Patents
Literature
5787results about "Projector focusing arrangement" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
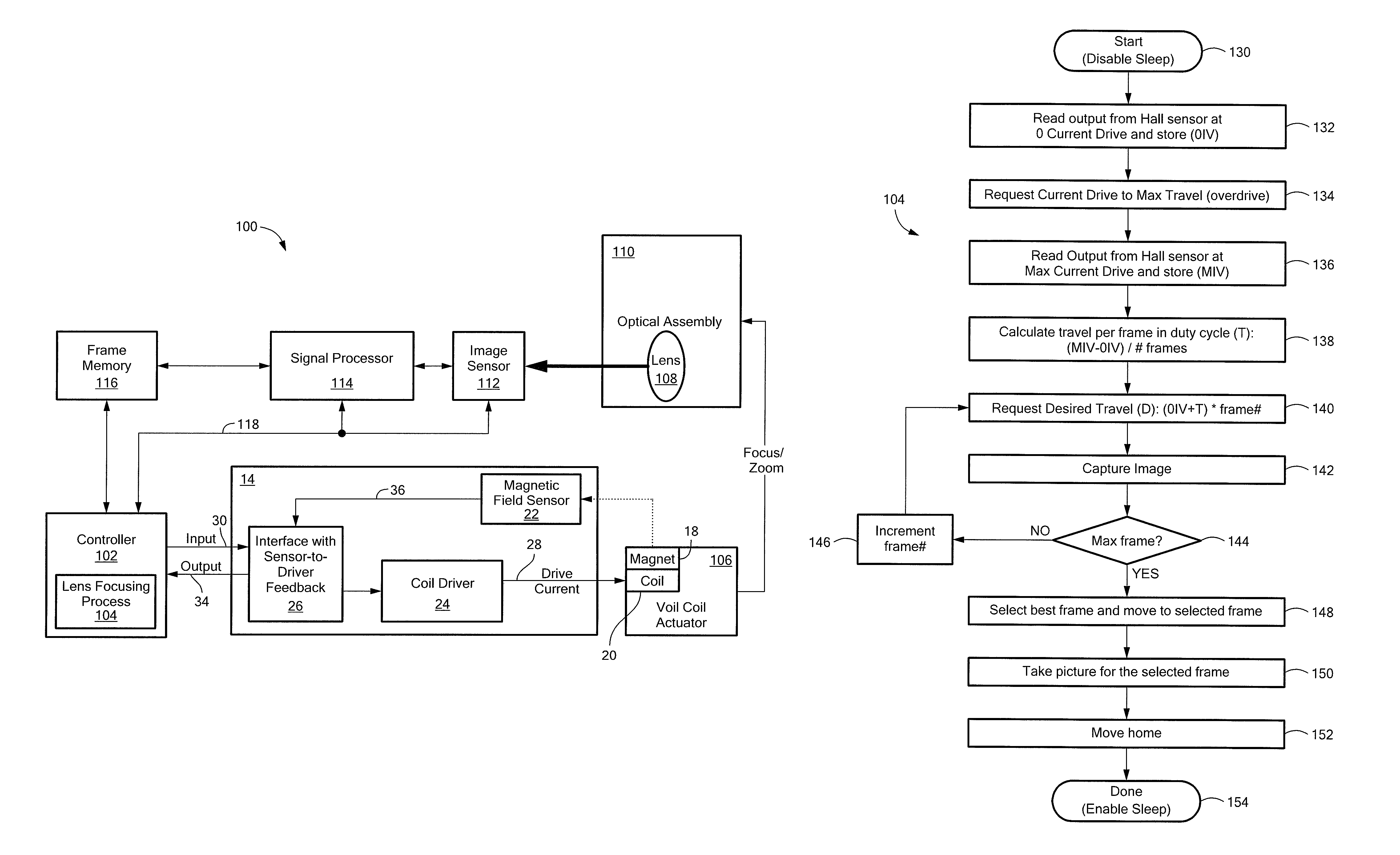
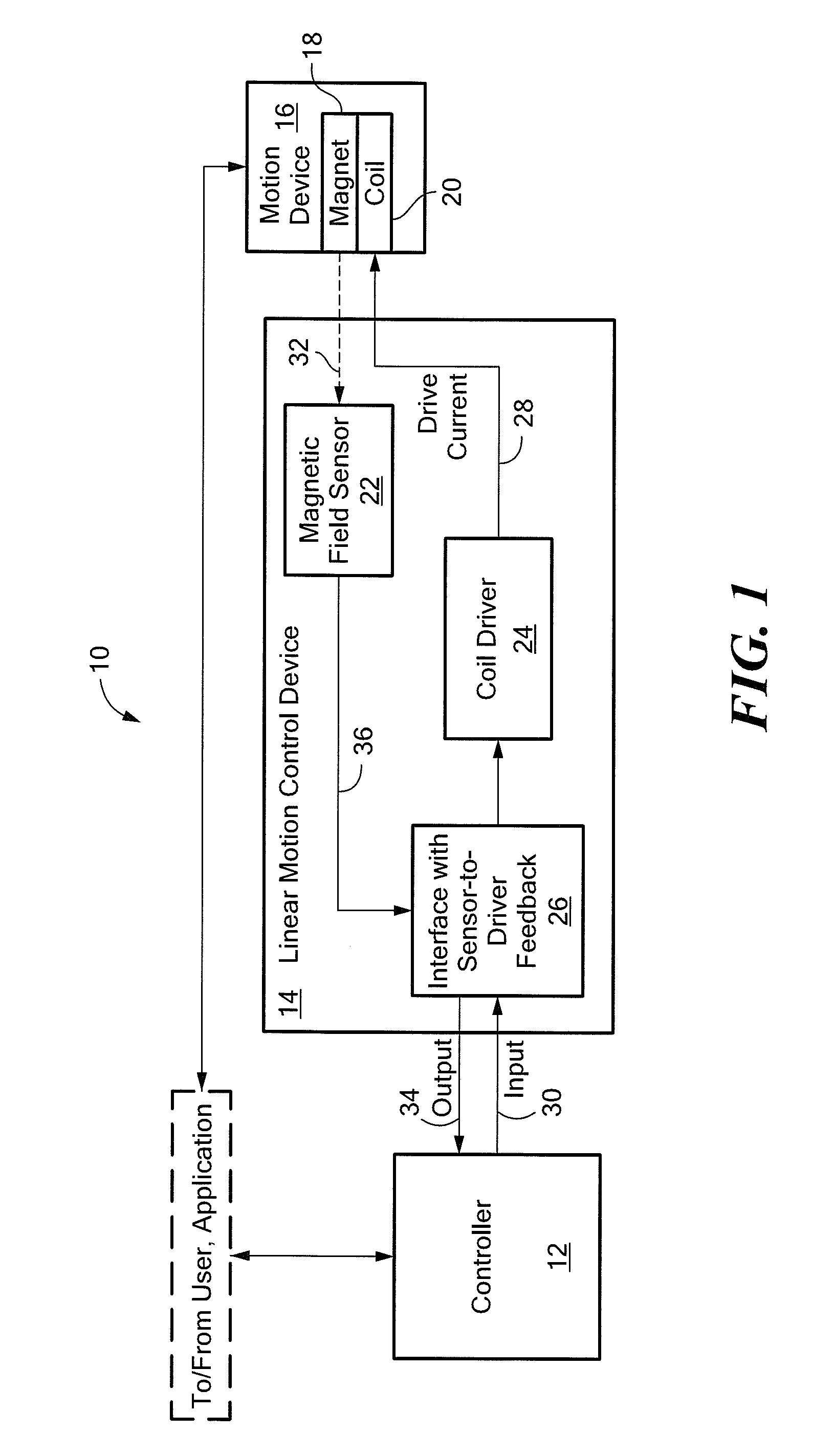
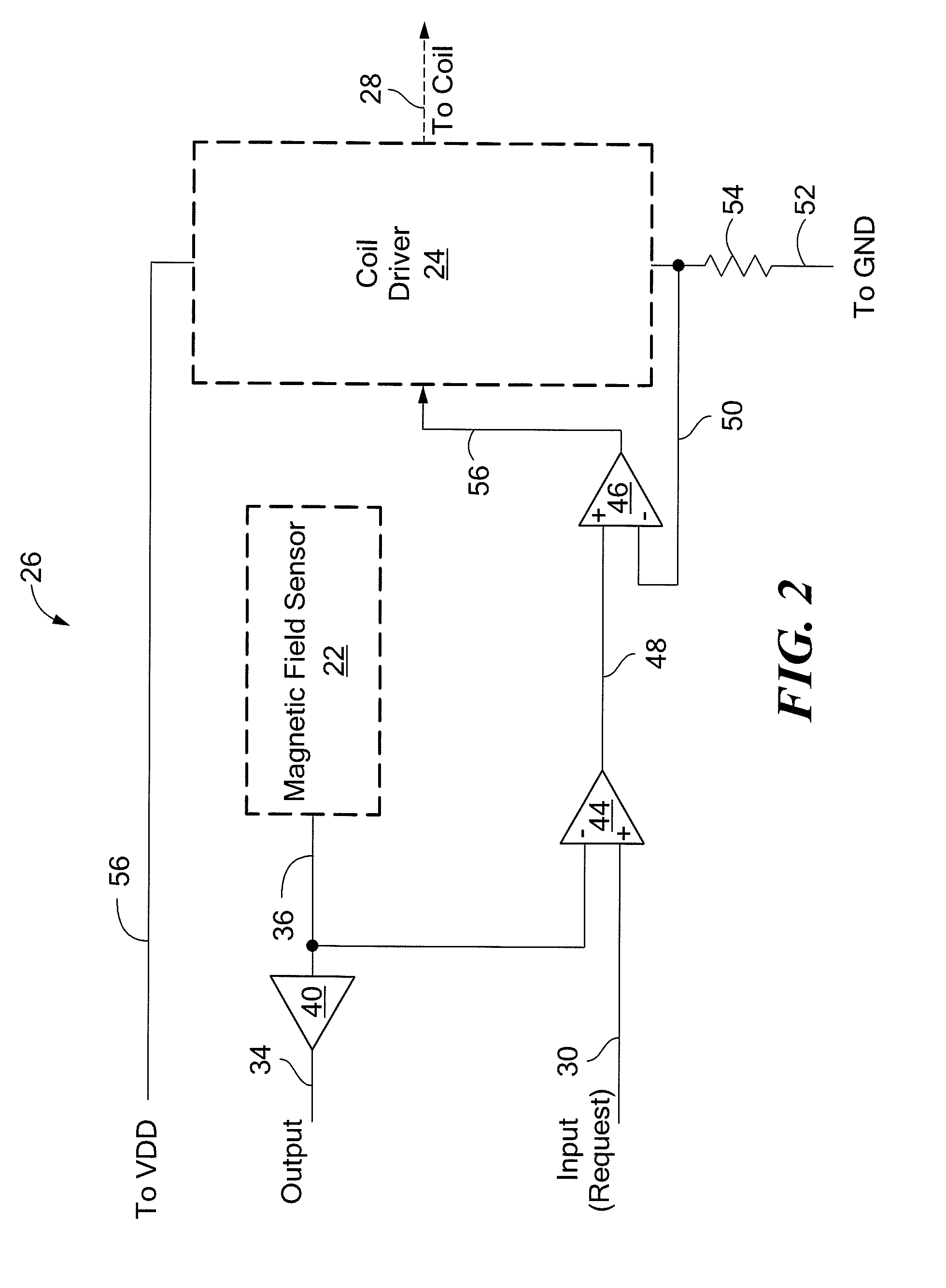
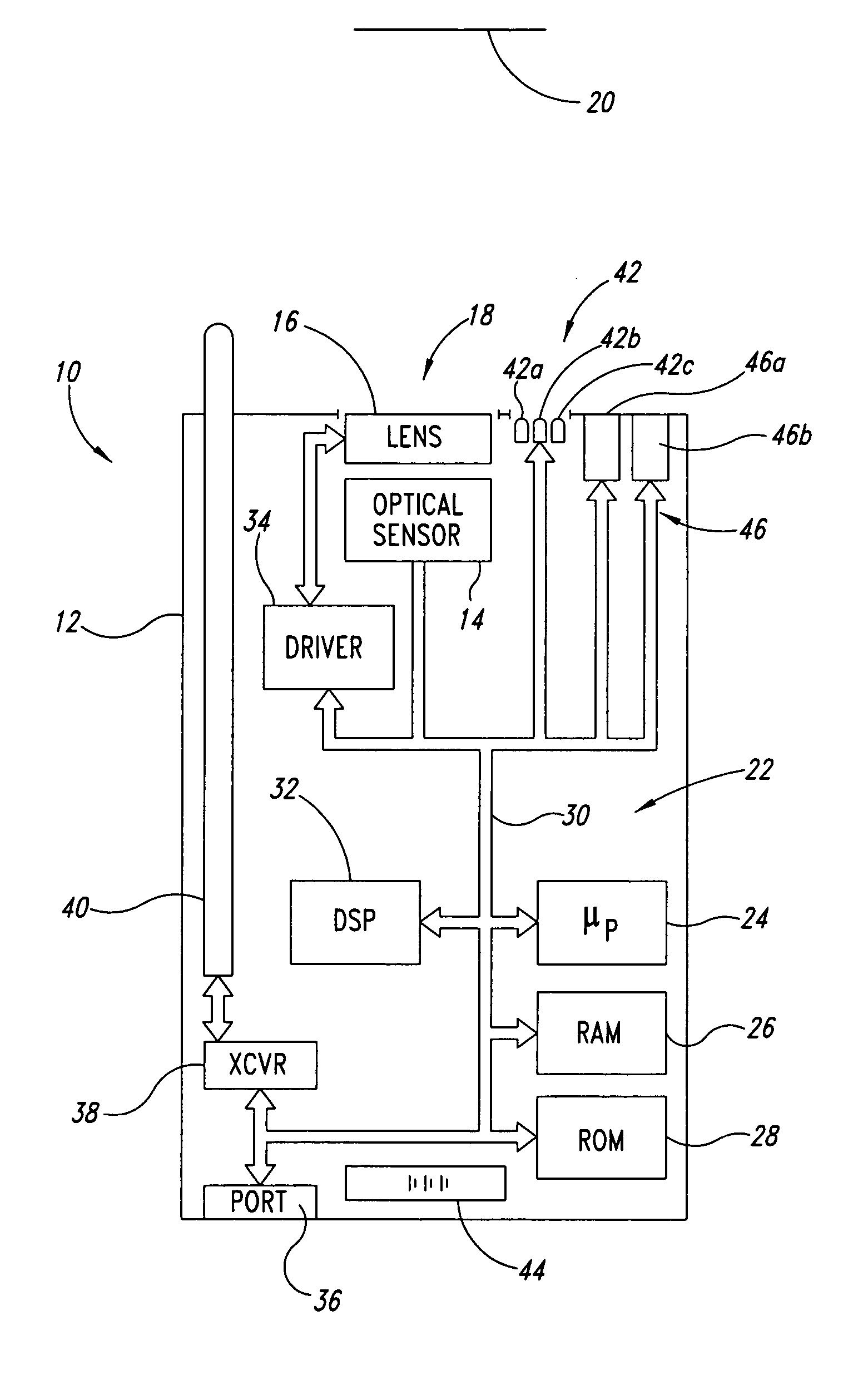
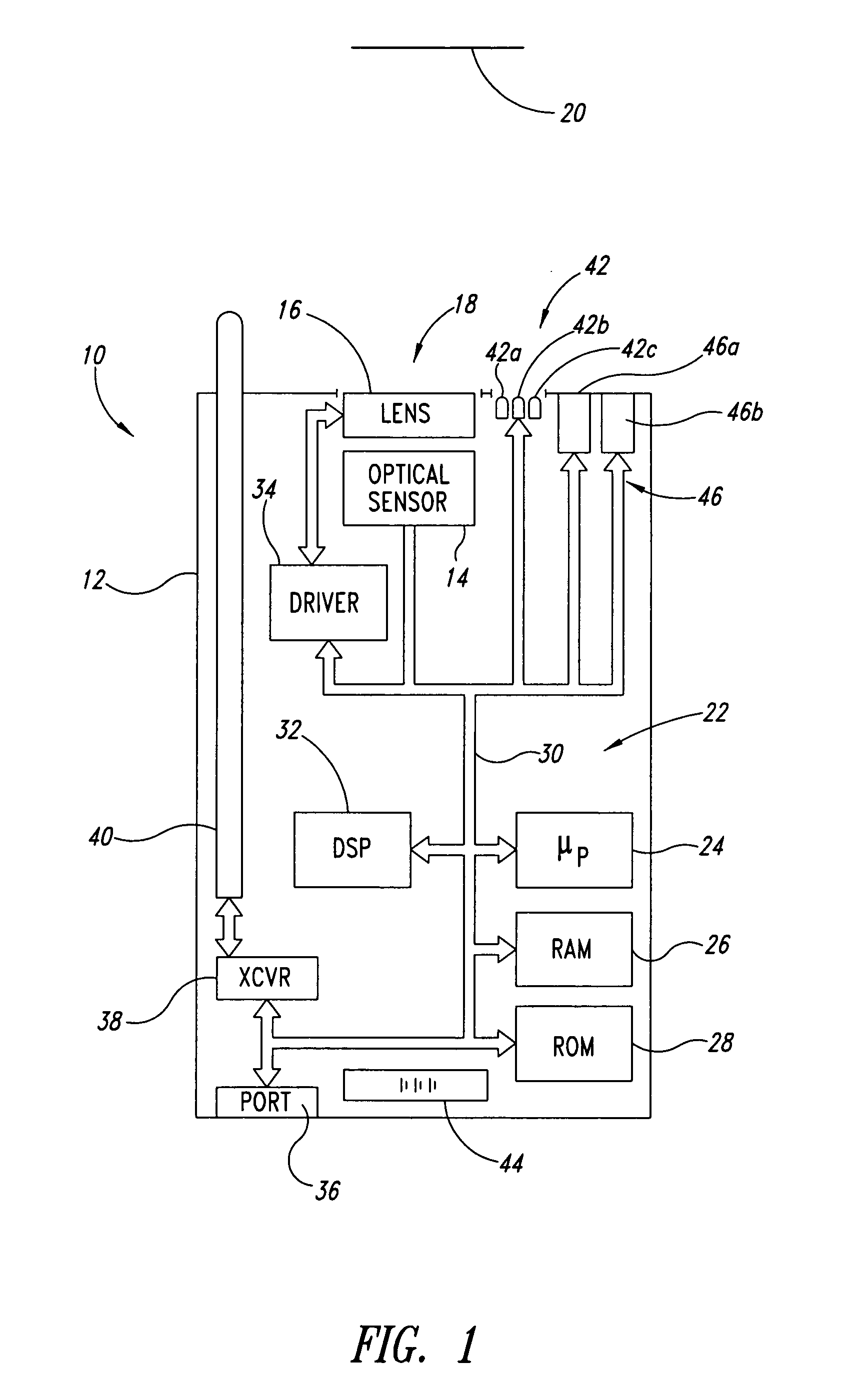
Hall-effect based linear motor controller
Owner:ALLEGRO MICROSYSTEMS INC
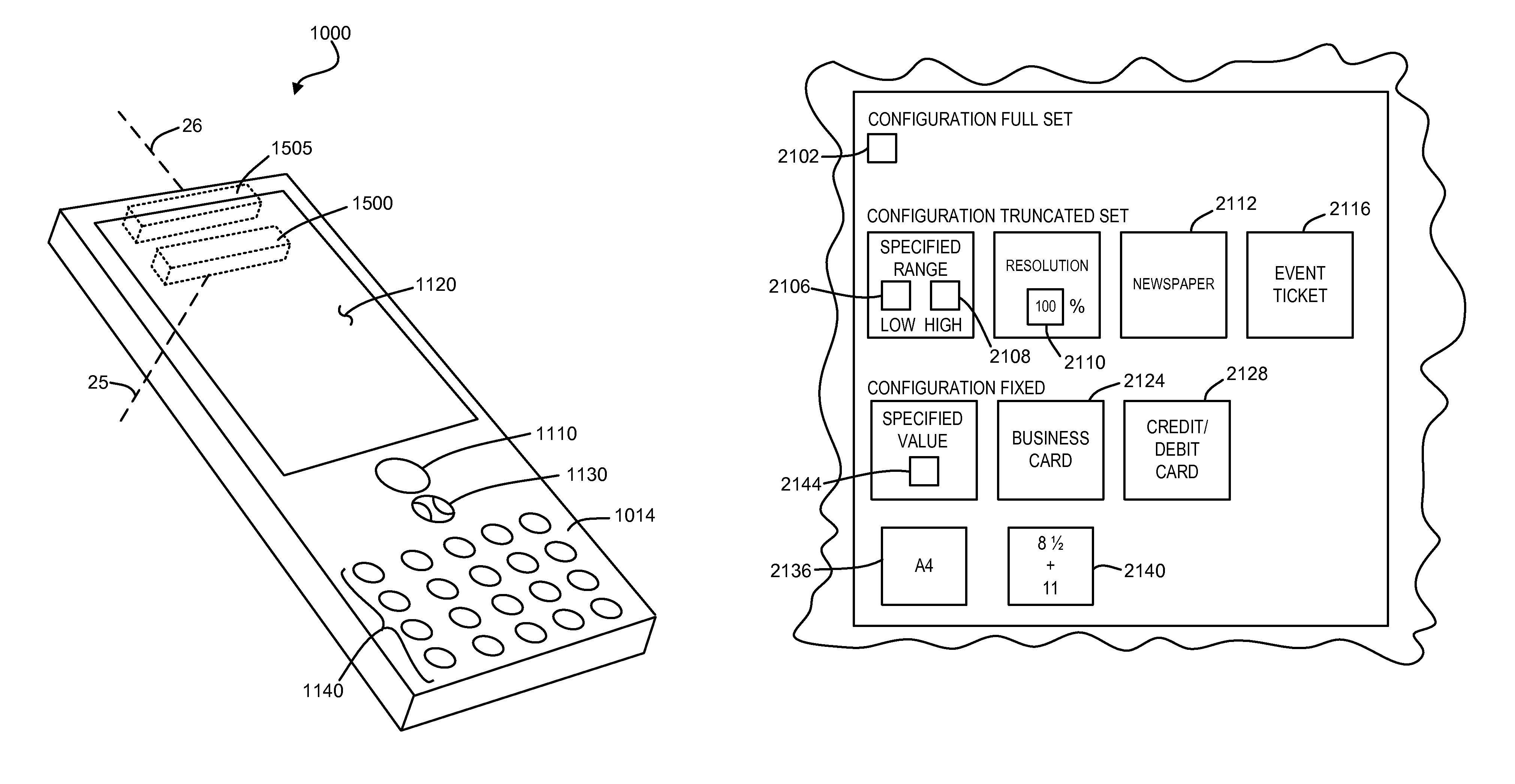
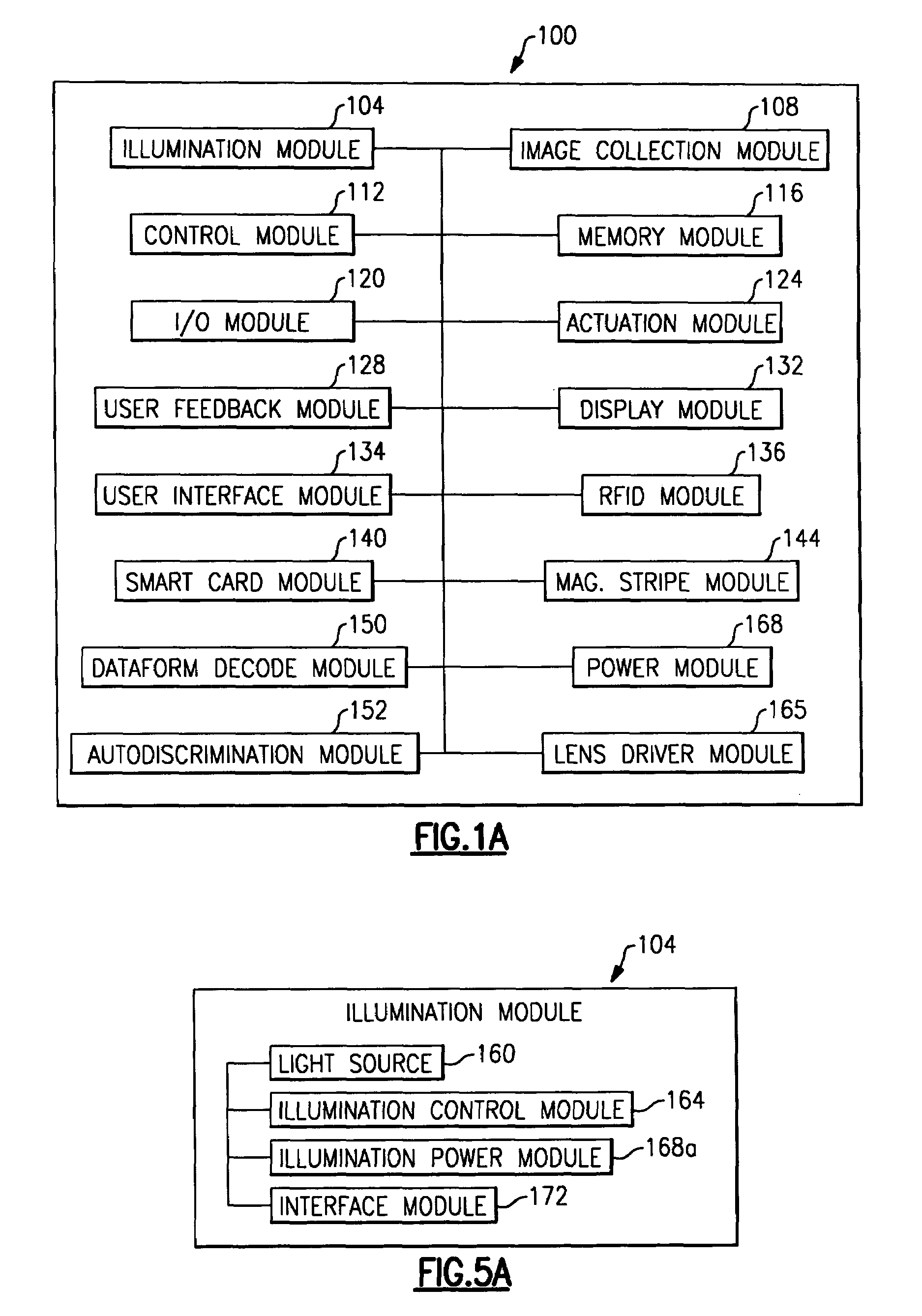
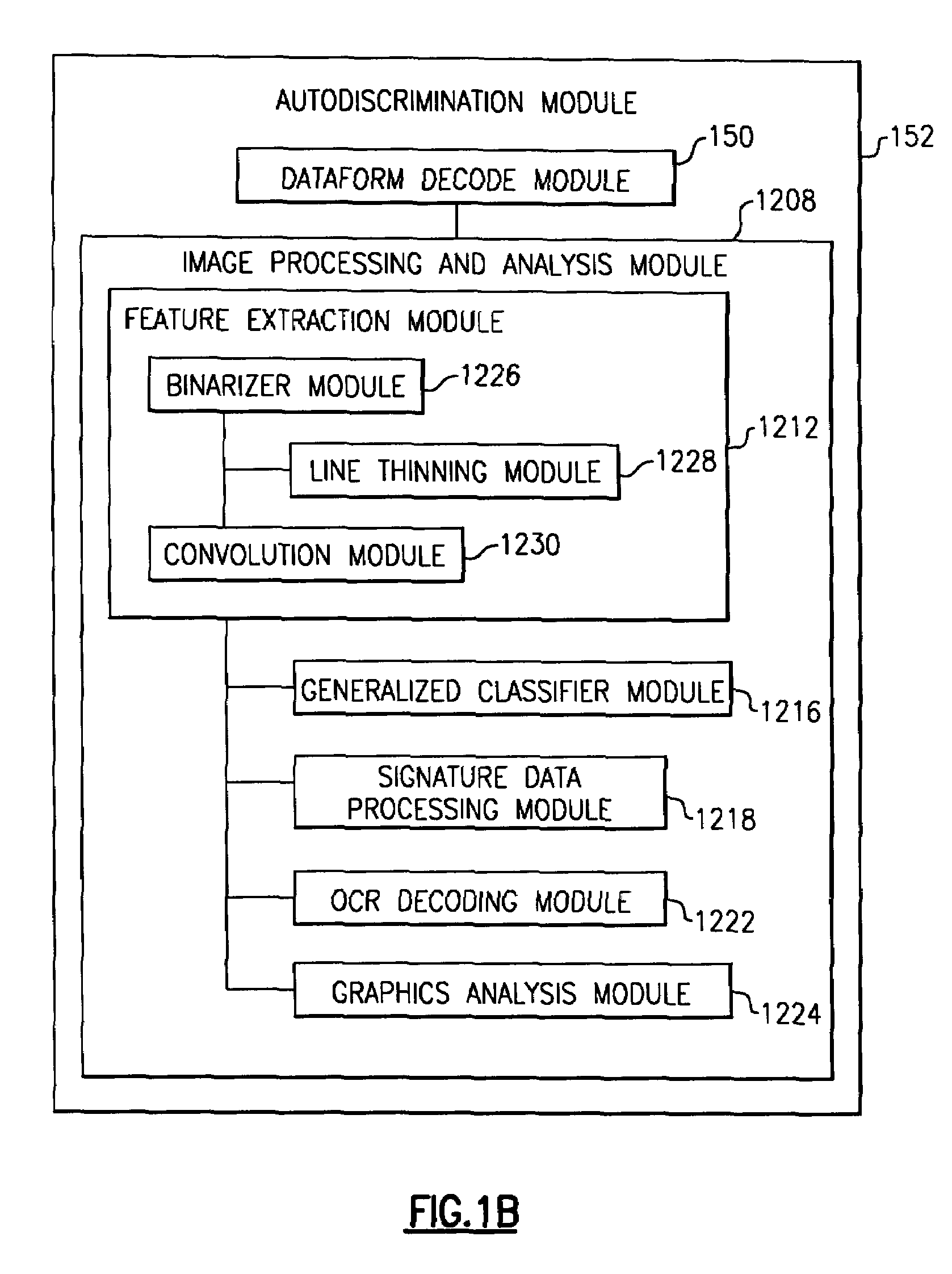
Imaging terminal having focus control
ActiveUS8692927B2Television system detailsTelevision system scanning detailsImaging lensBiological activation
There is set forth herein an imaging terminal having an image sensor array and a variable lens assembly for focusing an image onto the image sensor array. In one embodiment, an imaging terminal can include one or more focusing configuration selected from the group comprising a full set focusing configuration, a truncated set focusing configuration and a fixed focusing configuration. When a full set focusing configuration is active, a full set of candidate focus settings can be active when the imaging terminal determines a focus setting of the terminal responsively to a trigger signal activation. When a truncated set focusing configuration is active, a truncated range of candidate focus settings can be active when the imaging terminal determines a focus setting of the terminal responsively to a trigger signal activation. When a fixed focusing configuration is active, the focus setting of the imaging lens assembly can be fixed so that a predetermined lens assembly focus setting is active when a trigger signal is active.
Owner:HAND HELD PRODS
Multiple camera control system
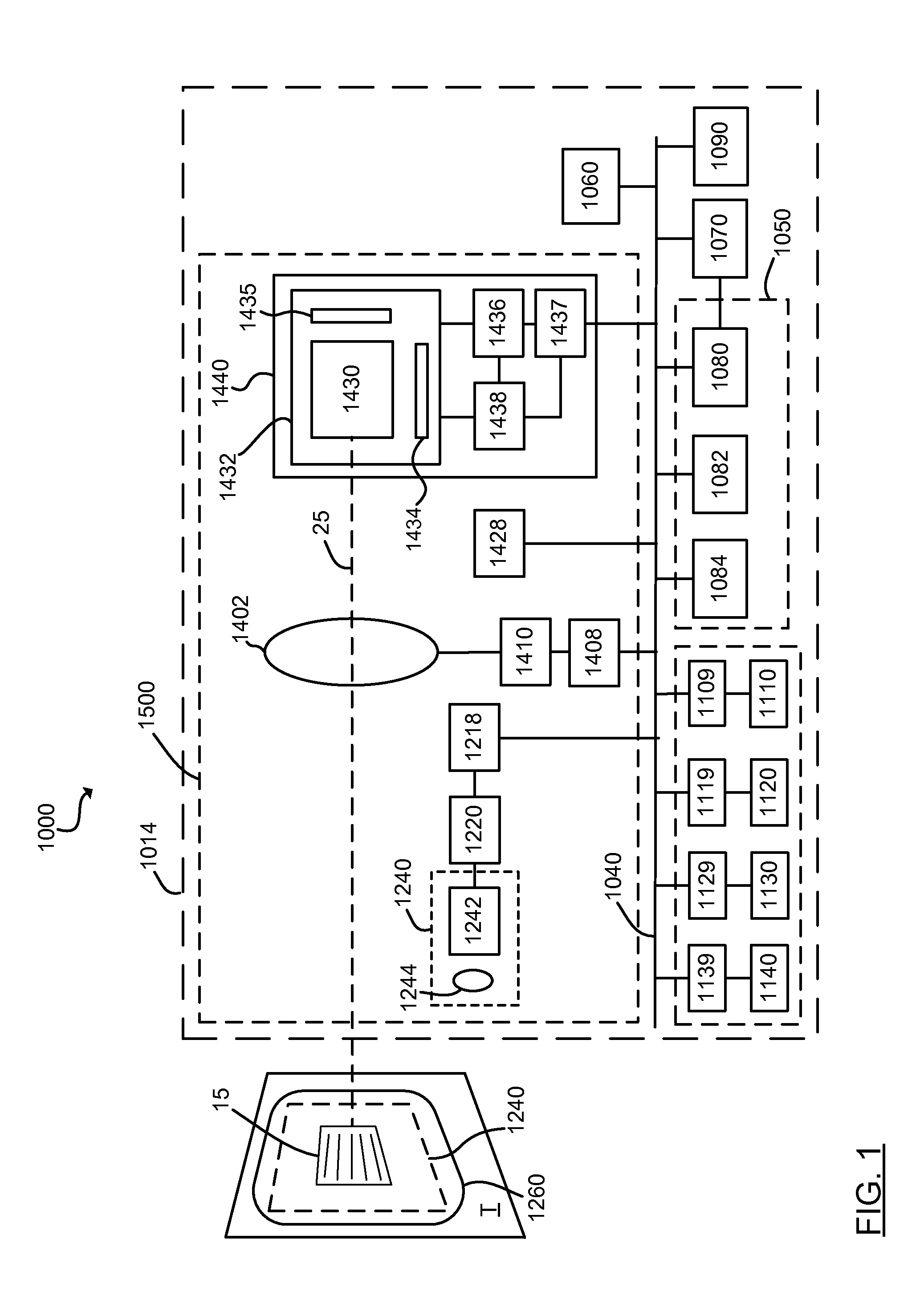
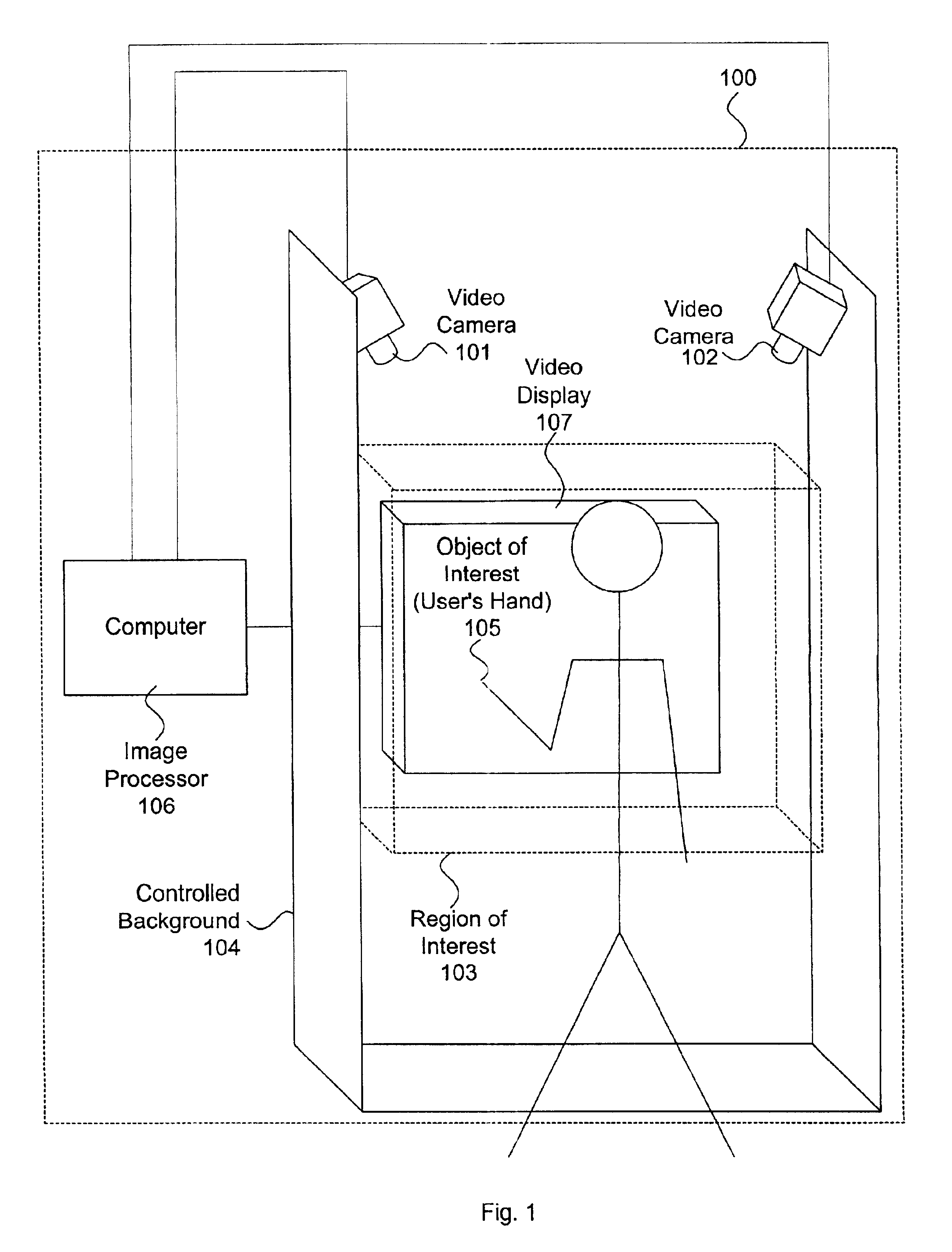
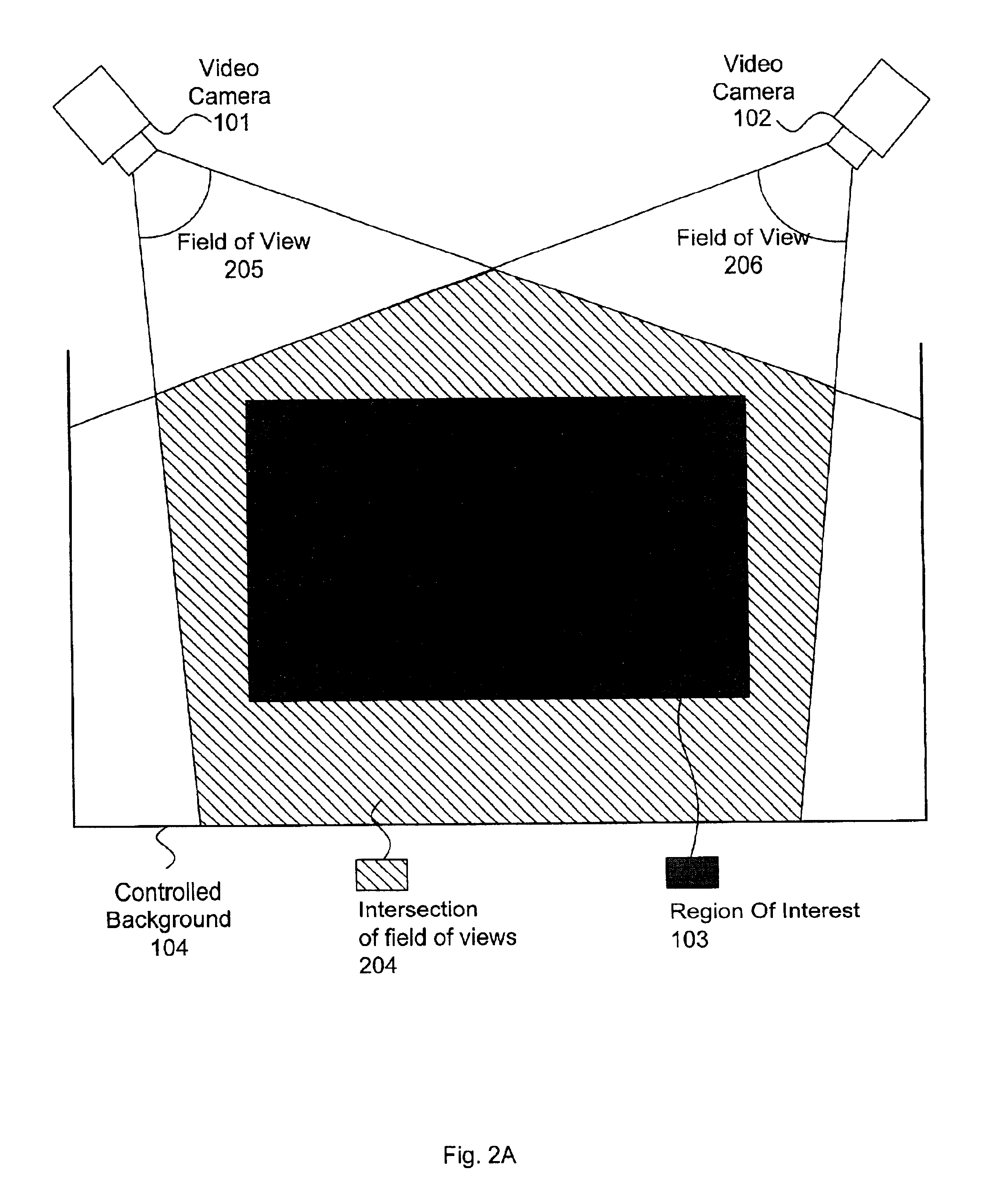
A multiple camera tracking system for interfacing with an application program running on a computer is provided. The tracking system includes two or more video cameras arranged to provide different viewpoints of a region of interest, and are operable to produce a series of video images. A processor is operable to receive the series of video images and detect objects appearing in the region of interest. The processor executes a process to generate a background data set from the video images, generate an image data set for each received video image, compare each image data set to the background data set to produce a difference map for each image data set, detect a relative position of an object of interest within each difference map, and produce an absolute position of the object of interest from the relative positions of the object of interest and map the absolute position to a position indicator associated with the application program.
Owner:QUALCOMM INC
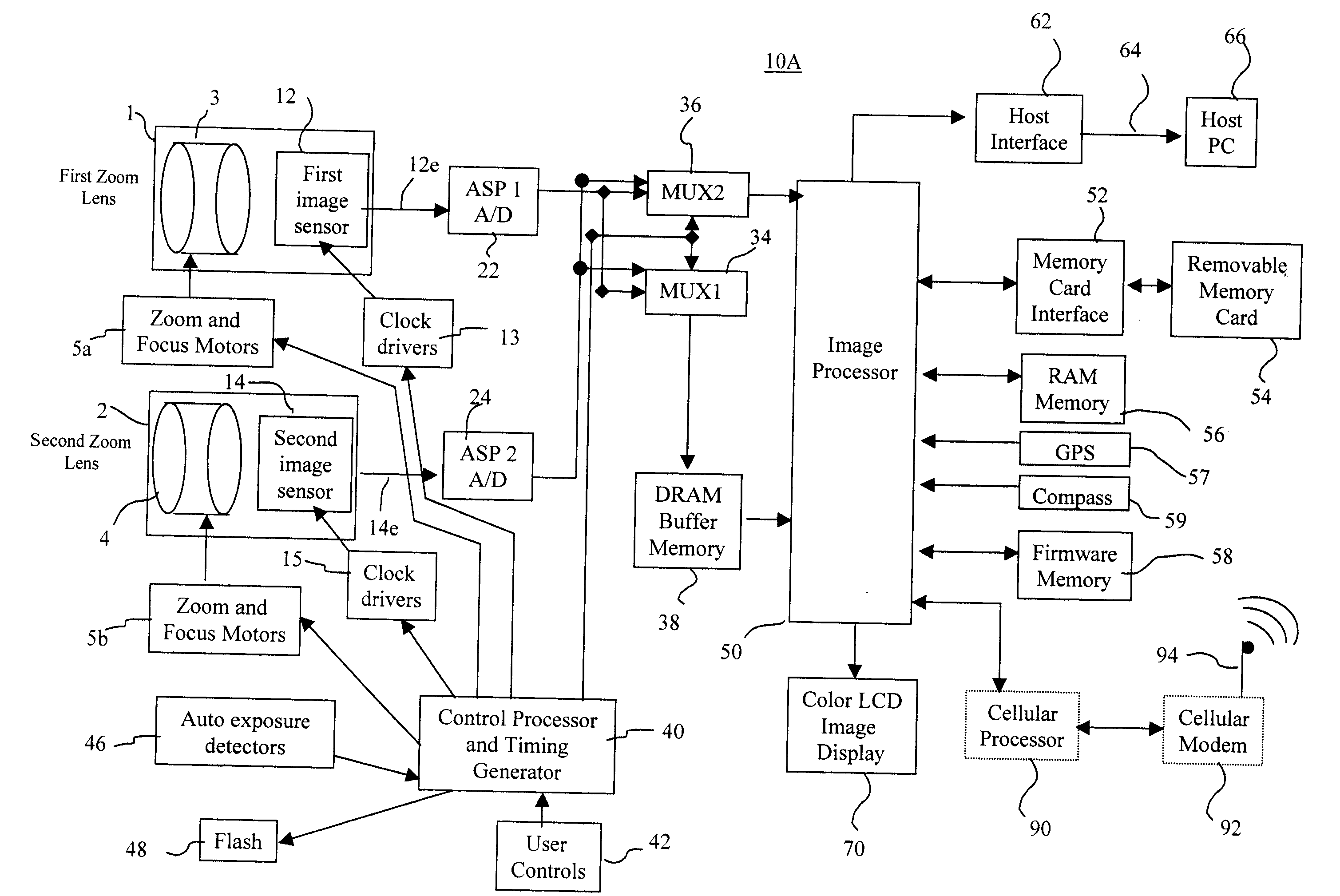
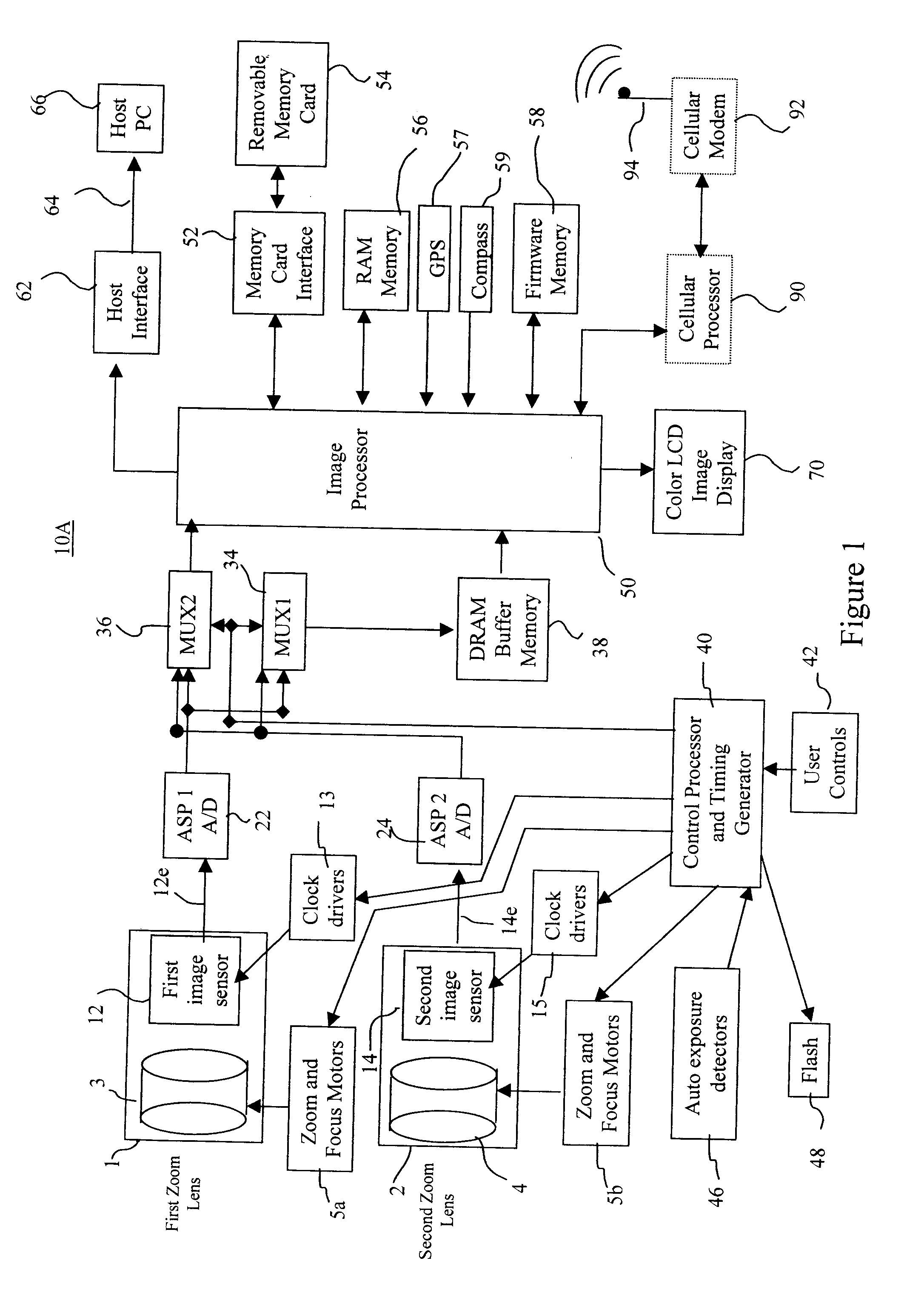
Camera using multiple lenses and image sensors to provide improved focusing capability
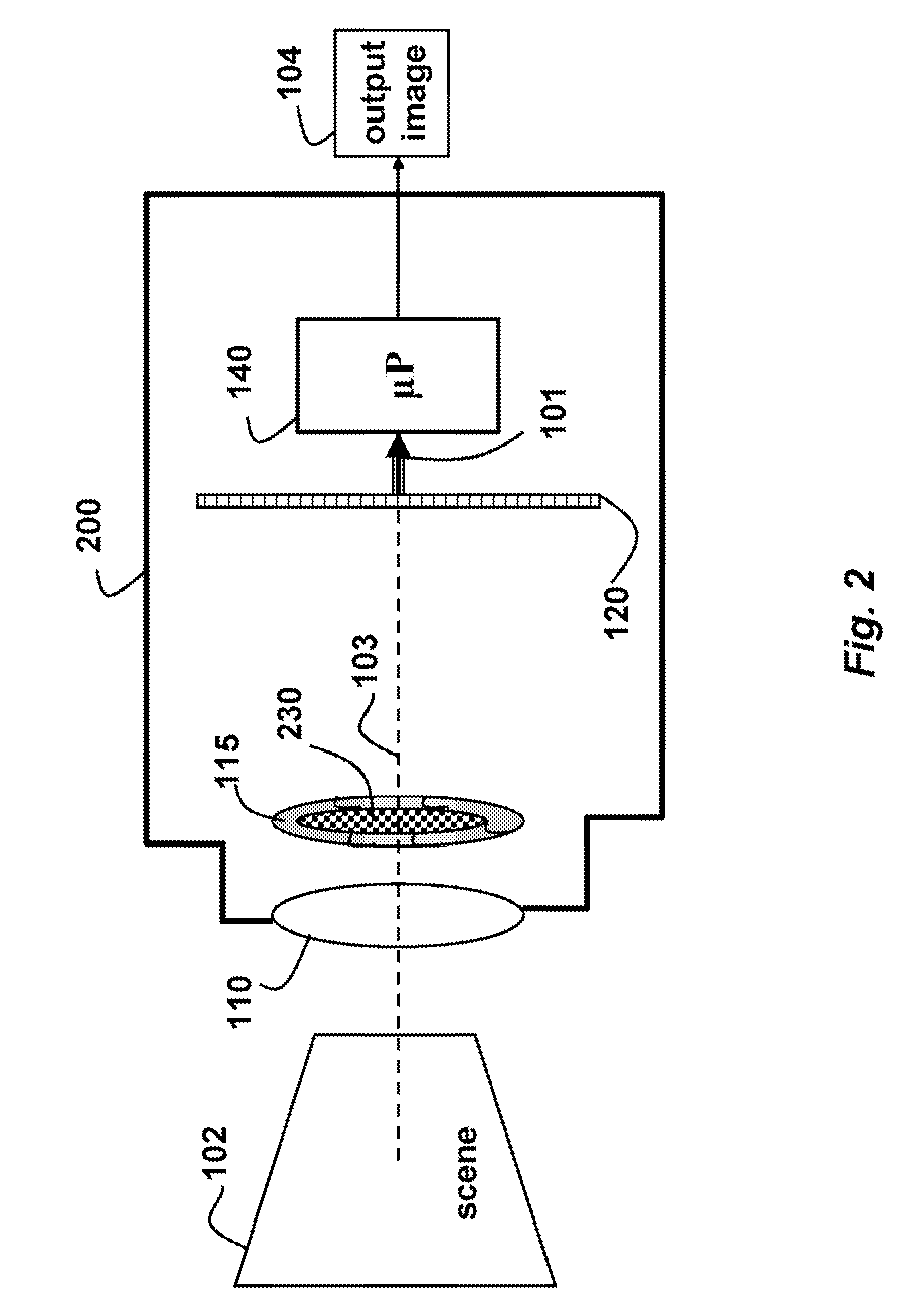
InactiveUS20080219654A1Increasing sizeIncreasing costTelevision system detailsProjector focusing arrangementCamera lensImage signal
An electronic camera for producing an output image of a scene from a captured image signal includes: (a) a first imaging stage comprising a first image sensor for generating a first sensor output; a first lens for forming a first image of the scene on the first image sensor; and a first lens focus adjuster for adjusting focus of the first lens responsive to a first focus detection signal; and (b) a second imaging stage comprising a second image sensor for generating a second sensor output; a second lens for forming a second image of the scene on the second image sensor; and a second lens focus adjuster for adjusting focus of the second lens responsive to a second focus detection signal. A processing stage either (a) selects the sensor output from the first imaging stage as the captured image signal and uses the sensor output from the second imaging stage to generate the first focus detection signal for the selected imaging stage, or (b) selects the sensor output from the second imaging stage as the captured image signal and uses the sensor output from the first imaging stage to generate the second focus detection signal for the selected imaging stage.
Owner:INTELLECTUAL VENTURES FUND 83 LLC
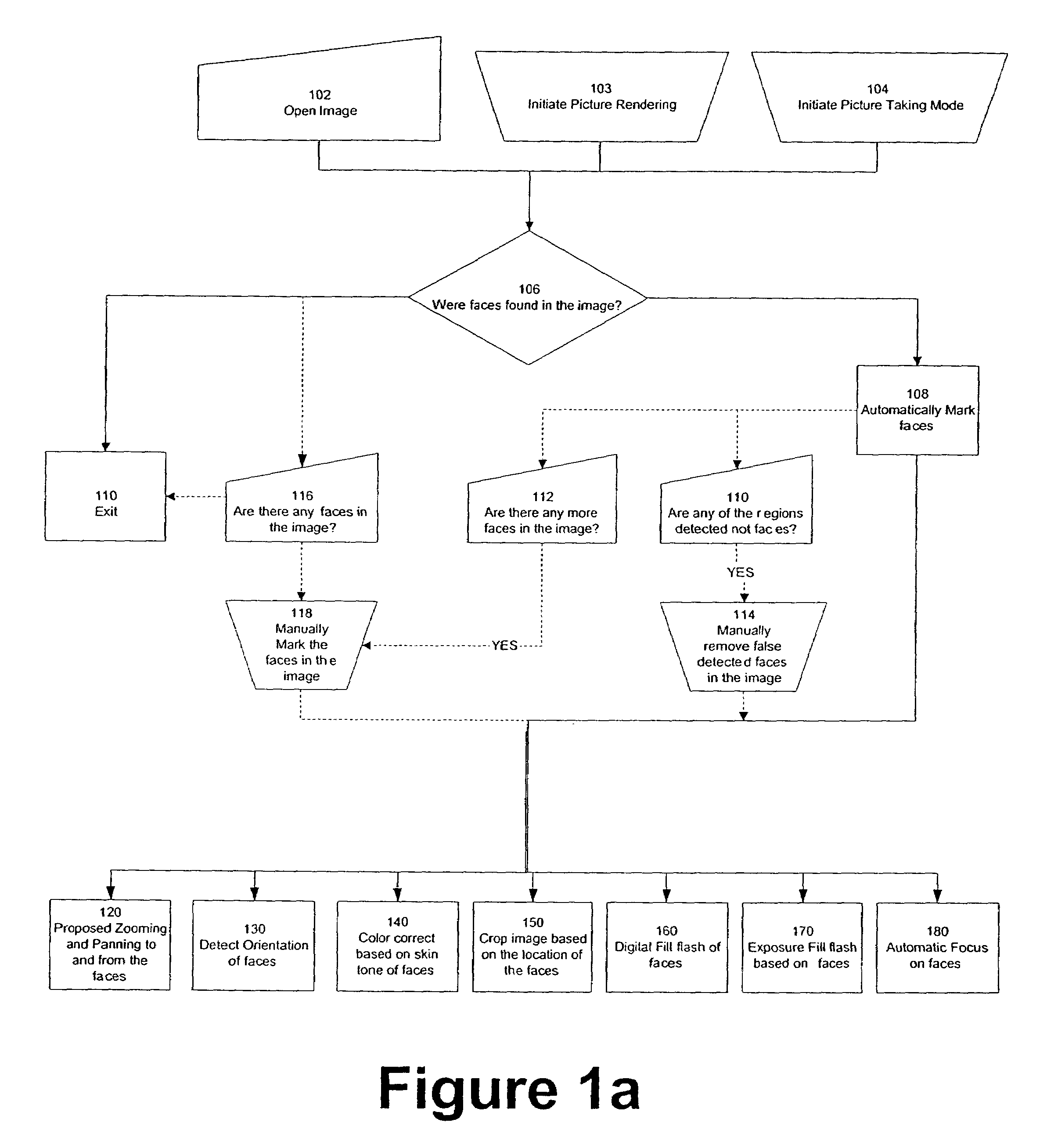
System and method for automatically setting image acquisition controls
InactiveUS6301440B1Television system detailsProjector focusing arrangementSubject matterComputer image
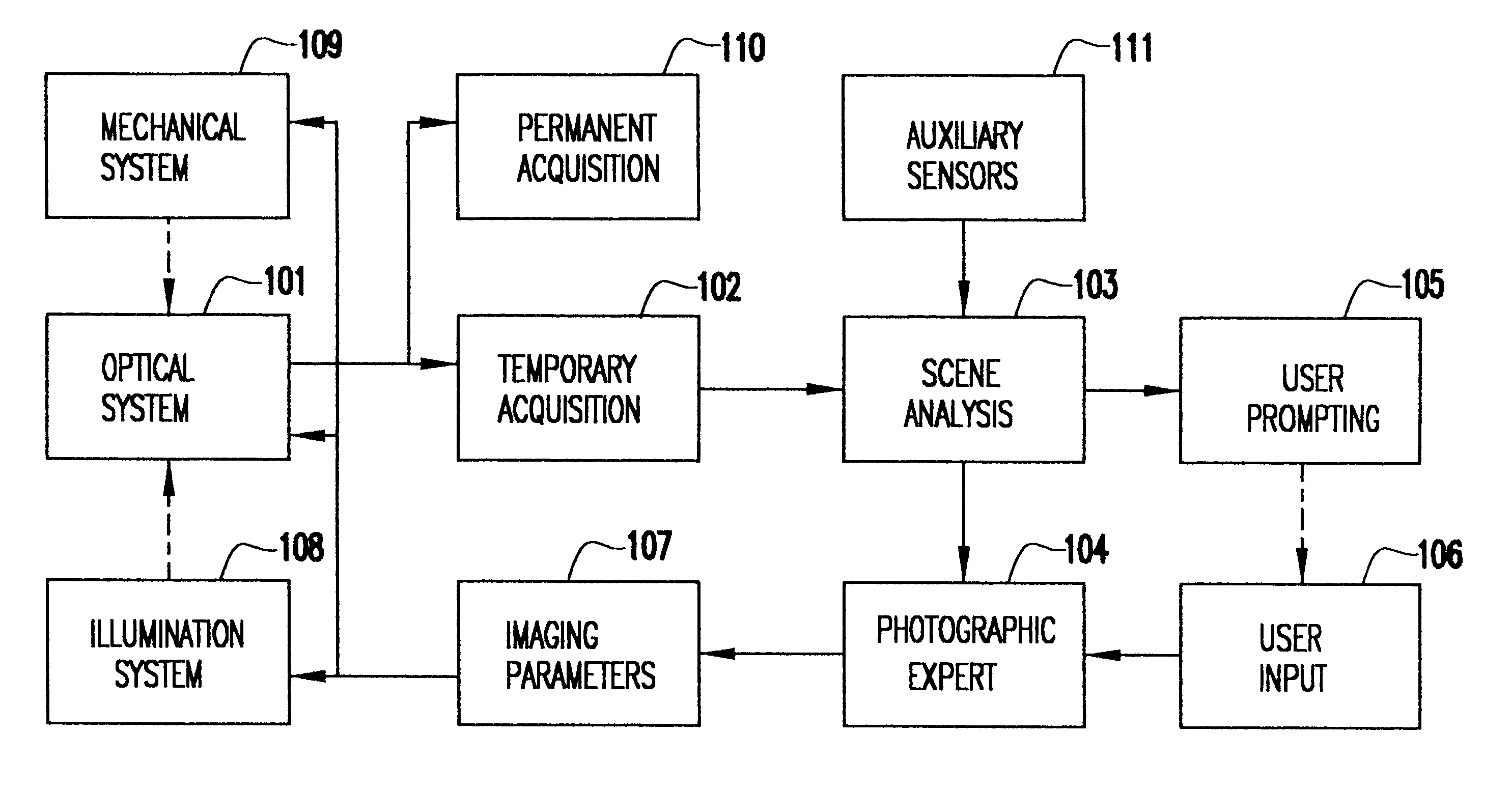
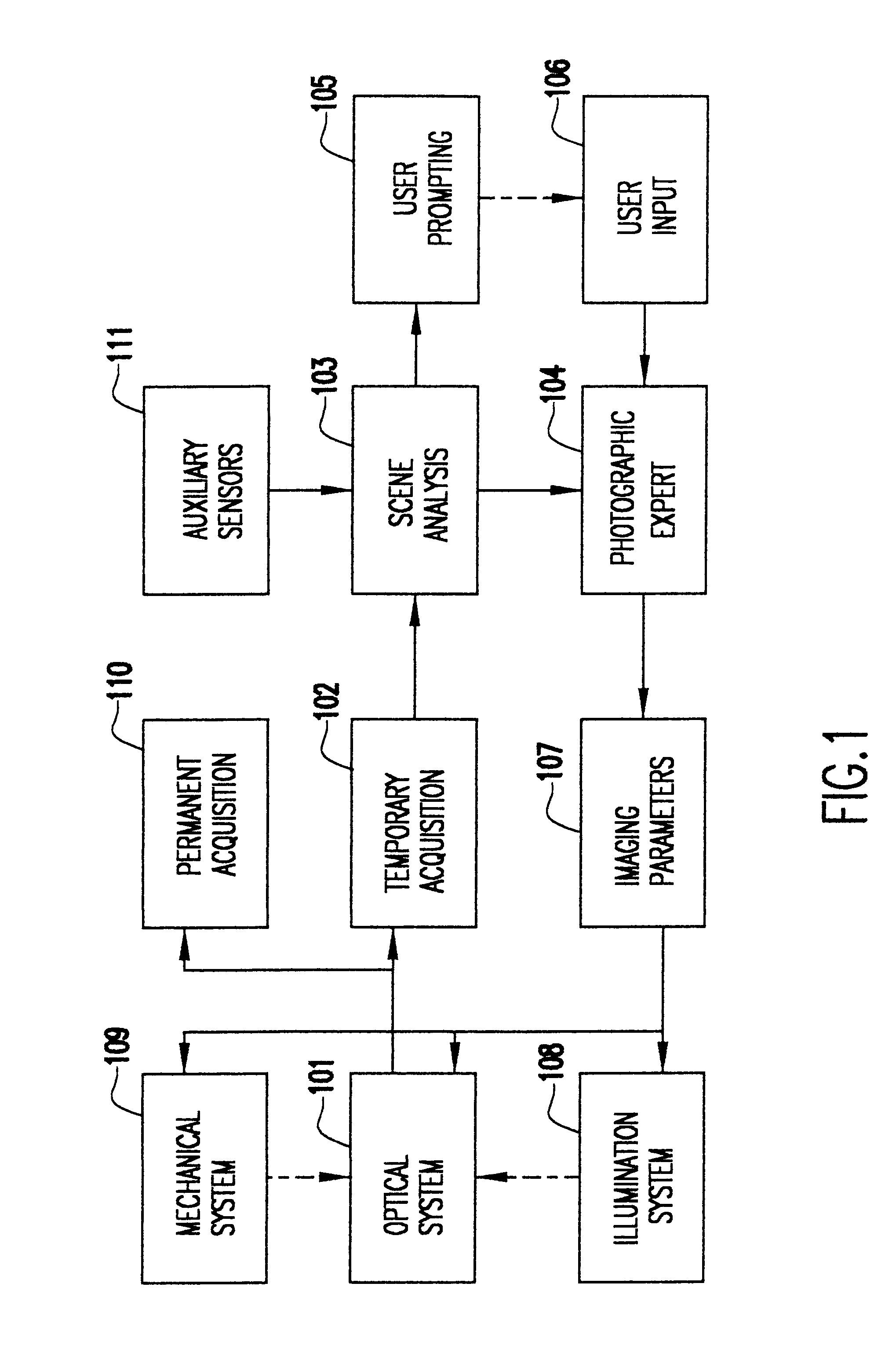
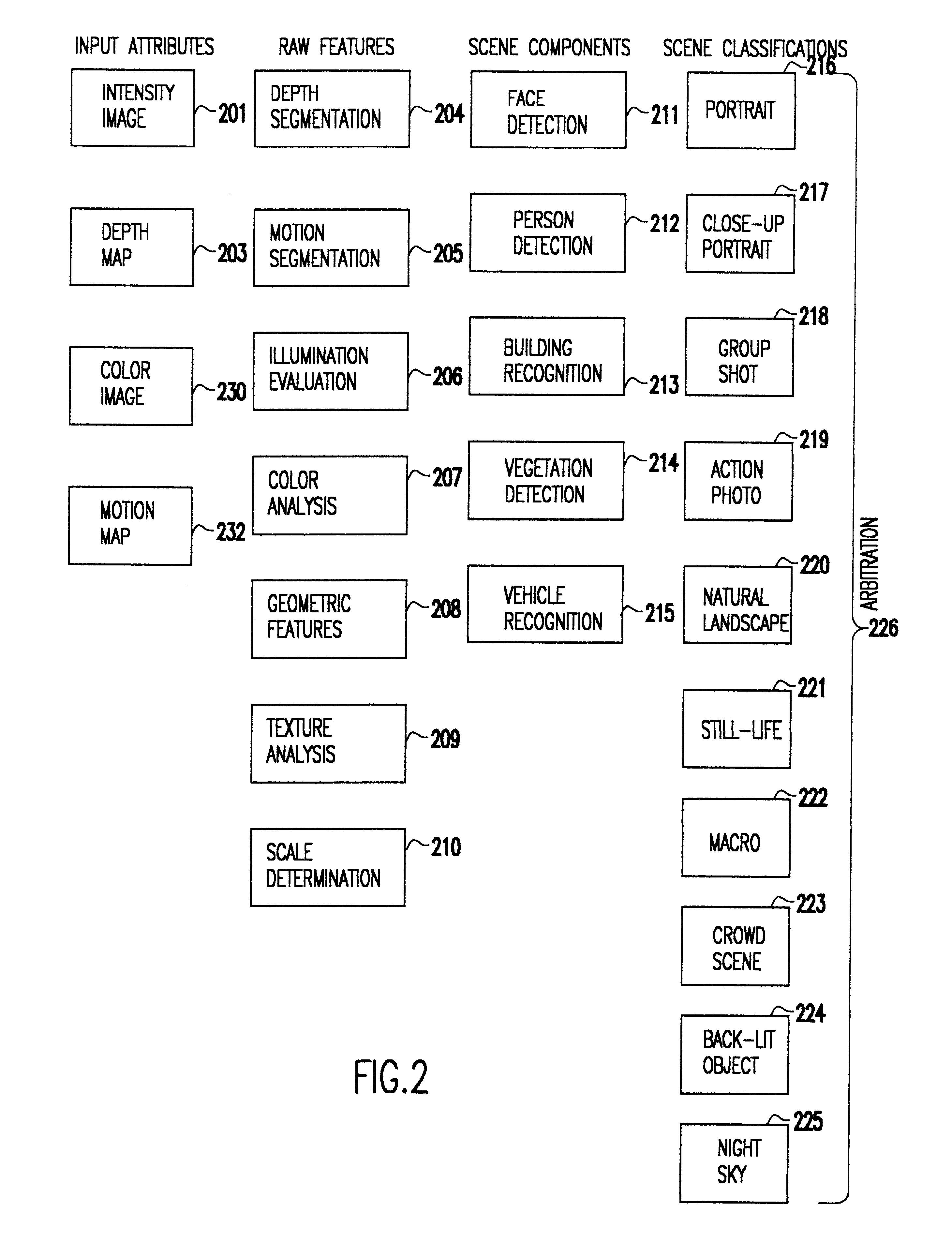
A system and method use computer image processing for setting the parameters for an image acquisition device of a camera. The image parameters are set automatically by analyzing the image to be taken, and setting the controls according to the subject matter, in the same manner as an expert photographer would be able to. The system can run in a fully automatic mode choosing the best image parameters, or a "guided mode" where the user is prompted with choices where a number of alternate settings would be reasonable.
Owner:ASML NETHERLANDS BV +1
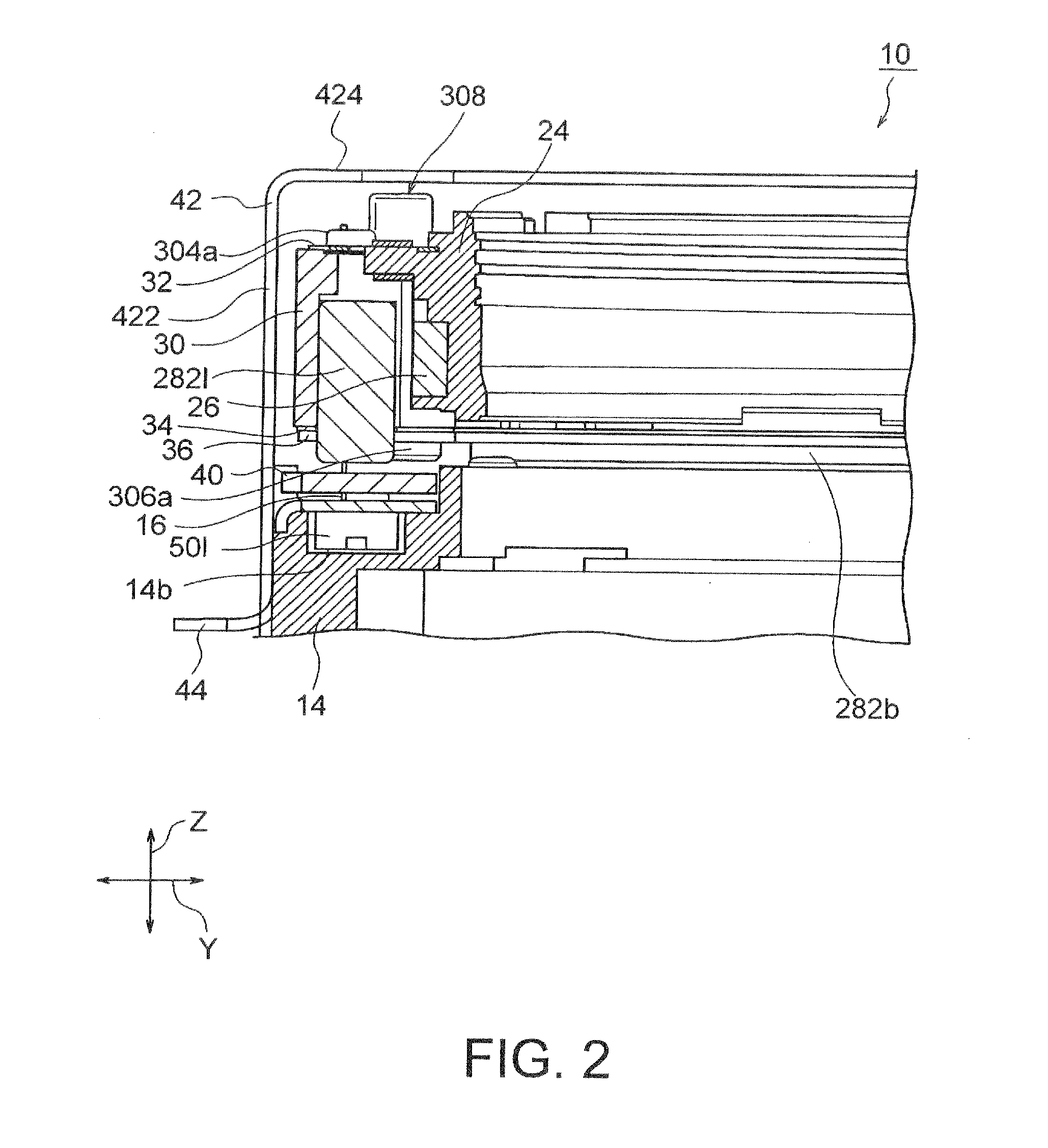
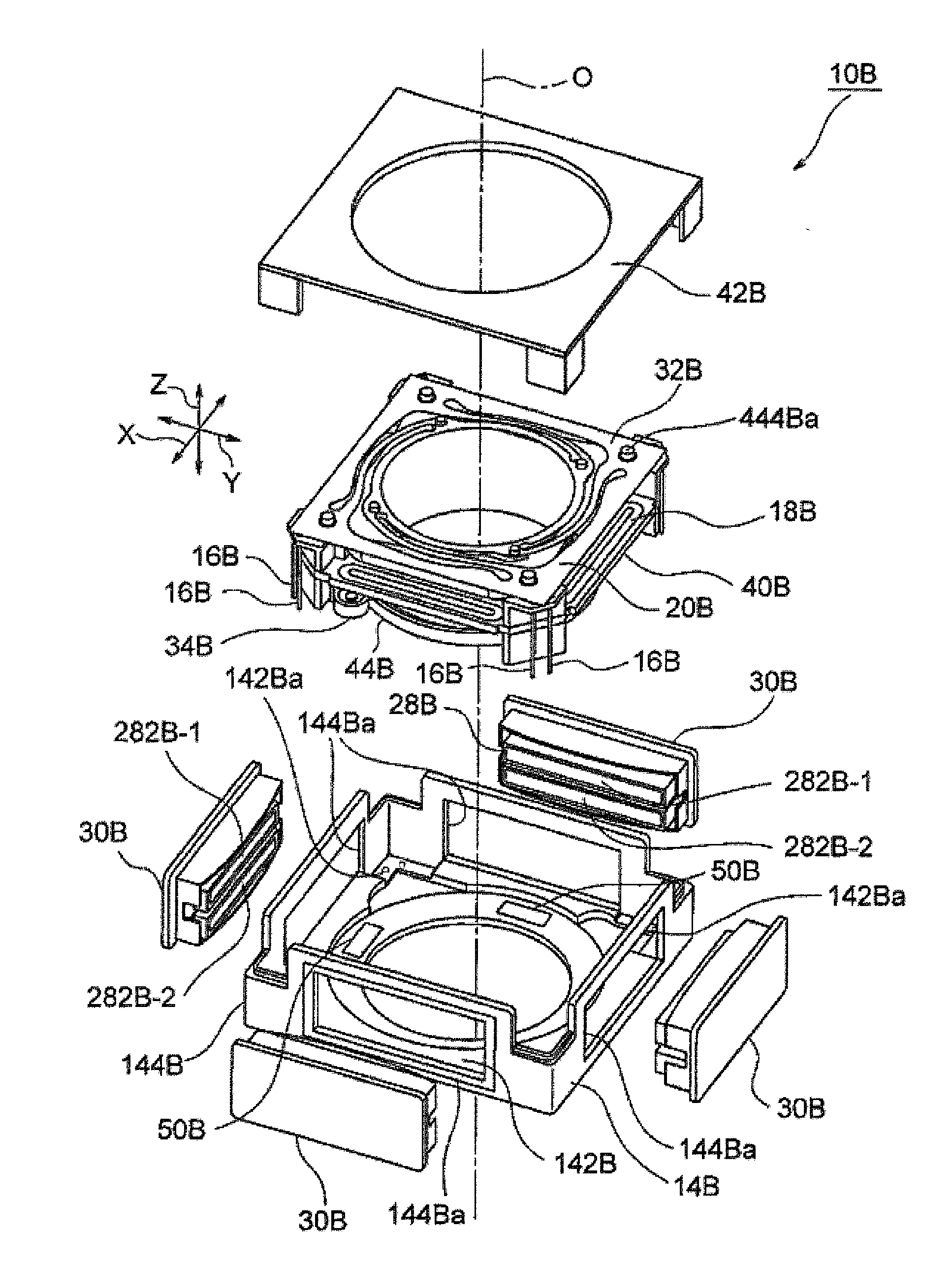
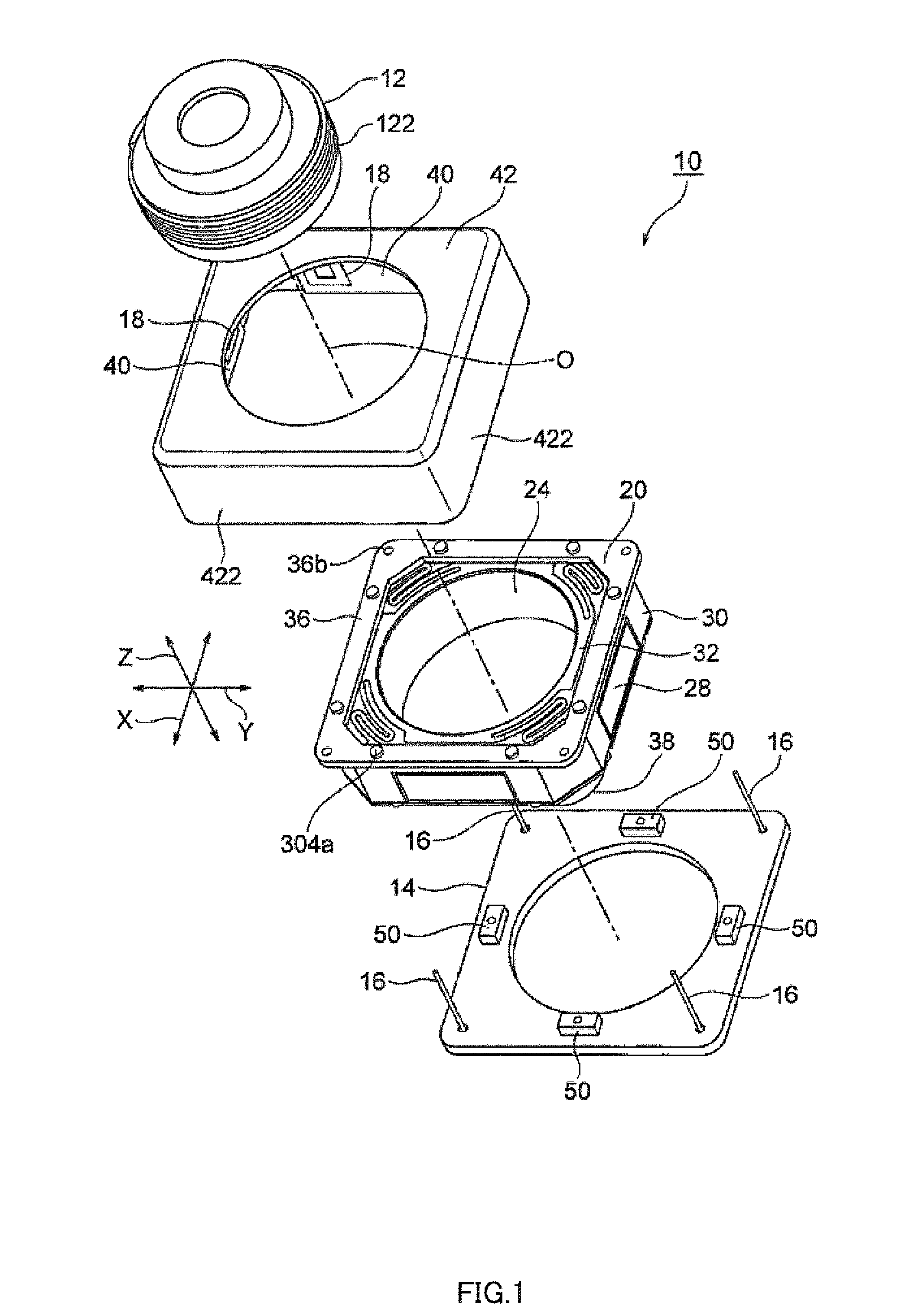
Camera-shake correction device
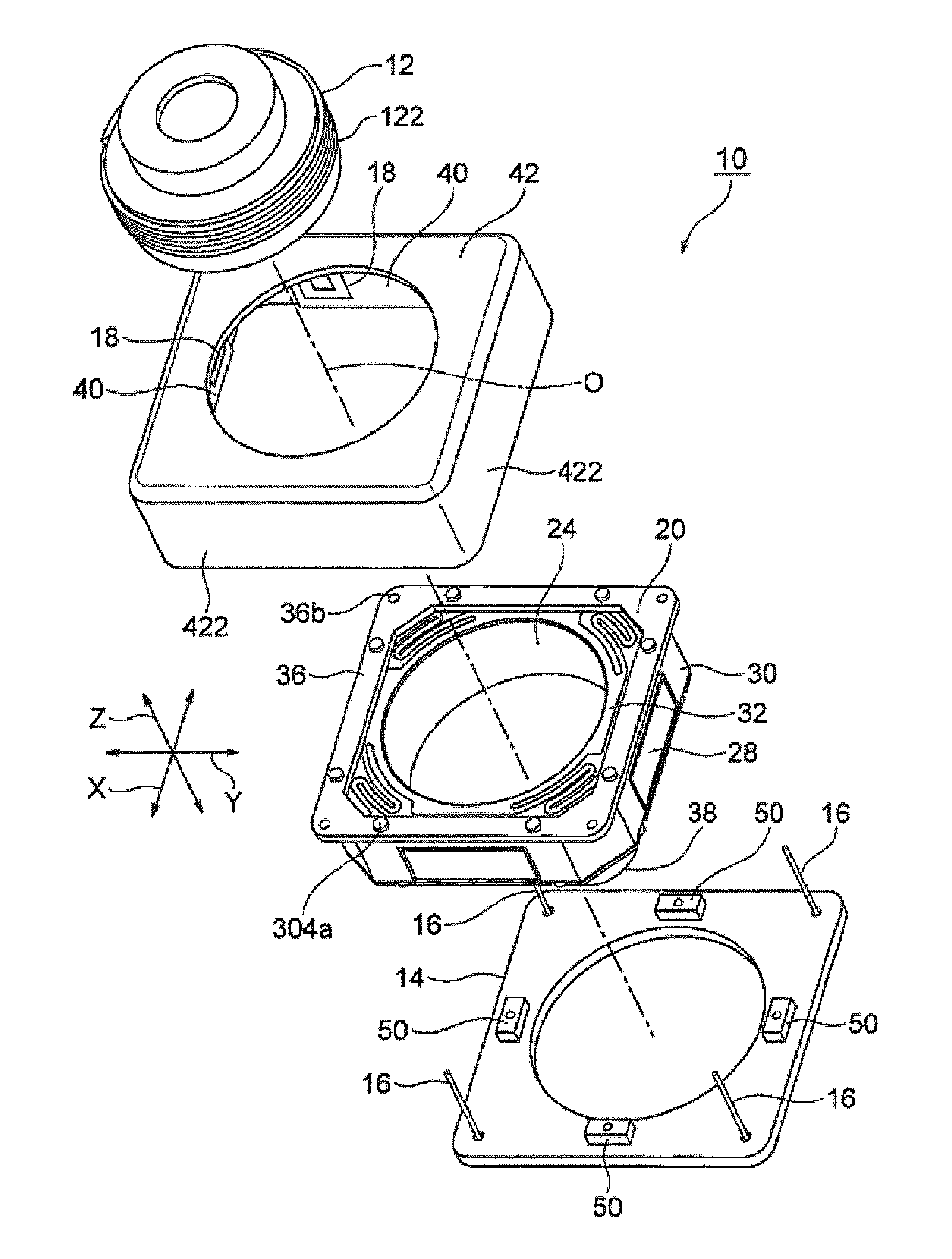
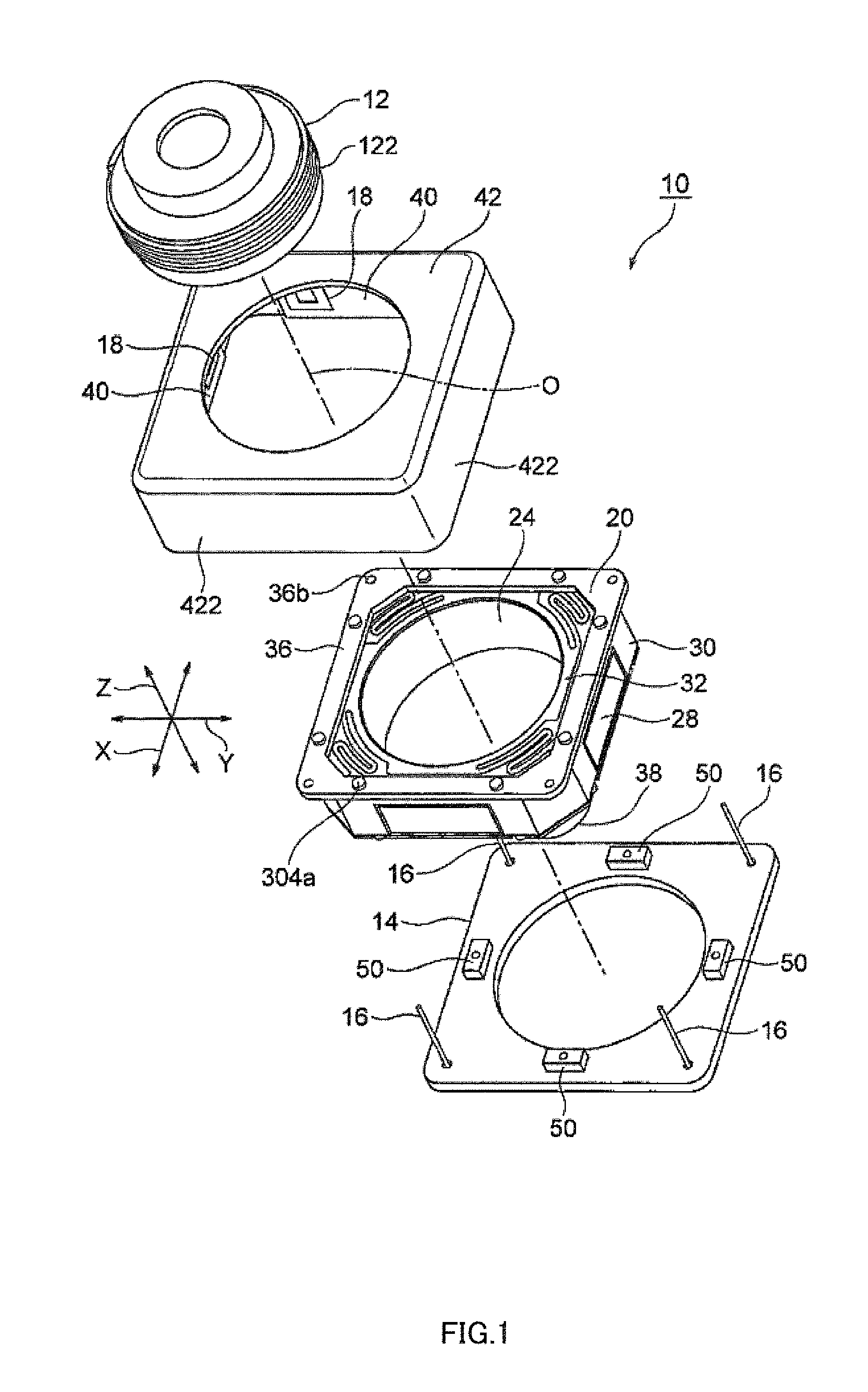
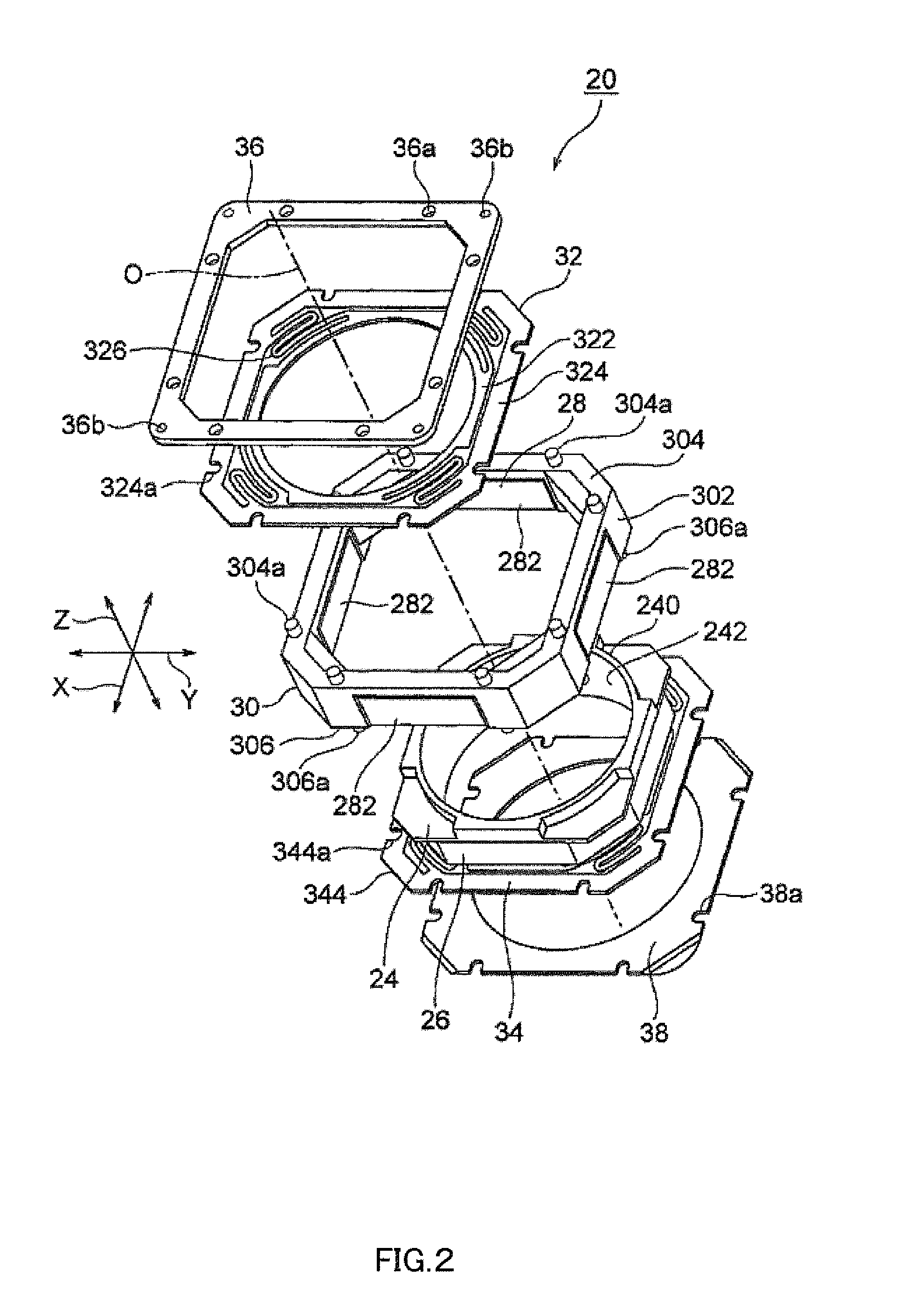
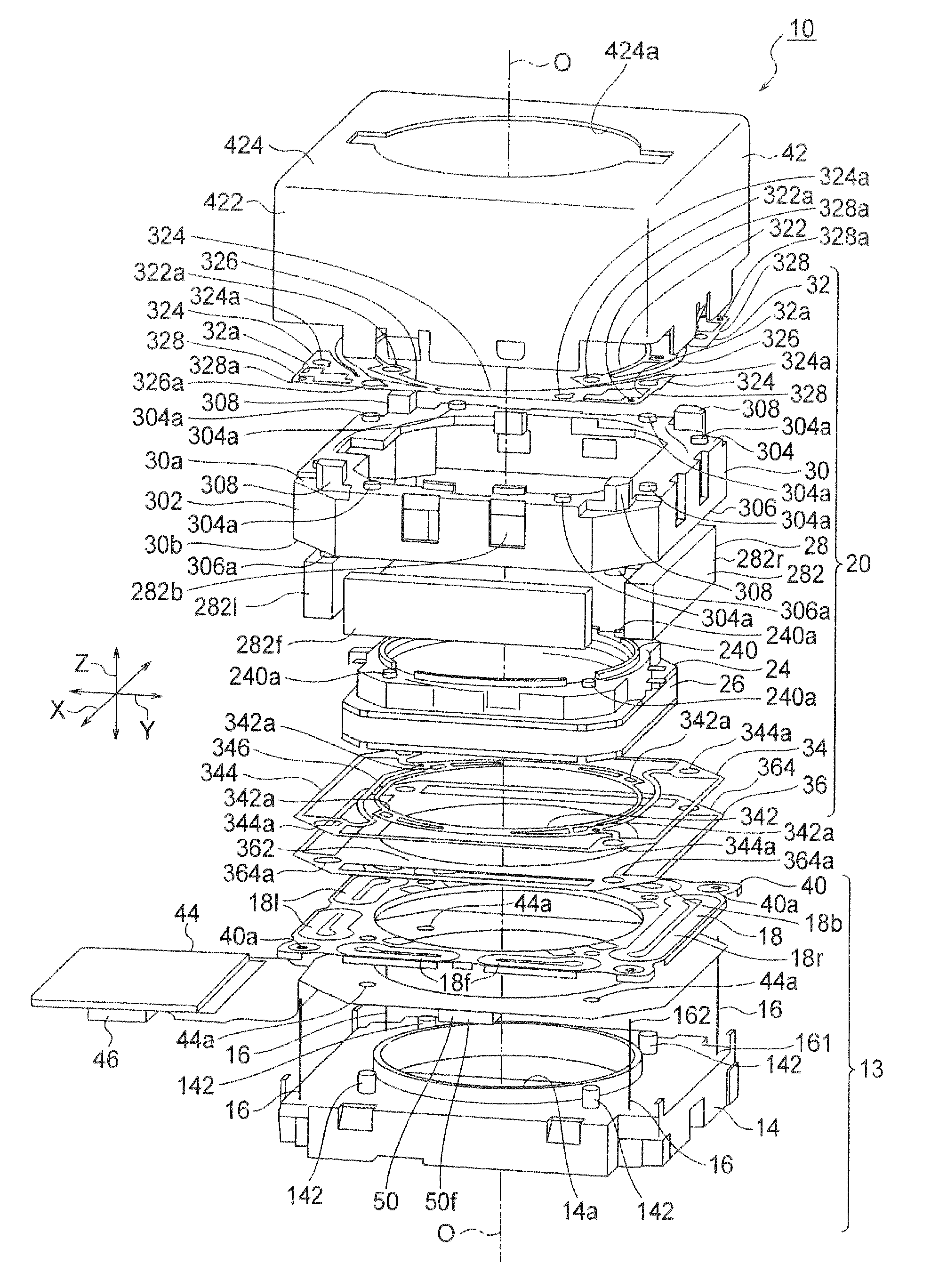
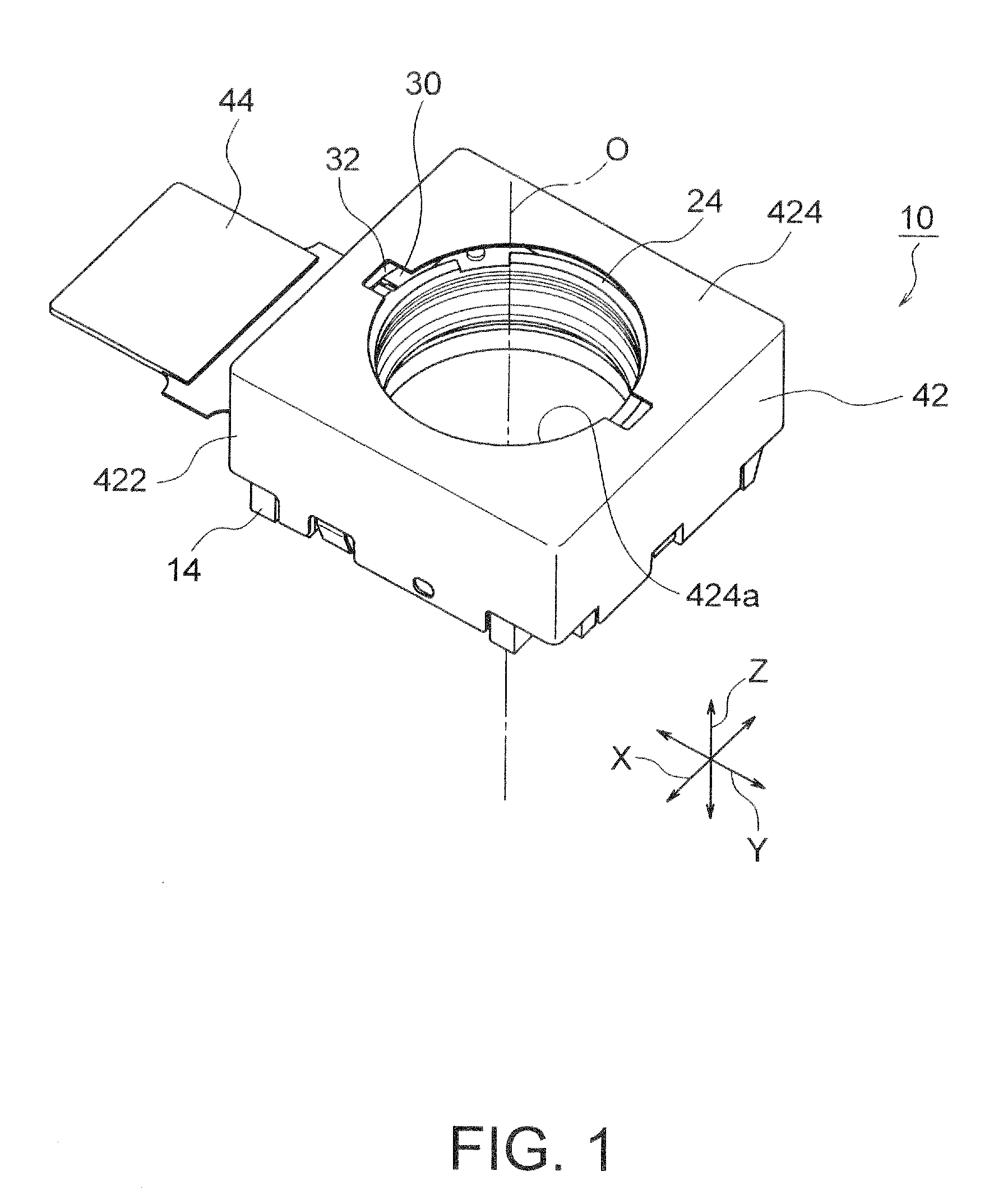
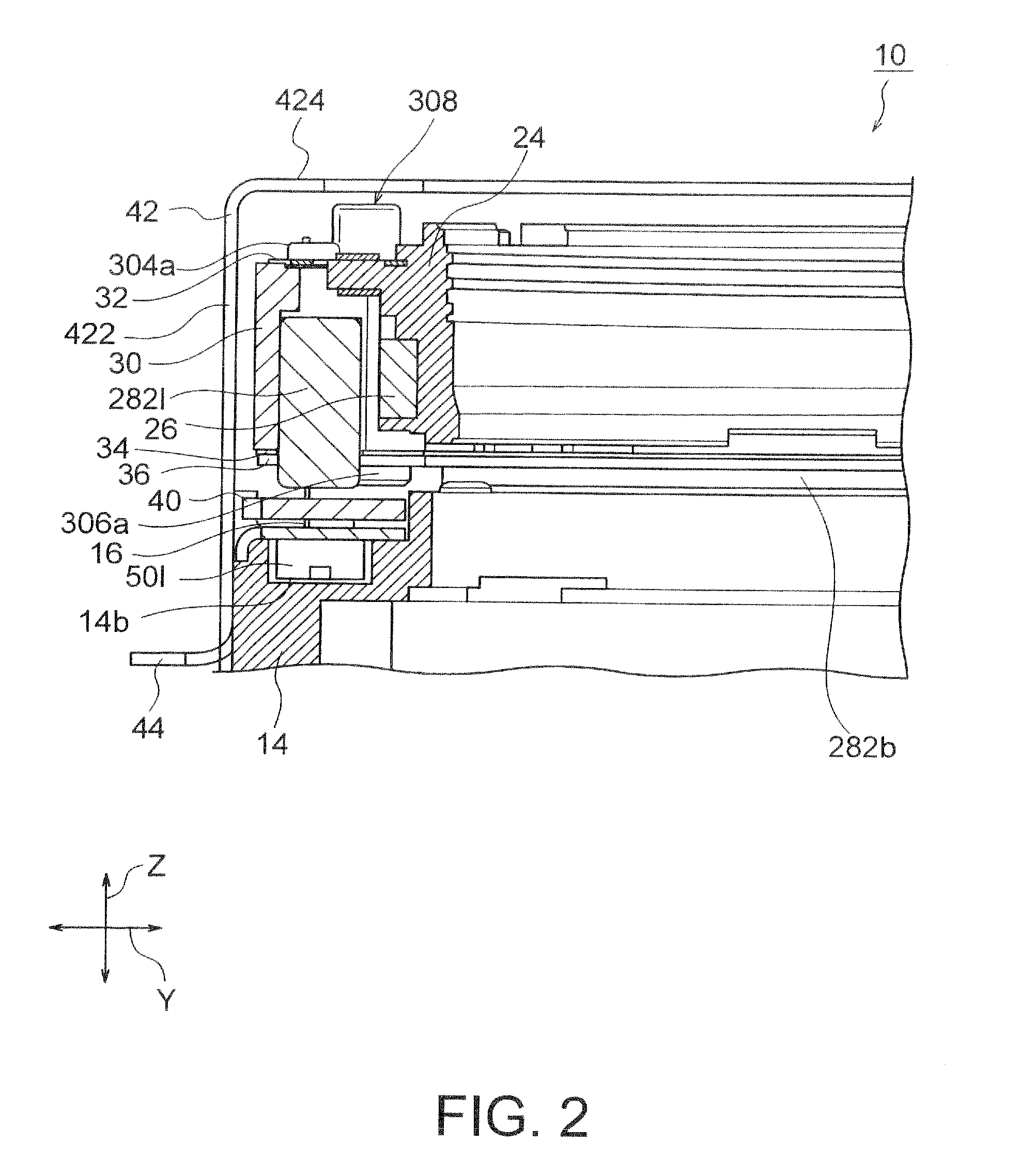
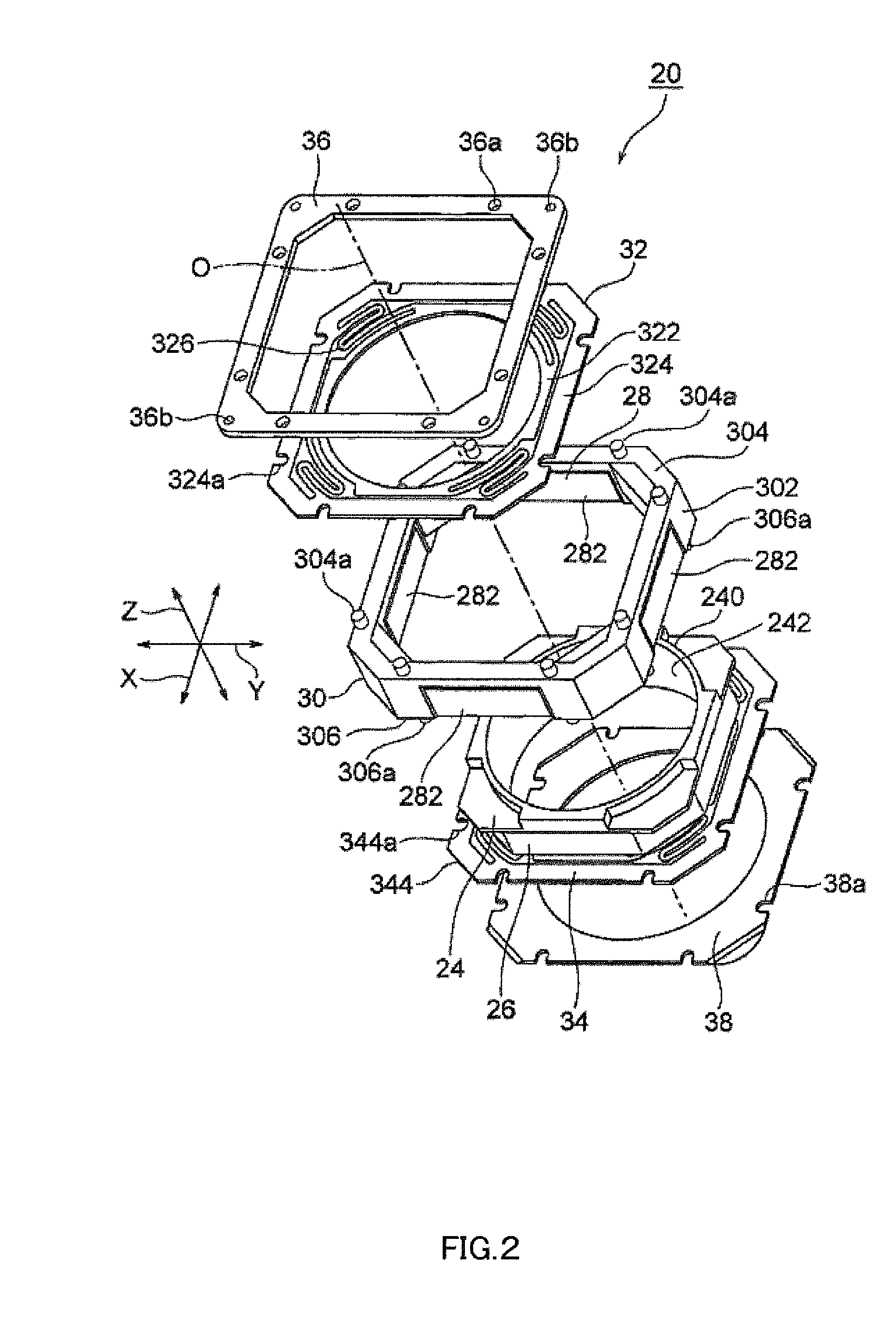
InactiveUS20120154614A1Small sizeLow profileTelevision system detailsProjector focusing arrangementOptical axisMagnet
A small size, low profile camera-shake correction device. A camera-shake correction device (10) corrects camera shake by moving the entire auto-focusing lens drive device (20) in a first direction (X) and a second direction (Y) which are perpendicular to the optical axis (O) and are perpendicular to each other, the auto-focusing lens drive device (20) being provided with a focusing coil (26) and a permanent magnet (28) which is disposed on the outside of the focusing coil. The camera-shake correction device (10) includes: a base (14) disposed so as to be spaced from the bottom surface of the auto-focusing lens drive device (20); suspension wires (16) which each have one end affixed to the outer peripheral section of the base, which extend along the optical axis (O), and which support the entire auto-focusing lens drive device (20) in such a manner that the auto-focusing lens drive device (20) is rockable in the first direction (X) and the second direction (Y); and a camera-shake correcting coil (18) disposed so as to face the permanent magnet (28).
Owner:MITSUMI ELECTRIC CO LTD
4D light field cameras
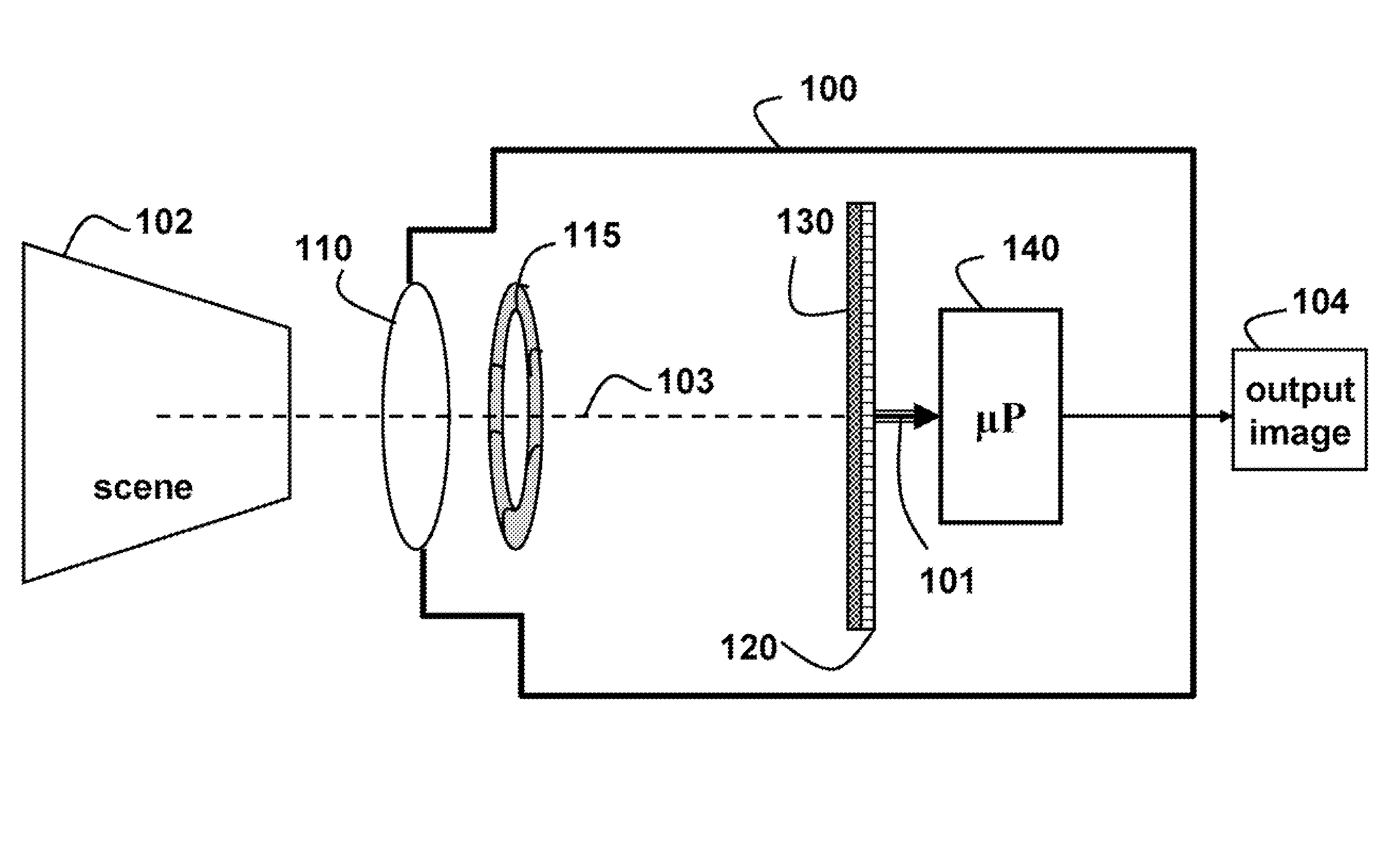
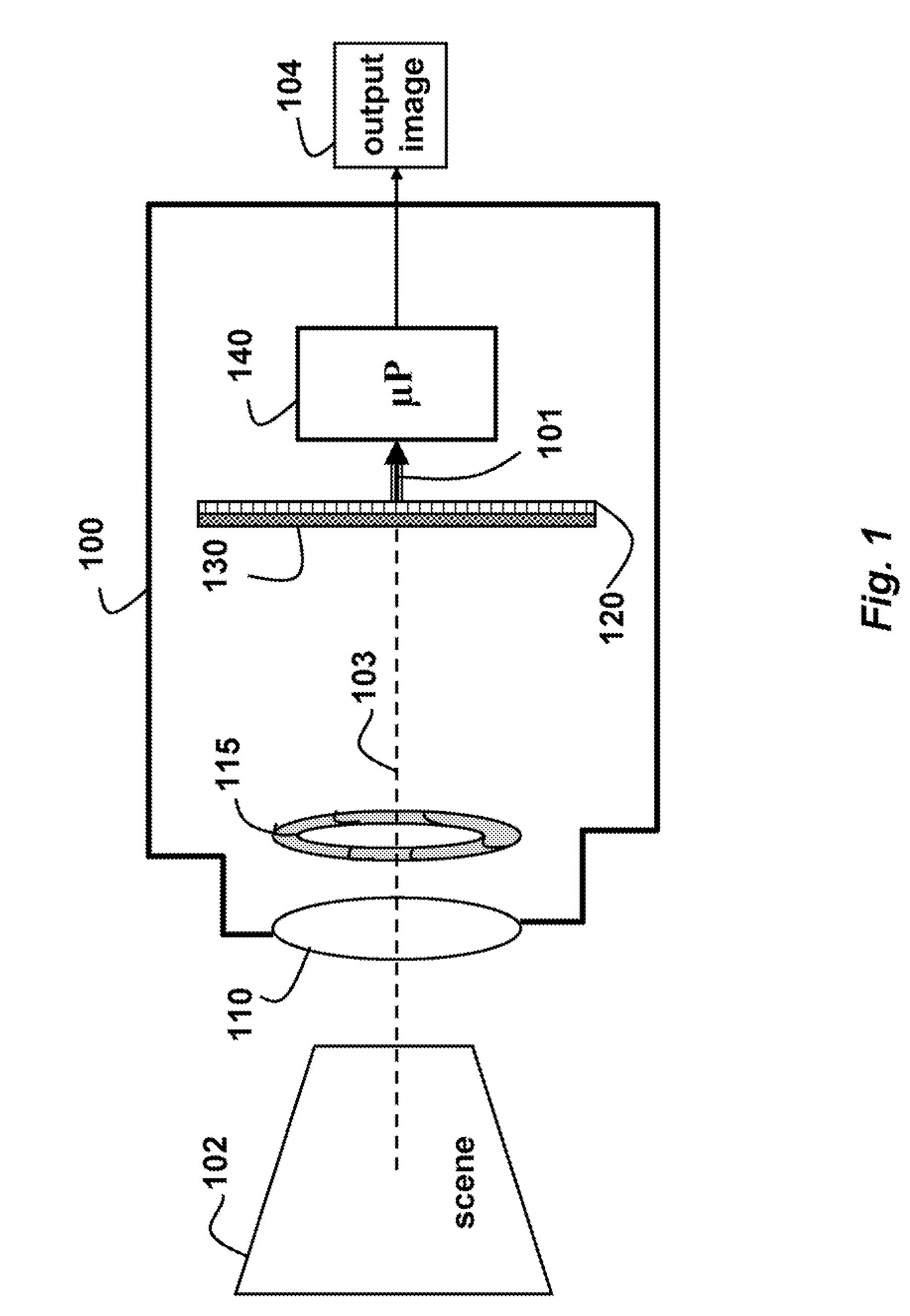
InactiveUS20080187305A1Simple attenuating maskSuppress unwanted occludersProjector focusing arrangementCamera focusing arrangementCamera lensUltrasound attenuation
A camera acquires a 4D light field of a scene. The camera includes a lens and sensor. A mask is arranged in a straight optical path between the lens and the sensor. The mask including an attenuation pattern to spatially modulate the 4D light field acquired of the scene by the sensor. The pattern has a low spatial frequency when the mask is arranged near the lens, and a high spatial frequency when the mask is arranged near the sensor.
Owner:MITSUBISHI ELECTRIC RES LAB INC
Method and apparatus for use in camera and systems employing same
ActiveUS20070002159A1High resolutionTelevision system detailsSolid-state devicesControl signalImage resolution
There are many inventions described herein. Some aspects are directed to methods and / or apparatus to provide relative movement between optics, or portion(s) thereof, and sensors, or portion(s) thereof, in a digital camera. The relative movement may be in any of various directions. In some aspects, relative movement between an optics portion, or portion(s) thereof, and a sensor portion, or portion(s) thereof, are used in providing any of various features and / or in the various applications disclosed herein, including, for example, but not limited to, increasing resolution, optical and electronic zoom, image stabilization, channel alignment, channel-channel alignment, image alignment, lens alignment, masking, image discrimination, range finding, 3D imaging, auto focus, mechanical shutter, mechanical iris, multi and hyperspectral imaging, and / or combinations thereof. In some aspects, movement is provided by actuators, for example, but not limited to MEMS actuators, and by applying appropriate control signal thereto.
Owner:INTELLECTUAL VENTURES II
Lens holder driving device capable of avoiding deleterious effect on hall elements
ActiveUS20130016427A1Television system detailsProjector focusing arrangementOptical axisHall element
An AF unit of a lens holder driving device includes a lens holder, a focusing coil, a permanent magnet having a plurality of permanent magnet pieces having first surfaces opposed to the focusing coil, a magnet holder holding the permanent magnet, and first and second leaf springs supporting the lens holder in a direction of an optical axis shiftably. An image stabilizer portion includes a fixed portion disposed near the second leaf spring, a supporting member swingably supporting the AF unit with respect to the fixed portion, an image stabilizer coil having a plurality of image stabilizer coil portions disposed so as to oppose to second surfaces of the plurality of permanent magnet pieces that are perpendicular to the first surfaces, and a plurality of Hall elements. Each Hall element is disposed at a position where the image stabilizer coil portion is separated into a plurality of coil parts.
Owner:MITSUMI ELECTRIC CO LTD
Apparatus for multiple camera devices and method of operating same
InactiveUS20070102622A1High resolutionExcellent color renditionTelevision system detailsSolid-state devicesSignal processing circuitsPhotovoltaic detectors
There are many, many inventions described herein. In one aspect, what is disclosed is a digital camera including a plurality of arrays of photo detectors, including a first array of photo detectors to sample an intensity of light of a first wavelength and a second array of photo detectors to sample an intensity of light of a second wavelength. The digital camera further may also include a first lens disposed in an optical path of the first array of photo detectors, wherein the first lens includes a predetermined optical response to the light of the first wavelength, and a second lens disposed in with an optical path of the second array of photo detectors wherein the second lens includes a predetermined optical response to the light of the second wavelength. In addition, the digital camera may include signal processing circuitry, coupled to the first and second arrays of photo detectors, to generate a composite image using (i) data which is representative of the intensity of light sampled by the first array of photo detectors, and (ii) data which is representative of the intensity of light sampled by the second array of photo detectors; wherein the first array of photo detectors, the second array of photo detectors, and the signal processing circuitry are integrated on or in the same semiconductor substrate.
Owner:OLSEN RICHARD IAN +8
Lens holder driving device including damper compound suppressing undesired resonance
ActiveUS20130050828A1Carrying out operation with stabilityTelevision system detailsProjector focusing arrangementCamera lensOptical axis
A lens holder driving device includes a lens holder moving portion, a fixed member, suspension wires, and a damper compound. In the lens holder moving portion, a lens holder moves in an optical axis and in first and second directions which are orthogonal to the optical axis and which are perpendicular to each other. The fixed member is disposed apart from the lens holder moving portion in the direction of the optical axis. The suspension wires have first end portions fixed to the fixed member at outer regions thereof, extending along the optical axis, having second end portions fixed to an elastic member mounted to the lens holder moving portion, and swingably supporting the lens holder moving portion in the first direction and the second direction. The damper compound is disposed so as to enclose at least one suspension wire and suppresses undesired resonance in the lens holder moving portion.
Owner:MITSUMI ELECTRIC CO LTD
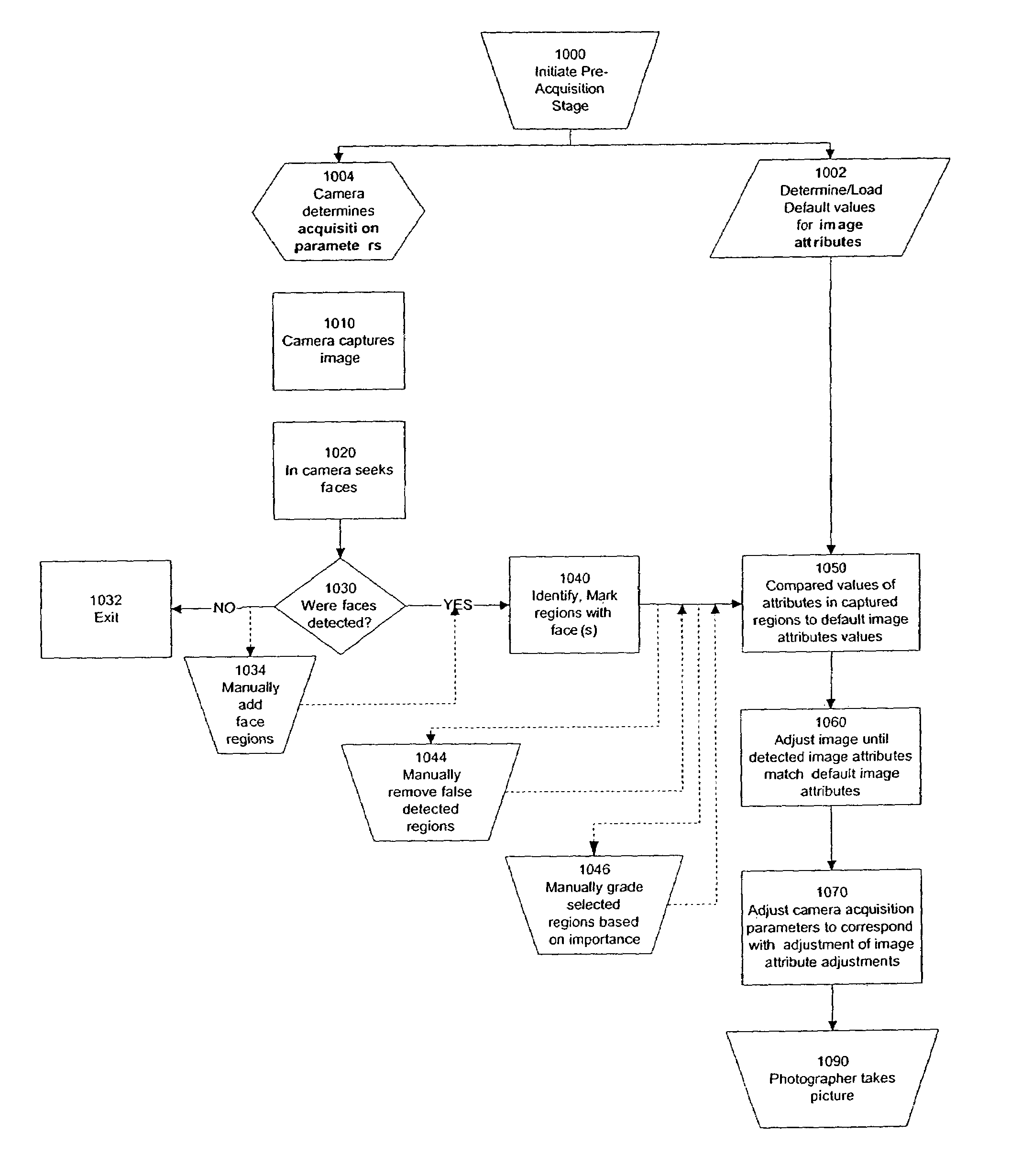
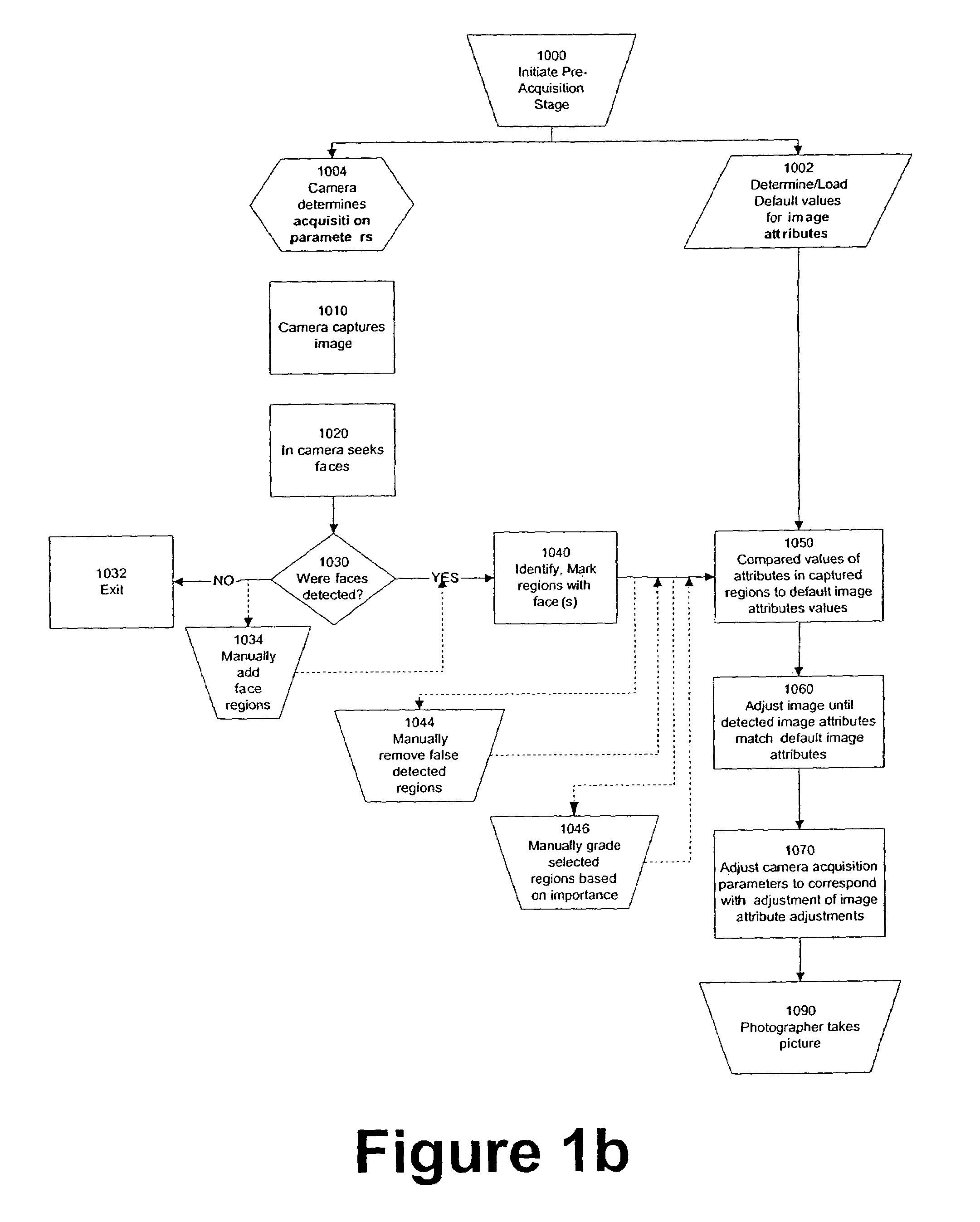
Perfecting the optics within a digital image acquisition device using face detection
ActiveUS7362368B2Television system detailsProjector focusing arrangementFace detectionAcquisition apparatus
Within a digital acquisition device, acquisition parameters of a digital image are perfected as part of an image capture process using face detection within said captured image to achieve one or more desired image acquisition parameters. Default values are determined of one or more image attributes of at least some portion of the digital image. Values of one or more camera acquisition parameters are determined. Groups of pixels are identified that correspond to an image of a face within the digitally-captured image. Corresponding image attributes to the groups of pixels are determined. One or more default image attribute values are compared with one or more captured image attribute values based upon analysis of the image of the face. Camera acquisition parameters are then adjusted corresponding to adjusting the image attribute values.
Owner:FOTONATION LTD
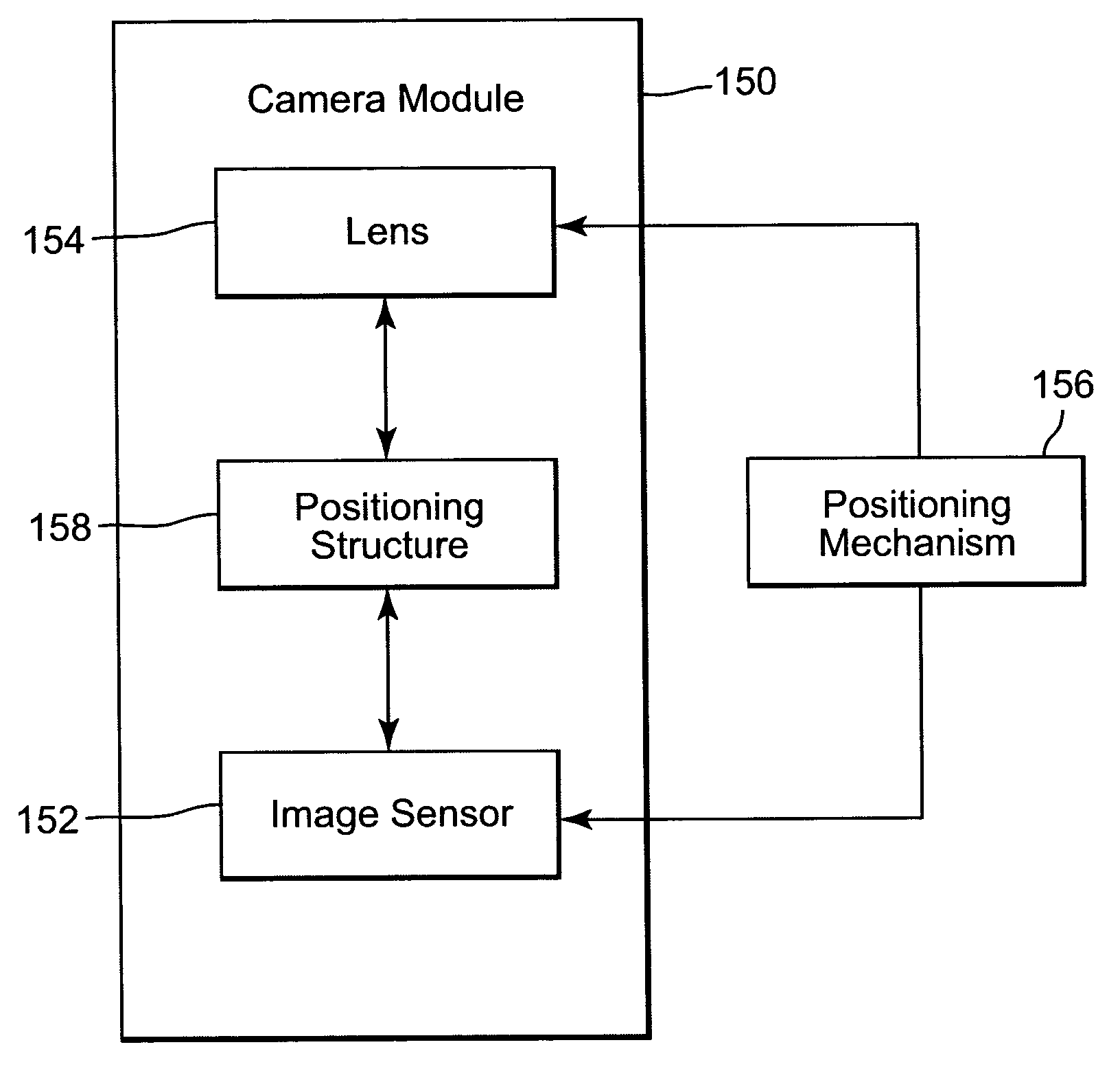
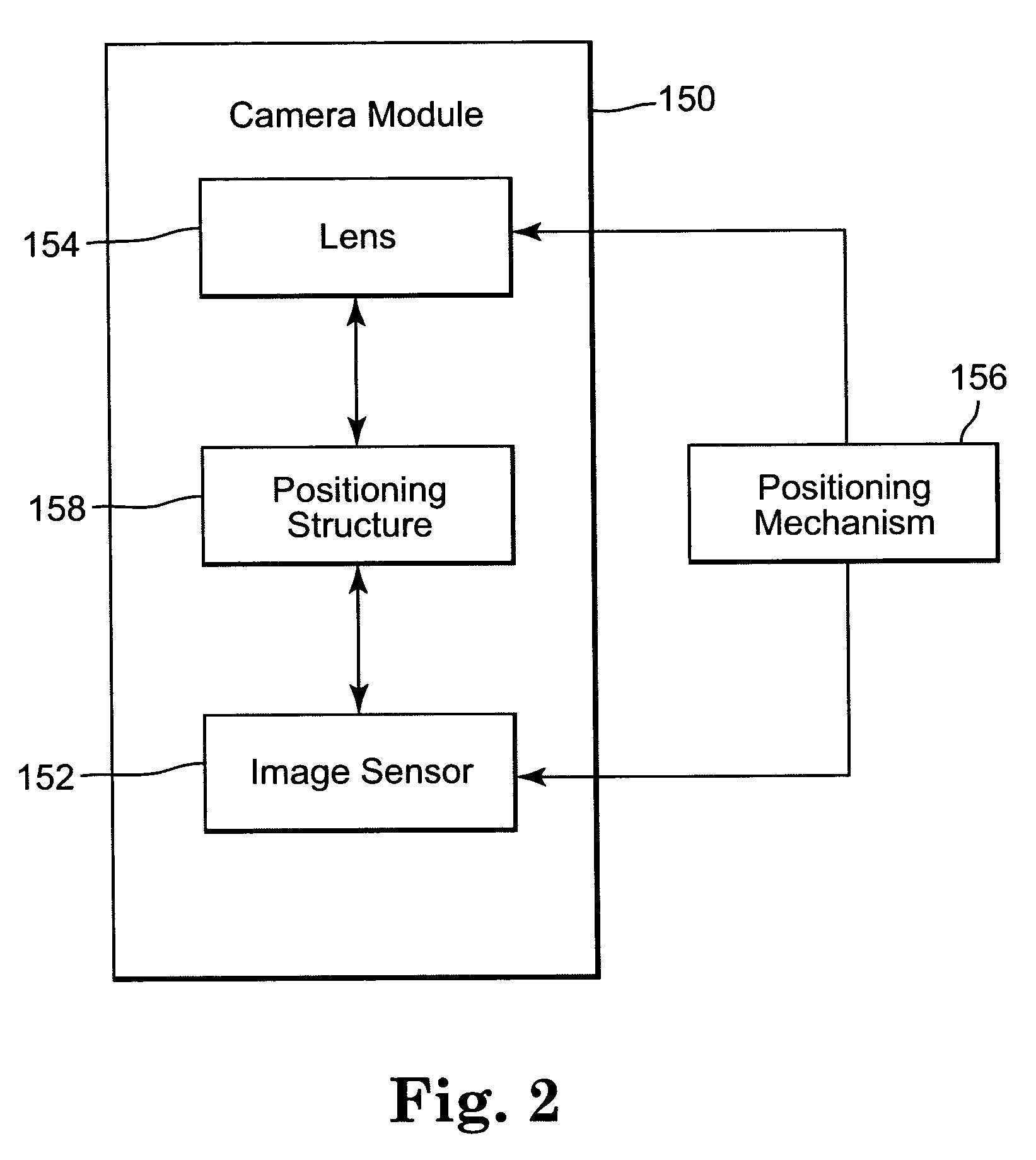
Fixed-focus camera module and associated method of assembly
InactiveUS20050036778A1Maintain alignmentTelevision system detailsProjector focusing arrangementImaging qualityCamera module
A fixed-focus camera module includes an image sensor, a lens for focusing an image onto the image sensor, and a positioning structure for maintaining an alignment of the lens and image sensor. The alignment provides a desired image quality of the image focussed onto the image sensor. The positioning structure includes a first unthreaded member coupled to the lens and a second unthreaded member coupled to the image sensor. One of the first and the second members is configured to be inserted into the other of the members to provide an adjustable relative position of the lens and the image sensor.
Owner:APTINA IMAGING CORP
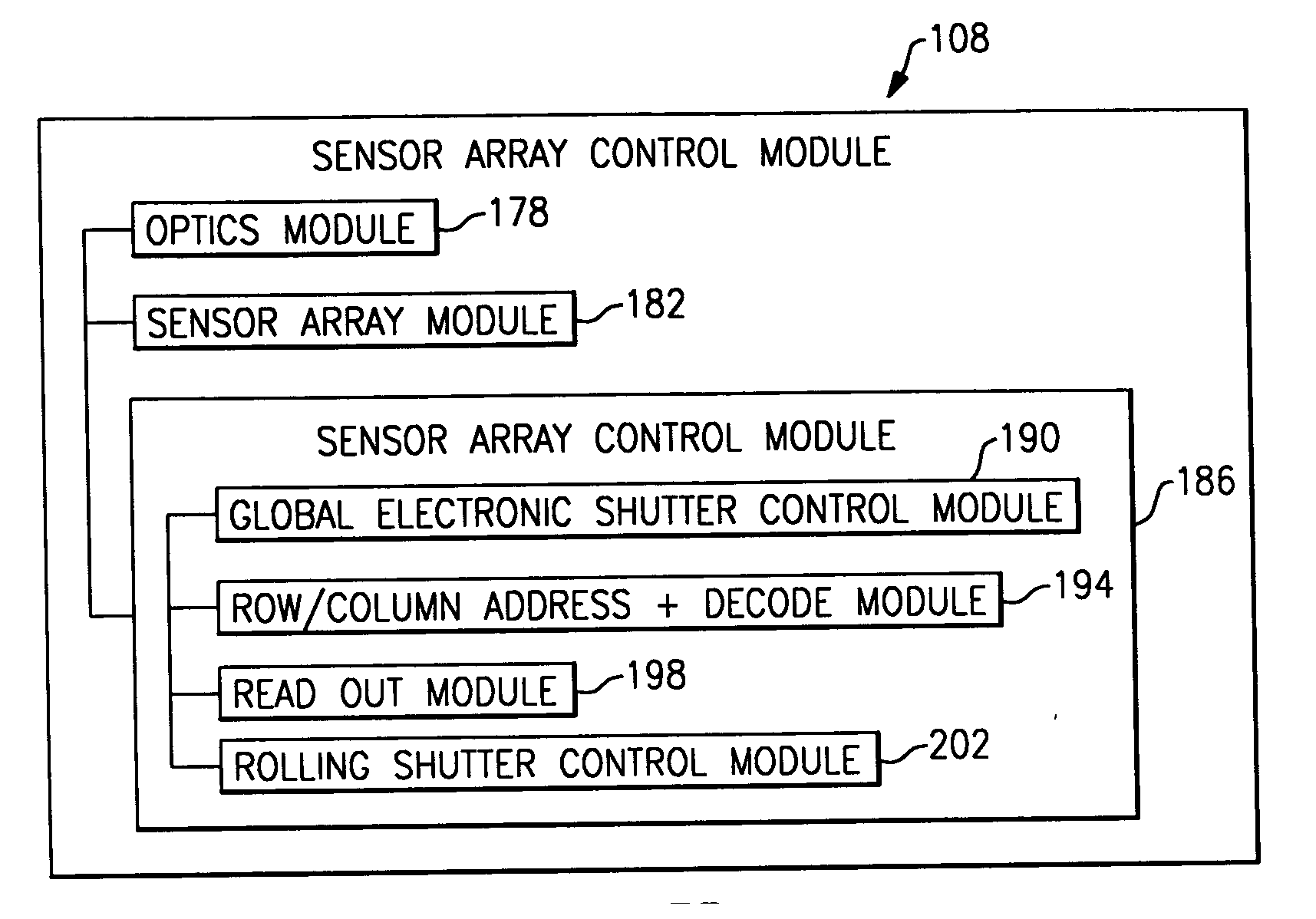
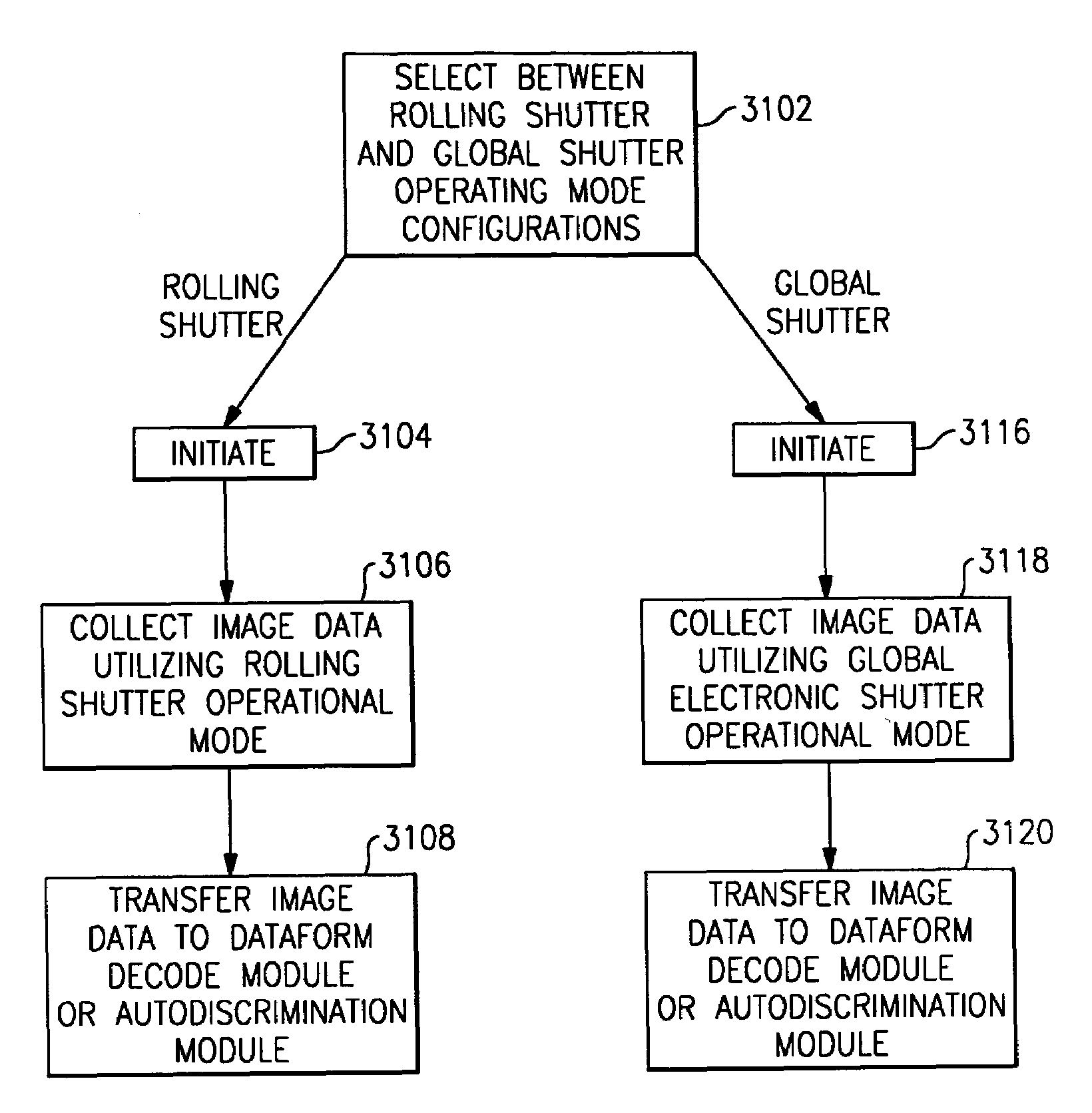
System and method to automatically focus an image reader
ActiveUS20060202038A1Minimize degradationProjector focusing arrangementCamera focusing arrangementImage formationImaging data
The invention features a system and method to automatically focus an image reader using a single frame of image data. The method comprises exposing sequentially a plurality of rows of pixels in the image sensor. The method further comprising varying in incremental steps the focus of the image reader's optical system from a first setting where a distinct image of objects located at a first distance from the image reader is formed on the image sensor to a second setting where a distinct image of objects located at a second distance from the image reader is formed on the image sensor. As part of the method, the varying of the focus of the optical system occurs during the exposure of the plurality of rows of pixels.
Owner:HAND HELD PRODS
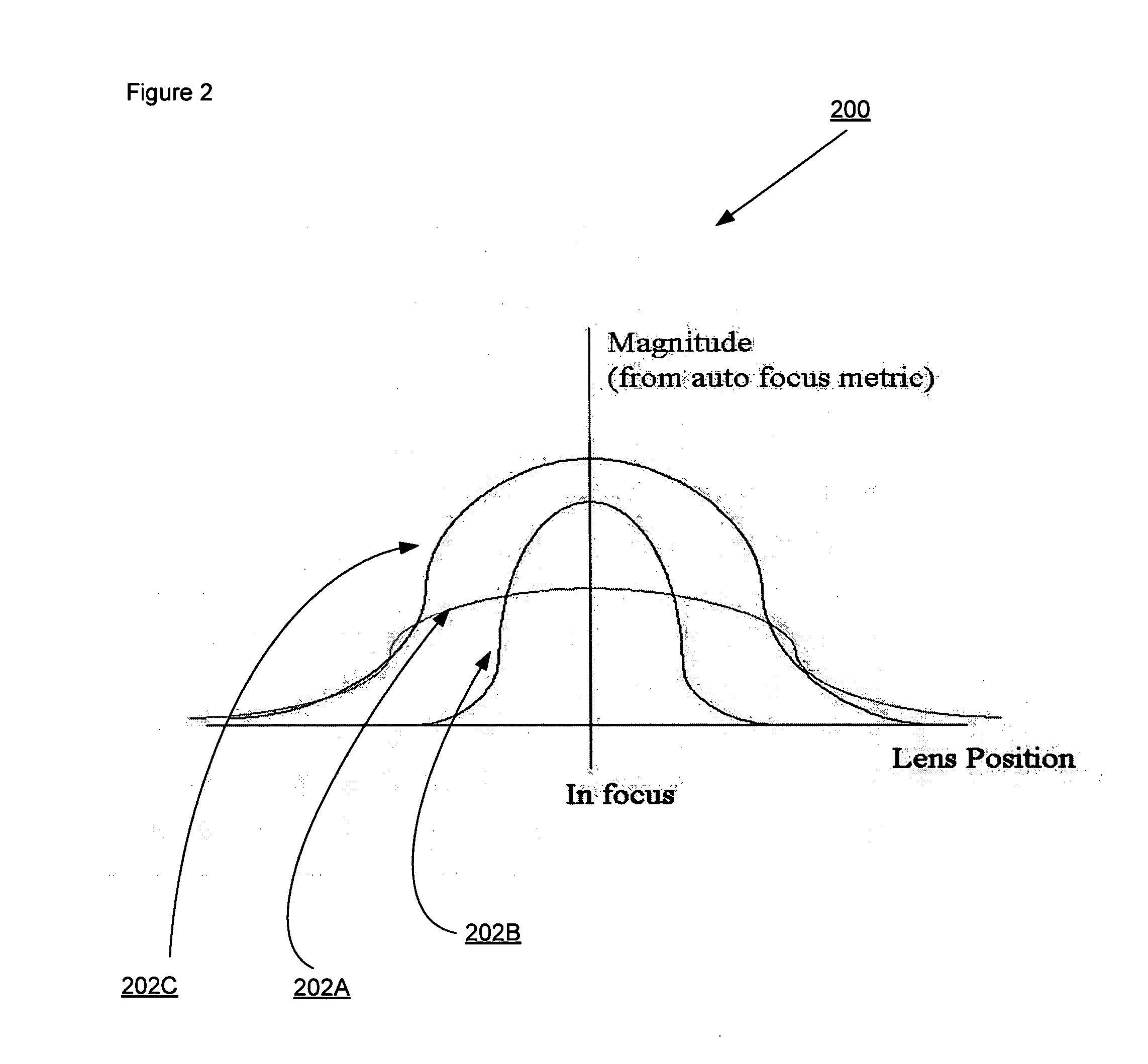
Simple method for calculating camera defocus from an image scene
ActiveUS20070216765A1Television system detailsProjector focusing arrangementThree-dimensional spaceAutofocus
An imaging acquisition system that generates a picture depth from an auto focus curve generated from picture of a three dimensional spatial scene is described. The auto focus curve comprises a step edge. The system generates the depth based on the step edge and a reference auto focus normalization curve.
Owner:SONY CORP +1
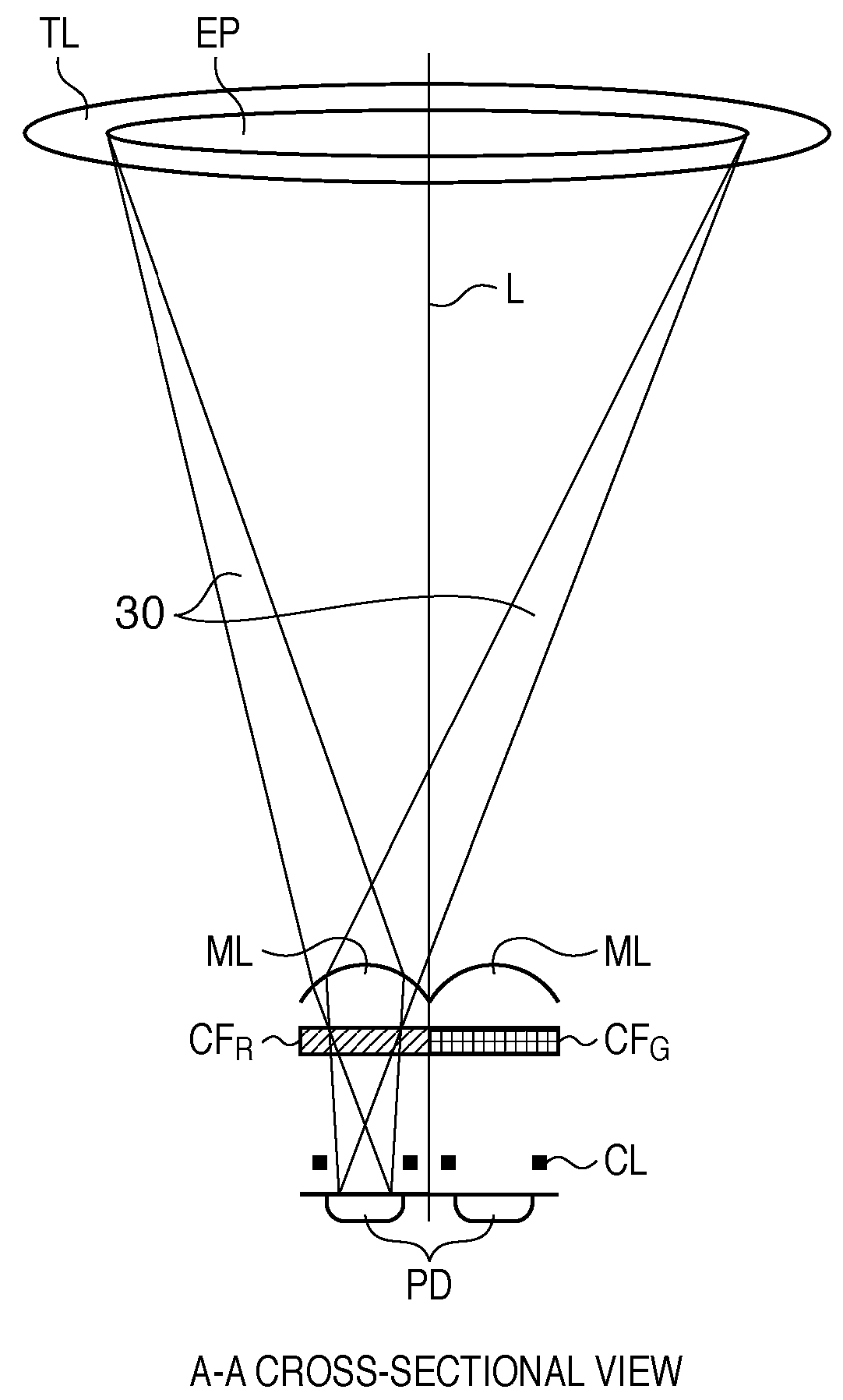
Image sensing apparatus, image sensing system and focus detection method
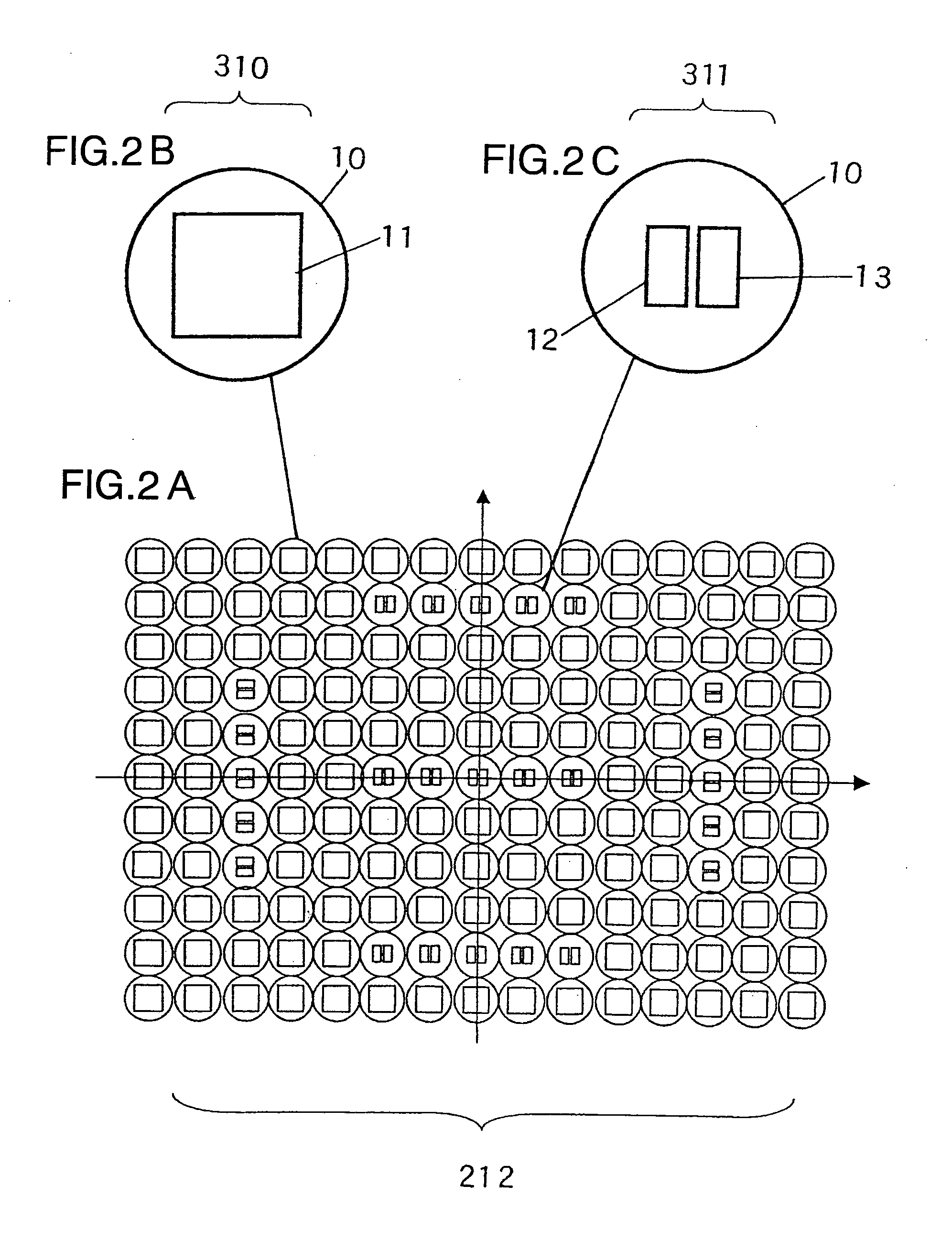
InactiveUS20100045849A1Improve accuracyMethod can be usedTelevision system detailsTelevision system scanning detailsCamera lensRelative shift
An image sensing apparatus including: an image sensor including a plurality of focus detection pixel pairs that perform photoelectric conversion on each pair of light beams that have passed through different regions of a photographing lens and output an image signal pair; a flash memory that stores shift information on relative shift between an optical axis of the photographing lens and a central axis of the focus detection pixel pairs; a correction unit that corrects a signal level of the image signal pair based on the shift information and exit pupil information of the photographing lens so as to compensate for an unbalanced amount of light that enters each of the focus detection pixel pairs; and a focus detection unit that detects a focus of the photographing lens using the image signal pair corrected by the correction unit.
Owner:CANON KK
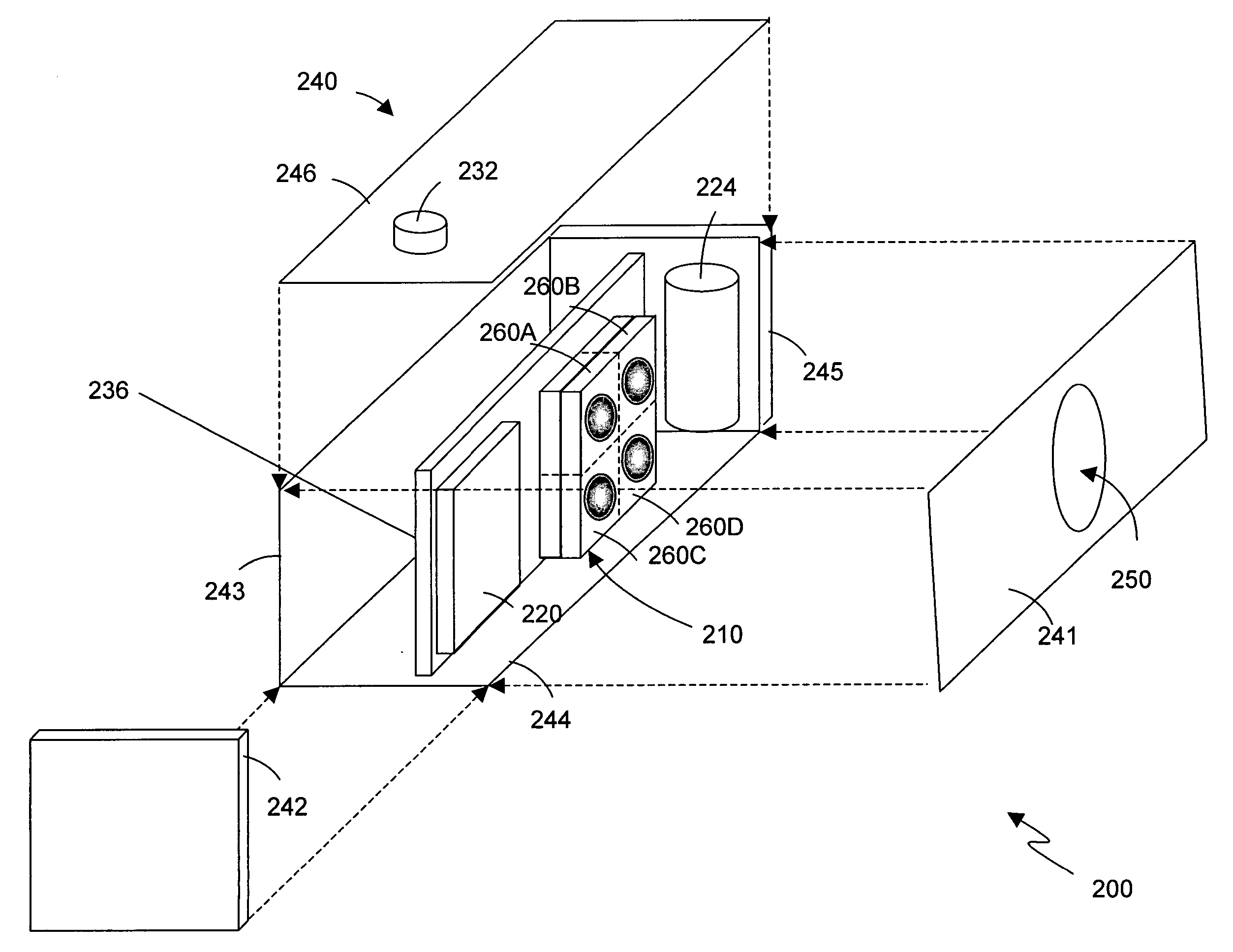
Focused plenoptic camera employing different apertures or filtering at different microlenses
ActiveUS8228417B1Increase and maximize spatial resolutionSharper and high spatial resolutionTelevision system detailsProjector focusing arrangementCamera lensMicro lens array
Owner:ADOBE INC
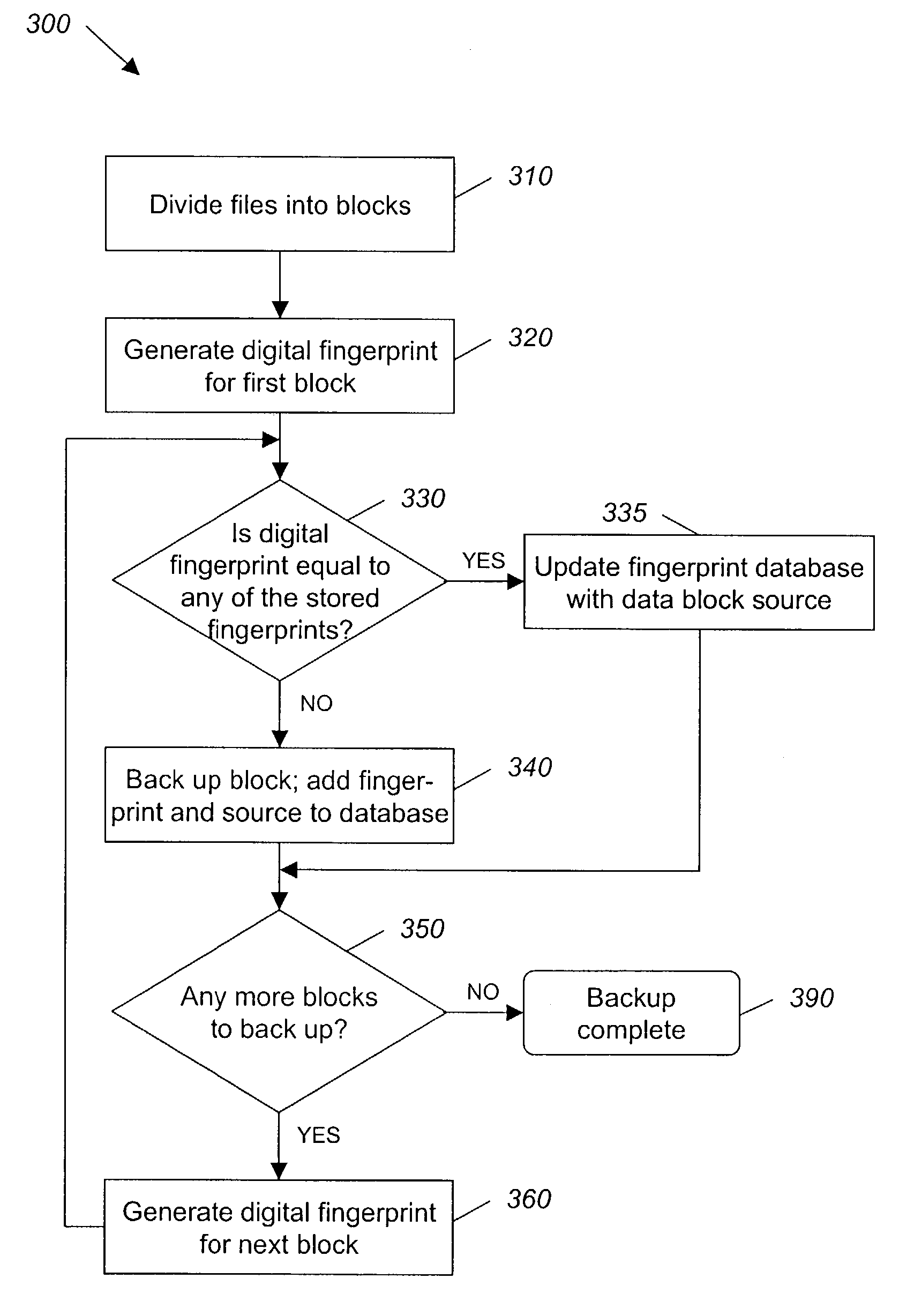
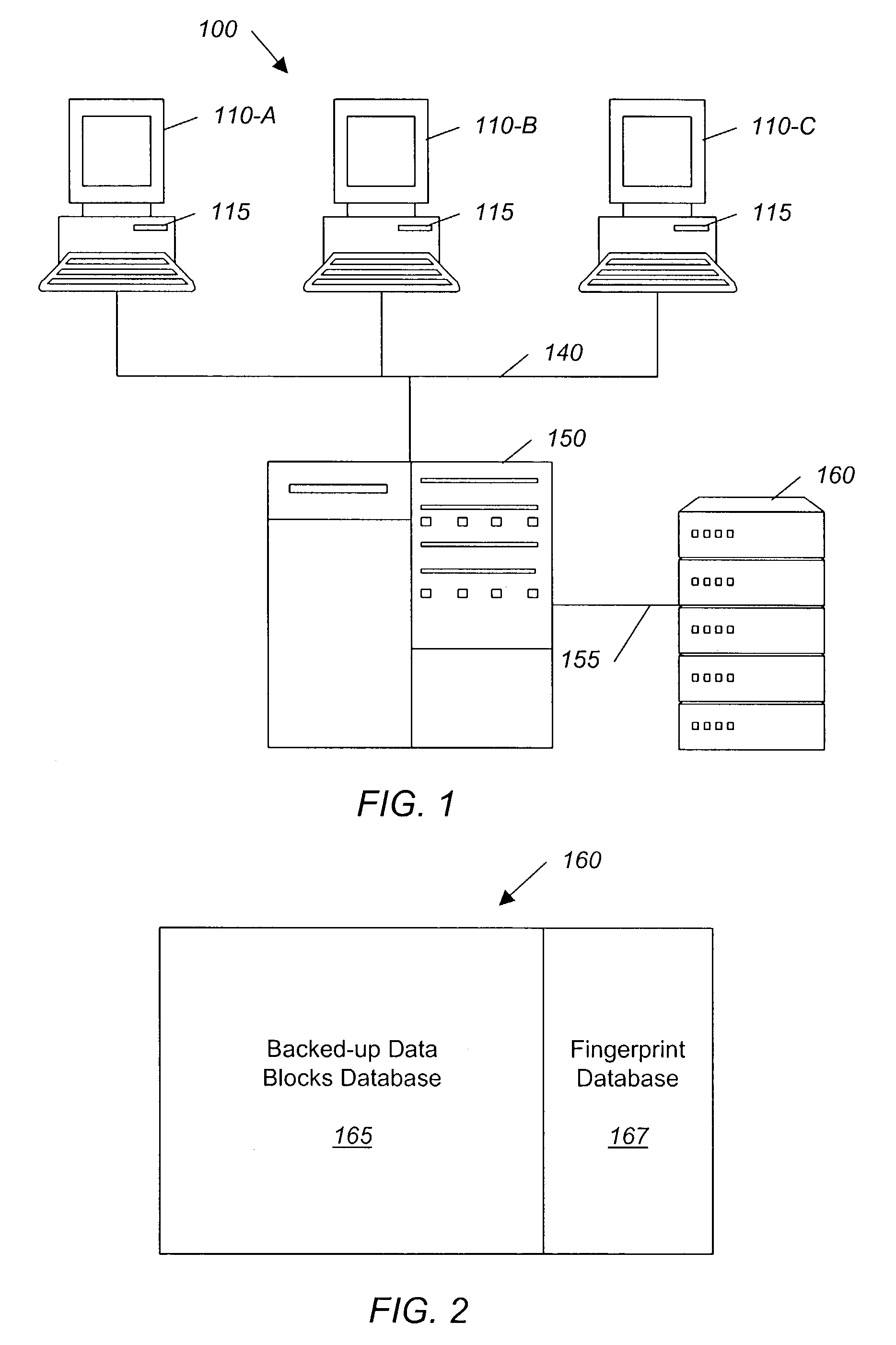
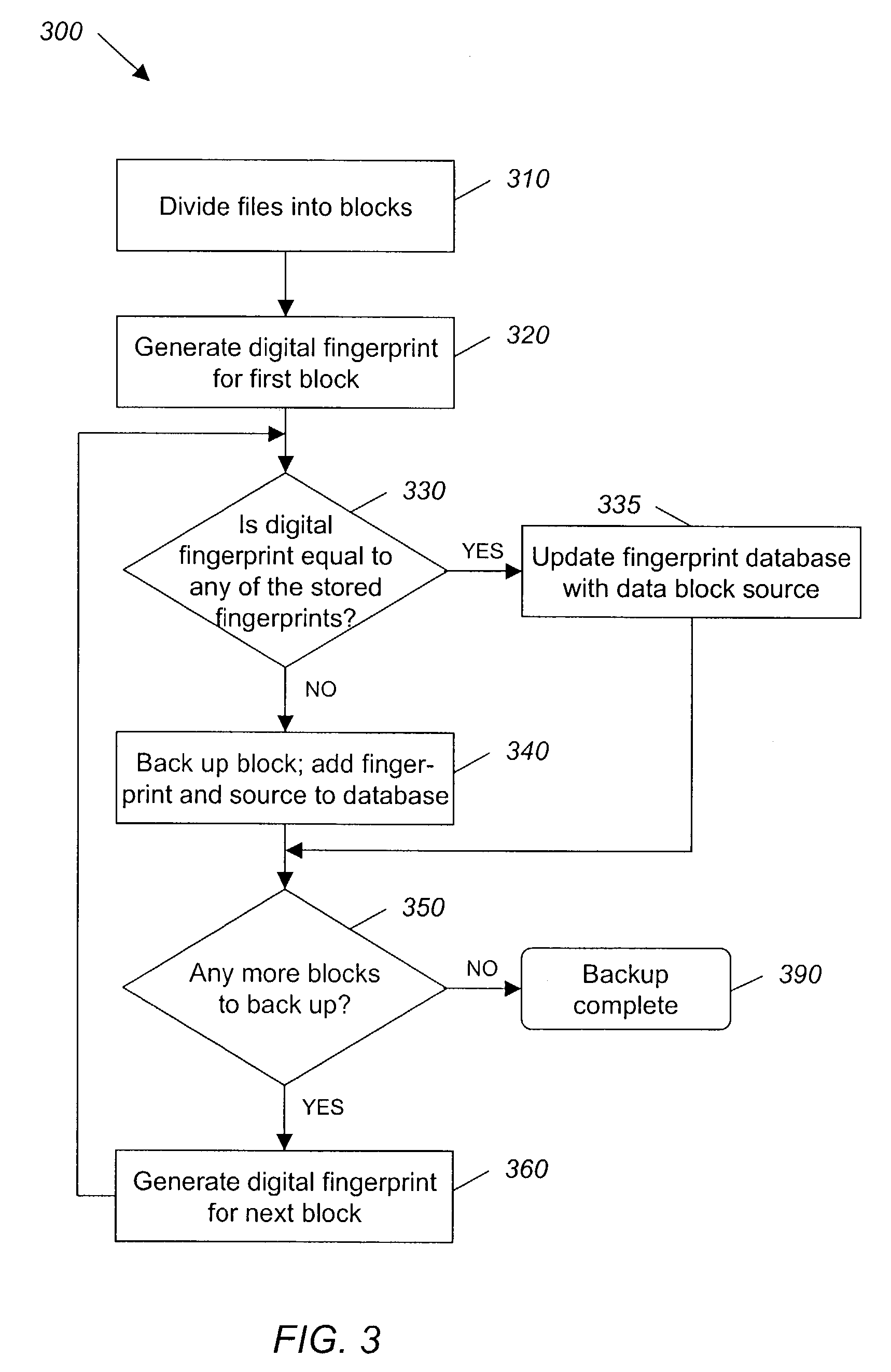
System and method for backing up data
ActiveUS7055008B2Avoid inefficiencyInefficiency of the Shnelvar patent can be avoidedCamera focusing arrangementPayment architectureSoftware licenseData content
A hash-optimized backup system and method takes data blocks and generates a probabilistically unique digital fingerprint of the content of each data block using a substantially collision-free algorithm. The process compares the generated fingerprint to a database of stored fingerprints and, if the generated fingerprint matches a stored fingerprint, the data block is determined to already have been backed up, and therefore does not need to be backed up again. Only if the generated fingerprint does not match a stored fingerprint is the data block backed up, at which point the generated fingerprint is added to the database of stored fingerprints. Because the algorithm is substantially collision-free, there is no need to compare actual data content if there is a hash-value match. The process can also be used to audit software license compliance, inventory software, and detect computer-file tampering such as viruses and malware.
Owner:FALCONSTOR
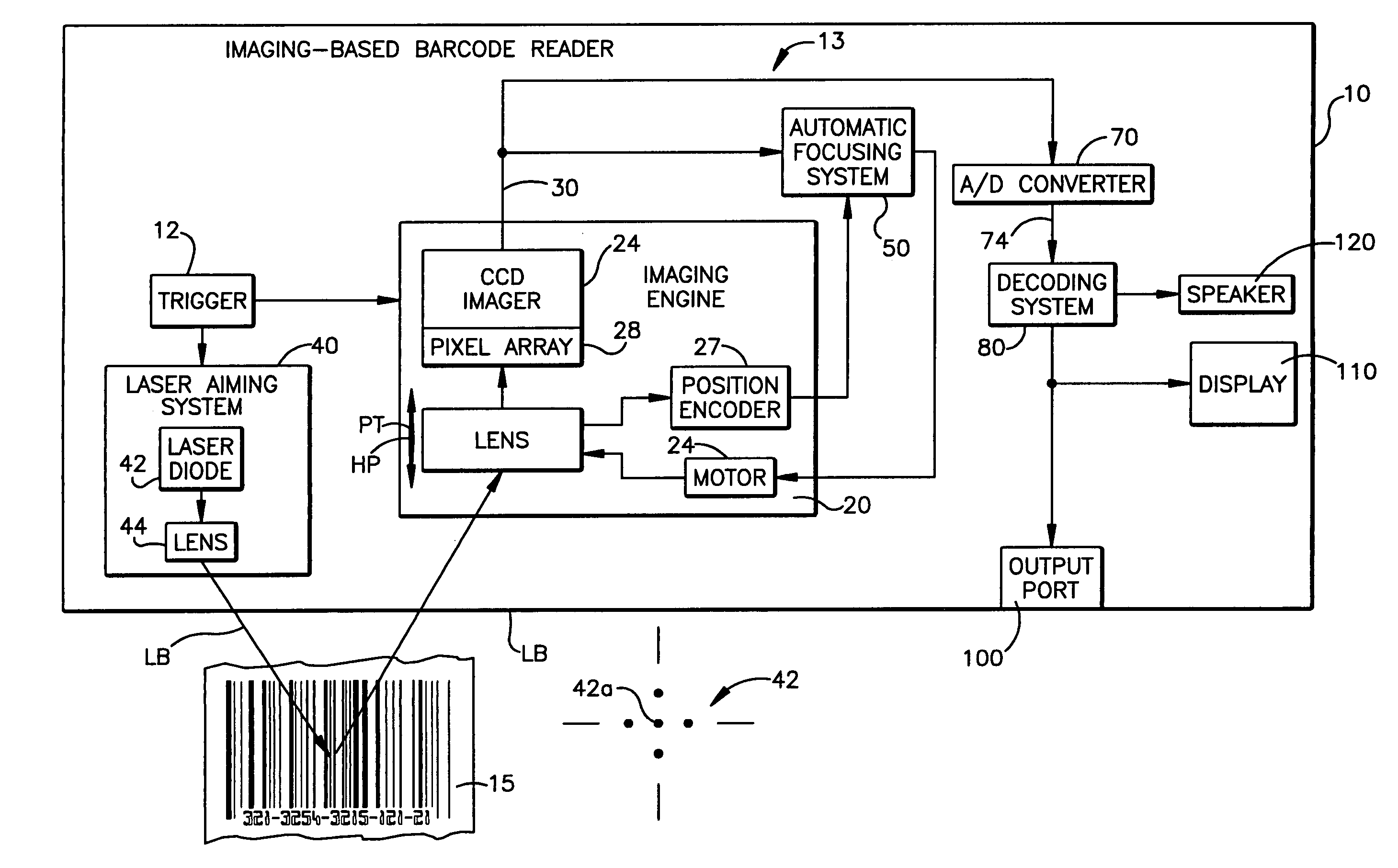
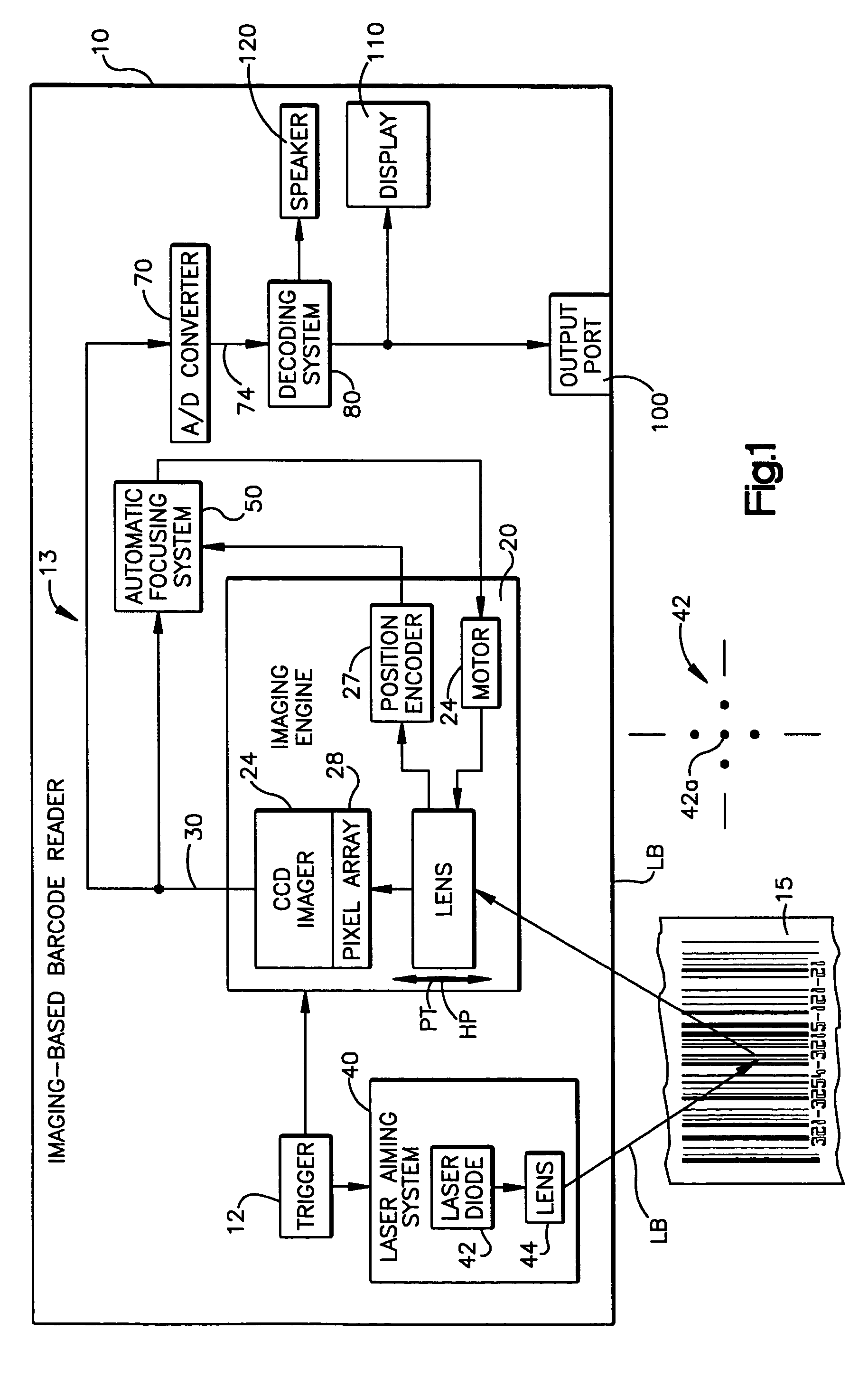
Automatic focusing system for imaging-based bar code reader
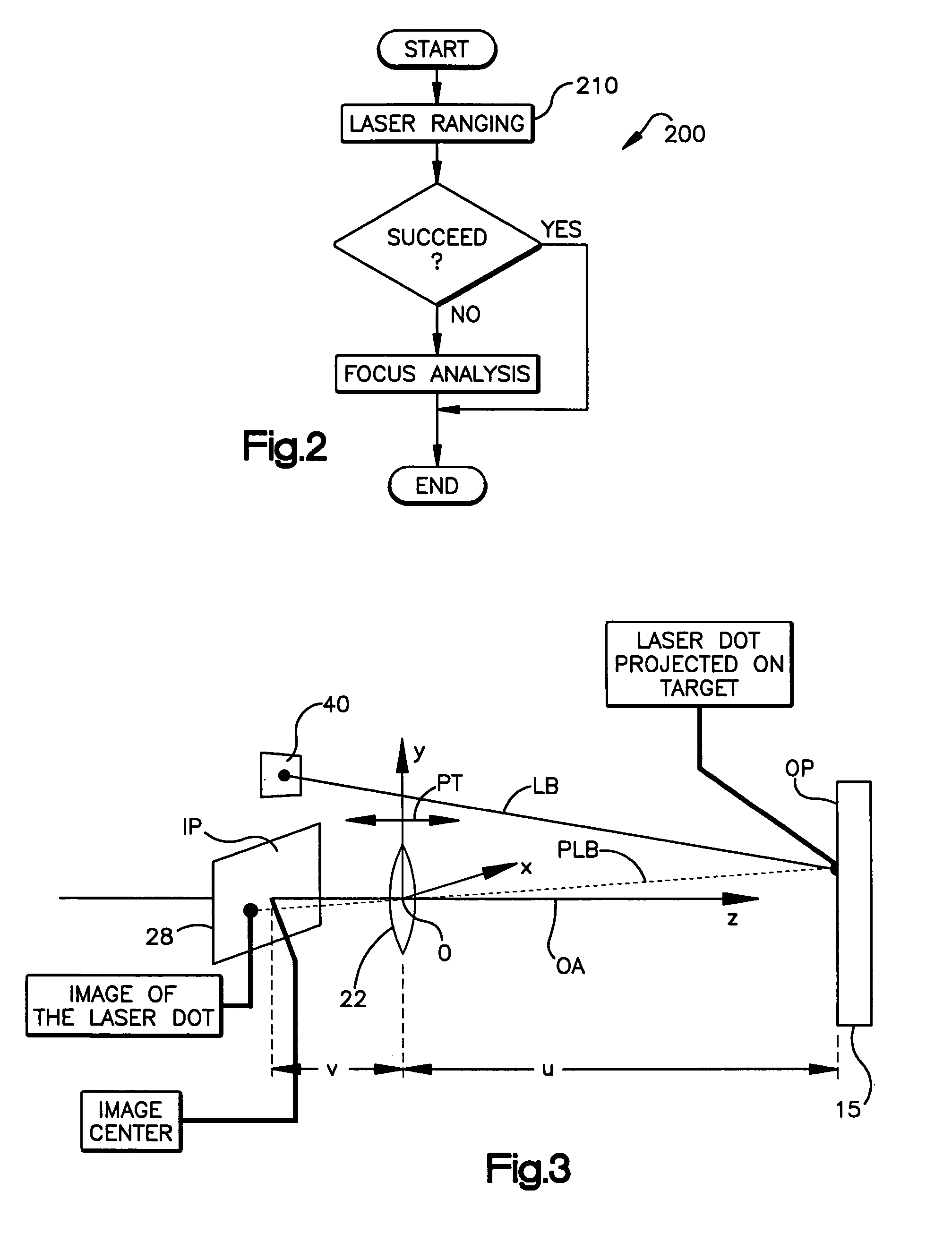
An automatic focusing system for an imaging-based bar code reader. The automatic focusing system employs a two step process for moving a lens of an imaging system along its path of travel such that a sharp image of a target bar code is projected or focused onto an imaging system pixel array. The first step is laser ranging which utilizes a laser beam for range finding. Laser ranging determines a distance between the imaging system pixel array and the target bar code. Given the determined distance, the automatic focusing system moves the lens to a suitable position for imaging the target bar code. If ambient conditions prevent laser ranging from properly working, the second step is focus analysis. Focus analysis involves moving the lens in accordance with a search routine and analyzing image frames of the target object to find a suitable focus position.
Owner:SYMBOL TECH LLC
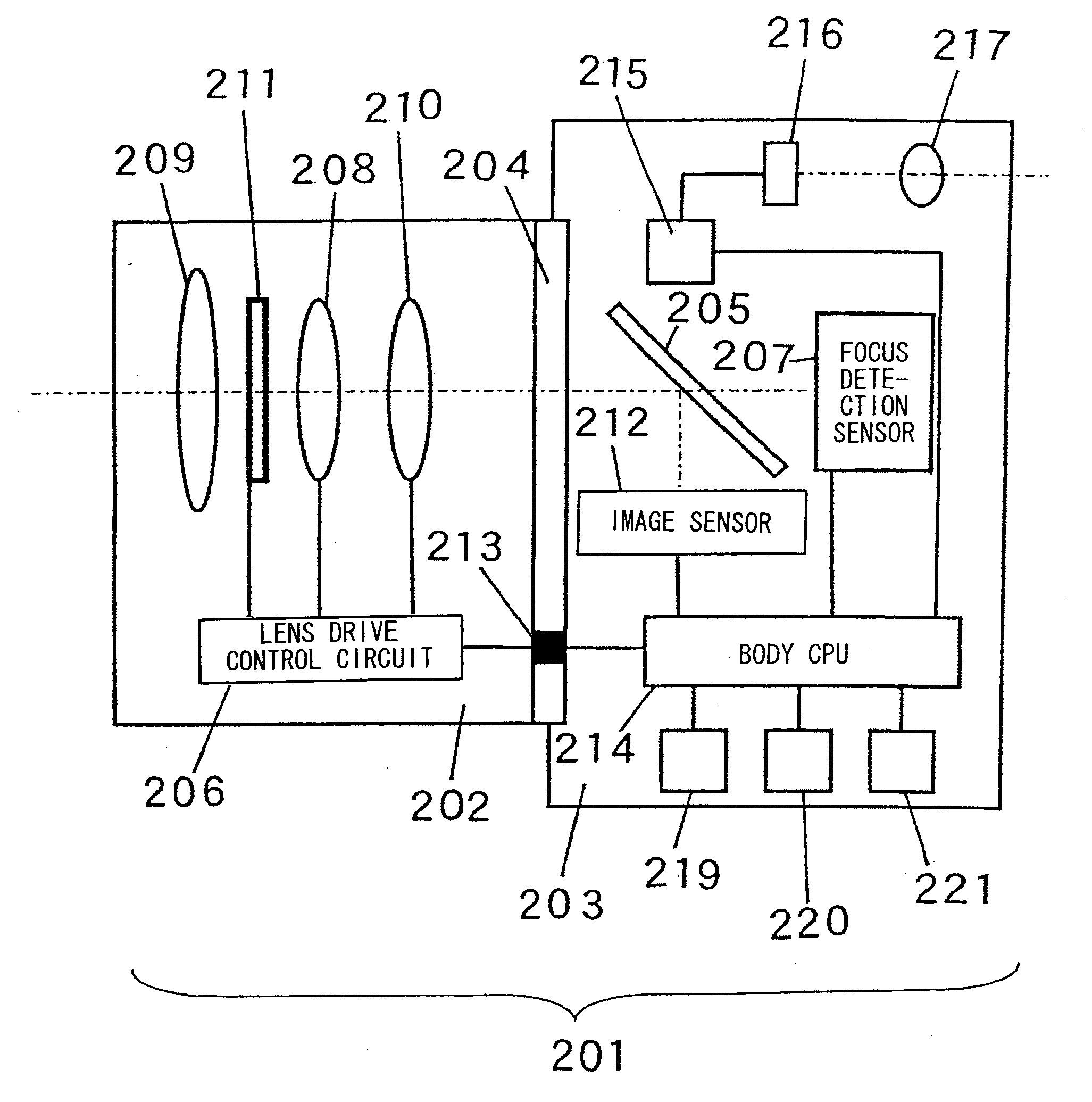
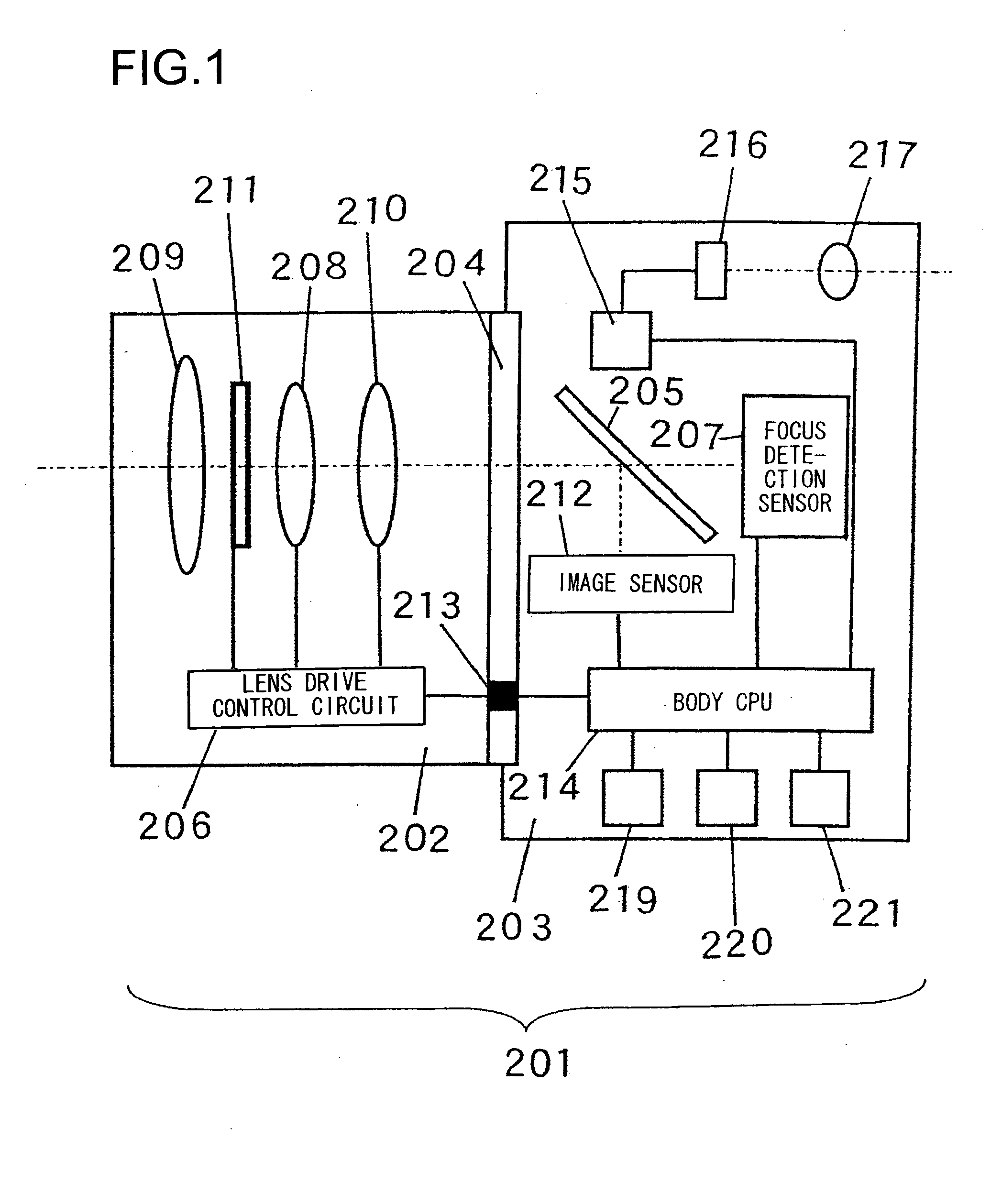
Focus adjustment device, imaging device and focus adjustment method
A focus adjustment device includes an image sensor that includes imaging pixels for capturing an image formed via an imaging optical system and focus detection pixels for detecting a focus adjustment state at the imaging optical system through a first pupil division-type image shift detection method, a focus detector that detects a focus adjustment state at the imaging optical system through a second pupil division-type image shift detection method different from the first pupil division-type image shift detection method, and a focus adjustment controller that executes focus adjustment for the imaging optical system based upon the focus adjustment states detected by the image sensor and the focus detector.
Owner:NIKON CORP
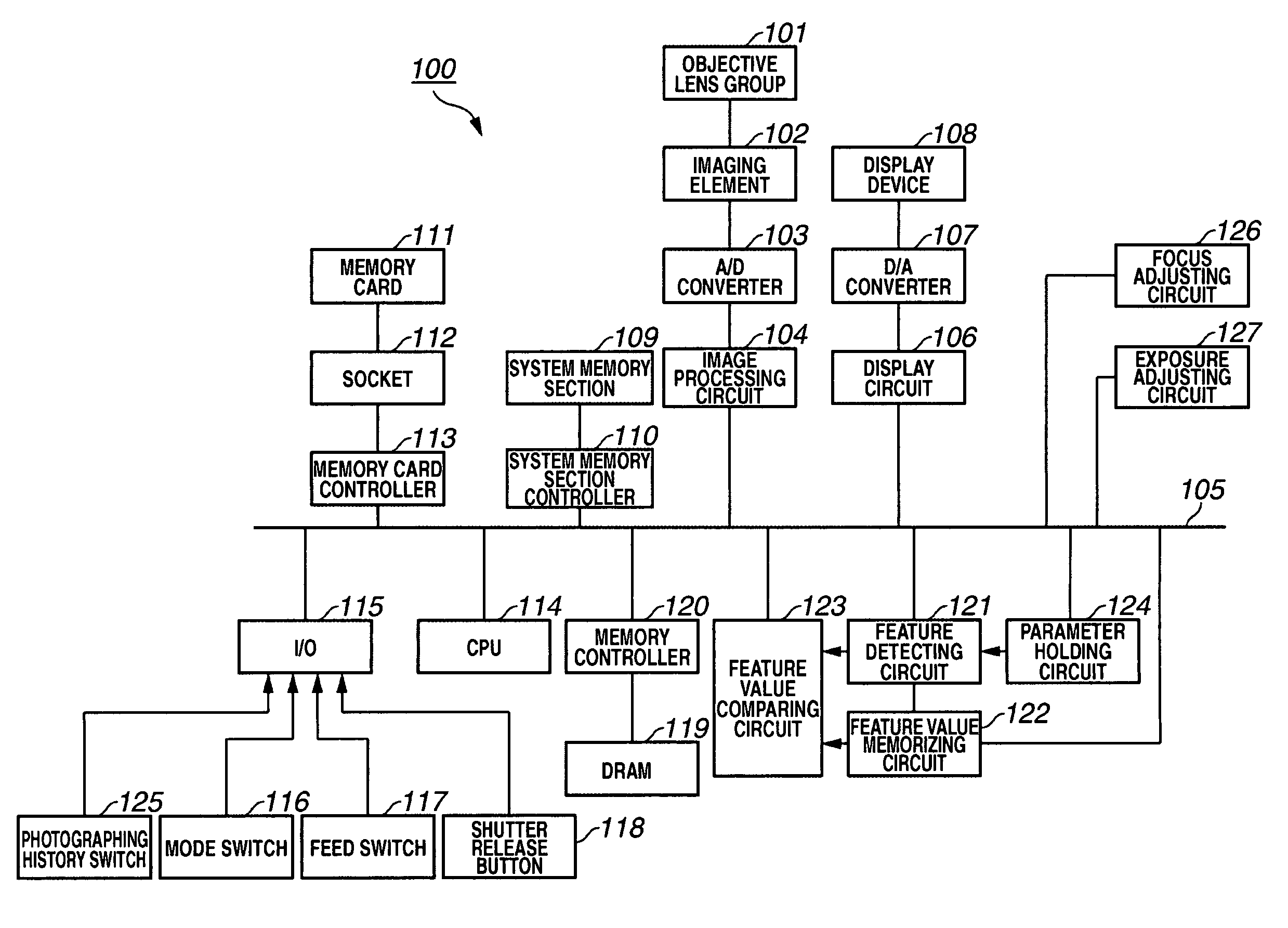
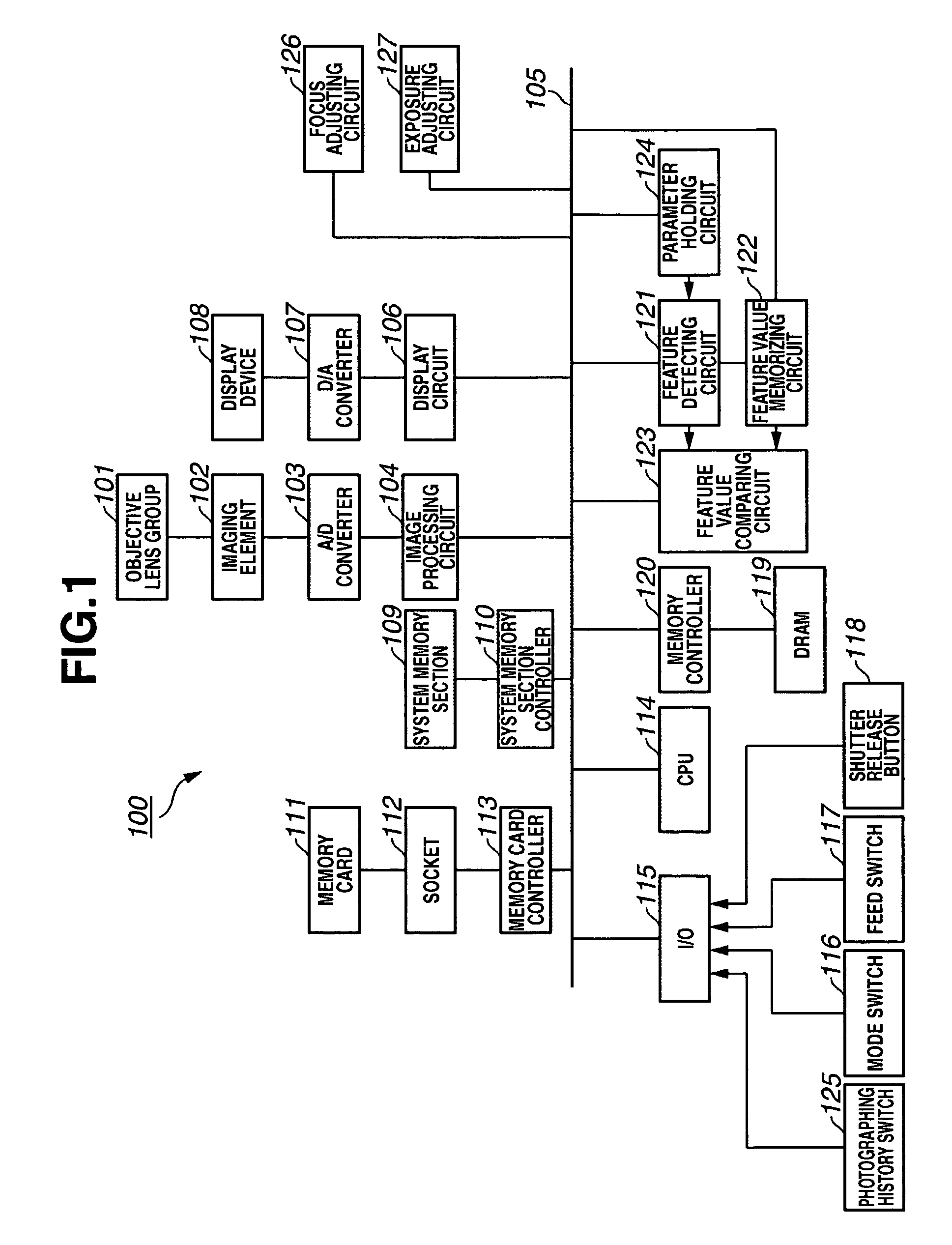
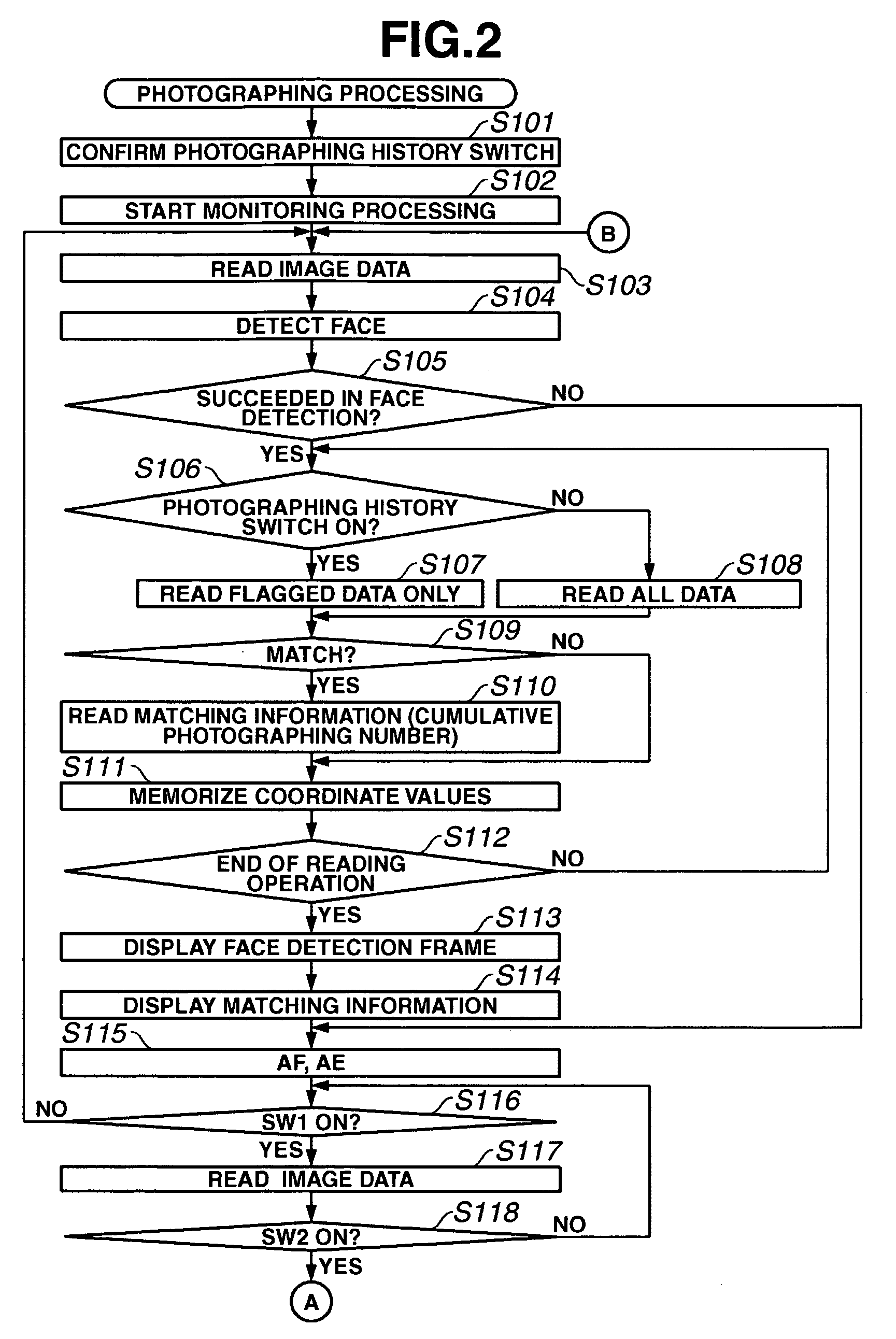
Imaging apparatus and method for controlling display device
InactiveUS20060210264A1Reduce user burdenTelevision system detailsProjector focusing arrangementImaging equipmentObject based
An imaging apparatus automatically detects an object and displays information on a display device based on a comparison between detected data and memorized (stored) data. The imaging apparatus includes a detecting circuit and a memorizing circuit. The detecting circuit detects the object based on the image data produced from an output of an imaging element and calculates a feature value representing a feature of the detected object. The memorizing circuit memorizes the feature value calculated by the detecting circuit. A feature value calculated by the detecting circuit based on the image data displayed on the display device is compared with the feature value memorized in the memorizing circuit. The display device displays information relating to the comparison result.
Owner:CANON KK
System and method to automatically focus an image reader
ActiveUS7611060B2Minimize degradationProjector focusing arrangementCamera focusing arrangementImaging dataSingle frame
The invention features a system and method to automatically focus an image reader using a single frame of image data. The method comprises exposing sequentially a plurality of rows of pixels in the image sensor. The method further comprising varying in incremental steps the focus of the image reader's optical system from a first setting where a distinct image of objects located at a first distance from the image reader is formed on the image sensor to a second setting where a distinct image of objects located at a second distance from the image reader is formed on the image sensor. As part of the method, the varying of the focus of the optical system occurs during the exposure of the plurality of rows of pixels.
Owner:HAND HELD PRODS
Lens holder drive apparatus, and camera equipped therewith
ActiveUS20120229901A1Small sizeProjector focusing arrangementCamera focusing arrangementCamera lensOptical axis
Provided is a small, low-profile lens holder apparatus. A lens holder apparatus includes: a lens holder to which a lens section can be attached; a first drive section that moves the lens holder in a first direction along the optical axis; a second drive section that moves the lens holder in a second direction and / or third direction that are perpendicular to the optical axis and differ from each other; a supporting section that includes a base disposed in a position spaced from the lens holder and a supporting member that supports the lens holder so as to be able to move in the second direction and / or third direction; and a position detection section that is disposed on the supporting section in order to detect a position in the second direction and / or third direction of the lens holder with respect to the base.
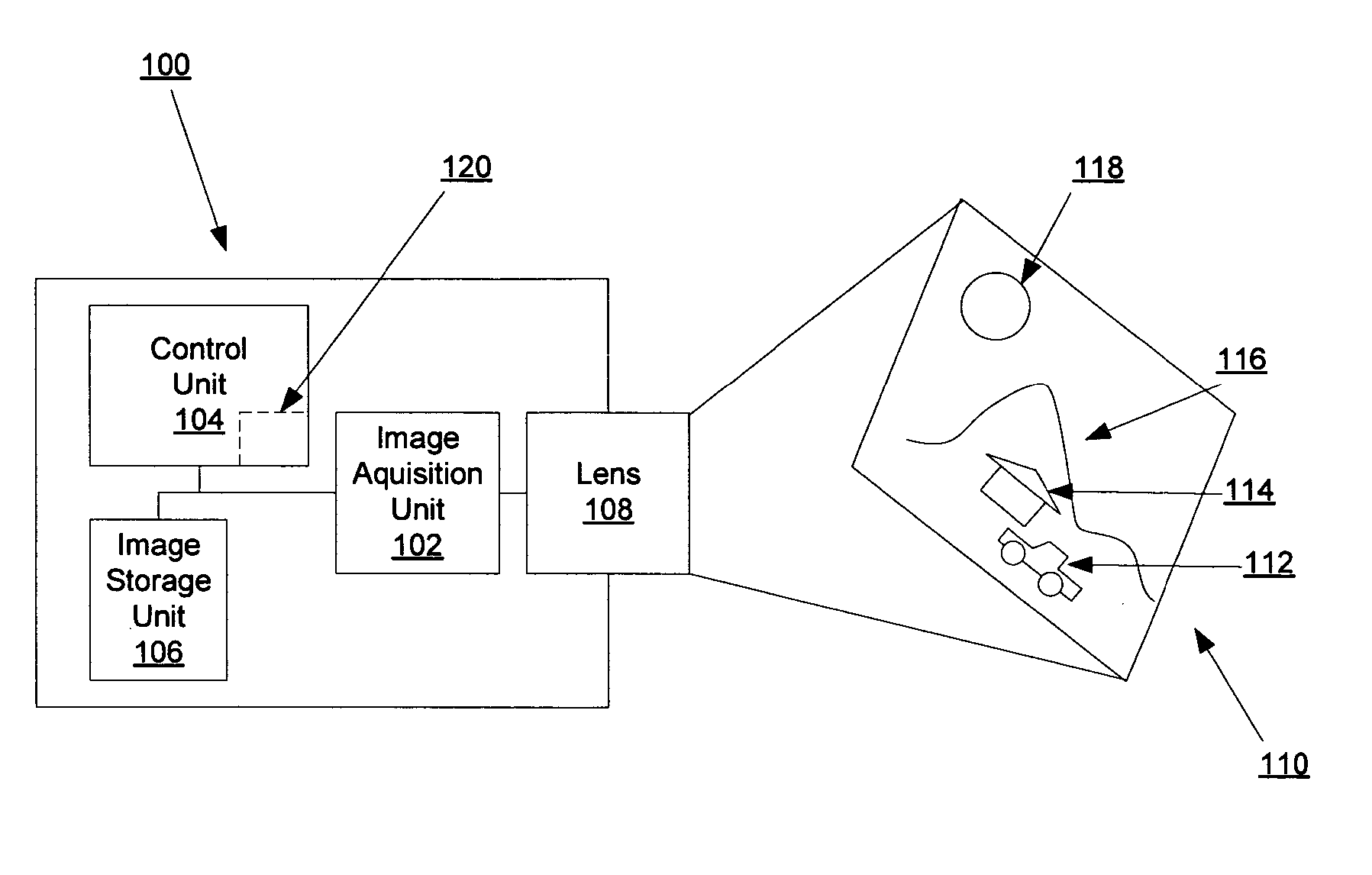
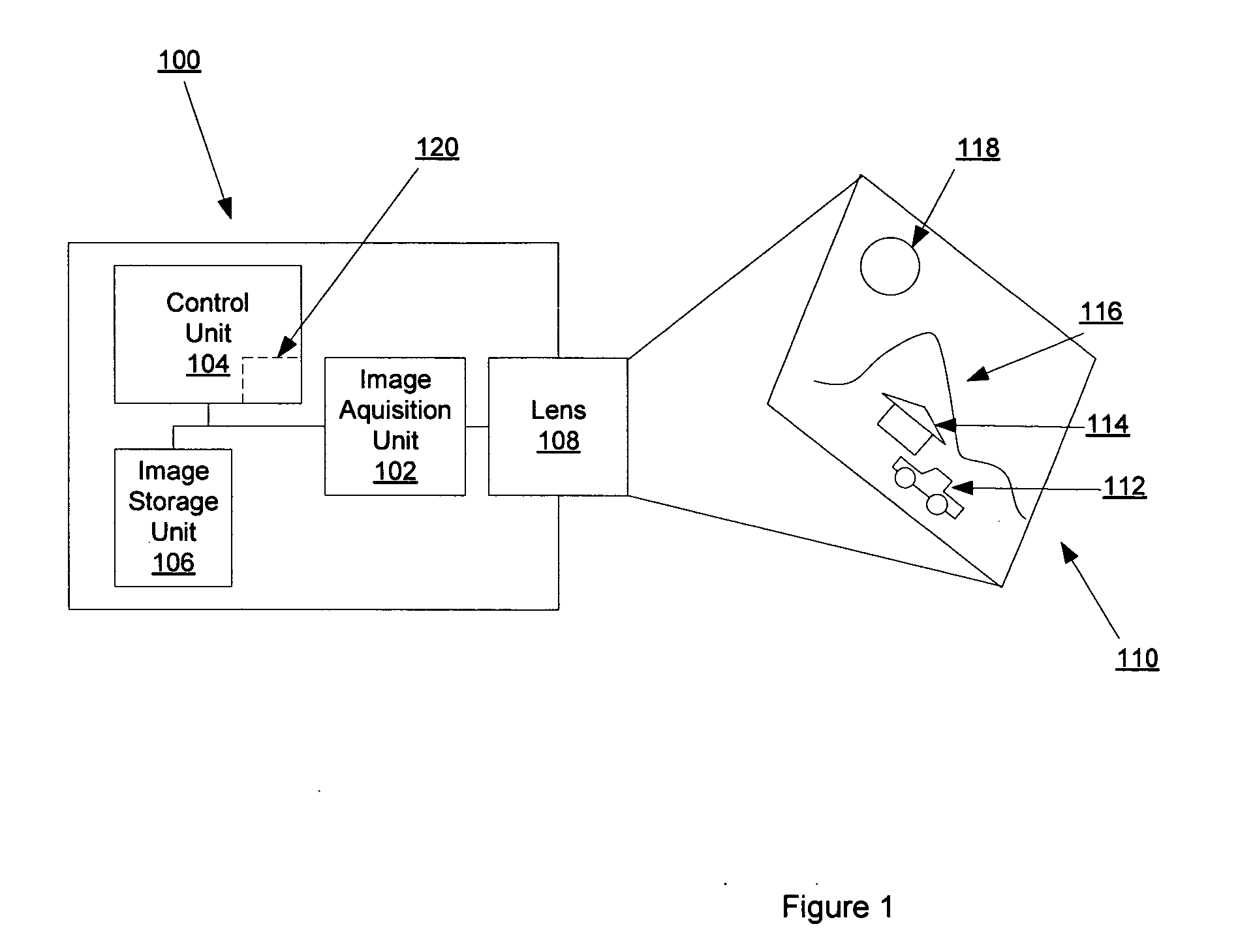
Owner:MITSUMI ELECTRIC CO LTD
Autofocus barcode scanner and the like employing micro-fluidic lens
ActiveUS20050218231A1Wide spatial resolution rangeReduce and eliminate needProjector focusing arrangementCamera focusing arrangementBarcodeAutofocus
A machine-readable symbol reader includes a microfluidic lens assembly providing responsive, reliable auto-focus functionality. A range finder may provide distance to a planar target (e.g., barcode symbol) information for use in auto-focusing, with or without localization. Illumination system, if included, is selectively controlled based on the distance to target and auto-focusing functionality to substantially reduce power consumption. The localization may color optical sensors.
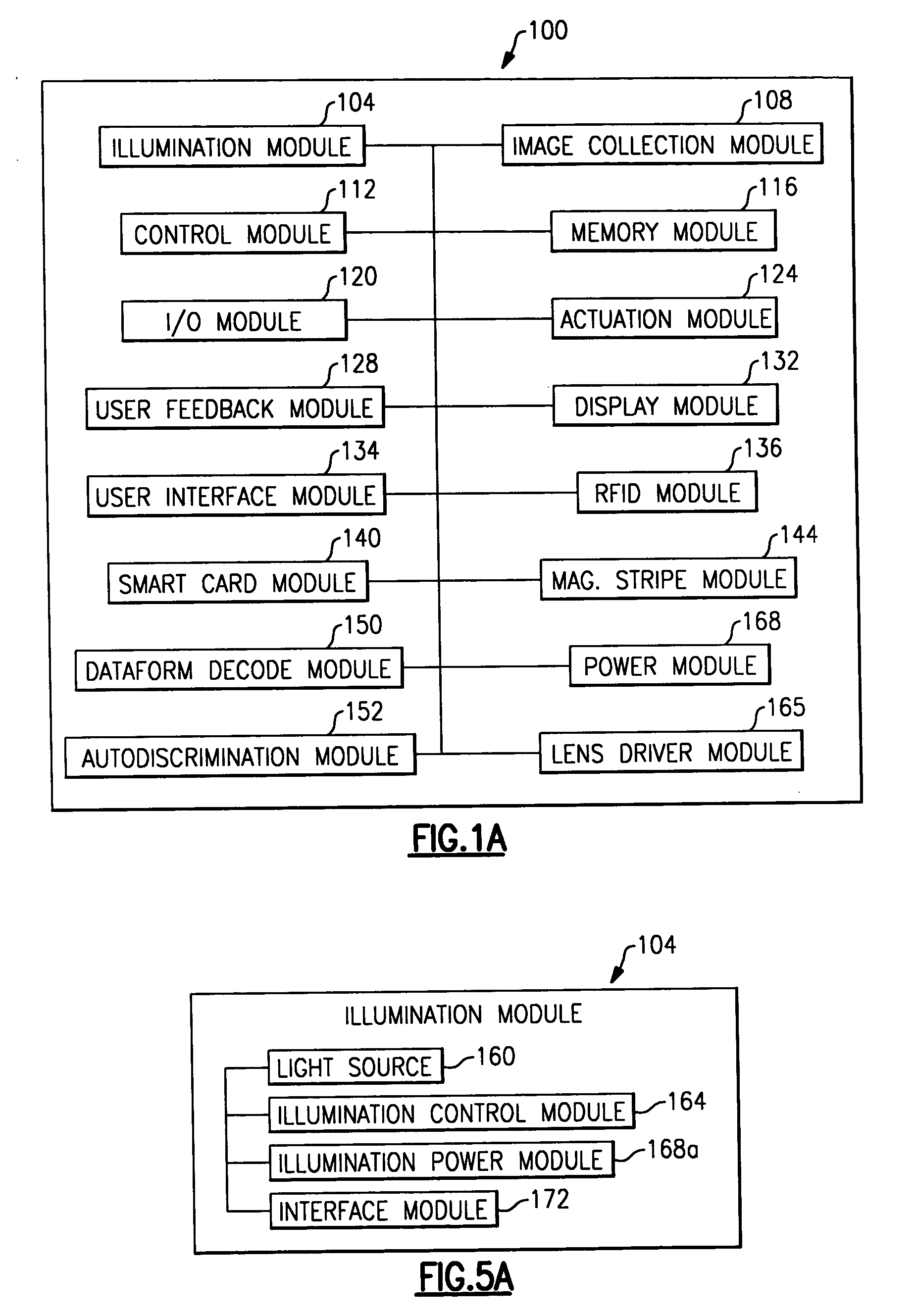
Owner:INTERMEC IP
Auto-focusing device with voice coil motor for position feedback and method for using same
InactiveUS20070047942A1Simple configurationSmall sizeTelevision system detailsProjector focusing arrangementMagnetic tension forceAutofocus
An auto-focusing device with voice coil motor for position feedback comprises a lens holder, a sensor holder, a permanent magnet set, a yoke and a base. The lens holder holds a lens barrel and is wound around with at least two coils wound in opposite directions. The sensor holder holds an image sensor. The permanent magnet set includes at least two permanent magnets stacked together with opposing poles to form a multi-pole permanent magnet set. The permanent magnet set is furnished on the periphery of lens holder and corresponds to the two coils on lens holder. The permanent magnet set is disposed on the yoke to form a close-loop magnetism so as to increase the density of magnetic lines and the efficiency of magnetic force, save power consumption, and extend the service life of device.
Owner:POWERGATE OPTICAL INC
Lens driving apparatus
ActiveUS20110176046A1Reduce manufacturing costImprove accuracyTelevision system detailsProjector focusing arrangementOptical axisOptoelectronics
Owner:TDK TAIWAN
Electronic camera
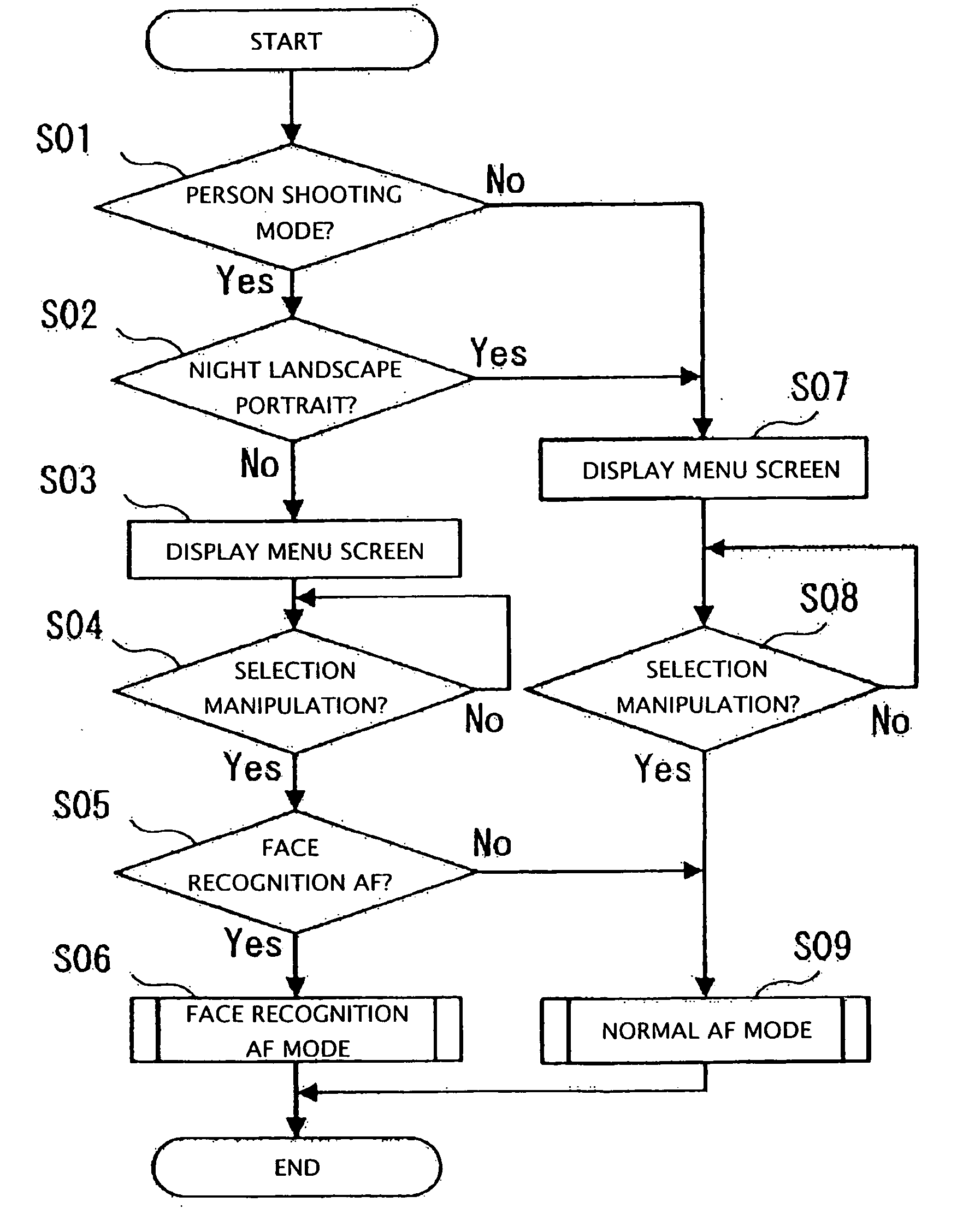
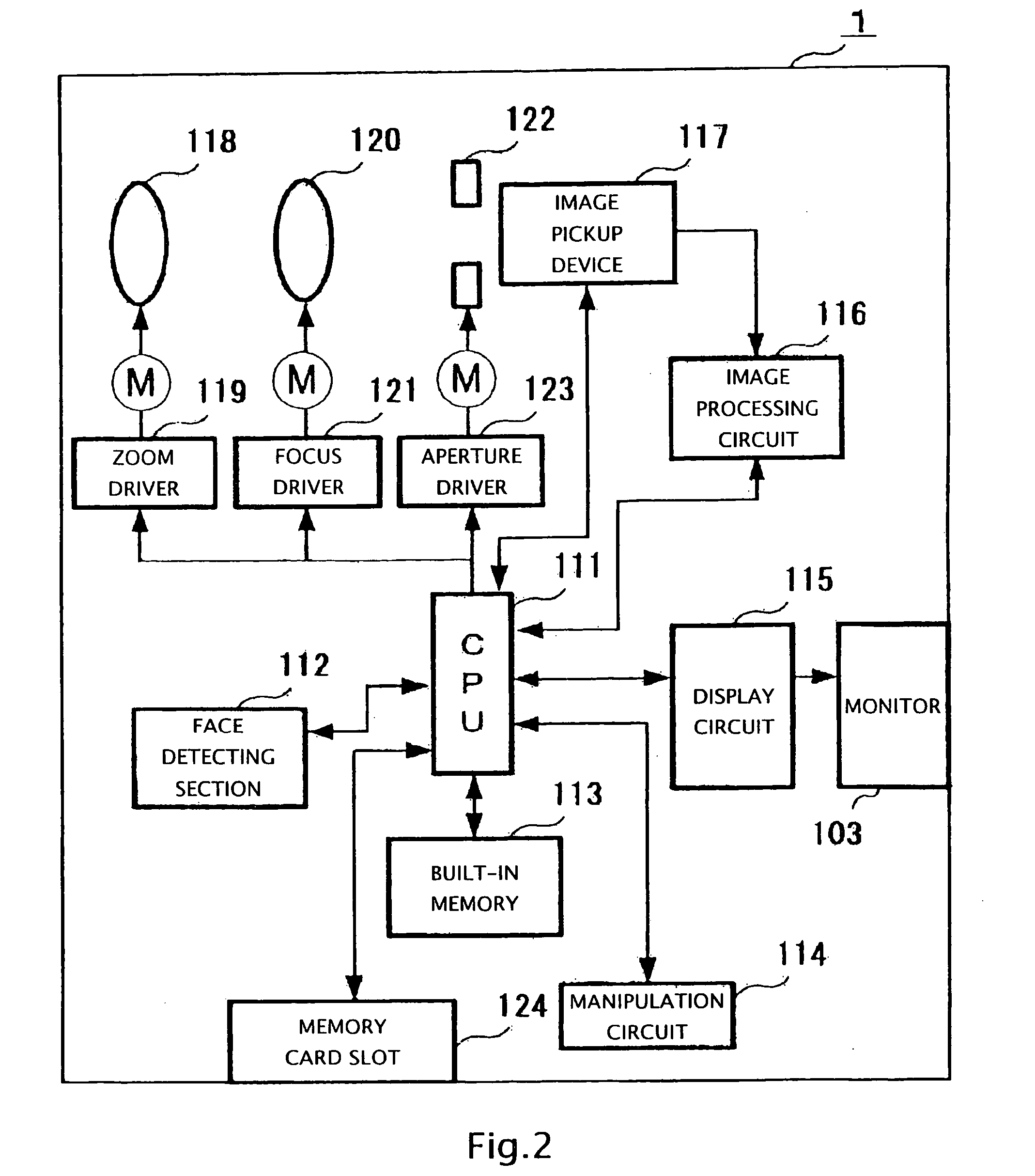
InactiveUS20060182433A1Stable focusAvoid confusionTelevision system detailsProjector focusing arrangementFace detectionComputer graphics (images)
An electronic camera includes a face detecting section, a setting section, and a controlling section. The face detecting section detects a face of a subject. The setting section sets a scene shooting mode to adjust a shooting condition to an optimum shooting condition in accordance with each pre-assumed shooting scene. The controlling section controls the face detection of the face detecting section only when the setting section has set a scene shooting mode for shooting a scene including a person.
Owner:NIKON CORP
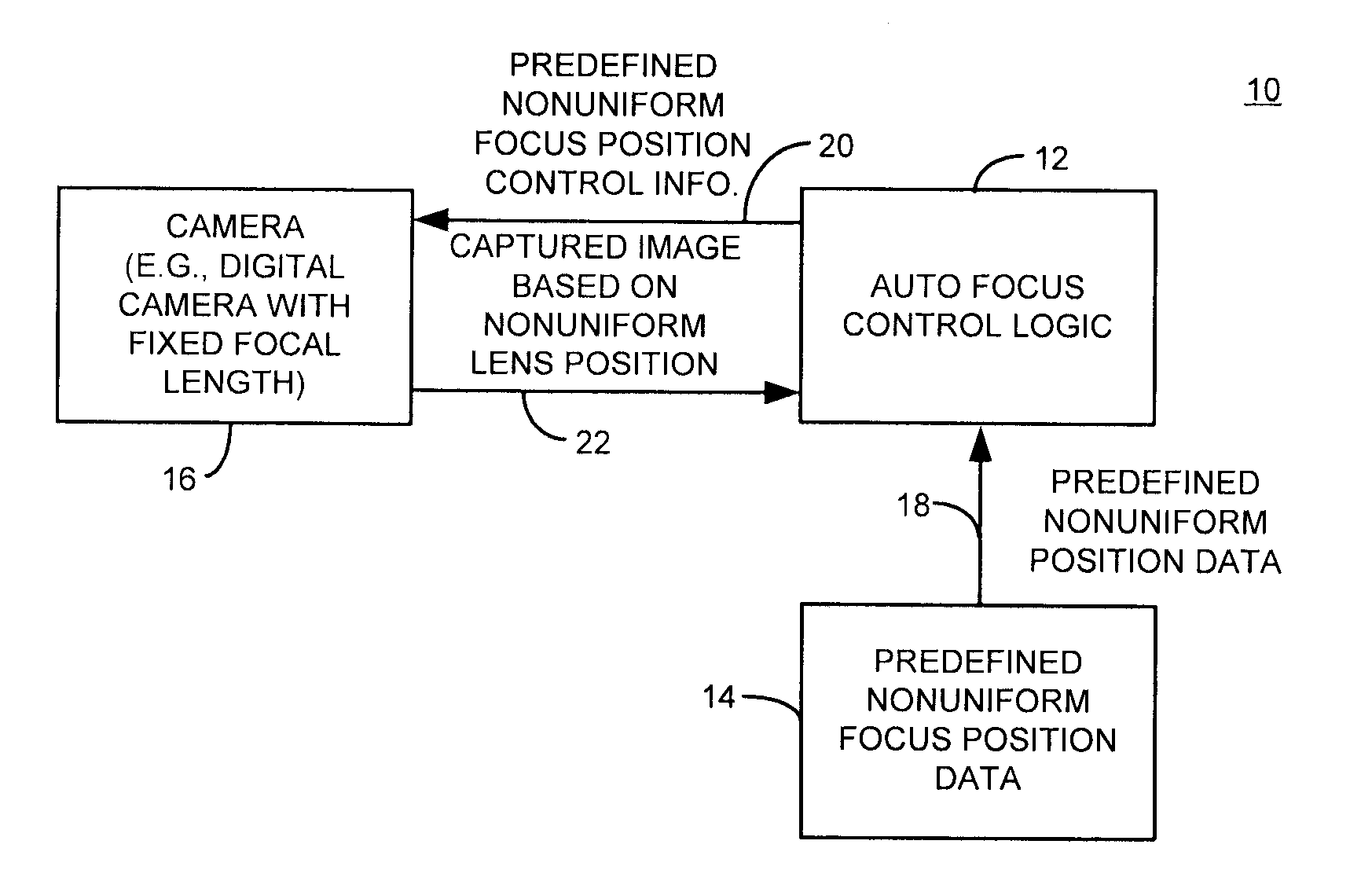
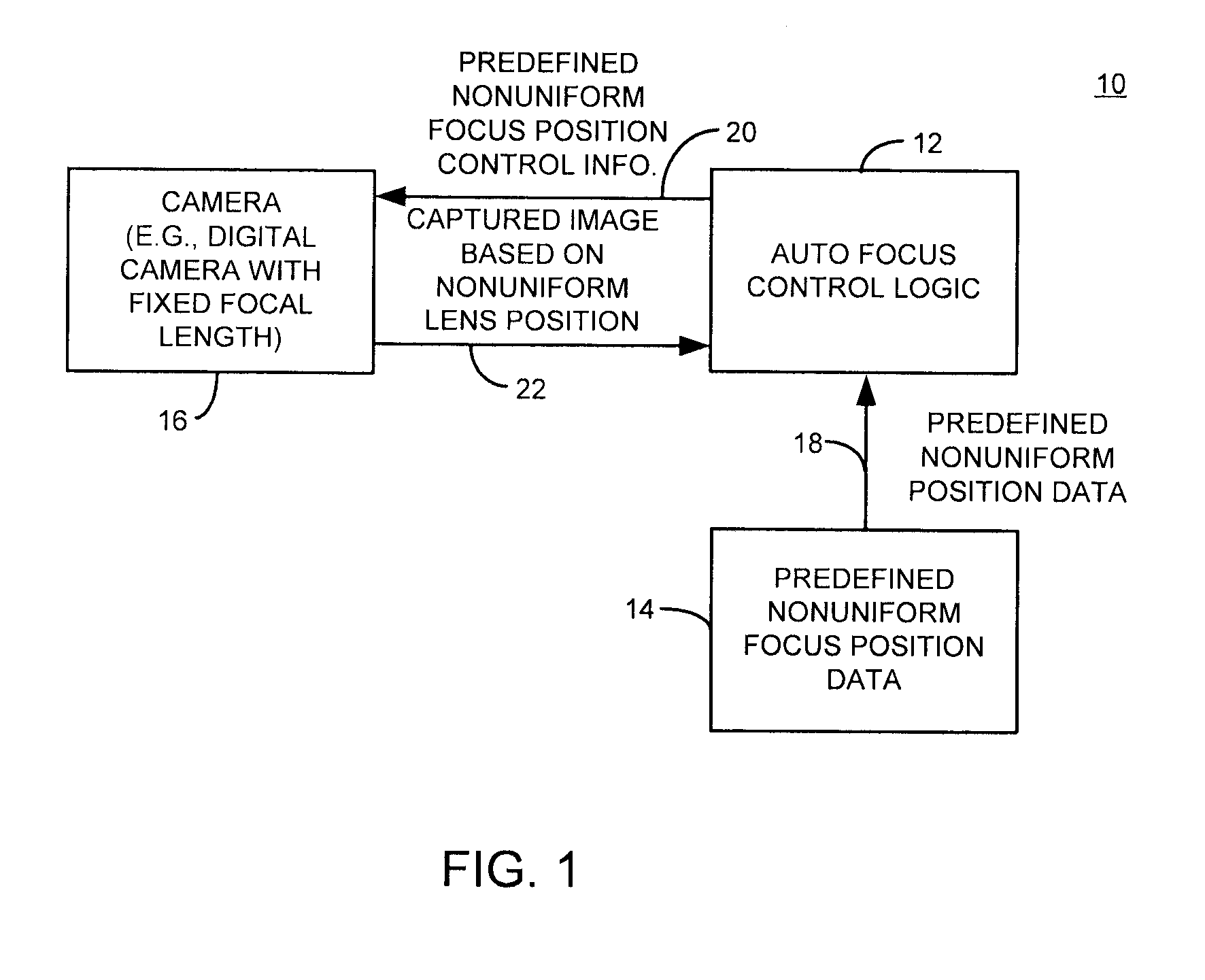
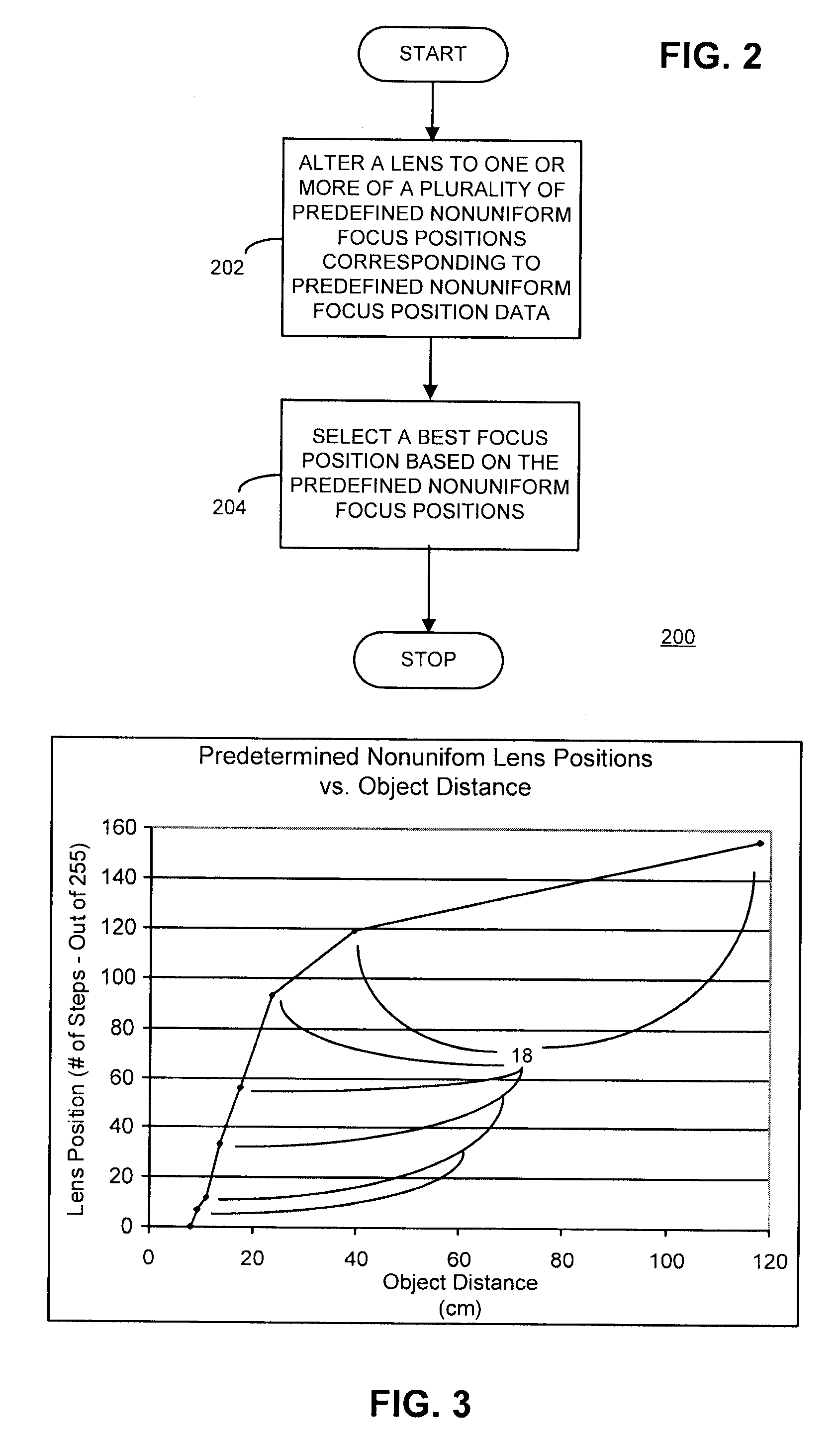
Method and apparatus with fast camera auto focus
A method and apparatus improves an auto focus system by altering, such as by positioning, at least one lens of a digital camera to a plurality of predetermined nonuniform lens positions corresponding to predetermined nonuniform lens position data. The method and apparatus selects a final lens position for the lens based on the predetermined nonuniform lens position data. In one example, a fixed number of predetermined nonuniform lens positions define a set of lens positions used to capture images during an auto focus operation. A final image is captured using a final lens position. The final lens position is determined by comparing focus metric information from each of the frames obtained at the various predetermined nonuniform focus lens positions and selecting the frame with, for example, the best focus metric as the lens position to be used for the final picture or image capture.
Owner:QUALCOMM INC
Image photographing device
ActiveUS20120320467A1Reduce noiseSimple structureTelevision system detailsProjector focusing arrangementOptical axisEngineering
Disclosed herein is an image photographing device capable of being auto-focused while moving a lens barrel in an optical axis direction. The image photographing device includes: a lens barrel having at least one lens; a housing receiving the lens barrel therein so that the lens barrel moves in an optical axis direction; and an impact reducing unit elastically supporting the lens barrel in the case in which the lens barrel deviates from a set movement range, thereby primarily damping the lens barrel before the lens barrel deviates from the movement range to collide with other components positioned at an outer side of the lens barrel.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRO MECHANICS CO LTD
Lens driving apparatus
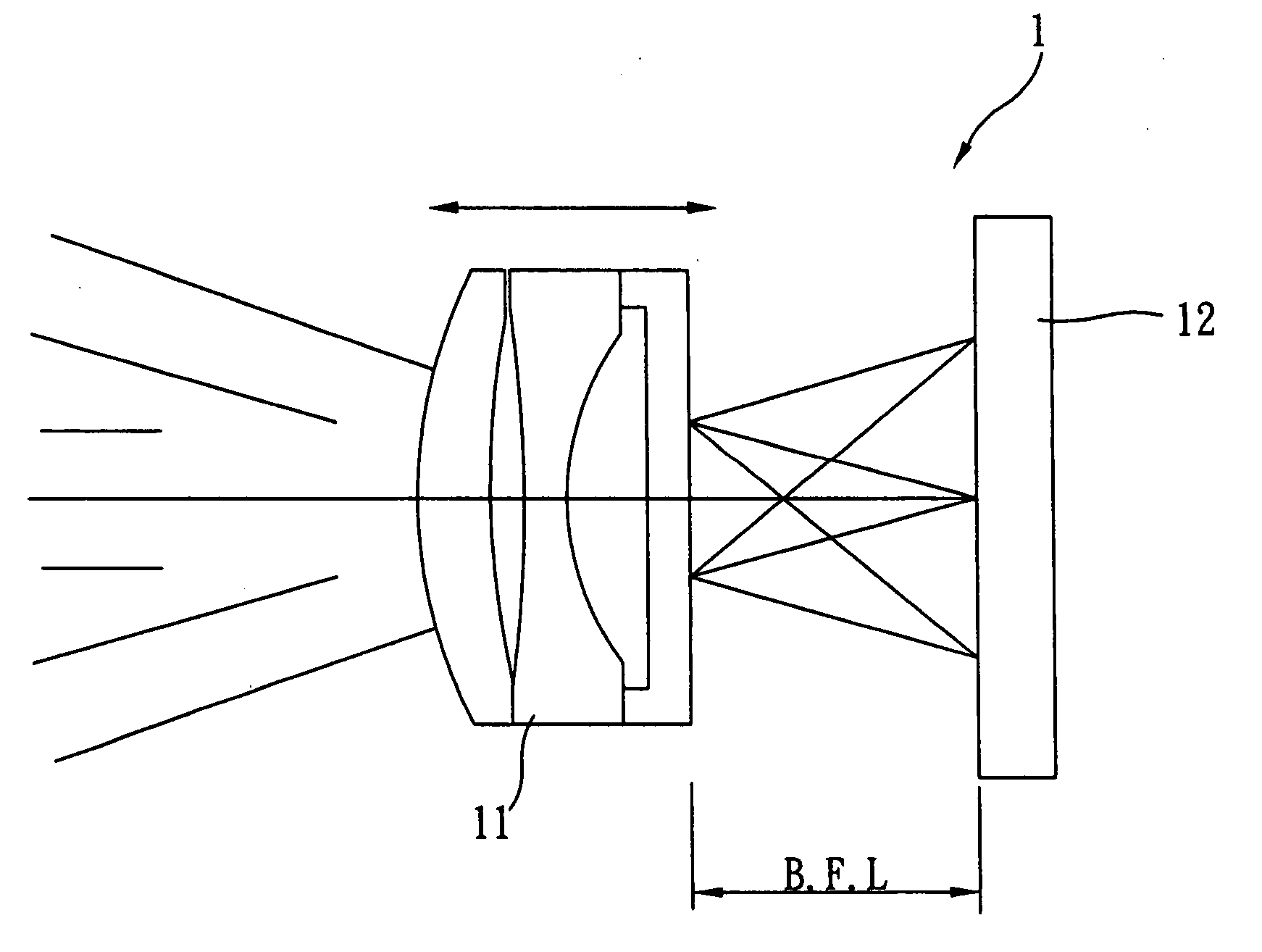
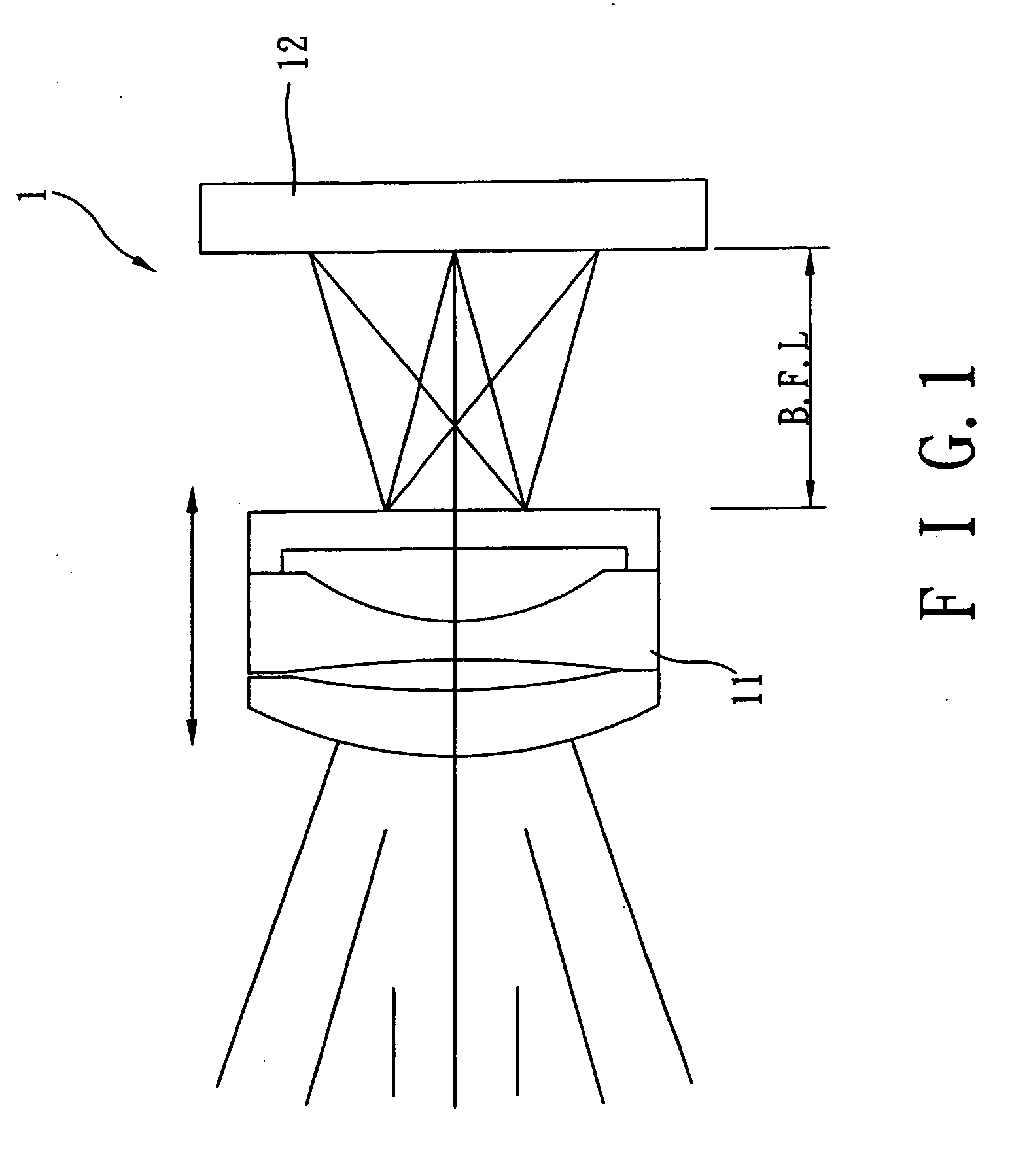
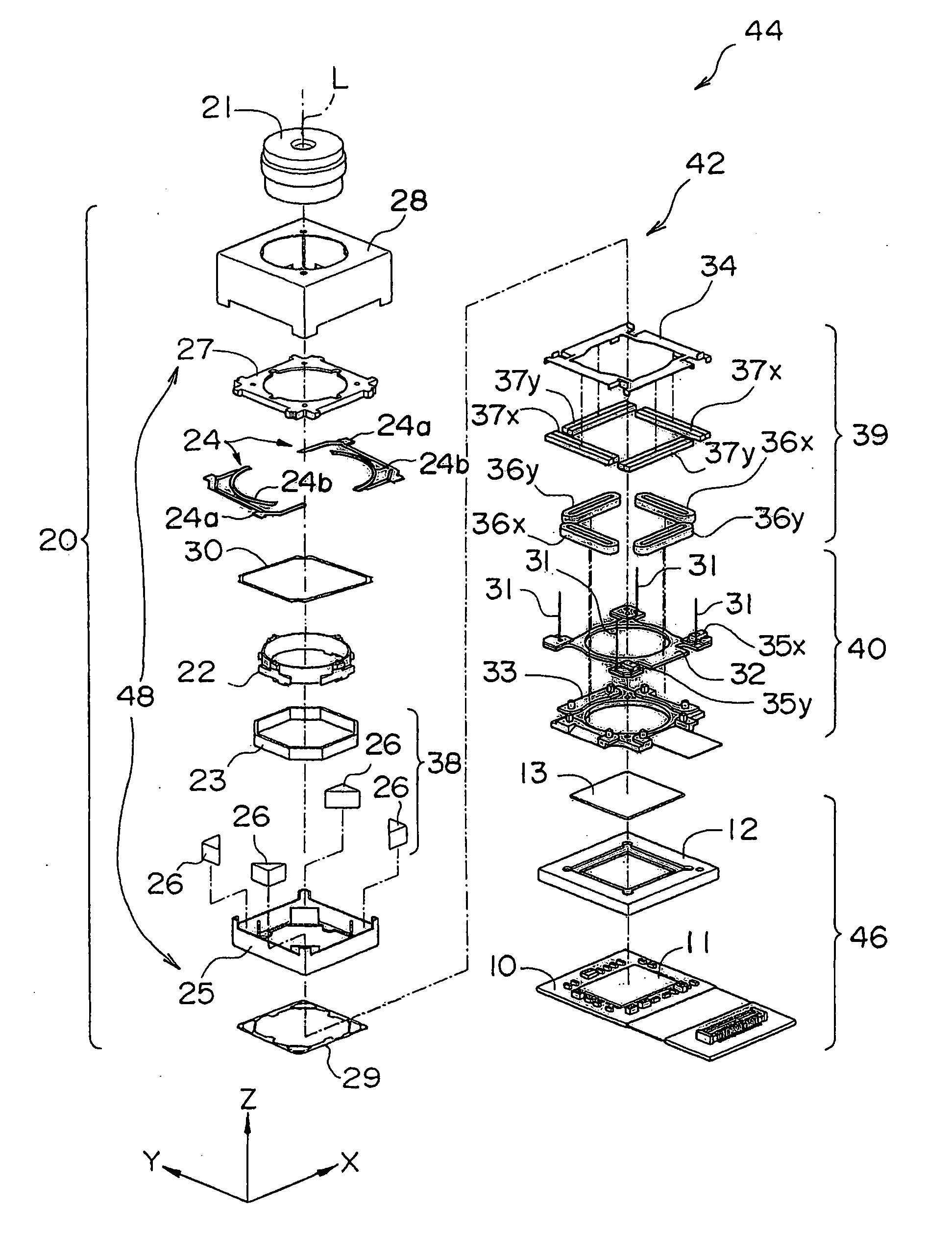
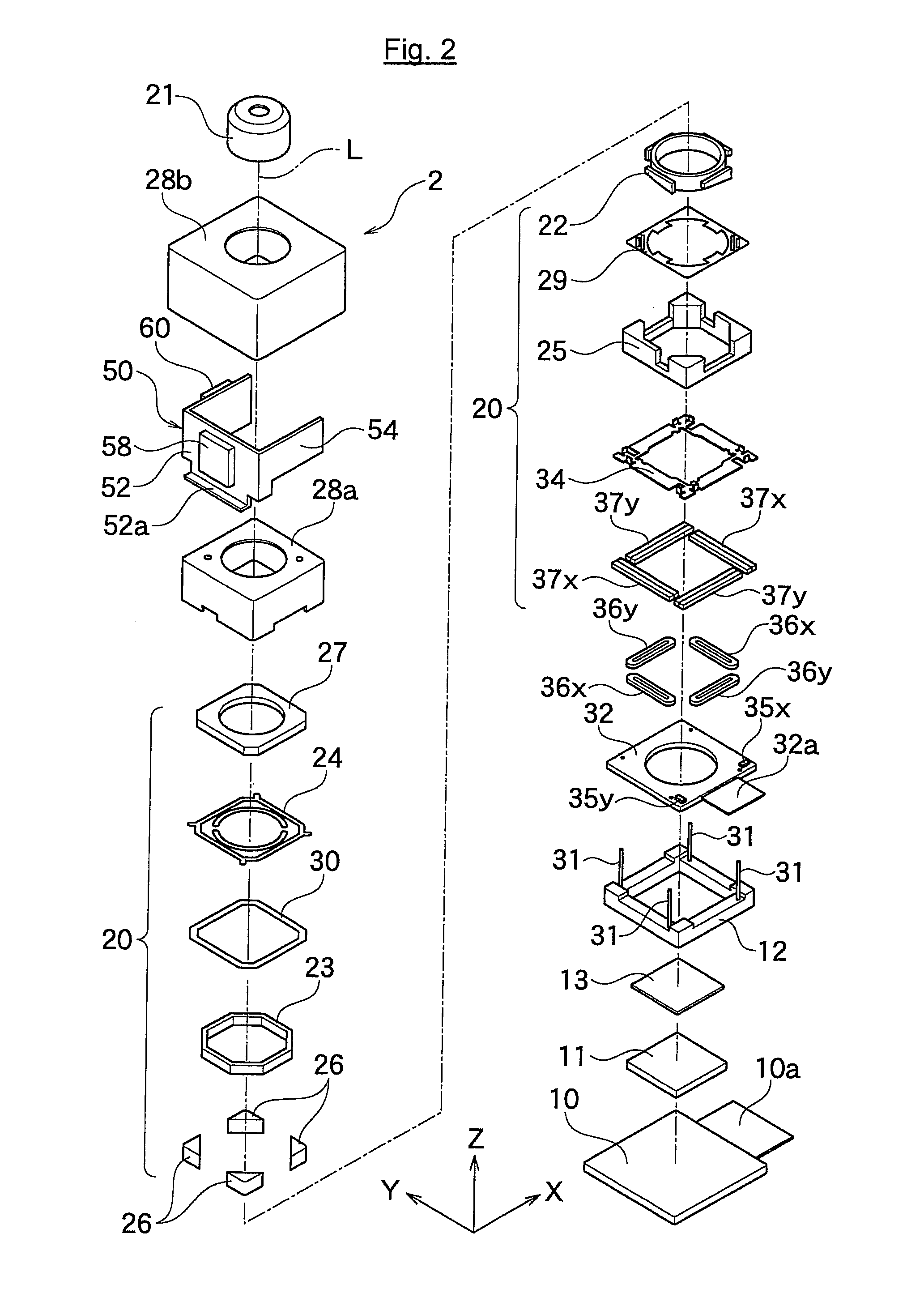
ActiveUS20110286732A1Precise motion controlEquipment miniaturizationProjector focusing arrangementCamera focusing arrangementCamera lensOptical axis
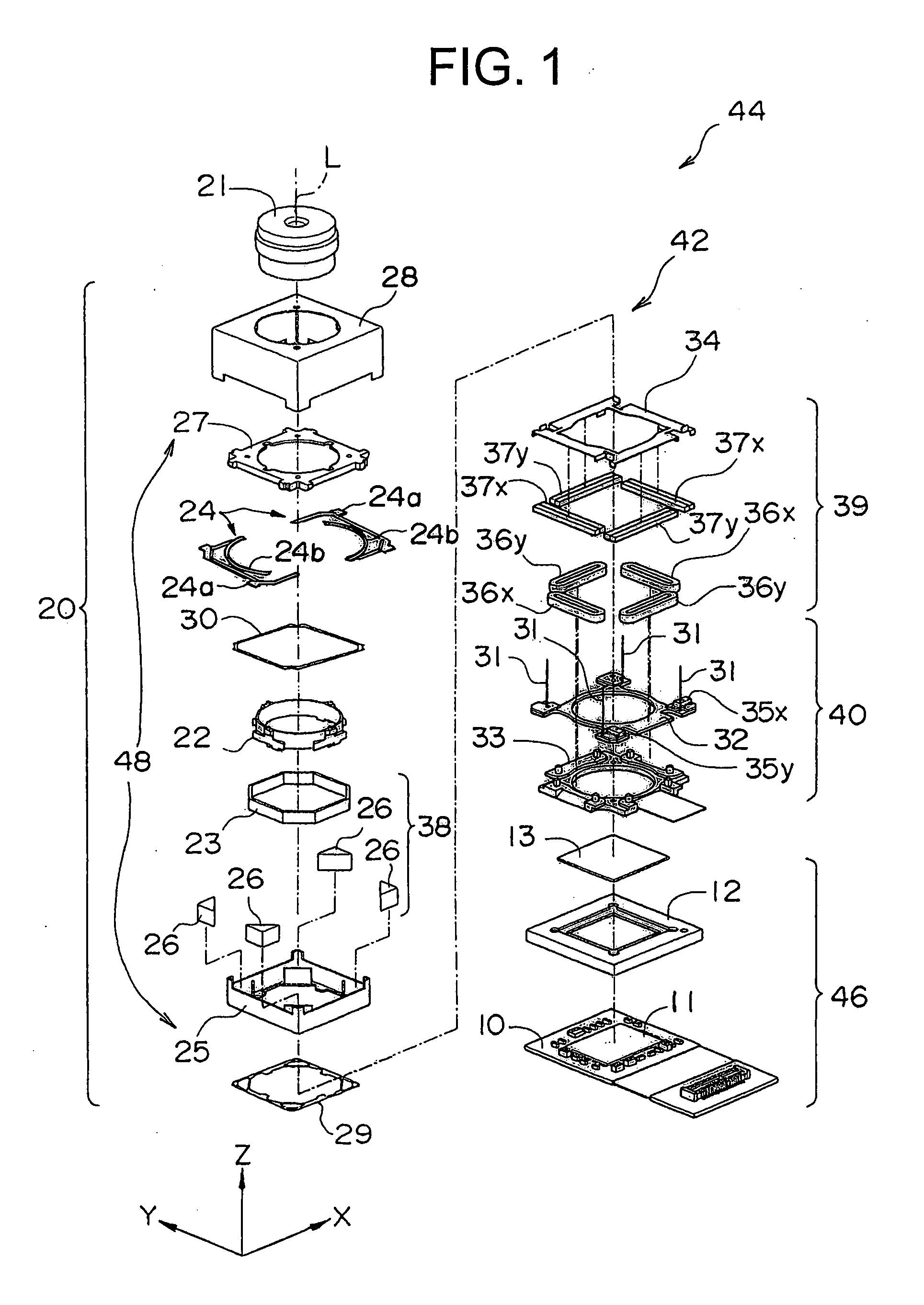
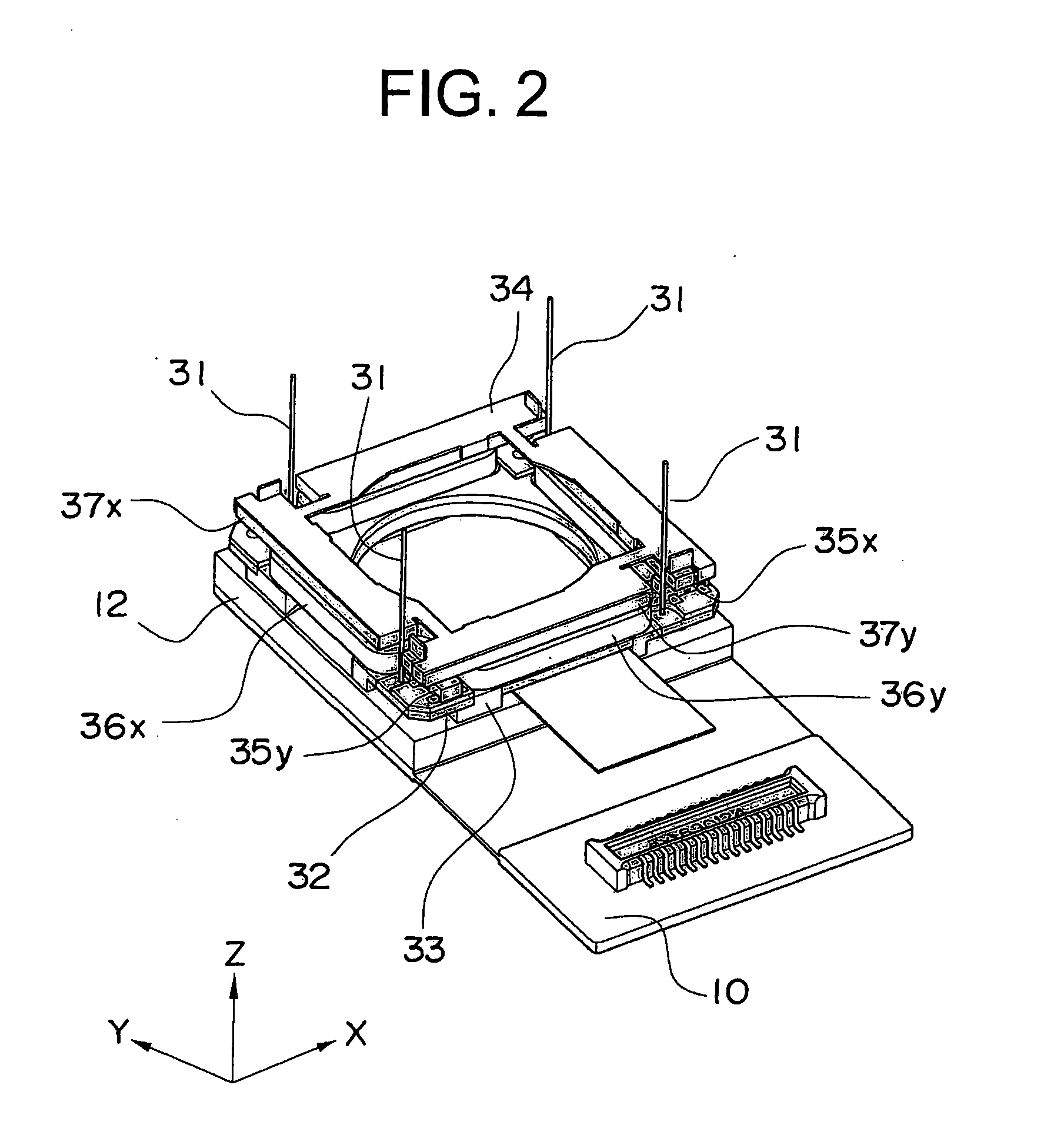
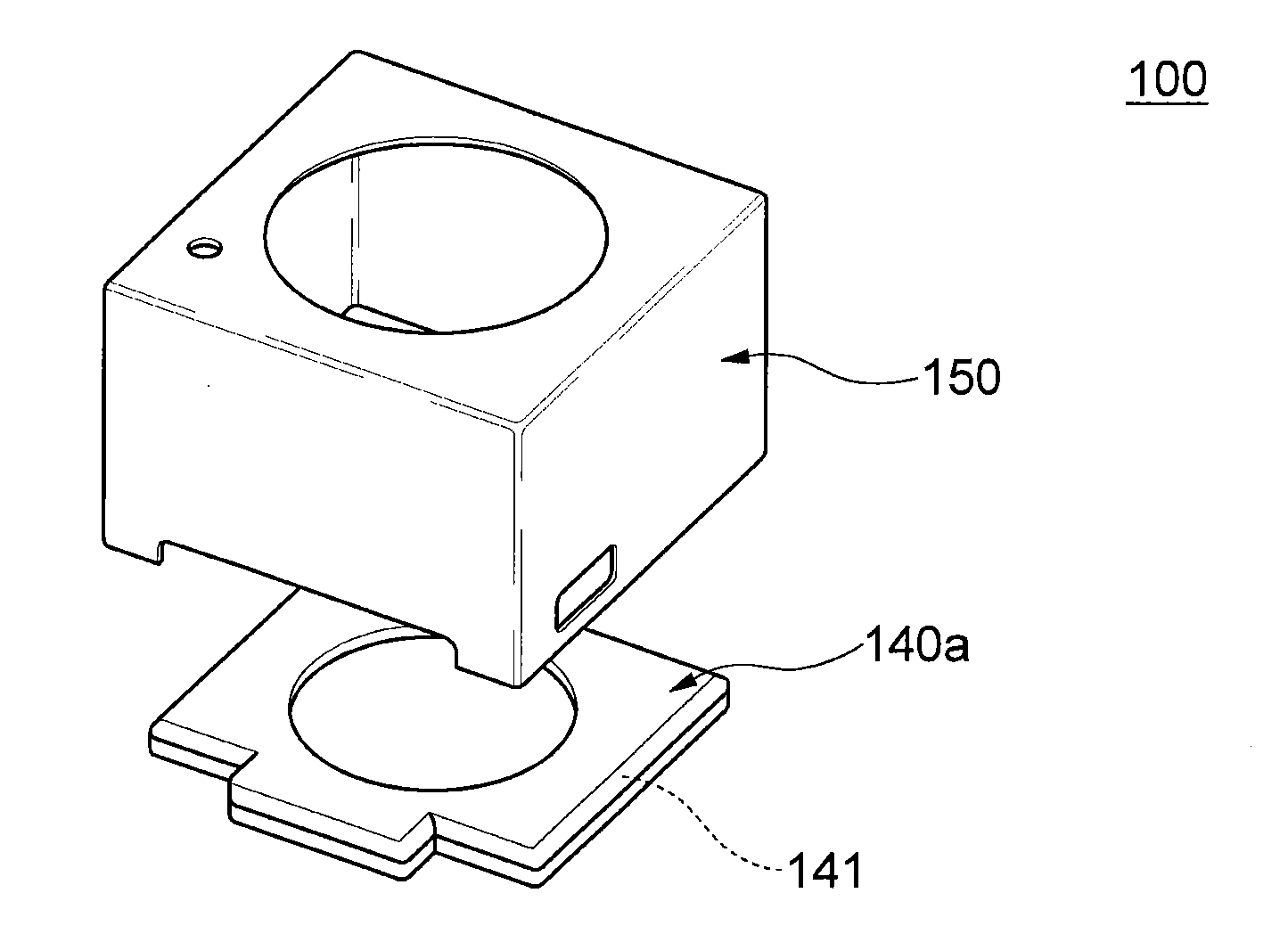
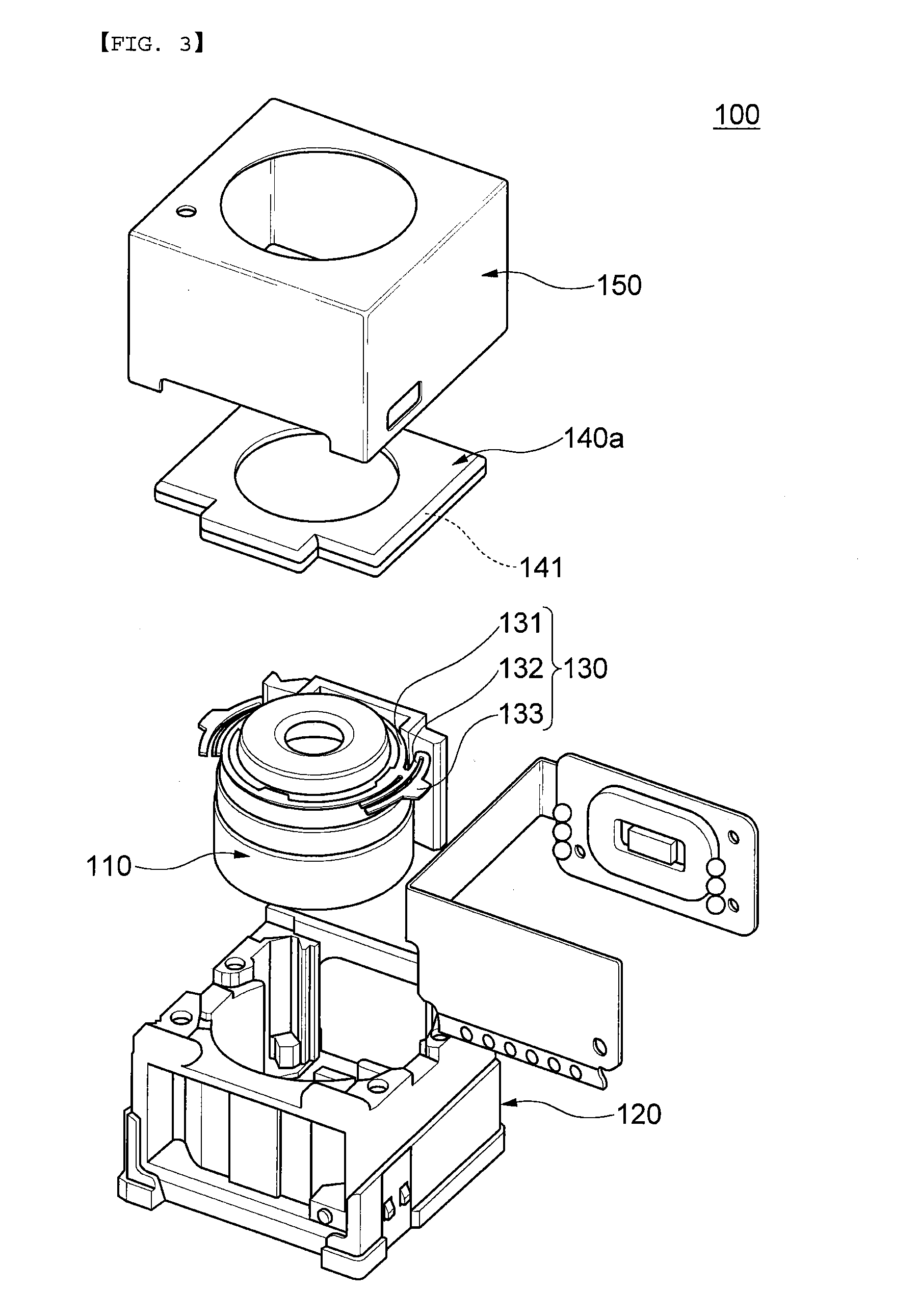
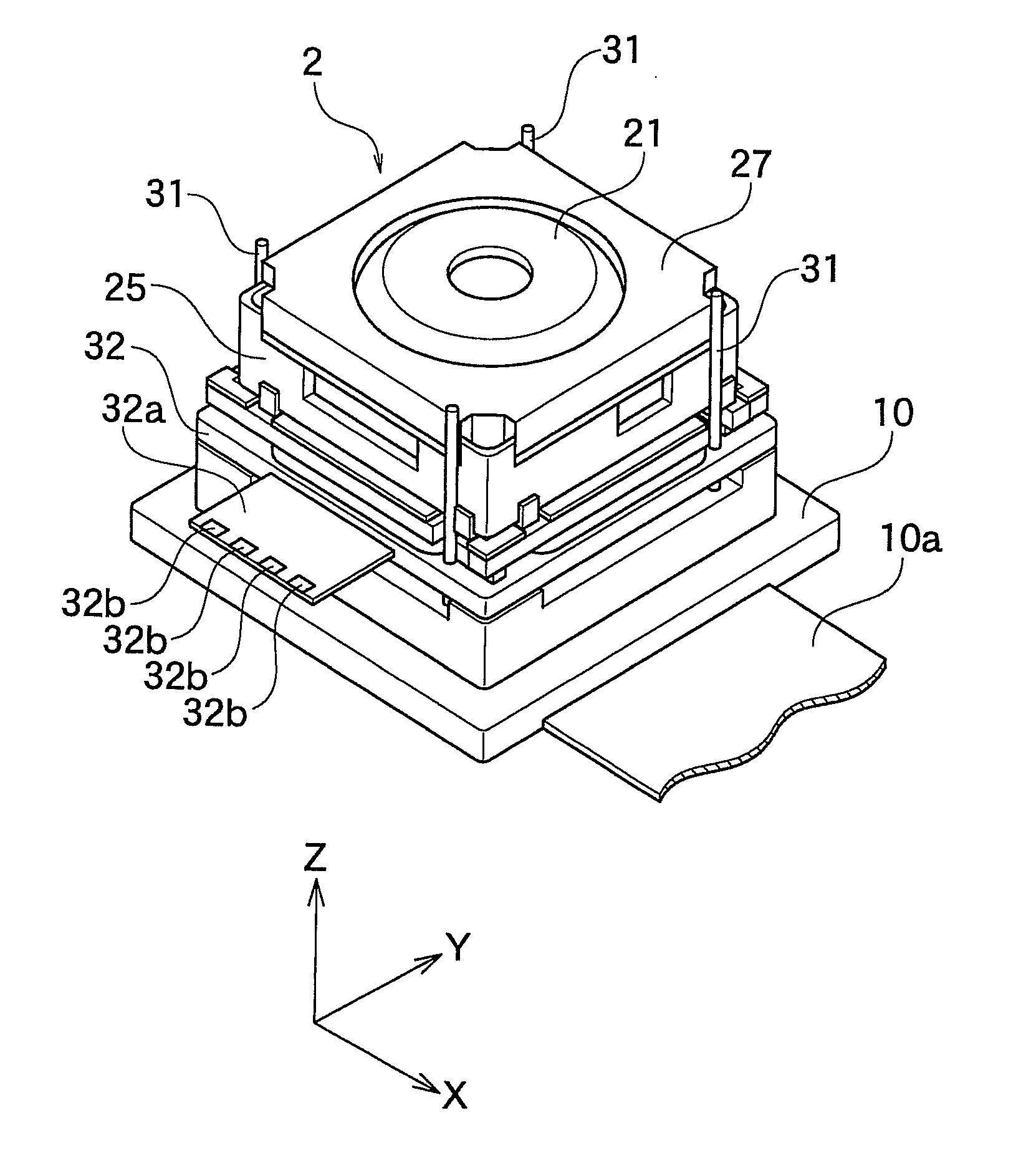
A lens driving apparatus has a lens portion 21, a first driving portion 36 and 37 to cause a movement of a movable unit 20 including said lens portion 21 relatively to a fixed portion 10 along a vertical direction of a light axis of said lens portion 21, a second driving portion 23 and 26 to cause a movement of said lens portion relatively to said fixed portion 10 along said light axis, an image sensor 11 held on said fixed portion 10 to detect a light which comes through said lens portion 21, an inner casing 28a held on said fixed portion 10 to cover said movable unit 20 and said image sensor 11, and a planar flexible printed circuit 50 to which a shake detection sensor 58 detecting a shake of said fixed portion 10 is connected. The planar flexible printed circuit 50 is attached to contact with a sidewall surface of said inner casing 28a parallel to the light axis of said lens.
Owner:TDK CORPARATION
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com