Patents
Literature
619 results about "Seismic survey" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
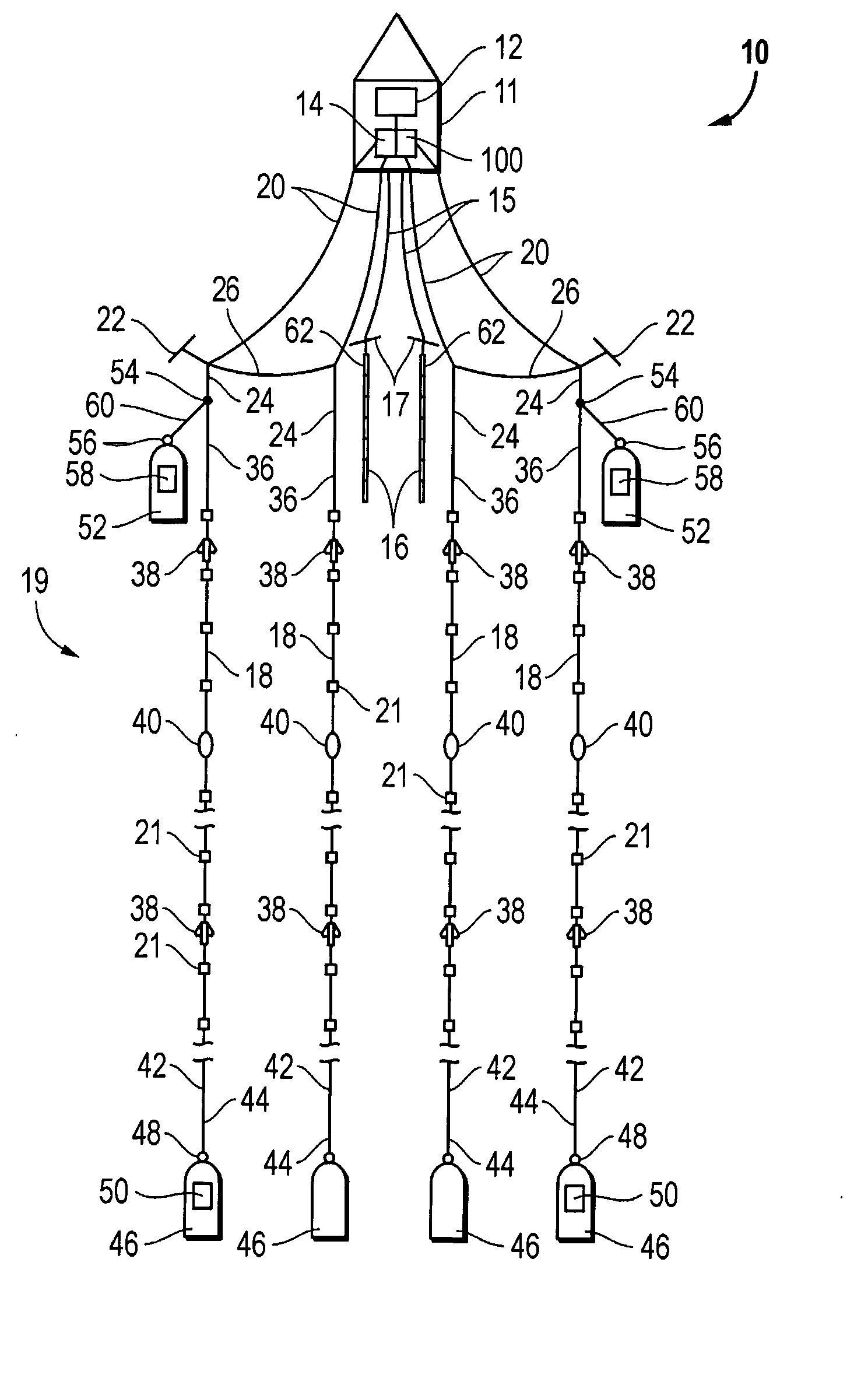
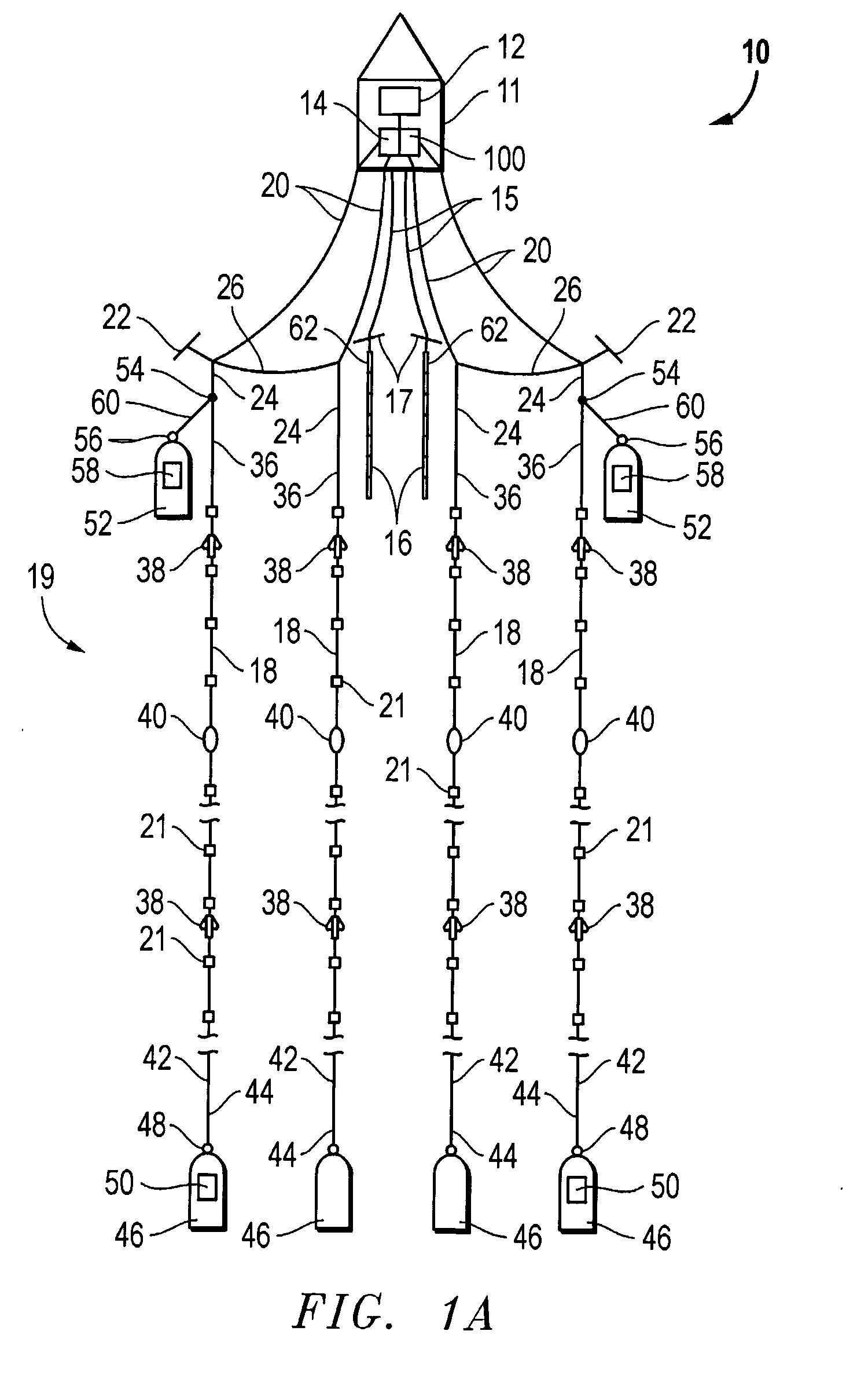
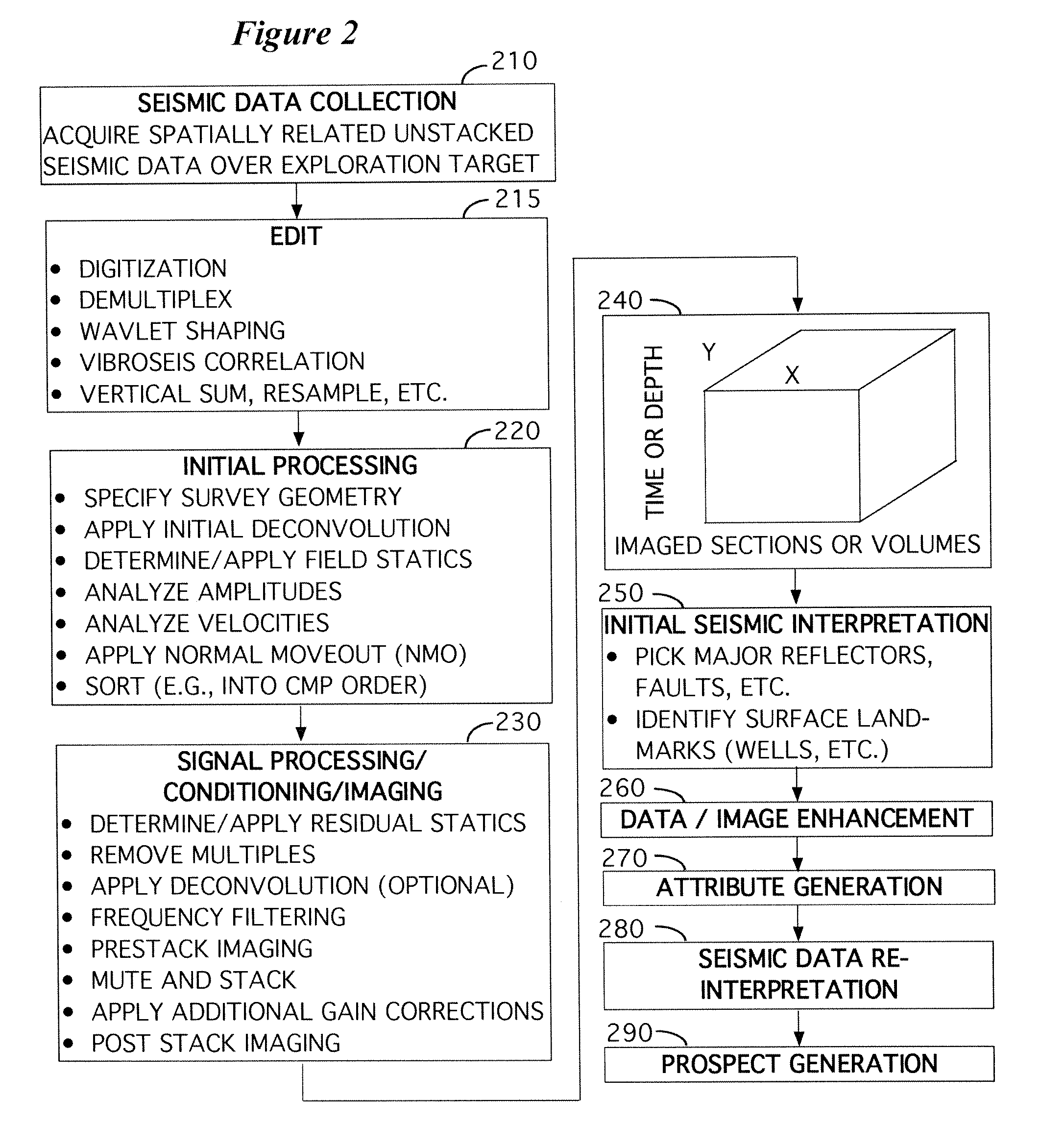
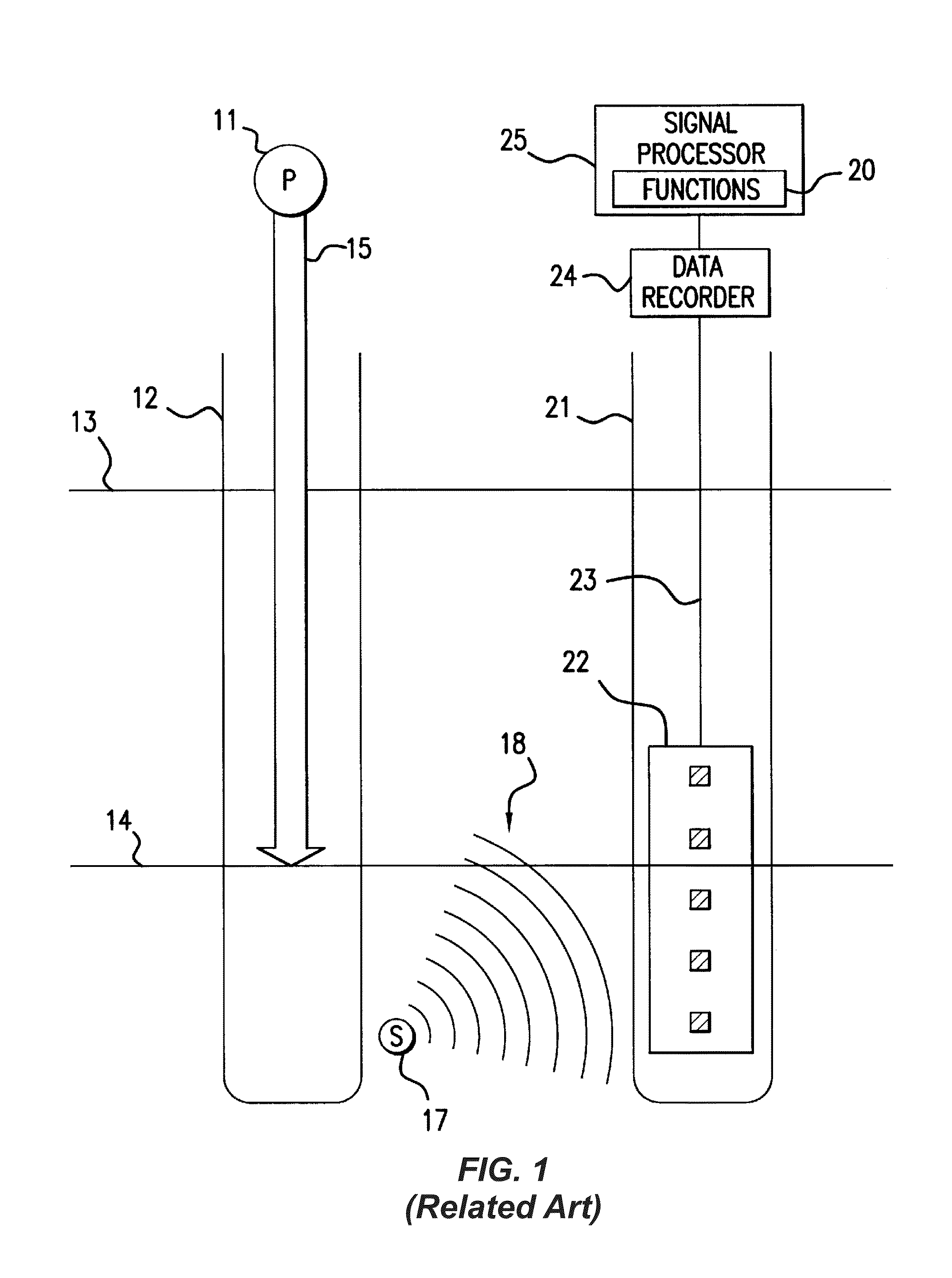
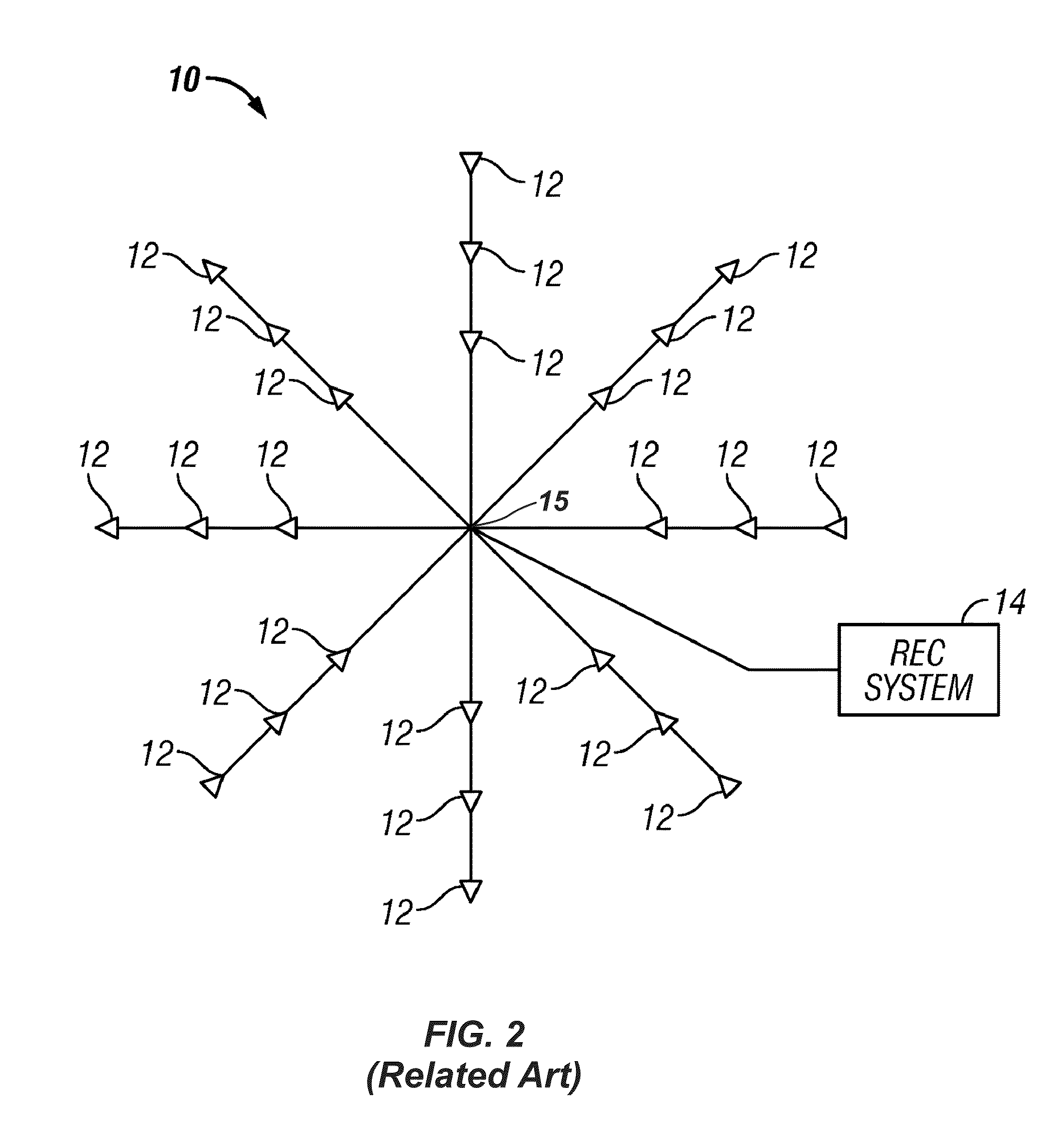
The seismic survey is one form of geophysical survey that aims at measuring the earth’s (geo-) properties by means of physical (-physics) principles such as magnetic, electric, gravitational, thermal, and elastic theories.
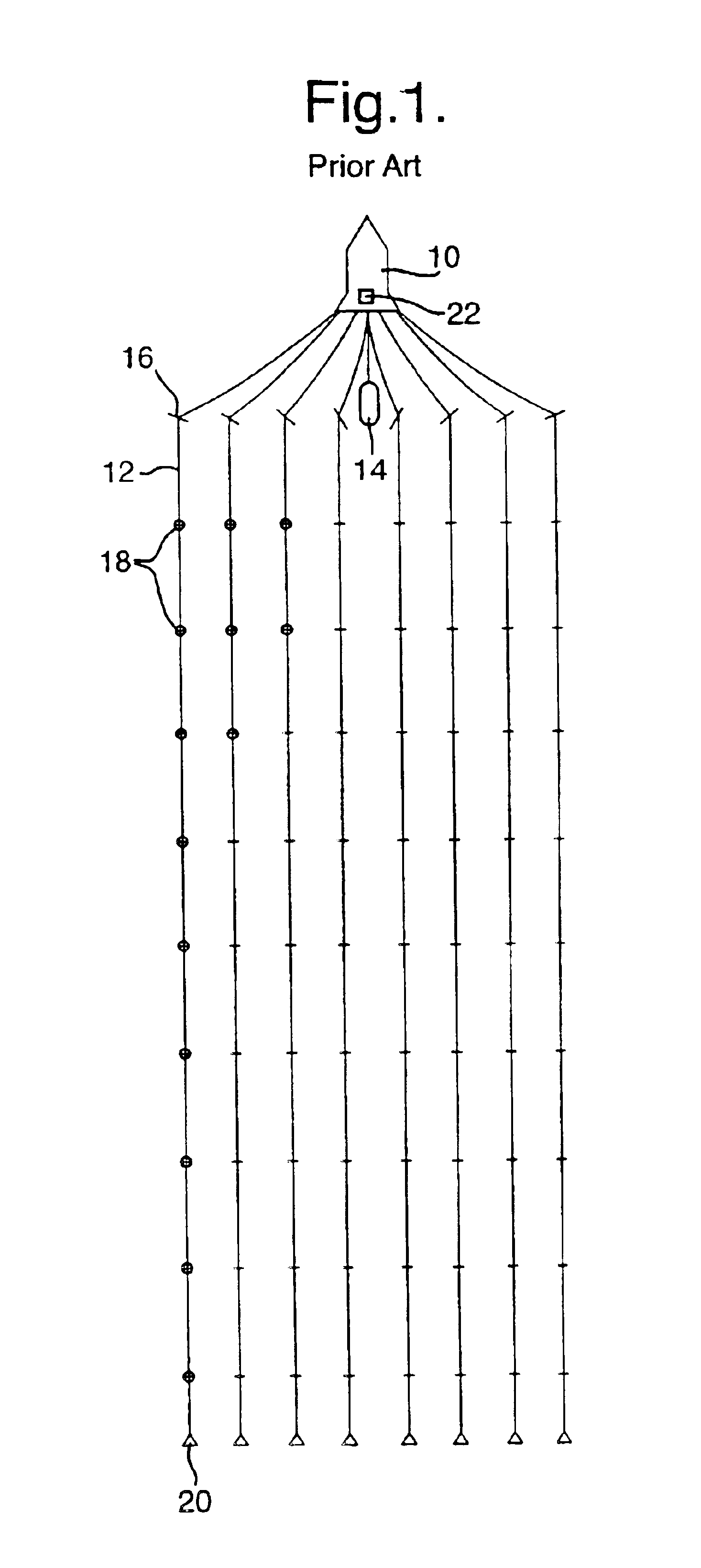
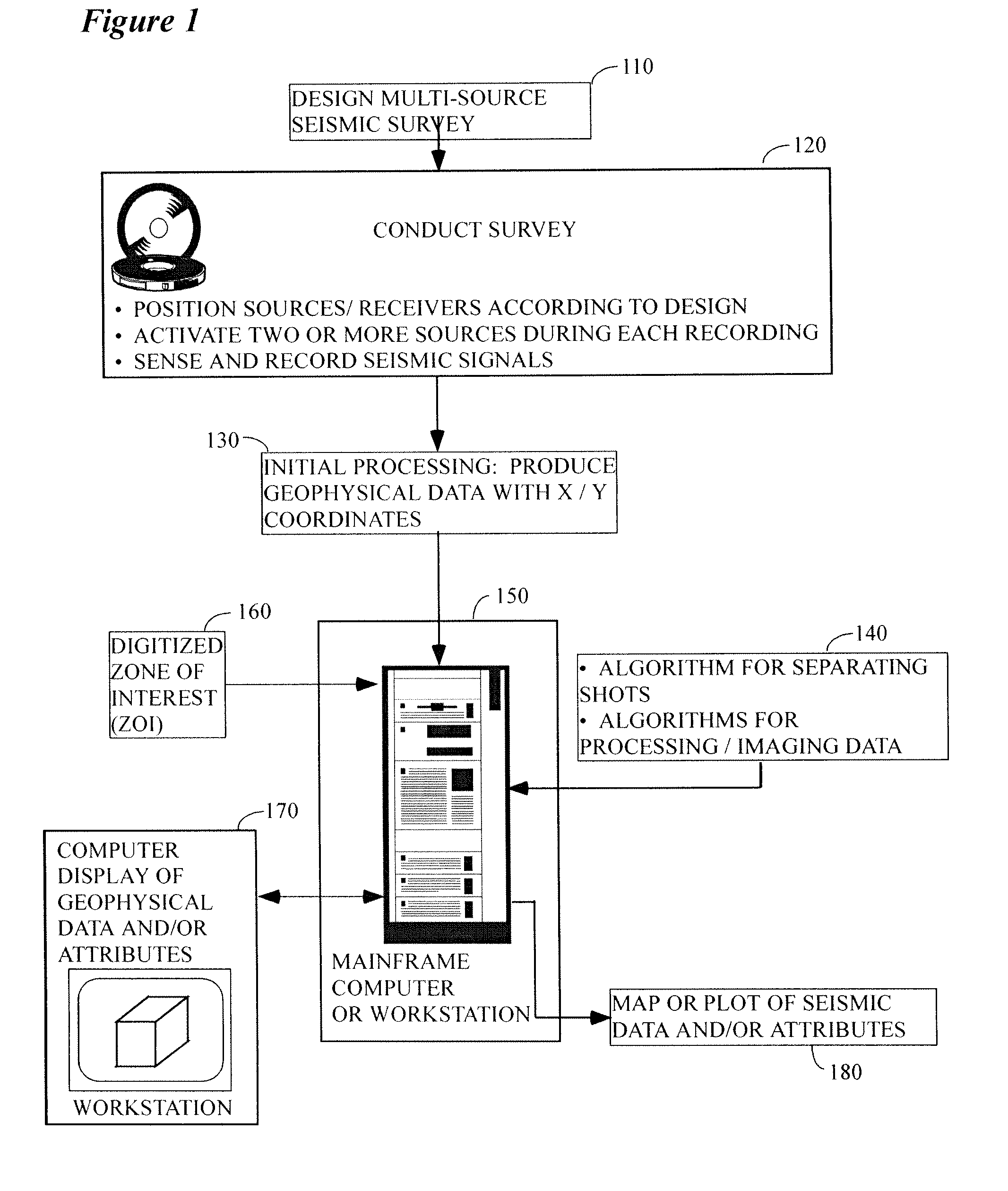
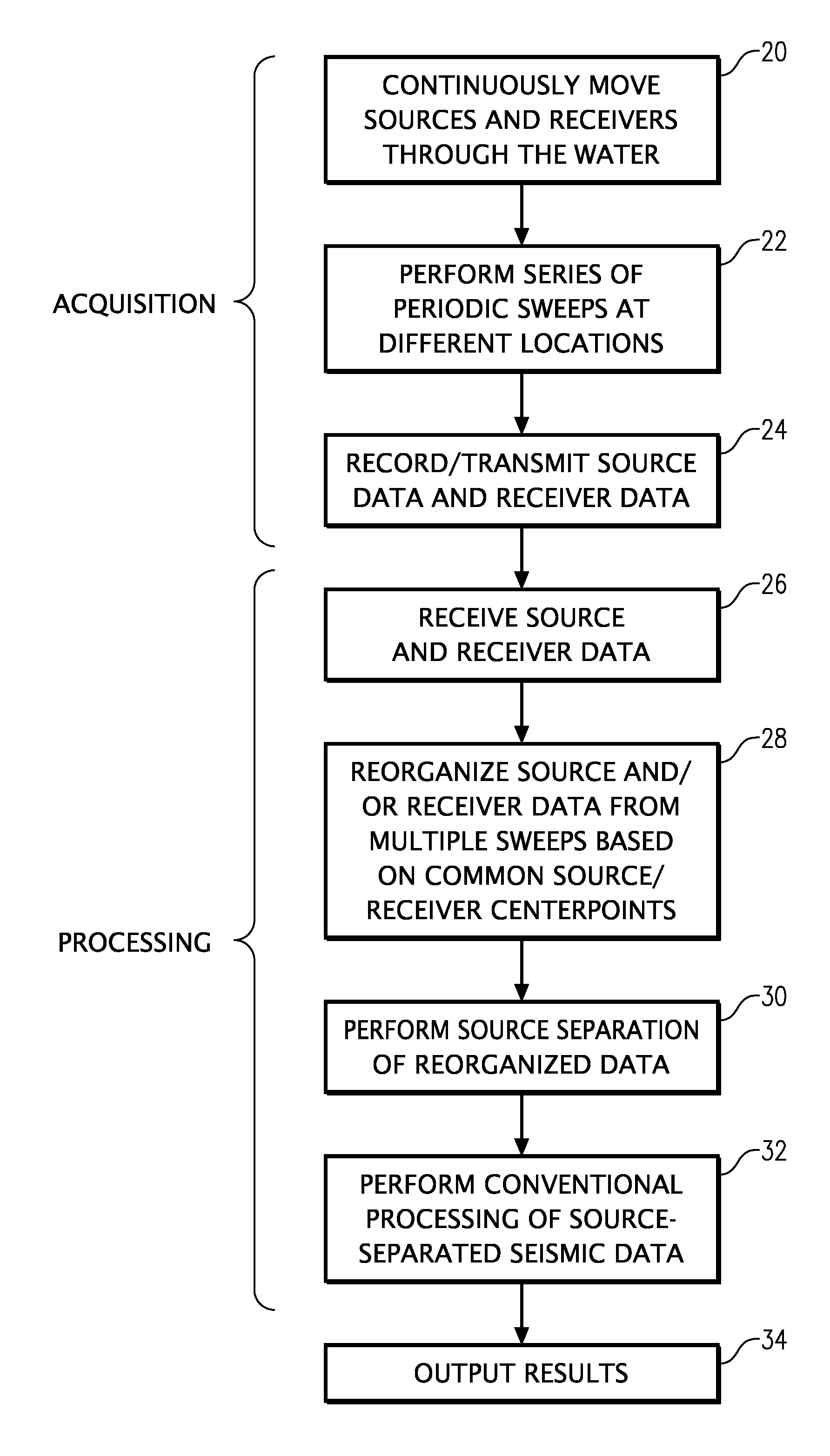
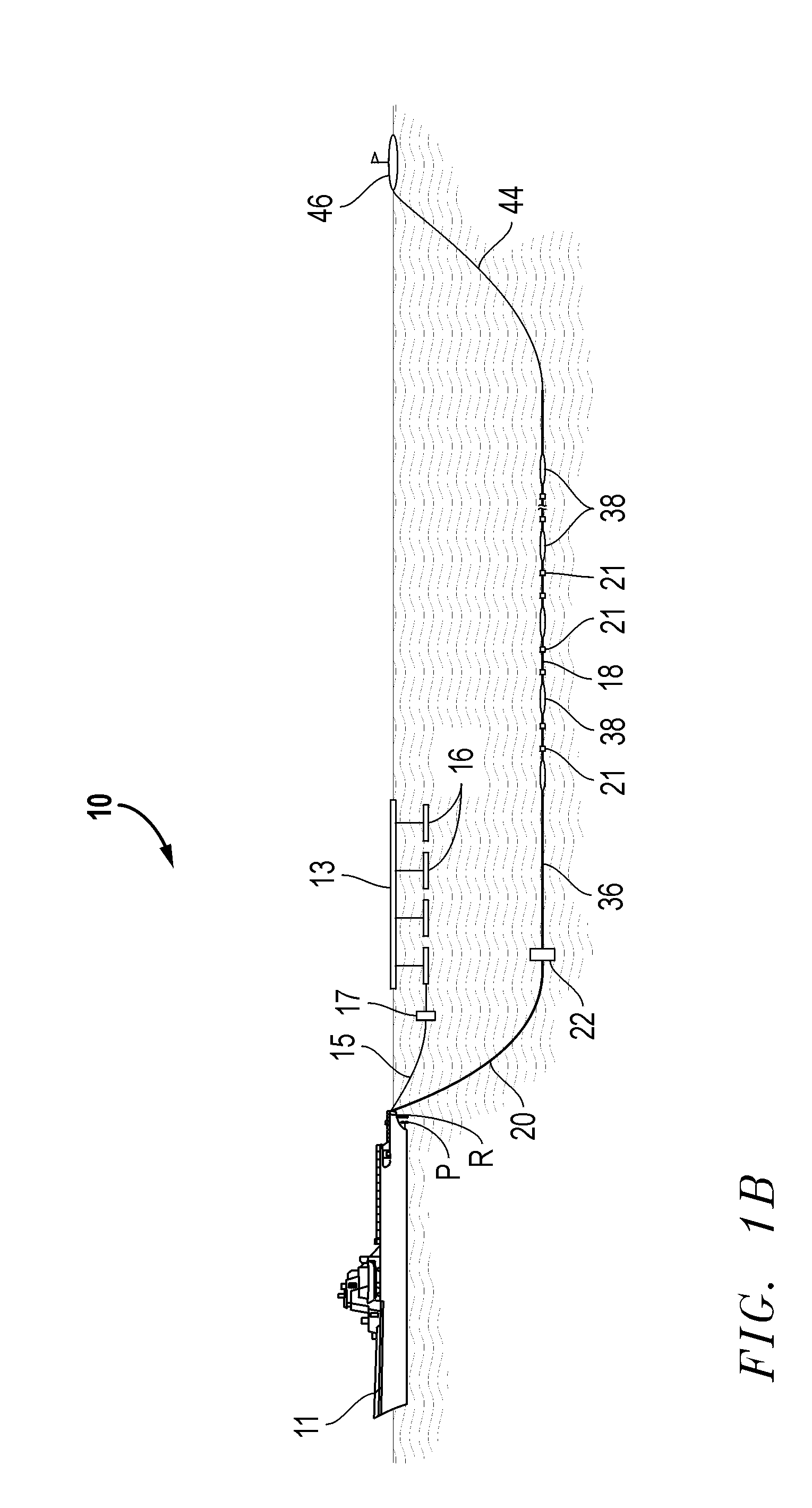
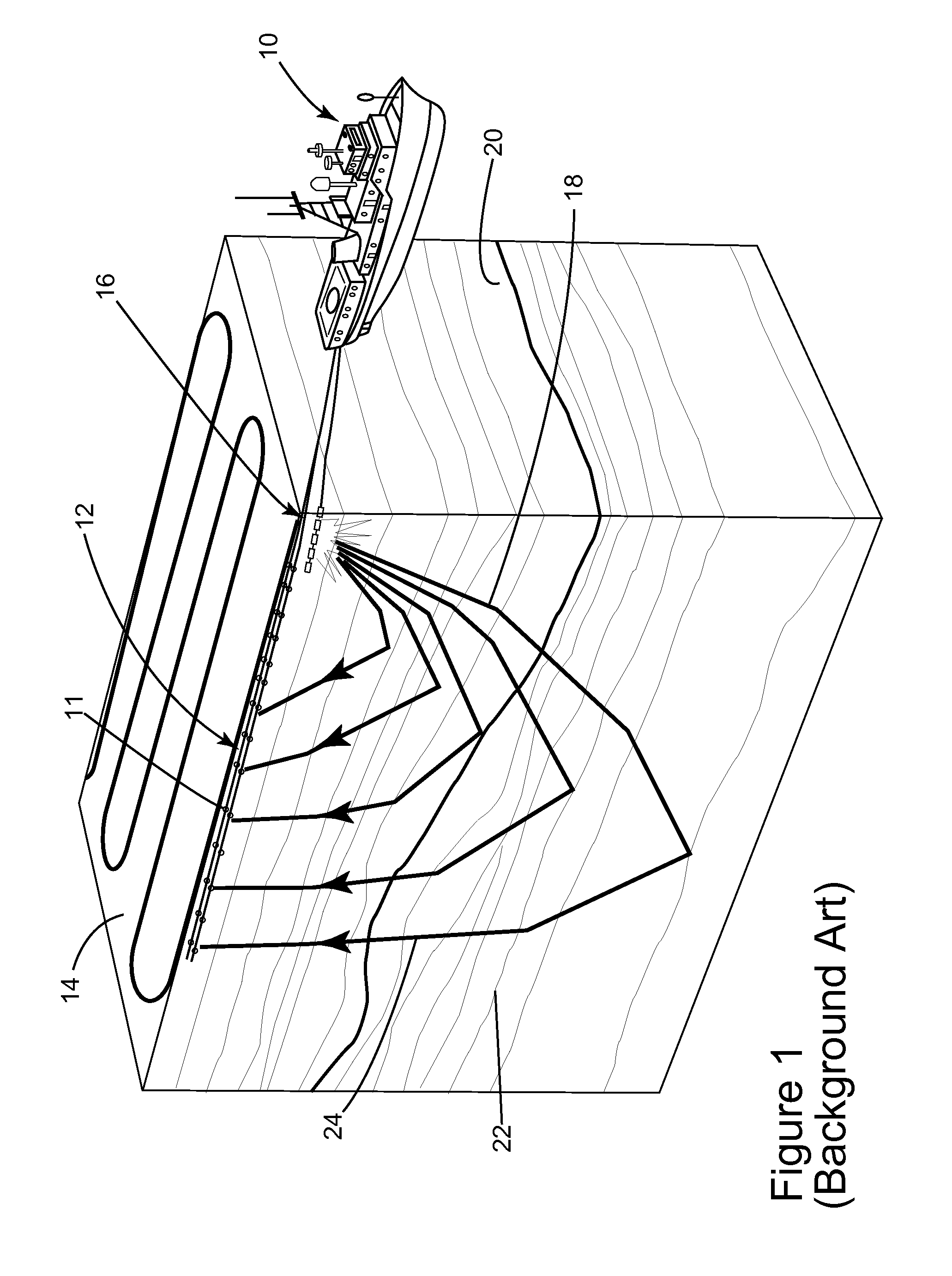
Marine seismic survey method and system
ActiveUS20090141587A1Reduce non-productive timeSeismic signal recordingSeismology for water-covered areasSeismic surveyEnvironmental data
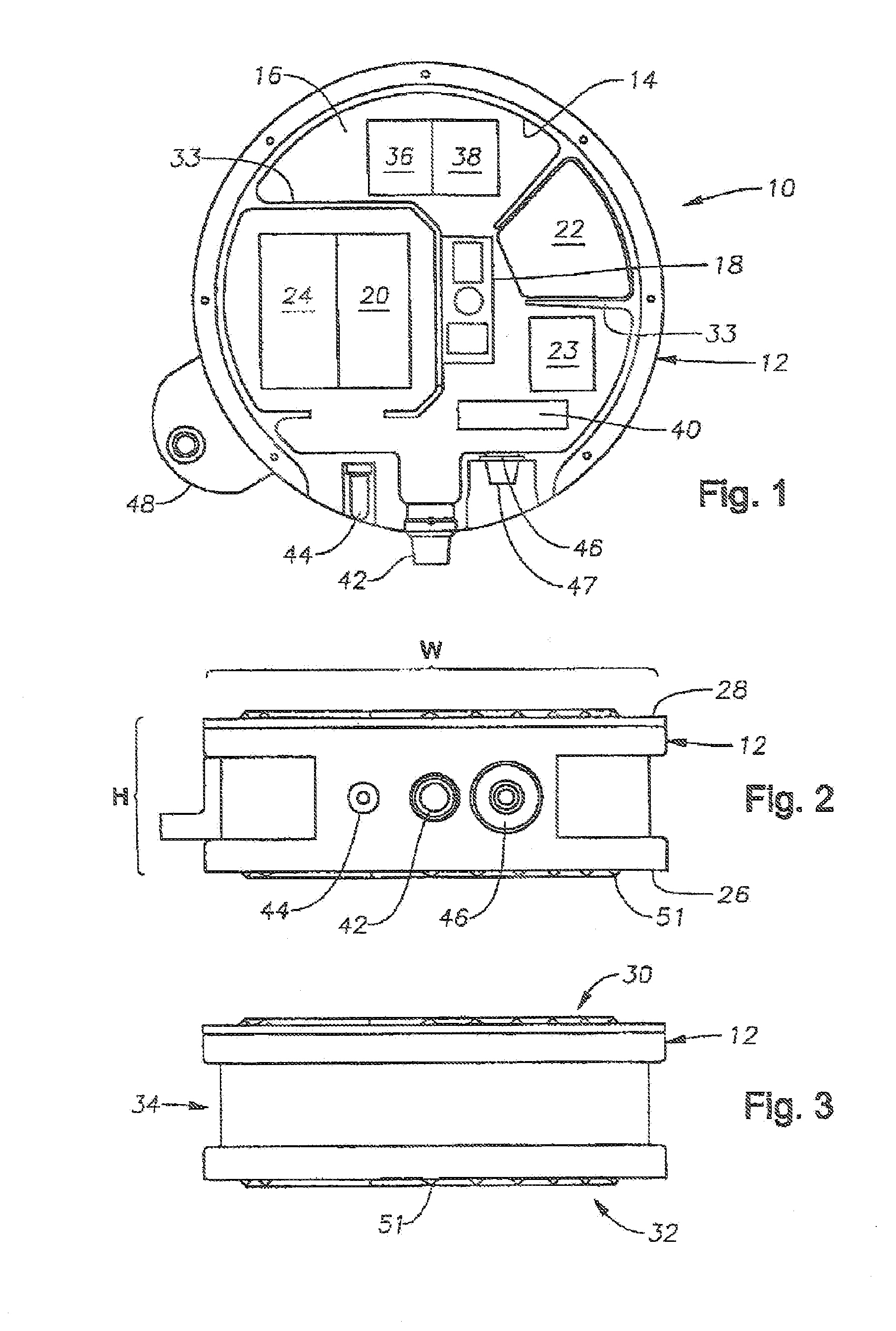
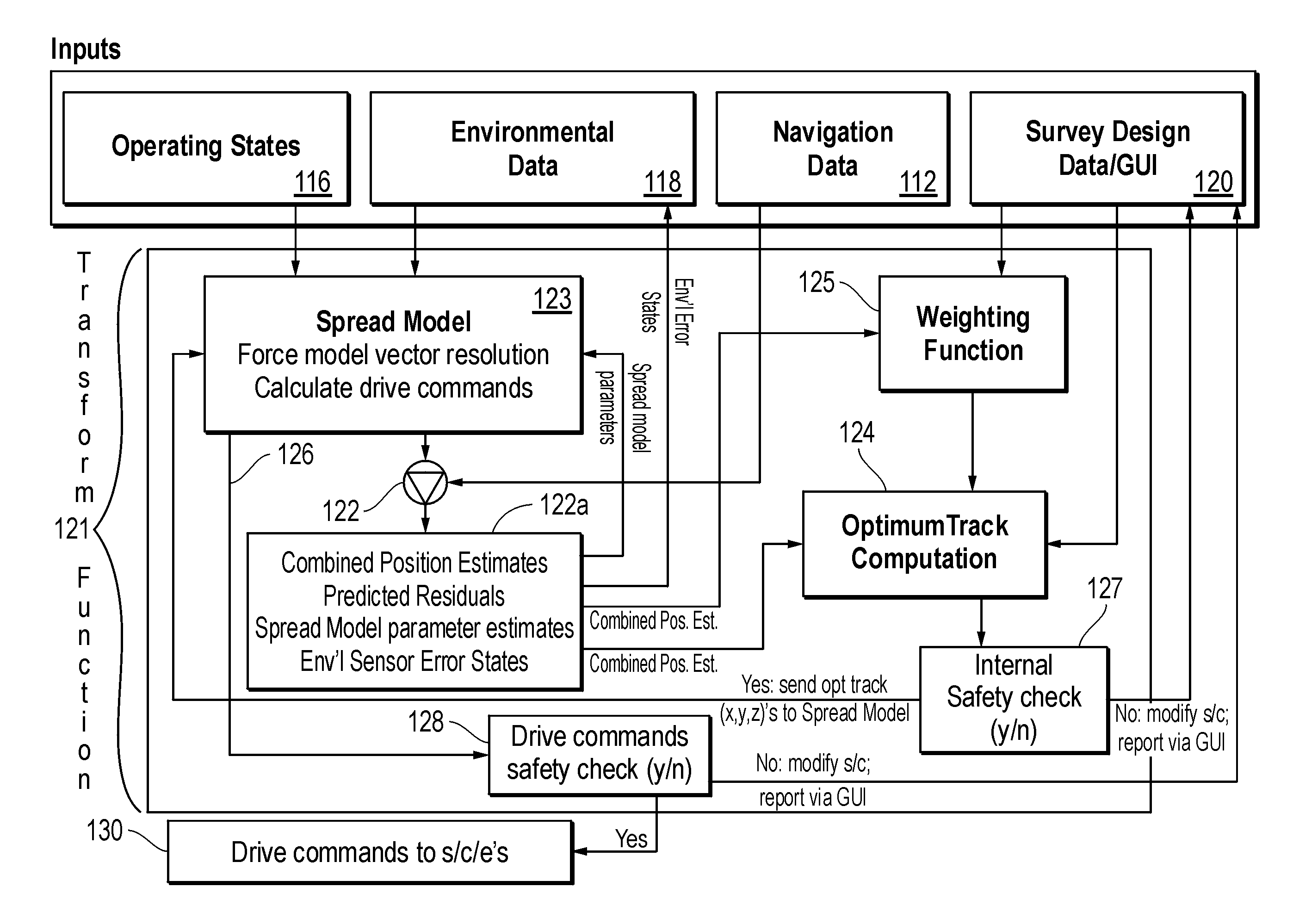
An inventive method provides for control of a seismic survey spread while conducting a seismic survey, the spread having a vessel, a plurality of spread control elements, a plurality of navigation nodes, and a plurality of sources and receivers. The method includes the step of collecting input data, including navigation data for the navigation nodes, operating states from sensors associated with the spread control elements, environmental data for the survey, and survey design data. The positions of the sources and receivers are estimated using the navigation data, the operating states, and the environmental data. Optimum tracks for the sources and receivers are determined using the position estimates and a portion of the input data that includes at least the survey design data. Drive commands are calculated for at least two of the spread control elements using the determined optimum tracks. The inventive method is complemented by an inventive system.
Owner:WESTERNGECO LLC
Control system for positioning of marine seismic streamers
InactiveUS6932017B1Reduce needEasy to controlDefensive equipmentTowing/pushing equipmentSeismic surveyControl system
A method of controlling a streamer positioning device (18) configured to be attached to a marine seismic streamer (12) and towed by seismic survey vessel (10) and having a wing and a wing motor for changing the orientation of the wing. The method includes the steps of: obtaining an estimated velocity of the streamer positioning device, calculating a desired change in the orientation of the wing using the estimated velocity of the streamer positioning device, and actuating the wing motor to produce the desired change in the orientation of the wing. The invention also involves an apparatus for controlling a streamer positioning device including means for obtaining an estimated velocity of the streamer positioning device, means for calculating a desired change in the orientation of the wing using the estimated velocity of the streamer positioning device, and means for actuating the wing motor to produce the desired change in the orientation of the wing.
Owner:SCHLUMBERGER TECH CORP
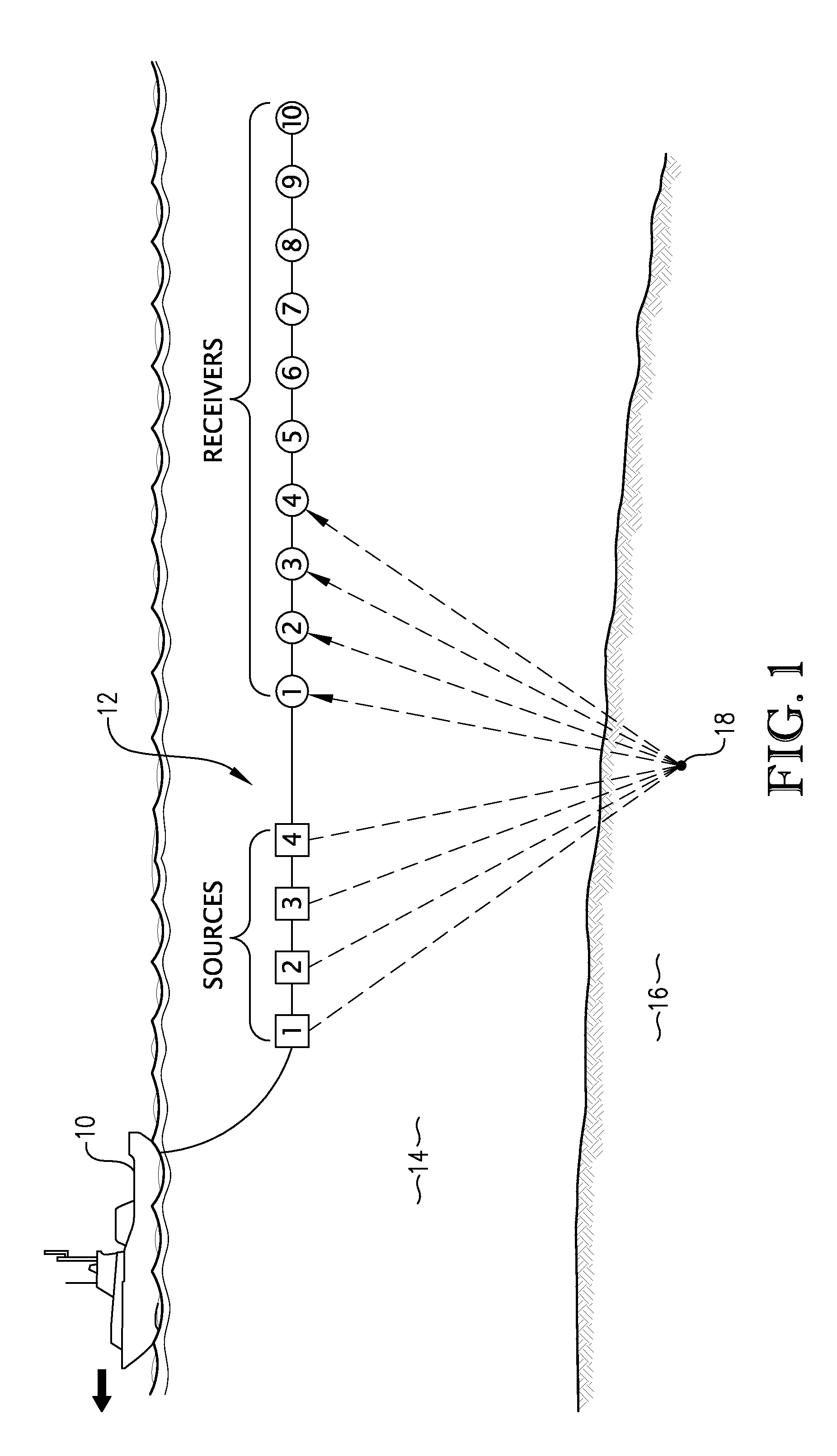
Method and system for acquiring marine seismic data using multiple seismic sources
InactiveUS6906981B2Easy to foldIncrease the lengthSeismic data acquisitionSeismic energy generationSeismic surveySurveyor
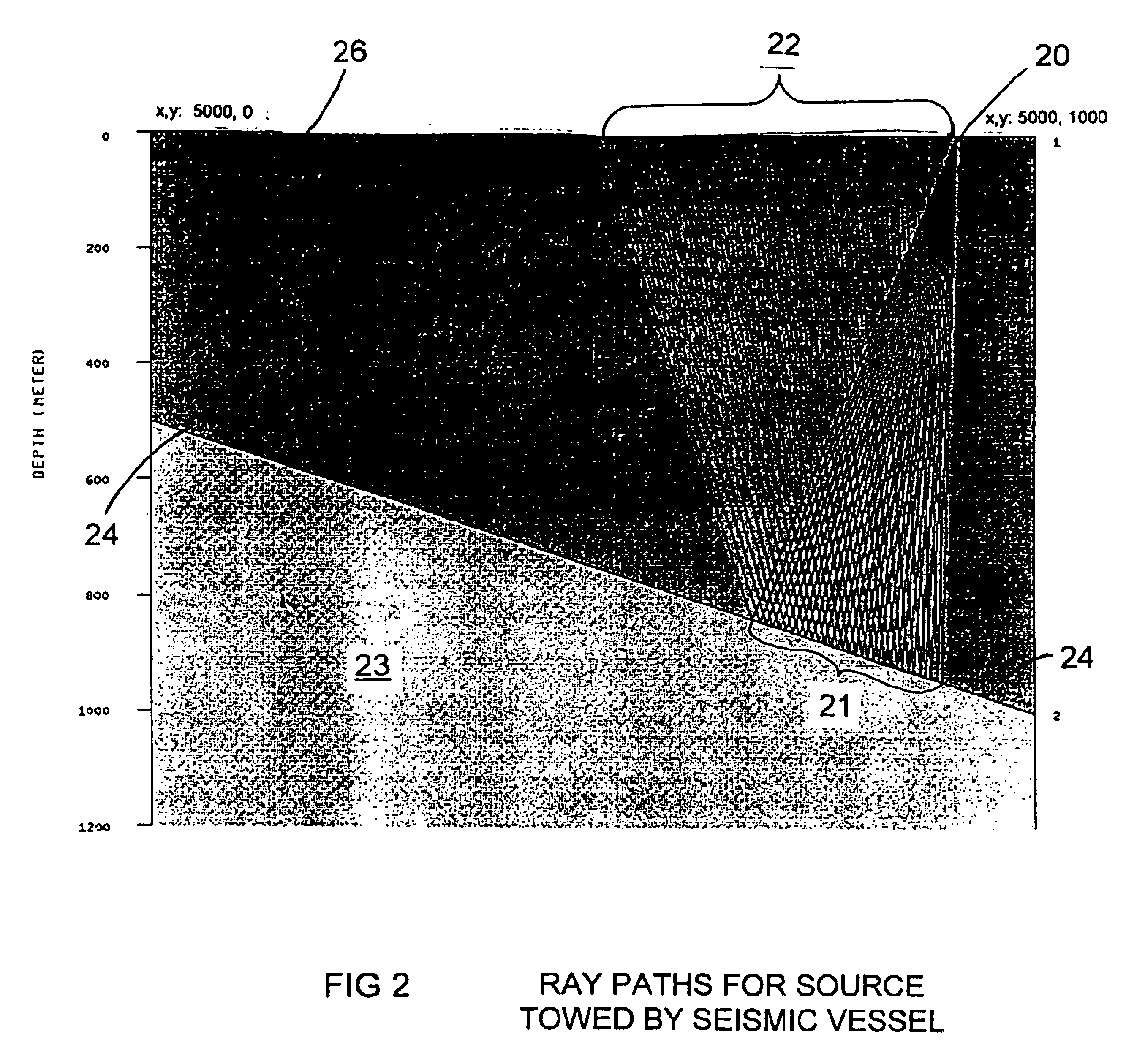
A method for seismic surveying is disclosed which includes towing a first seismic energy source and at least one seismic sensor system. A second seismic energy source is towed at a selected distance from the first source. The first seismic energy source and the second seismic energy source are actuated in a plurality of firing sequences. Each of the firing sequences includes firing of the first source, waiting a selected time firing the second source and recording signals generated by the seismic sensor system. The selected time between firing the first source and the second source is varied between successive ones of the firing sequences. The firing times of the first and second source are indexed so as to enable separate identification of seismic events originating from the first source and seismic events originating from the second source in detected seismic signals.
Owner:PGS GEOPHYSICAL AS
Methods and systems for efficiently acquiring towed streamer seismic surveys
ActiveUS20070165486A1Improved seismic imagingLess timeSeismic signal processingSeismology for water-covered areasSurveyorSeismic survey
Methods and systems for efficiently acquiring towed streamer marine seismic data are described. One method and system comprises positioning a plurality of source-only tow vessels and one or more source-streamer tow vessels to acquire a wide- and / or full-azimuth seismic survey without need for the spread to repeat a path once traversed. Another method and system allows surveying a sub-sea geologic feature using a marine seismic spread, the spread smartly negotiating at least one turn during the surveying, and shooting and recording during the turn. This abstract is provided to comply with the rules requiring an abstract, allowing a searcher or other reader to quickly ascertain the subject matter of the technical disclosure. It is submitted with the understanding that it will not be used to interpret or limit the scope or meaning of the
Owner:REFLECTION MARINE NORGE AS
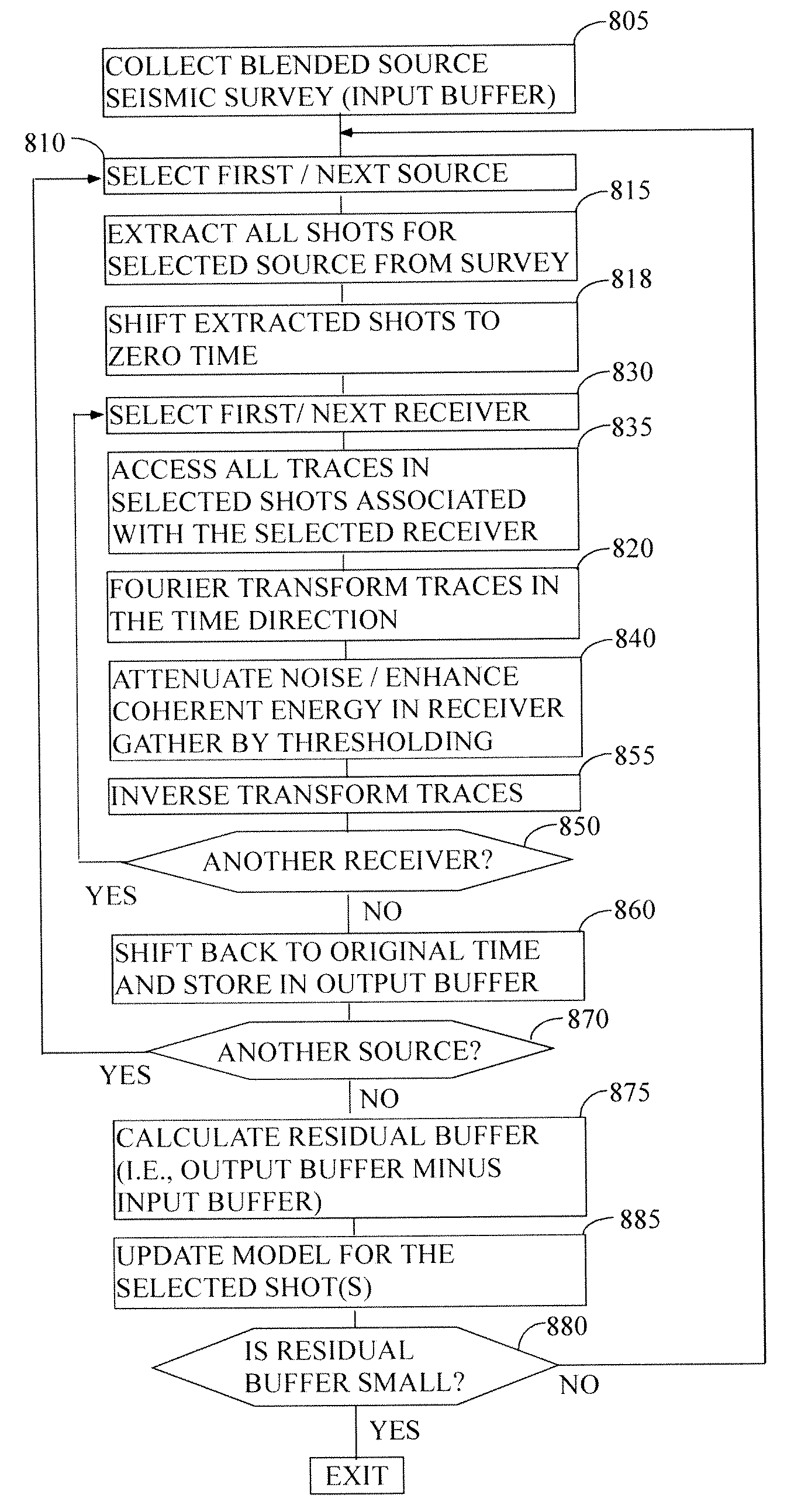
Method for separating independent simultaneous sources
ActiveUS20100039894A1Easy accessEfficient collectionSeismic data acquisitionSeismic signal processingSeismic surveyStart time
Owner:BP CORP NORTH AMERICA INC
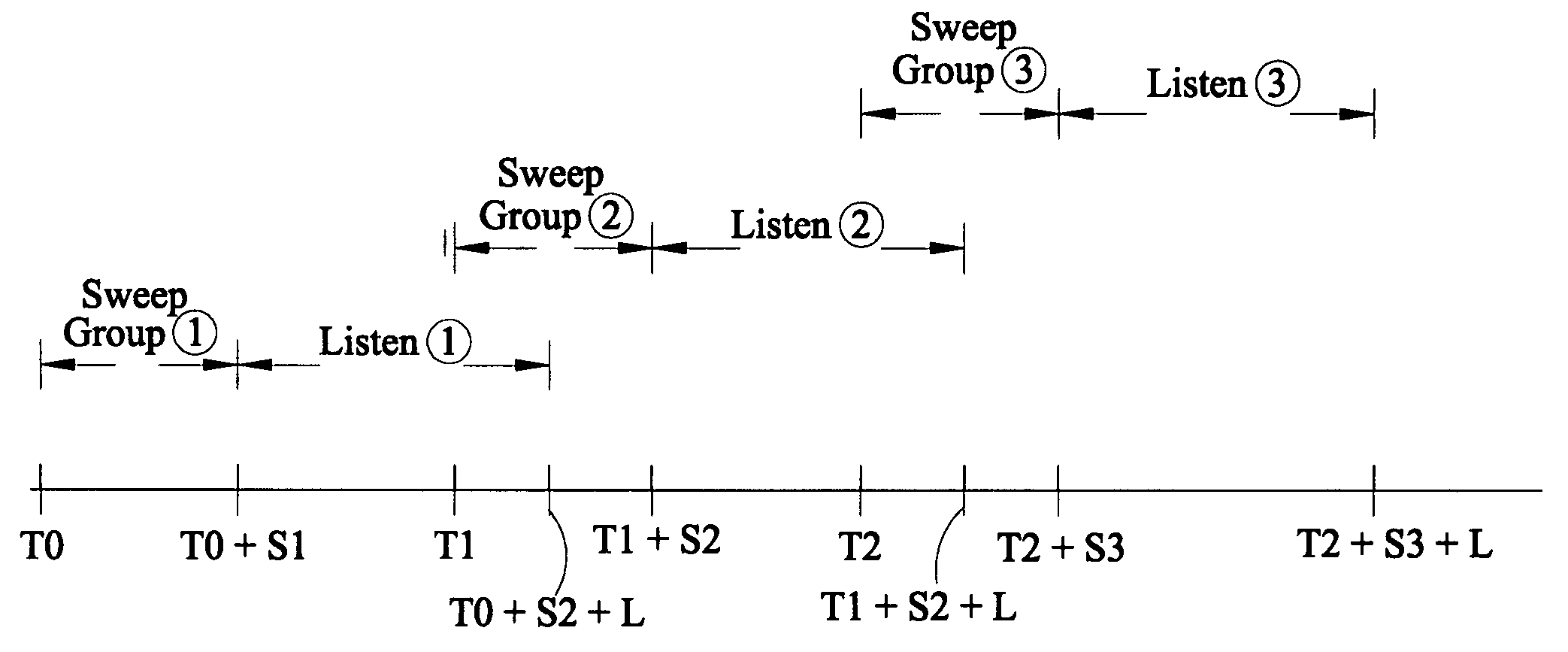
Method of seismic surveying
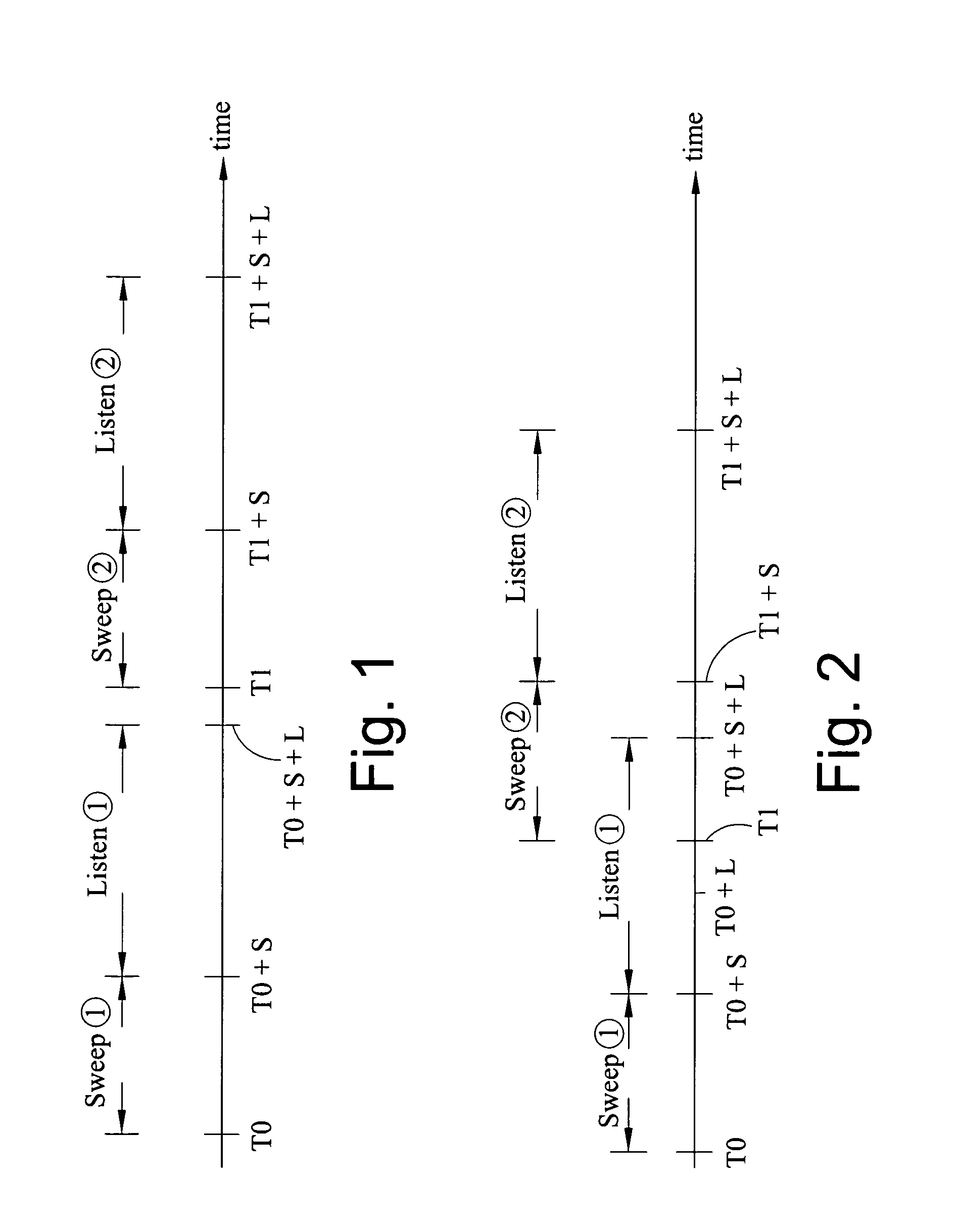
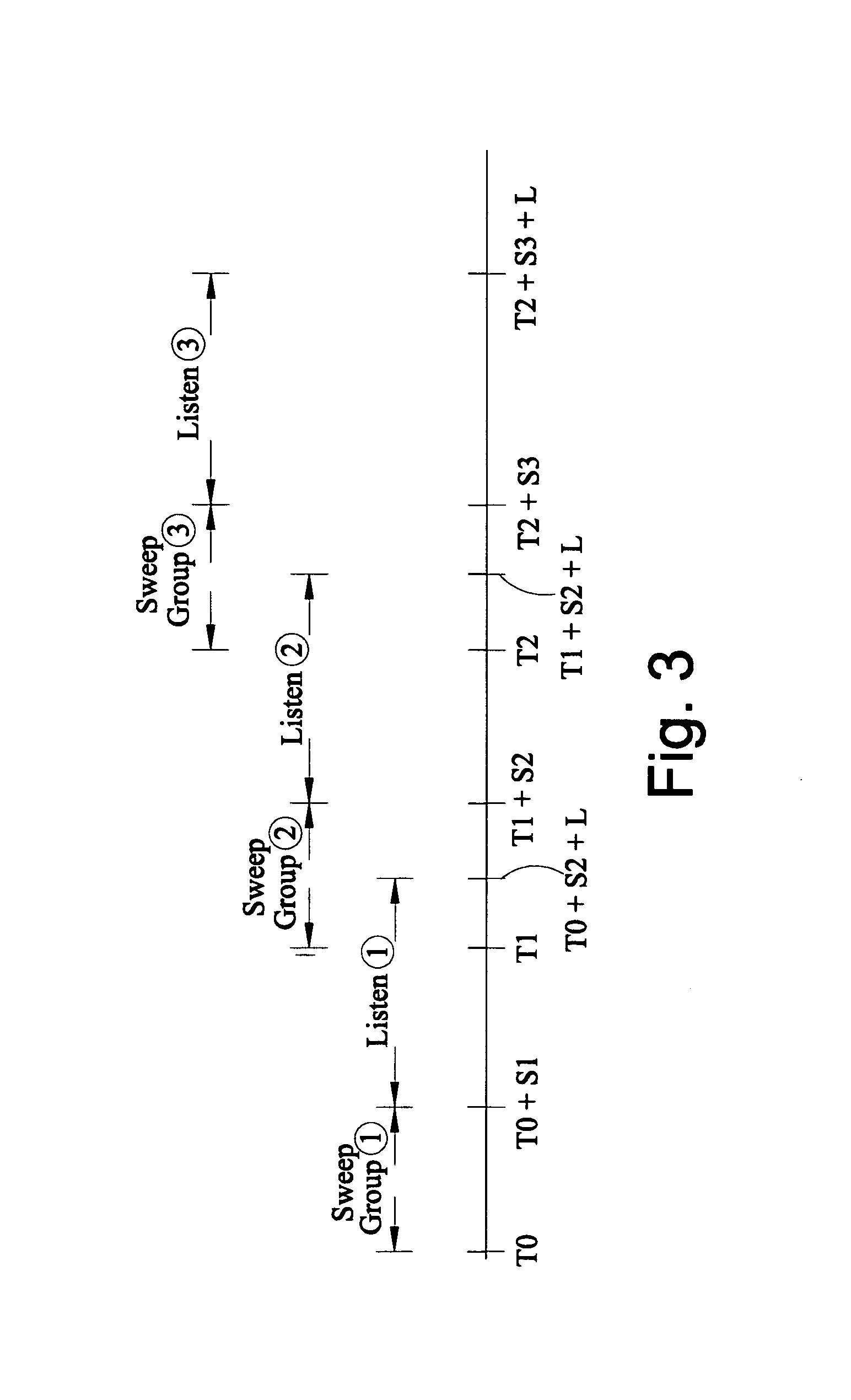
A method of seismic surveying comprising the steps of actuating the or each vibrator in a first vibrator group at time T0, and subsequently actuating the or each vibrator in a second vibrator group at time T1 that satisfies T0<T1<T0+S1+L where S1 is the sweep time of the first vibrator group and L is the listening time. At least one of the first vibrator group and the second vibrator group comprises at least two vibrators. The first group and the second group of vibrators may be the same group, or they may be different groups. This method enables the time required to complete a seismic survey to be reduced compared to the prior art “simultaneous shooting” and “slip-sweep shooting” techniques.In a case where the first group and the second group of vibrators are different, the method may further comprise actuating the or each vibrator in the first vibrator group at time T2, where T1<T2<T1+S2+L and S2 is the sweep time of the first vibrator group, and then actuating the or each vibrator in the second vibrator group at time T3 where T2<T3<T2+S1+L and where T3−T2≠T1−T0. The varying time delay between a shot of the first vibrator group and the corresponding shot of the second vibrator group means that harmonic noise will occur at different times in the shot records so that the noise may be eliminated by appropriately combining the shot records.
Owner:WESTERNGECO LLC
Marine seismic acquisition system and method
InactiveUS6684160B1Reduce contentReduce noiseSeismic signal receiversSeismic signal processingHydrophoneSeismic survey
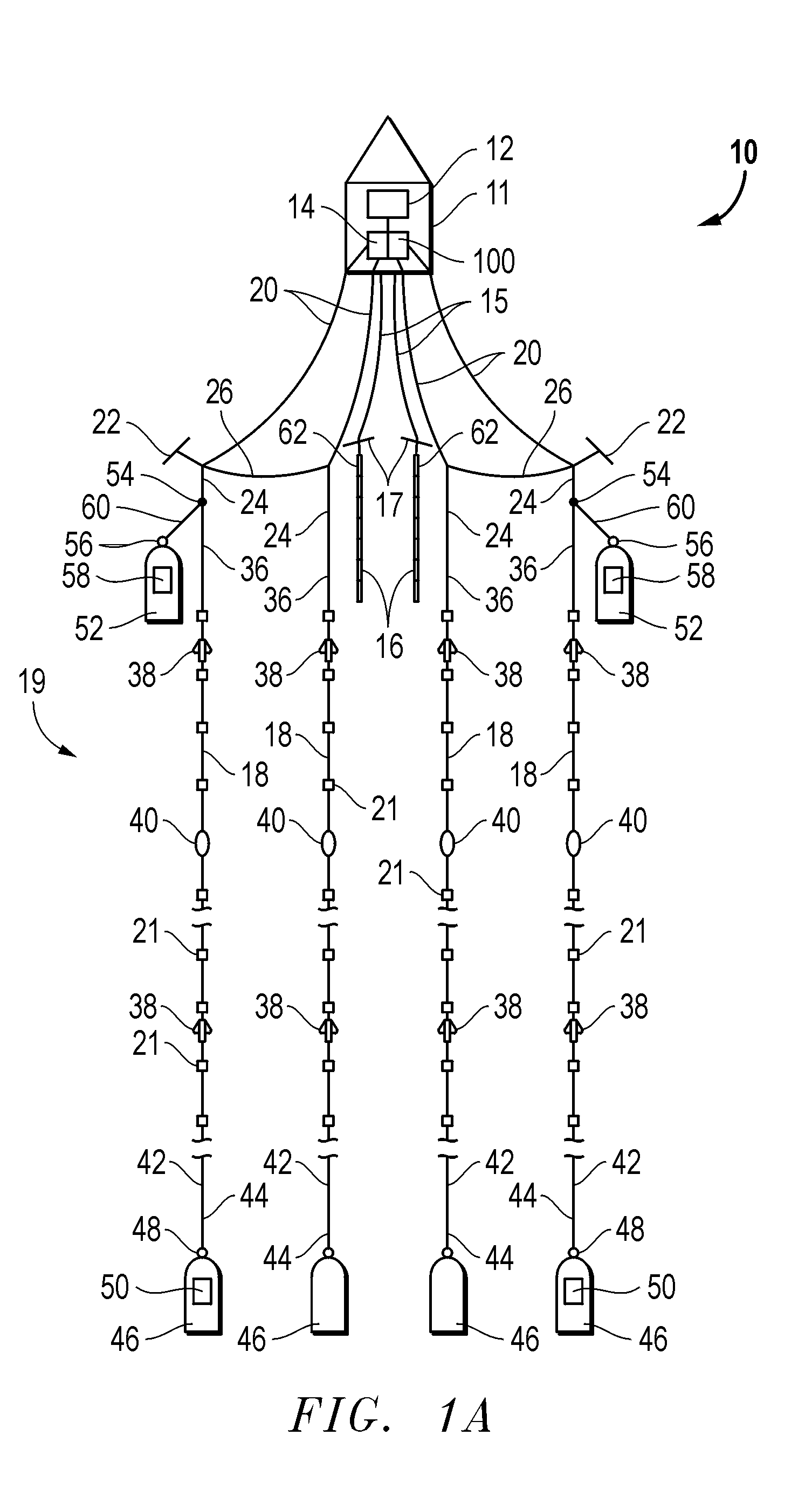
A method and system for performing a marine seismic survey is described, including towing at least one seismic streamer comprising a plurality of hydrophones distributed at average intervals of not more than 625 cm therealong in the water over the area to be surveyed; directing acoustic signals down through the water and into the earth beneath; receiving with the hydrophones seismic signals reflected from strata in the earth beneath the water; digitizing the output of each hydrophone separately; and filtering the output to reduce the noise present in the output and to generate a signal with a reduced noise content wherein the filtering process uses as further input the digitized output of at least one nearby hydrophone. The filtering is applied to single sensor recording prior to group-forming and thus able to detect and reduce coherent noise with a coherency length of 20 meters or less. It reduces noise such as streamer or bulge noise.
Owner:SCHLUMBERGER TECH CORP
Methods and systems for efficiently acquiring towed streamer seismic surveys
ActiveUS7400552B2Seismic signal processingSeismology for water-covered areasOcean bottomSeismic survey
Methods and systems for efficiently acquiring towed streamer marine seismic data are described. One method and system comprises positioning a plurality of source-only tow vessels and one or more source-streamer tow vessels to acquire a wide- and / or full-azimuth seismic survey without need for the spread to repeat a path once traversed. Another method and system allows surveying a sub-sea geologic feature using a marine seismic spread, the spread smartly negotiating at least one turn during the surveying, and shooting and recording during the turn. This abstract is provided to comply with the rules requiring an abstract, allowing a searcher or other reader to quickly ascertain the subject matter of the technical disclosure. It is submitted with the understanding that it will not be used to interpret or limit the scope or meaning of the claims. 37 CFR 1.72(b).
Owner:REFLECTION MARINE NORGE AS
Method for separating independent simultaneous sources
ActiveUS20100299070A1Easy accessEfficient collectionSeismic data acquisitionSeismic signal processingStart timeSeismic survey
Owner:BP CORP NORTH AMERICA INC
Workflow for processing streamer seismic data
ActiveUS20080049551A1Seismic signal processingSeismology for water-covered areasSeismic surveyWork flow
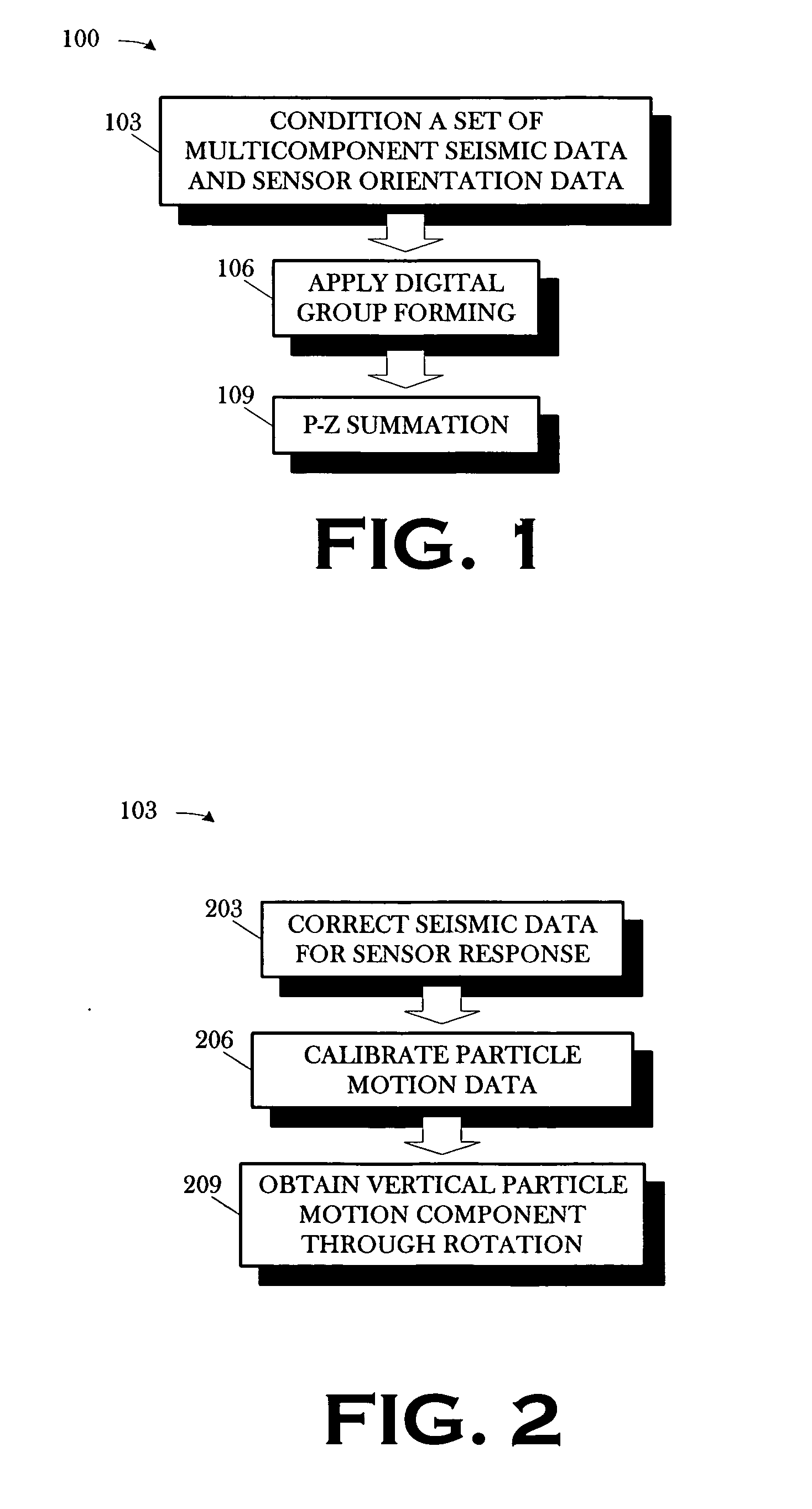
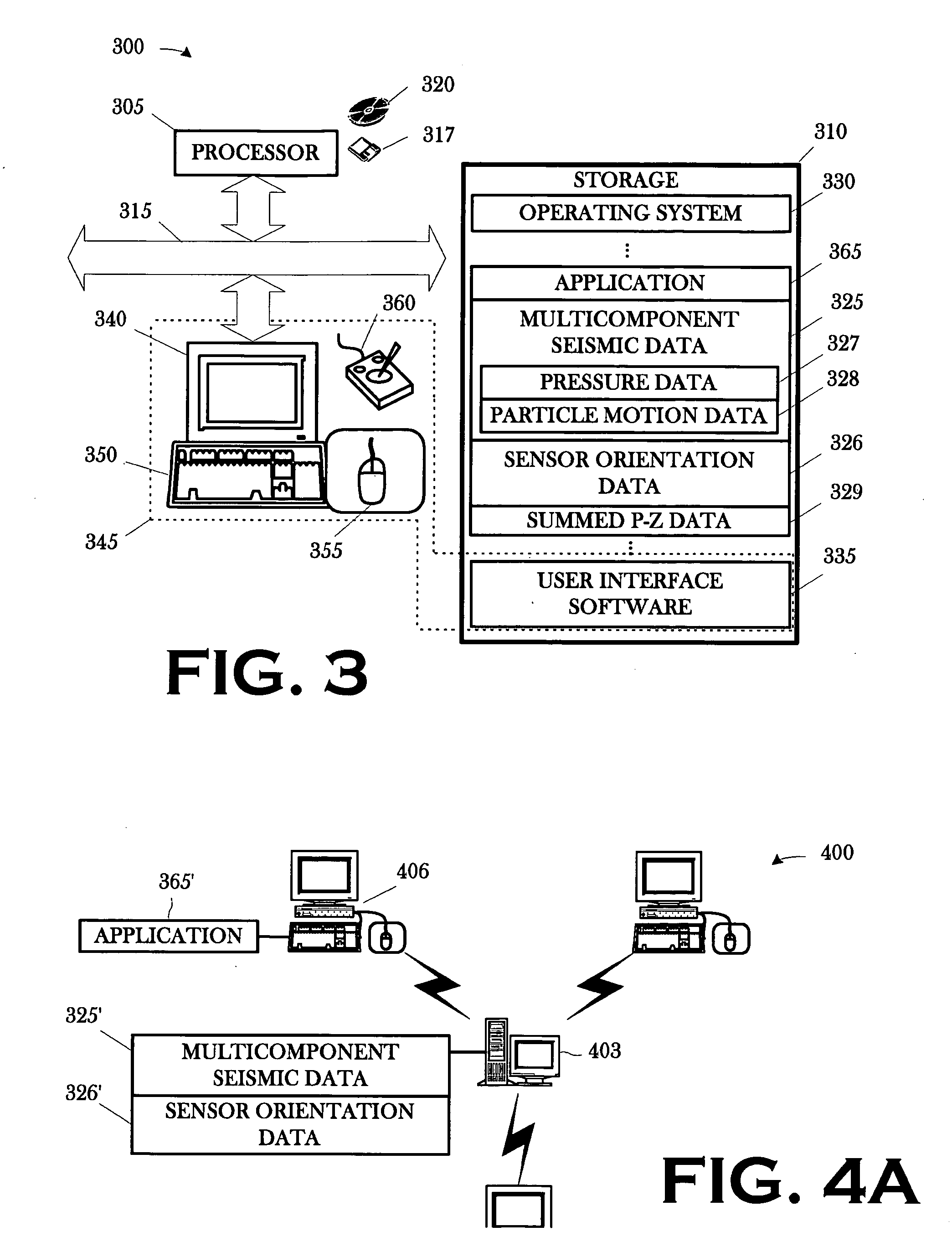
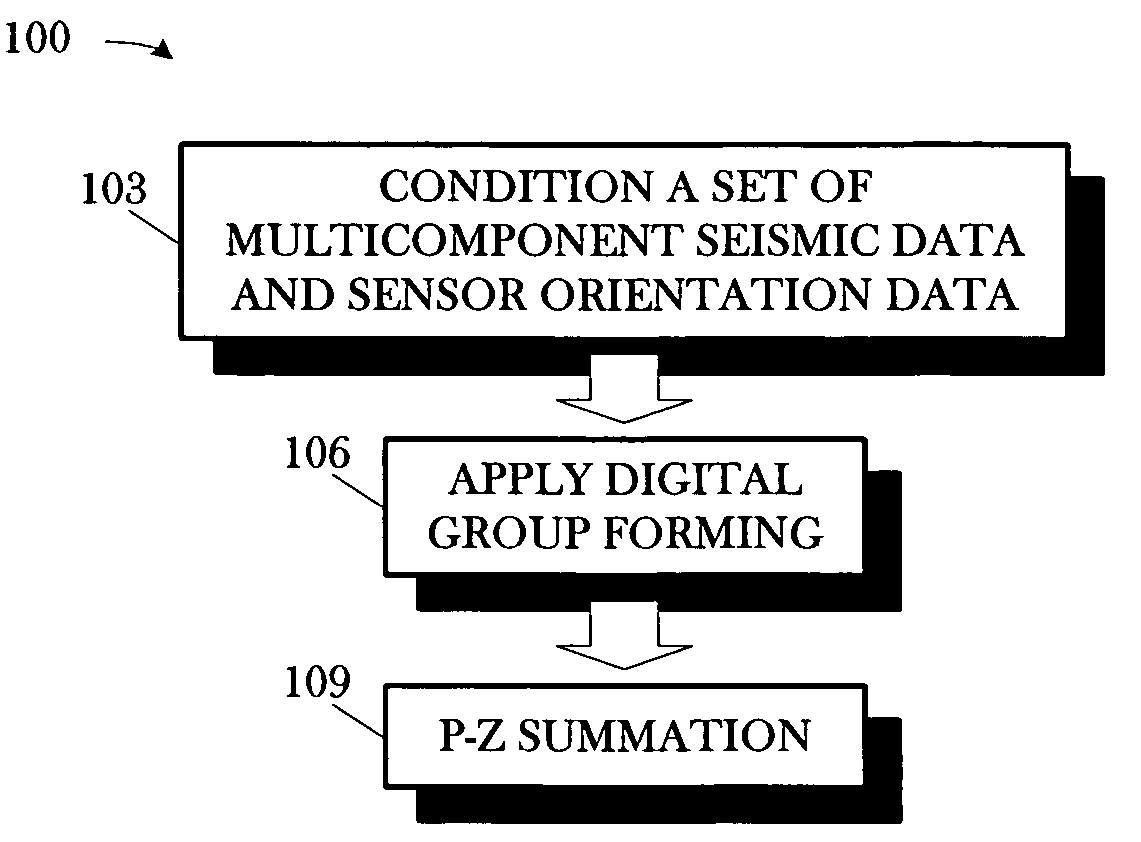
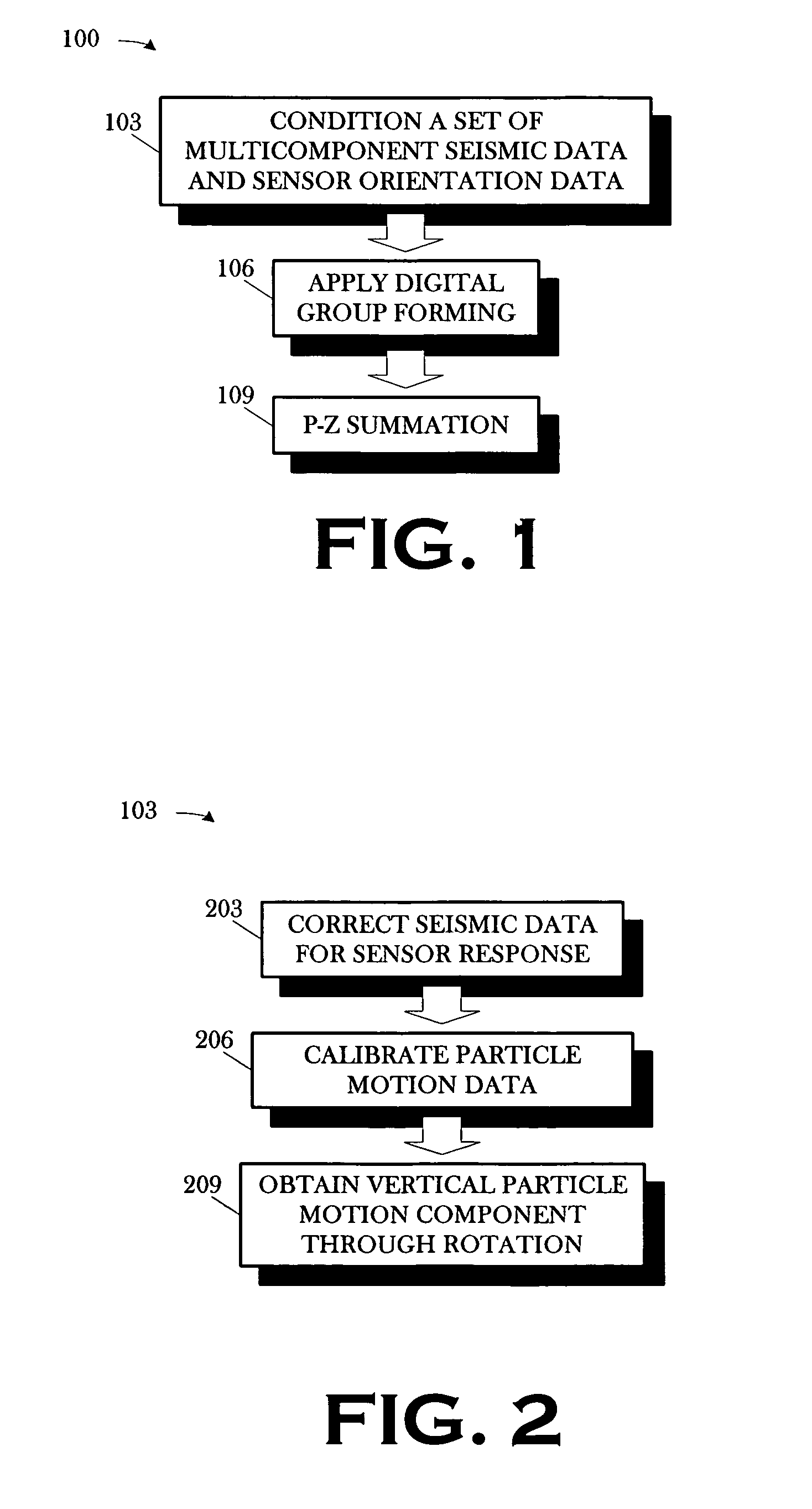
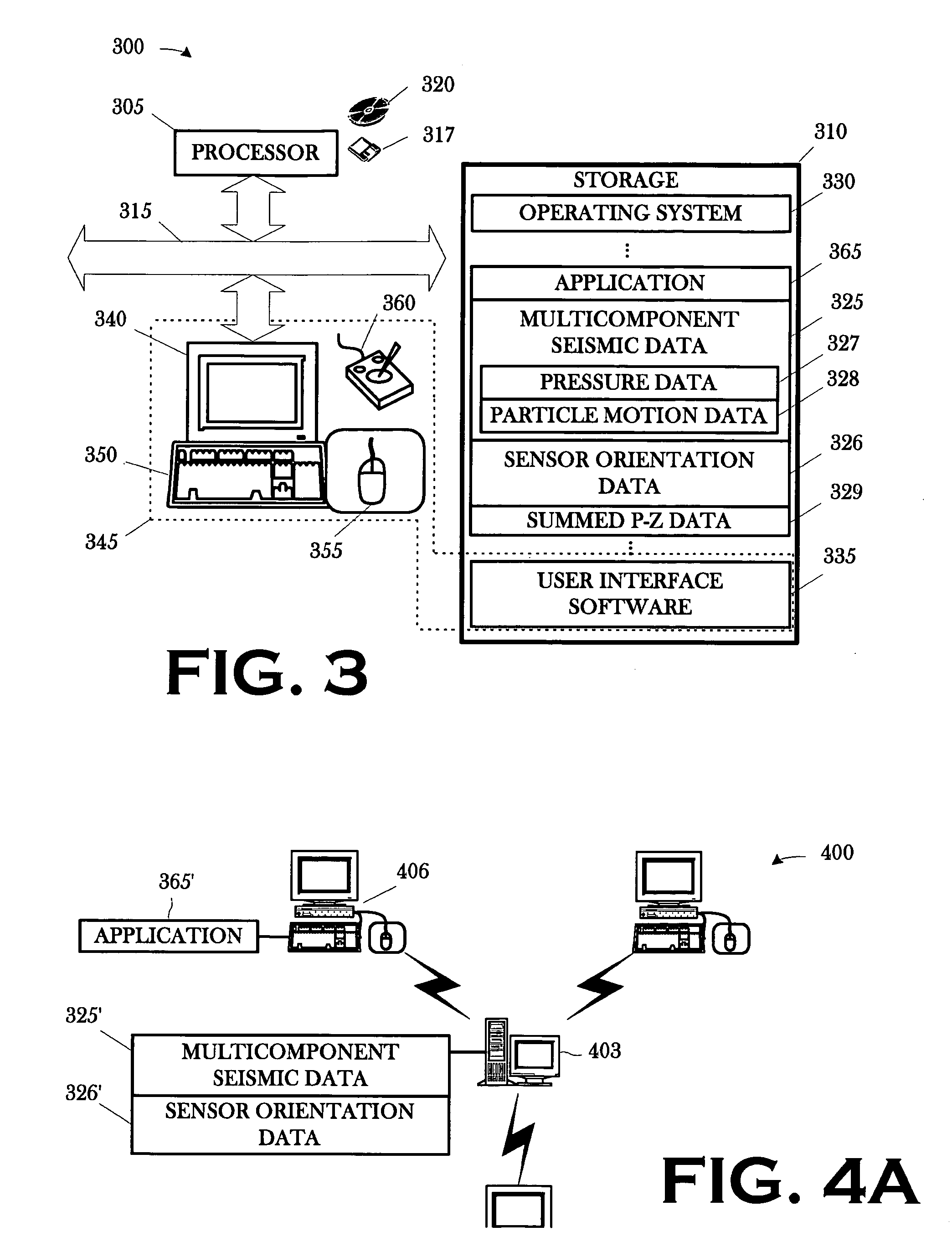
A method includes conditioning a set of multicomponent seismic data and sensor orientation data, the multicomponent seismic data including pressure data and particle motion data, acquired in a towed array, marine seismic survey; digital group forming the conditioned pressure data, a vertical particle motion component of the conditioned particle motion data, and the conditioned sensor orientation data; and summing the digitally group formed pressure data and the digitally group formed vertical particle motion component.
Owner:WESTERNGECO LLC
Geophysical method and apparatus
ActiveUS6975560B2Deploying seismic receivers on the seabed much quickerRapid deploymentSonic/ultrasonic/infrasonic transmissionSeismology for water-covered areasGeophoneSeismic survey
A method and apparatus is disclosed for performing a seismic survey below the surface of a body of water and on the seabed. In one embodiment, a plurality of seismic data receivers are removably loaded in a carrier located above the surface of the water and the carrier is lowered into the water and placed at a depth relatively close to the seabed. Each of the receivers has a memory for recording the vibrations of the seabed and has a switch for activating the memory. A ROV is used to unload the receivers from the carrier and to deposit each receiver on the seabed and along a survey line. In one embodiment, the receivers comprise a frame, a pressure vessel for housing the memory and remotely activated controls, and a geophone that is separately planted into the seabed at a relatively short distance from the frame.
Owner:BP CORP NORTH AMERICA INC
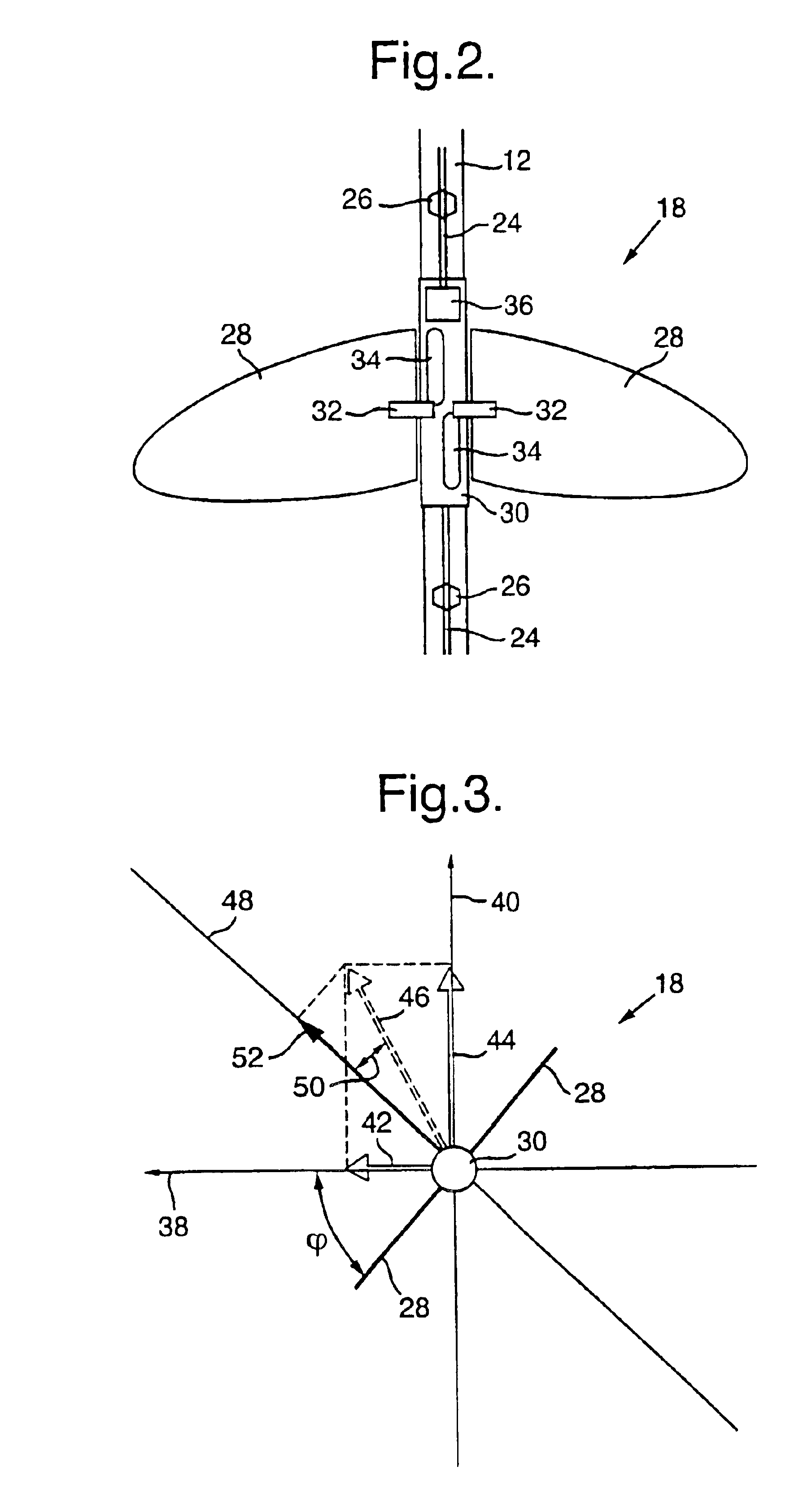
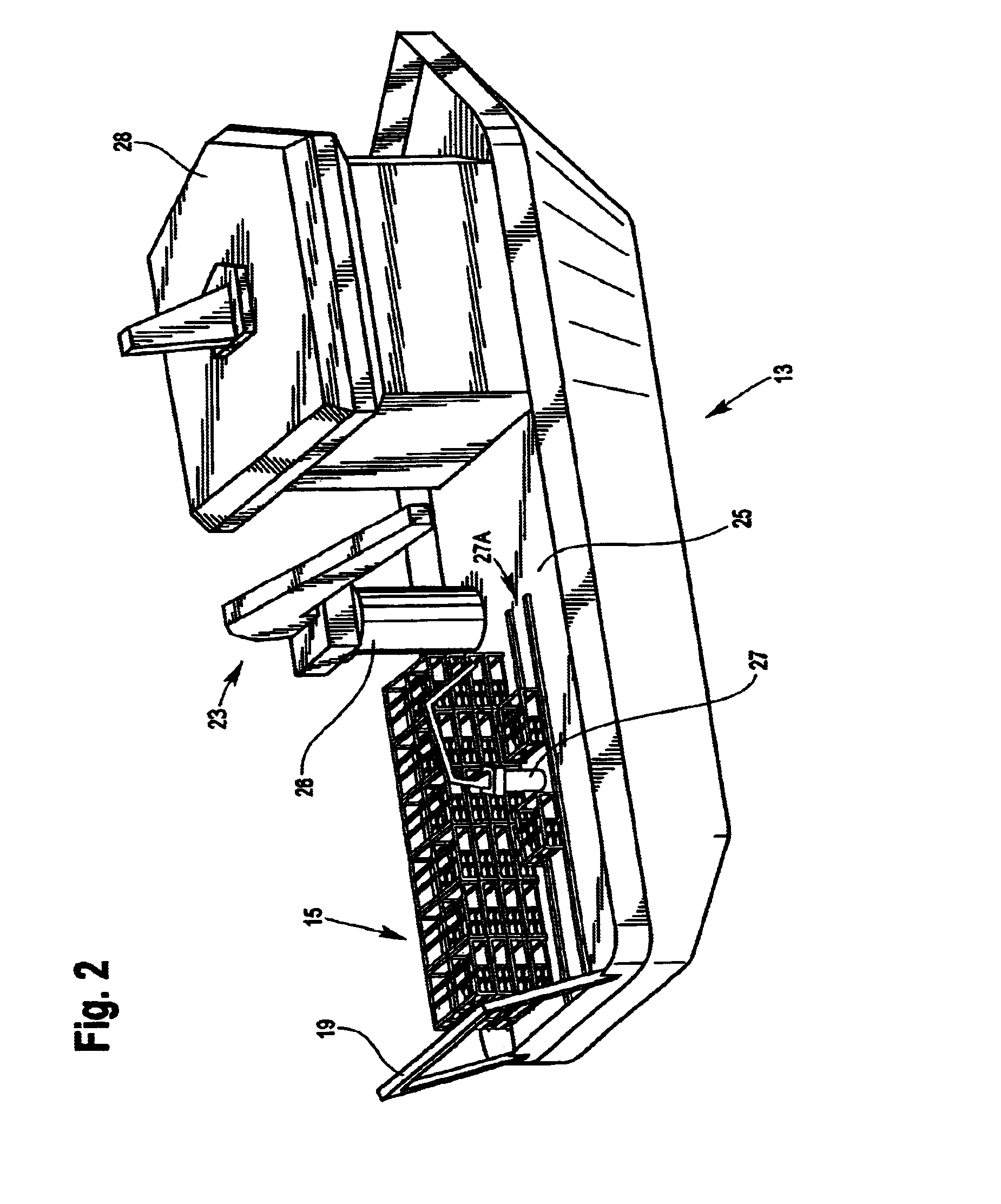
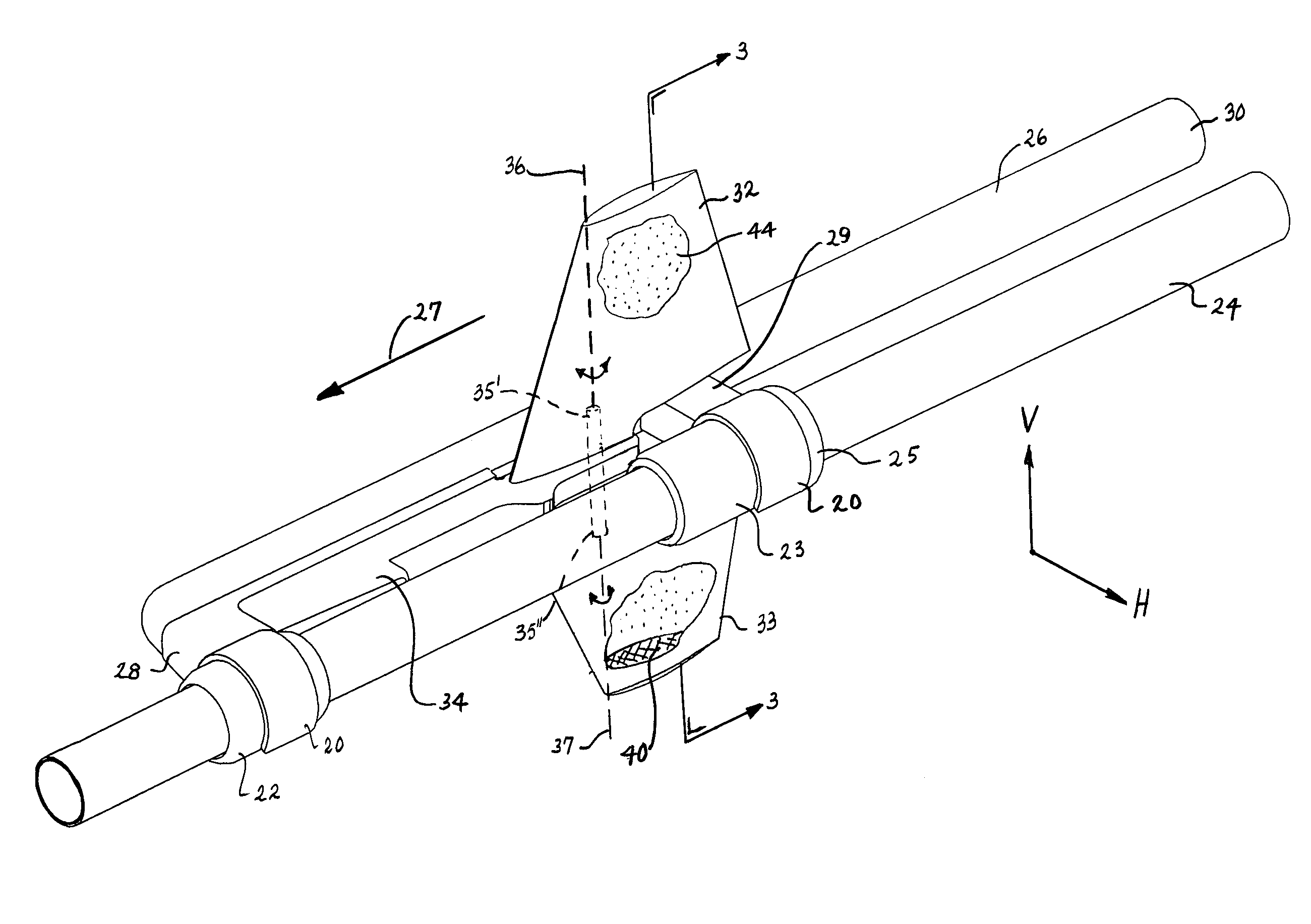
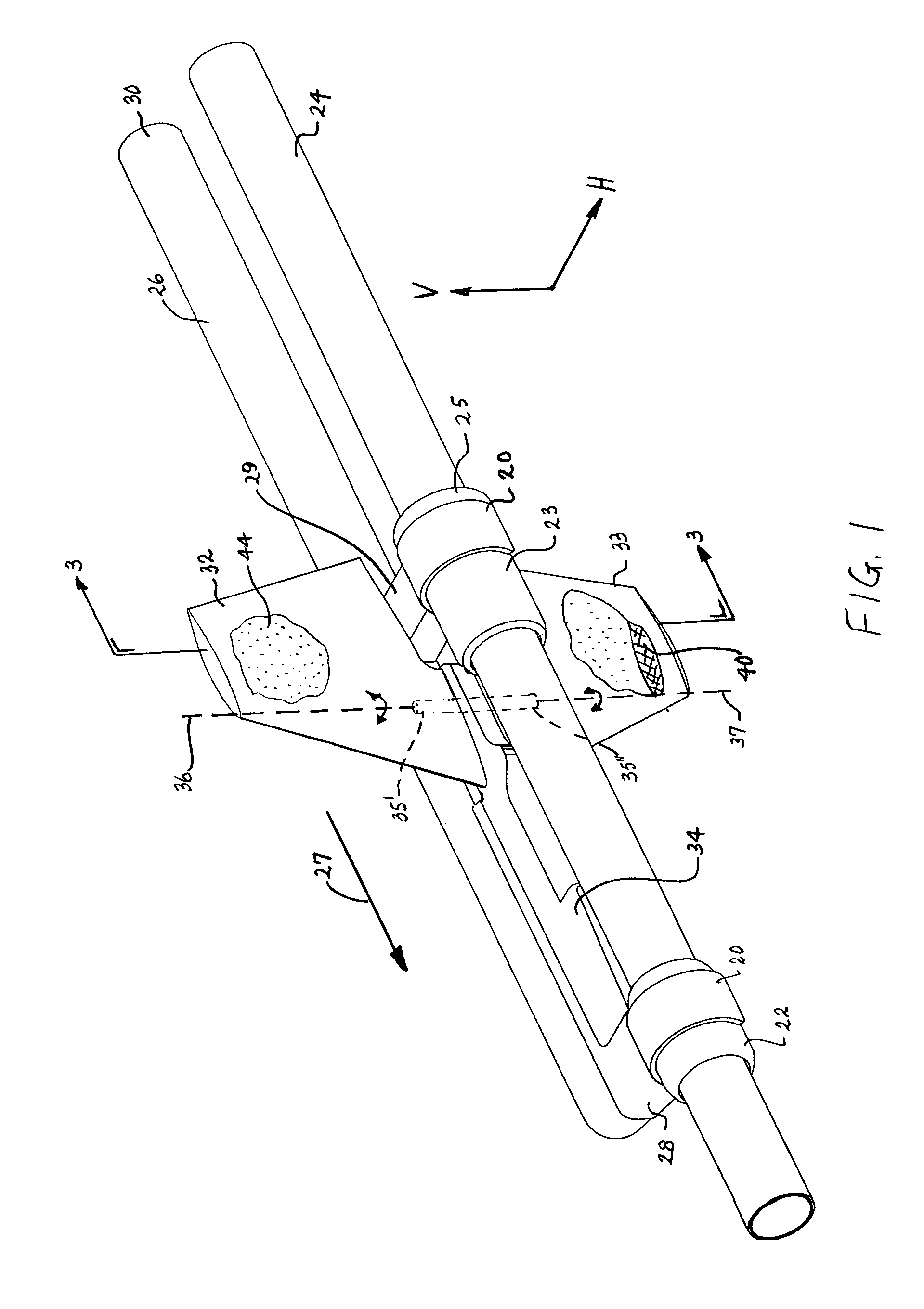
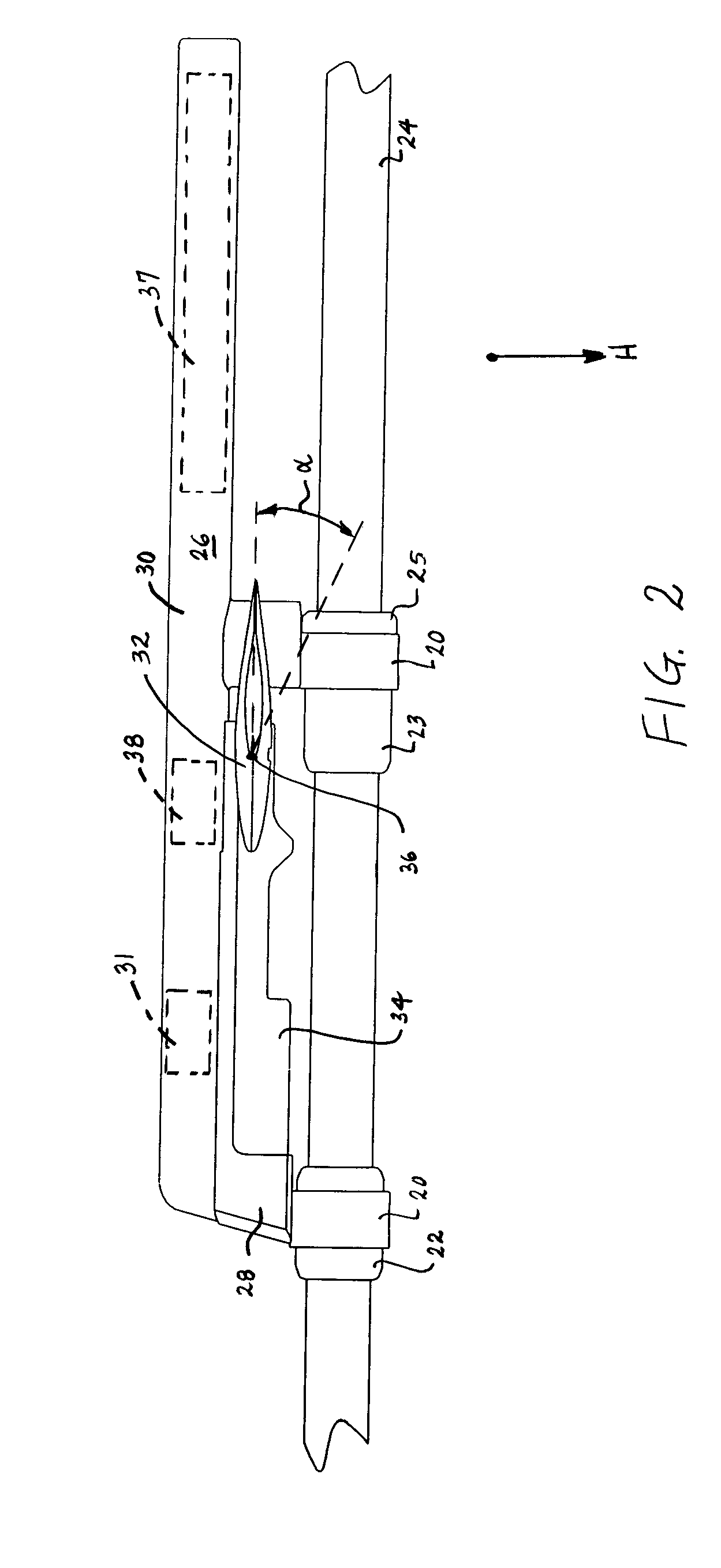
Device for laterally steering streamer cables
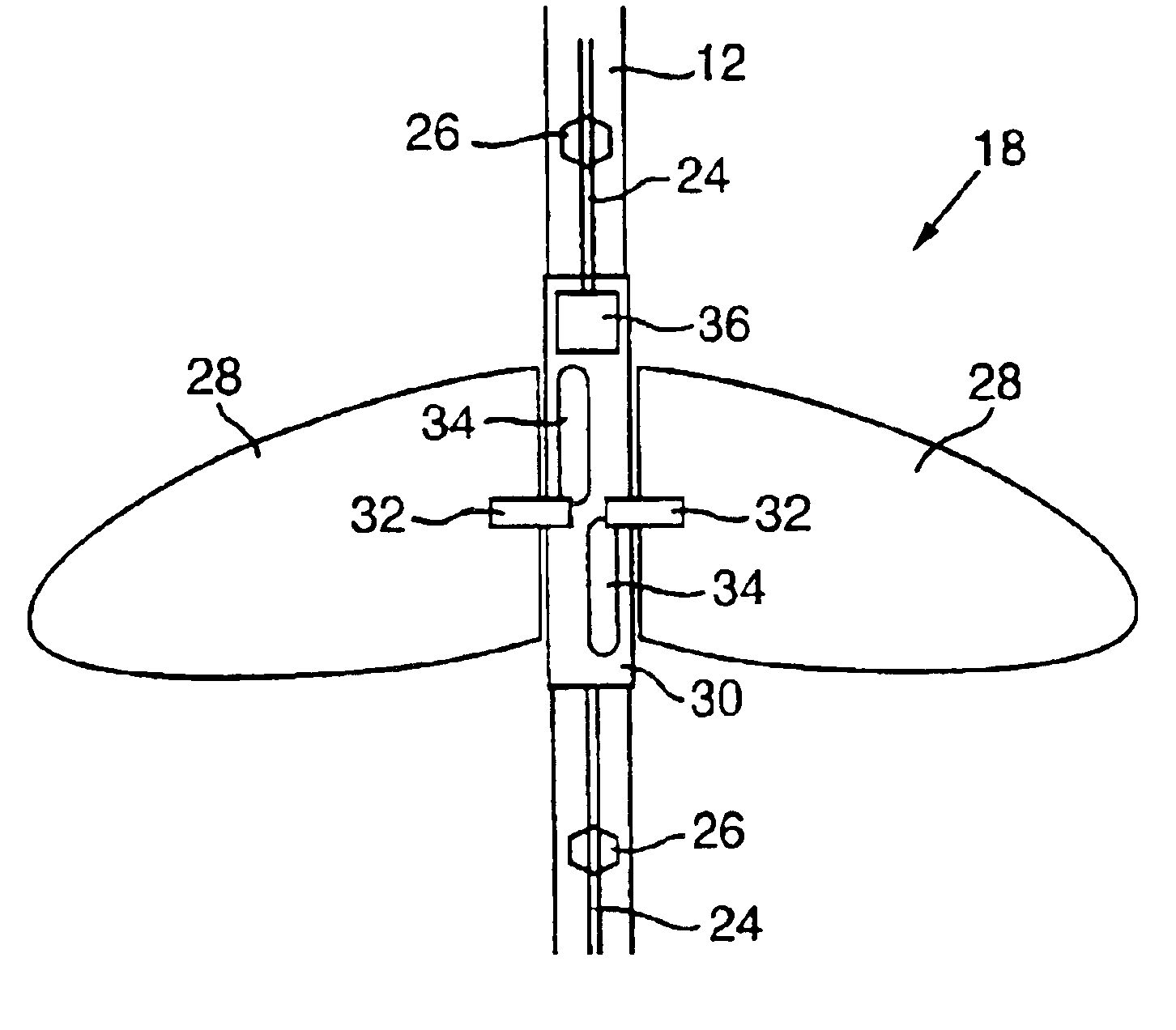
A device and a method for laterally steering a streamer cable towed underwater behind a seismic survey vessel. The device includes a cable-steering assembly rotatably attached to a streamer cable. The assembly includes a body to which one or more wings are mounted. The wings are arranged to pivot about pivot axes. The assembly is ballasted so that the pivot axes of the wings are largely in a vertical plane. A conventional cable-leveling bird is converted to one version of a cable-steering device by ballasting to maintain the pivot axes of the bird's wings largely vertical. With an orientation sensor for sensing the orientation of the wings, the cable-steering device adjusts the angle of the wings to provide a sideward component of force to steer the streamer.
Owner:INPUT OUTPUT INC
Methods for earth modeling and seismic imaging using interactive and selective updating
ActiveUS7480206B2Quality improvementEnhance the imageSeismic signal processingSeismic surveyGaussian beam
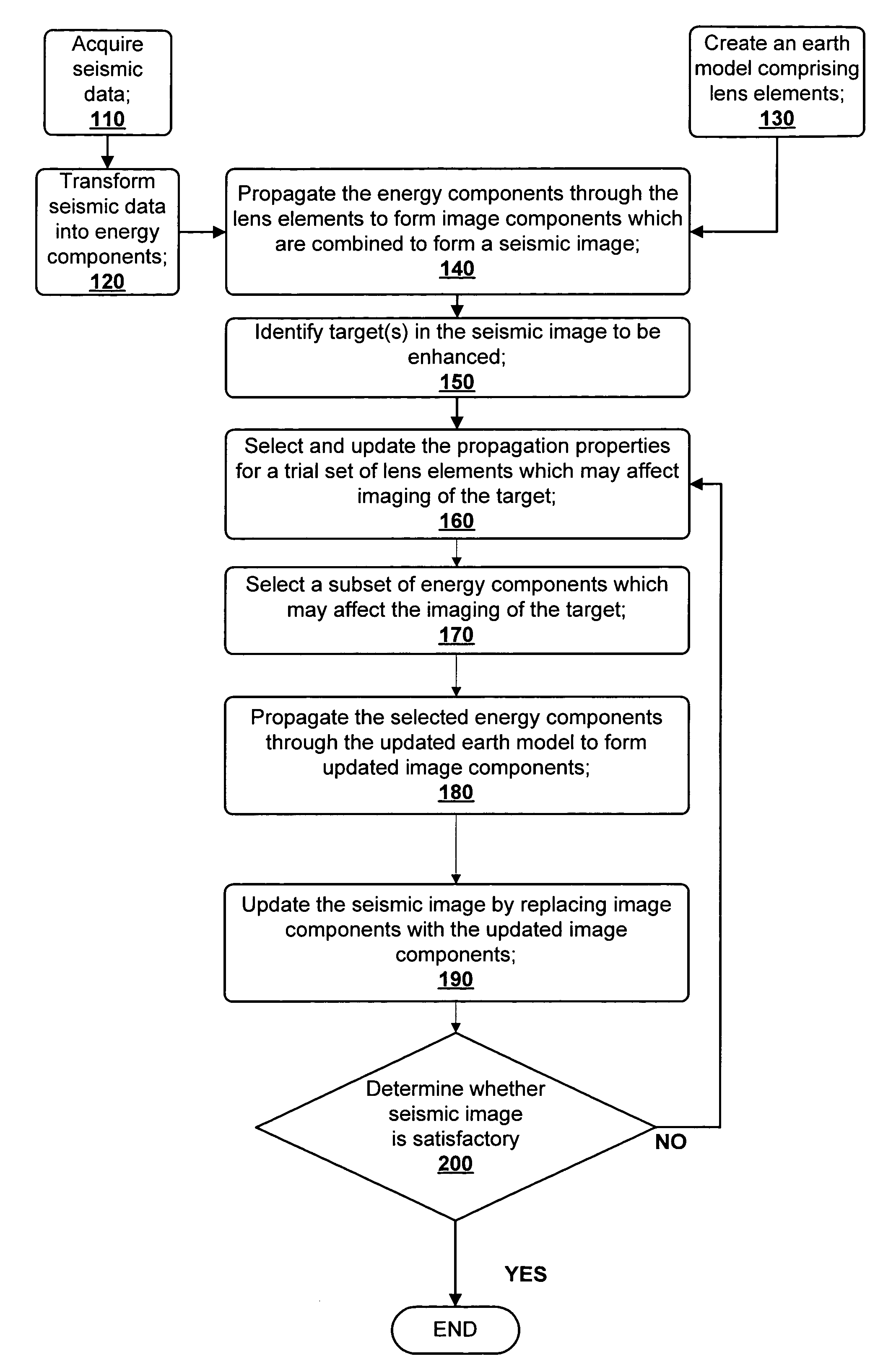
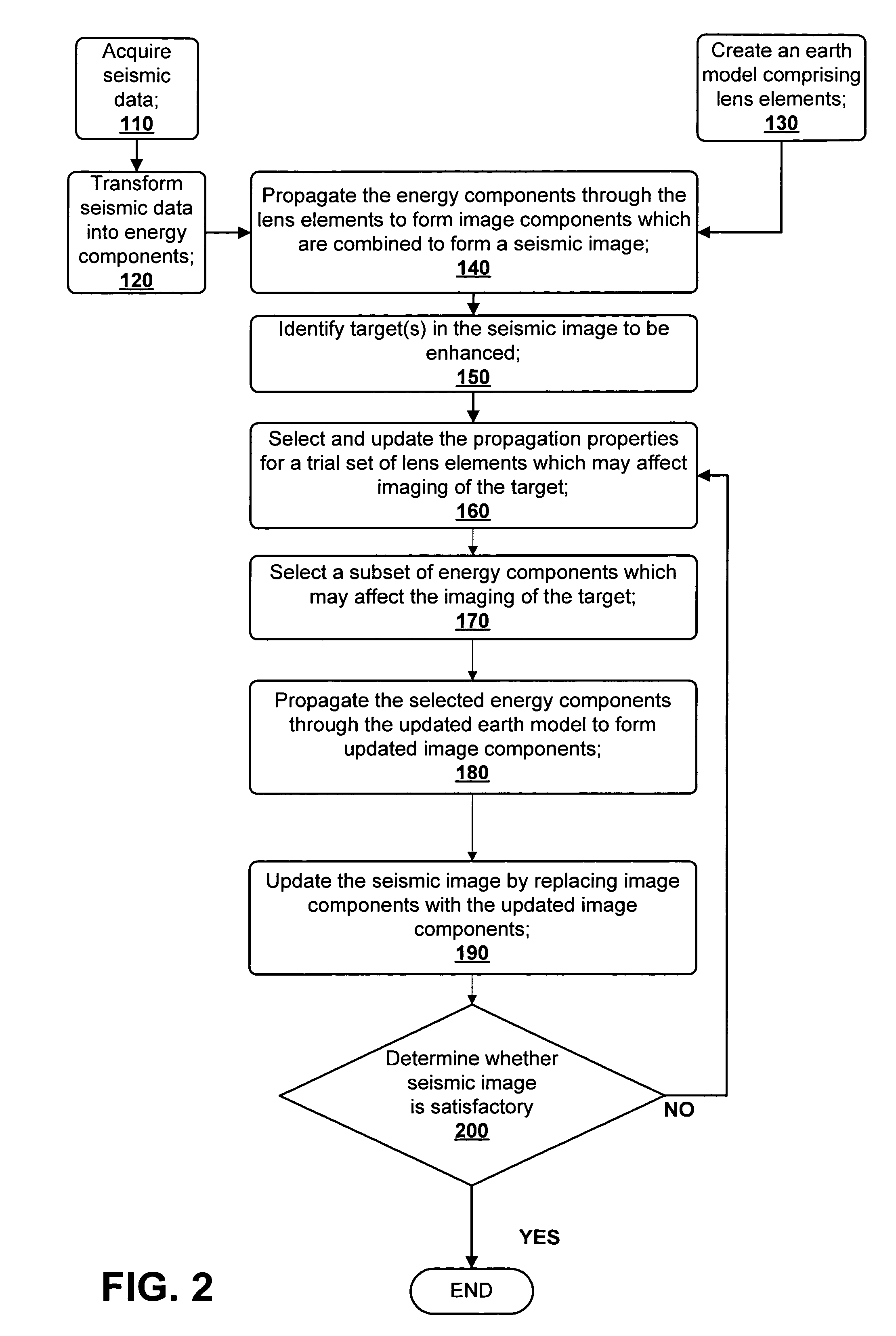
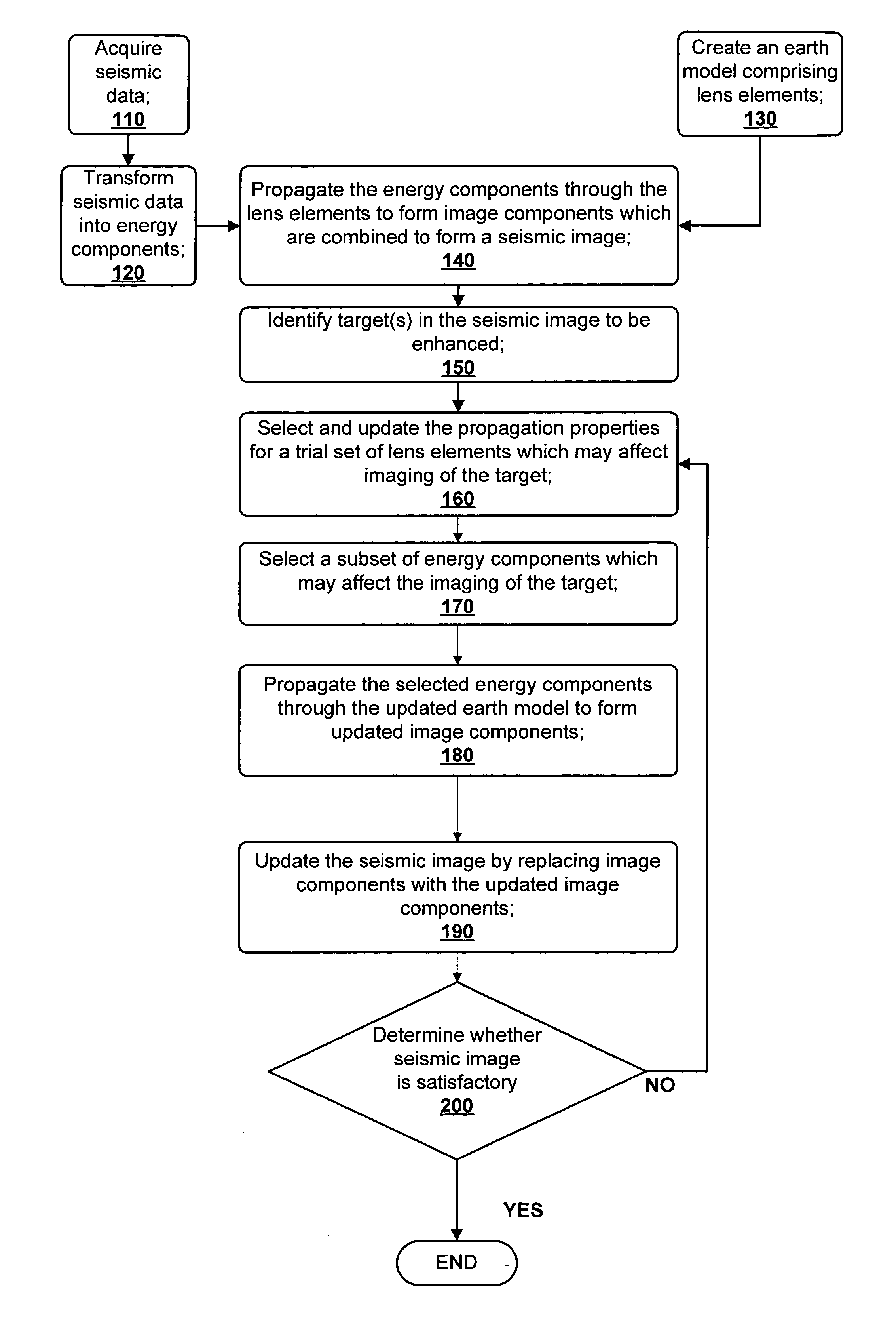
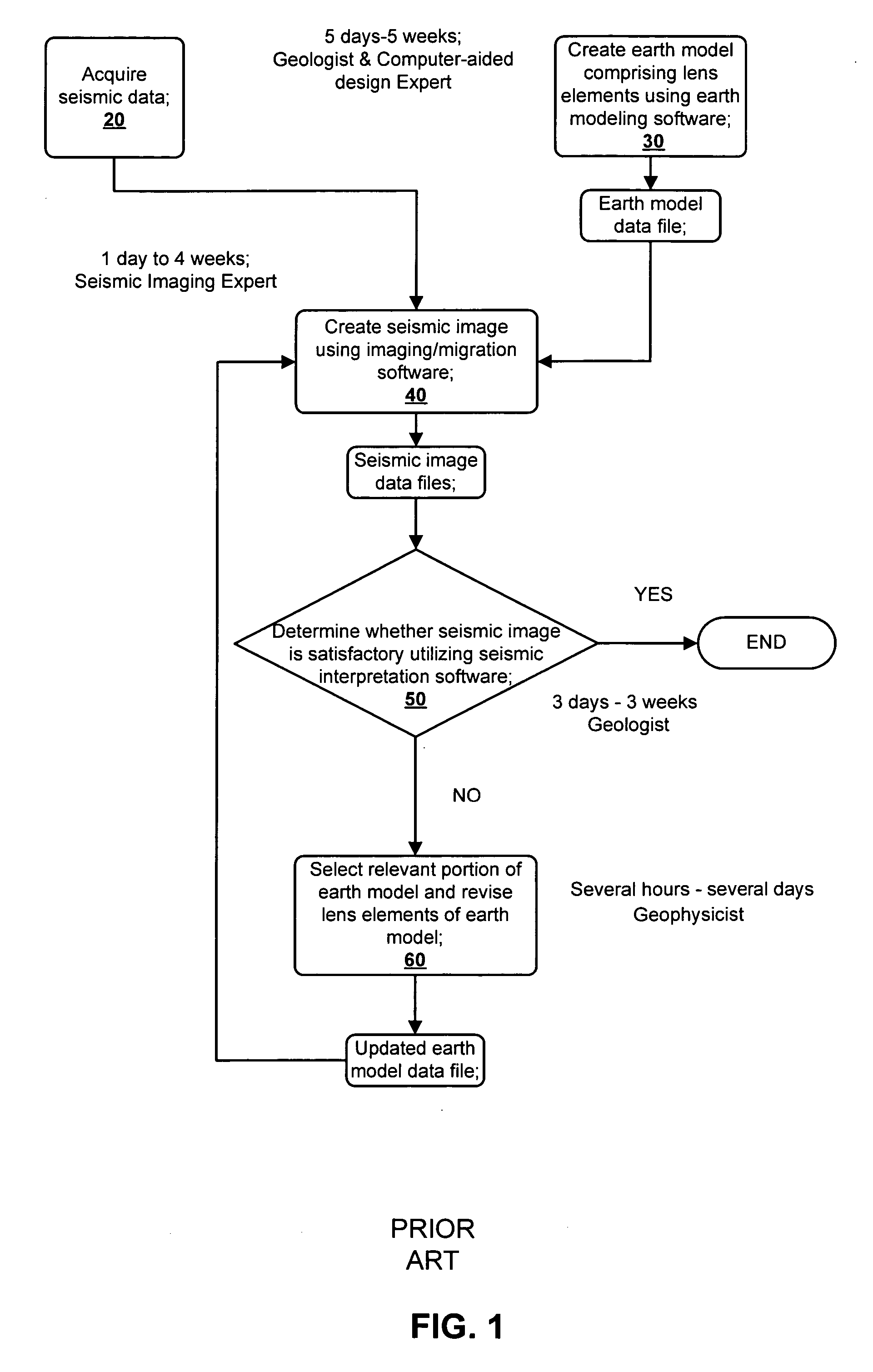
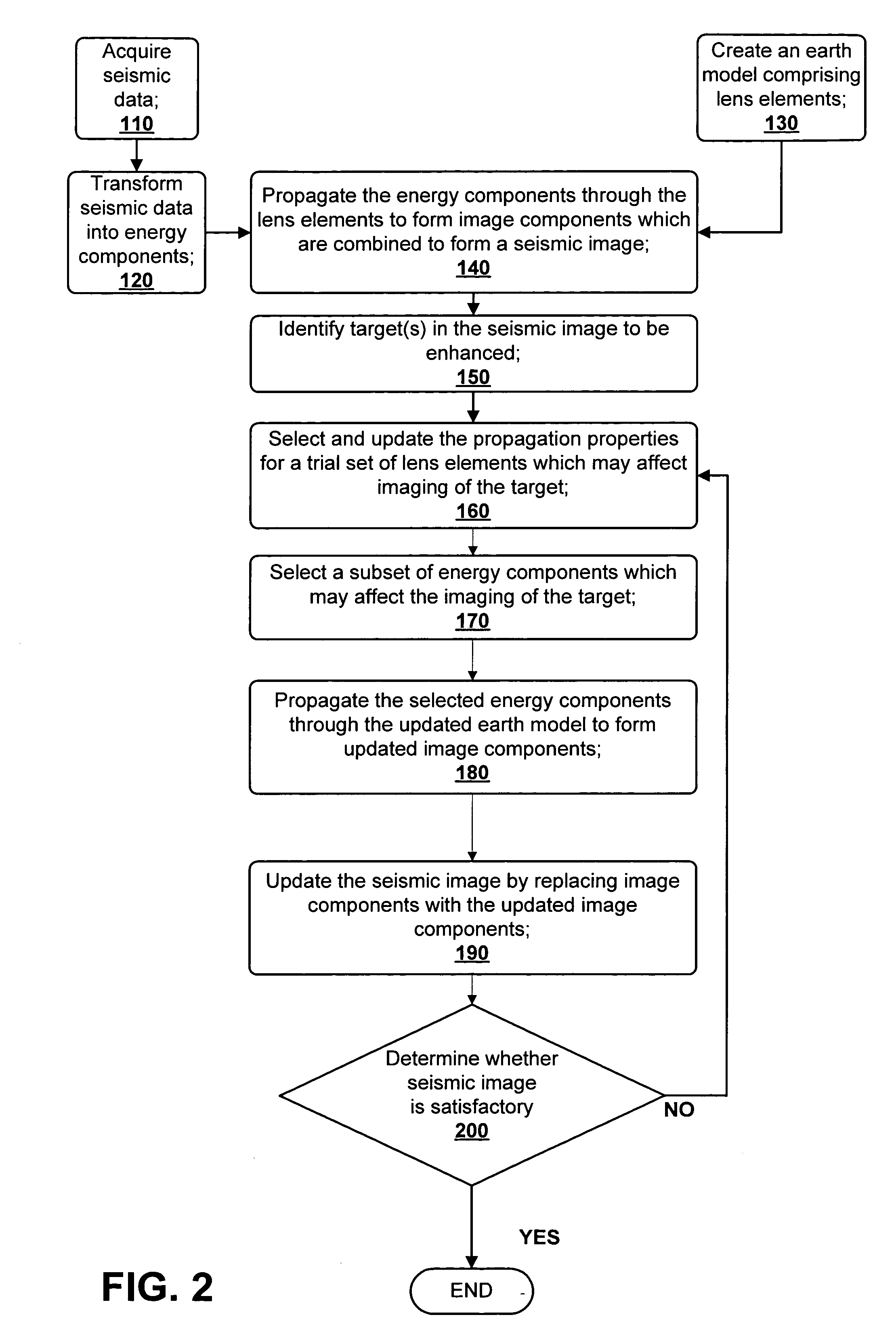
A method for creating an enhanced seismic image is described. Seismic data is acquired from a seismic survey conducted over a subterranean region. The seismic data is transformed into energy components, preferably Gaussian beam components. An earth model is created which is comprised of lens elements. The set of energy components is propagated or migrated through the lens elements to form image components which are combined into a seismic image. A target is identified in the seismic image for image enhancement. Ray tracing may be used to select the trial set of lens elements to be updated and to select a subset of energy components. The subset of energy components is propagated through updated earth model to form updated image components. The seismic image is updated by replacing image components with updated image components which are formed from the subset of selected energy components. This subset is ideally greatly reduced in size relative to the overall number of energy components, i.e., beam components.
Owner:CHEVROU USA INC
Reservoir architecture and connectivity analysis
InactiveUS20110040536A1GeomodellingComputation using non-denominational number representationBoundary element methodSeismic survey
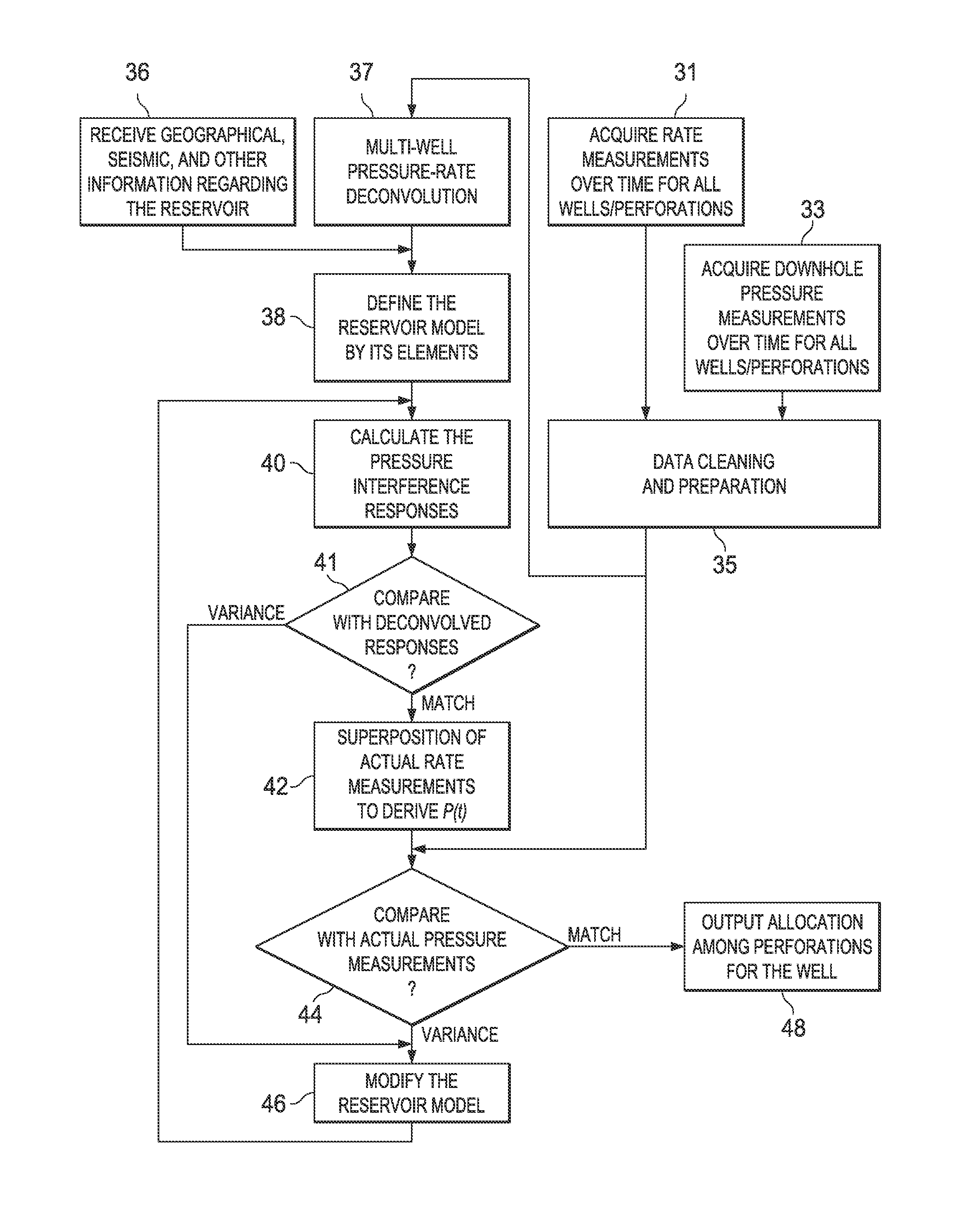
An interactive system and method of operating the system to define and evaluate a model of a hydrocarbon reservoir. The reservoir model is defined from extrinsic information such as seismic surveys, well logs, and the like, and is based on elements of formation regions, connections among the regions, wells, and perforations. A boundary-element method is used to determine pressure interference responses, corresponding to the pressure at a perforation in response to a single perforation producing fluid at a unit flow rate. These pressure interference responses are then convolved with measured well flow rates obtained during production to arrive at estimates of the wellbore pressure at one or more wells of interest. The estimated wellbore pressure can be compared with downhole pressure measurements to validate the reservoir model, or to provoke the user into modifying the model and repeating the evaluation of the model.
Owner:BP CORP NORTH AMERICA INC
Marine acoustic vibrator having enhanced low-frequency amplitude
InactiveUS20110317515A1Seismic energy generationSound producing devicesVibration amplitudeSeismic survey
A seismic source includes a flextensional shell defining a longer axis and a shorter axis and at least one driver coupled to the flextensional shell proximate an end of the shorter axis. The seismic source may be a component of a marine seismic survey system. The marine seismic survey system may be utilized in a method of marine seismic surveying.
Owner:PGS GEOPHYSICAL AS
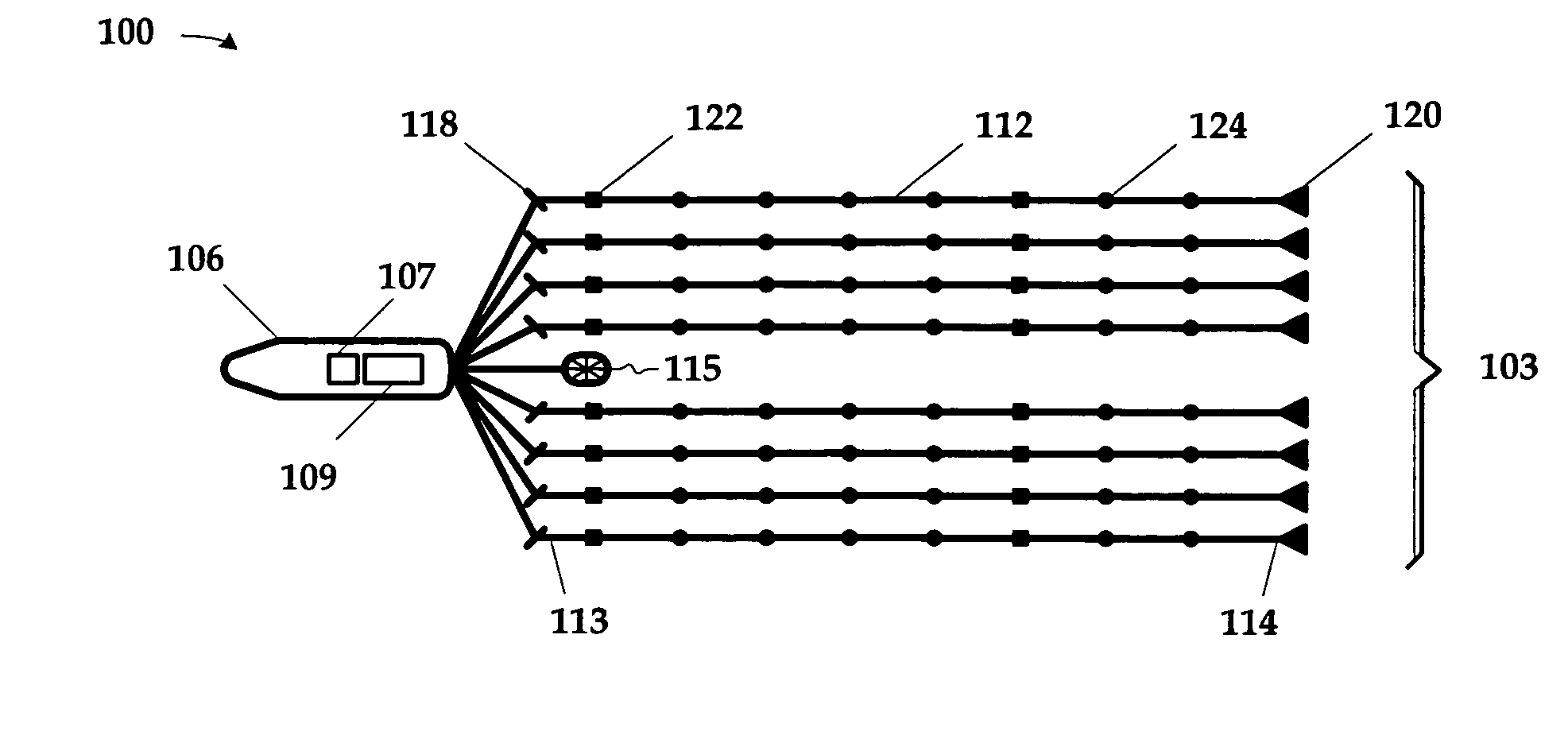
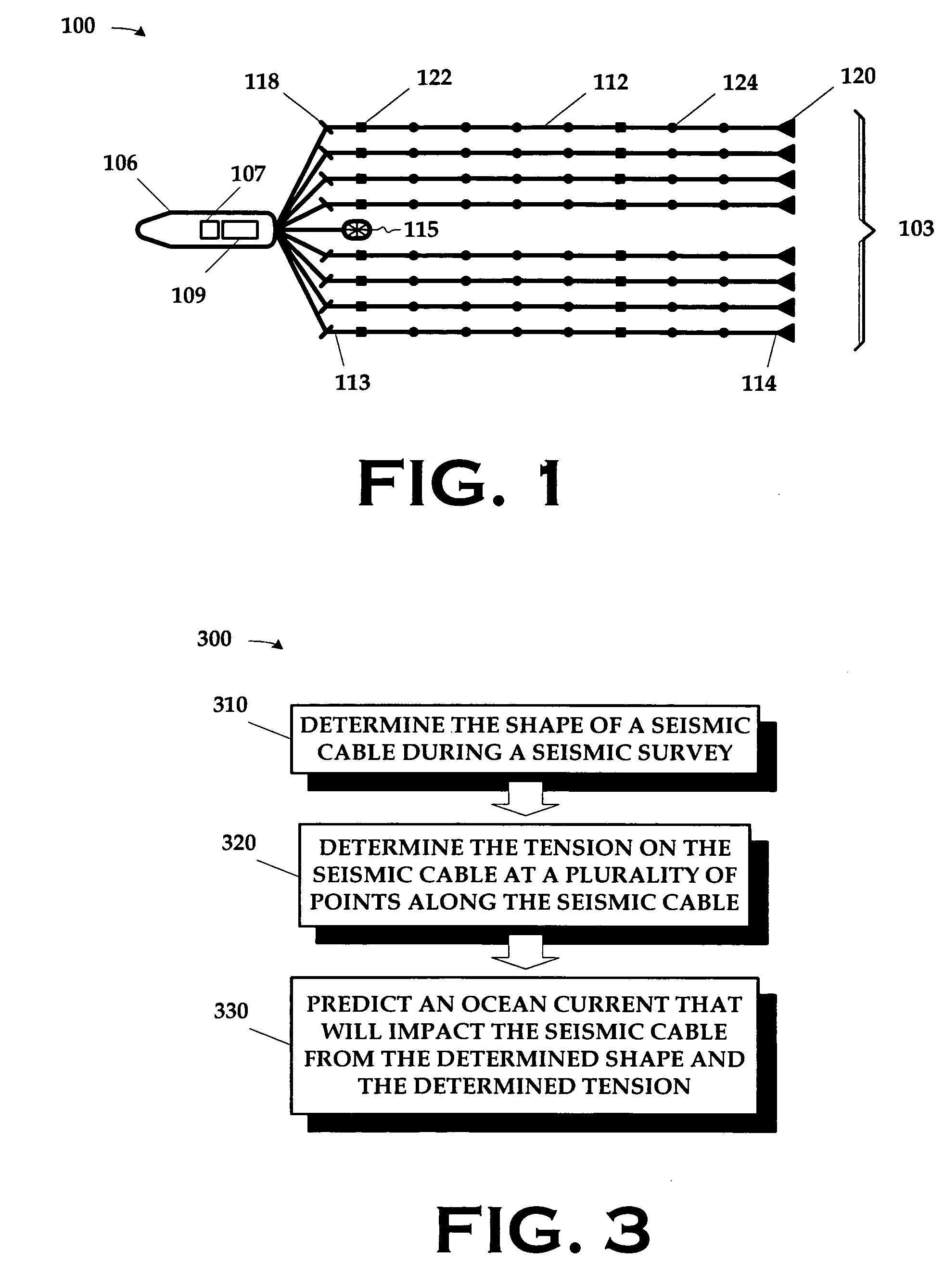
Current prediction in seismic surveys
ActiveUS20070127312A1Measuring open water movementSeismic signal processingOcean bottomSeismic survey
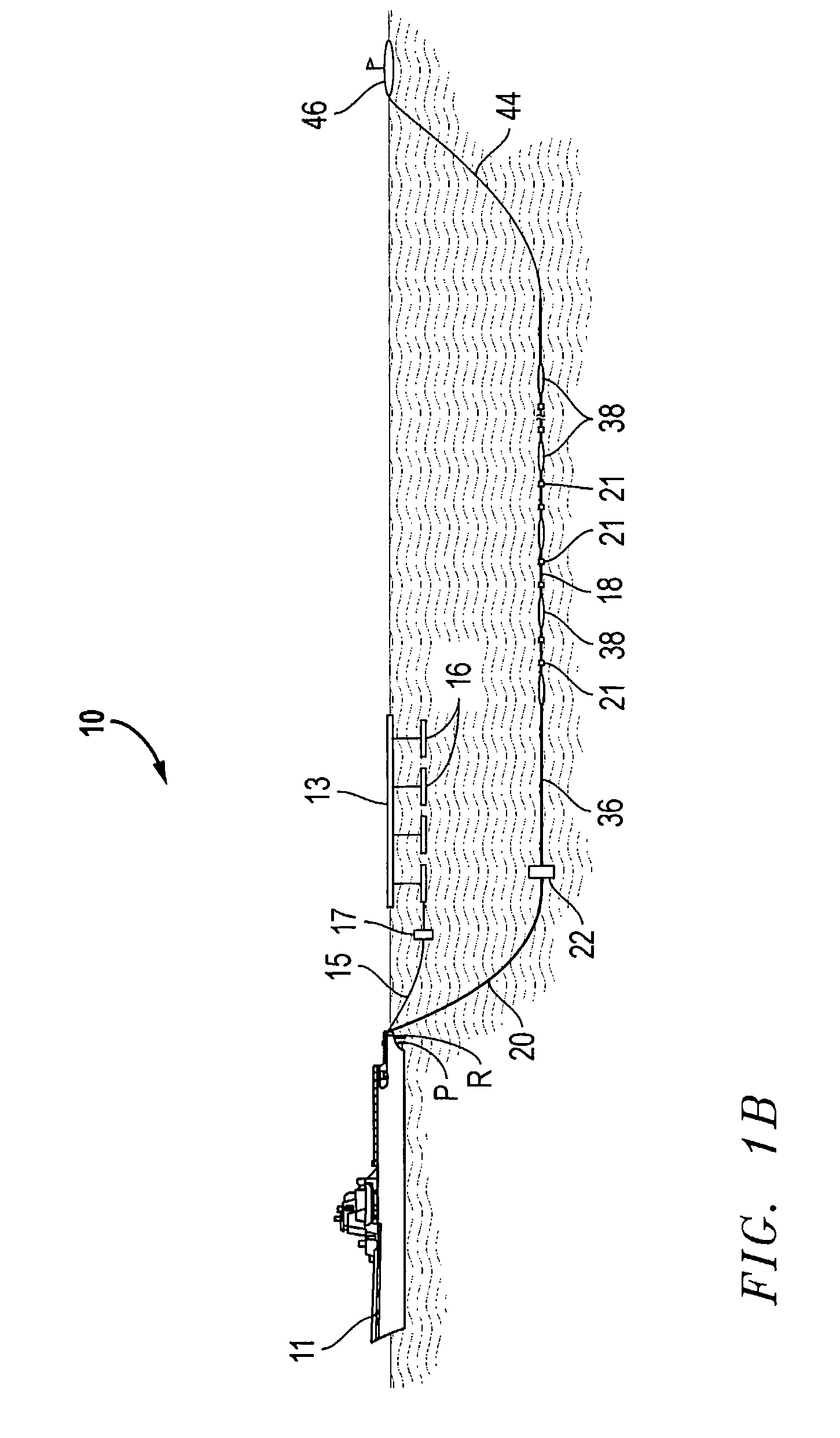
A method for use in seismic surveying includes determining the shape of a seismic cable during a seismic survey; determining the tension on the seismic cable at a plurality of points along the seismic cable; and predicting a current that will impact the seismic cable from the determined shape and the determined tension. The method may be practiced two-dimensionally in the context of a marine survey employing a towed streamer array or three-dimensionally in the context of laying an array of ocean bottom cables on the seabed. The predicted currents can, in some embodiments; be used to make steering corrections for the seismic cables.
Owner:REFLECTION MARINE NORGE AS
Marine Seismic Acquisition
ActiveUS20100103772A1Increase wider spreadReduces and eliminates needSeismic signal processingSeismology for water-covered areasSeismic surveyGeophysics
A method of conducting multiple source, multiple signal seismic surveys in a marine environment are provided.
Owner:CONOCOPHILLIPS CO
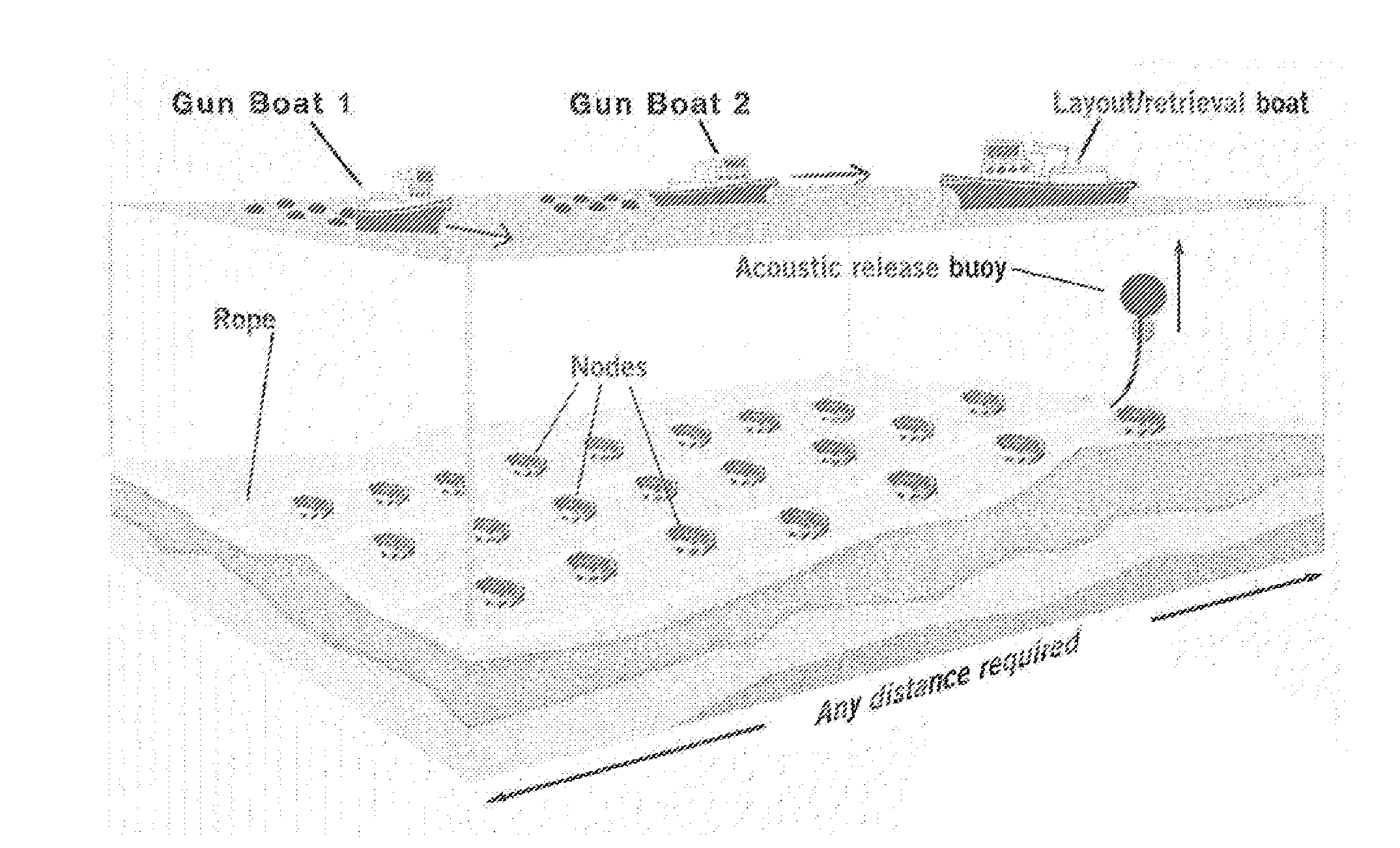
Simultaneous shooting nodal acquisition seismic survey methods
ActiveUS20140198607A1Avoid entrapmentMinimize the possibilitySeismic energy generationSeismology for water-covered areasNODALSeismic survey
A method of performing a seismic survey including: deploying nodal seismic sensors at positions in a survey region; activating a plurality of seismic sources; and using the nodal seismic sensors to record seismic signals generated in response to the activation of the plurality of signals.
Owner:MAGSEIS FF LLC
Marine Seismic Survey Method and System
InactiveUS20110286302A1Reduce non-productive timeSeismology for water-covered areasSeismic surveyAtmospheric sciences
An inventive method provides for control of a seismic survey spread while conducting a seismic survey, the spread having a vessel, a plurality of spread control elements, a plurality of navigation nodes, and a plurality of sources and receivers. The method includes the step of collecting input data, including navigation data for the navigation nodes, operating states from sensors associated with the spread control elements, environmental data for the survey, and survey design data. The positions of the sources and receivers are estimated using the navigation data, the operating states, and the environmental data. Optimum tracks for the sources and receivers are determined using the position estimates and a portion of the input data that includes at least the survey design data. Drive commands are calculated for at least two of the spread control elements using the determined optimum tracks. The inventive method is complemented by an inventive system.
Owner:WESTERNGECO LLC
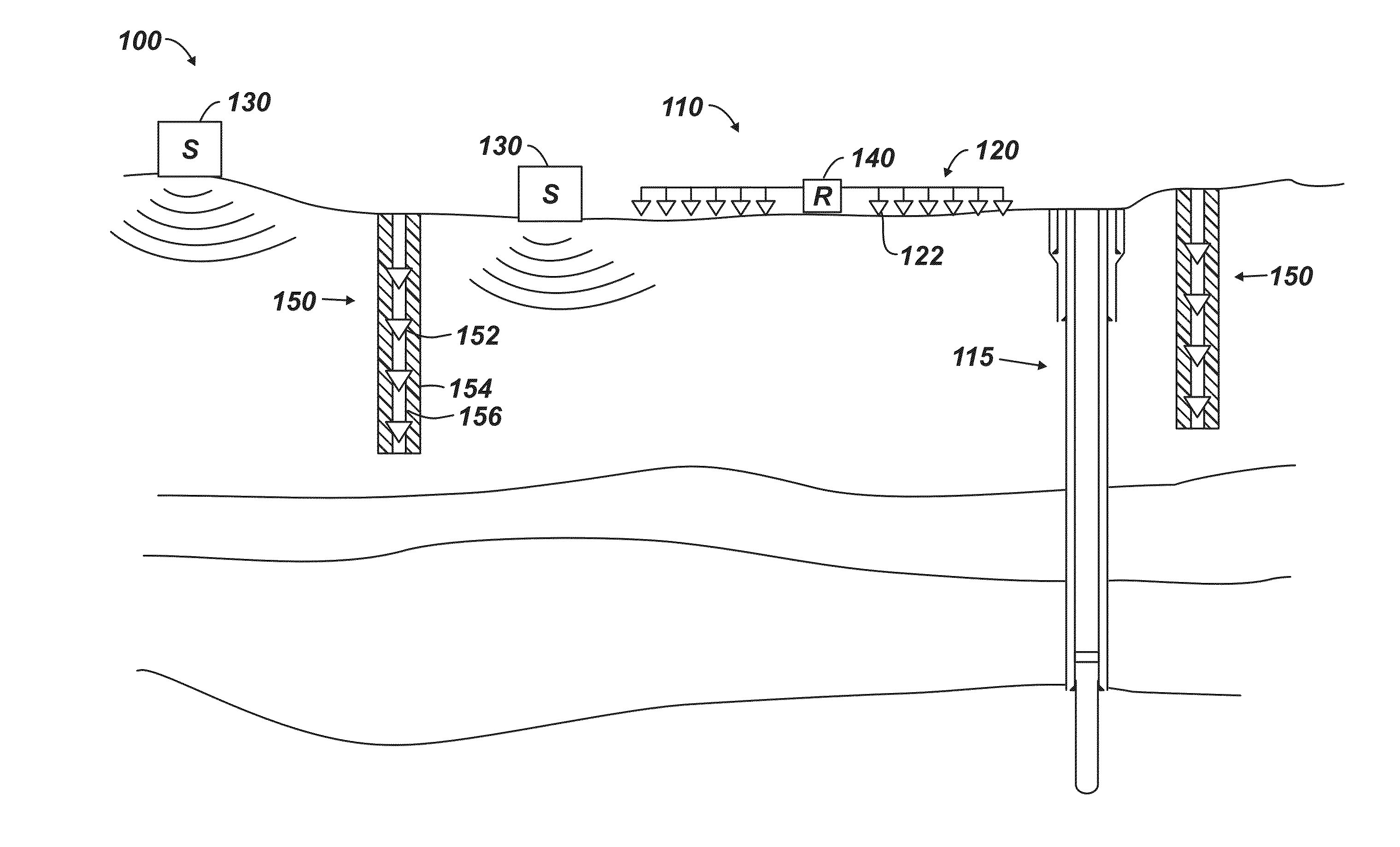
Sensor System of Buried Seismic Array
Microseismic mapping using buried arrays with the integration of passive and active seismic surveys provides enhanced microseismic mapping results. The system is initially set up by recording seismic data with the buried array installation while shooting a significant portion of the 3D surface seismic survey. The 3D surface seismic survey provides the following data: shallow 3D VSP data from the buried arrays; P-wave and converted wave data for the area covered by the buried array that benefits from the planned data integration processing effort; and microseismic data and associated analysis.
Owner:NUTEC SCI
Methods for earth modeling and seismic imaging using interactive and selective updating
ActiveUS20060056272A1Quality improvementEnhance the imageSeismic signal processingGaussian beamSeismic survey
A method for creating an enhanced seismic image is described. Seismic data is acquired from a seismic survey conducted over a subterranean region. The seismic data is transformed into energy components, preferably Gaussian beam components. An earth model is created which is comprised of lens elements. The set of energy components is propagated or migrated through the lens elements to form image components which are combined into a seismic image. A target is identified in the seismic image for image enhancement. Ray tracing may be used to select the trial set of lens elements to be updated and to select a subset of energy components. The subset of energy components is propagated through updated earth model to form updated image components. The seismic image is updated by replacing image components with updated image components which are formed from the subset of selected energy components. This subset is ideally greatly reduced in size relative to the overall number of energy components, i.e., beam components.
Owner:CHEVROU USA INC
Autonomous underwater vehicle for marine seismic surveys
An autonomous underwater vehicle (AUV) for recording seismic signals during a marine seismic survey. The AUV includes a body having a flush shape; an intake water element located on the body and configured to take in water; at least one propulsion nozzle located on the body and configured to eject the water from the intake water element for actuating the AUV; at least one guidance nozzle located on the body and configured to eject water to change a traveling direction of the AUV; and a seismic payload located on the body of the AUV and configured to record seismic signals.
Owner:SEABED GEOSOLUTIONS
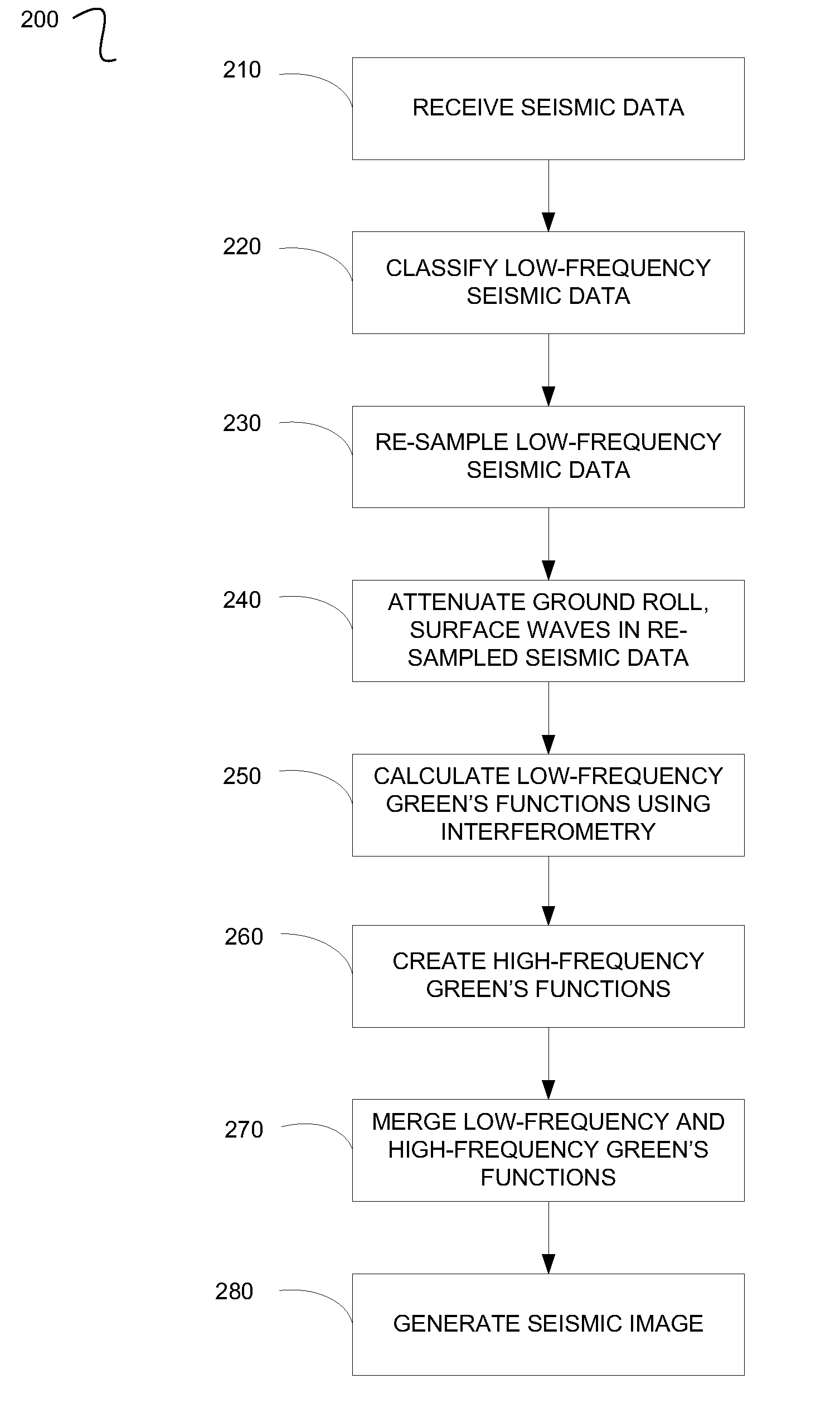
Interferometric seismic data processing
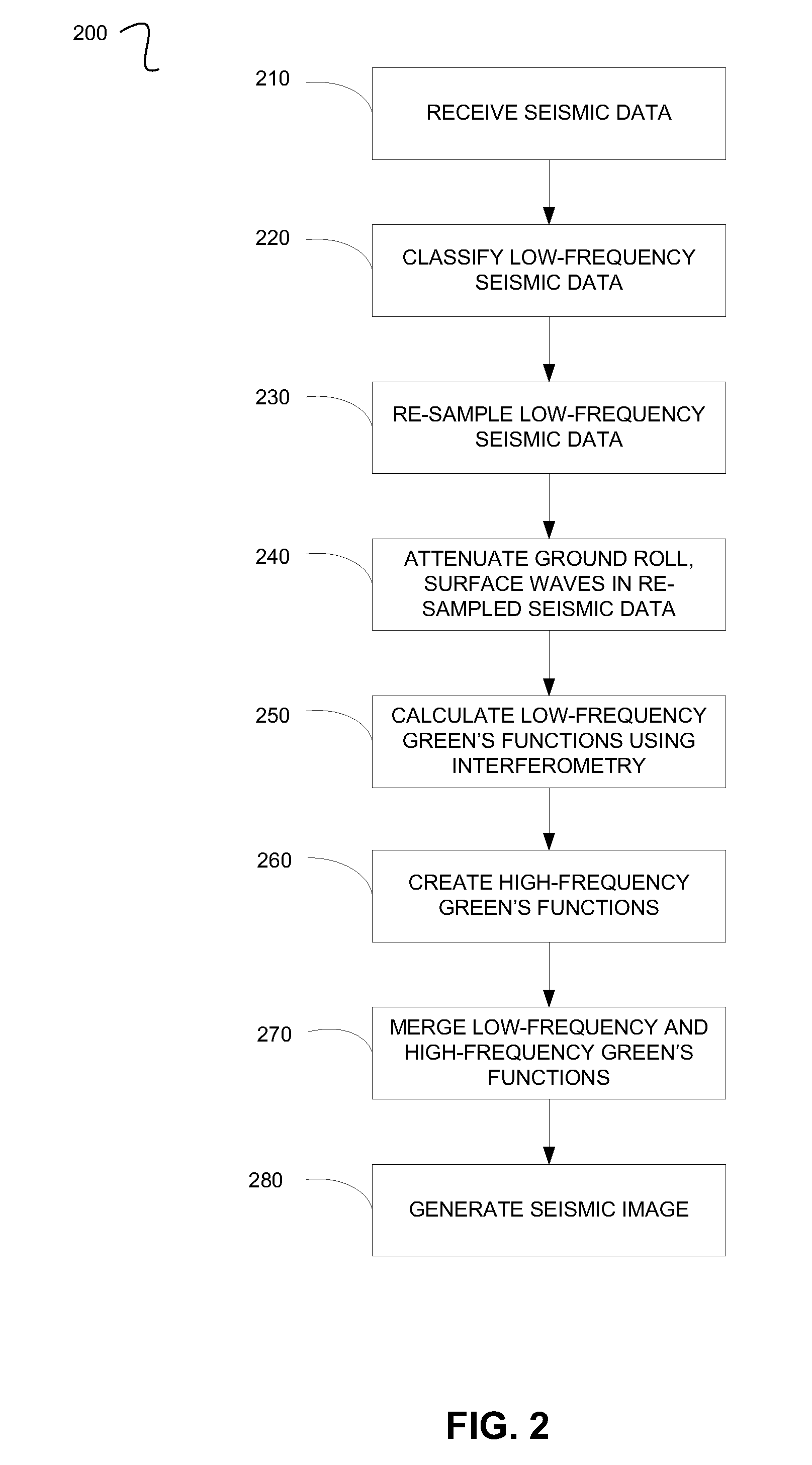
Implementations of various technologies for a method for generating a seismic image of a subsurface are described herein. Seismic data may be received from two sensors in a seismic survey. The seismic data below and equal to a predetermined frequency may be classified as low-frequency seismic data. The low-frequency seismic data may be re-sampled based on the predetermined frequency. A set of low-frequency Green's functions may be calculated using interferometry on the re-sampled low-frequency seismic data. High-frequency seismic data of the seismic data may be processed to create a set of high-frequency Green's functions at one or more source locations of the seismic survey. The set of high-frequency Green's functions may be merged with the set of low-frequency Green's functions to create a set of broad-band Green's functions. The seismic image may be generated using the set of broad-band Green's functions at the source locations.
Owner:WESTERNGECO LLC
Method for the measurement of multidirectional far-field source signatures from seismic surveys
InactiveUS6256589B1High resolutionImprove accuracySeismic signal processingSeismology for water-covered areasSeismic surveyAcquisition technique
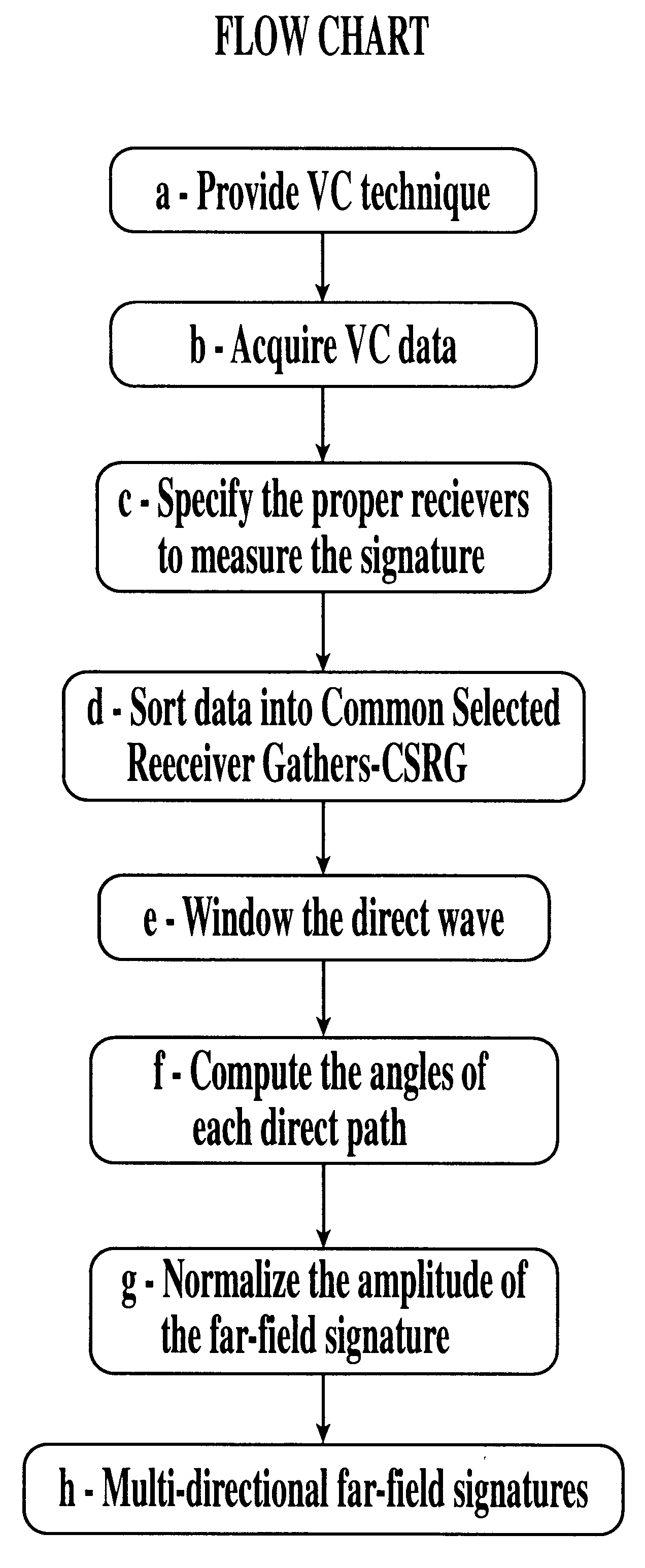
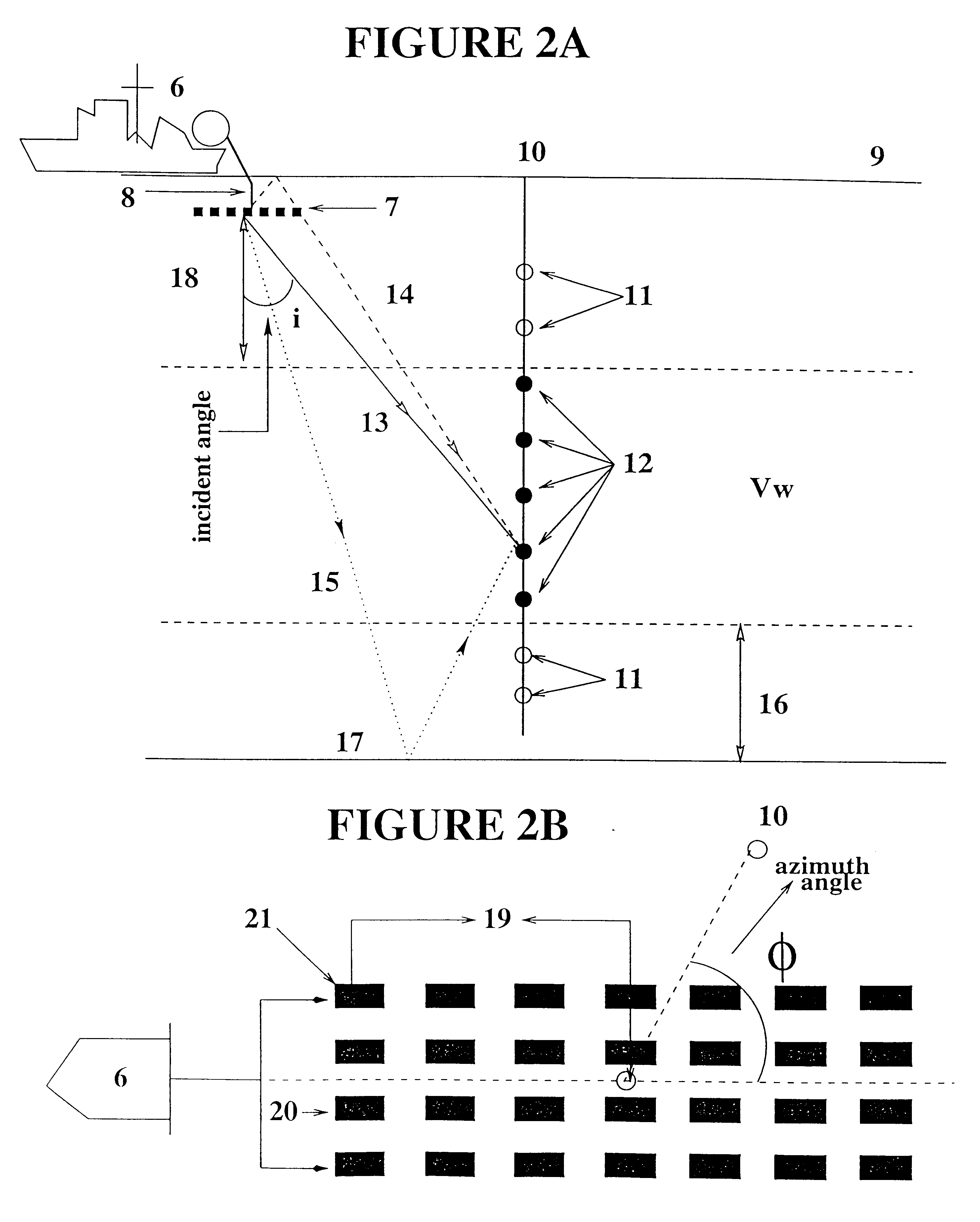
A method is described for the measurement of multidirectional far-field source signatures from seismic surveys whereby a vertical cable acquisition technique is provided, vertical cable data are acquired, the proper receivers are specified to measure the signature, data are sorted into common selected receiver gathers CSRG, the direct wave within common receiver gather is properly windowed, the angles of each direct path are computed and the amplitude of the signatures is normalized, so as to obtain the multidirectional far-field signatures of the seismic source array having the same characteristics as those that generated the seismic reflections.
Owner:PETROLEO BRASILEIRO SA (PETROBRAS)
Method and apparatus for locating gas hydrate
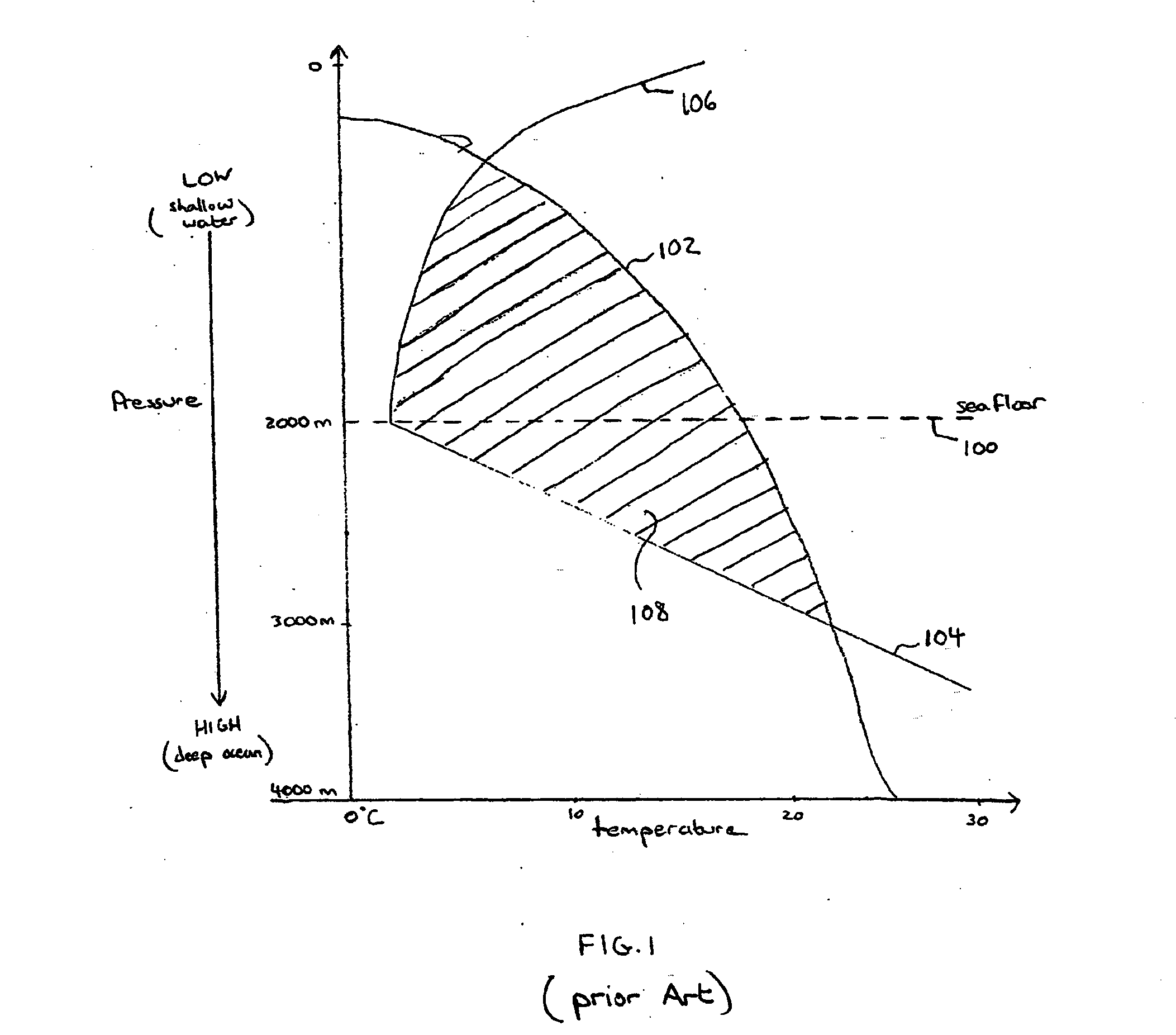
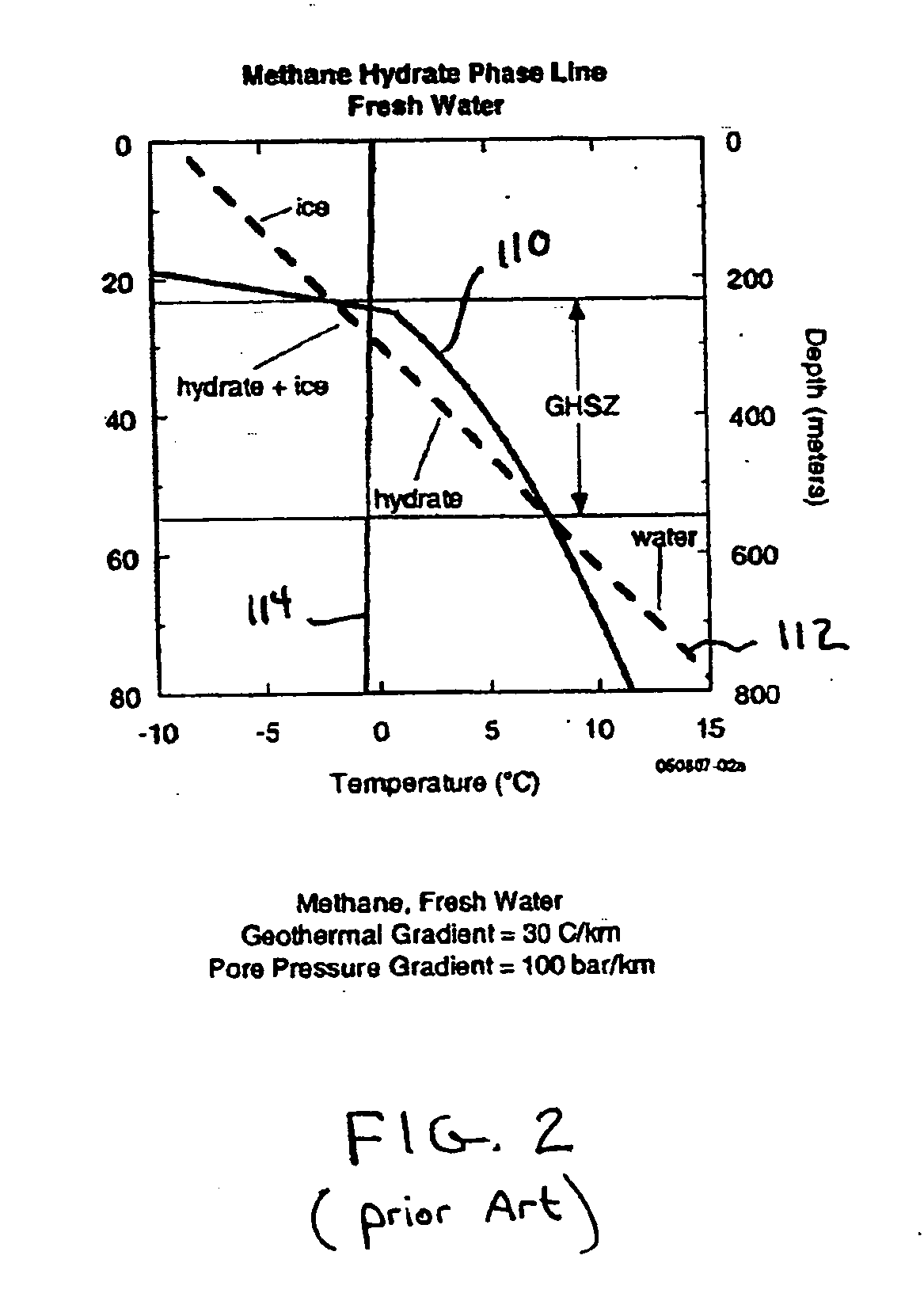
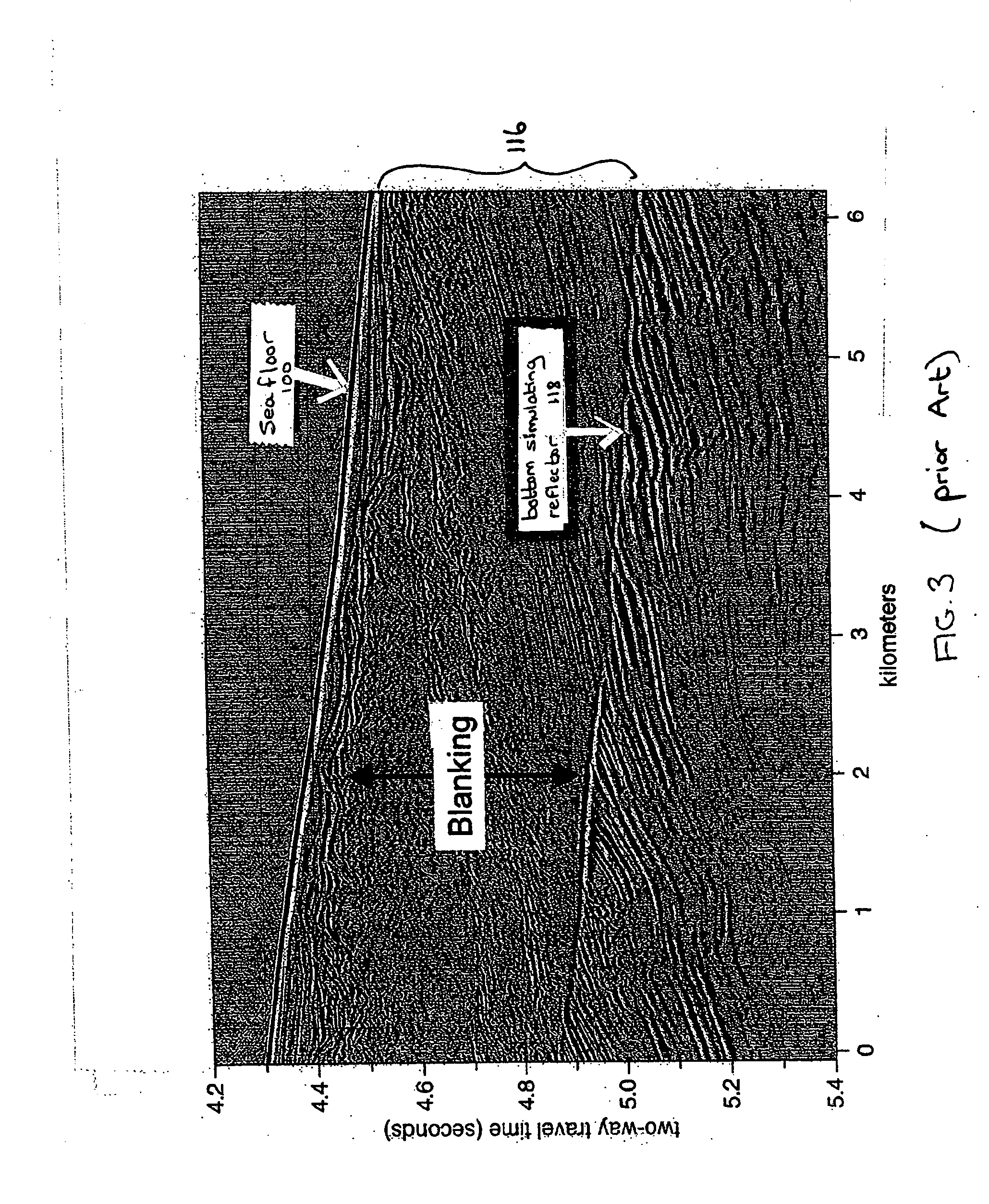
ActiveUS20070265782A1Reduce penetrationHigh porosityElectric/magnetic detection for well-loggingMaterial analysis using sonic/ultrasonic/infrasonic wavesGas hydrate stability zoneSeismic survey
An exploration paradigm for detecting and / or characterizing gas hydrate deposits using either electromagnetic or seismic surveys, that accounts for the possibility that gas hydrate may accumulate in vertical or subvertical dikes. Geologic factors, such as the presence of the gas hydrate stability zone, indications that a prolific source of gas exists (or existed) below the gas hydrate stability zone and indications that a high flux of gas could be transported into the gas hydrate stability zone, may be considered as part of an exploration strategy. Data may be collected using seismic techniques, such as a walk-away vertical seismic profile techniques, or electromagnetic surveys that are adapted to detecting the presence of vertical or subvertical dikes. In one example, data processing and acquisition techniques may be adapted to detect hydrate dikes, and do not assume a horizontally isotropic earth model.
Owner:SCHLUMBERGER TECH CORP
Workflow for processing streamer seismic data
A method includes conditioning a set of multicomponent seismic data and sensor orientation data, the multicomponent seismic data including pressure data and particle motion data, acquired in a towed array, marine seismic survey; digital group forming the conditioned pressure data, a vertical particle motion component of the conditioned particle motion data, and the conditioned sensor orientation data; and summing the digitally group formed pressure data and the digitally group formed vertical particle motion component.
Owner:WESTERNGECO LLC
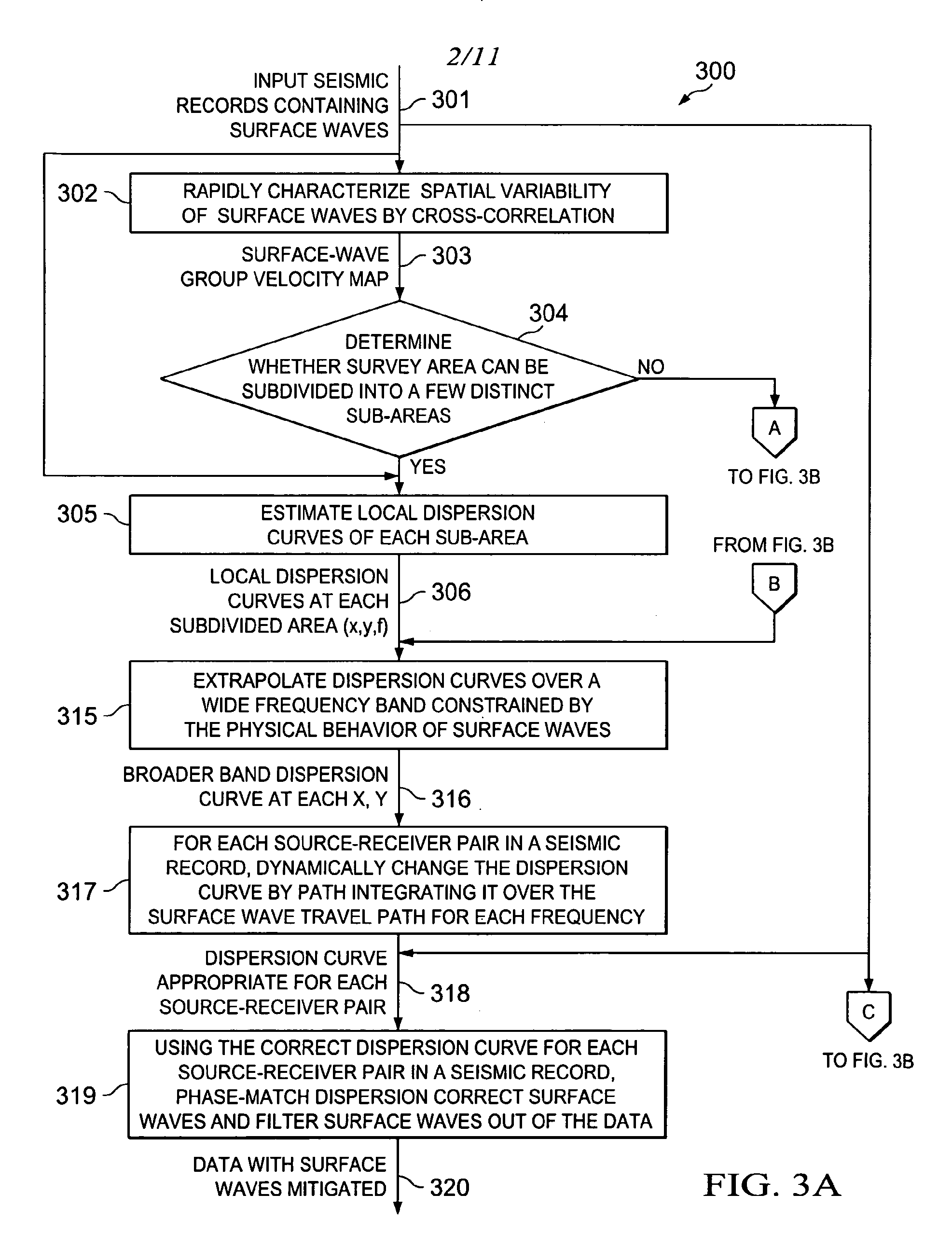
Characterizing Spatial Variability of Surface Waves In Seismic Processing
ActiveUS20100286919A1Seismic signal processingSpecial data processing applicationsSeismic surveySeismic processing
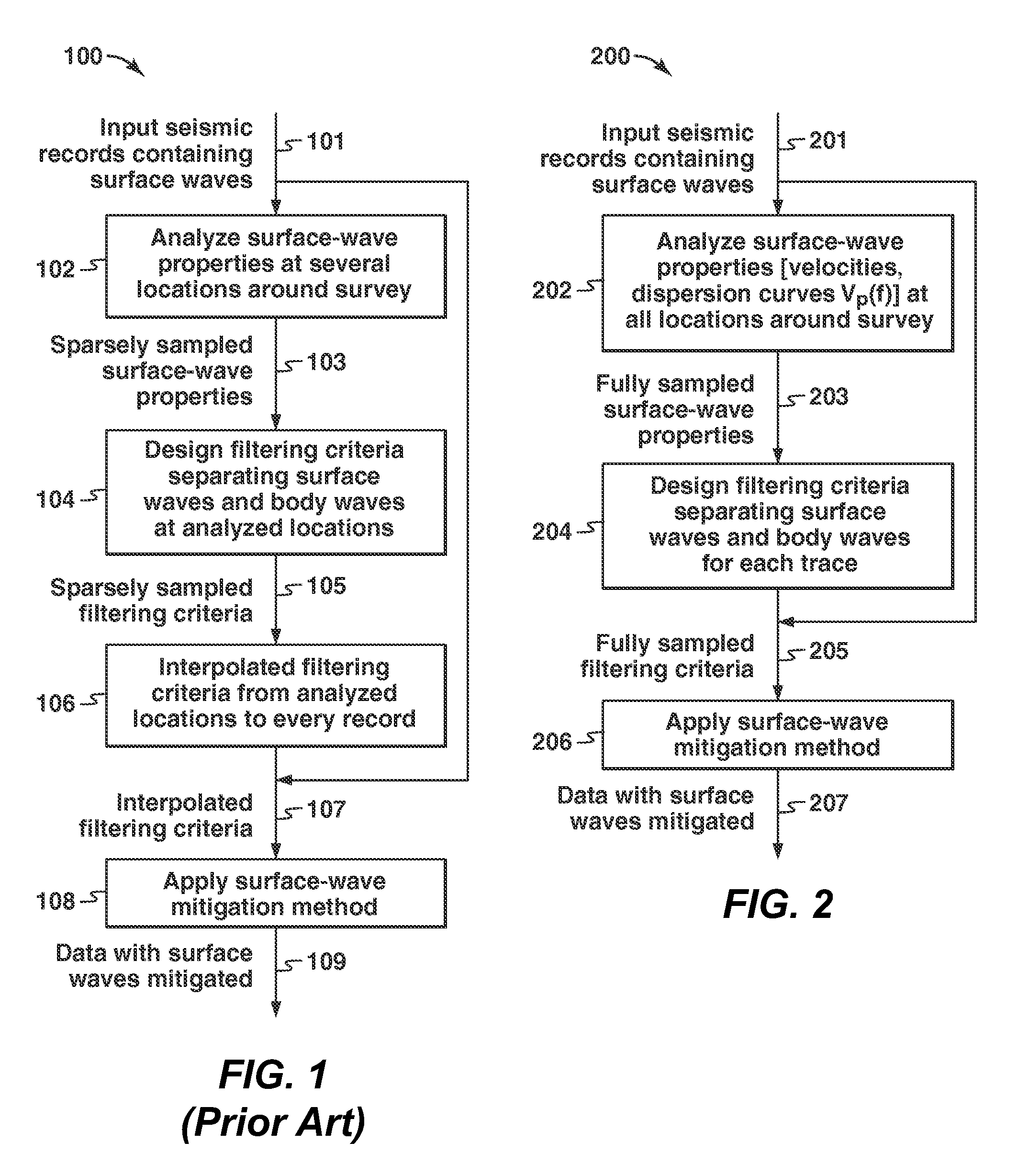
Embodiments use seismic processing methods that account for the spatial variability of surface wave velocities. Embodiments analyze surface wave properties by rapidly characterizing spatial variability of the surface waves in the seismic survey data (302). Filtering criteria are formed using the spatial variability of the surface waves (204). The filtering criteria can then be used to remove at least a portion of the surface waves from the seismic data (206, 319). The rapid characterization involves estimating a local group velocity of the surface waves by cross-correlation of the analytic signals (302).
Owner:EXXONMOBIL UPSTREAM RES CO
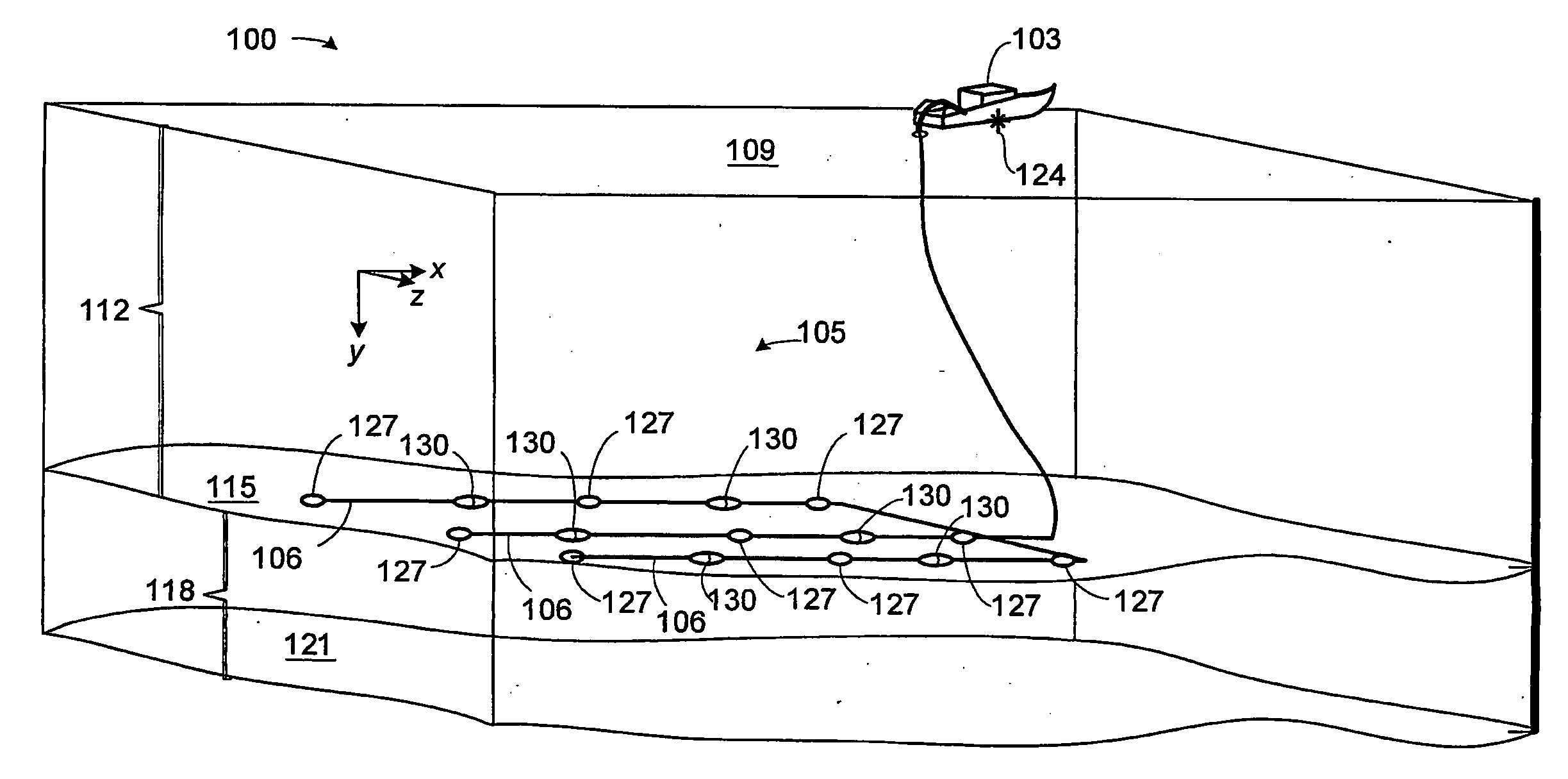
Acquiring azimuth rich seismic data in the marine environment using a regular sparse pattern of continuously curved sail lines
InactiveUS20090122640A1Well formedSeismic signal processingSeismology for water-covered areasRegular gridSeismic survey
A method for determining a sail plan for a towed-array marine seismic survey, includes: dividing a survey area into a regular grid of tiles; and identifying a subset of the tiles as nodes around which continuously curved sail lines are defined. The nodes define regular pattern further including: a first subpattern of nodes; and a second subpattern of nodes offset from the first subpattern. In alternative aspects, a computer-readable program storage medium may be encoded with instructions that, when executed by a processor, perform the method, or a computing apparatus may be programmed to perform the method. A method for conducting a towed array marine survey includes: traversing a plurality of continuously curved sail lines across a survey area, each sail line being relative to a node; and acquiring seismic data while traversing the continuously curved sail lines. The set of nodes defining a regular pattern further including: a first subpattern of nodes; and a second subpattern of nodes offset from the first subpattern.
Owner:REFLECTION MARINE NORGE AS
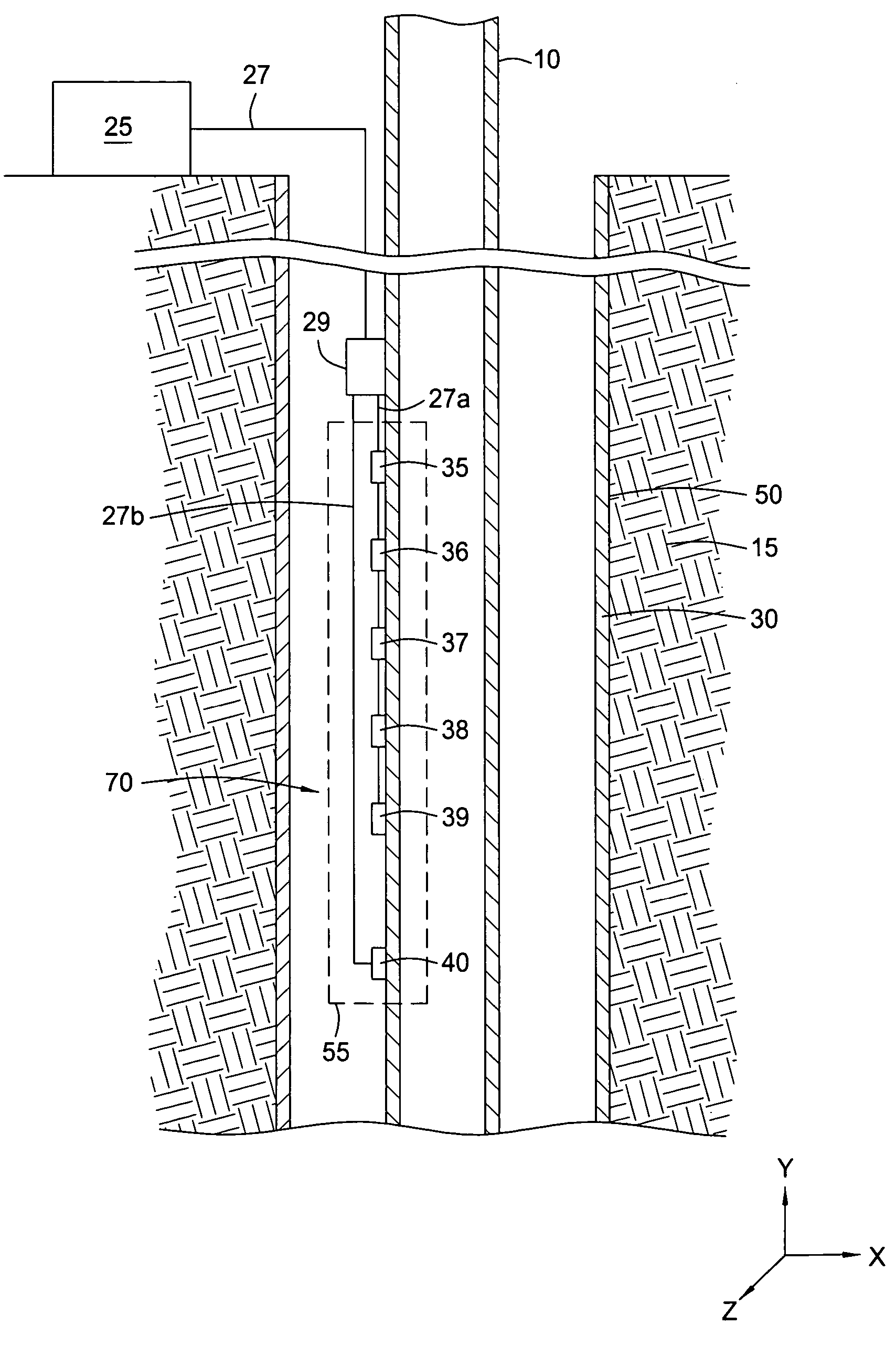
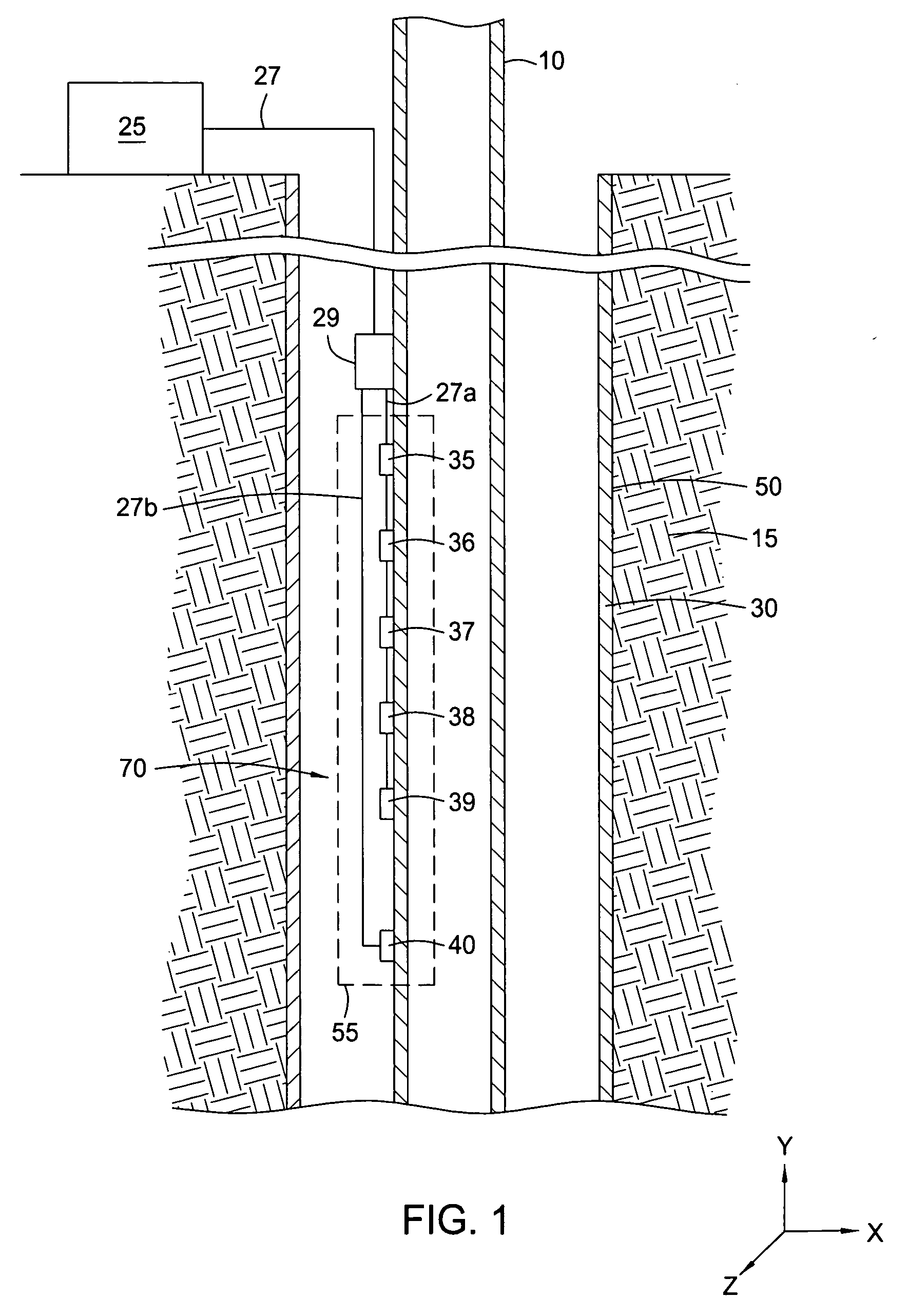
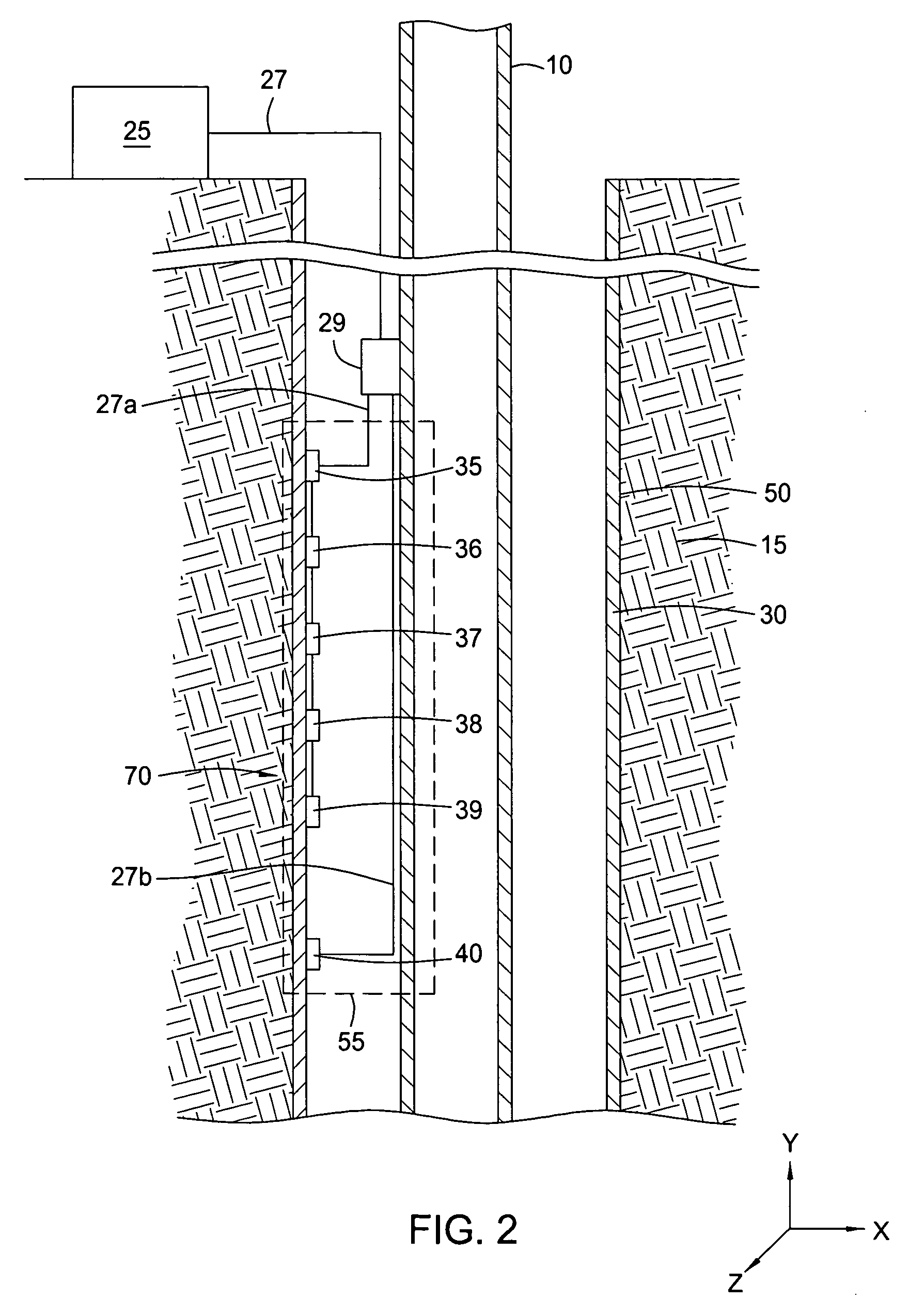
Permanently installed in-well fiber optic accelerometer-based seismic sensing apparatus and associated method
Embodiments of the present invention include a fiber optic seismic sensing system for permanent downhole installation. In one aspect, the present invention includes a multi-station, multi-component system for conducting seismic reservoir imaging and monitoring in a well. Permanent seismic surveys may be conducted with embodiments of the present invention, including time-lapse (4D) vertical seismic profiling (VSP) and extended micro-seismic monitoring. Embodiments of the present invention provide the ability to map fluid contacts in the reservoir using 4D VSP and to correlate micro-seismic events to gas injection and production activity.
Owner:WEATHERFORD TECH HLDG LLC
Seismic Cable Positioning Using Coupled Inertial System Units
InactiveUS20080253225A1Seismic signal receiversSeismology for water-covered areasSeismic surveyMeasurement device
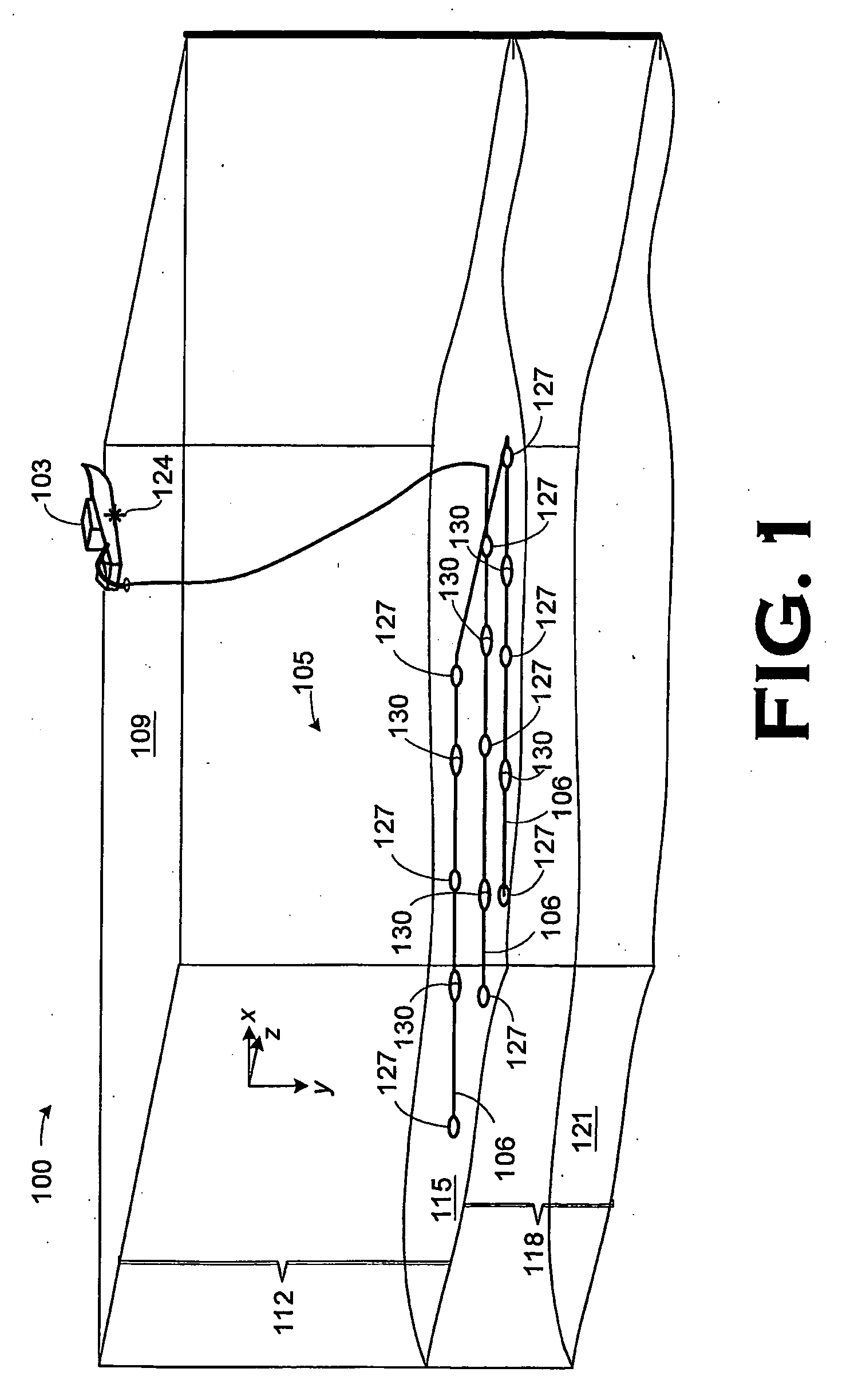
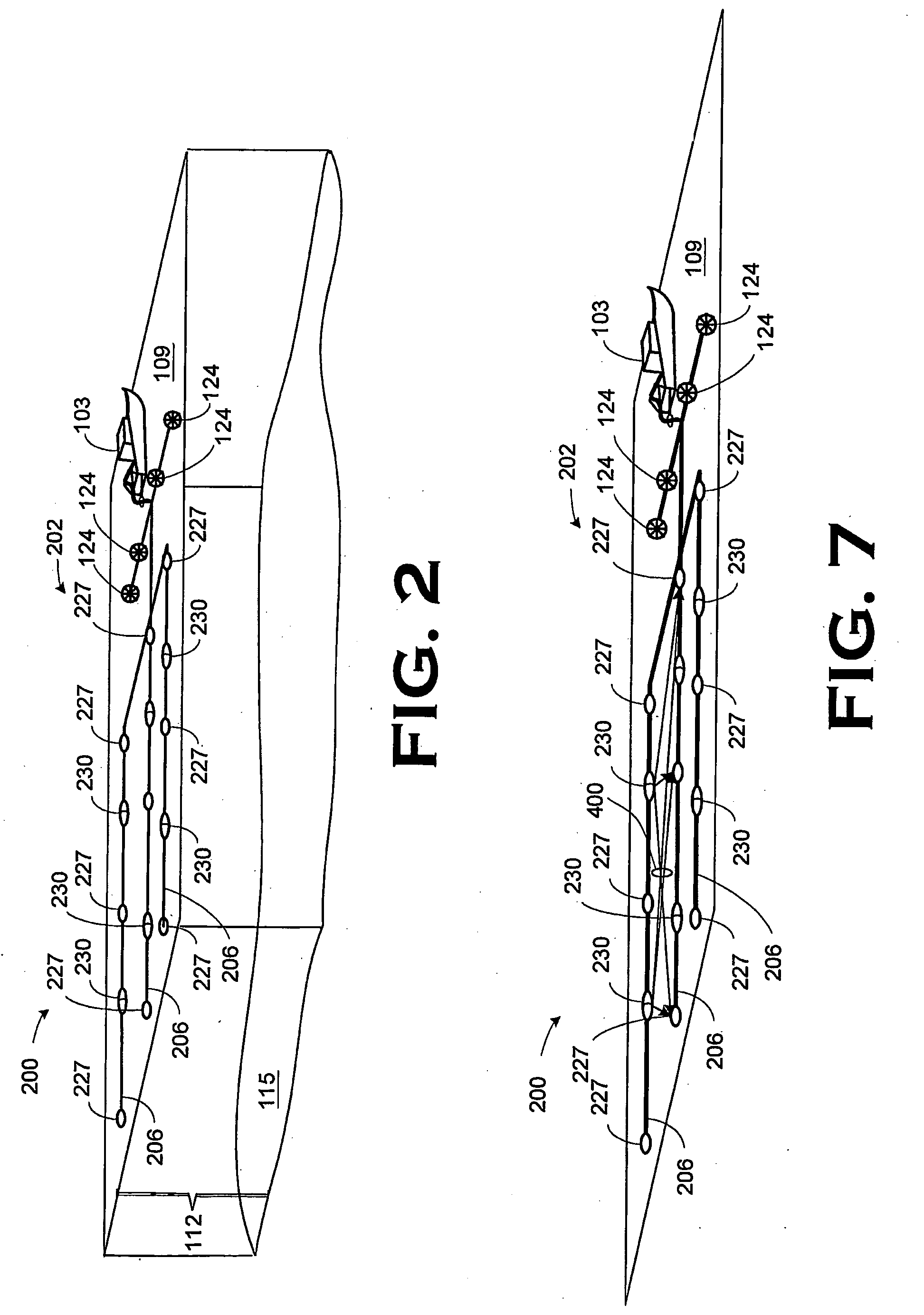
An apparatus and a method of its use in a marine seismic survey are disclosed. The apparatus includes a seismic survey object (106) and an inertial measurement device (130) coupled to the seismic survey object (106). The method includes taking inertial measurements of the movement of selected points on a seismic spread relative to at least one known point, and applying the inertial measurements to the known point to determine the positions of the selected points.
Owner:WESTERNGECO LLC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com