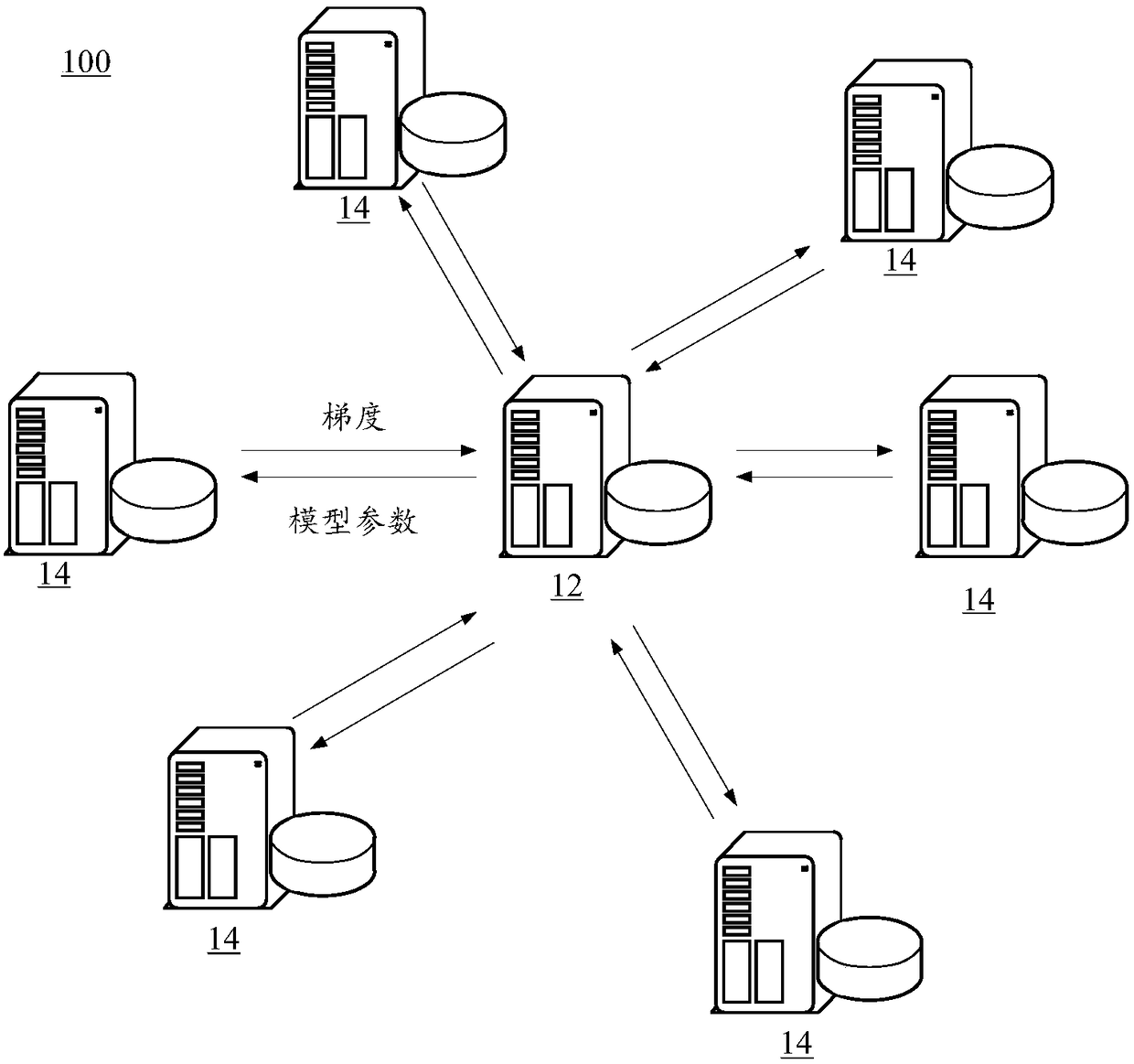
Patents
Literature
1257 results about "Attenuation coefficient" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
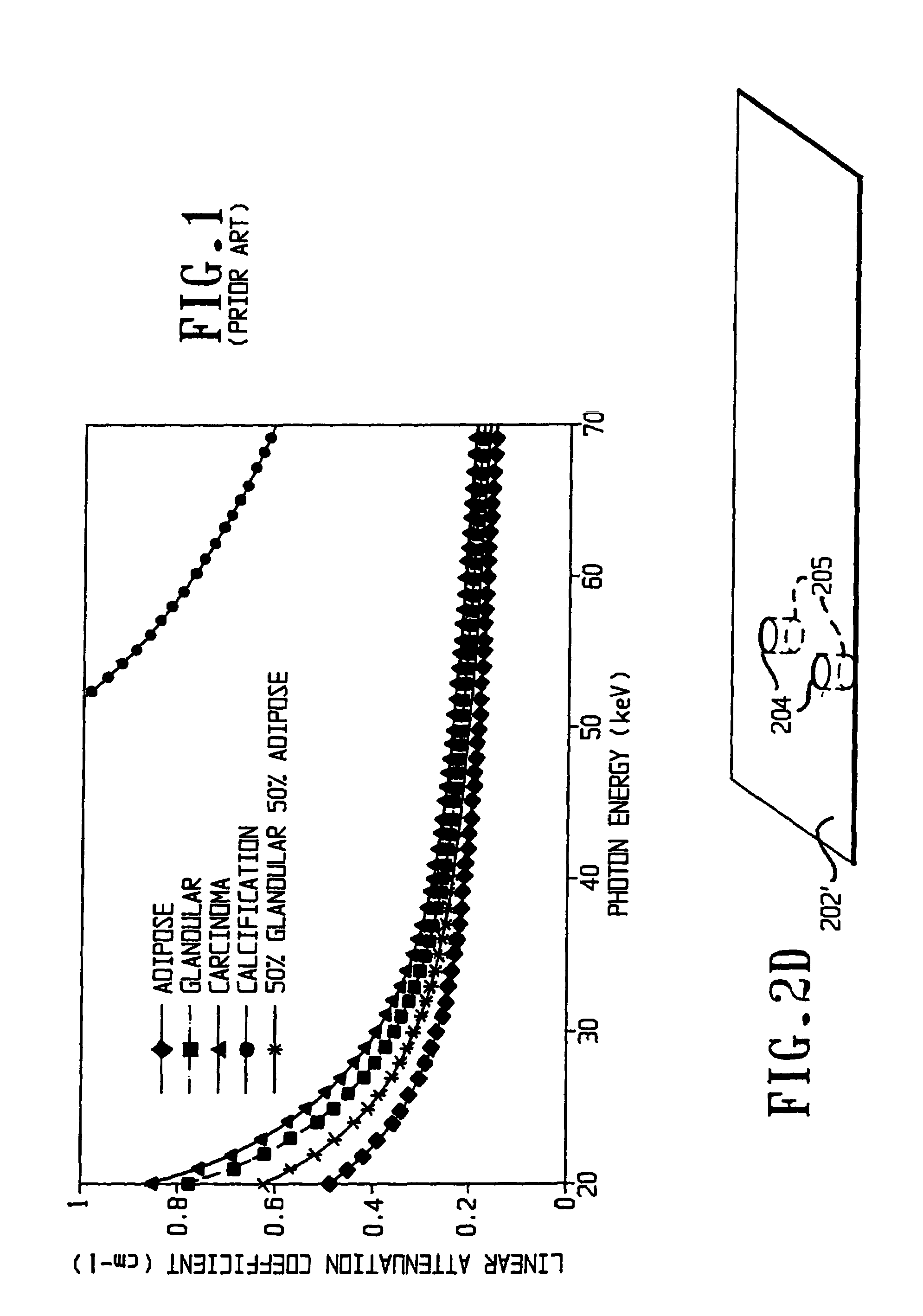
The linear attenuation coefficient, attenuation coefficient, or narrow-beam attenuation coefficient characterizes how easily a volume of material can be penetrated by a beam of light, sound, particles, or other energy or matter. A large attenuation coefficient means that the beam is quickly "attenuated" (weakened) as it passes through the medium, and a small attenuation coefficient means that the medium is relatively transparent to the beam. The SI unit of attenuation coefficient is the reciprocal metre (m⁻¹). Extinction coefficient is an old term for this quantity but is still used in meteorology and climatology. Most commonly, the quantity measures the number of downward e-foldings of the original intensity that will be had as the energy passes through a unit (e.g. one meter) thickness of material, so that an attenuation coefficient of 1 m⁻¹ means that after passing through 1 metre, the radiation will be reduced by a factor of e, and for material with a coefficient of 2 m⁻¹, it will be reduced twice by e, or e². Other measures may use a different factor than e, such as the decadic attenuation coefficient below. The broad-beam attenuation coefficient counts forward-scattered radiation as transmitted rather than attenuated, and is more applicable to radiation shielding.
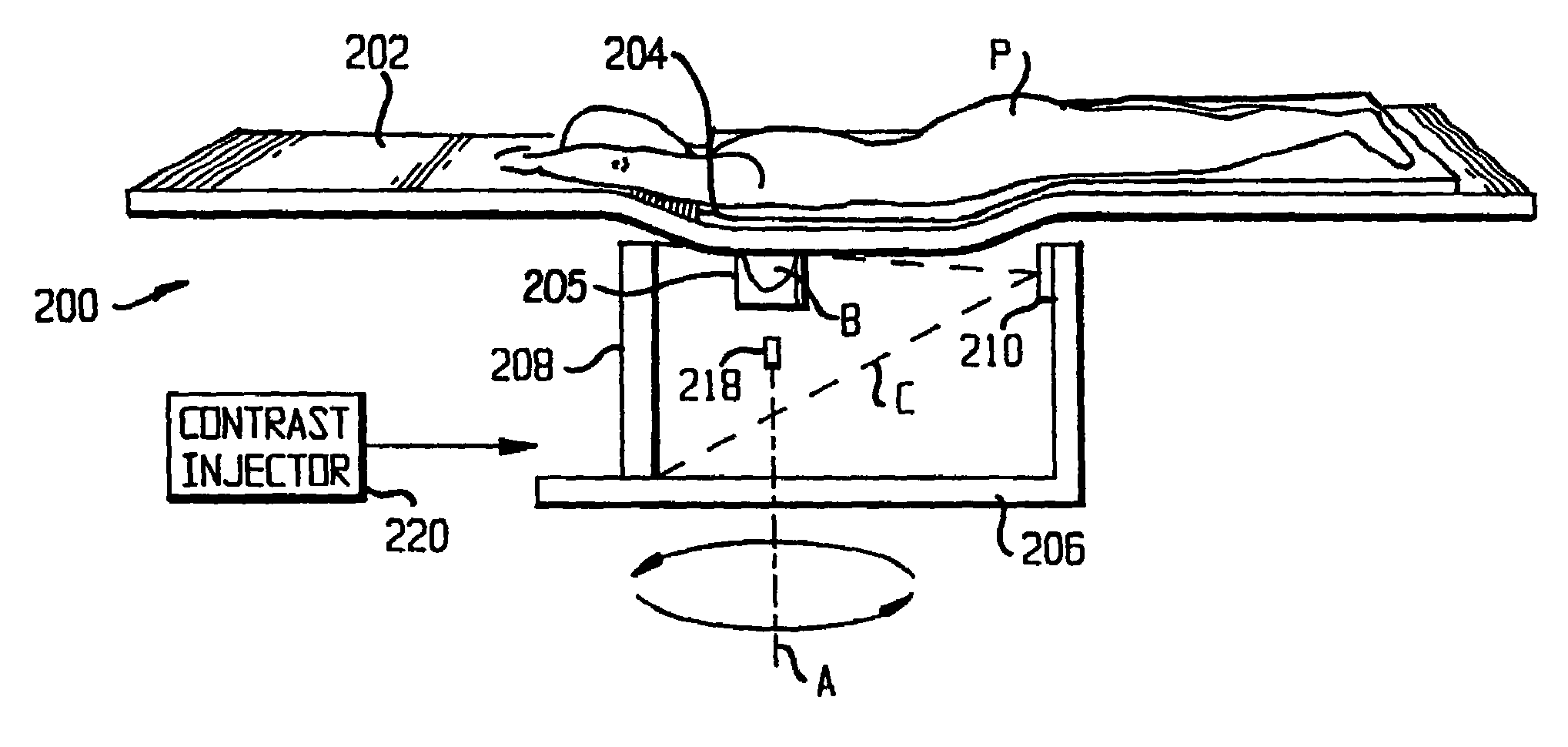
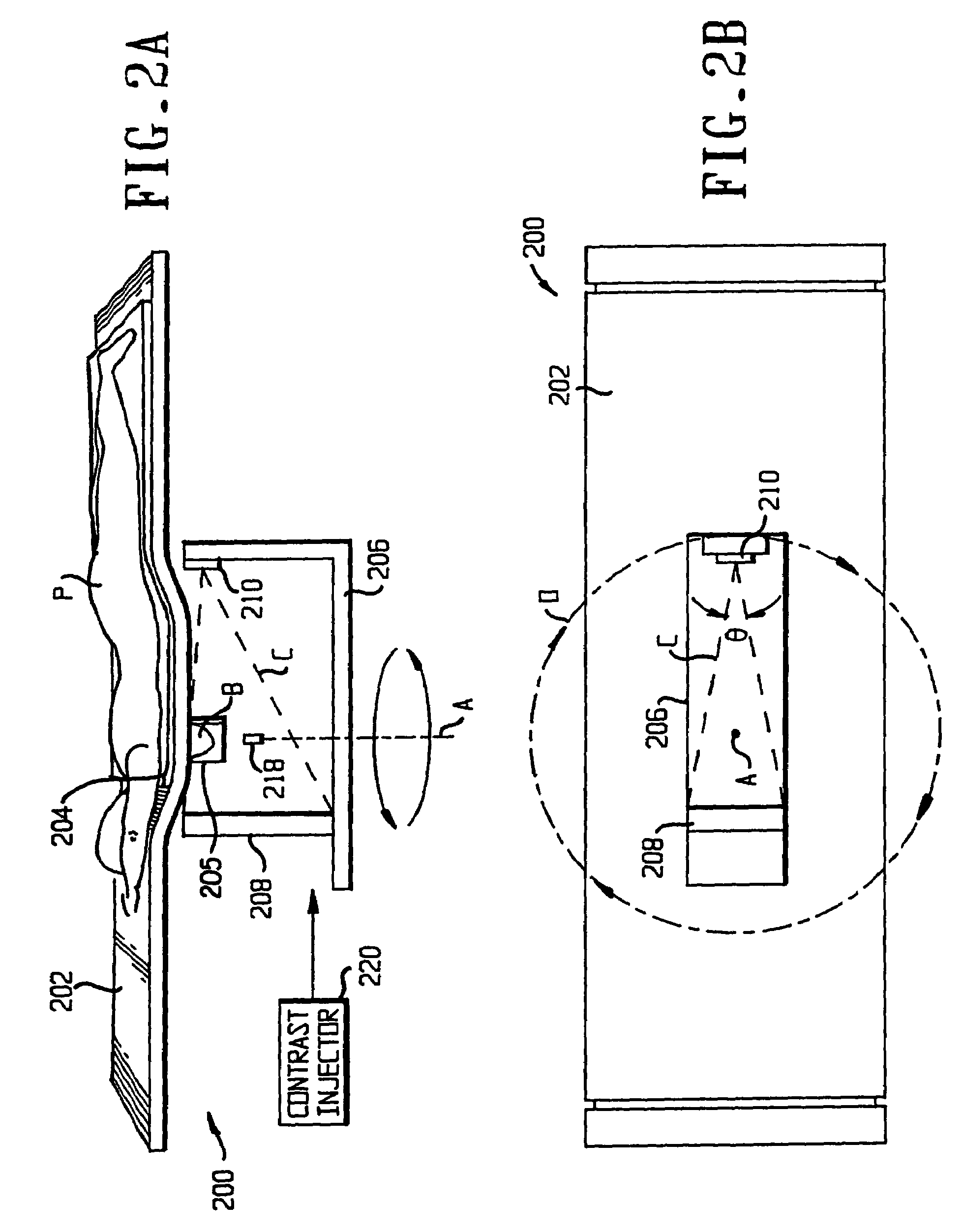
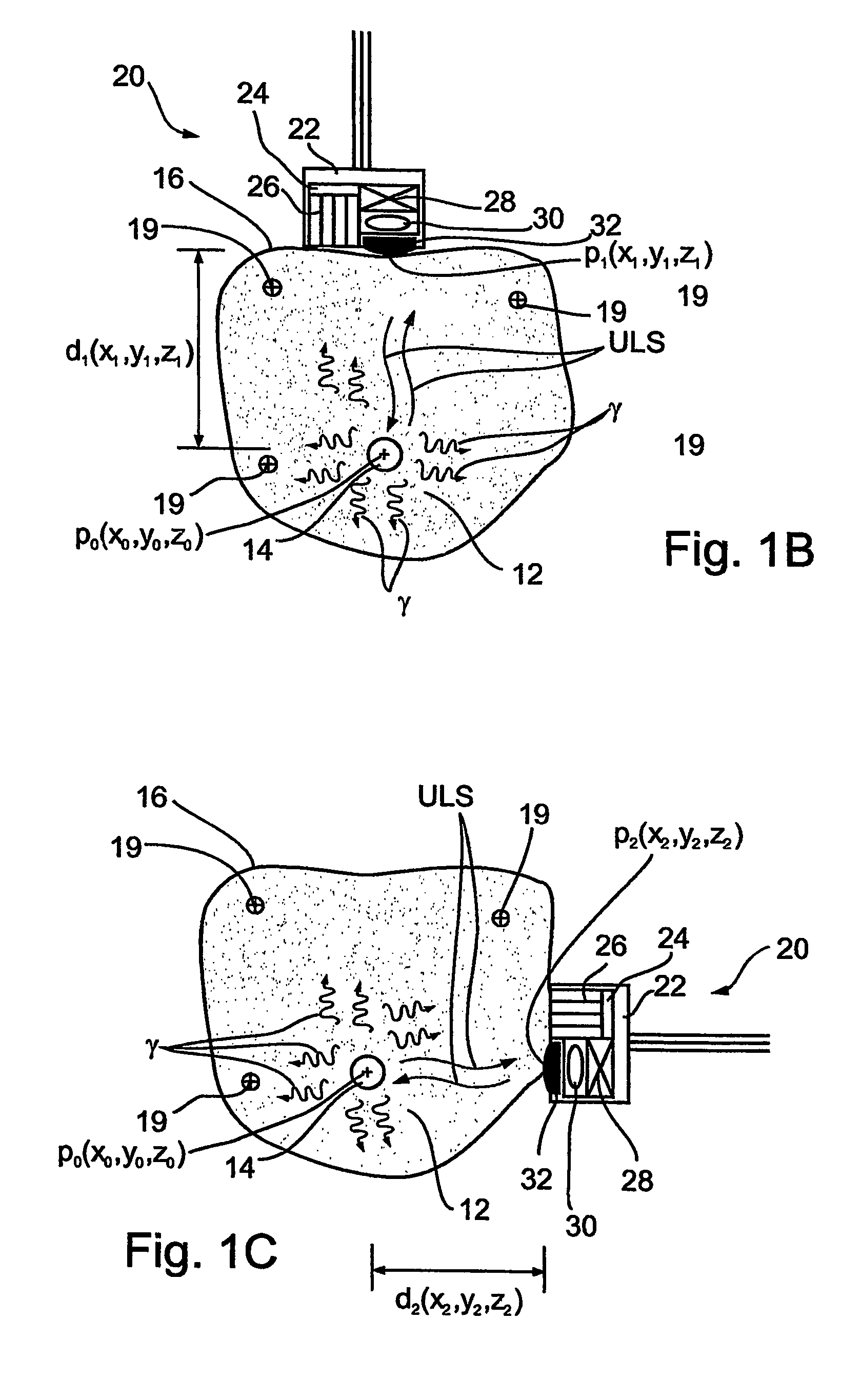
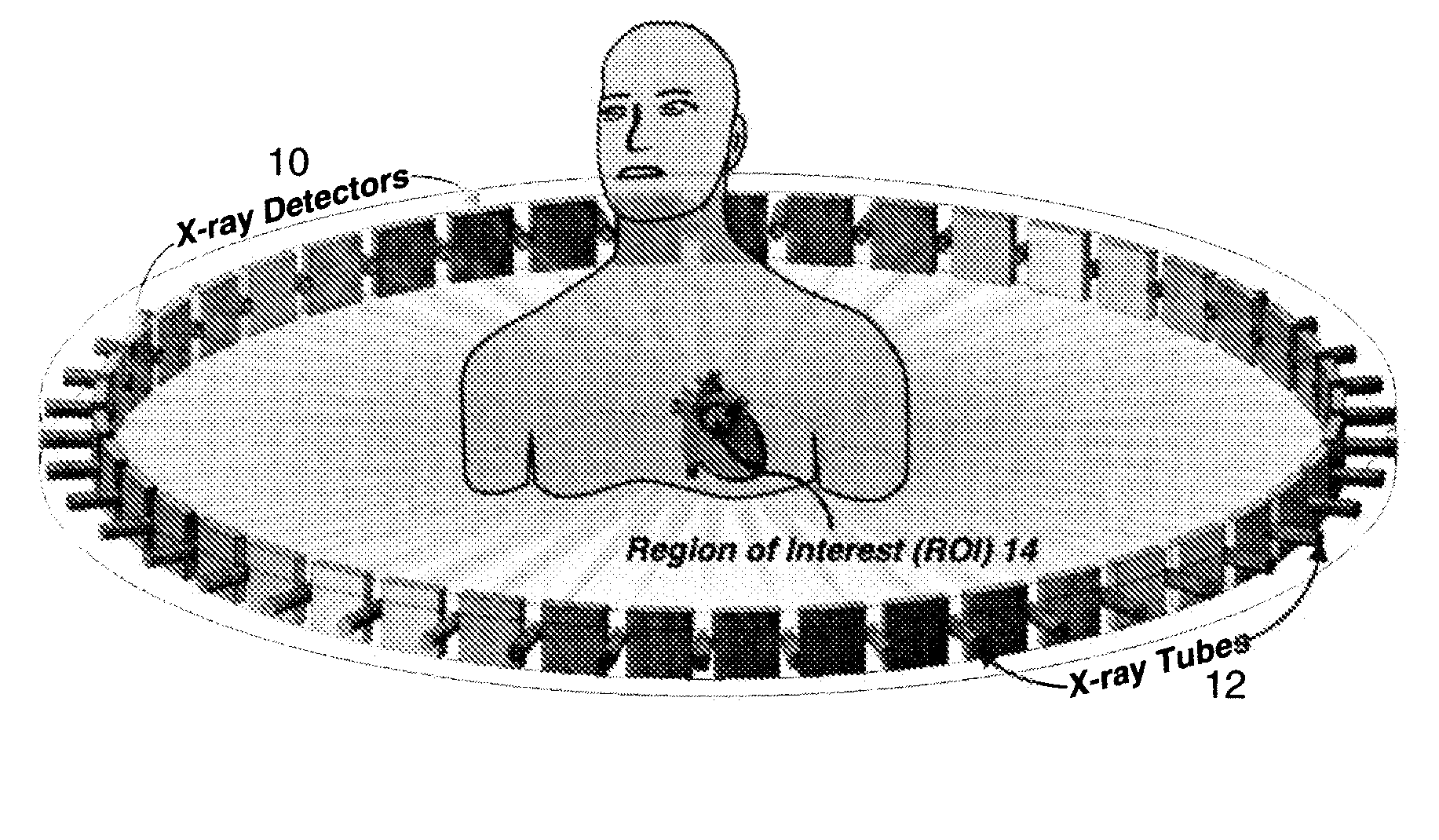
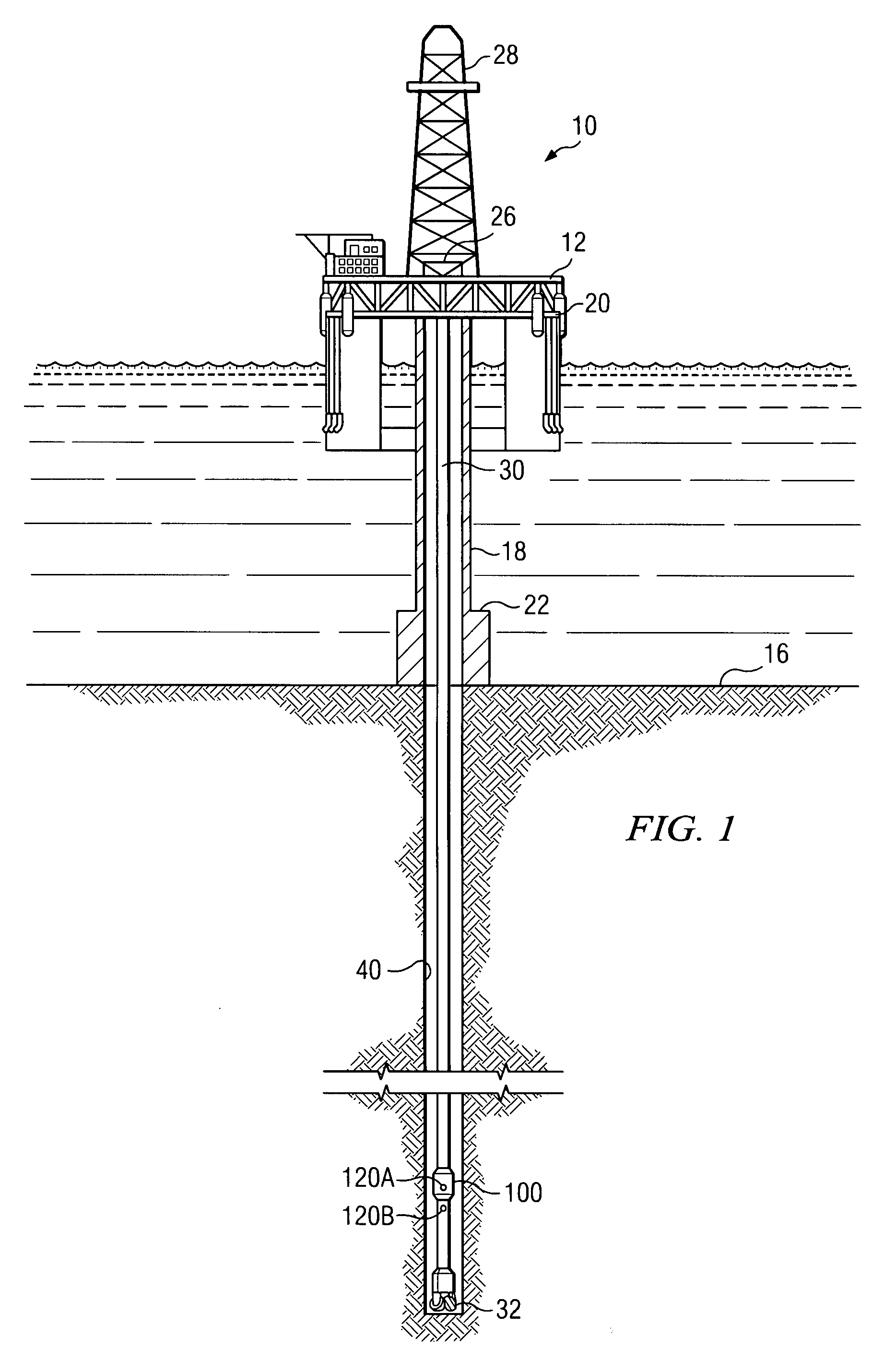
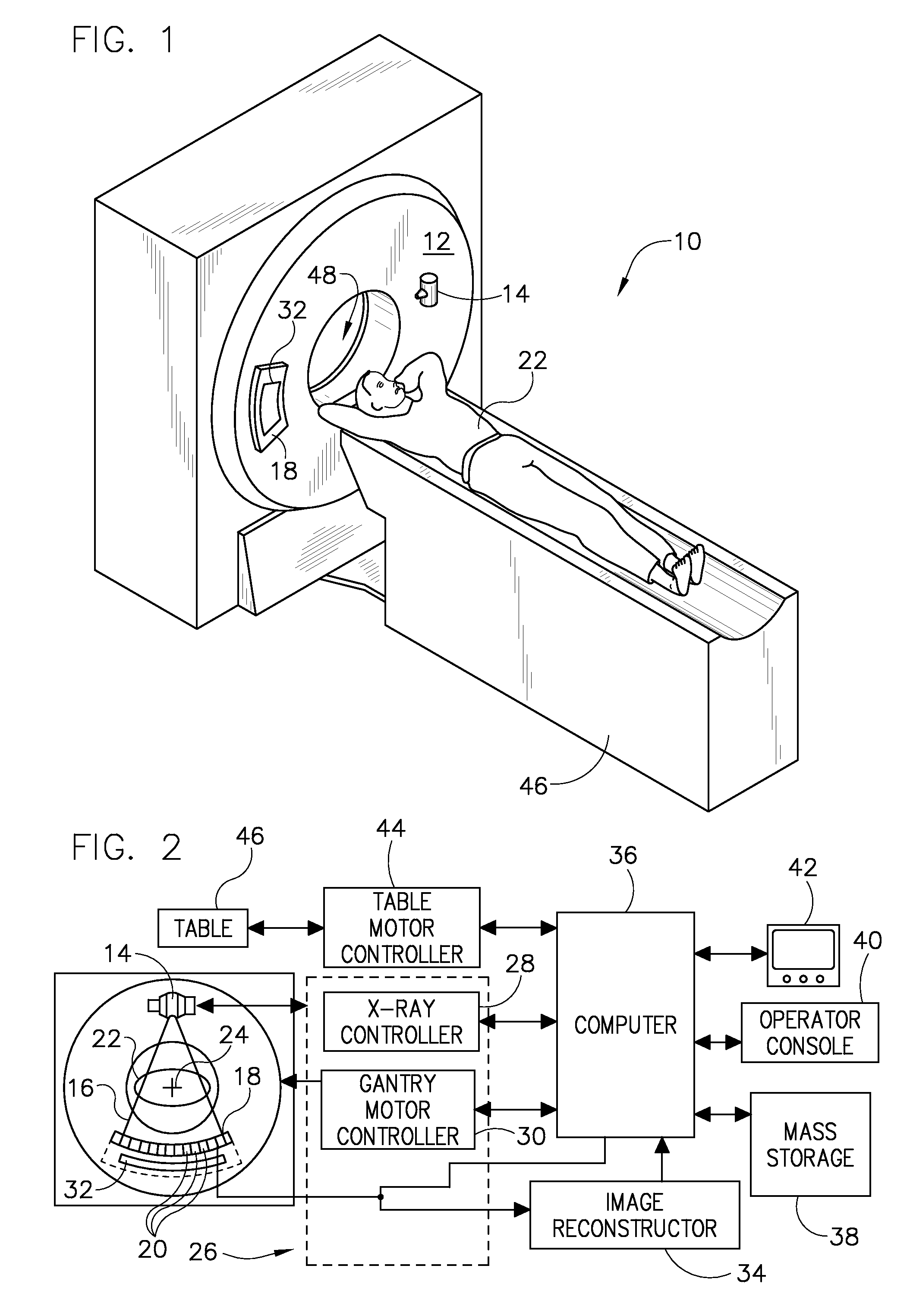
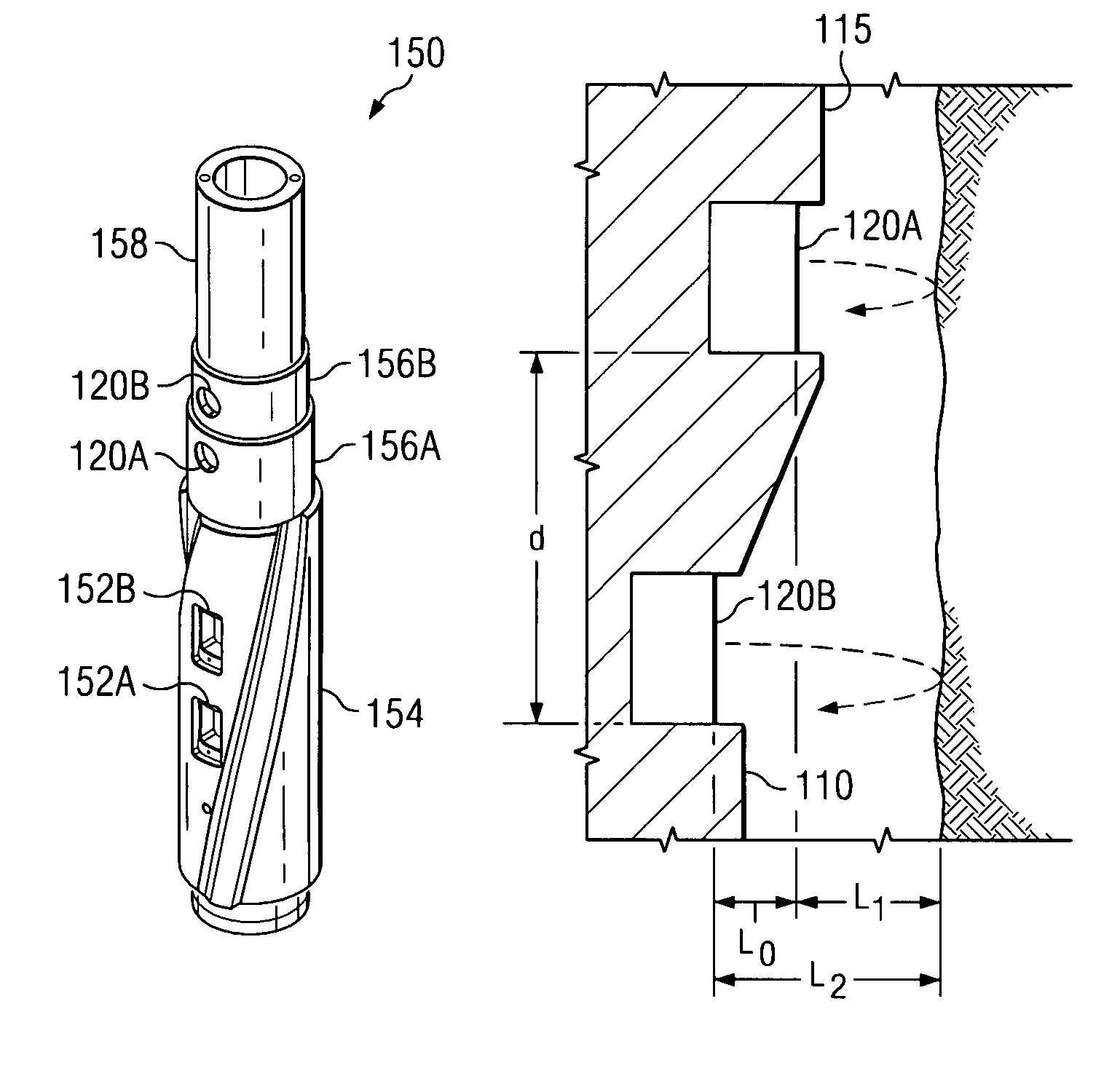
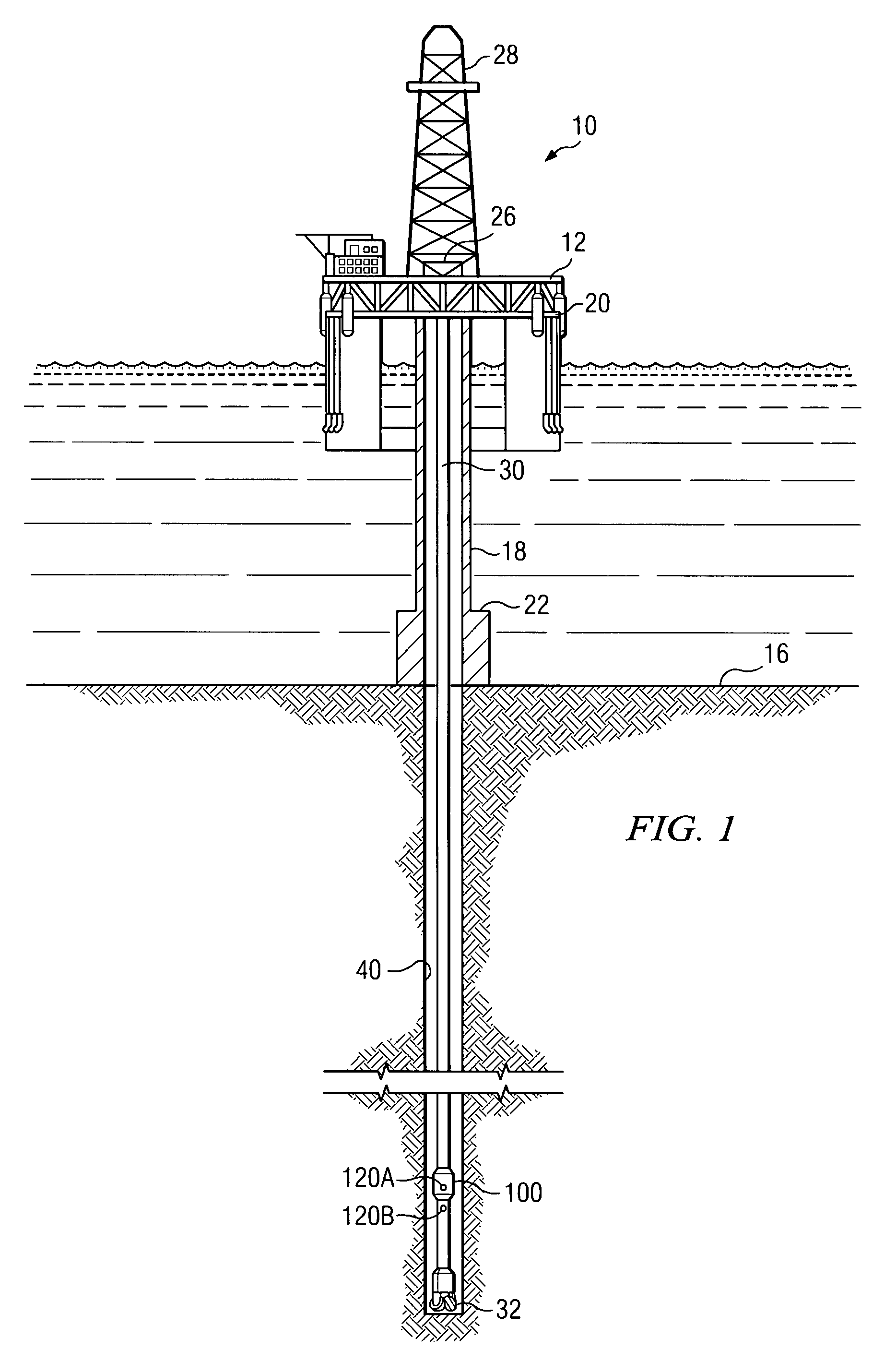
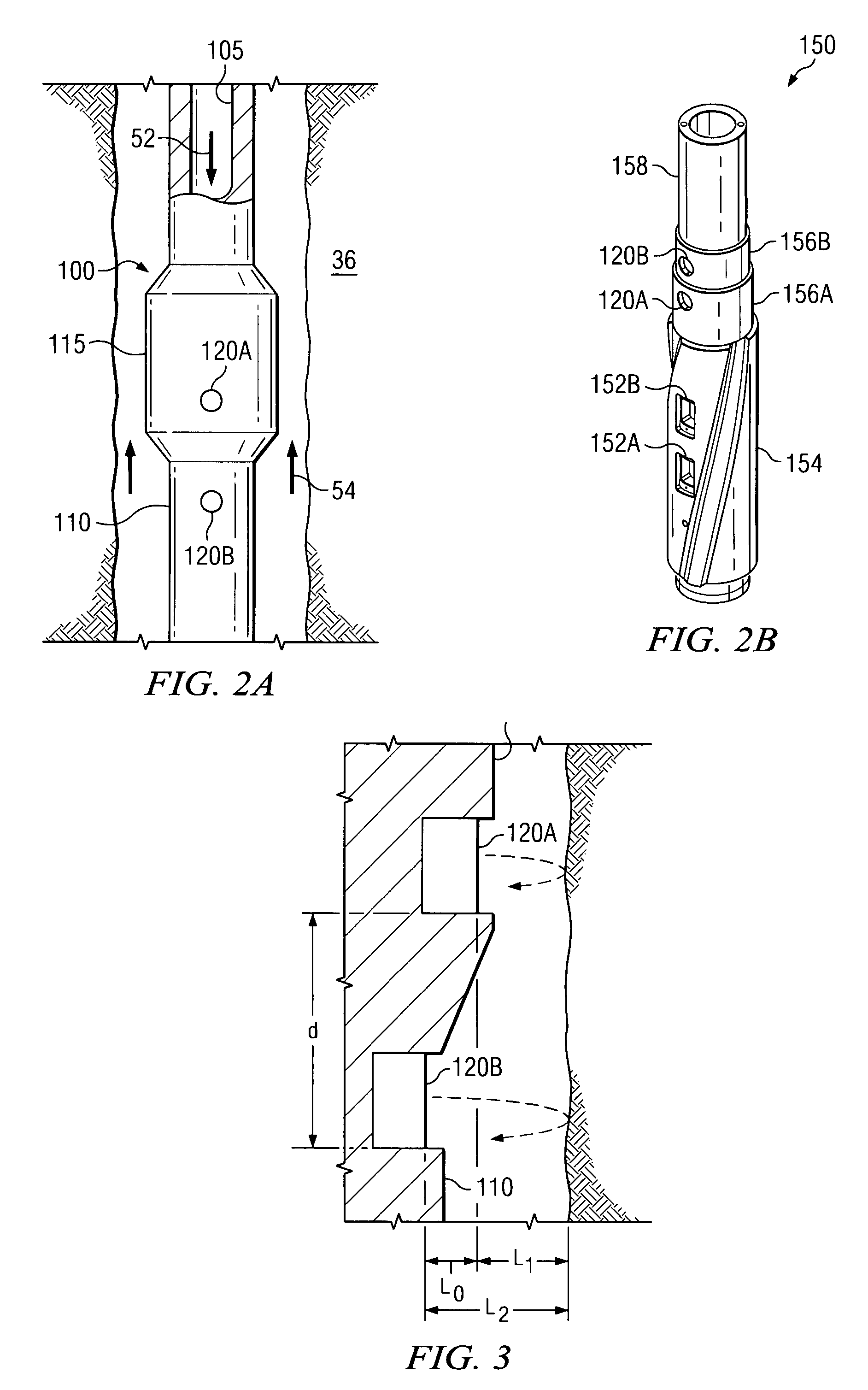
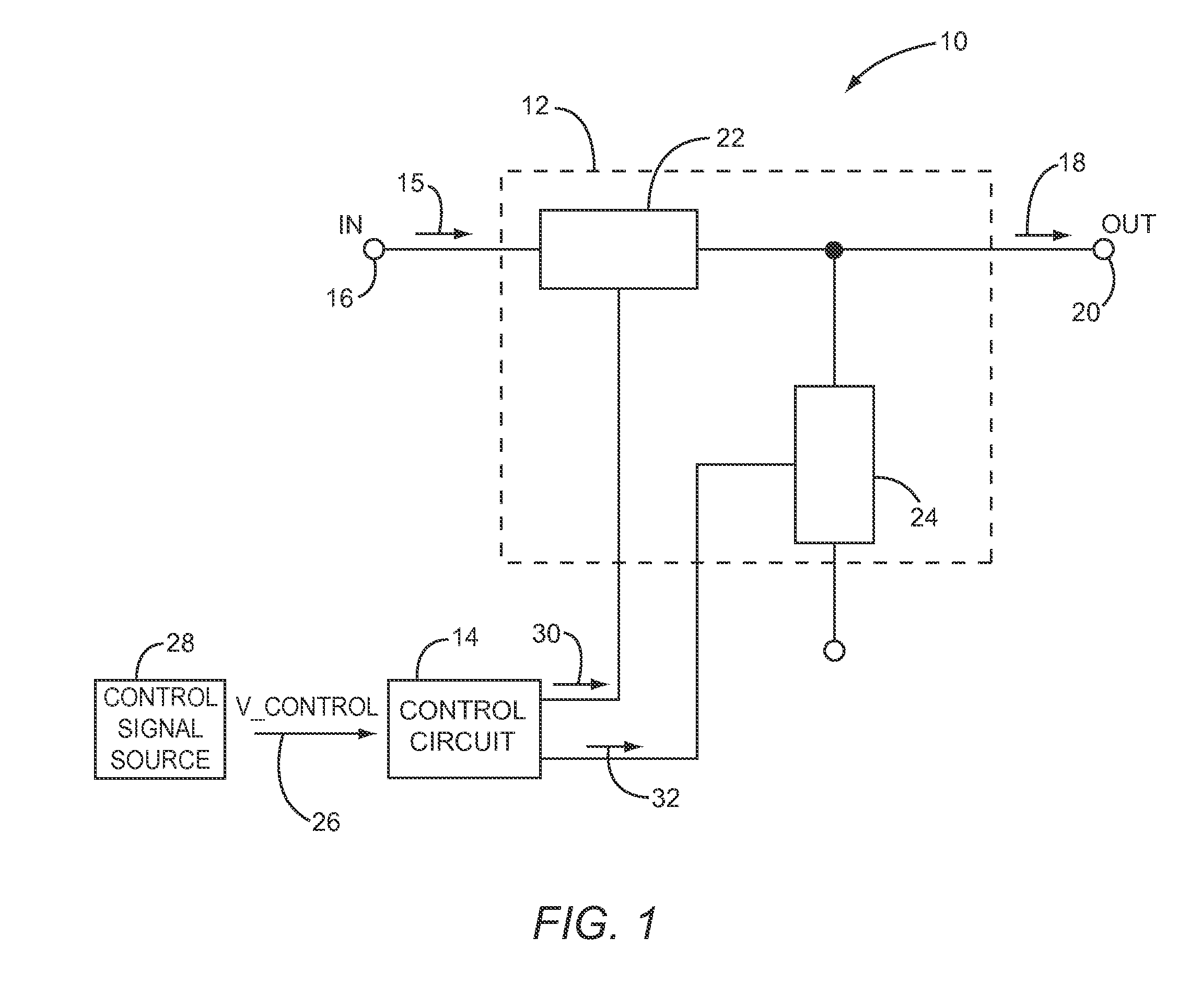
Apparatus and method for cone beam volume computed tomography breast imaging
InactiveUS6987831B2Promote quick completionGuaranteed continuous performanceSurgeryVaccination/ovulation diagnosticsX-rayEntire breast
Cone beam volume CT breast imaging is performed with a gantry frame on which a cone-beam radiation source and a digital area detector are mounted. The patient rests on an ergonomically designed table with a hole or two holes to allow one breast or two breasts to extend through the table such that the gantry frame surrounds that breast. The breast hole is surrounded by a bowl so that the entire breast can be exposed to the cone beam. Spectral and compensation filters are used to improve the characteristics of the beam. A materials library is used to provide x-ray linear attenuation coefficients for various breast tissues and lesions.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF ROCHESTER
X-ray scatter image reconstruction by balancing of discrepancies between detector responses, and apparatus therefor
ActiveUS7203276B2Duplicity of solutionNon-linearity of the inverse problem andMaterial analysis by optical meansPhotometry using electric radiation detectorsAttenuation coefficientUltrasound attenuation
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF NEW BRUNSWICK
Apparatus and methods for imaging and attenuation correction
InactiveUS7652259B2Ultrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsImage enhancementDiagnostic Radiology ModalitySonification
Owner:SPECTRUM DYNAMICS MEDICAL LTD
Apparatus and method for cone beam computed tomography breast imaging
InactiveUS20060094950A1Promote quick completionGuaranteed continuous performanceSurgeryVaccination/ovulation diagnosticsX-rayEntire breast
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF ROCHESTER
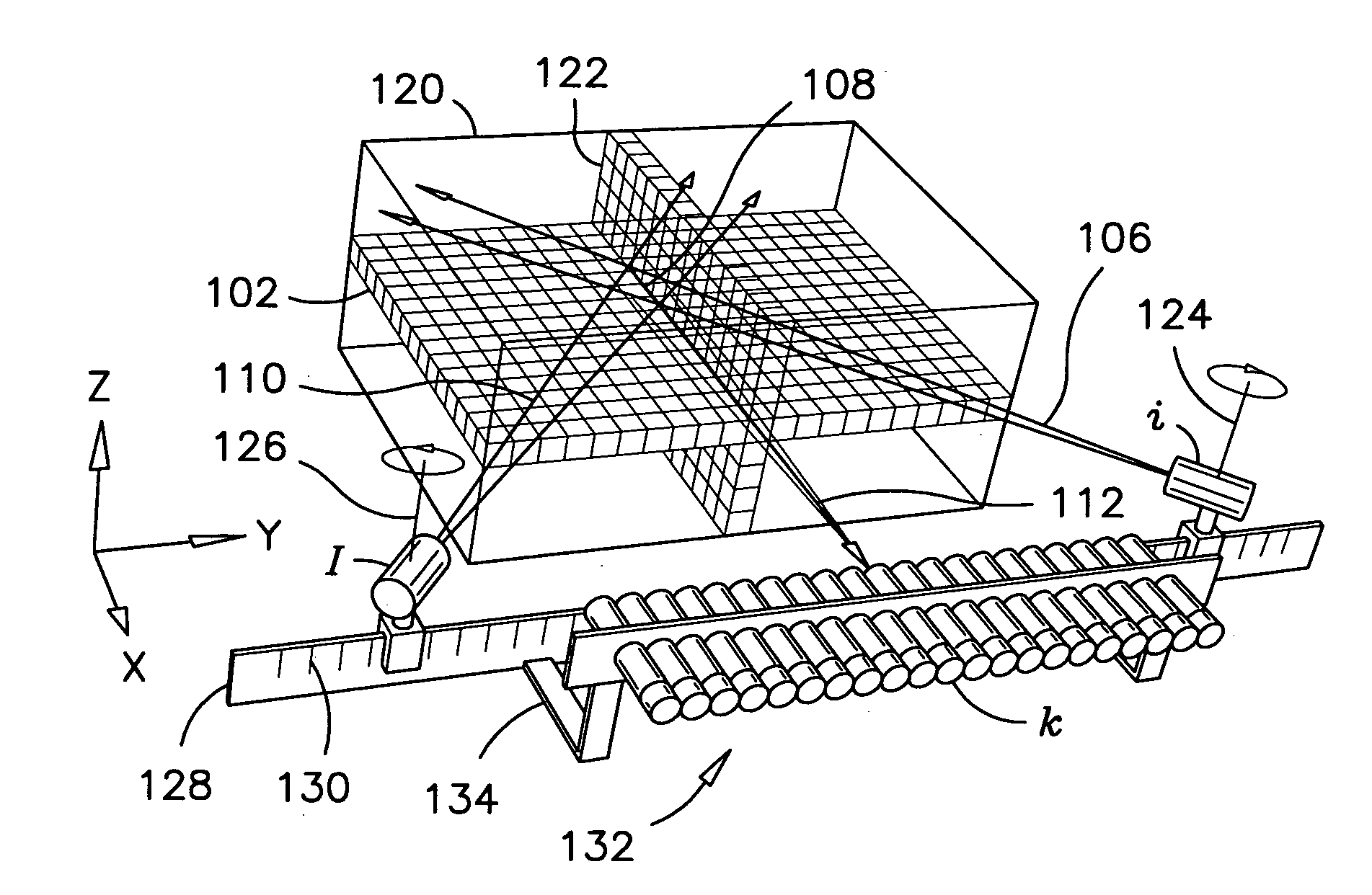
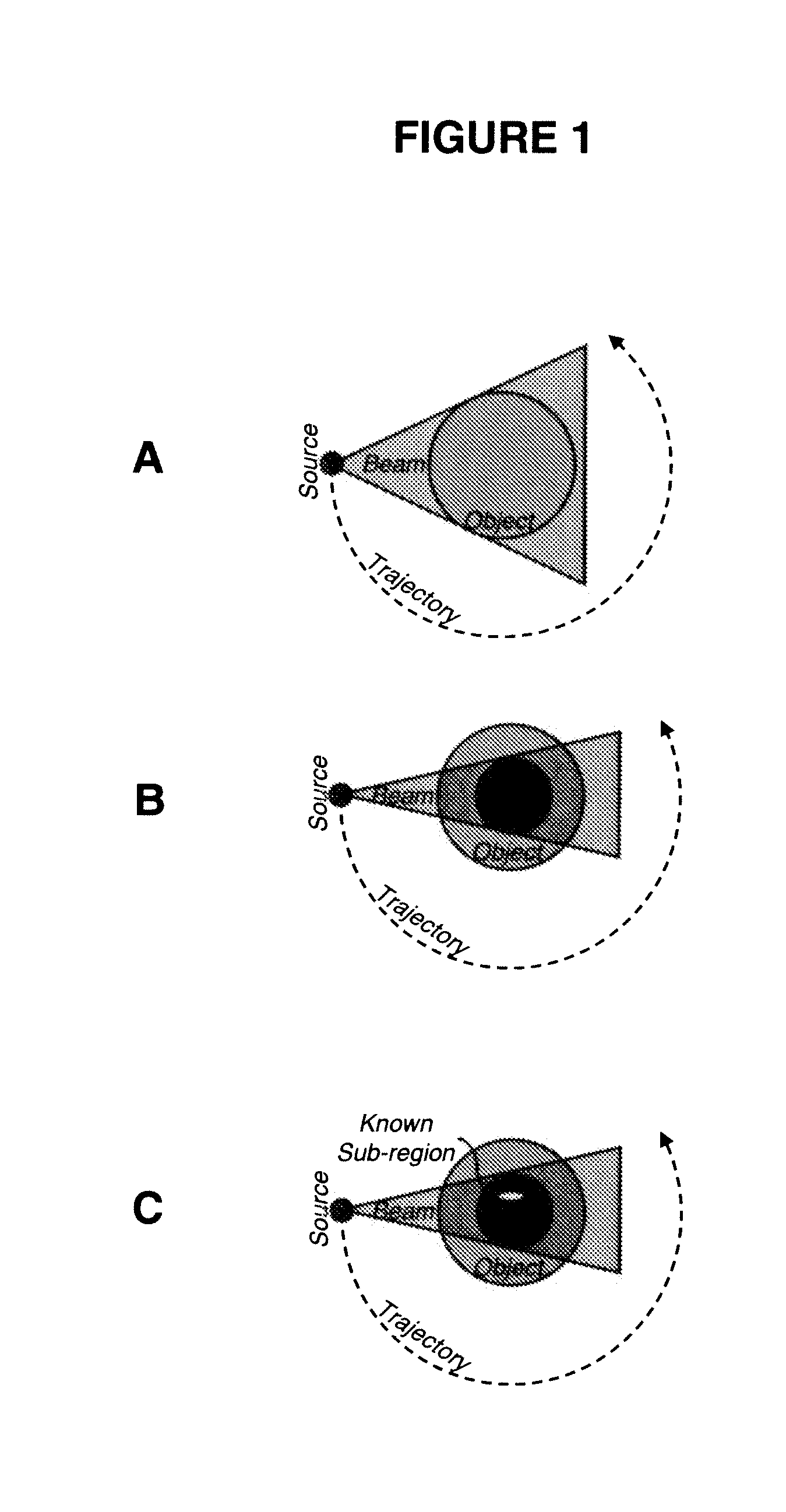
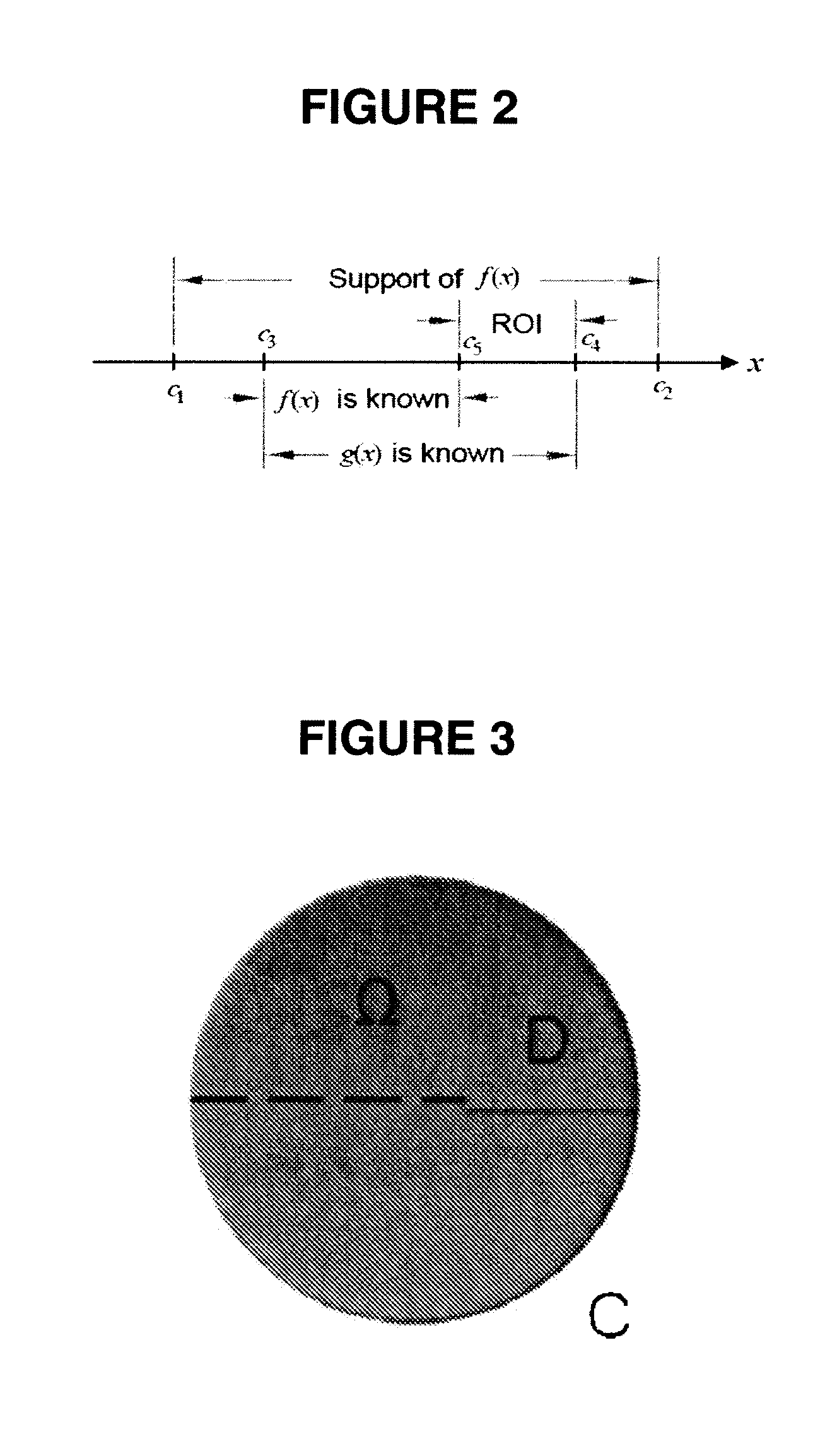
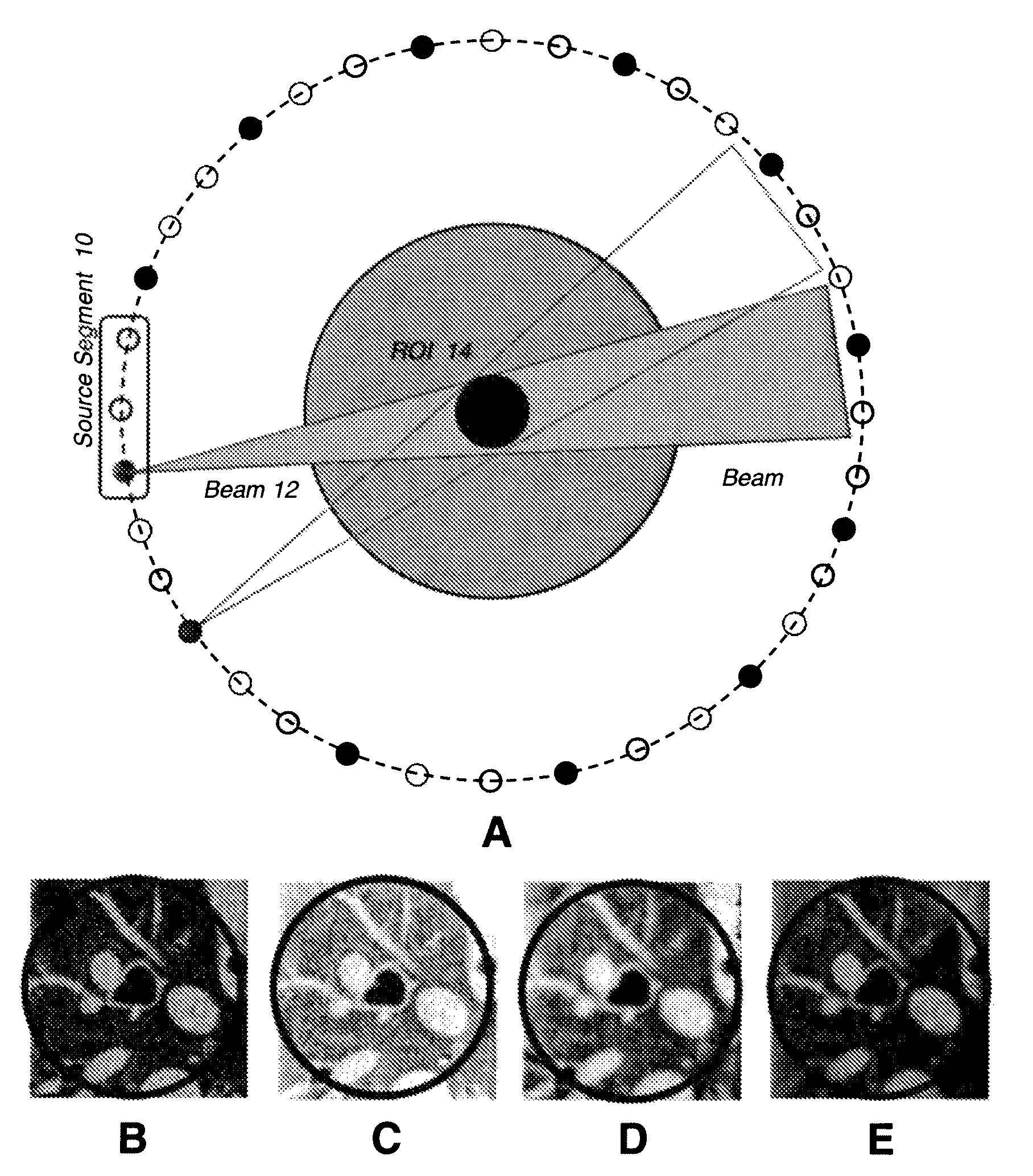
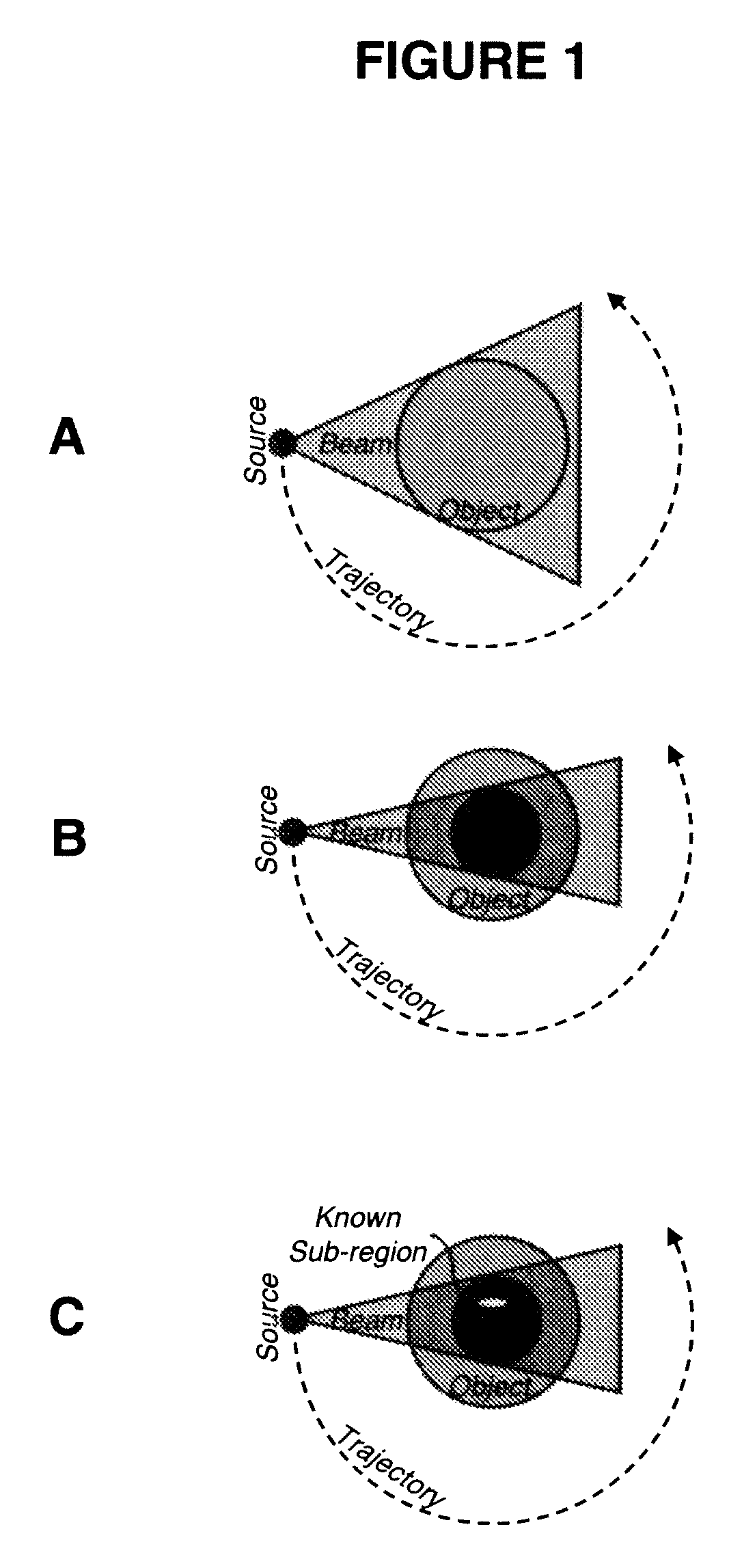
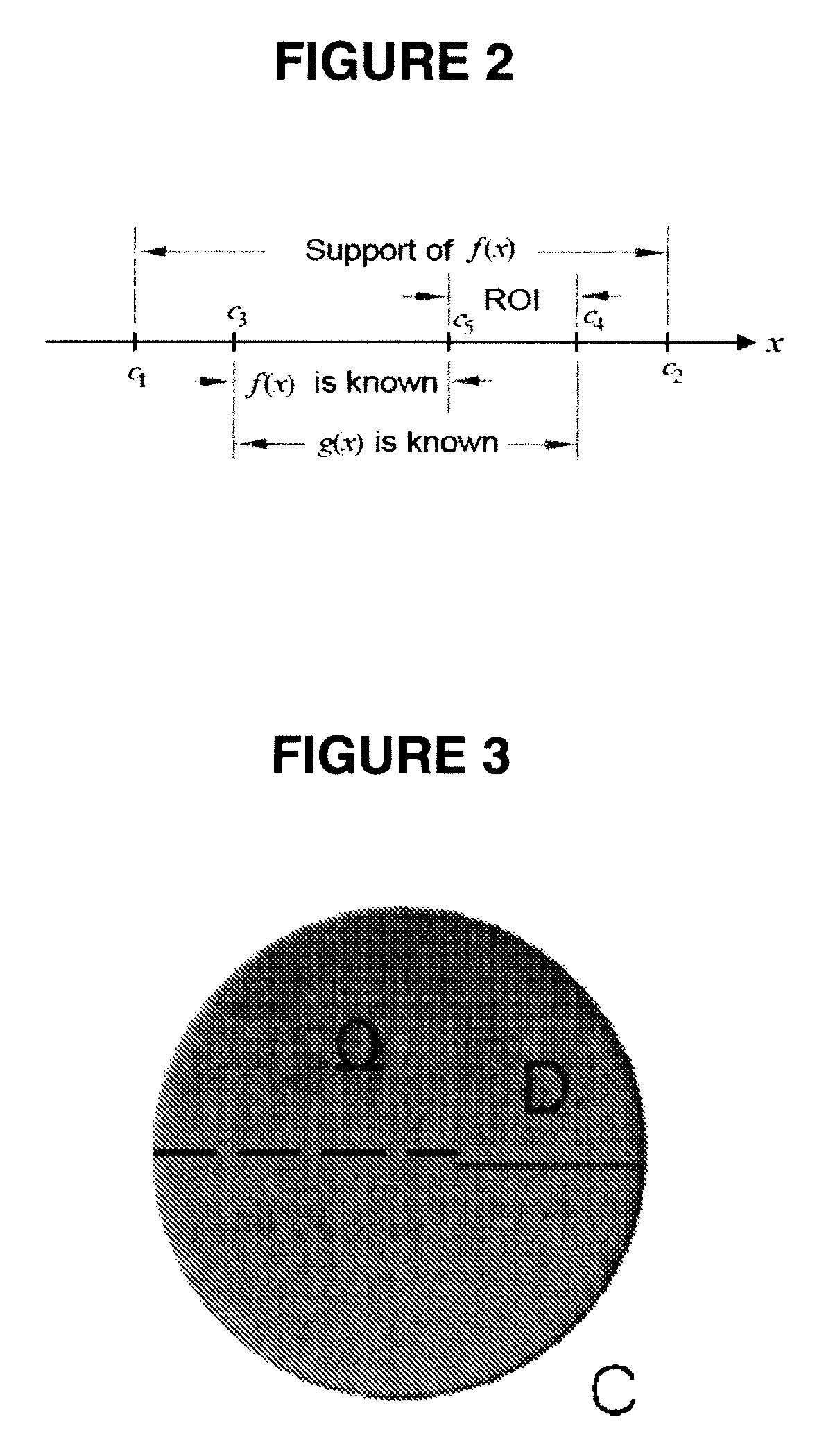
Interior Tomography and Instant Tomography by Reconstruction from Truncated Limited-Angle Projection Data
InactiveUS20090196393A1Faithful resolution of featureHigh spatial contrastReconstruction from projectionMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationAttenuation coefficientFractography
A system and method for tomographic image reconstruction using truncated limited-angle projection data that allows exact interior reconstruction (interior tomography) of a region of interest (ROI) based on the linear attenuation coefficient distribution of a subregion within the ROI, thereby improving image quality while reducing radiation dosage. In addition, the method includes parallel interior tomography using multiple sources beamed at multiple angles through an ROI and that enables higher temporal resolution.
Owner:UNIV OF IOWA RES FOUND +1
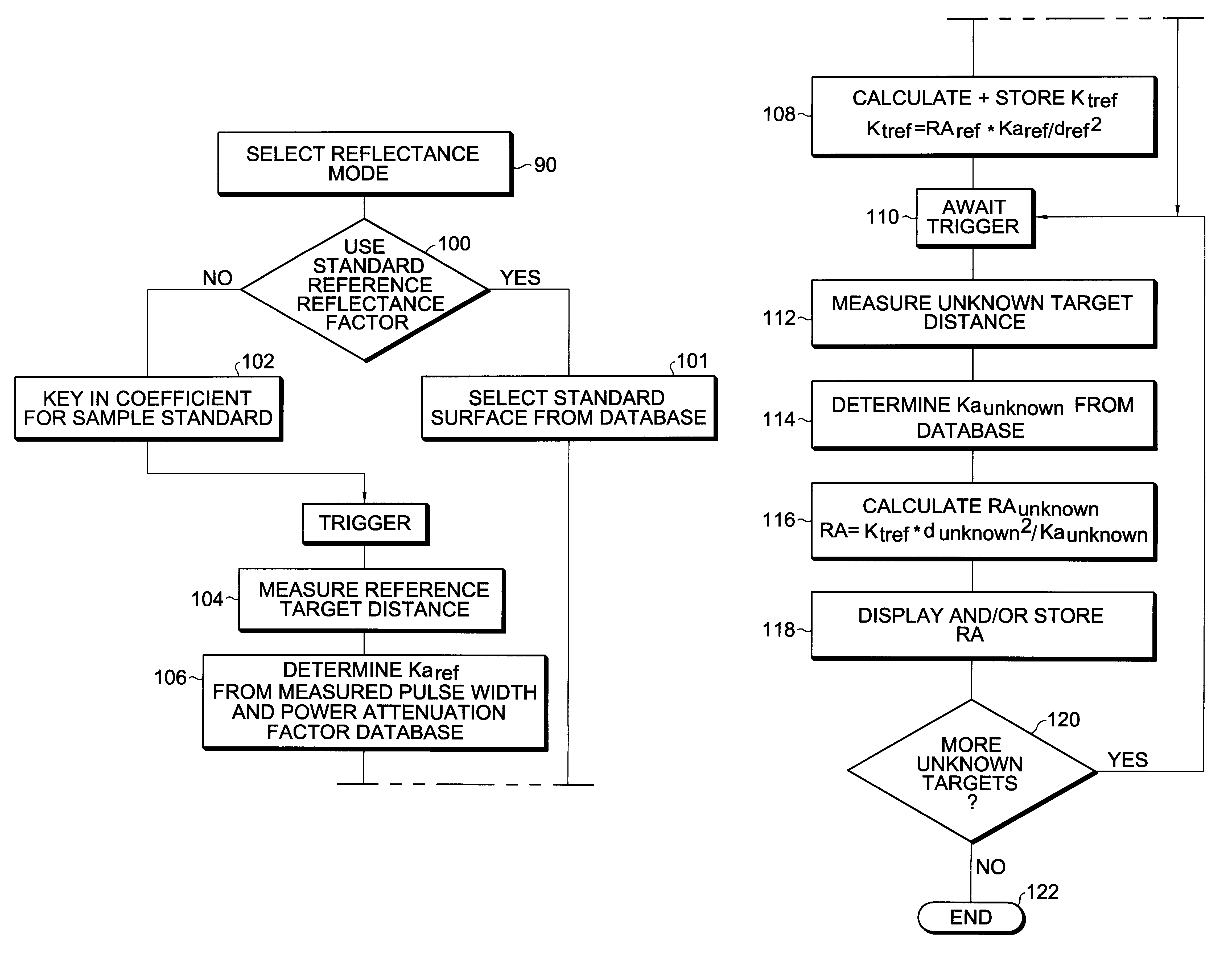
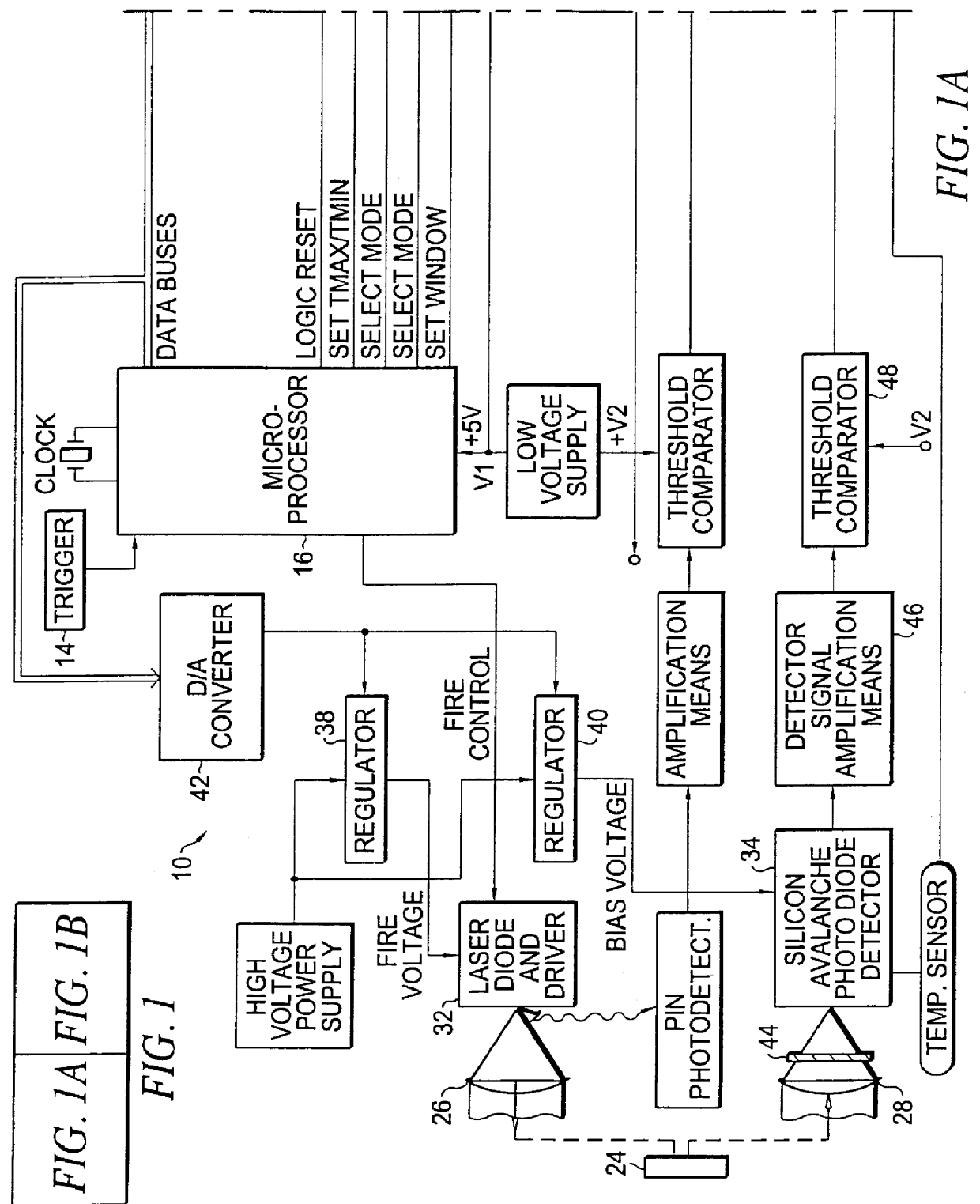
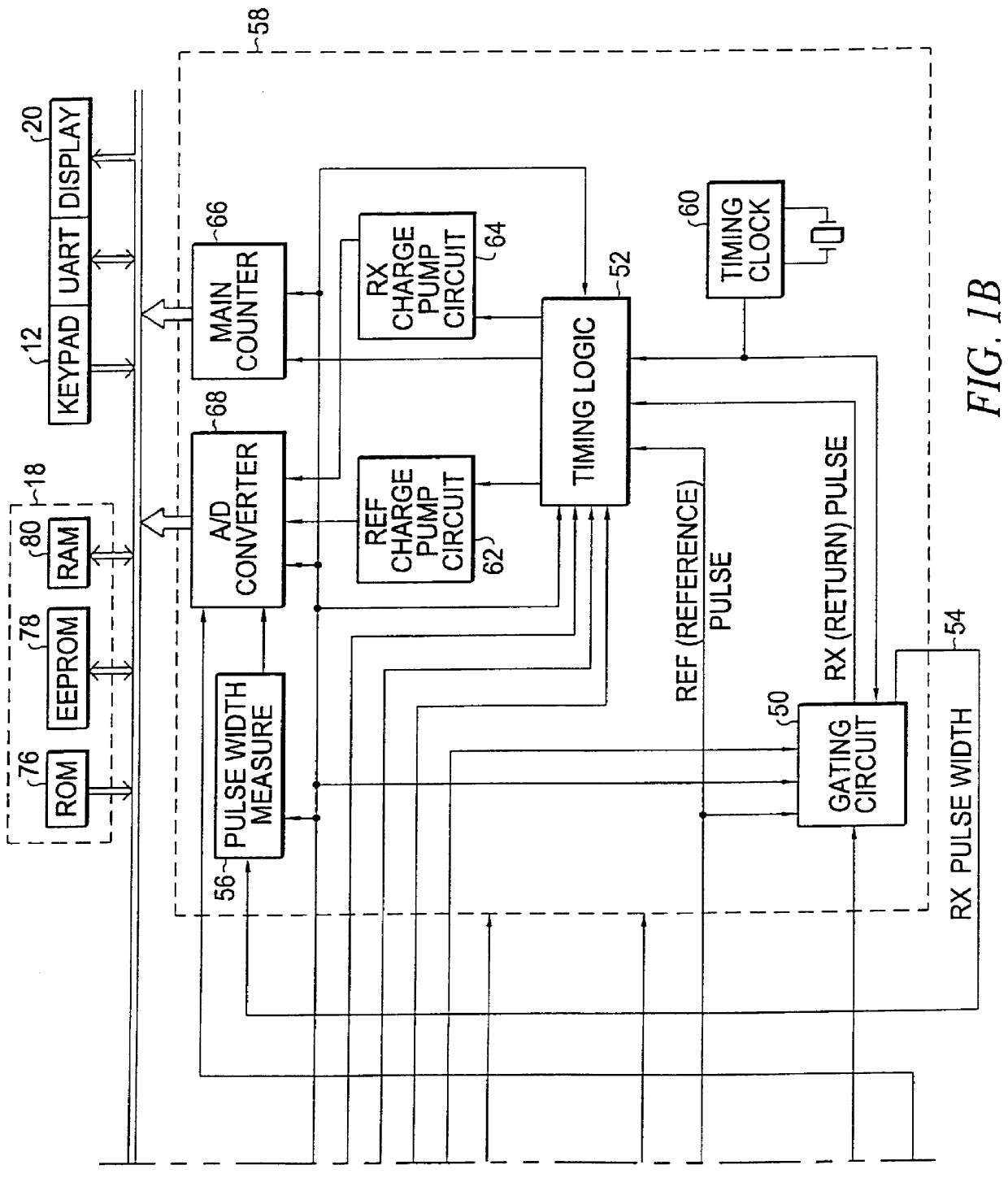
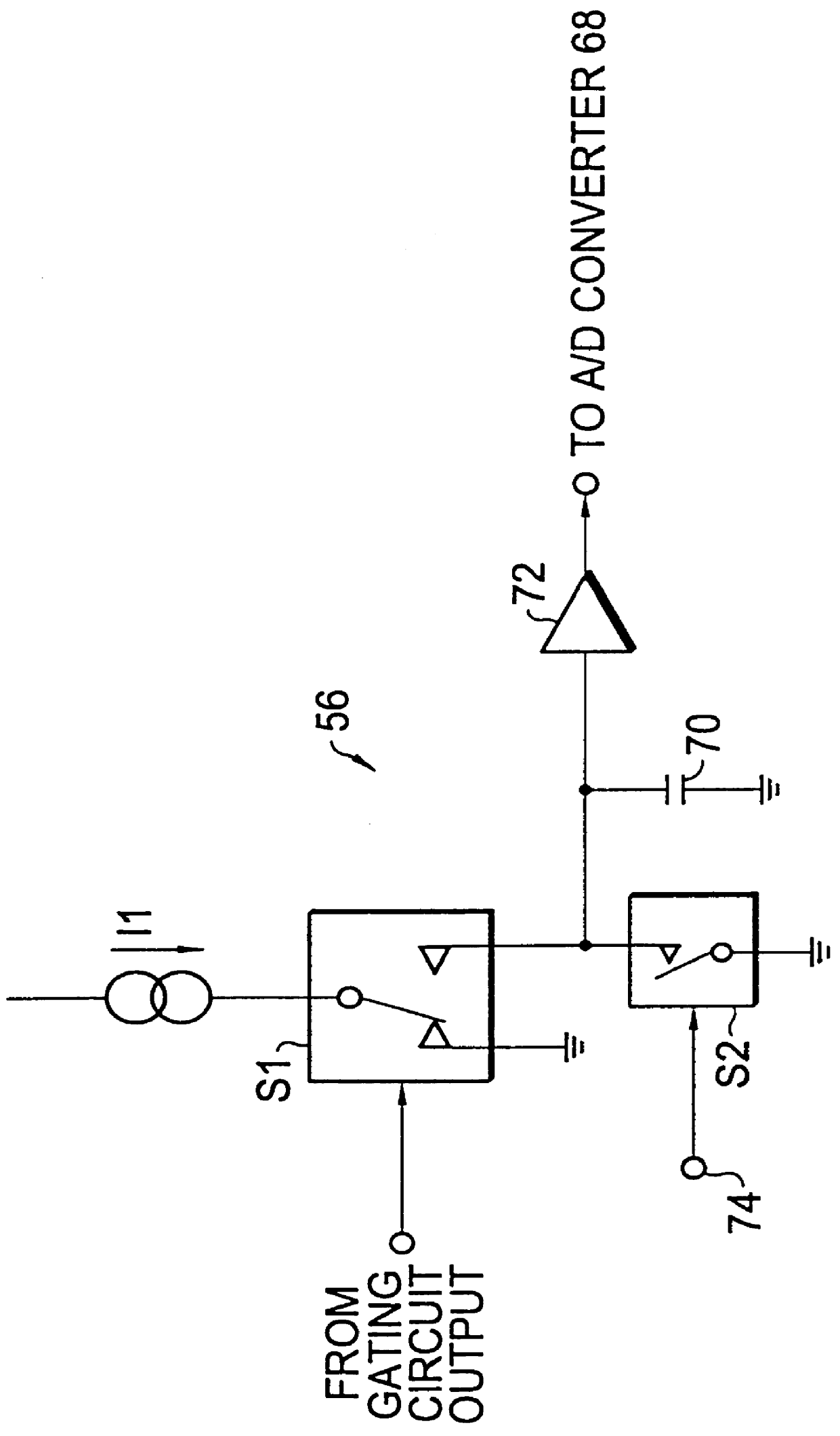
Apparatus and method for determining precision reflectivity of highway signs and other reflective objects utilizing an optical range finder instrument
An apparatus and method for measuring coefficients of retroreflectance of retroreflective surfaces such as road signs involves use of a modified light based range finder. The apparatus includes a power attenuation factor data base which relates pulse width of received pulses to power attenuation of the transmitted pulses. The range finder calculates target range based on time of flight of light pulses. The apparatus automatically calculates the absolute coefficient of retroreflectance for an unknown reflective surface being measured by comparison of the measurement to a reading with the same instrument of a known reflectance standard. The method involves either recalling a stored standard reference reflectance factor or determining a reflectance factor via the range finder for a sample of retroreflective material with a predetermined coefficient of retroreflectance, and then measuring the distance to an unknown target, determining a power attenuation factor from the received pulse width from the unknown target and then calculating the absolute coefficient of retroreflectance based upon these determined values of power attenuation factor, distance and the reference reflectance factor.
Owner:KAMA TECH CORP +1
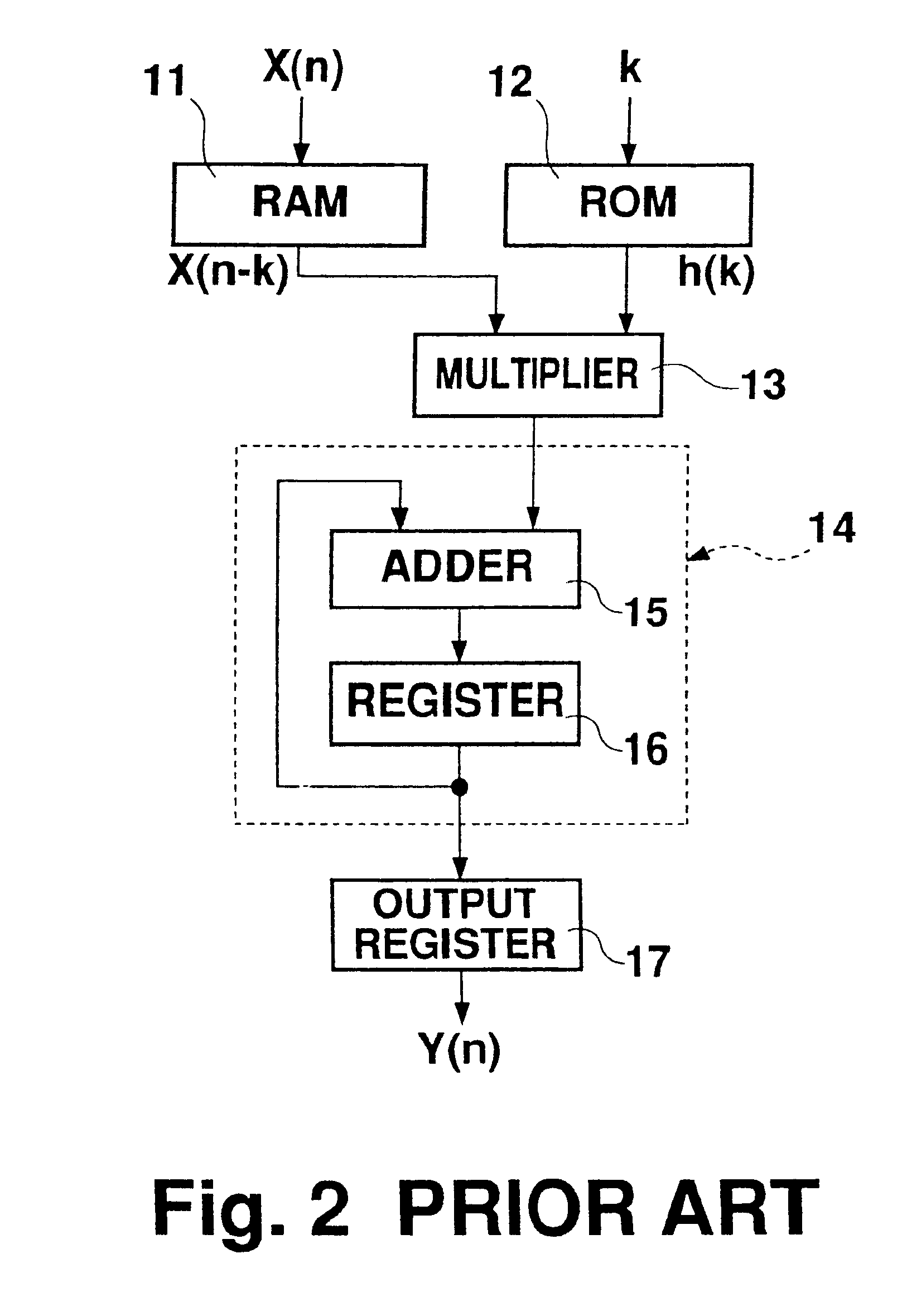
Digital filters
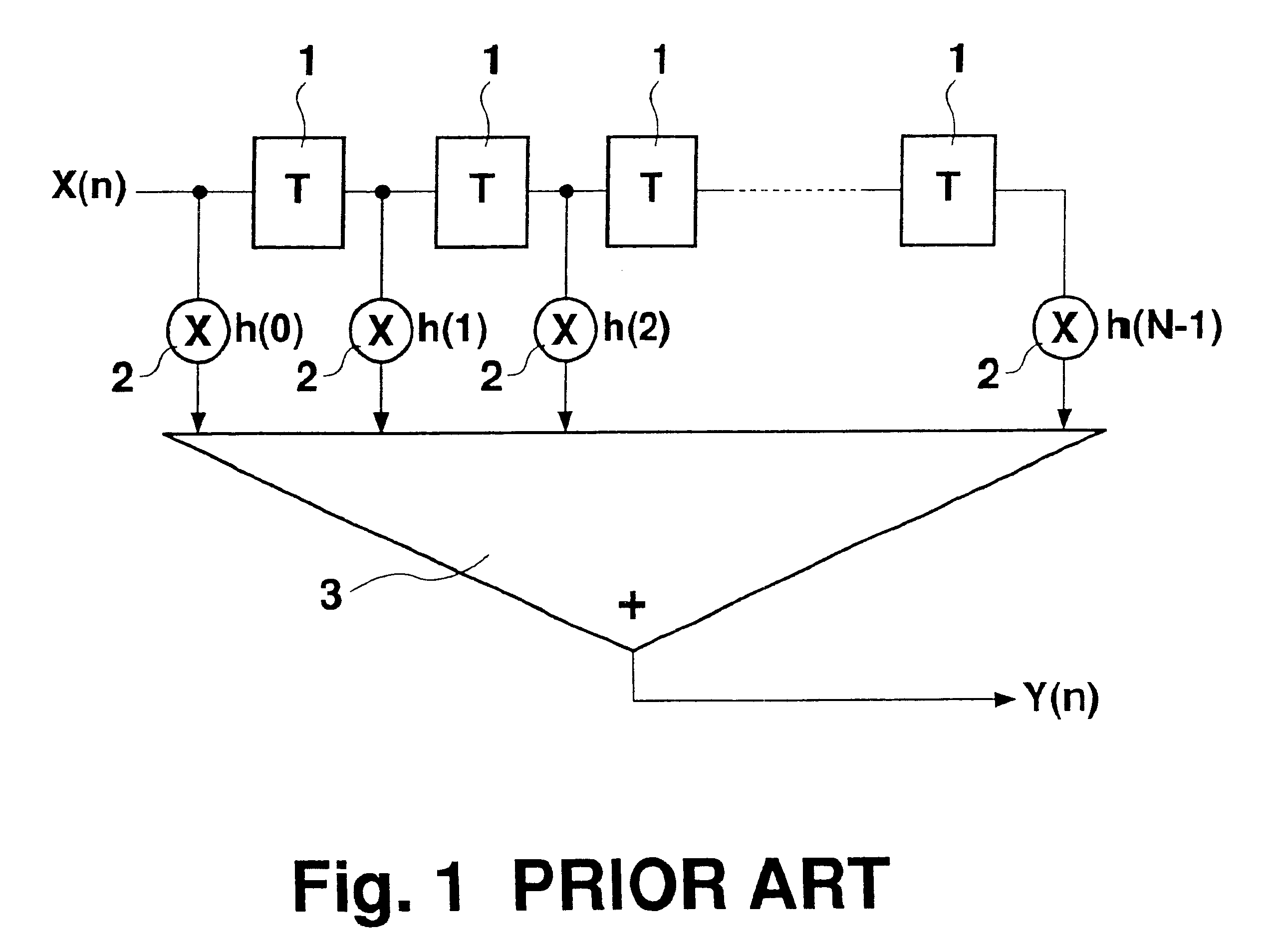
InactiveUS6360240B2Digital technique networkComplex mathematical operationsAttenuation coefficientDigital filter
A digital filter is provided with a plurality of selectors. Switchover from one selector to another switches the digital filter operation between a separation filter function and a synthesis filter function. When the digital filter functions as either separation filter or synthesis filter, it switches over between the functions of multiplying data by a filter coefficient and multiplying data by an attenuation coefficient. The entire digital filter circuit size can thus be reduced.
Owner:SEMICON COMPONENTS IND LLC
Measuring Cerebral Oxygen Saturation
ActiveUS20080316488A1Material analysis by optical meansDiagnostic recording/measuringAttenuation coefficientOxygen saturation
A device includes source and detector sensors. In a specific implementation, the device has two near detectors, two far detectors, and two sources. The two near detectors are arranged closer to the two sources than the two far detectors. A light-diffusing layer covers the two near detectors. The device may be part of a medical device that is used to monitor or measure oxygen saturation levels in a tissue. In a specific implementation, light is transmitted into the tissue and received by the detectors. An attenuation coefficient is first calculated for a shallow layer of tissue. The attenuation coefficient is then used to calculate an attenuation coefficient for a deep layer of tissue.
Owner:VIOPTIX
System, apparatus, and method for conducting electromagnetic induction surveys
InactiveUS7030617B2Electric/magnetic detection for well-loggingDetection using electromagnetic wavesAttenuation coefficientProximate
Owner:SCHLUMBERGER TECH CORP
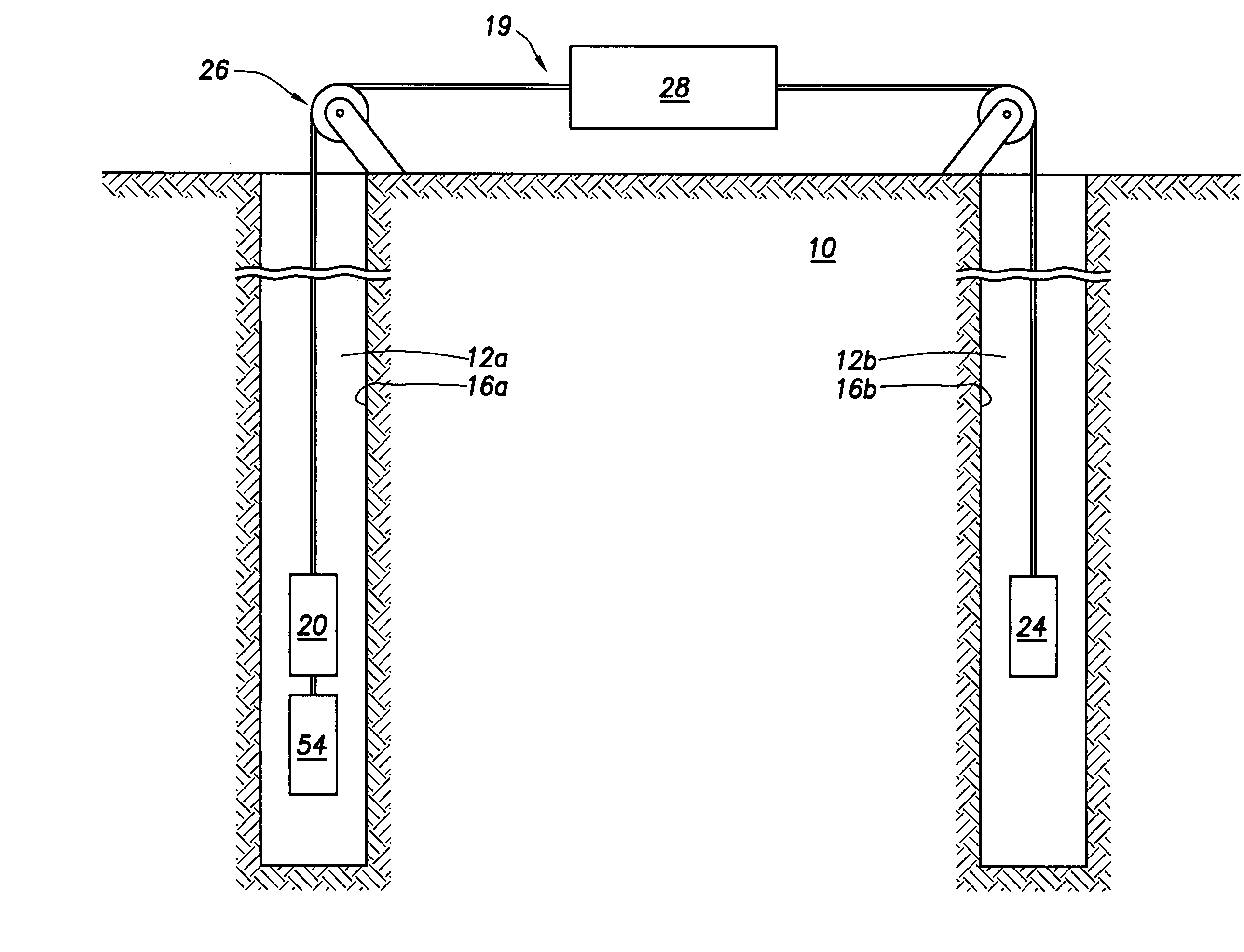
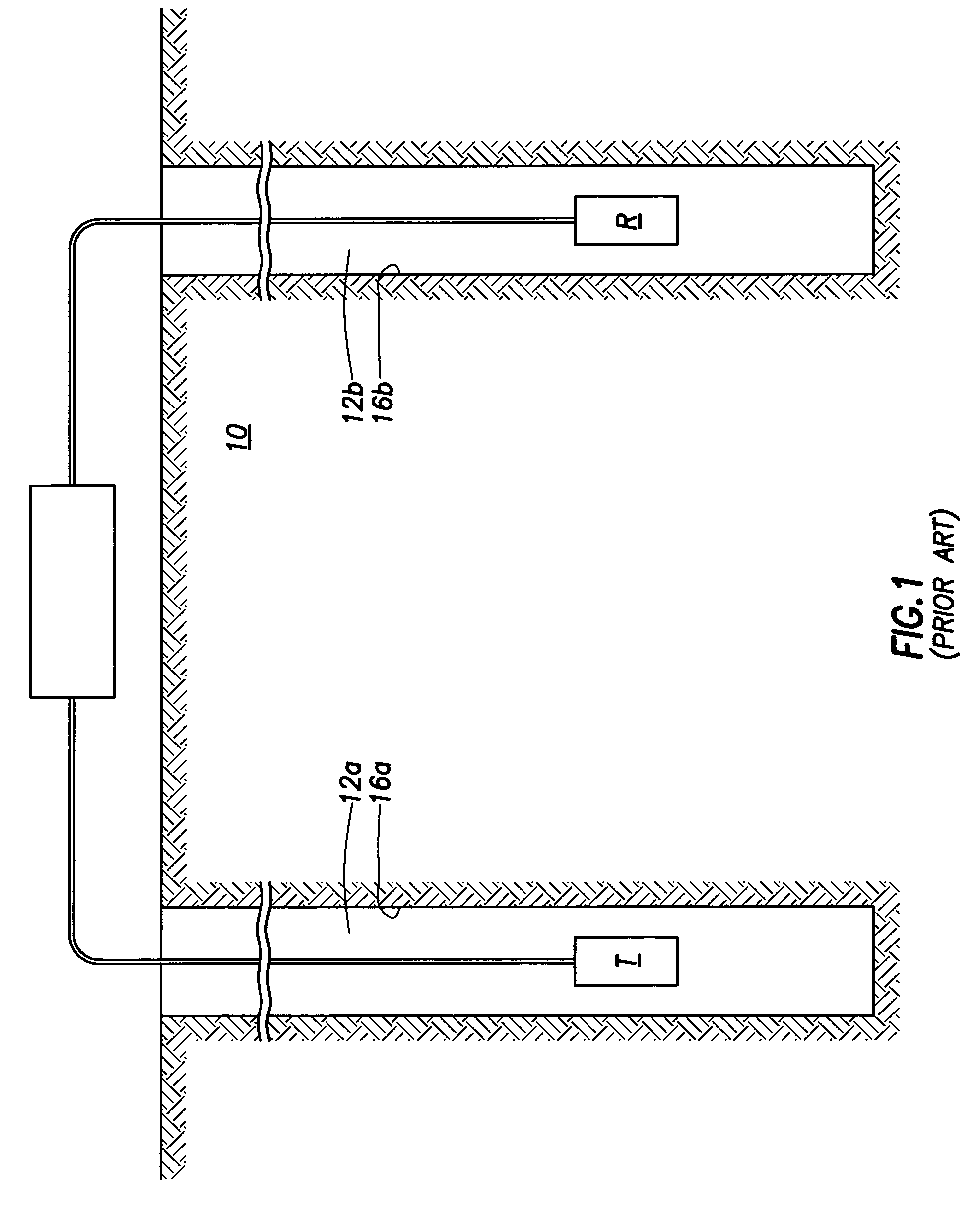
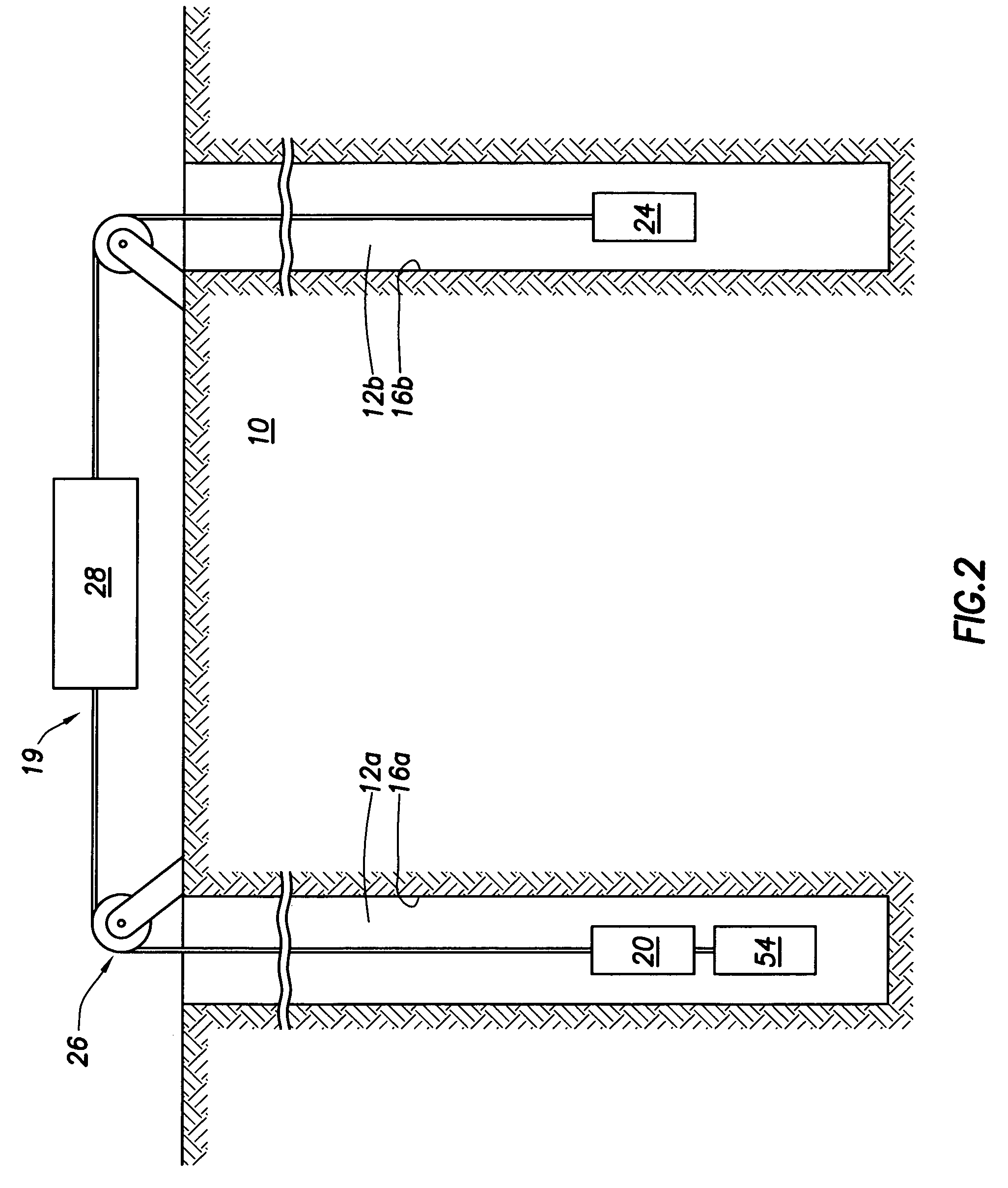
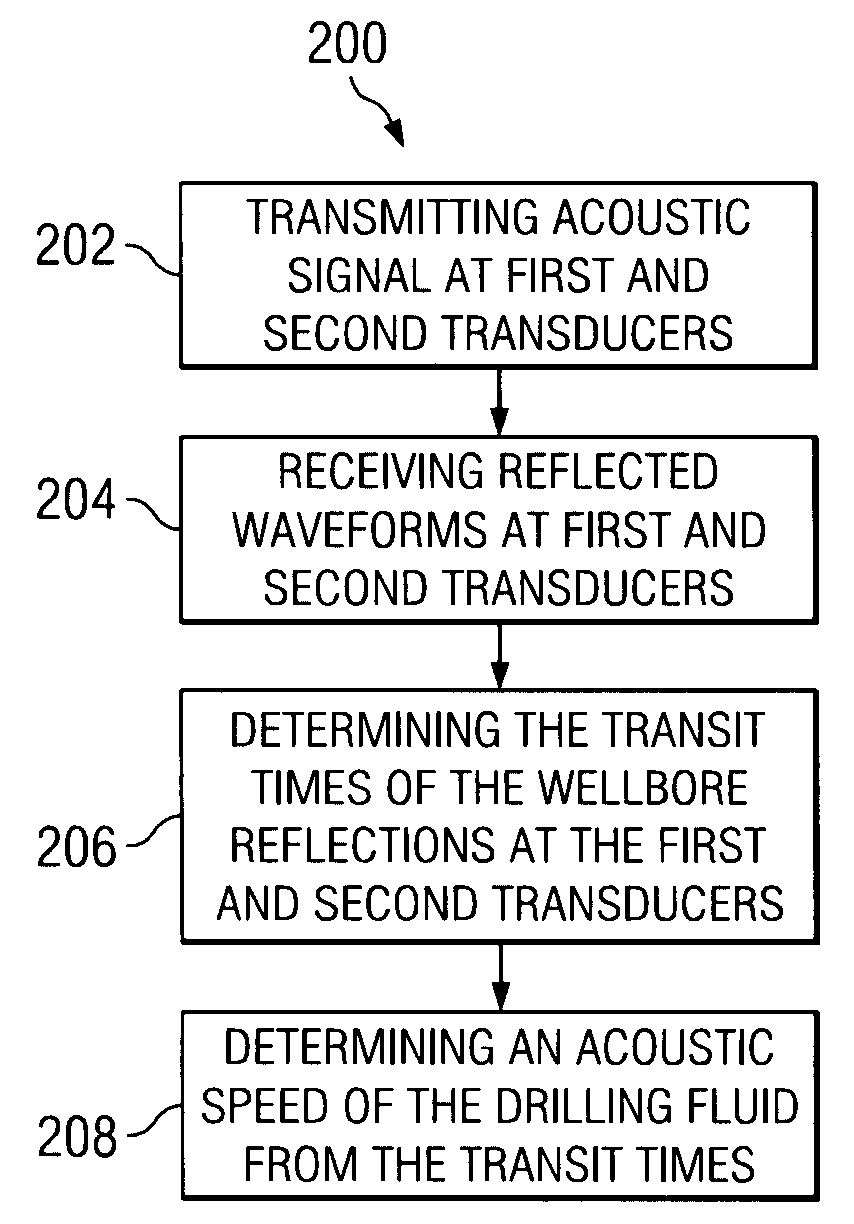
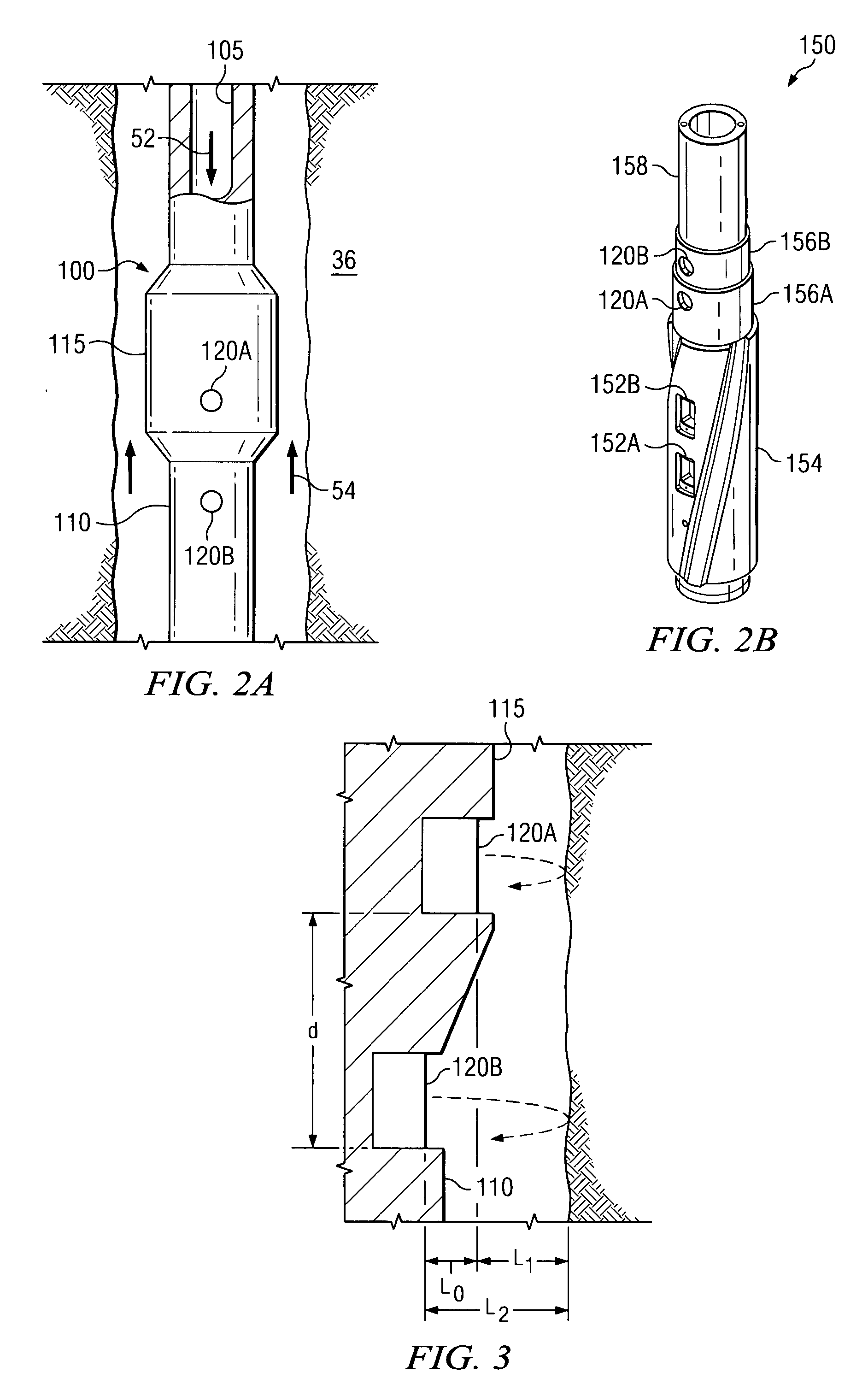
Apparatus and method for determining drilling fluid acoustic properties
ActiveUS20080186805A1Improve accuracyProvide goodAnalysing fluids using sonic/ultrasonic/infrasonic wavesSurveyReflection coefficientAttenuation coefficient
Aspects of this invention include a downhole tool having first and second radially offset ultrasonic standoff sensors and a controller including instructions to determine at least one of a drilling fluid acoustic velocity and a drilling fluid attenuation coefficient from the reflected waveforms received at the standoff sensors. The drilling fluid acoustic velocity may be determined via processing the time delay between arrivals of a predetermined wellbore reflection component at the first and second sensors. The drilling fluid attenuation coefficient may be determined via processing amplitudes of the predetermined wellbore reflection coefficients. The invention advantageously enables the acoustic velocity and attenuation coefficient of drilling fluid in the borehole annulus to be determined in substantially real-time.
Owner:SCHLUMBERGER TECH CORP
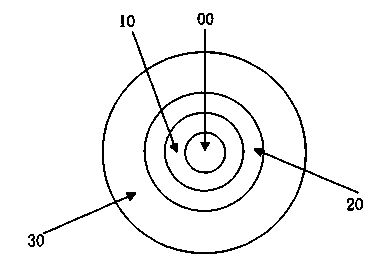
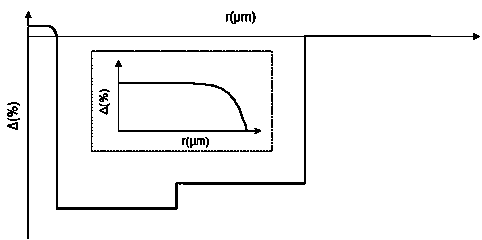
Single mode optical fiber
ActiveCN103454719AGood for drawing processReduce additional lossOptical fibre with multilayer core/claddingOptical waveguide light guideUltrasound attenuationAttenuation coefficient
The invention relates to a low-attenuation single mode optical fiber used in an optical fiber communication system. The single mode optical fiber comprises a core layer and a wrapping layer. The single mode optical fiber is characterized in that the refractive index distribution n (r) of the core layer and the g-type refractive index distribution of the core layer meet the formula: n (r)=n0*[1-2*delta 1*(r / R1)*g]*1 / 2 (r<=R1), the delta 1 of the core layer ranges from -0.05% to +0.05%, g ranges from 10 to 30, and the radius R1 of the core layer ranges from 4.0 microns to 5.0 microns; the wrapping layer sequentially comprises an inner wrapping layer, a middle wrapping layer and an outer wrapping layer from inner to outer, the delta 2 of the inner wrapping layer ranges from -0.3% to -0.45%, the radius R2 ranges from 20 microns to 30 microns, and the delta 3 of the middle wrapping layer is larger than delta 2, the numerical relationship between the relative refraction difference and the radius of the middle wrapping layer and the relative refraction difference and the radius of the inner wrapping layer is V=(R3-R2)*(delta 3-delta 2), and V ranges from 0.5*10-2-micron% to 7*10-2-micron%. The attenuation coefficient, at the 1550-nanometer position, of the optical fiber is smaller than or equal to 0.180dB / km. The low-attenuation single mode optical fiber is low in optical fiber loss, good in manufacturing technology, low in cost and suitable for scale production.
Owner:YANGTZE OPTICAL FIBRE & CABLE CO LTD
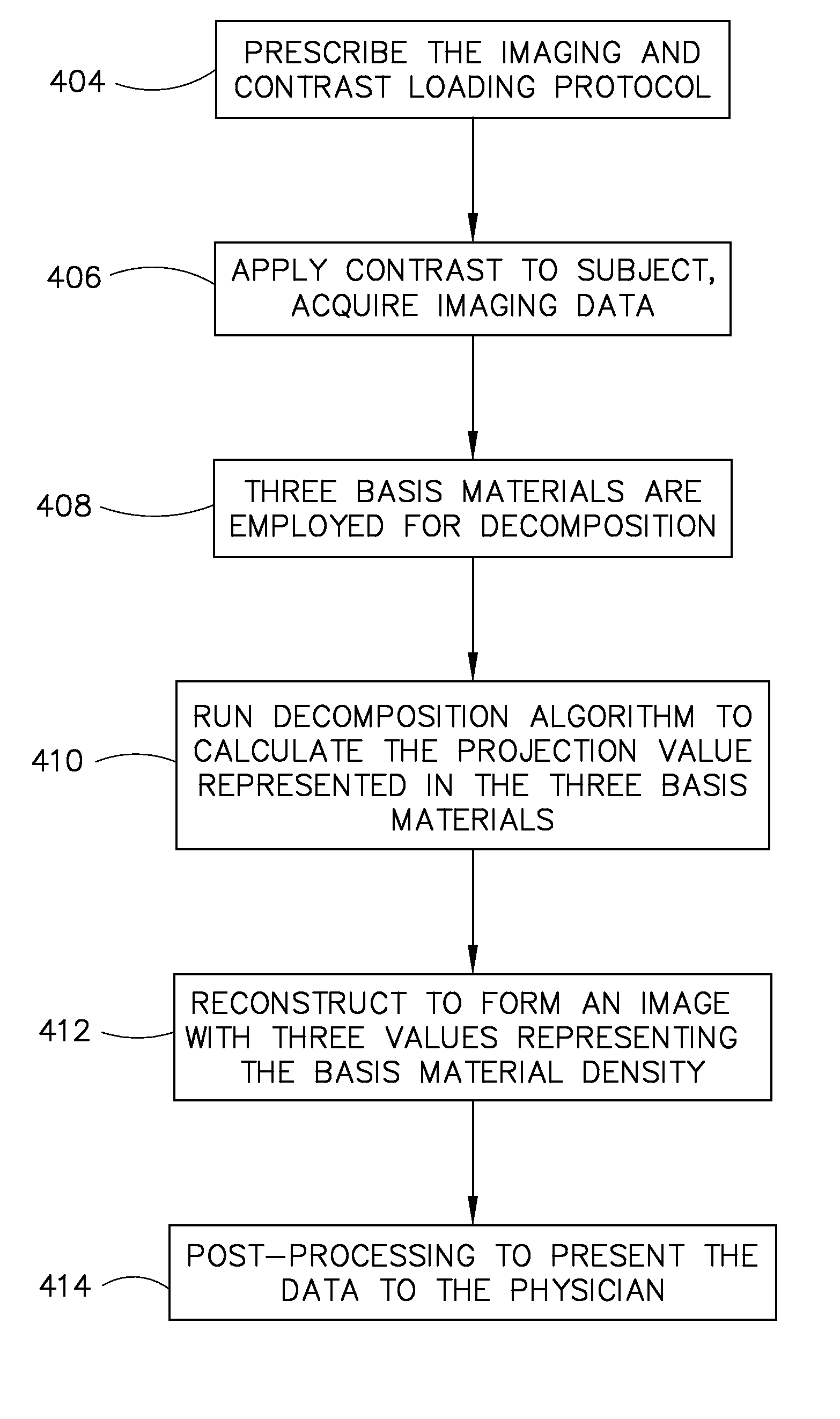
Method and apparatus for basis material decomposition with k-edge materials
InactiveUS20090052621A1Improve accuracyDiagnostic recording/measuringSensorsUltrasound attenuationAttenuation coefficient
A diagnostic imaging system includes a high frequency electromagnetic energy source that emits a beam of high frequency electromagnetic energy toward an object to be imaged, a detector that receives high frequency electromagnetic energy emitted by the high frequency electromagnetic energy source, and a data acquisition system (DAS) operably connected to the detector. A computer is operably connected to the DAS and is programmed to generate corresponding sets of projection values for three or more energy spectra through employment of attenuation coefficients of three or more basis materials to simulate responses of the diagnostic imaging system to a plurality of lengths of the three or more basis materials wherein the three or more basis materials comprise two or more non K-edge basis materials and one or more K-edge basis materials.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Apparatus and method for determining drilling fluid acoustic properties
ActiveUS7587936B2Improve accuracyImprove the accuracy of standoff measurementsAnalysing fluids using sonic/ultrasonic/infrasonic wavesSurveyAttenuation coefficientTime delays
Aspects of this invention include a downhole tool having first and second radially offset ultrasonic standoff sensors and a controller including instructions to determine at least one of a drilling fluid acoustic velocity and a drilling fluid attenuation coefficient from the reflected waveforms received at the standoff sensors. The drilling fluid acoustic velocity may be determined via processing the time delay between arrivals of a predetermined wellbore reflection component at the first and second sensors. The drilling fluid attenuation coefficient may be determined via processing amplitudes of the predetermined wellbore reflection coefficients. The invention advantageously enables the acoustic velocity and attenuation coefficient of drilling fluid in the borehole annulus to be determined in substantially real-time.
Owner:SCHLUMBERGER TECH CORP
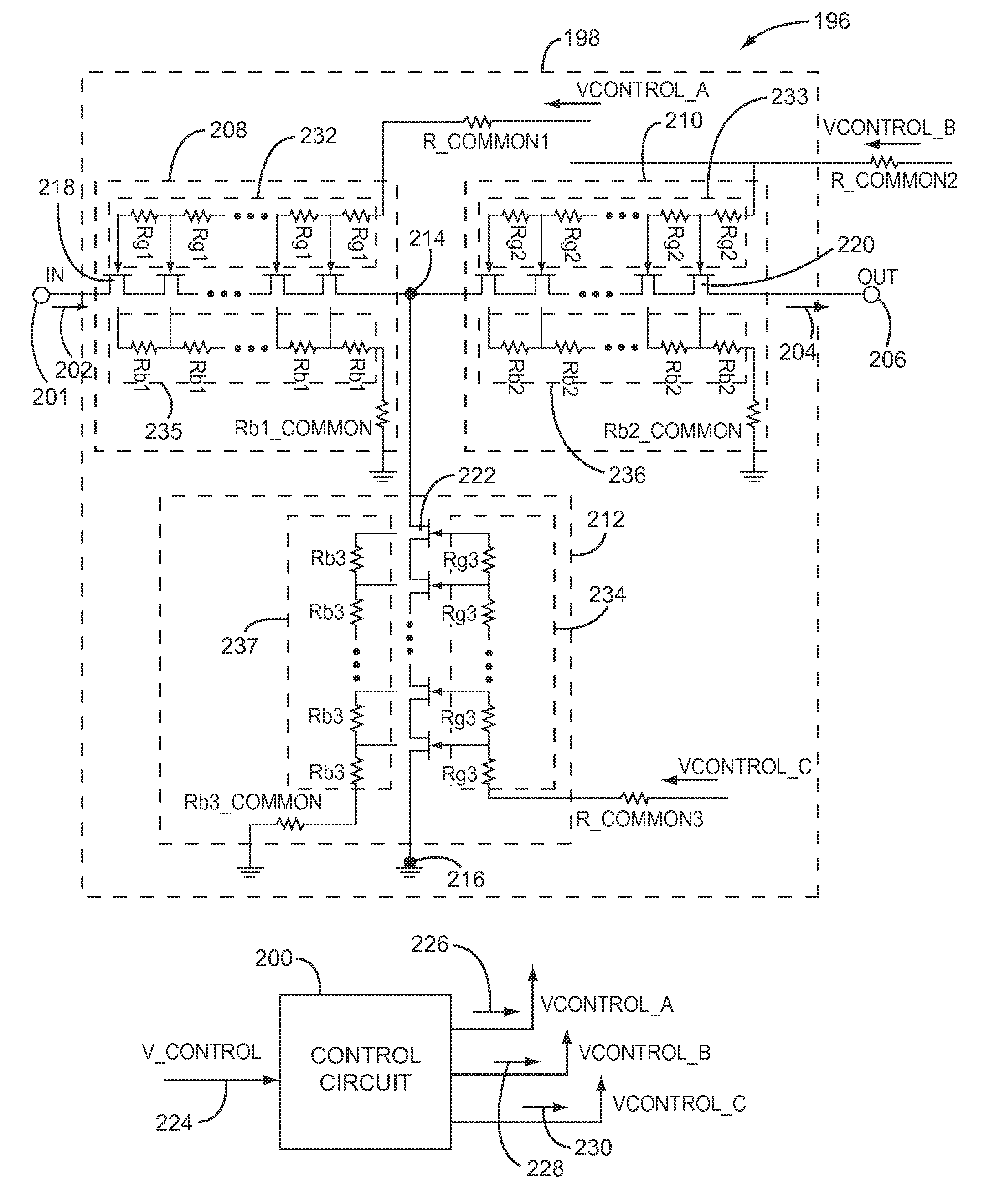
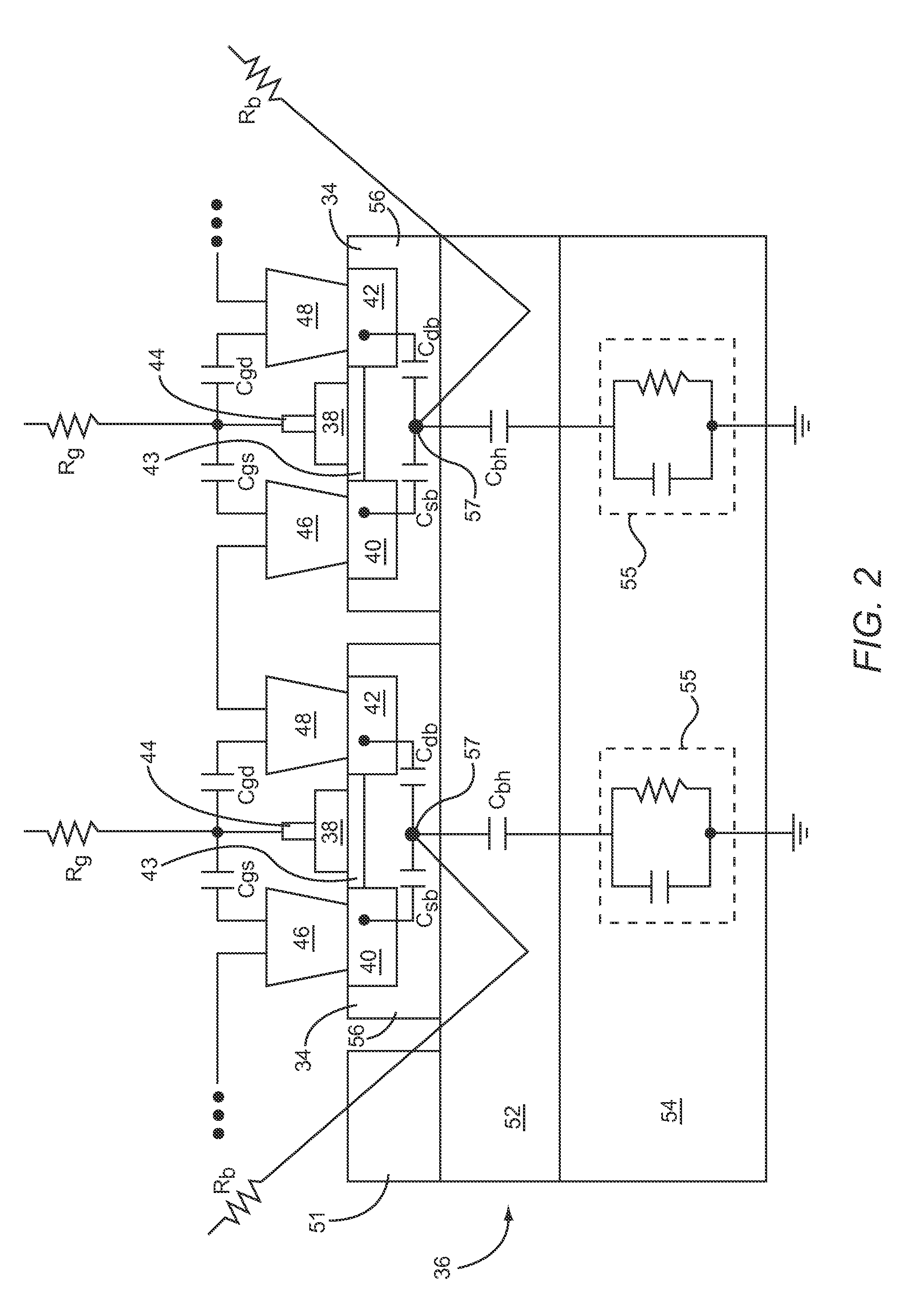
Variable attenuator having stacked transistors
ActiveUS20110148501A1Reduce distortion problemsWide bandwidthMultiple-port active networksPulse automatic controlUltrasound attenuationAttenuation coefficient
In one embodiment, a variable attenuator is disclosed having an attenuation circuit and a control circuit. The attenuation circuit may include a first series connected attenuation circuit segment and a shunt connected attenuation circuit segment, as well as additional attenuation circuit segments. Each attenuation circuit segment includes a stack of transistors that are coupled to provide the attenuation circuit segment with a variable impedance level having a continuous impedance range. In this manner, the control circuit may be operably associated with the stack of transistors in each attenuation circuit segment to control the variable attenuation level of the variable attenuator.
Owner:QORVO US INC
Interior tomography and instant tomography by reconstruction from truncated limited-angle projection data
InactiveUS7697658B2Faithful resolution of featureIncrease the number ofReconstruction from projectionMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationAttenuation coefficientRadiation Dosages
A system and method for tomographic image reconstruction using truncated limited-angle projection data that allows exact interior reconstruction (interior tomography) of a region of interest (ROI) based on the linear attenuation coefficient distribution of a subregion within the ROI, thereby improving image quality while reducing radiation dosage. In addition, the method includes parallel interior tomography using multiple sources beamed at multiple angles through an ROI and that enables higher temporal resolution.
Owner:UNIV OF IOWA RES FOUND +1
Apparatus and method for determining precision reflectivity of highway signs and other reflective objects utilizing an optical range finder instrument
An apparatus and method for measuring coefficients of retroreflectance of retroreflective surfaces such as road signs involves use of a modified light based range finder. The apparatus includes a power attenuation factor data base which relates pulse width of received pulses to power attenuation of the transmitted pulses. The range finder calculates target range based on time of flight of light pulses. The apparatus automatically calculates the absolute coefficient of retroreflectance for an unknown reflective surface being measured by comparison of the measurement to a reading with the same instrument of a known reflectance standard. The method involves either recalling a stored standard reference reflectance factor or determining a reflectance factor via the range finder for a sample of retroreflective material with a predetermined coefficient of retroreflectance, and then measuring the distance to an unknown target, determining a power attenuation factor from the received pulse width from the unknown target and then calculating the absolute coefficient of retroreflectance based upon these determined values of power attenuation factor, distance and the reference reflectance factor.
Owner:KAMA TECH (HK) LTD +1
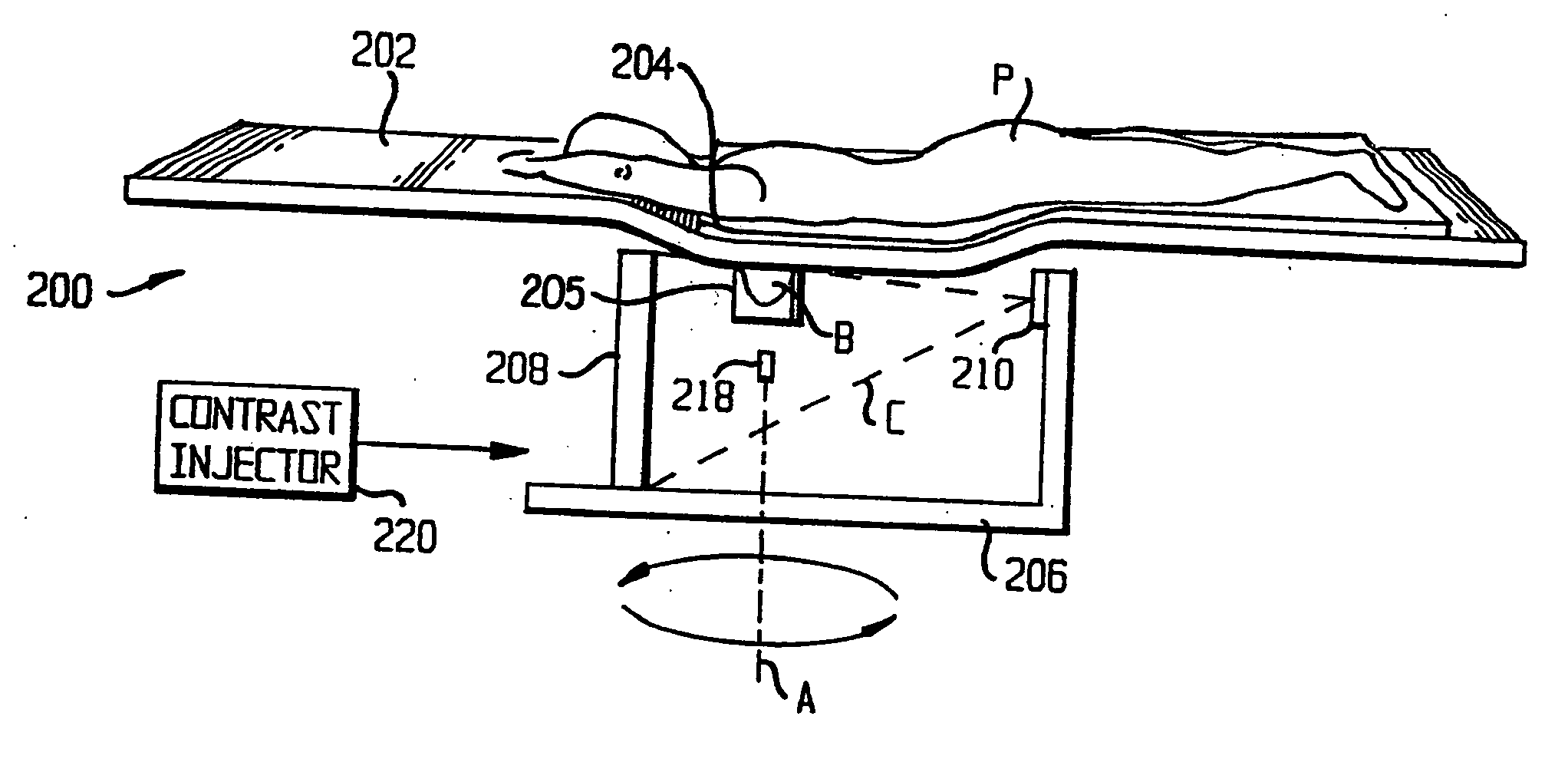
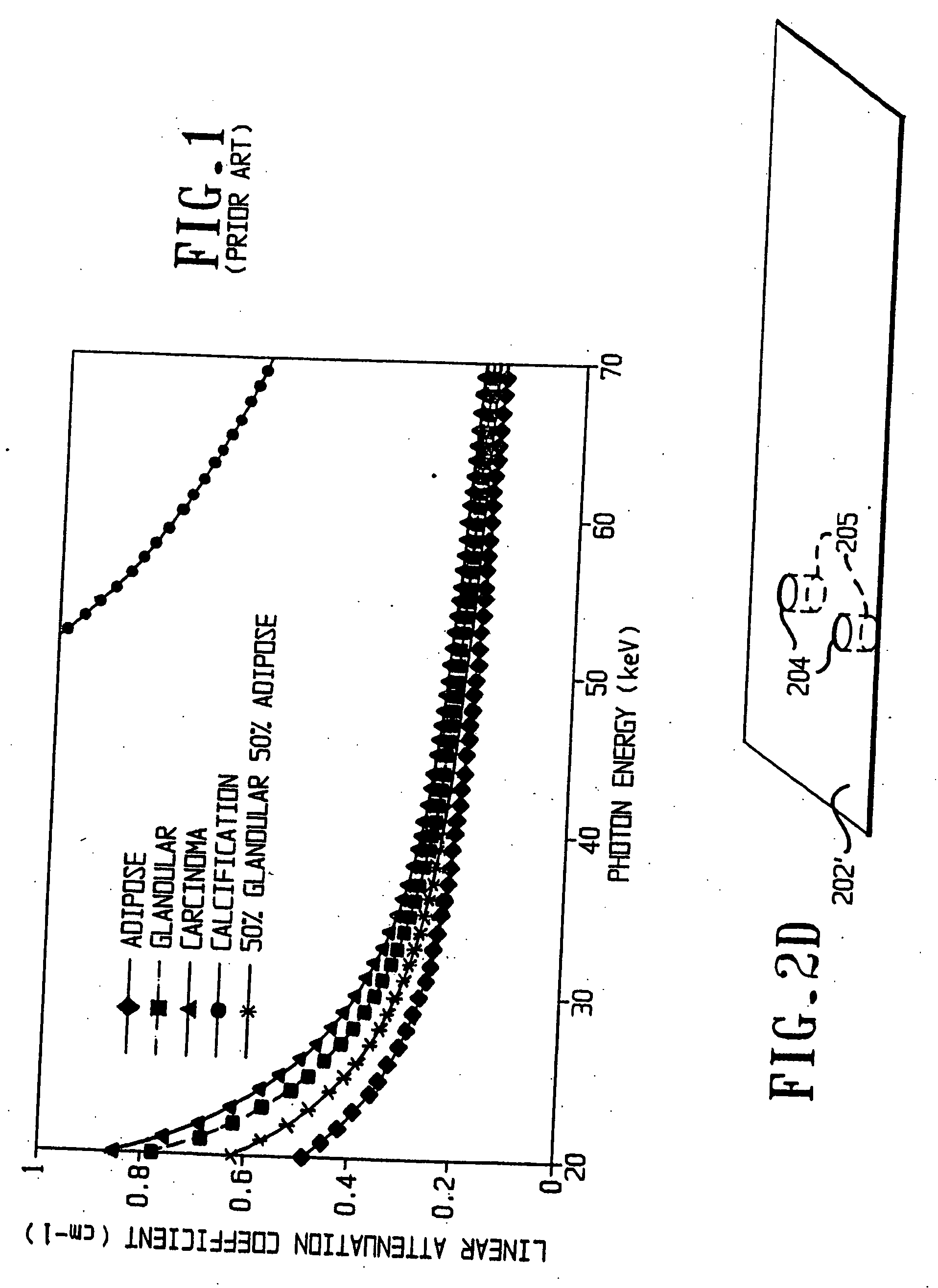
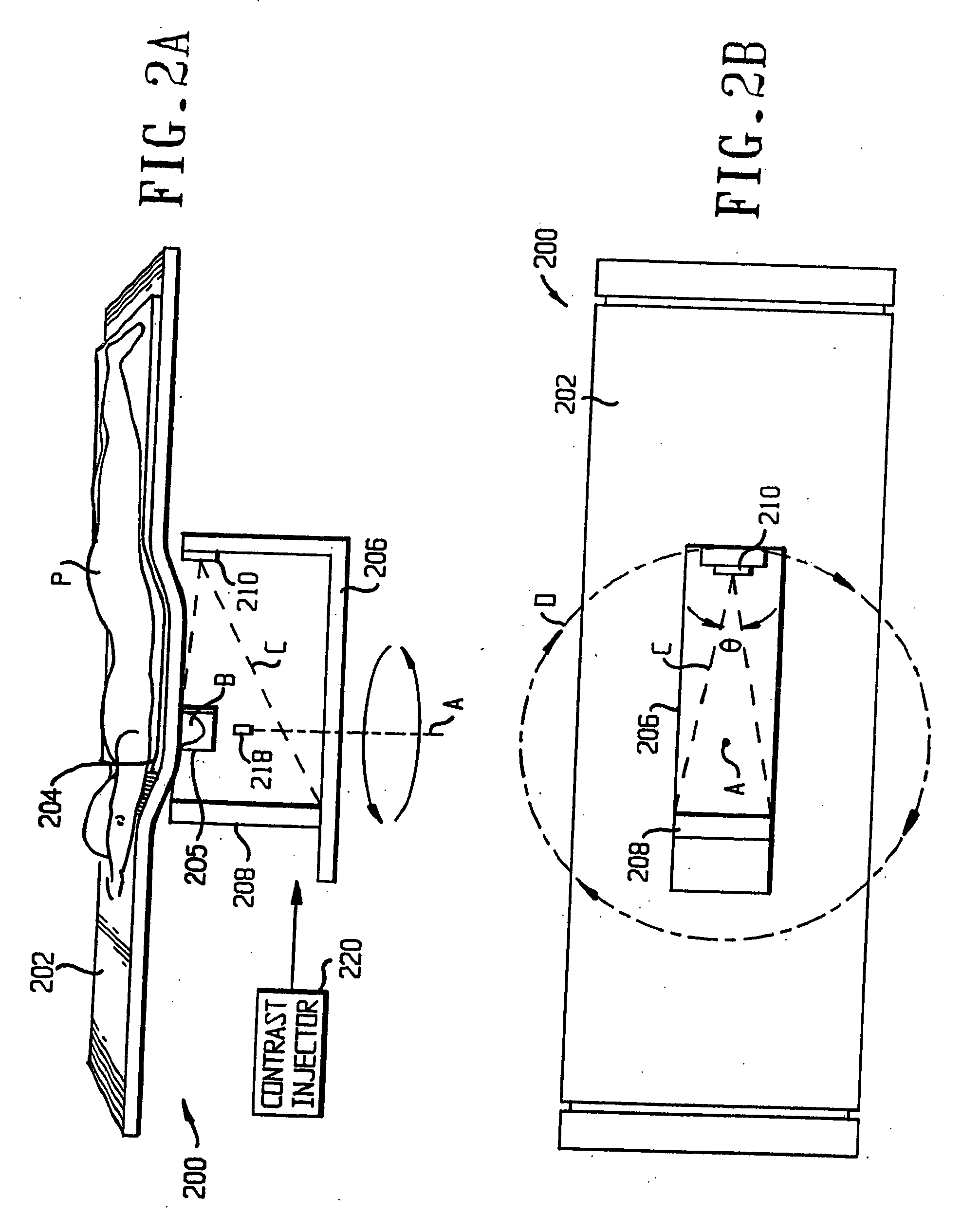
Method and apparatus for generating a density map using dual-energy CT
ActiveUS6904118B2Image enhancementReconstruction from projectionAttenuation coefficientComputer science
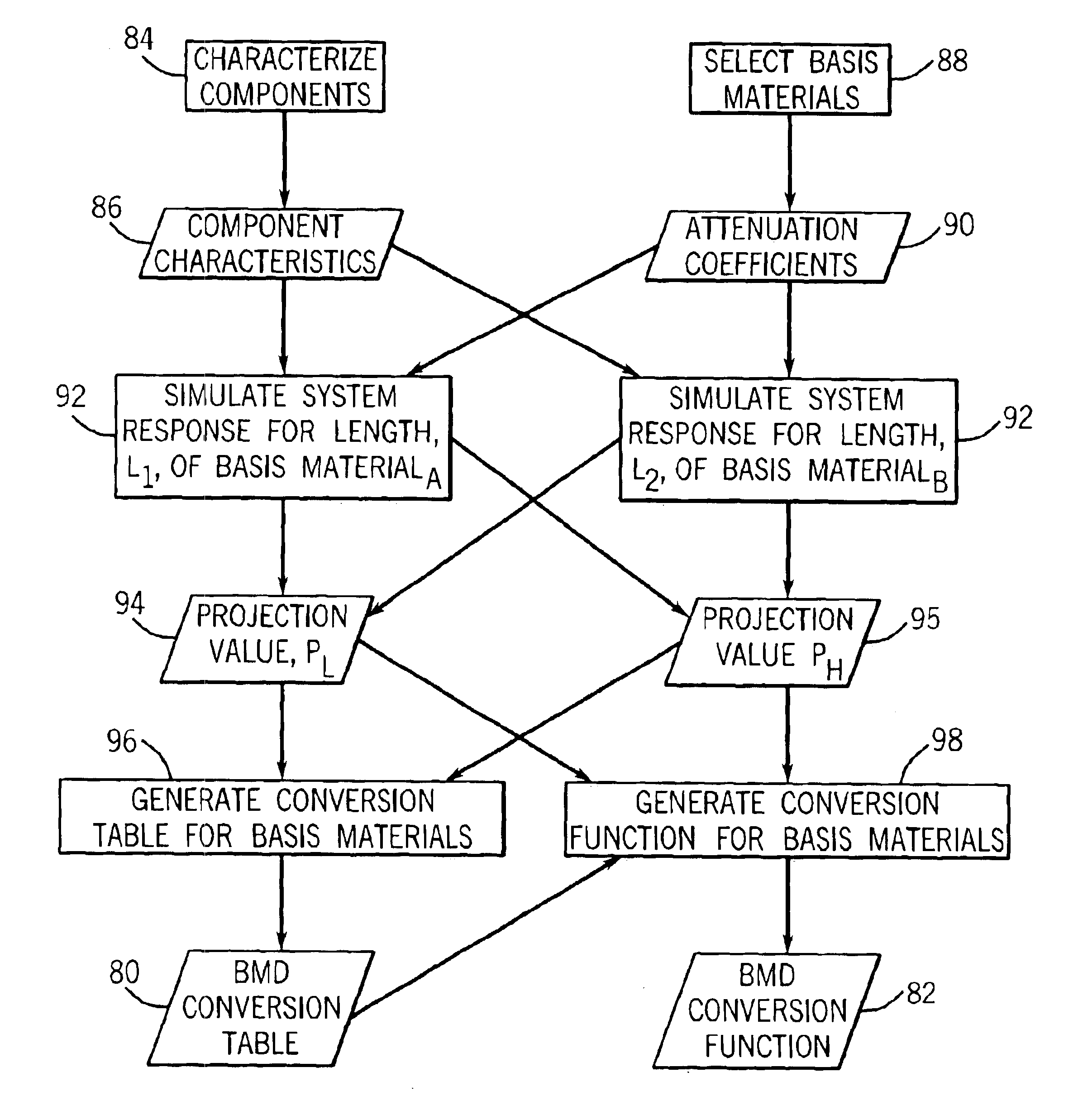
The present technique provides for the generation of density maps using one or more basis material decomposition tables or functions. The basis material decomposition tables or functions are generated by simulating the system response to various lengths of basis materials using component characteristics of the CT system as well as the attenuation coefficient for the desired basis material. Measured projection data may be processed using the basis material decomposition tables or functions to provide a set of density line-integral projections that may be reconstructed to form a density map or image.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
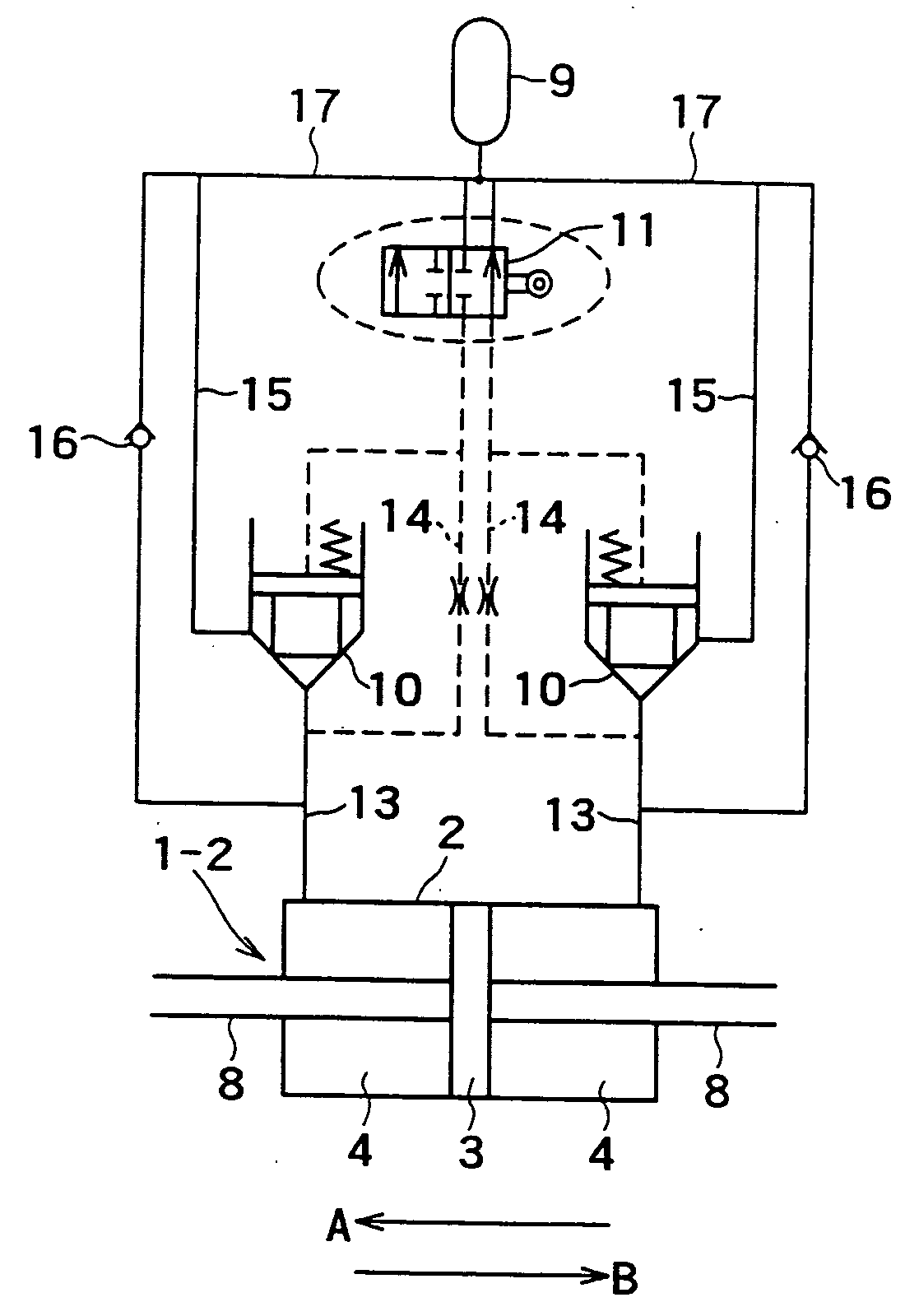
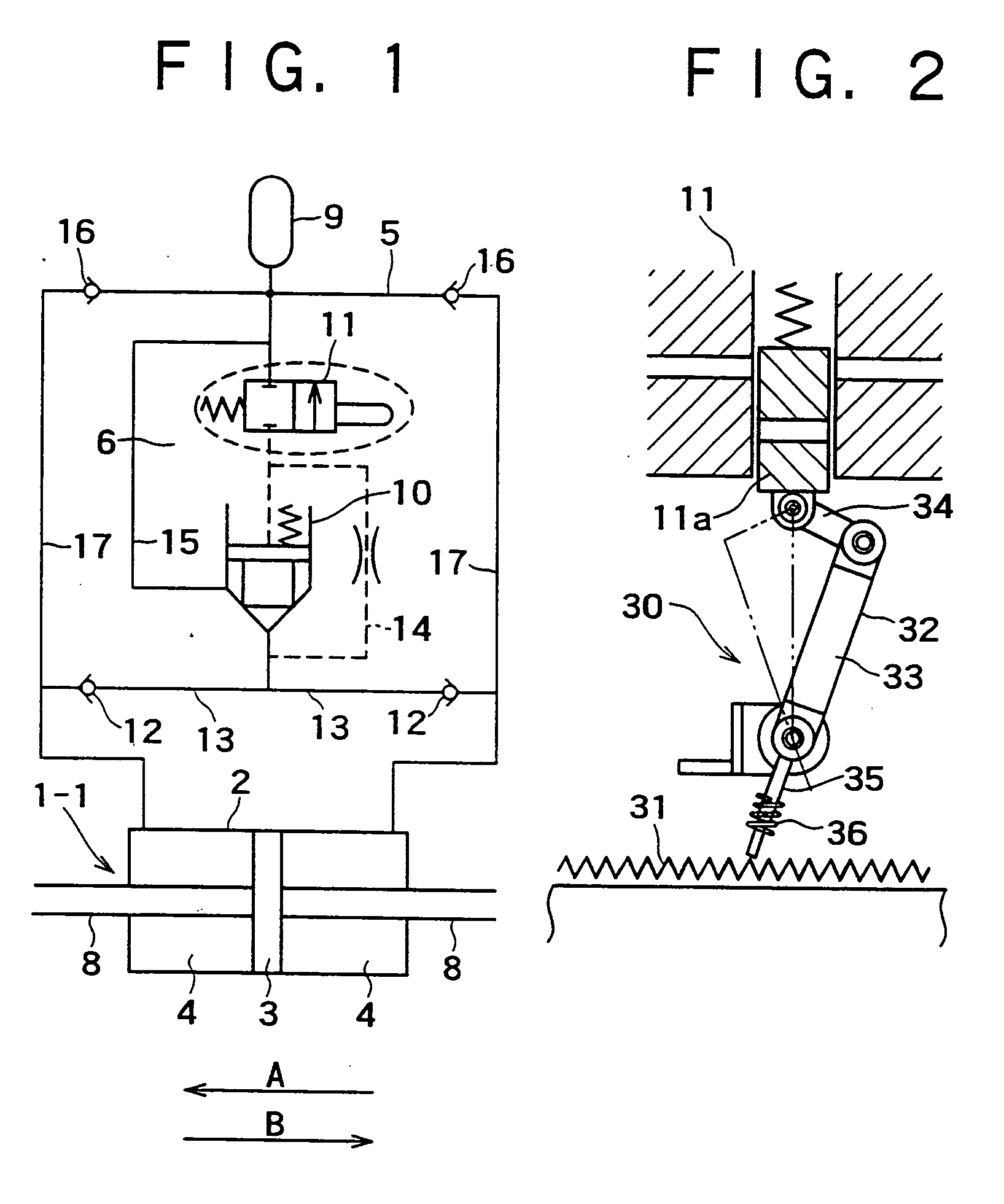
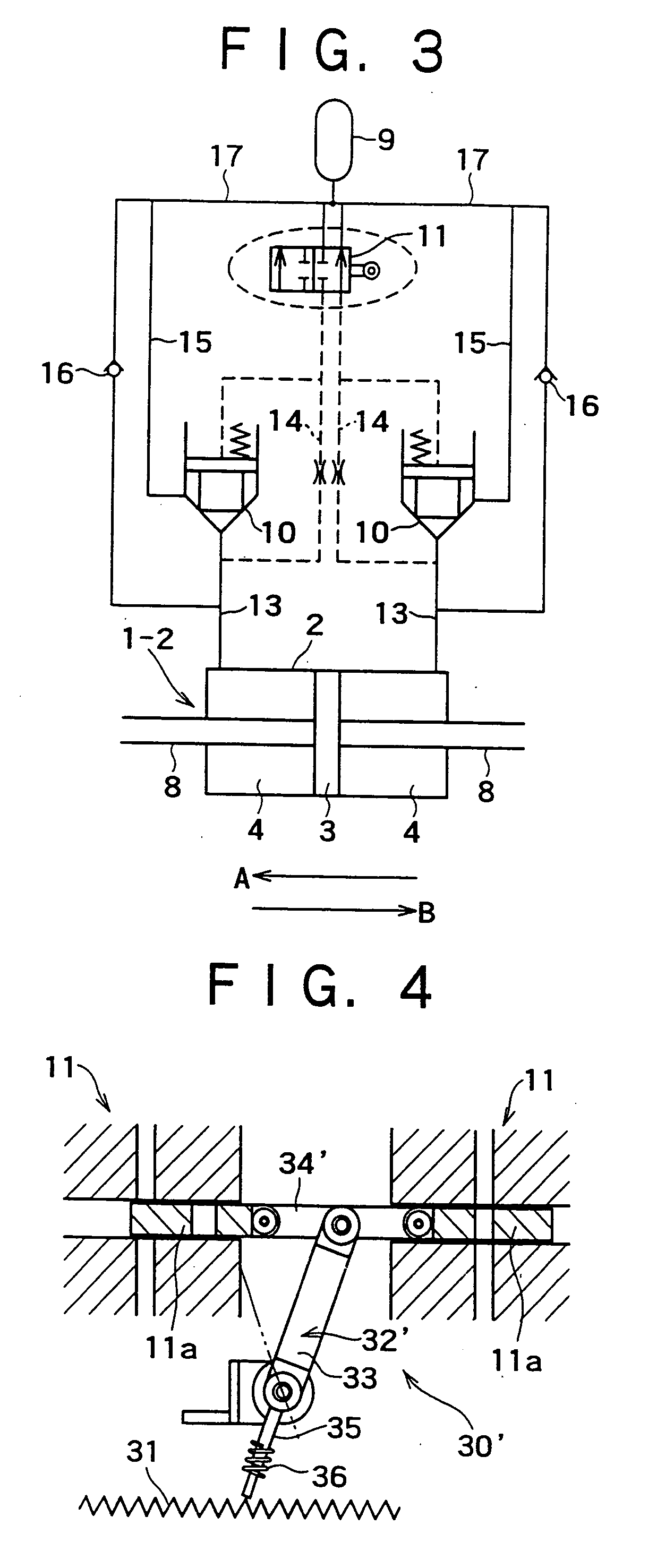
Attenuation coefficient switching type hydraulic damper
InactiveUS20050016086A1Improve energy absorptionOperating means/releasing devices for valvesSpringsAttenuation coefficientEnergy absorption
There is disclosed a damping coefficient switching-type hydraulic damper that may automatically switch a damping coefficient without needing supply of energy from the outside at all, and also may always surely exert an energy absorption capacity greater than that of a typical hydraulic damper. While a piston (3) is moving in a direction A, a mechanical drive means (30) composed of a straight gear (31) and a crank mechanism (31) allows an on-off control operation valve (11), that is, a flow regulating valve (10) to be placed in a closed state, and a damping coefficient is switched to a maximum value Cmax. When a movement of the piston (3) is turned in a direction B at a left-side maximum point of amplitude, the mechanical drive means (30) works to once open the flow regulating valve (10) to perform elimination of a load, so that the damping coefficient is switched to a minimum value (Cmin). When the piston (3) further moves in the direction B, the mechanical drive means (30) works to close the flow regulating valve (10) again, and the damping coefficient is returned to the maximum value (Cmax). Similar working to the above is also applied to a right-side maximum point of amplitude, and seismic response control is attained with repetition of the above operations.
Owner:KAJIMA CORP
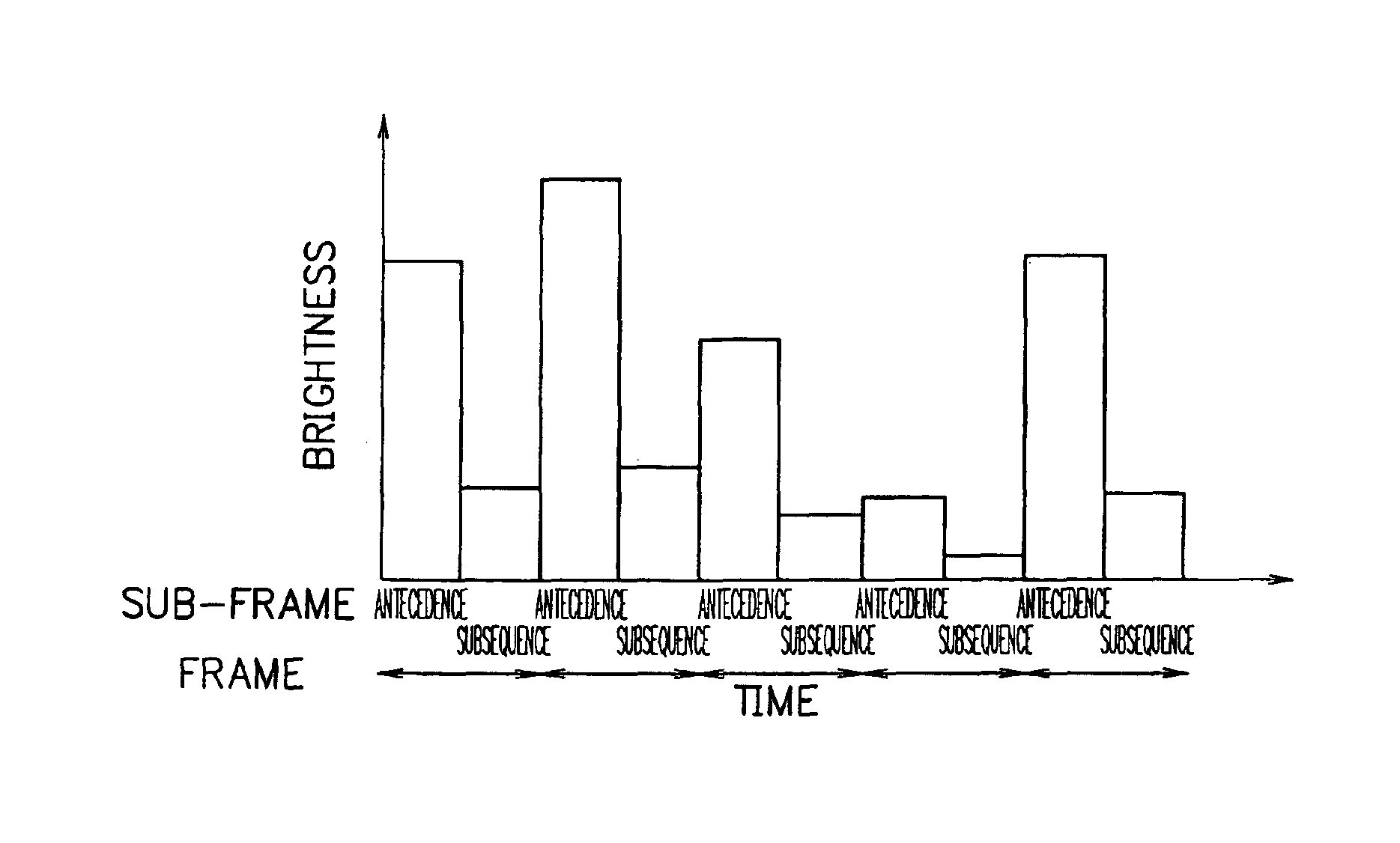
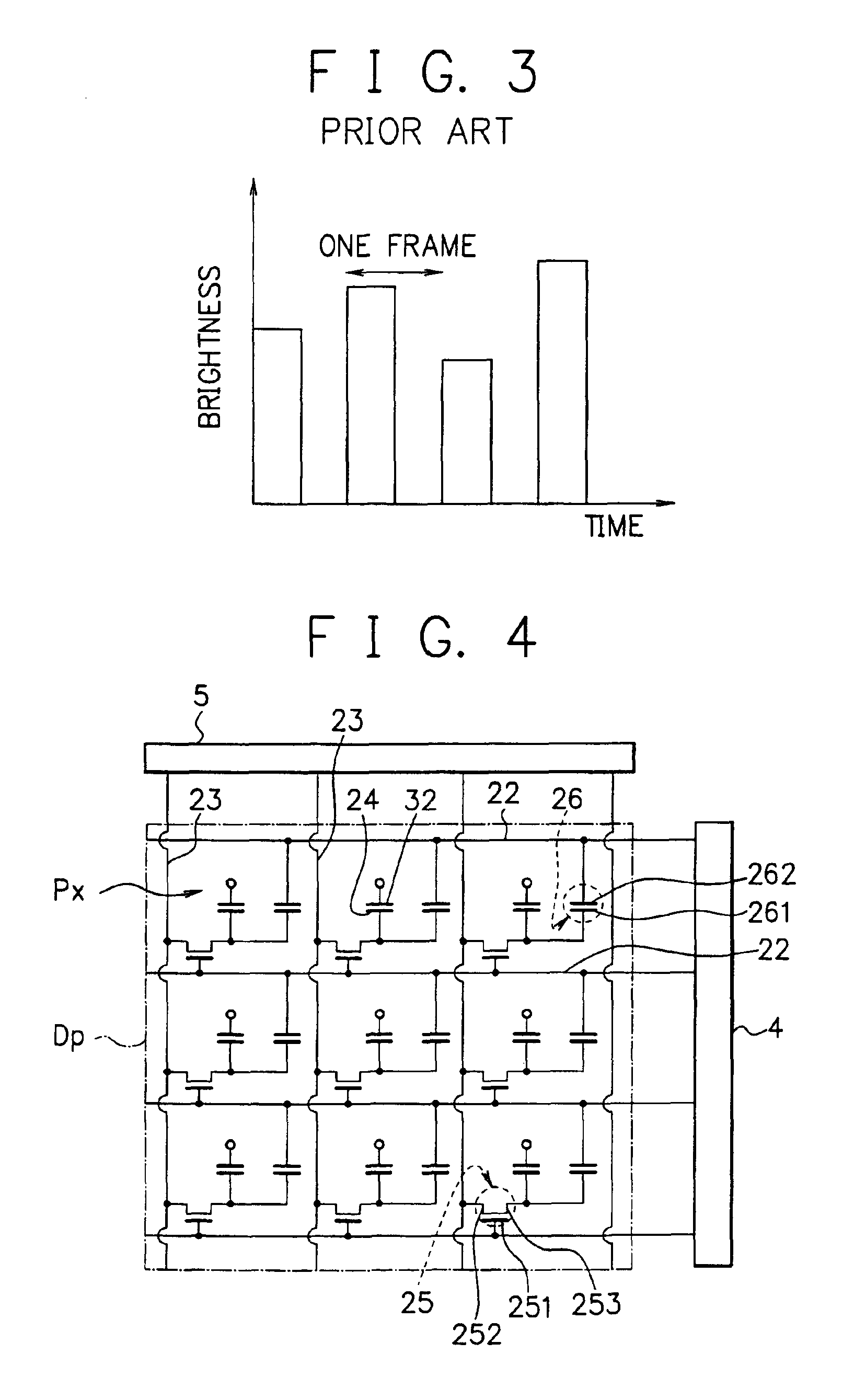
Display device
InactiveUS7002540B2Quality improvementSecuring contrast of pictureTelevision system detailsColor television detailsUltrasound attenuationAttenuation coefficient
A display device comprises a frame buffer which time-divides a frame displaying one picture into multiple sub-frames, an attenuation signal generating circuit which generates an attenuation signal by dividing the inputted luminosity signal by the designated attenuation coefficient, and a signal switching circuit which inputs luminosity signals before division to the antecedent sub-frame in the relevant frame, at the same time, inputs the above-mentioned attenuation signals after division to the subsequent sub-frame. Consequently, such a hold type display device is realized as is able to control the lowering of the picture brightness, as well as, prevent a moving picture from being unclear, blurred or disordered.
Owner:GOLD CHARM LTD
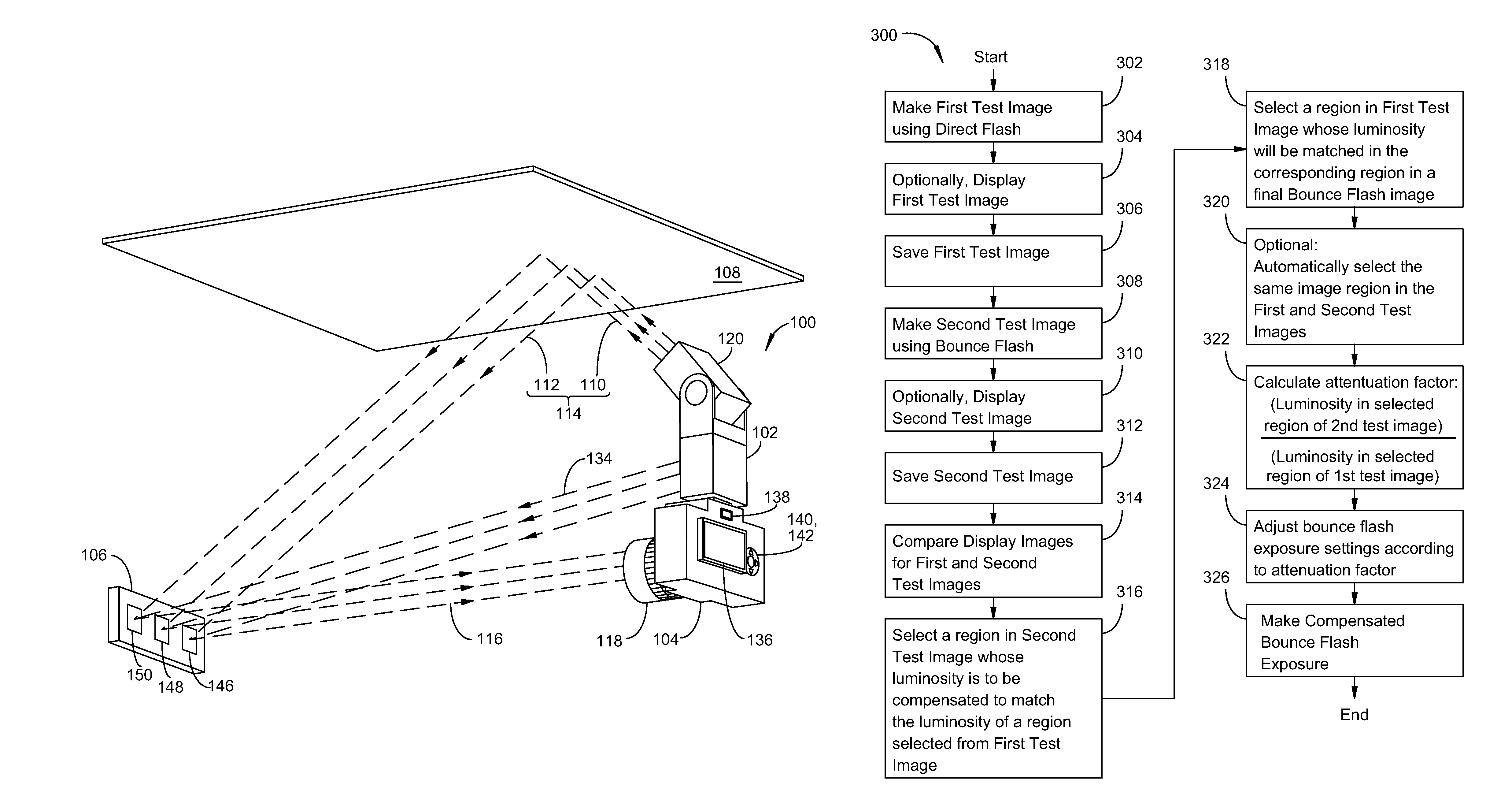
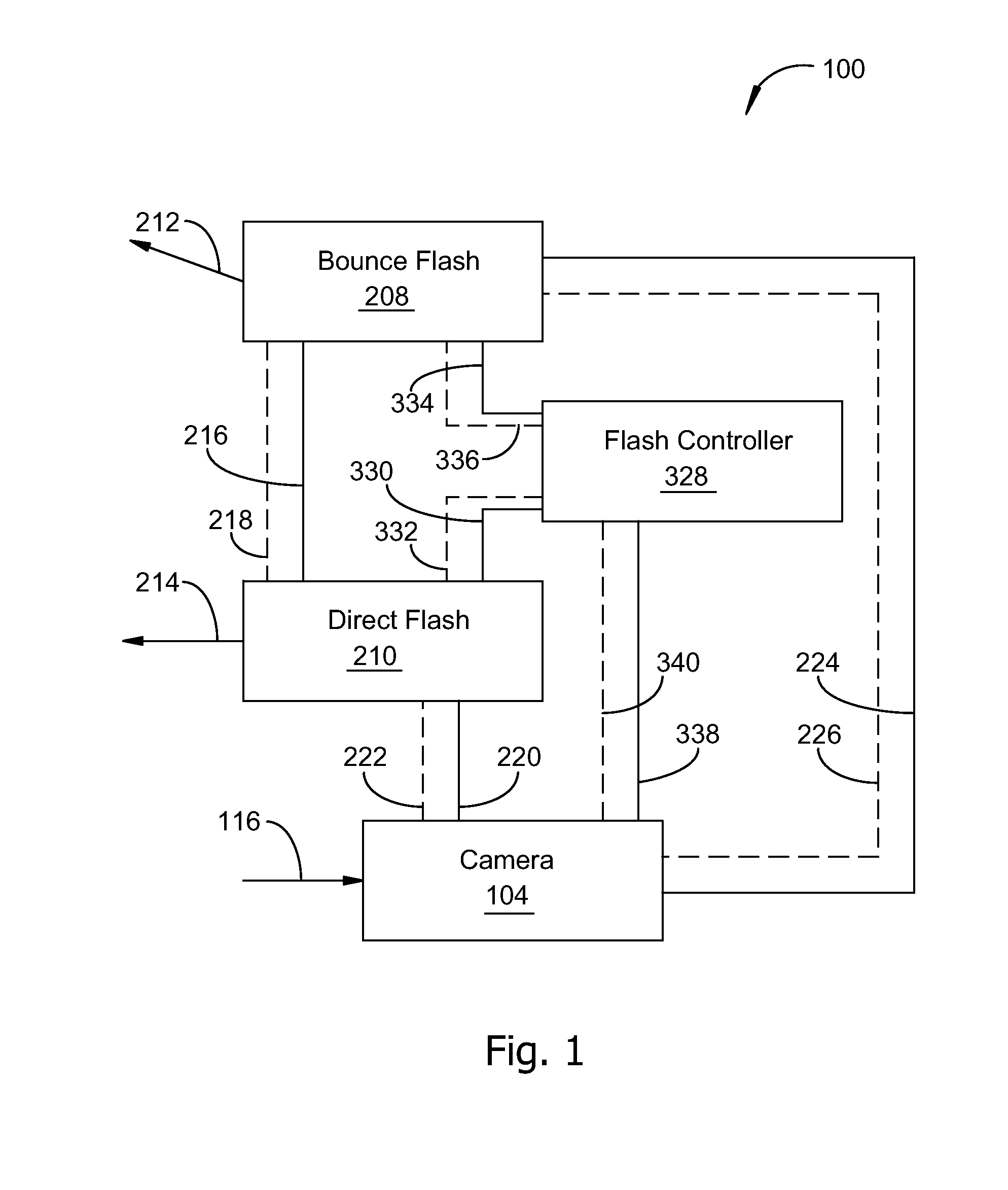
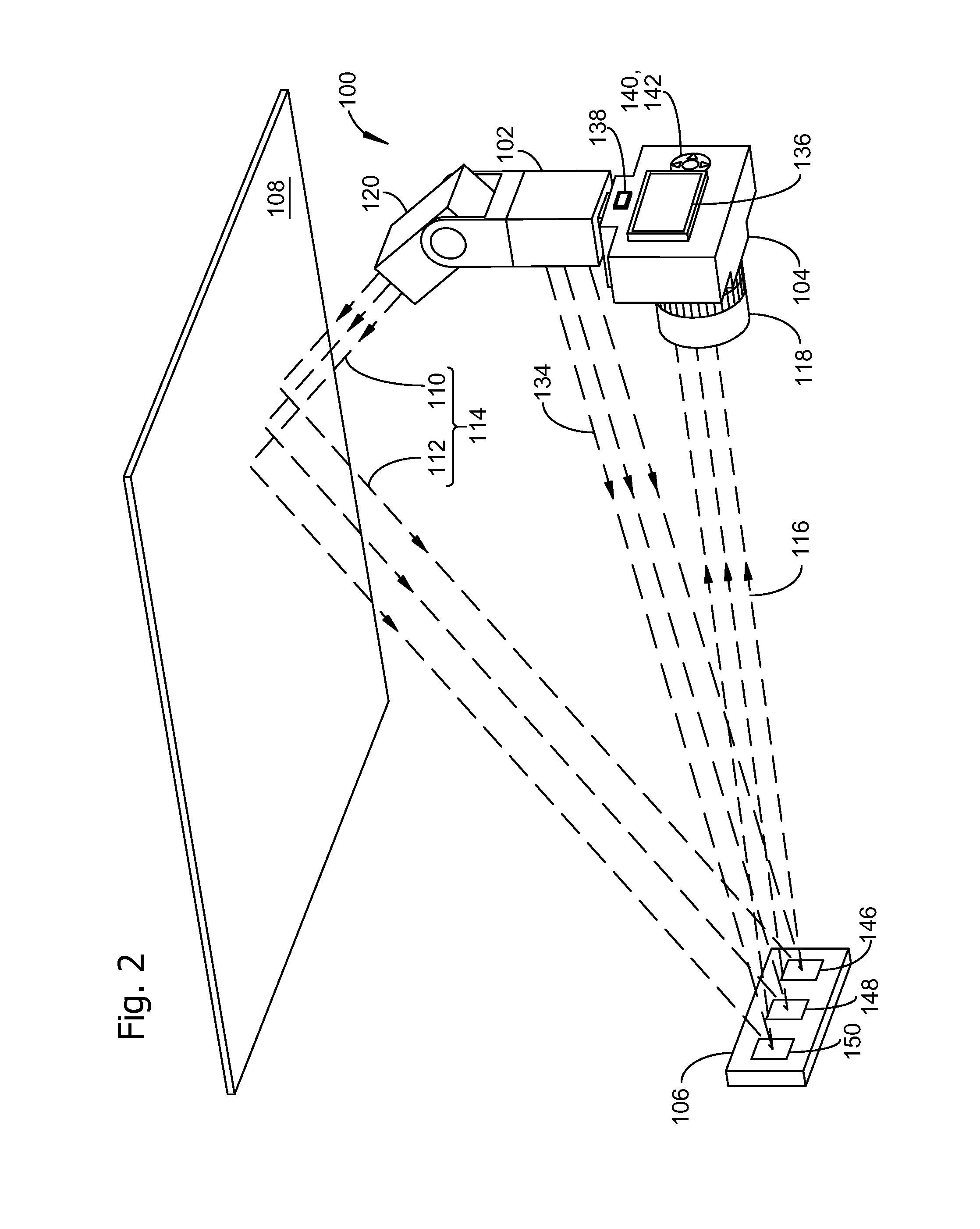
Automatic exposure control for flash photography
InactiveUS8736710B2Television system detailsColor signal processing circuitsAttenuation coefficientControl line
A photographic flash unit comprises a direct flash unit and a bounce flash unit rotatably connected to the direct flash unit. Status and control lines coupled between a hot shoe and each flash unit enable independent triggering and control of each flash unit. The direct and bounce flash units may be a part of a digital camera adapted to make a first test exposure using direct flash illumination and second test exposure using bounce flash illumination, then computing an attenuation factor for compensating a selected flash exposure parameter by dividing the selected parameter by the attenuation factor. Steps in a method embodiment include making a first test image, making a second test image, selecting regions in the first and second test images, computing an attenuation factor from luminosity values for the first and second test images, and compensating settings for a final bounce flash image by the attenuation factor.
Owner:INT BUSINESS MASCH CORP
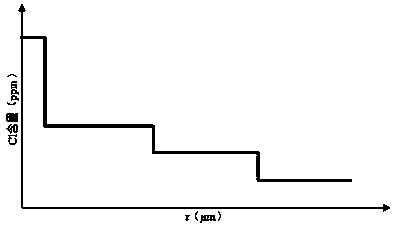
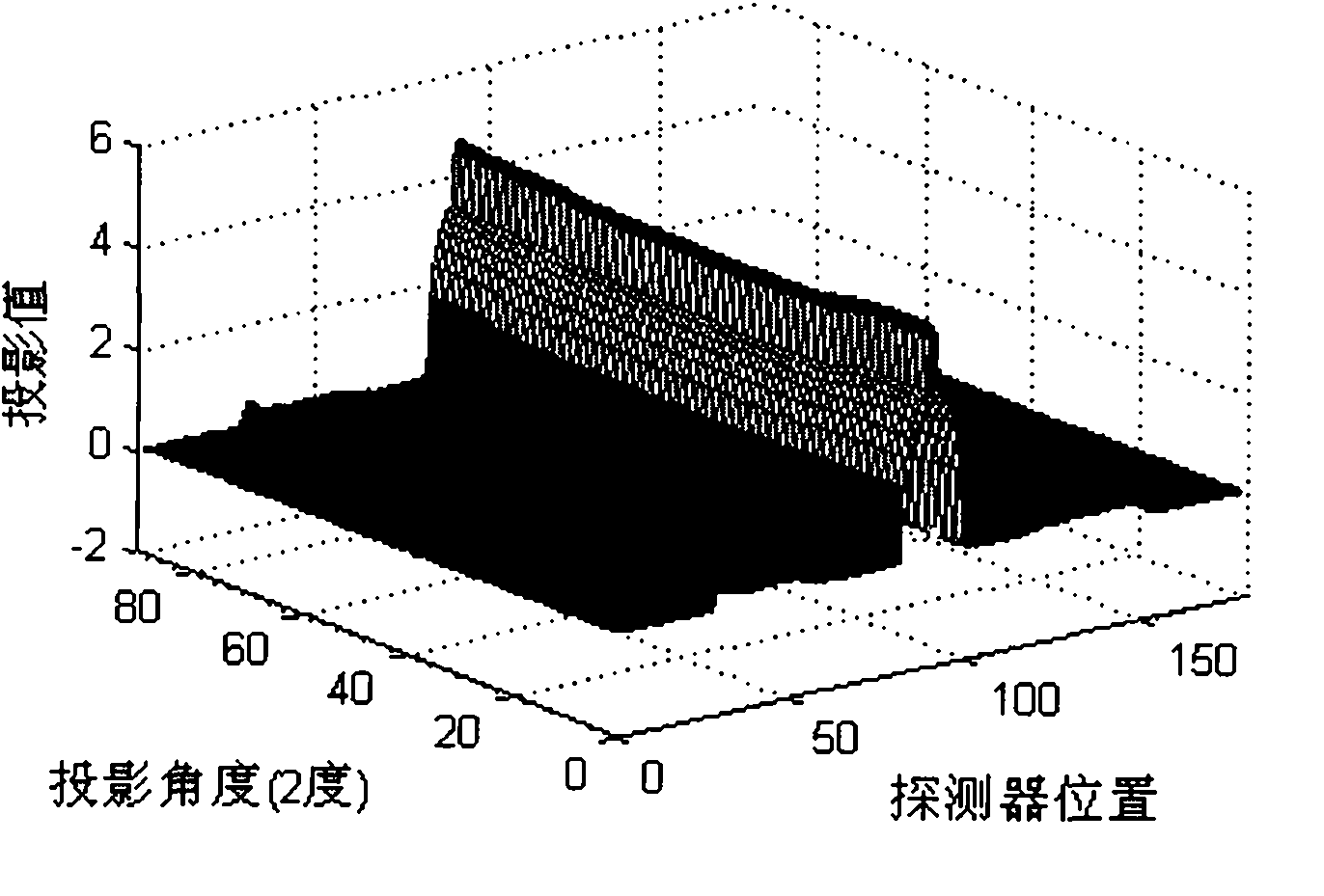
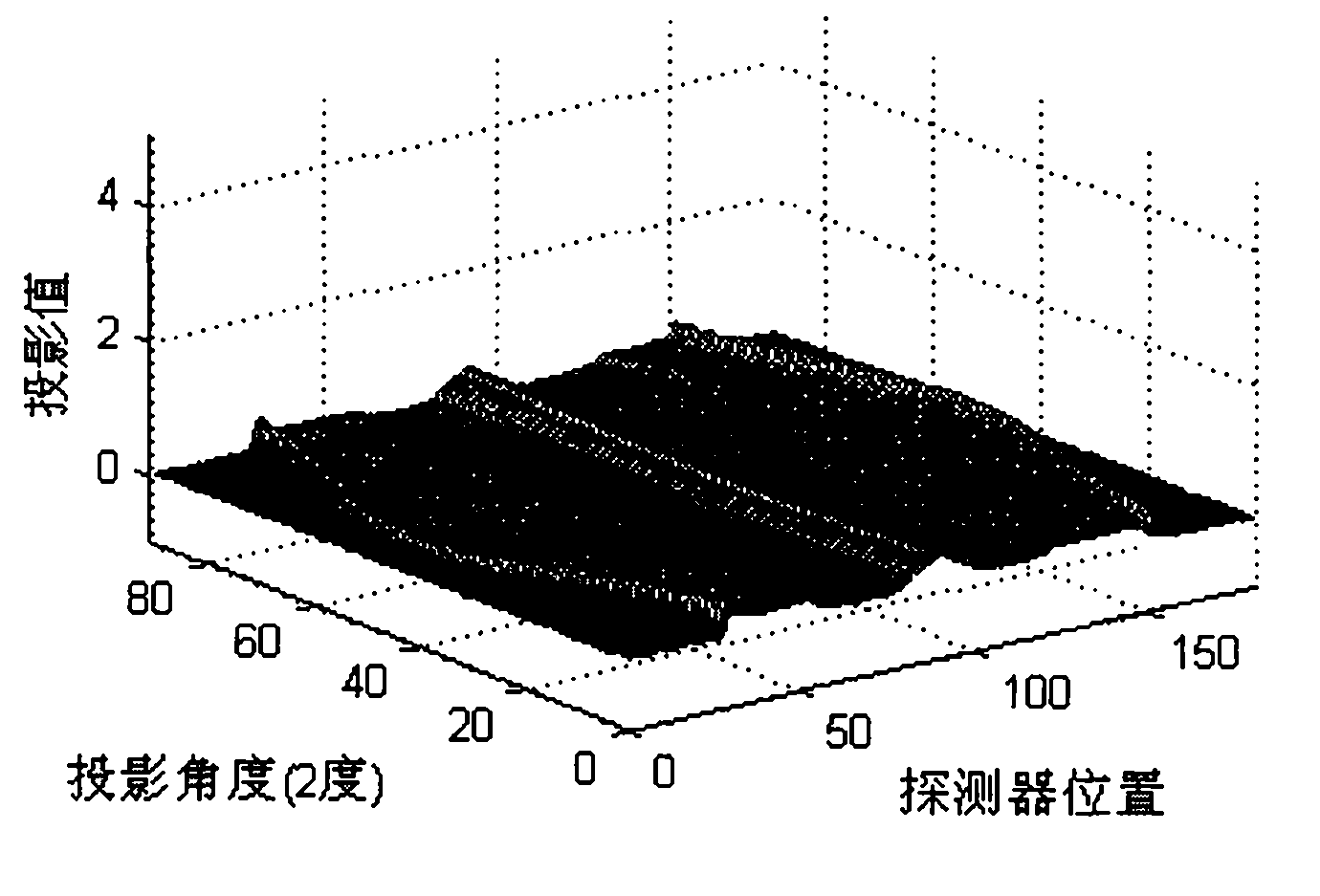
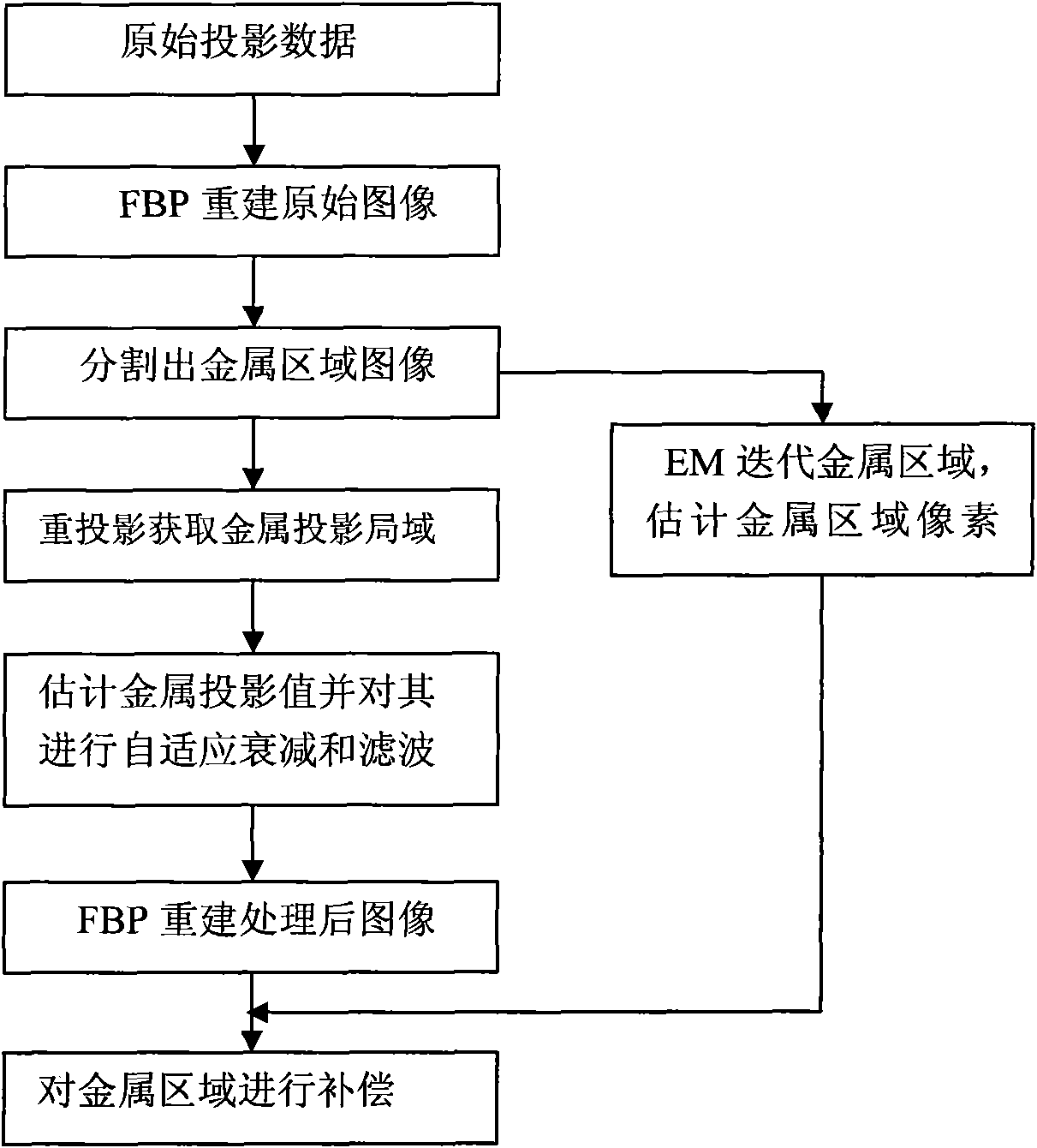
Attenuation filter-based metal artifact removing mixed reconstruction method for CT images
InactiveCN101777177AEfficient removalEasy to keepImage enhancement2D-image generationHigh absorptionComputation complexity
The invention discloses an attenuation filter-based metal artifact removing mixed reconstruction method for CT images. When a CT acquires data, if a scanned object contains a metal object with high absorption coefficients which comprises a tissue attenuation coefficient and a metal attenuation coefficient to cause projection data jump, the scanned object is considered to be destructive and should be corrected; thus, the metal artifact is greatly weakened during FPB reconstruction. The method comprises the following steps: after determining a metal projection area, performing adaptive attenuation adjustment and filter on the determined metal area; reconstructing an entire image through the FBP, performing EM iterative reconstruction on the metal area by using the primary projection data, and correcting the metal area after the adaptive attenuation filter and reconstruction; and compensating the metal projection area. The numerical simulation CT experiments prove that the method can effectively remove metal artifacts and well keep the information of the metal and the surrounding tissue of the metal. Particularly under the condition of multiple metal objects, the method has low calculation complexity and high practical value.
Owner:SHANGHAI WEIHONG ELECTRONICS TECH +1
Graphics accelerator with shift count generation for handling potential fixed-point numeric overflows
InactiveUS6037947ACathode-ray tube indicatorsProcessor architectures/configurationUltrasound attenuationAttenuation coefficient
A 3-D graphics accelerator for performing lighting operations using operands within a given fixed point numeric range. The 3-D graphics accelerator includes a first computational unit which is configured to compute a value of an attenuation factor usable for performing said lighting operation for local lights. The attenuation factor is represented in floating point format. The first computational unit is also configured to represent the attenuation factor in an intermediate format including a first intermediate value (a scaled attenuation factor value within the given fixed point numeric range), and a second intermediate value (a shift count usable to convert the scaled attenuation factor value back to the original attenuation factor value). The 3-D graphics accelerator further includes a lighting unit coupled to said first computational unit. The first computational unit is further configured to convey the intermediate representation of the attenuation factor to the lighting unit. The lighting unit performs lighting calculations in fixed point, using operands within the given numeric range (such as the scaled attenuation factors). The lighting unit generates intermediate color values as a result of these lighting calculations. The lighting unit then uses the shift count value to shift the intermediate color values by an appropriate amount, thereby generating a final color value. The lighting unit clamps said final color value to a predetermined maximum color value in response to said final color value exceeding said predetermined maximum color value.
Owner:ORACLE INT CORP
Composition for forming anti-reflective coating
ActiveUS20050118749A1Photosensitive materialsRadiation applicationsAnti-reflective coatingSolid component
There is provided a composition for forming anti-reflective coating for use in a lithography process with irradiation light from F2 excimer laser (wavelength 157 nm) which has a high effect of inhibiting reflected light and causes no intermixing with resist layers, and an anti-reflective coating prepared from the composition, and a method of controlling attenuation coefficient of the anti-reflective coating. Concretely, the composition is one containing a polymer compound containing halogen atom for forming anti-reflective coating for use in a lithographic process in manufacture of a semiconductor device. The polymer compound is one which halogen atom is introduced to a main chain thereof and / or a side chain bonded to the main chain. The attenuation coefficient can be controlled by changing the content of halogen atom in the solid content of the composition.
Owner:NISSAN CHEM IND LTD
Exposure apparatus, exposure method using the same, and method of manufacture of circuit device
InactiveUS20010043321A1Favorable imaging stateExposed to lightPhotomechanical exposure apparatusMicrolithography exposure apparatusAttenuation coefficientUltraviolet
A reflective member is fixedly or movably provided near the pupil plane of a projection optical system with which a projection exposure apparatus is equipped. A collimated measuring beam with an exposure wavelength is incident from the object plane side or image plane side of the projection optical system, and the intensity of the beam reflected by the reflective member is detected photoelectrically to measure a value corresponding to the attenuation factor (transmissivity or reflectivity) of the projection optical system or the variation with time of the attenuation factor (transmissivity or reflectivity) of the projection optical system. In accordance with the measurement results, the exposing conditions when a photosensitive substrate is exposed are corrected to avoid the deterioration of the exposure control precision due to the variation of the attenuation factor (transmissivity variation or reflectivity variation) which is caused in the projection optical system and illumination optical system of a projection exposure apparatus which uses ultraviolet illumination light.
Owner:NIKON CORP
System, apparatus, and method for conducting electromagnetic induction surveys
InactiveUS20050156602A1Electric/magnetic detection for well-loggingDetection using electromagnetic wavesAttenuation coefficientLinear relationship
A method is provided for conducting an electromagnetic induction survey of a geological formation penetrated by a borehole lined with a conductive casing. The method includes positioning a transmitter in the borehole, whereby the transmitter generates a transmitter magnetic moment, and positioning a distant receiver external of the borehole to detect a magnetic field induced by the transmitter, whereby the distant receiver is disposed across part of the formation from the borehole. Furthermore, an auxiliary receiver is positioned in the borehole proximate the transmitter to detect a magnetic field induced by the transmitter and attenuated by the conductive casing. Subsequently, a first casing attenuation factor that is applicable to the magnetic field measured by the auxiliary receiver is determined from a ratio of the measured magnetic field at the auxiliary receiver and the transmitter magnetic moment. A second casing attenuation factor applicable to the measurement of the magnetic field at the distant receiver is determined from a non-linear relationship (e.g., a power law relationship) between the first casing attenuation factor and the second attenuation factor, wherein the second attenuation factor is less than the first attenuation factor. Then, a formation attenuation factor applicable to the measured magnetic field at the distant receiver is determined from a relationship between the magnetic moment of the transmitter, the second casing attenuation factor, and the measured magnetic field at the distant receiver. Finally, the method correlates the determined value of the formation attenuation factor to a resistivity characteristic of the formation between the distant receiver and the transmitter.
Owner:SCHLUMBERGER TECH CORP
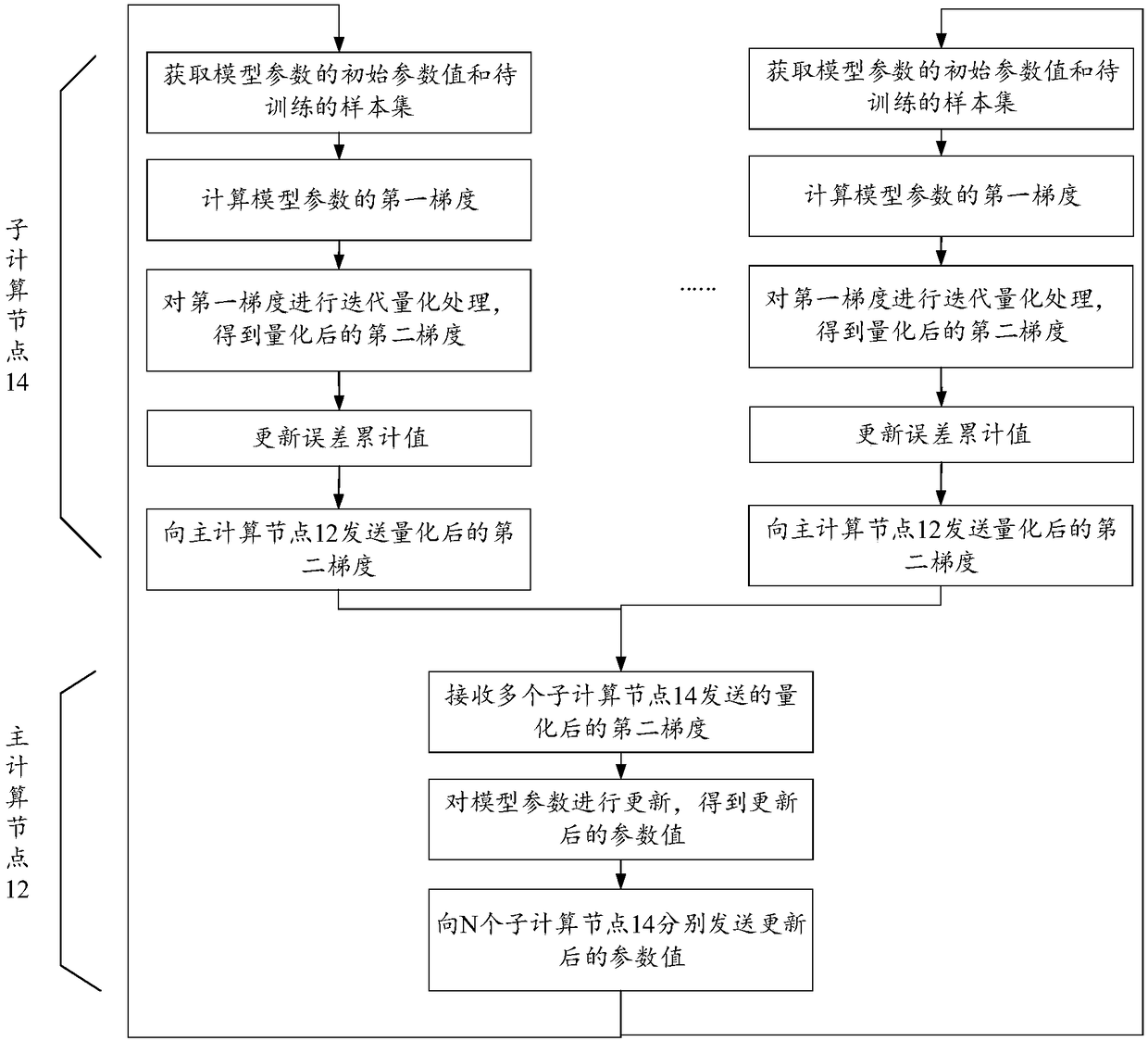
Model parameter training method and device, server and storage medium
ActiveCN108491928AReduce overheadImprove operational efficiencyNeural architecturesAttenuation coefficientAlgorithm
The invention discloses a model parameter training method and device, a server and a storage medium, which belongs to the technical field of information. The method comprises the steps that an initialparameter value and a sample set of a model parameter of a target model are acquired; the first gradient of the model parameter is calculated according to the initial parameter value and the sample set; iterative quantization processing is carried out on the first gradient to acquire a quantized second gradient, wherein the iterative quantization processing is quantization processing carried outbased on an error cumulative value corresponding to the t-1-th iteration round in the t-th iteration round, and the error cumulative value is a quantization error cumulative value calculated based ona preset time attenuation coefficient; and the quantized second gradient is transmitted to a primary computing node, wherein the quantized second gradient is used to instruct the primary computing node to update the initial parameter value according to the quantized second gradient to acquire an updated parameter value. According to the embodiment of the invention, a quantization error correctionmethod is used to quantize and compress the first gradient of the model parameter, which reduces the communication cost and network overhead of gradient transmission.
Owner:TENCENT TECH (SHENZHEN) CO LTD
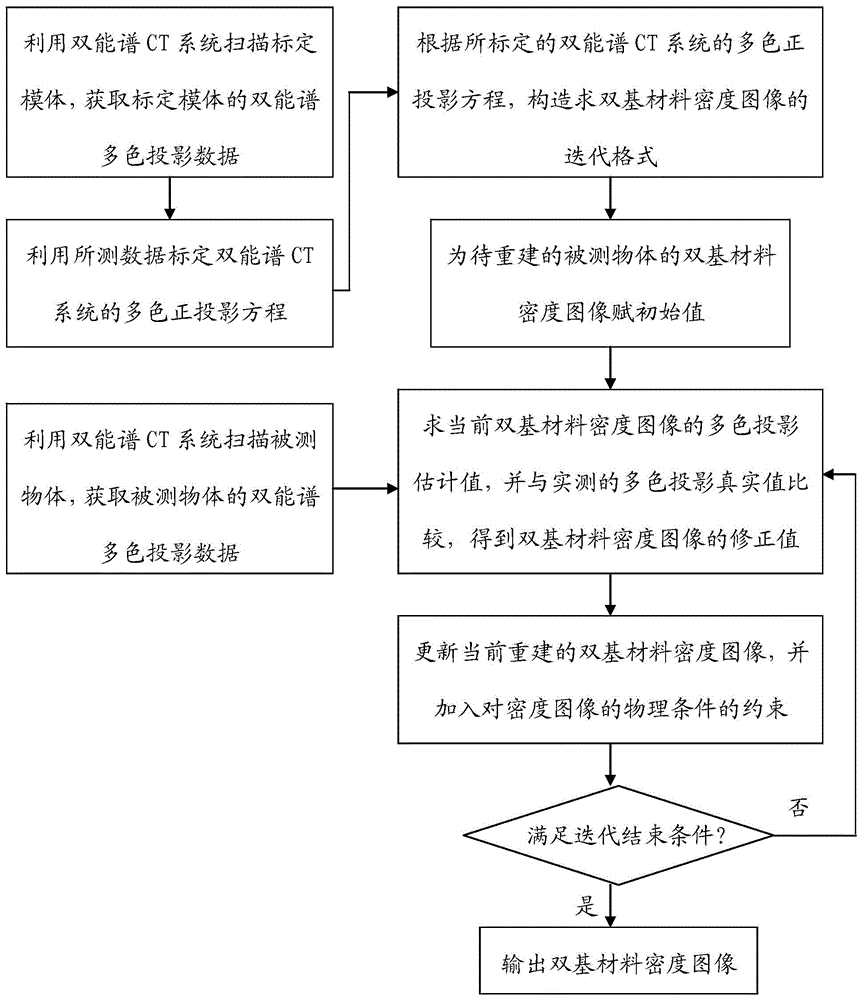
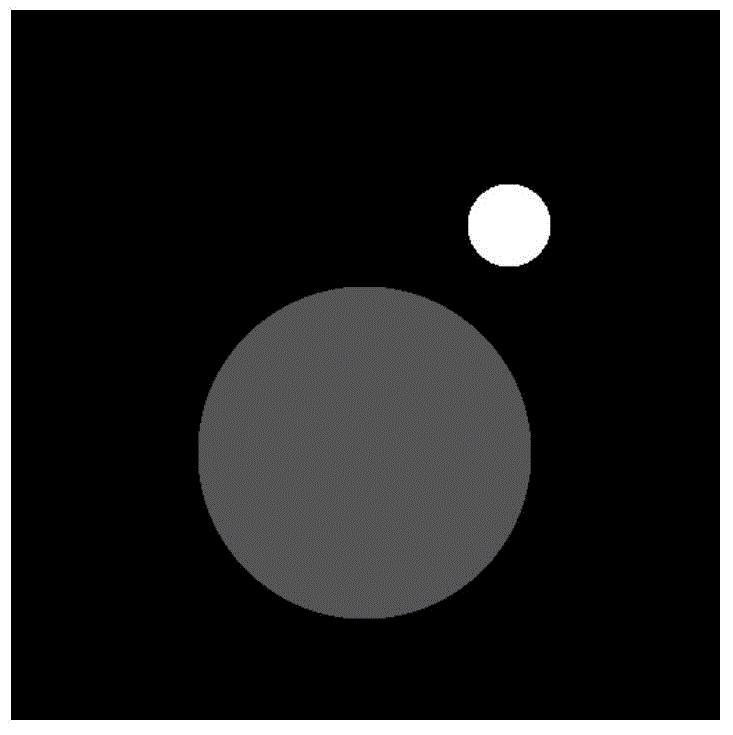
Method for iterating and reconstructing double-energy-spectrum CT image
InactiveCN103559729ALow energy spectrumImprove applicabilityImage enhancement2D-image generationAttenuation coefficientHigh energy
The invention discloses a method for iterating and reconstructing a double-energy-spectrum CT image. The method is used for reconstructing a base material density image of a measured object and comprises the following steps of (1) selecting a calibration model body containing tow types of different base materials according to the size of a material of the measured object; measuring the model body through a double-energy-spectrum CT system, and calibrating a double-energy-spectrum multi-color orthographic projection equation presenting a curvilinear relationship between a multi-color projection value and base material thickness combination; (2) collecting double-energy-spectrum multi-color projection data of the measured object by utilizing the double-energy-spectrum CT system; (3) constructing a iterative scheme according to the calibrated multi-color orthographic projection equation, and iterating and reconstructing the double-base-material density image of the measured object through comparison with the practically measured multi-color projection data and addition of a physical constraint condition. Compared with the existing method, the method for iterating and reconstructing the double-energy-spectrum CT image has the advantages that the high energy spectrum and the low energy spectrum of the double-energy-spectrum CT system and an attenuation coefficient of the base materials do not need to be detected in advance, and meanwhile the method is applied to the situation that the high energy spectrum and the low energy spectrum are matched with each other or not in geometry.
Owner:CAPITAL NORMAL UNIVERSITY +1
Onboard antenna system for satellite tracking with polarization control
InactiveUS20110006948A1Polarisation/directional diversityIndividually energised antenna arraysUltrasound attenuationAttenuation coefficient
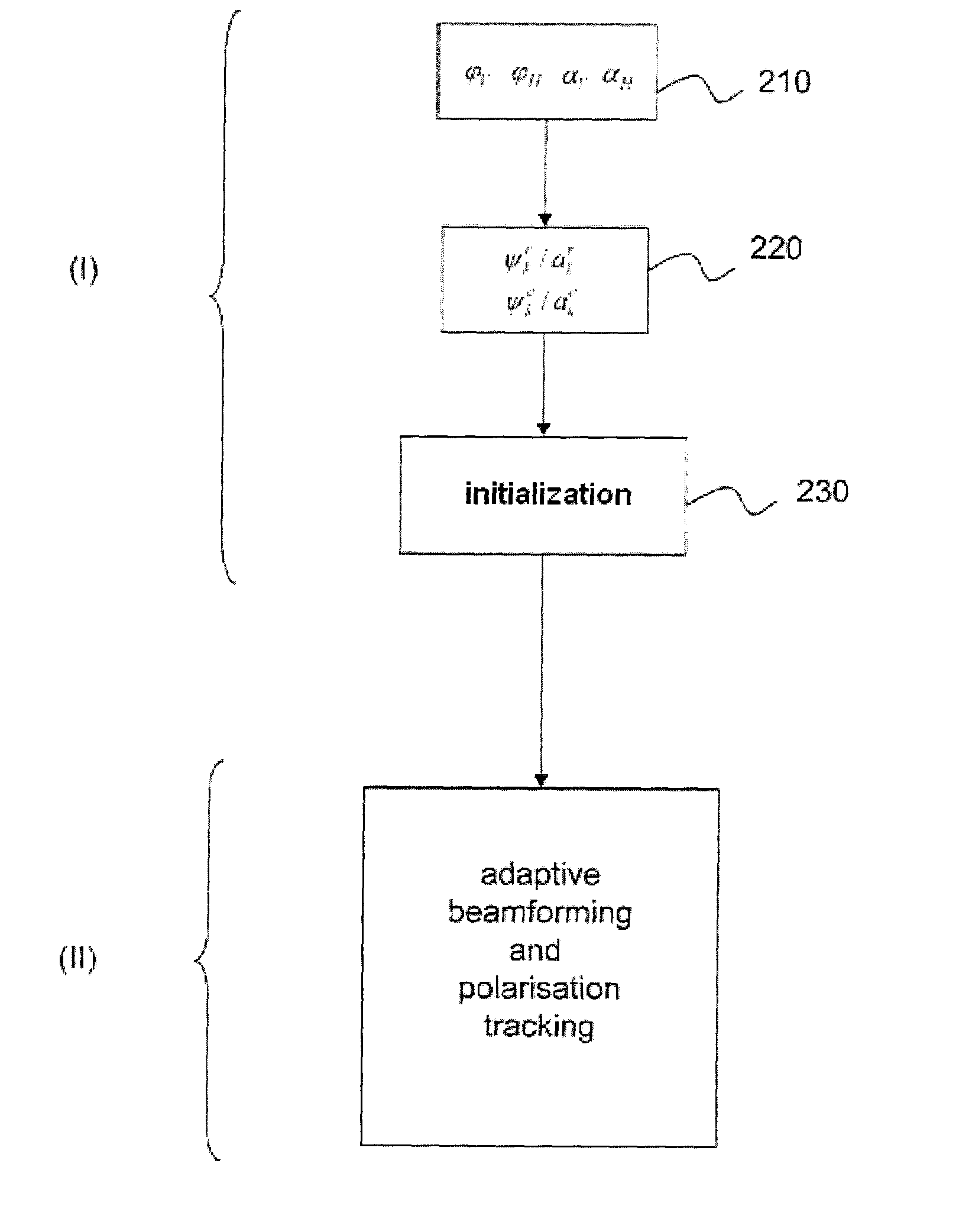
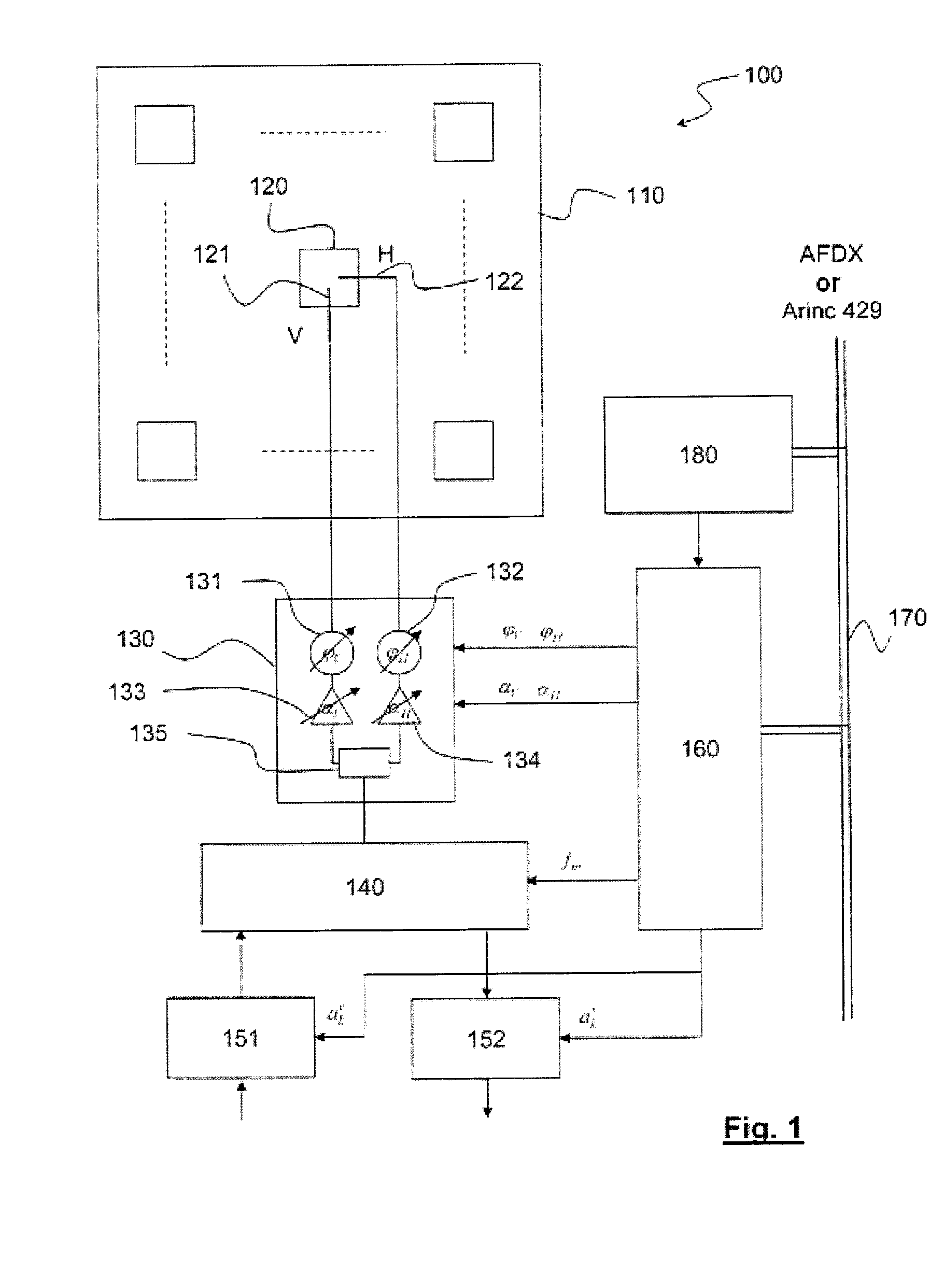
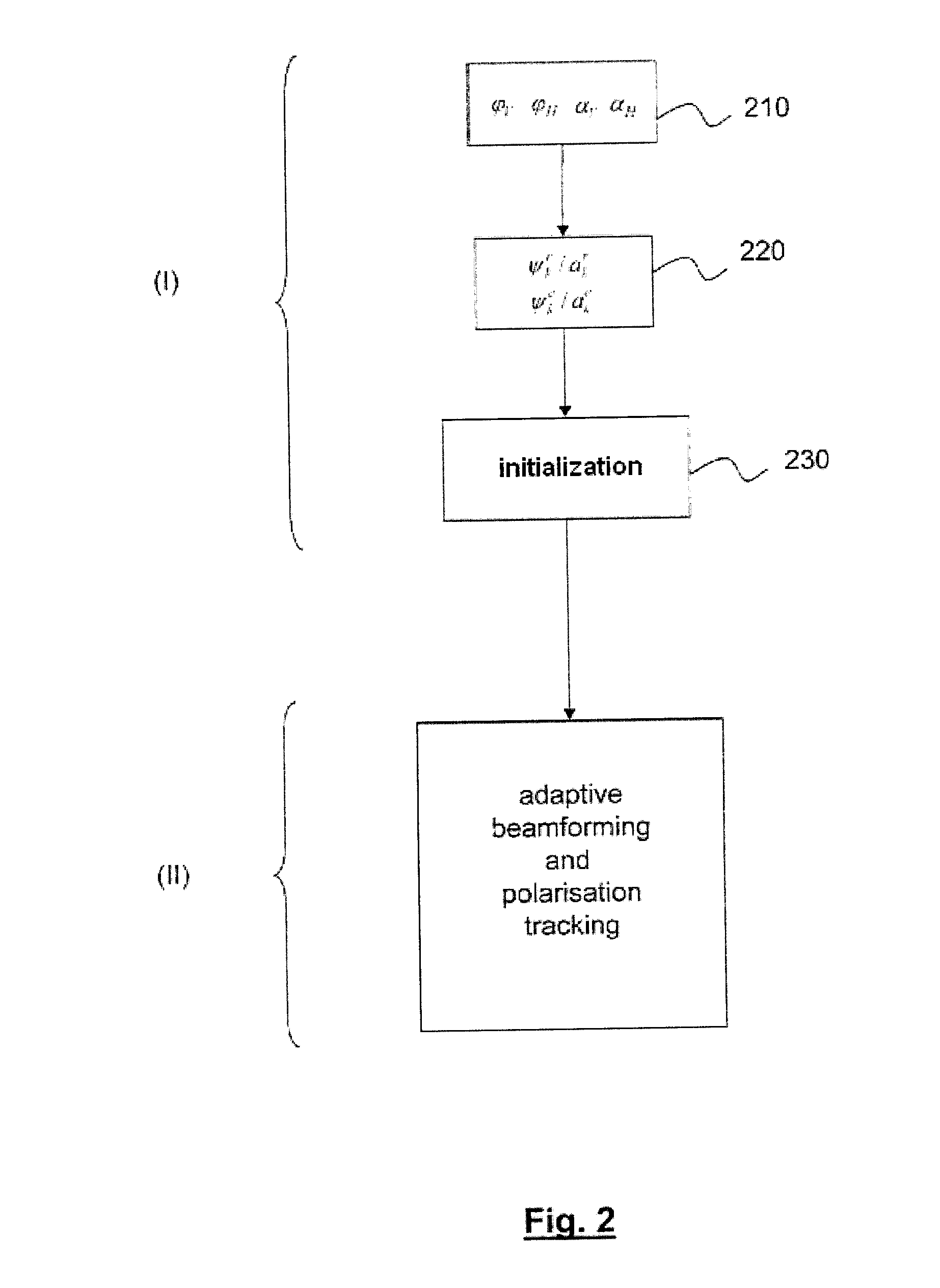
The present invention concerns an antenna system (100) intended to be embarked on an aircraft, comprising a phase-control array antenna (110) made up of a plurality of polarization-controlled elementary antennas (120), connected to at least one beamformer (151, 152), comprising:a calculator (160) adapted to calculate phase offset values (φV, φH) and attenuation coefficients (αV, αH) from position and attitude information of the aircraft, coordinates of a telecommunications satellite and polarization characteristics of a transponder of said satellite;a polarization control means (130) using said phase offset values and the attenuation coefficients to control the polarization of said elementary antennas.
Owner:AXESS EURO
Light emitter
InactiveUS20120008338A1Ensure transparencyHighly efficient light emissionOptical light guidesReflectorsAttenuation coefficientLight guide
Provided is a surface light emitter that supplies light using a light guide method, and ensures transparency by lowering a haze value in a thickness direction at the time when a light source is turned off, and enables highly efficient light emission by using plate-surface transversal radiant emitted light at the time when the light source is on. A surface light emitter (2) including light diffusing particles guides light in a length direction of the light guide while scattering the light in the thickness direction of the light guide while scattering the light in the thickness direction of the light guide, and a calculated value (m−1 / %) obtained by dividing a luminance attenuation coefficient E (m−1) by a haze value (%) per 5 (mm) thickness of the light guide is greater than or equal to 0.55 (m−1 / %) and less than or equal to 10.0 (m−1 / %).
Owner:KURARAY CO LTD
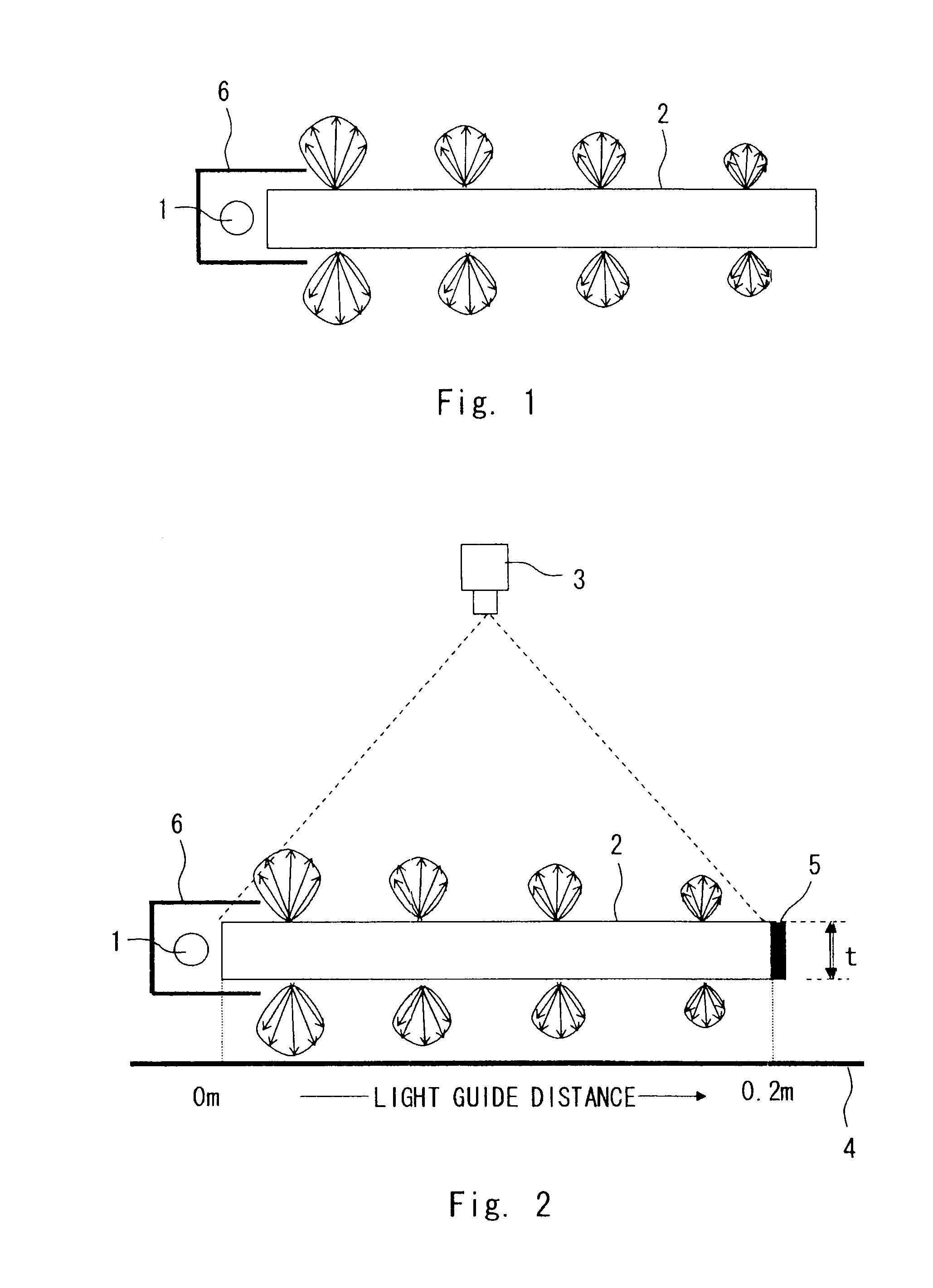
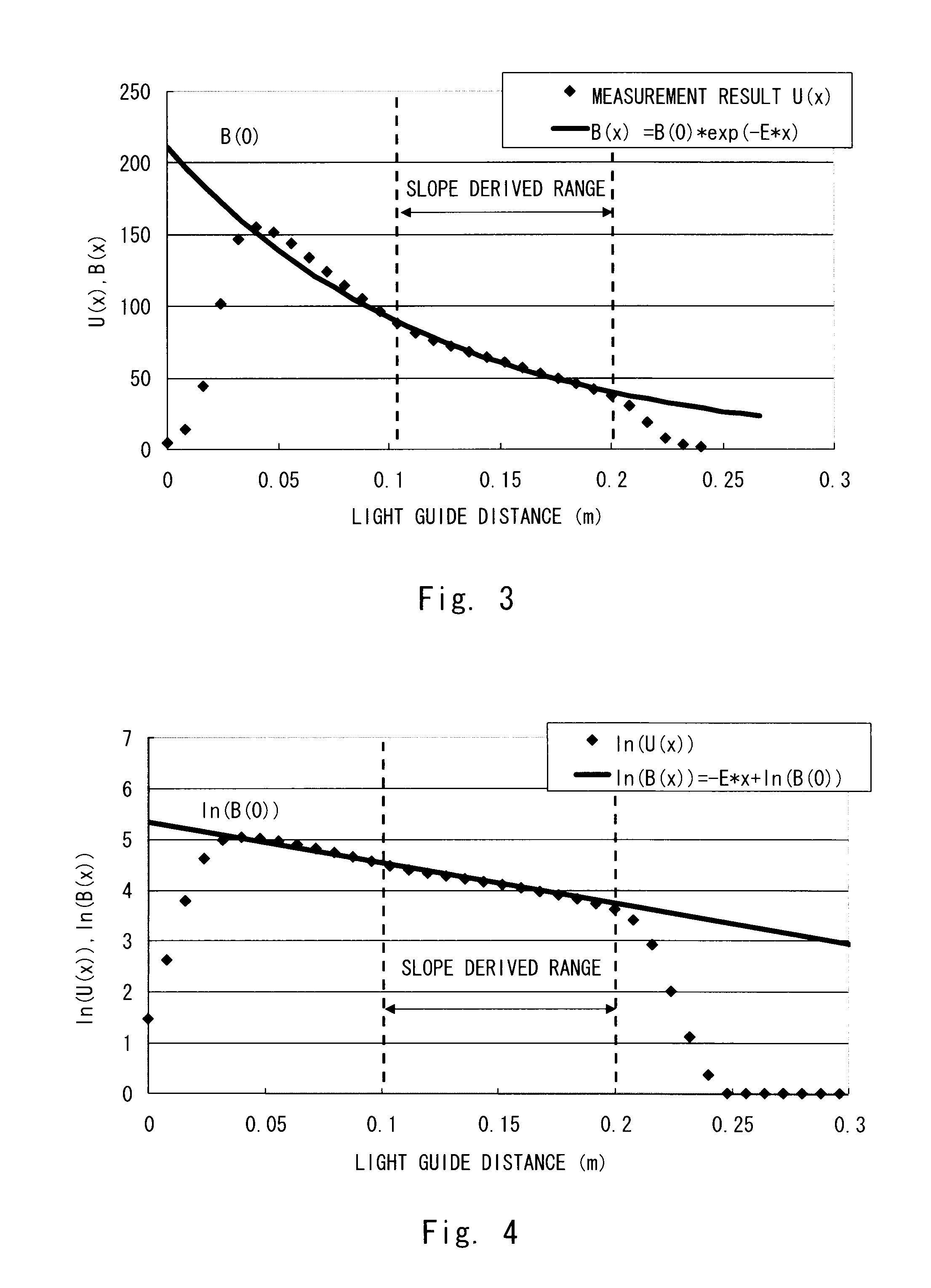
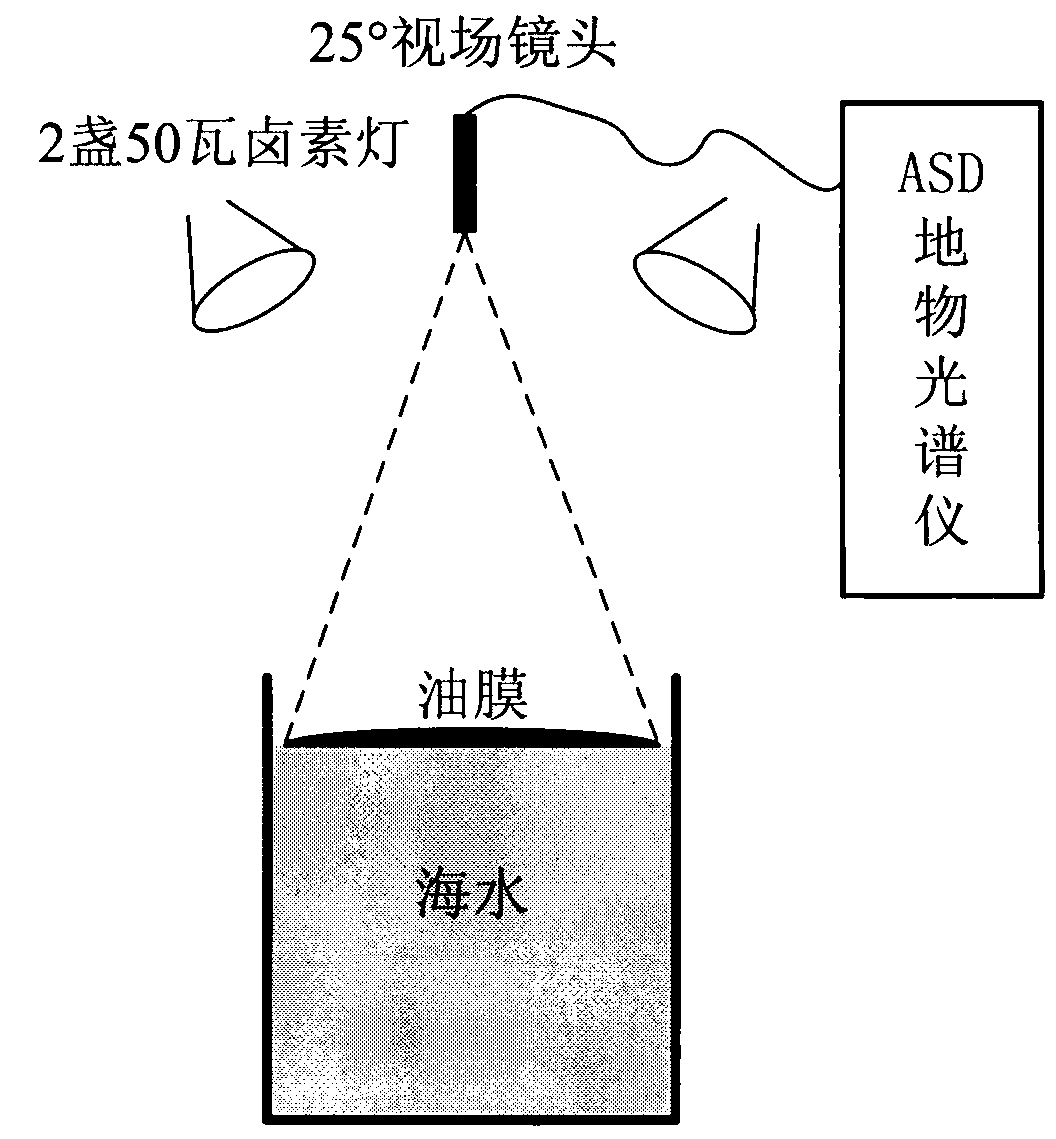
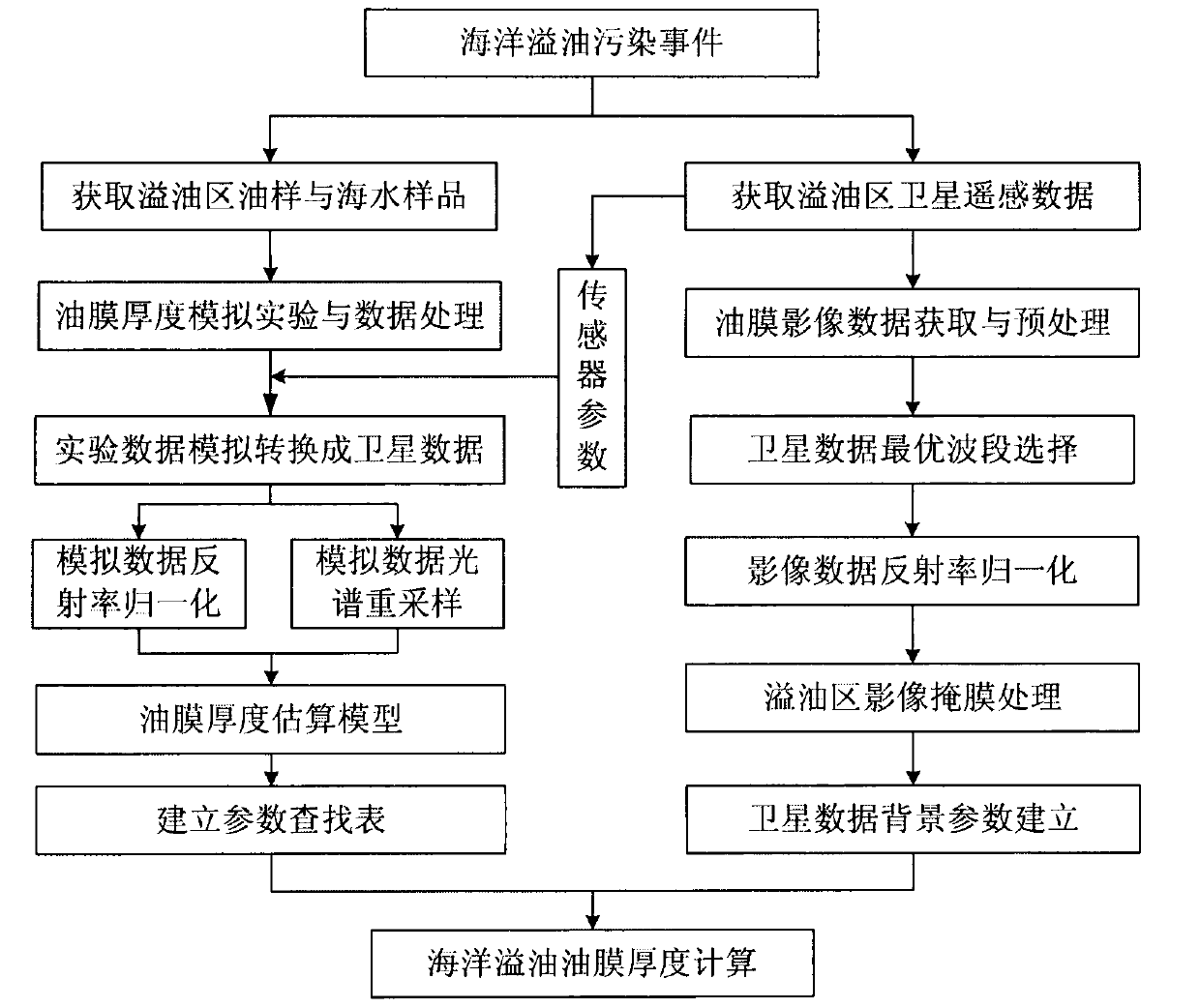
Ocean spilt oil film thickness hyperspectral remote sensing estimation method based on parameter lookup table
InactiveCN102997856AMeet the needs of emergency monitoringEstimation is objective and efficientUsing optical meansPerformance indexKnowledge Field
The invention relates to an ocean spilt oil film thickness hyperspectral remote sensing estimation method based on a parameter lookup table and belongs to the field of ocean environment monitoring research. The method includes the steps of obtaining and pre-processing standard oil film thickness continuous change hyperspectral data by designing a simulation experiment; obtaining and pre-processing ocean spilt oil satellite remote sensing data; resampling a standard oil film spectrum based on a satellite sensor performance index; normalizing spectral reflectivity; building an oil film thickness optical calculating model; building an attenuation parameter lookup table; normalizing the reflectivity of satellite data and conducting mask treatment; inquiring and building an optimal wave band of the satellite data and relevant parameters; and calculating the oil film thickness in the satellite data through the parameter lookup table and the optical model. Compared with a traditional observation means, by means of the ocean spilt oil film thickness hyperspectral remote sensing estimation method, field workload is less, the thickness of the spilt oil film can be quantized, the thickness of an oil film in a spilt oil area can be calculated without entering an ocean spilt oil pollution area, and requirements of ocean split oil emergency monitoring and evaluation can be met.
Owner:NANJING UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com