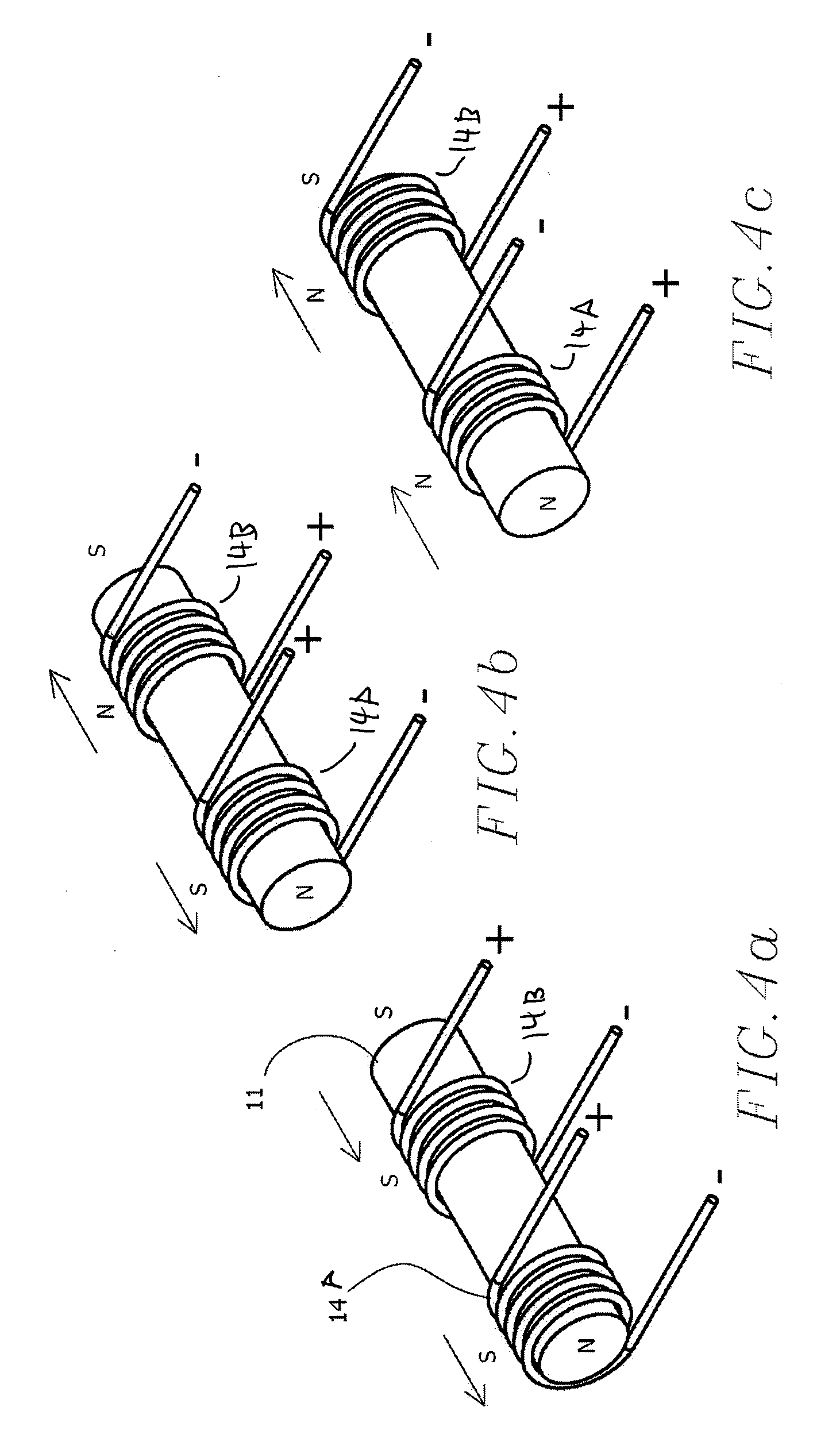
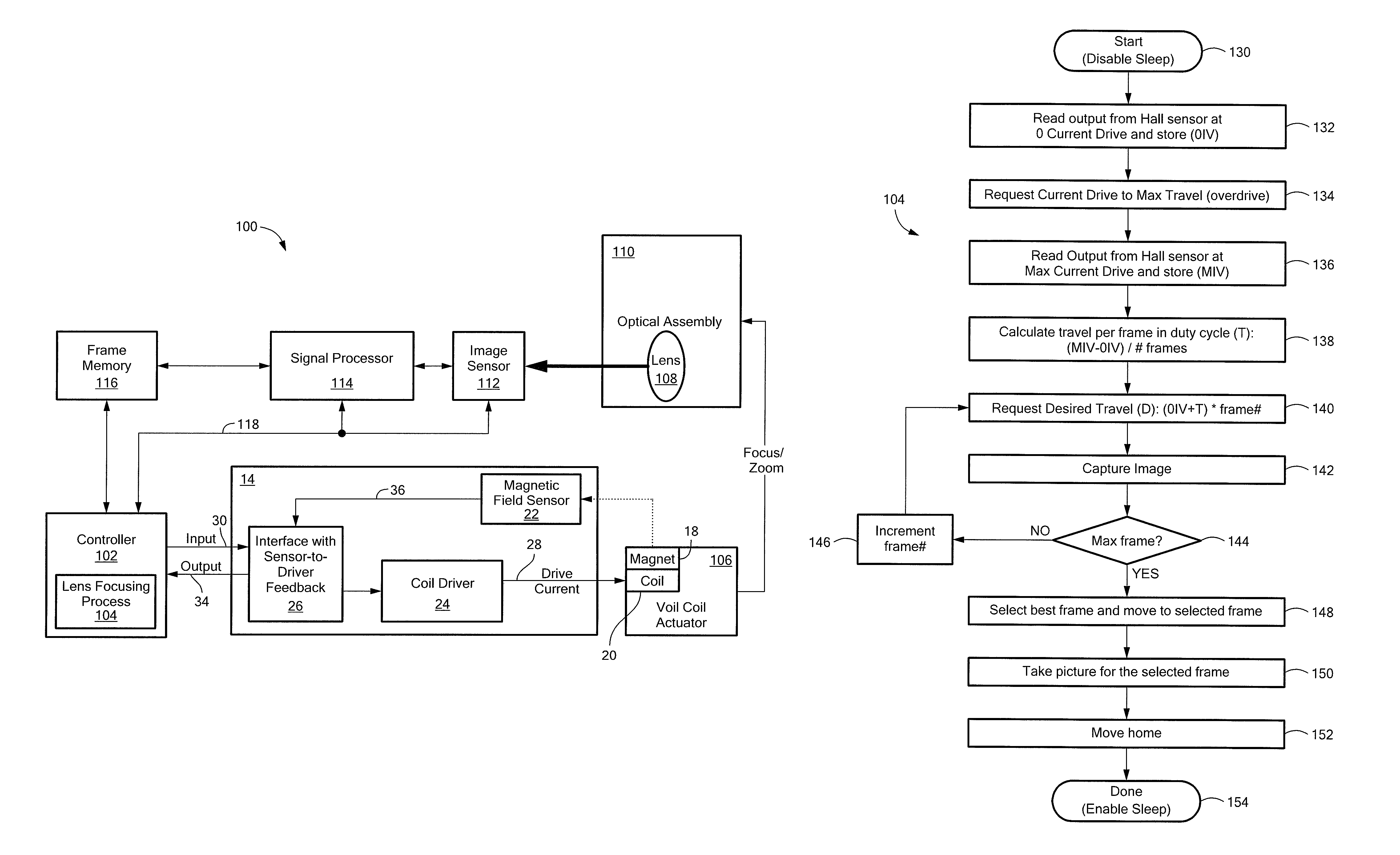
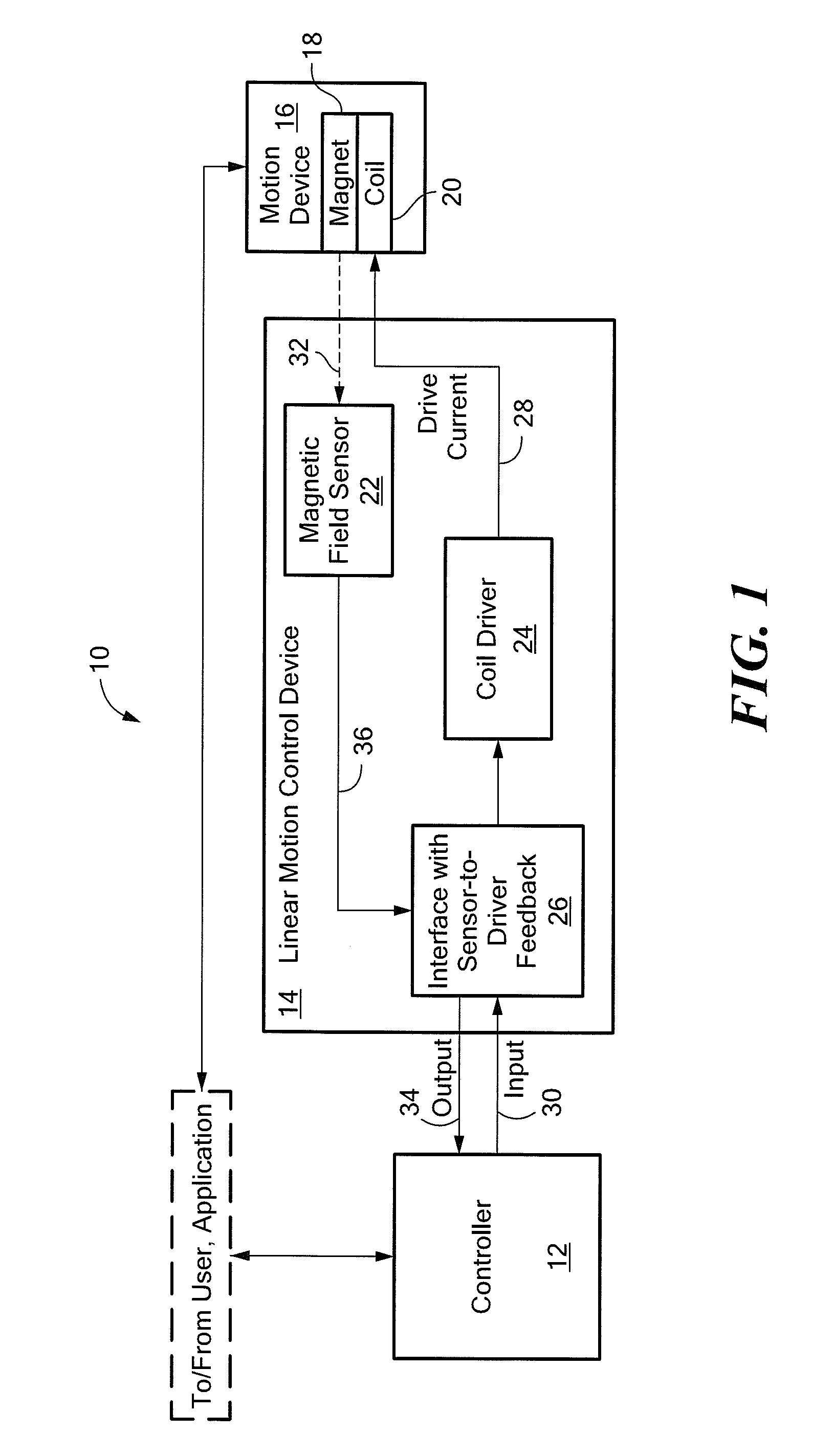
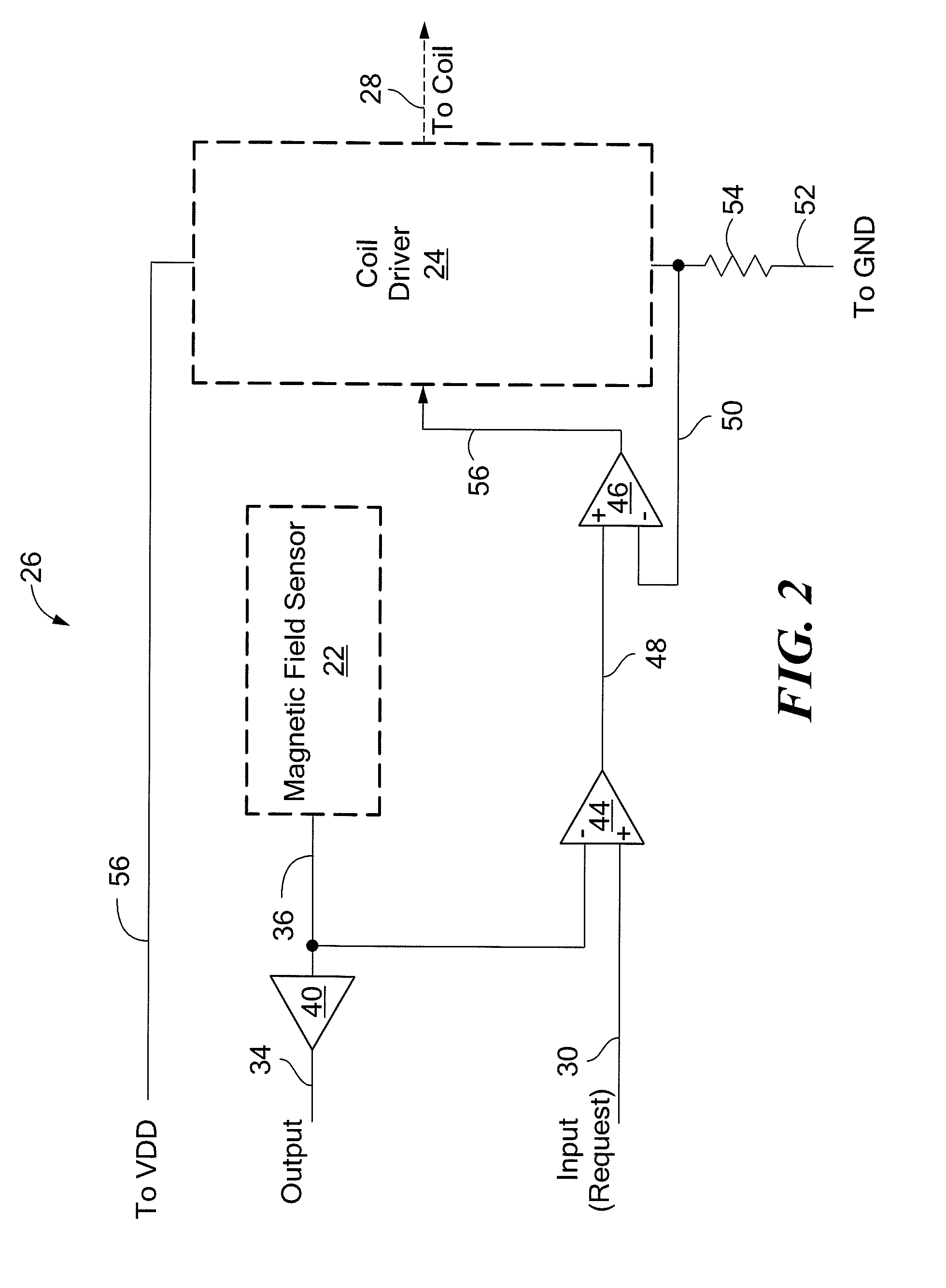
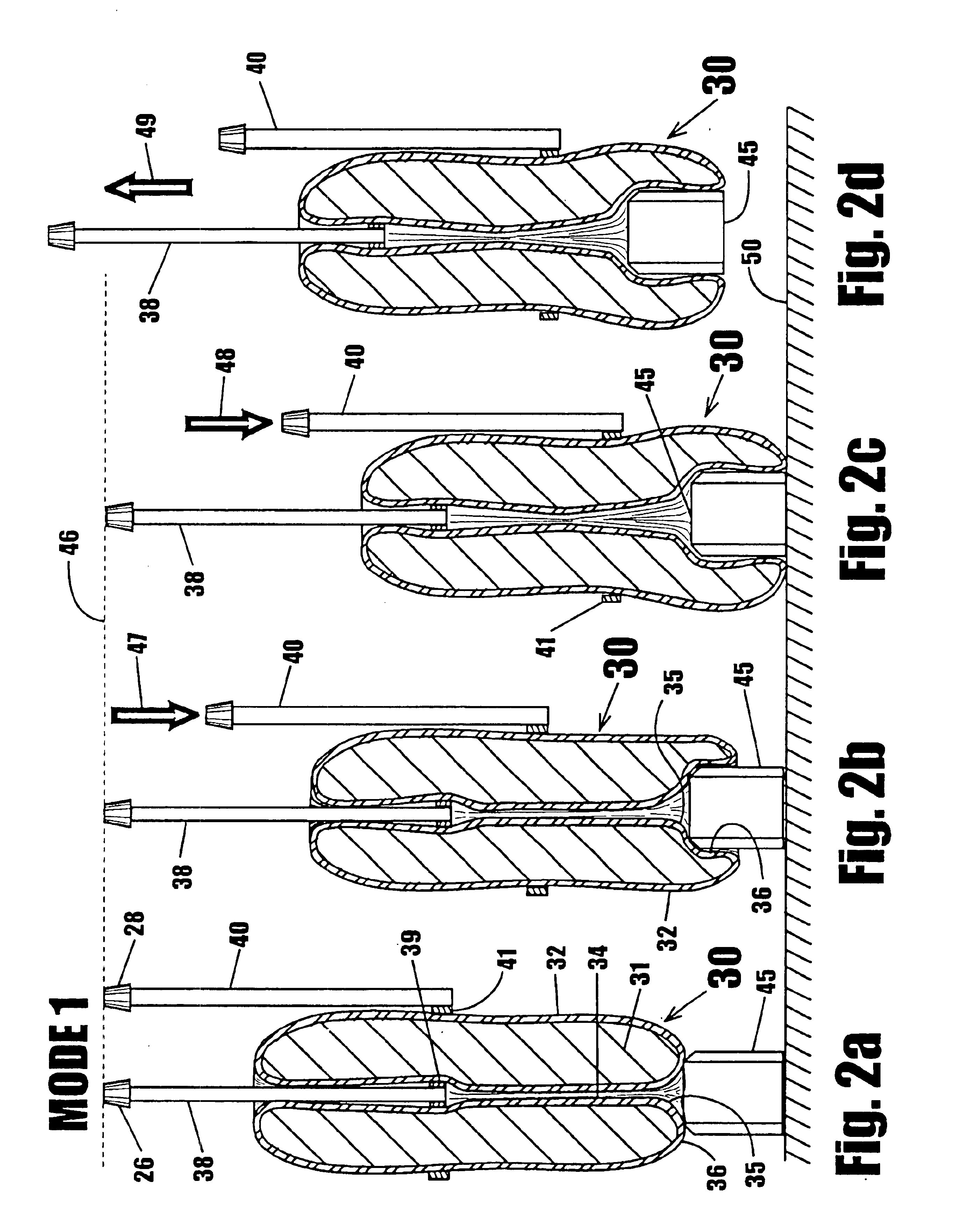
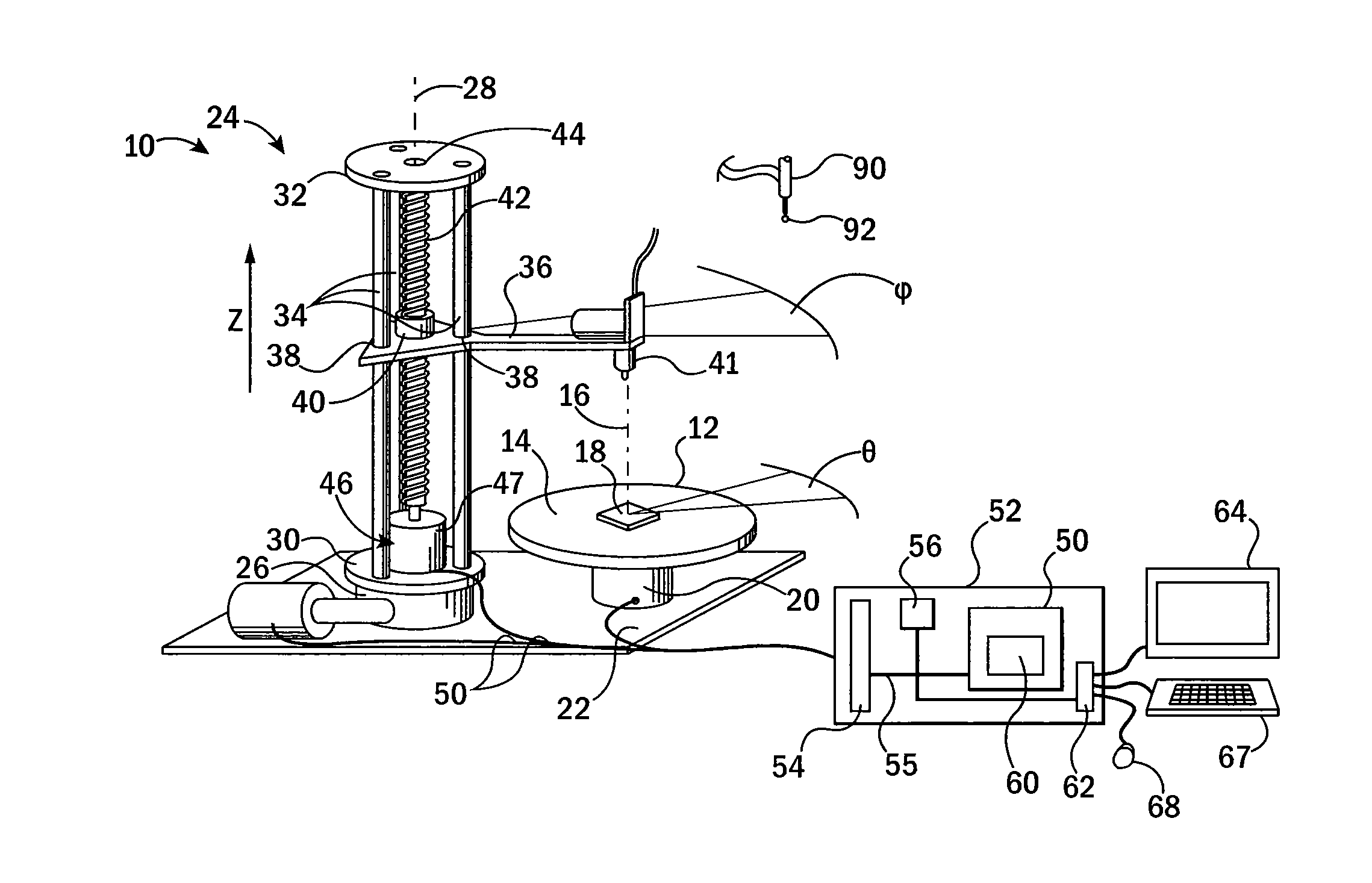
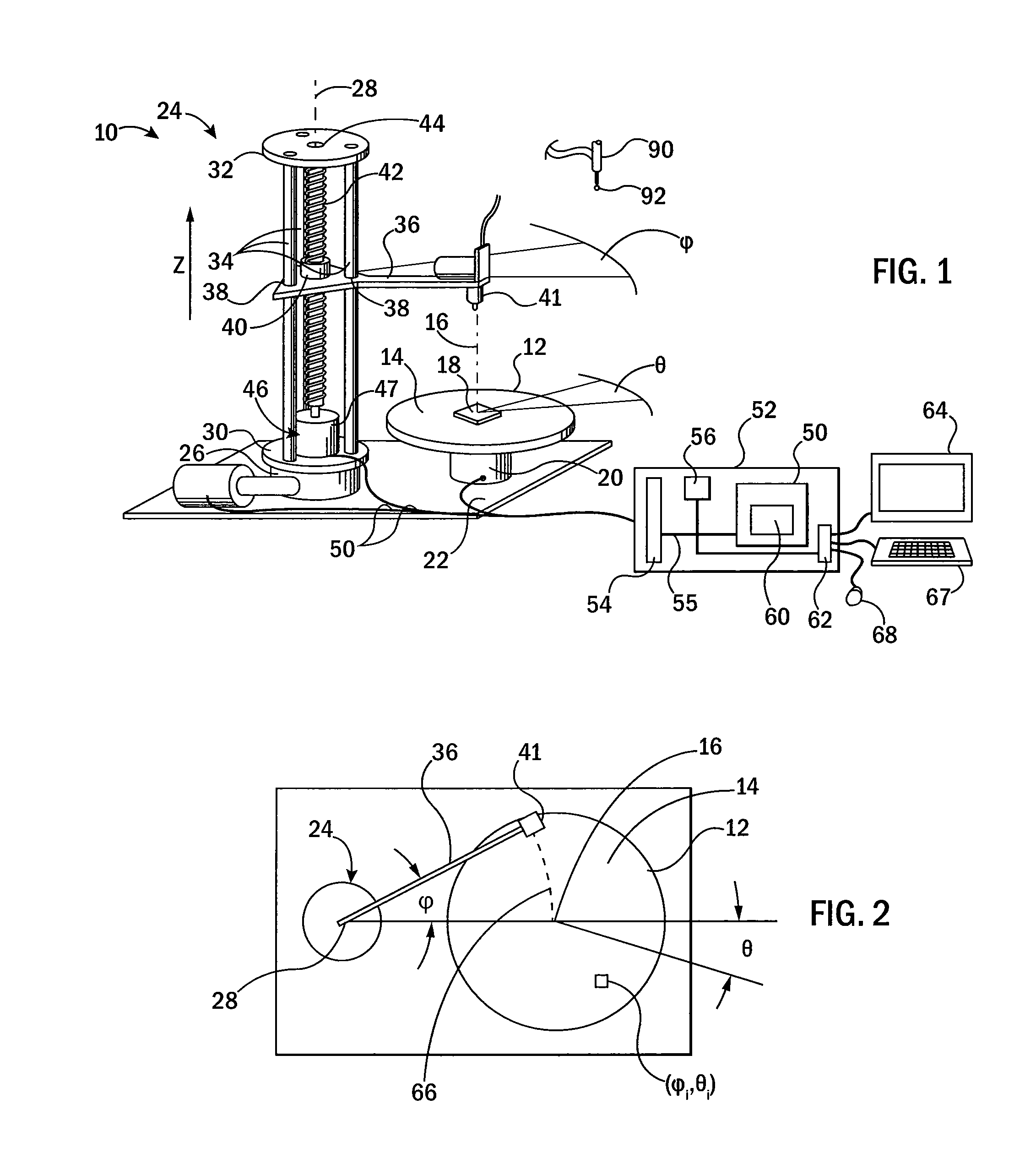
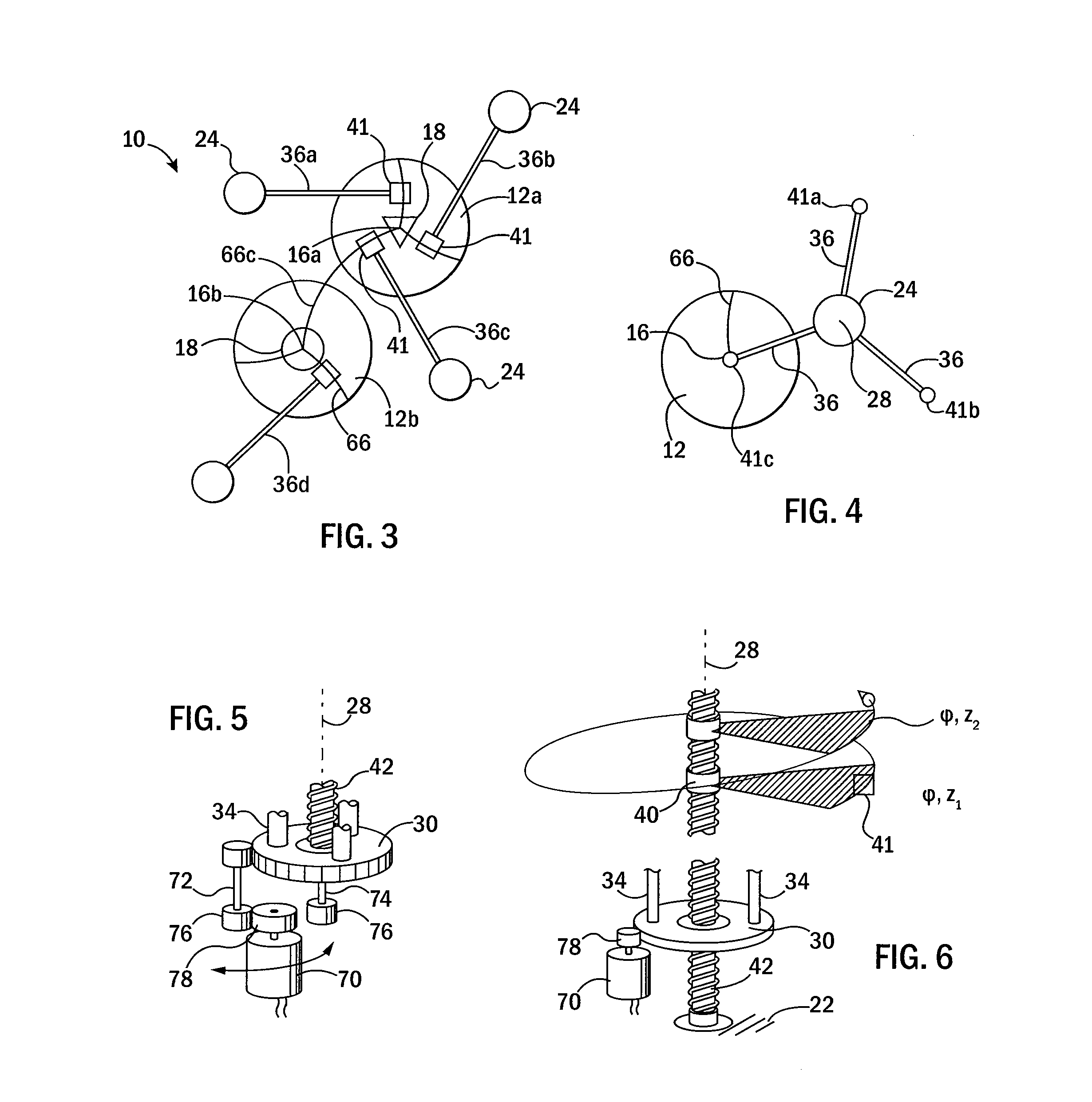
Patents
Literature
10319 results about "Linear motion" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Linear motion (also called rectilinear motion) is a one-dimensional motion along a straight line, and can therefore be described mathematically using only one spatial dimension. The linear motion can be of two types: uniform linear motion with constant velocity or zero acceleration; non uniform linear motion with variable velocity or non-zero acceleration. The motion of a particle (a point-like object) along a line can be described by its position x, which varies with t (time).
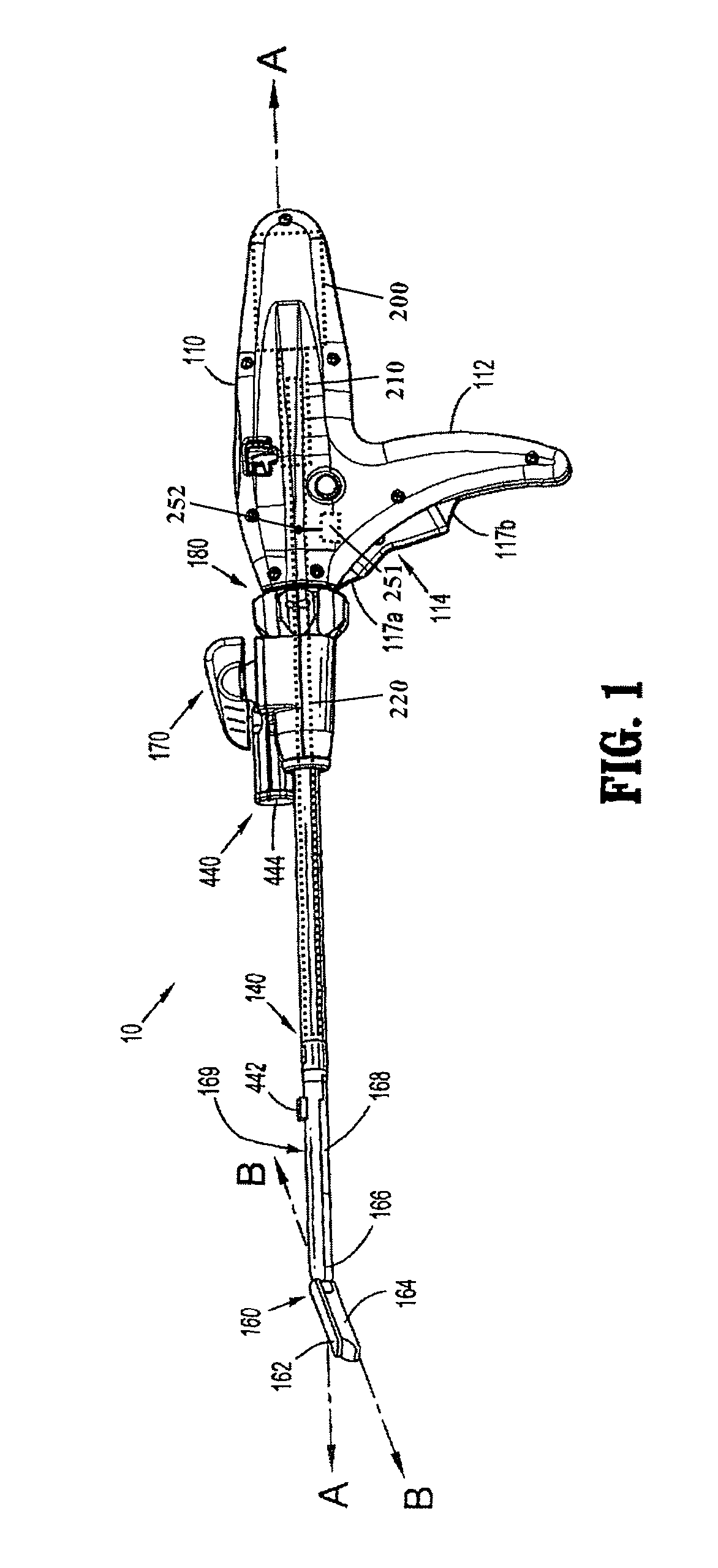
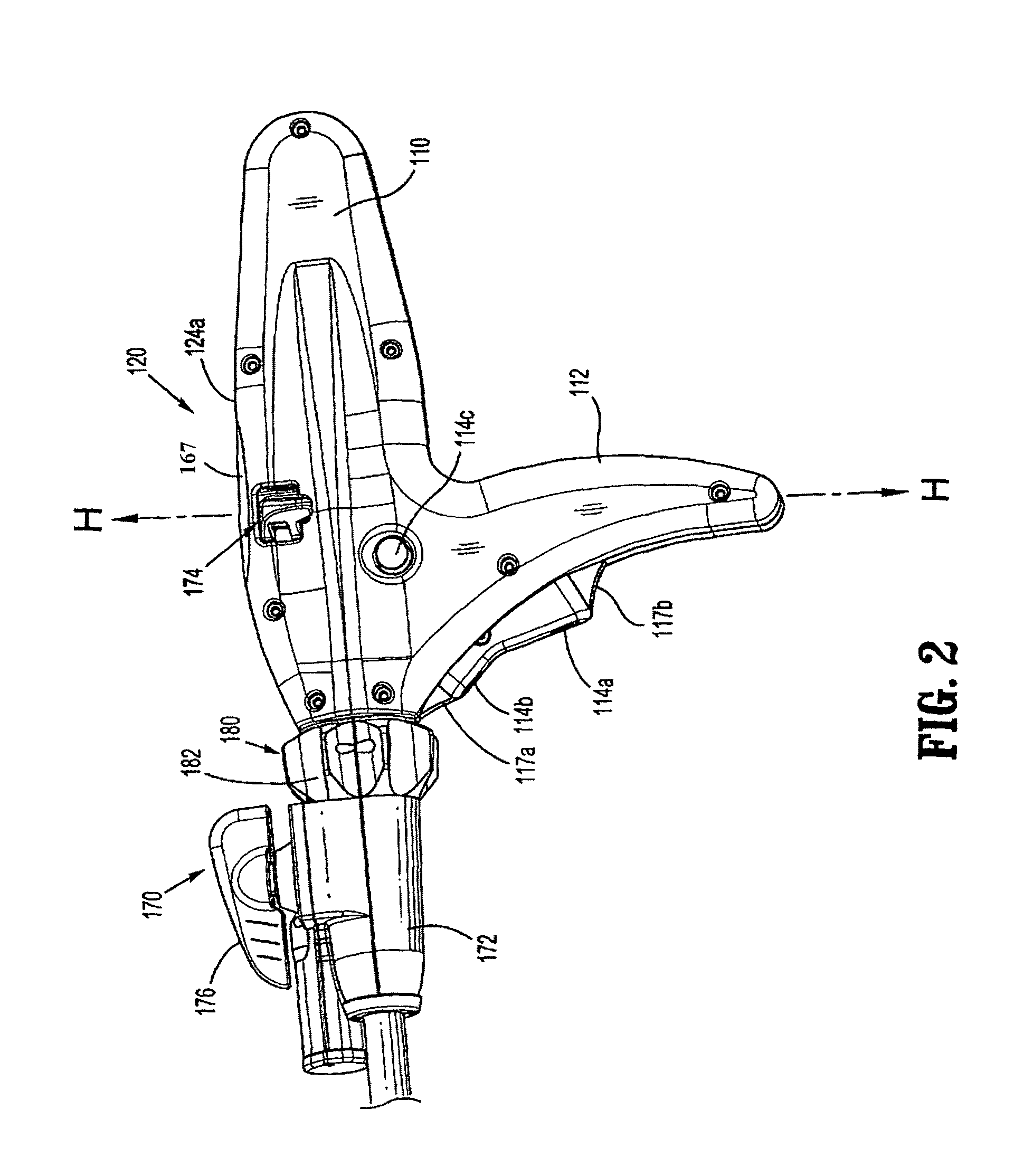
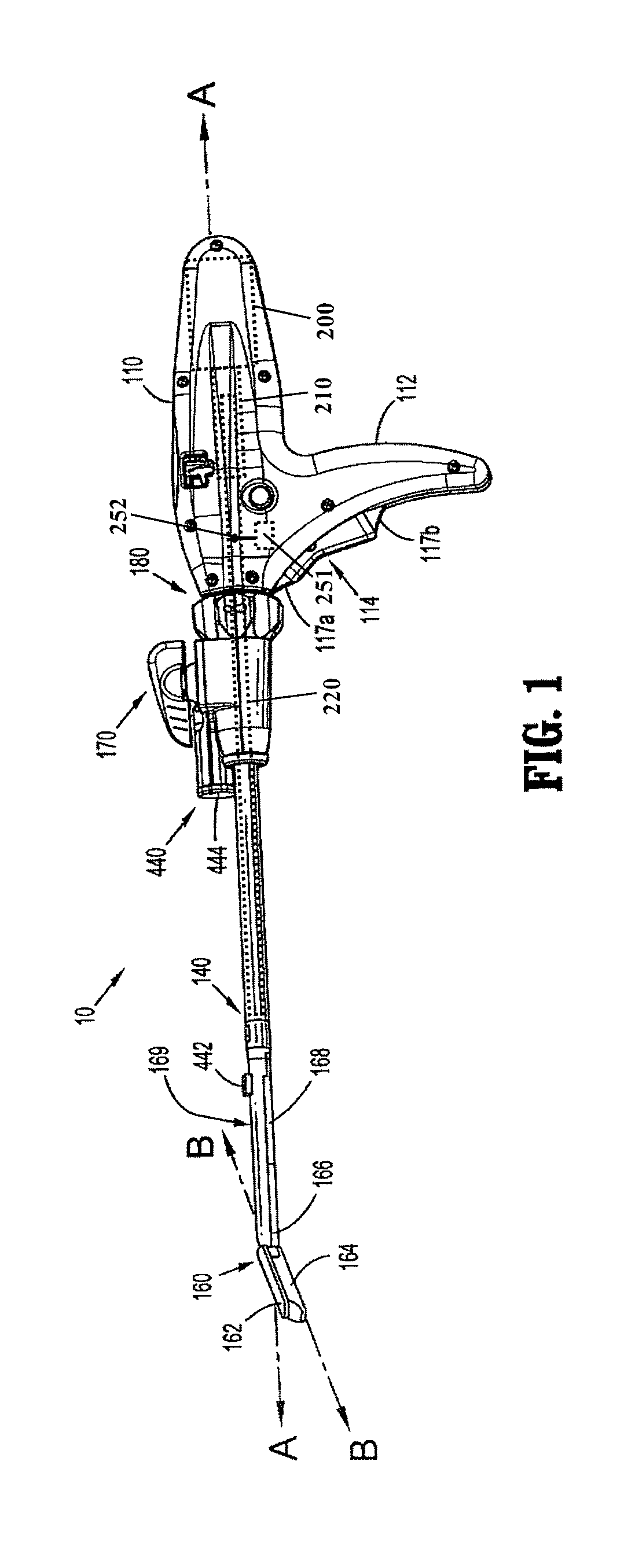
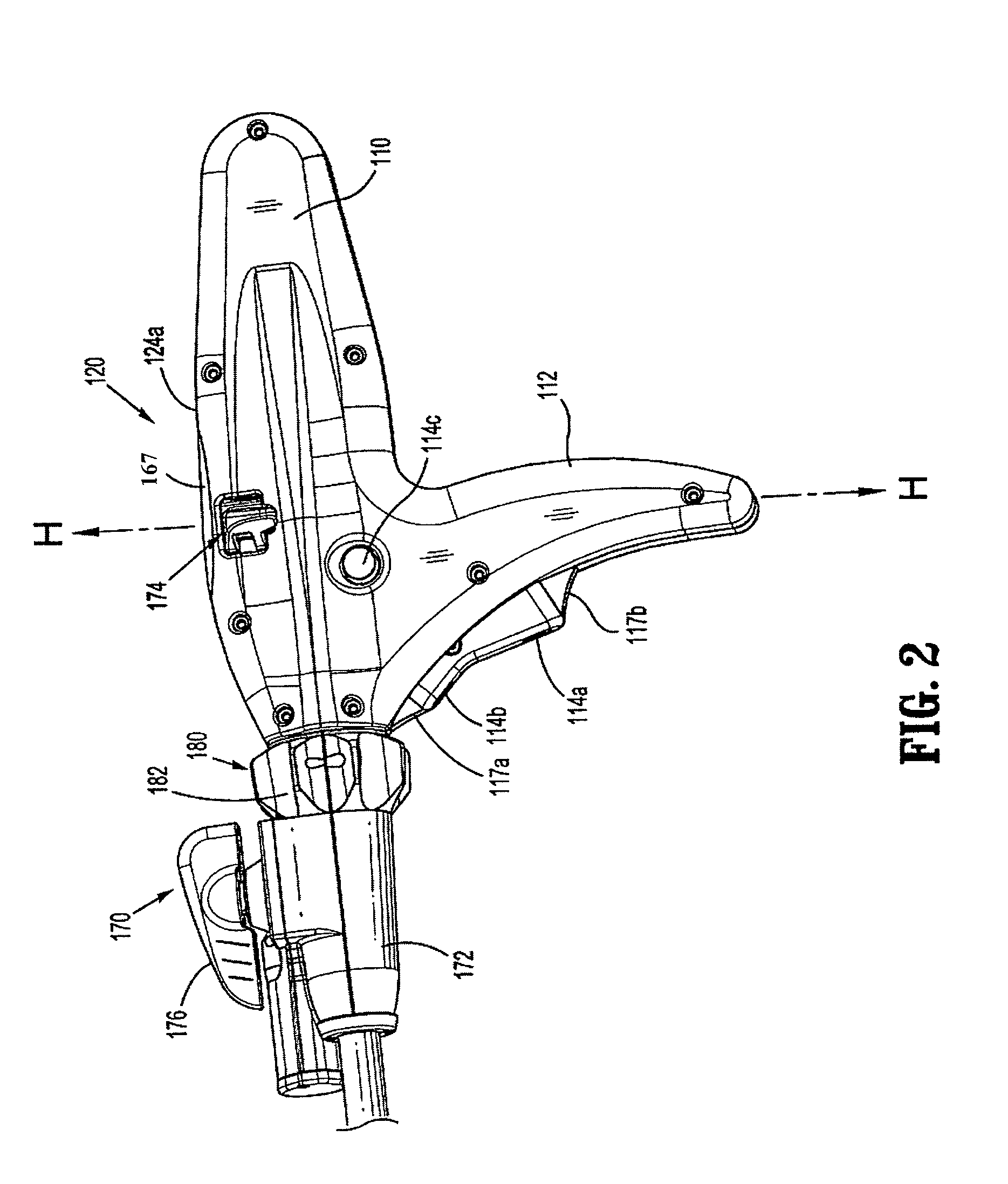
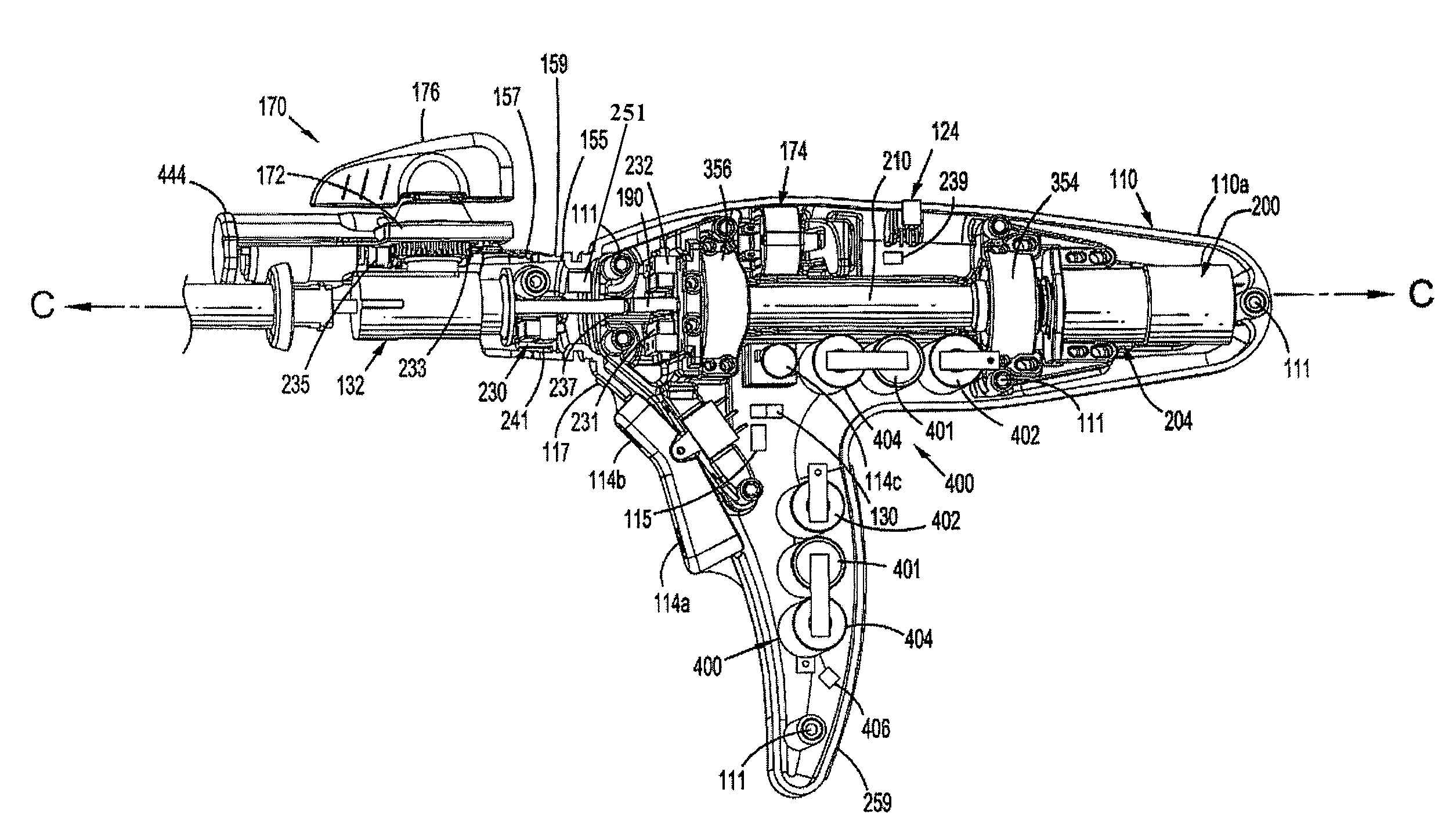
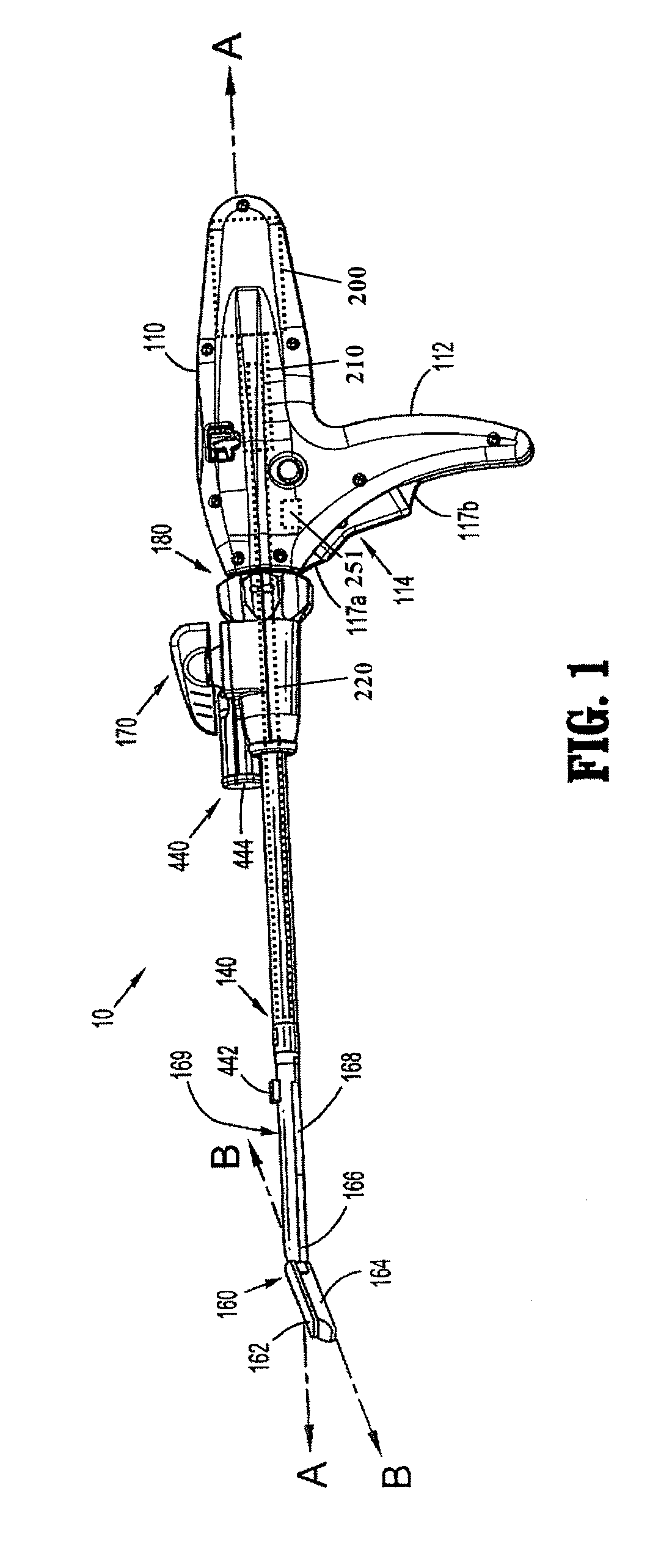
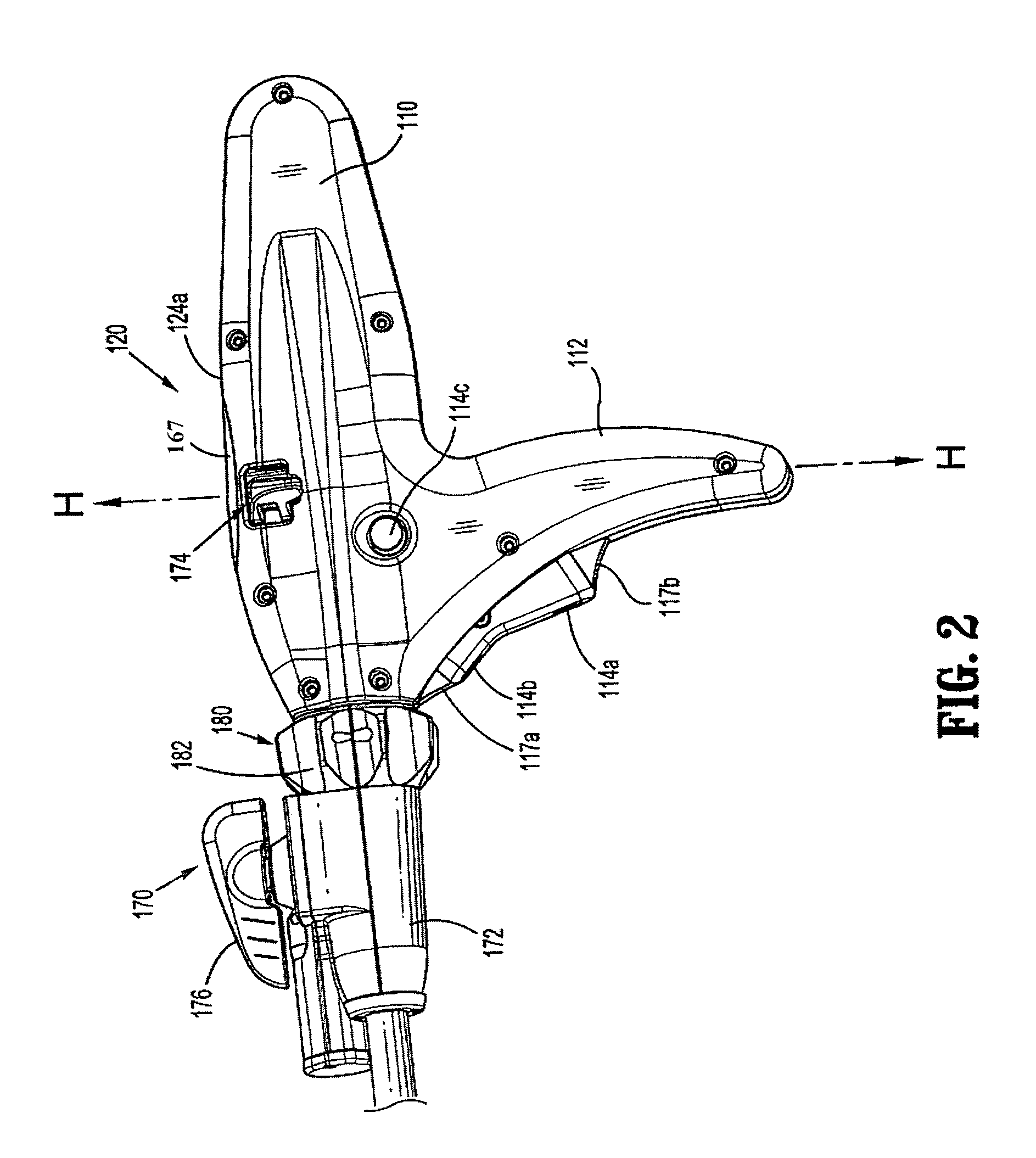
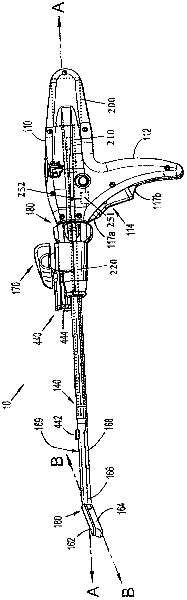
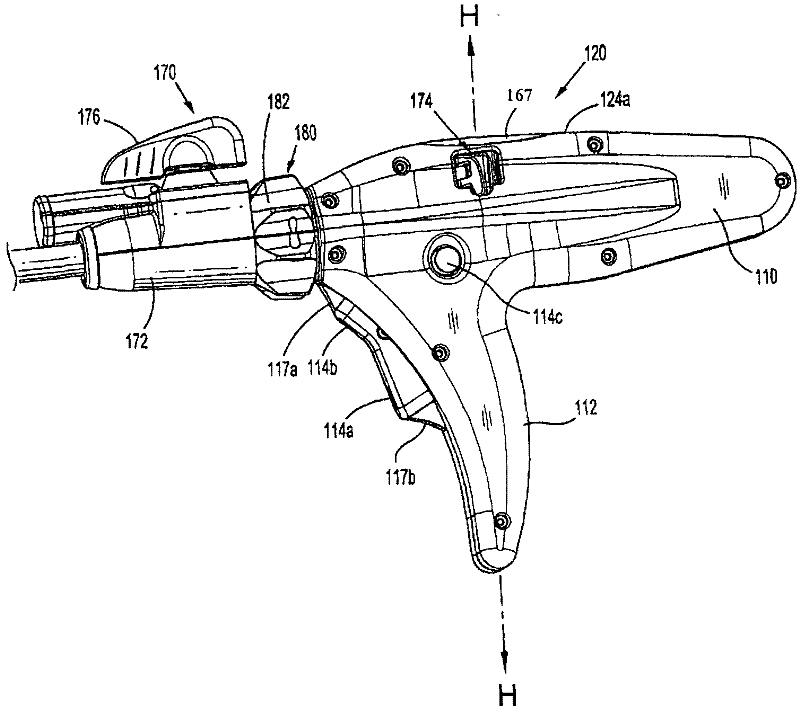
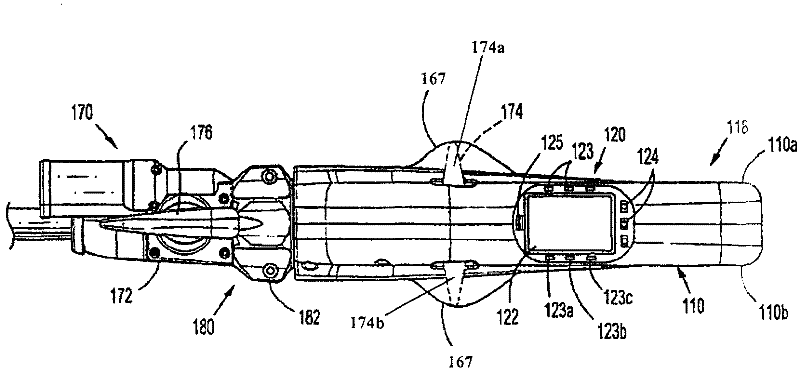
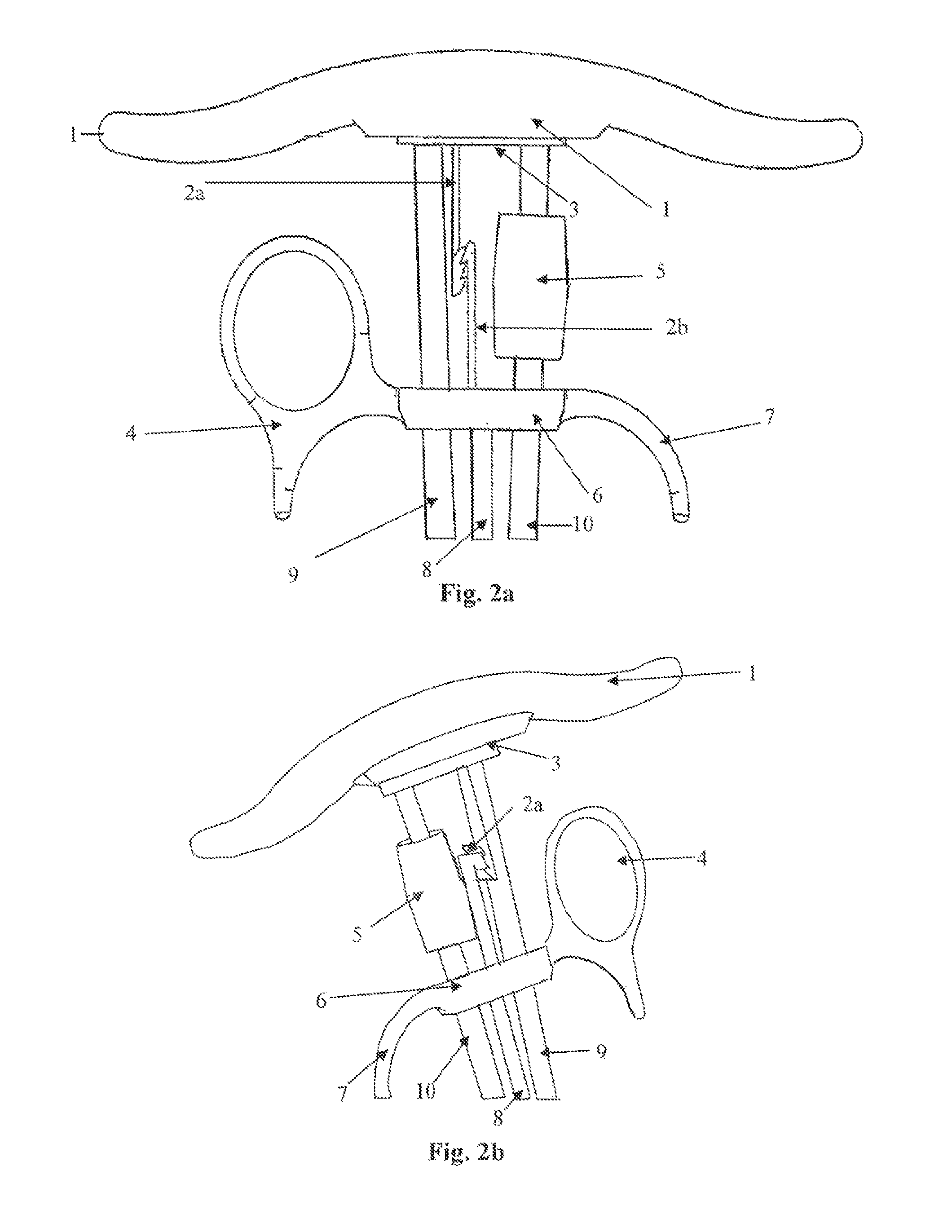
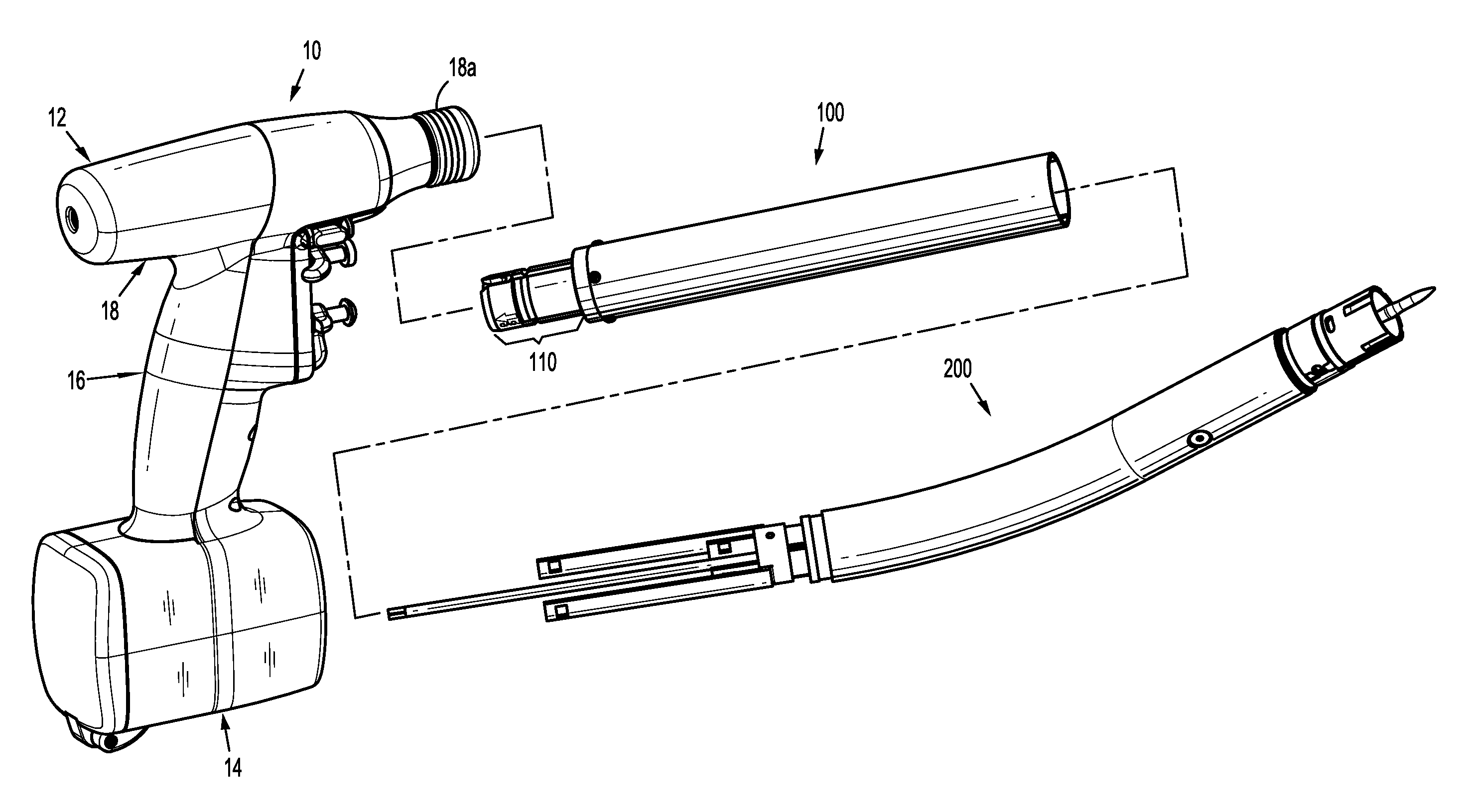
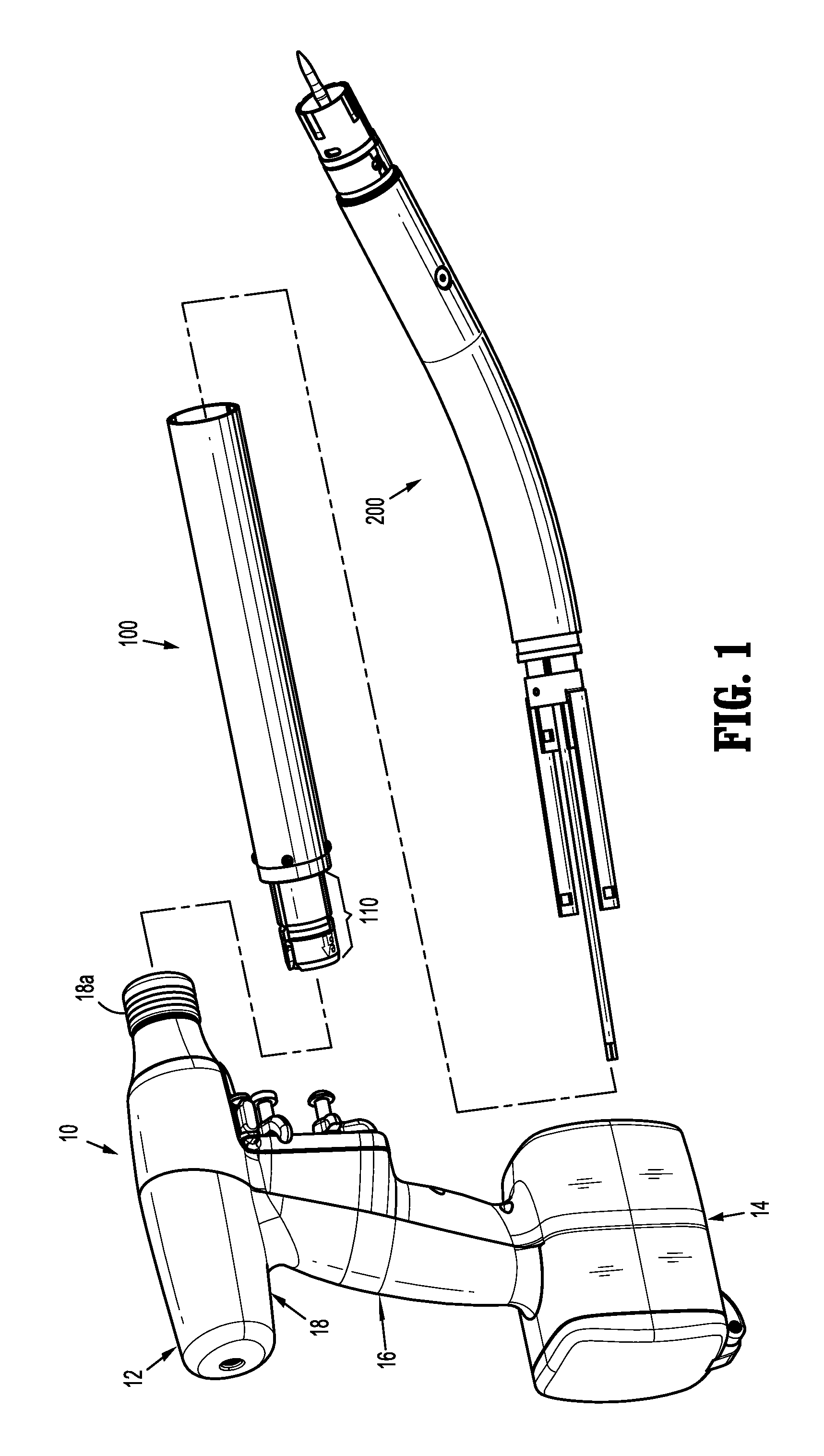
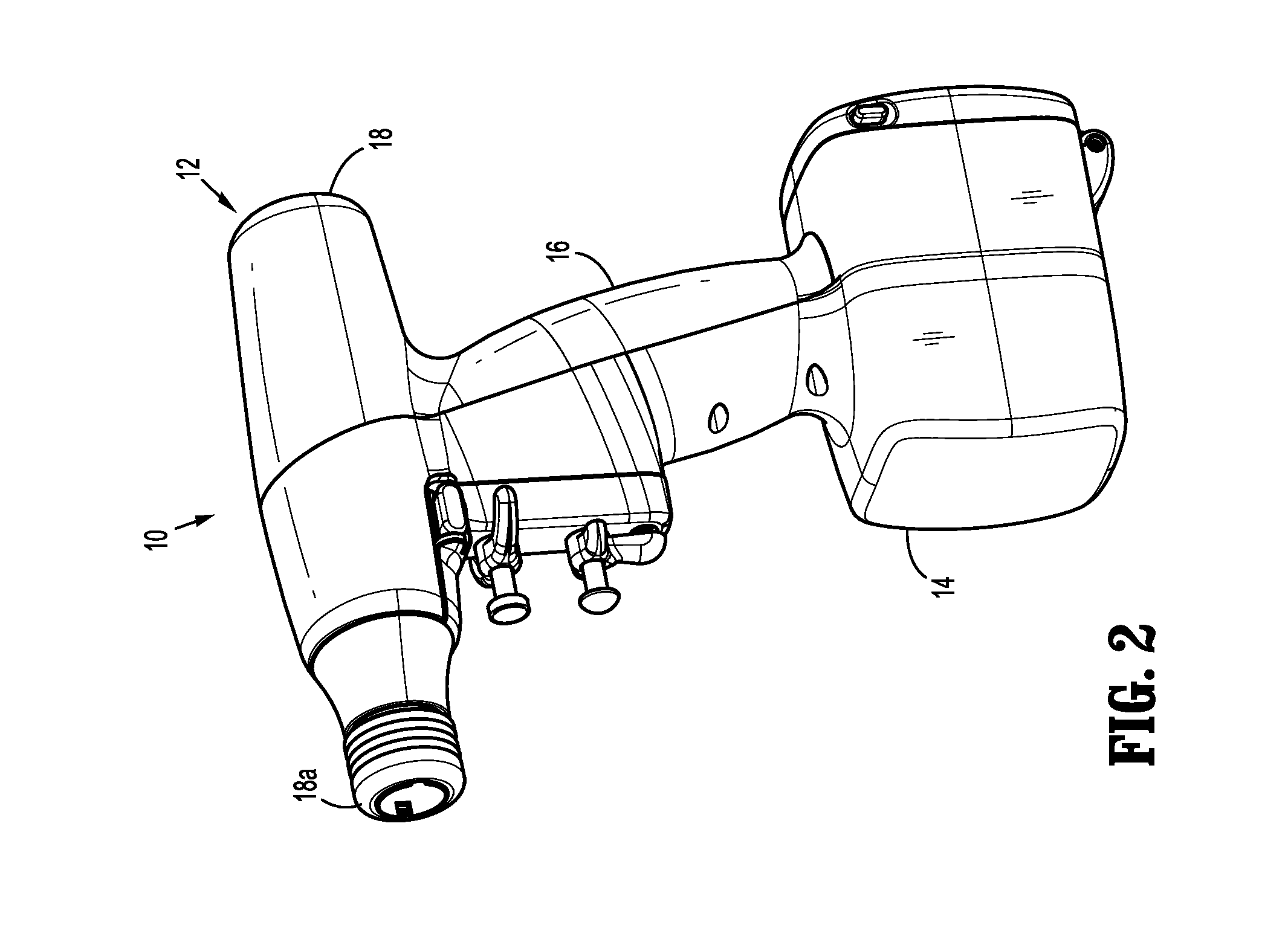
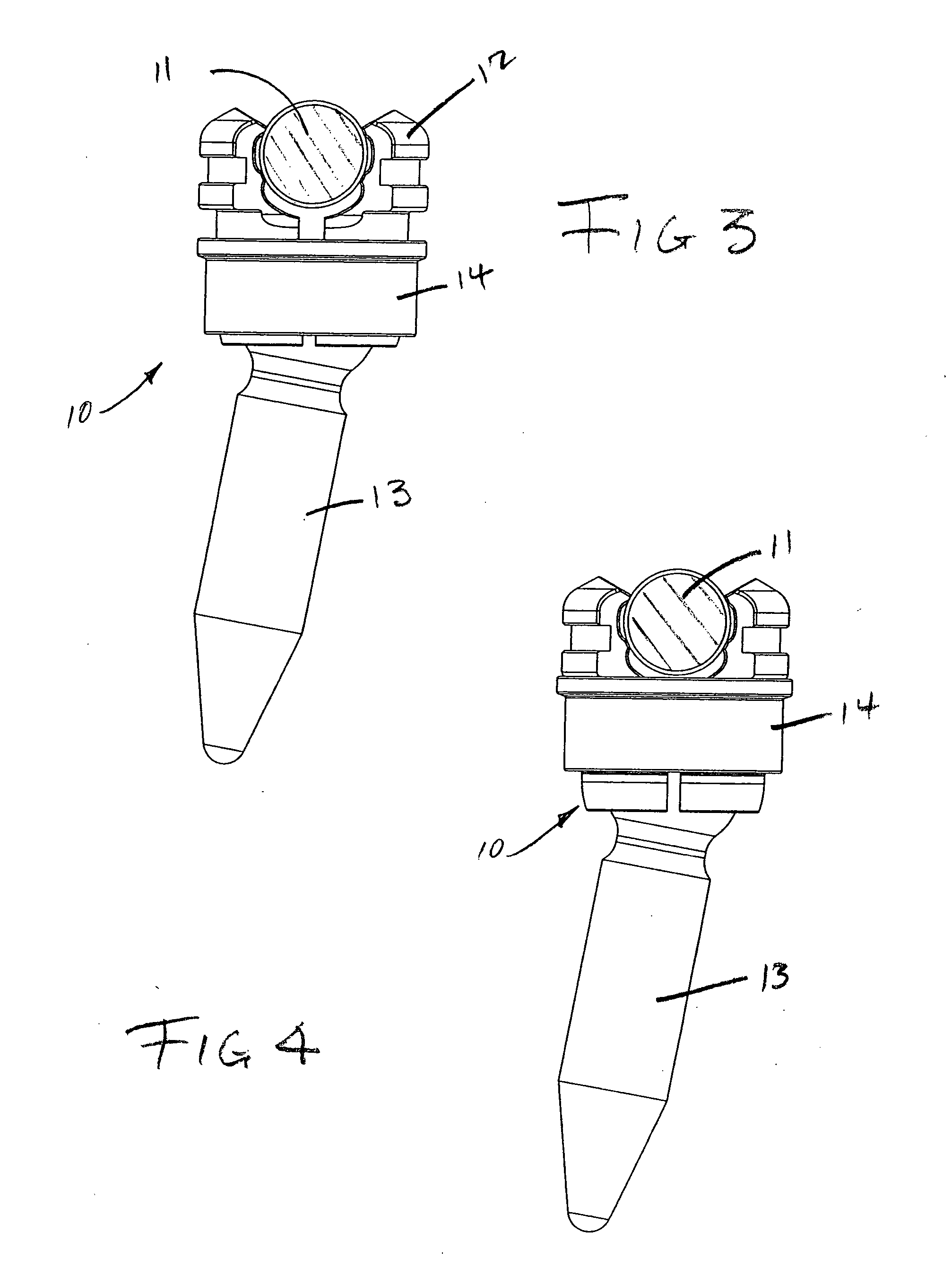
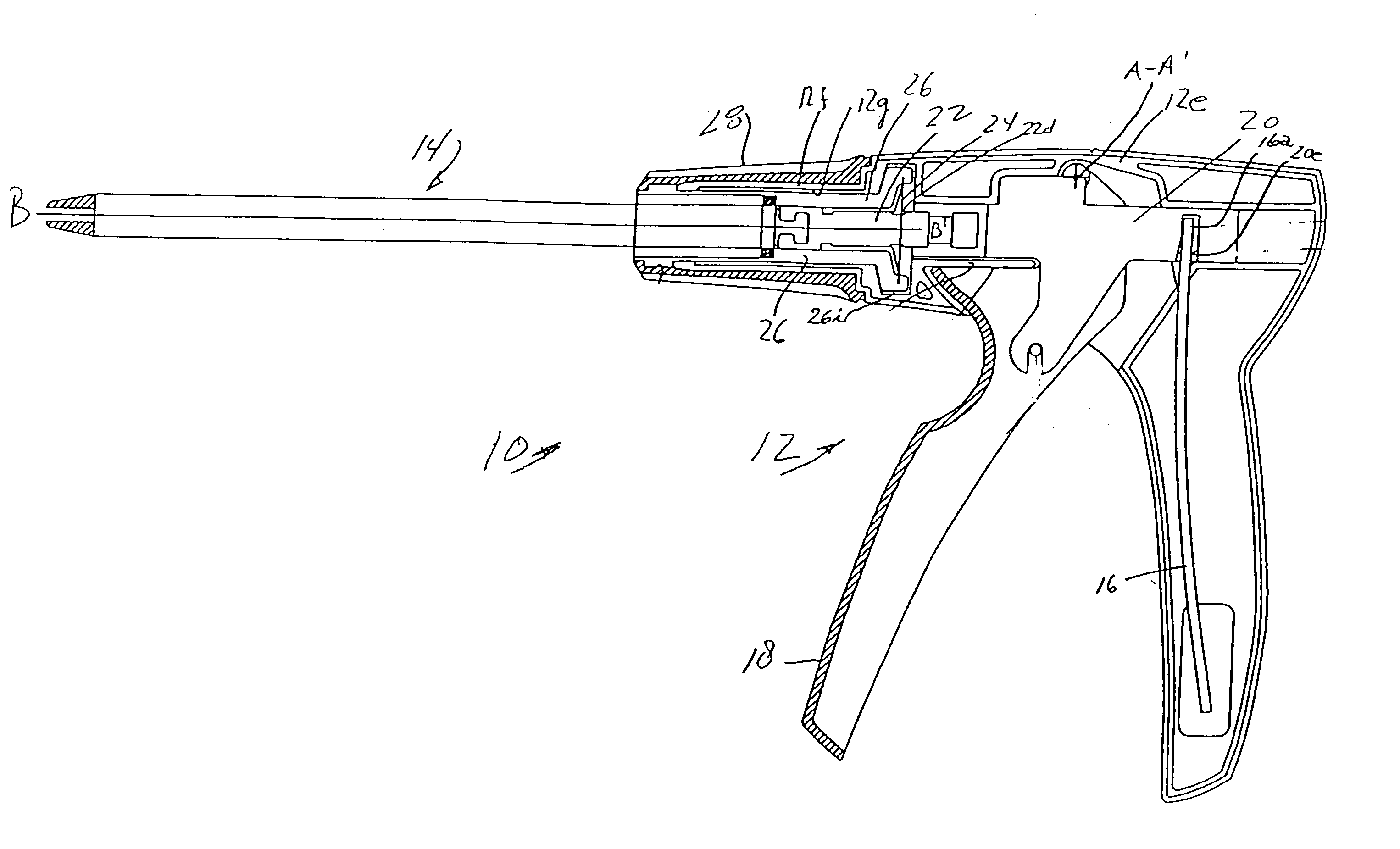
Method and apparatus for determining parameters of linear motion in a surgical instrument
ActiveUS8967443B2Reduce mechanical wearMinimized in sizeSuture equipmentsStapling toolsLinear motionMotion parameter
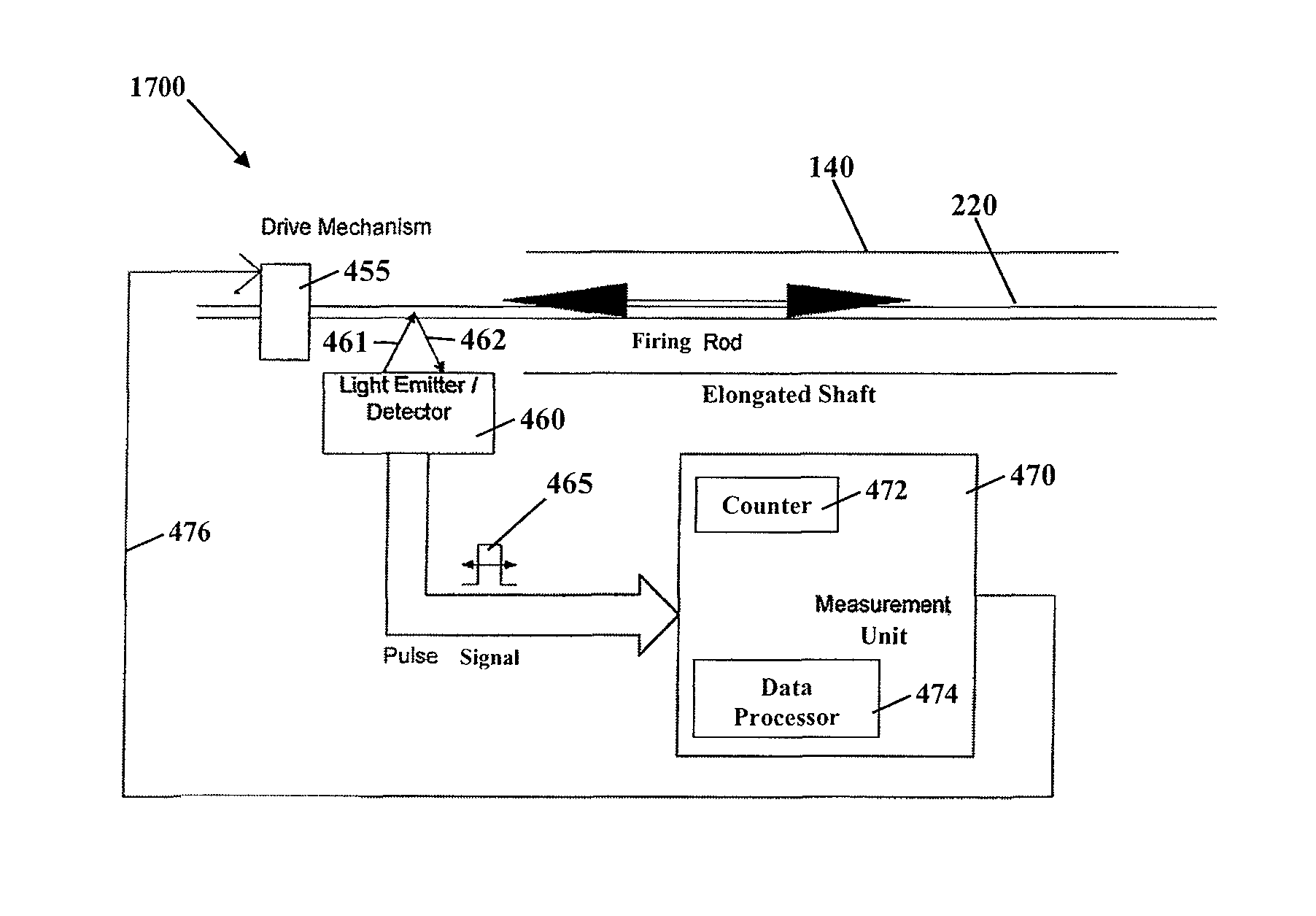
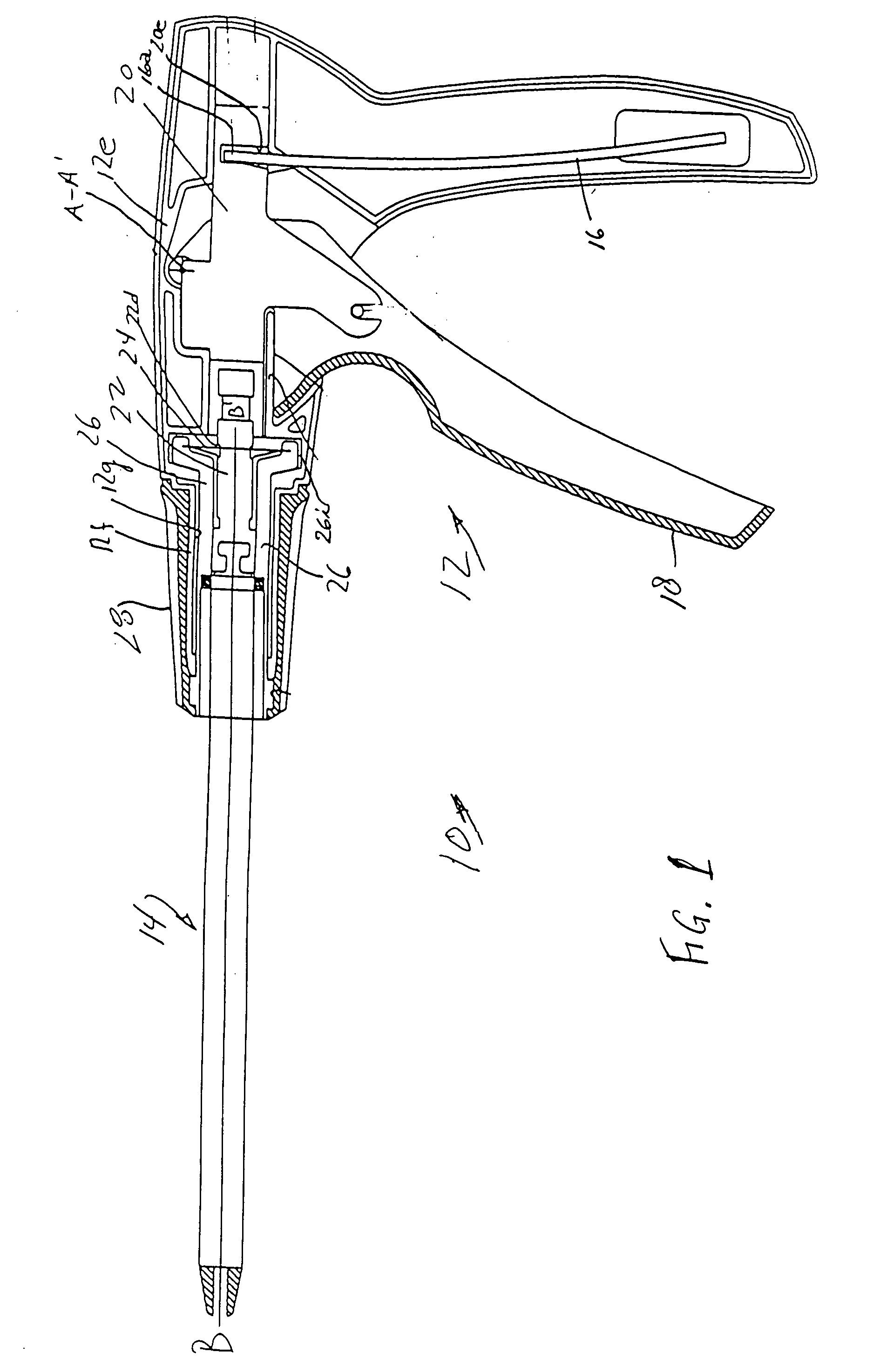
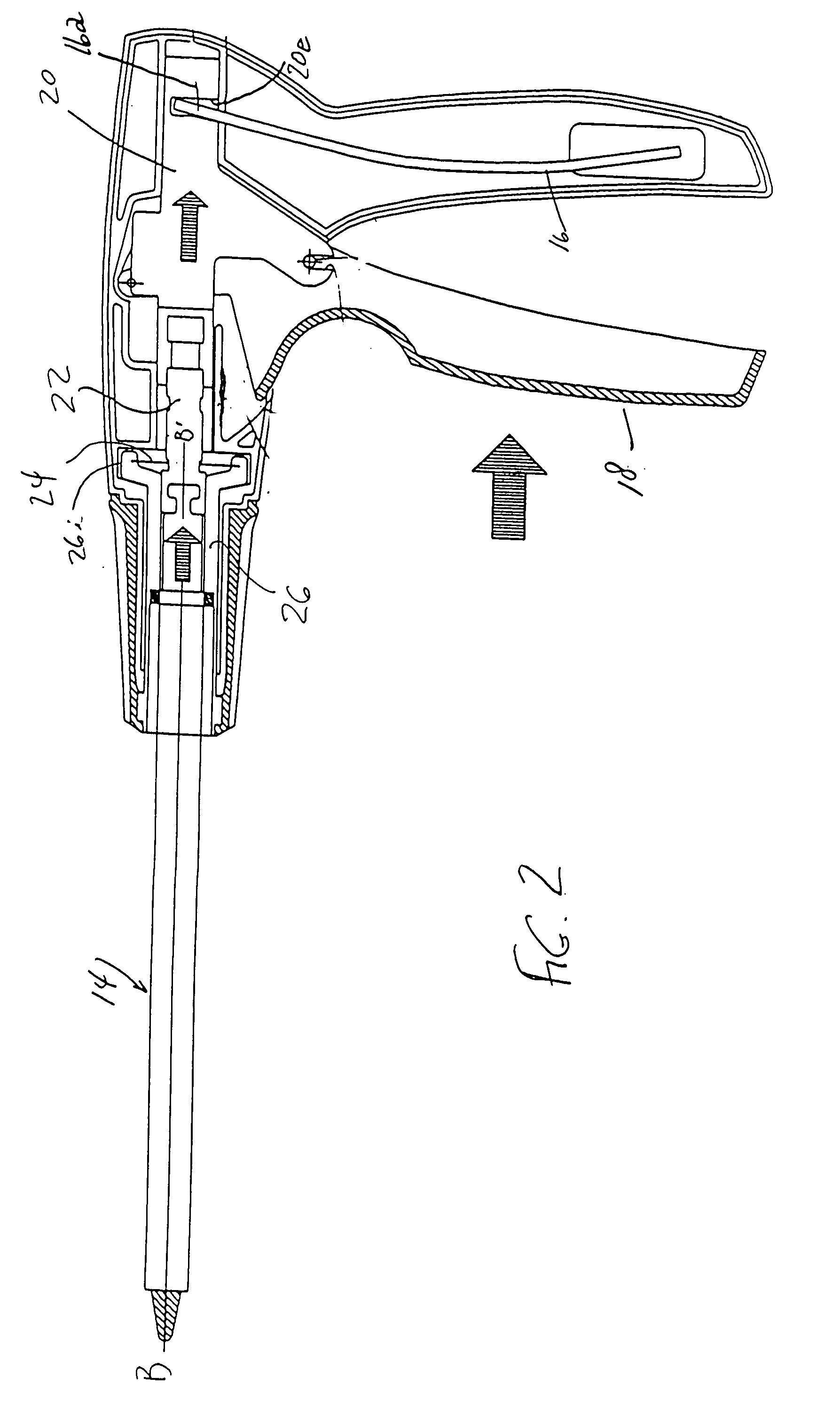
A surgical instrument and method of controlling the surgical instrument are disclosed. The surgical instrument includes a housing and an elongated shaft that extends distally from the housing and defines a first longitudinal axis. The surgical instrument also includes a firing rod disposed in the elongated shaft and a drive mechanism disposed at least partially within the housing. The drive mechanism mechanically cooperates with the firing rod to move the firing rod. A sensor senses a parameter of light reflected from the surface of the firing rod, which includes markings that change the reflectivity of the firing rod. The measurement unit determines a parameter of the motion of the firing rod, such as the position and speed of the firing rod, based on the sensed parameter of the light reflected from the surface of the firing rod.
Owner:TYCO HEALTHCARE GRP LP
Method and apparatus for determining parameters of linear motion in a surgical instrument
ActiveUS8960520B2Reduce mechanical wearMinimized in sizeSuture equipmentsStapling toolsCapacitanceLinear motion
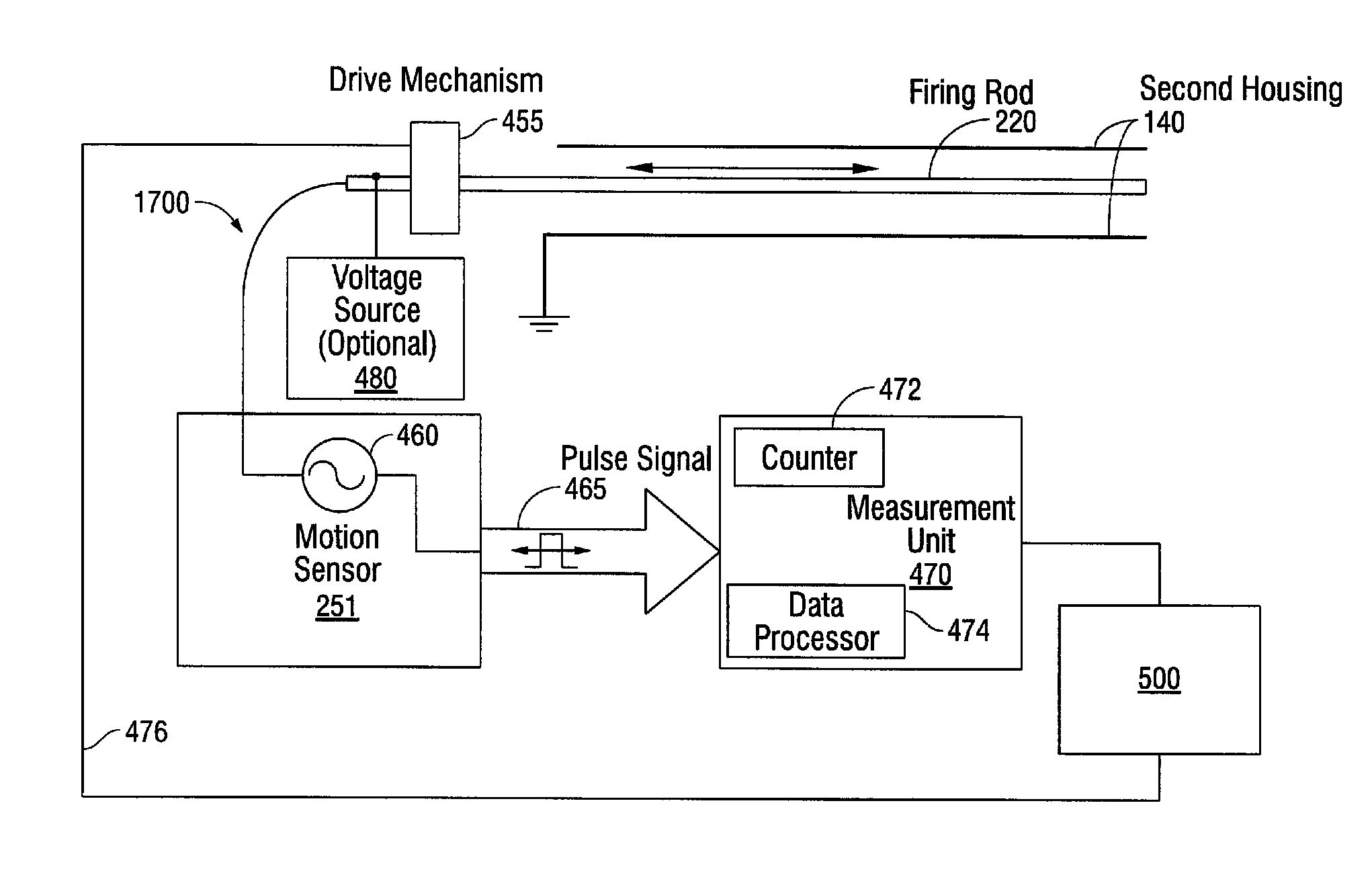
A surgical instrument and method of controlling the surgical instrument are disclosed. The surgical instrument includes a housing and an elongated shaft that extends distally from the housing and defines a first longitudinal axis. The surgical instrument also includes a firing rod disposed in the elongated shaft and a drive mechanism disposed at least partially within the housing. The drive mechanism mechanically cooperates with the firing rod to move the firing rod. A motion sensor senses a change in the electric field (e.g., capacitance, impedance, or admittance) between the firing rod and the elongated shaft. The measurement unit determines a parameter of the motion of the firing rod, such as the position, speed, and direction of the firing rod, based on the sensed change in the electric field. A controller uses the measured parameter of the motion of the firing rod to control the drive mechanism.
Owner:TYCO HEALTHCARE GRP LP
Magnetic linear actuator for deployable catheter tools
InactiveUS20080297287A1Easy to controlGood precisionDiagnostic recording/measuringSensorsDiagnostic Radiology ModalityLinear motion
Using the linear forces that are provided by an electromagnetic solenoid applied near the distal end of a medical catheter, various surgical instruments can be actuated or deployed for use in interventional medicine. The linear actuator uses the principles of magnetic repulsion and attraction as a means for moving a bobbin that can be attached to various types of moving components that translate linear movements into the actuation of a tool that is attached to the linear actuator. Using independent solenoid coils, movement modality is increased from two possible positions to three.
Owner:NEURO KINESIS CORP
Hall-effect based linear motor controller
Owner:ALLEGRO MICROSYSTEMS INC
Prophy angle and adapter
A dental prophy angle includes a housing and a rotor. The housing defines a first bore and a second bore in communication with the first bore, and rotor is disposed within the second bore. The rotor includes a gearing system, and rotor includes a lock having a lock channel configured to receive a tip of a drive shaft. The housing includes a lock receiver for receiving the lock receiver permits rotation of the lock within the lock receiver and restrains linear movement of the lock in a direction substantially parallel to a rotational axis of the rotor.
Owner:AVID INC
Method and apparatus for determining parameters of linear motion in a surgical instrument
ActiveUS20110204119A1Reduce mechanical wearMinimized in sizeSuture equipmentsStapling toolsLinear motionCapacitance
A surgical instrument and method of controlling the surgical instrument are disclosed. The surgical instrument includes a housing and an elongated shaft that extends distally from the housing and defines a first longitudinal axis. The surgical instrument also includes a firing rod disposed in the elongated shaft and a drive mechanism disposed at least partially within the housing. The drive mechanism mechanically cooperates with the firing rod to move the firing rod. A motion sensor senses a change in the electric field (e.g., capacitance, impedance, or admittance) between the firing rod and the elongated shaft. The measurement unit determines a parameter of the motion of the firing rod, such as the position, speed, and direction of the firing rod, based on the sensed change in the electric field. A controller uses the measured parameter of the motion of the firing rod to control the drive mechanism.
Owner:TYCO HEALTHCARE GRP LP
Method and apparatus for determining parameters of linear motion in a surgical instrument
ActiveUS20110139851A1Reduce mechanical wearMinimized in sizeSuture equipmentsStapling toolsLinear motionMotion parameter
A surgical instrument and method of controlling the surgical instrument are disclosed. The surgical instrument includes a housing and an elongated shaft that extends distally from the housing and defines a first longitudinal axis. The surgical instrument also includes a firing rod disposed in the elongated shaft and a drive mechanism disposed at least partially within the housing. The drive mechanism mechanically cooperates with the firing rod to move the firing rod. A sensor senses a parameter of light reflected from the surface of the firing rod, which includes markings that change the reflectivity of the firing rod. The measurement unit determines a parameter of the motion of the firing rod, such as the position and speed of the firing rod, based on the sensed parameter of the light reflected from the surface of the firing rod.
Owner:TYCO HEALTHCARE GRP LP
Method and apparatus for determining parameters of linear motion in a surgical instrument
ActiveCN102217961AFrequency increase or decreaseDiagnosticsSurgical manipulatorsLinear motionCapacitance
The invention discloses a surgical instrument and method of controlling the surgical instrument, especially discloses a method and apparatus for determining parameters of linear motion in a surgical instrument. The surgical instrument includes a housing and an elongated shaft that extends distally from the housing and defines a first longitudinal axis. The surgical instrument also includes a firing rod disposed in the elongated shaft and a drive mechanism disposed at least partially within the housing. The drive mechanism mechanically cooperates with the firing rod to move the firing rod. A motion sensor senses a change in the electric field (e.g., capacitance, impedance, or admittance) between the firing rod and the elongated shaft. The measurement unit determines a parameter of the motion of the firing rod, such as the position, speed, and direction of the firing rod, based on the sensed change in the electric field. A controller uses the measured parameter of the motion of the firing rod to control the drive mechanism.
Owner:TYCO HEALTHCARE GRP LP
Drive system for an infusion pump
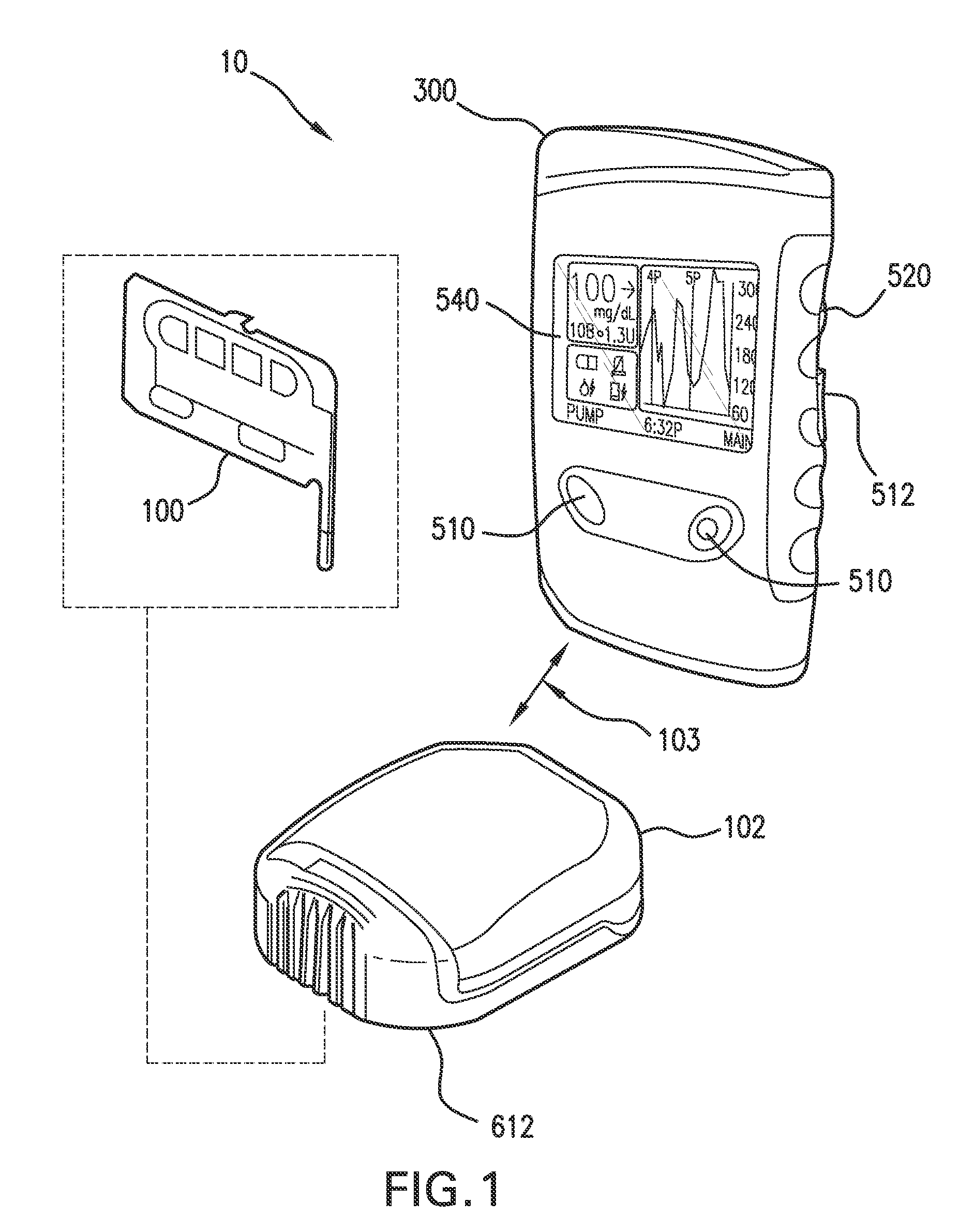
InactiveUS6854620B2Small sizeImprove portabilityClosure using stoppersLarge containersLinear motionProximity sensor
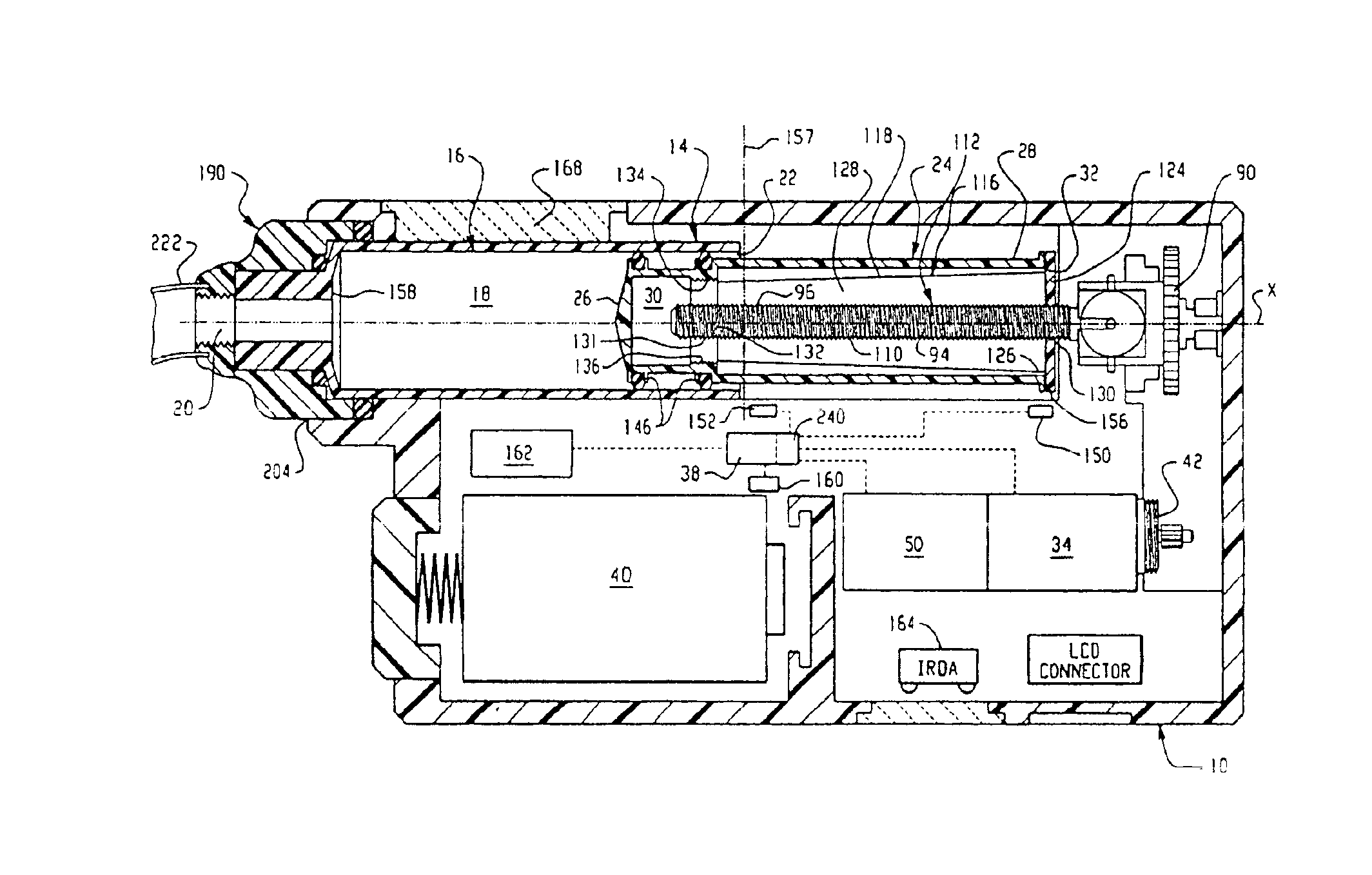
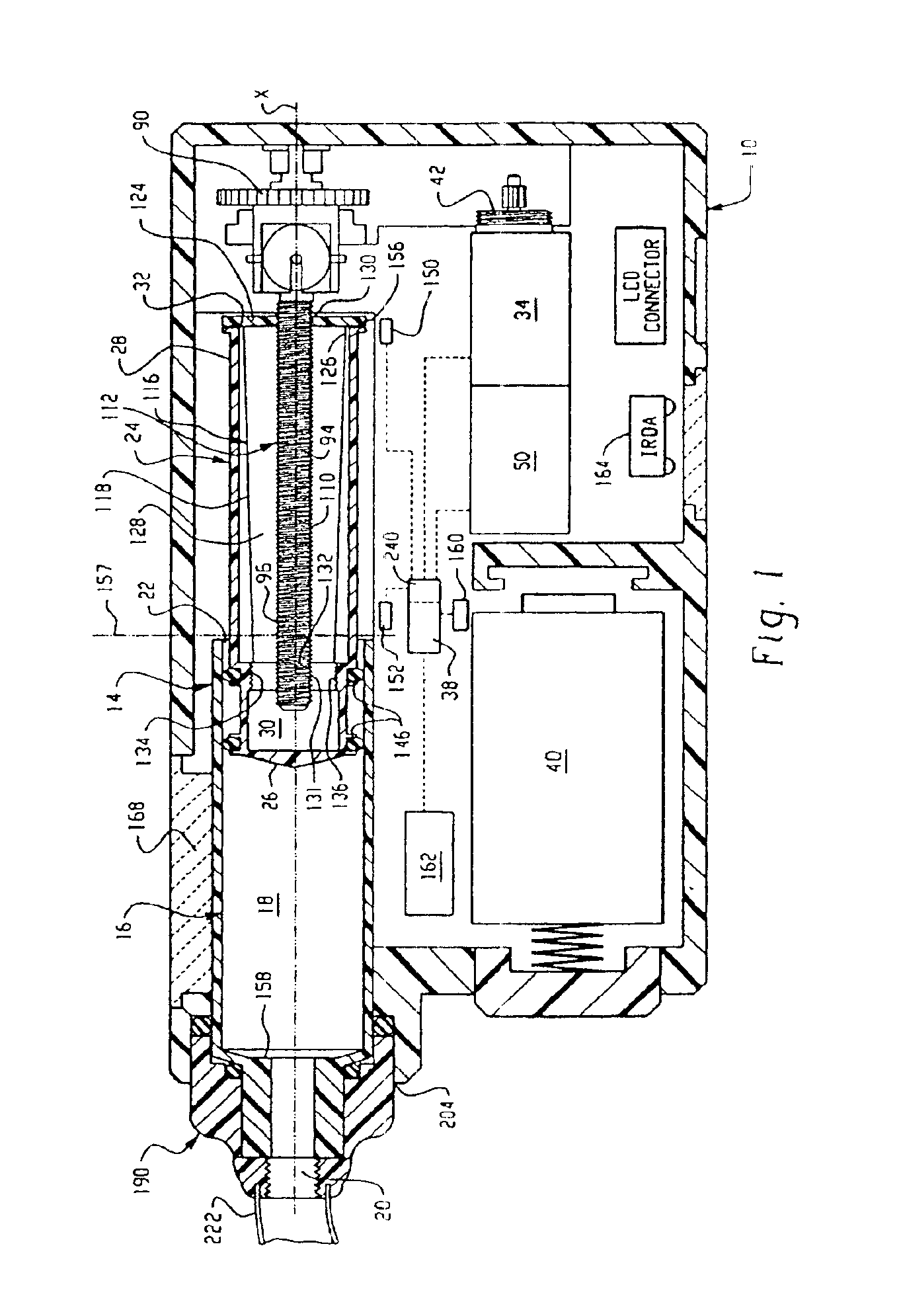
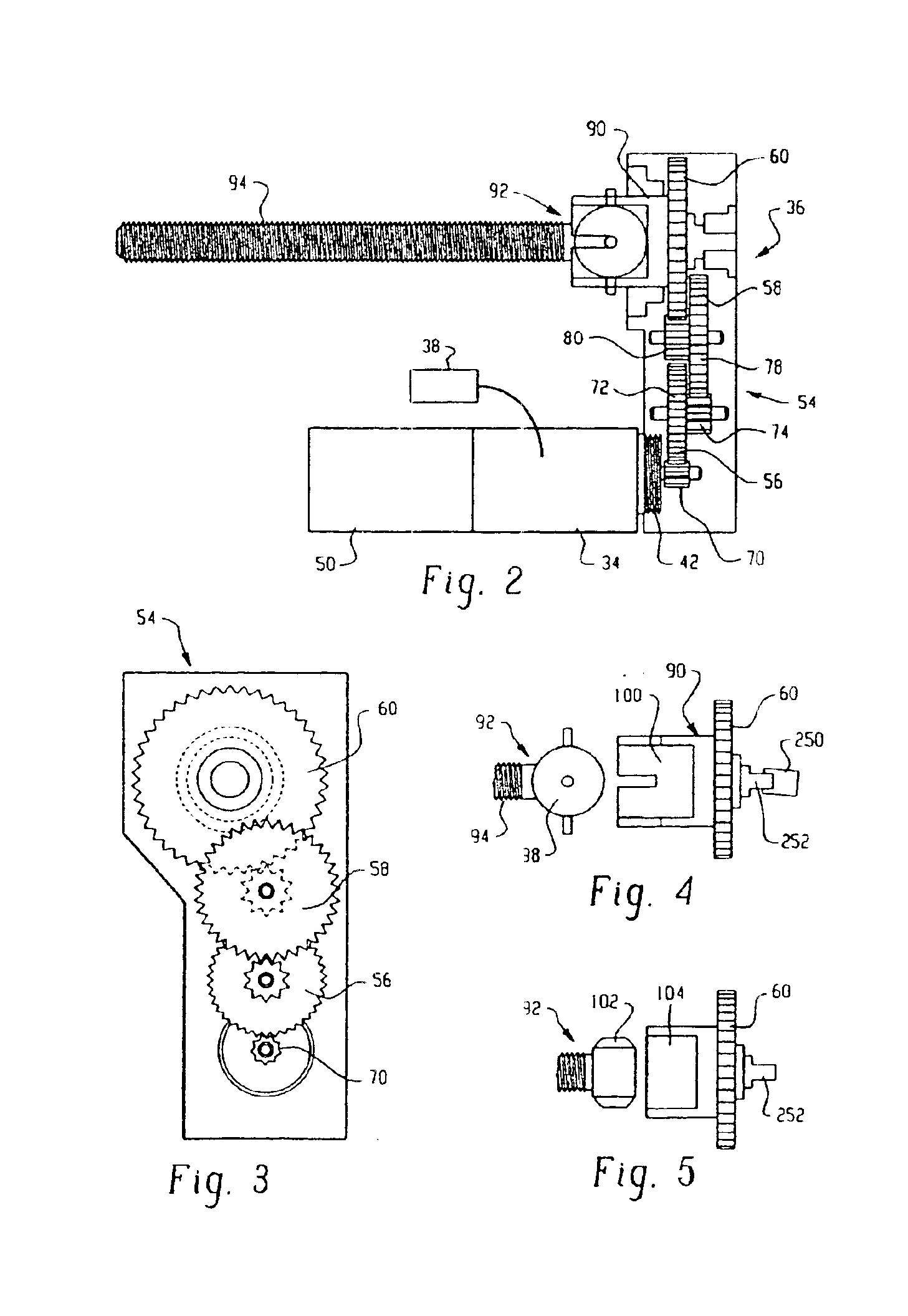
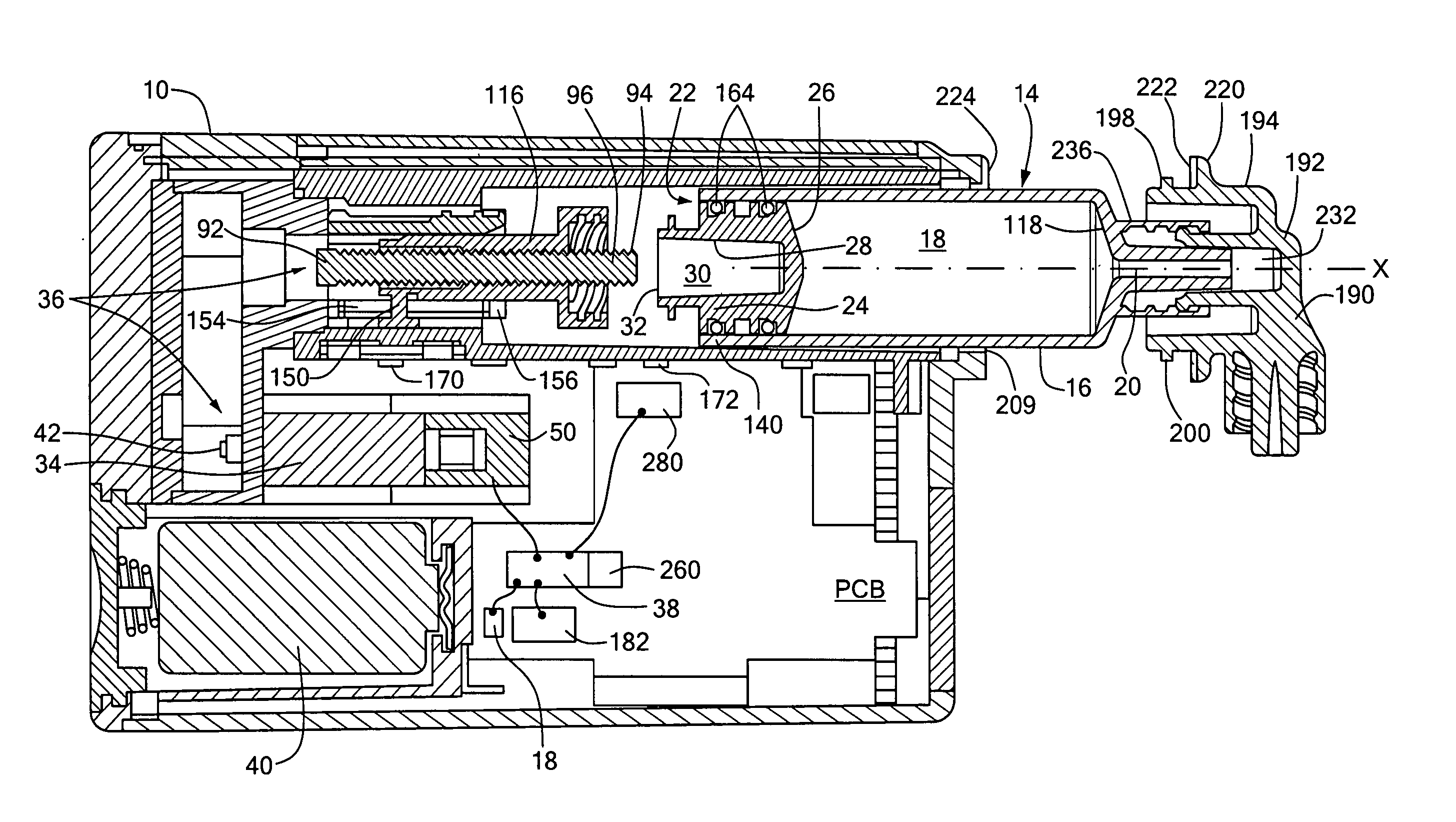
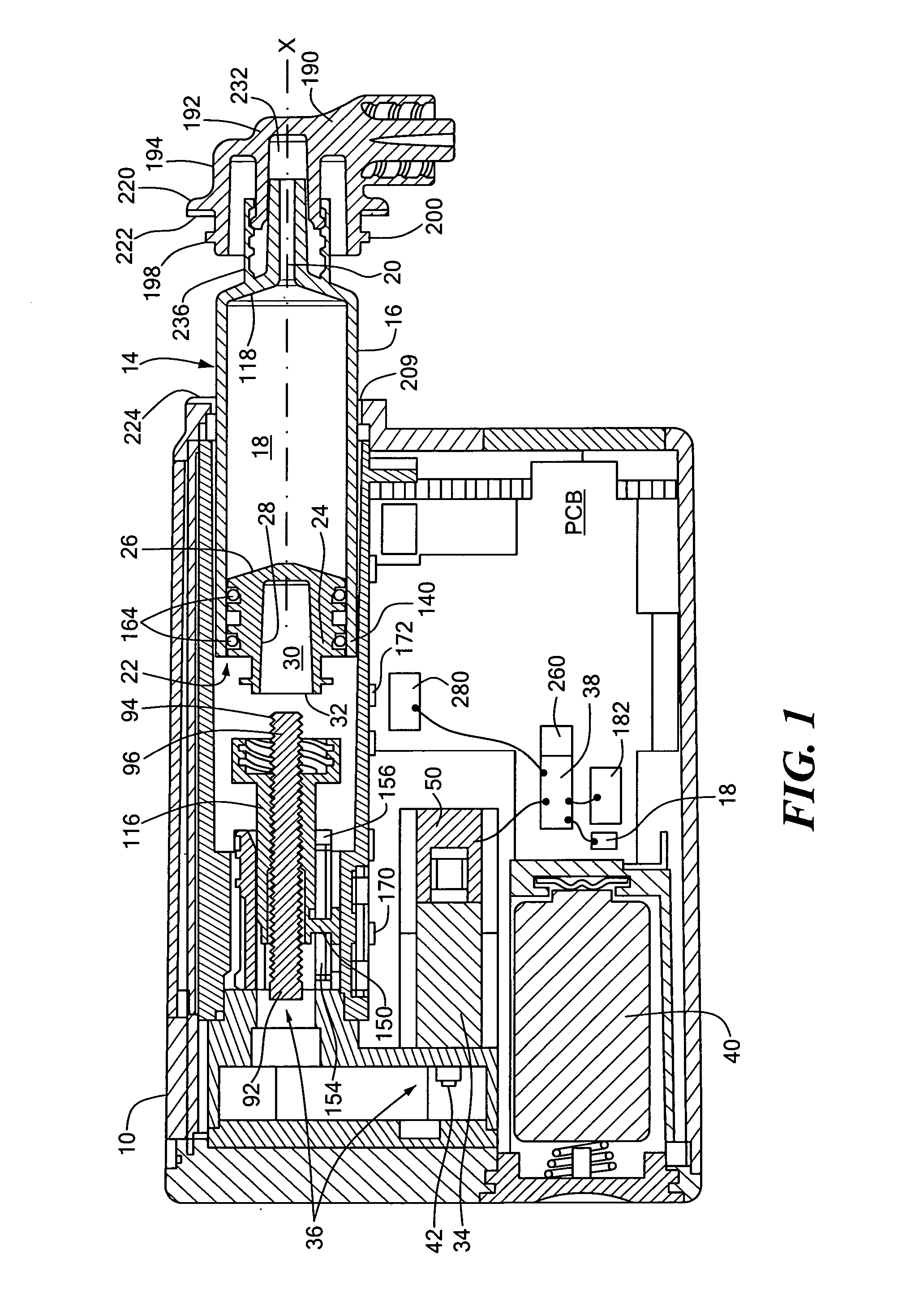
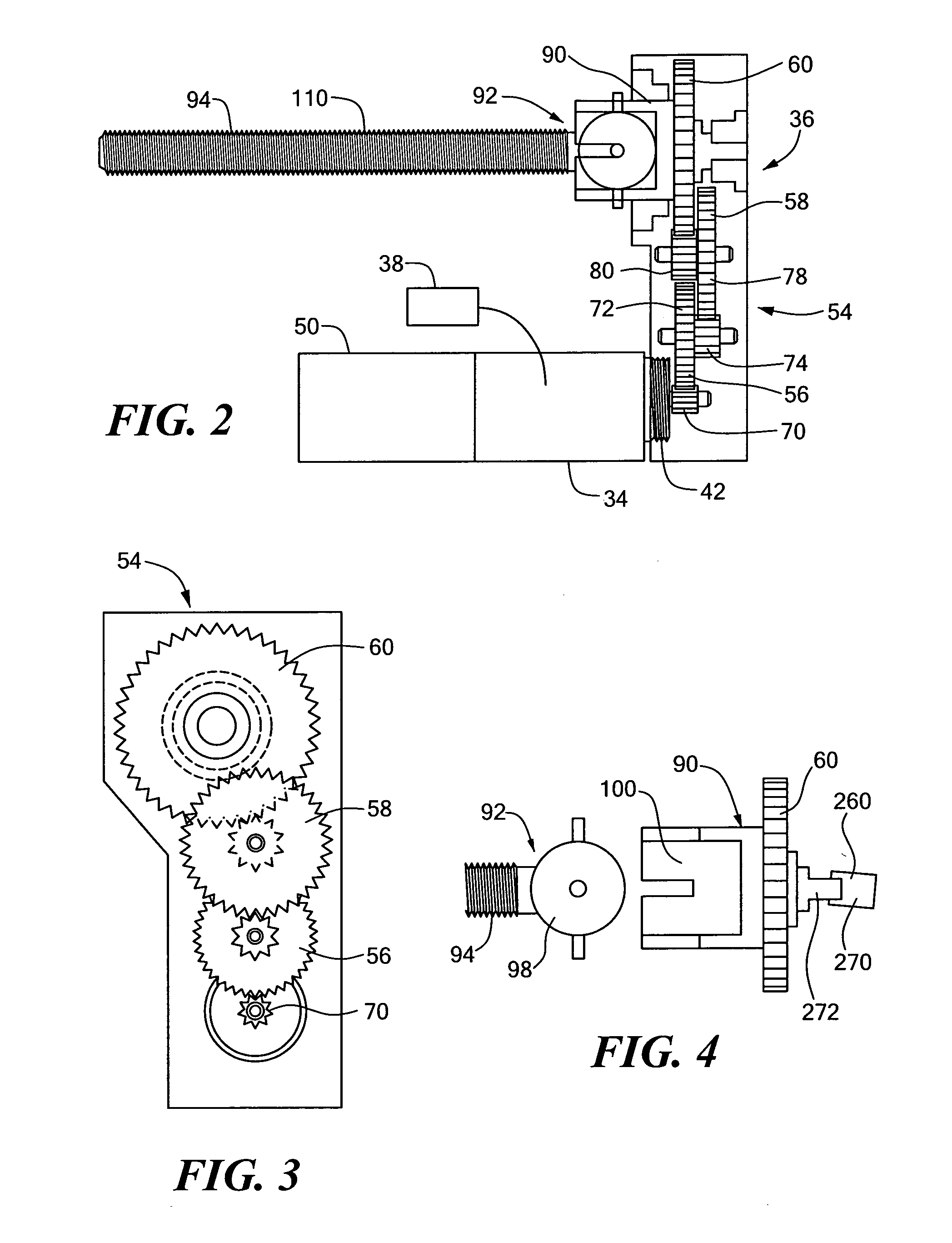
A pump system for an infusion system includes a linear drive (36, 36′) which minimizes the space occupied by the pump components in a portable housing (10, 10′). A motor (34) and a motor drive shaft (42) are arranged in parallel with, and adjacent to a syringe (14, 14′) and lead screw (94, 94′). A gear box (54) connects the drive shaft and lead screw to transfer rotational movements between them. A piston driving member, such as a cone (116) or drive nut (116′) converts the rotational movement of the lead screw into linear motion of a syringe piston (24). Sensors (150, 152) detect when the piston or cone is in a “home” position and in an “end” position, respectively. Optionally, a proximity sensor (170) is used to ensure that the cone and the piston (24) are abutting during dispensing. Alternatively, a clamping member (350) selectively clamps the lead screw (94′) against linear motion in at least a dispensing direction.
Owner:TRIVIDIA HEALTHCARE SYST LLC
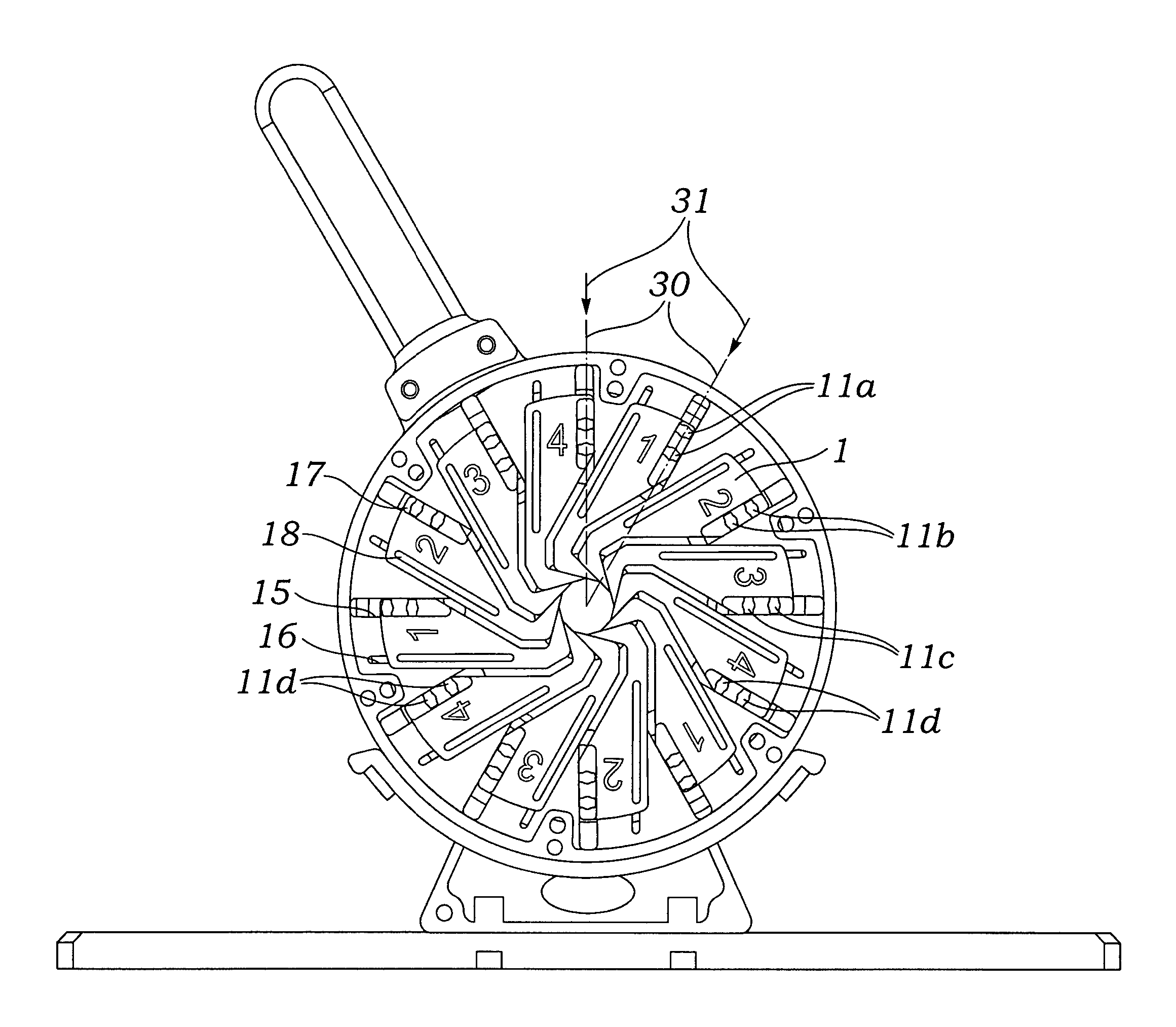
Straight seam cutter
ActiveCN103860225BAvoid surgeryAvoid medical malpracticeEndoscopic cutting instrumentsSurgical staplesLinear motionEngineering
The invention discloses a linear type suturing and excising device, comprising a body, a staple cartridge rack, a staple anvil, a staple cartridge, a cocking block and a knife pushing rod, wherein the staple cartridge rack, the staple anvil and the staple cartridge are arranged at the far end of the body, the cocking block is used for pushing a staple pushing piece and is arranged in a chute of the staple cartridge, the knife pushing rod pushes the cocking block to move, the staple cartridge rack is provided with a safety block for preventing secondary cocking, the safety block has a linear motion trail, the moving direction of the safety block is vertical to the moving direction of the knife pushing rod, and the safety block is arranged at the far end of the knife pushing rod and the excising knife, and is used for limiting the movement of the knife pushing rod and the excising knife from the near end of the linear suturing and excising device to the far end of the linear suturing and excising device when the linear type suturing and excising device is under the initial state and under the state of cocking completion. The linear type suturing and excising device has the beneficial effects that a doctor is effectively prevented from performing the next operation under the condition of not replacing a cocked staple cartridge, the occurrence of medical negligence is avoided, and the structure is simple and effective.
Owner:TOUCHSTONE INTERNATIONAL MEDICAL SCIENCE CO LTD
Rotational driver
ActiveUS9192376B2Enhances maneuvering and safetyEfficiently sutureSuture equipmentsDiagnosticsSuturing needleLinear motion
A rotational driver that comprises a interactive portion, wherein each interactive portion comprises a first extended member and a second extended member, a rotational system and a linear motion system, wherein the rotational driver permits a left or right handed surgeons to perform the surgical suturing procedure in a less complicated and more secure way by allowing more control over the suturing needle and the area to be stitched, even when the suturing area is small, deep, and / or restricted.
Owner:ERGOSURGICAL GRP CORP
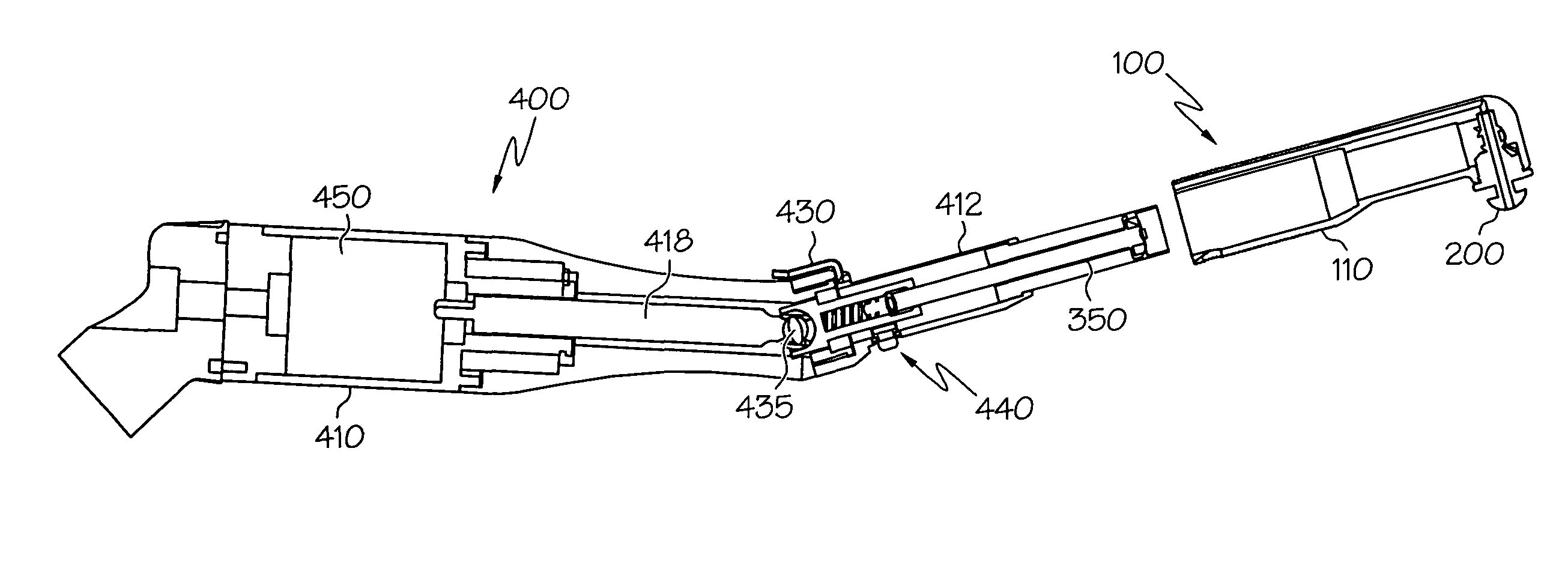
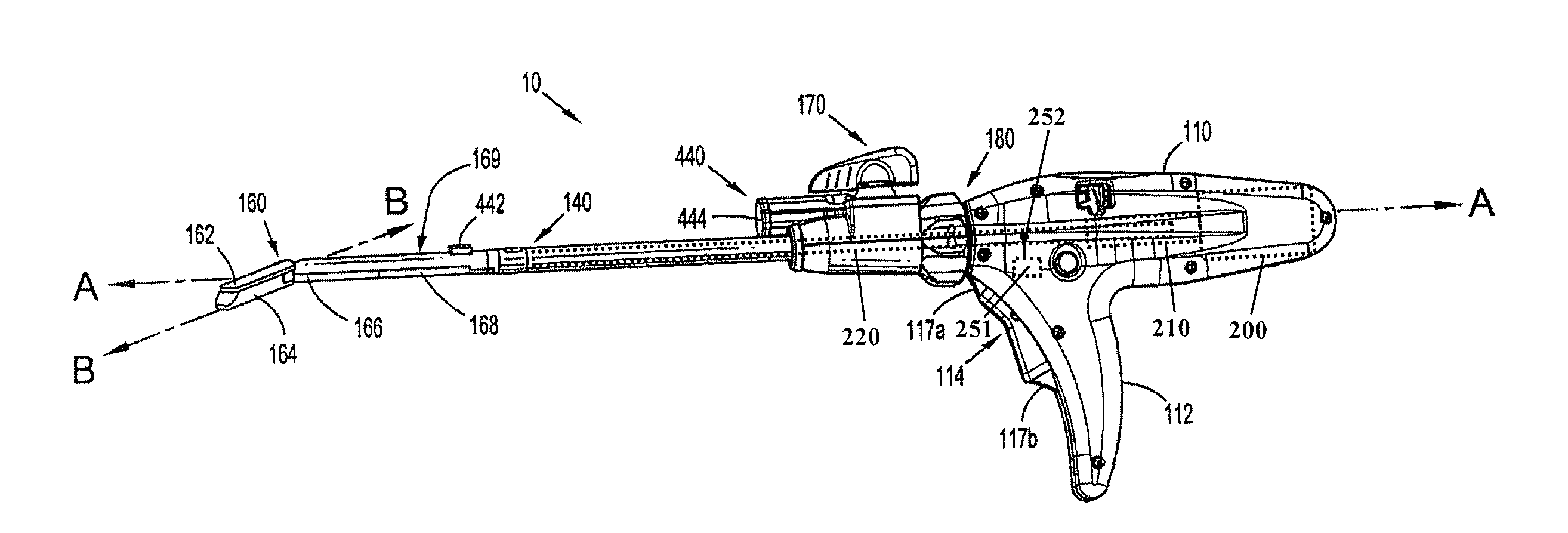
Adapter, extension, and connector assemblies for surgical devices
An assembly including an adapter assembly and an extension assembly for connecting an end effector to an electrosurgical instrument is provided. The adapter assembly includes first and second pusher assemblies configured for converting rotational motion into linear motion and a drive member for transferring rotational motion. The extension assembly includes at least one flexible band assembly for transferring the linear motion from the adapter assembly and a trocar assembly configured for converting rotational motion into linear motion. Also provided is a connection assembly for connecting a first tubular member to a second tubular member.
Owner:TYCO HEALTHCARE GRP LP
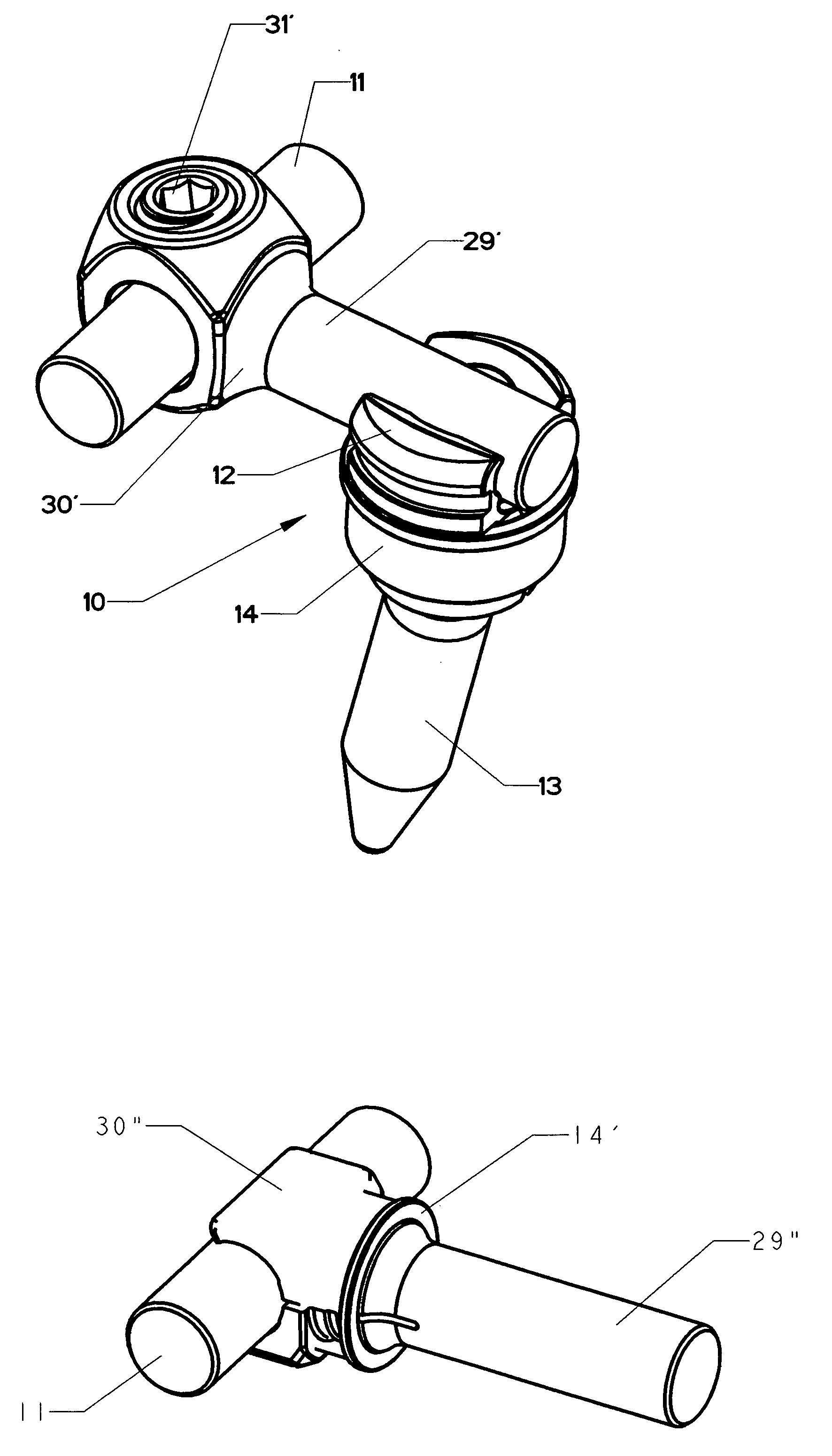
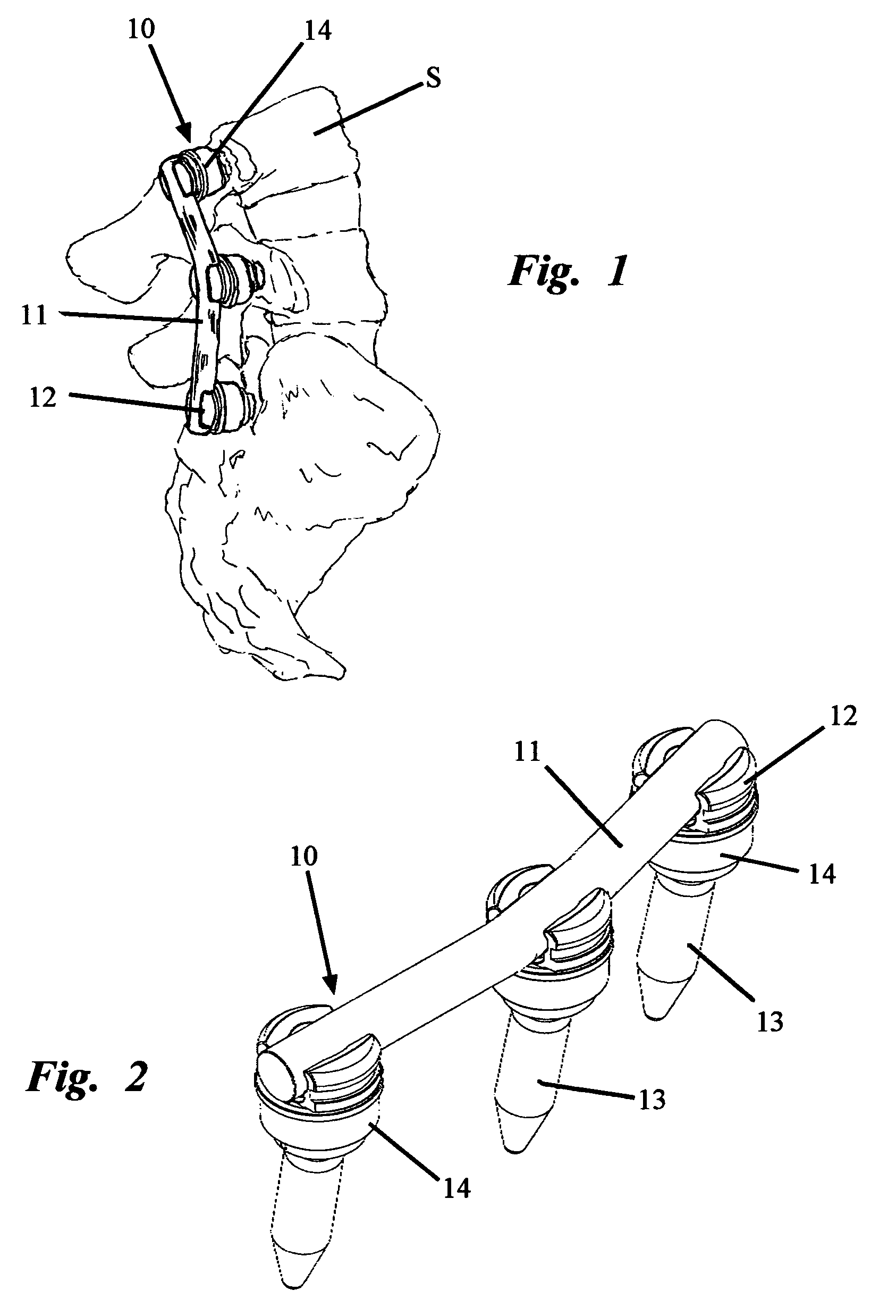
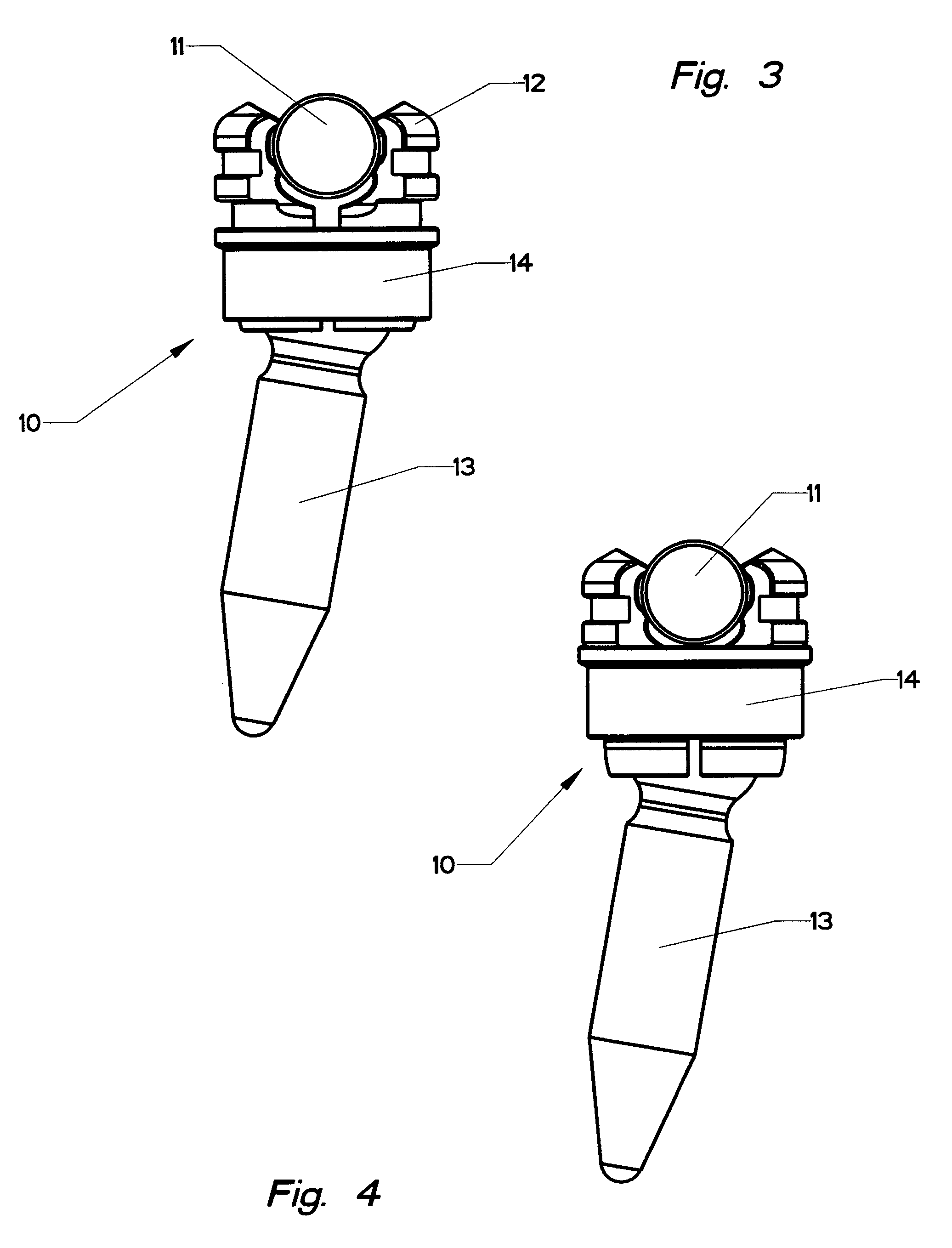
Bone fixation system with low profile fastener
A low profile orthopedic device is used to fix and stabilize bones to correct anomalies in skeletal structure occurring naturally or by trauma. Bone screws are screwed into bones by application of torque. Clamps are movably attached to the screws. Each clamp includes a compression ring. A connecting rod connects several screws through slots in the clamps. The clamps are tightened to hold the rod and the heads in a pre-selected position by linear movement of the compression rings.
Owner:SPINAL
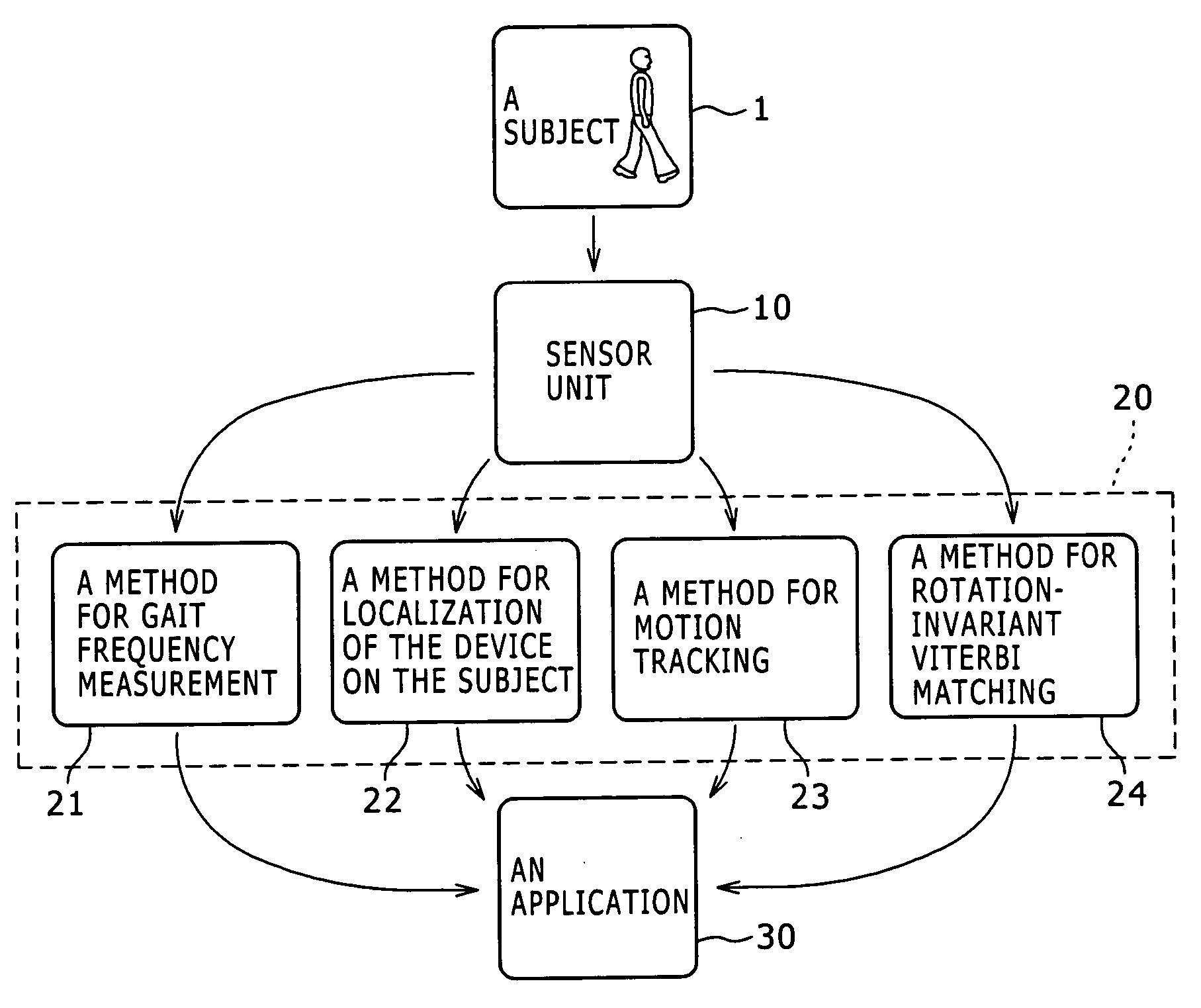
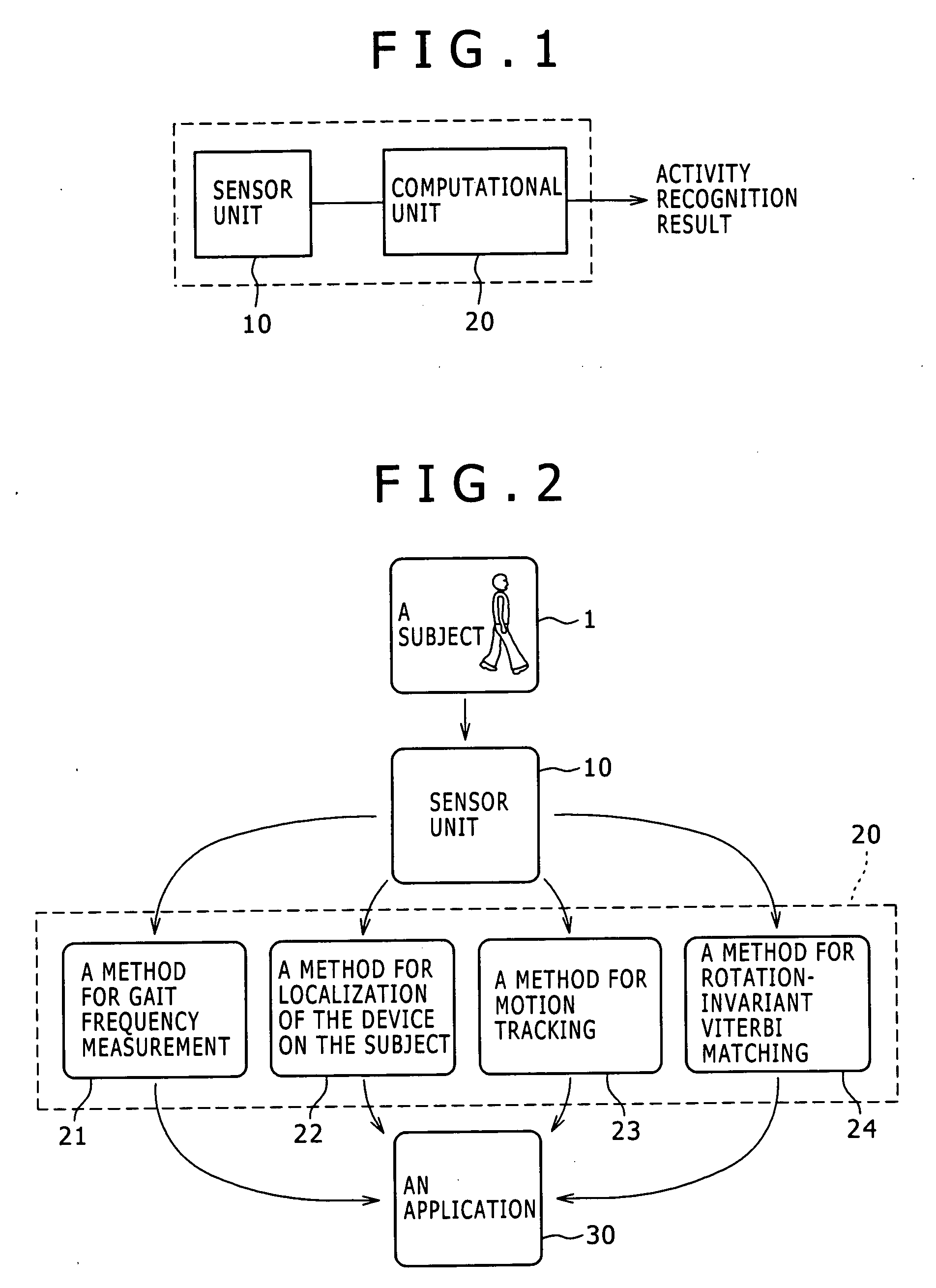
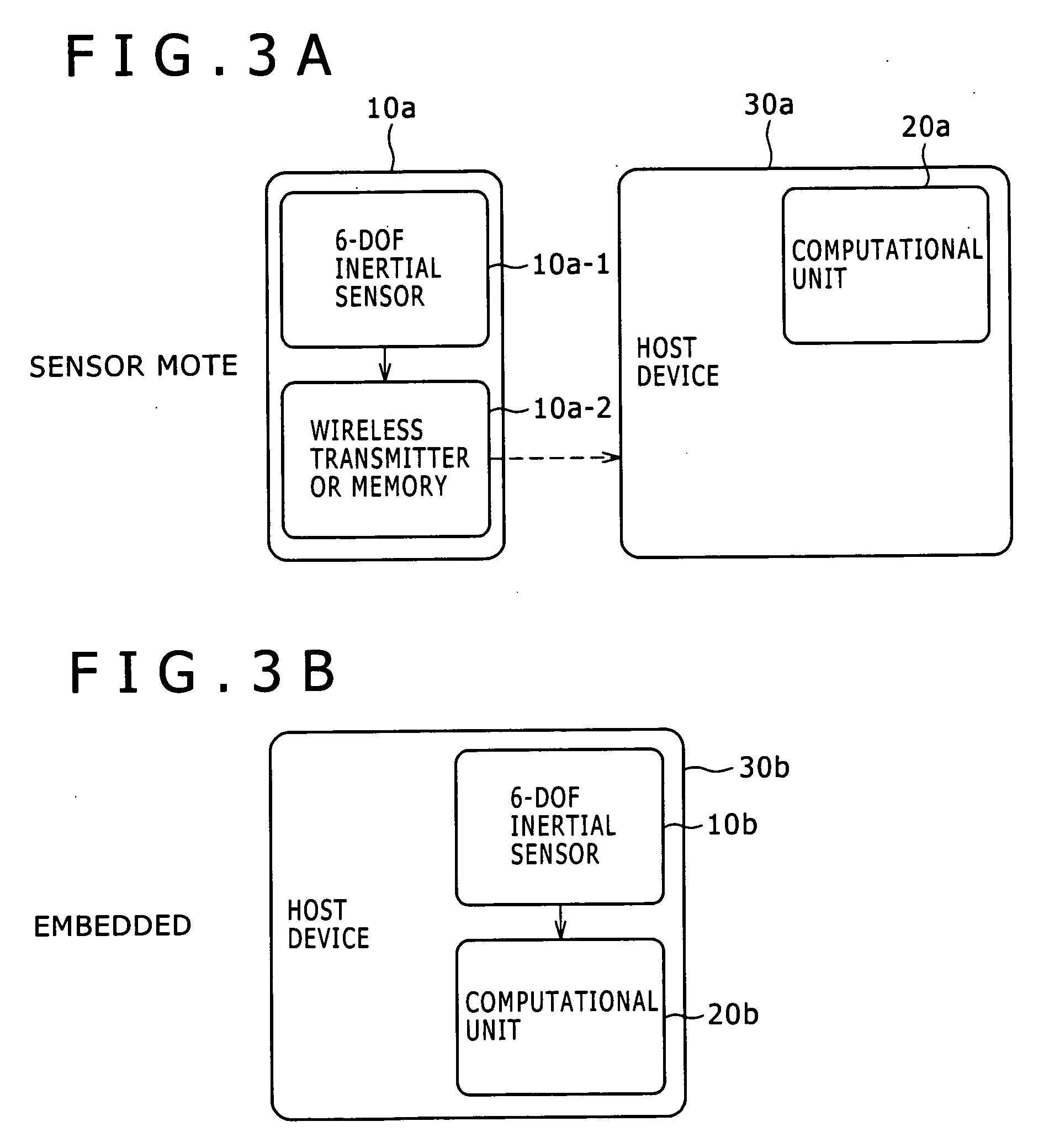
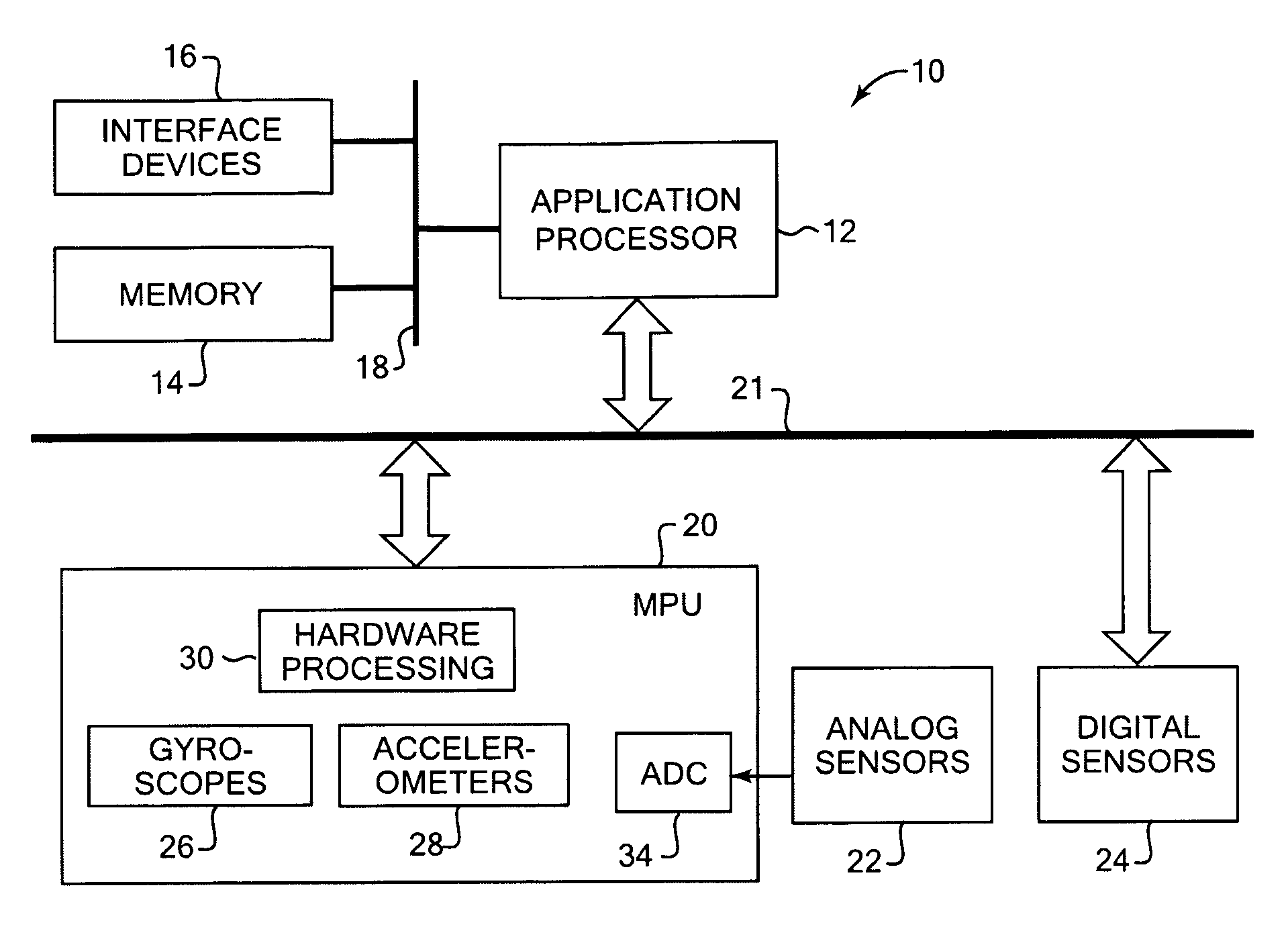
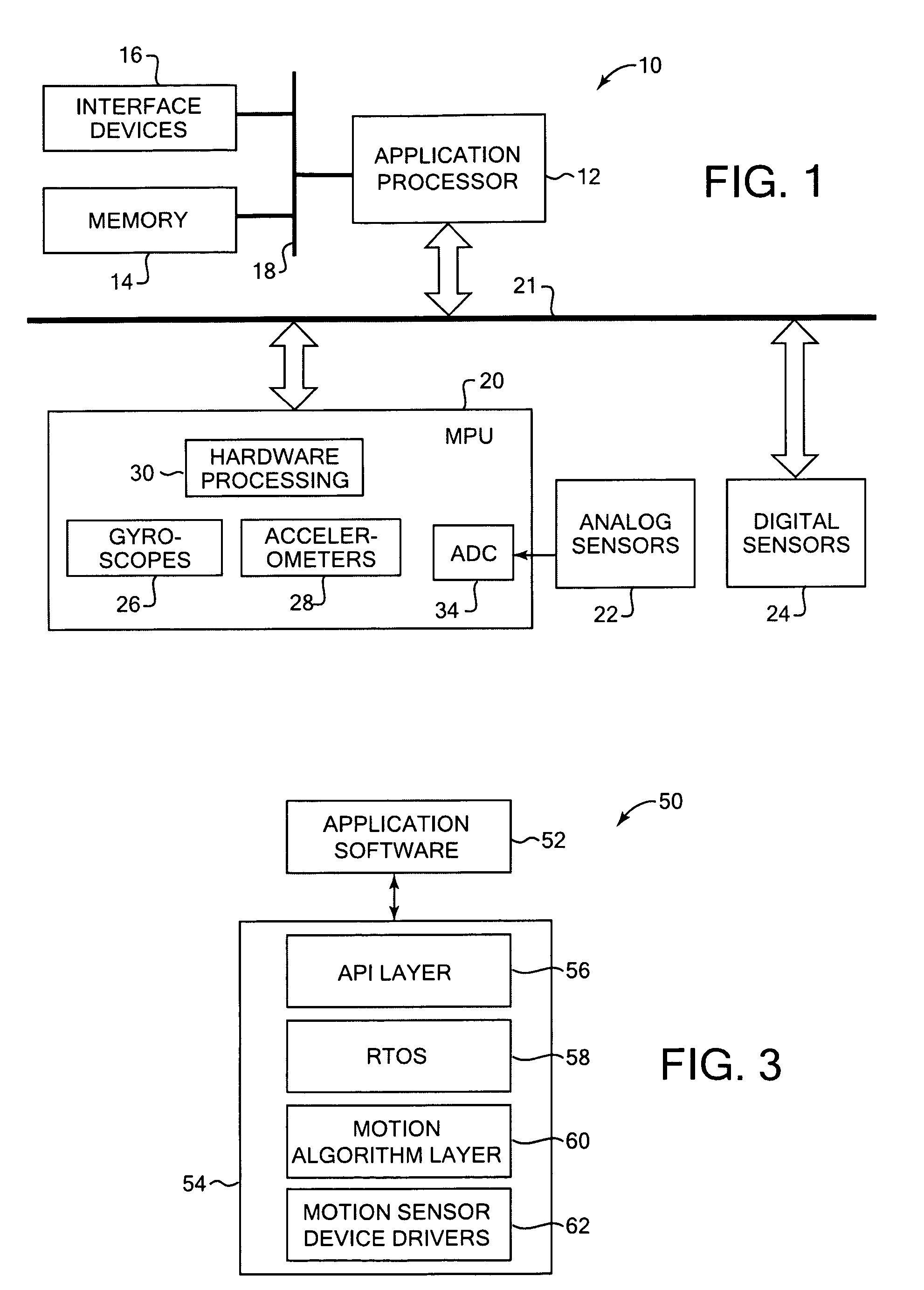
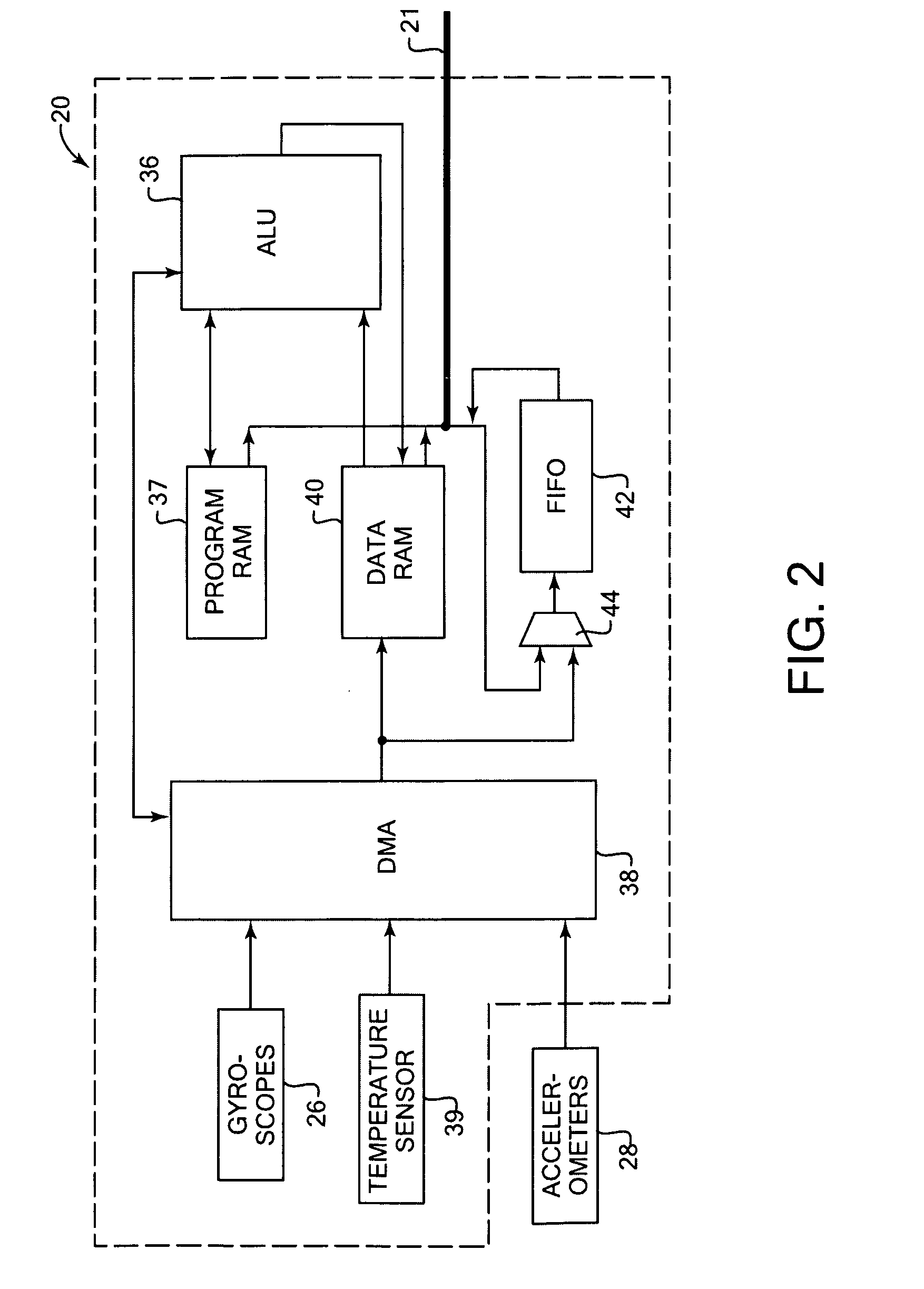
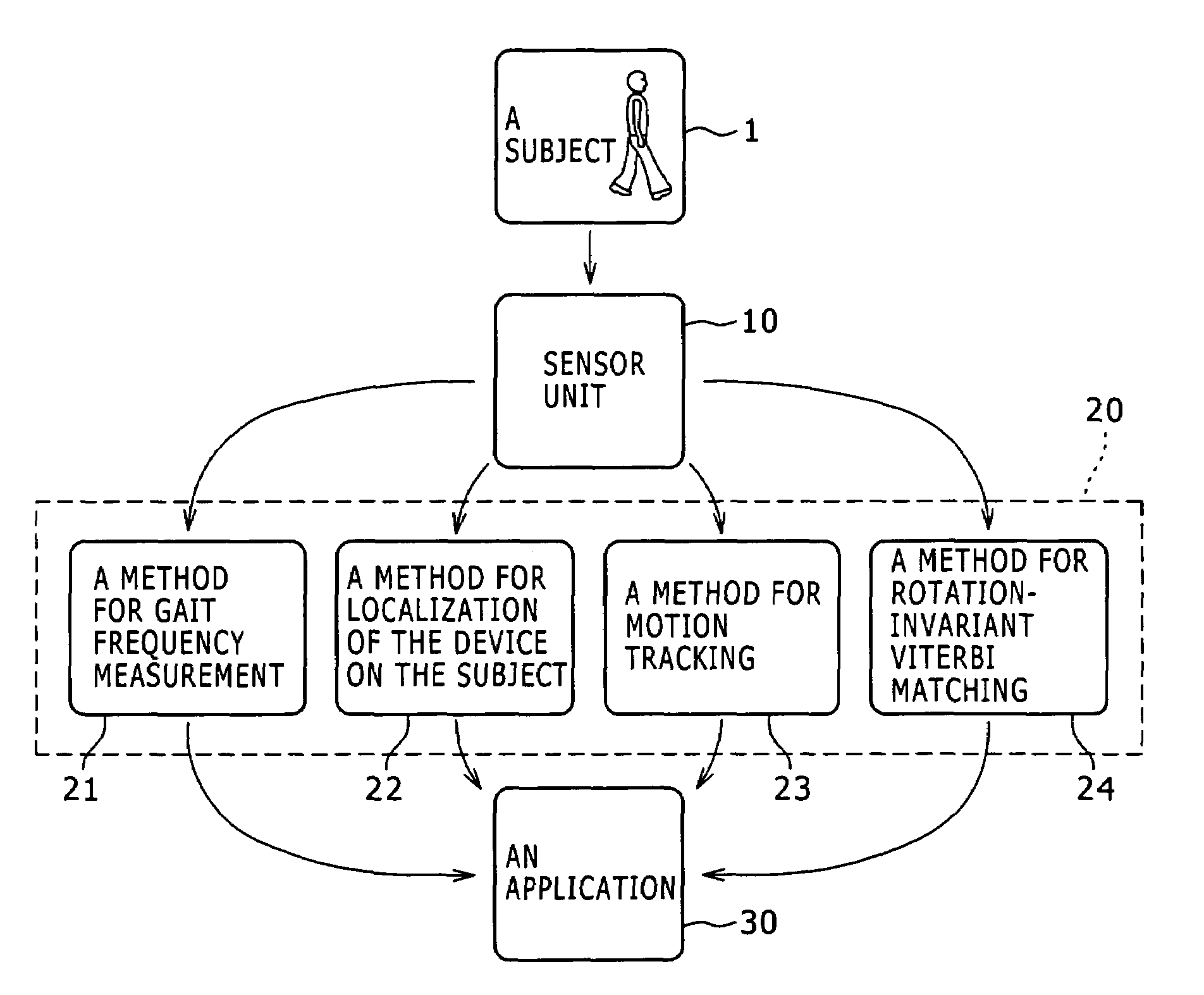
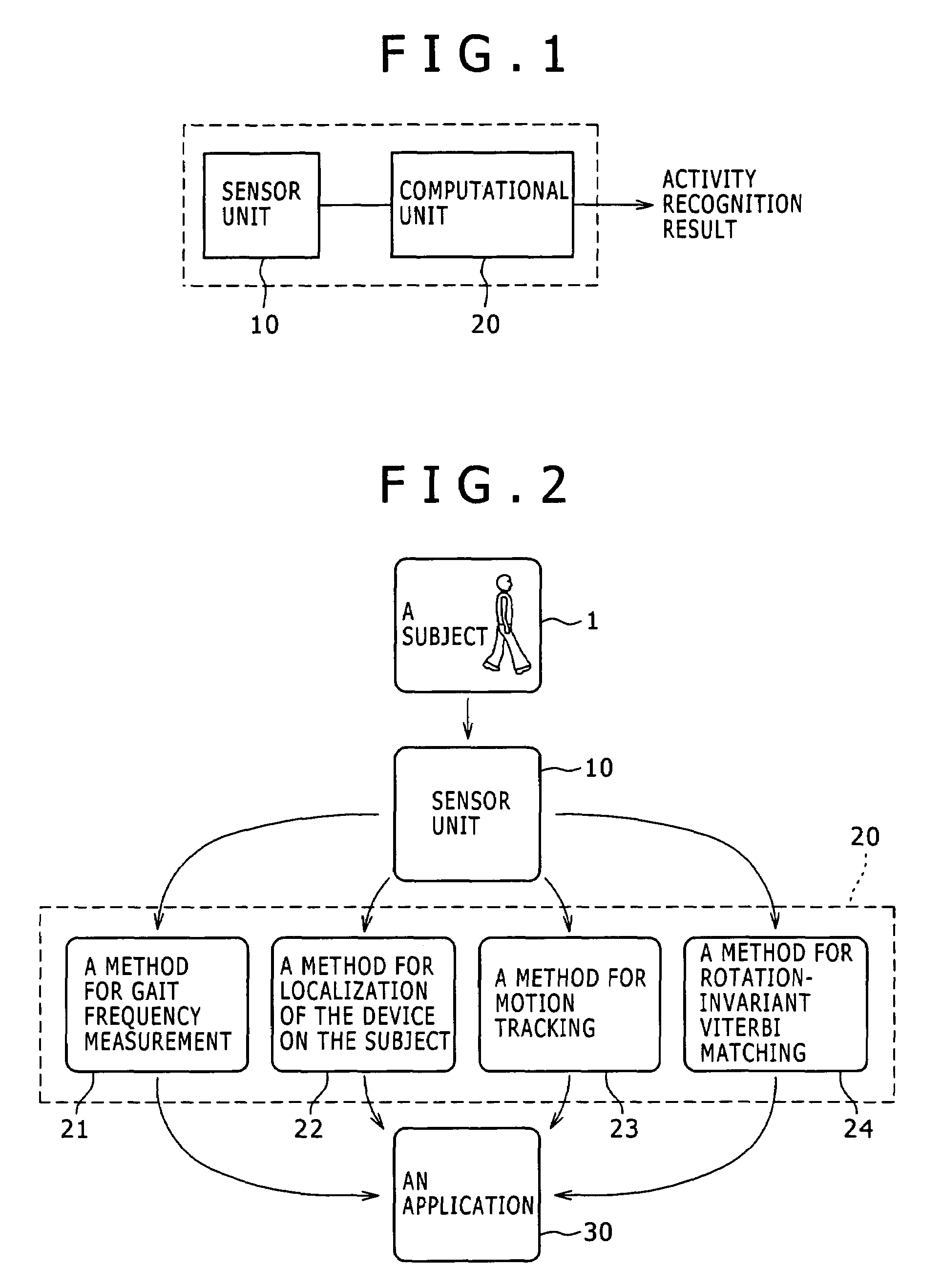
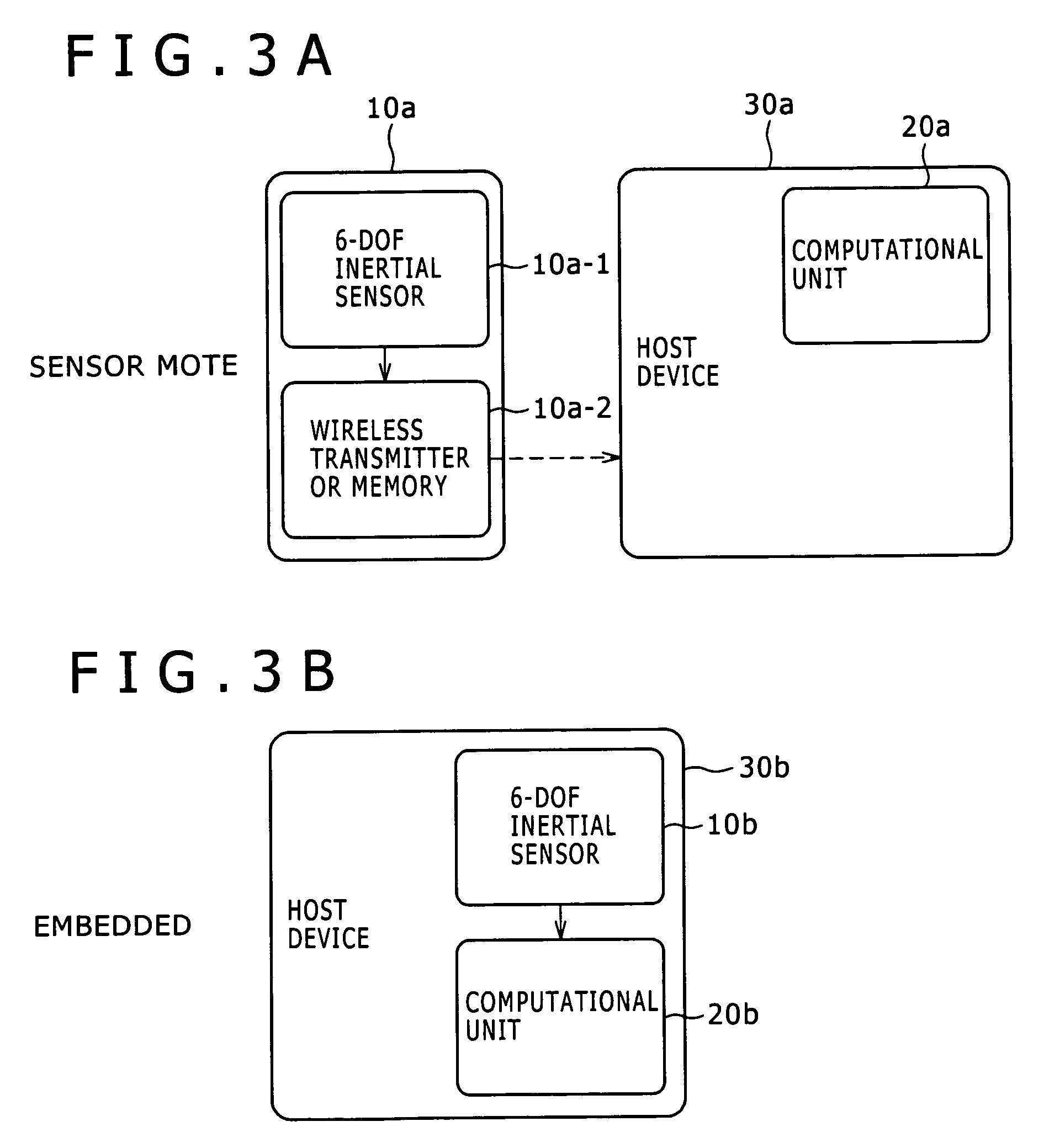
Activity recognition apparatus, method and program
ActiveUS20060284979A1Flexibility of implementationAvoid less flexibilityInertial sensorsNavigation by speed/acceleration measurementsLinear motionComputer science
There is provided an activity recognition apparatus for detecting an activity of a subject. The apparatus includes: a sensor unit including a plurality of linear motion sensors configured to detect linear motions and a plurality of rotational motion sensors, the linear motions being orthogonal to each other, the rotational motions being orthogonal to each other; and a computational unit configured to receive and process signals from the sensors included in the sensor unit so as to detect an activity of the subject. The sensor unit is directly or indirectly supported by the subject with an arbitrary orientation with respect to the subject. The computational unit performs a calculation that uses the signals from both linear motion sensors and rotational motion sensors to determine the activity of the subject independent of the orientation of the sensor unit.
Owner:SONY CORP
Bone fixation system with low profile fastener
A low profile orthopedic device is used to fix and stabilize bones to correct anomalies in skeletal structure occurring naturally or by trauma. Bone screws are screwed into bones by application of torque. Clamps are movably attached to the screws. Each clamp includes a compression ring. A connecting rod connects several screws through slots in the clamps. The clamps are tightened to hold the rod and the heads in a pre-selected position by linear movement of the compression rings.
Owner:SPINAL
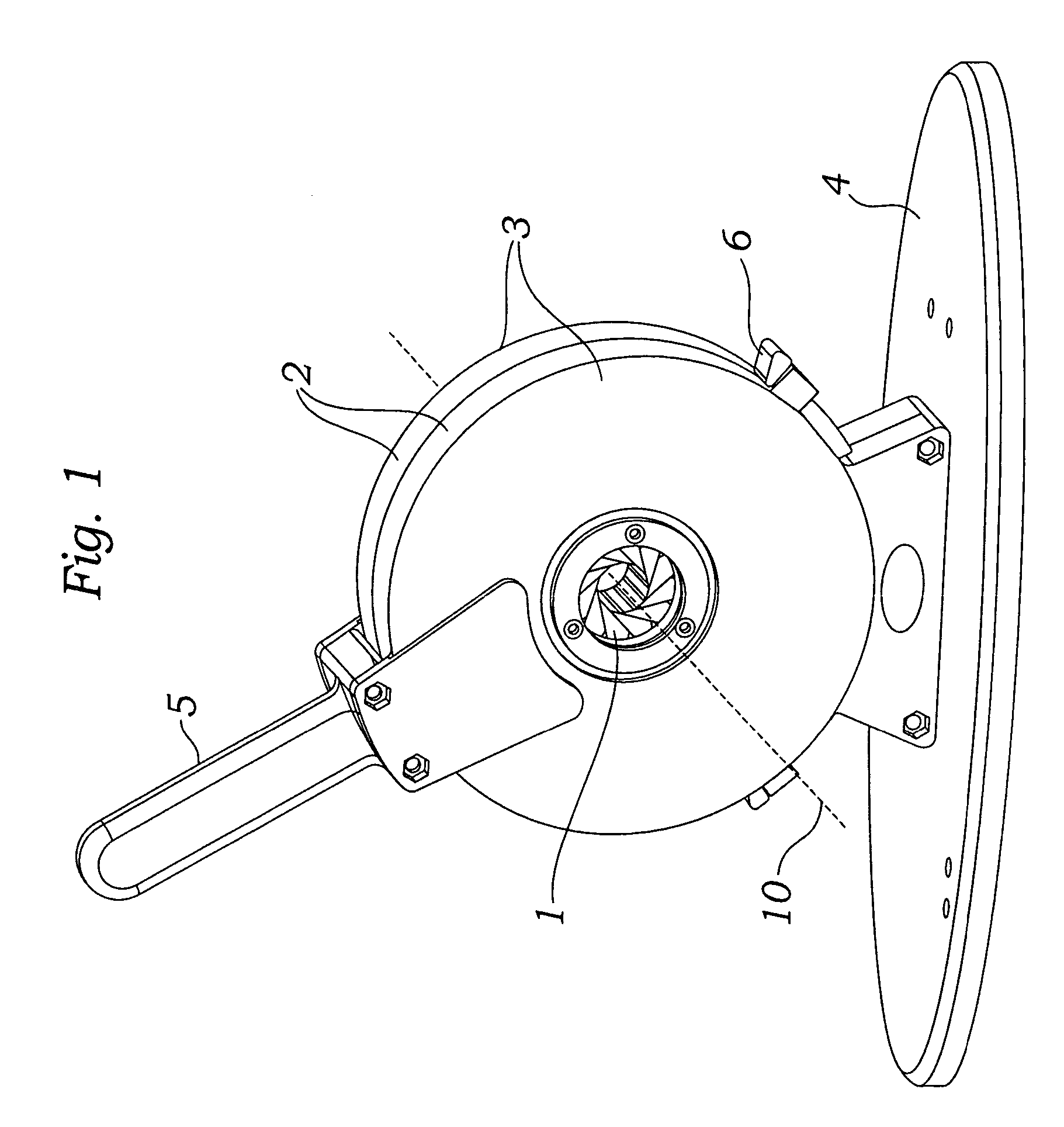
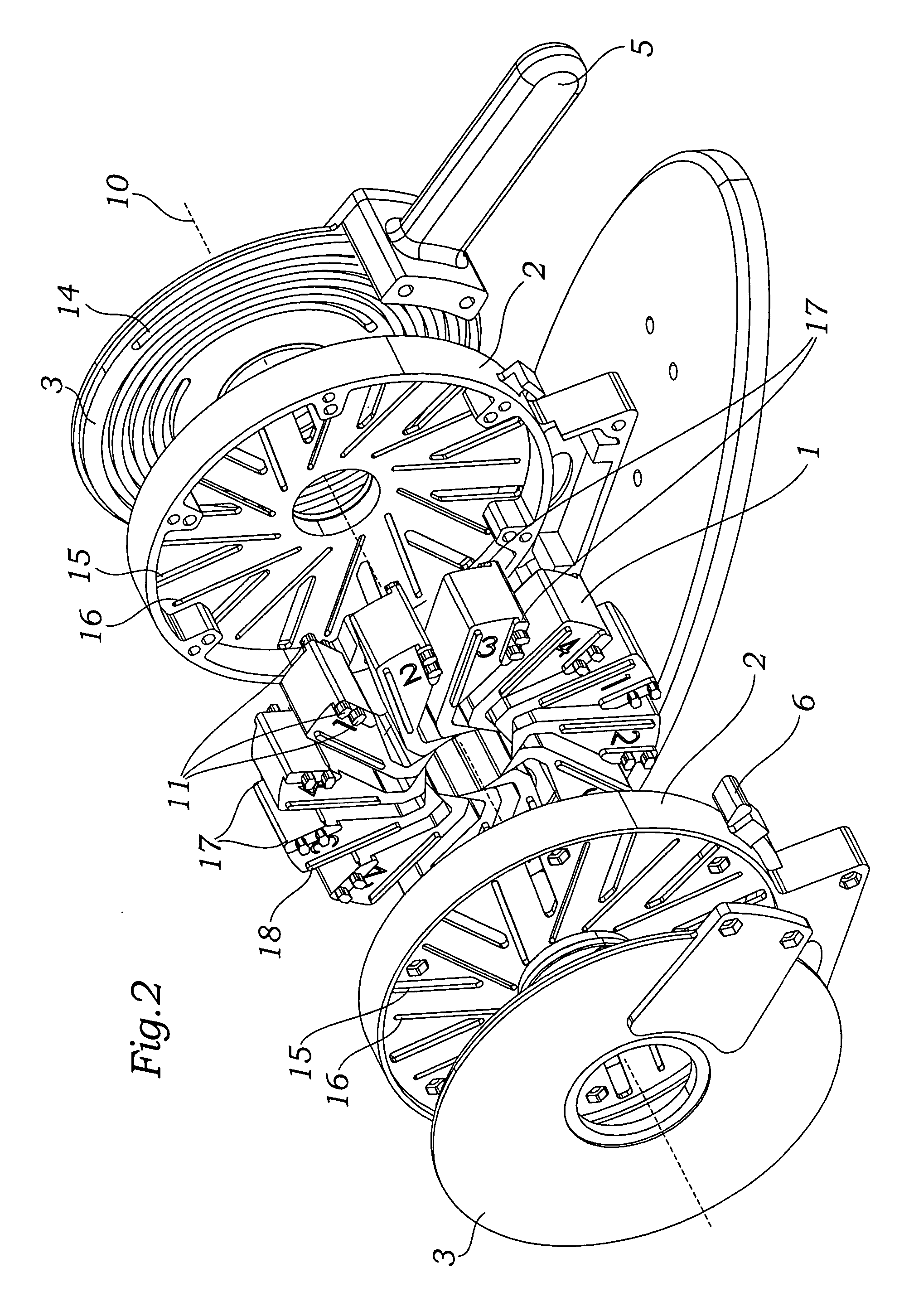
Prosthetic valve crimping device
ActiveUS20070056346A1Prevent rotationMost efficientStentsBalloon catheterProsthetic valveEngineering
An improved crimping mechanism well-suited for use with stented prosthetic heart valves. The crimping mechanism includes a plurality of jaws configured for linear non-rotational movement toward a central axis. A rotational plate is formed with a plurality of spiral grooves or tracks for engaging the jaws. Rotational movement of the spiral tracks produces linear movement of the jaws. Nesting of the inner ends of the jaws permits each to be acted on along different radial lines while their inner faces move together evenly to reduce the crimping aperture in a smooth fashion. The crimping mechanism is particularly well-suited for use with stented prosthetic heart valves, such as a prosthetic aortic valve, though it can also be applied to other stented heart valves, venous valves, and even stent grafts which tend to be fairly large.
Owner:EDWARDS LIFESCIENCES CORP
Interfacing application programs and motion sensors of a device
ActiveUS20090184849A1Easy maintenanceReduce processIndoor gamesElectronic switchingLinear motionSimulation
Interfacing application programs and motion sensors of a device. In one aspect, a high-level command is received from an application program running on a motion sensing device, where the application program implements one of multiple different types of applications available for use on the device. The high-level command requests high-level information derived from the output of motion sensors of the device that include rotational motion sensors and linear motion sensors. The command is translated to cause low-level processing of motion sensor data output by the motion sensors, the low-level processing following requirements of the type of application and determining the high-level information in response to the command. The application program is ignorant of the low-level processing, and the high-level information is provided to the application program.
Owner:INVENSENSE
Anti-backup mechanism for repeating multi-clip applier
InactiveUS20060009790A1Avoid dangerAvoid loadDisinfectionSurgical forcepsLinear motionSurgical operation
An instrument for applying clips in surgery having an operating handle with operating components and a clip cartridge with clip applying mechanism. The handle operating components generate reciprocal linear motion imparted to the clip applying mechanism and accommodate rotation of the cartridge about a cartridge axis. An anti-backup mechanism constrains operating components to complete first and second strokes of reciprocal linear motion.
Owner:BLAKE JOSEPH W III +1
Method and system for a static magnetic read/write head
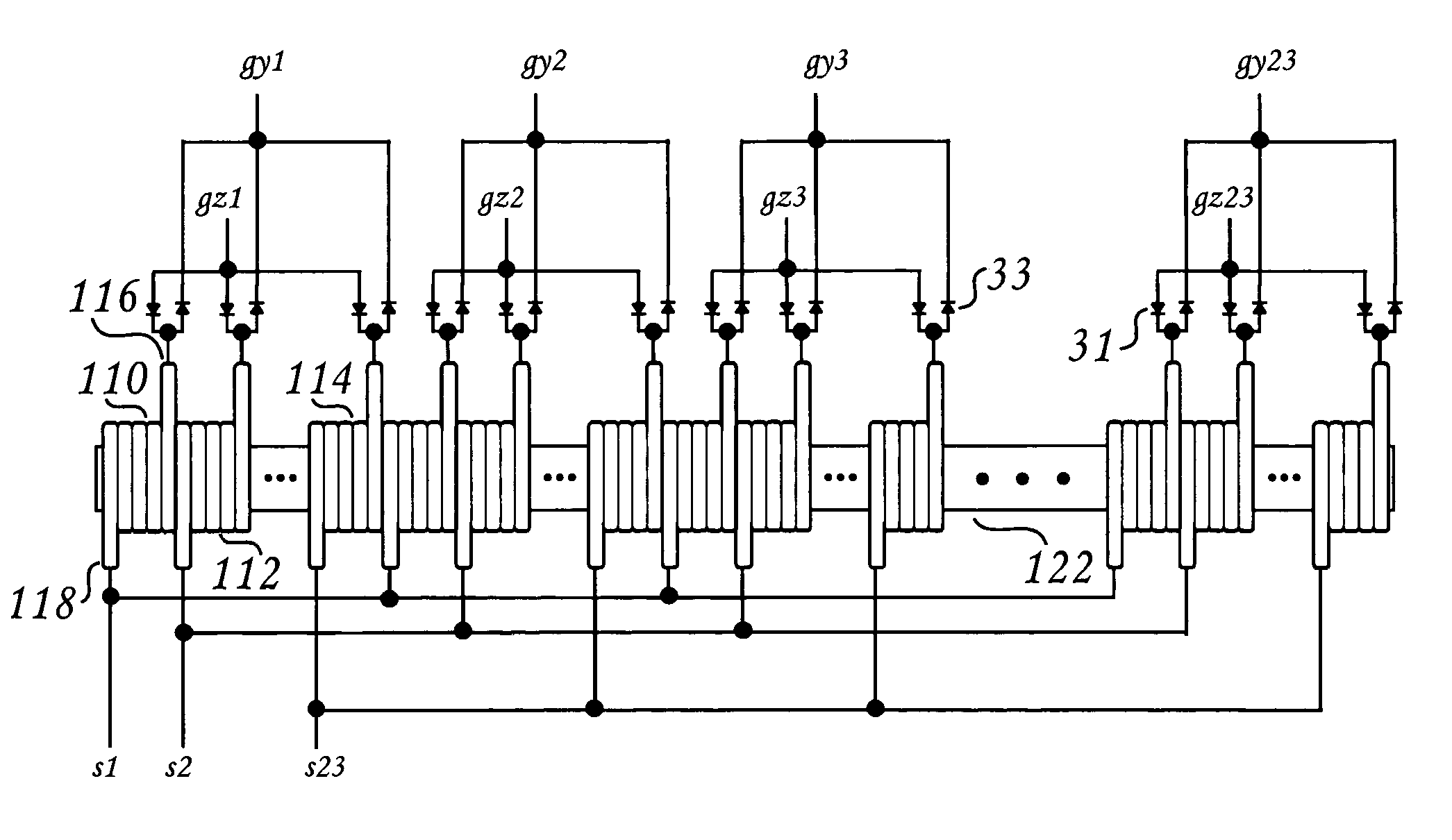
ActiveUS7591427B2Simplify complexityReduce complexitySensing record carriersDigital marking by magnetic meansLinear motionDriving current
The present invention enables reading from and writing onto a magnetic stripe medium with a static read / write head that does not require relative linear motion between the magnetic stripe medium and the head while reading or writing takes place. The reading and writing is accomplished using a stationary uni-dimensional, bi-dimensional, or multi-dimensional conductor array addressing and driving current through an individual conductor element. Reading from magnetic stripe is accomplished by using magnetic flux sensing method such as a fluxgate.
Owner:INTELLECTUAL VENTURES HOLDING 81 LLC
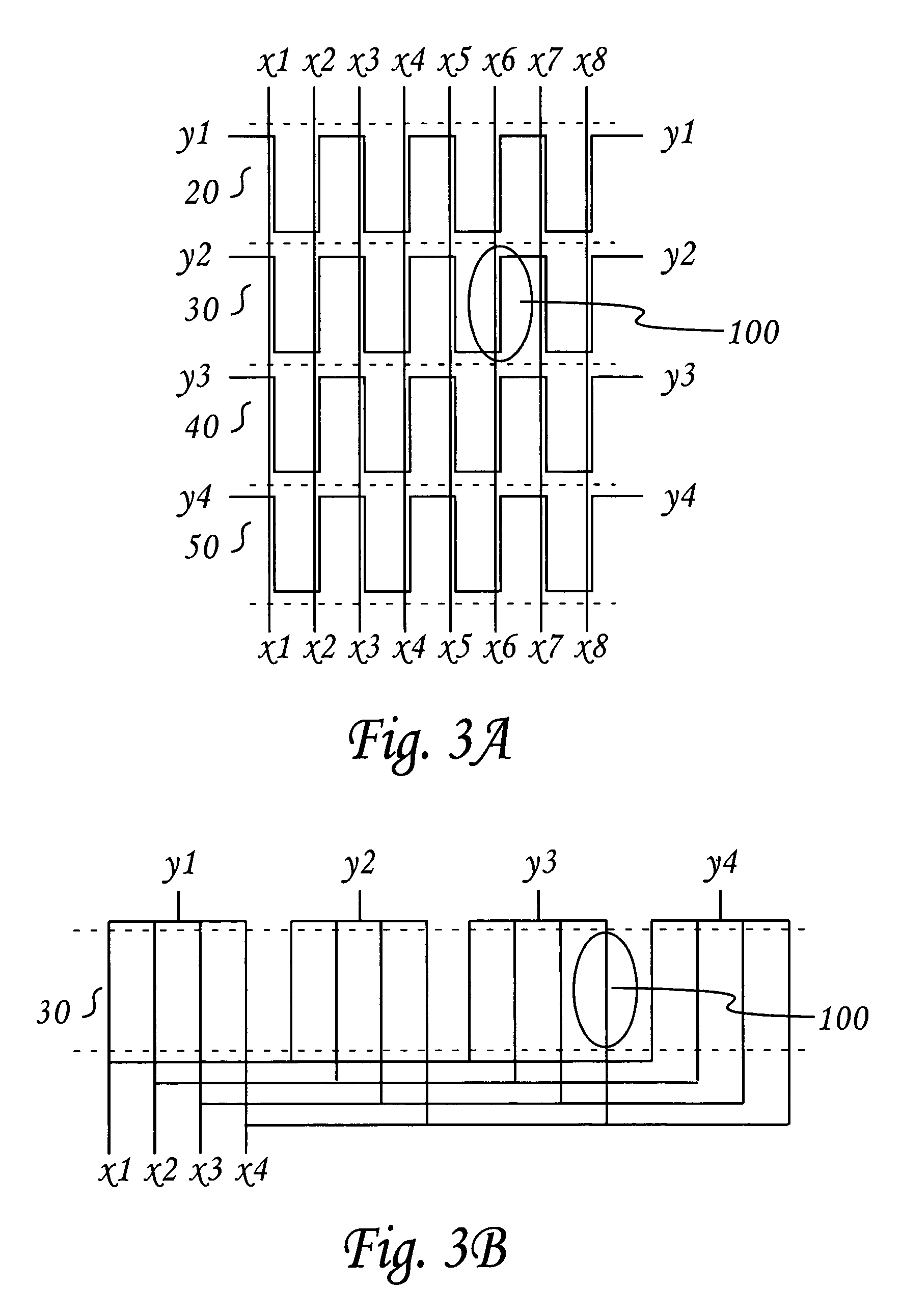
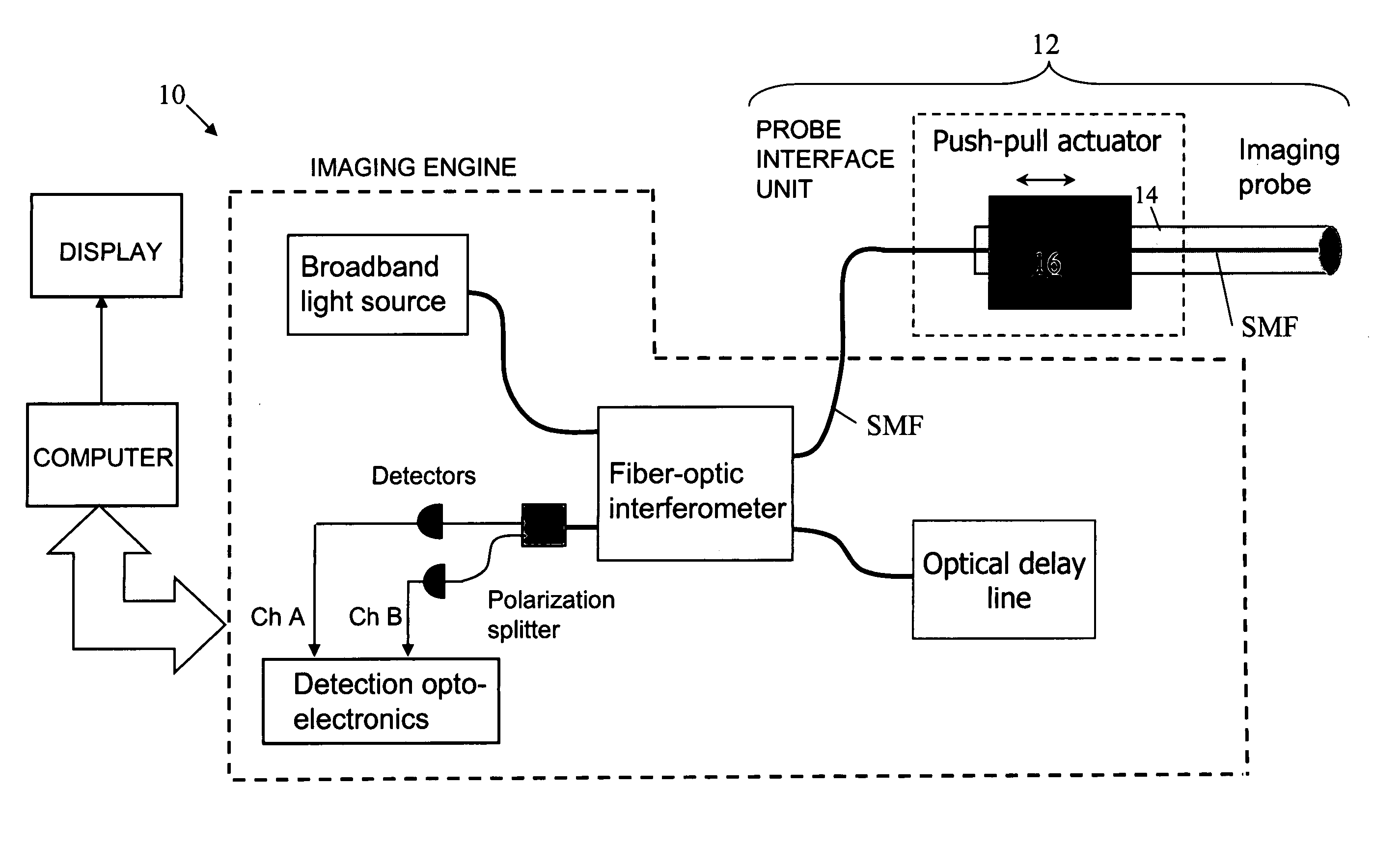
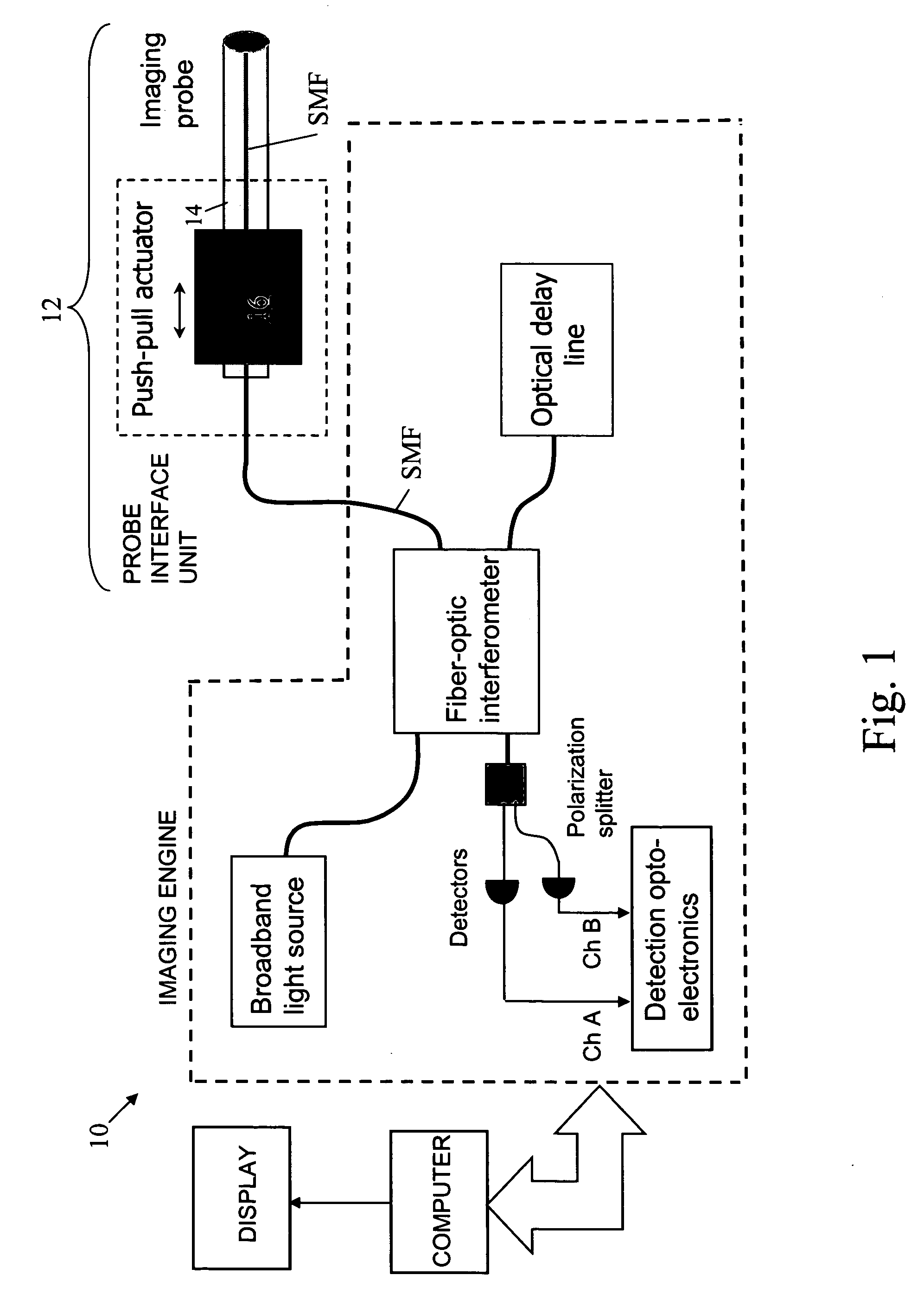
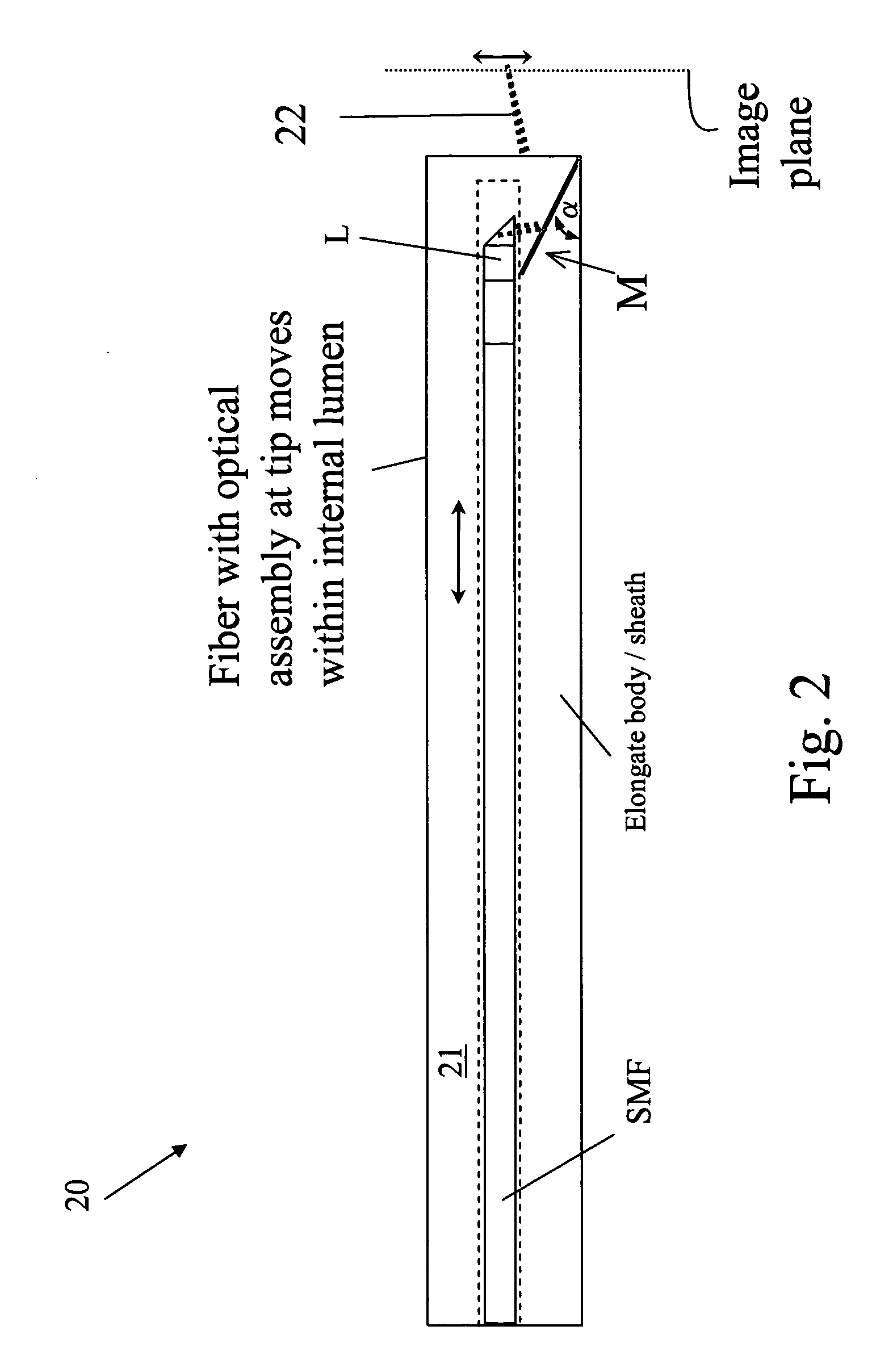
Optical coherence tomography apparatus and methods
In one aspect, the invention relates to an imaging probe. The imaging probe includes an elongate body having a proximal end and distal end, the elongate body adapted to enclose a portion of a slidable optical fiber, the optical fiber having a longitudinal axis; and a first optical assembly attached to a distal end of the fiber. The first optical assembly includes a beam director adapted to direct light emitted from the fiber to a plane at a predetermined angle to the longitudinal axis, a linear actuator disposed at the proximal portion of the elongated body, the actuator adapted to affect relative linear motion between the elongate body and the optical fiber; and a second optical assembly located at the distal portion of the elongate body and attached thereto, the second optical assembly comprising a reflector in optical communication with the first optical assembly, the reflector adapted to direct the light to a position distal to the elongate body.
Owner:LIGHTLAB IMAGING
Coupling system for an infusion pump
InactiveUS20050020980A1Small sizeImprove portabilityMedical devicesPressure infusionLinear motionMotor drive
A pump system for an infusion system includes a linear drive (36, 36′) which minimizes the space occupied by the pump components in a portable housing (10, 10′). A motor (34) and a motor drive shaft (42) are arranged in parallel with, and adjacent to a syringe (14, 14′) and lead screw (94, 94′). A gear box (54) connects the drive shaft and lead screw to transfer rotational movements between them. A piston driving member, such as a drive nut (116) converts the rotational movement of the lead screw into linear motion of a syringe piston (24). A cap (190, 190′) couples the syringe (14, 14′) to the housing and provides an outlet for the liquid to be dispensed. In one embodiment, the cap (190′) is configured to rotate relative to the housing in one direction only, during locking. Rotational movement is also used for locking the piston (24) to the drive nut (116) against relative axial movement. In another embodiment, the cap (190′) carries a rotatable hub (330) which is connected at a first end (336) with an infusion line (191) and at a second end defines a needle (338) for piercing a closure (340) on the syringe.
Owner:INOUE YOSHIO +4
Inserter device including rotor subassembly
InactiveUS20110106126A1Reduce manufacturing costImprove reliabilityCatheterSensorsLinear motionEngineering
An inserter subassembly including a rotor and drive member such that rotation of the rotor is translated to a linear motion including insertion and refraction paths.
Owner:ABBOTT DIABETES CARE INC
Torus-shaped mechanical gripper
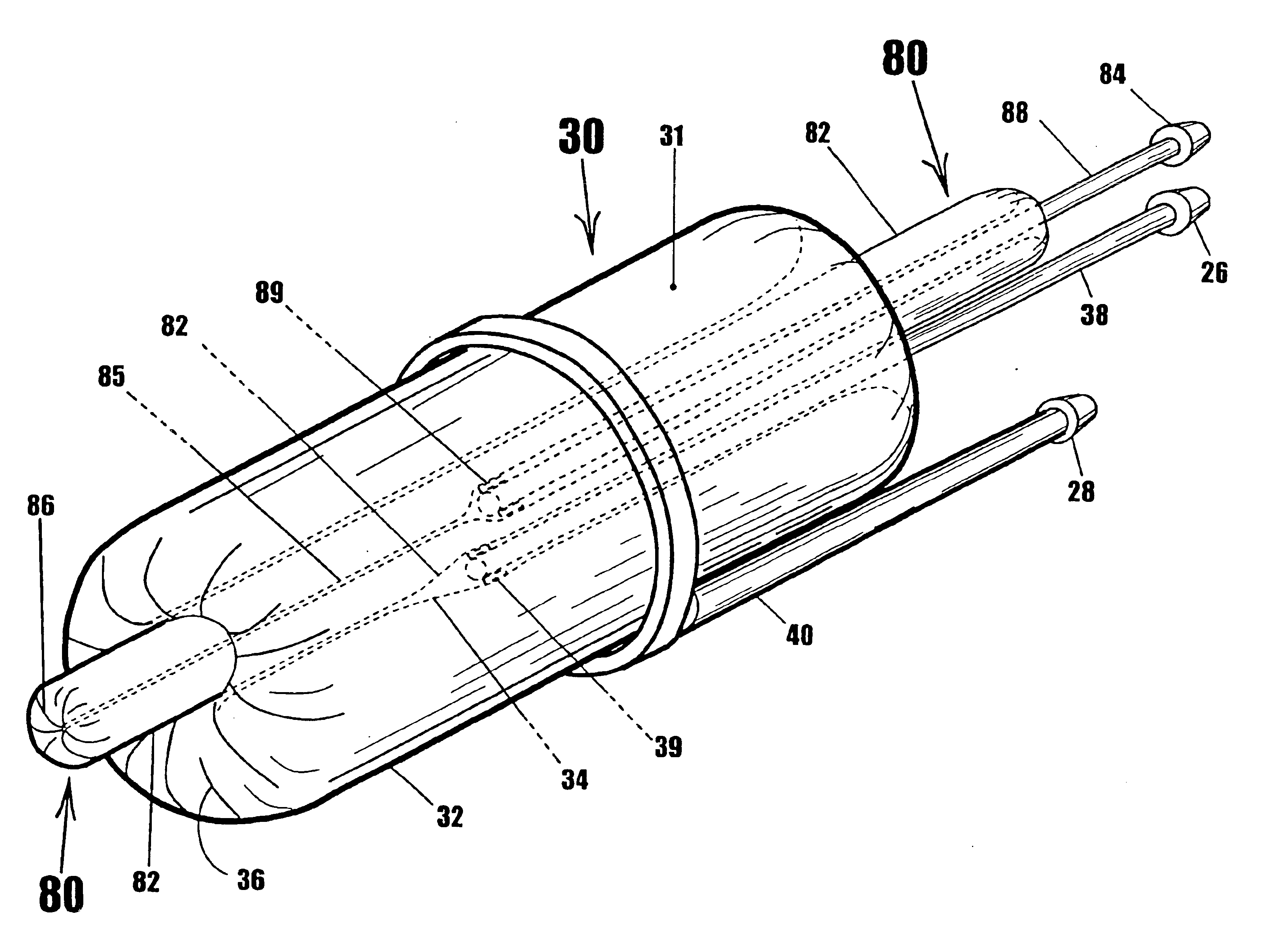
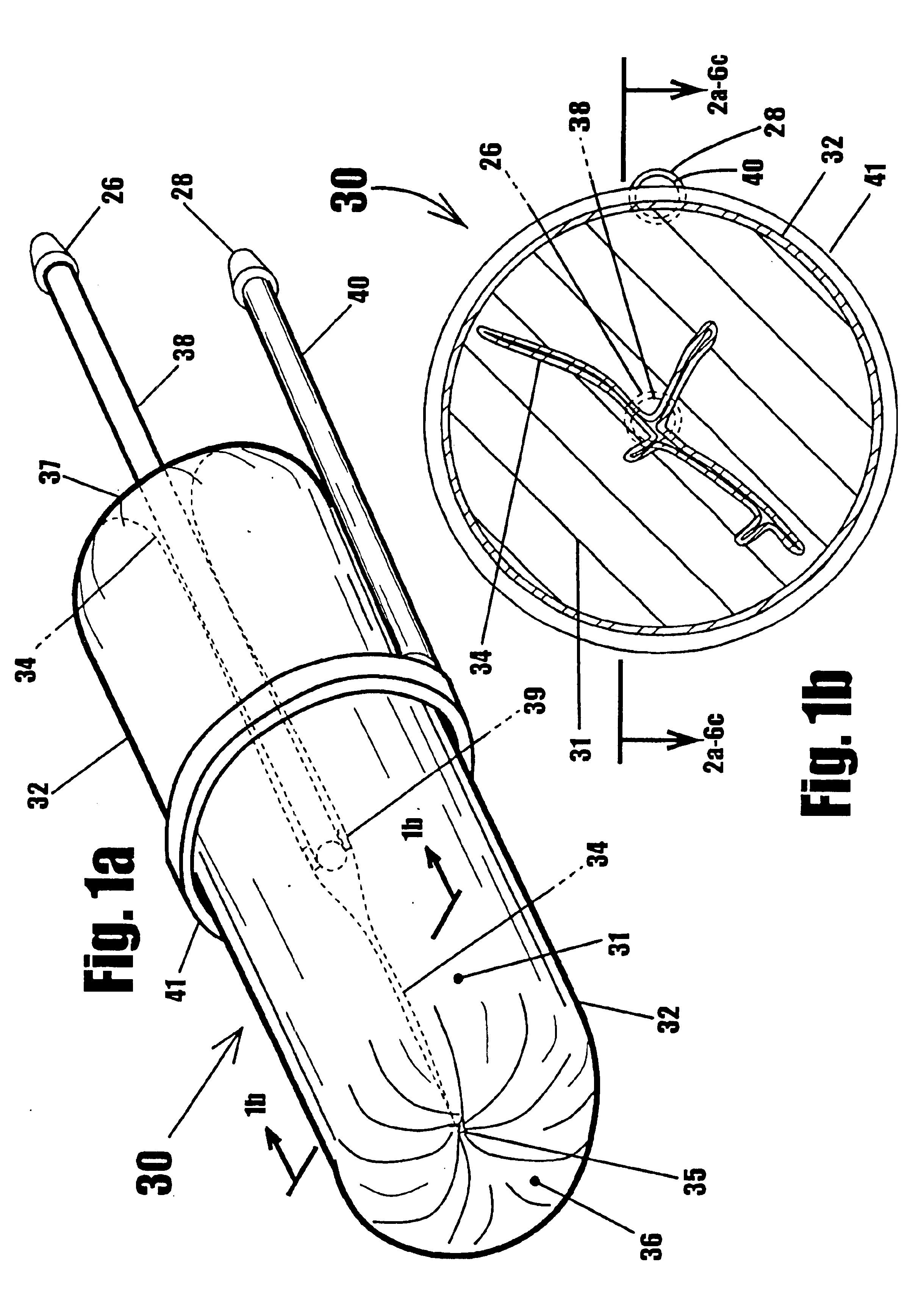
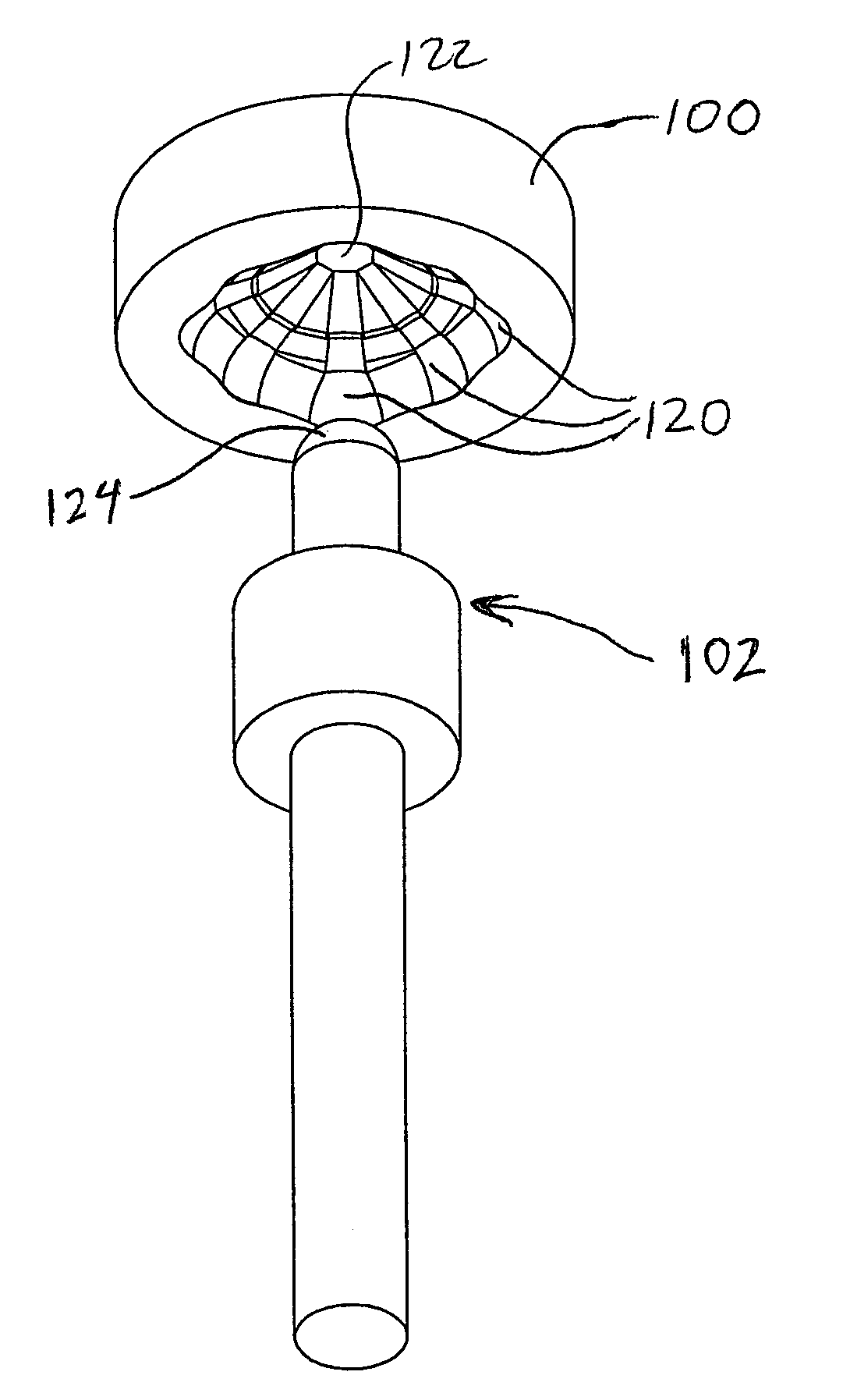
A device for gripping, holding, and releasing objects of varying sizes and shapes, which comprises an elongated torus (30) enclosing a fluid material (31), an external control rod (40), and an internal control rod (38). Torus (30) may be made of a flexible membrane and able to seal in fluid material (31). Fluid material (31) can be a gas, liquid, solid particles, semisolid particles, or mixtures of these. Central channel (34) of torus (30) is collapsed due to pressure of fluid material (31) within torus (30). Both control rods are securely attached to torus (30), with rod (38) attached to the interior portion of the torus along collapsed central channel (34), and rod (40) attached to the exterior portion of the torus on outer surface (32). Gripping action is achieved by differential linear motion of control rods (38) and (40) along the longitudinal (elongated) axis of torus (30). This causes front portion (36) of the torus to slide radially inward or outward to grip objects. Further movement of the control rods can cause the object to be pulled completely inside the collapsed channel for secure gripping by completely surrounding the object. The soft flexible nature of torus (30) allows grasping even the most delicate objects without damaging them. Even over-ripe strawberries can be rapidly grasped without bruising.
Owner:RAGNER GARY DEAN +1
Three-Dimensional Printing System Using Dual Rotation Axes
ActiveUS20130189435A1Promote sportsImprove throughputAdditive manufacturing apparatusAdditive manufacturing with liquidsRotational axisLinear motion
A 3-D printer system moves a printed tool over a print surface with a mechanism controlling a rotational angle of an arm holding the print tool and a revolutionary angle of axis of rotation of the printable area to eliminate the disadvantages of conventionally used linear motion mechanisms
Owner:WISCONSIN ALUMNI RES FOUND
Apparatus and method for resonant-vibratory mixing
ActiveUS7188993B1Reduce the overall heightImprove bearing lifeShaking/oscillating/vibrating mixersTransportation and packagingLinear motionElectronic controller
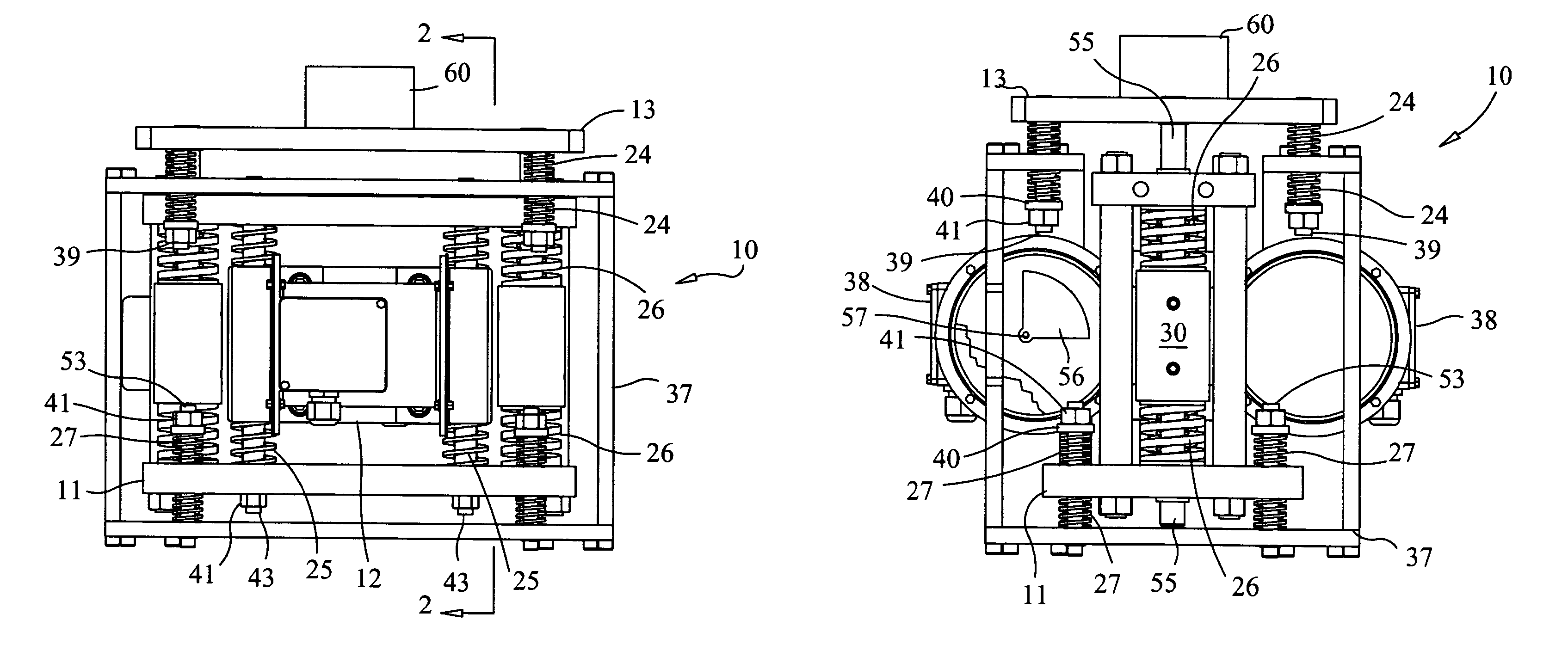
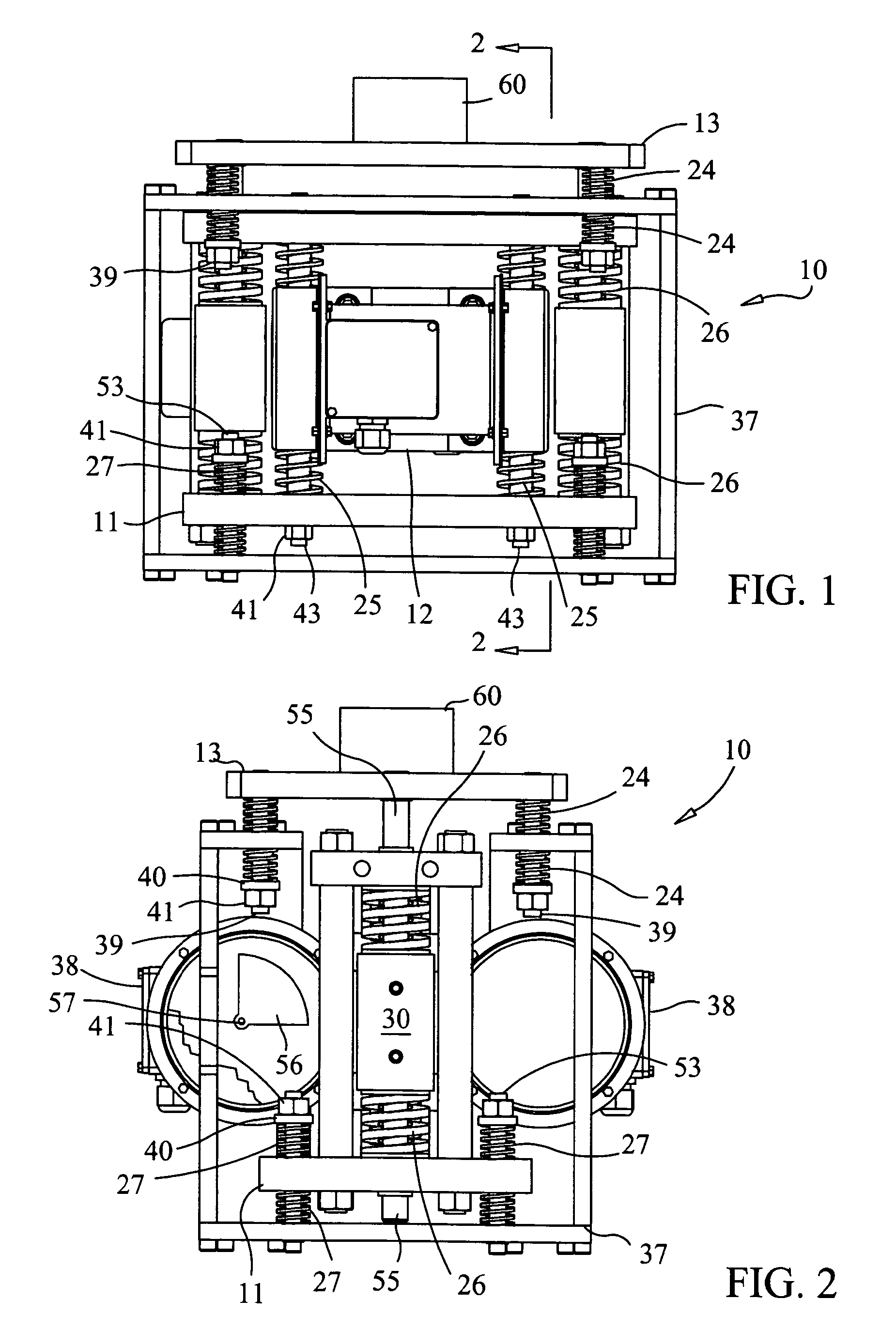
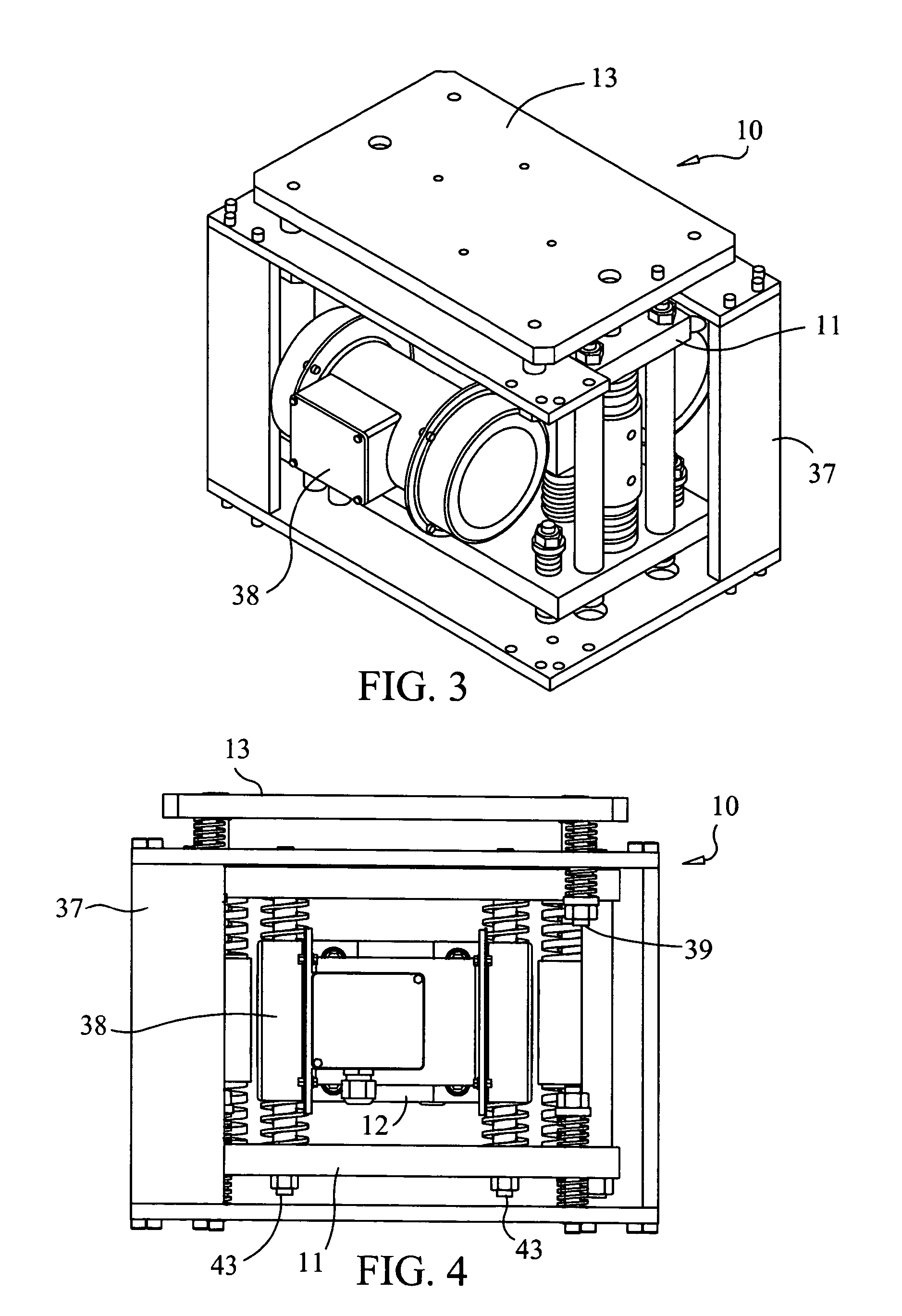
An apparatus and method for mixing fluids and / or solids in a manner that can be varied from maintaining the integrity of fragile molecular and biological materials in the mixing vessel to homogenizing heavy aggregate material by supplying large amounts of energy. Variation in the manner of mixing is accomplished using an electronic controller to generate signals to control the frequency and amplitude of the motor(s), which drive an unbalanced shaft assembly to produce a linear vibratory motion. The motor may be a stepper motors a linear motor or a DC continuous motor. By placing a sensor on the mixing vessel platform to provide feedback control of the mixing motor, the characteristics of agitation in the fluid or solid can be adjusted to optimize the degree of mixing and produce a high quality mixant.
Owner:RESODYN ACOUSTIC MIXERS
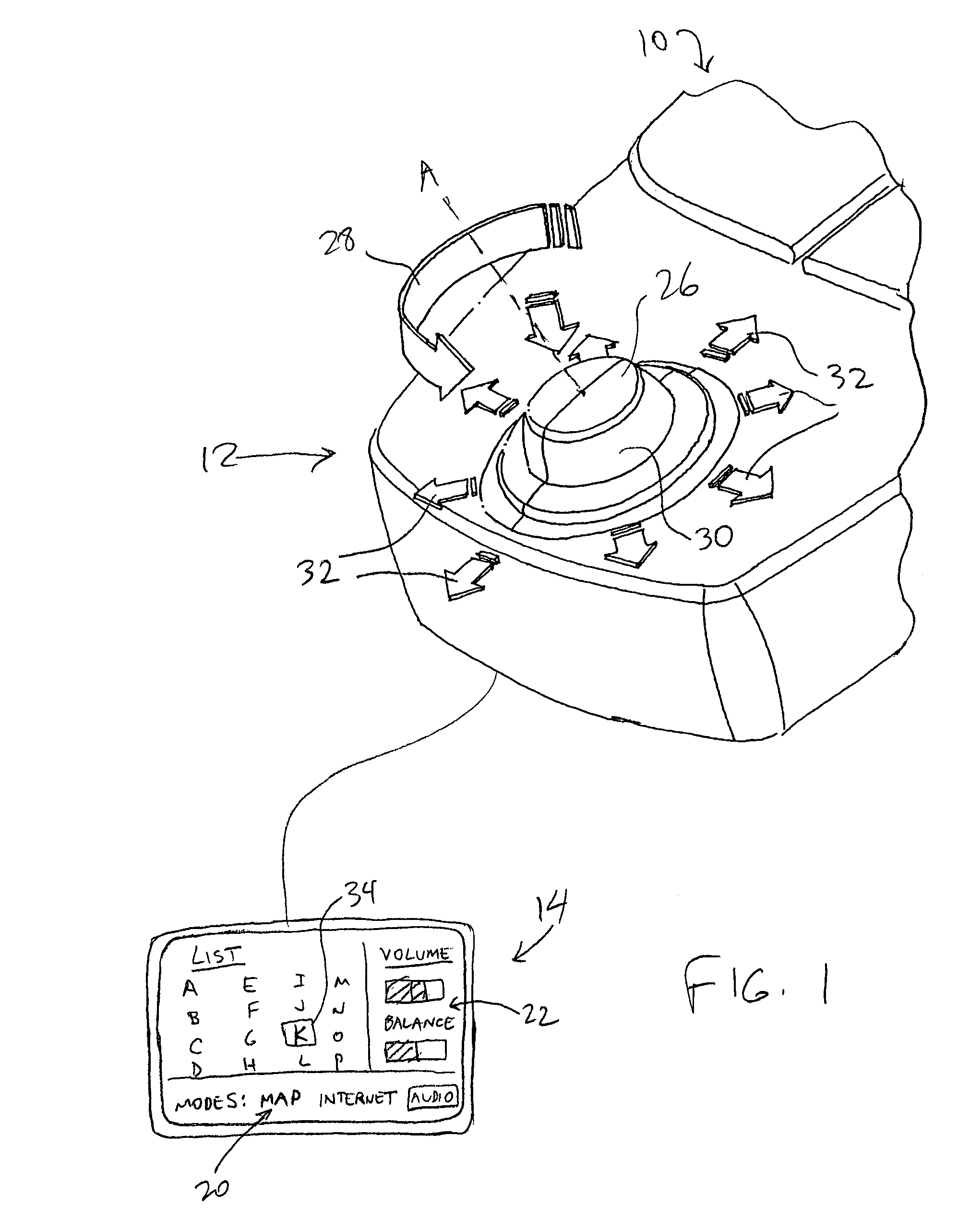
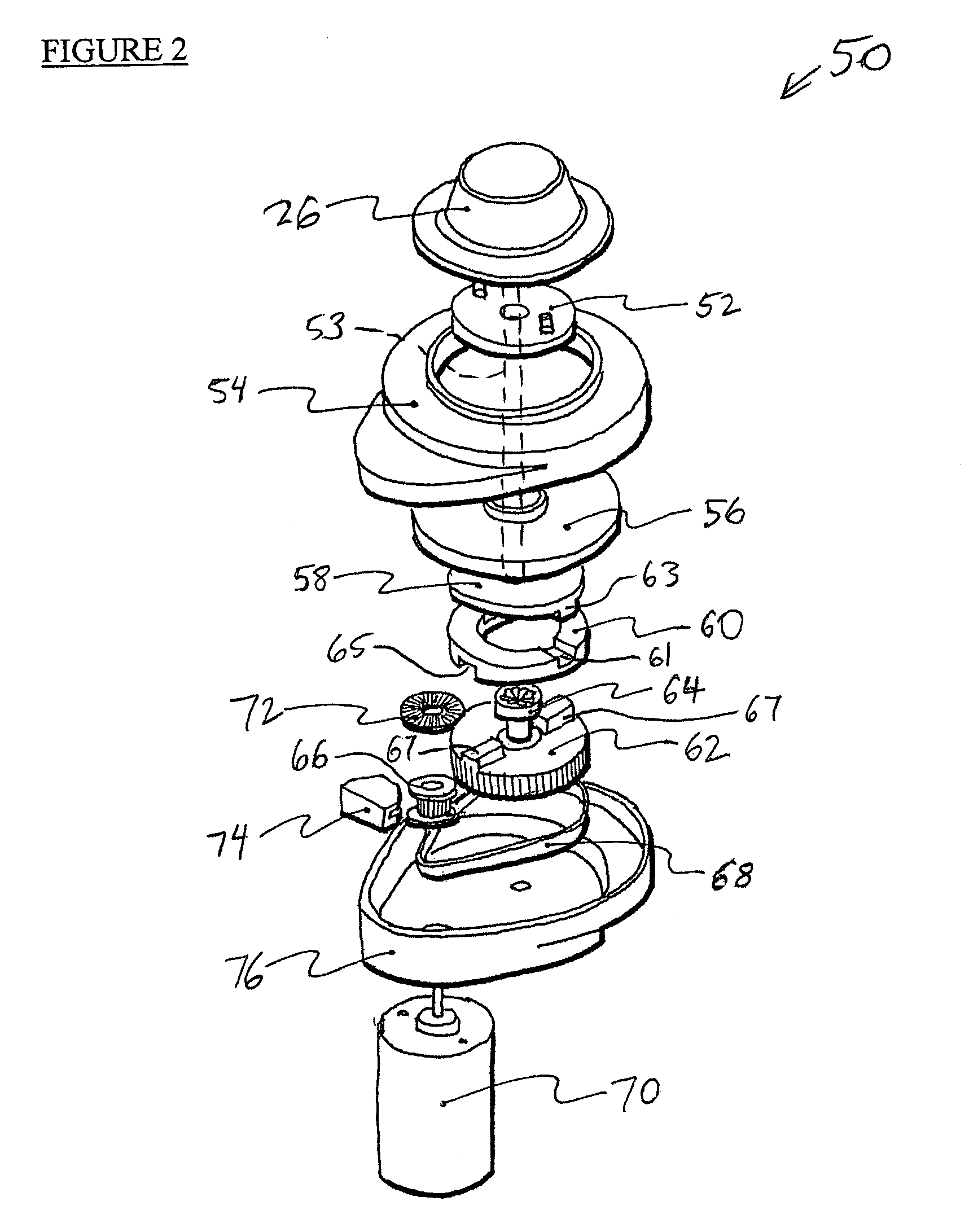
Mechanisms for control knobs and other interface devices
InactiveUS7038667B1Strong control functionGreat easeCathode-ray tube indicatorsElectrical haptic/tactile feedbackRotational axisLinear motion
Mechanisms for a control knob or other interface device providing additional degrees of freedom for the knob. One embodiment provides a rotatable knob moveable also in a lateral plane approximately perpendicular to the axis of rotation. A mechanism providing the lateral motion can include a gate member and a plunger member that engages grooves in the gate member. A rotational sensor detects a rotational position and a lateral sensor can detect a lateral position of the knob. Another embodiment provides an actuator that includes a shaft that is coaxial with the axis of rotation and which can be moved linearly along the axis of rotation with respect to actuator housing to accommodate linear motion of the knob. In another embodiment, a gear assembly including two interlocked gears is provided to transmit rotational motion from the knob to the sensor, and the interlocked gears translate with respect to each other when the knob is translated along the rotational axis.
Owner:IMMERSION CORPORATION
Activity recognition apparatus, method and program
ActiveUS7421369B2Flexibility of implementationAvoid less flexibilityVehicle testingTesting/calibration apparatusLinear motionComputer science
There is provided an activity recognition apparatus for detecting an activity of a subject. The apparatus includes: a sensor unit including a plurality of linear motion sensors configured to detect linear motions and a plurality of rotational motion sensors, the linear motions being orthogonal to each other, the rotational motions being orthogonal to each other; and a computational unit configured to receive and process signals from the sensors included in the sensor unit so as to detect an activity of the subject. The sensor unit is directly or indirectly supported by the subject with an arbitrary orientation with respect to the subject. The computational unit performs a calculation that uses the signals from both linear motion sensors and rotational motion sensors to determine the activity of the subject independent of the orientation of the sensor unit.
Owner:SONY CORP
Cam-follower release mechanism for fiber optic modules with side delatching mechanisms
InactiveUS6851867B2Limit to rotation angleCouplings bases/casesCoupling light guidesFiberLinear motion
A cam-follower release mechanism for fiber optic modules with side releases. The cam-follower release mechanism translates rotational motion into linear motion. The release mechanism has a rotatable bail lever with a cam lobe that pivots about a pivot point and presses against a bearing surface of the fiber optic module. The release mechanism further has a base with a pin about with the rotatable bail lever may pivot and a sliding fork with sliding side actuators and delatch actuators at each end. As a follower, the base and sliding fork is linearly pulled as the rotatable bail lever is rotated. As the sliding fork is pulled out, the delatch actuators at each end push in on side tabs of a cage into which the fiber optic module may be inserted. The release mechanism further has a spring to apply a force against the rotation of the rotatable bail lever to return it to home and retain the release mechanism moveable coupled to the fiber optic module. The fiber optic module further includes opto-electronic devices mounted to a printed circuit board, and a housing.
Owner:LUMENTUM OPERATIONS LLC
Robotic surgical system
InactiveUS20090228019A1Quicker procedureDiagnosticsSurgical instrument detailsSurgical operationEngineering
It is an object of the present invention to provide an automated, a semi-automated, a surgeon-guided quasi-automated and / or a fully surgeon's controlled surgical system surgical system useful for performing a fully automated medical procedure within a body cavity such that faultless and quick medical procedure is obtained. Each of the surgical systems comprises: (a) at least one effecter for performing the medical procedure; (b) at least one maneuverable platform reversibly coupled with the effecter; the platform provides the effecter with a scheduled set of independent displacements selected from a group consisting of up to six (degrees of freedom) DOFs, namely linear movement along the X,Y,Z-coordinates, and radial movement around the X,Y,Z coordinates, such that the time-resolved spatial position of the effecter is defined by the up to six coordinates (three-dimensional spatial position, 3DSP); and (c) sensing and processing means.
Owner:GROSS YOSEF +4
Microelectromechanical integrated sensor structure with rotary driving motion
ActiveUS20070214883A1Easy to manufactureSolve the low detection efficiencyAcceleration measurement using interia forcesSpeed measurement using gyroscopic effectsLinear motionEngineering
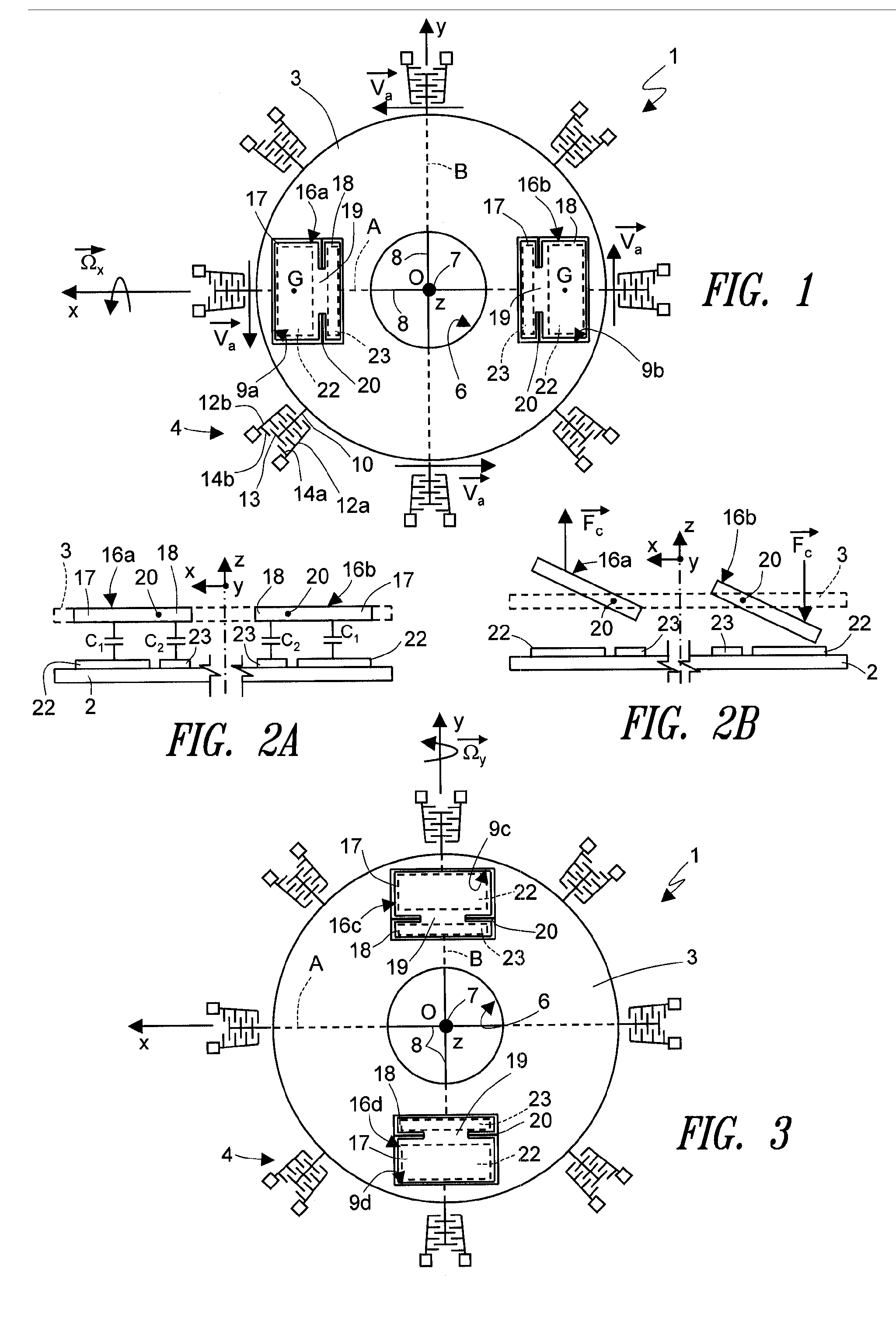
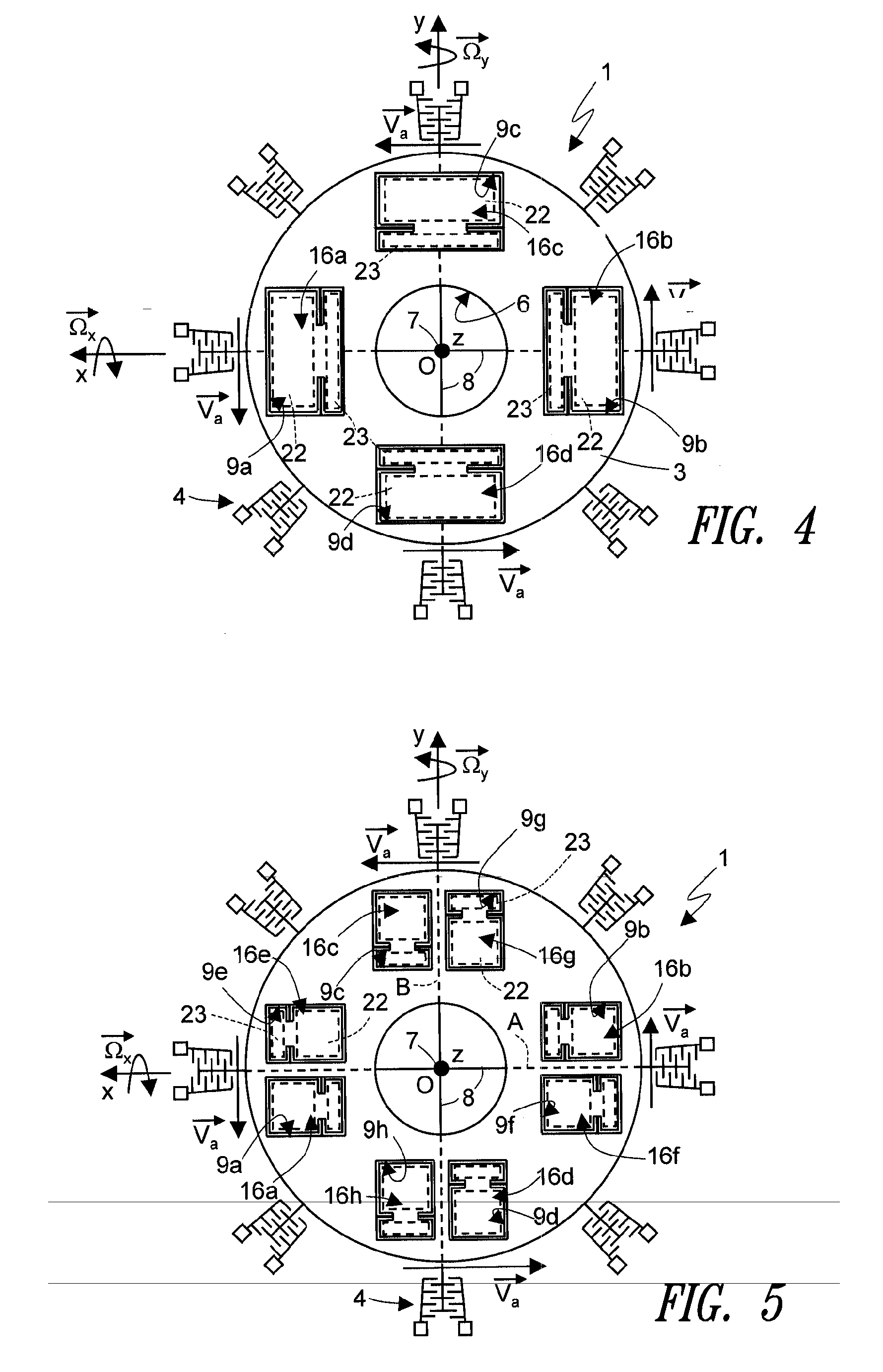
A driving mass of an integrated microelectromechanical structure is moved with a rotary motion about an axis of rotation, and a first sensing mass is connected to the driving mass via elastic supporting elements so as to perform a first detection movement in a presence of a first external stress. The driving mass is anchored to an anchorage arranged along the axis of rotation by elastic anchorage elements. An opening is provided within the driving mass and the first sensing mass is arranged within the opening. The elastic supporting and anchorage elements render the first sensing mass fixed to the driving mass in the rotary motion, and substantially decoupled from the driving mass in the first detection movement. A second sensing mass is connected to the driving mass so as to perform a second detection movement in a presence of a second external stress. A first movement is a rotation about an axis lying in a plane, and a second movement is a linear movement along an axis of the plane.
Owner:STMICROELECTRONICS SRL
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com