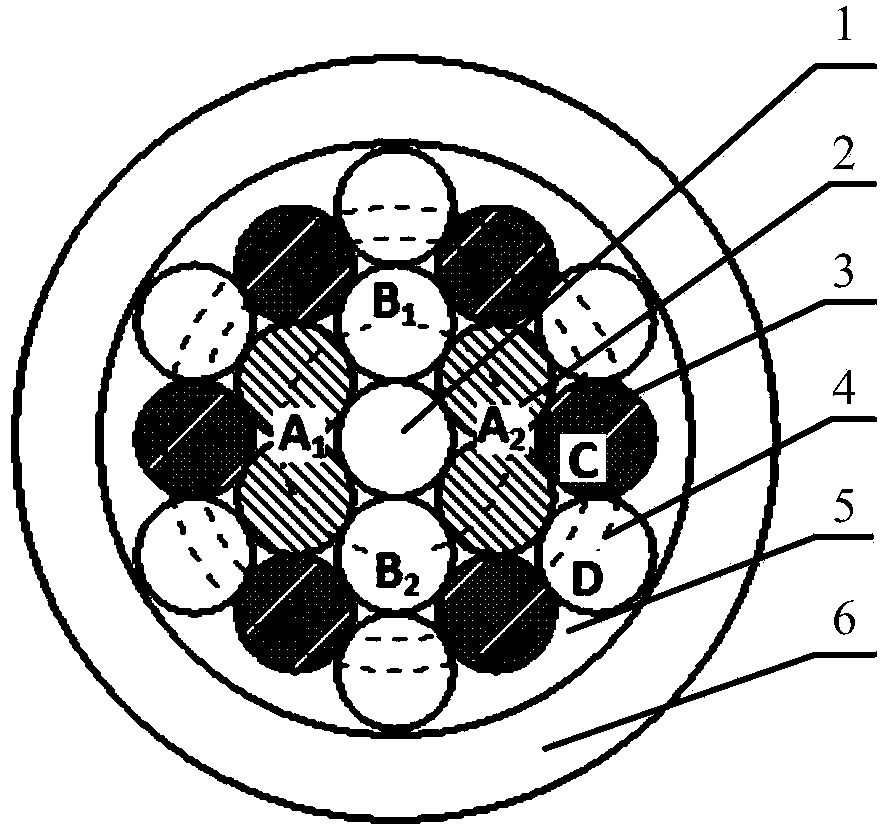
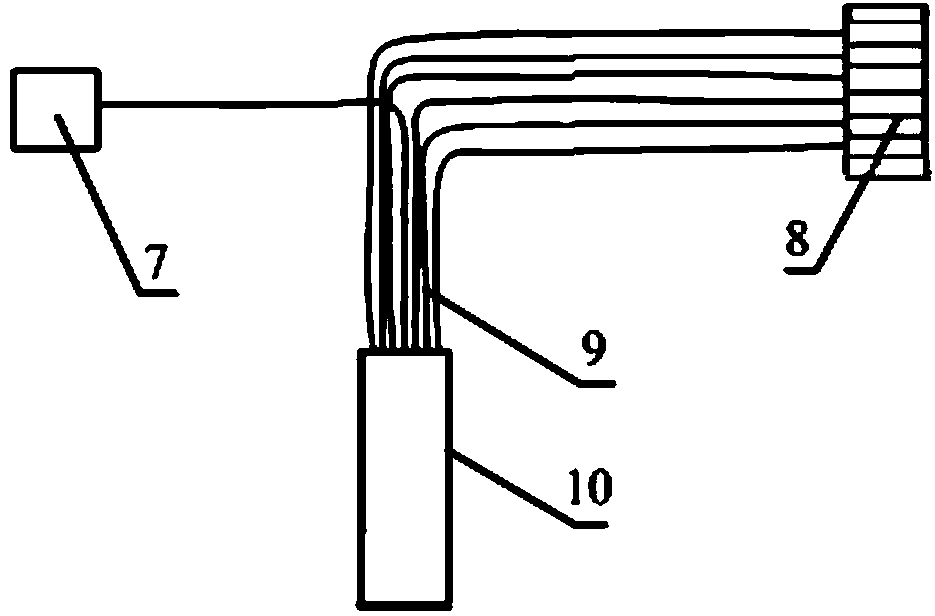
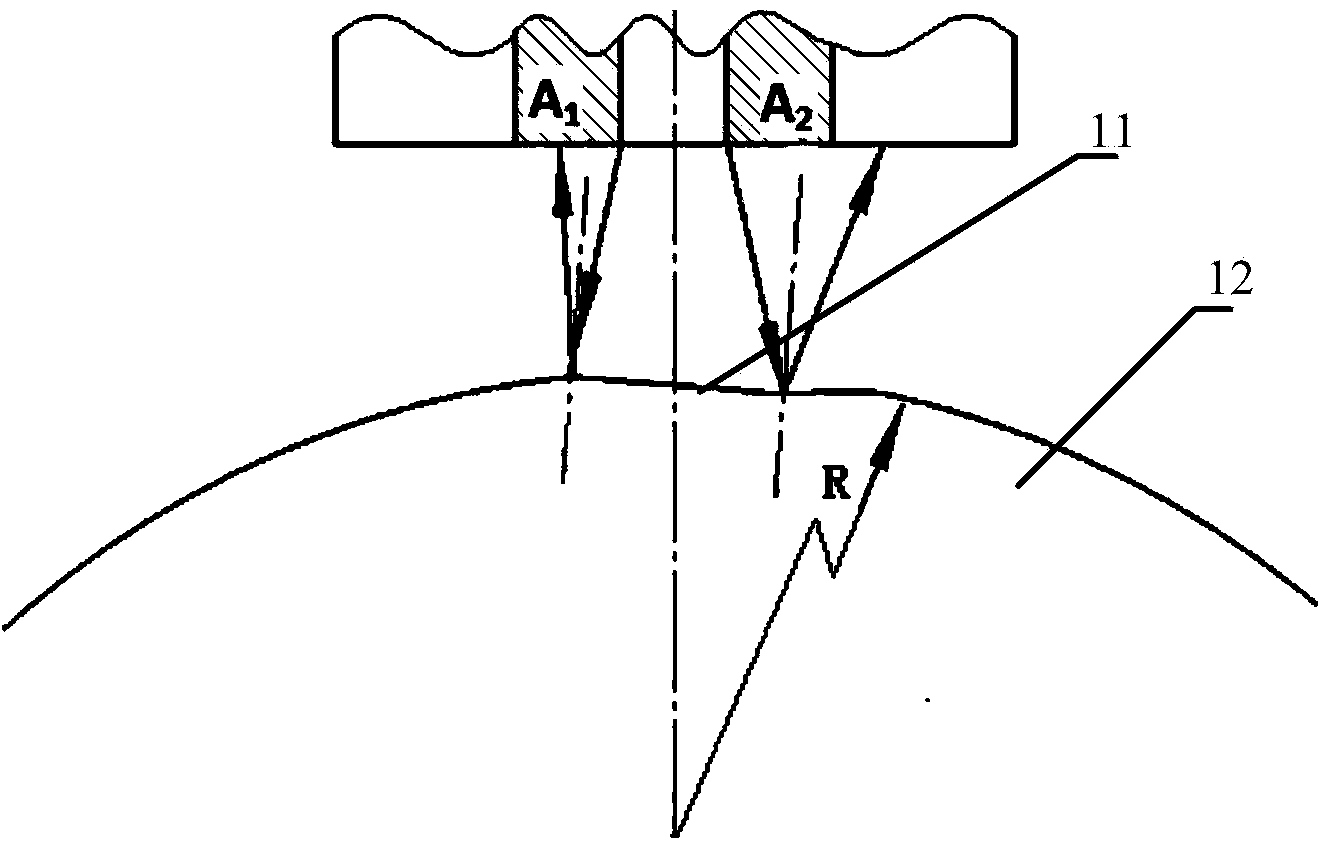
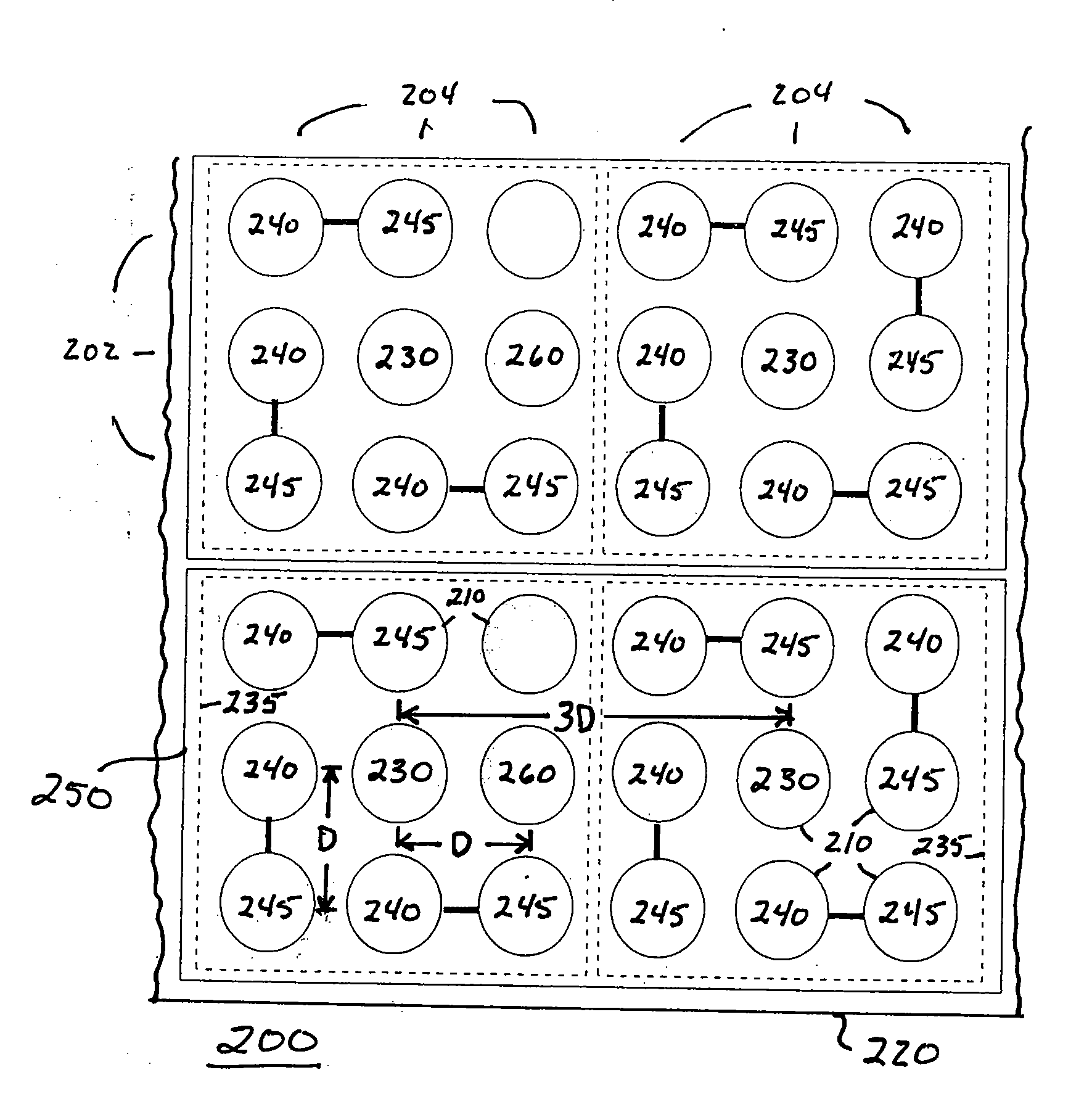
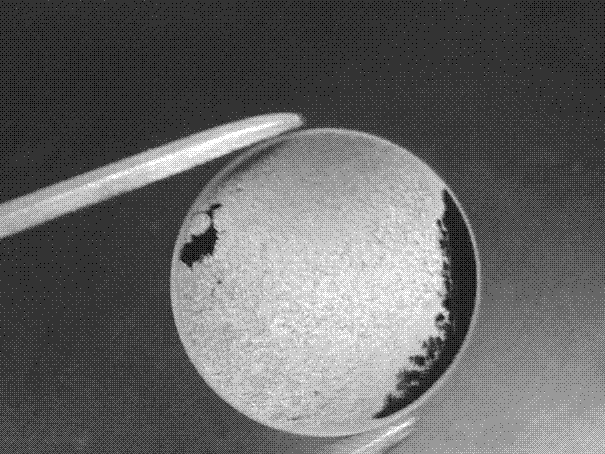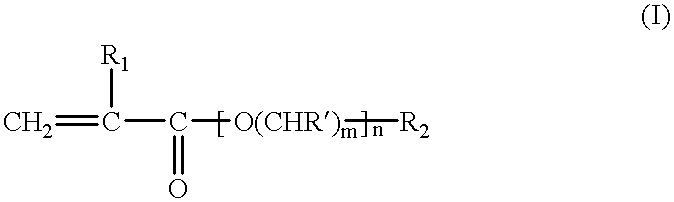Patents
Literature
128 results about "Hexagonal array" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
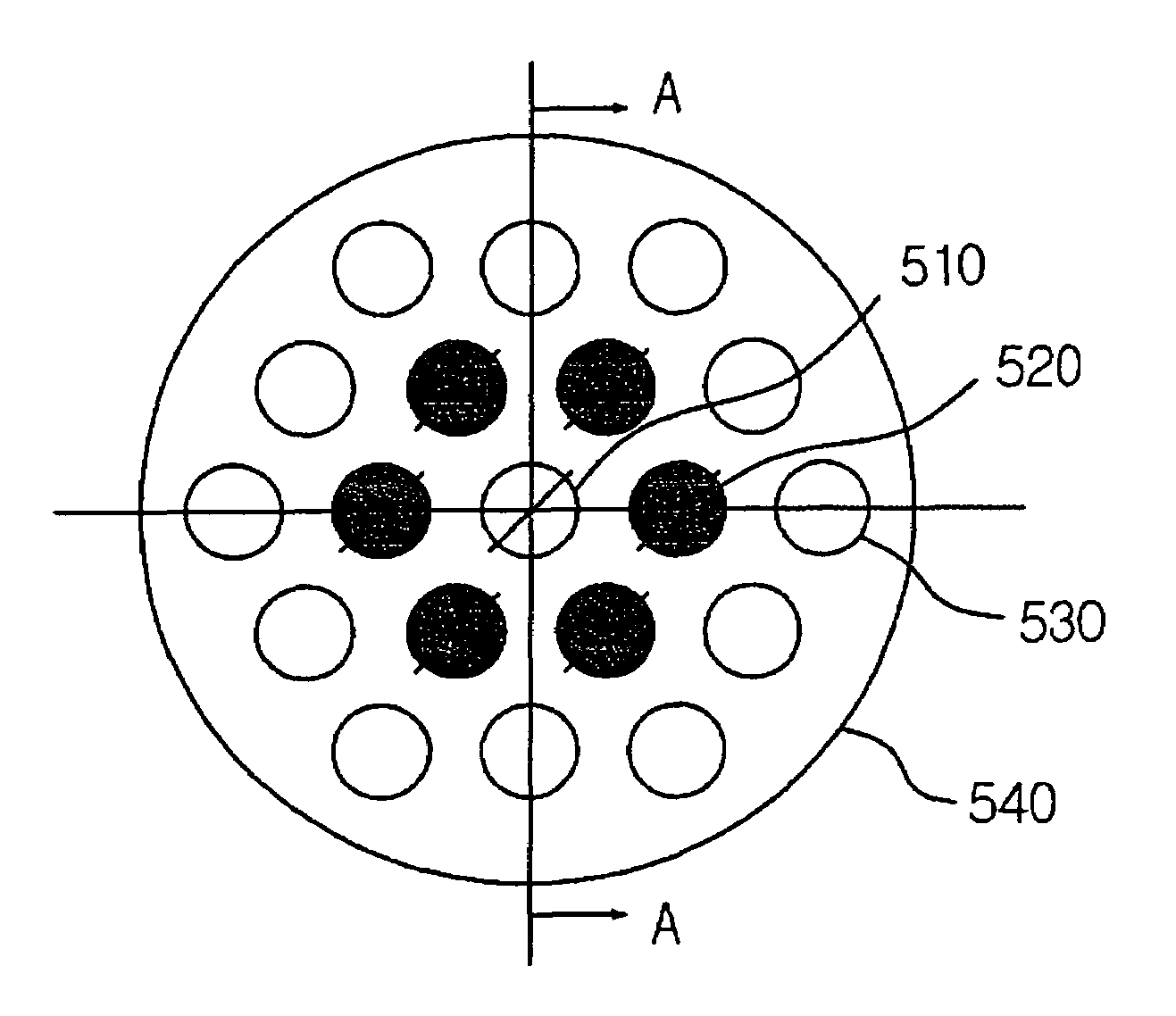
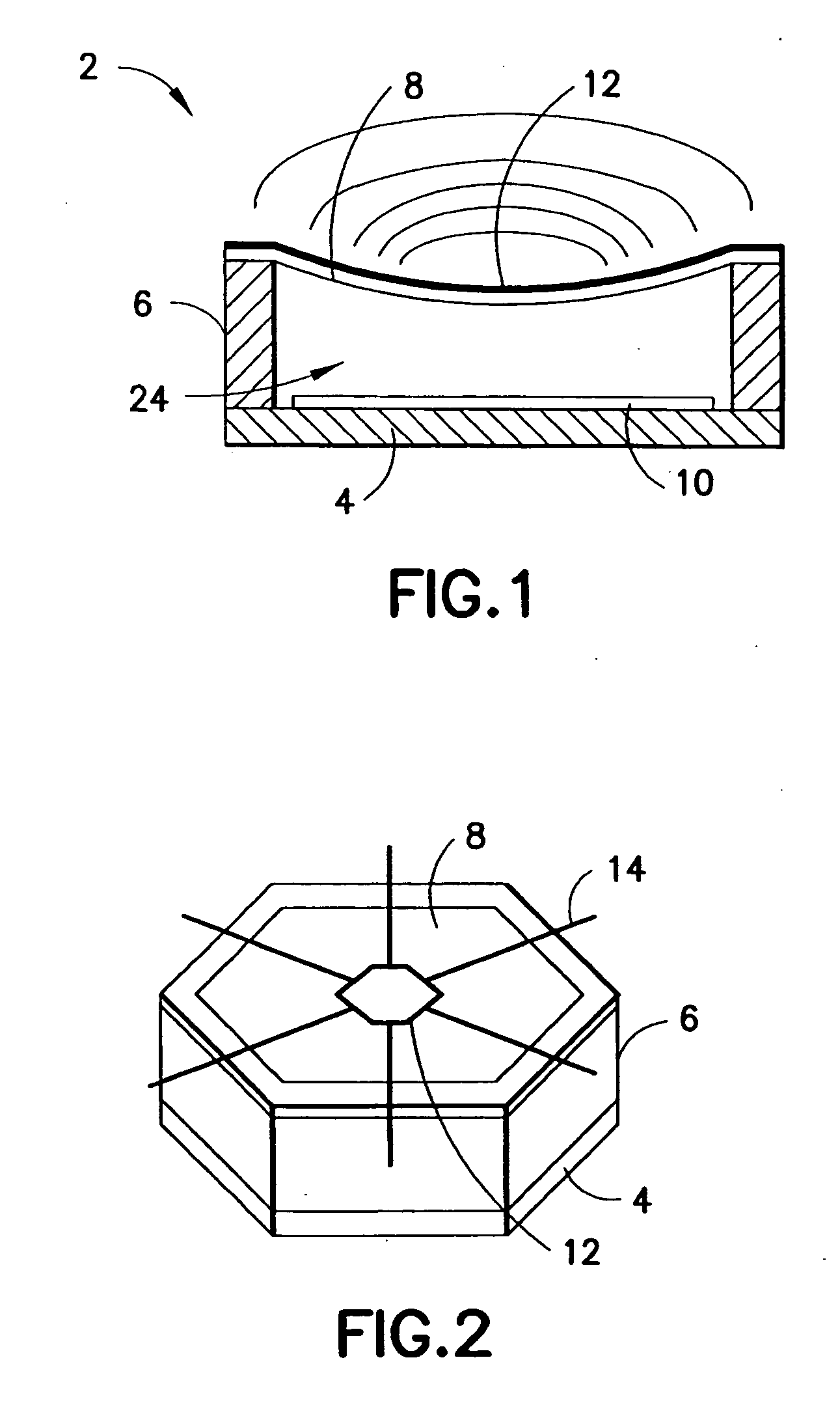
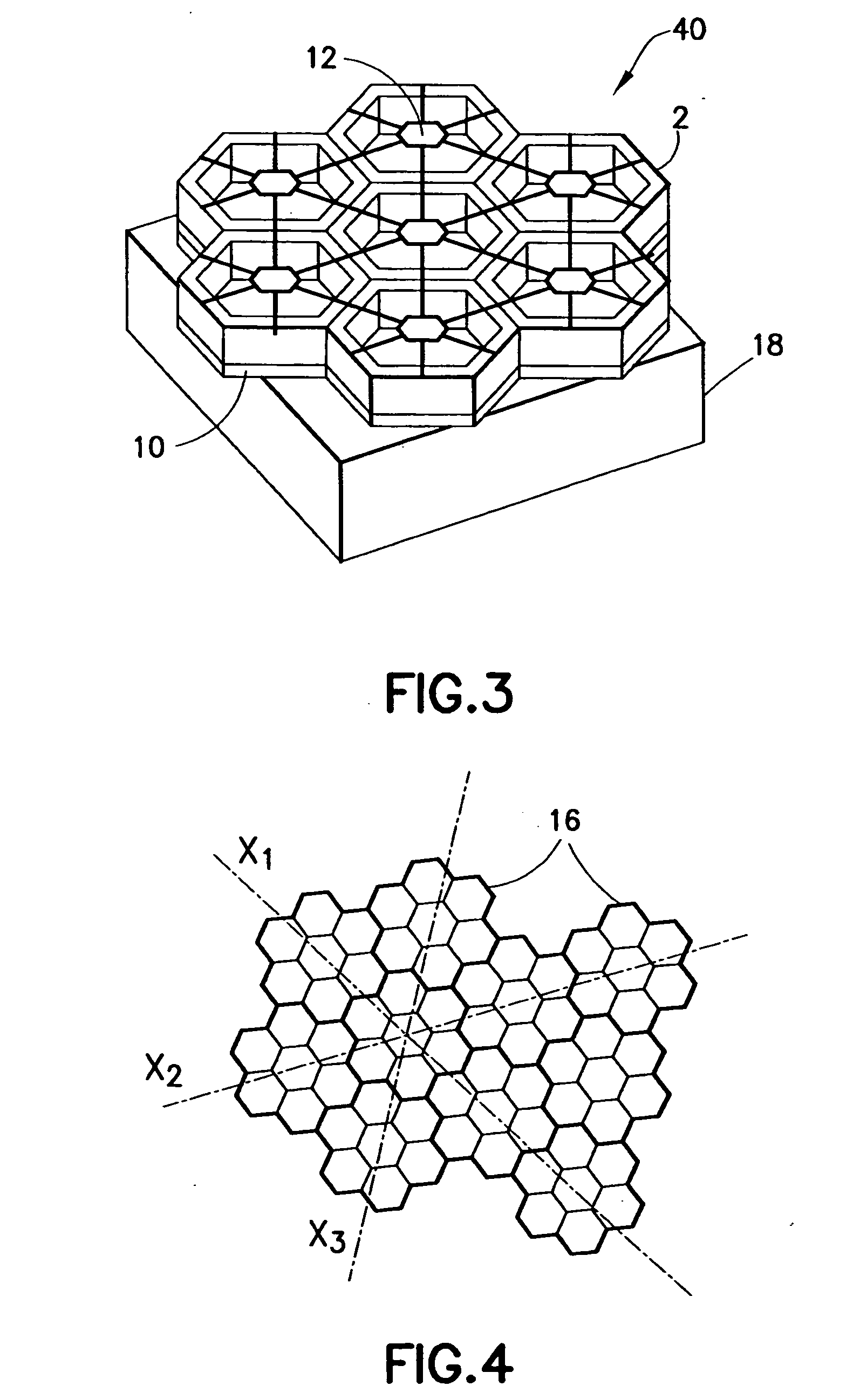
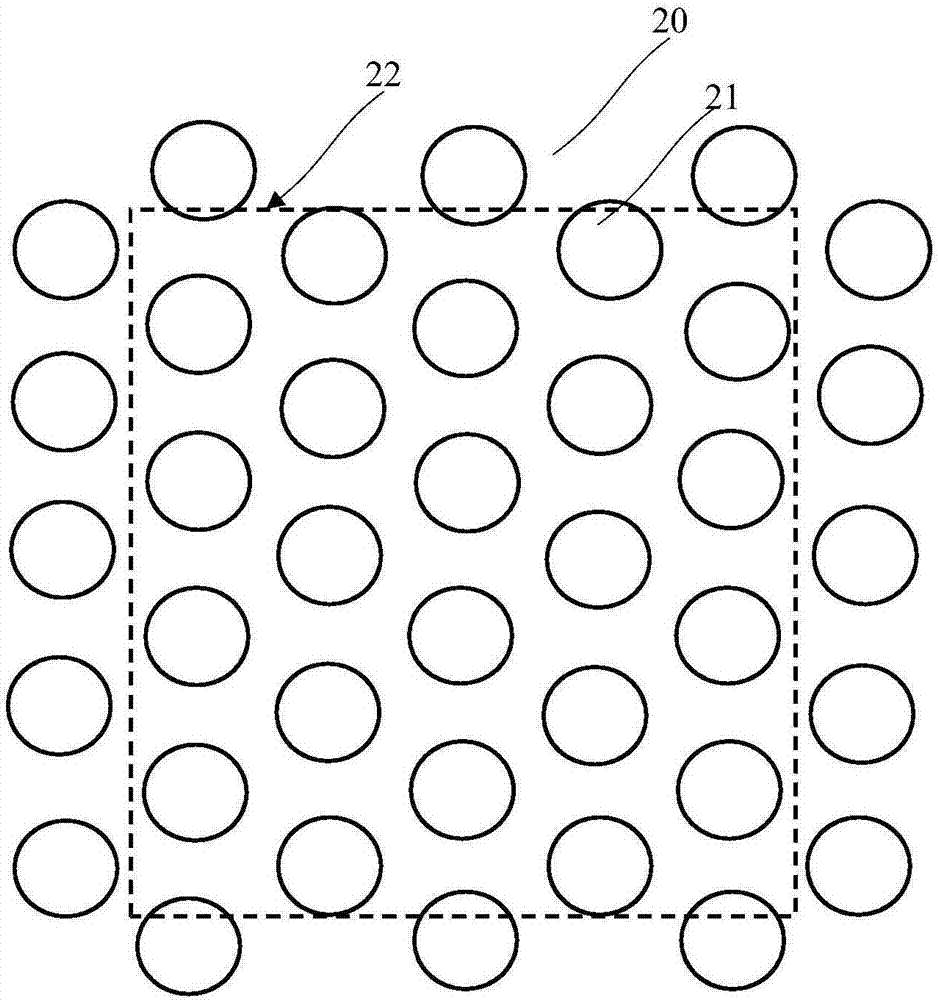
Hexagonal array structure of dielectric rod to shape flat-topped element pattern
InactiveUS7167139B2Wide beam scanning rangeConstant electric performanceIndividually energised antenna arraysLeaky-waveguide antennasCouplingEngineering
A hexagonal array structure of a dielectric rod for shaping a flat-topped element pattern (FTEP) is provided. The hexagonal structure of dielectric rods forming a flat-topped element pattern (FTEP) includes: a center element for forming a unit radiation pattern of the FTEP through an electromagnetic wave mutual coupling by receiving a polarization signal of a basic mode; a plurality of first ring elements arranged at vertexes of a regular hexagon based on the center element for forming the unit radiation pattern by electromagnetic wave mutual coupling with the center element and an electromagnetic wave; and a circular waveguide array supporting unit for supporting the center element and the plurality of first ring elements.
Owner:ELECTRONICS & TELECOMM RES INST
Multi-axis joystick and transducer means therefore
InactiveUS20050162389A1Reduce noiseLow costProgramme controlManual control with multiple controlled membersJoystickTransducer
The invention relates to improved multi-axis joysticks and associated multi-axis optical displacement measurement means. The displacement measuring means may include one or more light emitters and one or more light detectors, preferably mounted in a planar hexagonal array. The relative position of an adjacent movable reflector assembly can be measured in six degrees of freedom by variations in detected light amplitude. Various ergonomic configurations of six axis joystick embodiments which may be facilitated by the compact design of the transducer means are disclosed. Means for dynamically adjusting coordinate transformations for construction machinery control are also disclosed.
Owner:OBERMEYER HENRY K +1
Multi-axis joystick and transducer means therefore
InactiveUS7474296B2Facilitate exchange in positionFacilitate simple zero-backlash mounting of inexpensive displacement transducersProgramme controlManual control with multiple controlled membersJoystickClassical mechanics
The invention relates to improved multi-axis joysticks and associated multi-axis optical displacement measurement means. The displacement measuring means may include one or more light emitters and one or more light detectors, preferably mounted in a planar hexagonal array. The relative position of an adjacent movable reflector assembly can be measured in six degrees of freedom by variations in detected light amplitude. Various ergonomic configurations of six axis joystick embodiments which may be facilitated by the compact design of the transducer means are disclosed. Means for dynamically adjusting coordinate transformations for construction machinery control are also disclosed.
Owner:OBERMEYER HENRY K +1
Alignment method for fabrication of integrated ultrasonic transducer array
InactiveUS7052464B2Ultrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsDecorative surface effectsCMOSAxis of symmetry
An integrated circuit is fabricated by micromachining a hexagonal array of cMUT elements on top of a substrate comprising a hexagonal array of CMOS cells. Each cMUT element overlies a respective CMOS cell in one-to-one correspondence. During layout of the mask for micromachining the cMUT layer, either the hexagonal pattern or the alignment key is rotated until an axis of symmetry of the hexagonal pattern is aligned with an axis of the alignment key. Later, when the mask is superimposed on the CMOS substrate, the alignment key on the mask is aligned with an alignment key on the substrate. This ensures that the cMUT elements formed by optical lithography will be matched to the CMOS cells.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Thermoelectric device
InactiveUS8222511B2Vehicle seatsThermoelectric device with peltier/seeback effectElectrical conductorEngineering
A thermoelectric device comprises a plurality of semiconductor elements comprising a first set of semiconductor elements and a second set of semiconductor elements, which include dissimilar electrical properties. The semiconductor elements are oriented in a substantially hexagonal array that includes rows in which semiconductor elements of the first and second sets of semiconductor elements alternate. The thermoelectric device also comprises a first set of electrical conductors and a second set of electrical conductors; each of the first set of electrical conductor being electrically coupled to the first end of a semiconductor element of the first set of semiconductor elements and the first end of a semiconductor element of the second set of semiconductor elements, each of the second set of electrical conductors are electrically coupled to the second end of a semiconductor element of the first set of semiconductor elements and the a second end of a semiconductor element of the second set of semiconductor elements such that the plurality of semiconductor elements are electrically coupled to each other in series.
Owner:GENTHERM INC
Alignment method for fabrication of integrated ultrasonic transducer array
InactiveUS20050148132A1Ultrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsDecorative surface effectsCMOSAxis of symmetry
An integrated circuit is fabricated by micromachining a hexagonal array of cMUT elements on top of a substrate comprising a hexagonal array of CMOS cells. Each cMUT element overlies a respective CMOS cell in one-to-one correspondence. During layout of the mask for micromachining the cMUT layer, either the hexagonal pattern or the alignment key is rotated until an axis of symmetry of the hexagonal pattern is aligned with an axis of the alignment key. Later, when the mask is superimposed on the CMOS substrate, the alignment key on the mask is aligned with an alignment key on the substrate. This ensures that the cMUT elements formed by optical lithography will be matched to the CMOS cells.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
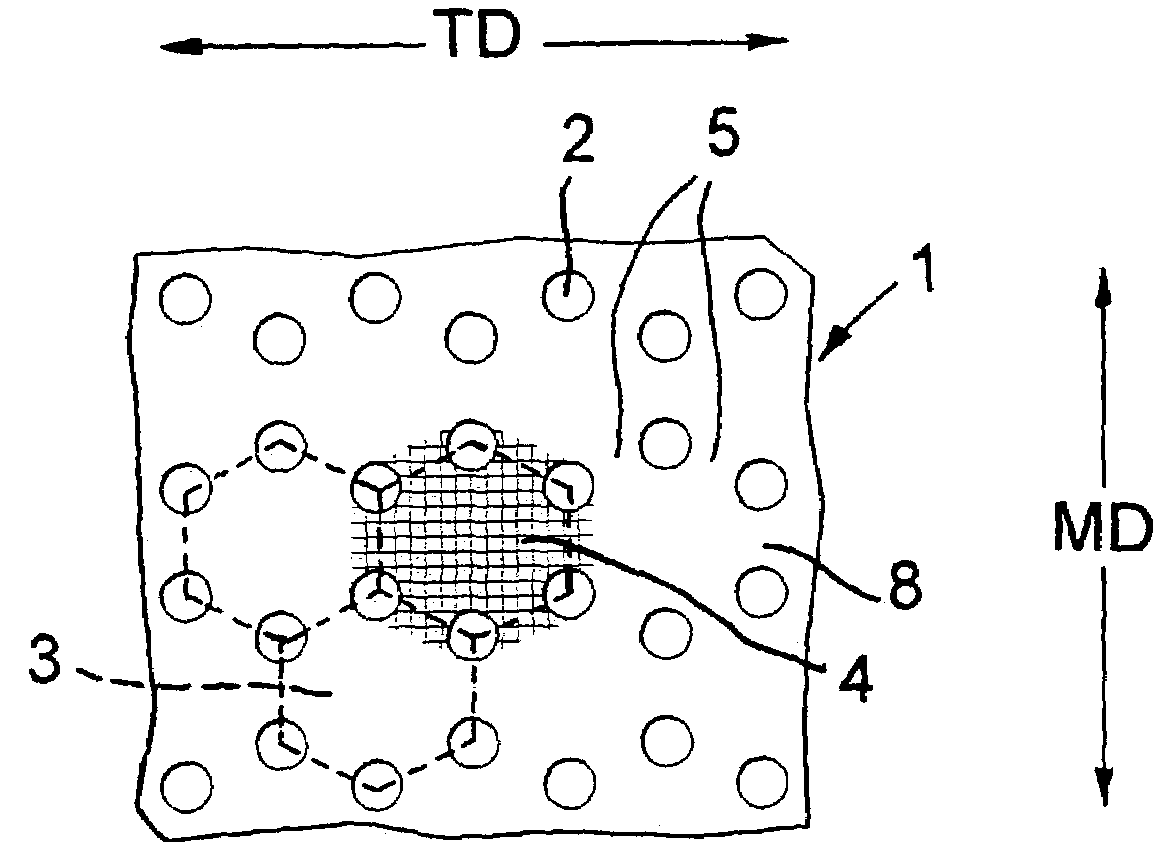
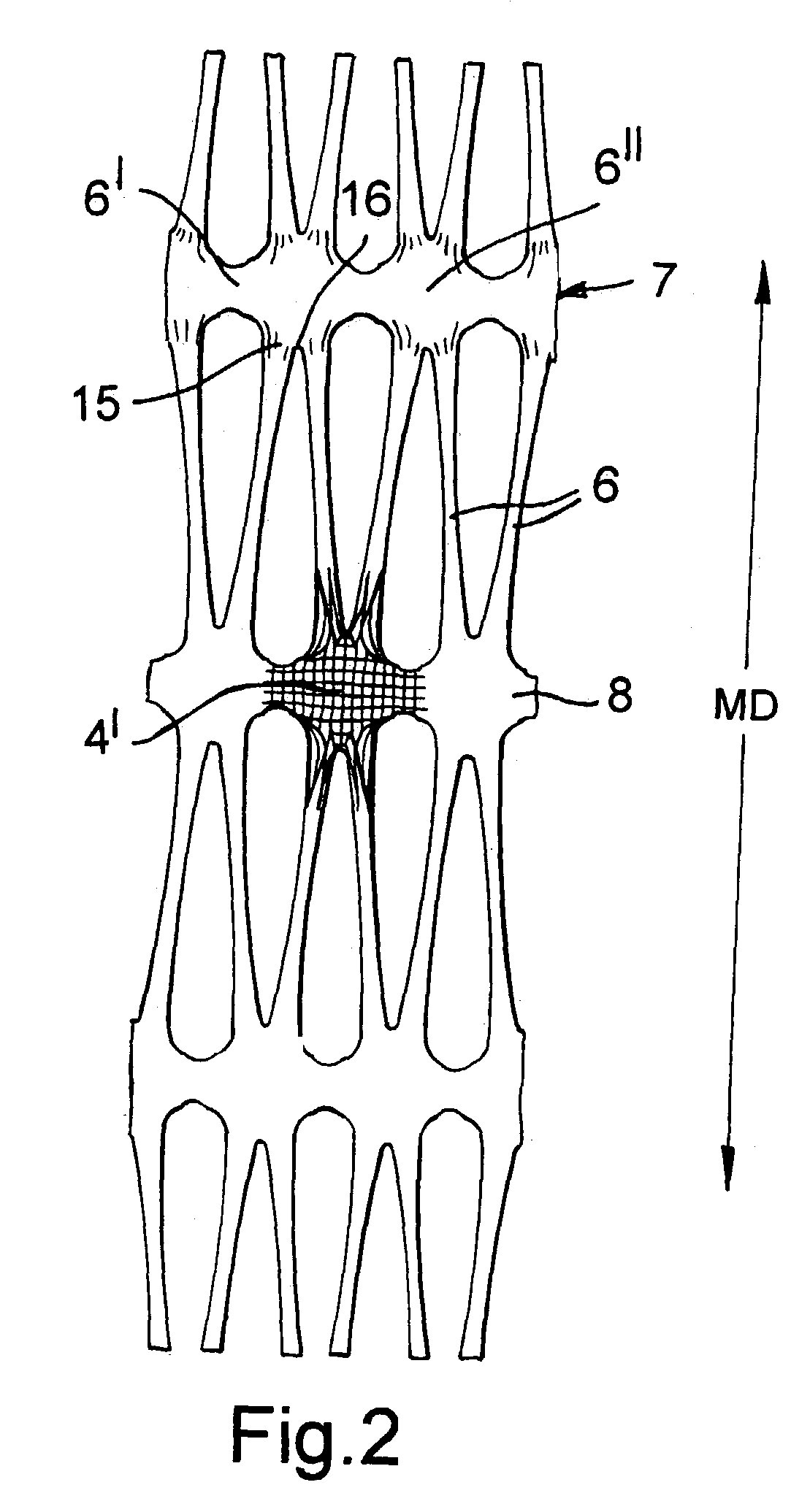
Geogrid or mesh structure
ActiveUS7001112B2Increase torsional stiffnessEnhance abilityArtificial islandsLayered productsEngineeringPlastic materials
To make an oriented plastics material geogrid 10 in which oriented strands 6, 9 form triangular meshes with a junction 11 at each corner and six of the strands 6, 9 meet at each junction 11, a plastics material sheet starting material 1 has holes 2 in an array of hexagons 3, opposite holes 2 of each hexagon being aligned in the machine direction, and the starting material 1 is stretched first in the machine direction and secondly in the transverse direction. In the eventual geogrid 10, the centre portions of the hexagons in the starting material 1 form the junctions 11. The centres of the junctions 11 are slightly biaxially oriented, but at the edges of the junctions 11, the orientation of the edge of substantially each strand 6 or 9 runs around the edge of the respective junction 11 and into the edge of the next strand 6 or 9. During the second stretch, restraint can be applied in the first stretch direction and discontinued before the material is allowed to relax in the second stretch direction. If desired, the procedure can be terminated after the first stretch, to produce a uniaxially-oriented geogrid. By using a starting material 21 which has through holes 22 and weakened zones 23, it is possible to form the geogrid of the invention from a starting material 21 having a rectangular array of through holes 22.
Owner:TENSAR TECH
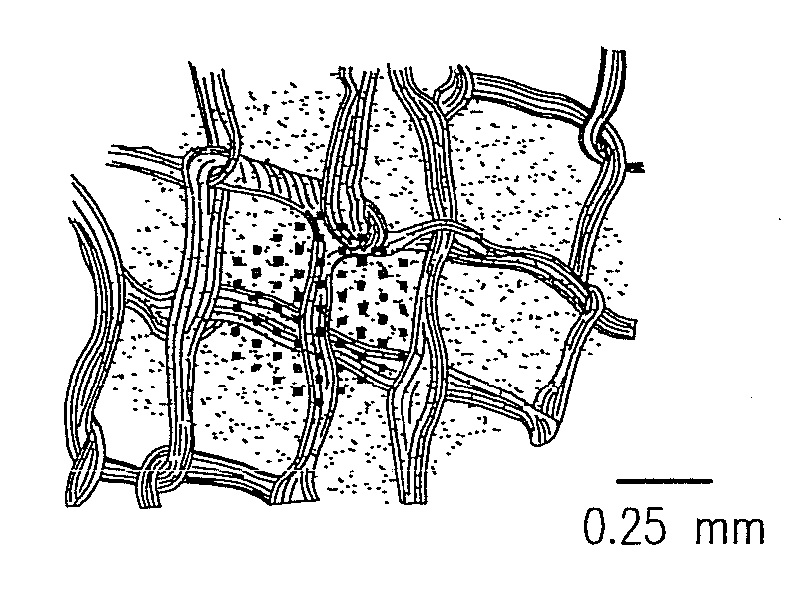
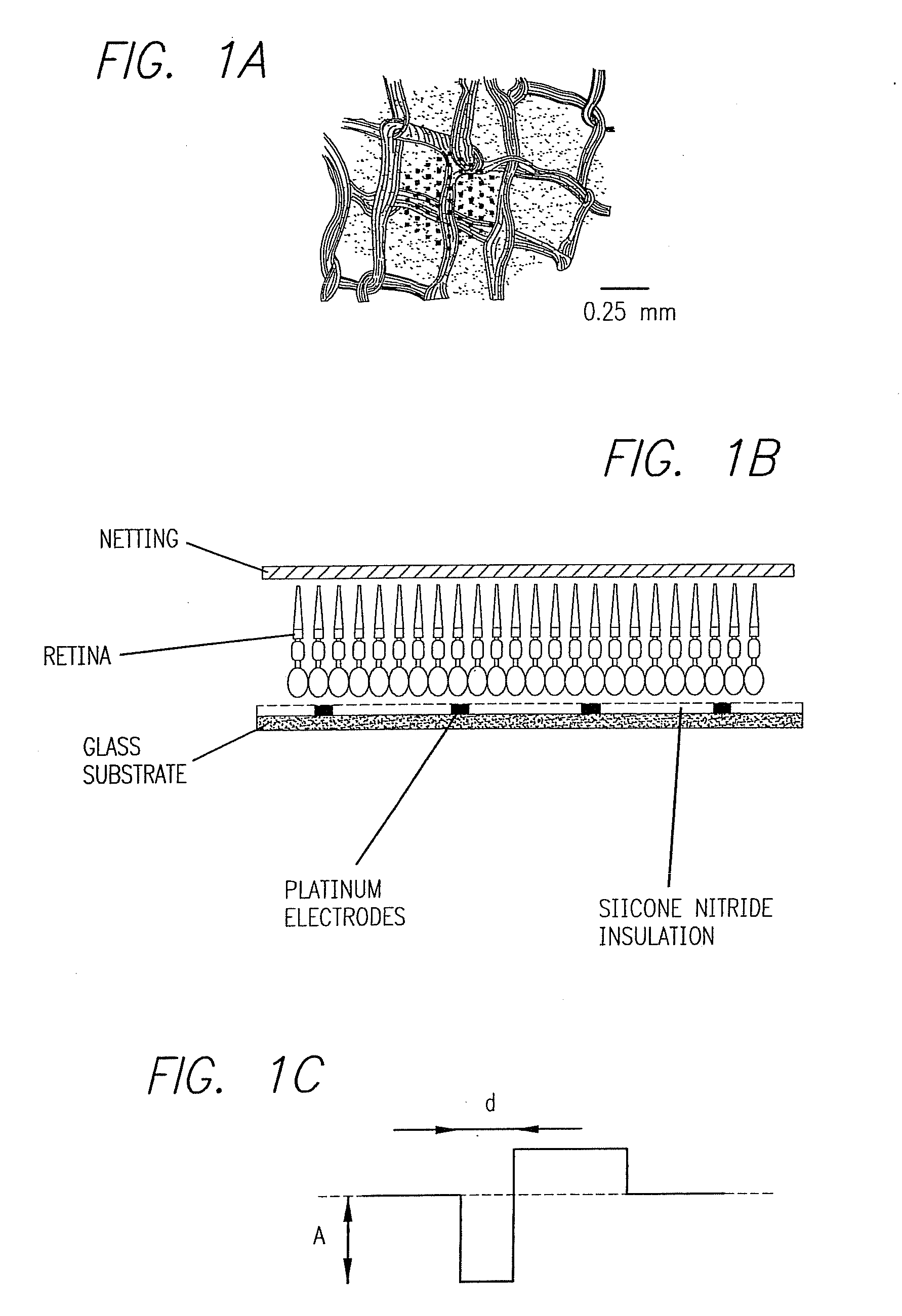
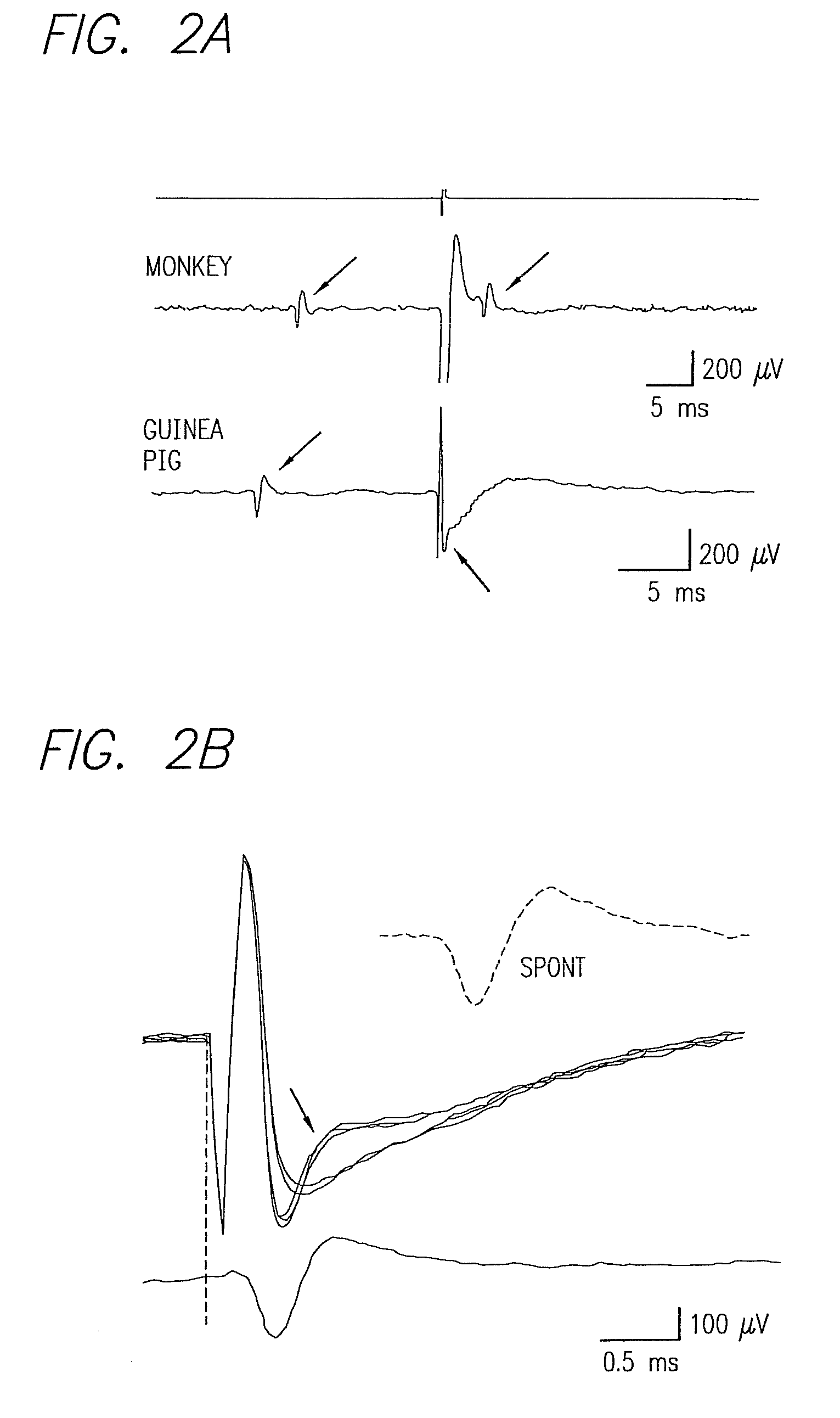
Method and apparatus for visual neural stimulation
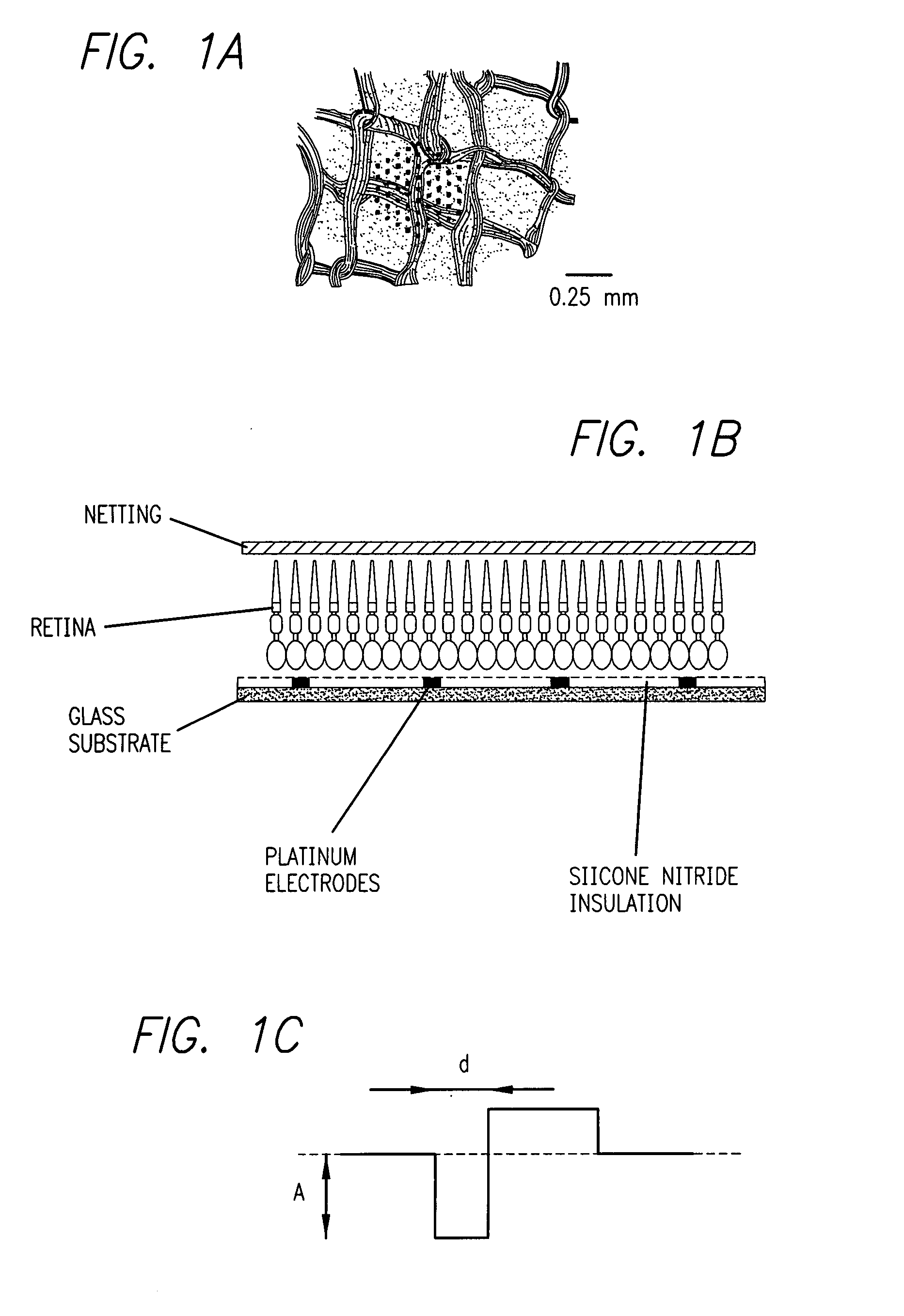
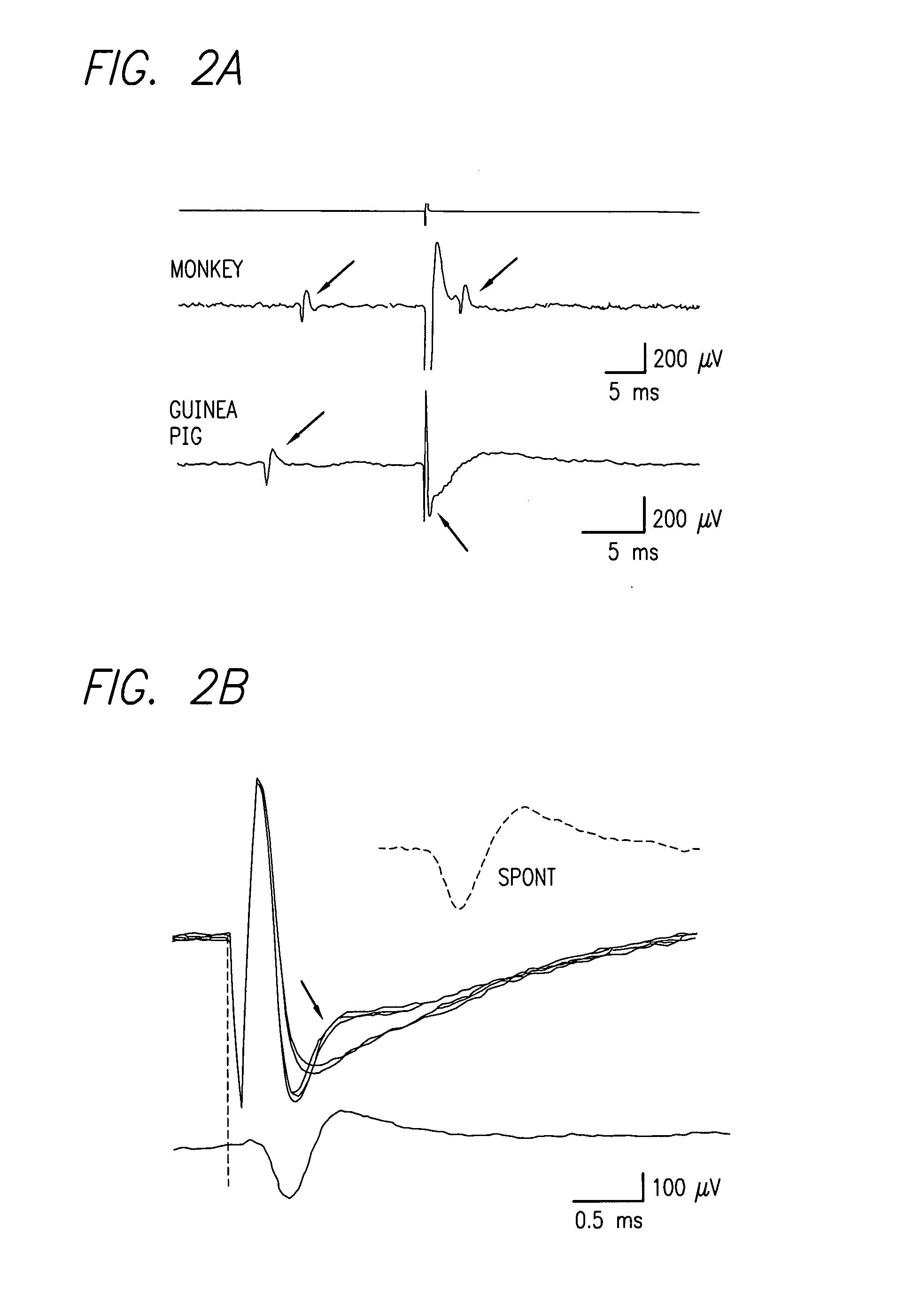
Existing epiretinal implants for the blind are designed to electrically stimulate large groups of surviving retinal neurons using a small number of electrodes with diameters of several hundred μm. To increase the spatial resolution of artificial sight, electrodes much smaller than those currently in use are desirable. In this study we stimulated and recorded ganglion cells in isolated pieces of rat, guinea pig, and monkey retina. We utilized micro-fabricated hexagonal arrays of 61 platinum disk electrodes with diameters between 6 and 25 μm, spaced 60 μm apart. Charge-balanced current pulses evoked one or two spikes at latencies as short as 0.2 ms, and typically only one or a few recorded ganglion cells were stimulated. Application of several synaptic blockers did not abolish the evoked responses, implying direct activation of ganglion cells. Threshold charge densities were typically below 0.1 mC / cm2 for a pulse duration of 100 μs, corresponding to charge thresholds of less than 100 pC. Stimulation remained effective after several hours and at high frequencies. To demonstrate that closely spaced electrodes can elicit independent ganglion cell responses, we utilized the multi-electrode array to stimulate several nearby ganglion cells simultaneously. From these data we conclude that electrical stimulation of mammalian retina with small-diameter electrode arrays is achievable and can provide high temporal and spatial precision at low charge densities. We review previous epiretinal stimulation studies and discuss our results in the context of 32 other publications, comparing threshold parameters and safety limits.
Owner:SALK INST FOR BIOLOGICAL STUDIES +1
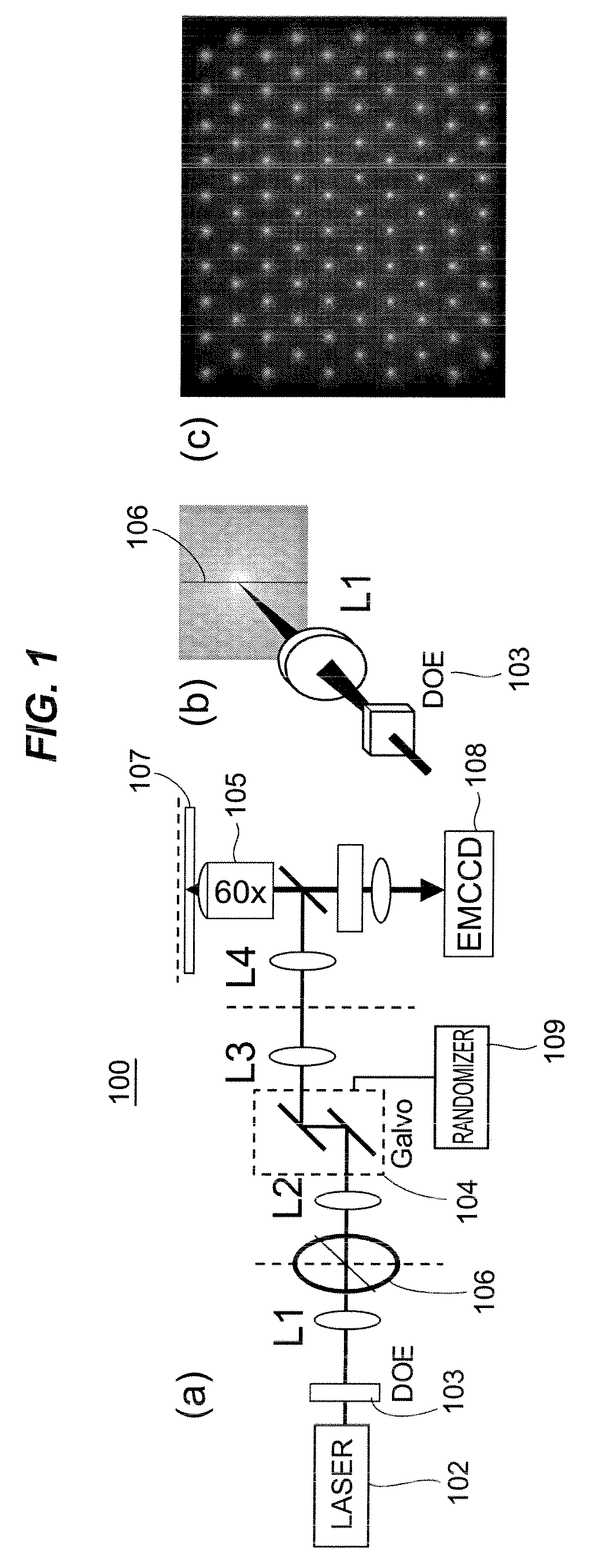
Stochastic scanning apparatus using multiphoton multifocal source
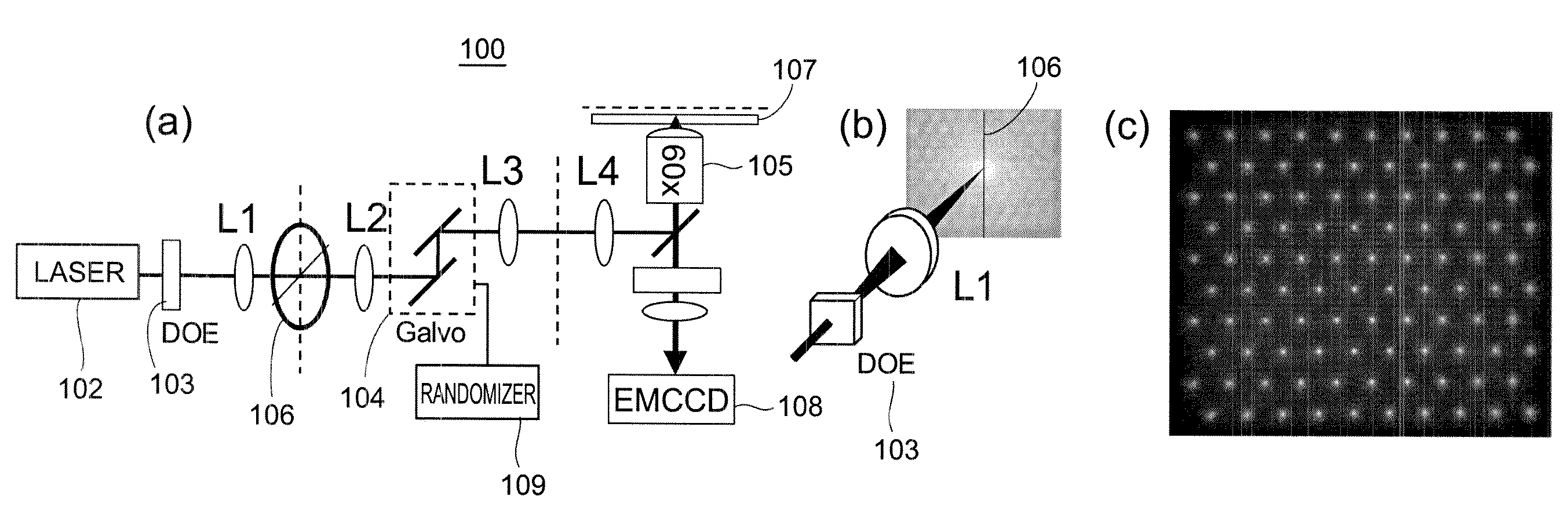
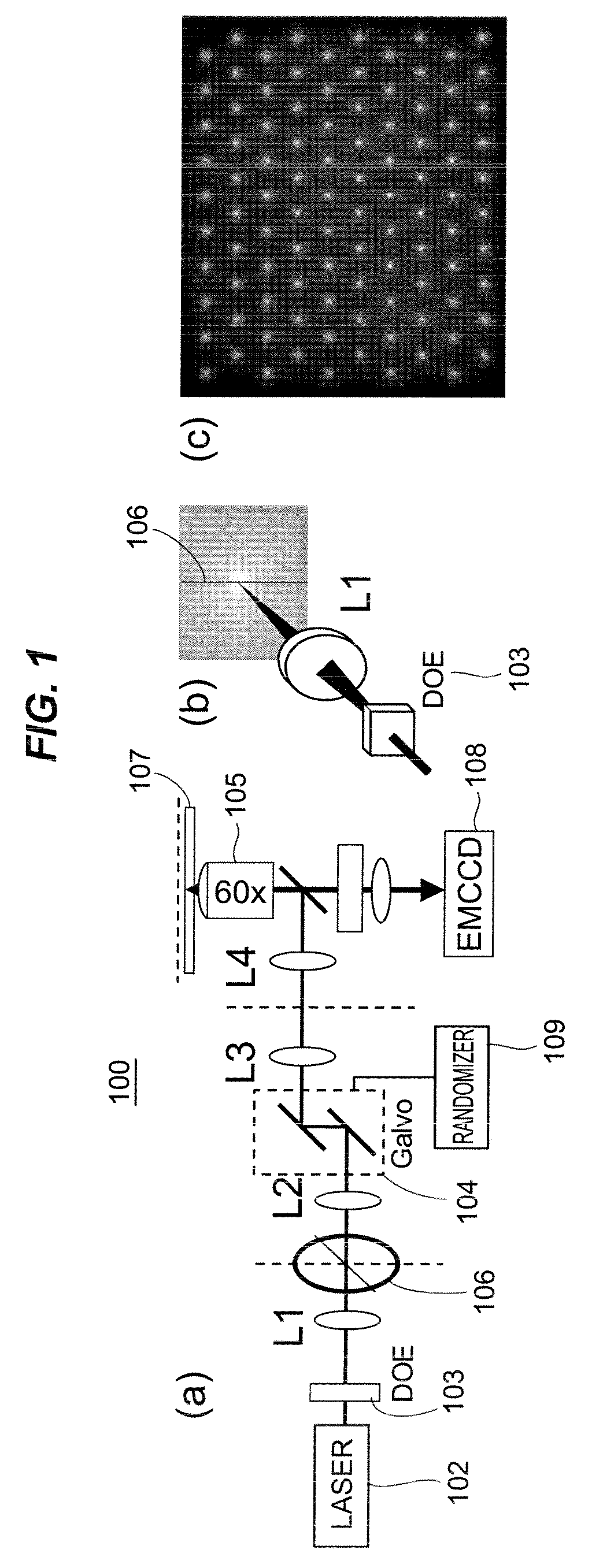
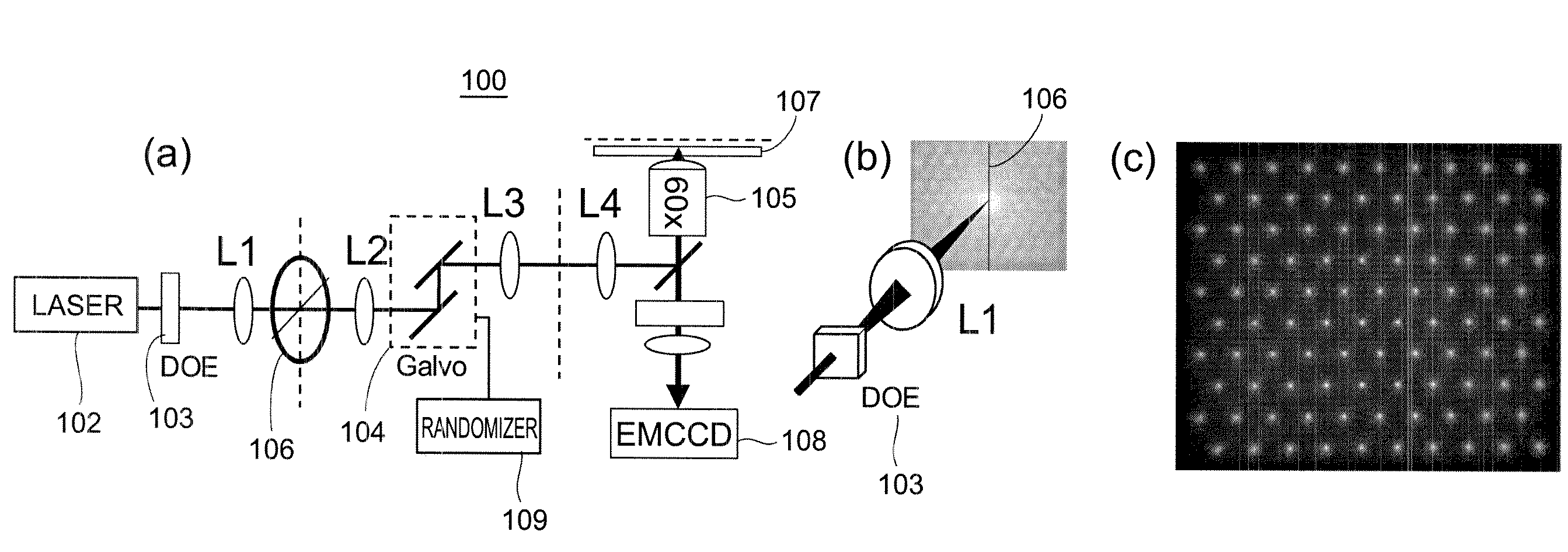
A rapid-sampling stochastic scanning multiphoton multifocal microscopy (SS-MMM) fluorescence imaging technique enables multiparticle tracking at rates upwards of 1,000 times greater than conventional single point raster scanning. Stochastic scanning of a diffractive optical element may generate a 10×10 hexagonal array of foci with a white noise driven galvanometer to yield a scan pattern that is random yet space-filling. SS-MMM may create a more uniformly sampled image with fewer spatio-temporal artifacts than obtained by conventional or multibeam raster scanning.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF CHICAGO
Stochastic Scanning Apparatus Using Multiphoton Multifocal Source
A rapid-sampling stochastic scanning multiphoton multifocal microscopy (SS-MMM) fluorescence imaging technique enables multiparticle tracking at rates upwards of 1,000 times greater than conventional single point raster scanning. Stochastic scanning of a diffractive optical element may generate a 10×10 hexagonal array of foci with a white noise driven galvanometer to yield a scan pattern that is random yet space-filling. SS-MMM may create a more uniformly sampled image with fewer spatio-temporal artifacts than obtained by conventional or multibeam raster scanning.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF CHICAGO
Micro-fastening system and method of manufacture
This application relates to a micro-fastening system and, more particularly, to a mechanical micro-fastening system employing a plurality of mating nanoscale fastening elements (16, 18) and a method of manufacturing a micro-fastening system. The mating nanoscale fastening elements (16, 18) are formed by functionalizing nanotubes having an ordered array of hexagons with pentagons and heptagons at particular heterojunctions.
Owner:BOARD OF TRUSTEES OPERATING MICHIGAN STATE UNIV
Large field-of-view bionic compound eye visual system adopting dome light cone
InactiveCN102819053ASolve the problem of severe imaging defocusCompact structureCoupling light guidesMountingsCouplingSurface type
The invention discloses a large field-of-view bionic compound eye visual system adopting a dome light cone. The system comprises a curved surface compound eye lens, an aperture diaphragm, the light cone and an image detector, which are connected with one another in sequence; the curved surface compound eye lens comprises sub eyes and a substrate, the sub eyes are hermetically bonded in the hexagonal array mode, the surface type of the sub eyes are non-spherical, the substrate is a curved surface substrate, the aperture diaphragm is a stepped type aperture diaphragm, and the light cone is a dome light cone. According to the invention, the dome light cone coupling strategy is used as the light path conduction mode, on one hand, a curved image formed by the compound eye lens is converted into a planar image, so as to be received by a plane detector, on the other hand, the large field of view image formed by the compound eye lens is compressed into a smaller image according to an equal ratio, so that the large field of view image can be completely imaged in a small-sized detector in a lossless mode, the coupling is realized, and the technical requirements on the size of detectors are accordingly reduced.
Owner:MDTP OPTICS
Method and Apparatus for Visual Neural Stimulation
Existing epiretinal implants for the blind are designed to electrically stimulate large groups of surviving retinal neurons using a small number of electrodes with diameters of several hundred μm. To increase the spatial resolution of artificial sight, electrodes much smaller than those currently in use are desirable. In this study we stimulated and recorded ganglion cells in isolated pieces of rat, guinea pig, and monkey retina. We utilized micro-fabricated hexagonal arrays of 61 platinum disk electrodes with diameters between 6 and 25 μm, spaced 60 μm apart. Charge-balanced current pulses evoked one or two spikes at latencies as short as 0.2 ms, and typically only one or a few recorded ganglion cells were stimulated. Application of several synaptic blockers did not abolish the evoked responses, implying direct activation of ganglion cells. Threshold charge densities were typically below 0.1 mC / cm2 for a pulse duration of 100 μs, corresponding to charge thresholds of less than 100 pC. Stimulation remained effective after several hours and at high frequencies. To demonstrate that closely spaced electrodes can elicit independent ganglion cell responses, we utilized the multi-electrode array to stimulate several nearby ganglion cells simultaneously. From these data we conclude that electrical stimulation of mammalian retina with small-diameter electrode arrays is achievable and can provide high temporal and spatial precision at low charge densities. We review previous epiretinal stimulation studies and discuss our results in the context of 32 other publications, comparing threshold parameters and safety limits.
Owner:SECOND SIGHT MEDICAL PRODS +1
Self-assembly preparation method of colloid microsphere single-layer film
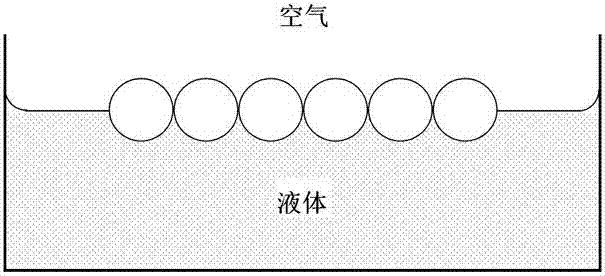
The invention discloses a self-assembly preparation method of a colloid microsphere single-layer film. In the self-assembly preparation method, after the colloid microsphere single-layer film with large area and high coverage rate is obtained by utilizing a spin-coating method, colloid microspheres are extruded into a compactly stacked hexagon array by adopting a liquid-vapor interface method and utilizing the surface tension of liquid. Equipment used in the self-assembly preparation method is simple and cheap and is simple to operate and controllable; and the colloid microsphere single-layer film array prepared by the method has high efficiency, high yield and good film formation quality.
Owner:UNIV OF ELECTRONICS SCI & TECH OF CHINA
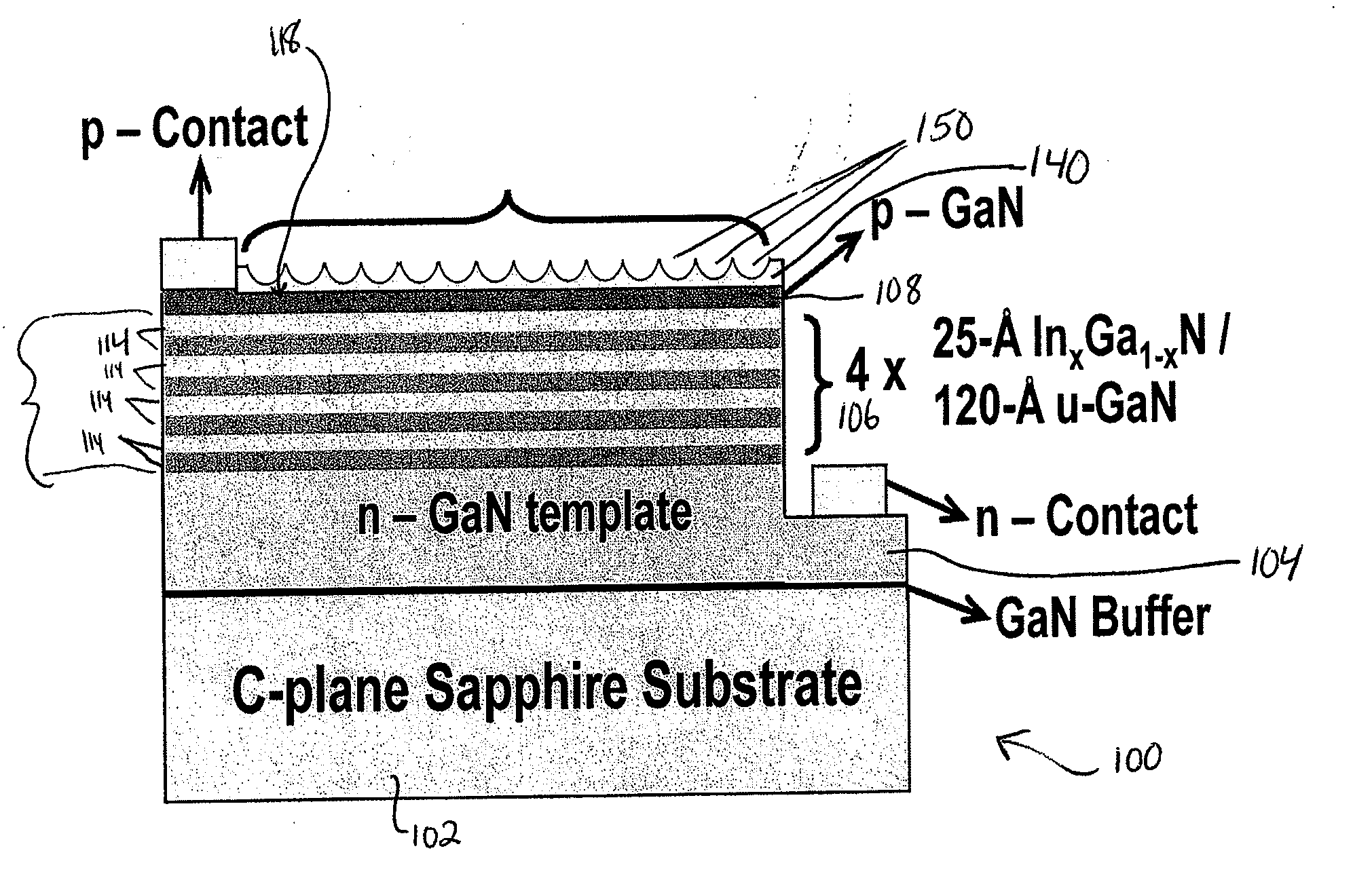
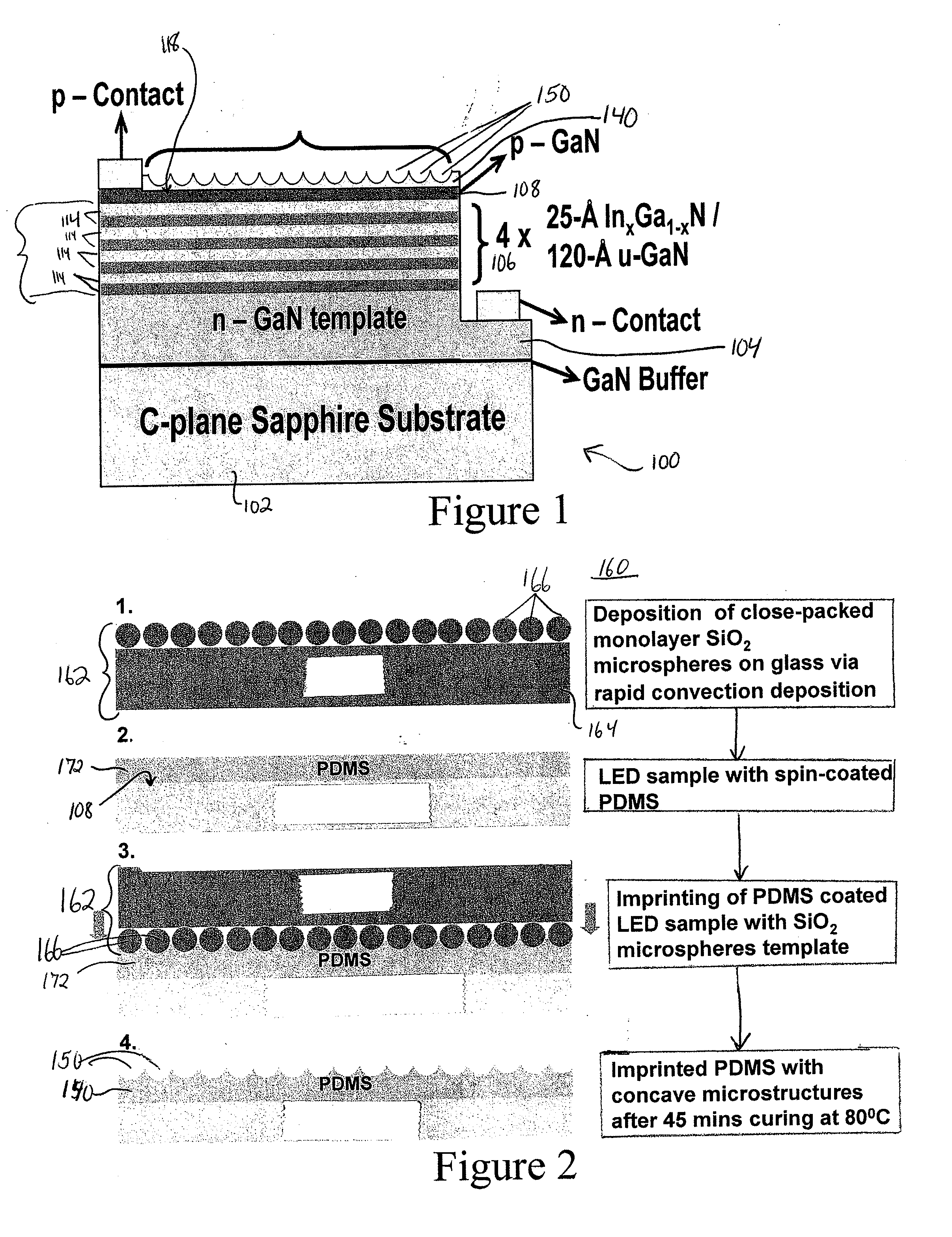
Semiconductor light-emitting devices having concave microstructures providing improved light extraction efficiency and method for producing same
ActiveUS20110155999A1Light extraction efficiency can be improvedIncrease light escape coneSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSemiconductor devicesMicrosphereQuantum well
A conventional semiconductor LED is modified to include a microlenslayer over its light-emitting surface. The LED may have an active layer including at least one quantum well layer of InGaN and GaN. The microlens layer includes a plurality of concave microstructures that cause light rays emanating from the LED to diffuse outwardly, leading to an increase in the light extraction efficiency of the LED. The concave microstructures may be arranged in a substantially uniform array, such as a close-packed hexagonal array. The microlens layer is preferably constructed of curable material, such as polydimethylsiloxane (PDMS), and is formed by soft-lithography imprinting by contacting fluid material of the microlens layer with a template bearing a monolayer of homogeneous microsphere crystals, to cause concave impressions, and then curing the material to fix the concave microstructures in the microlens layer and provide relatively uniform surface roughness.
Owner:LEHIGH UNIVERSITY
X-ray fluuorroscopy device
To make an oriented plastics material geogrid in which oriented strands form triangular meshes with a junction at each corner and six of the strands meet at each junction, a plastics material sheet starting material has holes in an array of hexagons, opposite holes of each hexagon being aligned in the machine direction, and the starting material is stretched first in the machine direction and secondly in the transverse direction. In the eventual geogrid, the centre portions of the hexagons in the starting material form the junctions. The centres of the junctions are slightly biaxially oriented, but at the edges of the junctions, the orientation of the edge of substantially each strand runs around the edge of the respective junction and into the edge of the next strand. During the second stretch, restraint can be applied in the first stretch direction and discontinued before the material is allowed to relax in the second stretch direction.
Owner:TENSAR TECH
Coating compositions having a geometrically ordered array of polymeric particles and substrates coated therewith
Coating materials comprising polymeric particles in a geometrically ordered array are disclosed. The particles can be formed from materials having different glass transition temperatures; this allows for phase segregation between areas of different glass transition temperatures within each particle. Typically, at least 50 percent of the particles will form a hexagonal array, capable of exhibiting Bragg diffraction. Because the particles within the array do not coalesce to any appreciable extent, significant surface area is provided by the present coating materials. Thus, the present materials have particularly good sound deadening properties. Substrates coated with the present materials are also disclosed, as are methods for inhibiting sound transmission through a substrate using these coatings.
Owner:PPG IND OHIO INC
Stereo grid shaped bone filler and manufacturing method thereof
The invention provides a bone filling material of three-dimensional grid structure and a preparation method thereof. The material is characterized in that the material comprises a three-dimensional structure body and alveolate cavities are distributed at all the surfaces of the three-dimensional structure body. The alveolate cavities are in regular grid arrangement and the regular grid is of square array, rectangular array, triangular array, rhombic array or hexagonal array constructed by cylindrical boundaries. The bone filling material is suitable for mixed repair of bone injury.
Owner:北京吉马飞科技发展有限公司
Double-face capacitor and manufacturing method thereof
The invention provides a double-face capacitor and a manufacturing method thereof. The double-face capacitor includes: a semiconductor substrate, wherein multiple pads in memory array structures are formed on the semiconductor substrate; and a double-face capacitor array, which is formed on the first pad, wherein each double-face capacitor includes a first double-U conductive layer, a second double-U conductive layer, a capacitor dielectric, and a third conductive layer. Through a multi-pattern method and a support frame structure strengthened by a boundary process, the hexagonal-array-arranged double-face capacitor with a double-U bottom electrode is manufactured. The capacitor has a great height and a great width ratio, and is effectively improved in capacitance value per unit area.
Owner:CHANGXIN MEMORY TECH INC
Coating compositions having a geometrically ordered array of polymeric particles and substrates coated therewith
Coating materials comprising polymeric particles in a geometrically ordered array are disclosed. The particles can be formed from materials having different glass transition temperatures; this allows for phase segregation between areas of different glass transition temperatures within each particle. Typically, at least 50 percent of the particles will form a hexagonal array, capable of exhibiting Bragg diffraction. Because the particles within the array do not coalesce to any appreciable extent, significant surface area is provided by the present coating materials. Thus, the present materials have particularly good sound deadening properties. Substrates coated with the present materials are also disclosed, as are methods for inhibiting sound transmission through a substrate using these coatings.
Owner:PPG IND OHIO INC
Novel optical fiber sensor for detecting surface defects of steel balls and detection method
InactiveCN104390987AEliminate the effect of reflectivityEasy and accurate installation and positioningOptically investigating flaws/contaminationSteel ballLaser light
The invention discloses a novel optical fiber sensor for detecting surface defects of steel balls and a detection method. The sensor mainly comprises a laser light source, a sensor probe comprising an optical fiber bundle, an optical fiber fixing filler and a casing, and a photoelectric converter, wherein the laser light source emits infrared light with 820 nanometer wavelength; the optical fiber bundle comprises 19 optical fibers which comprise 1 emitting optical fiber and 18 receiving optical fibers; the emitting optical fiber and the receiving optical fibers are closely arranged to form a two-dimensional equilateral hexagon array; the axis of the array adopts the emitting optical; the cross orthometric receiving optical fibers are sequentially outward from the axis; the cross orthometric receiving optical fibers comprise 6 optical fibers, and are divided into four ways to perform photovoltaic conversion, and are arranged in a cross orthometric way; two ways of ratio processing receiving receiving optical fiber bundles perform photovoltaic conversion singly. The sensor has the benefits that the optical fiber sensing technology is applied to the detection of surface defects of steel balls, multi-parameter automatic nondestructive detection and real-time processing can be performed, the structure is simple, the volume is small, and the measurement accuracy is high.
Owner:UNIV OF JINAN
Interconnect pattern for high performance interfaces
ActiveUS20110192640A1Improve performanceElectrically conductive connectionsSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsGround contactDifferential signaling
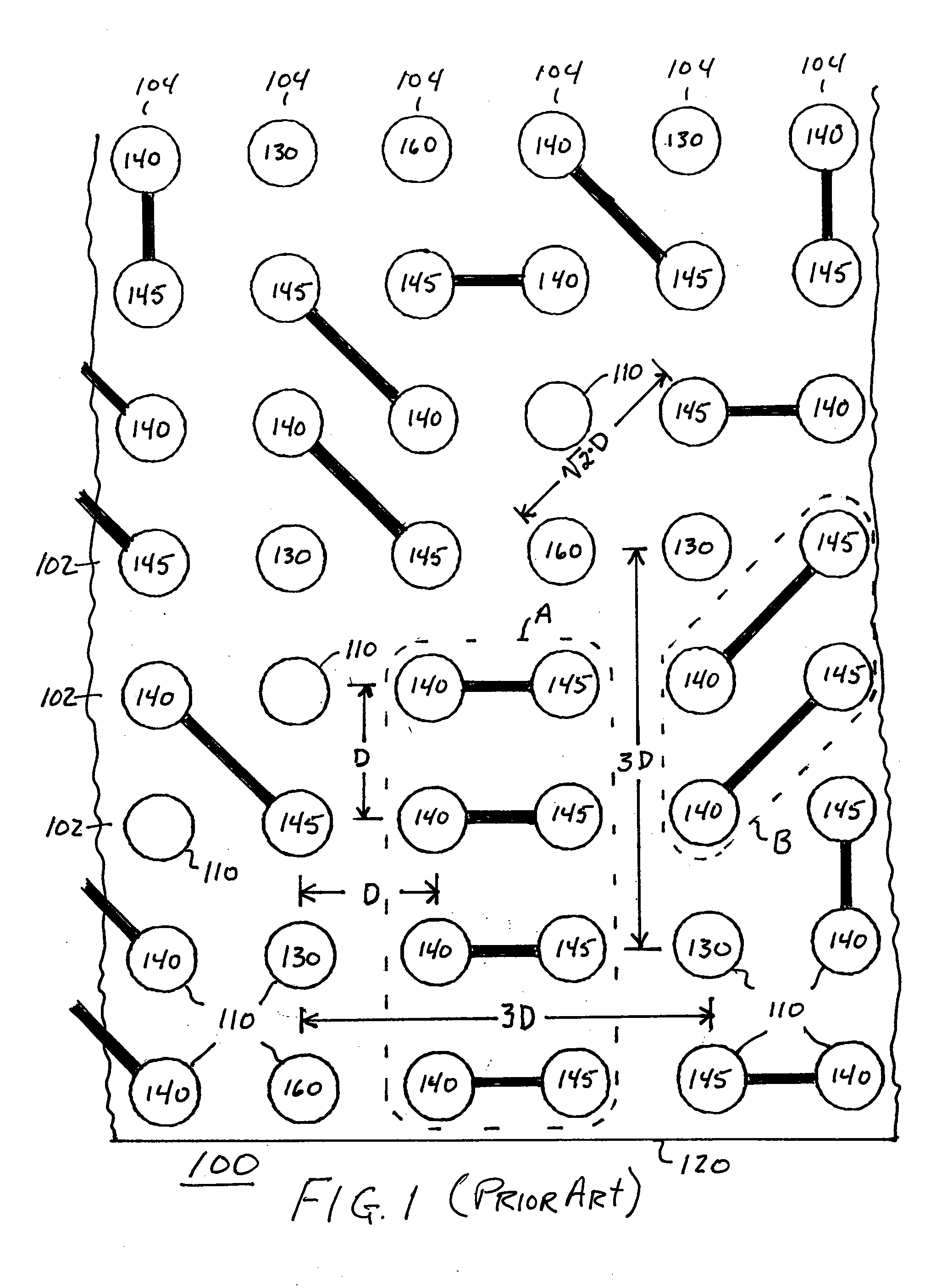
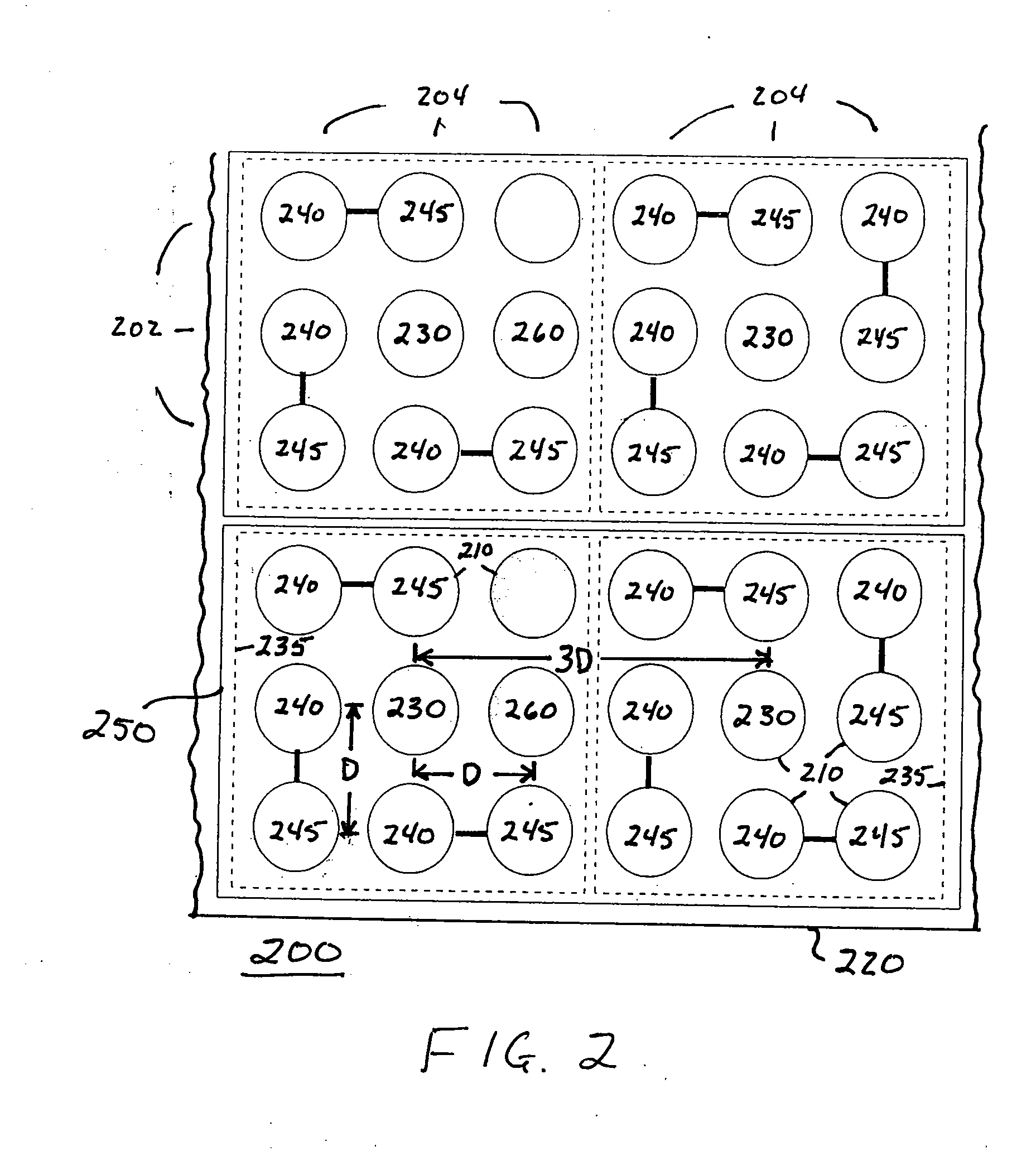
In one embodiment, differential signaling and ground contacts are located in a rectilinear array of rows and columns with ground contacts spaced apart by three times the pitch distance between adjacent rows or columns and signaling contacts are located immediately adjacent the ground contacts. In particular, the two contacts of each differential pair are located one pitch distance apart from each other and one contact of each differential pair of contacts is located one pitch distance from a ground contact and the other contact of the differential pair is located approximately sqrt(2)*pitch distance from the same ground contact. In a second embodiment, differential signaling and ground contacts are located in a hexagonal array with ground contacts located three times the pitch distance between adjacent contacts and signaling contacts located immediately adjacent the ground contacts. In particular, the two contacts of each differential pair are located one pitch distance apart from each other and both contacts of each differential pair of contacts are located one pitch distance from a ground contact.
Owner:ALTERA CORP
Semiconductor memory and manufacturing method thereof
InactiveCN107301976AHighWideTransistorSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingCapacitanceDielectric
The invention provides a semiconductor memory and a manufacturing method thereof. The semiconductor memory comprises a semiconductor substrate, a double-sided capacitor array, a support cylinder. The semiconductor substrate is provided with a plurality of first pads in a memory array structure and a plurality of second pads located outside the memory array structure and on the periphery of the first pads. The double-sided capacitor array is formed on the first pads, and each double-sided capacitor comprises a first conductive layer and a second conductive layer forming a double-U-shaped structure, a capacitor dielectric and a third conductive layer. The support cylinder is formed on the second pads, and comprises dummy holes with no electrical function. In the invention, the double-sided capacitor with a double-U-shaped lower electrode arranged in a hexagonal array is manufactured by using a multi-patterning method and a support structure reinforced by a boundary process, and has a large height-to-width ratio and can effectively increase the capacitance per unit area.
Owner:CHANGXIN MEMORY TECH INC
Production of organic luminescent diode element
InactiveCN1819303AImprove light extraction efficiencyQuality improvementElectroluminescent light sourcesSolid-state devicesDirect heatingUltraviolet irradiation
On the glass substrate a large area corpuscle hexagonal array made of monolayer polymers material is formed by using spin coating method and adjusting the ratio of powder size to nonionic surfactant and methanol. The ultraviolet irradiation or direct heating are used to prepare the micro convex lens array layer made of polymers materials. The micro convex lens can be directly used to prepare OLED component.
Owner:EAST CHINA NORMAL UNIV
Preparation method for micro-texturing three-layer composite lubricant thin film
ActiveCN106179906AImprove surface activityImprove joint strengthPretreated surfacesSpecial surfacesSilanesPolymer thin films
The invention discloses a preparation method for a micro-texturing three-layer composite lubricant thin film. The surface of monocrystalline silicon is etched to obtain a microcosmic rough structure with regular equilateral-hexagon array morphology, and then through molecular self-assembly, polymer and ionic liquid technologies, a (3-aminopropyl) trimethoxy silane (APS) substrate fixation thin film layer, a polydopamine (PDA) intermediate junction thin film layer, and a carboxyl imidazolium ionic liquid (IL-COOH) fixation / flow two-phase lubricant thin film are sequentially obtained on the surface of a micro-texturing silicon slice, and the micro-texturing three-layer composite lubricant thin film is formed. According to the micro-texturing three-layer composite lubricant thin film prepared through the preparation method, surface texture, a self-assembled molecular film, a polymer thin film and an ionic liquid thin film are integrated reasonably, and the tribology performance of the surface of the monocrystalline silicon is effectively improved. The preparation method has good application prospects in the micro electro mechanical system surface protection field.
Owner:XIANGTAN UNIV
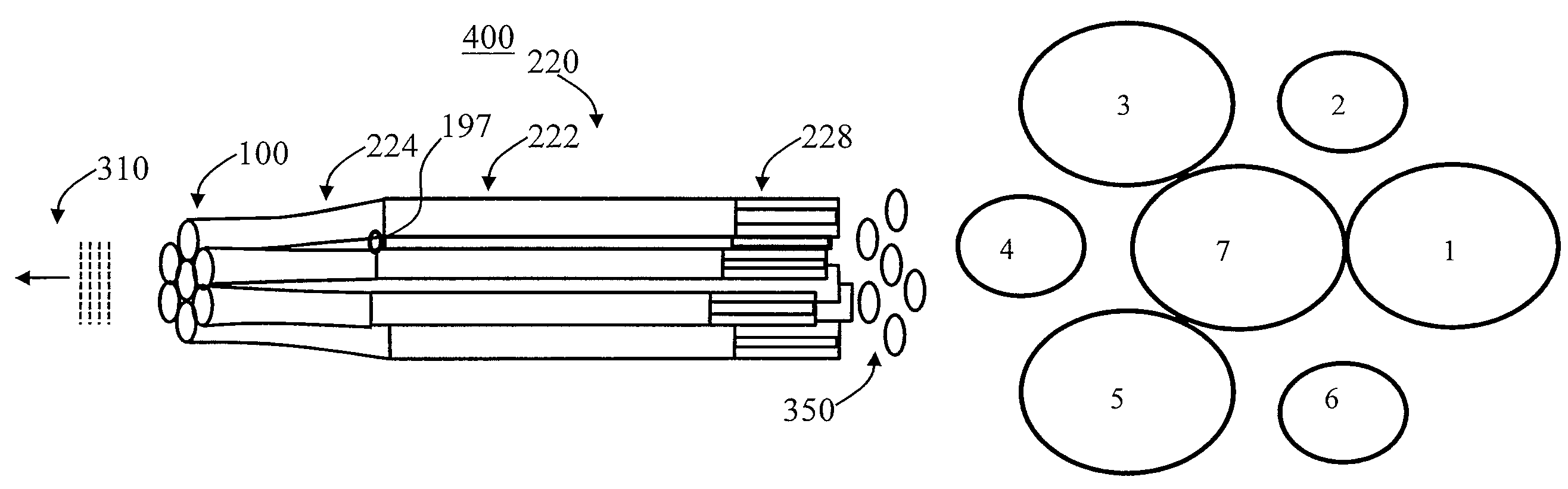
All-fiber laser coupler with high stability
InactiveUS7738751B1Laser using scattering effectsCoupling light guidesAudio power amplifierOptical coupler
An optical coupler is provided for a passive coherent combination of fiber lasers / amplifiers. A plurality of optical fibers are arranged in a close-packed hexagonal array having 1+3n(n+1) fibers with (3 / 2)(n2−n)+3 interferometrically dark fibers and (3 / 2)(n2+3n)−2 light fibers, where n is an integer greater than or equal to 1. Each optical fiber has a first end and a second end. The plurality of optical fibers are fused together along a section of each optical fiber proximate the first end of each optical fiber to form a fused section having a fiber axis. The fused section of the plurality of optical fibers is tapered to form a tapered region. A facet is at an end of the fused section. The facet is disposed in a direction perpendicular to the fiber axis. The coherent pattern is highly stable against perturbation.
Owner:HRL LAB
Organic electroluminescent device
InactiveUS20110279027A1Preventing electrical shortsDistribution moreDischarge tube luminescnet screensElectroluminescent light sourcesOrganic electroluminescenceElectrode pair
The present invention relates to an organic electroluminescent device comprising a substrate (40) and on top of the substrate (40) a substrate electrode (20), a counter electrode (30) and an electroluminescent layer stack (50) with at least one organic electroluminescent layer arranged between the substrate electrode (20) and the counter electrode (30), an encapsulation means (90) encapsulating at least the electroluminescent layer stack (50) and at least one non-conductive spacer means (70) arranged on the substrate electrode (20) to mechanically support the encapsulation means (90) and to prevent an electrical short between the substrate electrode (20) and the counter electrode (30) during the mechanical support, wherein the spacer means (70) comprise at least one light scattering means (80) for redirecting at least a part of light (65) trapped in the substrate (40), to a method of manufacturing such an encapsulated electroluminescent device and to the use of an array, preferably a hexagonal array, of non-conductive spacer means.
Owner:KONINKLIJKE PHILIPS ELECTRONICS NV
Reconfigurable hunting blind
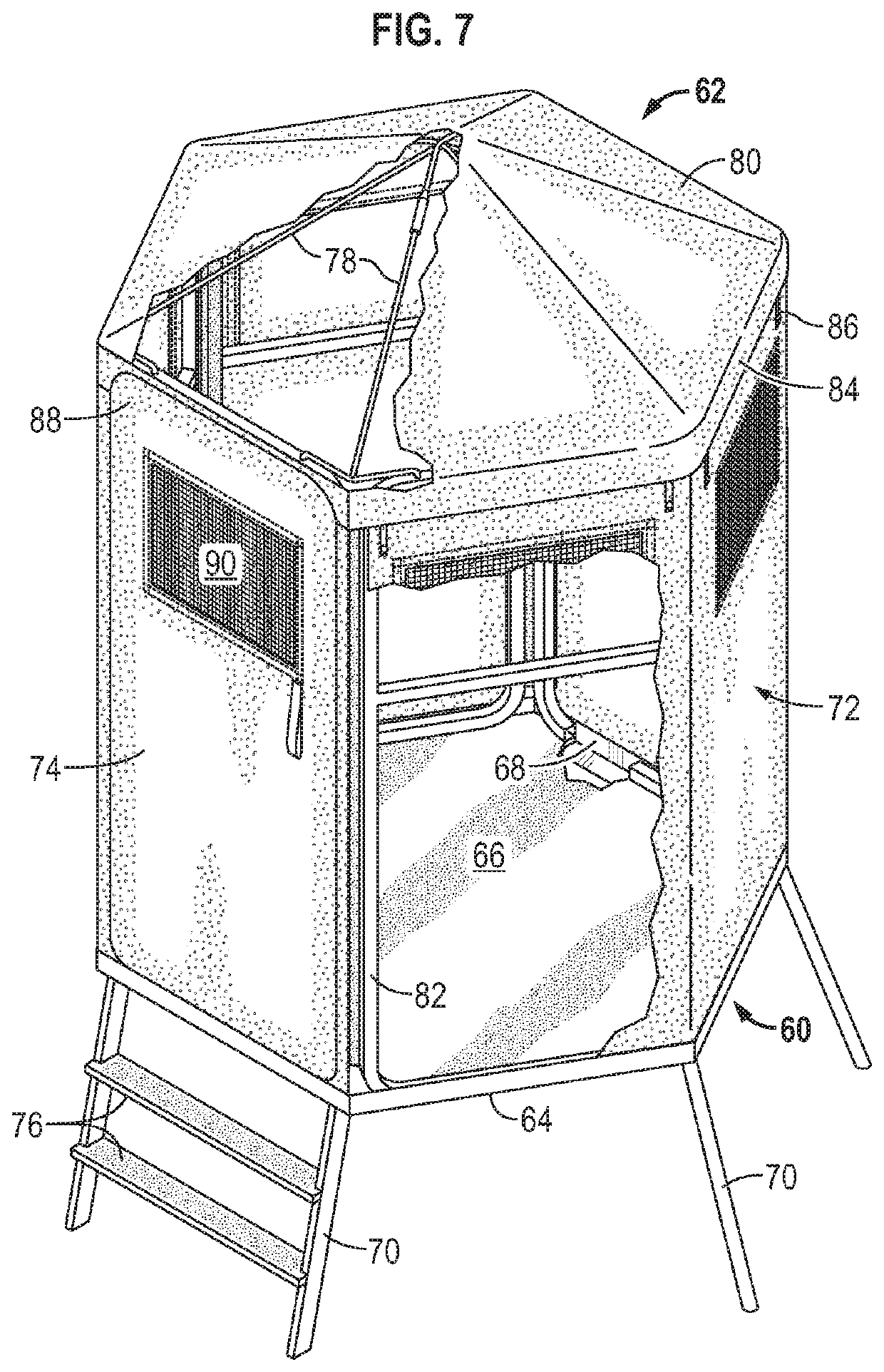
ActiveUS10584511B1Expand coverageImproved connection systemAnimal huntingTents/canopiesWindow shutterWindow opening
A duck blind is formed from first and a second panel assemblies. The first panel assembly has a first height and the second panel assembly has a second height that is less than the first height. Hunters can sit with their backs to the first panel assembly and stand to shoot over the second panel assembly. Improvements for blind windows in the panel coverings are disclosed. A flexible clear window cover covers the window opening from the inside. When a hunter wants to open the window, a releasable fastener system along the upper edge of the window cover can be disconnected and the clear window cover will swing down out of the way. An elevated blind formed from panels is disclosed. A hexagonal array of panels is positioned on a hexagonal platform to improve visibility from the blind in all directions.
Owner:GOOD SPORTSMAN MARKETING LLC
CMOS image sensor, image processing method and storage medium
PendingCN110379824AIncrease pixel densityImprove the layout densityTelevision system detailsSolid-state devicesImaging processingCmos pixels
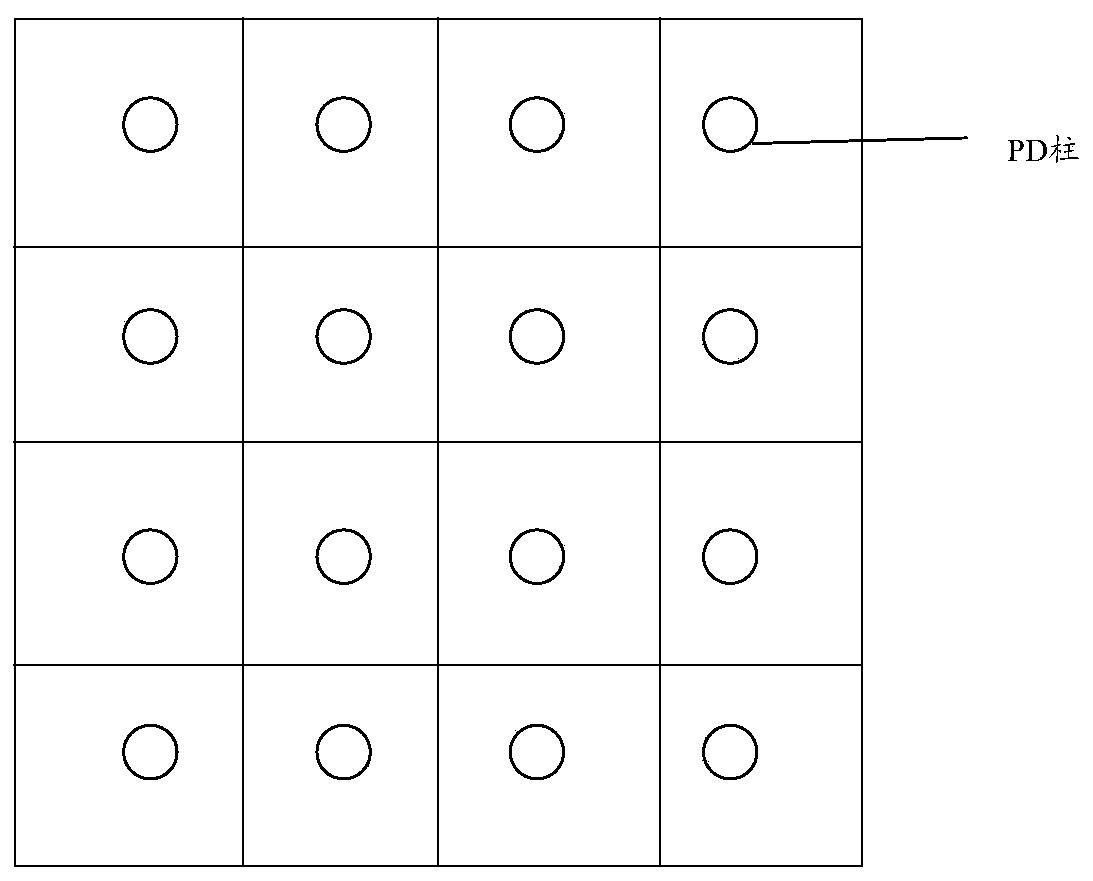
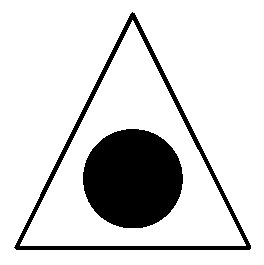
The embodiment of the application provides a CMOS image sensor, an image processing method and a storage medium. The CMOS image sensor comprises triangular pixel units arranged in a hexagonal array and a CMOS pixel readout circuit connected with the triangular pixel units, wherein each triangular pixel unit is internally provided with a photodiode PD column and uses the photodiode PD column to absorb RGB monochromatic light and convert a corresponding optical signal into an electric signal, and the CMOS pixel readout circuit is used for amplifying and reading out the electric signals.
Owner:GUANGDONG OPPO MOBILE TELECOMM CORP LTD
Achromatic optical metasurface focusing element
InactiveCN111679351AEliminate chromatic aberrationVersatile and strongOptical elementsNanopillarLight beam
The invention provides an achromatic optical metasurface focusing element. The achromatic optical metasurface focusing element comprises a substrate and a plurality of cuboid nanorods generated on thesubstrate, wherein the nanorods are divided into a first size, a second size and a third size and correspond to a first wavelength lambda 1, a second wavelength lambda 2 and a third wavelength lambda3; the nanorods of the first size, the second size and the third size are alternately arranged in a regular hexagon array at intervals; the length and the width of the nanorods are coupled with the wavelength of an incident light beam, and rotation angles of the nanorods are coupled with the wavelength, the focal length, an additional phase modulation value and a position of the incident light beam, so that the focal lengths of the element to parallel incident light with three wavelengths are the same. According to the achromatic optical metasurface focusing element, the achromatic adaptationof incident beams with various wavelengths can be realized by adjusting the length, width and rotation angle of the nanorod, and the universality of the design scheme is greatly higher than that of the existing scheme.
Owner:FUZHOU UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com