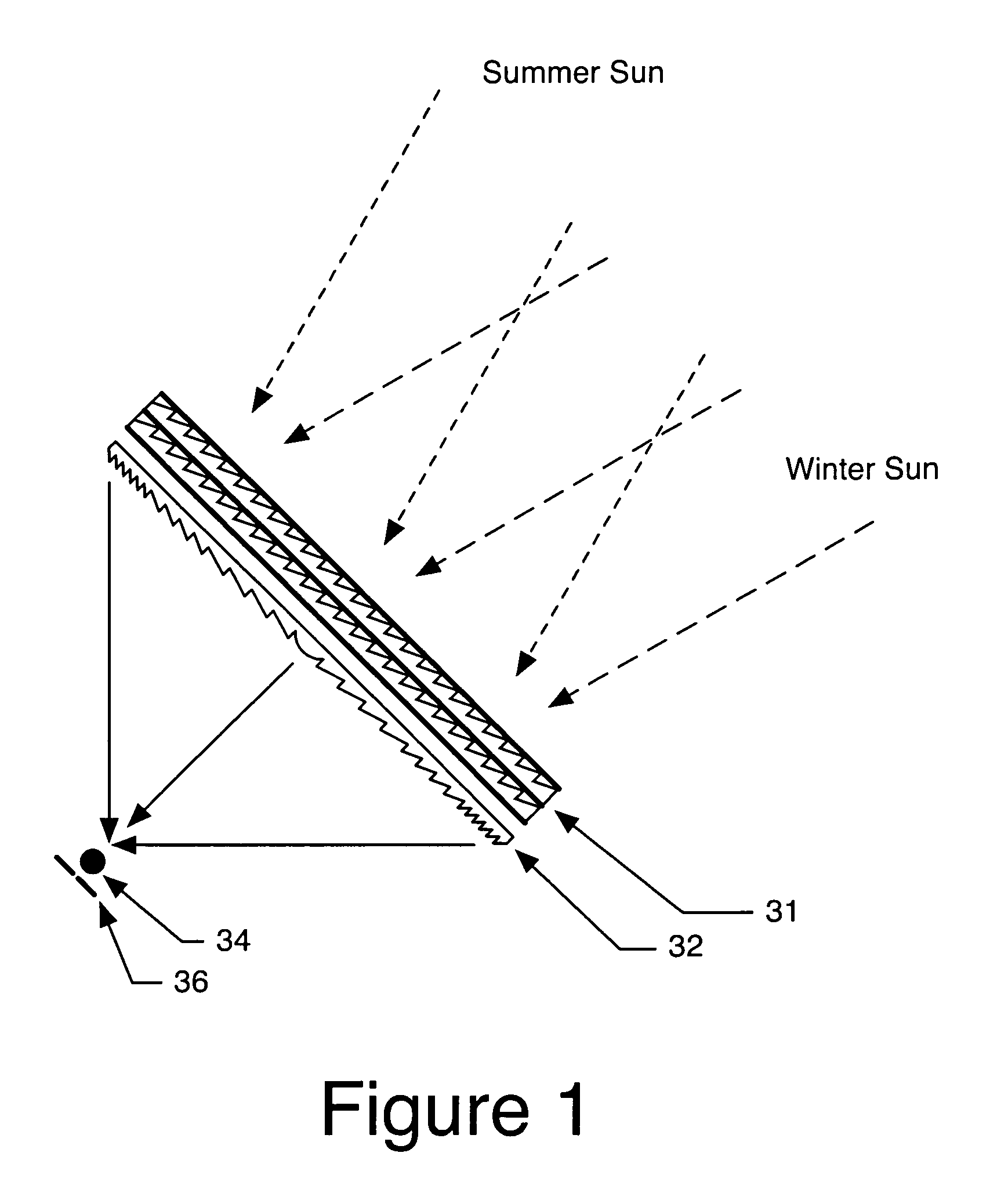
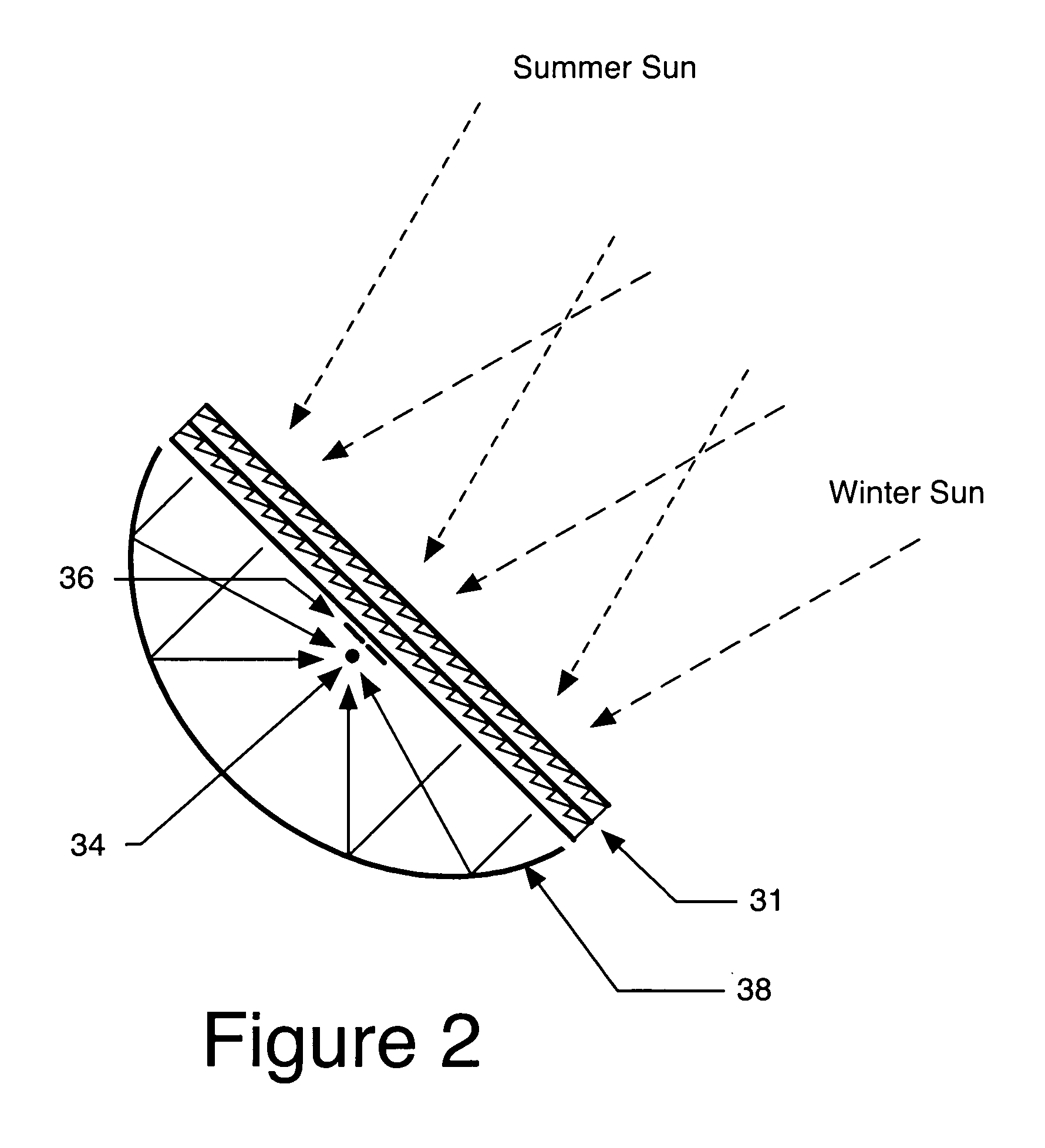
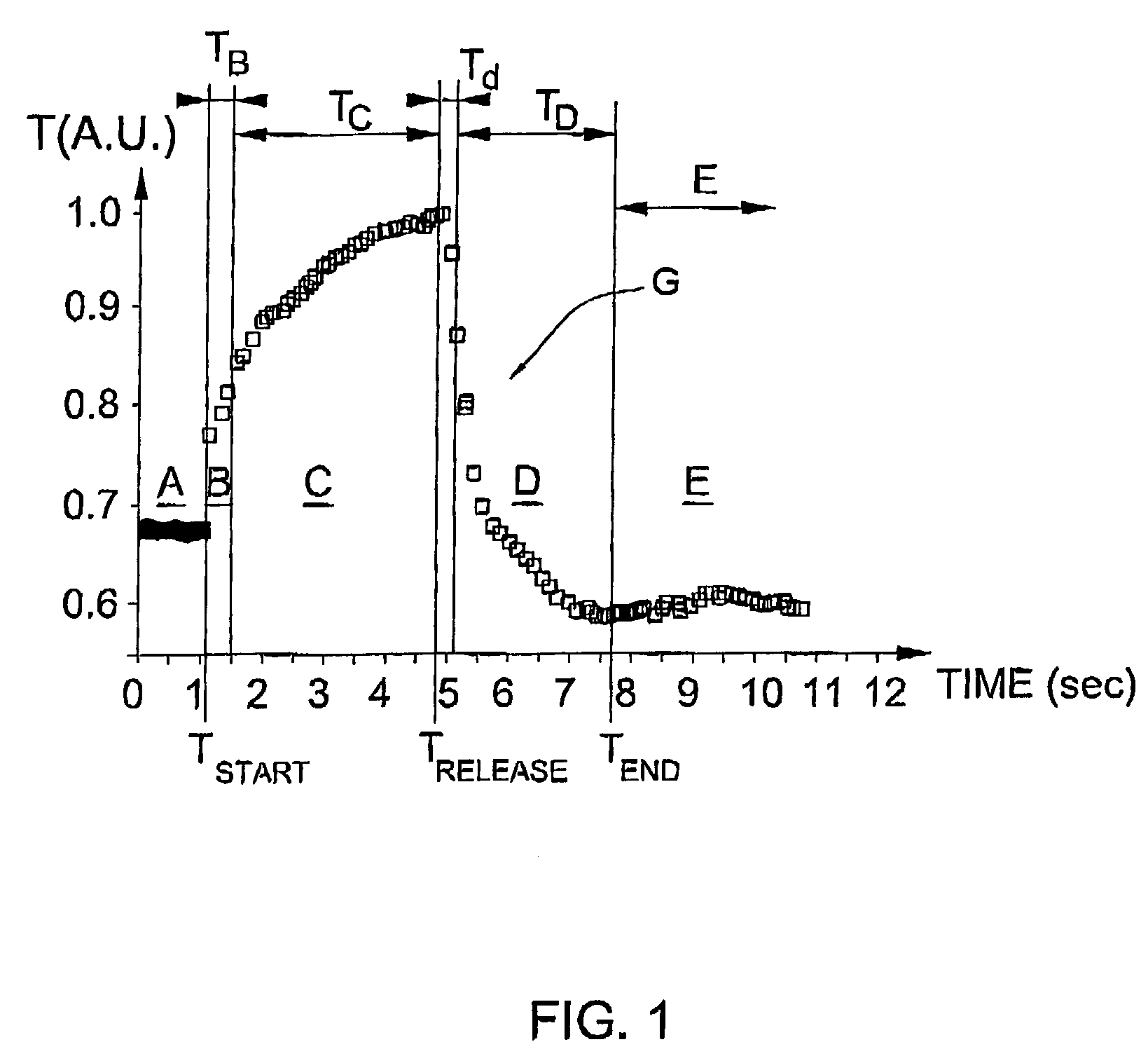
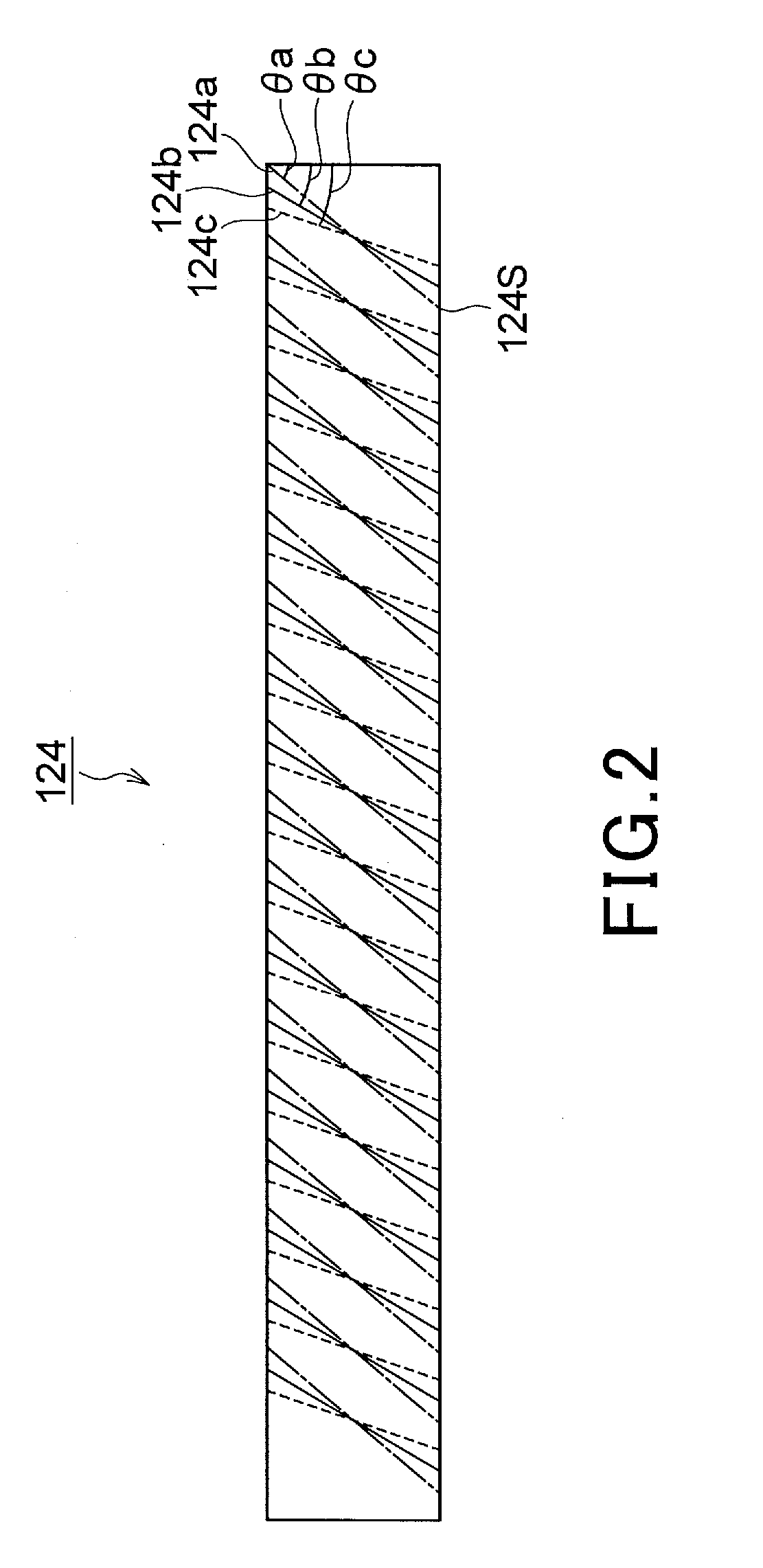
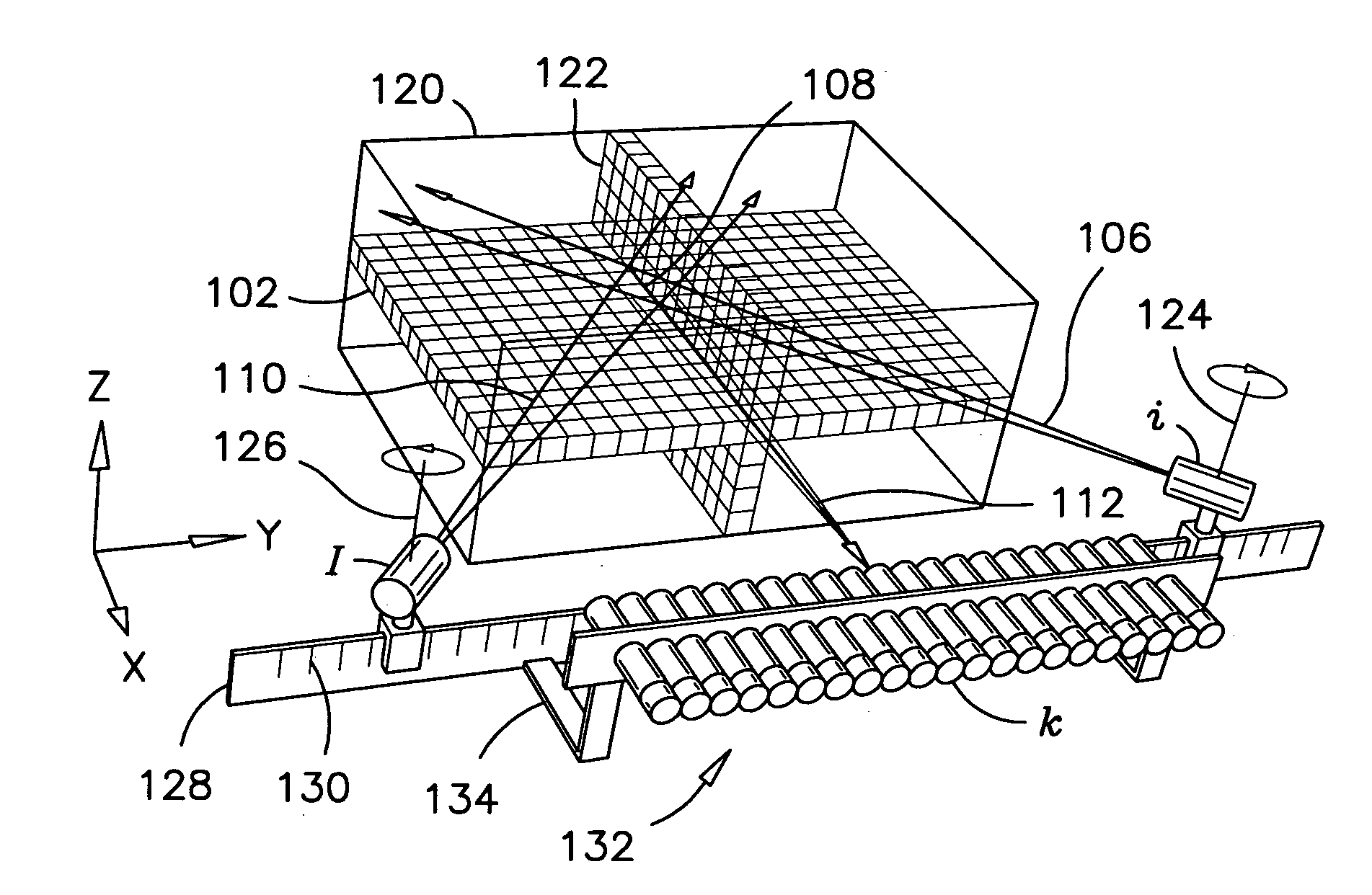
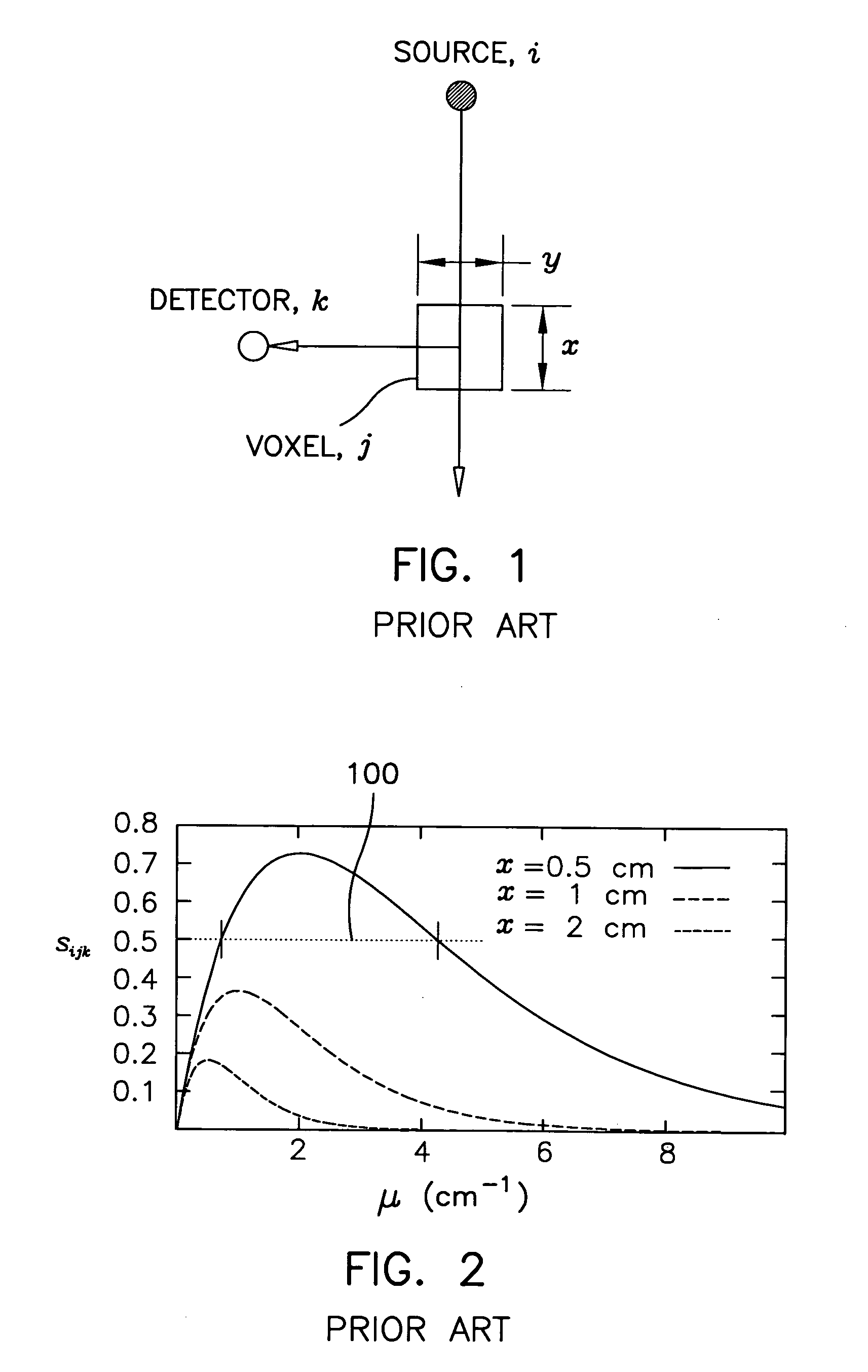
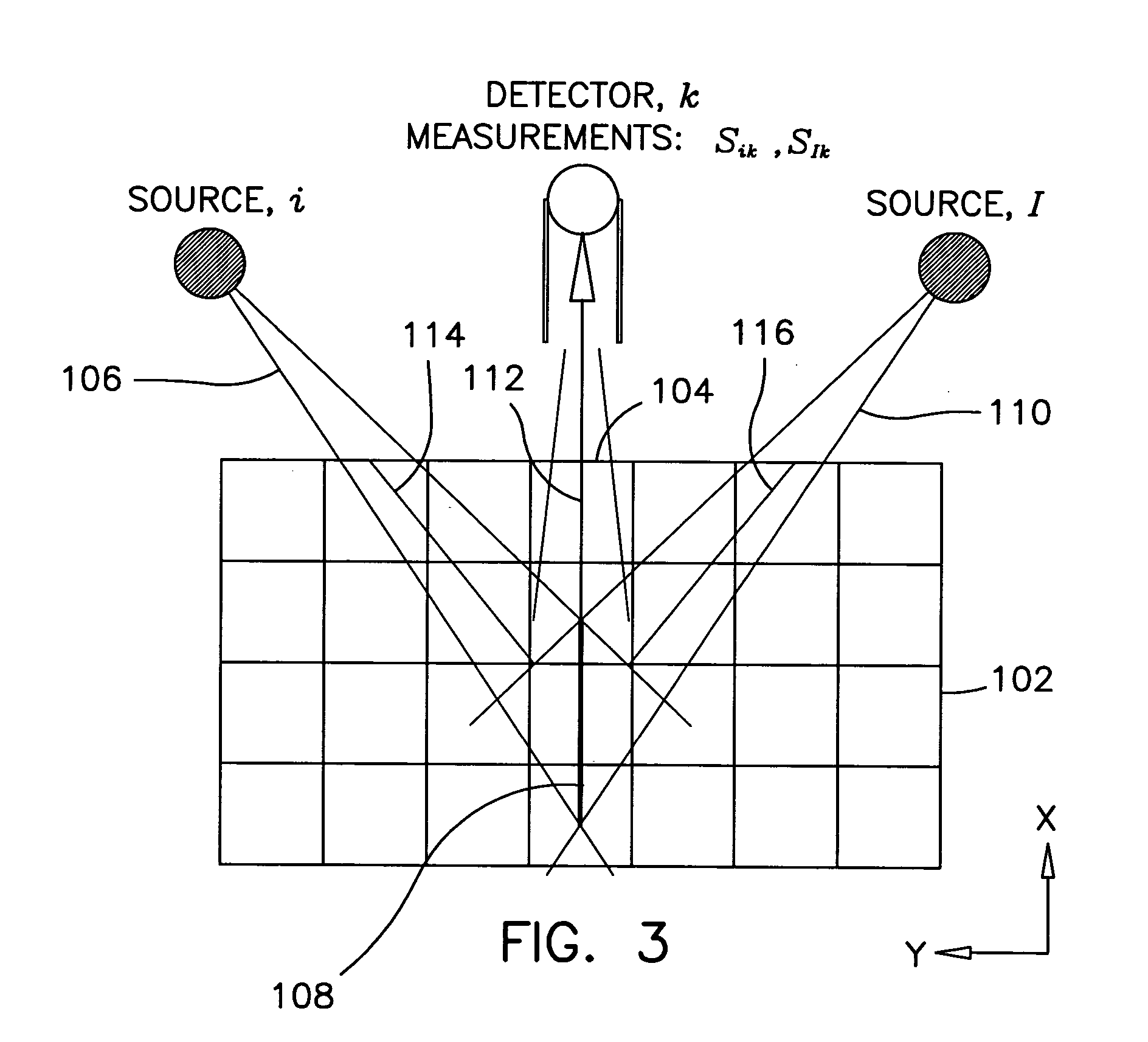
Patents
Literature
2692 results about "Incident beam" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
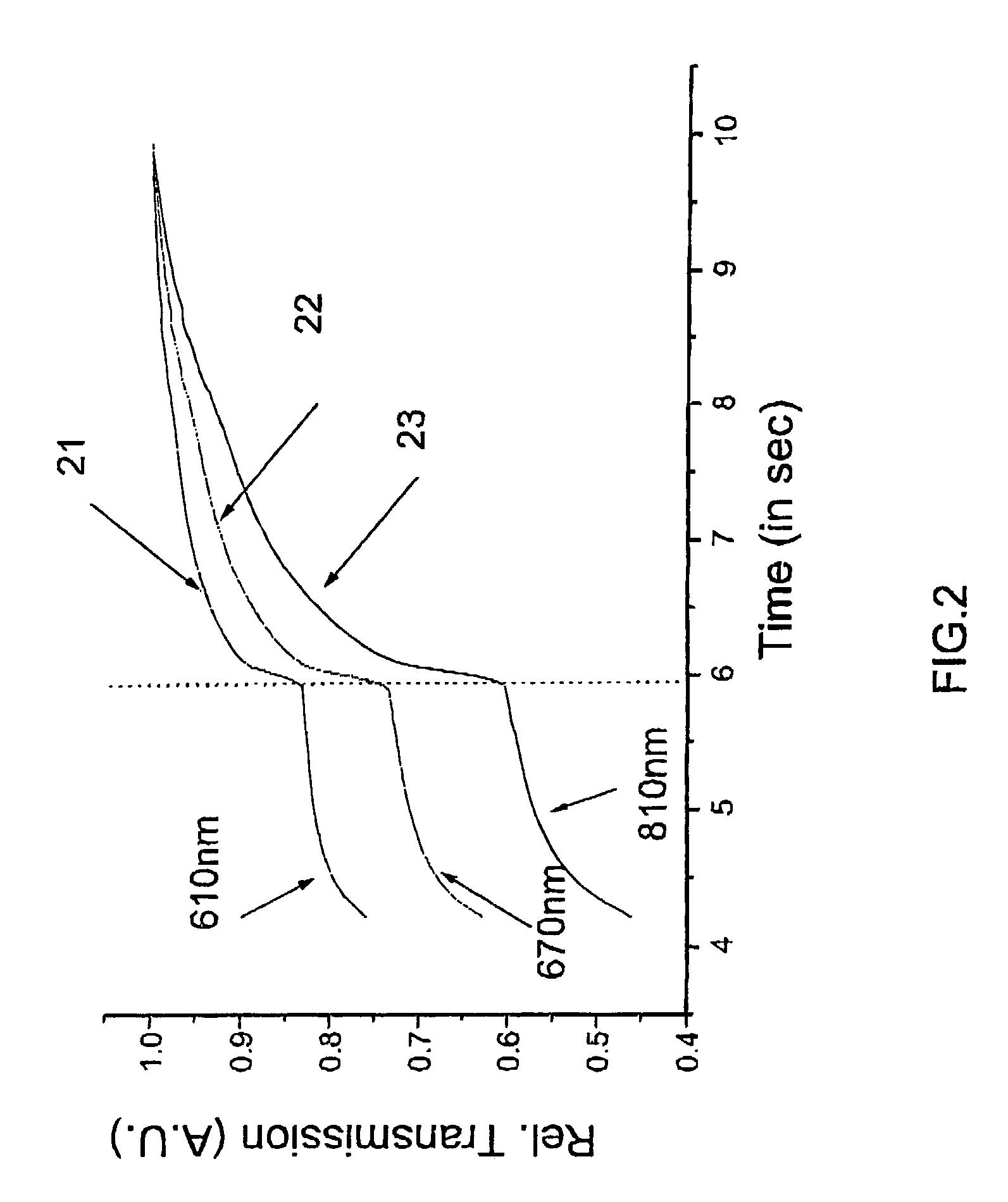
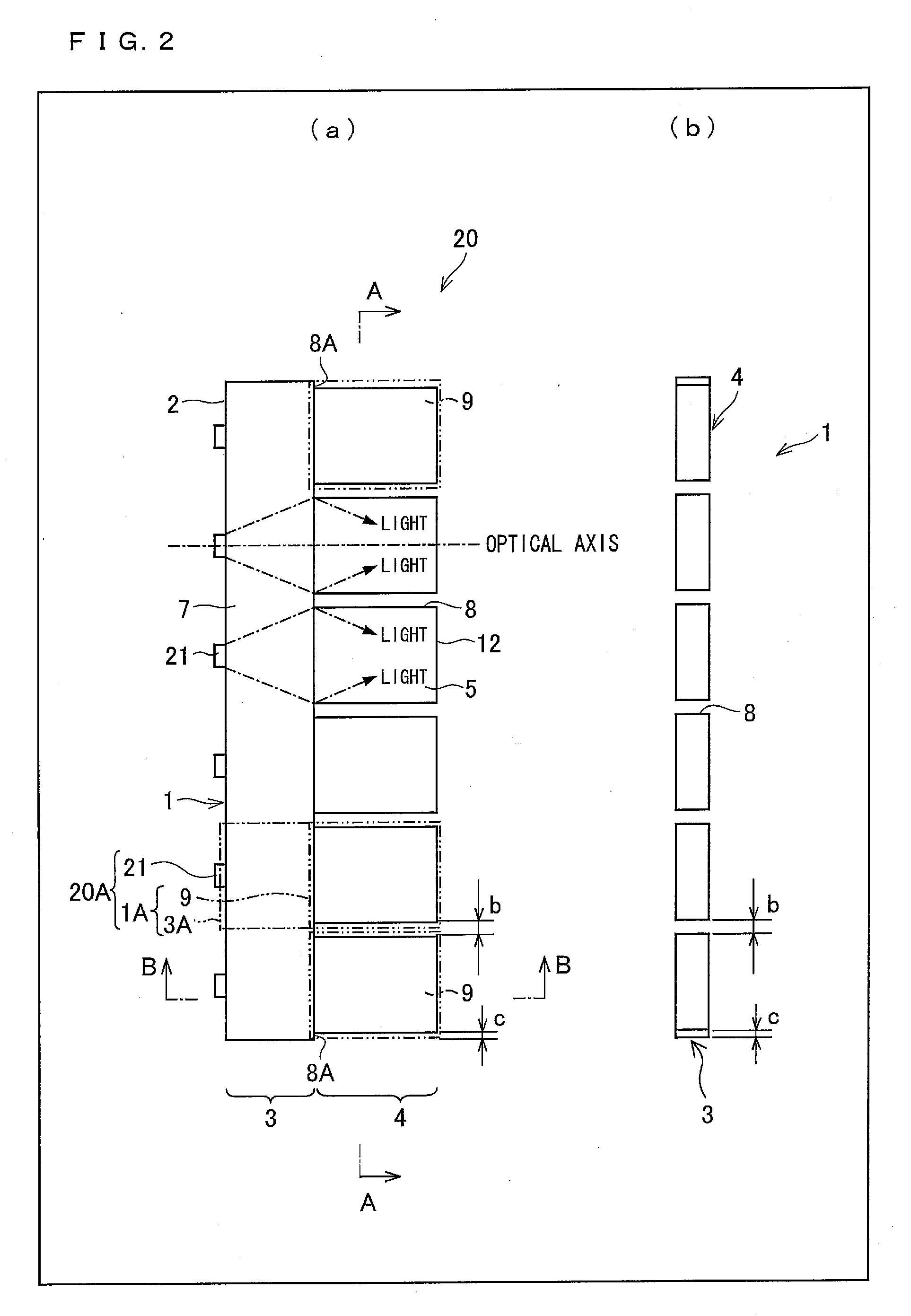
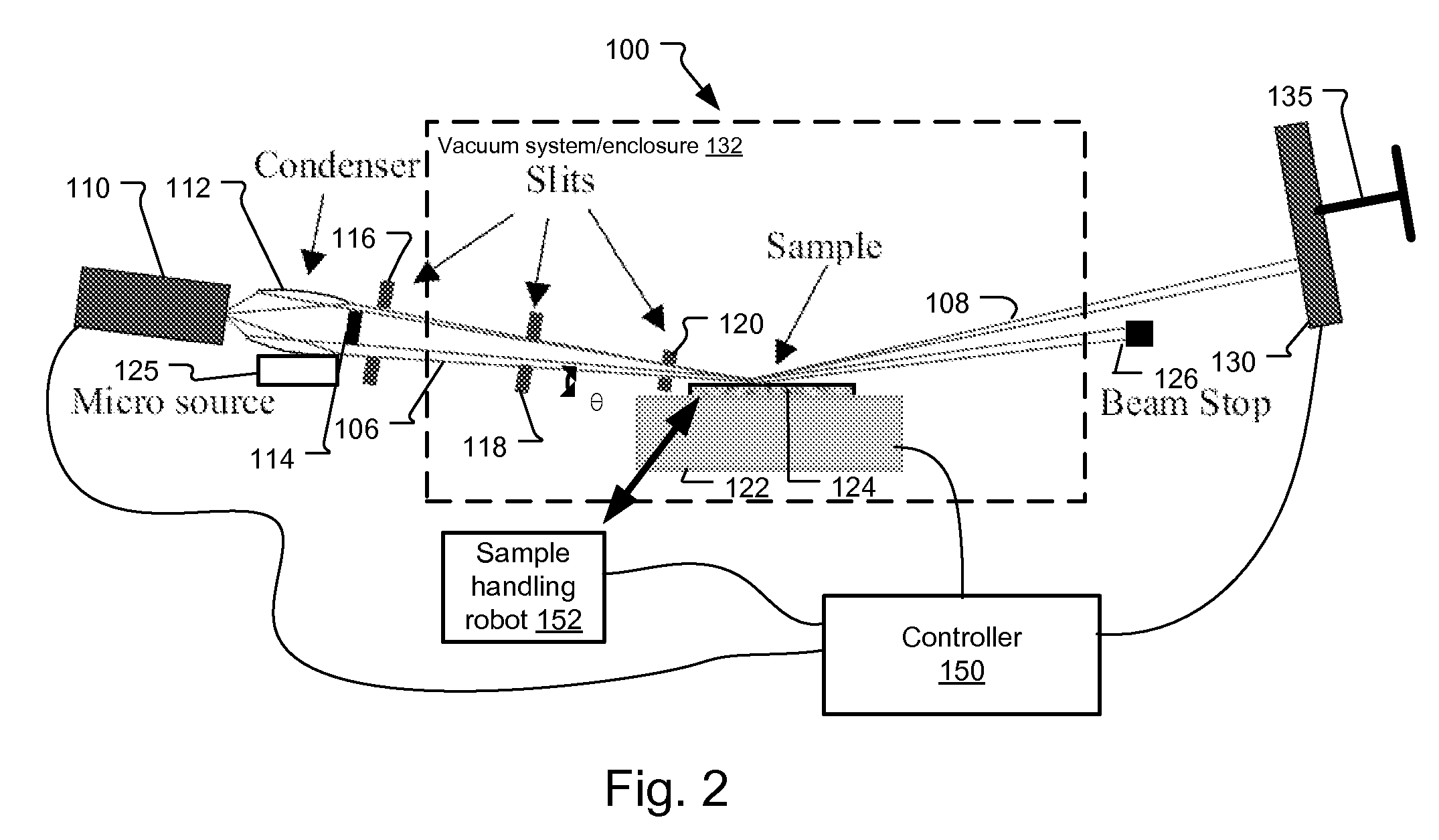
Incident Beam Masks. Beam masks are fitted in the incident beam path to control the axial width of the incident beam, defining the amount (width) of the sample that is irradiated by the incident x-ray beam.
Illumination system particularly for microlithography
InactiveUS6438199B1Reduced beam diameterReduce the overall diameterNanoinformaticsHandling using diffraction/refraction/reflectionExit pupilGrating
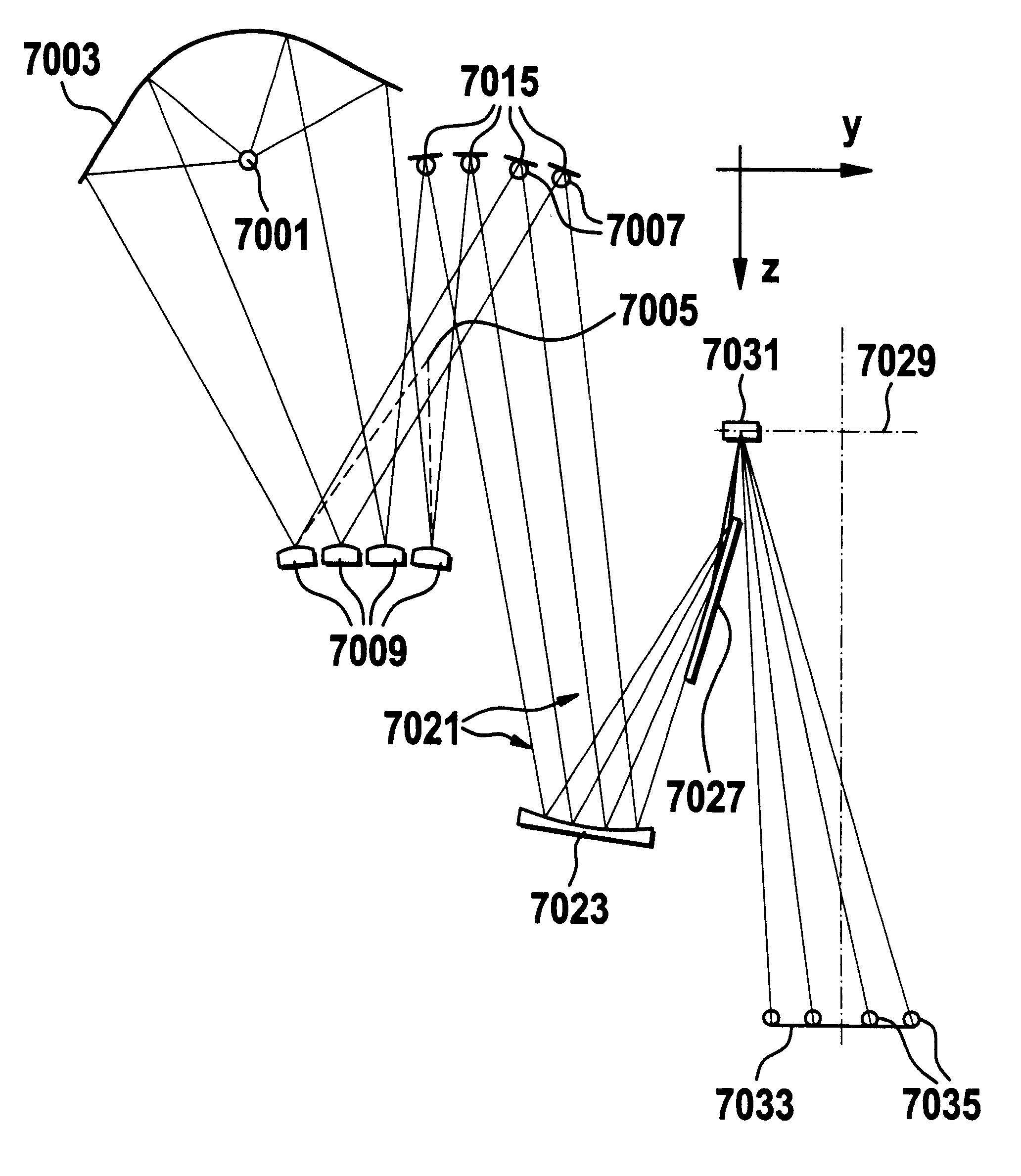
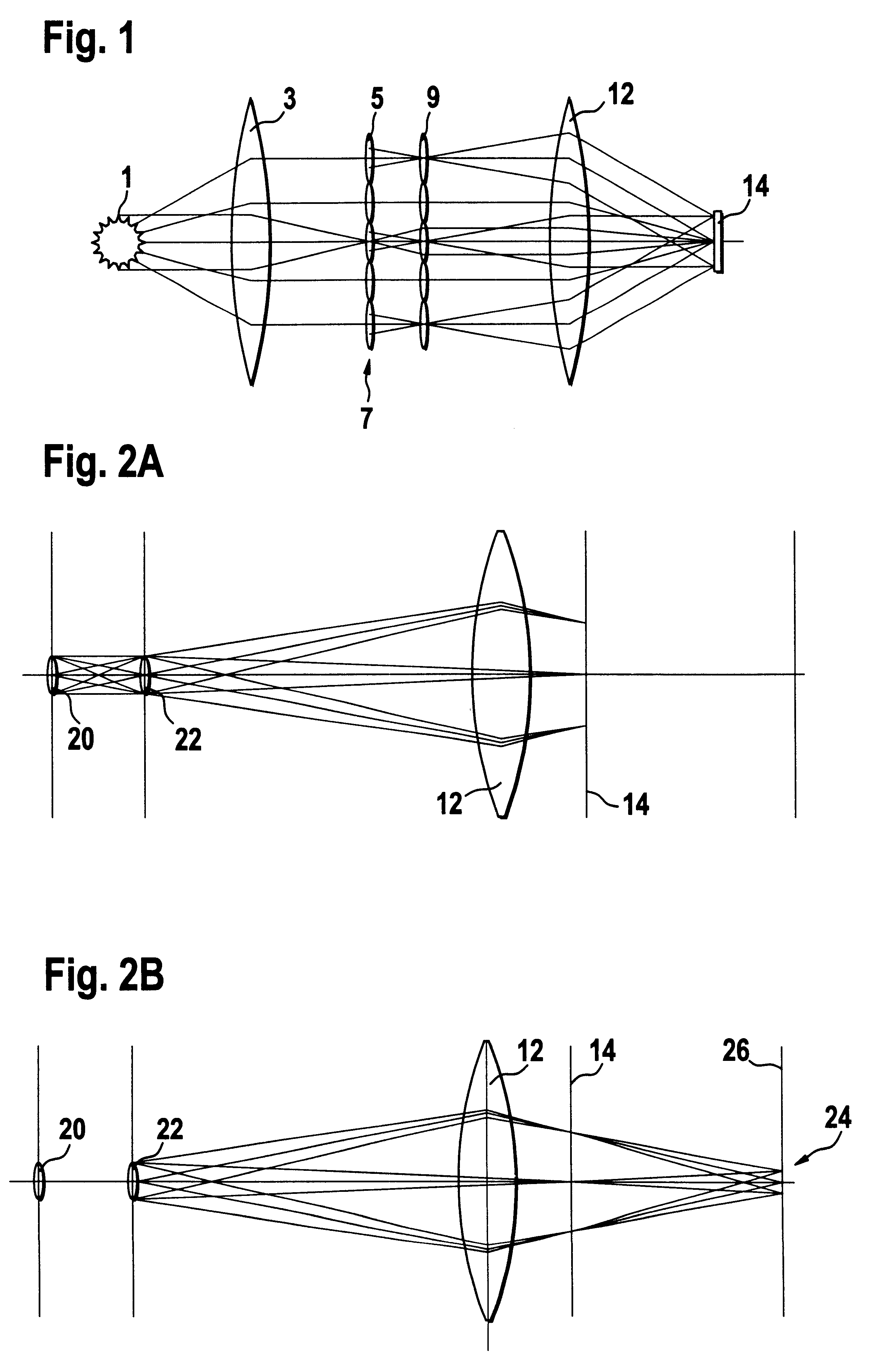
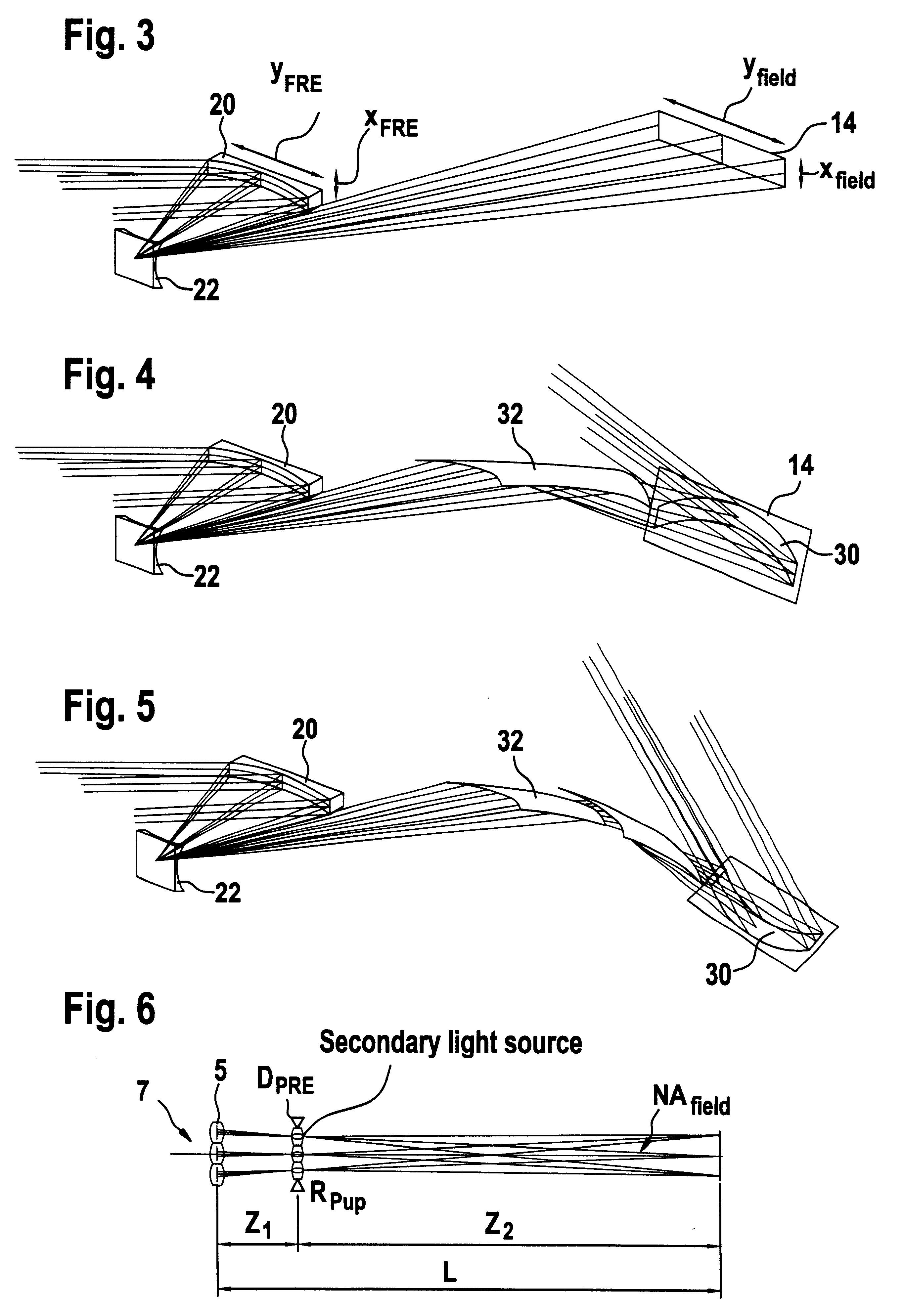
The invention concerns an illumination system, particularly for microlithography with wavelengths <=193 nm, comprising a light source, a first optical component, a second optical component, an image plane and an exit pupil. The first optical component transforms the light source into a plurality of secondary light sources being imaged by the second optical component in said exit pupil. The first optical component comprises a first optical element having a plurality of first raster elements, which are imaged into said image plane producing a plurality of images being superimposed at least partially on a field in said image plane. The first raster elements deflect incoming ray bundles with first deflection angles, wherein at least two of the first deflection angles are different. The first raster elements are preferably rectangular, wherein the field is a segment of an annulus. To transform the rectangular images of the first raster elements into the segment of the annulus, the second optical component comprises a first field mirror for shaping the field to the segment of the annulus.
Owner:CARL-ZEISS-STIFTUNG TRADING AS CARL ZEISS
Motion-free tracking solar concentrator
ActiveUS6958868B1Improve reliabilityReduce weightSolar heating energyPrismsRefractive indexLight beam
An integrated solar concentrator and tracker is constructed from a beam deflector for unpolarized light in combination with a fixed optical condenser. The one-dimensional beam deflector consists of a pair of prism arrays made from a material whose refractive index can be varied by applying an electric field. Two of the one-dimensional concentrators can be arranged with their faces in contact and with their prism arrays perpendicular to construct a two-dimensional beam deflector. The intensity and distribution of an applied field modifies the refractive index of the individual prisms in order to keep direction of the deflected beam fixed as the incident beam shifts. When the beam deflector is used with the fixed concentrator the result is that the position of the focus remains fixed as the source moves.
Owner:PENDER JOHN GEORGE
Method and system for use in non-invasive optical measurements of blood parameters
InactiveUS6993372B2Modulate scattering propertySufficient pressureDiagnostics using lightSensorsMedicineOptical measurements
A method and device are presented for use in non-invasive optical measurements of at least one desired characteristic of patient's blood. A condition of artificial blood kinetics is created at a measurement location in a patient's blood perfused fleshy medium and maintained for a certain time period. This condition is altered over a predetermined time interval within said certain time period so as to modulate scattering properties of blood. Optical measurements are applied to the measurement location by illuminating it with incident light beams of at least two different wavelengths in a range where the scattering properties of blood are sensitive to light radiation, detecting light responses of the medium, and generating measured data indicative of time evolutions of the light responses of the medium for said at least two different wavelengths, respectively, over at least a part of said predetermined time interval.
Owner:ORSENSE LTD
Device and method to realize a light processor
A device for light processing includes a first housing having a reflective bottom surface and walls defining a first cavity. A first fluid or gel has a meniscus disposed within the first cavity. A control means is coupled with the first fluid or gel for adjusting the curvature of the meniscus. The bottom surface is configured to reflect an incident light beam through the first fluid or gel and toward the meniscus.
Owner:AGENCY FOR SCI TECH & RES
Structured screens for controlled spreading of light
InactiveUS20020034710A1Increased peak intensityIncrease the number ofRadiation applicationsDiffusing elementsDiffusionLight beam
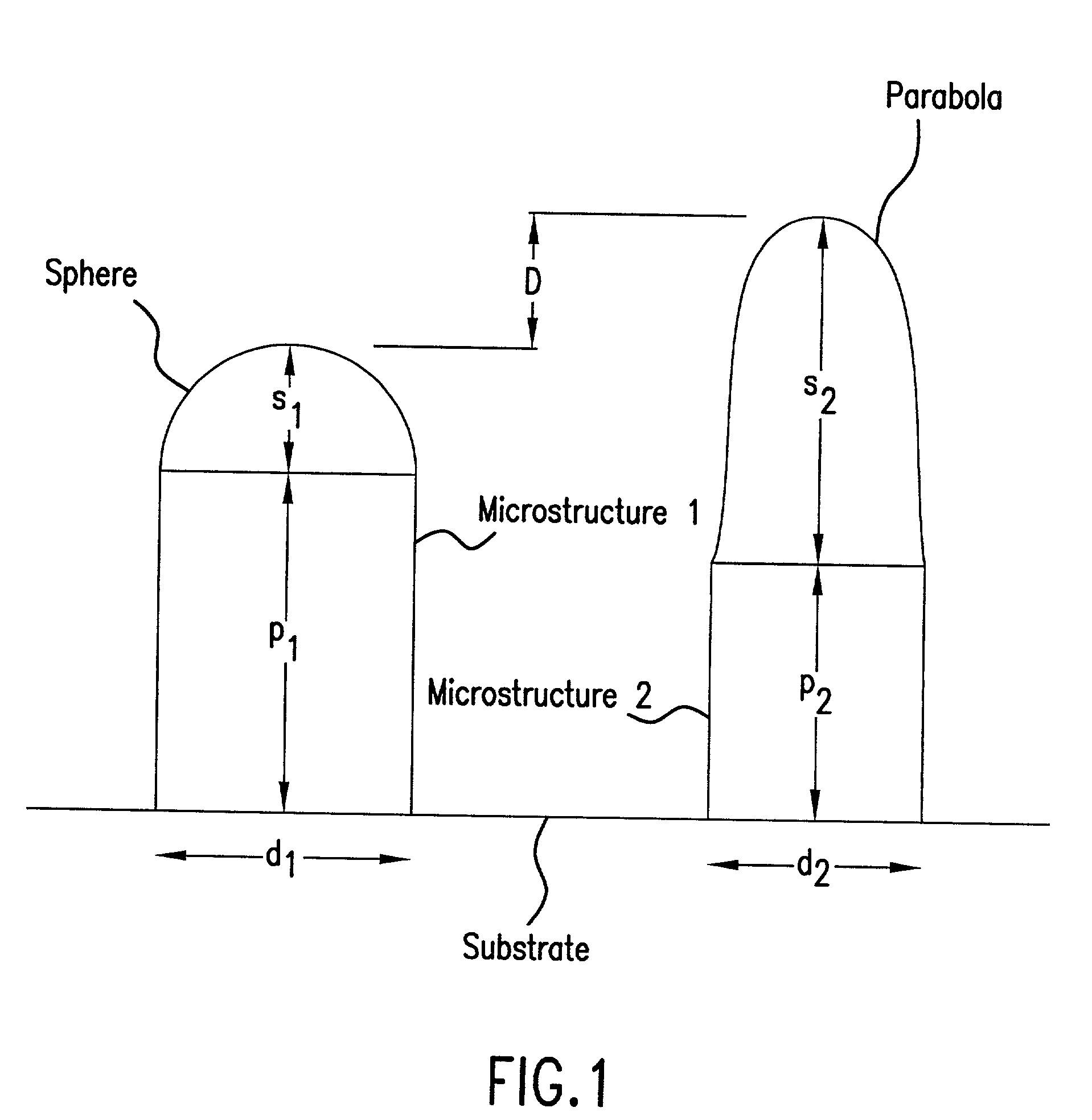
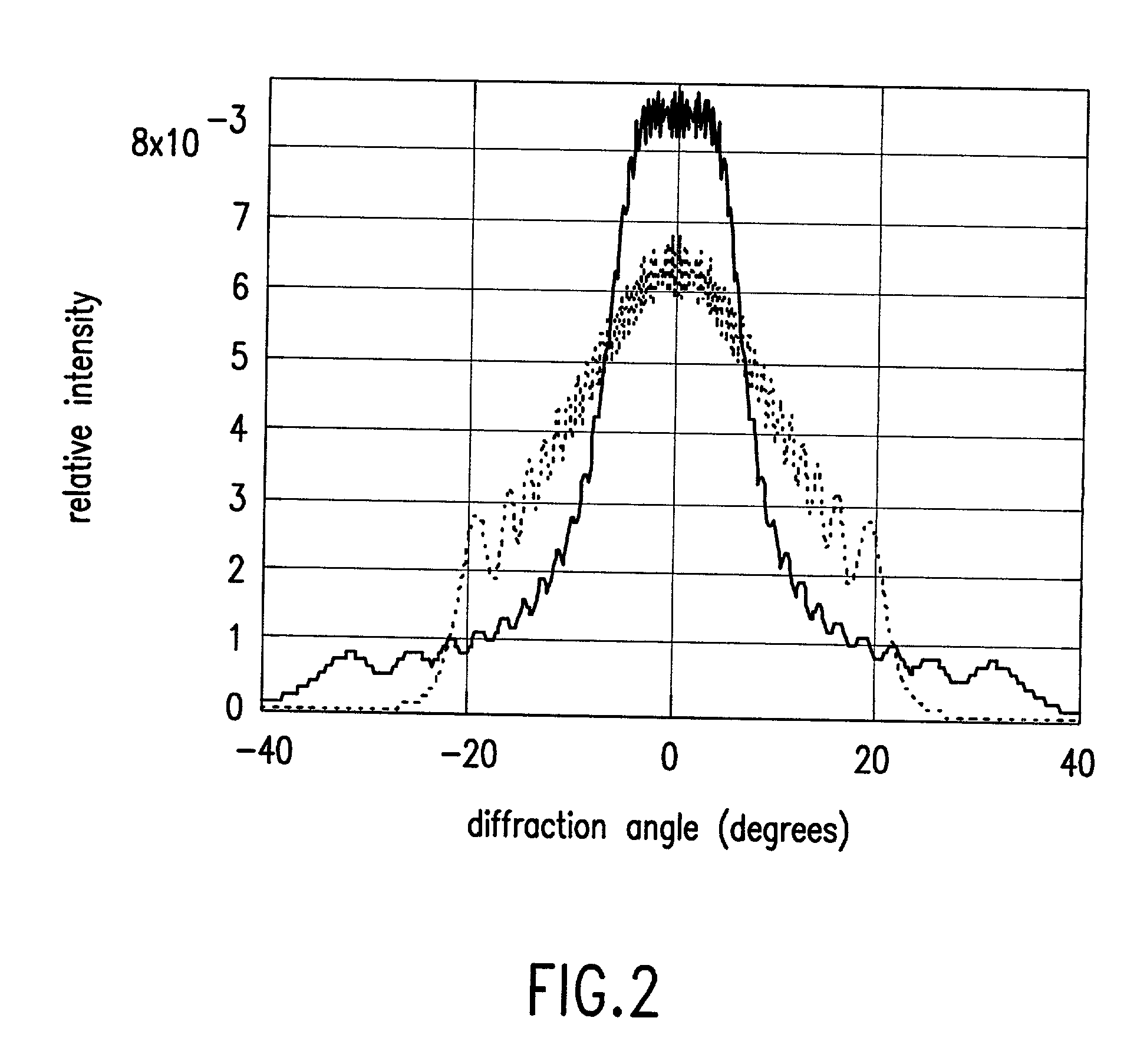
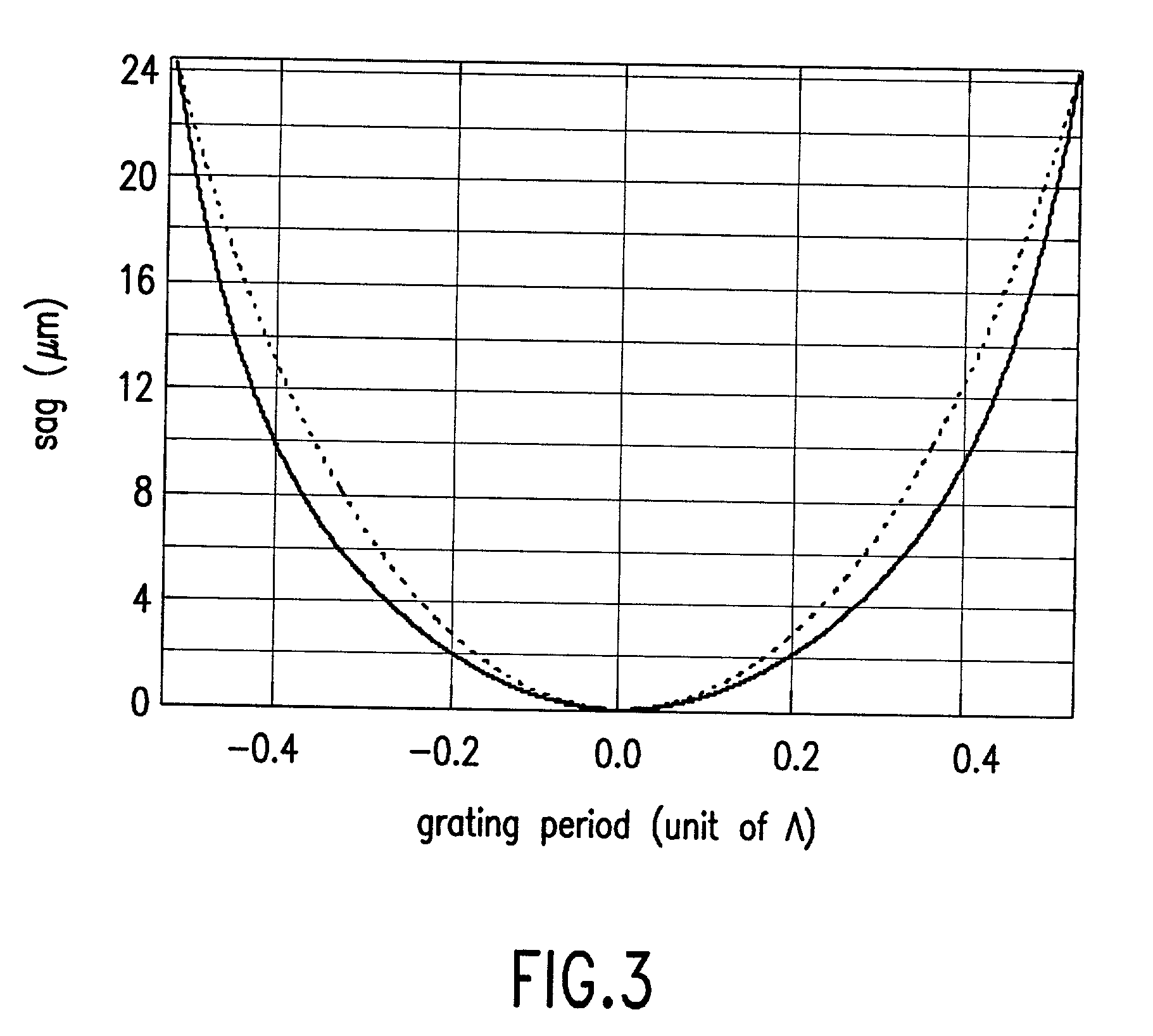
Structured screens for the controlled spreading, diffusion, or scattering of an incident beam are provided. The screens are composed of microstructures (1,2) whose configurations and distribution on the surfaces of the screen are precisely determined. In certain embodiments, the configurations and / or their distribution is randomized. The structured screens can be used as diffusing screens or display screens.
Owner:CORNING INC
Data storage system having an optical processing flying head
InactiveUS6781927B1Low costOptical flying-type headsOptical beam sourcesDigital dataData information
An optical data storage and retrieval system uses a flying head. The flying head is supported on a moving media having information stored in a plurality of stored data locations thereon. Information is stored in each of the plurality of media locations as physical structures capable of modulating the polarization state of incident light into one of two output polarization states. The flying head includes an optical processing assembly which directs an incident light beam having a source polarization state onto the moving media, accessing successive data locations. A reflected light beam having the source polarization state of the incident light beam modulated by a respective polarization modifying data location into one of the output polarization states is received by the flying head. The optical processing assembly optically transforms the modulated output polarization state of the reflected light beam into two return light beams having differentially modulated intensity related to the output polarization state of the reflected light beam. The two intensity modulated return light beams are optically coupled to a distal differential detector which outputs digital data representing the stored data information for the subject data location. A preferred embodiment includes optical fibers for coupling the incident and return light beams between the detector and the flying head. The optical assembly of a preferred embodiment includes an optical plate having pre-shaped and dimensioned recesses for automatically locating and aligning multiple optical components comprising the assembly. The flying head may also include a servo-controlled micro machined mirror for directing the incident and reflected light beams to and from the media.
Owner:WESTERN DIGITAL (FREMONT LLC)
Optical device, and virtual image display
ActiveUS20060291021A1Reduce color unevennessReduce unevennessDiffraction gratingsOptical light guidesGratingLight beam
There is provided an optical device including an optical waveguide upon which a group of parallel light beams different in traveling direction from each other are incident and from which the group of parallel light beams go out after propagated by repeated total reflection through it. The optical waveguide includes a first reflection-type volume hologram grating, and a second reflection-type volume hologram grating. The pitches of interference fringes on the hologram surfaces of the first and second reflection-type volume hologram gratings are equal to each other. In at least the second reflection-type volume hologram grating, the angle formed between the interference fringes and hologram surfaces are varied continuously or stepwise within the hologram in relation to the main incident light beam so as to meet the Bragg condition. Therefore, it is possible to reduce the unevenness of color and brightness due to angles of view.
Owner:SONY CORP
X-ray scatter image reconstruction by balancing of discrepancies between detector responses, and apparatus therefor
ActiveUS7203276B2Duplicity of solutionNon-linearity of the inverse problem andMaterial analysis by optical meansPhotometry using electric radiation detectorsAttenuation coefficientUltrasound attenuation
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF NEW BRUNSWICK
Method And Apparatus For Generating 3D Images
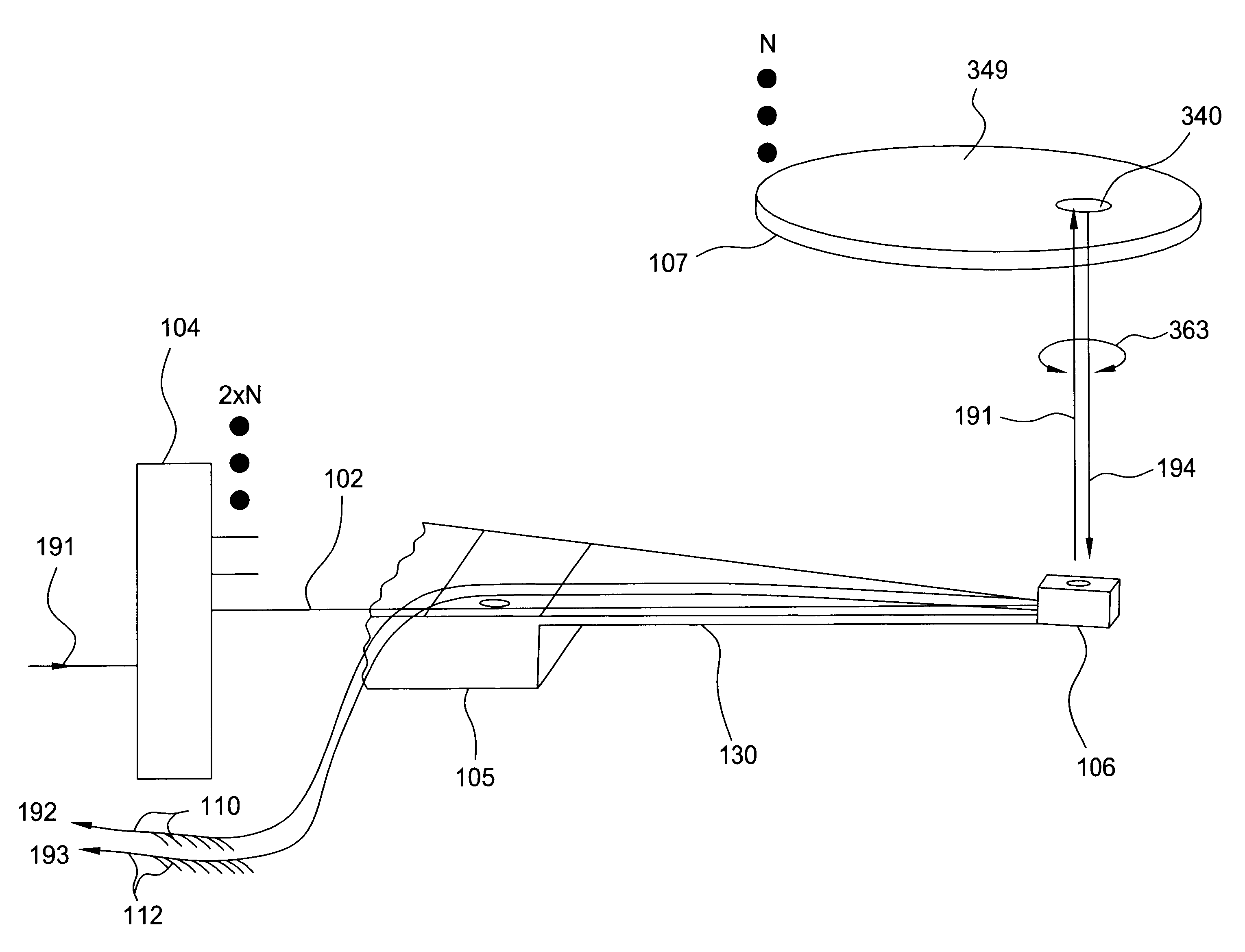
The present invention is directed to an apparatus and method for displaying 3D images. The apparatus comprises: a) a screen with angular dependent diffusion characteristics for direction selectively forwarding light; b) a screen illuminating system, the screen illuminating system comprising multiple modules for generating multiple light beams incident on points of the screen, the modules being arranged so that each point of the screen is illuminated by multiple modules, and the incident light beams generated by one module are projected into multiple different directions from the module towards multiple different points of the screen, and further the different incident light beams generated by one module are forwarded towards different emitting directions from the screen, means for coding each incident light beam with the image information of a single image point in the module, where the 3D image perceived by an observer being generated by multiple modules; c) a control system to control the modules; and d) means for imparting an exit divergence to the exiting light beams being transmitted through or reflected from the screen, the measure of the exit divergence substantially corresponding to the angle between neighbouring emitting directions associated with the optically neighbouring modules, go as to provide a substantially continuous motion parallax in the 3D image perceived by an observer. The apparatus according to the invention comprises imaging means for generating the incident light beams with a convergent section converging substantially towards a point of the screen, where a convergence of the incident light beams is substantially equal to the exit divergence of the light beams exiting the screen. The modules can be video projectors, LED projectors, the optical engines of these, or the like, arranged periodically shifted, preferably in the horizontal direction and the diffuser screen is realised as a holographic screen, arrays of diffractive or refractive elements, retroreflective surfaces, or any combination thereof, for imparting a larger divergence to the exit light beams along at least one, preferably in the vertical direction, while in the other direction the angle of divergence provided by the screen is smaller than the angle between the neighbouring emitting directions associated with the optically neighbouring modules. The invention is also directed to a method implemented by the apparatus according to the invention.
Owner:BALOGH
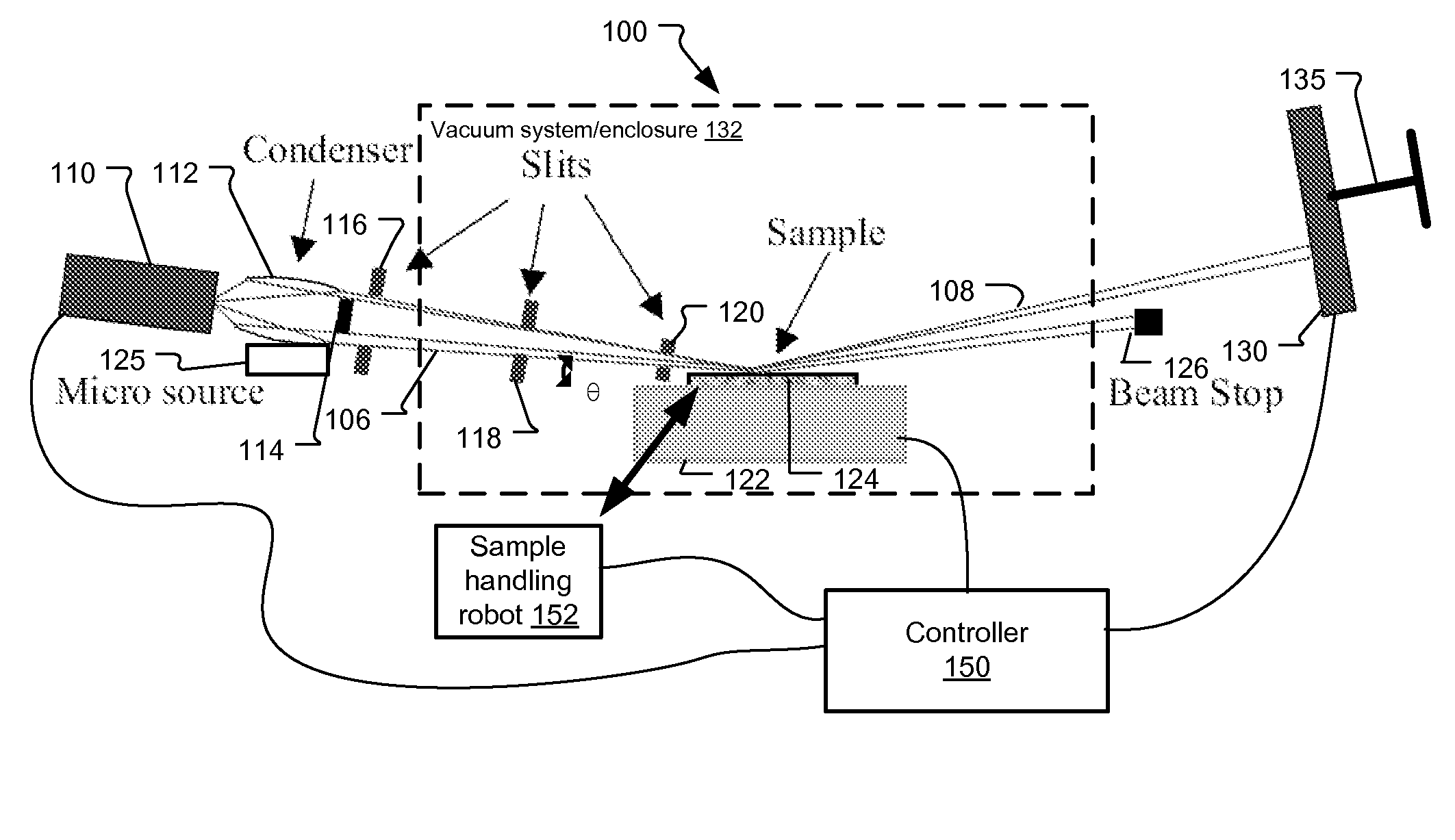
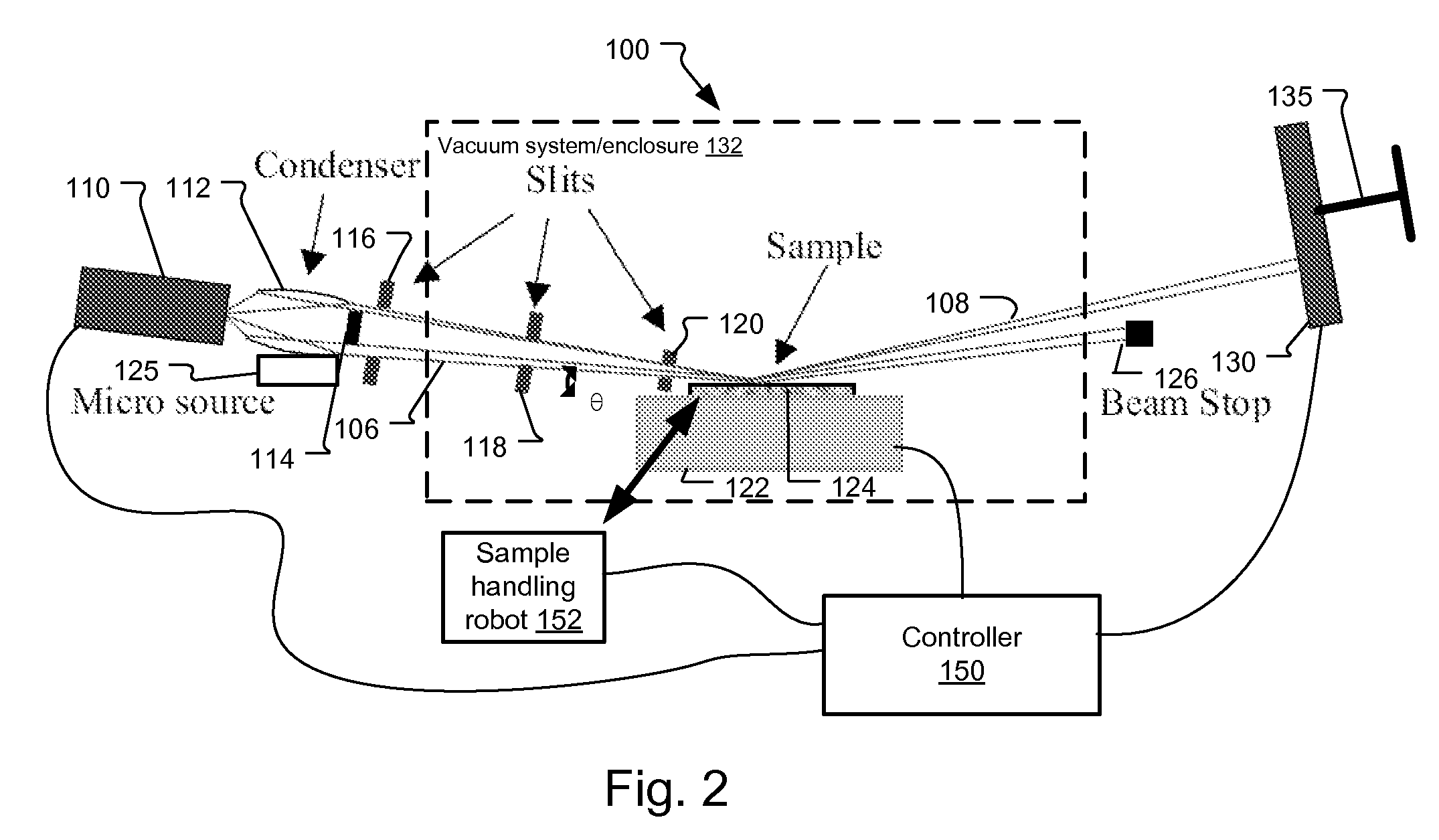
Small-angle scattering x-ray metrology systems and methods
ActiveUS20150110249A1Material analysis using wave/particle radiationTesting semiconductor materialsSoft x rayMetrology
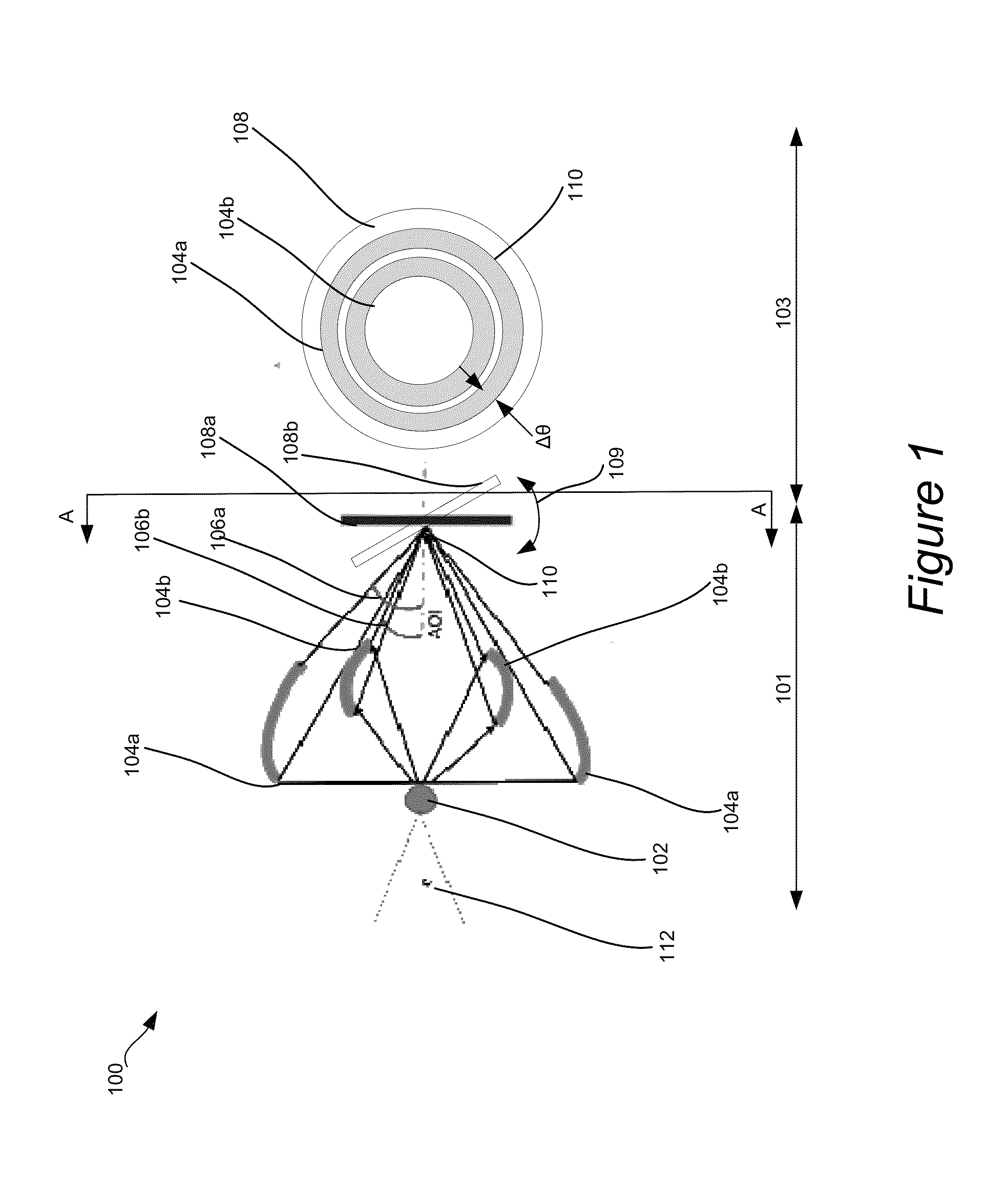
Disclosed are apparatus and methods for performing small angle x-ray scattering metrology. This system includes an x-ray source for generating x-rays and illumination optics for collecting and reflecting or refracting a portion of the generated x-rays towards a particular focus point on a semiconductor sample in the form of a plurality of incident beams at a plurality of different angles of incidence (AOIs). The system further includes a sensor for collecting output x-ray beams that are scattered from the sample in response to the incident beams on the sample at the different AOIs and a controller configured for controlling operation of the x-ray source and illumination optics and receiving the output x-rays beams and generating an image from such output x-rays.
Owner:KLA CORP
Illumination device, display device, and light guide plate
InactiveUS20110025730A1Reduce light leakageRetention strengthCathode-ray tube indicatorsPlanar/plate-like light guidesLight guideOptical axis
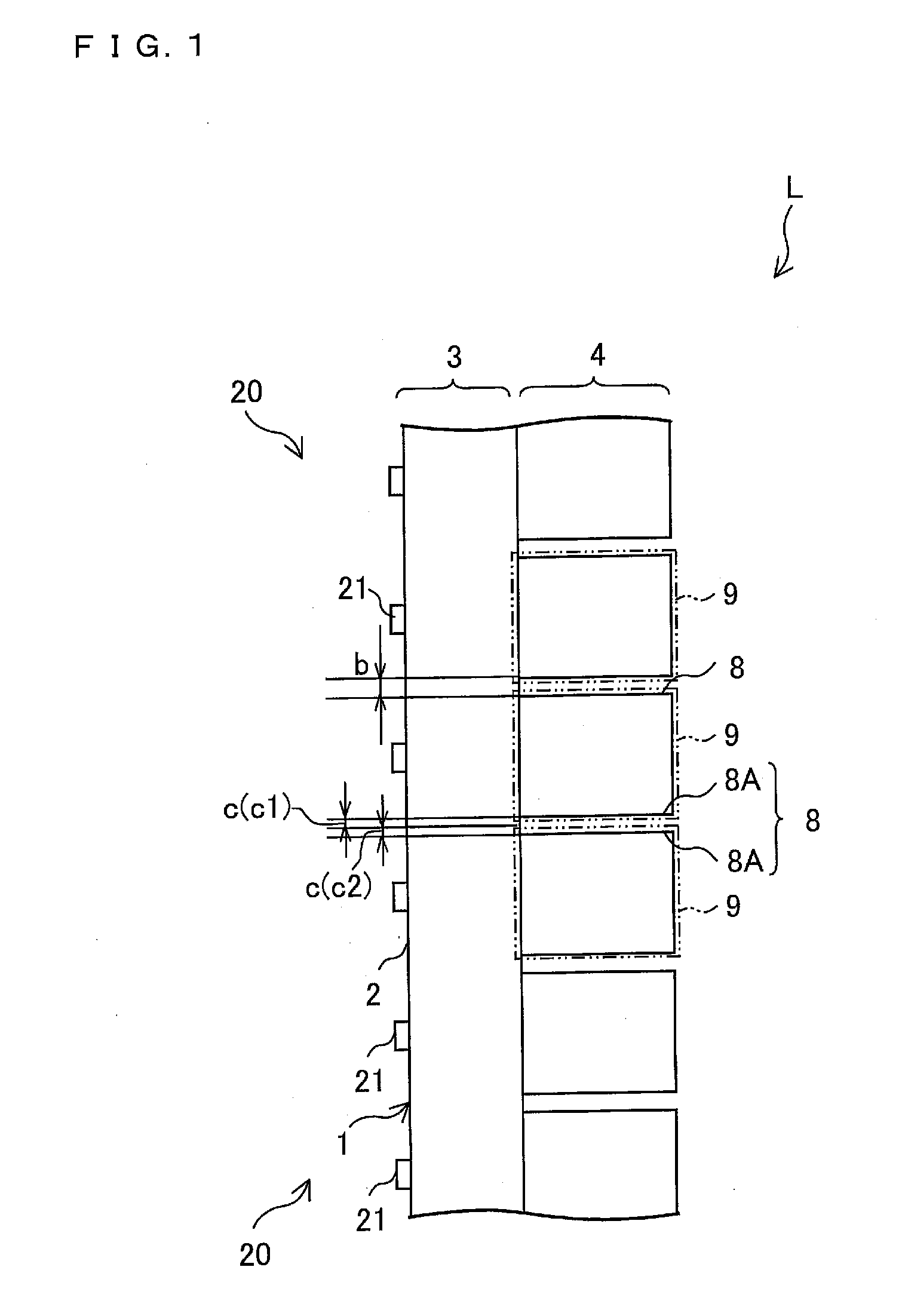
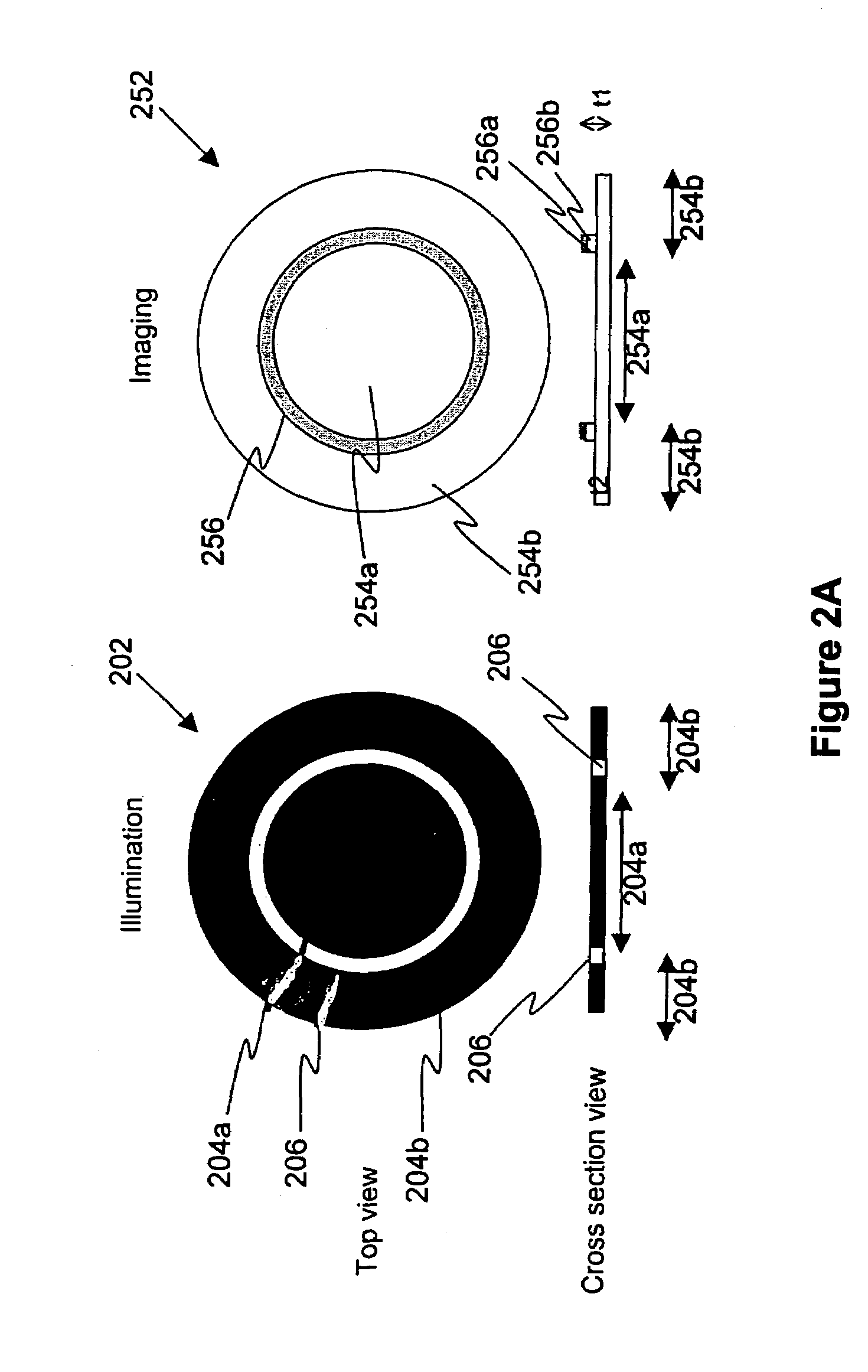
An illumination device (L) includes a plurality of light source units (20) each having a light guide plate (1) and a plurality of light sources (21). The light guide plate (1) has an illumination region (4) through which incident beams of light from the light sources (21) are emitted outward and a light guide region (3) through which the incident beams of light from the light sources (21) are guided toward the illumination region (4), with the light guide region (3) and the illumination region (4) laid side-by-side. The illumination region (4) is divided into a plurality of light-emitting sections (9) by slit sections (8), provided in such a way as to extend along directions of optical axes of the light sources (21), which restrict transmission of light. At least one of the light sources (21) is provided to each of the light-emitting sections (9) in such a way as to be placed side-by-side along the light guide region (3). The light source units (20) are provided in such a way as to be placed side-by-side along at least along a first direction along which the light-emitting sections (9) are arranged in the illumination region (4). There is also provided a slit section (8) in at least part of a space between light-emitting sections (9) between light source units (20) adjacent to each other along the first direction. This makes it possible to provide an illumination device (L) capable of retaining its strength as a combination of light guide blocks while reducing leakage of light into an adjacent area and capable of emitting uniform light.
Owner:SHARP KK
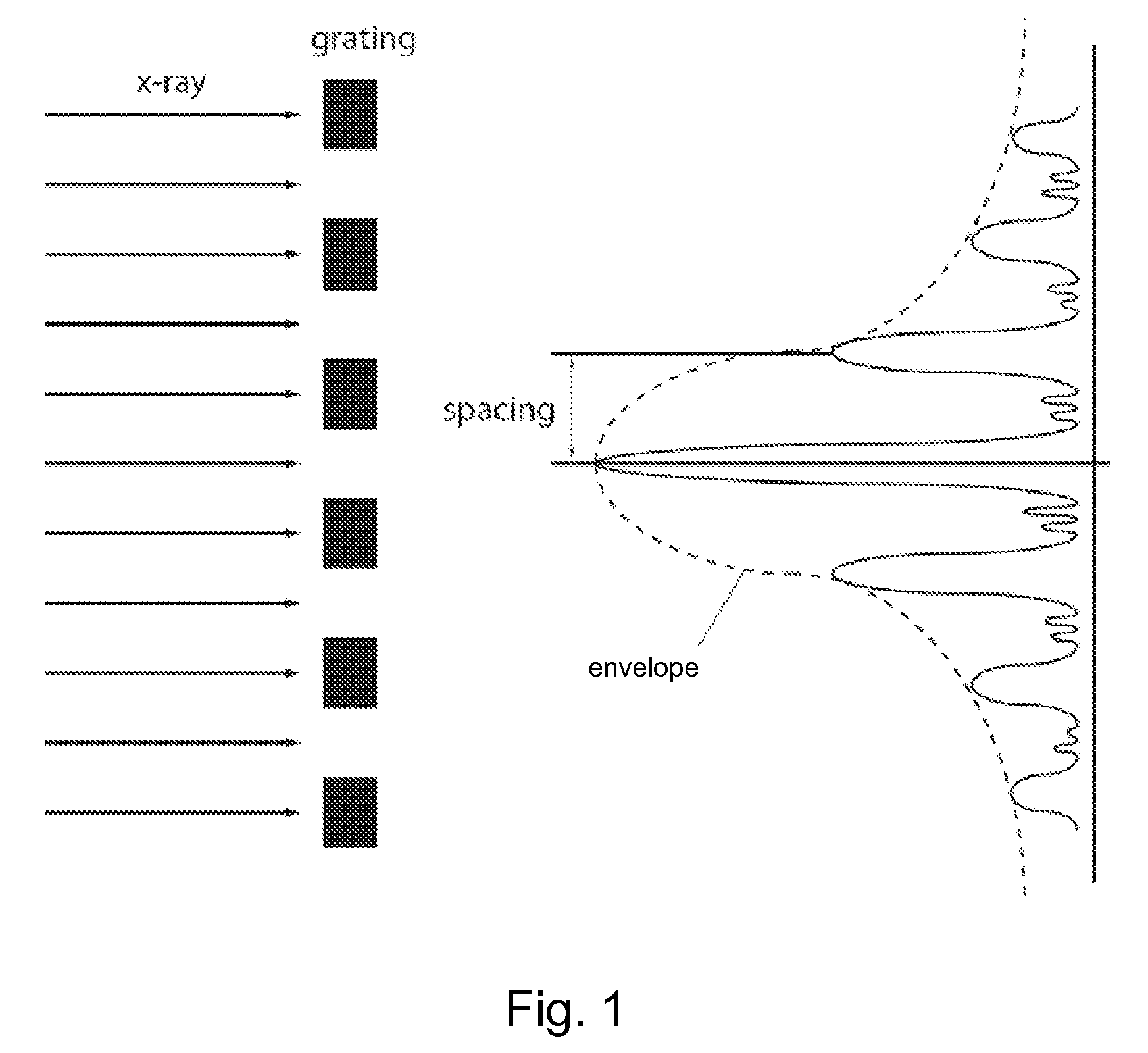
CD-GISAXS System and Method
ActiveUS20080273662A1High measurement accuracyHigh sensitivityPhotomechanical apparatusMaterial analysis using radiation diffractionMetrologyX-ray
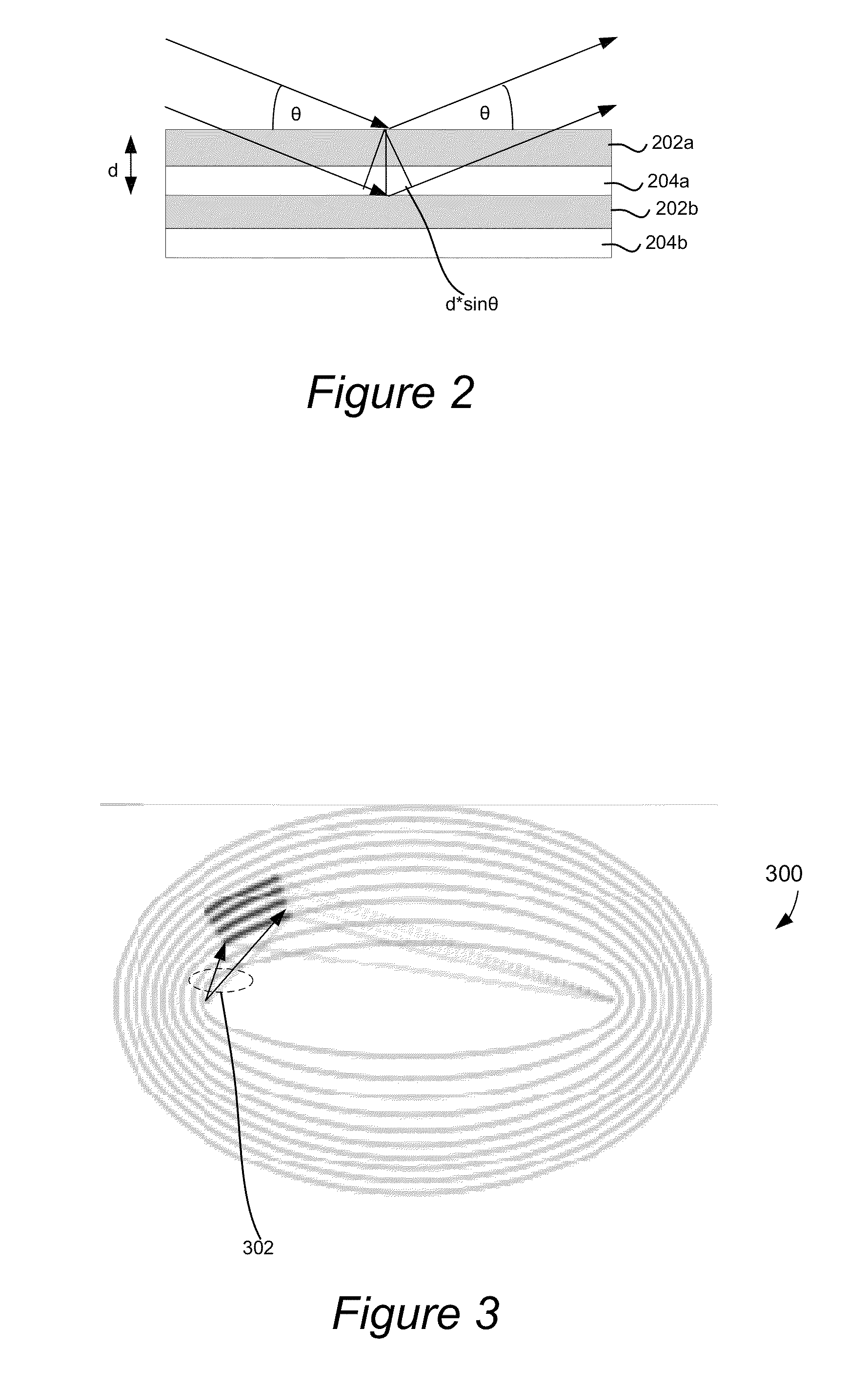
CD-GISAXS achieves reduced measurement times by increasing throughput using longer wavelength radiation (˜12×, for example) such as x-rays in reflective geometry to increase both the collimation acceptance angle of the incident beams and the scattering signal strength, resulting in a substantial combined throughput gain. This wavelength selection and geometry can result in a dramatic reduction in measurement time. Furthermore, the capabilities of the CD-GISAXS can be extended to meet many of the metrology needs of future generations of semiconductor manufacturing and nanostructure characterization, for example.
Owner:CARL ZEISS X RAY MICROSCOPY
Methods and apparatus for generating spatially resolved voltage contrast maps of semiconductor test structures
InactiveUS6445199B1Reduce pressureSemiconductor/solid-state device testing/measurementElectric discharge tubesSpatially resolvedEngineering
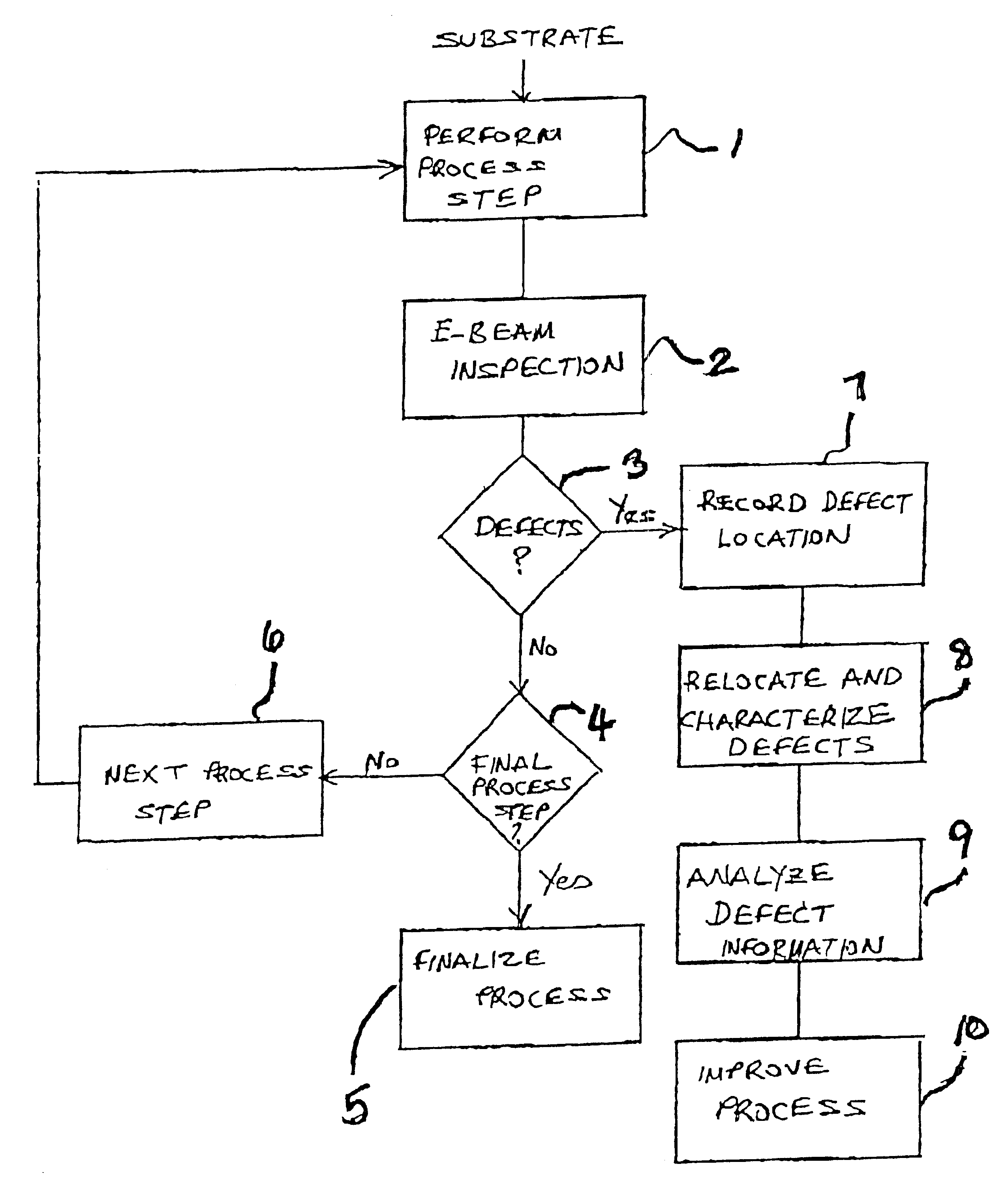
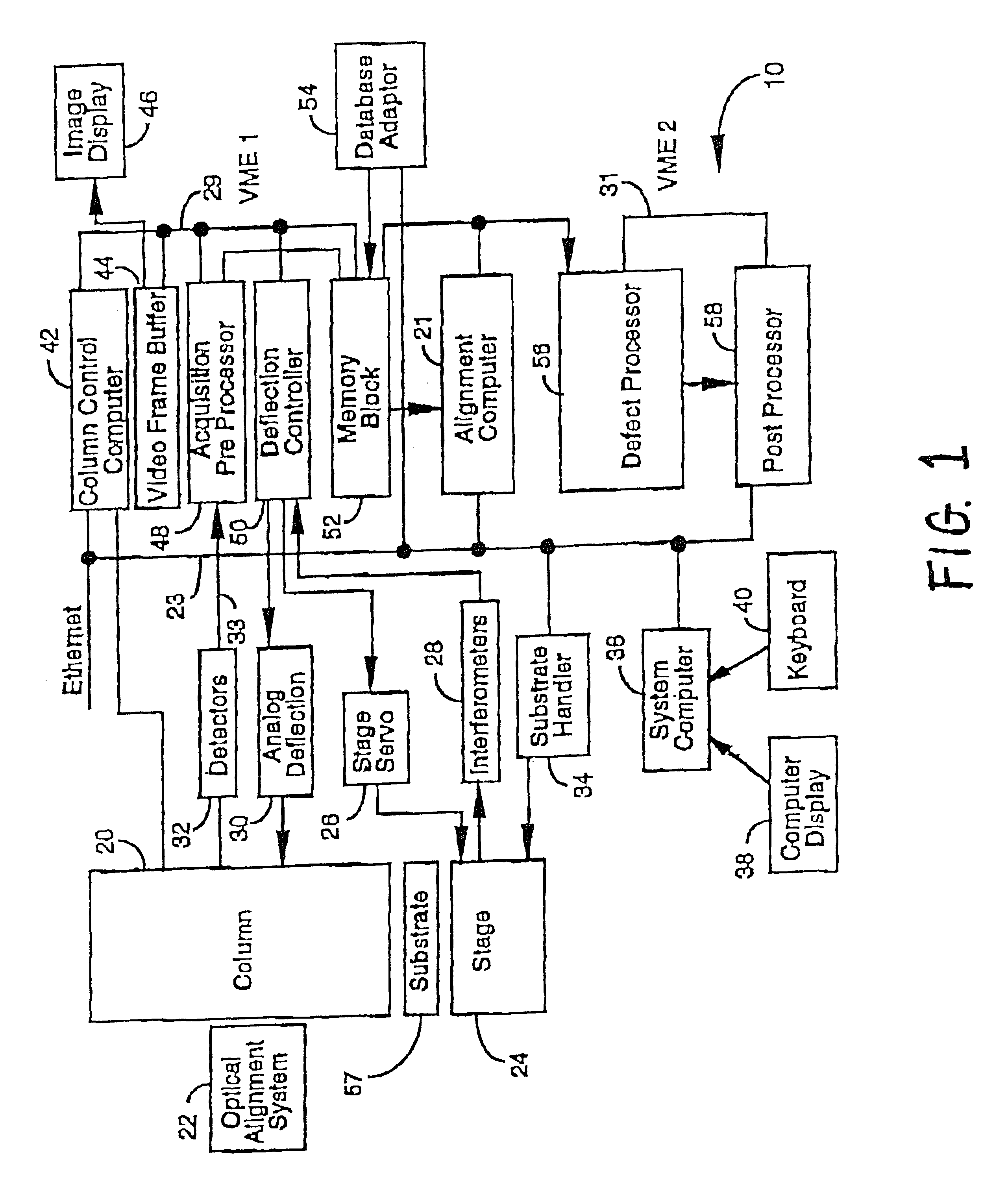
Disclosed is a method of inspecting a sample. The sample is illuminated with an incident beam, thereby causing voltage contrast within structures present on the sample. Voltage contrast is detected within the structures. Information from the detected voltage contrast is stored, and position data concerning the location of features corresponding to at least a portion of the stored voltage contrast information is also stored. In a specific embodiment, the features represent electrical defects present on the sample. In another embodiment, the stored position data is in the form of a two dimensional map. In another aspect, the sample is re-inspected and the stored position data is used in analyzing data resulting from the re-inspection.
Owner:KLA CORP
Spectral instrument using multiple non-interfering optical beam paths and elements for use therewith
InactiveUS6714298B2Good dispersionReduce dispersionRadiation pyrometrySpectrum investigationAngle of incidencePrism
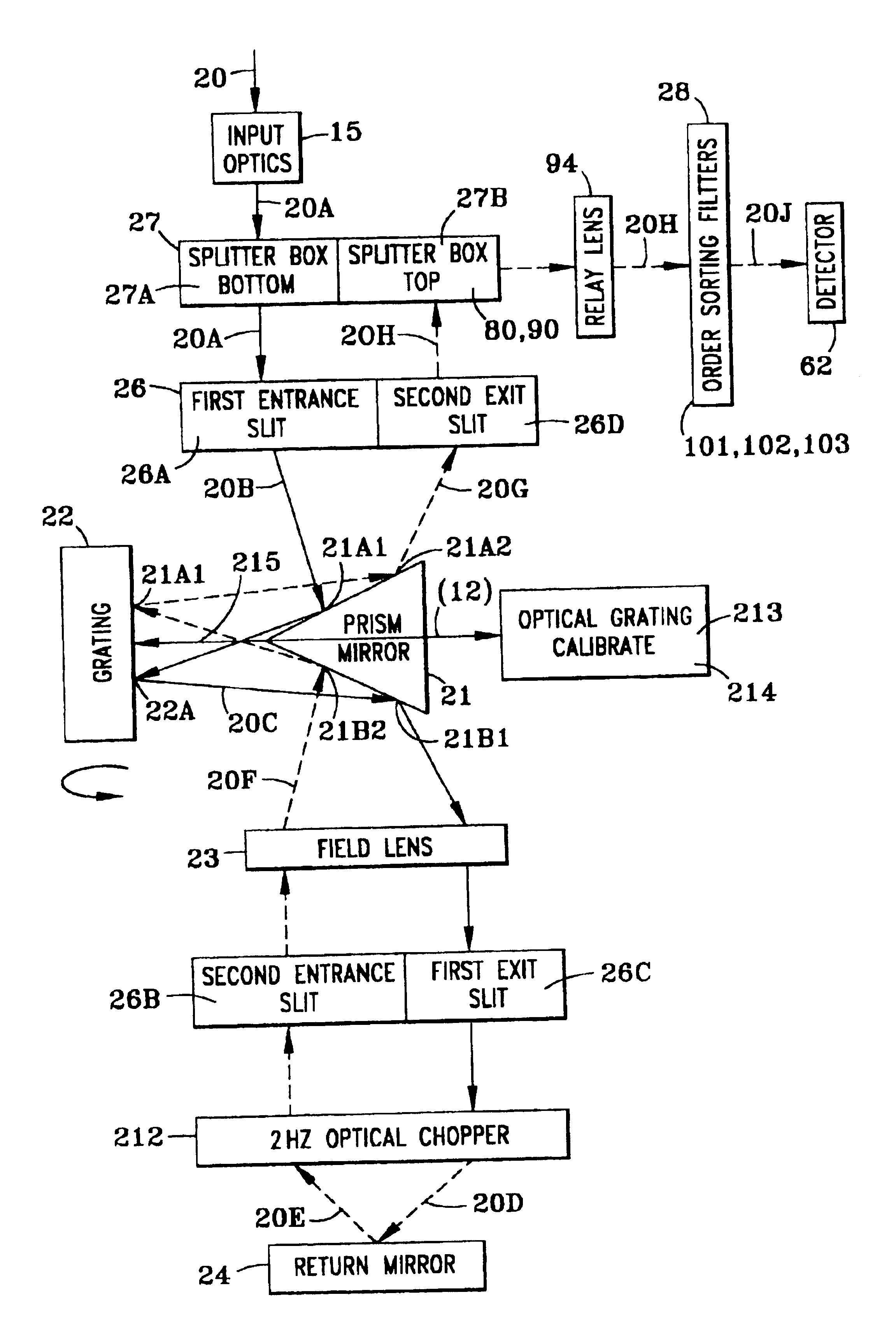
A spectrometer, or a spectral instrument using multiple non-interfering optical beam paths and special optical elements. The special optical elements for use with the instrument are used for directing the optical beam and / or altering the form of the beam. The instrument has the potential, depending upon the totality of the optical components incorporated into the instrument, to be a monochromator, a spectroradiometer, a spectrophotometer and a spectral source. The spectral instrument may further be a part of the spectral system. The system may include the spectral instrument, a power module and means for remote control of the instrument. Such remote control may be by use of a personal computer or a control system dedicated to the control, measurement and analysis of the collected information. The multiple non-interfering beam paths are created using specially designed optical elements such as a diffraction grating, a splitter box, a zero back-lash drive system for movement of the grating element. The orientation of and a physical / spatial relationship between the field lenses, slits, return mirror, reflecting prism, turning lenses all define the multiple, preferably two paths. Particularly, there is a double pass through the grating to increase dispersion, reduce scatter while maintaining a perfect temperature independent spectral match for the second pass. Using the same grating twice reduces scatter by about a factor of 1000, increases the dispersion by a factor of two, and eliminates any temperature-related mechanical spectral drift which often is present with two separate monochromators. Because of the specially designed grating structure, the grating can cause the concurrent diffraction of a plurality of incident optical beams, each of which beams have different angles of incidence and different angles of reflection. The path of the incident and the reflected beam to and from the grating is "off-axis". That is, the beams going to and from the grating do not use the optical axis of the grating structure.
Owner:RYER DAMOND V
Measuring an alignment target with a single polarization state
ActiveUS6992764B1Polarisation-affecting propertiesPhotomechanical apparatusLight beamSingle polarization
An alignment target includes periodic patterns on two elements. The periodic patterns are aligned when the two elements are properly aligned. By measuring the two periodic patterns with an incident beam having a single polarization state and detecting the intensity of the resulting polarized light, it can be determined if the two elements are aligned. The same polarization state may be detected as is incident or different polarization states may be used. A reference measurement location may be used that includes a third periodic pattern on the first element and a fourth periodic pattern on the second element, which have a designed in offset, i.e., an offset when there is an offset of a known magnitude when the first and second element are properly aligned. The reference measurement location is similarly measured with a single polarization state.
Owner:ONTO INNOVATION INC
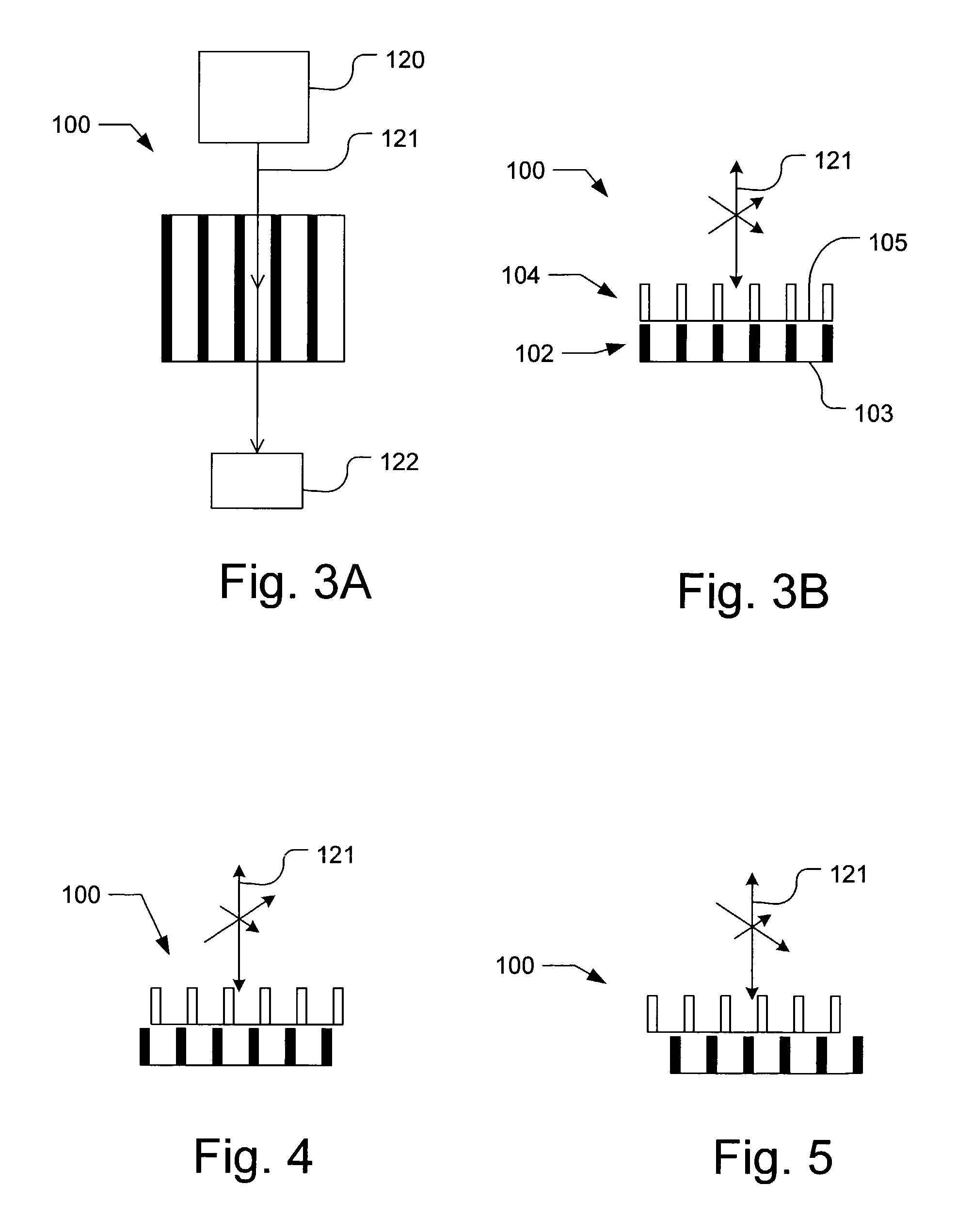
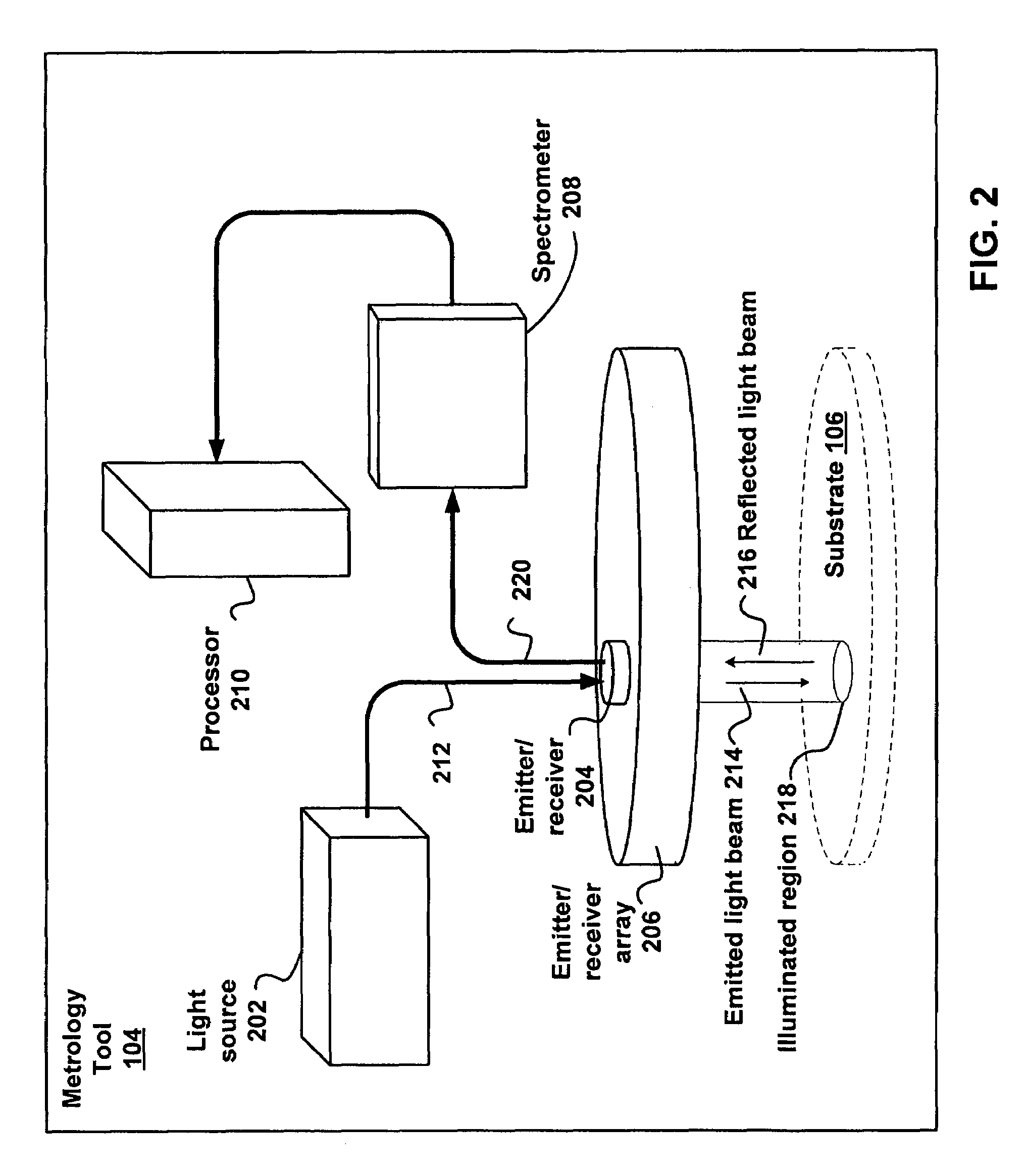
Method and apparatus for process control with in-die metrology
ActiveUS7469164B2Semiconductor/solid-state device testing/measurementScattering properties measurementsLight beamEngineering
Various embodiments include a method for providing instructions to a process tool. The method includes emitting an incident light beam at a substrate, receiving a reflected light beam from the substrate and determining a spectrum of the reflected light beam. The method further includes determining a first property of a first layer of the substrate and a second property of a second layer of the substrate, based on the spectrum determination. The method further includes comparing the first property of the first layer to a first reference property and comparing the second property of the second layer to a second reference property. The method further includes determining the instructions based on the first property comparison and the second property comparison; and providing the instructions to the process tool.
Owner:TEVET PCT
Film mapping system
ActiveUS20050046850A1Radiation pyrometrySpectrum generation using diffraction elementsLight beamElectromagnetic radiation
Owner:SVT ASSOCS
Color laser printer
A color laser printer producing a color image using a single laser scanning unit includes a lighting unit including first and second laser diodes emitting beams of one polarization, a polarization prism transmitting or reflecting incident beams depending on a direction of polarization, and third and fourth laser diodes disposed in a different direction from the first and second laser diodes with respect to the polarization prism, a rotary polygon mirror that reflects the beam emitted along the same path from the lighting unit, an f-θ lens that focuses the beam reflected by the rotary polygon mirror, first and second polarization beam splitters, each of which transmits or reflects the beam passing through the f-θ lens depending on the direction of the polarization, and first through fourth photoconductive units on which the beams reflected and transmitted through the first and second polarization beam splitters are incident. In the color laser printer, lengths of optical paths between the f-θ lens and each of the first through fourth photoconductive units are equal. The color laser printer is constructed such that a plurality of light sources emitting the beams of one polarization are arranged separately and the beams emitted from the light sources are combined by the polarization prism to enter the f-θ lens, thereby reducing a thickness of the f-θ lens.
Owner:HEWLETT PACKARD DEV CO LP
Optical device, and virtual image display
ActiveUS7453612B2Reduce color unevennessReduce unevennessDiffraction gratingsOptical light guidesGratingWaveguide
An optical device including an optical waveguide upon which a group of parallel light beams different in traveling direction from each other are incident and from which the group of parallel light beams go out after propagated by repeated total reflection through it. The optical waveguide includes a first reflection-type volume hologram grating, and a second reflection-type volume hologram grating. The pitches of interference fringes on the hologram surfaces of the first and second reflection-type volume hologram gratings are equal to each other. In at least the second reflection-type volume hologram grating, the angle formed between the interference fringes and hologram surfaces are varied continuously or stepwise within the hologram in relation to the main incident light beam so as to meet the Bragg condition. Therefore, it is possible to reduce the unevenness of color and brightness due to angles of view.
Owner:SONY CORP
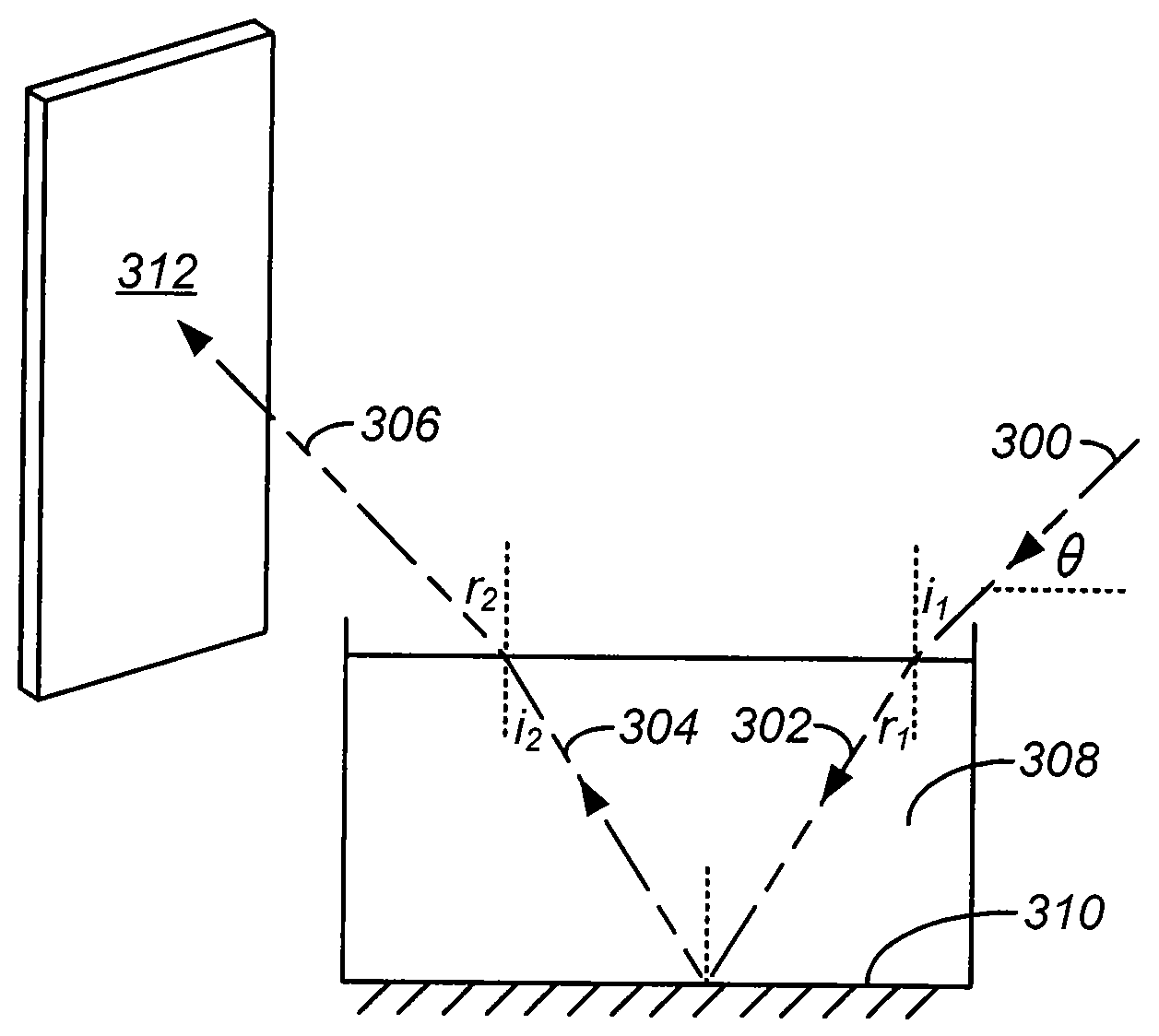
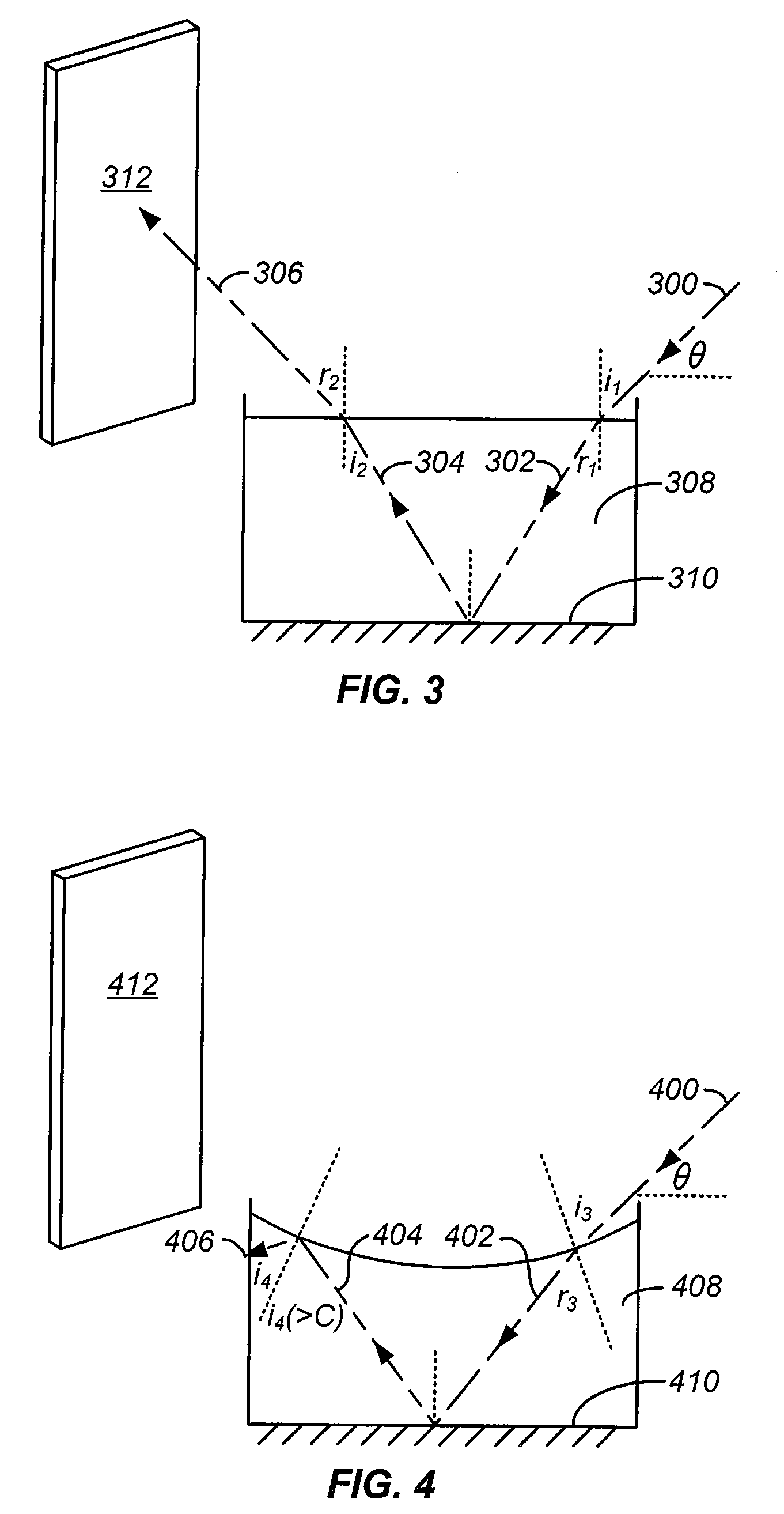
Optical apparatus
InactiveUS7221453B2Improve transmission efficiencyPrismsScattering properties measurementsCombined usePrism
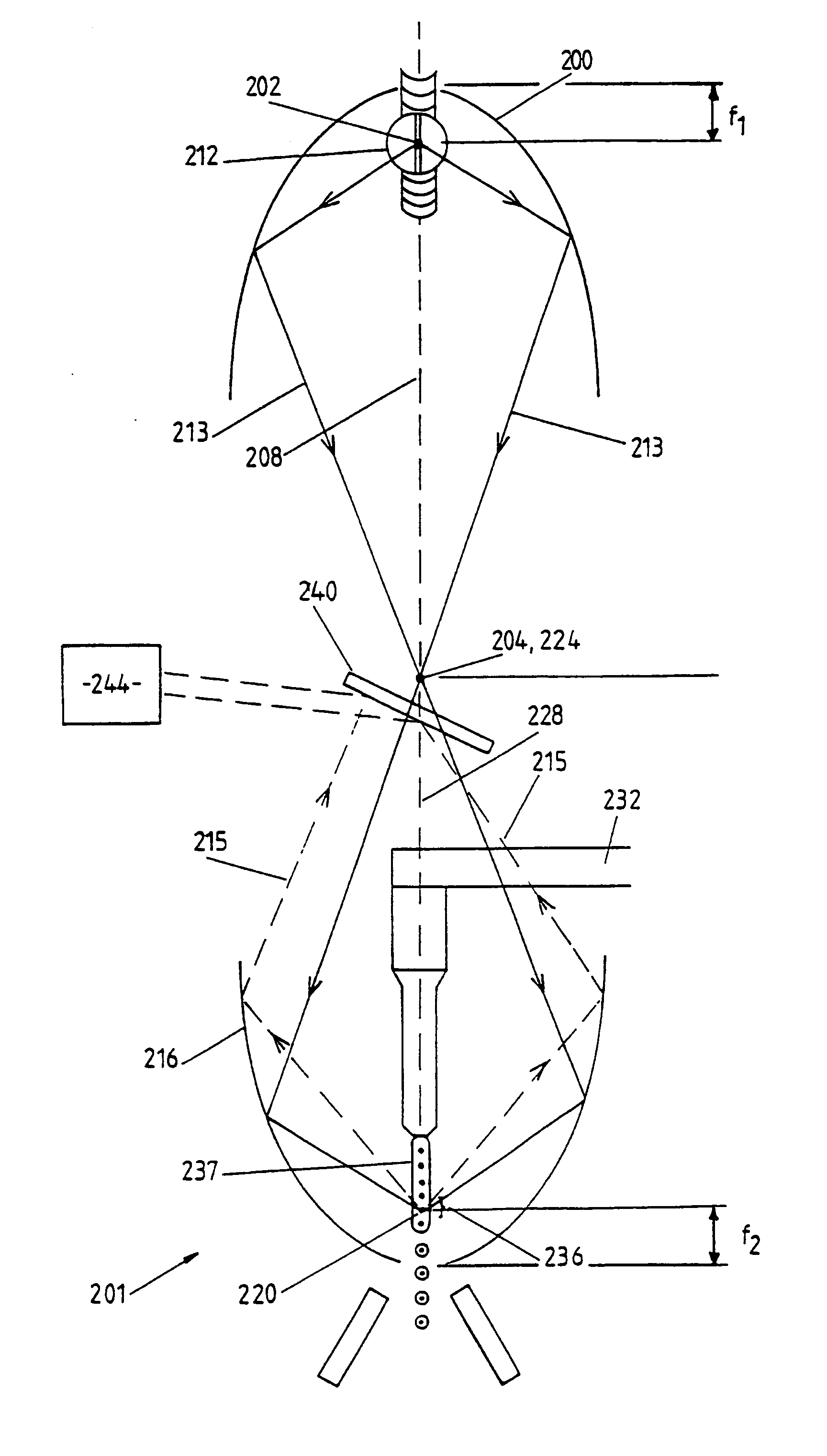
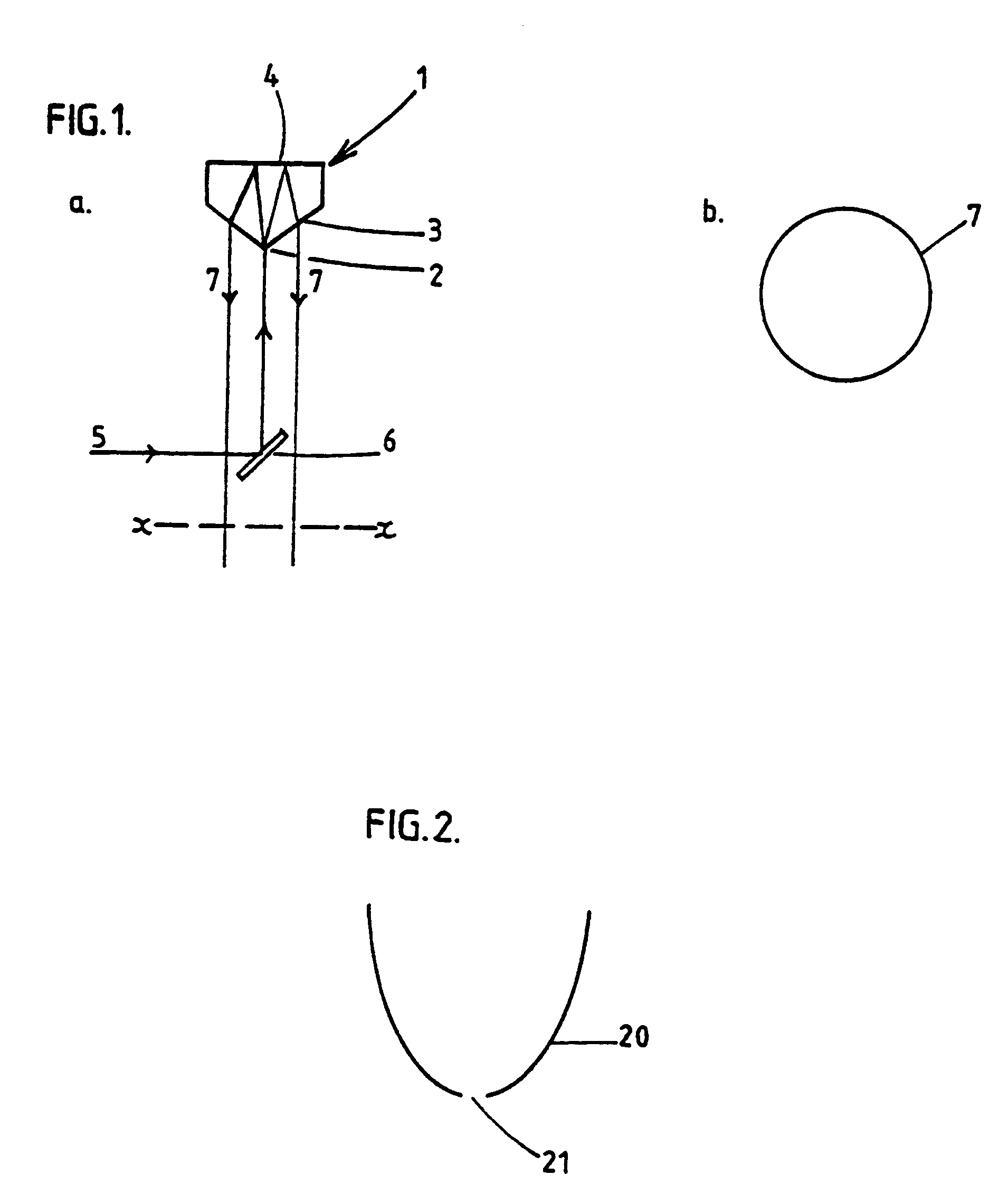
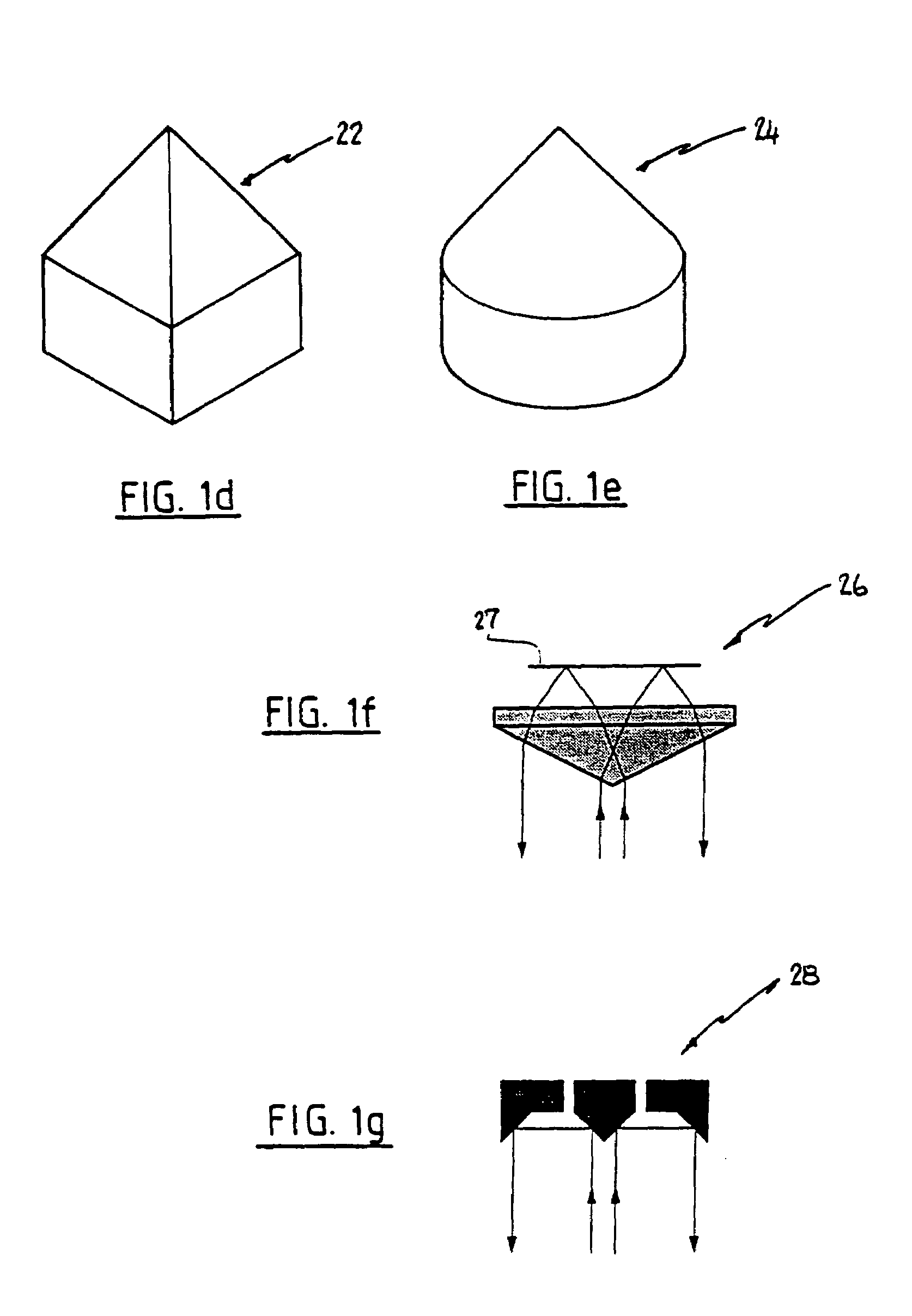
Various optical apparatus provide a source of parallel light (7, 75). The parallel light (7, 75) is generally achieved by directing an incident beam at the apex of a prism (1, 22, 24, 26, 28). The prism may have varying configurations. One configuration has a forward conical face (24). Another configuration has a pyramidal forward end (22). Other configurations are also disclosed. The application also discloses the use of reflectors (20, 78, 216, 316, 400) having internal reflective surfaces shaped as three-dimensional figures of revolution, for example paraboloid or ellipsoid. The reflectors (20, 78, 216, 316) focus light incident onto the reflectors at one or more foci (F, 220, 320, 420). The reflectors may be used in combination with the optical apparatus including the prisms (1, 22, 24, 26, 28). The reflectors (20, 78, 216,316) may be used in flow cytometers for focusing light at a sample stream (237, 337) passing through the focus (F, 220, 320, 420) of the reflector (20, 78, 216, 316). The collection of scattered and / or fluorescent light from an illuminated sample stream (237, 337) in a flow cytometer may be achieved with the use of a collector shaped as a figure of revolution e.g. paraboloid or ellipsoid. Various optical methods and methods for flow cytometry are also disclosed.
Owner:XY
Laser nanomachining device and method
ActiveUS20150158120A1Eliminate the effects ofSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingPrinted circuit manufactureSpectral bandsOptical axis
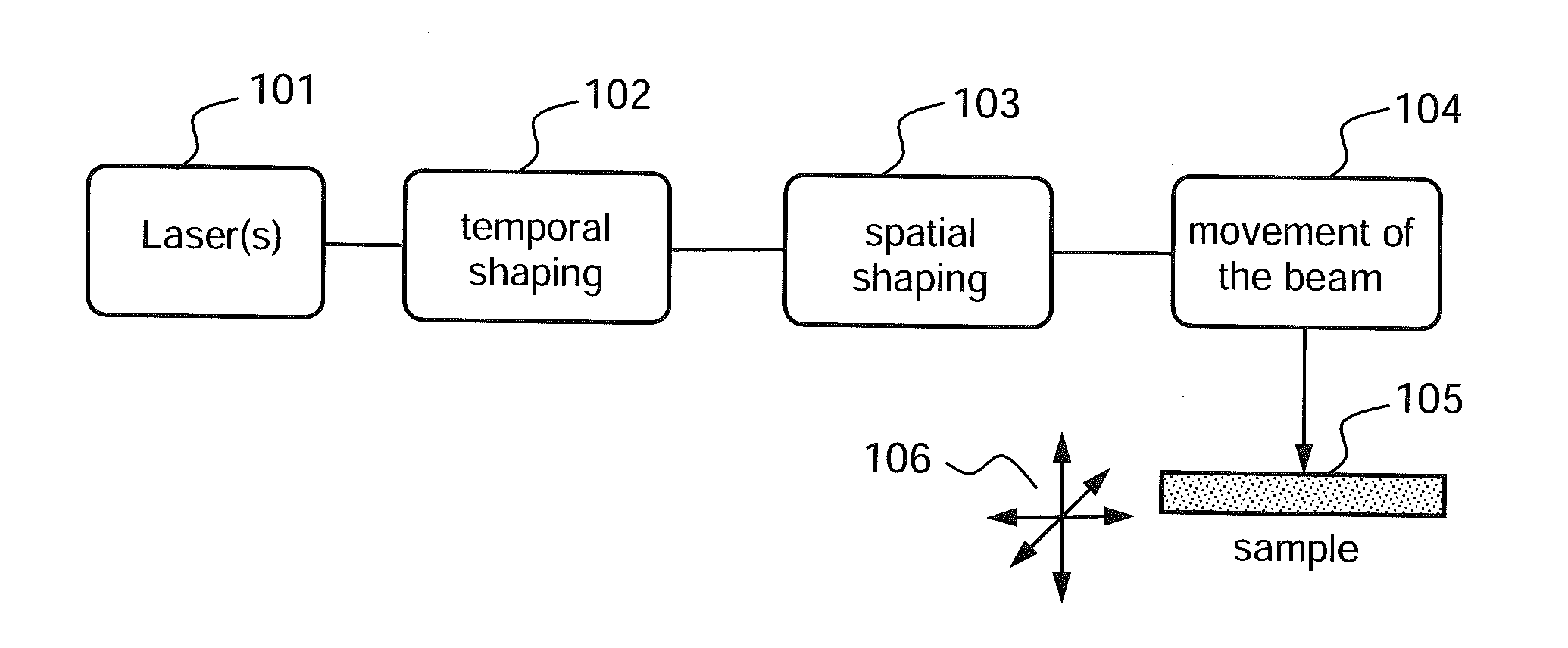
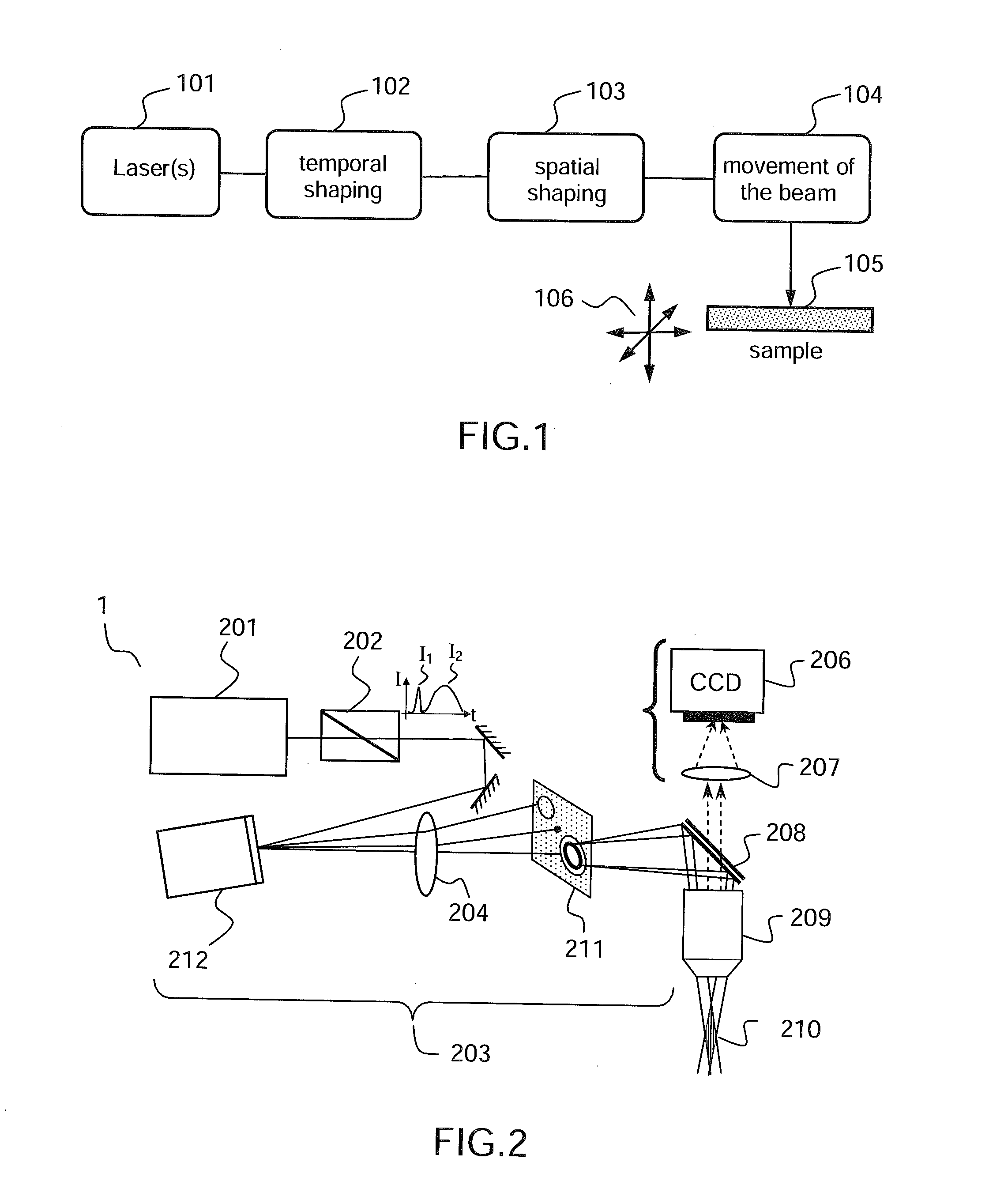
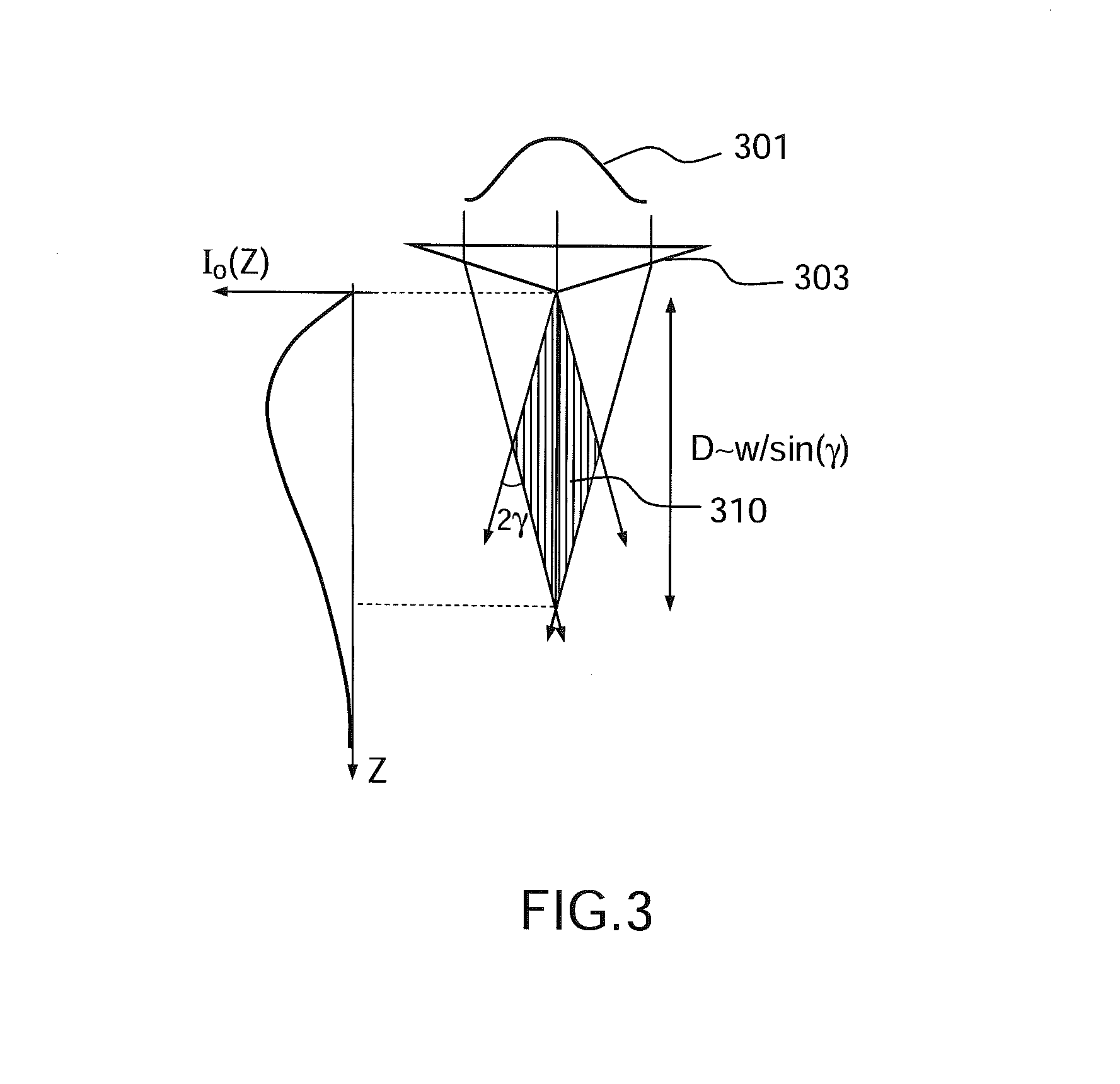
According to one aspect, the invention relates to a device (1, 2, 3) for laser nanomachining a sample made of a material having a given transparency band, the device comprising: a focusing module (203, 703) allowing a nondiffracting beam (210, 710) to be generated, along a focusing line generally oriented along the optical axis of the focusing module, from a given incident beam; first means (202, 702) for emitting a first light pulse (I1) of spectral band comprised in the transparency band of said material, able to generate in said material, after focusing by said focusing module, a plasma of free charges along said focusing line via multiphoton absorption, thus forming a “plasma channel”; and second means (202, 702) for emitting at least one second electromagnetic wave (I2) of spectral band comprised in the transparency band of said material, which wave(s) is / are intended to be spatially superposed on said plasma channel in order to heat said material via absorption by the free charges of the plasma.
Owner:CENT NAT DE LA RECHERCHE SCI +1
Optical mouse having an optical structure capable of high sensibility
InactiveUS20070222756A1Increased sensitivityConsiderable precisionCathode-ray tube indicatorsInput/output processes for data processingTarget surfaceLight beam
An optical structure of the optical mouse is disclosed, which comprises a light source providing an incident light beam transmitted onto a target surface at a specific incident angle and a photosensor pre-disposed at an angle of between 1 and 179 degrees or between 181 and 359 degrees so as to be aligned to stand at a right angle with respect to a path of the reflected version and thus achieve a proper acquirement of luminance and image of the reflected version of the incident light from the target surface.
Owner:CHIC TECH CORP
CD-GISAXS system and method
ActiveUS7920676B2Improve accuracyHigh sensitivityPhotomechanical apparatusMaterial analysis using radiation diffractionMetrologyX-ray
CD-GISAXS achieves reduced measurement times by increasing throughput using longer wavelength radiation (˜12×, for example) such as x-rays in reflective geometry to increase both the collimation acceptance angle of the incident beams and the scattering signal strength, resulting in a substantial combined throughput gain. This wavelength selection and geometry can result in a dramatic reduction in measurement time. Furthermore, the capabilities of the CD-GISAXS can be extended to meet many of the metrology needs of future generations of semiconductor manufacturing and nanostructure characterization, for example.
Owner:CARL ZEISS X RAY MICROSCOPY
Diffusion plate used in direct-type backlight module and method for making the same
ActiveUS20070014034A1Increase brightnessReduce variablesDiffusing elementsElectric lightingDiffusionLight beam
The present invention relates to a diffusion plate used in a direct-type backlight module and a method for making the same. At least one of the surfaces of the diffusion plate has a microstructure constituted by repeated undulation that can refract and diffuse the incident light beams that enter the diffusion plate. Therefore, the paths of the light beams after entering the diffusion plate are changed, which raises the luminance of the backlight module.
Owner:CHI MEI CORP
Methods and apparatus for inspecting a sample
ActiveUS7295303B1Increase contrastEliminate the effects ofMaterial analysis by optical meansMicroscopesCombined useLight beam
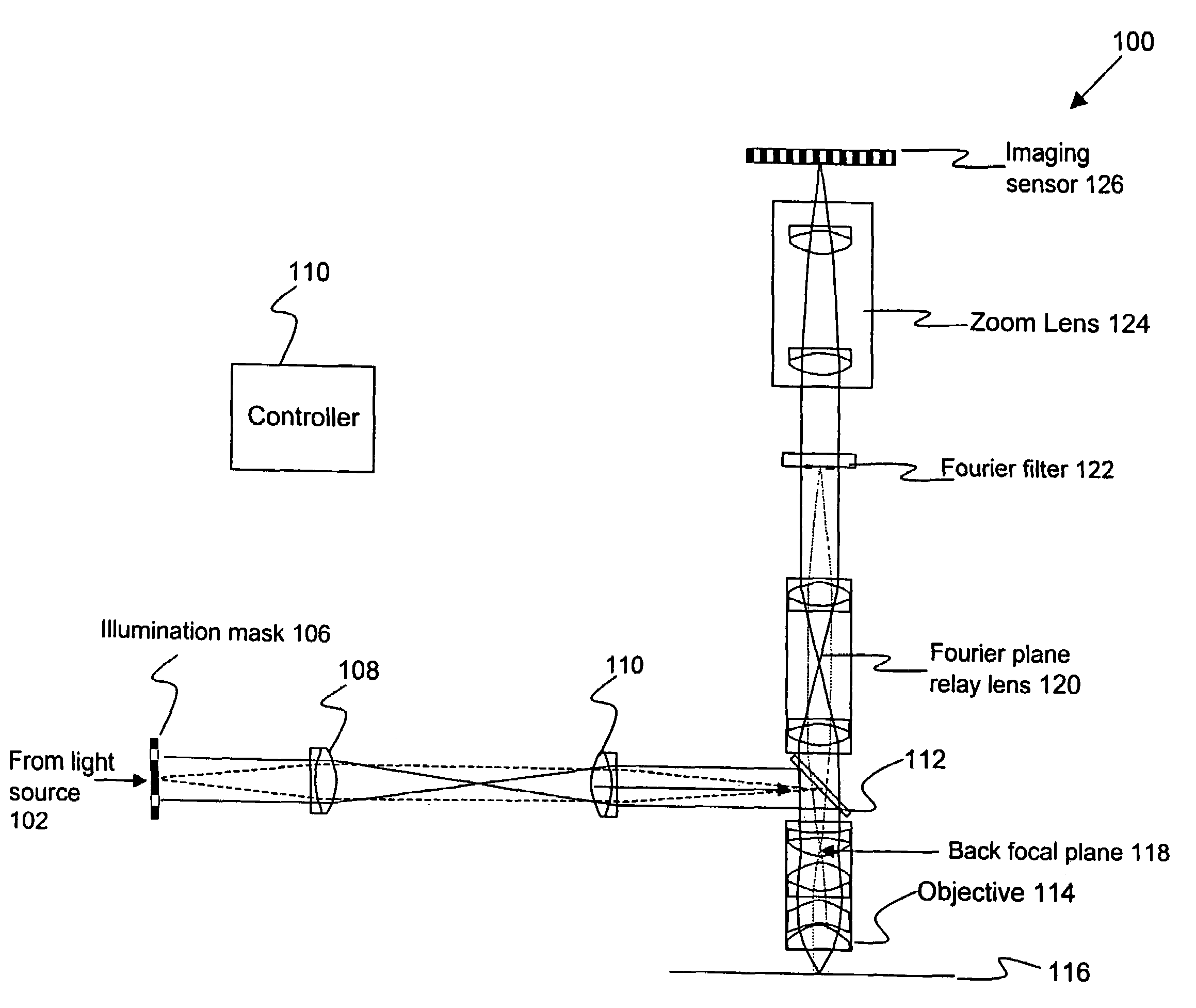
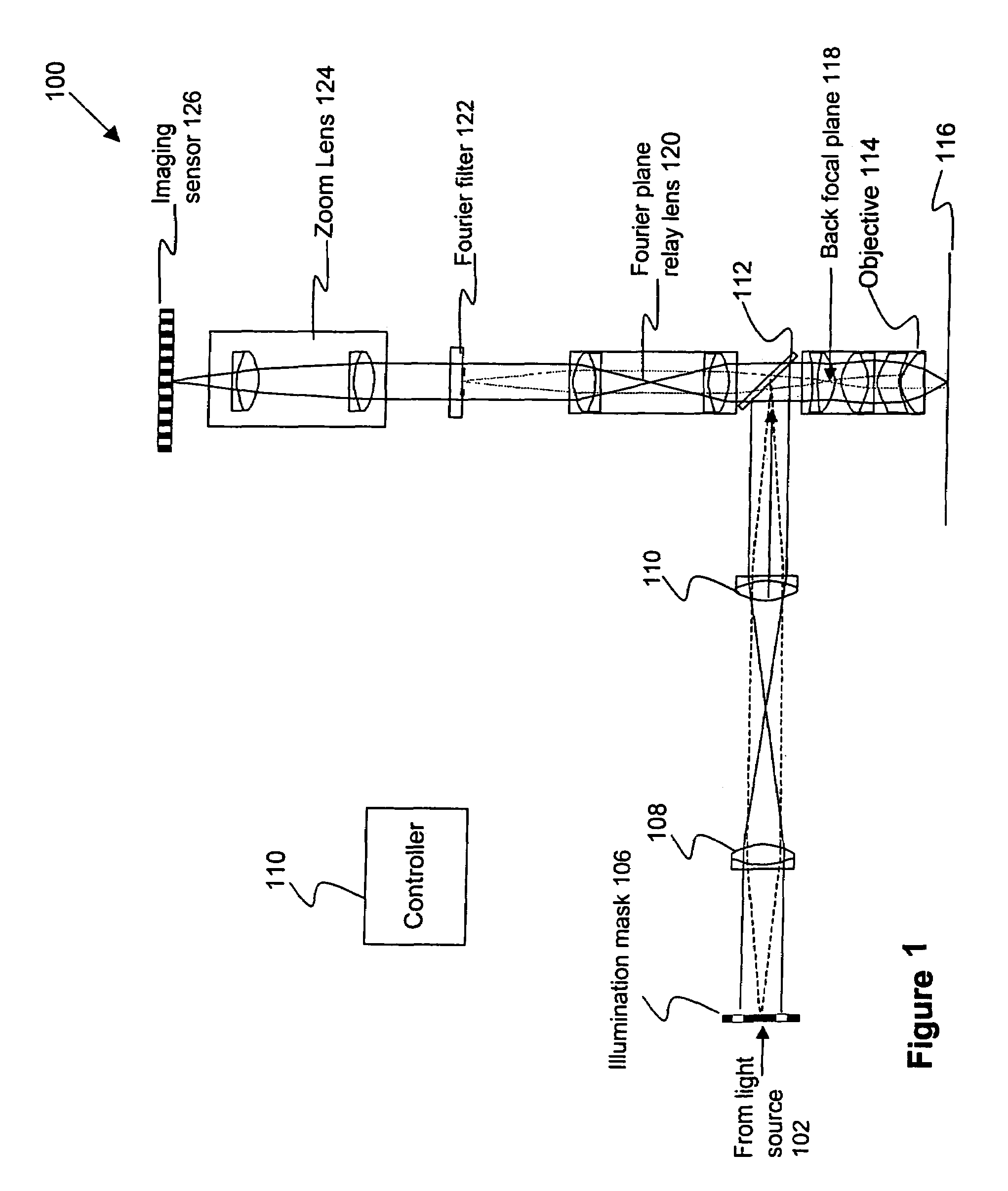
Disclosed are methods and apparatus for inspecting or imaging a sample, such as a semiconductor wafer or reticle. In general, an optical inspection or microscopy tool that has a complex Fourier filter positioned in the Fourier plane of the radiation beam output from the sample in response to an incident beam striking the sample is provided. Use of such Fourier filter is also disclosed. In one implementation, the complex Fourier is designed to alter a phase, and possibly amplitude, of the scattered spatial portions of the output beam relative to the specular spatial portions of the output beam so as to enhance the contrast between the two. In another implementation, the complex Fourier serves to filter the effects of repeating structures on the sample from the output beam. The complex Fourier filter is used in conjunction with a complementary illumination aperture.
Owner:KLA TENCOR TECH CORP
Optical recording systems
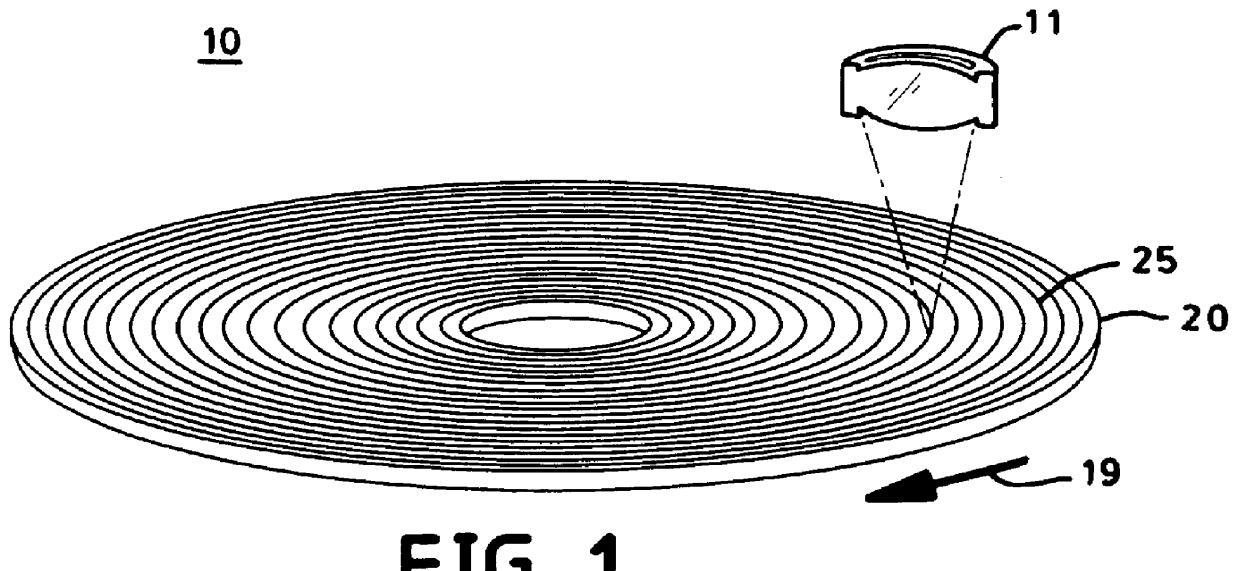
InactiveUS6094413AIncrease contrastImprove signal-to-noise ratioNanoinformaticsOptical beam sourcesOptical storageOptical recording
An optical storage system suitable for optical storage and retrieval of information using a storage medium comprising a substrate, an active layer for retention of the data, and an overlying optical layer, or layers for double-sided. The optical layer serves to produce an evanescent field in or adjacent to the active layer in response to an incident beam of radiation. The evanescent field is frustrated or attenuated by the data in the active layer and produces a signal.
Owner:SENSHIN CAPITAL +1
Micromirror elements, package for the micromirror elements, and projection system therefor
InactiveUS6962419B2Minimize light diffractionContrast ratio is reducedTelevision system detailsProjectorsLight beamLight diffraction
In order to minimize light diffraction along the direction of switching and more particularly light diffraction into the acceptance cone of the collection optics, in the present invention, micromirrors are provided which are not rectangular. Also, in order to minimize the cost of the illumination optics and the size of the display unit of the present invention, the light source is placed orthogonal to the rows (or columns) of the array, and / or the light source is placed orthogonal to a side of the frame defining the active area of the array. The incident light beam, though orthogonal to the sides of the active area, is not however, orthogonal to any substantial portion of sides of the individual micromirrors in the array. Orthogonal sides cause incident light to diffract along the direction of micromirror switching, and result in light ‘leakage’ into the ‘on’ state even if the micromirror is in the ‘off’ state. This light diffraction decreases the contrast ratio of the micromirror. The micromirrors of the present invention result in an improved contrast ratio, and the arrangement of the light source to micromirror array in the present invention results in a more compact system. Another feature of the invention is the ability of the micromirrors to pivot in opposite direction to on and off positions (the on position directing light to collection optics), where the movement to the on position is greater than movement to the off position. A further feature of the invention is a package for the micromirror array, the package having a window that is not parallel to the substrate upon which the micromirrors are formed. One example of the invention includes all the above features.
Owner:VENTURE LENDING & LEASING IV +1
Image recording device
InactiveUS6900901B2Prevents generation of crosstalkSmall and inexpensiveDigitally marking record carriersOptical filtersLight beamImage recording
When a recording starting point of a color photosensitive material reaches a position on which light beams are focused by a condenser lens and a reflecting mirror, a light beam is emitted from a red organic EL element of a light source by a controller, and red image data corresponding to a plurality of lines is transferred to a DMD. In accordance with the image data, on-off control of micromirrors of the DMD is carried out, and the red light beam emitted from the light source is made incident on the DMD. When the micromirrors are on, the incident light beam is reflected toward the reflecting mirror. The light beam is focused onto a recording surface of the color photosensitive material by the condenser lens and the reflecting mirror, and red exposure is carried out. Subsequently, green exposure and blue exposure are carried out in the same way.
Owner:FUJIFILM HLDG CORP +1
Optical devices with fluidic systems
Fluidic systems, including microfluidic systems, are used to manipulate light by light-fluid interaction so as to affect reflection, refraction, absorption, optical filtering, or scattering of the beam. One or more fluids may be provided to a channel or chamber and exposed to an incident beam, and the proportion of at least one of a plurality of fluids may be varied. Light may interact with a discrete fluid plug subject to movement within a channel. One or more flexible members may be employed, such as to provide a variable lens. Fluidic optical devices may be used in applications including optical switching, optical filtering, or optical processing. Multiplexed fluidic optical systems are further provided.
Owner:AGILENT TECH INC
Rectangular flat-top beam shaper
The invention relates to a beam shaping system for providing a square or rectangular laser beam having a controlled intensity profile (uniform, super gaussian or cosine corrected for example) from an incident non-uniform beam intensity profile laser beam source (a Gaussian profile, a profile with astigmatism or any non-rotationally symmetric and non-uniform profile for example). The beam shaping system uses a first acylindrical lens for shaping the incident laser beam along a first axis and a second acylindrical lens orthogonally disposed relative to the first acylindrical lens and for shaping the incident beam along a second axis. The thereby provided light beam is a rectangular beam having a controlled intensity distribution in the far field.
Owner:COHERENT INC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com