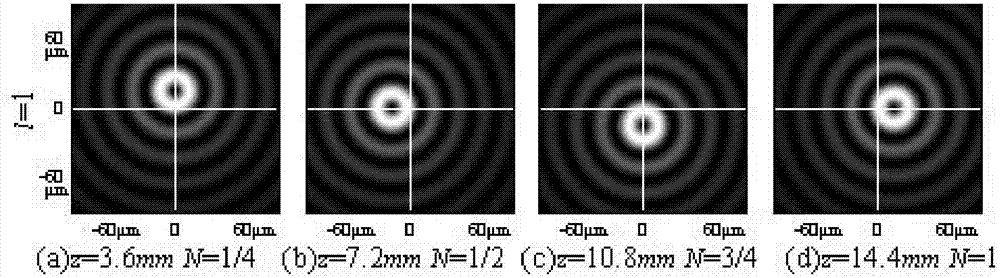
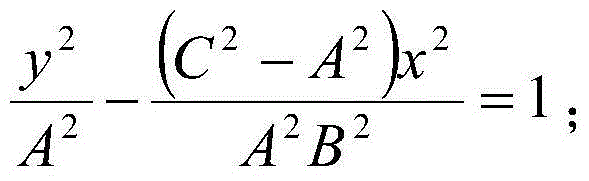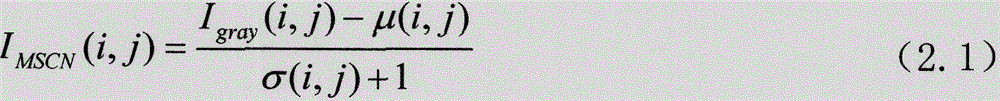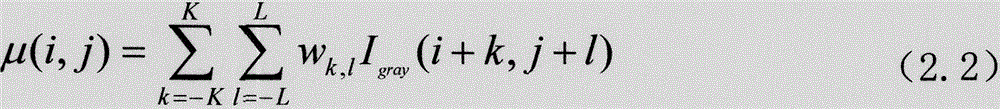Patents
Literature
724 results about "Gaussian beam" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
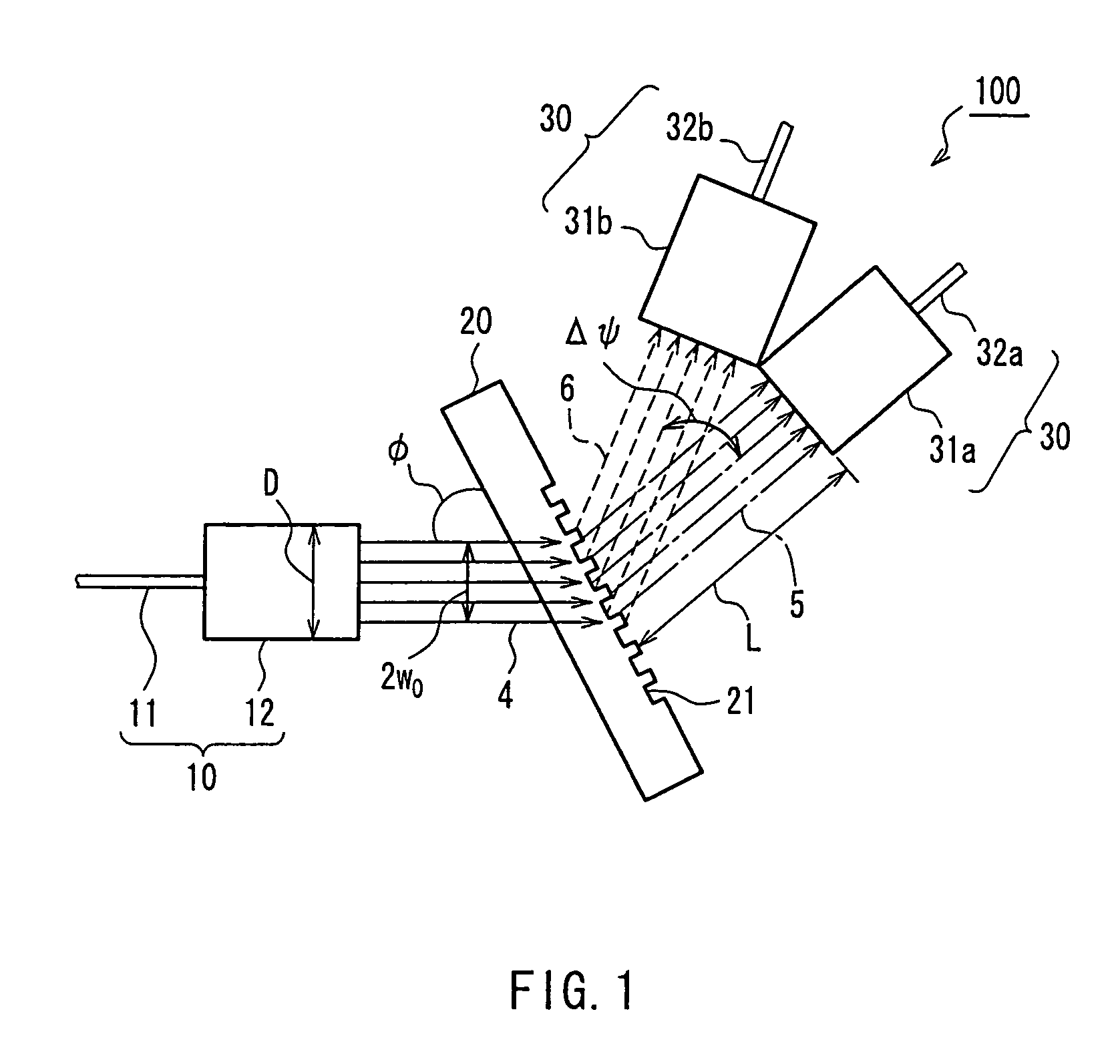
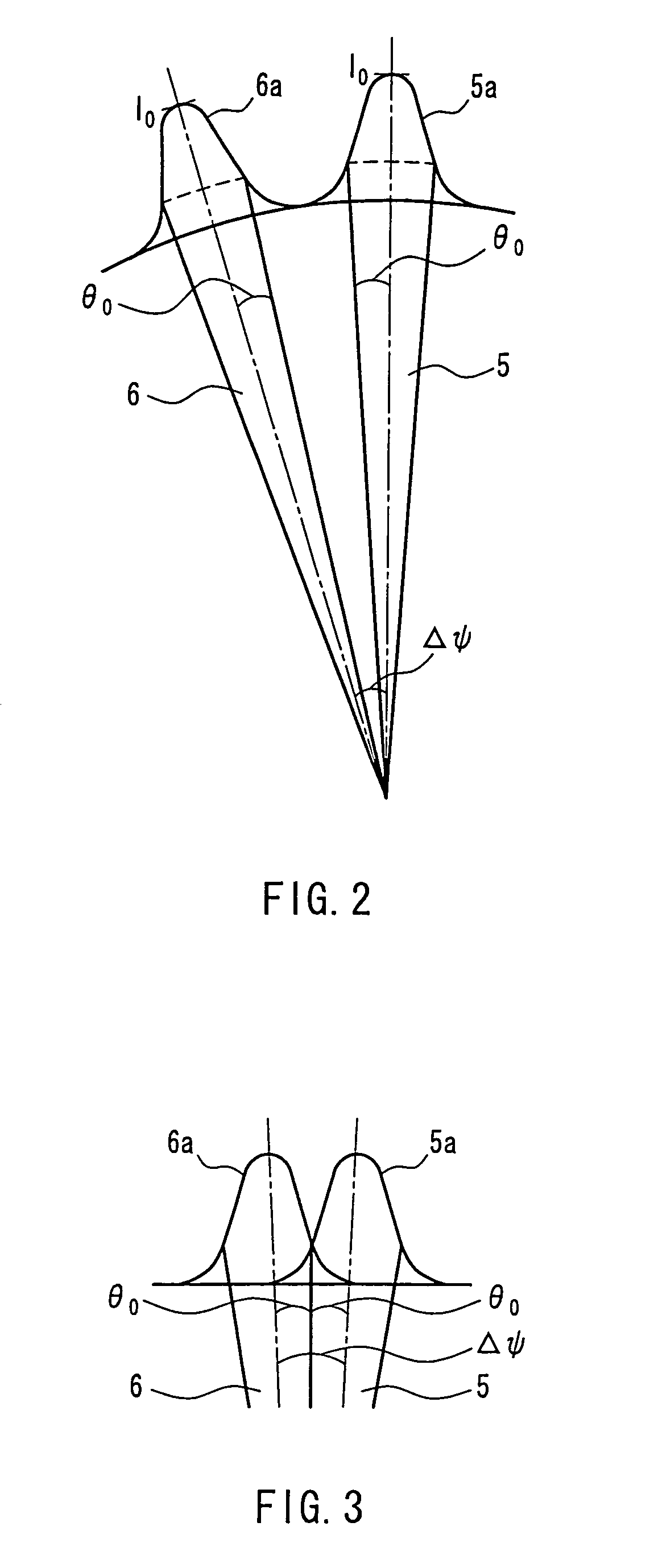
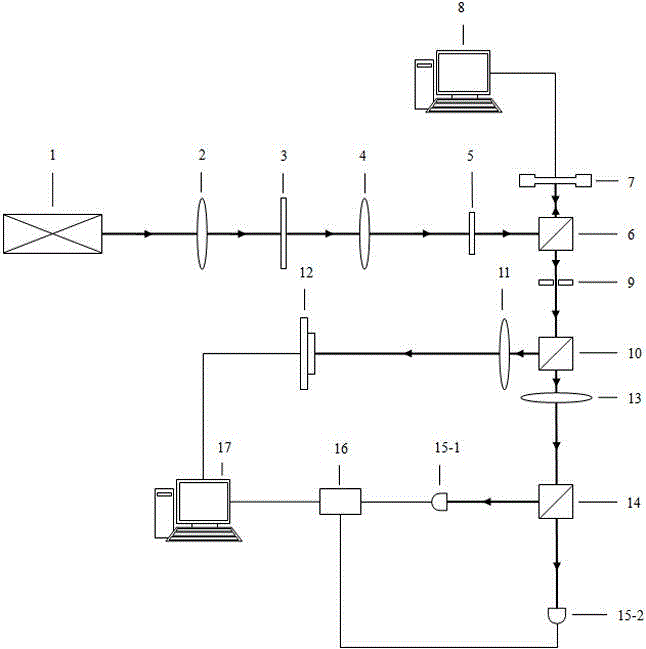
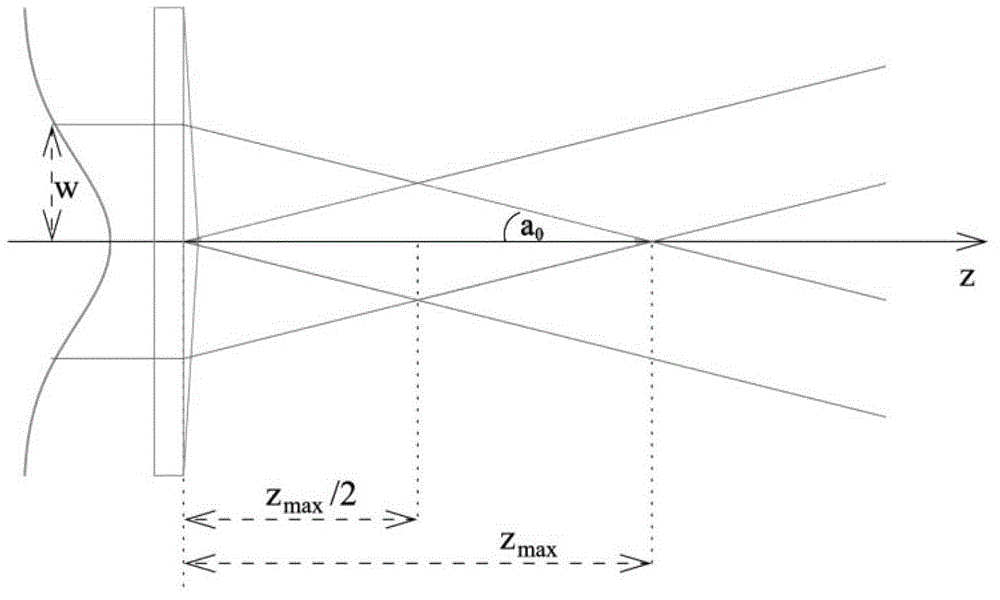
In optics, a Gaussian beam is a beam of monochromatic electromagnetic radiation whose transverse magnetic and electric field amplitude profiles are given by the Gaussian function; this also implies a Gaussian intensity (irradiance) profile. This fundamental (or TEM₀₀) transverse gaussian mode describes the intended output of most (but not all) lasers, as such a beam can be focused into the most concentrated spot. When such a beam is refocused by a lens, the transverse phase dependence is altered; this results in a different Gaussian beam. The electric and magnetic field amplitude profiles along any such circular Gaussian beam (for a given wavelength and polarization) are determined by a single parameter: the so-called waist w₀. At any position z relative to the waist (focus) along a beam having a specified w₀, the field amplitudes and phases are thereby determined as detailed below.
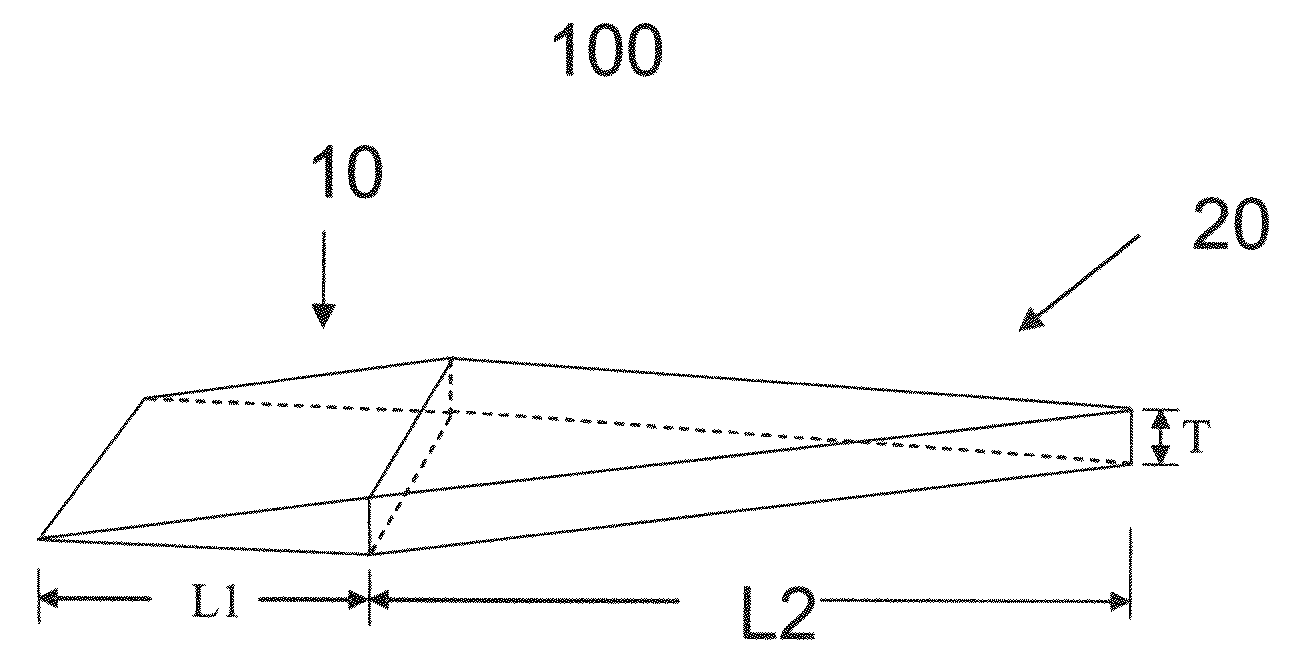
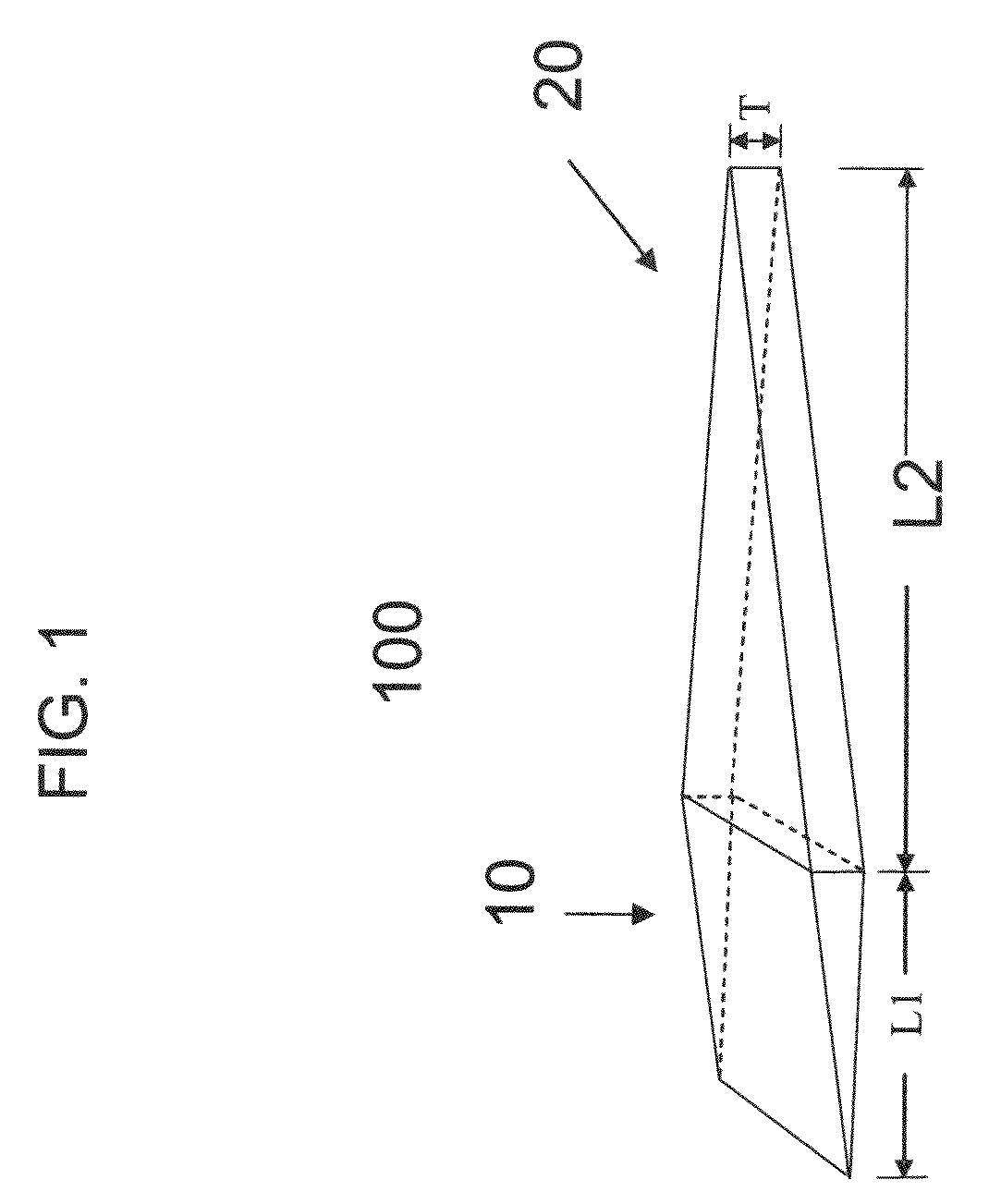
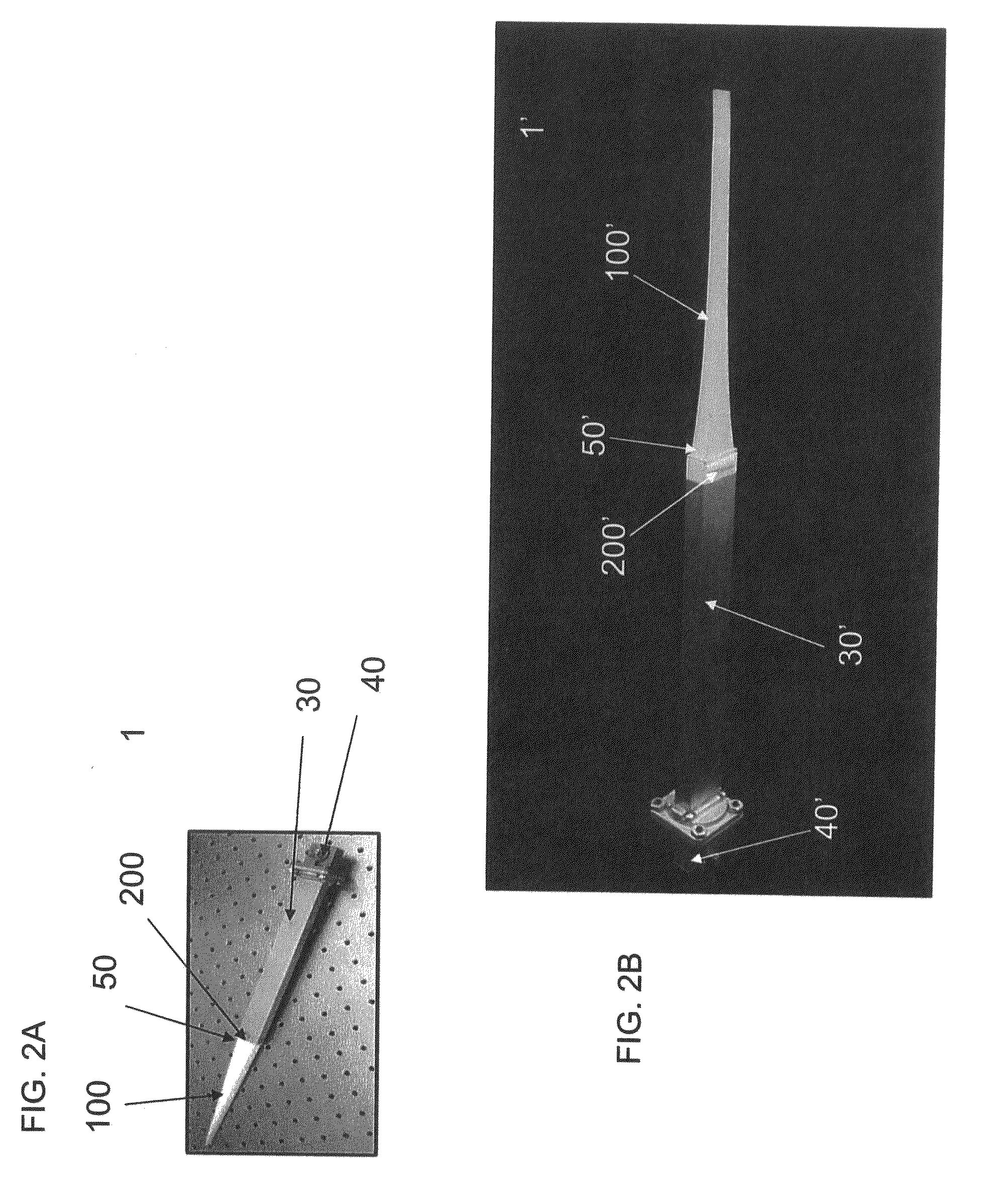
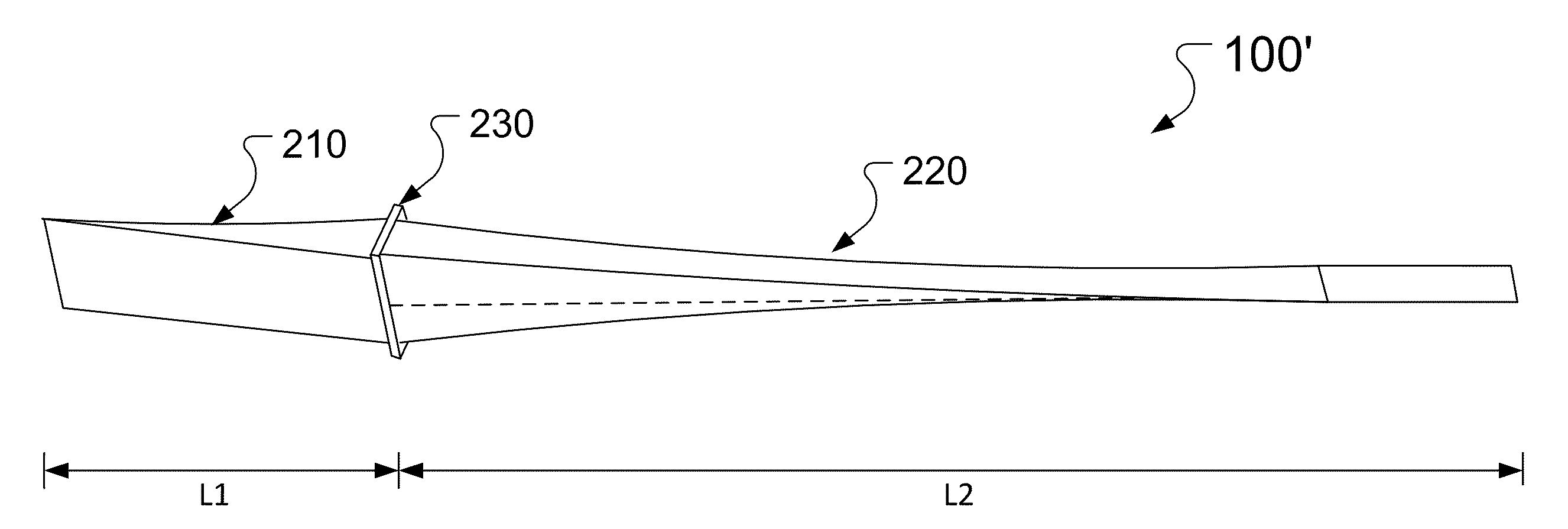
Aperture matched polyrod antenna
InactiveUS20080252541A1Minimizes and reduces end reflection and phase variationMinimizing and reducing diameterAdditive manufacturing apparatusWaveguide type devicesGaussian beamLight beam
A dielectric polyrod having at least one tapered section, where a section exposed outside of the waveguide is tapered a long a curve that depends on the dielectric constant of the material used. The invention also relates to an aperture matched polyrod antenna which includes the same and an inductive tuning element used to achieve wideband impedance match and to create a Gaussian beam in the radiating near field of the antenna, suitable to mimic a small region plane wave.
Owner:ARIZONA STATE UNIVERSITY
Aperture matched polyrod antenna
InactiveUS7889149B2Minimizes and reduces end reflection and phase variationMinimizing and reducing diameterAdditive manufacturing apparatusCoupling devicesGaussian beamLight beam
A dielectric polyrod having at least one tapered section, where a section exposed outside of the waveguide is tapered a long a curve that depends on the dielectric constant of the material used. The invention also relates to an aperture matched polyrod antenna which includes the same and an inductive tuning element used to achieve wideband impedance match and to create a Gaussian beam in the radiating near field of the antenna, suitable to mimic a small region plane wave.
Owner:ARIZONA STATE UNIVERSITY
Compact broad-band admittance tunnel incorporating gaussian beam antennas
Owner:ARIZONA STATE UNIVERSITY
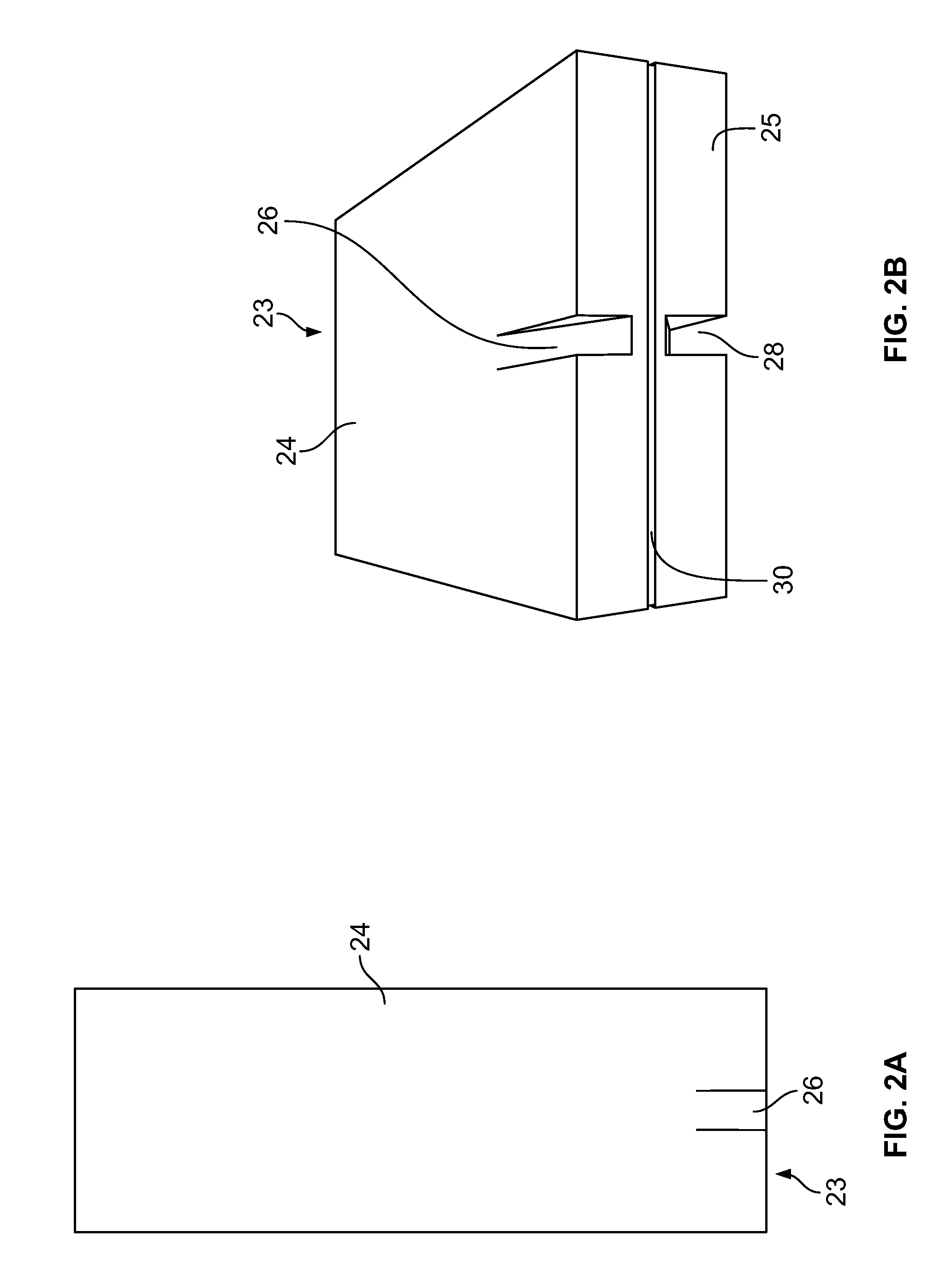
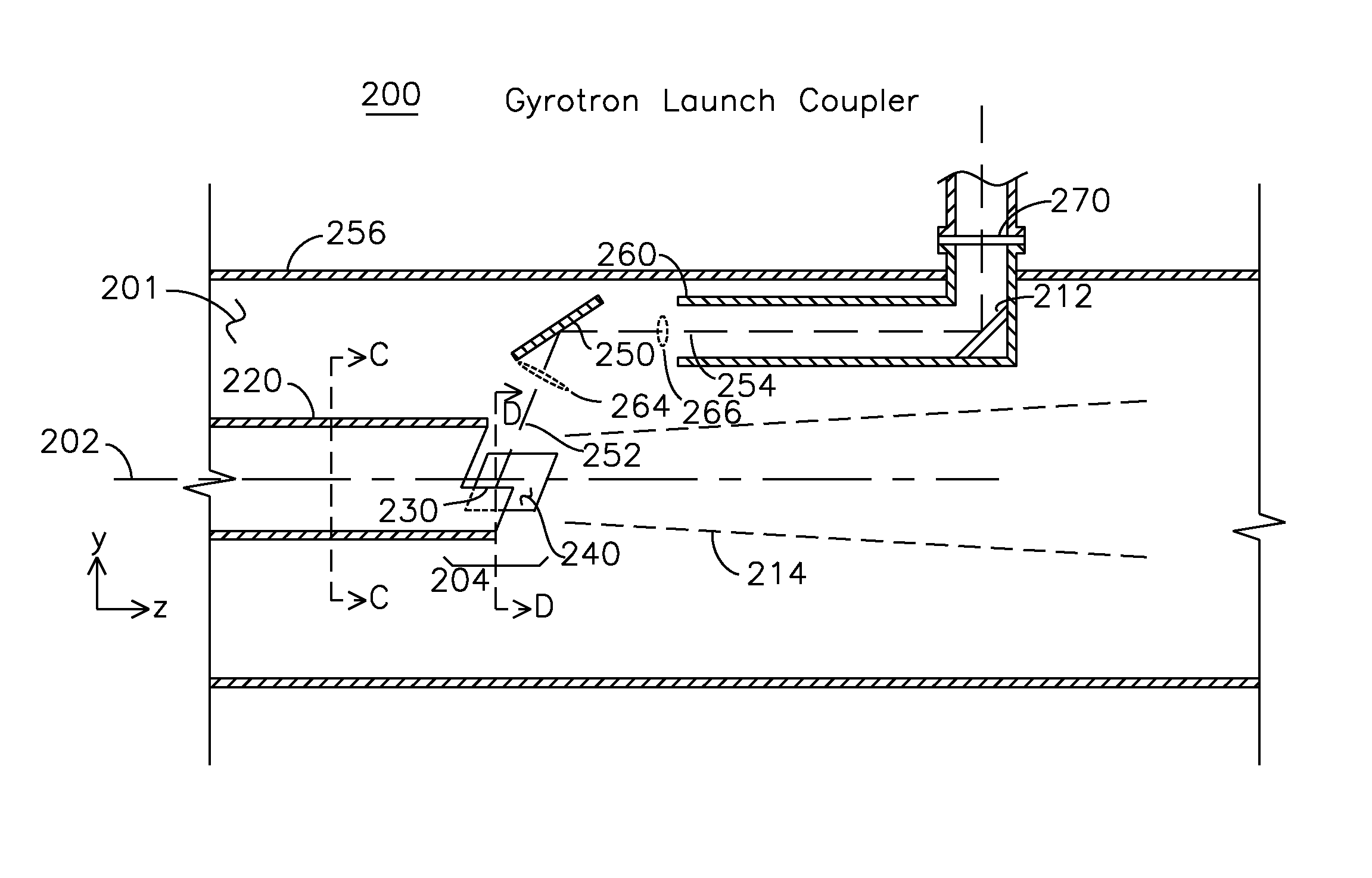
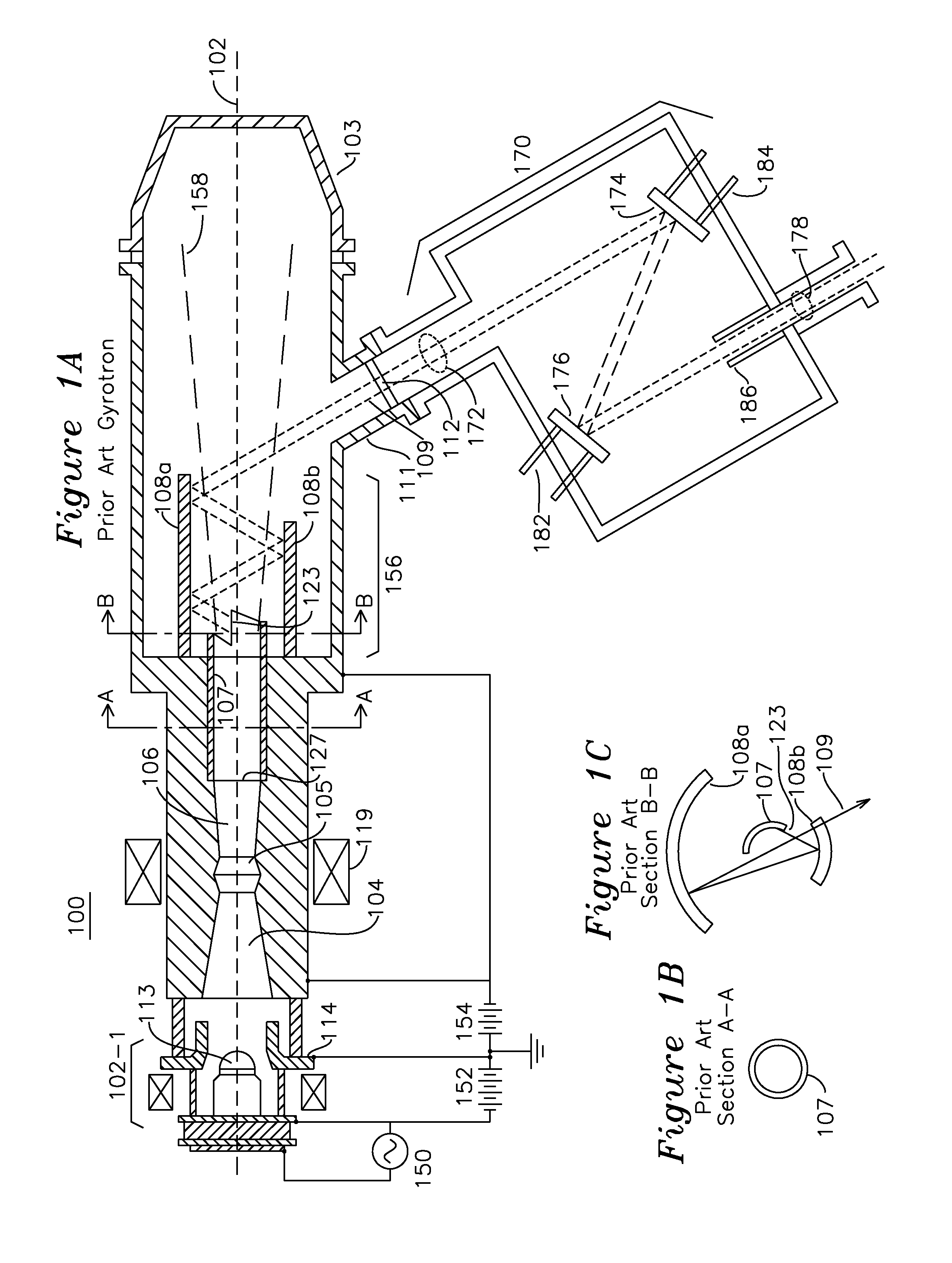
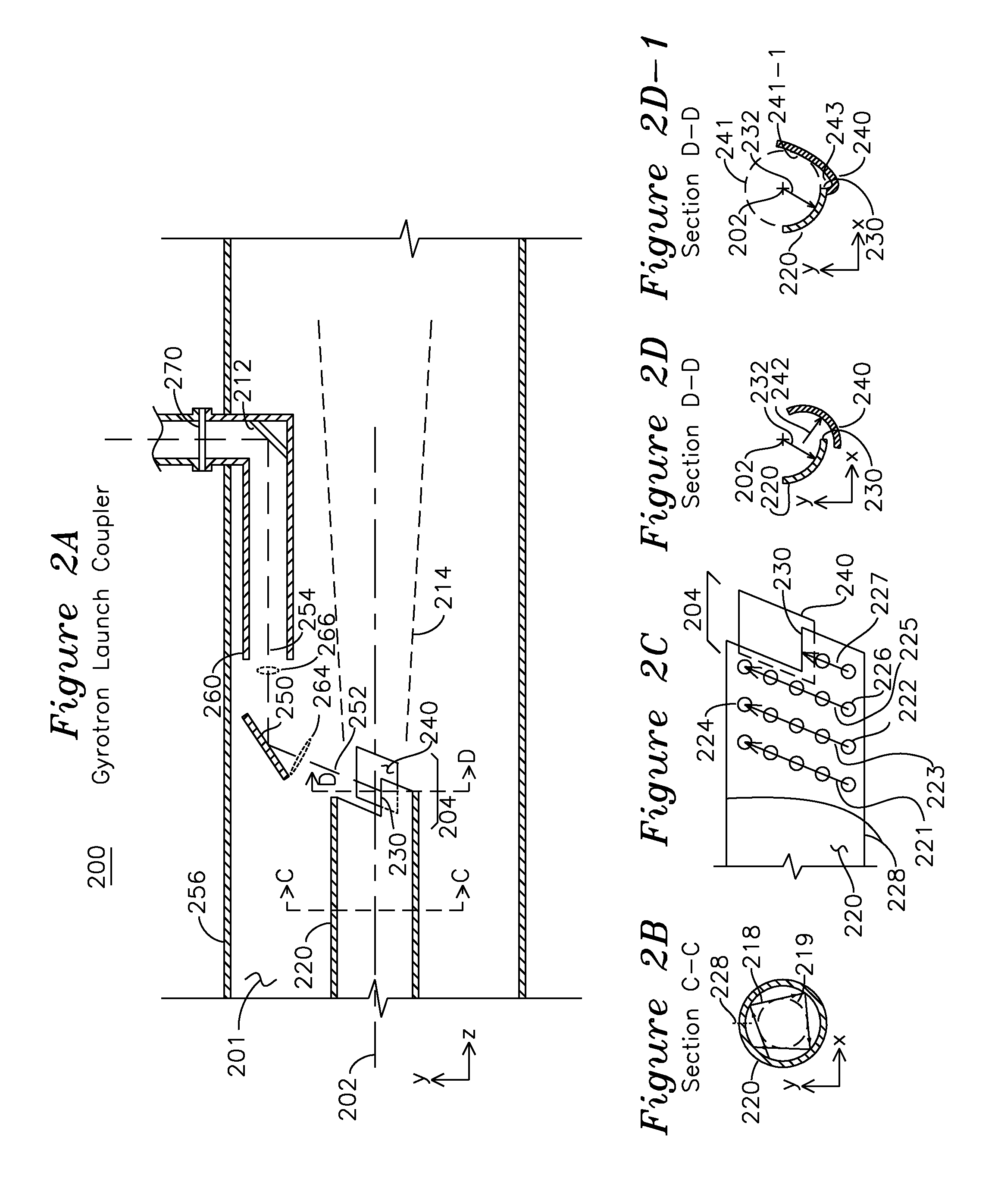
Coupler for coupling gyrotron whispering gallery mode RF into HE11 waveguide
ActiveUS8963424B1Increase generationEfficient couplingTubes with helical electron streamCoupling devicesGaussian beamWhispering gallery
A cylindrical waveguide with a mode converter transforms a whispering gallery mode from a gyrotron cylindrical waveguide with a helical cut launch edge to a quasi-Gaussian beam suitable for conveyance through a corrugated waveguide. This quasi-Gaussian beam is radiated away from the waveguide using a spiral cut launch edge, which is in close proximity to a first mode converting reflector. The first mode converting reflector is coupled to a second mode converting reflector which provides an output free-space HE11 mode wave suitable for direct coupling into a corrugated waveguide. The radiated beam produced at the output of the second mode converting reflector is substantially circular.
Owner:CALABAZAS CREEK RES
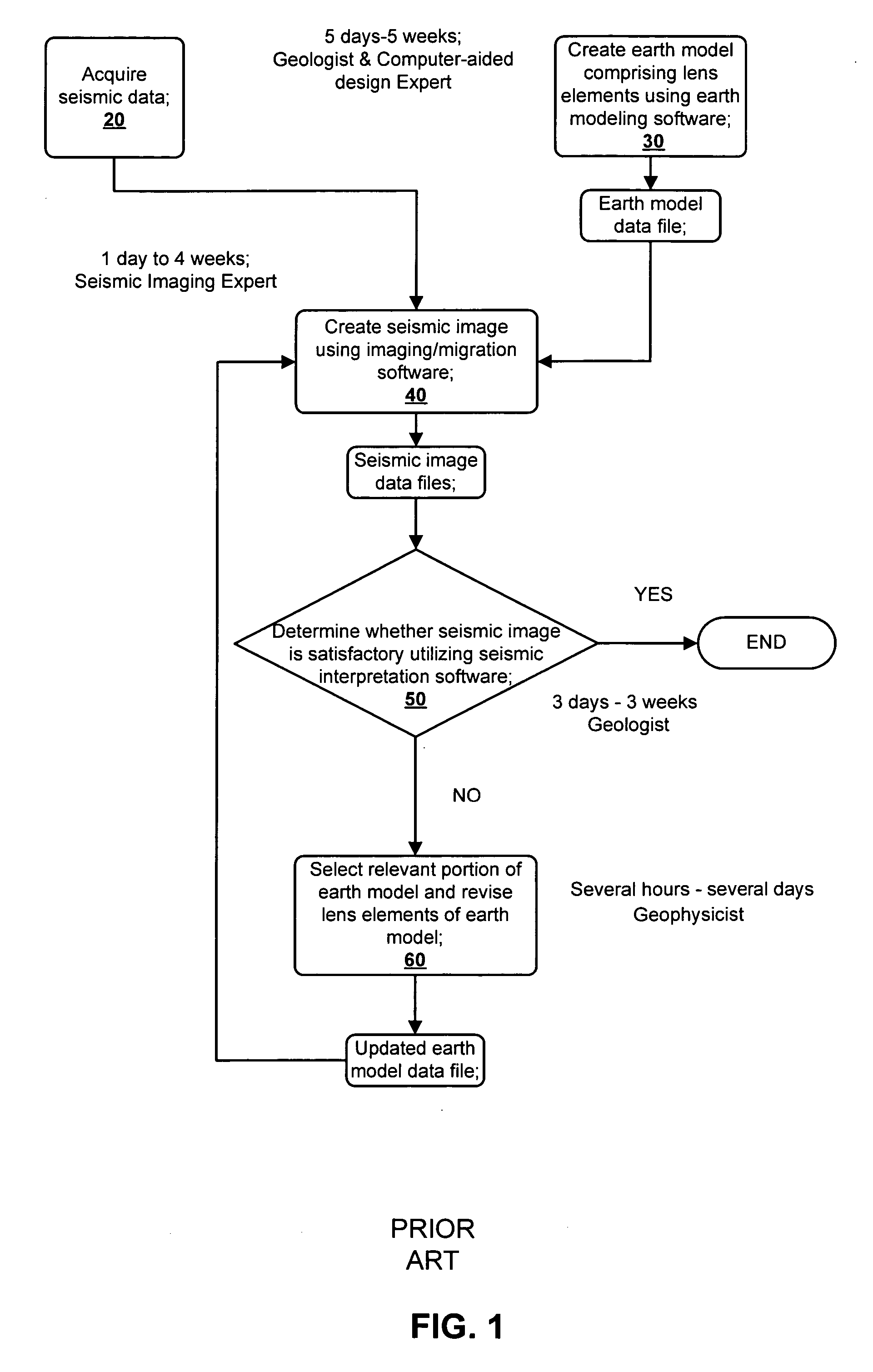
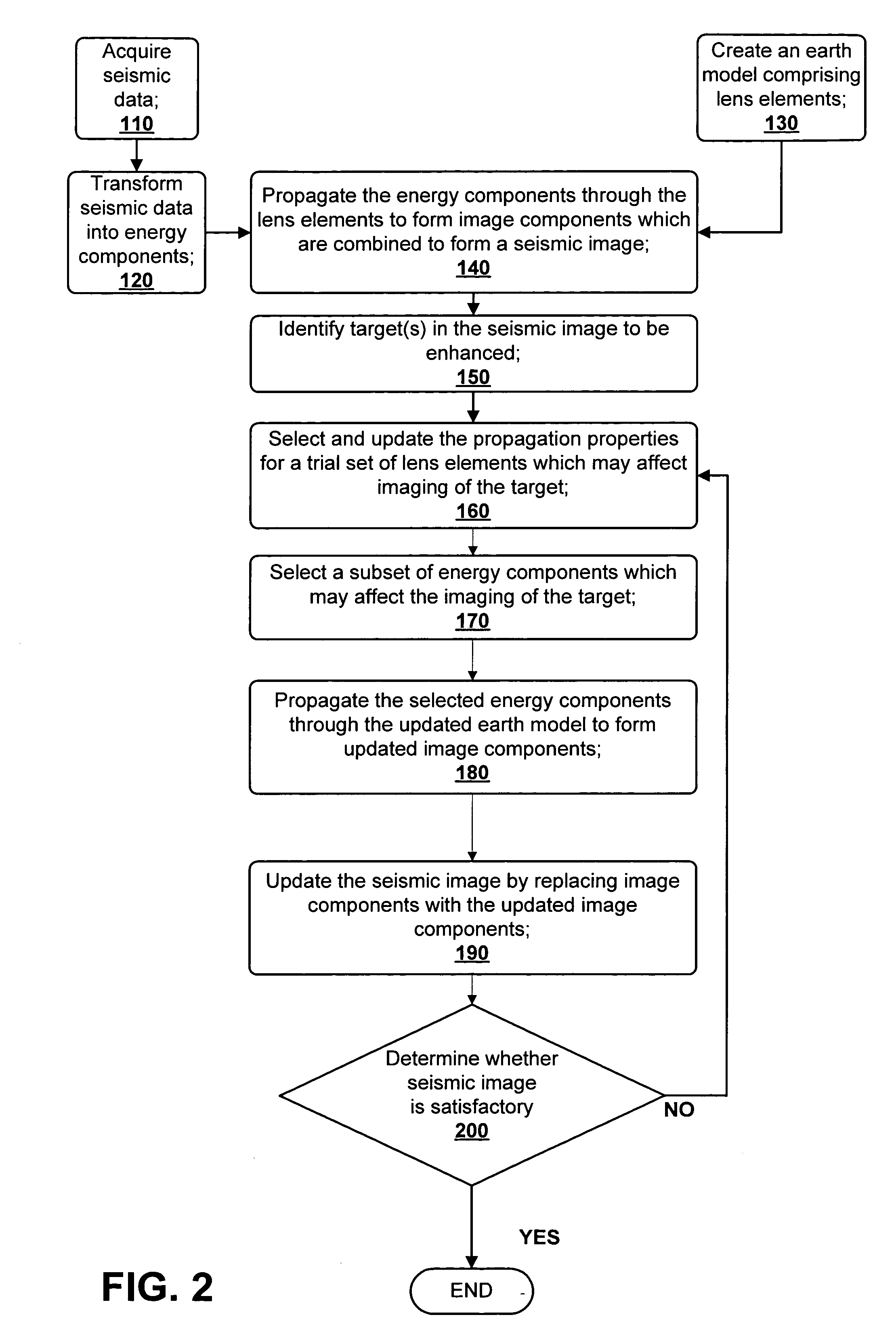
Methods for earth modeling and seismic imaging using interactive and selective updating
ActiveUS7480206B2Quality improvementEnhance the imageSeismic signal processingSeismic surveyGaussian beam
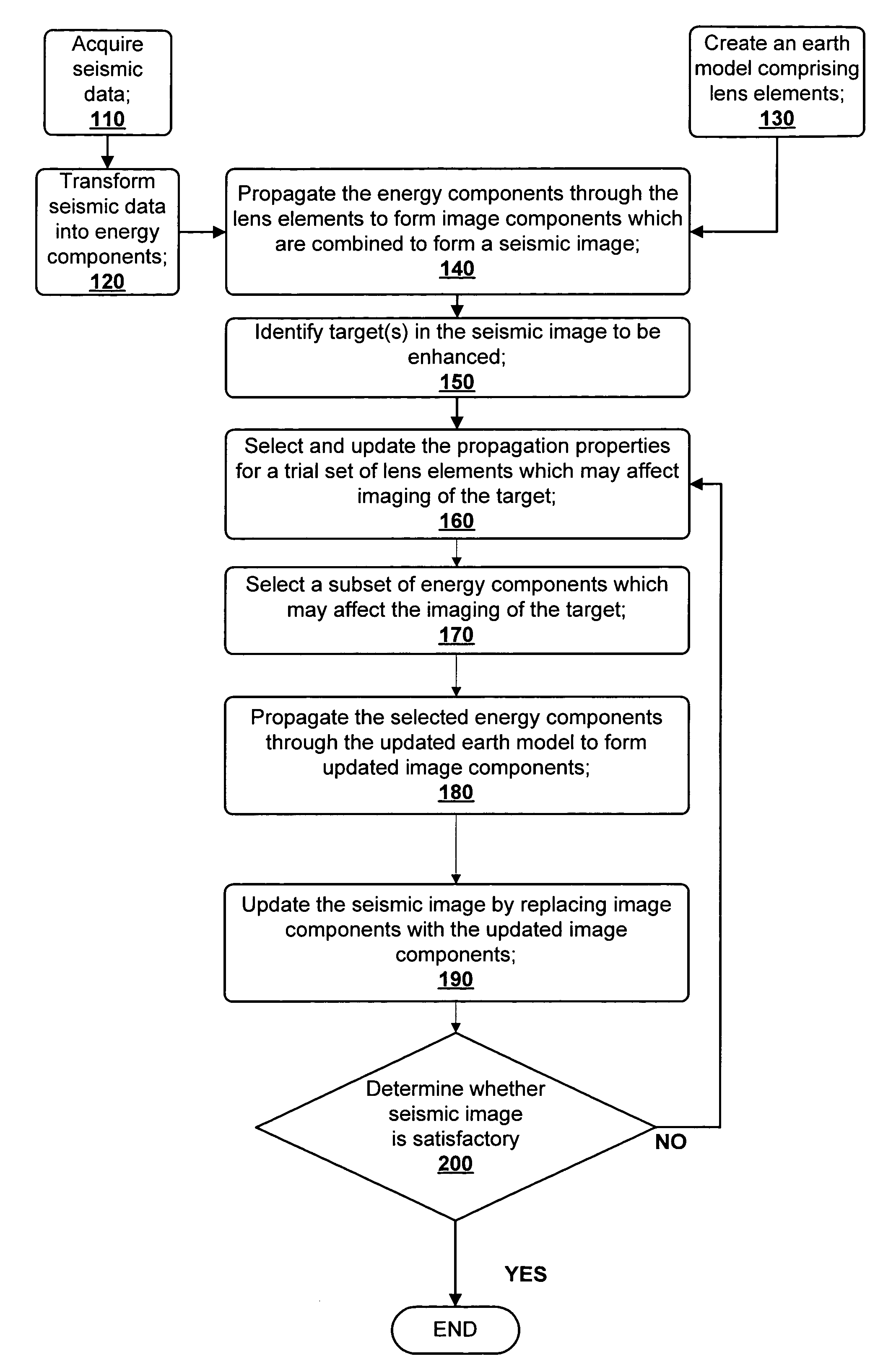
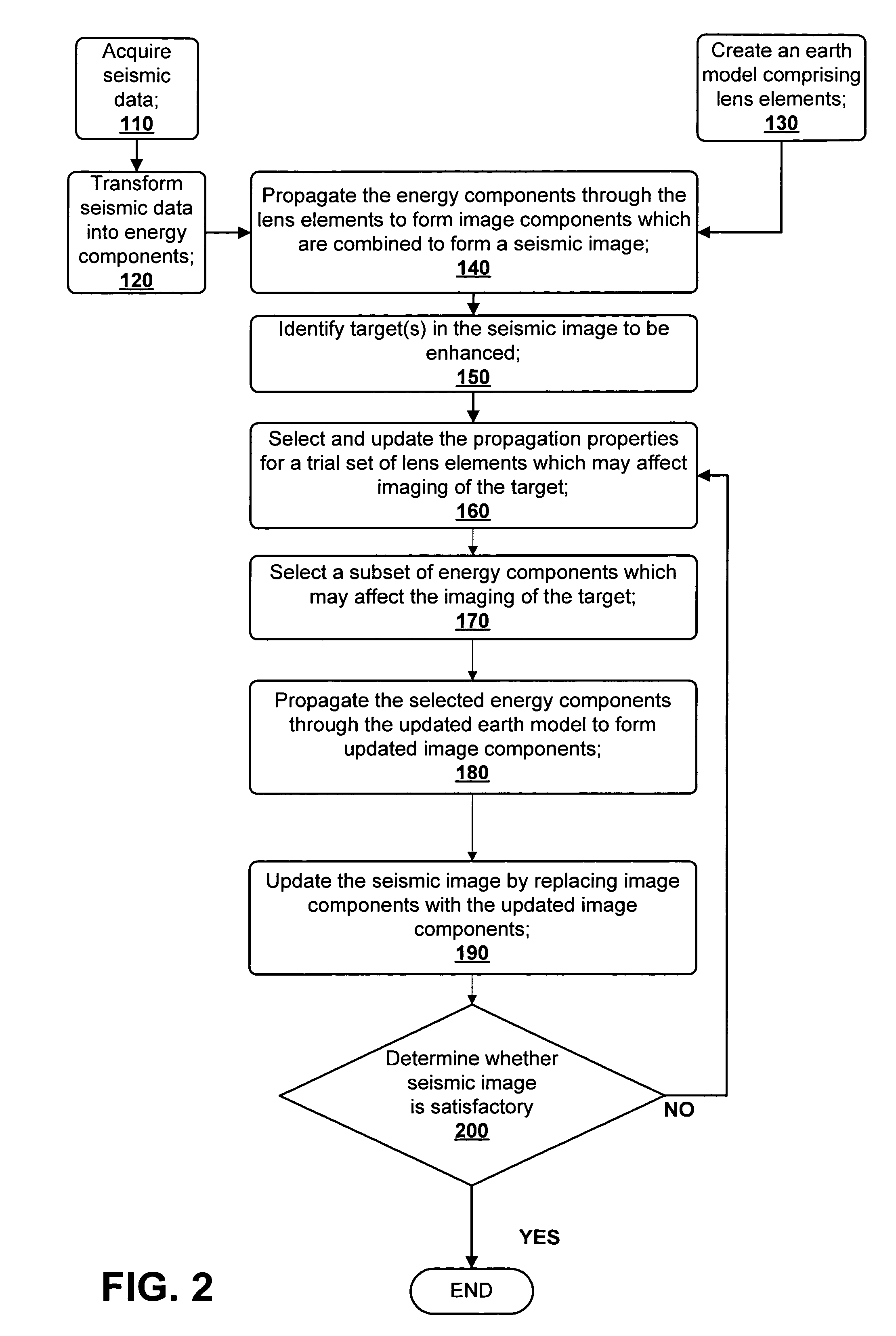
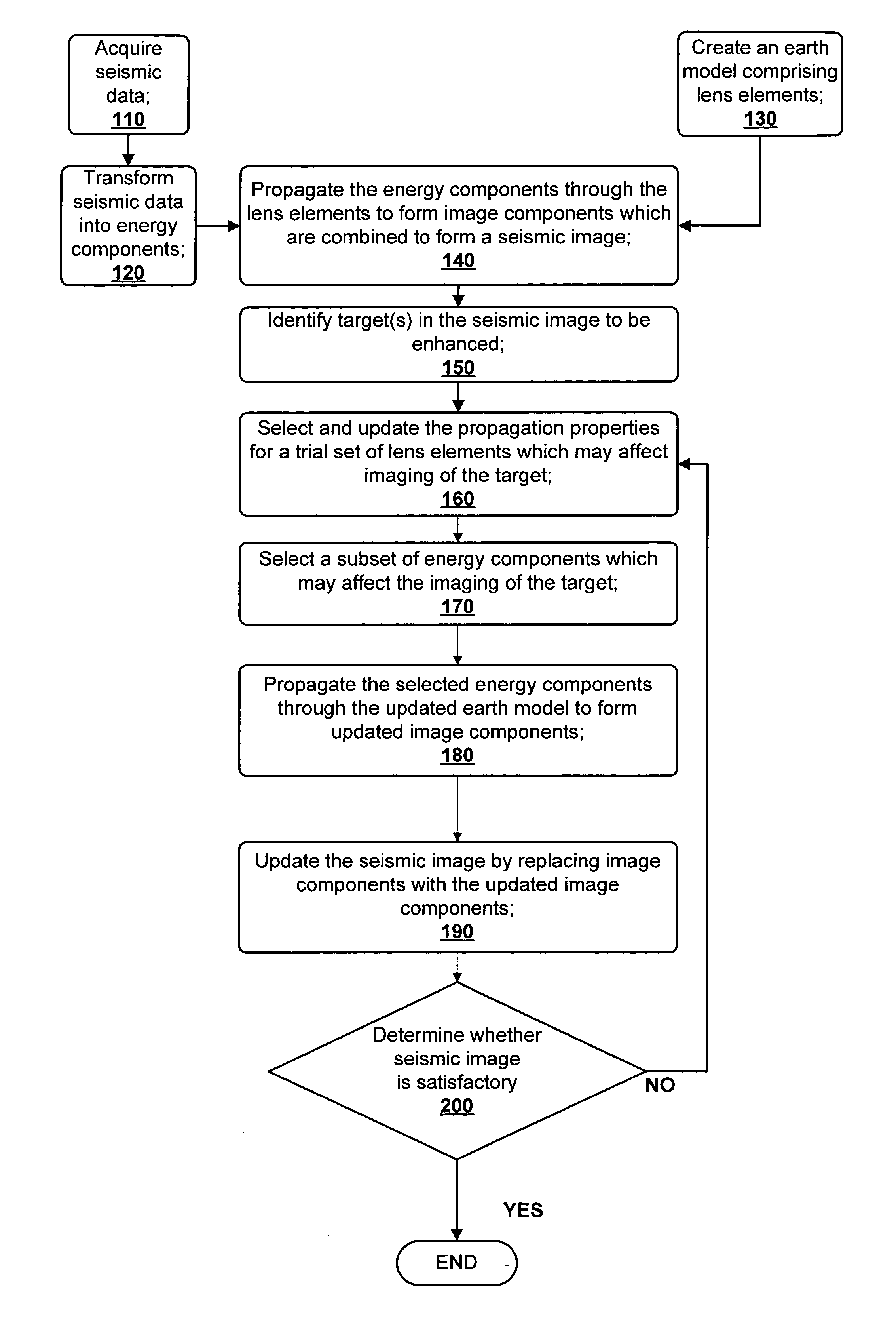
A method for creating an enhanced seismic image is described. Seismic data is acquired from a seismic survey conducted over a subterranean region. The seismic data is transformed into energy components, preferably Gaussian beam components. An earth model is created which is comprised of lens elements. The set of energy components is propagated or migrated through the lens elements to form image components which are combined into a seismic image. A target is identified in the seismic image for image enhancement. Ray tracing may be used to select the trial set of lens elements to be updated and to select a subset of energy components. The subset of energy components is propagated through updated earth model to form updated image components. The seismic image is updated by replacing image components with updated image components which are formed from the subset of selected energy components. This subset is ideally greatly reduced in size relative to the overall number of energy components, i.e., beam components.
Owner:CHEVROU USA INC
Methods for earth modeling and seismic imaging using interactive and selective updating
ActiveUS20060056272A1Quality improvementEnhance the imageSeismic signal processingGaussian beamSeismic survey
A method for creating an enhanced seismic image is described. Seismic data is acquired from a seismic survey conducted over a subterranean region. The seismic data is transformed into energy components, preferably Gaussian beam components. An earth model is created which is comprised of lens elements. The set of energy components is propagated or migrated through the lens elements to form image components which are combined into a seismic image. A target is identified in the seismic image for image enhancement. Ray tracing may be used to select the trial set of lens elements to be updated and to select a subset of energy components. The subset of energy components is propagated through updated earth model to form updated image components. The seismic image is updated by replacing image components with updated image components which are formed from the subset of selected energy components. This subset is ideally greatly reduced in size relative to the overall number of energy components, i.e., beam components.
Owner:CHEVROU USA INC
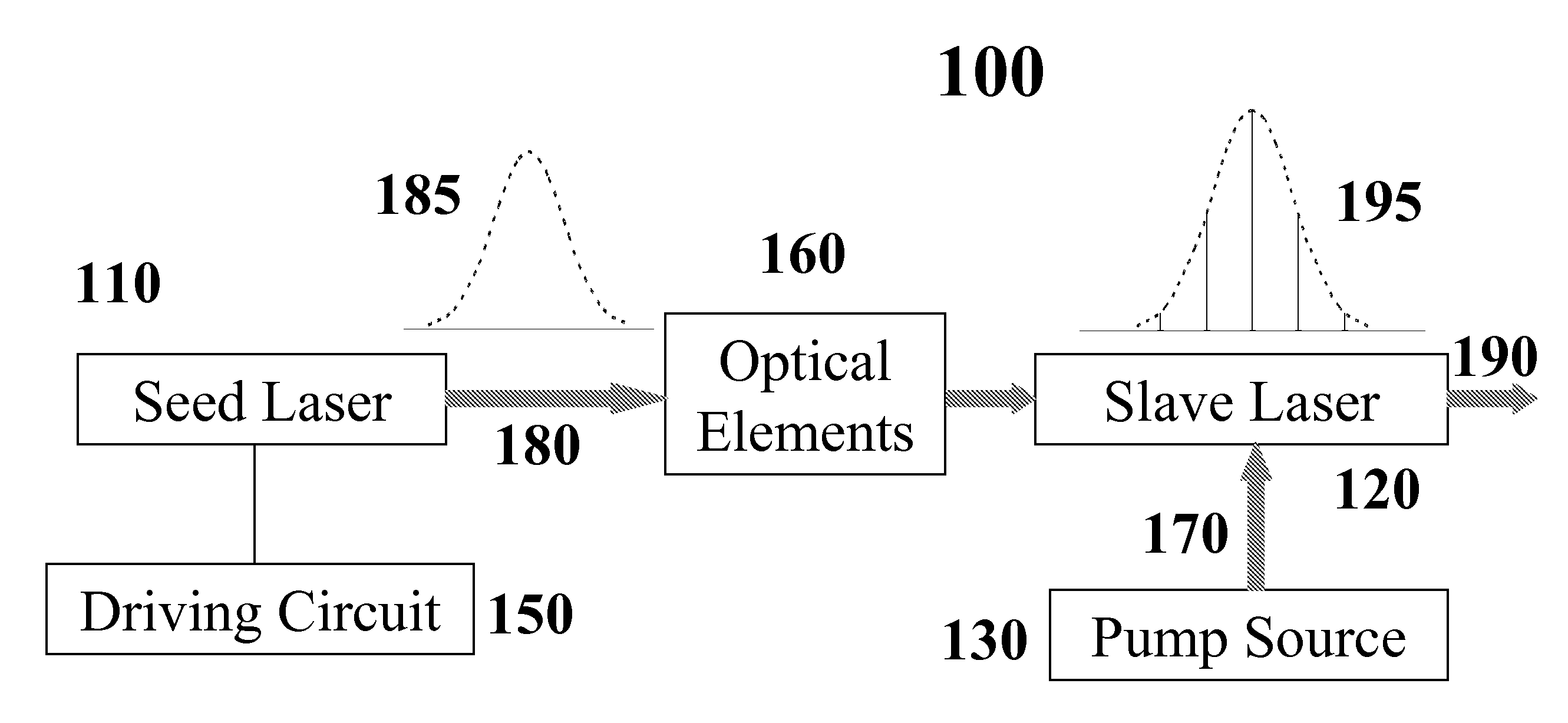
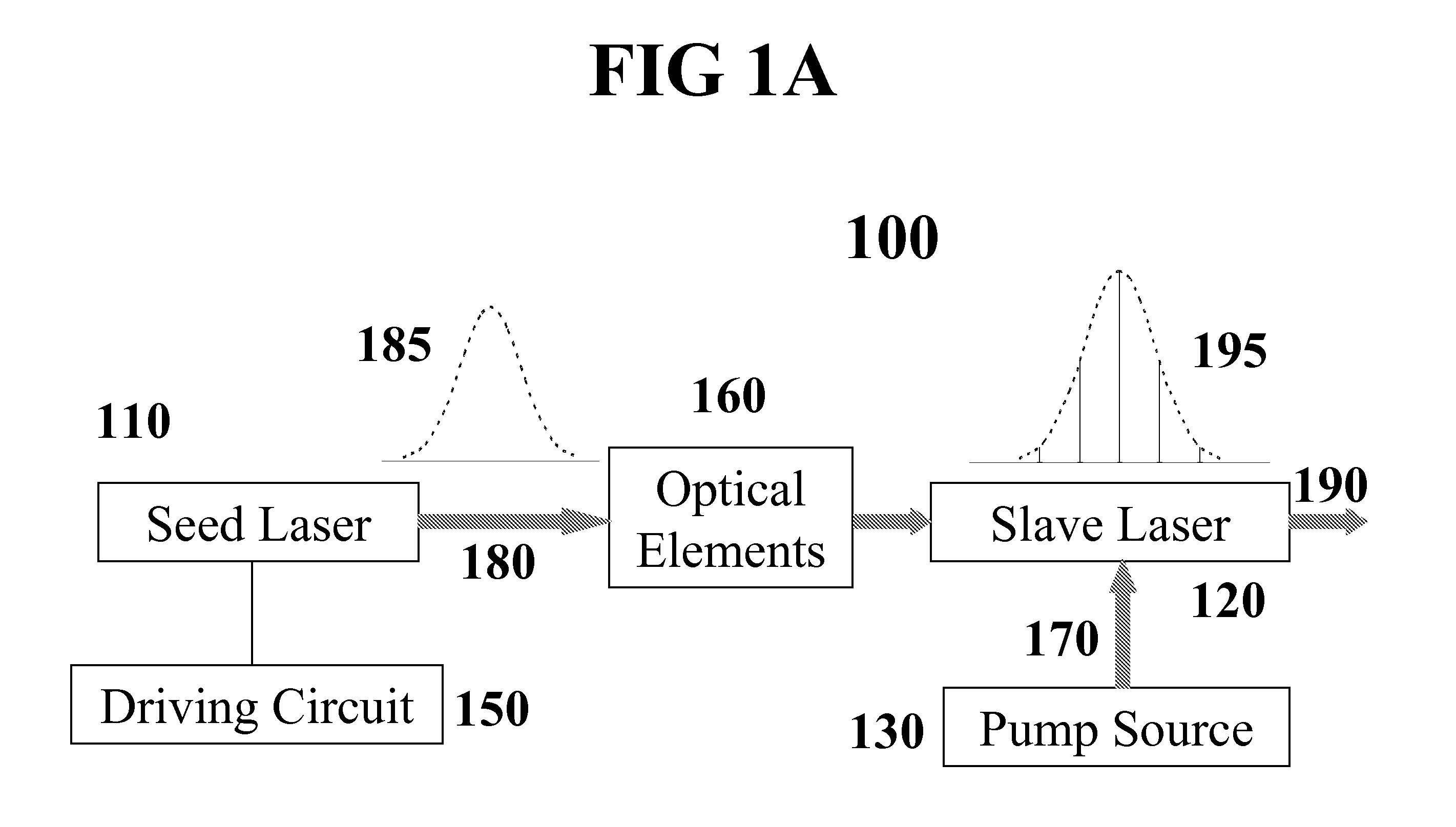
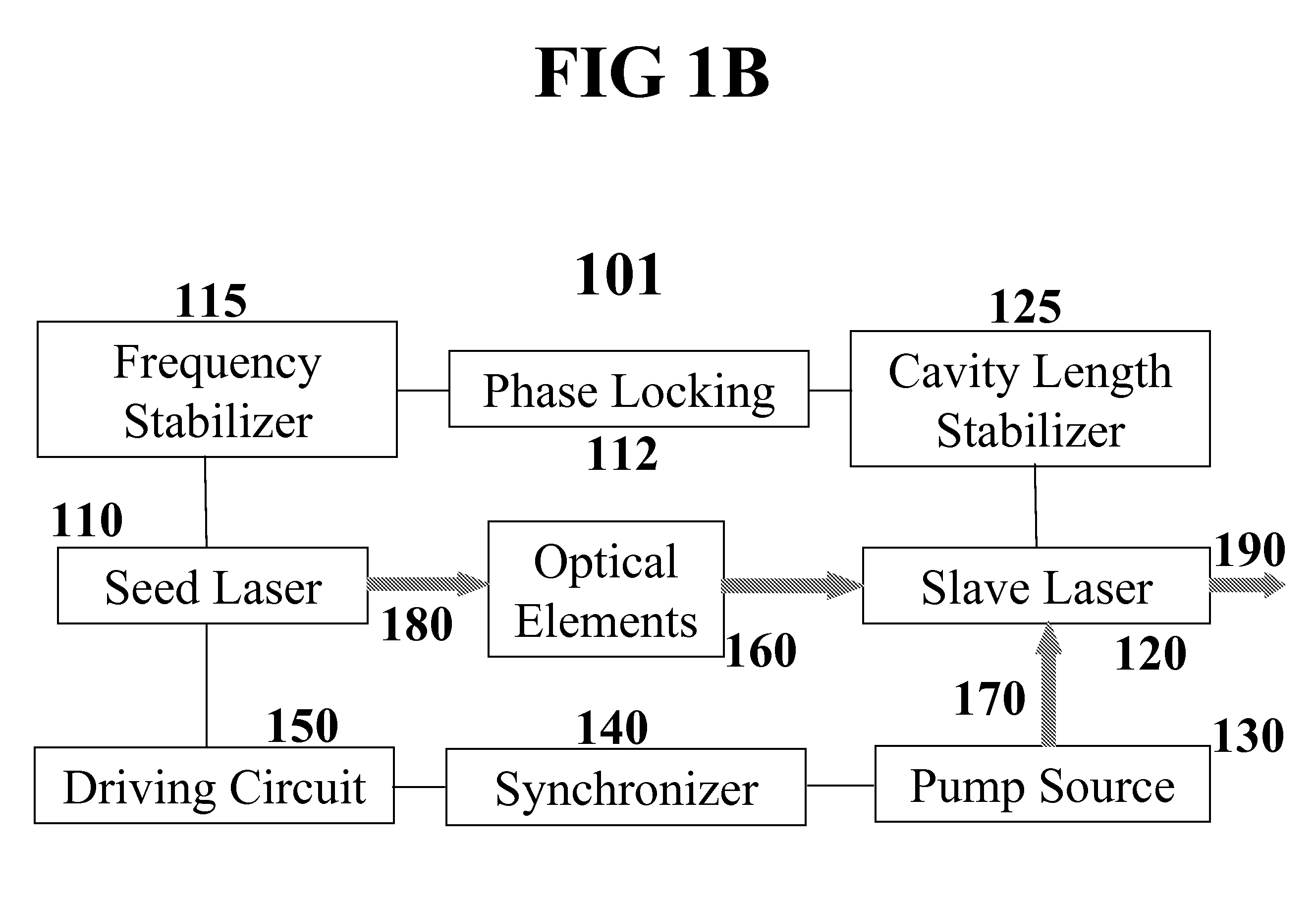
Injection seeding employing continuous wavelength sweeping for master-slave resonance
InactiveUS20080089369A1Convenient and cost-effectiveHigh beam qualityLaser detailsDriving currentGaussian beam
A method for effective injection seeding is based on continuous wavelength sweeping for matching the injected seeds with one or more longitudinal mode(s) of the slave oscillator in every pulse. This is achieved through rapidly varying laser drive current, as a result of RF modulation. Depending on the modulation parameters, the seeder may be operated in CW or quasi-CW or pulsed mode, with a narrow or broad bandwidth, for injection seeding of single longitudinal mode or multimode. The wavelength and bandwidth of the laser output can be tuned according to the needs. Injection seeding of high repetition rates is achievable. From pulse to pulse, the master-slave resonance persists though may occur at different longitudinal modes upon cavity length fluctuations. Cavity length control and phase locking schemes are consequently not required. The present invention also encompasses an injection seeding laser system, which is constructed in accordance with the inventive method, and a novel application of RF modulated laser diode to spectrum / wavelength control and to producing high power Gaussian beam with narrow pulse width in a stable, reliable, and cost-effective manner.
Owner:PAVILION INTEGRATION
Optical beam-shaper
InactiveUS20060256335A1Refined reshapingCloser approximationLight polarisation measurementOptical elementsGaussian beamLight beam
The present invention provides beam-shaping optics for transforming an approximately gaussian beam profile into a (nearly) uniform distribution over a specified spot area. The beam-shaping optics provide significant advantages over existing beam-shapers in that they are less sensitive to variations in the input beam profiles and can be used over a range of frequencies.
Owner:BECTON DICKINSON & CO
Retrieval method for chromatography speed based on undulating surface
InactiveCN102841376AFine velocity modelImplement tomographic velocity inversionSeismic signal processingGaussian beamVelocity inversion
The invention provides a retrieval method for a chromatography speed based on an undulating surface. The retrieval method comprises the following steps of: performing Gaussian beam shifting imaging based on the undulating surface on an initial speed model, extracting an angle region co-imaging point channel set and judging the correctness of an initial speed; taking a plurality of points from an in-phase axis of an angle channel set, fitting the in-phase axis of the angle channel set according to a shifting depth formula of the in-phase axis of the angle channel set, calculating a residual depth difference, and converting the residual depth difference into a traveling residual error according to a quantitative relation between the residual depth difference of an imaging channel set and the traveling residual error; taking a position interface on a shifting profile, establishing a reference speed model required by ray tracing forward modeling, and improving a constant-speed gradient method to obtain a sensitivity matrix suitable for the undulating surface; on the basis of considering the retrieval precision and calculation efficiency, introducing a regularizing factor and performing chromatography retrieval according to an LSQR method to obtain speed updating volume and updating the speed model; and applying the speed model obtained after updating to pre-stack depth migration and extracting the angle region co-imaging point channel set.
Owner:CHINA UNIV OF PETROLEUM (EAST CHINA)
Spectrometer using diffraction grating
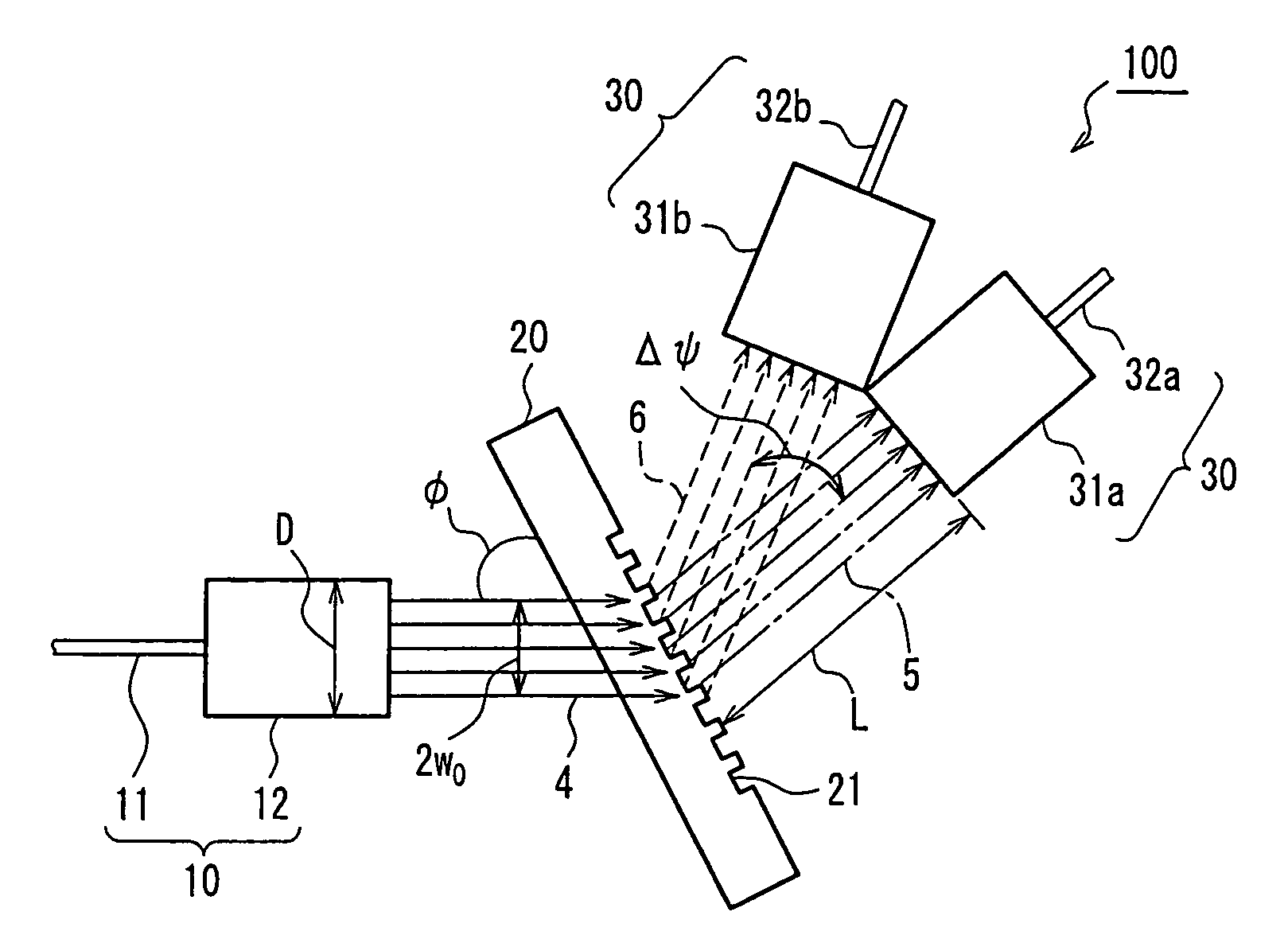
A spectrometer using a diffraction grating includes a light-incident portion including an incident-side optical waveguide emitting a light beam that includes a plurality of wavelength components and that approximates a Gaussian beam, and a collimating lens that is arranged on an emission side of the incident-side optical waveguide and that converts the light beam approximating a Gaussian beam that is emitted from the incident-side optical waveguide into a substantially collimated light beam; a diffraction grating having grooves on its surface, on which the light beam that has been converted into the substantially collimated light beam by the collimating lens is incident, the diffraction grating spectrally separating the light beam by emitting light beams whose emission direction depends on their wavelength; and a light-emitting portion having a plurality of focusing lenses that respectively condense the light beams that have been spectrally separated by the diffraction grating.
Owner:NIPPON SHEET GLASS CO LTD +1
Method for measuring partially coherent vortex light beam topological charge number
InactiveCN102944312AEasy to implementEasy to measureOptical measurementsBeam splitterCorrelation function
The invention discloses a method for measuring partially coherent vortex light beam topological charge number. A measured light beam passes through an imaging convex lens and then passes through a beam splitter to be divided into a transmission light beam and a reflection light beam, optical fiber scanning probes of two single-photon counters are respectively arranged at the centers of the transmission light beam and the reflection light beam, the position of a single-photon counter optical fiber probe is fixed, the position of the other single-photon counter optical fiber probe is regulated to perform point-by-point scanning measurement, correlation function values of the two beams on measuring position points are recorded, a spatial distribution image of a fourth-order correlation function is output through computer processing according to fourth-order correlation function relationship of partially coherent laguerre-gaussian beams, and the topological charge number of the beam to be measured is obtained through the number of dark rings on the image. The method is based on the fourth-order correlation function, a novel method for measuring the partially coherent vortex light beam topological charge number is provided, an adopted measuring device is simple in light path and easy to achieve, measuring method is simple, data processing is convenient, and result is reliable.
Owner:SUZHOU UNIV
Method for engraving materials using laser etched V-grooves
Disclosed is a method for engraving materials such as fused silica or ceramic by continuously actuating a laser producing a Gaussian beam, directing the beam towards the surface of the substrate and moving the beam relative to the surface of the substrate so that a V-groove is obtained by laser ablation of the substrate. The depth of the groove, the angle of the top of the groove, can be controlled by the relative speed between the laser beam and the substrate, the power density and the width of the laser beam, the polarization of the laser beam and the incident angle of the laser beam with respect to the surface. A method for treating an optical fiber connector is also disclosed.
Owner:INSTITUT NATIONAL D'OPTIQUE
Pulse laser beam quality synchronous measuring system and synchronous control method thereof
The invention discloses a pulse laser beam quality synchronous measuring system which comprises a facula test light path and a clock synchronous control module. The facula test light path comprises a straight line guide rail, two beam splitters, a reflector, a focus lens, a laser attenuator and two CCDs. Incident laser is divided into two beams by the first beam splitter, one beam enters a quick response photoelectric detector, and time domain information of the beam is measured; the other beam enters the test light path. Appropriate attenuation is carried out on the incident laser by the attenuator, beam waist regeneration is achieved through the focus lens, and the light beam is divided by the other beam splitter into two beams perpendicular to each other and emits into the two CCDs for facula measurement. One of the CCDs measures the size of a facula at a fixed position, and the other CCD determines the position of a beam waist through movement of the guide rail and measures the size of the beam waist. By means of measurement of the three values, a gauss beam analysis formula after beam waist regeneration can be obtained. A beam quality parameter of the incident gauss beam is obtained through lens transformation.
Owner:HUBEI SANJIANG AEROSPACE HONGFENG CONTROL
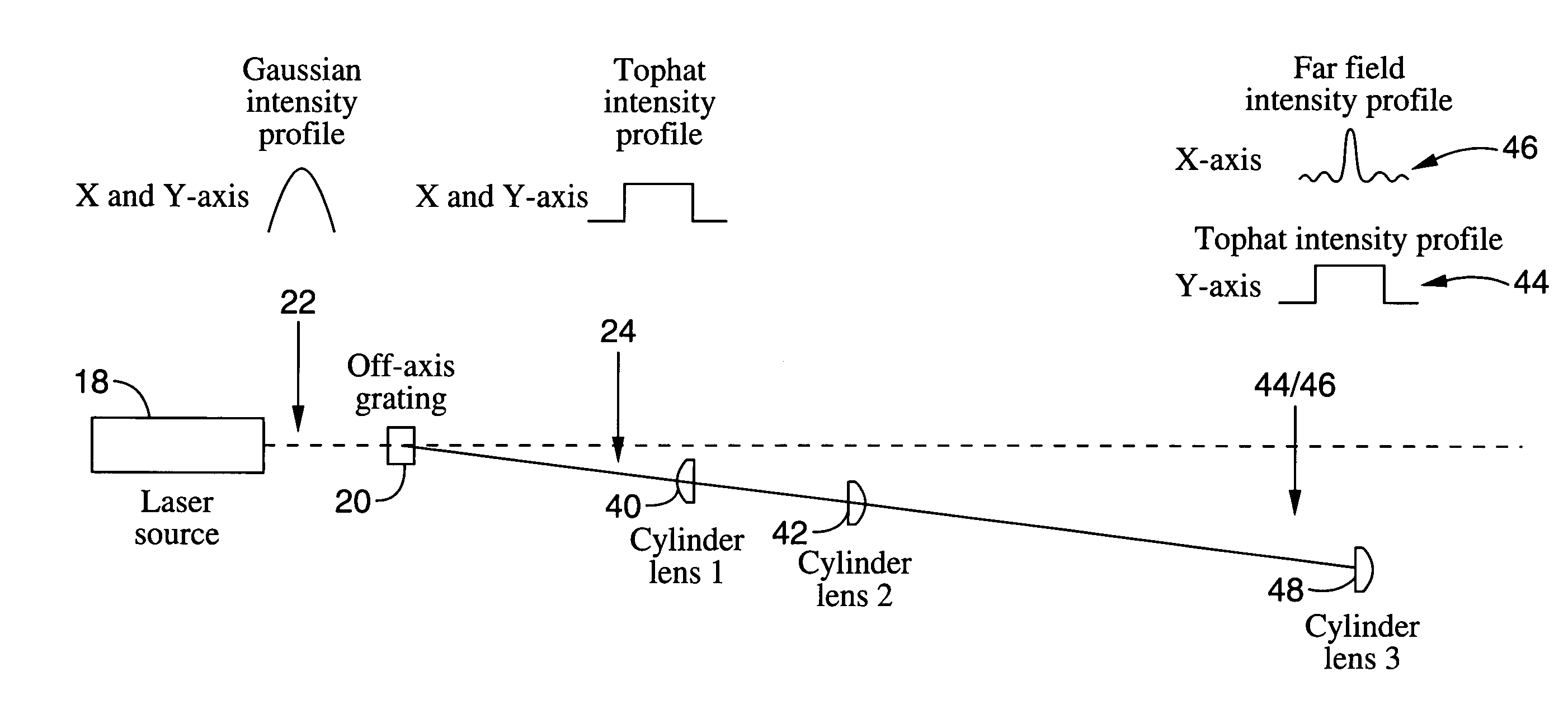
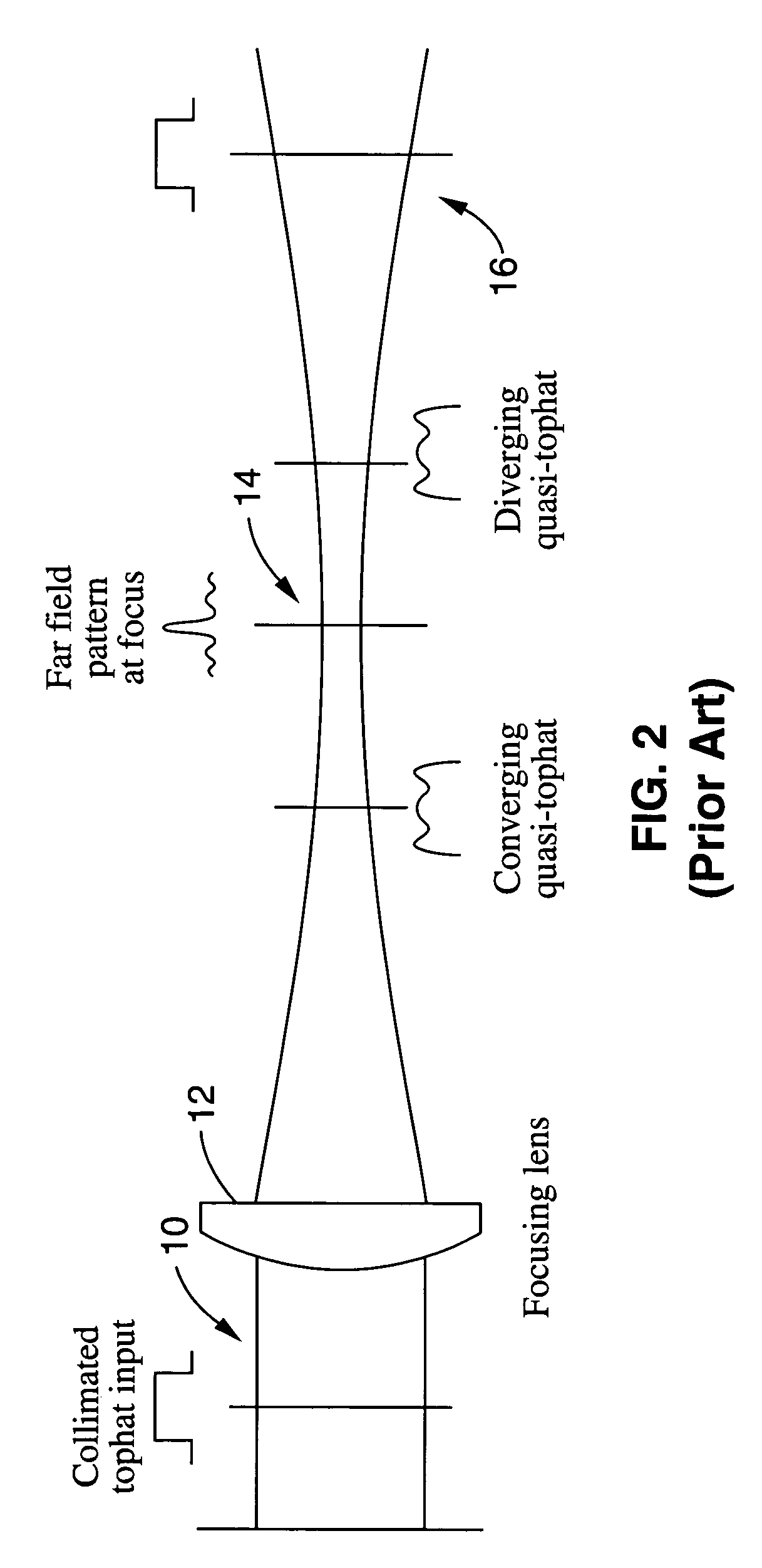
Method and apparatus for transformation of a gaussian laser beam to a far field diffraction pattern
InactiveUS6975458B1Optical resonator shape and constructionDiffraction gratingsGaussian beamFourier transform on finite groups
A method and apparatus for converting a Gaussian laser beam into a propagating far field diffraction pattern using an off-axis diffractive optic. This propagating far field pattern is focused by a lens to obtain a flattop intensity at the focal plane. The technique is based on the idea of Fourier transform pairs and produces a small spot diameter with a useable depth of field. A focused uniform intensity profile can be useful for many laser applications.
Owner:KANZLER KURT
Generation/three g dimensional reconstruction apparatus and method for Laguerre Gaussian vortex beam
InactiveCN106896498AHigh damage thresholdQuick responseOptical elementsGaussian beamInformation transmission
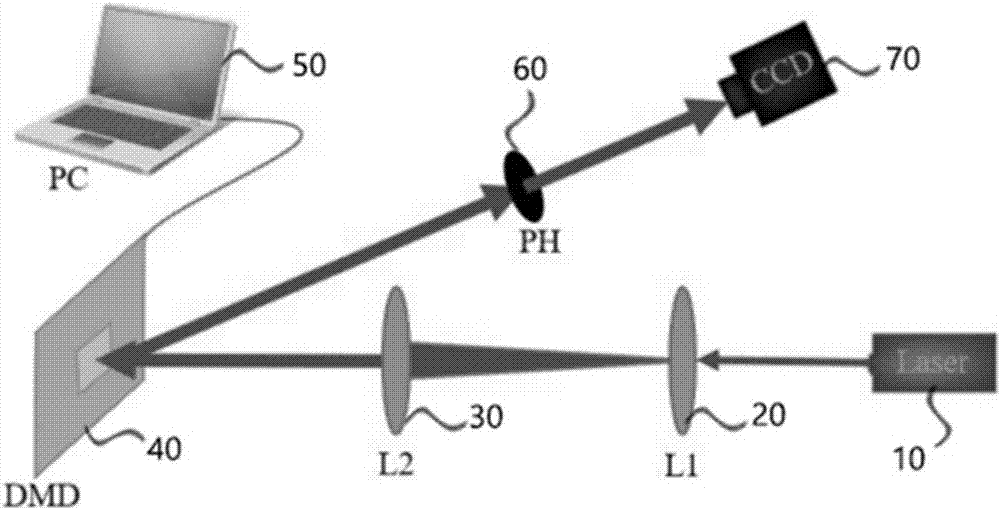
The invention discloses a generation / three-dimensional reconstruction apparatus and method for a Laguerre Gaussian vortex beam. The Laguerre Gaussian vortex beam generation apparatus comprises: a laser for emitting a Gaussian beam; a first convex lens for expanding the Gaussian beam; a second convex lens for collimating the expanded Gaussian beam; a computer for generating a fork-shaped diffraction grating and loading the fork-shaped diffraction grating onto a digital micromirror device, and subjecting the incident beam of the digital micromirror device to amplitude and / or phase modulation; and the digital micromirror device for subjecting a part of the collimated Gaussian beam to amplitude or / and phase modulation to produce Laguerre Gaussian vortex beams with different orders. The generation / three-dimensional reconstruction apparatus has a high damage threshold and a very fast response speed, is simple in structure, good in stability, and low in manufacturing cost, and is widely used in the fields of mechanical processing, biomedical treatment, military field, information transmission, micro-control and the like.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA NORMAL UNIVERSITY
Method and device for generating perfect Laguerre-Gaussian beam
InactiveCN103941405ASimple methodReliable methodOptical elementsSpatial light modulatorGaussian beam
The invention relates to a method and device for generating a perfect Laguerre-Gaussian beam. After a Gaussian beam is expanded, a spatial light modulator of a computer-generated hologram is loaded and used for regulating a light field, a first-level diffraction beam emitted by the spatial light modulator is captured, and then a hollow Gaussian beam is obtained; phase modulation is conducted through a spiral phase plate, so that a hollow beam carrying orbital angular momentum is obtained; focusing is conduced through a convex lens, so that the perfect Laguerre-Gaussian beam is obtained. According to the method and device for generating the perfect Laguerre-Gaussian beam, the perfect Laguerre-Gaussian beam is generated through the hollow beam carrying the orbital angular momentum, the method is simple and reliable, and the device is simple in structure, easy to adjust and good in stability; the generated beam can be applied to the fields such as the particle capturing field, the free space optical communication and the beam transmission characteristic research field.
Owner:SUZHOU UNIV
System and method for generating radial Bessel-Gaussian beam
The invention discloses a system for generating a radial Bessel-Gaussian beam. The system comprises a beam expander, a computer-controlled spatial light modulator, a vortex phase plate and a radial polarization convertor that are sequentially arranged in a light direction of a light source generating linearly polarized light, wherein a topological charge of the vortex phase plate is 1; and a calculation hologram generated by a computer is loaded to the spatial light modulator to form a calculation holographic grating, so that a first order Bessel-Gaussian beam is generated. The vortex phase plate is rotated to ensure that phase structure distribution of the vortex phase plate is right opposite to the phase structure distribution of the Bessel-Gaussian beam coming out of the spatial light modulator, and a vortex phase of the Bessel-Gaussian beam is eliminated. Then, the Bessel-Gaussian beam with the vortex phase being eliminated passes through the radial polarization convertor. Radial polarization Bessel-Gaussian beams with different ring numbers can be generated by generating different holograms due to the flexibility of the holograms of the computer, and have self-restorability.
Owner:SUZHOU UNIV
Light-splitting device and method
ActiveCN104174994AIncrease the number ofReduce heat damageMetal working apparatusLaser beam welding apparatusGaussian beamBeam splitting
The invention provides a light-splitting device and method. The light-splitting device comprises a pair of lenses between which the distance is adjustable, a planar reflecting mirror, a Gauss beam shaping element, a beam-splitting element and a focusing mirror, wherein the lenses are used for adjusting the light spot size and the diverging angles of Gauss beams emerged by a laser; the planar reflecting mirror is used for deflecting horizontal beams emerged by the lenses into vertical beams; the Gauss beam shaping element is used for converting light spots of the vertical beams which penetrate the Gauss beam shaping element into flat light spots with uniform energy density; the beam-splitting element is used for splitting the flat light spots into a one-dimensional or two-dimensional beam array; the focusing mirror is used for focusing the beams in the beam array to form a focus lattice.
Owner:北京中科镭特电子有限公司
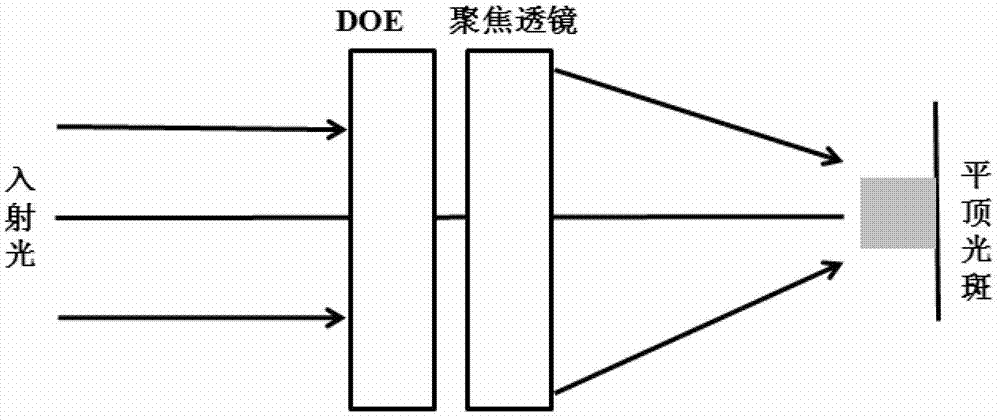
Diffractive optical element for shaping gauss beam into flat-topped beam, and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN103399406AImprove energy transmittanceEasy to usePhotomechanical exposure apparatusMicrolithography exposure apparatusGaussian beamTransmittance
The invention provides a new diffractive optical element for shaping a gauss beam into a flat-topped beam, and the diffractive optical element is called DOE for short; the invention also provides a preparation method of the DOE. Grooves or steps with different shapes and sizes are prepared in the center of a quartz substrate, and the DOE is then arranged at the different positions of a light path and is matched with a beam expanding collimation lens and a focusing lens, so that the flat-topped beam can be realized. The DOE has the outstanding advantages of being high in energy transmittance, less sensitive to the incident laser mode change, and simple and flexible in installation and use.
Owner:北京润和微光科技有限公司
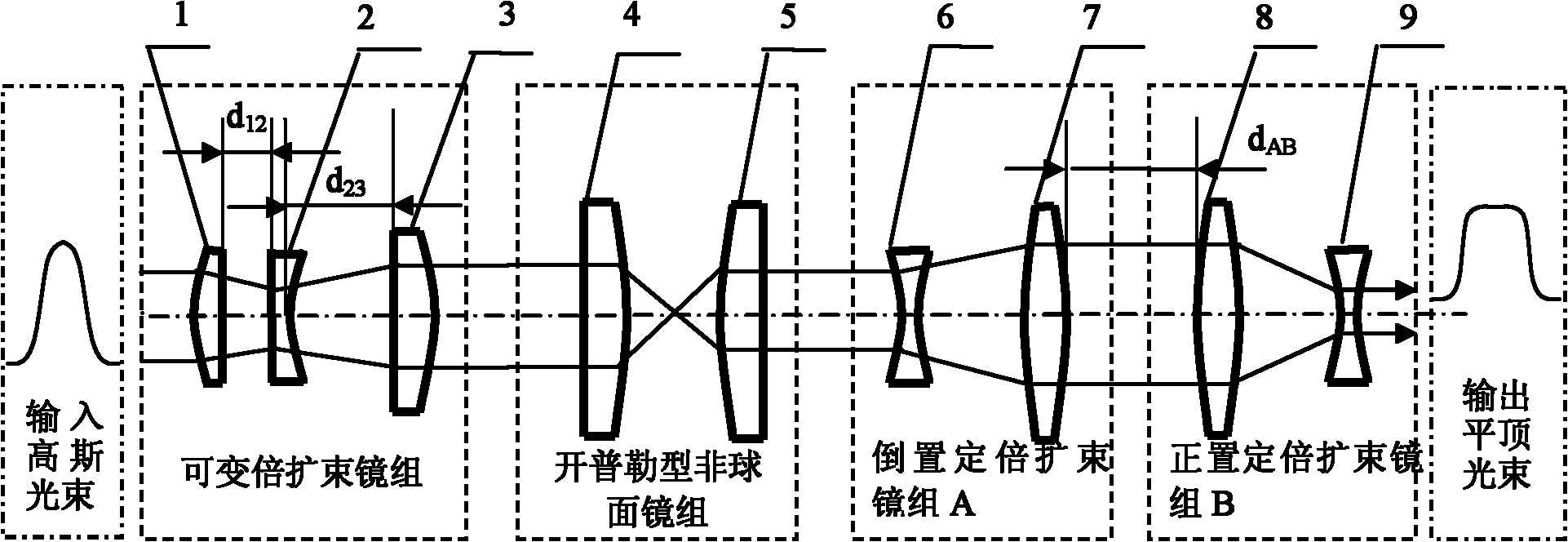
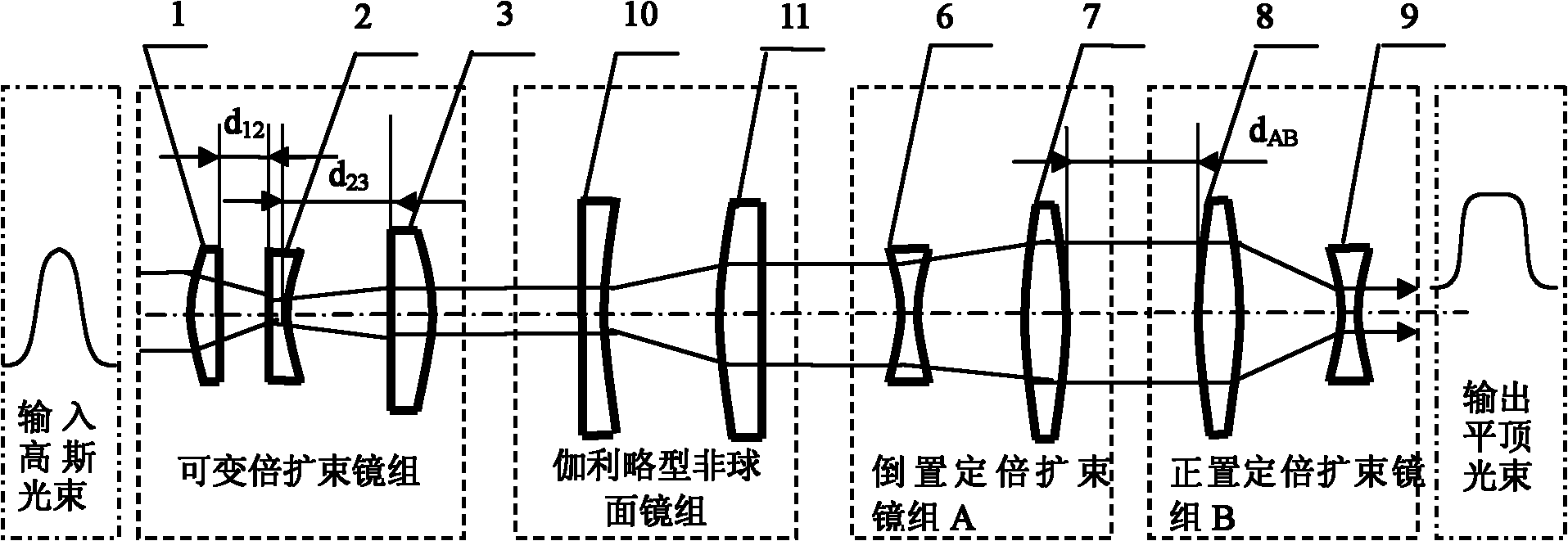
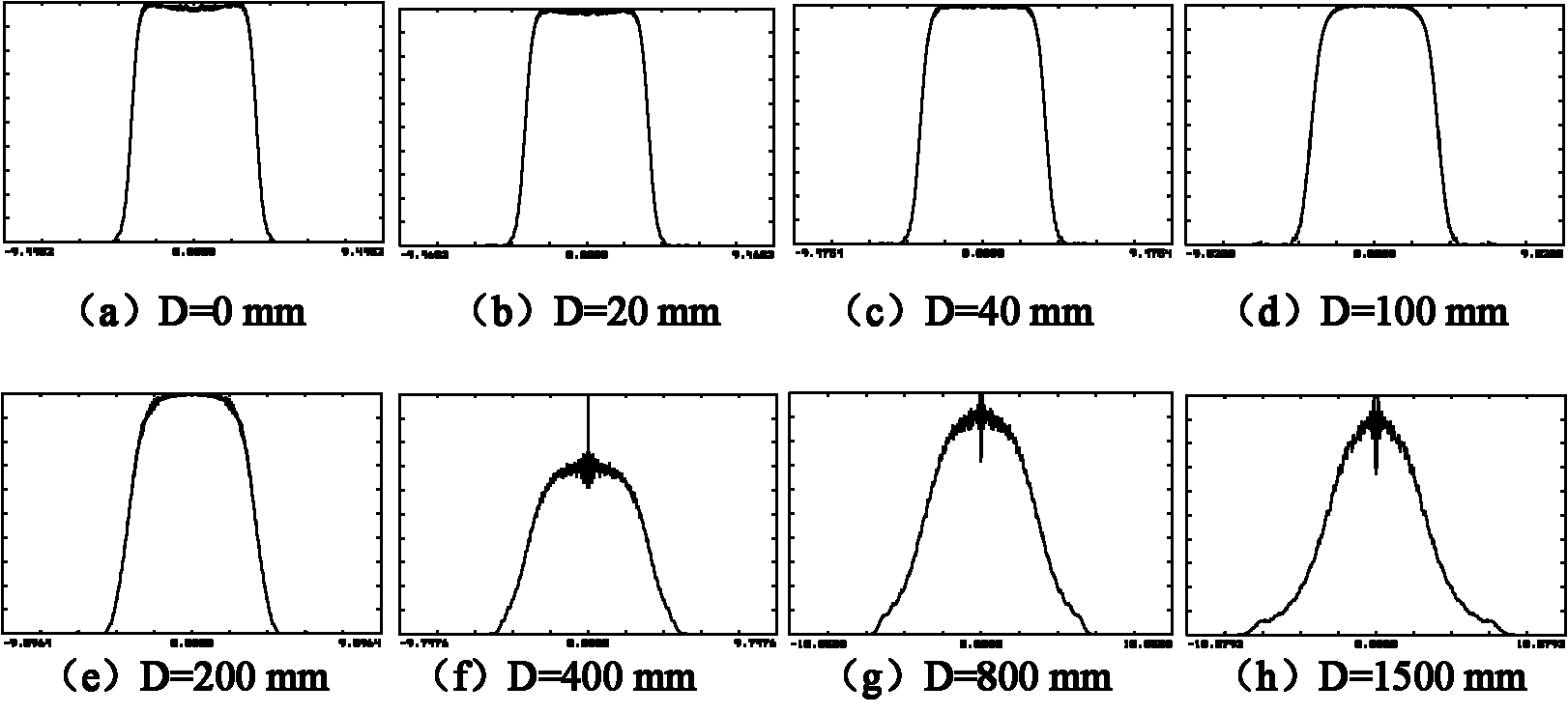
Device and method for shaping Gaussian beam to flat-topped beam
The invention discloses a device and a method for shaping a Gaussian beam to a flat-topped beam. The device mainly comprises four parts, which are a variable focus beam expanding mirror group, an aspherical mirror group, an inverted fixed focus beam expanding mirror group and an upright fixed focus beam expanding mirror group sequentially. At the front end, the variable focus beam expanding mirror group is adopted for firstly performing beam expanding matching on the input Gaussian beam with arbitrary waist radius and the further inputting into the aspherical mirror group, thereby getting the flat-topped beam which is only applicable to near-field propagation. In order to get the flat-topped beam which has better beam quality and can be applicable to far-field propagation, the inverted fixed focus beam expanding mirror group is further used for performing beam expanding, beam reducing is further performed after far-field propagation for a certain distance, and then the flat-topped beam with good uniformity in light intensity distribution is obtained at the output end of a system. The device is very high in flexibility and good in controllability, and can perform the beam expanding on the Gaussian beam with the arbitrary waist radius, and simultaneously overcome the problem that the beam quality of the flat-topped beam which directly goes out of the aspherical mirror group becomes poor.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF TECH
Three-dimensional imaging system and method in deep scattering medium
ActiveCN102944540ARealize 3D spatial distribution imagingEasy accessFluorescence/phosphorescenceFluorescenceCollection system
A three-dimensional imaging system in a deep scattering medium includes a light source, a Bessel light beam generating and scanning device, a fluorescence collection system, a signal detection component, and an image acquisition system which are arranged in order along the optical path propagation direction, wherein the Bessel light beam generating and scanning device includes a translation stage, a cone mirror, a first lens, a galvanometer and a 4f system which are arranged along the optical path. The system and method help to solve the technical problems of inefficiency that conventional three-dimensional imaging technology uses point by point scanning to obtain a three-dimensional image and the phosphor in the scattering medium can not be imaged, use standard Bessel light beam which can generate a line focusing along light propagation direction as excitation light to replace conventional Gaussian beam which produces point focusing in the two-photon excitation fluorescence scanning microtechnic, and change original flat scaning into volume scanning to achieve quick acquisition the internal fluorescence distribution images in the scattering medium.
Owner:BEIJING LUSTER LIGHTTECH
Quality blind evaluation method for unmanned aerial vehicle image
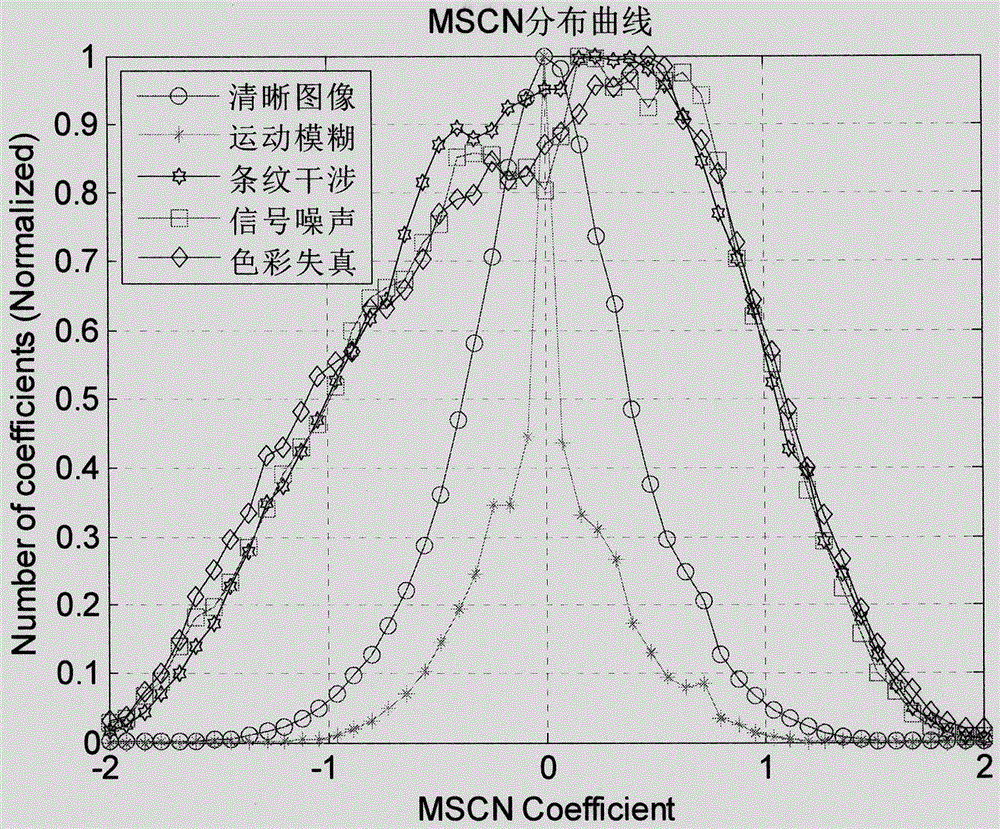
InactiveCN106447646ASolve the problem of lack of training set for blind evaluationEase of evaluationImage analysisGaussian beamImaging quality
The present invention relates to a quality blind evaluation method for an unmanned aerial vehicle image. The method comprises the steps: S1, obtaining an unmanned aerial vehicle image, and performing analysis at three aspects of the image information structure character, the image information integrity and the image information color character; constructing the corresponding quality evaluation measurement; and constructing a standard MVG model by employing a multi-Gaussian beam model, and finally obtaining the quality equal division of the whole image by employing a mean value method. On the basis of comprehensively analyzing the classic no-reference image quality evaluation method and unmanned aerial vehicle image features, aiming at the unmanned aerial vehicle image multi-distortion and mixture problem, the quality blind evaluation method for an unmanned aerial vehicle image extracts three types of quality feature factor sets capable of showing the unmanned aerial vehicle image multi-distortion scenes for perception expression for three types of main distortion of information entropy integrity, structure information changing and color loss.
Owner:中国人民解放军陆军军官学院
Fidelity amplitude gaussian beam pre-stack depth migration method under double complex conditions
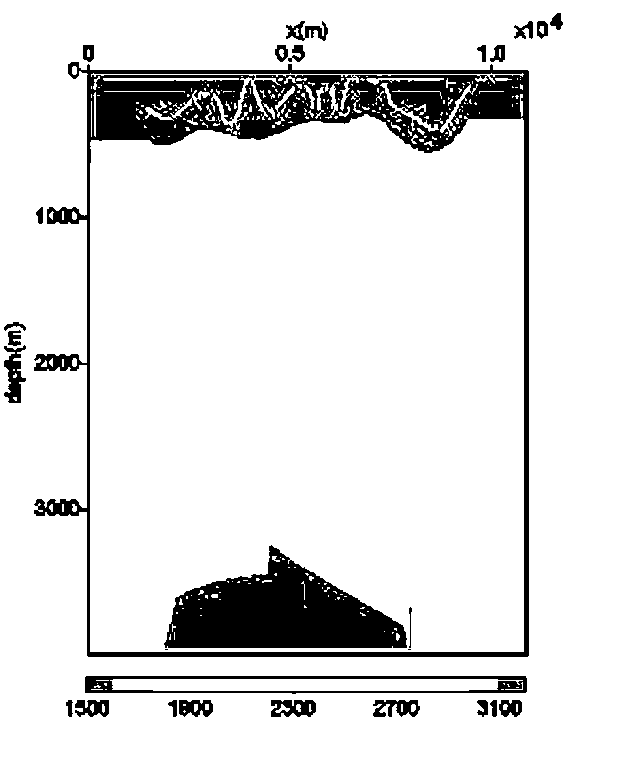
InactiveCN102183786ASignificant speed changeTypical complex surface structureSeismic signal processingGaussian beamClassical mechanics
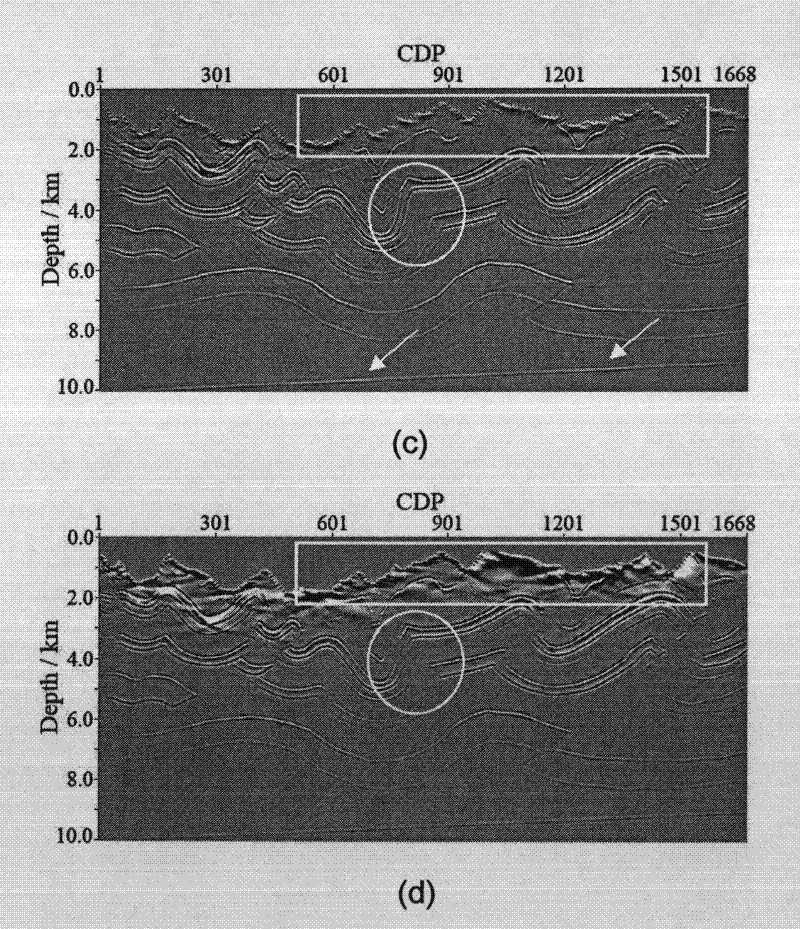
The invention provides a fidelity amplitude gaussian beam pre-stack depth migration method under double complex conditions. The specific realizing process comprises the following steps: firstly, according to the initial width of a selected gaussian beam, a single shot record is divided into a series of overlaid areas through a gaussian window, and the center of each area is a beam center; secondly, through considering the slant stack of earth surface elevation, the shot record corresponding to a beam center is divided into plane waves in different directions; thirdly, the gaussian beams are respectively test-fired from a vibration source and the beam centers, and the travel time and amplitude information in the effective range of each gaussian beam are calculated; fourthly, according to an deduced fidelity amplitude imaging formula, the imaging value corresponding to one beam center is calculated by utilizing calculated travel time, amplitude, and the local inclination angle information of earth surface; and fifthly, the operation of the step three and step four are repeated to obtain the imaging result of the single shot, all single shot imaging results are overlaid to obtain the final offset result. With the invention, the energy strength of a deep layer (the position indicated by an arrow) is effectively strengthened, and the light layer noise (the position indicated by the frame) is suppressed, so that the imaging accuracy of near earth surface is improved.
Owner:CHINA UNIV OF PETROLEUM (EAST CHINA)
Laser cutting equipment and method
ActiveCN107199410AEfficient cuttingImprove static strengthGlass severing apparatusWelding/soldering/cutting articlesGaussian beamLight beam
The invention provides laser cutting equipment and method. The laser cutting equipment comprises a feeding assembly, a first dual-linkage mechanical arm, a cutter wheel cutting assembly, a front laser cutting assembly, a turning-over assembly, a reverse laser cutting assembly, a second dual-linkage mechanical arm, a laser broken piece assembly and a sorting assembly. The front laser cutting assembly and the reverse laser cutting assembly perform laser cutting on a sample through bessel beams, and the focused bessel beams are focused light beams with a large focal depth, so that compared with gauss beams, the thick sample to be cut can be cut effectively, and thus the application range of the laser cutting equipment is broadened. Besides, the laser cutting assemblies and the laser broken piece assembly are adopted to cut the sample twice correspondingly, a finished product can be separated from waste, and cutting efficiency is high. In addition, the laser cutting equipment has the advantages that the cutting path is narrow, edge breakage of the surface of the cut product is small, the conical degree is small, the static pressure strength is high, an abnormally-shaped product can be cut, and the like.
Owner:东莞市盛雄激光先进装备股份有限公司
Optical system generating screw type Bessel beams and generating method
ActiveCN103792663ASimple secondary processing designPromote conversionOptical elementsGratingDiffraction order
The invention discloses an optical system generating screw type Bessel beams and a generating method. The optical system is composed of a He-Ne laser device, a polarizer, a first beam expander, a binary amplitude grating, a second beam expander, an aperture diaphragm, a liquid crystal spatial light modulator, an axicon and a CCD camera. Gauss beams emitted from the He-Ne laser device are converted into 0-degree linearly polarized light after passing through the polarizer with a 0-degree polarizing direction, beam expanding is carried out on the 0-degree linearly polarized light through the first beam expander, the 0-degree linearly polarized light is vertically emitted into the binary amplitude grating, generated diffracted light passes through the second beam expander, the diffraction angles of all diffraction orders of the diffracted light are enlarged, single-ring Laguerre-Guss beams are obtained through the aperture diaphragm and are sent to the liquid crystal spatial light modulator, the Bessel beams which are off an axis and are transmitted around the axis in a screw mode are generated by passing through the axicon, and the Bessel beams are irradiated to the CCD camera to obtain light distribution. The optical system generating the screw type Bessel beams and the generating method achieve generation of the Bessel beams which are off the optical axis and are transmitted around the optical axis in the screw mode.
Owner:BEIJING RES INST OF SPATIAL MECHANICAL & ELECTRICAL TECH
Device for generating arbitrary vector beams based on Mach-Zehnder interferometer
InactiveCN103293696ARapid regulationNon-linear opticsOptical elementsGaussian beamMach–Zehnder interferometer
The invention relates to a device for generating arbitrary vector beams based on a Mach-Zehnder interferometer. The device comprises a fundamental-mode linear polarization laser source, a half-wave plate, two polarization splitting prisms, two totally reflecting mirrors, two discontinuous wave plates and an electro-optic phase modulator, and the fundamental-mode linear polarization laser source generates a fundamental-mode Gaussian beam which is divided into two paths of orthogonal linearly-polarized light via the half-wave plate and the first polarization splitting prism. The vertically polarized light is converted into TEM01 vertically polarized light via the first 45-degree totally reflecting mirror and the first discontinuous wave plate; the horizontally polarized light is converted into TEM10 horizontally polarized light via the second discontinuous wave plate, and the TEM10 horizontally polarized light is reflected by the electro-optic phase modulator and the second 45-degree totally reflecting mirror and then is coaxially and coherently superposed with the TEM01 vertically polarized light at the position of the second polarization splitting prism to generate to vector polarized light. By the device, arbitrary phi0 and delta combined vector beams can be generated, and continuous and quick switching between different vector beams can be realized.
Owner:NORTHWEST UNIV
Laser cutting device and cutting method
ActiveCN106994564AEfficient cuttingGlass severing apparatusWelding/soldering/cutting articlesPicosecond laserGaussian beam
The invention provides a laser cutting device and a cutting method. The laser cutting device comprises a laser, a light beam shaping system and a first collecting lens; the laser is a picosecond laser; the laser is used for emitting laser; the laser is a Gaussian beam; the light beam shaping system is used for converting the Gaussian beam to a Bessel beam; and the first collecting lens is used for focusing the Bessel beam to an area to be cut of samples to be cut, so that the area to be cut is precut by the Bessel beam. As the focused Bessel beam is the focused beam with longer focal depth, compared with the Gaussian beam, the Bessel beam can effectively cut the samples to be cut with greater thicknesses to widen the application range of the laser cutting device.
Owner:东莞市盛雄激光先进装备股份有限公司
Power scalable waveguide amplifier and laser devices
InactiveUS6894828B2Preservation of polarization andUndesirable nonlinear effectOptical wave guidanceLaser optical resonator constructionNonlinear distortionGaussian beam
The present invention is directed to guided wave systems, beam transport and waveguide techniques. The invention may comprise passive or active, hollow and dielectric core self-imaging mode wave guide systems, beam amplifiers (10, 40), laser resonators (70), beam transports, and waveguides. Embodiments may include rectangular cross-section waveguides, and preferably maintaining spatial profile of an input beam, such as a Gaussian beam, through the self-imaging period of the waveguide while unique new capabilities to mitigate non-linear distortions that corrupt spatial, spectral and temporal coherence and polarization. Additional aspects may include, for example, transport, amplification, phase / frequency control or modulation, deflection, conversion, synthetic aperture, distributed aperture, beam forming, beam steering, beam combining, power sampling, power combining and power splitting, among other features. Some embodiments may provide a self-imaging, multimode, waveguide (10) and self-imaging guided wave systems and beam transport. Embodiments of the present invention may further provide a method of self-imaging, multimode beam transport and other self-imaging wave guidance techniques.
Owner:LOCKHEED MARTIN COHERENT TECH
Compact broad-band admittance tunnel incorporating Gaussian beam antennas
A plane wave antenna including: a horn antenna; a waveguide at least partially inside the horn antenna, wherein the waveguide includes: a central dielectric slab increasing in width toward the horn antenna and with a first dielectric constant, an upper slab above the central dielectric slab with a second dielectric constant, and a lower slab below the central dielectric slab with the second dielectric constant; wherein the central dielectric slab has a substantially constant thickness less than a quarter of a wavelength at a highest frequency of operation of the plane wave antenna.
Owner:ARIZONA STATE UNIVERSITY
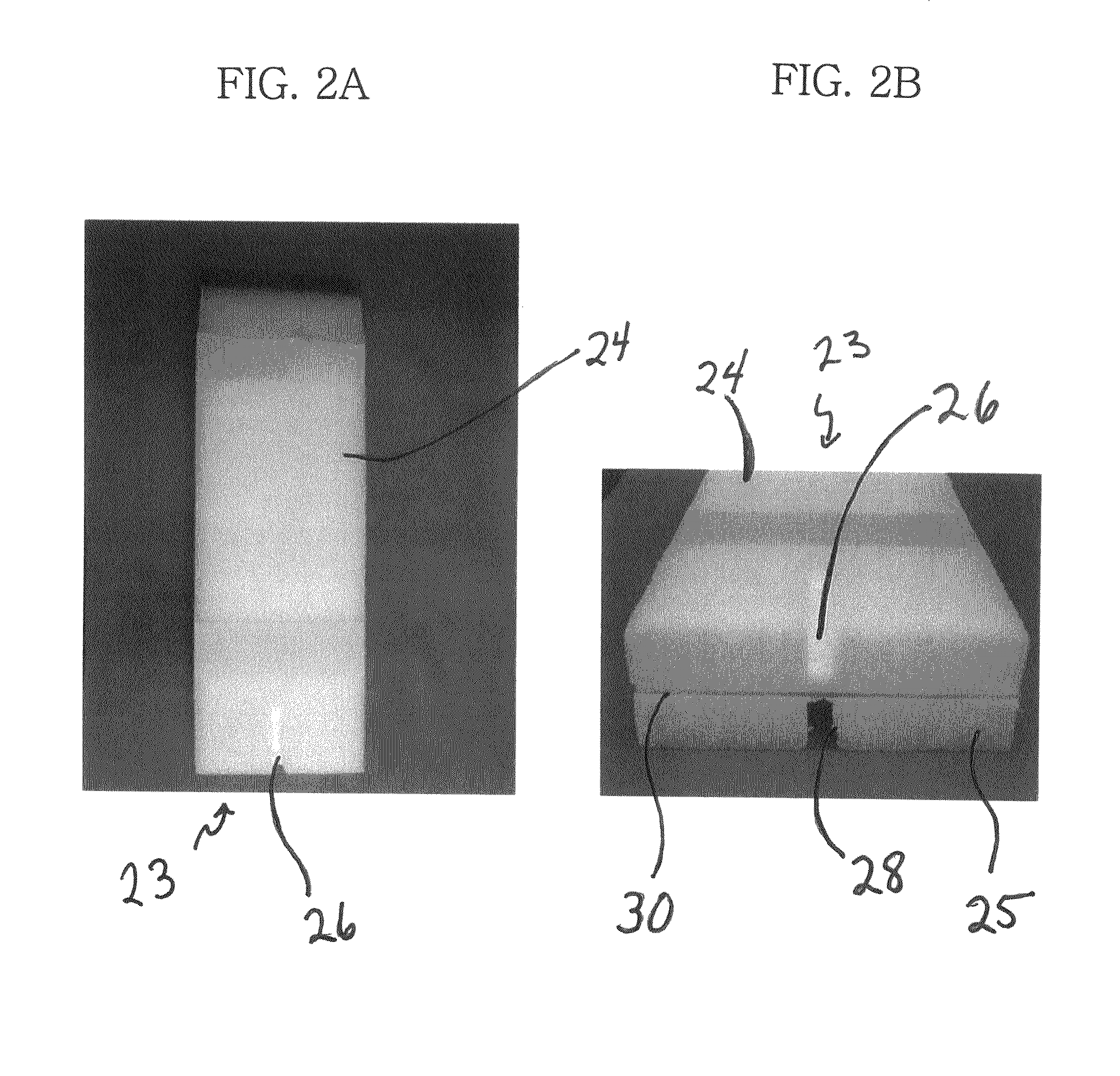
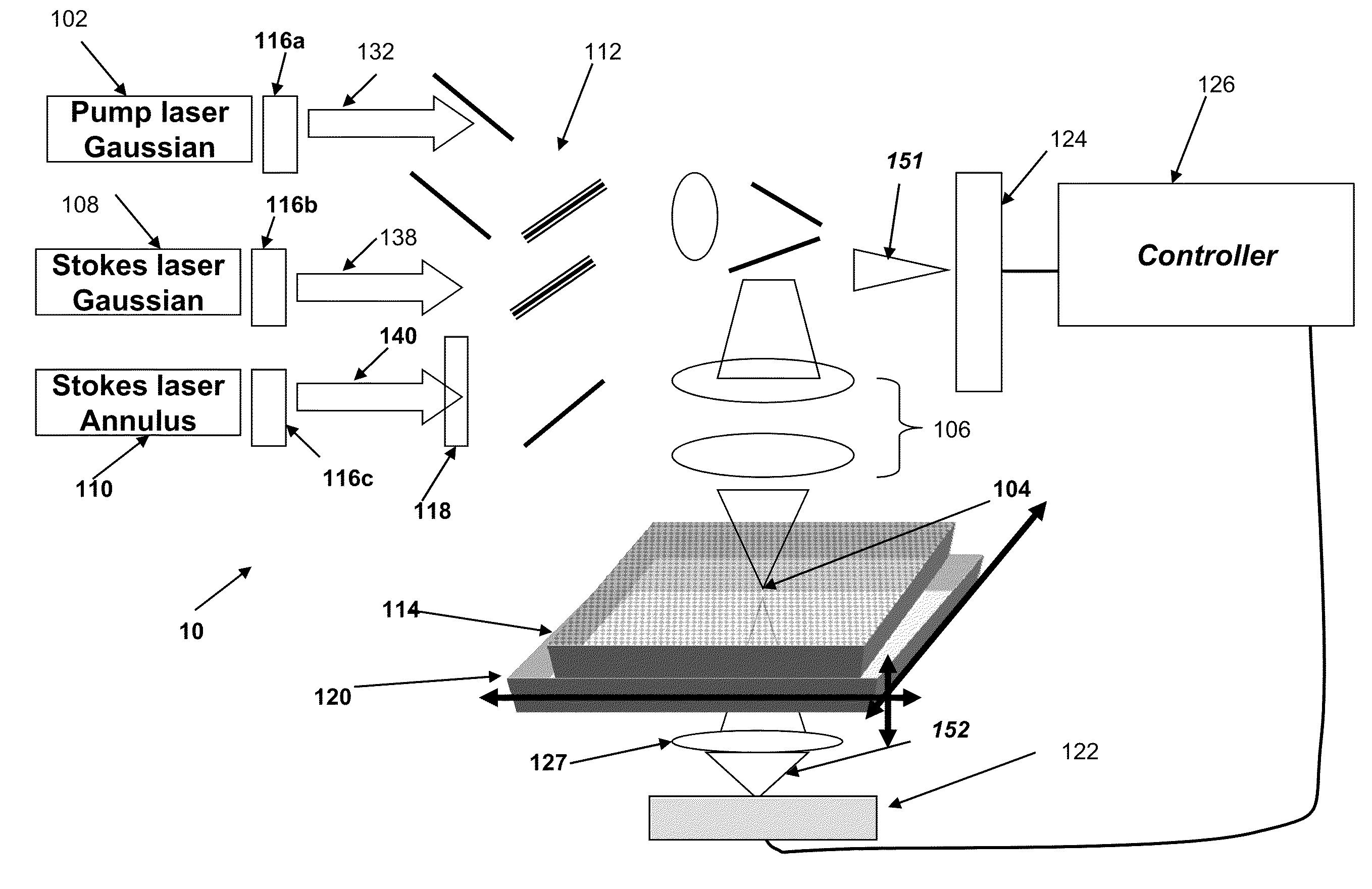
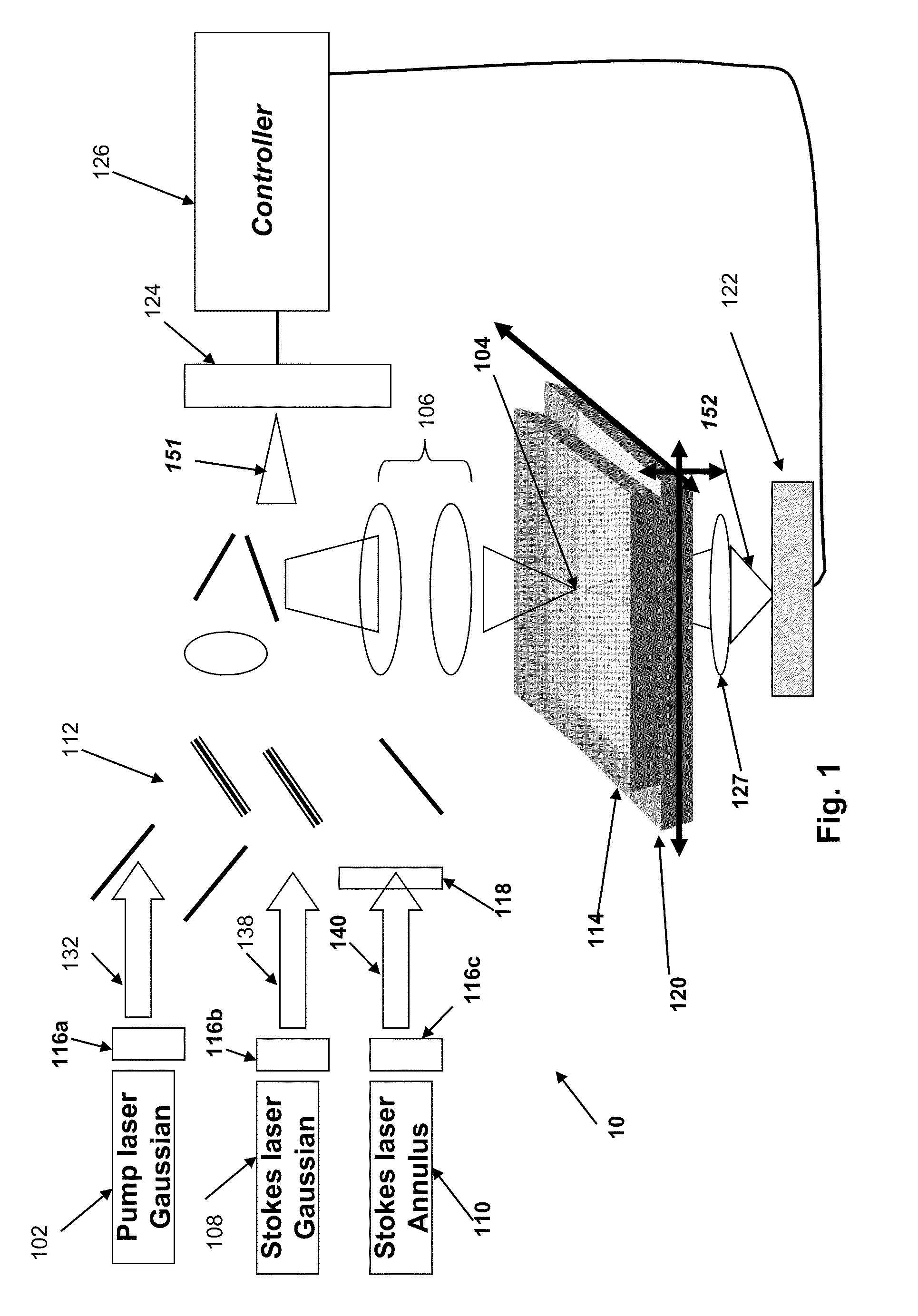
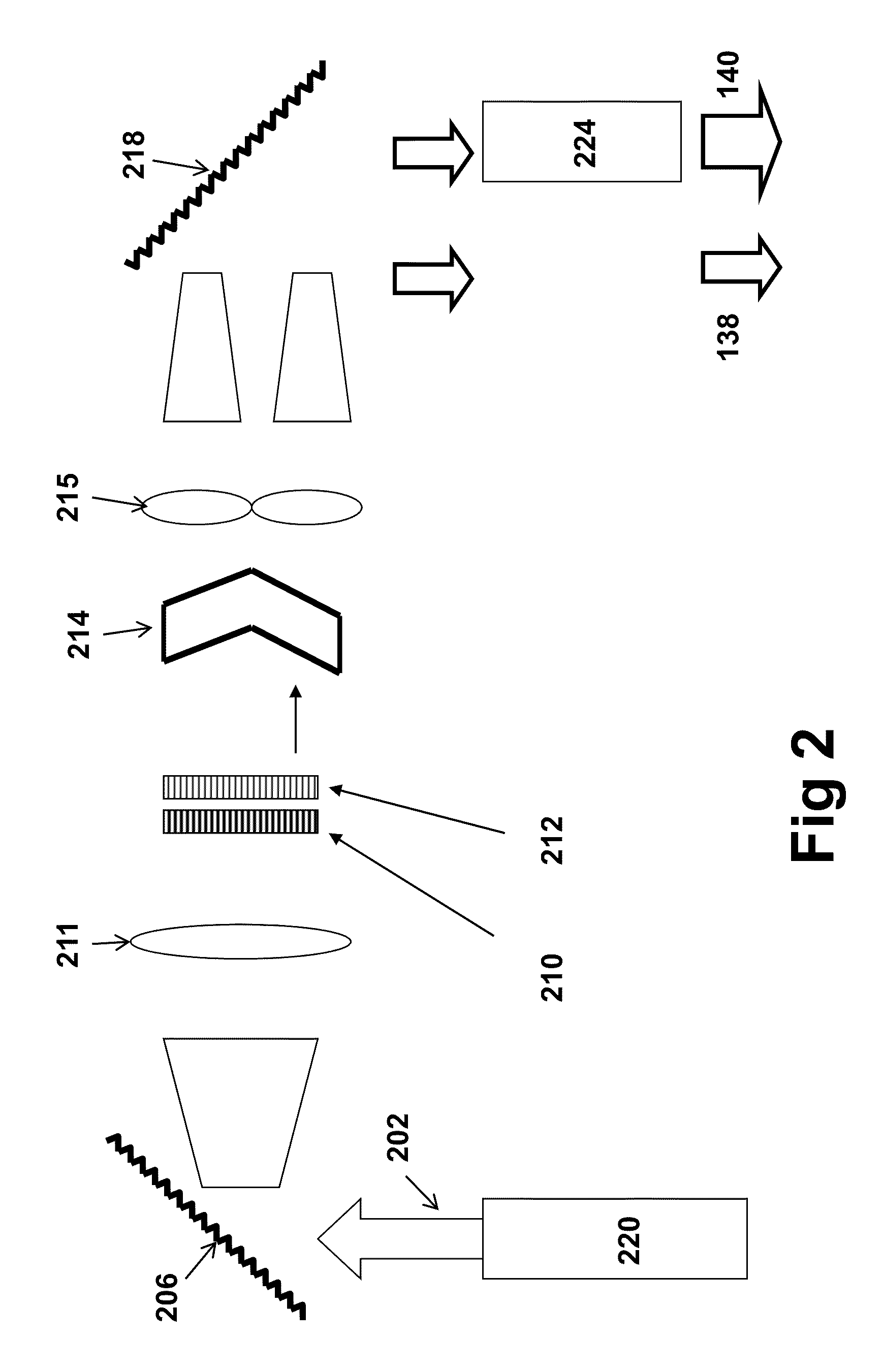
Method and system for stimulated Raman microscopy beyond the diffraction limit
Systems and methods for probing a Raman signature of a sample with a resolution exceeding the diffraction limit are described. These systems, called GASSE (Gain Saturated Stimulated Emission) and iGASSE (interferometric GASSE), are detecting a Raman signal produced in a sample located at the focal spot of a Gaussian pump pulse. Two additional pulsed laser beams (Stokes beams), a central Stokes beam having a Gaussian beam profile and another Stokes beam having an annular beam profile, are also focused to the focal spot. The spatial and temporal phases of the laser pulses are adjusted to produce destructive interference over most of the temporal width of Stokes pulses, which causes emission from the central Stokes beam to narrow well below the diffraction limit. A two-dimensional image of the sample is produced by scanning the combined beams across the sample. The system may find applications in biomedical and semiconductor technology.
Owner:FREL ROBERT D
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com