Patents
Literature
80 results about "Negative buoyancy" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Negative buoyancy is what causes objects to sink. It refers to an object whose weight is more than the weight of the liquid it displaces. For example, a pebble may weigh 25 grams, but if it only displaces 15 grams of water, it cannot float.
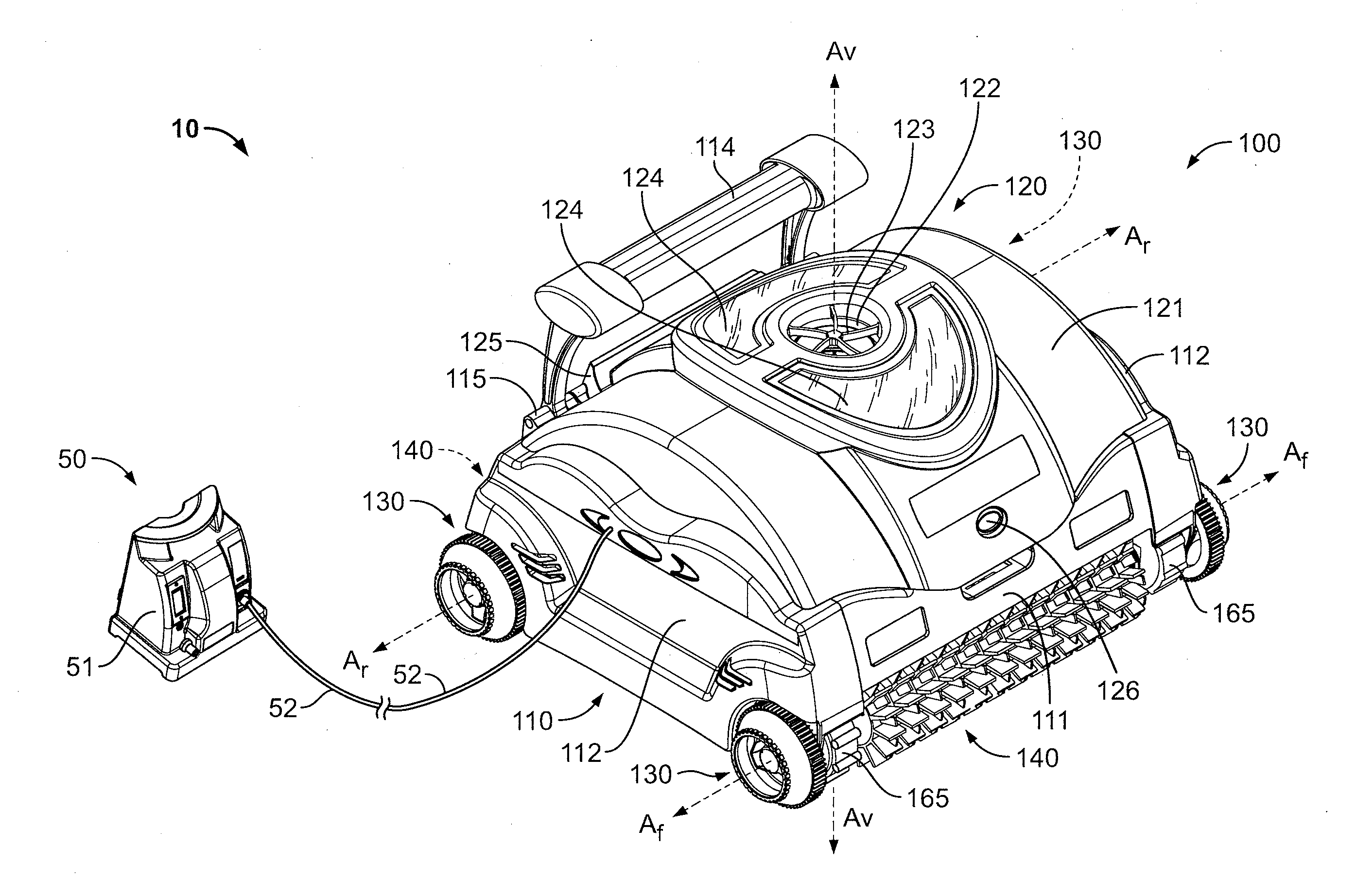
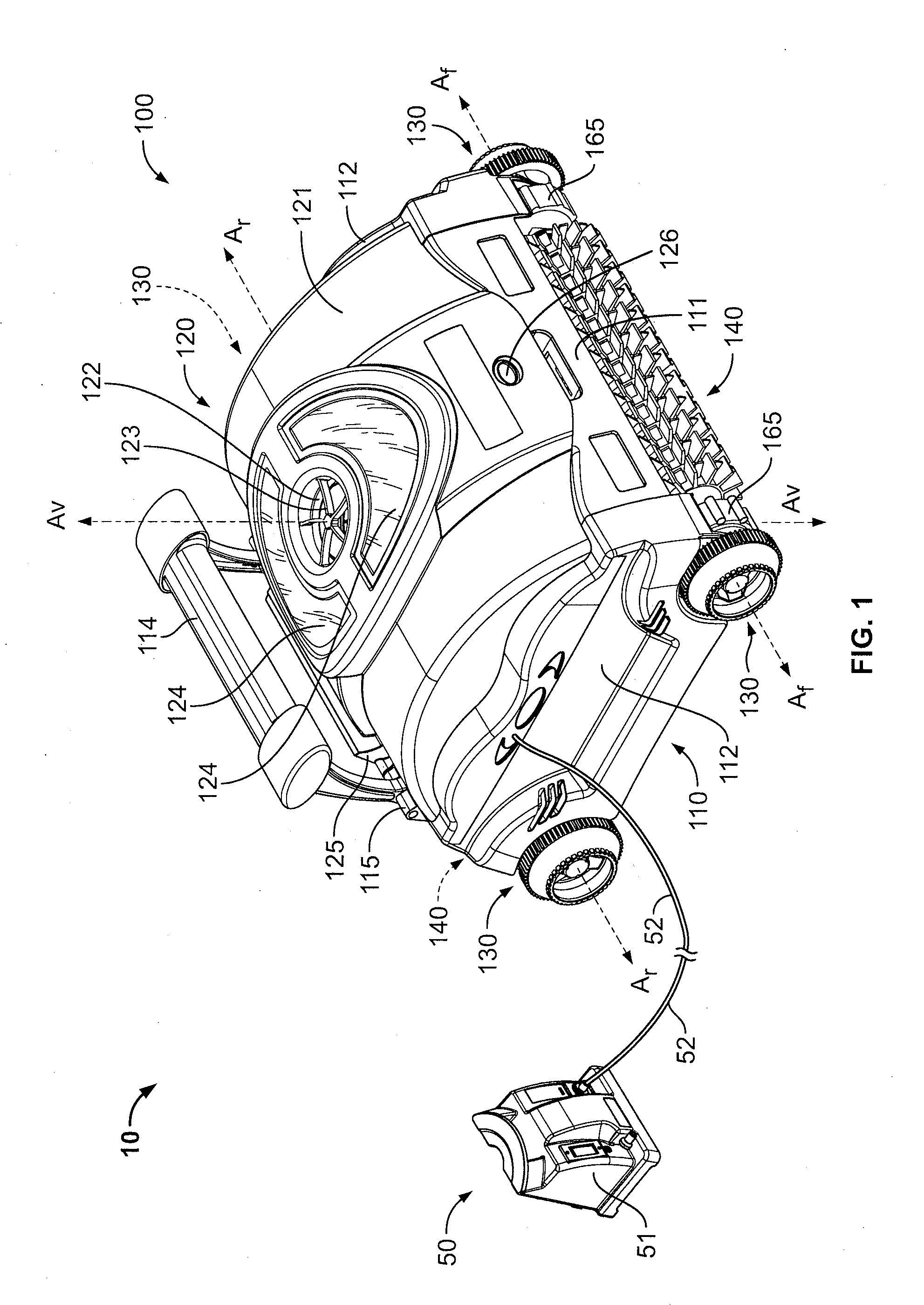
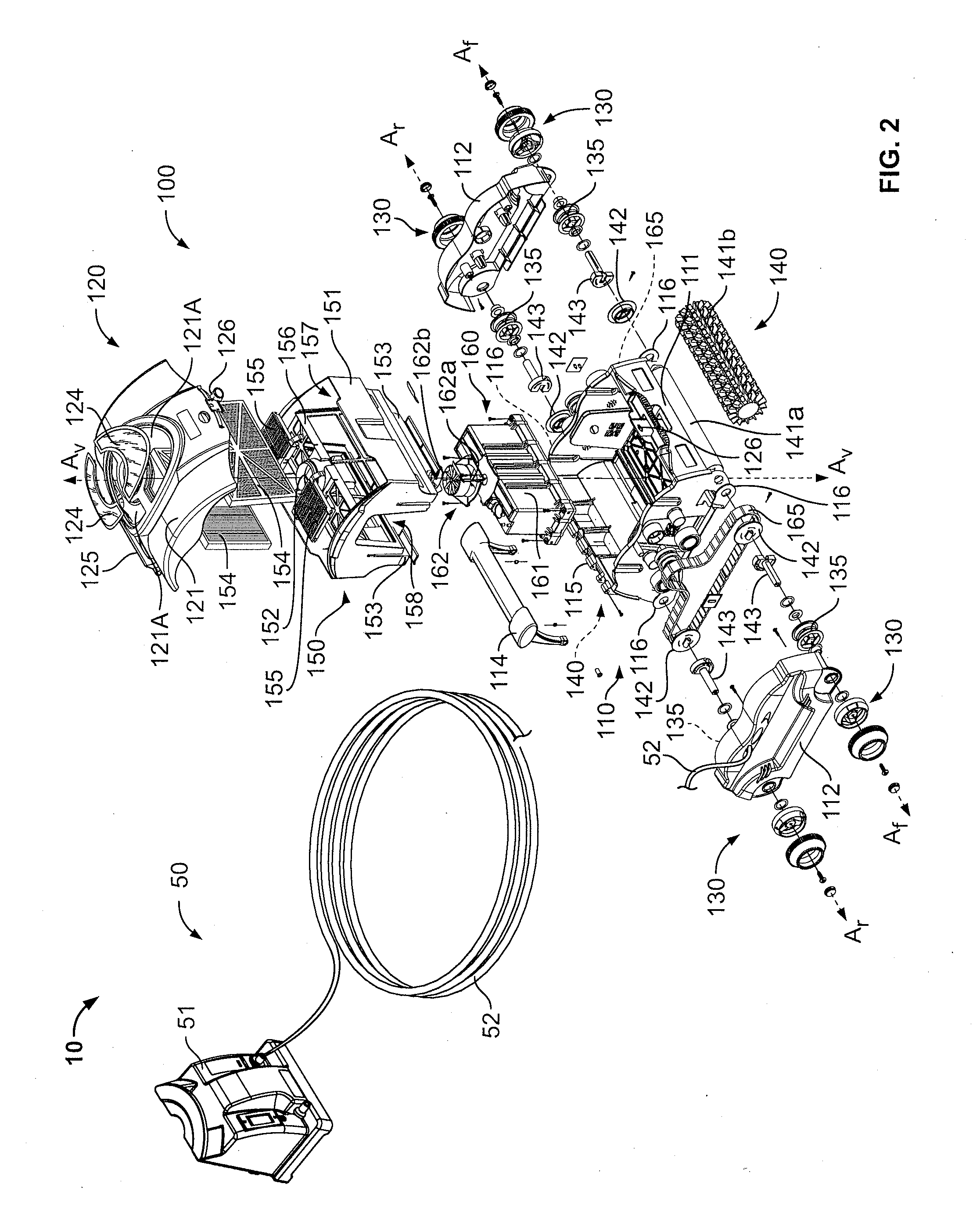
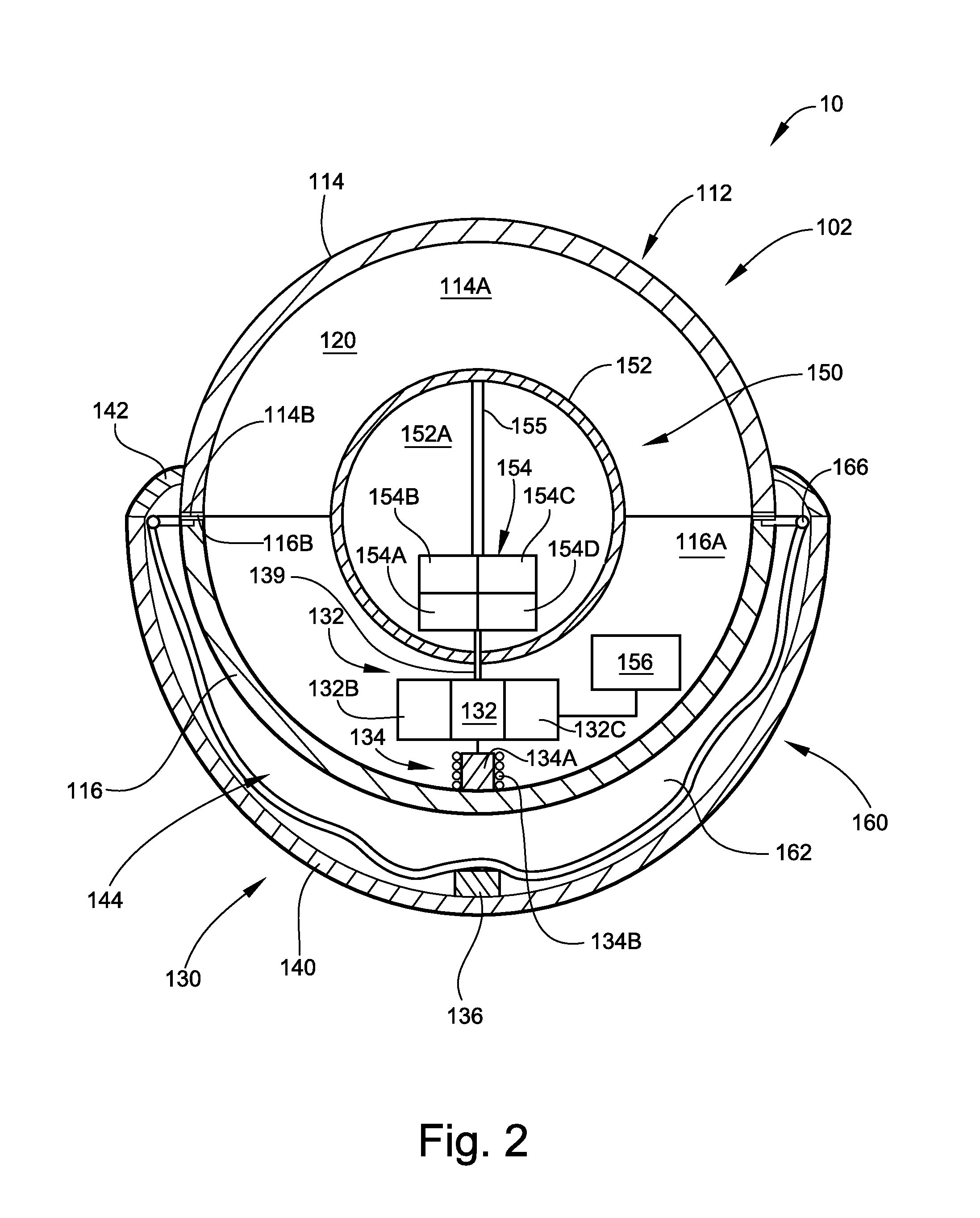
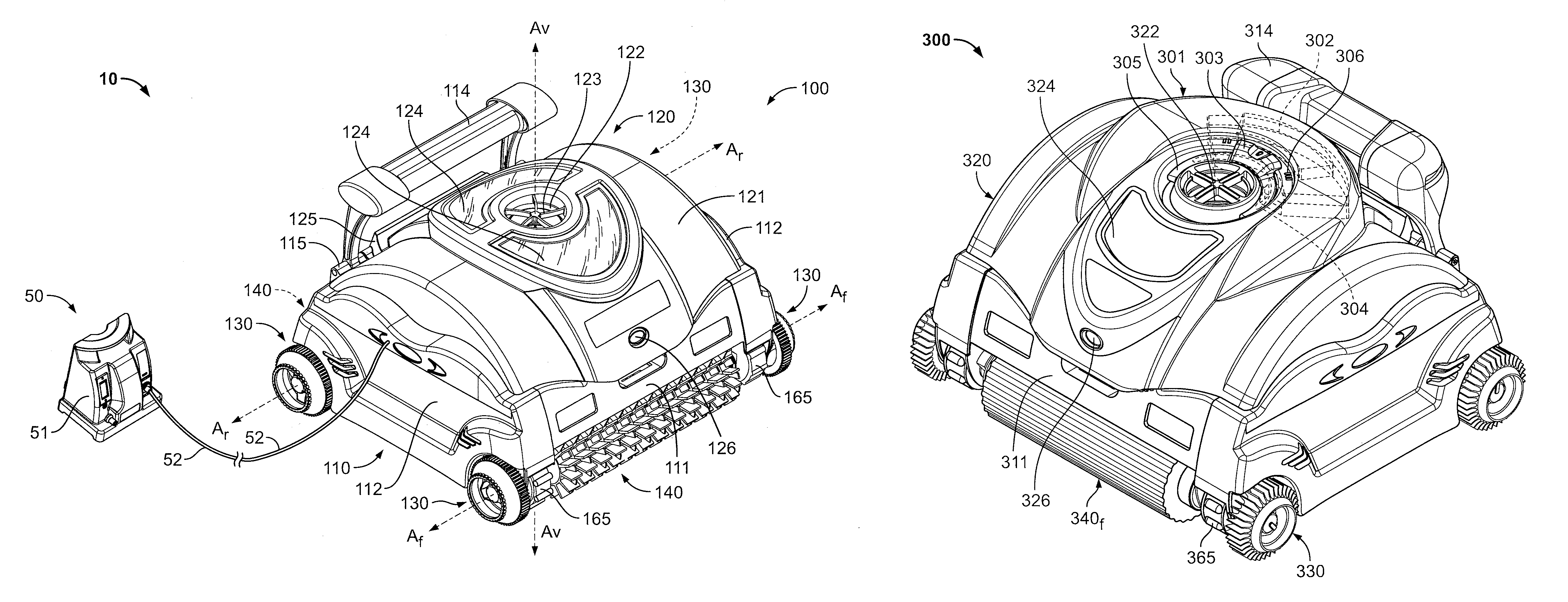
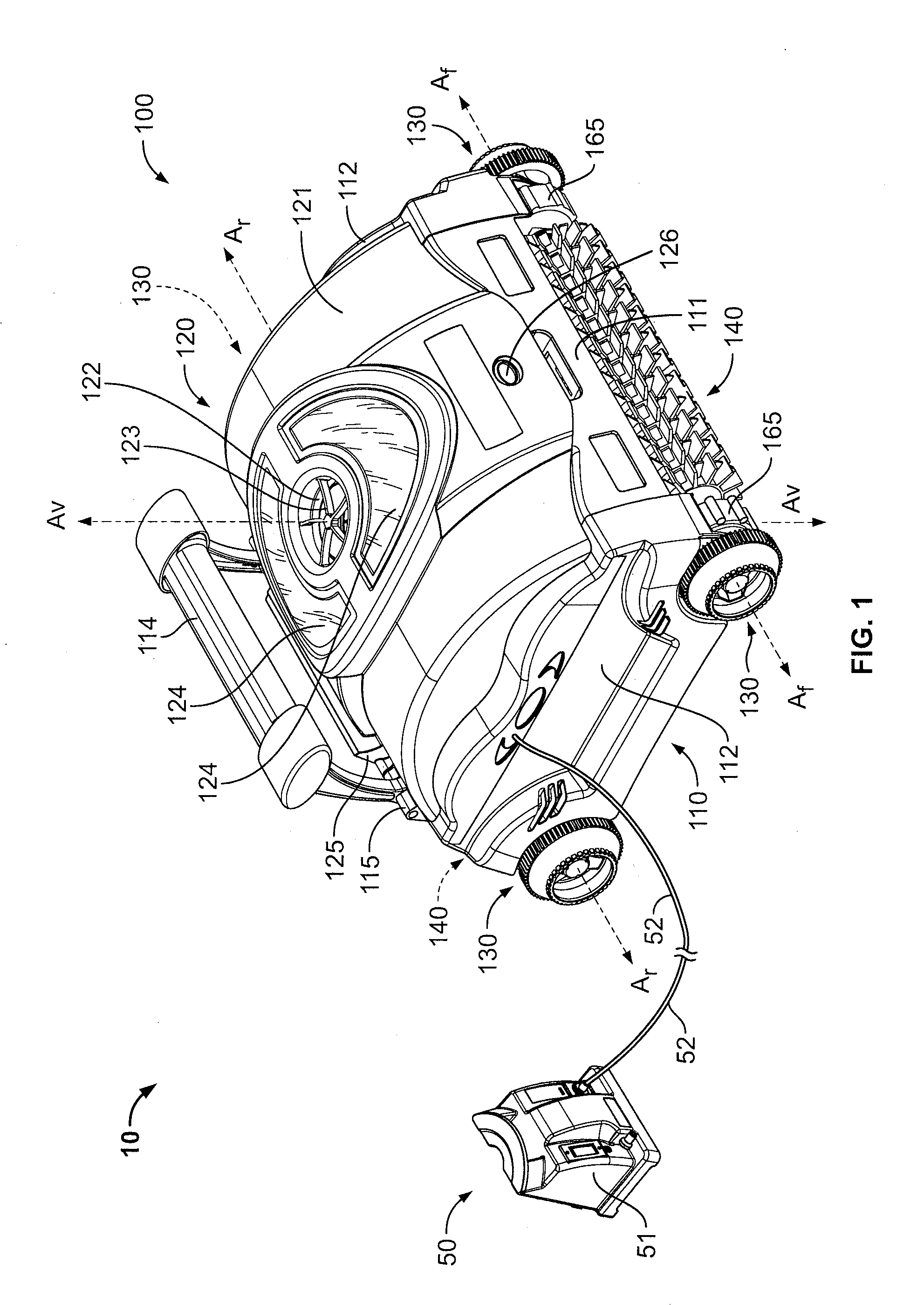
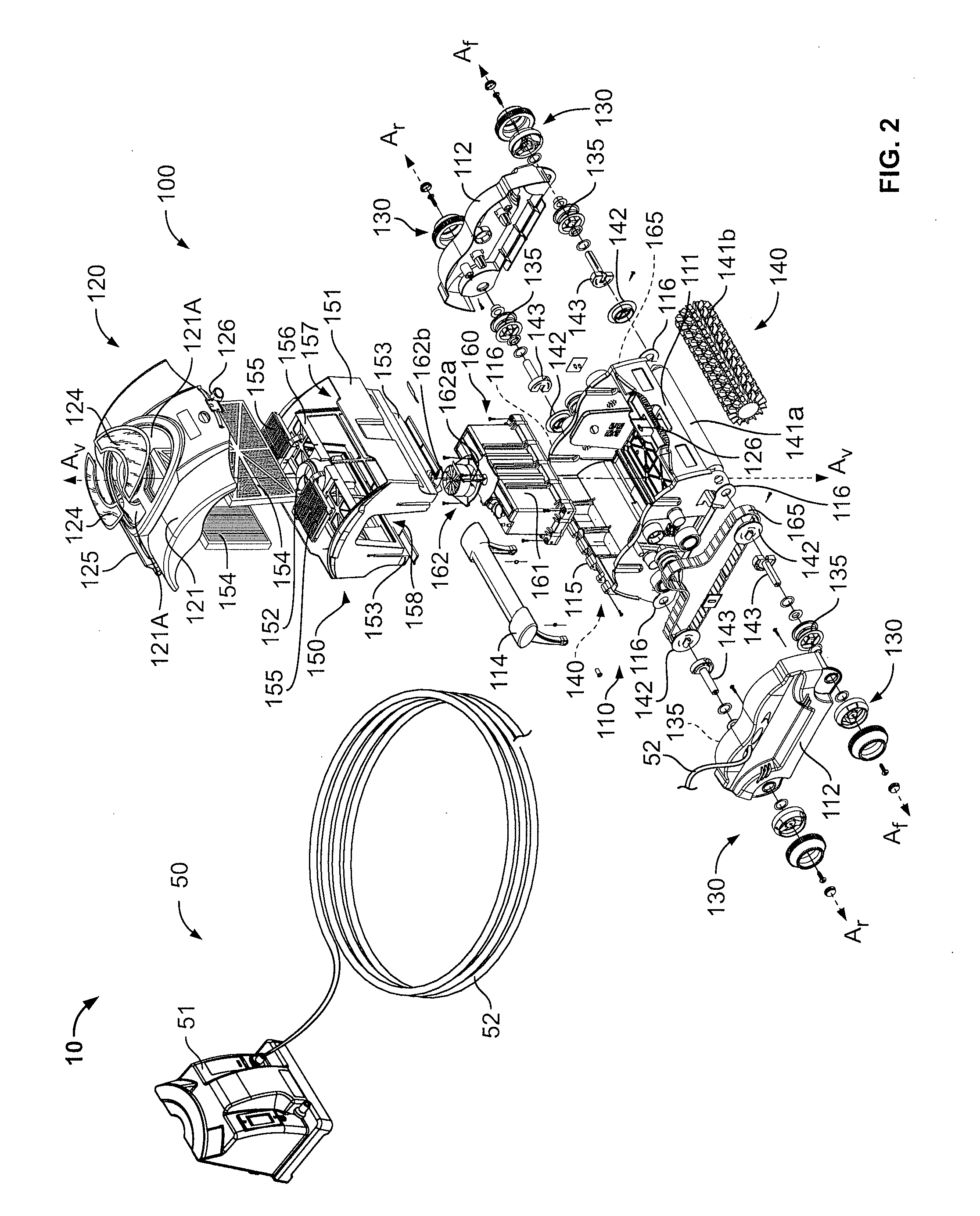
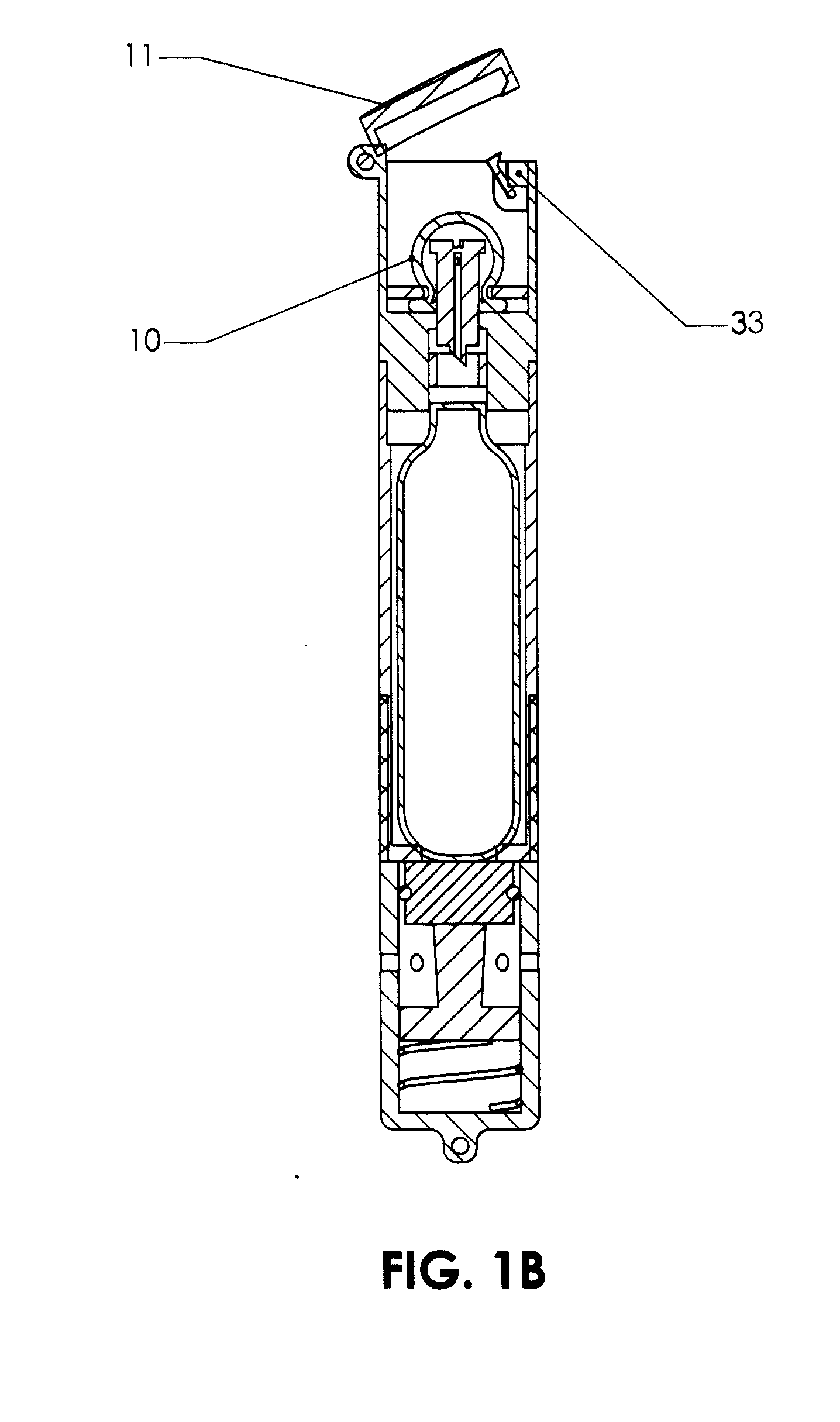
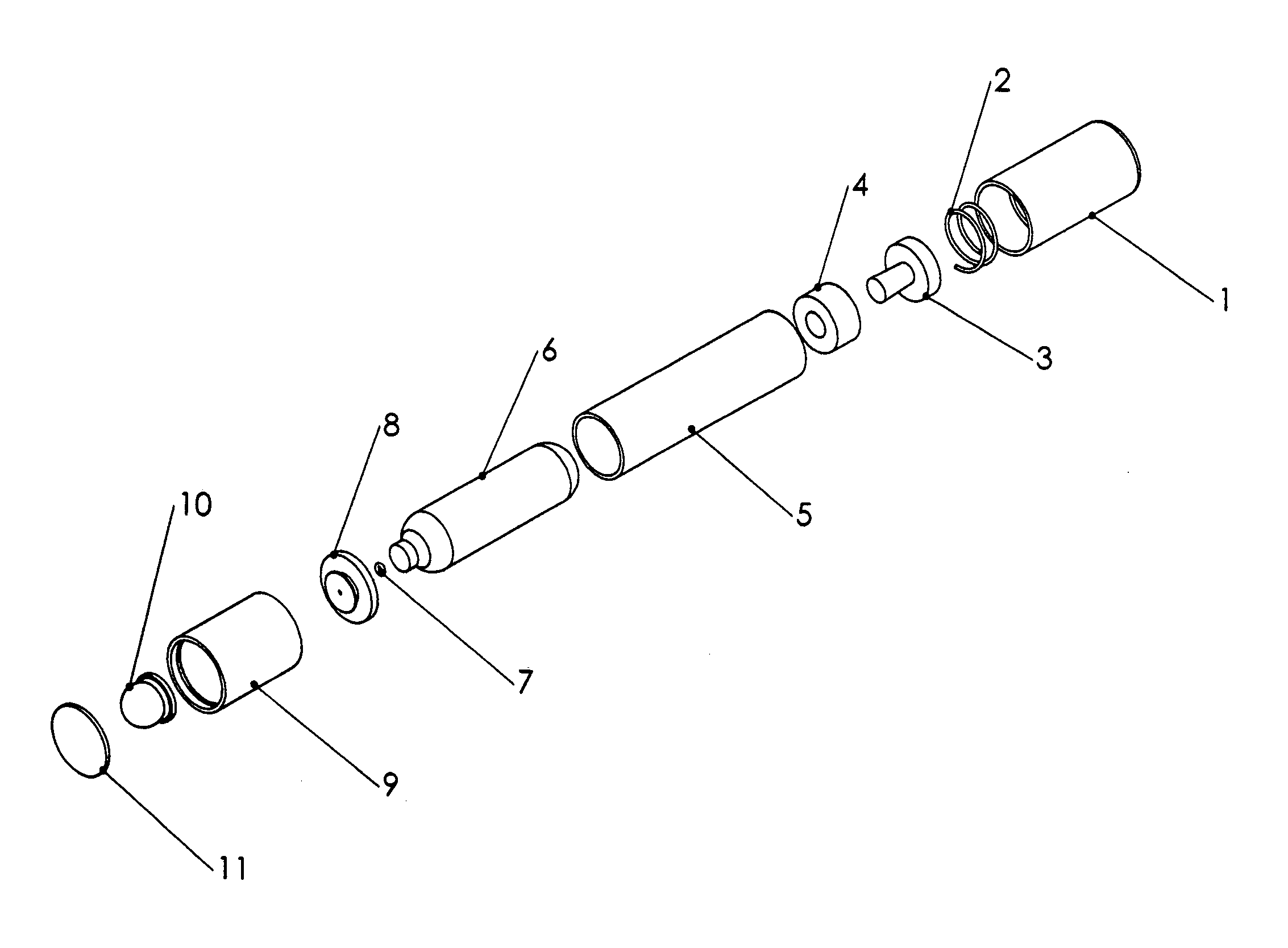
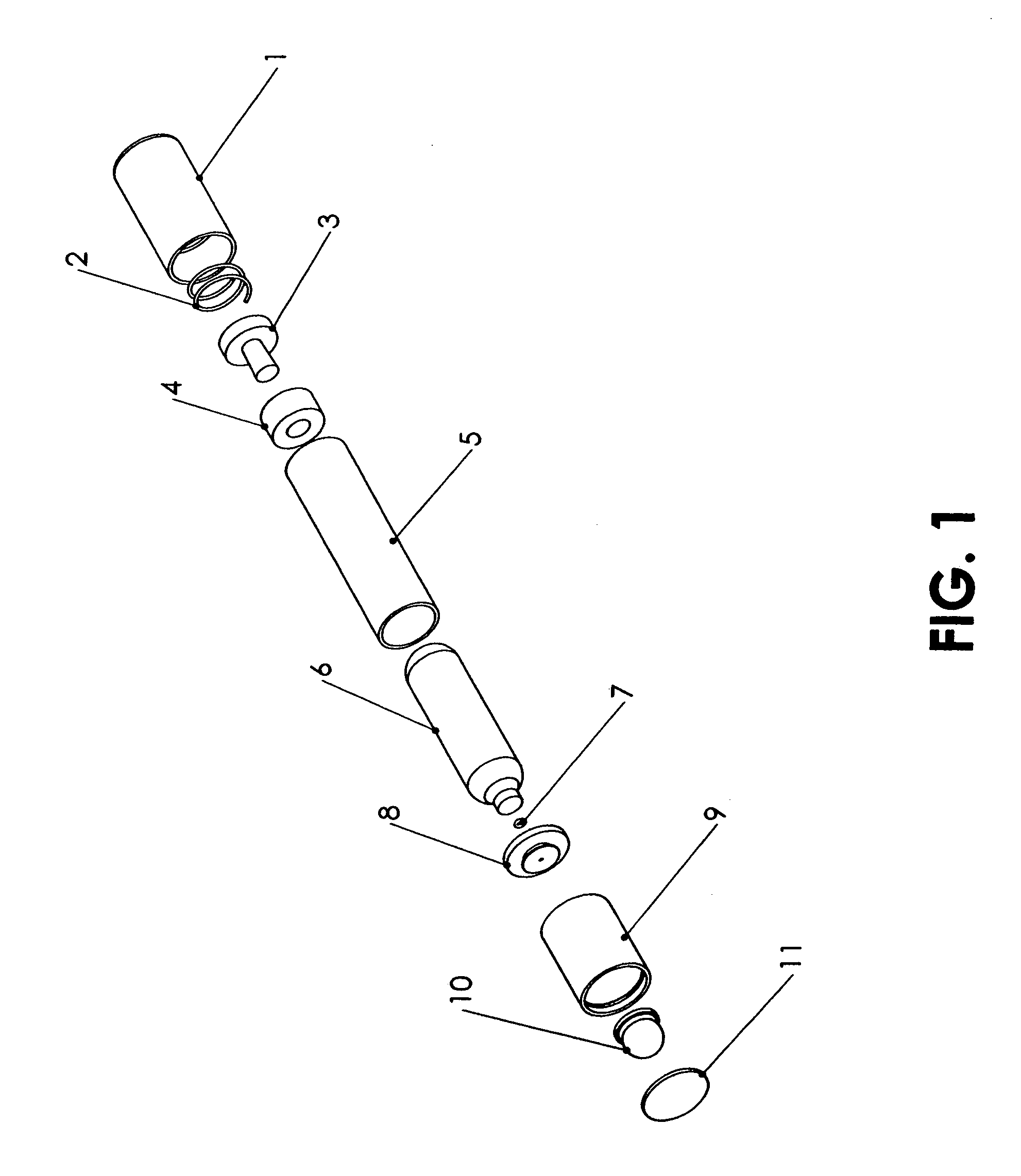
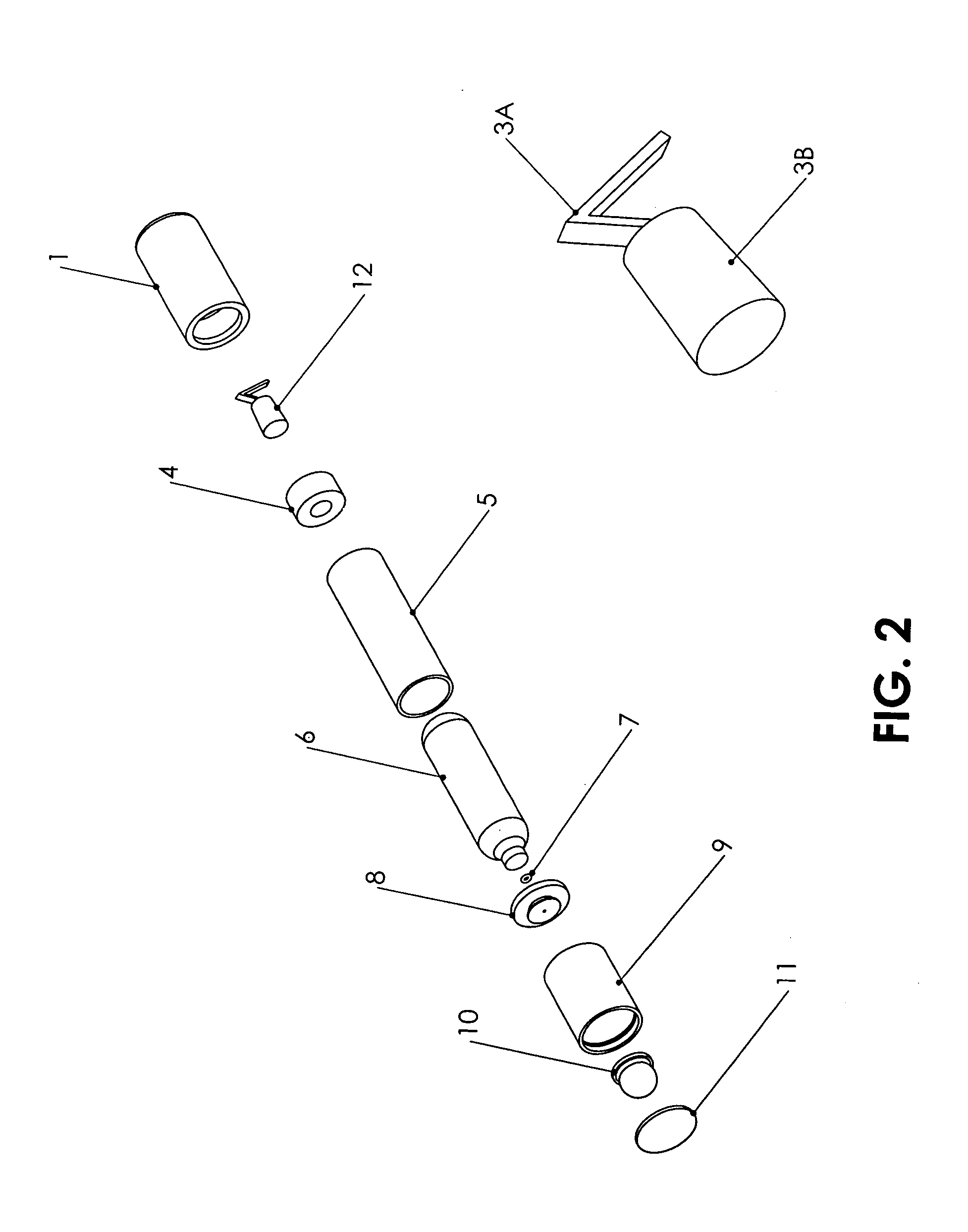
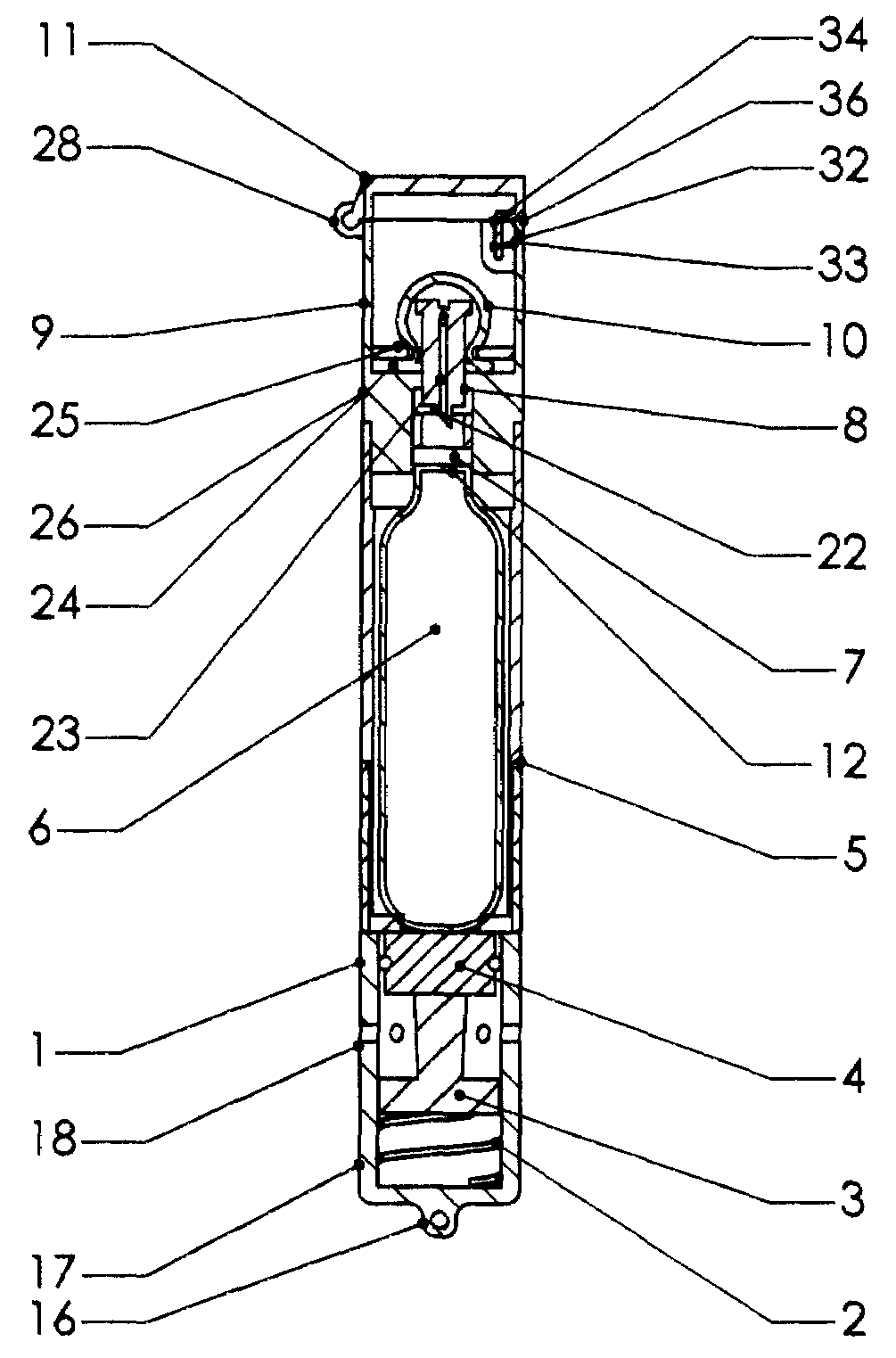
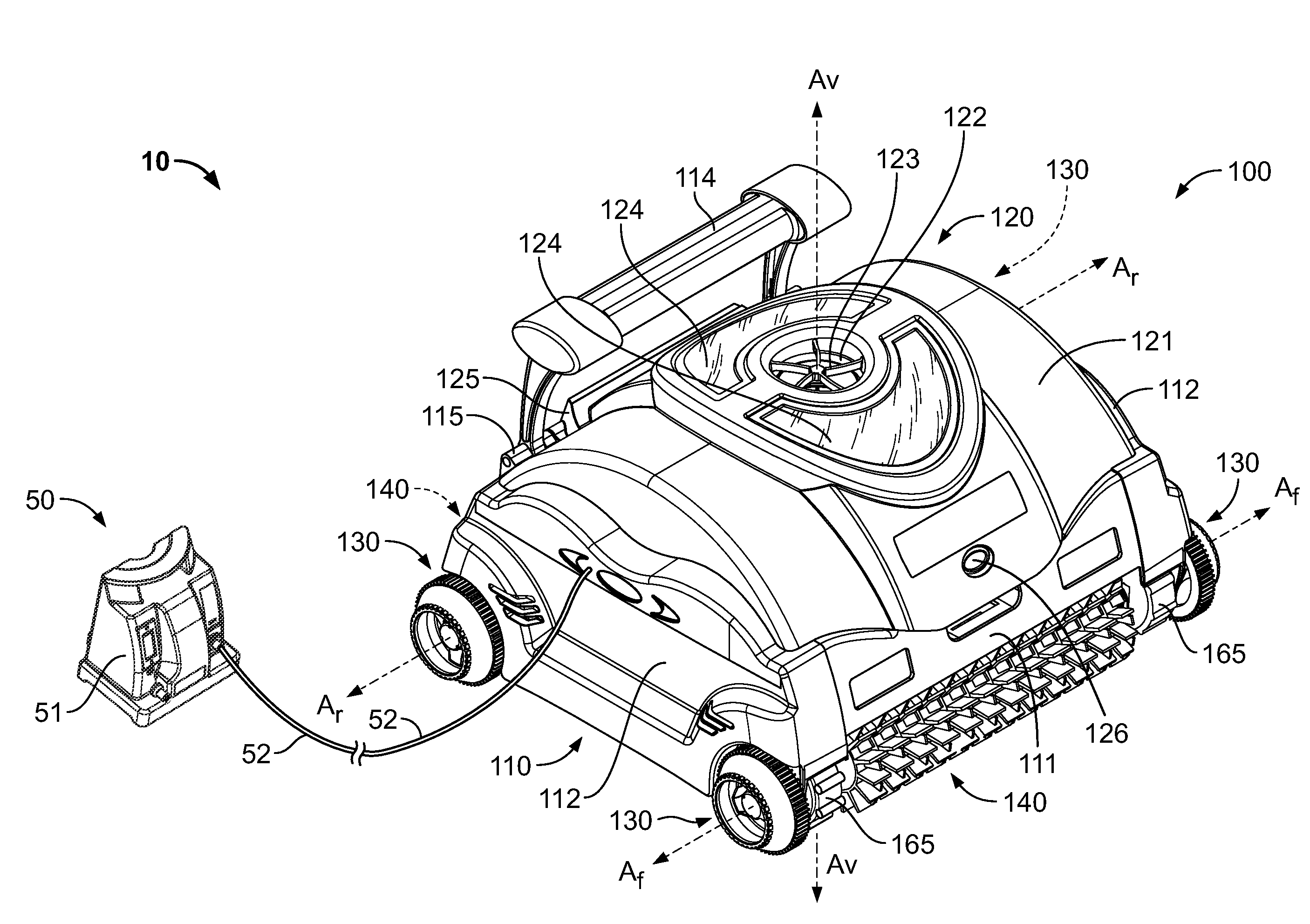
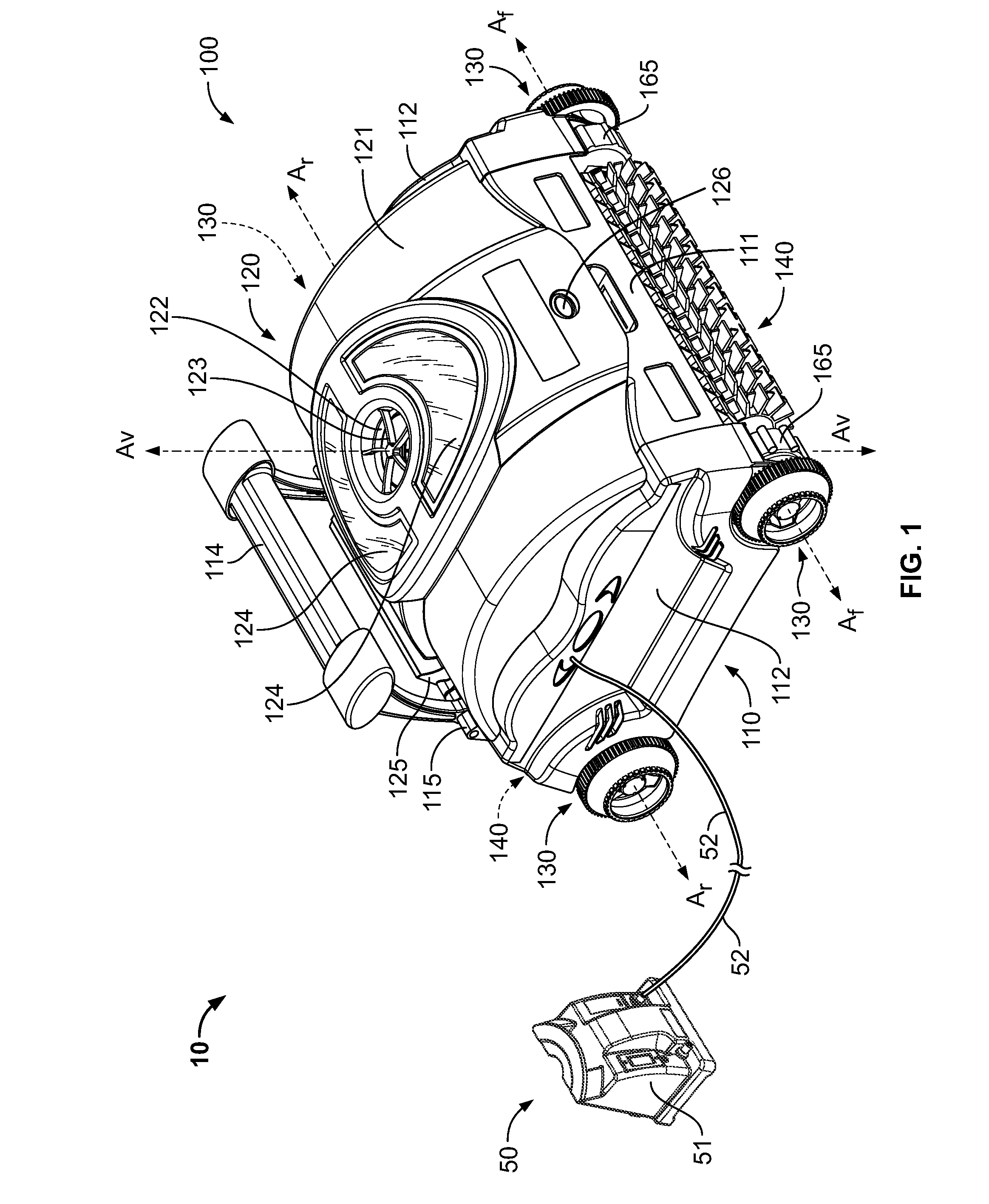
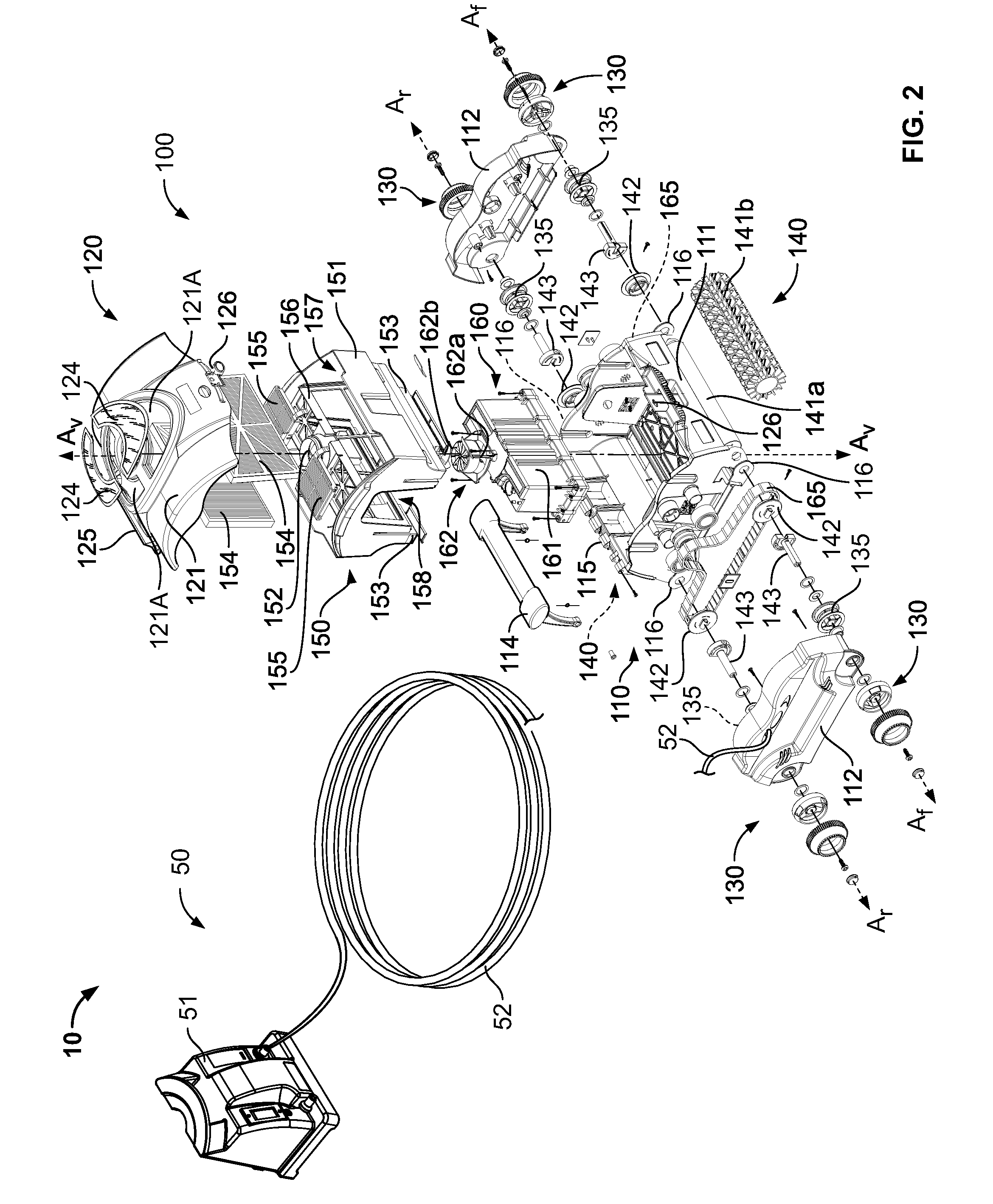
Pool Cleaning Device With Adjustable Buoyant Element
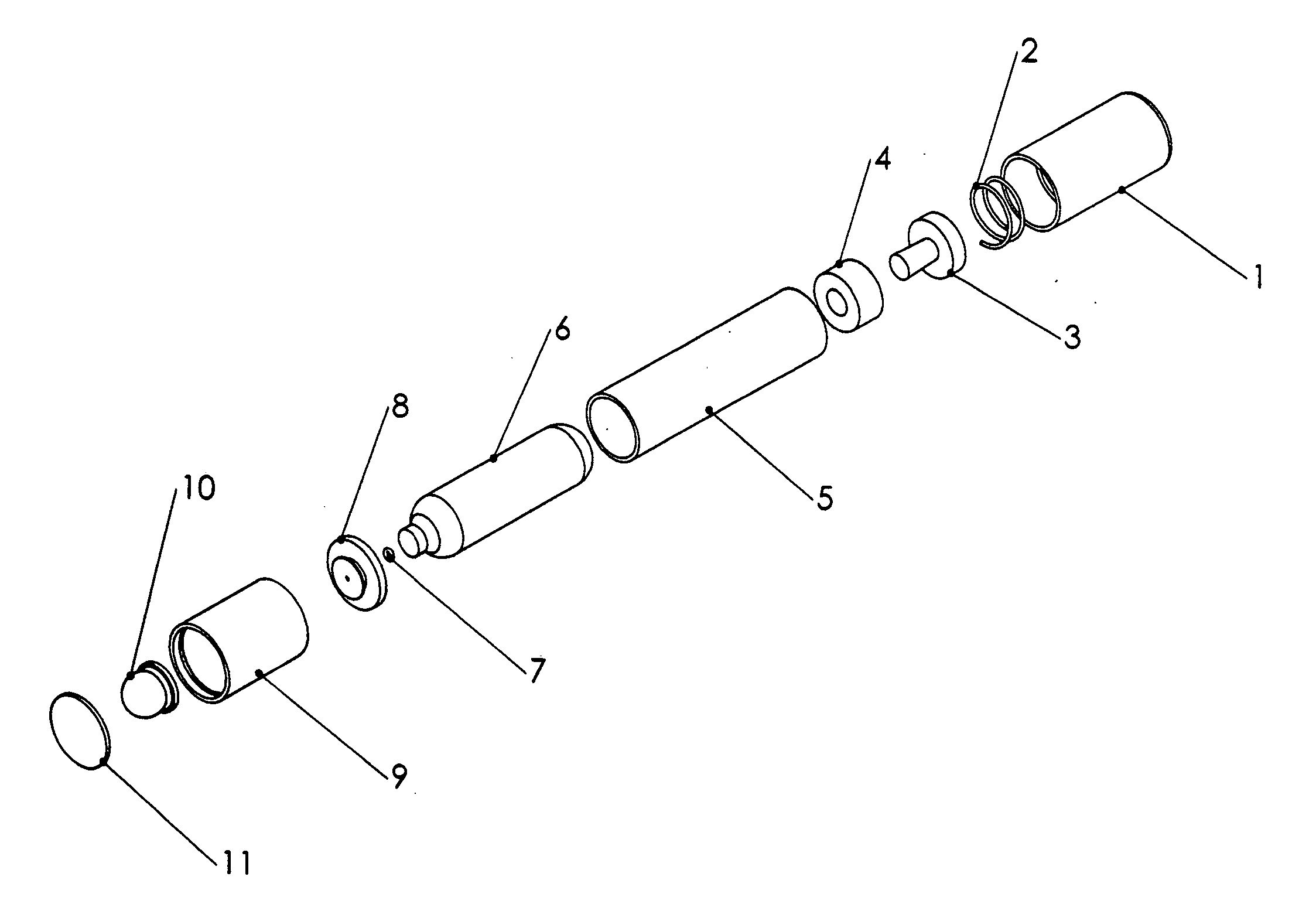
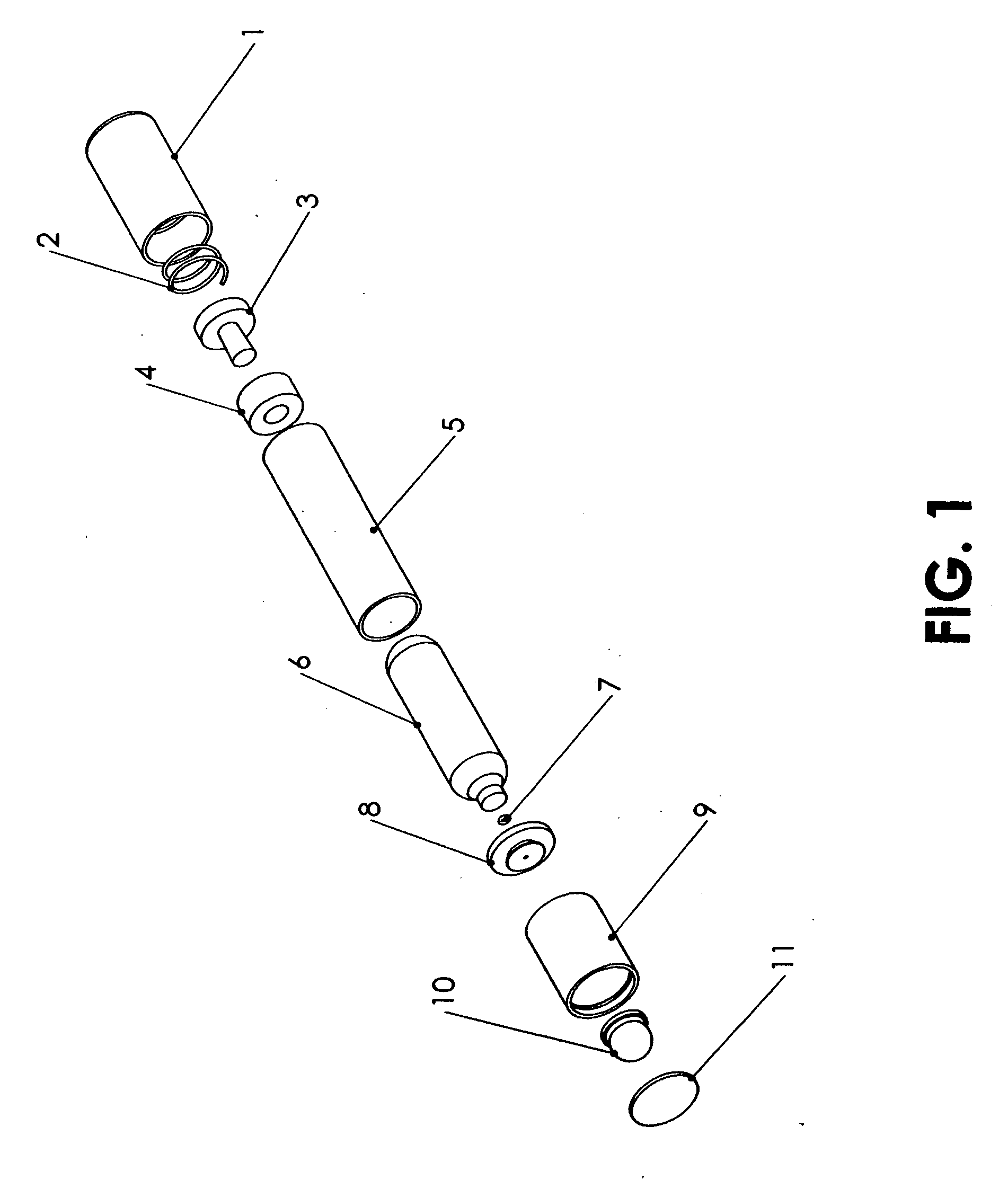
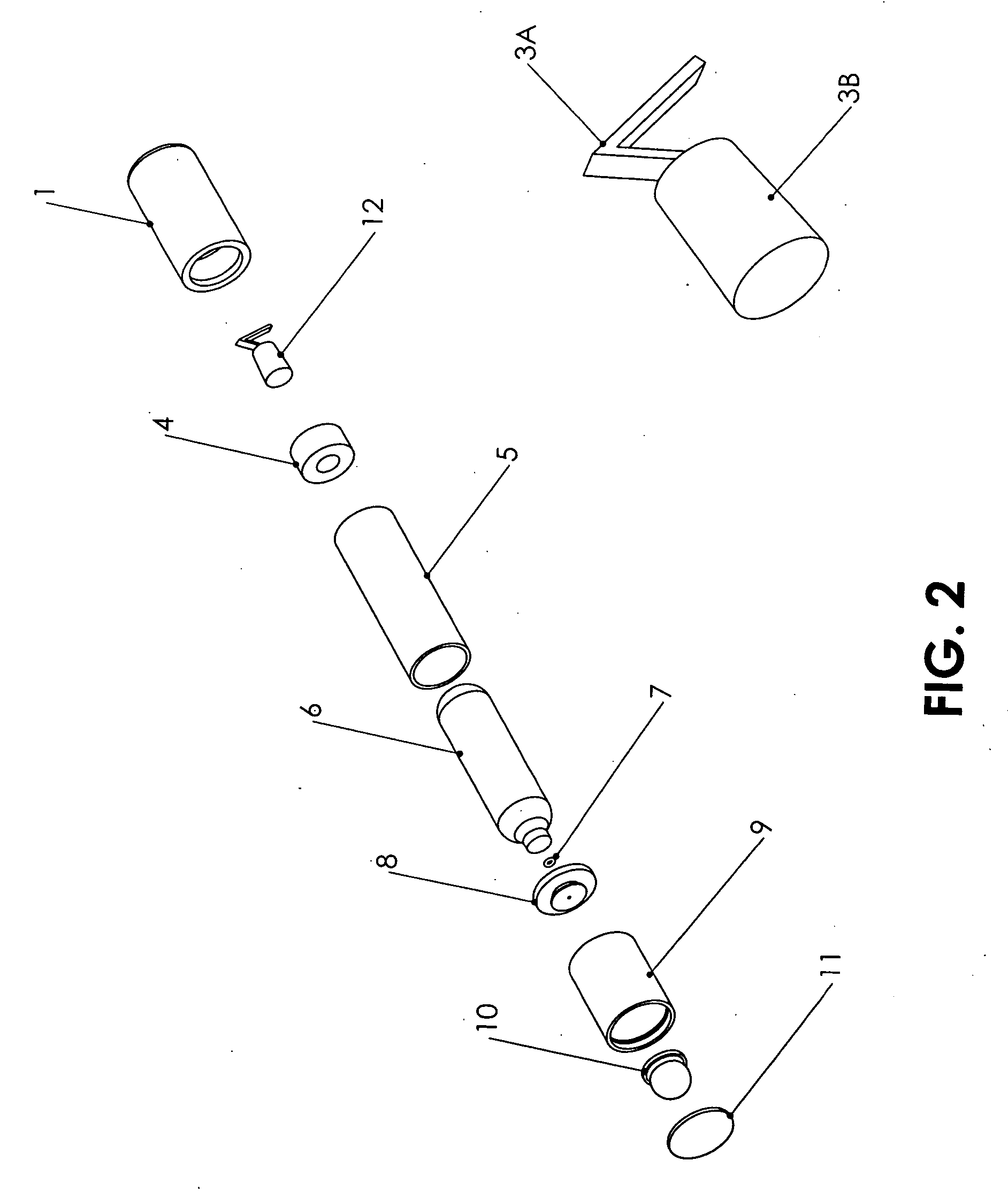
ActiveUS20120103365A1Negative buoyancyEasy to operateGymnasiumCleaning processes and apparatusAutomated pool cleanerDetent
An automatic pool cleaner has a plurality of components, some of which have a density greater than water, giving the cleaner an overall negative buoyancy. The cleaner has a buoyant element which is adjustable in position relative to the center of gravity of the cleaner. Adjusting the position of the buoyant element changes the probable motion path of the cleaner on the pool floor and on the walls to allow the cleaner to execute a variety of motion paths to clean various parts of the pool. The adjustable element may be slidably positioned by a handle extending through a slot in the housing or be slidable on a slide band attached to the housing, which may be pivotable, translatable and rotatable, providing an additional range of position alternatives. A selected position is held by a detent or other holding mechanism. The adjustable element permits the cleaner to be adapted to clean various pool shapes and surfaces.
Owner:HAYWARD IND INC
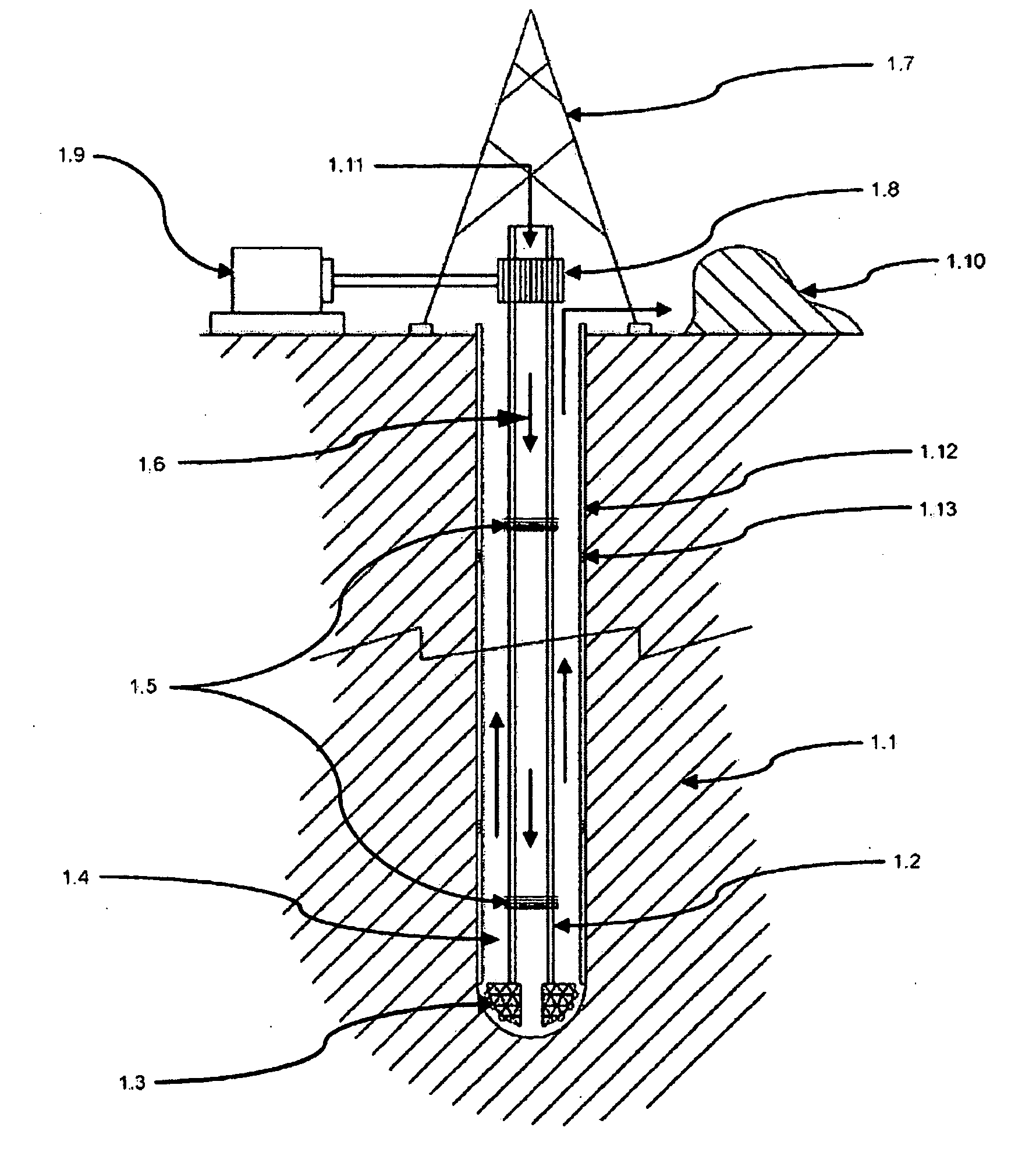
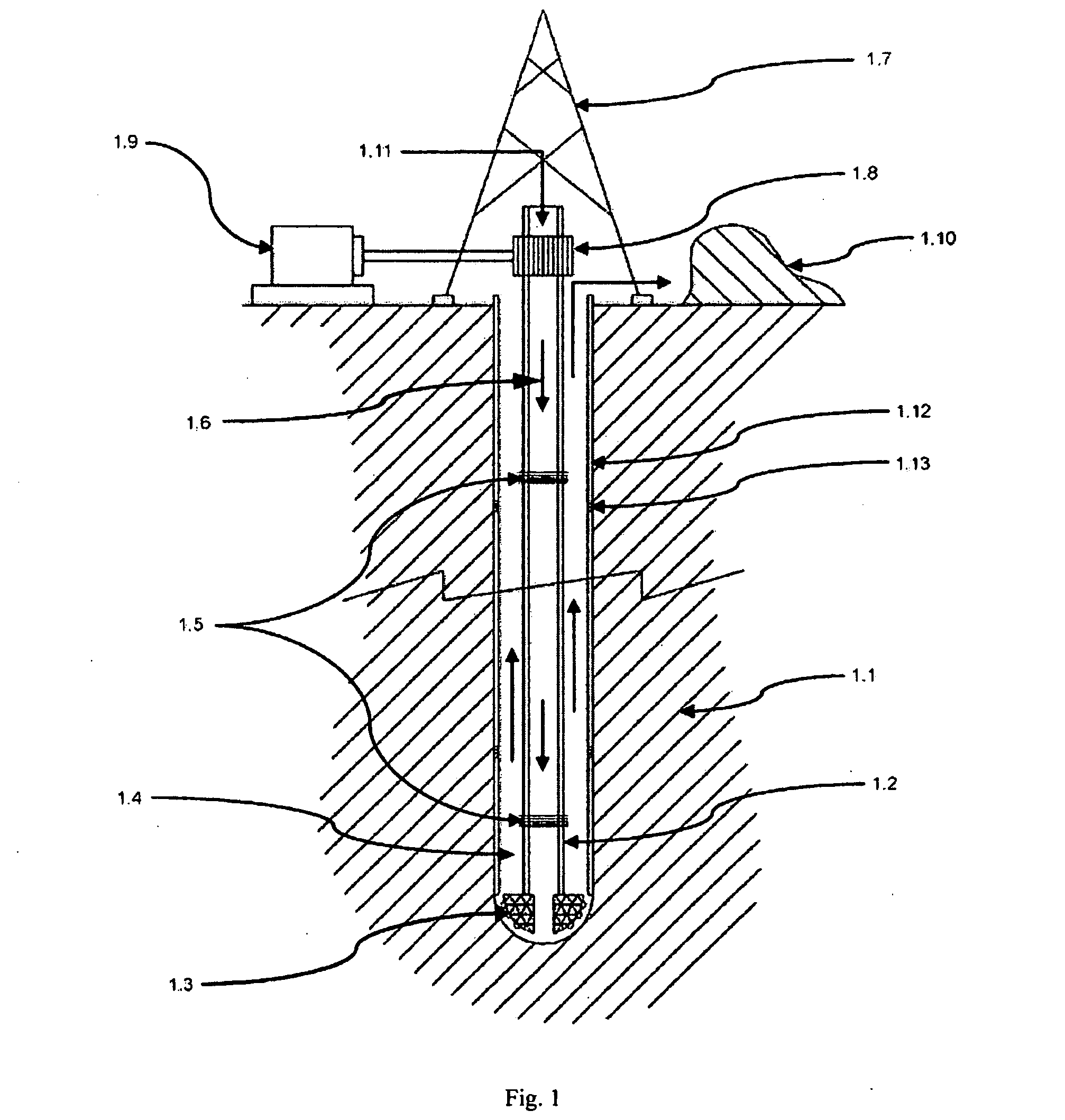
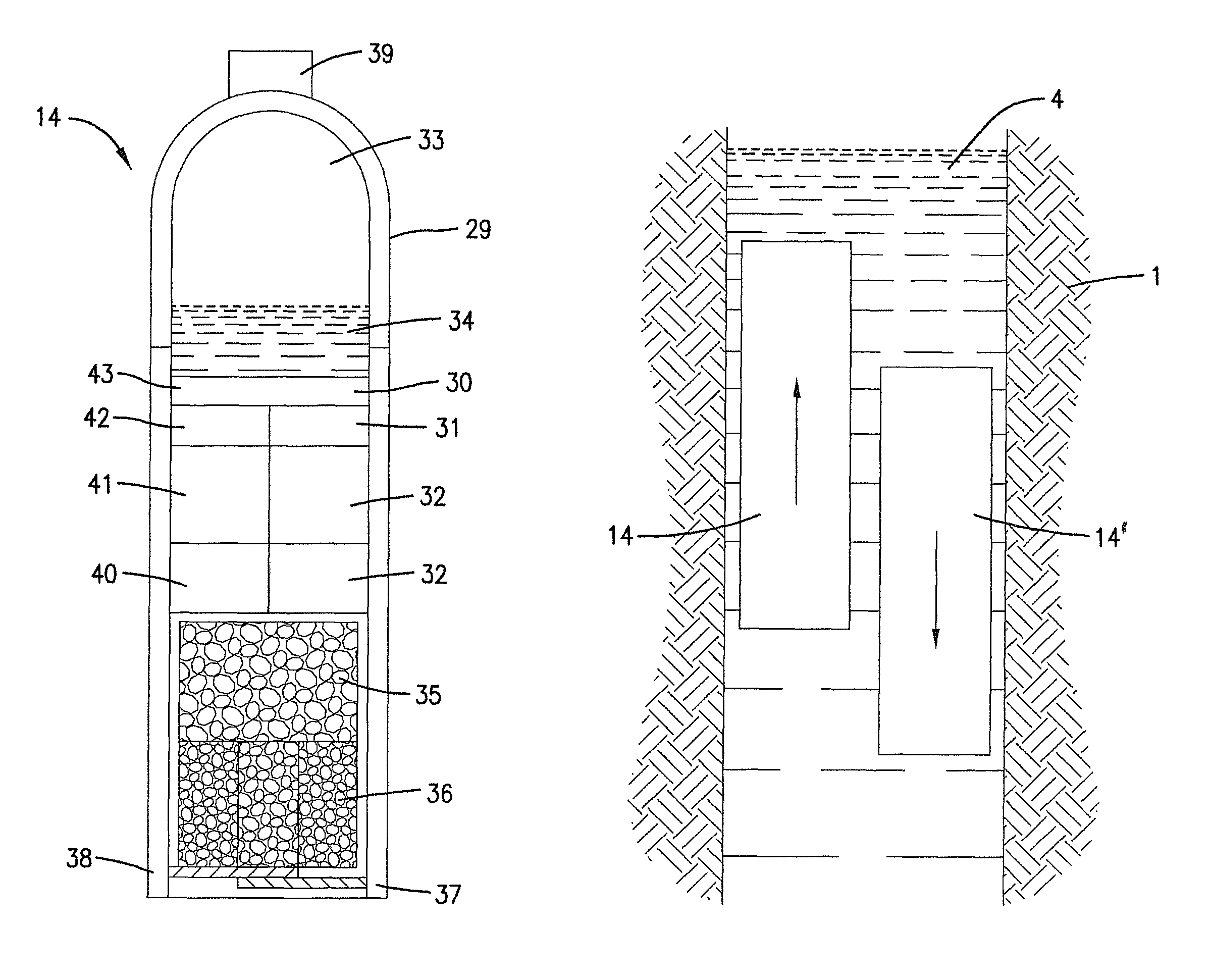
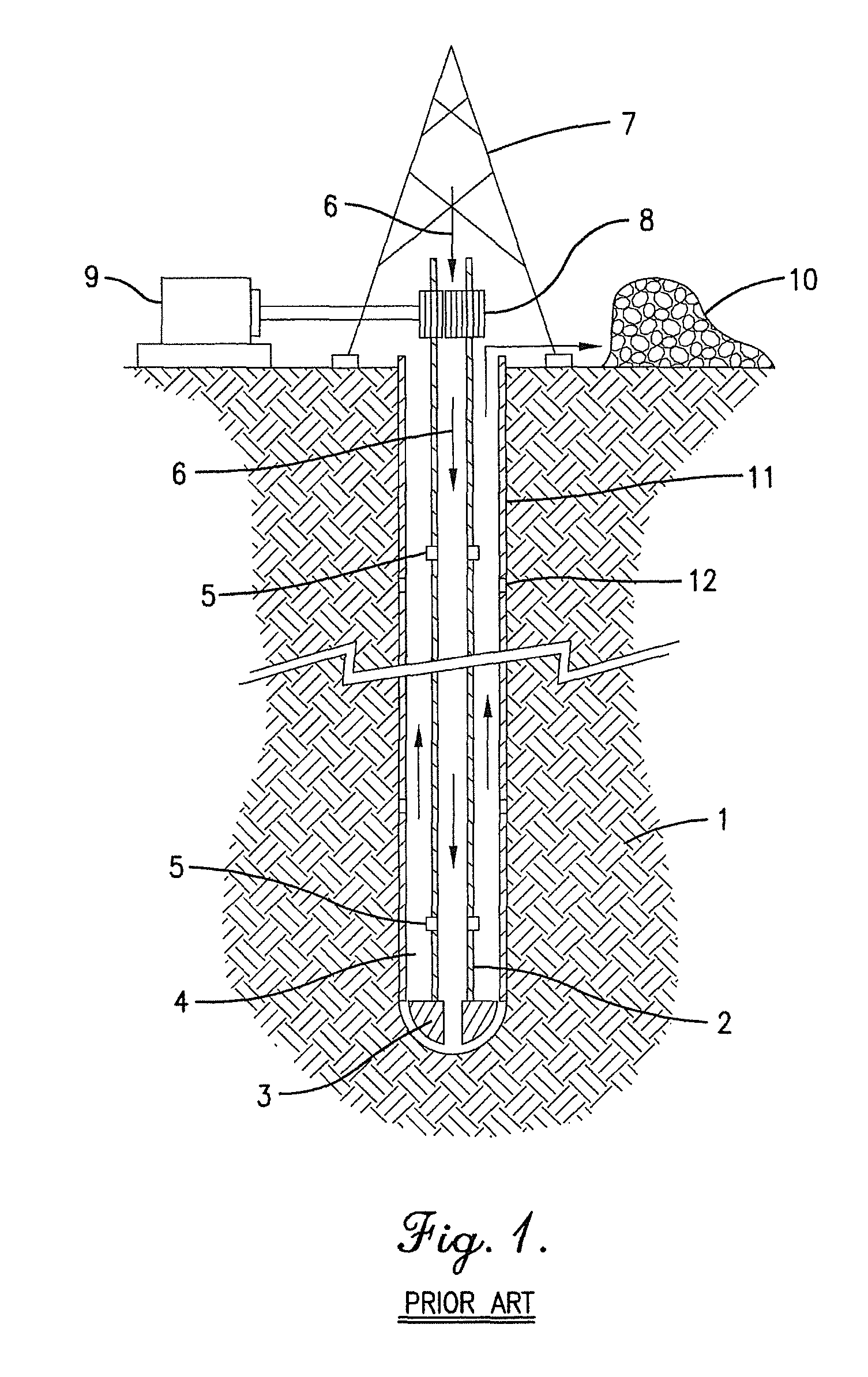
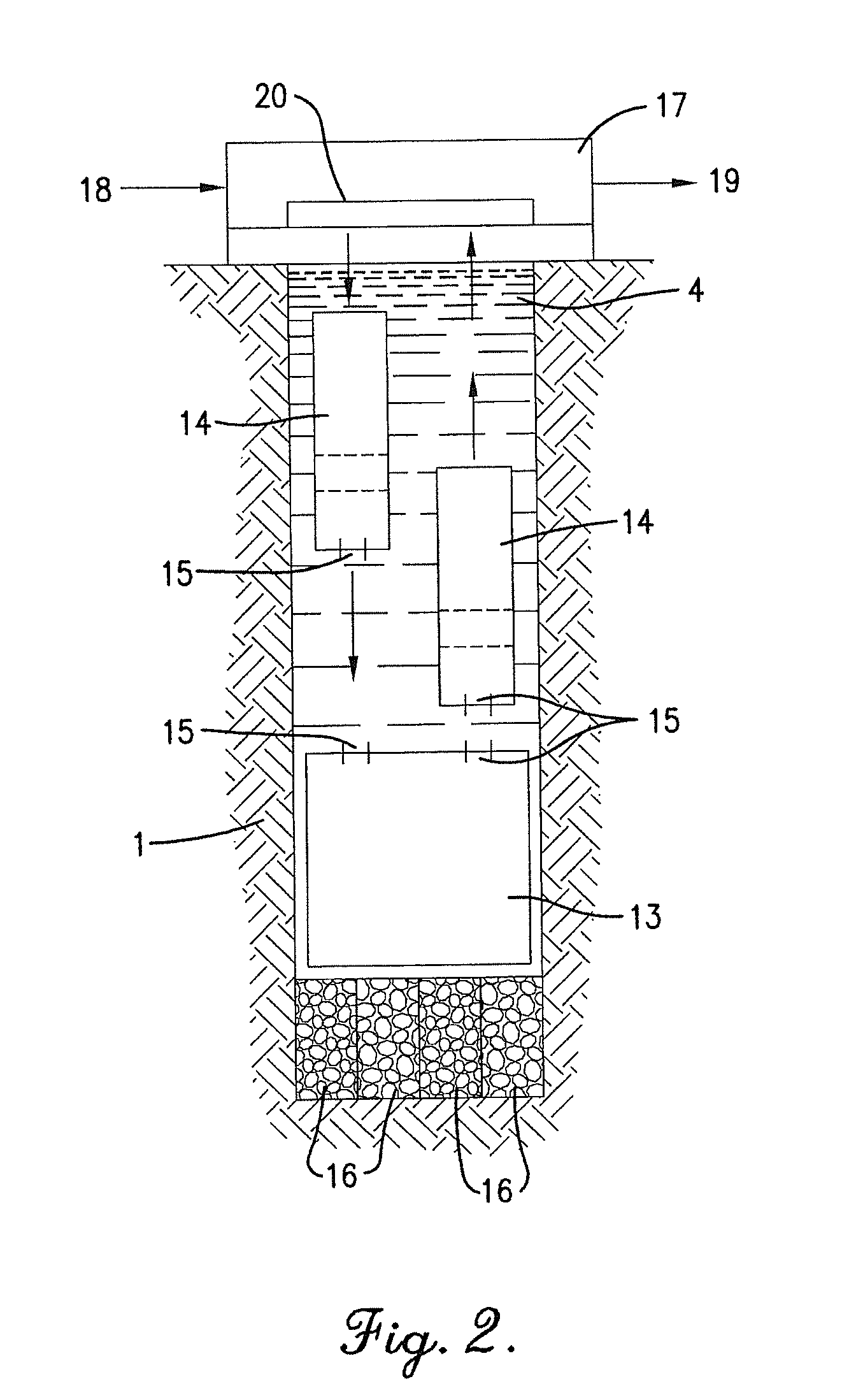
Equipment for excavation of deep boreholes in geological formation and the manner of energy and material transport in the boreholes
InactiveUS20100224408A1Considerable energy savingLarge boreholeDisloding machinesThermal drillingEngineeringEnergy depletion
Utilisation of geothermal energy in depths above 5 km could contribute considerably to resolving the global problems related to a lack of energy and to glasshouse gases from fossil fuels. The invention describes innovative equipment which makes deep holes in geological formations (rock) by disintegrating the soil into blocks carried to the land surface through the excavated hole filled with liquid, using transport modules yielded up by gas buoyancy interaction in the transport module utilising supercavitation. In an opposite direction—by help of negative buoyancy—the necessary energy carriers, materials and components, or entire devices required for rock excavation, are carried to the bottom. The opportunity to transport rock in entire blocks reduces energy consumption considerably, because the rock is disintegrated in the section volumes only. Some of the extracted rock and material carried from the surface is used to make a casing of the hole using a part of the equipment. The equipment also allows the generation of the necessary high pressure of liquid at the bottom of the hole, to increase permeability of adjacent rock. The equipment as a whole allows by its function that there is almost linear dependence between the price and depth (length) of the produced hole (borehole).
Owner:GA DRILLING AS
Payload delivery units for pressure protecting and delivering a submerged payload and methods for using the same
A payload delivery unit for protecting and delivering a payload submerged in a submersion medium includes an unmanned buoy, a drop weight member, and a retention system. The buoy includes a container. The container includes a pressure-resistant shell defining a sealed containment chamber. The drop weight member is mounted on the shell and has a negative buoyancy with respect to the submersion medium. The retention system is operative to retain the drop weight member on the buoy and selectively release the drop weight member from the buoy.
Owner:IROBOT CORP
Equipment for excavation of deep boreholes in geological formation and the manner of energy and material transport in the boreholes
InactiveUS8082996B2Increase speedReduce frictionDisloding machinesCleaning apparatusEngineeringEnergy depletion
Utilization of geothermal energy in depths above 5 km could contribute considerably to resolving the global problems related to a lack of energy and to glasshouse gases from fossil fuels. The invention describes innovative equipment which makes deep holes in geological formations (rock) by disintegrating the soil into blocks carried to the land surface through the excavated hole filled with liquid, using transport modules yielded up by gas buoyancy interaction in the transport module utilizing supercavitation. In an opposite direction—by help of negative buoyancy—the necessary energy carriers, materials and components, or entire devices required for rock excavation, are carried to the bottom. The opportunity to transport rock in entire blocks reduces energy consumption considerably, because the rock is disintegrated in the section volumes only. Some of the extracted rock and material carried from the surface is used to make a casing of the hole using a part of the equipment. The equipment also allows the generation of the necessary high pressure of liquid at the bottom of the hole, to increase permeability of adjacent rock. The equipment as a whole allows by its function that there is almost linear dependence between the price and depth (length) of the produced hole (borehole).
Owner:GA DRILLING AS
Pool cleaning device with adjustable buoyant element
An automatic pool cleaner has a plurality of components, some of which have a density greater than water, giving the cleaner an overall negative buoyancy. The cleaner has a buoyant element which is adjustable in position relative to the center of gravity of the cleaner. Adjusting the position of the buoyant element changes the probable motion path of the cleaner on the pool floor and on the walls to allow the cleaner to execute a variety of motion paths to clean various parts of the pool. The adjustable element may be slidably positioned by a handle extending through a slot in the housing or be slidable on a slide band attached to the housing, which may be pivotable, translatable and rotatable, providing an additional range of position alternatives. A selected position is held by a detent or other holding mechanism. The adjustable element permits the cleaner to be adapted to clean various pool shapes and surfaces.
Owner:HAYWARD IND INC
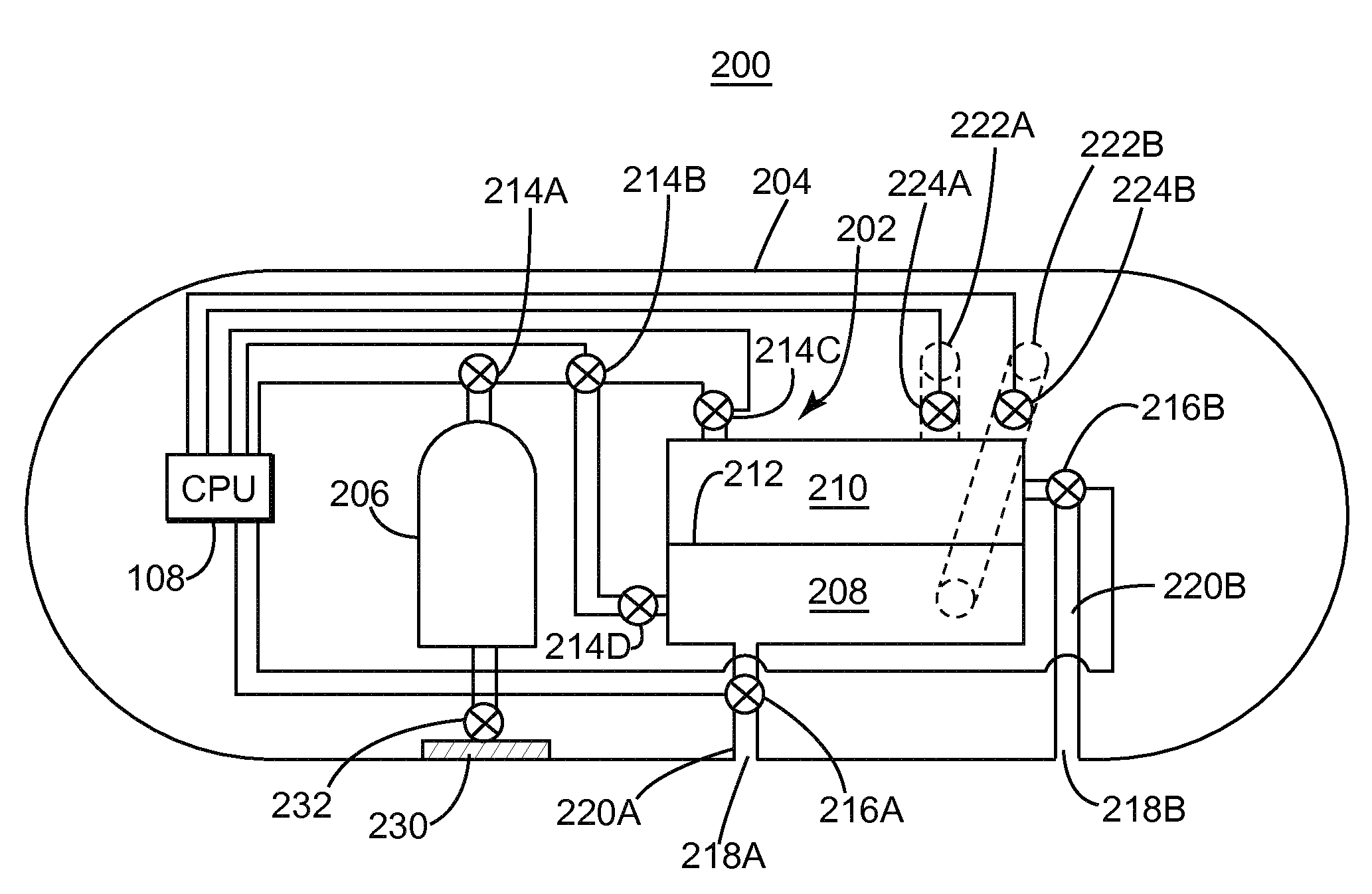
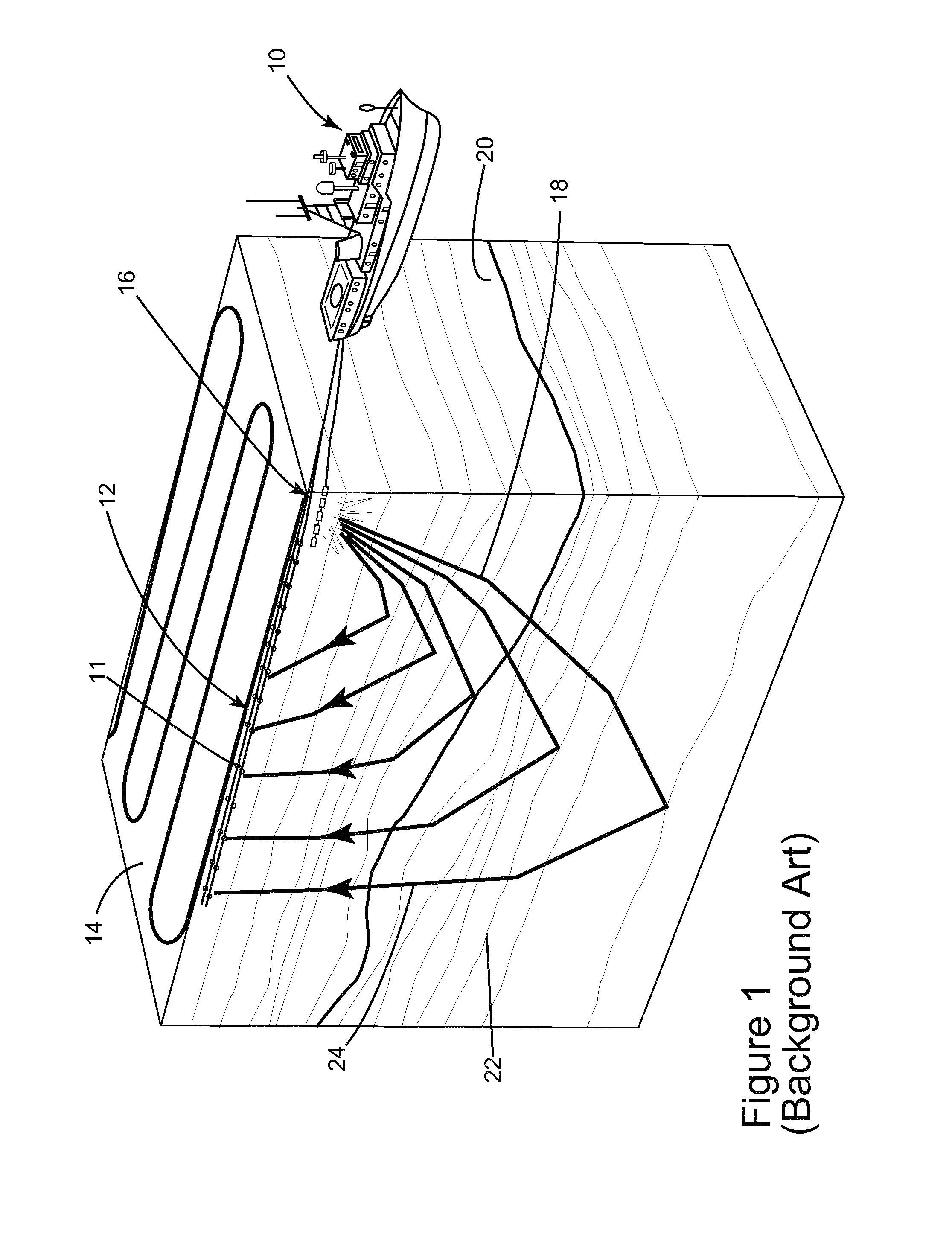
Autonomous underwater vehicle marine seismic surveys
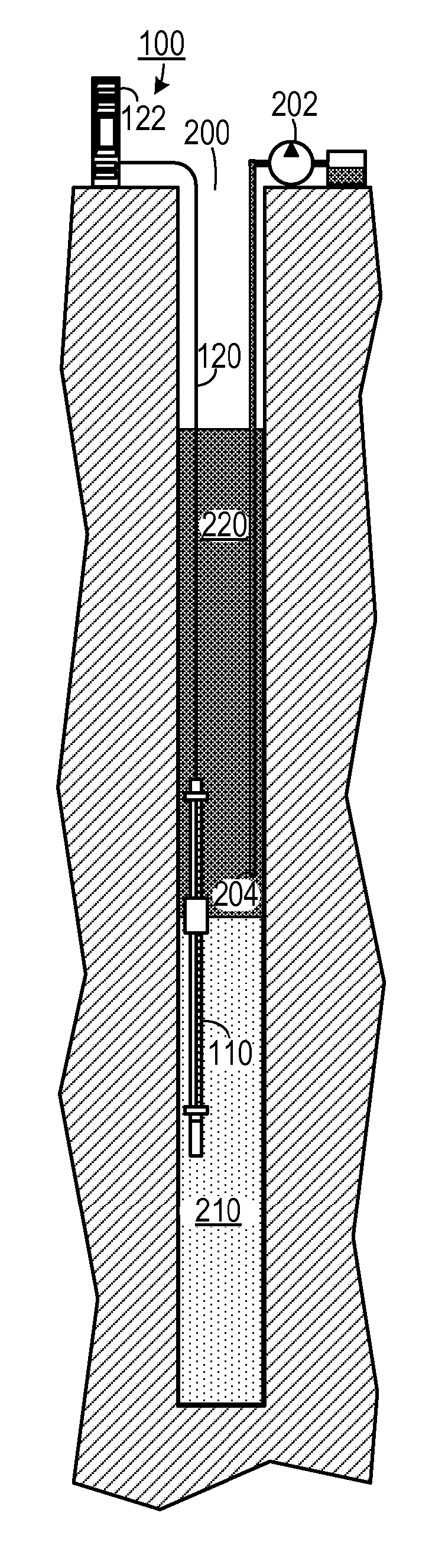
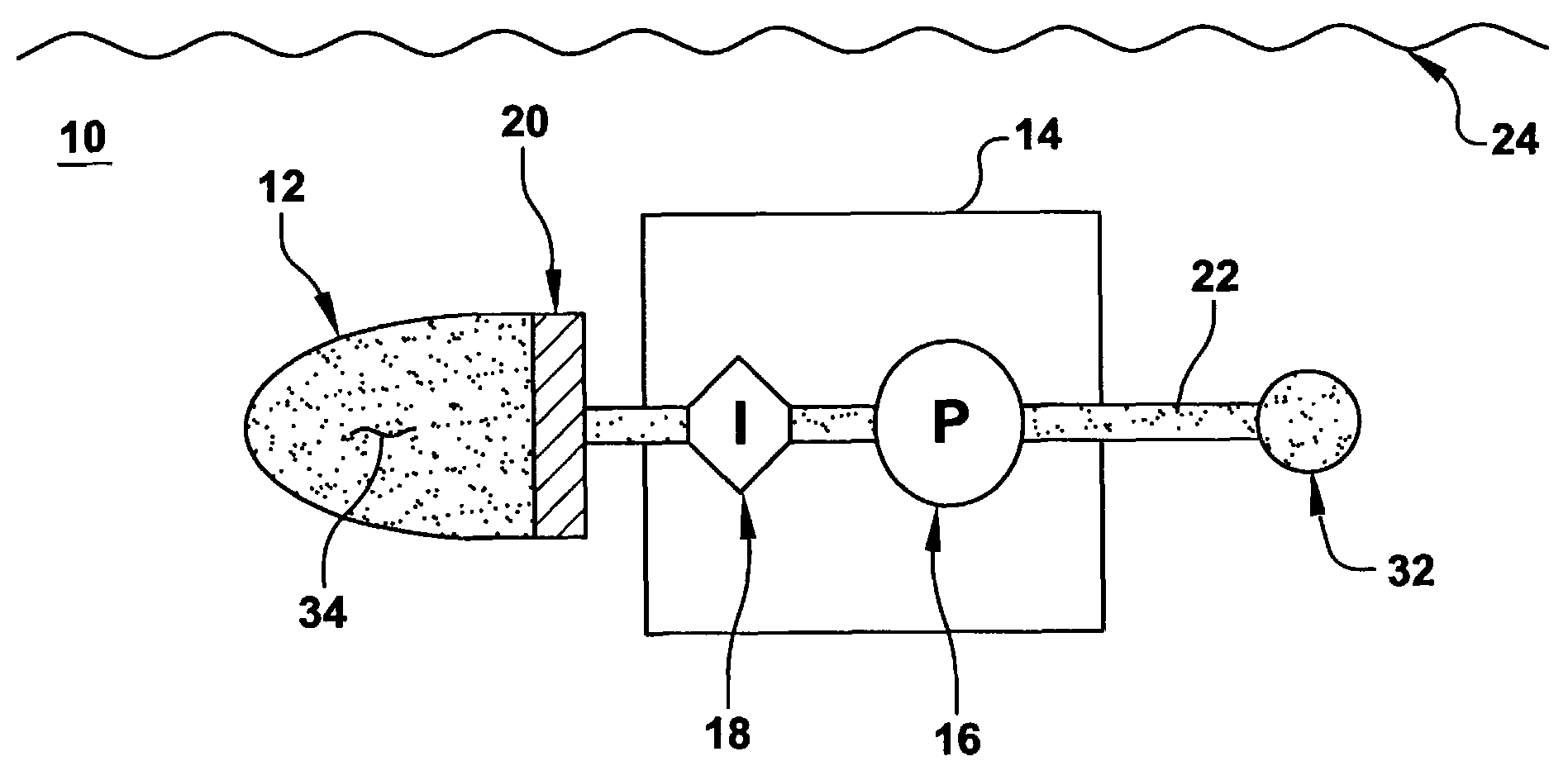
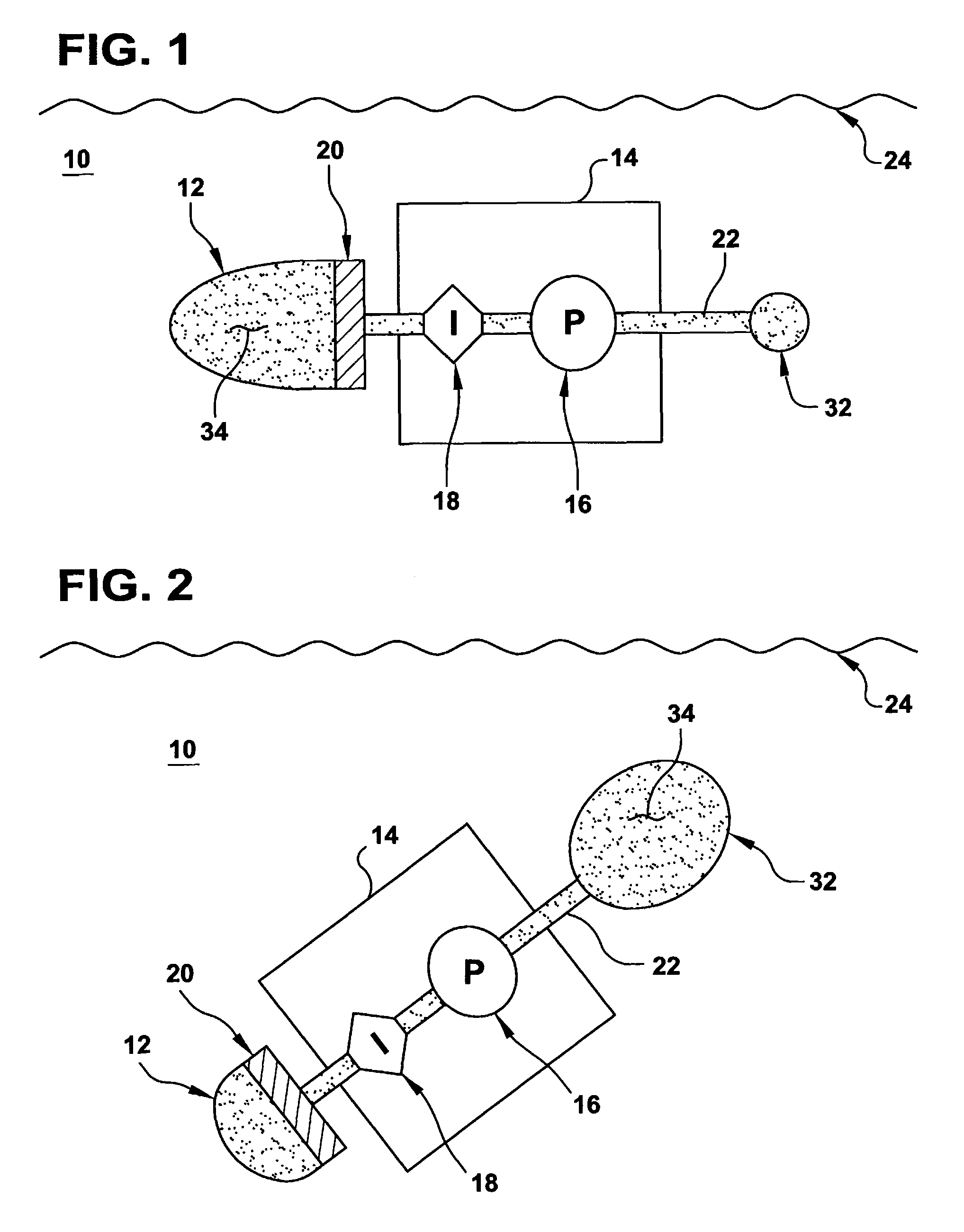
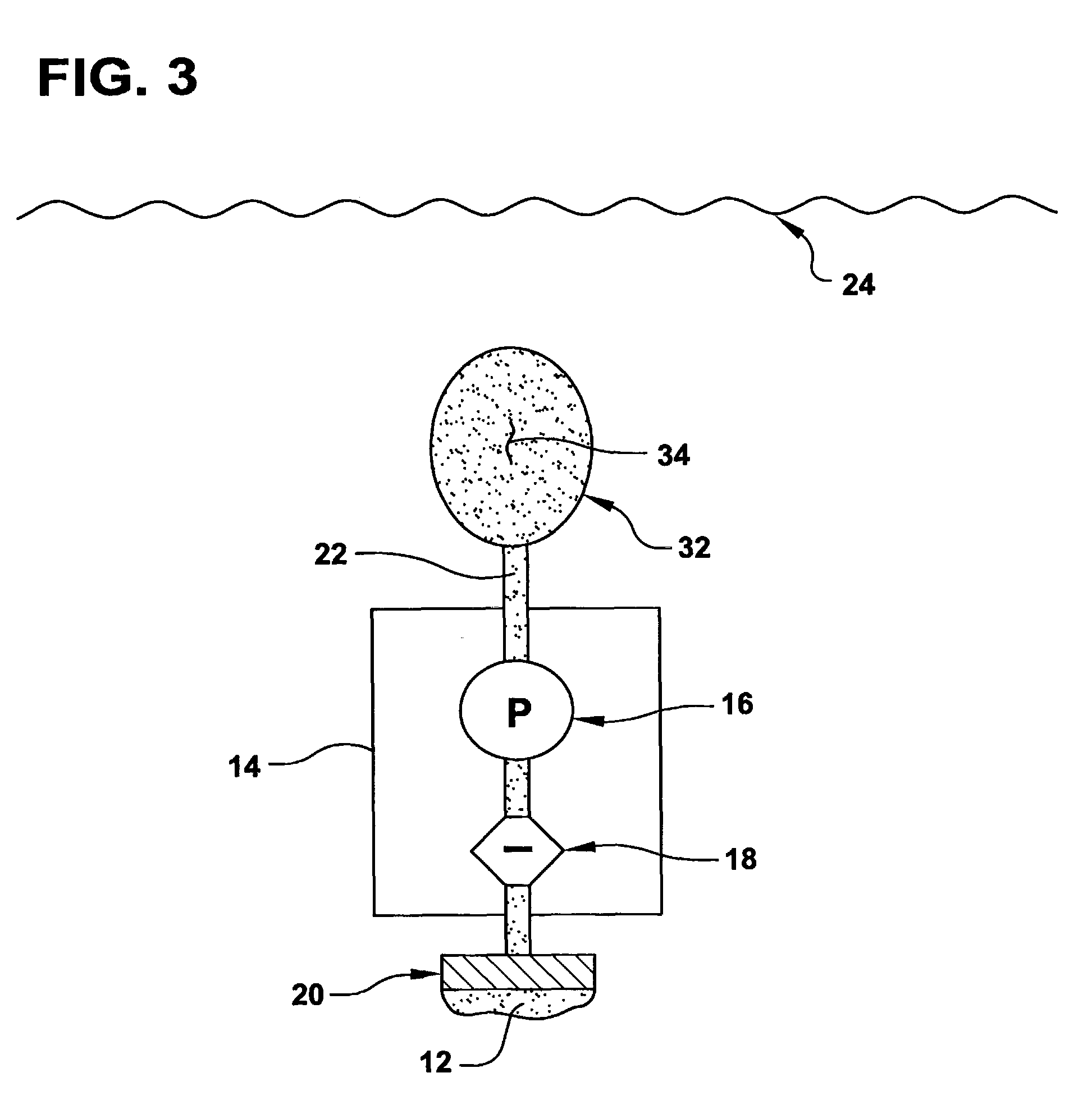
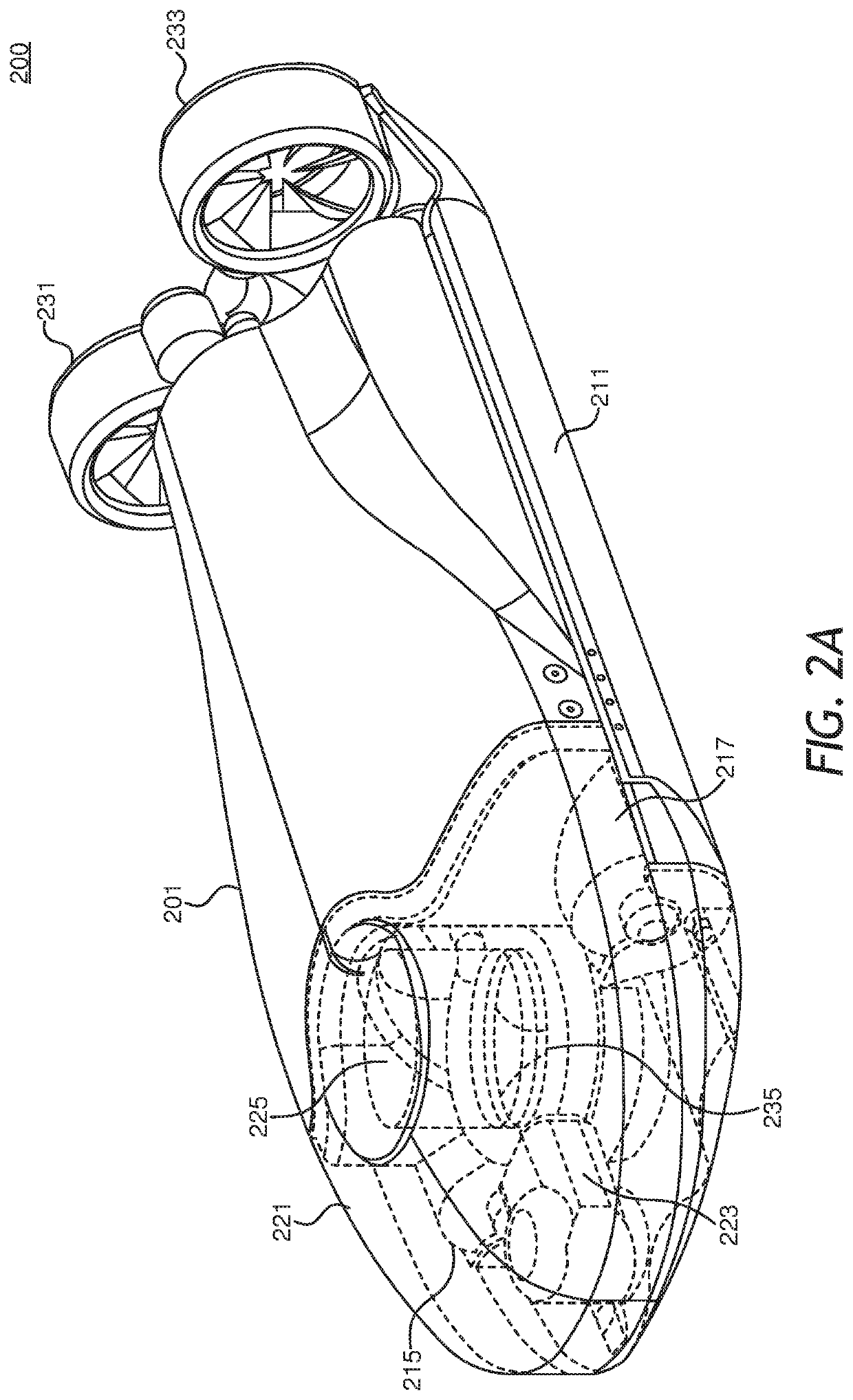
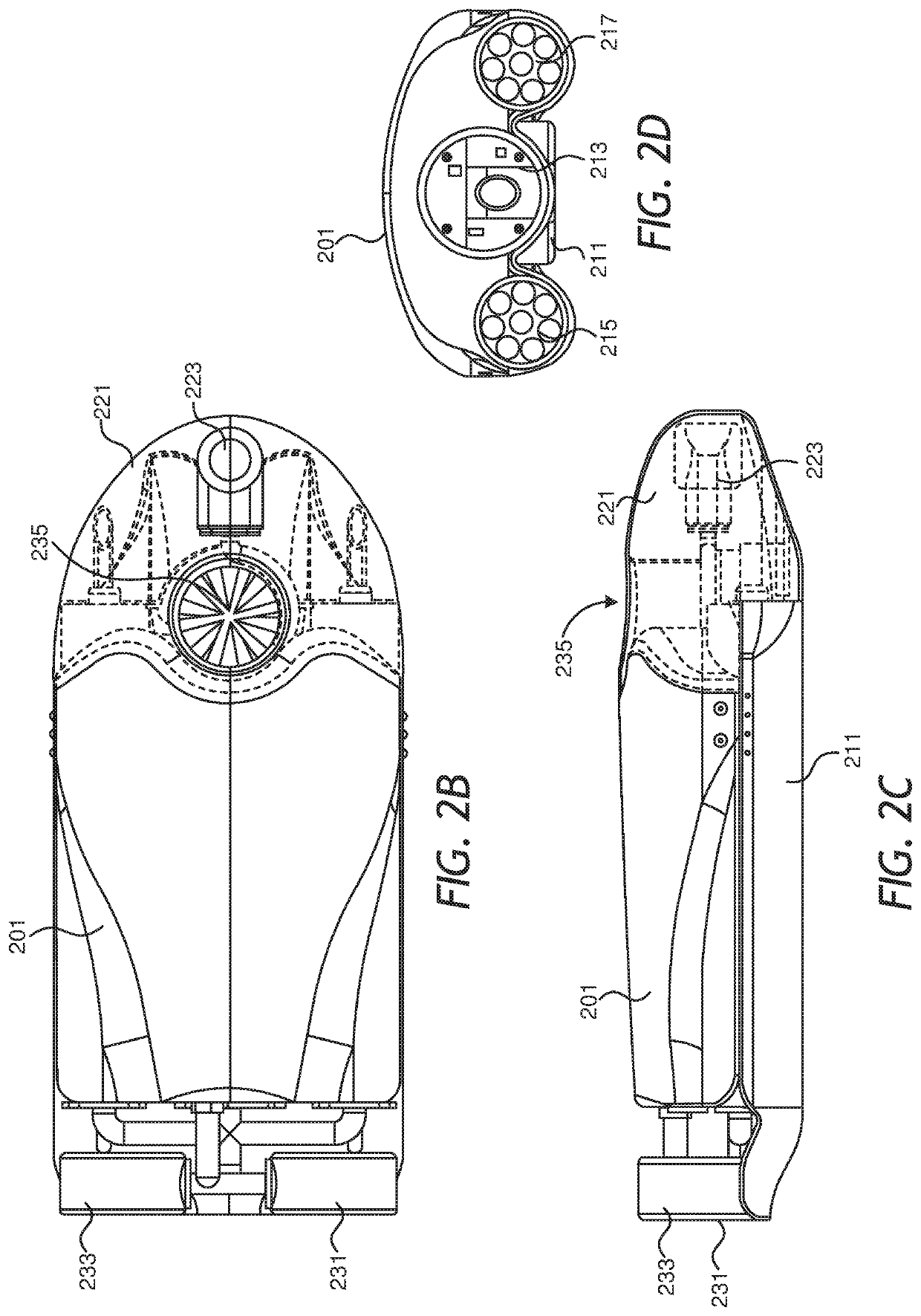
An autonomous underwater vehicle (AUV) for recording seismic signals during a marine seismic survey. The AUV (200) includes a body (204) having a flush shape; a buoyancy system (202) located inside the body and configured to control a buoyancy of the AUV while traveling underwater; a processor (108) connected to the buoyancy system and configured to select one of plural phases for the buoyancy system at different times of the seismic survey, wherein the plural phases include a neutral buoyancy, a positive buoyancy and a negative buoyancy; and a seismic sensor (110) for recording seismic signals.
Owner:SEABED GEOSOLUTIONS
Inflatable buoyancy device with water-dependant triggering mechanism.
InactiveUS20080311805A1Keep the surfaceWaterborne vesselsBuoysChemical reactionVariable Characteristic
This invention is directed toward a device which provides buoyancy to objects with negative buoyancy in water. The invention comprises a water-sensitive trigger which, when activated, causes a balloon to inflate, causing the object to float upon the surface where the user can then easily and safely retrieve it, through one of two mechanisms: first, a compressed gas is allowed to exit a canister and enter a balloon, second, one or more substances which, when mixed with water will produce bubbles are exposed to water and the balloon is filled with bubbles from the chemical reaction. There are a number of variable characteristics, including canister size and shape, trigger fuse length, balloon configuration, and housing material that allow a user tremendous flexibility in selecting a proper size of the invention for the user's intended purpose.
Owner:SPEARS FREDRICK +1
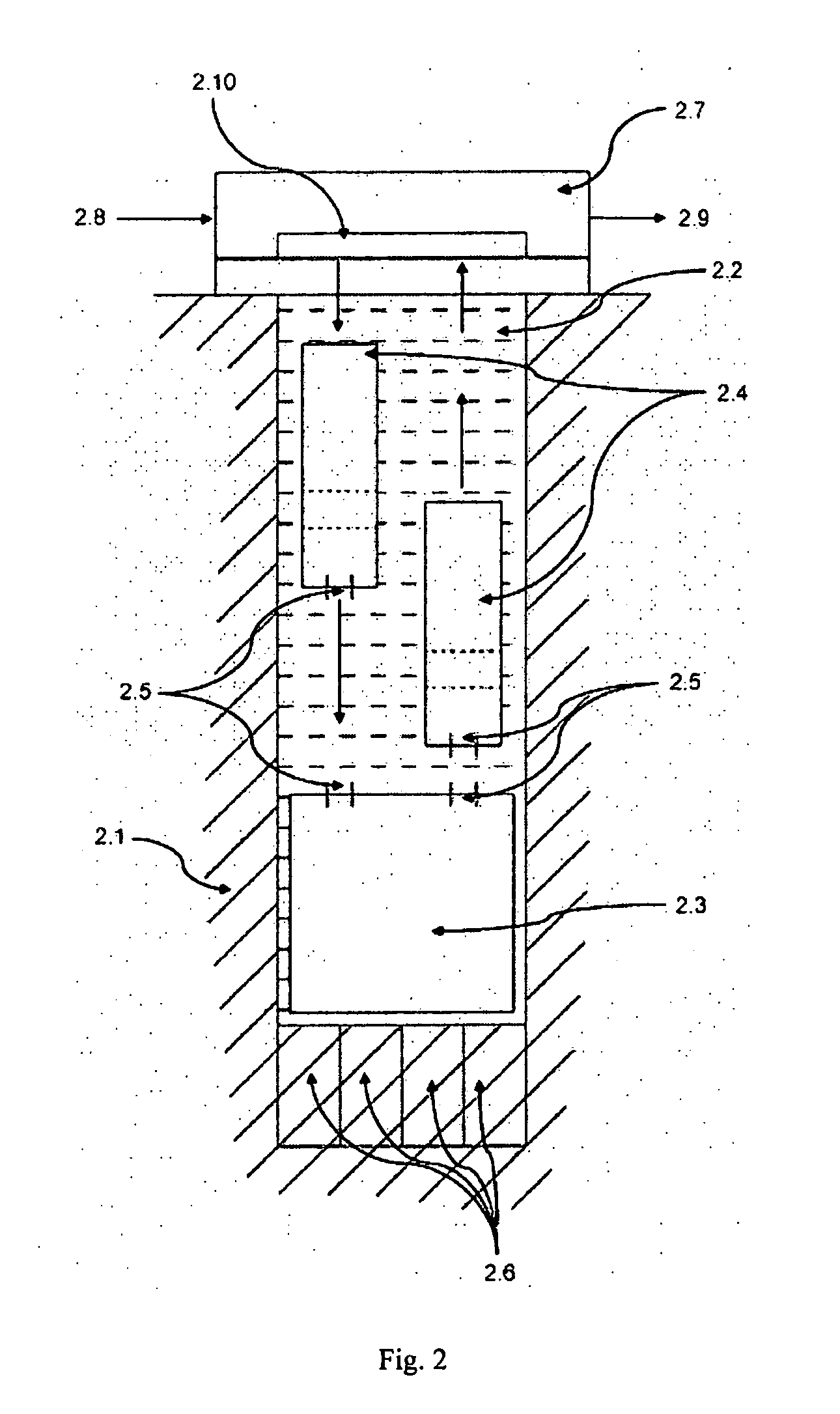
Submersible pump apparatus and method for using same
ActiveUS7713031B2Positive displacement pump componentsFlexible member pumpsSurface levelNegative buoyancy
A submersible pump apparatus comprising a housing containing all the components of the pump assembly for using the submersible pump apparatus in a body of water. A float or a plurality of floats are attached to the top side of the housing for providing a positive buoyancy to the submersible pump apparatus. The float is provided with a channel for slidably receiving a single weight or a plurality of weights. The weight is used to overcome the positive buoyancy of the float and achieve a negative buoyancy for submerging the submersible pump apparatus to the bottom of the body of water. A sled is attached to the bottom side of the housing and comprises the combination of both legs and feet for supporting the submersible pump apparatus at the bottom of a body of water. A finder float floating at the water surface level is attached using a rope to both the weight and the housing. By removing the weight or weights from the float, a positive buoyancy is restored to raise the submersible pump apparatus.
Owner:AQUA CONTROL
Inflatable buoyancy device with water-dependant triggering mechanism
Owner:OLSON MANFRED BRADLEY +1
Inflatable buoyancy device with water-dependant triggering mechanism
This invention is directed toward a device which provides buoyancy to objects with negative buoyancy in water. The invention comprises a water-sensitive trigger which, when activated, causes a balloon to inflate, causing the object to float upon the surface where the user can then easily and safely retrieve it, through one of two mechanisms: first, a compressed gas is allowed to exit a canister and enter a balloon, second, one or more substances which, when mixed with water will produce bubbles are exposed to water and the balloon is filled with bubbles from the chemical reaction. There are a number of variable characteristics, including canister size and shape, trigger fuse length, balloon configuration, and housing material that allow a user tremendous flexibility in selecting a proper size of the invention for the user's intended purpose.
Owner:SPEARS FREDRICK +1
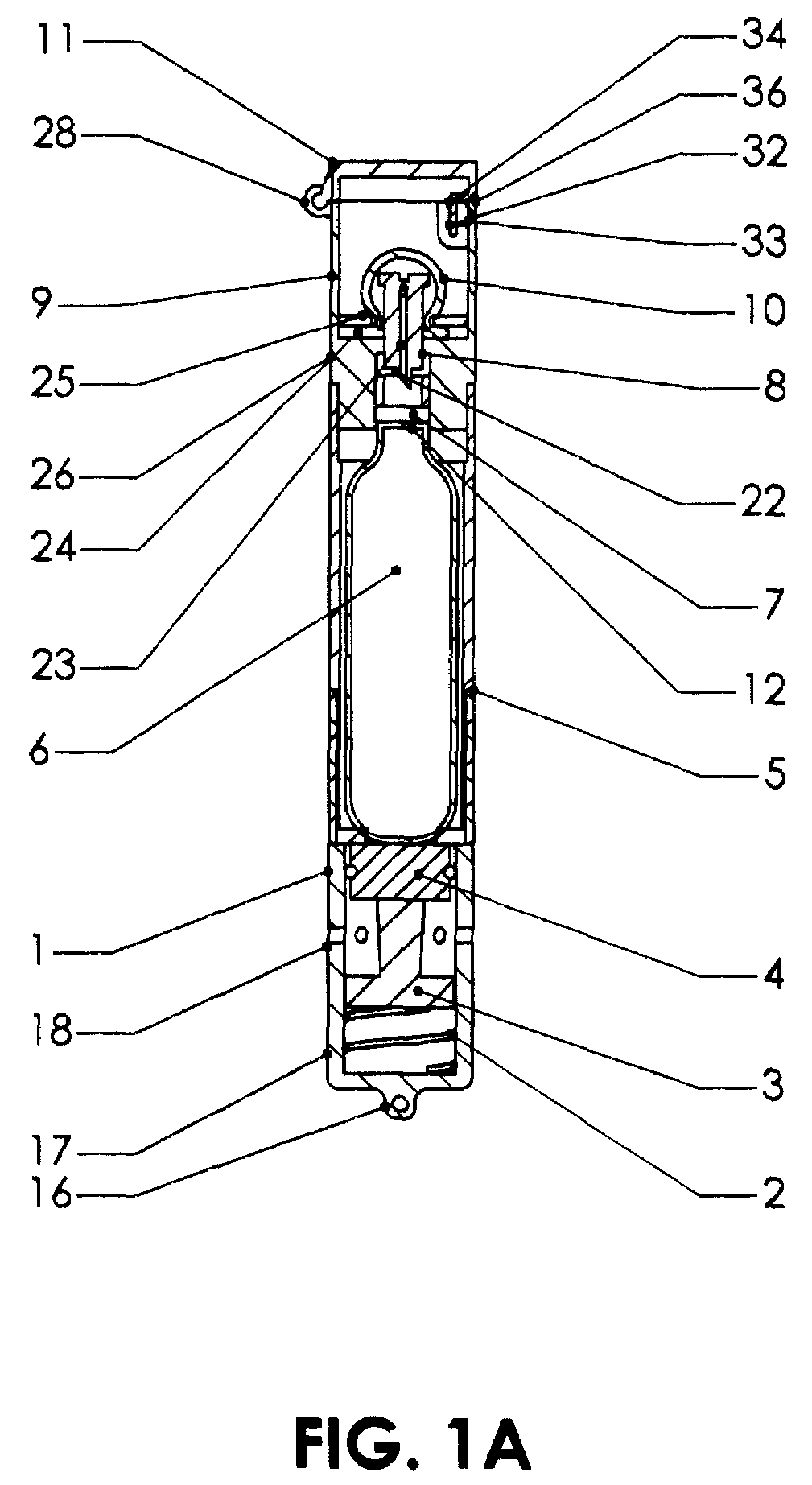
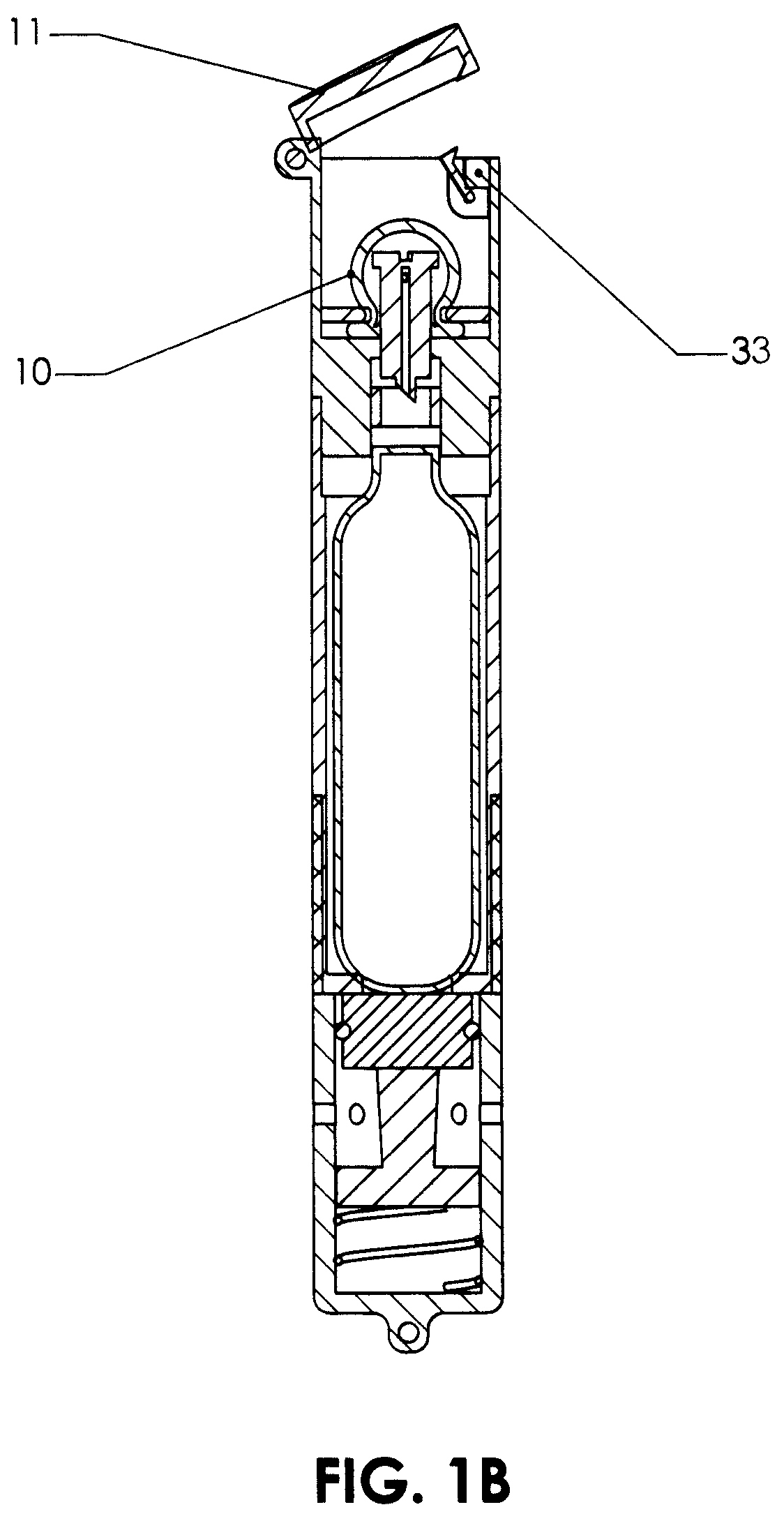
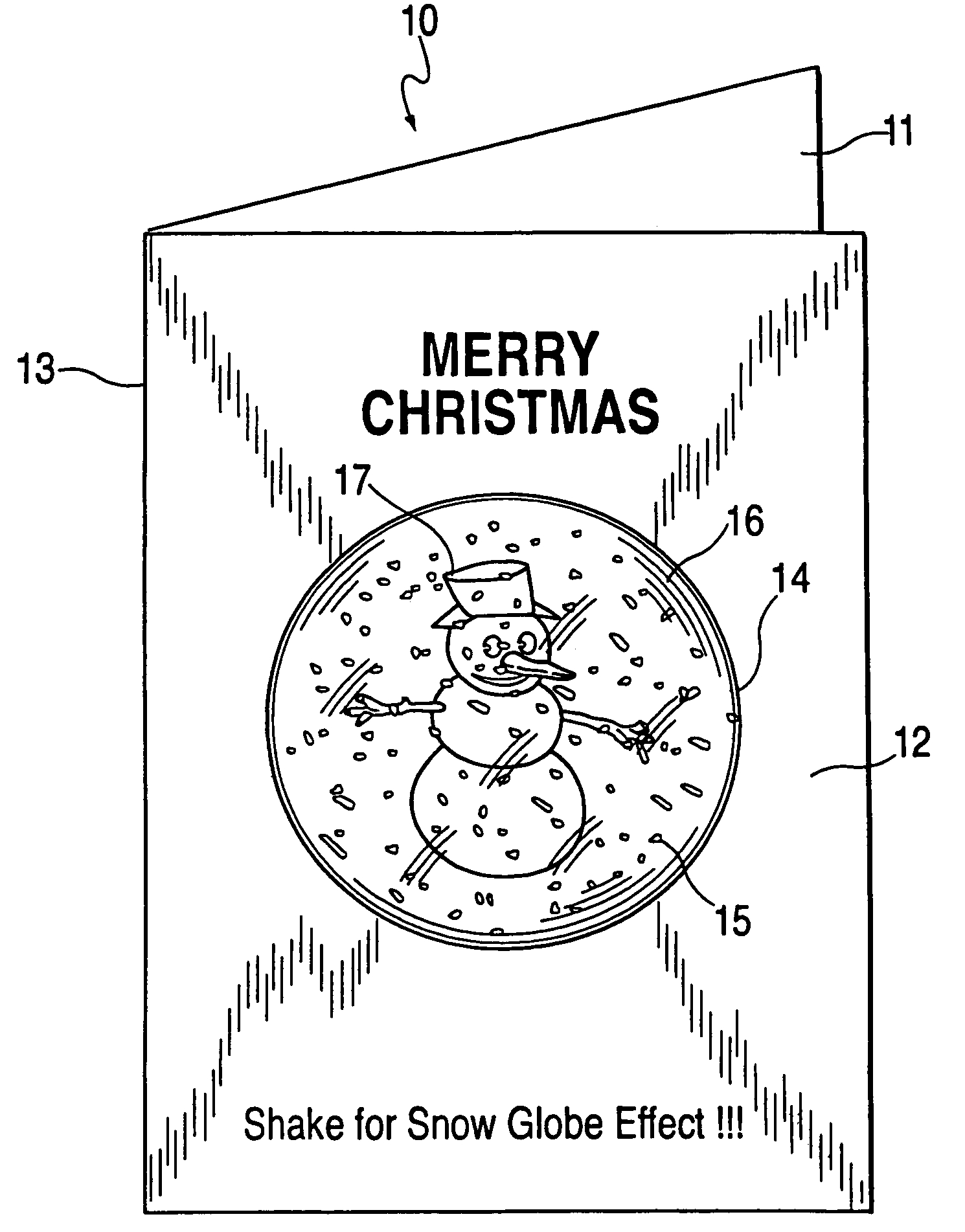
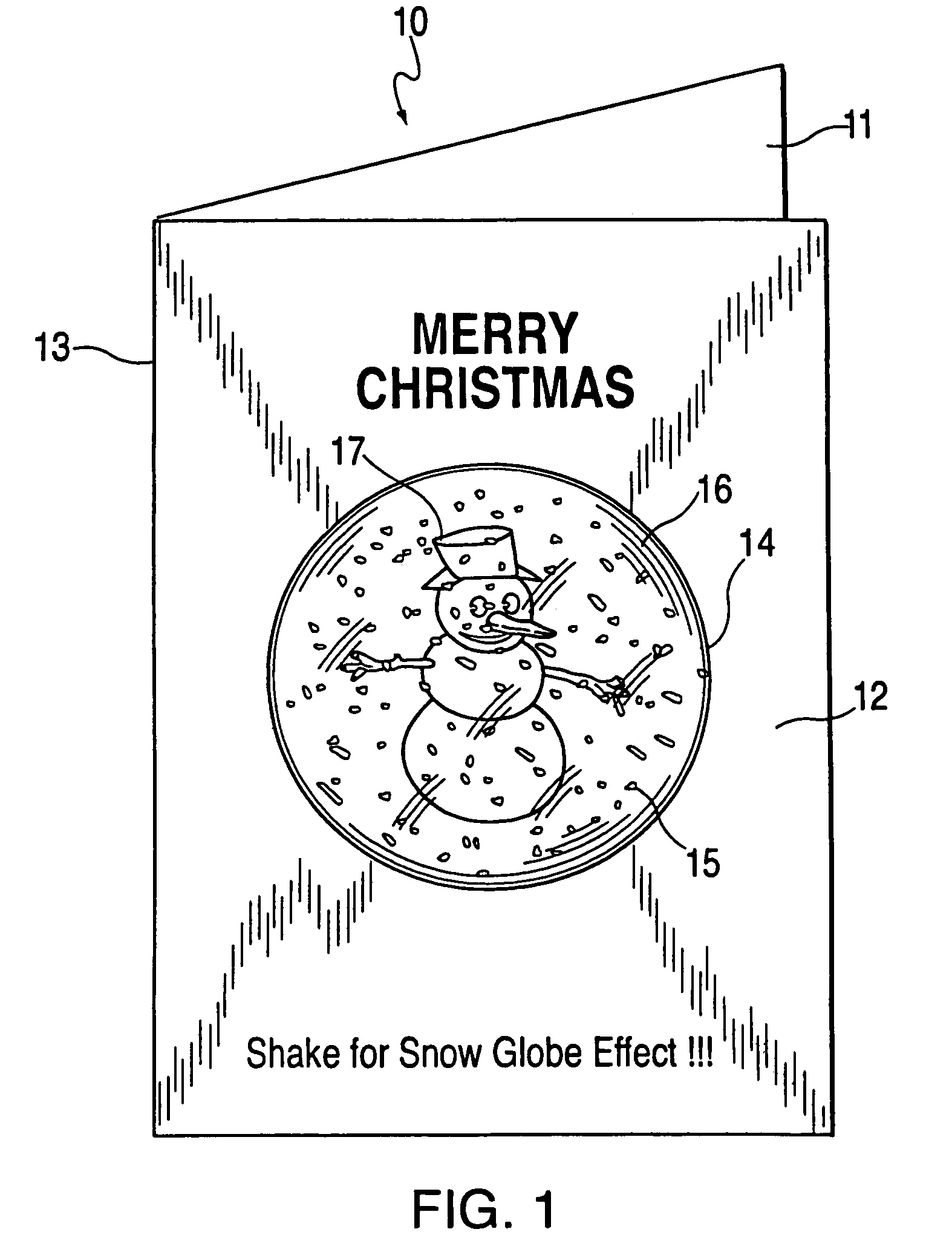
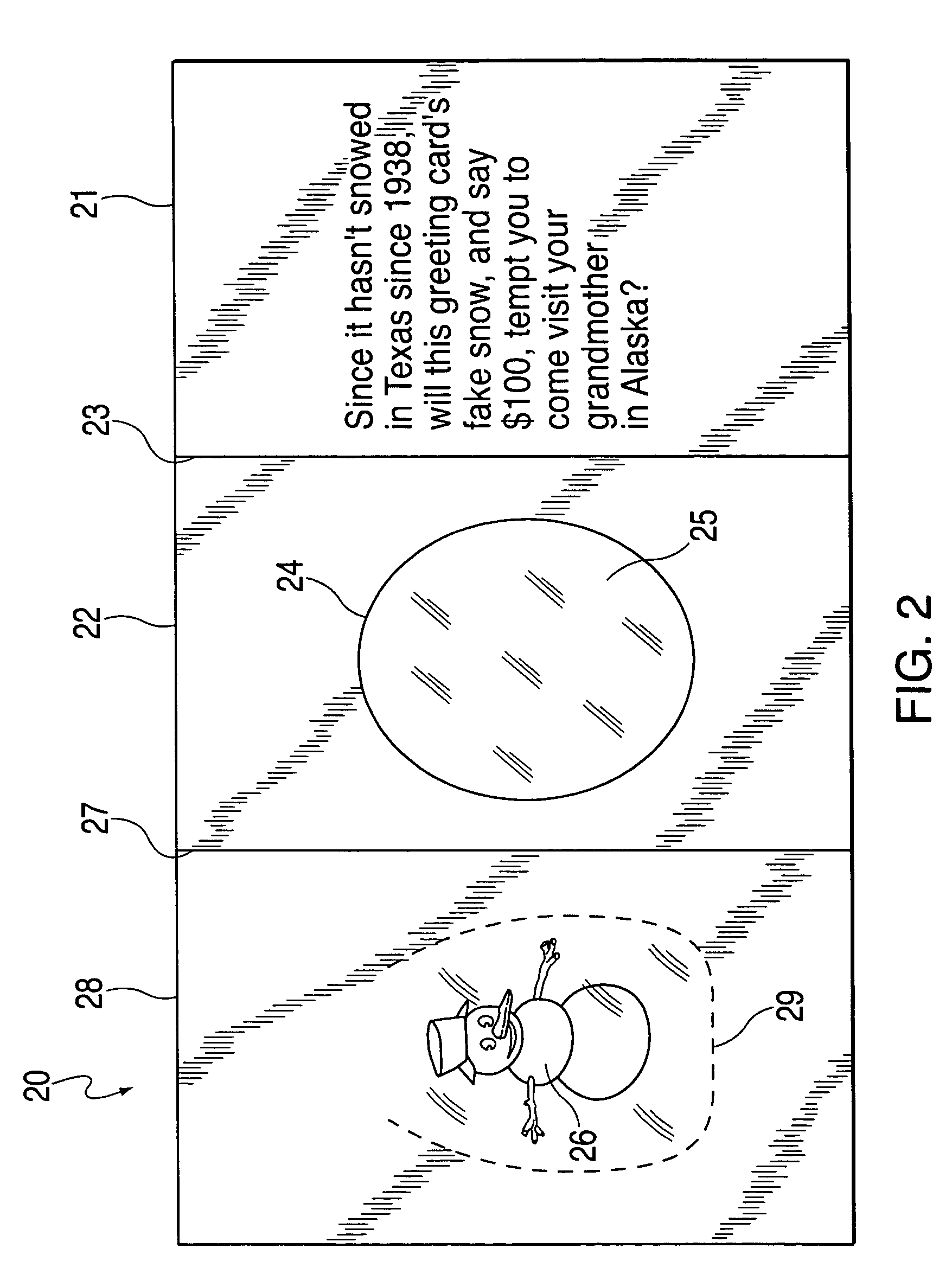
Greeting cards, postcards, gift bags, and the like employing a special effects container
InactiveUS7322134B2Improve whimsical festive natureIncrease profitContainer decorationsLevel indicationsMedicineNegative buoyancy
Special effects containers that include a special effects substance are provided in, for example, greeting cards, gift bags, photo albums, postcards. This substance may comprise particles (e.g., a glitter or confetti) and a liquid (e.g., water) such that when the special effects container is shaken, a visual effect is produced. One type of visual effect produced is similar to that of a snow globe. For example, pieces of a polymer confetti, each having the shape of a snowflake, may be included in a special effects container with a liquid. Such confetti may have a negative buoyancy with respect to the liquid such that after the special effects container is shaken, the pieces of confetti sink. The rate of descent / ascent of the container particles can be configured by changing the specific weight of the liquid or particles.
Owner:ANDERSON PRESS +1
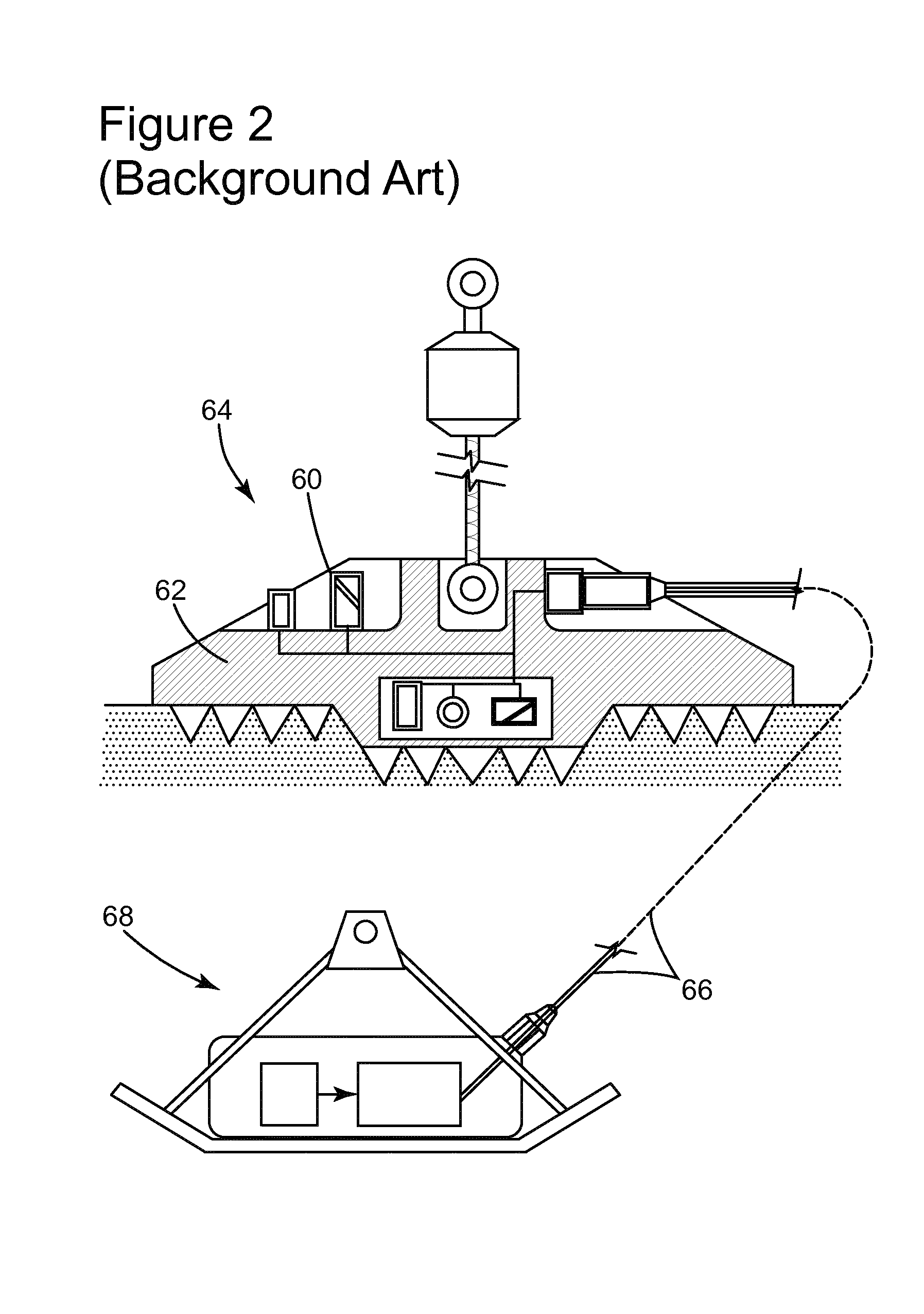
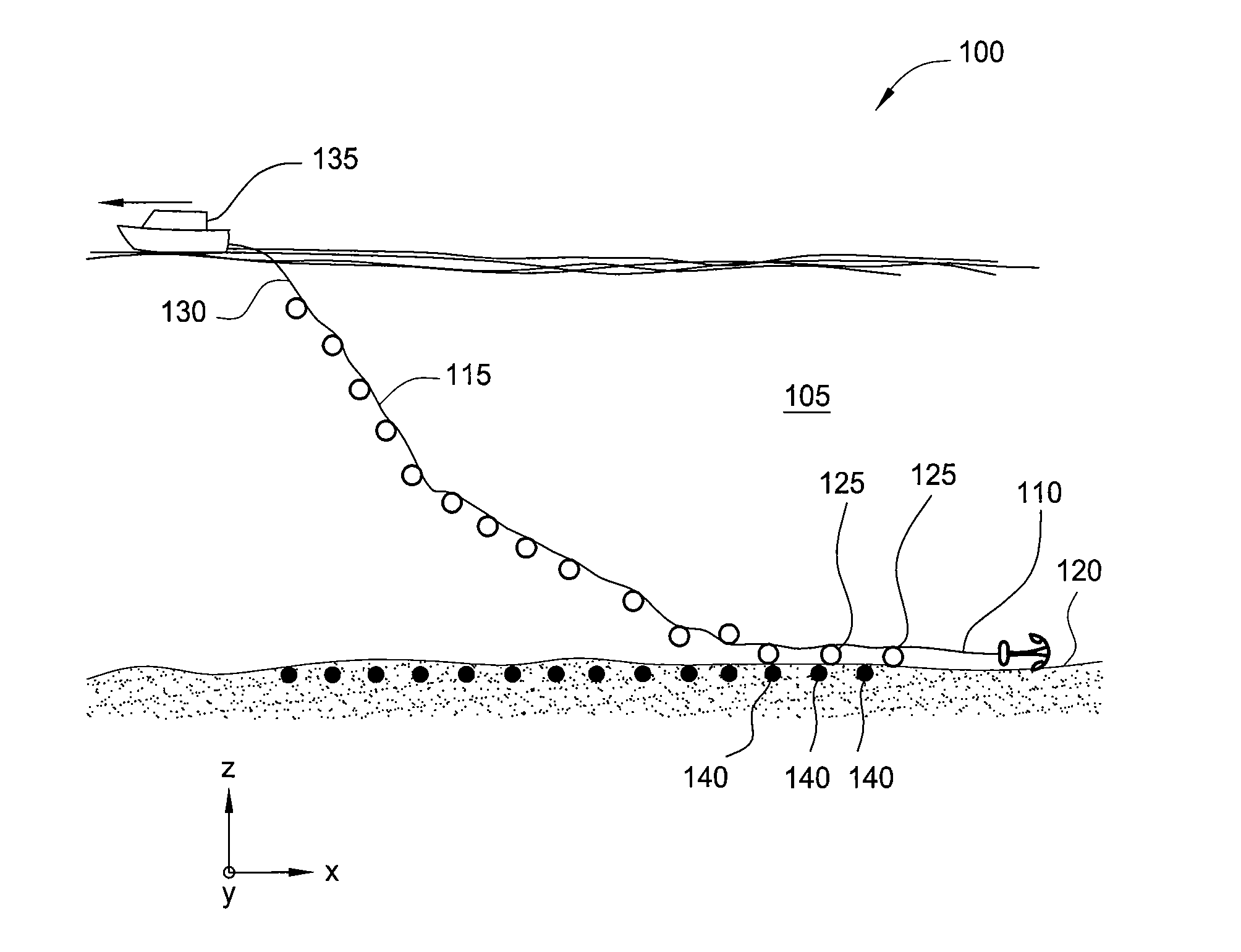
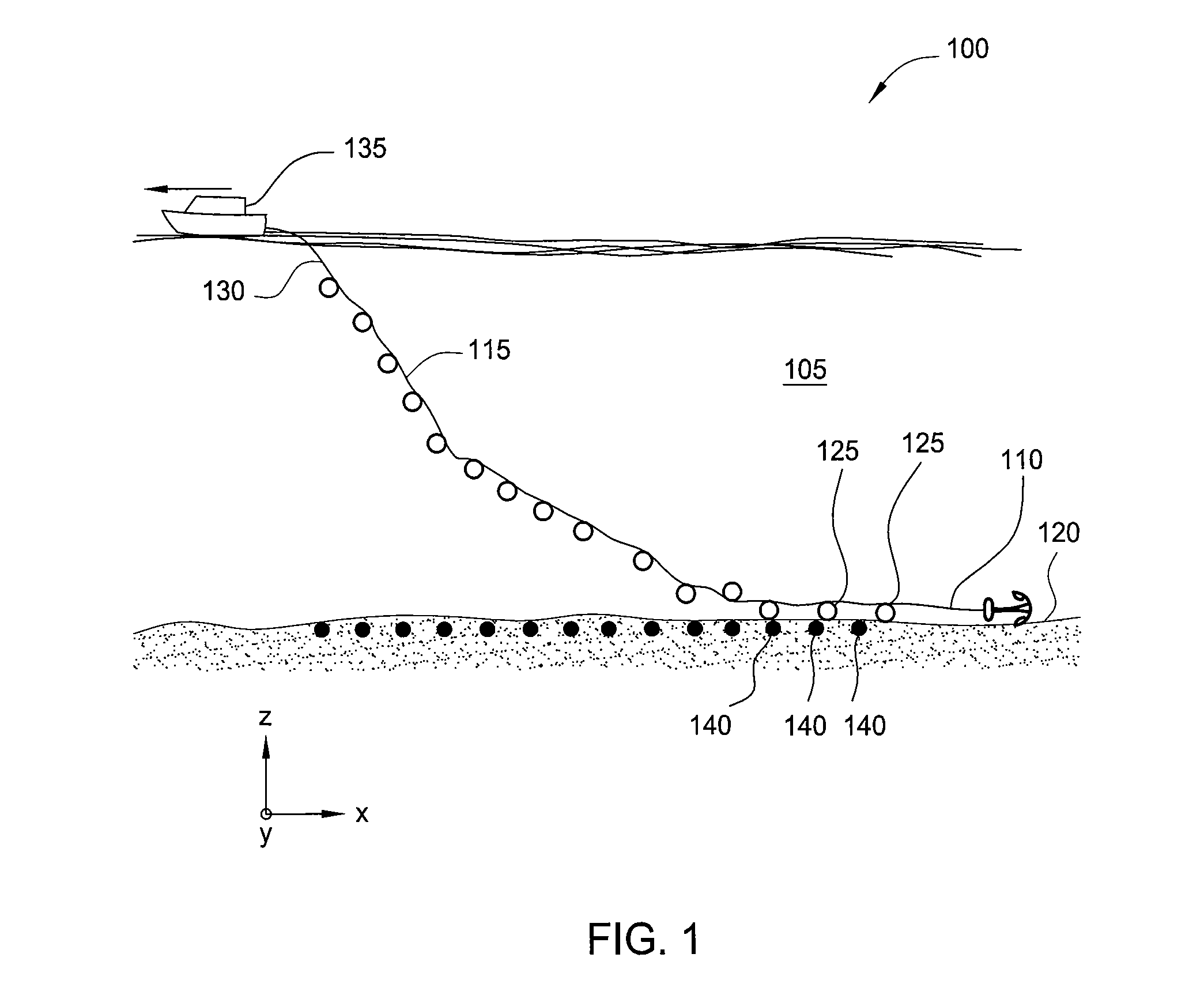
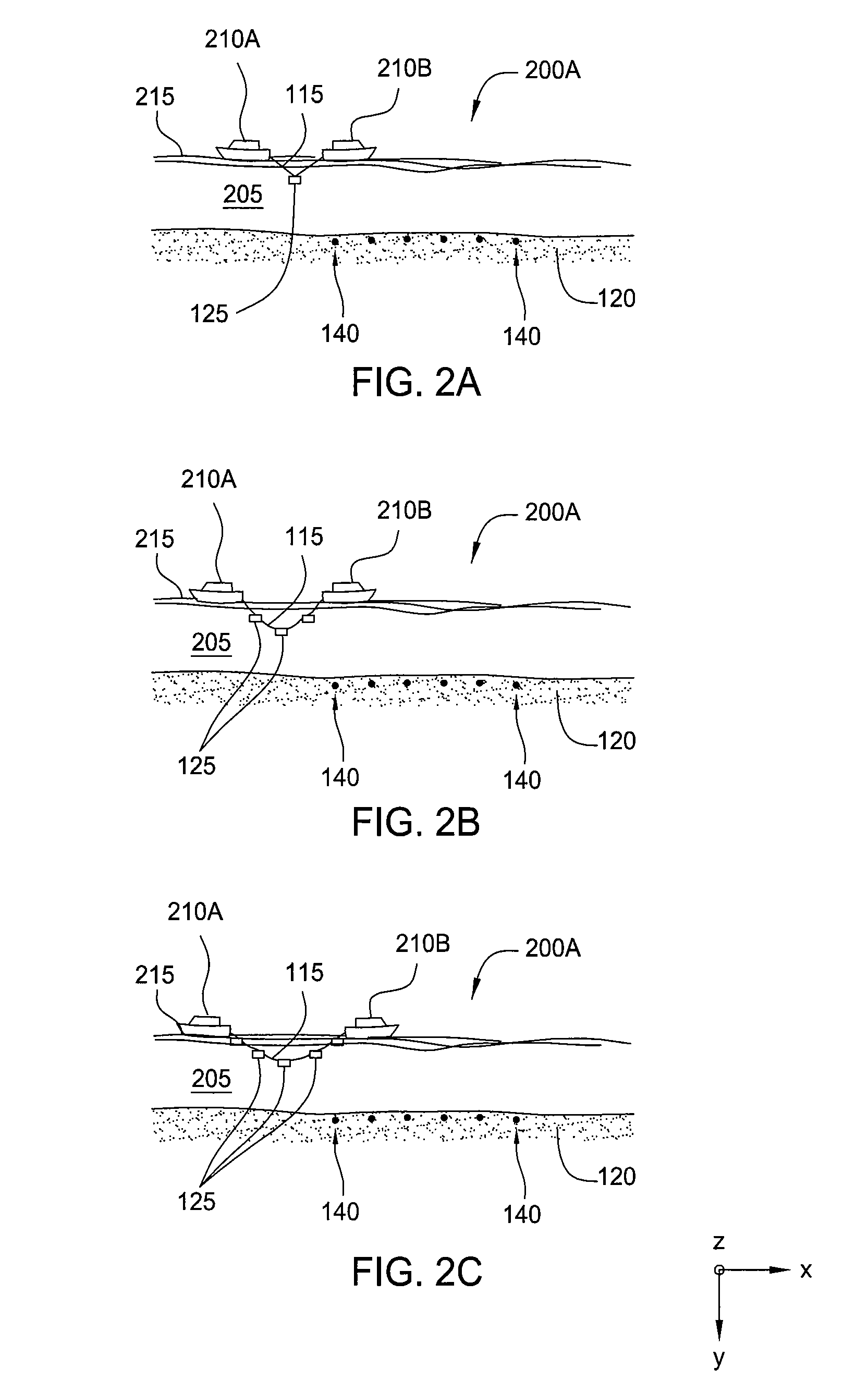
Method and apparatus for accurate placement of ocean bottom seismic instrumentation
InactiveUS20110176383A1Pipe laying and repairSeismology for water-covered areasOcean bottomMarine engineering
Embodiments described herein relate to an apparatus and method for deployment and retrieval of one or more seismic devices in a deep water marine environment. In one embodiment, a method for deploying and positioning ocean bottom equipment is described. The method includes attaching at least one article having a negative buoyancy to a support cable, lowering the at least one article into the water column from two or more points of suspension on a surface of the water column, at least one of the two or more points of suspension being movable relative to the other point of suspension, and manipulating tension of the support cable, length of the support cable, position of the support cable, and distance between the two or more points of suspension to cause the at least one article to fall to a bottom of the water column at a predetermined location on the bottom.
Owner:FAIRFIELD INDUSTRIES INC
Inflatable buoyancy device with water-dependant triggering mechanism
Owner:OLSON MANFRED BRADLEY +1
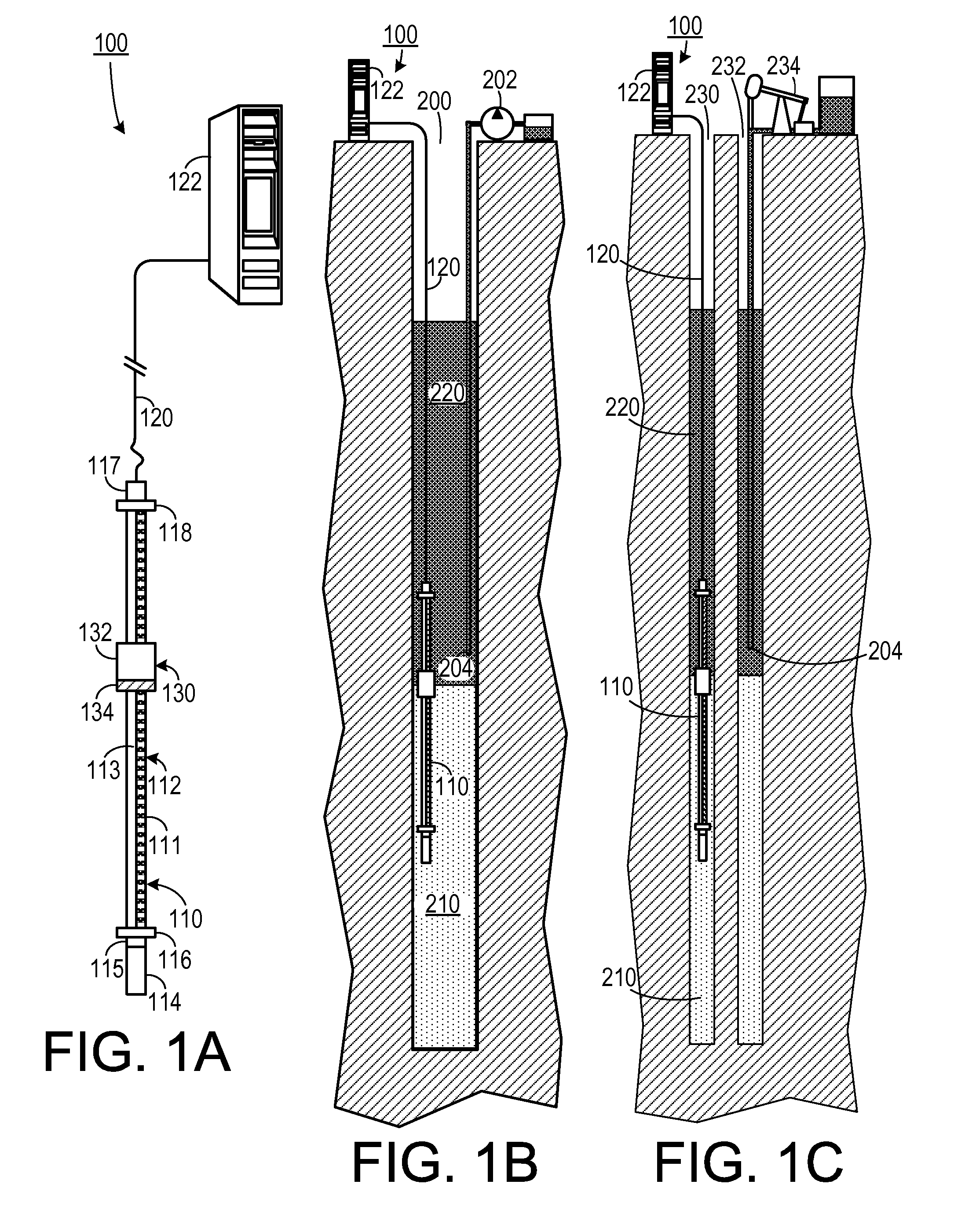
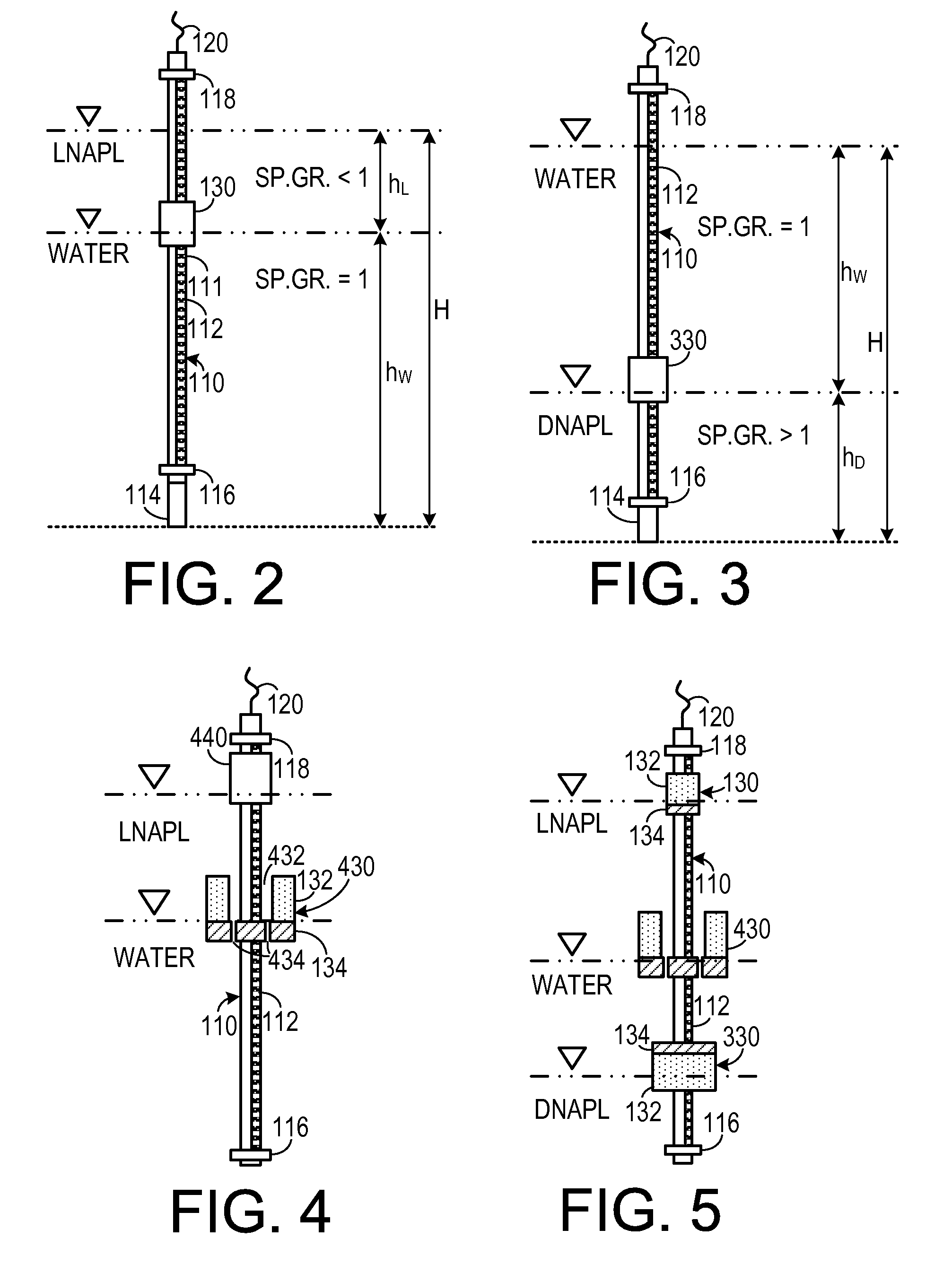
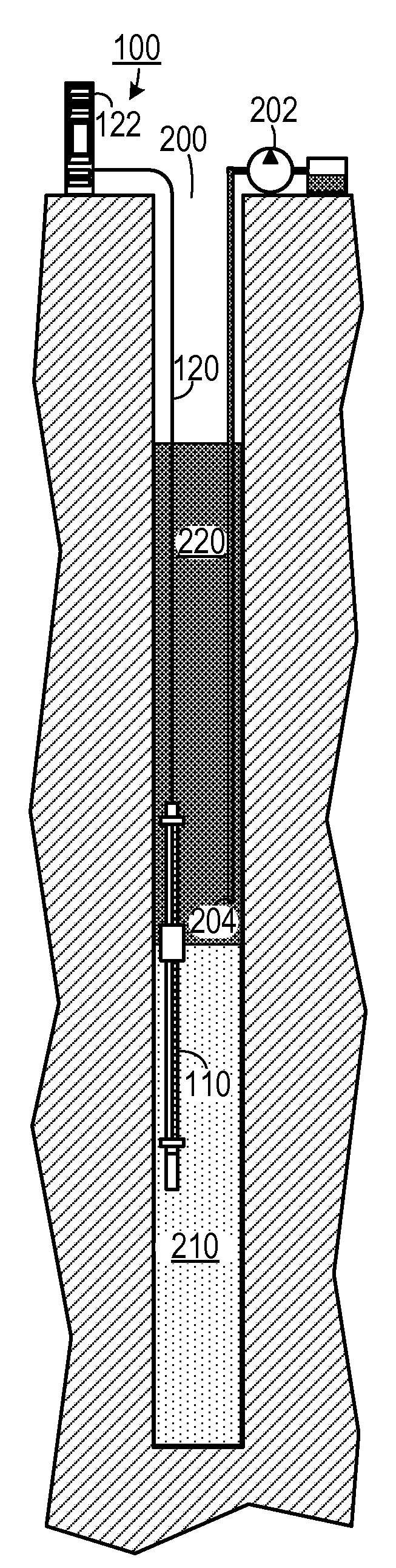
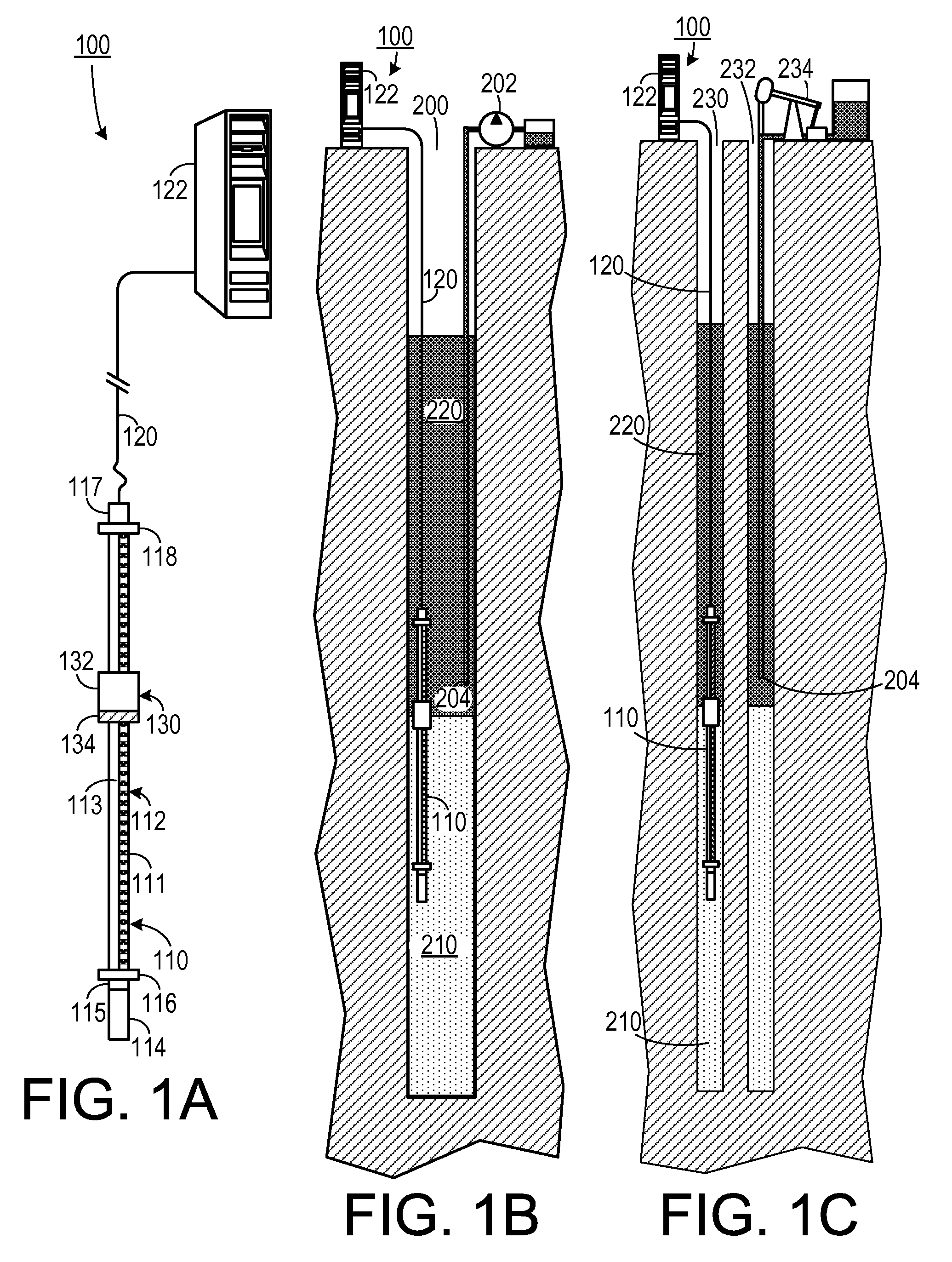
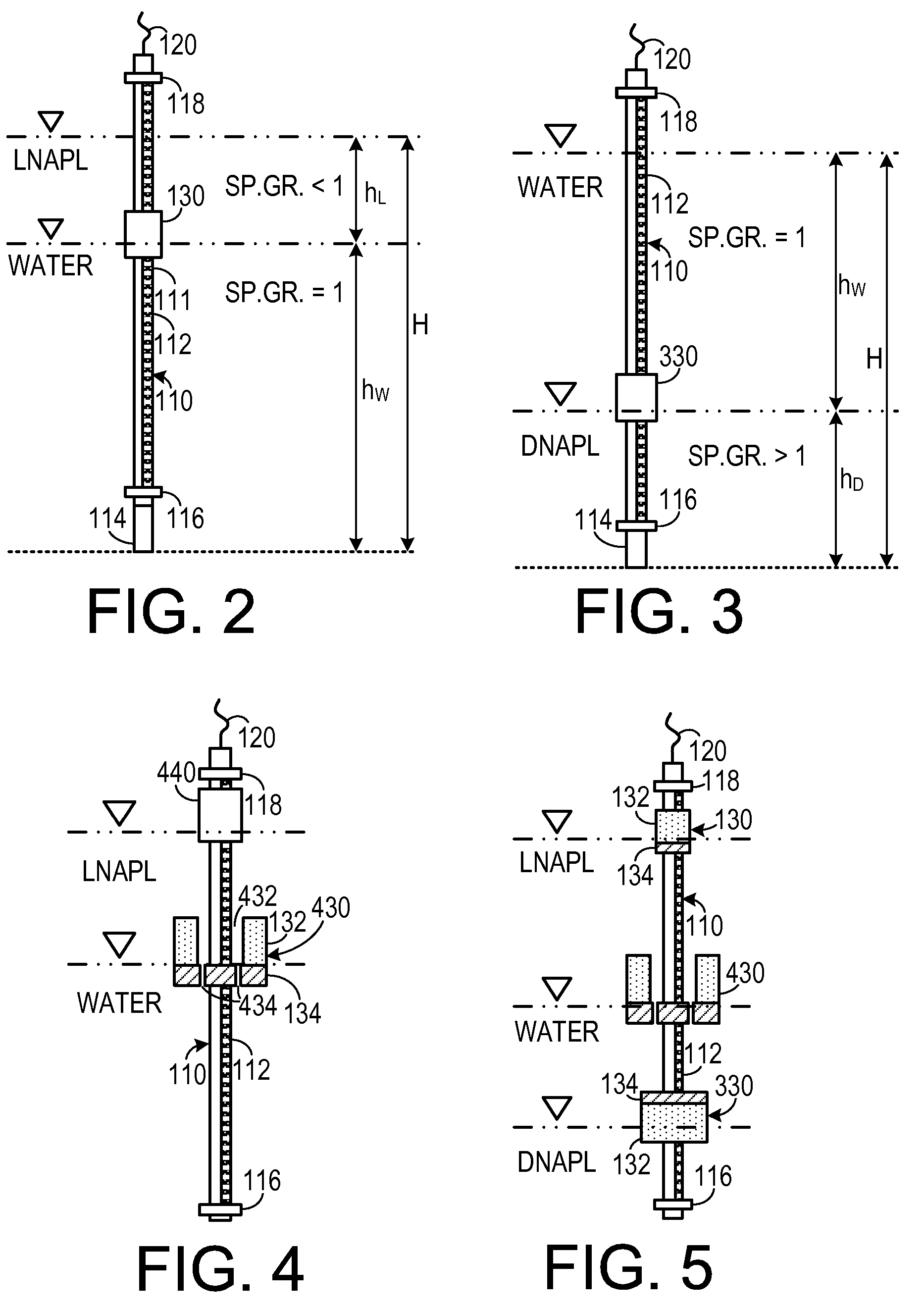
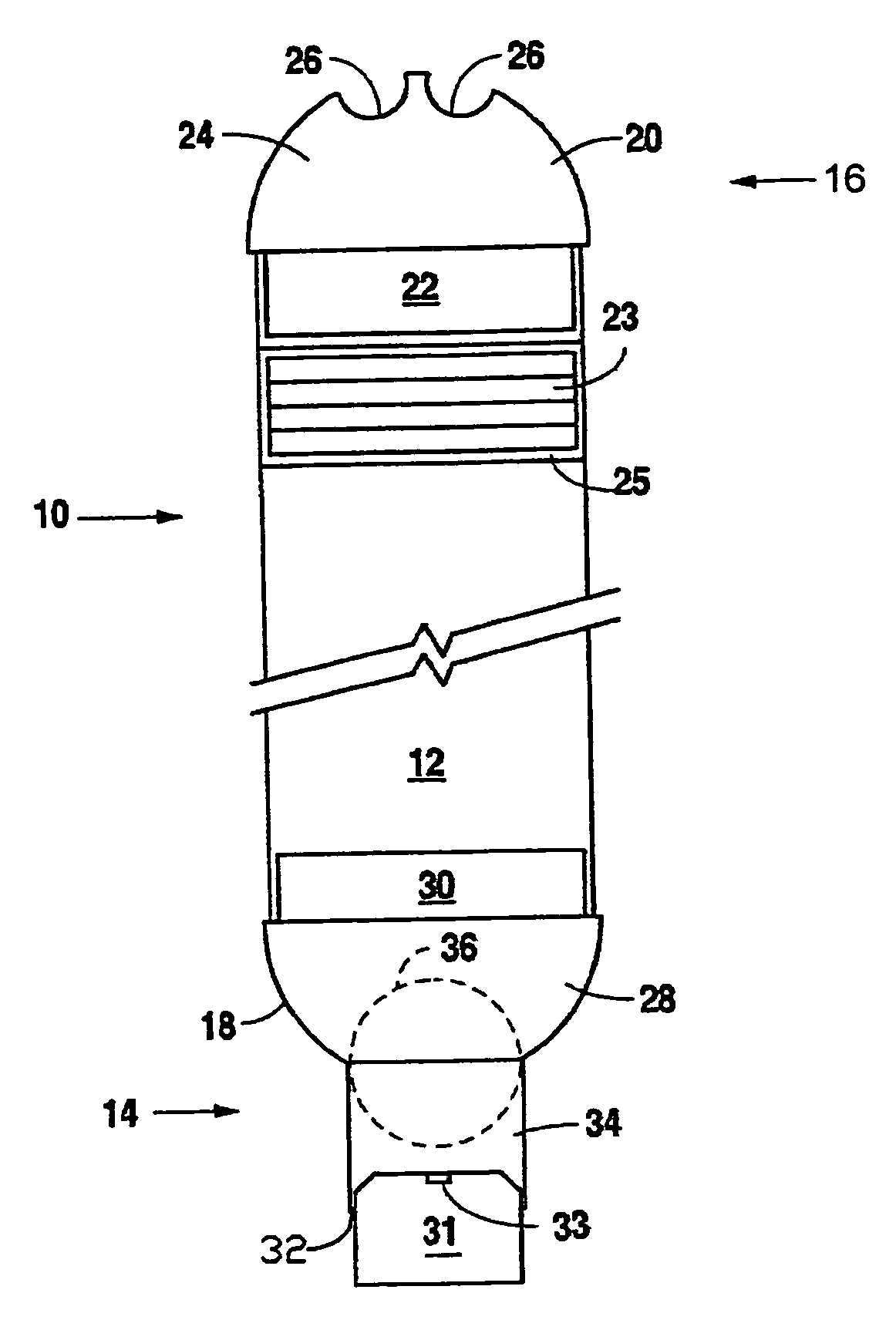
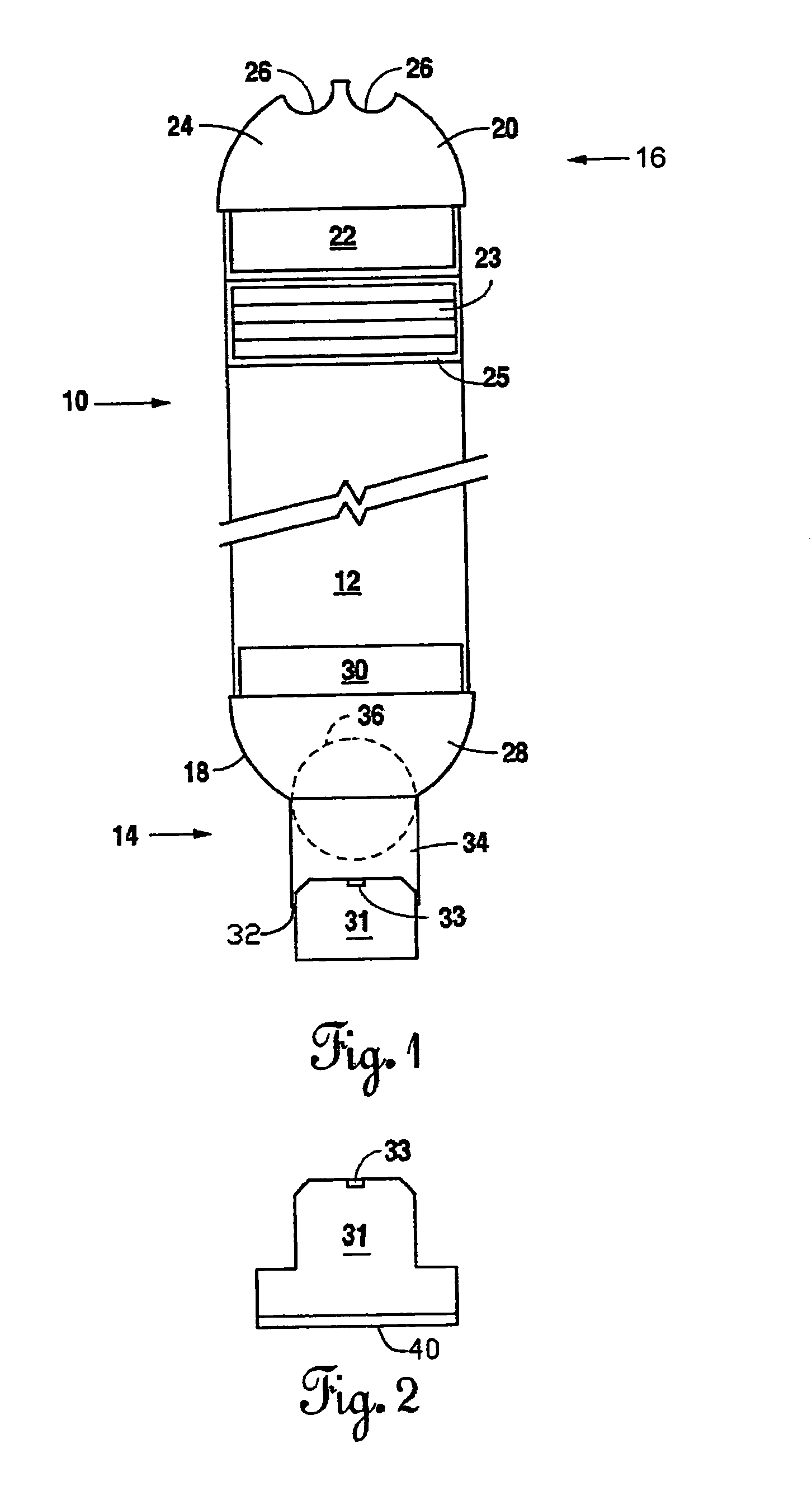
Multiphase-liquid level data logger
A multiphase-liquid level sensing system for sensing a layer depth and thickness of a liquid of a first phase that floats on a liquid of a different second phase includes an elongated stem that defines an elongated cavity. A float, which exhibits a sensible property, is disposed coaxially around the elongated stem and has negative buoyancy relative to the liquid of the first phase and positive buoyancy relative to the liquid of the second phase. A level sensor senses the sensible property and indicates a second phase liquid distance from the float to the bottom of the stem. An overburden sensor extends downwardly from the stem senses total liquid thickness of the liquid above the overburden sensor. A computational circuit calculates a layer depth and thickness of the liquid of the first phase, based on input from the level sensor and the overburden sensor.
Owner:MAHADEVAIAH BASAVARAJ
Self-filling modular barrier
A flood barrier comprises hollow self-filling units (10, 12, 14, 16) placed end-to-end and connected at their ends by downwardly tapered bilobal (46) keys inserted into sockets (26, 28) at the ends of the units, wherein the keys incorporate concrete or other ballast for negative buoyancy.
Owner:BU INNOVATIONS LTD
Neutrally buoyant submerged system using lesser density ballast fluid
InactiveUS7987805B1Avoid excessive densityVessel partsVessel safetyMarine engineeringNeutral buoyancy
The invention provides a means by which the attitude or orientation of a submerged object can be changed or altered using a fixed quantity of transferable ballast fluid which has a density less than that of the surrounding fluid in which the object is submerged. In one embodiment, the process utilizes a static negatively buoyant material (which could be a lead weight) to offset the net negative buoyancy of the transferable ballast fluid. In this way, the total overall buoyancy of the system does not change, but by transferring ballast fluid into expandable reservoirs which are physically separated from the static negatively buoyant material, the separation between the center of buoyancy and the center of mass of the object can be changed, and thus the attitude or orientation of the object, if it is unrestrained, may be changed.
Owner:THE UNITED STATES OF AMERICA AS REPRESENTED BY THE SECRETARY OF THE NAVY
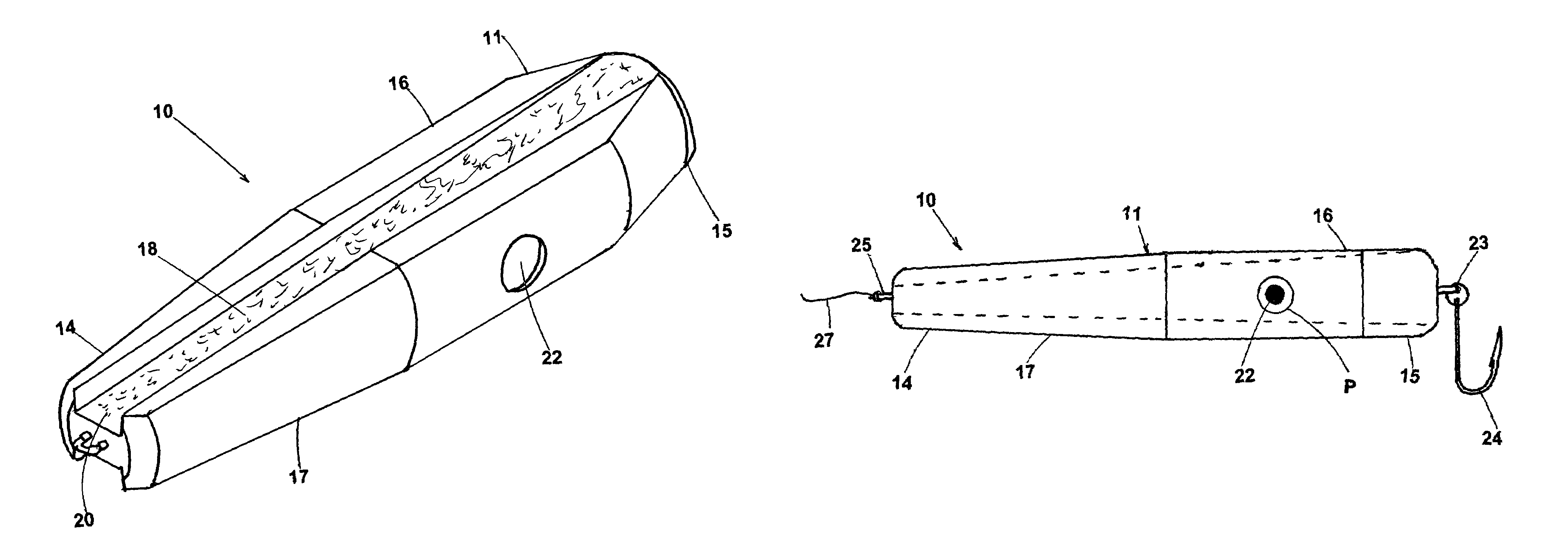
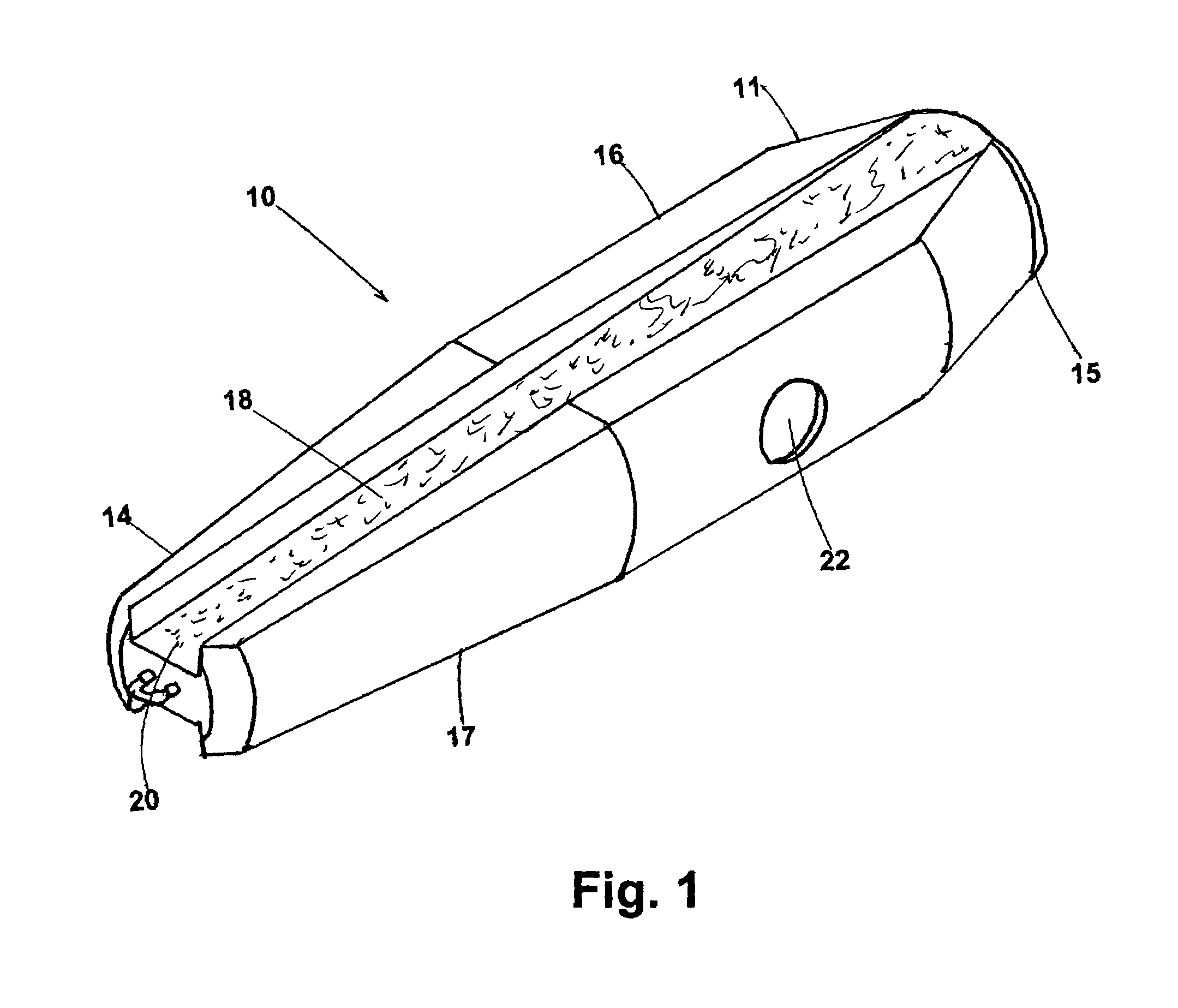
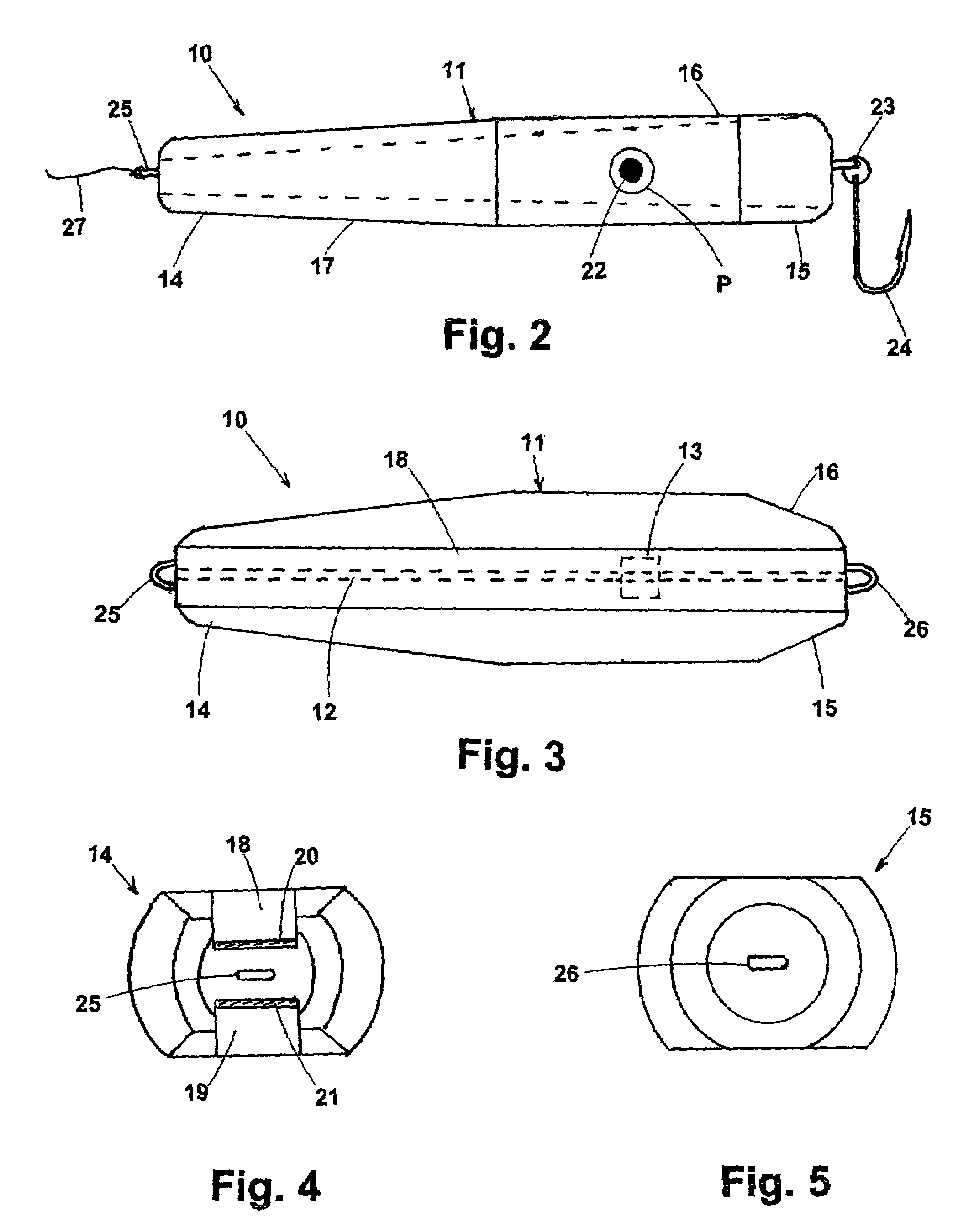
Fishing lure
A fishing lure for use as a top water lure having a construction of negative buoyancy. The lure has an elongated weighted body resembling a squid with angled channels defined in the top and bottom surfaces of the body. Upon the lure being retrieved by an angler, water gushes through one of the channels and splashes over and about the leading end of the lure, causing the lure to “swim” over the water surface with the trailing end submersed in the water. This presents the appearance of a fleeting baitfish. By careful selection of colors and reflective strips the lure will have an appearance that is very visually stimulating to game fish.
Owner:JUSSAUME RAYMOND G
Neutrally buoyant submerged system using greater density ballast fluid
The system provides a means by which the attitude or orientation of a submerged object can be changed using a fixed quantity of transferable ballast fluid which has a density greater than that of the surrounding fluid in which the object is submerged. In one embodiment, the process utilizes a static flotation shell offset the net negative buoyancy of the transferable ballast fluid. In this way, the total overall buoyancy of the system does not change, but by transferring fluid into expandable reservoirs which are physically separated from the static flotation shell, the separation between the center of buoyancy and the center of mass of the object can be changed, and thus the attitude or orientation of the object, if it is unrestrained, may be changed.
Owner:THE GOVERNMENT OF THE UNITED STATES OF AMERICA AS REPRESENTED BY THE SEC OF THE NAVY NAVAL RES LAB WASHINGTON
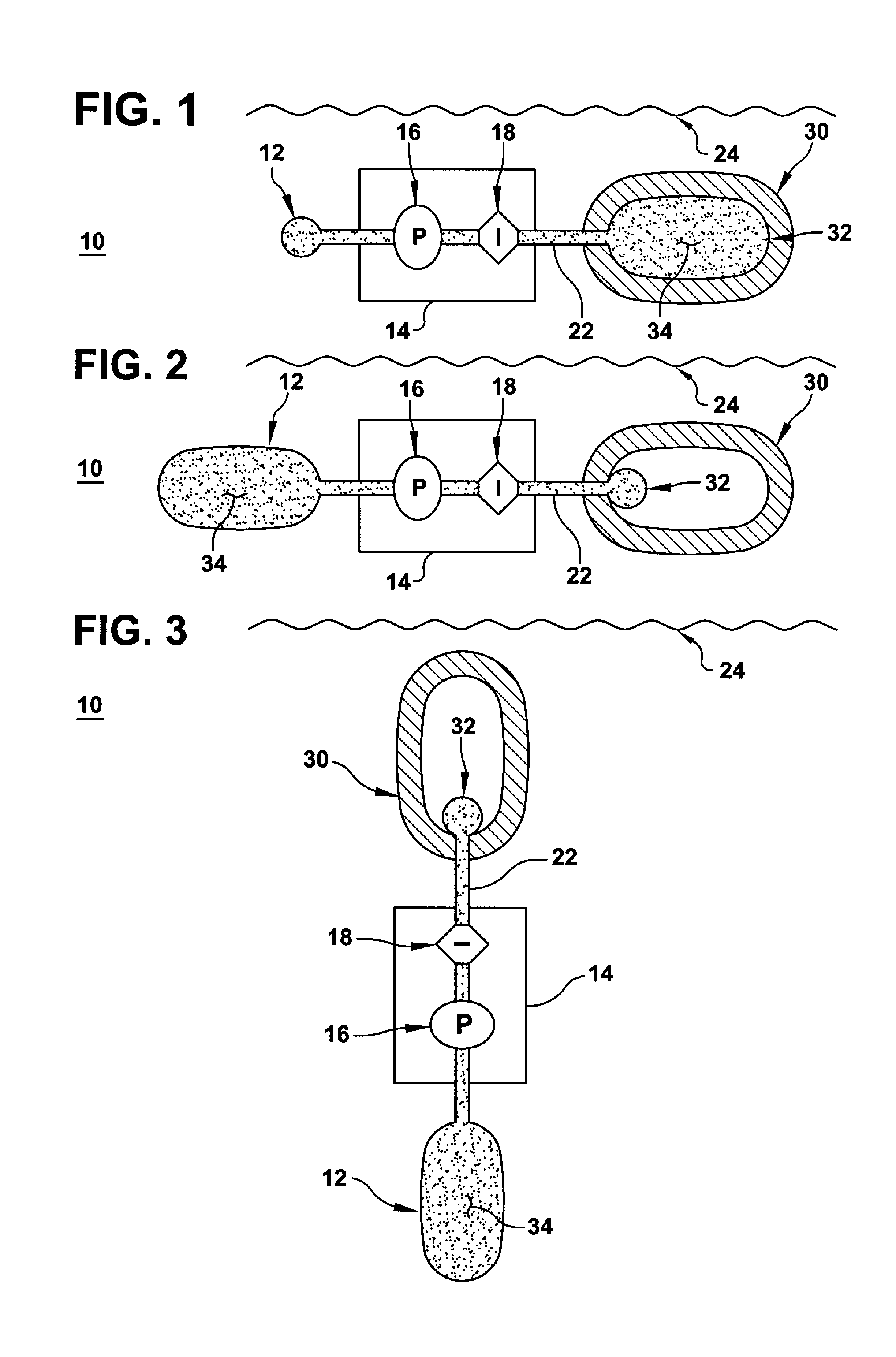
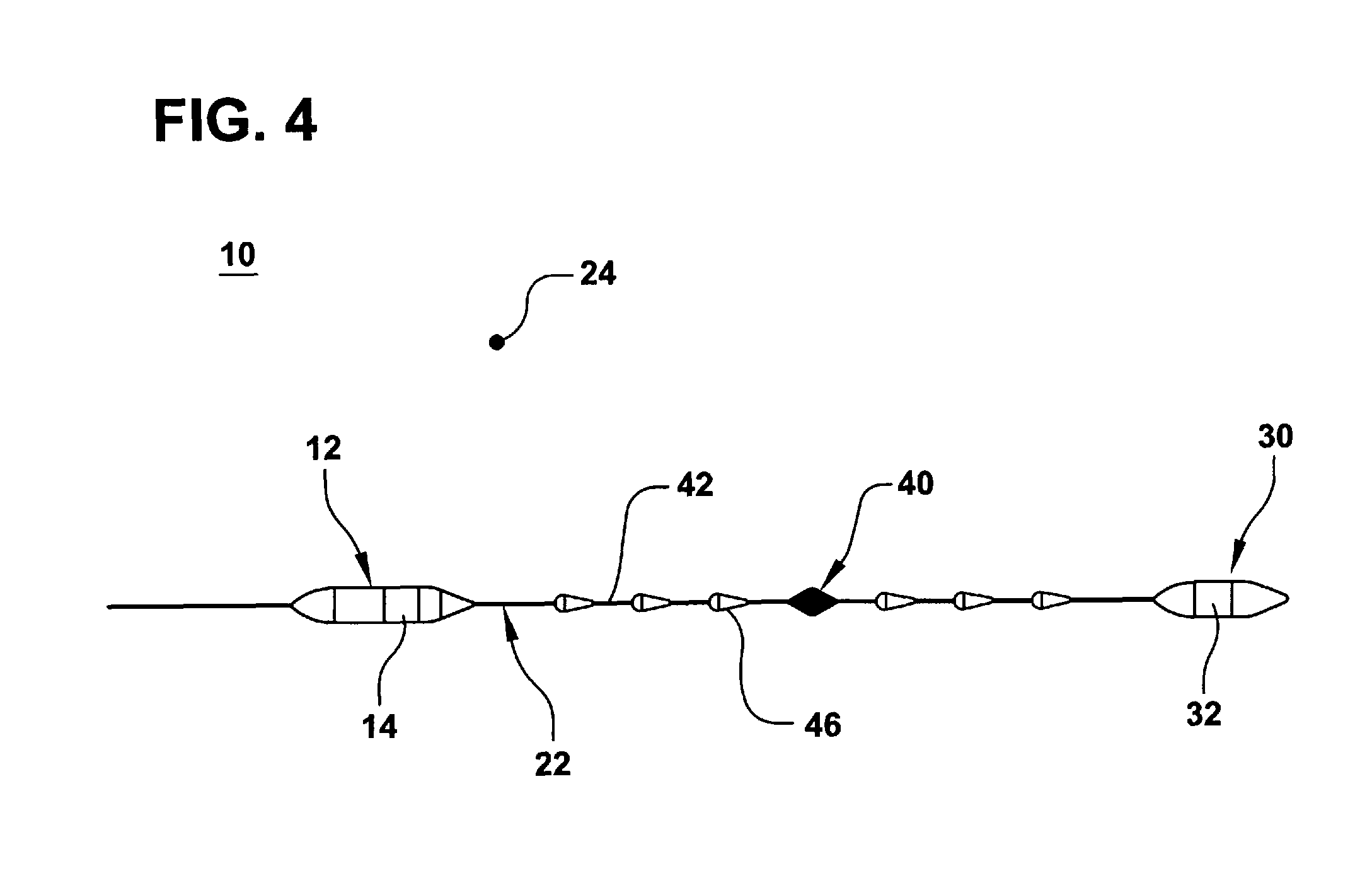
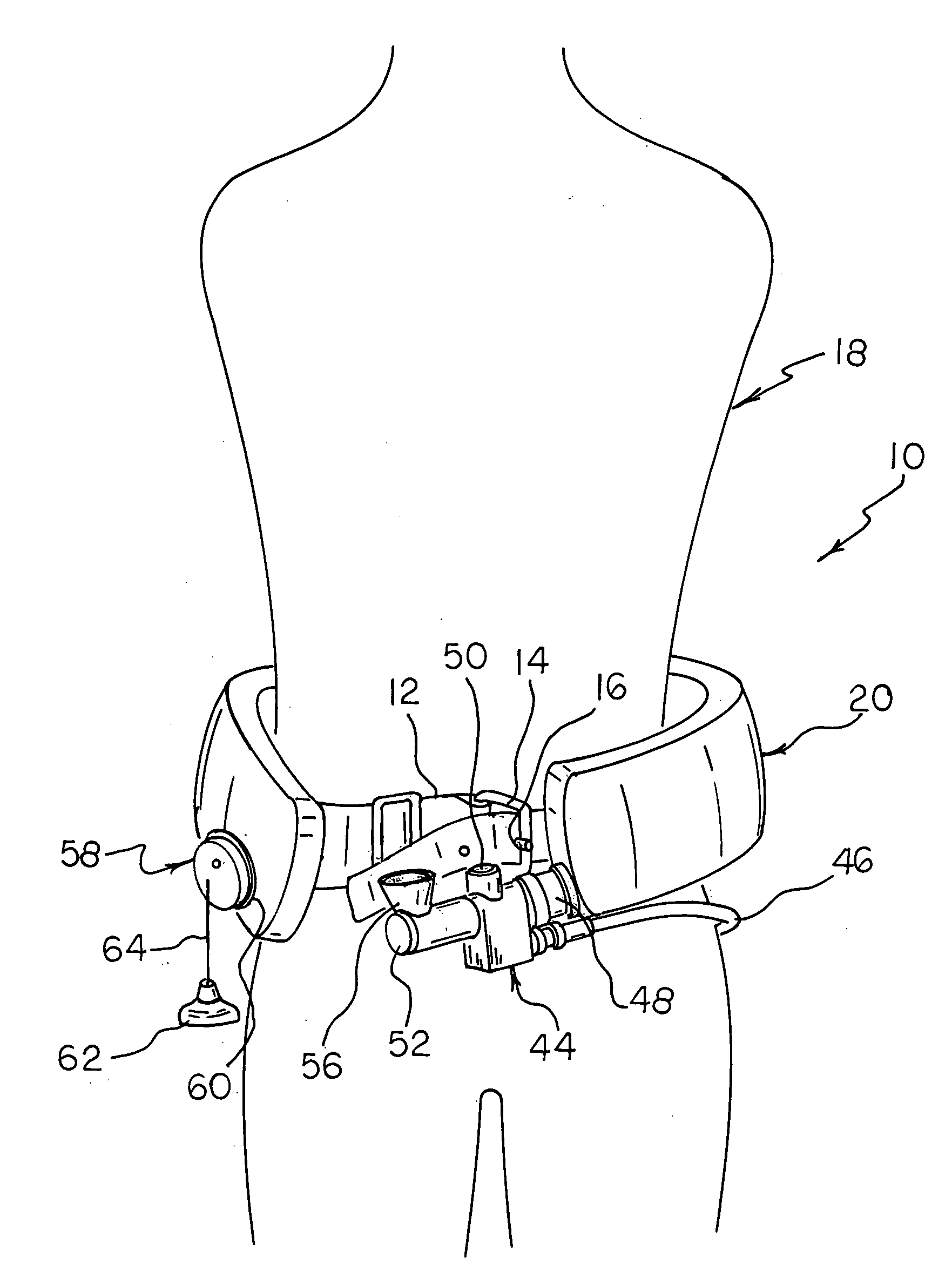
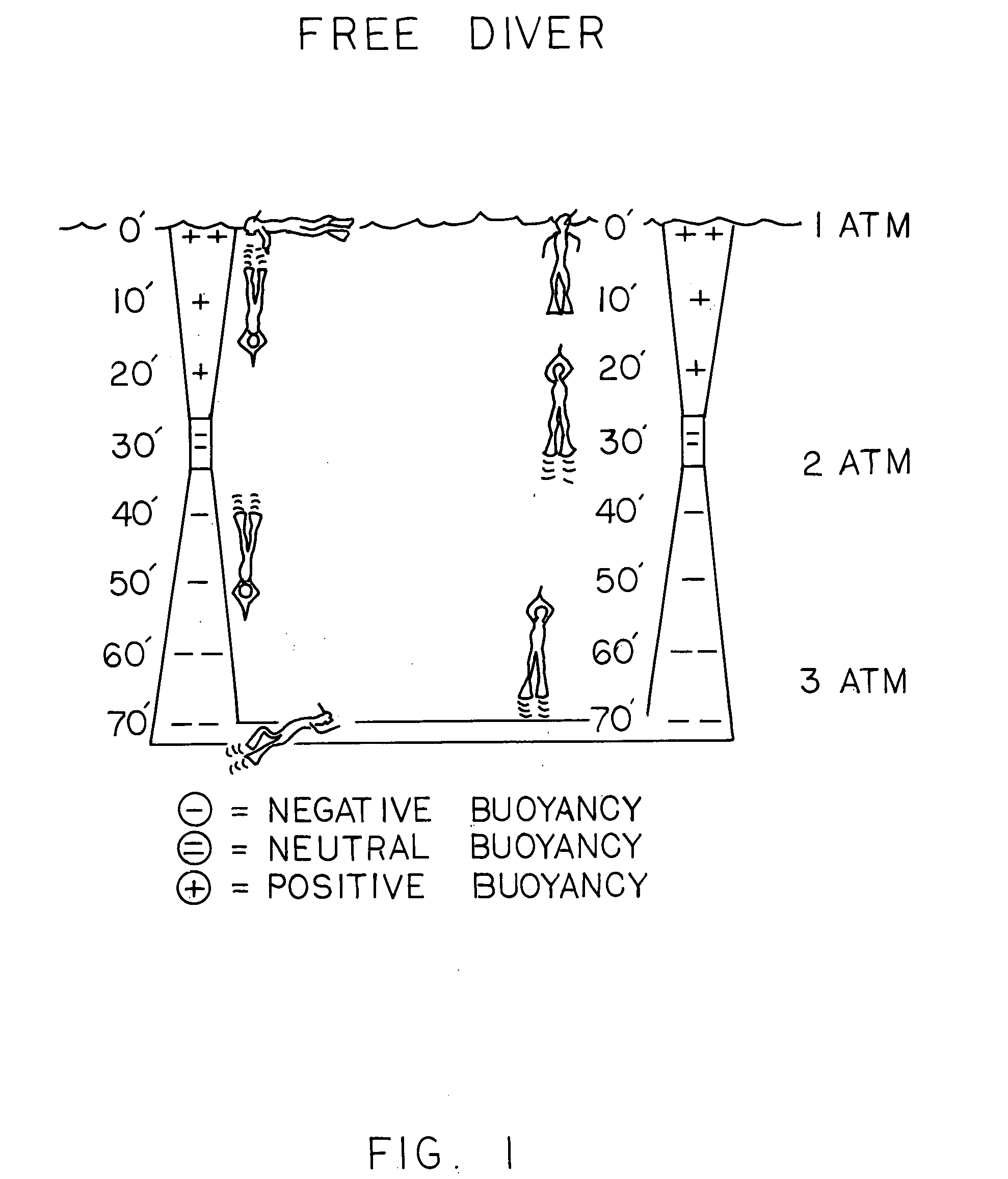
Buoyancy compensator belt
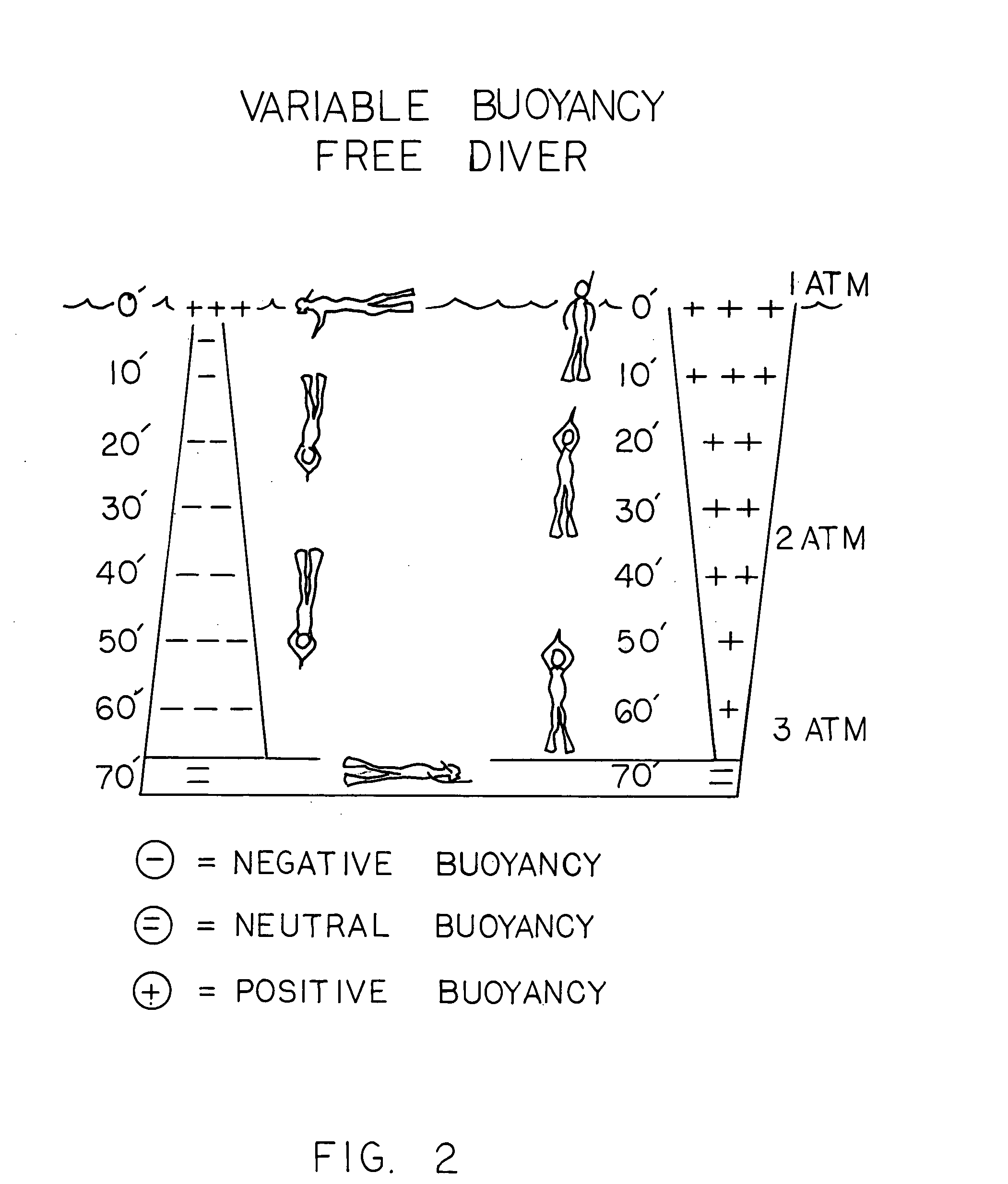
A buoyancy compensator belt comprising a belt to which is mounted a tubular inflatable bladder positioned within a flexible housing and a small gas cylinder. In one embodiment, one or more weights are mounted onto the belt. A combination power inflation / bleed valve is operatively connected to the inflatable bladder and is fluidly connected to a first stage regulator of the gas cylinder by a hose. A dump valve is operatively connected to the bladder to prevent over-inflation and allow dumping of the air from the bladder. The buoyancy compensator belt is particularly suitable for use by free divers to allow the diver to rapidly descend to the desired depth due to the negative buoyancy produced by the weight of the belt, to allow the diver to partially inflate the inflator bladder to achieve neutral buoyancy at the desired depth, and then, when the diver wishes to ascend, to more fully inflate the inflator bladder to achieve positive buoyancy and rapidly ascend to the surface.
Owner:HUISH OUTDOORS
Autonomous Underwater Vehicle
ActiveUS20180346082A1Avoid gasSeismic signal receiversSeismology for water-covered areasAmbient waterMarine engineering
A method of obtaining data with a sensor of an autonomous underwater vehicle (AUV), the AUV comprising a bladder which contains a gas and is exposed to ambient water pressure. A downward thrust force is generated which causes the AUV to descend through a body of water, wherein the bladder contracts as the AUV descends due to an associated increase in the ambient water pressure, the contraction of the bladder causing the gas to compress and the AUV to become negatively buoyant. Next the AUV lands on a bed of the body of water. After the AUV has landed on the bed, the sensor is operated to obtain data with the AUV stationary and negatively buoyant and a weight of the AUV supported by the bed. After the data has been obtained, an upward thrust force is generated which overcomes the negative buoyancy of the AUV and causes the AUV to ascend through the body of water, the ascent of the AUV causing the bladder to expand due to the associated decrease in the ambient water pressure, the expansion of the bladder causing the gas to decompress and the AUV to become neutrally buoyant.
Owner:AUTONOMOUS ROBOTICS
Multiphase-liquid level data logger
A multiphase-liquid level sensing system for sensing a layer depth and thickness of a liquid of a first phase that floats on a liquid of a different second phase includes an elongated stem that defines an elongated cavity. A float, which exhibits a sensible property, is disposed coaxially around the elongated stem and has negative buoyancy relative to the liquid of the first phase and positive buoyancy relative to the liquid of the second phase. A level sensor senses the sensible property and indicates a second phase liquid distance from the float to the bottom of the stem. An overburden sensor extends downwardly from the stem senses total liquid thickness of the liquid above the overburden sensor. A computational circuit calculates a layer depth and thickness of the liquid of the first phase, based on input from the level sensor and the overburden sensor.
Owner:MAHADEVAIAH BASAVARAJ
Device for skimming oil from the surface of water
InactiveUS20130313181A1Improve reliabilityImprove efficiencyWater cleaningWaterborne vesselsMarine engineeringWater oil emulsion
The dock vessel has the tow compartment for placement of tug-boats, and technological compartment. The technological compartment is made as a hangar at the bottom of which a central channel is located, along its upper boundaries, the rack-ledges with symmetrical location to the right and left, toward the hull, are placed on which the technological equipment for the water-oil emulsion treatment is placed. Between the dock-vessel hull walls and side walls of the central channel, the containers for collection of the emulsified oil are placed. The central channel of the technological compartment is equipped with, at least, two bulkheads in which, the hermetically pluggable openings located at different levels are made. The floating boom is made as the sectional net sleeve filled with elastic porous adsorbent and provided with positive buoyancy in the top edge of doubled net forming the net sleeve and negative buoyancy at its lower edge.
Owner:ZOTOV IGOR A +1
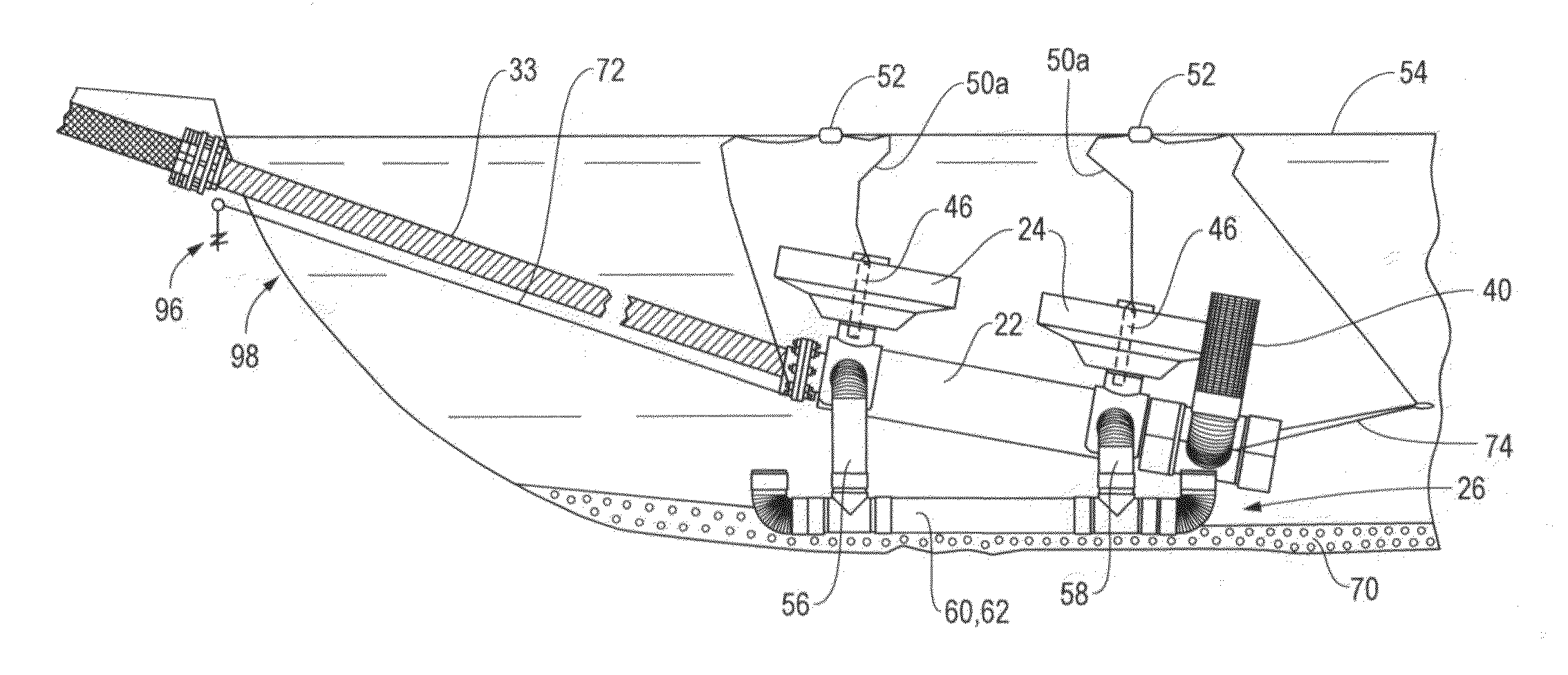
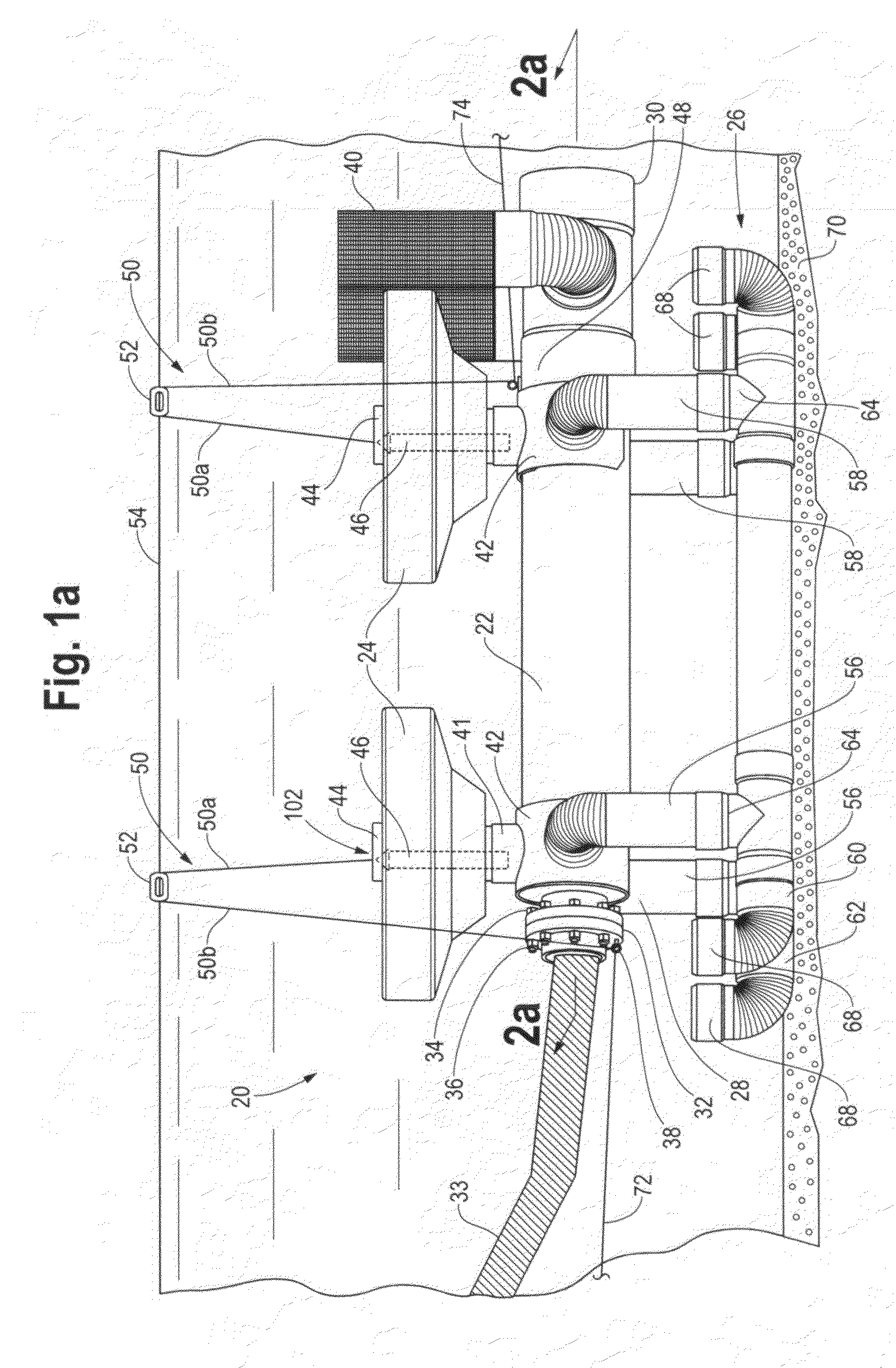
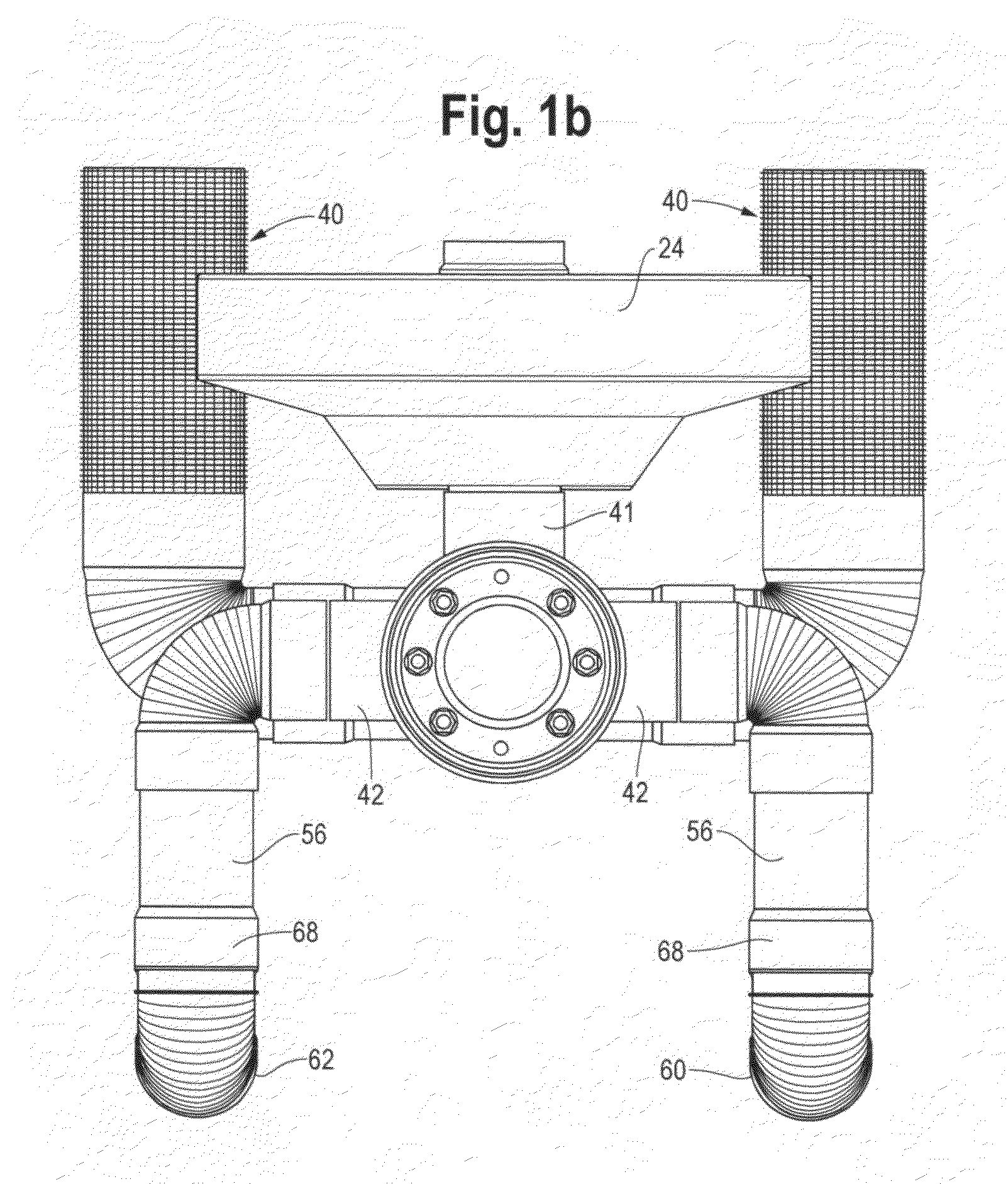
Towing and subsea installation of long articles
ActiveUS7993077B2Reduce deformationReduce fatigueDefensive equipmentTowing/pushing equipmentOcean bottomEngineering
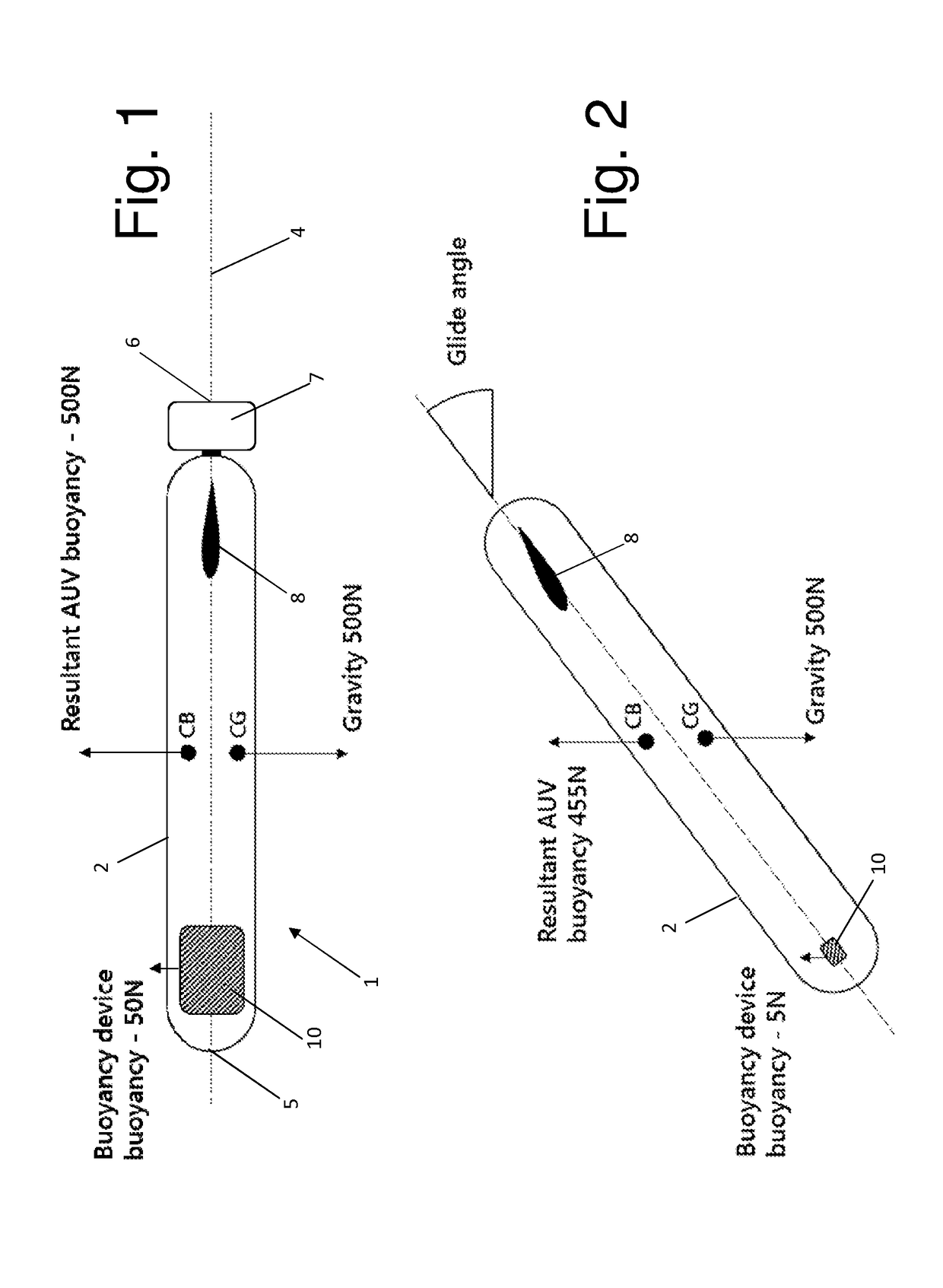
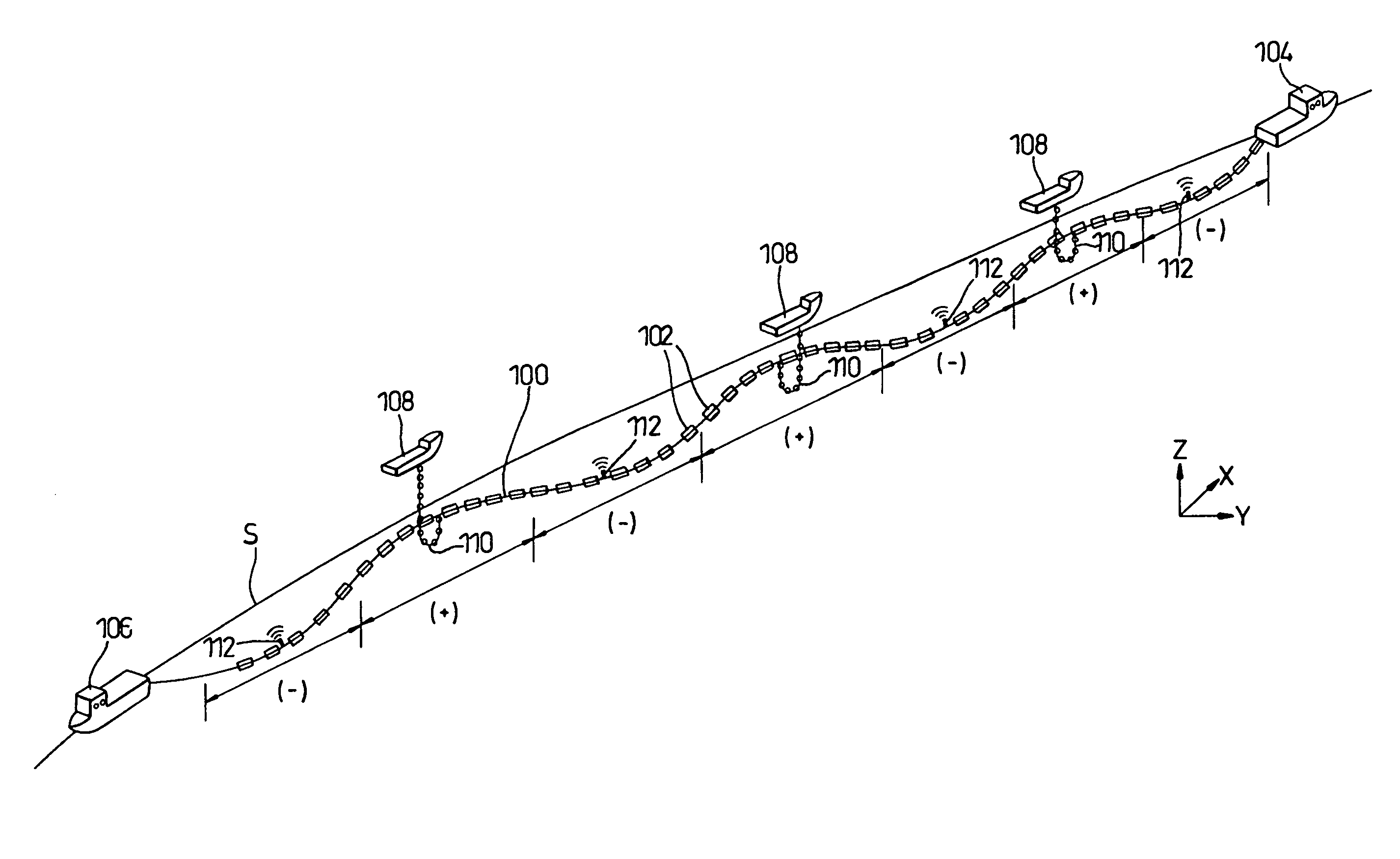
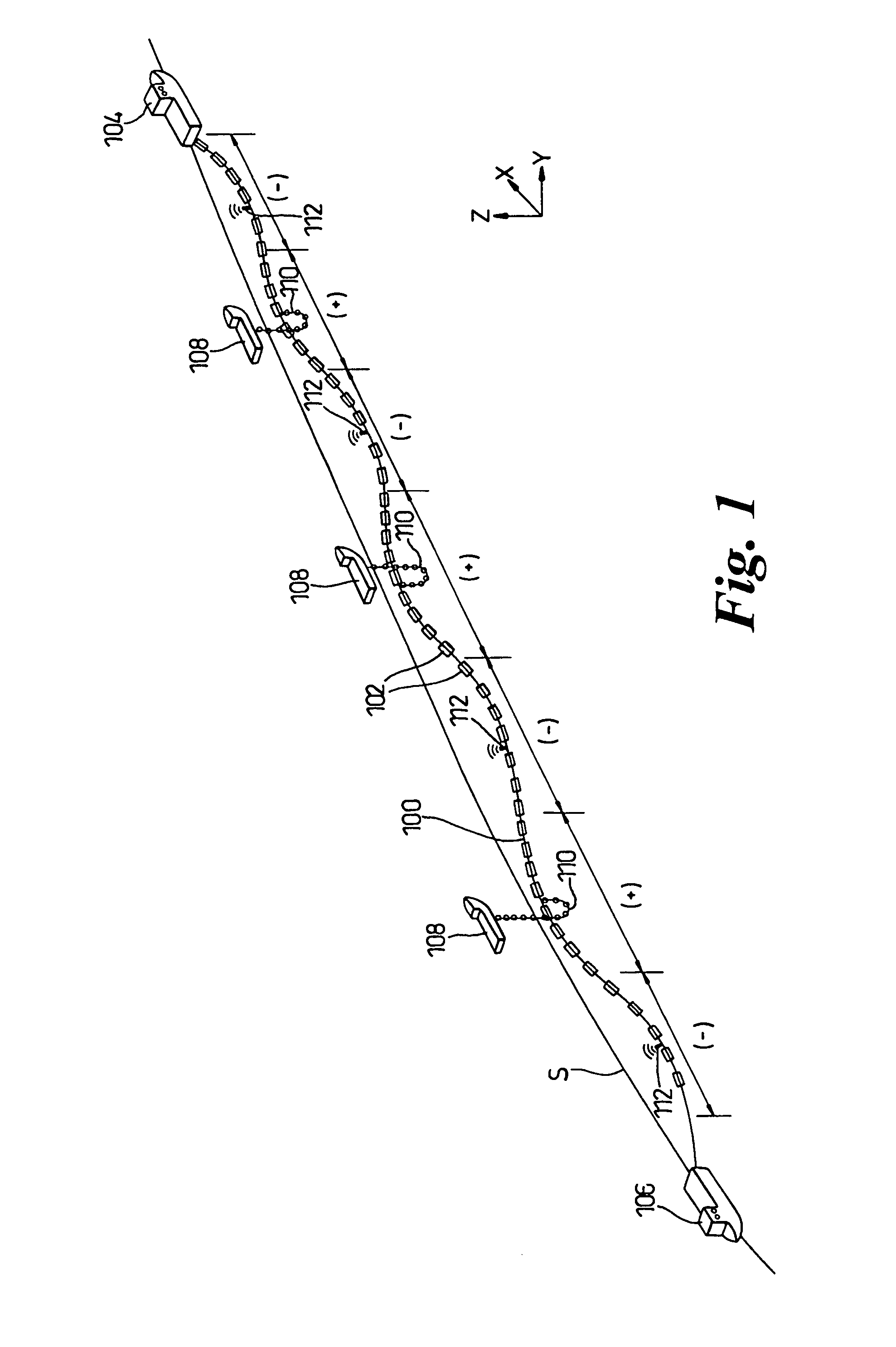
An elongate article (100) such as a prefabricated pipeline of several kilometers length is towed through water. The article is provided along its length with buoyancy adjusting material (102) fitted closely to the article. The buoyancy adjusting material is sufficient to give the article overall a positive buoyancy so that it will not sink to the seabed, and is distributed unevenly along the length of the article so as to create regions of negative buoyancy. This causes the article to adopt a wave profile with peaks (+) and troughs (−) along its length. The article is connected at its extremities to lead and trail tugs (104, 106) for controlling movement of the article through the water. Intermediate peaks are optionally coupled to intermediate tugs (108) or buoys (702) via self-adjusting ballast chains (110). The wave profile allows the towed structure to extend without undue tension on the article itself. The article can be laid to the seabed progressively removing buoyancy elements (102) using an ROV (302).
Owner:ACERGY FRANCE
Water bag ballast method for immersed tube tunnel construction
ActiveCN109056817AEasy to assembleEasy constructionArtificial islandsUnderwater structuresWater storageEnvironmental engineering
The invention discloses a water bag ballast method for immersed tube tunnel construction. The water bag ballast method for immersed tube tunnel construction comprises the following steps of firstly, calculating the number and arrangement positions of water bags needing to be laid in a water bag ballast system according to the buoyancy stressed by an immersed tube; secondly, arranging and installing the water bag ballast system in the immersed tube; thirdly, carrying out water storage and leak detection on the water bags; fourthly, during floating transportation and immersion placement of the immersed tube, controlling and regulating negative buoyancy and gesture of the immersed tube in the process of transverse movement, floating transportation and immersion installation of the immersed tube in a dock by carrying out water storage and drainage on the water bags; and fifthly, detaching the water bag ballast system after the installation process of the immersed tube is completed. The water bag ballast method for immersed tube tunnel construction has the advantages of being simple in construction process, high in operation efficiency and control accuracy, and low in construction costand labor cost, and is very high in practicability.
Owner:CCCC SECOND HARBOR ENG +1
Whale safe groundline
InactiveUS20050150152A1Improve wear resistanceLess likely to cutAgriculture tools and machinesFishing netsFiberYarn
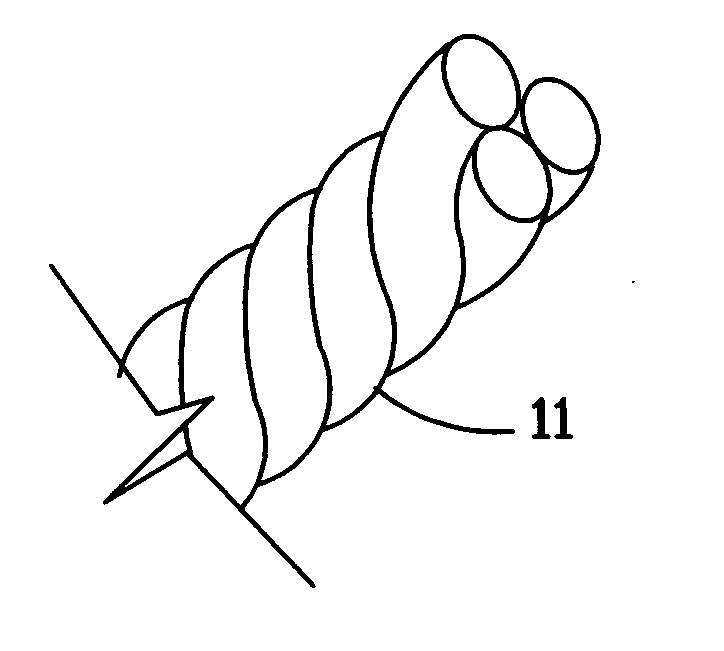
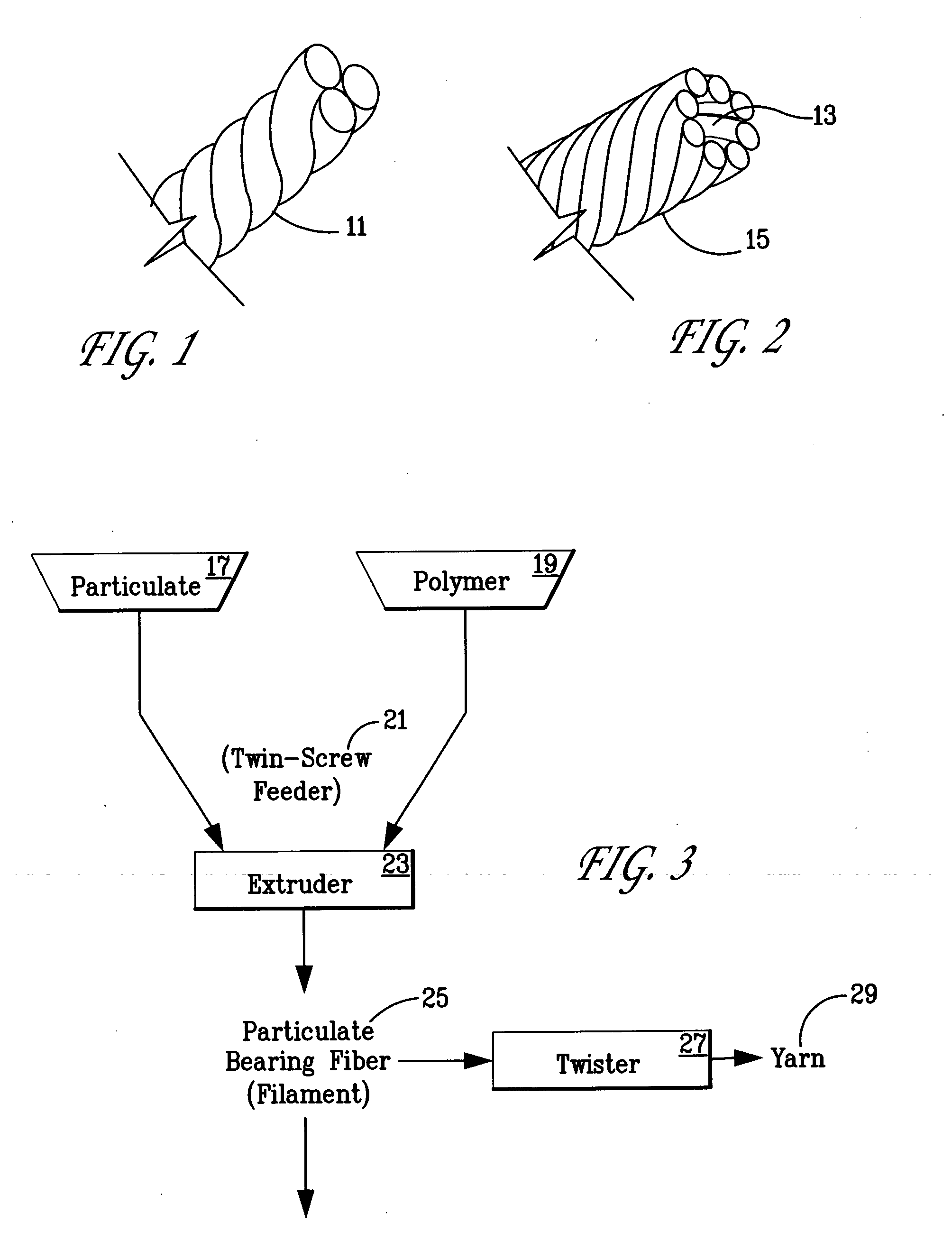
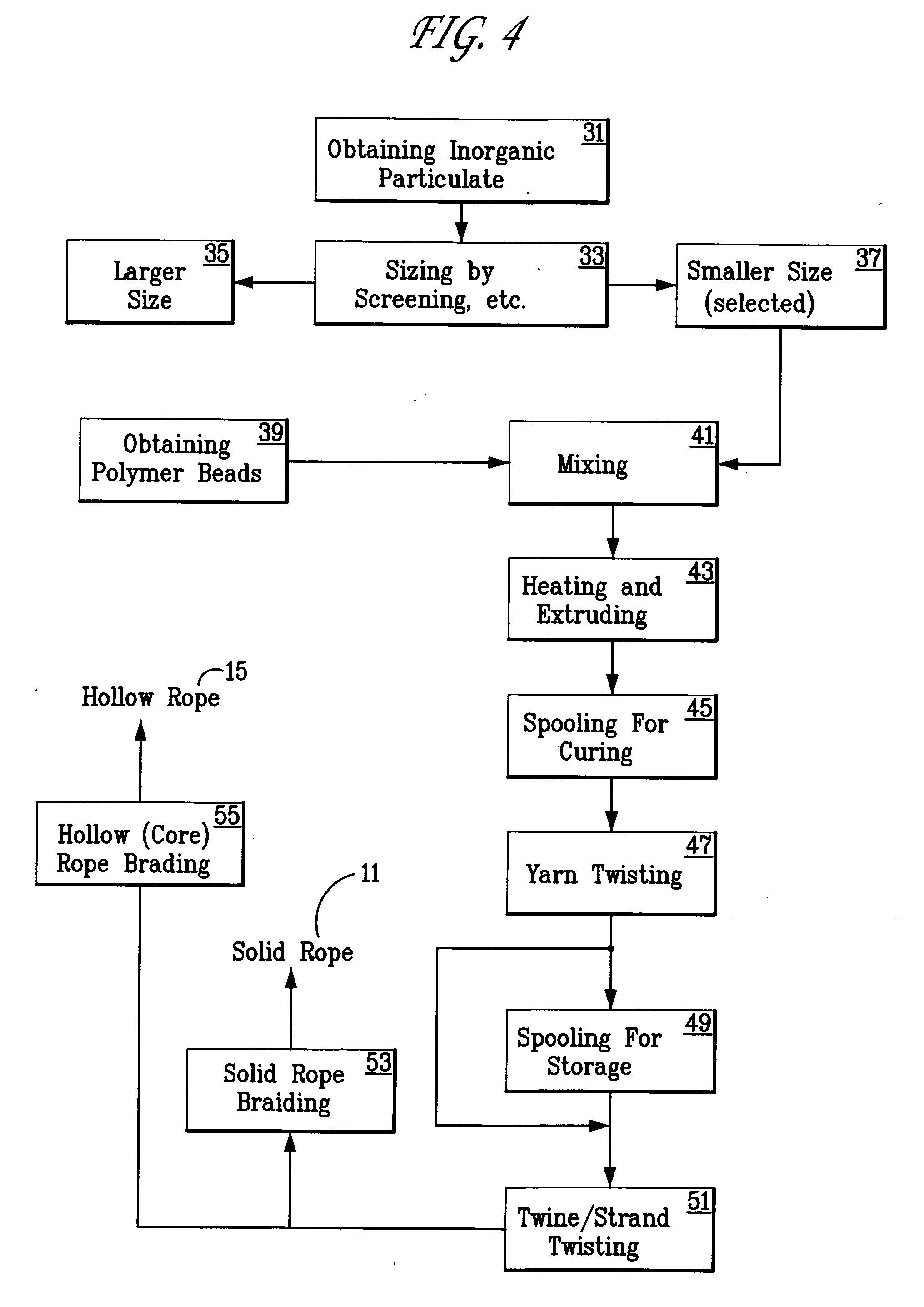
A whale-safe goundline rope for attachment to undersea traps and seagoing buoys. This rope is made of melt-processable polymers having filler particulate distributed uniformly throughout the polymer, prior to it being extruded into a fiber or yarn. The manufacturing process generates a hollow rope, with that being a rope made from hollow fibers or yarn. The filler particulate is sufficient to provide a rope with negative buoyancy.
Owner:BETTER GEAR
Ocean bottom seismic autonomous underwater vehicle
ActiveUS10543892B2Improve abilitiesSeismic signal recordingSeismology for water-covered areasSignal onElectrical conduit
Seismic autonomous underwater vehicles (AUVs) for recording seismic signals on the seabed. The AUV may be negatively buoyant and comprise an external body (which may be formed of multiple housings) that substantially encloses a plurality of pressure housings. Portions of the external body housing may be acoustically transparent and house one or more acoustic devices for the AUV. The AUV may comprise a main pressure housing that holds substantially all of the electronic components of the AUV, while a second and third pressure housing may be located on either side of the main pressure housing for other electronic components (such as batteries). A plurality of external devices (such as acoustic devices or thrusters) may be coupled to the main pressure housing by external electrical conduit. The AUV may comprise fixed or retractable wings for increased gliding capabilities during subsea travel.
Owner:PXGEO UK LTD
Low flow bailer system
InactiveUS7028564B2Negative buoyancy of the apparatusSimple designComponent separationWithdrawing sample devicesParticulatesEngineering
An improved bailer which allows for the variance of flow into the bailer through use of attachments with varying inflow orifice sizes. As the size of the orifice changes, the weight of the apparatus can also be changed allowing for an only slightly negative buoyancy of the apparatus. The attachment may also be designed to include features for filtering unwanted particulates from the sample.
Owner:LOW FLOW BAILER SYST
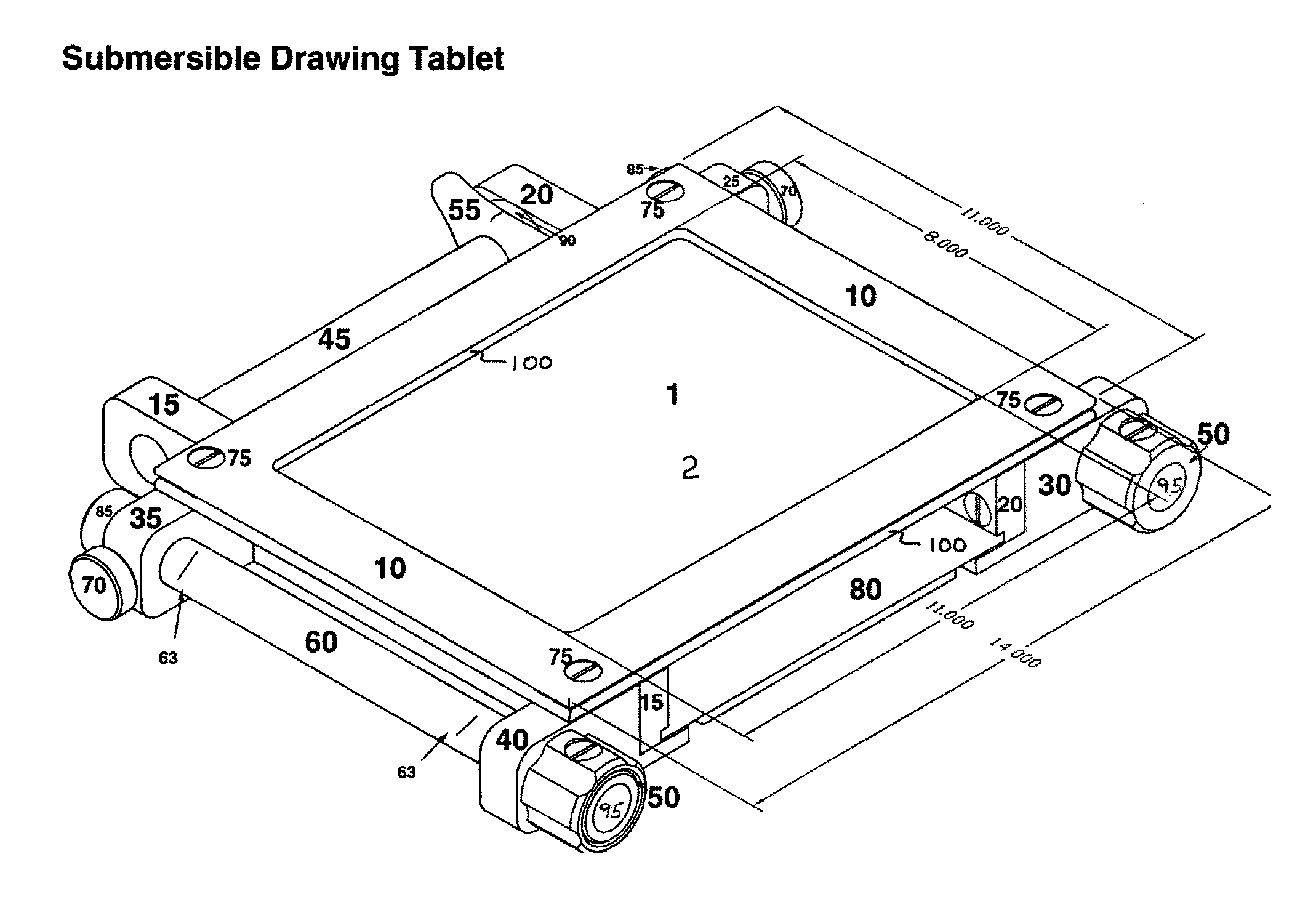
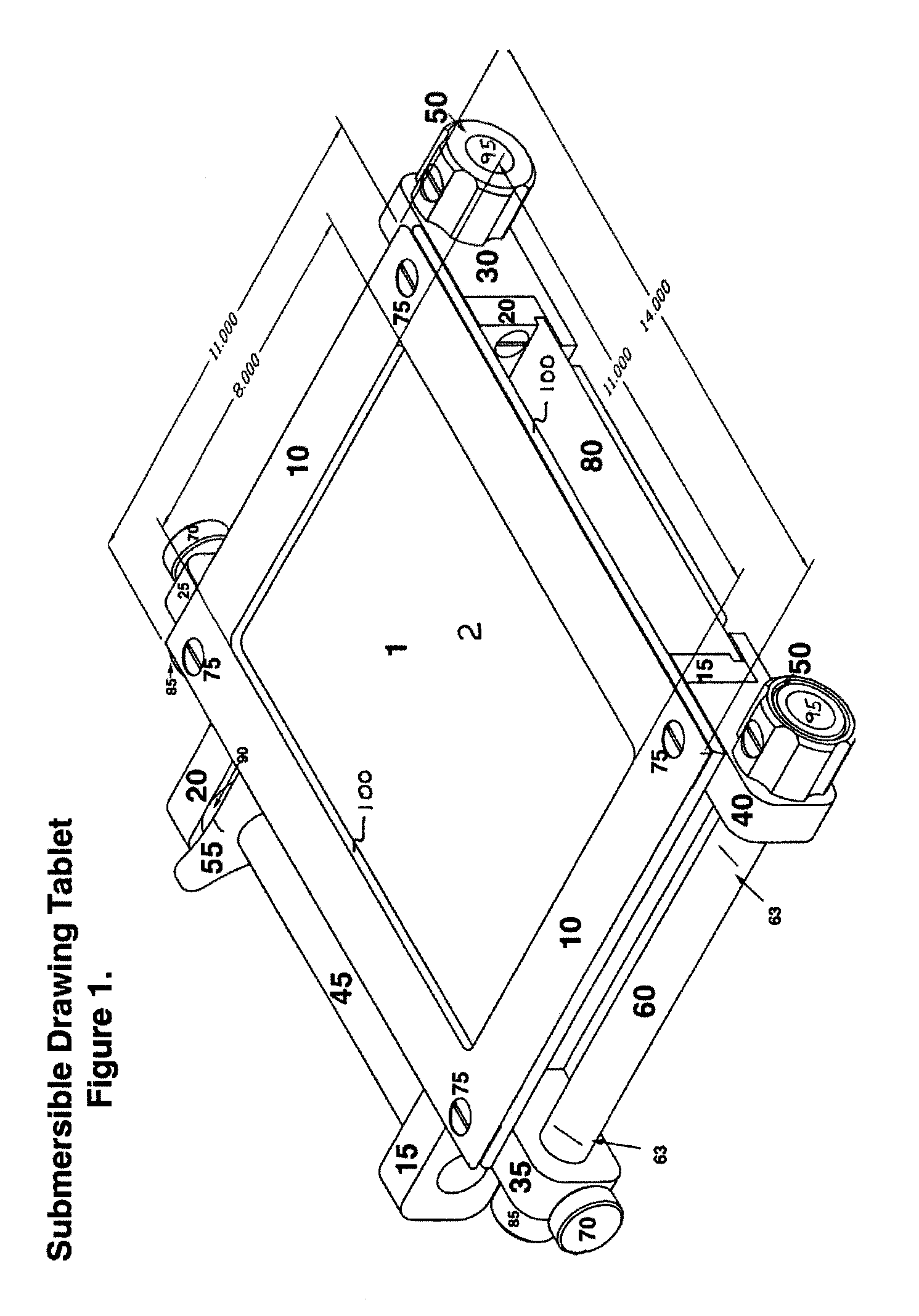
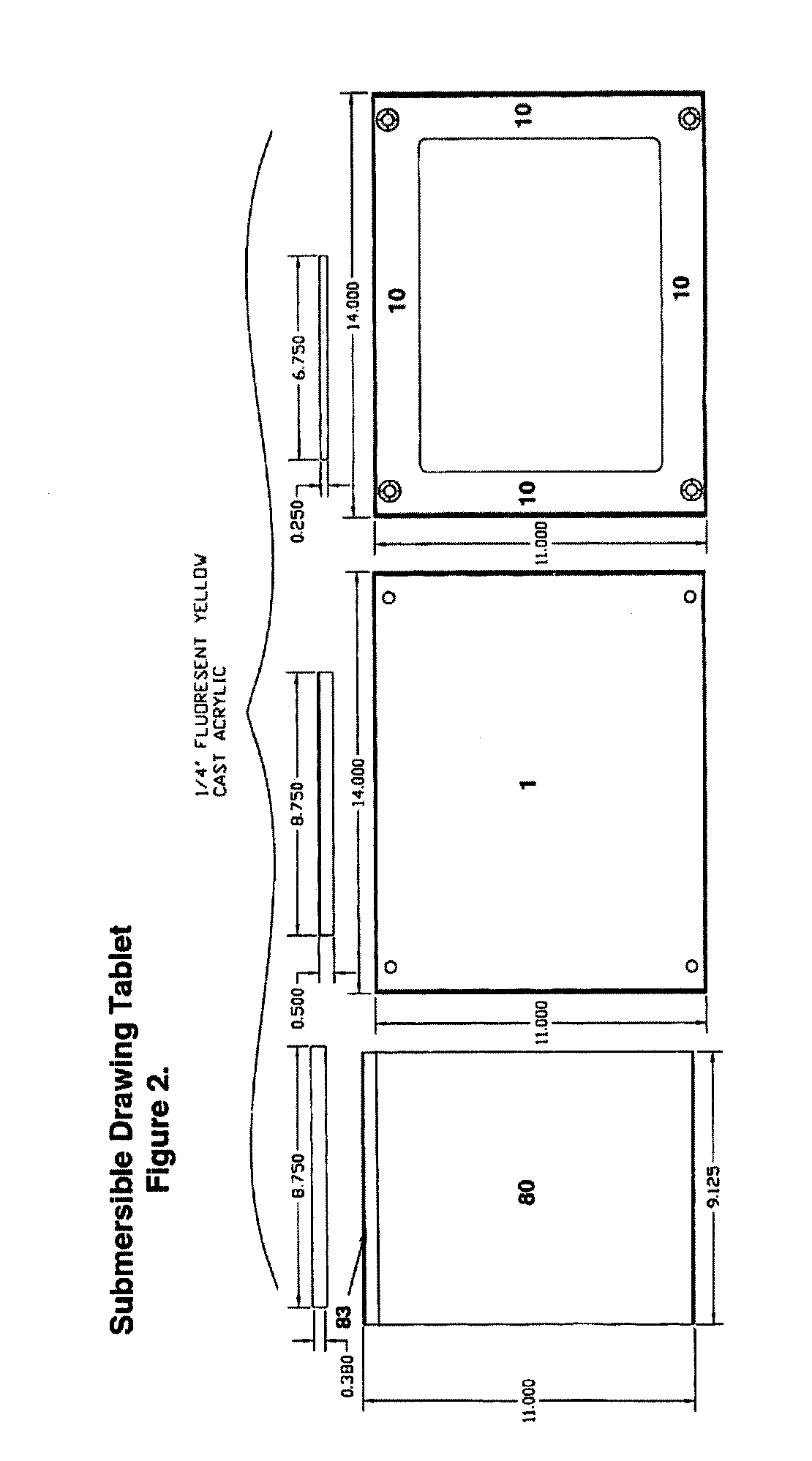
Submersible tablet for underwater or extreme environment
A tablet that is suitable for use underwater or in any extreme environment is provided. The tablet is designed, through the use of buoyant materials such as polystyrene, to have a slightly negative buoyancy at a depth of about fifty feet so that it can be very easy to manipulate underwater and will not sink or ascend rapidly if let go. A length of waterproof (plastic) vellum is stretched between two rollers to form a drawing or writing surface thereby enabling the user to easily record information on the vellum.
Owner:HAGAN MARK L
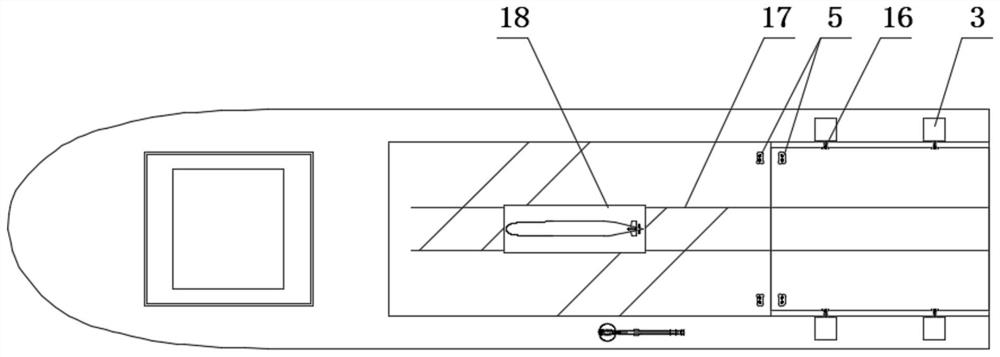
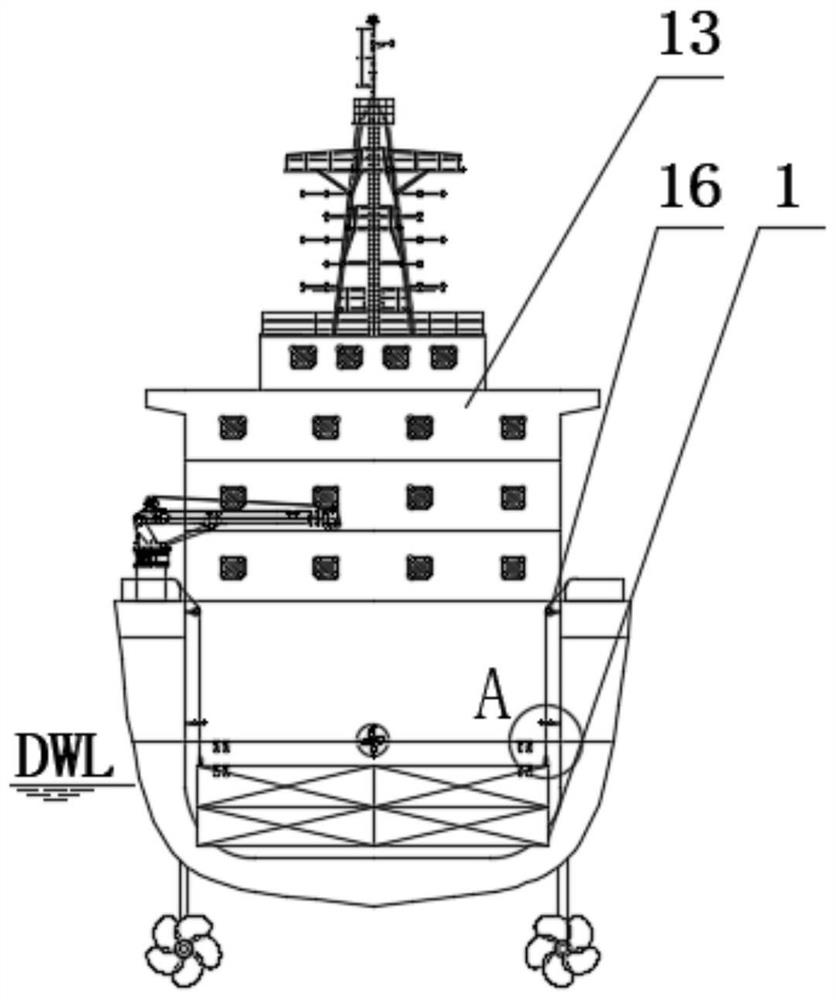
Multifunctional workboat with buoyancy adjusting carrying platform and operation method of multifunctional working ship
ActiveCN111645810ALower performance requirementsCompact structureTowing/pushing equipmentCargo handling apparatusBuoyancy regulationMarine equipment
According to the multifunctional workboat with the buoyancy adjusting carrying platform and the operation method of the multifunctional workboat, during marine transportation, marine equipment can becarried on a loading deck of a water surface boat in a dry mode and can also be tied and fixed to the deck of the buoyancy adjusting carrying platform; during laying, the ocean equipment is transferred to the buoyancy adjusting carrying platform by means of a rail and a flatcar on the loading deck, and laying and recycling operation of the ocean equipment is implemented by means of linkage of a buoyancy adjusting system of the buoyancy adjusting carrying platform and a plurality of winches on the main deck of the working ship. The buoyancy adjusting system of the carrying platform is used forbalancing the gravity and buoyancy of the carrying platform and the ocean equipment as a whole. Therefore, the requirement for the performance of the winch on the main deck is greatly lowered, only small tension needs to be provided to maintain the depth of the carrying platform, and the carrying platform is lighter, more flexible, economical and reliable compared with an A frame, a floating craneand the like used for offshore hoisting.
Owner:CHINA SHIP SCIENTIFIC RESEARCH CENTER (THE 702 INSTITUTE OF CHINA SHIPBUILDING INDUSTRY CORPORATION)
Pool Cleaning Device With Adjustable Buoyant Element
A pool cleaner has a plurality of components, some having a density greater than water, giving the cleaner an overall negative buoyancy. The cleaner has a buoyant element which is adjustable in position relative to the center of gravity of the cleaner. Adjusting the position of the buoyant element changes the probable motion path of the cleaner on the pool floor and walls, allowing the cleaner to execute a variety of motion paths to clean various parts of the pool. The adjustable element may be slidably positioned by a handle extending through a slot in the housing or be slidable on a slide band attached to the housing, which may be pivotable, translatable and rotatable, providing an additional range of position alternatives. A detent or other holding mechanism holds a selected position. The adjustable element permits the cleaner to be adapted to clean various pool shapes and surfaces.
Owner:HAYWARD IND INC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com