Patents
Literature
226 results about "Wedge prism" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
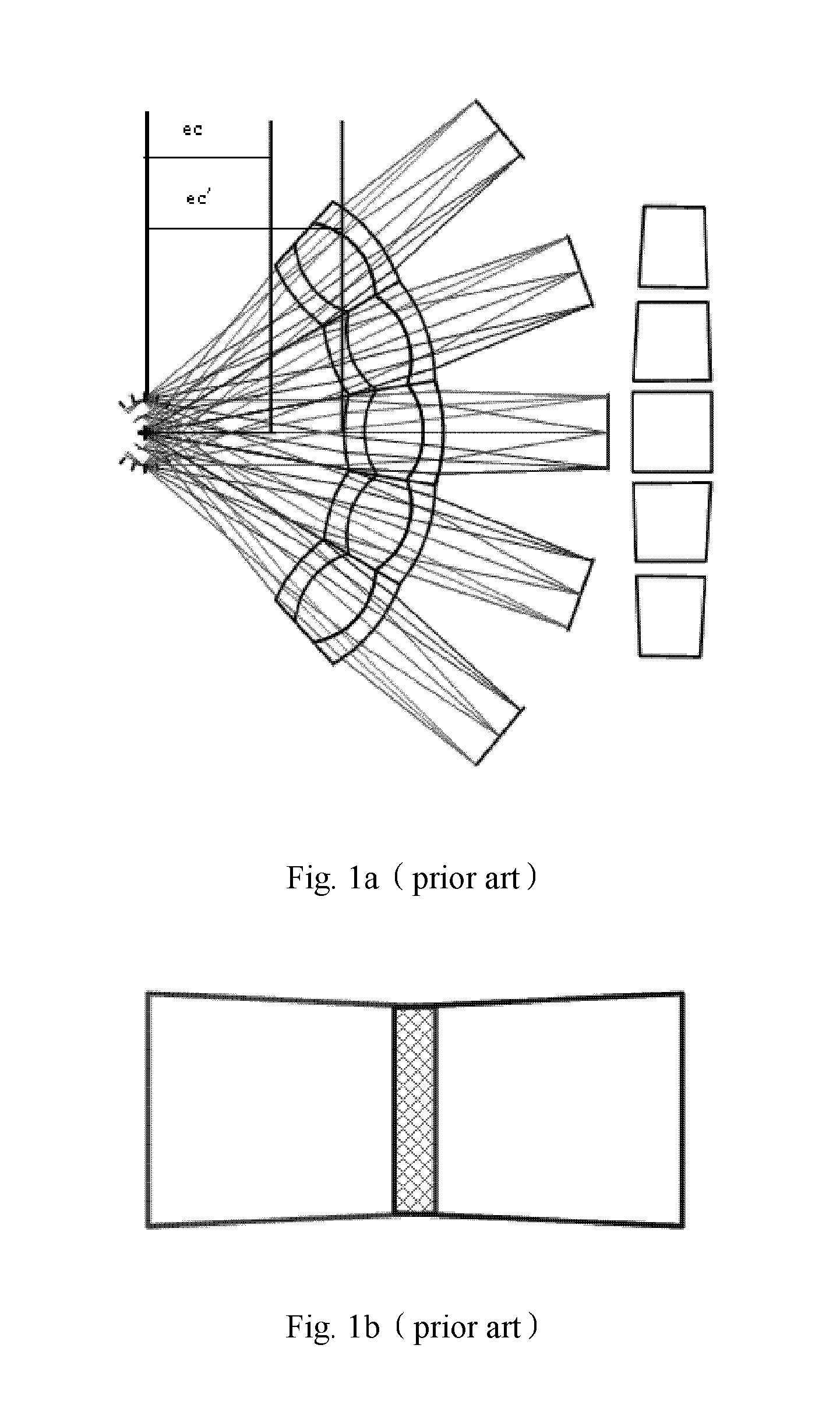
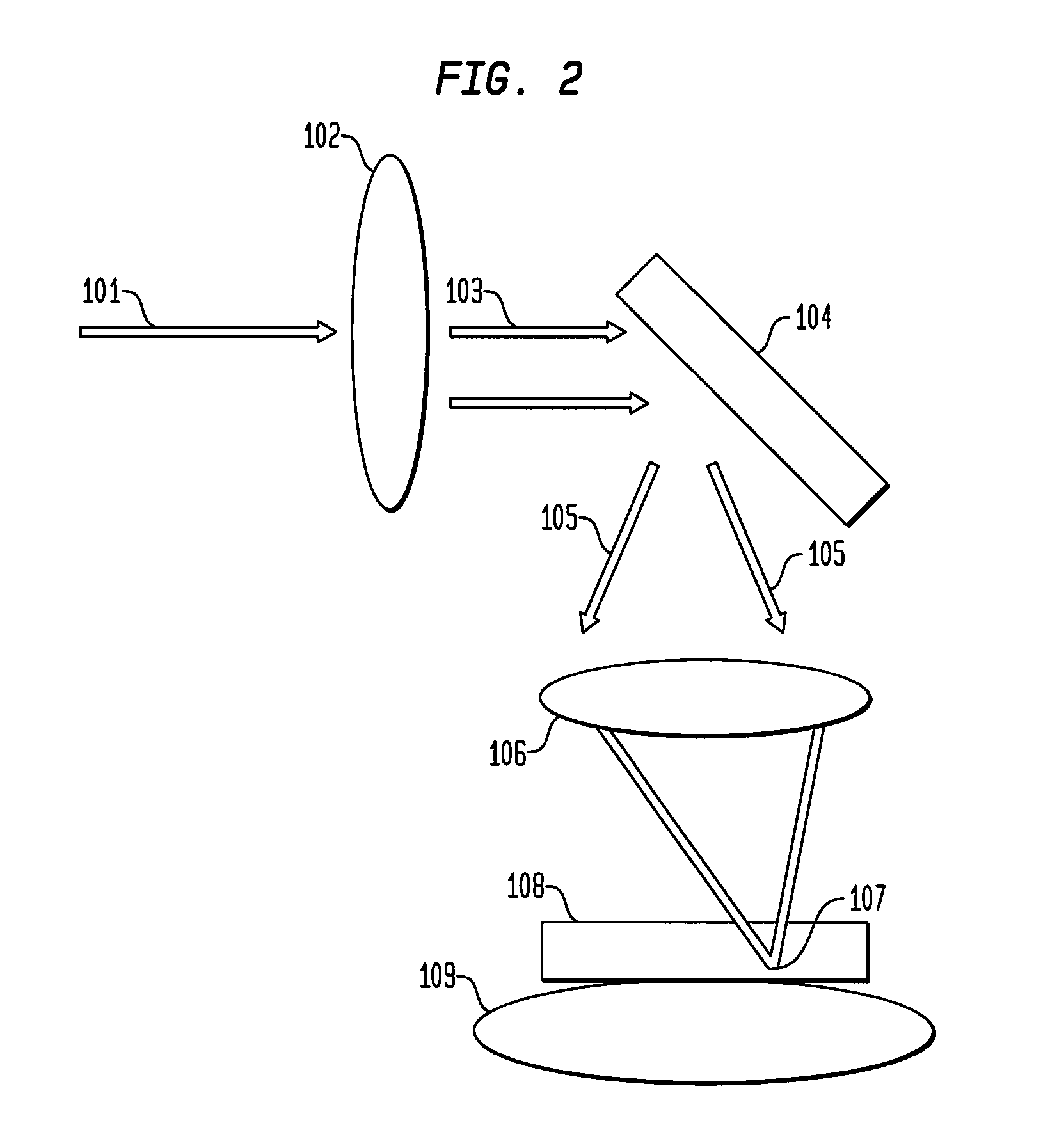
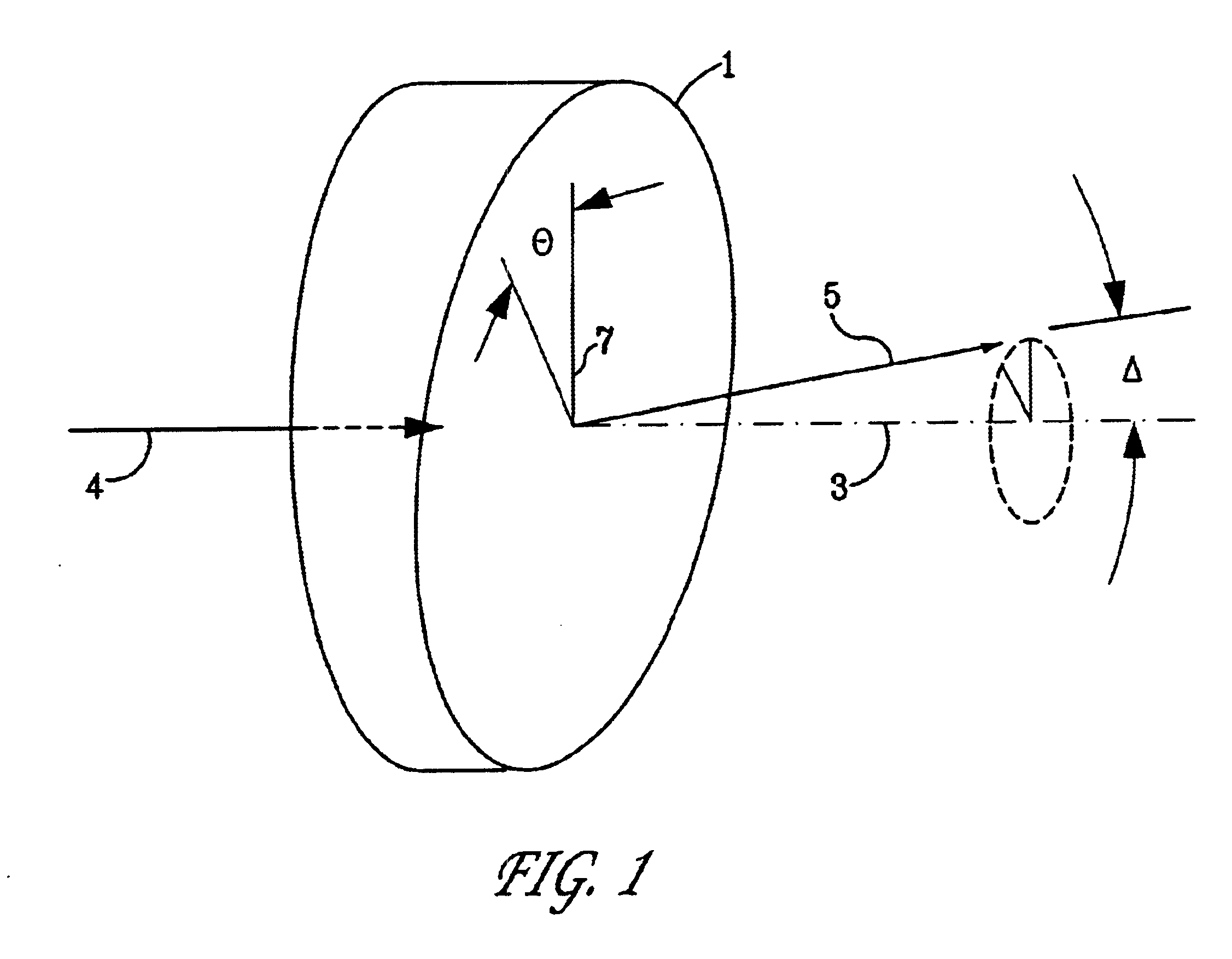
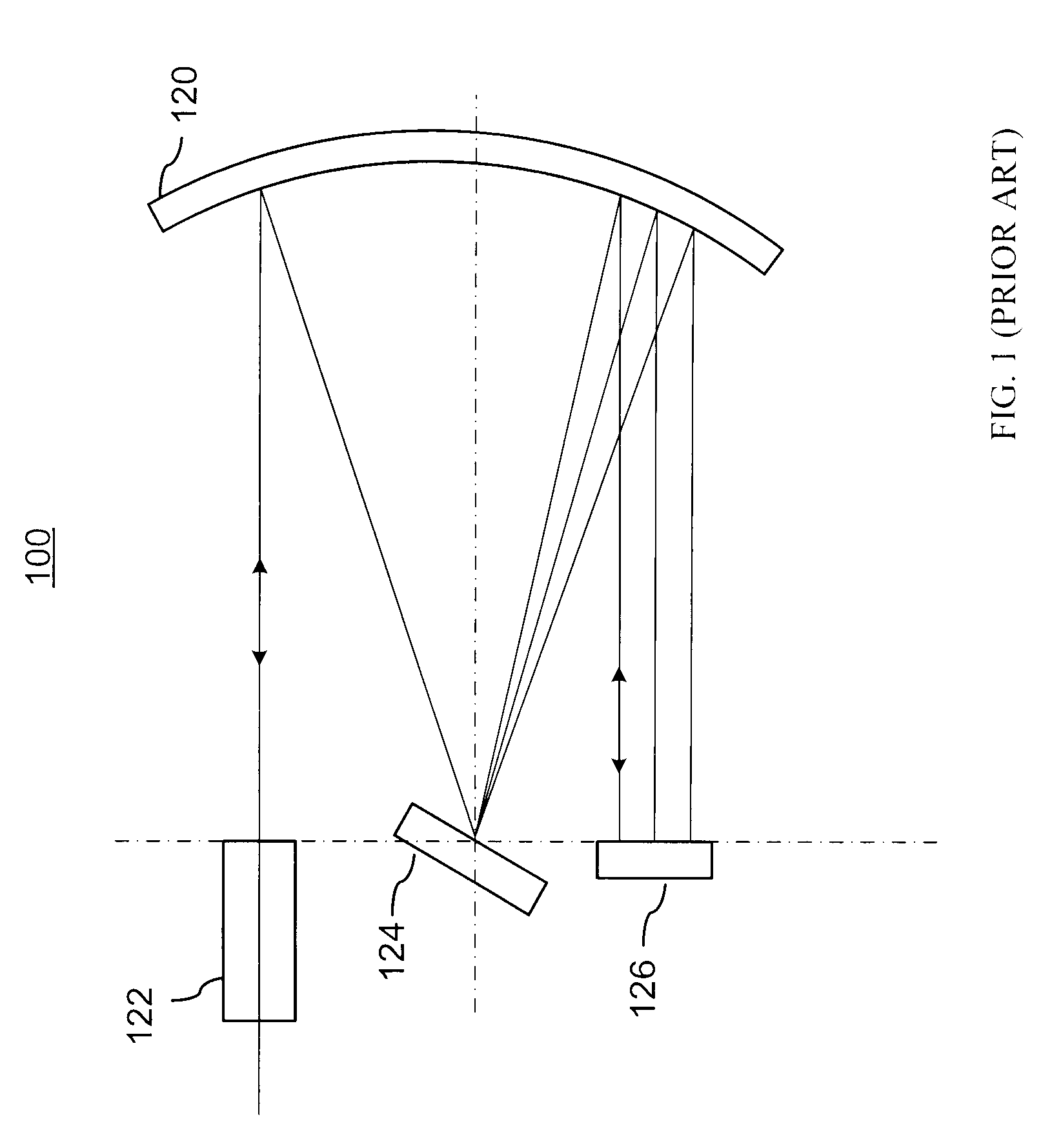
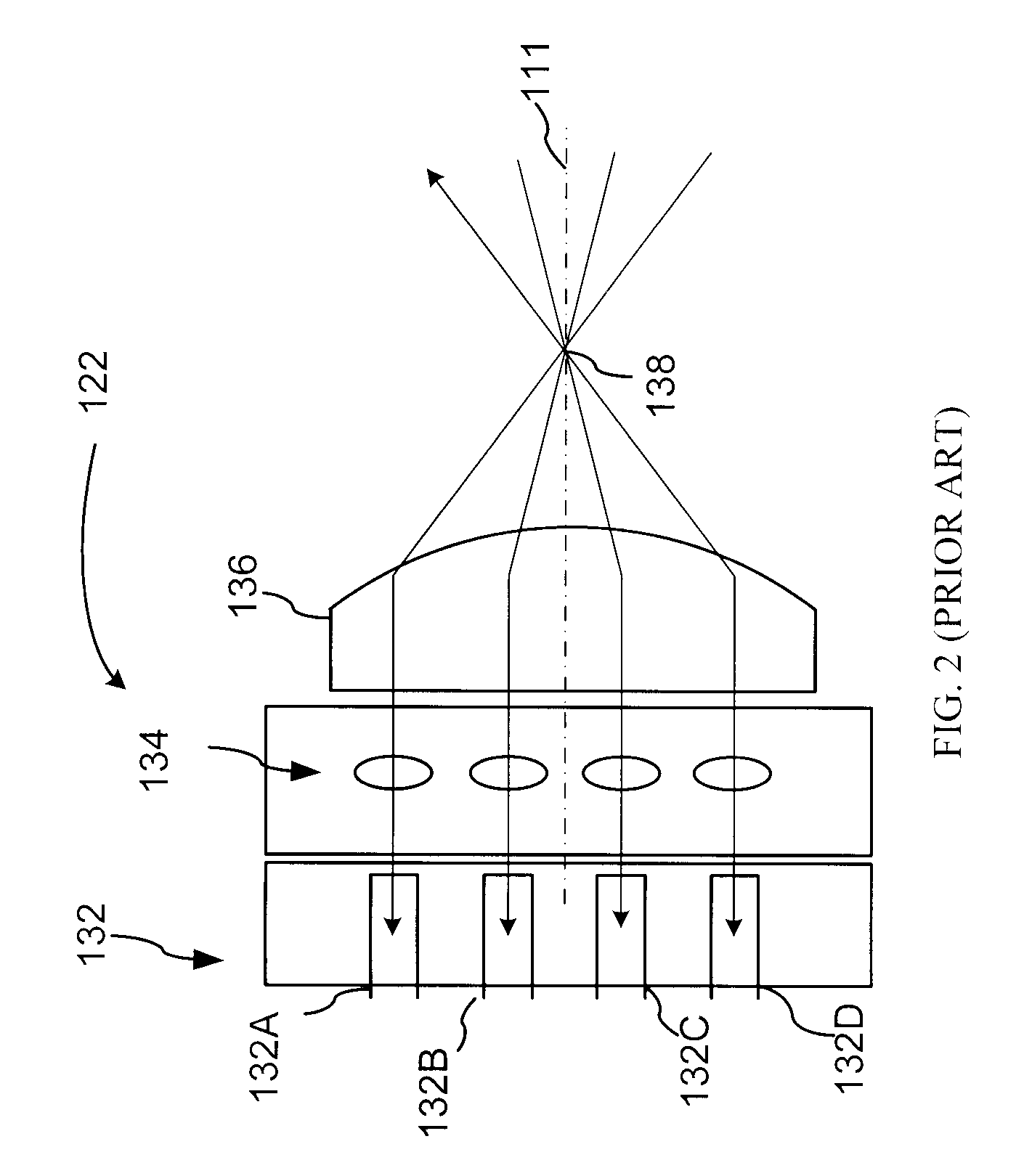
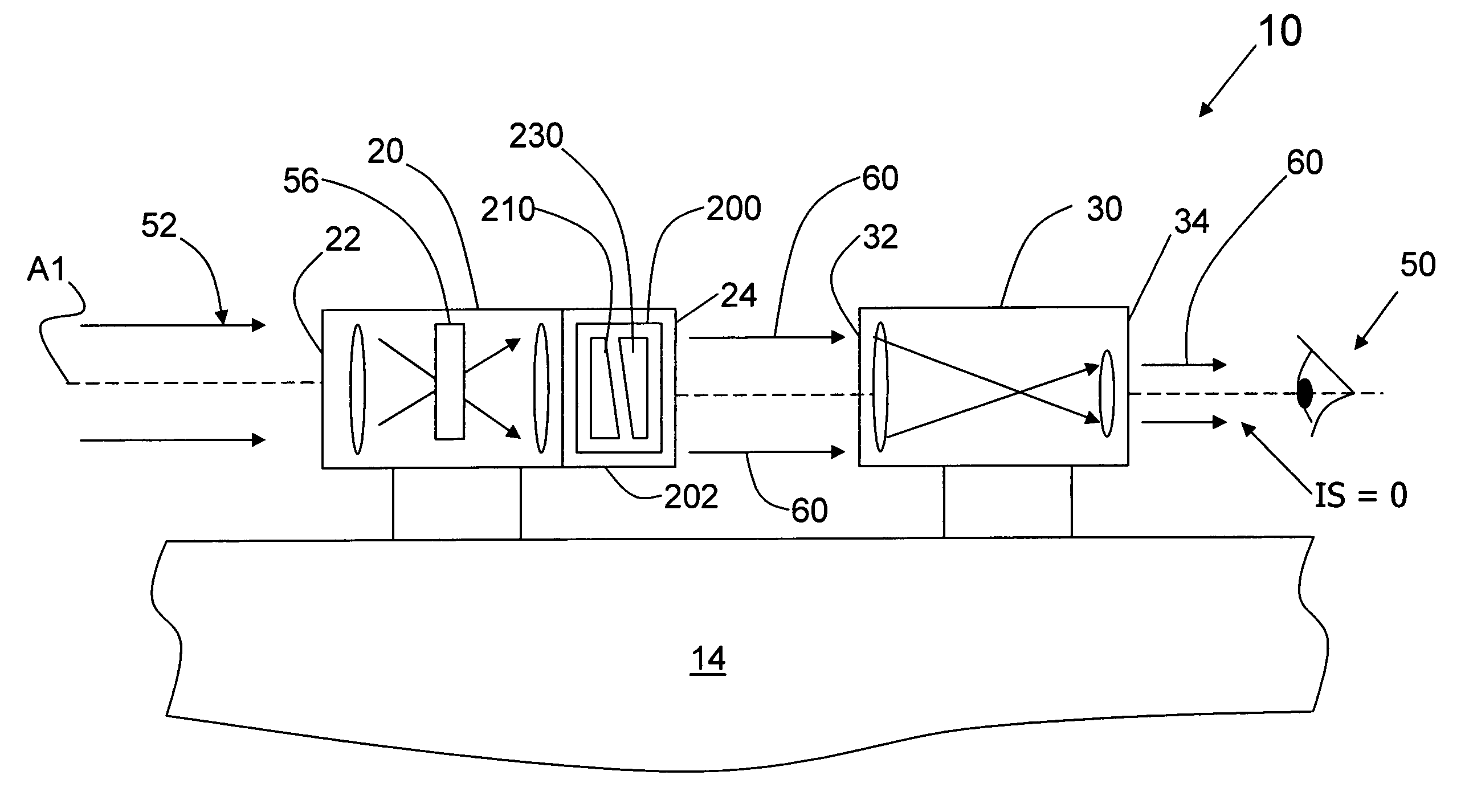
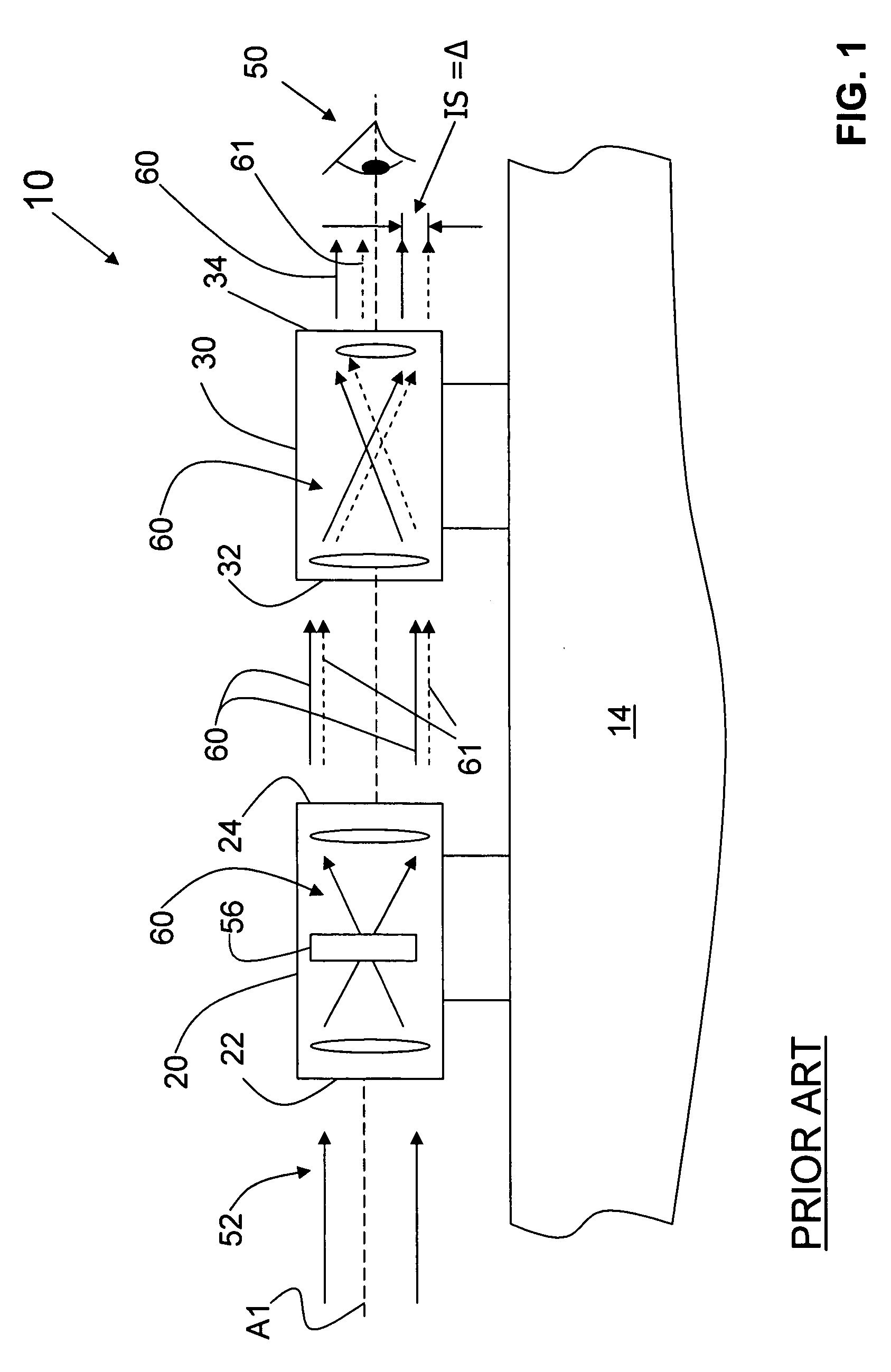
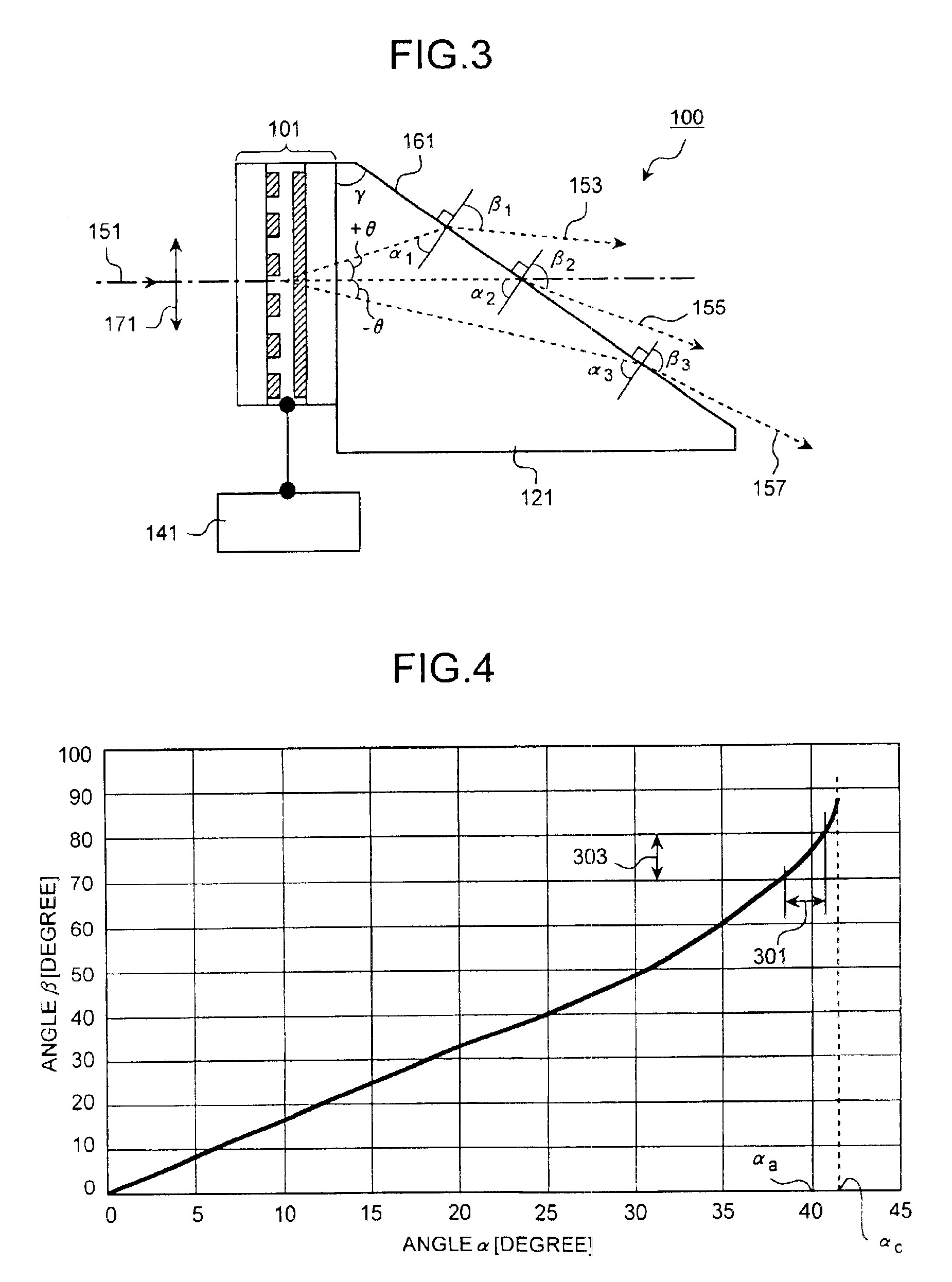
The wedge prism is a prism with a shallow angle between its input and output surfaces. This angle is usually 3 degrees or less. Refraction at the surfaces causes the prism to deflect light by a fixed angle. When viewing a scene through such a prism, objects will appear to be offset by an amount that varies with their distance from the prism.
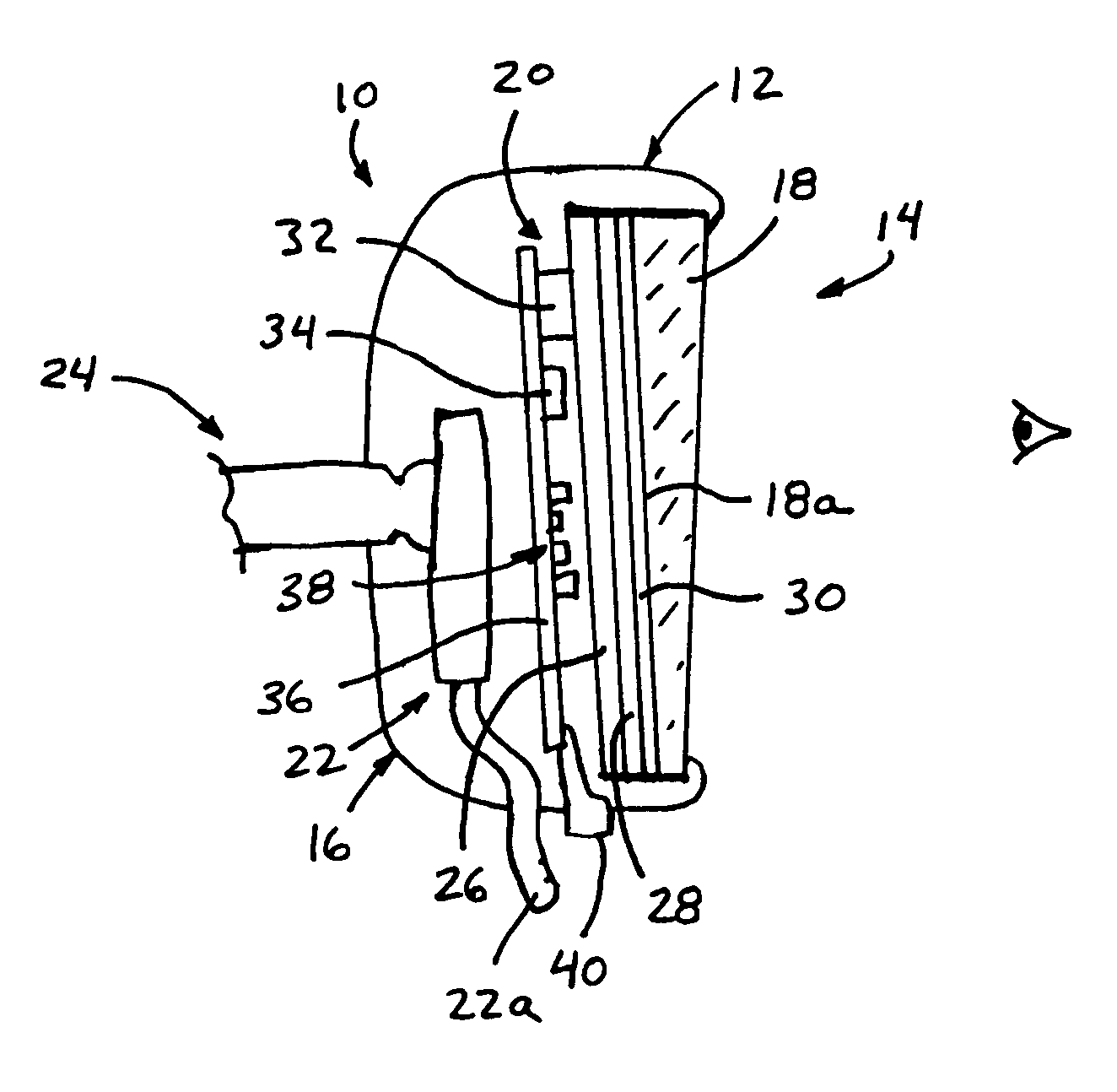
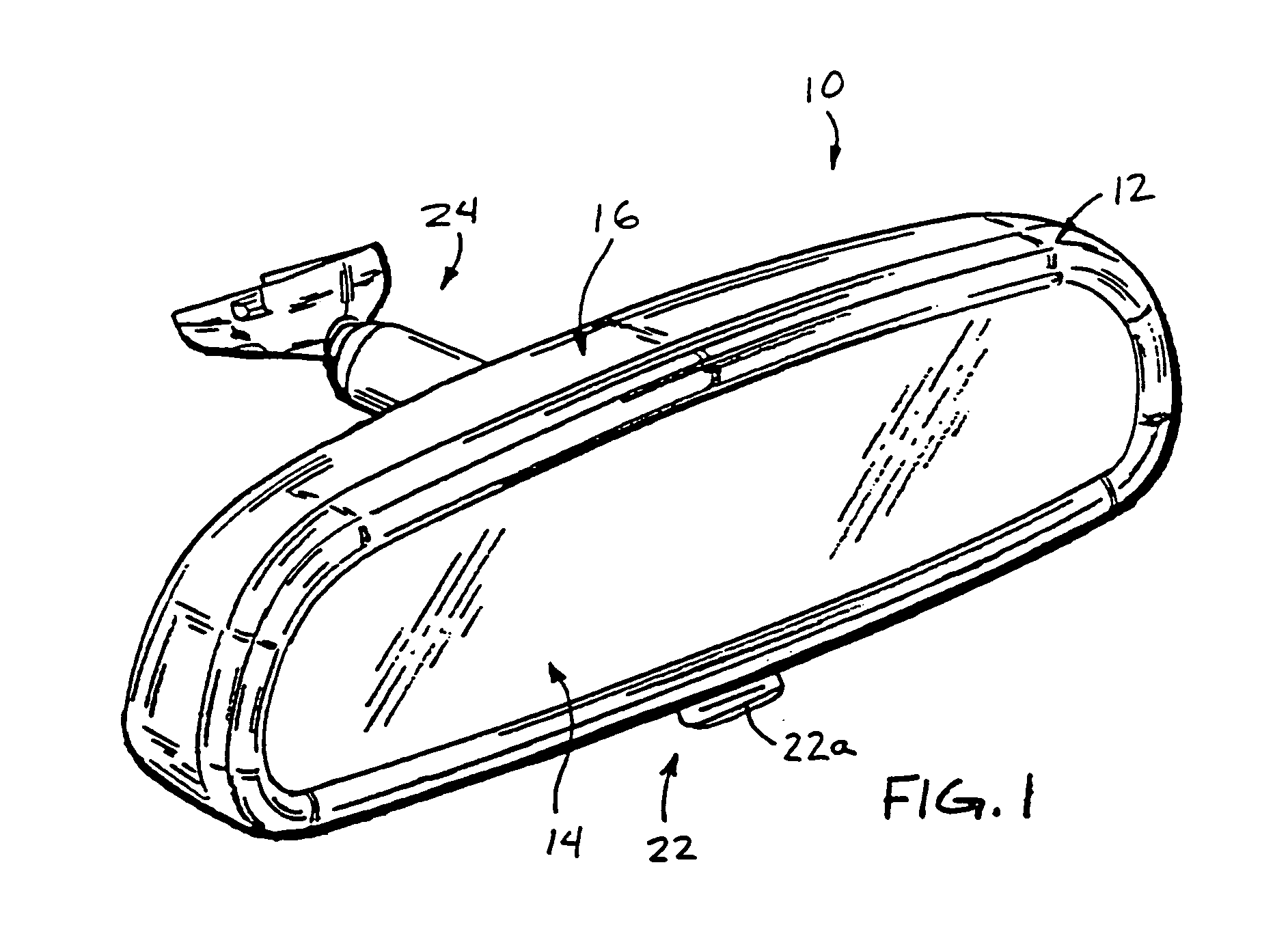
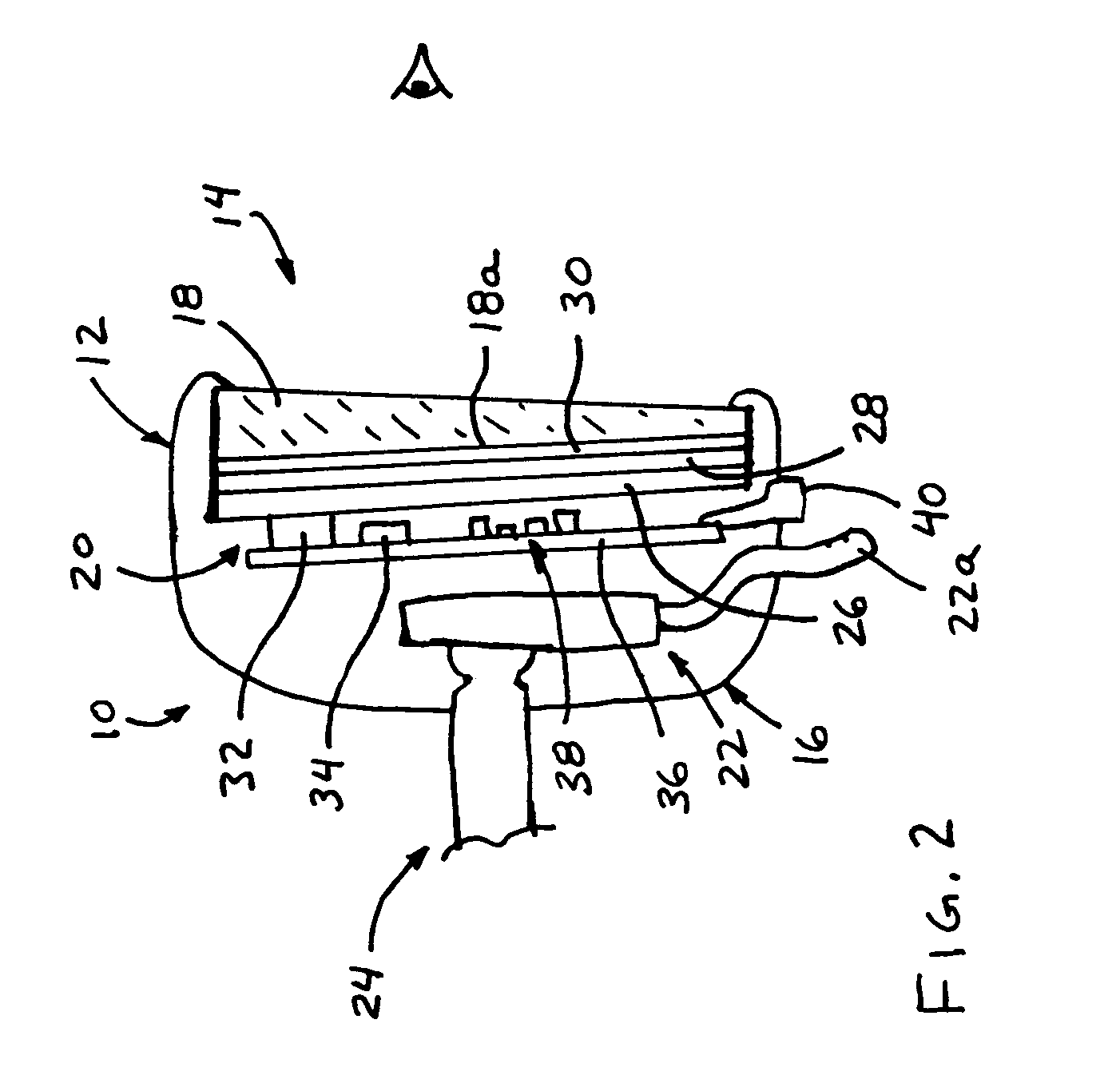
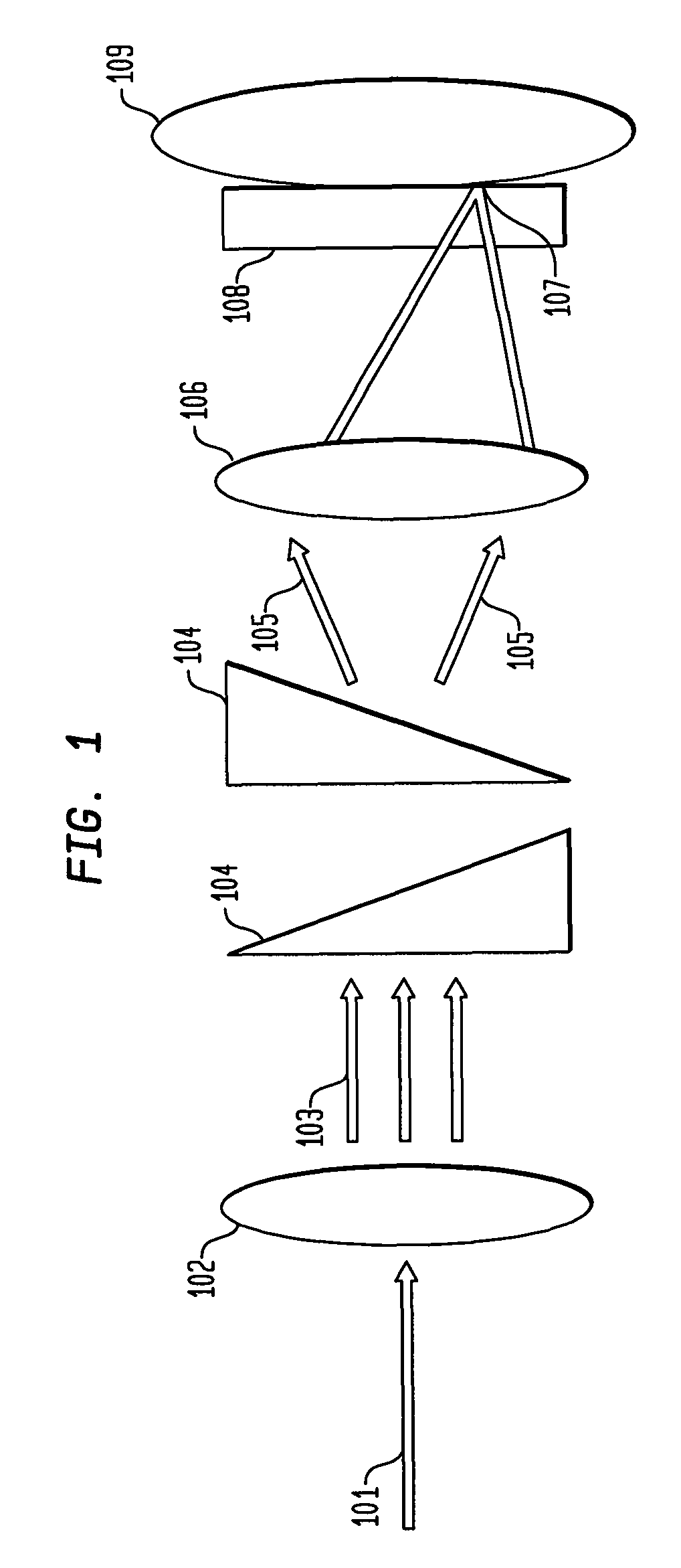
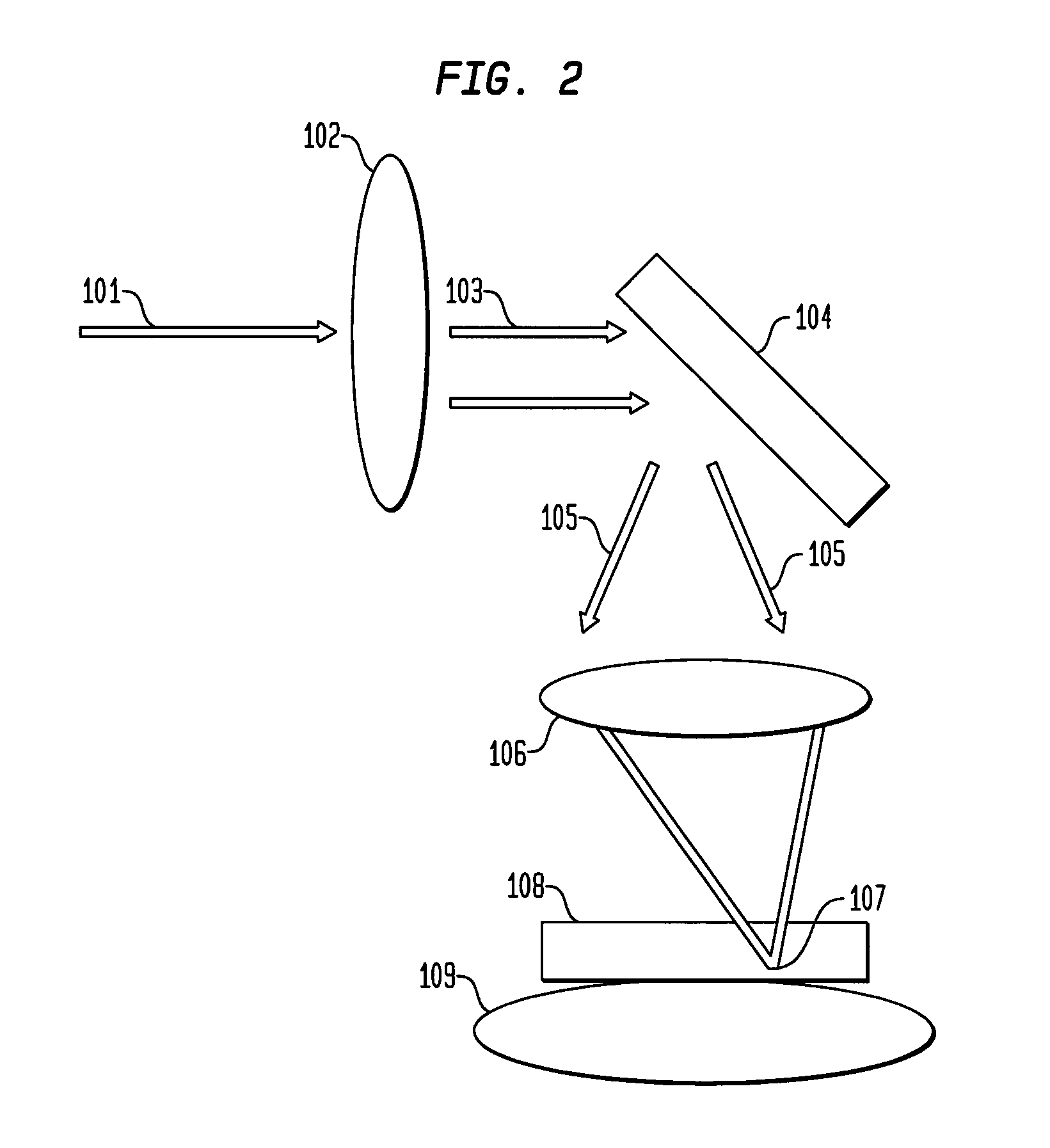
Mirror reflective element for a vehicle
InactiveUS7338177B2Low costEconomically manufacturedMirrorsVisible signalling systemsDriver/operatorEngineering
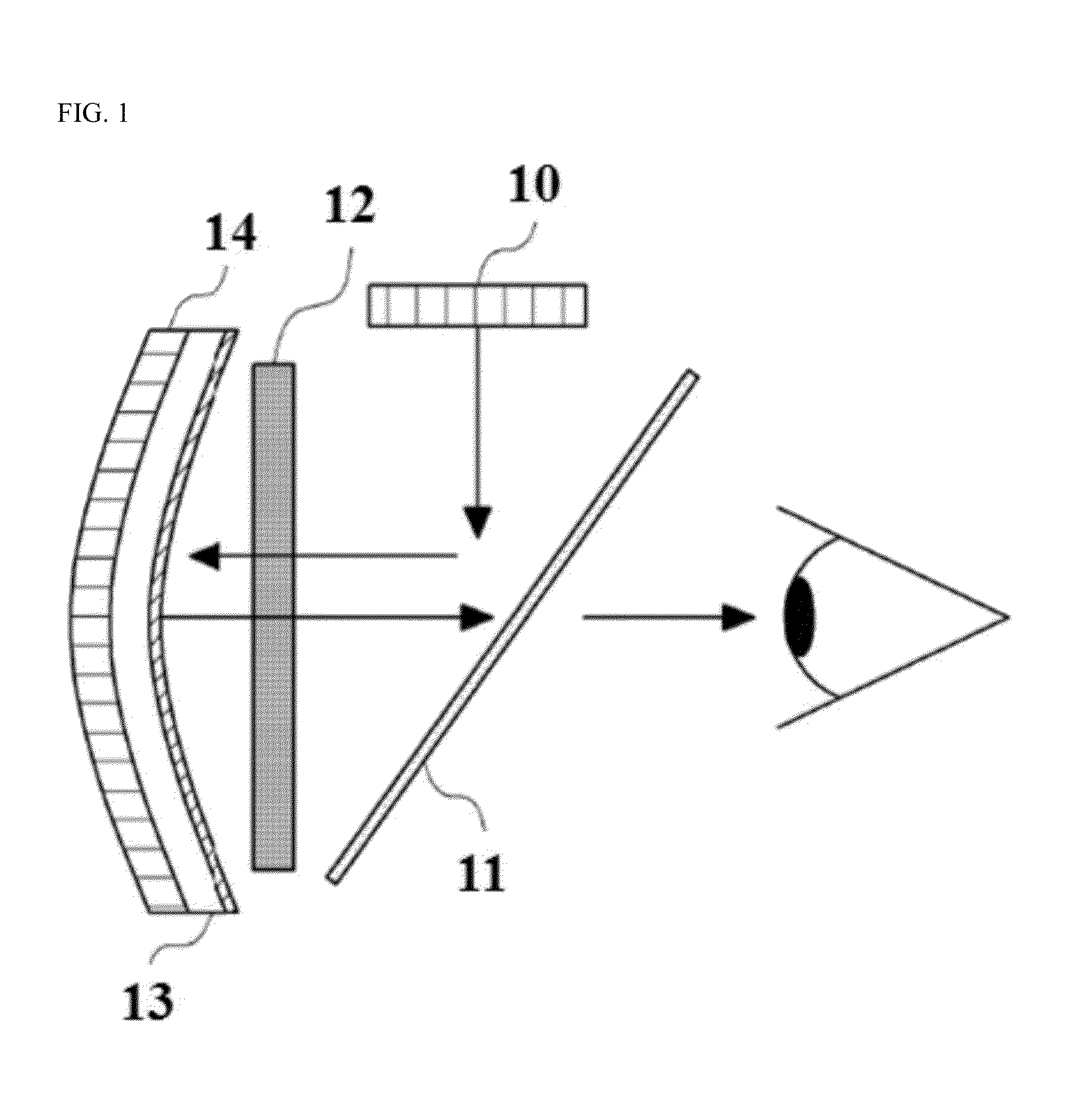
An interior rearview mirror assembly for a vehicle includes a prismatic mirror element and a display element. The prismatic mirror element includes a wedge-shaped prism element having a front surface and a rear surface and a second element having a transflective reflector on a first surface thereof. The front surface of the prism element generally faces a driver of the vehicle when the mirror assembly is installed in the vehicle, and the rear surface is opposite the front surface. The transflective reflector coated first surface of the second element is attached to the rear surface of the prism element via an optically matching medium. The display element is positioned to the rear of the prismatic mirror element and operates to display information through the prismatic mirror element so as to be viewable by a driver of the vehicle when the display element is operated to emit visible light.
Owner:DONNELLY CORP
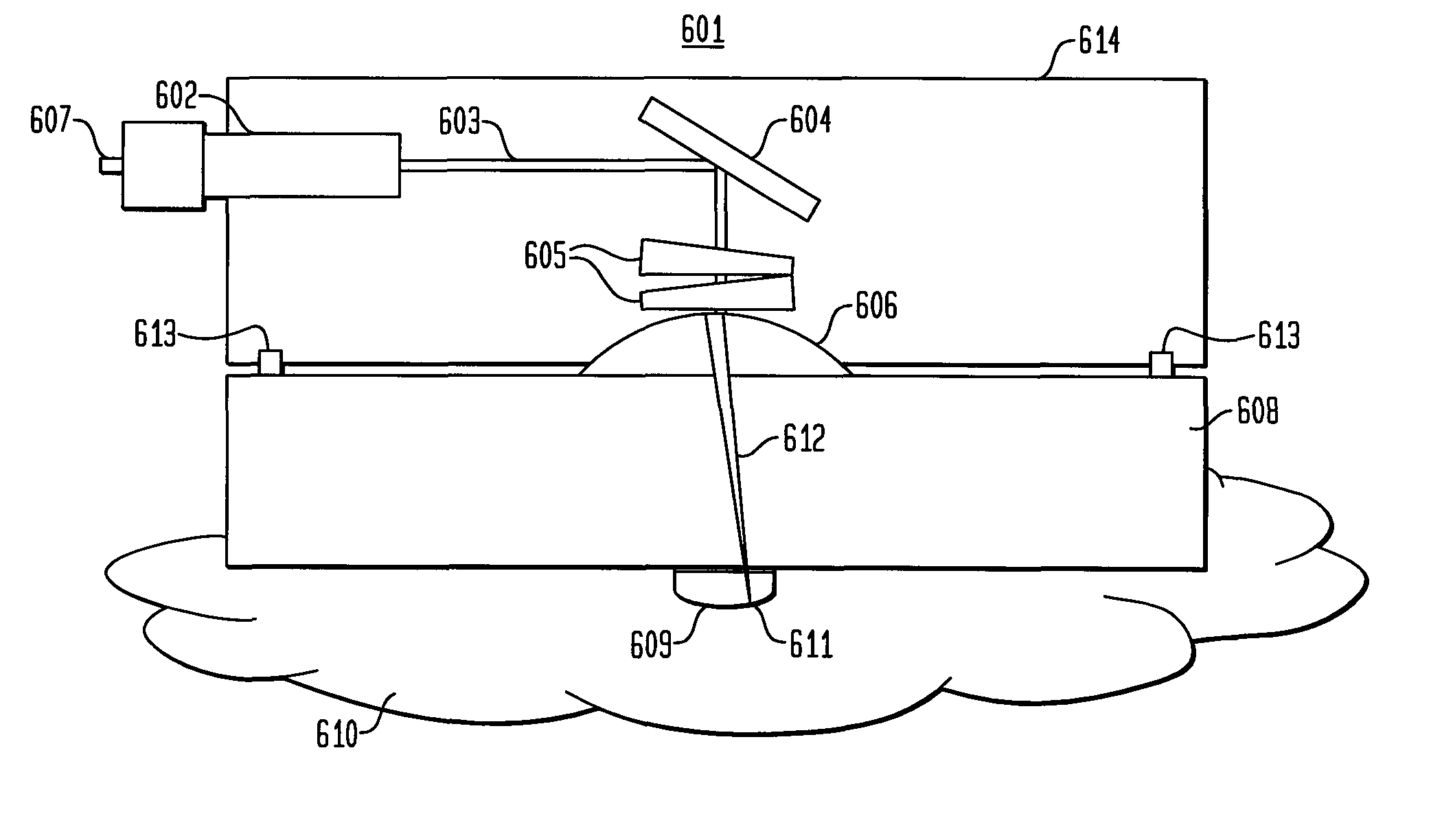
System and method for creating a stable optical interface
ActiveUS8219172B2High bandwidthReduce coherenceDiagnostic recording/measuringSensorsRefractive indexLight beam
Owner:MASIMO CORP
Mirror reflective element for a vehicle
InactiveUS20050134983A1Low costEconomically manufacturedMirrorsVisible signalling systemsEngineeringSpecular reflection
An interior rearview mirror assembly for a vehicle includes a prismatic mirror element and a display element. The prismatic mirror element includes a wedge-shaped prism element having a front surface and a rear surface and a second element having a transflective reflector on a first surface thereof. The front surface of the prism element generally faces a driver of the vehicle when the mirror assembly is installed in the vehicle, and the rear surface is opposite the front surface. The transflective reflector coated first surface of the second element is attached to the rear surface of the prism element via an optically matching medium. The display element is positioned to the rear of the prismatic mirror element and operates to display information through the prismatic mirror element so as to be viewable by a driver of the vehicle when the display element is operated to emit visible light.
Owner:DONNELLY CORP
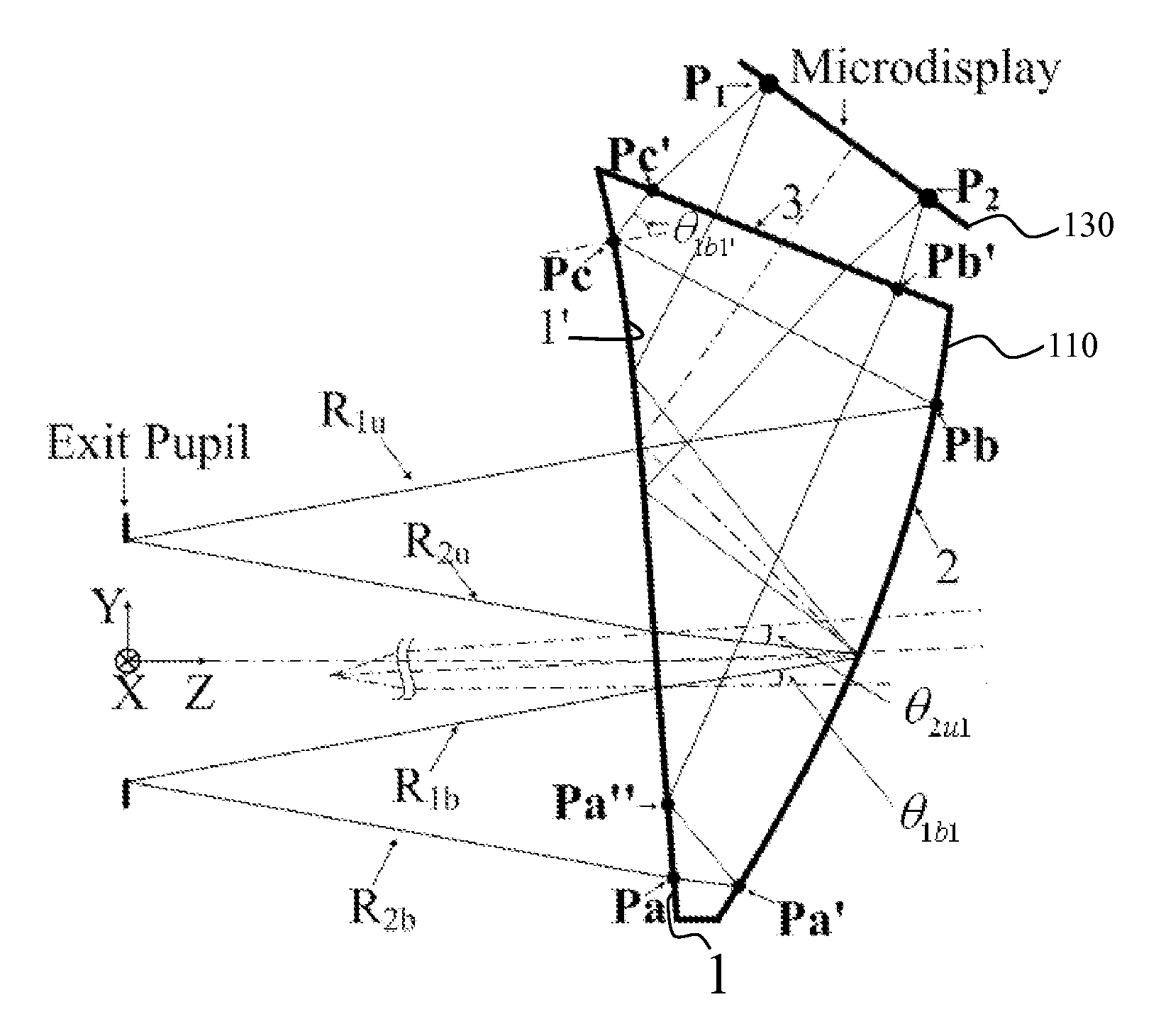
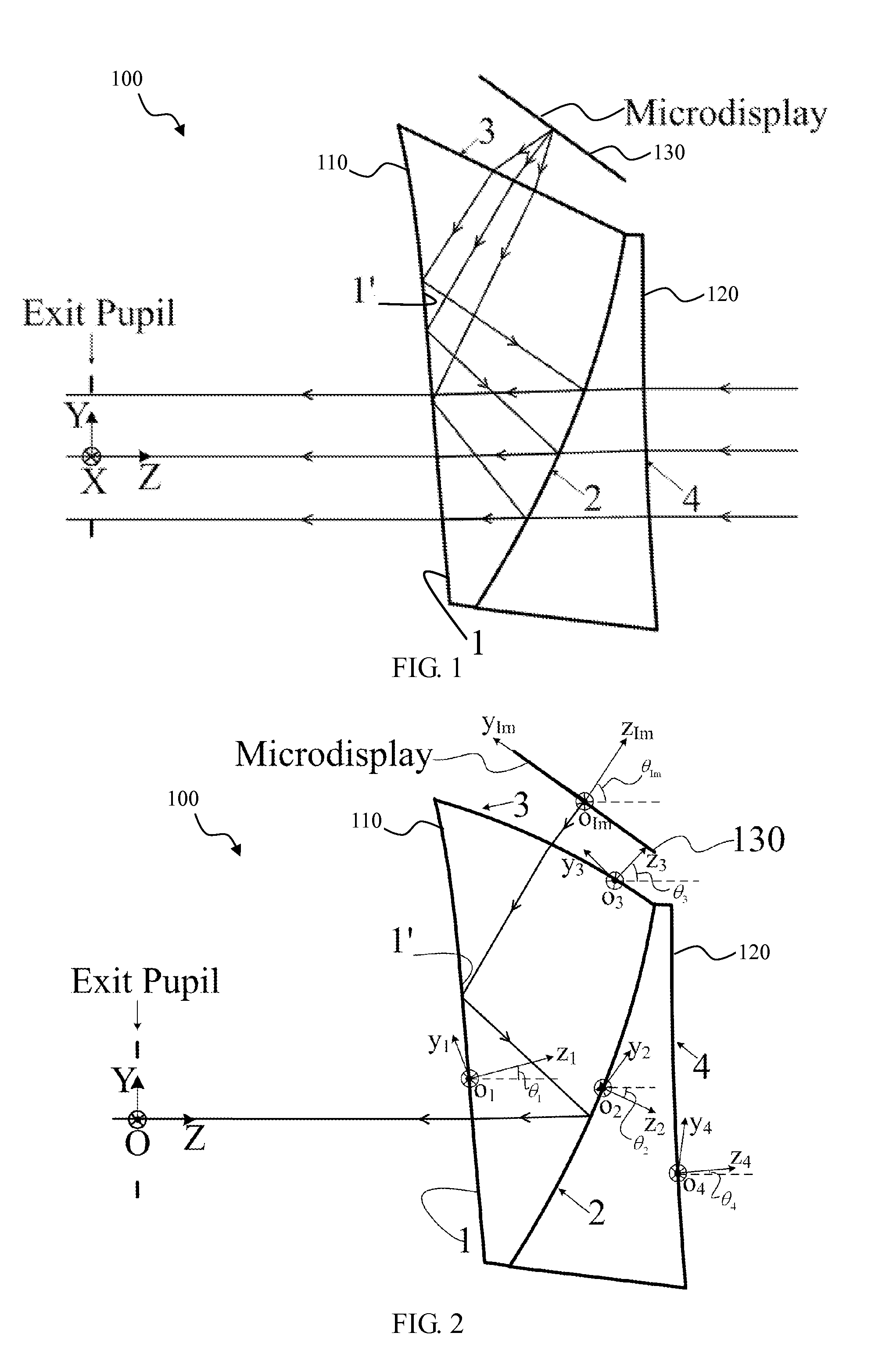
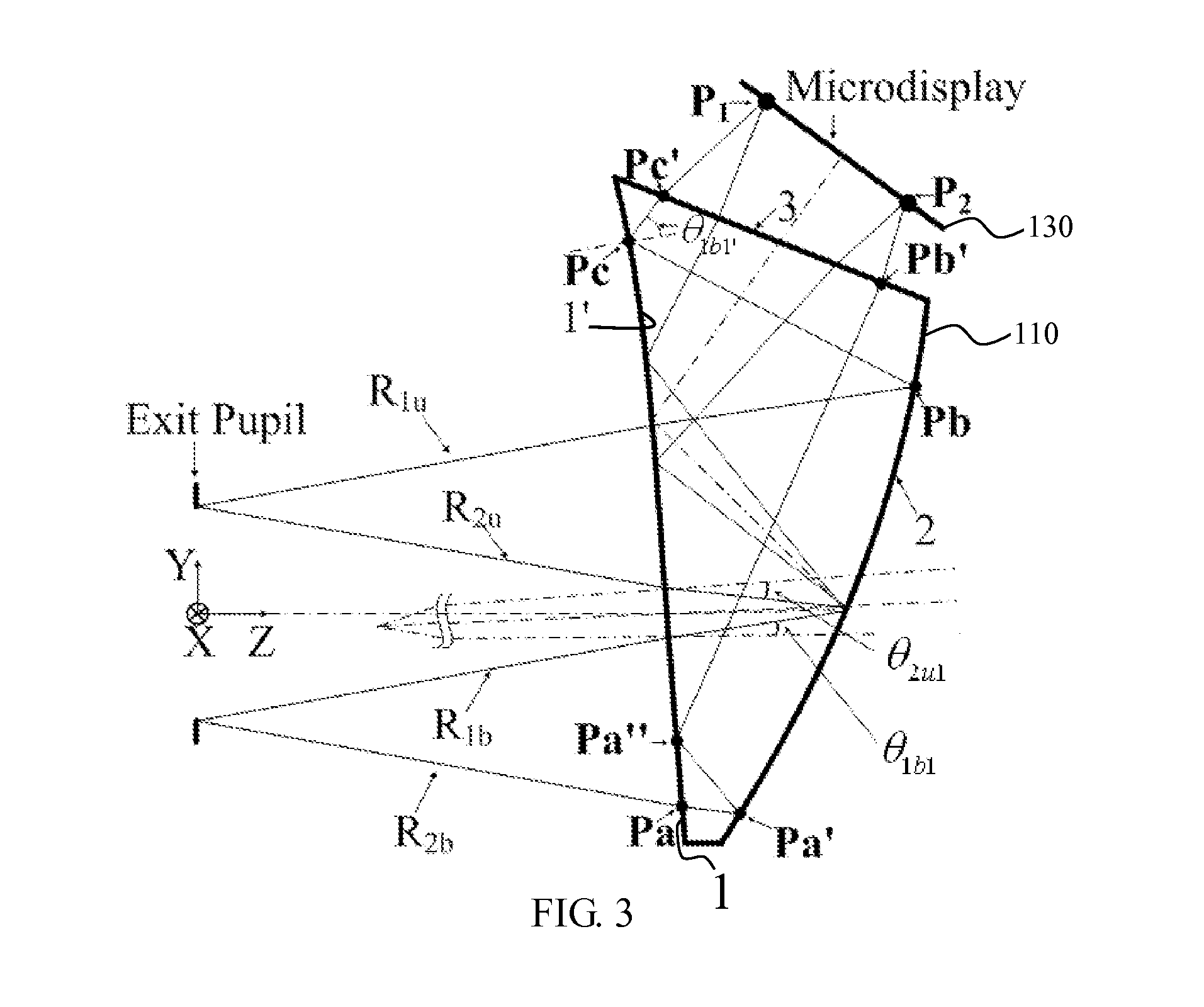
Optical see-through free-form head-mounted display
A see-through free-form head-mounted display including a wedge-shaped prism-lens having free-form surfaces and low F-number is provided.
Owner:CHENG DEWEN +2
Wide angle and high resolution tiled head-mounted display device
ActiveUS20130187836A1Avoiding pupil aberrationAvoid distortionPrismsCathode-ray tube indicatorsWide fieldExit pupil
Owner:THE ARIZONA BOARD OF REGENTS ON BEHALF OF THE UNIV OF ARIZONA +1
Optical scanner and image forming apparatus
InactiveUS20060232660A1Correct difference of colorEasy to correctInking apparatusVisual representatino by photographic printingColor imageResist
An optical scanner is capable of effectively correcting a difference with respect to the sub-scanning direction between the positions of optical spots for scanning photoconductor drums of a tandem type color image forming apparatus. The optical scanner includes an optical axis adjusting part. The optical axis adjusting part uses a deflecting mirror or a wedge-shaped prism to deflect the optical axis of an optical beam with respect to the sub-scanning direction. As a result, it is possible to accurately correct a resist difference among individual image forming stations and form a high-quality color image without any color displacement.
Owner:RICOH KK
Optical see-through free-form head-mounted display
A see-through free-form head-mounted display including a wedge-shaped prism-lens having free-form surfaces and low F-number is provided.
Owner:BEIJING INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGYGY +1
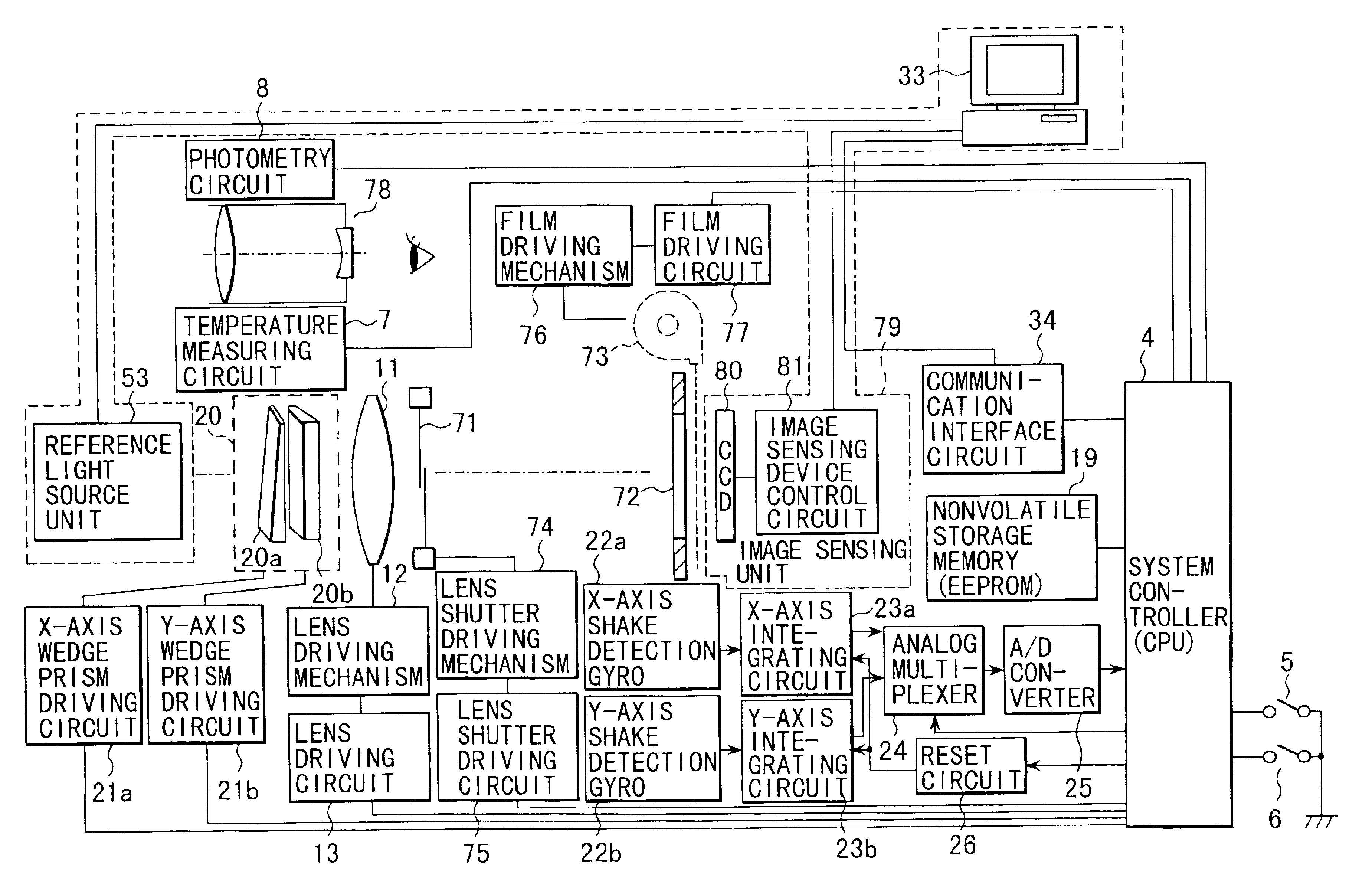
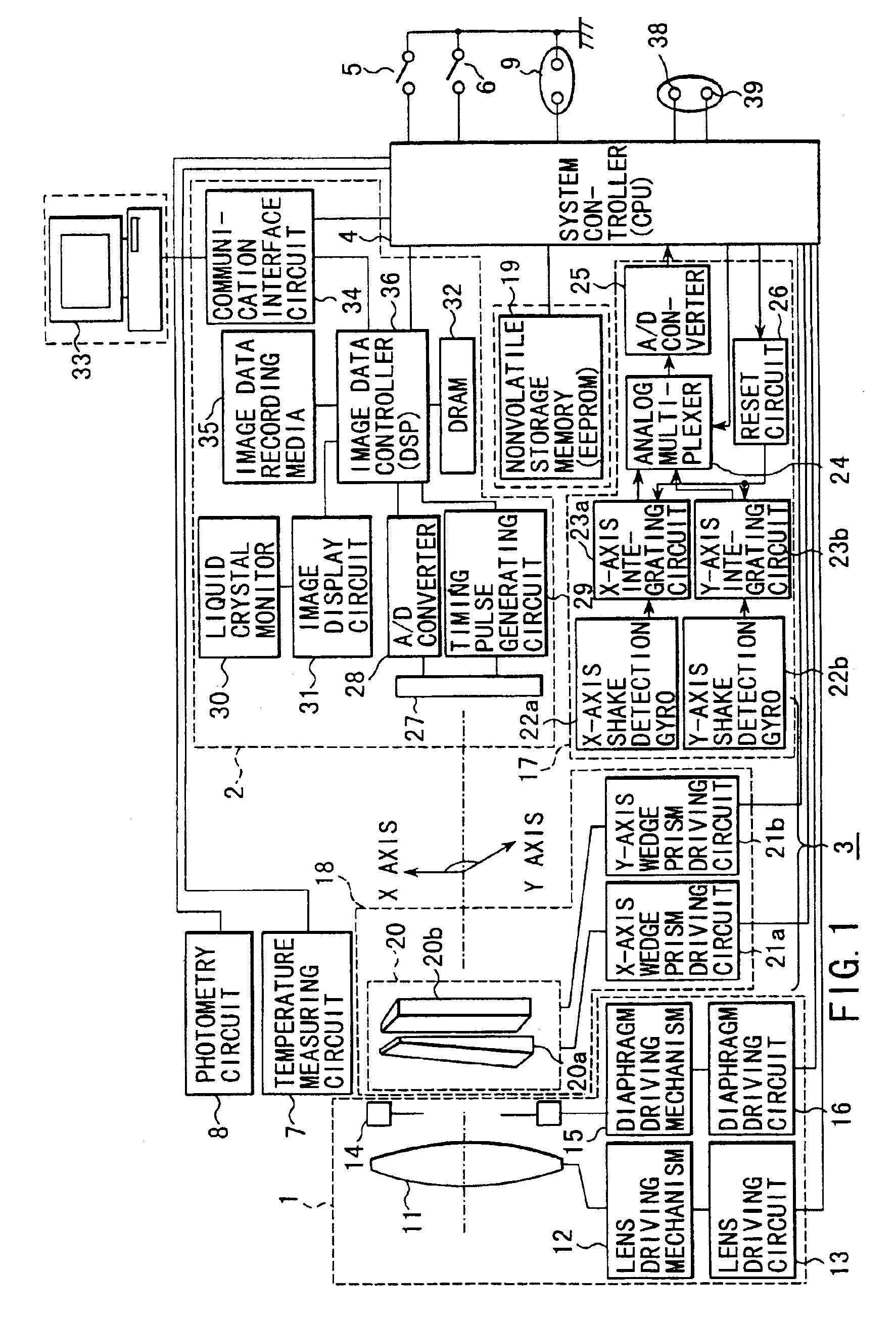
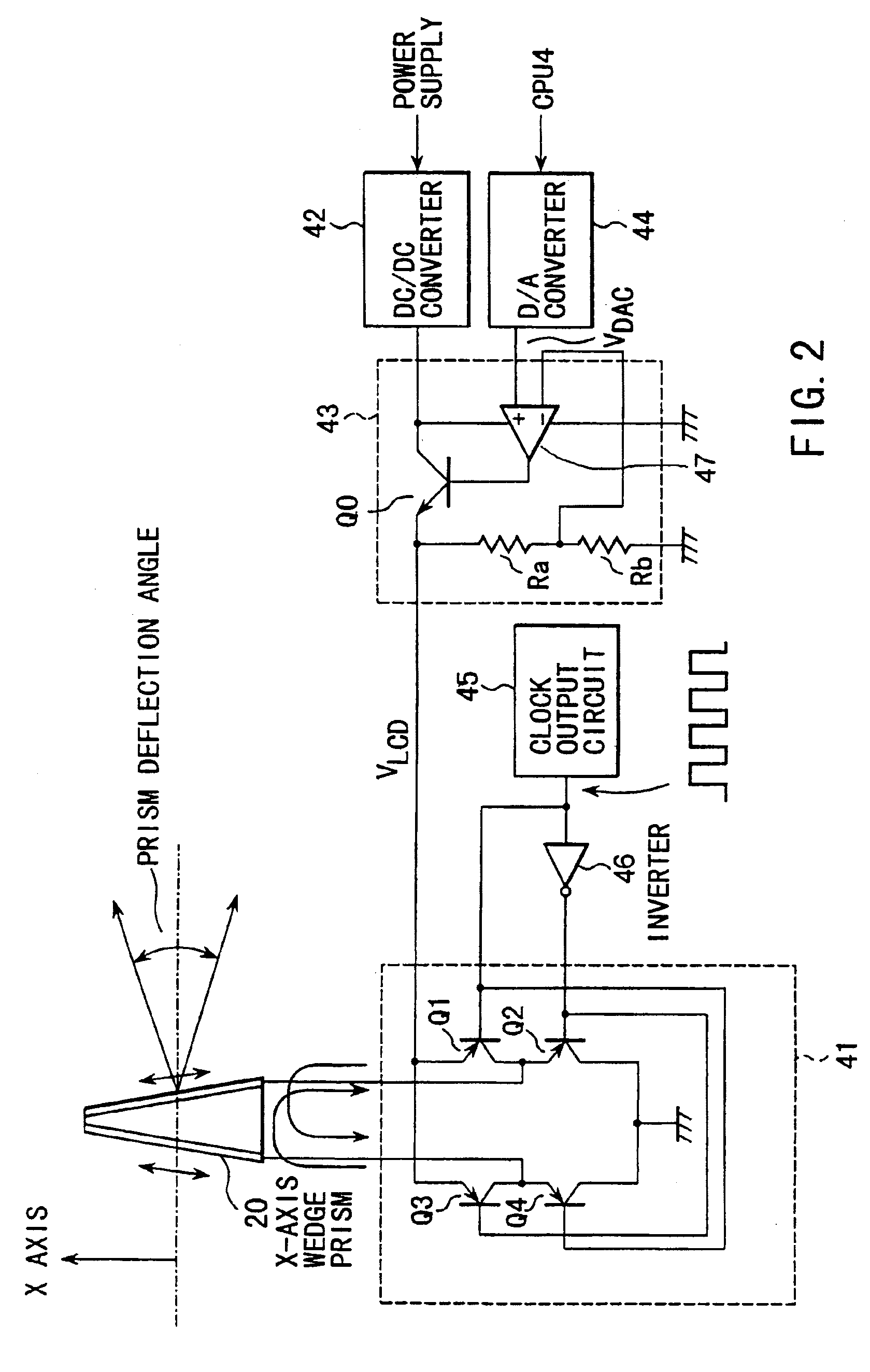
Camera having shake correction device mounted thereon
A camera of this invention is a camera containing a shake correction device for correcting the shake by reading out application voltage data corresponding to a detected shake amount by use of parameters stored in an EEPROM indicating the relation between a voltage applied to a wedge prism and a deflection angle of a light beam and applying a voltage subjected to the temperature correcting process to the wedge prism to change the index of refraction of the wedge prism and deflect the light beam in a direction opposite to the shake direction. The parameters are determined by deriving the relation between the application voltage and the inclination of the light beam by detecting the inclination of a reference light beam from the illuminating position of the image sensing device while changing the index of refraction of the wedge prism by applying a voltage to the wedge prism and then stored into an EEPROM as a data table
Owner:OLYMPUS OPTICAL CO LTD
Wide angle and high resolution tiled head-mounted display device
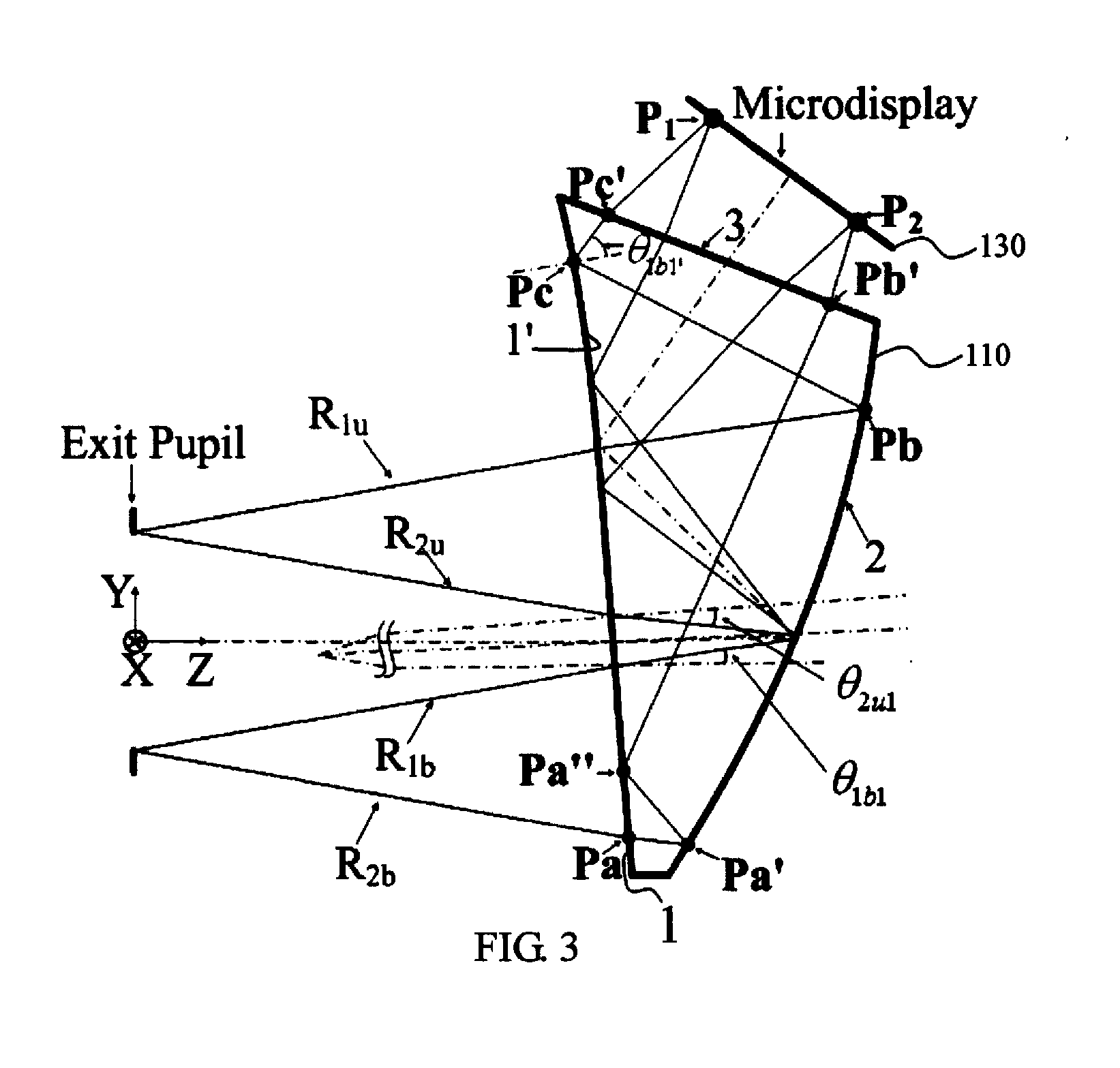
ActiveUS9244277B2Avoid aberrationsKeep constantPrismsCathode-ray tube indicatorsWide fieldExit pupil
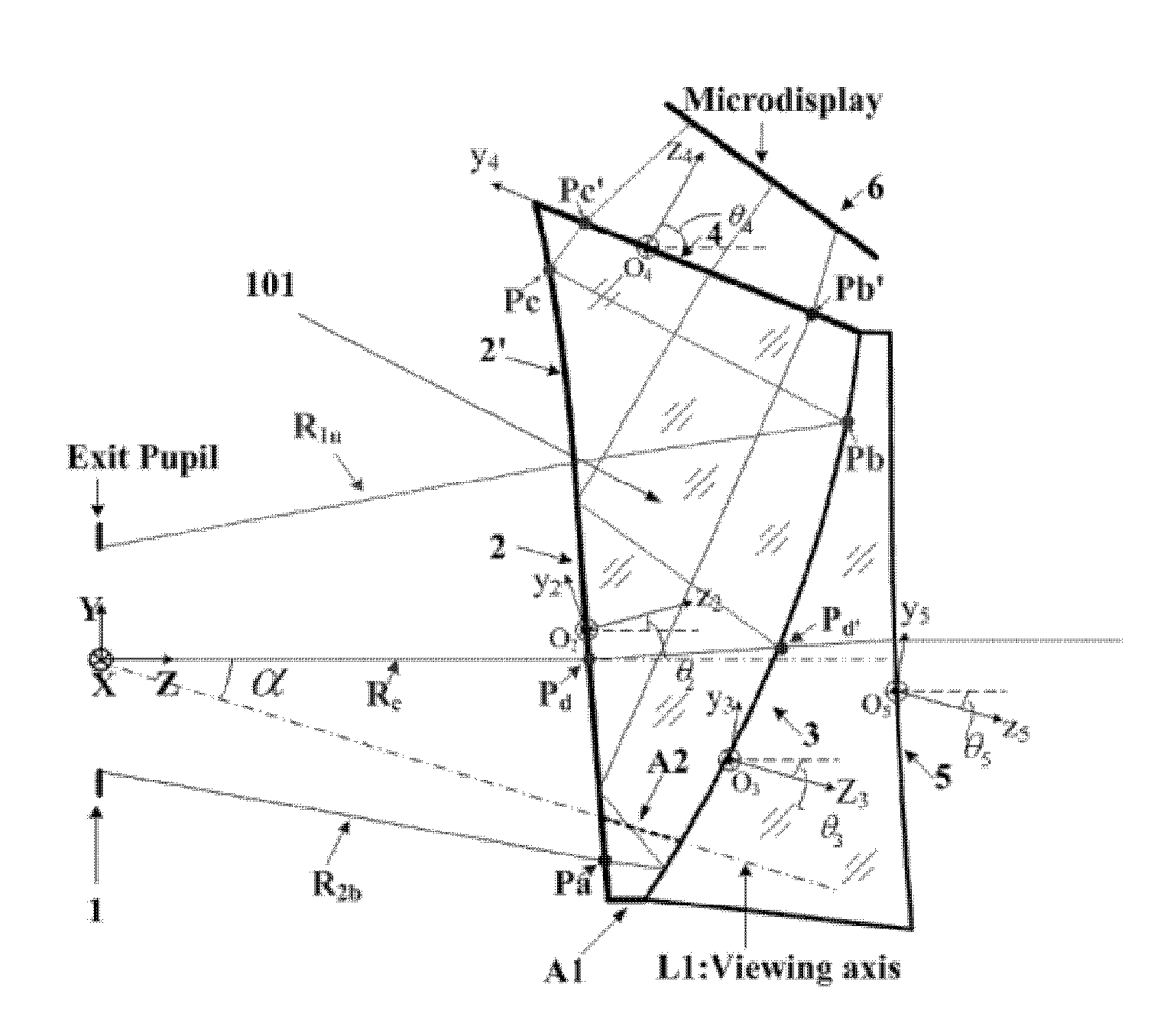
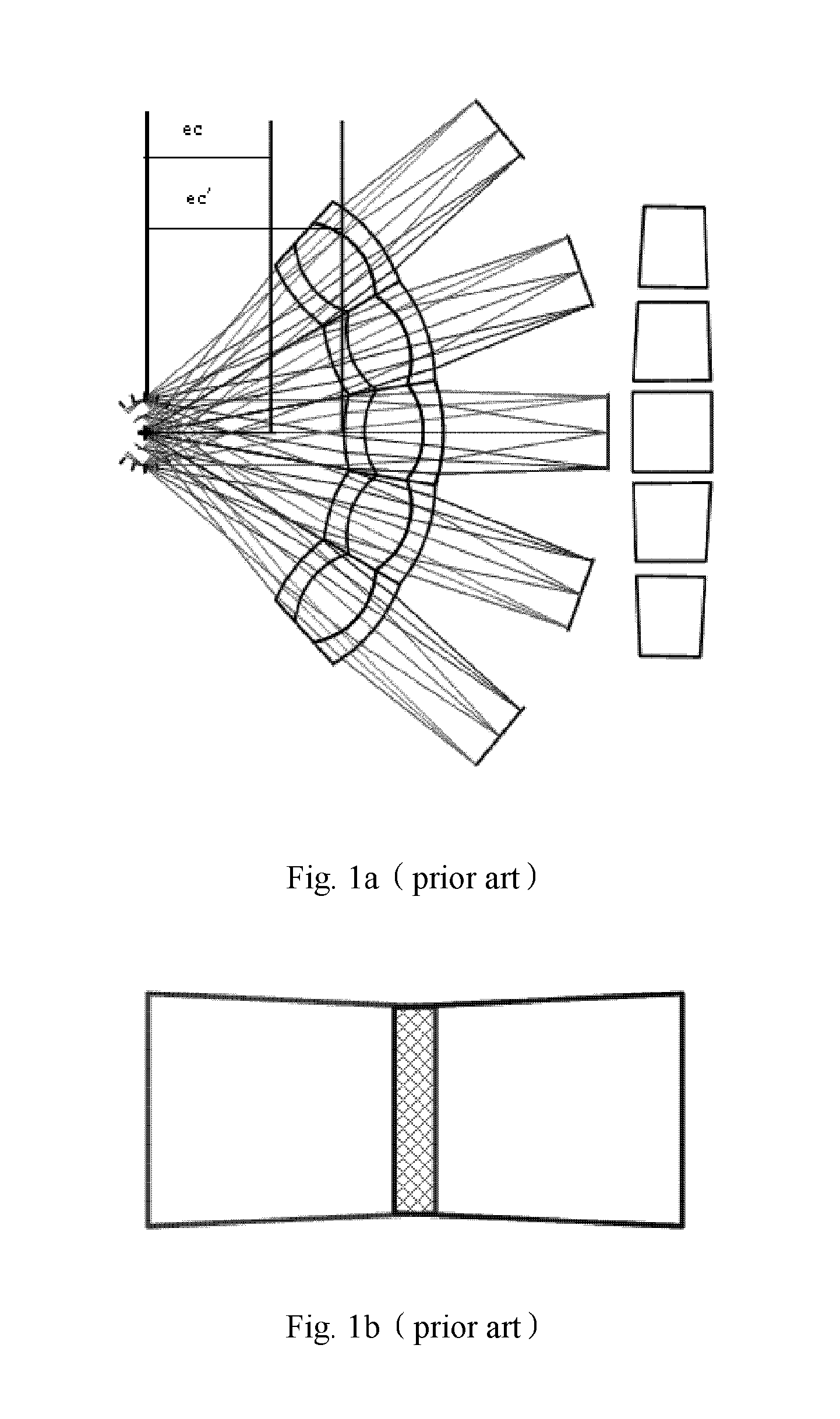
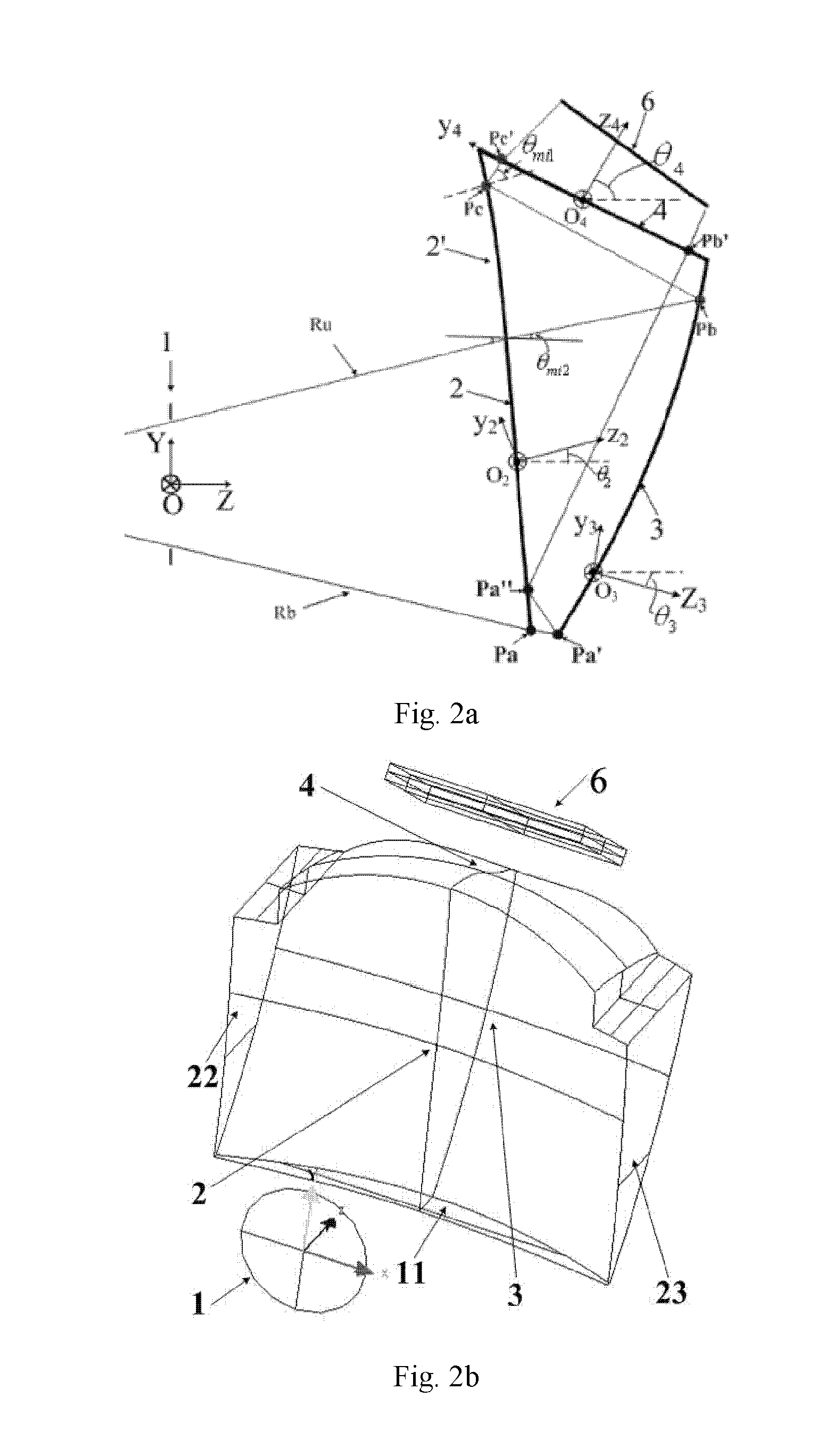
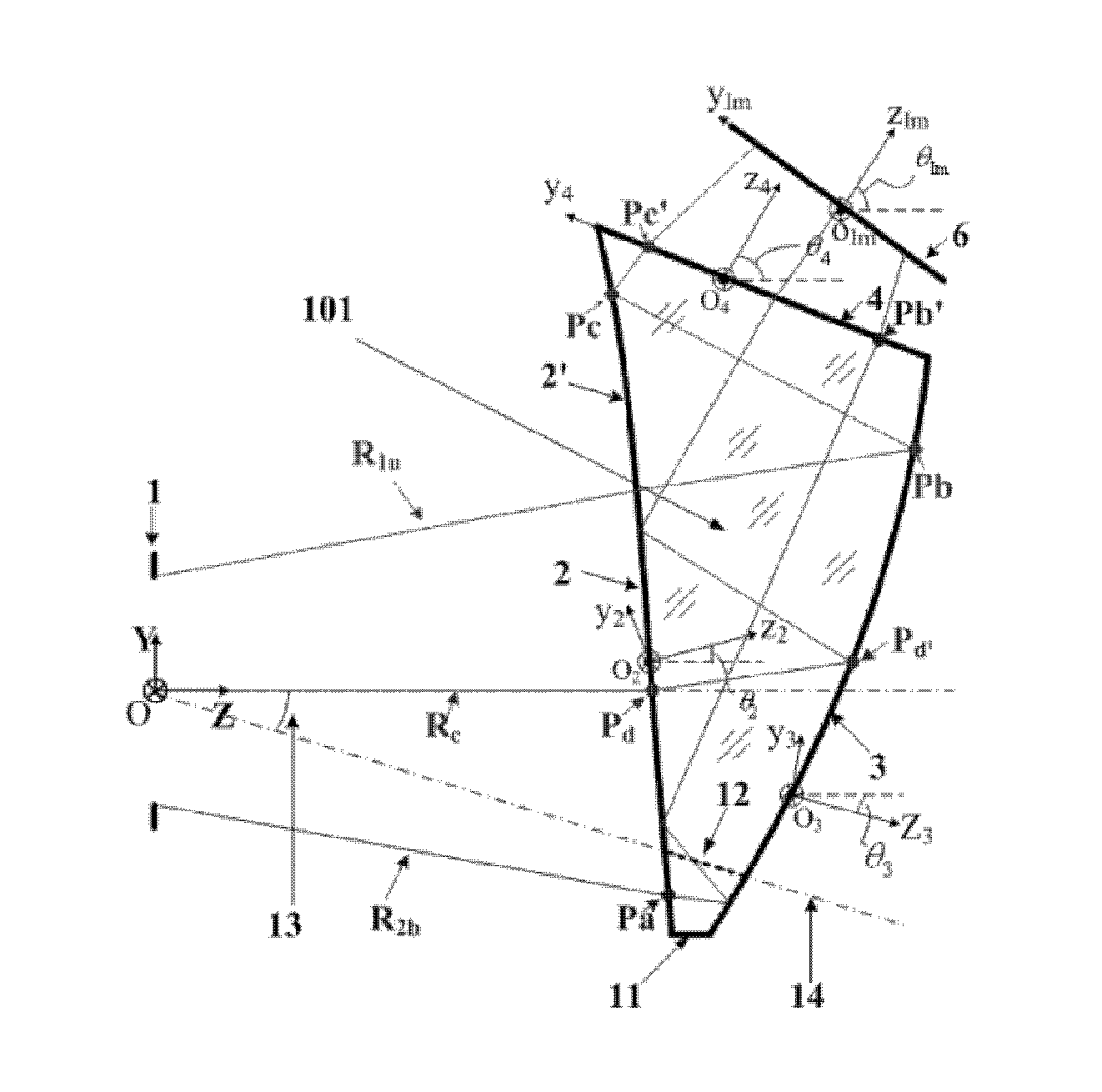
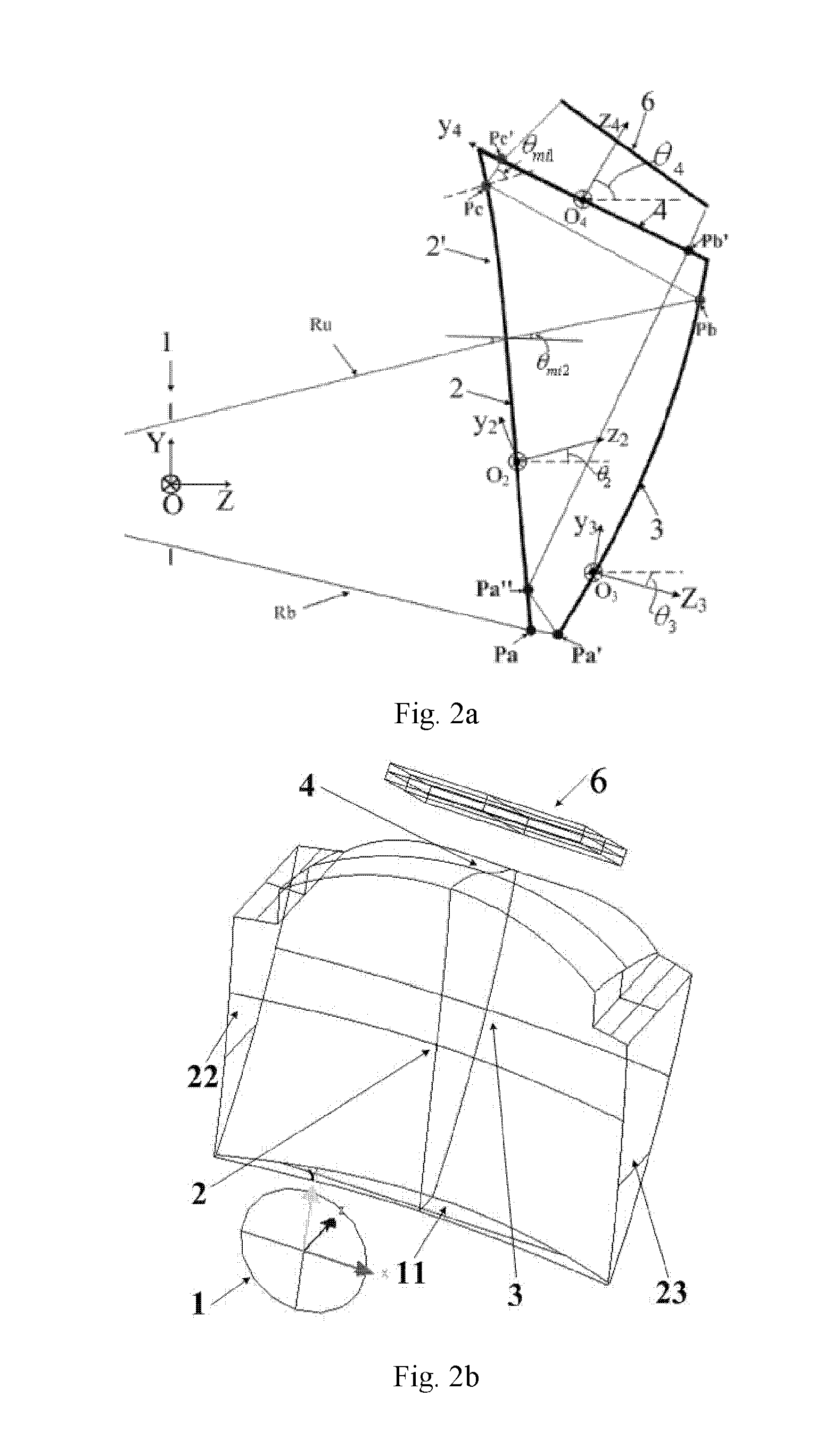
A tiled head-mounted display device comprises an optical component including a plurality of prisms with free-form surfaces, and a display component including a plurality of micro-displays (6), wherein the number of the micro-displays (6) and the number of the prisms with free-form surfaces is identical, and each prism with free-form surfaces and the corresponding micro-display (6) constitute a display channel. Each prism is a wedge prism including a first surface (2), a second surface (3) and a third surface (4). The exit pupil planes of each display channel are coincident, thus avoiding pupil aberration and keeping exit pupil diameter and eye clearance same as a single ocular. There is no resolution variance throughout the entire field of view, thus preventing extra trapezoid distortion. The tiled head-mounted display device is compact and lightweight, and provides wide field of view and high resolution. The tiled head-mounted display device can be readily applicable to augmented environments applications by simply adding an auxiliary free-form lens behind the prism with free-form surfaces.
Owner:THE ARIZONA BOARD OF REGENTS ON BEHALF OF THE UNIV OF ARIZONA +1
Methods and Systems of Rapid Focusing and Zooming for Volumetric 3D Displays and Cameras
InactiveUS20090080048A1Quick changeZoom in fastProjector focusing arrangementCamera focusing arrangement3d imageDisplay device
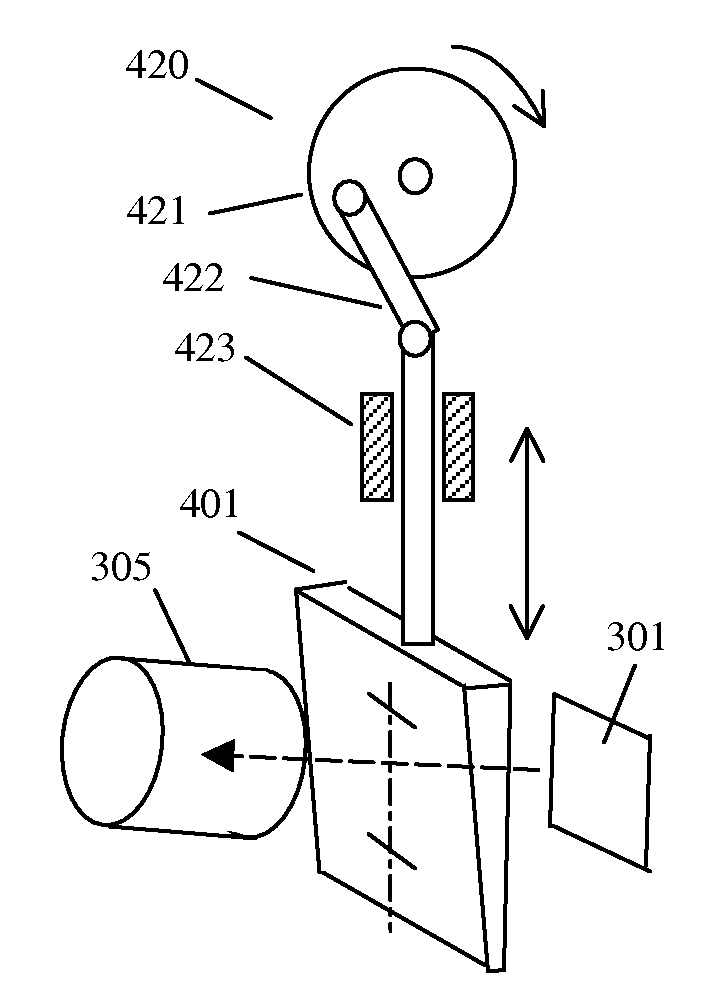
This invention relates in general to methods and systems of rapid focusing and zooming for the applications in the projection of volumetric 3D images and in the imaging of 3D objects. Rapid variable focusing or zooming is achieved by rapid and repeated change of the object distance or the spacing between lens groups of the projection lens or a combination of both. One preferred approach inserts thin wedge prisms into the optical path and changes their positions relative to the optical path. This changes the thickness traveled through by the optical path and results in effective optical path length change. Another approach folds an optical path by mirrors and moves the mirrors to change the optical path length. For focusing purpose, small and precise displacement is achieved by moving a wedge-shaped optical device obliquely with respect to the optical path. The wedge-shaped optical device can be a thin wedge prism or a mirror on a wedge-shaped base. Optical layout analysis shows that the changes of the object distance, of the spacing between two lens groups and of the image distance are almost in proportion and can be correlated by linear relations. Therefore, the same type of motion function can be used to change these three optical path lengths to achieve focusing and constant magnification.
Owner:TSAO CHE CHIH
System and method for creating a stable optical interface
ActiveUS20070219437A1Simple interfaceOptical coupling efficiency is decreasedDiagnostic recording/measuringSensorsSkin surfaceRefractive index
A system and a method for creating a stable and reproducible interface of an optical sensor system for measuring blood glucose levels in biological tissue include a dual wedge prism sensor attached to a disposable optic that comprises a focusing lens and an optical window. The disposable optic adheres to the skin to allow a patient to take multiple readings or scans at the same location. The disposable optic includes a Petzval surface placed flush against the skin to maintain the focal point of the optical beam on the surface of the skin. Additionally, the integrity of the sensor signal is maximized by varying the rotation rates of the dual wedge prisms over time in relation to the depth scan rate of the sensor. Optimally, a medium may be injected between the disposable and the skin to match the respective refractive indices and optimize the signal collection of the sensor.
Owner:MASIMO CORP
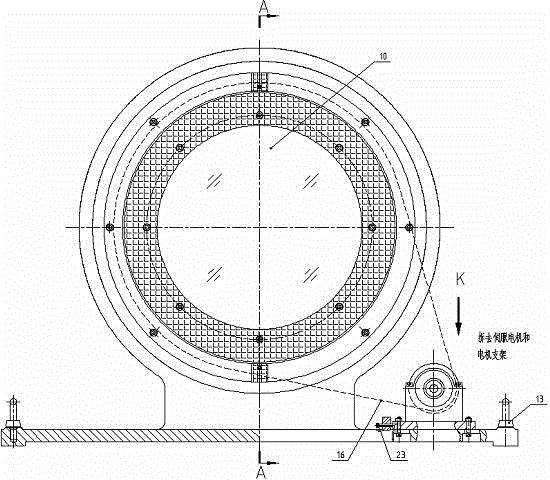
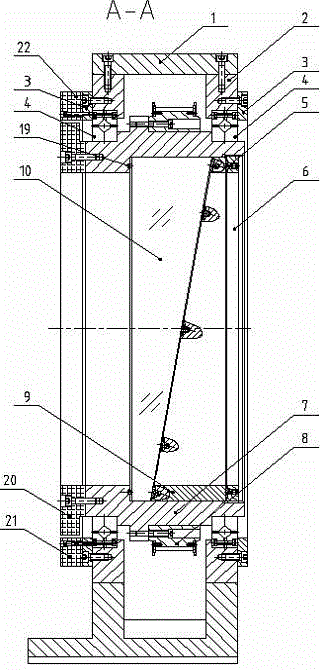
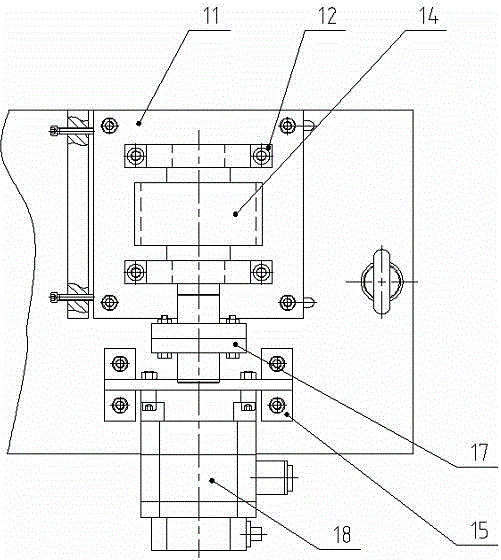
Synchronous belt drive rotary prism device
The invention relates to a synchronous belt drive rotary prism device, which comprises a mirror frame and scanning frame assembly, a synchronous belt mechanism, rotary encoder assemblies and a machine seat assembly, wherein the machine seat assembly comprises a machine seat and two machine seat inserts; the mirror frame and scanning frame assembly comprises a rubber pad, a prism check ring, a mirror frame, a big pulley, a wedge-shaped check ring and a wedge-shaped prism; the synchronous belt mechanism comprises a small pulley axle support, a small bearing pressing block, a small pulley axle, a motor support, a synchronous belt, a coupling and a servo motor; and two sets of rotary encoder assemblies are arranged and respectively comprise an encoder rotary ring, a first reading head and a second reading head. According to the synchronous belt drive rotary prism device provided by the invention, the center distance between two synchronous pulleys is adjustable within limits; the strain of the synchronous belt can be conveniently adjusted to ensure transmission reliability; the structure is compact; and the arrangement is flexible.
Owner:TONGJI UNIV
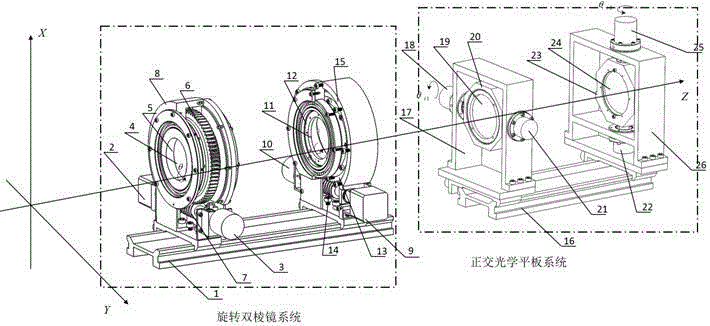
Cascading coarse-fine data coupling optical scanning device
InactiveCN104793334ARealize coarse and fine scanningRealize fine scanningOptical elementsPlane mirrorOptical axis
The invention relates to a cascading coarse-fine data coupling optical scanning device. The cascading coarse-fine data coupling optical scanning device is formed by a rotation double-prism system and an orthogonal deflection optical panel system in the direction of an optical axis; the rotation double-prism system adopts two rotation stepping motors to respectively drive two wedge-shaped prisms to rotate surrounding a Z axis to achieve coarse scanning; the orthogonal deflection optical panel system adopts the two rotation stepping motors to respectively drive two optical panels to deflect surrounding a Y axis and a Z axis; displacement translation of light beams within local ranges through the displacement translation of refraction light beams and an exquisite scanning requirement is satisfied; two sets of prim systems of the rotation double-prism system are both formed by a base, a rotation stepping motor, an encoder, a wedge-shaped prism, an optical frame, a worm gear, a worm and a mirror bracket; the orthogonal deflection optical panel system is formed by a second base, a third mirror bracket, a third rotation stepping motor, a first plane mirror, a third mirror frame, a third encoder, a fourth encoder, a fourth mirror frame, a second plane mirror, a fourth rotation stepping motor and a fourth mirror frame. According to the cascading coarse-fine data coupling optical scanning device, the light beam propagation direction is easy to control and control is convenient.
Owner:TONGJI UNIV
Compact optical engine for very small personal projectors using LED illumination
ActiveUS7360905B2Produce heatPower can be minimalTelevision system detailsProjectorsLight pipeLens plate
Owner:TEXAS INSTR INC
Protective film for a prism lens
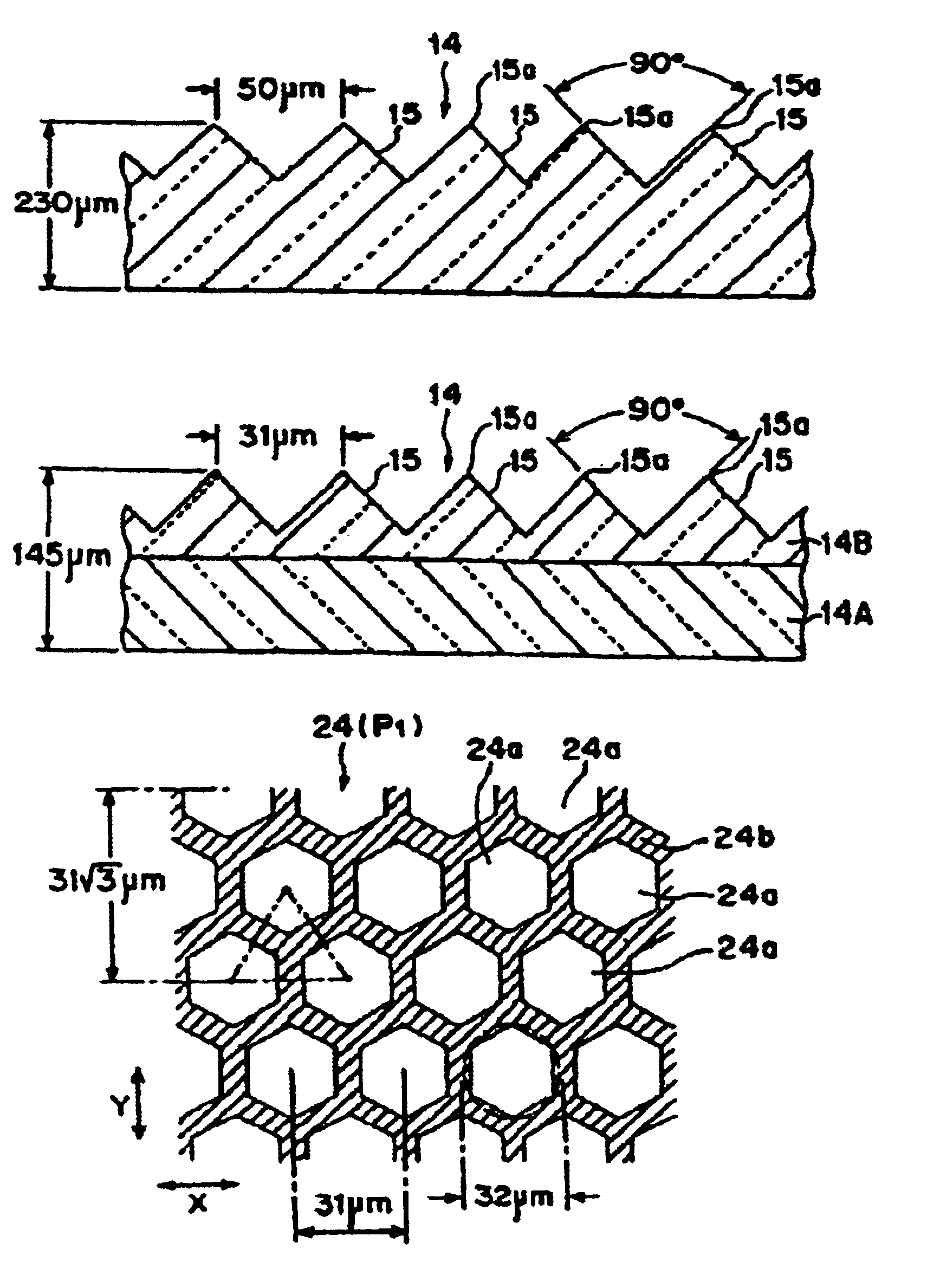
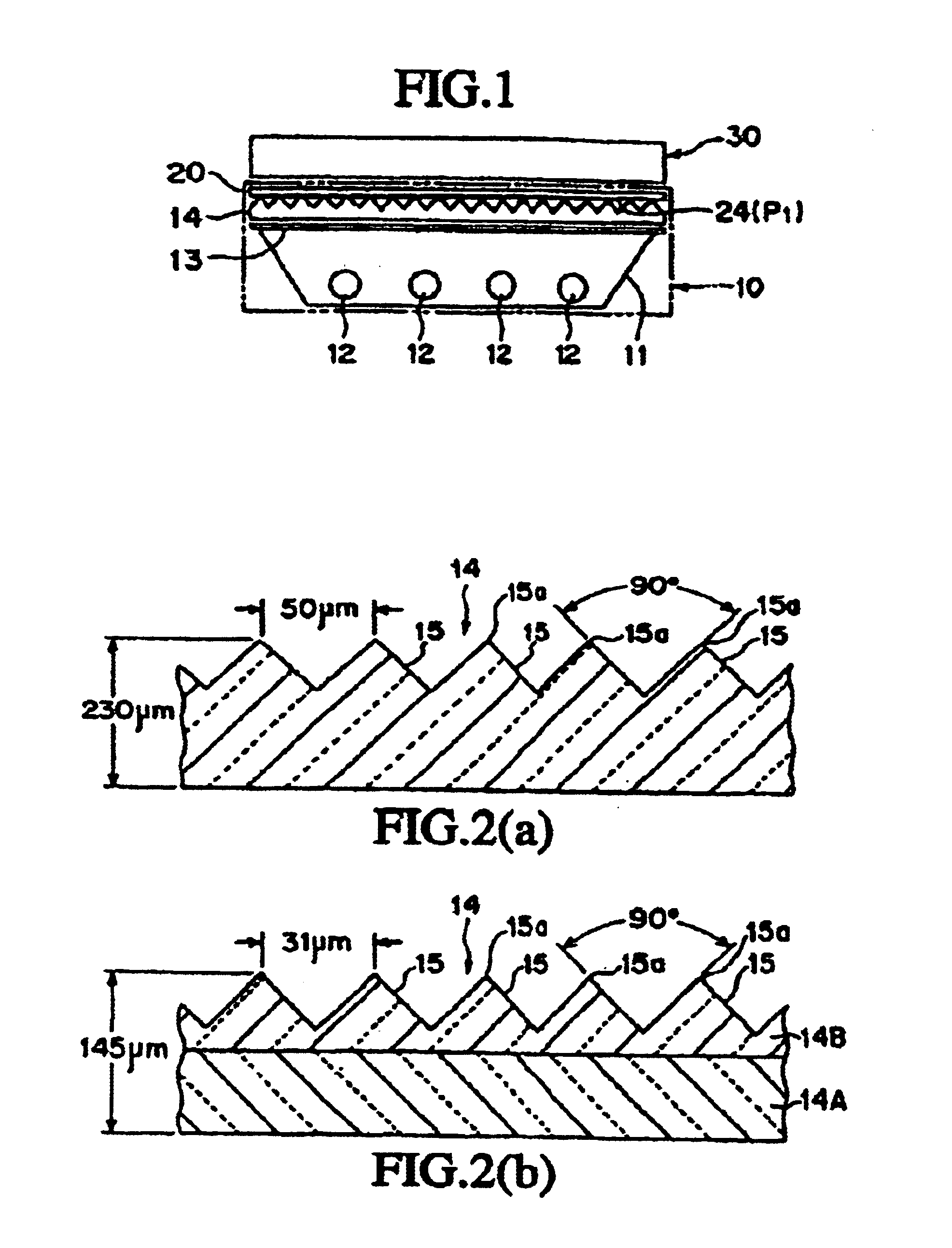
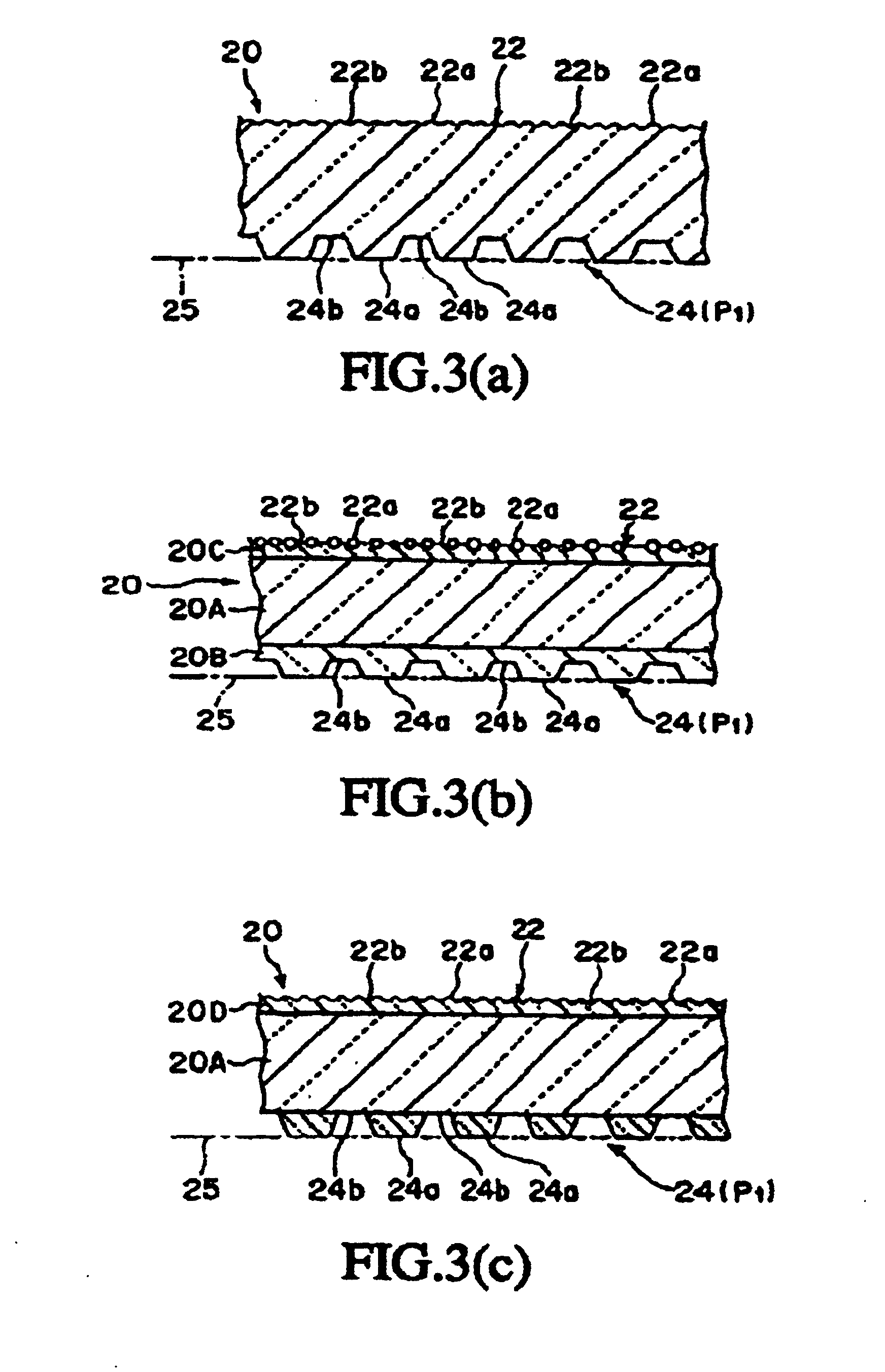
A transparent synthetic resin protective film to be mounted on prisms (15) of a synthetic resin prism lens (14) where a light entering from the side face or the back face emerges from the prism forming face on the front side formed with ridge prisms (15) continuously. A rough surface (24) comprising micro protrusions and recesses for suppressing moire fringes, blur, glare, and inversion is provided at least to the protective film facing the prism (15). The top part of each protrusion (24a) constituting the rough surface (24) is a flat face substantially contained in a single plane (25) and having such a predetermined small extent not recognizable by naked eyes or a convex face of small curvature. The flat faces of the protrusions (24a) is continuous with the edges (15a) of the prisms (15) in any relative position of the protective film (20) and the prism lens (14) in the two-dimensional direction. Since the protrusions (24a) on the protective film (20) side slide smoothly on the prism (15) when the protective film (20) moves relatively to the prism lens (14), the conventional drawback that the edges (15a) of the prism (15) of the prism lens (14) is rubbed and worn by (the protrusions (24a) of) the rough surface (22) on the protective film (20) side is overcome.
Owner:TSUJIDEN
Optical switch using risley prisms
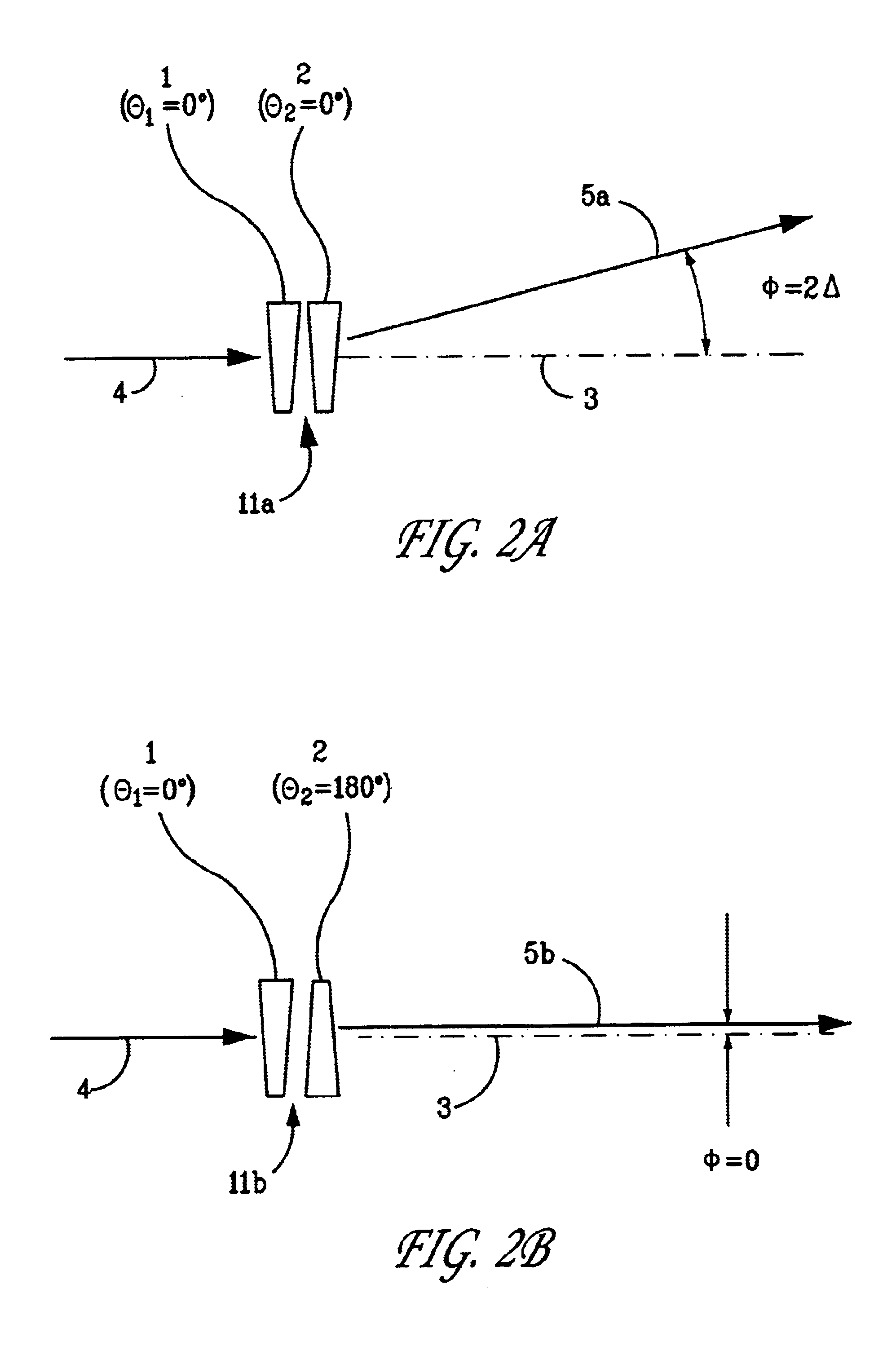
InactiveUS6859120B2Precise and independent rotationPrecise rotationElectrostatic generators/motorsCoupling light guidesLight beamEngineering
An optical switch using Risley prisms and rotary microactuators to independently rotate the wedge prisms of each Risley prism pair is disclosed. The optical switch comprises an array of input Risley prism pairs that selectively redirect light beams from a plurality of input ports to an array of output Risley prism pairs that similarly direct the light beams to a plurality of output ports. Each wedge prism of each Risley prism pair can be independently rotated by a variable-reluctance stepping rotary microactuator that is fabricated by a multi-layer LIGA process. Each wedge prism can be formed integral to the annular rotor of the rotary microactuator by a DXRL process.
Owner:NAT TECH & ENG SOLUTIONS OF SANDIA LLC
Wavelength dispersive device with temperature compensation
The invention relates to fiber-optic wavelength dispersive devices incorporating a wavelength dispersive reflector that provides auto-compensation of variations of output spectral characteristic with temperature and includes a transmissive dispersion that is followed by a beam-folding reflecting surface in a double-pass configuration grating and is coupled to a wedged shaped prism.
Owner:LUMENTUM OPERATIONS LLC
Night-day boresight with adjustable wedge-prism assembly
ActiveUS7142357B2Reduce and eliminate image shiftPrismsSighting devicesCost effectivenessEngineering
An in-line night-day boresight with an adjustable wedge-prism assembly is disclosed. The adjustable wedge-prism assembly includes two opposing wedge prisms that are axially rotatable relative to each other. The assembly is arranged in the optical path between the night optics and the day optics. The adjustable wedge-prism assembly allows for compensation of image shift errors introduced by the night optics due to manufacturing errors in the night optics. This in turn allows for a cost-effective and easily aligned in-line night-day boresight.
Owner:KNIGHT VISION LLLP
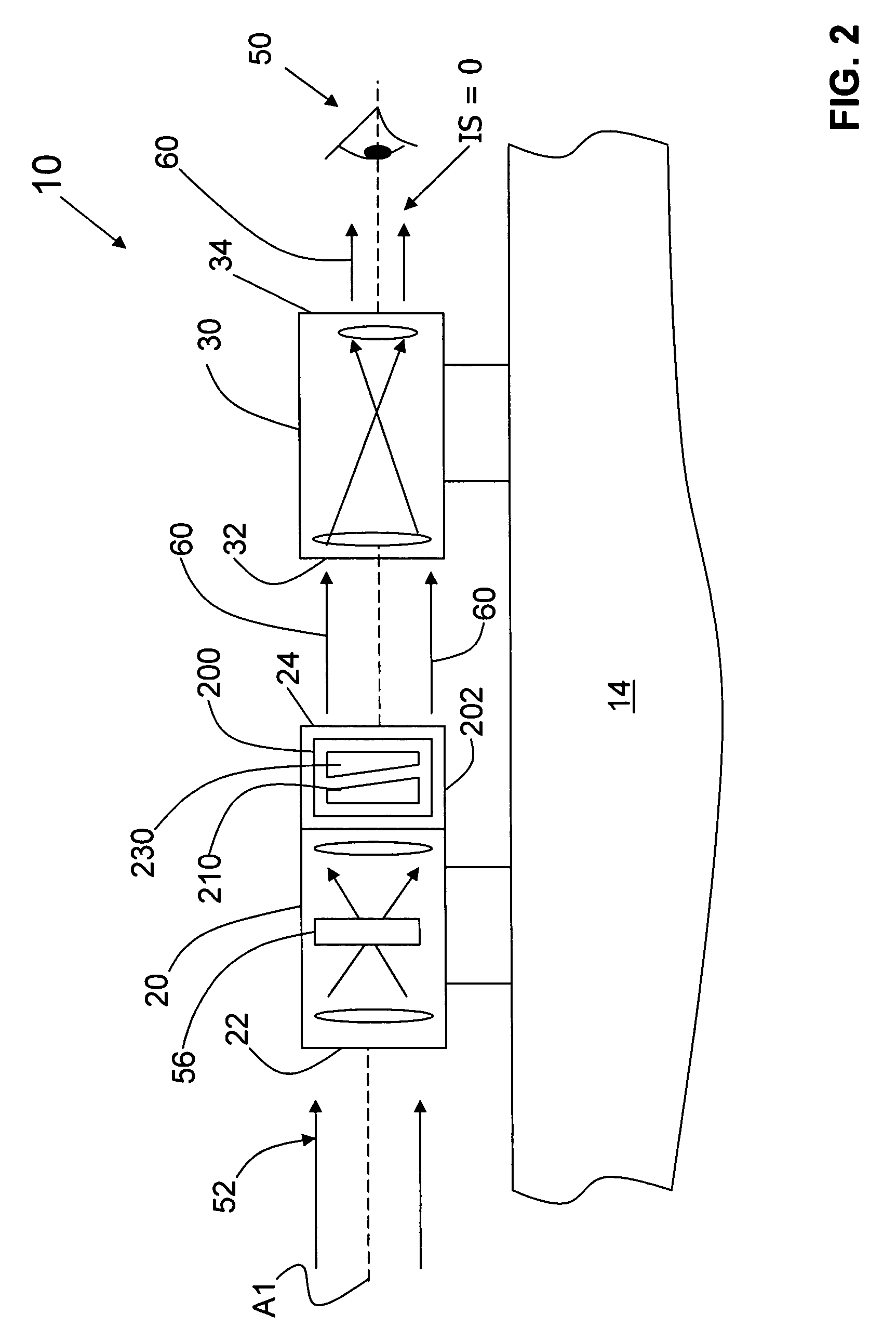
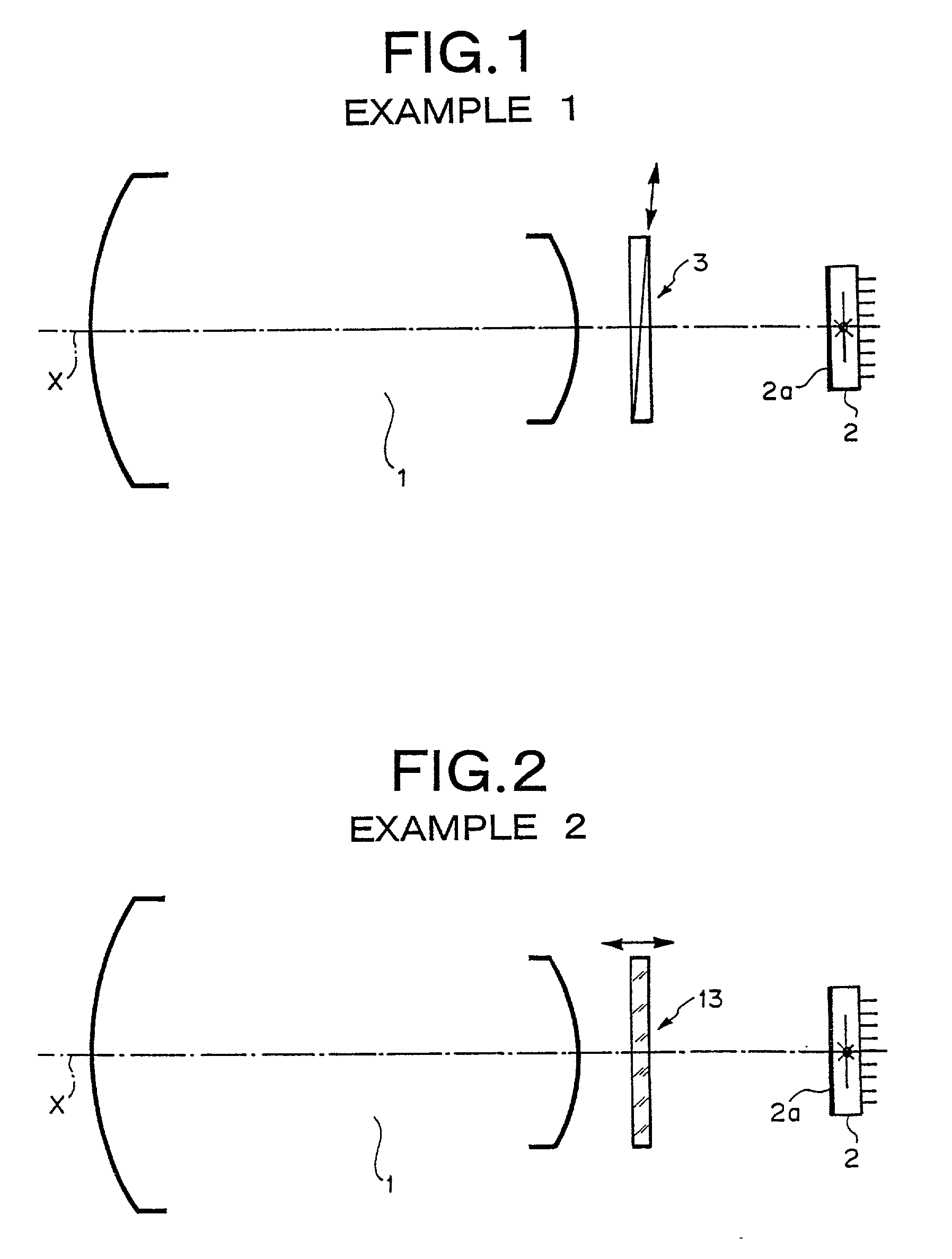
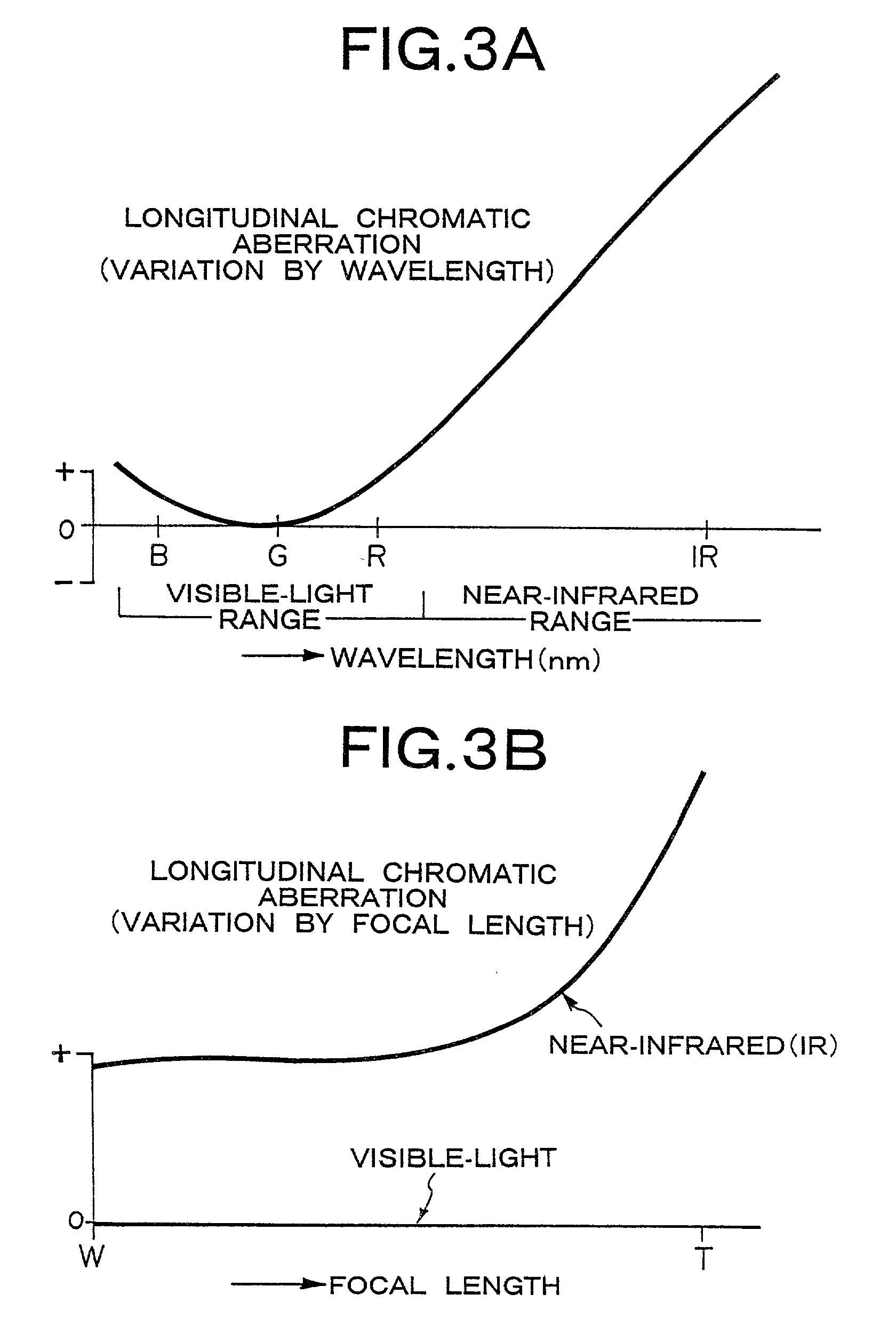
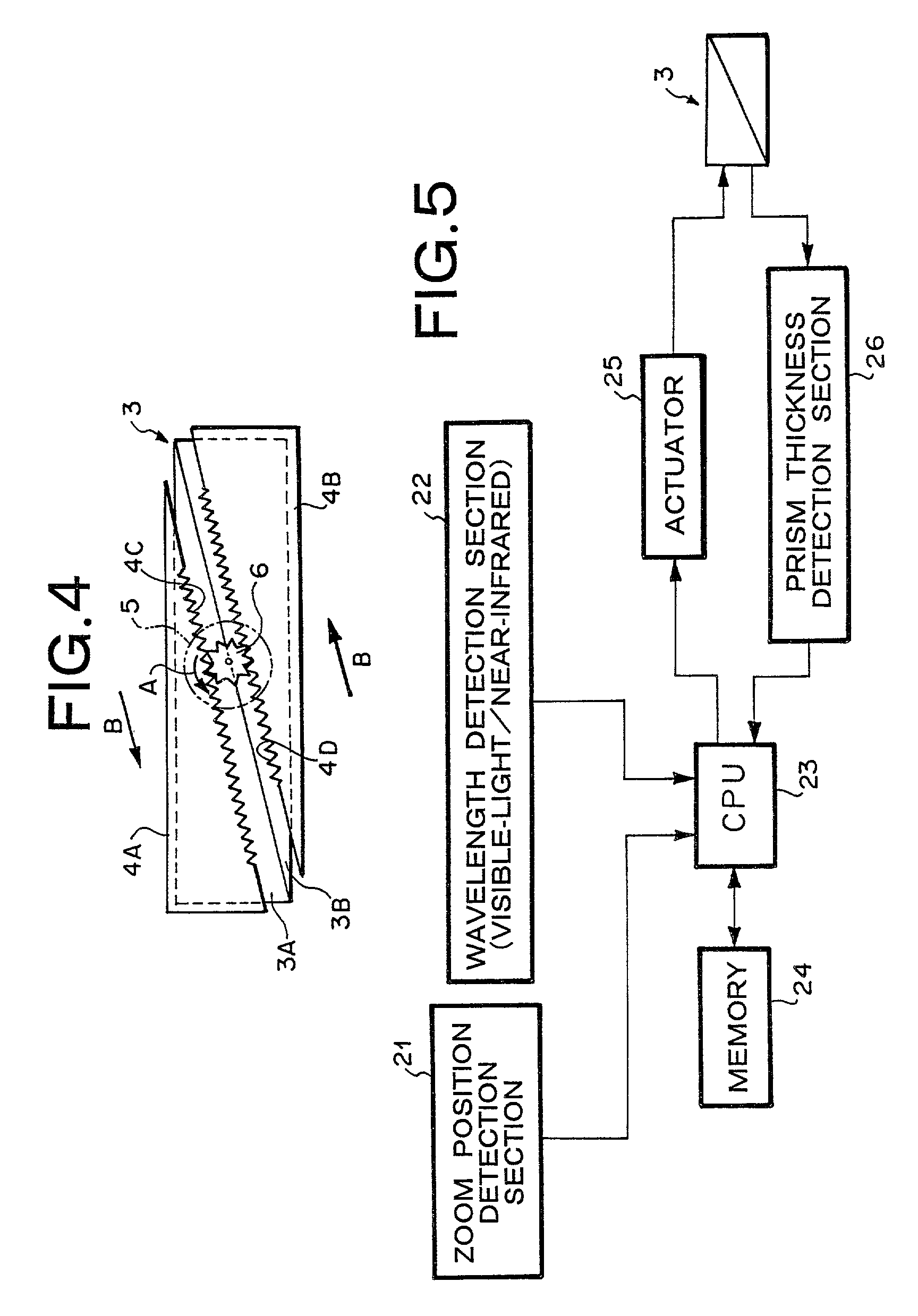
Dual-use visible-light/infrared image pickup device
InactiveUS20010026400A1Television system detailsProjector focusing arrangementCamera lensVariable thickness
A shift in focal point due to longitudinal chromatic aberration of a photographing lens is properly corrected in accordance with various photographing conditions, by means of controlling the thickness of a variable-thickness optical filter interposed between an image pickup lens system and a solid-state image pickup element, on the basis of a correlation table defining the correlation between photographing conditions and the thickness of the variable-thickness optical filter that can correct a shift in focal point. A variable-thickness optical filter is interposed between a photographing lens system and a CCD having sensitivity ranging from the visible-light range to the infrared range. The thickness of the optical filter is changed, by means of controlling an actuator on the basis of a correlation table defining the correlation between the photographing conditions and the thickness of the variable-thickness optical filter which can correct the shift in optical focal point. The variable-thickness optical filter is formed from two wedge-shaped prisms combined together to form a parallel-plane plate, and the overall thickness of the variable-thickness optical filter can be changed, by means of moving the prisms in opposite directions while oblique lines of the prisms remain in contact with each other.
Owner:FUJI PHOTO OPTICAL CO LTD
Exposure apparatus and exposure method
InactiveCN101142534ASmall sizeKeep stableSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingPhotomechanical exposure apparatusWedge prismOptical path length
An exposure apparatus (10) includes a light source unit (60) for emitting exposure light, a DMD (90) for performing spatial light modulation, based on an image signal, on the exposure light, an imaging optical system (50) for forming an image on a photosensitive material (12) with the exposure light on which spatial light modulation has been performed, and a pair (54) of wedge prisms for adjusting focus by changing the optical path length of the modulated exposure light when an image is formed on the photosensitive material (12) with the modulated exposure light. In the imaging optical system (50), distortion at a peripheral portion of a projection lens is increased, and optical performance of the lens at a region including a central portion is improved. An image is formed only by a substantially rectangular region of the projection lens, including the central portion, with the modulated exposure light.
Owner:FUJIFILM CORP
Method for measuring thickness of measured article and its device
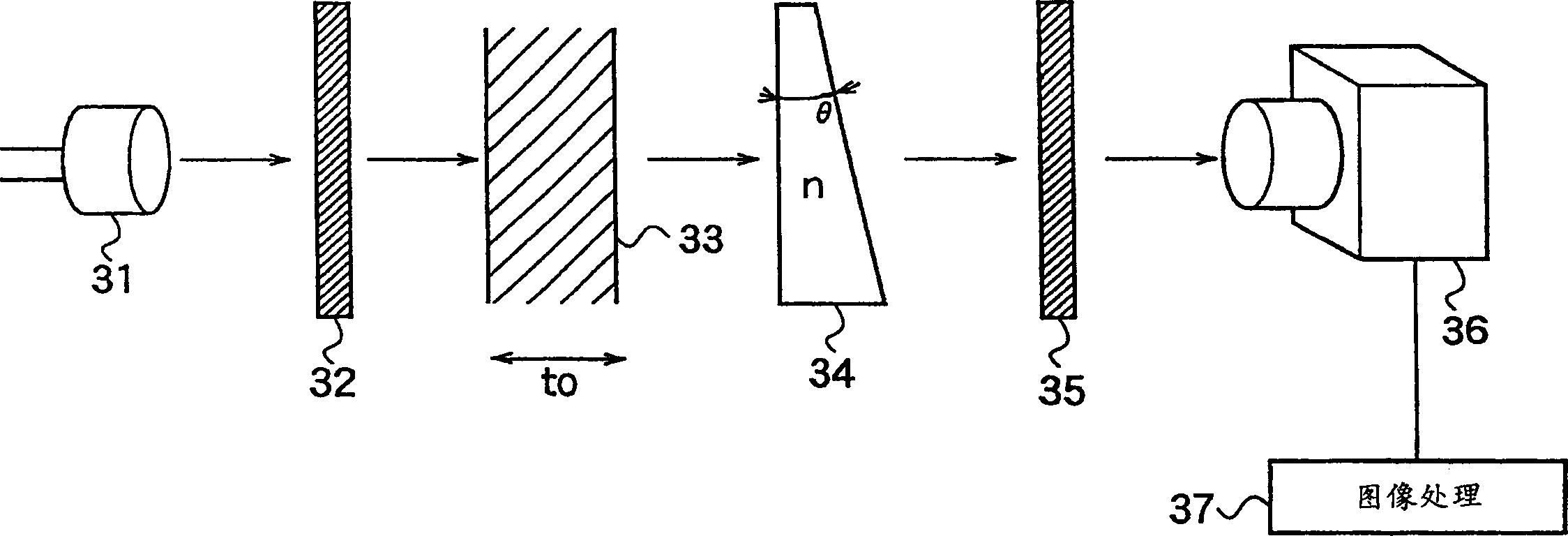
A method and device for measuring the thickness of a measured object, which can perform high-speed, high-precision, stable measurement and are easy to maintain. The coherent light emitted from the light source 31 is converted into the desired linearly polarized light by the polarizer 32, and the linearly polarized light is incident on the object 33 having birefringence, and the normal light and the extraordinary light are taken out, and the taken out light is further incident on the wedge shape. The prism 34 extracts the light having a phase difference that changes according to the thickness of the measured object 33 and the wedge prism 34 that passes through the measured object 33 at the measurement site. The light taken out is received by the analyzer 35, and a component of a polarization direction is extracted from the normal light and the extraordinary light, and the interference of the normal light component and the extraordinary light component of a polarization direction is generated, and the generated interference is reflected on the camera as interference fringes. By observing the reflected interference fringes on the screen of the device 36, the image processing device 37 measures the thickness of the object 33 depending on the displacement of the interference fringes.
Owner:日本マクシス
Composite type beam coarse and fine coupling scanning device
The invention relates to a composite type beam coarse and fine coupling scanning device which comprises a base, a spring, a middle lens frame, an inner lens frame, a wedge prism, a large bearing end cover, a rotary encoder rotor, a rotary encoder stator, an outer lens frame, a large bearing retainer ring, a large bearing, a nylon pad, a wedge retainer ring, a threaded pressing ring, a prism tightening screw, a torque motor stator, a torque motor rotor, a voice coil motor rotor, a push rod, a voice coil motor stator, a push groove, a third nylon pad, a small bearing, a small bearing end cover, a half shaft, and a small rotary encoder assembly. Through the rotation of the wedge prism, the beam large range coarse scanning is realized, through the deflection of the wedge prism, the beam local range high precision scanning is realized. One set of the device or multiple sets of the devices can be used together, the scanning range of the beam can be increased further when the multiple sets of the devices are used, the rich scanning styles are realized, and the device has extensive prospect in the application fields with high requirements of a beam scanning range and precision such as photoelectric imaging detection, free space laser communication, and dynamic target laser tracking.
Owner:TONGJI UNIV
Rotating triple-prism beam scanning device
InactiveCN106249405AControl rotation angleAvoid empty backOptical elementsCouplingRolling-element bearing
The invention relates to a rotating triple-prism beam scanning device comprising a rotating double-prism system, a rotating single-prism system, a guide rail, an adjustable support, and a fixed support. The rotating single-prism system comprises a base component, a prism and frame assembly, and a worm-and-gear mechanism. The prism and frame assembly comprises a flat washer, a wedge prism, a rubber pad, a wedge retainer ring, a threaded retainer ring, and a frame. The base component comprises a base, a base baffle, and a base insert. The worm-and-gear mechanism comprises a rotary motor, a motor stand, a coupling, a worm, a bearing support, a rolling bearing, a worm gear, an encoder support, and a rotary encoder. The rotating double-prism system is formed by assembling two rotating single-prism systems together. In the invention, the three wedge prisms are driven by the worm-and-gear mechanisms to do full-circumferential rotation, transmission is stable and accurate, and the scanning precision and stability of dynamic beams can be ensured; the prisms are independent of one another in rotation control, and diversified scanning modes can be achieved; and by introducing the third prism to the double-prism system, the scanning field of beams is enlarged significantly, and the problem that a double-prism system has scanning blind areas and control singular points is solved effectively.
Owner:TONGJI UNIV
Optical head and optical disk apparatus
There are provided an interference type optical head and an optical disk apparatus, which have a signal amplification effect and which can be manufactured in sizes comparable to conventional optical heads. In an optical disk apparatus that performs signal amplification by making a light, which is used as a reference light without being irradiated on an optical disk and, interfere with reflected light from the optical disk, a corner cube prism that reflects the reference light is mounted on the same actuator as an objective lens. Further, there is provided a movable portion that adjusts the optical path length of the interfering light in accordance with the kind of optical disk being read and the recording layer being read. A wedge prism may be used for the movable portion, and a spherical aberration correction lens and an optical path length adjusting component may be moved integrally. Thus, a stable amplification effect may be obtained while keeping the overall size comparable to conventional apparatuses.
Owner:HITACHI CONSUMER ELECTRONICS CORP
Optical system for see-through head mounted display
Provided is a see-through head mounted display (HMD) optical system which includes a display device, a collimation lens that parallelizes image lights emitted from the display device, a first wedge prism that includes a first enlargement unit for enlarging an image in a horizontal direction, a second wedge prism that includes a second enlargement unit for enlarging the image in a vertical, and a third wedge prism that has an inverse shape of the second wedge prism so as to prevent the image lights which have been reflected in the second wedge prism and enlarged in the vertical direction and an external image which has passed through the second wedge prism and been provided to a user from being distorted.
Owner:GREEN OPTICS CO LTD
Optical deflection apparatus and optical deflection method
A liquid crystal optical phase modulator includes first and second substrates. A plurality of strip-shaped individual electrodes that are arranged parallel to each other on one surface of the first substrate. A common electrode is arranged on one surface, which faces towards the surface of the first substrate, of the second substrate. Both the individual electrodes and the common electrode are made of a conductive material that is transparent. A driver unit drives the liquid crystal optical phase modulator. A wedge-shaped prism is located near another surface of the second substrate of the liquid crystal optical phase modulator. The prism is such that a surface of it from where a light enters and a surface of it from where the entered light is output make a predetermined angle with each other.
Owner:CITIZEN WATCH CO LTD
Image position adjustment device and optical device
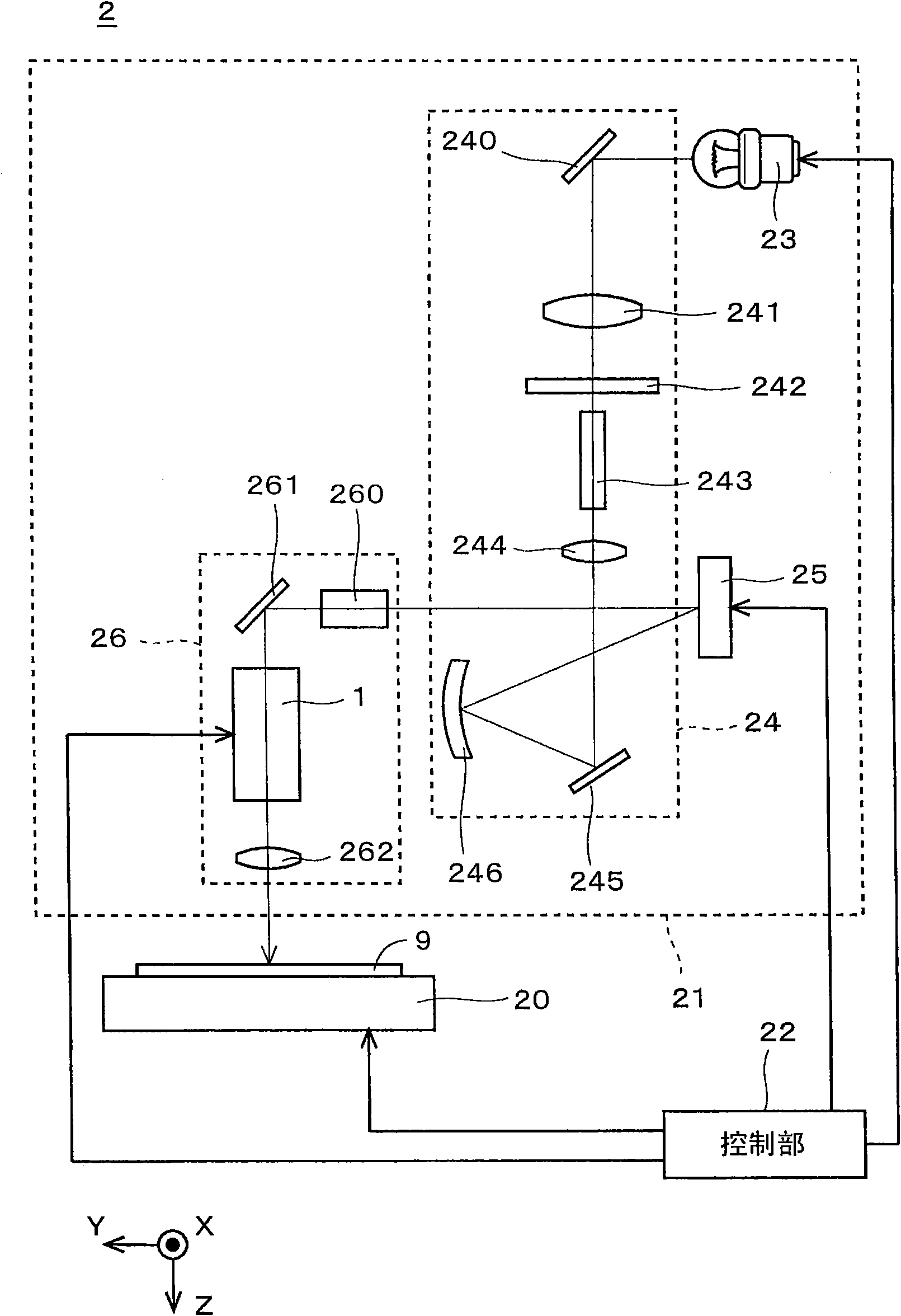
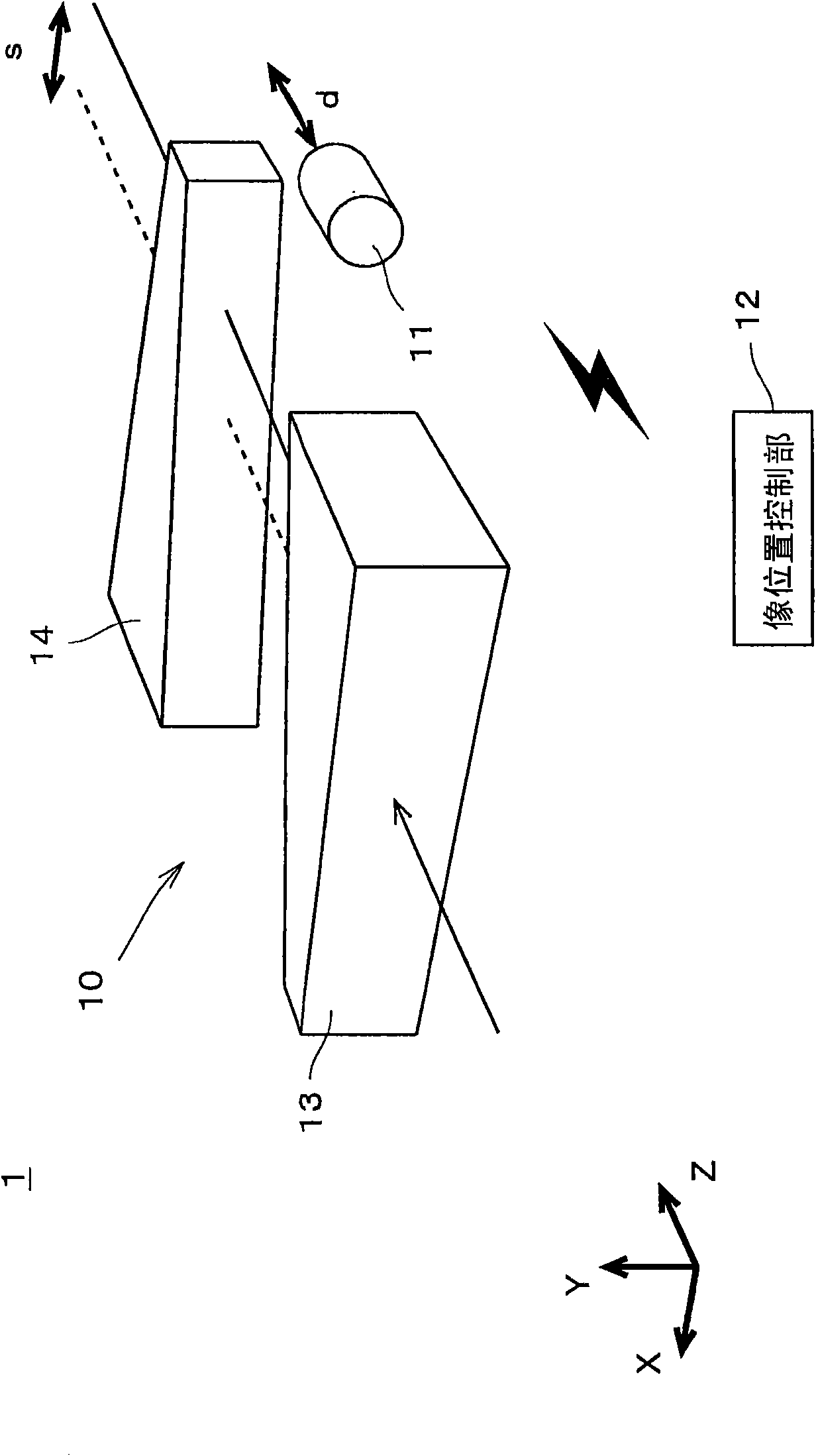
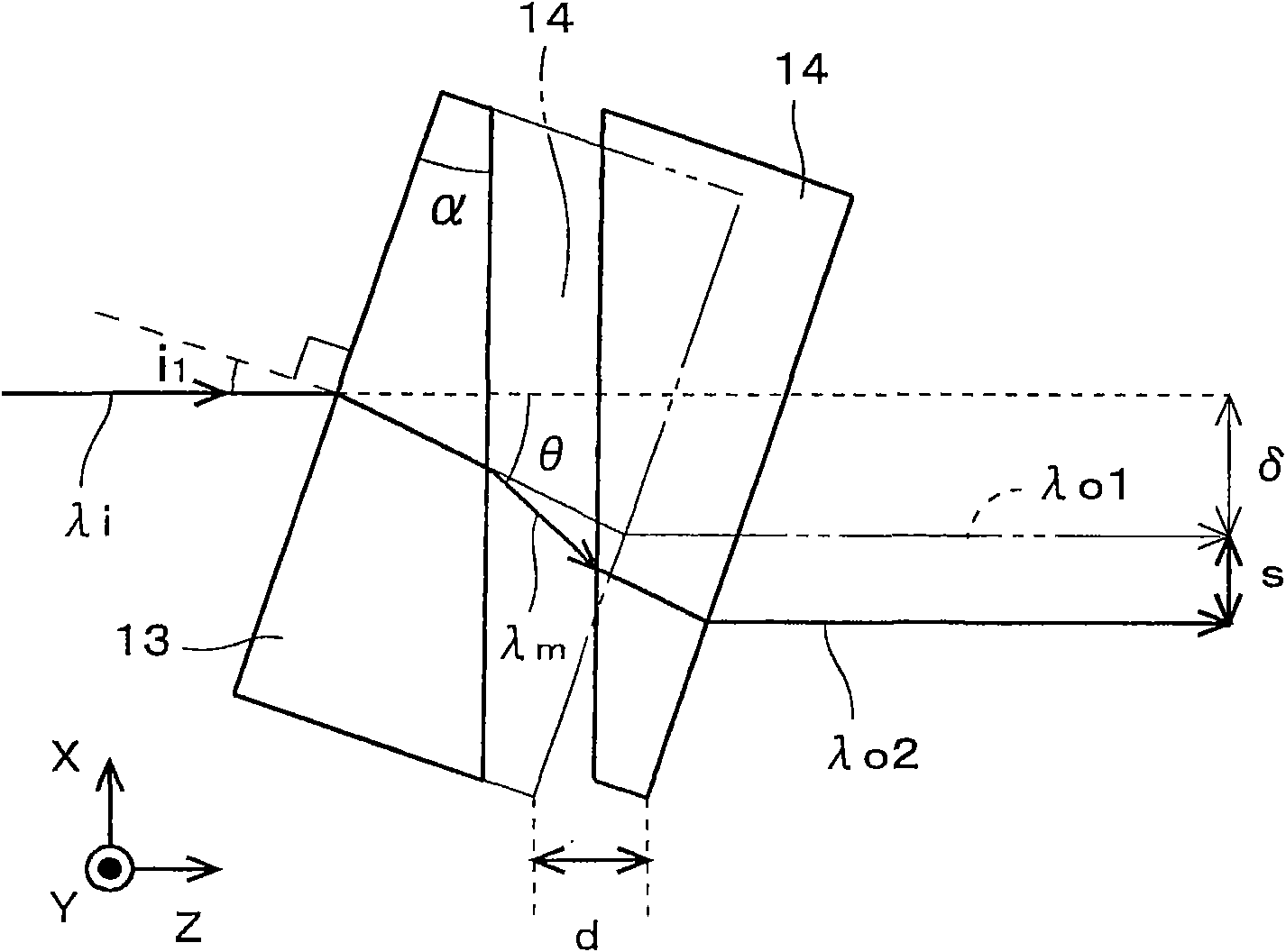
Provided is an image position adjustment device and an optical device, capable of shifting the image arbitrarily and compactly with a high precision without infection of the optical performance. the image position adjustment device (1) for shifting the image on an image surface is provided with an adjustment mechanism (11), a first wedge-shaped prism (13) and a second wedge-shaped prism (14). Thefirst wedge-shaped prism (13) is fixed that an incident light has a prescribed incidence angle, and the second wedge-shaped prism (14) is arranged in an opposition direction, such that the second wedge-shaped prism (14) is opposite with the first wedge-shaped prism (13). By means of moving the second wedge-shaped prism (14) in a Z axis direction (optical axis direction), a relative distance between the first and the second wedge-shaped prisms (13, 14) is altered, so as to adjust an offset on the image surface in a X axis direction.
Owner:DAINIPPON SCREEN MTG CO LTD
Wavelength dispersive device with temperature compensation
The invention relates to fiber-optic wavelength dispersive devices incorporating a wavelength dispersive reflector that provides auto-compensation of variations of output spectral characteristic with temperature and includes a transmissive dispersion that is followed by a beam-folding reflecting surface in a double-pass configuration grating and is coupled to a wedged shaped prism.
Owner:LUMENTUM OPERATIONS LLC
Liquid crystal variable wavelength filter unit, and driving method thereof
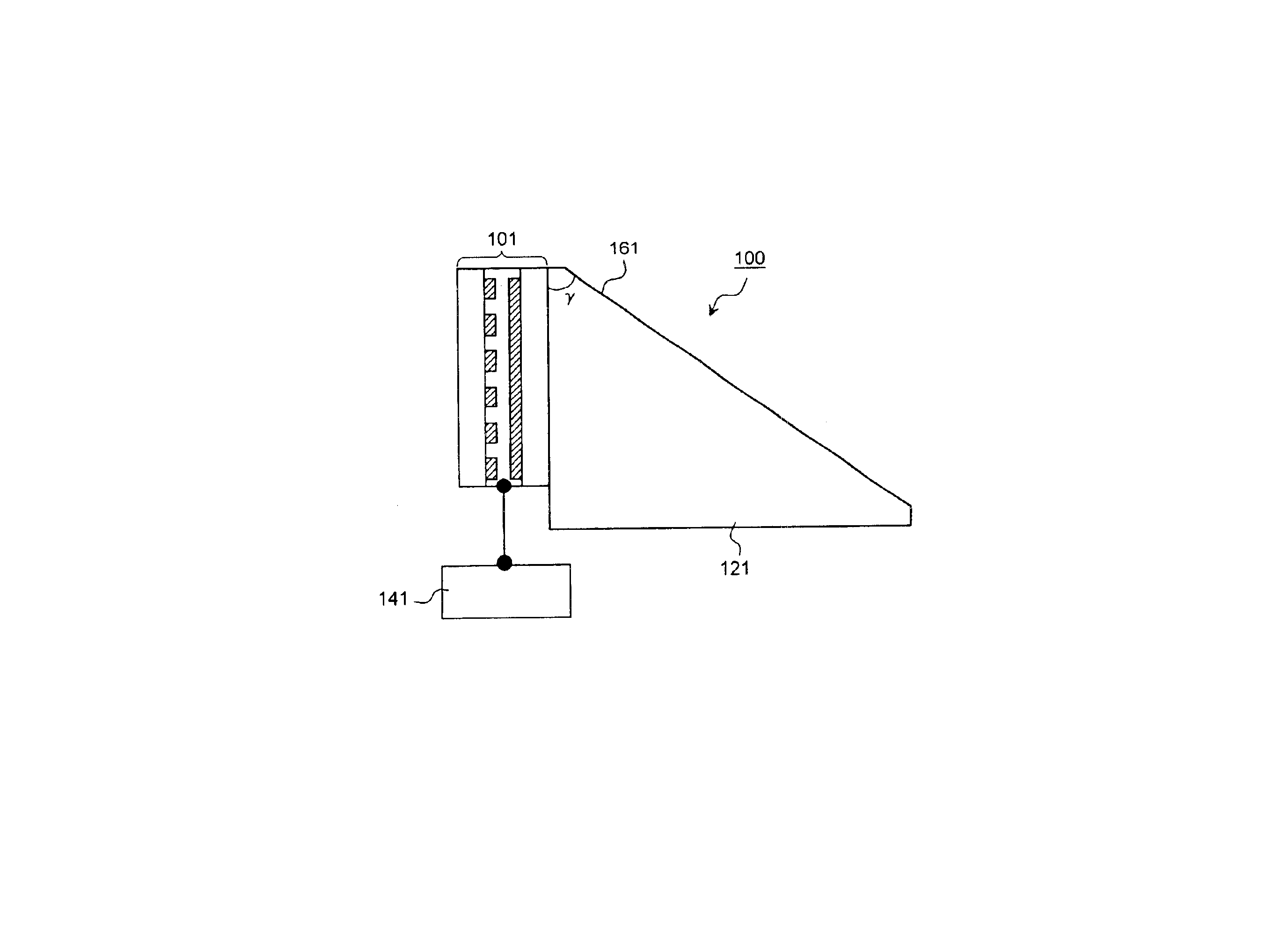
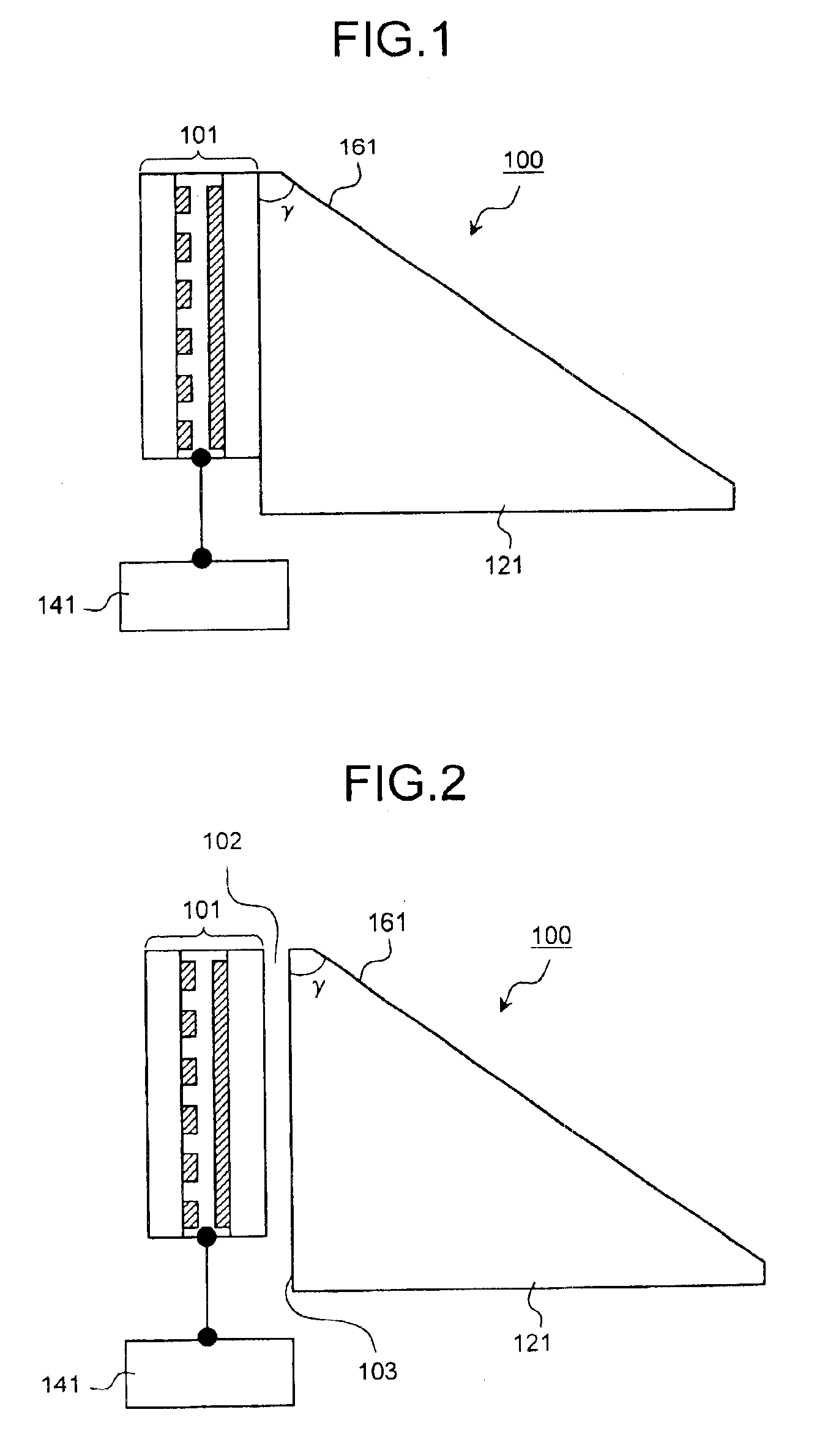
ActiveUS20050078237A1Simple structureStatic indicating devicesCoupling light guidesWavelength filterCommunications system
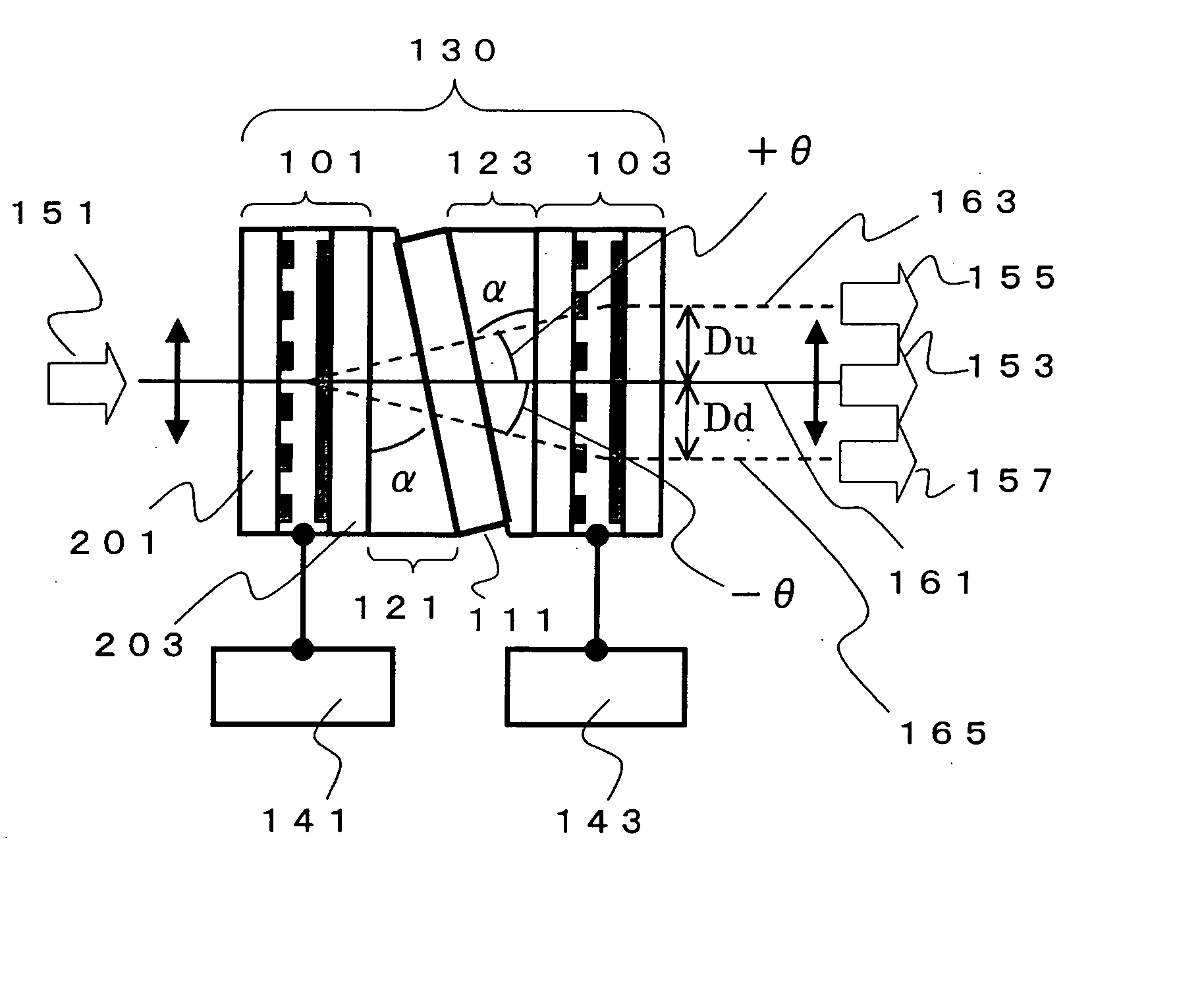
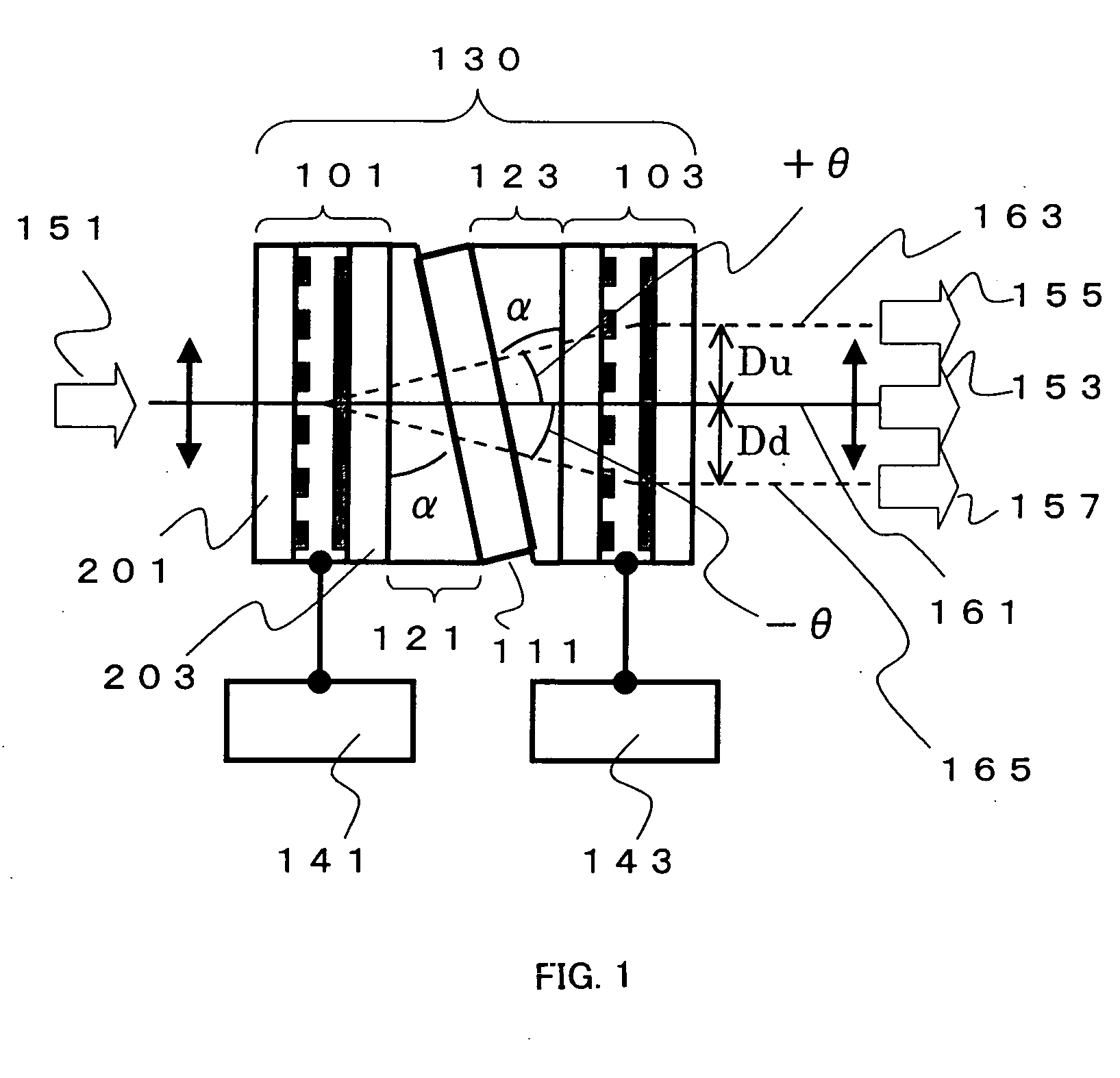
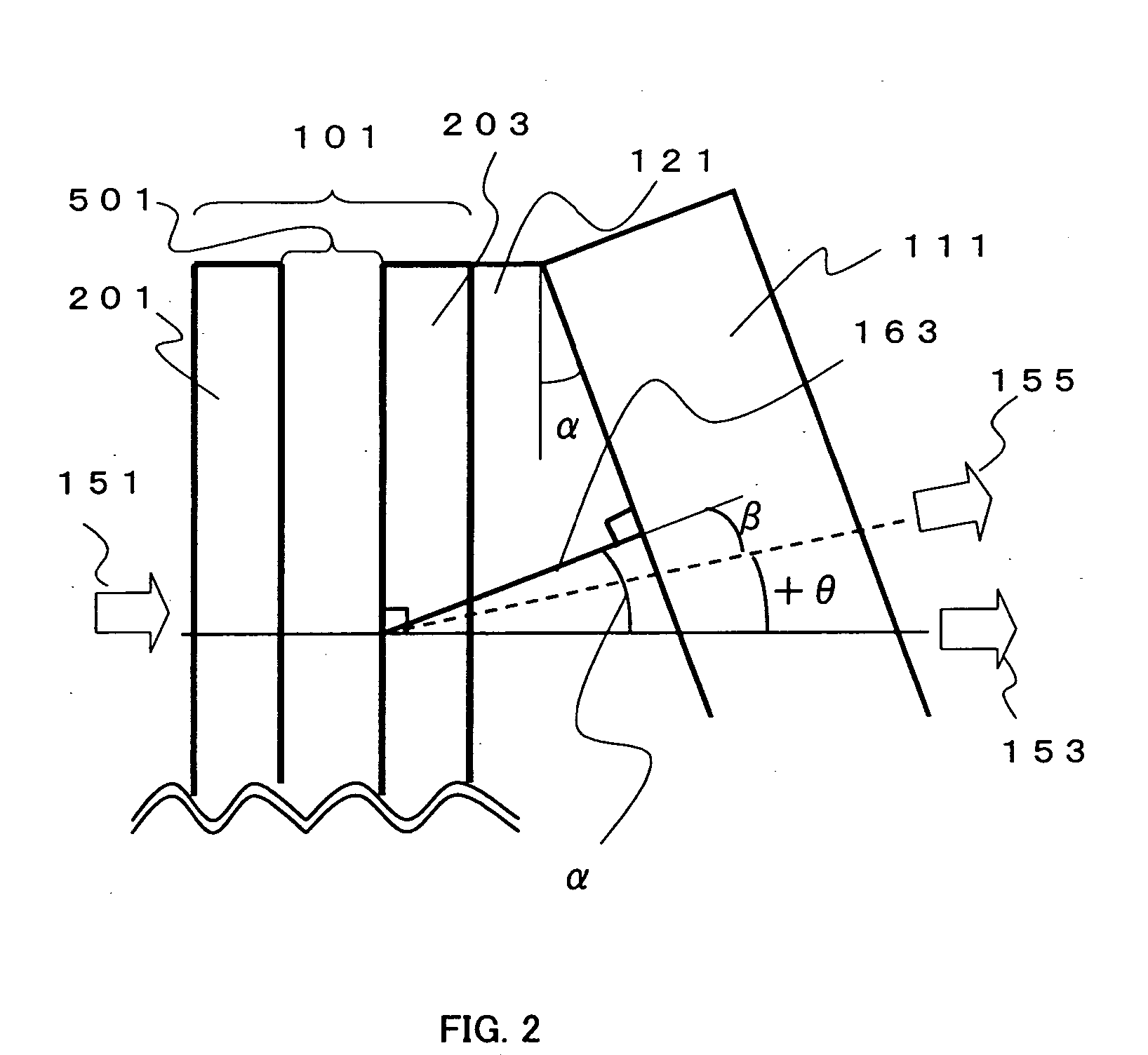
A liquid crystal variable wavelength filter unit and its driving method applicable for a Wavelength Division Multiplexing (WDM) communication system and an optical network using an optical fiber. The liquid crystal variable wavelength filter unit (130) includes a band pass filter (111) configured of a dielectric multi-layered film inclined by a predetermined angle of a between a first liquid crystal beam deflector (101) and a second liquid crystal beam deflector (103) and held between a first wedge prism (121) and a second wedge prism (123). The first drive device (141) is connected to the first liquid crystal beam deflector (101), and the second drive device (143) is connected to the second liquid crystal beam deflector (103). The wavelength is selected by the liquid crystal beam deflector by making the outgoing angle variable with respect to the band pass filter.
Owner:CITIZEN WATCH CO LTD
Compact optical engine for very small personal projectors using LED illumination
ActiveUS20060290899A1Produce heatSolution be minimalTelevision system detailsProjectorsTotal internal reflectionLight pipe
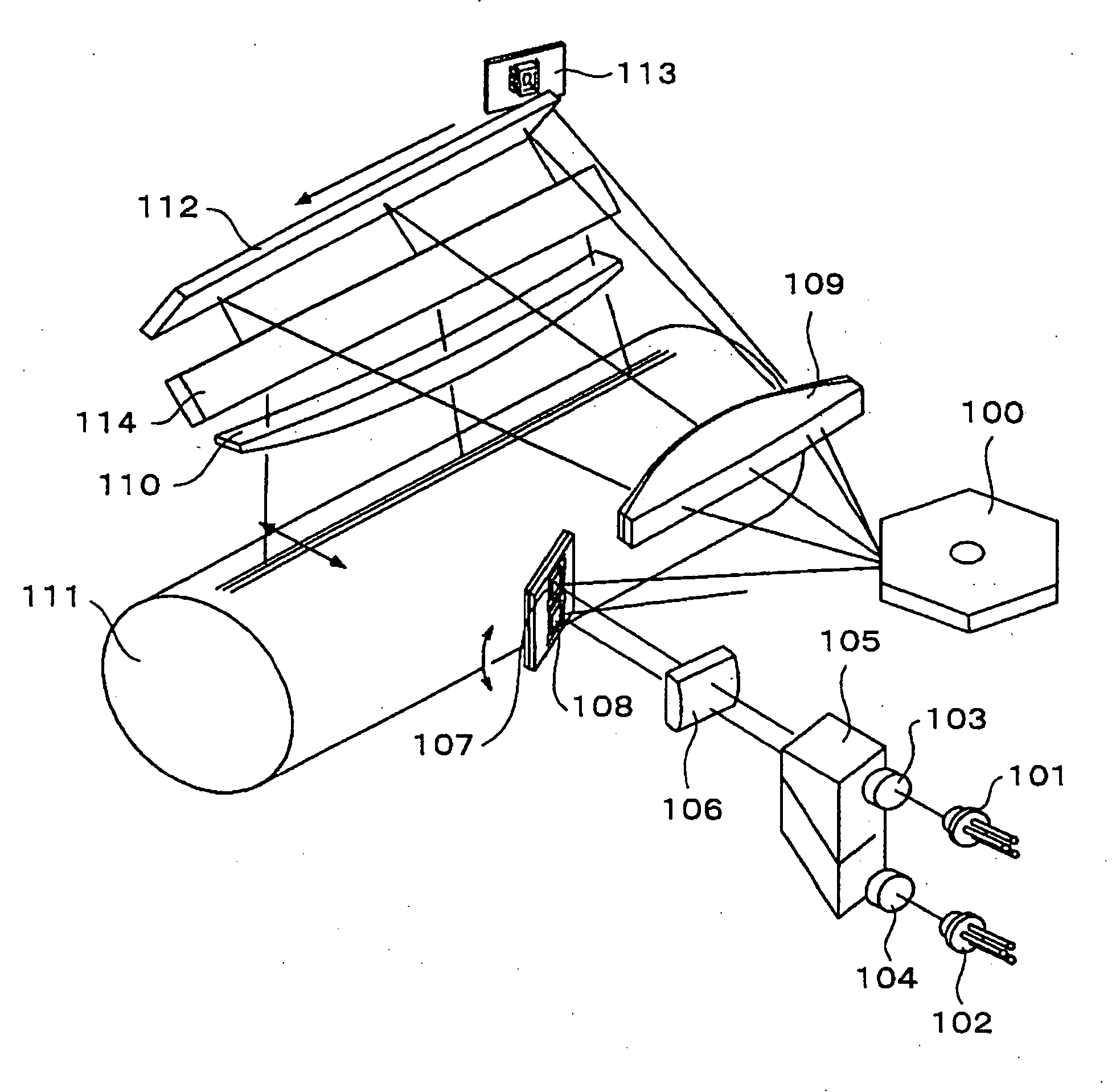
According to various illustrative embodiments of the present invention, a device for a light projection system includes a single light emitting diode array comprising at least one green die, at least one blue die, and at least one red die, a single light collection, integration, and etendue-matching optic element comprising a tapered light pipe capable of collecting substantially all light emitted by the single light emitting diode array and spatially integrating the substantially all the light emitted by the single light emitting diode array, and a telecentric relay using at least one of spherical and aspherical refractive and reflective components. The device also includes an illumination wedge prism, a digital micromirror device capable of modulating the substantially all the light emitted by the single light emitting diode array, and a projection total internal reflection prism, the projection total internal reflection prism disposed between the illumination wedge prism and the digital micromirror device. The device also includes a projection lens, wherein the telecentric relay provides the substantially all the light emitted by the single light emitting diode array through the illumination wedge prism and through the projection total internal reflection prism to the digital micromirror device that reflects the substantially all the light emitted by the single light emitting diode array back through the projection total internal reflection prism that totally internally reflects the substantially all the light emitted by the single light emitting diode array through the projection lens.
Owner:TEXAS INSTR INC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com