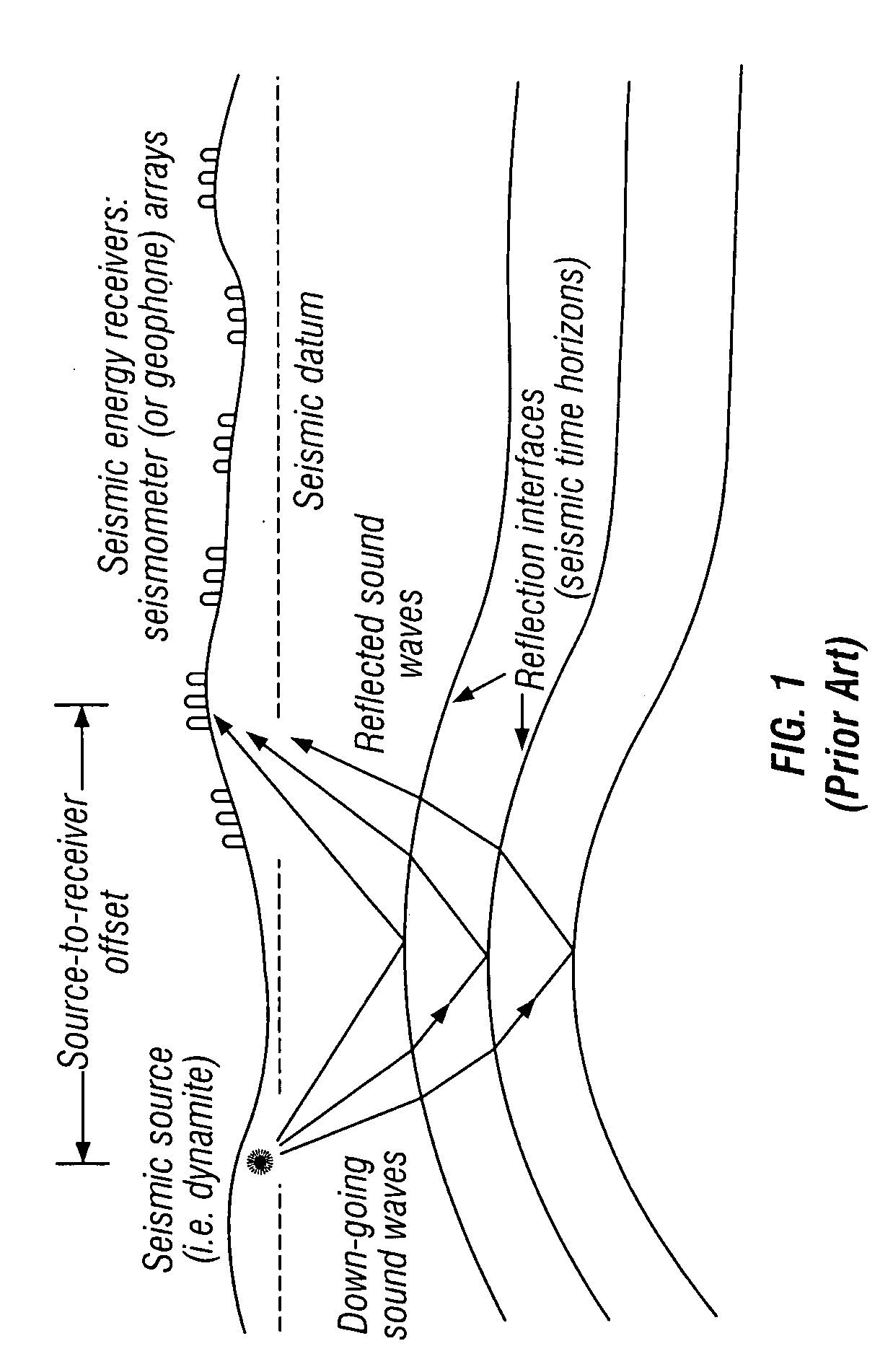
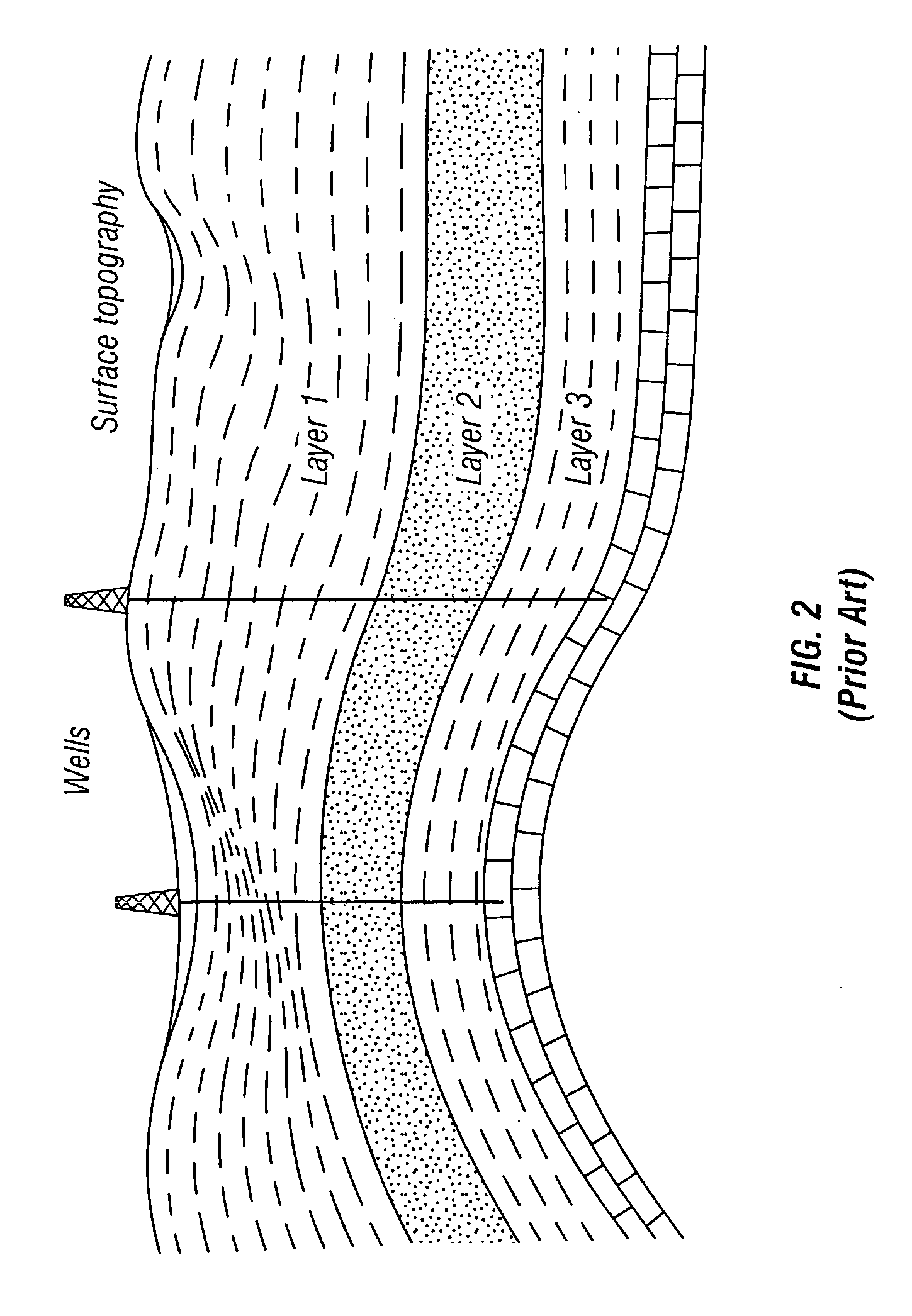
Patents
Literature
499 results about "Geological formation" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
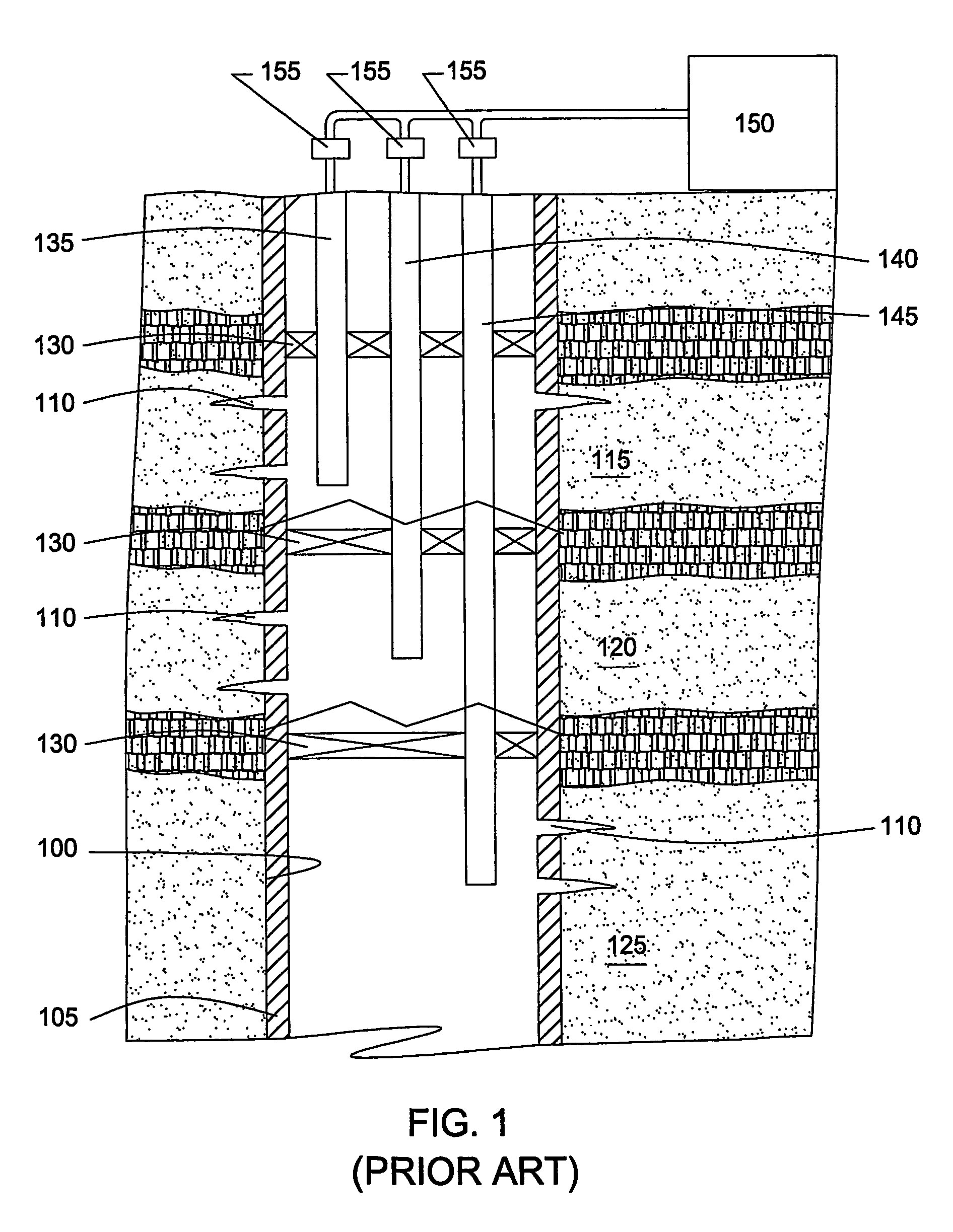
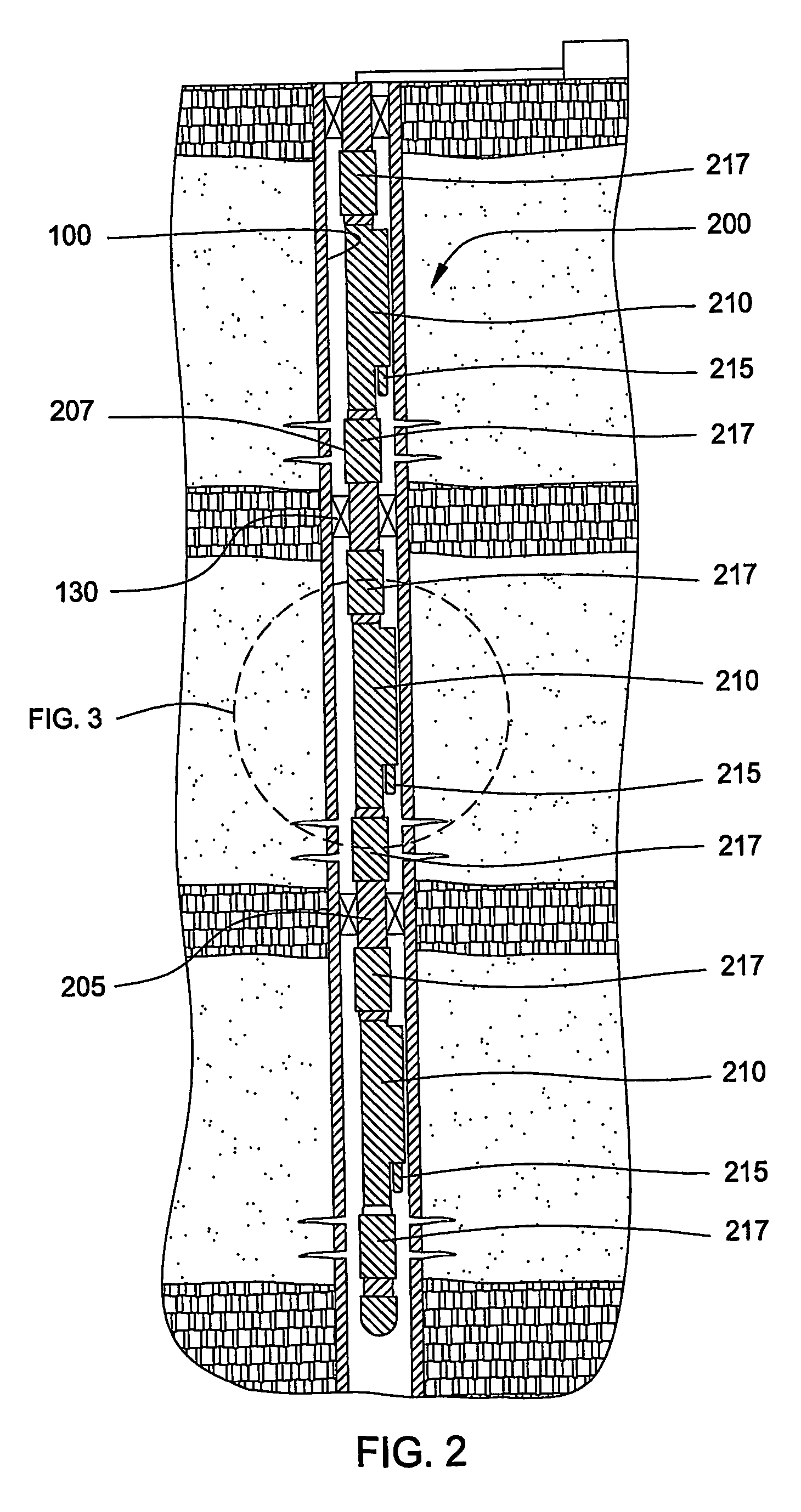
A formation or geological formation is the fundamental unit of lithostratigraphy. A formation consists of a certain amount of rock strata that have a comparable lithology, facies or other similar properties. Formations are not defined by the thickness of their rock strata; therefore the thickness of different formations can vary widely.
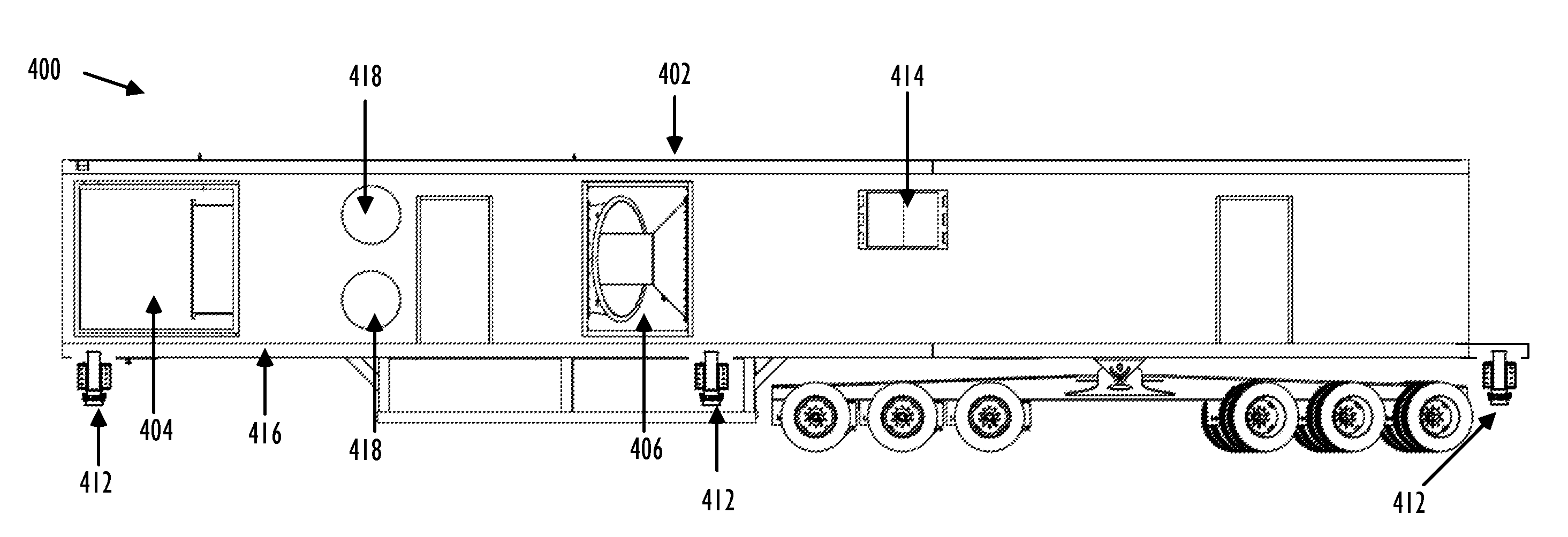
Mobile fracturing pump transport for hydraulic fracturing of subsurface geological formations
ActiveUS20160369609A1Well formedMechanical actuated clutchesGas turbine plantsCouplingFracturing fluid
Providing pressurized fracturing fluid with a fracturing pump transport comprising a first fracturing pump and a second fracturing pump that are coupled on opposite sides of a dual shaft electric motor. A first drive line assembly comprising a first engagement coupling that allows for selective engagement and / or disengagement of the first fracturing pump with the dual shaft electric motor. A second drive line assembly comprising a second engagement coupling that allows for selective engagement and / or disengagement of the second fracturing pump with the dual shaft electric motor. The fracturing pump transport also comprising an engagement panel that allows for selective engagement or disengagement at the first engagement coupling based on receiving a remote command.
Owner:TYPHON TECH SOLUTIONS (U S) LLC
Multi-resolution graph-based clustering
InactiveUS6295504B1Electric/magnetic detection for well-loggingCharacter and pattern recognitionReference sampleData set
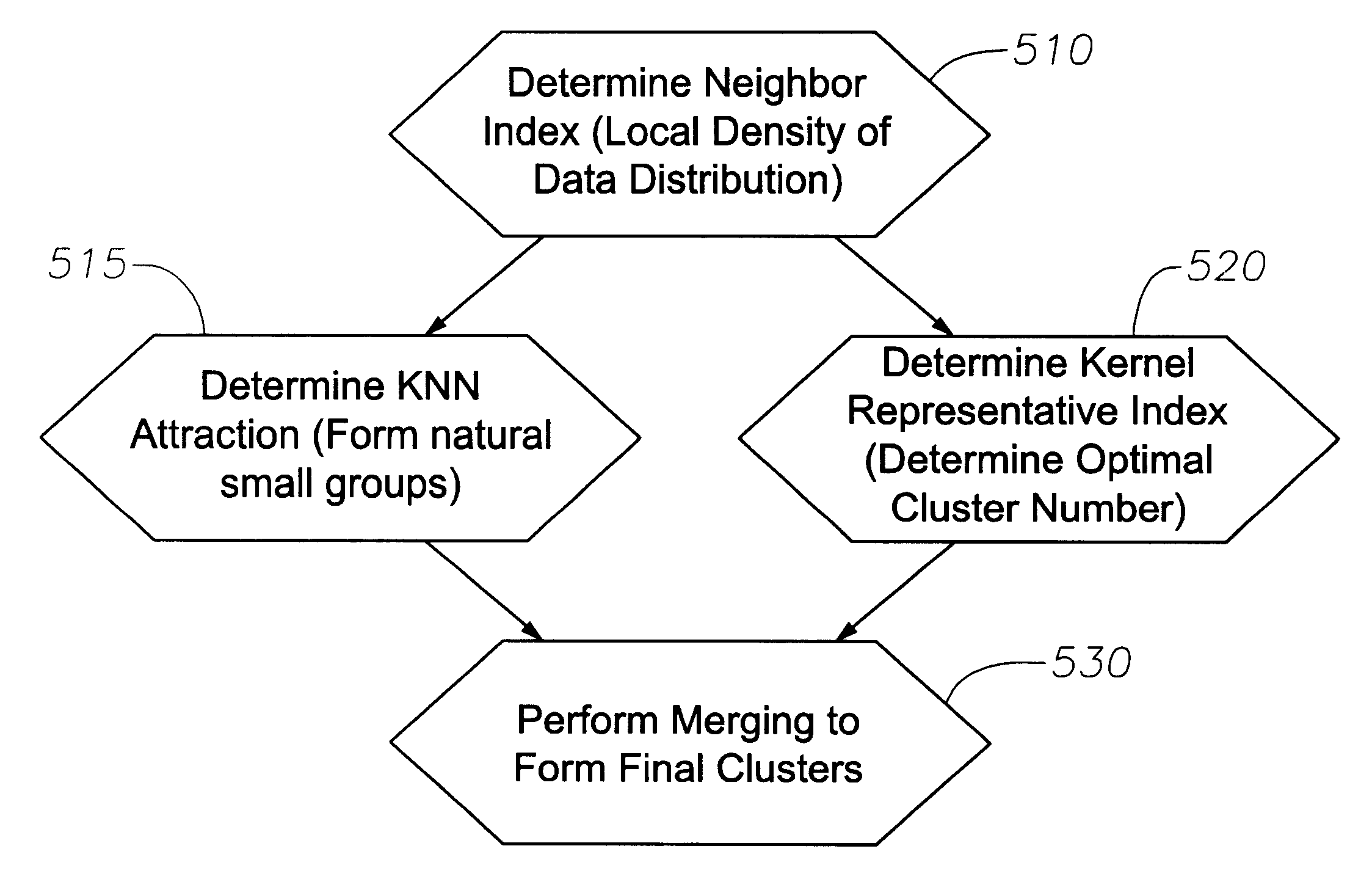
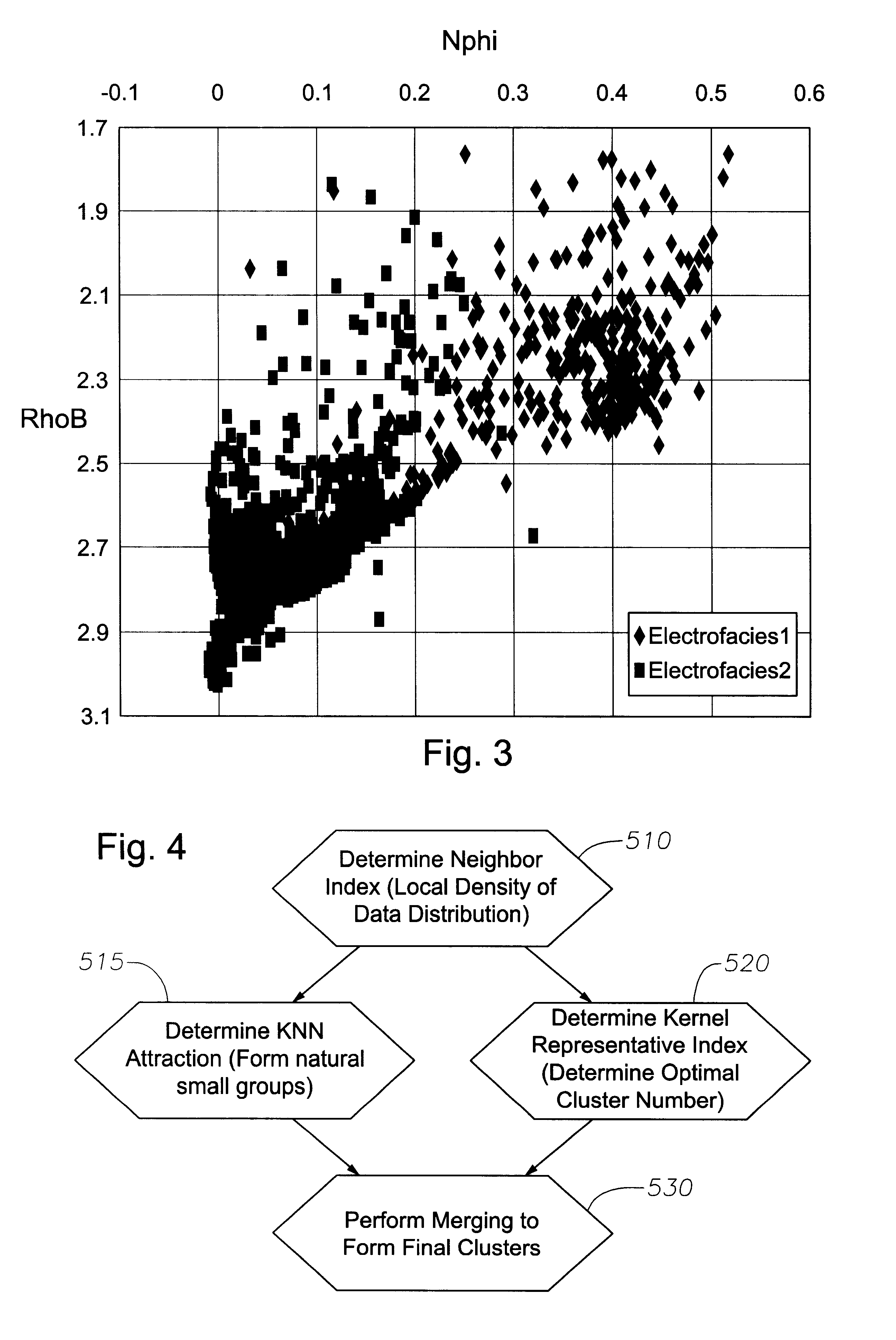
An apparatus and method for obtaining facies of geological formations for identifying mineral deposits is disclosed. Logging instruments are moved in a bore hole to produce log measurements at successive levels of the bore hole. The set of measurements at each such level of the bore hole interval is associated with reference sample points within a multidimensional space. The multidimensional scatter of sample points thus obtained is analyzed to determine a set of characteristic modes. The sample points associated with characteristic modes are grouped to identify clusters. A facies is designated for each of the clusters and a graphic representation of the succession of facies as a function of the depth is thus obtained. To identify the clusters, a "neighboring index" of each log measurement point in the data set is calculated. Next, small natural groups of points are formed based on the use of the neighboring index to determine a K-Nearest-Neighbor (KNN) attraction for each point. Independently of the natural group formation, an optimal number of clusters is calculated based on a Kernel Representative Index (KRI) and based on a user-specified resolution. Lastly, based on the data calculated from the prior steps, final clusters are formed by merging the smaller clusters.
Owner:HALLIBURTON ENERGY SERVICES INC
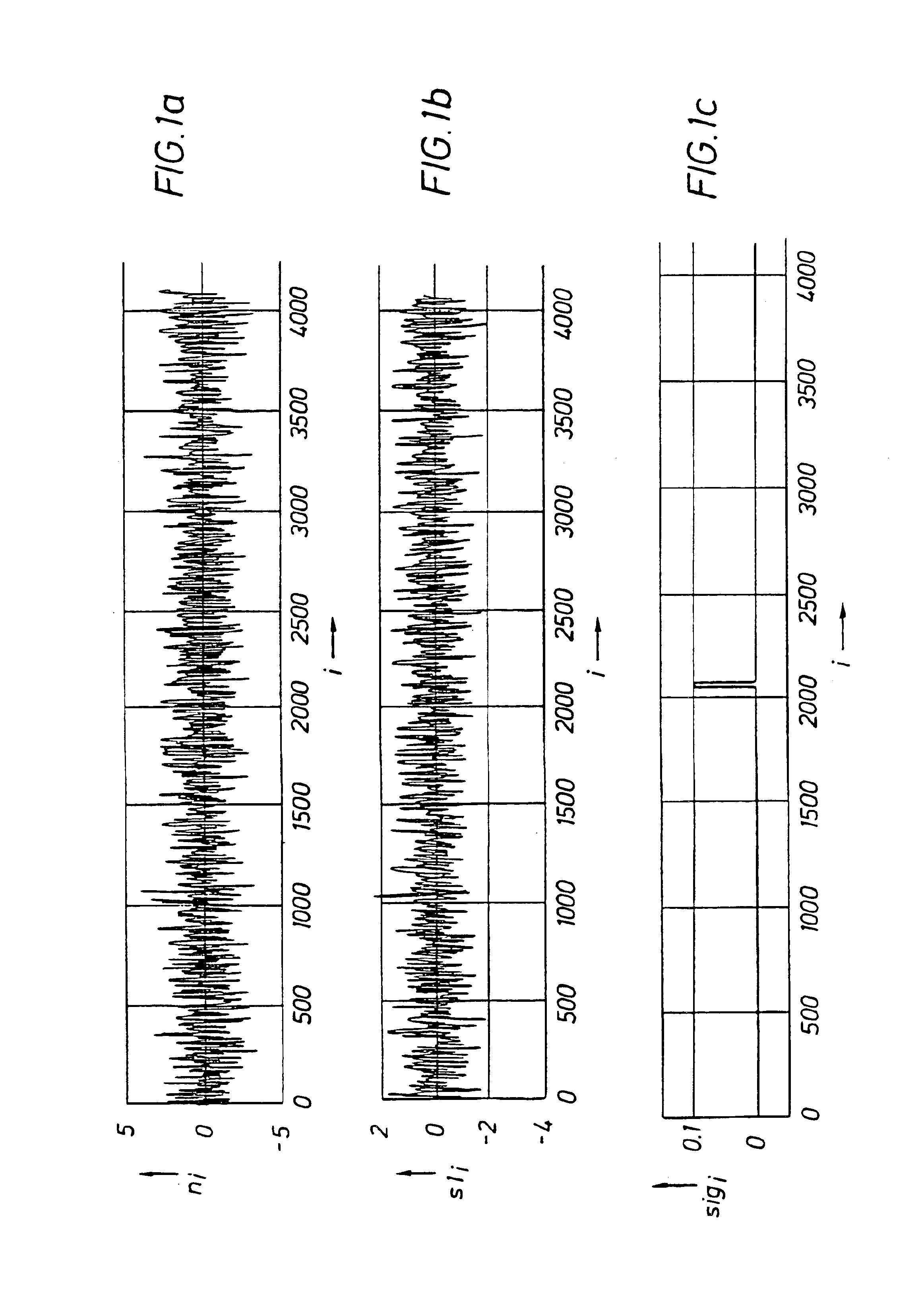
Method and apparatus for cancellation of unwanted signals in MWD acoustic tools
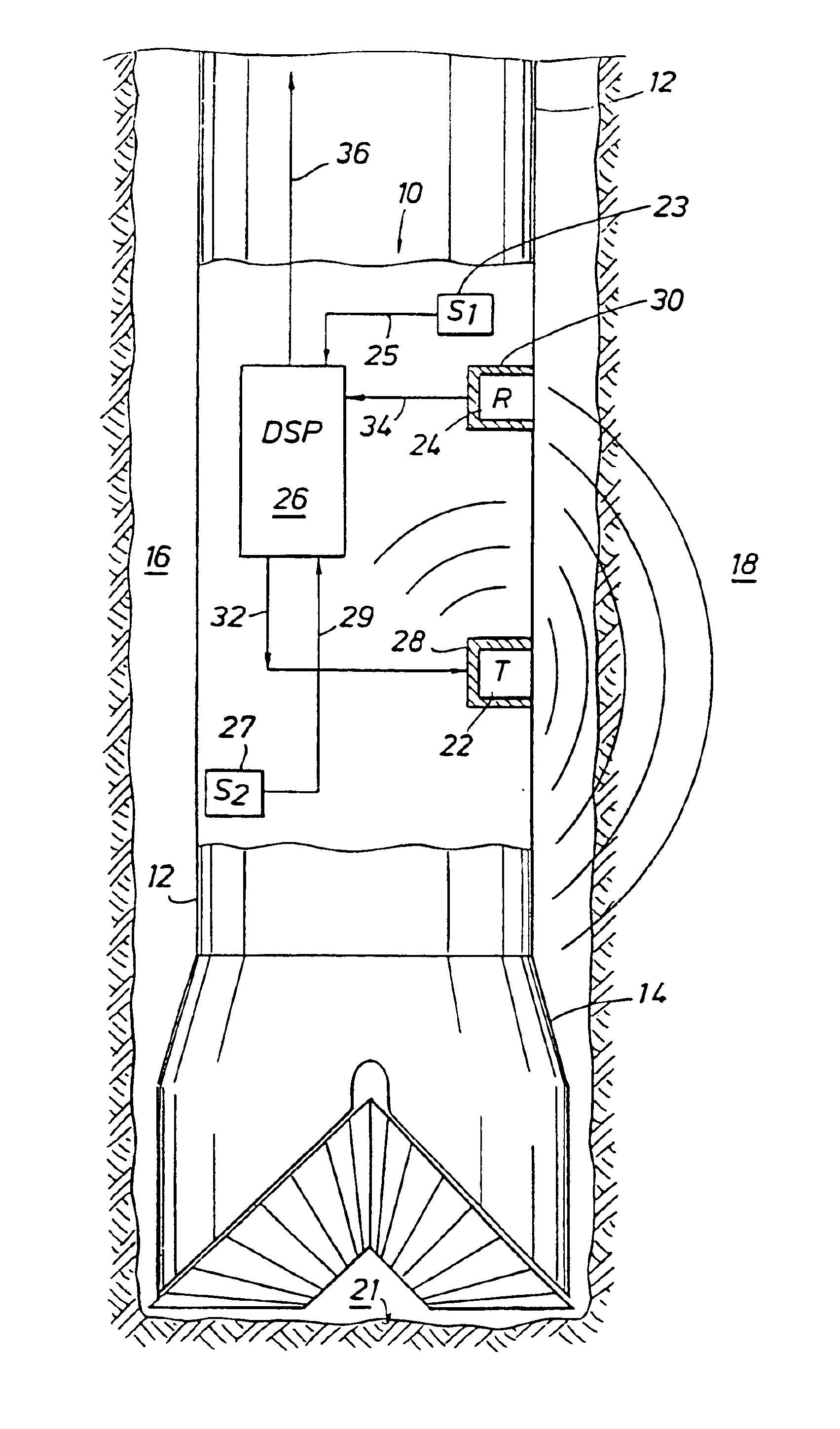
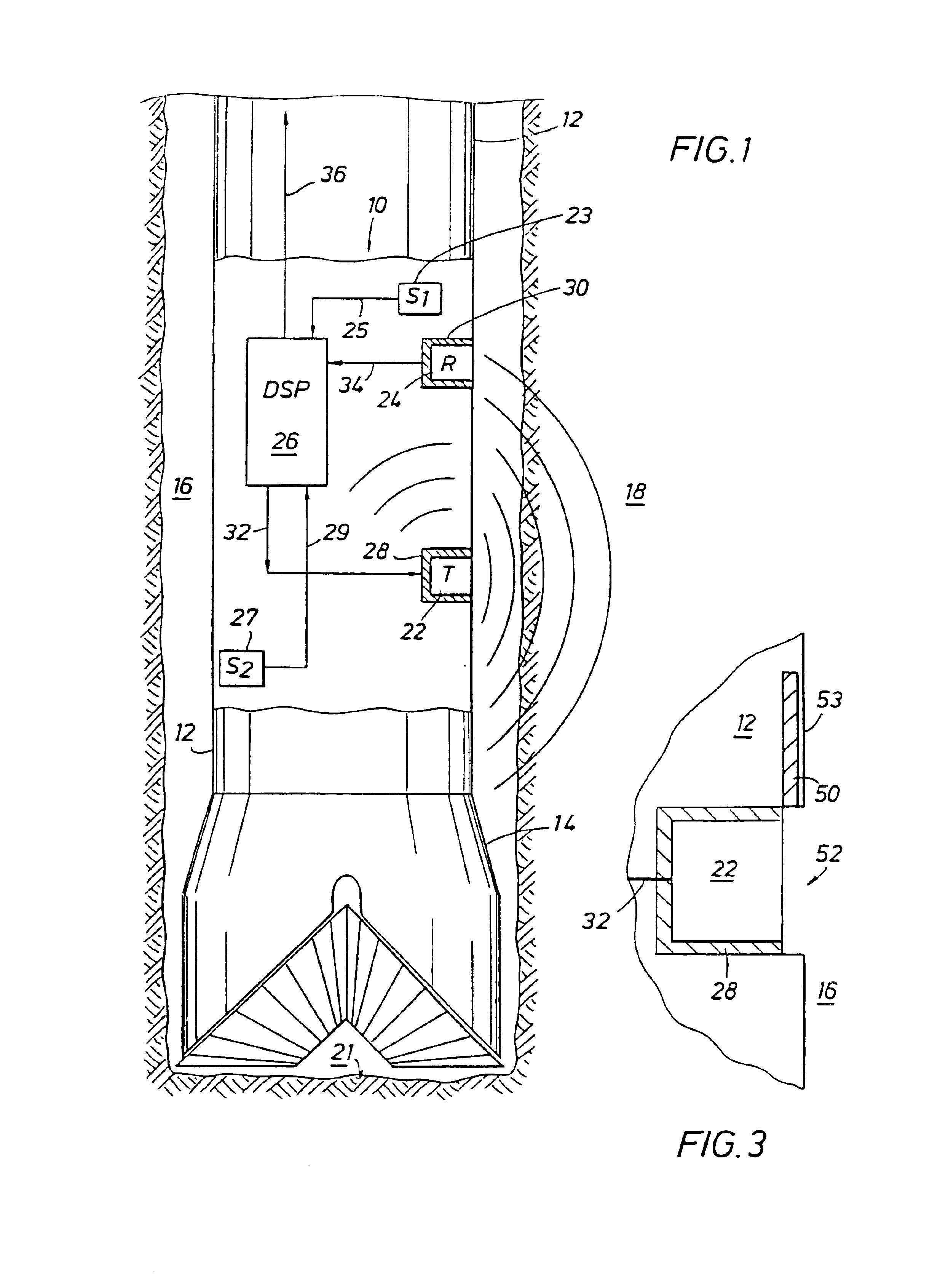
An apparatus (10) and method are disclosed for eliminating a noise signal from at least one source during an acoustic measurement of a subsurface geological formation or borehole. The apparatus (10) includes a longitudinal body for positioning in the borehole and a transmitter (22) supported by the body for transmitting acoustic signals into the formation and borehole. A sensor (23), substantially isolated within the body, is used to detect one or more noise signals and a receiver (24) is carried by the body for receiving acoustic signals traversing the formation and borehole, and for receiving one or more noise signals. A processor (26) is connected to the sensor (23) and receiver (24) for processing the acoustic signals and noise signals coupled from the receiver (24) and the noise signal coupled from the sensor (23) into a preferred formation or borehole signal by determining the noise signal received at the receiver (24) using the noise signal received in the sensor (23) and a propagation factor for the noise signal between the sensor (23) and receiver (24). The determined noise signal is used to identify and eliminate the noise signals from the acoustic signals traversing the formation and borehole.
Owner:HALLIBURTON ENERGY SERVICES INC
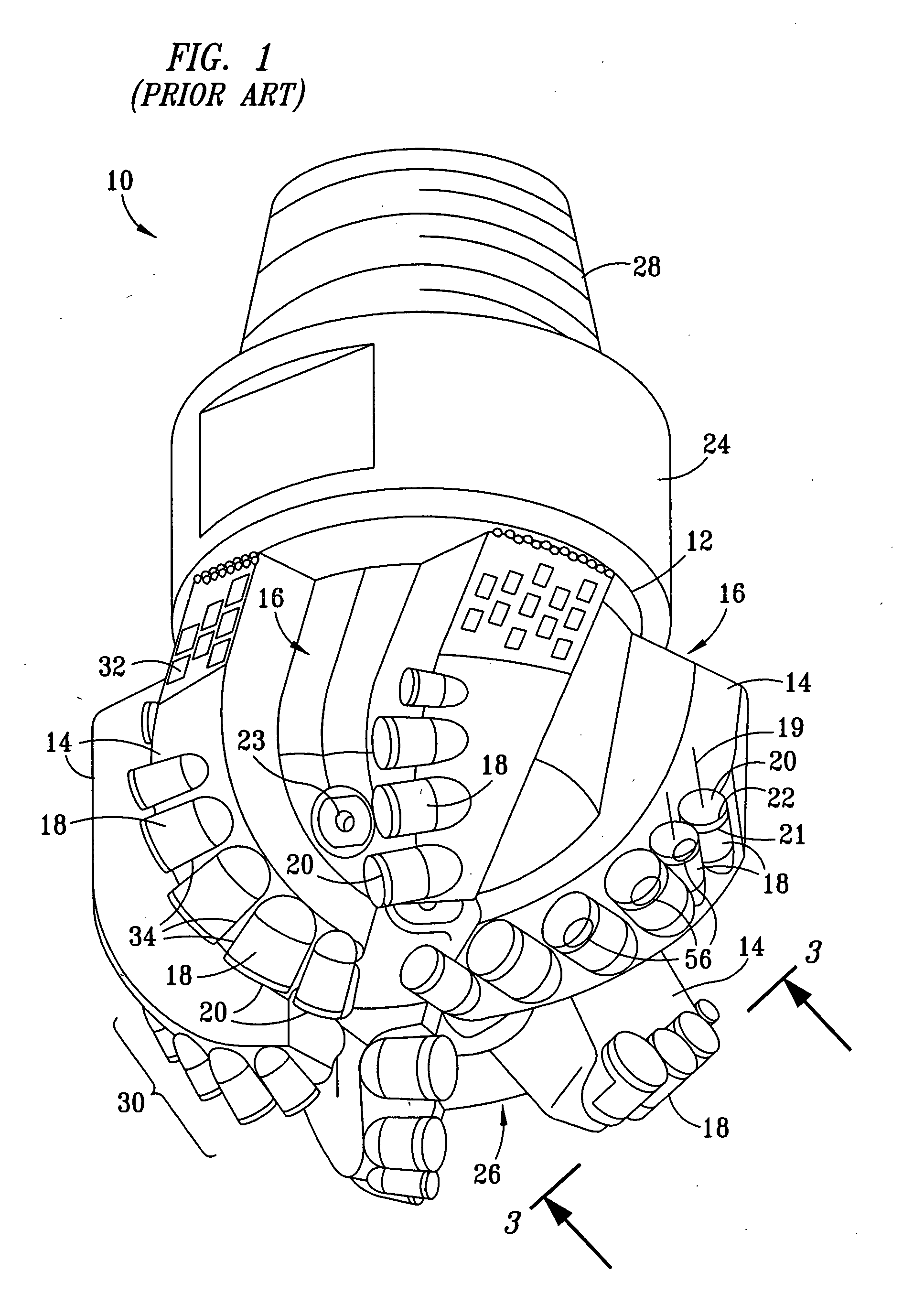
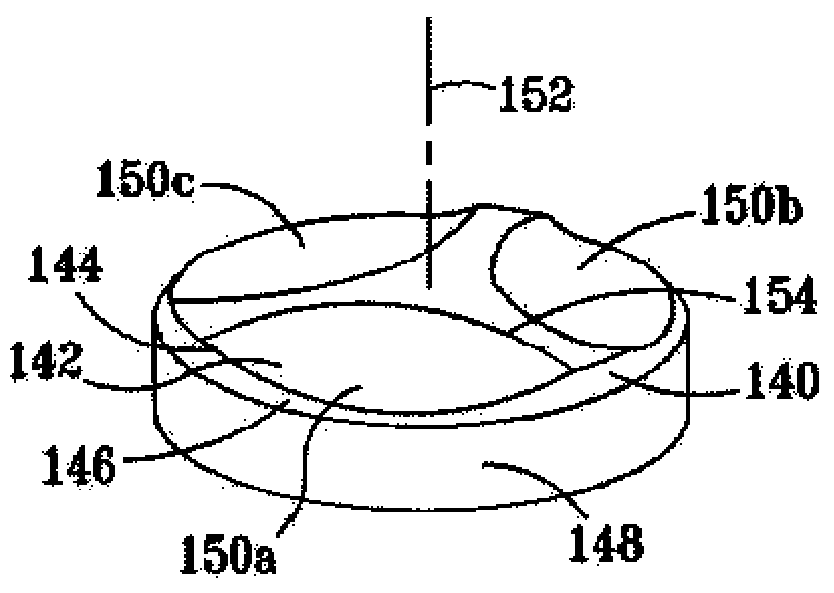
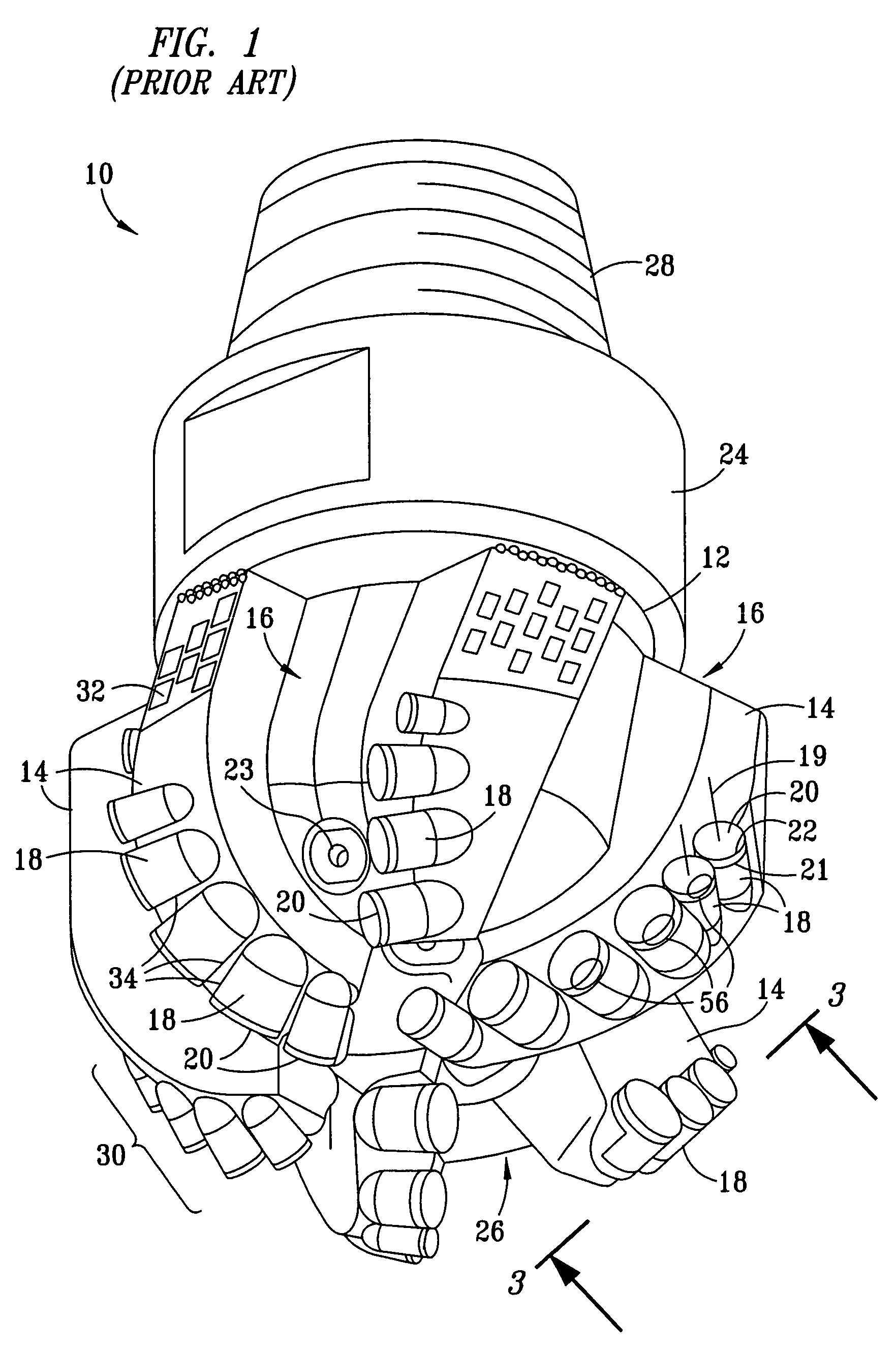
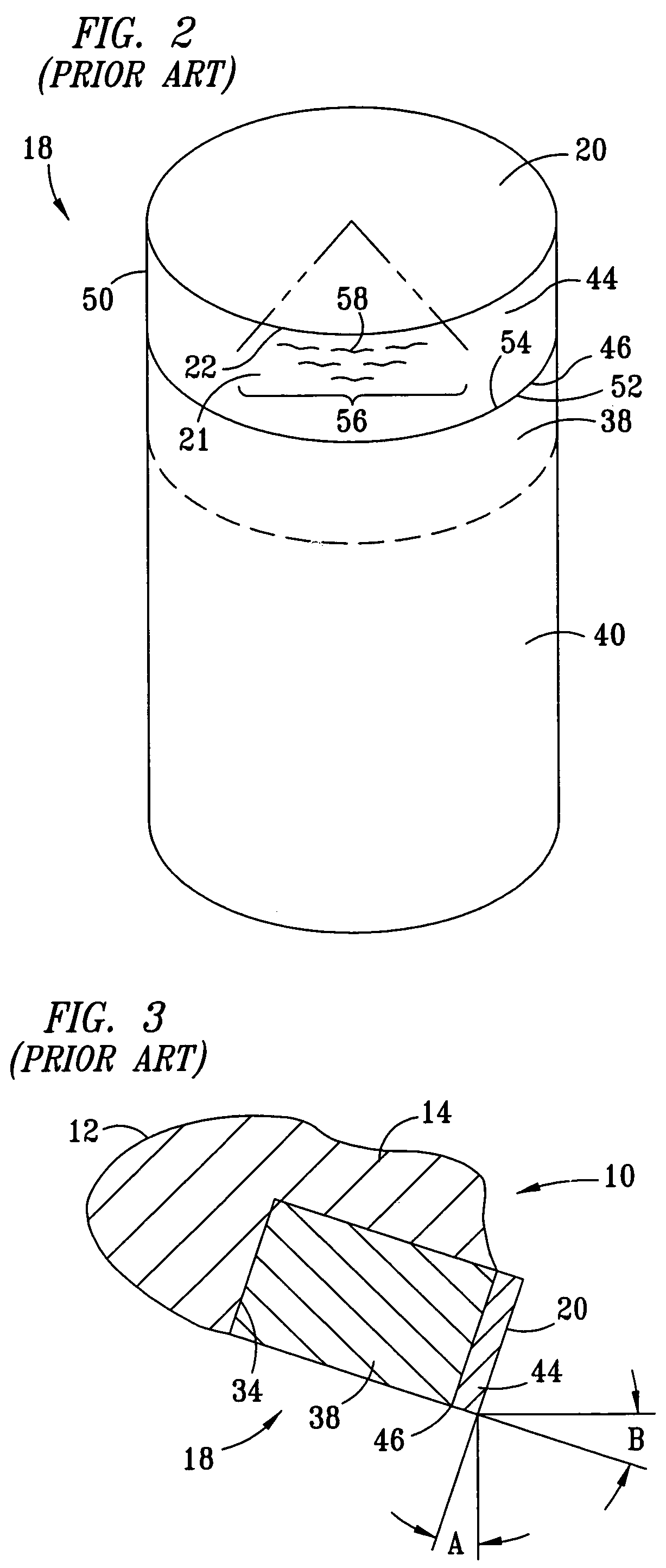
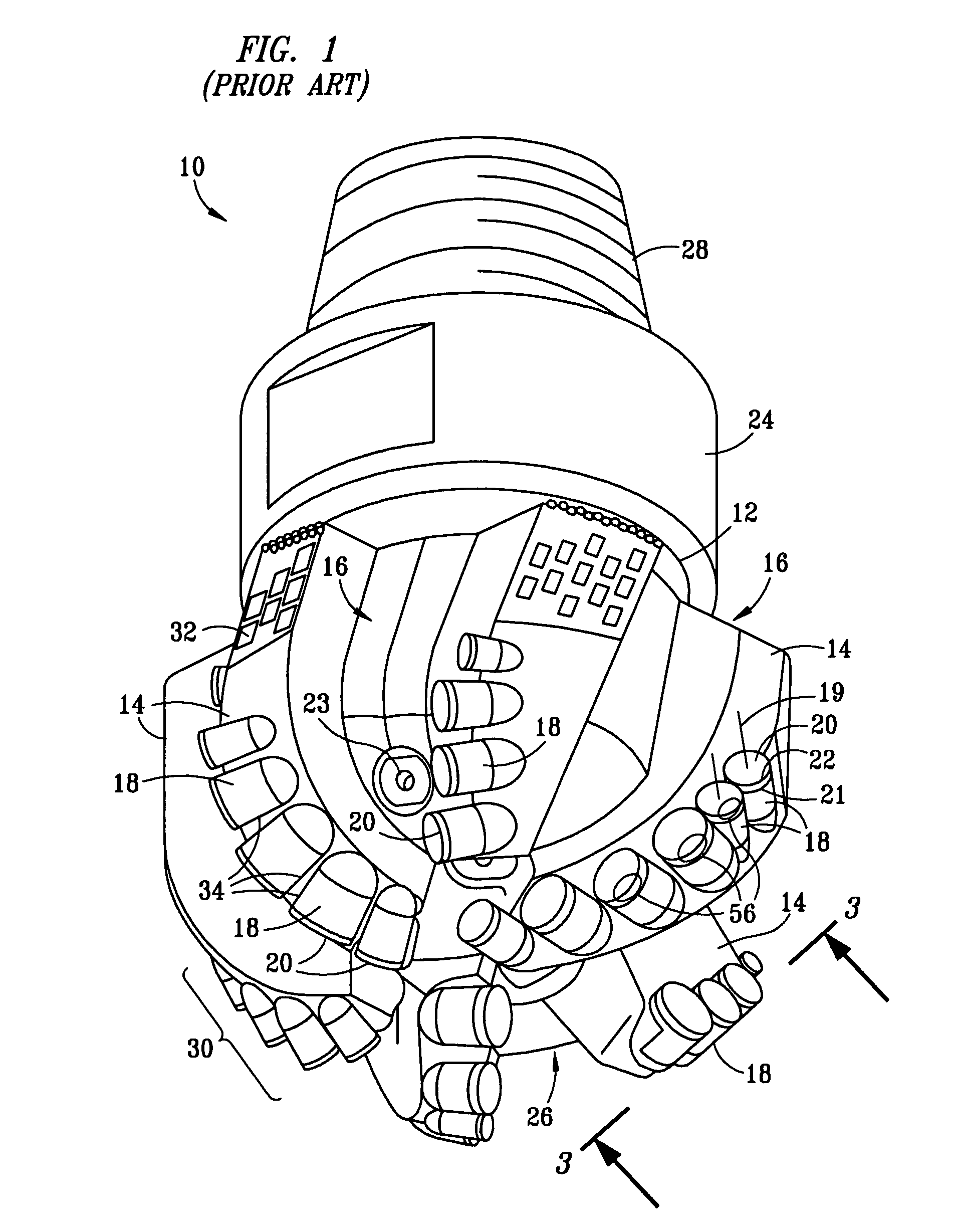
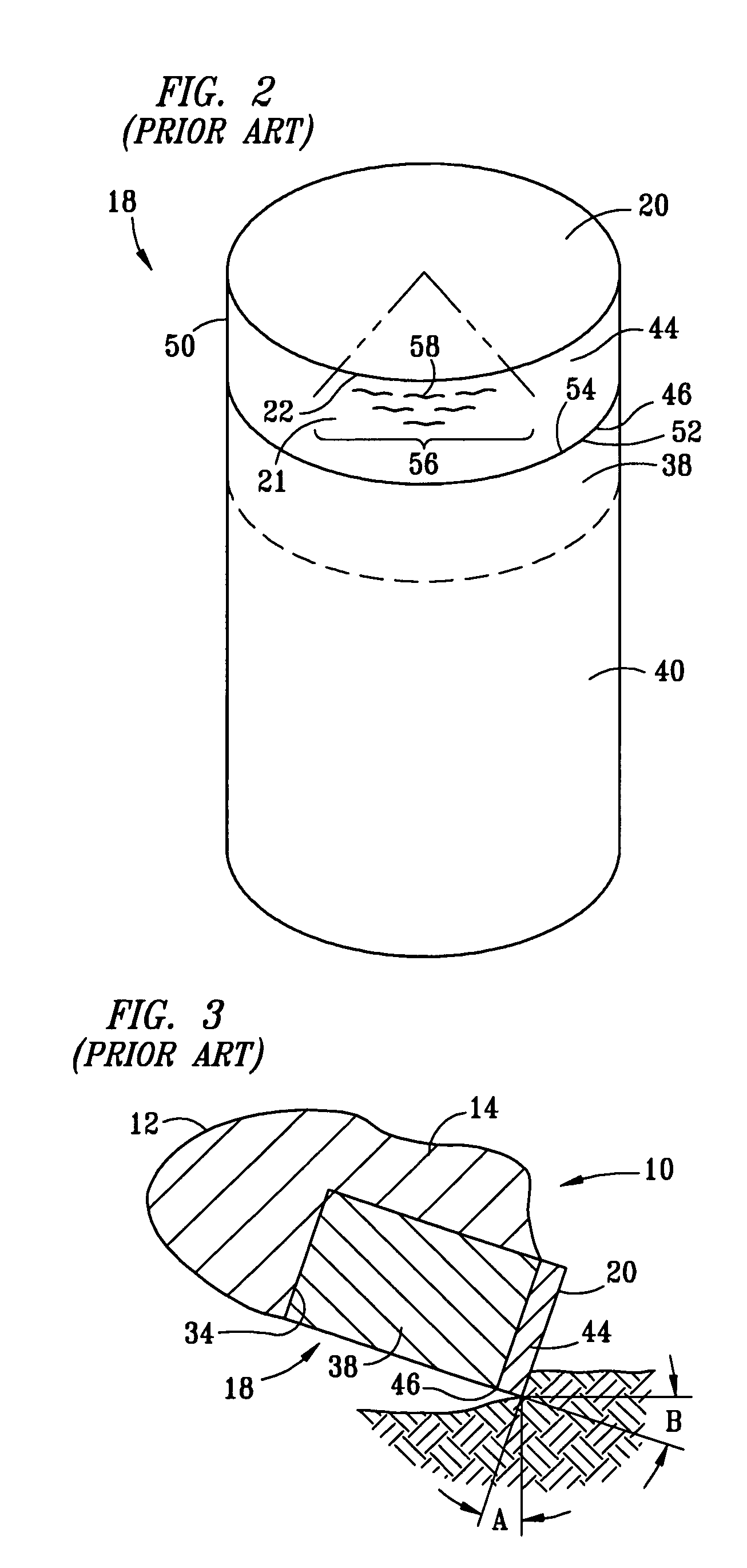
Cutter having shaped working surface with varying edge chamber
ActiveUS20050247492A1Reduce certain adverse consequenceDrill bitsConstructionsEngineeringMechanical engineering
Owner:SMITH INT INC
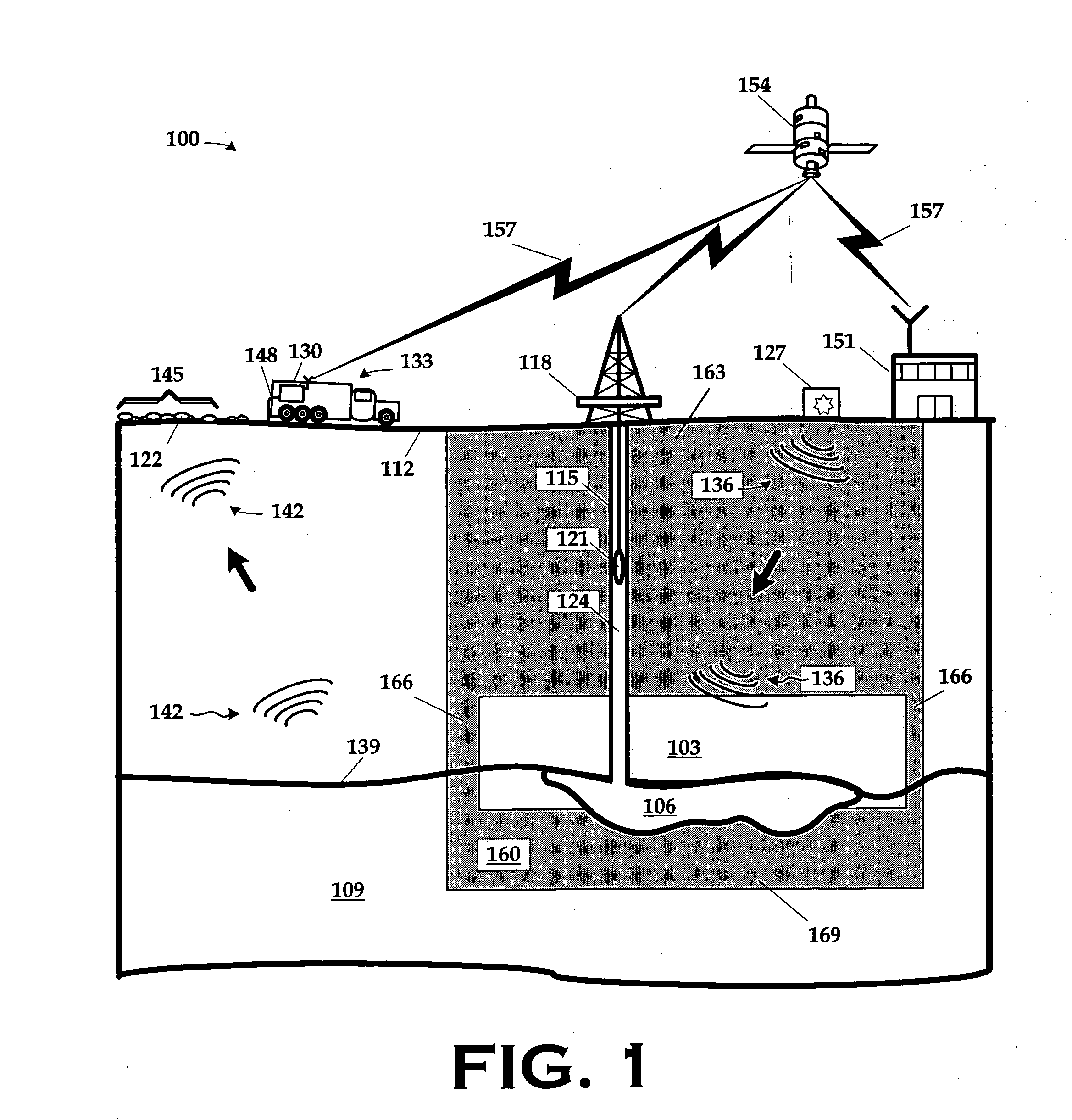
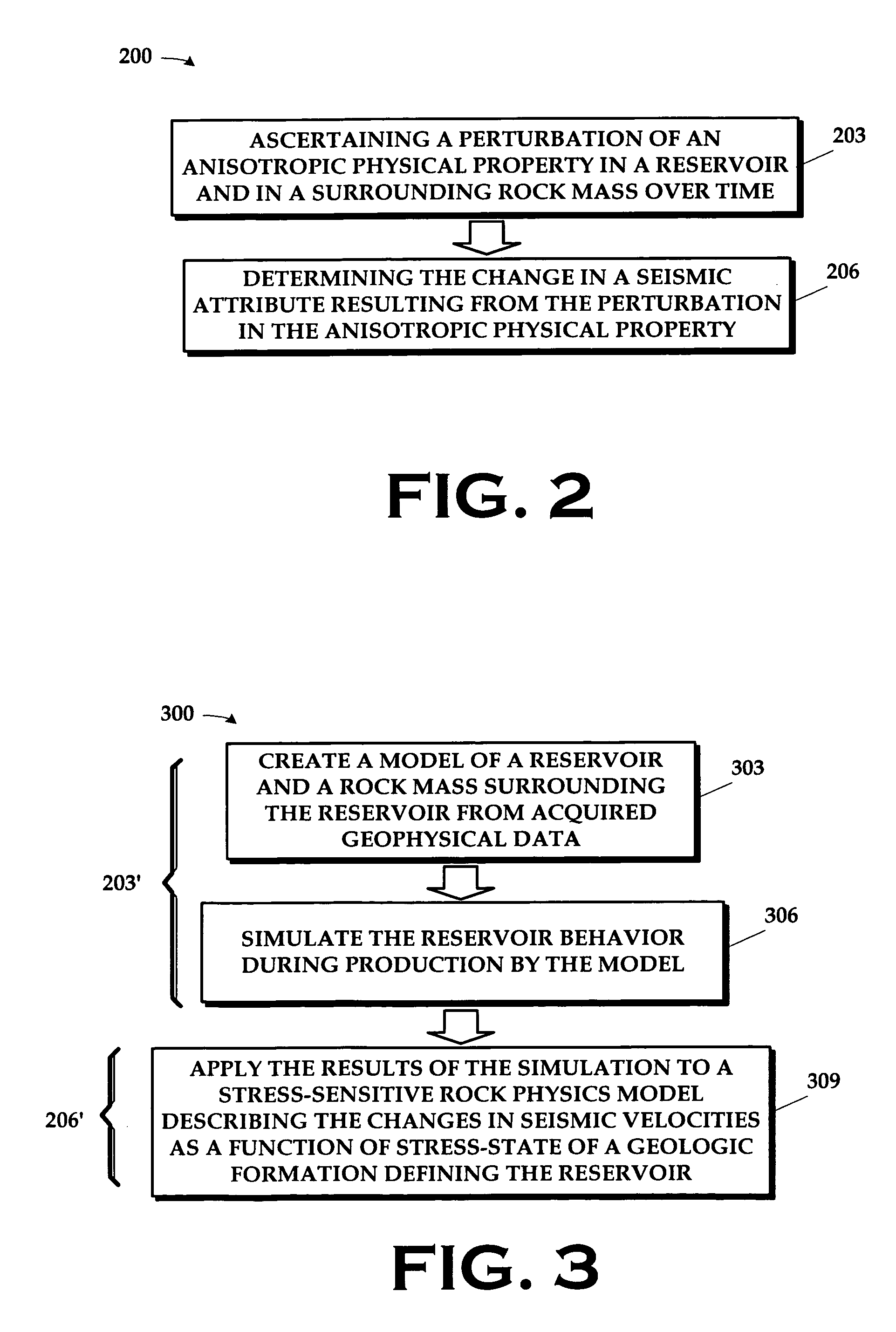
Determination of anisotropic physical characteristics in and around reservoirs
InactiveUS20060153005A1Carbon-dioxide storageSeismic signal processingSeismic attributeStressed state
A method and apparatus for use in estimating stress fields in a geological formation are disclosed. The method includes ascertaining a perturbation of stress in the triaxial stress state in a reservoir and in a surrounding rock mass over time; and determining the change in a seismic attribute resulting from the perturbation in the stress. The apparatus includes a program storage medium encoded with instructions that, when executed by a computing device, perform such a method or a computing system programmed to perform such a method.
Owner:WESTERNGECO LLC
Imaging near-borehole structure using directional acoustic-wave measurement
Directional acoustic measurements made in the borehole are used for imaging a near-borehole geological formation structure and determination of its orientation. Four-component cross-dipole data set measured in a deviated borehole in combination with the directionality of the compressional waves in the dipole data give the orientation of bed boundaries crossing the borehole. The low-frequency content (2˜3 kHz) of the data allows for imaging the radial extent of the formation structure up to 15 m, greatly enhancing the penetration depth as compared to that obtained using conventional monopole compressional-wave data. A combination monopole / dipole arrangement of sources and receivers may also be used for imaging of bed boundaries.
Owner:BAKER HUGHES INC
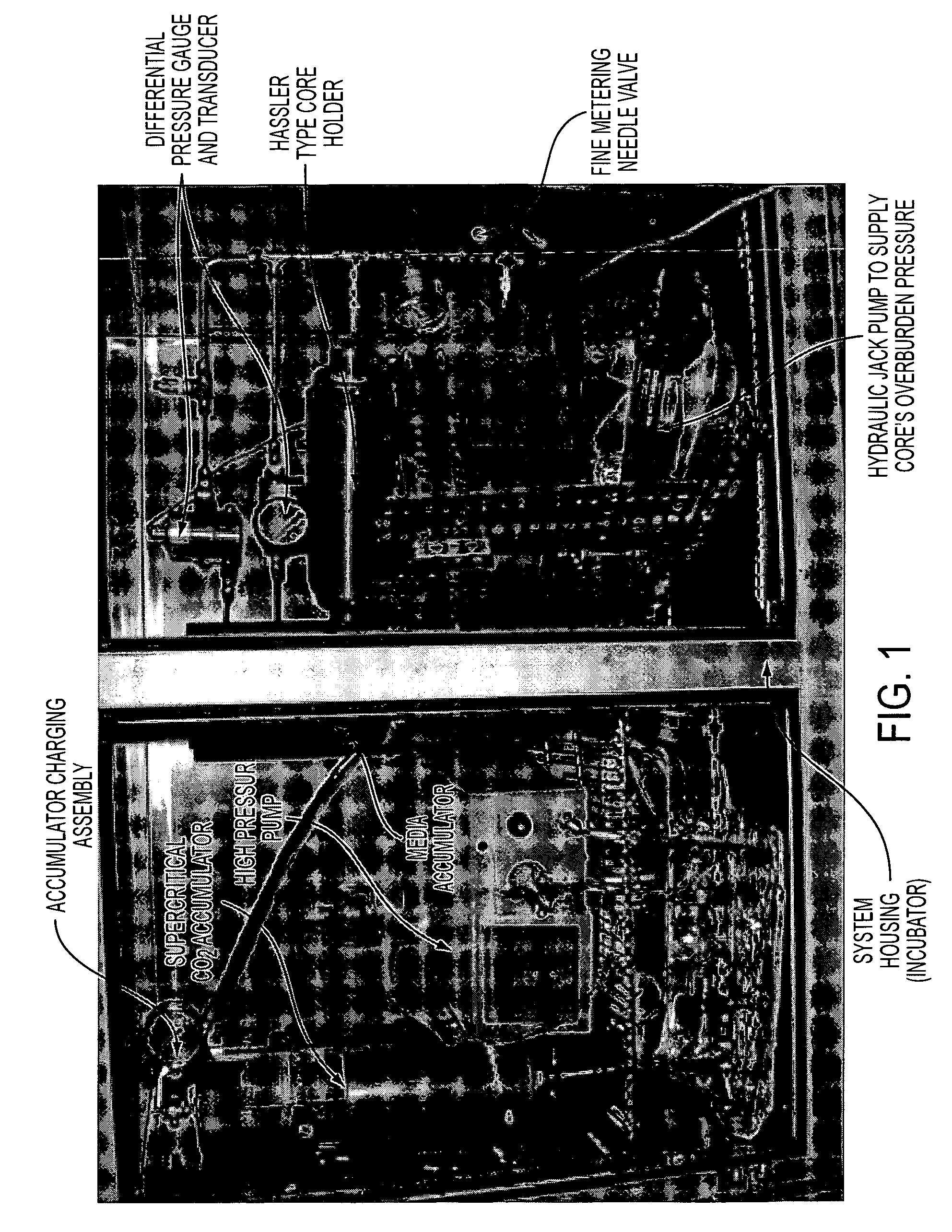
Method of detecting leakage from geologic formations used to sequester CO2
InactiveUS7704746B1Low costLow detection limitDetection of fluid at leakage pointConstructionsGas phaseLeak detection
The invention provides methods for the measurement of carbon dioxide leakage from sequestration reservoirs. Tracer moieties are injected along with carbon dioxide into geological formations. Leakage is monitored by gas chromatographic analyses of absorbents. The invention also provides a process for the early leak detection of possible carbon dioxide leakage from sequestration reservoirs by measuring methane (CH4), ethane (C2H6), propane (C3H8), and / or radon (Rn) leakage rates from the reservoirs. The invention further provides a method for branding sequestered carbon dioxide using perfluorcarbon tracers (PFTs) to show ownership.
Owner:THE UNITED STATES AS REPRESENTED BY THE DEPARTMENT OF ENERGY
System, apparatus, and method for conducting electromagnetic induction surveys
InactiveUS7030617B2Electric/magnetic detection for well-loggingDetection using electromagnetic wavesAttenuation coefficientProximate
Owner:SCHLUMBERGER TECH CORP
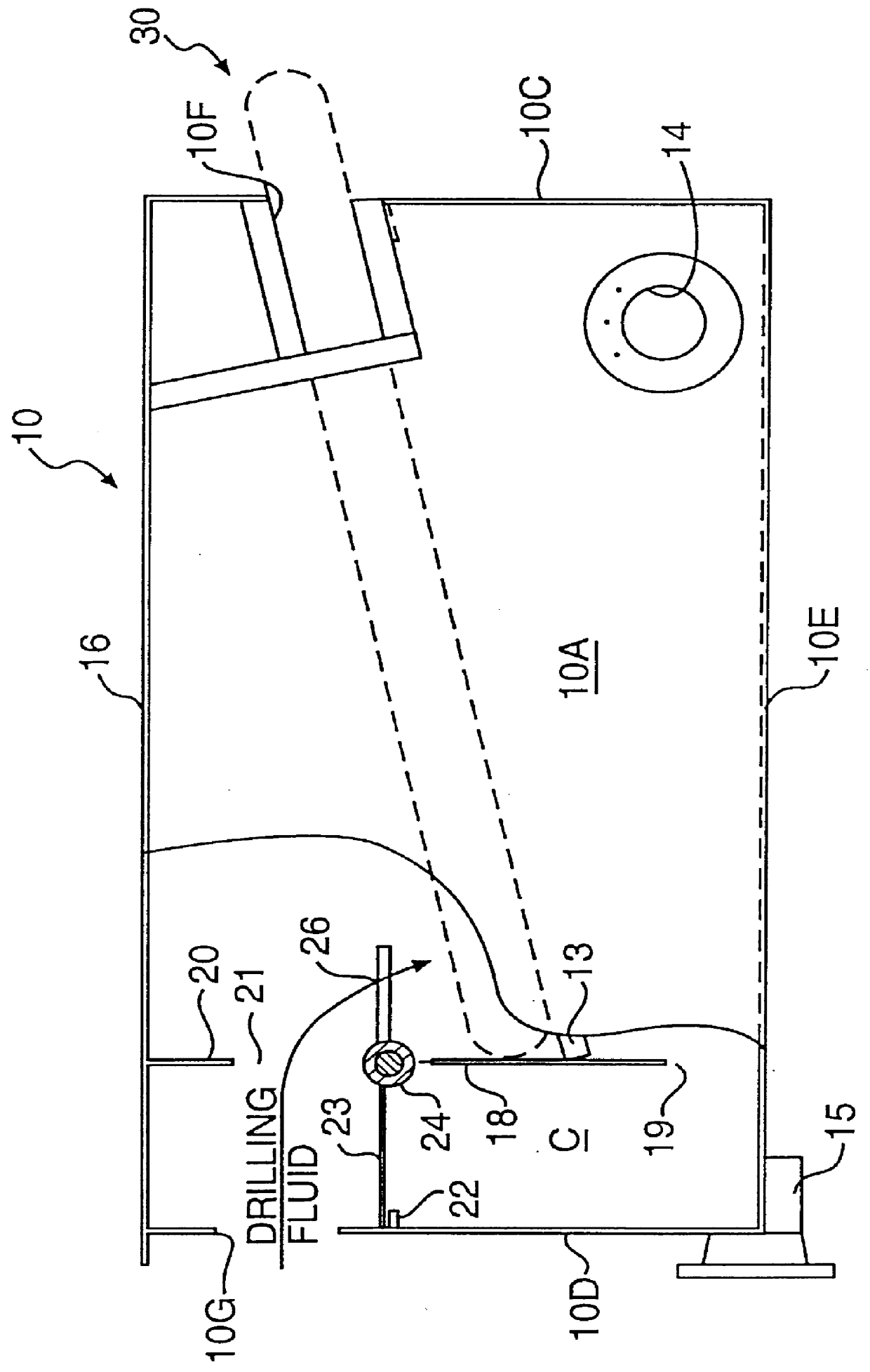
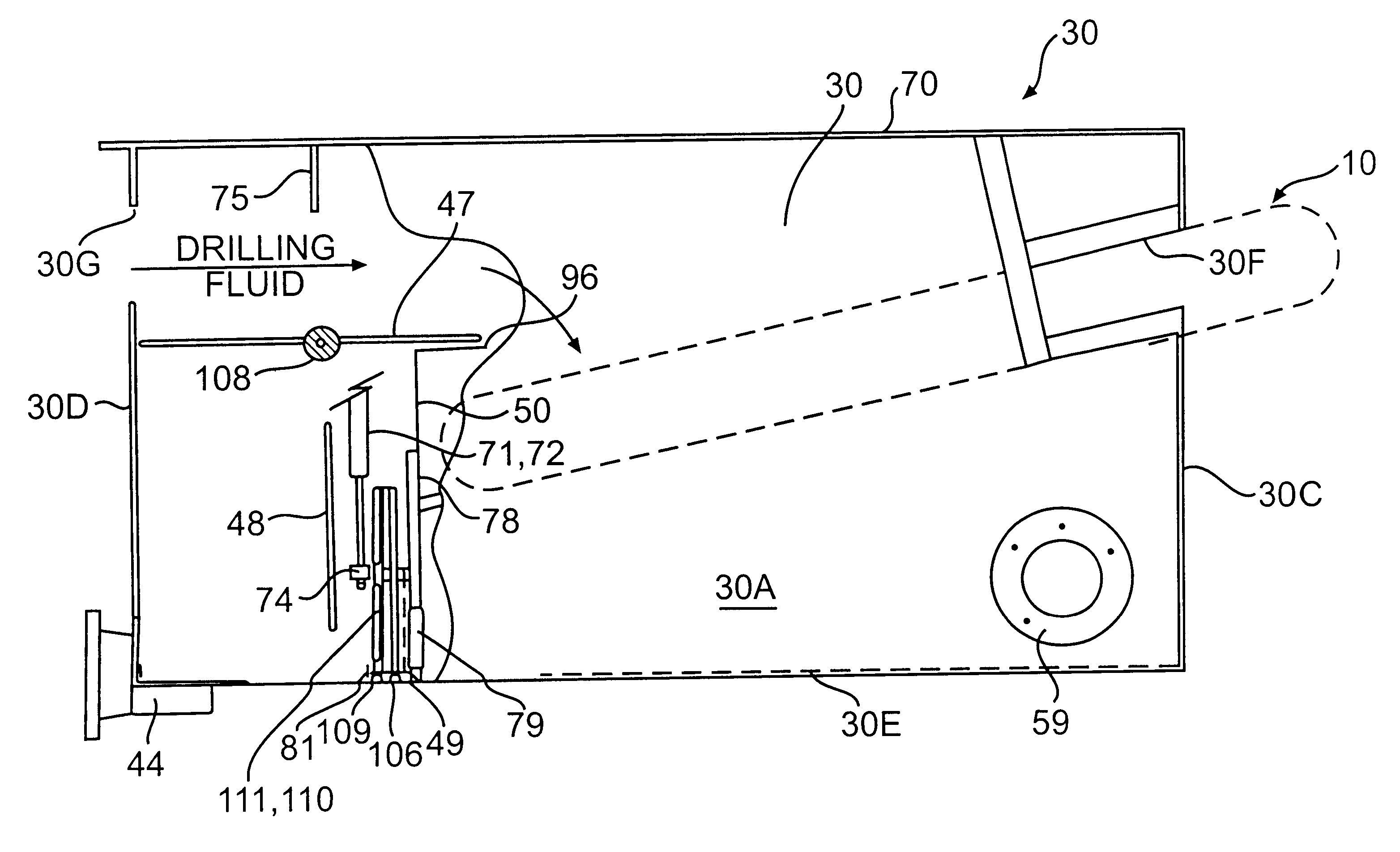
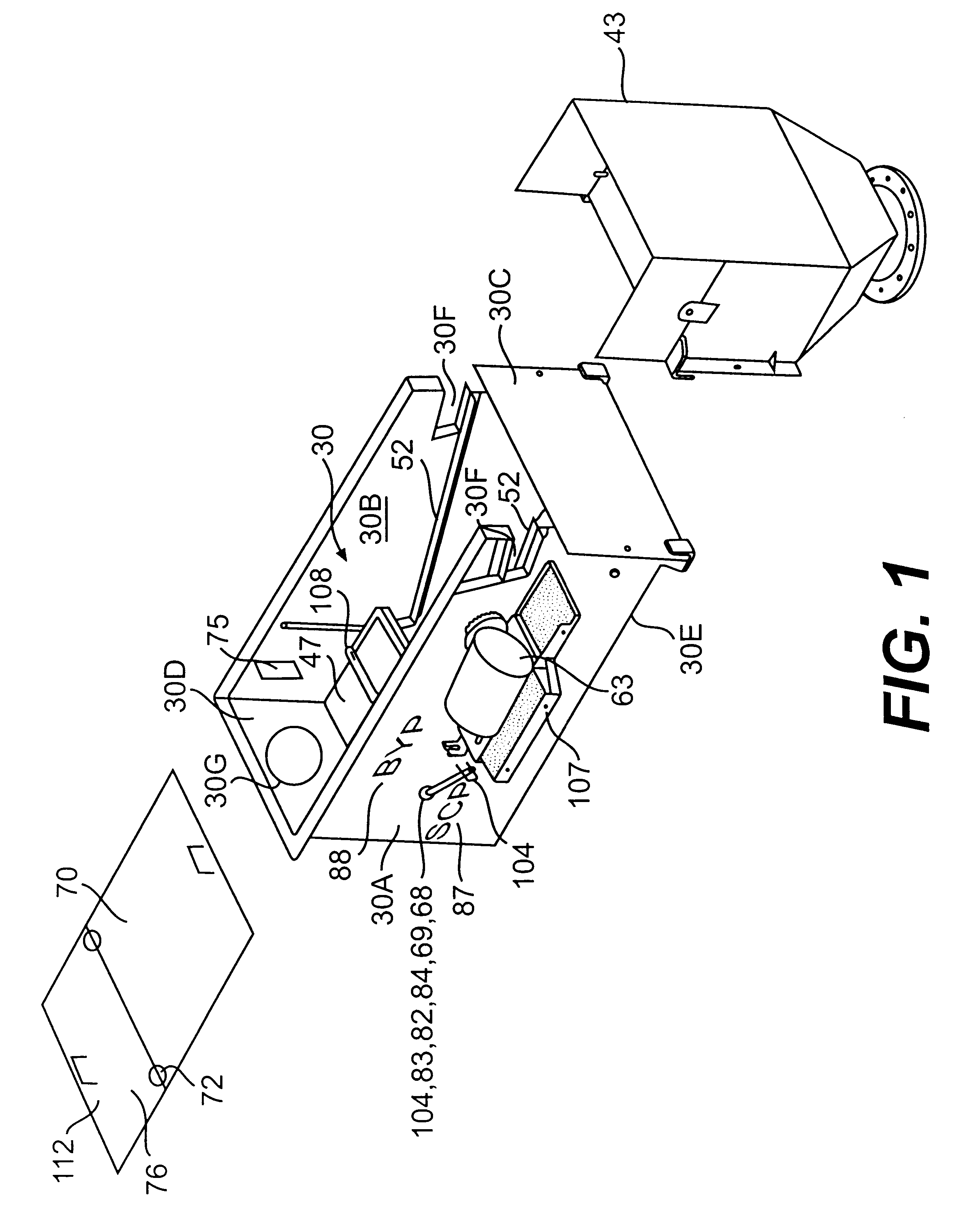
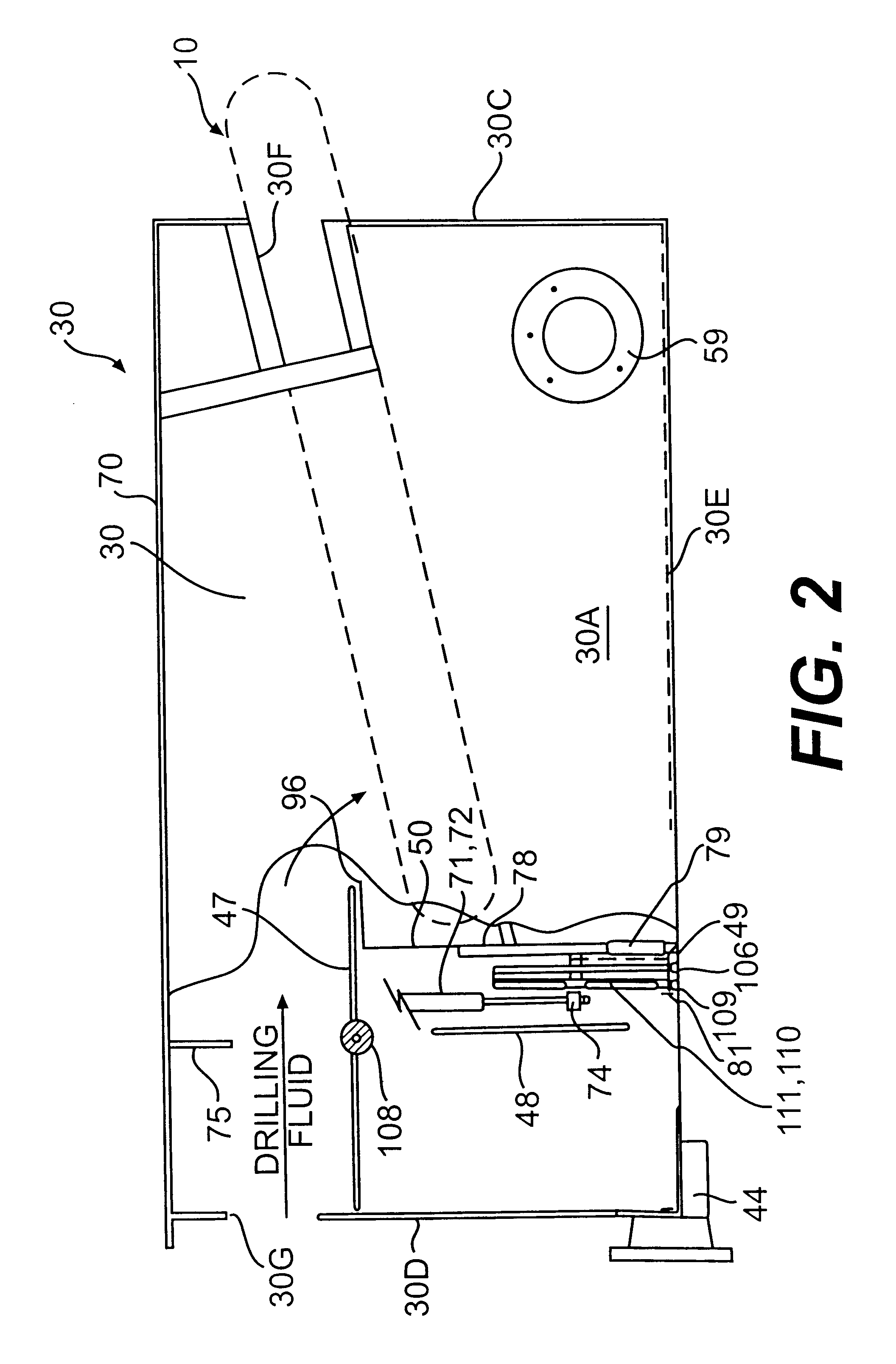
Bypass diverter box for drilling mud separation unit
A bypass diverter box disposed upstream from conventional solids control equipment of a mud system of a drilling rig contains a drilling mud separation unit having a continuous-loop scalper screen that is driven in a continuous loop to separate, convey and discharge large amounts of gumbo, heavy clays and drill solids at the end of the separation unit. The flow divider box is a box-like housing with a verter plate, upper and lower baffle plates and a grate that allows drilling fluid or drilling mud to be selectively directed to the mud separation unit to be separated prior to passing to the conventional downstream solids control equipment or allows the fluid to bypass the separation unit and flow directly to the conventional solids control equipment. The bypass diverter box baffle plates, diverter plate and grate, and selective utilization of the mud separation unit removes large amounts of gumbo, heavy clays and drill solids from the drilling mud and allows high flow rates to be easily processed by shale shakers and other conventional downstream solids control equipment of the mud system and compliments the drilling operations with respect to changes in the lithology, geological formations, or loss of returns in relation to the gallons pumped or folume of drilling fluid or drilling mud entering the bypass diverter box.
Owner:TUBOSCOPE NU TECGNT
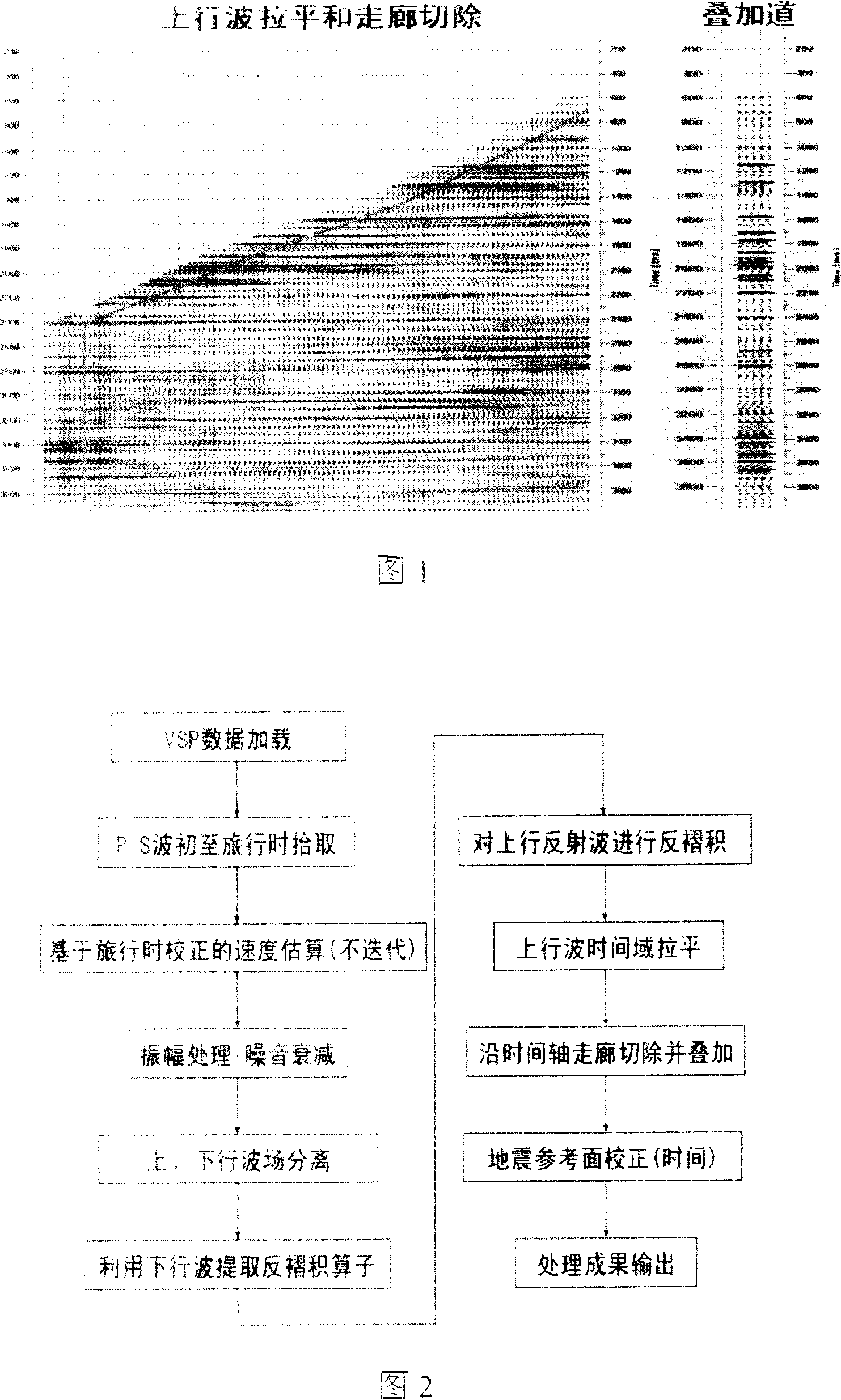
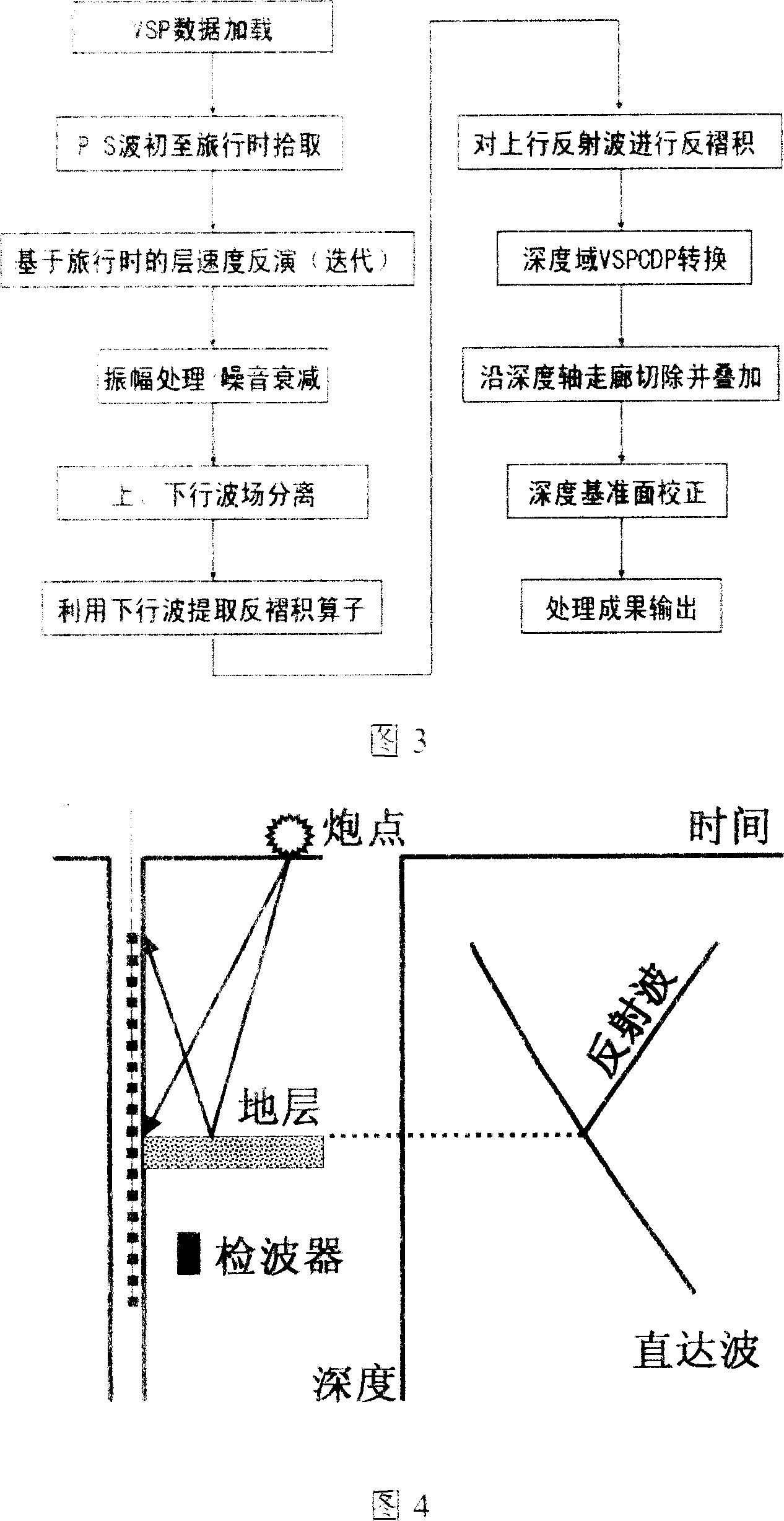
Zero hypocentral distance vertical seismic section compressional-shear wave data depth field corridor stacked section processing method
Geophysical exploration for oil wells, the source from the vertical seismic profile aspect wave data stack depth domain Corridor profile approach is the use of in situ collection of well spacing VSP data, which will all receive points drilling depth of information and hierarchical data with the depth of information, the use of direct wave VSP data travel through and optimization algorithms are highly accurate anti-layer velocity model, the direct wave to the beginning of the reflected wave in the vicinity of the depth and precision homing imaging, further in-depth domain Corridor section and with the superposition of alternative conventional method leveled in the time domain, with corridors and the superposition method, the results can be superimposed for direct comparison with the drilling and seismic data stratified layer identification. More intuitive, but also made full use of VSP data in the depth of information, make geological formation of the earthquake response and drilling, logging data in depth domain direct contrast, a more intuitive geological layer and the relationship between seismic horizon, thereby enabling layer of identification and calibration more reliable.
Owner:BGP OF CHINA NAT GASOLINEEUM CORP
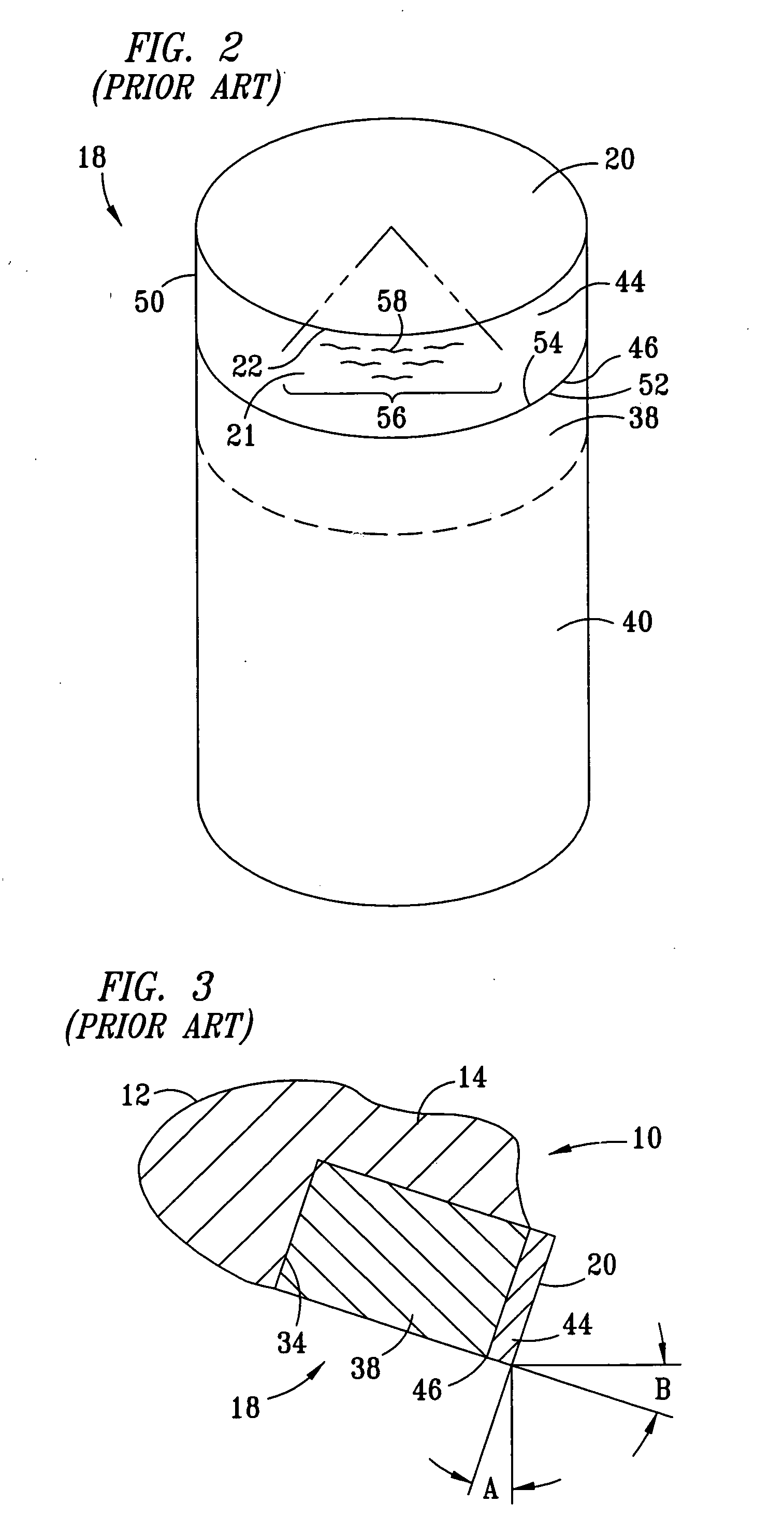
Cutter having shaped working surface with varying edge chamfer
ActiveUS7726420B2Reduce certain adverse consequenceIncreasing the thicknessDrill bitsConstructionsWell drillingEngineering
A cutter for a drill bit used for drilling wells in a geological formation includes an ultra hard working surface and a chamfer along an edge of the working surface, wherein the chamfer has a varied geometry along the edge. The average geometry of the chamfer varies with cutting depth. A depression in the shaped working surface is oriented with the varied chamfer and facilitates forming the varied chamfer. A non-planar interface has depressions oriented with depressions in the shaped working surface to provide support to loads on the working surface of the cutter when used.
Owner:SMITH INT INC
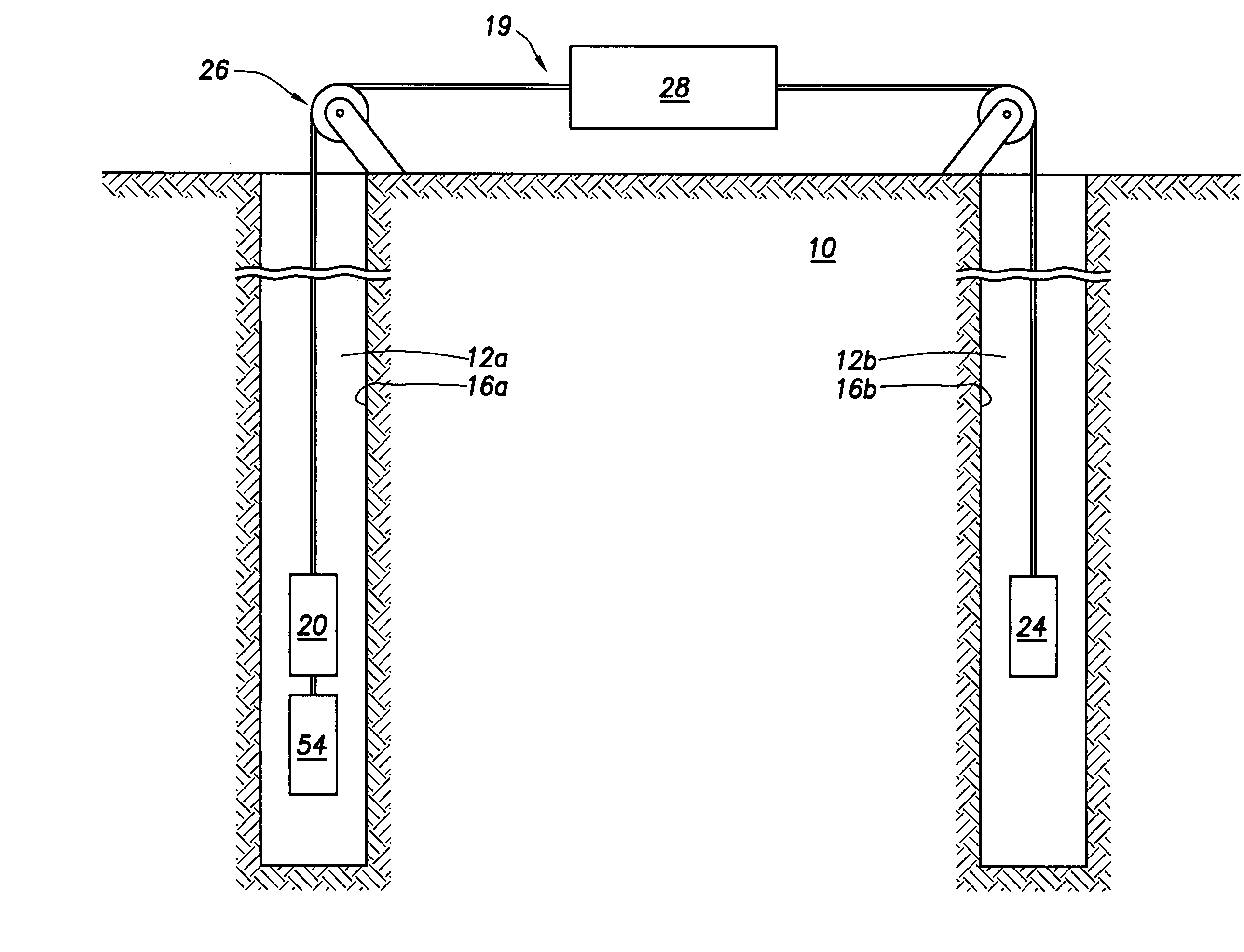
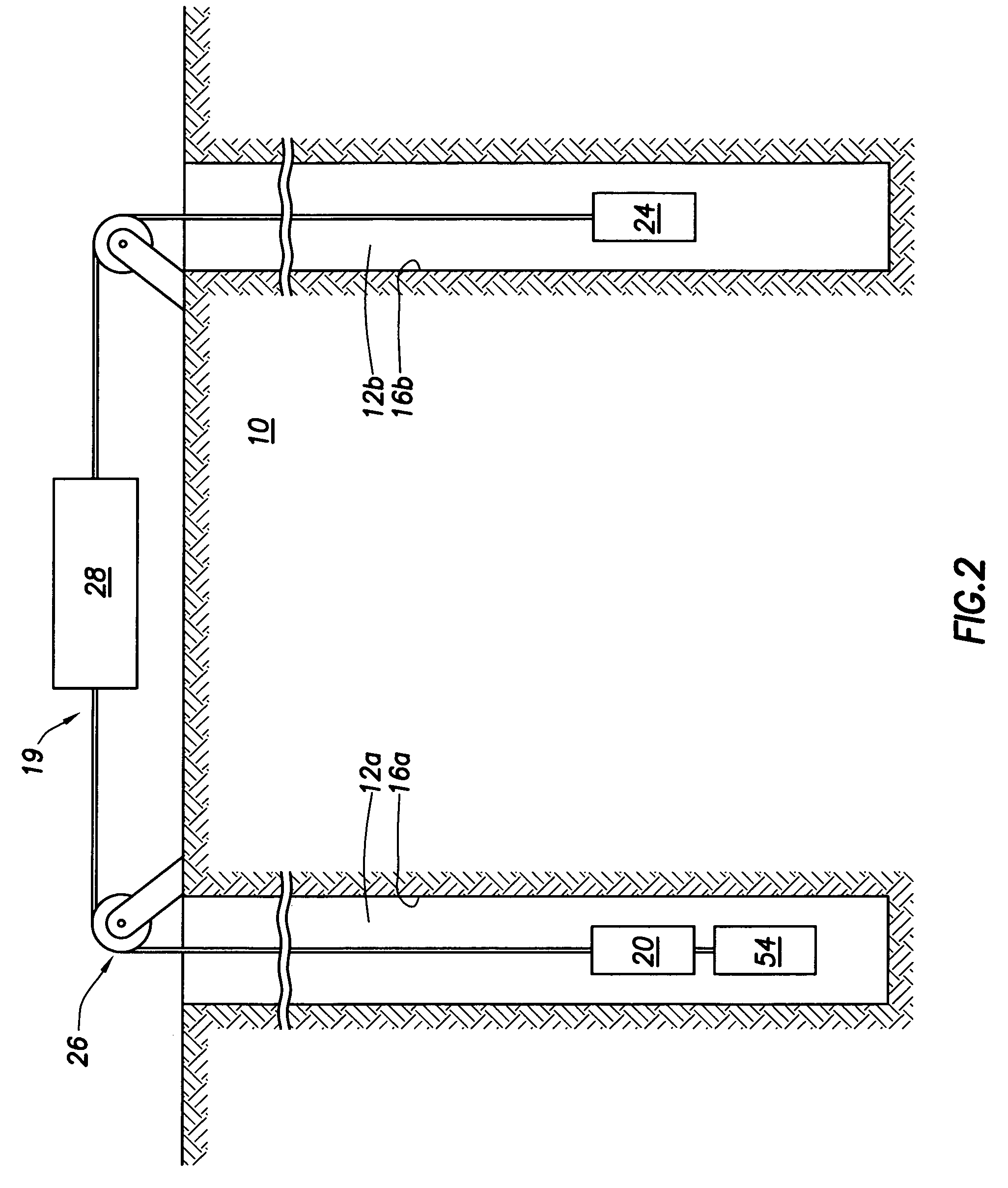
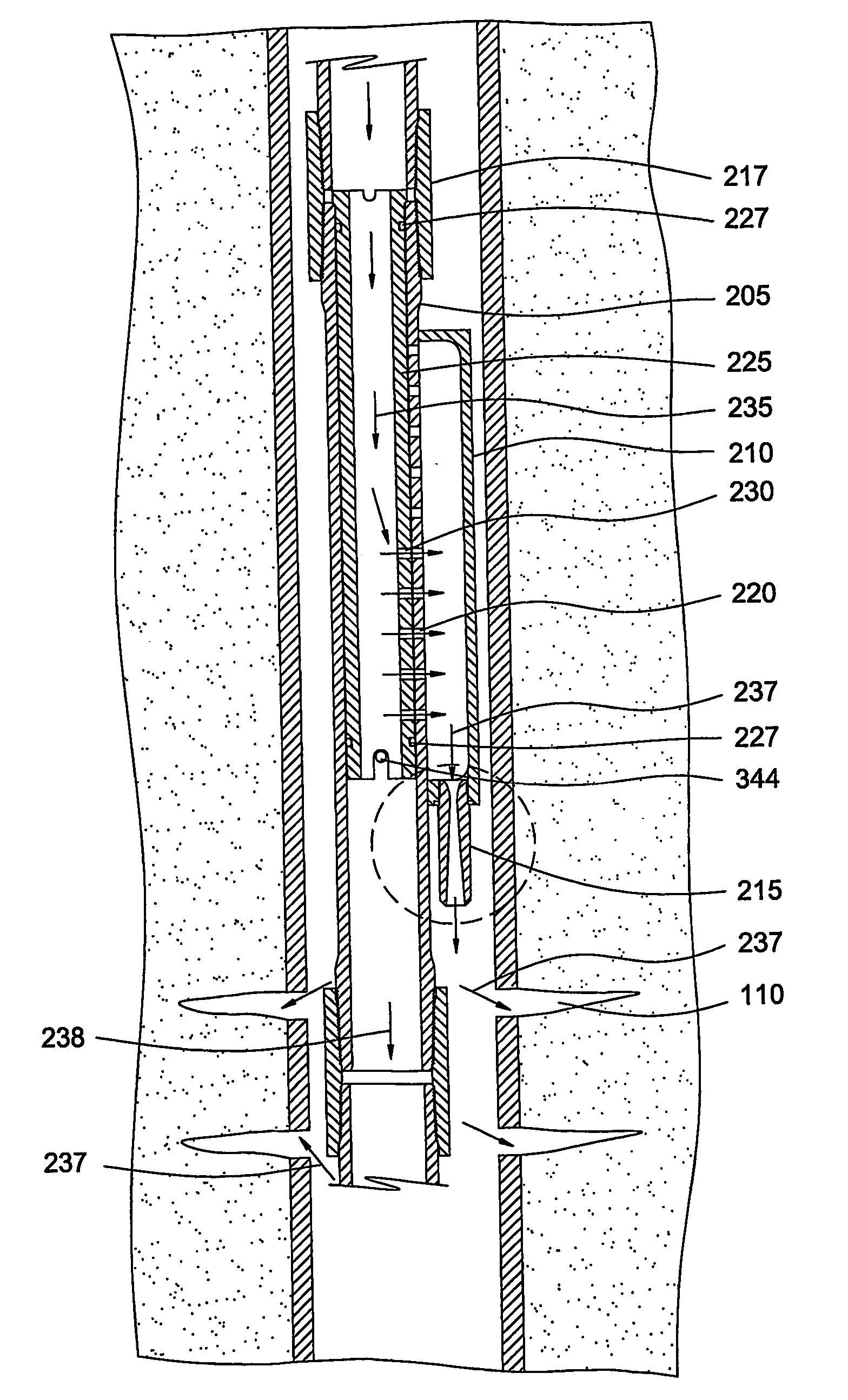
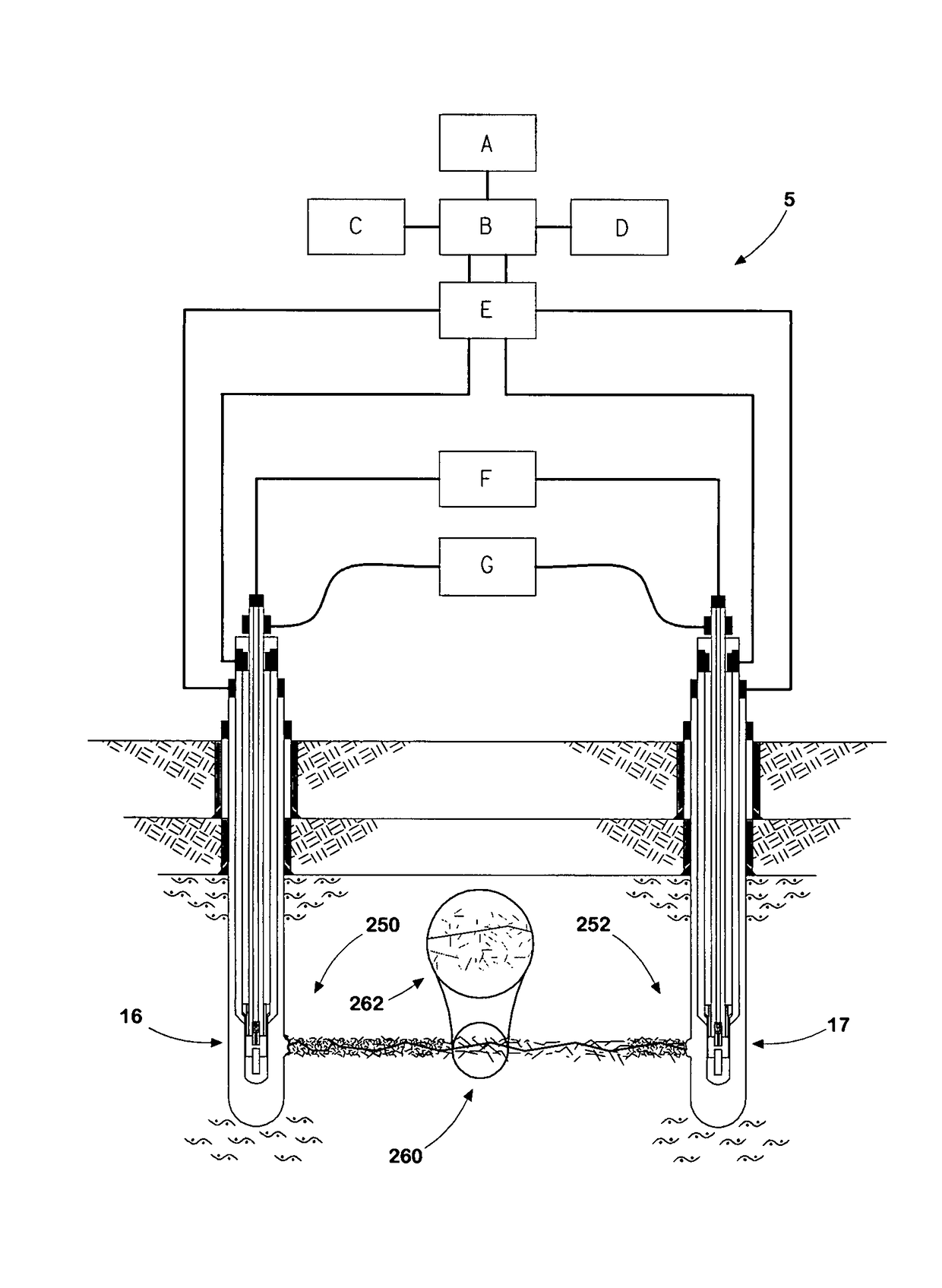
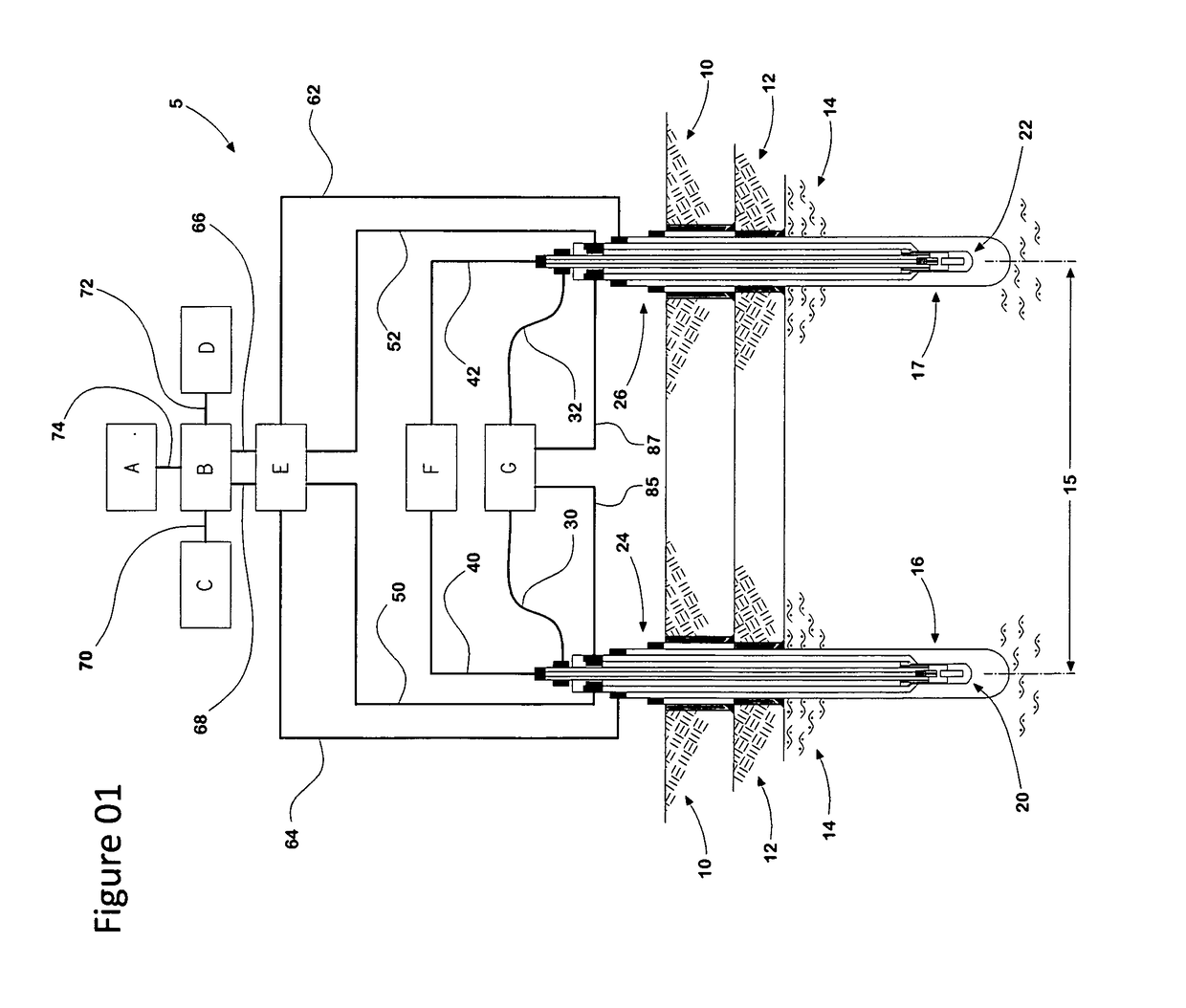
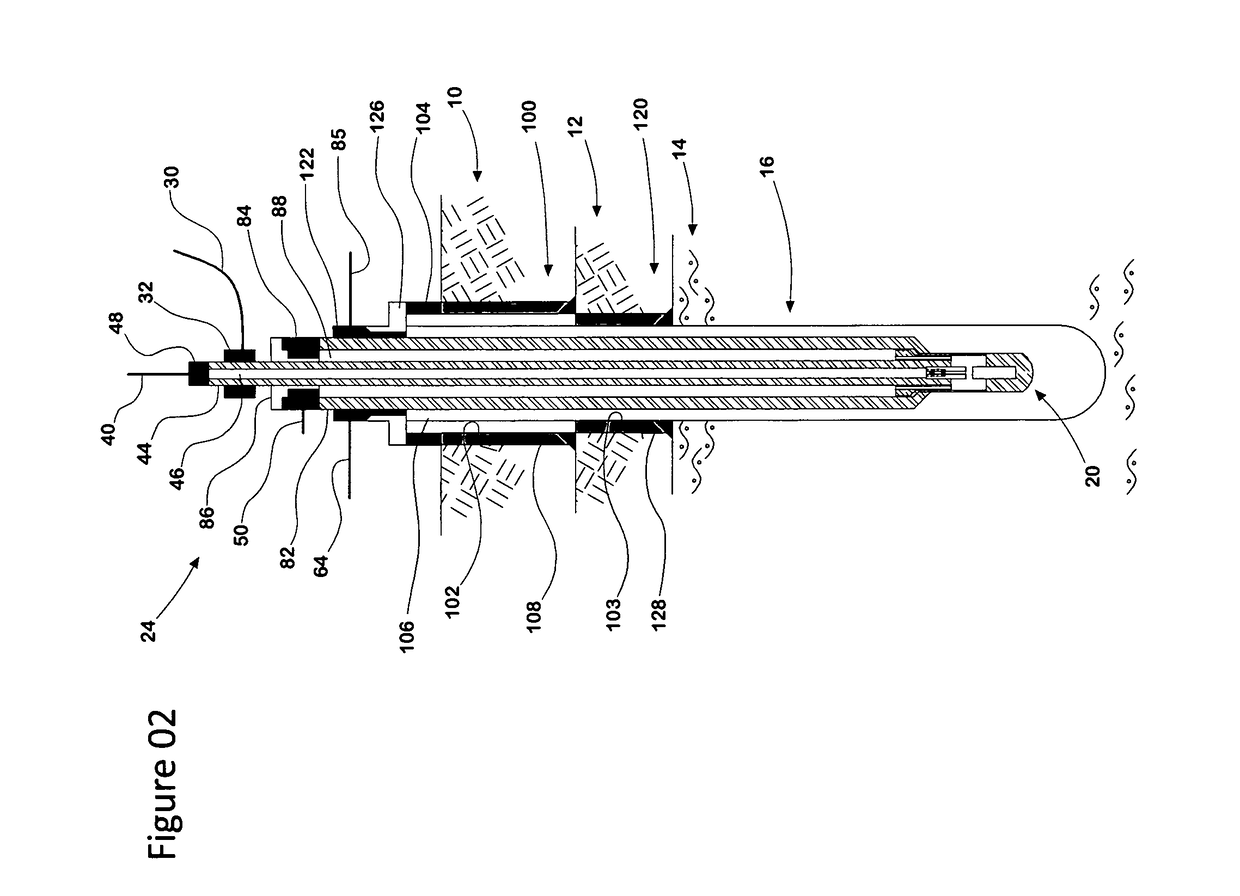
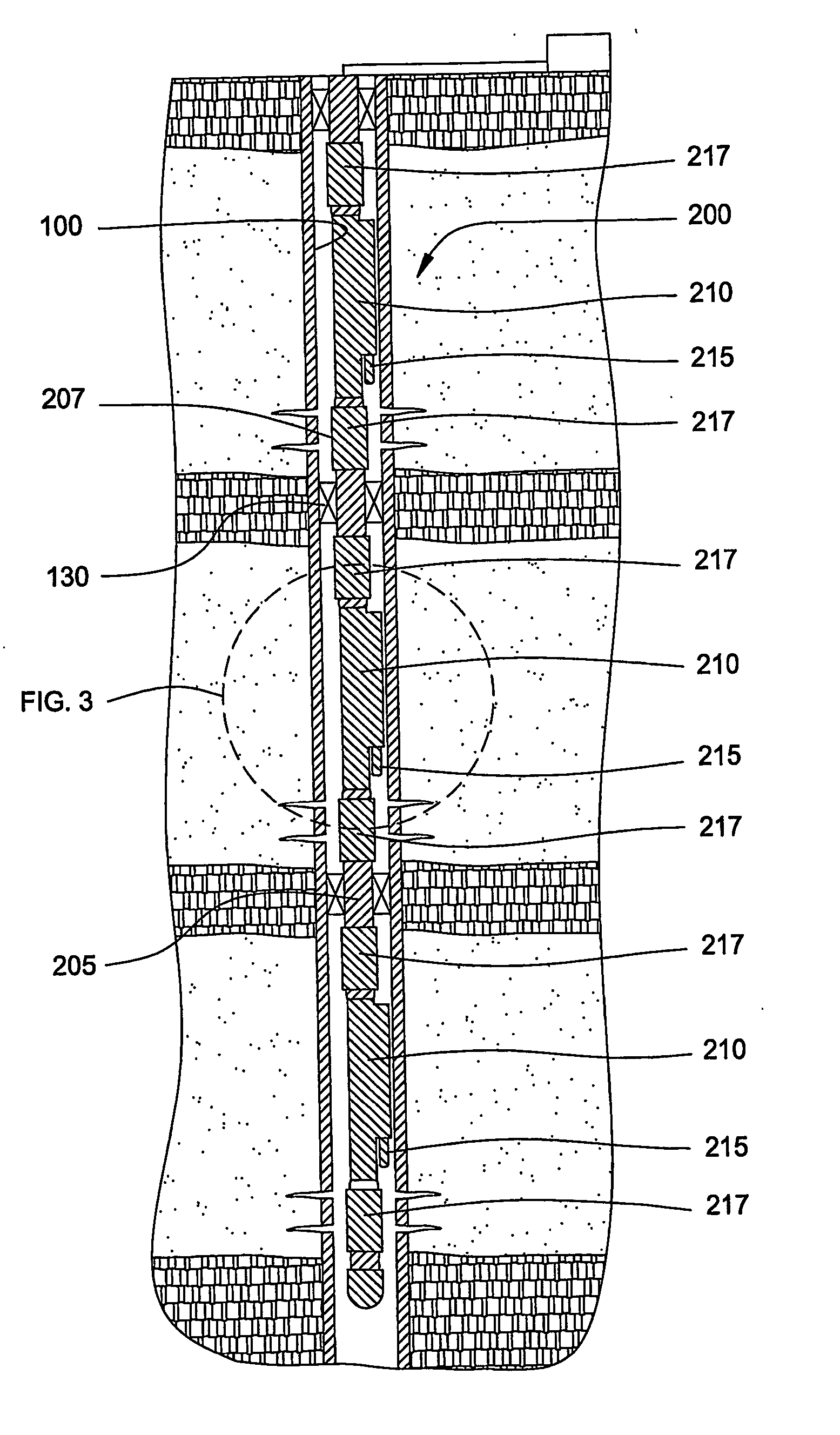
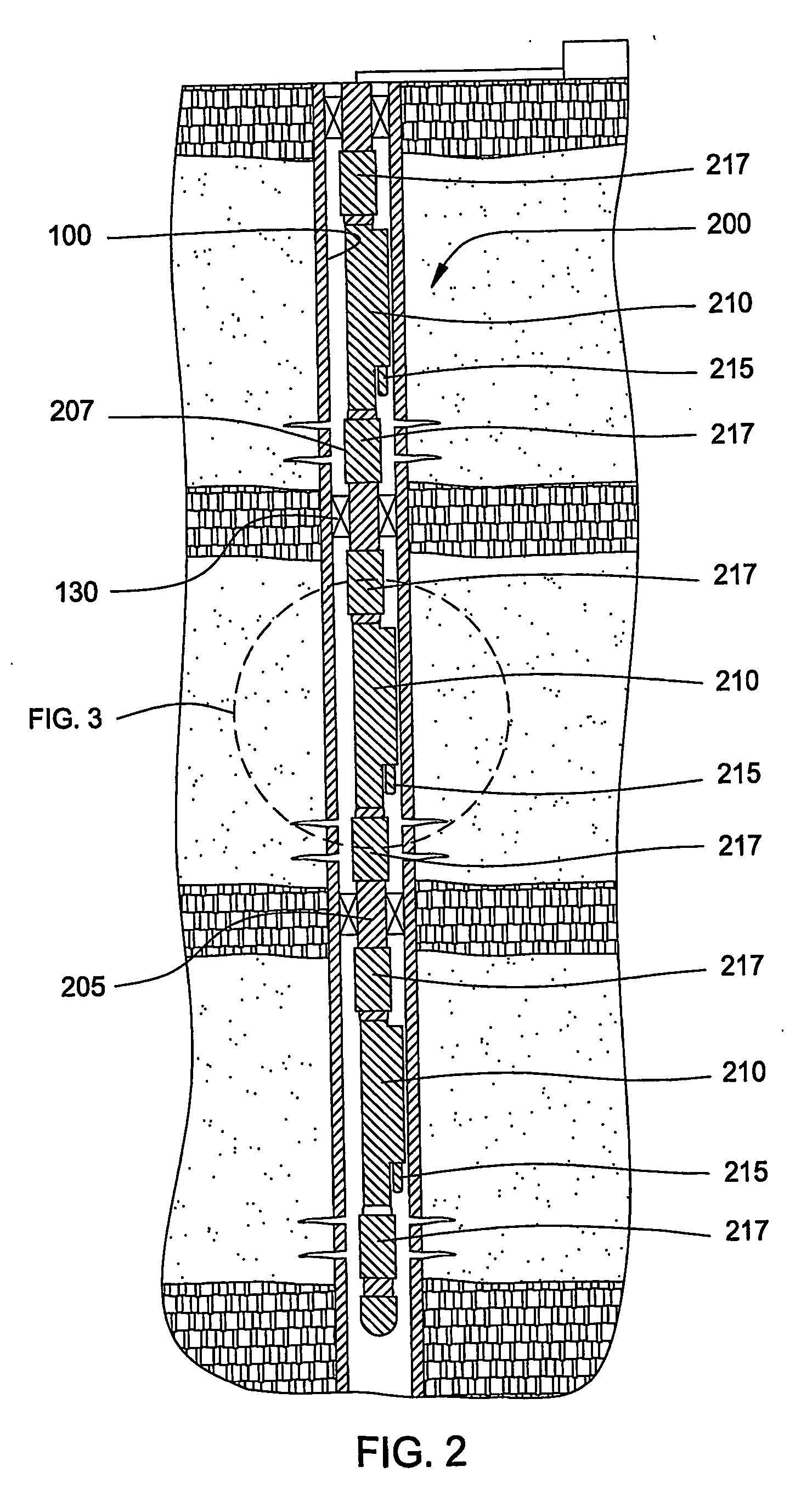
Method and apparatus for injecting steam into a geological formation
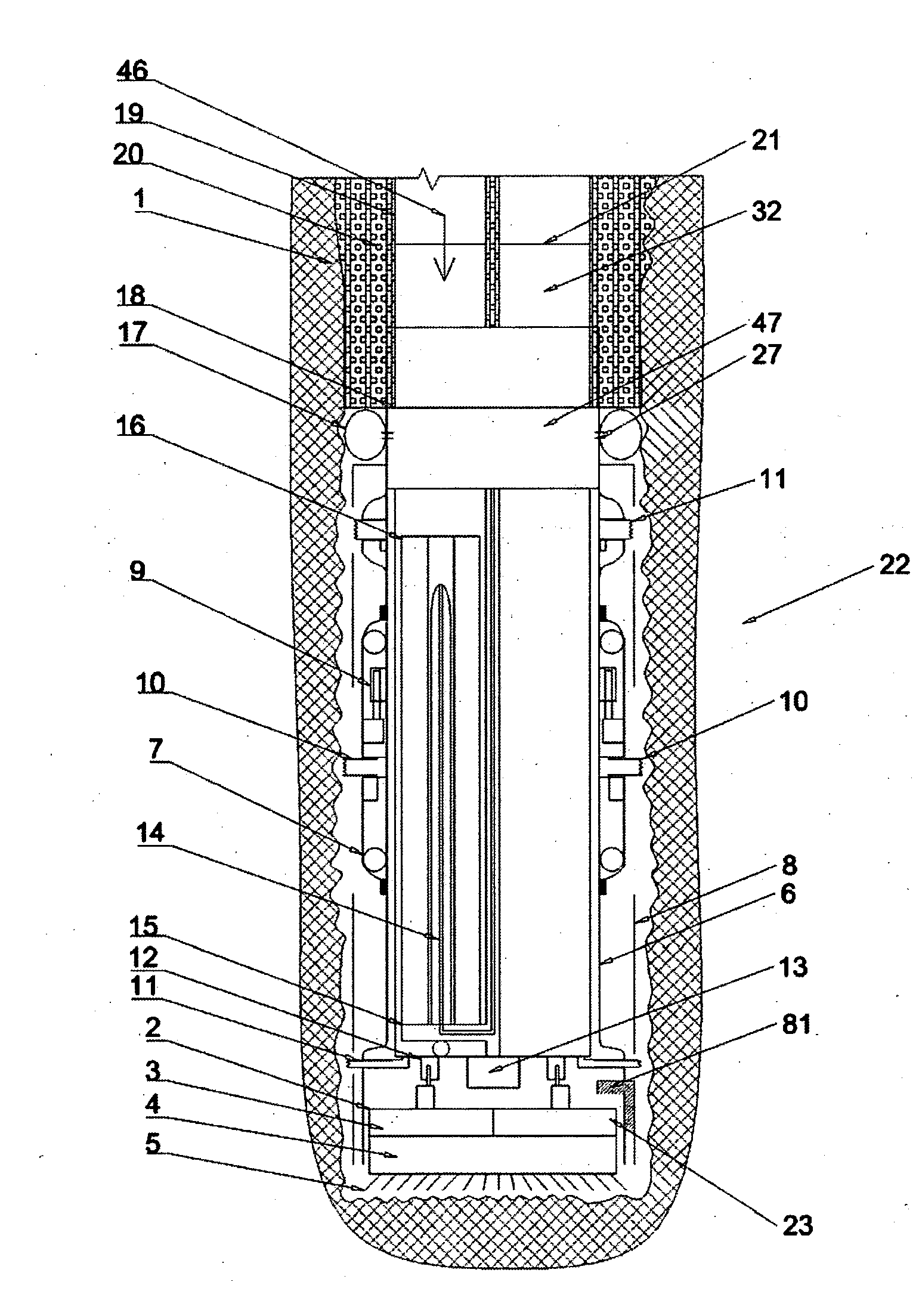
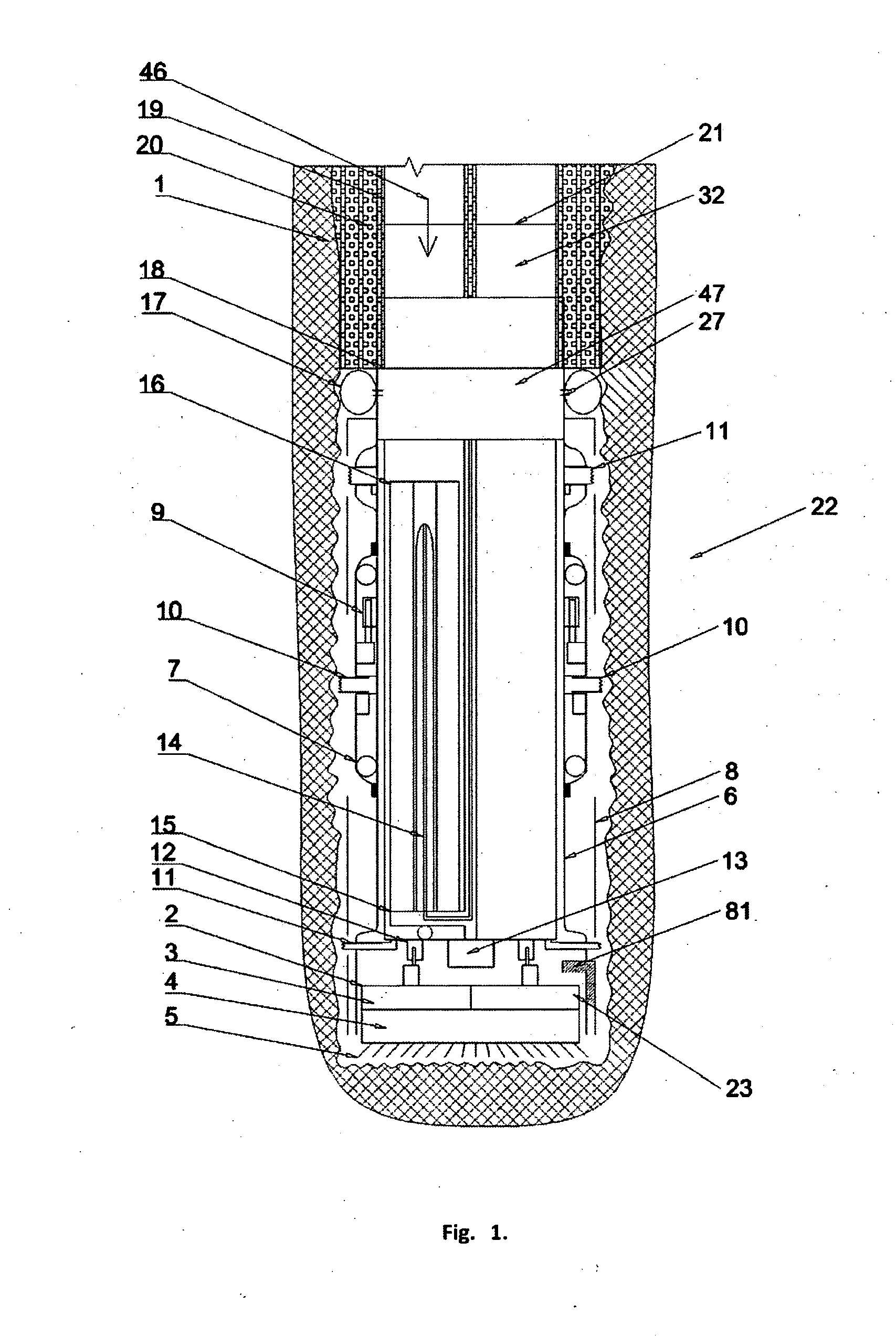
The present invention generally provides a method and apparatus for injecting a compressible fluid at a controlled flow rate into a geological formation at multiple zones of interest. In one aspect, the invention provides a tubing string with a pocket and a nozzle at each isolated zone. The nozzle permits a predetermined, controlled flow rate to be maintained at higher annulus to tubing pressure ratios. In another aspect, the present invention assures that the fluid is supplied uniformly to a long horizontal wellbore by providing controlled injection at multiple locations that are distributed throughout the length of the wellbore. In another aspect, the invention ensures that saturated steam is injected into a formation in a predetermined proportion of water and vapor by providing a plurality of apertures between a tubing wall and a pocket.
Owner:WEATHERFORD TECH HLDG LLC
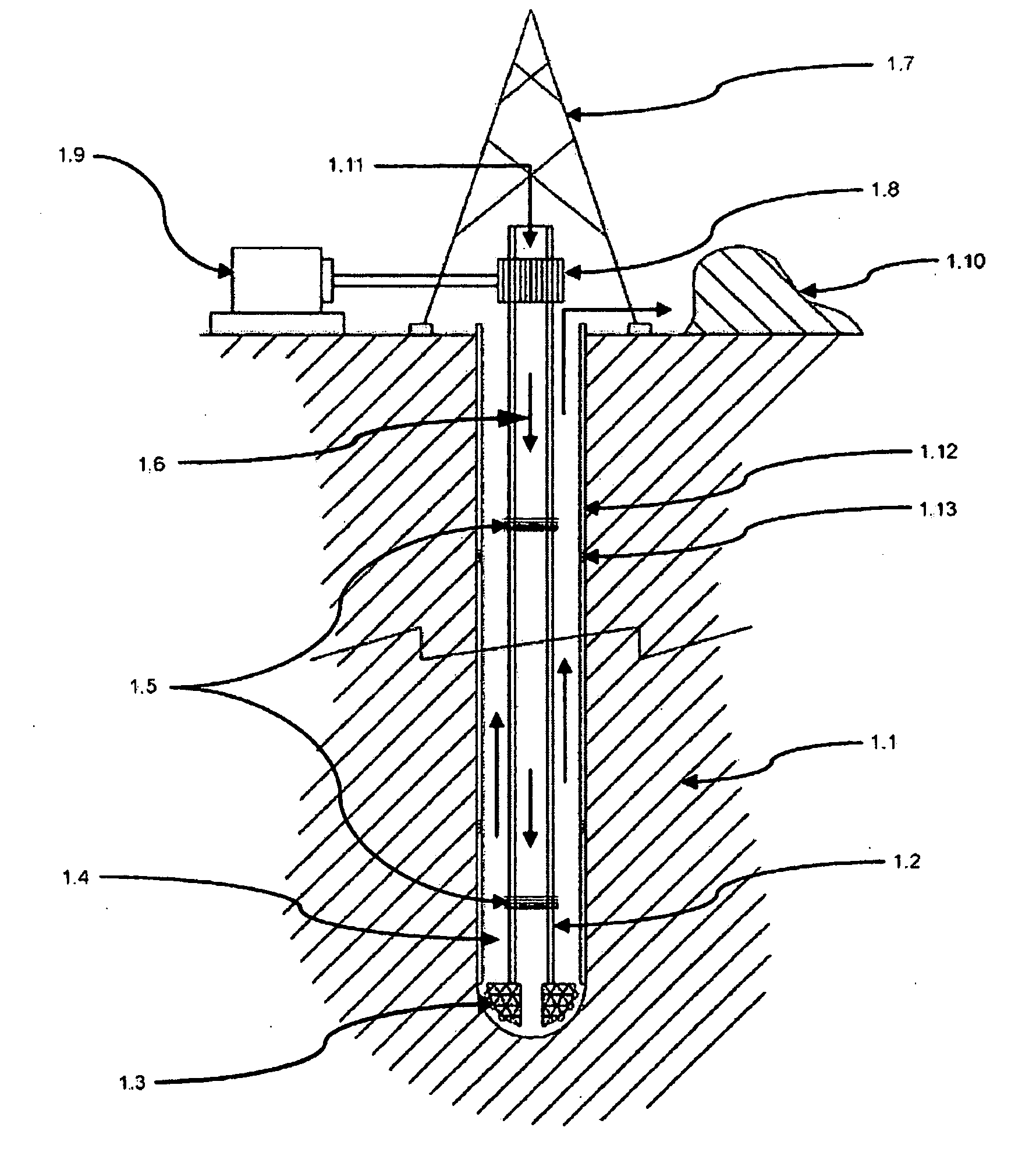
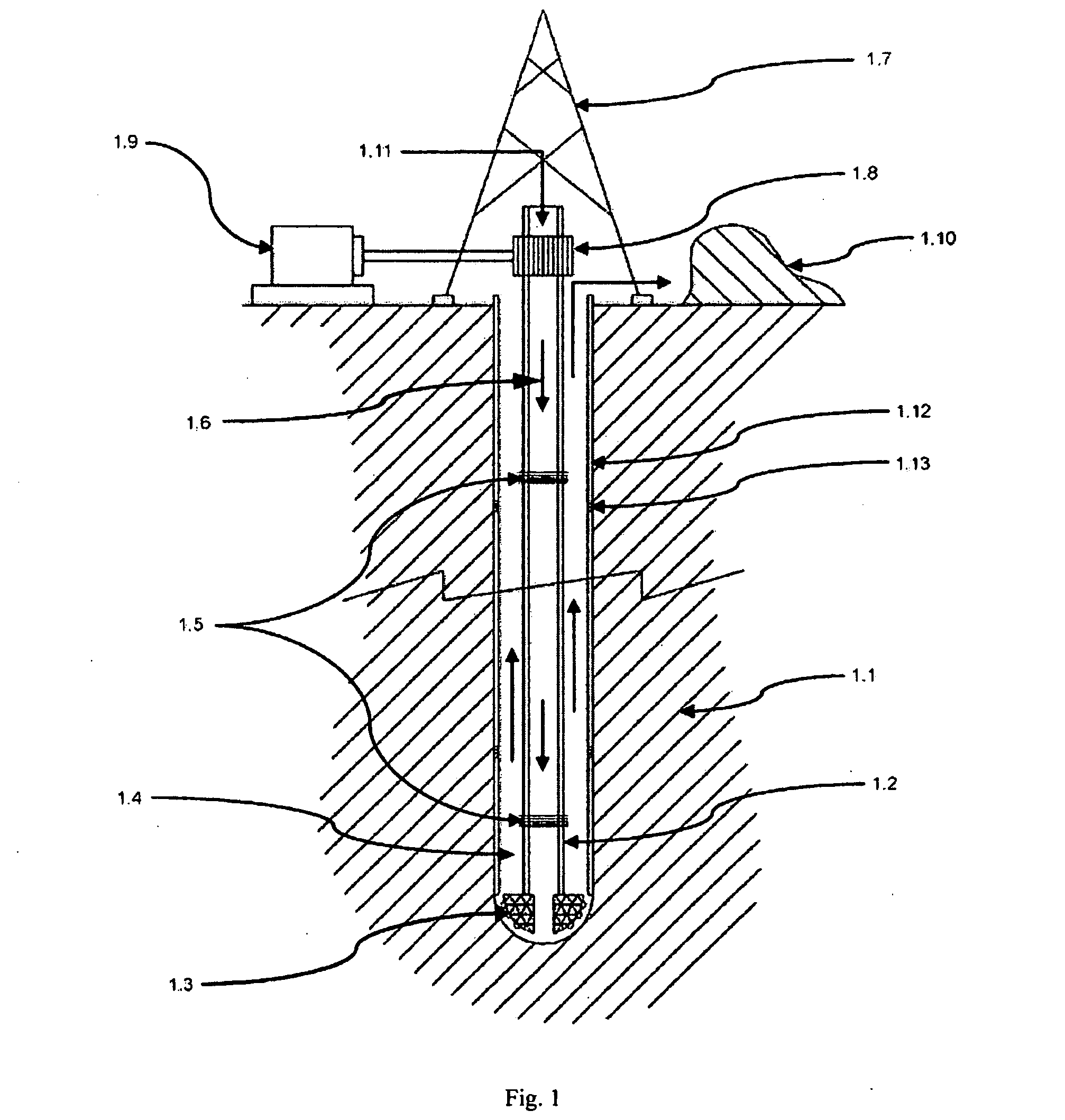
Device for performing deep drillings and method of performing deep drillings
InactiveUS20110290563A1Improve equipment efficiencyRobotic multi-functional underground drilling platform can beDrilling rodsThermal drillingTransport infrastructureWater channel
Device for performing deep drillings, especially geothermal, may include a surface base, a borehole in a geological formation, filled with fluid, and a robotic multi-functional underground drilling platform, which contains especially a block (2) for crushing rock (1), a block for continuous formation of casing profile, a block of casing as transfer and transport infrastructure, a block (16) of transport container, a control and communication block (39), an energy block (4), a block of operating transport containers, and a block of removing and loading rock (1) from the place of crushing. The block (2) for rock crushing may be interconnected with block of removing and loading rock (1) from the place of crushing by means of water channels, ensuring removal of the crushed rock 107. The block of removing and loading rock (1) from the place of crushing may be interconnected with block (16) of transport container by means of water channels. The block of casing as transfer and transport infrastructure may be connected to block of continuous forming the casing profile by means of moving formworks.
Owner:GA DRILLING AS
Sensor arrangement for seismic waves
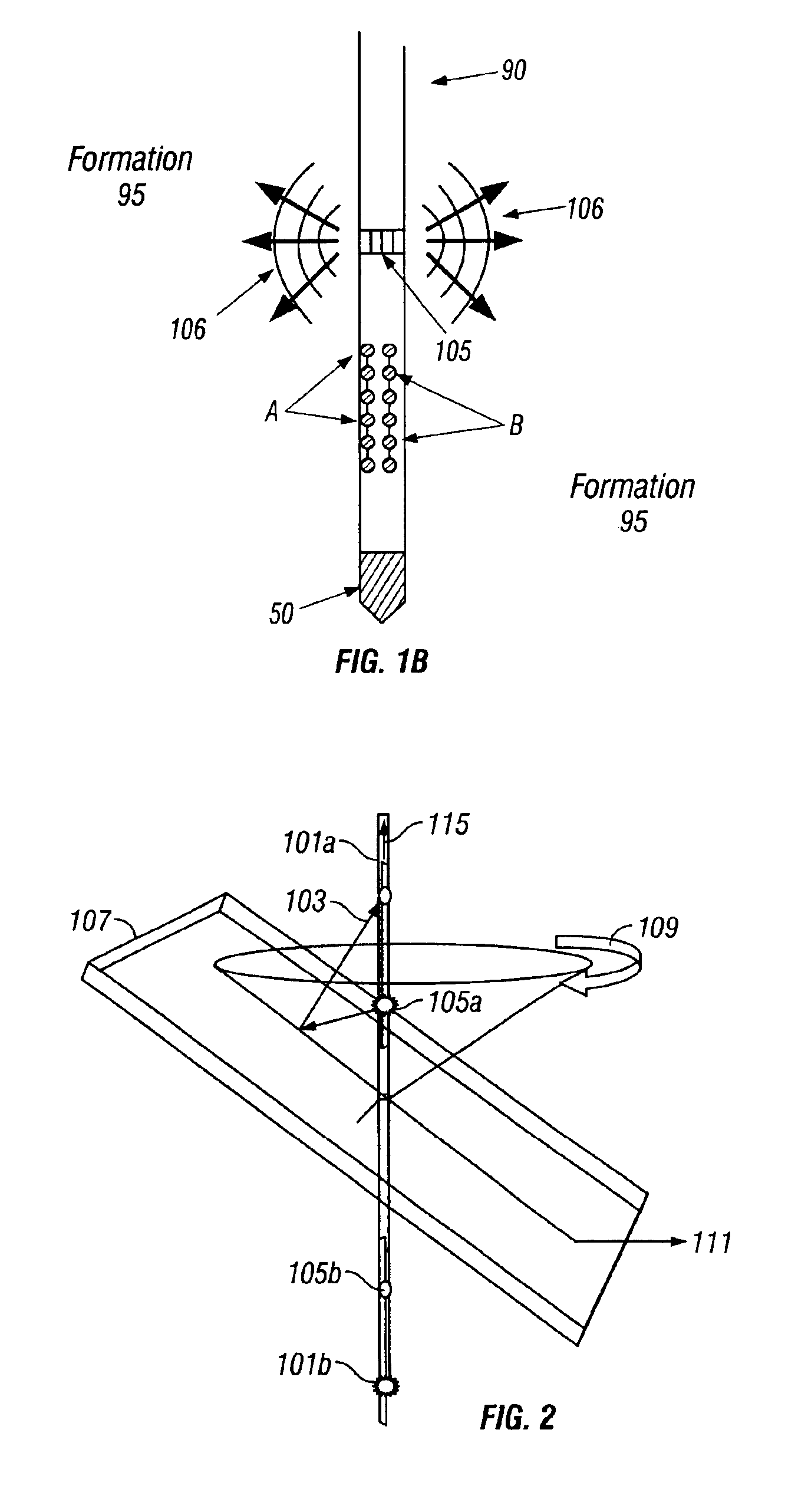
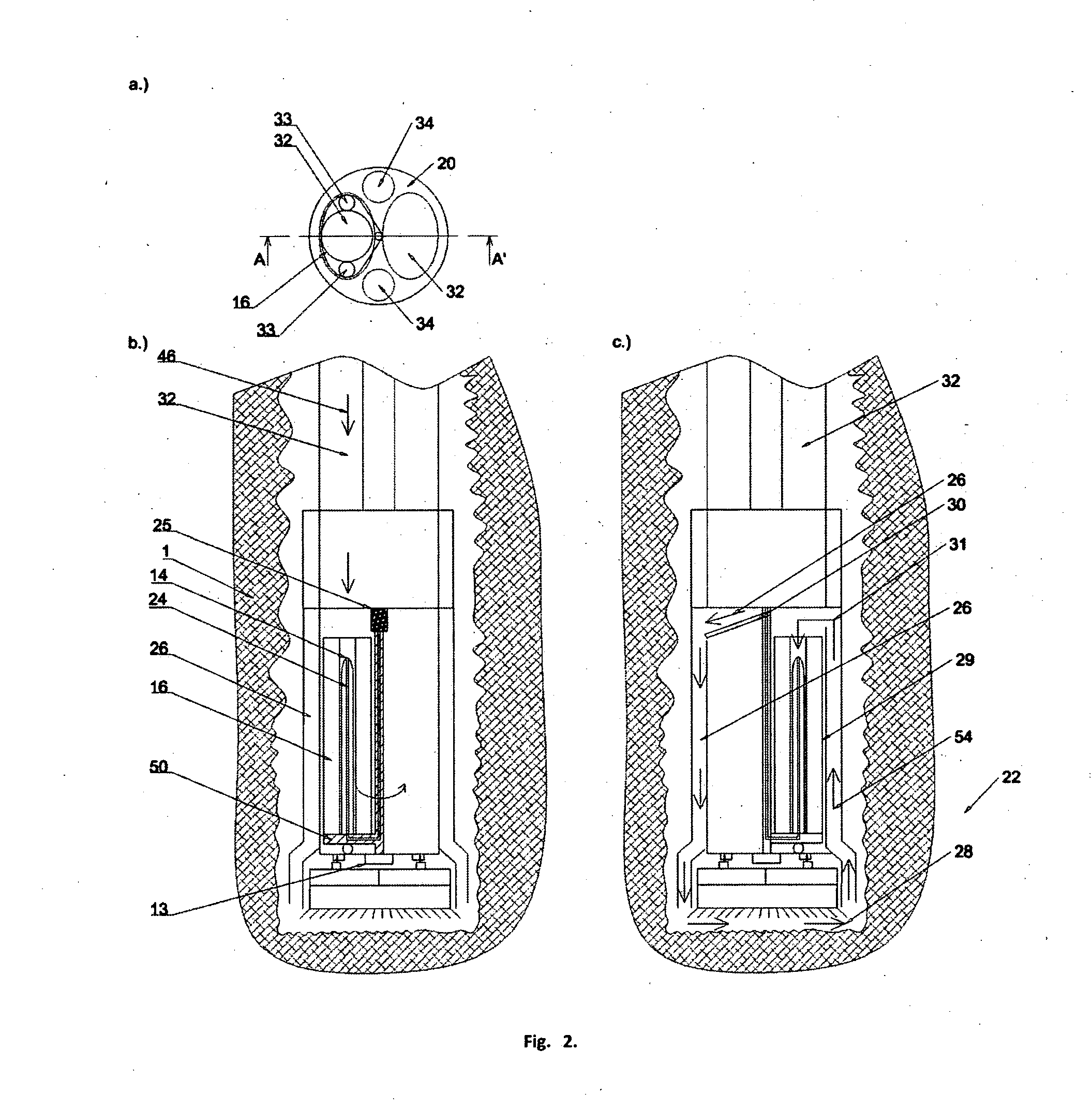
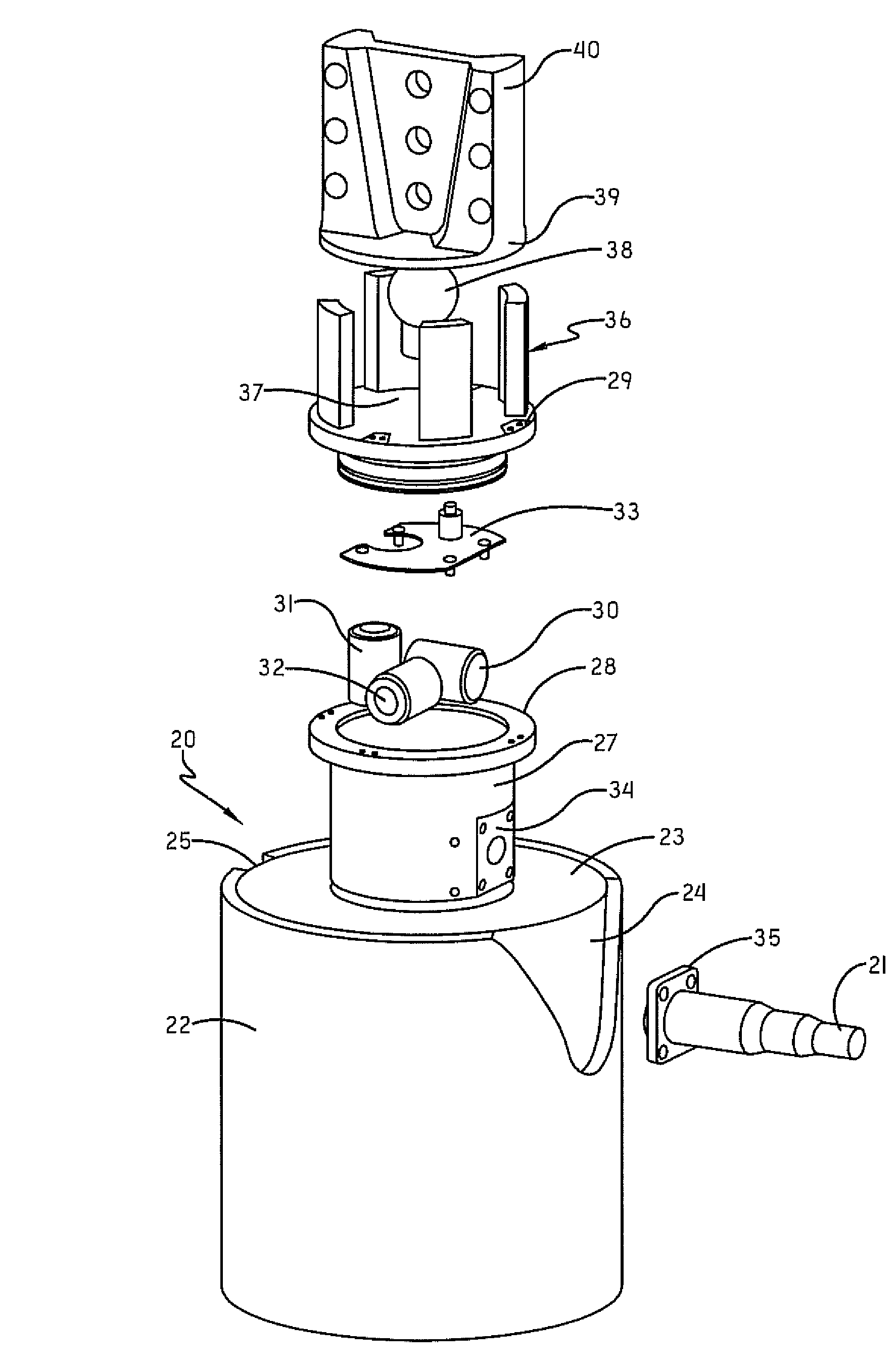
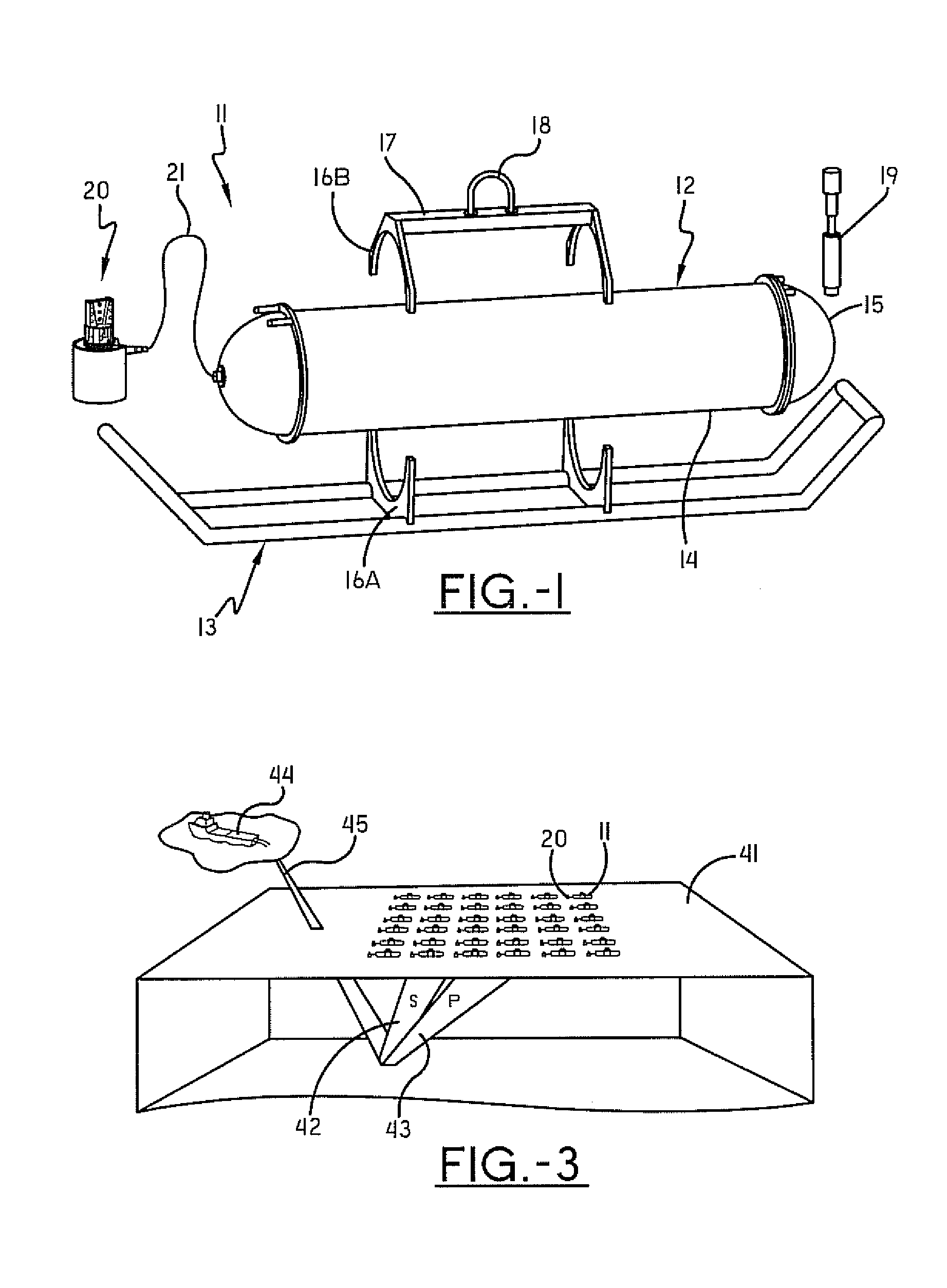
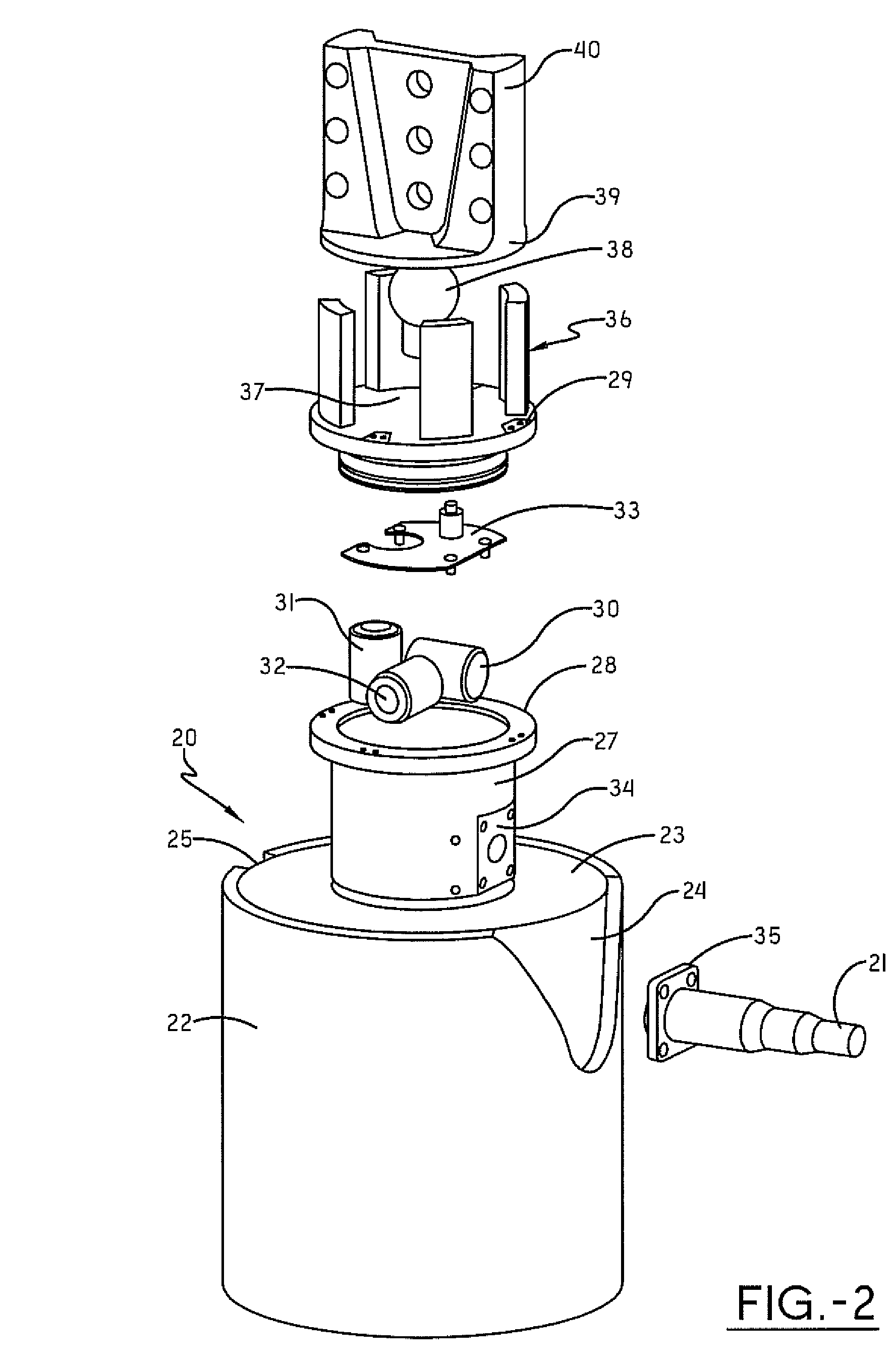
A sensor arrangement is provided for use in the seismic investigation of geological formations below the seabed. A plurality of sensor nodes (20) are provided and are positioned gfor deployment on the seabed to collect pressure waves and shear waves from the geological formations and to transfer seismic data to a surface receiver. Each sensor node (20) may include a cylindrical structure (22), which is intended to penetrate downwardly into the seabed. At least one, preferably three, geophones (30-32) are positioned in connection with this structure (22). An advantageous method for operating a seismic mapping system with sensor arrangements orderly deployed on the seabed records data concerning system behavior and seismic data. This data may be further processed separately.
Owner:SEABED GEOSOLUTIONS
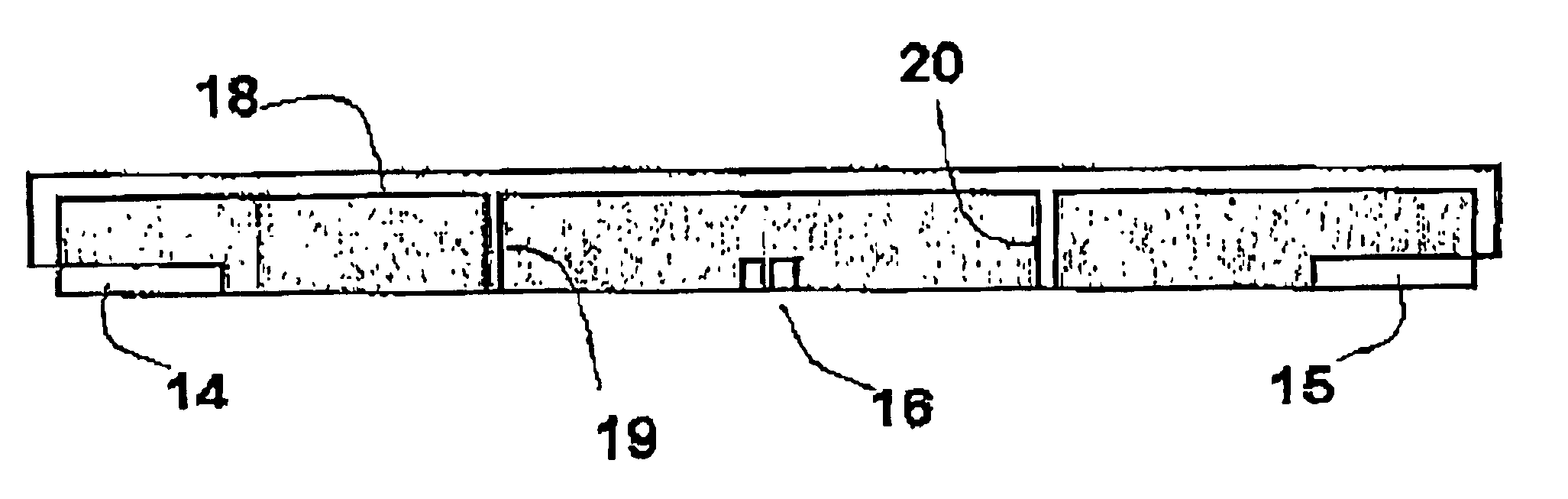
Conductive pad around electrodes for investigating the wall of a borehole in a geological formation
InactiveUS6891377B2Shorten the lengthSimple technologyElectric/magnetic detection for well-loggingAcoustic wave reradiationPotential differenceElectrical current
The present invention relates to apparatus for a tool for investigating the wall of a borehole in a geological formation, the apparatus comprising: a non-conductive pad having an inside face and an outside face for pressing against the wall; a set of measurement electrodes mounted on the outside face of the pad and means for measuring the potential difference between two measurement electrodes; and both a source electrode adapted to inject current into the geological formation and a return electrode, the set of measurement electrodes being situated between the source electrode and the return electrode for the current; the apparatus being characterized in that the pad comprises an electrically conductive portion covering the entire measurement electrode zone and electrically insulated from the measurement electrodes.
Owner:SCHLUMBERGER TECH CORP
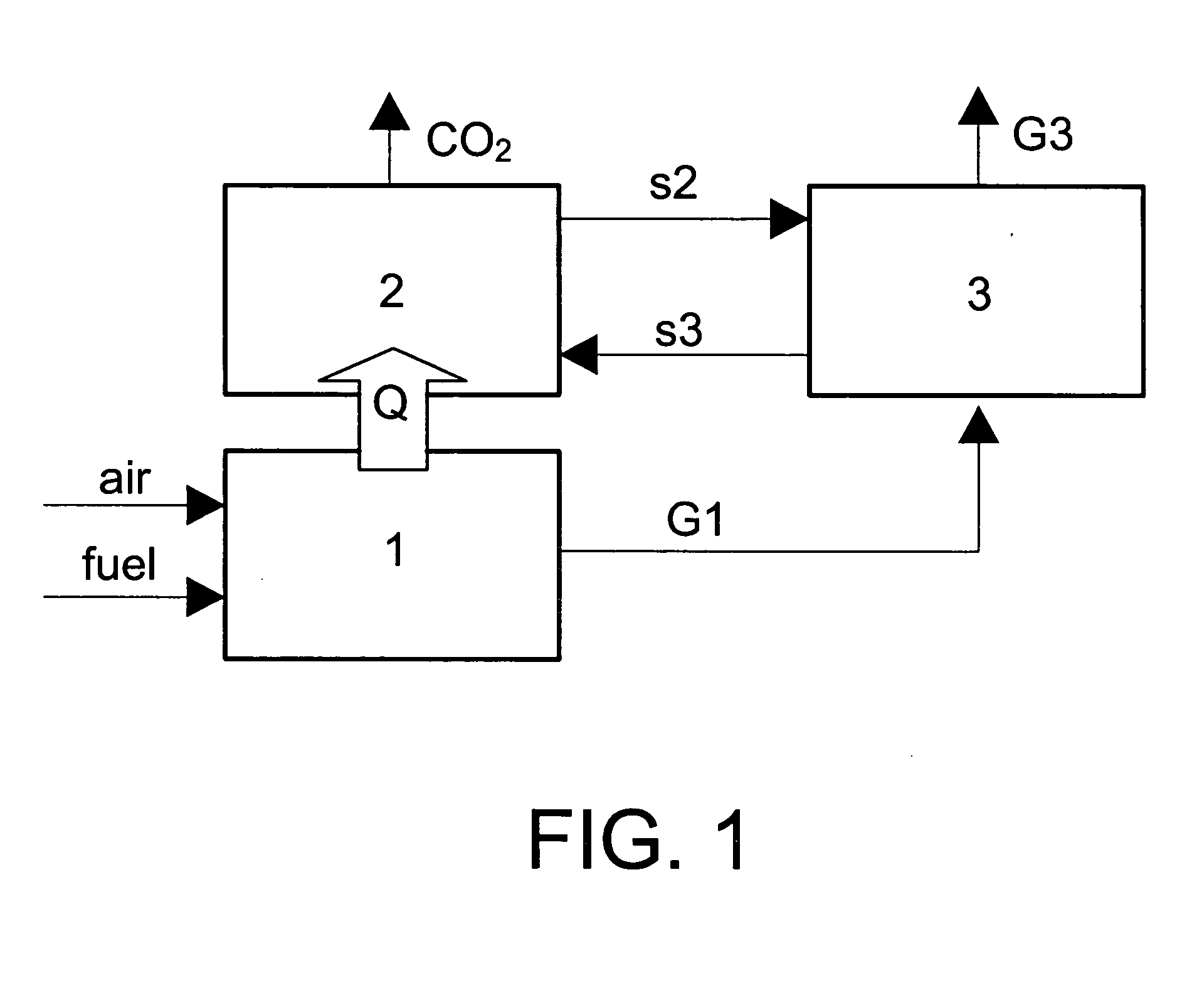
Combustion method with integrated CO2 separation by means of carbonation
InactiveUS20050060985A1Easy to separateReduce the temperatureGas treatmentOther chemical processesCalcium in biologyCombustion
The invention relates to a method for separating CO2 from combustion gases, which can be used at areas with large emissions (thermal power stations using any carbonaceous fuel). The separated CO2 stream can be used and / or contained in geological formations. The inventive method aims to reduce the high costs involved in CO2 separation which prevent large-scale use of the CO2 confinement options included in the UN's IPCC reports. Said method consists of bringing the combustion gases into contact with a calcareous sorbent (limestone, calcined dolomite) at 650-750° C., thereby producing the CO2 capture reaction by means of the rapid carbonation of the sorbent. The sorbent is regenerated in another reactor (calciner) which operates in CO2 or CO2 / H2O atmospheres.
Owner:CONSEJO SUPERIOR DE INVESTIGACIONES CIENTIFICAS (CSIC) +1
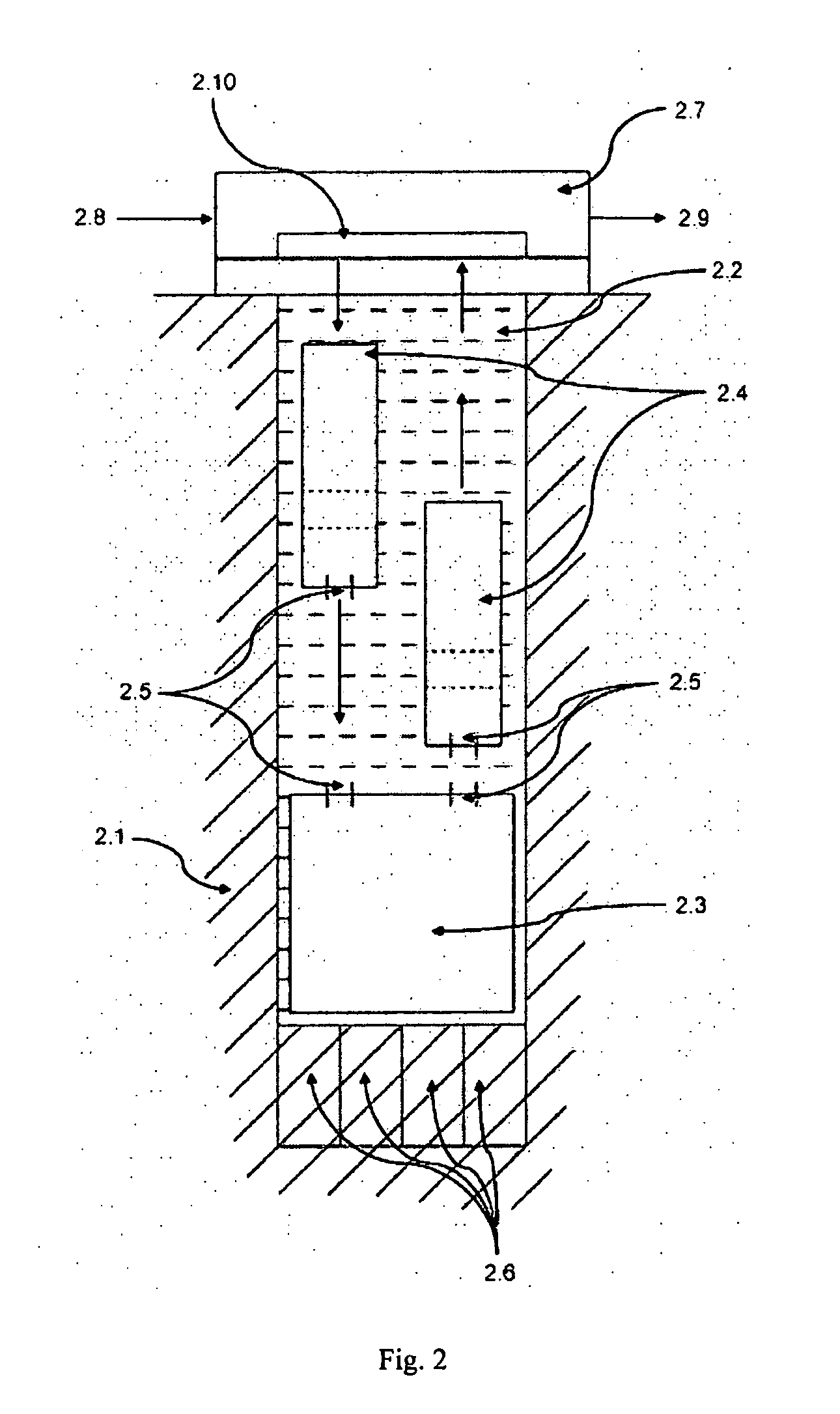
Equipment for excavation of deep boreholes in geological formation and the manner of energy and material transport in the boreholes
InactiveUS20100224408A1Considerable energy savingLarge boreholeDisloding machinesThermal drillingEngineeringEnergy depletion
Utilisation of geothermal energy in depths above 5 km could contribute considerably to resolving the global problems related to a lack of energy and to glasshouse gases from fossil fuels. The invention describes innovative equipment which makes deep holes in geological formations (rock) by disintegrating the soil into blocks carried to the land surface through the excavated hole filled with liquid, using transport modules yielded up by gas buoyancy interaction in the transport module utilising supercavitation. In an opposite direction—by help of negative buoyancy—the necessary energy carriers, materials and components, or entire devices required for rock excavation, are carried to the bottom. The opportunity to transport rock in entire blocks reduces energy consumption considerably, because the rock is disintegrated in the section volumes only. Some of the extracted rock and material carried from the surface is used to make a casing of the hole using a part of the equipment. The equipment also allows the generation of the necessary high pressure of liquid at the bottom of the hole, to increase permeability of adjacent rock. The equipment as a whole allows by its function that there is almost linear dependence between the price and depth (length) of the produced hole (borehole).
Owner:GA DRILLING AS
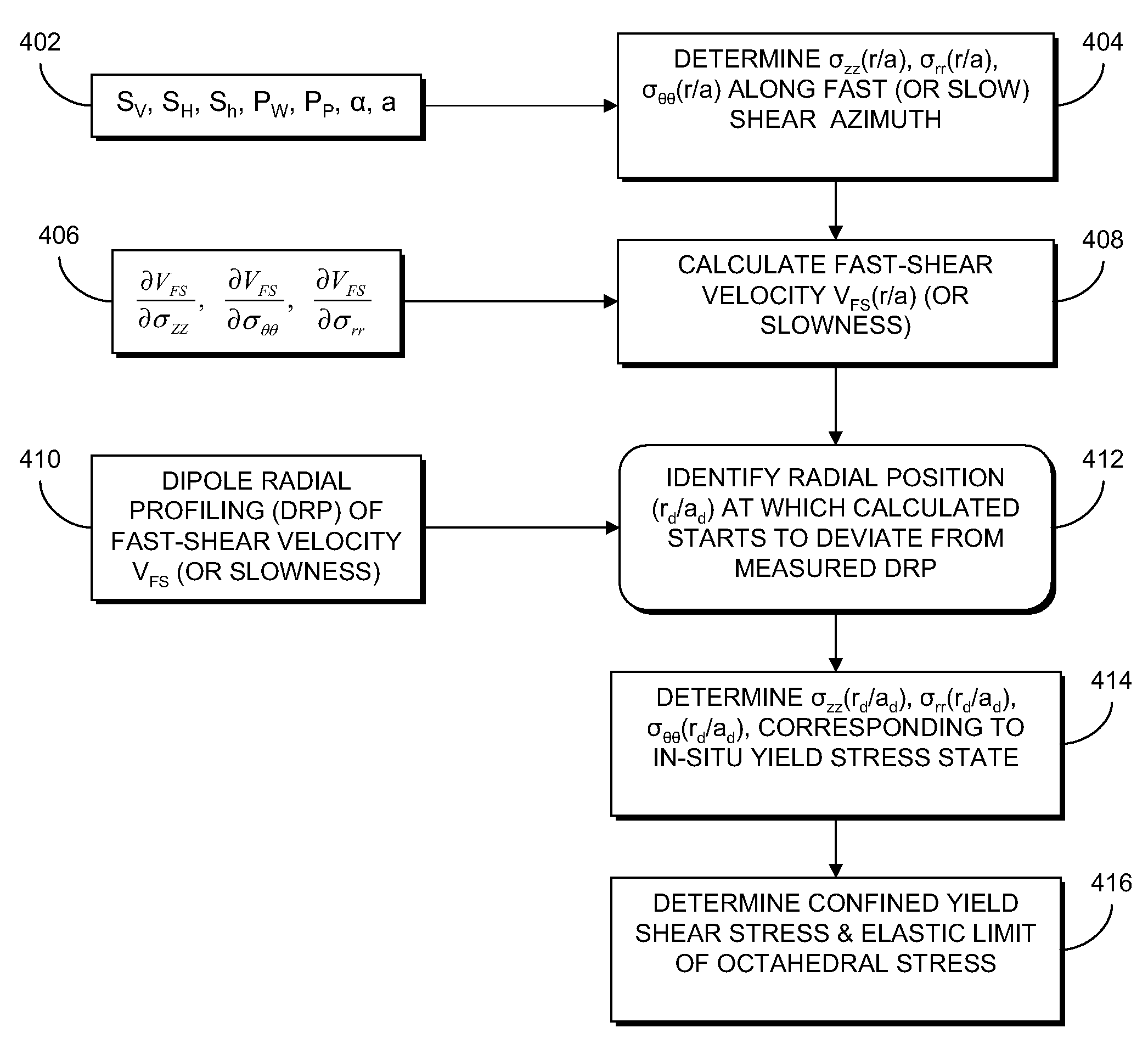
In-situ determination of yield stress state of earth formations
ActiveUS20090109794A1Reliable estimateAccurate representationSeismic signal processingSeismology for water-loggingStressed stateEffective stress
Determination of in-situ rock yield stress state of a geological formation surrounding a borehole includes determining a profile for each of an axial effective, a radial effective, and a hoop effective stress within at least one axial plane containing a borehole axis. A predicted radial shear response radial profile is calculated from the effective stresses within the at least one axial plane. A measurement-based estimate of a shear response radial profile within the at least one axial plane is determined from measured data. A maximum radial distance at which a difference between the predicted and measurement-based shear response radial profiles is identified within the at least one axial plane as being greater than a difference threshold. The respective axial, radial, and hoop stresses, are determined at the identified maximum radial distance. The identified stresses are indicative of an in-situ yield stress state of the rock.
Owner:SCHLUMBERGER TECH CORP
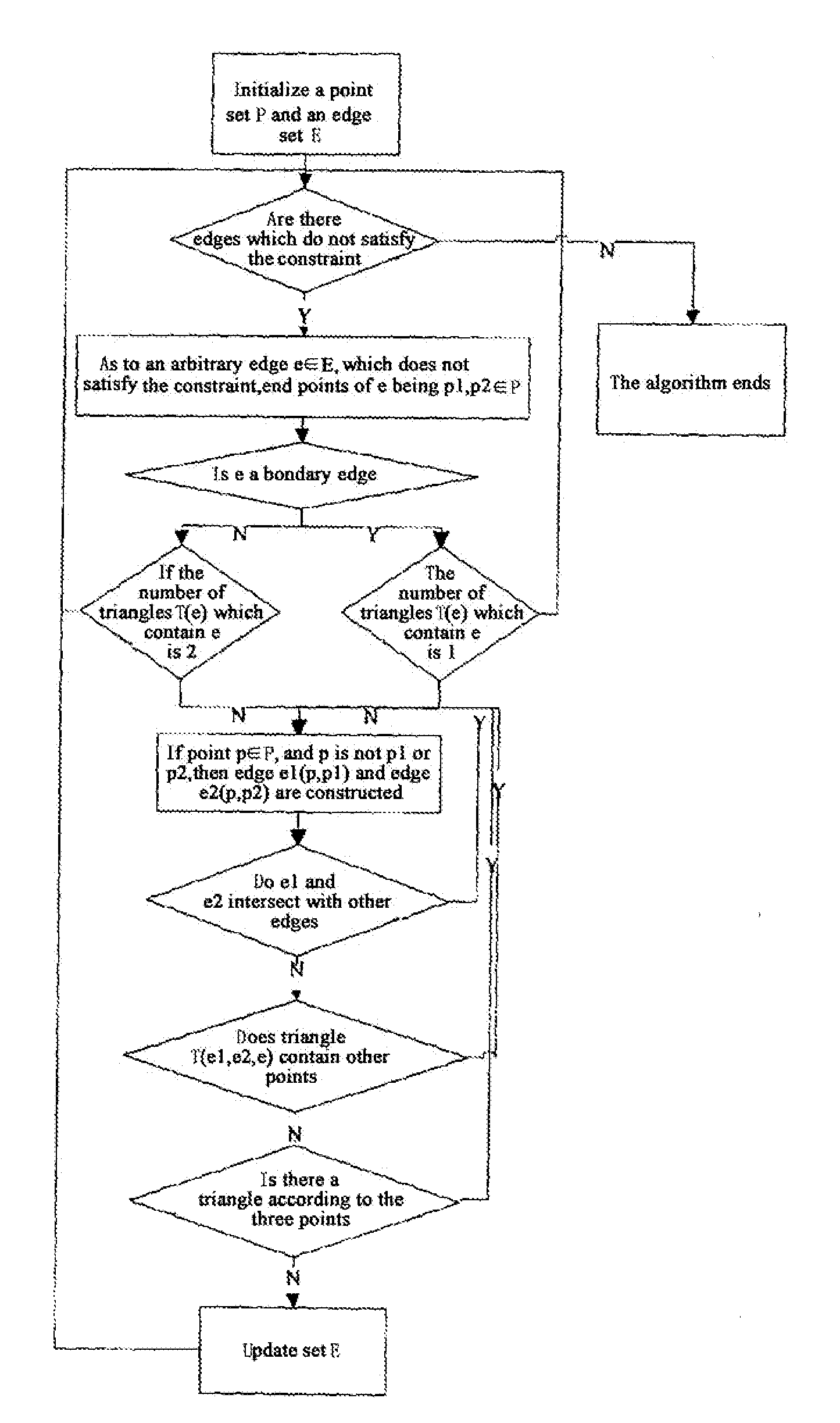
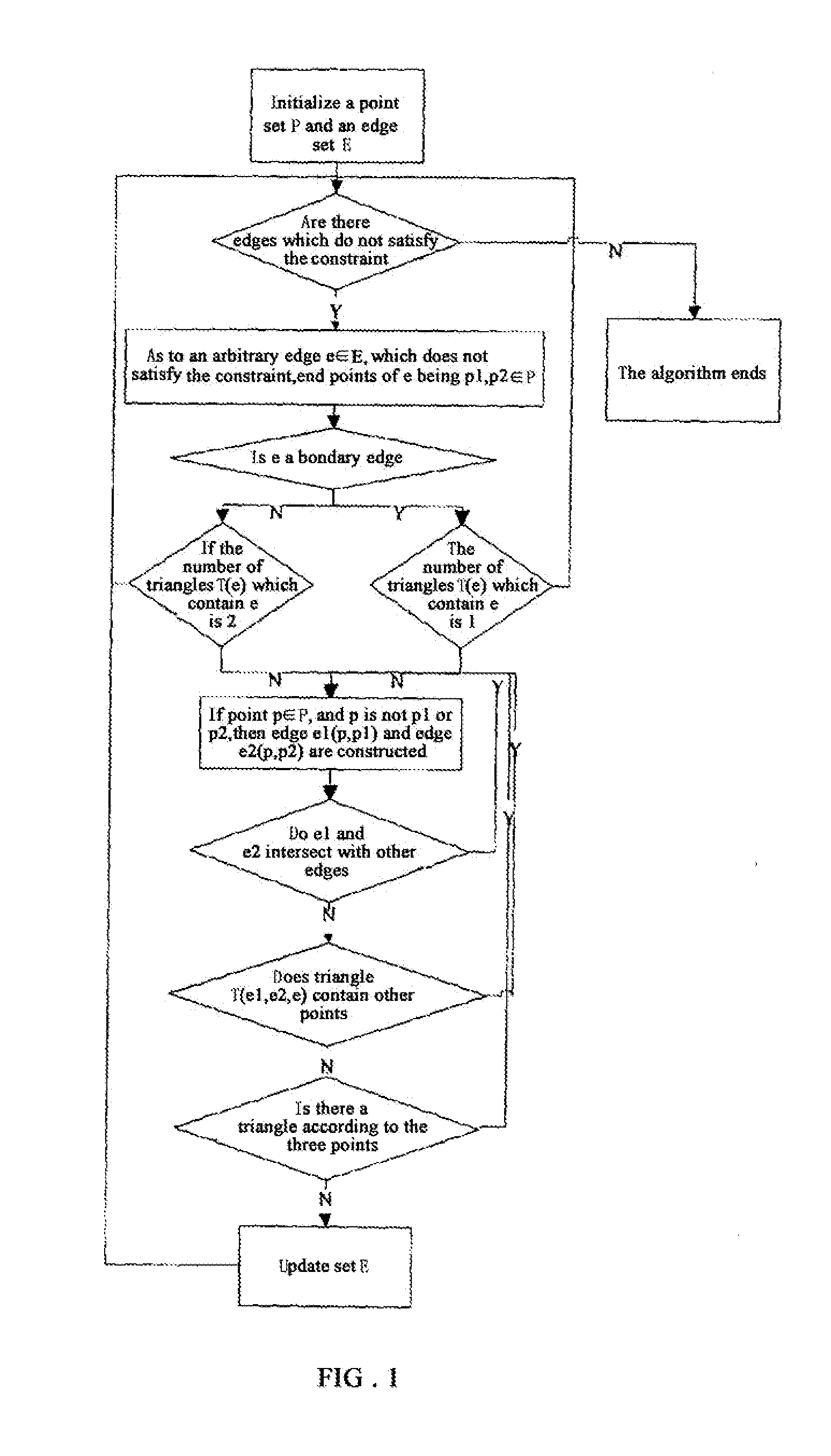
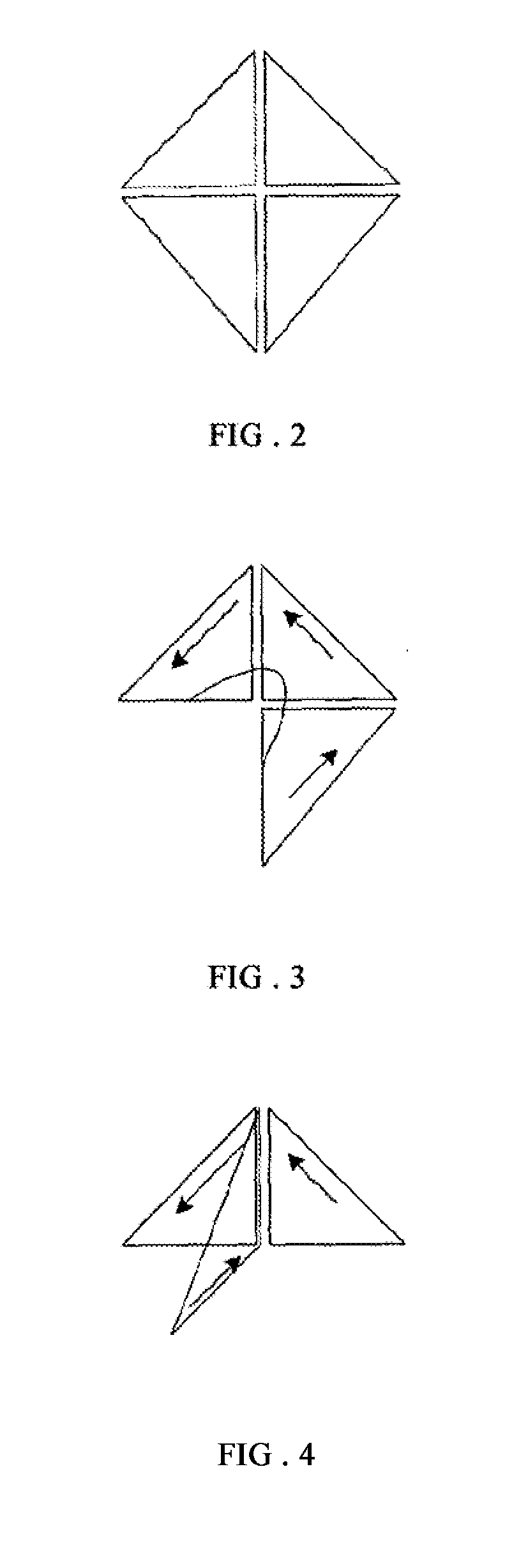
Block model constructing method for complex geological structures
InactiveUS20120166160A1High computation loadHigh solving difficultyGeomodellingComputation using non-denominational number representationTopological consistencyGeometric consistency
A block model constructing method for complex geological structures is provided. The method comprises the following steps: a) making a triangle mesh description of a layer plane or a fault plane; b) judging whether two triangles intersect, and finding out the intersection points if they intersect; c) performing a geometric consistency and topological consistency processing within every intersectant triangle; d) extracting an enclosing block to acquire an interface constituted of peripheral edges of the enclosing block, and defining a geological attribute of the enclosing block to form a three-dimensional model block. The method needs not to solve difficult equation sets with large computation, thus simplifying the constructing method.
Owner:BC P INC CHINA NAT PETROLEUM CORP
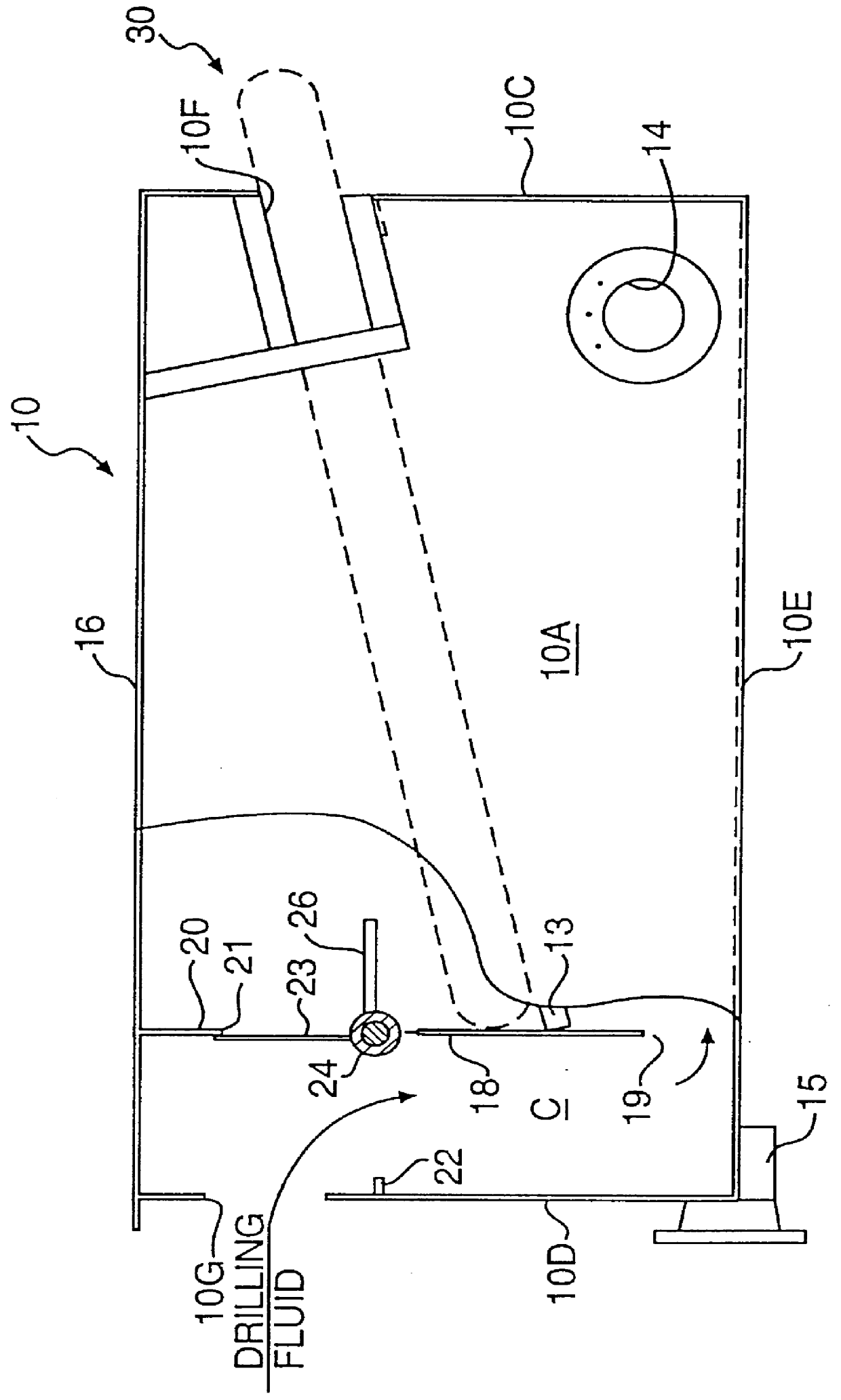
Weir box for drilling mud separation unit
InactiveUS6244362B1Settling tanks feed/dischargeLoose filtering material filtersLithologyShale shakers
A weir box disposed upstream from conventional solids control equipment of a mud system of a drilling rig contains a drilling mud separation unit having a continuous-loop scalper screen that is driven in a continuous loop to separate, convey and discharge large amounts of gumbo, heavy clays and drill solids at the end of the separation unit. The flow divider box is a box-like housing with a diverter plate, weir baffle plates and a sliding gate that allows drilling fluid or drilling mud to be selectively directed to the mud separation unit to be separated prior to passing to the conventional downstream solids control equipment or allows the fluid to bypass the separation unit and flow directly to the conventional solids control equipment. The sliding gate is adjustable to selectively control or meter the flow rate and to create a hydrostatic head upstream from the conventional solids control equipment. The weir box baffle plates, sliding gate, and selective utilization of the mud separation unit allows the operator to produce an increased hydrostatic head, which enables high flow rates to be easily processed by shale shakers and other conventional downstream solids control equipment of the mud system and to compliment the drilling operation with respect to changes in the lithology, geological formations, or loss of returns in relation to the gallons pumped or volume of drilling fluid or drilling mud entering the weir box.
Owner:WILLIAMS J TERRELL
Use of bacteria to prevent gas leakage
InactiveUS20060216811A1Reduce leakageReduce penetrationCarbon-dioxide storageFermentationGas leakMicrobial Biofilms
The present invention relates to the use of microbial biofilms and microbial induction of calcium carbonate precipitation to sequester gases in underground geological formations. In one embodiment, methods of the invention can be used to prevent the leakage of supercritical CO2 in underground geological formations such as aquifers.
Owner:MONTANA STATE UNIVERSITY
Shaped cutter surface
ActiveUS7798257B2Reduce certain adverse consequenceSmooth curveDrill bitsConstructionsEngineeringAbnormal shaped
Owner:SMITH INT INC
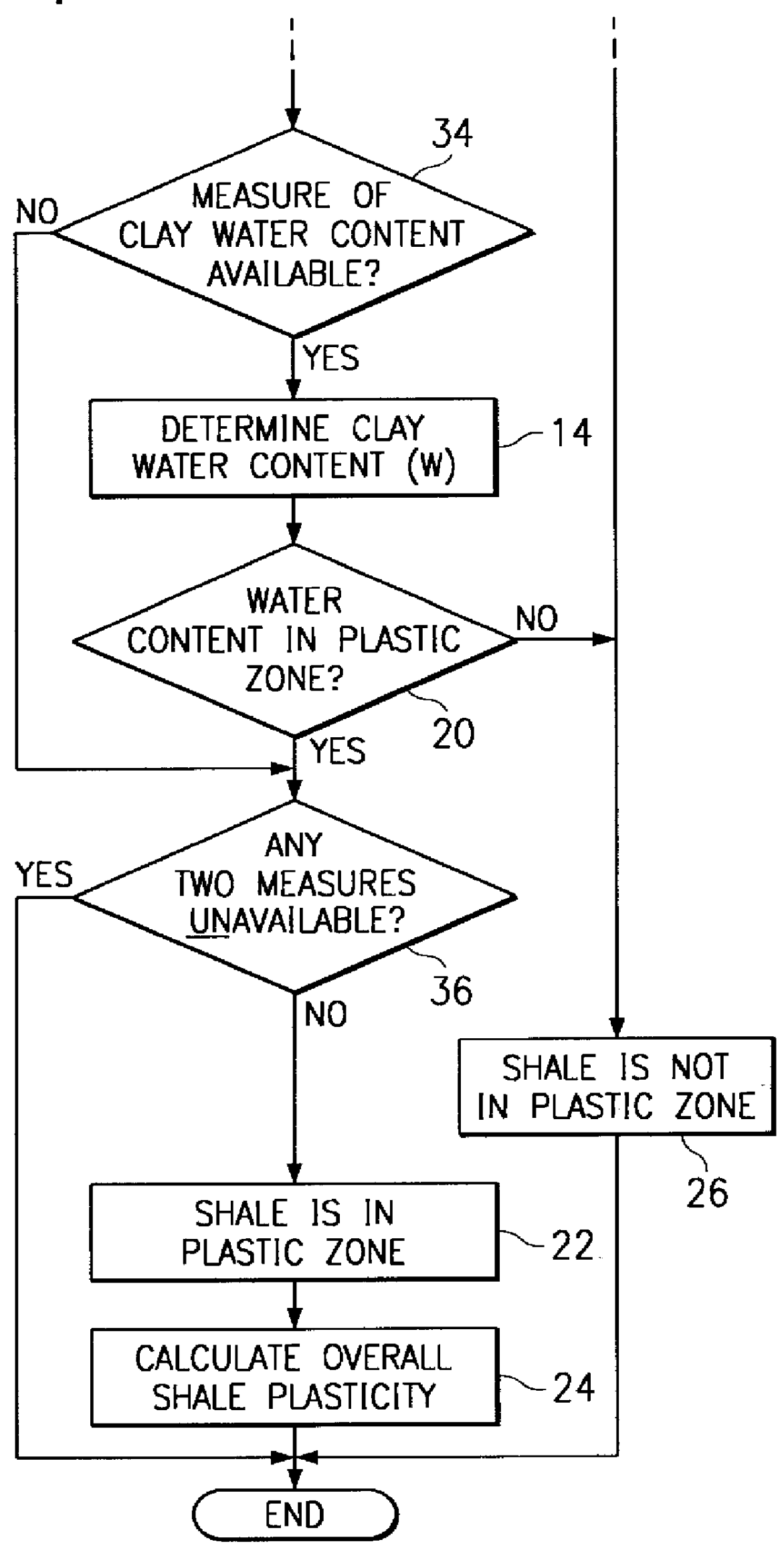
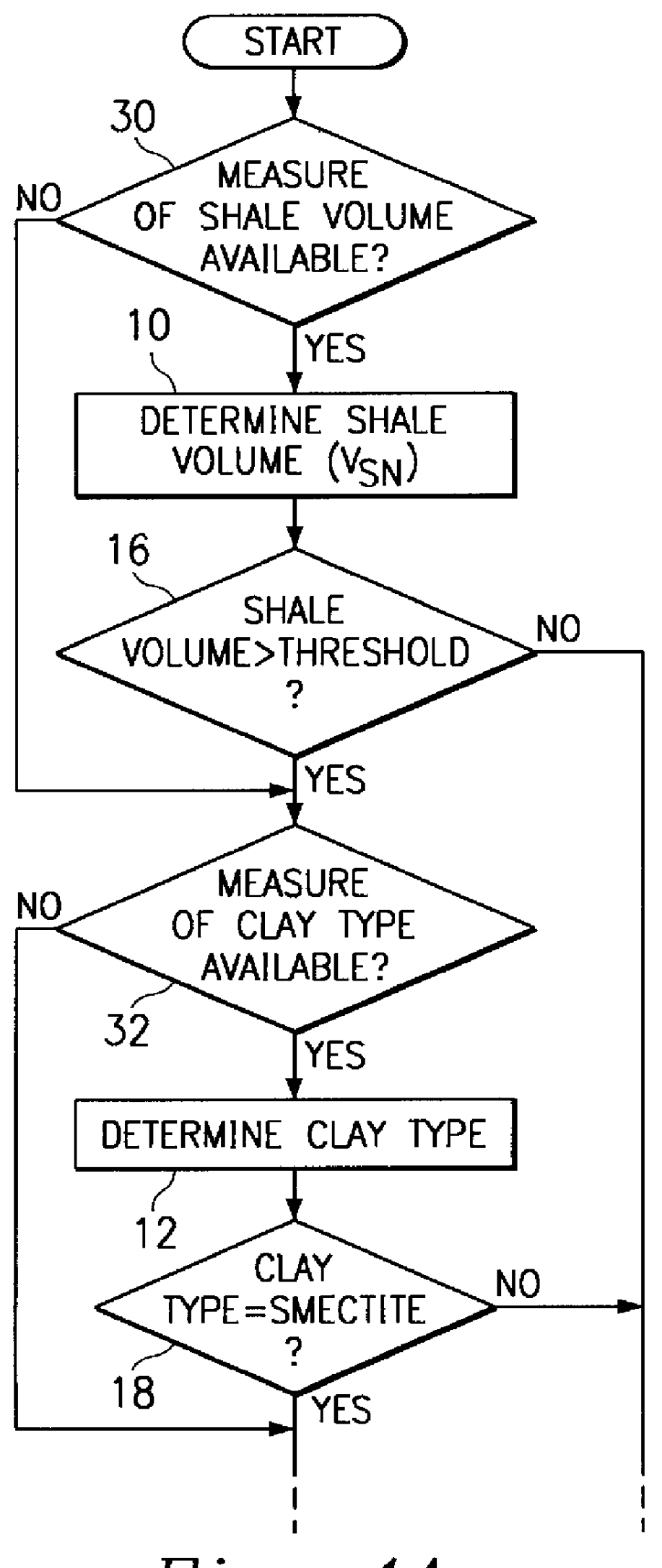
Method and apparatus for quantifying shale plasticity from well logs
InactiveUS6052649AApparent advantageAccurate modelingElectric/magnetic detection for well-loggingSeismology for water-loggingWell loggingWater content
Shale plasticity in a geological formation is quantified by the steps of measuring a shale volume of the formation, measuring a shale composition of the formation, measuring a shale water content of the formation, and determining a measure of shale plasticity of the formation in response to the measured shale volume, shale composition, and shale water content according to a shale plasticity model. An apparatus for quantifying shale plasticity is disclosed also.
Owner:HALLIBURTON ENERGY SERVICES INC
High-density rapid detection method based on z-component transmitting channel waves
ActiveCN102788991AImprove work efficiencyIncreased Ray Coverage DensitySeismic signal processingBandpass filteringAlgorithm
The invention relates to a high-density rapid detection method based on z-component transmitting channel waves. The method is achieved by the following steps: (1) collecting data; (2) processing the data by firstly setting an observation system (that is, inputting shots and receiver points coordinates), collecting z-component channel waves by the observation system, and then performing channel wave data analysis, bandpass filtering and imaging in sequence; (3) interpreting the data by comprehensively judging chasms, falling columns and other geological abnormal developmental conditions in the working face based on the combination of the imaging result and the geological data disclosed by the working face laneway, and making an integrated interpretation map of the geological structure in the working face. The method greatly increases the work efficiency, allows the construction of the wide-span working face (more than 1000 m) to be completed within 8 hours, collects the Z-component channel wave signals at the same time by the measurement points which are arranged on the laneway lateral walls, increases the ray coverage density, collects the information as much as possible, and improves the detection precision.
Owner:XIAN RES INST OF CHINA COAL TECH& ENG GROUP CORP
Method and System for Subsurface Resource Production
ActiveUS20170175505A1Improve breathabilityHigh densityGeothermal energy generationFluid removalPower flowMagneto hydrodynamic
A means to generate increasing geological permeability to produce greater volumes of various subsurface geological resources when compared to the current conventional production methods is disclosed. The means include a Pulsed Power Plasma Emitter System capable of substantially increasing the available electrical energy for use in high power compression surge currents that can be discharged and transmitted to power a simplified downhole Plasma Emitter Tool subsystem. The simplified downhole Plasma Emitter Tool sub-system is capable of generating a broad range of precisely controlled magnetohydrodynamic plasma spark discharges that produce a broad range of high power electromagnetic, acoustic and hydrodynamic surge waves. These powerful surge waves are generated at energy and power levels that are necessary to physically modify all types of geological formation permeability and to energize the mobilization of various subsurface fluids and fluidized resources.
Owner:GREEN CHEM ENERGY LLC
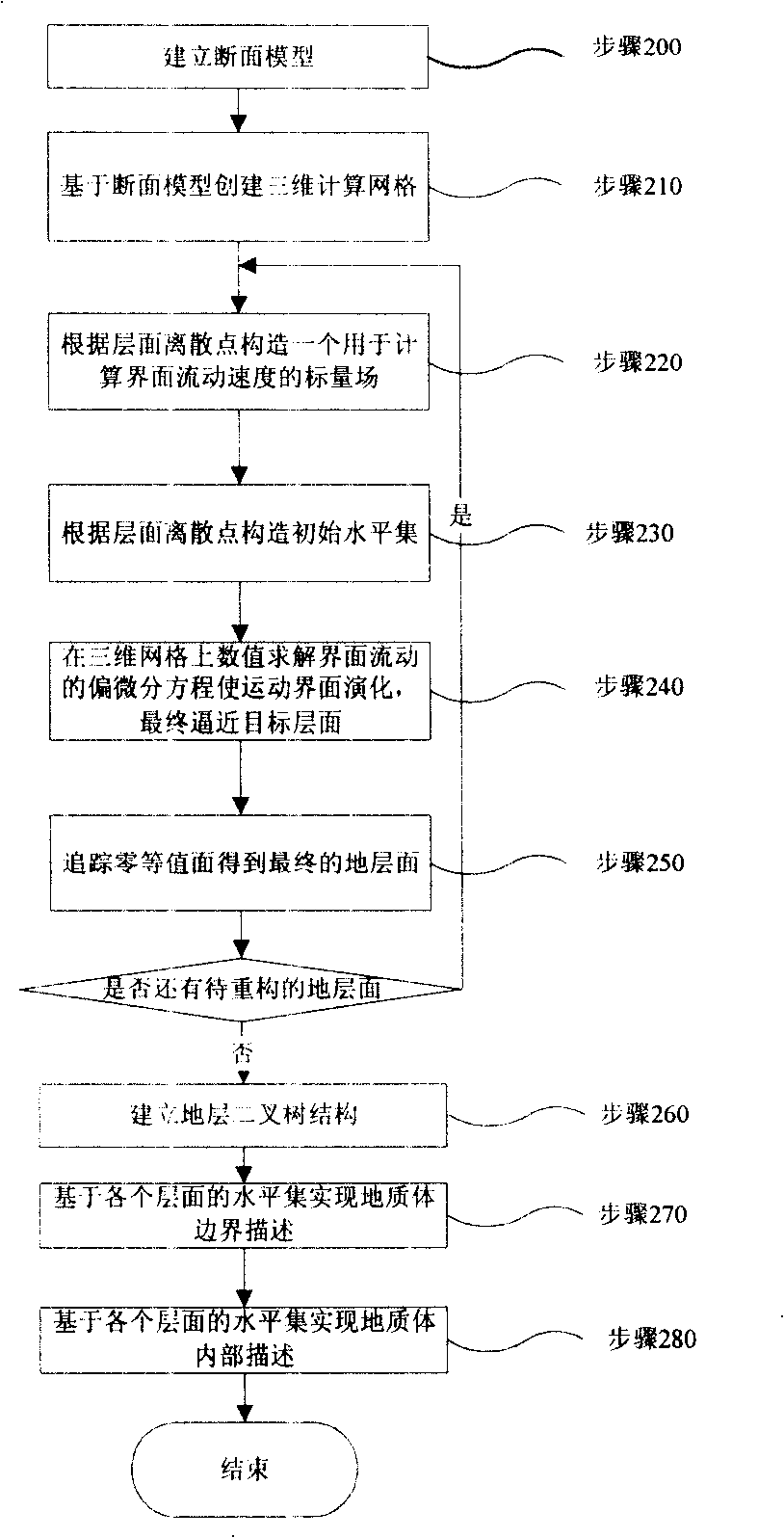
Method for generating ground layer surface and geologic body based on level set
ActiveCN101303414AImprove efficiencyHigh precisionSeismic signal processingSalt domePartial differential equation
The invention discloses a bedding surface based on a level set and a method for generating a geologic body, which is applied to a system for geologic modeling, simulation and analysis. The method is characterized by comprising the steps: a sectional model is built, and a three-dimensional computational grid is formed on the basis of the sectional model; a scalar field used for calculating the flowing speed of a computational interface is formed in each bedding surface according to bedding surface discrete points; an initial level set is built according to the bedding surface discrete points; numerical solutions to the partial differential equation about the flowing of the interface are carried out in the three-dimensional grid, which causes the level set to update so as to lead to the evolution of the moveable interface, finally drawing near to a target bedding surface; a final strata surface is obtained by tracing a zero contour surface; the level set corresponding to each bedding surface is utilized to realize the description of the boundary and interior of the geologic body. The invention can realize the automatic reconstruction of bedding surfaces and geologic bodies of a plurality of faults at complicated geologic states, such as overthrust faults, mushroom bodies, salt domes, lenticular bodies, and the like, and effectively improve the generating efficiency and precision of complicated geologic structure models.
Owner:北京网格天地软件技术股份有限公司
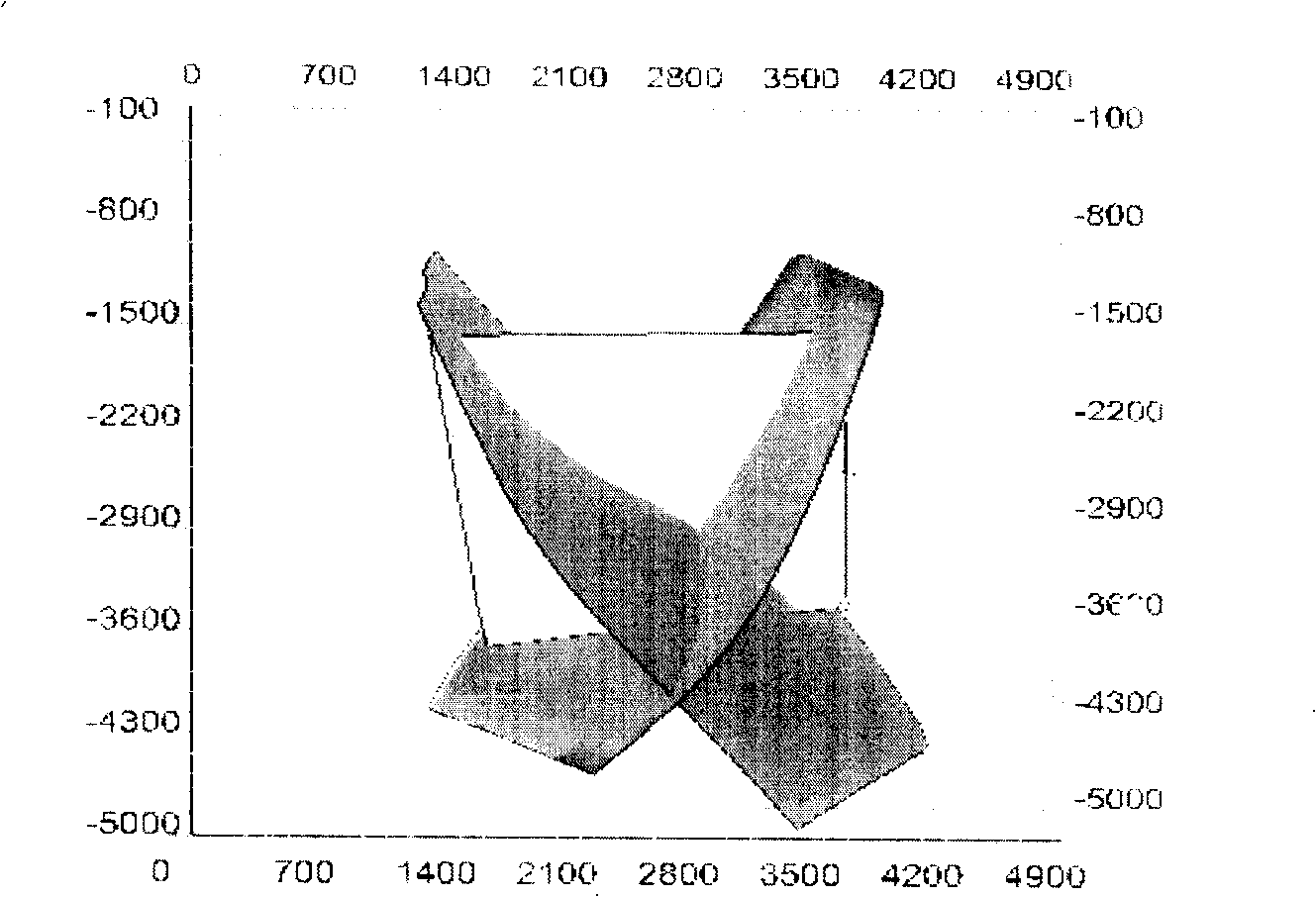
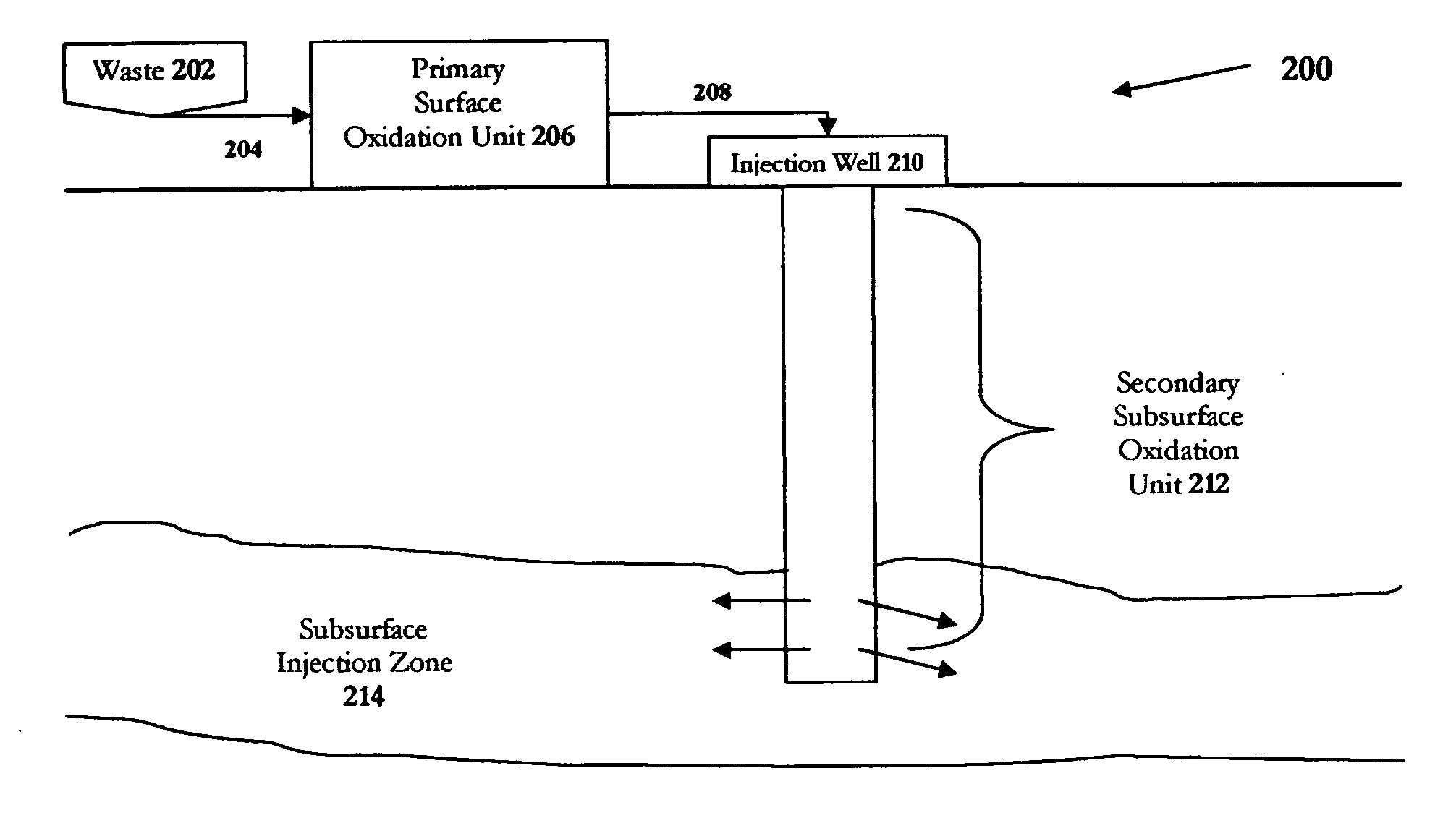
Waste disposal method and apparatus using wet oxidation and deep well injection
InactiveUS20060060541A1Sludge treatmentWater/sewage treatment by substance additionEnvironmental engineeringEngineering
The present invention relates generally to waste treatment methodologies and technologies for treatment and disposal of organic wastes. More specifically, in a preferred embodiment of the present invention, there is described a system and methodology for treating organic waste by wet oxidation processes or wet air oxidation processes (carried out on the surface or subsurface) followed by introduction of the treated waste mixture into a disposal well and injection of the mixture into a suitable geological formation. Ideally, the mixture is filtered prior to injection into the formation. The method and apparatus of the present invention provide increased waste treatment throughput as compared to conventional use of wet oxidation or wet air oxidation followed by surface biotreatment.
Owner:TM DEER PARK SERVICES
Oil and Gas Well Proppants Of Silicone-Resin-Modified Phenolic Resins
InactiveUS20140124200A1Stable and long lasting and cost-effectiveLong and stableFluid removalFlushingPolyresinCopolymer
Owner:WACKER CHEM CORP
Method and apparatus for injecting steam into a geological formation
The present invention generally provides a method and apparatus for injecting a compressible fluid at a controlled flow rate into a geological formation at multiple zones of interest. In one aspect, the invention provides a tubing string with a pocket and a nozzle at each isolated zone. The nozzle permits a predetermined, controlled flow rate to be maintained at higher annulus to tubing pressure ratios. The nozzle includes a diffuser portion to recover lost steam pressure associated with critical flow as the steam exits the nozzle and enters a formation via perforations in wellbore casing. In another aspect, the present invention assures that the fluid is supplied uniformly to a long horizontal wellbore by providing controlled injection at multiple locations that are distributed throughout the length of the wellbore. In another aspect, the invention ensures that saturated steam is injected into a formation in a predetermined proportion of water and vapor by providing a plurality of apertures between a tubing wall and a pocket. The apertures provide distribution of steam that maintains a relative mixture of water and vapor. In another aspect of the invention, a single source of steam is provided to multiple, separate wellbores using the nozzle of the invention to provide a controlled flow of steam to each wellbore.
Owner:WEATHERFORD TECH HLDG LLC
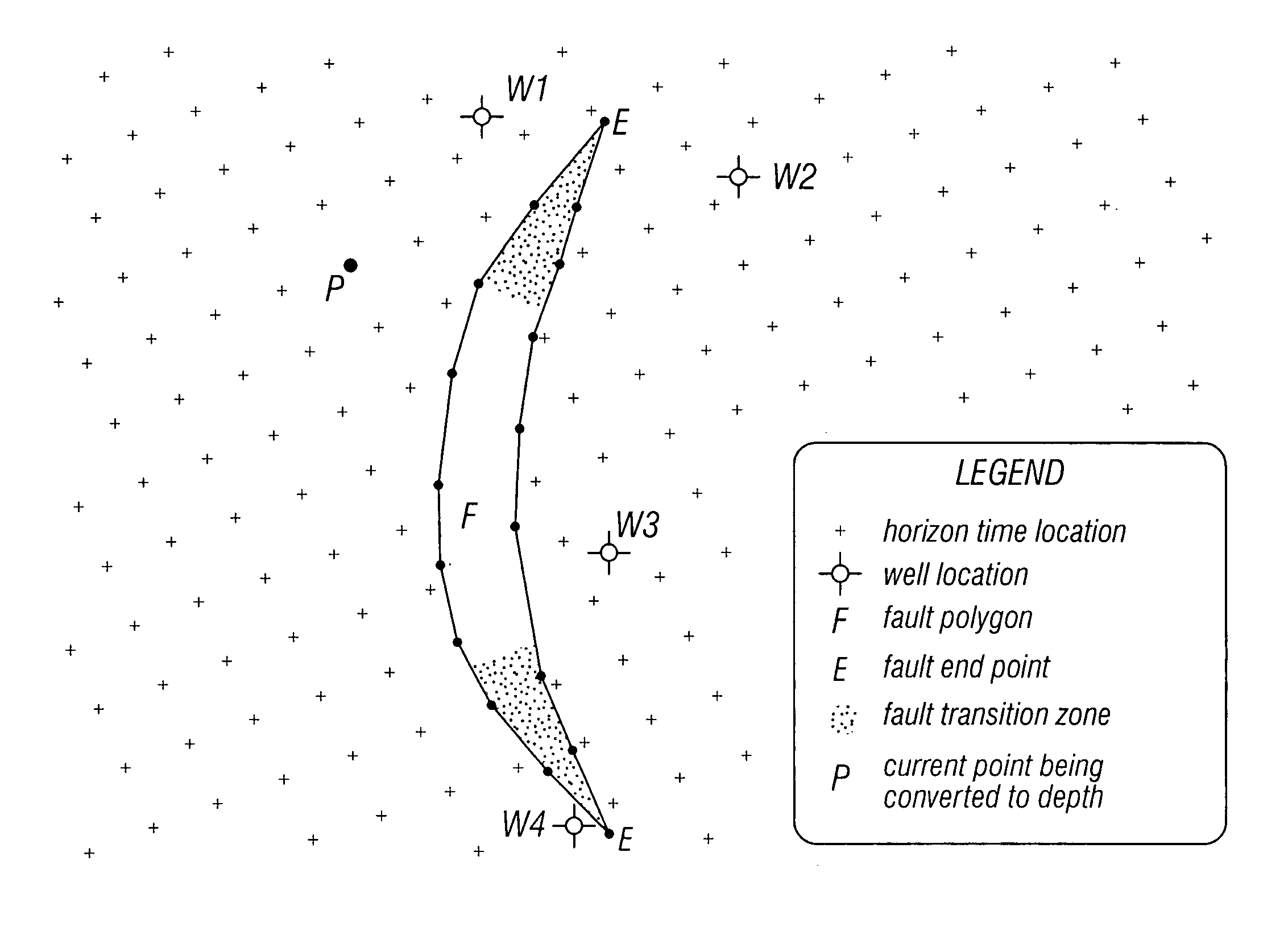
Method of estimating geological formation depths by converting interpreted seismic horizons from the time domain to the depth domain
InactiveUS20060047429A1Electric/magnetic detection for well-loggingSeismic signal processingHorizonData set
According to one aspect of the invention, a method of estimating geological location depths by converting horizon data from the time domain to the depth domain is provided, wherein the method comprises at least a data accumulation step and a data evaluation step, wherein the data evaluation step further comprises assignment of greater statistical weight to data derived from closer data acquisition points than to data derived from further data acquisition points using a weighted regression analysis, with distance being one of several weighting criteria. According to a further aspect of the invention, a method of estimating geological location depths is provided, wherein the method comprises a continuous, layer-by-layer computation of geological formation depths achieved by extracting values from horizon time data set at an exact geographic location of the next deeper horizon, thereby allowing interval computations to be carried out without the need for gridding. According to a still further aspect of the invention, a method of estimating geological formation depths is provided, wherein the method comprises estimating an expected error based on data scatter, and then allowing an alternative solution to be either partially or fully employed in areas where the accumulated data is insufficient to determine an acceptably reliable geophysical model.
Owner:ADAMS STEVEN L
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com