Patents
Literature
2766 results about "Collimated light" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
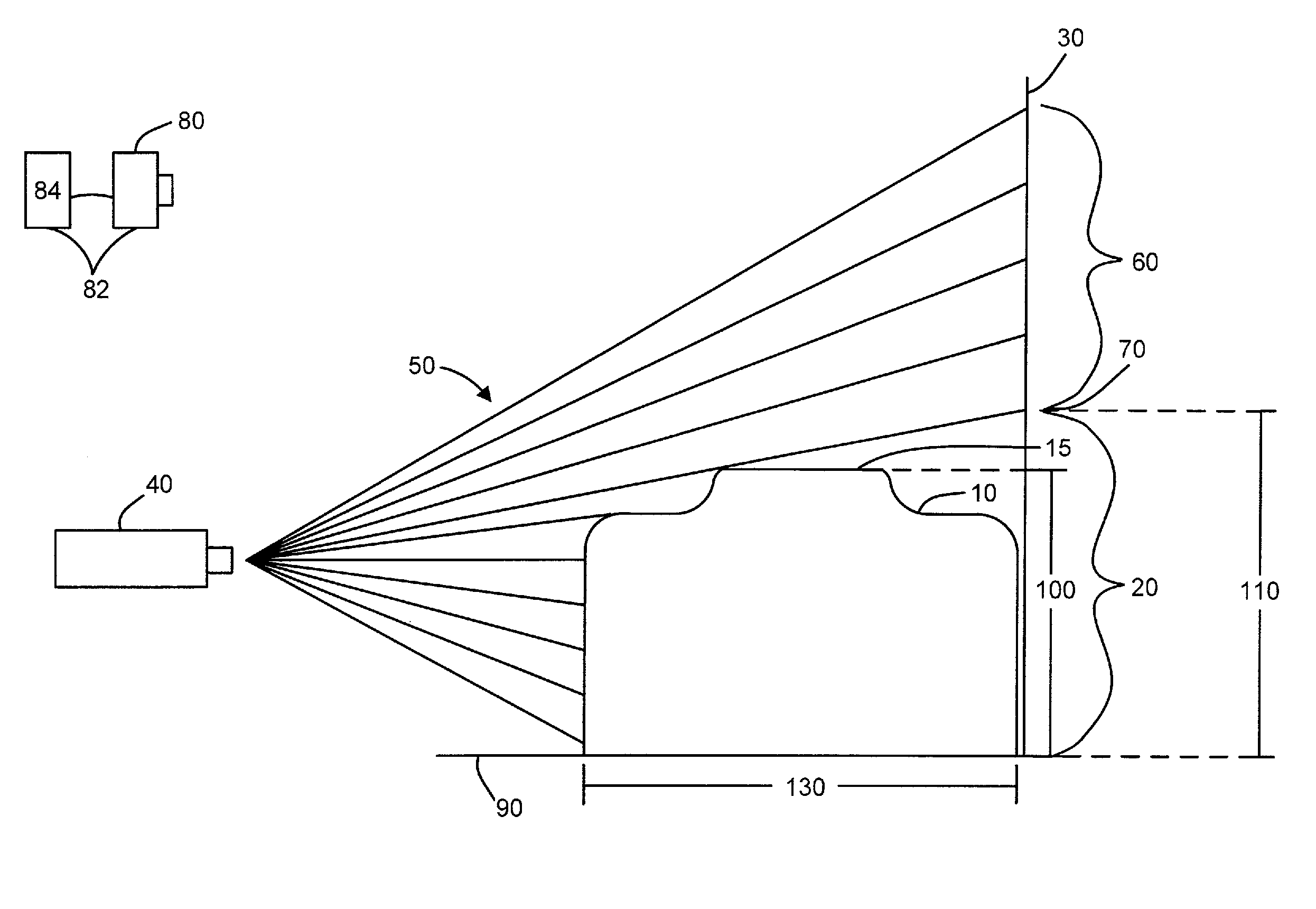
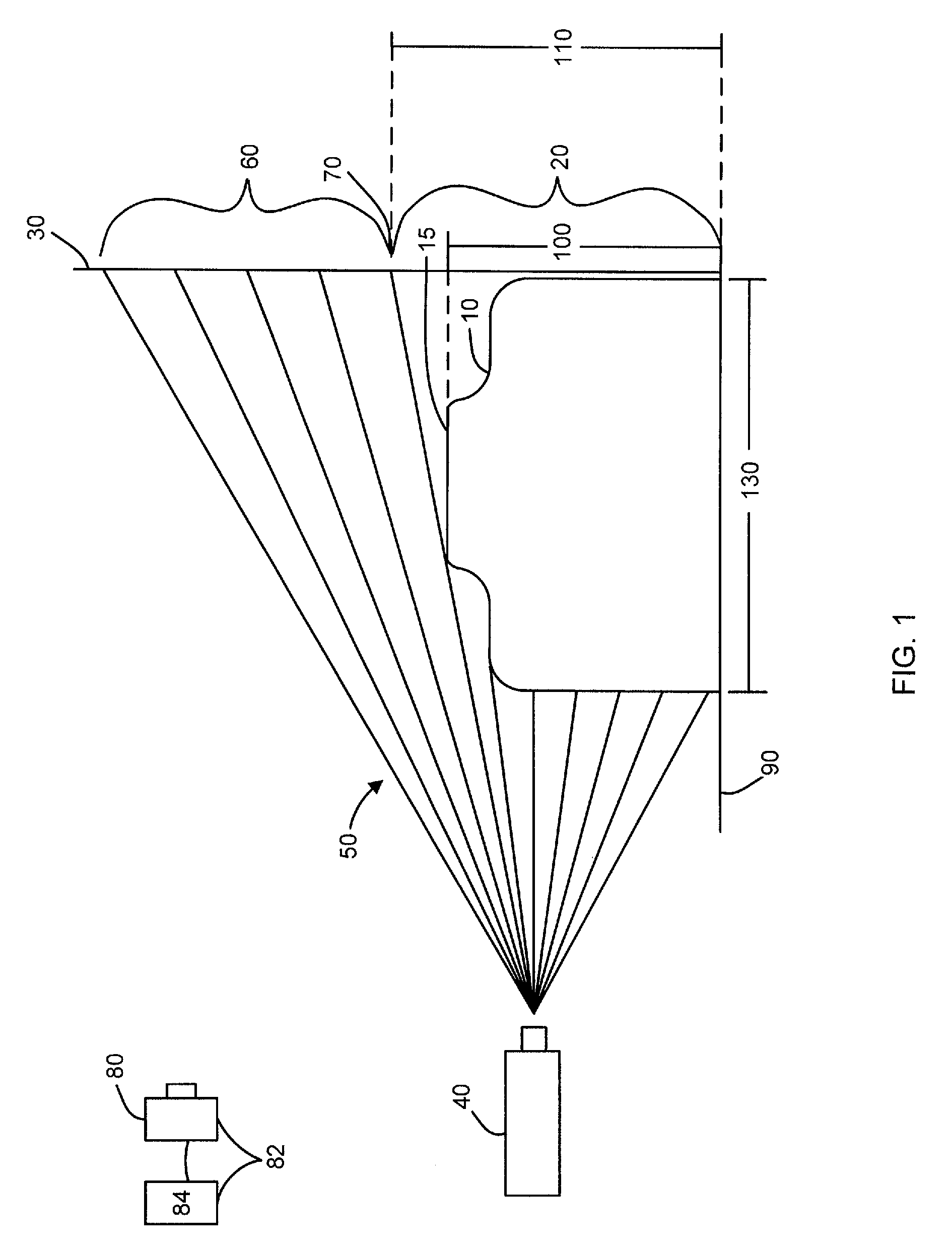
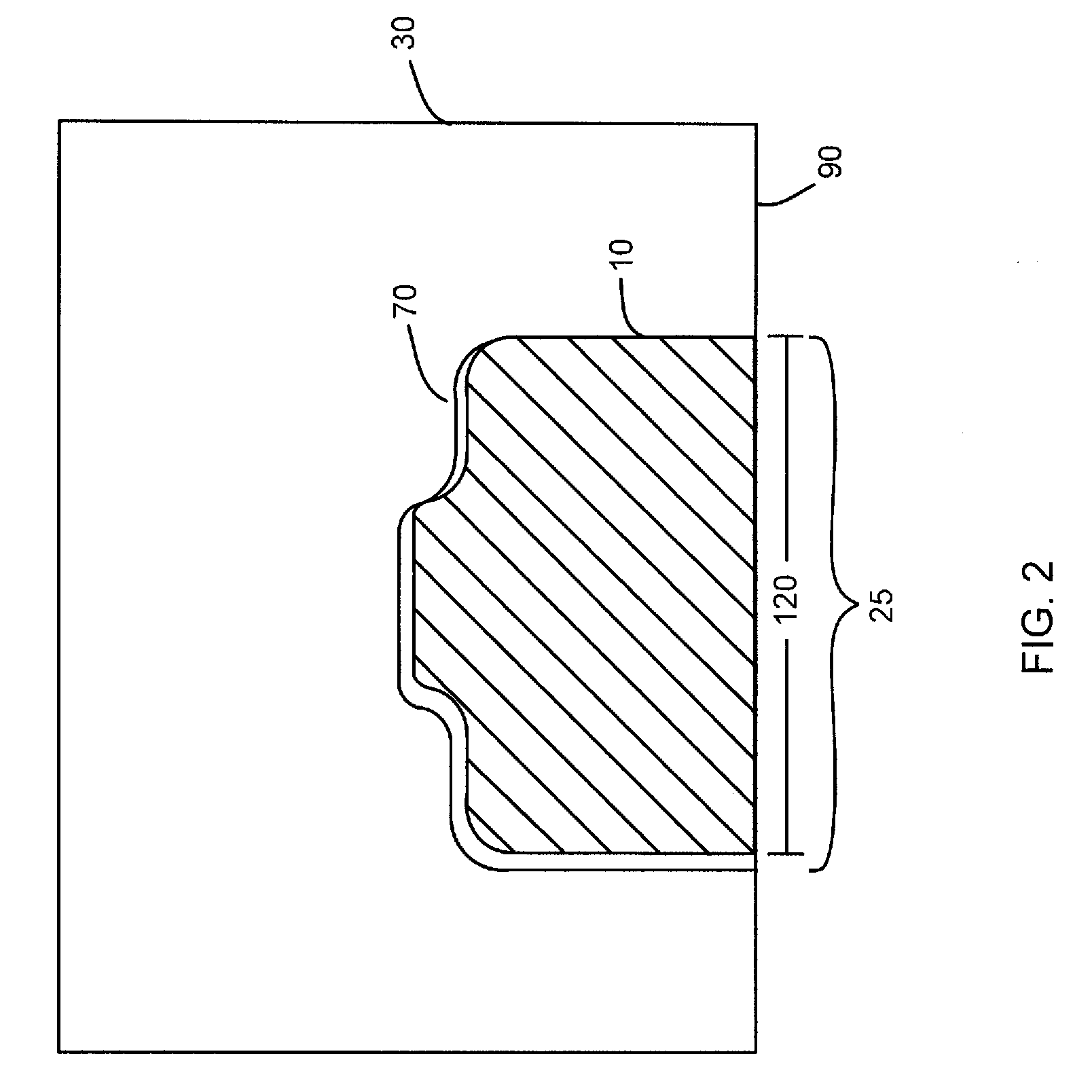
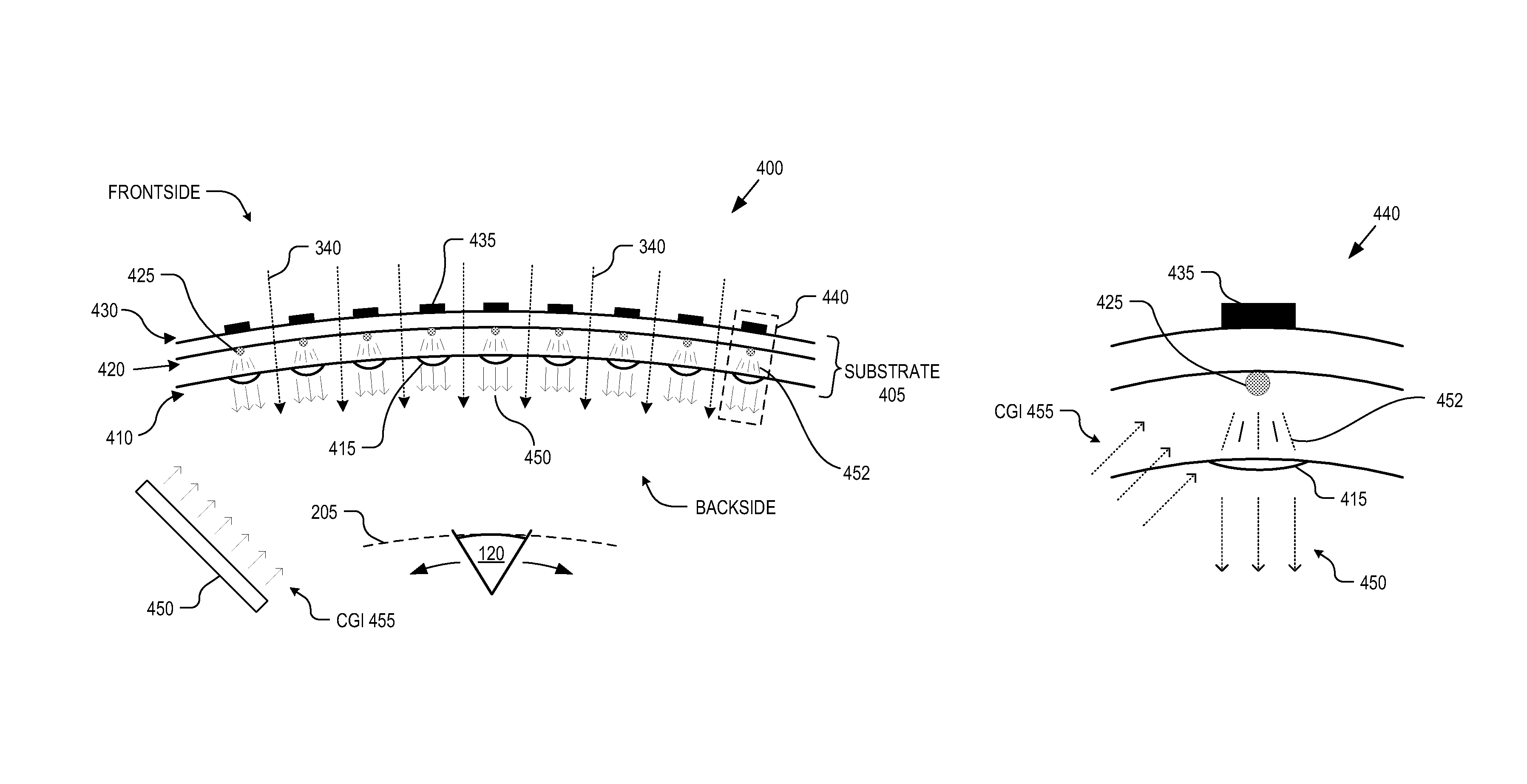
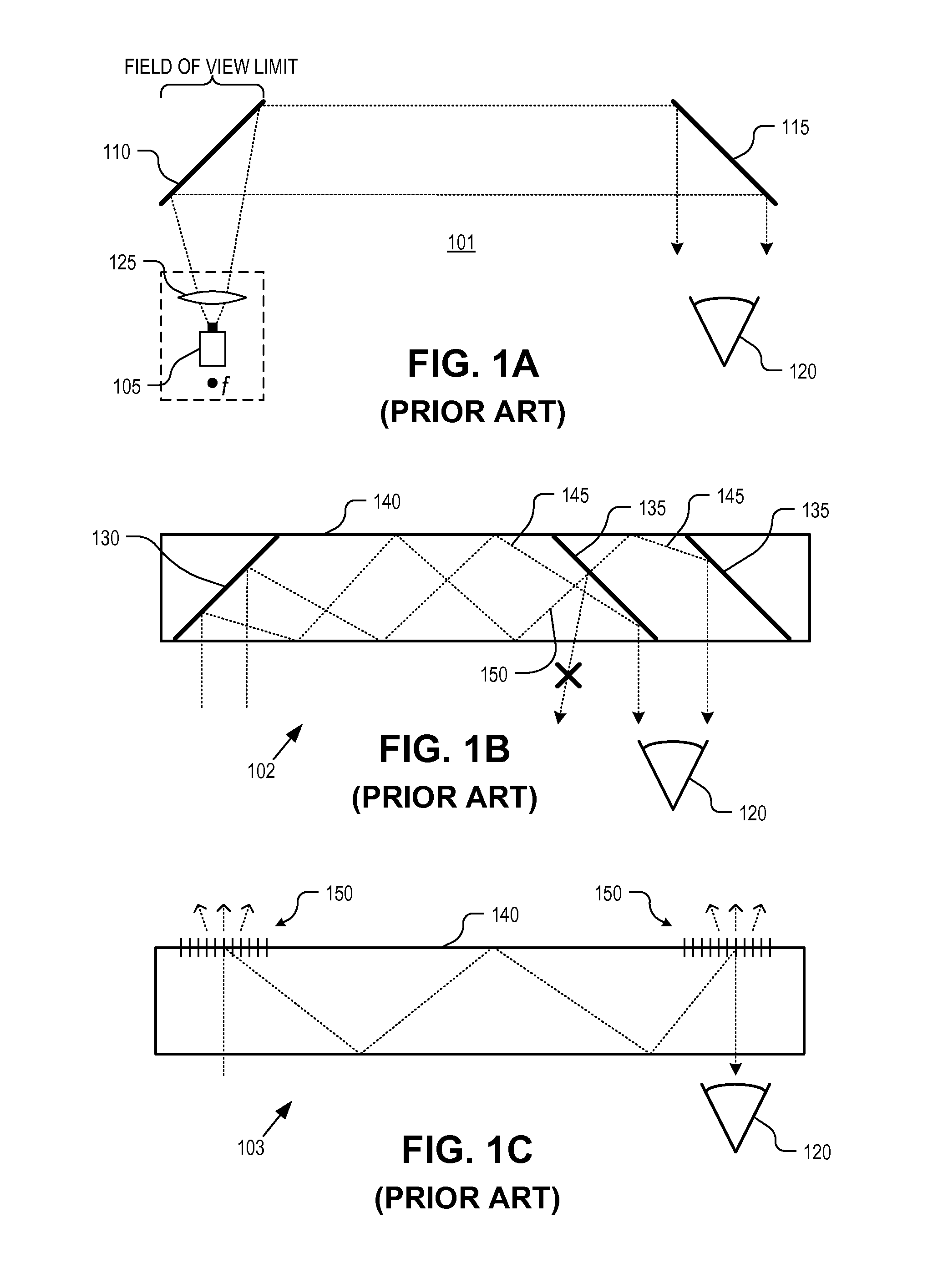
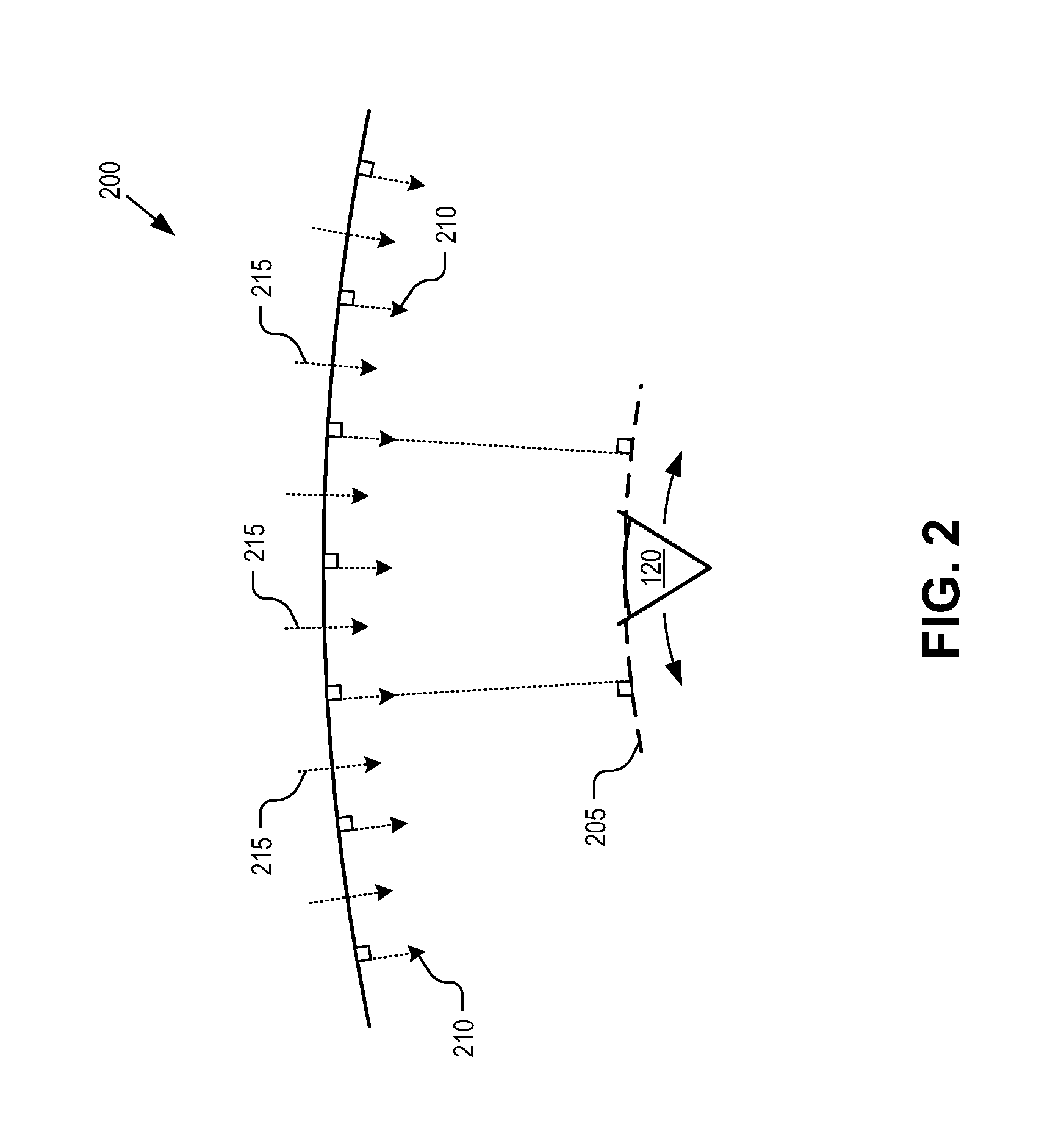
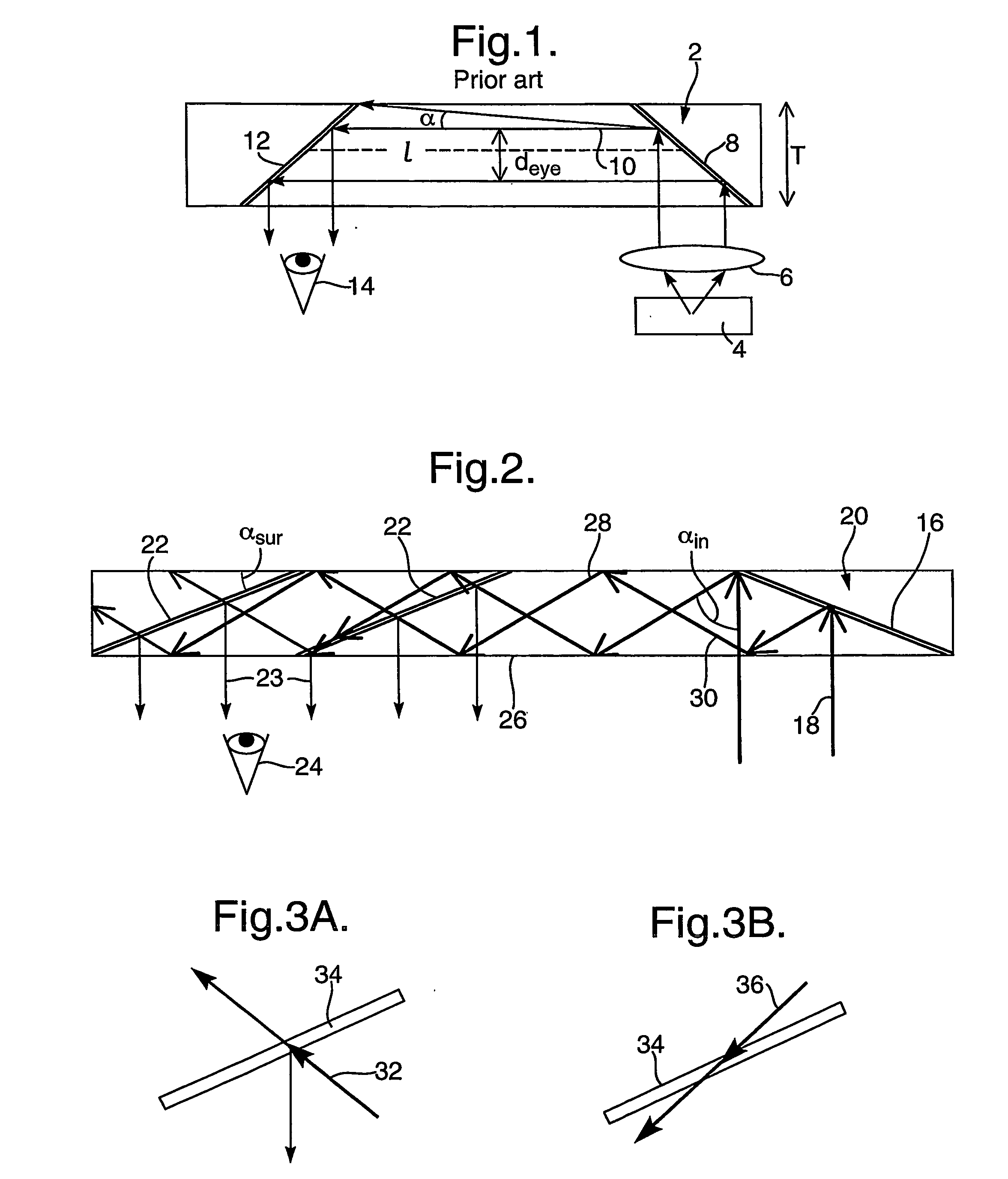
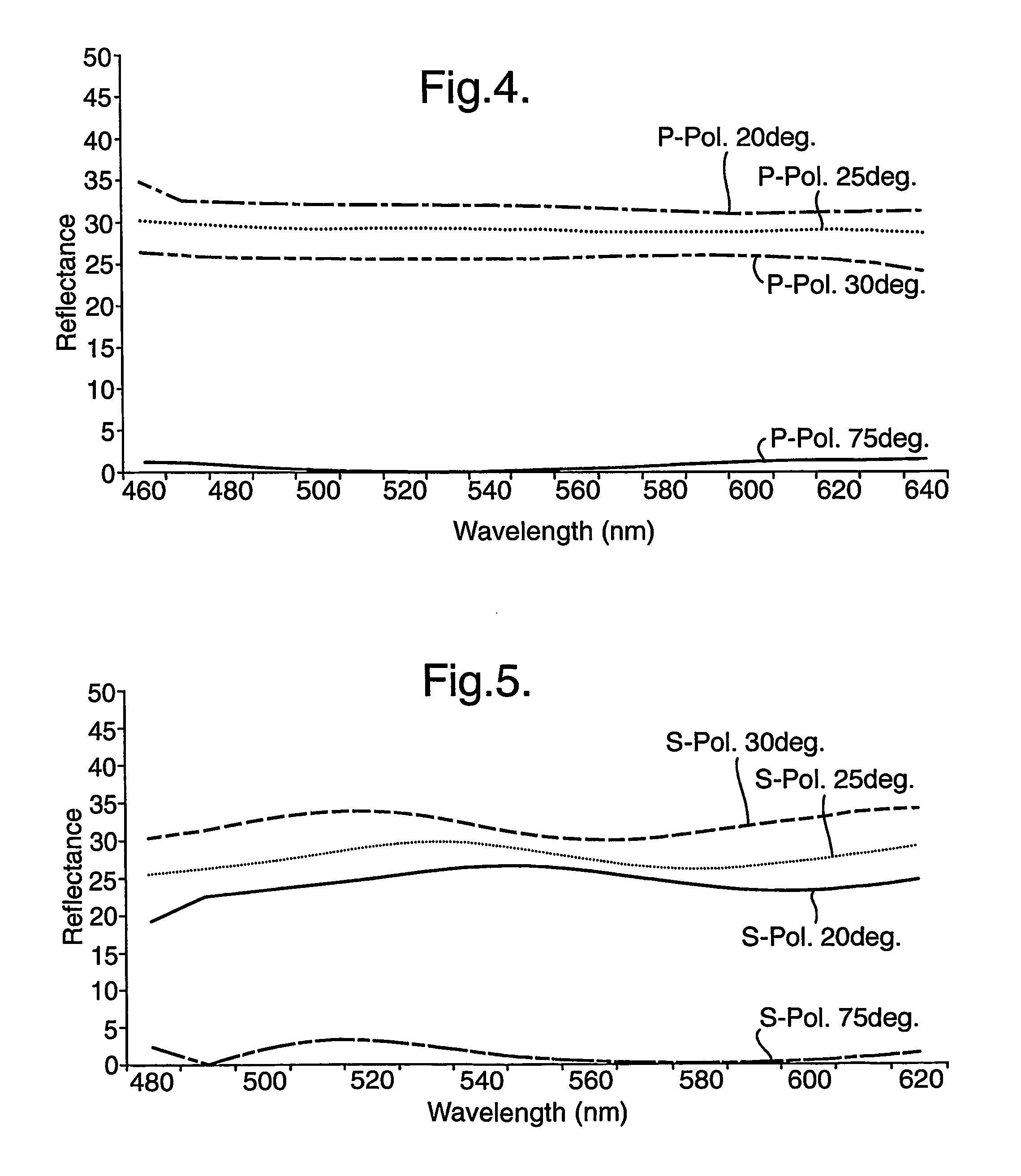
A collimated beam of light or other electromagnetic radiation has parallel rays, and therefore will spread minimally as it propagates. A perfectly collimated light beam, with no divergence, would not disperse with distance. Such a beam cannot be created, due to diffraction.
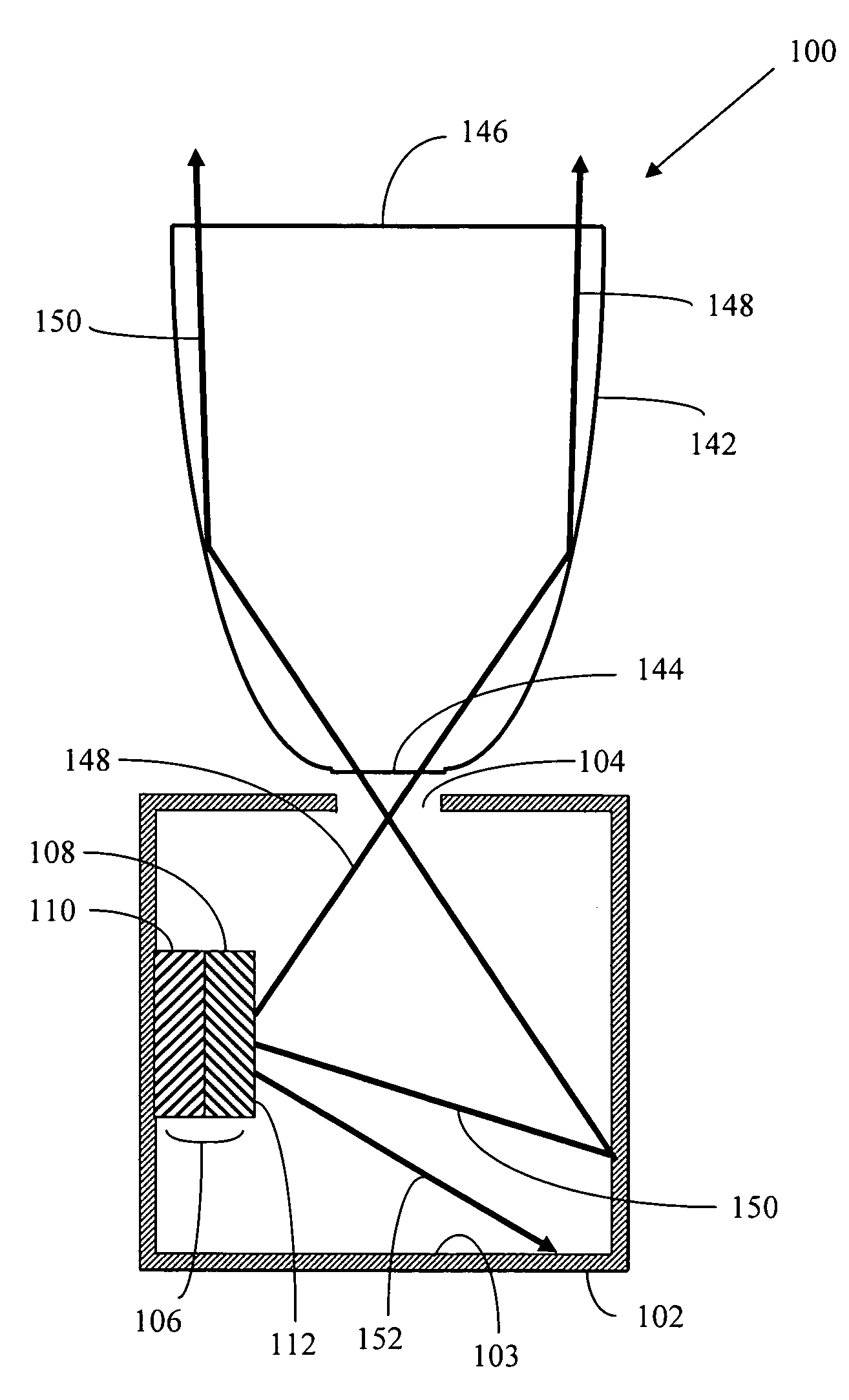
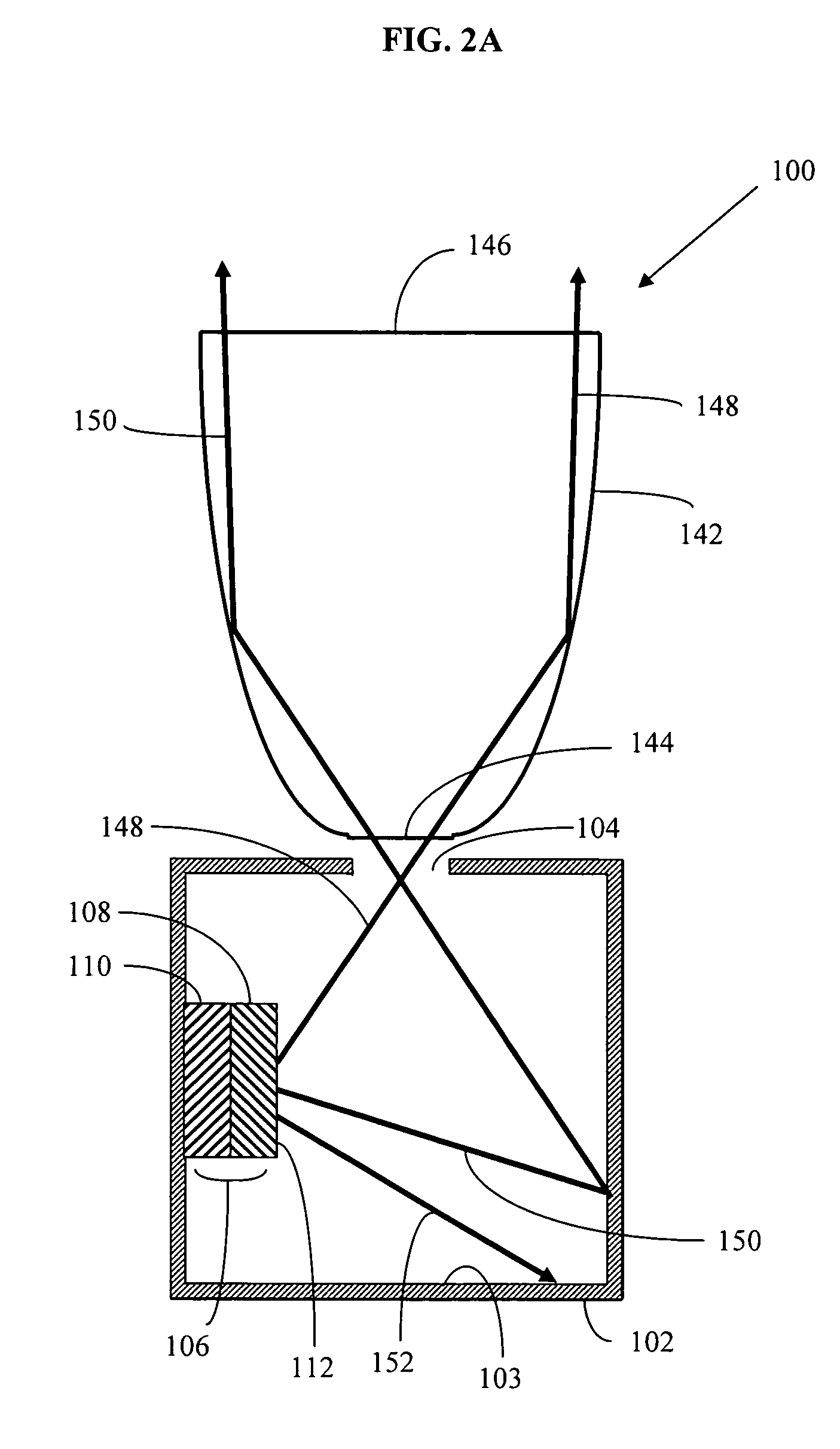
System and method for measuring irregular objects with a single camera
ActiveUS8643717B2Rapid and efficient mannerAccurate chargesCharacter and pattern recognitionColor television detailsFresnel lensSize measurement
Owner:HAND HELD PRODS
Optically oriented three-dimensional polymer microstructures
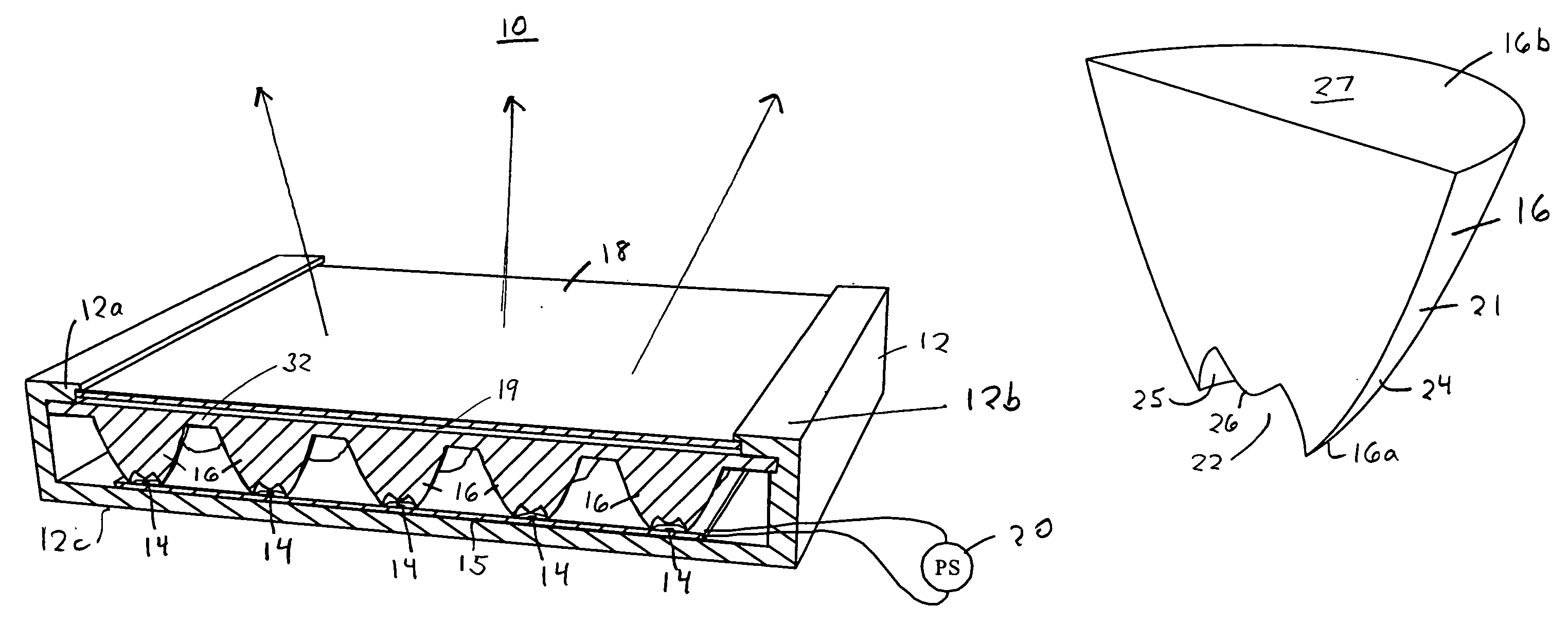
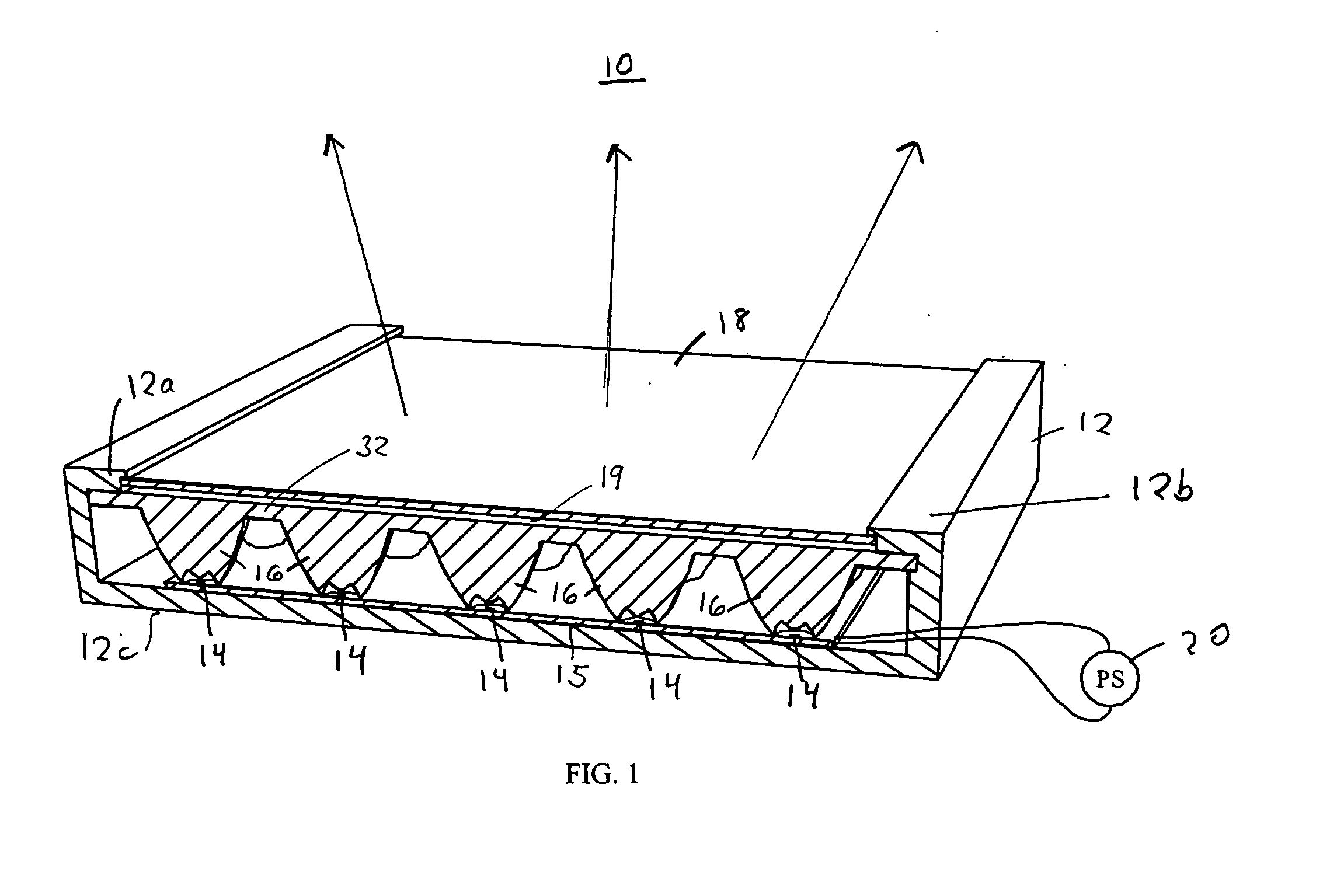
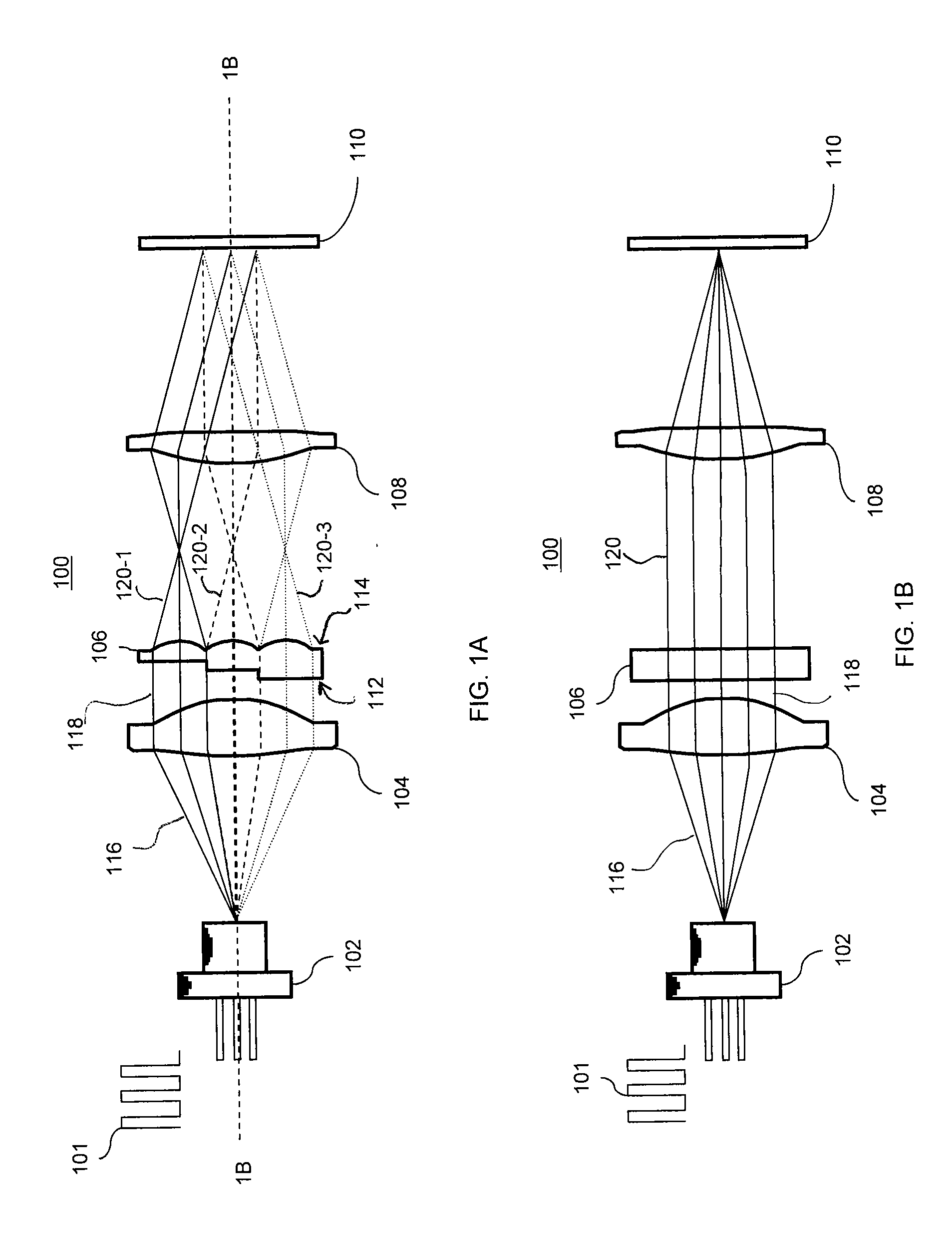
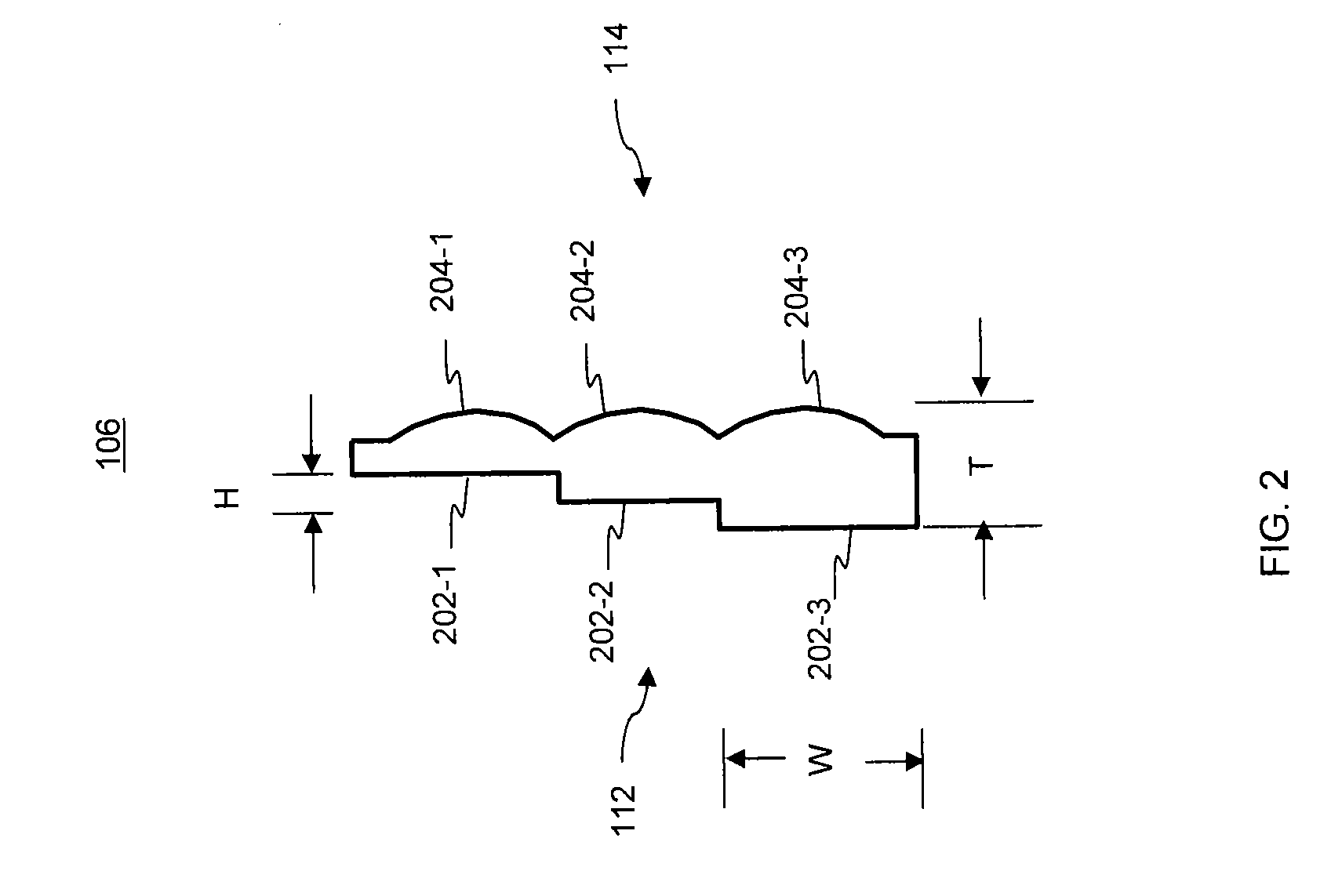
A method and system of creating one or more waveguides and / or patterning these waveguides to form a 3D microstructure that uses mask and collimated light. In one embodiment, the system includes at least one collimated light source selected to produce a collimated light beam; a reservoir having a photo-monomer adapted to polymerize by the collimated light beam; and a mask having at least one aperture and positioned between the at least one collimated light source and the reservoir. Here, the at least one aperture is adapted to guide a portion of the collimated light beam into the photo-monomer to form the at least one polymer waveguide through a portion of a volume of the photo-monomer.
Owner:HRL LAB
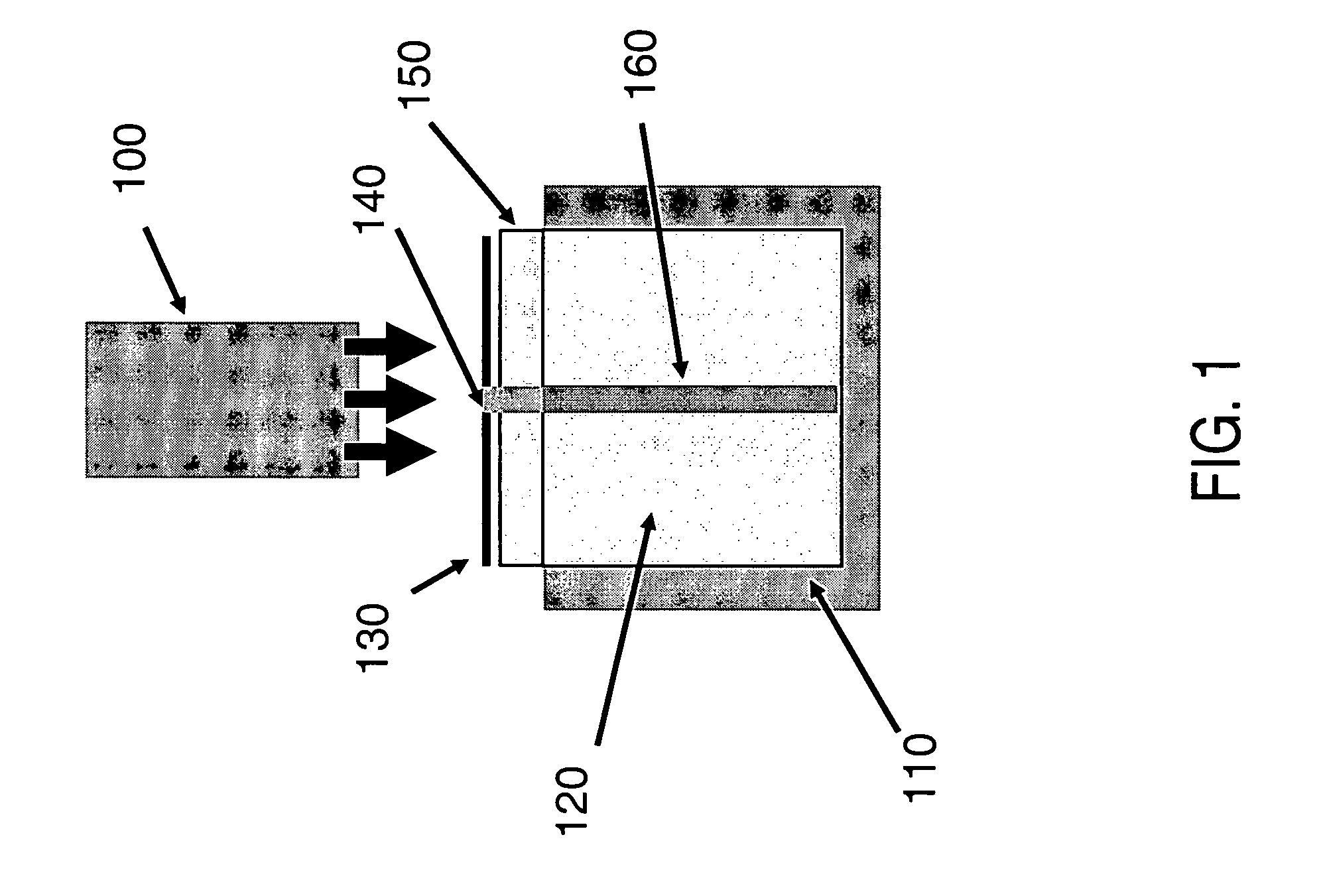
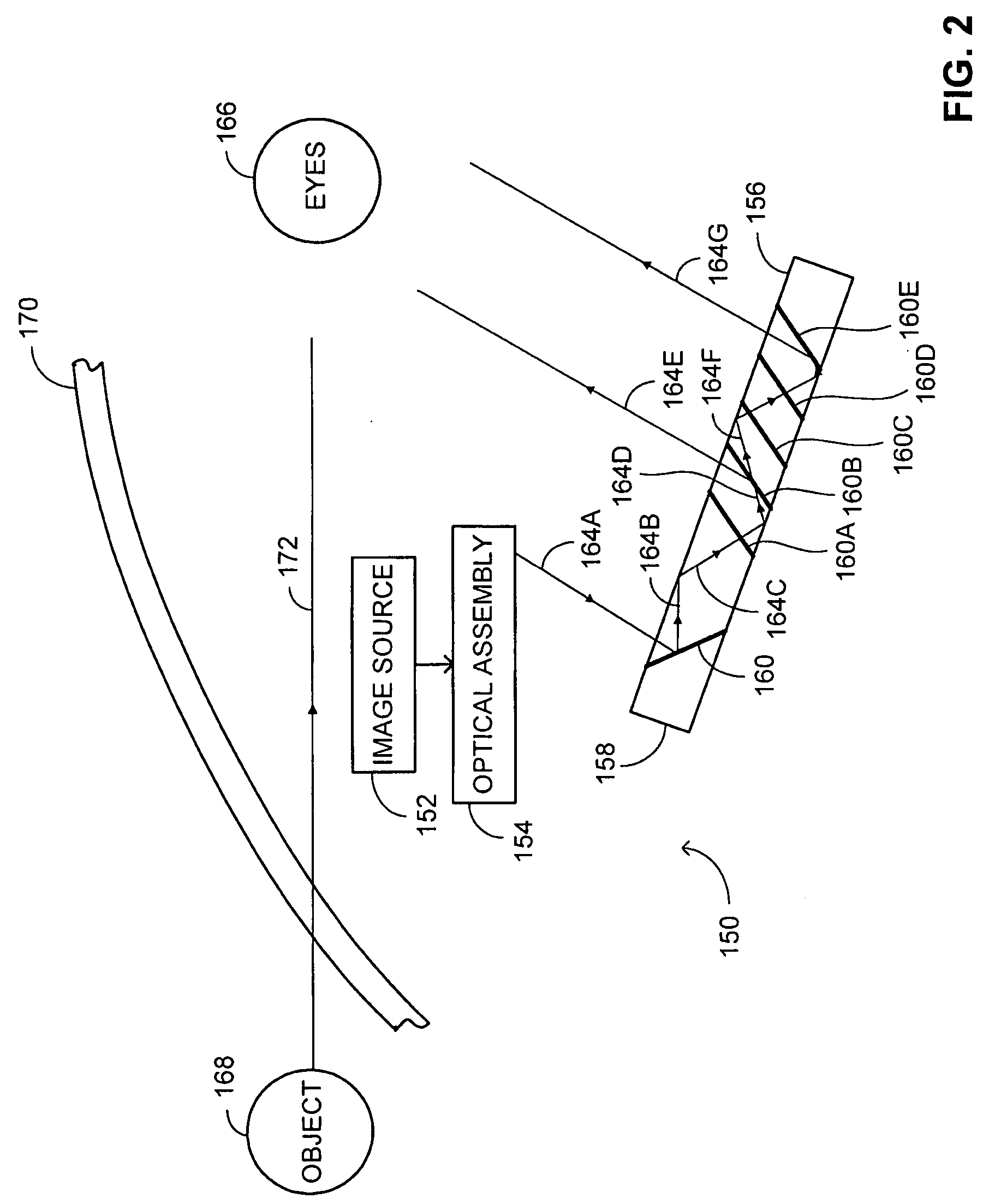
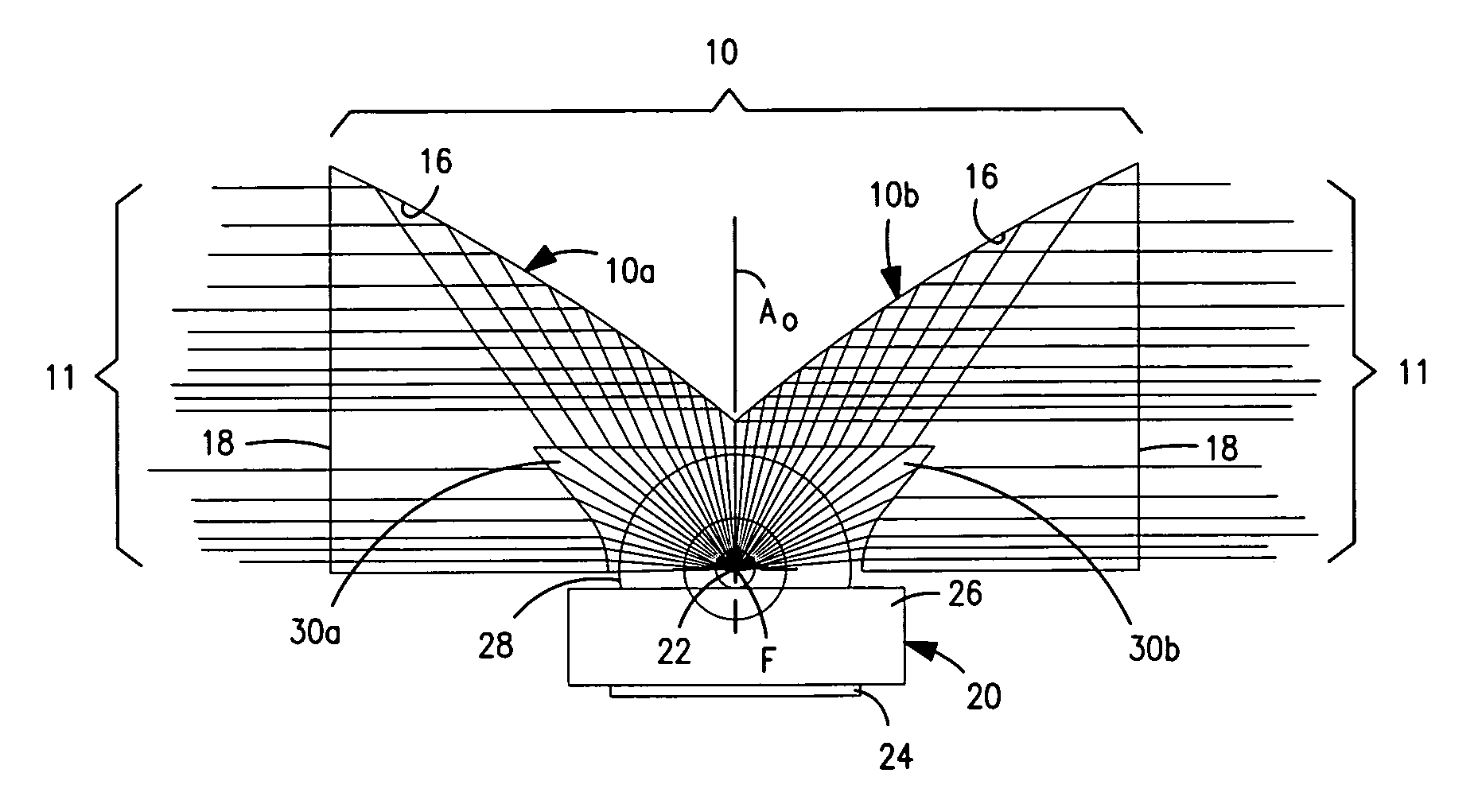
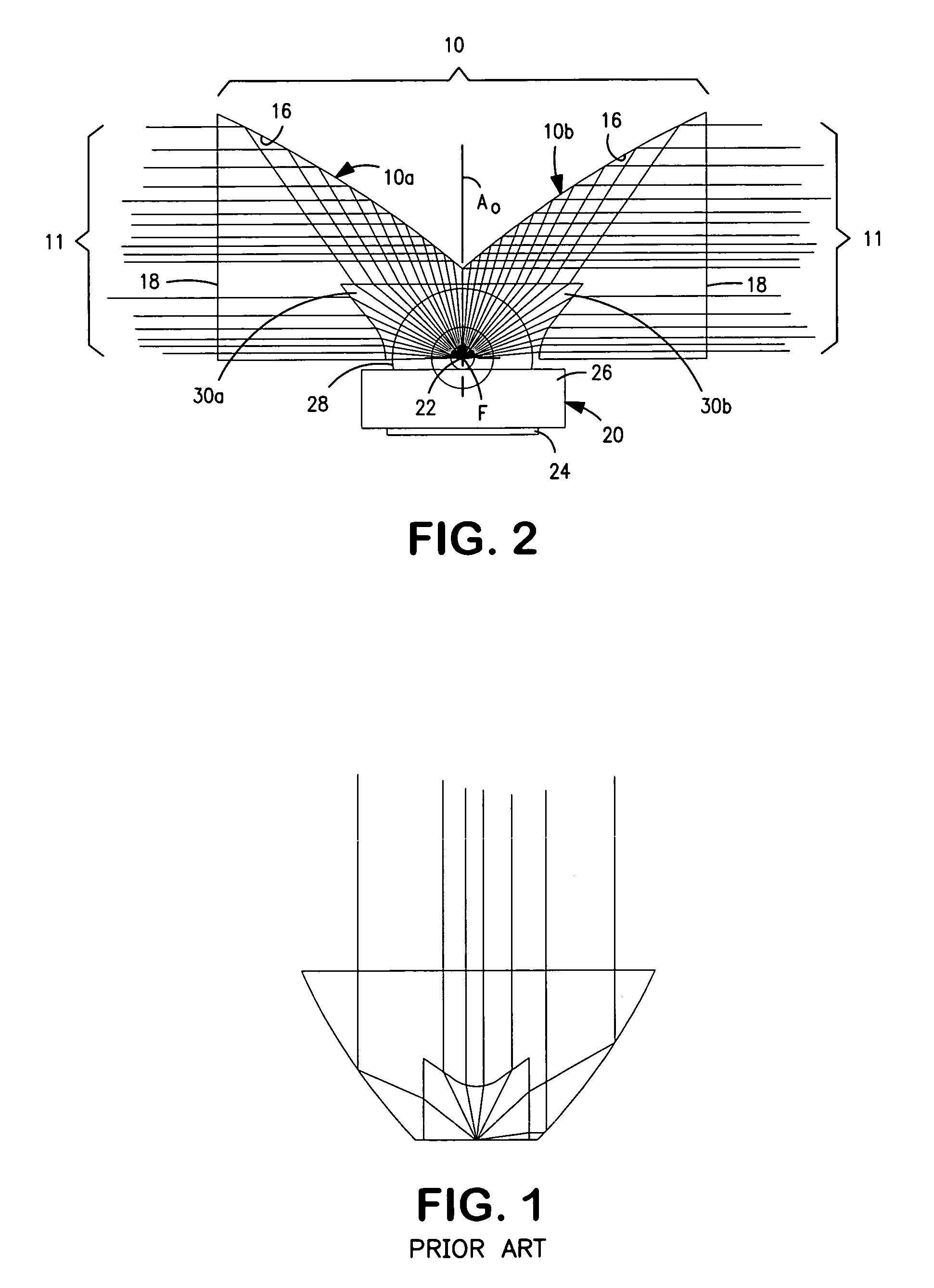
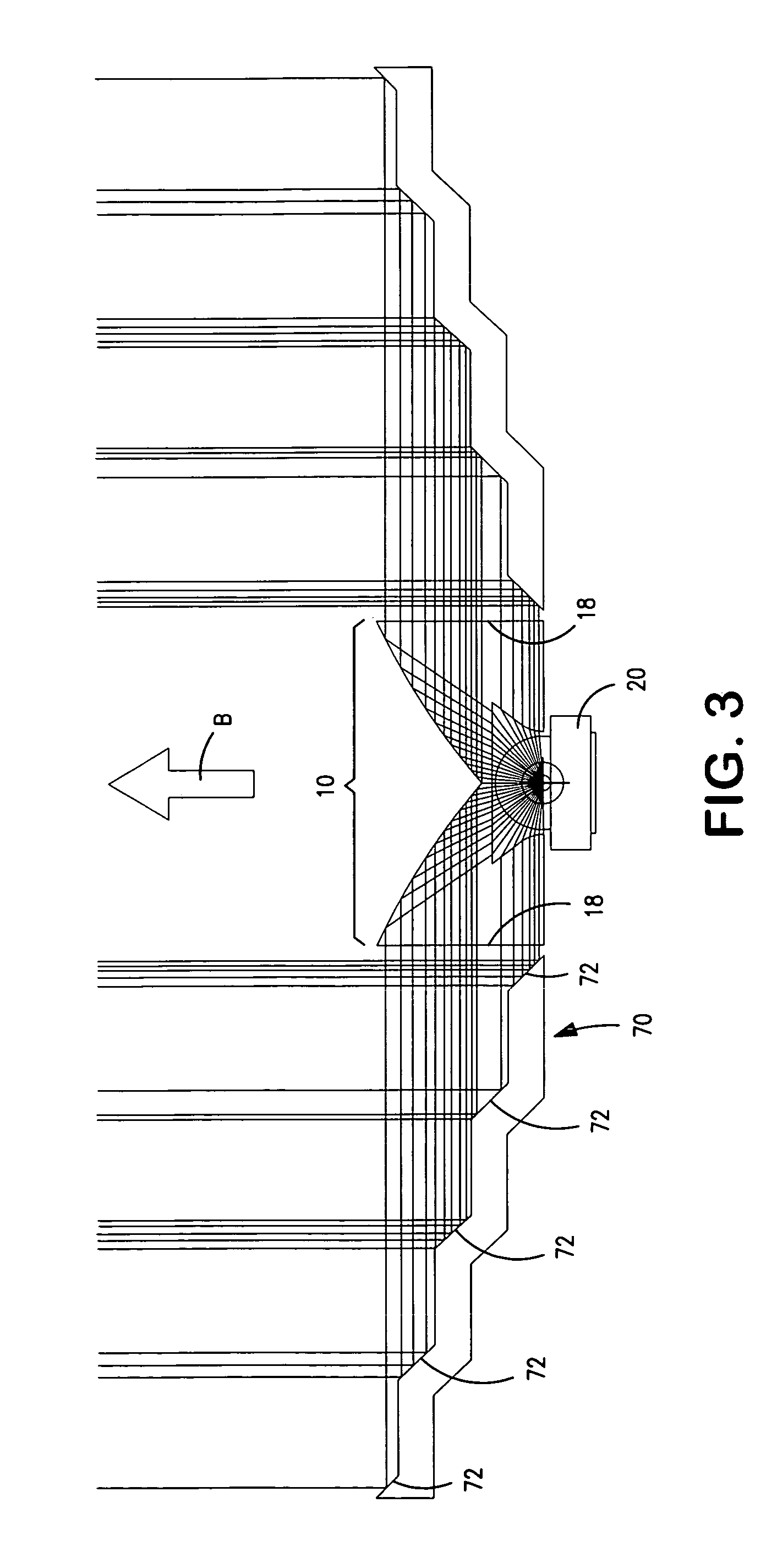
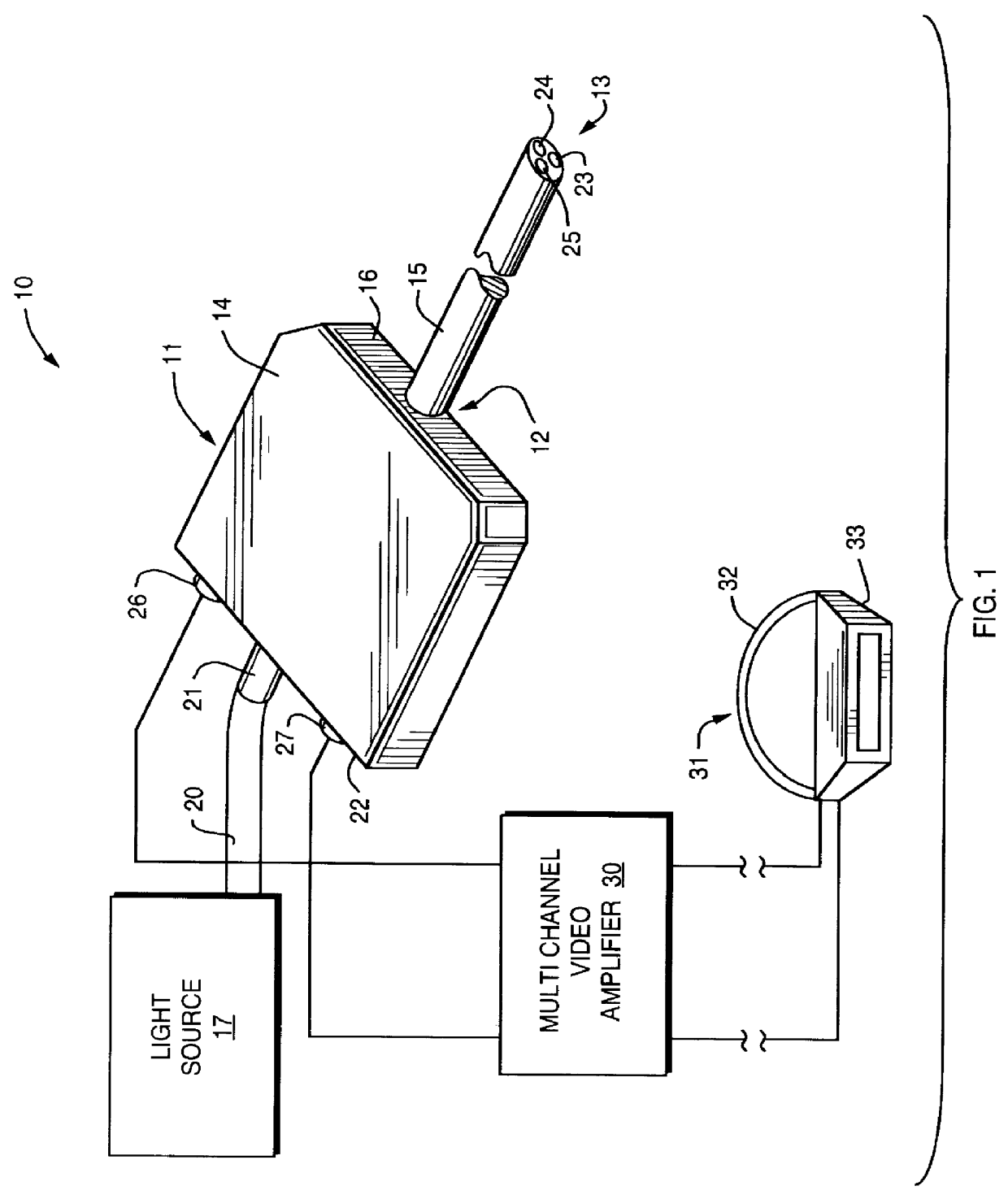
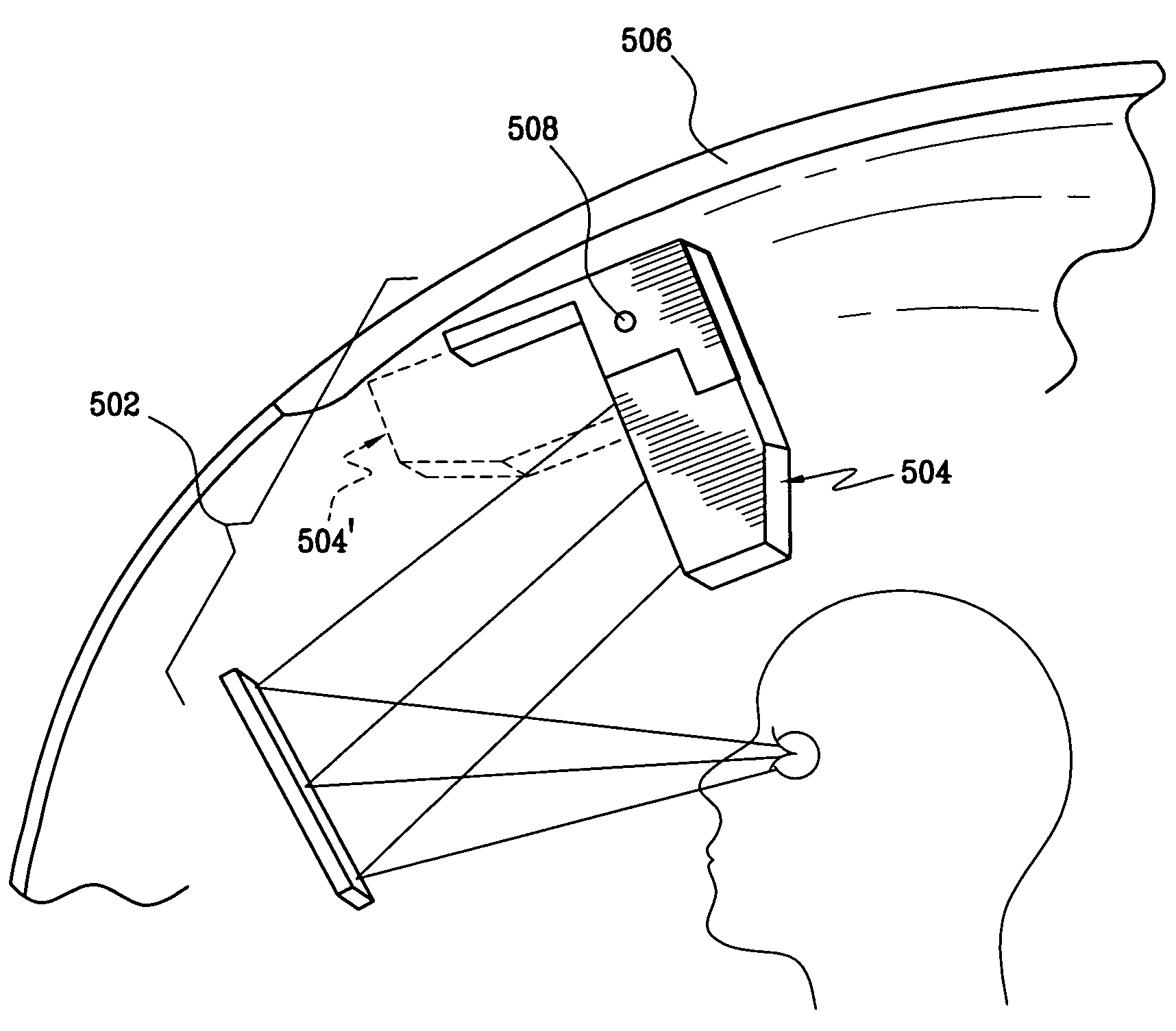
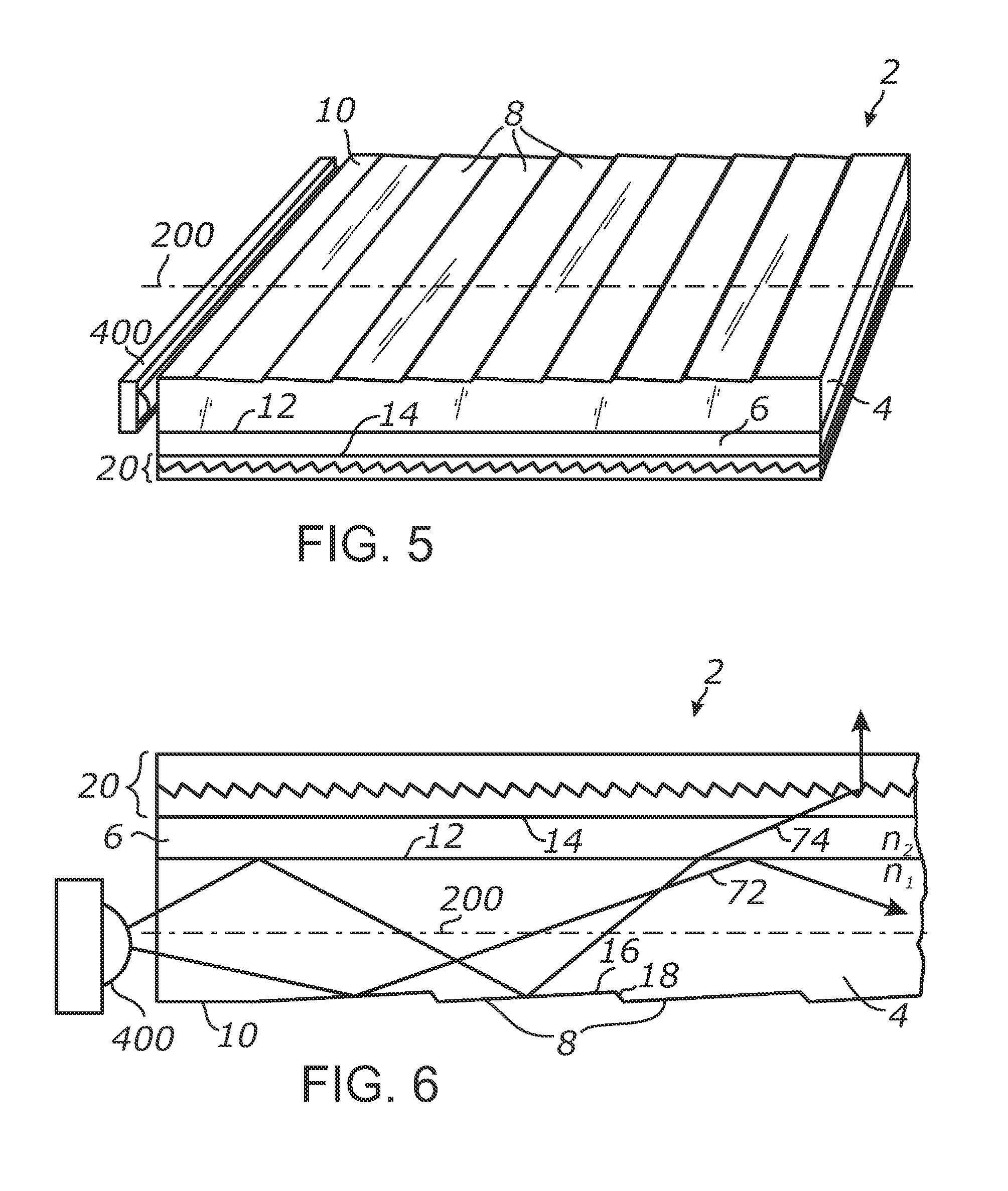
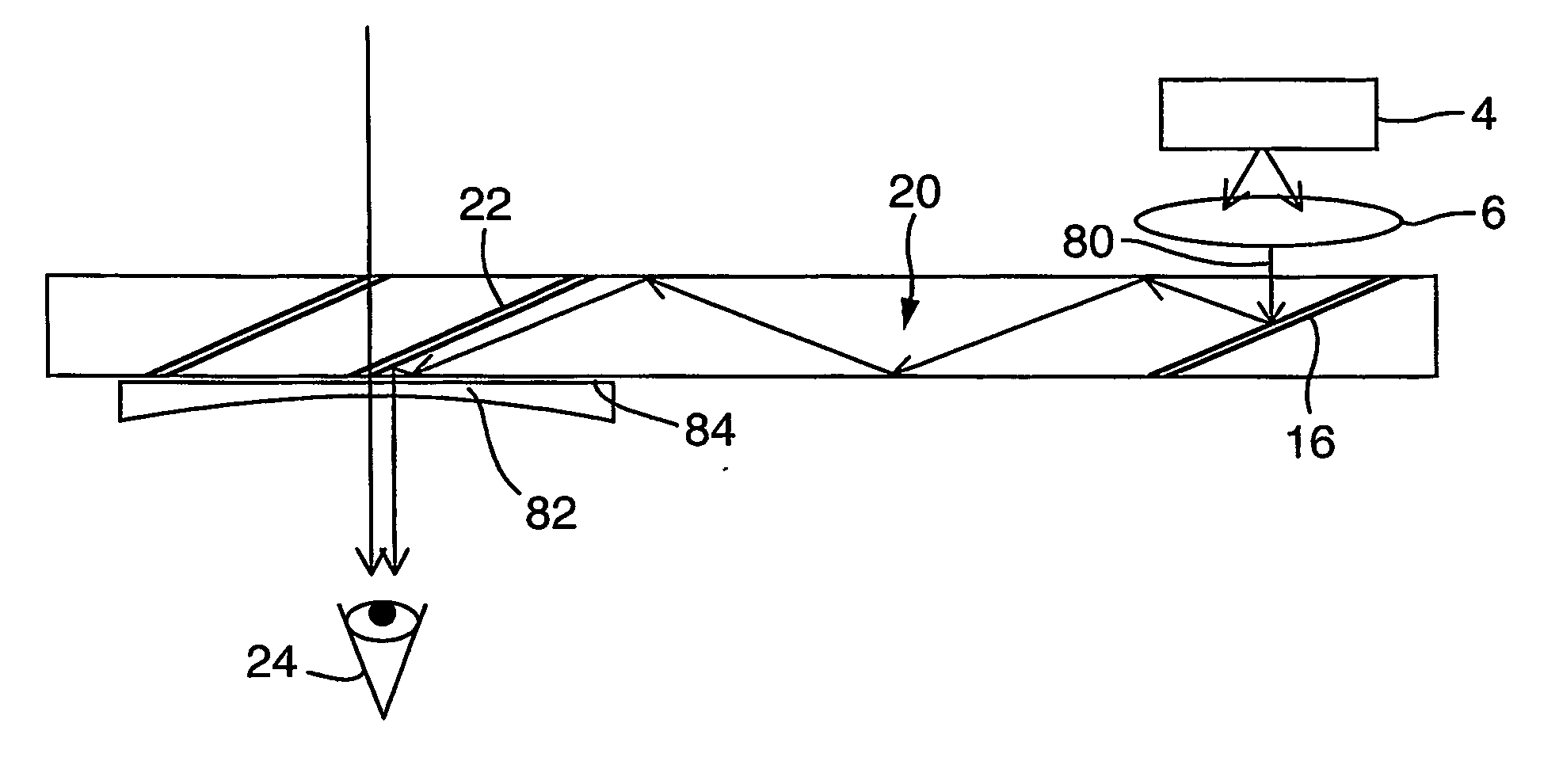
Vehicle display system
System for displaying an incident image for an operator of a vehicle, the system including an optical assembly receiving the incident image from an image source, and a planar optical module optically coupled with the optical assembly, the optical assembly producing a collimated light beam according to the incident image, the planar optical module being located in a line of sight of the operator, the planar optical module displaying a set of output decoupled images, each of the output decoupled images being similar to the incident image, and each of the output decoupled images having a focal point substantially located at an infinite distance from the operator.
Owner:EL OP ELECTRO OPTICS INDS
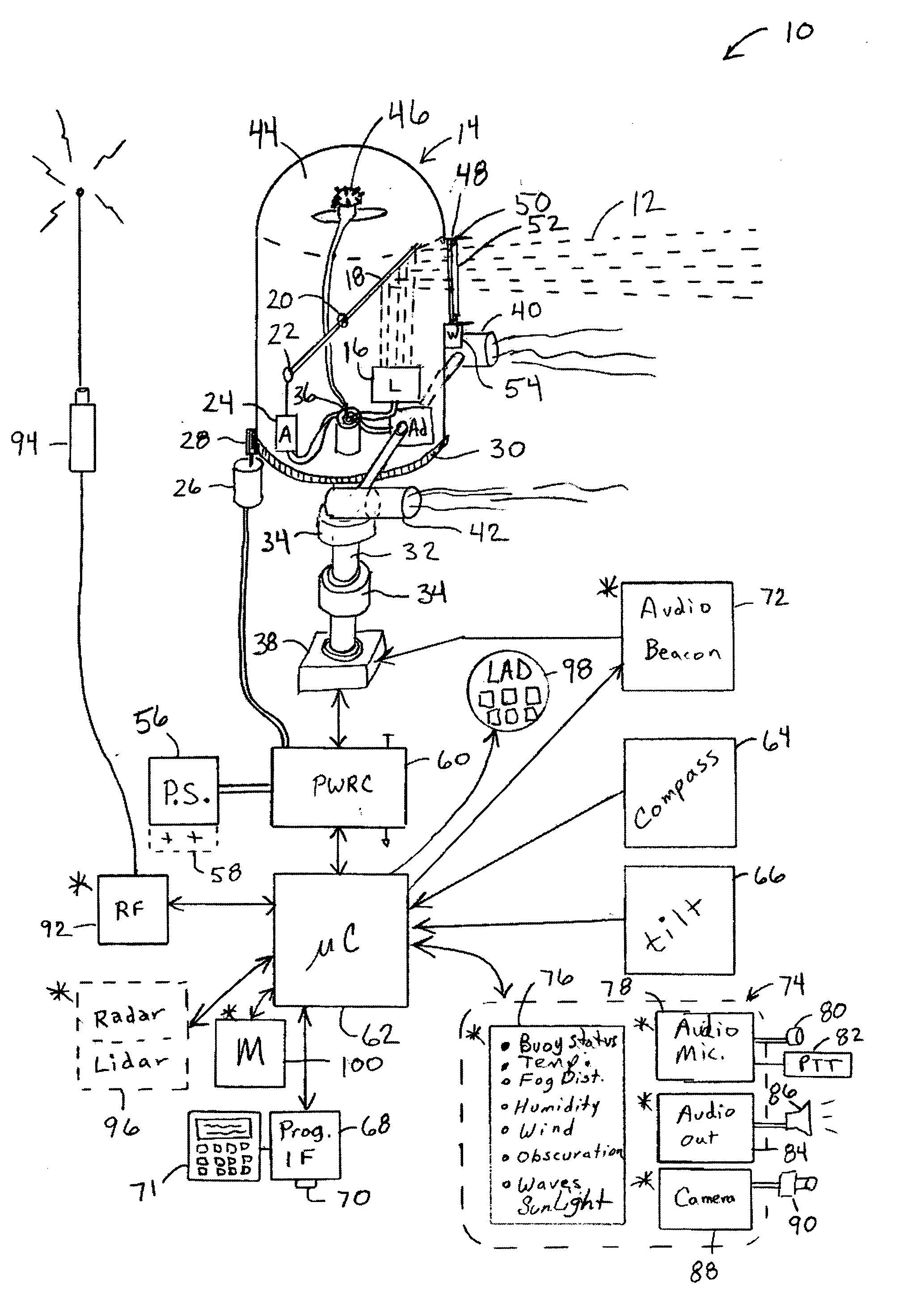
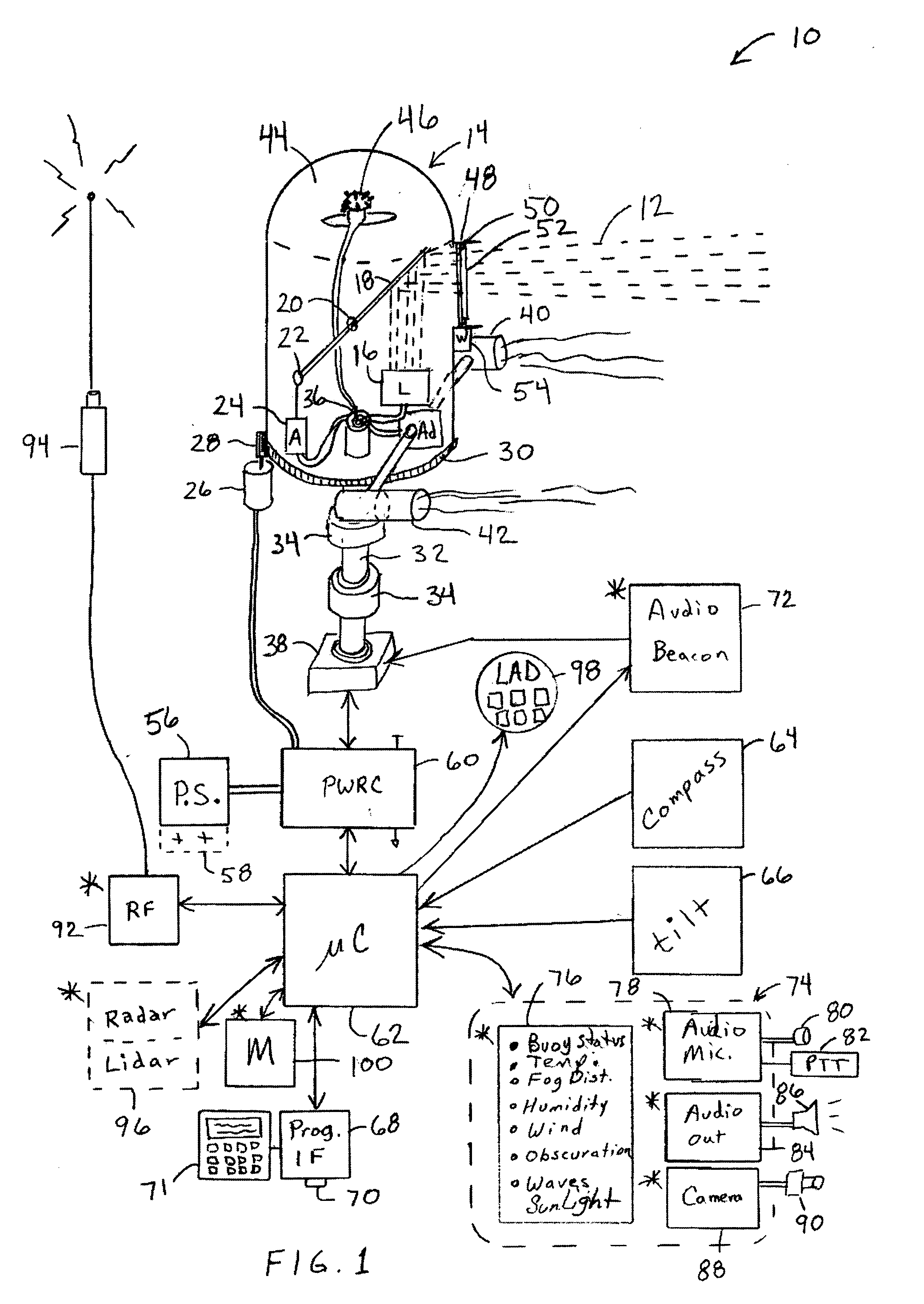
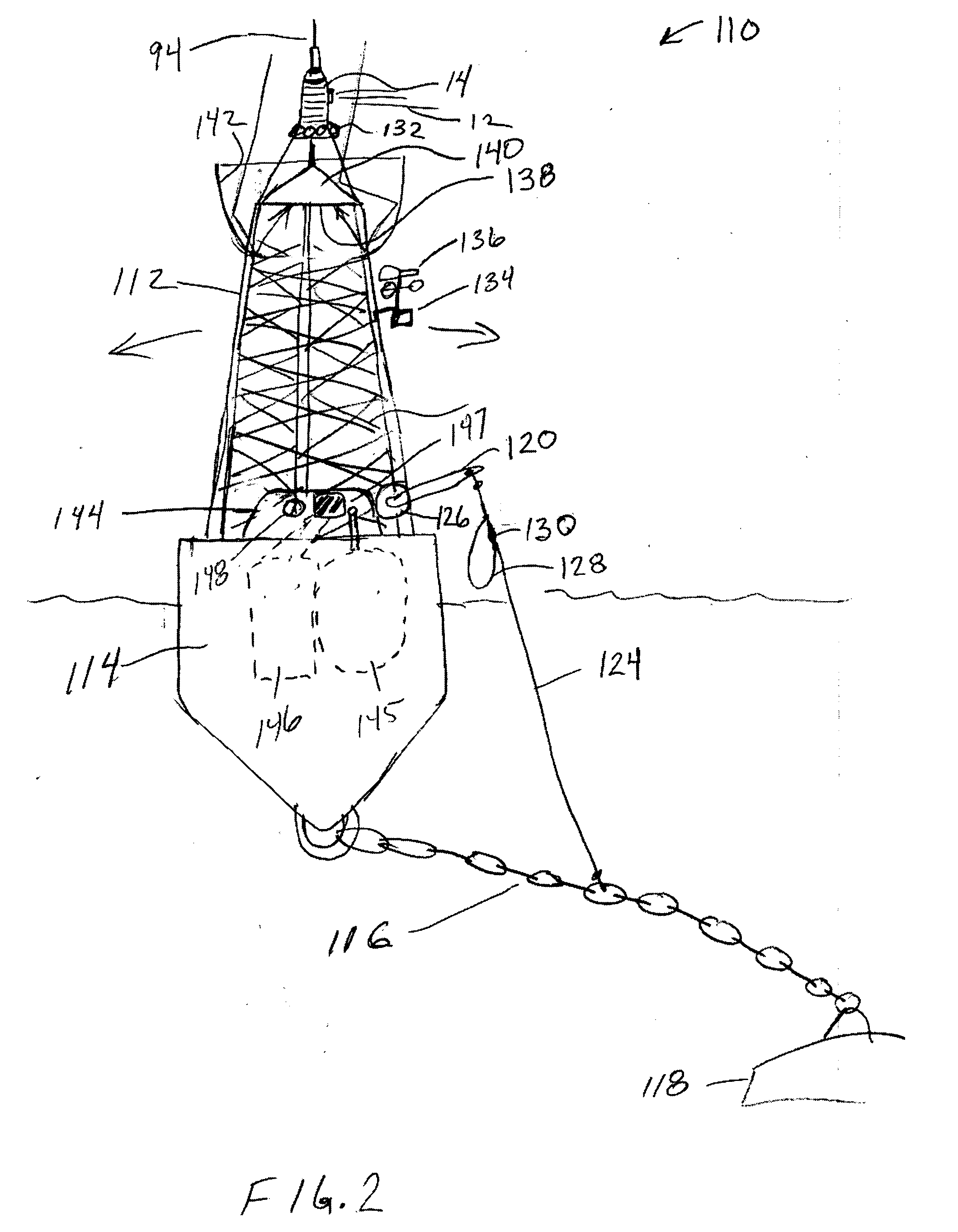
Transportation signaling device
An apparatus for generating buoy light signals using a collimated light source. The system provides for communication of system conditions and ambient conditions, and can provide homeland security monitoring. The system senses motion of the buoy and compensates the direction of lighting, and optionally acoustics, being generated out over a body of water. Numerous other transportation related embodiments are described including devices for providing user comfort when flying, automotive signaling, auto parking control, sports bottles, visors, and lures.
Owner:RAST RODGER H
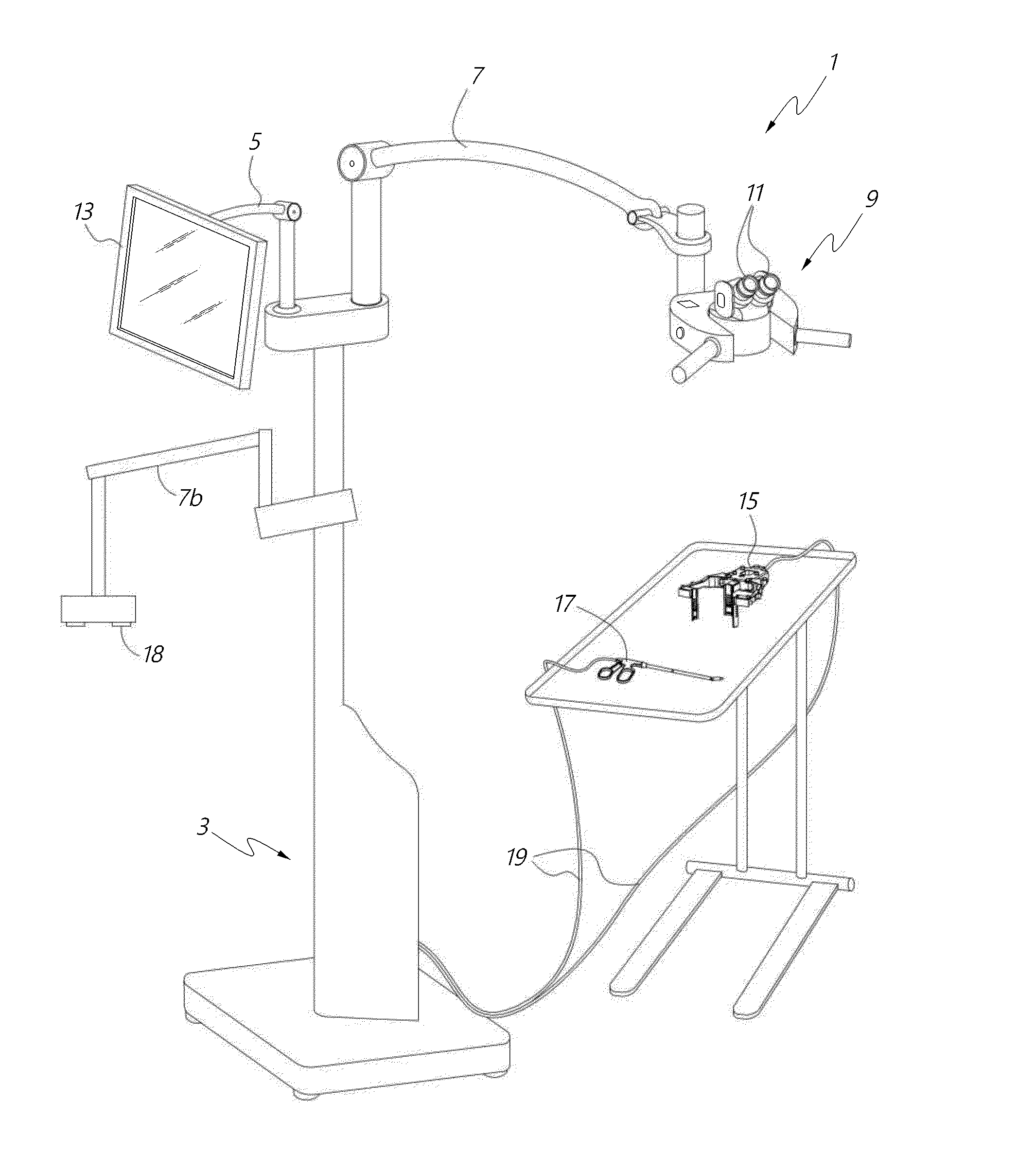
Surgical visualization systems
InactiveUS20150297311A1Minimize and reduce sizeSave spaceUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsImage enhancementEyepieceDisplay device
A medical apparatus is described for providing visualization of a surgical site. The medical apparatus includes an electronic display disposed within a display housing, the electronic display configured to produce a two-dimensional image. The medical apparatus includes a display optical system disposed within the display housing, the display optical system comprising a plurality of lens elements disposed along an optical path. The display optical system is configured to receive the two-dimensional image from the electronic display, produce a beam with a cross-section that remains substantially constant along the optical path, and produce a collimated beam exiting the opening in the display housing. The medical apparatus can also include an auxiliary video camera configured to provide an oblique view of a patient on the electronic display without requiring a surgeon to adjust their viewing angle through oculars viewing the electronic display.
Owner:CAMPLEX
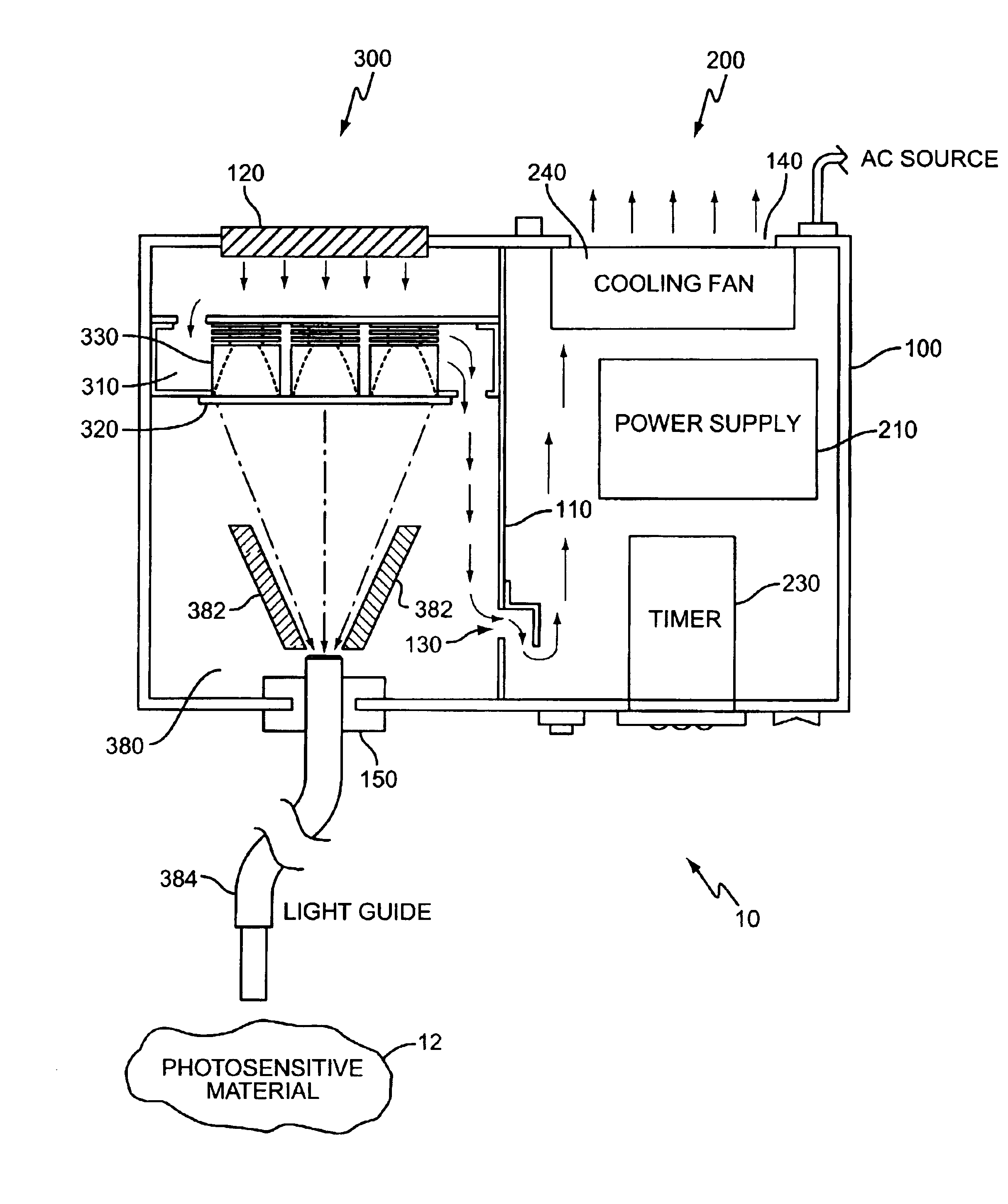
High intensity photocuring system
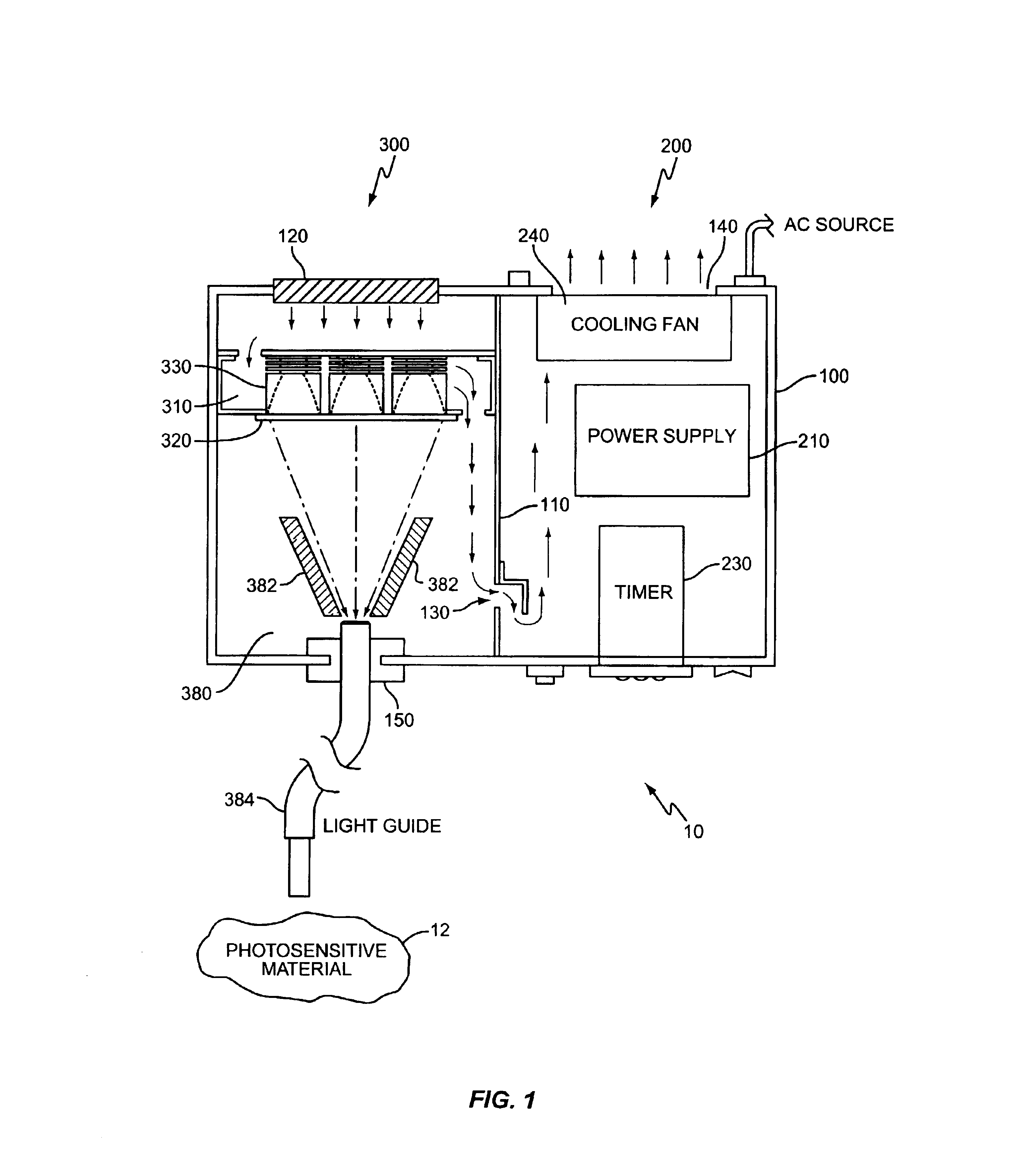
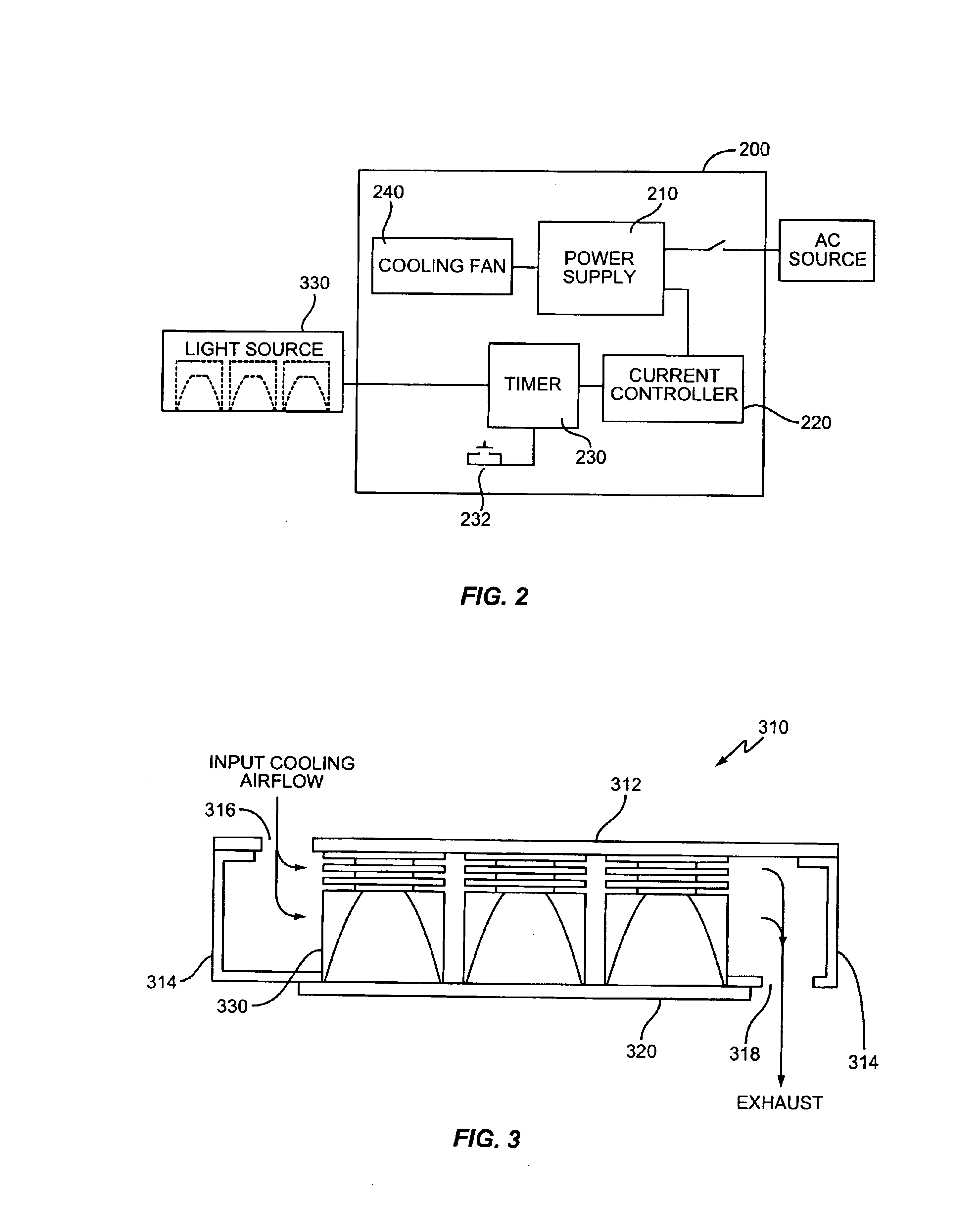
A method and apparatus for curing photosensitive materials uses LEDs and an optical concentrator to generate high optical power intensities. An LED array, comprising a plurality of LED assemblies, generates collimated light. A collection lens functions as an optical concentrator and focuses the collimated light to a desired spot size at a desired location. The LED assemblies may be at least partially disposed in a cooling plenum, where the cooling plenum is at least partially defined by the collection lens. Each LED assembly within the LED array may be detachably coupled to a mounting surface, enabling easy replacement of individual LED assemblies within the LED array. The photocuring assembly may also include a redirecting assembly disposed between the collection lens and the desired location that may further concentrate the light at the desired location. The photocuring assembly may include more than one of the above features.
Owner:SMD SOFTWARE
Illumination devices
ActiveUS20080043466A1Uniform lightPlanar light sourcesPoint-like light sourceEffect lightLight emitting device
Lighting devices are provided for efficiently distributing light over an area to provided uniform illumination over a wide angle or other tailored illumination patterns. Each light device has at least one light source, at least one collimator for partially collimating light from the light source, and at least one diffuser for diffusing light from the collimator. The diffuser provides diffused light over an area from the diffuser having an intensity that is angularly dependent in accordance with the angular distribution intensity of light outputted from the collimator, so as to provide a predetermined illumination pattern from the device. The light sources and collimators may be provided in one or two-dimensional arrays, and a single diffuser may be formed on each collimator or the diffuser may be along a plate spaced from the collimators.
Owner:VIAVI SOLUTIONS INC
Augmented reality glasses for medical applications and corresponding augmented reality system
Owner:BADIALI GIOVANNI +3
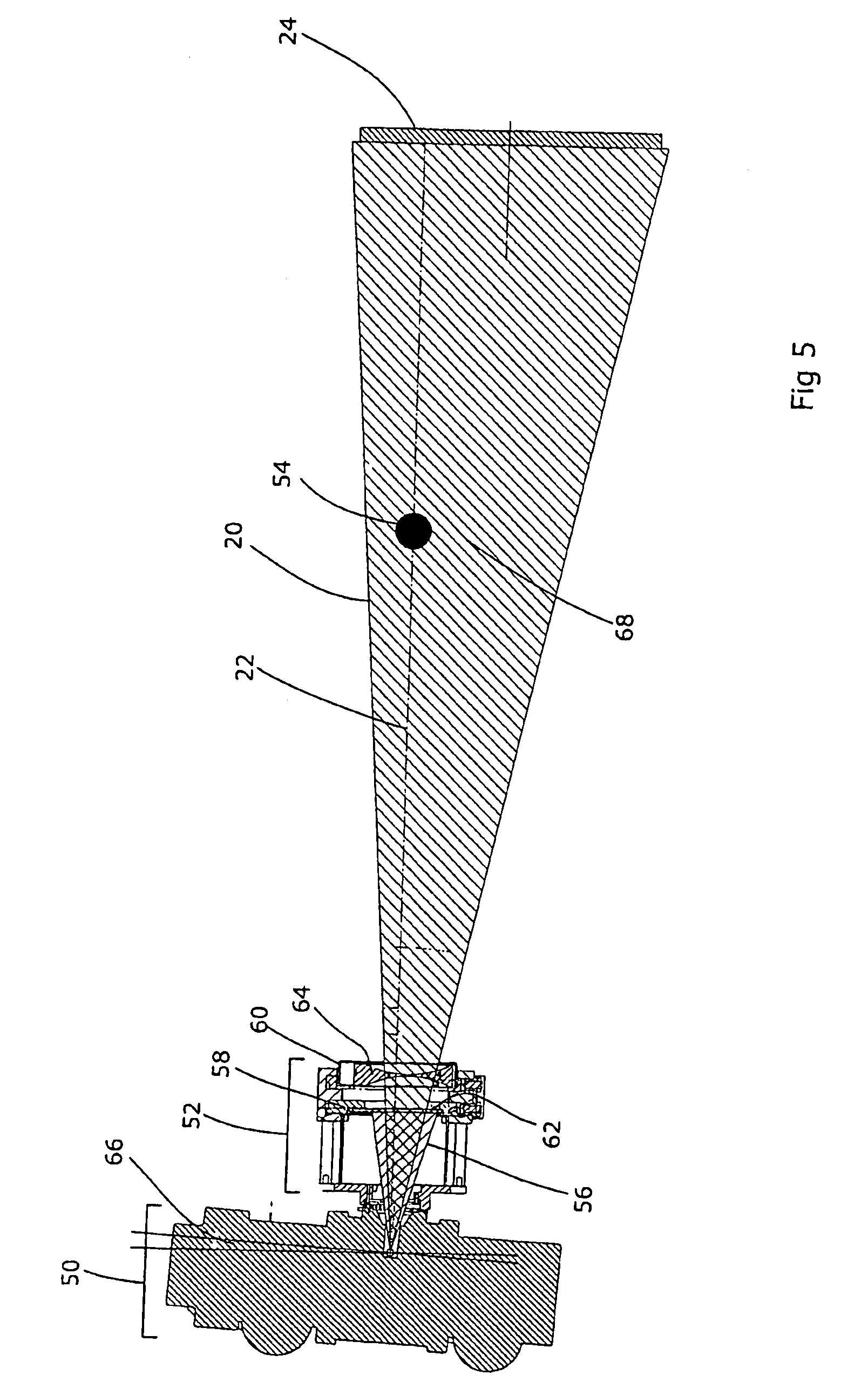
Side-emitting collimator
A side-emitting collimator employs a combination of refraction and internal reflection to organize light from a light source into oppositely directed collimated beams. A light source chamber over the light source is defined by substantially cylindrical and aspheric refracting surfaces positioned to gather light into the collimating lens. The aspheric refracting surfaces redirect a portion of the light from the light source into a direction perpendicular to the optical axis of the light source. The substantially cylindrical surfaces refract light from the light source onto an aspheric upper reflecting surface. Light incident upon the aspheric upper reflecting surface is collimated into a direction perpendicular to the optical axis of the light source. The side-emitting collimator includes mirror image collimator halves, each producing a collimated beam. The collimator halves are rotationally symmetric about a common axis of symmetry above a plane including the axis of symmetry.
Owner:WHELEN ENGINEERING COMPANY
Stereoscopic endoscope with virtual reality viewing
InactiveUS6139490AHigh contrast and spatial resolutionMinimal eye fatigueSurgeryEndoscopesProximateComputer graphics (images)
A stereoscopic endoscope system for producing images that can be perceived in three dimensions. An endoscope apparatus includes a sheath carrying a light source and two independent fixed lens endoscopes. Collimated light from the proximal ends of each endoscope are directed along folded optical paths to independent video cameras. The images generated by the video cameras energize monitors in a virtual reality display device that can be positioned proximate an observer's eyes. Adjustable mirrors and the provision of the rotation of at least one of the video cameras on its axis facilitate the alignment of the images for maximum effect.
Owner:INTUITIVE SURGICAL OPERATIONS INC
Optical manifold for light-emitting diodes
ActiveUS20060239006A1Easy to useImprove color uniformityMechanical apparatusLight source combinationsPhotoluminescencePhosphor
An optical manifold for efficiently combining a plurality of blue LED outputs to illuminate a phosphor for a single, substantially homogeneous output, in a small, cost-effective package. Embodiments are disclosed that use a single or multiple LEDs and a remote phosphor, and an intermediate wavelength-selective filter arranged so that backscattered photoluminescence is recycled to boost the luminance and flux of the output aperture. A further aperture mask is used to boost phosphor luminance with only modest loss of luminosity. Alternative non-recycling embodiments provide blue and yellow light in collimated beams, either separately or combined into white.
Owner:SEOUL SEMICONDUCTOR
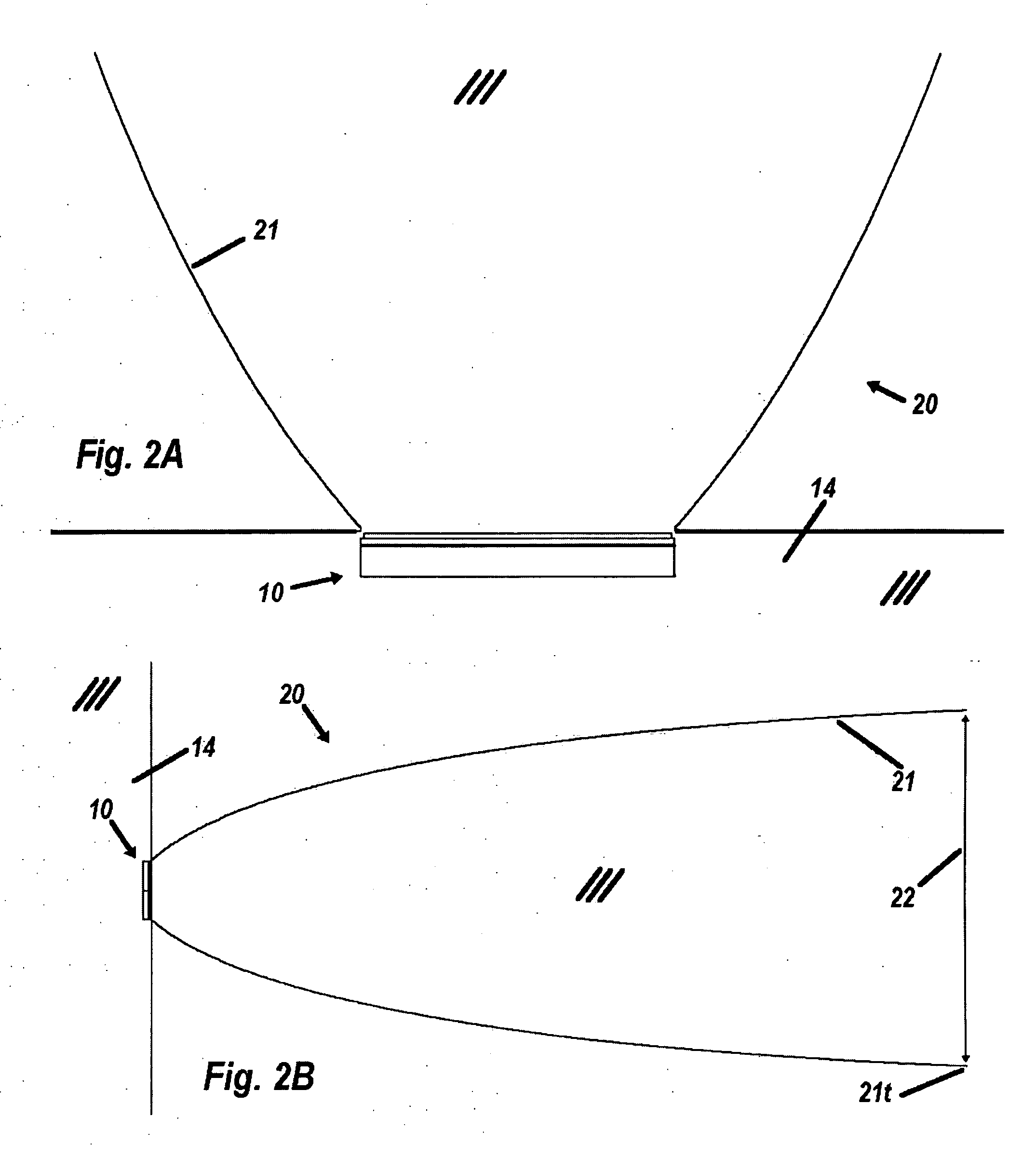
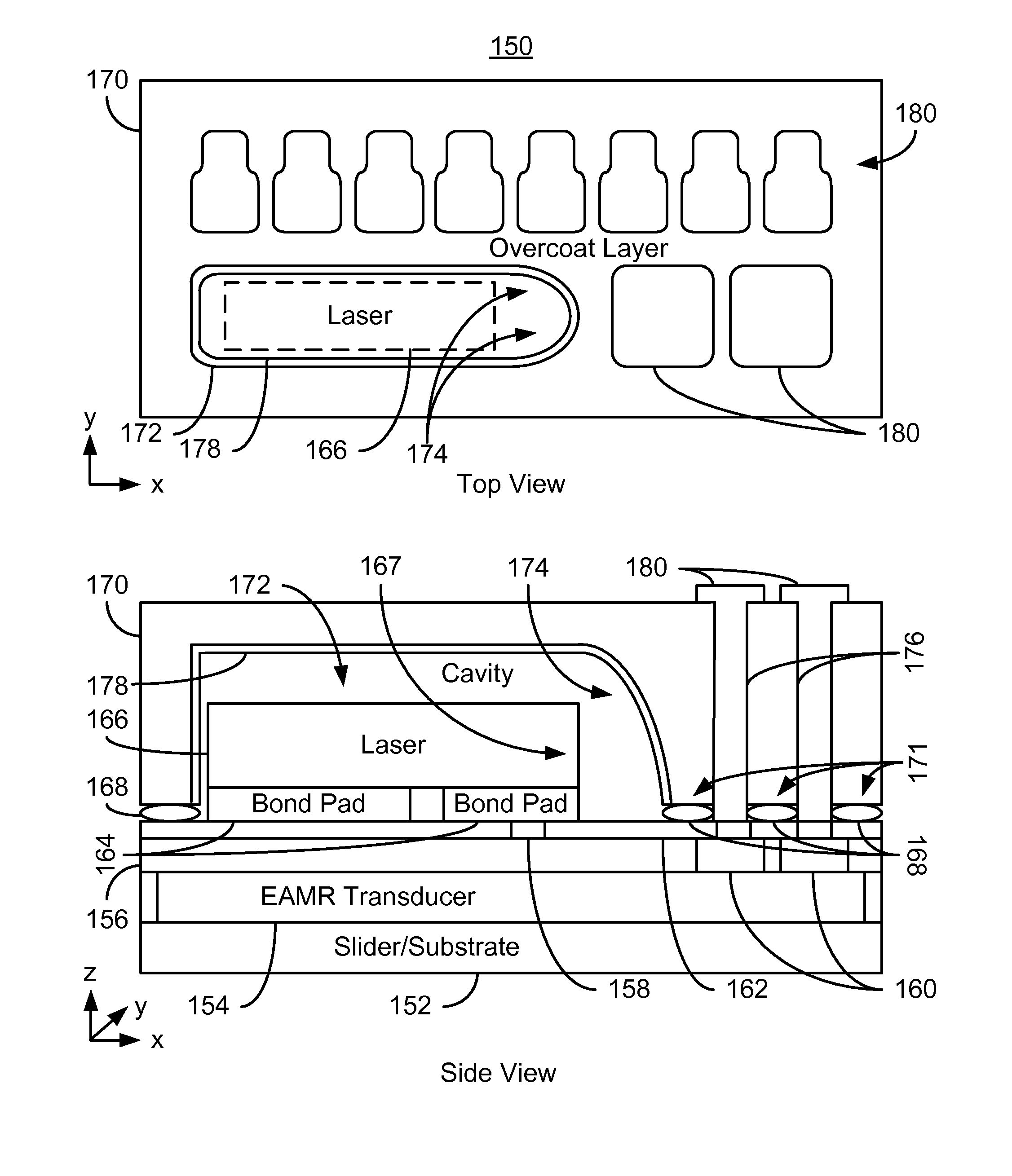
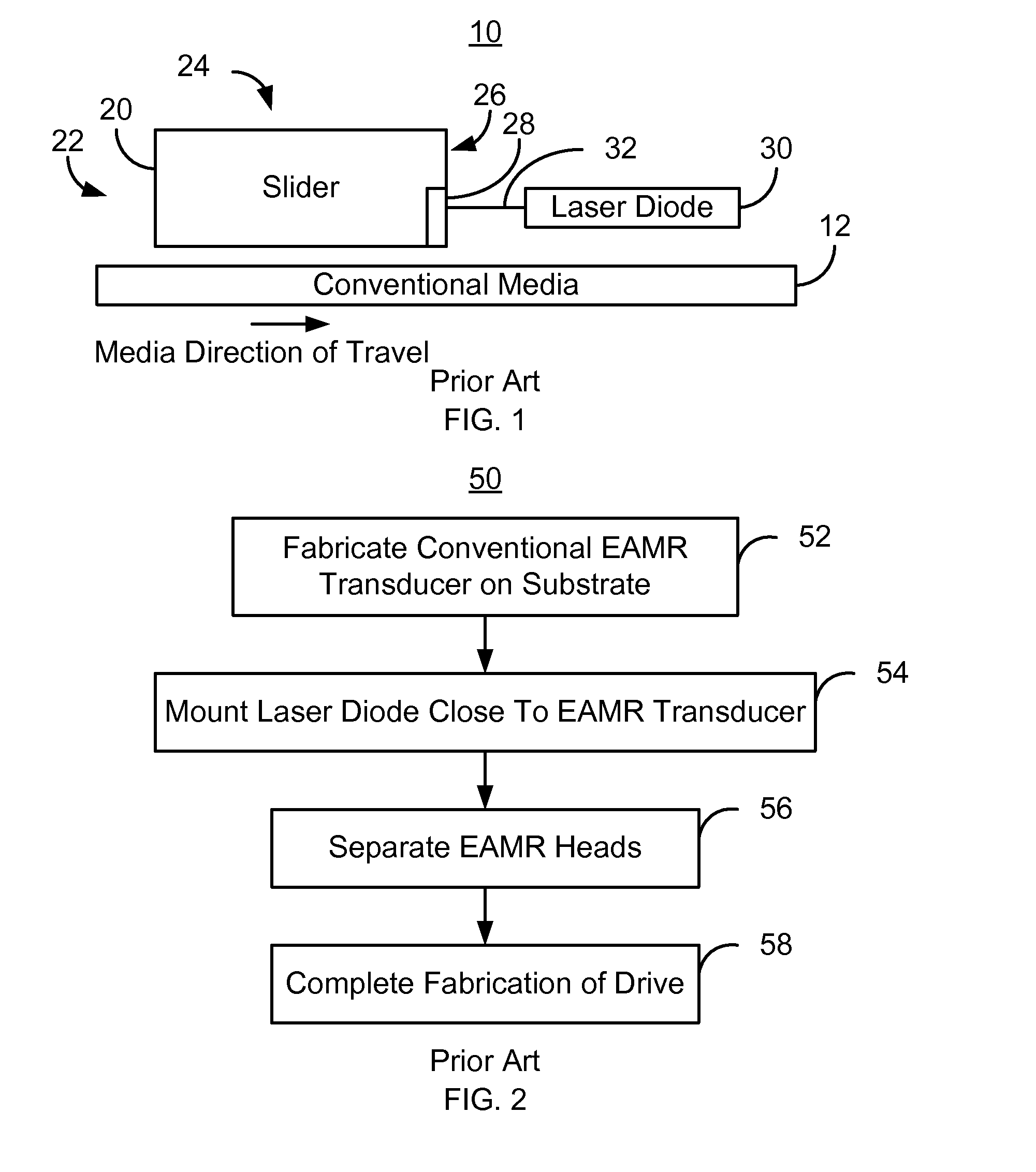
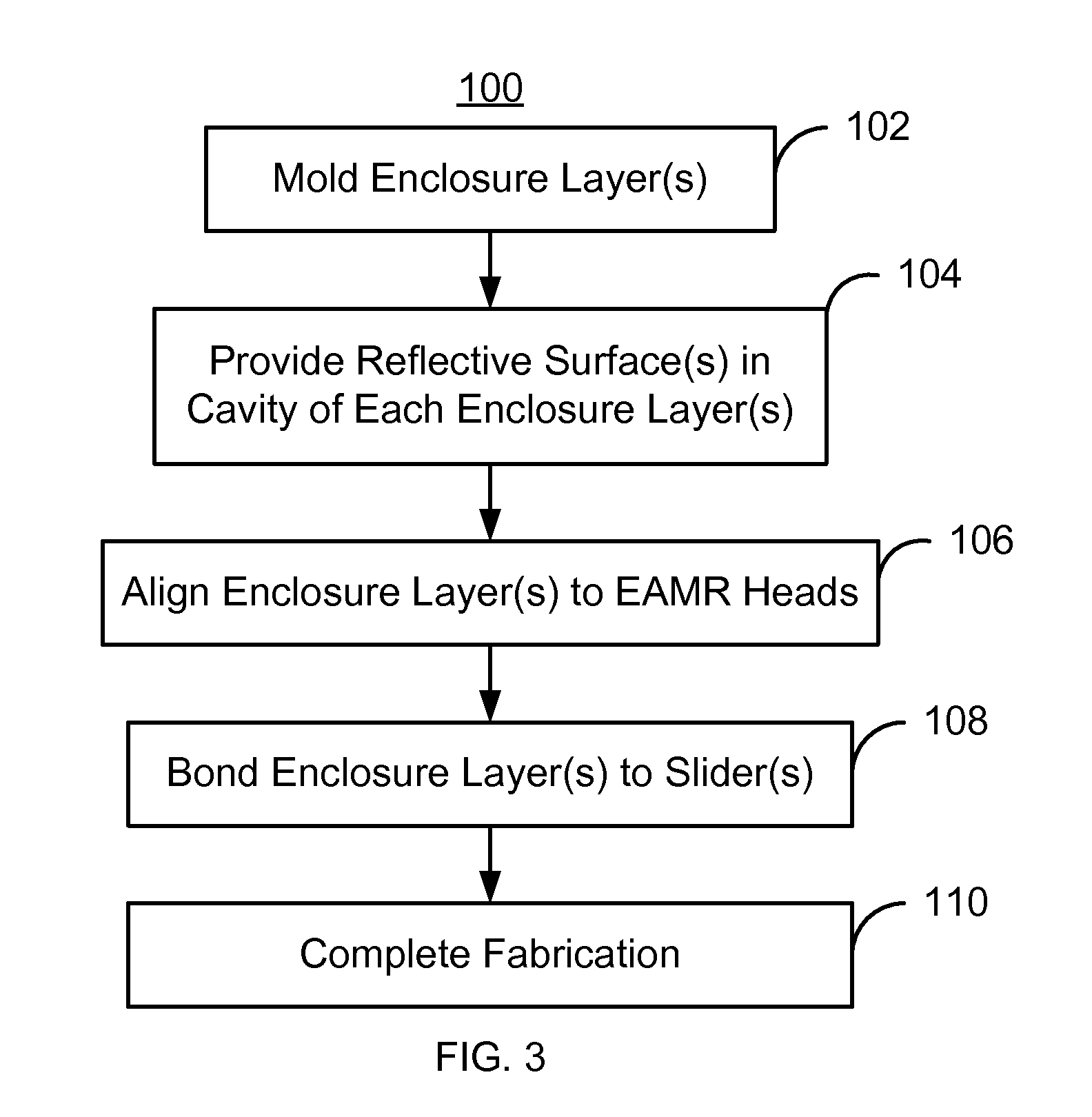
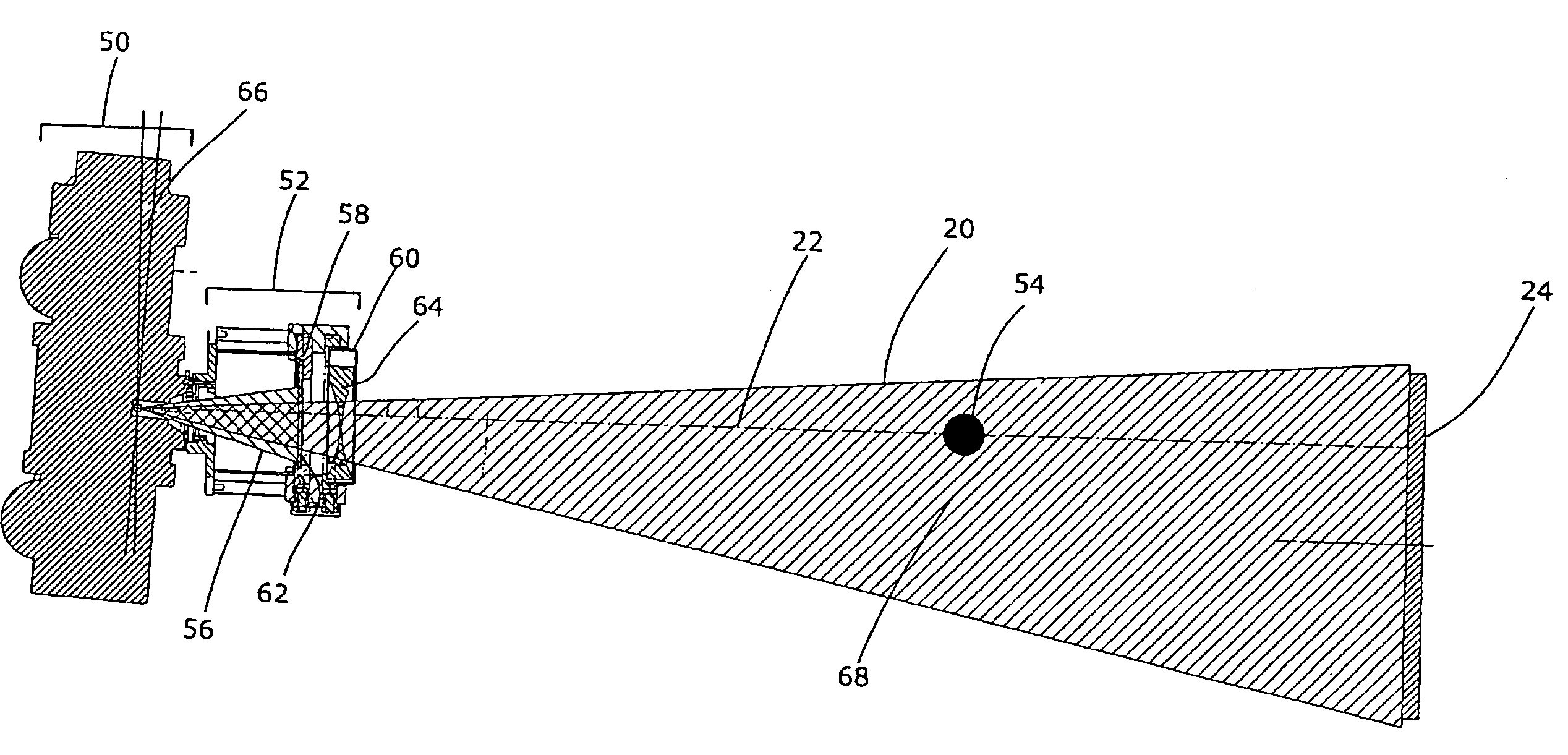
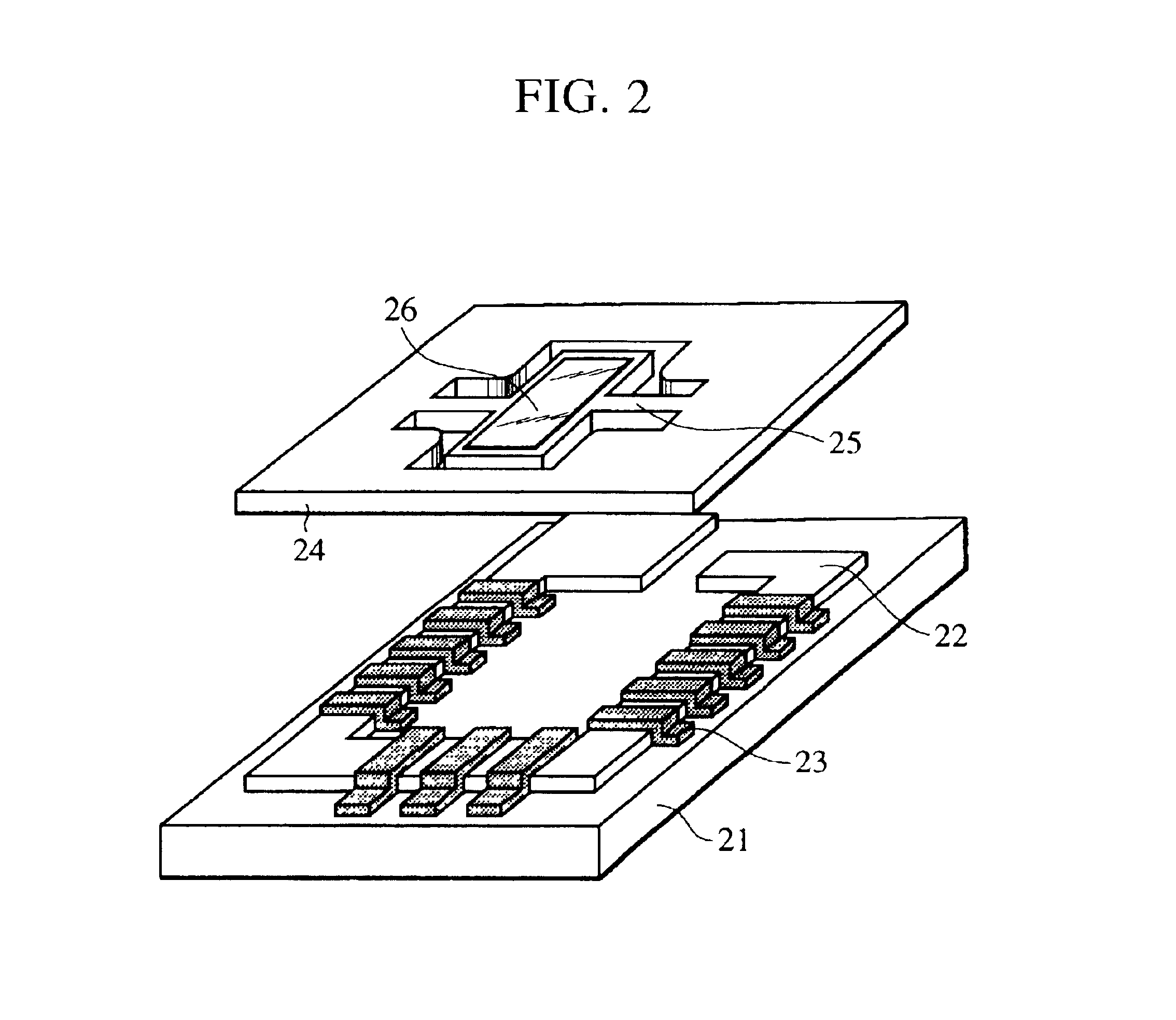
Method and system for providing a molded capping layer for an energy assisted magnetic recording head
A method and system for providing energy assisted magnetic recording (EAMR) heads are described. The heads include sliders and lasers coupled with the sliders. The method and system include molding an enclosure layer. The enclosure layer has a laser-facing surface and a top surface opposing the laser-facing surface. The laser-facing surface has a cavity including a concave section. The method and system further includes providing a reflective layer on the cavity. A portion of the reflective layer resides on the concave section, collimates light from the laser, and provides the collimated light to the EAMR transducer. The method and system further includes aligning the concave section of the cavity with a light emitting portion of the laser. The enclosure layer is also bonded to the slider.
Owner:WESTERN DIGITAL TECH INC
Curved near-to-eye display
A display apparatus includes an array of microlenses disposed in or on a substrate. In one embodiment, the apparatus includes scattering centers disposed in or on the substrate and offset relative to the microlenses. The scattering centers are positioned substantially at focal points of the microlenses such that light incident upon a first side the substrate is scattered off of the scattering centers and collimated by corresponding ones of the microlenses before emission from the display apparatus. In another embodiment, the apparatus includes light emitting pixels disposed in or on the substrate and offset relative to the microlenses. The light emitting pixels are positioned substantially at focal points of the microlenses such that non-collimated light emitted from the light emitting pixels is collimated by the microlenses upon emission from the display apparatus.
Owner:GOOGLE LLC
Projection display systems utilizing light emitting diodes and light recycling
InactiveUS7025464B2Incadescent screens/filtersElectric discharge tubesEngineeringLight-emitting diode
Owner:GOLDENEYE
Thin illumination system
ActiveUS20100315833A1Without compromise in sharpnessModerate brightnessPlanar light sourcesMechanical apparatusLight beamEffect light
The present invention introduces a new class of thin doubly collimating light distributing engines for use in a variety of general lighting applications, especially those benefiting from thinness. Output illumination from these slim-profile illumination systems whether square, rectangular or circular in physical aperture shape is directional, square, rectangular or circular in beam cross-section, and spatially uniform and sharply cutoff outside the system's adjustable far-field angular cone. Field coverage extends from + / −5- to + / −60-degrees and more in each meridian, including all asymmetric combinations in between, both by internal design, by addition of angle spreading film sheets, and angular tilts. Engine brightness is held to safe levels by expanding the size of the engine's output-aperture without sacrifice in the directionality of illumination. One form of the present invention has a single input light emitter, a square output aperture and the capacity to supply hundreds of lumens per engine. A second multi-segment form of the invention deploys one light emitter in each engine segment, so that total output lumens is determined by the number of segments. Both types of thin light distributing engines provide input light collimated in one meridian and a light distributing element that maintains input collimation while collimating output light in the un-collimated orthogonal meridian, in such a manner that the system's far-field output light is collimated in both its orthogonal output meridians. The present invention also includes especially structured optical films that process the engine's doubly collimated output illumination so as to increase its angular extent one or both output meridians without changing beam shape or uniformity.
Owner:SNAPTRACK +1
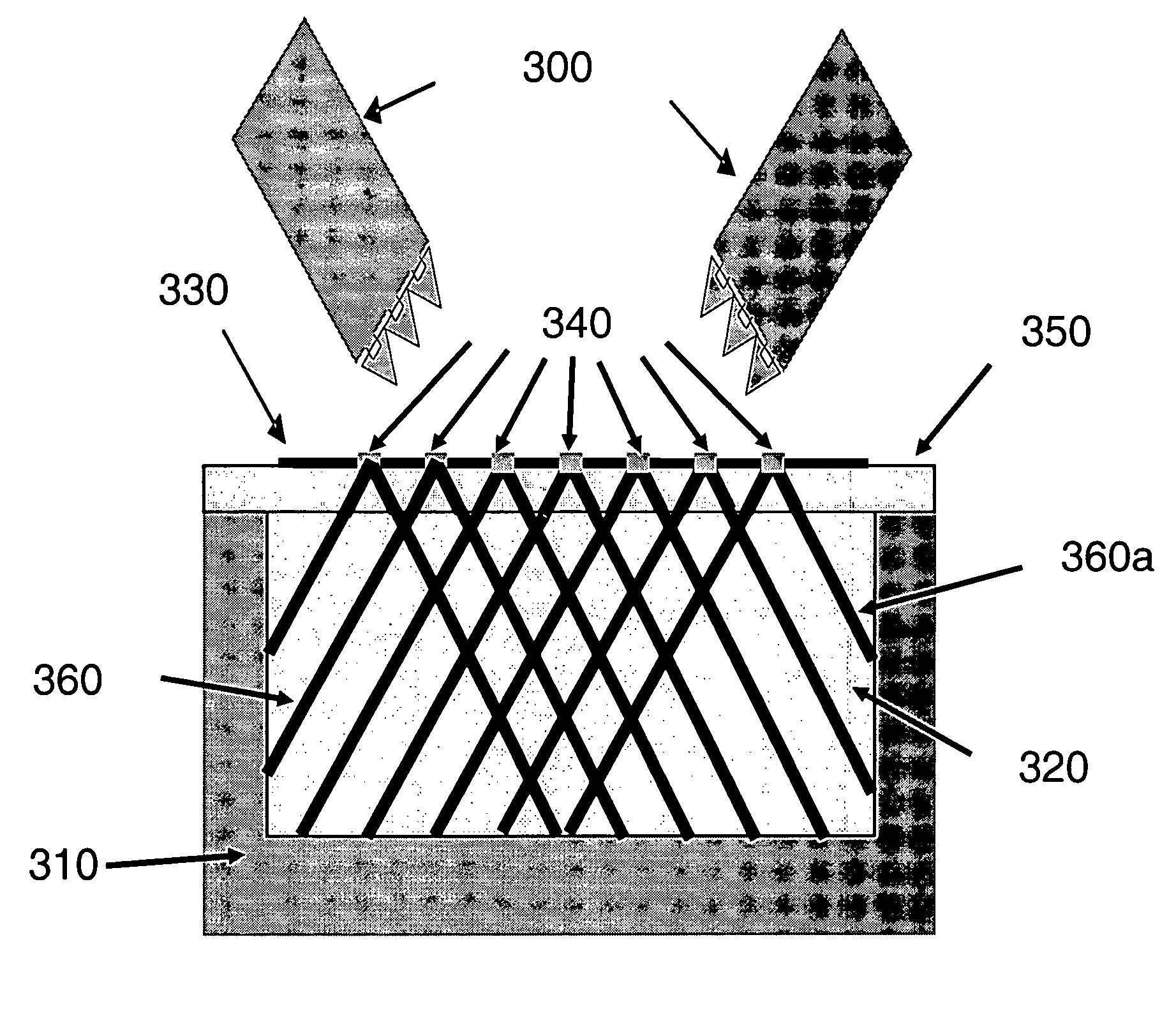
X-ray imaging of baggage and personnel using arrays of discrete sources and multiple collimated beams
ActiveUS7505562B2Material analysis by transmitting radiationNuclear radiation detectionSpatial OrientationsCarbon nanotube
A system and methods are provided for imaging an object, based on activating an array of discrete X-ray sources in a prescribed temporal pattern so as to illuminate the object with a beam varying in spatial orientation, and detecting X-rays of the beam after interaction with the object and generating a detector signal. An image of the object may then be constructed on the basis of the time variation of the detector signal. The discrete X-ray sources may be moved during the course of inspection, moreover, the prescribed temporal pattern may constitute a Hadamard code. The discrete sources may be carbon nanotube x-ray sources.
Owner:AMERICAN SCI & ENG INC
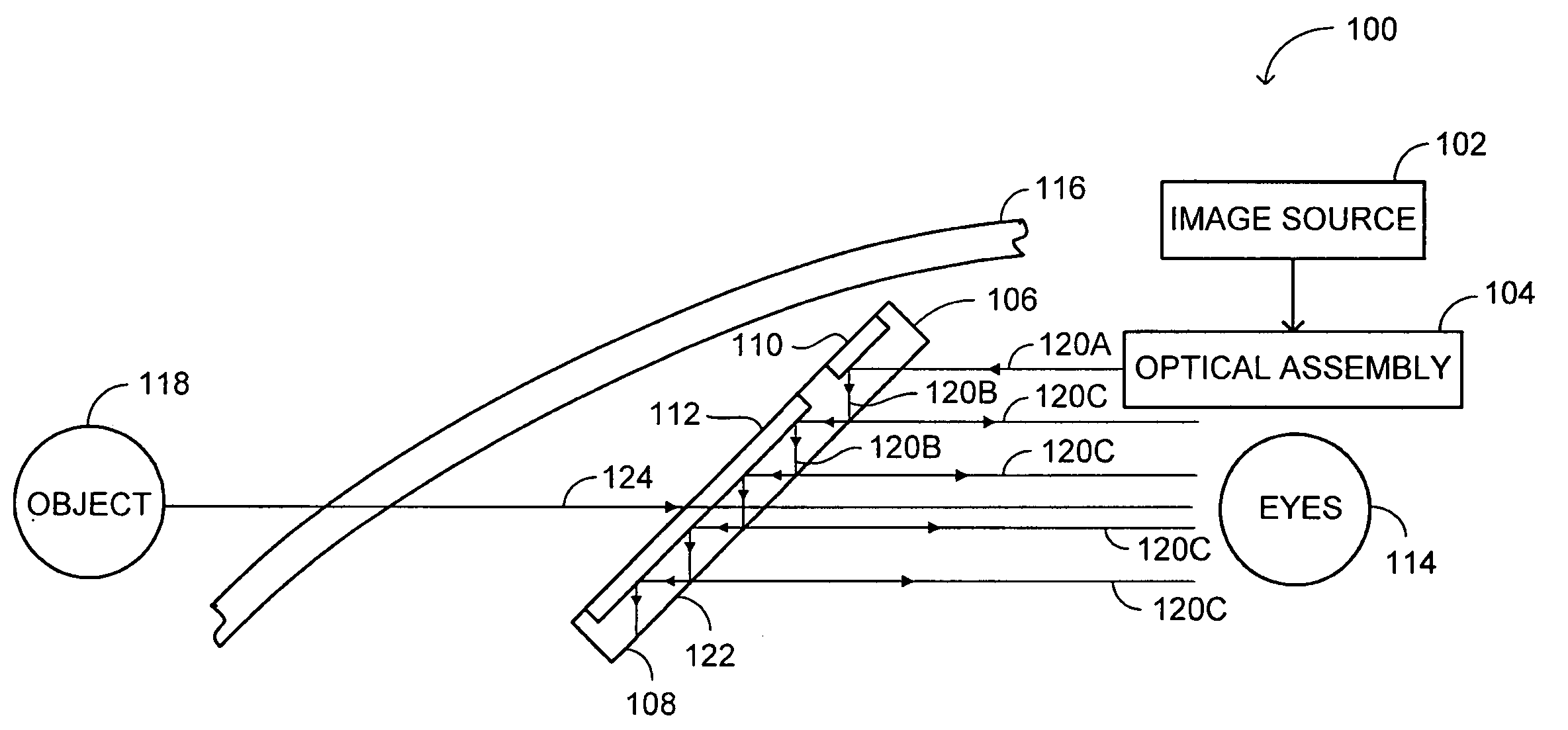
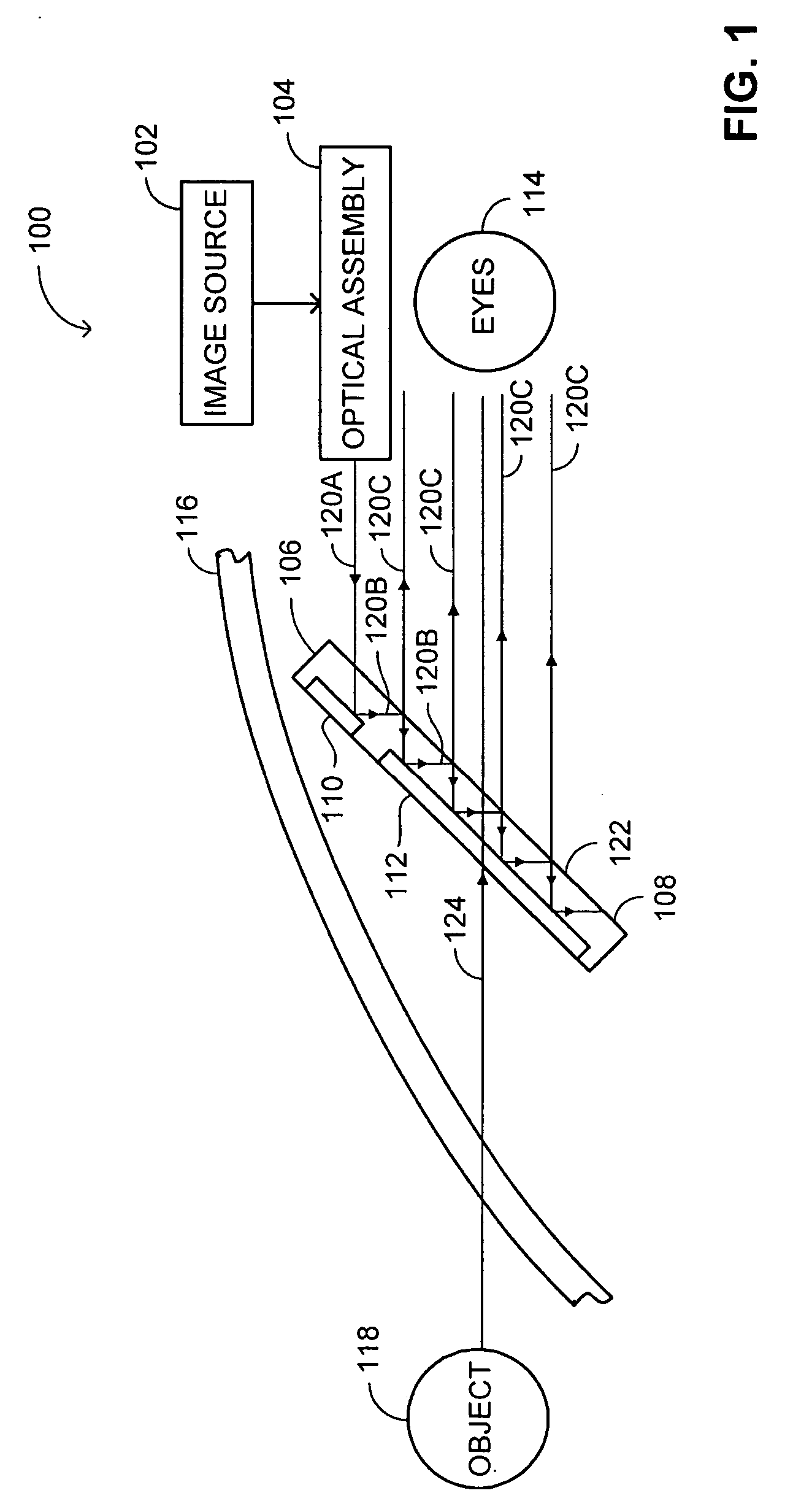
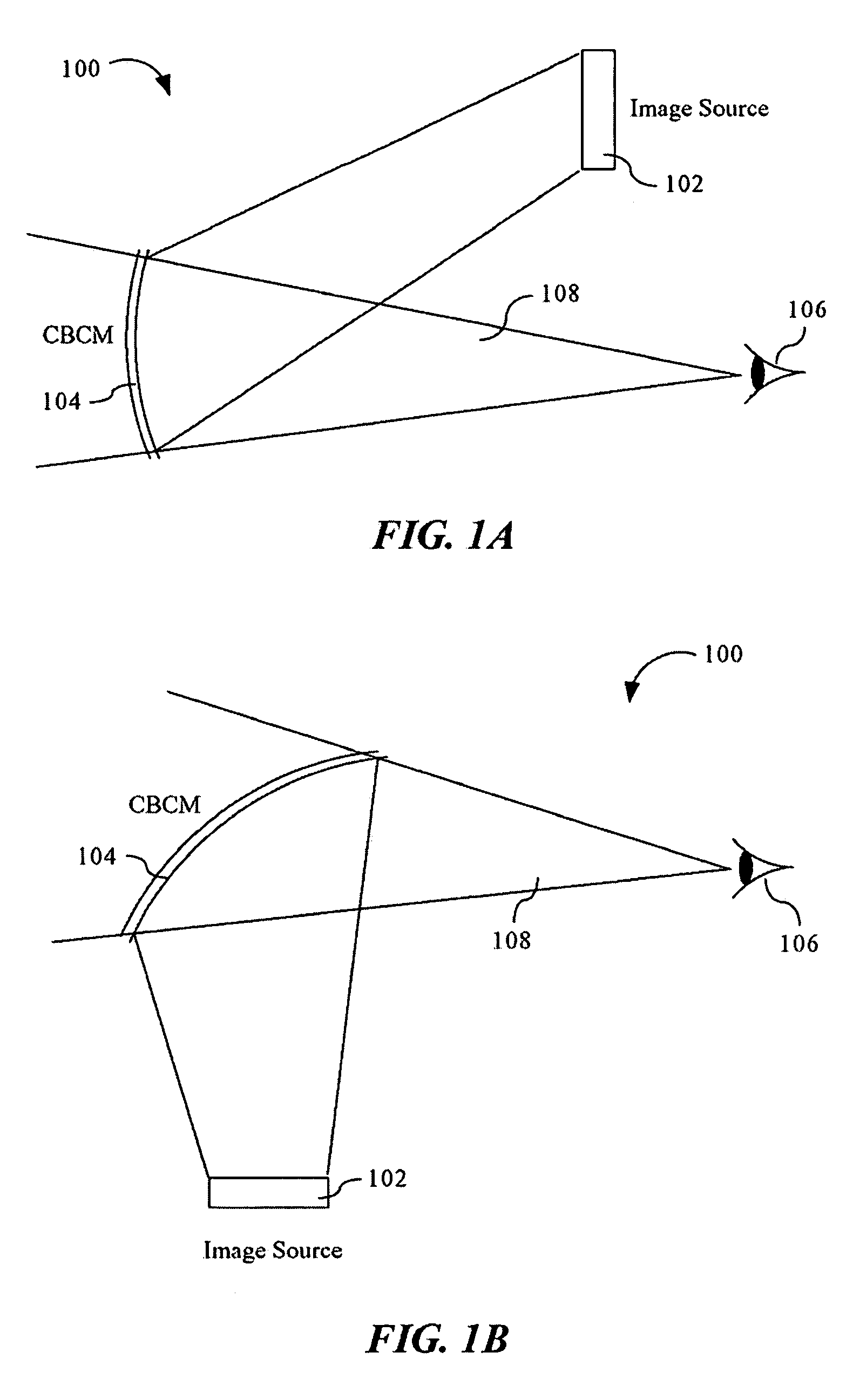
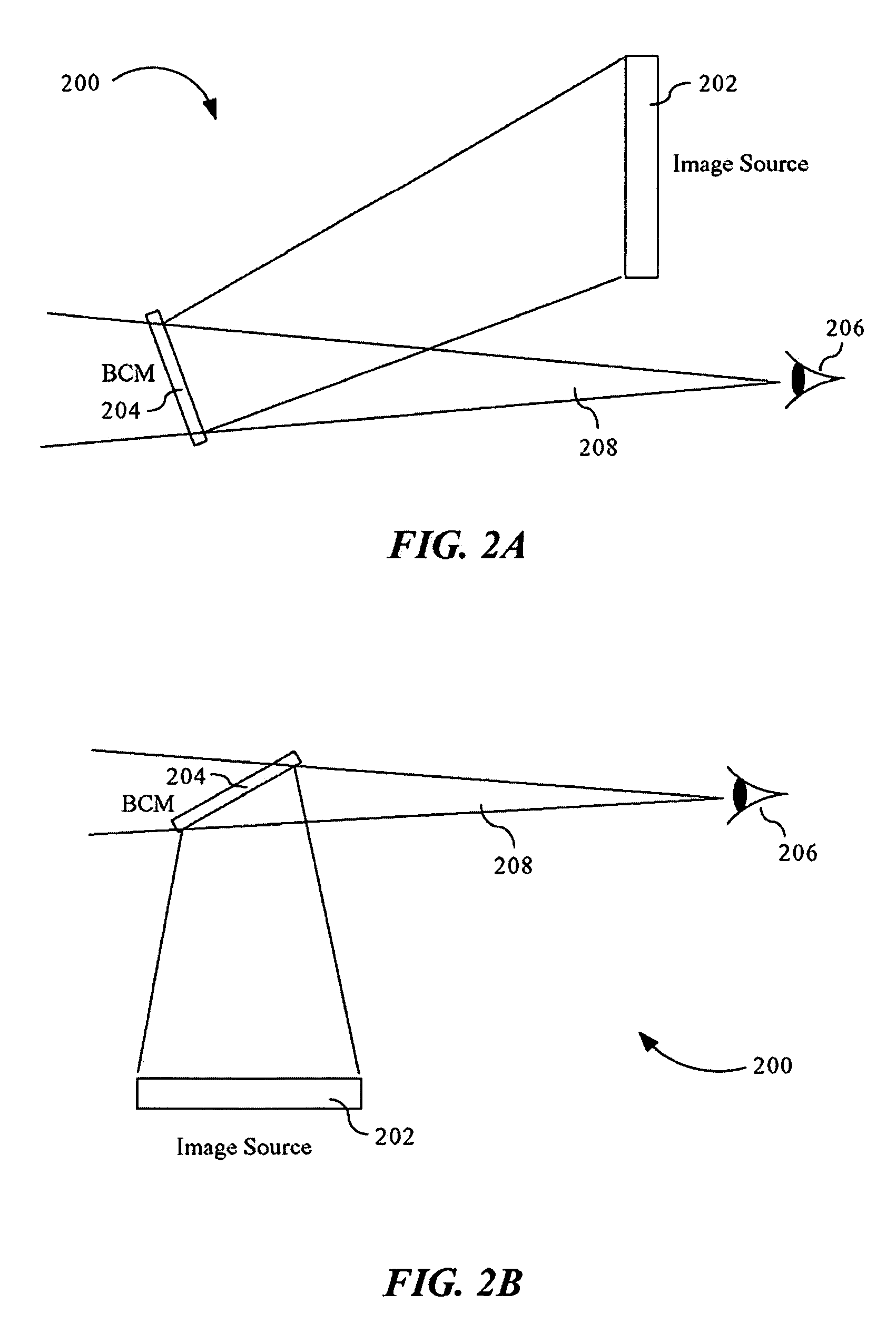
Advanced compact head up display
ActiveUS7095562B1Simplifies optical systemMinimize aberrationLighting support devicesCathode-ray tube indicatorsHead-up displayDashboard
A head up display system for a vehicle that includes a compact image source for projecting an image. The compact image source may be foldable up toward or into a cockpit ceiling of the vehicle, be positioned within a dashboard of the vehicle, or located at another suitable position. A combiner reflects the projected image with optical power toward an observer for observation. The combiner is positioned so that the observer, in a line of sight, may see a visual exterior view of an outside scene through the combiner and the projected image in the combiner. In a preferred embodiment, the image source includes an illumination system that includes a high power light emitting diode (LED) array assembly. A Fresnel lens array is operatively associated with the LED array assembly for receiving light produced by the LED and providing a nearly collimated light output. A spatial light modulator receives the nearly collimated light output. The preferred combiner is a meniscus combiner that includes a meniscus lens; a multi-layer dichroic coating formed on a first surface of the meniscus lens; and, an anti-reflection coating formed on a second, opposite surface of the meniscus lens. The meniscus combiner preferably utilizes a non-symmetric aspheric meniscus lens.
Owner:ROCKWELL COLLINS INC
X-ray apparatus
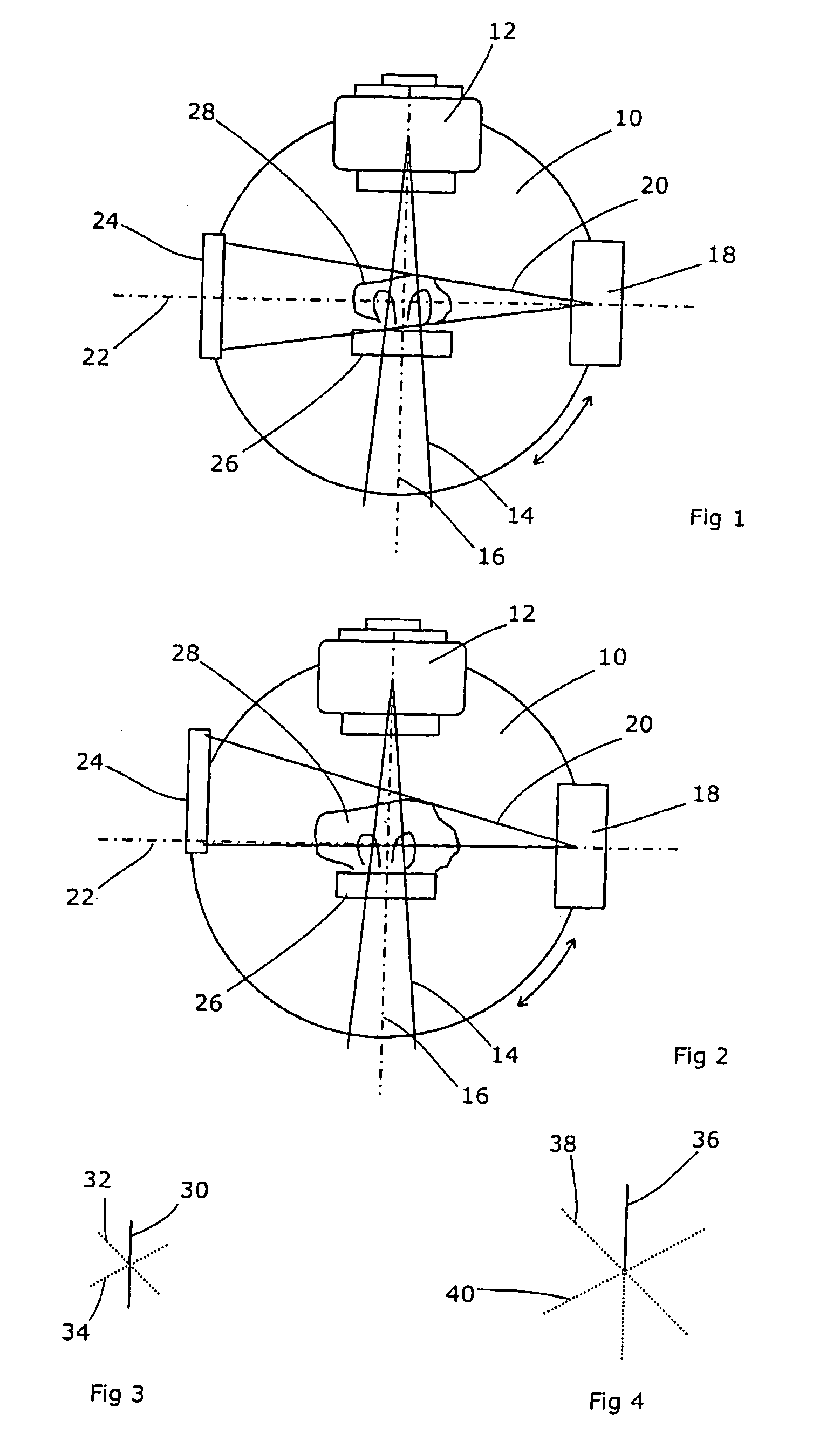
ActiveUS7796728B2Improve performanceIncrease capacityHandling using diaphragms/collimetersComputerised tomographsTwo dimensional detectorX-ray
An investigative X-ray apparatus comprises a source of X-rays emitting a cone beam centred on a beam axis, a collimator to limit the extent of the beam, and a two-dimensional detector, the apparatus being mounted on a support which is rotatable about a rotation axis, the collimator having a first state in which the collimated beam is directed towards the rotation axis and the second state in which the collimated beam is offset from the rotation axis, the two-dimensional detector being movable accordingly, the beam axis being offset from the rotation axis by a lesser amount than the collimated beam in the second state. The X-ray source is no longer directed towards the isocentre as would normally be the case; the X-ray source is not orthogonal to the collimators. This is advantageous in that the entire field of the X-ray tube can be utilised. As a result, a lesser field is required of the X-ray tube and the choice of tube designs and capacities can be widened so as to optimise the performance of the X-ray tube in other aspects.
Owner:ELEKTA AB
Waveguide illumination system
InactiveUS20140140091A1Reduce light lossMinimizes lightMechanical apparatusElectric lightingForward scatterTotal internal reflection
An illumination system employing a waveguide. Light received from an edge or an end of a waveguide is propagated in response to transmission and total internal reflection. Light deflecting elements distributed along the propagation path of light continuously change the out-of-plane propagation angle of light rays and cause decoupling of portions of the propagated light from the core of the waveguide at different distances from the light input edge or end. Light escapes from the waveguide into an intermediate layer at low out-of-plane angles and is further redirected by light extraction features out of the system. In one embodiment, the illumination system is configured to emit collimated light. In one embodiment, the illumination system includes shallow surface relief features. In one embodiment, the light deflecting elements include forward-scattering particles distributed throughout the volume of the waveguide. Additional collimating and non-collimating illumination units and methods are also disclosed.
Owner:VASYLYEV SERGIY VICTOROVICH
Projection display device
InactiveUS6945652B2Less expensiveAccurate color reproductionTelevision system detailsTelevision system scanning detailsColor imageProjection plane
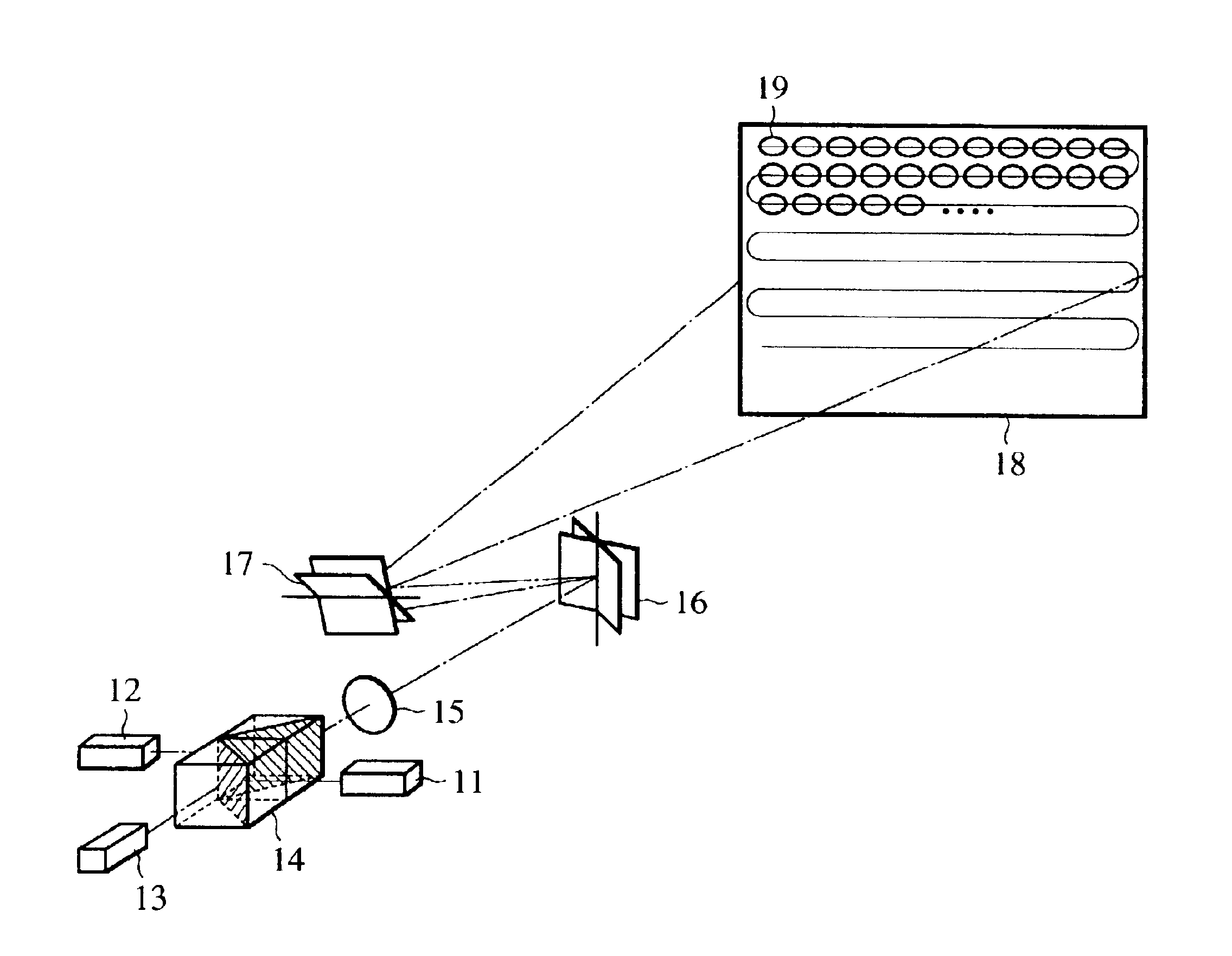
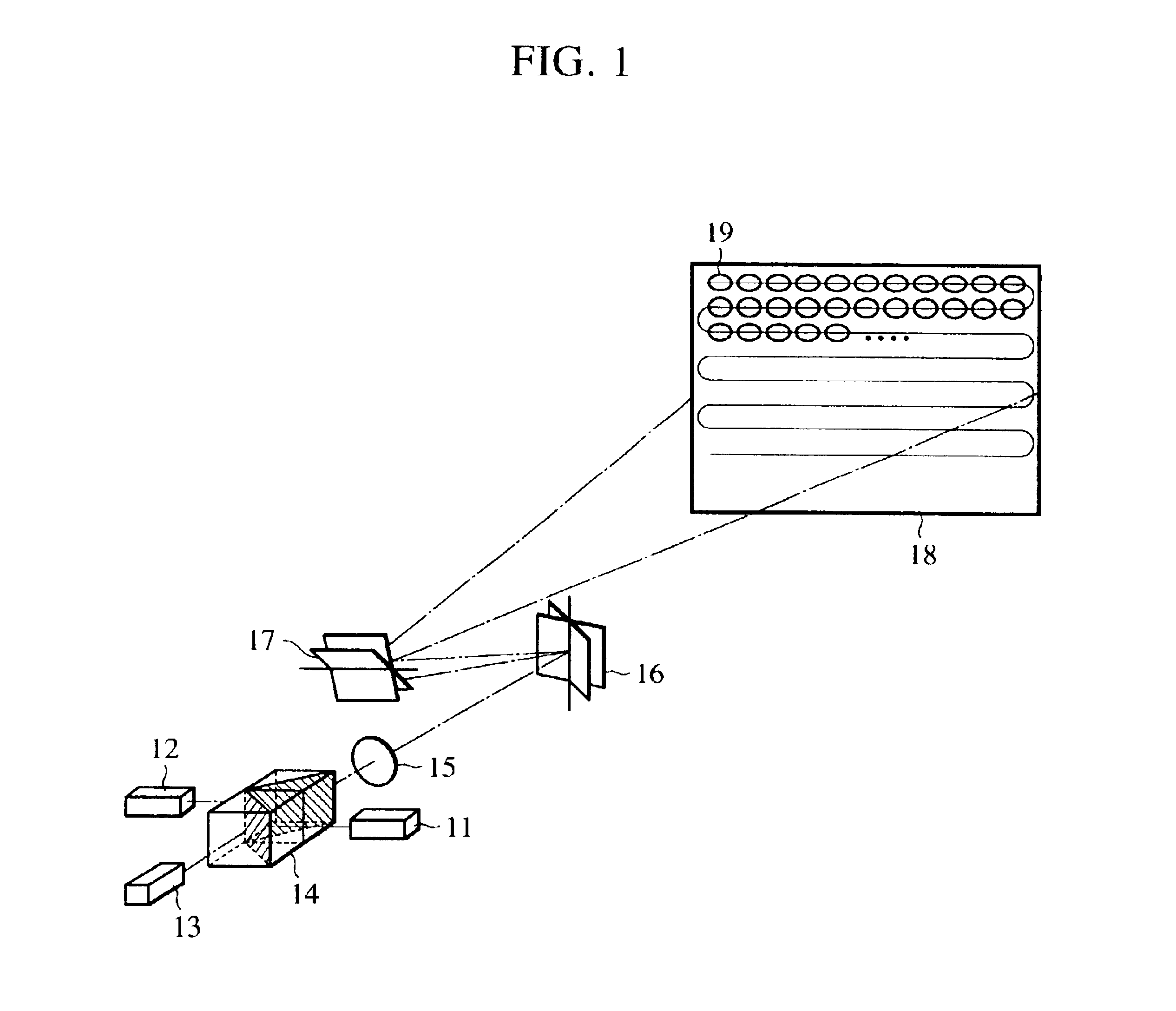
Light beams having different wavelengths emitted from red and blue semiconductor lasers and a laser diode pumped green solid-state laser are incident on respectively different surfaces of a color combining element and are overlaid on a single light path. Multiple beam interference films of the color combining element allow only the light beams having the oscillating wavelengths corresponding to the respective light sources to pass therethrough or reflect thereon so as to combine the light beams. A collimator collimates the light beams so that the beam waist of the light beams lies around a projection plane. When two-dimensional scanning is performed by radiating the light beams onto a micromechanical mirror and then onto a galvanometer mirror for scanning light in the horizontal and vertical directions, respectively, a color image is displayed on the projection plane by arranging pixels in array, each pixel consisting of overlapping pulses of light of three colors.
Owner:CANON KK
High repetition rate laser produced plasma EUV light source
An EUV light source apparatus and method are disclosed, which may comprise a pulsed laser providing laser pulses at a selected pulse repetition rate focused at a desired target ignition site; a target formation system providing discrete targets at a selected interval coordinated with the laser pulse repetition rate; a target steering system intermediate the target formation system and the desired target ignition site; and a target tracking system providing information about the movement of target between the target formation system and the target steering system, enabling the target steering system to direct the target to the desired target ignition site. The target tracking system may provide information enabling the creation of a laser firing control signal, and may comprise a droplet detector comprising a collimated light source directed to intersect a point on a projected delivery path of the target, having a respective oppositely disposed light detector detecting the passage of the target through the respective point, or a detector comprising a linear array of a plurality of photo-sensitive elements aligned to a coordinate axis, the light from the light source intersecting a projected delivery path of the target, at least one of the which may comprise a plane-intercept detection device. The droplet detectors may comprise a plurality of droplet detectors each operating at a different light frequency, or a camera having a field of view and a two dimensional array of pixels imaging the field of view. The apparatus and method may comprise an electrostatic plasma containment apparatus providing an electric plasma confinement field at or near a target ignition site at the time of ignition, with the target tracking system providing a signal enabling control of the electrostatic plasma containment apparatus. The apparatus and method may comprise a vessel having and intermediate wall with a low pressure trap allowing passage of EUV light and maintaining a differential pressure across the low pressure trap. The apparatus and method may comprise a magnetic plasma confinement mechanism creating a magnetic field in the vicinity of the target ignition site to confine the plasma to the target ignition site, which may be pulsed and may be controlled using outputs from the target tracking system.
Owner:ASML NETHERLANDS BV
Backlight unit and display device including the same
InactiveUS20120008067A1Quickly and sequentially controlledPlanar/plate-like light guidesNon-linear opticsLight guideDisplay device
A backlight unit and a display device including the backlight unit are provided. The backlight unit includes at least one light source unit and a light guide plate. The light source unit provides collimated light and controls light such that it is emitted in a plurality of light exit directions.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
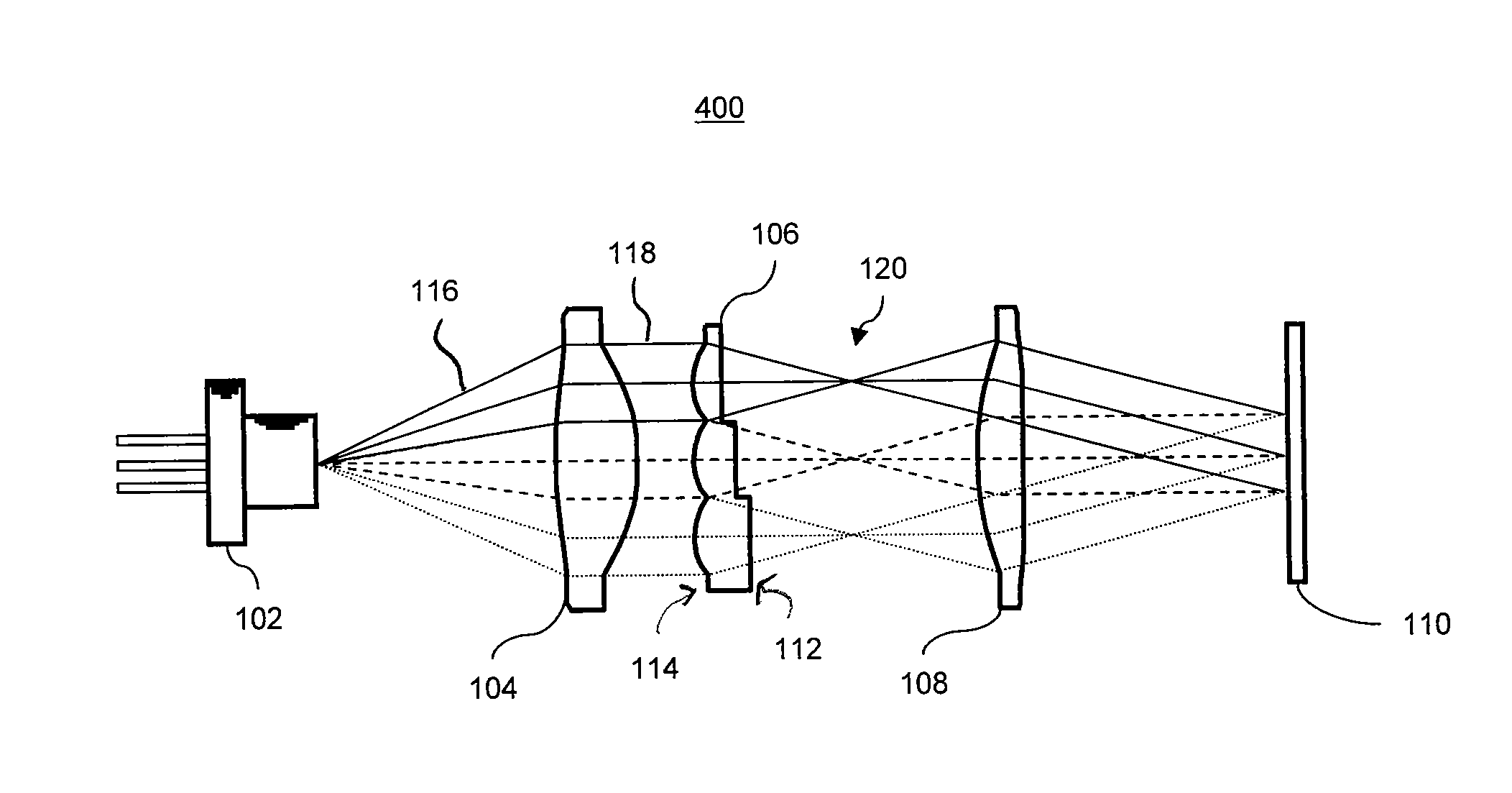
Compact optical detection system for a microfluidic device
ActiveUS7518726B2Large numerical apertureLow powerWithdrawing sample devicesMaterial analysis by optical meansFluorescenceOptical alignment
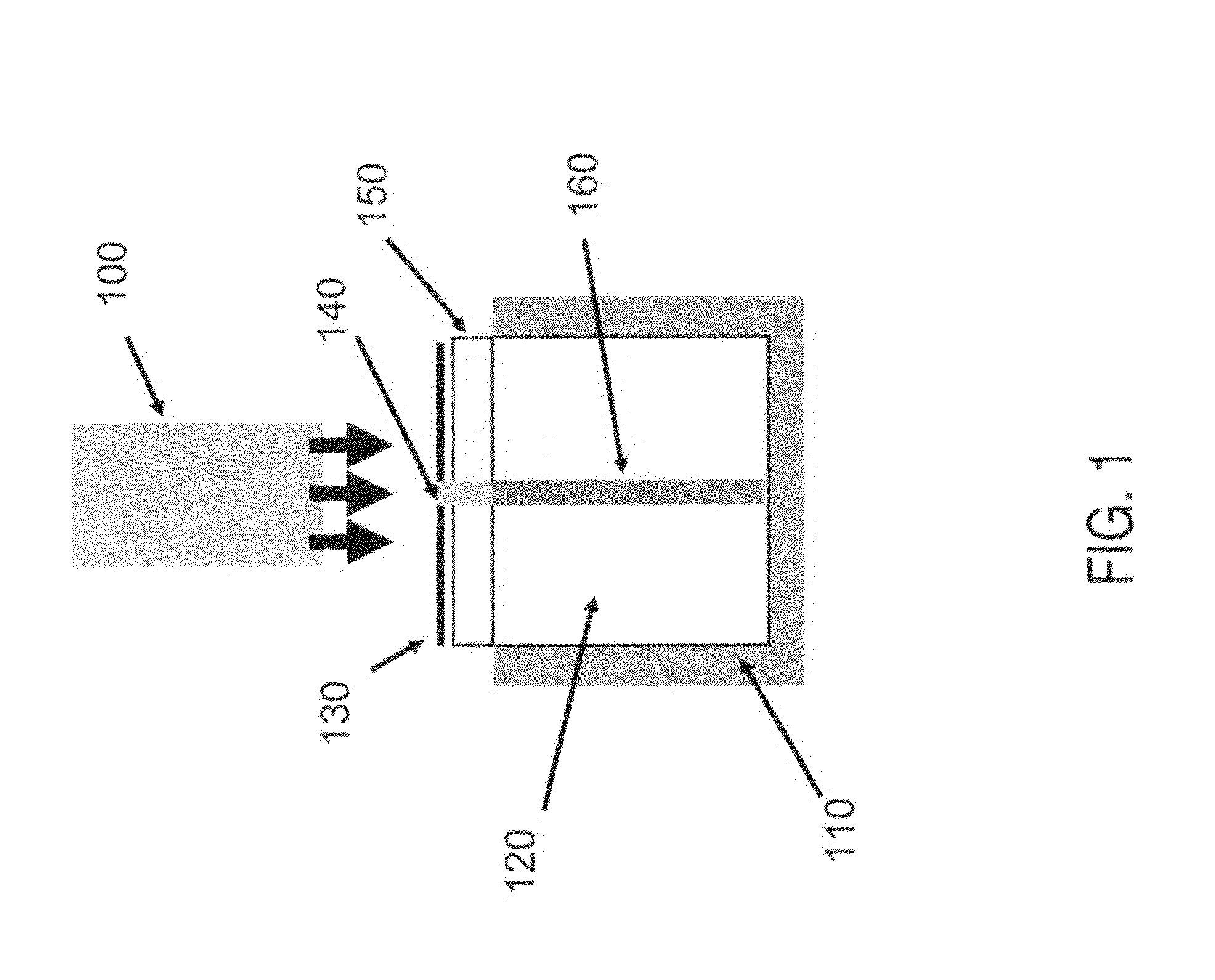
An optical detection system for a microfluidic device and a dry-focus microfluidic device compatible with the compact optical detection system are described. The system includes an LED; means for collimating light emitted by the LED; an aspherical, fused-silica objective lens; means for directing the collimated light through the objective onto a microfluidic device; and means for detecting a fluorescent signal emitted from the microfluidic device. The working distance between the objective and the device allows light from an external LED or laser to be brought in along a diagonal path to illuminate the microfluidic device. The dry-focus microfluidic device includes multiple channels and multiple closed optical alignment marks having curved walls. At least one of the channels is positioned between at least two of the marks. The marks are illuminated for alignment and focusing purposes by light brought in on a diagonal path from an external white LED.
Owner:CAPLIPER LIFE SCI INC
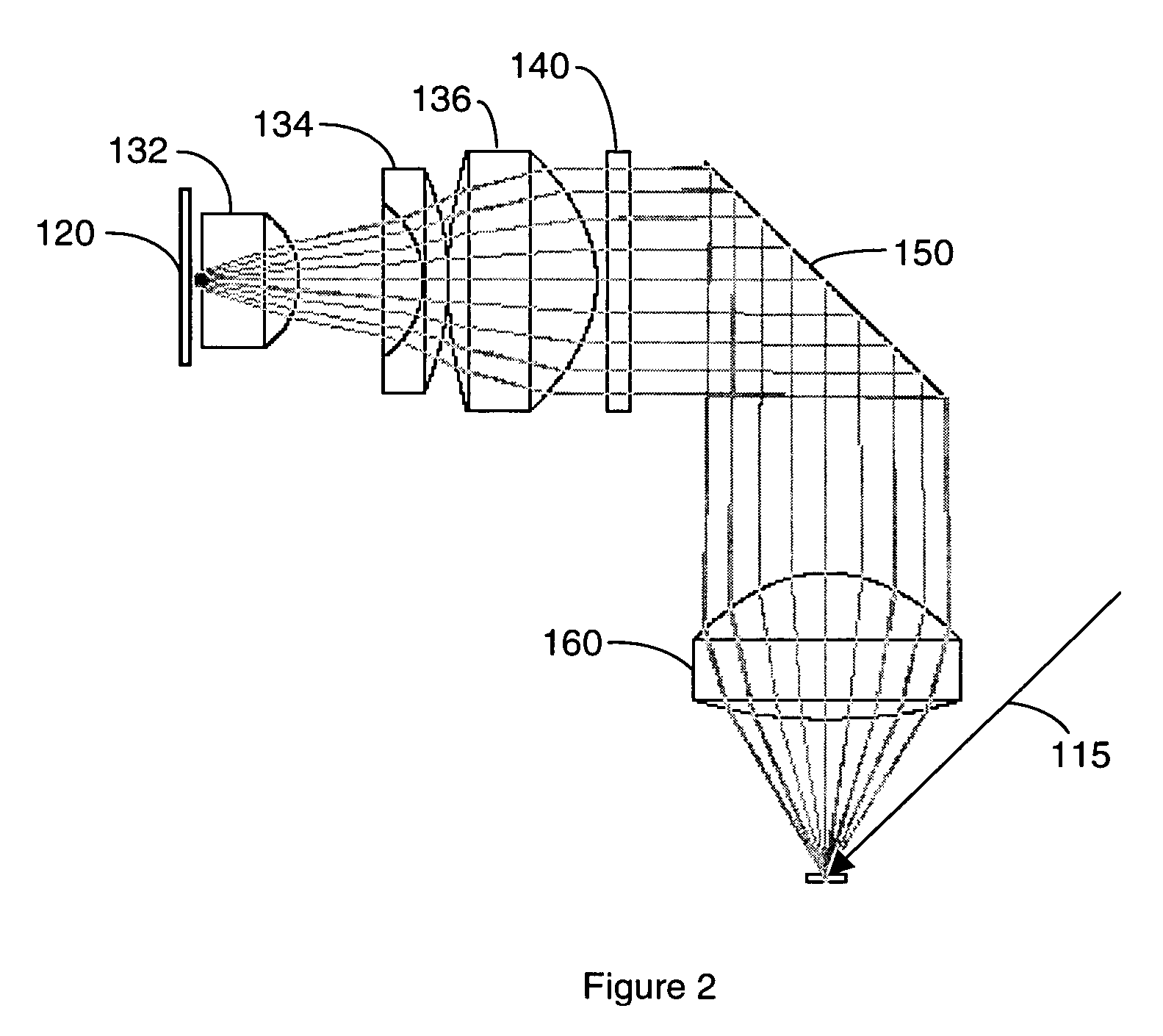
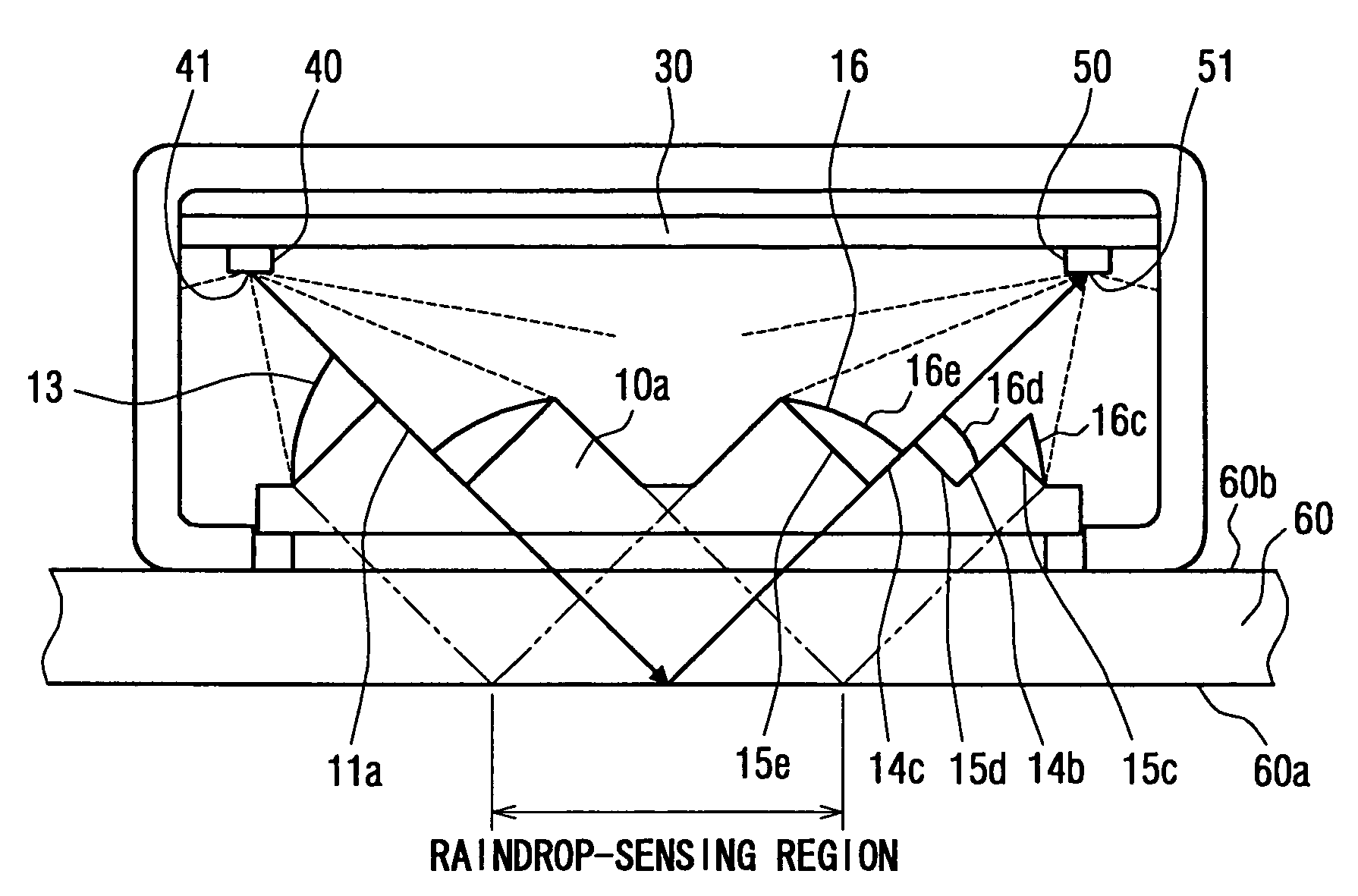
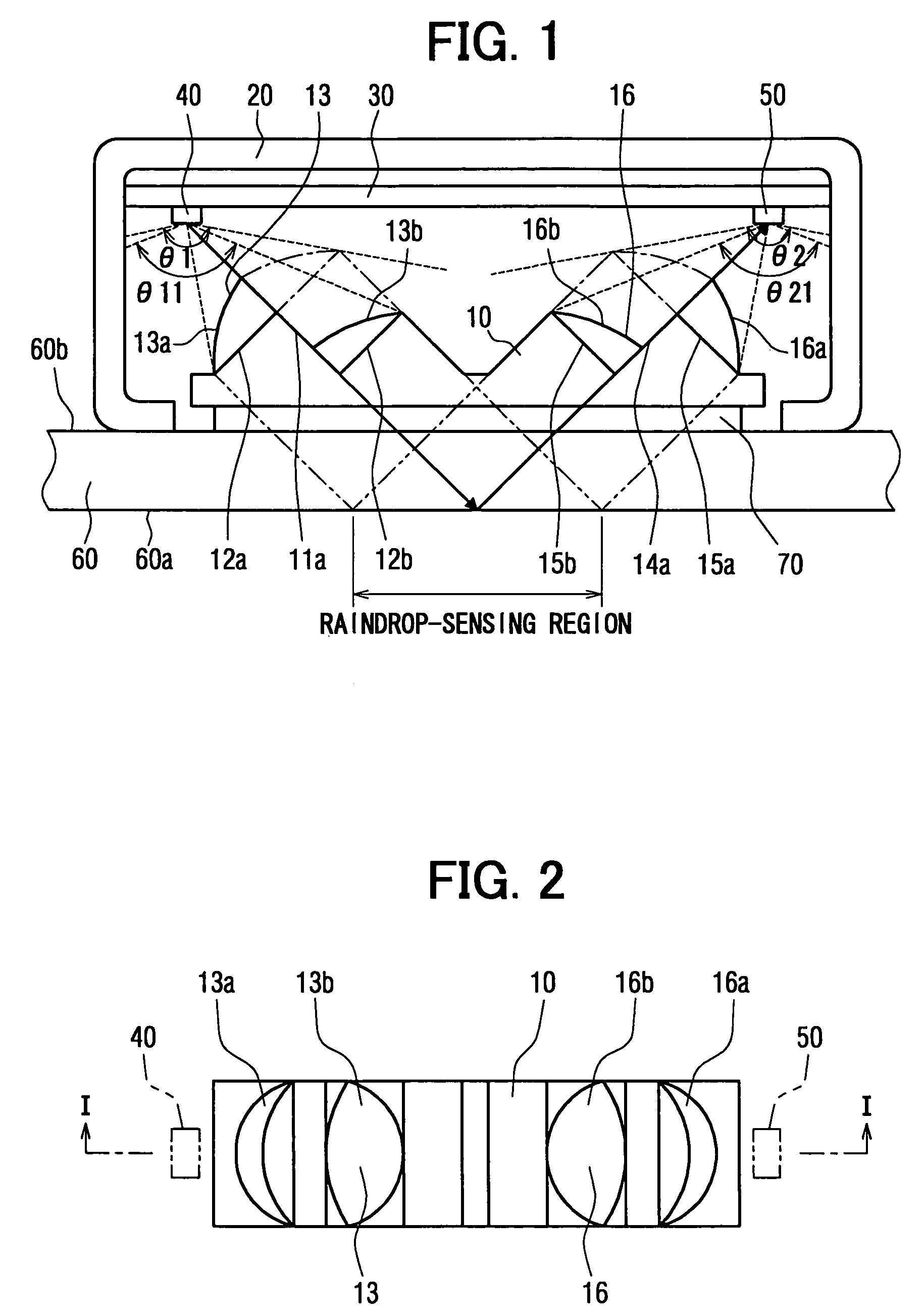
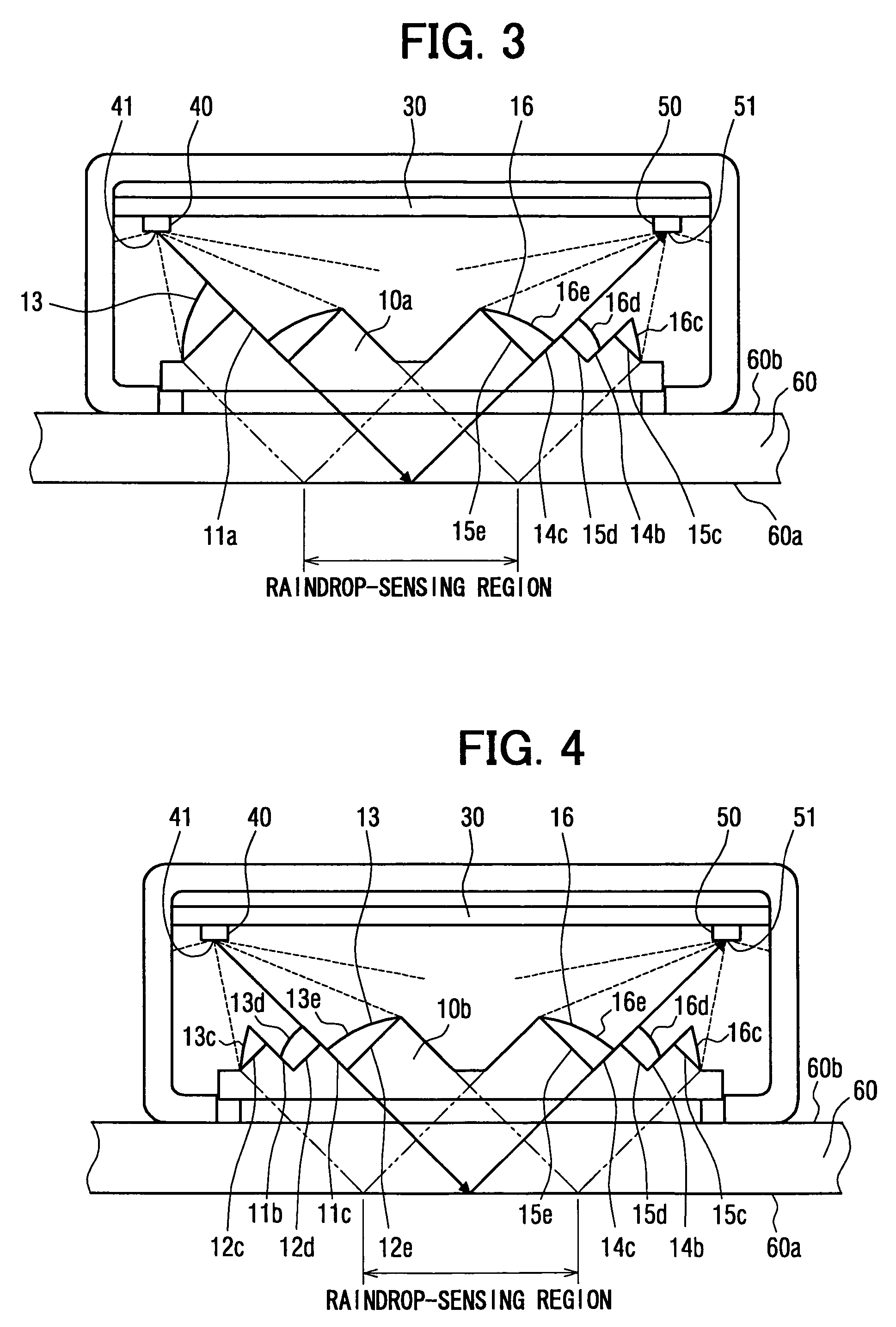
Raindrop sensor
ActiveUS7309873B2Phase-affecting property measurementsInvestigating moving fluids/granular solidsLight guideLight beam
A raindrop sensor includes a light-emitting element, a light-receiving element and a light guide body. The light-emitting element and the light-receiving element face a transparent panel. The light guide body, which is mounted on the transparent panel, includes an input lens, an input side dividing surface, an output lens and an output side dividing surface. The input lens collimates light emitted by the light-emitting element to form an input side collimated light beam. The output lens receives the collimated light beam, which is collimated by the input lens and is reflected by a reference surface of the transparent panel, to which the raindrop attaches. The output lens converges the reflected collimated light beam toward the light-receiving element. An intersection between an imaginary extension of the input side dividing surface and an imaginary extension of the output side dividing surface is located on the reference surface of the transparent panel.
Owner:DENSO CORP
Projection display systems utilizing color scrolling and light emitting diodes
A projection display system has at least one light-recycling illumination system, a color scroller and an imaging light modulator. The light-recycling illumination system includes a light source that is enclosed within a light-recycling envelope. The light source is a light-emitting diode that emits light, and a fraction of that light will exit the light-recycling envelope through an aperture. The light-recycling envelope recycles a portion of the light emitted by the light source back to the light source in order to enhance the luminance of the light exiting the aperture. The fraction of the light that exits the aperture is partially collimated and is directed to a color scrolling means. The color scroller scans the partially collimated light across the face of the imaging light modulator. The imaging light modulator spatially modulates the scrolled beam of light to form an image.
Owner:GOLDENEYE
Substrate-guided optical devices
ActiveUS20070091445A1Simple structureFacilitates fabricationMechanical apparatusLight guides for lighting systemsImage resolutionAngular deviation
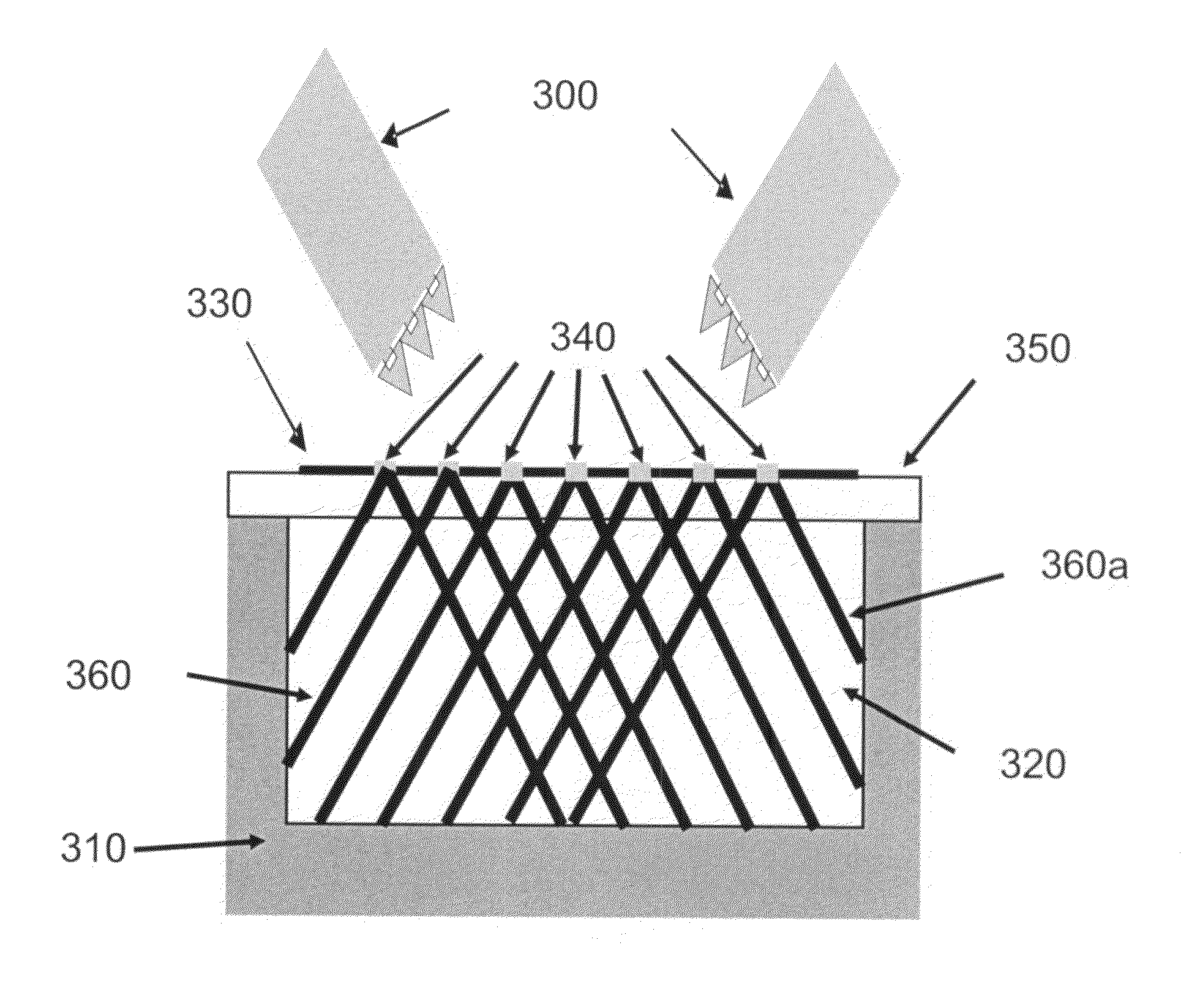
There is provided an optical device, having a light-transmitting substrate (20) having at least two major surfaces parallel to each other and edges; a display light source; optical means for coupling light from the light source into the substrate (20) by internal reflection, and at least one partially reflecting surface (22) located in the substrate (20) which is non-parallel to the major surfaces of the substrate wherein the source emits light waves located in a given field-of-view, that the light waves are collimated, that an angular resolution is defined for the optical device, and wherein the angular deviation between any two different rays located in one of the collimated light waves, is smaller than the angular resolution.
Owner:LUMUS LTD
Optically oriented three-dimensional polymer microstructures
A three-dimensional (3D) ordered polymer microstructure having a length, a width and a height and including a plurality of waveguides that can be formed utilizing a mask and collimated light. The plurality of waveguides includes a first waveguide having a first finite propagation distance extended along a first direction, a second waveguide having a second finite propagation distance extended along a second direction and a third waveguide having a third finite propagation distance extended along a third direction. Here, only one of the length, width and height of the 3D ordered polymer microstructure is limited by the first finite propagation distance of the first waveguide, the second finite propagation distance of the second waveguide and the third finite propagation distance of the third waveguide.
Owner:HRL LAB
Side-emitting collimator
ActiveUS20050286251A1Effective lightingLighting support devicesPoint-like light sourceAxis of symmetryOptical axis
A side-emitting collimator employs a combination of refraction and internal reflection to organize light from a light source into oppositely directed collimated beams. A light source chamber over the light source is defined by substantially cylindrical and aspheric refracting surfaces positioned to gather light into the collimating lens. The aspheric refracting surfaces redirect a portion of the light from the light source into a direction perpendicular to the optical axis of the light source. The substantially cylindrical surfaces refract light from the light source onto an aspheric upper reflecting surface. Light incident upon the aspheric upper reflecting surface is collimated into a direction perpendicular to the optical axis of the light source. The side-emitting collimator includes mirror image collimator halves, each producing a collimated beam. The collimator halves are rotationally symmetric about a common axis of symmetry above a plane including the axis of symmetry.
Owner:WHELEN ENGINEERING COMPANY
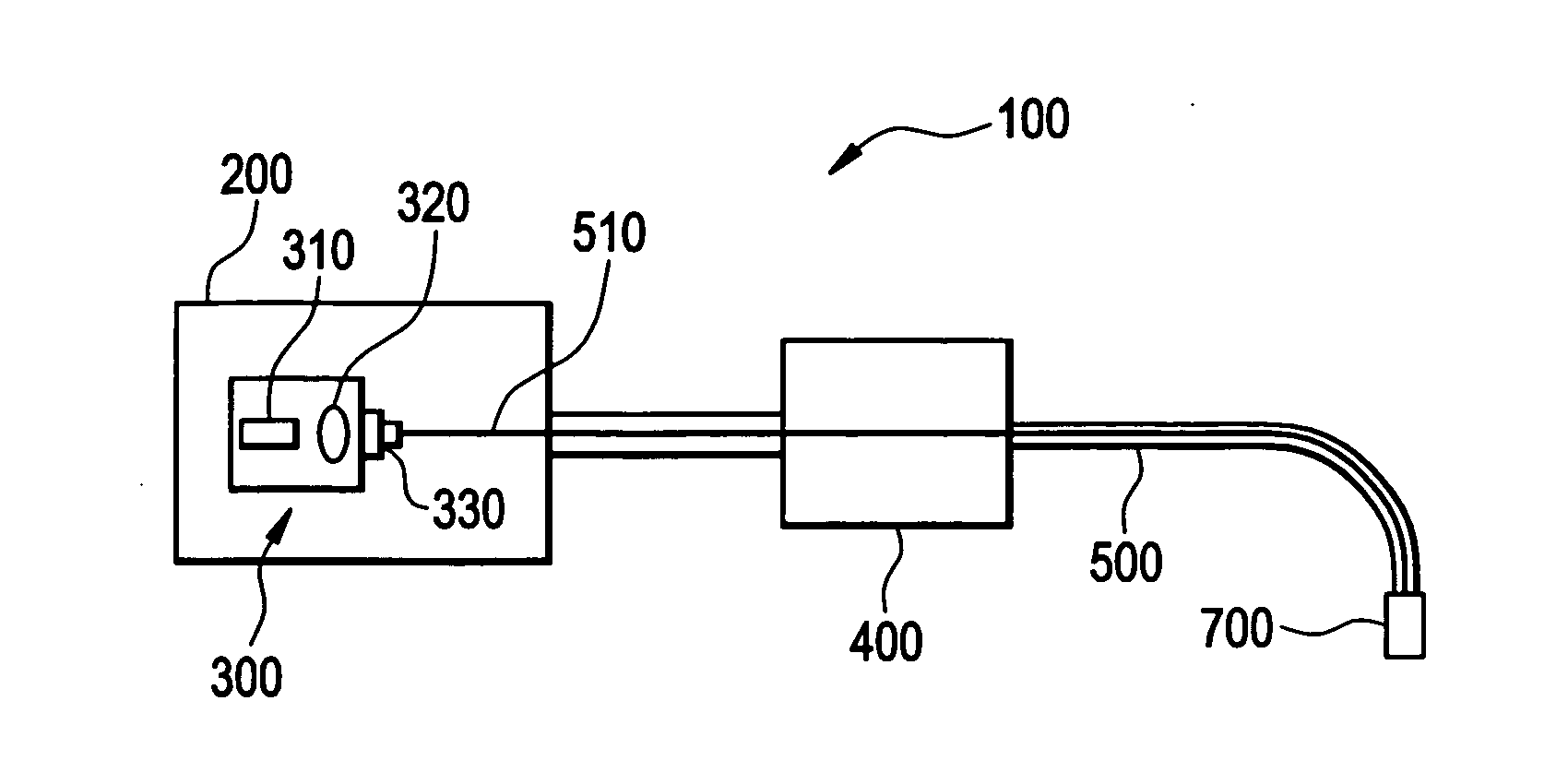
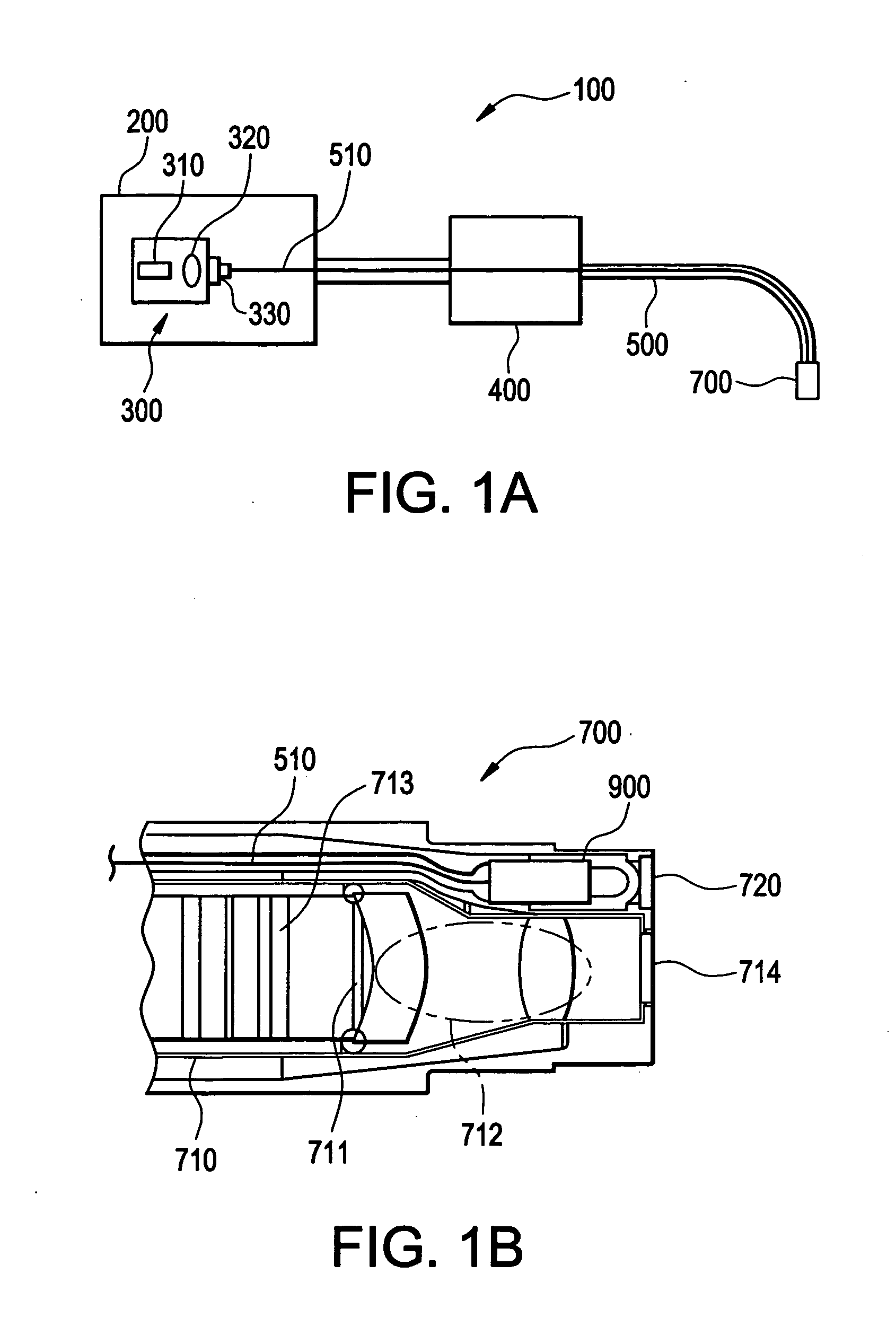
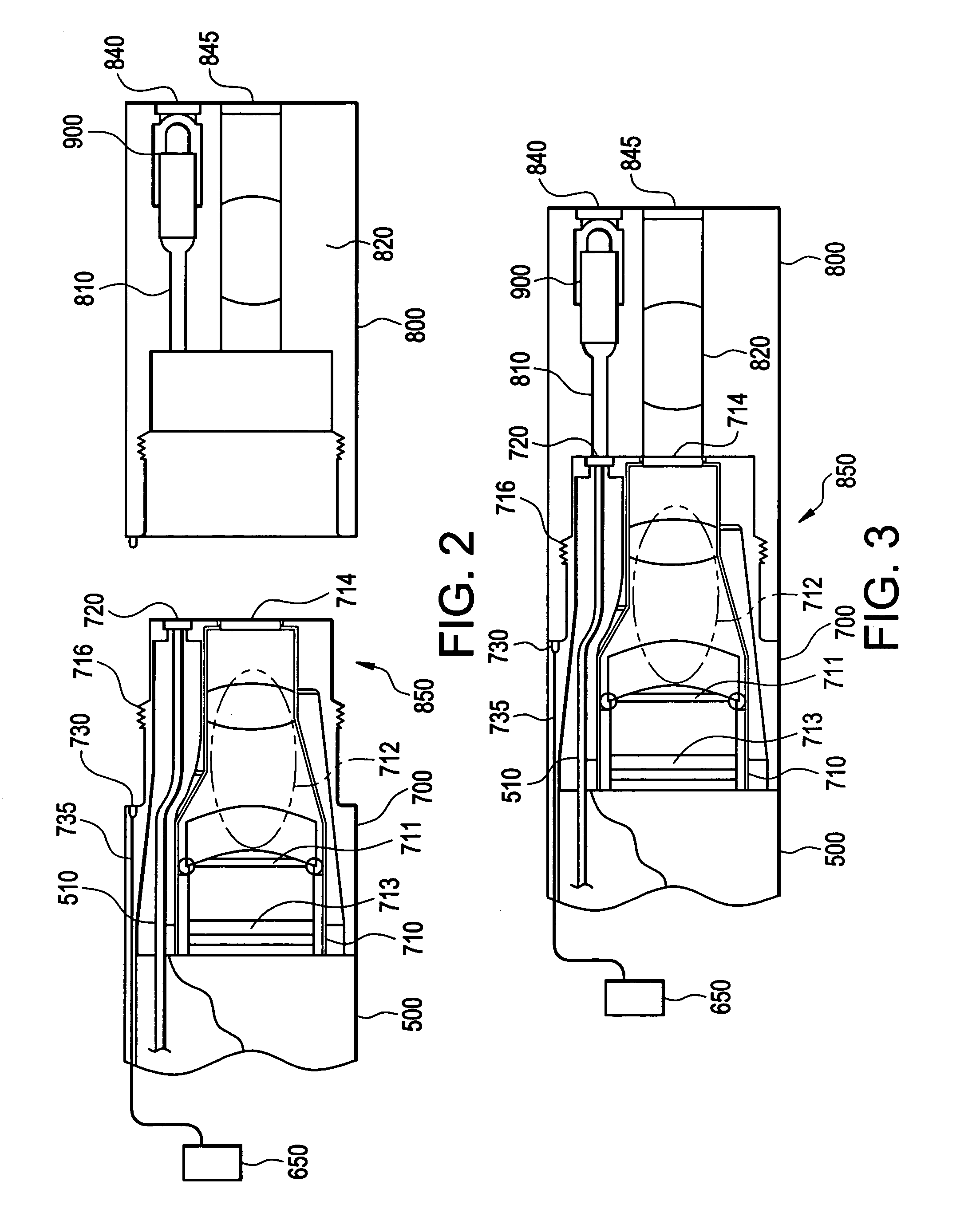
Light assembly for remote visual inspection apparatus
An apparatus for use as a light assembly in remote visual inspection devices is provided. The light assembly may consist of a laser diode coupled to a fiber optic bundle that transmits collimated laser light onto a wavelength converter located in the distal end of the remote video inspection system. Wavelength converters consisting of phosphorescent materials can be used to convert collimated laser light into white light for inspection illumination purposes.
Owner:GE INSPECTION TECH LP
Laser speckle reduction element
ActiveUS20120081786A1Reduce coherenceBroaden wavelength bandwidthPolarising elementsLight beamOptical pathlength
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com