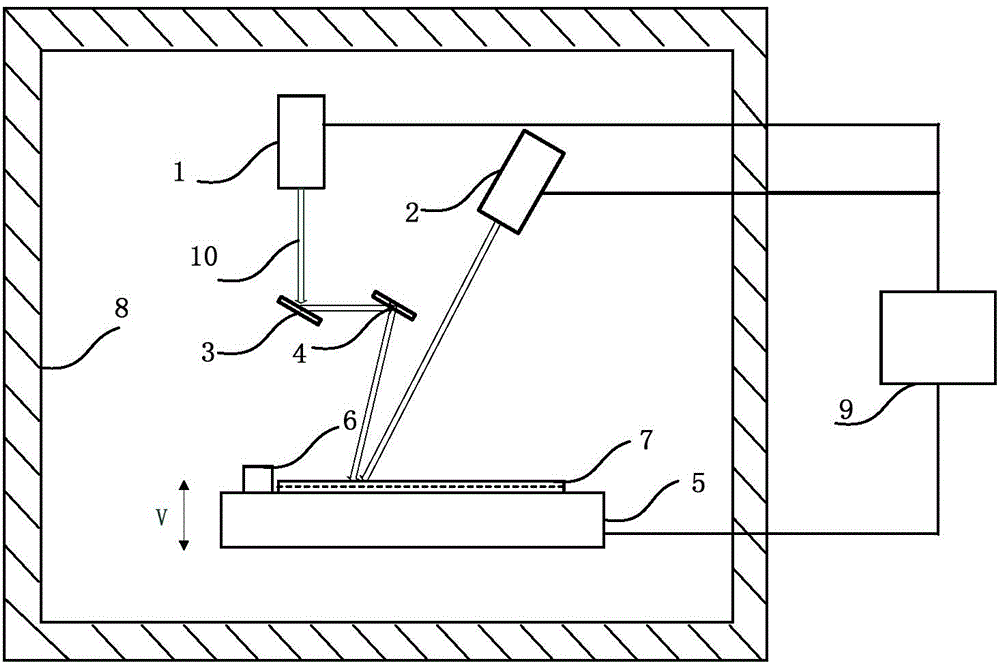
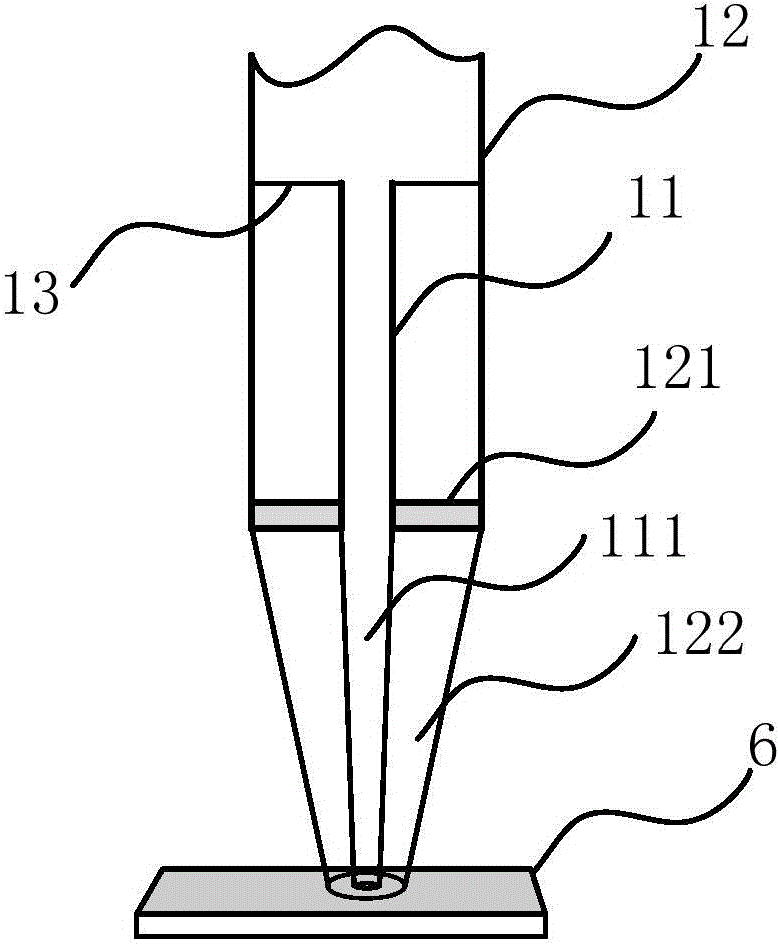
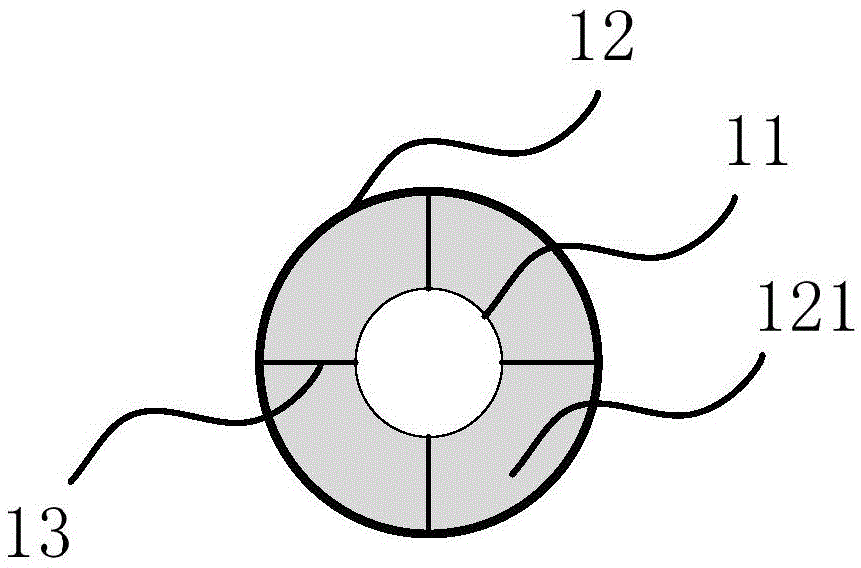
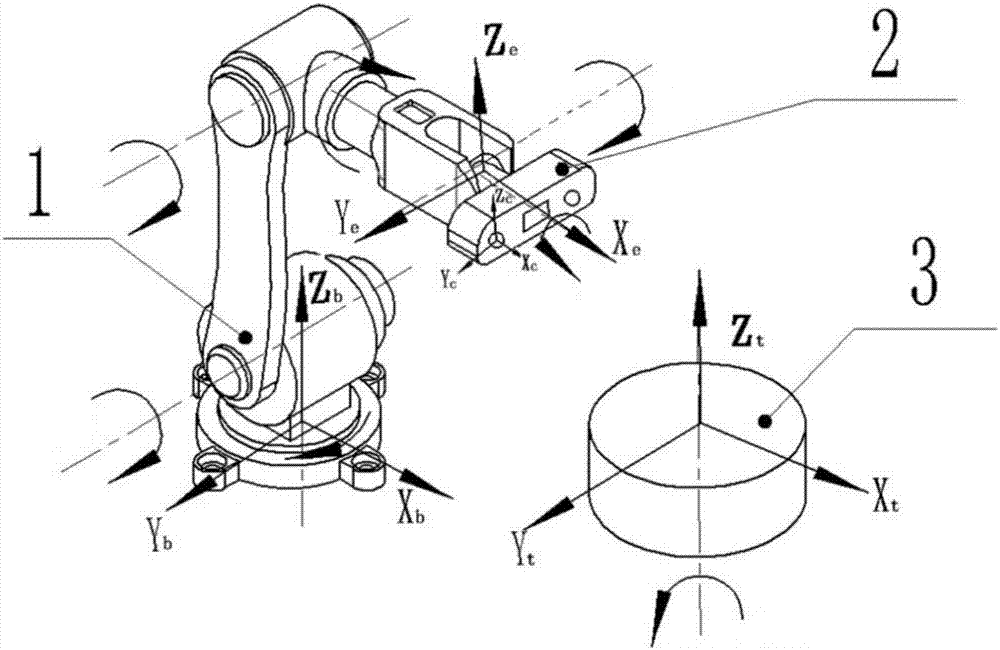
Patents
Literature
3614 results about "Galvanometer" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
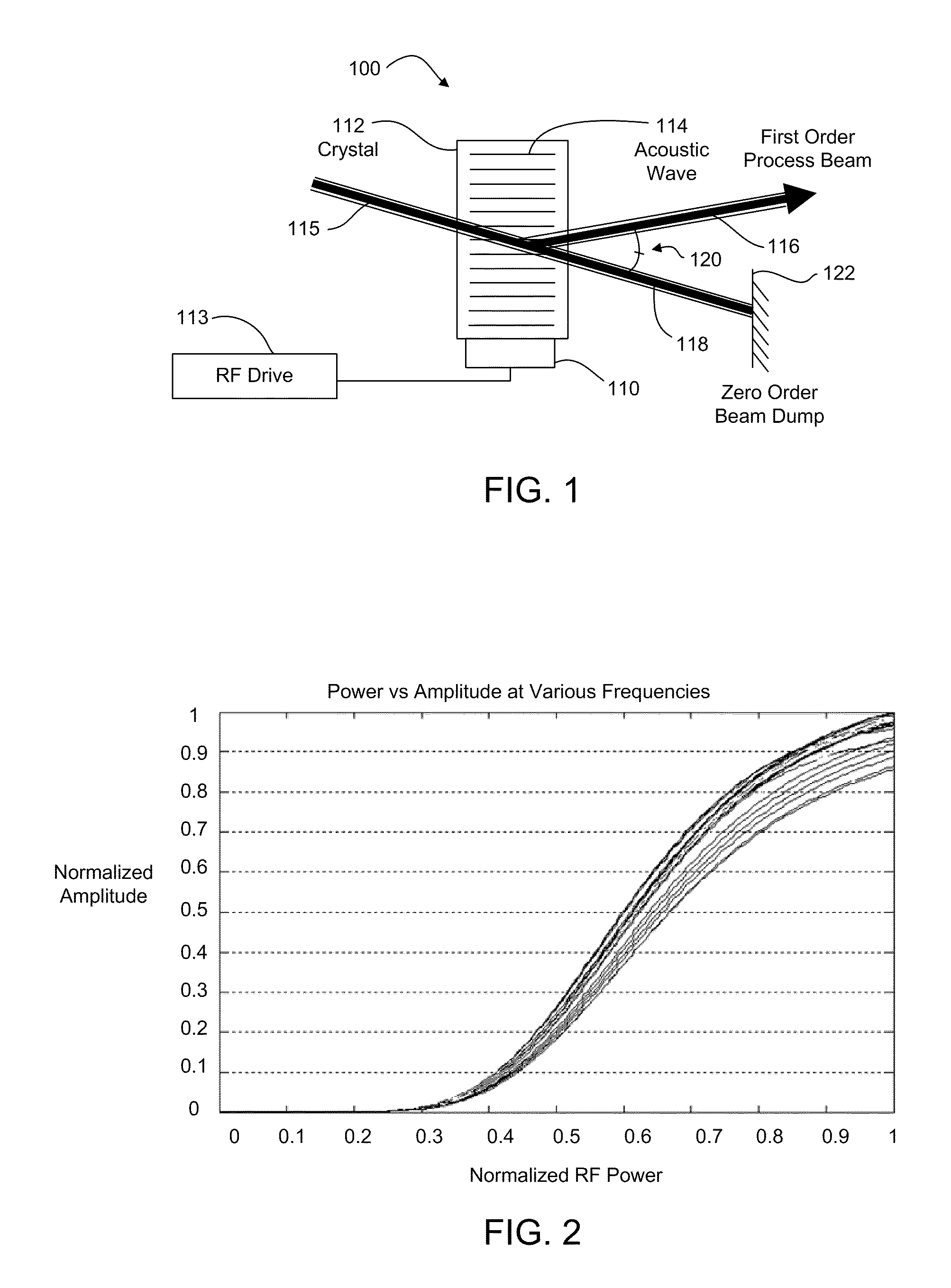
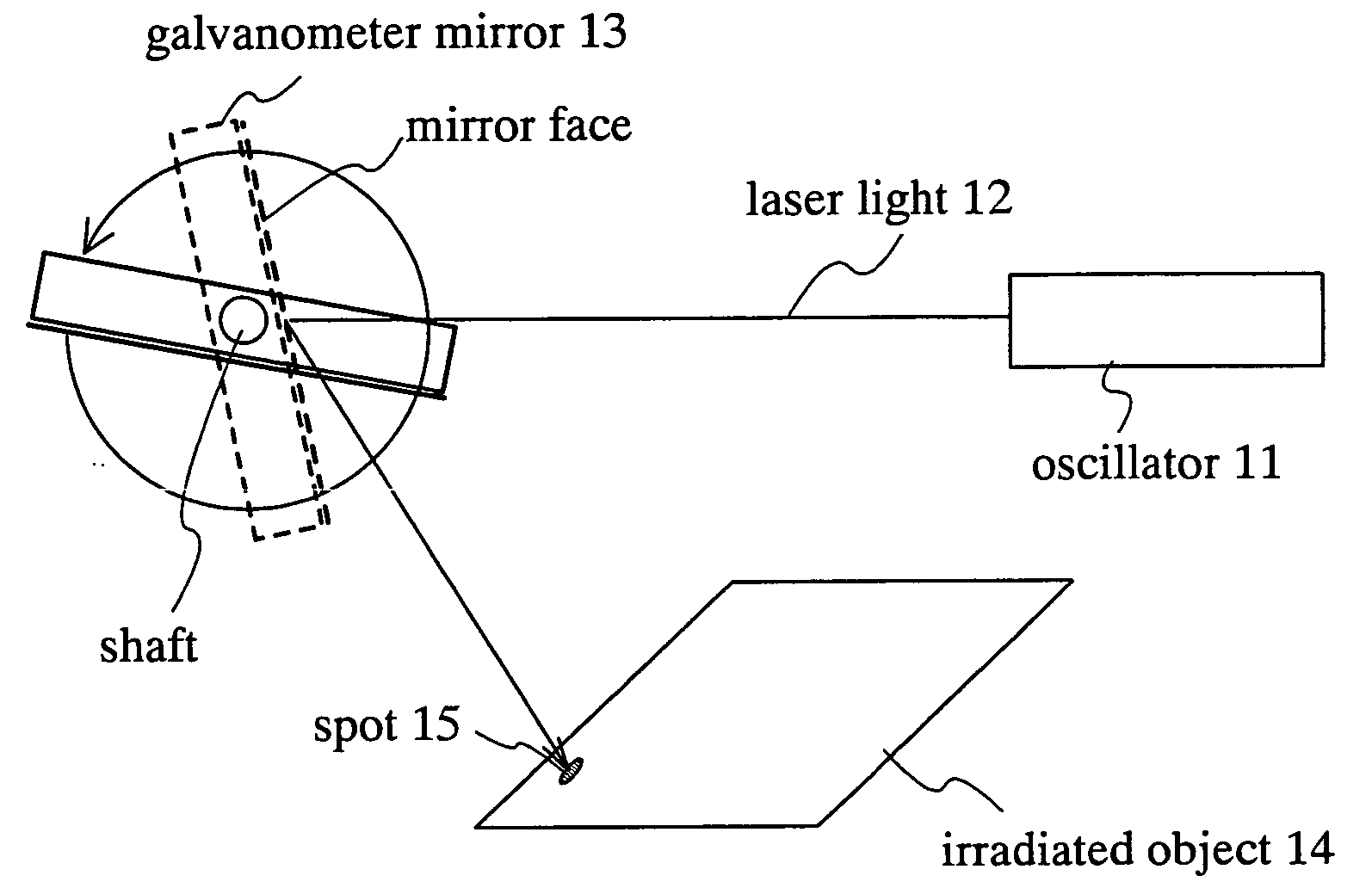
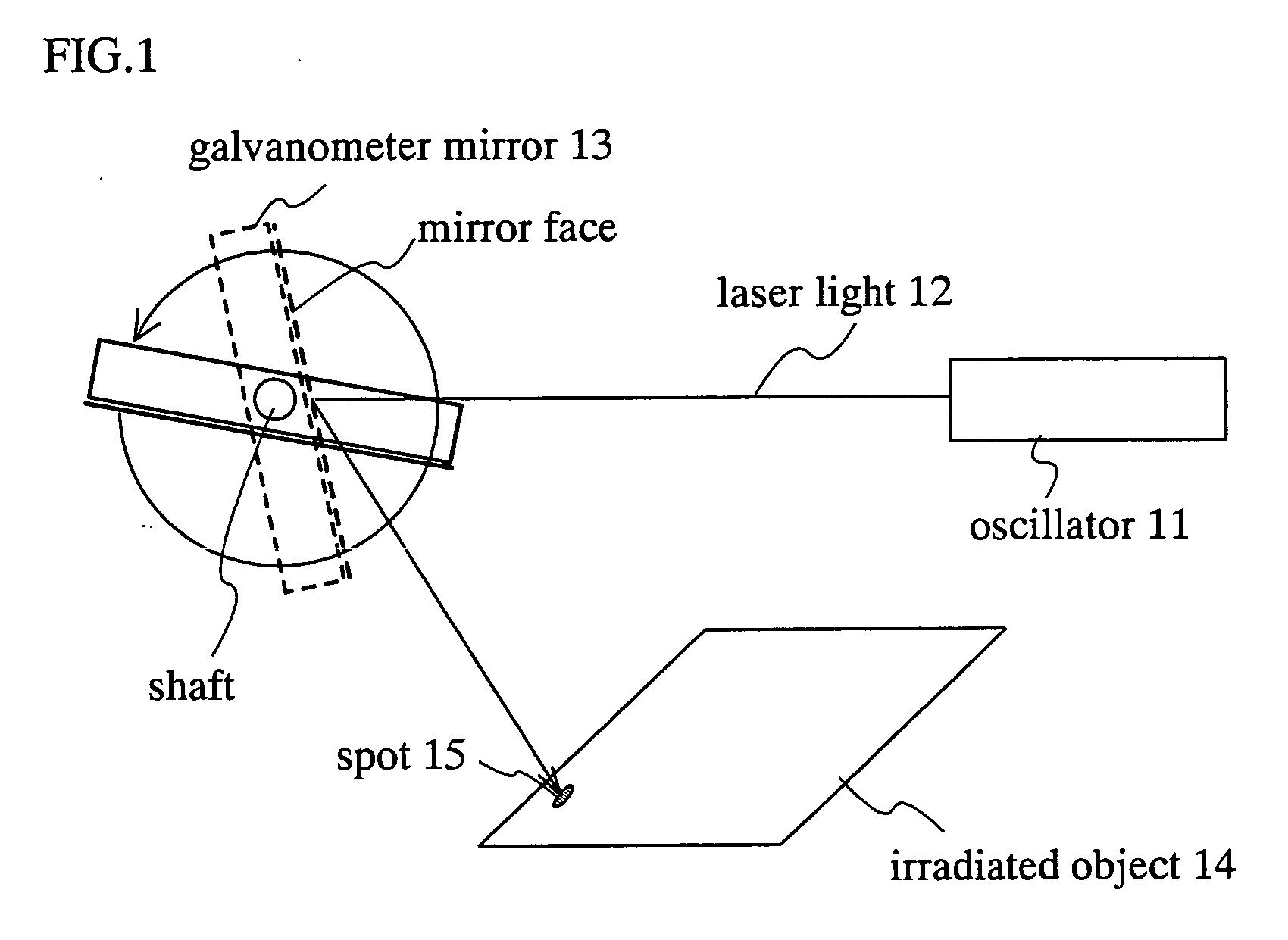
A galvanometer is an electromechanical instrument used for detecting and indicating an electric current. A galvanometer works as an actuator, by producing a rotary deflection (of a "pointer"), in response to electric current flowing through a coil in a constant magnetic field. Early galvanometers were not calibrated, but their later developments were used as measuring instruments, called ammeters, to measure the current flowing through an electric circuit.
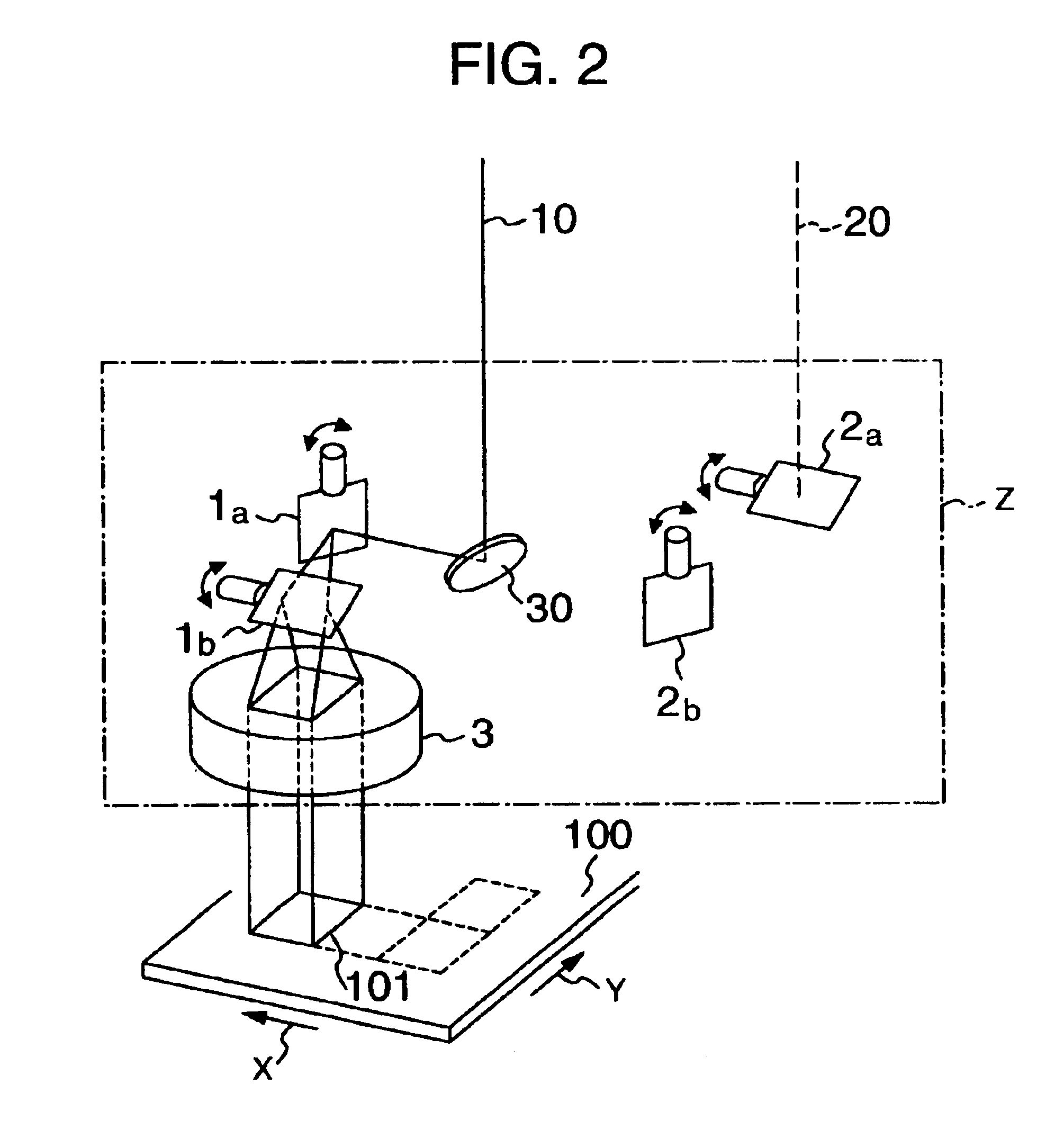
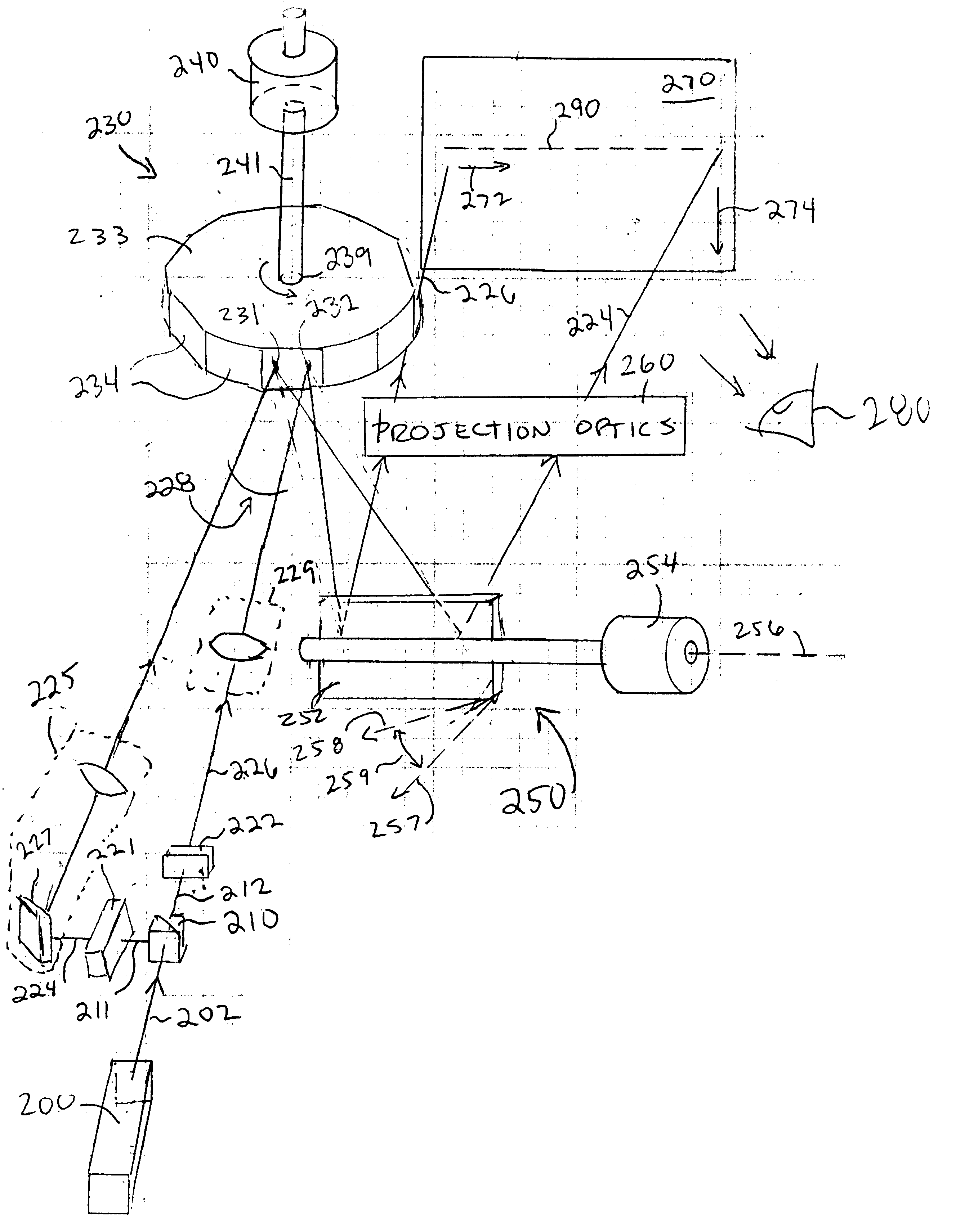
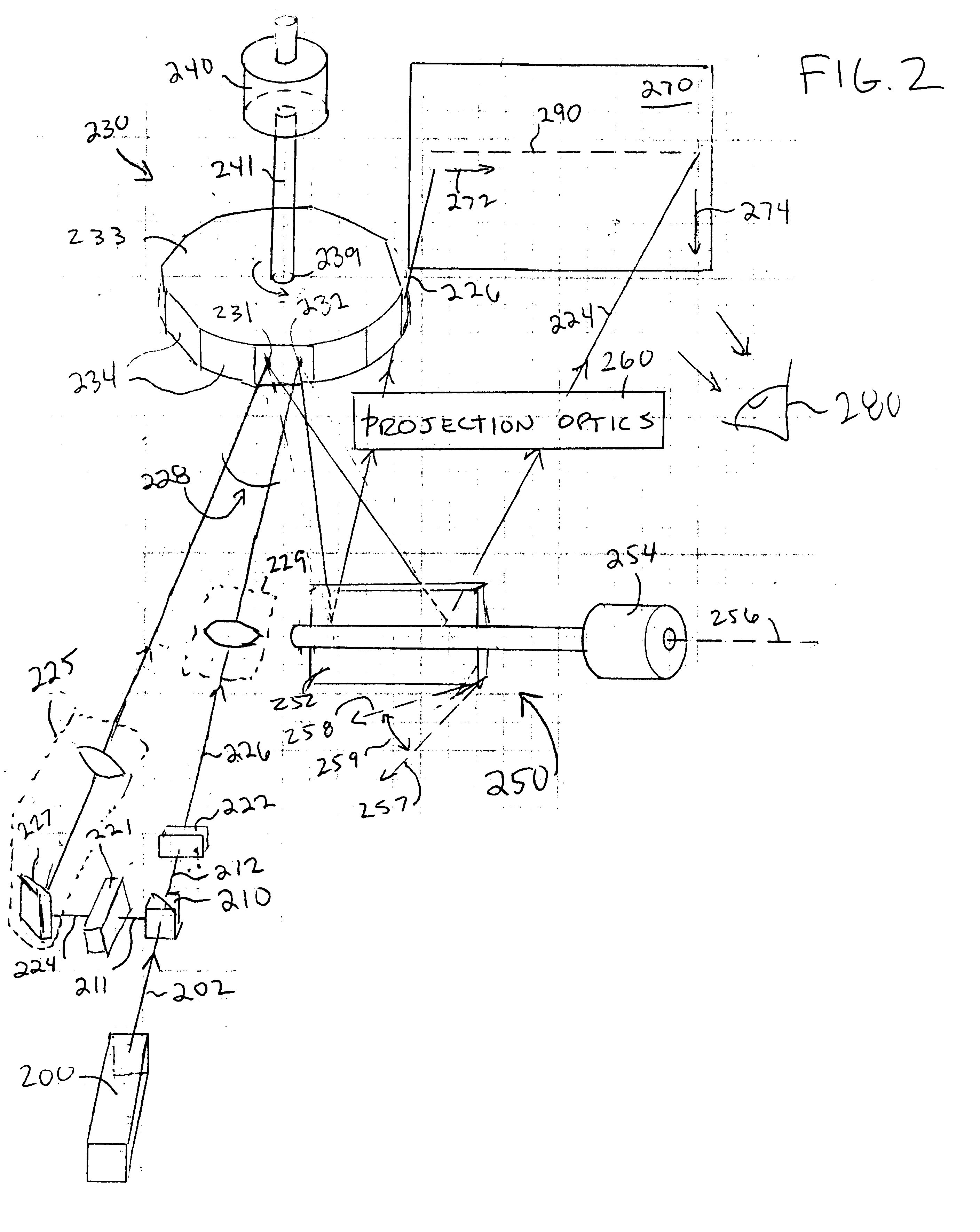
Projection display device
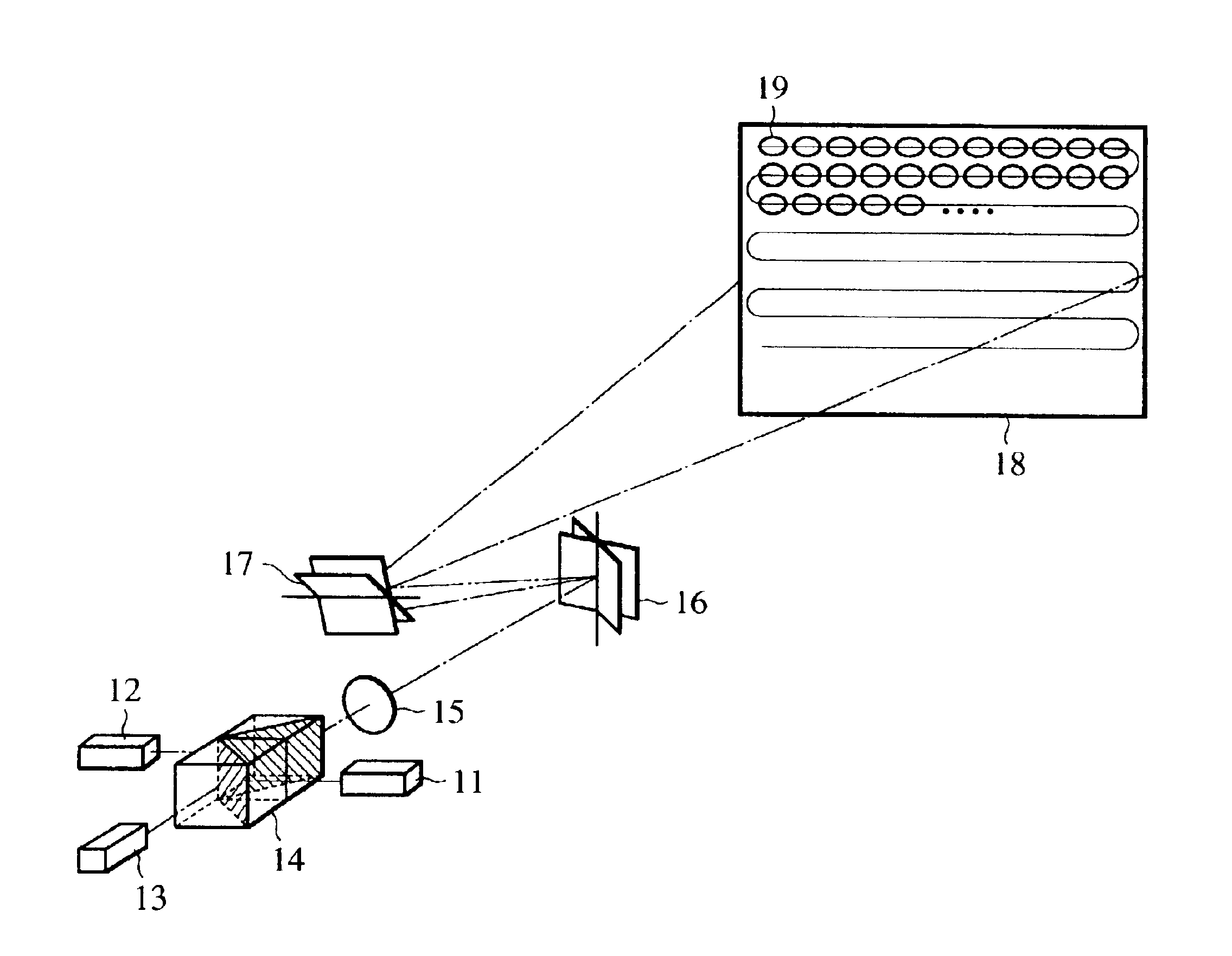
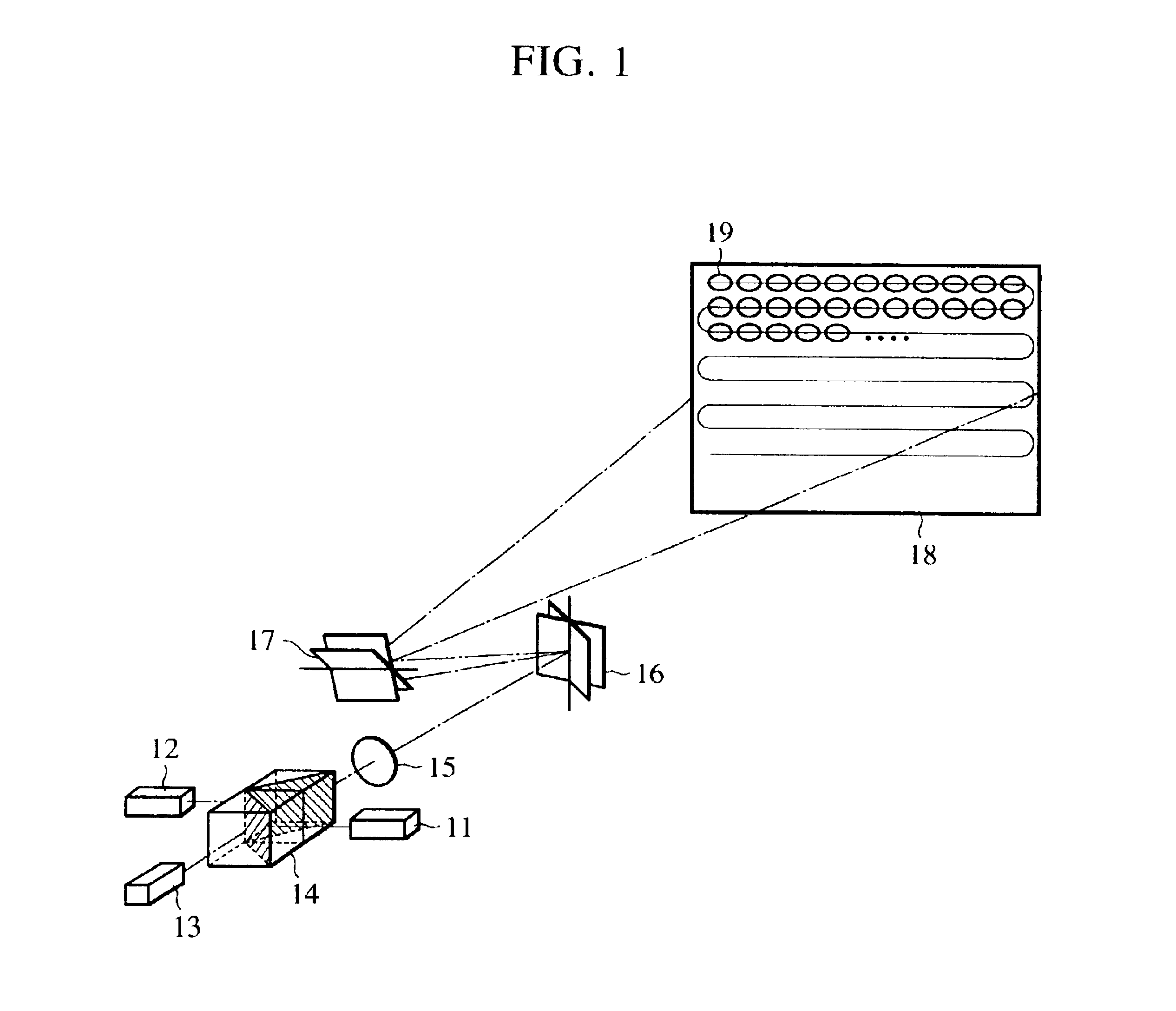
InactiveUS6945652B2Less expensiveAccurate color reproductionTelevision system detailsTelevision system scanning detailsColor imageProjection plane
Light beams having different wavelengths emitted from red and blue semiconductor lasers and a laser diode pumped green solid-state laser are incident on respectively different surfaces of a color combining element and are overlaid on a single light path. Multiple beam interference films of the color combining element allow only the light beams having the oscillating wavelengths corresponding to the respective light sources to pass therethrough or reflect thereon so as to combine the light beams. A collimator collimates the light beams so that the beam waist of the light beams lies around a projection plane. When two-dimensional scanning is performed by radiating the light beams onto a micromechanical mirror and then onto a galvanometer mirror for scanning light in the horizontal and vertical directions, respectively, a color image is displayed on the projection plane by arranging pixels in array, each pixel consisting of overlapping pulses of light of three colors.
Owner:CANON KK
Laser machining device
InactiveUS6875951B2Low costSmall sizeWelding/soldering/cutting articlesLaser beam welding apparatusLaser processingGalvanometer
A laser machining device according to the invention is provided with a laser oscillator for generating a laser beam, a main deflecting galvannometer mirror, an Fθ lens, and a sub-deflecting means arranged in an optical path between the laser oscillator and the main deflecting galvanometer mirror. A means for splitting a laser beam is provided, and the sub-deflecting means is inserted into the optical path of one of the split laser beams. At the same time, both the split laser beams are incident from the same main deflecting galvannometer mirror to the Fθ lens, and a numerical aperture in the optical system constituted by the main deflecting galvannometer mirror, the Fθ lens, and an object is set to be not more than 0.08.
Owner:MITSUBISHI ELECTRIC CORP
Multibeam laser drilling apparatus
ActiveUS6849824B2Avoid it happening againSuppress errorPrinted circuit manufactureWelding/soldering/cutting articlesPower flowGalvanometer
Provided is a multi-beam laser drilling apparatus for drilling a workpiece, simultaneously at two positions while telecentric errors are suppressed, in which a conventional optical system in which galvanometer mirrors are used for a first laser beam, and a galvanometer-mirror system is located close to an fθ lens in order to prevent occurrence of telecentric error. A second laser beam which has been deflected by a second galvanometer-mirror system, transmits through a polarized beam mixers and is incident upon the first galvanometer-mirror system and the fθ lens, and accordingly, the workpiece is drilled simultaneously at two positions with the use of both first and second laser beams.
Owner:HITACHI SEIKO LTD
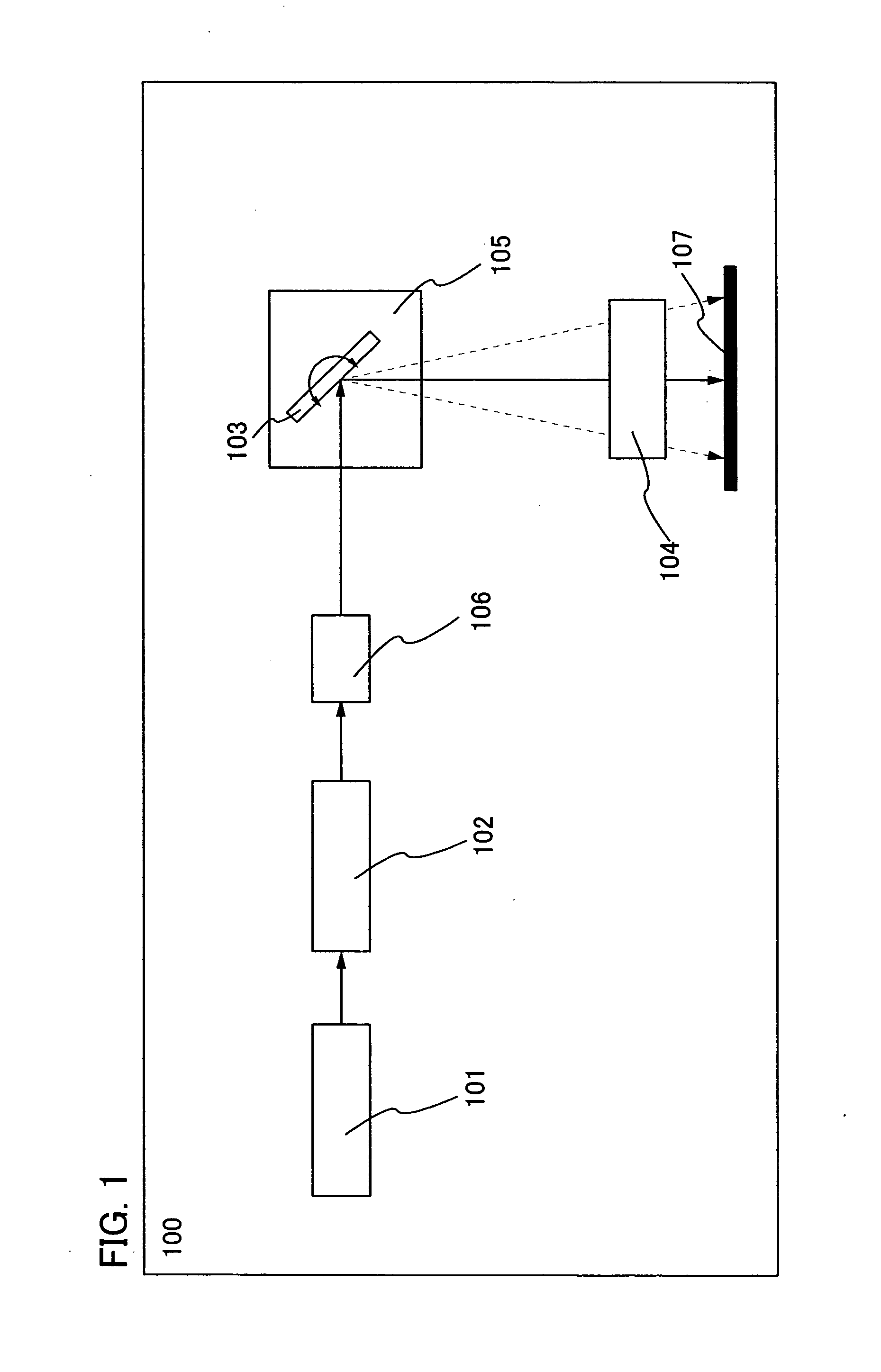
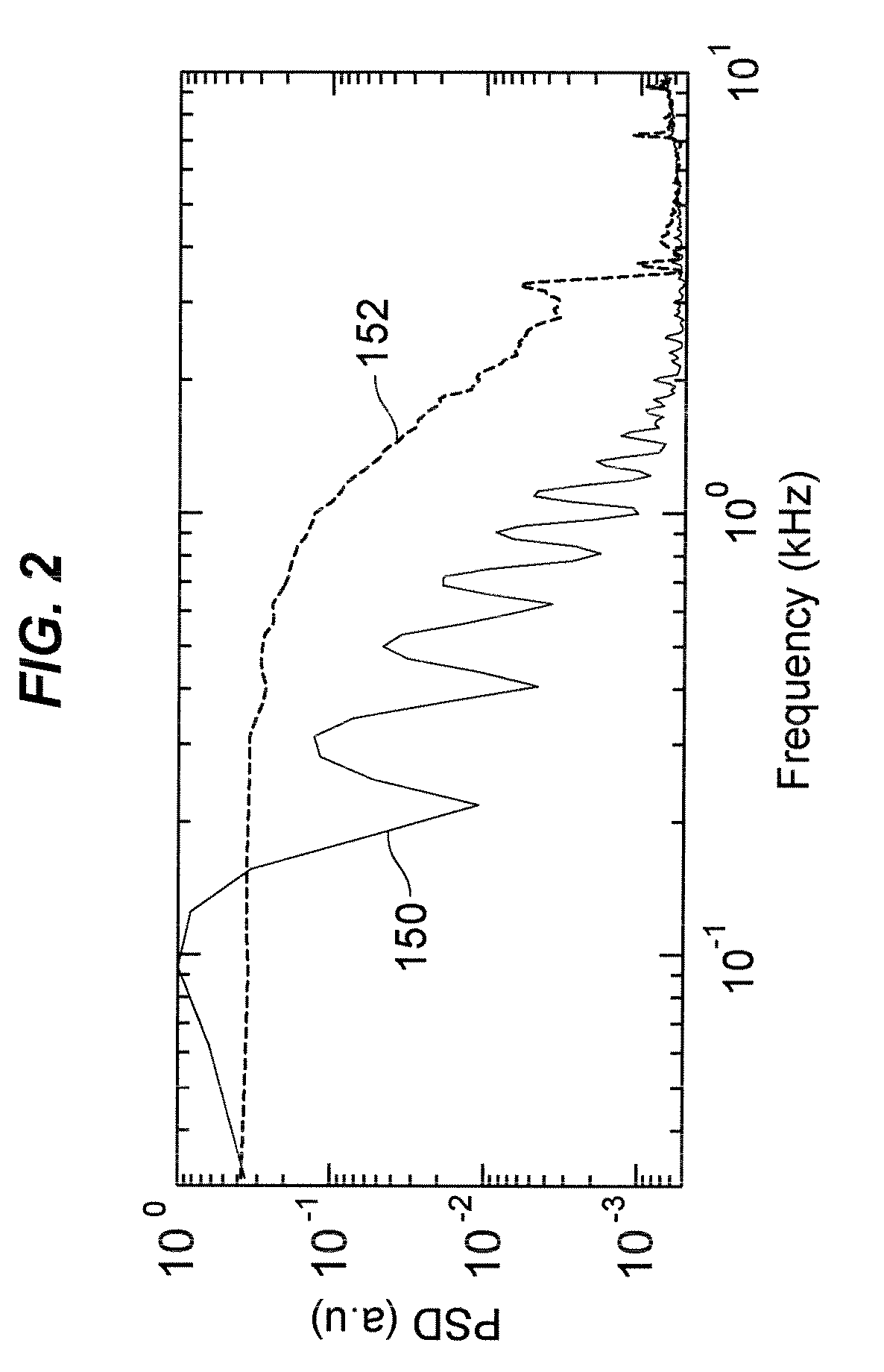
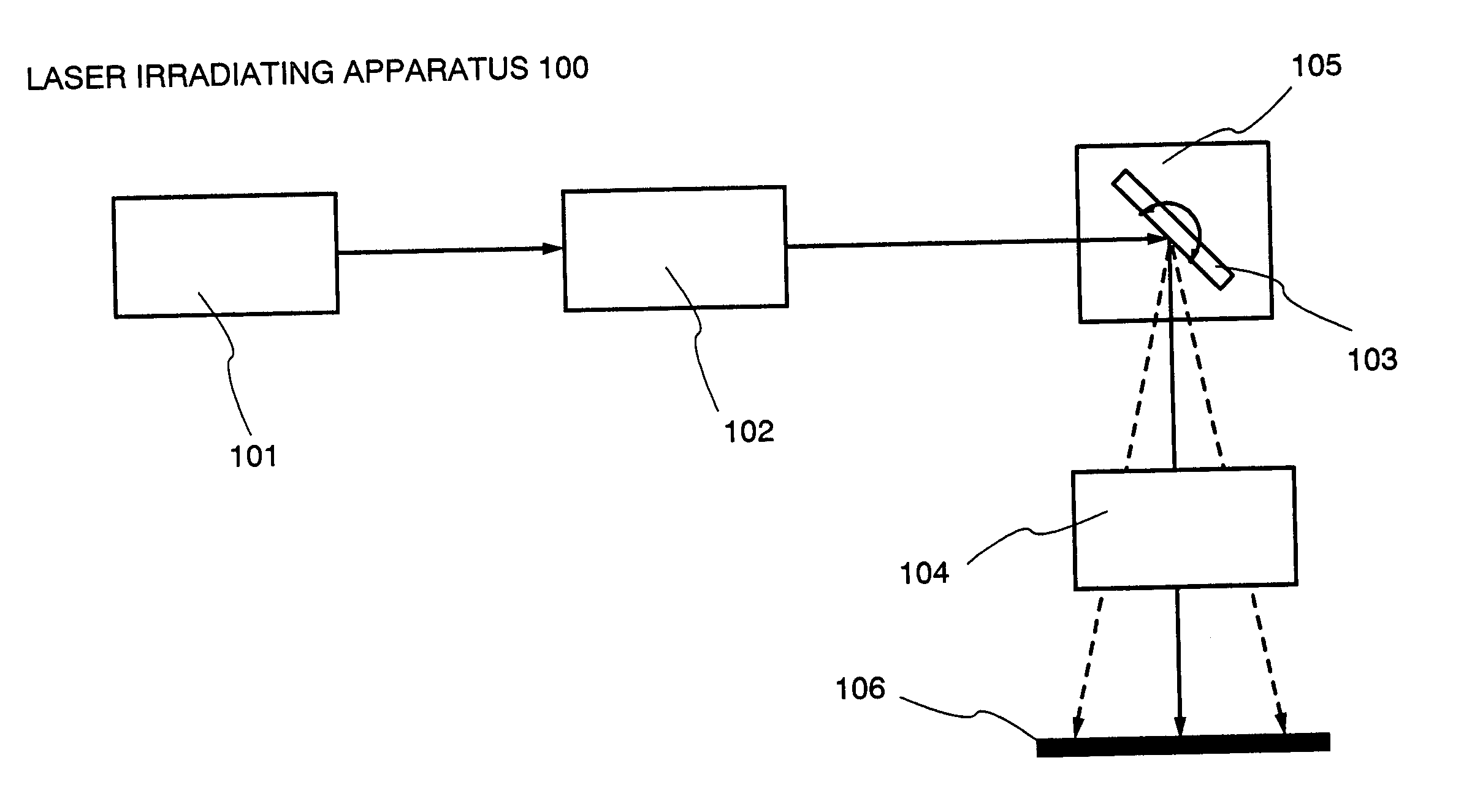
Laser irradiation apparatus and method of manufacturing semiconductor device by using the laser irradiation apparatus
InactiveUS20040074881A1Offset changeSuppress fluctuationsTransistorSolid-state devicesEnergy variationLight beam
The present invention provides the laser irradiation apparatus that has a galvanometer mirror and an f-theta lens optical system, can offset the change of the energy due to the transmittance change of the f-theta lens, and can scan a laser beam while the change of the energy on a substrate is suppressed. Further, the laser beam energy that is incident on the lens is controlled in advance by combining the optical system changing the branching ratio of polarization of the laser beam and the optical system having dependence on direction of polarization of the laser beam and changed continuously according to the transmittance of the lens on which the laser beam is incident. The laser energy is controlled to offset the transmittance of the lens, and thereby energy fluctuation of the laser beam irradiation of a substrate can be prevented.
Owner:SEMICON ENERGY LAB CO LTD
Device for manufacturing three-dimensional objects using superimposed layers, and associated method of manufacture
ActiveUS20150210013A1Additive manufacturing apparatusAuxillary shaping apparatusElectricityMetallurgy
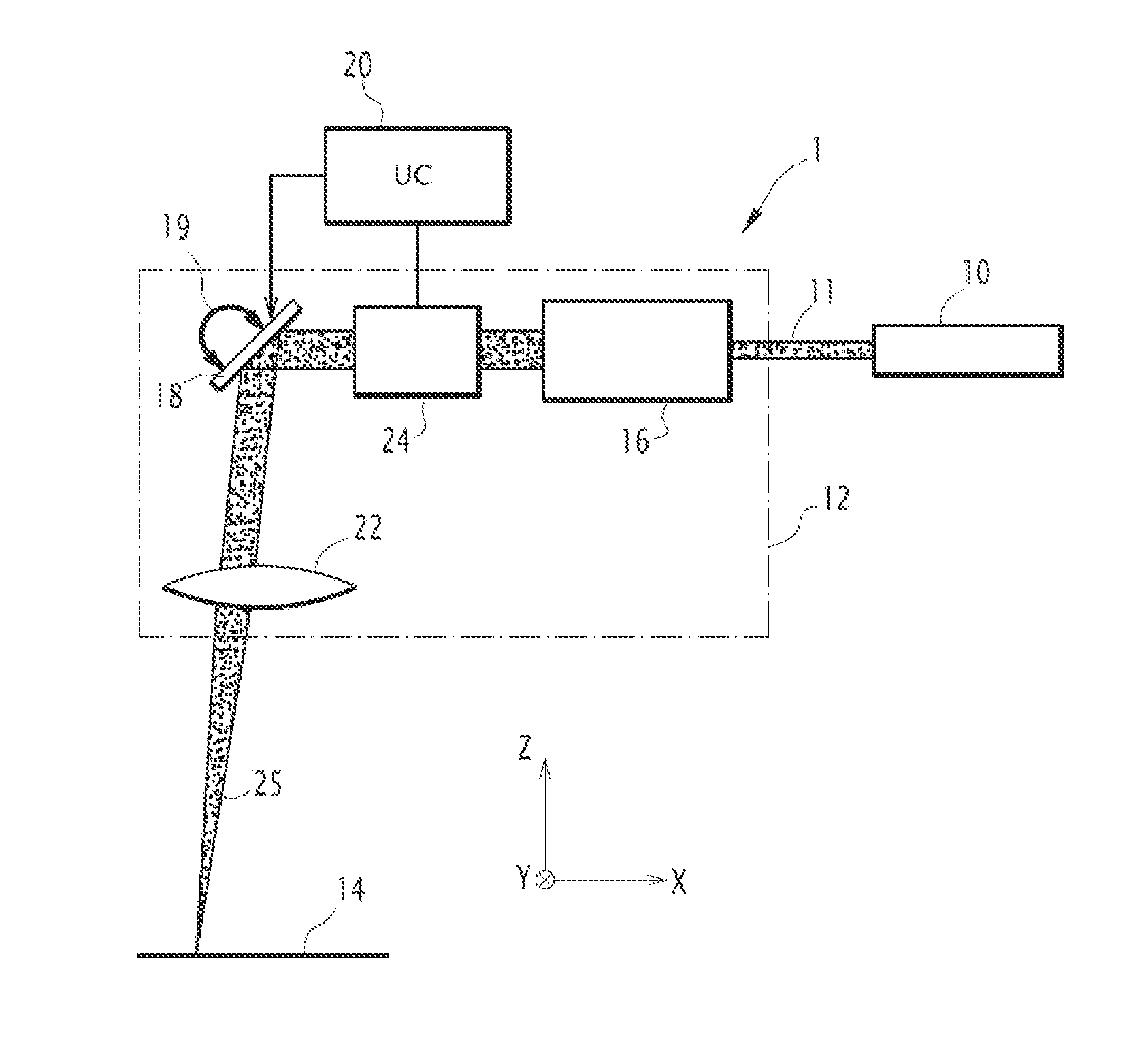
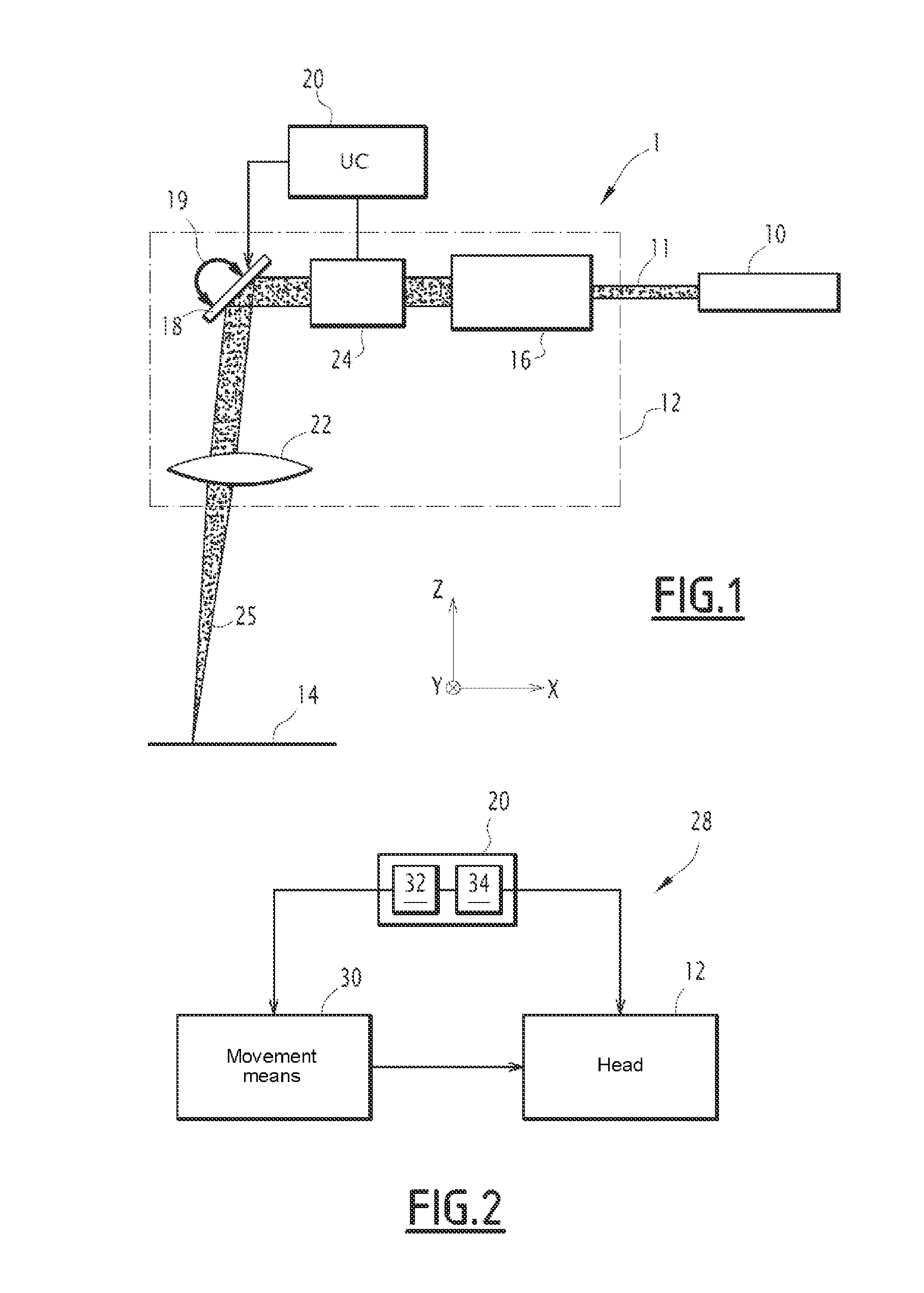
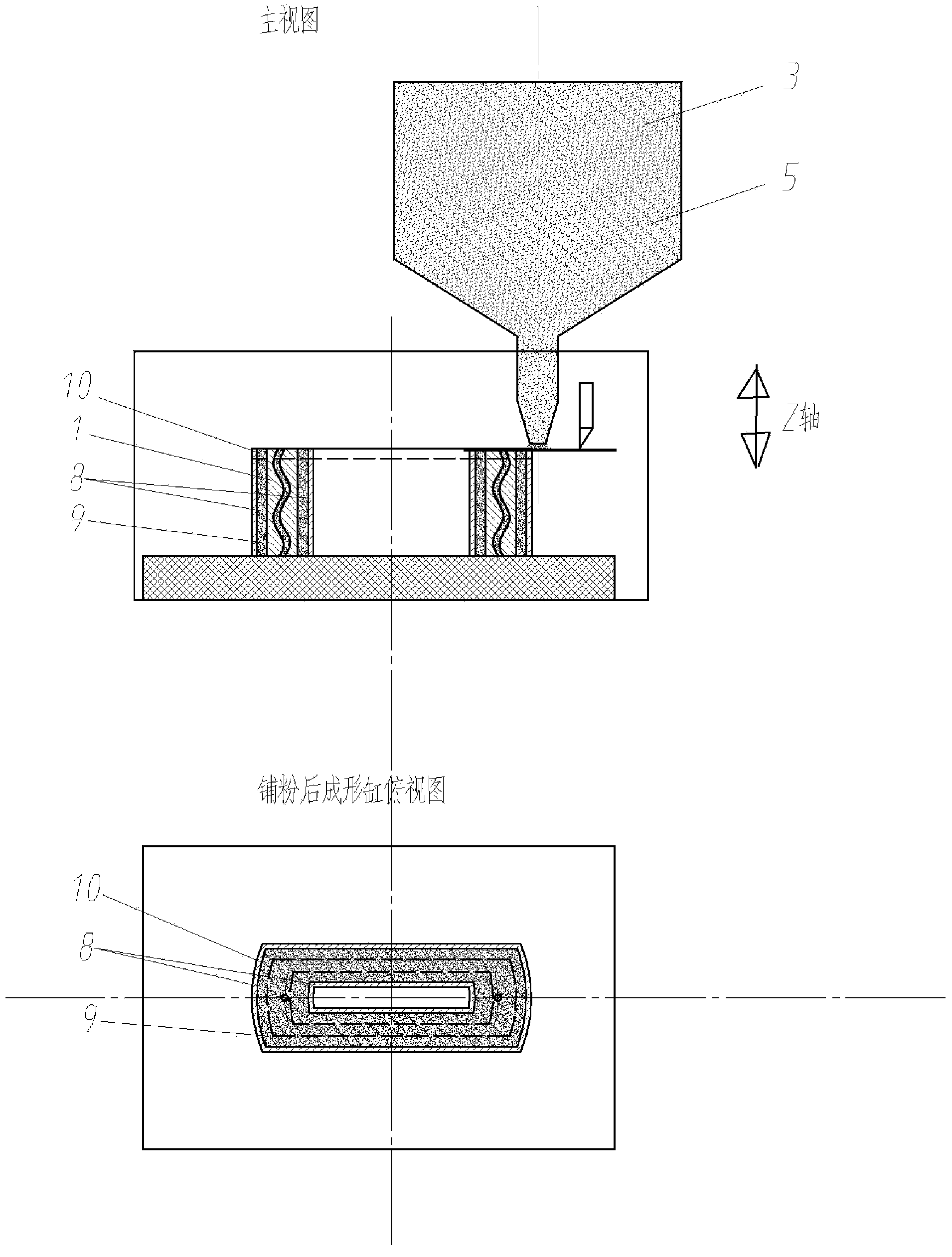
A device for manufacturing three-dimensional objects using superimposed layers is capable, for each layer to be manufactured, of applying a laser beam treatment to a layer of a pulverulent material or liquid placed in a sintering field. The device includes a galvanometric head able to steer a laser beam toward each point of a maximum sintering zone of the sintering field when the galvanometric head is positioned at a predetermined position. The device further includes limiting elements for limiting the steering of the laser beam to an effective sintering zone situated inside the maximum sintering zone, and movement elements for moving the galvanometric head in a plane parallel to that of the sintering field, allowing the galvanometric head to be positioned at at least two different positions, an effective sintering zone being associated with each position of the galvanometric head. An associated method of manufacturing three-dimensional objects is described.
Owner:PHENIX SYST
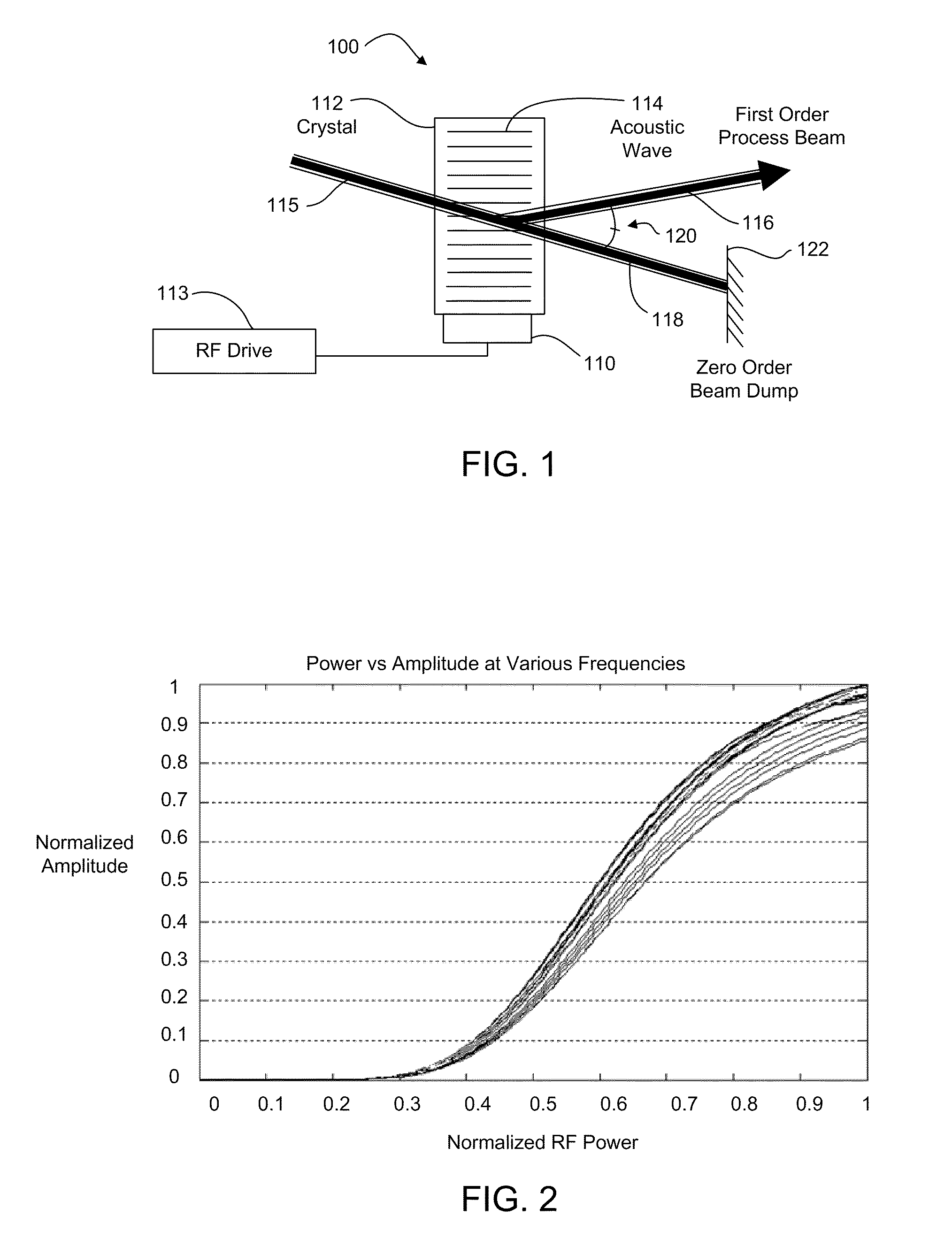
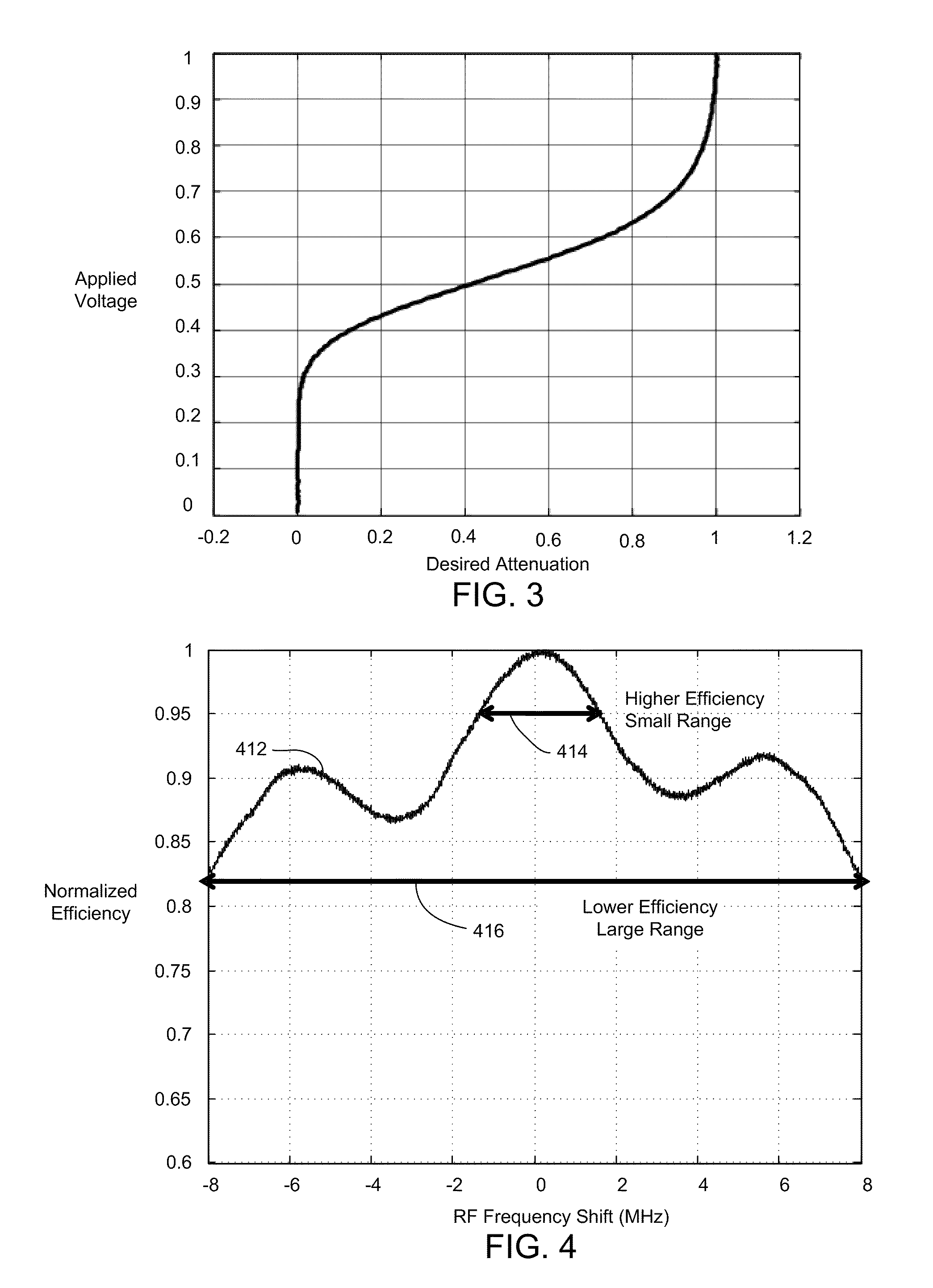
Acousto-optic deflector applications in laser processing of dielectric or other materials
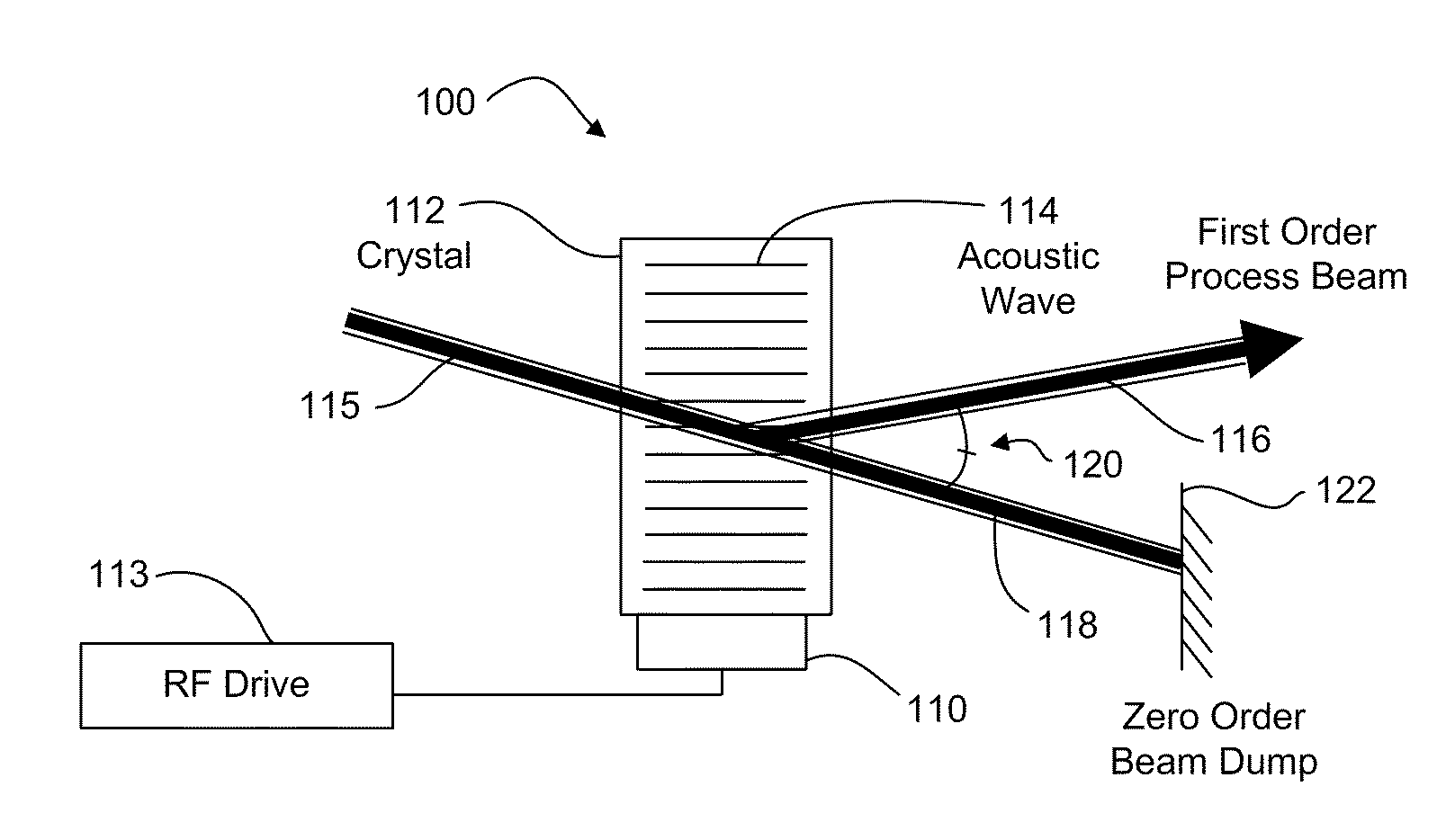
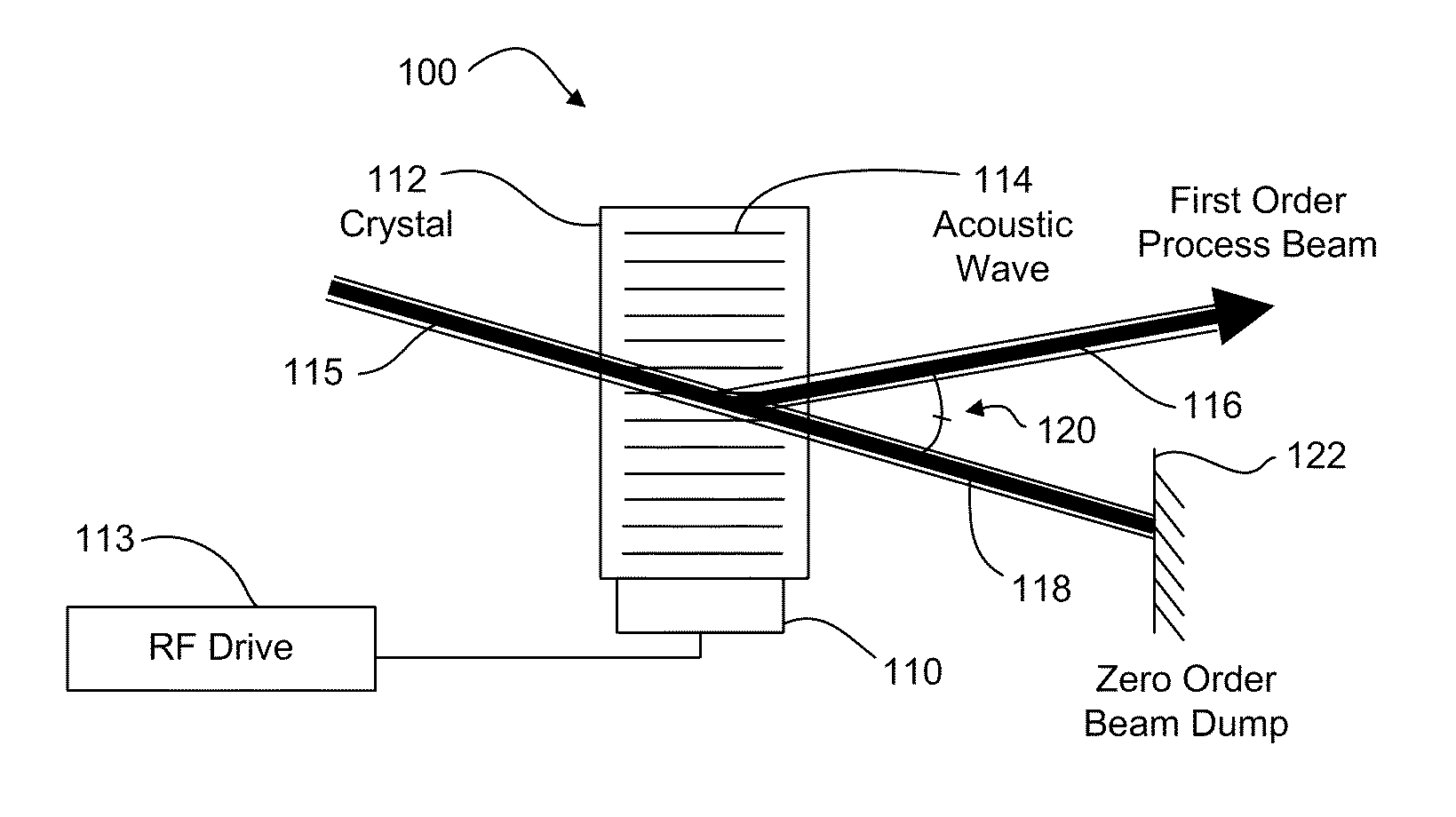
ActiveUS20100301023A1Effective expansionIncrease speedWelding/soldering/cutting articlesMetal working apparatusPower modulationAcousto optic deflector
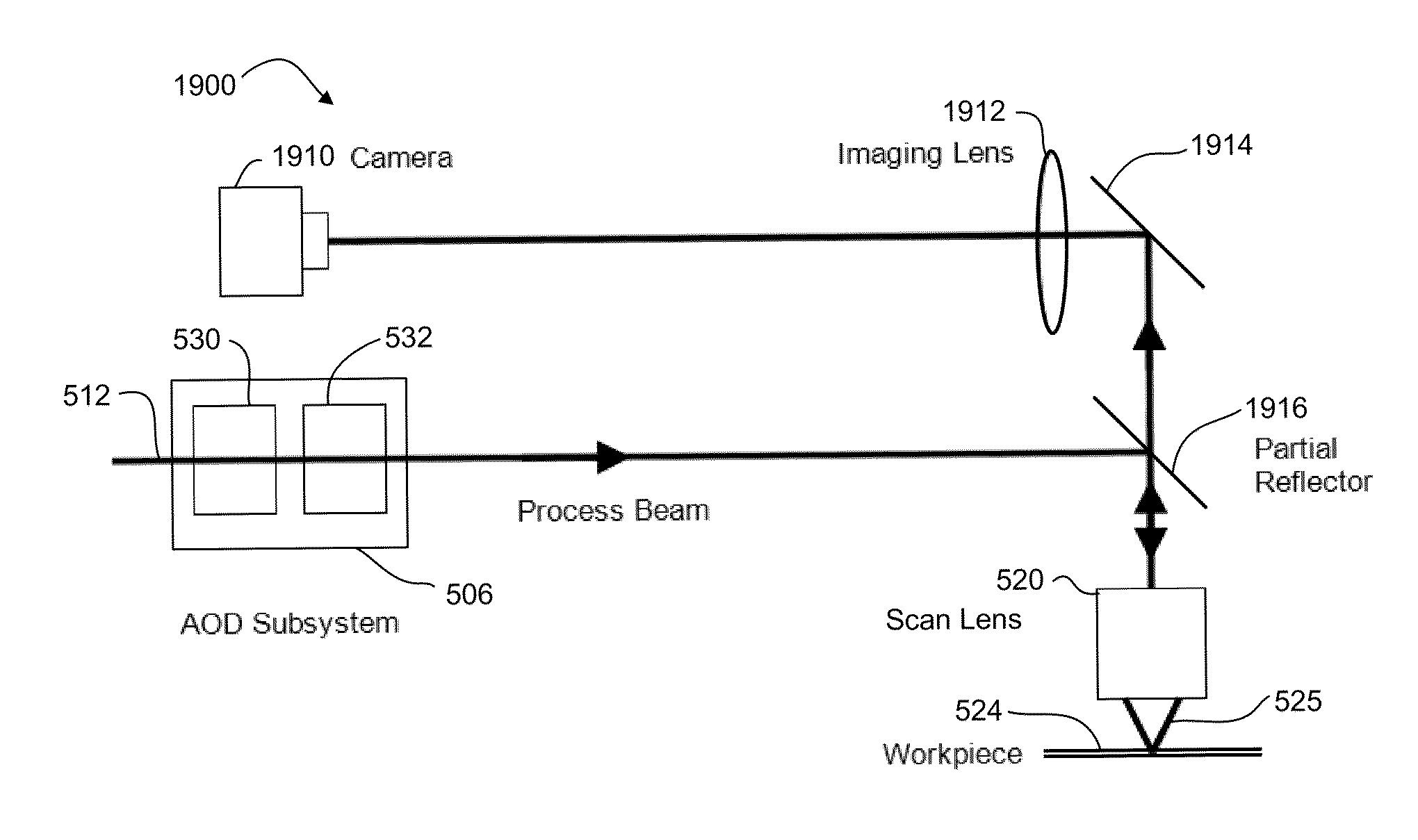
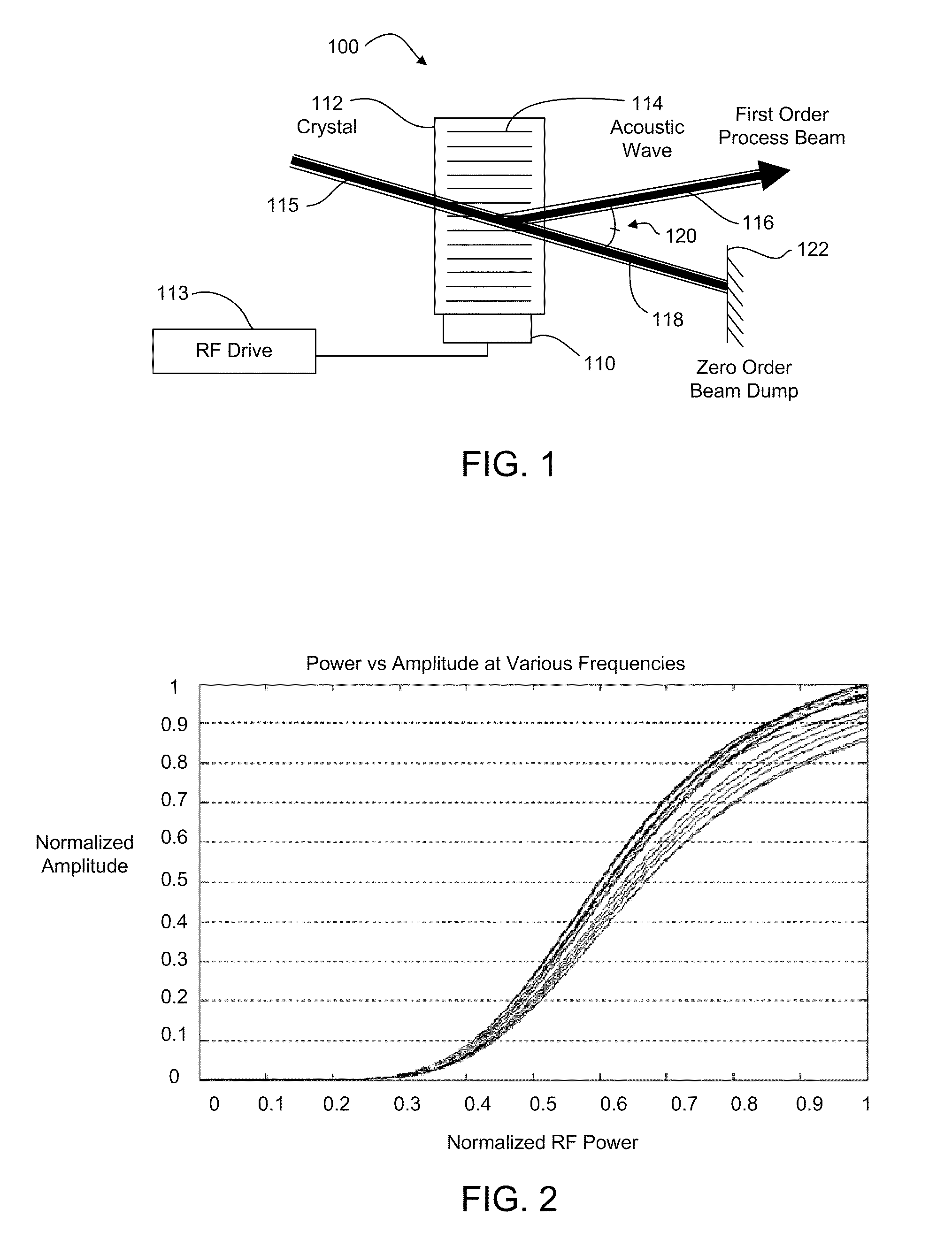
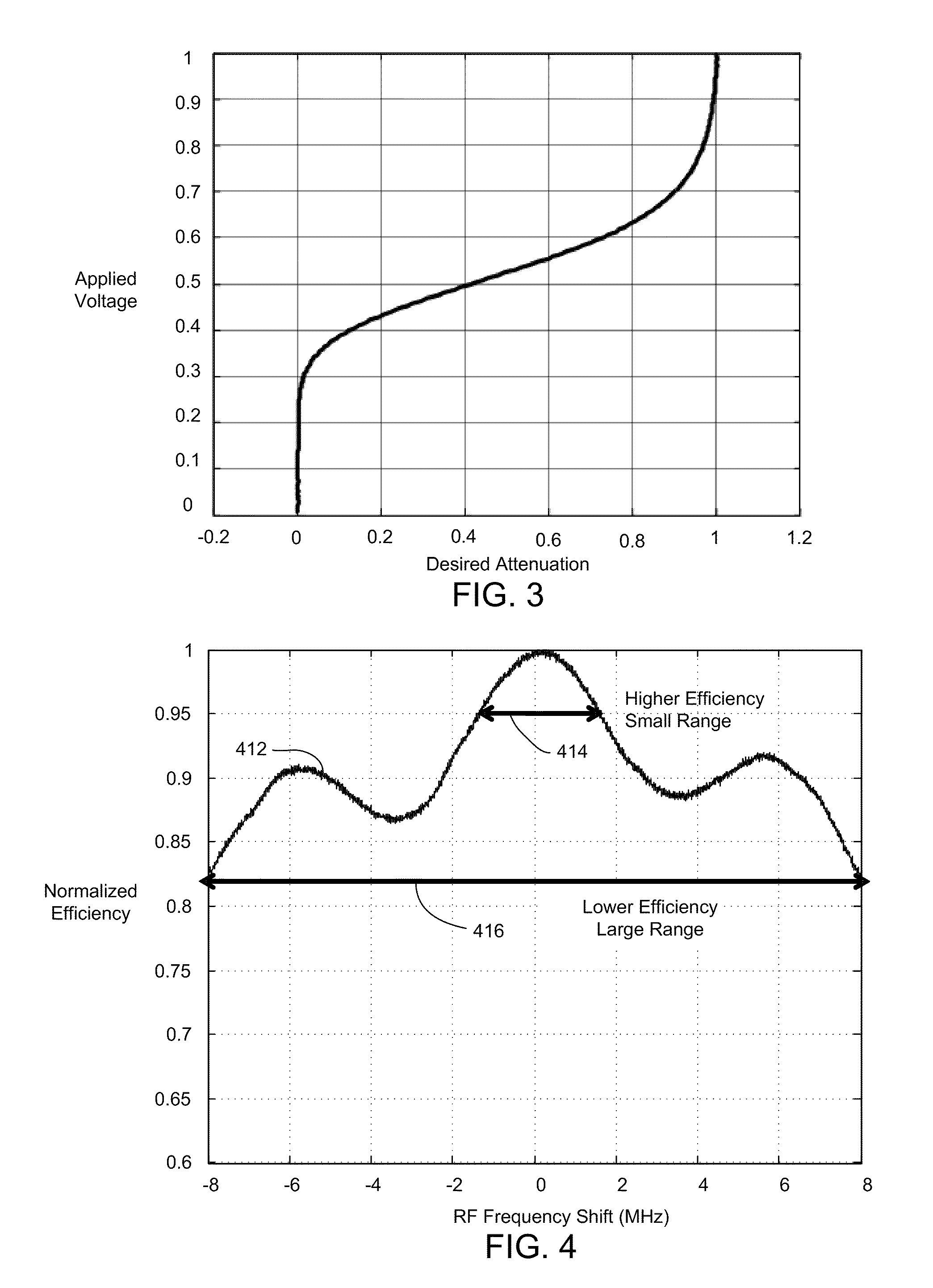
A laser processing system for micromachining a workpiece includes a laser source to generate laser pulses for processing a feature in a workpiece, a galvanometer-driven (galvo) subsystem to impart a first relative movement of a laser beam spot position along a processing trajectory with respect to the surface of the workpiece, and an acousto-optic deflector (AOD) subsystem to effectively widen a laser beam spot along a direction perpendicular to the processing trajectory. The AOD subsystem may include a combination of AODs and electro-optic deflectors. The AOD subsystem may vary an intensity profile of laser pulses as a function of deflection position along a dither direction to selectively shape the feature in the dither direction. The shaping may be used to intersect features on the workpiece. The AOD subsystem may also provide rastering, galvo error position correction, power modulation, and / or through-the-lens viewing of and alignment to the workpiece.
Owner:ELECTRO SCI IND INC
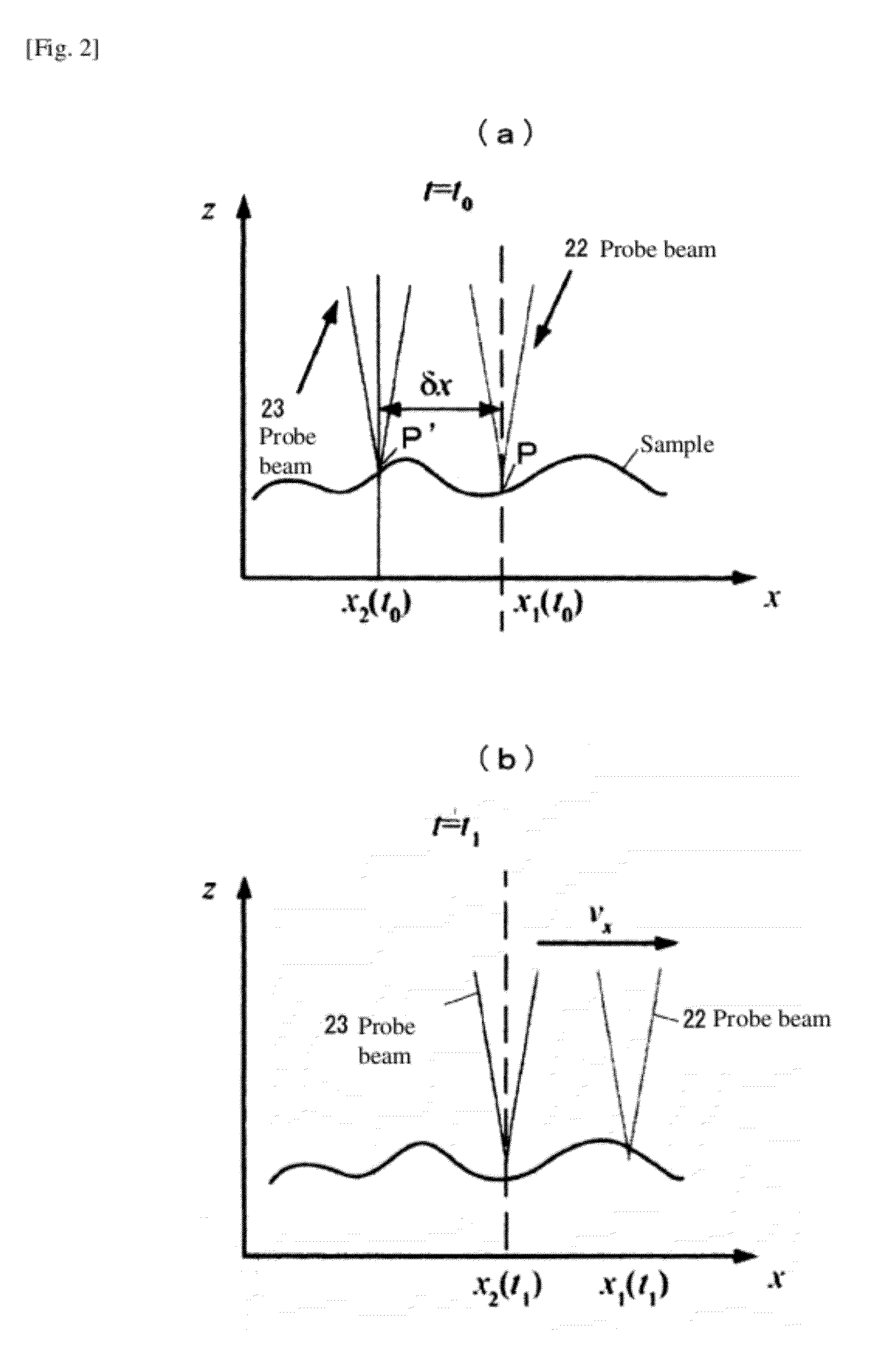
Two-beam optical coherence tomography apparatus
ActiveUS20120120408A1Solve the slow scanning speedHigh measurement sensitivityMaterial analysis by optical meansDiagnostic recording/measuringBeam splitterSpectroscopy
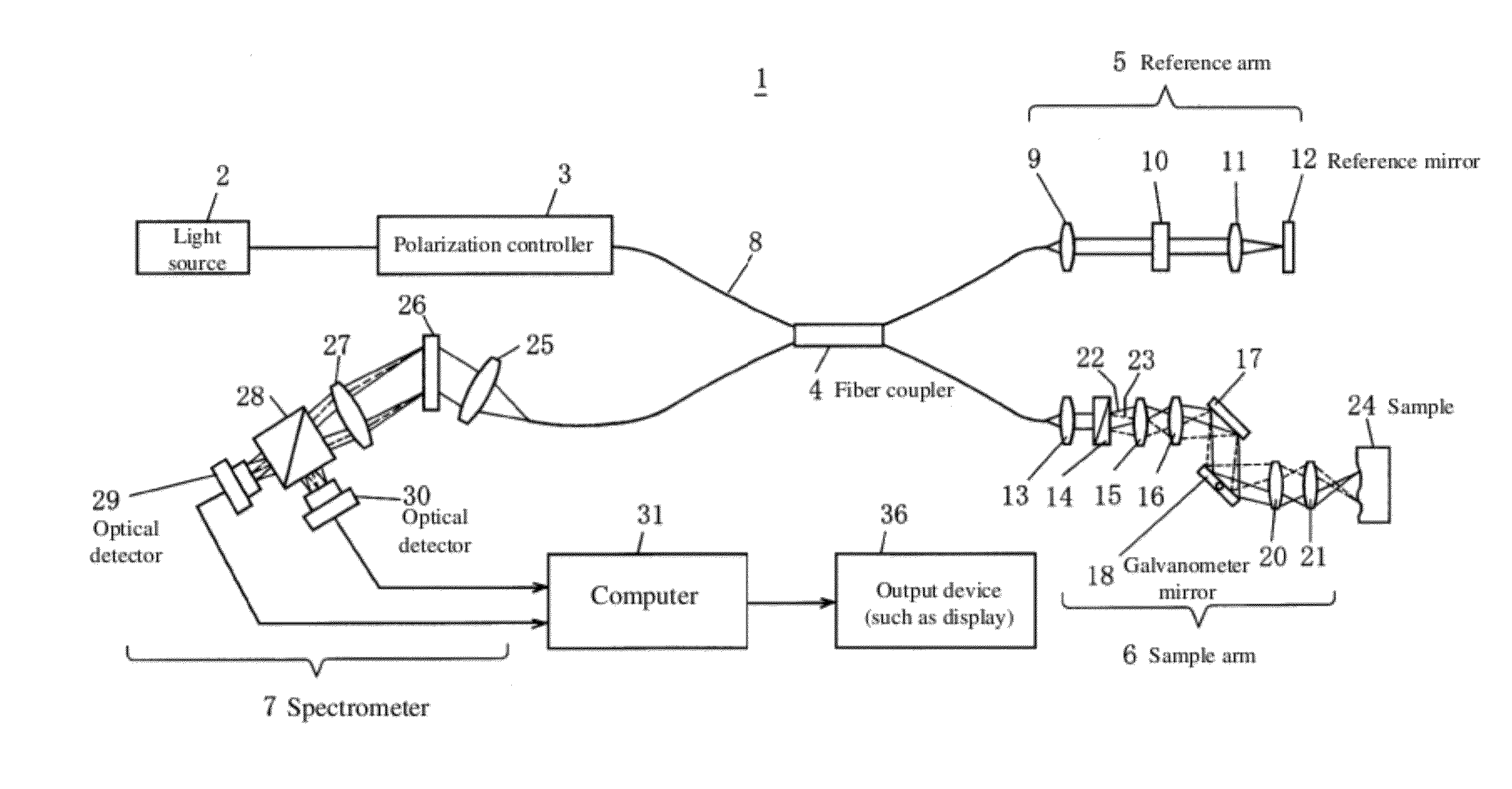
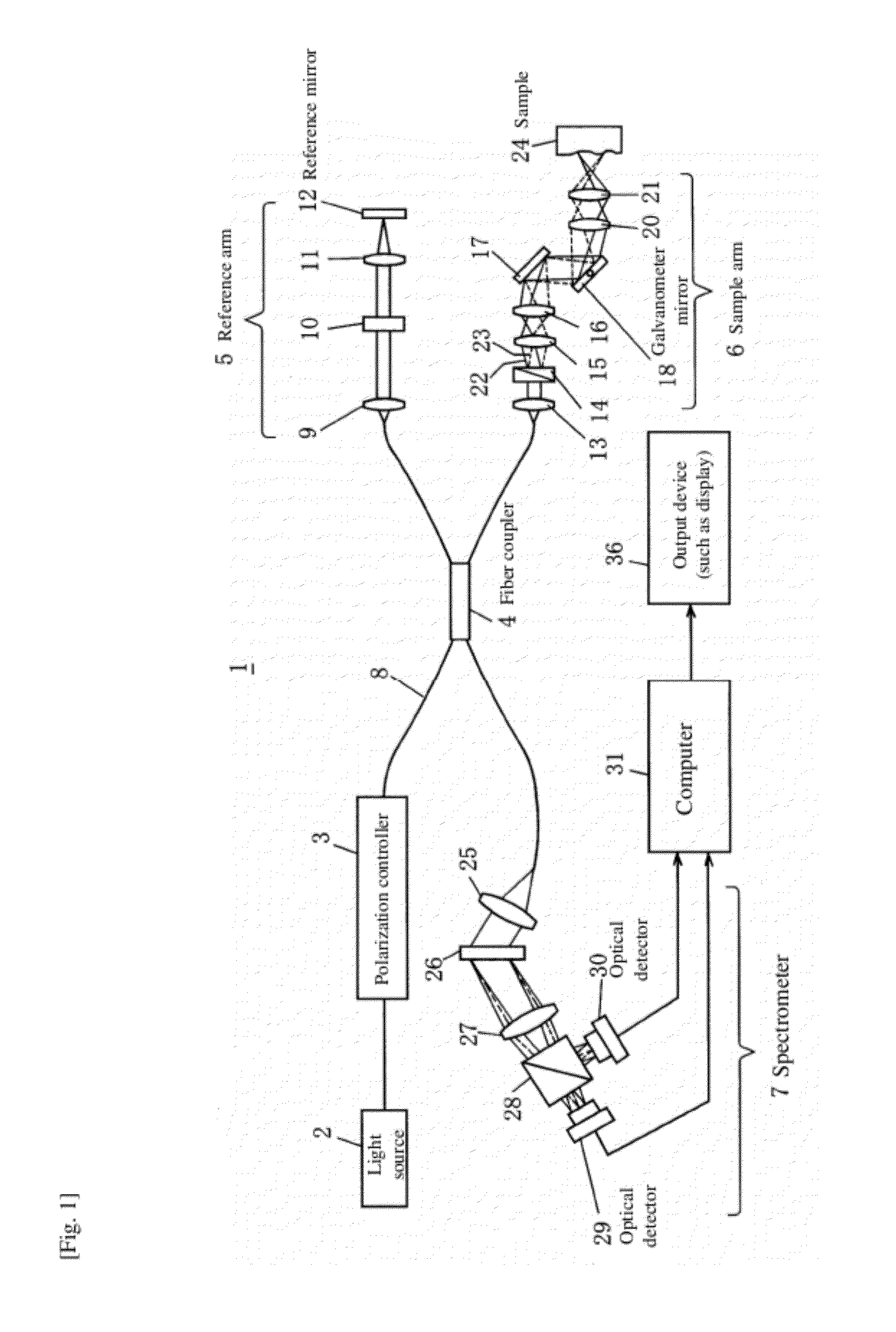
The scanning speed of a sample in Doppler OCT, etc., is increased to enable quick measurement of blood flow rate, blood flow volume, etc. Wideband light from a light source 2 is linearly polarized by a polarization controller 3 and this linearly polarized beam is split into vertically polarized light and horizontally polarized light using a Wollaston prism 14 at a sample arm, which are then irradiated simultaneously onto two different locations of the sample in the scanning direction using a galvanometer mirror18, and reference light from a reference arm 5 and object light from a sample arm 6 are merged and caused to interfere with each other, with the resulting interference signal light passed through a diffraction grating 26 for spectroscopy, while the horizontal component and vertical component are separated by a polarized beam splitter 28, to simultaneously measure the components with two polarization-sensitive optical detectors 29, 30 and thereby obtain two tomography images of the same location at different times by one mechanical scan, thus allowing the amount of temporal change in phase to be measured using the two tomography images.
Owner:UNIV OF TSUKUBA
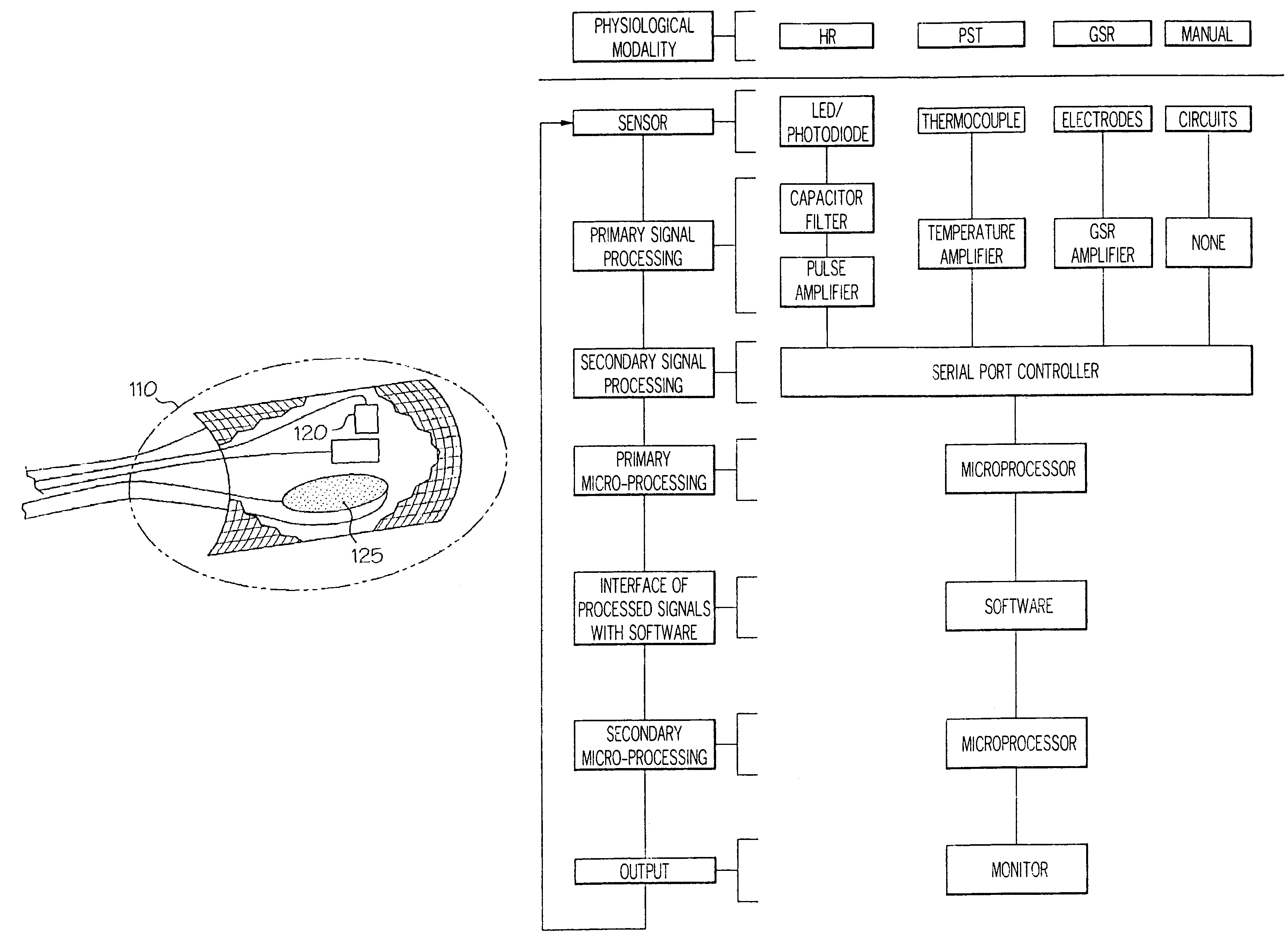
Video game system and game controller
InactiveUS7625285B2Overcome disadvantagesDiagnostic recording/measuringSensorsGalvanometerCommunication link
Game controllers having a communication link to a game systems, a processor, and a photoelectric plethysmography, a galvanometer, or a thermocouple. Video game systems having a video game processor, a computer readable medium containing executable instructions for providing a video game and the game controller.
Owner:BREVING JOEL S
Method for projection-type laser etching on free curved surface
ActiveCN101786200AImprove efficiencySimple processLaser beam welding apparatusLaser etchingLaser processing
The invention discloses a method for projection-type laser etching on a free curved surface. By combining a laser galvanometer as well as a triaxial coordinate positioning technology and adopting the principles of partitioned parallel projection as well as height mapping, the invention directly conducts precise surface laser etching on the basis of a discrete point cloud model of a free curved surface part. The method has the characteristic that the laser etching properties such as the shape and size of a spot and the energy distribution remain unchanged within the focal depth range of a focusing lens, so that the free curved surface is converted into a plurality of plane subblocks for processing, and the high-precision processing efficiency of the free curved surface can be improved even by adopting the existing laser etching technology. The diameter of the focusing spot of a laser beam can reach tens of microns and is much smaller than the size of the part processed by a traditional knife tool; and the processing precision of nearly 10 microns can be realized by controlling the laser energy property. Under the premise of meeting the demands for high precision and high efficiency of pattern etching on the free curved surface, the method can realize high reliability and high flexibility in the processing of the free curved surface.
Owner:武汉飞能达激光技术有限公司
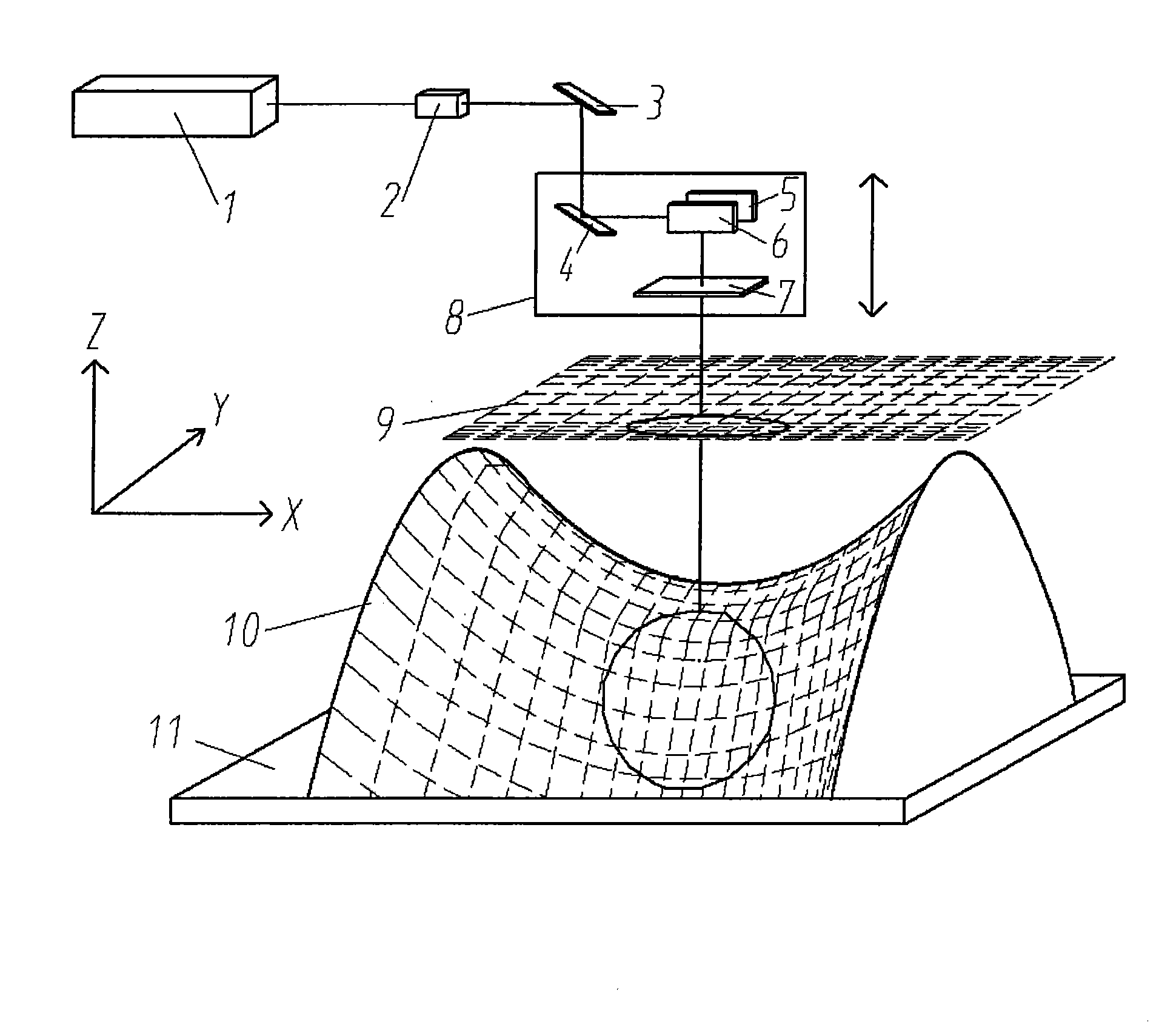
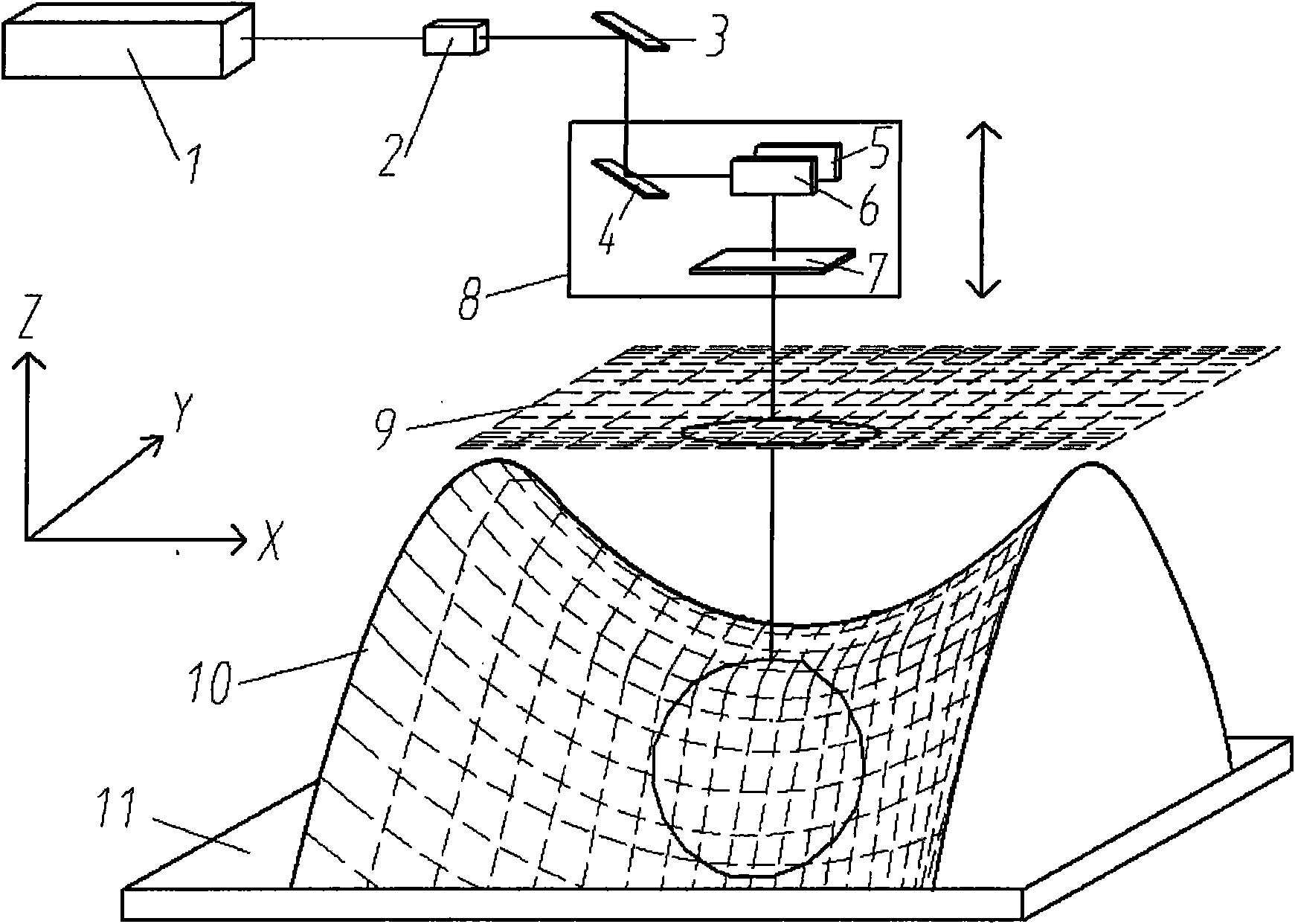
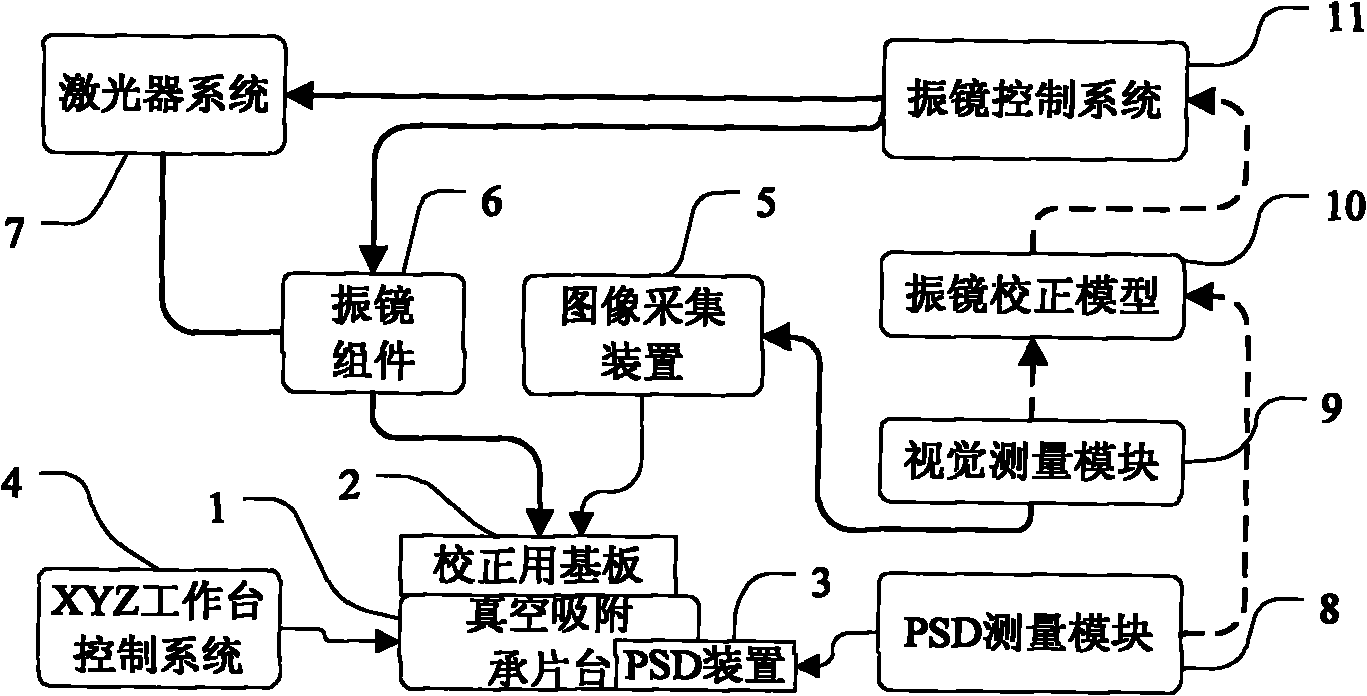
Galvanometer system correction device and correction method thereof
InactiveCN101804521AGood dynamic tracking abilitySolve the problem of calibration inefficiencyLaser beam welding apparatusGalvanometerCorrection method
The invention provides a galvanometer system correction device and a correction method thereof, and relates to the technical field of precision laser processing equipment. A honeycomb panel is arranged in the middle of the outer frame of a bearing platform, a base plate for corrective is absorbed on the honeycomb panel, and the vacuum chamber of the honeycomb panel is connected with a dust collector; a PSD sensor for measuring the actual output light spot center position of the laser of a galvanometer system is arranged on the vacuum absorption bearing platform; a CCD image acquisition device is arranged above the base plate for correcting, and then is provided with a light intensity regulating module and an image acquisition board card; and a visual measurement algorithm module is arranged. The invention can effectively inhibit the precision drift of the galvanometer system, improve the efficiency of the galvanometer system when in correction model updating and in real-time correction calculation operation, improve the automatic degree of equipment, reduce the labor intensity of an operator, greatly improve the processing precision of equipment, product quality and production efficiency, has simple structure and unique principle and method, and is particularly suitable for precision laser processing equipment to use.
Owner:THE 45TH RES INST OF CETC
Laser imaging system with progressive multi-beam scan architecture
InactiveUS6351324B1Big cost advantageImprove system efficiencyPicture reproducers using projection devicesPicture signal generatorsColor imageBeam scanning
A progressive scan architecture for displaying a two-dimensional image by alternately scanning two or more laser beams, one after the other with a time delay between adjacent beams. The beams are arranged to become incident upon a polygon scanner in a row with an approximately uniform spatial separation and an approximately equal angle between adjacent beams. The polygon scanner scans horizontally and a galvanometer-driven mirror scans vertically. Adjacent lines are progressively scanned in sequence from top to bottom, which advantageously reduces or eliminates psycho-visual effects and is tolerant of non-linearities in the vertical scanner, allowing use of a low-cost galvo mirror. Typically, the beams in the row are arranged in pairs, and only one beam from each pair will be scanning at any one time. Embodiments are described in which the duty cycle is slightly less than 50% and the laser illumination is switched between two interleaved beam scans thereby allowing a single modulator to be used for both beams which provides significant cost advantages and improves system efficiency. For full-color images, each of the beams described can incorporate separate red, green and blue (RGB) components which are individually modulated by separate red, green, and blue modulators. The system can be scaled up with one or more additional pairs of beams to improve resolution and / or increase pixel count without requiring a high-speed polygon scanner or a highly-linear galvo scanner. Furthermore, the height of each facet in the polygon mirror need be only one beam diameter and its length need only be two beam diameters, which allows the system to approach the minimum pixel size attainable, which is useful to provide high efficiency and high brightness in the image.
Owner:PHOTERA TECH
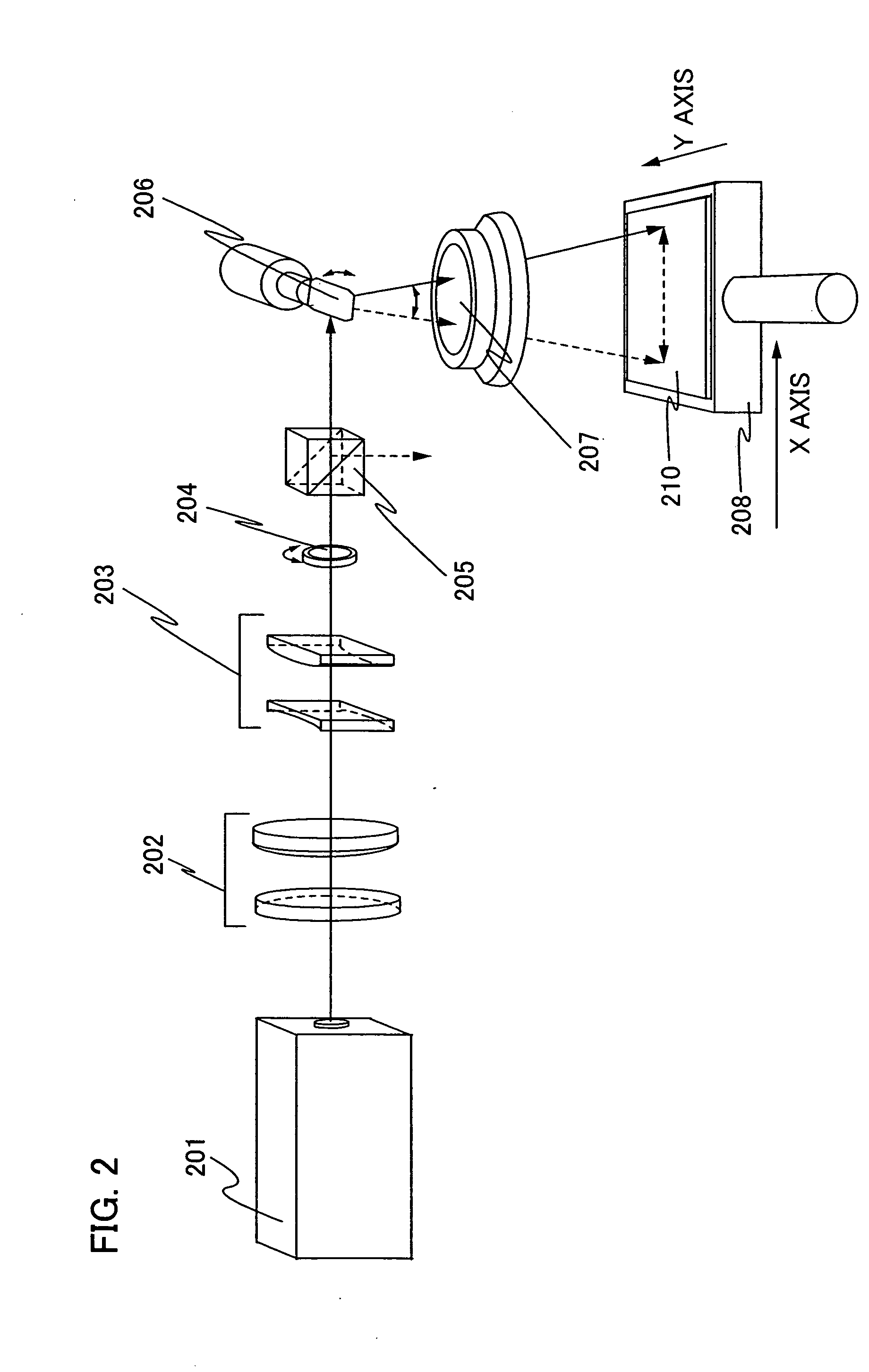
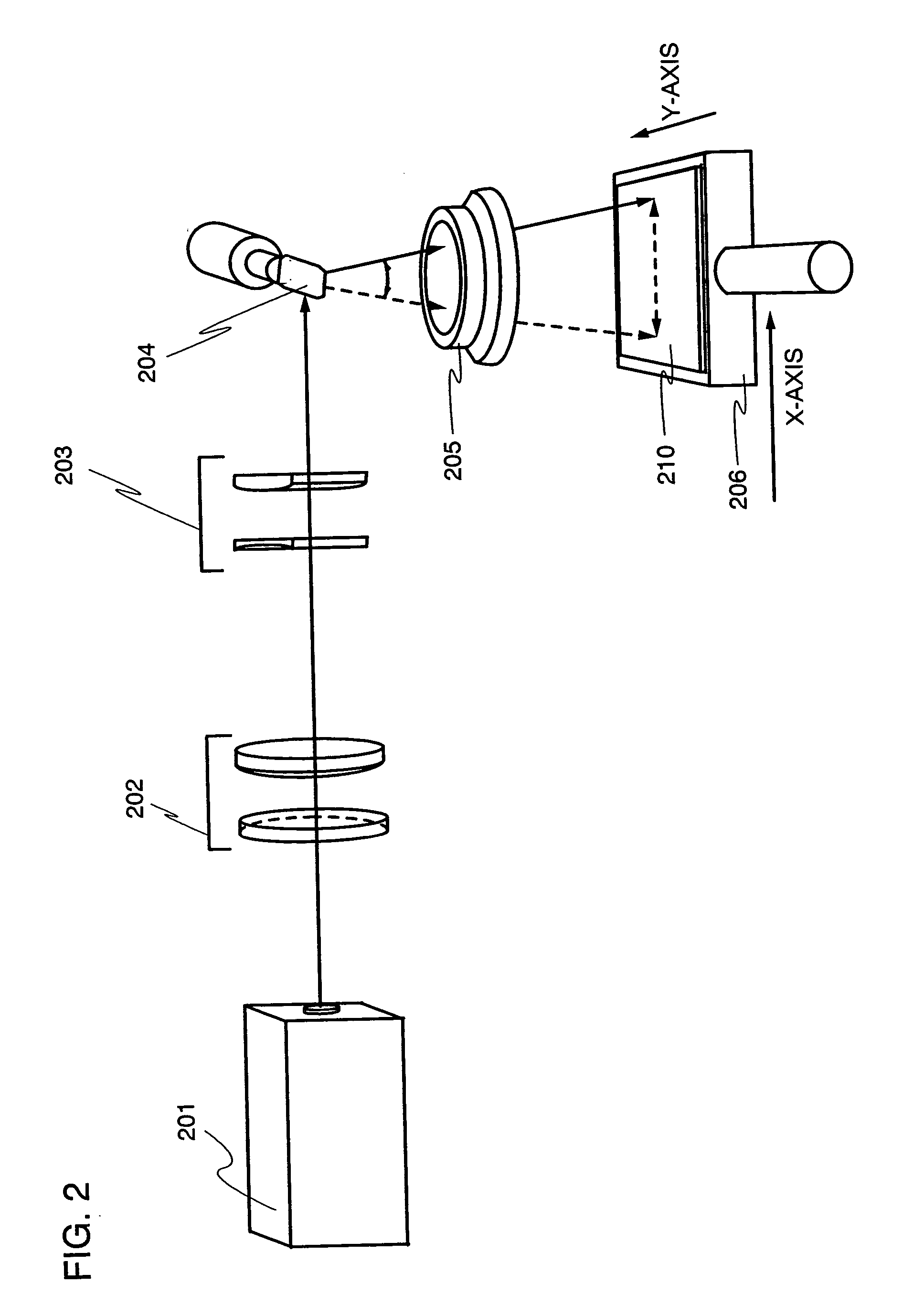
Beam irradiation apparatus, beam irradiation method, and method for manufacturing a thin film transistor
InactiveUS20050036190A1Uniform crystallinityUniform characteristicsLaser beam welding apparatusOptical elementsGalvanometerLight beam
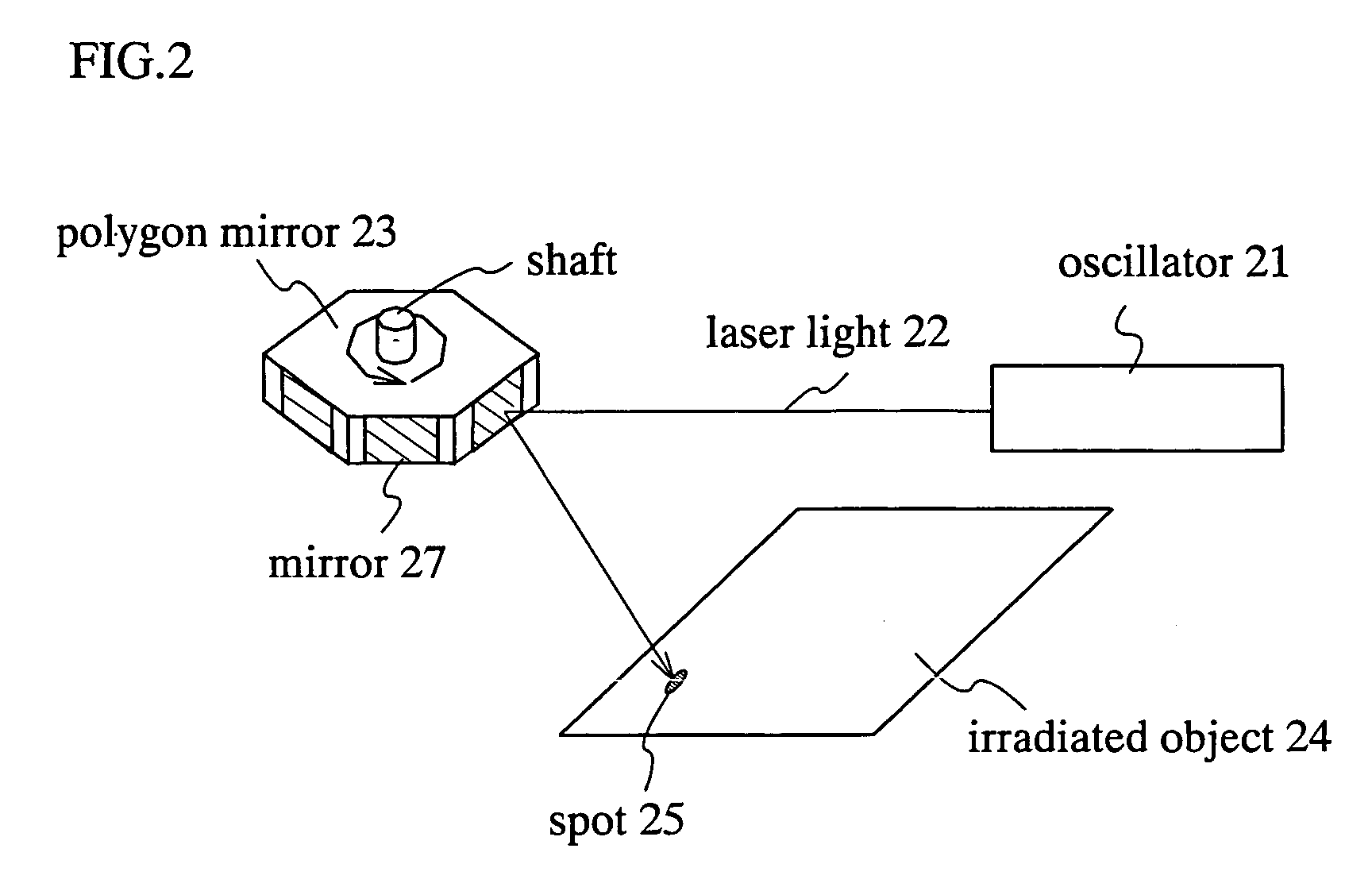
A galvanometer mirror rotates in one direction when the galvanometer mirror is used. A spot can be scanned on an irradiated surface at a more constant speed by rotating the galvanometer mirror and by using the inertia. Moreover, it is preferable to make the galvanometer mirror heavy because the inertia becomes higher so that the spot is scanned at a more constant speed. In addition, in a polygon mirror of this invention, mirrors are arranged so as not to contact each other because a change time of the scanning position between the mirrors is provided. By moving the irradiated object with timing together when the laser light is not irradiated, the laser process can be performed efficiently.
Owner:SEMICON ENERGY LAB CO LTD
Laser processing systems using through-the-lens alignment of a laser beam with a target feature
ActiveUS20100301024A1Welding/soldering/cutting articlesMetal working apparatusAcousto optic deflectorLaser processing
A laser processing system for micromachining a workpiece includes a laser source to generate laser pulses for processing a feature in a workpiece, a galvanometer-driven (galvo) subsystem to impart a first relative movement of a laser beam spot position along a processing trajectory with respect to the surface of the workpiece, and an acousto-optic deflector (AOD) subsystem. The AOD subsystem may include a combination of AODs and electro-optic deflectors. The AOD subsystem may vary an intensity profile of laser pulses as a function of deflection position along a dither direction. The AOD subsystem may be used for aligning a processing laser beam to workpiece features.
Owner:ELECTRO SCI IND INC
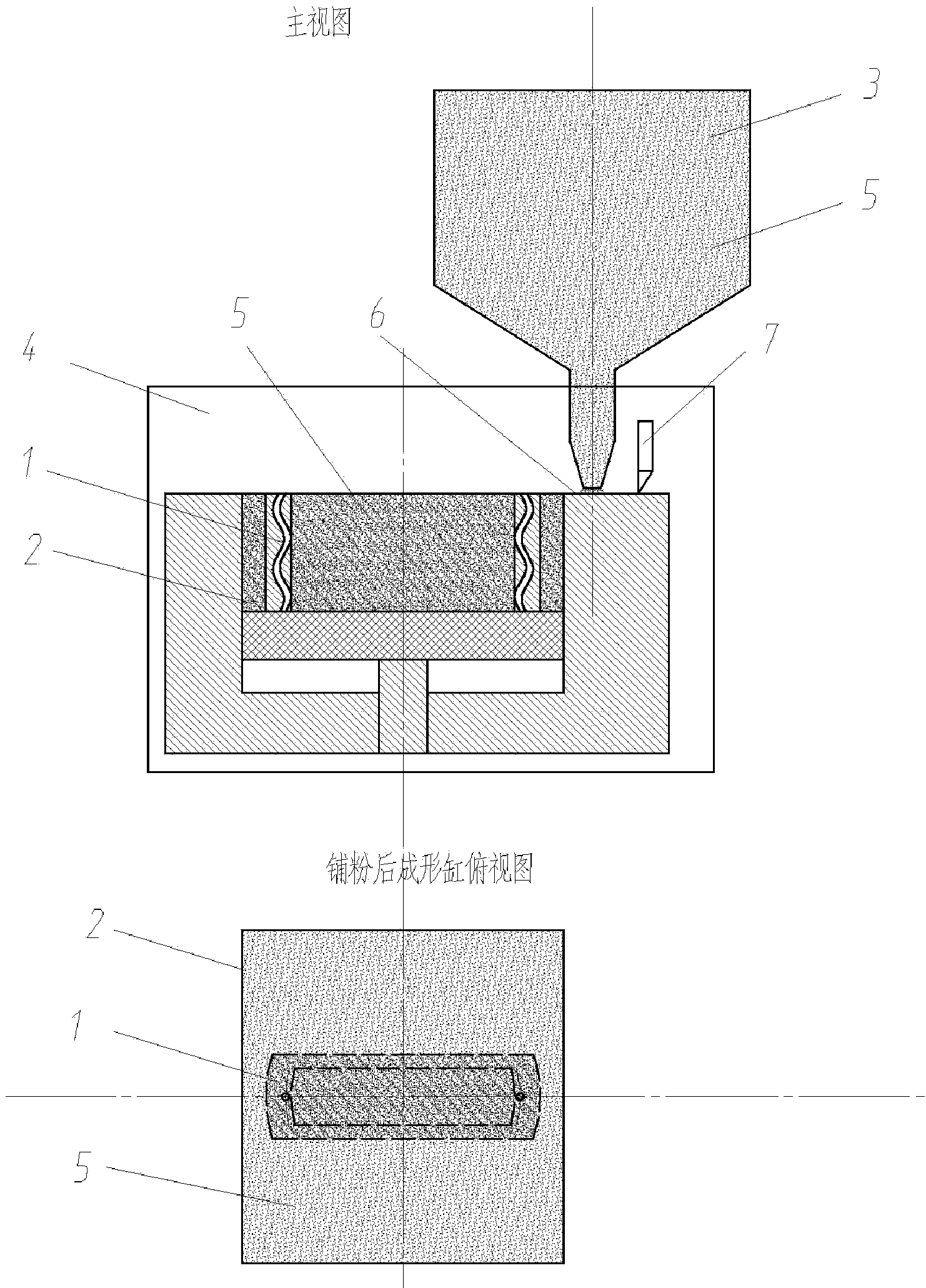
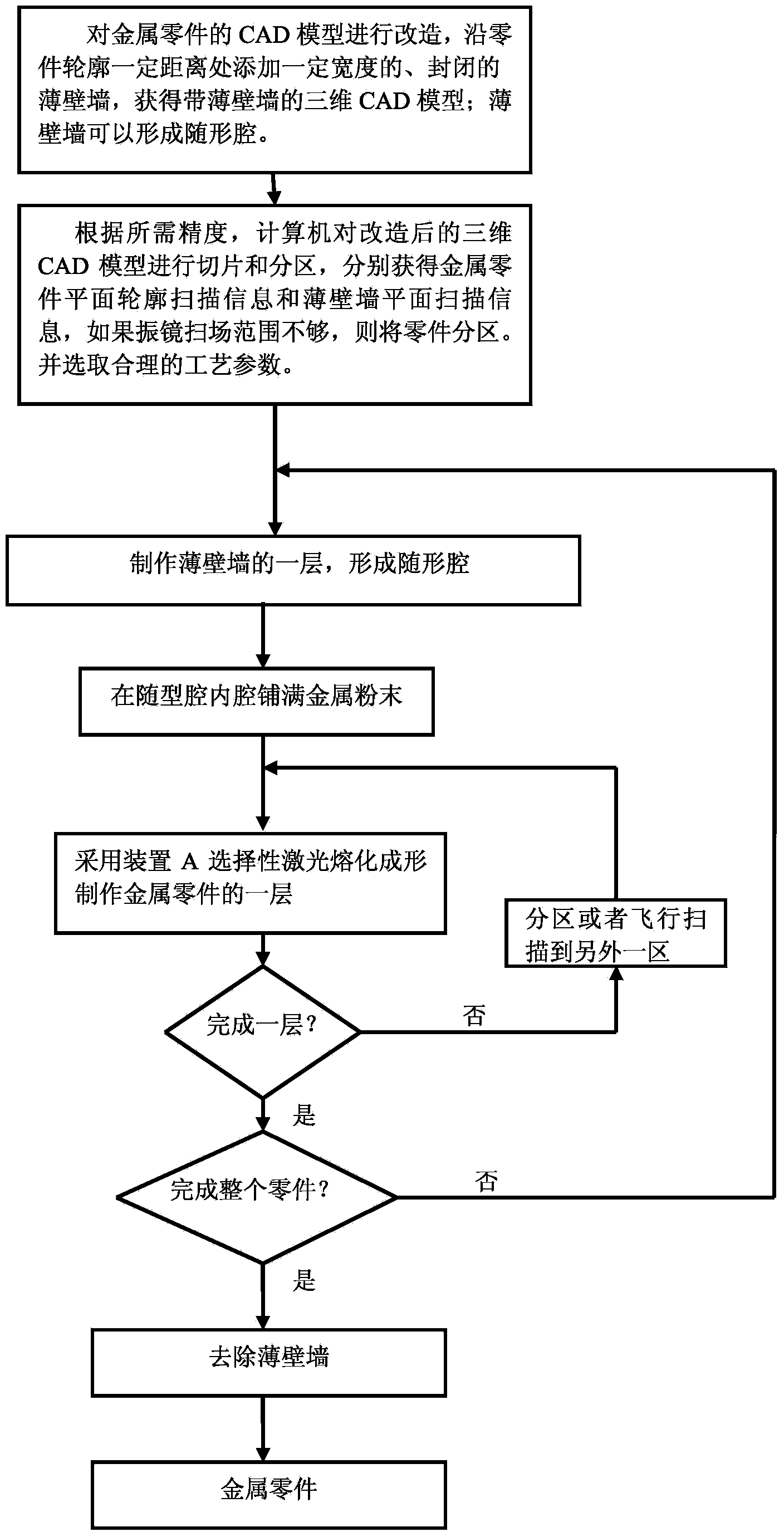
Laser additive manufacturing method and device of metal parts
ActiveCN103726049AMeet the requirements of high precision formingRealization of high-precision forming requirementsMetallic material coating processesSelective laser meltingManufacturing technology
The invention discloses a laser additive manufacturing method and a laser additive manufacturing device of metal parts. In the laser additive manufacturing method, a layered-manufactured profile-followed cylinder is used as a forming cylinder, namely before each metal part layer is manufactured, a layer of closed thin wall is manufactured, the formed cavity is used as the profile-followed cavity, the height of the profile-followed cavity is the same as that of the metal part layer to be manufactured, and the shape of the profile-followed cavity is adapted to that of the metal part layer to be manufactured, so as to provide a plane reference and a cavity for laying powder; the layered-manufactured profile-followed cylinder is used, a scanning galvanometer is used for performing selective laser melting and forming, the metal part layers are manufactured layer by layer, layers of the profile-followed cavities are finally stacked to form the profile-followed cylinder, and the layers of metal parts are stacked to form metal parts. The laser additive manufacturing device comprises a laser galvanometer melting and forming device and a thin wall preparation device which alternatively work, so as to accomplish the selective laser melting and forming process. The method and the device keep the advantages of the selective laser melting (SLM) metal additive manufacturing technology, uses the profile-followed cylinder to break the limit of the conventional SLM device fixed-size forming cylinder, and thus achieving the high-precision manufacture of the large-size even over-sized parts.
Owner:TECH LASER TECH SHANGHAI CO LTD
Method and Apparatus for Improving Image Clarity and Sensitivity in Optical Tomography Using Dynamic Feedback to Control Focal Properties and Coherence Gating
InactiveUS20110201924A1Accurately determineMoved much faster and more accuratelyInterferometersScattering properties measurementsOptical tomographyFeedback control
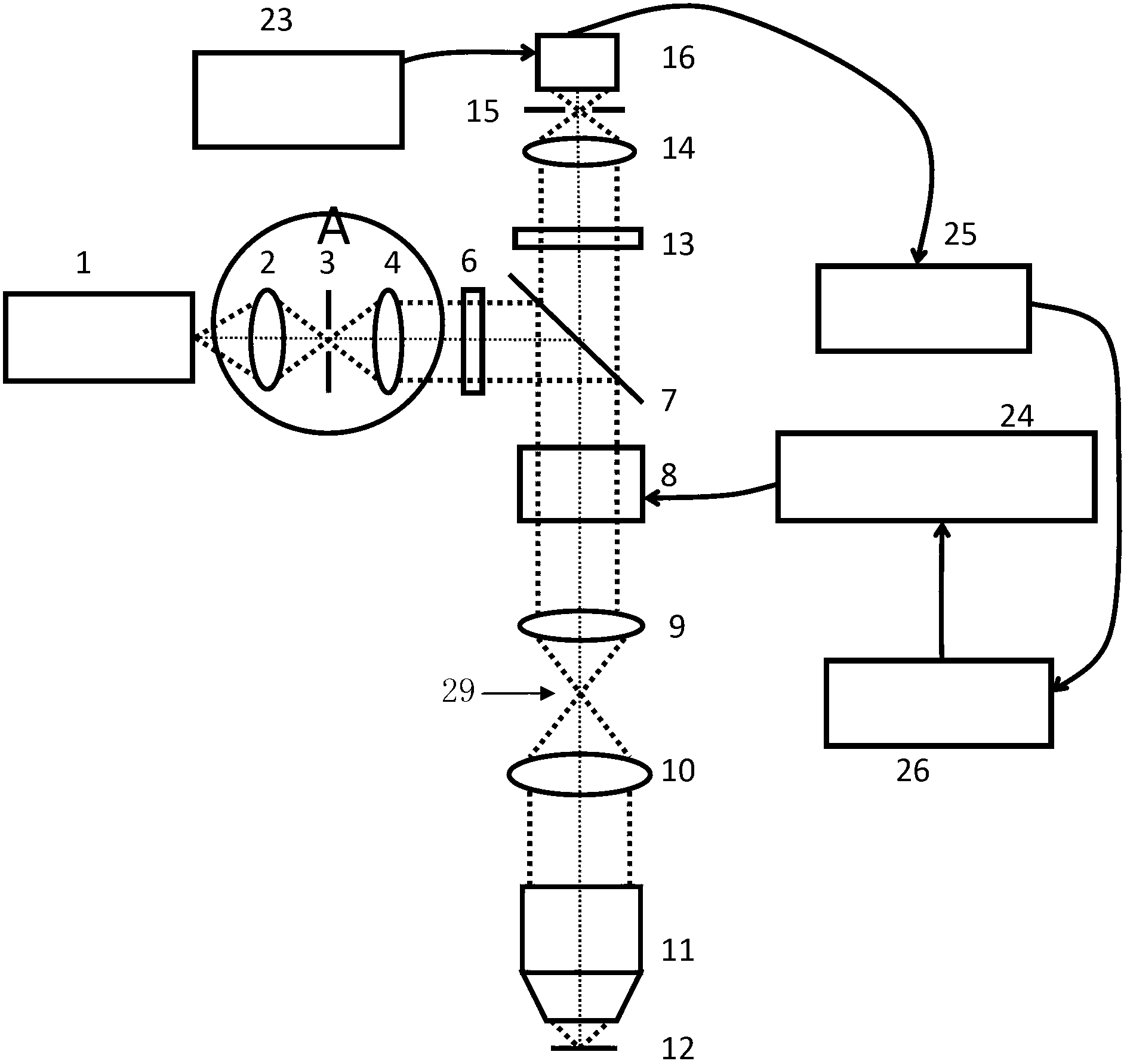
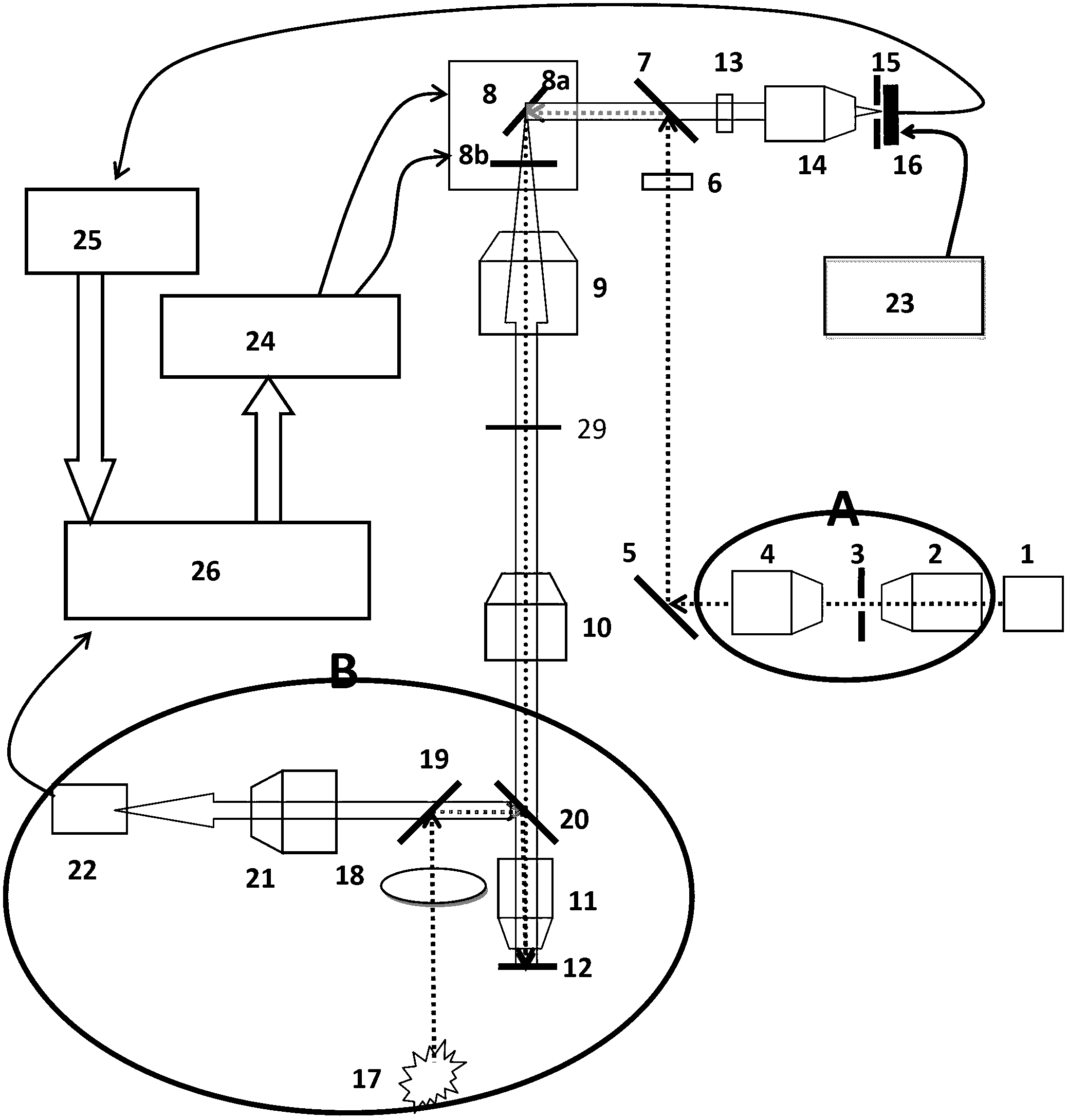
Methods for optical imaging, particularly with optical coherence tomography, using a low coherence light beam reflected from a sample surface and compared to a reference light beam, wherein real time dynamic optical feedback is used to detect the surface position of a tissue sample with respect to a reference point and the necessary delay scan range. The delay is provided by a tilting / rotating mirror actuated by a voltage adjustable galvanometer. An imaging probe apparatus for implementing the method is provided. The probe initially scans along one line until it finds the tissue surface, identifiable as a sharp transition from no signal to a stronger signal. The next time the probe scans the next line it adjusts the waveform depending on the previous scan. An algorithm is disclosed for determining the optimal scan range.
Owner:THE GENERAL HOSPITAL CORP
Laser processing systems using through-the-lens alignment of a laser beam with a target feature
ActiveUS8288679B2Welding/soldering/cutting articlesMetal working apparatusAcousto optic deflectorLaser processing
A laser processing system for micromachining a workpiece includes a laser source to generate laser pulses for processing a feature in a workpiece, a galvanometer-driven (galvo) subsystem to impart a first relative movement of a laser beam spot position along a processing trajectory with respect to the surface of the workpiece, and an acousto-optic deflector (AOD) subsystem. The AOD subsystem may include a combination of AODs and electro-optic deflectors. The AOD subsystem may vary an intensity profile of laser pulses as a function of deflection position along a dither direction. The AOD subsystem may be used for aligning a processing laser beam to workpiece features.
Owner:ELECTRO SCI IND INC
Solid-state laser radar system
InactiveCN106443634ARealize 2D scanningRealize scanningElectromagnetic wave reradiationRadar systemsGalvanometer
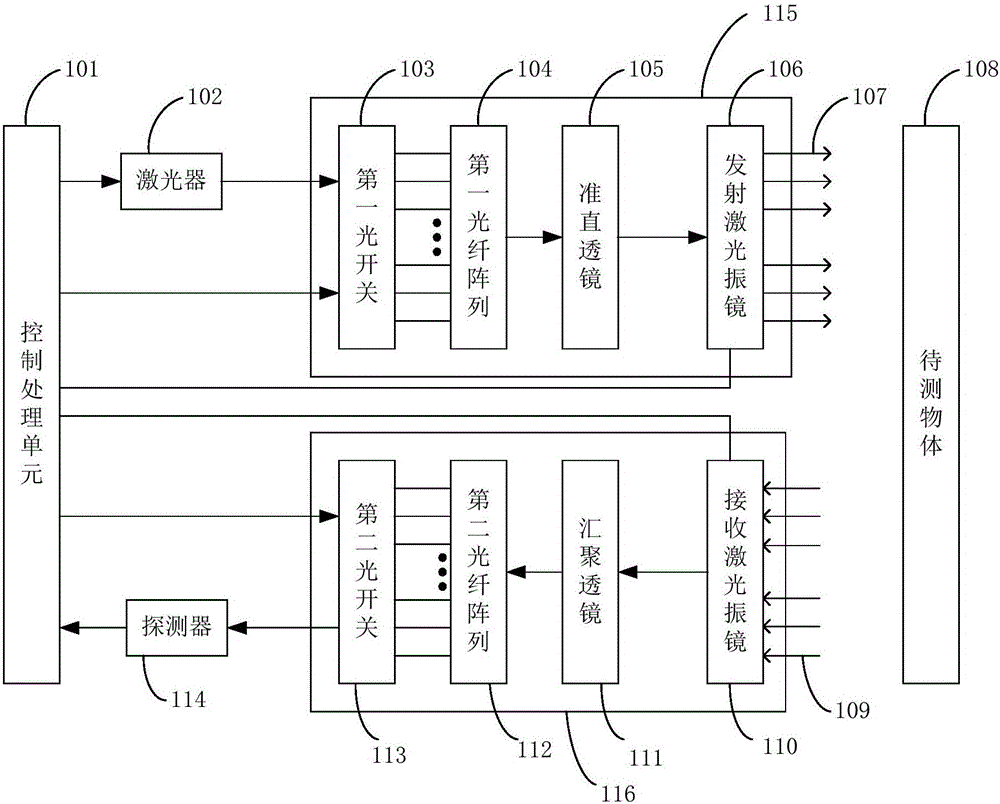
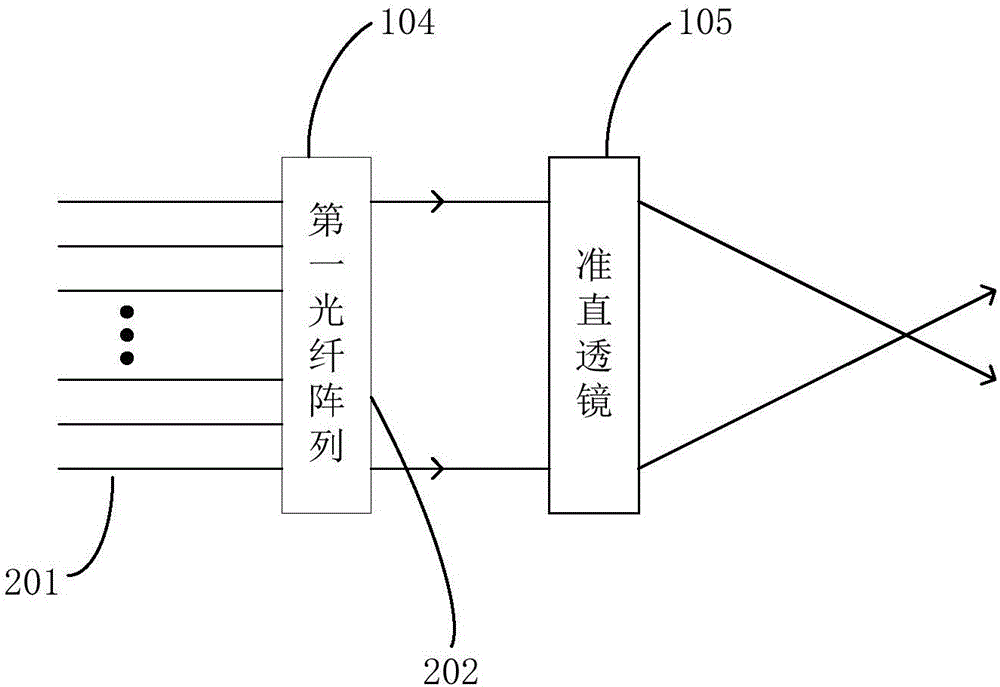
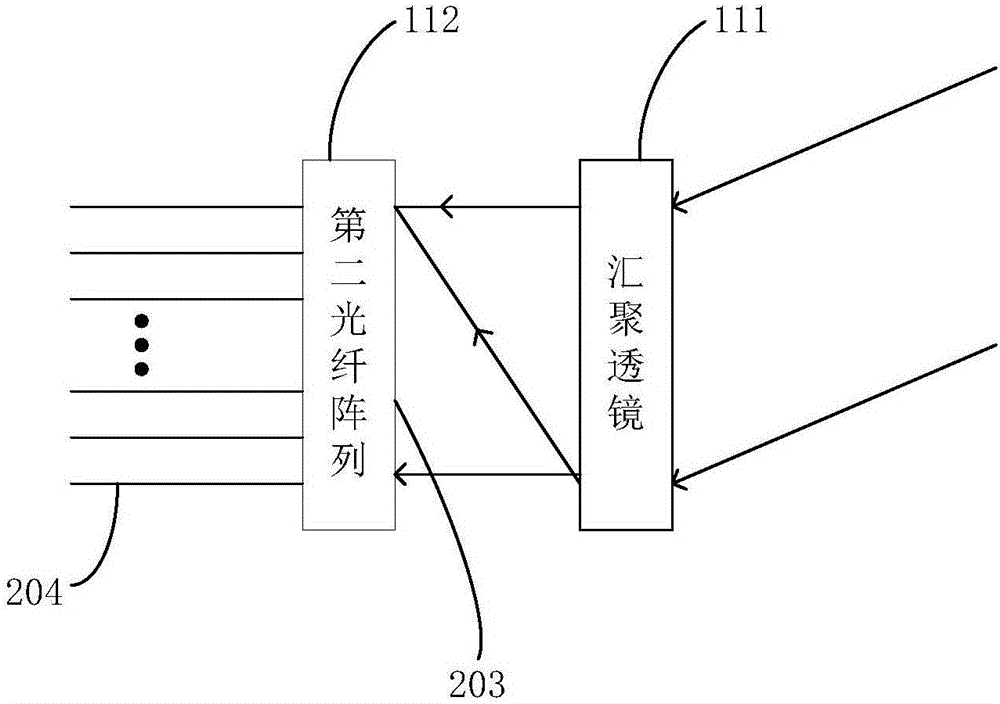
The invention discloses a solid-state laser radar system, which comprises a laser, a detector, an emitting optical system, a receiving optical system and a control processing unit. The emitting optical system comprises a first optical switch, a first fiber array, a collimating lens and an emission laser galvanometer. The receiving optical system comprises a second optical switch, a second fiber array, a convergence lens and a receiving laser galvanometer. By utilizing functions of optical path selection and time division multiplexing of the optical switches, multi-line measurement can be realized through one laser and one detector; through cooperation of the first fiber array and the collimating lens as well as cooperation of the second fiber array and the convergence lens, scanning of a first dimension of a space is realized; and through deflection functions of the emission laser galvanometer and the receiving laser galvanometer on the laser, scanning of a second dimension vertical to the first dimension of the space is realized. The system is low in cost and small in size; and the laser radar system can be driven to rotate without a mechanical scanning mechanism.
Owner:上海博未传感技术有限公司
Near-infrared laser scanning confocal imaging system
ActiveCN102706846AImaging RealizationReduce absorptionFluorescence/phosphorescenceFluorescenceLaser scanning
The invention discloses a near-infrared laser scanning confocal imaging system, which comprises a light path scanning unit and a control unit which adopt a confocal structure, wherein the light path scanning unit comprises a near-infrared laser source, a collimation and extension module, a laser optical filter, a dichroic reflector, a scanning galvanometer, an f-theta lens, a tube lens, an imaging objective lens, a fluorescent optical filter, a convergent lens, a pinhole, a detector and the like, the control unit comprises a motion control module used for controlling the scanning galvanometer, a data acquisition module used for acquiring an output signal of the detector, a data processing module connected with the motion control module and the data acquisition module, and the like. The method matched with the system is characterized in that a sample is marked with near-infrared quantum dots with the fluorescence emission spectrums between 932nm and 1250nm, and then the sample is detected by the near-infrared laser scanning confocal imaging system. According to the system disclosed by the invention, deep-level imaging of samples such as biological tissues can be accurately and efficiently realized, and the system has a simple structure and is easy to operate.
Owner:SUZHOU INST OF NANO TECH & NANO BIONICS CHINESE ACEDEMY OF SCI
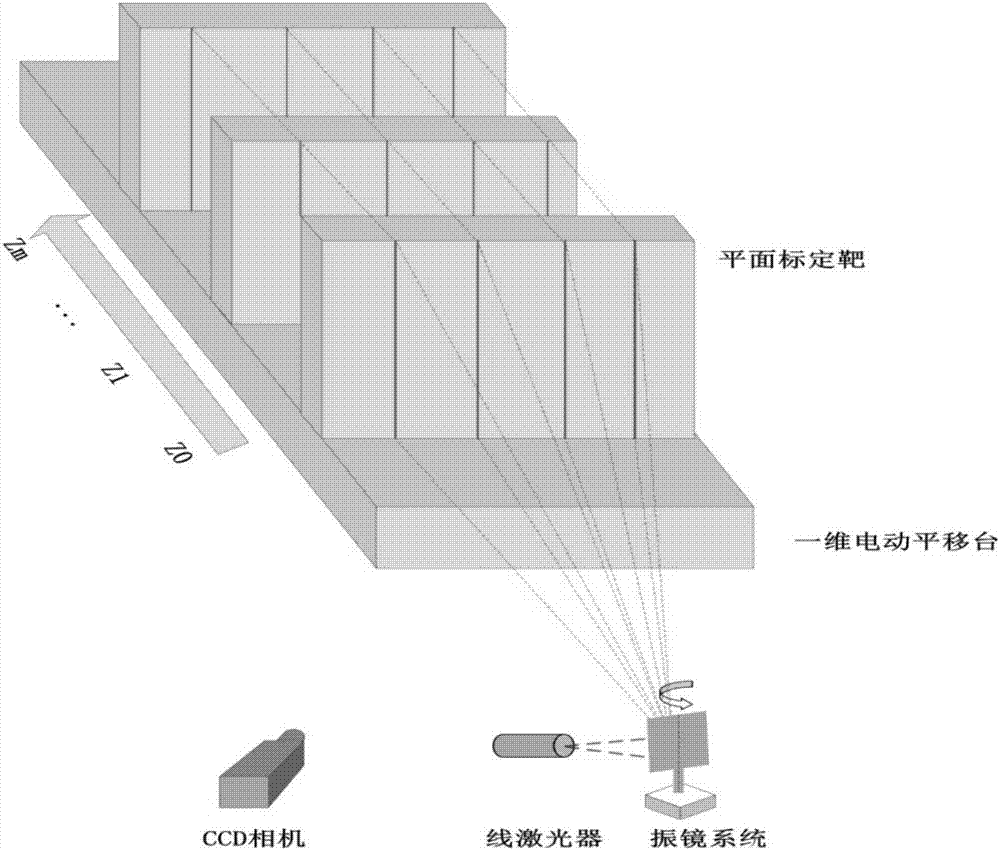
Method for overall calibration of galvanometer type line laser scanning three-dimensional measuring system
ActiveCN107014312AReduce the impactFlexible calibration schemeUsing optical meansLaser scanningGalvanometer
The invention discloses a method for overall calibration of a galvanometer type line laser scanning three-dimensional measuring system. First two lenses whose effective focal lengths are f1 and f2 are selected, and a camera is utilized to shoot a plane target and feature point coordinates are extracted, and main point coordinates of an image are calculated according to a varifocal method; then the lens whose focal length is f1 is used as a lens of the system, and for the feature point coordinates on the plane target which are obtained by the lens, intrinsic parameters and extrinsic parameters of the camera are calibrated; next, by changing galvanometer control voltage and driving a one-dimensional translation table to move, line laser stripes in different depth directions and different optical planes are obtained, and through operation of plane fitting and intersecting line obtaining, a transformation relation between a target coordinate system and a world coordinate system is obtained; and finally, coordinates under a system model are all unified to an image pixel coordinate system and the world coordinate system, thereby completing calibration of the whole system. The method has the advantages of simple calibration process, high calibration precision, fast calibration speed and the like.
Owner:XI AN JIAOTONG UNIV
Moving coil motor and implementations in MEMS based optical switches
InactiveUS20020130561A1Expand the working areaSmall device footprintMagnetic circuitCoupling light guidesOptical cavityGalvanometer
A moving coil motor has an axisymmetric magnetic field applied to the drive coils on the movable member of the motor. The movable member is suspended by springs. The moving coil motor may be configured in a MEMS format, with the movable member and its suspension springs fabricated from a mono-crystalline substance to improve structural integrity. MEMS based moving coil motors may be configured in an array. Sensors are provided to detect the relative spatial positions of the movable member. The movable member may include several tiers. In one application, the moving coil motor may be configured to support and drive a mirror surface on the movable member to form a galvanometer, optical switch, or other optical component. Singular moving coil motors may be configured in an optical cavity to facilitate the tuning of specific wavelengths while a number of moving coil motors may be configured to form an array of optical switches to facilitate switching in a multi-channel optical network.
Owner:INTEGRATED MICROMACHINES
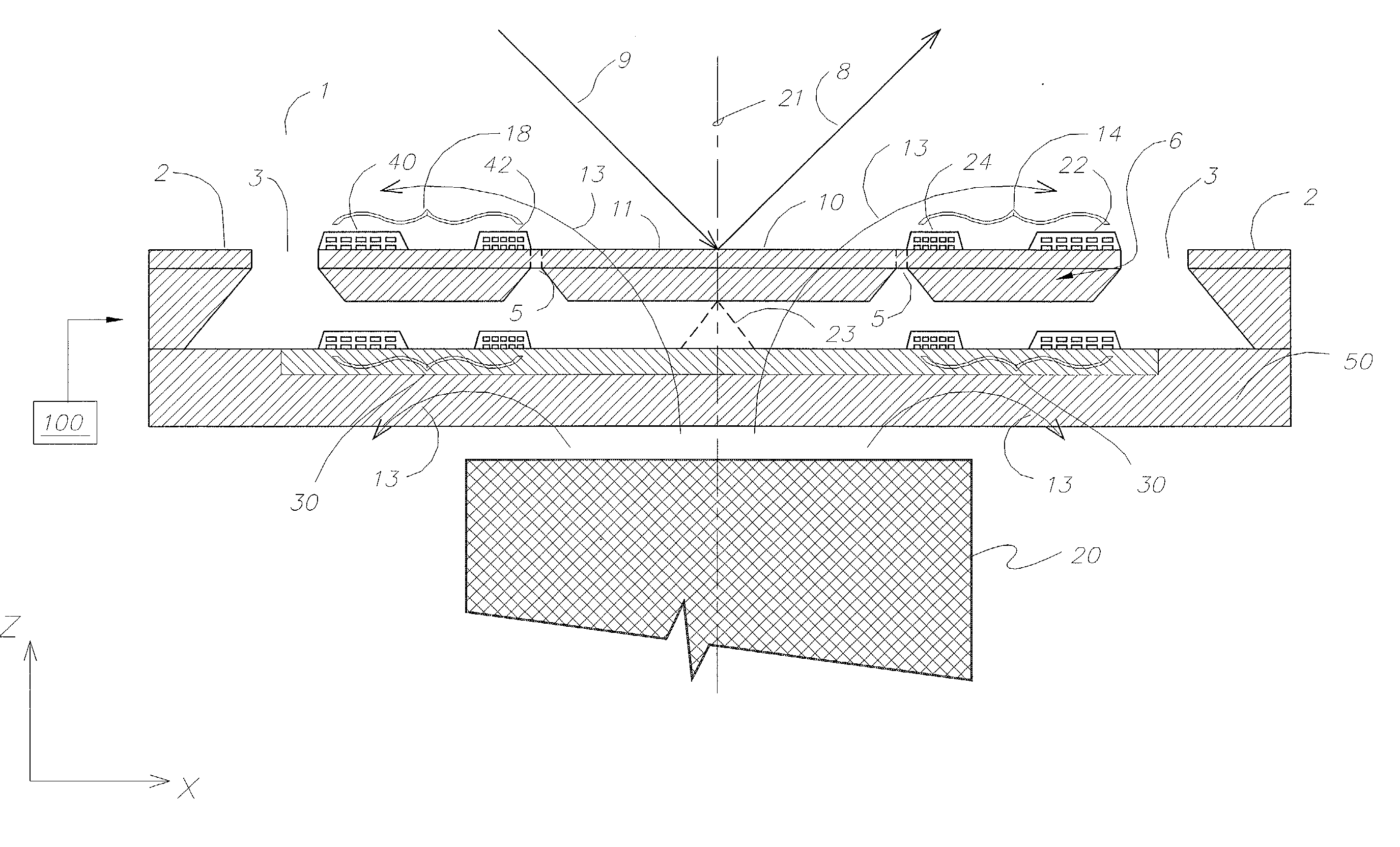
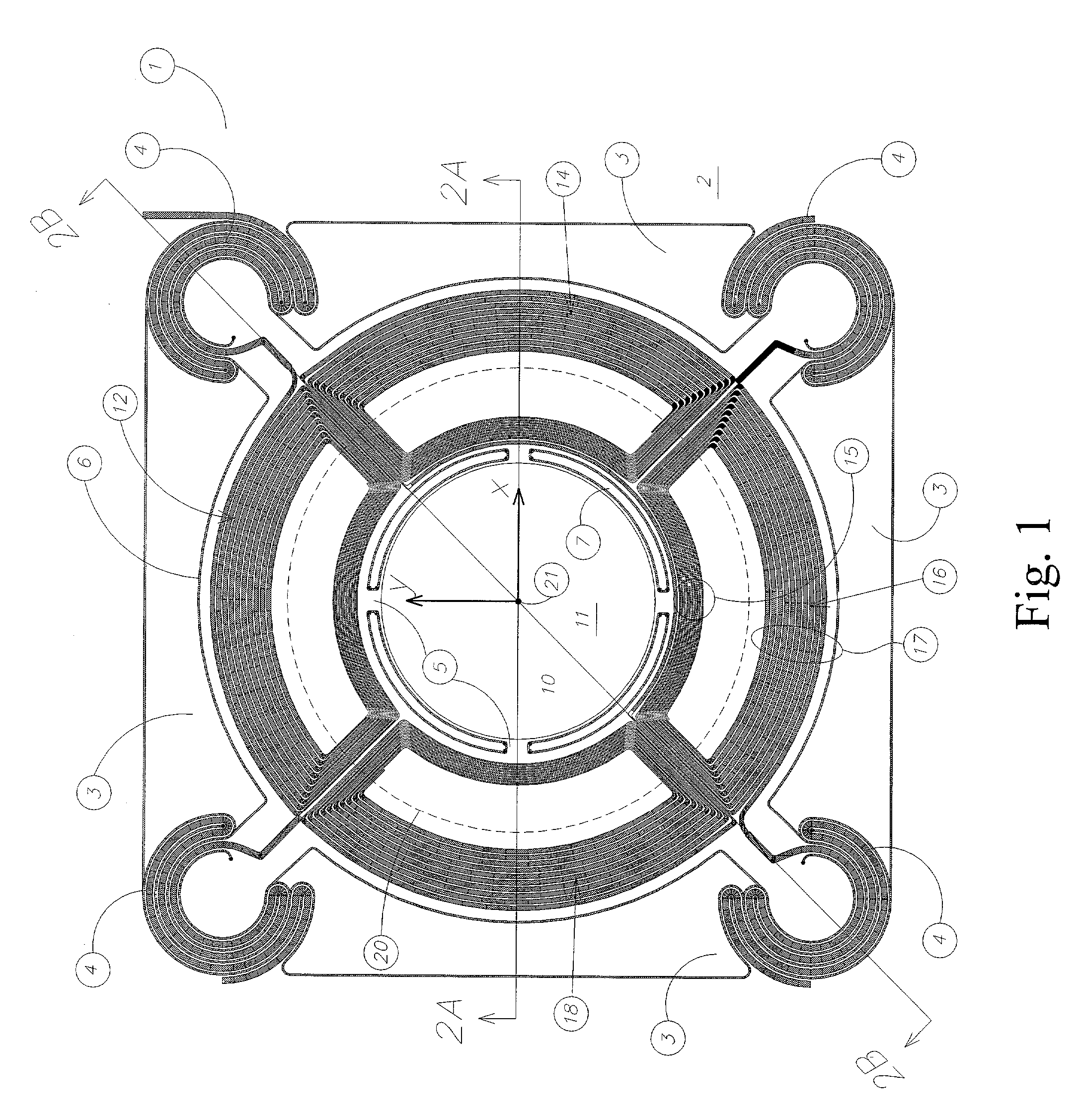
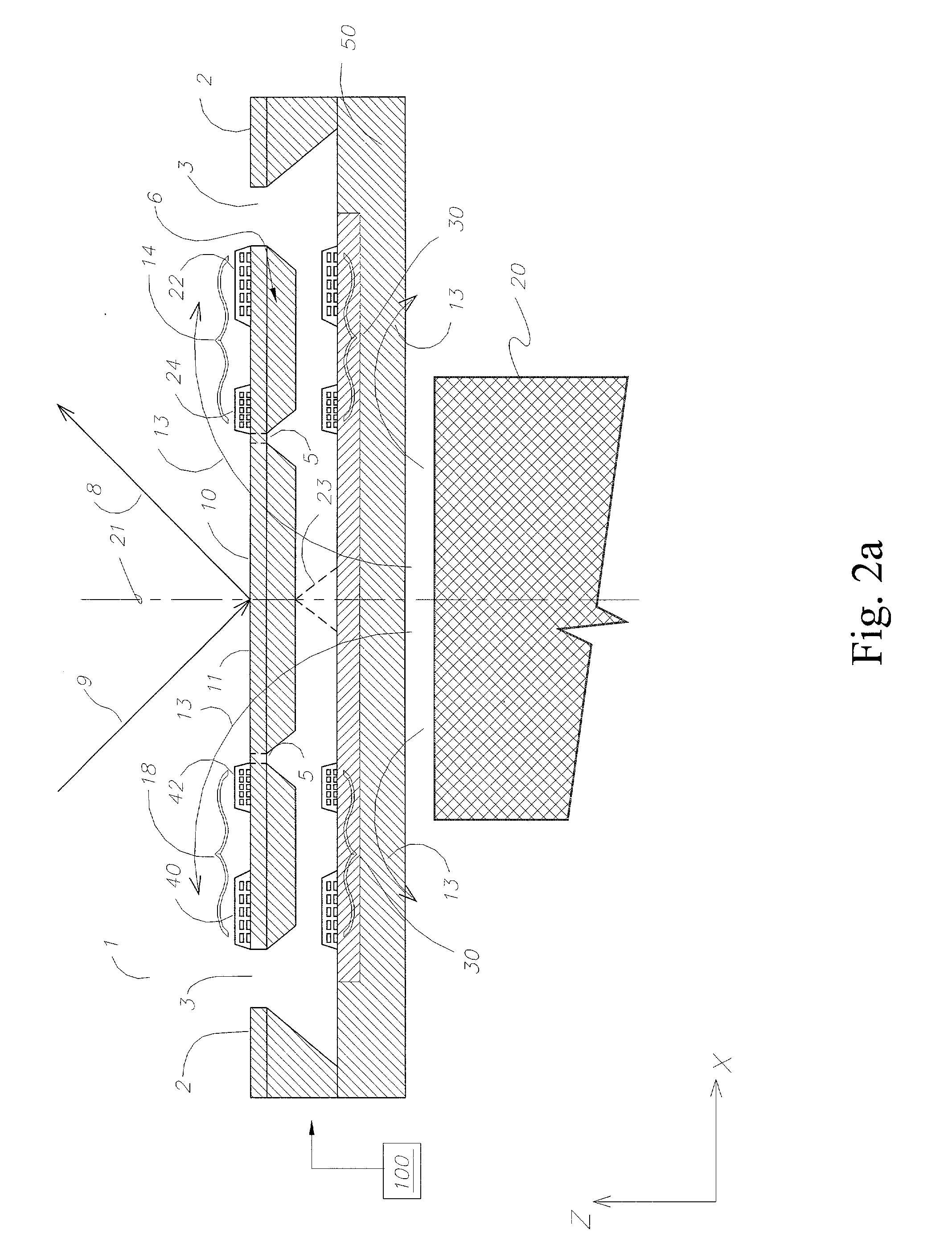
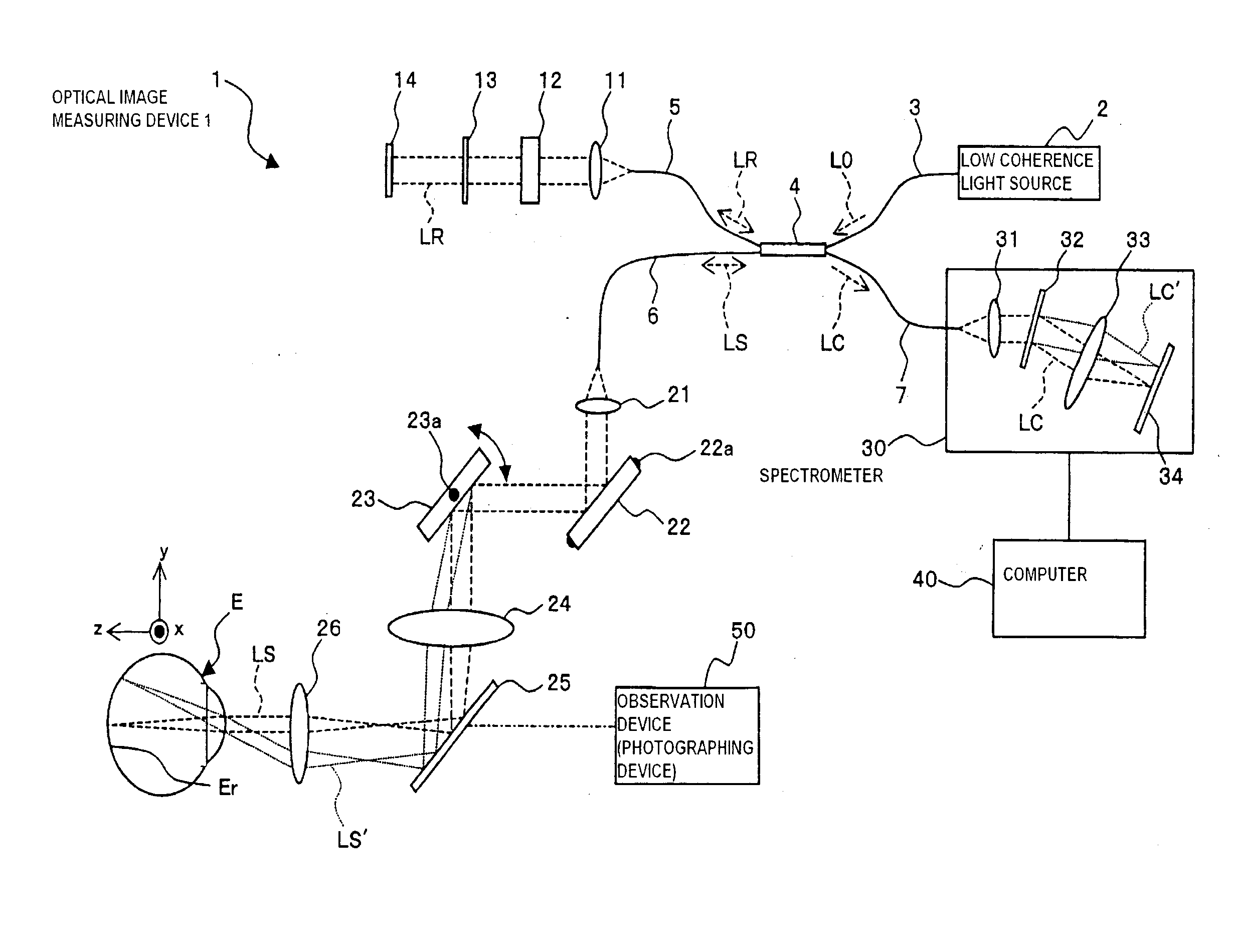
Optical image measuring device, optical image measuring program, fundus observation device, and fundus observation program
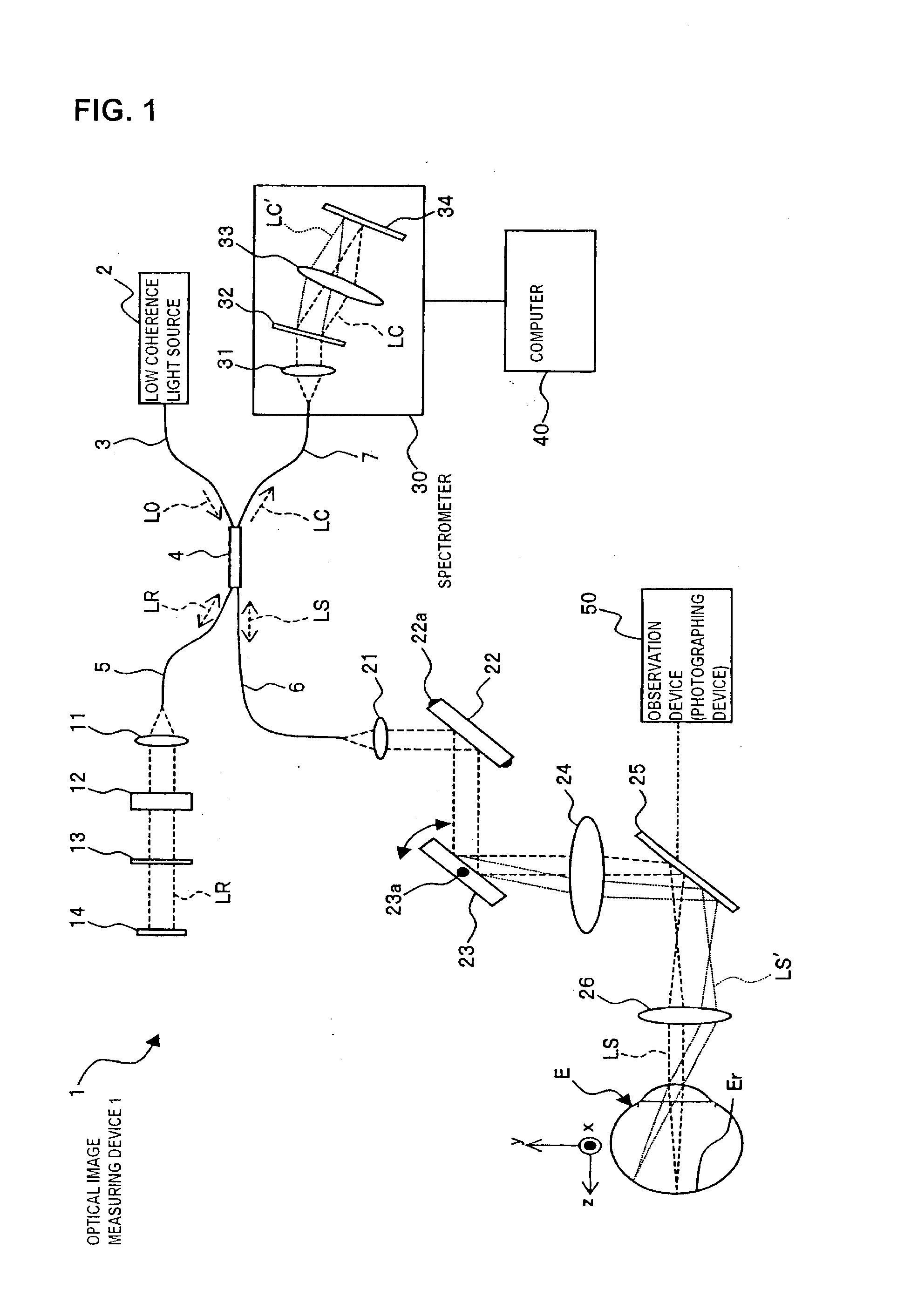
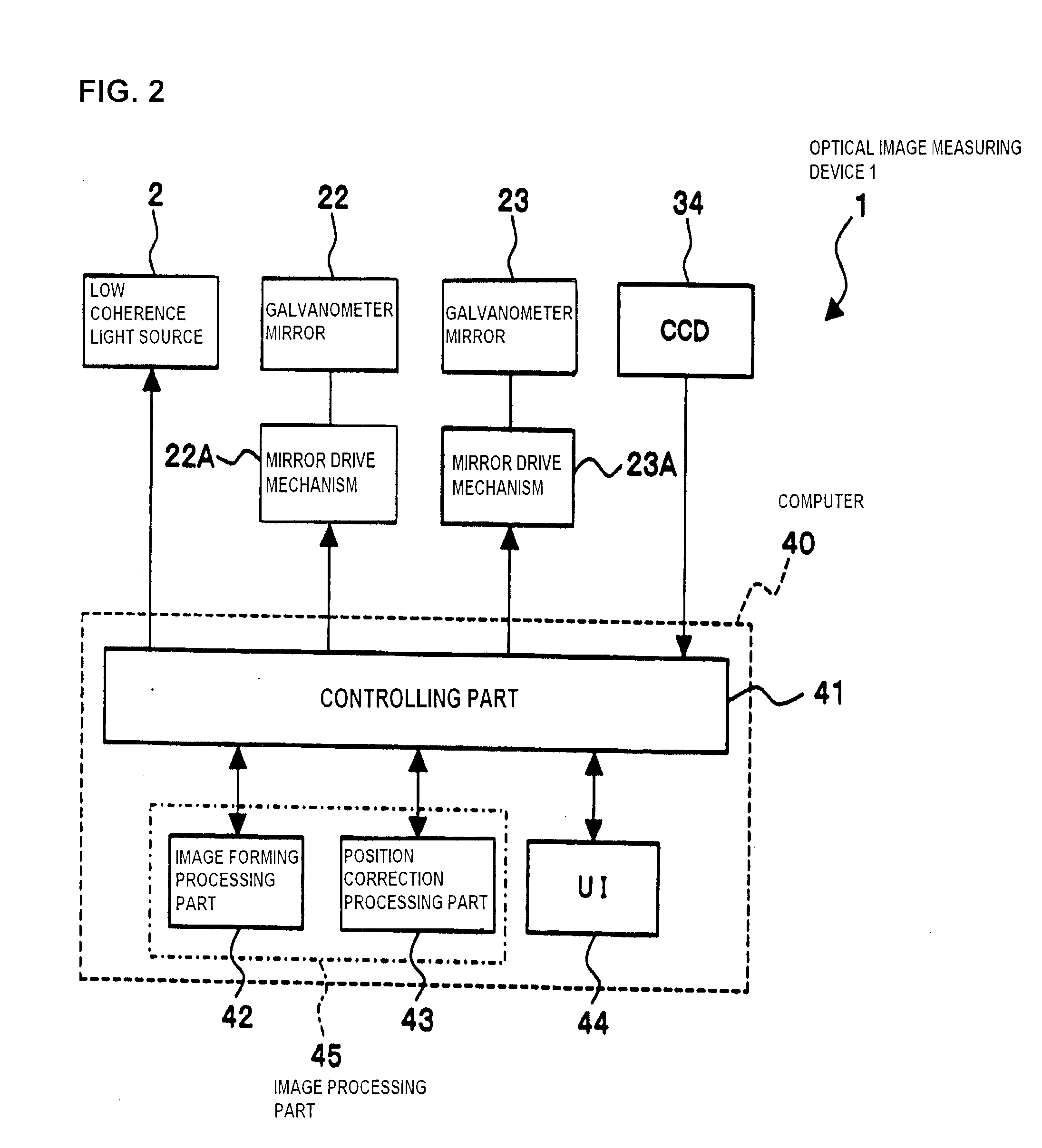
ActiveUS20100142780A1Accurate imagingAccurate displacementMaterial analysis by optical meansCharacter and pattern recognitionGalvanometerSignal light
An optical image measuring device which can form a highly reliable image even if an object moves during scanning of a signal light is provided. An optical image forming device 1 comprises: an interferometer that splits a low coherence light L0 into a signal light LS and a reference light LR and generates an interference light LC by overlaying the signal light LS reflected by a fundus oculi with the reference light LR reflected by a reference mirror 14; a CCD 34 which receives the interference light LC and outputs a detection signal; Galvanometer mirrors 22 and 23 to scan the signal light LS in a main scanning direction and a sub-scanning direction; and a computer 40 forming tomographic images G1 to Gm along the main scanning direction at different positions of the sub-scanning direction. The Galvanometer mirrors 22 and 23 scan the signal light LS in a given direction crossing the main scanning direction, and the computer 40 forms a tomographic image for correction GR along the given direction to correct displacement of each topographic image Gi based on the tomographic image for correction GR.
Owner:KK TOPCON
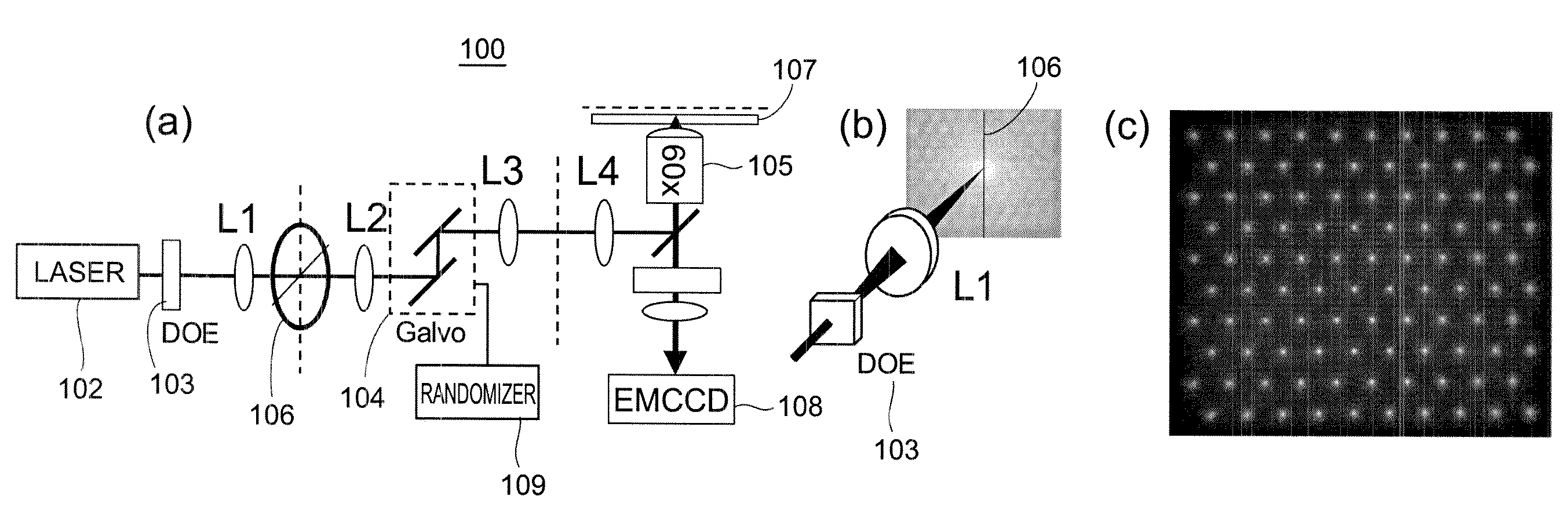
Stochastic scanning apparatus using multiphoton multifocal source
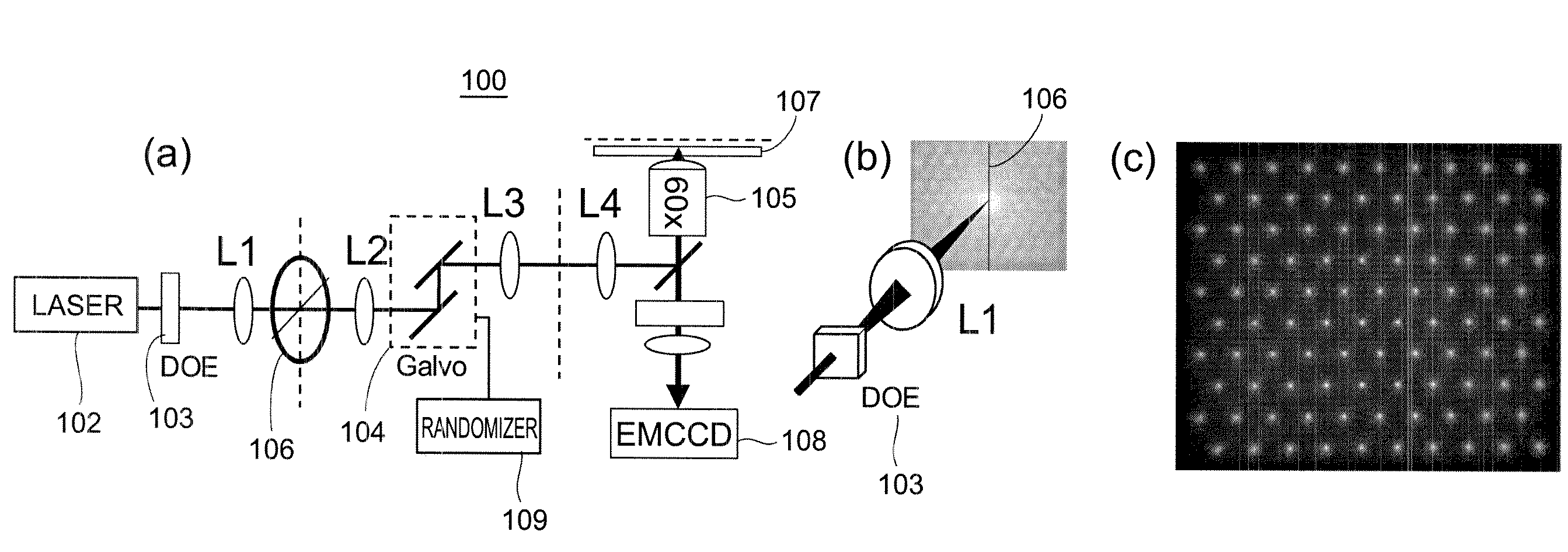
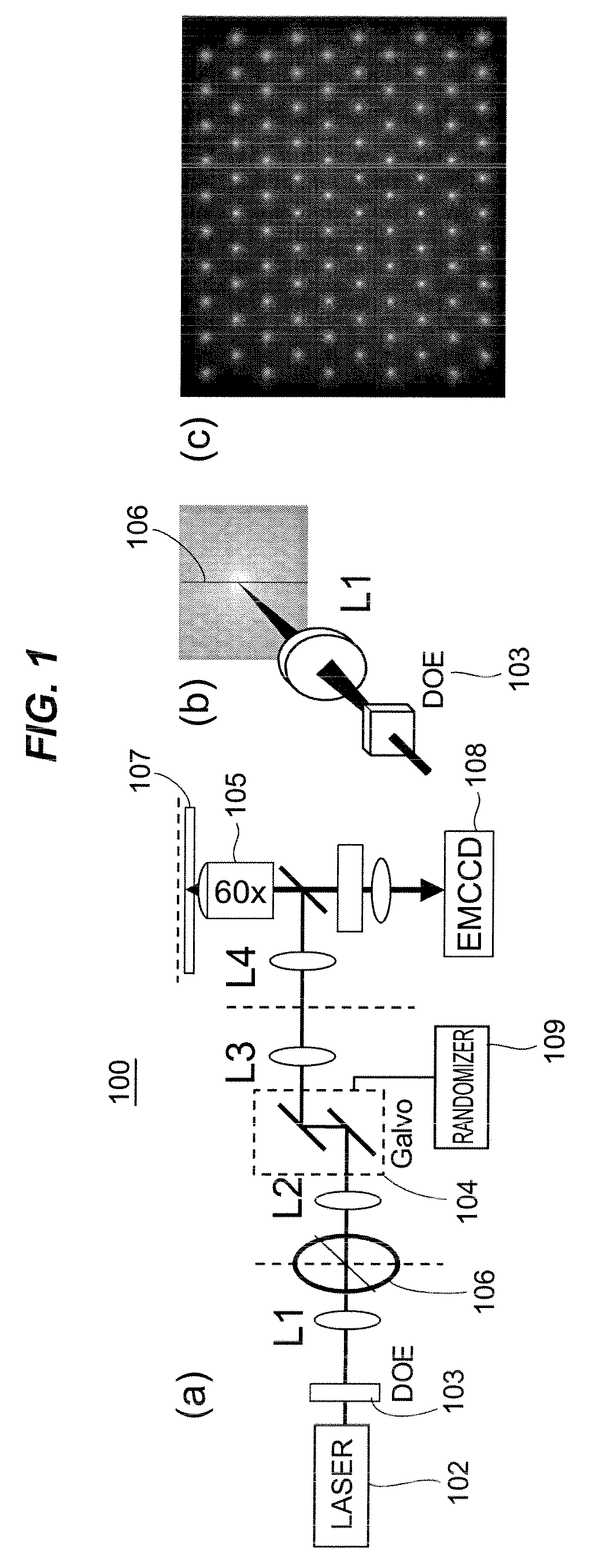
A rapid-sampling stochastic scanning multiphoton multifocal microscopy (SS-MMM) fluorescence imaging technique enables multiparticle tracking at rates upwards of 1,000 times greater than conventional single point raster scanning. Stochastic scanning of a diffractive optical element may generate a 10×10 hexagonal array of foci with a white noise driven galvanometer to yield a scan pattern that is random yet space-filling. SS-MMM may create a more uniformly sampled image with fewer spatio-temporal artifacts than obtained by conventional or multibeam raster scanning.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF CHICAGO
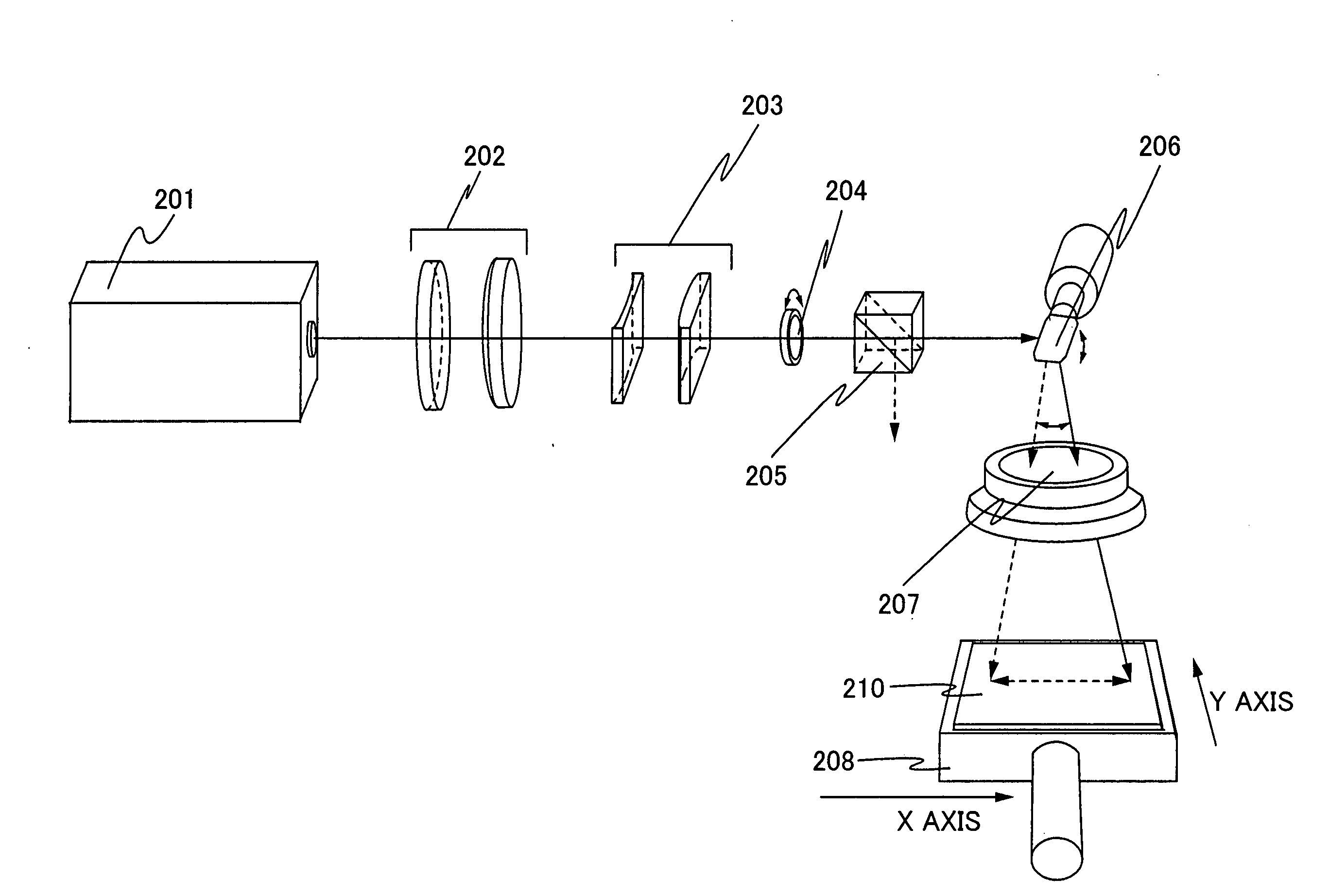
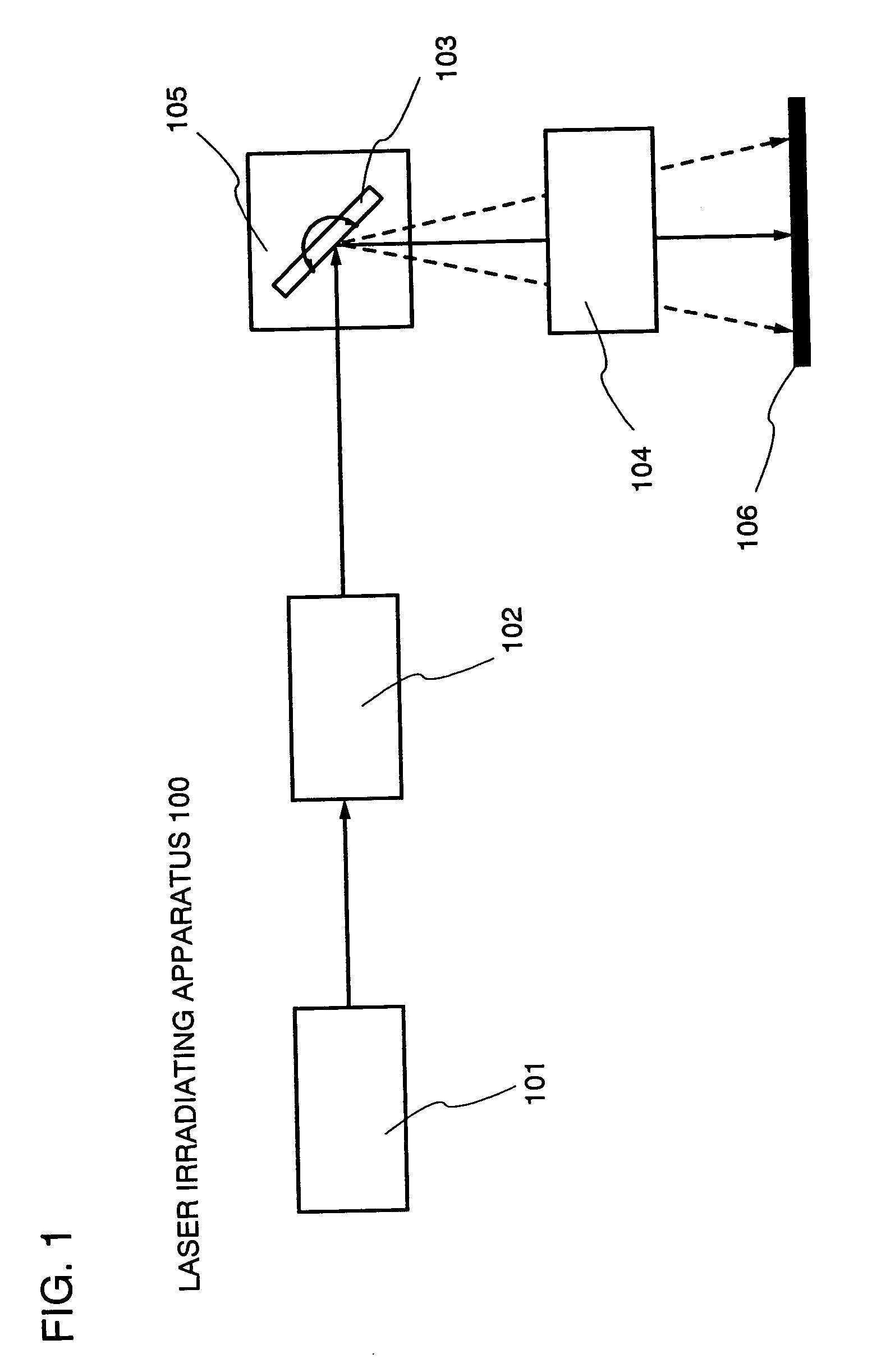
Laser irradiation apparatus and method of manufacturing semiconductor device
ActiveUS20040065643A1Avoid changeReduce variationSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingLaser beam welding apparatusEnergy variationTransmittance
The transmissivity of an ftheta lens which is used as a means for converging laser light differs in the center and in the edge thereof. As a result, when the ftheta lens is used as it is with the purpose of crystallizing by laser irradiation, energy distribution of the laser light which is irradiated on the semiconductor film is not uniform so that the whole surface of the semiconductor film could not be irradiated uniformly. Therefore, the present invention provides a laser irradiation apparatus including a galvanometer mirror and an ftheta lens that can offset the change of the energy due to the change of transmissivity of the ftheta lens and can scan the laser light while controlling the change of the energy on the object to be irradiated. Moreover, the invention provides a manufacturing method of a semiconductor device including the laser irradiation apparatus described above.
Owner:SEMICON ENERGY LAB CO LTD
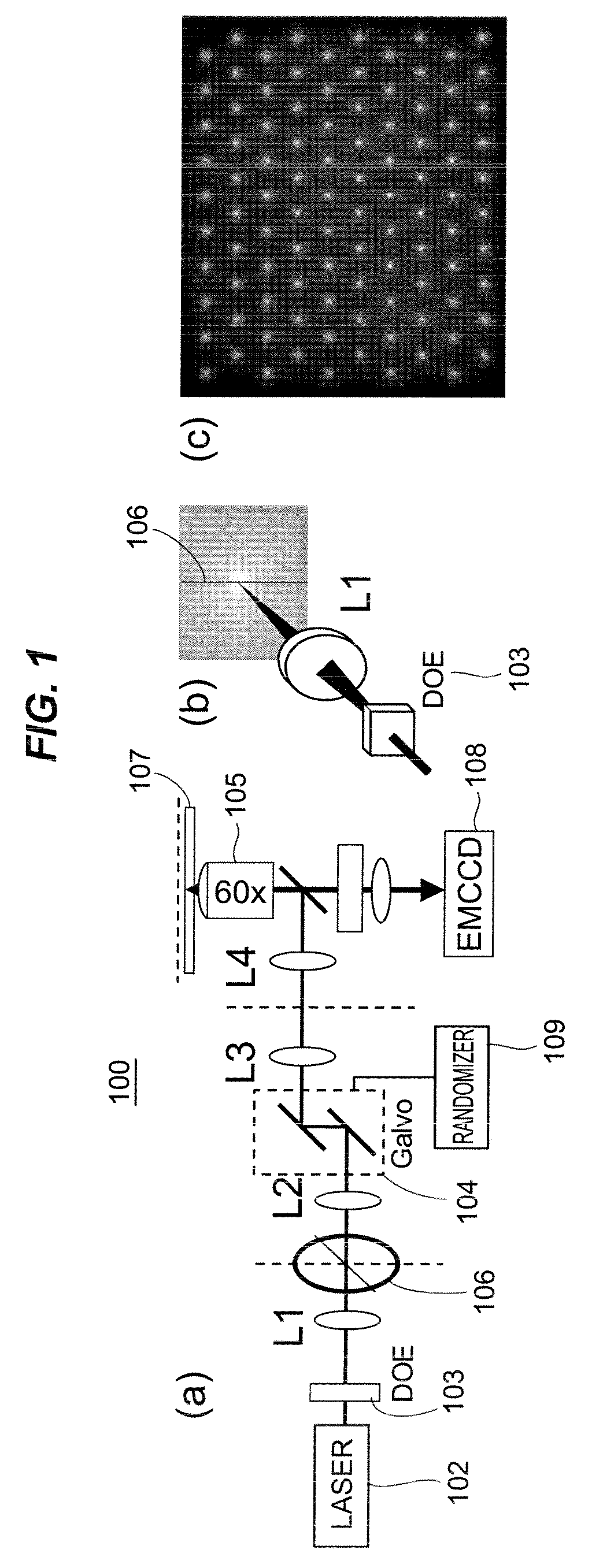
Stochastic Scanning Apparatus Using Multiphoton Multifocal Source
A rapid-sampling stochastic scanning multiphoton multifocal microscopy (SS-MMM) fluorescence imaging technique enables multiparticle tracking at rates upwards of 1,000 times greater than conventional single point raster scanning. Stochastic scanning of a diffractive optical element may generate a 10×10 hexagonal array of foci with a white noise driven galvanometer to yield a scan pattern that is random yet space-filling. SS-MMM may create a more uniformly sampled image with fewer spatio-temporal artifacts than obtained by conventional or multibeam raster scanning.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF CHICAGO
Device and method for laser remote removal of foreign matter on transmission line
ActiveCN104064989AClear in timeQuick clearApparatus for overhead lines/cablesNumerical controlForeign matter
The invention discloses a device and method for laser remote removal of foreign matter on a transmission line. The device comprises a laser, a numerical control base, a light beam collimator, a visible indicating light unit, a scanning galvanometer, a distance measuring instrument, an electronic telescoping sighting device, a controller and an emitting barrel. By the adoption of the device and method, only one operator is needed, large-sized equipment or other auxiliary equipment is not needed, the operator does not have to climb a tower or a rope ladder, environment conditions such as the terrain and the line height do not needed to be considered, the device simply needs to be adjusted so as to be aligned to a target and emit lasers, the foreign matter can be removed or shot down within tens of seconds, the operator do not make any contact with facilities and equipment of the transmission line in the whole process, hot-line work can be conducted, the foreign matter on the transmission line can be remotely, rapidly and safely removed in time, and the application prospect is good.
Owner:STATE GRID CORP OF CHINA +2
Illumination light source and two-dimensional image display using same
ActiveUS20060285078A1Uniform lightIlluminating the screen or the like uniformlyProjectorsPicture reproducers using projection devicesResonanceLight beam
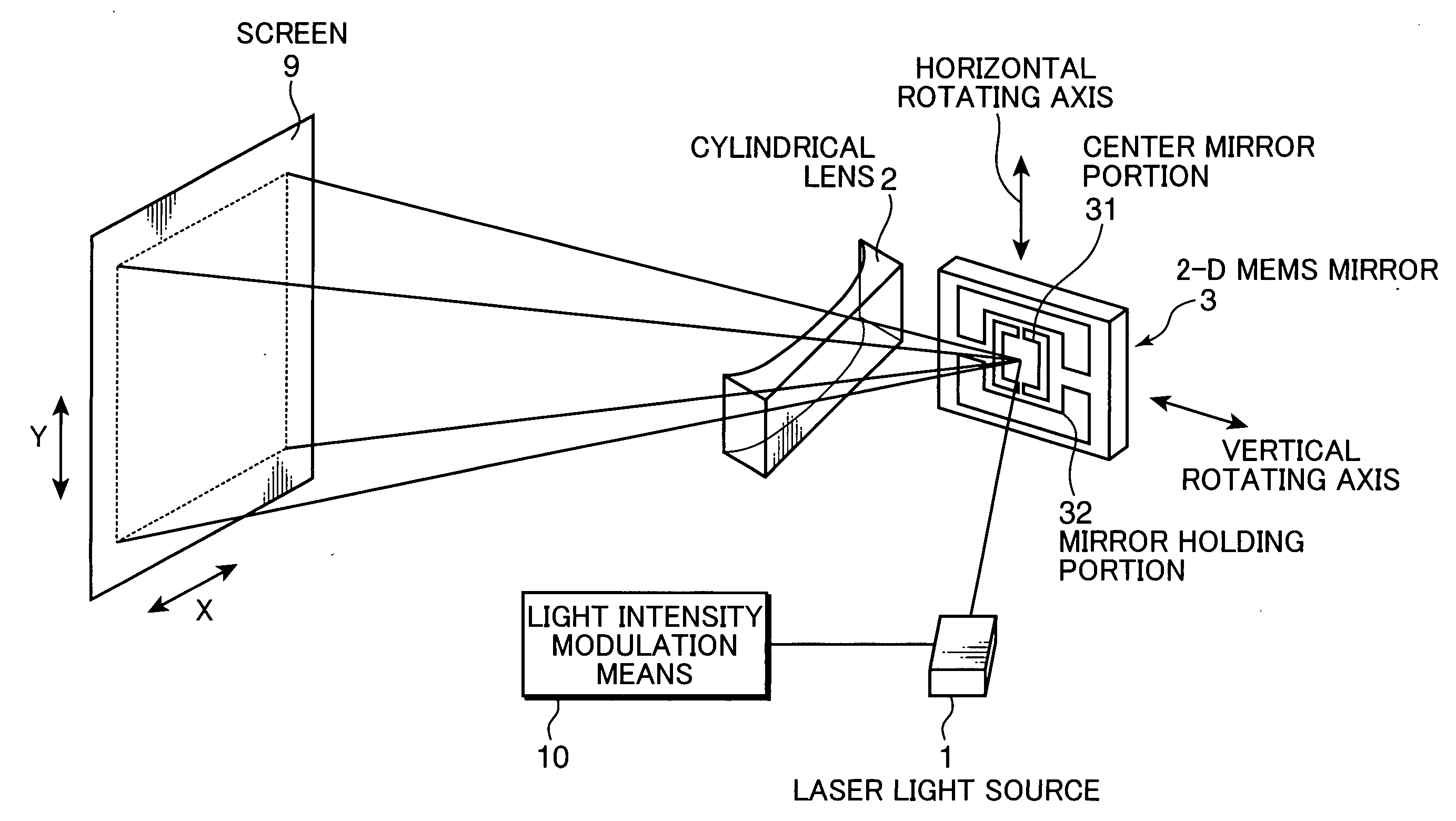
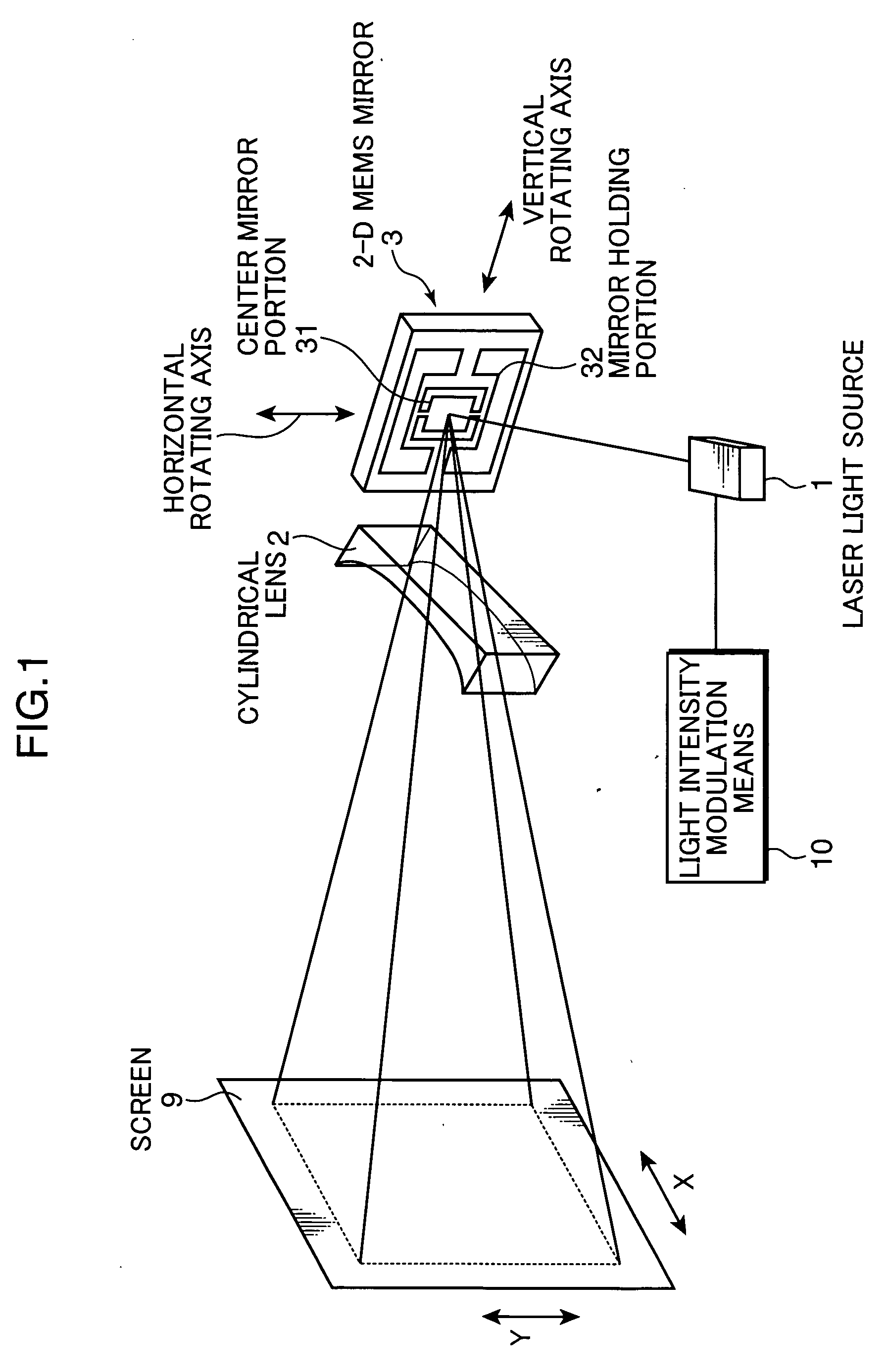
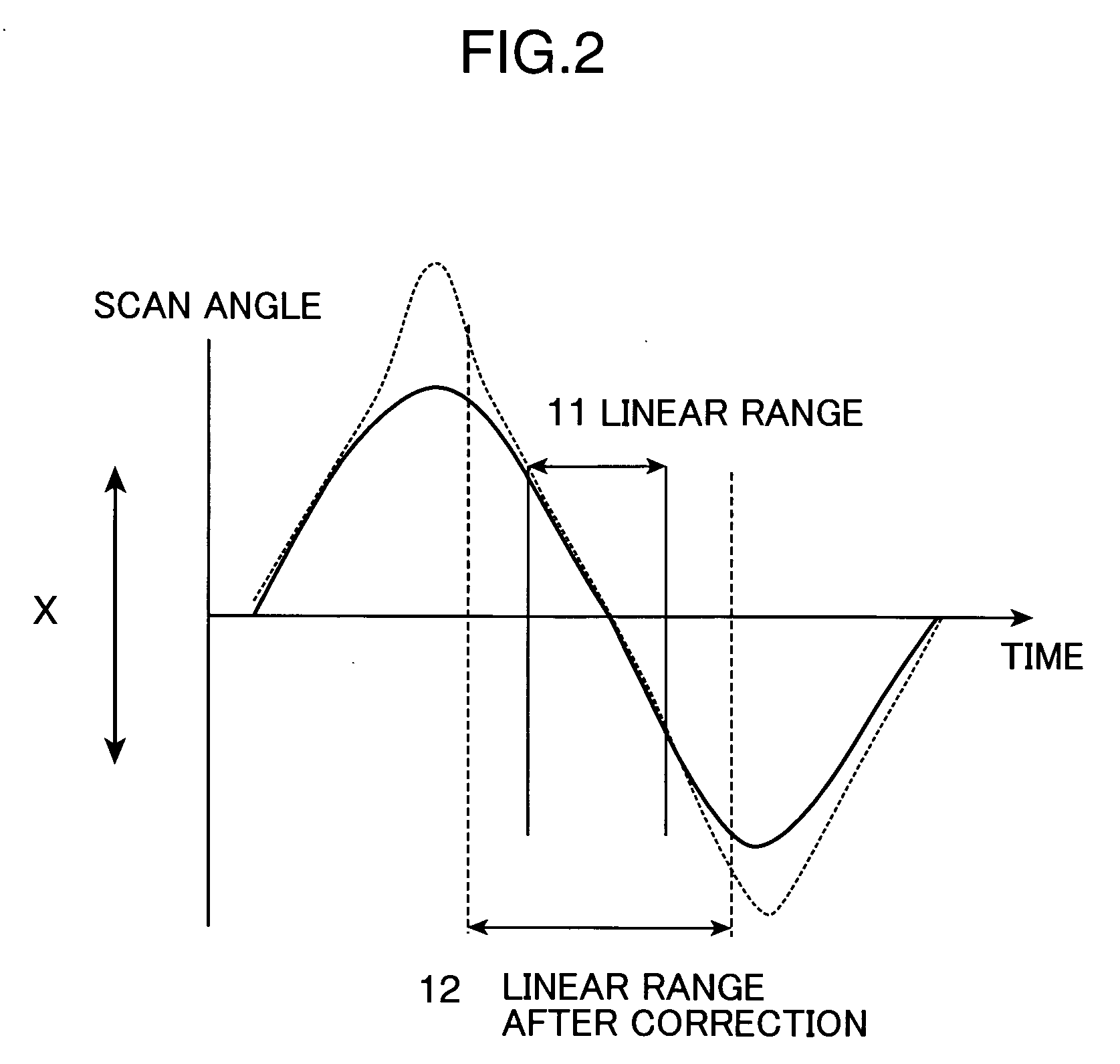
A 2-D beam scan method using a galvanometer mirror and a polygon scanner has a problem that the polygon scanner is large and noises are increased. Also, a method of oscillating a compact mirror has a problem that a brightness distribution is produced depending on a scan angle. Hence, a beam is scanned while a relatively small mirror, such as an MEMS mirror, is oscillated at or in the vicinity of the resonance frequency. In this instance, the scan angle is corrected with the use of a correction optical system for uniform illumination to be achieved.
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
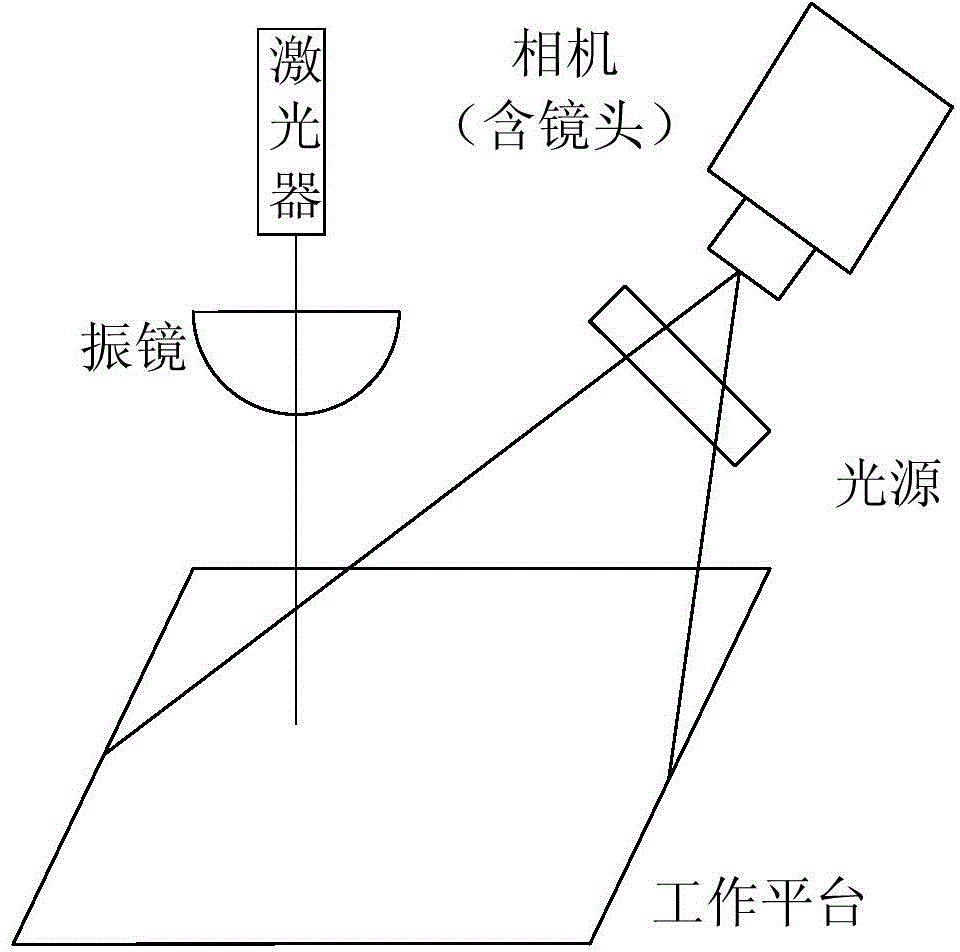
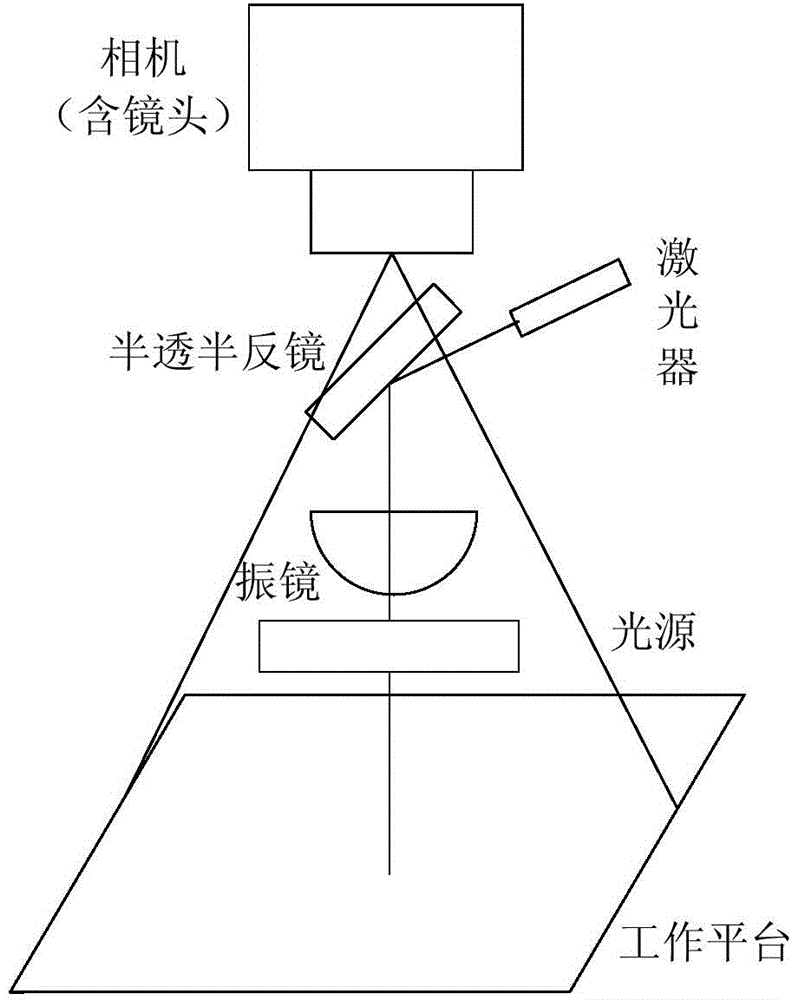
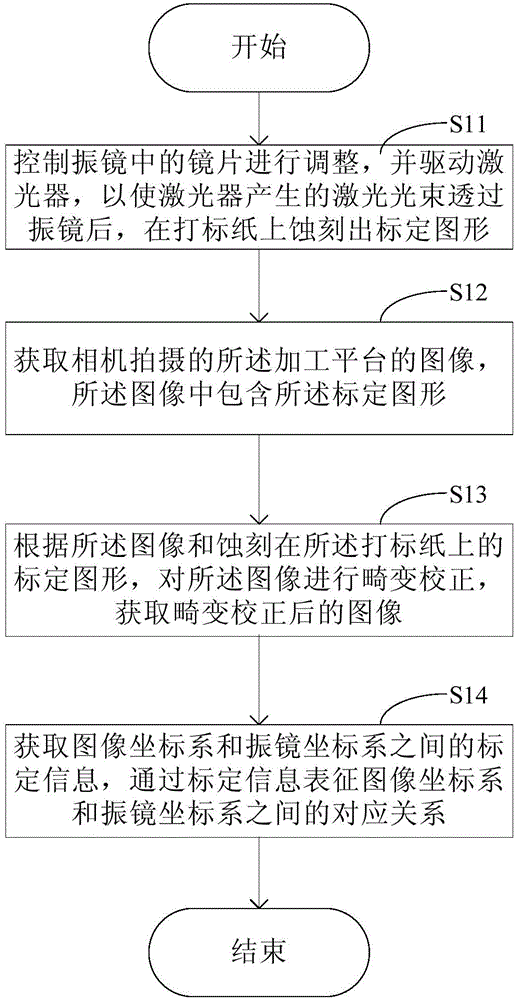
Calibration method and device used for laser processing system
The invention discloses a calibration method and device used for a laser processing system. The calibration method includes the steps that firstly, a lens in a galvanometer is controlled to be adjusted according to a calibration picture which is edited in advance, a laser device is driven, a laser beam generated by the laser device is made to penetrate through the galvanometer, and the calibration picture is etched on marking paper which is placed on a processing platform in advance; secondly, an image, photographed by a camera, of the processing platform is obtained, and the image includes the calibration picture; thirdly, distortion correction is conducted according to the image and the calibration picture etched on the marking paper, and the corresponding relation between an image coordinate system and a galvanometer coordinate system is obtained. According to the calibration method and device used for the laser processing system, distortion correction is achieved through the calibration picture on the marking paper, a target does not need to be used, cost is saved under the premise that precision is ensured, and the calibration operation is simplified.
Owner:BEIJING LUSTER LIGHTTECH
Reflection-type confocal scanning retina imaging system based on adaptive optics
ActiveCN101862178AIncrease horizontal resolutionIncrease vertical resolutionOthalmoscopesRetinal imagingData acquisition
The invention relates to a reflection-type confocal scanning retina imaging system based on adaptive optics, which can accurately obtain the high-resolution images of vital human eye retinae in real time and comprises a light source, a reflection-type beam shrinking and expanding system, a two-dimension scanning galvanometer, a Hartmann sensor, a deformable mirror, a photoelectric detection system, a data acquisition and processing system and a contraocular sighting target system. Lasers emitted from the light source are hit into human eye ground; light reflected from the eye ground returns along the original path, enters the photoelectric detection system and passes through the data acquisition and processing system to obtain the real-time images of the human eye ground. Simultaneously, an adaptive optics system comprising the Hartmann sensor and the deformable mirror can synchronously detect and correct human eye aberration, and thereby, the high resolution of the images is ensured.
Owner:INST OF OPTICS & ELECTRONICS - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
High polymer material ultraviolet laser 3D (three-dimensional) printing method and device for precise temperature control
ActiveCN103978307ALess frizzReduce temperature gradientAdditive manufacturing apparatus3D object support structuresUltravioletThermostat
The invention discloses a high polymer material ultraviolet laser 3D (three-dimensional) printing method and device for precise temperature control. The device comprises a thermostat, a laser head, a non-contact type temperature monitoring device, a scanning galvanometer, a machining platform, a powder paving device, a machining material and a computer control system. The laser head adopts a dual-tube core structure, an inner tube and an outer tube are coaxially fixed, one or more than one gradual-change neutral filter piece is arranged between the two tubes, and the laser transmittance of the filter piece(s) is radially reduced from the inner tube to the outer tube. The method comprises the following steps: presetting the machining temperature by the control system, in the process of machining, monitoring the temperature rise condition of an object to be machined in real time under the irradiation of laser by the non-contact type temperature monitoring device, feeding back to the control system, recording the increased value of the temperature within a certain time, and obtaining the absorption capability of the material to be machined to the laser and the temperature rise degree by the system, so that according to the preset machining temperature value, the laser output power can be calculated, the laser power can be timely adjusted, and the machining temperature can be precisely controlled.
Owner:INST OF CHEM CHINESE ACAD OF SCI +1
Robot three-dimensional scanning device and robot three-dimensional scanning method
InactiveCN107121062ASolve the problems of blind spots in scanning, long scanning time and low scanning accuracyExpand the scope of workUsing optical meansGratingPoint cloud
The invention discloses a robot three-dimensional scanning device and a robot three-dimensional scanning method. The device comprises an MEMS scanning galvanometer laser three-dimensional probe for generating three-dimensional point cloud data, a six-axis machine arm for clamping the MEMS scanning galvanometer laser three-dimensional probe, a turntable for placing a measured object and a controller for controlling the robot and the turntable, wherein the MEMS scanning galvanometer laser three-dimensional probe is arranged at the tail end of the machine arm; and the measured object is placed in the center of the turntable. In comparison with a digital and physical grating technology, the robot three-dimensional scanning device has the advantages of large depth of field, fast scanning speed, small size and high scanning accuracy; the device combines the high-accuracy turntable and the six-degree-of-freedom robot to a seven-degree-of-freedom device, the working range of the machine arm can be increased, flexibility of scanning on a large object can be improved, scanning dead angles can be reduced, and finally, fully-automatic three-dimensional scanning can be realized.
Owner:SUZHOU DEKA TESTING TECH CO LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com