Patents
Literature
1212 results about "Stepper" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
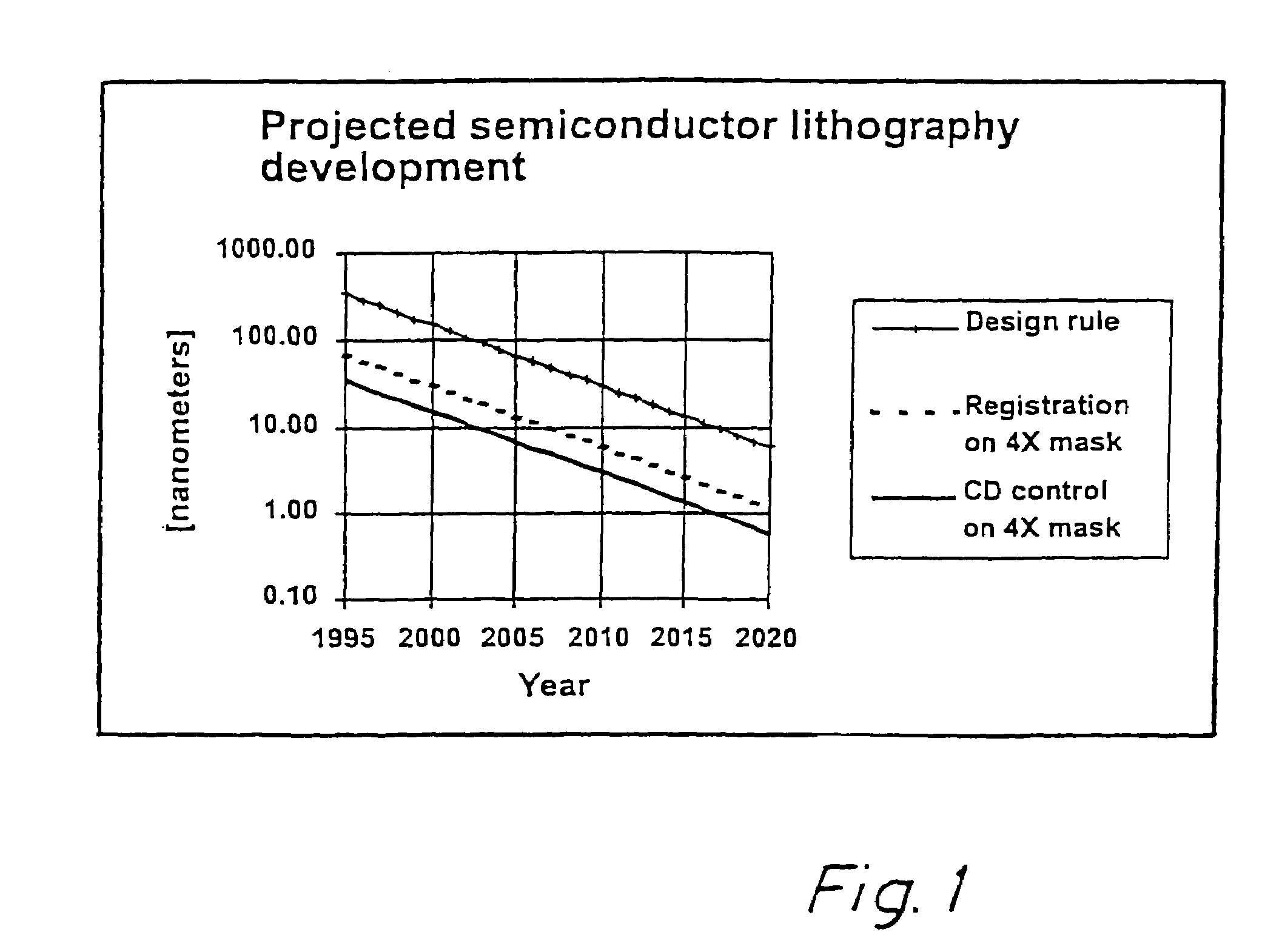
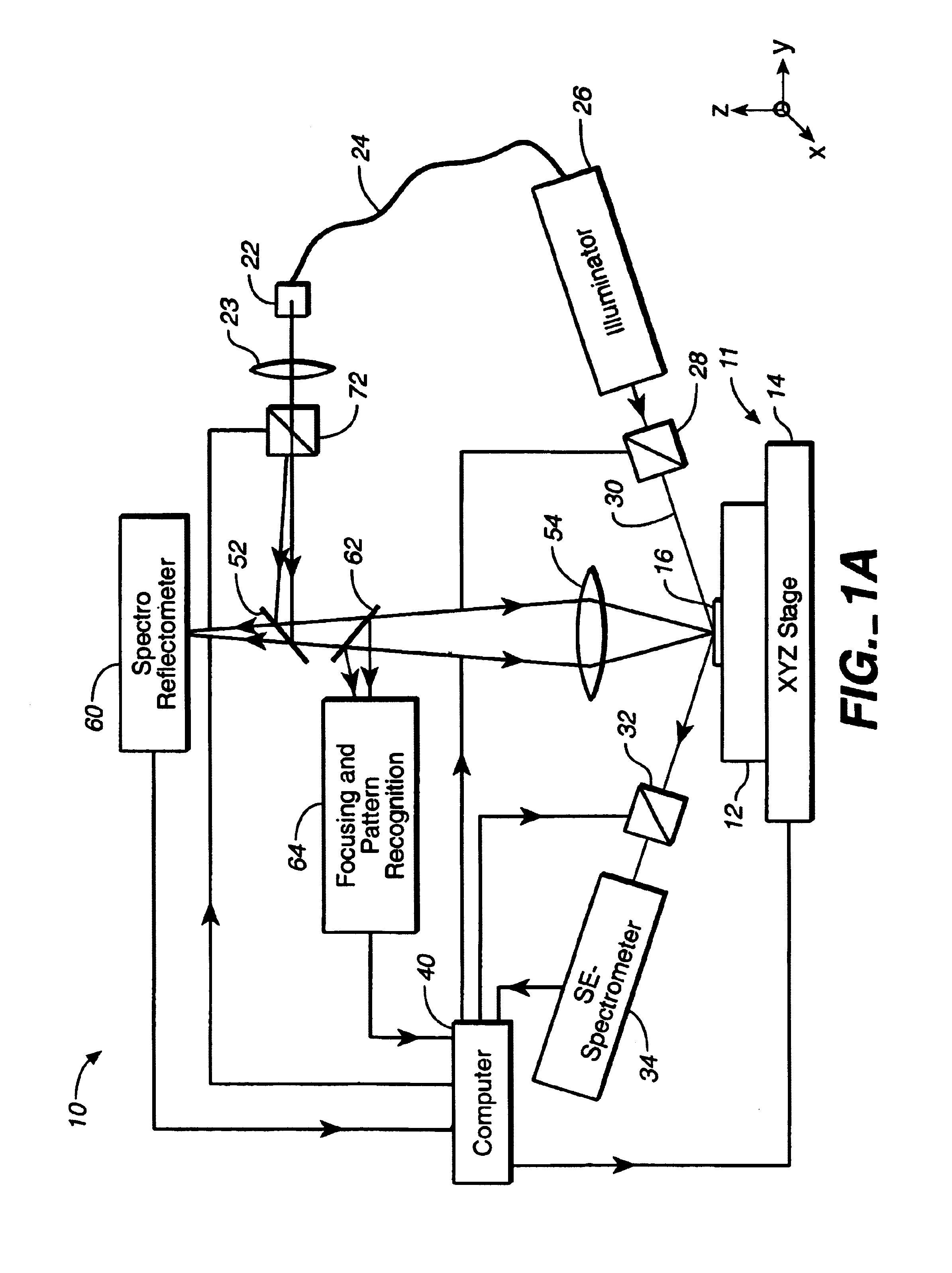
A stepper is a device used in the manufacture of integrated circuits (ICs) that is similar in operation to a slide projector or a photographic enlarger. The term "stepper" is short for step-and-repeat camera. Steppers are an essential part of the complex process, called photolithography, that creates millions of microscopic circuit elements on the surface of tiny chips of silicon. These chips form the heart of ICs such as computer processors, memory chips, and many other devices.
Portable apparatus for peritoneal dialysis therapy
A portable peritoneal dialysis apparatus having (1) a hinged door for enclosing a disposable cassette that seals tightly shut using air pressure; (2) accurate pressure sensing of pressures applied to the patient through an enclosure in the disposable cassette; (3) two pumps that can operate separately or in tandem actuated by two separate stepper motors; and (4) a touch screen user interface where indicia of the operating mode is always visible along with indicia for the other possible operating modes and the mode can be changed by touching one of these indicia.
Owner:FRESENIUS MEDICAL CARE HLDG INC
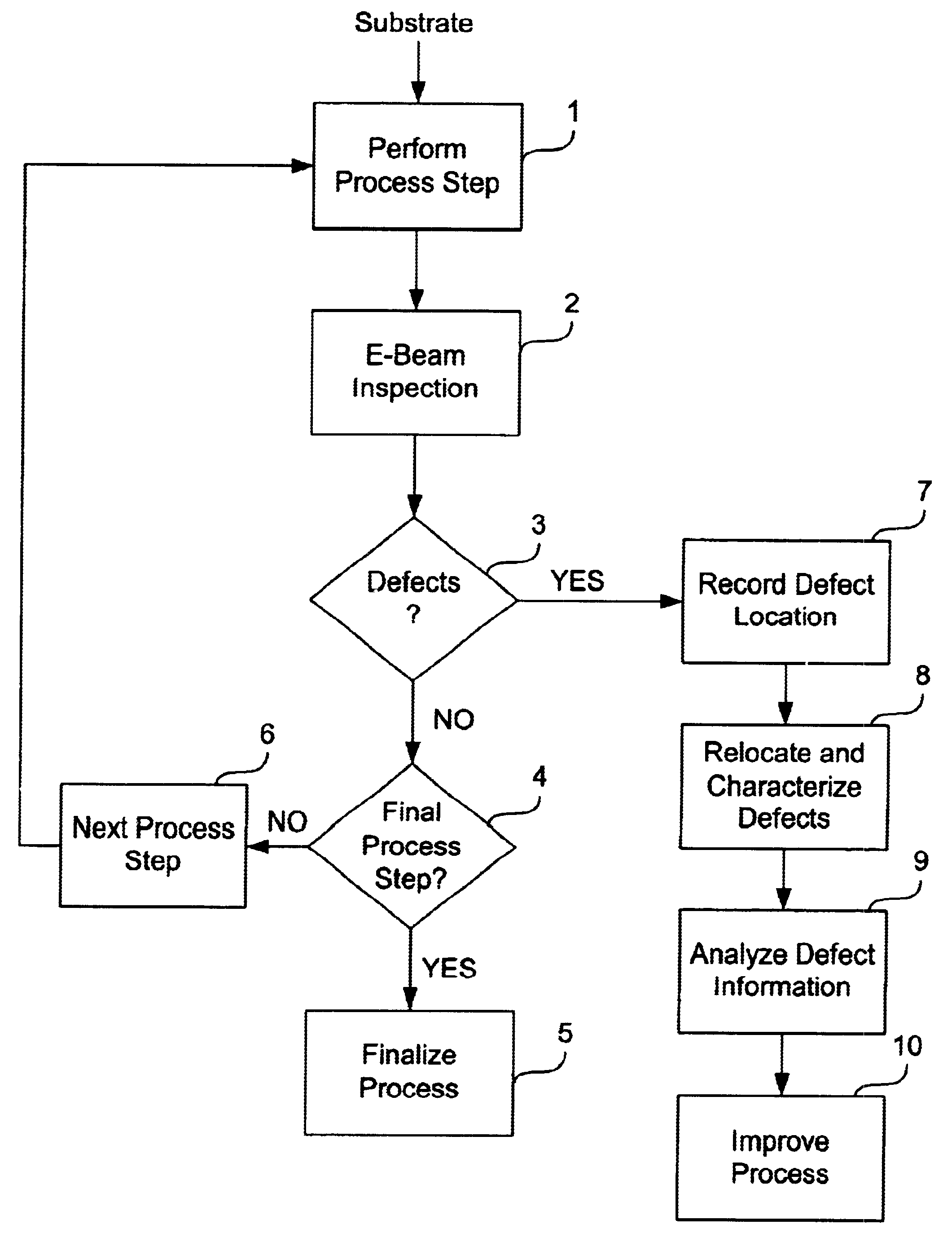
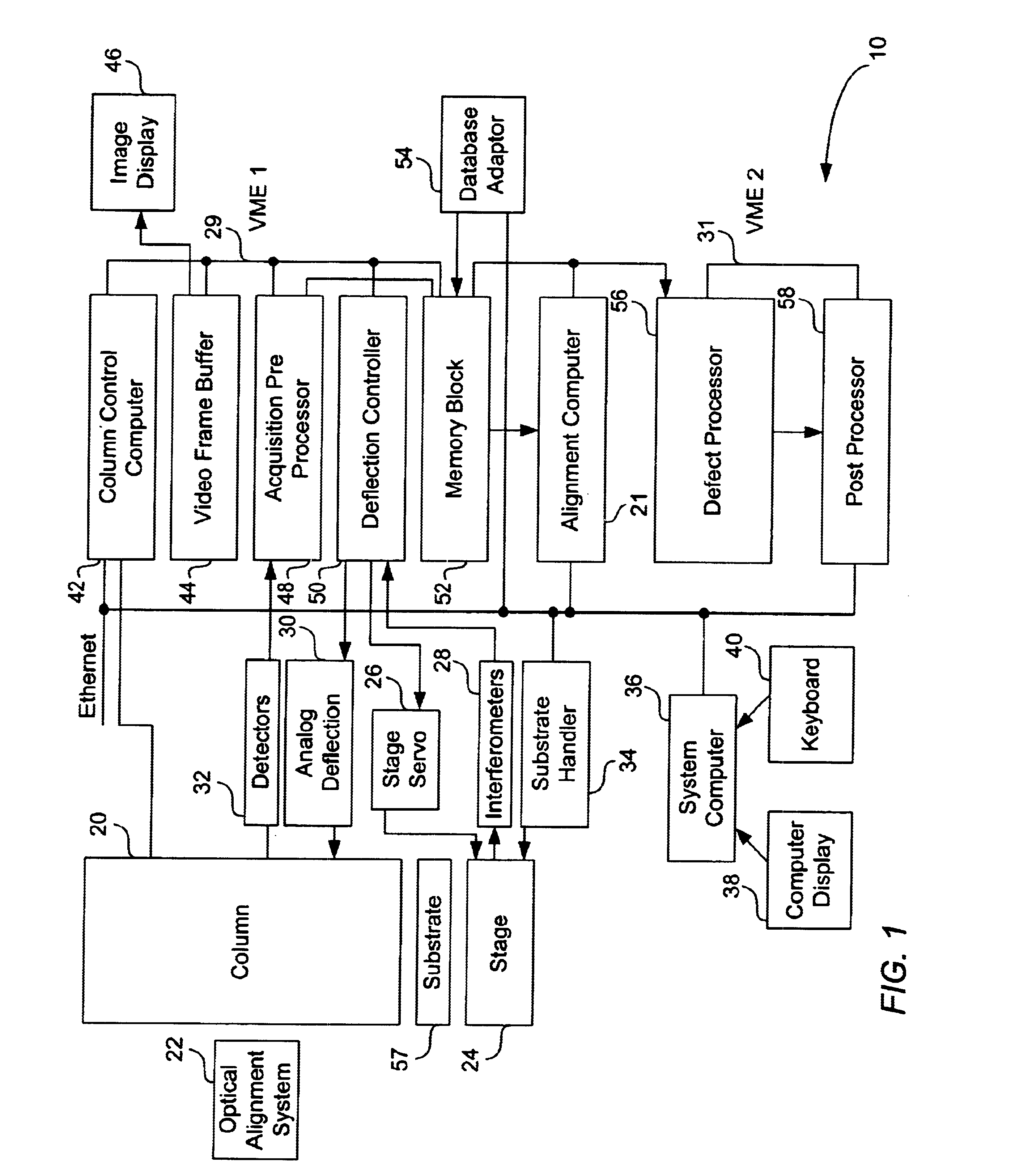
Stepper type test structures and methods for inspection of semiconductor integrated circuits
InactiveUS6633174B1Reduce pressureNanotechSemiconductor/solid-state device testing/measurementEngineeringSemiconductor
Disclosed is a method of inspecting a sample. The method includes moving to a first field associated with a first group of test structures. The first group of test structures are partially within the first field. The method further includes scanning the first field to determine whether there are any defects present within the first group of test structures. When it is determined that there are defects within the first group of test structures, the method further includes repeatedly stepping to areas and scanning such areas so as to determine a specific defect location within the first group of test structures. A suitable test structure for performing this method is also disclosed.< / PTEXT>
Owner:KLA TENCOR TECH CORP
3D printer and printhead unit with multiple filaments
InactiveUS8827684B1Reduce complexityIncrease speedConfectionerySweetmeatsFused filament fabricationMetal filament
A fused filament fabrication printer has a fixed extrusion module having multiple printheads having print tips. The fixed arrangement of the printing heads allows the close spacing of multiple print tips in a printhead unit, and the simple routing of multiple plastic or metal filaments to the individual printing heads. The closely spaced print tips in the printhead unit share common components. An exemplary printhead unit has four printing heads which share a common heating block and heating block temperature sensor. The heating block incorporates a group of four print tips evenly spaced along a line. Each printing head has a separate filament which is controlled and driven by its own stepper motor through the heating block to one of the print tips. Printing of a part is by control of individual stepper motors which drive filaments through the heating block and through one of the printing tips.
Owner:RADIANT FABTION
Apparatus and method for resonant-vibratory mixing
ActiveUS7188993B1Reduce the overall heightImprove bearing lifeShaking/oscillating/vibrating mixersTransportation and packagingLinear motionElectronic controller
An apparatus and method for mixing fluids and / or solids in a manner that can be varied from maintaining the integrity of fragile molecular and biological materials in the mixing vessel to homogenizing heavy aggregate material by supplying large amounts of energy. Variation in the manner of mixing is accomplished using an electronic controller to generate signals to control the frequency and amplitude of the motor(s), which drive an unbalanced shaft assembly to produce a linear vibratory motion. The motor may be a stepper motors a linear motor or a DC continuous motor. By placing a sensor on the mixing vessel platform to provide feedback control of the mixing motor, the characteristics of agitation in the fluid or solid can be adjusted to optimize the degree of mixing and produce a high quality mixant.
Owner:RESODYN ACOUSTIC MIXERS
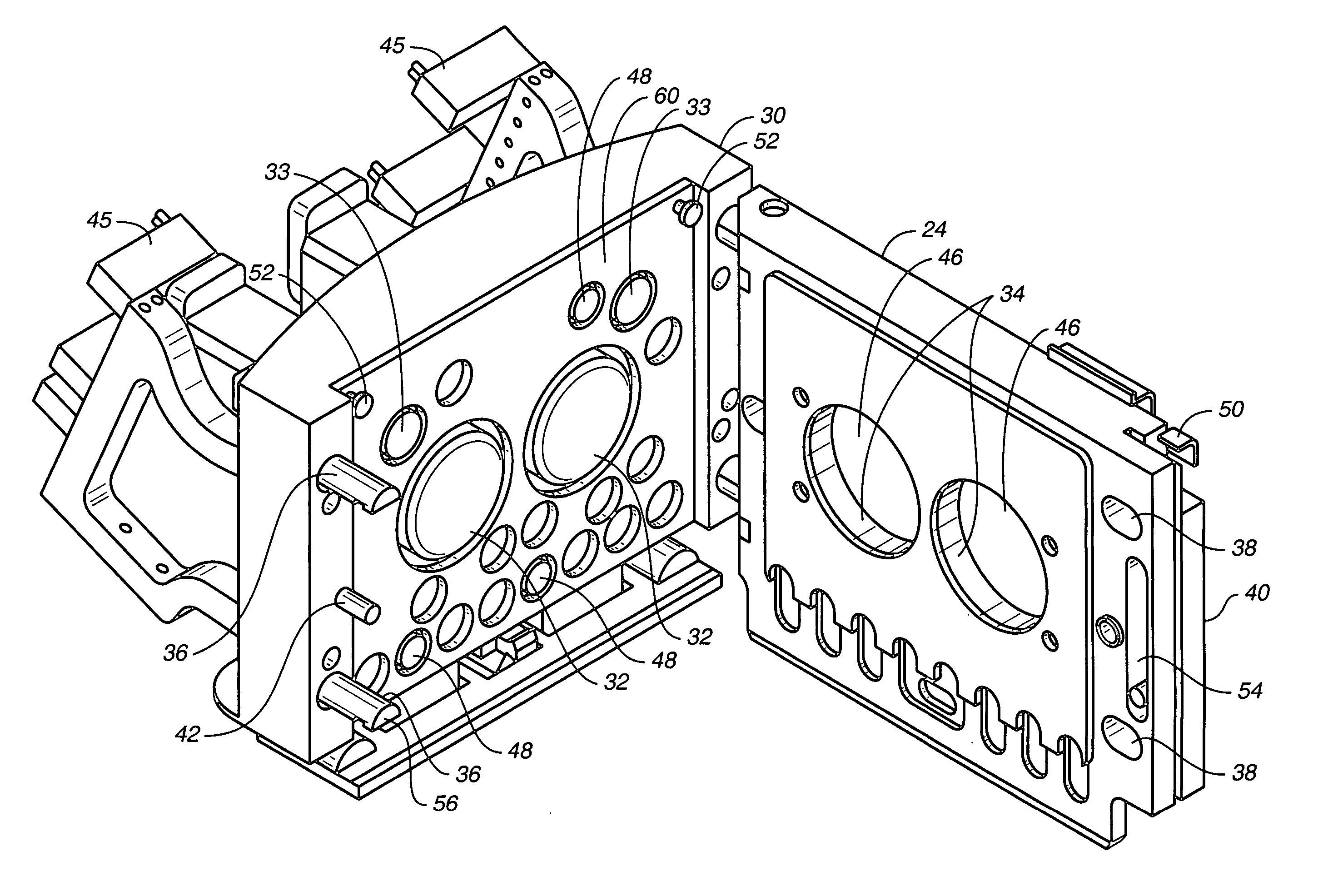
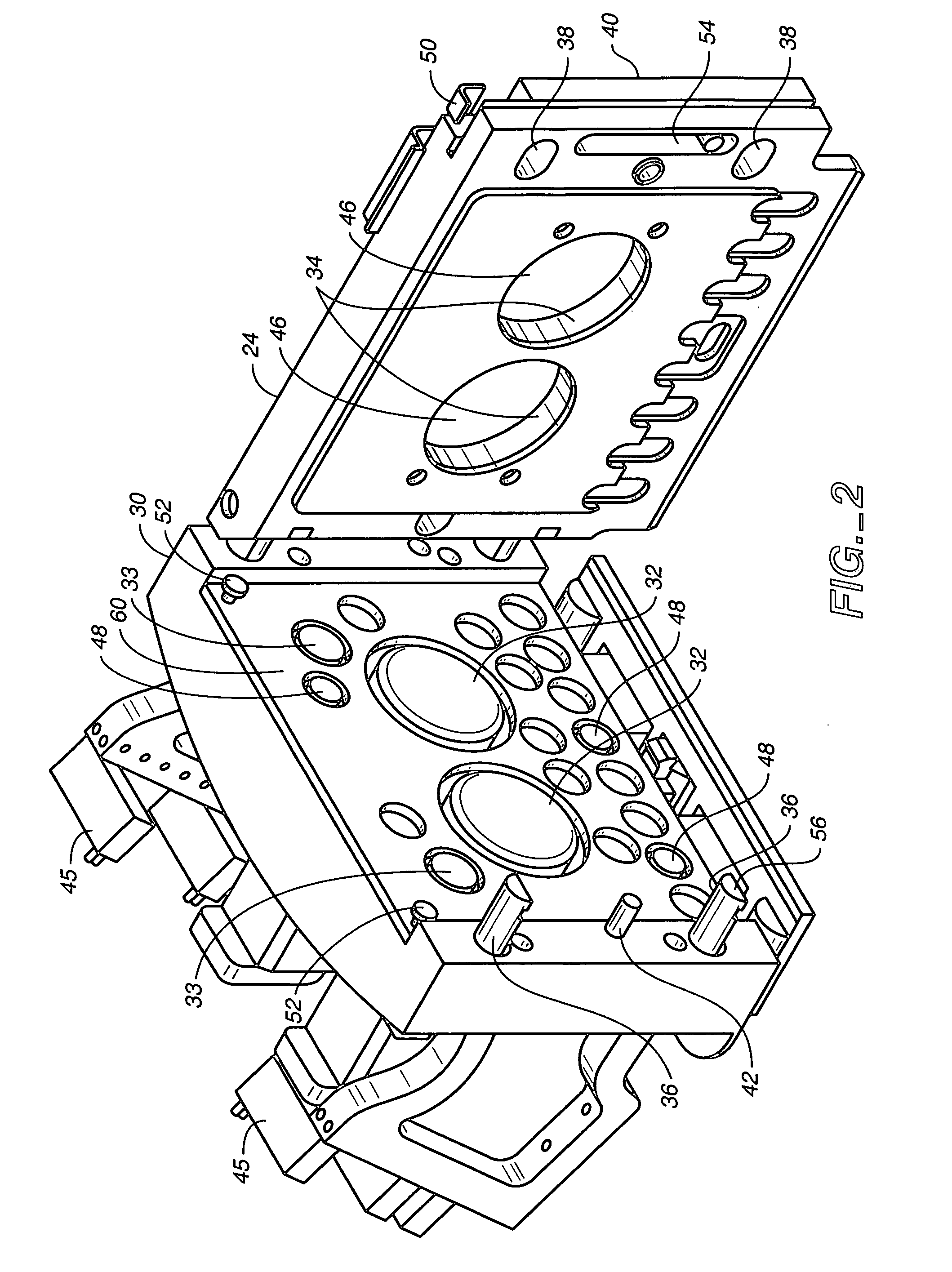
Positioning device having dynamically isolated frame, and lithographic device provided with such a positioning device
InactiveUS6989647B1Small distortionSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingPhotomechanical exposure apparatusDrive motorEngineering
A guided stage mechanism suitable for supporting a reticle in a photolithography machine includes a stage movable in the X-Y directions on a base. Laterally surrounding the stage is a rectangular window frame guide which is driven in the X-axis direction on two fixed guides by means of motor coils on the window frame guide cooperating with magnetic tracks fixed on the base. The stage is driven inside the window frame guide in the Y-axis direction by motor coils located on the stage cooperating with magnetic tracks located on the window frame guide. Forces from the drive motors of both the window frame guide and the stage are transmitted through the center of gravity of the stage, thereby eliminating unwanted moments of inertia. Additionally, reaction forces caused by the drive motors are isolated from the projection lens and the alignment portions of the photolithography machine. This isolation is accomplished by providing a mechanical support for the stage independent of the support for its window frame guide. The window frame guide is a hinged structure capable of a slight yawing (rotational) motion due to hinged flexures which connect the window frame guide members.
Owner:NIKON CORP
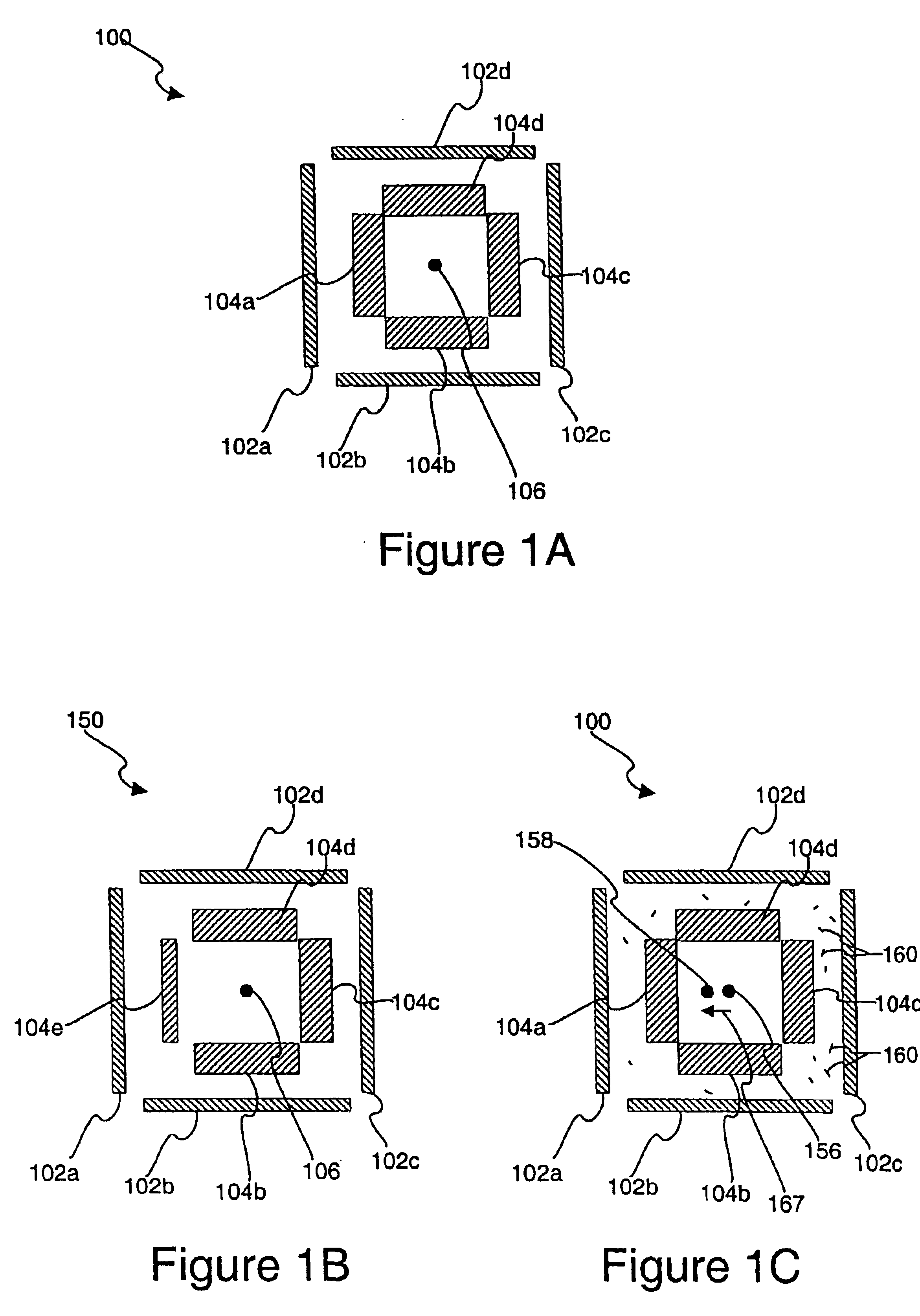
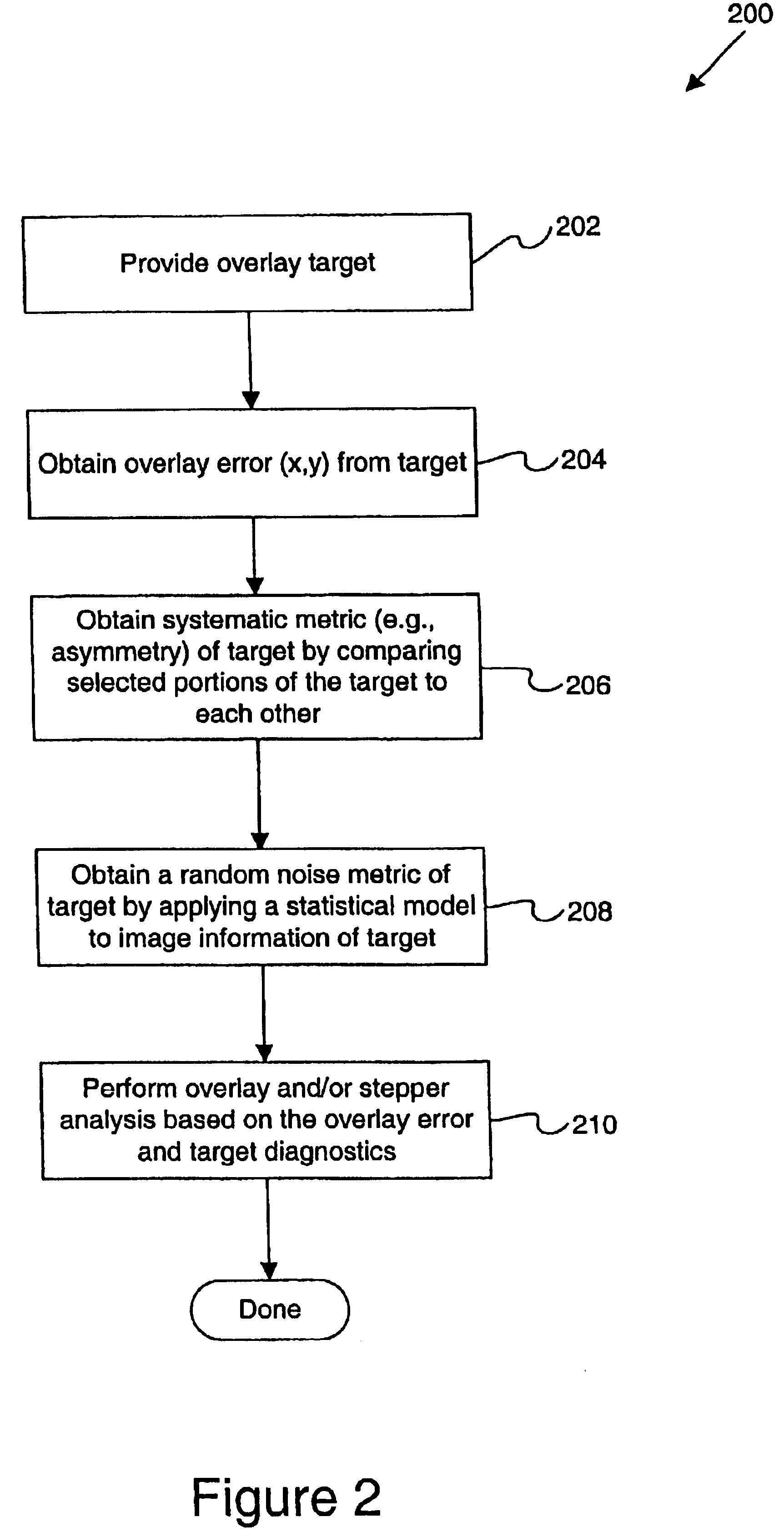
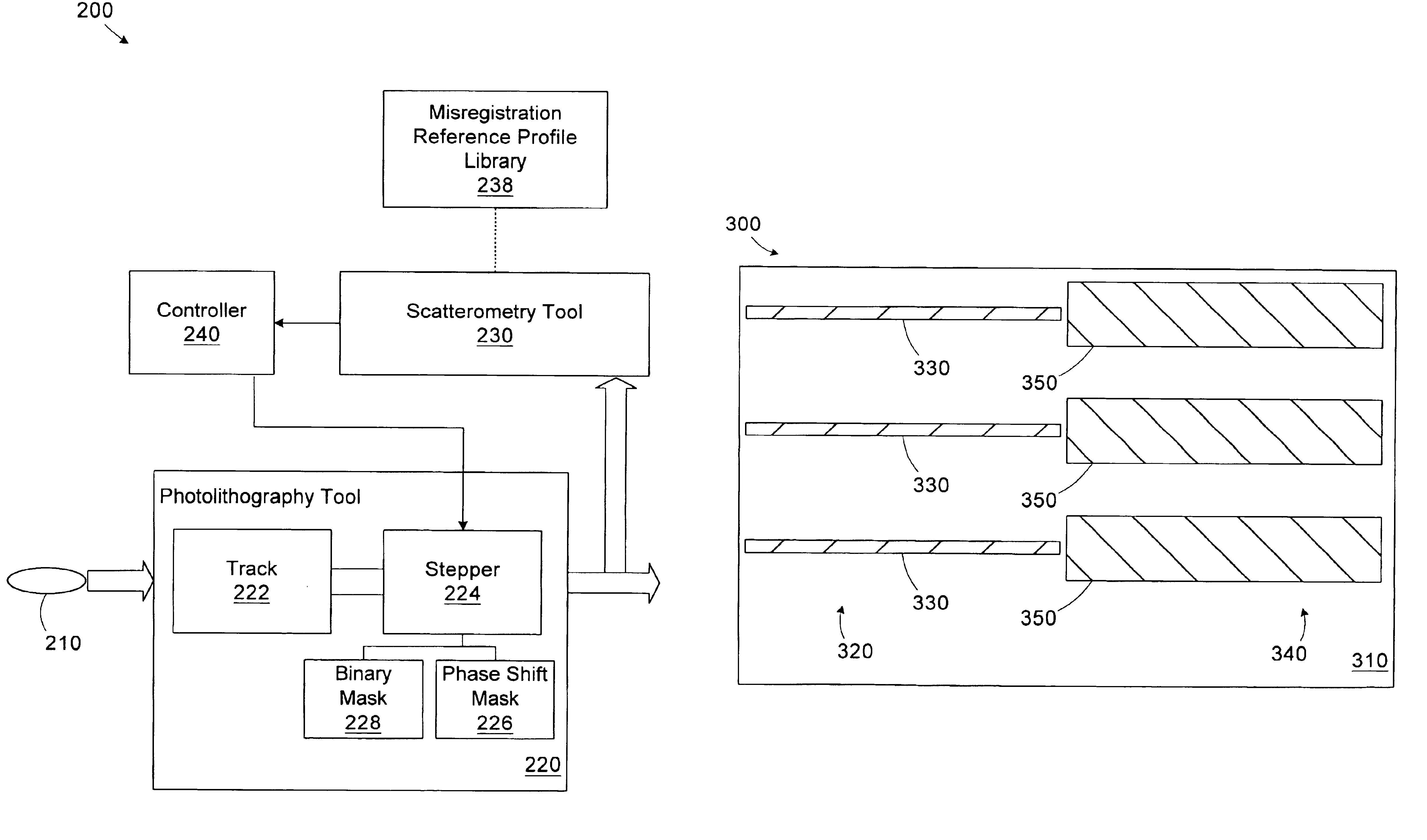
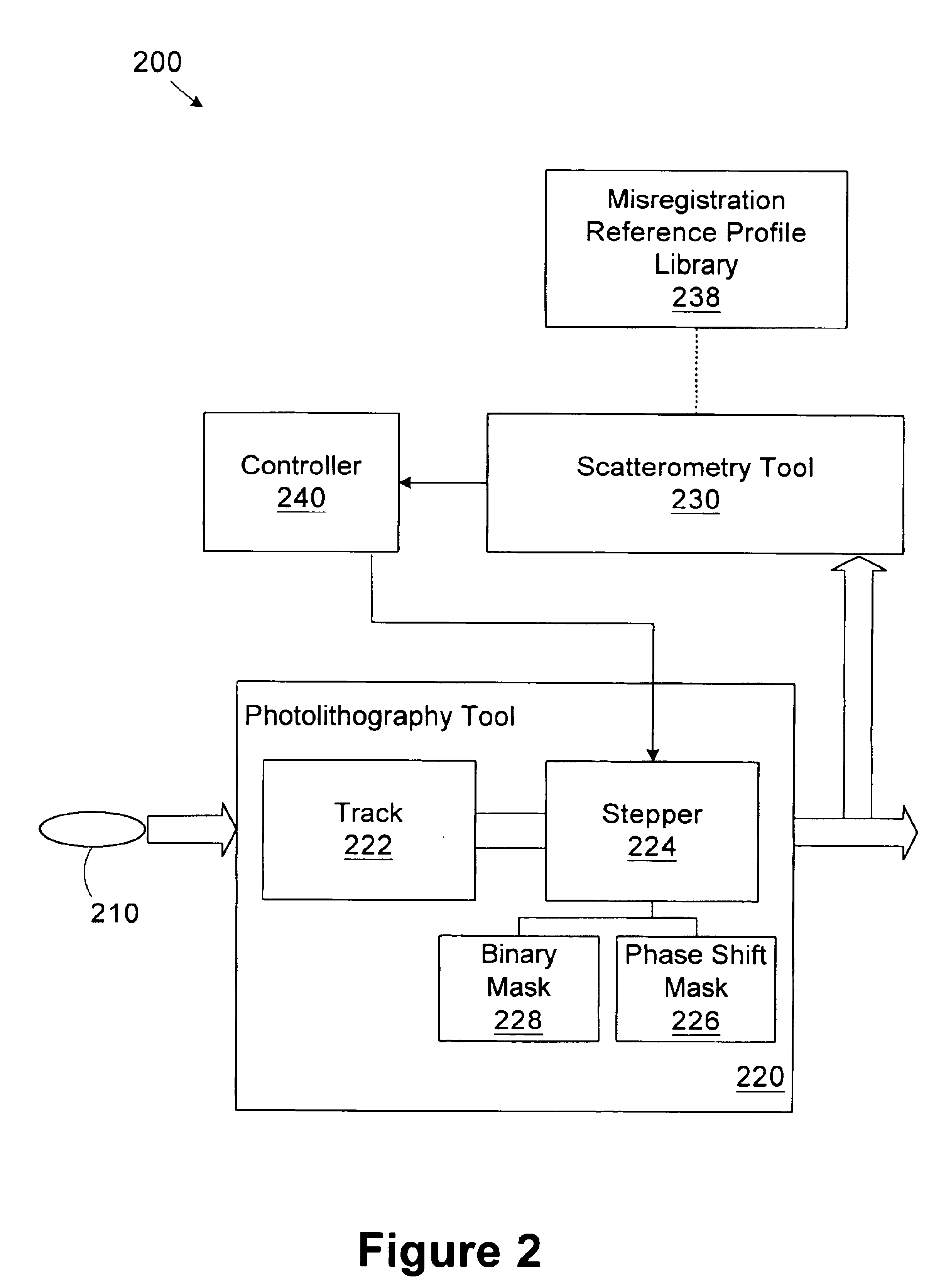
Use of overlay diagnostics for enhanced automatic process control
ActiveUS6928628B2Easy to operateSemiconductor/solid-state device testing/measurementSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingAutomatic controlInternet privacy
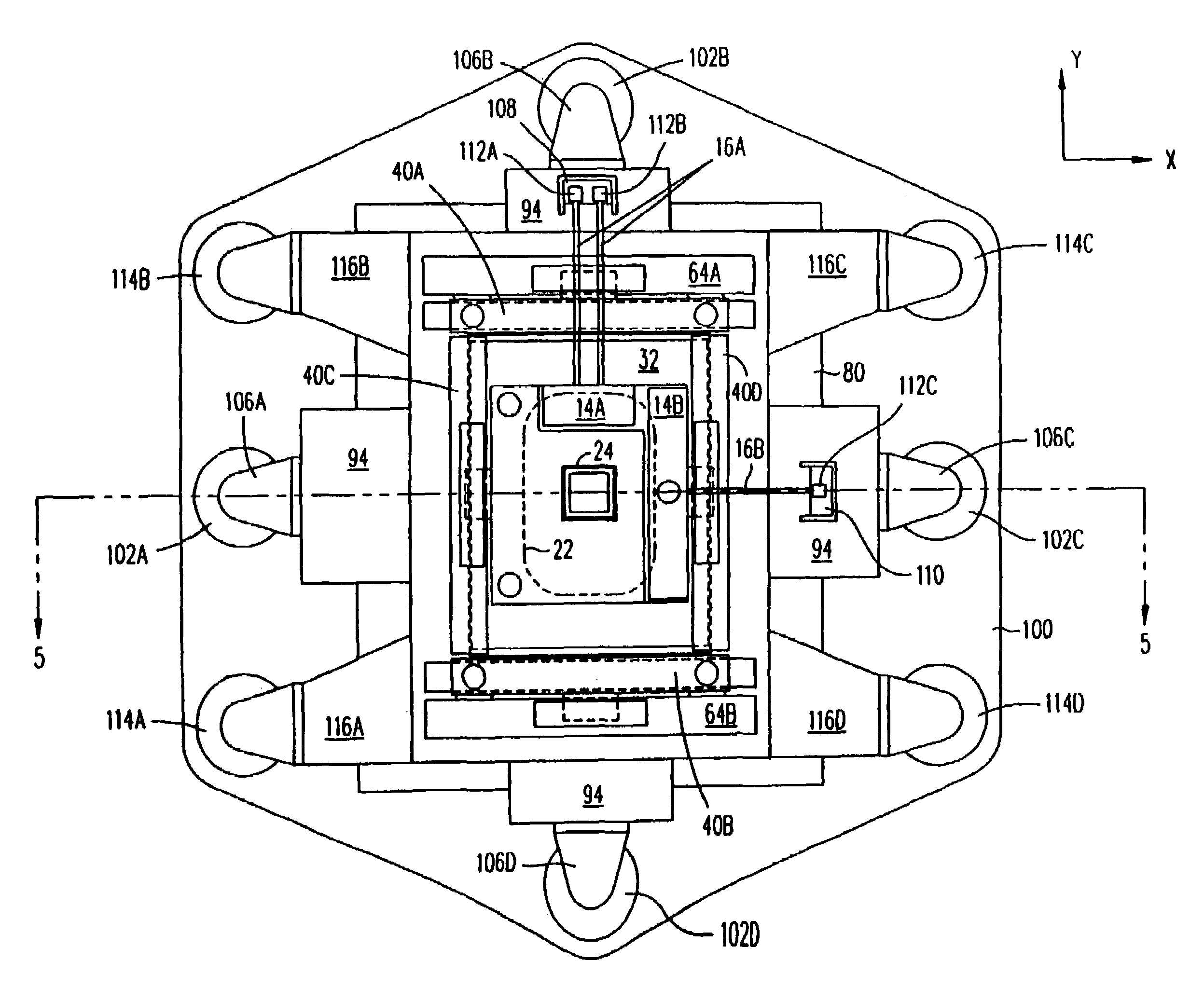
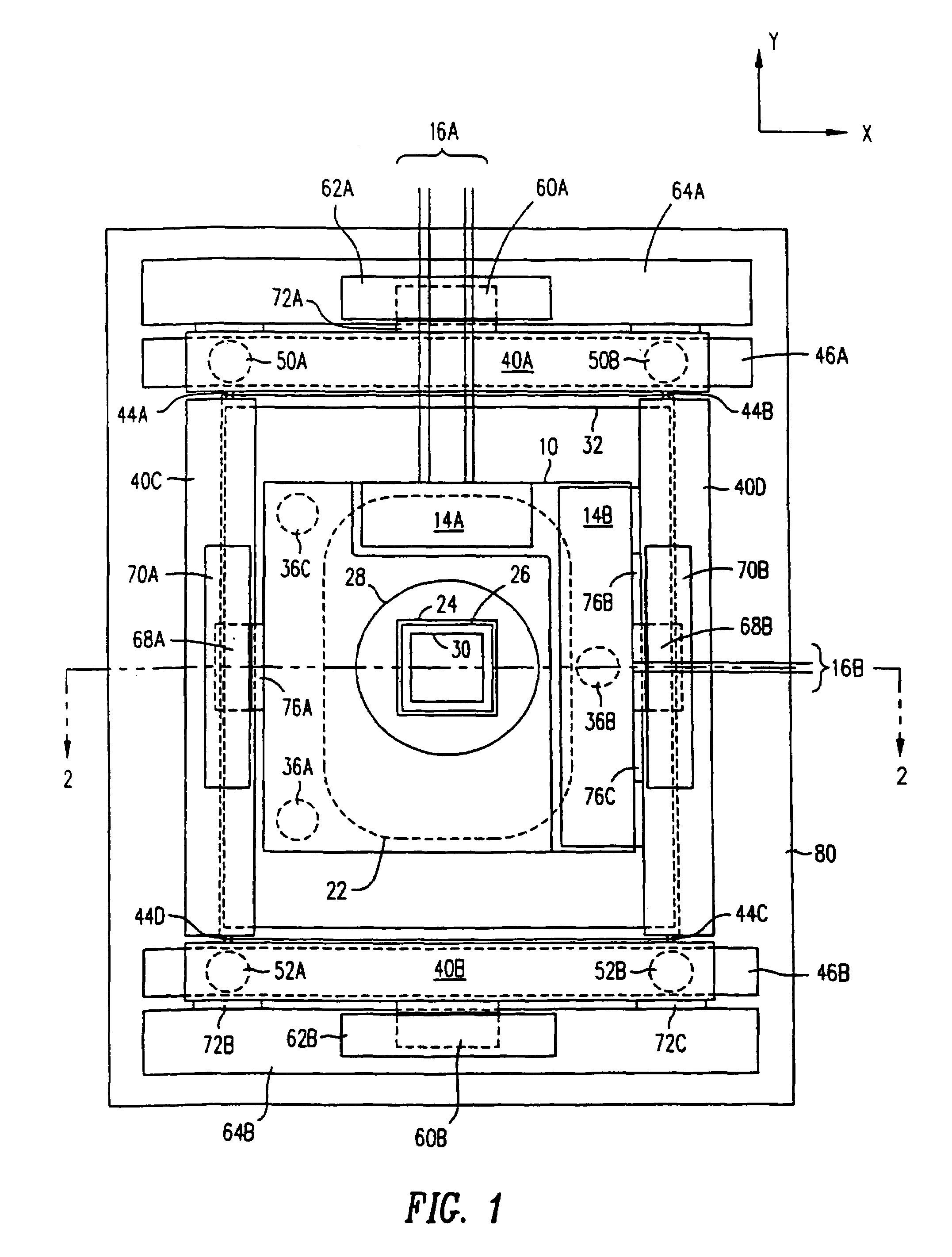
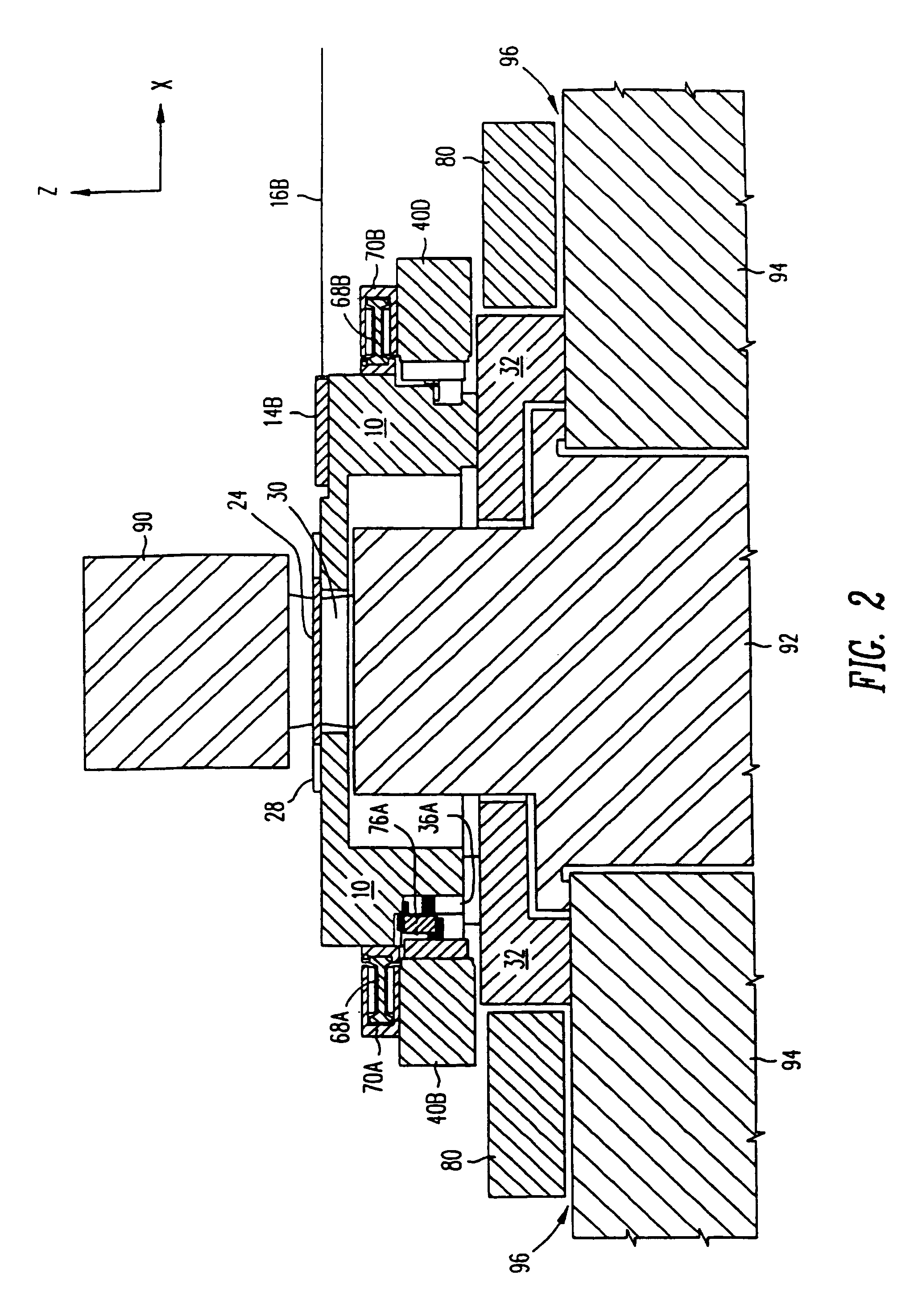
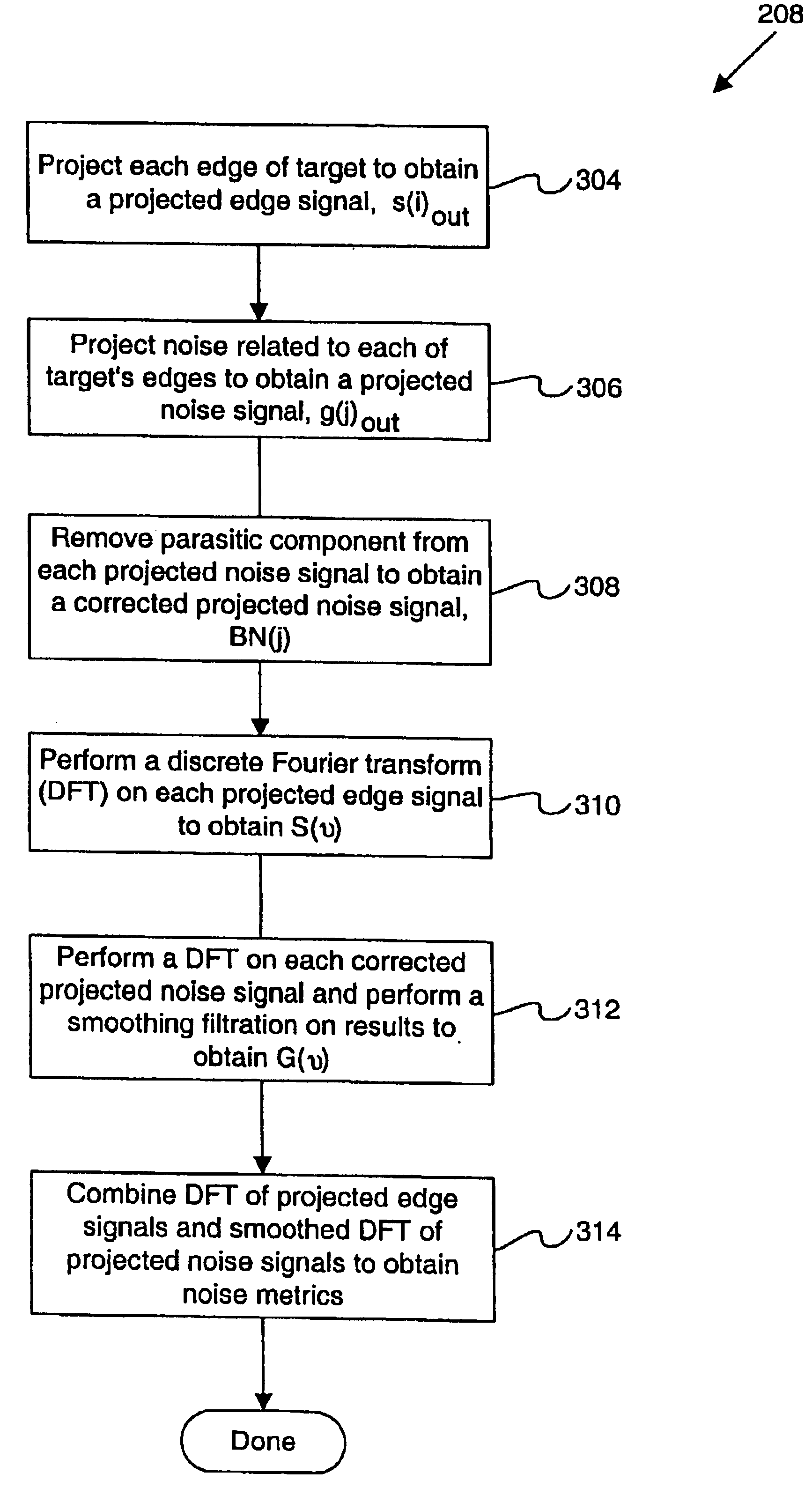
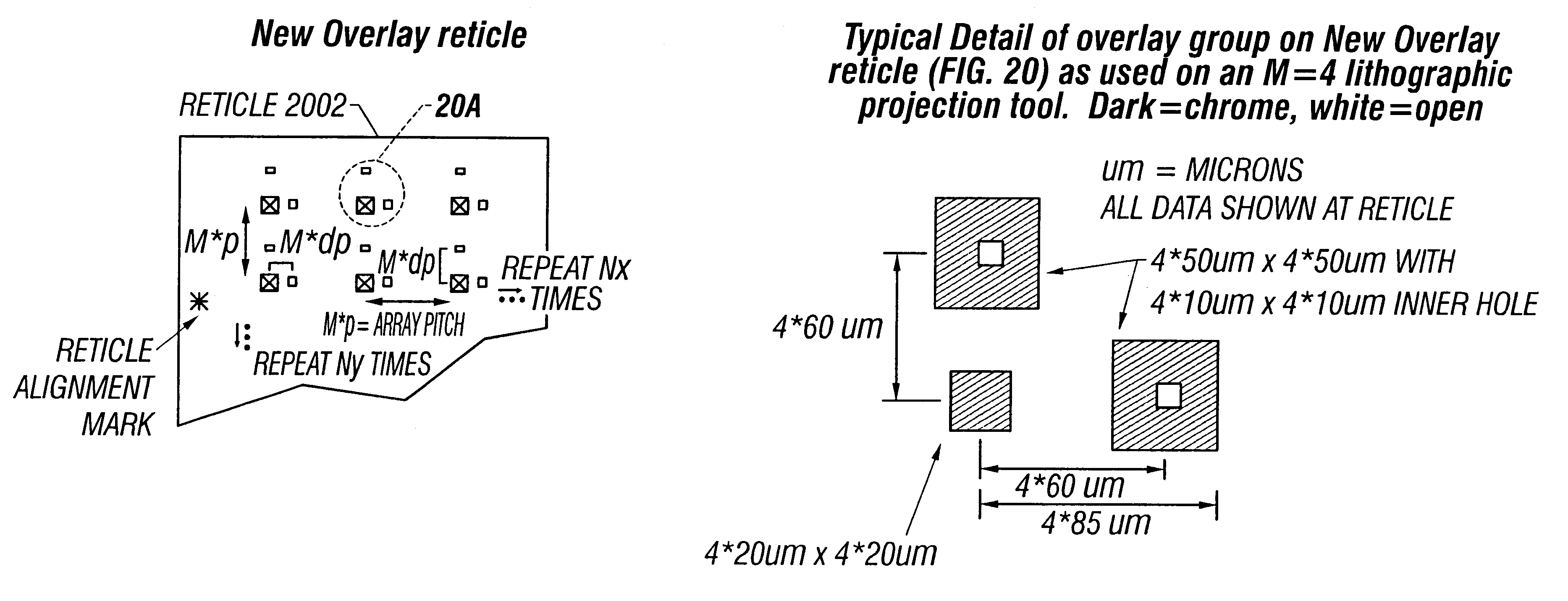
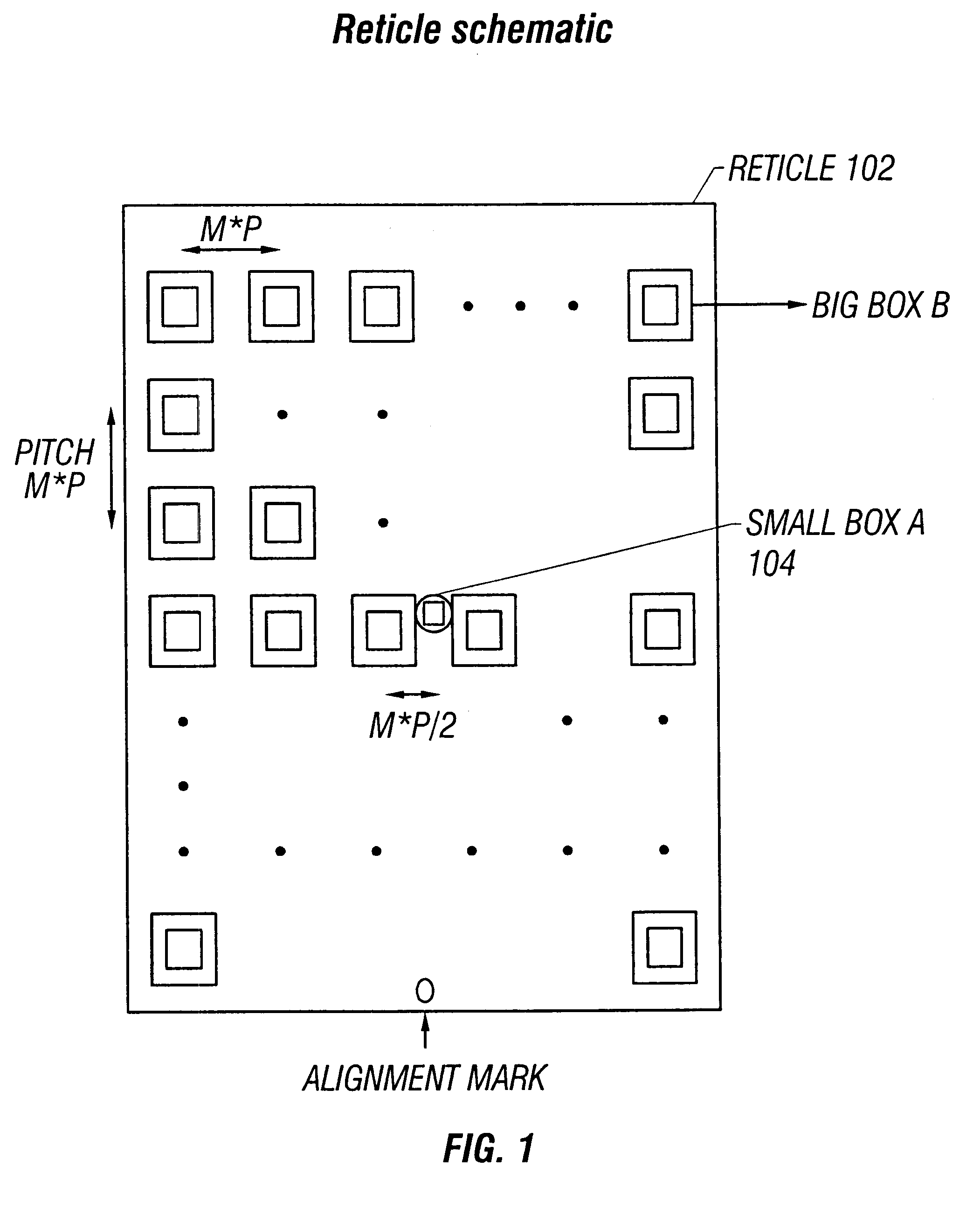
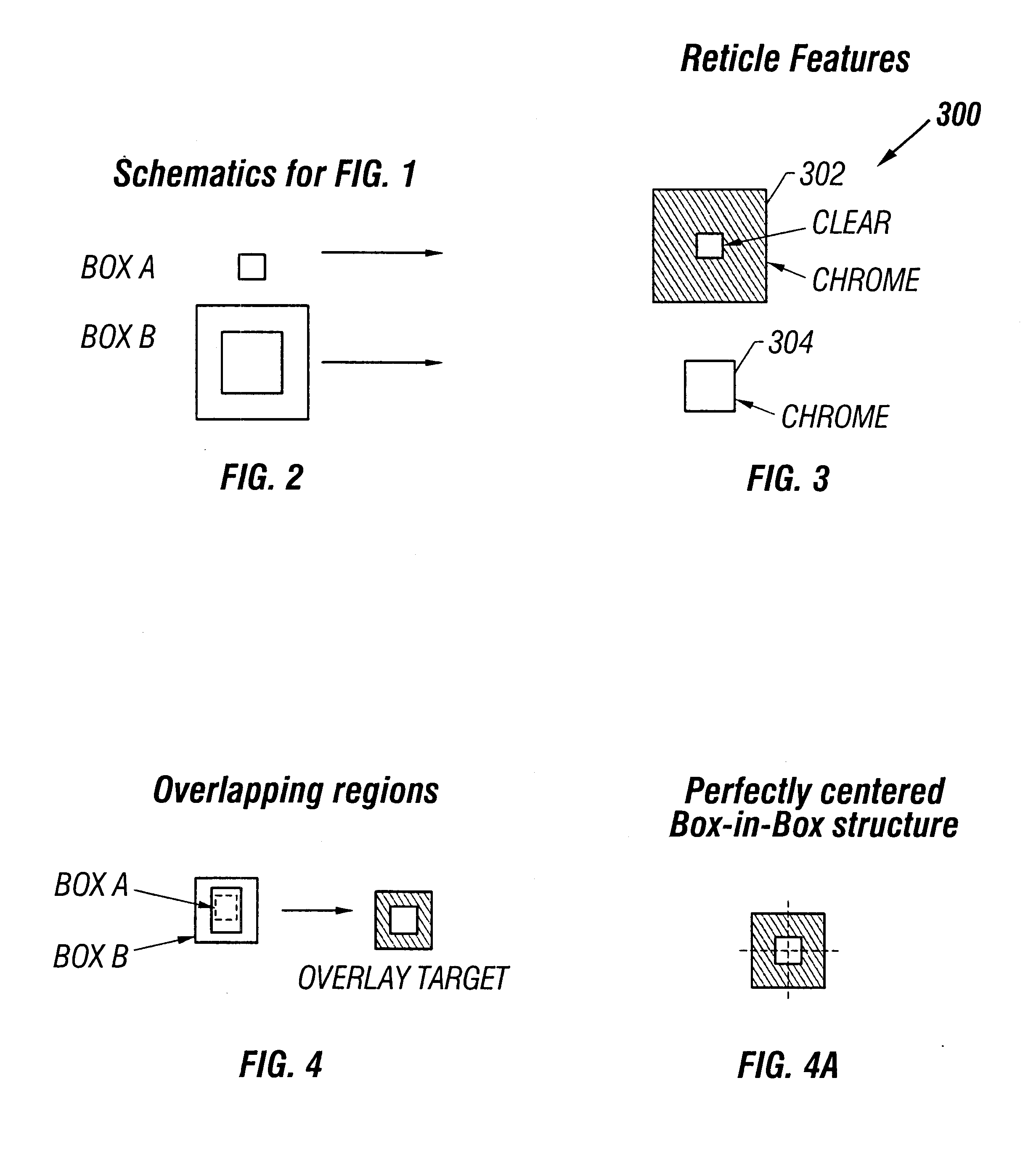
Disclosed are methods and apparatus for analyzing the quality of overlay targets. In one embodiment, a method of extracting data from an overlay target is disclosed. Initially, image information or one or more intensity signals of the overlay target are provided. An overlay error is obtained from the overlay target by analyzing the image information or the intensity signal(s) of the overlay target. A systematic error metric is also obtained from the overlay target by analyzing the image information or the intensity signal(s) of the overlay target. For example, the systematic error may indicate an asymmetry metric for one or more portions of the overlay target. A noise metric is further obtained from the overlay target by applying a statistical model to the image information or the intensity signal(s) of the overlay target. Noise metric characterizes noise, such as a grainy background, associated with the overlay target. In other embodiments, an overlay and / or stepper analysis procedure is then performed based on the systematic error metric and / or the noise metric, as well as the overlay data.
Owner:KLA TENCOR TECH CORP
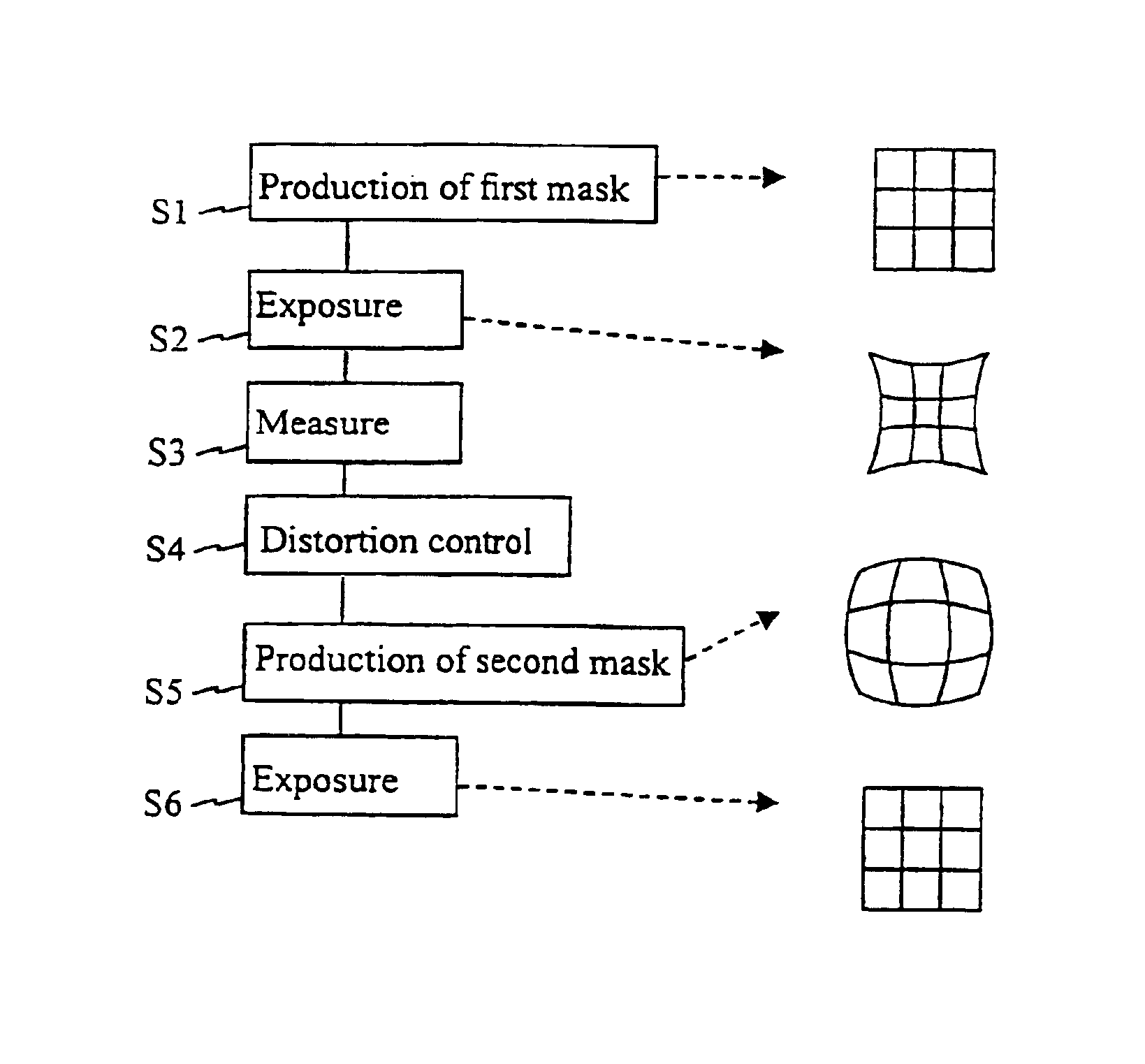
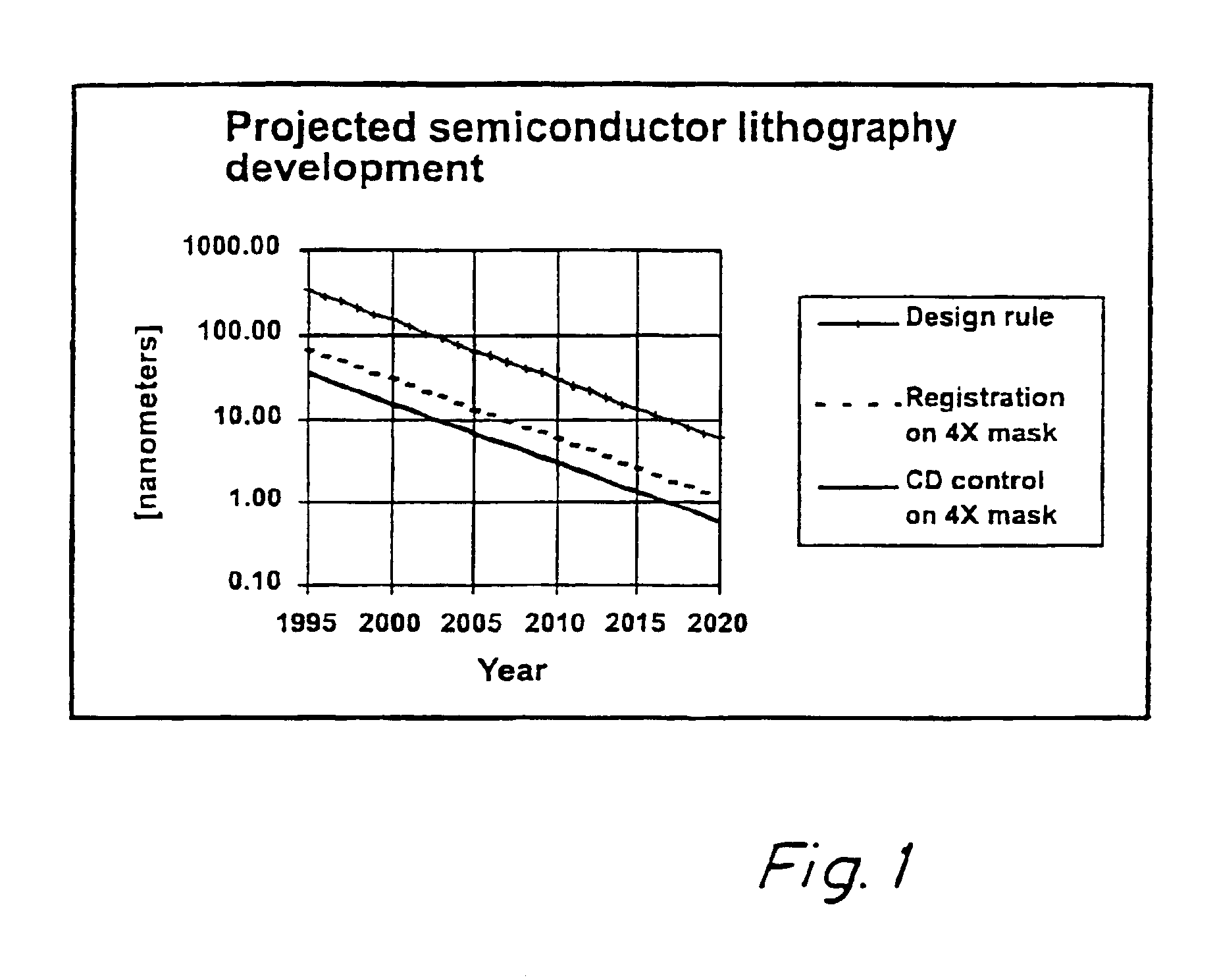
Method for error reduction in lithography
InactiveUS6883158B1High precisionSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingPhotomechanical exposure apparatusError reductionEngineering
The present invention relates to a method and a system for predicting and correcting geometrical errors in lithography using masks, such as large-area photomasks or reticles, and exposure stations, such as wafer steppers or projection aligners, printing the pattern of said masks on a workpiece, such as a display panel or a semi-conductor wafer. The method according to the invention comprises the steps of collecting information about a mask substrate, a mask writer, an exposure stati n, and / or about behavior of a processing step that will occur after the writing of the mask. Further the method comprises predicting from the combined information distorsions occuring in the pattern, when it is subsequently printed on the workpiece; calculating from said prediction a correction to diminish said predicted distorsion, and exposing said pattern onto said mask substrate while applying said correction for said distorsions.
Owner:MICRONIC LASER SYST AB
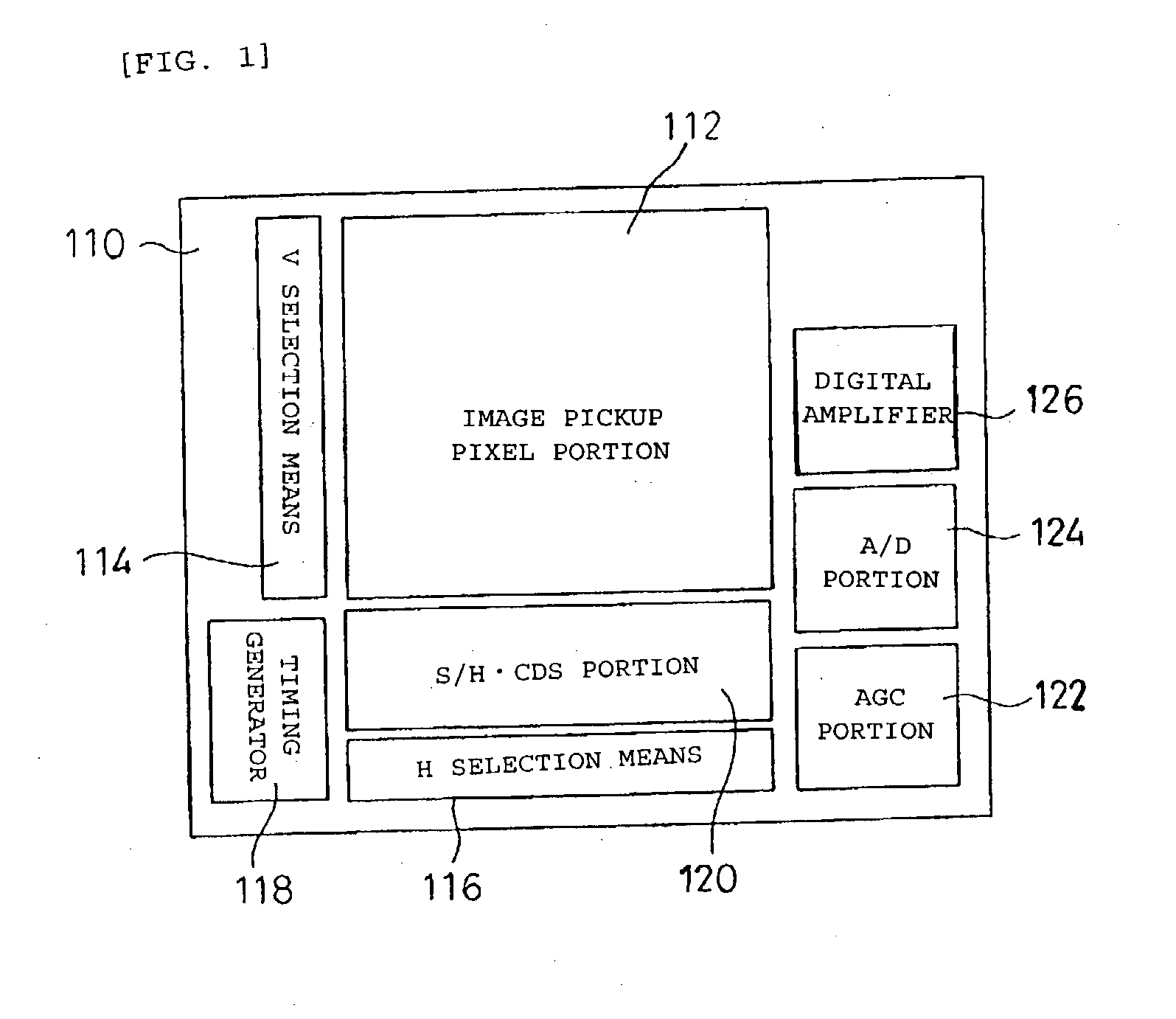
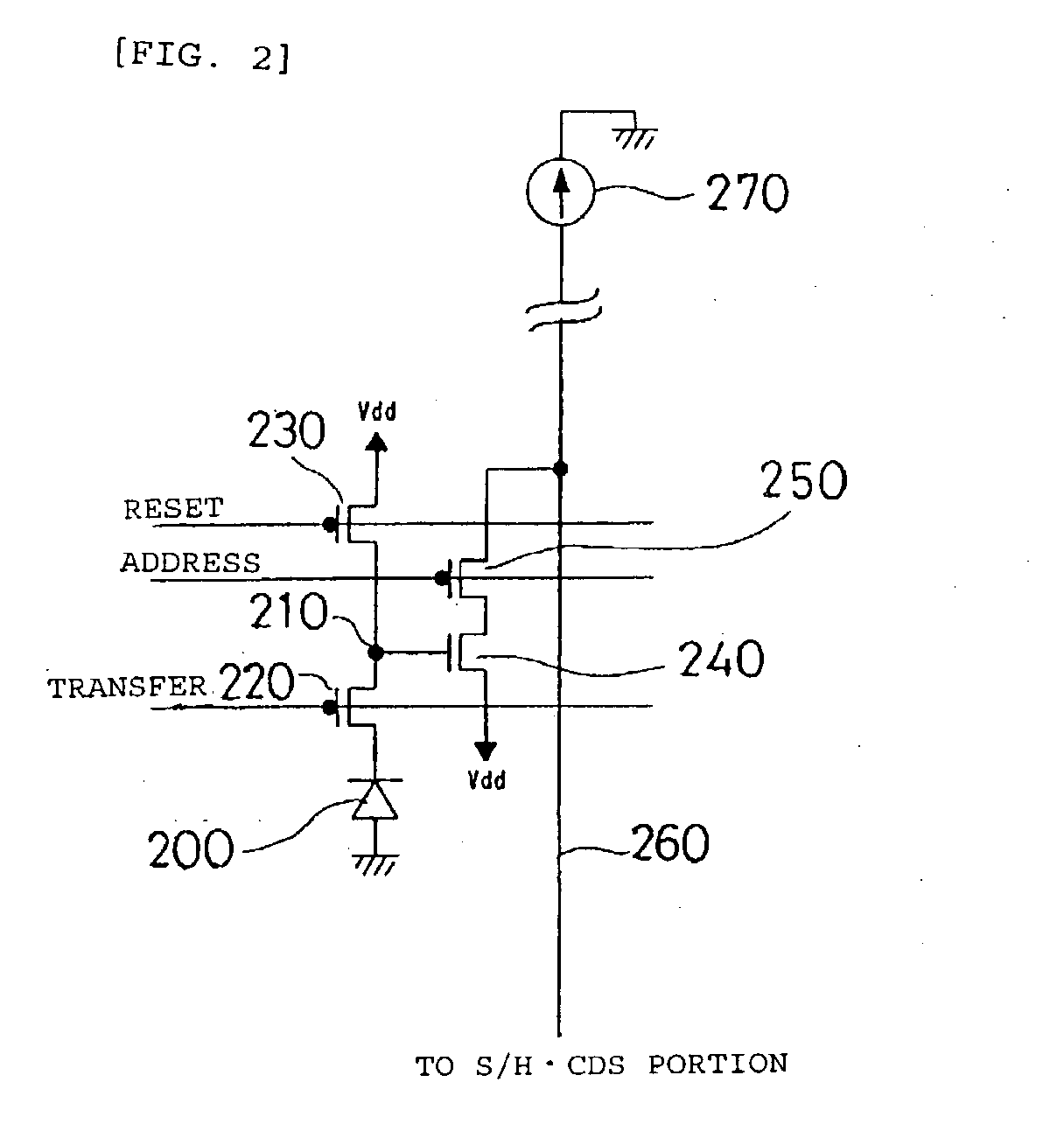
Solid state image pickup device and method of producing solid state image pickup device
Owner:SONY CORP
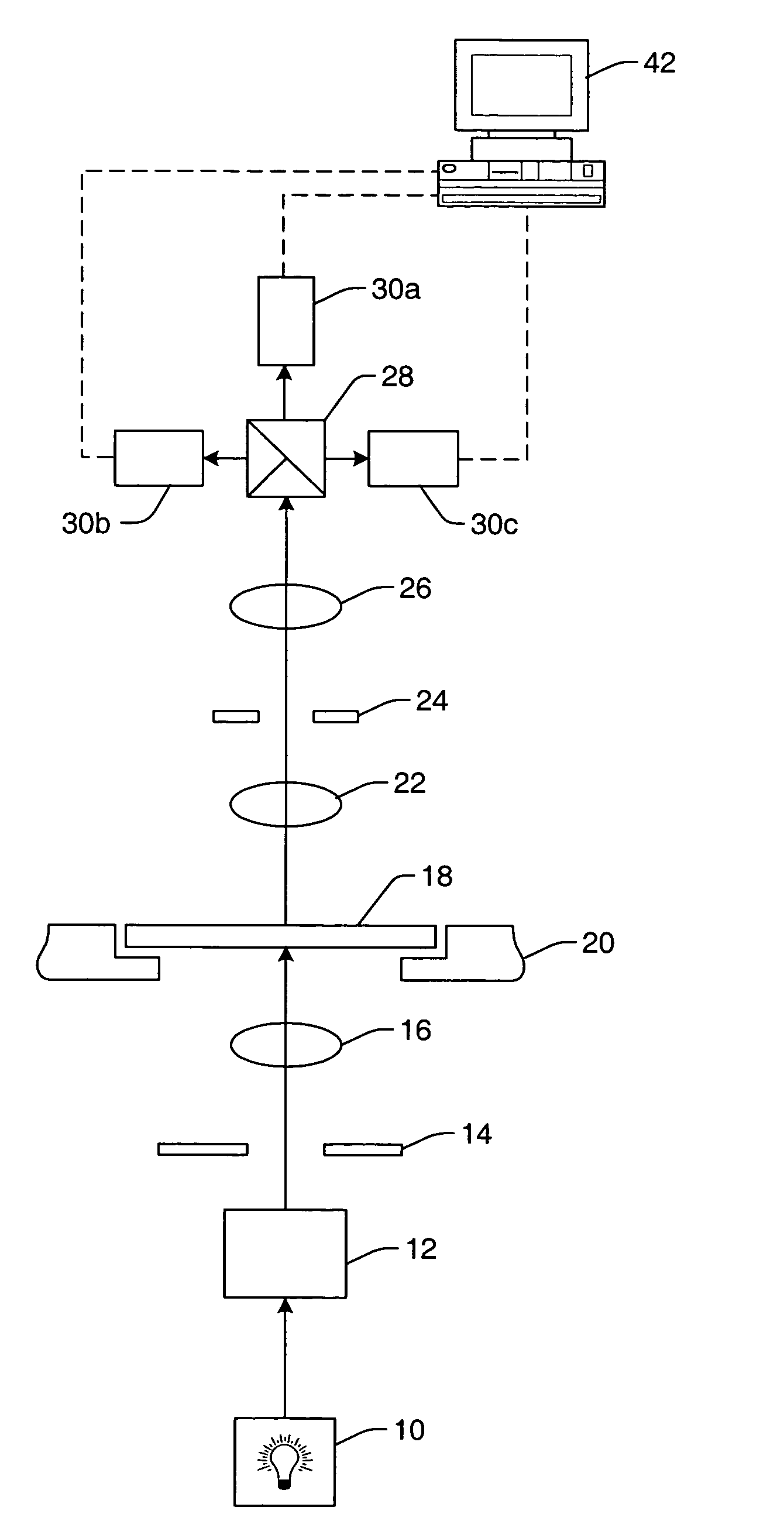
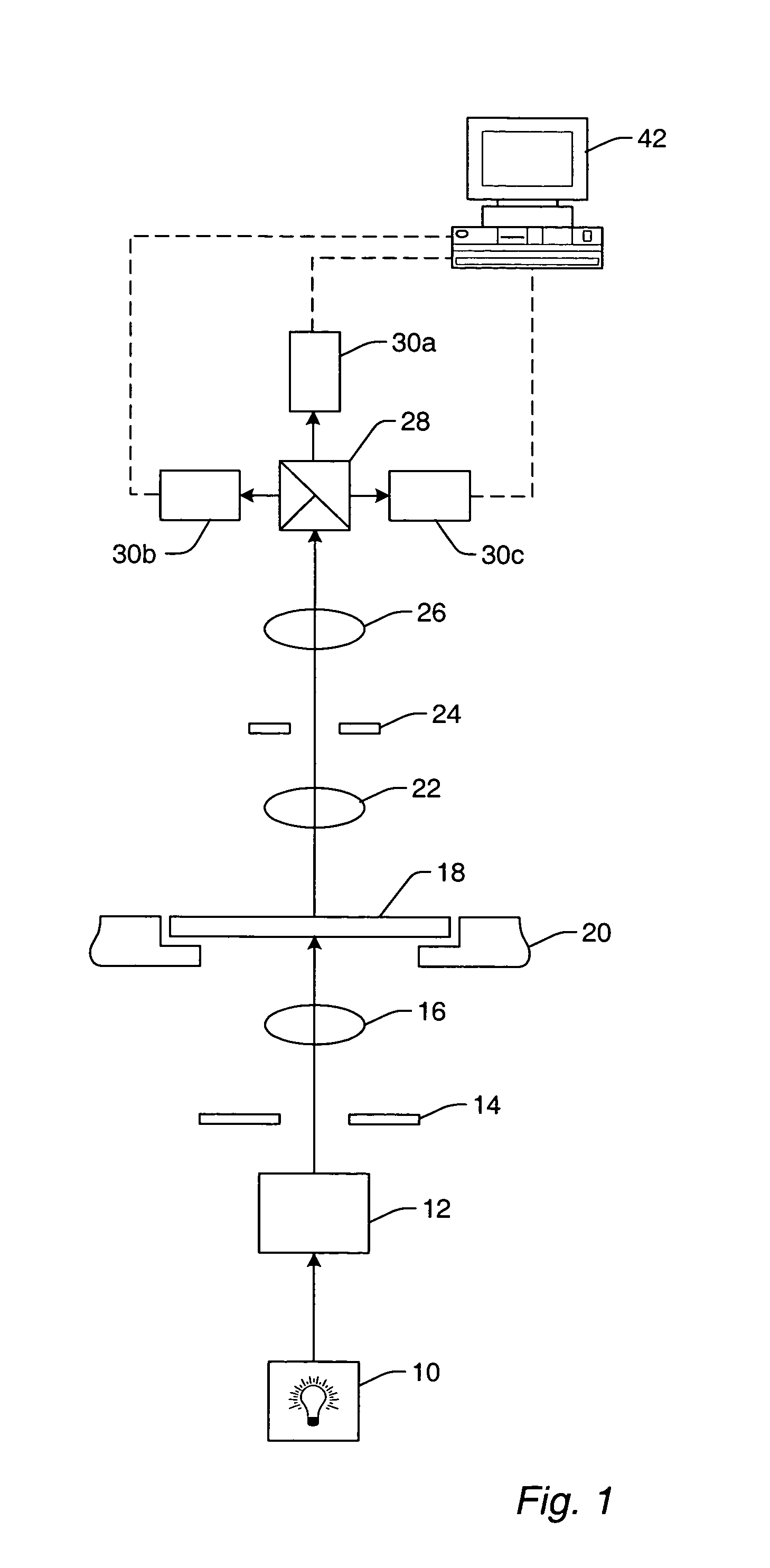
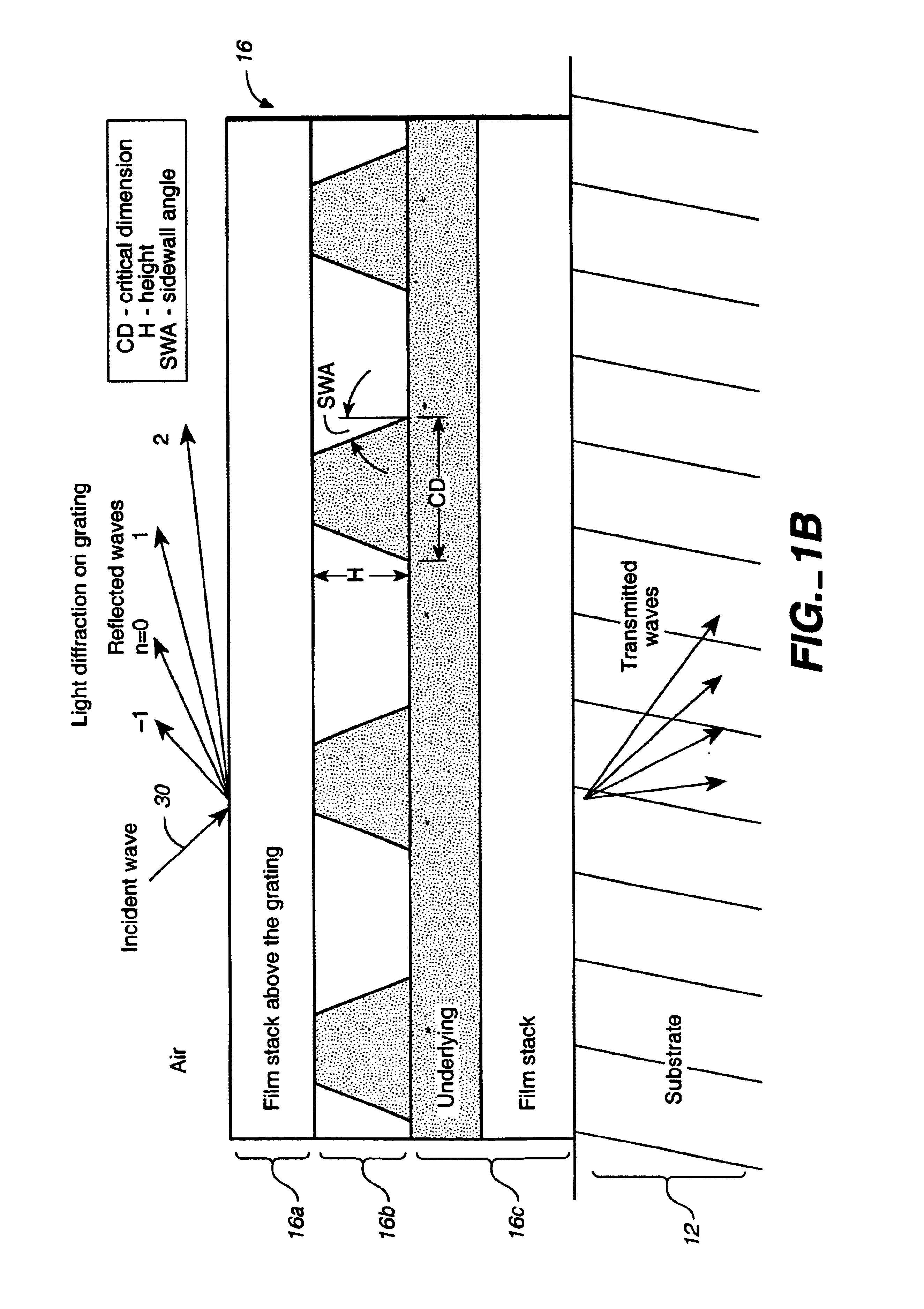
Method and apparatus for controlling photolithography parameters based on photoresist images
InactiveUS6259521B1Material analysis by optical meansPhotomechanical exposure apparatusScatterometerPhotoresist
A method for controlling uniformity in a wafer is provided. A wafer is provided. A layer of photoresist is formed on the wafer, and the photoresist layer is patterned. A portion of the patterned photoresist layer is illuminated in at least first and second positions. Light reflected at the two positions is measured to generate first and second measurements. A recipe of a stepper is adjusted in response to the first measurement differing from the second measurement. A wafer processing system includes a stepper, a scatterometer, and a process controller. The stepper is adapted to expose a layer of photoresist in accordance with a recipe to generate an exposed layer of photoresist. The scatterometer is adapted to take first and second measurements in at least first and second positions on the exposed layer of photoresist. The process controller is adapted to compare the first and second measurements and adjust the recipe based on the first and second measurements.
Owner:GLOBALFOUNDRIES INC
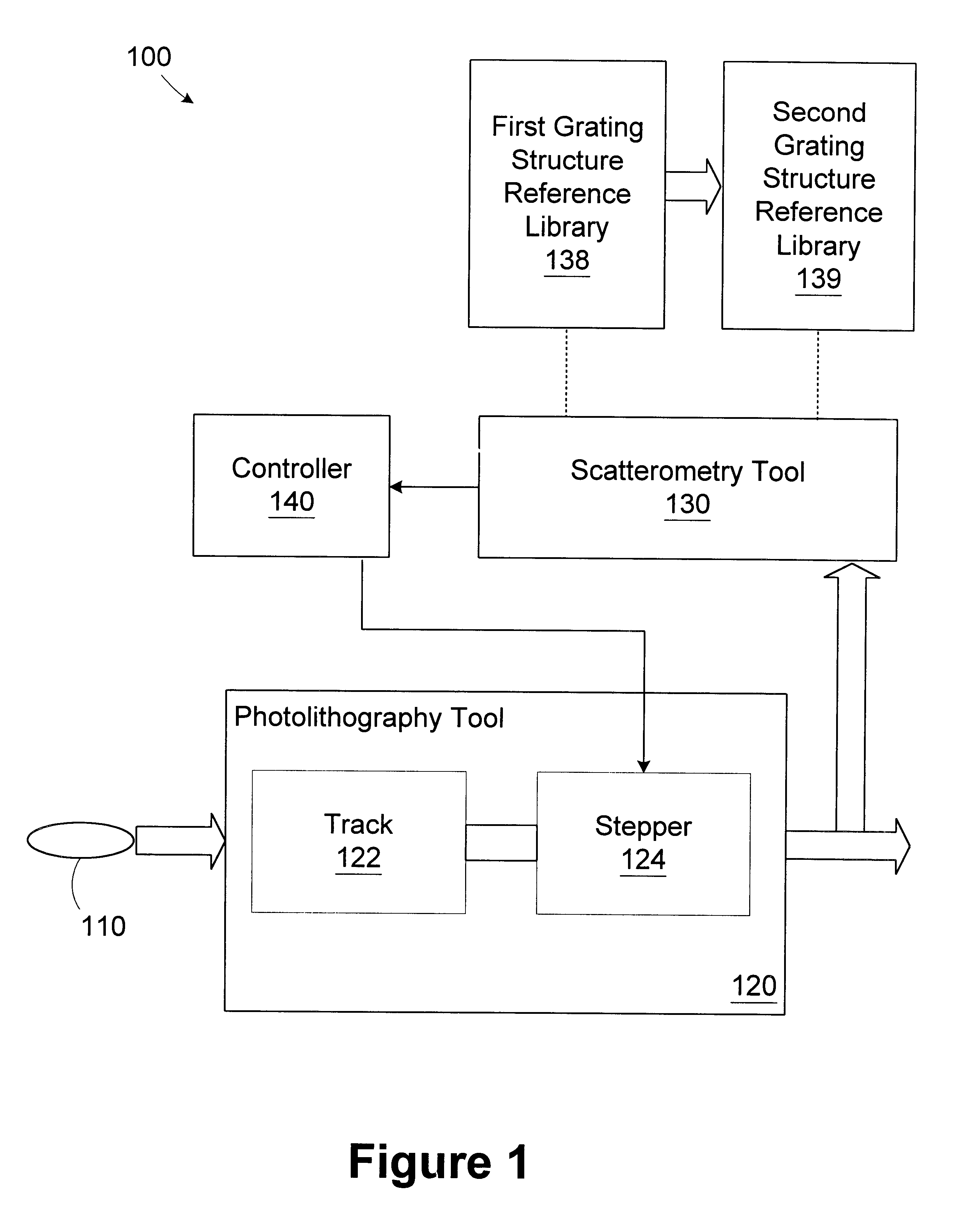
Method and apparatus for controlling photolithography overlay registration
InactiveUS6458605B1Electrolytic capacitorsSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingGratingMetrology
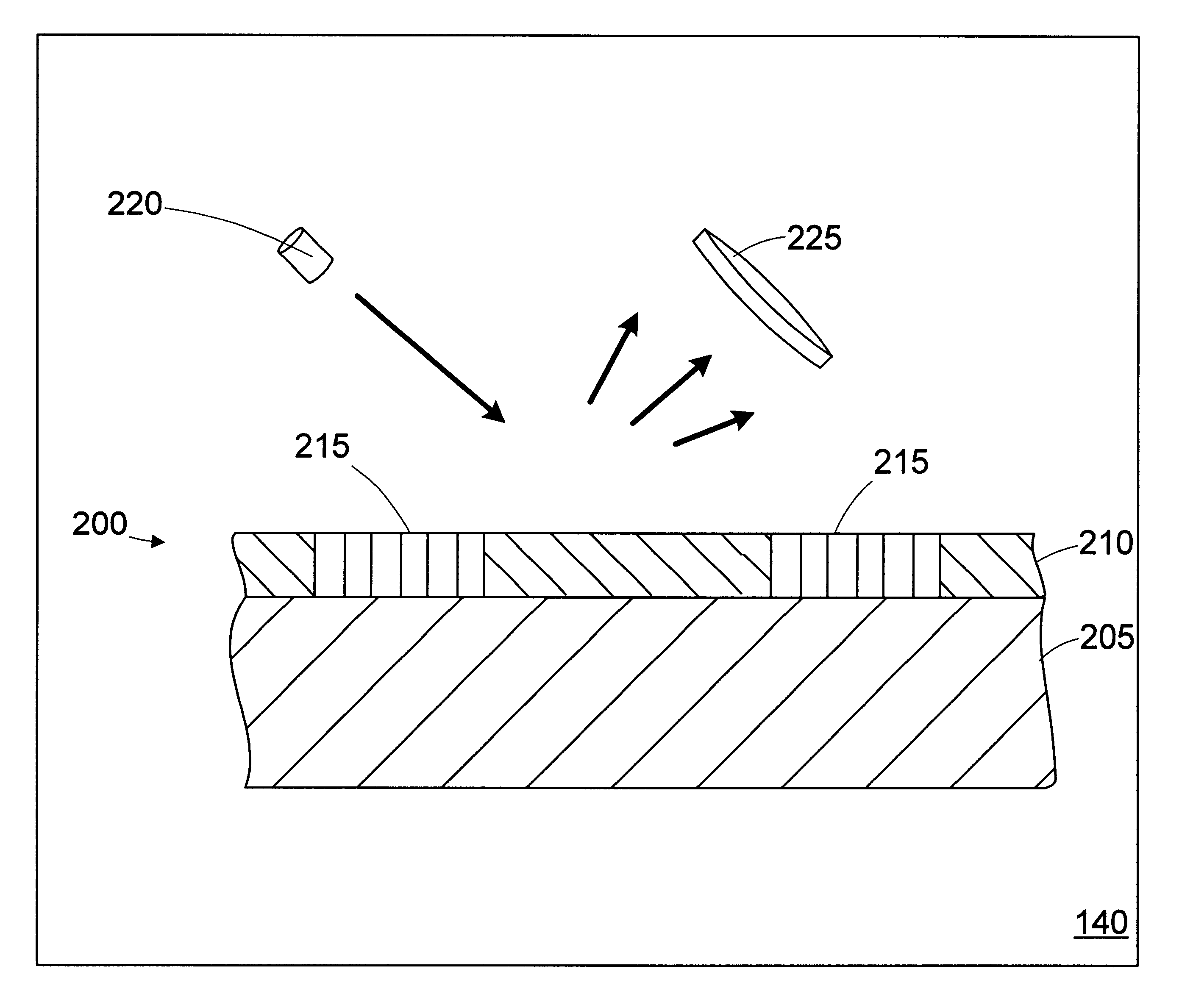
A method for controlling a photolithography process includes providing a wafer having a first grating structure and a second grating structure overlying the first grating structure; illuminating at least a portion of the first and second grating structures with a light source; measuring light reflected from the illuminated portion of the first and second grating structures to generate a reflection profile; determining an overlay error between the first and second grating structures based on the reflection profile; and determining at least one parameter of an operating recipe for a photolithography stepper based on the determined overlay error. A processing line includes a photolithography stepper, a first metrology tool, and a controller. The photolithography stepper is adapted to process wafers in accordance with an operating recipe. The first metrology tool is adapted to receive a wafer having a first grating structure and a second grating structure overlying the first grating structure. The metrology tool includes a light source, a detector, and a data processing unit. The light source is adapted to illuminate at least a portion of the first and second grating structures. The detector is adapted to measure light reflected from the illuminated portion of the first and second grating structures to generate a reflection profile. The data processing unit is adapted to determine an overlay error between the first and second grating structures based on the reflection profile. The controller is adapted to determine at least one parameter of the operating recipe of the photolithography stepper based on the determined overlay error.
Owner:FULLBRITE CAPITAL PARTNERS
Methods and systems for inspecting reticles using aerial imaging at off-stepper wavelengths
ActiveUS7027143B1Material analysis by optical meansCharacter and pattern recognitionAerial imagingSpatial image
Methods and systems for inspecting a reticle are provided. A method may include forming an aerial image of the reticle with an inspection system at a wavelength different from a wavelength of an exposure system. The method may also include correcting the aerial image for differences between modulation transfer functions (MTF) of the inspection system and the exposure system. In this manner, the corrected aerial image may be substantially equivalent to an image of the reticle that would be printed onto a specimen by the exposure system at the wavelength of the exposure system. In addition, the method may include detecting defects on the reticle using the corrected aerial image. The detected defects may include approximately all of the defects that would be printed onto a specimen by the exposure system using the reticle.
Owner:KLA TENCOR TECH CORP
Portable apparatus for peritoneal dialysis therapy
A portable peritoneal dialysis apparatus having (1) a hinged door for enclosing a disposable cassette that seals tightly shut using air pressure; (2) accurate pressure sensing of pressures applied to the patient through an enclosure in the disposable cassette; (3) two pumps that can operate separately or in tandem actuated by two separate stepper motors; and (4) a touch screen user interface where indicia of the operating mode is always visible along with indicia for the other possible operating modes and the mode can be changed by touching one of these indicia.
Owner:FRESENIUS MEDICAL CARE HLDG INC
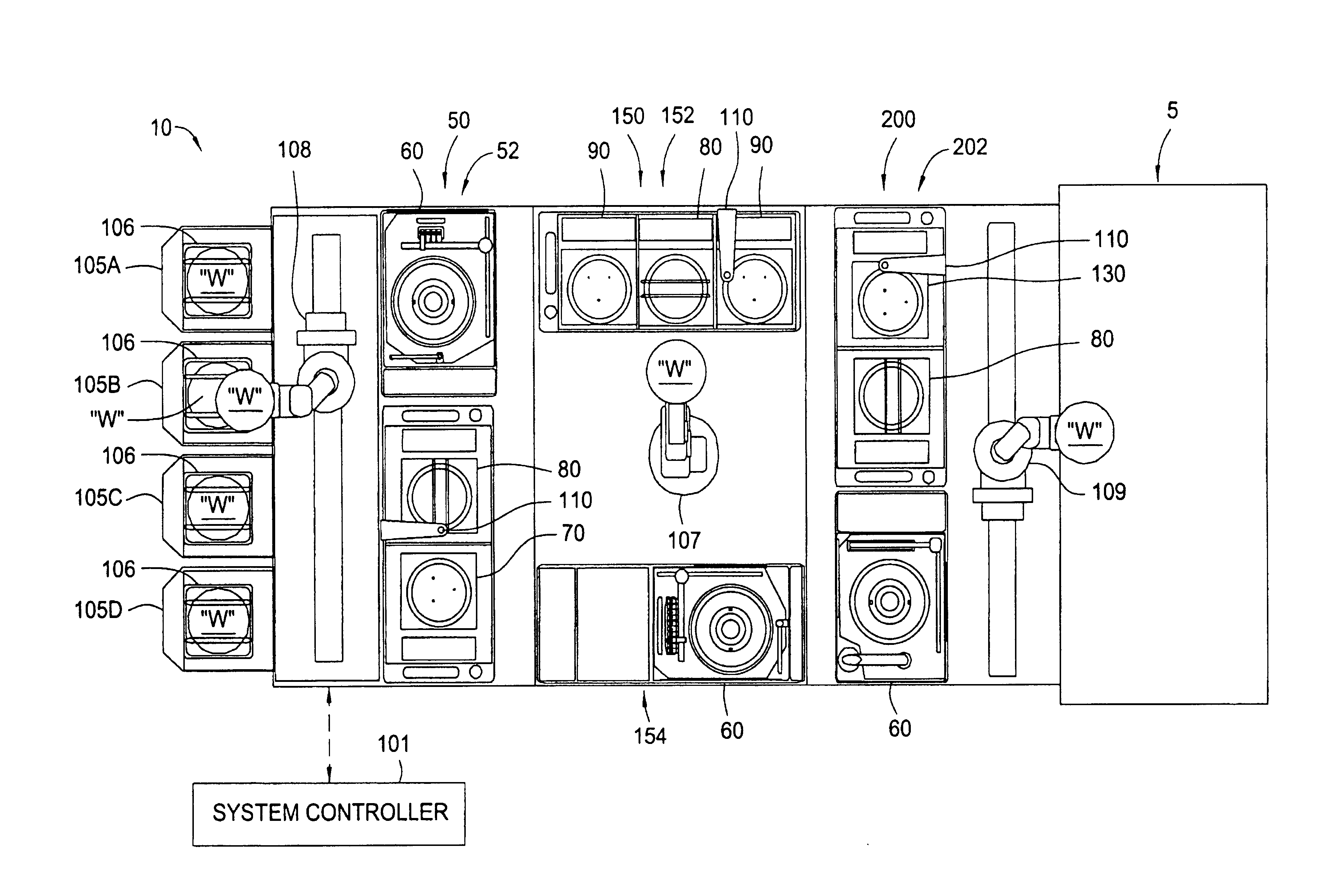
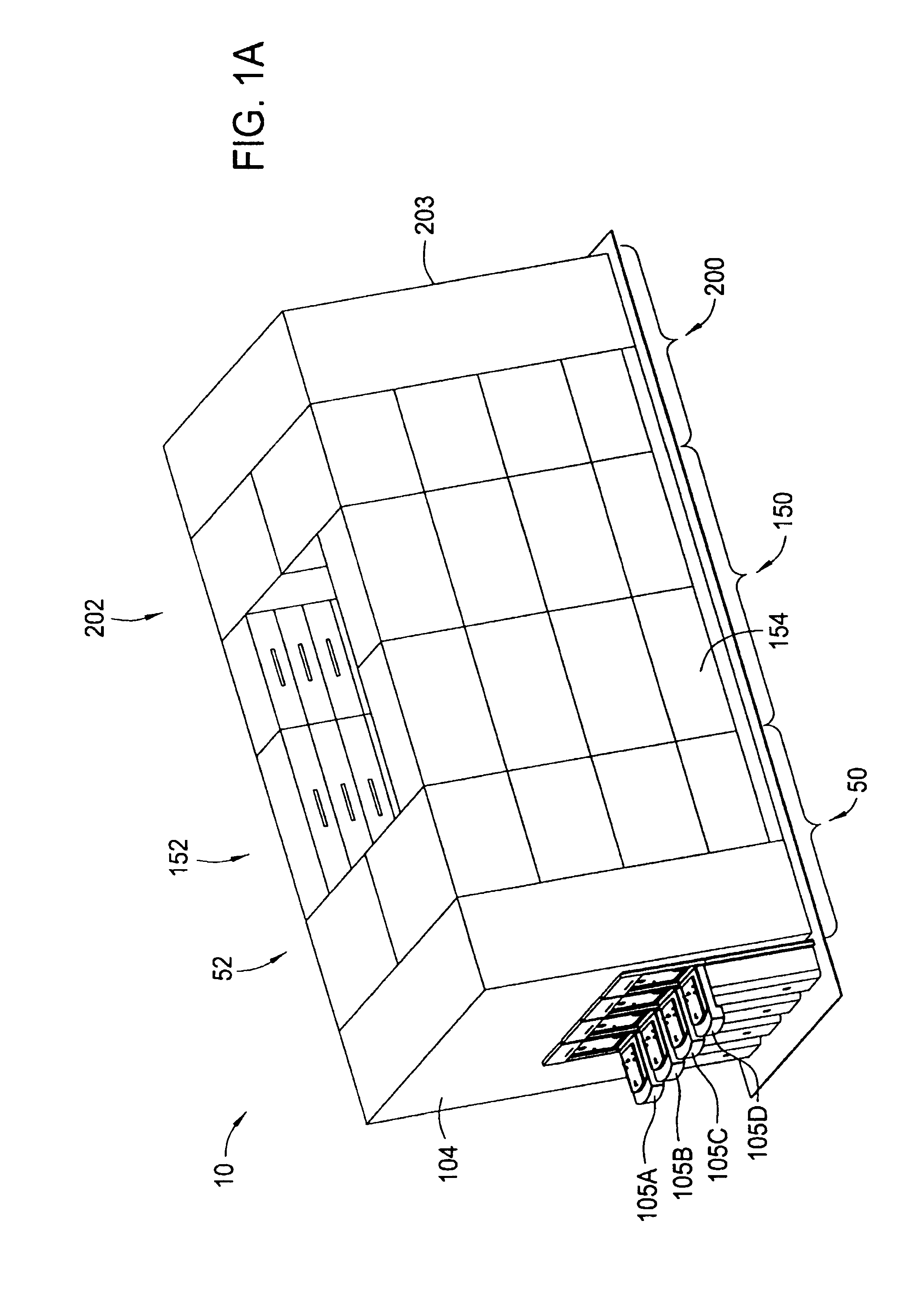
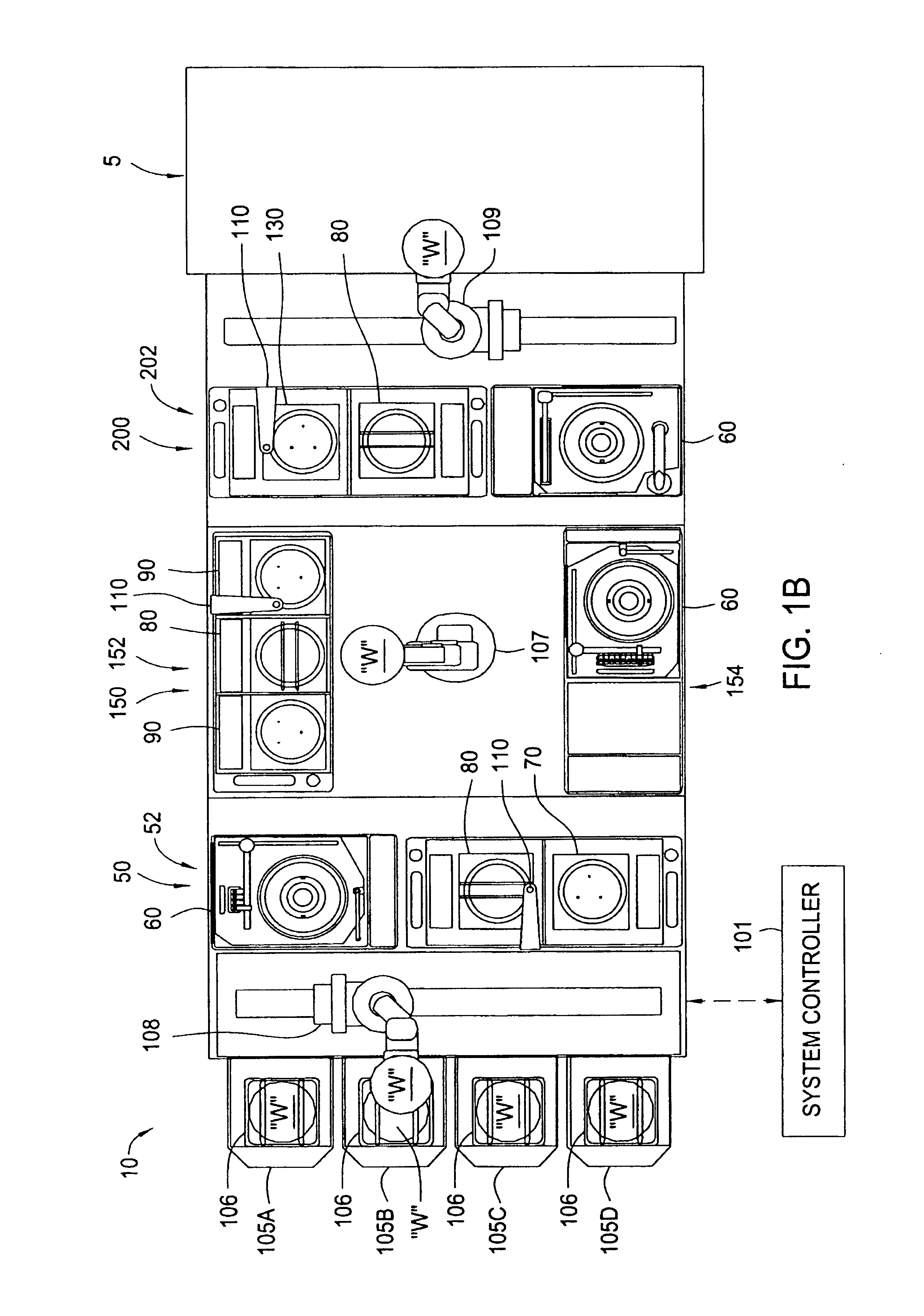
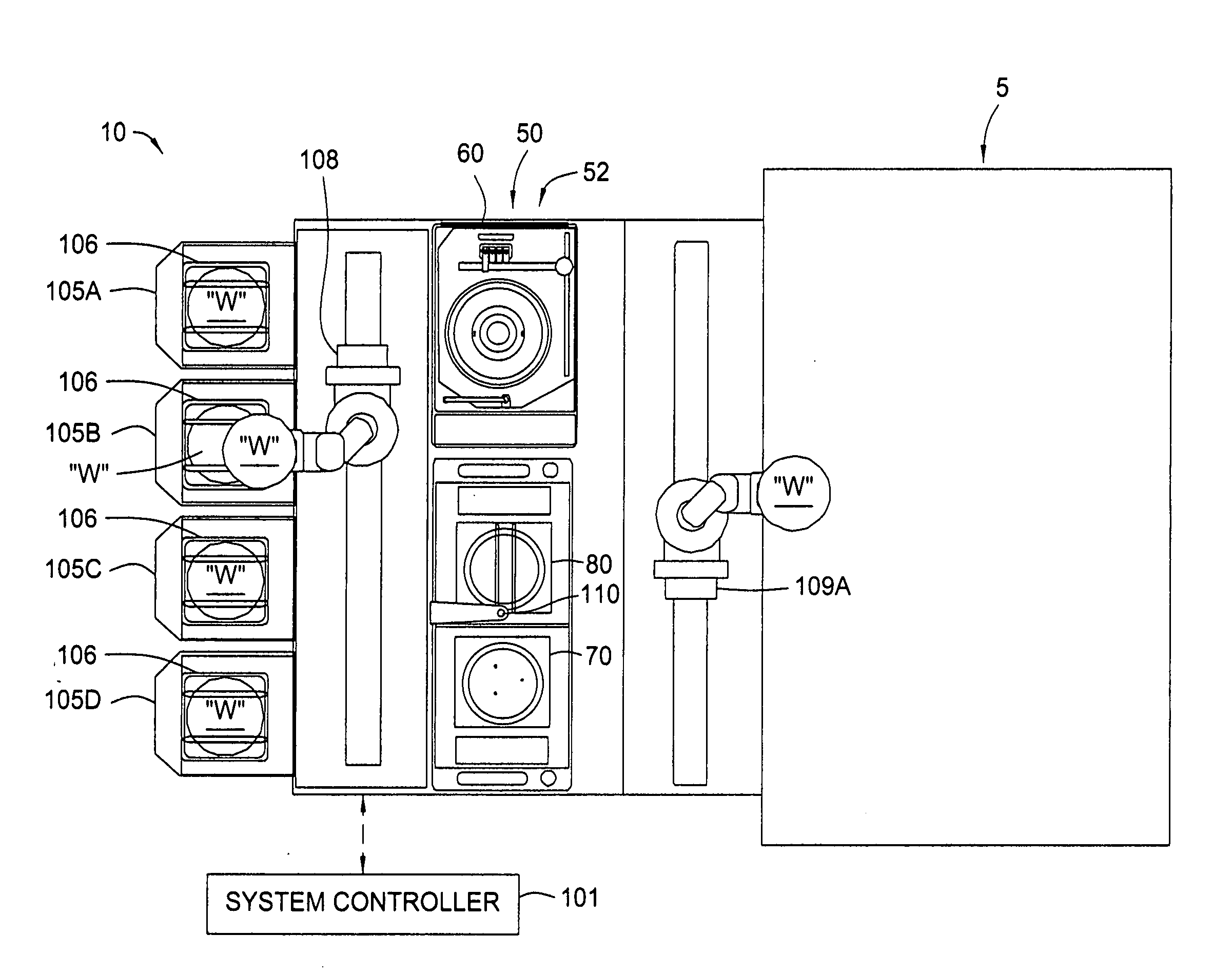
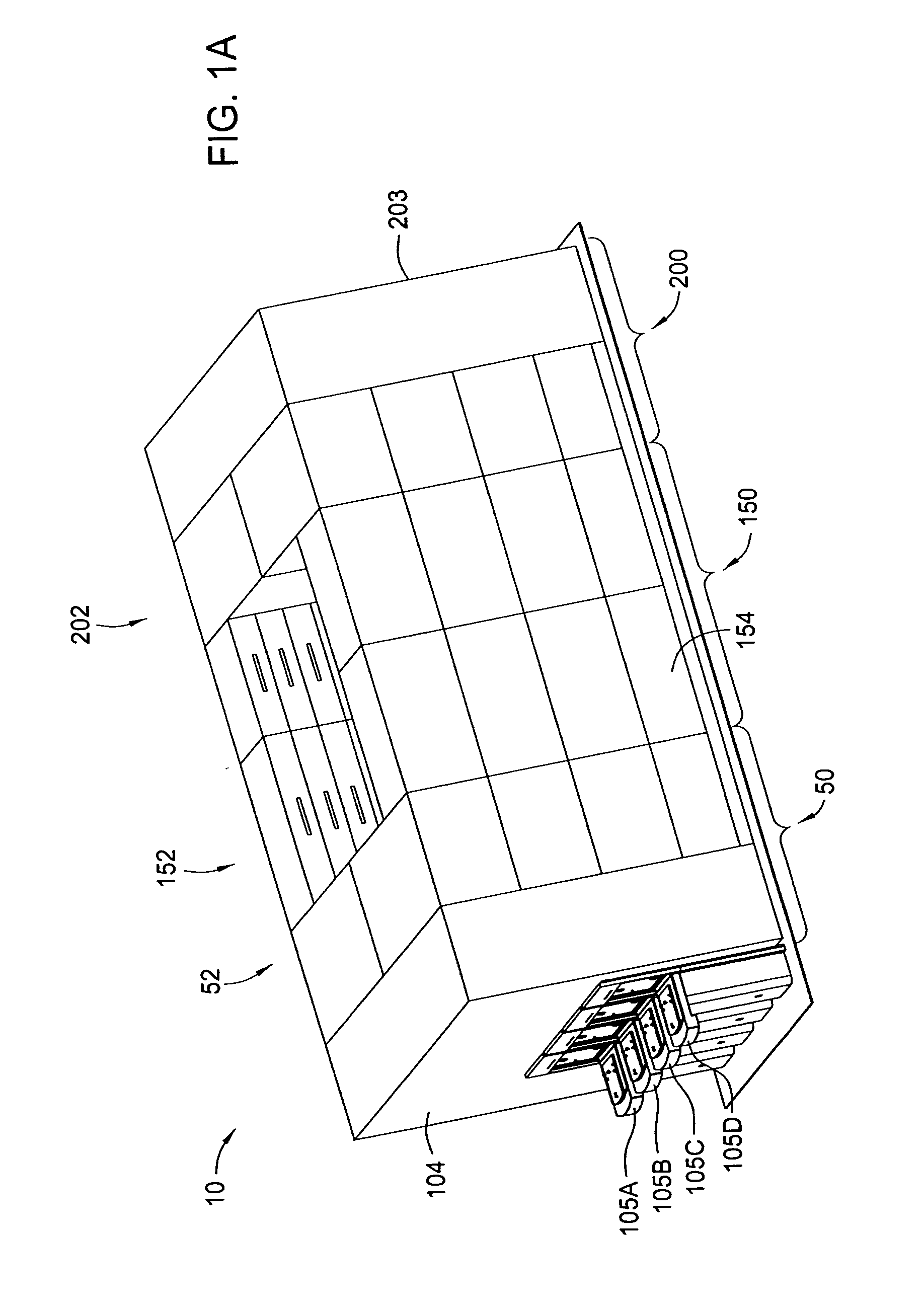
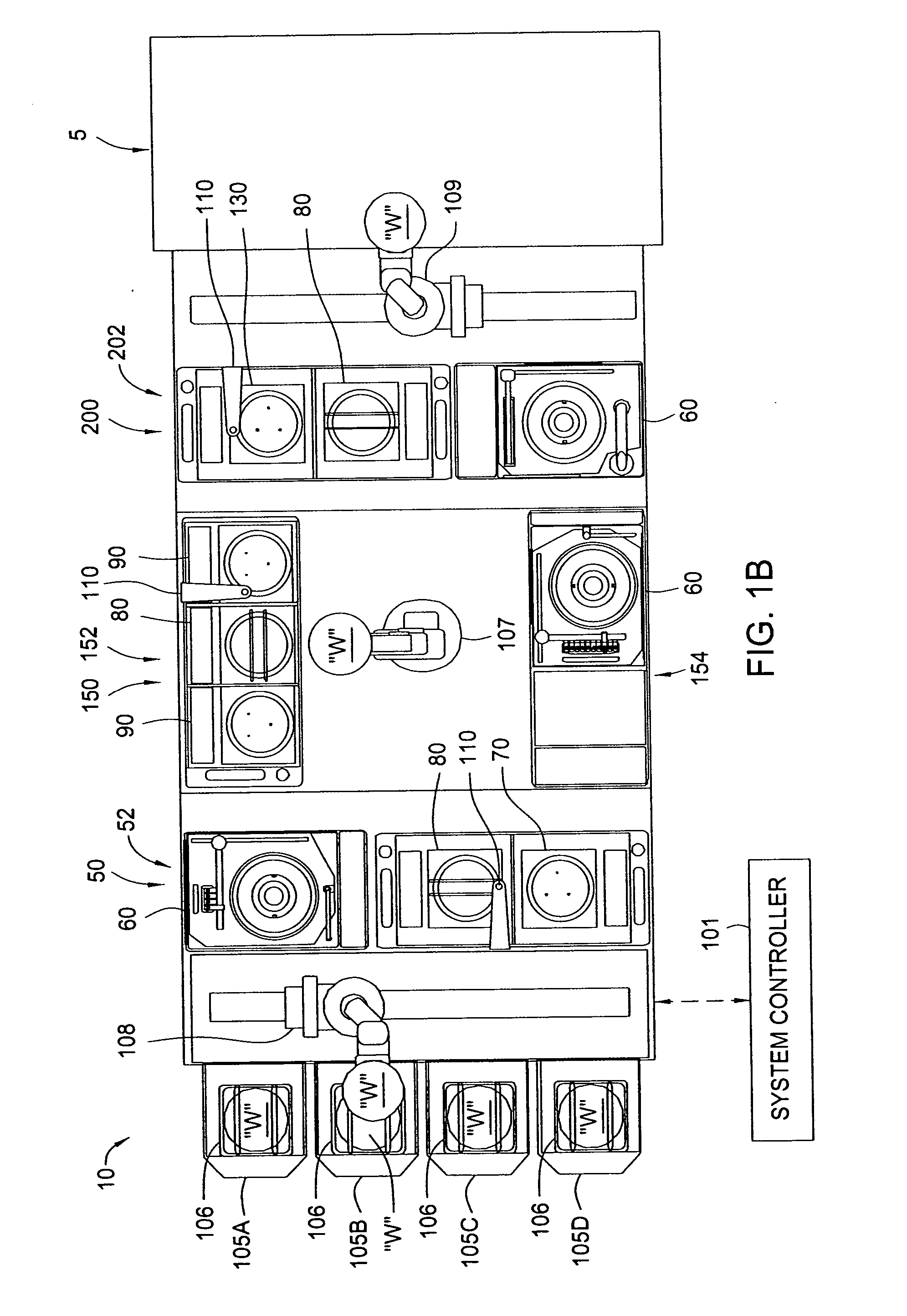
Cluster tool architecture for processing a substrate
ActiveUS20060130750A1Temperature controlMore repeatable wafer processing historyLiquid surface applicatorsSemiconductor/solid-state device testing/measurementLithography processEngineering
Embodiments generally provide an apparatus and method for processing substrates using a multi-chamber processing system (e.g., a cluster tool) that has an increased system throughput, increased system reliability, substrates processed in the cluster tool have a more repeatable wafer history, and also the cluster tool has a smaller system footprint. In one embodiment, the cluster tool is adapted to perform a track lithography process in which a substrate is coated with a photosensitive material, is then transferred to a stepper / scanner, which exposes the photosensitive material to some form of radiation to form a pattern in the photosensitive material, which is then removed in a developing process completed in the cluster tool. In track lithography type cluster tools, since the chamber processing times tend to be rather short, and the number of processing steps required to complete a typical track system process is large, a significant portion of the time it takes to process a substrate is taken up by the processes of transferring the substrates in a cluster tool between the various processing chambers. In one embodiment of the cluster tool, the cost of ownership is reduced by grouping substrates together and transferring and processing the substrates in groups of two or more to improve system throughput, and reduces the number of moves a robot has to make to transfer a batch of substrates between the processing chambers, thus reducing wear on the robot and increasing system reliability. In one aspect of the invention, the substrate processing sequence and cluster tool are designed so that the substrate transferring steps performed during the processing sequence are only made to chambers that will perform the next processing step in the processing sequence. Embodiments also provide for a method and apparatus that are used to improve the coater chamber, the developer chamber, the post exposure bake chamber, the chill chamber, and the bake chamber process results. Embodiments also provide for a method and apparatus that are used to increase the reliability of the substrate transfer process to reduce system down time.
Owner:SCREEN SEMICON SOLUTIONS CO LTD
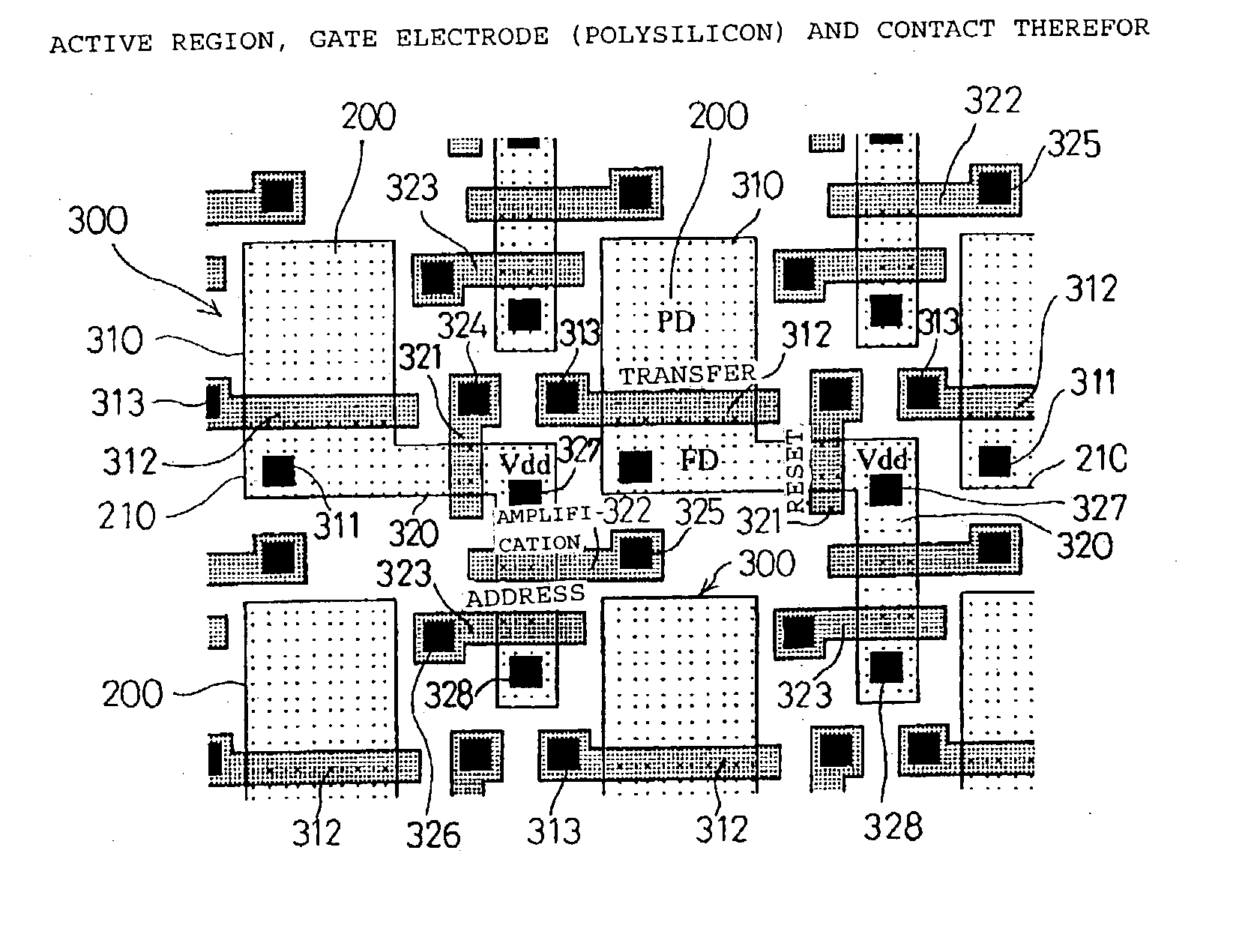
Solid state image pickup device and method of producing solid state image pickup device
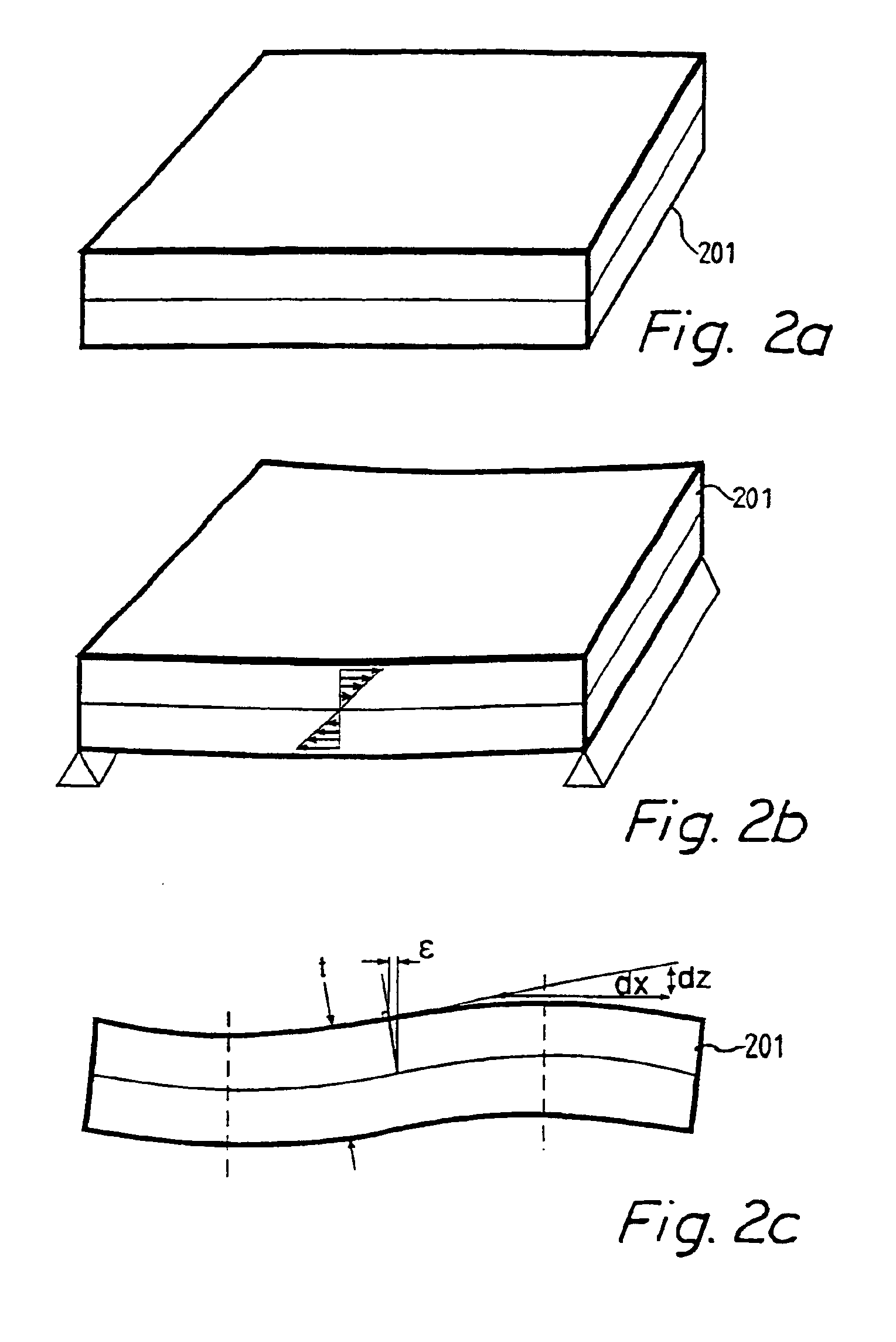
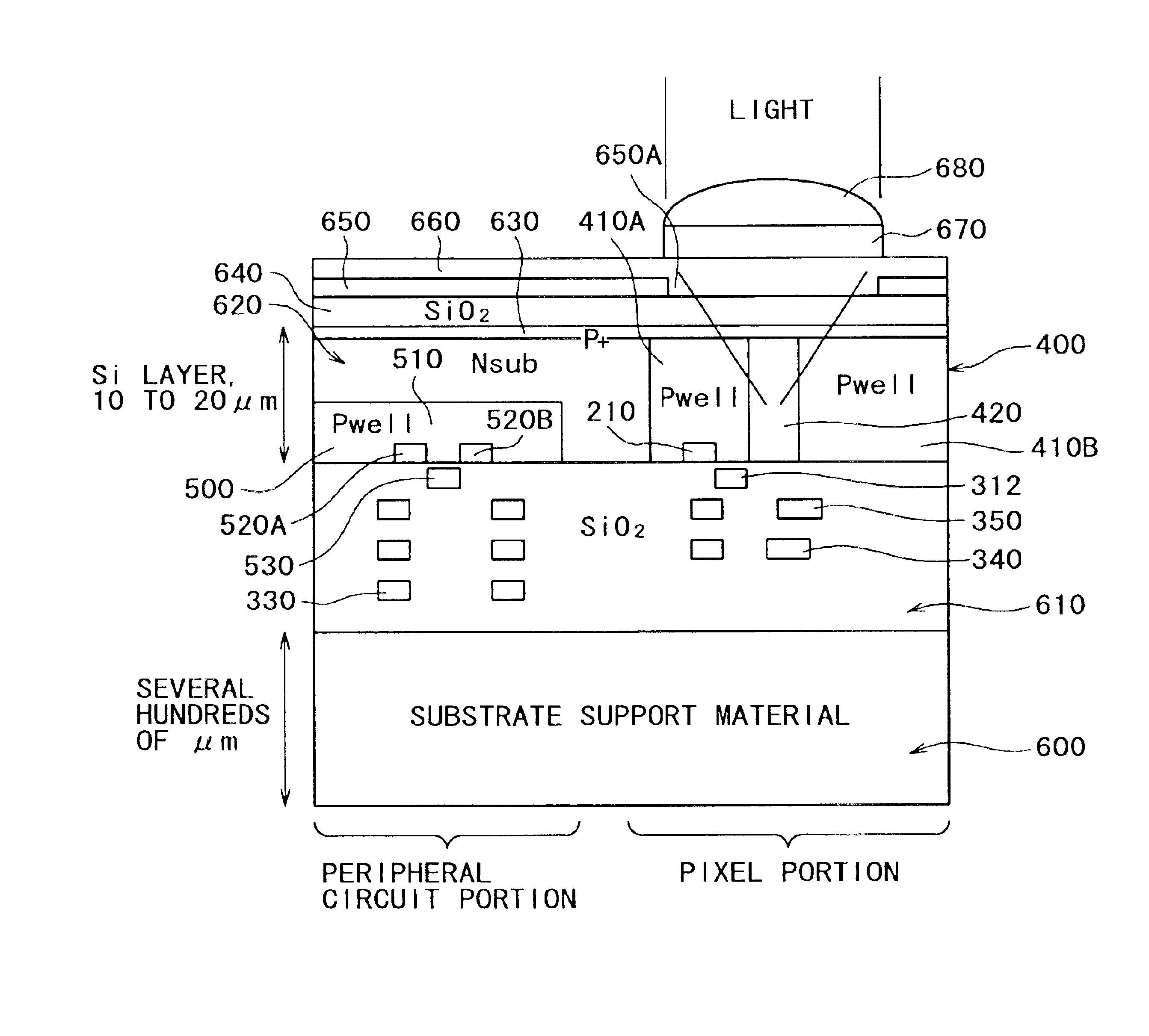
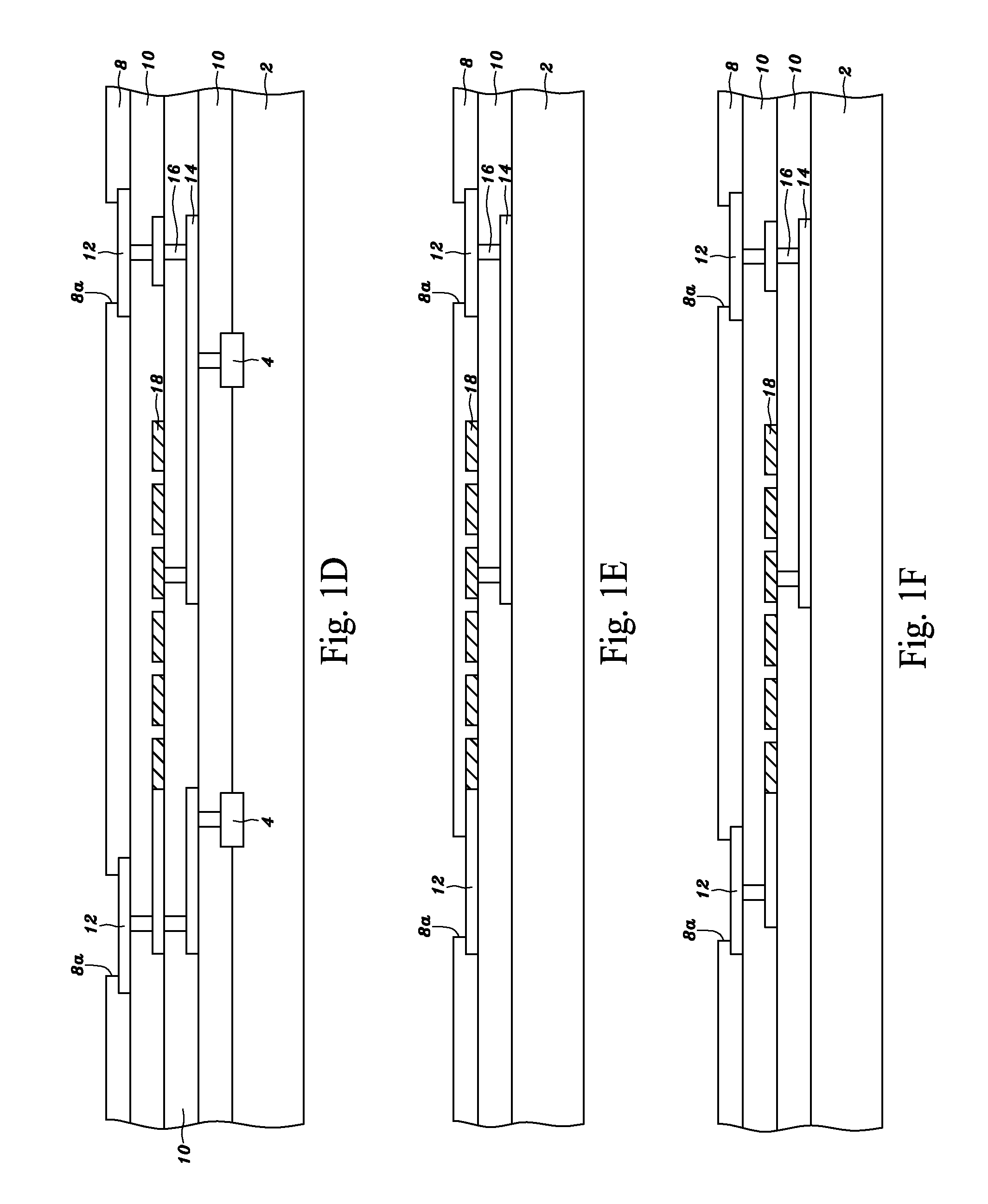
Forming a back-illuminated type CMOS image sensor, includes process for formation of a registration mark on the wiring side of a silicon substrate during formation of an active region or a gate electrode. A silicide film using an active region may also be used for the registration mark. Thereafter, the registration mark is read from the back side by use of red light or near infrared rays, and registration of the stepper is accomplished. It is also possible to form a registration mark in a silicon oxide film on the back side (illuminated side) in registry with the registration mark on the wiring side, and to achieve the desired registration by use of the registration mark thus formed.
Owner:SONY CORP
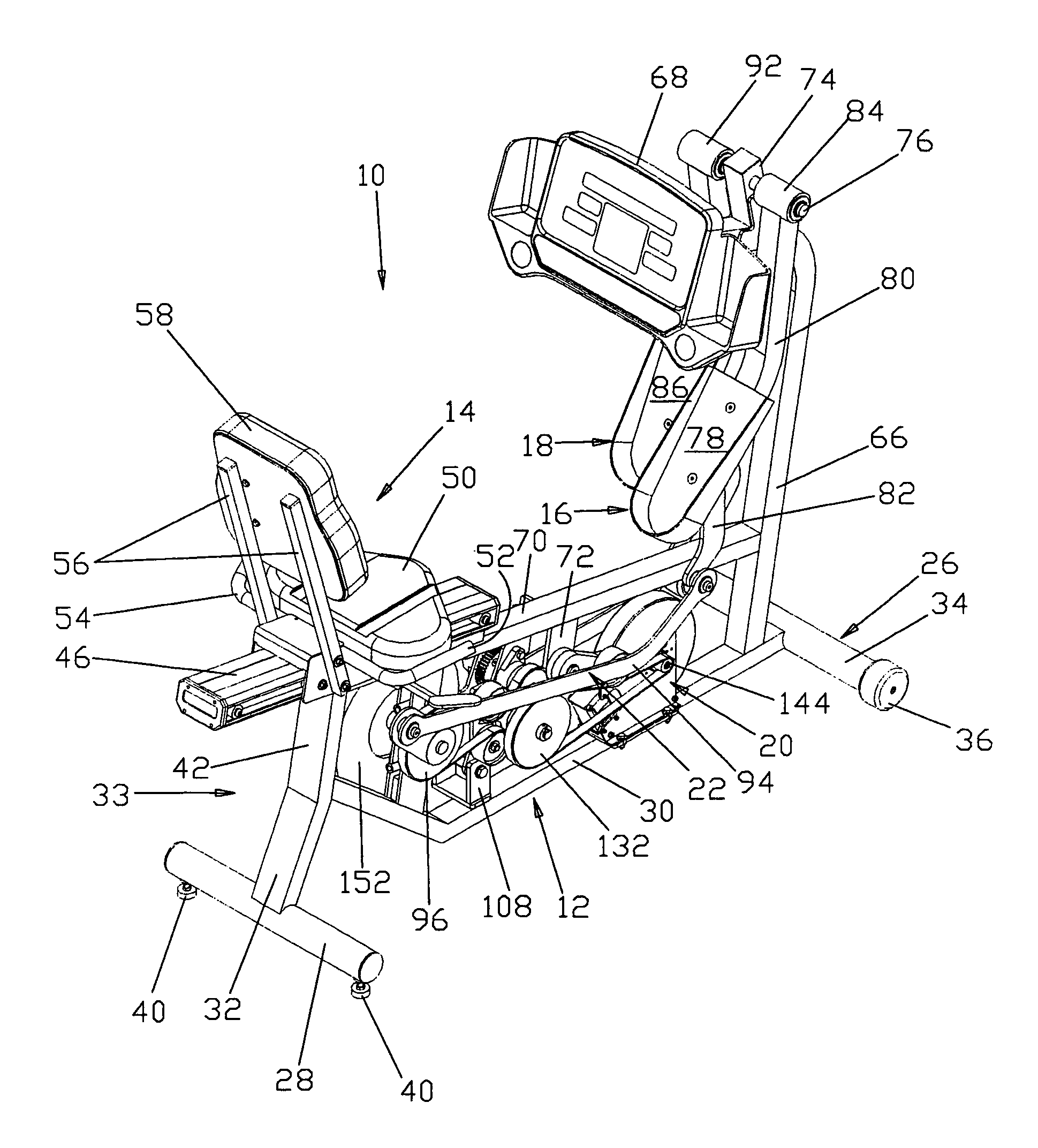
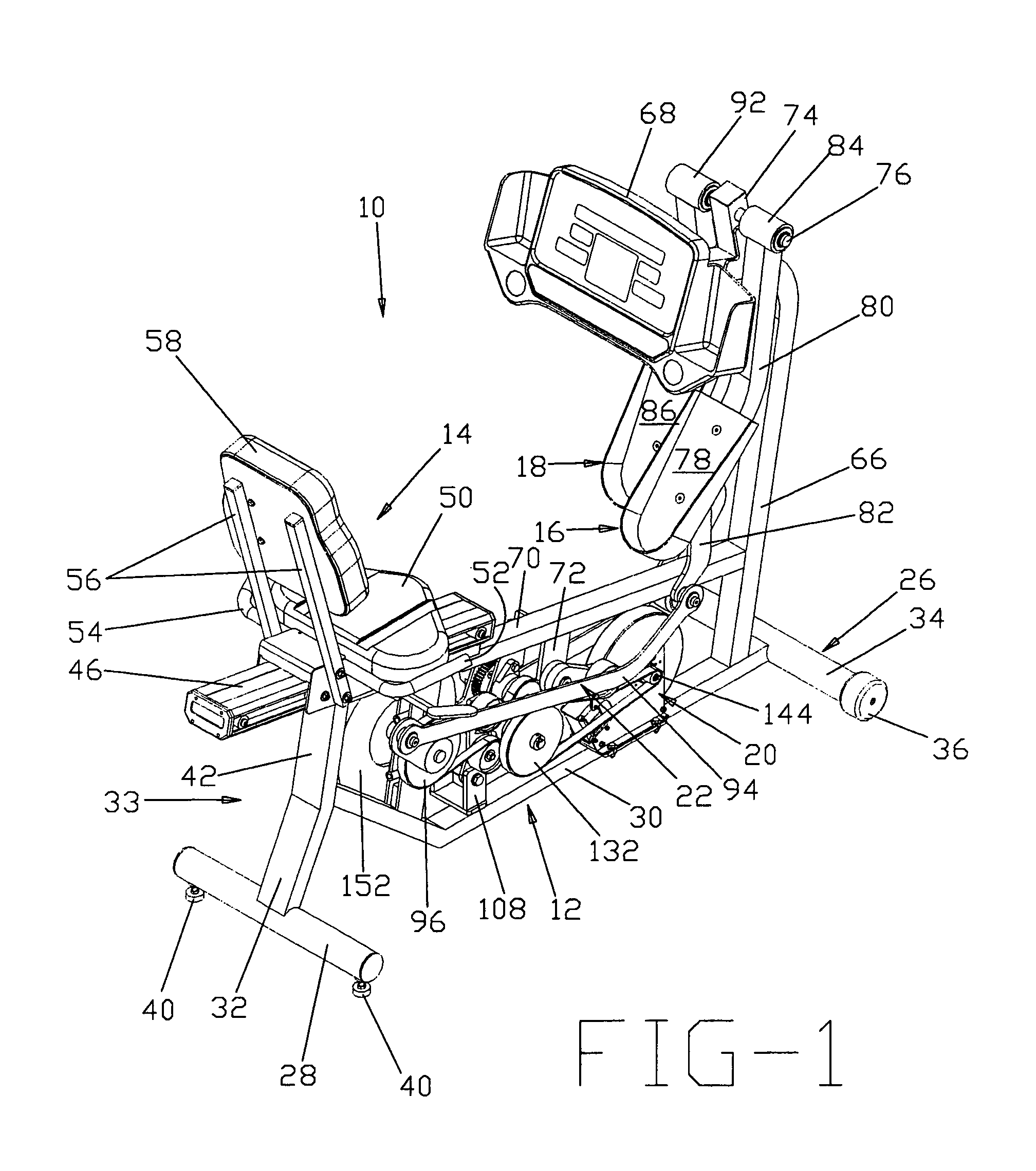
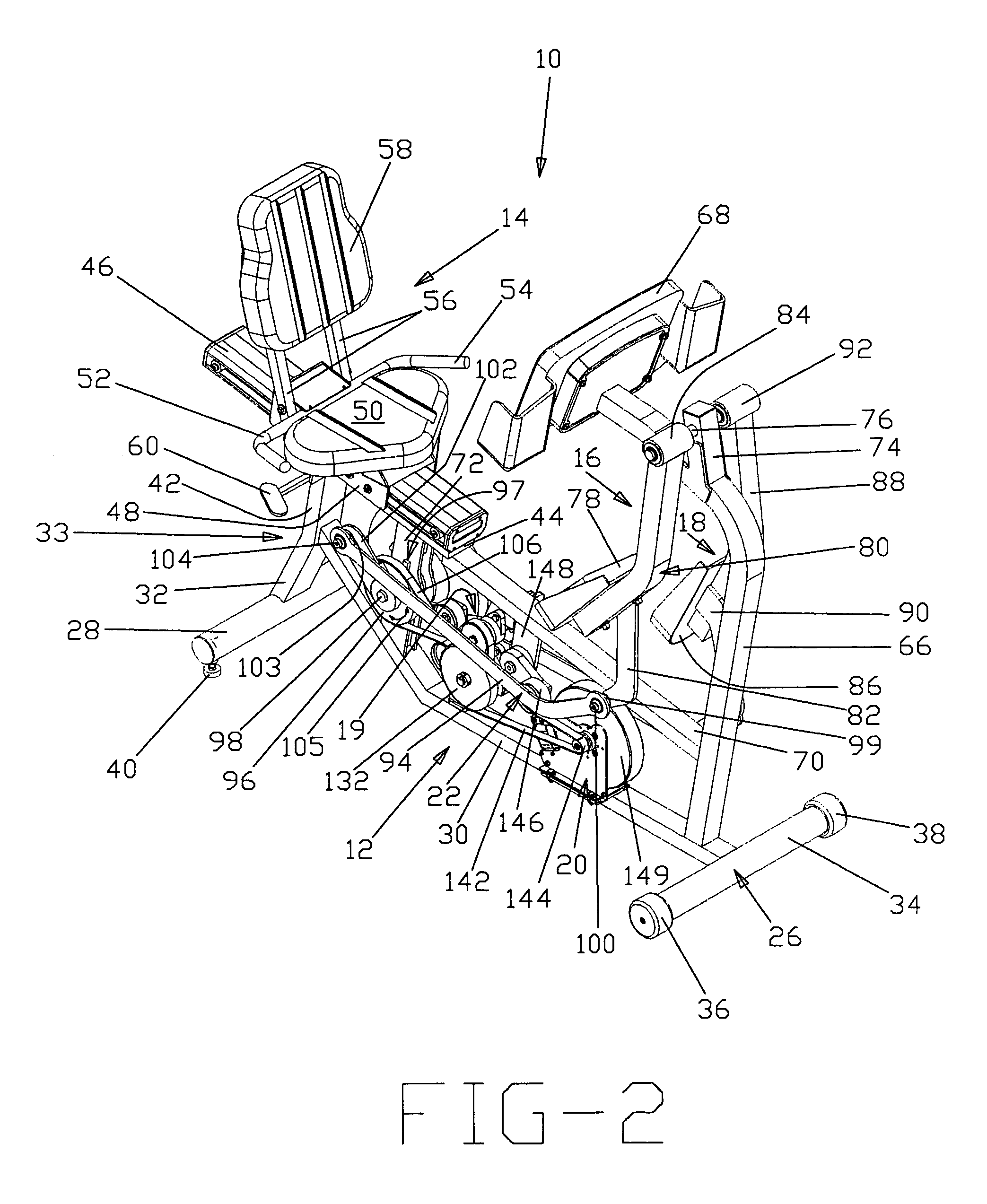
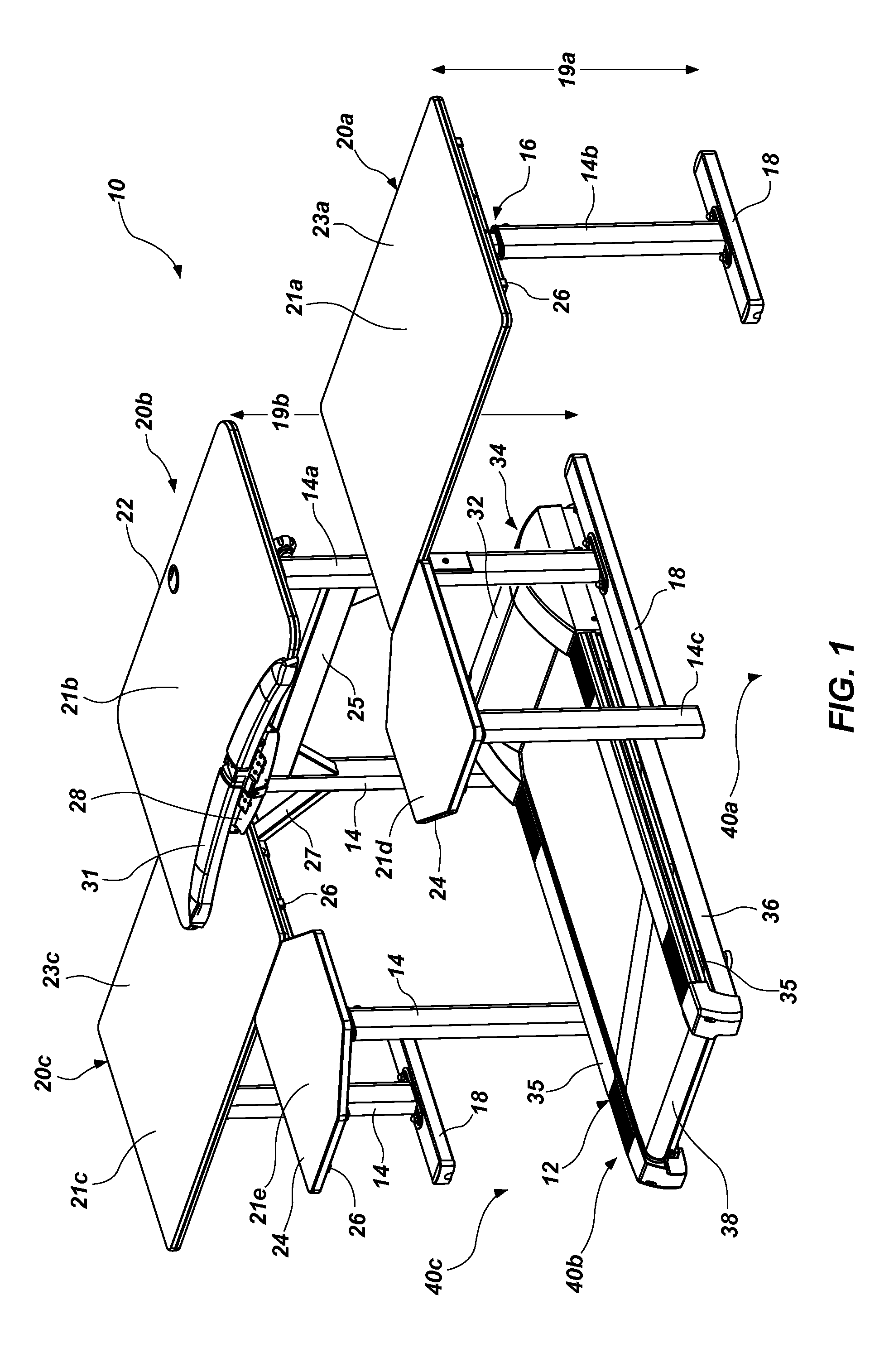
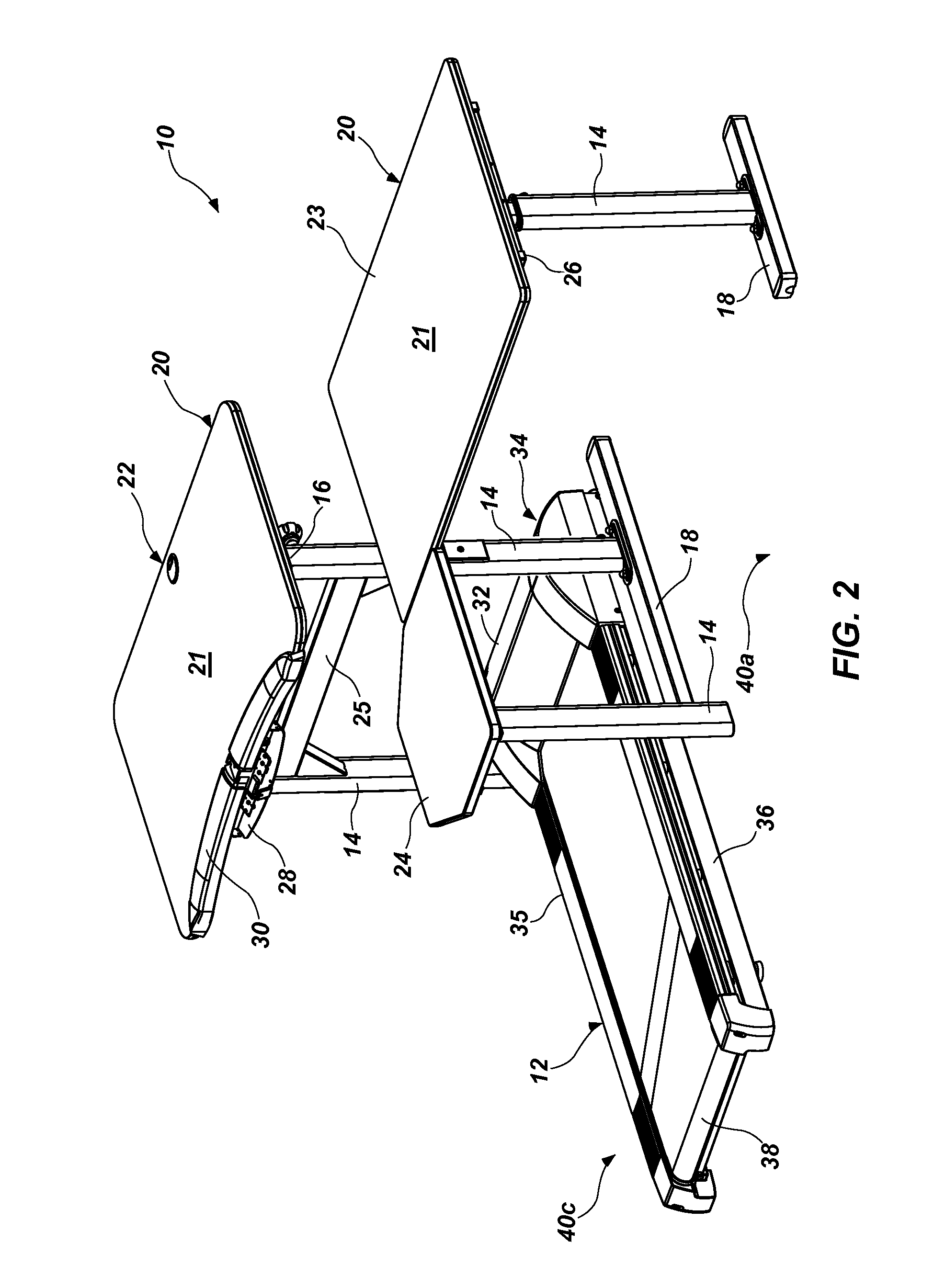
Seated stepper
InactiveUS6932745B1Body workoutLower body workoutMuscle exercising devicesMovement coordination devicesGear wheelReciprocating motion
The seated stepper is provided for exercising the lower body. The stepper includes a frame having opposite sides and a longitudinal axis, and a seat attached to the frame. First and second foot lever arrangements are pivotally coupled together on opposite sides of the frame to move alternately in forward and rearward directions towards forward and rearward positions. The foot lever arrangements have linearly moveable right and left foot receptacles adapted to be engaged by an exerciser's feet. First and second motion transfer arrangements are mounted on opposite sides of the frame and coupled to the foot lever arrangements for enabling reciprocating movement of one foot lever arrangement relative to the other foot lever arrangement. A transmission arrangement is mounted on the frame and is operably connected to the first and second motion transfer arrangements. The transmission arrangement includes upper and lower pulley and gear trains in meshing relationship with one another. A resistance structure is mounted to the frame and is operably connected to the transmission arrangement for resisting pivotal movement of each foot lever arrangement in one of the forward and rearward directions. The transmission arrangement enables either of the foot receptacles to be moved and prevents any inertia from the resistance structure from being transferred back to the foot lever arrangements.
Owner:NORTHLAND INDS
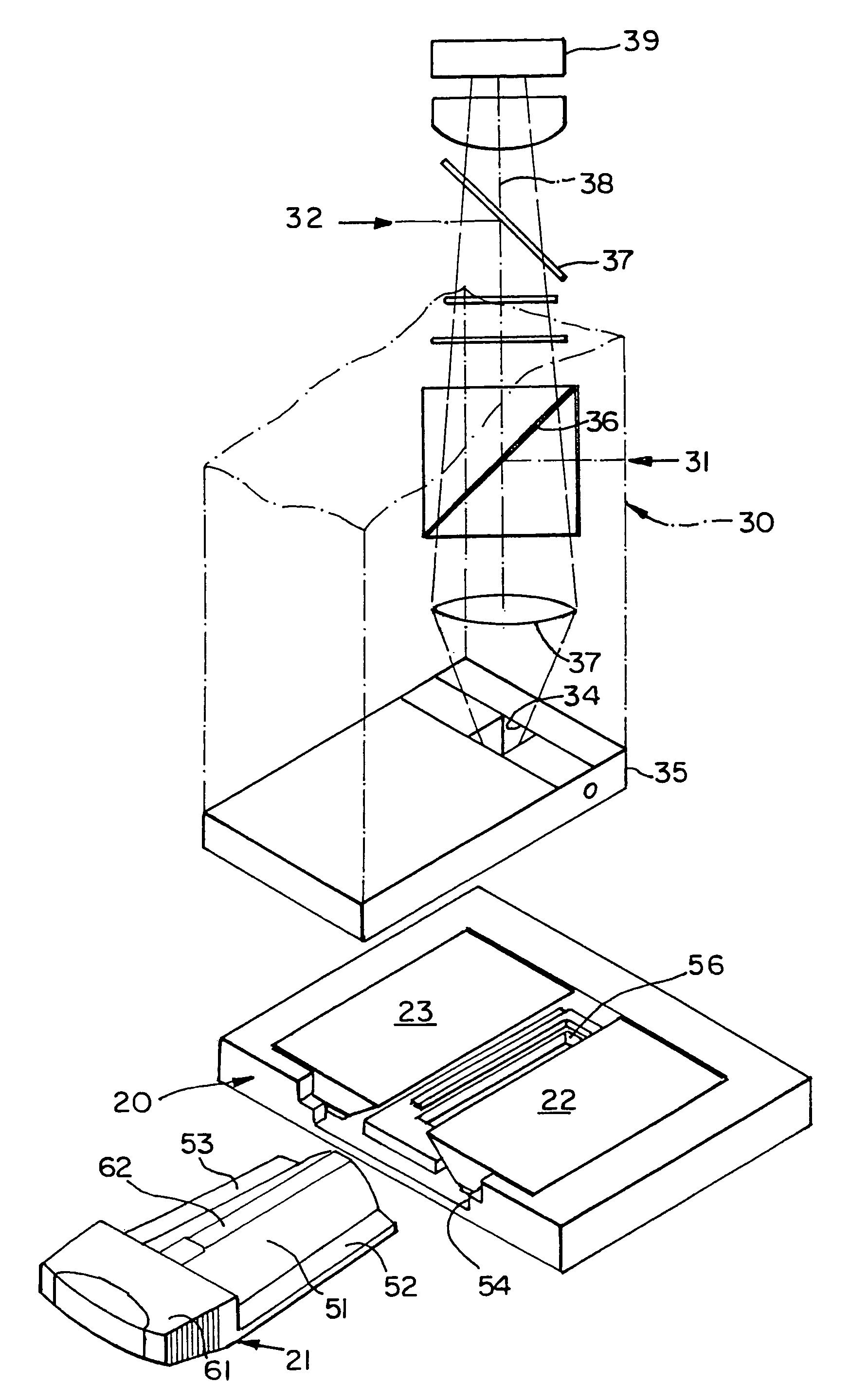
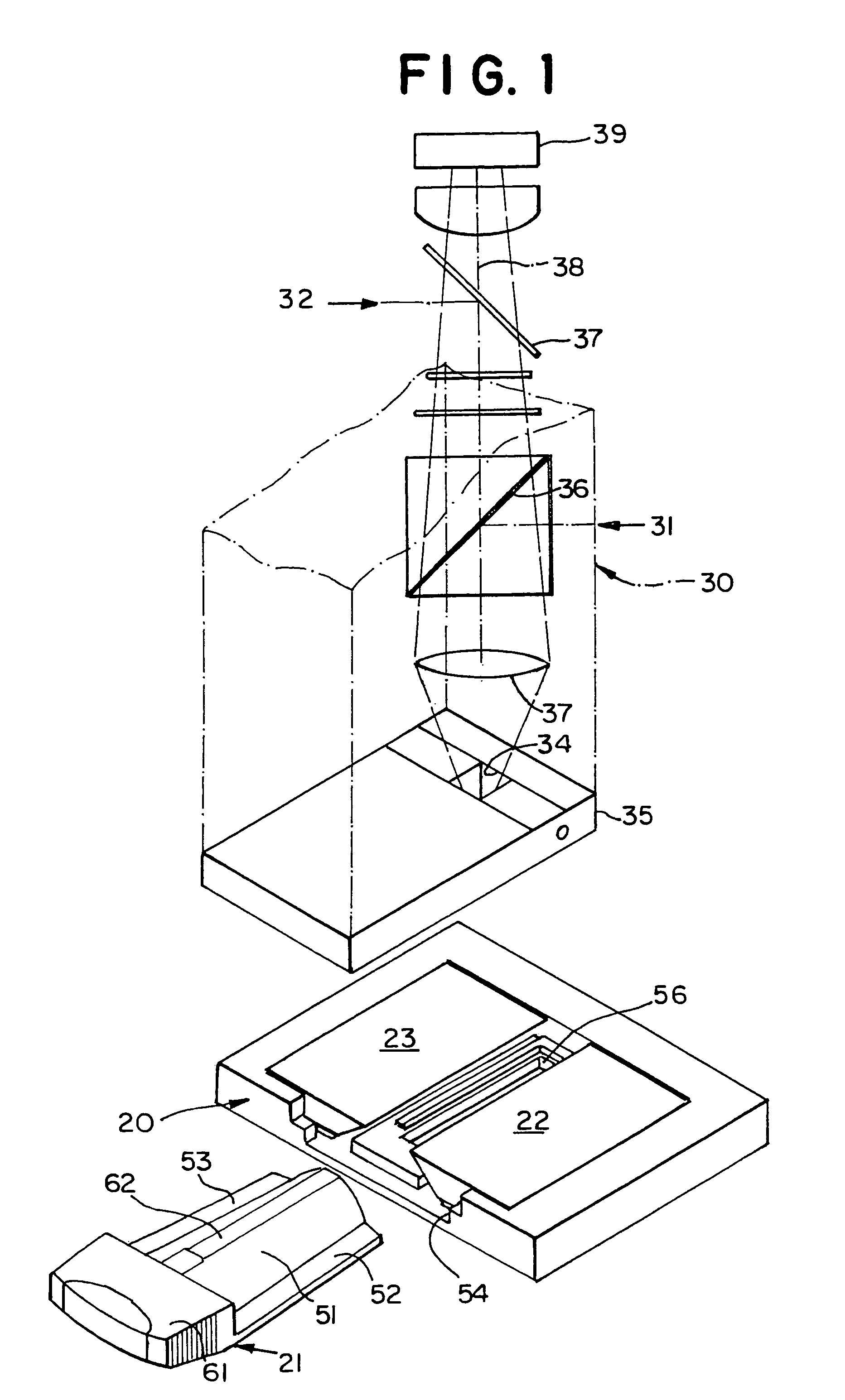
Cartridge for containing a specimen sample for optical analysis
InactiveUS7604777B2Without riskBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsTest chamberEngineering
A cartridge for holding a test specimen with an extremely small volume. The cartridge has a test chamber and a vestibule through which the test fluids are inserted into the test chamber. The cartridge has a stopper having a pair of seals, the first of which seals the test chamber inlet between the vestibule and the test chamber, and the second, of which seals the mouth of the vestibule so that when the stepper is in place, the test chamber is closed to the admission of air or other contaminants and the vestibule is similarly closed against escape of the overflow from the test chamber.
Owner:MENARINI SILICON BIOSYSTEMS SPA
Mechanics sensor array calibrating apparatus and working method thereof
ActiveCN101281073APrecision mechanical designQuick start and stopForce/torque/work measurement apparatus calibration/testingSensor arrayElectricity
The present invention discloses a mechanical sensor array calibration device and the working method thereof. The device comprises locating transmission part and control part which is electrically connected with the locating transmission part; wherein, the locating transmission part comprises calibrated working platform and pressure head testing part; the pressure head testing part is connected with a force sensor through an extension head of a Z-directional linear stepper motor. Using the working method of the device adopts three stepper motors as the driving source; two stepper motors drive the coordinate motion of the slides on the guide rail to finish the location of coordinate point on the working platform; an extension of a linear stepper motor drives the pressure head to exert force on the tested sensor; when the force exerted by the pressure head achieves the set pressure valve, the singlechip collects the output of the tested sensor and the force sensor and the position coordinate of the tested sensor. The present invention is able to execute the choose and configuration of the calibrating mode and process according to the specific sensor array and the specific calibrating demand so as to enlarge the using range of the device.
Owner:ANHUI ZHONGKE BENYUAN INFORMATION TECH CO LTD
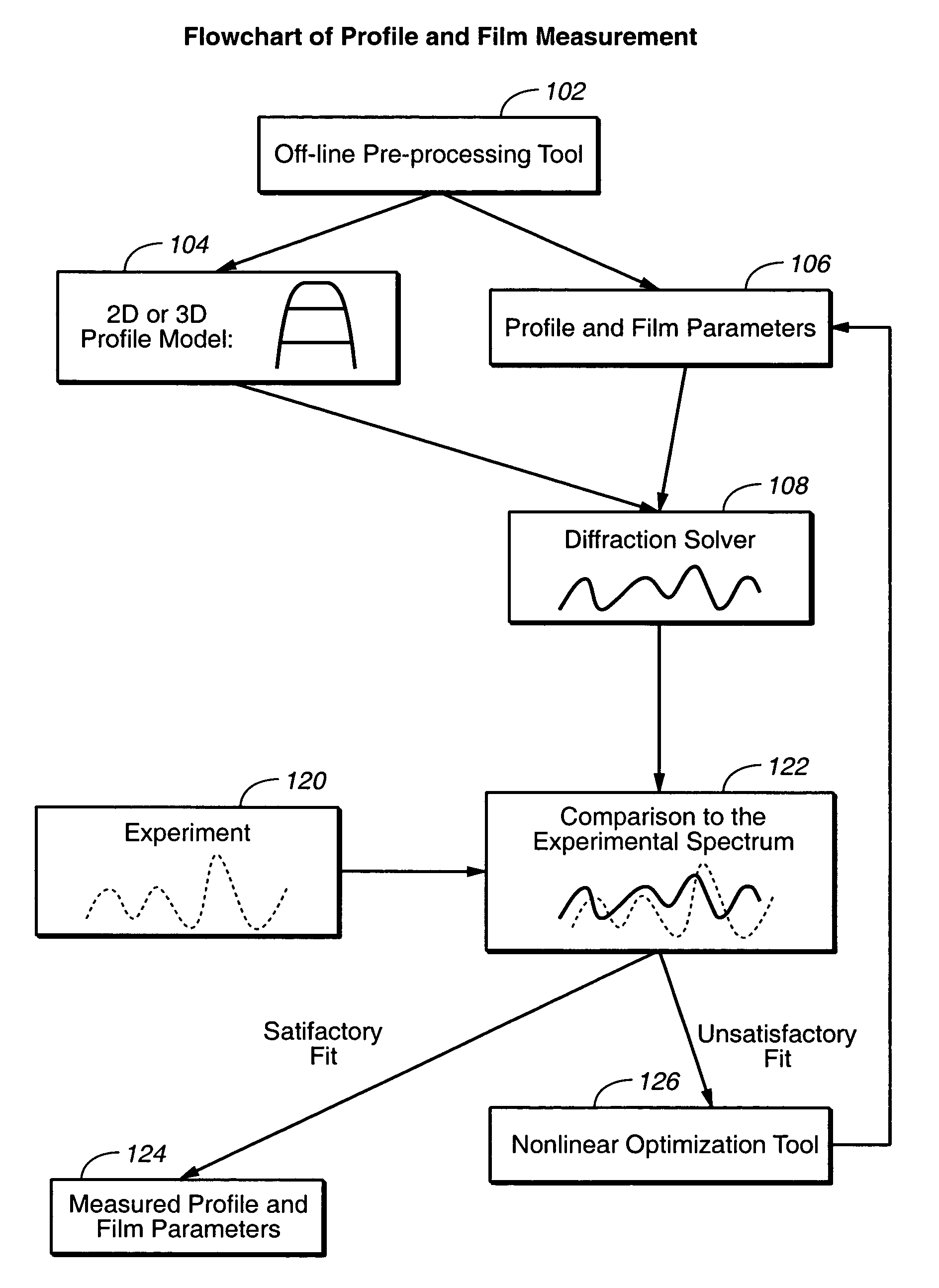
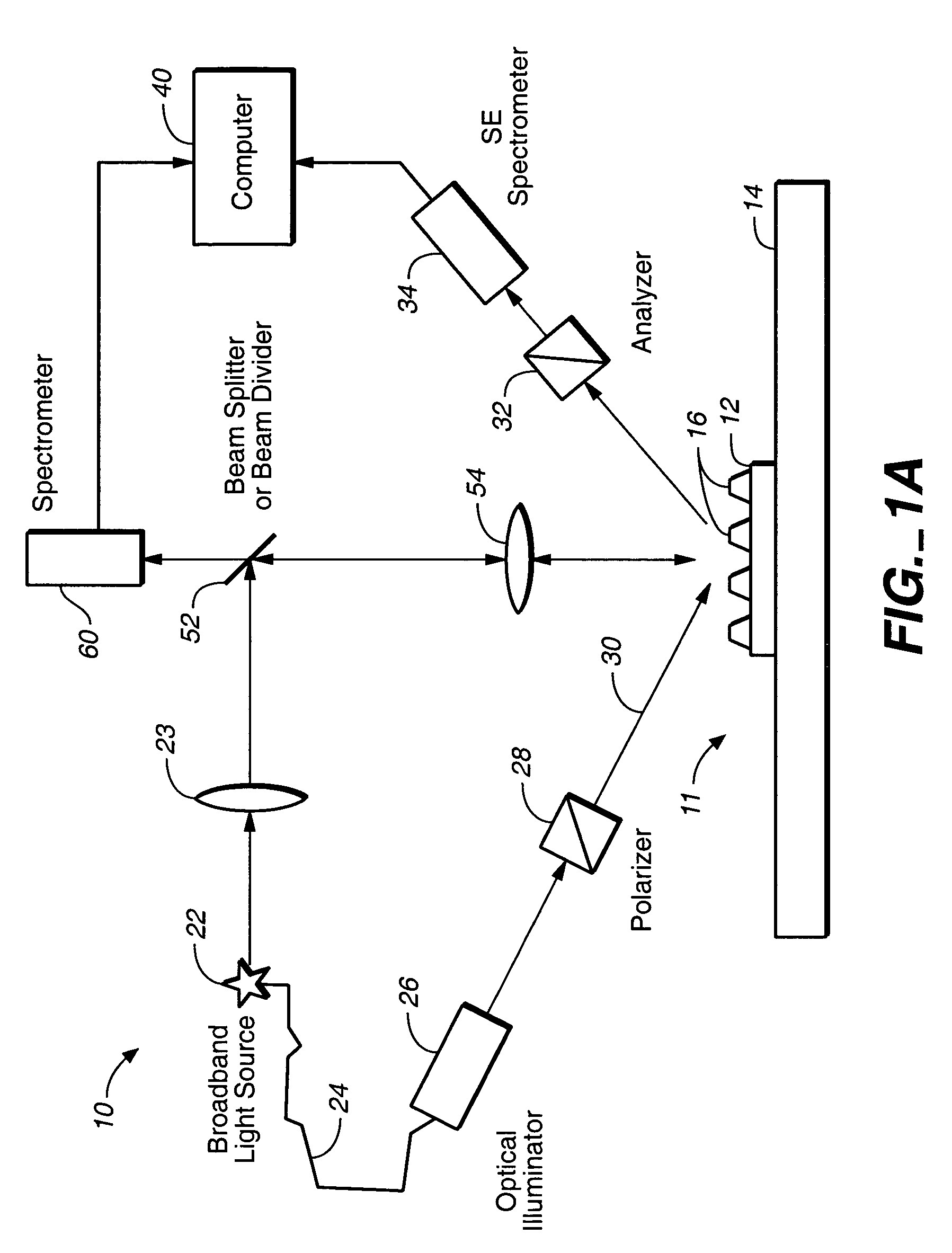
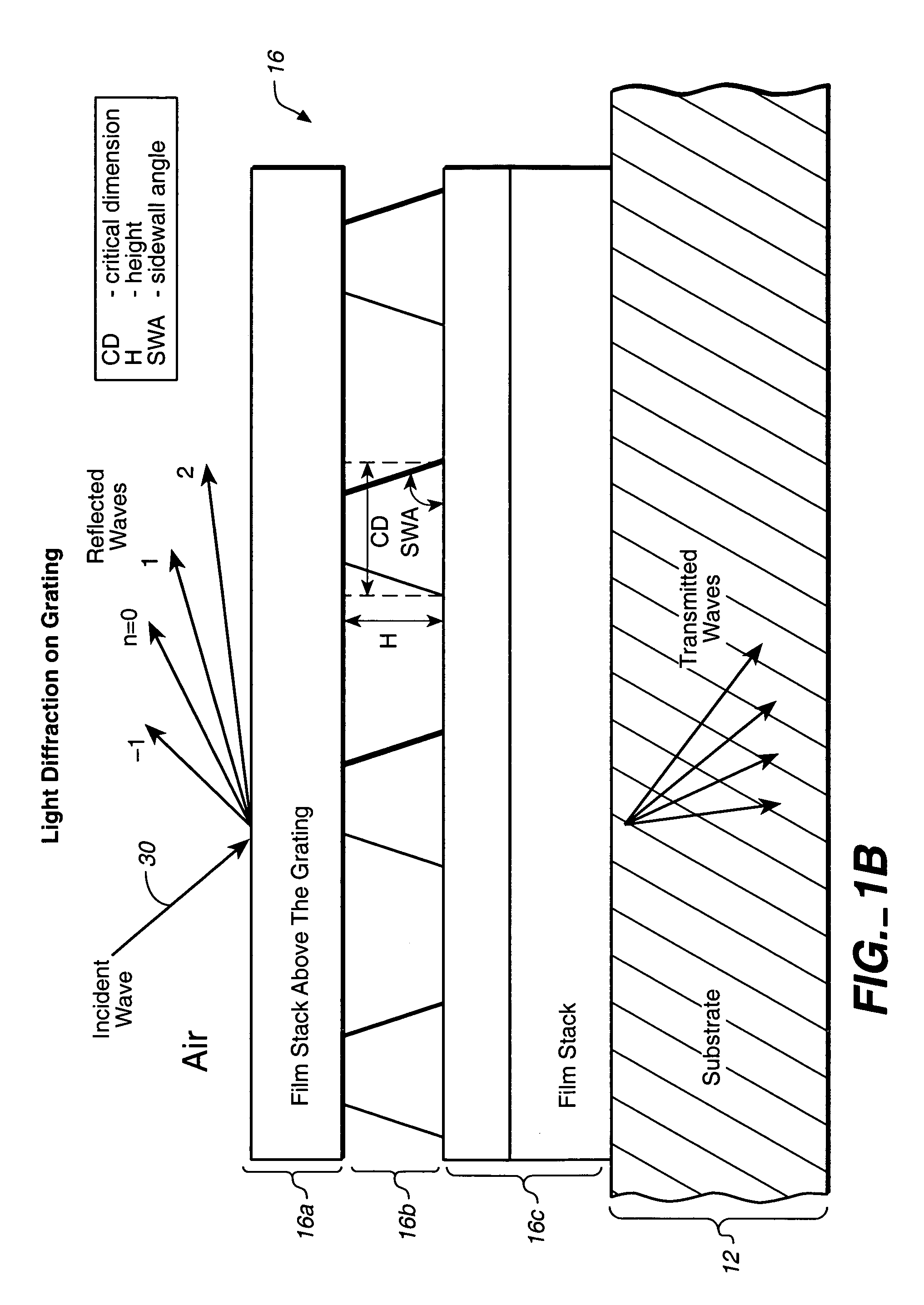
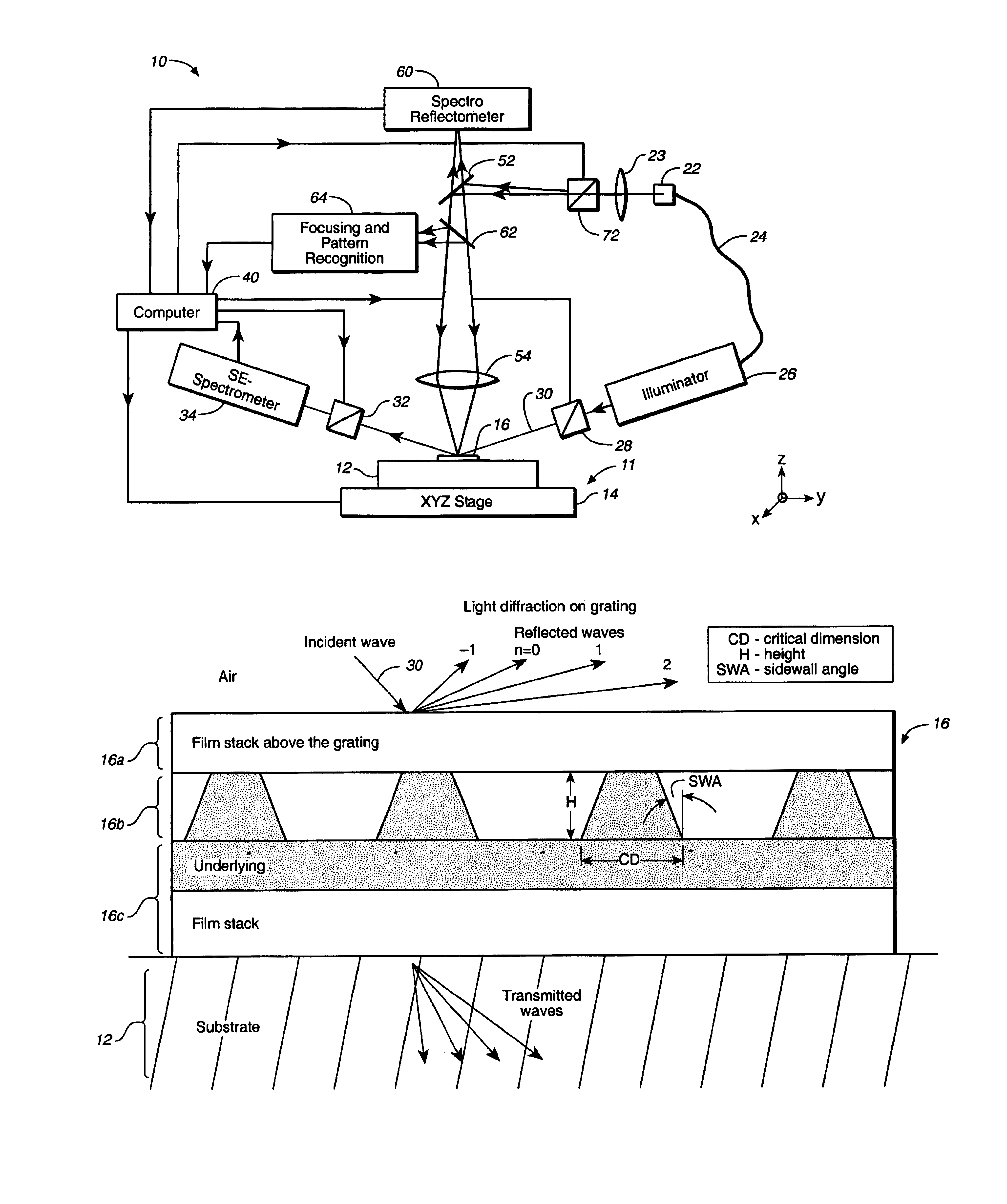
Parametric profiling using optical spectroscopic systems
InactiveUS7280230B2Simplify profile measurementRemove uncertaintyPolarisation-affecting propertiesScattering properties measurementsComputer scienceSemiconductor
A gallery of seed profiles is constructed and the initial parameter values associated with the profiles are selected using manufacturing process knowledge of semiconductor devices. Manufacturing process knowledge may also be used to select the best seed profile and the best set of initial parameter values as the starting point of an optimization process whereby data associated with parameter values of the profile predicted by a model is compared to measured data in order to arrive at values of the parameters. Film layers over or under the periodic structure may also be taken into account. Different radiation parameters such as the reflectivities Rs, Rp and ellipsometric parameters may be used in measuring the diffracting structures and the associated films. Some of the radiation parameters may be more sensitive to a change in the parameter value of the profile or of the films then other radiation parameters. One or more radiation parameters that are more sensitive to such changes may be selected in the above-described optimization process to arrive at a more accurate measurement. The above-described techniques may be supplied to a track / stepper and etcher to control the lithographic and etching processes in order to compensate for any errors in the profile parameters.
Owner:KLA TENCOR TECH CORP
Method for fabricating chip package
InactiveUS20070275503A1Solid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingGold layerPhotoresist
The present invention provides a method for fabricating chip package comprises the following steps: forming a photoresist layer on a metal layer over a passivation layer, an opening in the photoresist layer exposing the metal layer, wherein said forming the photoresist layer comprises exposing the photoresist layer using 1X stepper with at least two of G-line, H-line and I-line; electroplating a gold layer over the metal layer exposed by the opening with an electroplating solution containing gold and sulfite ion; removing the photoresist layer and the metal layer not under the gold layer.
Owner:QUALCOMM INC
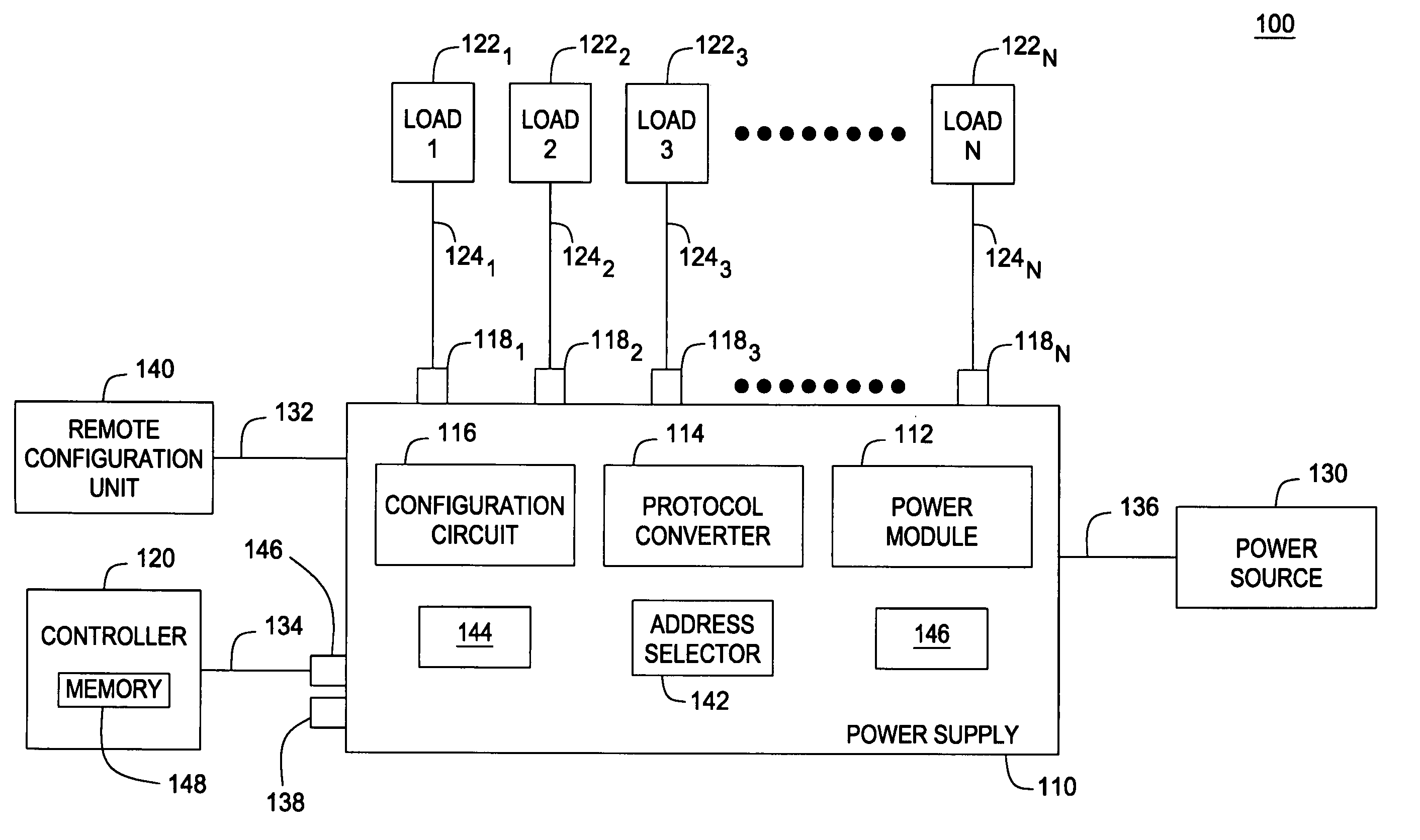
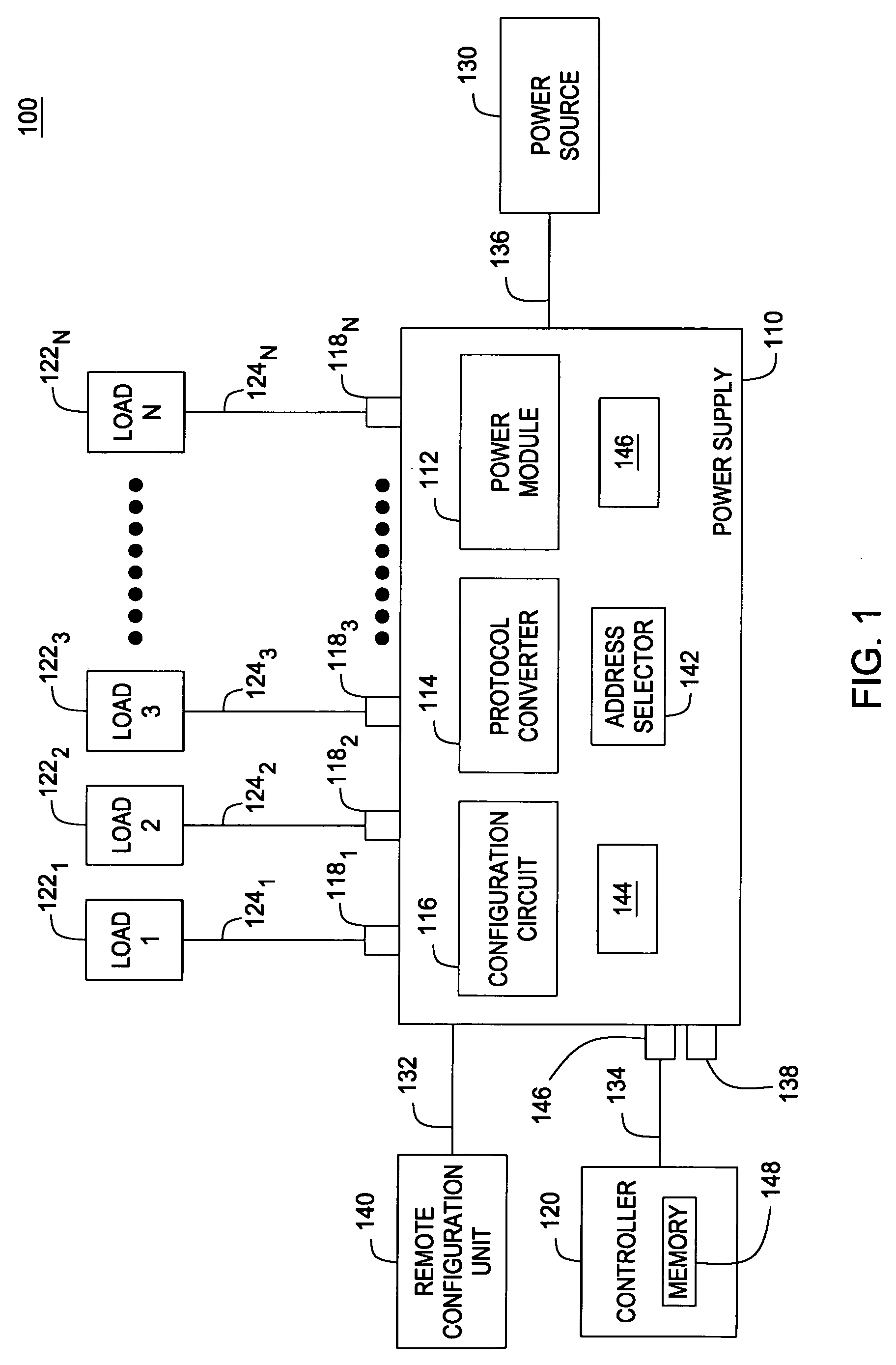
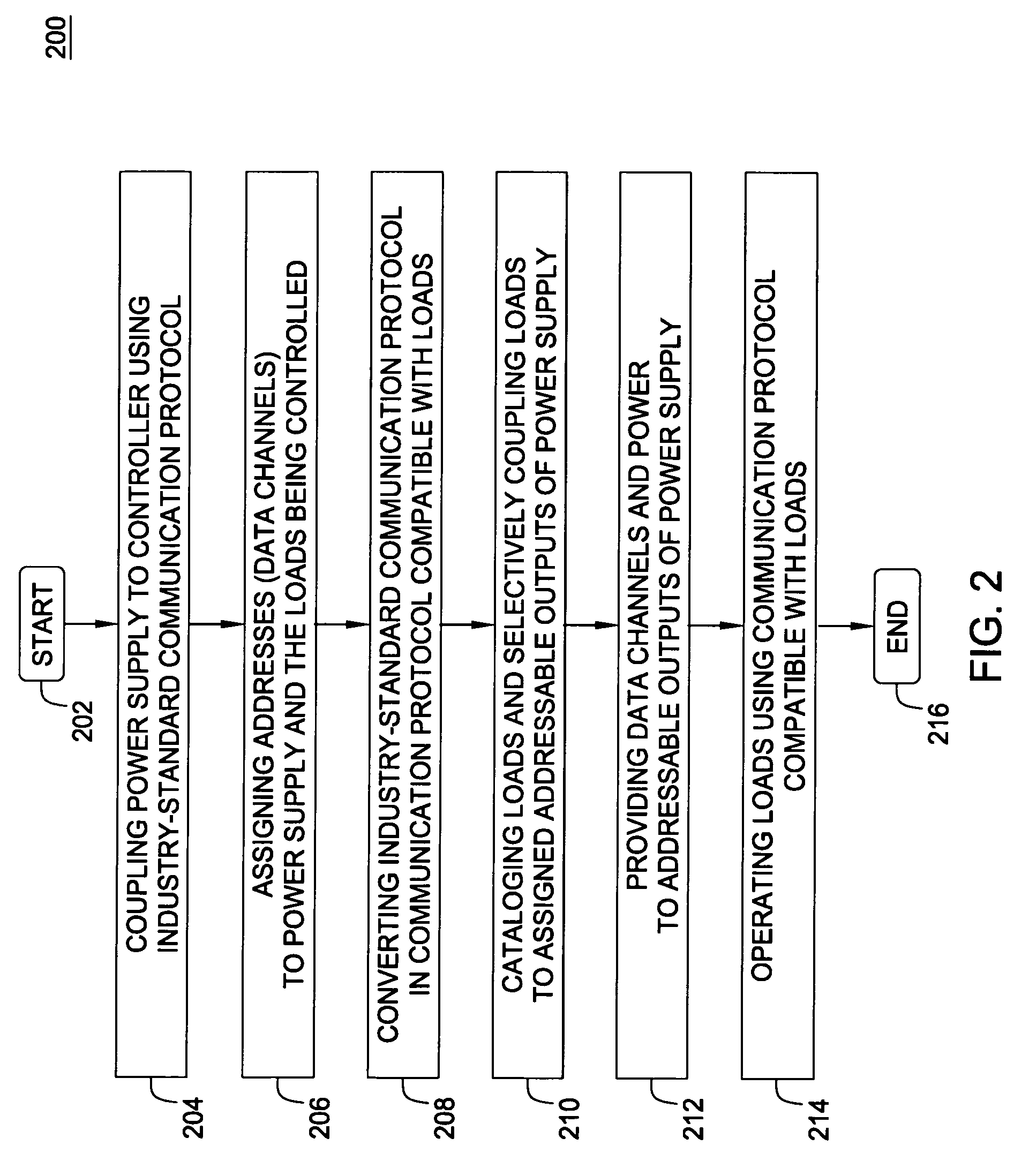
Power supply system and method thereof
A system and a method for operating devices (e.g., luminaries, light dimmers, effect devices, stepper motors, and the like) used in entertainment lighting applications is disclosed. Embodiments include a power supply operating a plurality of such devices coupled to selectively addressable outputs and having a converter of an industry-standard communication protocol (e.g., DMX512, RDM, or ACN protocol) in a communication protocol compatible with such devices.
Owner:CITY THEATRICAL
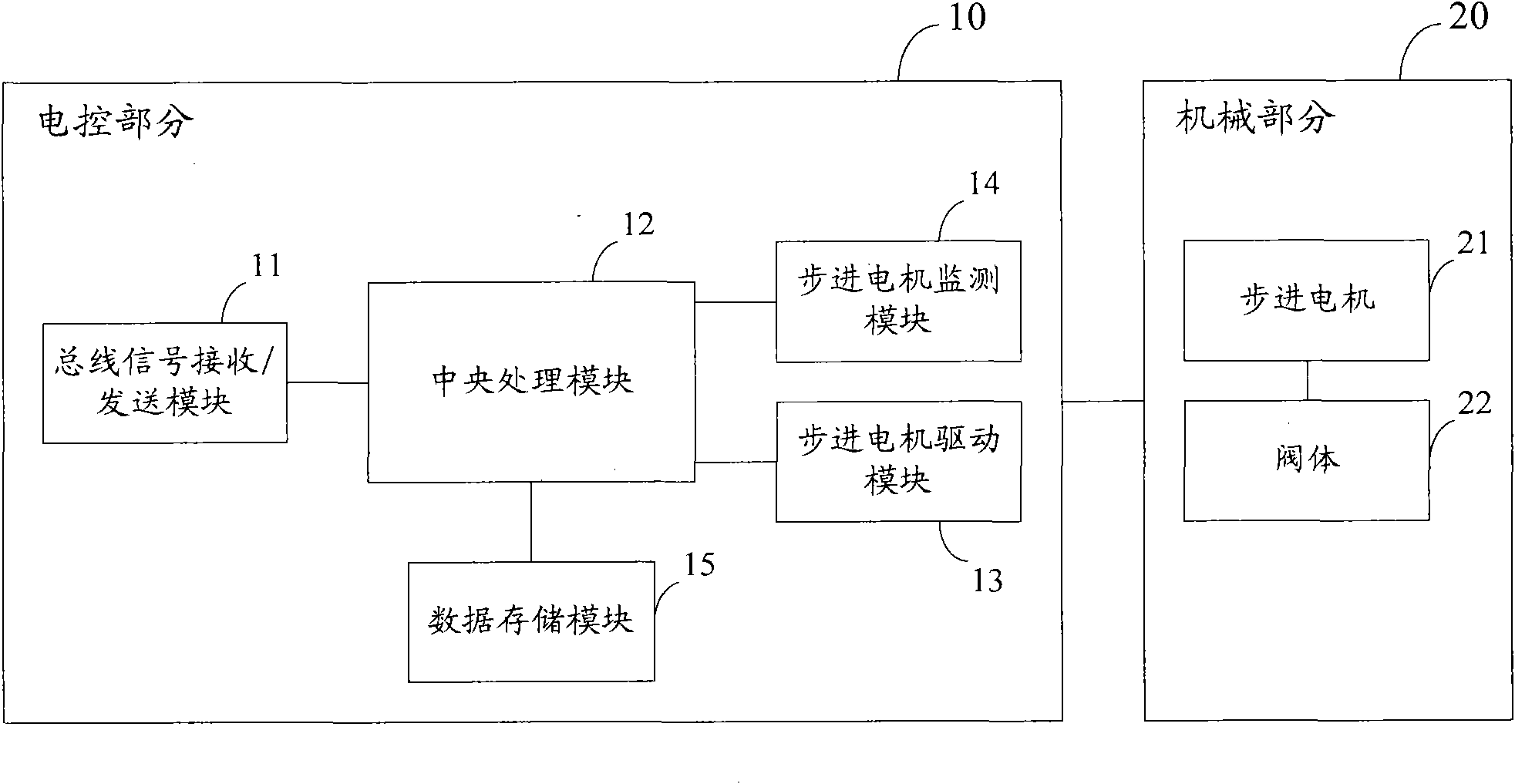
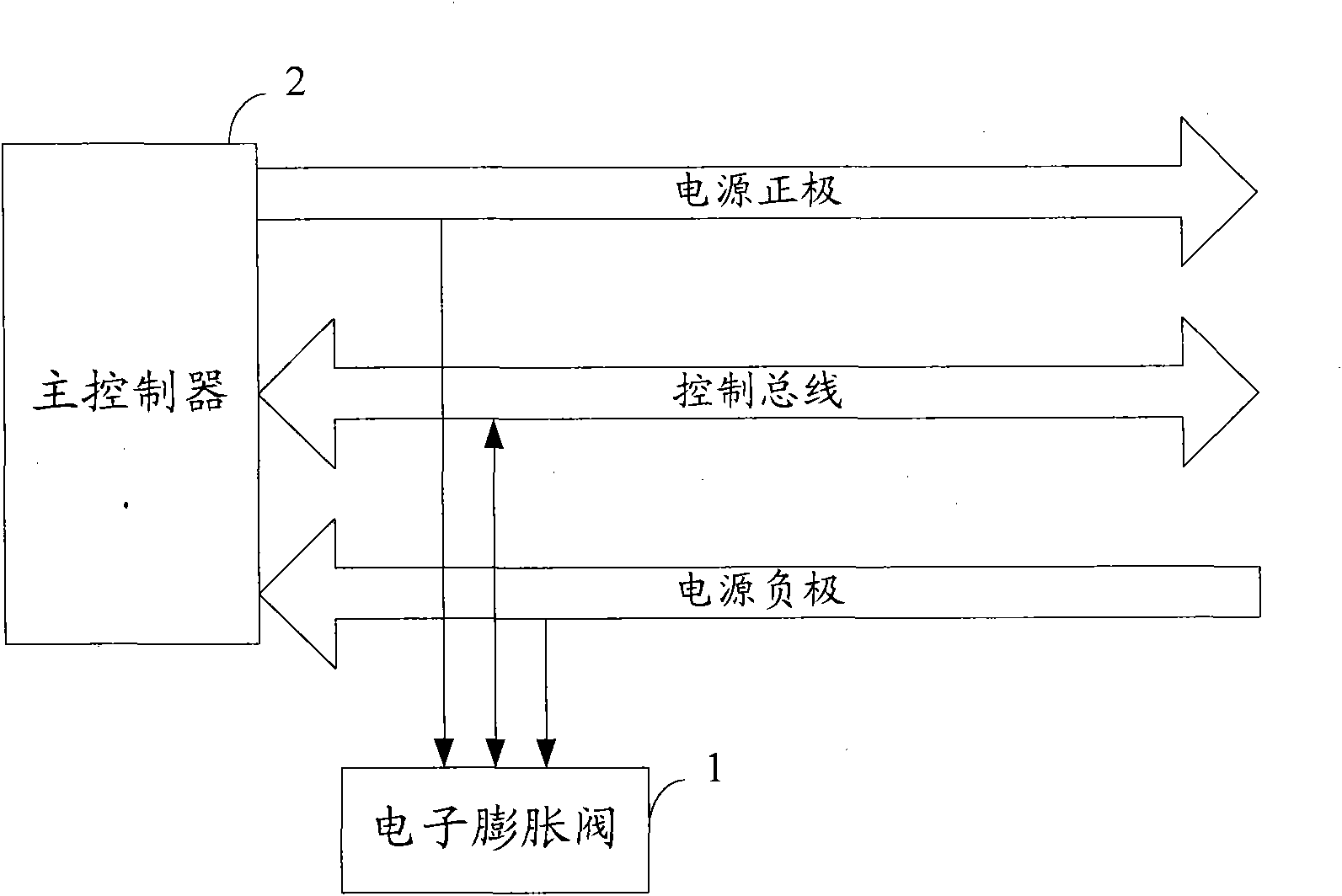
Electronic expansion valve, stepper motor and reversing valve
ActiveCN102374328AReduce in quantitySimple structureOperating means/releasing devices for valvesDynamo-electric converter controlPulse controlControl signal
The invention discloses an electronic expansion valve, which comprises an electrical control part and a mechanical part. The electrical control part comprises a bus signal reception / transmission module, a central processing module and a stepper motor driving module; wherein the bus signal reception / transmission module is used for receiving a bus control signal and transmitting the bus control signal to the central processing module; the central processing module is used for extracting valve opening information included in the bus control signal, generating a corresponding pulse control signalin combination with current position information of a stepper motor read from a data storage module, and outputting the pulse control signal to the stepper motor driving module; and the stepper motordriving module is used for driving the stepper motor to adjust the valve opening according to the pulse control signal. The invention also discloses a stepper motor and a reversing valve. The number of drive wires directly connected with a main control board can be reduced, the structure of the main control board can be simplified, and the manufacturing cost can be saved.
Owner:ZHEJIANG SANHUA AUTOMOTIVE COMPONENTS CO LTD
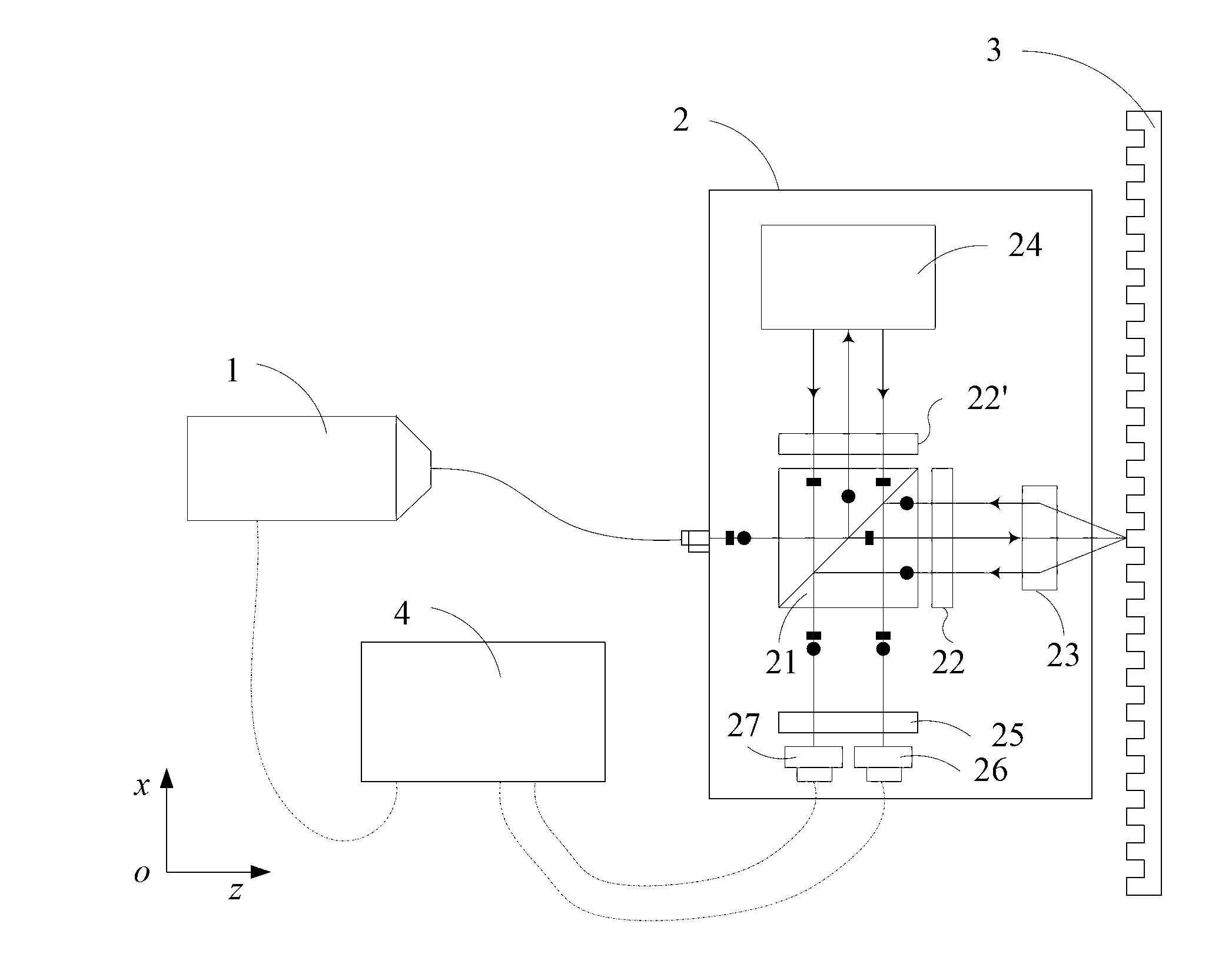
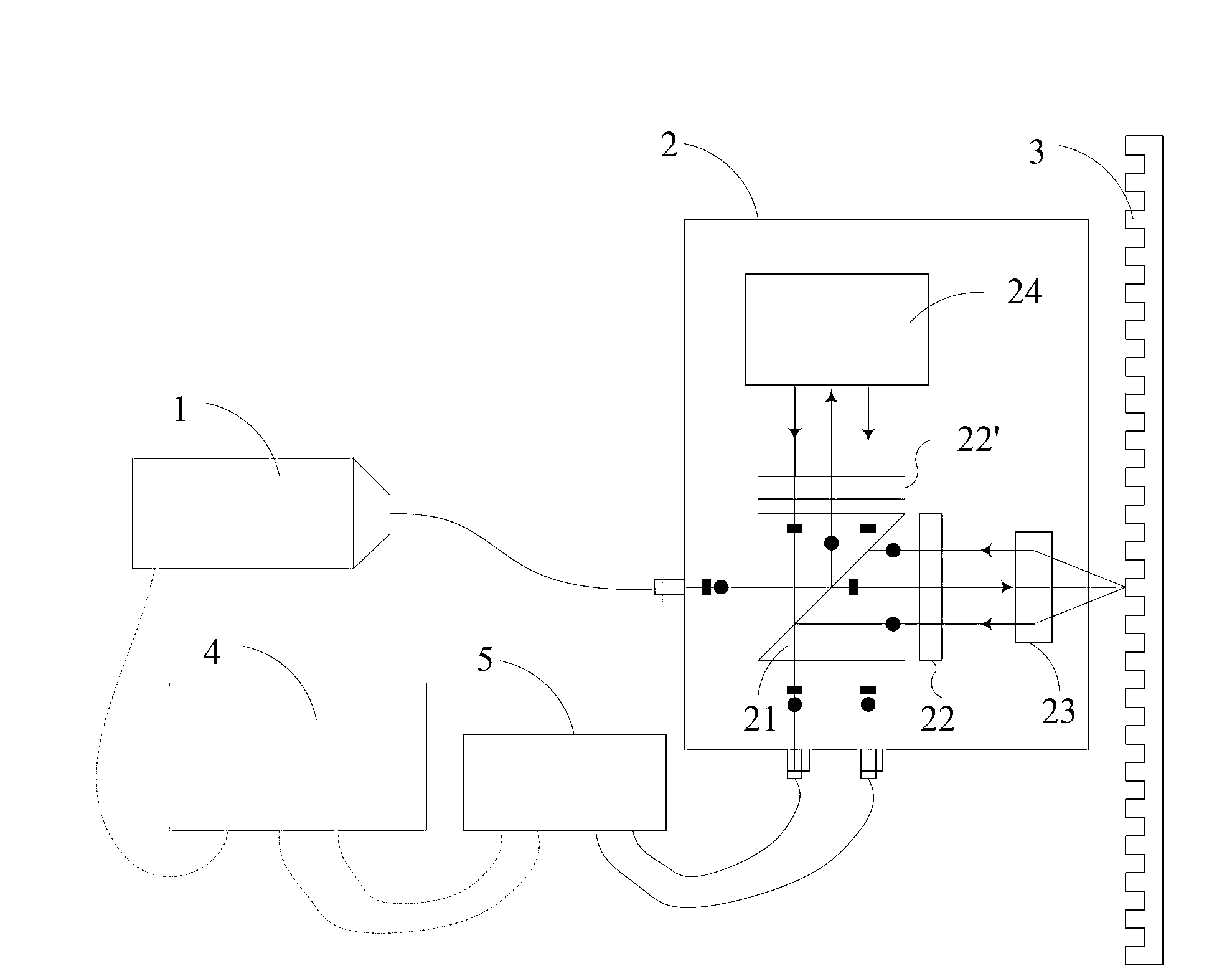
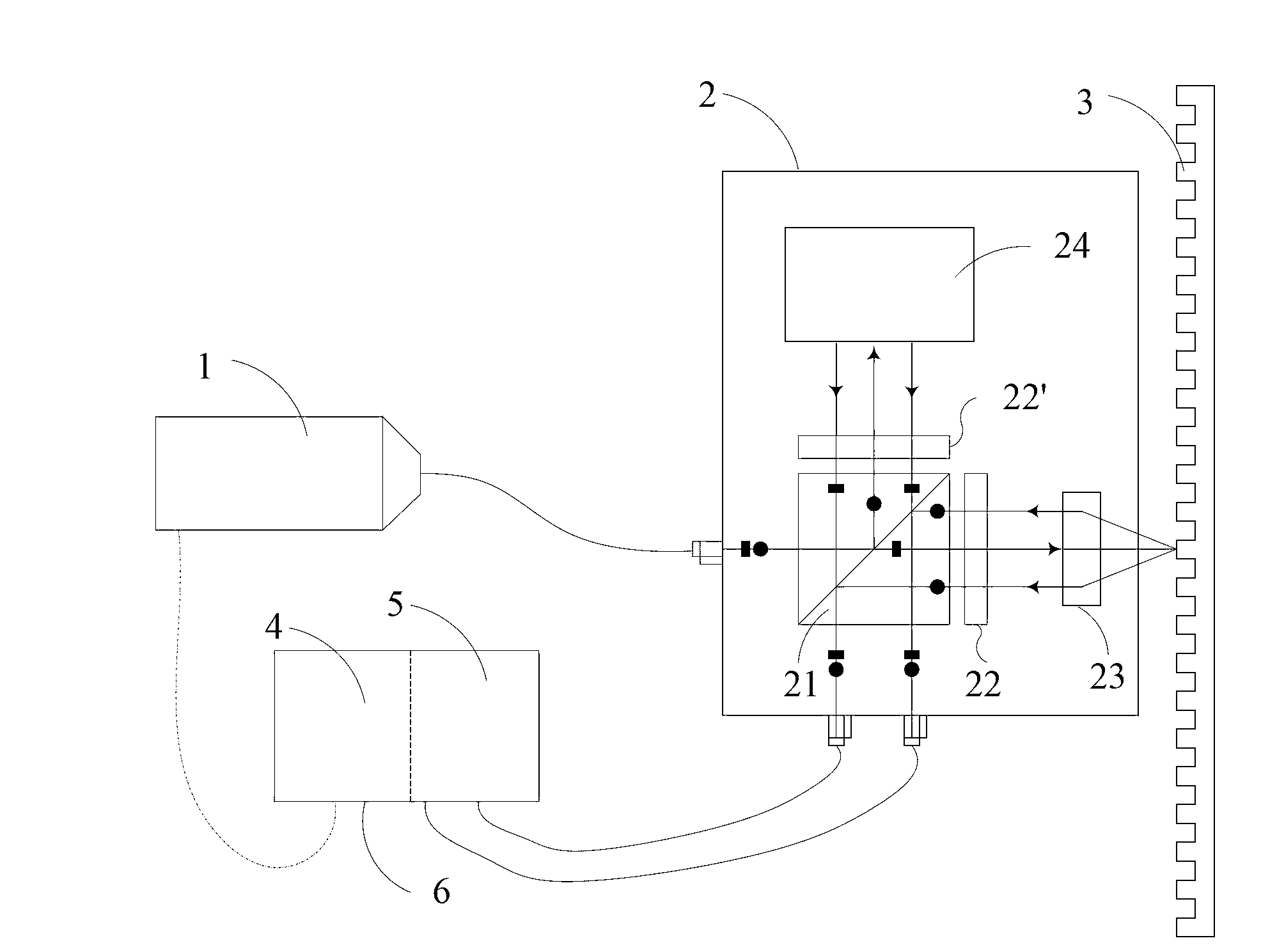
Double-frequency grating interferometer displacement measurement system
ActiveCN102937411AReduce volumeLight in massUsing optical meansConverting sensor output opticallyGratingBeam splitter
The invention discloses a double-frequency grating interferometer displacement measurement system. The system comprises a double-frequency laser device, an interferometer, a measuring grating and an electrical signal processing portion. The measurement system achieves displacement measurement based on optical grating diffraction, the optical doppler principle and an optical beat frequency principle. The double-frequency laser device transmits double-frequency laser, the laser is divided into reference light and measuring light through a polarizing beam splitter, the measuring light transmits into a position of the measuring grating, positive and negative first-order diffraction occurs, diffraction light and the reference light form a beat frequency signal which contains displacement information in two directions at the position of a light detection unit, and linear displacement output is achieved through signal processing. According to the system, the sub-nanometer-grade or even higher grade of resolution ratio and accuracy can be achieved, and horizontal large-stroke displacement and horizontal displacement can be measured at the same time. The system has the advantages of being insensitive to the environment, high in measuring accuracy, small in volume and light in weight. The system serves as a lithography machine ultraprecise workpiece platform position measurement system, the comprehensive performance of the workpiece platform can be improved.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV +1
Interactive computer simulation enhanced exercise machine
InactiveUS20070117680A1Improve sports experienceEfficient executionIndoor gamesSpace saving gamesExercise machineVisual perception
A computer simulation enhanced exercise device is provided which engages the user by directly relating the users exercise motion in real time to a visual simulation or interactive game. The exercise device may comprise any variety of machines including, stationary bikes, rowing machines, treadmills, stepper, elliptical gliders or under desk exercise. These exercise devices are configured with sensors to measure physical movements as the user exercises and are coupled to computer hardware with modeling and virtualization software to create the system. These sensor measurements are then sent to a computer for use in the physics based modeling and real-time visual simulation. The computer simulation enhanced exercise device is further provided with features including manual and automatic adjustment of resistance levels, visualization of accurate caloric burn rates and correlation to everyday food items, and network connectivity providing for multiplayer network simulations and directed advertising.
Owner:CUBEX
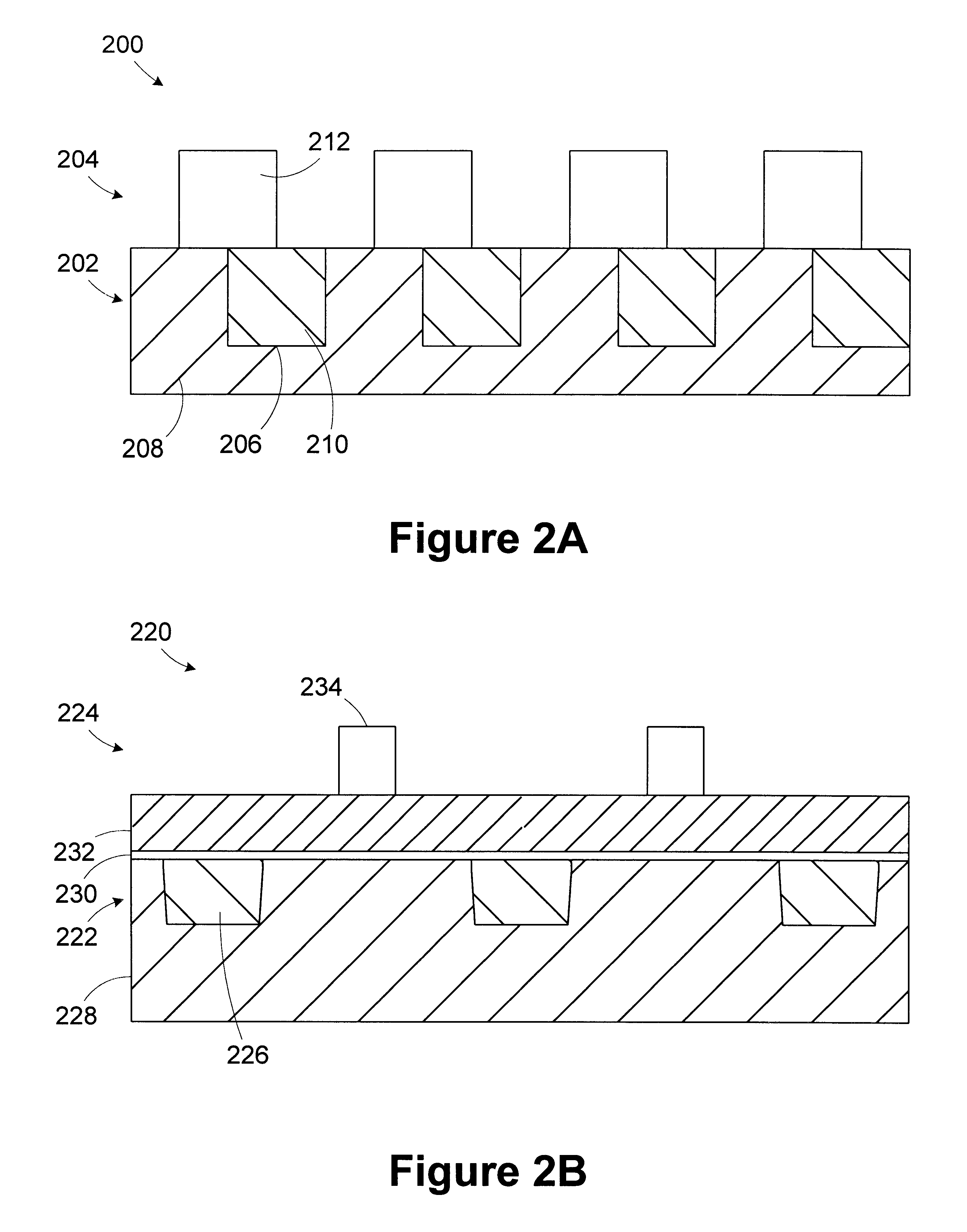
Method and apparatus for identifying misregistration in a complimentary phase shift mask process
InactiveUS6774998B1Semiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingUsing optical meansMetrologyGrating
A method includes providing a wafer having a first grating structure and a second grating structure formed in a photoresist layer. At least a portion of the first and second grating structures is illuminated with a light source. Light reflected from the illuminated portion of the first and second grating structures is measured to generate a reflection profile. Misregistration between the first and second grating structures is determined based on the reflection profile. A processing line includes a photolithography stepper, a metrology tool, and a controller. The photolithography stepper is adapted to process wafers in accordance with an operating recipe. The metrology tool is adapted to receive a wafer processed in the stepper. The wafer has a first grating structure and a second grating structure formed in a photoresist layer. The metrology tool includes a light source, a detector, and a data processing unit.
Owner:GLOBALFOUNDRIES US INC
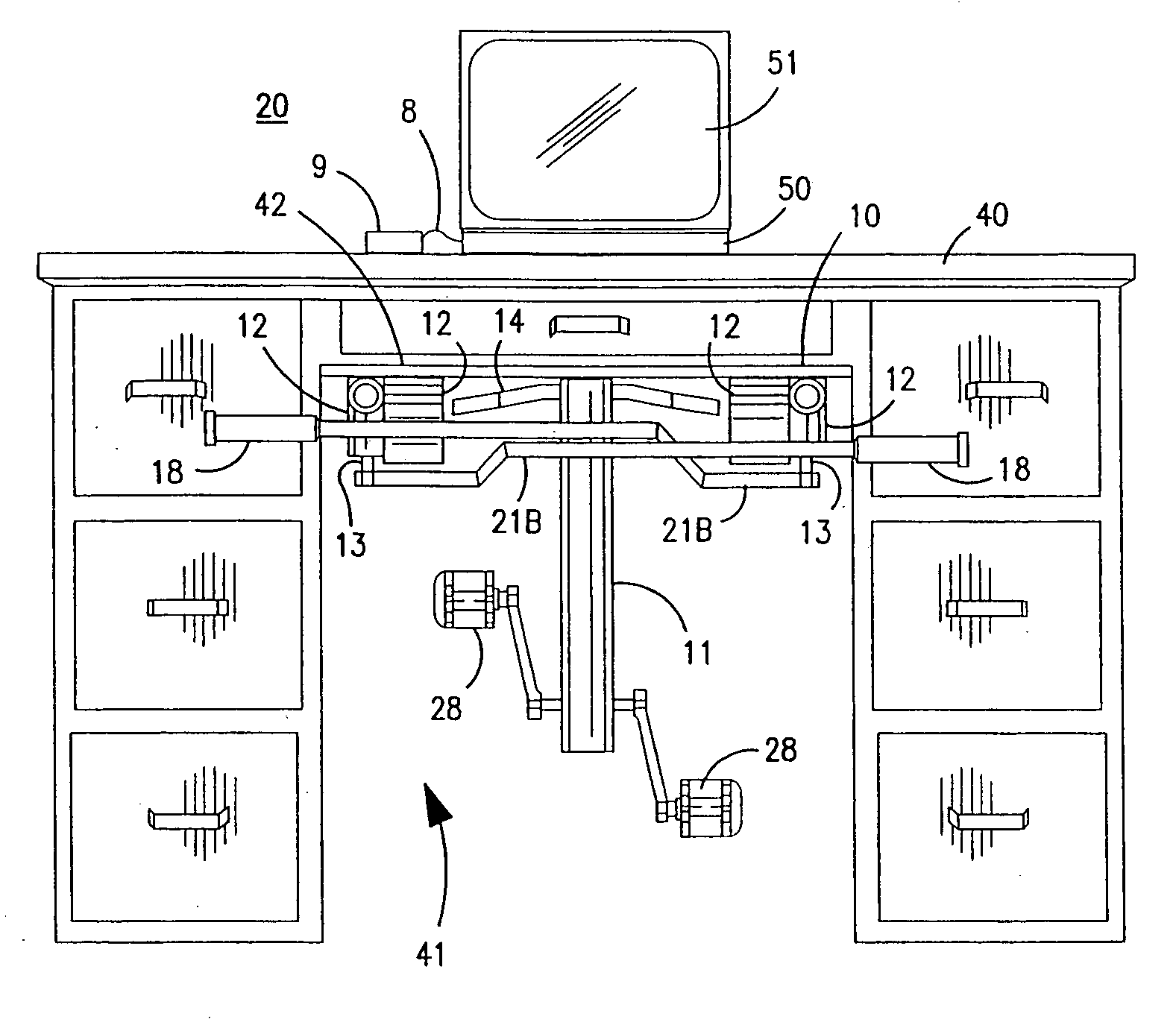
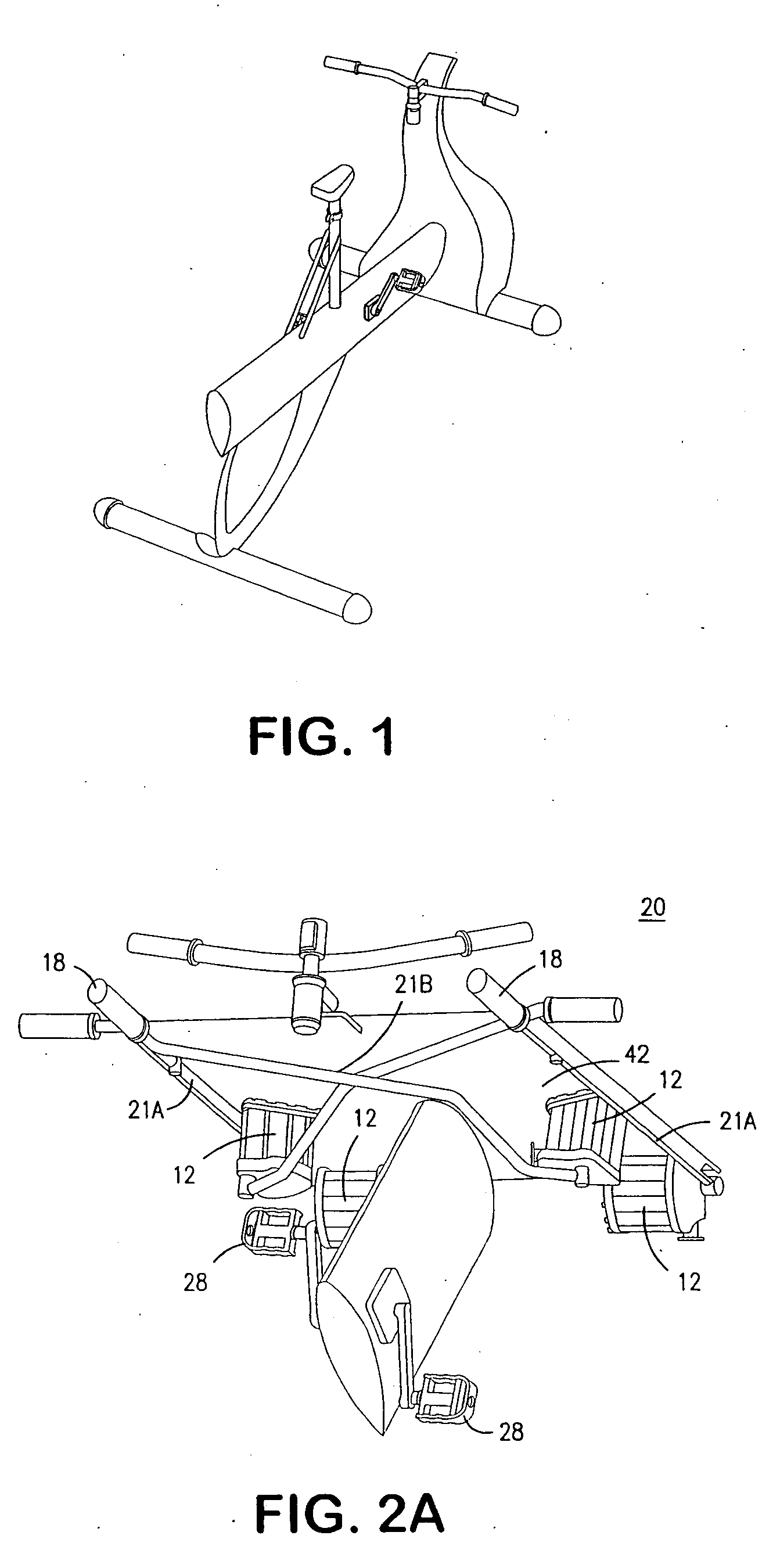
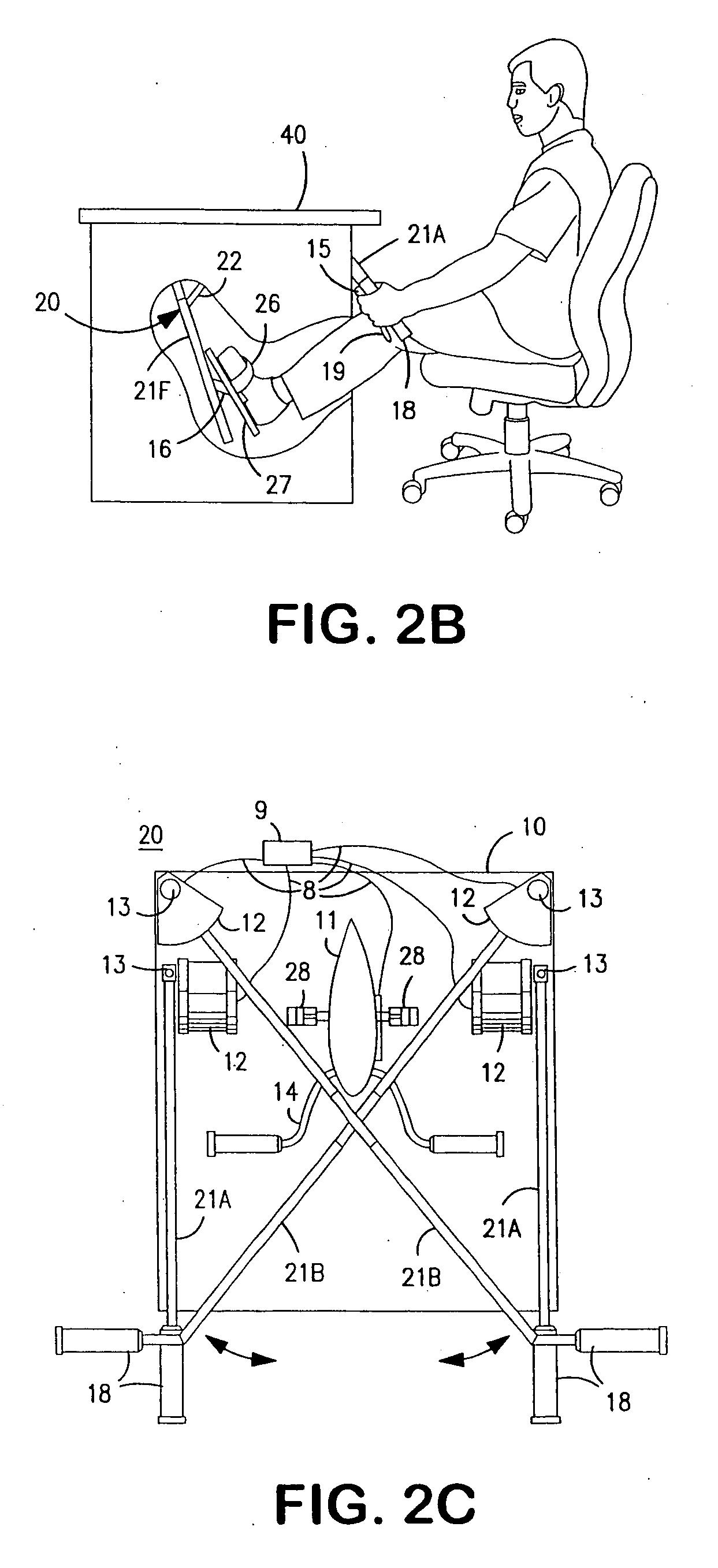
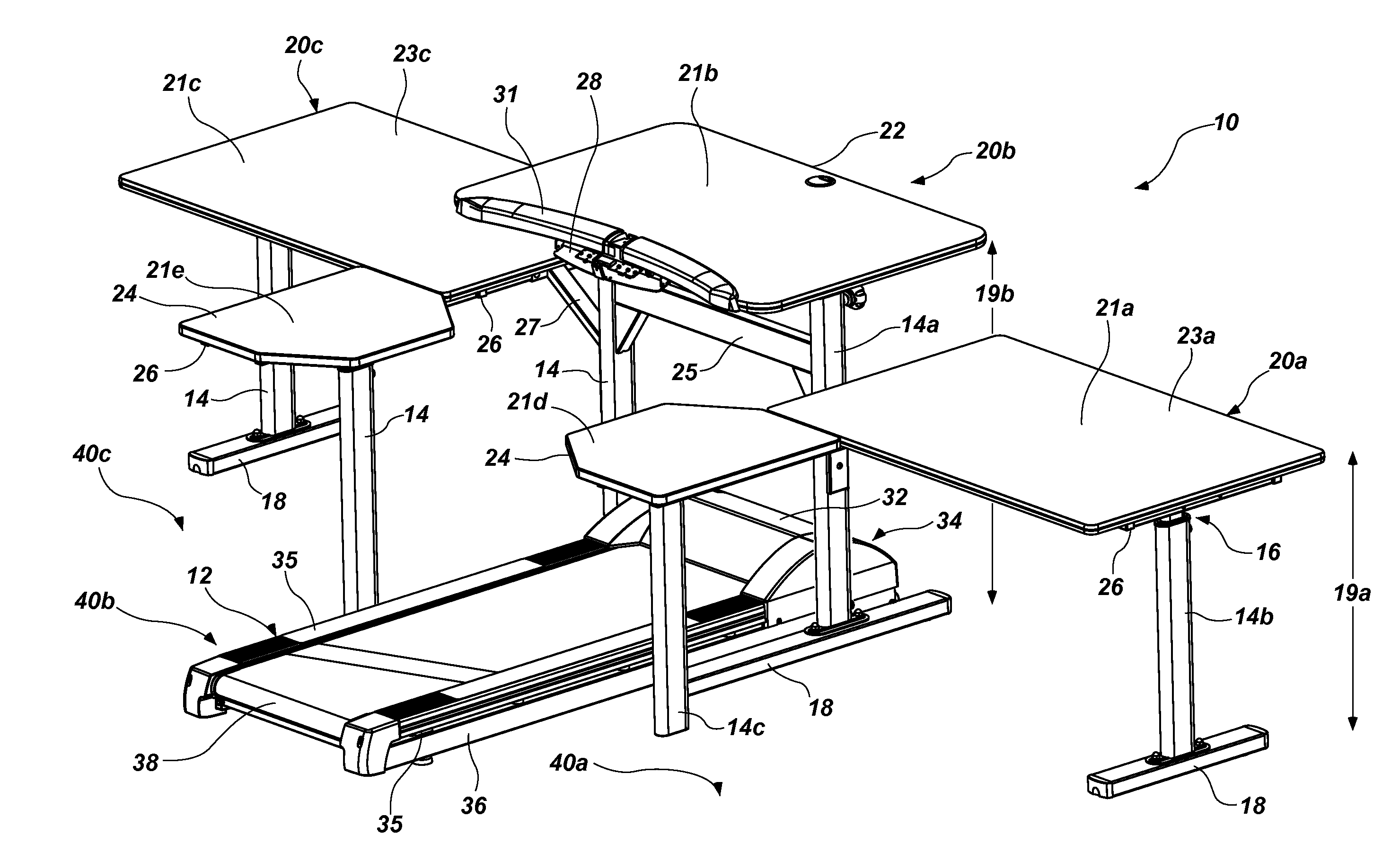
Active workstation apparatus and method
InactiveUS20140360413A1Easy to adjustEasy accessOffice tablesSectional furnitureEngineeringWorkstation
An apparatus and method provide various desk structures as workstations to receive a user, standing or sitting, walking or stationary, exercising or sedentary. A double duty desk system may include multiple, dedicated “sitting desks” at seated height and fixed to a shared “standing desk,” the height of whose desktop stands accessible to a user exercising on an exercise bike, treadmill, stepper, or the like. A user in an exercise (e.g., standing) position may view materials set on the standing desk and on the attached sitting desks and returns. Heights of desks may be permanently fixed, adjustable, powered, mechanized, manual, or a combination. A user may selectively exercise or sit, in order to read, browse online, attend webinars, edit, monitor, handwrite, type, lecture, listen, answer phones, make calls, develop software, or the like from a standing or sitting position, at will.
Owner:SCHENK PETER
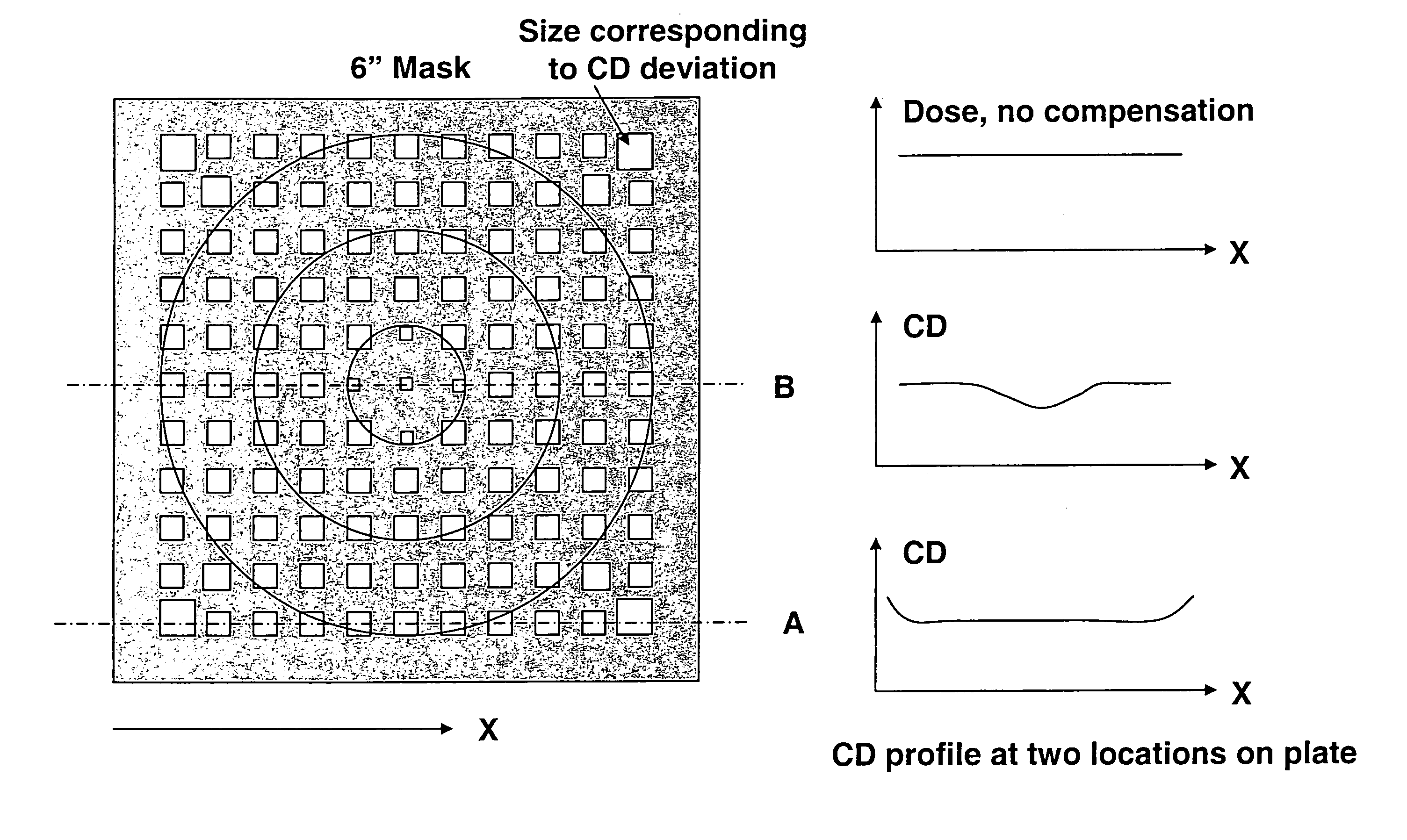
Method for error reduction in lithography
InactiveUS7444616B2High precisionCharacter and pattern recognitionPhotomechanical exposure apparatusError reductionEngineering
The present invention relates to a method and a system for predicting and / or measuring and correcting geometrical errors in lithography using masks, such as large-area photomasks or reticles, and exposure stations, such as wafer steppers or projection aligners, printing the pattern of said masks on a workpiece, such as a display panel or a semiconductor wafer. A method to compensate for process variations when printing a pattern on a workpiece, including determining a two-dimensional CD profile in said pattern printed on said workpiece, generating a two-dimensional compensation file to equalize fluctuations in said two-dimensional CD-profile, and patterning a workpiece with said two-dimensional compensation file.
Owner:MICRONIC LASER SYST AB
Interactive computer simulation enhanced exercise machine
InactiveUS7497812B2Improve sports experienceLow costInput/output for user-computer interactionIndoor gamesPhysics basedVirtualization
A computer simulation enhanced exercise device is provided which engages the user by directly relating the users exercise motion in real time to a visual simulation or interactive game. The exercise device may comprise any variety of machines including, stationary bikes, rowing machines, treadmills, stepper, elliptical gliders or under desk exercise. These exercise devices are configured with sensors to measure physical movements as the user exercises and are coupled to computer hardware with modeling and virtualization software to create the system. These sensor measurements are then sent to a computer for use in the physics based modeling and real-time visual simulation. The computer simulation enhanced exercise device is further provided with features including manual and automatic adjustment of resistance levels, visualization of accurate caloric burn rates and correlation to everyday food items, and network connectivity providing for multiplayer network simulations and directed advertising.
Owner:CUBEX
Cluster tool architecture for processing a substrate
InactiveUS20060134330A1More repeatable wafer processing historyReduced footprintProgramme controlSemiconductor/solid-state device testing/measurementLithography processEngineering
Embodiments generally provide an apparatus and method for processing substrates using a multi-chamber processing system (e.g., a cluster tool) that has an increased system throughput, increased system reliability, substrates processed in the cluster tool have a more repeatable wafer history, and also the cluster tool has a smaller system footprint. In one embodiment, the cluster tool is adapted to perform a track lithography process in which a substrate is coated with a photosensitive material, is then transferred to a stepper / scanner, which exposes the photosensitive material to some form of radiation to form a pattern in the photosensitive material, which is then removed in a developing process completed in the cluster tool. In track lithography type cluster tools, since the chamber processing times tend to be rather short, and the number of processing steps required to complete a typical track system process is large, a significant portion of the time it takes to process a substrate is taken up by the processes of transferring the substrates in a cluster tool between the various processing chambers. In one embodiment of the cluster tool, the cost of ownership is reduced by grouping substrates together and transferring and processing the substrates in groups of two or more to improve system throughput, and reduces the number of moves a robot has to make to transfer a batch of substrates between the processing chambers, thus reducing wear on the robot and increasing system reliability. In one aspect of the invention, the substrate processing sequence and cluster tool are designed so that the substrate transferring steps performed during the processing sequence are only made to chambers that will perform the next processing step in the processing sequence. Embodiments also provide for a method and apparatus that are used to improve the coater chamber, the developer chamber, the post exposure bake chamber, the chill chamber, and the bake chamber process results. Embodiments also provide for a method and apparatus that are used to increase the reliability of the substrate transfer process to reduce system down time.
Owner:SOKUDO CO LTD
System for scatterometric measurements and applications
InactiveUS7099005B1Robust partSimple processSemiconductor/solid-state device testing/measurementPolarisation-affecting propertiesTime efficientEstimation methods
Instead of constructing a full multi-dimensional look up table as a model to find the critical dimension or other parameters in scatterometry, regression or other optimized estimation methods are employed starting from a “best guess” value of the parameter. Eigenvalues of models that are precalculated may be stored and reused later for other structures having certain common characteristics to save time. The scatterometric data that is used to find the value of the one or more parameter can be limited to those at wavelengths that are less sensitive to the underlying film characteristics. A model for a three-dimensional grating may be constructed by slicing a representative structure into a stack of slabs and creating an array of rectangular blocks to approximate each slab. One dimensional boundary problems may be solved for each block which are then matched to find a two-dimensional solution for the slab. A three-dimensional solution can then be constructed from the two-dimensional solutions for the slabs to yield the diffraction efficiencies of the three-dimensional grating. This model can then be used for finding the one or more parameters of the diffracting structure in scatterometry. Line roughness of a surface can be measured by directing a polarized incident beam in an incident plane normal to the line grating and measuring the cross-polarization coefficient. The value of the one or more parameters may then be supplied to a stepper or etcher to adjust a lithographic or etching process.
Owner:KLA TENCOR TECH CORP
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com