Patents
Literature
2349 results about "Optical beam" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
An optical beam smoke detector is a device that uses a projected beam of light to detect smoke across large areas, typically as an indicator of fire. They are used to detect fires in buildings where standard point smoke detectors would either be uneconomical or restricted for use by the height of the building. Optical beam smoke detectors are often installed in warehouses as a cost effective ...
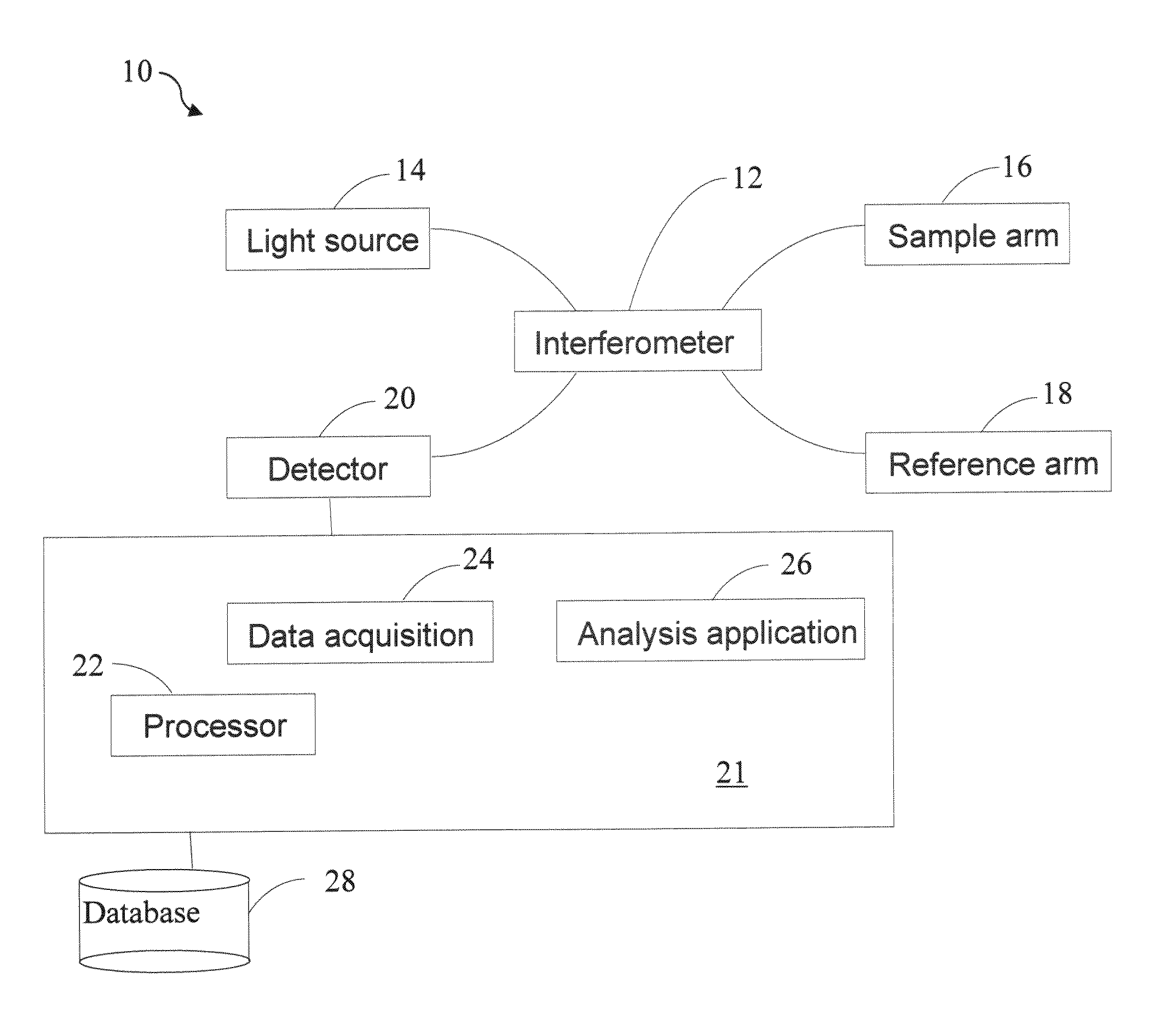
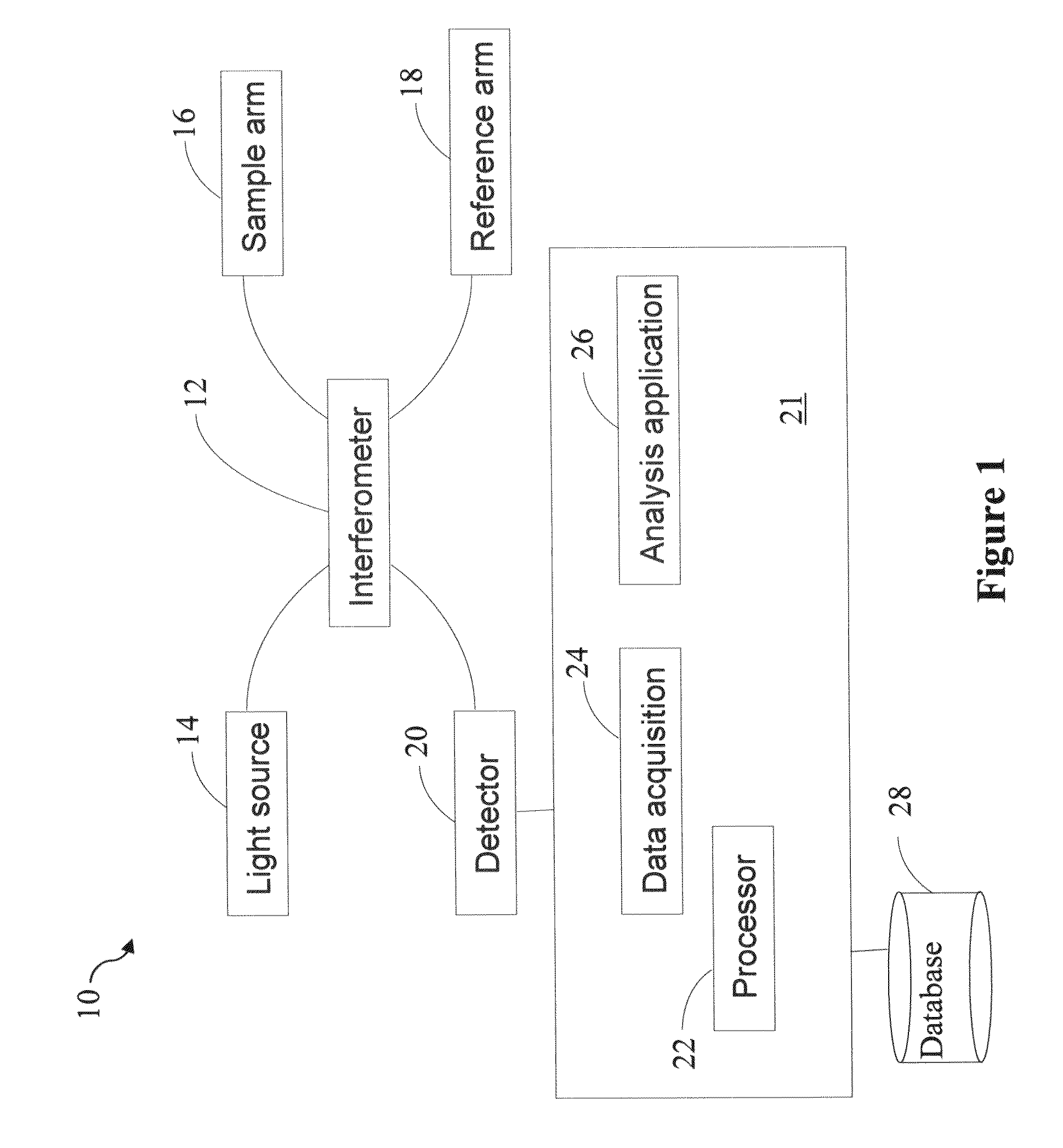
System and method for creating a stable optical interface
ActiveUS8219172B2High bandwidthReduce coherenceDiagnostic recording/measuringSensorsRefractive indexLight beam
Owner:MASIMO CORP
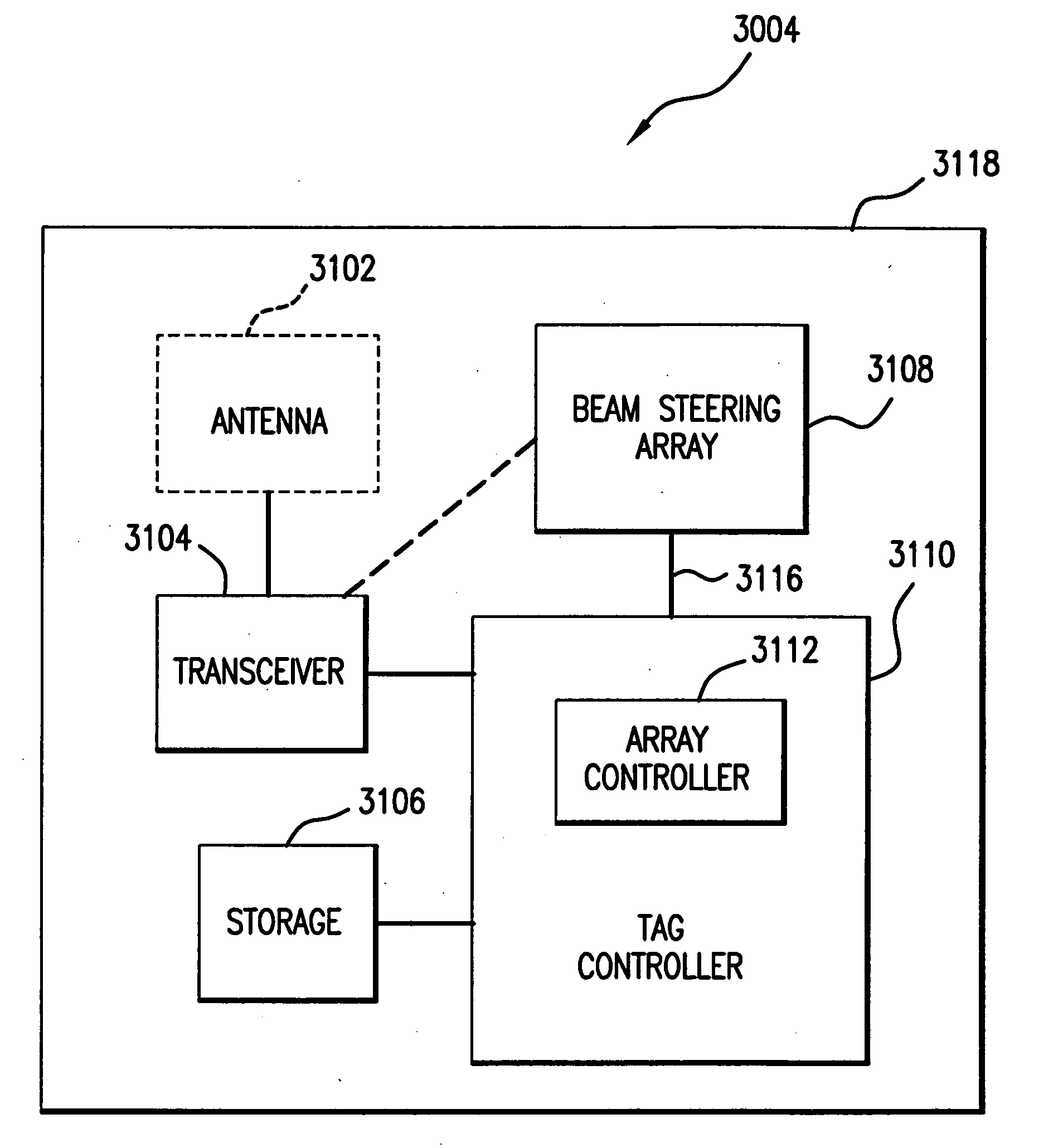
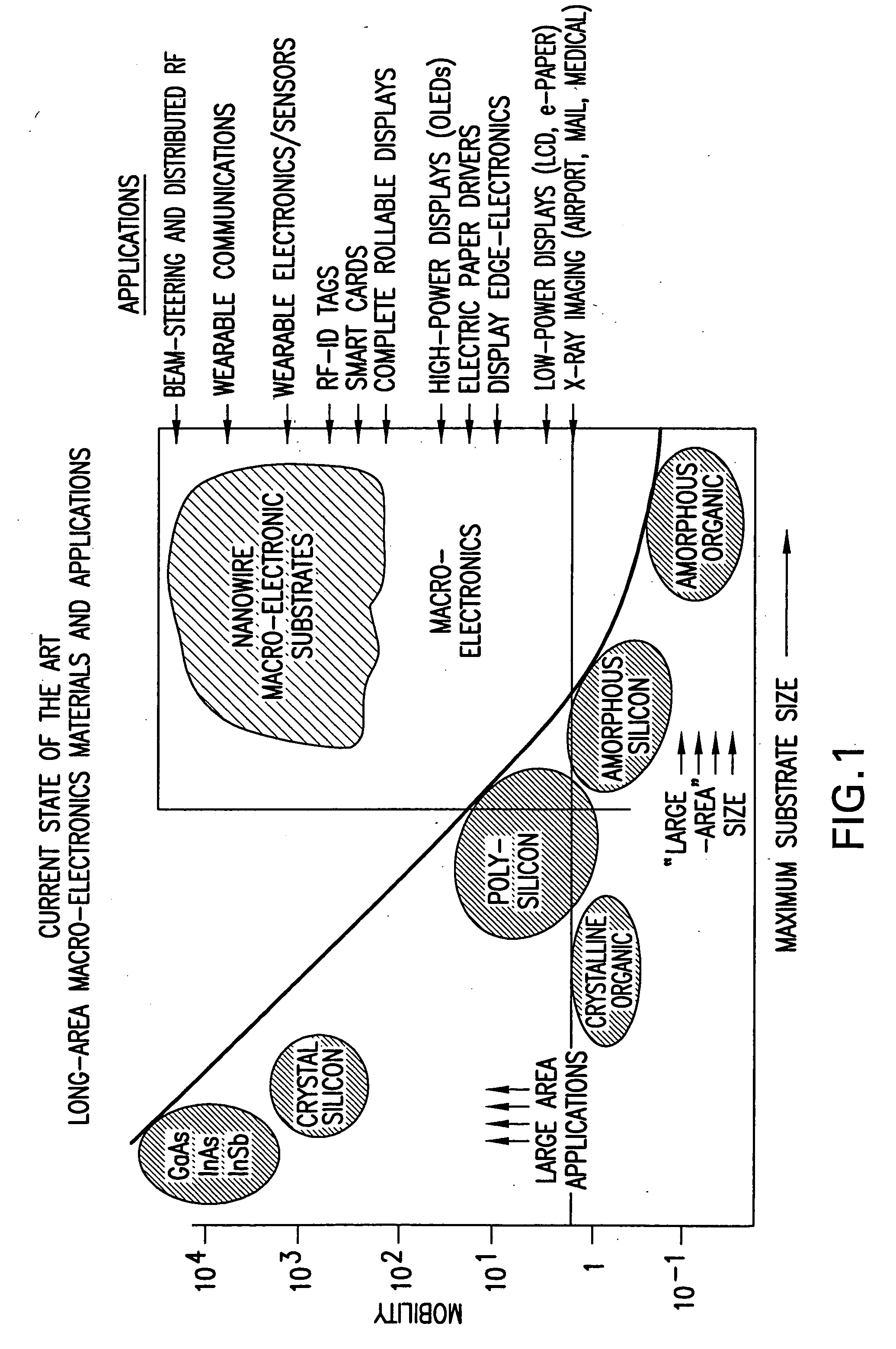
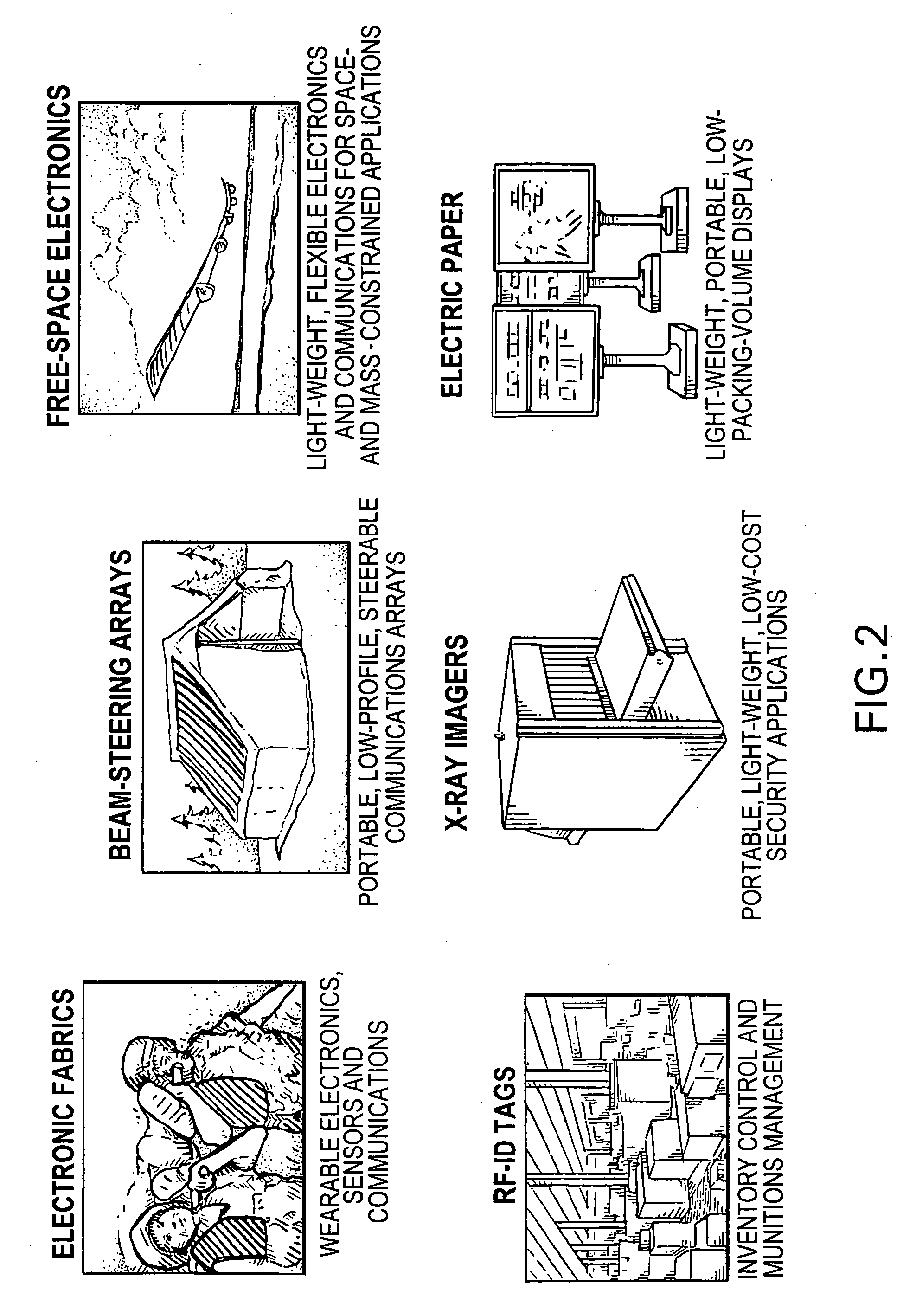
Applications of nano-enabled large area macroelectronic substrates incorporating nanowires and nanowire composites
Macroelectronic substrate materials incorporating nanowires are described. These are used to provide underlying electronic elements (e.g., transistors and the like) for a variety of different applications. Methods for making the macroelectronic substrate materials are disclosed. One application is for transmission an reception of RF signals in small, lightweight sensors. Such sensors can be configured in a distributed sensor network to provide security monitoring. Furthermore, a method and apparatus for a radio frequency identification (RFID) tag is described. The RFID tag includes an antenna and a beam-steering array. The beam-steering array includes a plurality of tunable elements. A method and apparatus for an acoustic cancellation device and for an adjustable phase shifter that are enabled by nanowires are also described.
Owner:ONED MATERIAL INC
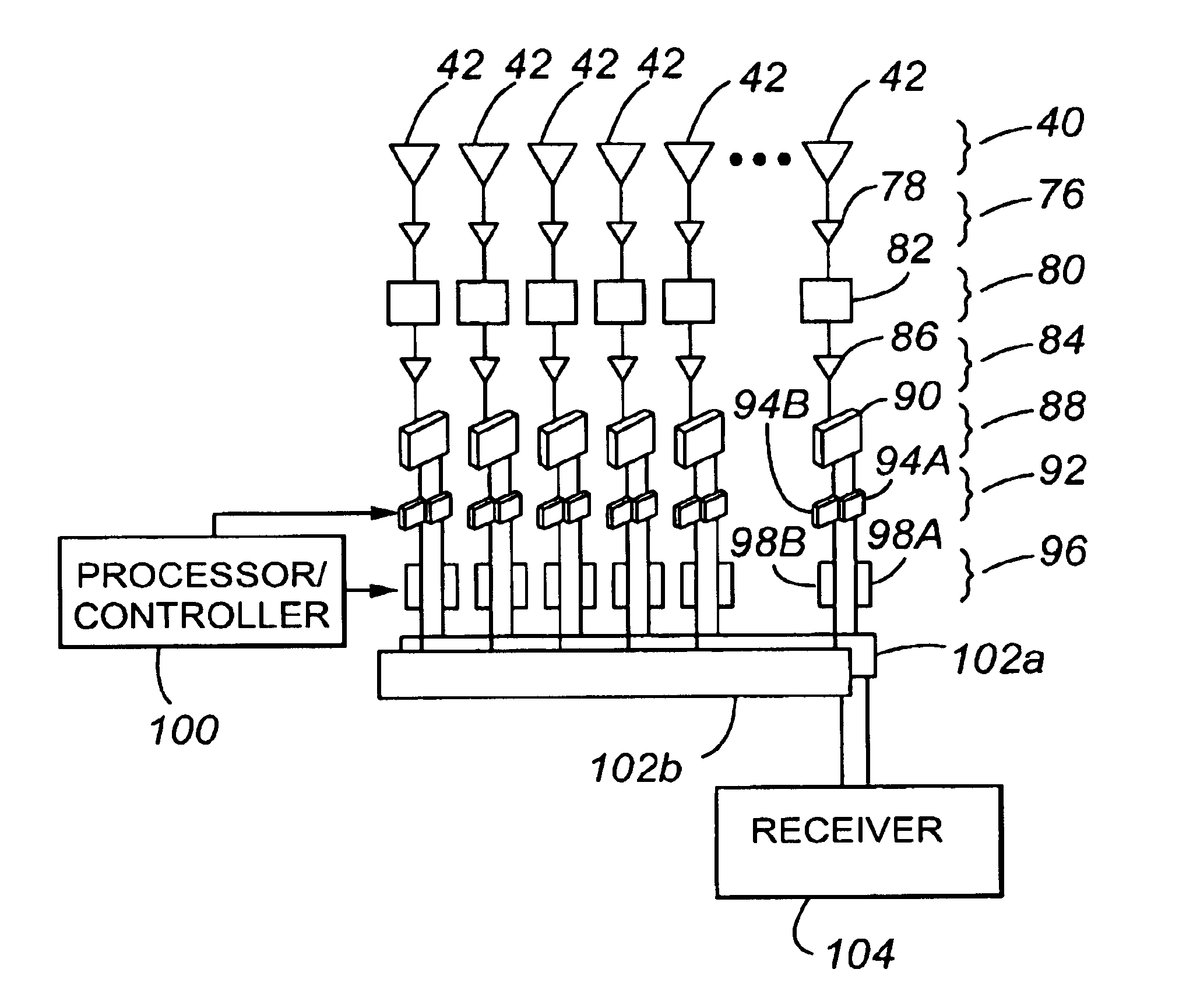
Electronically agile dual beam antenna system
InactiveUS6768456B1Reduce needSimple and reliable processAntenna adaptation in movable bodiesIndividually energised antenna arraysDual beamMulti beam
The present invention provides an improved antenna system that, in one embodiment, includes an antenna array comprised of a plurality of elements, each of which is capable of providing a signal. Also included in the improved antenna system is a multi-beam beamformer for producing two spatially independent overlapping beams from the signals provided by two different subsets of the antenna array. The phase of the two beams is compared to realize an interferometer that can provide high or fine resolution data on the position of an object relative to the antenna system. The amplitude of the two beams can also be compared to obtain coarse data on the position of the object. The beamformer includes a switching network for selecting which elements of the antenna array form the two subsets. This permits, for example, the position of the beams to moved, the baseline of the two beams to be varied, and / or the beam width of the beams to be altered. To reduce adverse aerodynamic effects in certain applications, the antenna array is located conformal to the exterior surface of the body on which the array is mounted. Further, to reduce temperature related problems associated with high speed movement of the body on which the array is located, the array is located on the side of the body, as opposed to the front of the body. The side location also provides space for other types of sensors that are preferably located adjacent to the front surface of the body.
Owner:BALL AEROSPACE & TECHNOLOGIES
Optical phased array lidar system and method of using same
A lidar-based system and method are used for the solid state beamforming and steering of laser beams using optical phased array (OPA) photonic integrated circuits (PICs) and the detection of laser beams using photodetectors. Transmitter and receiver electronics, power management electronics, control electronics, data conversion electronics and processing electronics are also included in the system and used in the method.Laser pulses beamformed by the OPA PIC reflect from objects in the field of view (FOV) of said OPA, and are detected by a detector or a set of detectors.A lidar system includes at least one lidar, and any subset and any number of complementary sensors, data processing / communication / storage modules, and a balance of system for supplying power, protecting, connecting, and mounting the components of said system.Direct correlation between the 3D point cloud generated by the lidar and the color images captured by an RGB (Red, Green, Blue) video camera can be achieved by using an optical beam splitter that sends optical signals simultaneously to both sensors.A lidar system may contain a plurality of lidar sensors, a lidar sensor may contain a plurality of optical transmitters, and an optical transmitter may contain a plurality of OPA PICs.
Owner:QUANERGY SOLUTIONS INC
Quantitative methods for obtaining tissue characteristics from optical coherence tomography images
InactiveUS20090306520A1Improve tissue type classificationCatheterDiagnostic recording/measuringUltrasound attenuationLight beam
A method and apparatus for determining properties of a tissue or tissues imaged by optical coherence tomography (OCT). In one embodiment the backscatter and attenuation of the OCT optical beam is measured and based on these measurements and indicium such as color is assigned for each portion of the image corresponding to the specific value of the backscatter and attenuation for that portion. The image is then displayed with the indicia and a user can then determine the tissue characteristics. In an alternative embodiment the tissue characteristics is classified automatically by a program given the combination of backscatter and attenuation values.
Owner:LIGHTLAB IMAGING
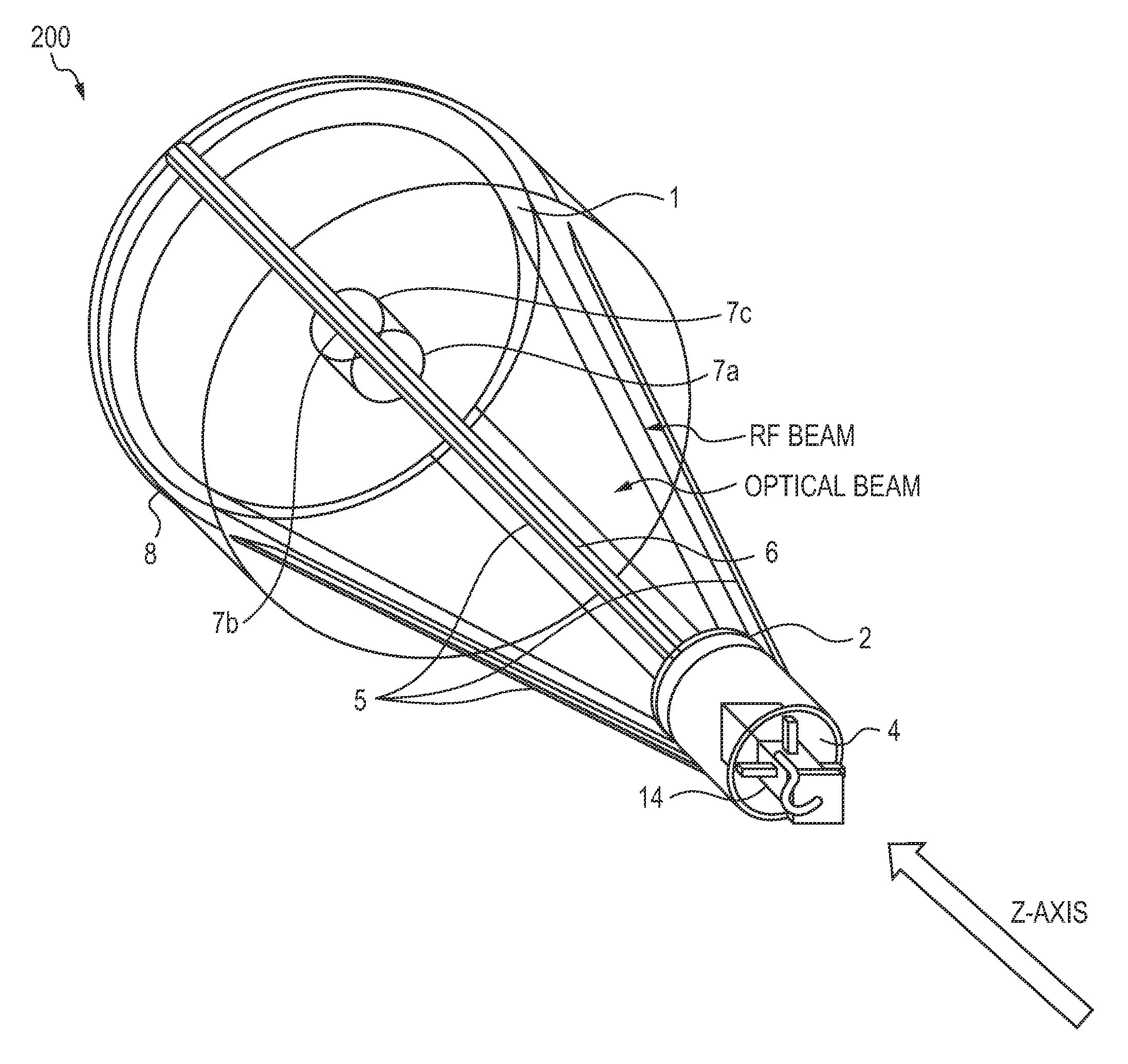
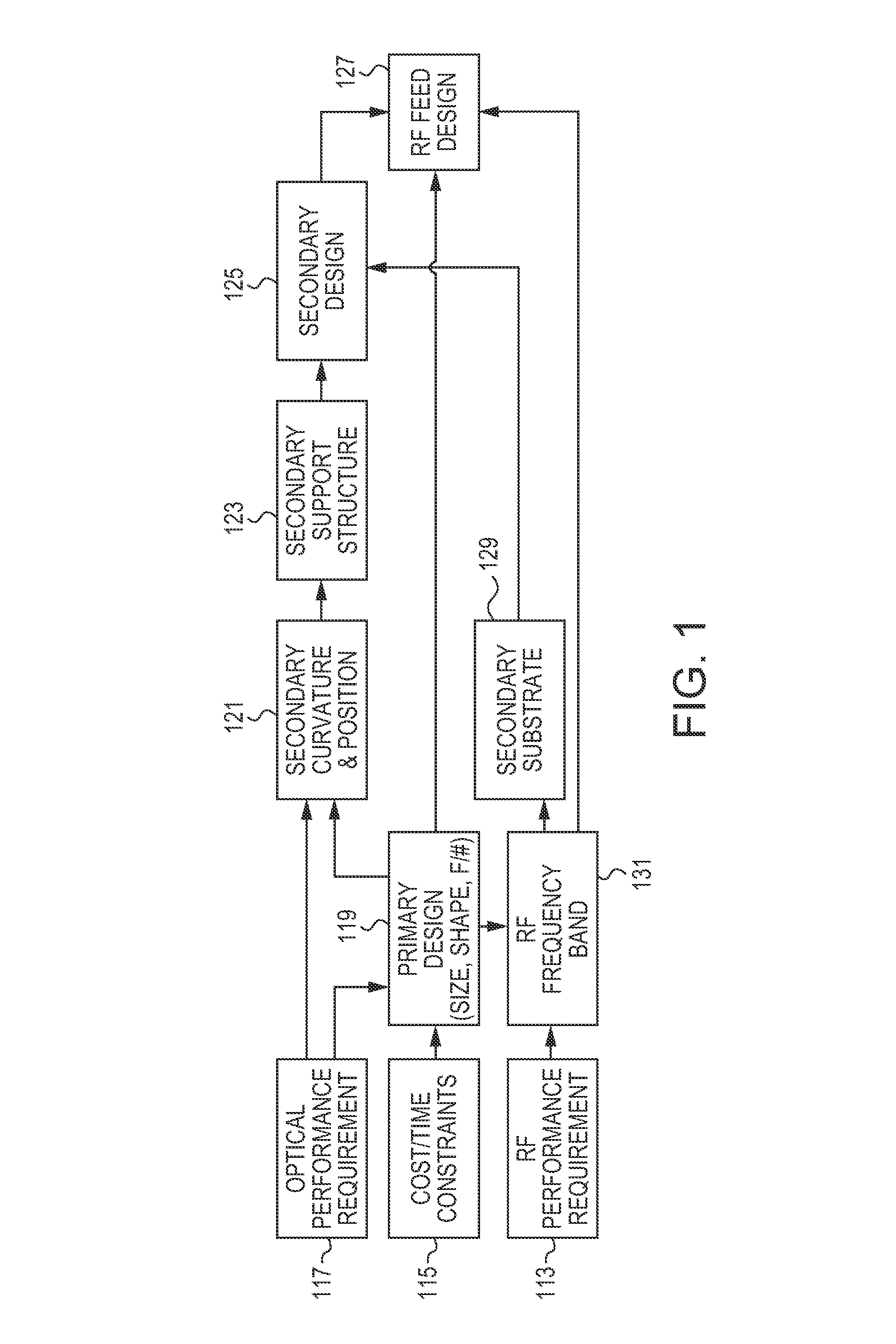
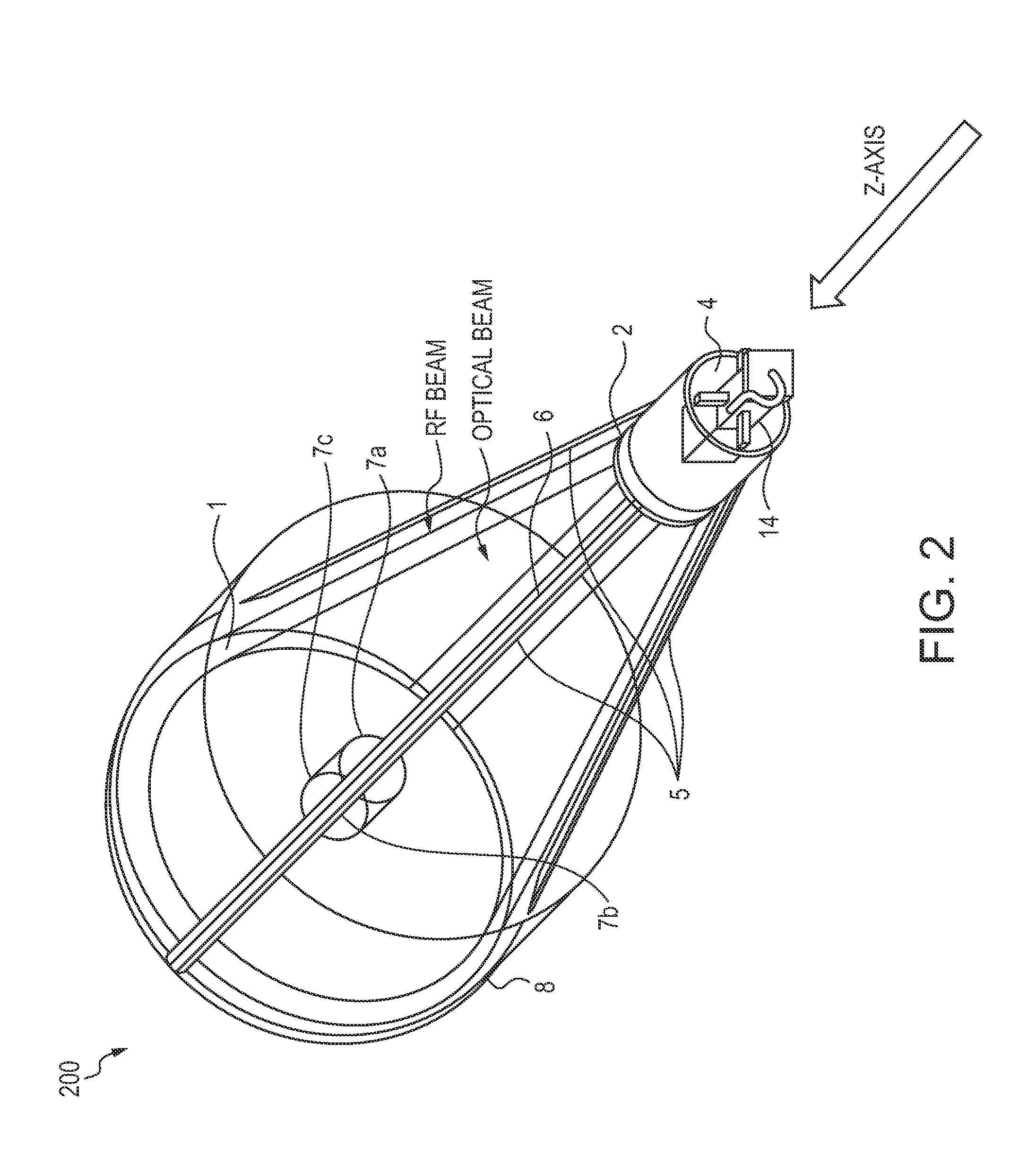
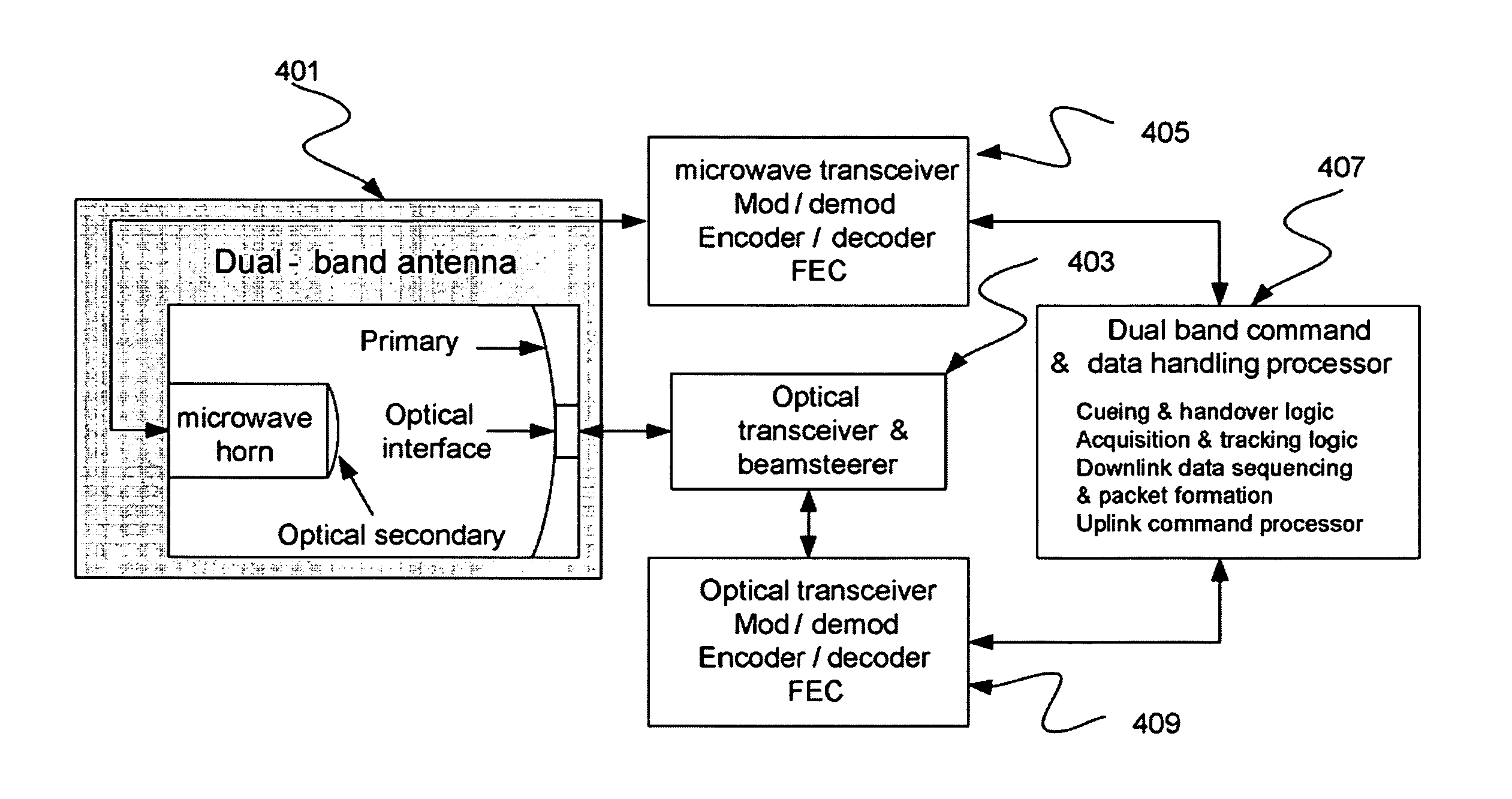
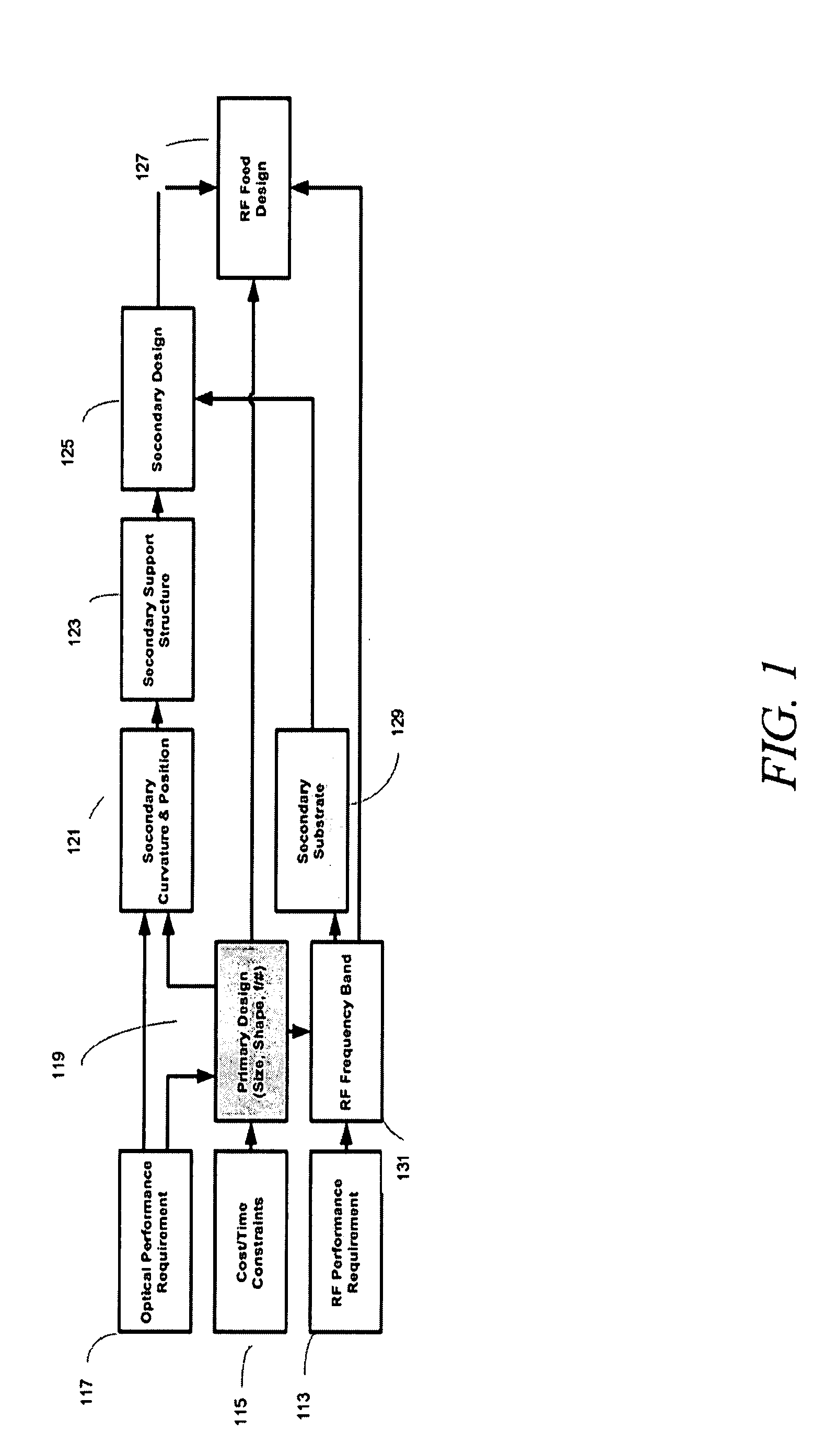
Dual band radio frequency (RF) and optical communications antenna and terminal design methodology and implementation
ActiveUS8094081B1High bandwidthMinimized massAntenna arraysSimultaneous aerial operationsAntenna designTransceiver
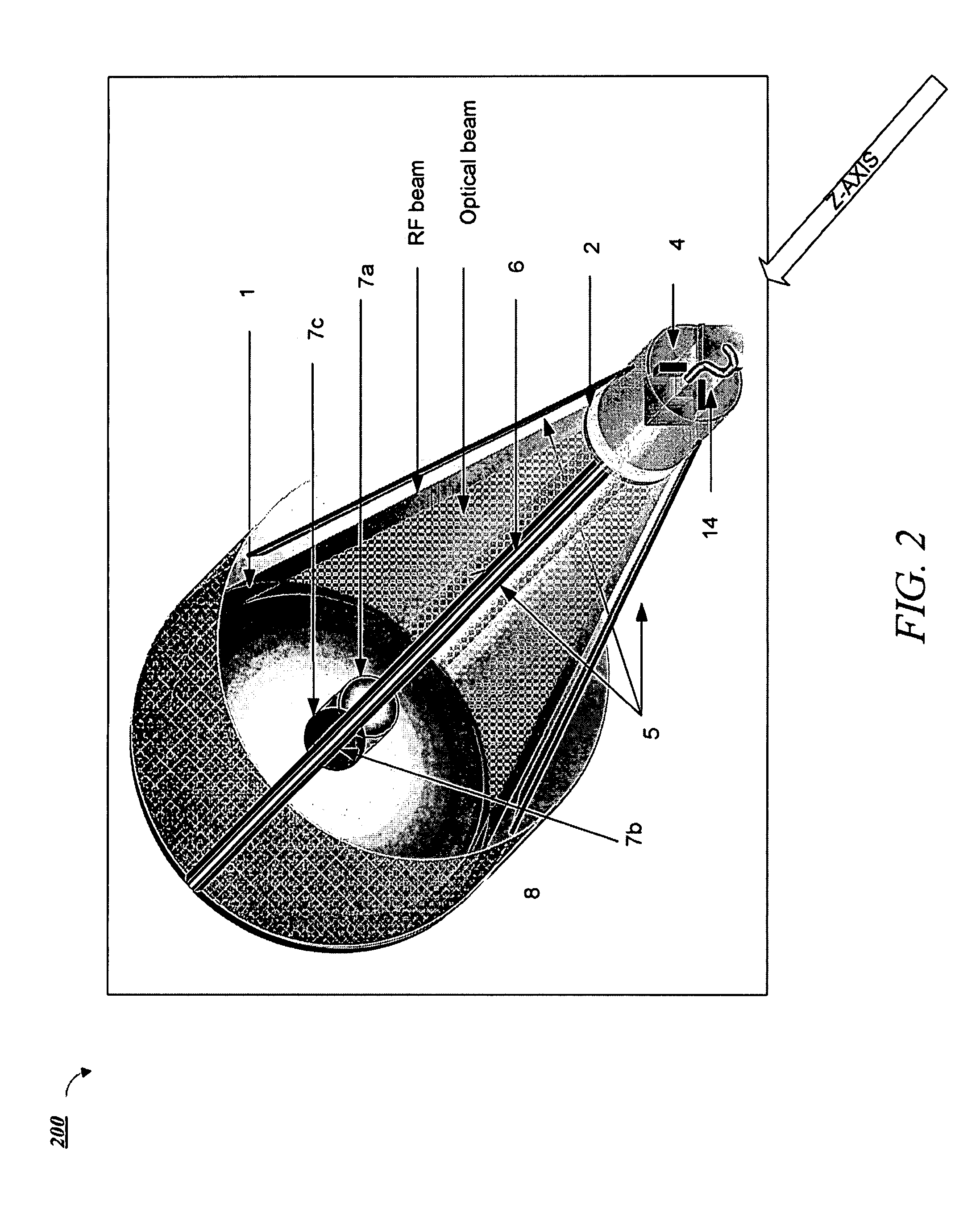
A dual-band antenna is provided that combines two normally disparate communications modes into a single compact aperture minimizing overall mass and volume, while maintaining high performance efficiency and reciprocity of each individual mode. The antenna is compatible with both optical (near-IR / visible) and RF (microwave / millimeter-wave) transceiver subsystems for high bandwidth communications, applicable primarily to long- to extremely long-range (space-to-ground) link distances. The optical link provides high bandwidth while the RF provides a lower data-rate weather backup, accommodation for traditional navigation techniques, and assistance in cueing the extremely tight optical beam by matching the RF beamwidth to an optical fine-steering mechanism field-of-regard. The configuration is built around a near-diffraction-limited high performance primary mirror shared by both a direct-fed RF antenna design and a Cassegrain optical telescope. Material properties are exploited to combine the optical secondary mirror with the RF feed structure, providing a collimated optical beam interface at the antenna vertex.
Owner:THE JOHN HOPKINS UNIV SCHOOL OF MEDICINE
Dual band radio frequency (RF) & optical communications antenna and terminal design methodology and implementation
ActiveUS20120002973A1Increase system capacityLink robustnessWaveguide hornsAntenna arraysAntenna designTransceiver
A dual-band antenna is provided that combines two normally disparate communications modes into a single compact aperture minimizing overall mass and volume, while maintaining high performance efficiency and reciprocity of each individual mode. The antenna is compatible with both optical (near-IR / visible) and RF (microwave / millimeter-wave) transceiver subsystems for high bandwidth communications, applicable primarily to long- to extremely long-range (space-to-ground) link distances. The optical link provides high bandwidth while the RF provides a lower data-rate weather backup, accommodation for traditional navigation techniques, and assistance in cueing the extremely tight optical beam by matching the RF beamwidth to an optical fine-steering mechanism field-of-regard. The configuration is built around a near-diffraction-limited high performance primary mirror shared by both a direct-fed RF antenna design and a Cassegrain optical telescope. Material properties are exploited to combine the optical secondary mirror with the RF feed structure, providing a collimated optical beam interface at the antenna vertex.
Owner:THE JOHN HOPKINS UNIV SCHOOL OF MEDICINE
Thin film organic position sensitive detectors
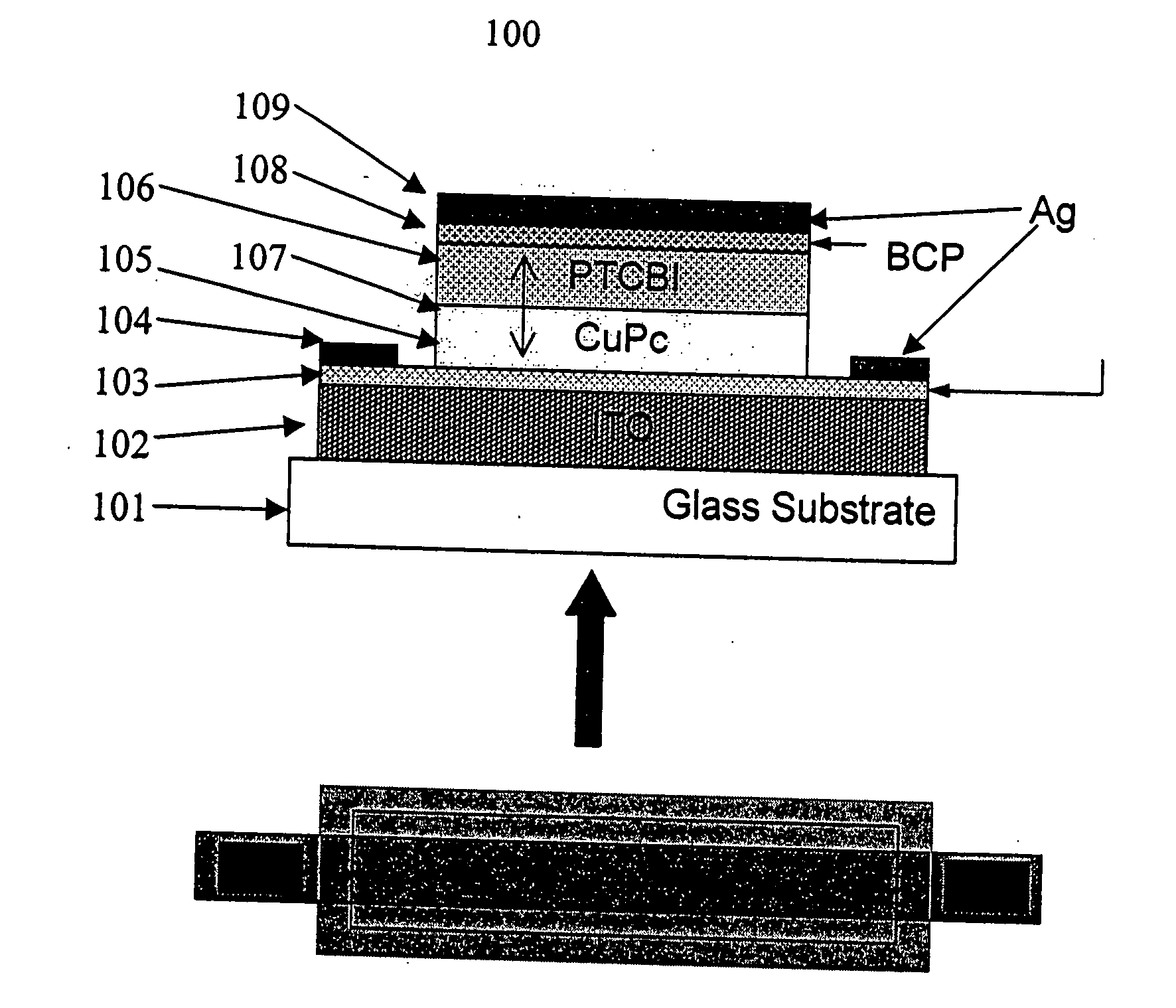
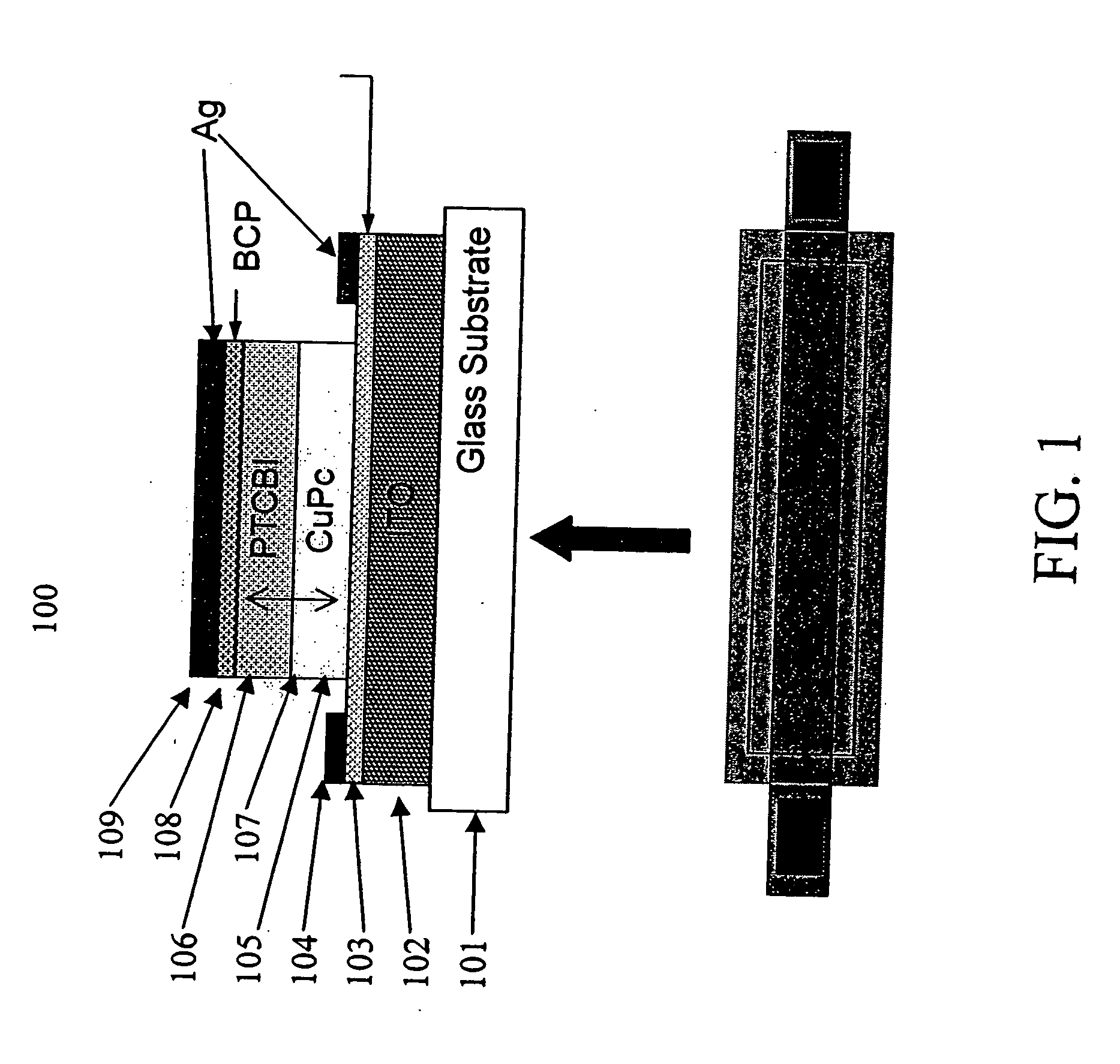
The present invention is directed to organic photosensitive optoelectronic devices and methods of use for determining the position of a light source. Provided is an organic position sensitive detector (OPSD) comprising: a first electrode, which is resistive and may be either an anode or a cathode; a first contact in electrical contact with the first electrode; a second contact in electrical contact with the first electrode; a second electrode disposed near the first electrode; a donor semiconductive organic layer disposed between the first electrode and the second electrode; and an acceptor semiconductive organic layer disposed between the first electrode and the second electrode and adjacent to the donor semiconductive organic layer. A hetero-junction is located between the donor layer and the acceptor layer, and at least one of the donor layer and the acceptor layer is light absorbing. The OPSD has an optical beam spatial resolution of 20 μm and measurements are insensitive to fluctuations in incident light beam intensity and background illumination. The response of the OPSD shows high linearity, low positional error, high spatial resolution, and good beam tracking velocity. The OPSDs exhibited linearities and positional uncertainties of <1%.
Owner:FORREST STEPHEN R +2
Multiple plane scanning system for data reading applications
InactiveUS6991169B2Character and pattern recognitionVerifying markings correctnessBeam splitterScan line
An optical system and method for data reading. The preferred system is directed to a scanner which includes a laser diode and a beam splitter for generating first optical beam and a second optical beam, the first optical beam being directed toward one side of a scanning optical element such as a rotating polygon mirror and to a first mirror array, the second optical beam is being simultaneously directed toward a second optical element such as another side of the rotating polygon mirror and then to a second and a third mirror array. The first mirror array is configured to generate a scan pattern through a vertical window and the second and third mirror arrays are configured to generate scan patterns passing through a horizontal window. In combination, the three mirror arrays generate three sets of scan lines so as to scan the bottom and all lateral sides of an object being passed through the scan volume.
Owner:DATALOGIC SCANNING
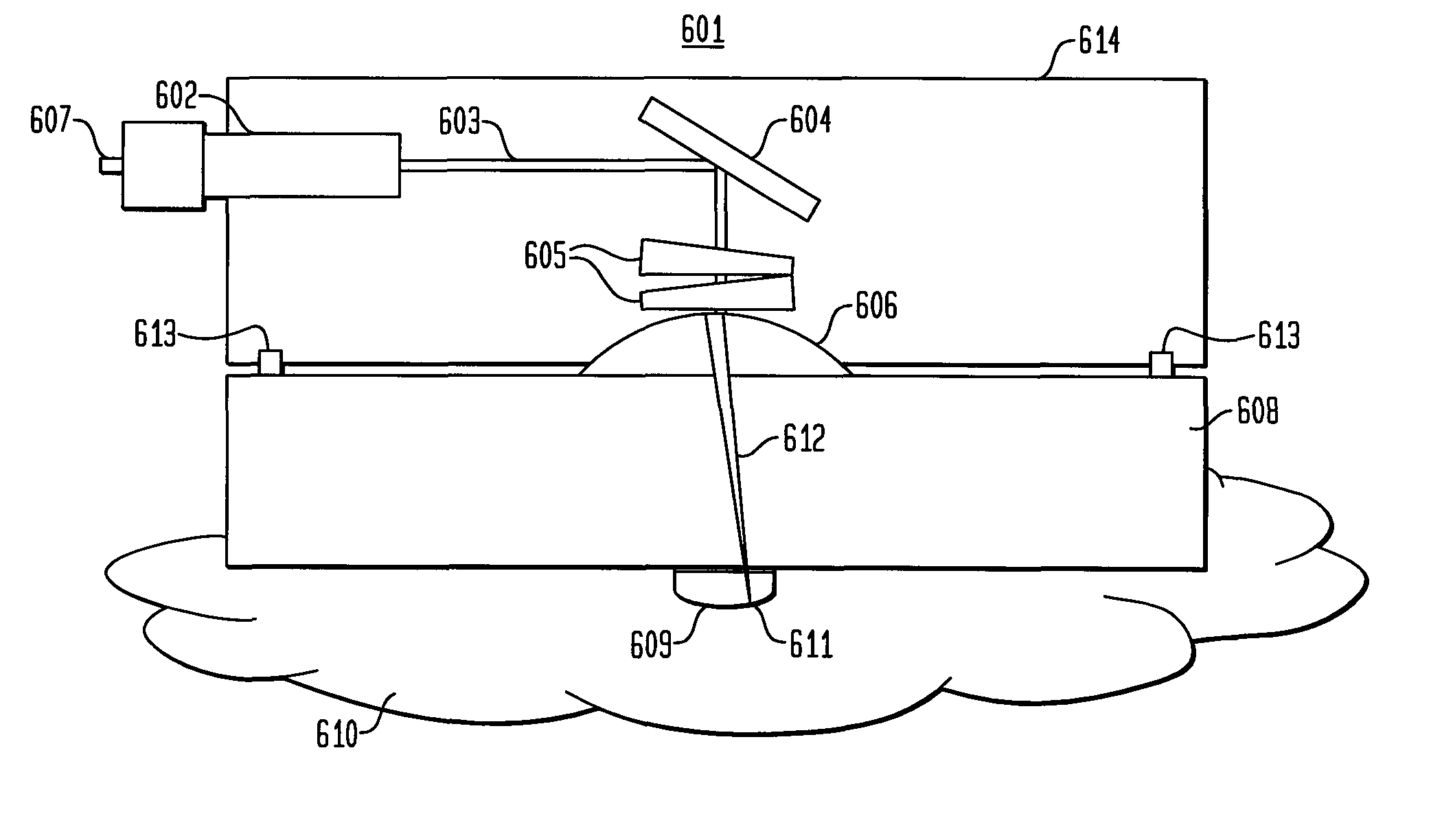
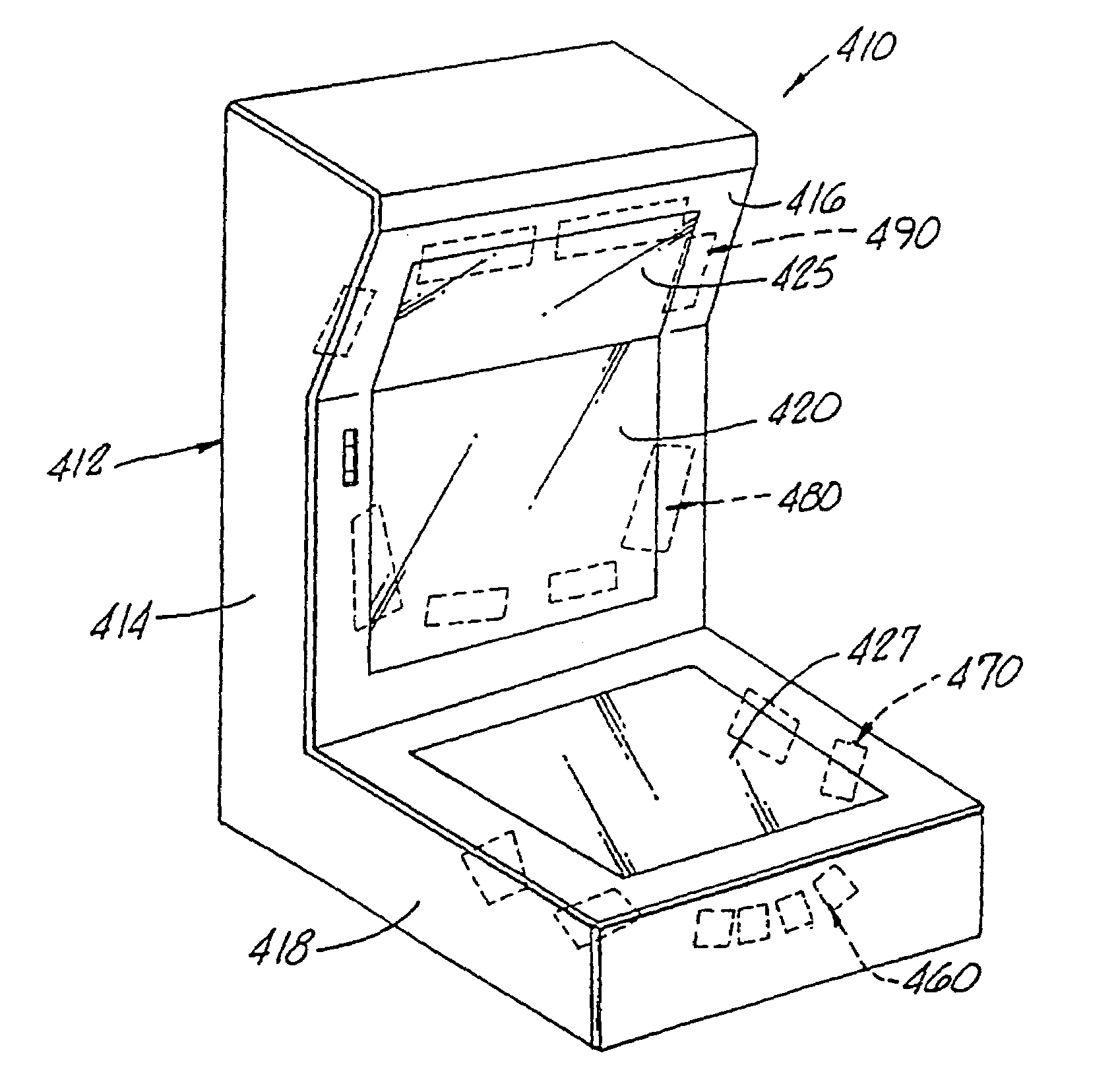
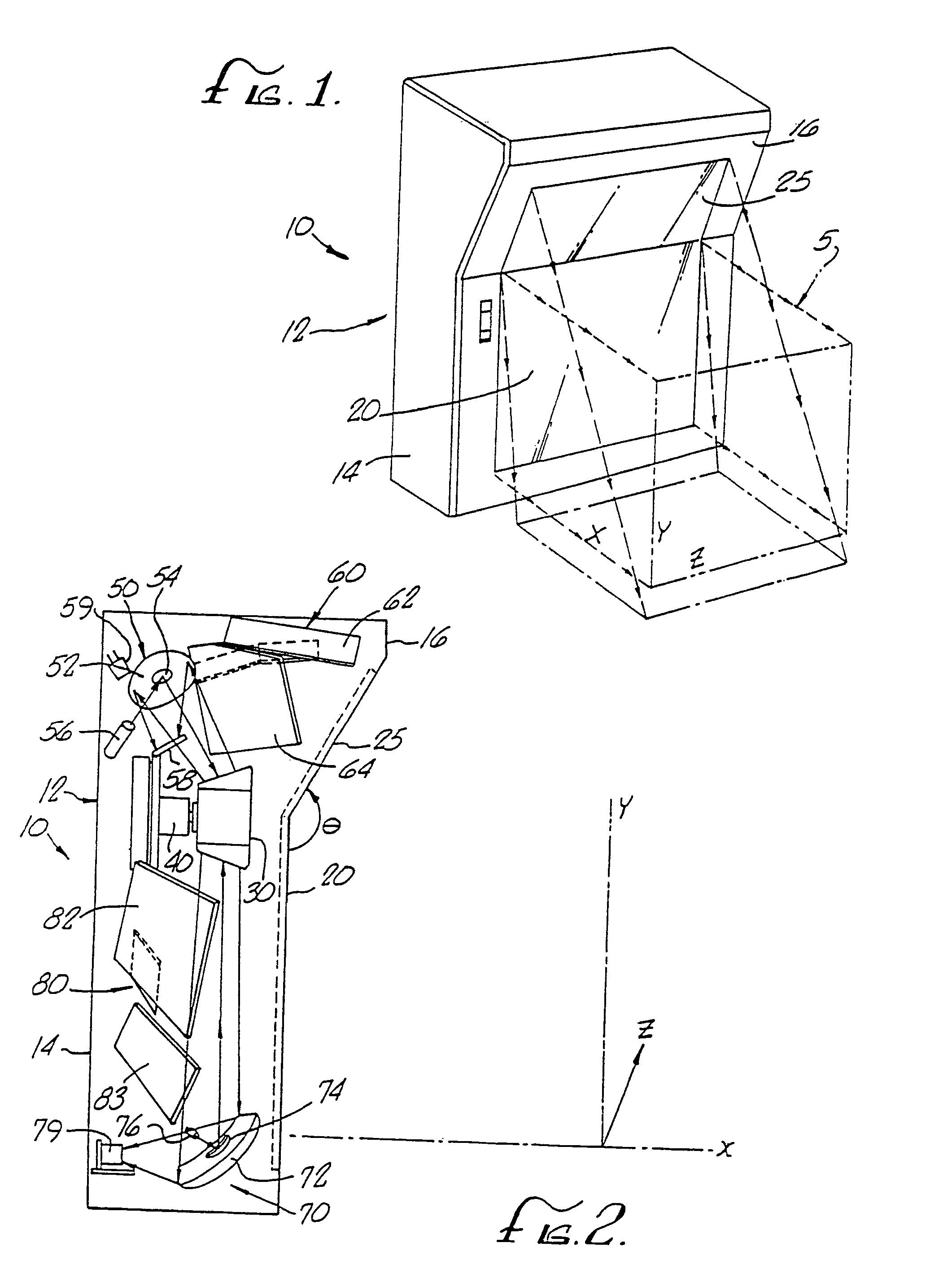
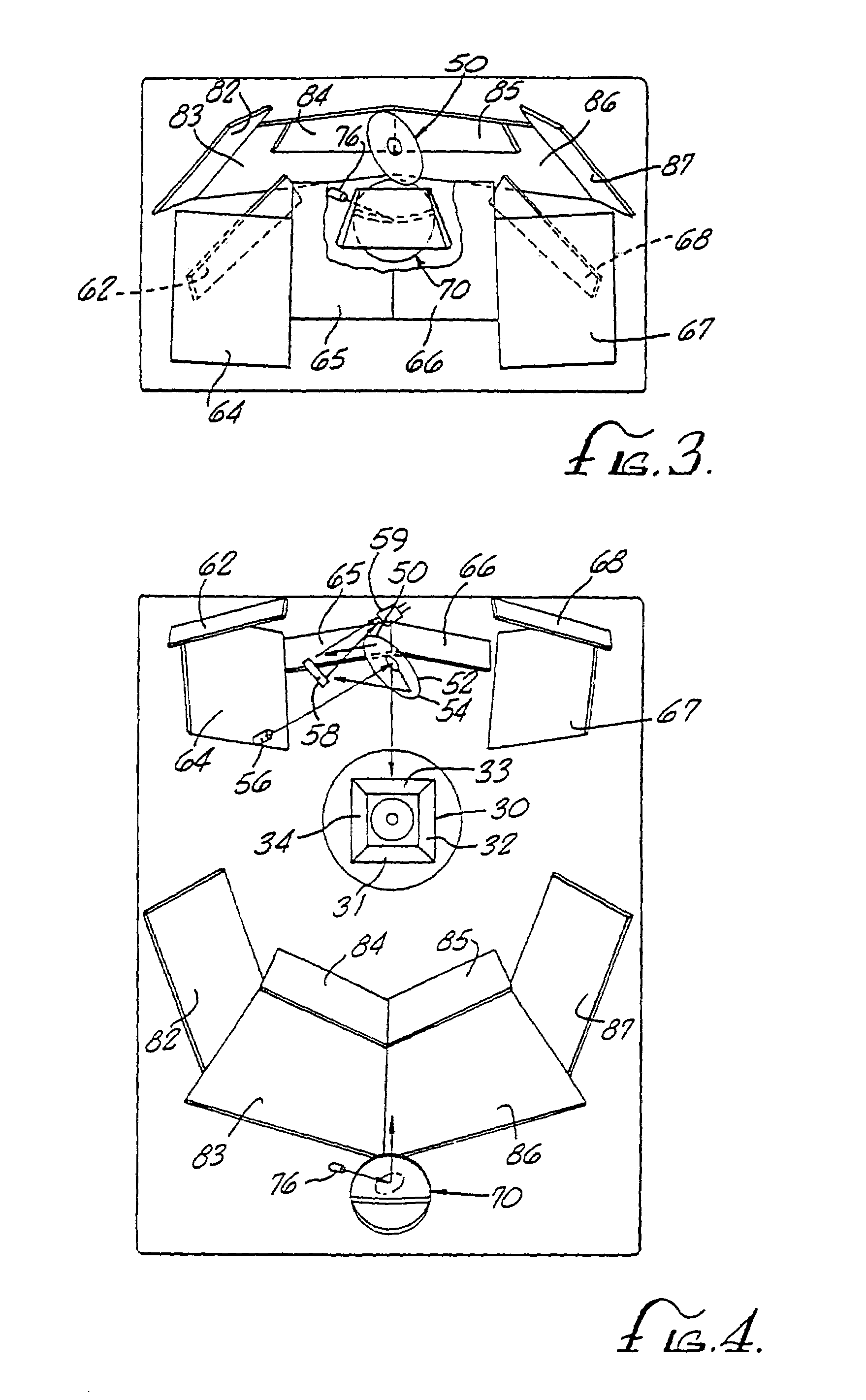
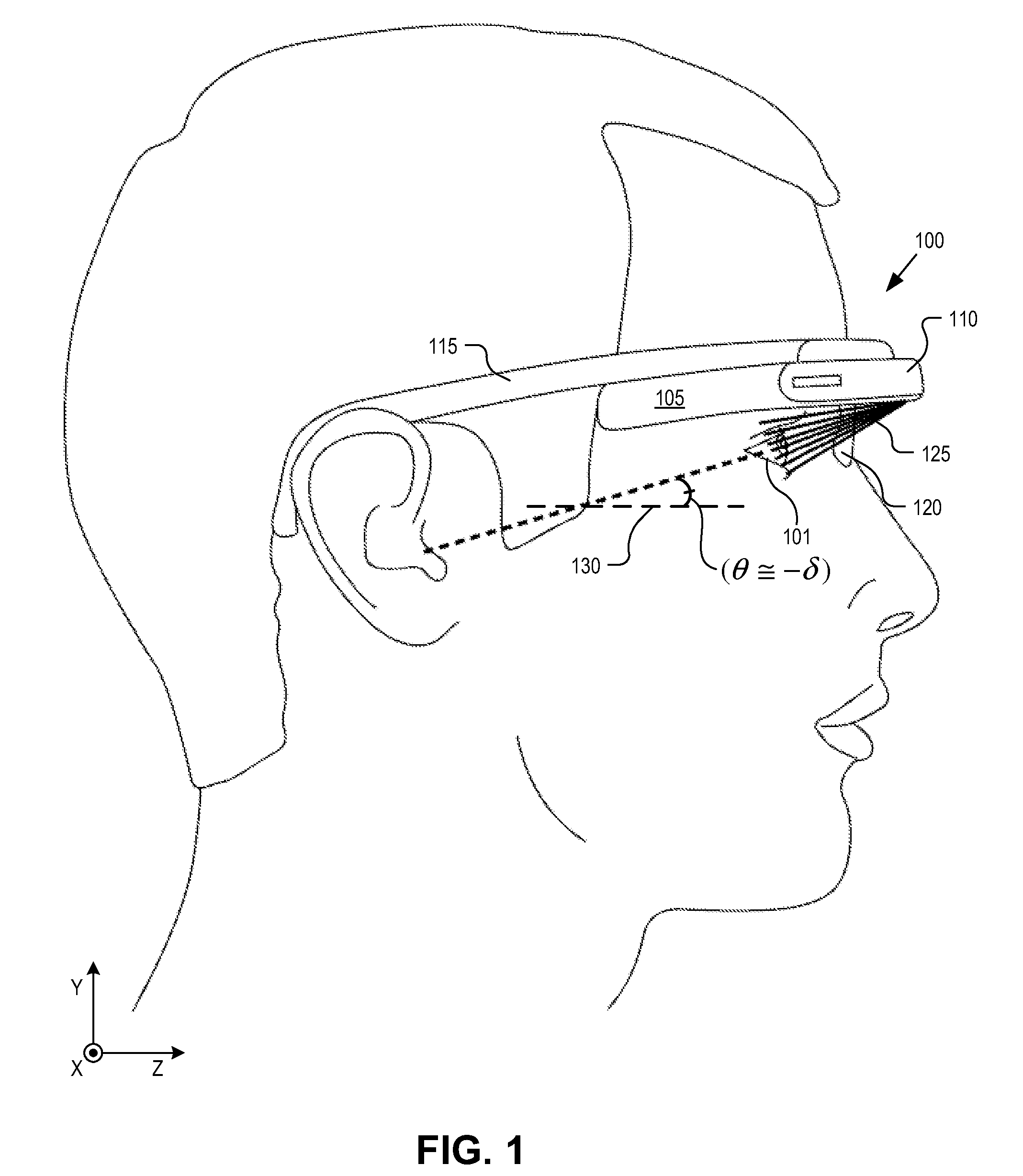
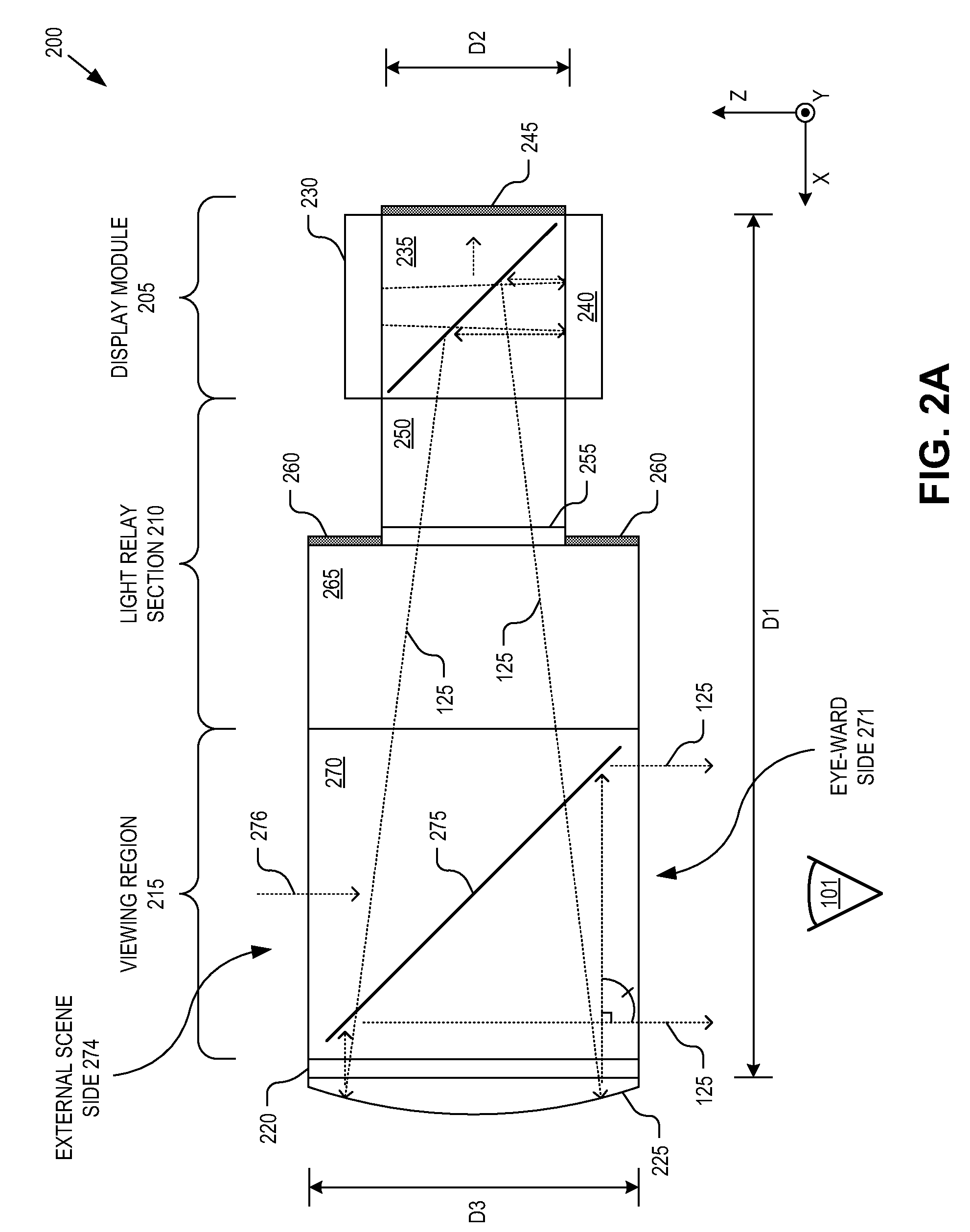
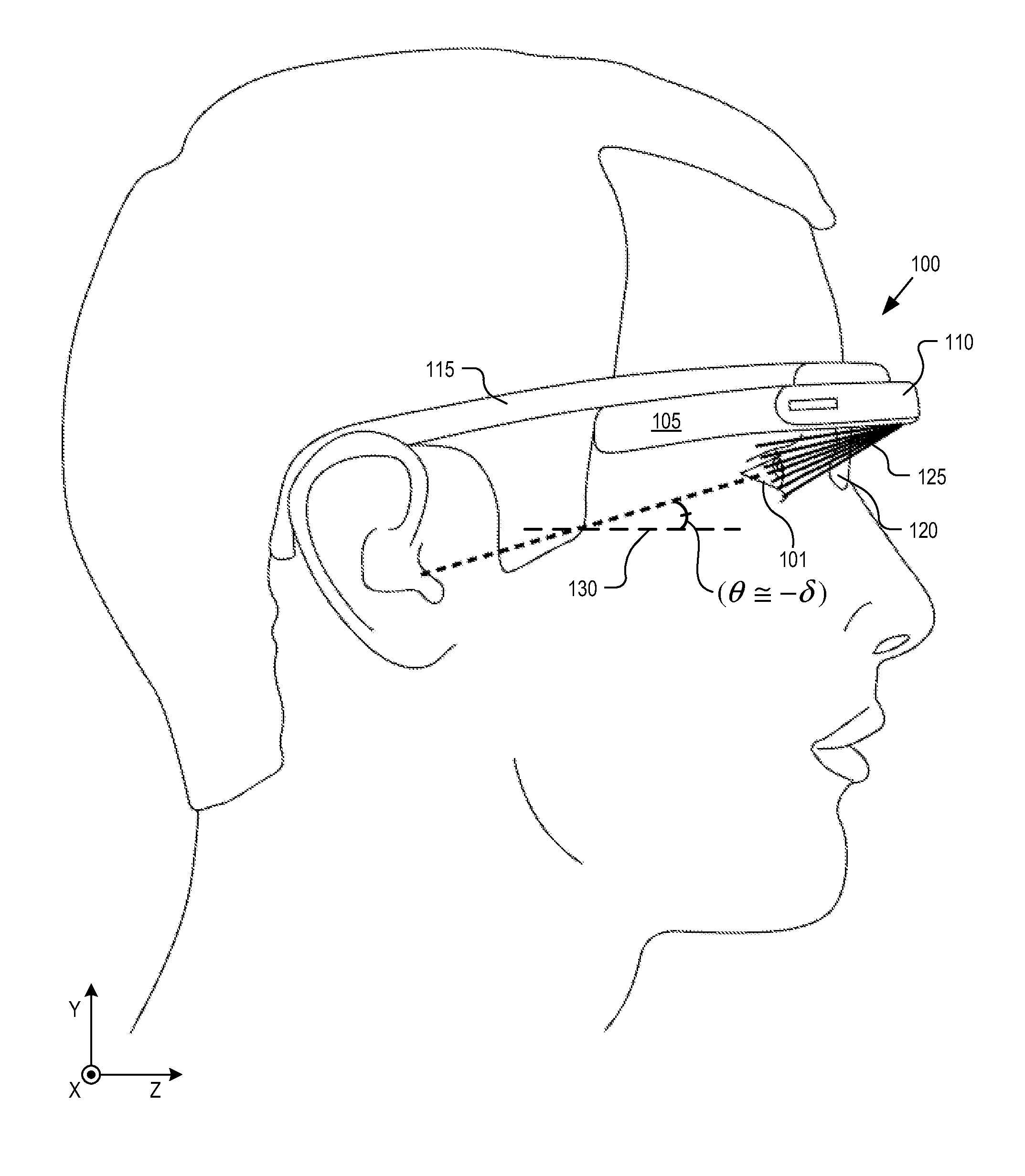
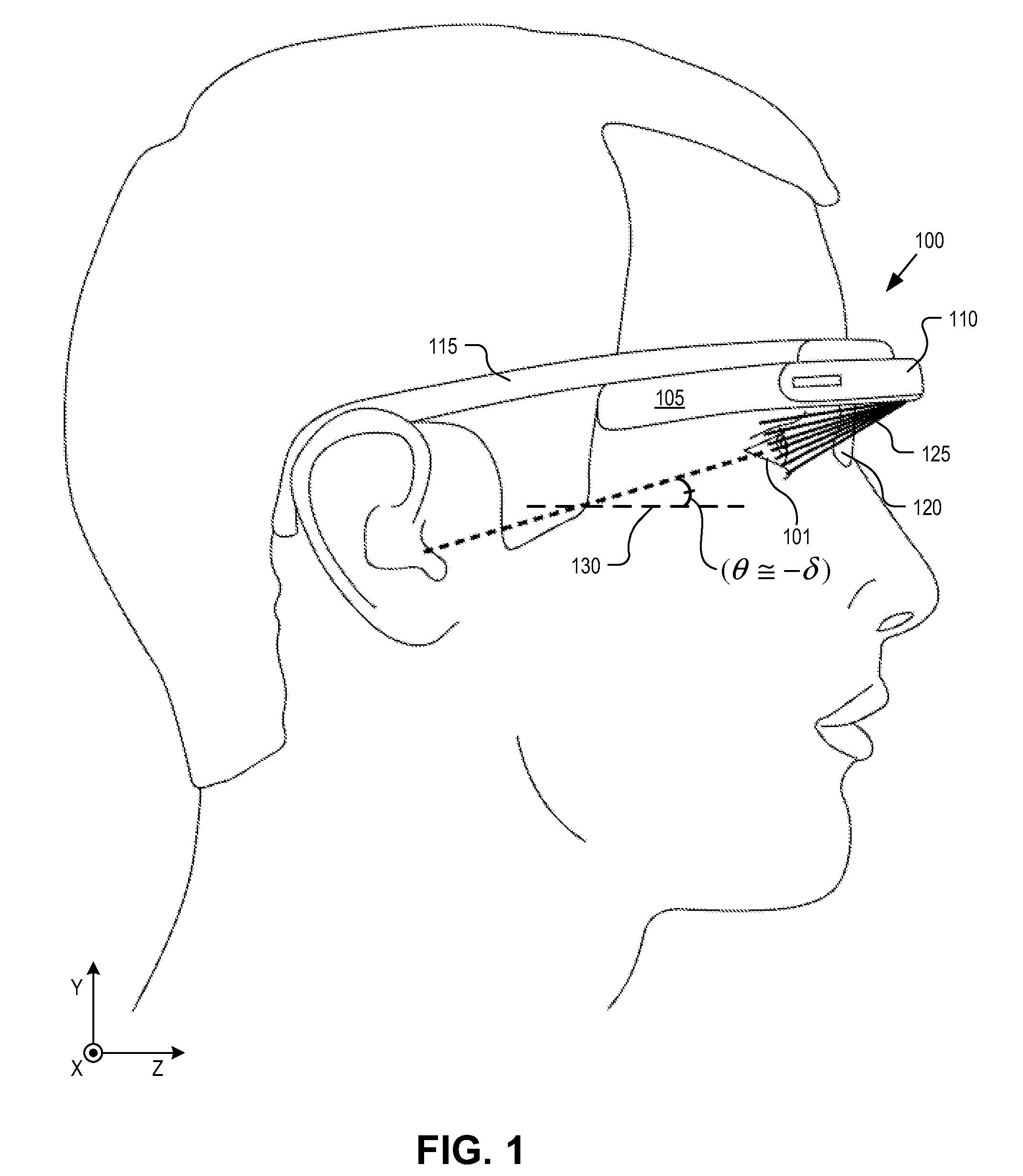
Optical beam tilt for offset head mounted display
Owner:GOOGLE LLC
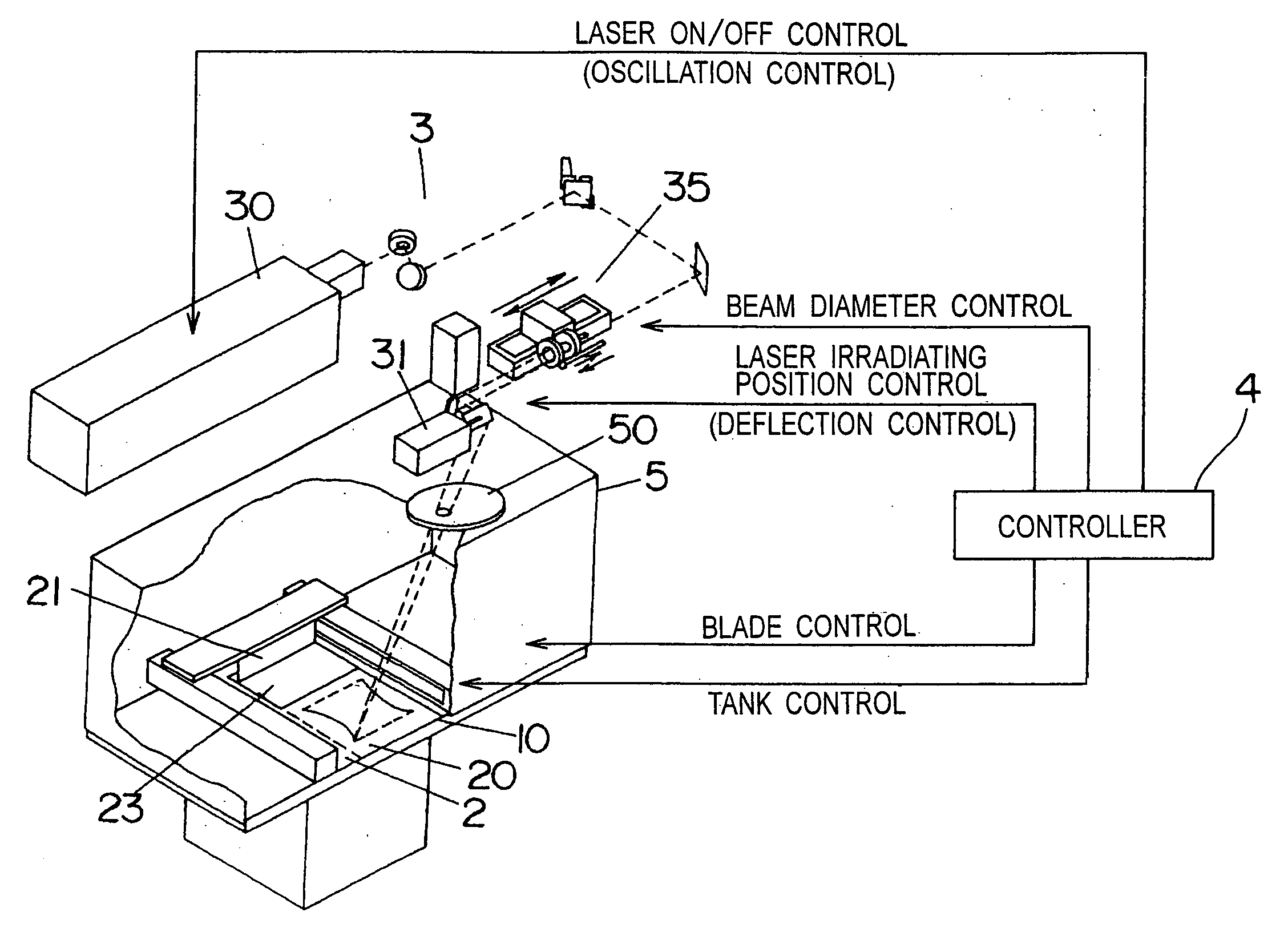
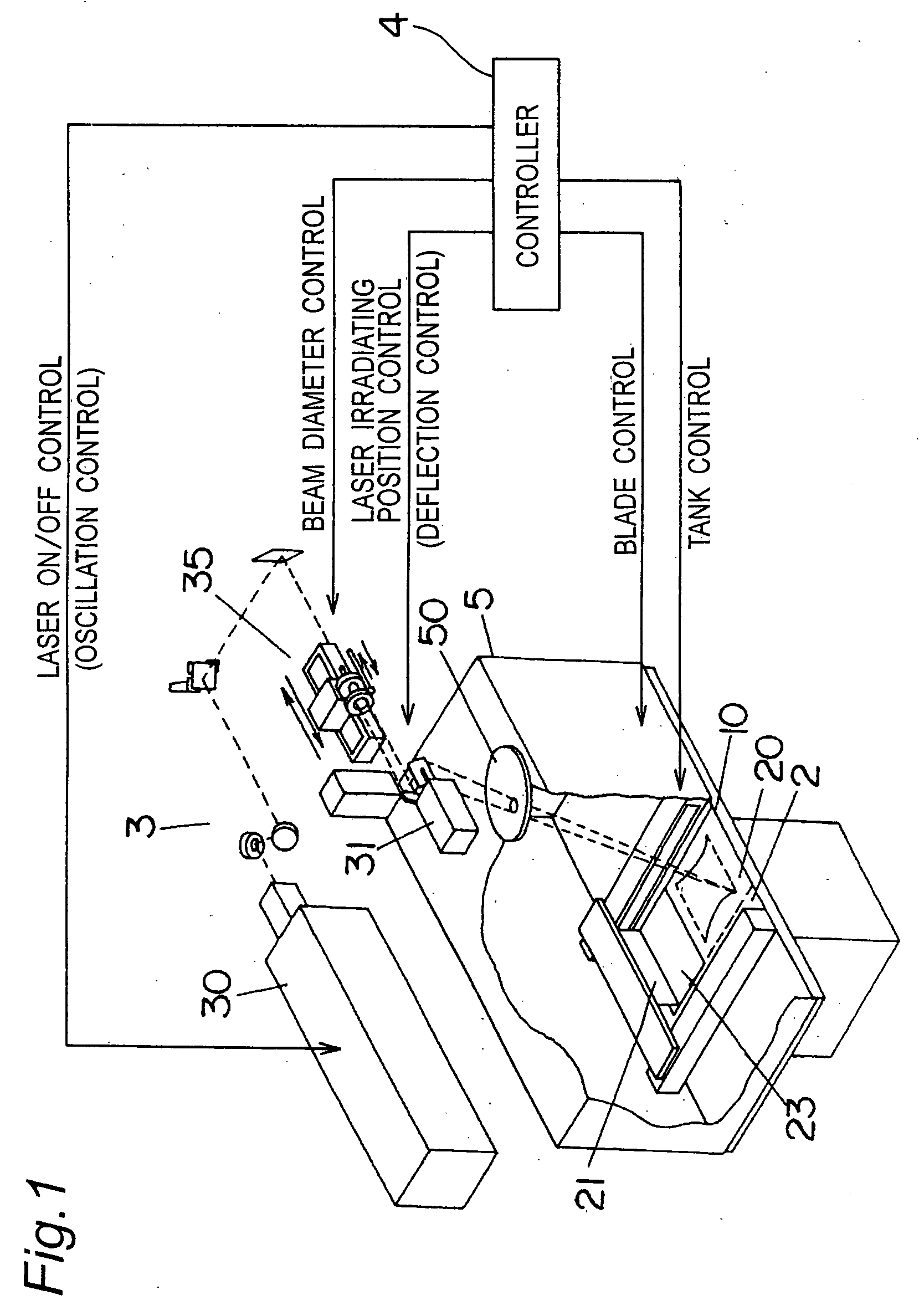
Three dimensional structure producing device and producing method
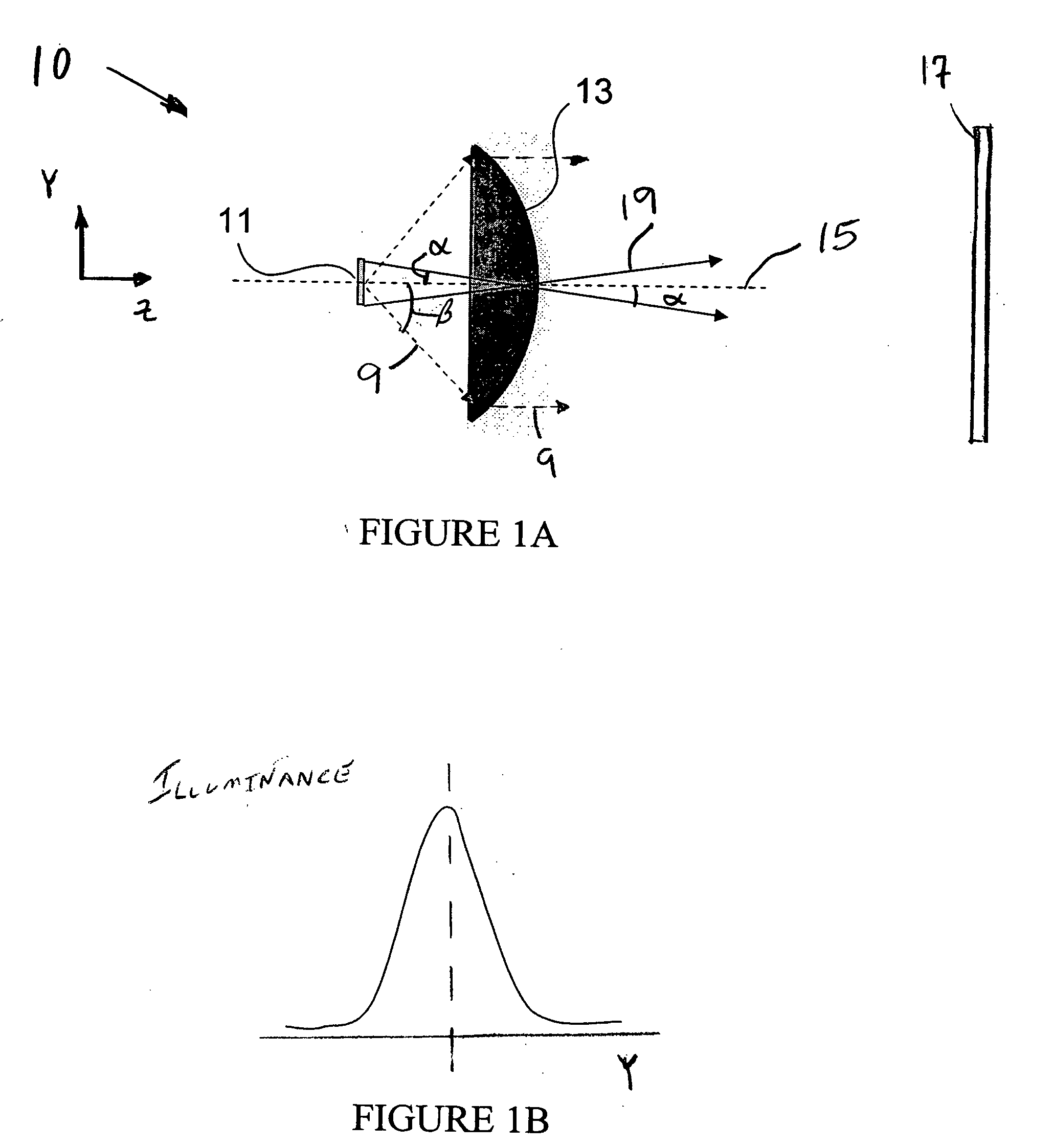
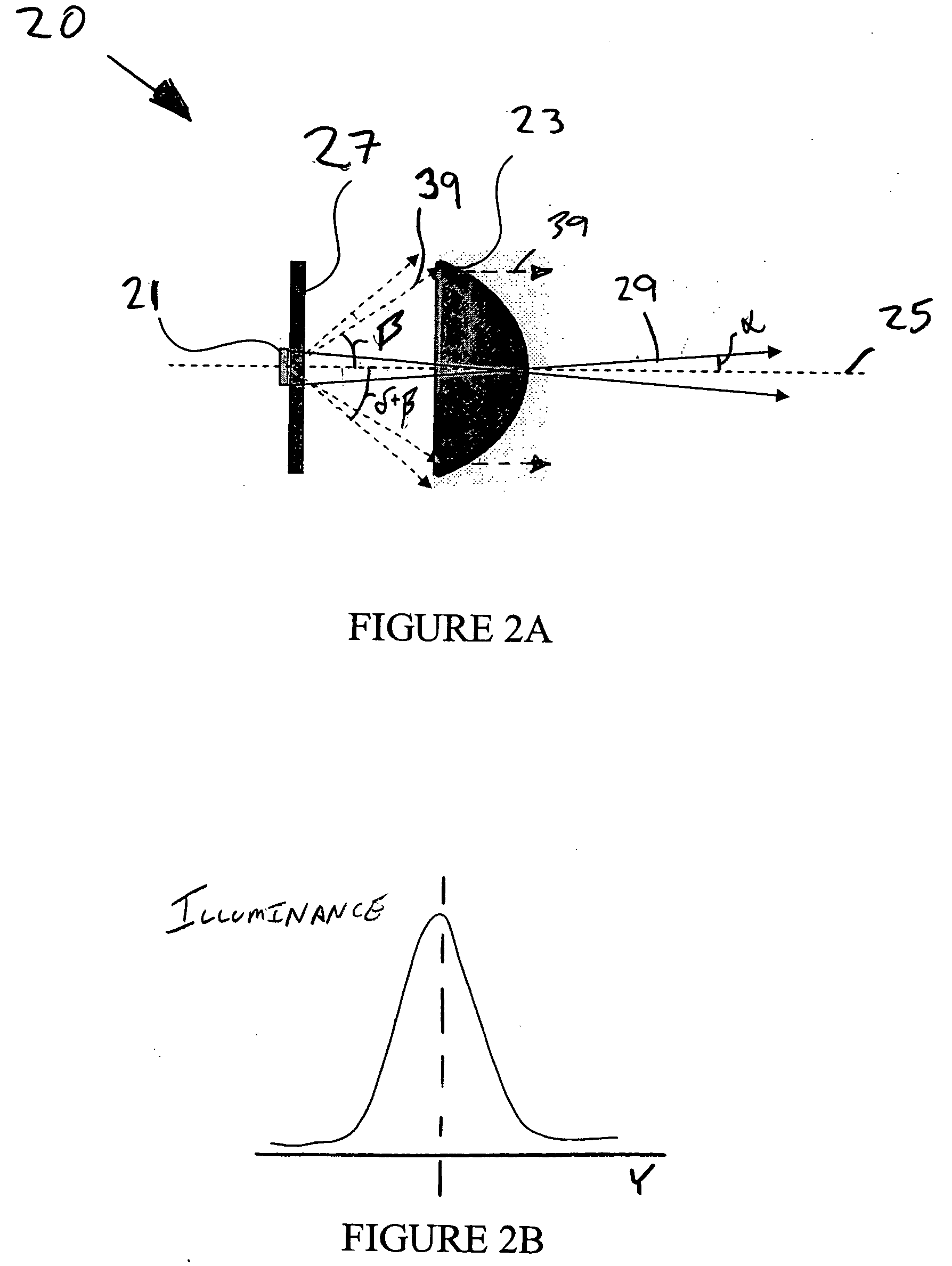
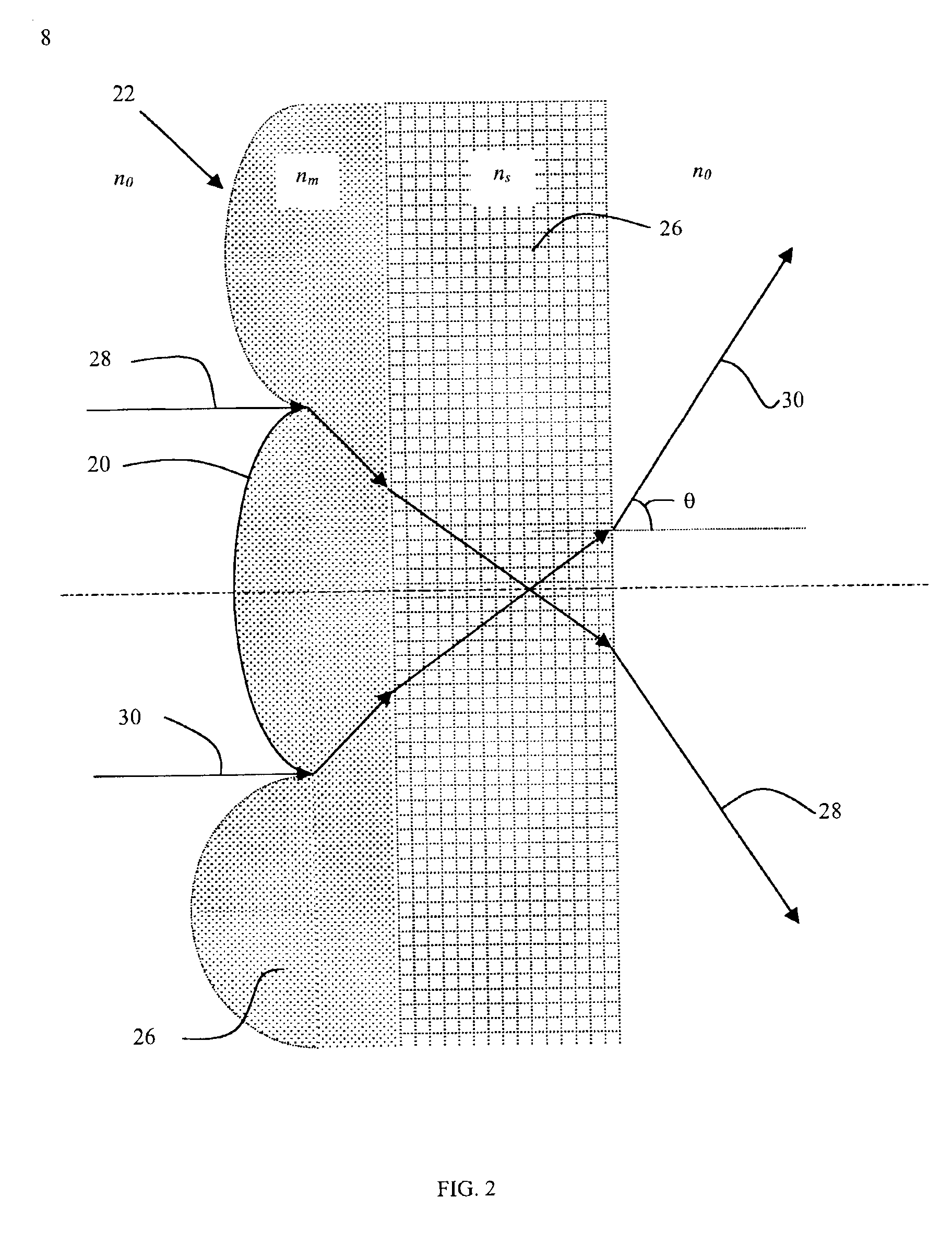
An apparatus for making a three-dimensional object includes a powdery layer-forming unit for forming a powdery layer on a table and an optical beam-irradiating unit for irradiating an optical beam on a predetermined region of the powdery layer to sinter the predetermined region. The optical beam-irradiating unit is disposed at a position spaced from immediately above an optical beam-irradiating range to obliquely irradiate the optical beam on the powdery layer. Because fumes generated by irradiating and heating the powdery layer with the optical beam rise towards a position immediately above them, the optical beam is irradiated from the position spaced from immediately above the optical beam-irradiating range, thereby reducing a cloud of the optical beam-irradiating unit that may be caused by the fumes.
Owner:MATSUSHITA ELECTRIC WORKS LTD
General diffractive optics method for expanding an exit pupil
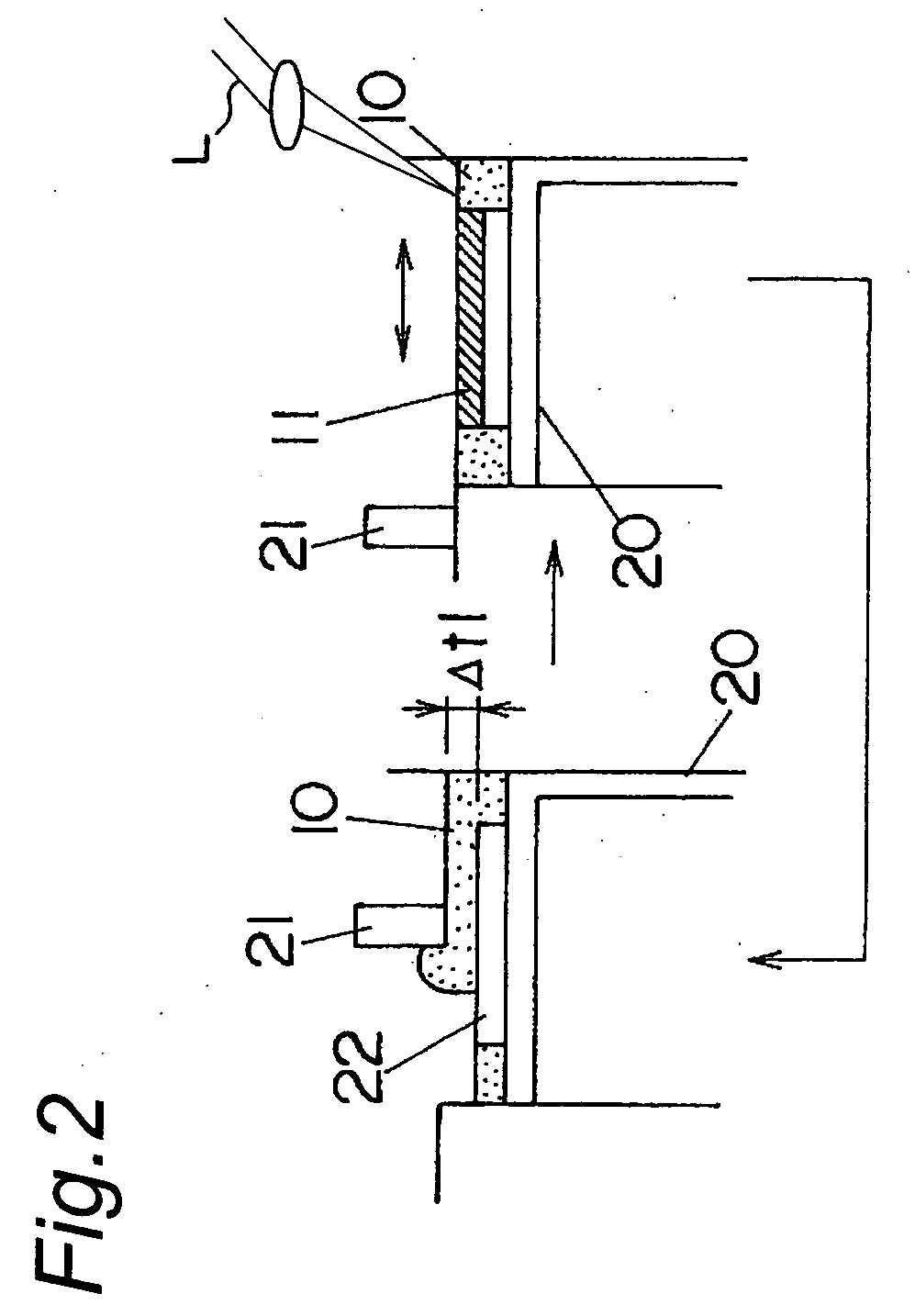
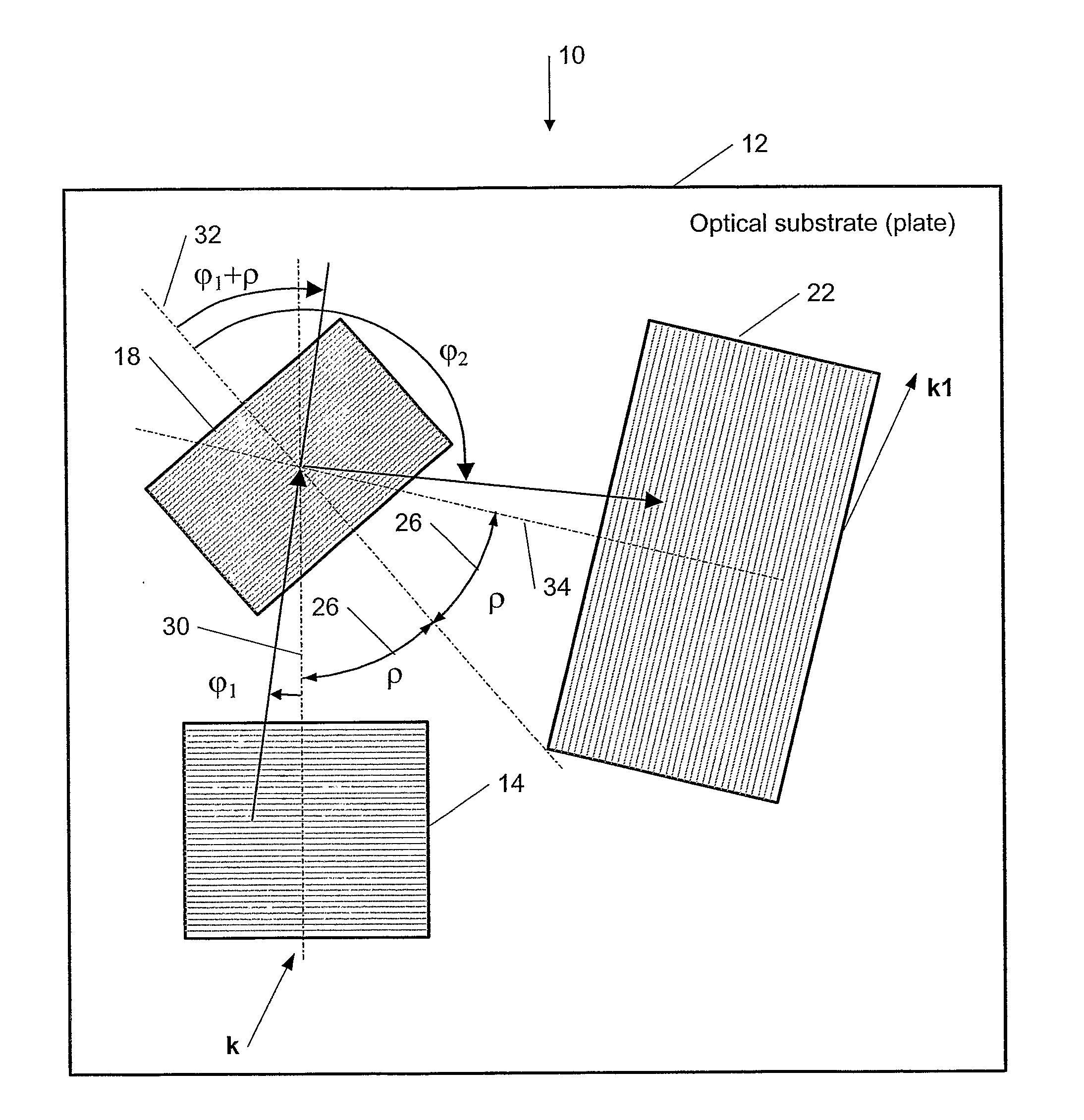
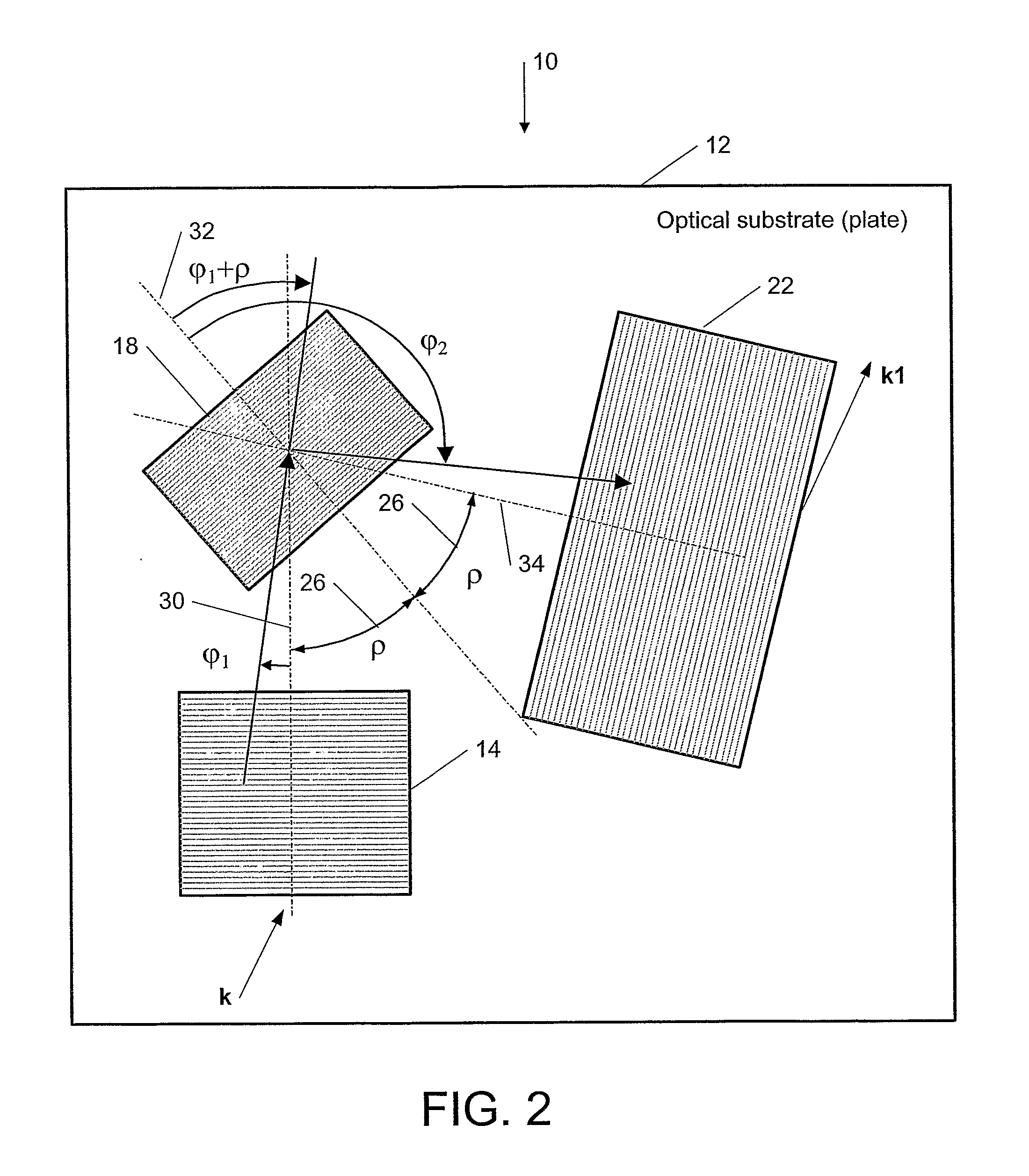
This invention describes a general diffractive optics method that uses a plurality of diffractive elements on an optical substrate for expanding the exit pupil of a display of an electronic device for viewing. The method can be used for optical coupling in an optical device and it is characterized by extending of an exit pupil of an input optical beam in an output optical beam wherein the optical device comprises: an optical substrate and in-coupling, intermediate and out-coupling diffractive element disposed on the optical substrates, wherein periodic lines of the intermediate diffractive element comprise an angle ρ with periodic lines of the in-coupling and of the out-coupling diffractive elements, respectively. The system can support a broad range of rotation angles (e.g., 0<ρ<70°) and corresponding conical angles and remains geometrically accurate.
Owner:NOKIA CORP
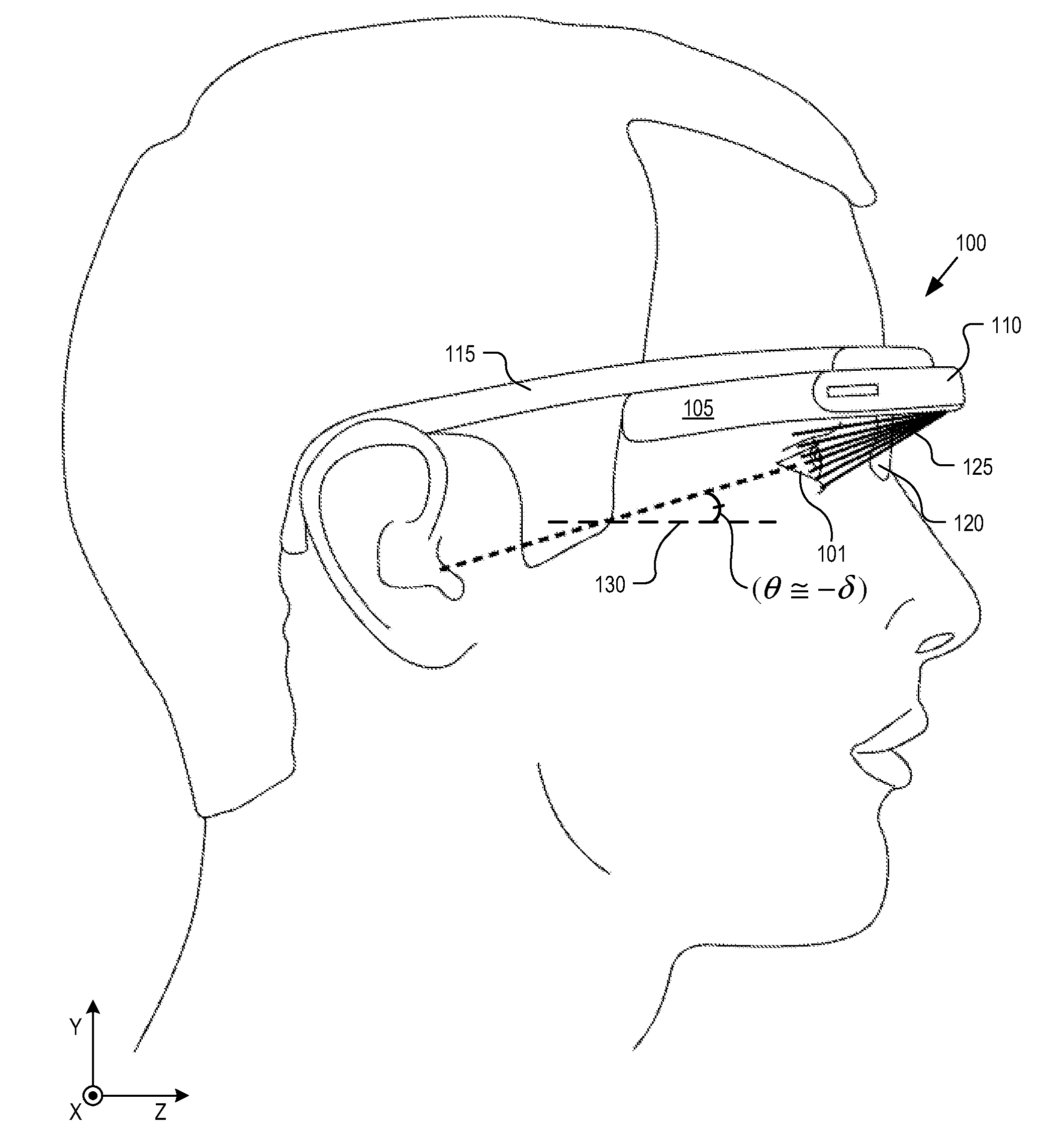
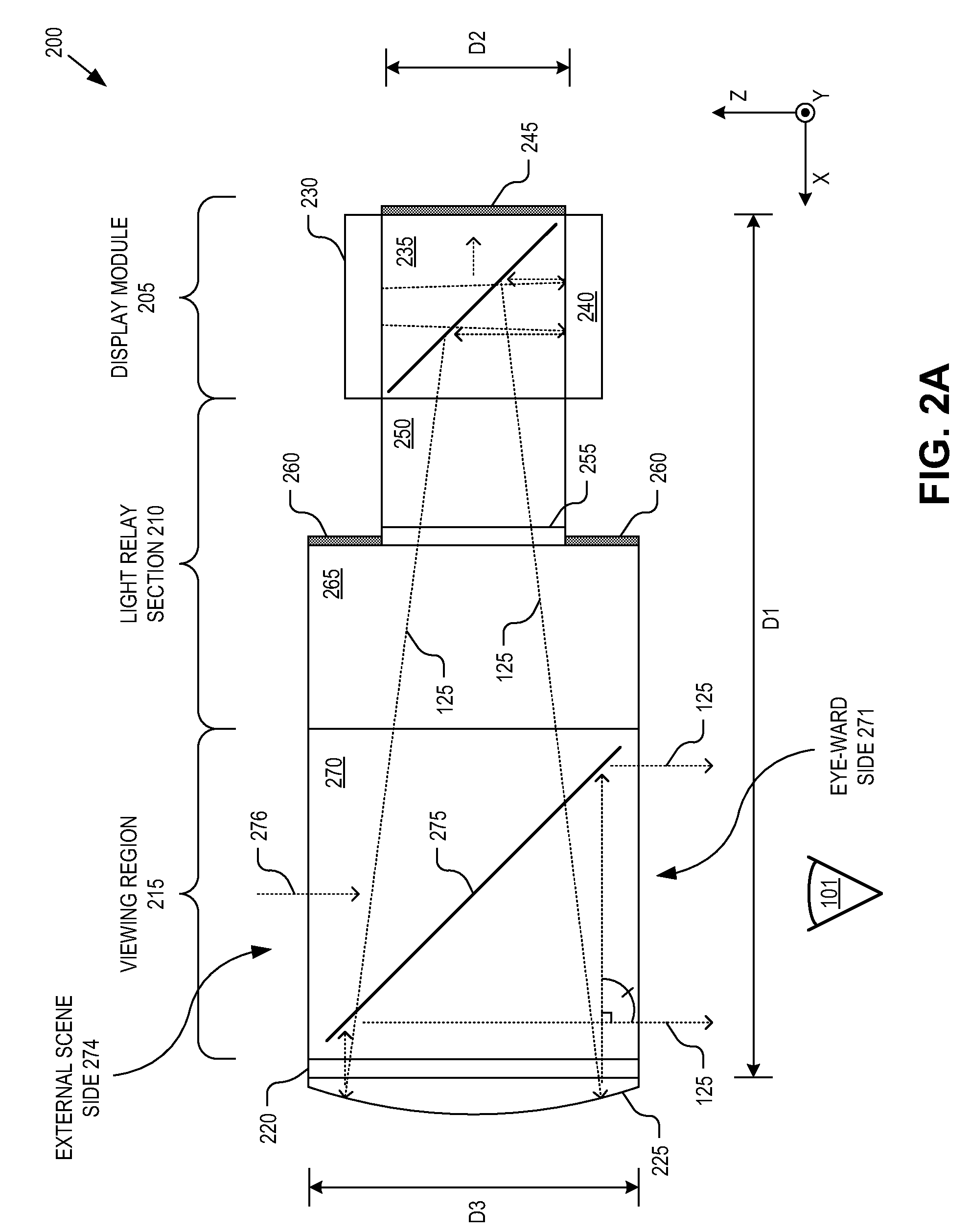
Optical beam tilt for offset head mounted display
An eyepiece for a head mounted display includes a display module, end reflector, and viewing region. The end reflector is disposed at an opposite end of the eyepiece from the display module to reflect the display light back from a forward propagation path to a reverse propagation path. The viewing region is disposed between the display module and the end reflector and includes a partially reflective surface, that passes the display light traveling along the forward propagation path and redirects the display light traveling along the reverse propagation path out of an eye-ward side of the eyepiece along an emission path. The partially reflective surface has a compound folding angle such that the emission path of the display light emitted from the eyepiece is folded along two axes relative to the reverse propagation path between the end reflector and the partially reflective surface.
Owner:GOOGLE LLC
Broadband optics for manipulating light beams and images
InactiveUS20110188120A1Enhancing optical manipulation capabilityDiffraction gratingsLight beamDivergence angle
The objective of the present invention is providing optical systems for controlling with propagation of light beams in lateral and angular space, and through optical apertures. Said light beams include laser beams as well as beams with wide spectrum of wavelengths and large divergence angles. Said optical systems are based on combination of diffractive waveplates with diffractive properties that can be controlled with the aid of external stimuli such as electrical fields, temperature, optical beams and mechanical means.
Owner:UNITED STATES OF AMERICA THE AS REPRESENTED BY THE SEC OF THE ARMY
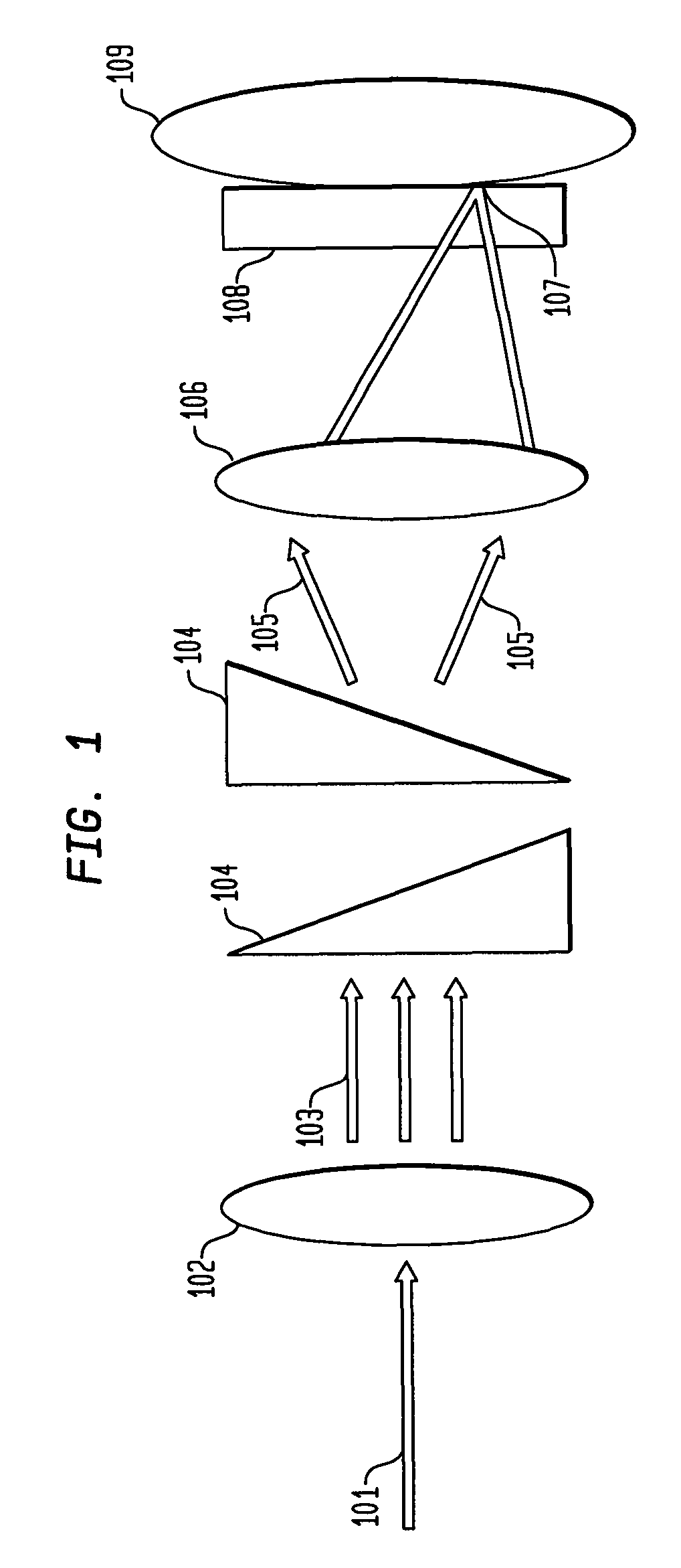
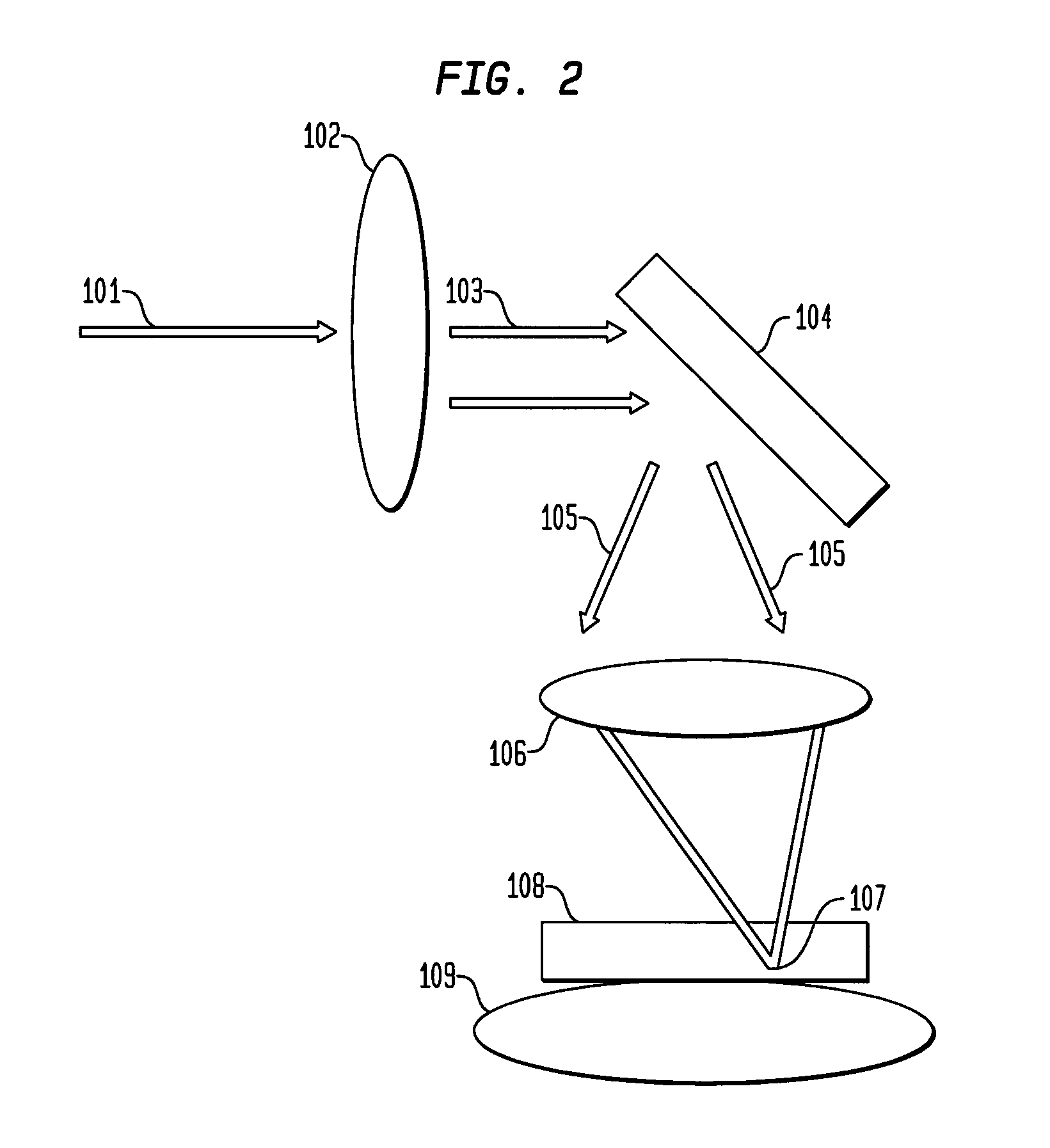
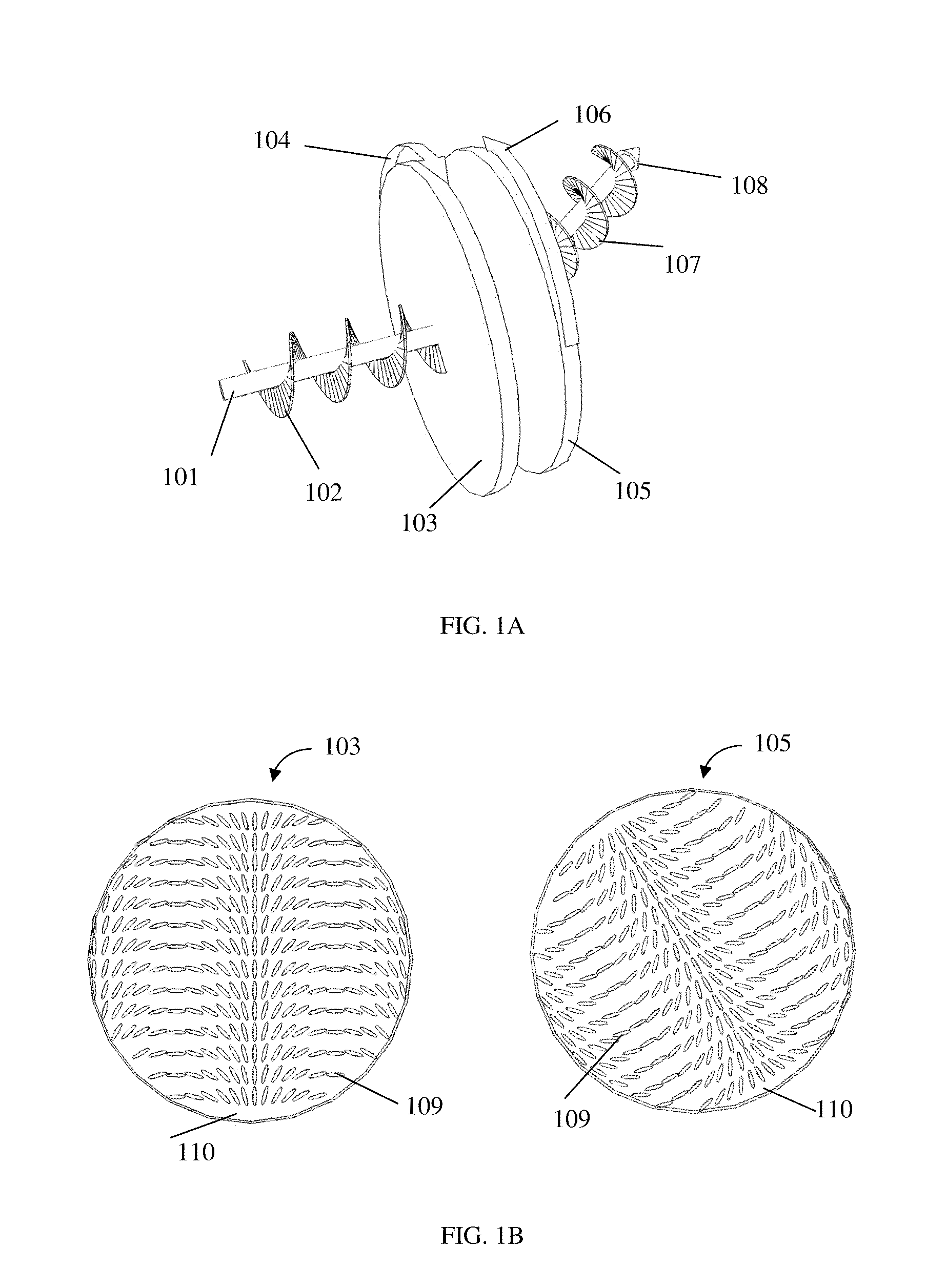
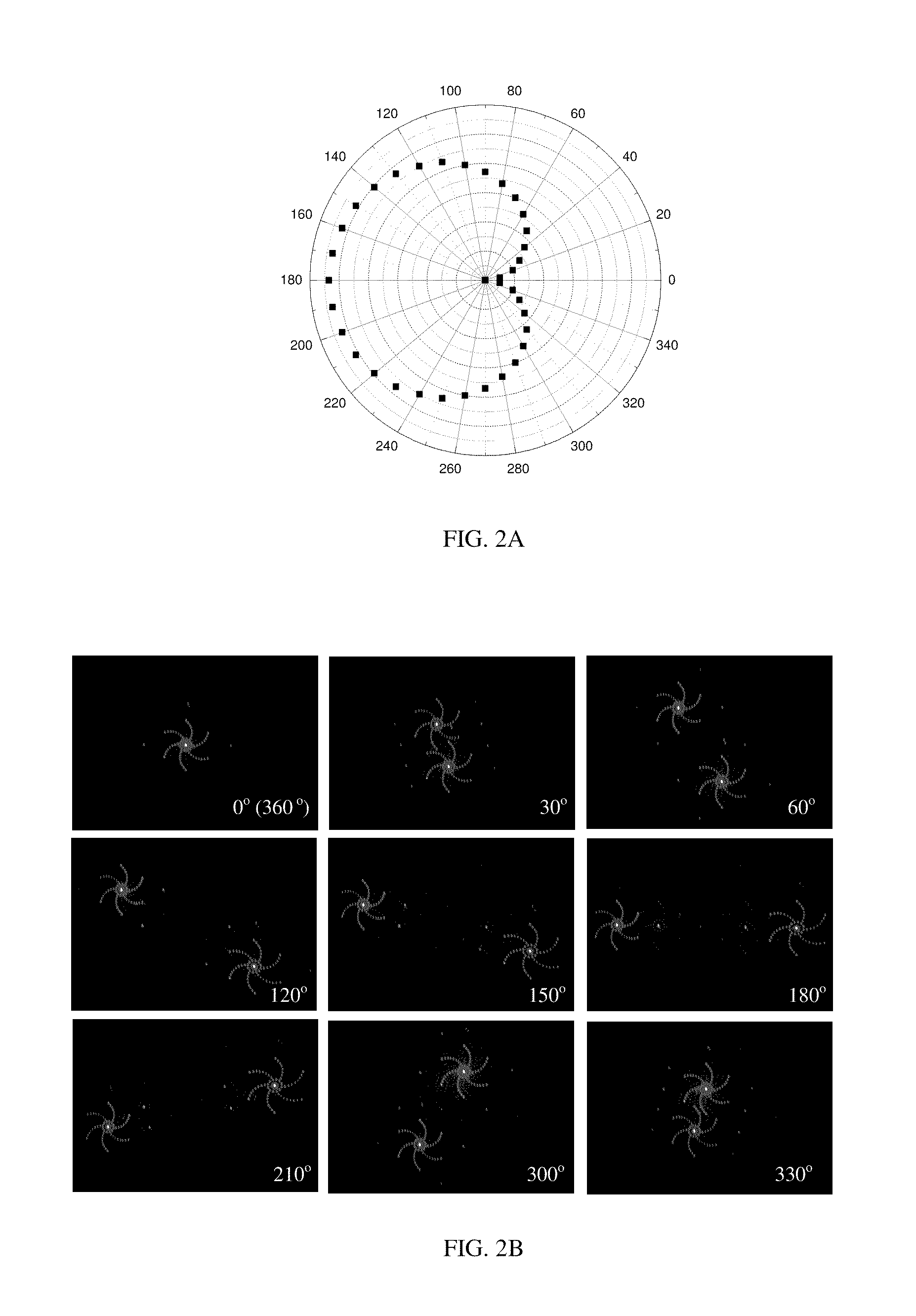
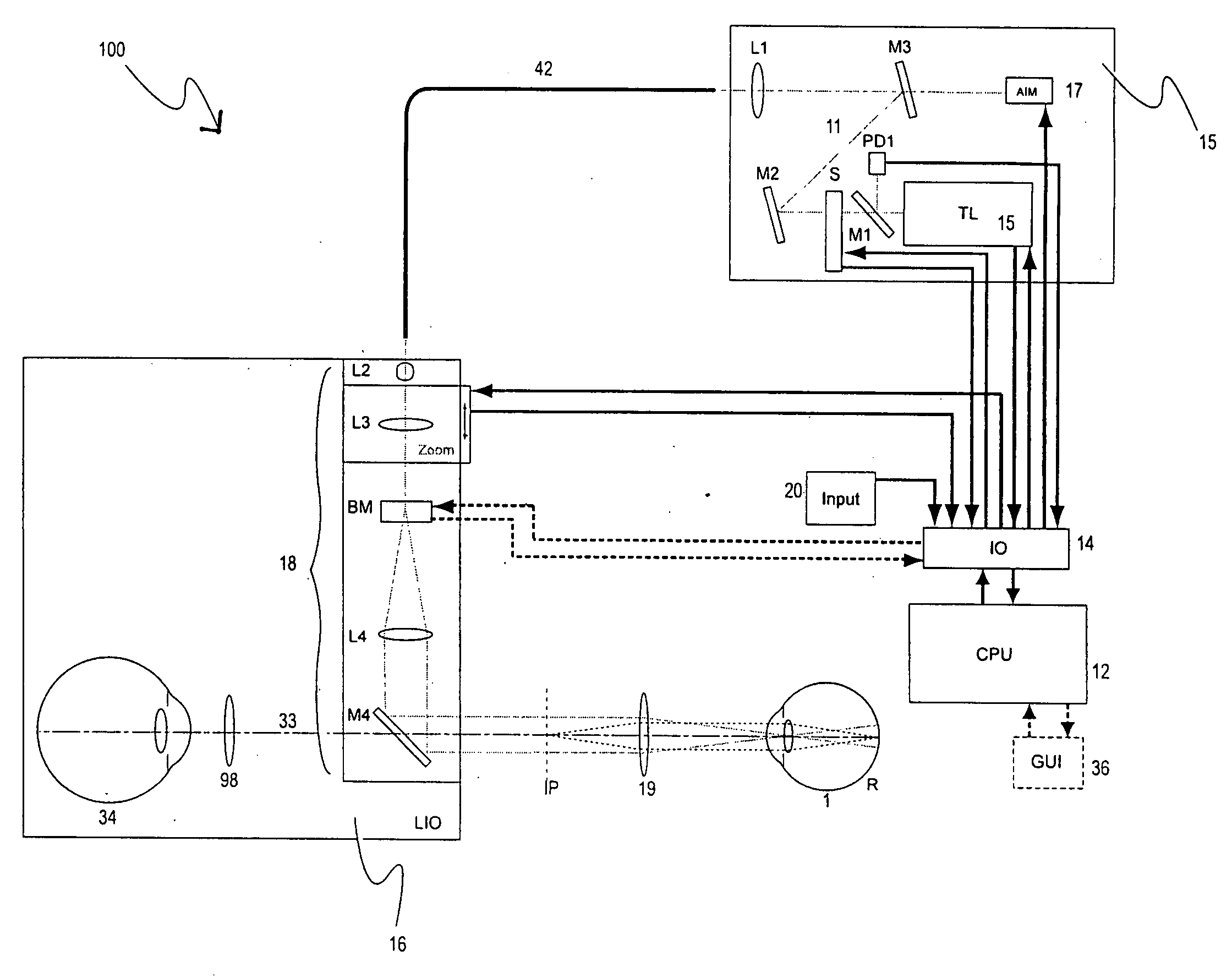
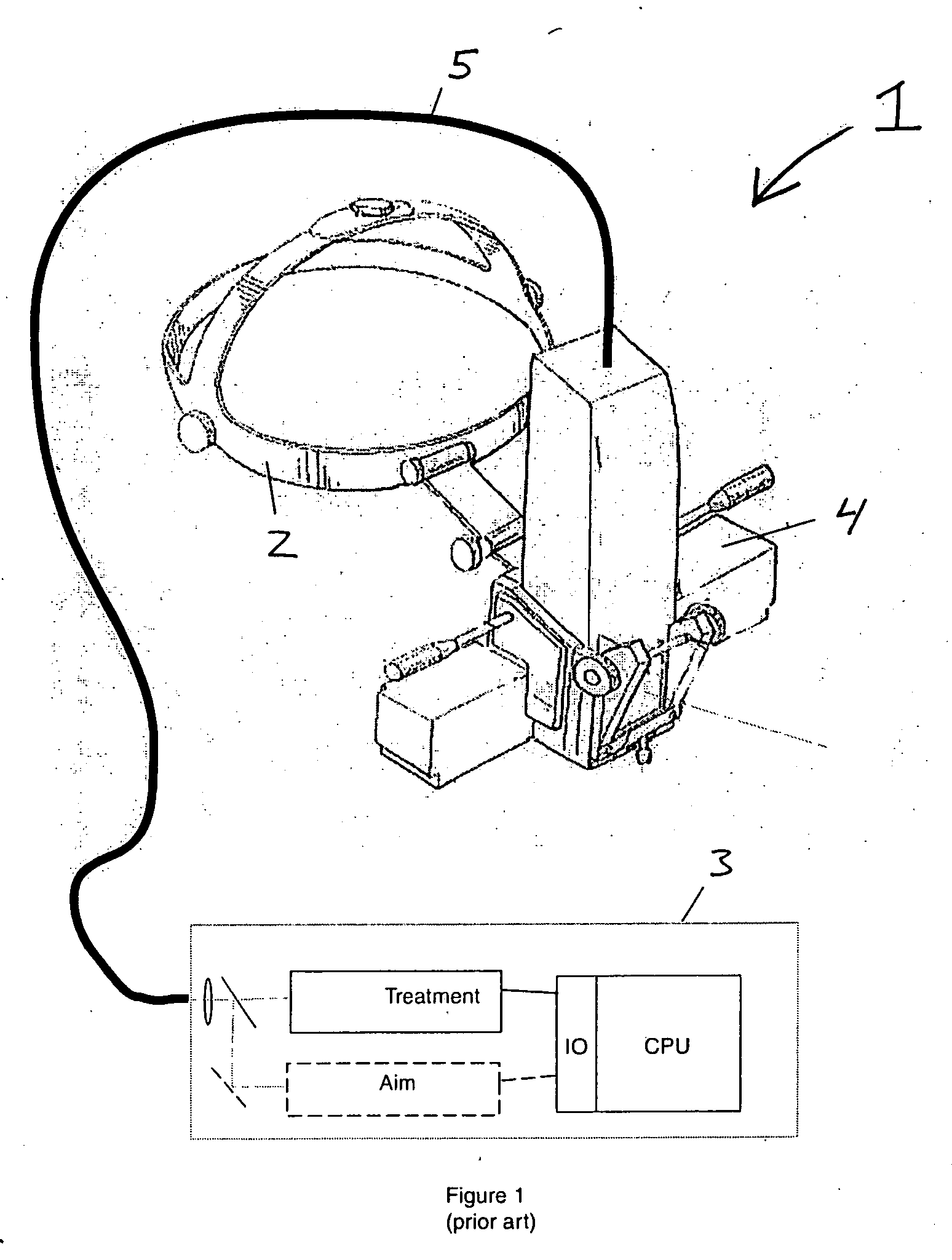
Multiple spot photomedical treatment using a laser indirect ophthalmoscope
A laser indirect ophthalmoscope (LIO) apparatus for photomedical treatment and / or diagnosis is presented. The LIO apparatus allows multiple spot ophthalmic surgery to be performed in a wider range of patient positions and less intrusively than currently available methods. The LIO apparatus utilizes a separate or integral beam multiplier that generates one or more optical beams via spatial and / or temporal separation, and an optical system that conditions and directs the one or more optical beams to a target to form a pattern. The LIO apparatus includes a headset, and is therefore wearable by the user (e.g., a physician).
Owner:TOPCON MEDICAL LASER SYST INC
Intraocular Camera for Retinal Prostheses
ActiveUS20080086206A1Enhanced patient acceptabilityAdd depthHead electrodesEye treatmentControl signalRetinal Prosthesis
An intraocular camera for retinal prostheses may include an optical imaging system comprising a set of optical elements for forming an image of the external world on an image sensor array, wherein the optical elements and the image sensor array may be enclosed in an implantable biocompatible housing that may employ haptic elements for stabilization within the eye. The set of optical elements may be designed to have a short focal length and to provide adequate resolution images that can be transformed into a set of stimulation signals applied to a pixellated microstimulator array. Transmission of the signals from the intraocular camera to a microstimulator driver circuit may be accomplished either by a wired or wireless communication device. Power and control signals may be provided to the intraocular camera by a wired or wireless communication device, or optically by means of ambient illumination or an optical beam.
Owner:UNIV OF SOUTHERN CALIFORNIA
Free space optical communications link tolerant of atmospheric interference
InactiveUS20040208602A1Improve reliabilityIncrease resistanceElectromagnetic transmissionUltrasound attenuationTransceiver
Free space optical communications systems which resist atmospheric attenuation of optical beams is presented. Very long link distances remain highly reliable despite fog and other inclement weather conditions which otherwise tend to hamper optical transmissions in an atmospheric air column. Systems include primary elements as follows: a plurality of transceivers and at least one air column optical path. Each transceiver includes specialized light sources which produce radiation in the Mid-IR spectral region. In addition, these sources are very compact and well organized in view of their intended deployment environment. Further, special modulation means are joined with particular light sources to address high bandwith needs. In addition, specialized detection strategies are presented whereby sensitivity is improved. Alternative versions and configurations directed to specialized function are also described in detail.
Owner:PLANTE JAMES
Multi-beam multi-column electron beam inspection system
InactiveUS6844550B1Material analysis using wave/particle radiationRadiation/particle handlingSystems designData stream
A multi-column electron beam inspection system is disclosed herein. The system is designed for electron beam inspection of semiconductor wafers with throughput high enough for in-line use. The system includes field emission electron sources, electrostatic electron optical columns, a wafer stage with six degrees of freedom of movement, and image storage and processing systems capable of handling multiple simultaneous image data streams. Each electron optical column is enhanced with an electron gun with redundant field emission sources, a voltage contrast plate to allow voltage contrast imaging of wafers, and an electron optical design for high efficiency secondary electron collection.
Owner:MULTIBEAM CORP
Method and apparatus for measuring motion of a subject using a series of partial images from an imaging system
ActiveUS20060228011A1Accurate placementCharacter and pattern recognitionCathode-ray tube indicatorsOptical radiationReference image
A line scan imager is used to determine the motion of a subject. Each line of image data from the line scan imager is compared with a reference image. The location of a matching line in the reference image reveals the displacement of the subject. The current subject displacement can be determined based on each line of image data. The resulting displacement information can be used to correctly place other optical beams on the subject. The method can be applied to tracking the human eye to facilitate measurement, imaging, or treatment with a beam of optical radiation.
Owner:CARL ZEISS MEDITEC INC
Transmitter-receiver with integrated modulator array and hybrid bonded multi-wavelength laser array
InactiveUS7257283B1Coupling light guidesOptical waveguide light guideSemiconductor materialsOptical cavity
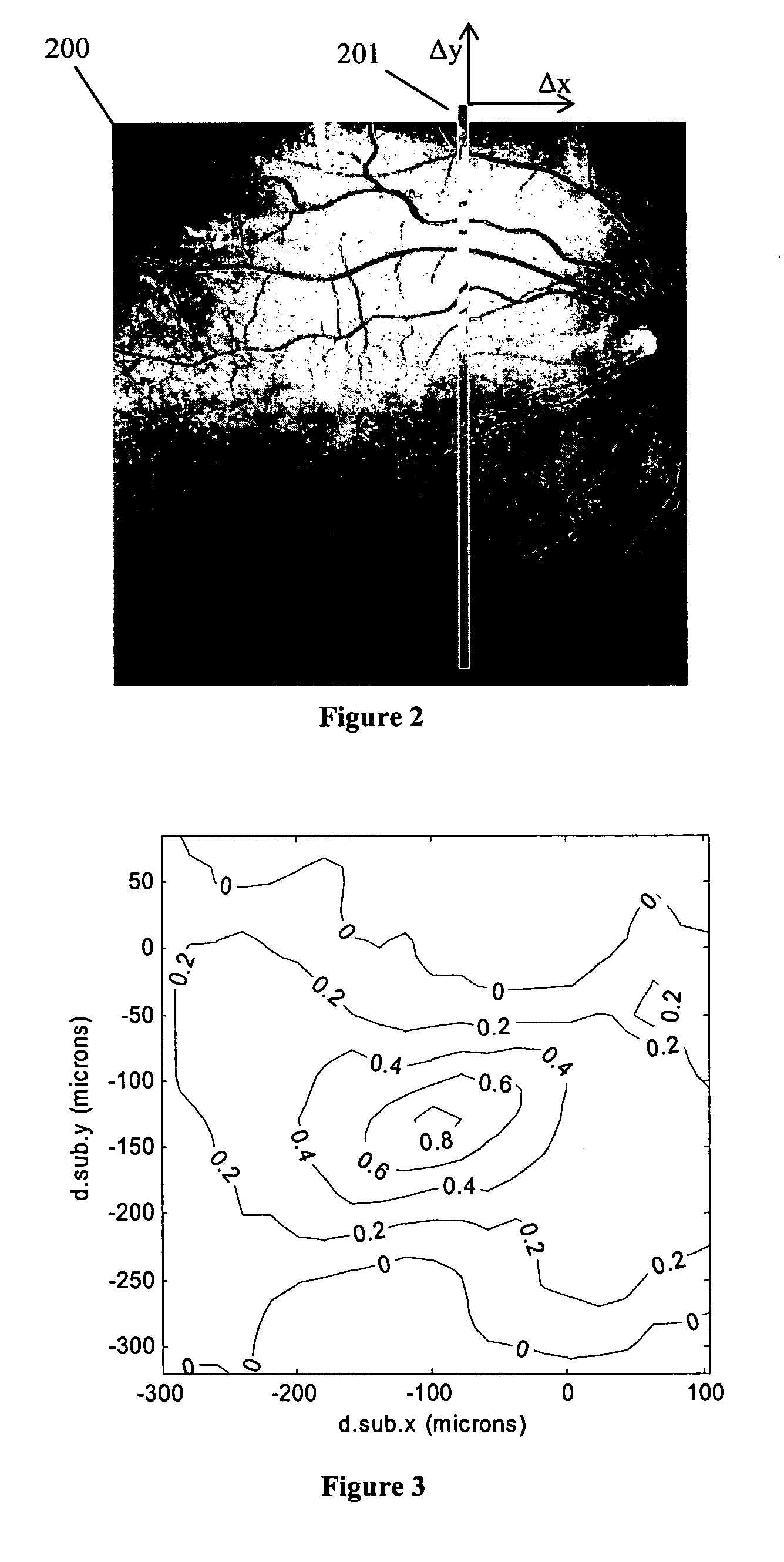
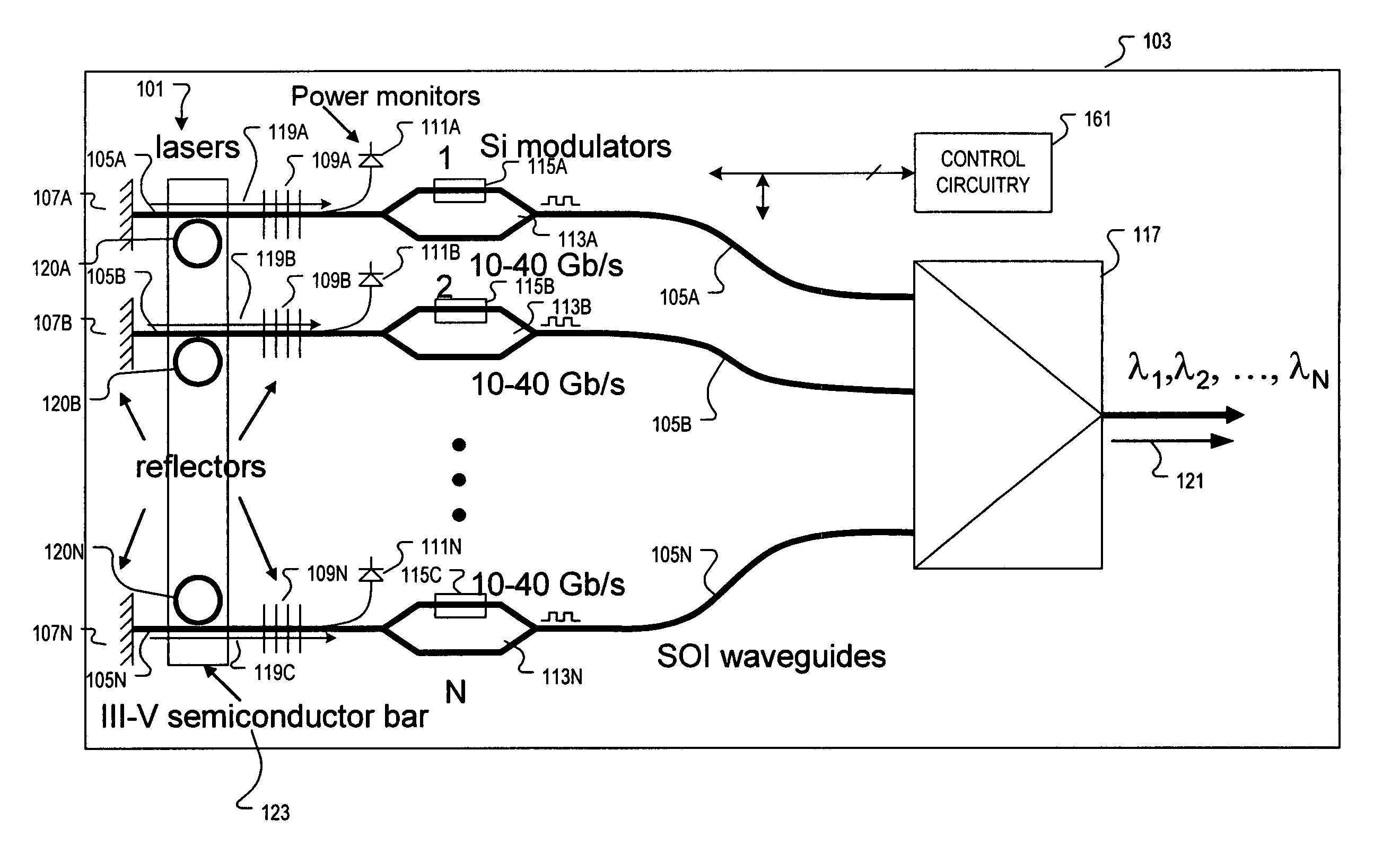
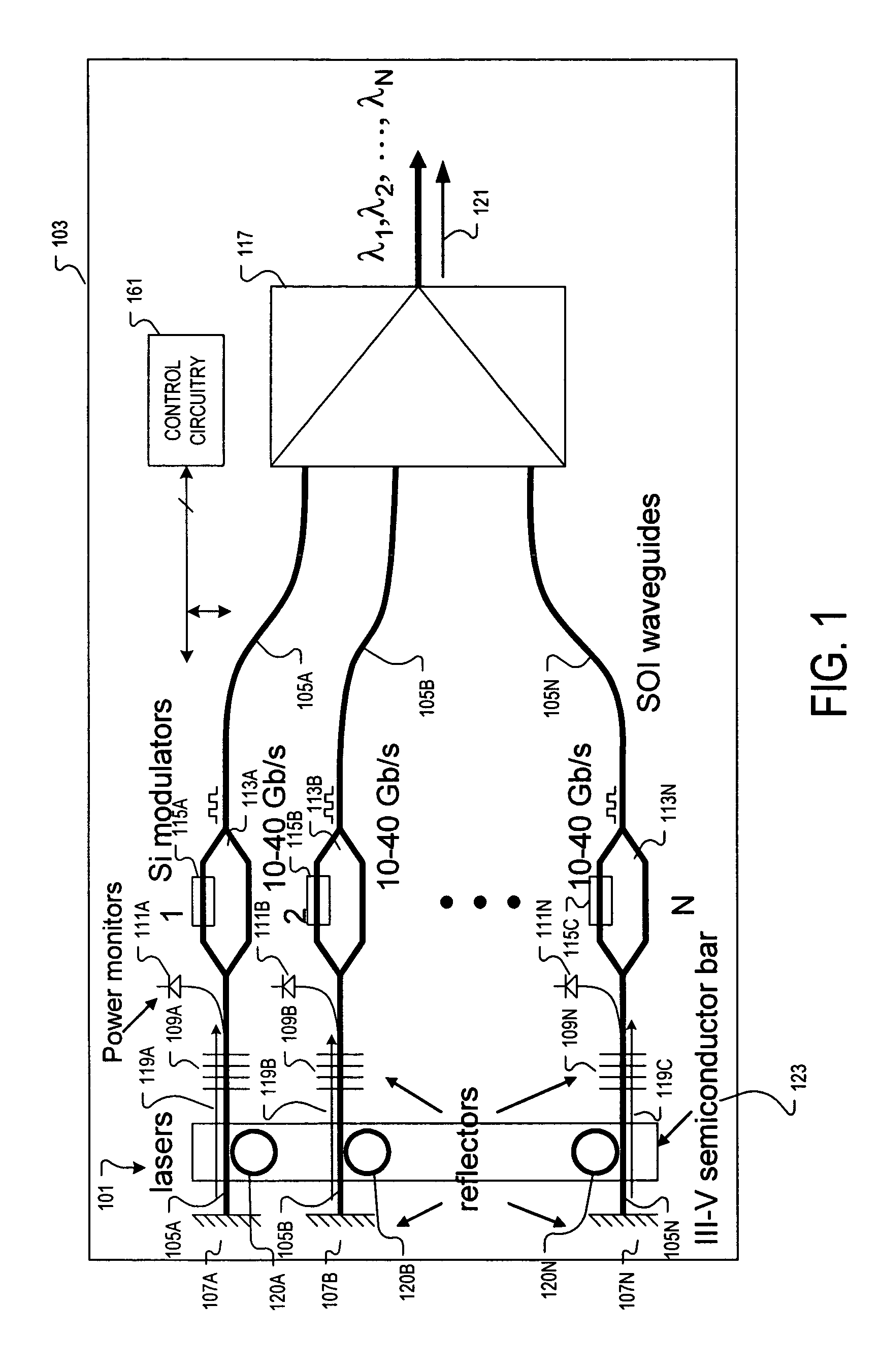
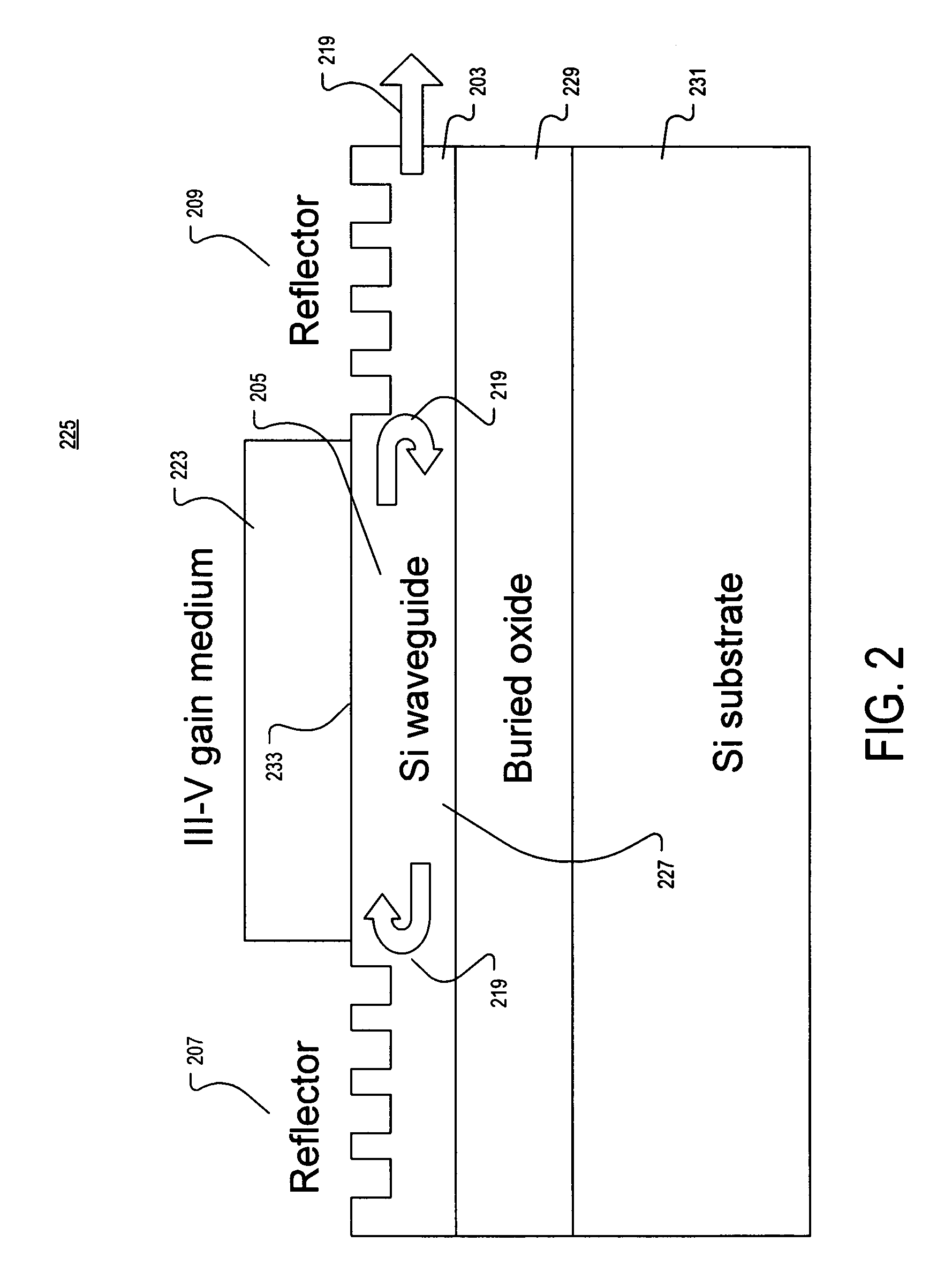
An apparatus and method providing a plurality of modulated optical beams from a single layer of semiconductor material. For one example, an apparatus includes a plurality of optical waveguides disposed in a single layer of semiconductor material. Each one of the plurality of optical waveguides includes an optical cavity defined along the optical waveguide. A single bar of gain medium material adjoining the single layer of semiconductor material across the plurality of optical waveguides is included. The gain medium-semiconductor material interface is defined along each of the plurality of optical waveguides. A plurality of optical modulators is disposed in the single layer of semiconductor material. Each one of the plurality of optical modulators is optically coupled to a respective one of the plurality of optical waveguides to modulate a respective optical beam directed from the optical cavity.
Owner:INTEL CORP
Method and arrangement for generating a laser beam having a differing beam profile characteristic by means of a multi-clad fiber
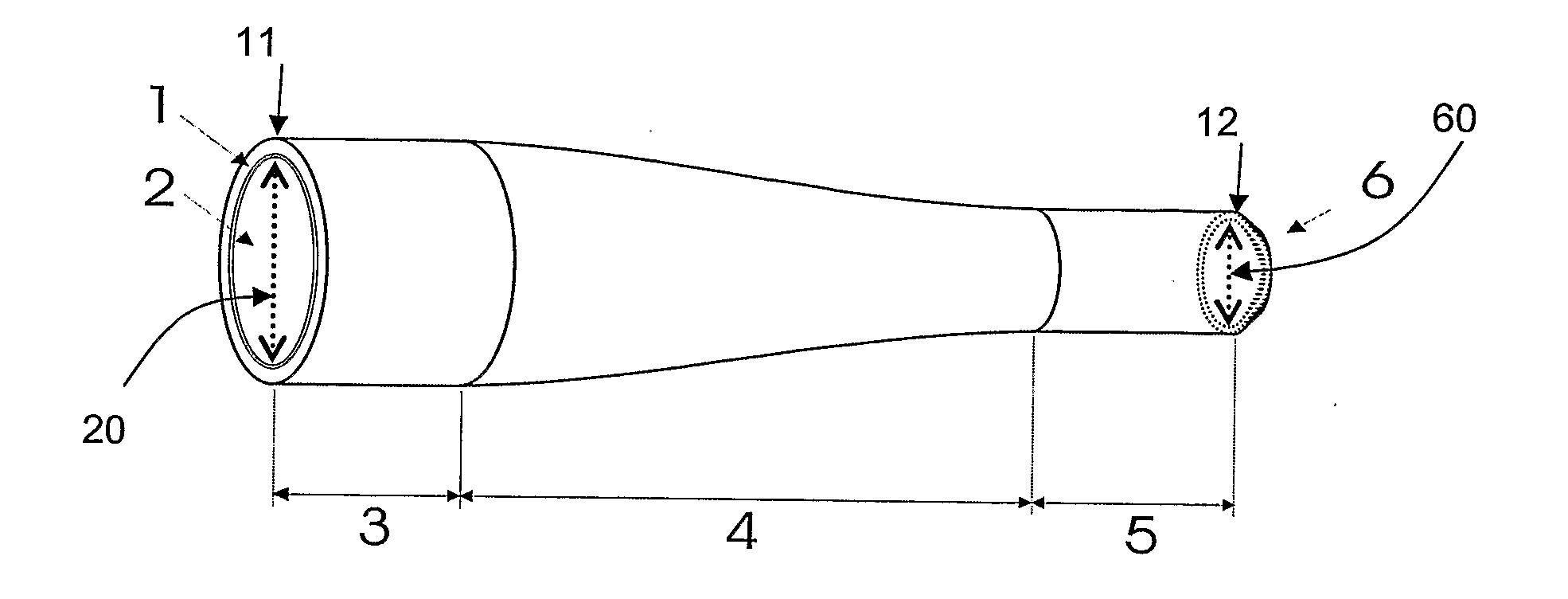
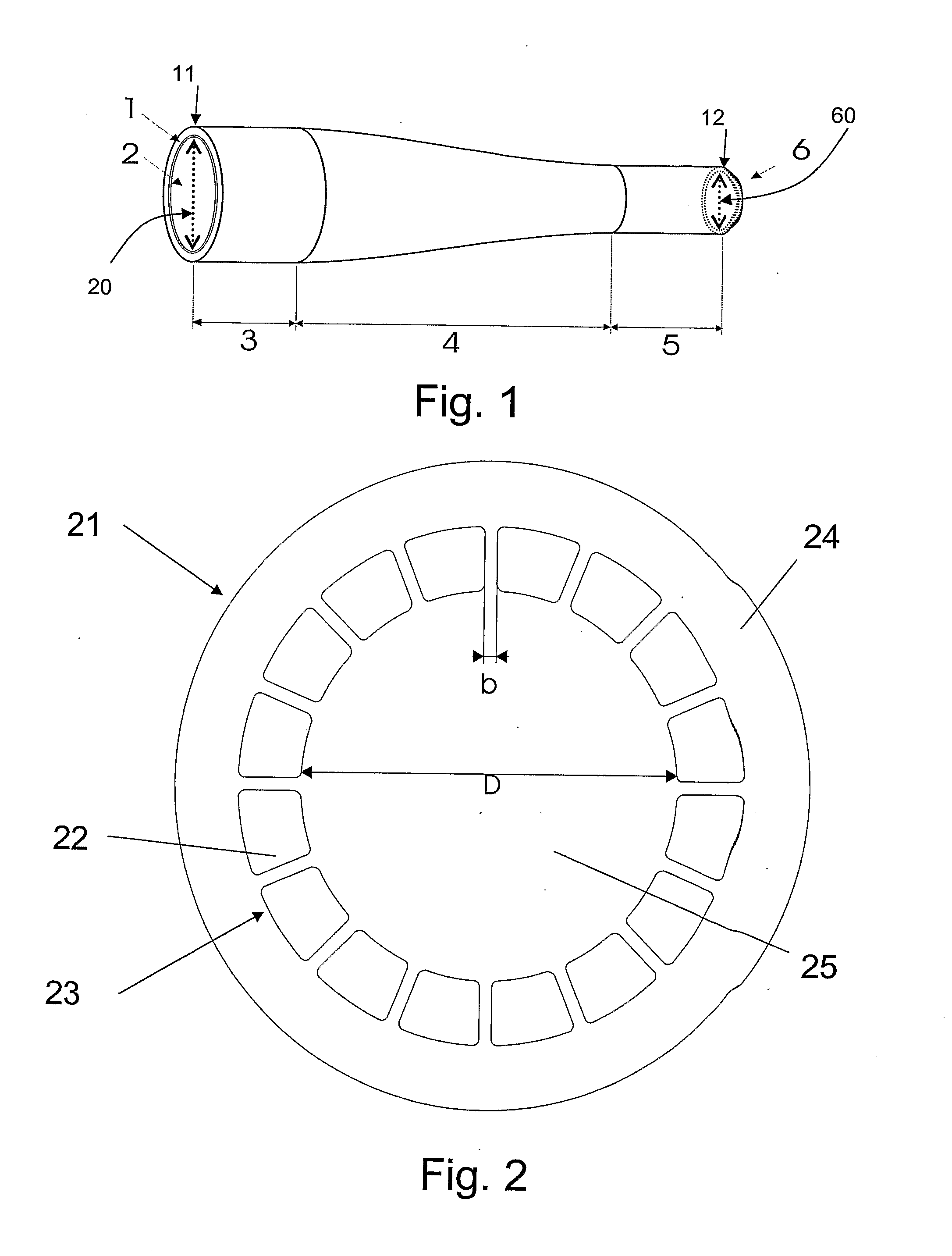
ActiveUS8781269B2Expand the range of adaptation potential of beam profile characteristicsReduce complexityLaser detailsOptical fibre with multilayer core/claddingFiberDouble-clad fiber
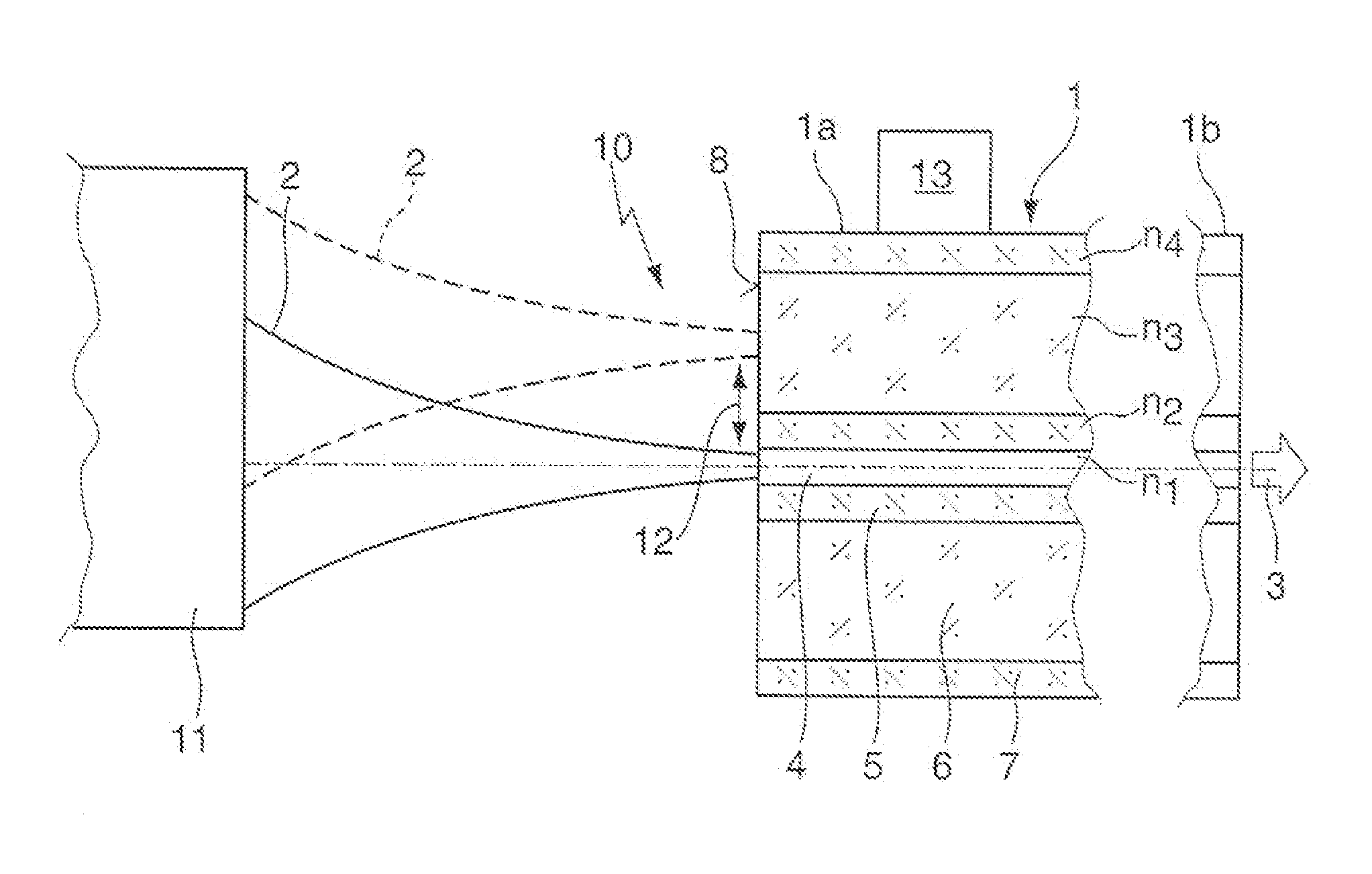
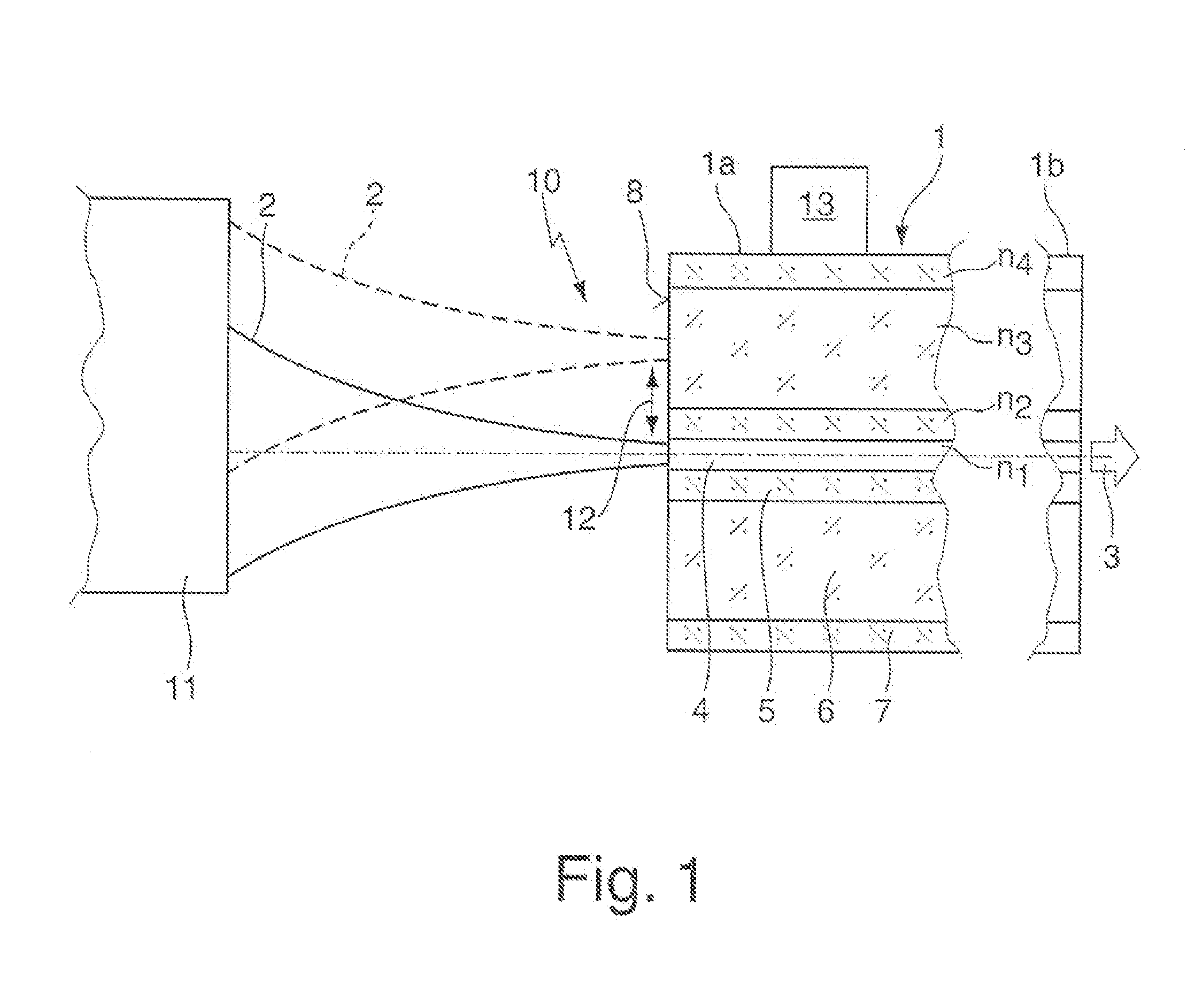
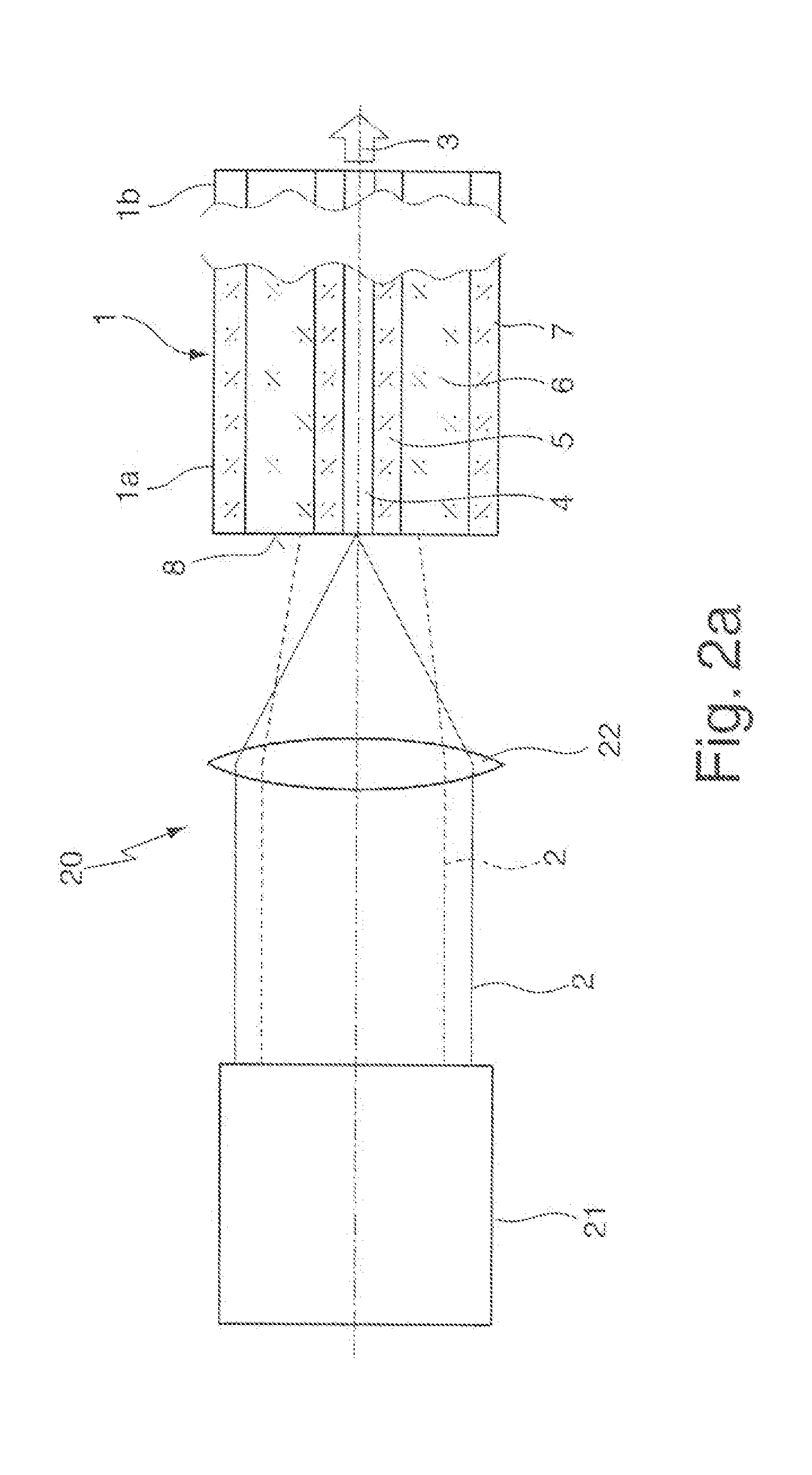
The invention concerns a method for generating a laser beam (3) with different beam profile characteristics, whereby a laser beam (2) is coupled into one fiber end (1a) of a multi-clad fiber (1), in particular a double-clad fiber, and emitted from the other fiber end (1b) of the multi-clad fiber (1) and whereby, to generate different beam profile characteristics of the output laser beam (3), the input laser beam (2) is electively coupled either at least into the inner fiber core (4) of the multi-clad fiber (1) or at least into at least one outer ring core (6) of the multi-clad fiber (1), as well as a corresponding arrangement (10).
Owner:TRUMPF LASERSYST FOR SEMICON MFG
Lighting systems for producing different beam patterns
InactiveUS20060039160A1Secure attachmentMechanical apparatusPoint-like light sourceWide beamBeam pattern
Various embodiments described herein include lighting systems that produce an optical beam. Moreover, in various embodiments, the beam may be altered to provide, for example, a narrow beam or a wide beam. One such lighting system includes a light source, a diffusing optical element, and a projection lens. The diffusing optical element is disposed between the light source and the projection lens and can be translated to provide zoom capability.
Owner:OPTICAL RES ASSOCS
Random microlens array for optical beam shaping and homogenization
Microlens arrays are defined with microlens elements that differ from each other in accordance with a probability distribution for shaping an optical beam having a prescribed intensity profile within a desired far-field scatter pattern. The differences include random variations in a sag profile corresponding to a surface shape of the microlenses, a boundary profile corresponding to a boundary of the microlenses, and a spatial distribution corresponding to the relative position of the microlenses within the array. The sag profile variations can be used to homogenize an intensity profile of the optical beam. The boundary profile variations within an irregular spatial distribution can be used to apply the prescribed intensity profile of the optical beam within the desired scatter pattern.
Owner:CORNING INC
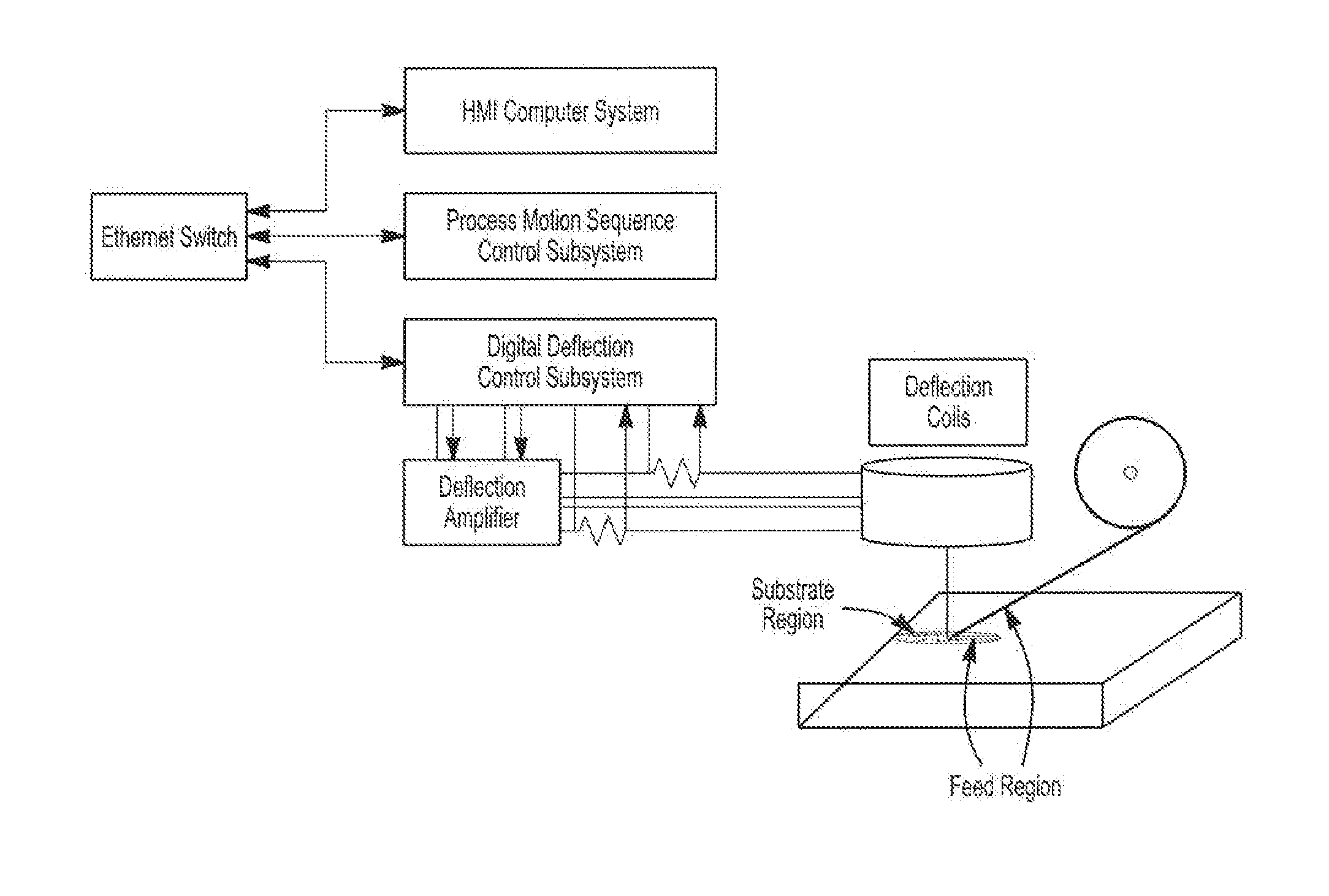
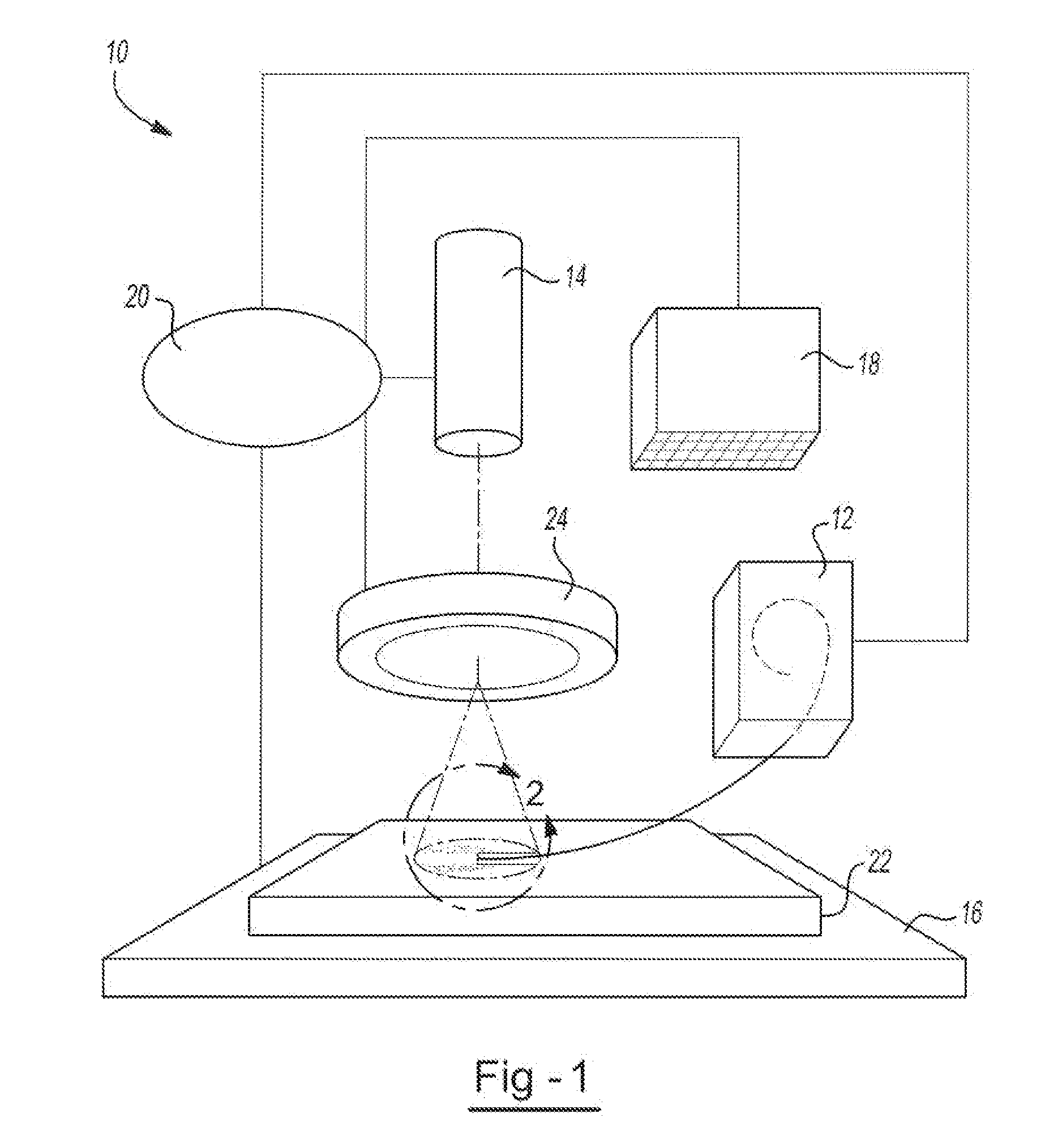
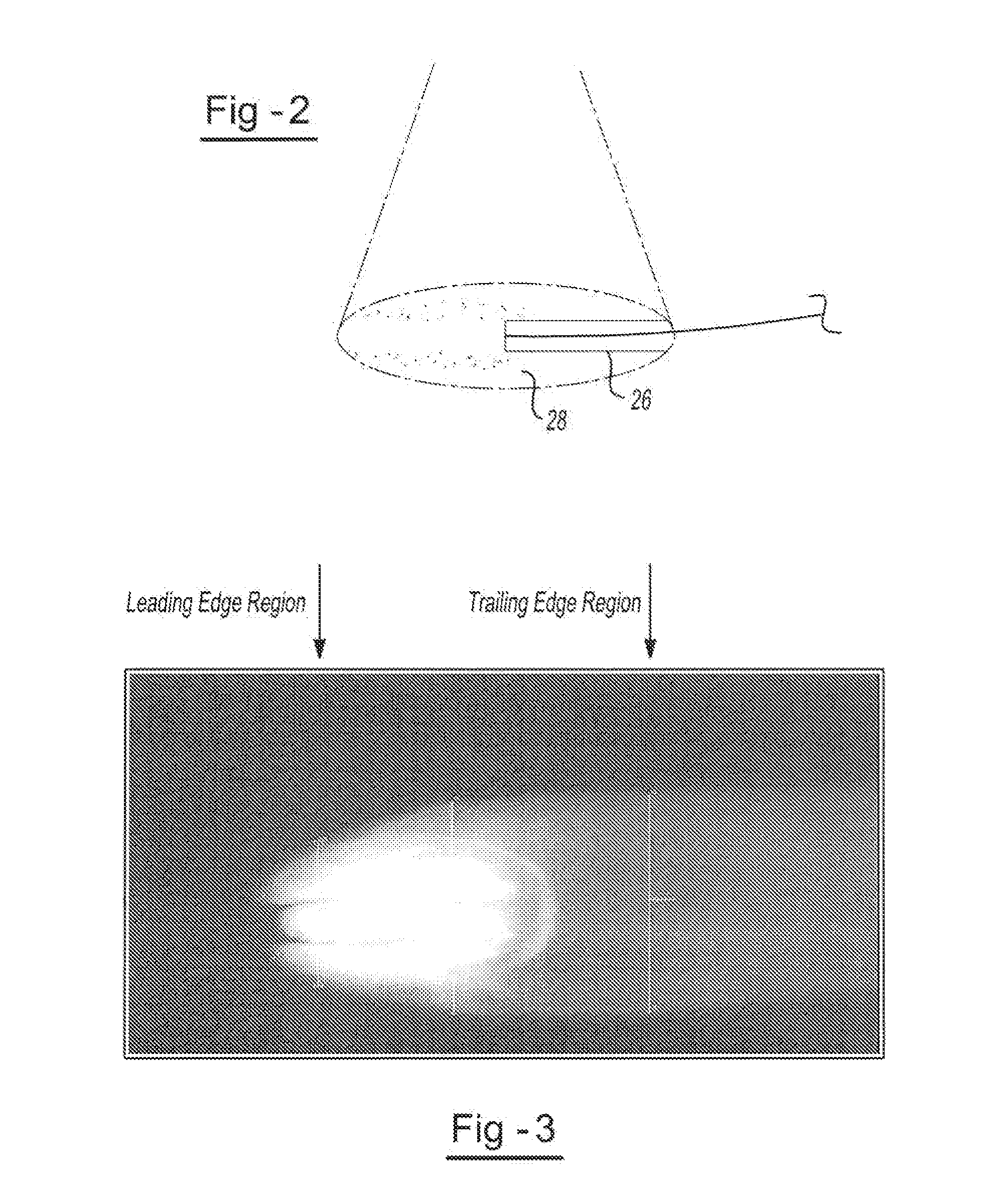
Raster methodology, apparatus and system for electron beam layer manufacturing using closed loop control
ActiveUS20110240607A1Constant feed rateConstant frame rateLiquid surface applicatorsAdditive manufacturing apparatusGratingClosed loop
A method for layer-by-layer manufacturing of a three-dimensional metallic work piece, comprising the steps of: delivering a metallic feed material in a substantially solid state into a feed region; emitting an electron beam having one or more predetermined electrical currents; translating the electron beam through a first predetermined raster pattern frame in an x-y plane that includes: a plurality of points within the feed region sufficient so that the metallic feed material is subjected to a melting beam power density level sufficient to cause melting of the metallic feed material and formation of a molten pool deposit; and a plurality of points in a substrate region that is outside of the feed region, sufficient so that the plurality of points outside the feed region is subjected to a substrate beam power density level that is different from (e.g., lower than) the melting beam power density level; monitoring a condition of one or both of the feed region or the substrate region substantially in real time for the occurrence of any deviation from a predetermined condition; upon detecting of any deviation, translating the electron beam through at least one second predetermined raster pattern frame in the x-y plane that maintains the melting beam power density level substantially the same as the first predetermined raster pattern frame, but alters the substrate beam power density level in a manner so that the monitored condition returns to the predetermined condition; and repeating the above steps at one or more second locations for building up layer by layer, generally along a z-axis that is orthogonal to the x-y plane, a three-dimensional layered metallic work piece. The teachings herein also contemplate an apparatus that includes an electronic control device that performs any of the methods herein, as well as articles made according to such methods.
Owner:SCIAKY SA
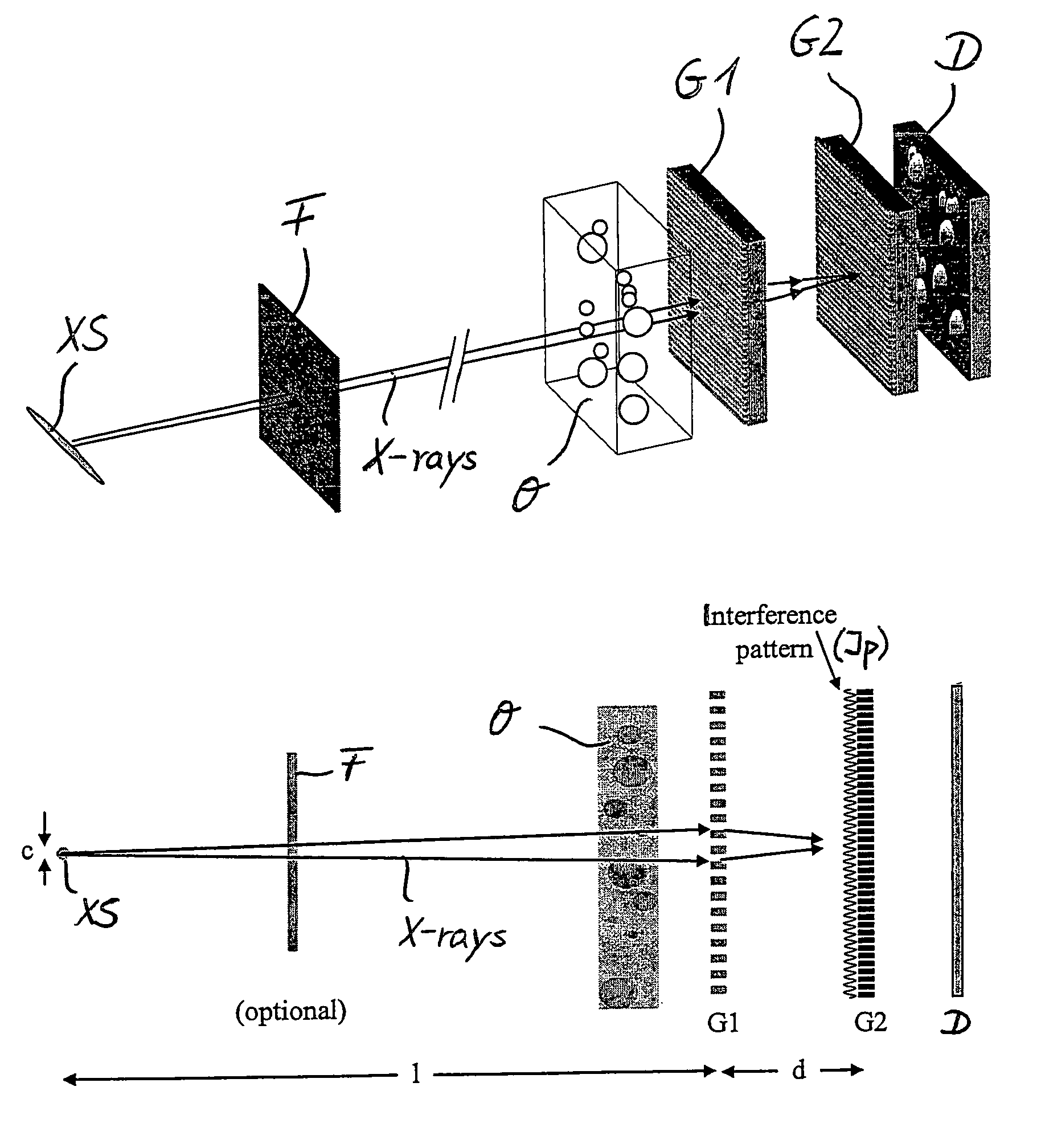
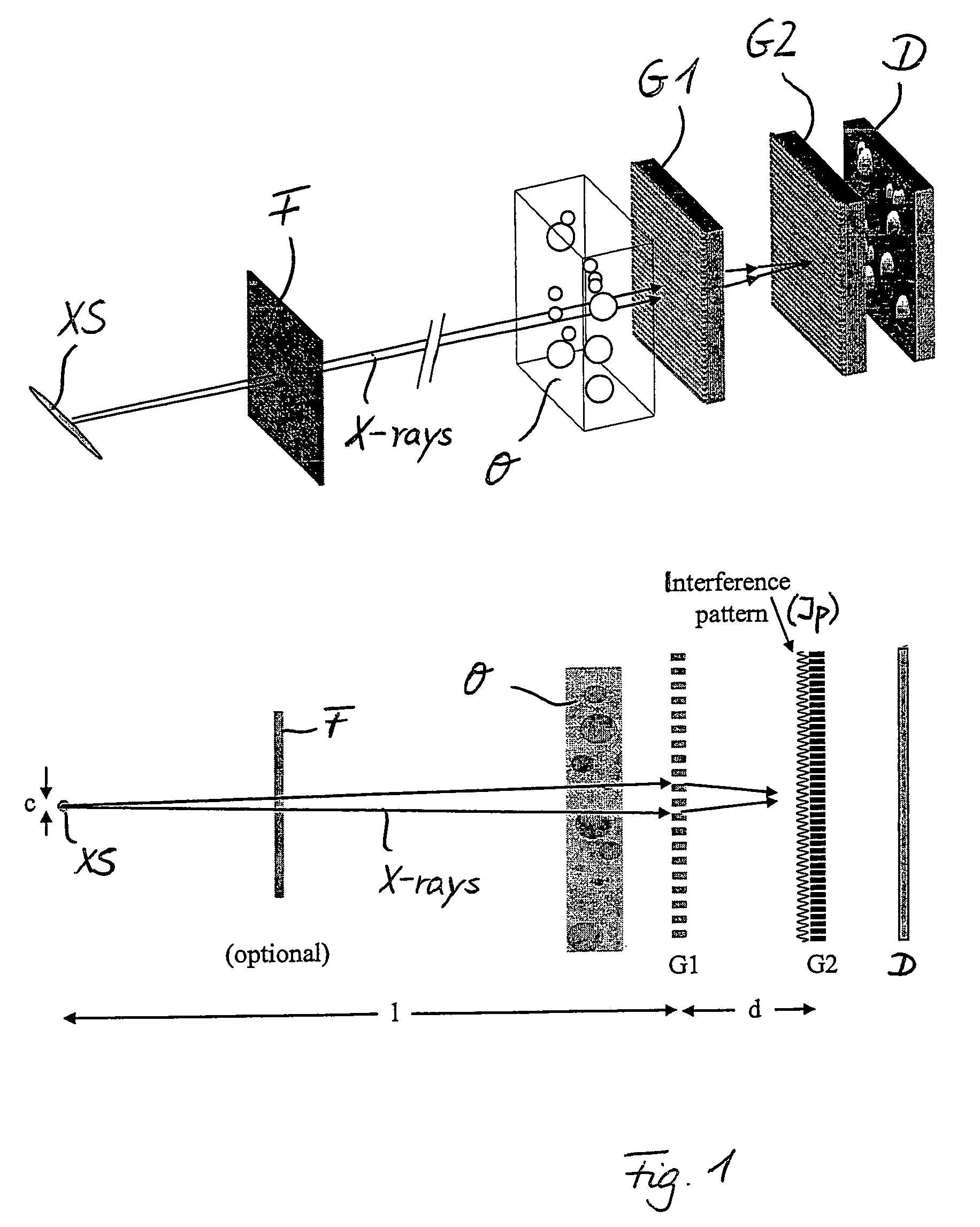
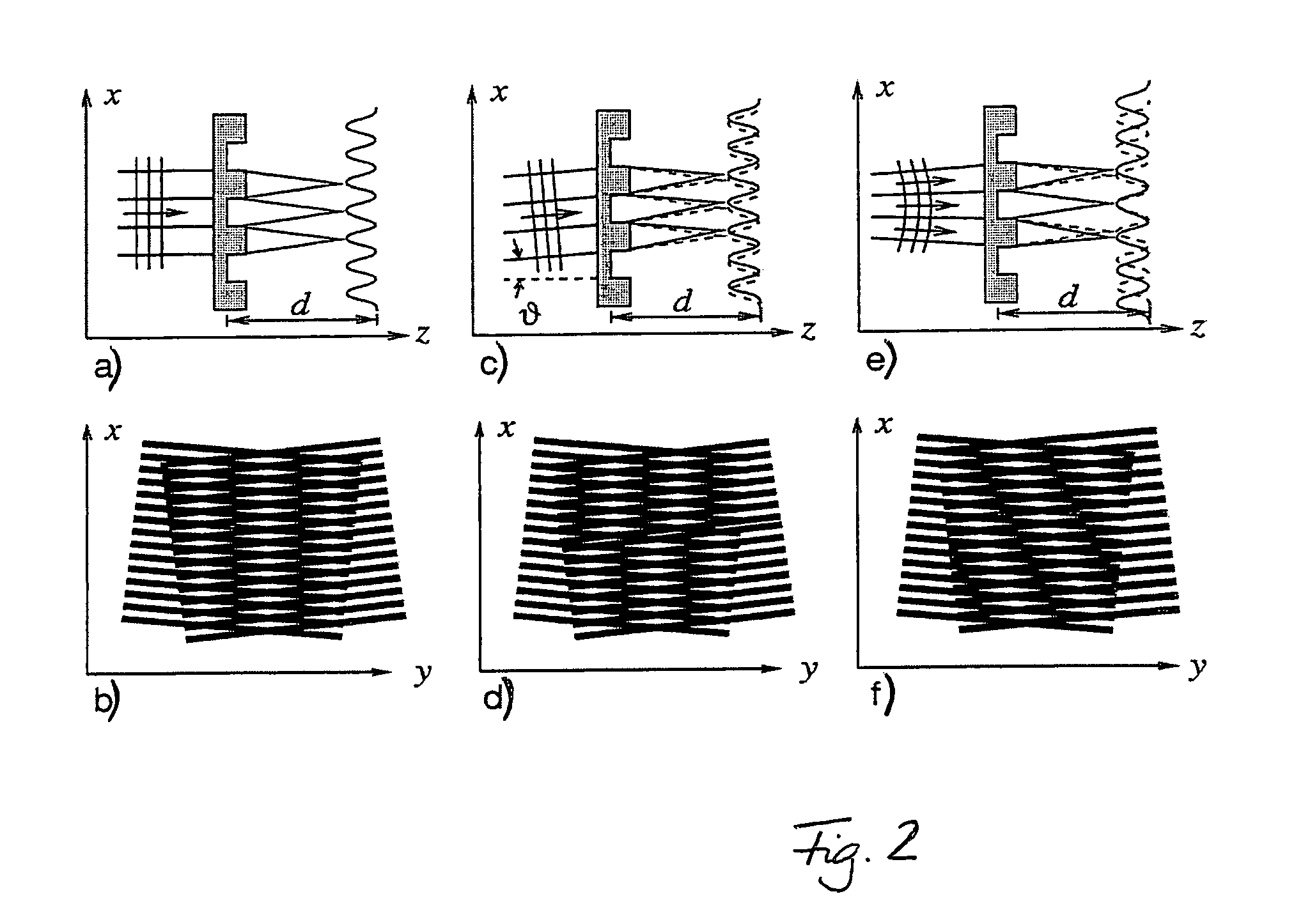
Interferometer for quantitative phase contrast imaging and tomography with an incoherent polychromatic x-ray source
ActiveUS7889838B2Little effortAlleviate scattering artifactImaging devicesTomographyHard X-raysTransmission geometry
Owner:PAUL SCHERRER INSTITUT
Optical System and Assembly Method
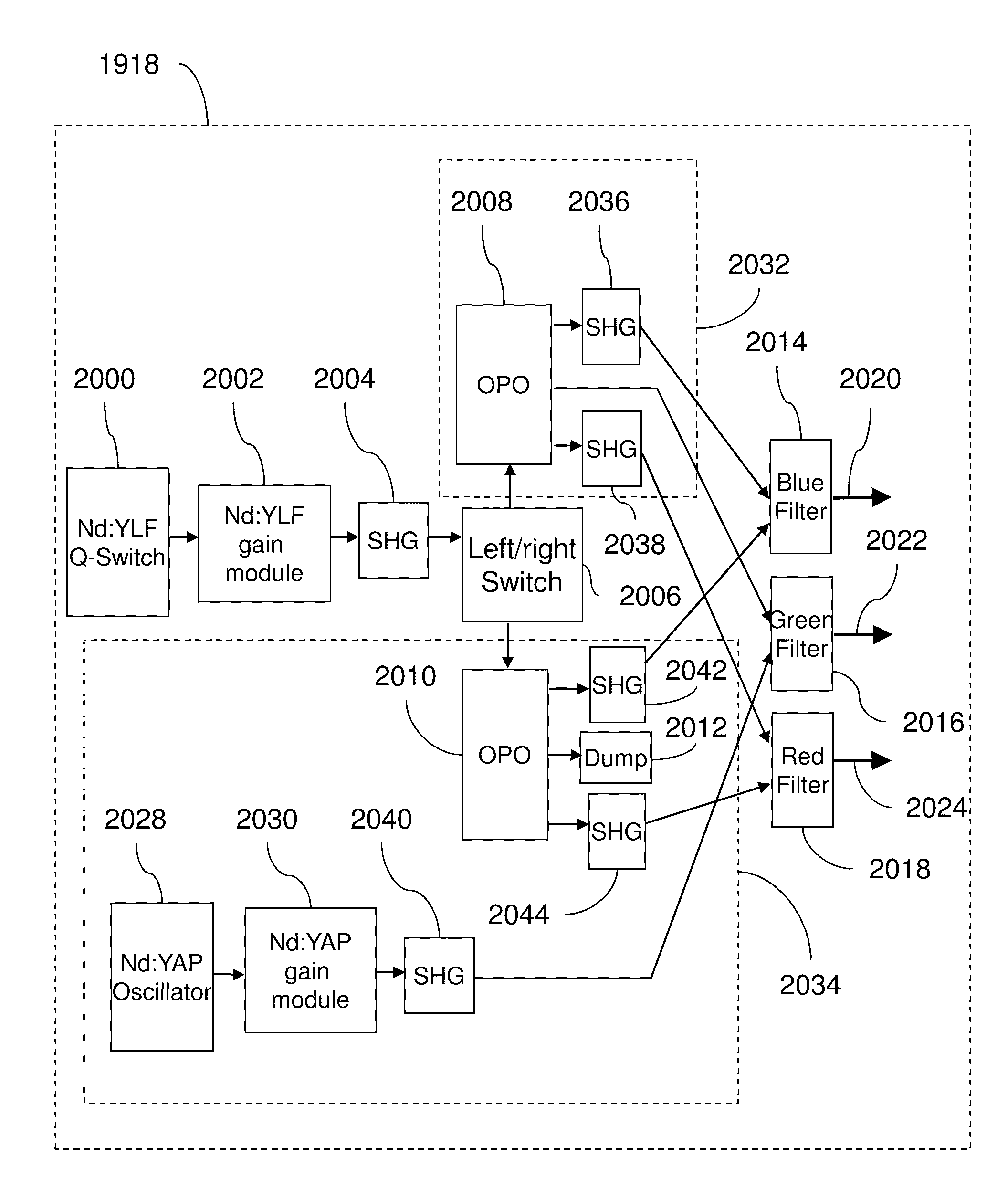
InactiveUS20100253769A1Need long operating lifetimesMethod is feasibleLaser arrangementsColor television detailsSpatial light modulatorDisplay device
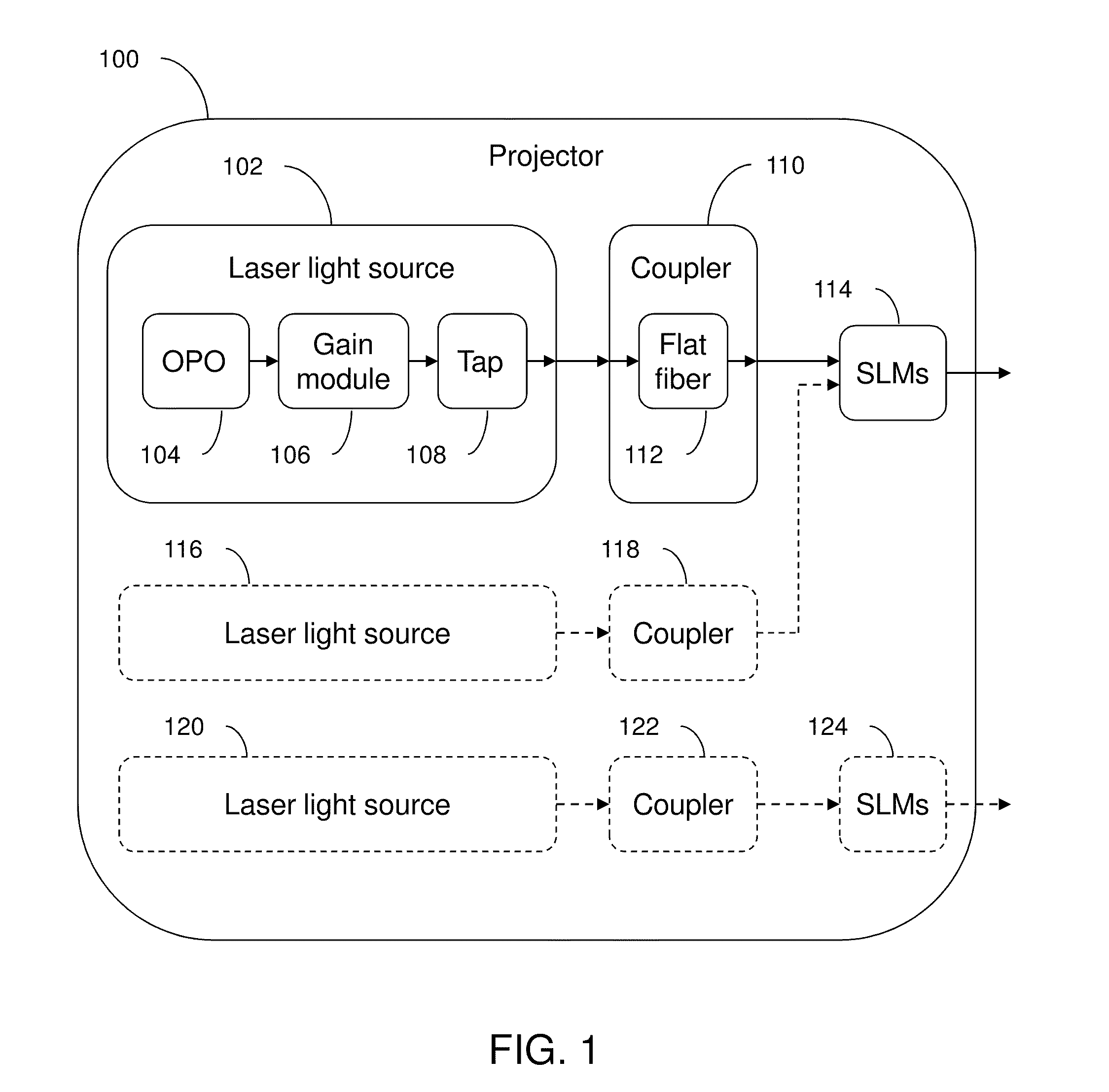
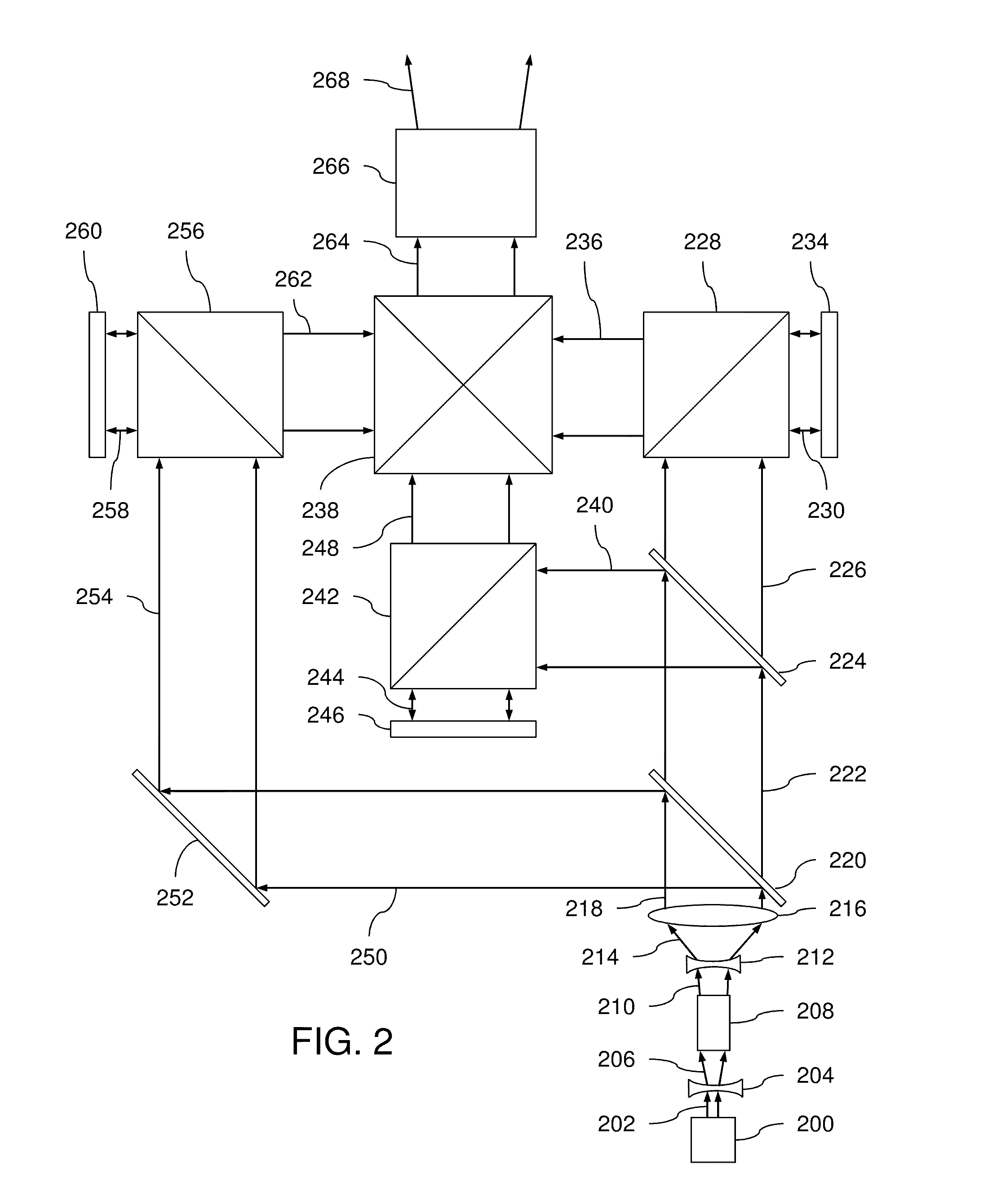
An optical system which includes some or all of the following parts: a laser light source which illuminates a spatial light modulator such that optical characteristics are preserved; a stereoscopic display which has a polarization-switching light source; a stereoscopic display which includes two infrared lasers, two optical parametric oscillators, and six second harmonic generators; two light sources processed by two parts of the same spatial light modulator; a method of assembly using an alignment plate to align kinematic rollers on a holding plate; an optical support structure which includes stacked, compartmented layers; a collimated optical beam between an optical parametric oscillator and a second harmonic generator; a laser gain module with two retroreflective mirrors; an optical tap which keeps the monitored beam co-linear; an optical coupler which includes an optical fiber and a rotating diffuser; and an optical fiber that has a core with at least one flat side.
Owner:PROJECTION VENTURES INC
Optical scanner and image forming apparatus
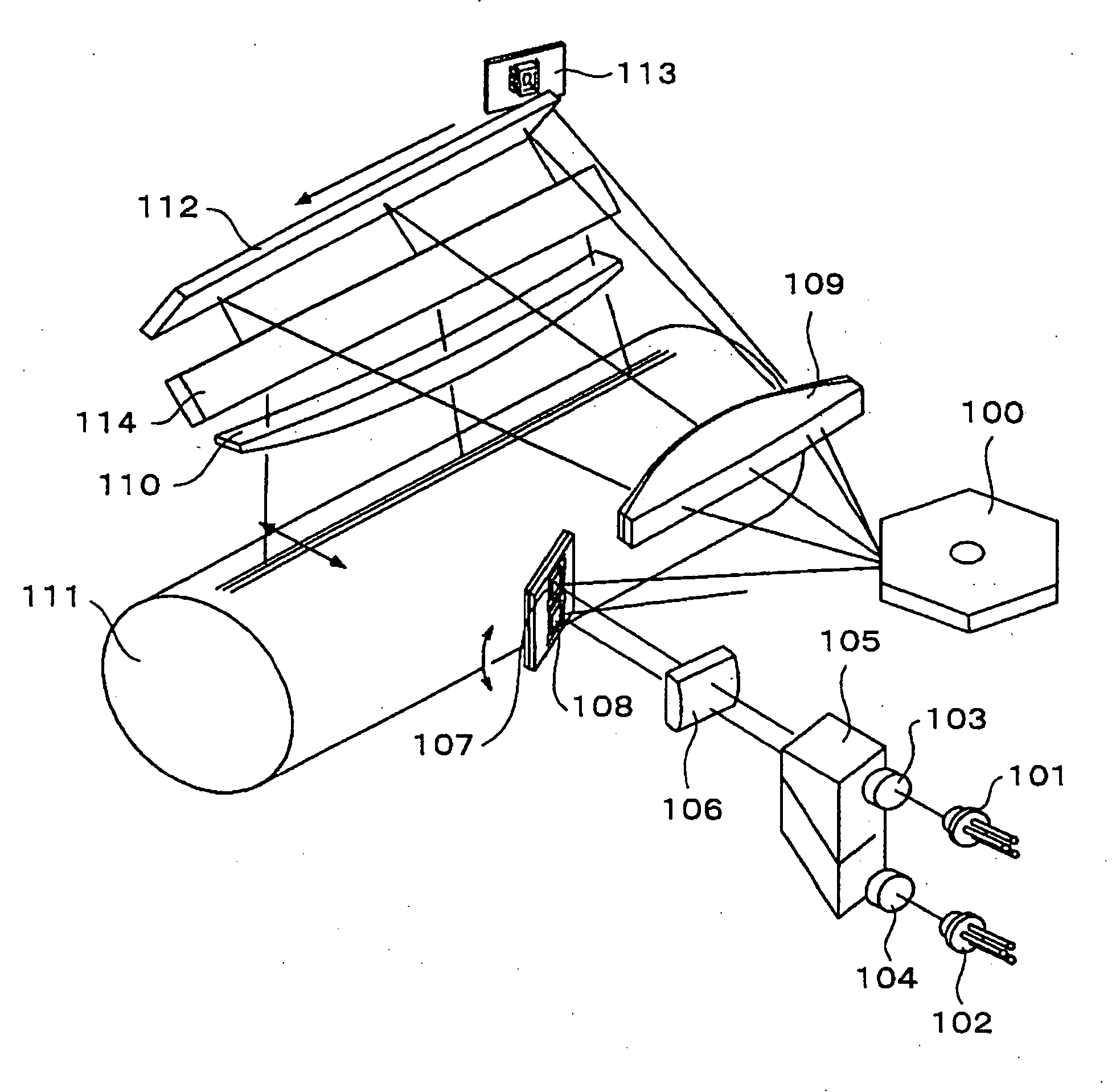
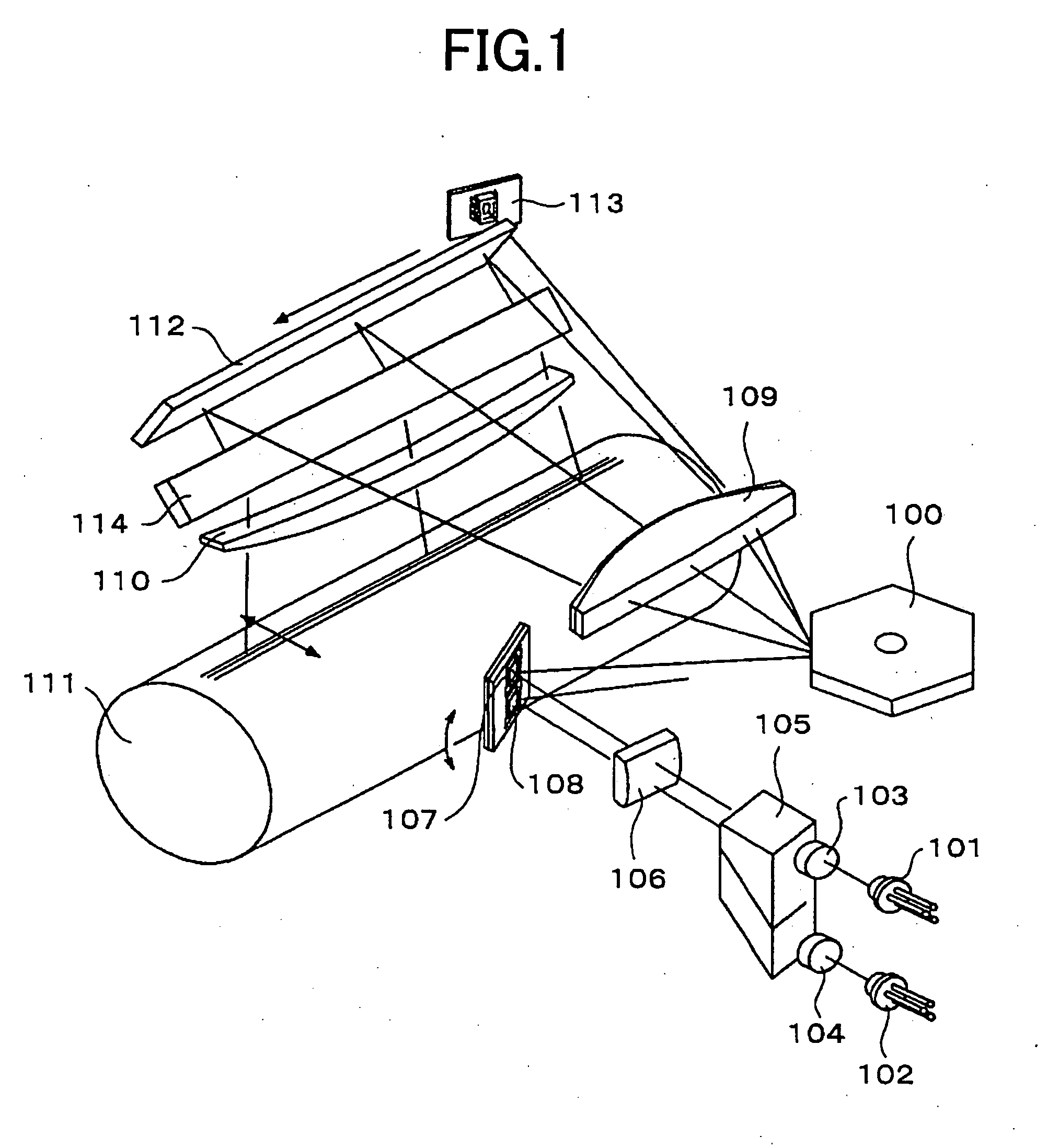
InactiveUS20060232660A1Correct difference of colorEasy to correctInking apparatusVisual representatino by photographic printingColor imageResist
An optical scanner is capable of effectively correcting a difference with respect to the sub-scanning direction between the positions of optical spots for scanning photoconductor drums of a tandem type color image forming apparatus. The optical scanner includes an optical axis adjusting part. The optical axis adjusting part uses a deflecting mirror or a wedge-shaped prism to deflect the optical axis of an optical beam with respect to the sub-scanning direction. As a result, it is possible to accurately correct a resist difference among individual image forming stations and form a high-quality color image without any color displacement.
Owner:RICOH KK
Gimbal-less micro-electro-mechanical-system tip-tilt and tip-tilt-piston actuators and a method for forming the same
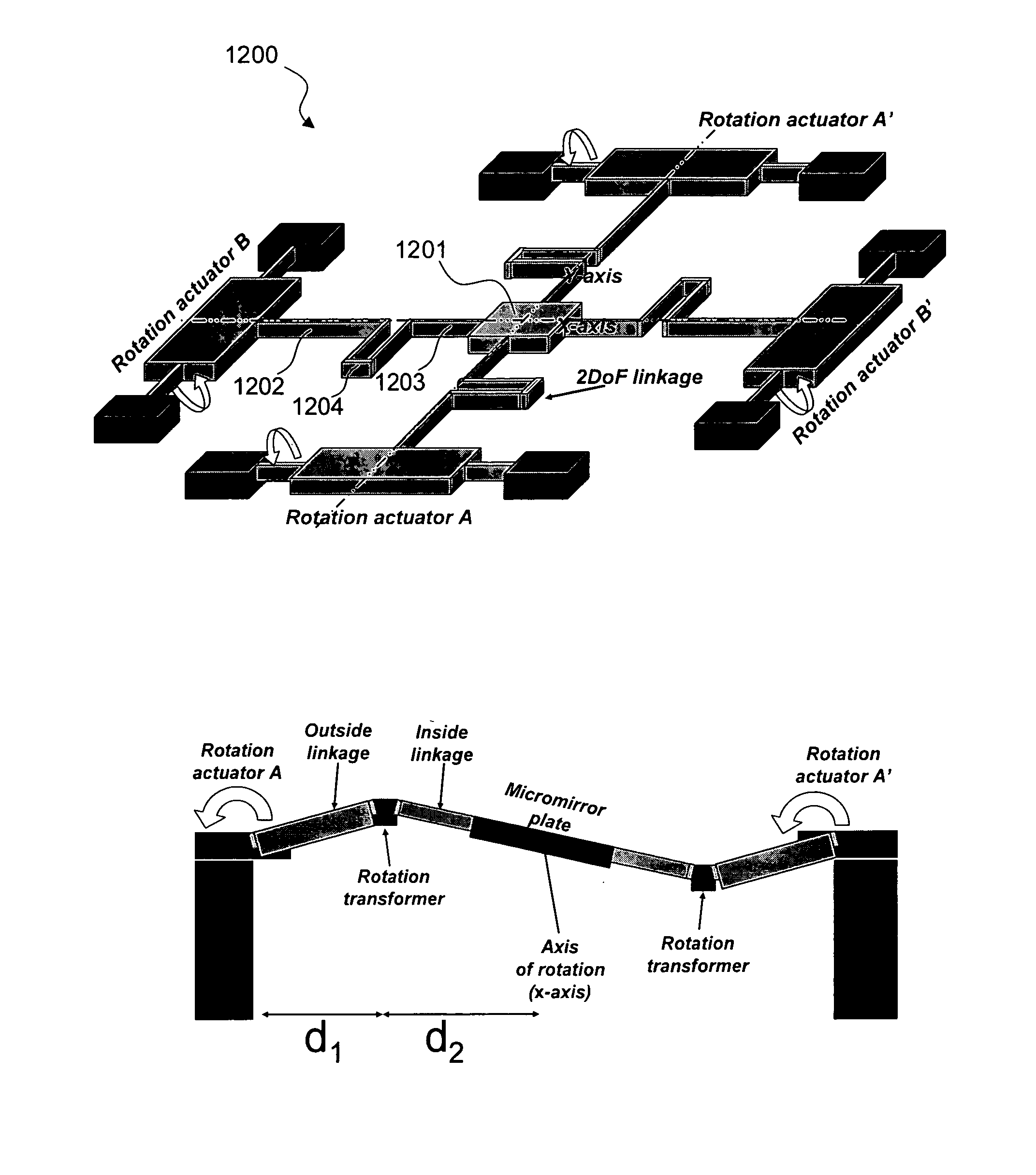
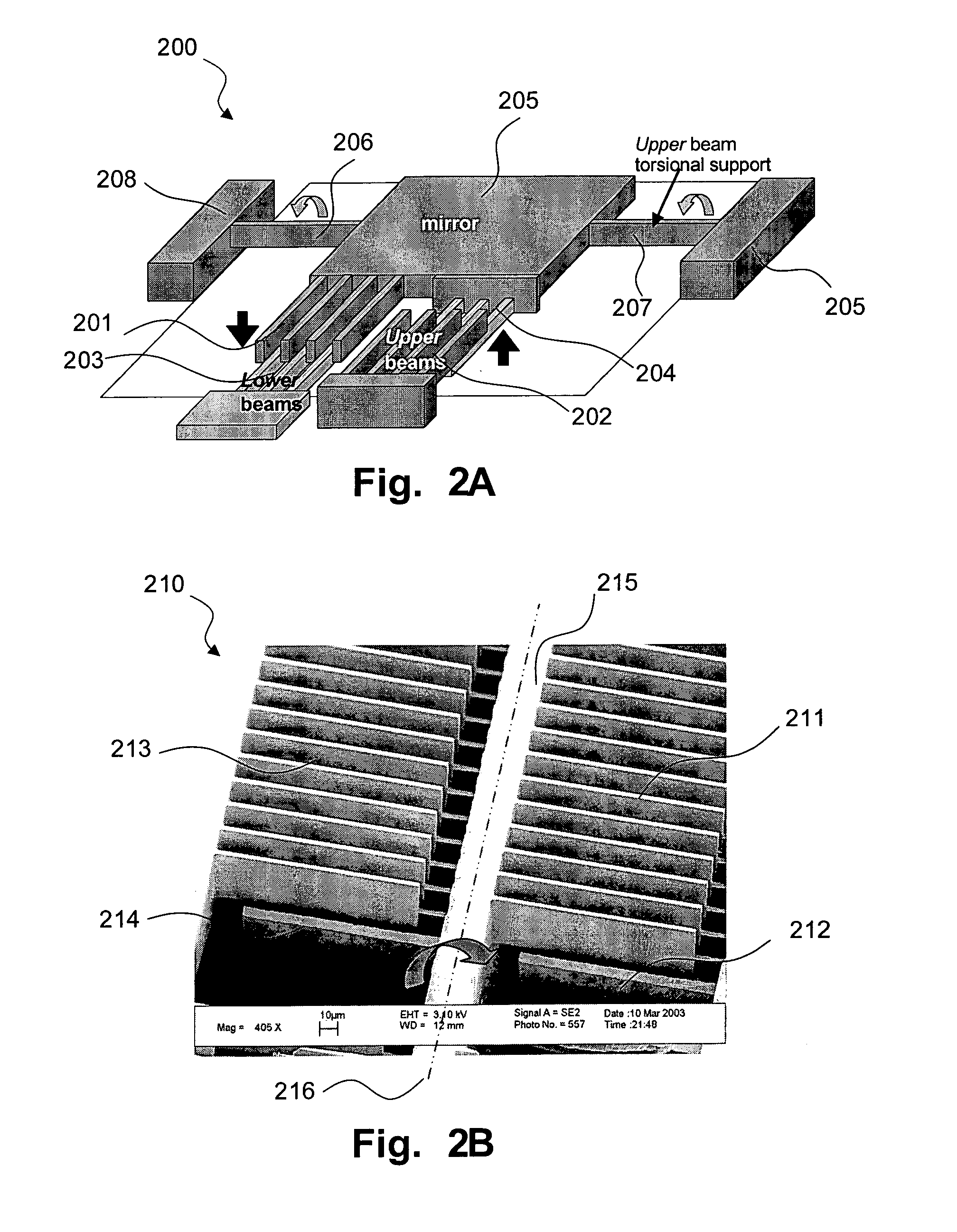
Fully monolithic gimbal-less micro-electro-mechanical-system (MEMS) devices with large static optical beam deflection and fabrications methods are disclosed. The devices can achieve high speed of operation for both axes. Actuators are connected to a device, or device mount by linkages that allow static two-axis rotation in addition to pistoning without the need for gimbals, or specialized isolation technologies. The device may be actuated by vertical comb-drive actuators, which are coupled by bi-axial flexures to a central micromirror or device mount. Devices may be fabricated by etching an upper layer both from the top side and from the bottom side to form beams at different levels, The beams include a plurality of lower beams, a plurality of full-thickness beams, and a plurality of upper beams, the lower, full-thickness and upper beams That form vertical combdrive actuators, suspension beams, flexures, and a device mount.
Owner:ADRIATIC RES INST
Optical Coupler Devices, Methods of Their Production and Use
InactiveUS20070237453A1Laser using scattering effectsOptical fibre with multilayer core/claddingDouble-clad fiberWaveguide
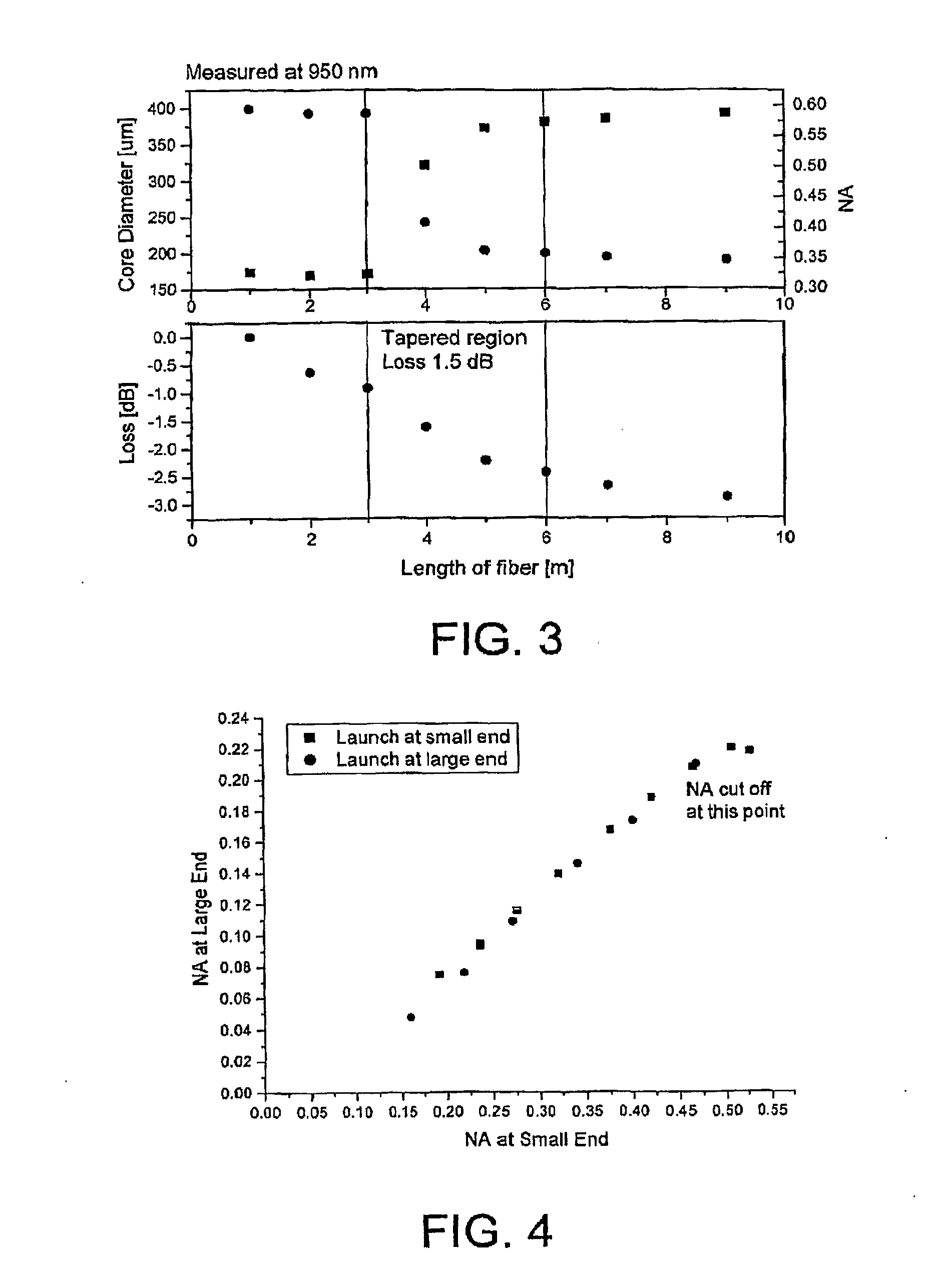
The present invention relates in general to coupling of light from one or more input waveguides to an output waveguide or output section of a waveguide having other physical dimensions and / or optical properties than the input waveguide or waveguides. The invention relates to an optical component in the form of a photonic crystal fibre for coupling light from one component / system with a given numerical aperture to another component / system with another numerical aperture. The invention further relates to methods of producing the optical component, and articles comprising the optical component, and to the use of the optical component. The invention further relates to an optical component comprising a bundle of input fibres that are tapered and fused together to form an input coupler e.g. for coupling light from several light sources into a single waveguide. The invention still further relates to the control of the spatial extension of a guided mode (e.g. a mode-field diameter) of an optical beam in an optical fibre. The invention relates to a tapered longitudinally extending optical waveguide having a relatively larger cross section that over a certain longitudinal distance is tapered down to a relatively smaller cross section wherein the spatial extent of the guided mode is substantially constant or expanding from the relatively larger to the relatively smaller waveguide cross section. The invention may e.g. be useful in applications such as fibre lasers or amplifiers, where light must be coupled efficiently from pump sources to a double clad fibre.
Owner:CRYSTAL FIBRE AS
Apparatus and methods for fluorescence imaging using radiofrequency-multiplexed excitation
ActiveUS9423353B2Reduce image noiseScalable approachMicroscopesFluorescence/phosphorescenceBeam splitterLaser scanning microscope
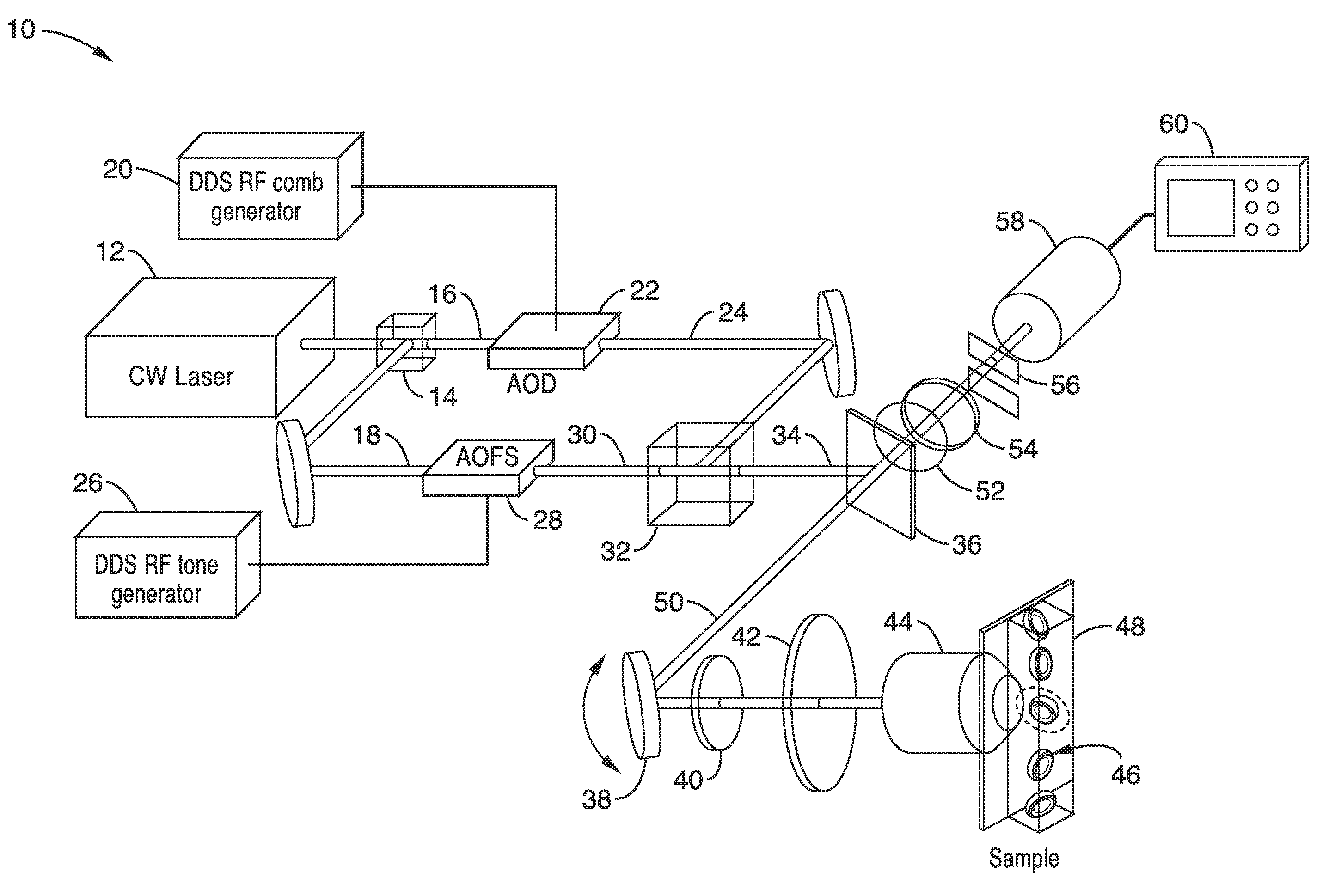
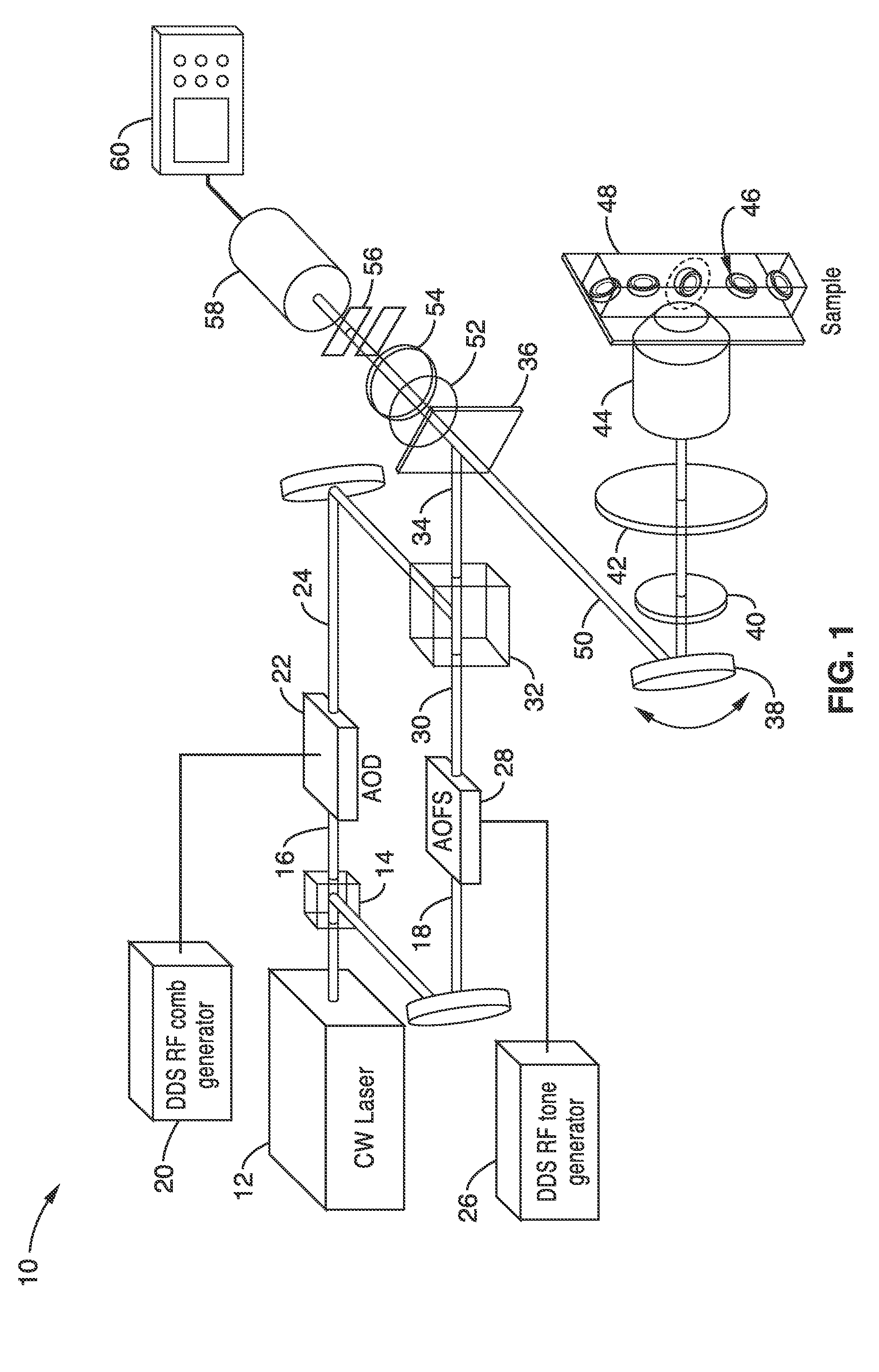
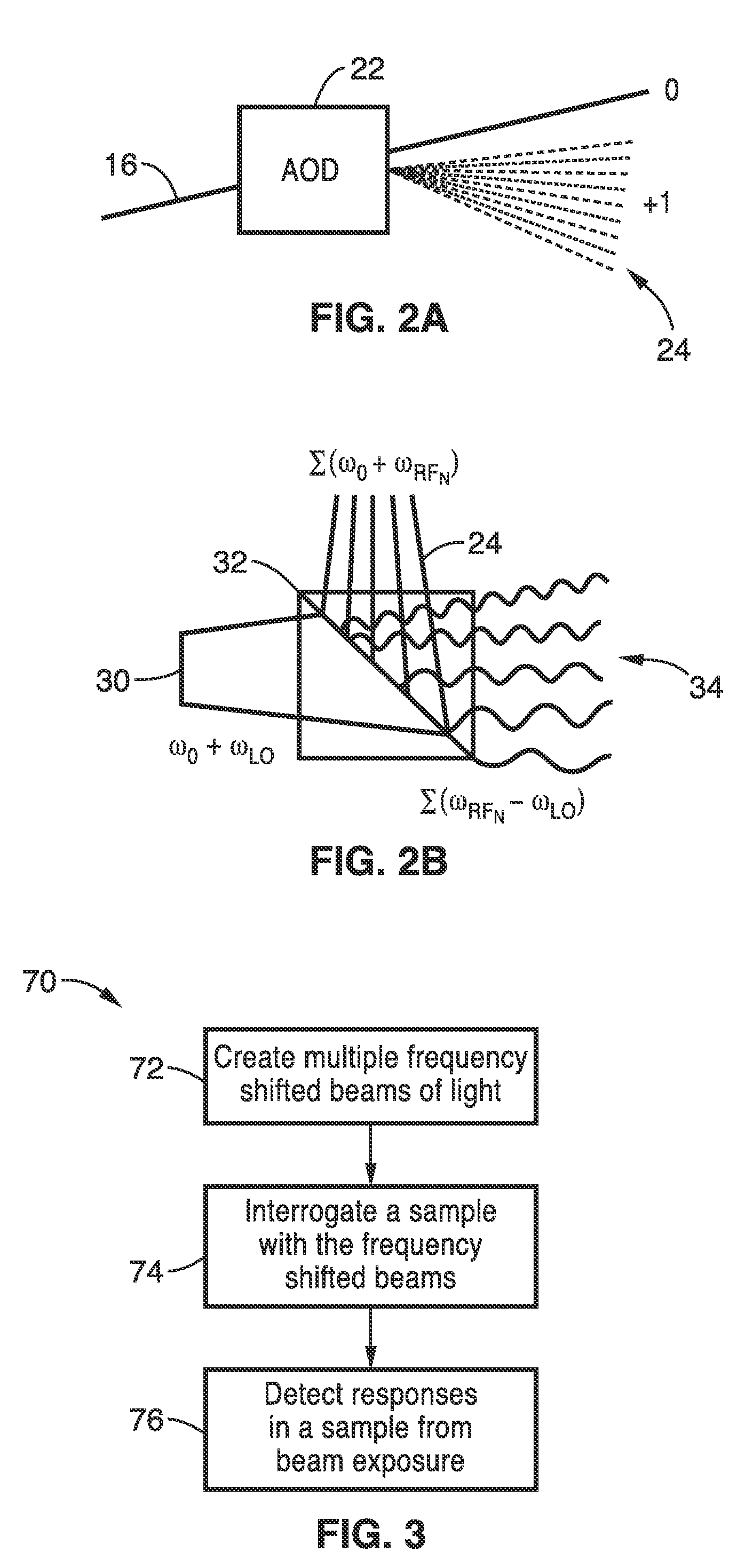
Apparatus and methods for fluorescence imaging using radiofrequency multiplexed excitation. One apparatus splits an excitation laser beam into two arms of a Mach-Zehnder interferometer. The light in the first beam is frequency shifted by an acousto-optic deflector, which is driven by a phase-engineered radiofrequency comb designed to minimize peak-to-average power ratio. This RF comb generates multiple deflected optical beams possessing a range of output angles and frequency shifts. The second beam is shifted in frequency using an acousto-optic frequency shifter. After combining at a second beam splitter, the two beams are focused to a line on the sample using a conventional laser scanning microscope lens system. The acousto-optic deflectors frequency-encode the simultaneous excitation of an entire row of pixels, which enables detection and de-multiplexing of fluorescence images using a single photomultiplier tube and digital phase-coherent signal recovery techniques.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com