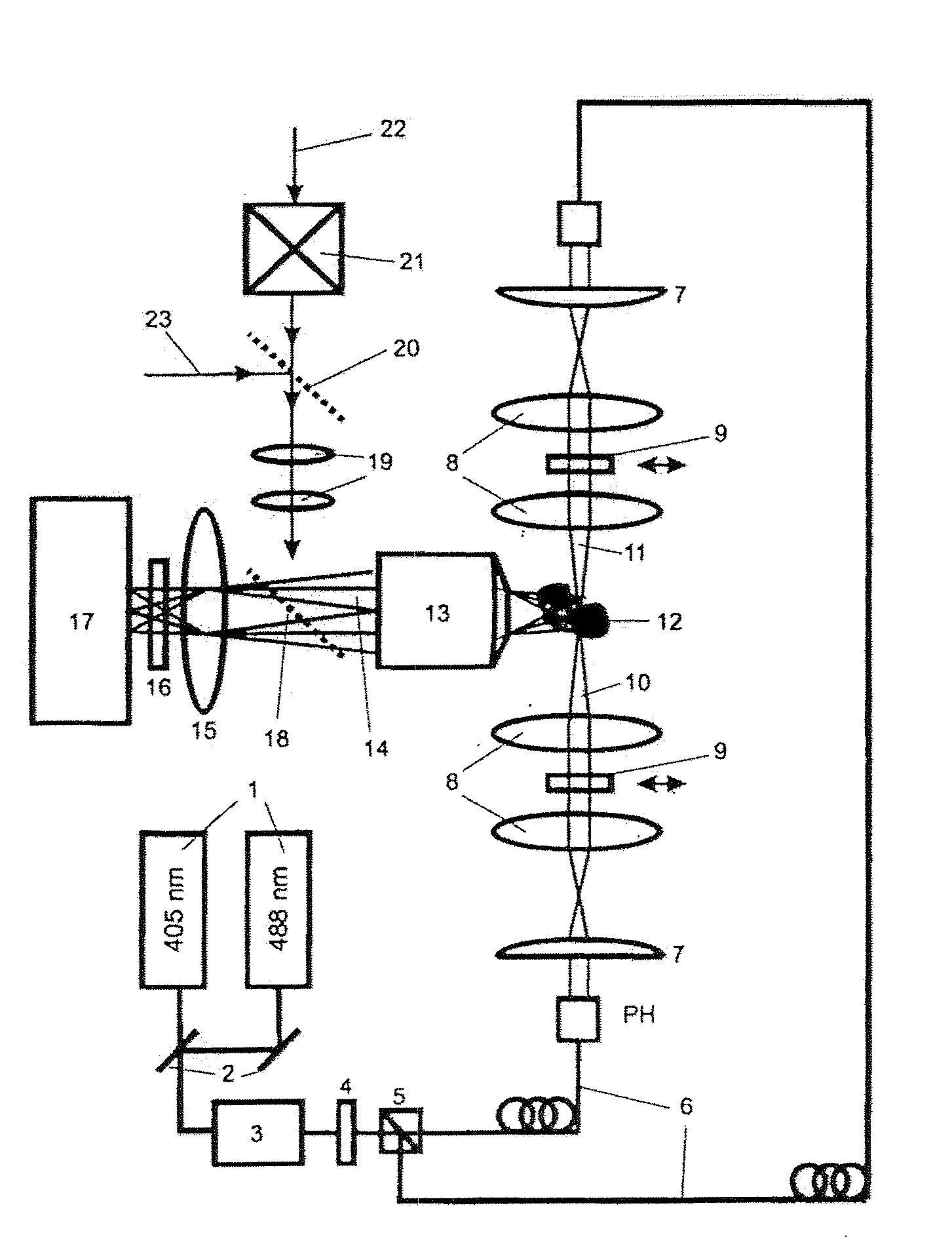
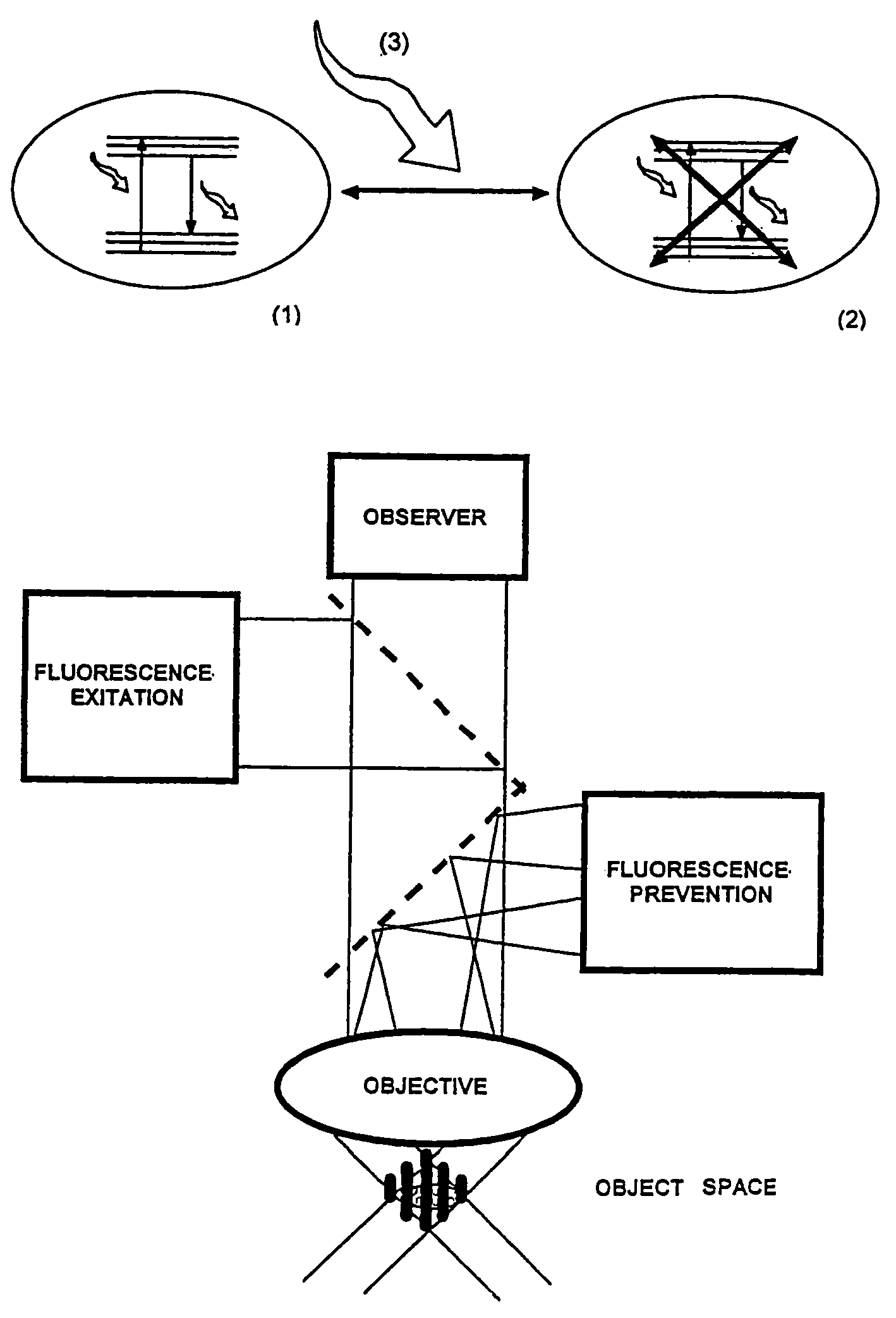
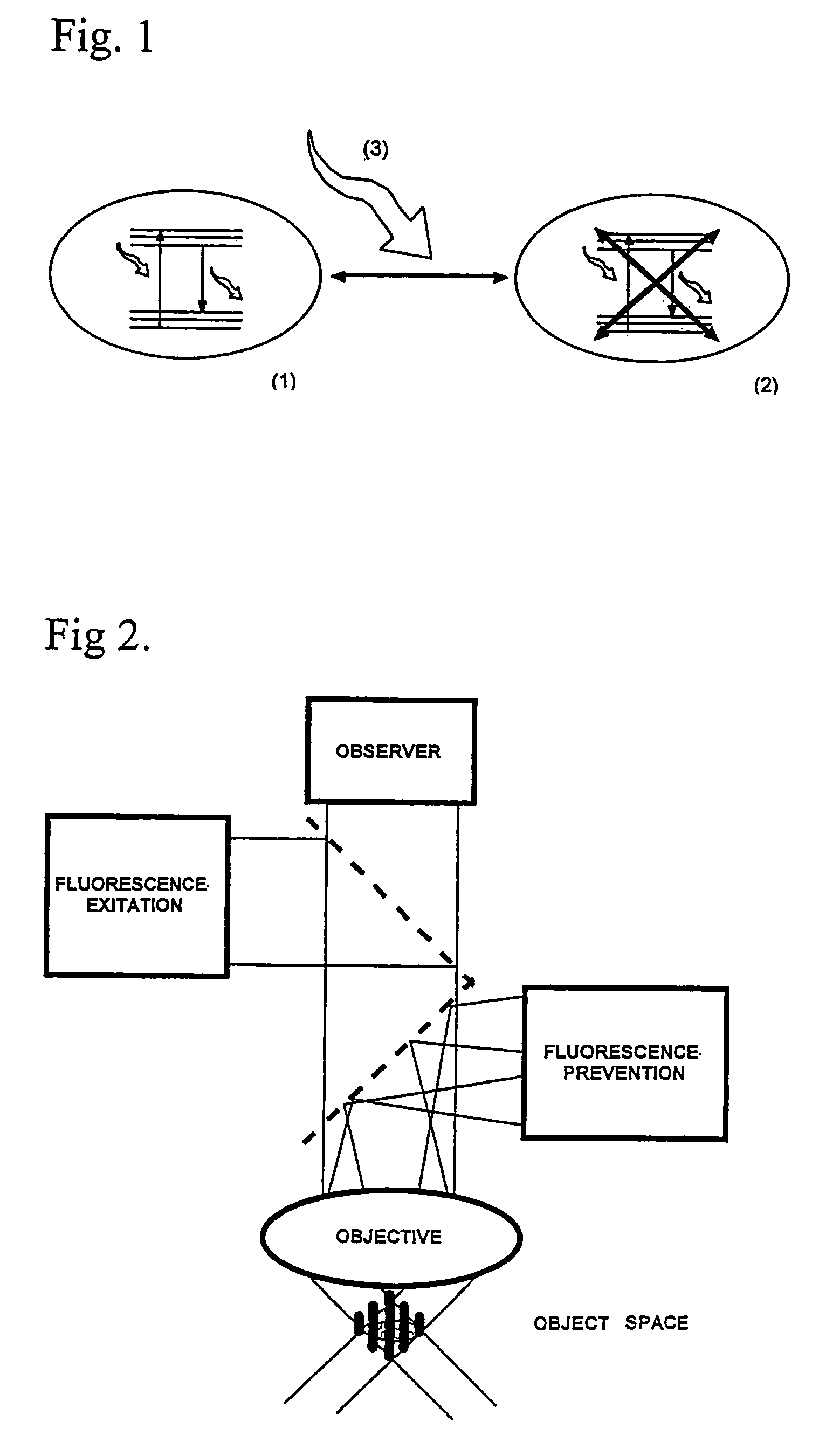
High spatial resolution imaging of a structure of interest in a specimen
ActiveUS20090134342A1Reduces yield of fluorescent lightHigh resolutionMicrobiological testing/measurementPreparing sample for investigationSensor arrayFluorescence
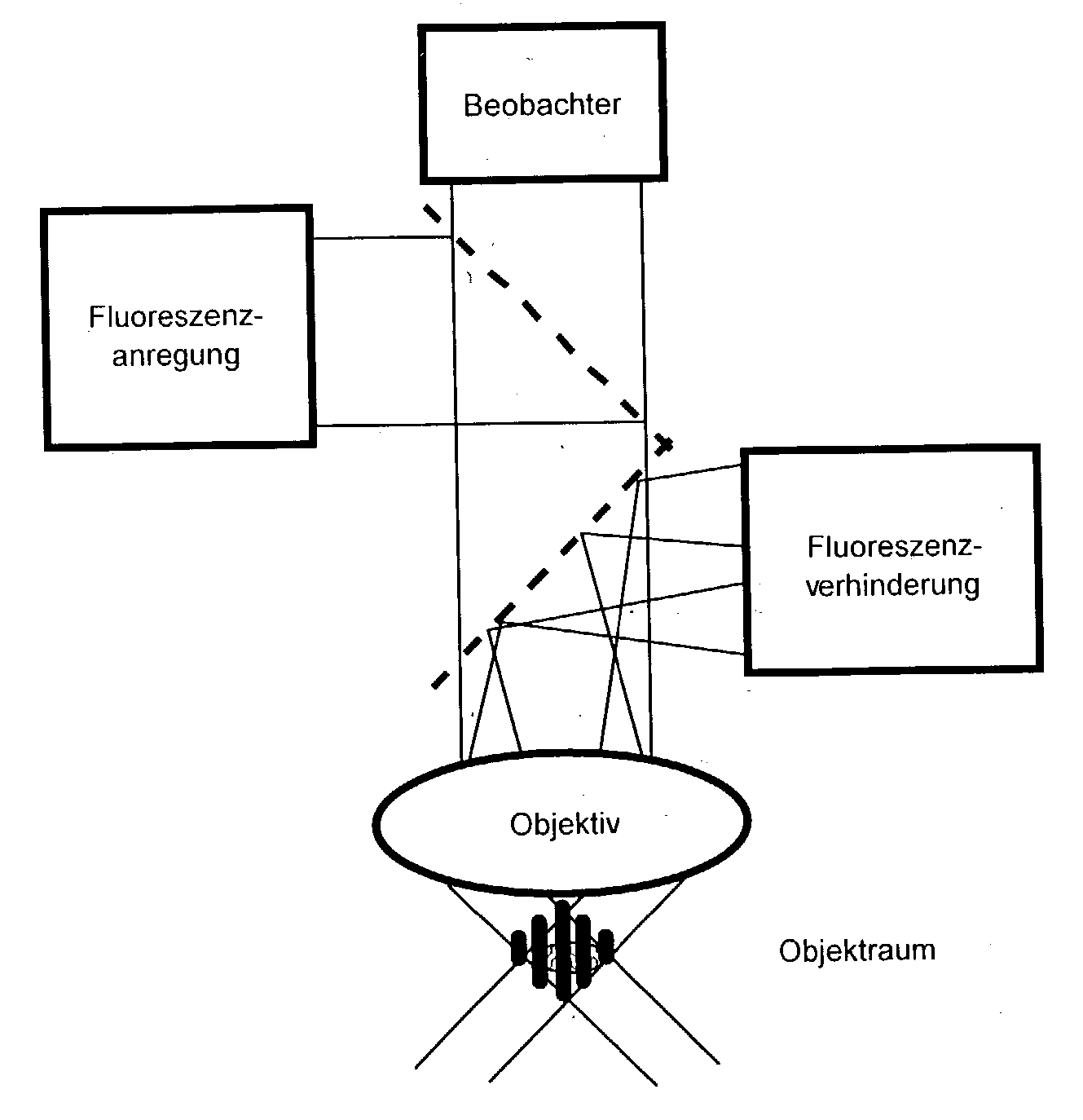
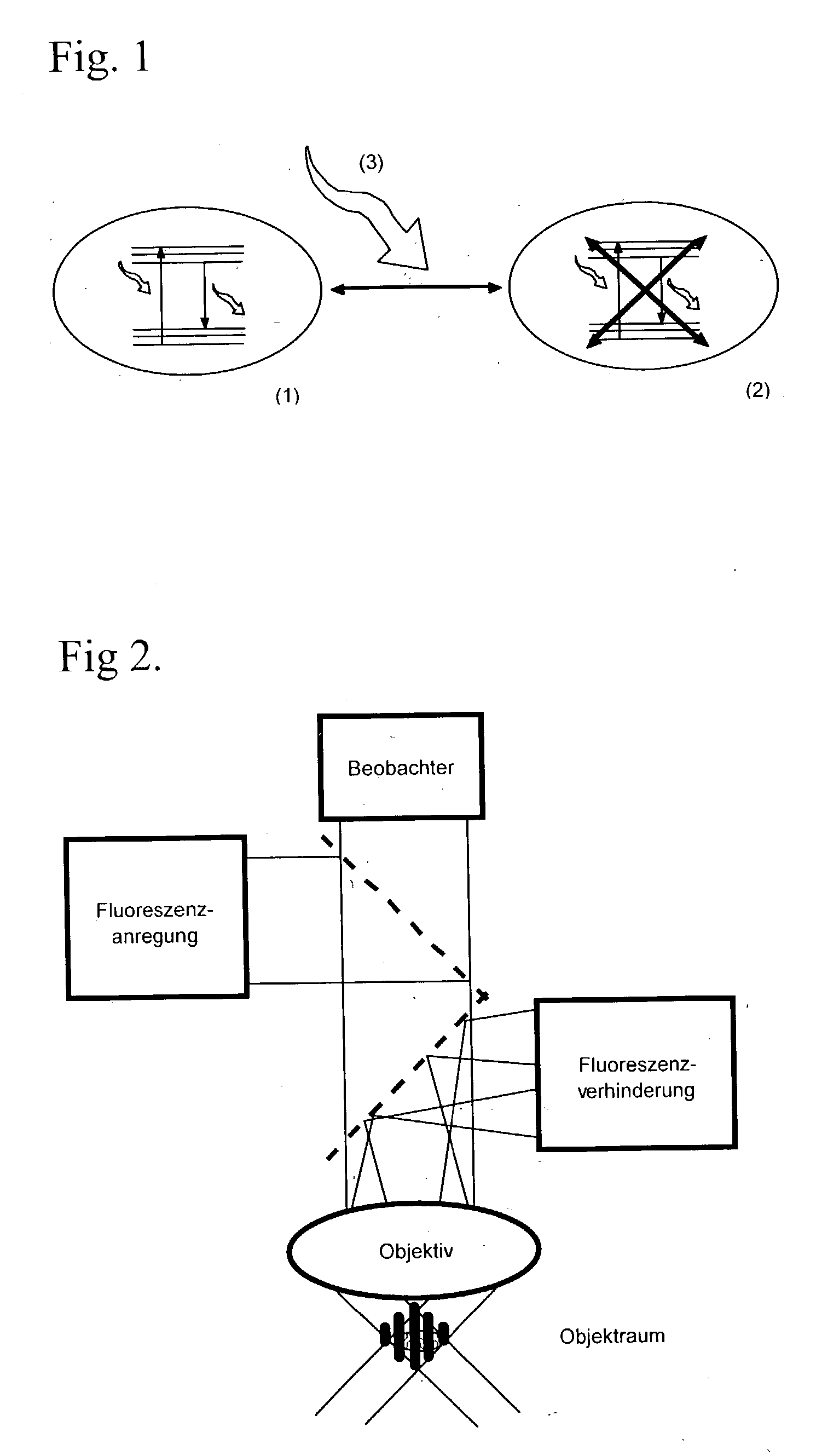
For the high spatial resolution imaging of a structure of interest in a specimen, a substance is selected from a group of substances which have a fluorescent first state and a nonfluorescent second state; which can be converted fractionally from their first state into their second state by light which excites them into fluorescence, and which return from their second state into their first state; the specimen's structure of interest is imaged onto a sensor array, a spatial resolution limit of the imaging being greater (i.e. worse) than an average spacing between closest neighboring molecules of the substance in the specimen; the specimen is exposed to light in a region which has dimensions larger than the spatial resolution limit, fractions of the substance alternately being excited by the light to emit fluorescent light and converted into their second state, and at least 10% of the molecules of the substance that are respectively in the first state lying at a distance from their closest neighboring molecules in the first state which is greater than the spatial resolution limit; and the fluorescent light, which is spontaneously emitted by the substance from the region, is registered in a plurality of images recorded by the sensor array during continued exposure of the specimen to the light.
Owner:MAX PLANCK GESELLSCHAFT ZUR FOERDERUNG DER WISSENSCHAFTEN EV
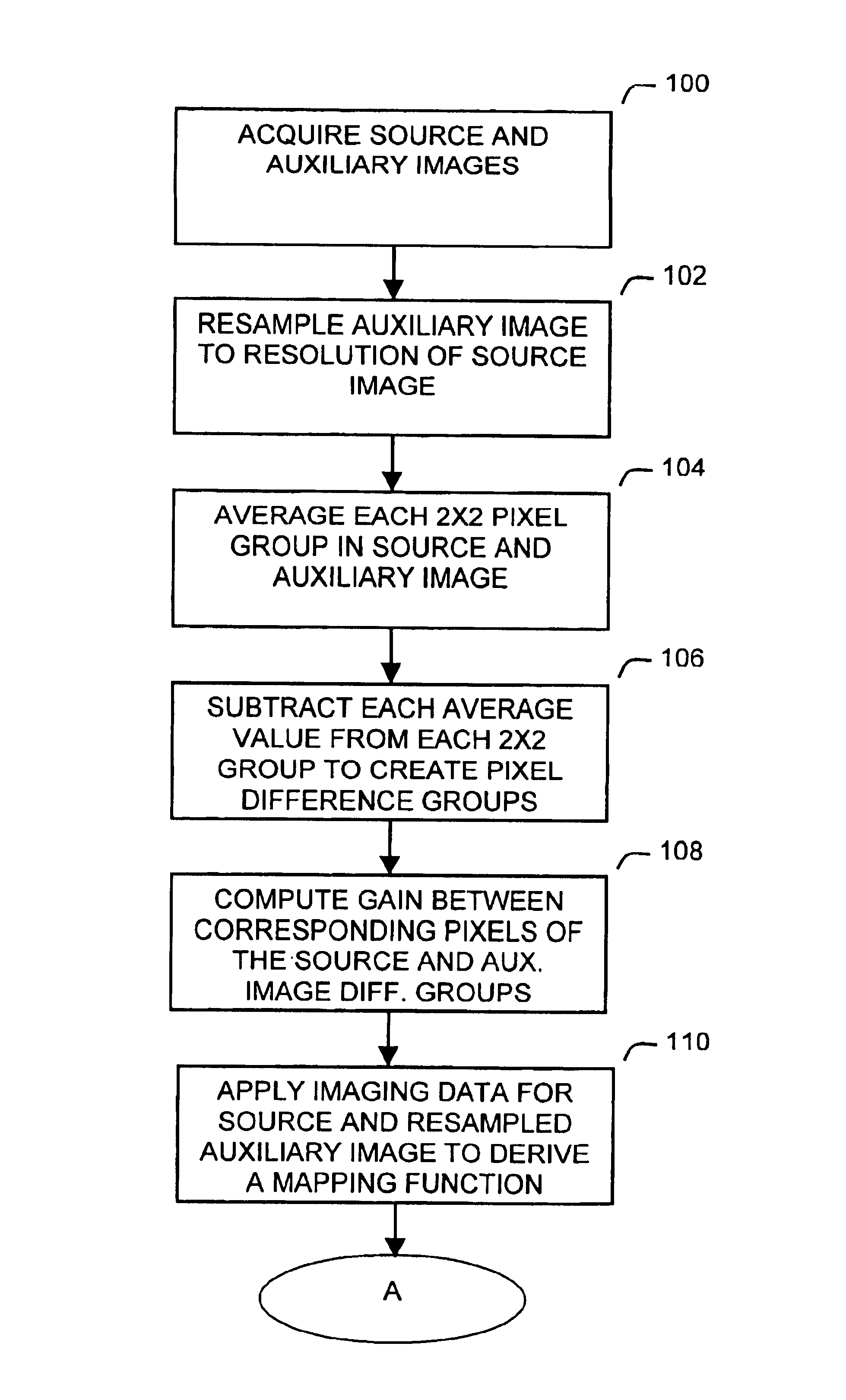
Apparatus and method for efficiently increasing the spatial resolution of images
InactiveUS6937774B1Improve spatial resolutionTelevision system detailsGeometric image transformationImage resolutionHigh spatial resolution
A method increases the spatial resolution of a source image based on an auxiliary, co-registered image of a higher spatial resolution. Each of the source and auxiliary images includes a plurality of pixels with corresponding spectral intensities and the method includes reducing, identifying, deriving, subdividing and modifying steps. Multiple auxiliary images can be used with the method.In the reducing step, a spatial resolution of the auxiliary image is reduced to a common resolution with the source image. Then in the identifying step, corresponding groups of pixels at the common resolution in the source and auxiliary images are identified. Then in the deriving step, a mapping function is derived which relates the rate of change of intensity of each group in the auxiliary image and the corresponding rate of change of intensity in the corresponding group in the source image to the intensity vector. This map can be conditioned on any number of auxiliary image planes.In the subdividing step, each source pixel is subdivided. Then in the modifying step, the spectral intensity of each subdivided source pixel is modifying based on the map and the local intensity variations of the auxiliary image. This results in increasing the resolution of the source image.
Owner:LOCKHEED MARTIN CORP
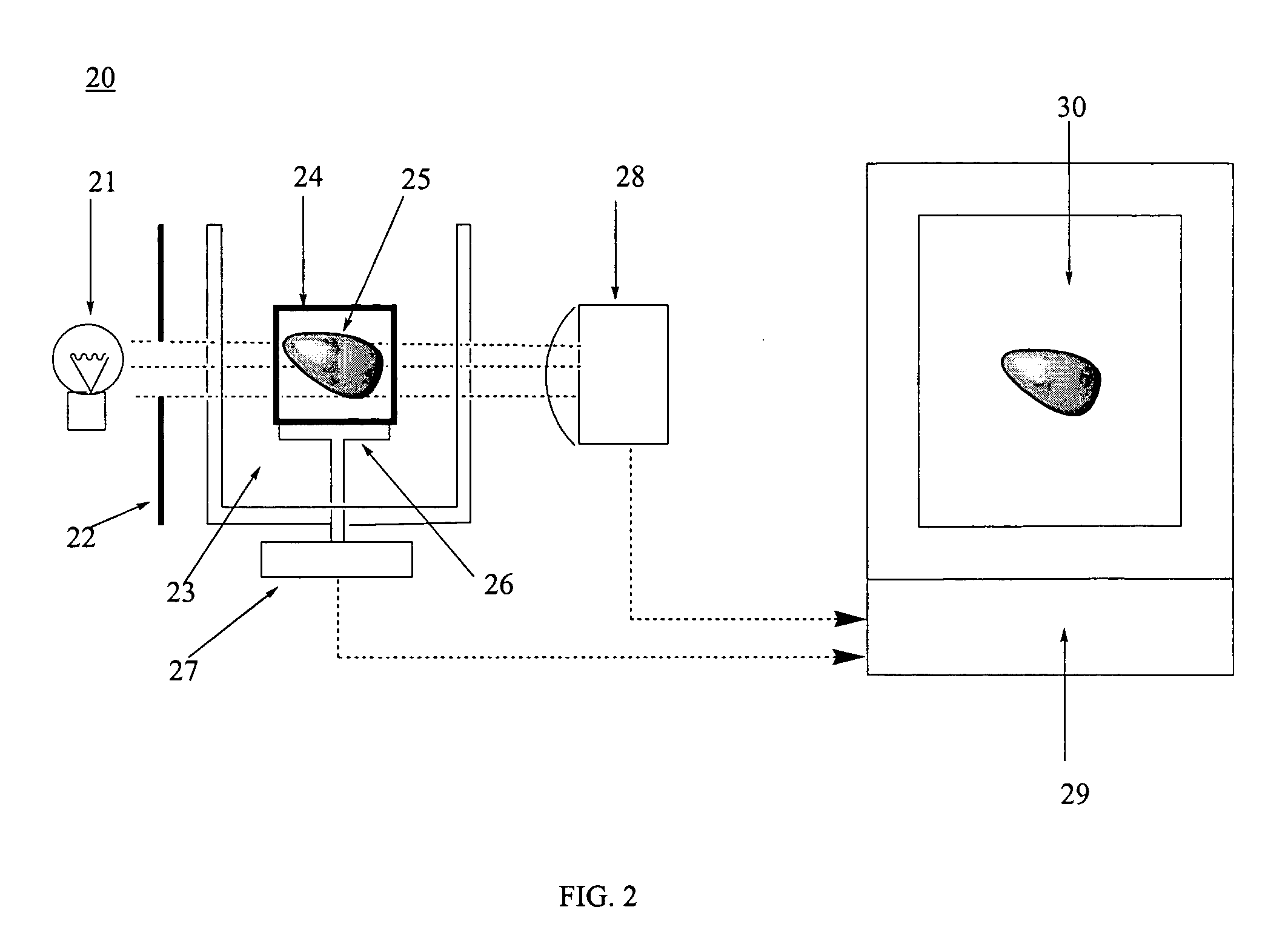
Device and method for analyzing an organic sample
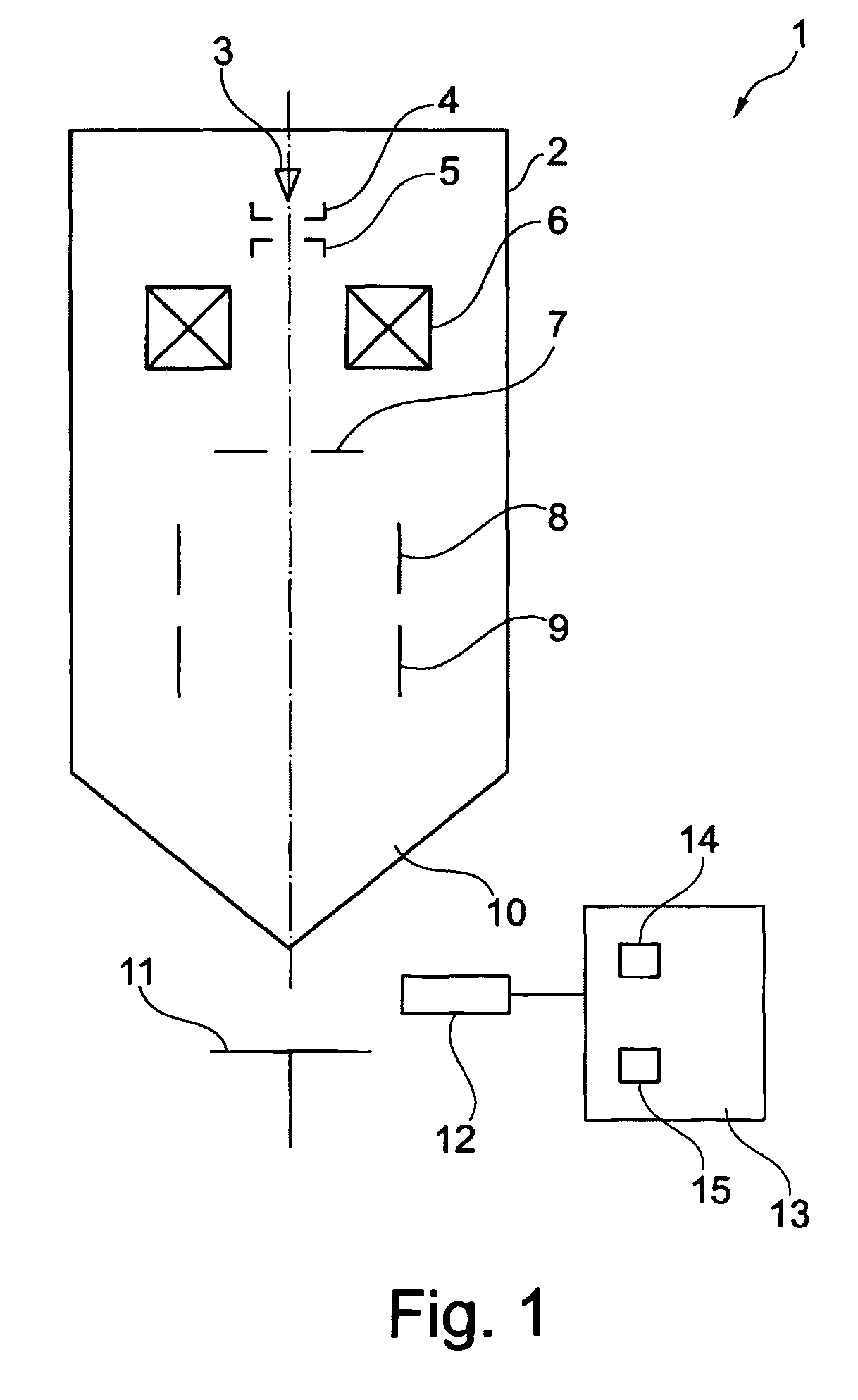
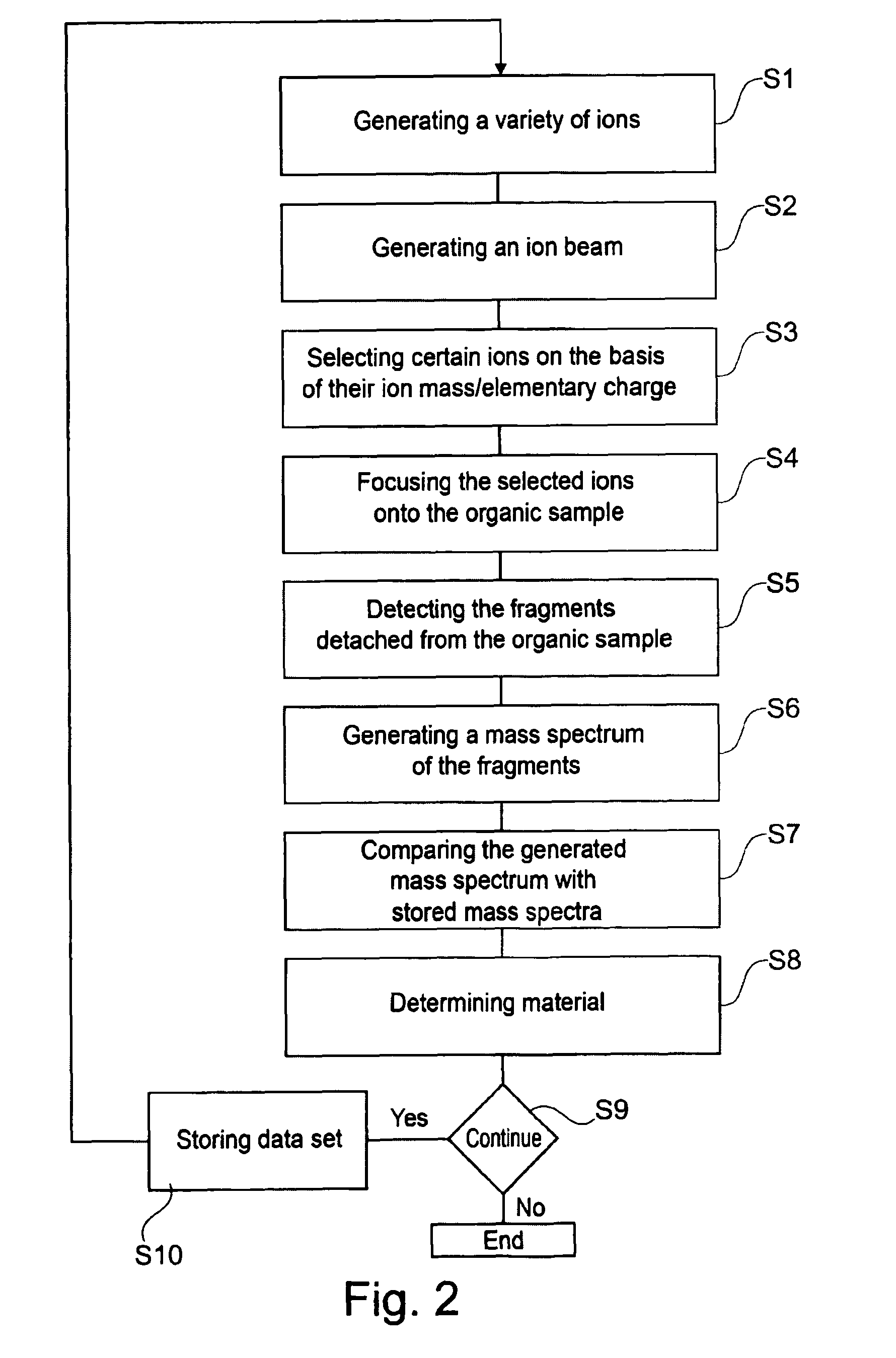
ActiveUS8263933B2Easy to analyzeHigh resolutionMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationMaterial analysis by optical meansImage resolutionHigh spatial resolution
A device and method for analyzing an organic sample provide high spatial resolution. A focused ion beam is directed onto the organic sample. Fragments detached from the sample are examined using mass spectroscopy.
Owner:CARL ZEISS SMT GMBH
Differential confocal scanning detection method with high spatial resolution
InactiveCN1527026AImprove axial resolutionImprove horizontal resolutionUsing optical meansLine widthHigh spatial resolution
The present invention belongs to the field of fine surface structure measuring technology, and relates to one kind of differential confocal scanning detection method with high spatial resolution. Differential confocal microscopic double receiving light path configuration and double detector subtraction form the differential confocal signal in measuring the workpiece. Optical super-resolution confocal microscopic detection method is adopted to raise the transverse resolution, and differential confocal microscopic detection method is adopted to raise the longitudinal resolution, so as to reach differential confocal scanning detection of high spatial resolution. The method can meet the requirements in high spatial resolution, high precision and great measurement range, and is especially suitable for the measurement of fine surface 3D structure, miniature steps, miniature grooves, line width, surface appearance, etc.
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH
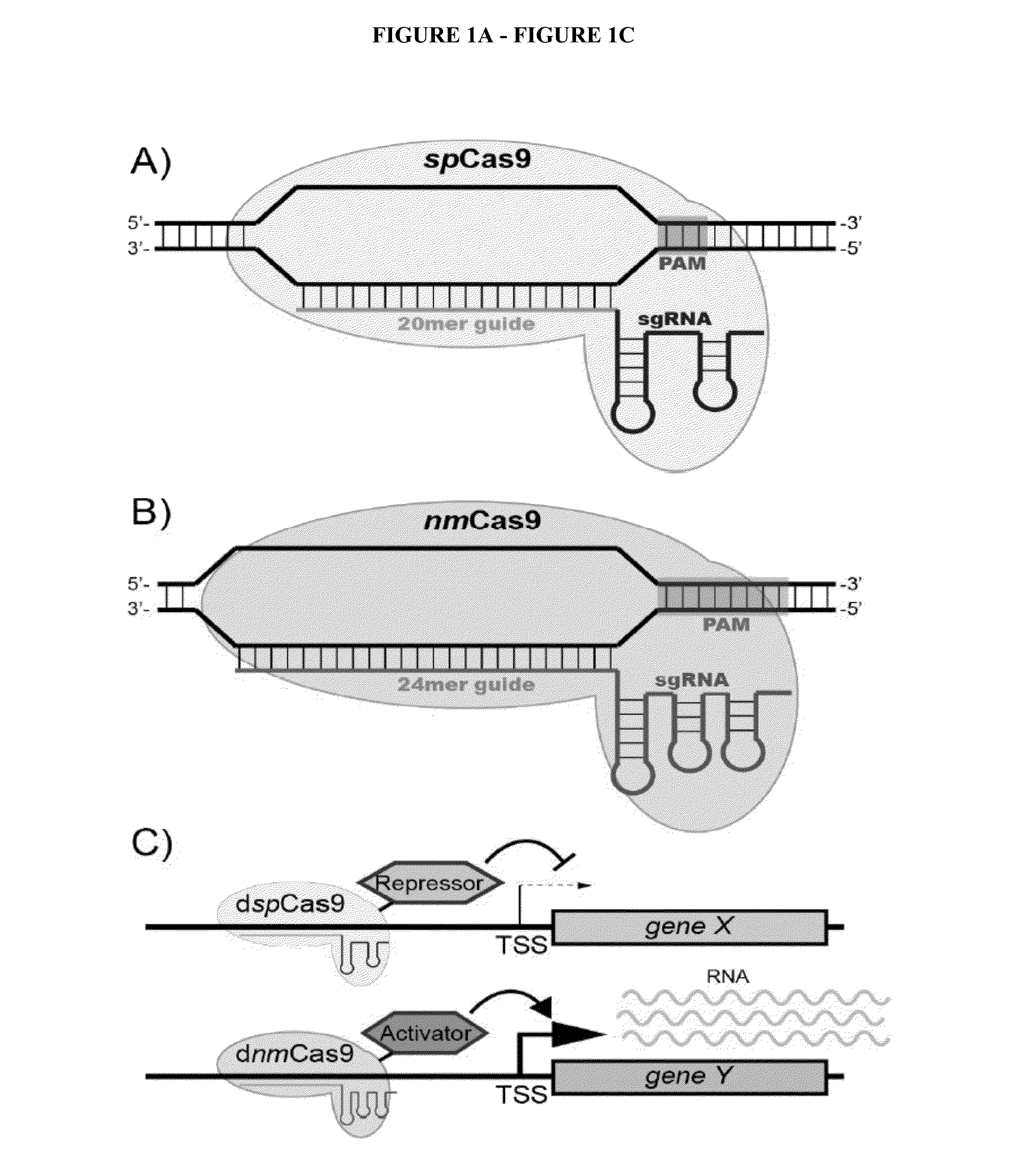
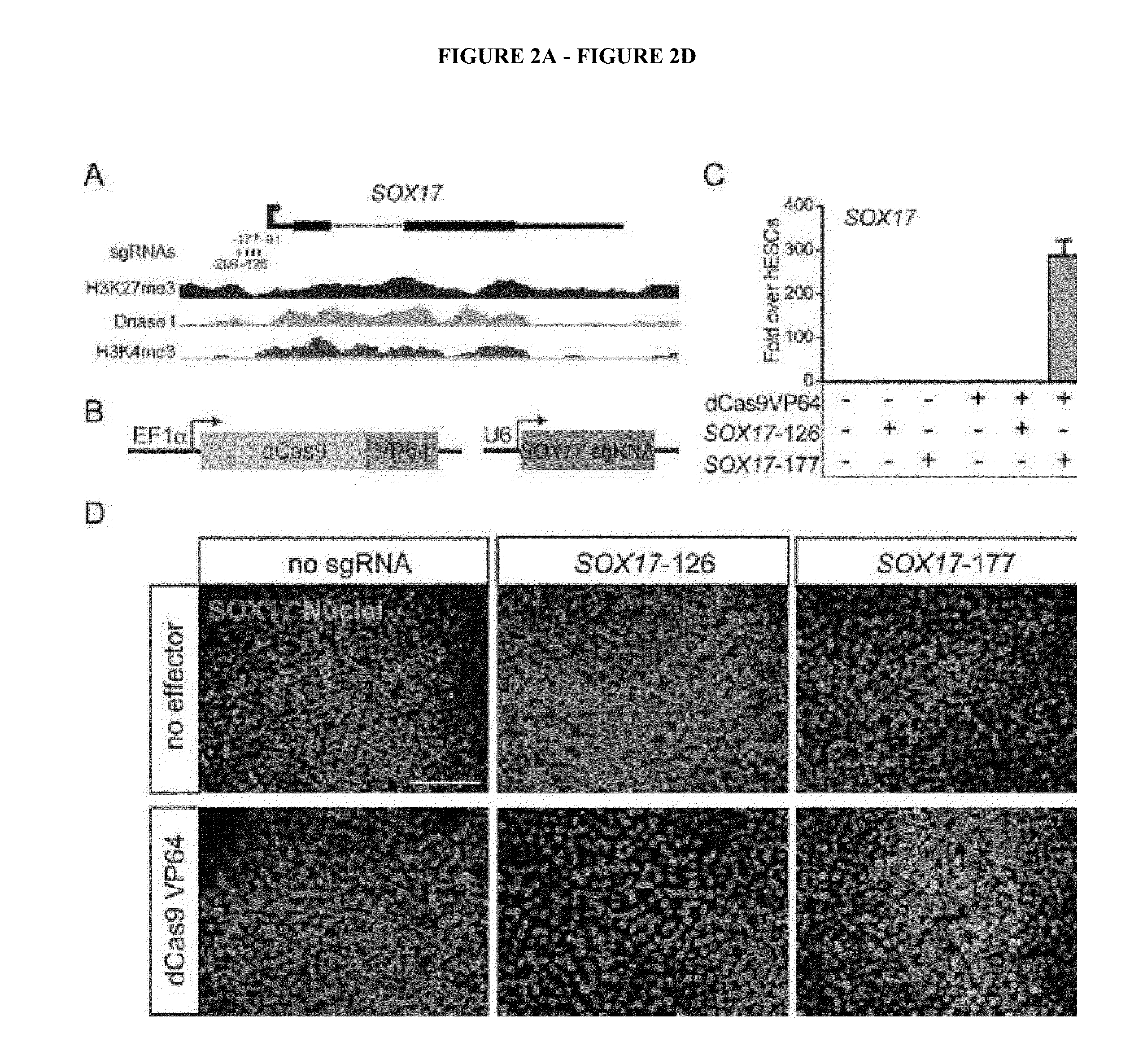
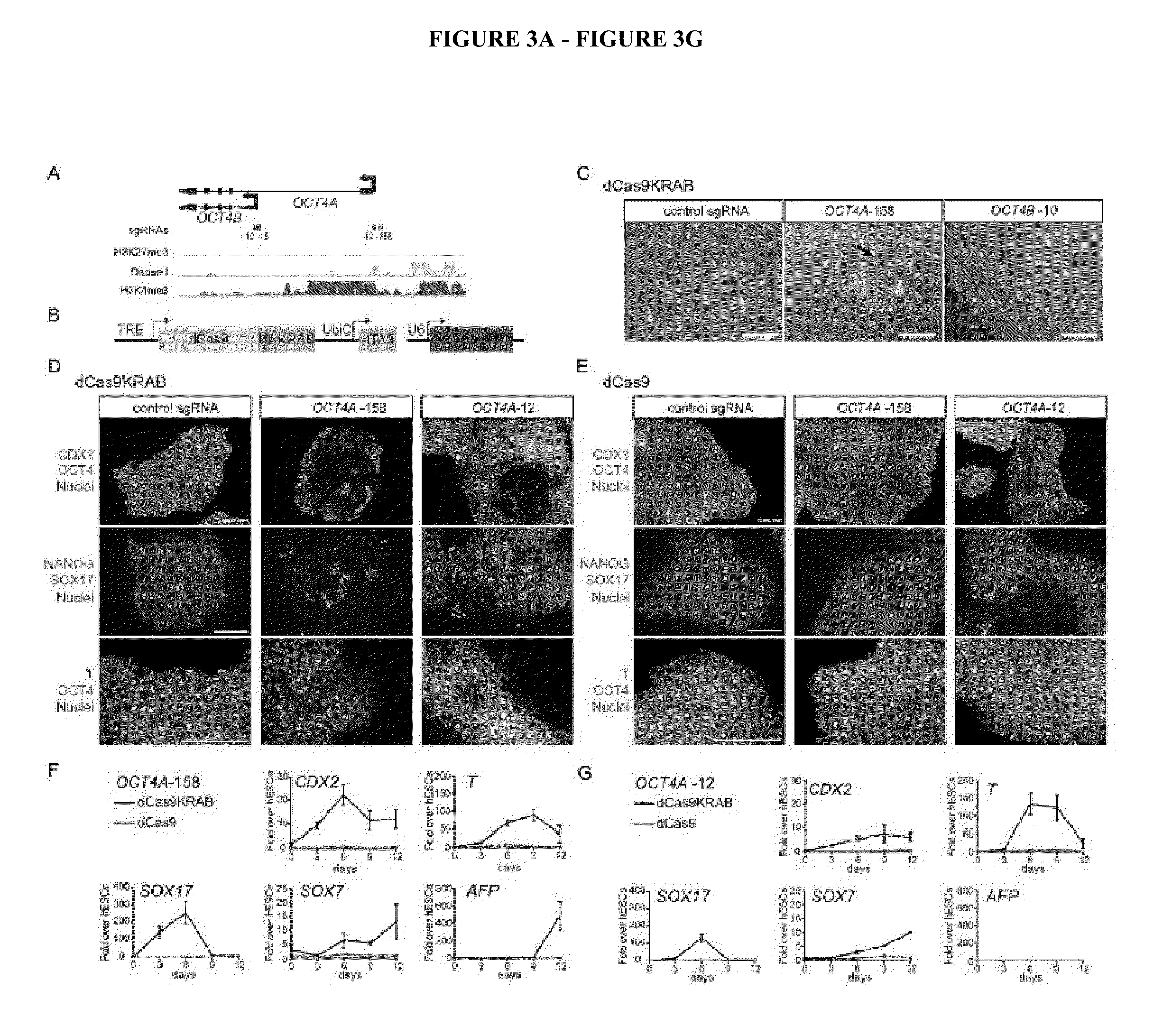
Cas9 effector-mediated regulation of transcription, differentiation and gene editing/labeling
InactiveUS20150191744A1Prevent degradationHydrolasesMicrobiological testing/measurementProgenitorReprogramming
The present disclosure relates to methods of and systems for modifying the transcriptional regulation of stem or progenitor cells to promote their differentiation or reprogramming of somatic cells. Further, the labeling and editing of human genomic loci in live cells with three orthogonal CRISPR / Cas9 components allow multicolor detection of genomic loci with high spatial resolution, which provides an avenue for barcoding elements of the human genome in the living state.
Owner:UNIV OF CENT FLORIDA RES FOUND INC +1
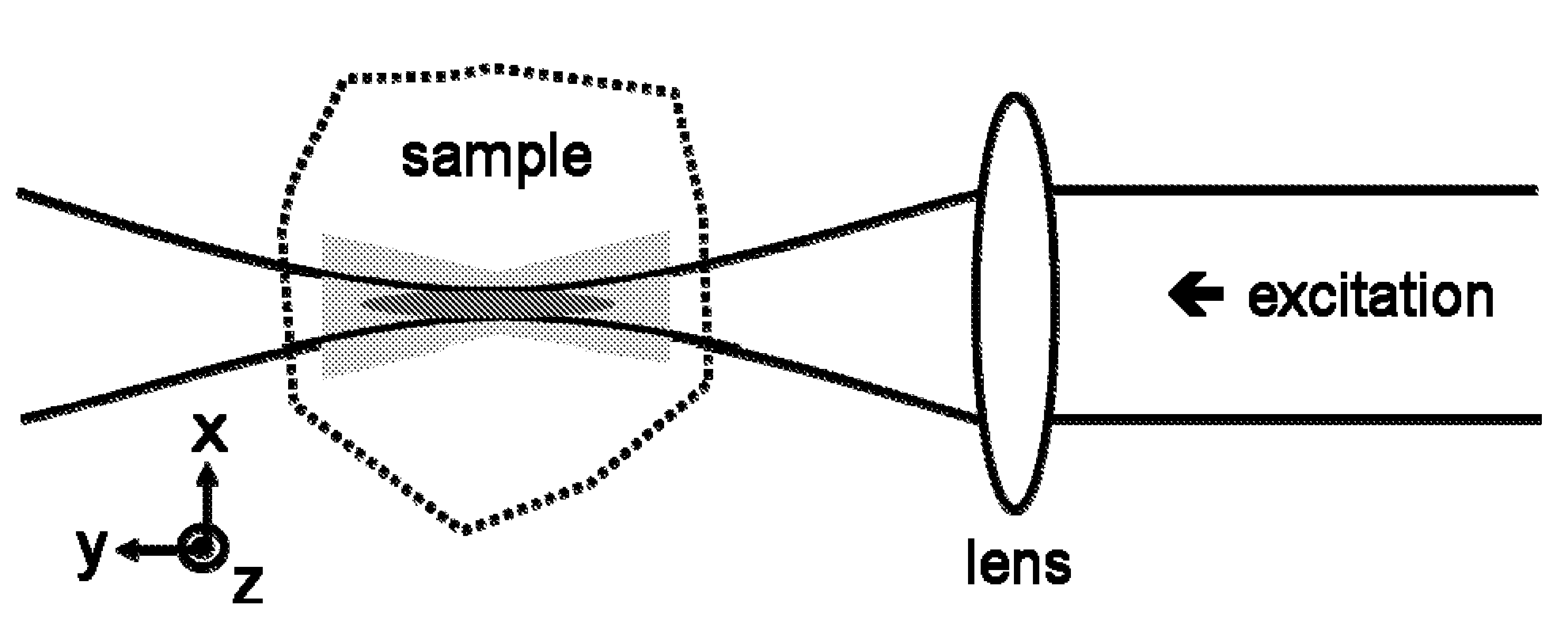
Multiple-photon excitation light sheet illumination microscope
ActiveUS20110122488A1Radiation pyrometrySpectrum investigationDiagnostic Radiology ModalityFluorescence
An apparatus for and method of performing multi-photon light sheet microscopy (MP-LISH), combining multi-photon excited fluorescence with the orthogonal. illumination of light sheet microscopy are provided. With live imaging of whole Drosophila and zebrafish embryos, the high performance of MP-LISH compared to current state-of-the-art imaging techniques in maintaining good signal and high spatial resolution deep inside biological tissues (two times deeper than one-photon light sheet microscopy), in acquisition speed (more than one order of magnitude faster than conventional two-photon laser scanning microscopy), and in low phototoxicity are demonstrated. The inherent multi-modality of this new imaging technique is also demonstrated second harmonic generation light sheet microscopy to detect collagen in mouse tail tissue. Together, these properties create the potential for a wide range of applications for MP-LISH in 4D imaging of live biological systems.
Owner:CALIFORNIA INST OF TECH
Electro-optical Foveated Imaging and Tracking System
InactiveUS20090080695A1Improve spatial resolutionWide field-of-viewCharacter and pattern recognitionSensor arrayHigh resolution image
Conventional electro-optical imaging systems can not achieve wide field of view (FOV) and high spatial resolution imaging simultaneously due to format size limitations of image sensor arrays. To implement wide field of regard imaging with high resolution, mechanical scanning mechanisms are typically used. Still, sensor data processing and communication speed is constrained due to large amount of data if large format image sensor arrays are used. This invention describes an electro-optical imaging system that achieves wide FOV global imaging for suspect object detection and local high resolution for object recognition and tracking. It mimics foveated imaging property of human eyes. There is no mechanical scanning for changing the region of interest (ROI). Two relatively small format image sensor arrays are used to respectively acquire global low resolution image and local high resolution image. The ROI is detected and located by analysis of the global image. A lens array along with an electronically addressed switch array and a magnification lens is used to pick out and magnify the local image. The global image and local image are processed by the processor, and can be fused for display. Three embodiments of the invention are descried.
Owner:NEW SPAN OPTO TECH
Real-time Elastic Registration to Determine Temporal Evolution of Internal Tissues for Image-Guided Interventions
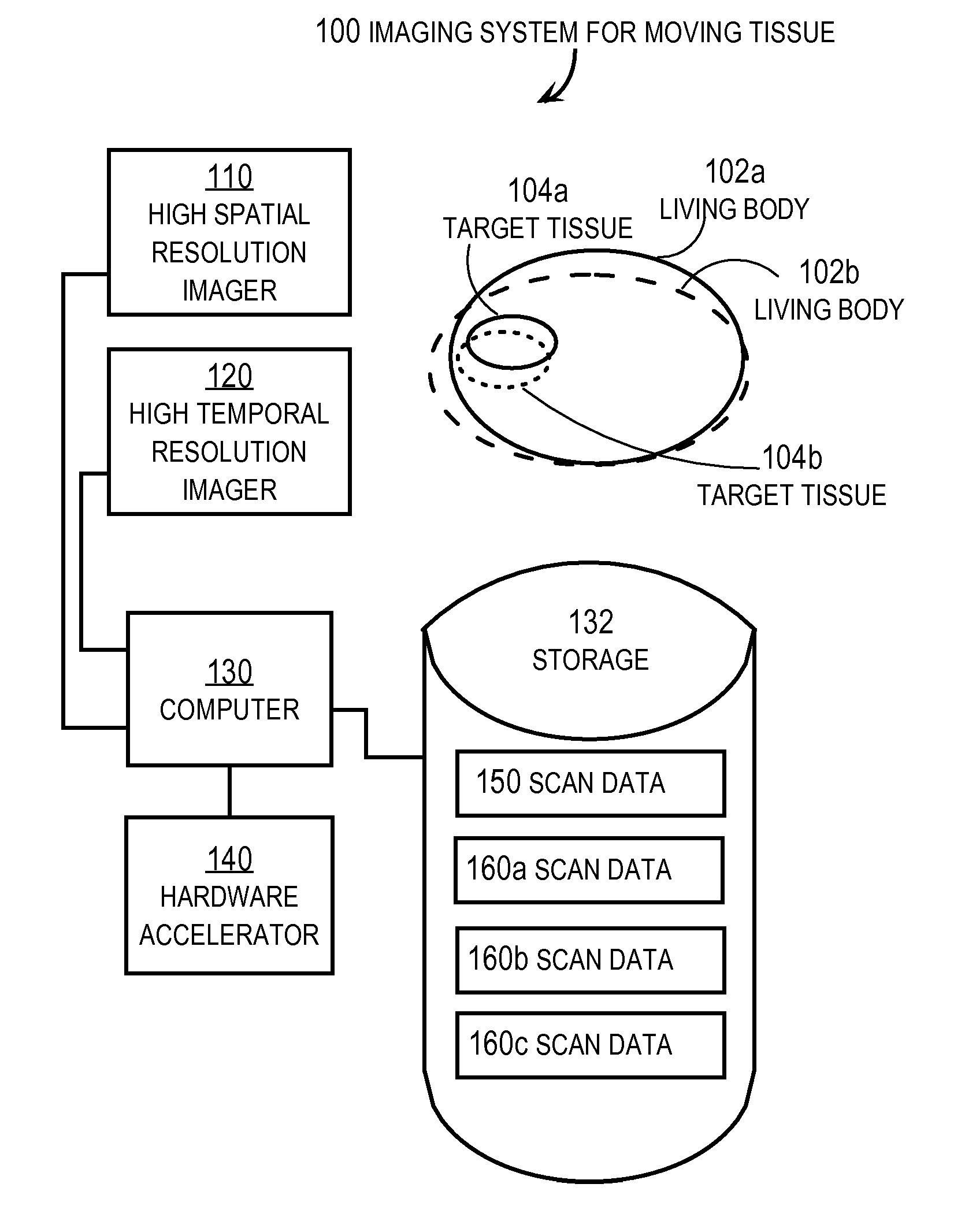
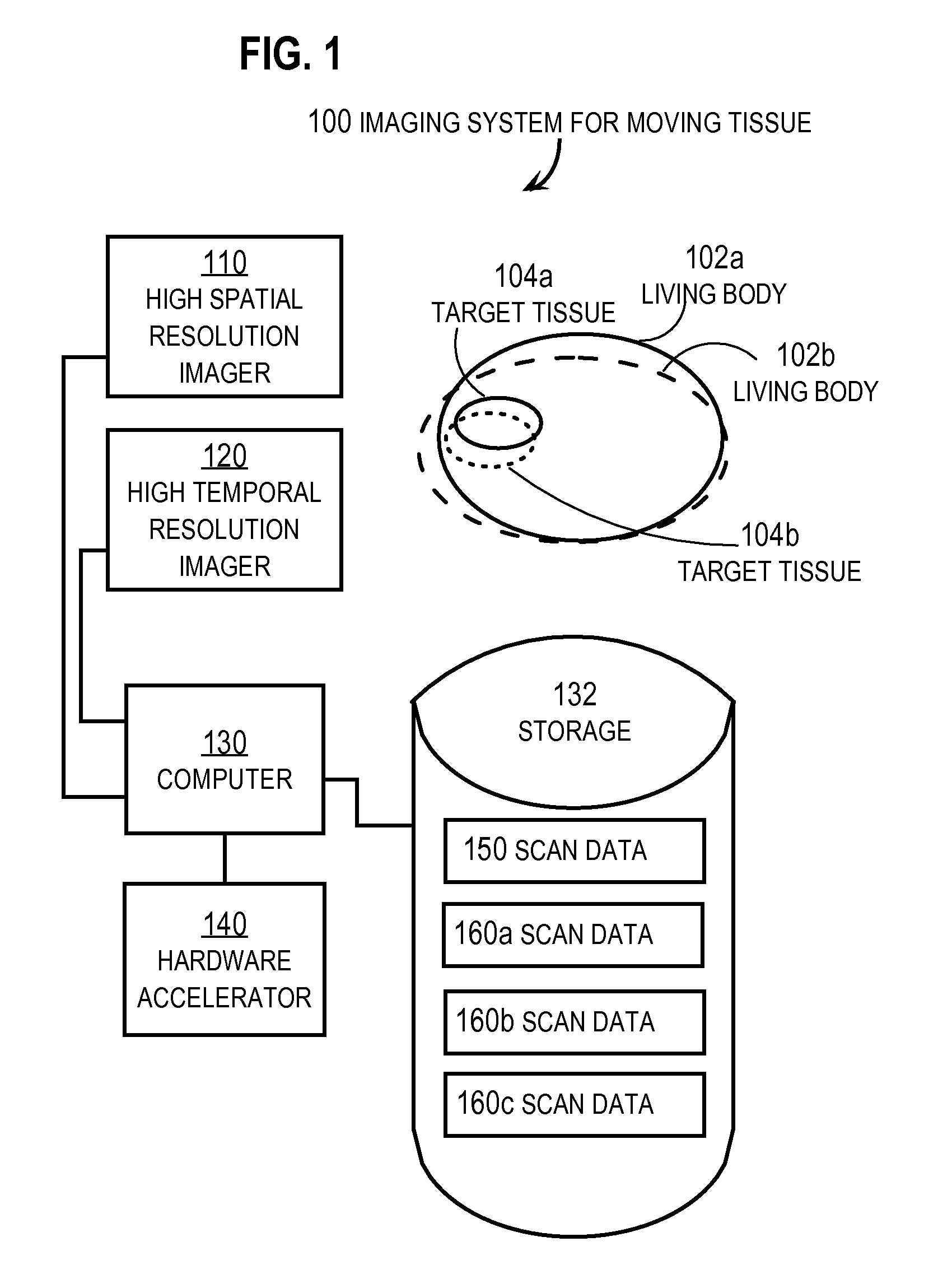
Techniques for indicating arrangement of moving target tissue in a living body include receiving first scan data based at least in part on a first mode of measuring with high spatial resolution over a first duration at a first time. Also received is second scan data representing a scan of the living body based at least in part on a second mode of measuring at a second time. The second mode can be different with a second duration and a repeat rate greater than a repeat rate for the first scan data. An elastic transform is determined that registers the first scan data elastically to the second scan data. A particular spatial arrangement of the moving target tissue is indicted based on the elastic transform. These techniques can be used to update a pre-intervention plan and highlight target detail by registering pre-intervention data to second scan data during the intervention.
Owner:UNIV OF MARYLAND
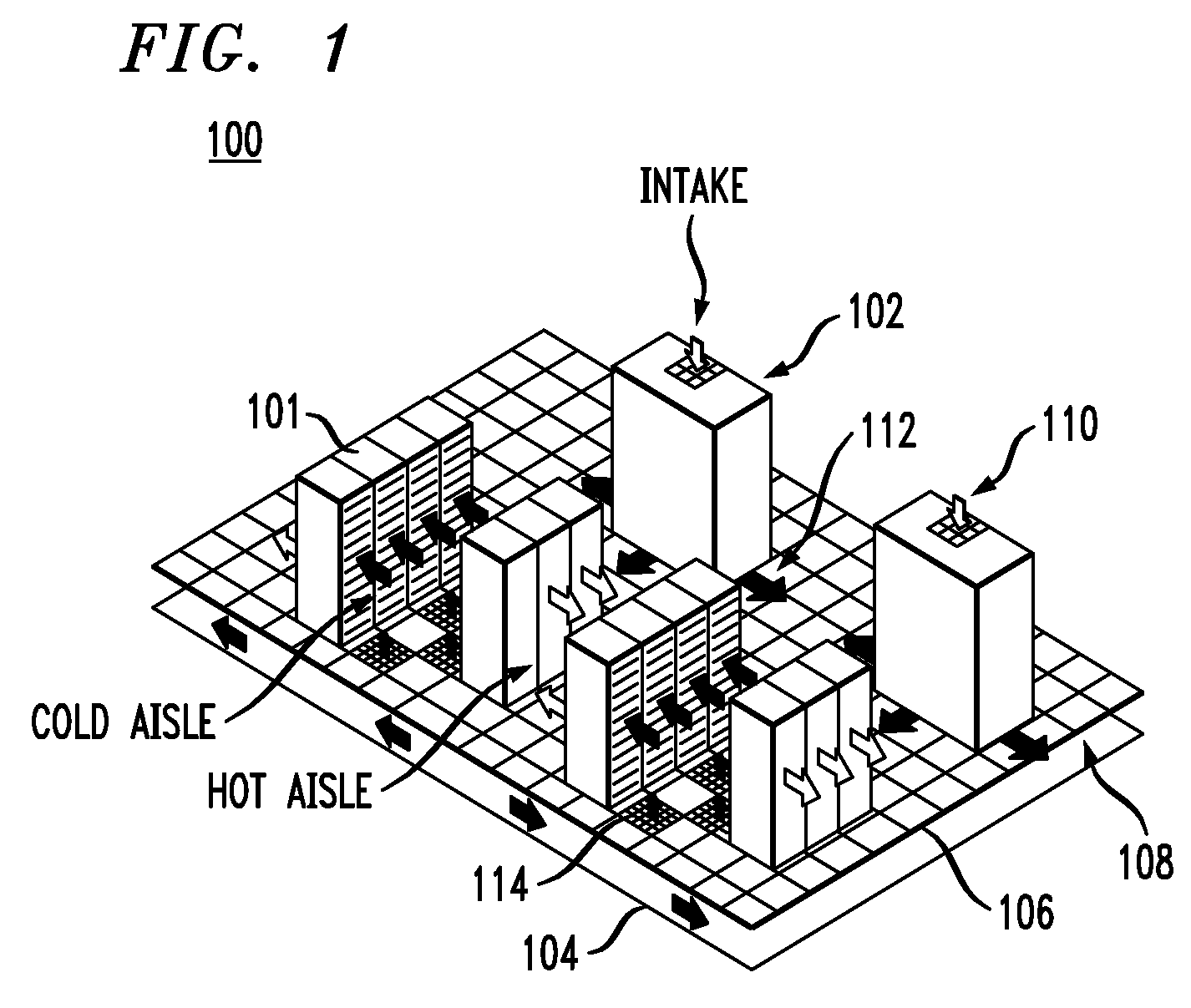
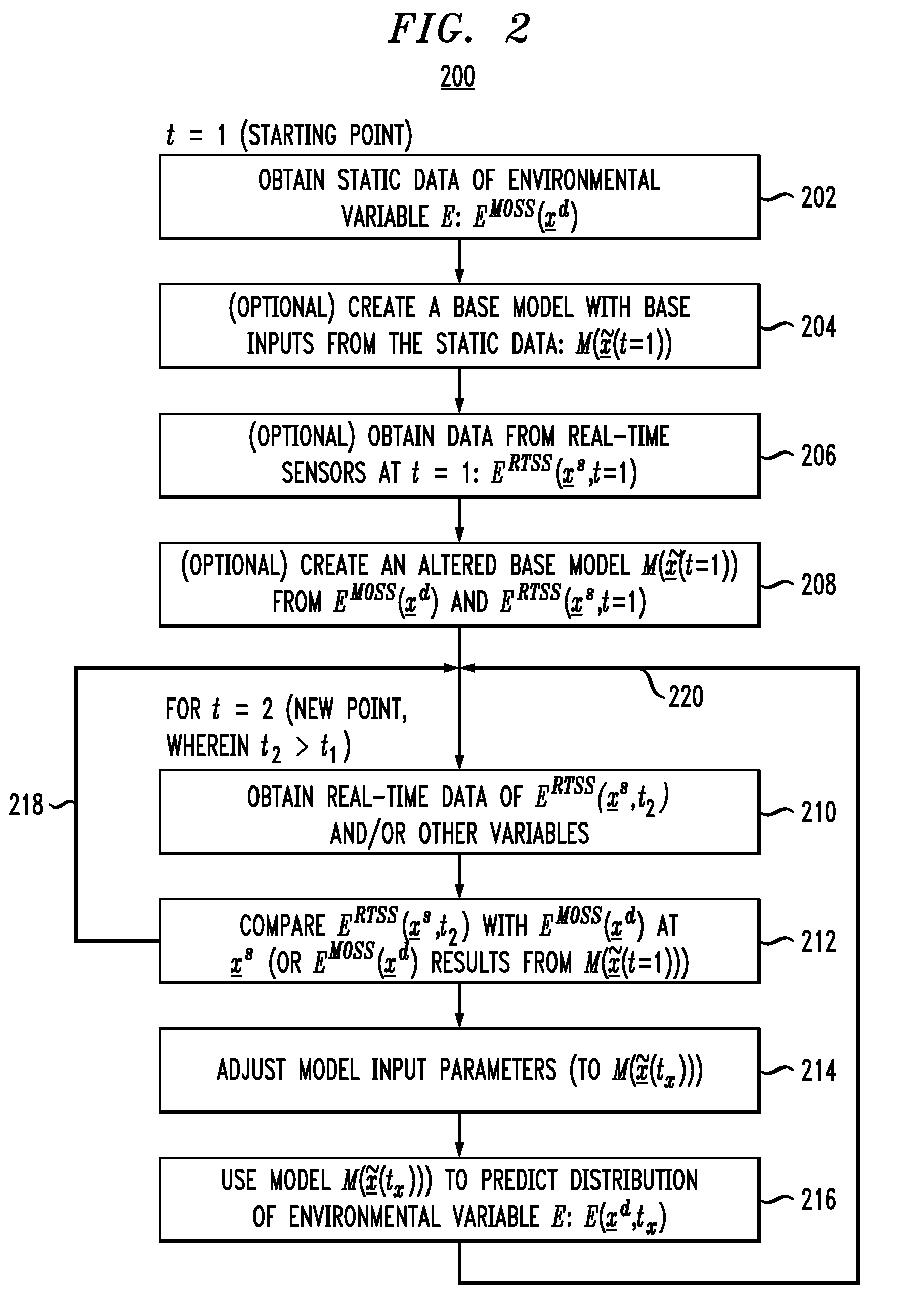
Techniques to Predict Three-Dimensional Thermal Distributions in Real-Time
ActiveUS20090326884A1Improve spatial resolutionMeasurement resolutionEnergy efficient ICTComputation using non-denominational number representationImage resolutionHigh spatial resolution
Techniques for monitoring and predicting environmental operating conditions in a data center are provided. In one aspect, a method for real-time, three-dimensional analysis of environmental operating conditions in a data center includes the following steps. High spatial resolution three-dimensional measurements of one or more environmental variables in the data center made at a time t1 are obtained. Real-time measurements of the environmental variables in the data center made at a time t2, wherein t2 is later in time than t1, are obtained. The high spatial resolution three-dimensional measurements are combined with the real-time measurements to derive a model for the environmental variables in the data center at the time t2. The model is used to predict three-dimensional distributions of the environmental variables in the data center at the time t2. A base model can be created and used to derive the model for the data center at the time t2.
Owner:IBM CORP
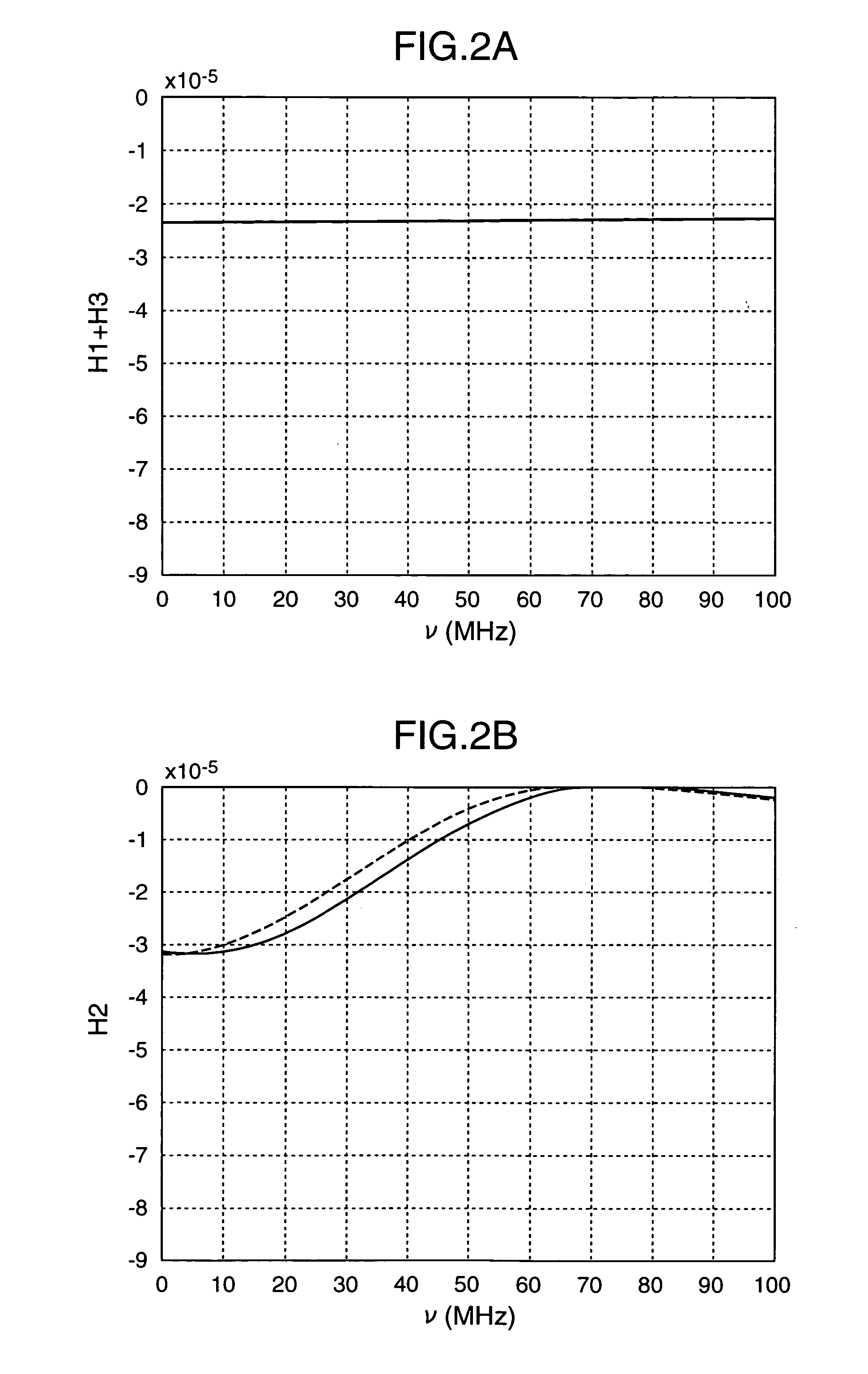
High spatial resolution imaging
ActiveUS20060038993A1Improve spatial resolutionRadiation pyrometrySpectrum investigationComing outOptical property
Owner:MAX PLANCK GESELLSCHAFT ZUR FOERDERUNG DER WISSENSCHAFTEN EV
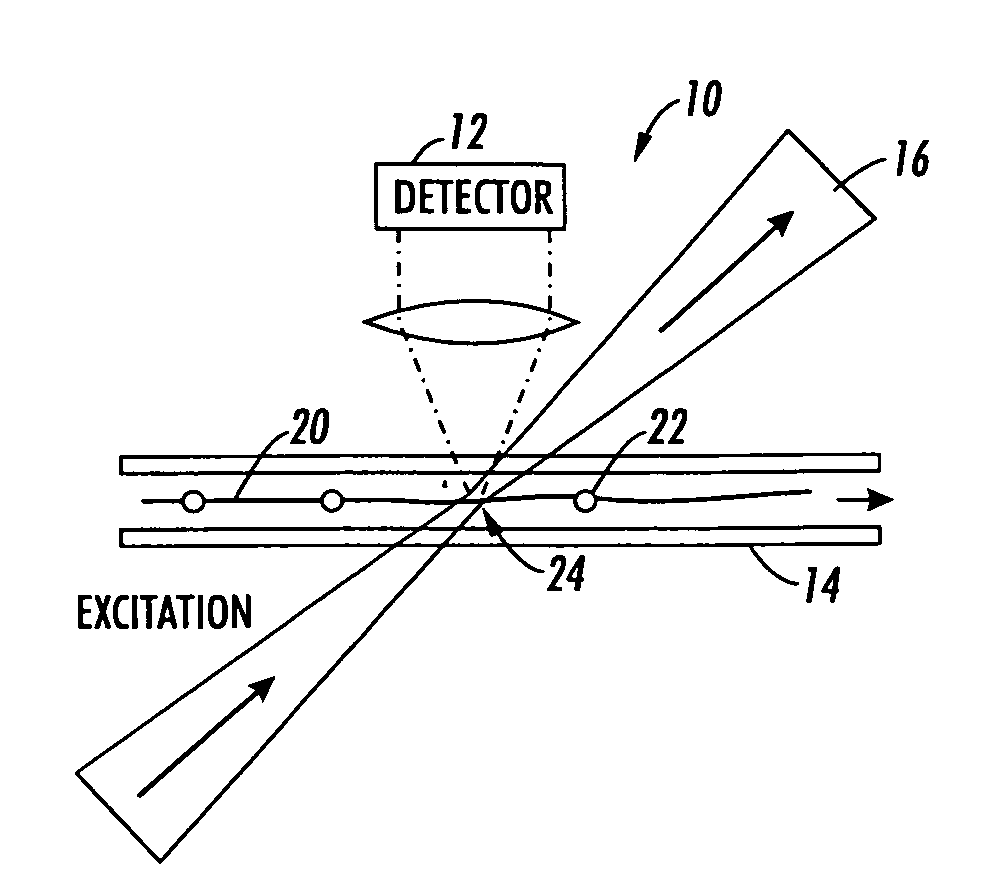
Method and system implementing spatially modulated excitation or emission for particle characterization with enhanced sensitivity
ActiveUS20080181827A1SamplingChemiluminescene/bioluminescenceRelative motionSignal-to-quantization-noise ratio
A method and system for using spatially modulated excitation / emission and relative movement between a particle (cell, molecule, aerosol, . . . ) and an excitation / emission pattern are provided. In at least one form, an interference pattern of the excitation light with submicron periodicity perpendicular to the particle flow is used. As the particle moves along the pattern, emission is modulated according to the speed of the particle and the periodicity of the stripe pattern. A single detector, which records the emission over a couple of stripes, can be used. The signal is recorded with a fast detector read-out in order to capture the “blinking” of the particles while they are moving through the excitation pattern. This concept enables light detection with high signal-to-noise ratio and high spatial resolution without the need of expensive and bulky optics.
Owner:XEROX CORP
High spatial resoulution imaging and modification of structures
ActiveUS20040212799A1Small intensityLong lastingSpectrum investigationMaterial analysis by optical meansOptical propertyImage resolution
In a method of high spatial resolution imaging or modifying a structure, the structure is marked with a substance which is selected from the group of substances which can be transferred from a first state having first optical properties to a second state having second optical properties by means of an optical switch over signal. Then, the second state of the substance is adjusted with the switch over signal except for a spatially limited area. If the substance and the switch over signal are adapted to each other in such a way, that everywhere where the switch over signal exceeds a threshold value essentially the second state of the substance is adjusted, and if the spatial area purposefully omitted by the switch over signal is an intensity minimum of an interference pattern, the spatial area of the structure in which the substance is within the first state becomes smaller than the diffraction limit for the switch over signal.
Owner:MAX PLANCK GESELLSCHAFT ZUR FOERDERUNG DER WISSENSCHAFTEN EV
Distributed Optical Fiber Sensor
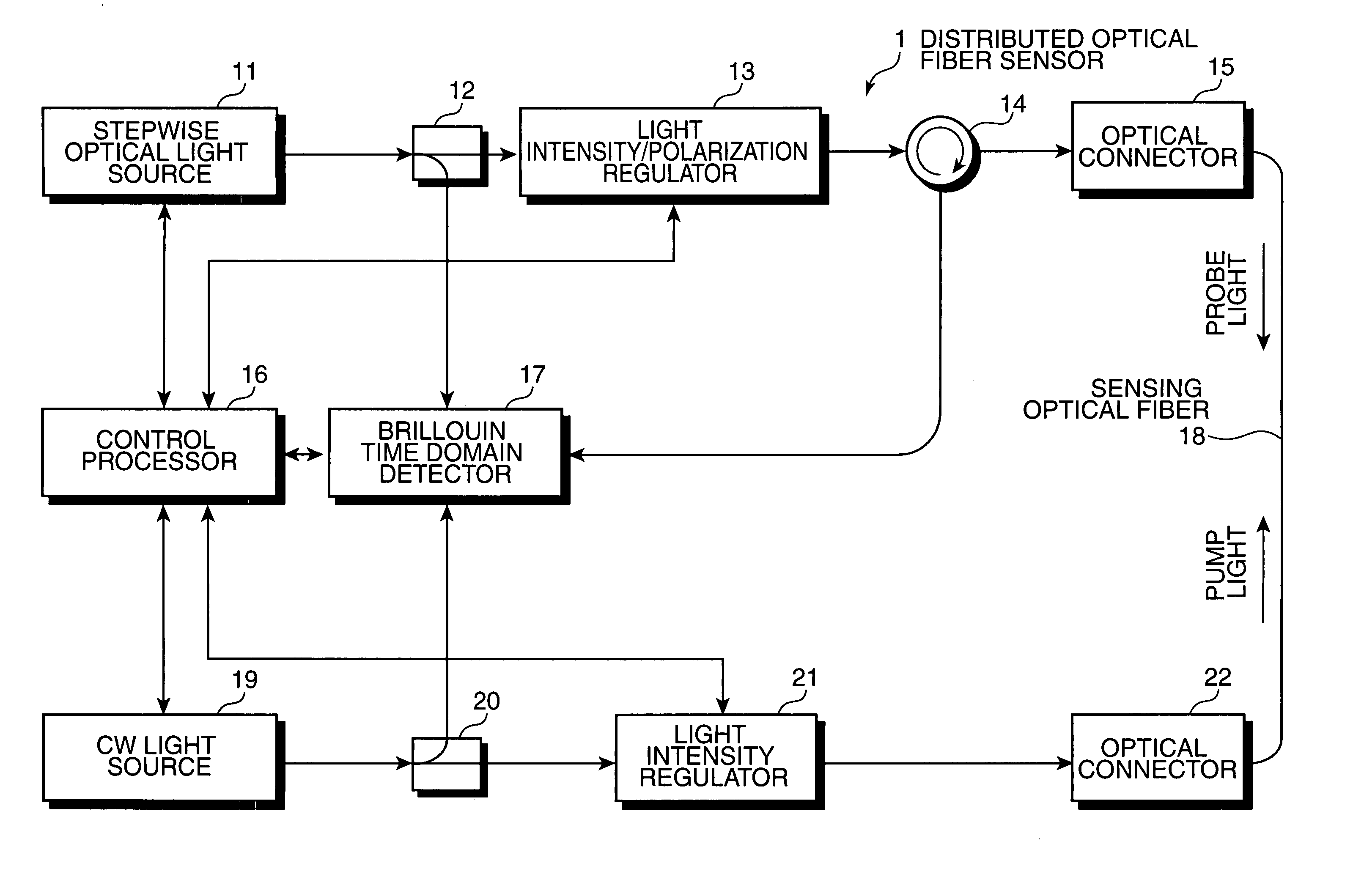
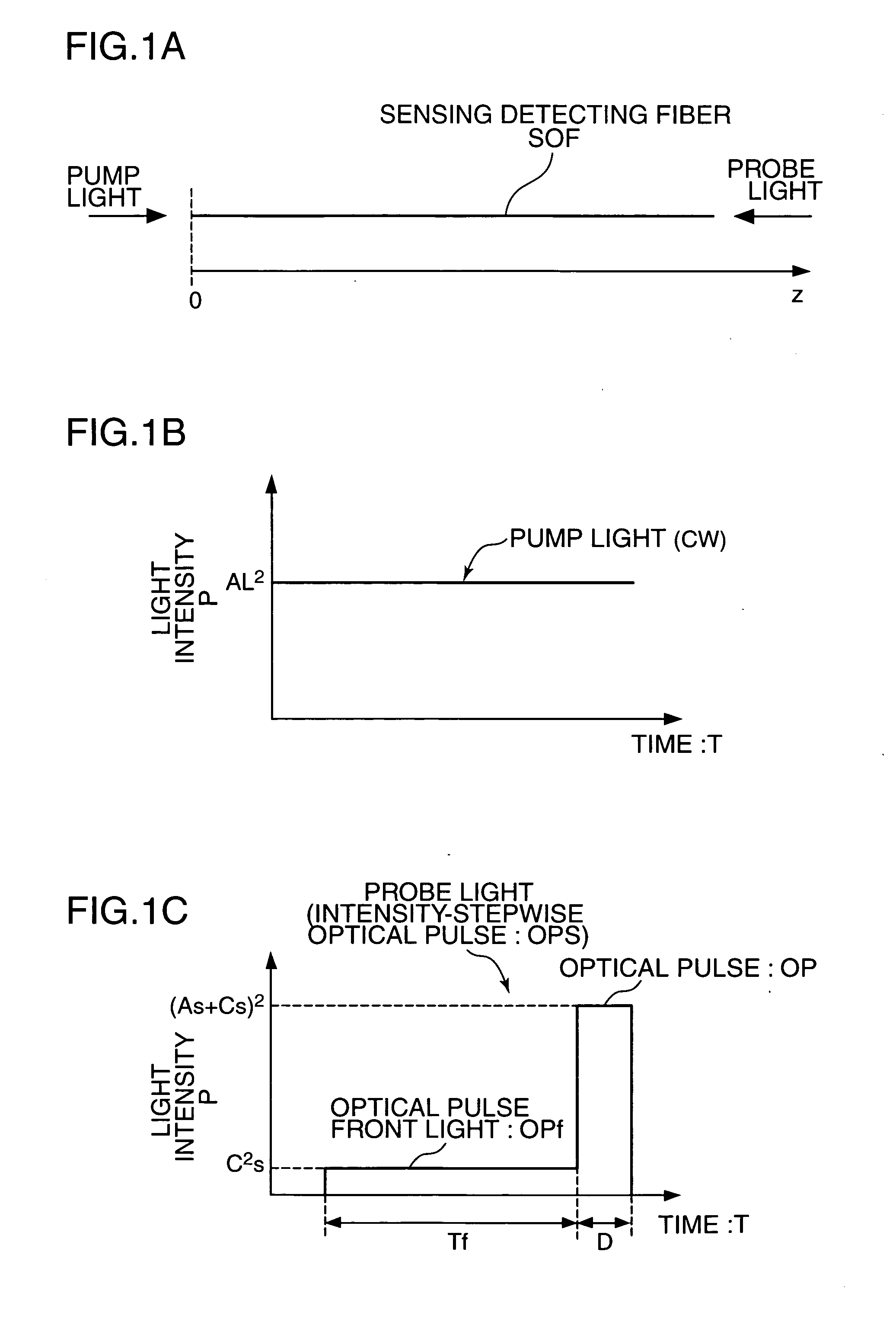
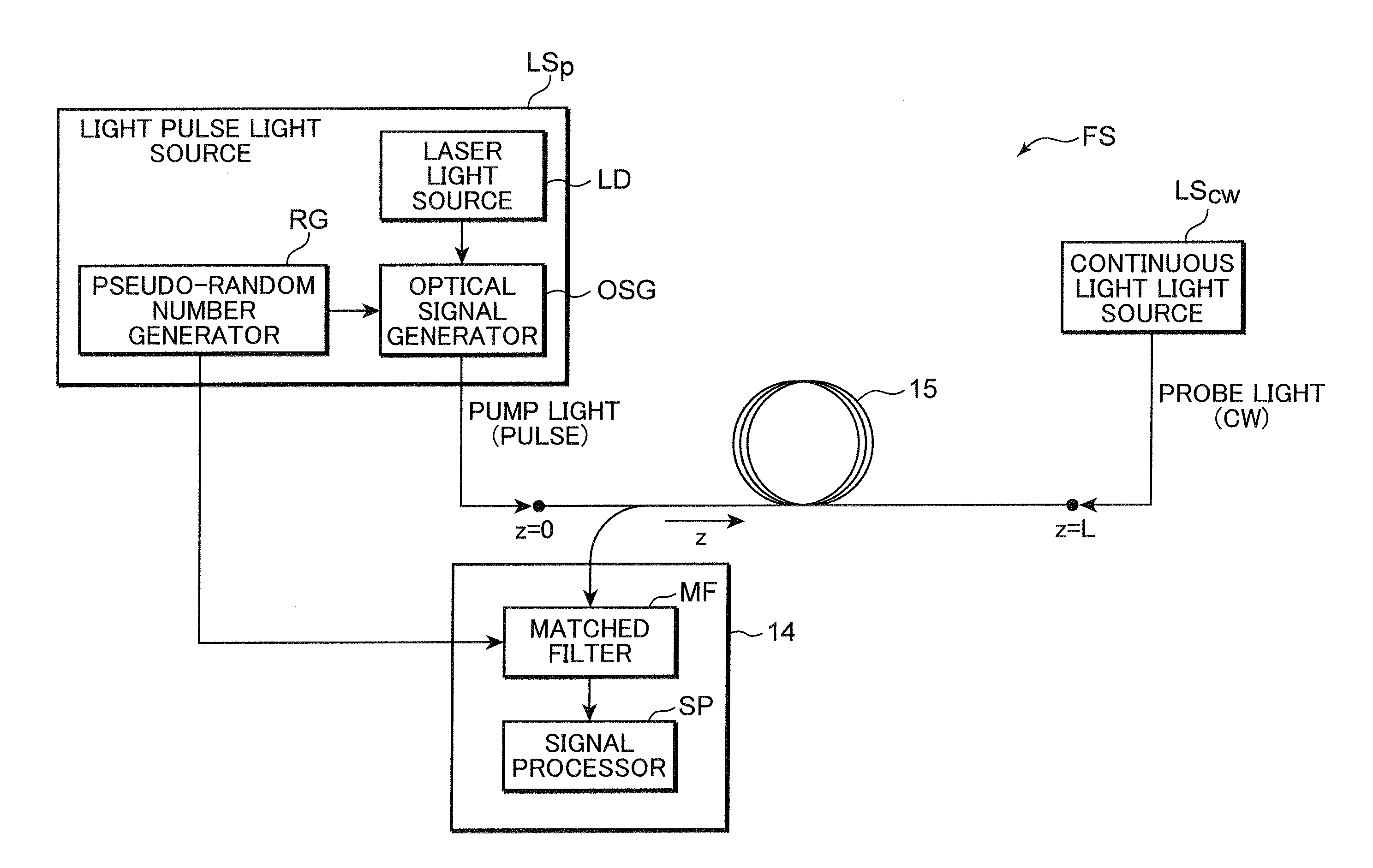
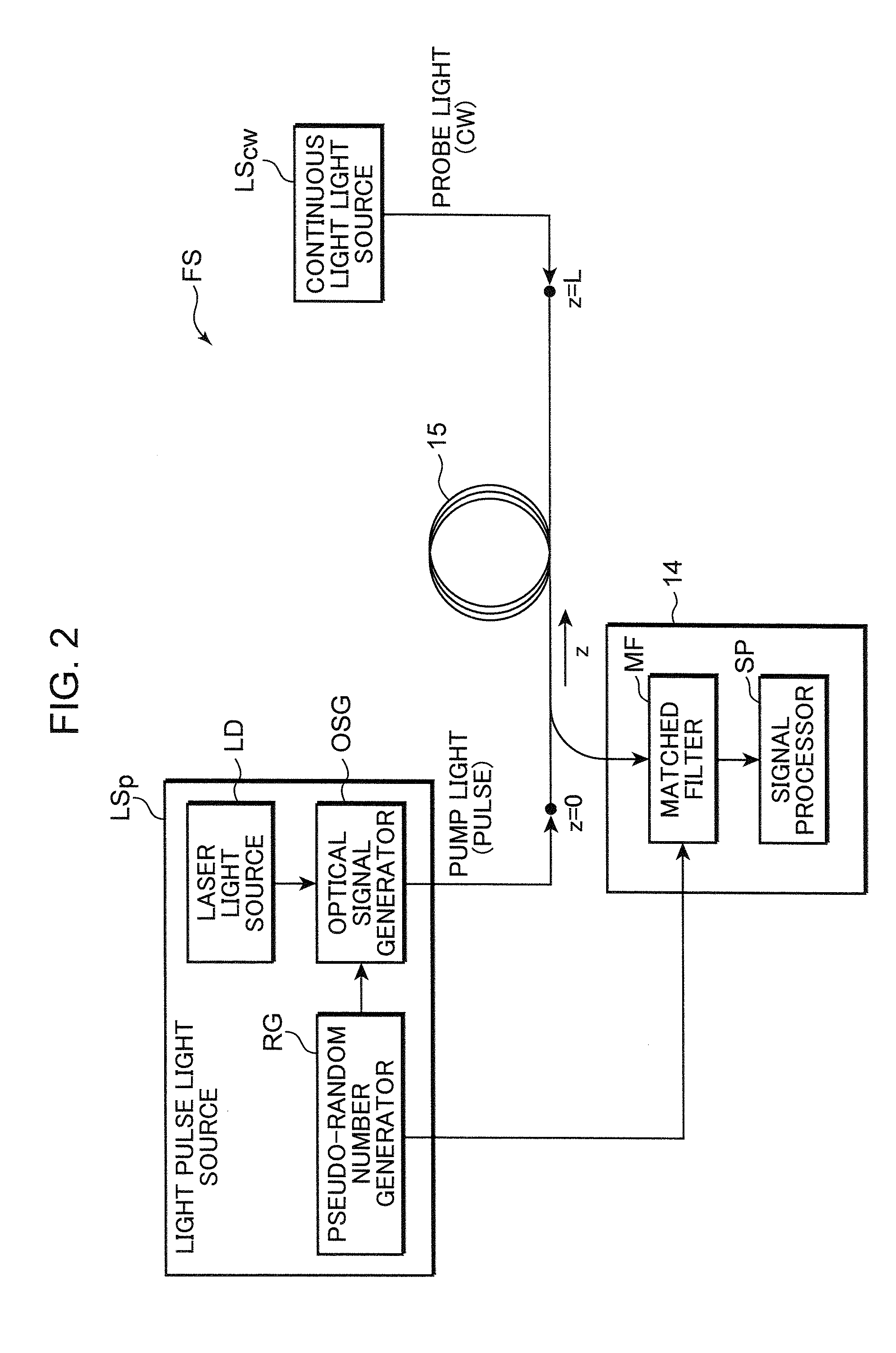
A distributed optical fiber sensor uses a Brillouin scattering phenomenon to avoid manual adjustment and to measure strain and / or temperature with high accuracy and high spatial resolution. A stepwise optical light source generates an optical pulse having a stepwise distribution of intensity to increase toward the center, and a continuous light source generates continuous light on. The optical pulse is incident on a sensing optical fiber as probe light and the continuous light is incident as pump light to cause a Brillouin scattering phenomenon between the probe light and the pump light. A Brillouin time domain detector determines a Brillouin loss or gain spectrum from the light emerging from the sensing optical fiber and attributed to the Brillouin scattering phenomenon, and measures strain in and / or temperature of the sensing optical fiber in the longitudinal direction thereof based on the determined Brillouin loss or gain spectrum.
Owner:NEUBREX
Apparatus and method for high spatial resolution imaging of a structure of a sample
ActiveUS20110036996A1High image rateReducing out-of-focus autofluorescencePhotometryMaterial analysis by optical meansSpatially resolvedImage resolution
Apparatus and method for high spatial resolution imaging of a sample's structure, including a diffraction-limited resolution volume with a plurality of dye molecules which can be switched between different states and have a distribution density which is greater than the inverse of the diffraction-limited resolution volume, where at least one state is fluorescing, the fluorescence being collected by an objective lens and imaged on a spatially resolving detector by an optical system. At least one light source provided for emitting a switching radiation and for emitting an excitation radiation. At least one of the light sources is arranged to radiate through the sample, and a switching and / or fluorescence excitation of the dye molecules is carried out. The switching is a photoactivation or a photodeactivation of the dye molecules. A focusing arrangement is provided for switching and / or for excitation to generate a line-like illumination region extending in a direction of illumination.
Owner:CARL ZEISS MICROSCOPY GMBH
Distributed optical fiber sensor
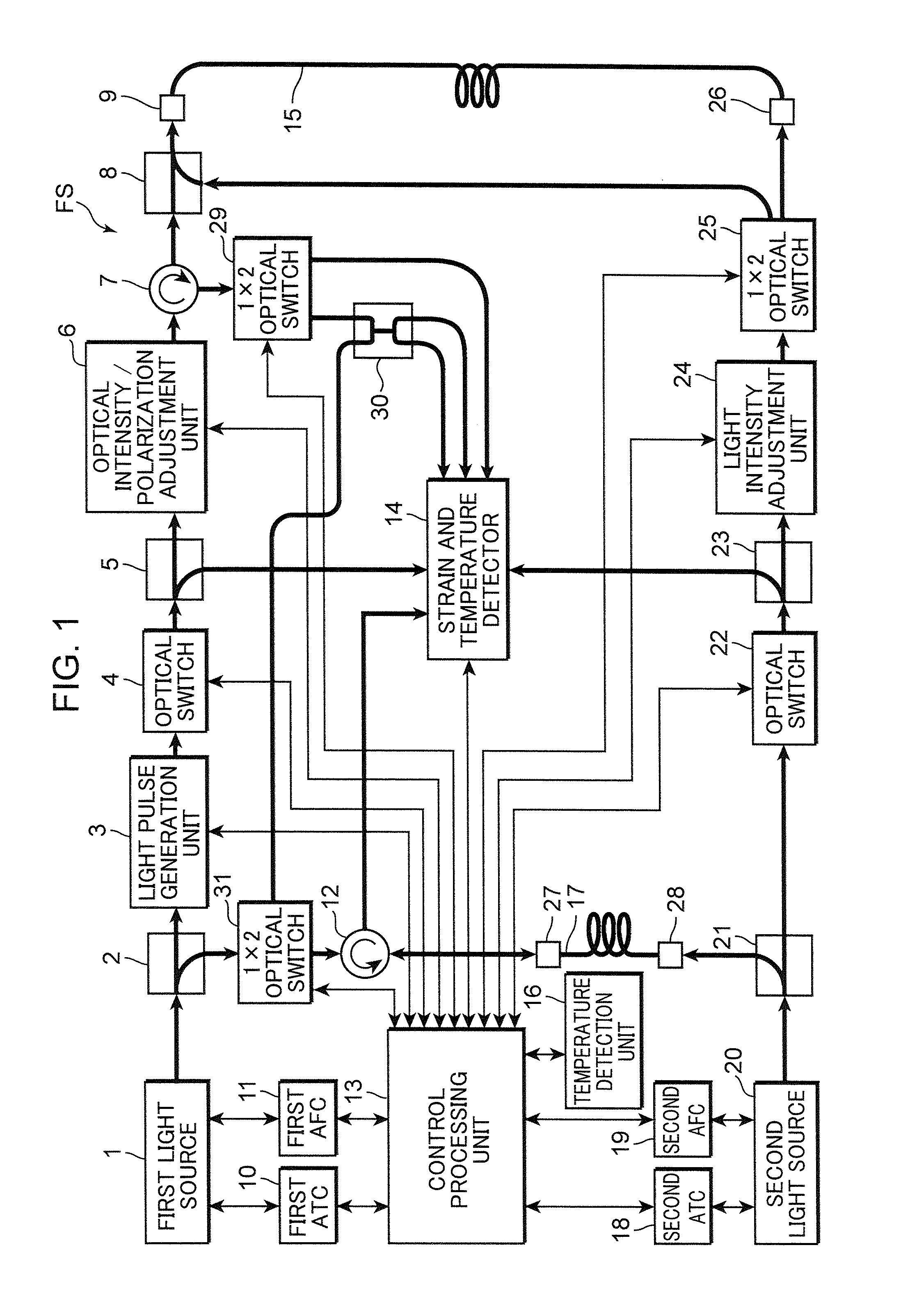
ActiveUS20110228255A1Improve spatial resolutionPolarisation-affecting propertiesForce measurementRayleigh scatteringRayleigh Light Scattering
The present invention provides a distributed optical fiber sensor capable of measuring the strain and temperature of an object to be measured simultaneously and independently with high spatial resolution. A distributed optical fiber sensor FS is a distributed optical fiber sensor which uses an optical fiber 15 as a sensor, and a strain and temperature detector 14 measures a Brillouin frequency shift amount caused by a strain and a temperature generated in the optical fiber 15 by using a Brillouin scattering phenomenon, measures a Rayleigh frequency shift amount caused by the strain and temperature generated in the optical fiber 15 by using a Rayleigh scattering phenomenon, and calculates the strain and temperature generated in the optical fiber 15 from the measured Brillouin frequency shift amount and Rayleigh frequency shift amount.
Owner:NEUBREX
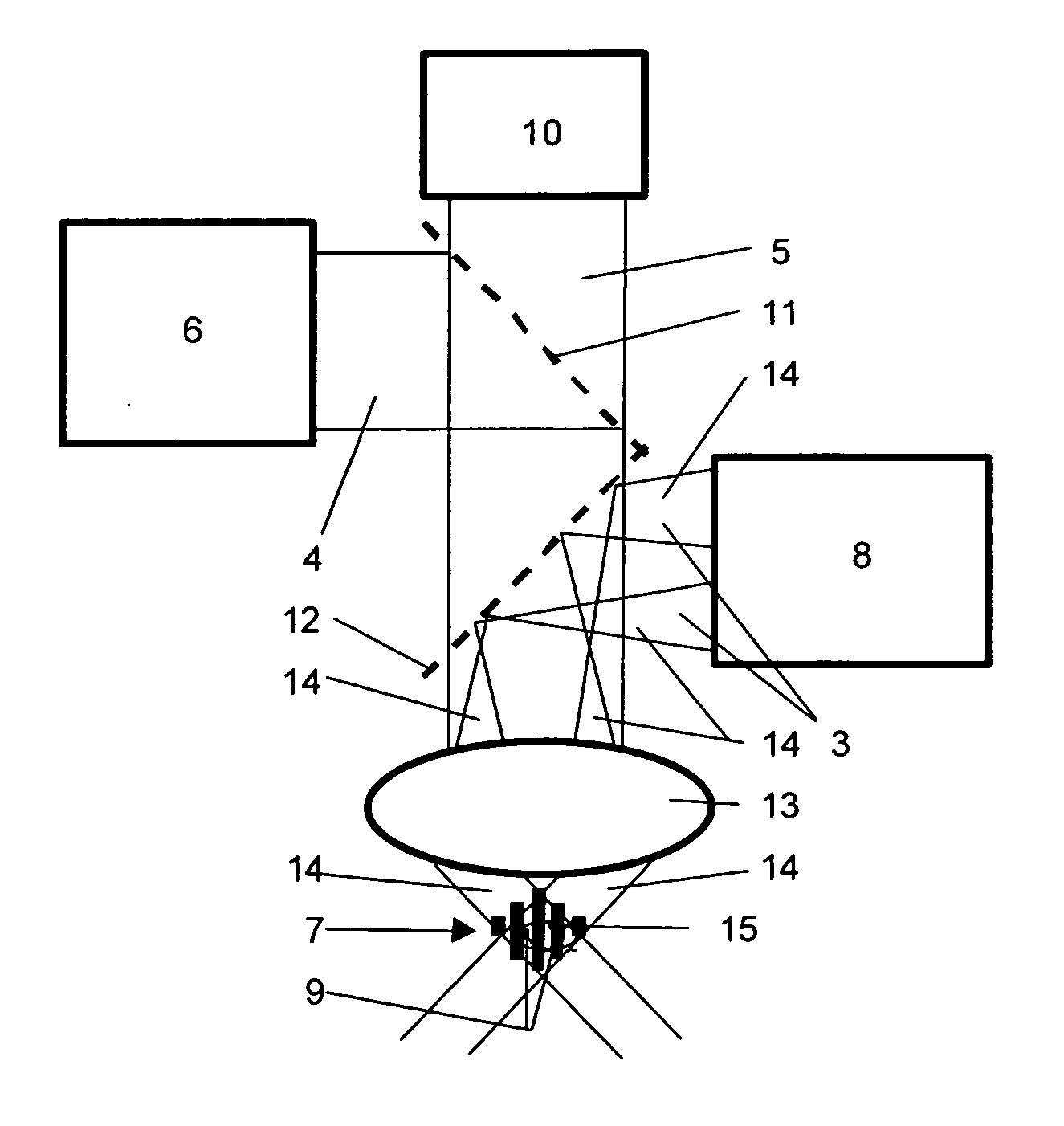
Optical field imaging device and method
ActiveCN102739945ASolve the problem that the resolution cannot meet the demandSolve problems that do not meet needsTelevision system detailsColor television detailsCamera lensImaging processing
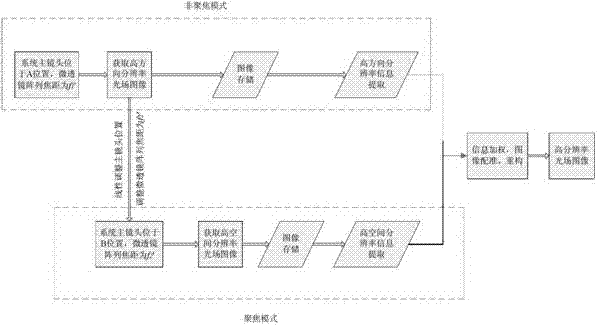
The invention provides an optical field imaging device and method. A device corresponding to the optical filed imaging method enables an image plane of a main lens to be overlapped with the a variable-zoom micro lens array through horizontally moving the main lens; the focal length of the variable-zoom micro lens array is an initial focal length, and the distance between a sensor and the variable-zoom micro lens array is equal to the initial focal length; a first image is obtained by the sensor and the main lens is horizontally moved to enable the image plane to be deviated from the position of the variable-zoom micro lens array; the focal length of the variable-zoom micro lens array is correspondingly adjusted to a second focal length so that the image plane of the main lens is conjugated and imaged on the sensor through the variable-zoom micro lens array to obtain a second image; in the process, the change of the horizontal movement position of the main lens and the focal length of the variable-zoom micro lens array abides by a Gaussian optical law; high-direction resolution rate information of the first image and high-direction resolution rate information of the second image are extracted through an extracting part; and an image processing part is used for carrying out weighting recombination on the extracted information and carrying out registration and reconfiguration on the image to obtain the best imaging effect.
Owner:SHENZHEN KECHUANG DIGITAL DISPLAY TECH
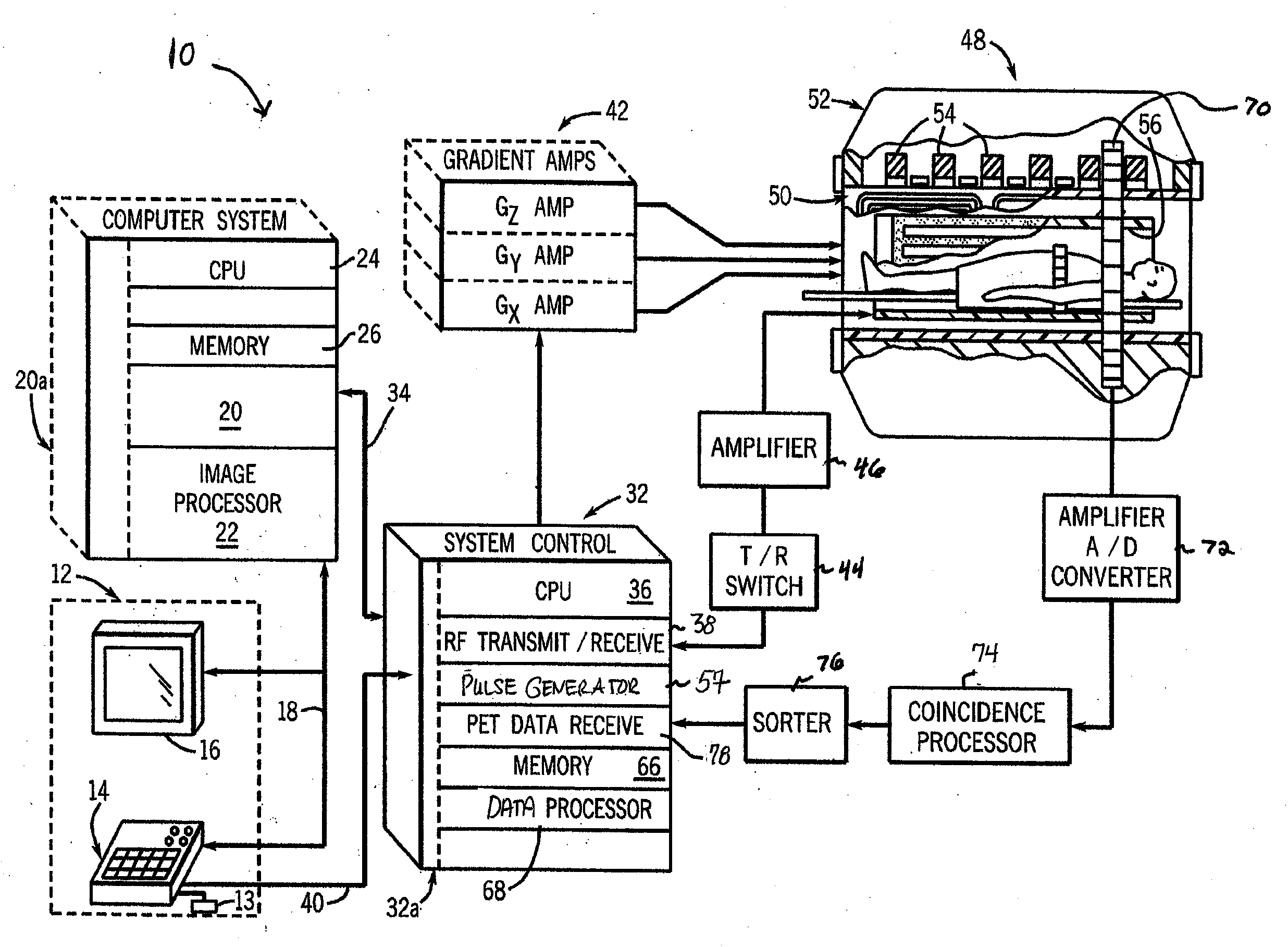
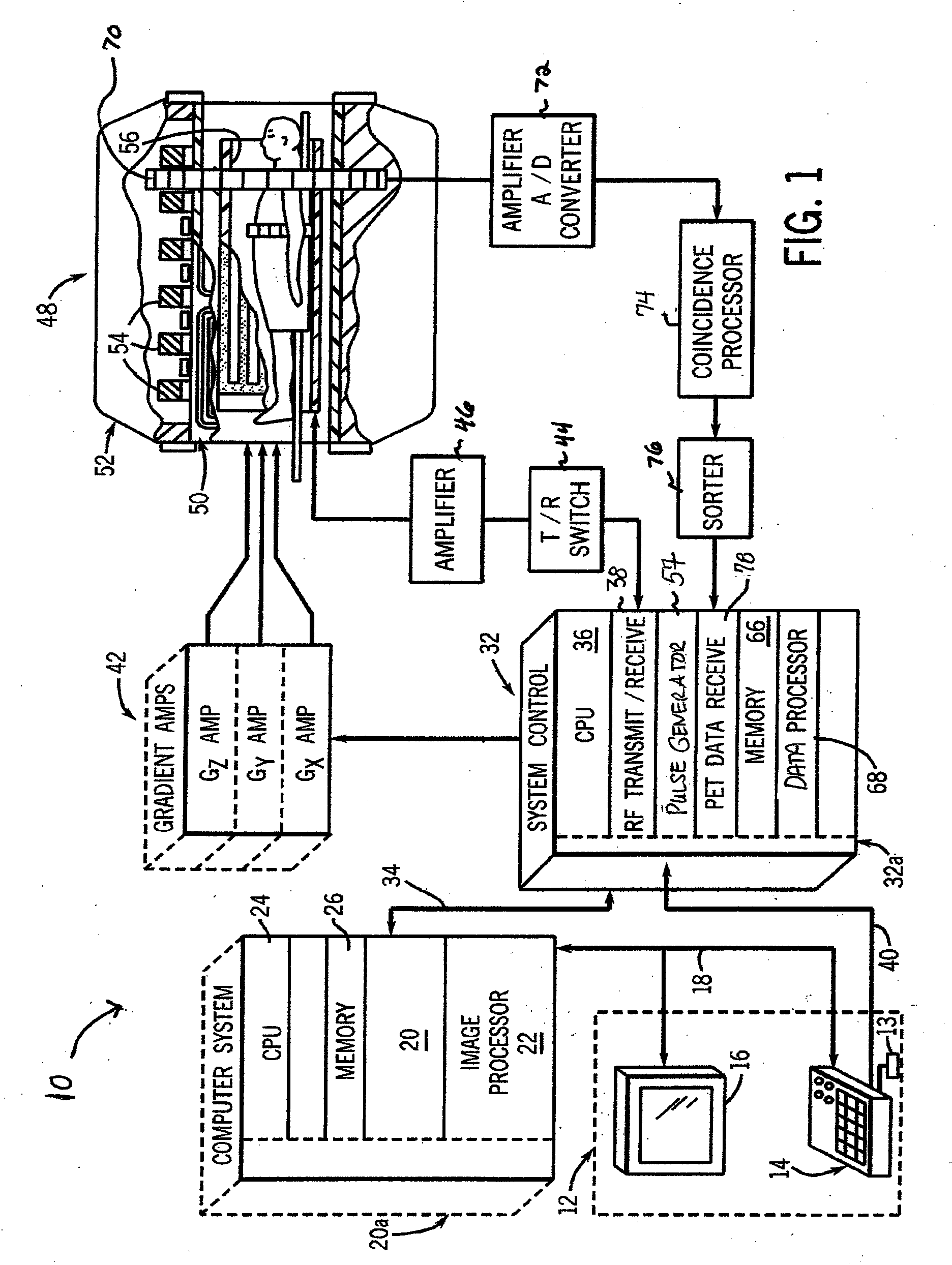
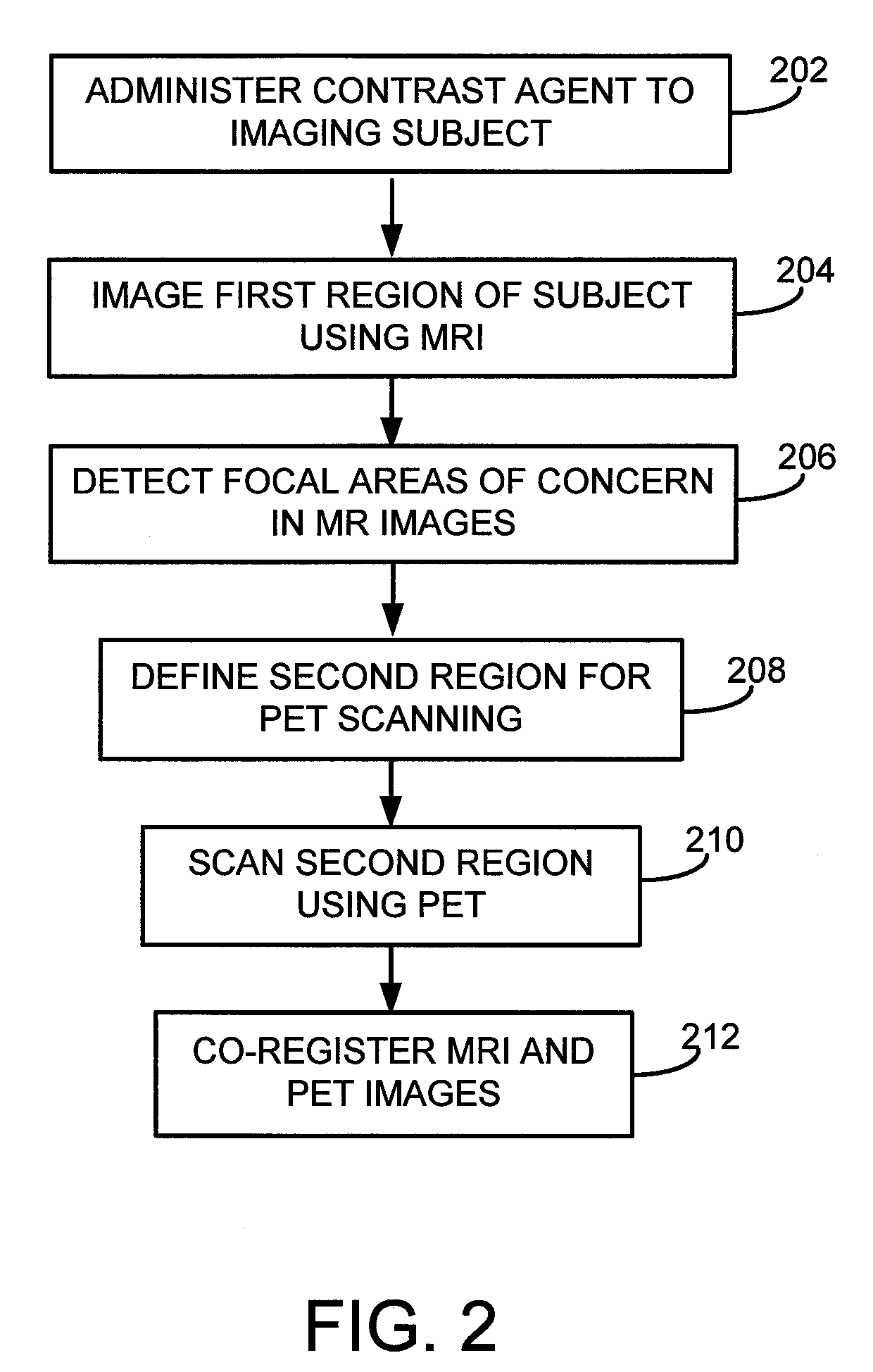
System, method and apparatus for cancer imaging
InactiveUS20080146914A1Diagnostic recording/measuringTomographyImage resolutionHigh spatial resolution
A method for imaging cancer using a combined PET-MRI system takes advantage of the performance characteristics for both PET and MRI in the context of cancer imaging. MRI is used to assess a large area of the body with high sensitivity for cancer and PET is then used in localized areas of concern to provide physiological information. Optionally, MRI may also then be used to re-scan the localized areas of concern with high spatial resolution and additional tissue contrasts to provide anatomical information and soft tissue contrast to supplement the PET information. The use of a combined PET-MRI system ensures that the imaging data from both modalities is accurately referenced to the same locations in the body.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
High spatial resoulution imaging and modification of structures
InactiveUS7064824B2Spectrum investigationMaterial analysis by optical meansOptical propertyImage resolution
In a method of high spatial resolution imaging or modifying a structure, the structure is marked with a substance which is selected from the group of substances which can be transferred from a first state having first optical properties to a second state having second optical properties by means of an optical switch over signal. Then, the second state of the substance is adjusted with the switch over signal except for a spatially limited area. If the substance and the switch over signal are adapted to each other in such a way, that everywhere where the switch over signal exceeds a threshold value essentially the second state of the substance is adjusted, and if the spatial area purposefully omitted by the switch over signal is an intensity minimum of an interference pattern, the spatial area of the structure in which the substance is within the first state becomes smaller than the diffraction limit for the switch over signal.
Owner:MAX PLANCK GESELLSCHAFT ZUR FOERDERUNG DER WISSENSCHAFTEN EV
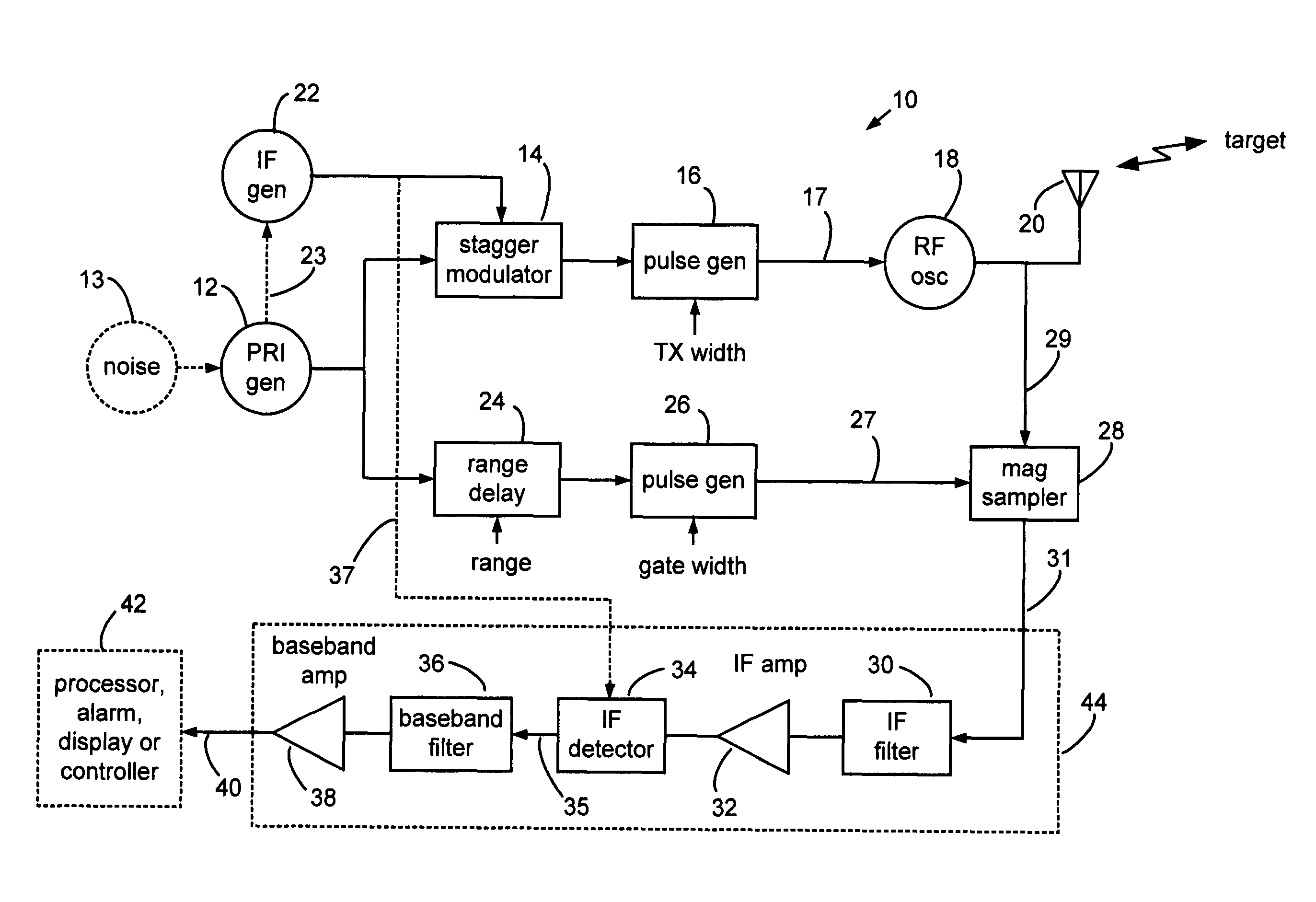
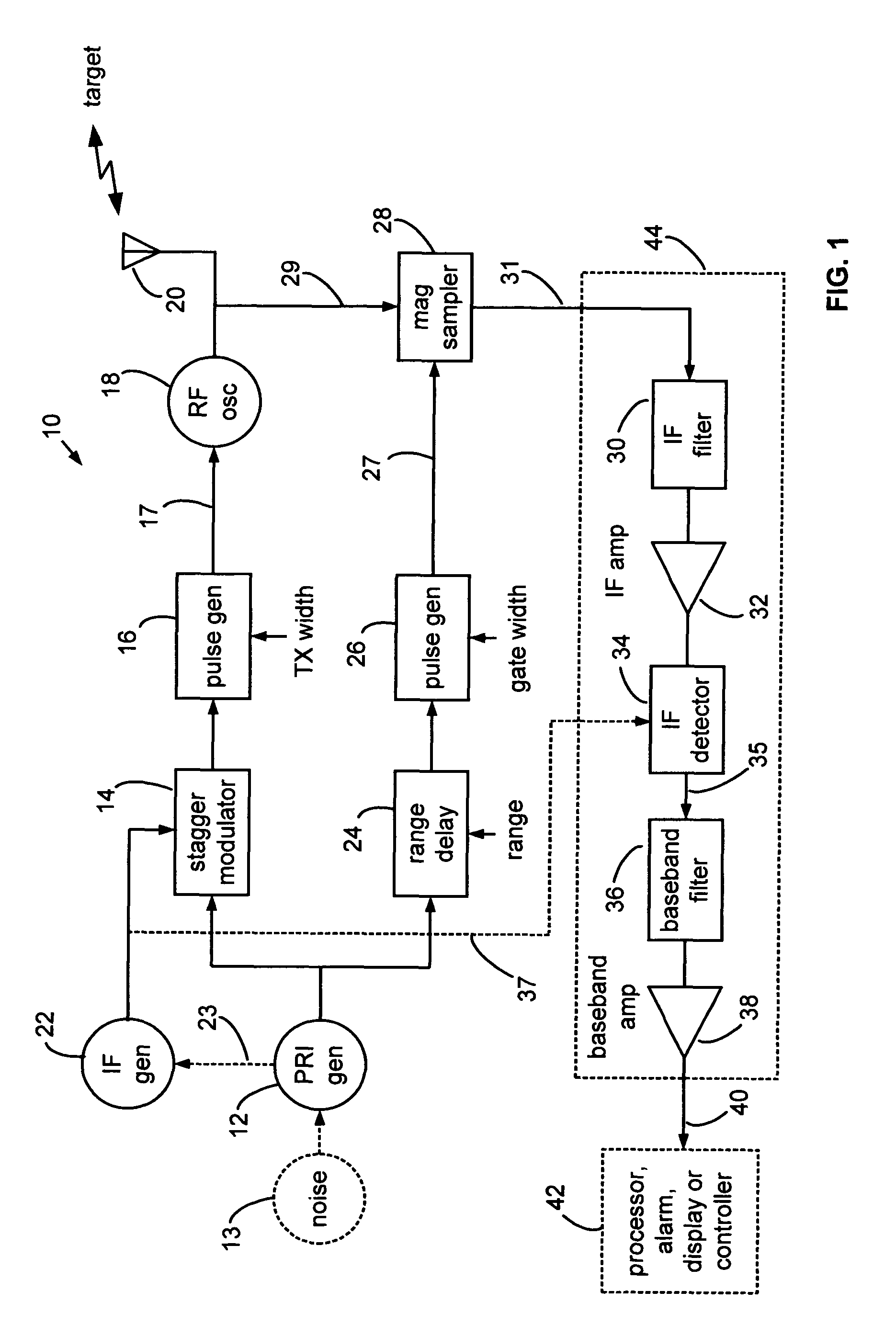
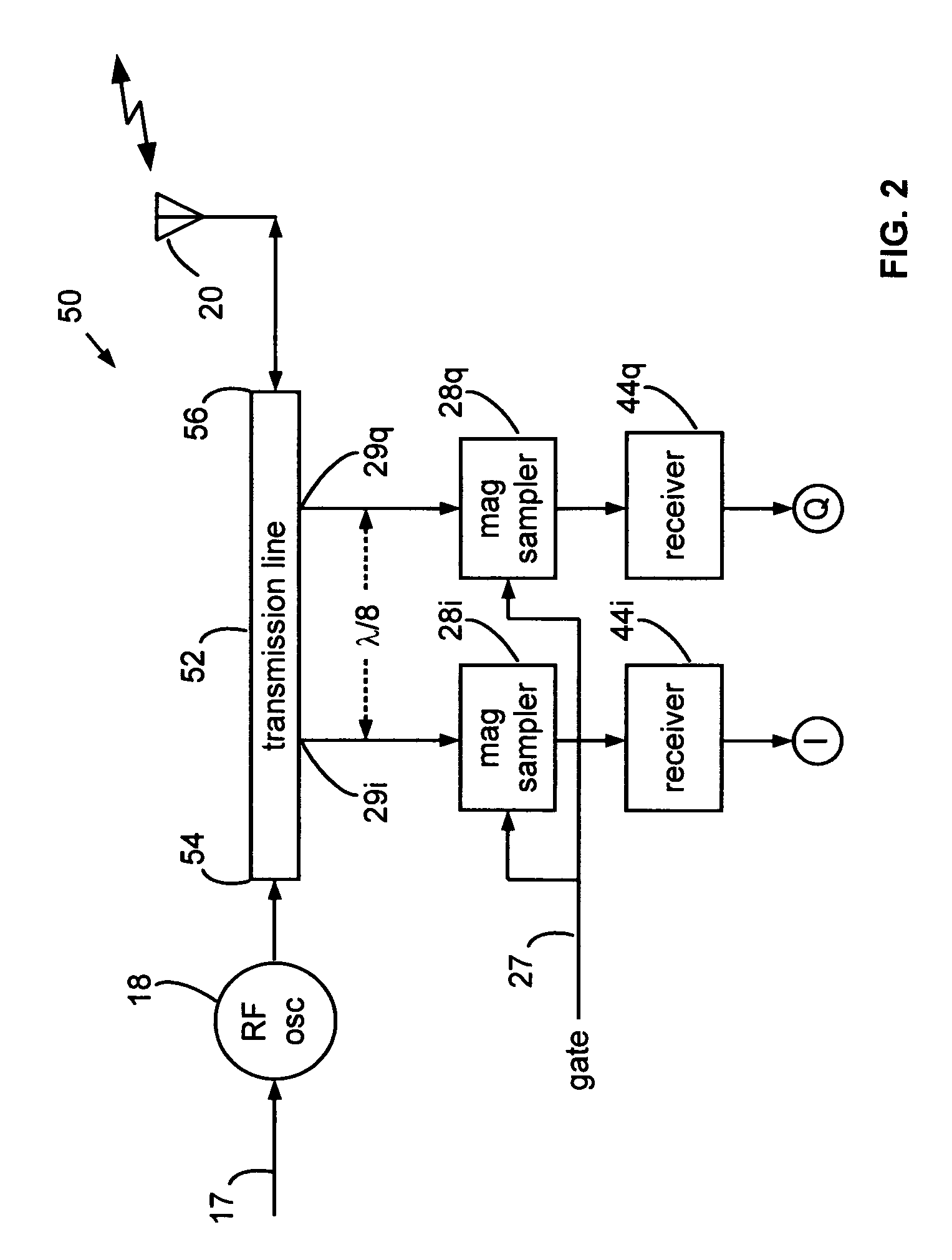
Range gated holographic radar
Narrow virtual transmit pulses are synthesized by differencing long-duration, staggered pulse repetition interval (PRI) transmit pulses. PRI is staggered at an intermediate frequency IF. Echoes from virtual pulses form IF-modulated interference patterns with a reference wave. Samples of interference patterns are IF-filtered to produce high spatial resolution holographic data. PRI stagger can be very small, e.g., 1-ns, to produce a 1-ns virtual pulse from very long, staggered transmit pulses. Occupied Bandwidth (OBW) can be less than 10 MHz due to long RF pulses needed for holography, while spatial resolution can be very high, corresponding to ultra-wideband (UWB) operation, due to short virtual pulses. X-Y antenna scanning can produce range-gated surface holograms from quadrature data. Multiple range gates can produce stacked-in-range holograms. Motion and vibration can be detected by changes in interference patterns within a range-gated zone.
Owner:MCEWAN TECH
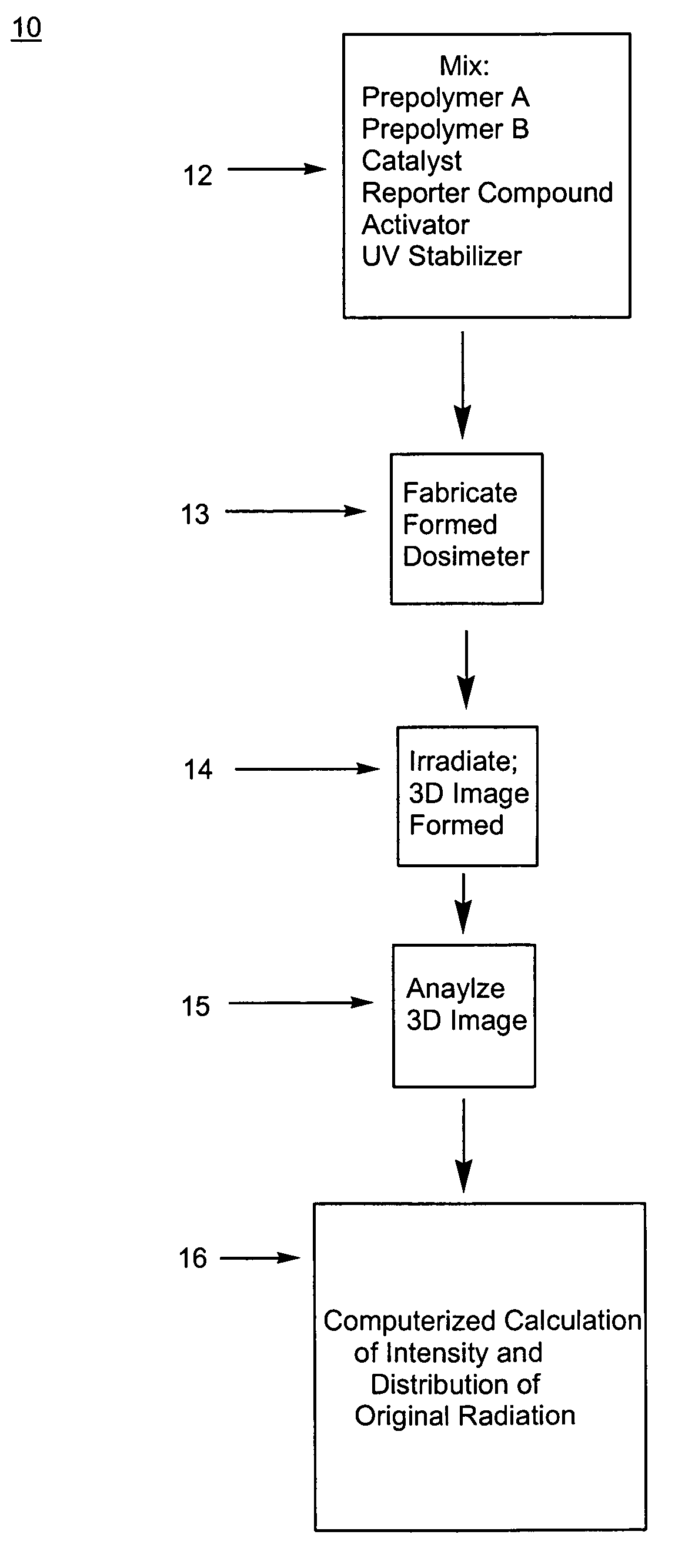
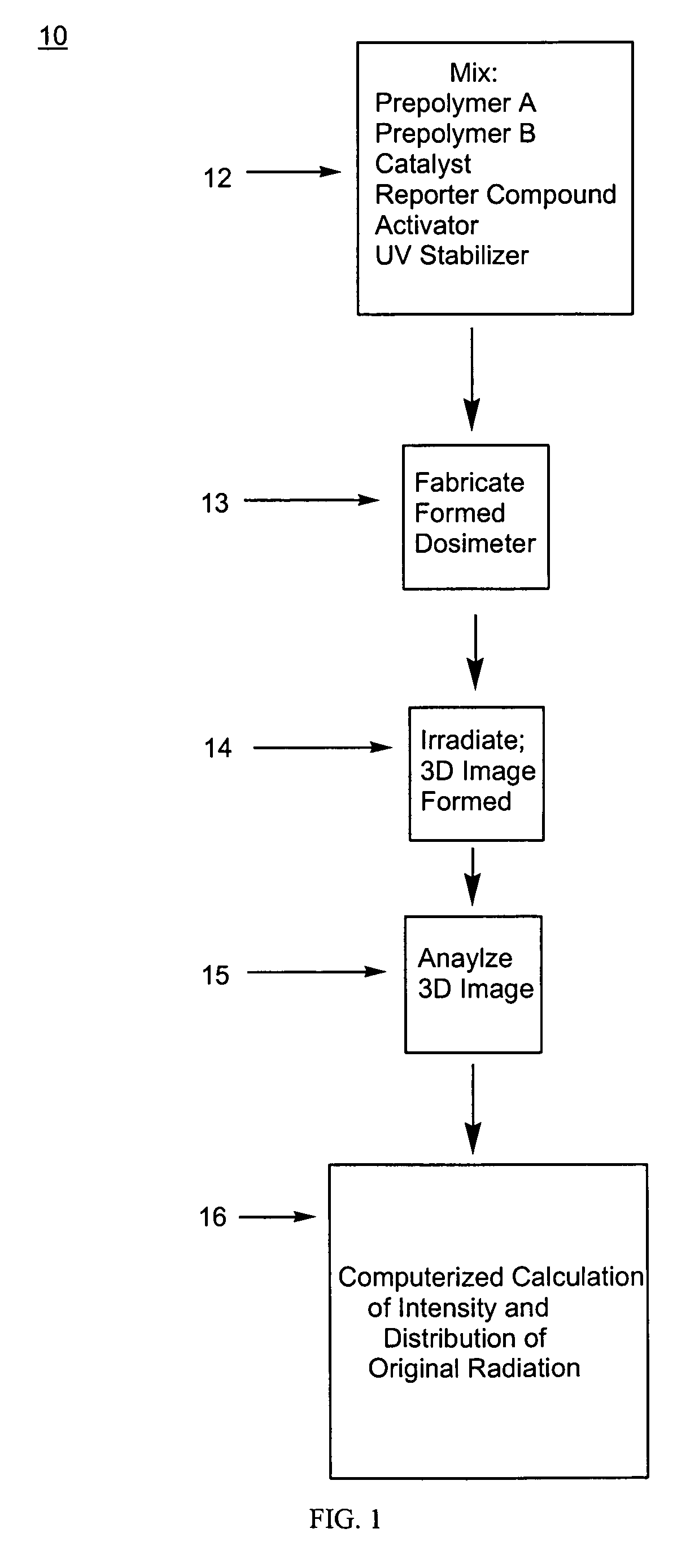
Three-dimensional dosimeter for penetrating radiation and method of use
ActiveUS7098463B2High resolutionRobust and safe processPhotosensitive materialsGlass dosimetersPolymer scienceImage resolution
This invention relates to a method of forming a three-dimensional (3D) dosimetric map in a solid translucent or transparent polymer and to an article of manufacture comprising a polymer formulated to capture data imparted by incident penetrating radiation. The present invention provides a method of preparation of a solid translucent or transparent polymer matrix capable of detecting and displaying a dose or doses of penetrating radiation by forming within the polymeric matrix a 3D dosimetric map which is measurable and quantifiable by various known procedures. The dosimetric map is representative of the 3D distribution of the dose or doses of the penetrating radiation to which the polymer had been exposed and can be quantified at high spatial resolution, thereby providing an accurate, stable, storable record in three dimensions of the radiation exposure or dosing event(s).
Owner:HEURIS PHARMA
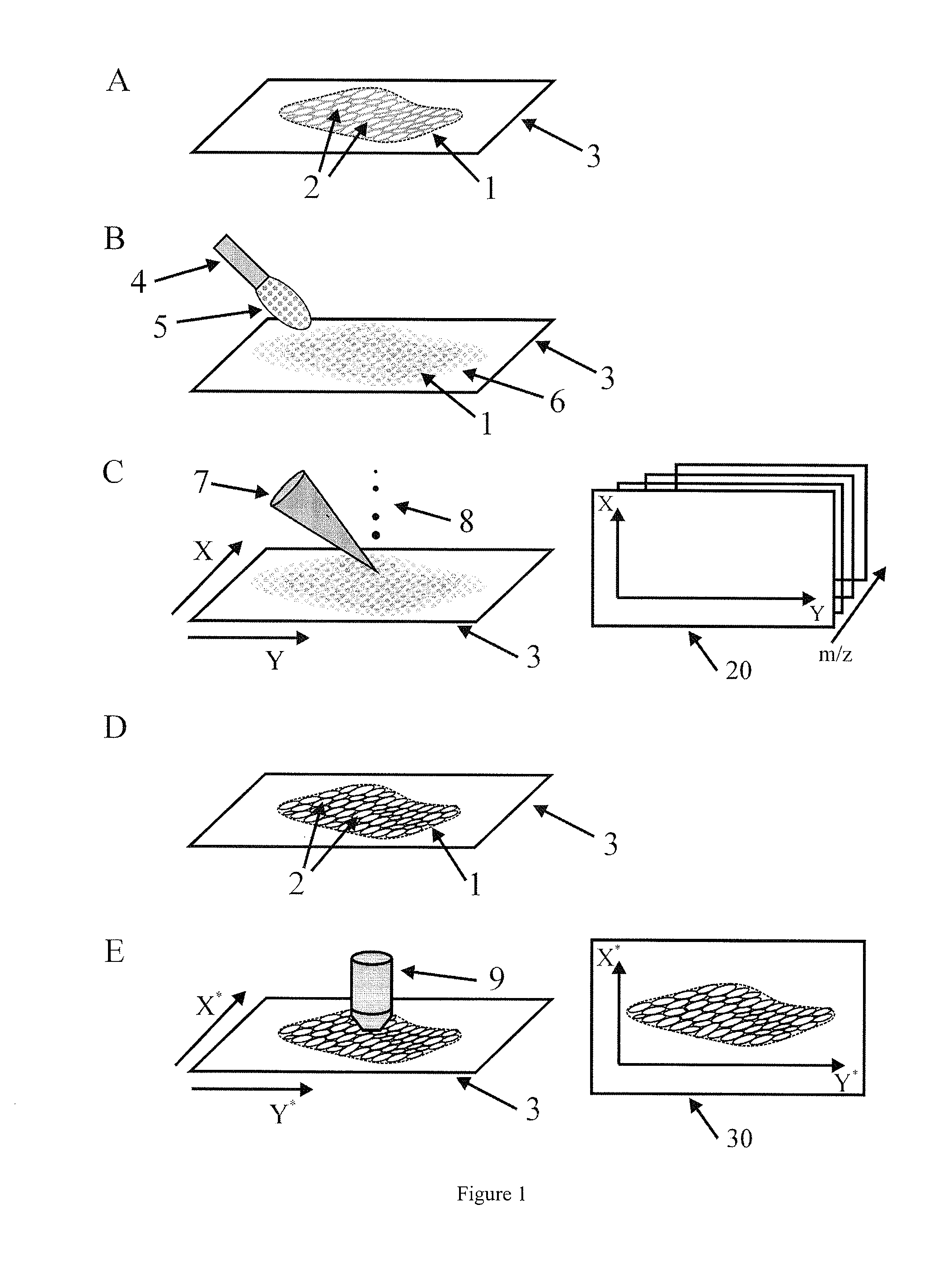
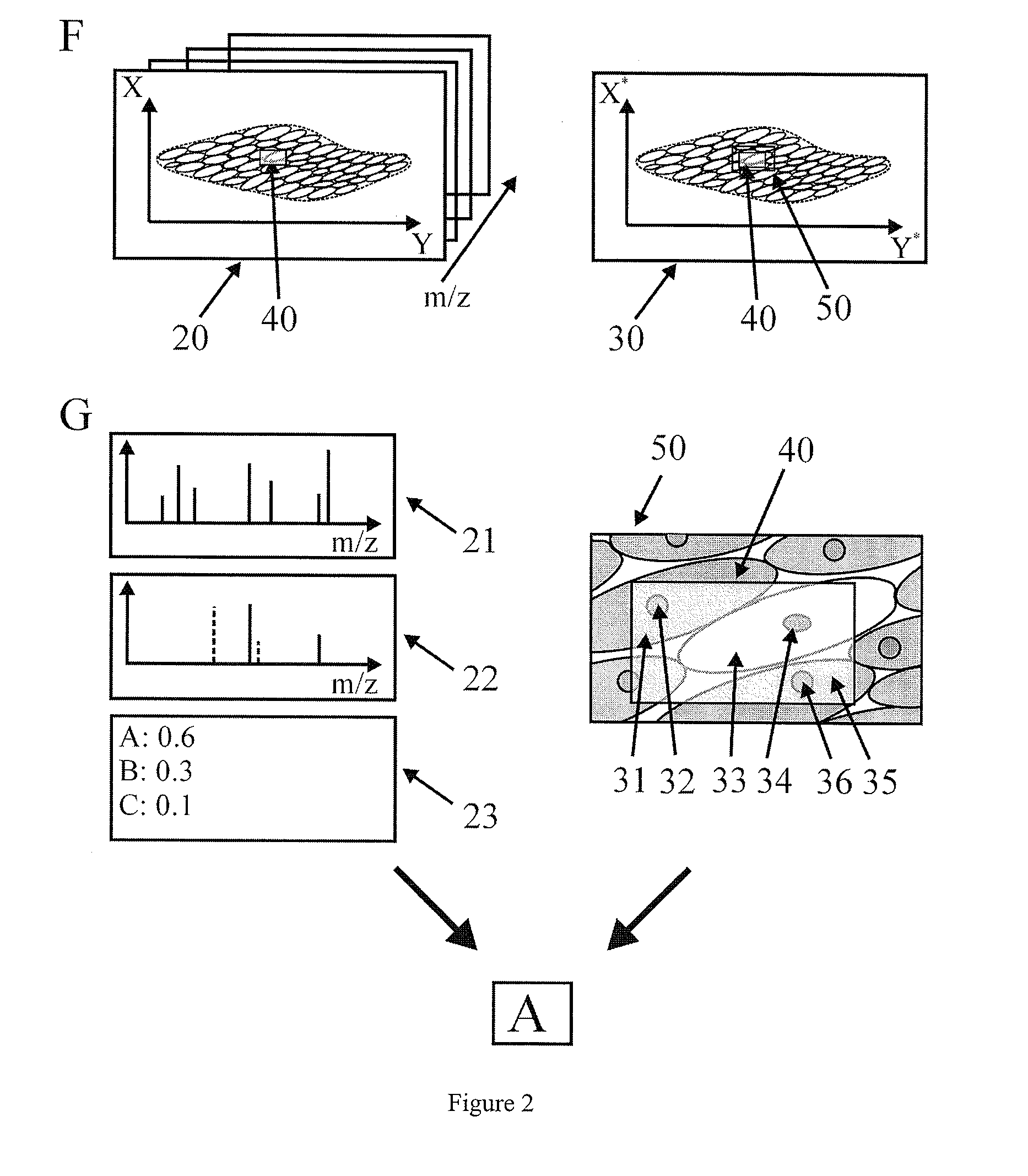
Method for the analysis of tissue sections
InactiveUS20090289184A1Reduce spatial resolutionIncrease contentImage enhancementImage analysisSpatially resolvedImage resolution
The present invention relates to a method for the histologic classification of a tissue section. The method includes acquiring a mass spectrometric image and a light-optical image of the same tissue section (the optical image having a higher spatial resolution than the mass spectrometric image) and combining optical information on the structures of a subarea of the tissue section with mass spectrometric information on the subarea (the structures not being spatially resolved in the mass spectrometric image).
Owner:BRUKER DALTONIK GMBH & CO KG
Superresolution parallel magnetic resonance imaging
InactiveUS20090285463A1Increase spatio-temporal resolutionReduce acquisition timeGeometric image transformationCharacter and pattern recognitionVoxelReceiver coil
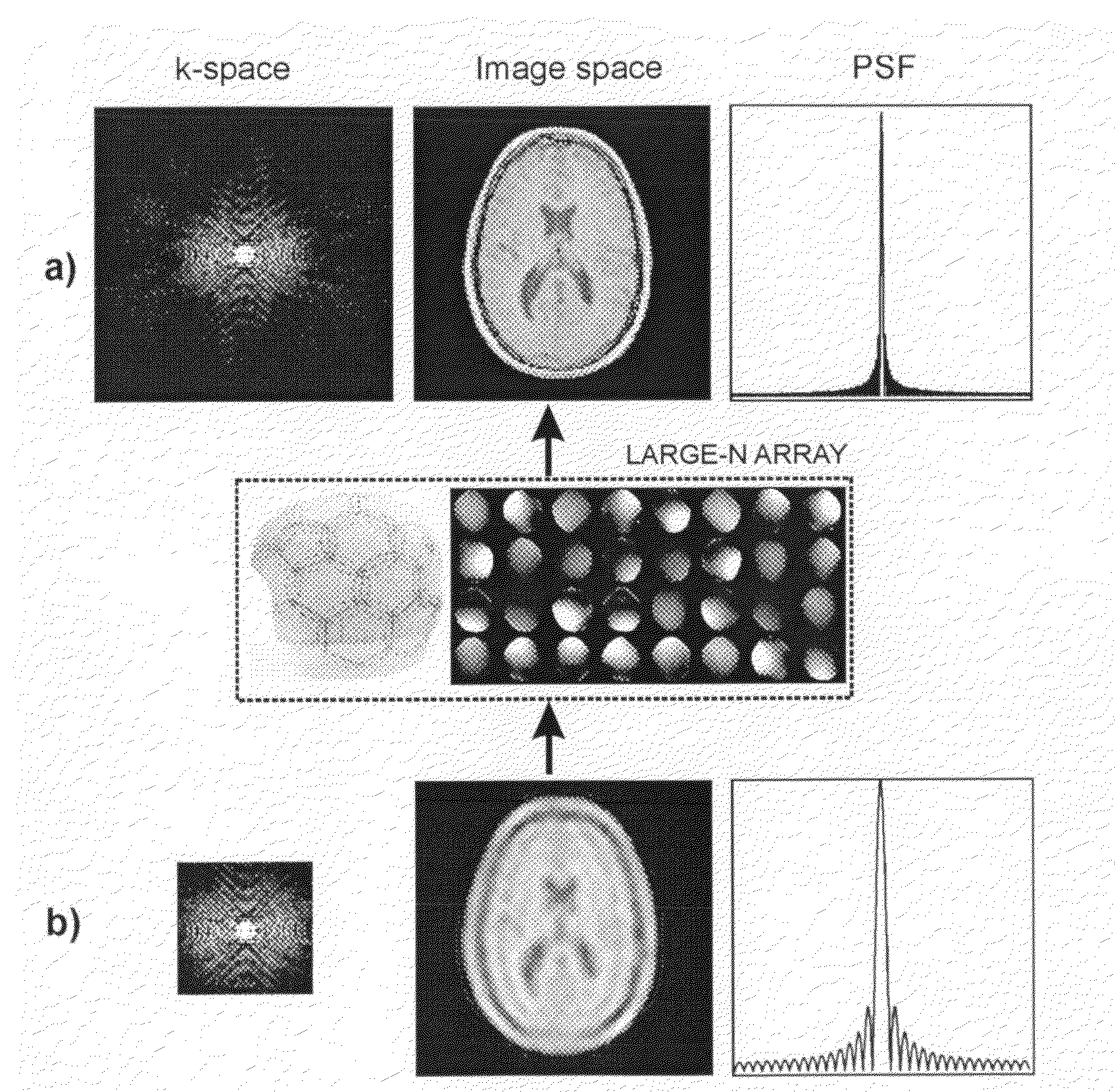
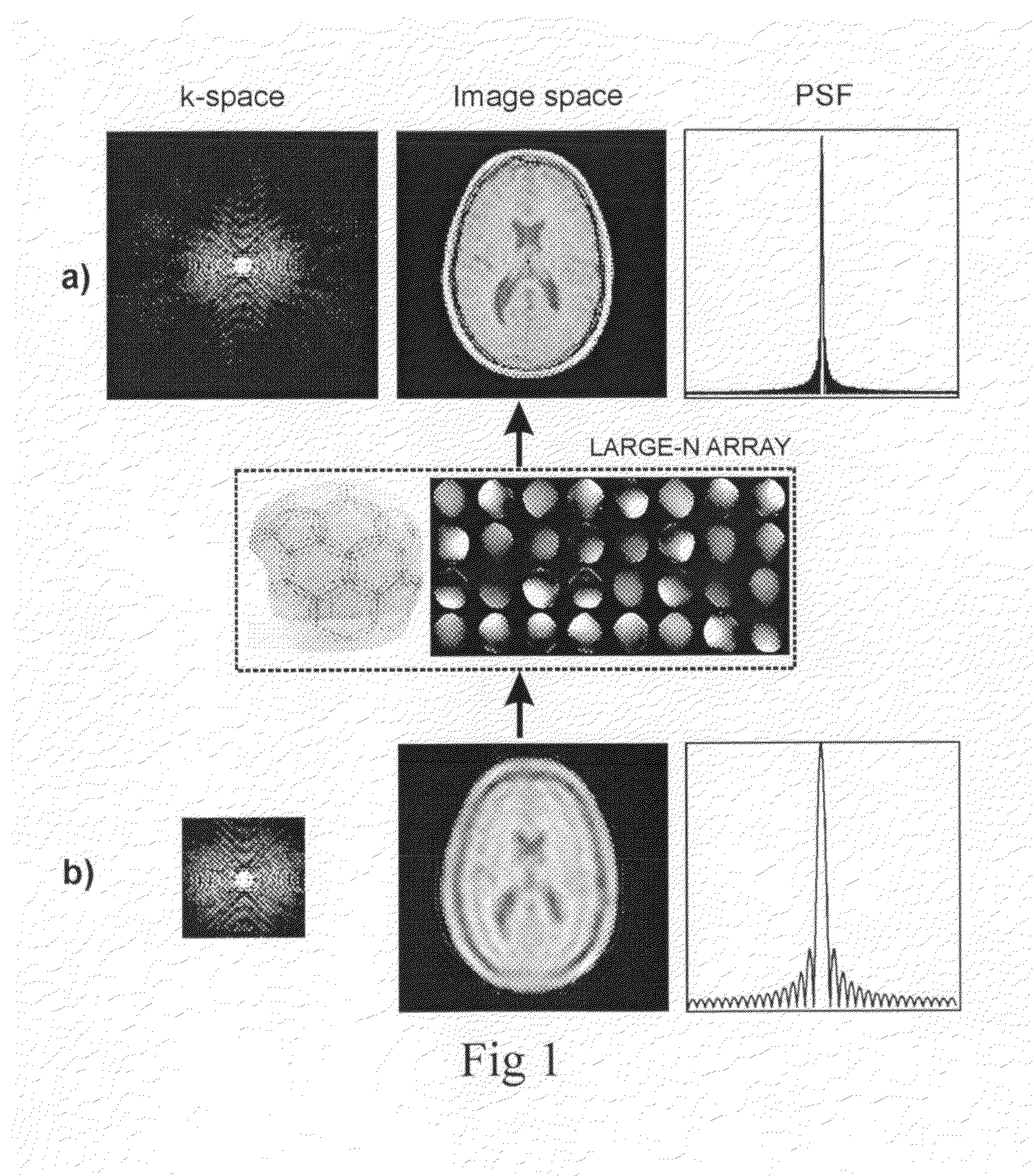
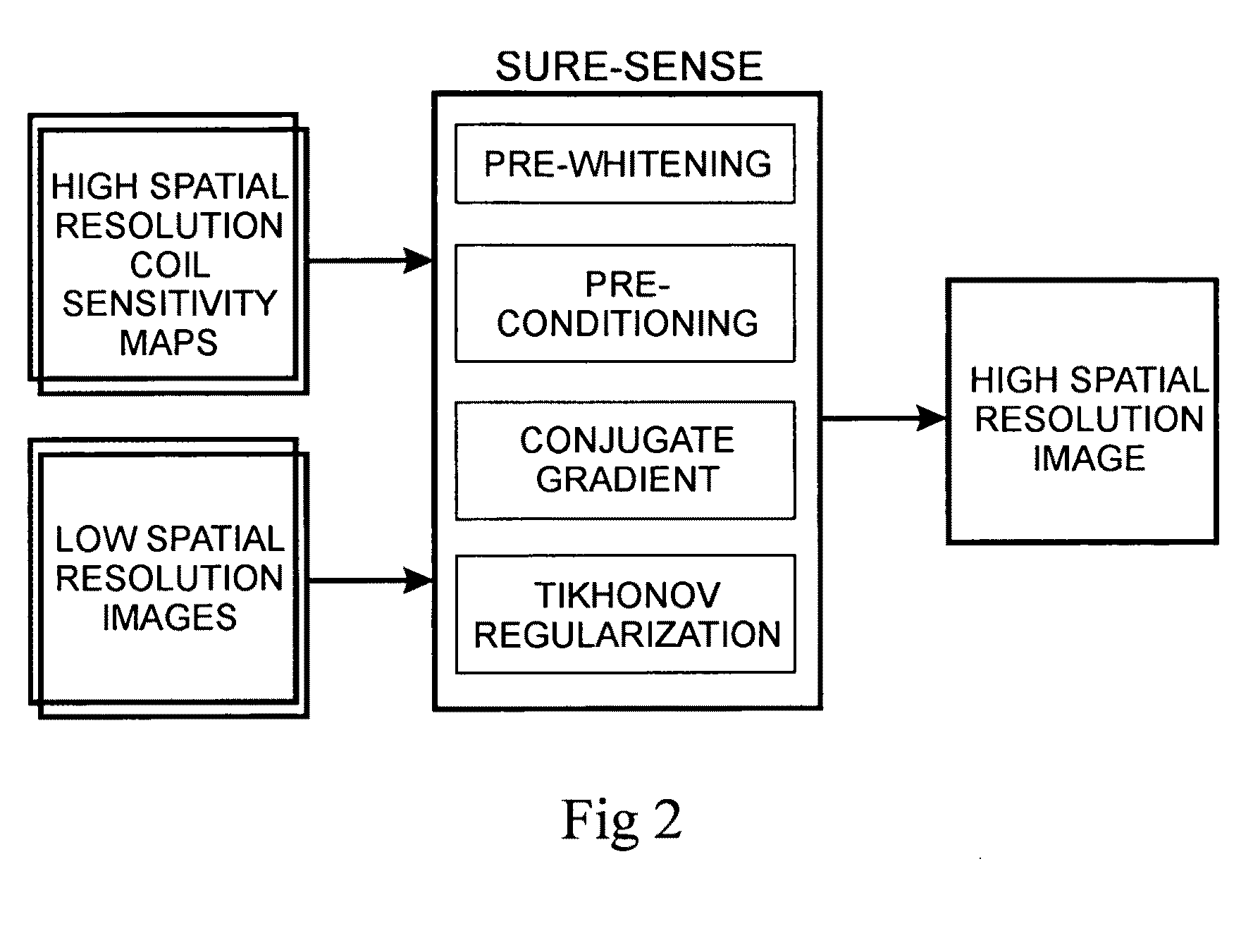
The present invention includes a method for parallel magnetic resonance imaging termed Superresolution Sensitivity Encoding (SURE-SENSE) and its application to functional and spectroscopic magnetic resonance imaging. SURE-SENSE acceleration is performed by acquiring only the central region of k-space instead of increasing the sampling distance over the complete k-space matrix and reconstruction is explicitly based on intra-voxel coil sensitivity variation. SURE-SENSE image reconstruction is formulated as a superresolution imaging problem where a collection of low resolution images acquired with multiple receiver coils are combined into a single image with higher spatial resolution using coil sensitivity maps acquired with high spatial resolution. The effective acceleration of conventional gradient encoding is given by the gain in spatial resolution Since SURE-SENSE is an ill-posed inverse problem, Tikhonov regularization is employed to control noise amplification. Unlike standard SENSE, SURE-SENSE allows acceleration along all encoding directions.
Owner:OTAZO RICARDO +1
Radiation detectors
InactiveUS7304309B2Improve efficiencyEasy accessMaterial analysis by optical meansNanoopticsRecoil electronPhotonic bandgap
The invention consists in structuring scintillation radiation detectors as Photonic Bandgap Crystals or 3D layers of thin filaments, thus enabling extremely high spatial resolutions and achieving virtual voxellation of the radiation detector without physical separating walls. The ability to precisely measure the recoil electron track in a Compton camera enables to assess the directions of the gamma rays hitting the detector and consequently dispensing with collimators that strongly reduce the intensity of radiation detected by gamma cameras. The invention enables great enhancements of the capabilities of gamma cameras, SPECT, PET, CT and DR machines as well as their use in Homeland Security applications. Methods of fabrication of such radiation detectors are described.
Owner:SUHAMI AVRAHAM
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com