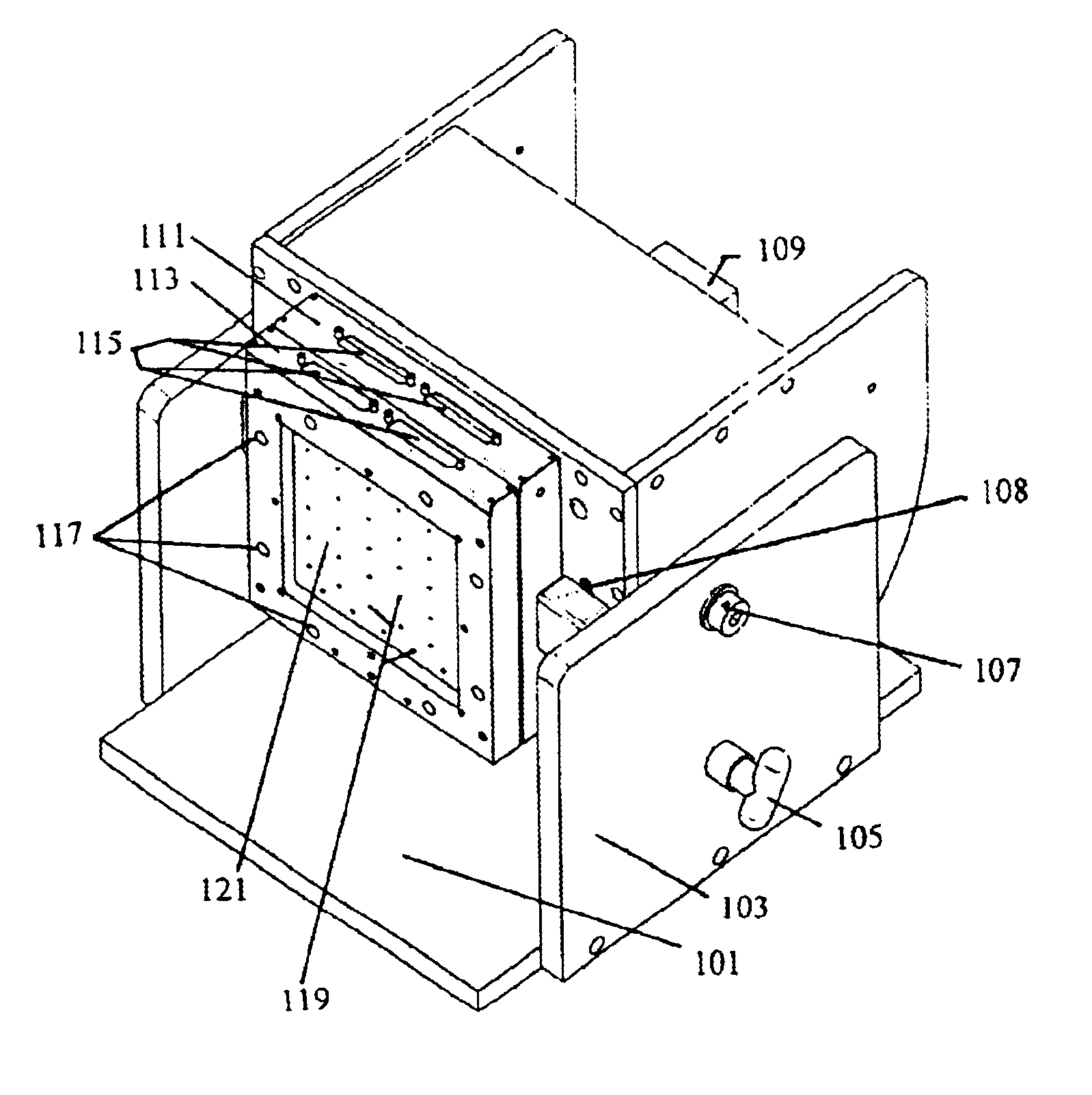
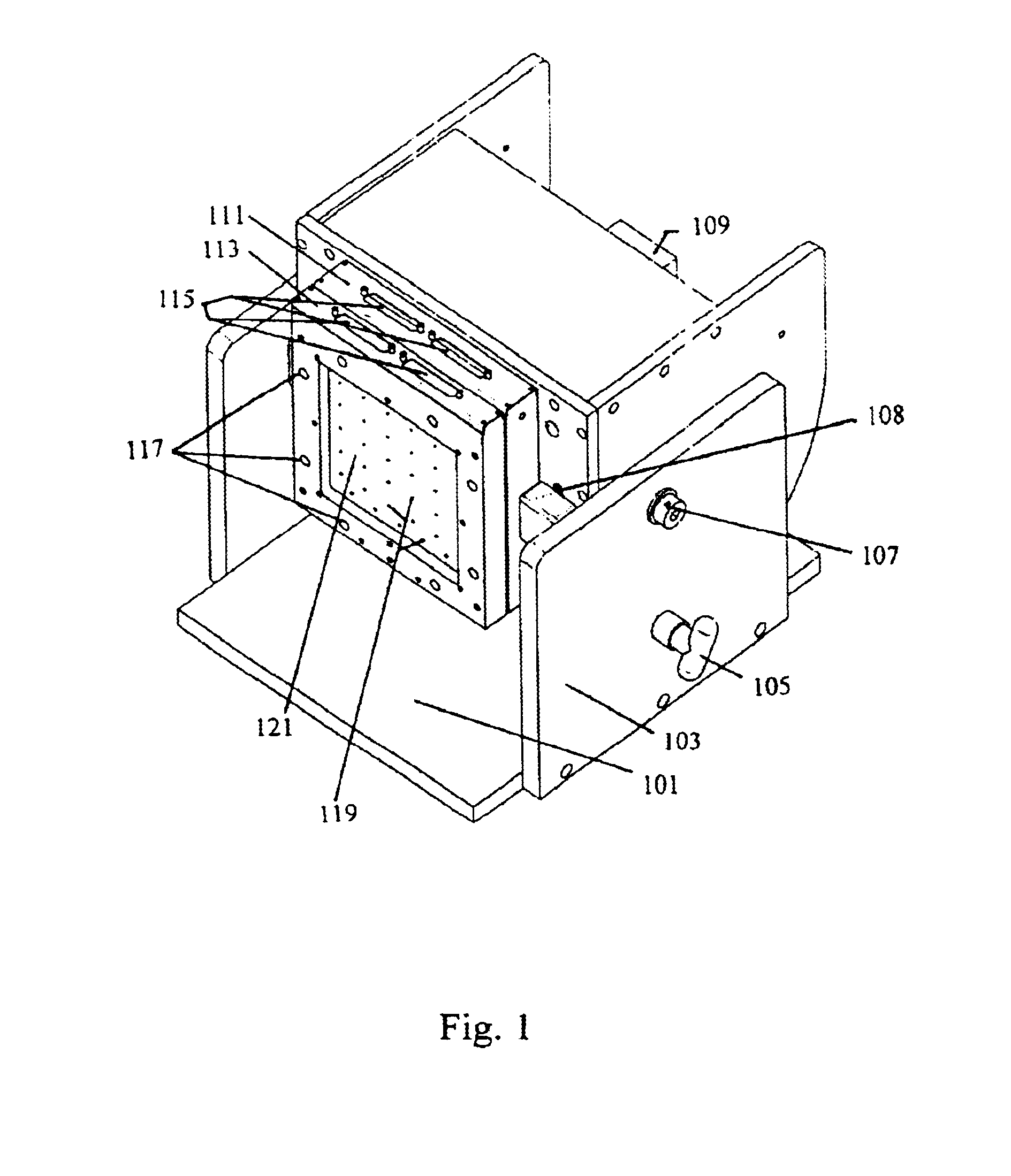
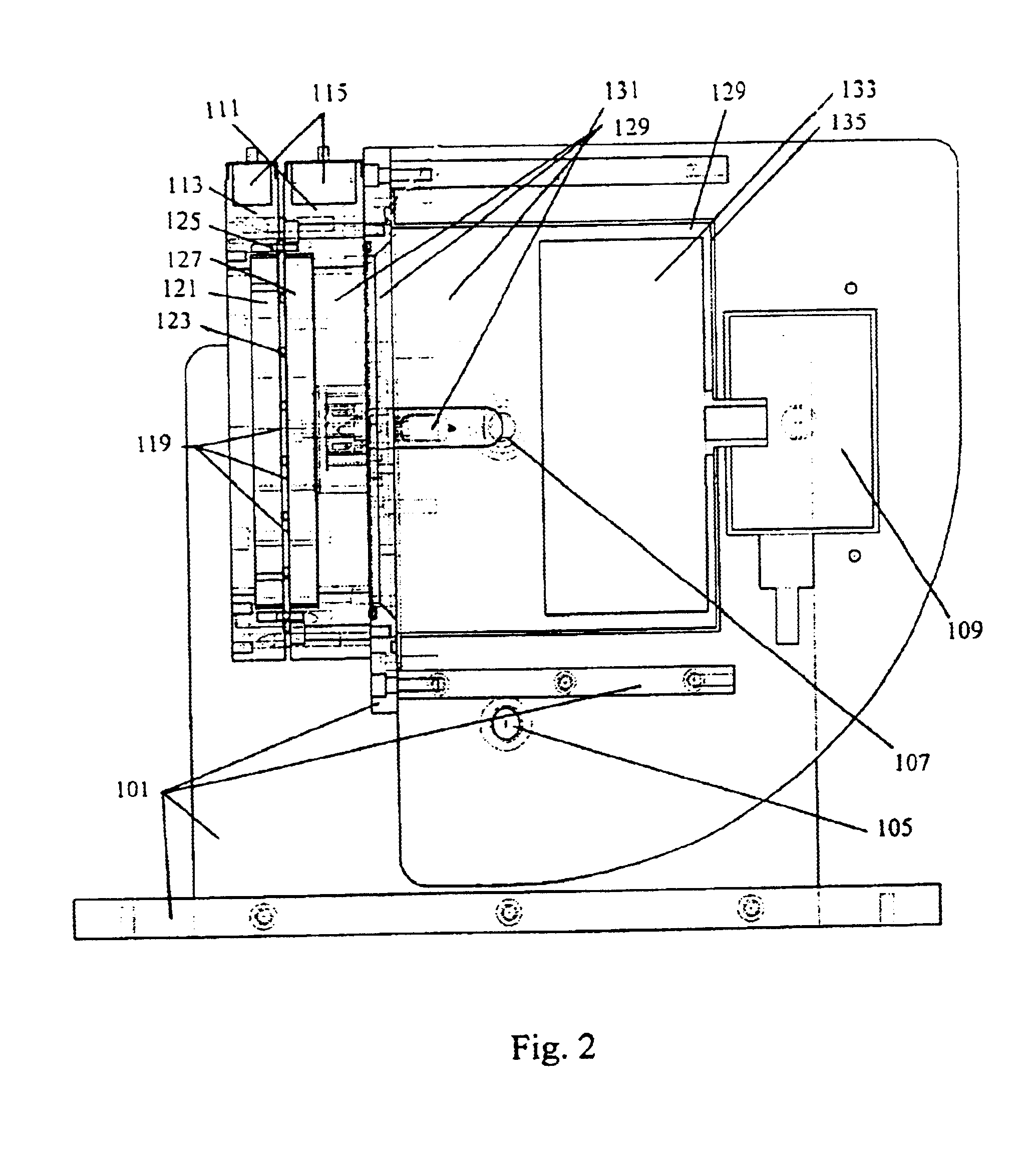
Patents
Literature
4495 results about "Nanorod" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
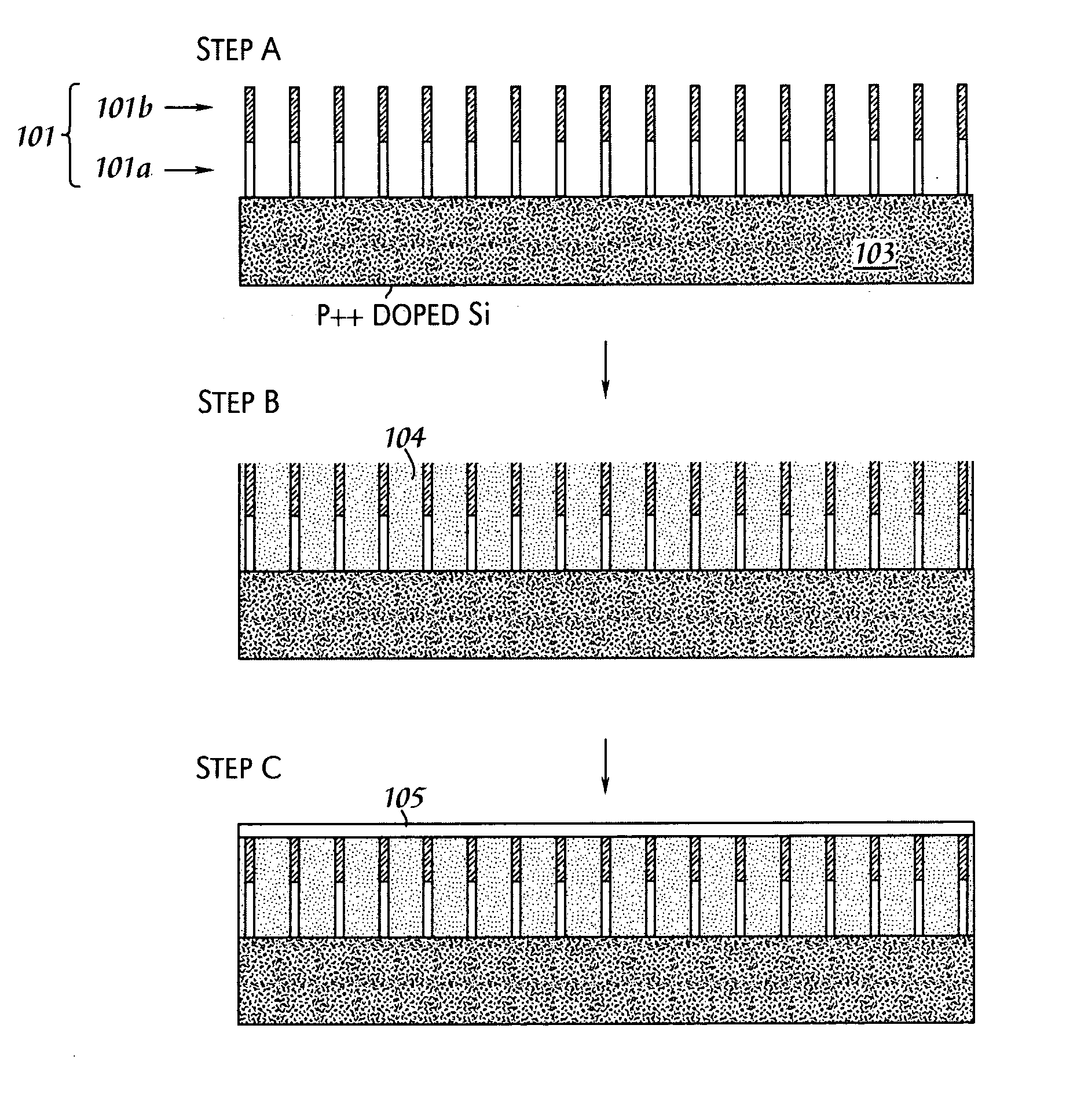
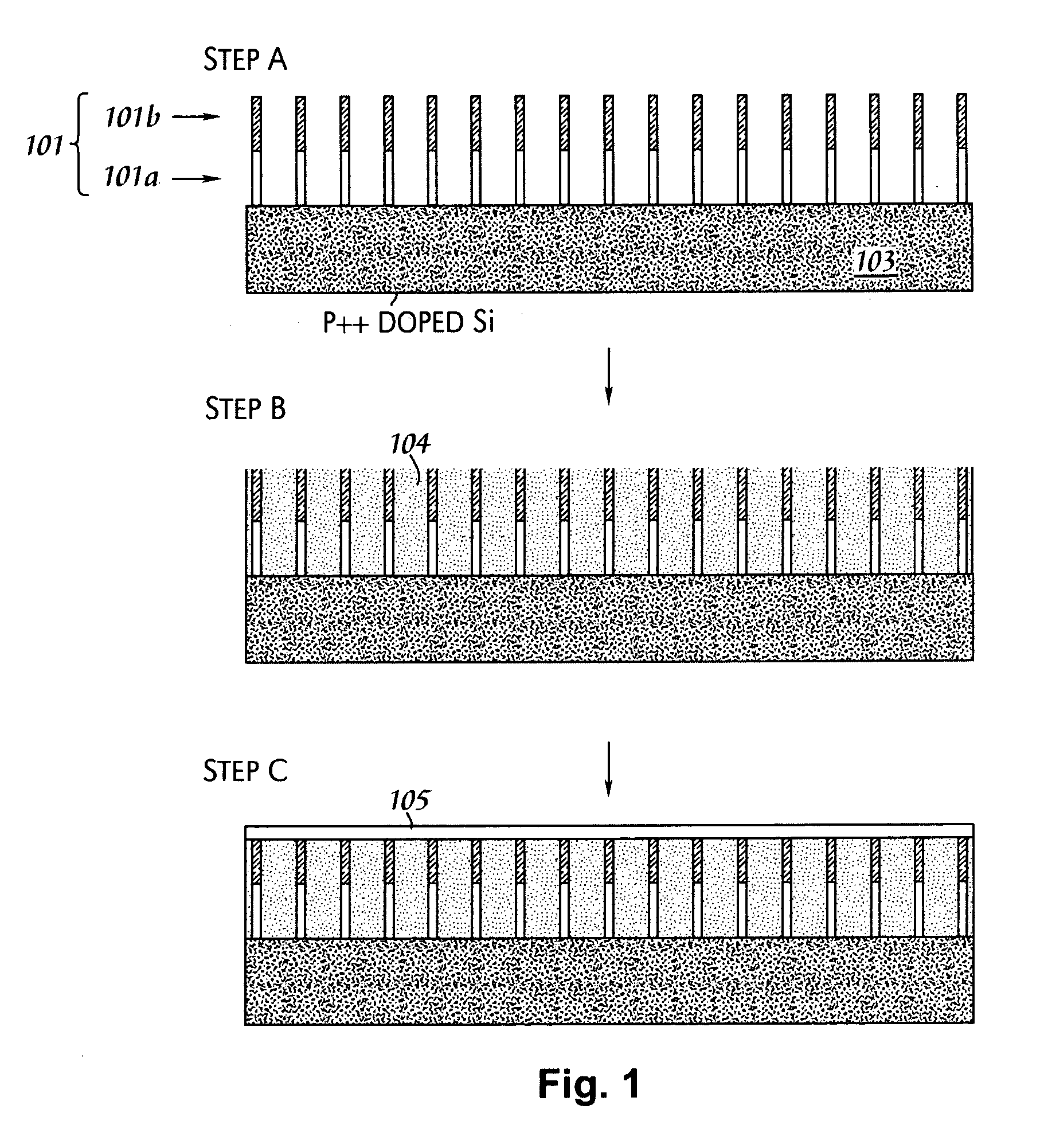
In nanotechnology, nanorods are one morphology of nanoscale objects. Each of their dimensions range from 1–100 nm. They may be synthesized from metals or semiconducting materials. Standard aspect ratios (length divided by width) are 3-5. Nanorods are produced by direct chemical synthesis. A combination of ligands act as shape control agents and bond to different facets of the nanorod with different strengths. This allows different faces of the nanorod to grow at different rates, producing an elongated object.
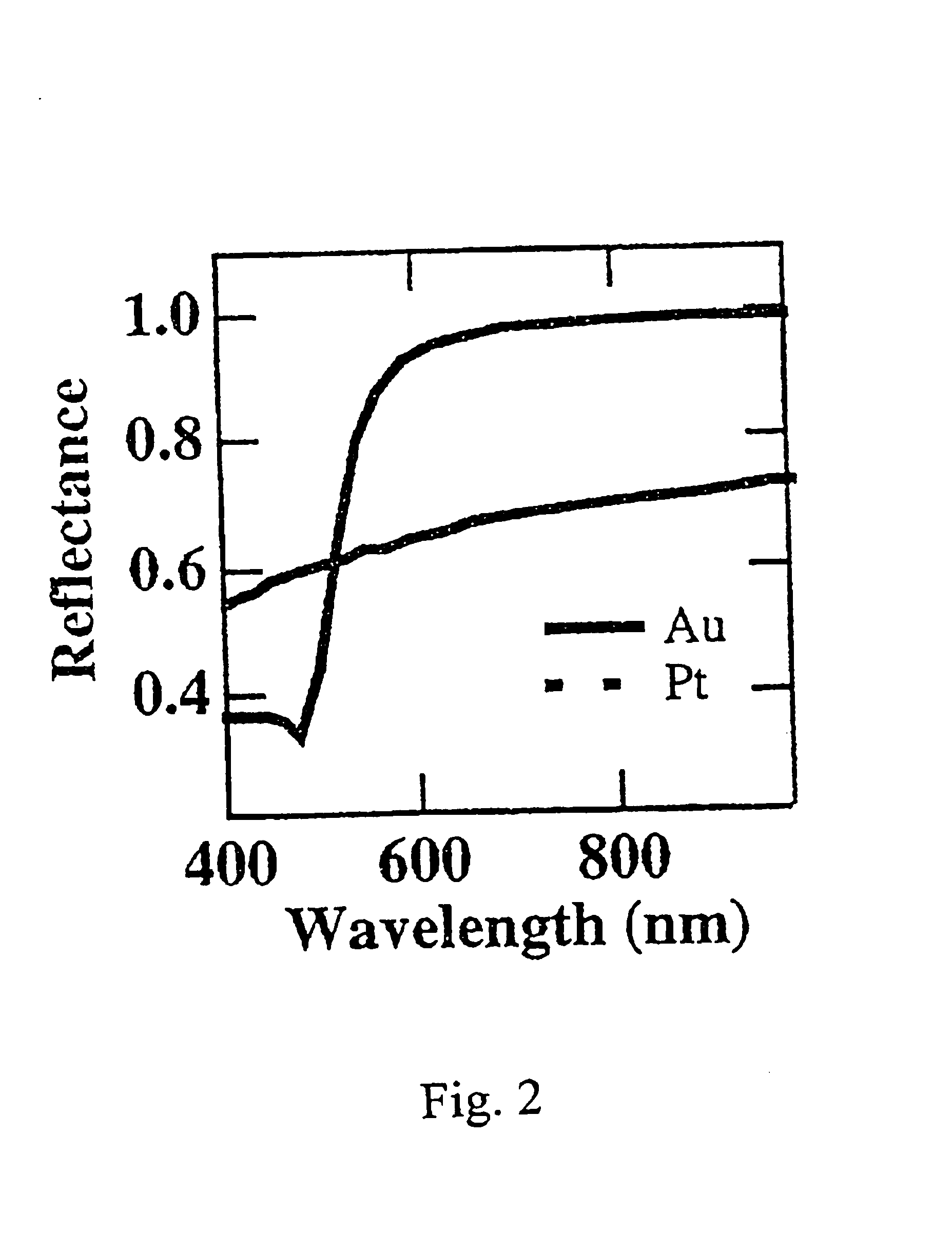
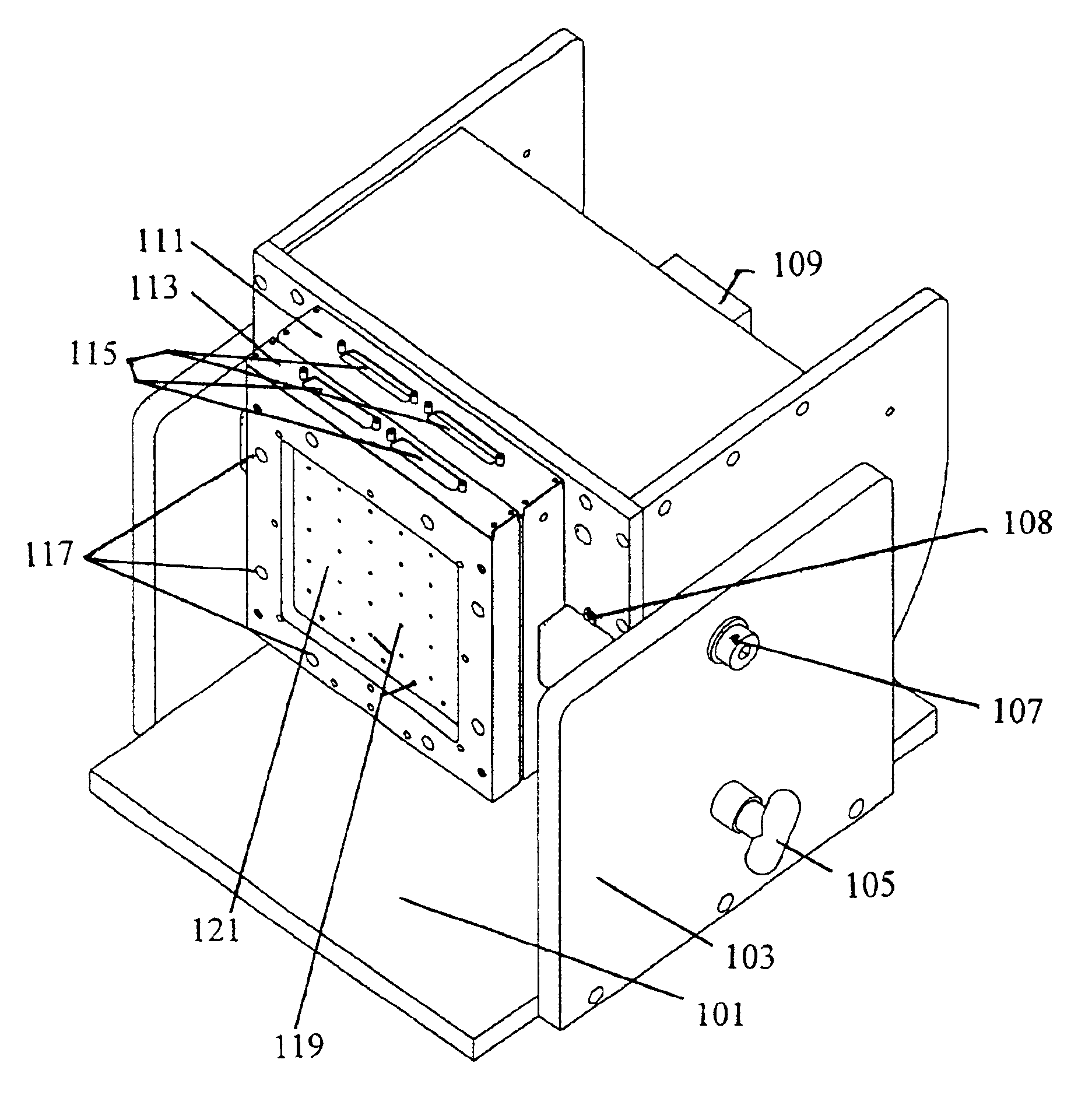
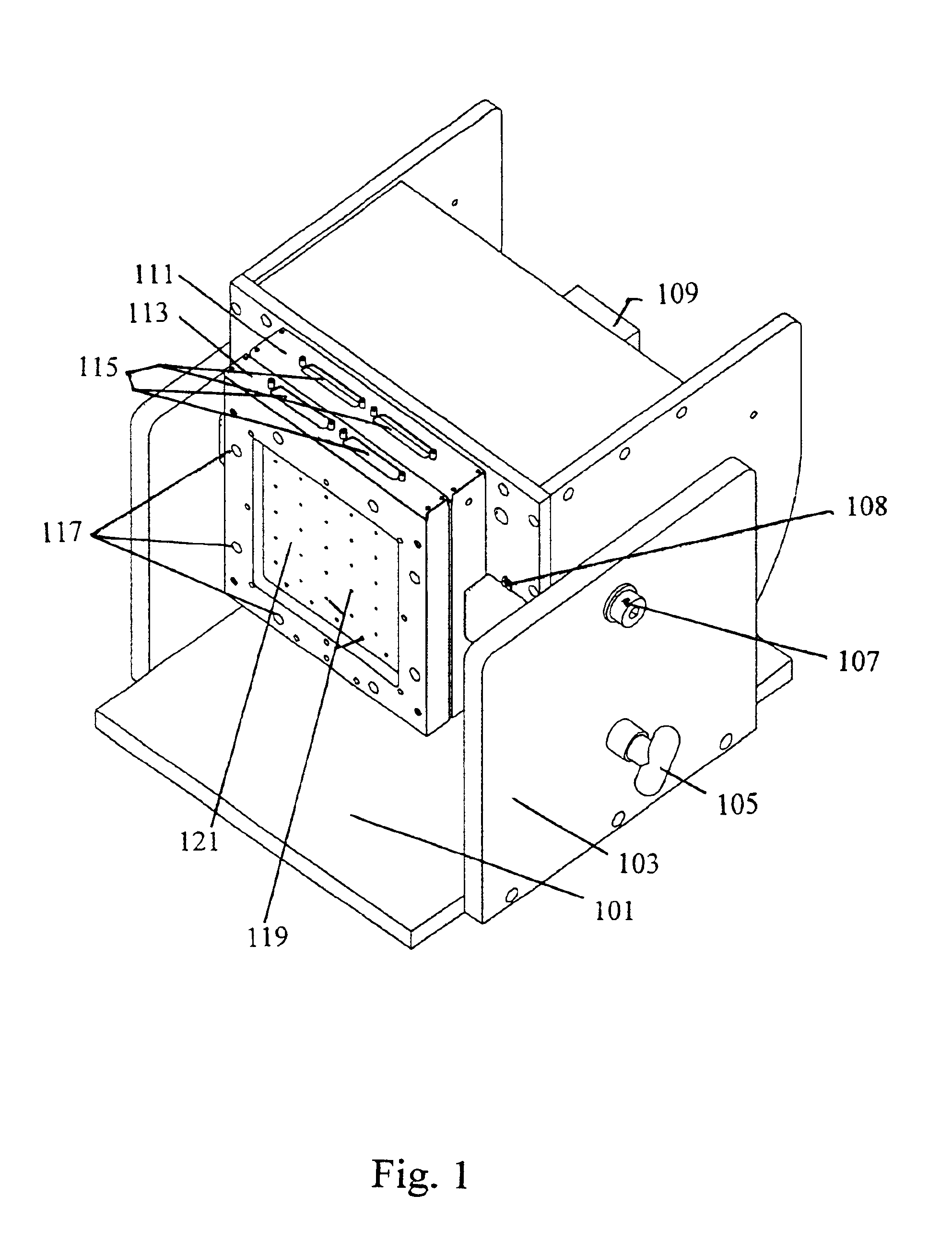
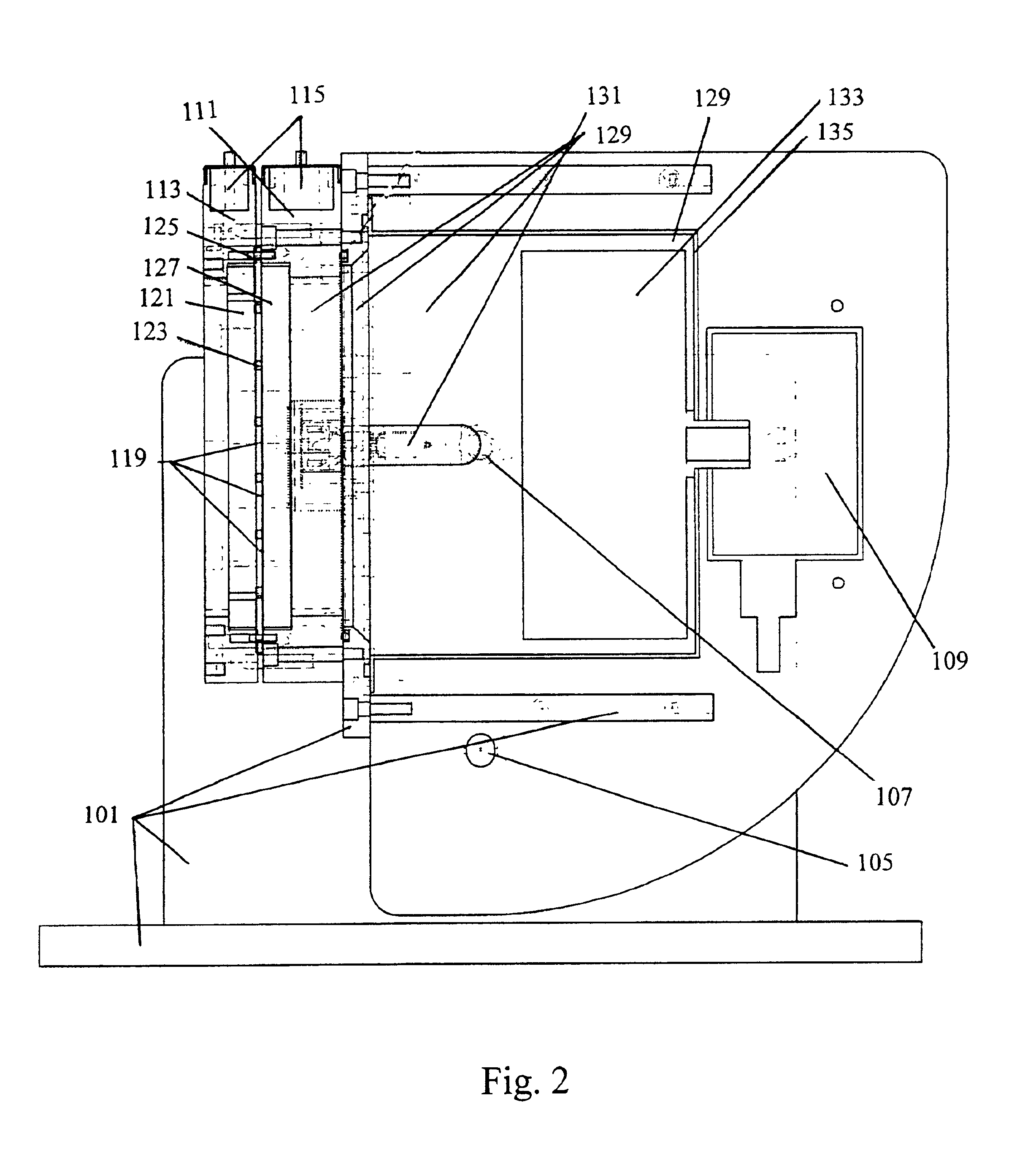
High efficiency inorganic nanorod-enhanced photovoltaic devices
InactiveUS20060207647A1Reduce weight and sizeImprove reliabilityNanoopticsSemiconductor devicesSolar cellNanostructured materials
The present invention is directed to photovoltaic devices comprising nanostructured materials, wherein such photovoltaic devices are comprised exclusively of inorganic components. Depending on the embodiment, such nanostructured materials are either 1-dimensional nanostructures or branched nanostructures, wherein such nanostructures are used to enhance the efficiency of the photovoltaic device, particularly for solar cell applications. Additionally, the present invention is also directed at methods of making and using such devices.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Chemical manufacture of nanostructured materials
InactiveUS6872330B2High strengthIncrease volumeMaterial nanotechnologyOxide/hydroxide preparationInorganic compoundTe element
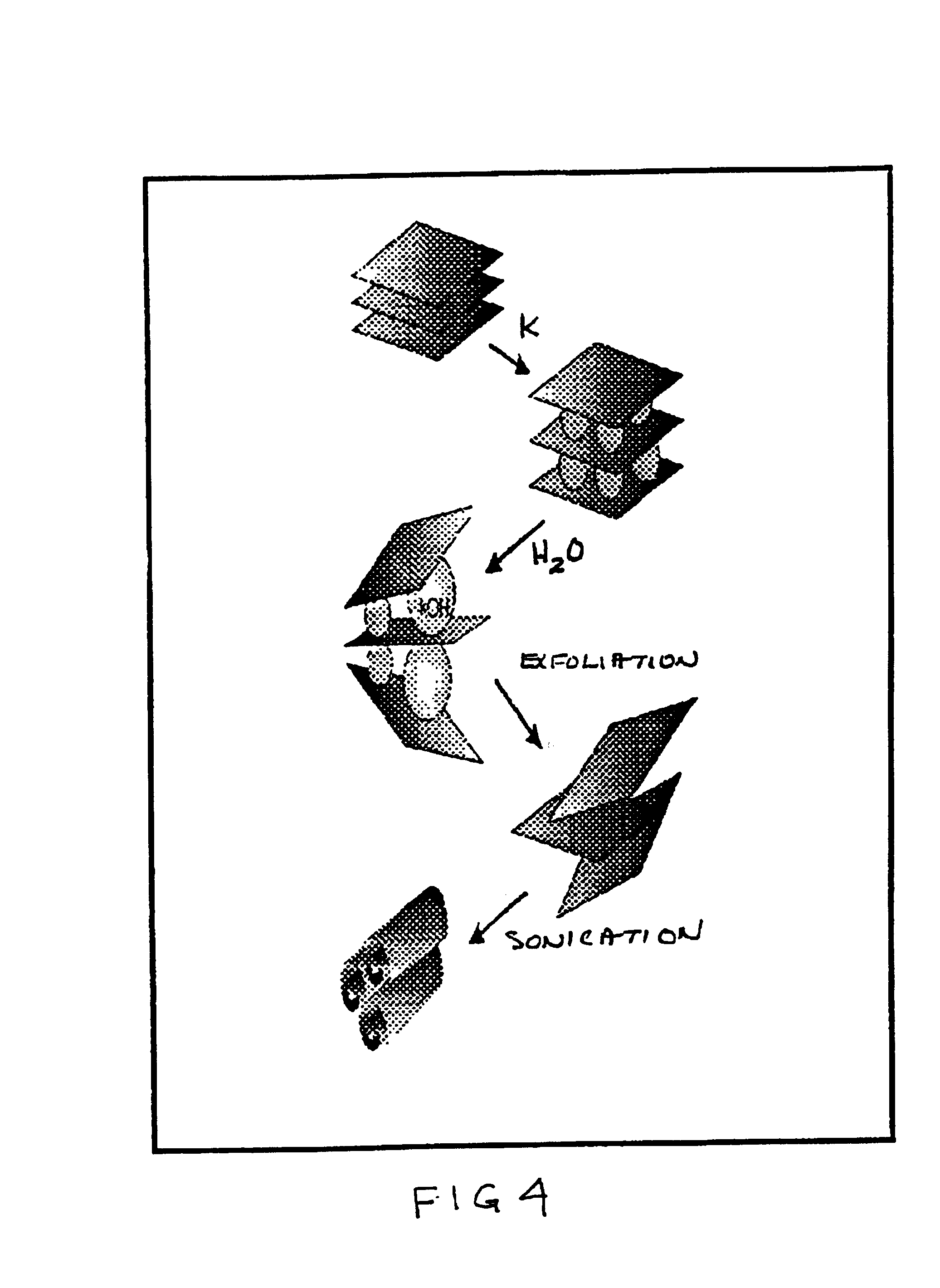
A low temperature chemical route to efficiently produce nanomaterials is described. The nanomaterials are synthesized by intercalating ions into layered compounds, exfoliating to create individual layers and then sonicating to produce nanotubes, nanorods, nanoscrolls and / or nanosheets. It is applicable to various different layered inorganic compounds (for example, bismuth selenides / tellurides, graphite, and other metal complexes, particularly transition metal dichalcogenides compounds including oxygen, sulfur, tellurium or selenium).
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Semiconductor nano-rod devices
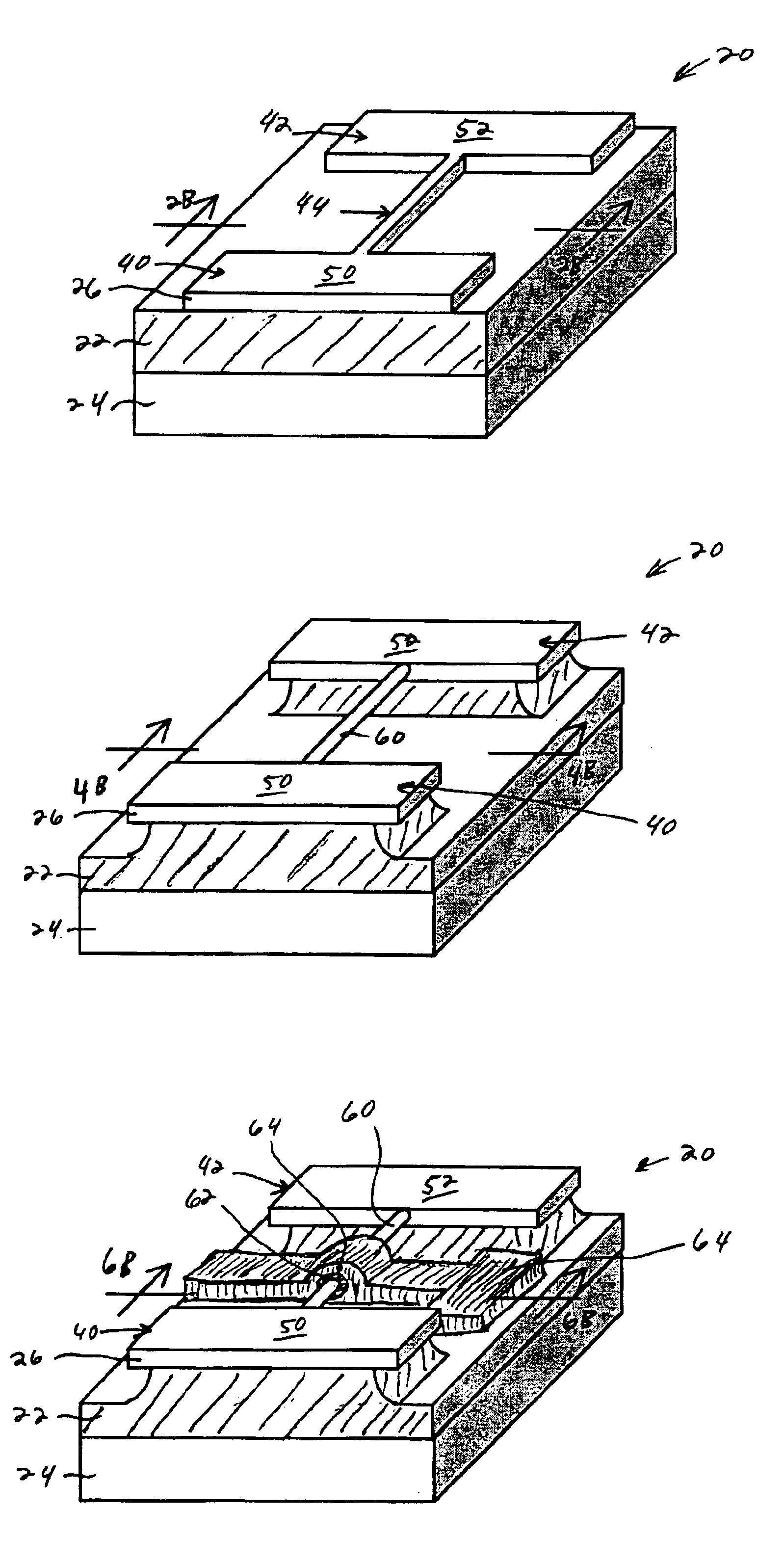
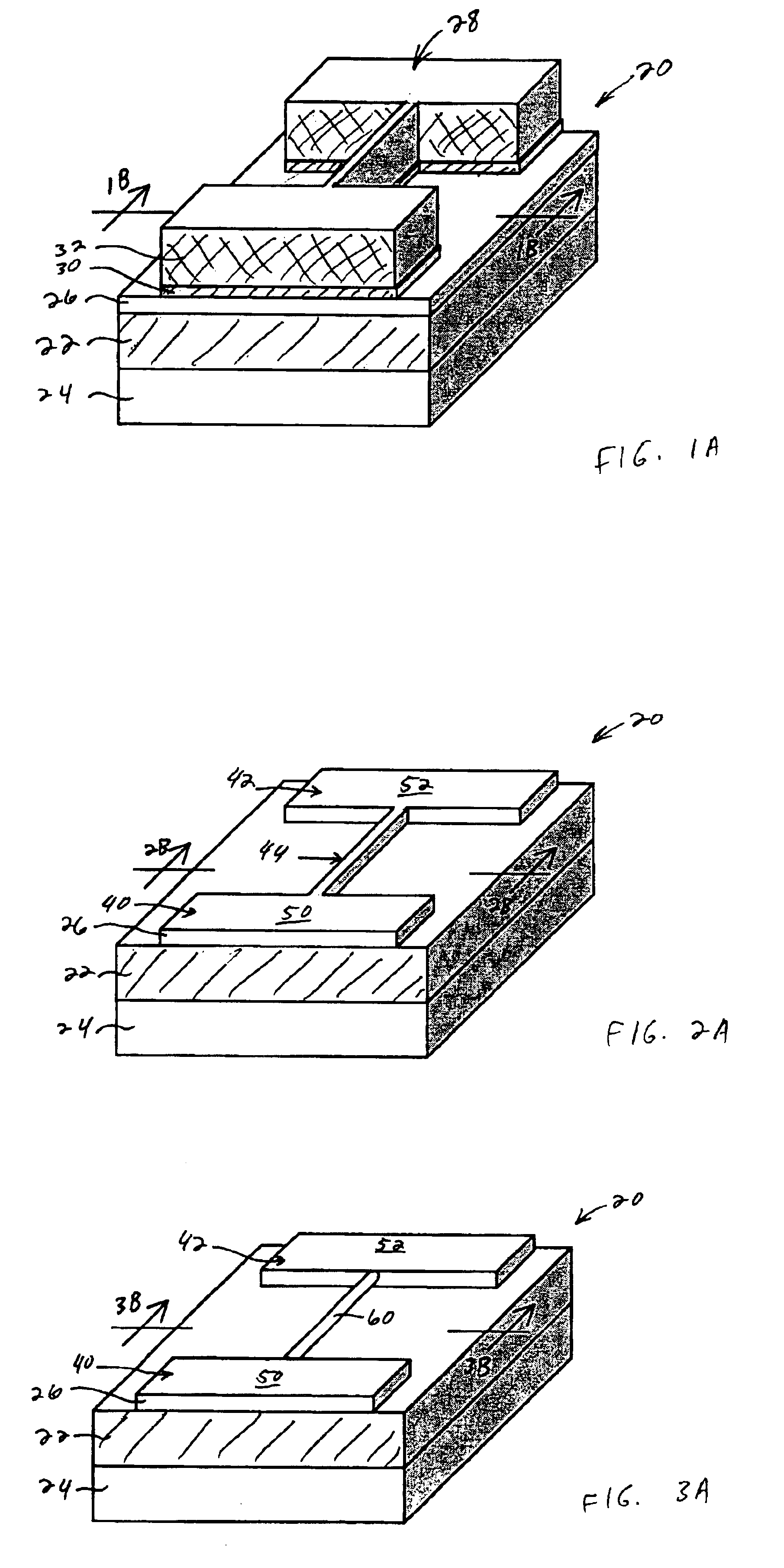
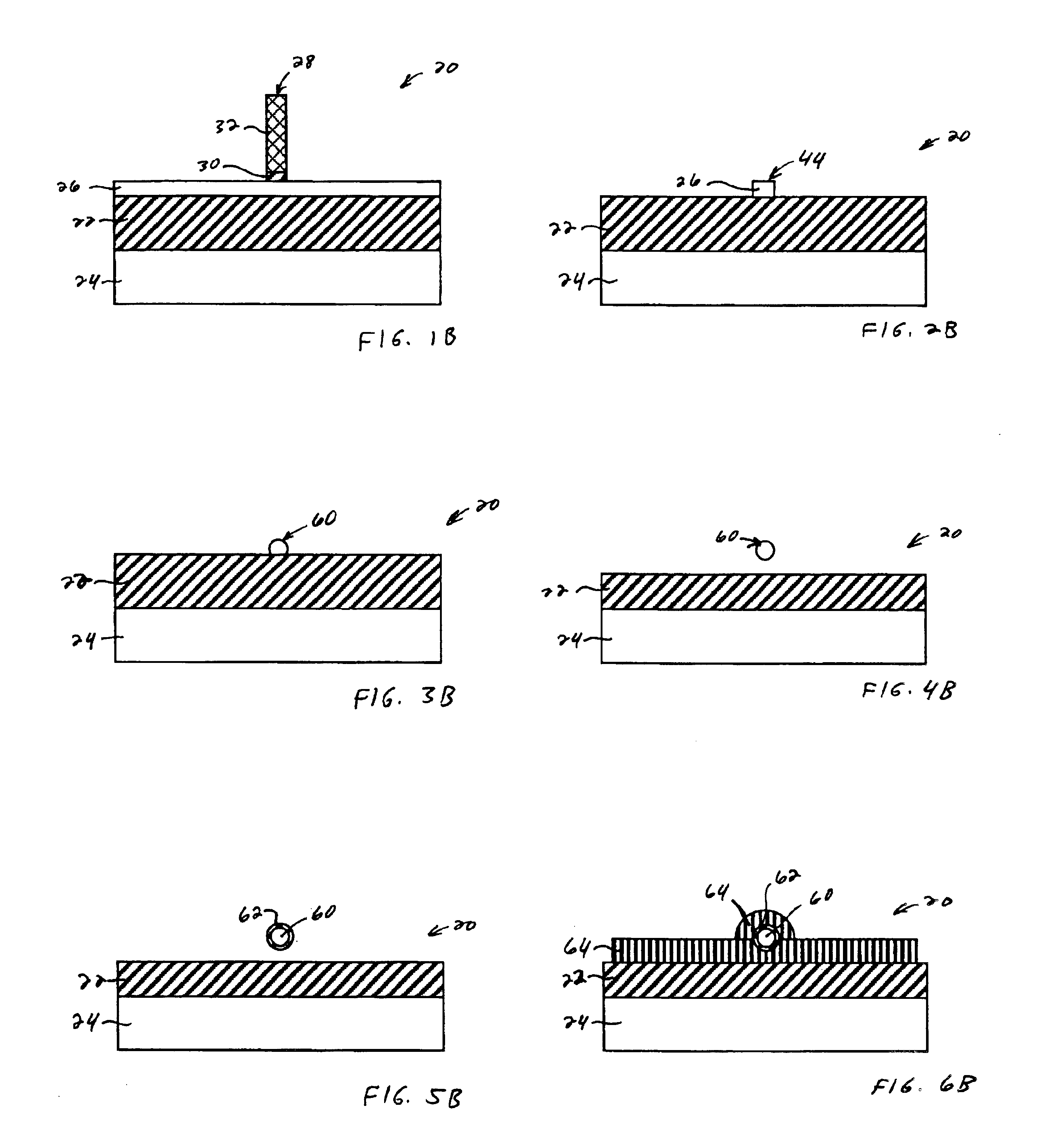
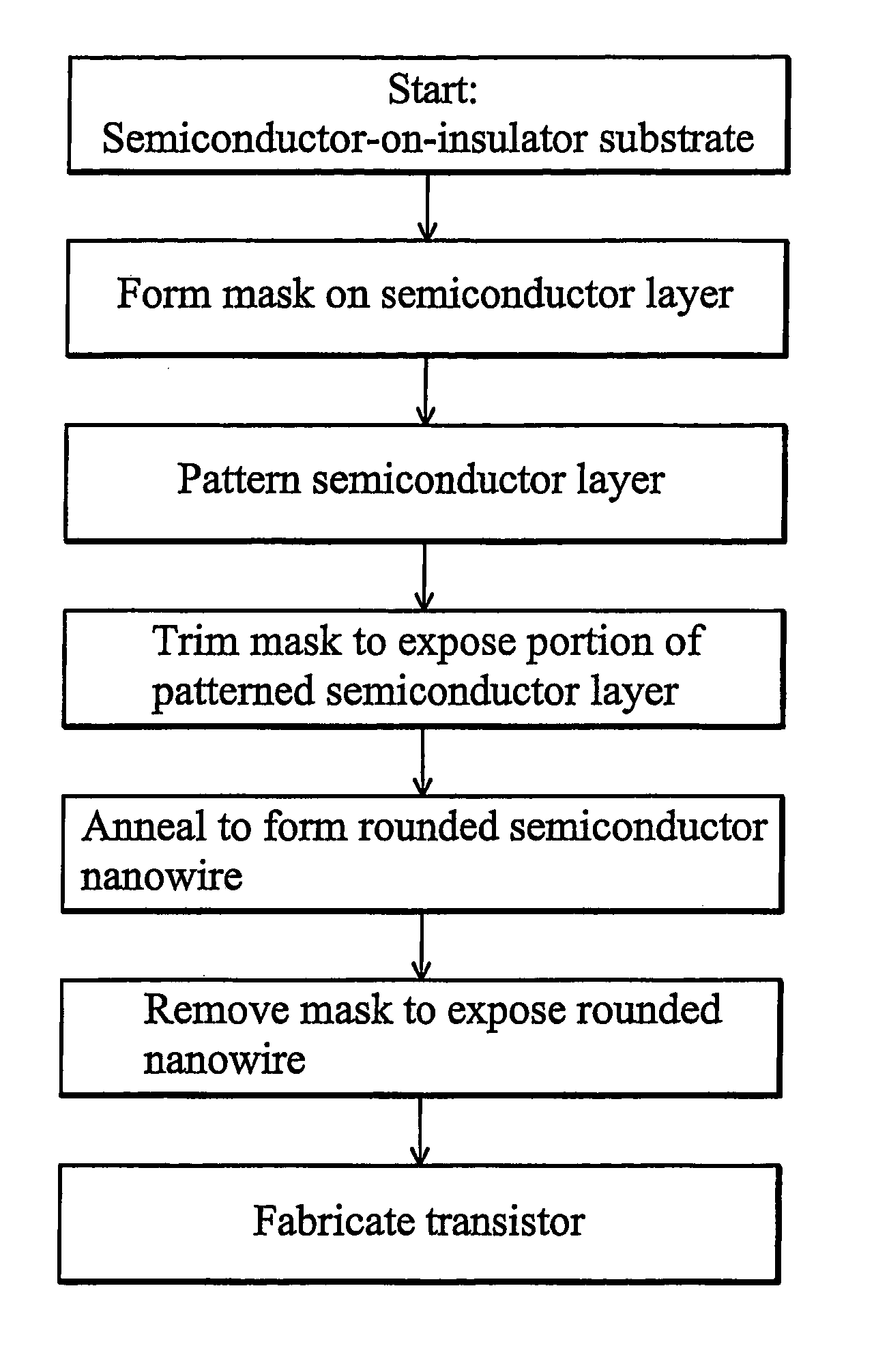
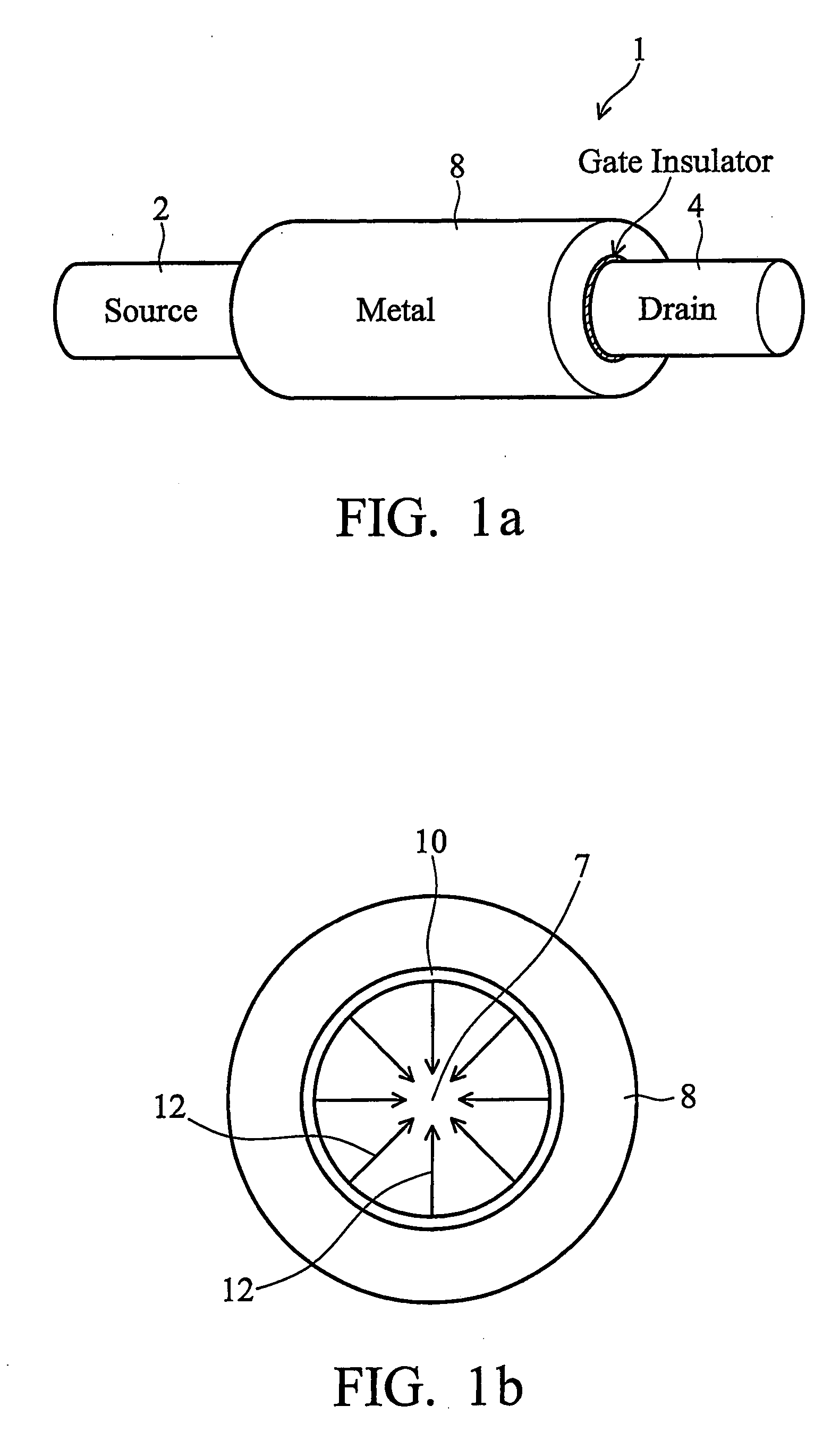
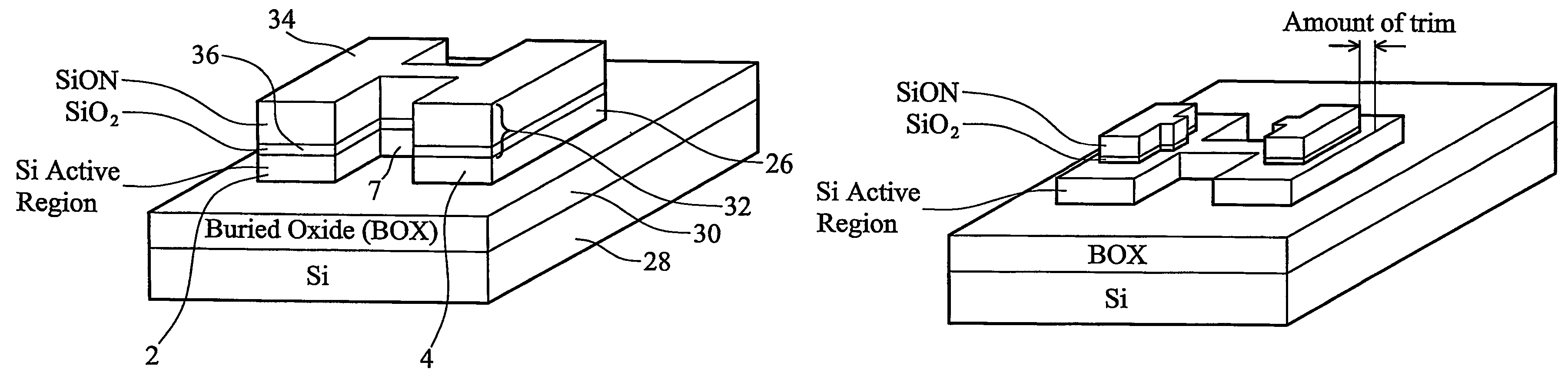
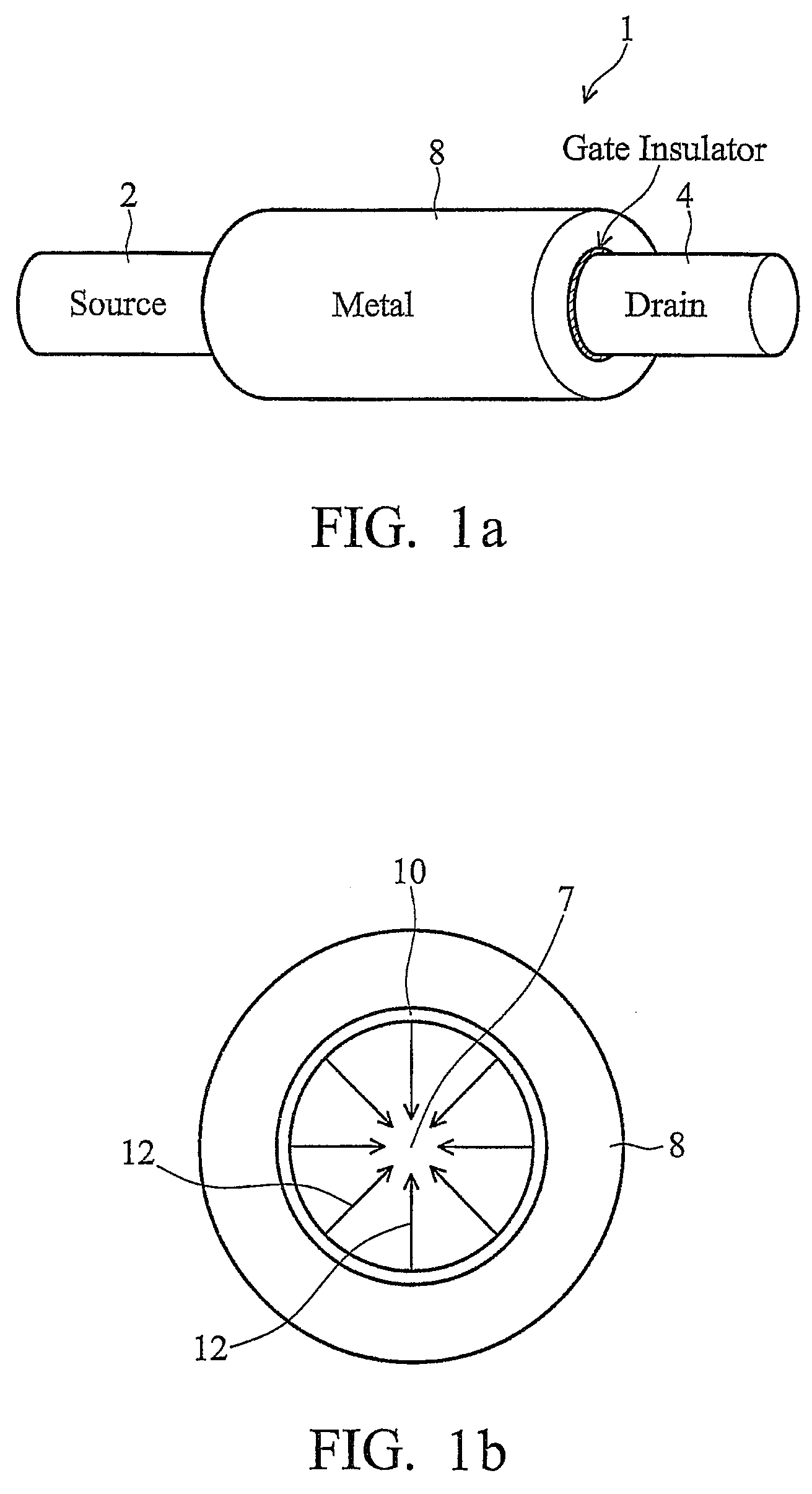
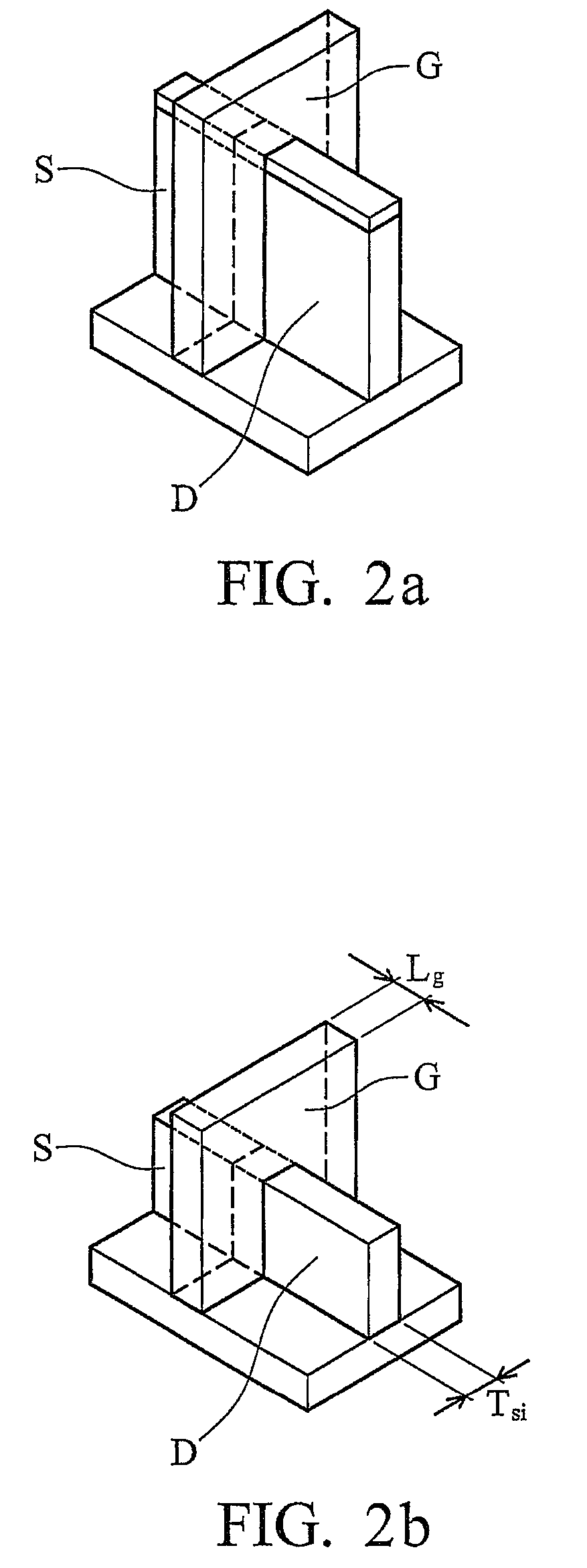
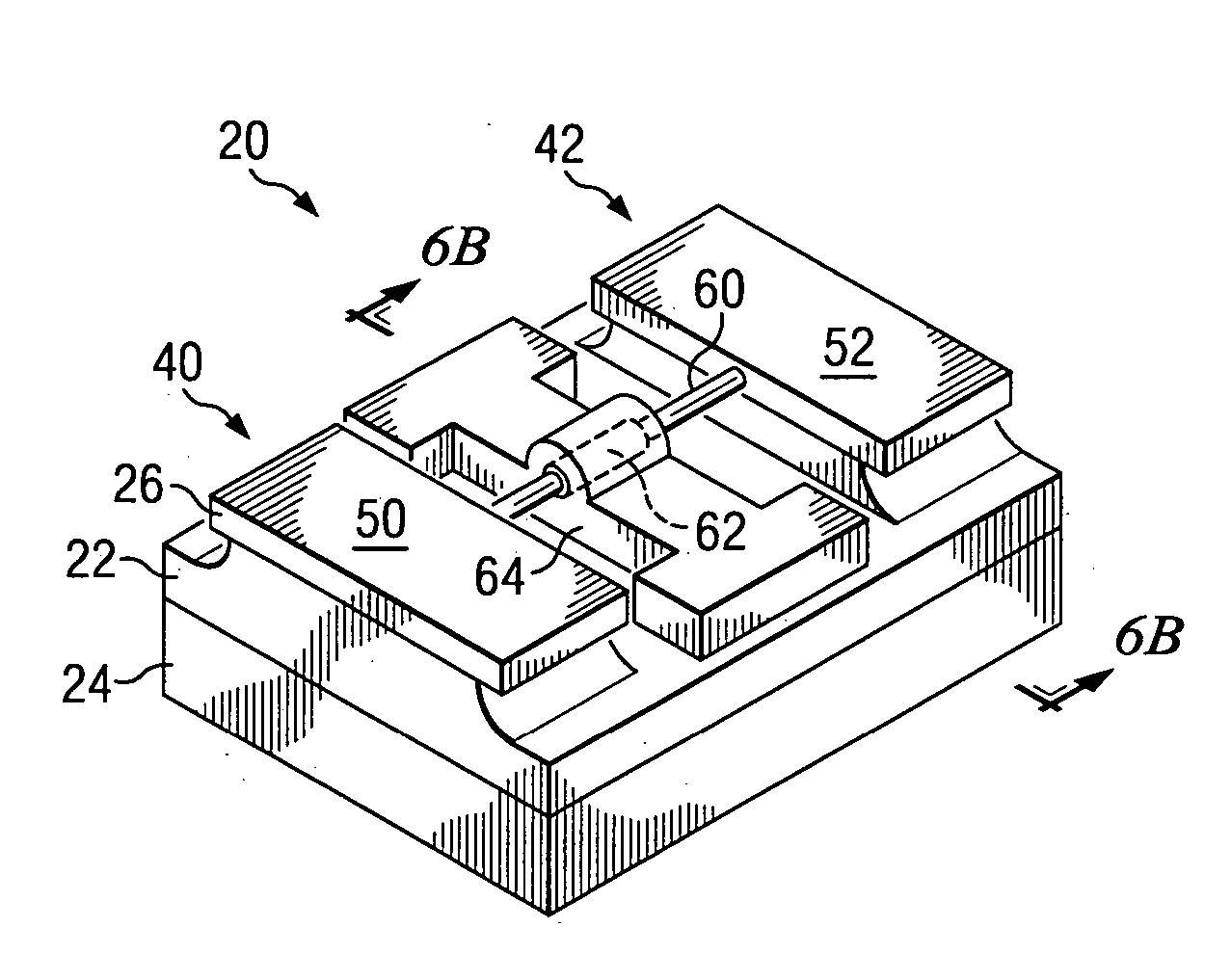
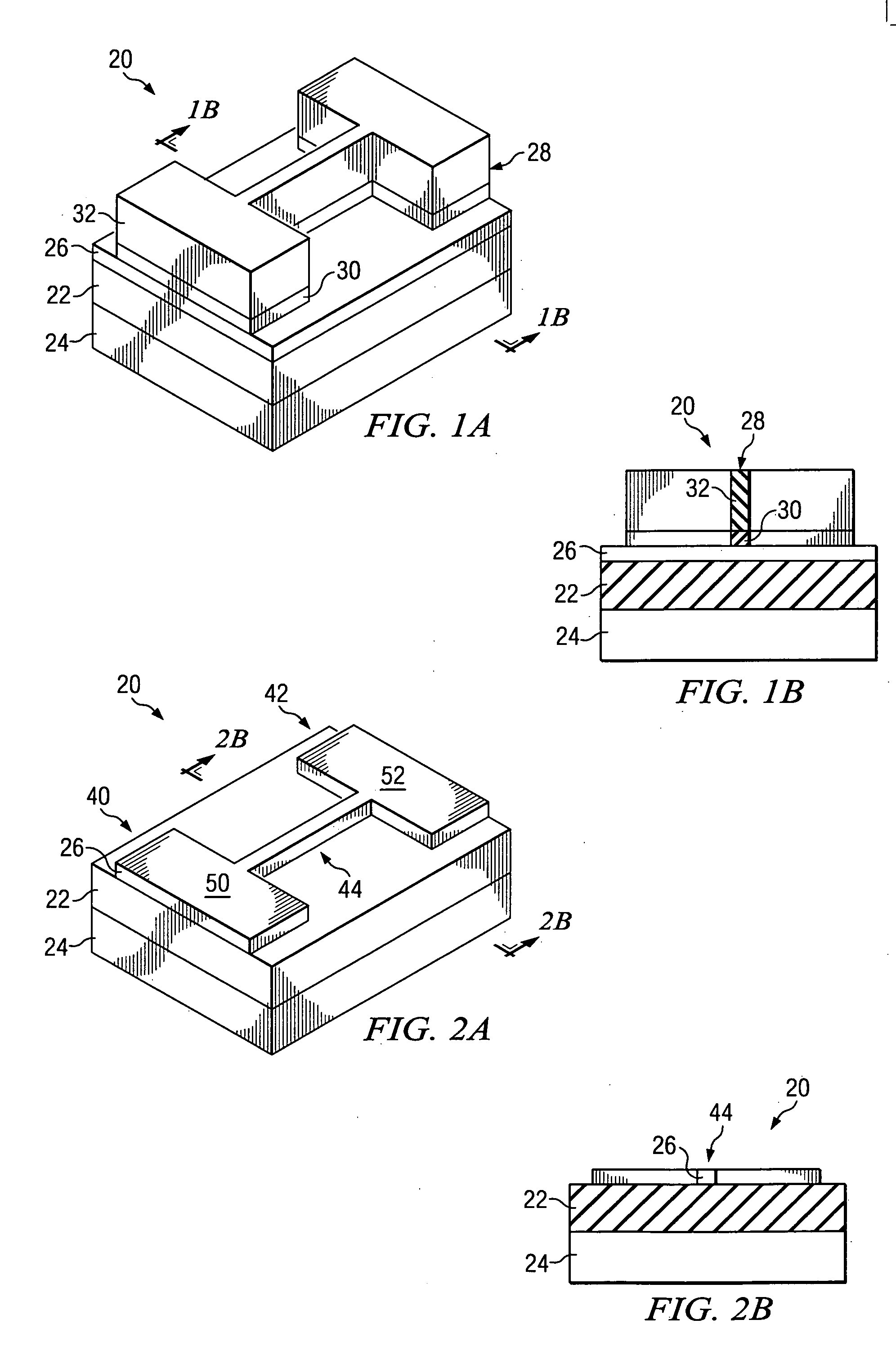
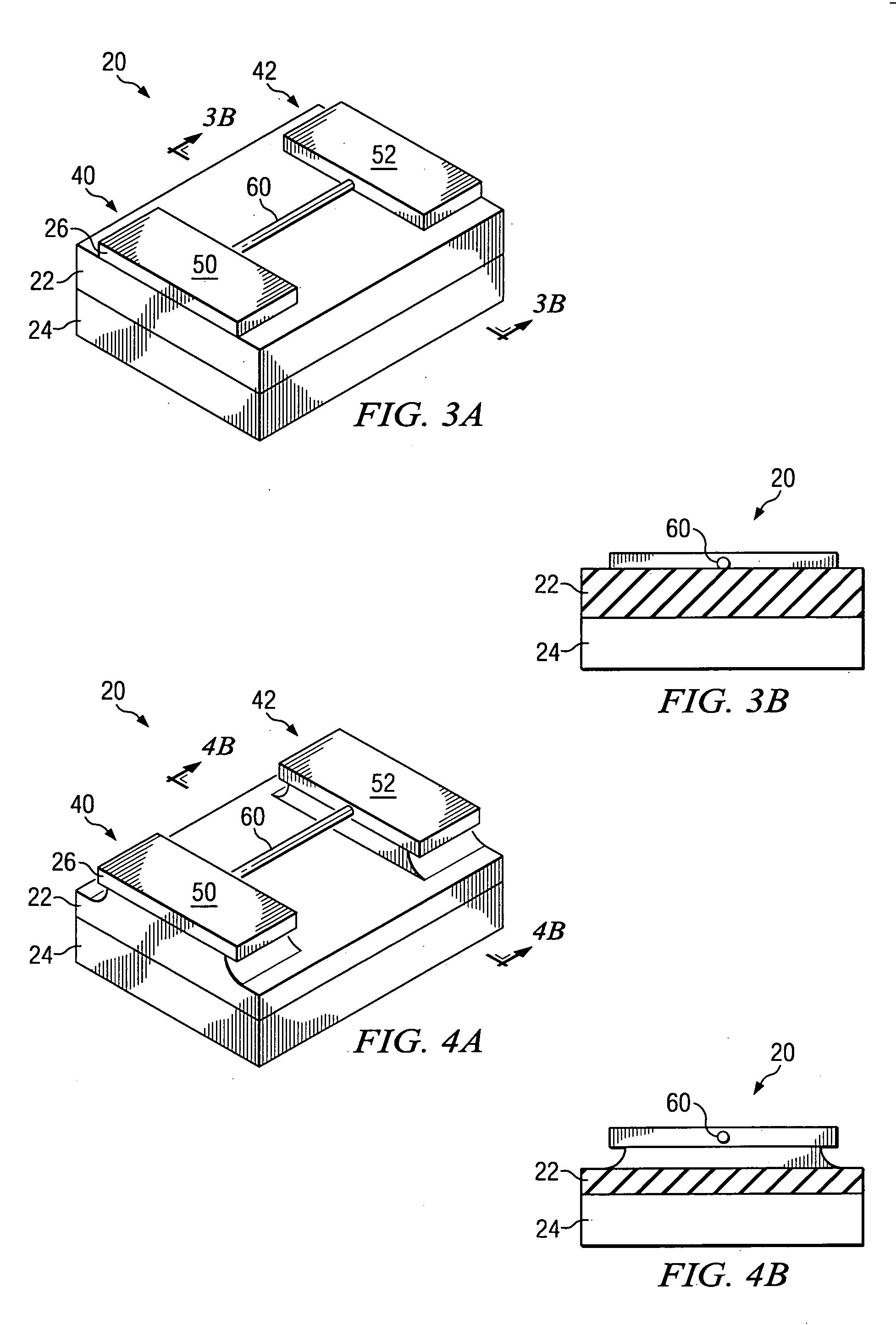
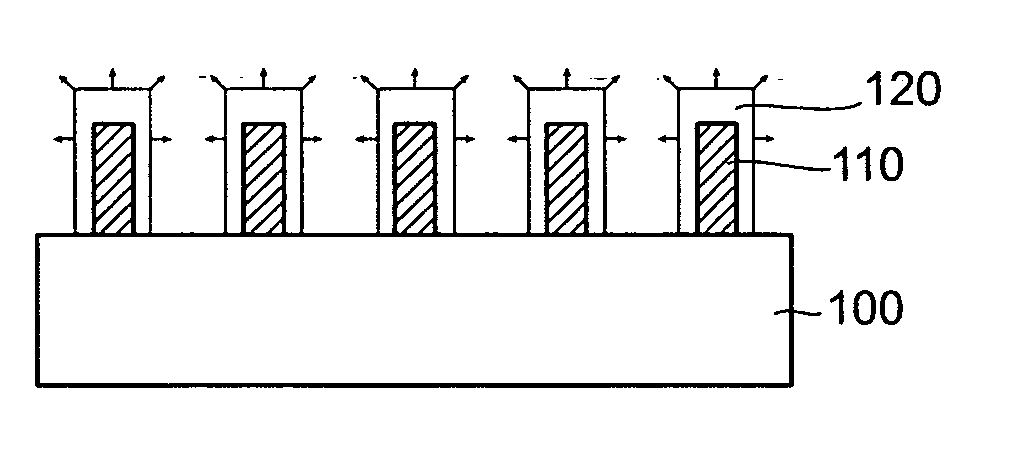
In a method of manufacturing a semiconductor device, a semiconductor layer is patterned to form a source region, a channel region, and a drain region in the semiconductor layer. The channel region extends between the source region and the drain region. Corners of the channel region are rounded by annealing the channel region to form a nano-rod structure. Part of the nano-rod structure is then used as a gate channel. Preferably, a gate dielectric and a gate electrode both wrap around the nano-rod structure, with the gate dielectric being between the nano-rod structure and the gate electrode, to form a transistor device.
Owner:TAIWAN SEMICON MFG CO LTD
Semiconductor nano-wire devices and methods of fabrication
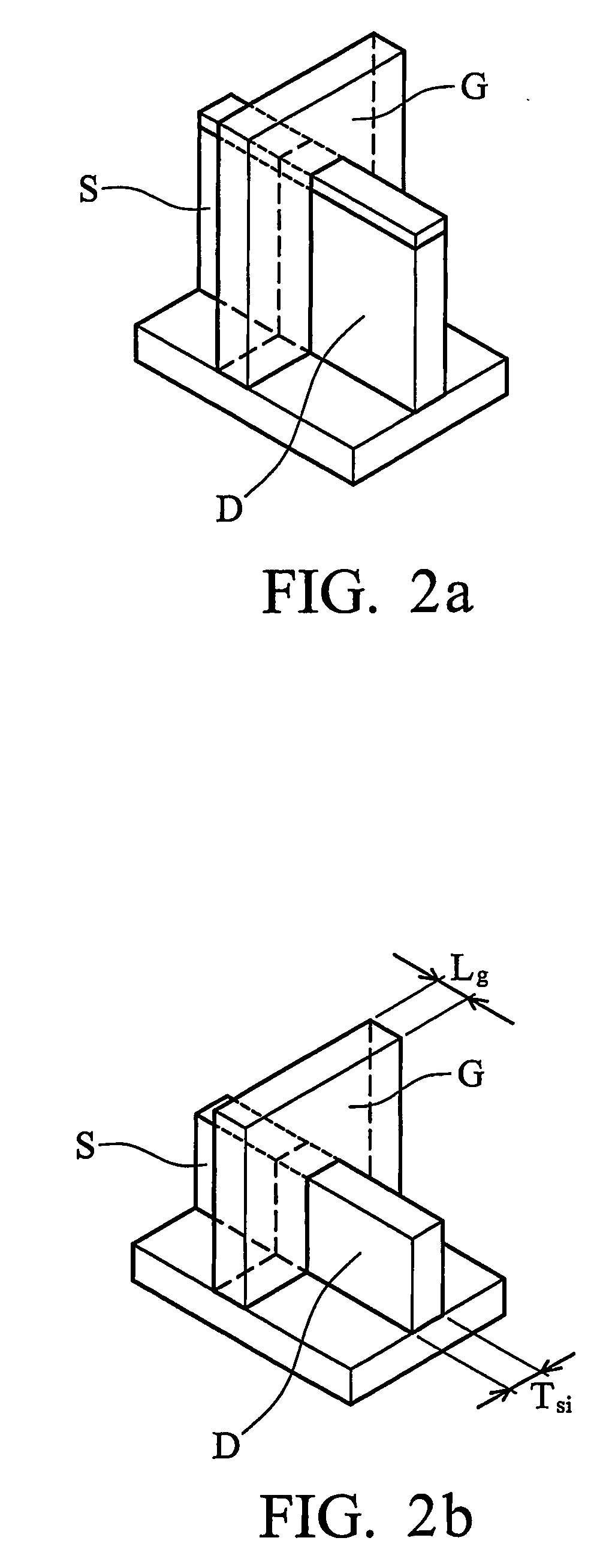
InactiveUS20050275010A1Rule out the possibilityReduce agglomerationTransistorNanoinformaticsDielectricNanowire
Nano-wires, preferably of less than 20 nm diameter, can be formed with minimized risk of narrowing and breaking that results from silicon atom migration during an annealing process step. This is accomplished by masking portion of the active layer where silicon atomer would otherwise agglomerate with a material such as silicon dioxide, silicon nitride, or other dielectric that eliminates or substantially reduces the silicon atom migration. Nano-wires, nanotubes, nano-rods, and other features can be formed and can optionally be incorporated into devices, such as by use as a channel region in a transistor device.
Owner:TAIWAN SEMICON MFG CO LTD
Compositions Including Nano-Particles and a Nano-Structured Support Matrix and Methods of preparation as reversible high capacity anodes in energy storage systems
The present invention relates to compositions including nano-particles and a nano-structured support matrix, methods of their preparation and applications thereof. The compositions of the present invention are particularly suitable for use as anode material for lithium-ion rechargeable batteries. The nano-structured support matrix can include nanotubes, nanowires, nanorods, and mixtures thereof. The composition can further include a substrate on which the nano-structured support matrix is formed. The substrate can include a current collector material.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF PITTSBURGH
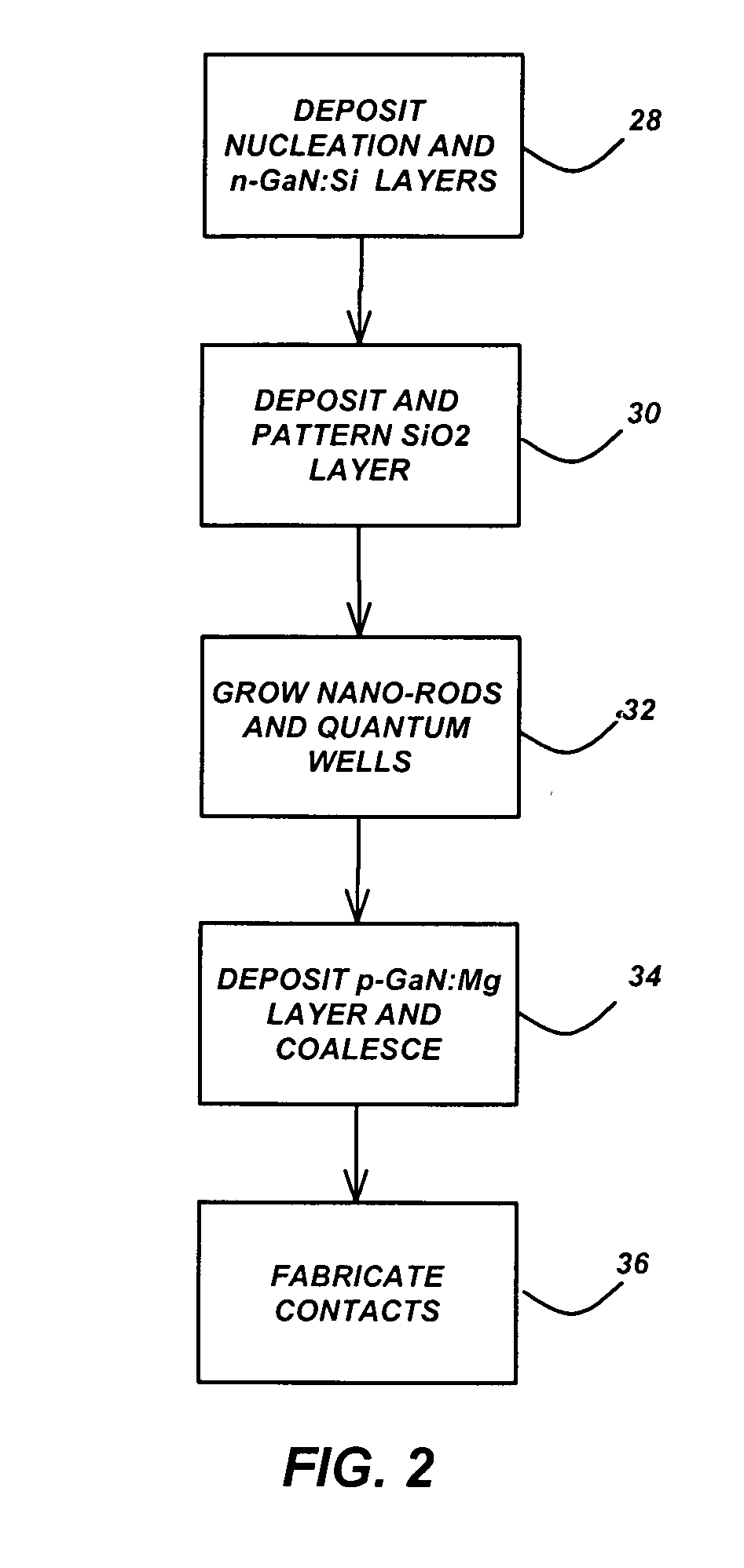
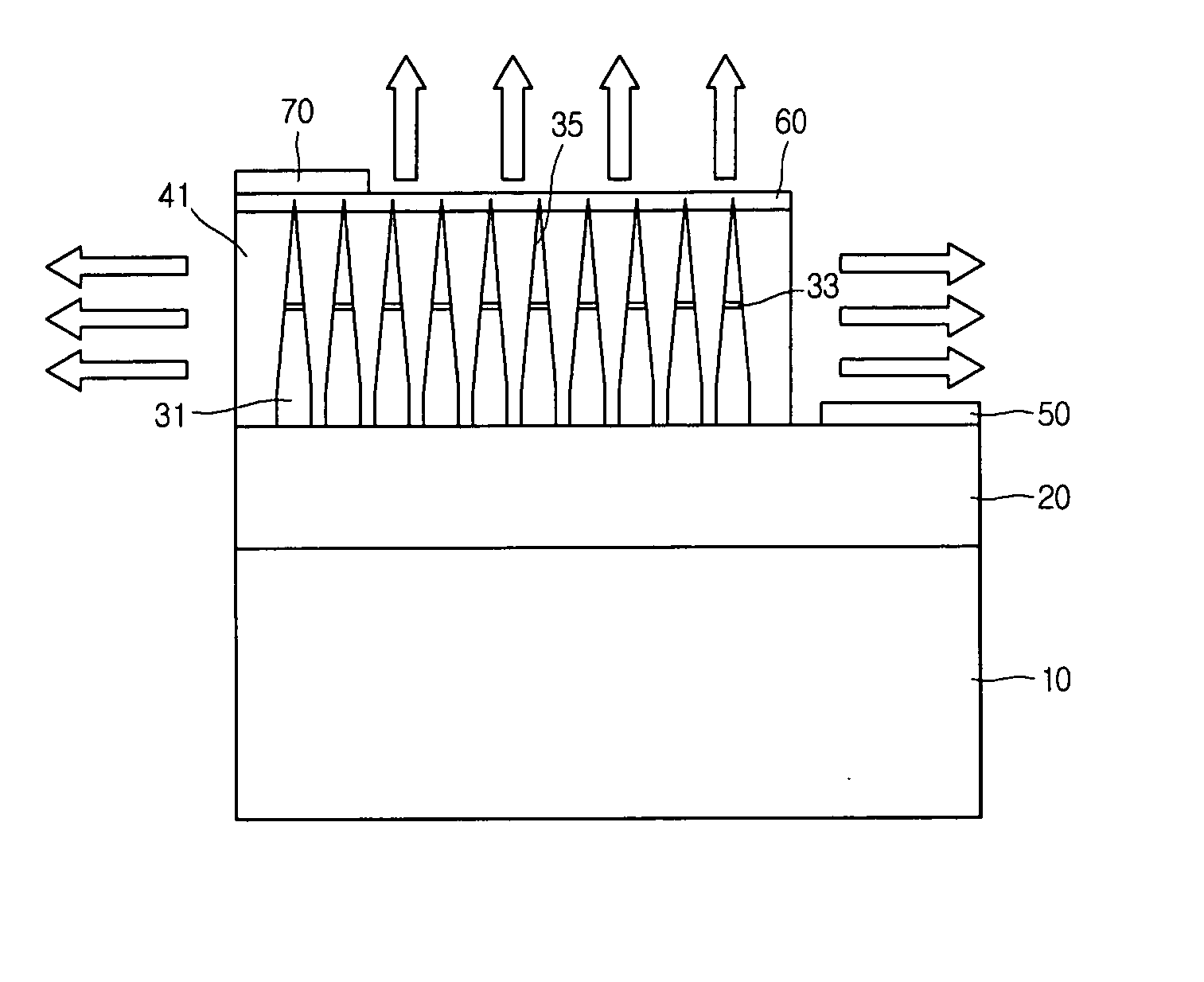
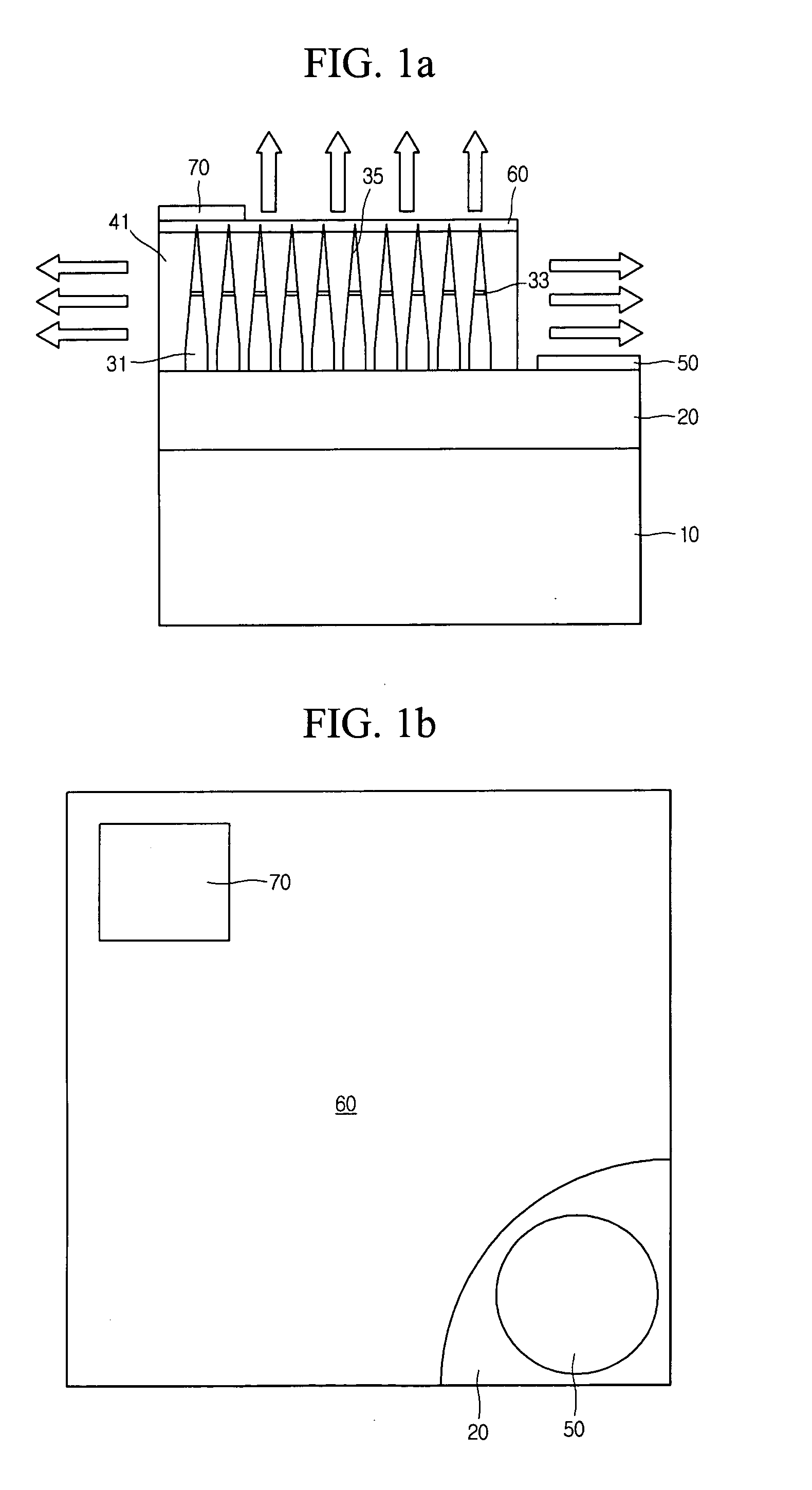
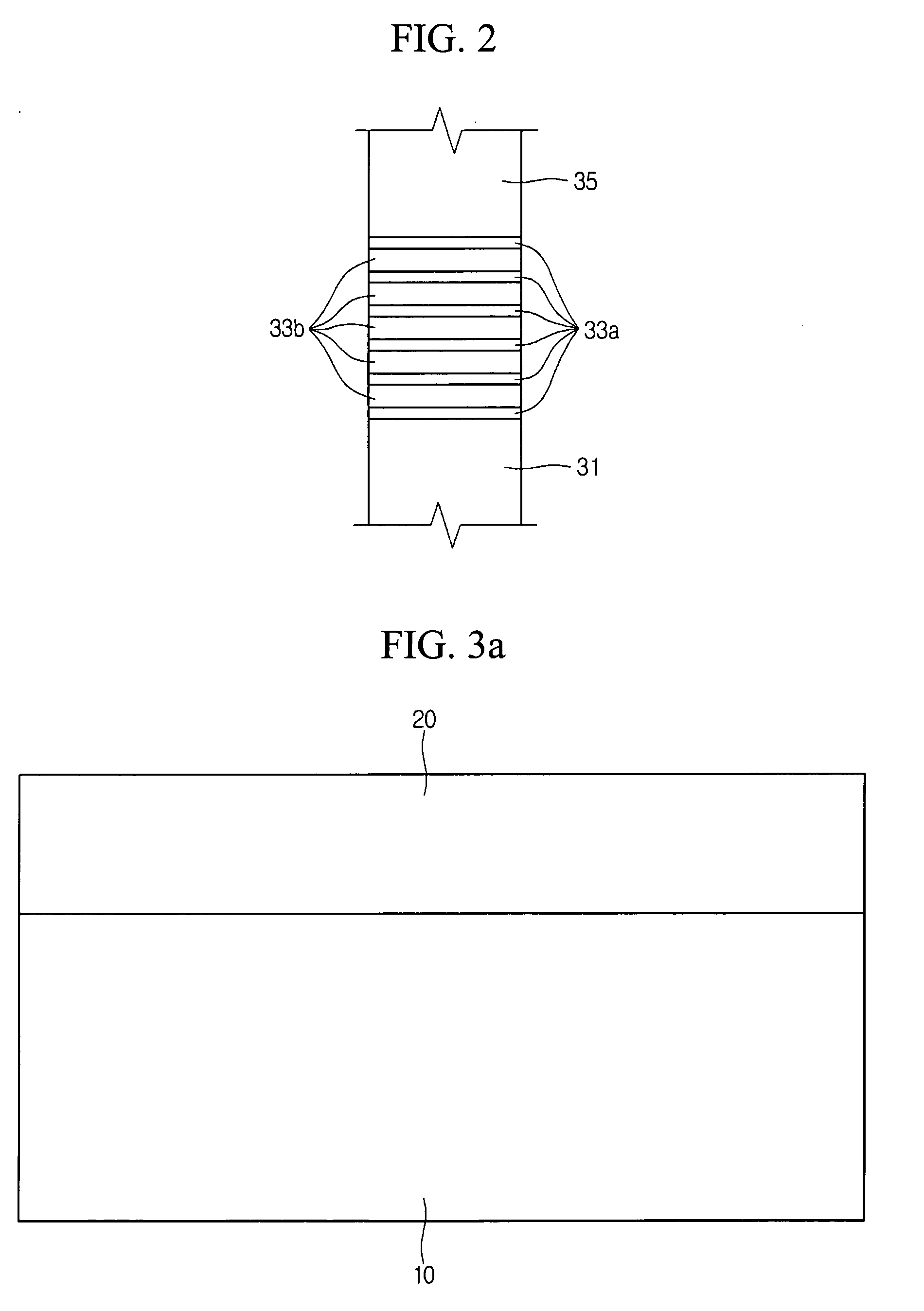
Semiconductor devices based on coalesced nano-rod arrays
InactiveUS20060223211A1NanoinformaticsSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingEtchingDevice material
Semiconductor devices are fabricated using semiconductor nano-rod arrays, which are merged through coalescence into a continuous planar layer after the nano-rods in the nano-rod array are fabricated by growth or etching. Merging of the nano-rods through coalescence into a continuous layer is achieved by tuning the growth conditions into a regime allowing epitaxial lateral overgrowth.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
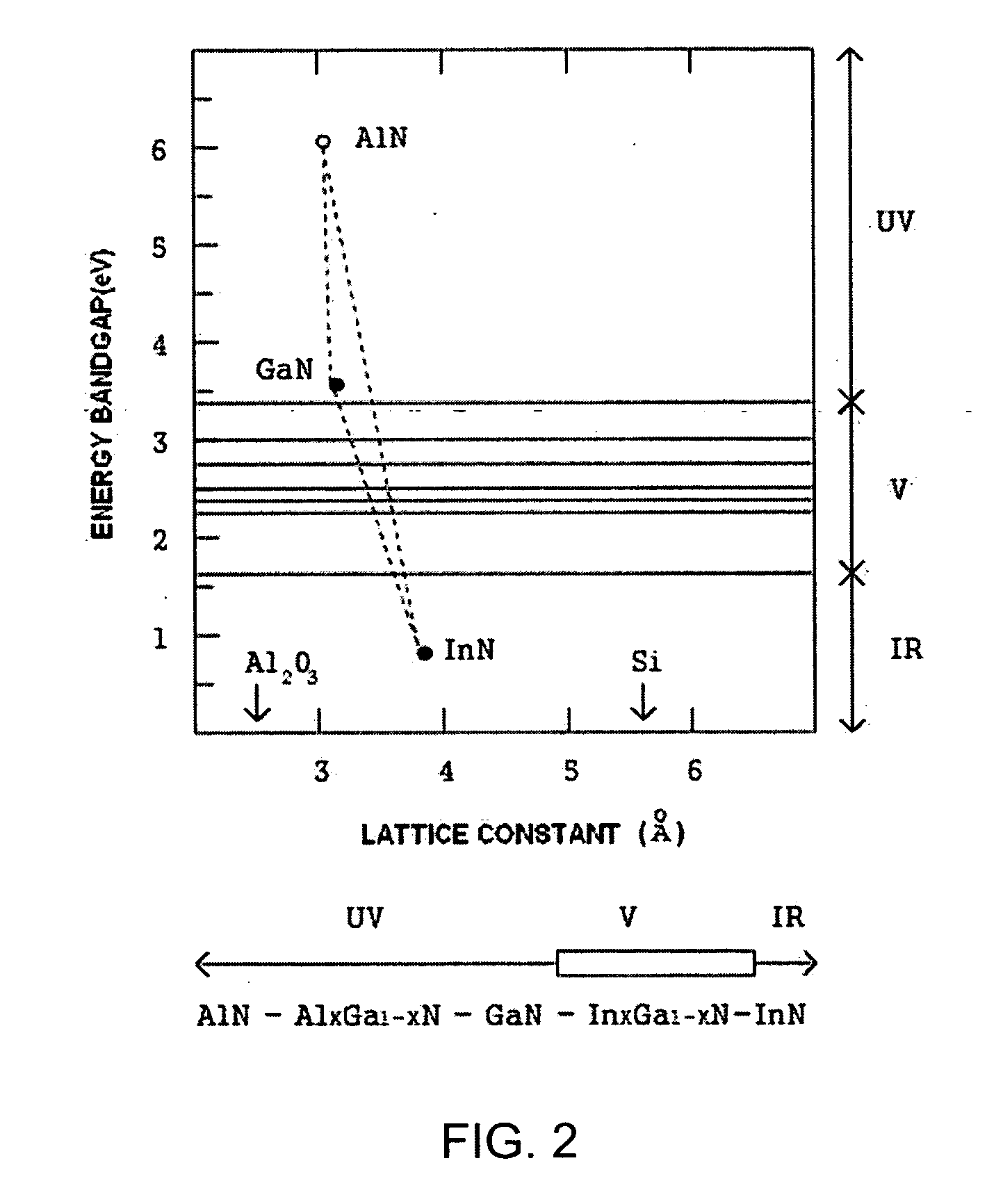
Super bright light emitting diode of nanorod array structure having InGaN quantum well and method for manufacturing the same
ActiveUS20050194598A1Increase brightnessHigh light emitting efficiencyMaterial nanotechnologySemiconductor/solid-state device detailsNanowireQuantum well
An GaN light emitting diode (LED) having a nanorod (or, nanowire) structure is disclosed. The GaN LED employs GaN nanorods in which a n-type GaN nanorod, an InGaN quantum well and a p-type GaN nanorod are subsequently formed in a longitudinal direction by inserting the InGaN quantum well into a p-n junction interface of the p-n junction GaN nanorod. In addition, a plurality of such GaN nanorods are arranged in an array so as to provide an LED having much greater brightness and higher light emission efficiency than a conventional laminated-film GaN LED.
Owner:DONGGUK UNIV IND ACADEMIC COOPERATION FOUND
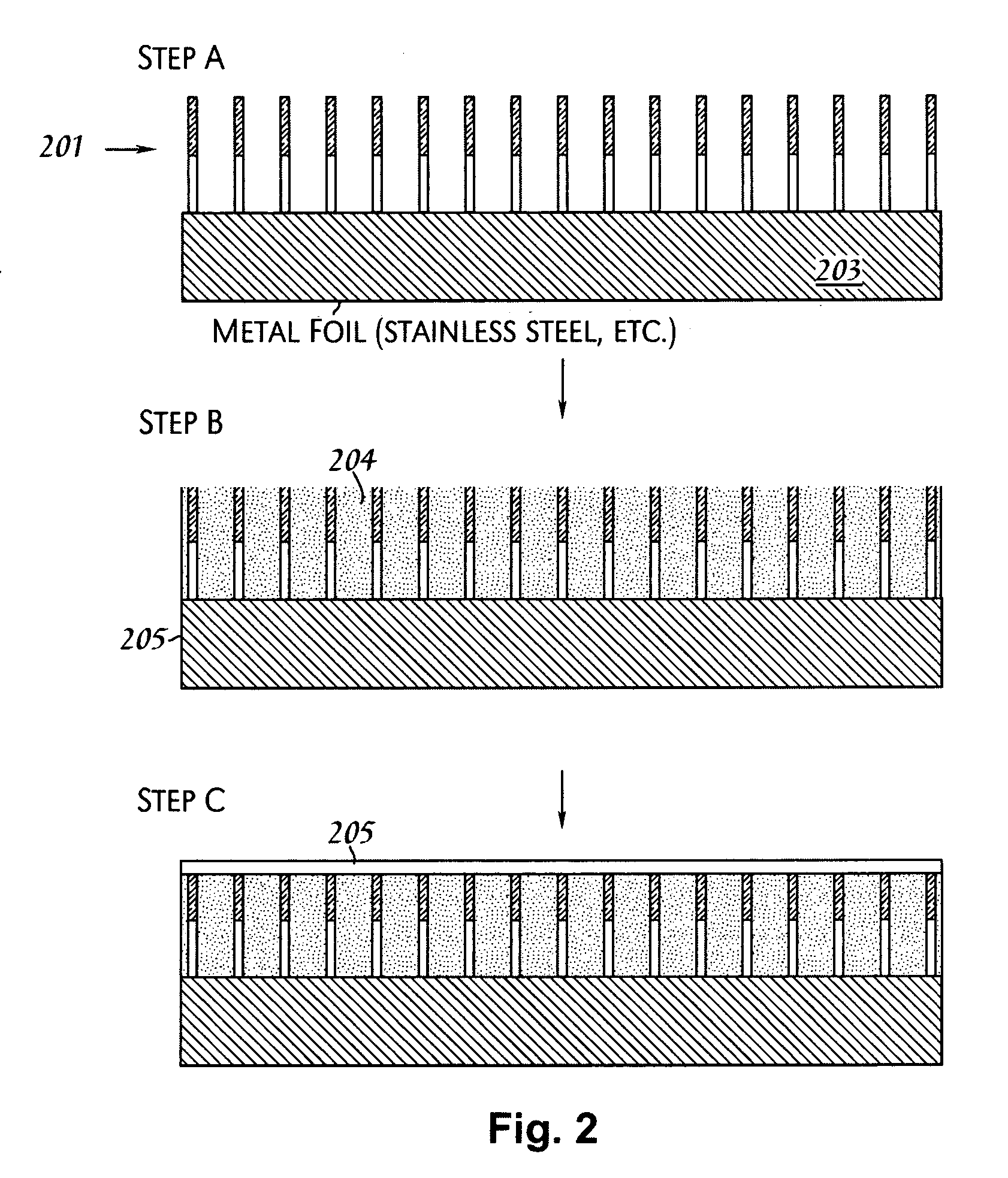
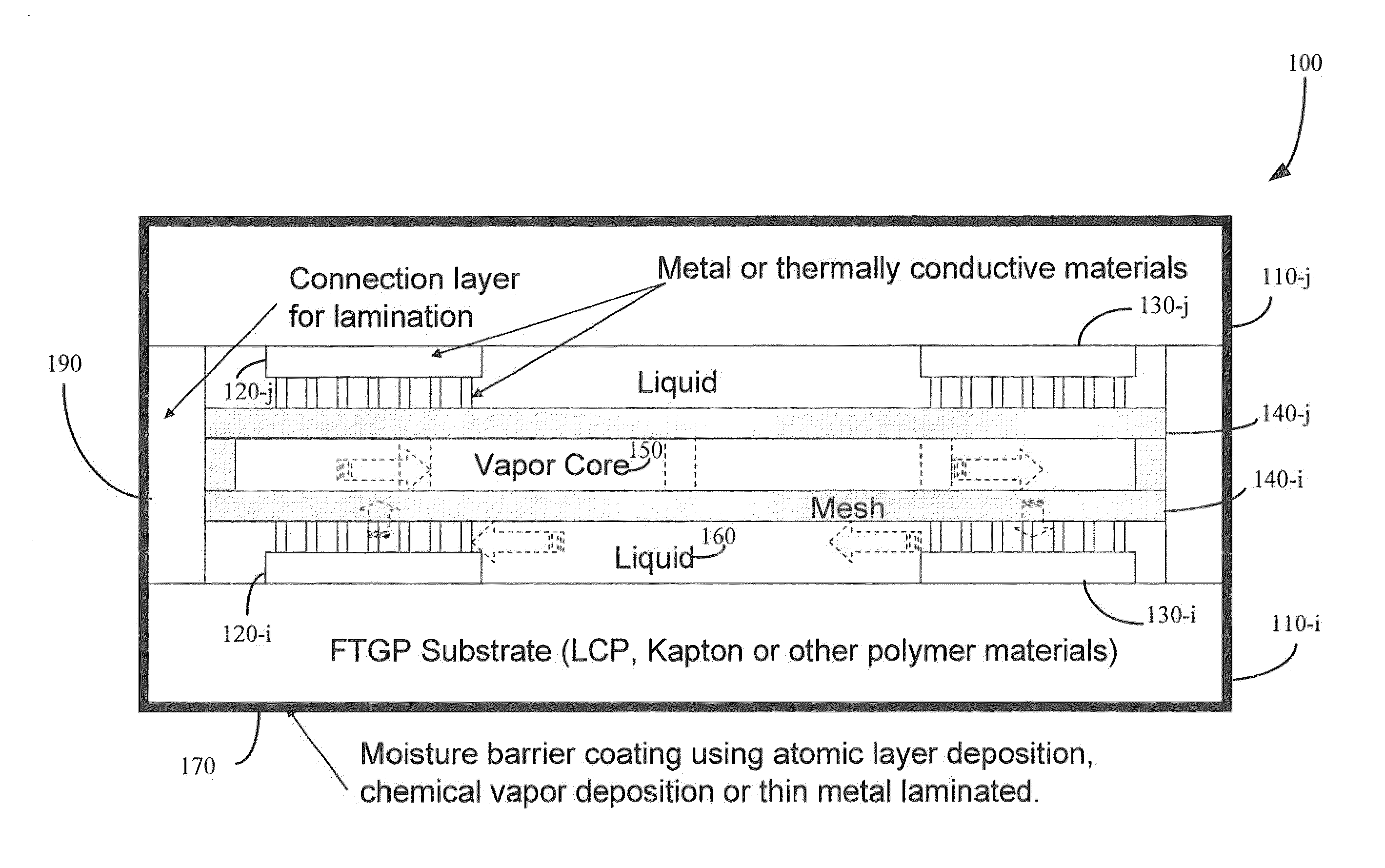
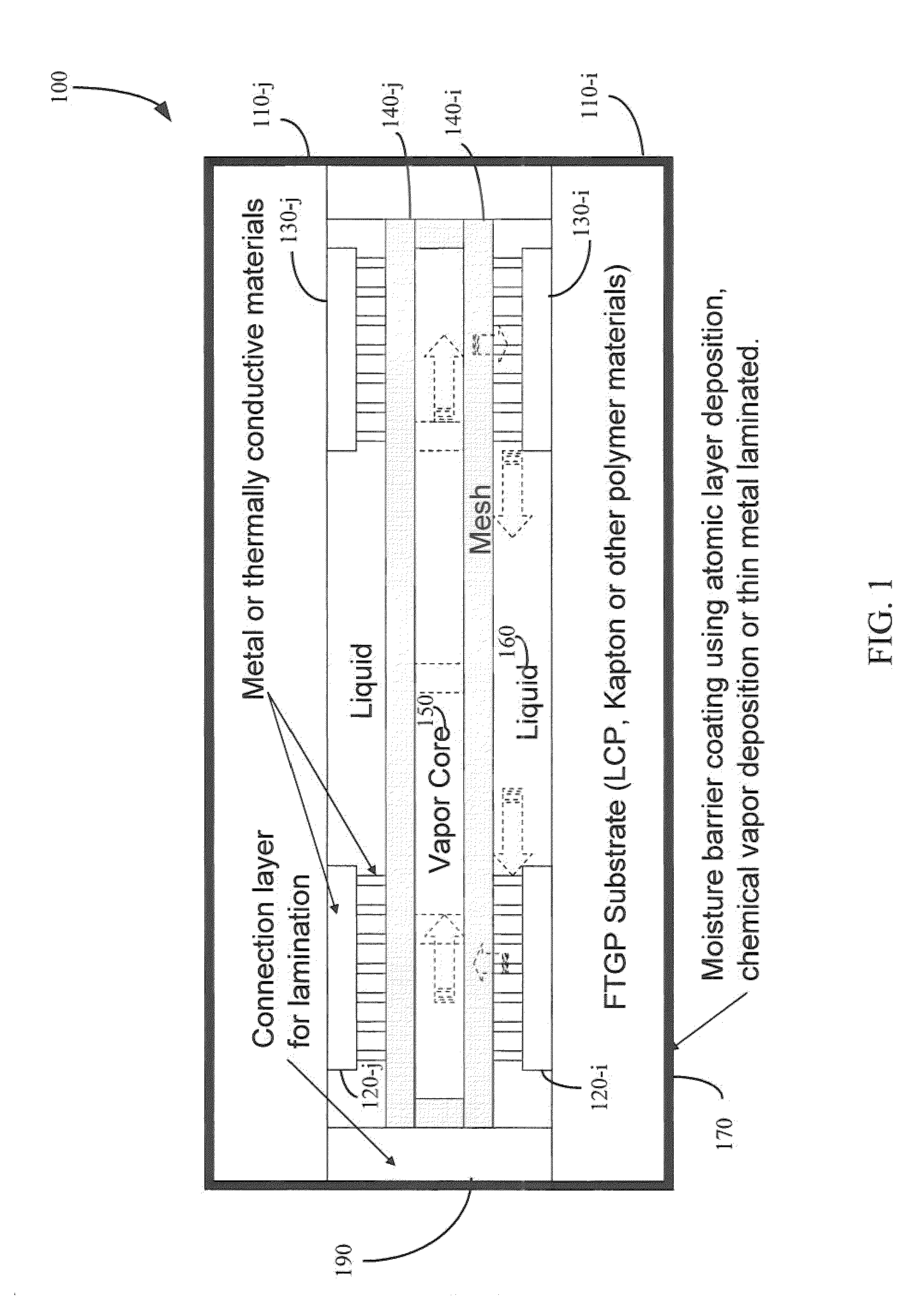
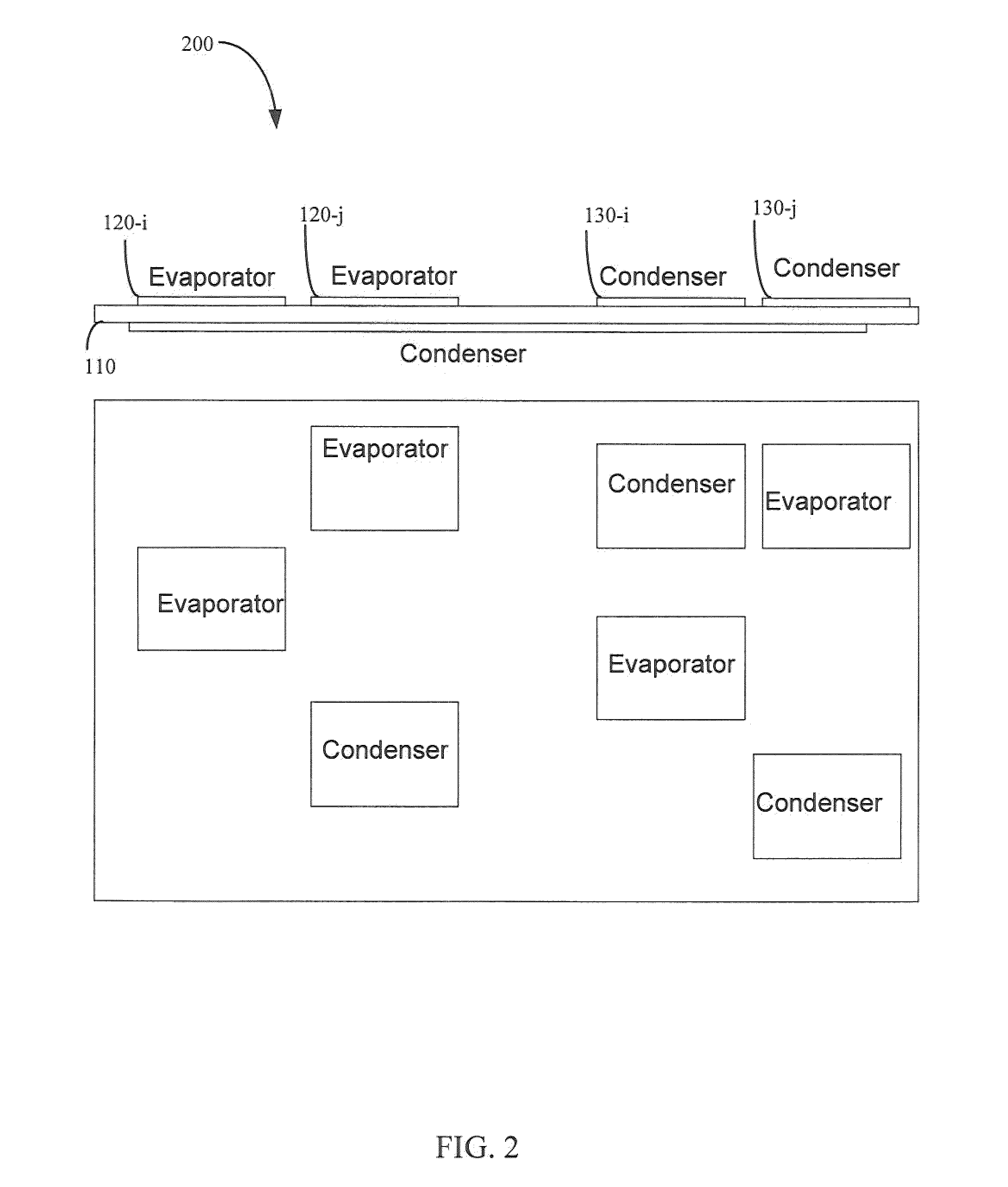
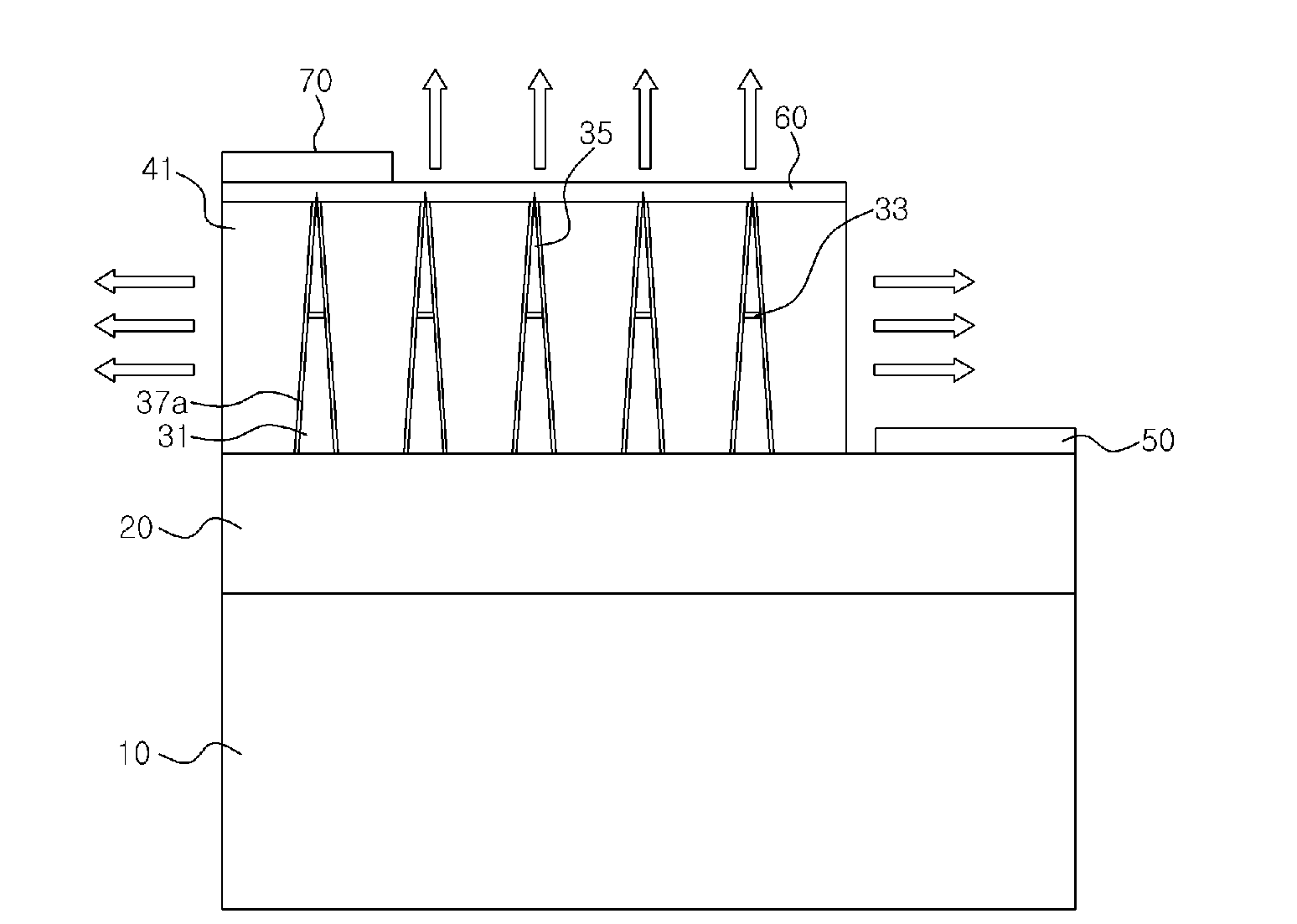
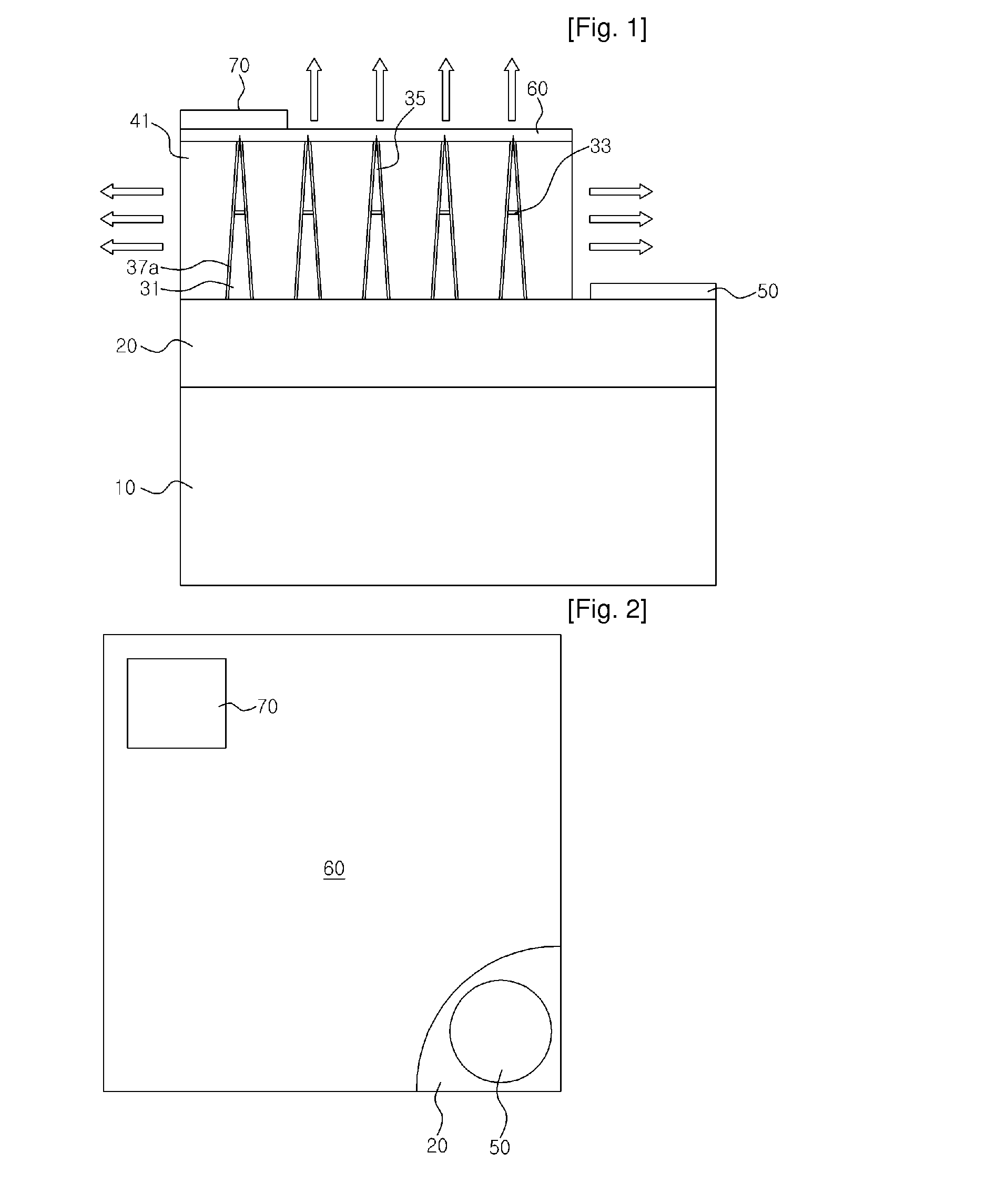
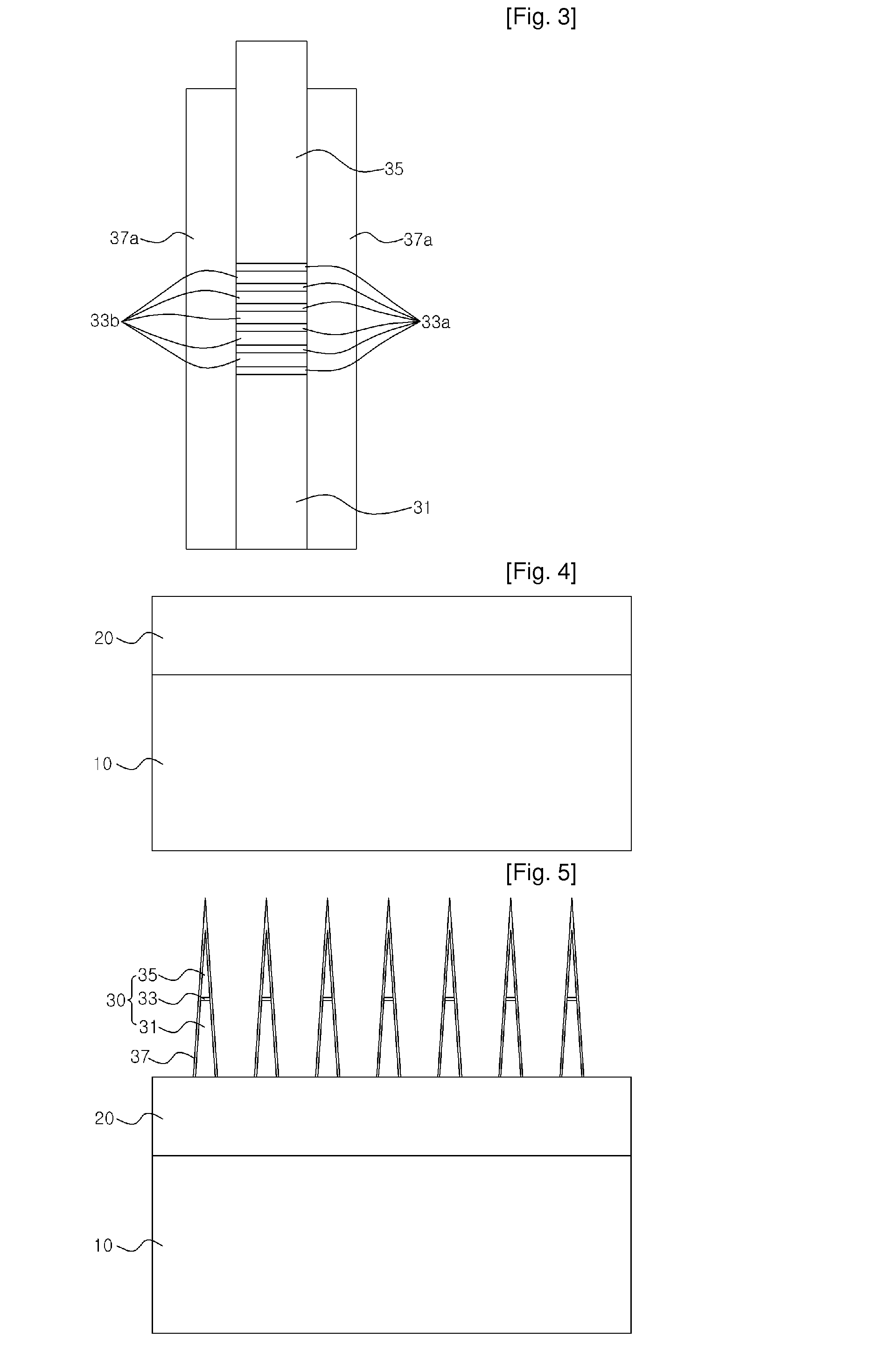
Flexible thermal ground plane and manufacturing the same
ActiveUS20110017431A1Improve thermal performanceEffective liquid supplySemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesGround planeNanorod
Methods, apparatuses, and systems are disclosed for flexible thermal ground planes. A flexible thermal ground plane may include a support member. The flexible thermal ground plane may include an evaporator region or multiple evaporator regions configured to couple with the support member. The flexible thermal ground plane may include a condenser region or multiple condenser regions configured to couple with the support member. The evaporator and condenser region may include a microwicking structure. The evaporator and condenser region may include a nanowicking structure coupled with the micro-wicking structure, where the nanowicking structure includes nanorods. The evaporator and condenser region may include a nanomesh coupled with the nanorods and / or the microwicking structure. Some embodiments may include a micromesh coupled with the nanorods and / or the microwicking structure.
Owner:KELVIN THERMAL TECH
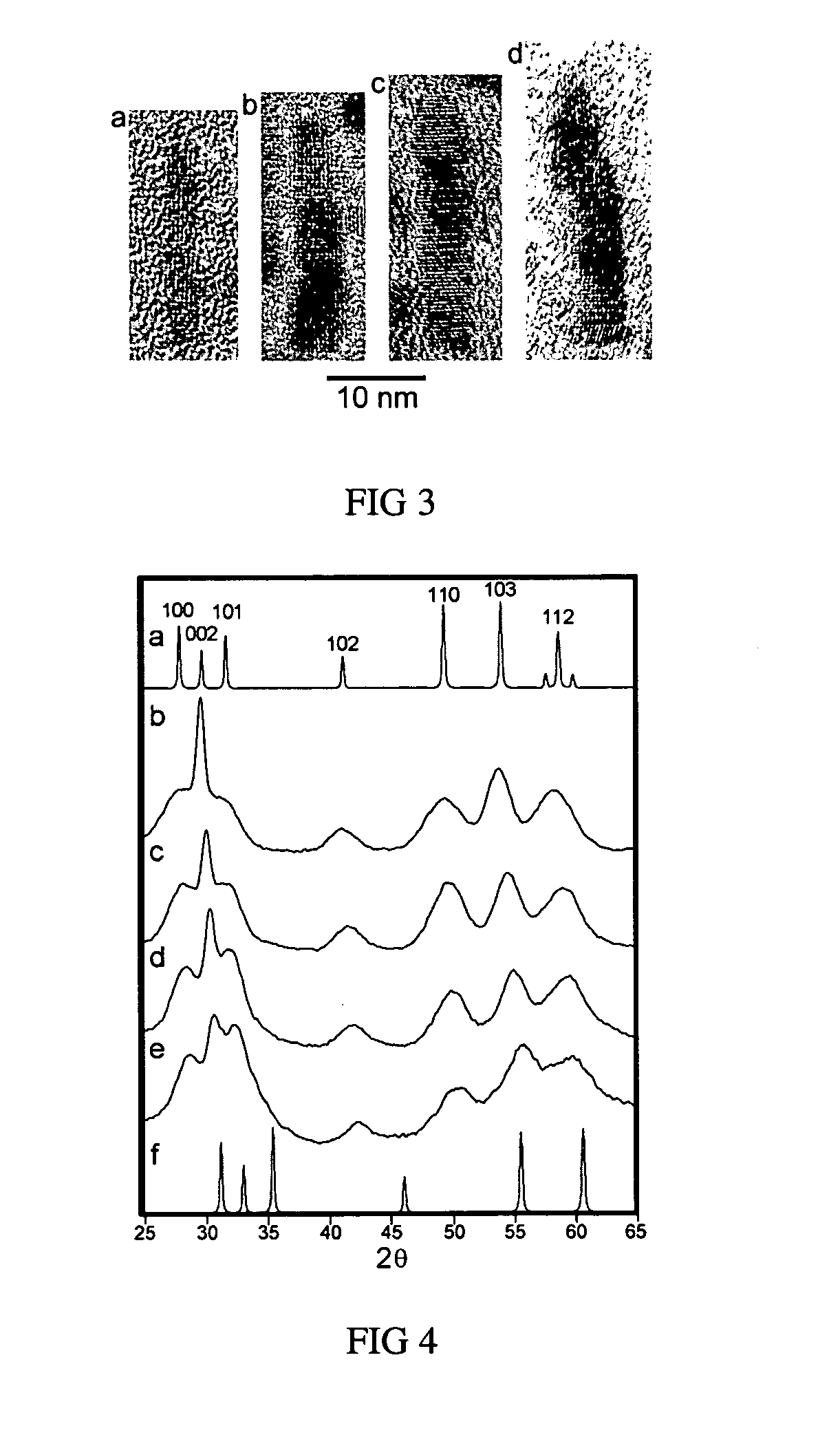
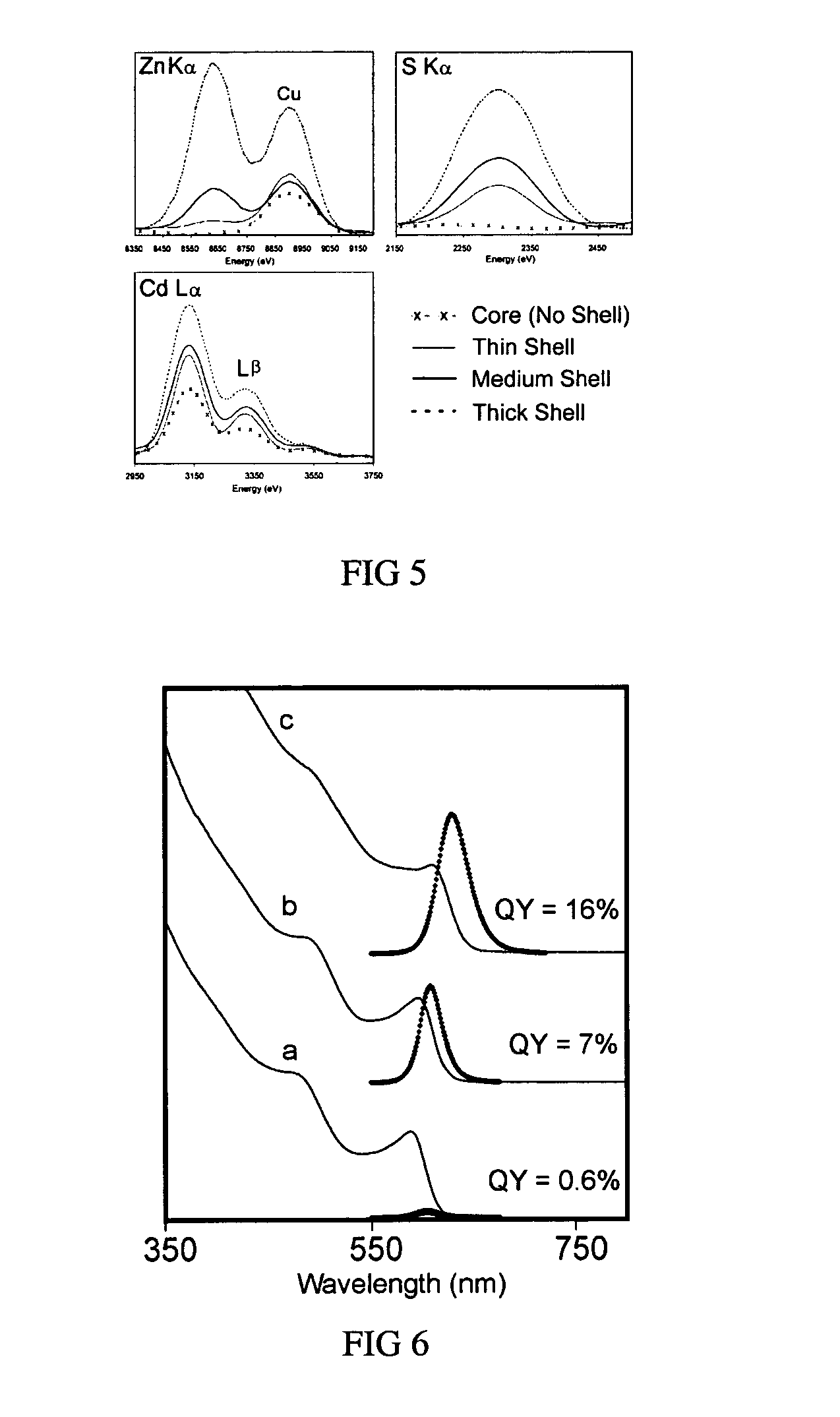
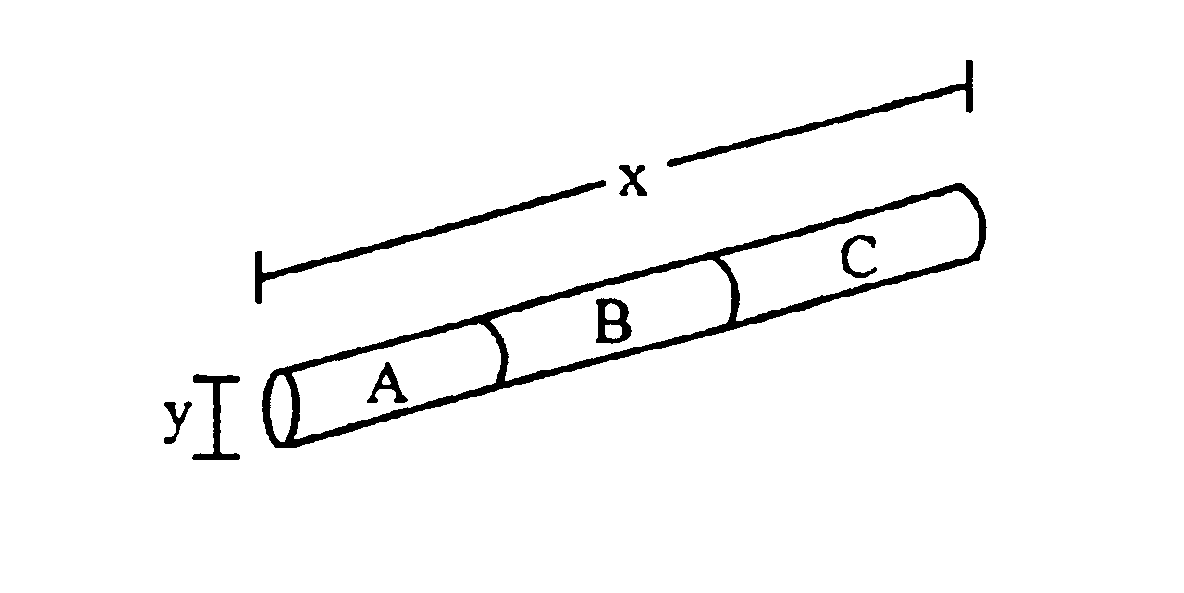
Graded core/shell semiconductor nanorods and nanorod barcodes
InactiveUS20050054004A1Improve quantum efficiencyIncrease in photoluminescence QYMaterial nanotechnologyNanosensorsGroup iiSemiconductor
Disclosed herein is a graded core / shell semiconductor nanorod having at least a first segment of a core of a Group II-VI, Group III-V or a Group IV semiconductor, a graded shell overlying the core, wherein the graded shell comprises at least two monolayers, wherein the at least two monolayers each independently comprise a Group II-VI, Group III-V or a Group IV semiconductor.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Colloidal rod particles as nanobar codes
Owner:SURROMED +1
Method of manufacture of colloidal rod particles as nanobarcodes
Owner:SURROMED +1
Semiconductor nano-wire devices and methods of fabrication
InactiveUS7452778B2Rule out the possibilityReduce agglomerationTransistorNanoinformaticsDielectricNanowire
Nano-wires, preferably of less than 20 nm diameter, can be formed with minimized risk of narrowing and breaking that results from silicon atom migration during an annealing process step. This is accomplished by masking portion of the active layer where silicon atomer would otherwise agglomerate with a material such as silicon dioxide, silicon nitride, or other dielectric that eliminates or substantially reduces the silicon atom migration. Nano-wires, nanotubes, nano-rods, and other features can be formed and can optionally be incorporated into devices, such as by use as a channel region in a transistor device.
Owner:TAIWAN SEMICON MFG CO LTD
Semiconductor nano-rod devices
In a method of manufacturing a semiconductor device, a semiconductor layer is patterned to form a source region, a channel region, and a drain region in the semiconductor layer. The channel region extends between the source region and the drain region. Corners of the channel region are rounded by annealing the channel region to form a nano-rod structure. Part of the nano-rod structure is then used as a gate channel. Preferably, a gate dielectric and a gate electrode both wrap around the nano-rod structure, with the gate dielectric being between the nano-rod structure and the gate electrode, to form a transistor device.
Owner:CHEN HAO YU +3
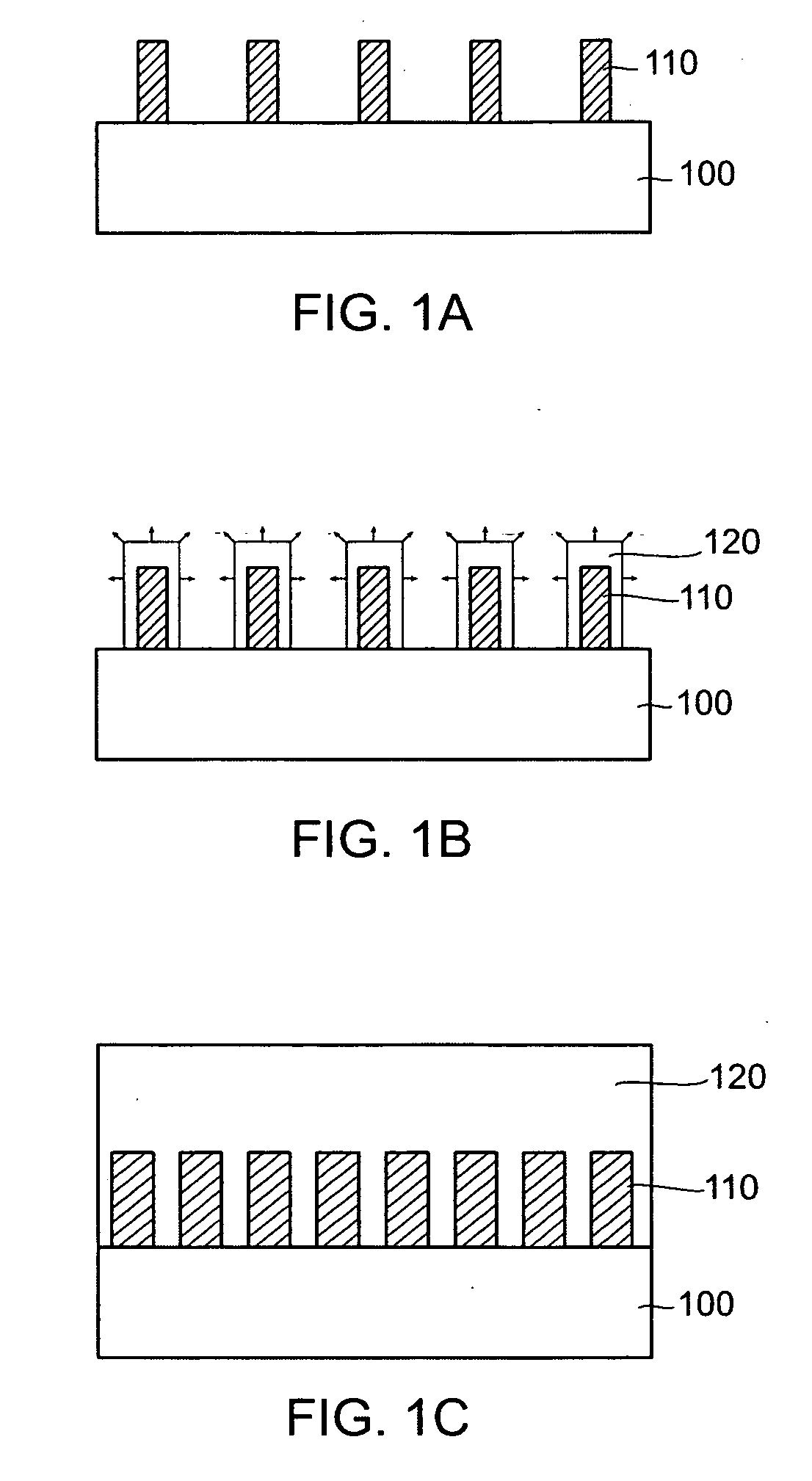
Nitride based semiconductor device using nanorods and process for preparing the same
ActiveUS20060091408A1Reduce thermal stressInhibit the generation of cracksSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSemiconductor devicesDevice materialAmorphous matrix
Disclosed are a nitride based semiconductor device, including a high-quality GaN layer formed on a silicone substrate, and a process for preparing the same. A nitride based semiconductor device in accordance with the present invention comprises a plurality of nanorods aligned and formed on the silicone substrate in the vertical direction; an amorphous matrix layer filling spaces between nanorods so as to protrude some upper portion of the nanorods; and a GaN layer formed on the matrix layer.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
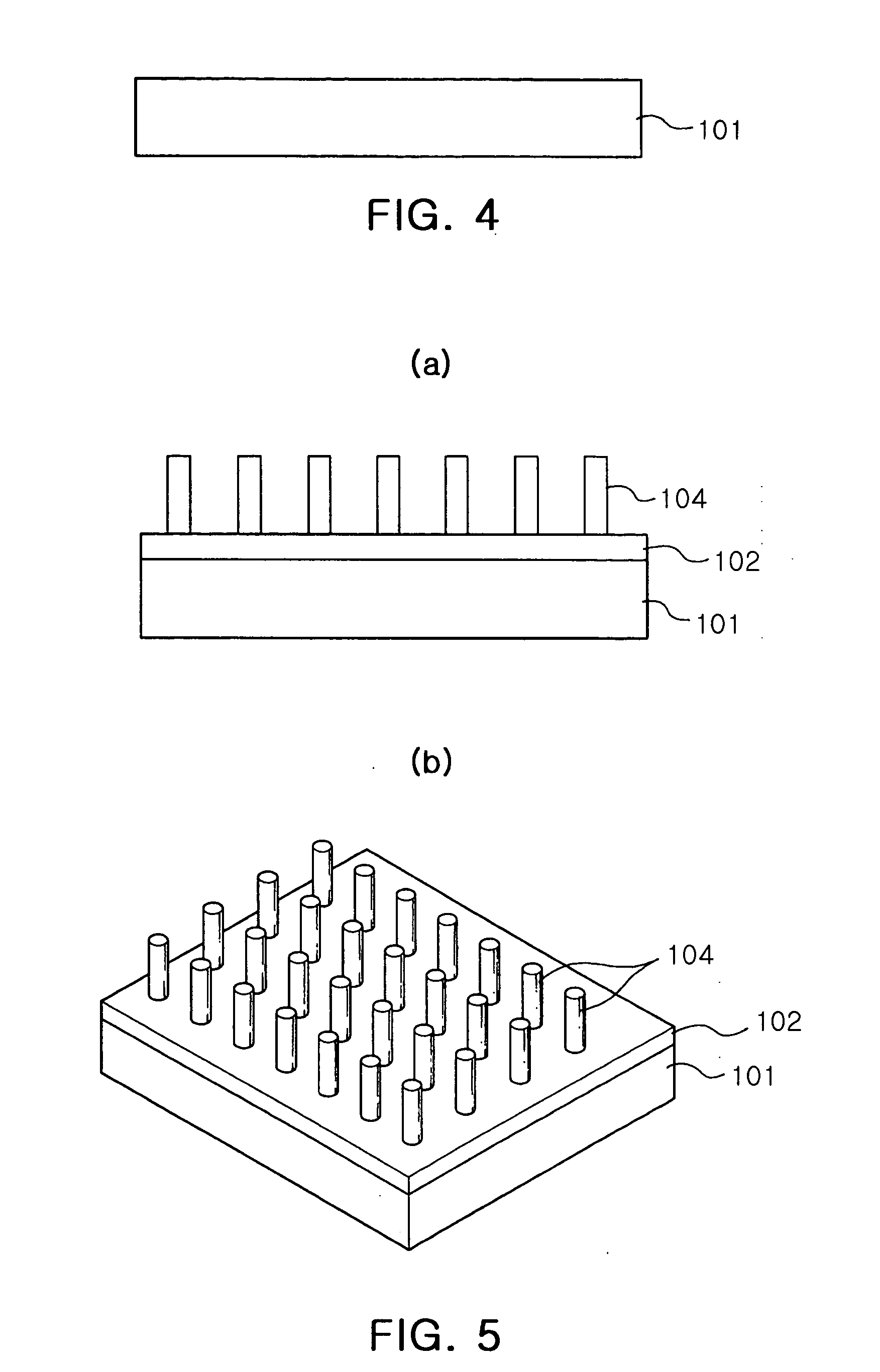
Large scale patterned growth of aligned one-dimensional nanostructures
A method of making nanostructures using a self-assembled monolayer of organic spheres is disclosed. The nanostructures include bowl-shaped structures and patterned elongated nanostructures. A bowl-shaped nanostructure with a nanorod grown from a conductive substrate through the bowl-shaped nanostructure may be configured as a field emitter or a vertical field effect transistor. A method of separating nanoparticles of a desired size employs an array of bowl-shaped structures.
Owner:GEORGIA TECH RES CORP
Printable compositions having anisometric nanostructures for use in printed electronics
Compositions and methods for production of conductive paths can include a printable composition including a liquid carrier and a plurality of nanostructures. The plurality of nanostructures can have an aspect ratio of at least about 5:1 within the liquid carrier. Examples of nanostructures include nanobelts, nanoplates, nanodiscs, nanowires, nanorods, and mixtures of these materials. These printable compositions can be used to form a conductive path on a substrate. The printable composition can be applied to a substrate using any number of conventional printing techniques. Following application of the printable composition, at least a portion of the liquid carrier can be removed such that the nanostructures can be in sufficient contact to provide a conductive path. The nanostructures arranged in a conductive path can be sintered or used as a conductive material without sintering.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
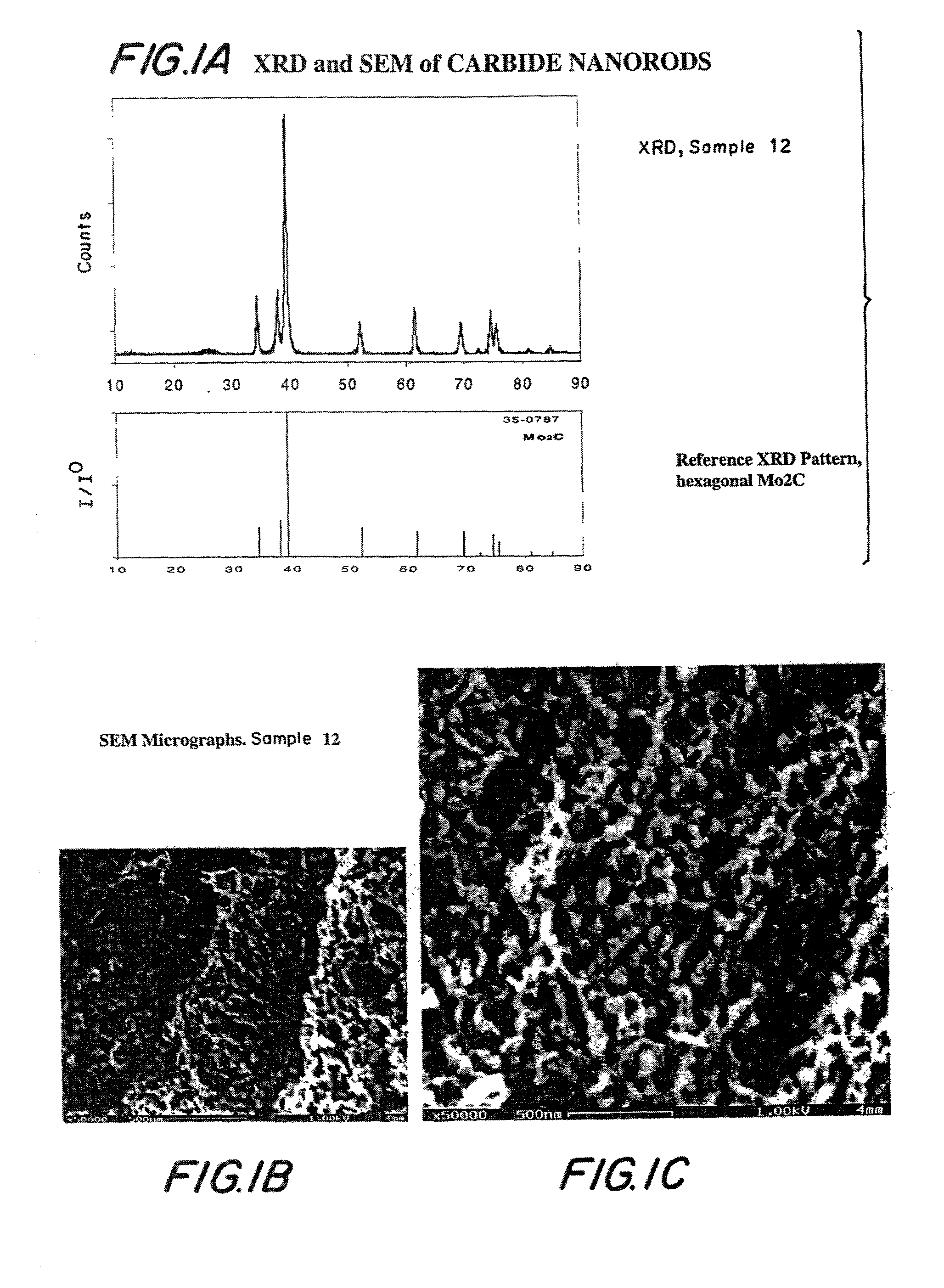
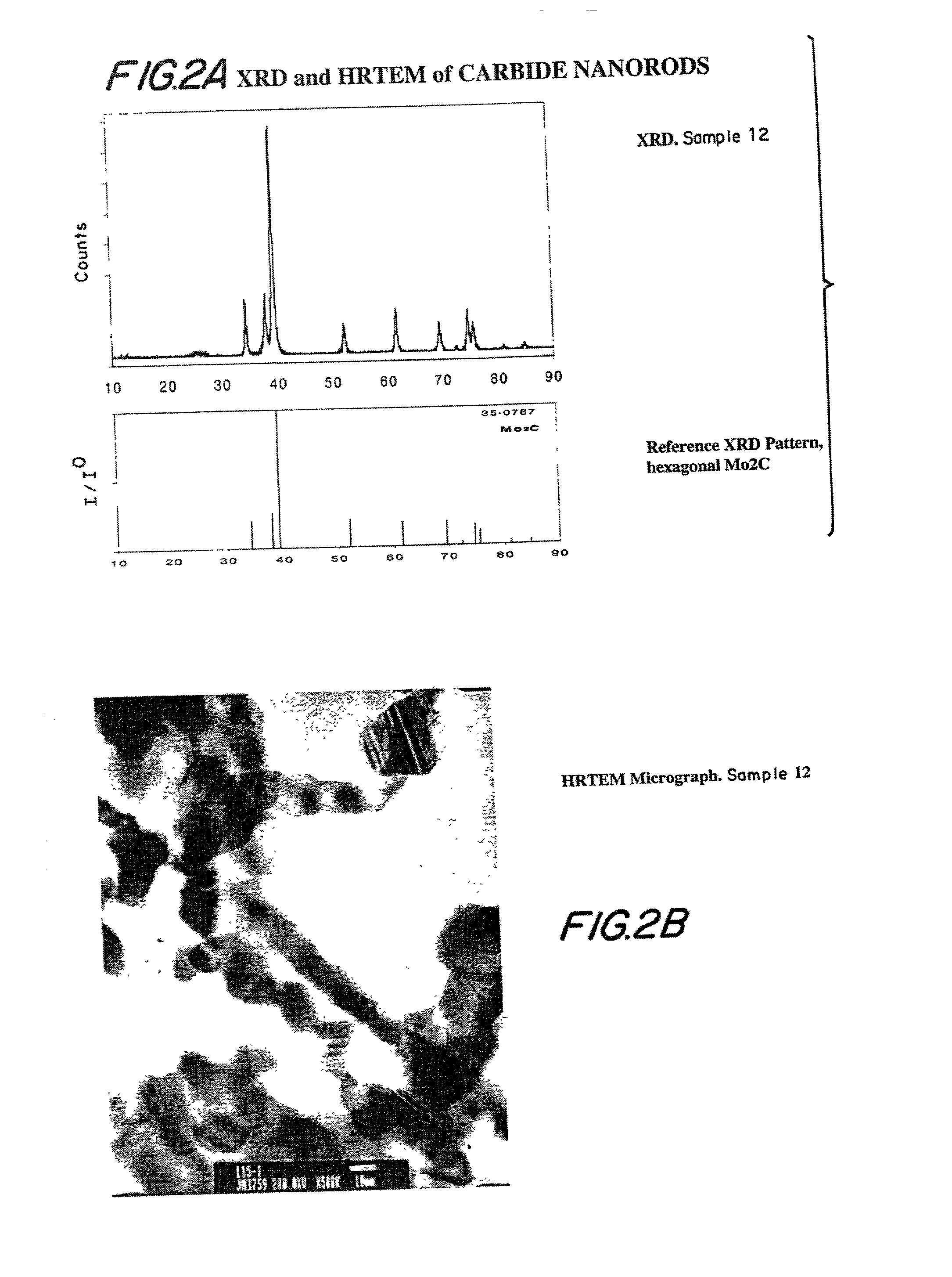
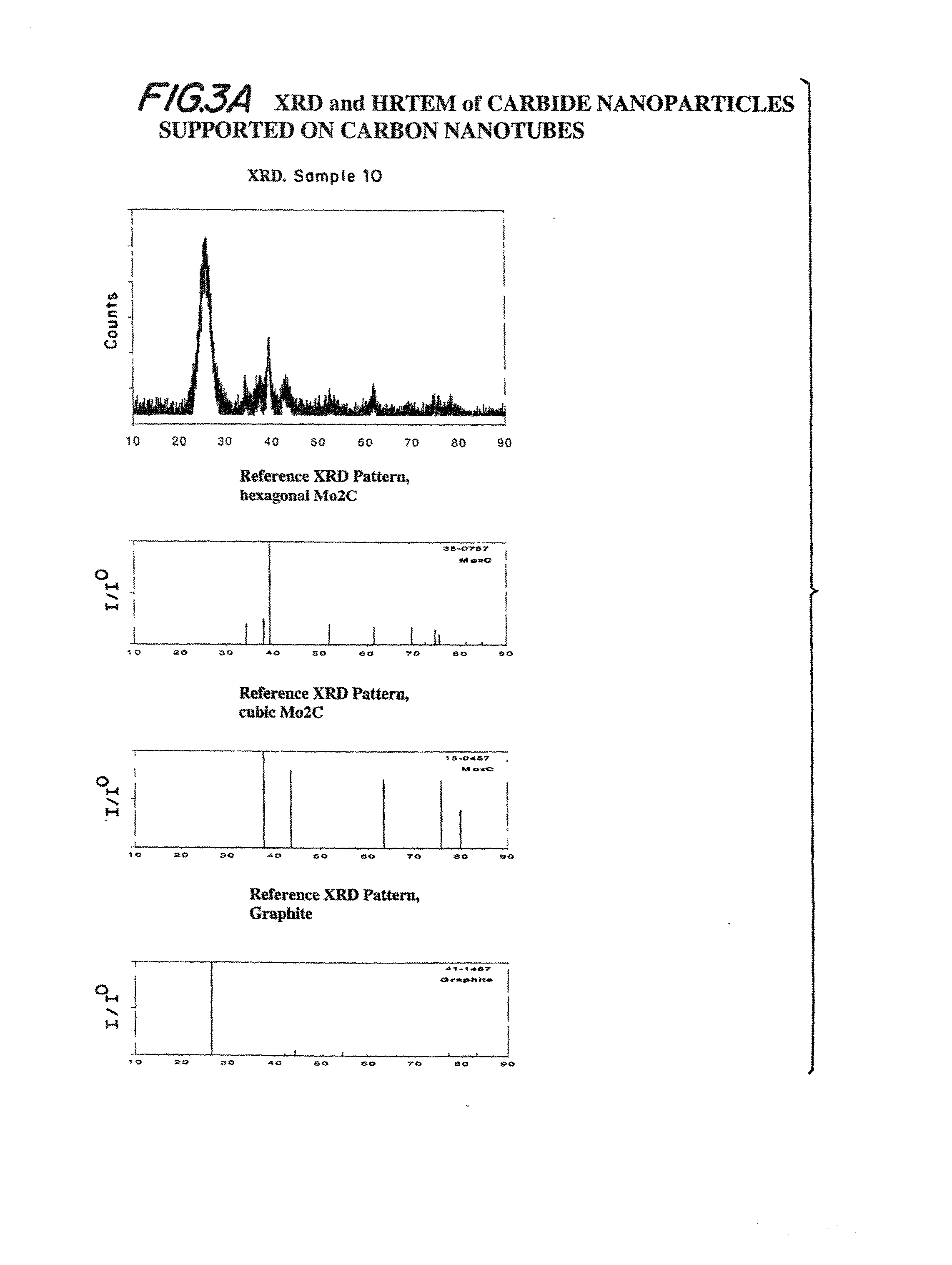
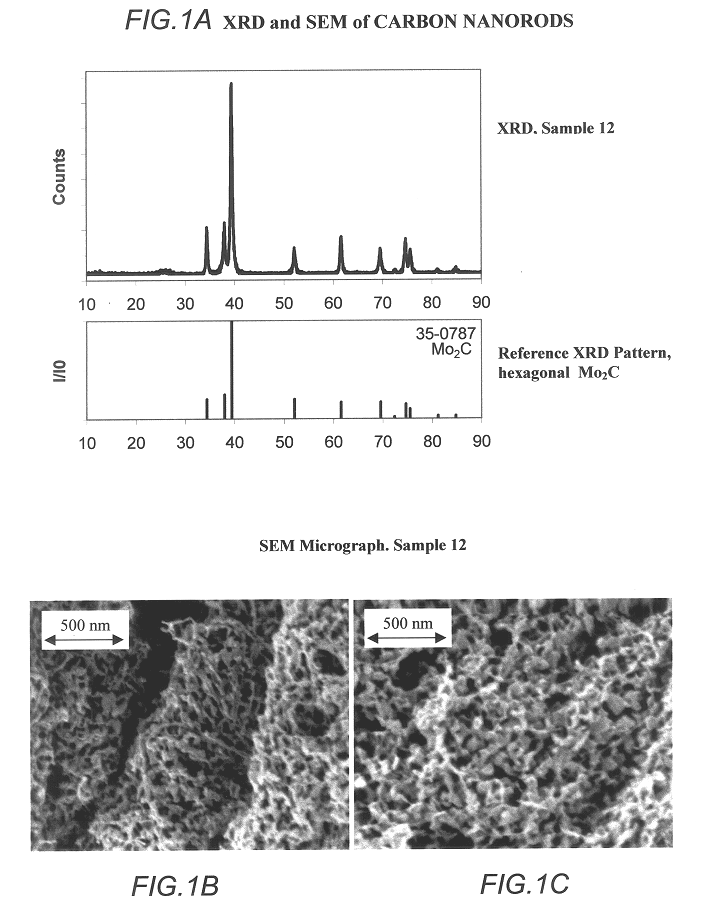
Method of using carbide and/or oxycarbide containing compositions
InactiveUS20020121460A1Facilitated DiffusionHigh porosityMaterial nanotechnologyHydrocarbon by isomerisationFluid phaseChemical reaction
Compositions including carbide-containing nanorods and / or oxycarbide-containing nanorods and / or carbon nanotubes bearing carbides and oxycarbides and methods of making the same are provided. Rigid porous structures including oxycarbide-containing nanorods and / or carbide containing nanorods and / or carbon nanotubes bearing carbides and oxycarbides and methods of making the same are also provided. The compositions and rigid porous structures of the invention can be used either as catalyst and / or catalyst supports in fluid phase catalytic chemical reactions. Processes for making supported catalyst for selected fluid phase catalytic reactions are also provided.
Owner:HYPERION CATALYSIS INT
Open porous electrically conductive nanocomposite material
ActiveUS20100233538A1Easy to getFaster and energy efficientElectrode manufacturing processesFinal product manufactureHigh energyConductive polymer
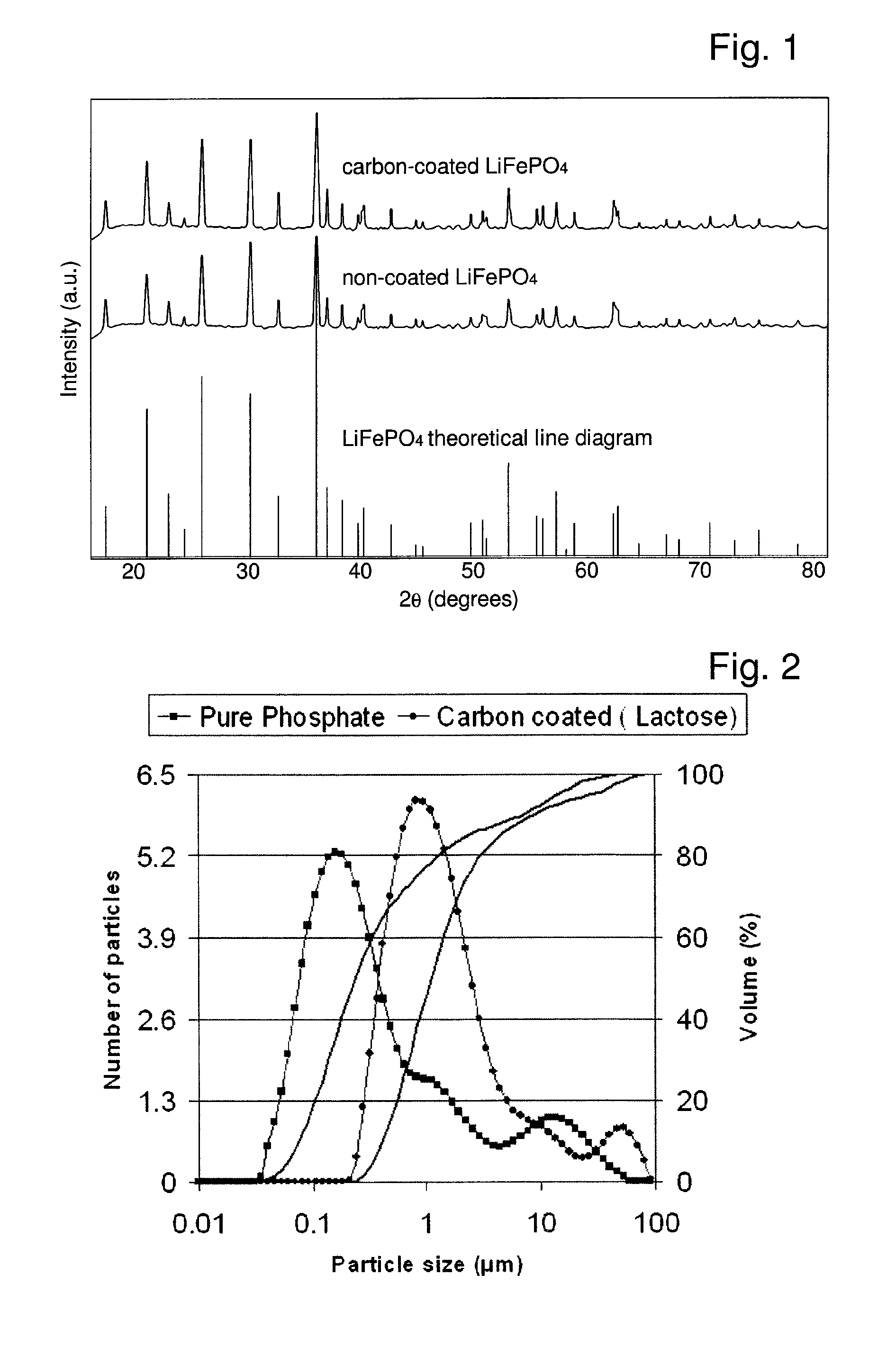
Nanocomposits of conductive, nanoparticulate polymer and electronically active material, in particular PEDOT and LiFePO4, were found to be significantly better compared to bare and carbon coated LiFePO4 in carbon black and graphite filled non conducting binder. The conductive polymer containing composite outperformed the other two samples. The performance of PEDOT composite was especially better in the high current regime with capacity retention of 82% after 200 cycles. Hence an electrode based on composite made of conductive, nanoparticulate polymer and electronically active material, in particular LiFePO4 and PEDOT nanostubs, with its higher energy density and increased resistance to harsh charging regimes proved to dramatically extend the high power applicability of materials such as LiFePO4.
Owner:BELENOS CLEAN POWER HLDG
Nanostructured Metal Oxides Comprising Internal Voids and Methods of Use Thereof
InactiveUS20100258759A1Controllable sizeEasy to useMaterial nanotechnologyElectrolytic capacitorsNanoparticleNanostructured metal
The present invention relates to nano structures of metal oxides having a nanostructured shell (or wall), and an internal space or void. Nanostructures may be nanoparticles, nanorod / belts / arrays, nanotubes, nanodisks, nanoboxes, hollow nanospheres, and mesoporous structures, among other nanostructures. The nanostructures are composed of polycrystalline metal oxides such as SnO2. The nanostructures may have concentric walls which surround the internal space of cavity. There may be two or more concentric shells or walls. The internal space may contain a core such ferric oxides or other materials which have functional properties. The invention also provides for a novel, inexpensive, high-yield method for mass production of hollow metal oxide nanostructures. The method may be template free or contain a template such as silica. The nanostructures prepared by the methods of the invention provide for improved cycling performance when tested using rechargeable lithium-ion batteries.
Owner:CORNELL RES FOUNDATION INC
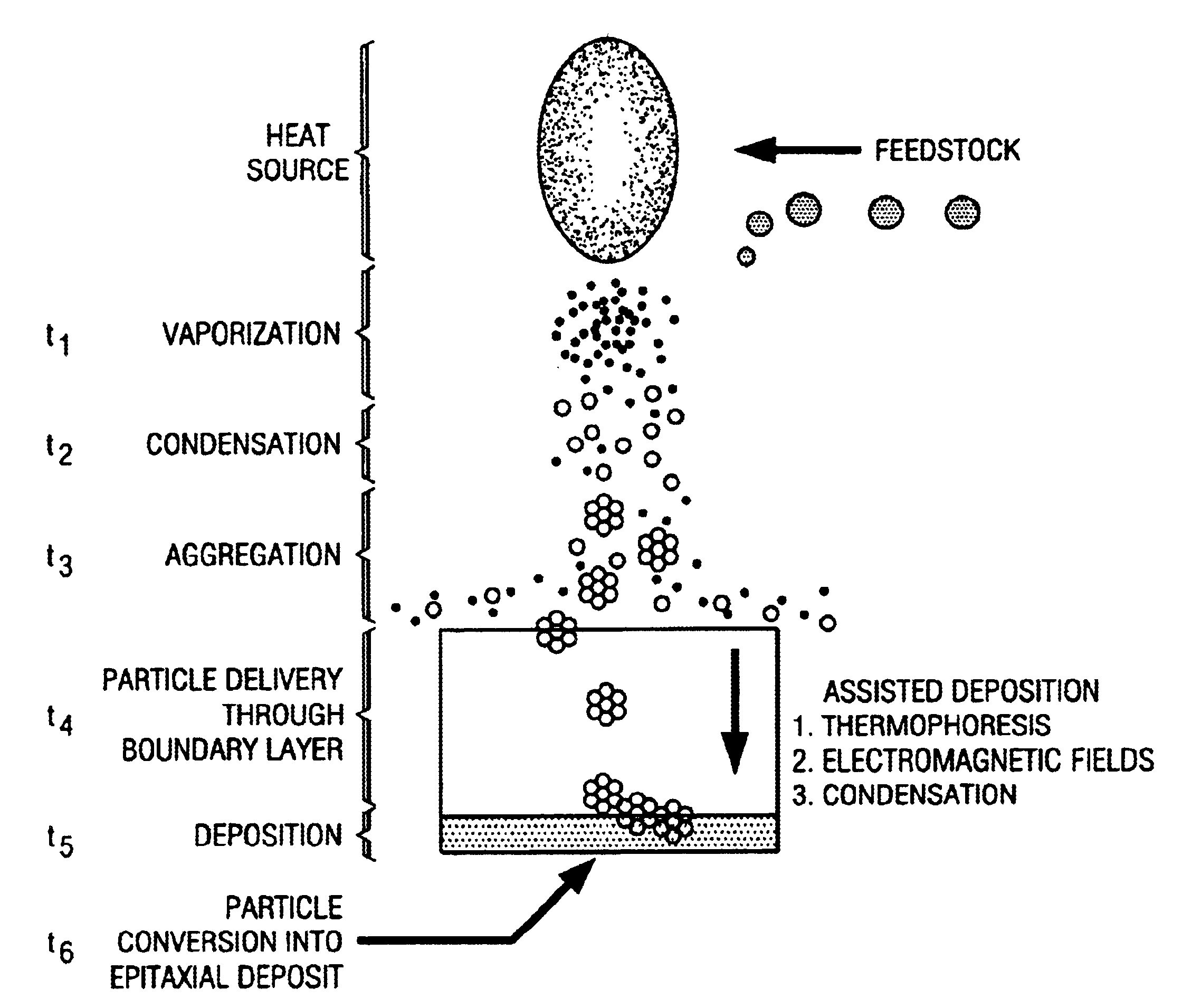
Condensed phase conversion and growth of nanorods instead of from vapor
Compositions, systems and methods are described for condensed phase conversion and growth of nanorods and other materials. A method includes providing a condensed phase matrix material; and activating the condensed phase matrix material to produce a plurality of nanorods by condensed phase conversion and growth from the condensed chase matrix material instead of from vacor. The compositions are very strong. The compositions and methods provide advantages because they allow (1) formation rates of nanostructures necessary for reasonable production rates, and (2) the near net shaped production of component structures.
Owner:UT BATTELLE LLC
Nitride semiconductor device and method of manufacturing the same
ActiveUS20050199886A1Improve optical efficiencyQuality improvementNanotechSolid-state devicesLight-emitting diodeElectron
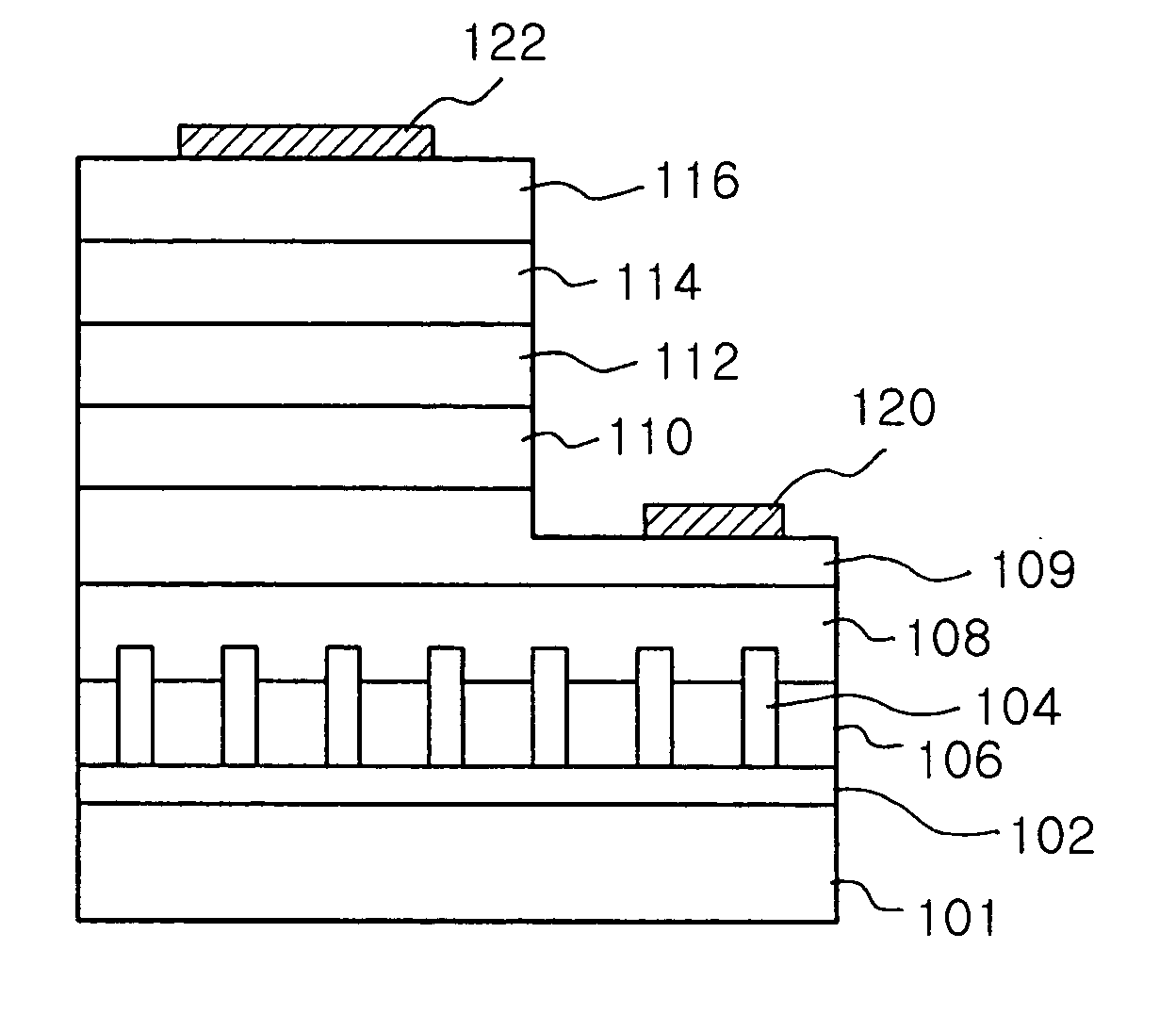
Provided are a nitride semiconductor device and method of manufacturing the same. In the method, semiconductor nanorods are vertically grown on a substrate, and then a nitride semiconductor thin film is deposited on the substrate having the semiconductor nanorods. Accordingly, a high-quality nitride semiconductor thin film can be deposited on a variety of inexpensive, large-sized substrates. Also, because the nitride semiconductor thin film containing the semiconductor nanorods can easily emit light through openings between the nanorods, internal scattering can be greatly reduced. Thus, the nitride semiconductor thin film can be usefully employed in optical devices such as light emitting diodes and electronic devices.
Owner:LG SILTRON +1
Carbide and oxycarbide based compositions, rigid porous structures including the same, methods of making and using the same
InactiveUS6514897B1Easy to diffuseSpeed up the flowMaterial nanotechnologyHydrocarbon by isomerisationIsomerizationChemical reaction
The present invention relates to compositions and rigid porous structures that contain nanorods having carbides and / or oxycarbides and methods of making and using such compositions and such rigid porous structures. The compositions and rigid porous structures can be used either as catalysts and / or catalyst supports in fluid phase catalytic chemical reactions. Processes for making supported catalyst for selected fluid phase catalytic reactions are also provided. The fluid phase catalytic reactions catalyzed include hydrogenation hydrodesulfuriaation, hydrodenitrogenation, hydrodemetallization, hydrodeoxygenation, hydrodearomatization, dehydrogenation, hydrogenolyis, isomerization, alkylation, dealkylation, oxidation and transalkylation.
Owner:HYPERION CATALYSIS INT
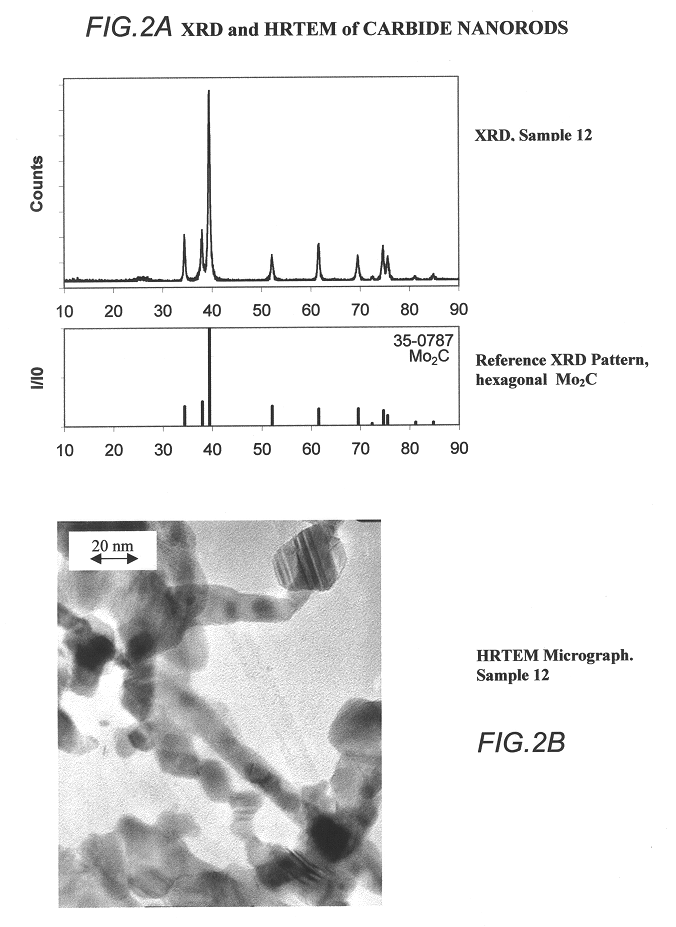
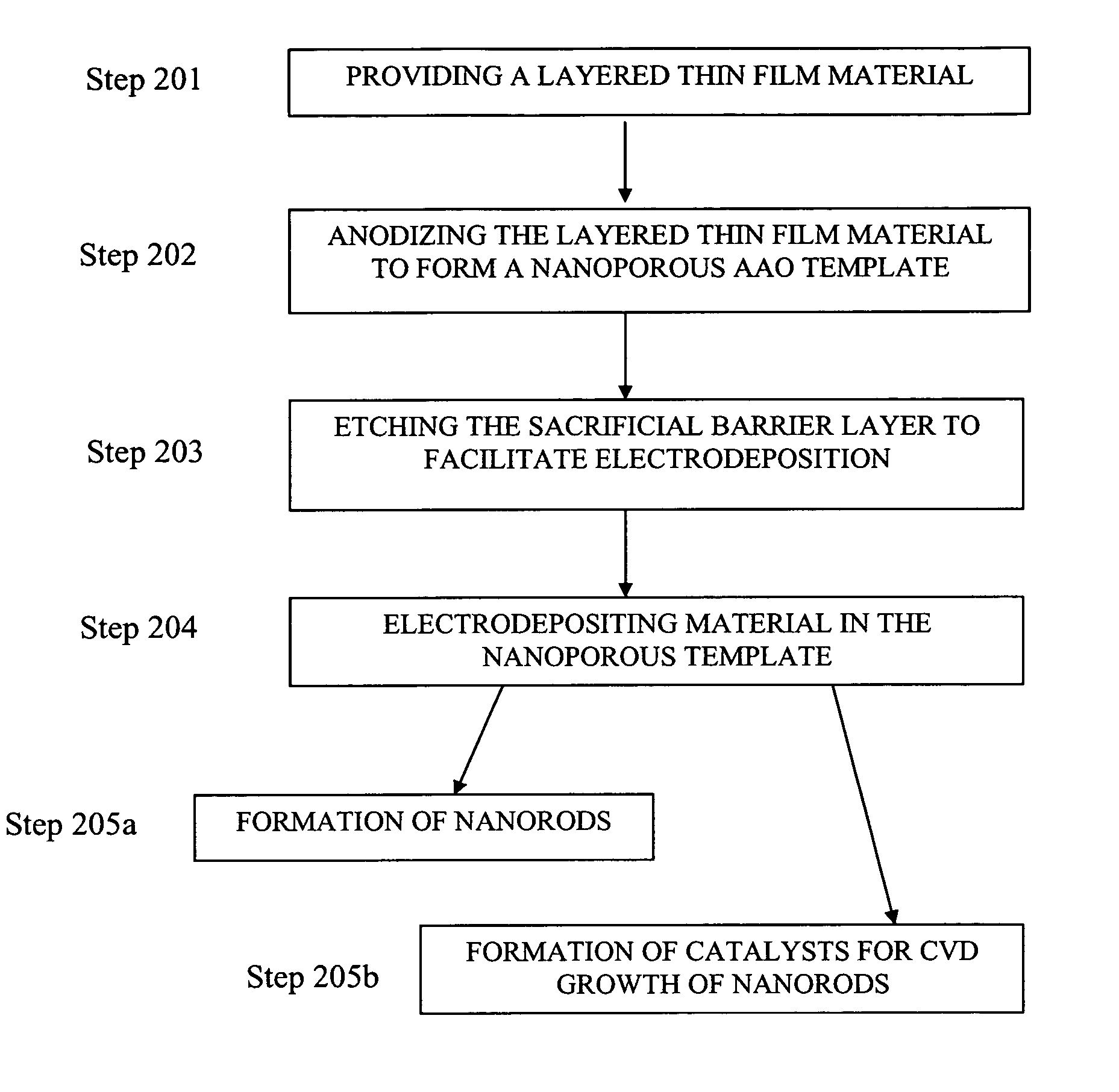
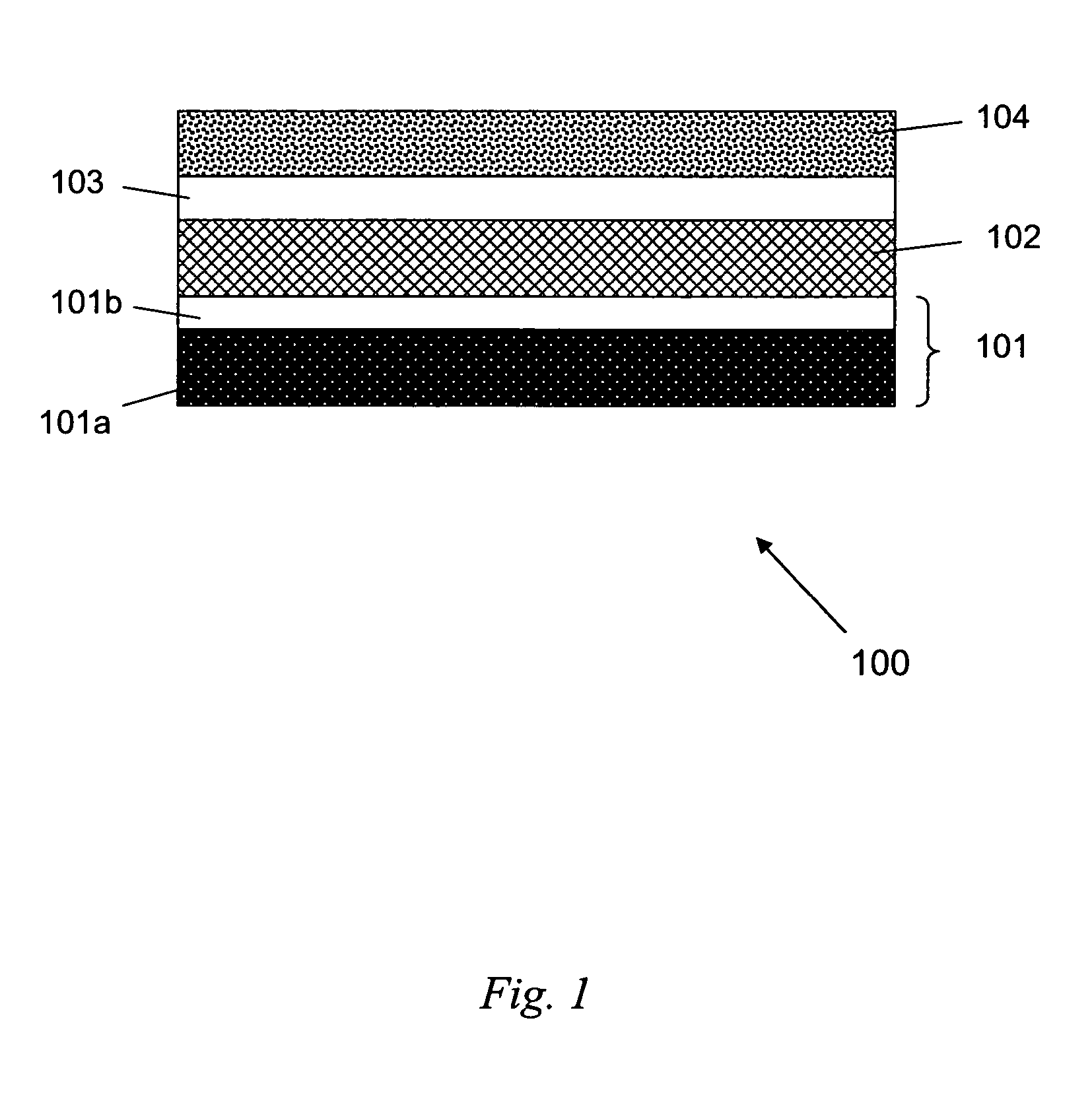
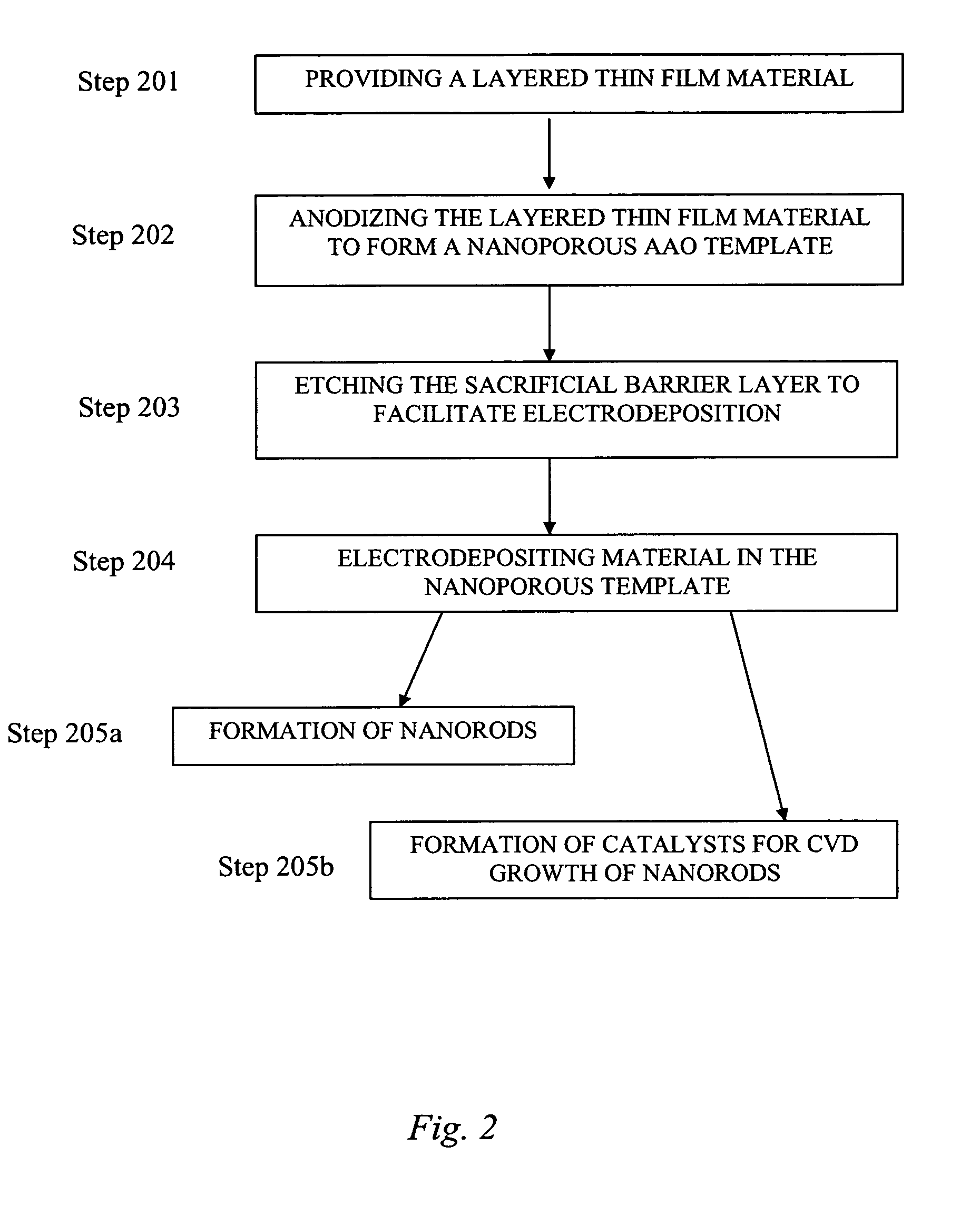
Anodized aluminum oxide nanoporous template and associated method of fabrication
In some embodiments, the present invention is directed to nanoporous anodized aluminum oxide templates of high uniformity and methods for making same, wherein such templates lack a AAO barrier layer. In some or other embodiments, the present invention is directed to methods of electrodepositing nanorods in the nanopores of these templates. In still other embodiments, the present invention is directed to electrodepositing catalyst material in the nanopores of these templates and growing nanorods or other 1-dimensional nanostructures via chemical vapor deposition (CVD) or other techniques.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
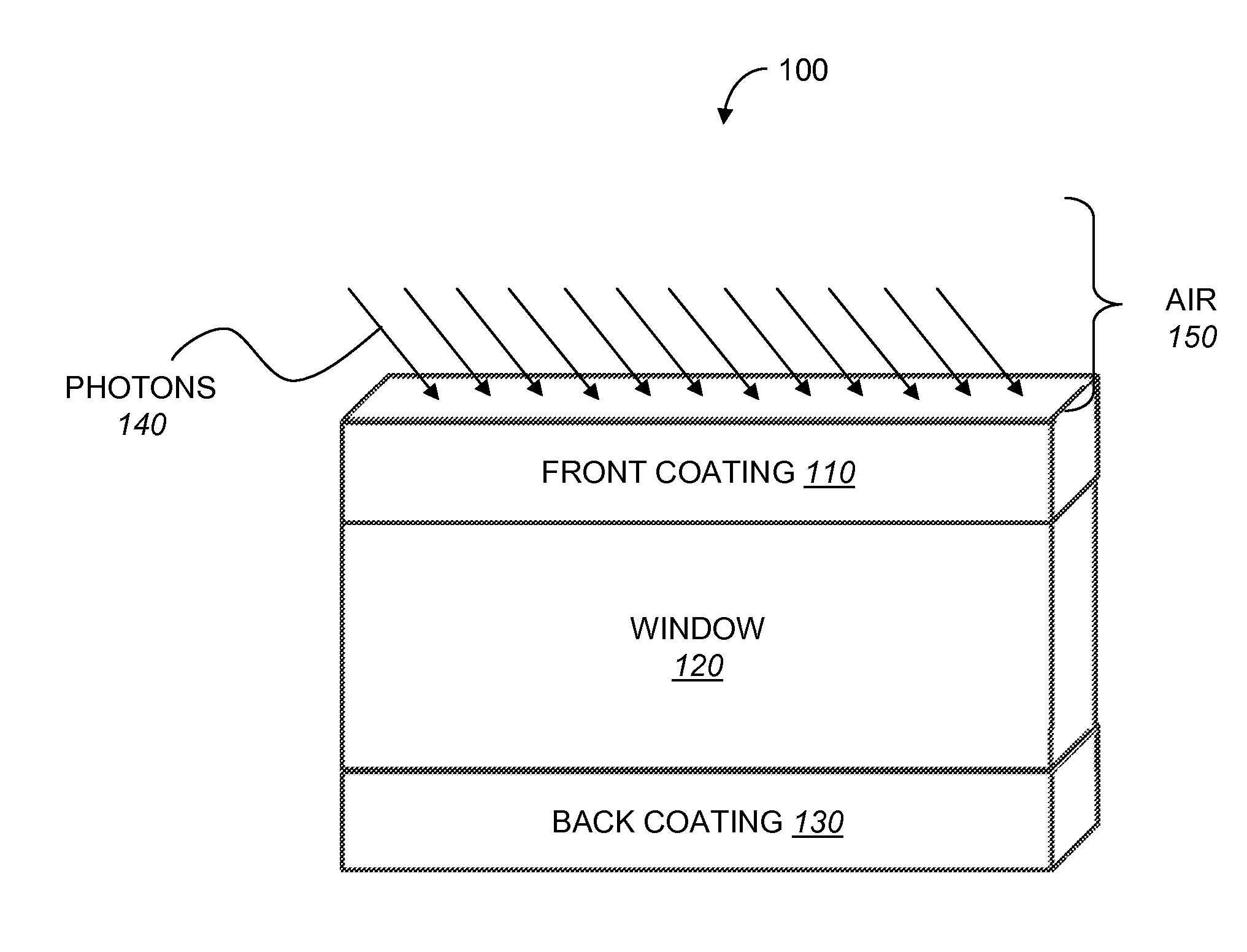
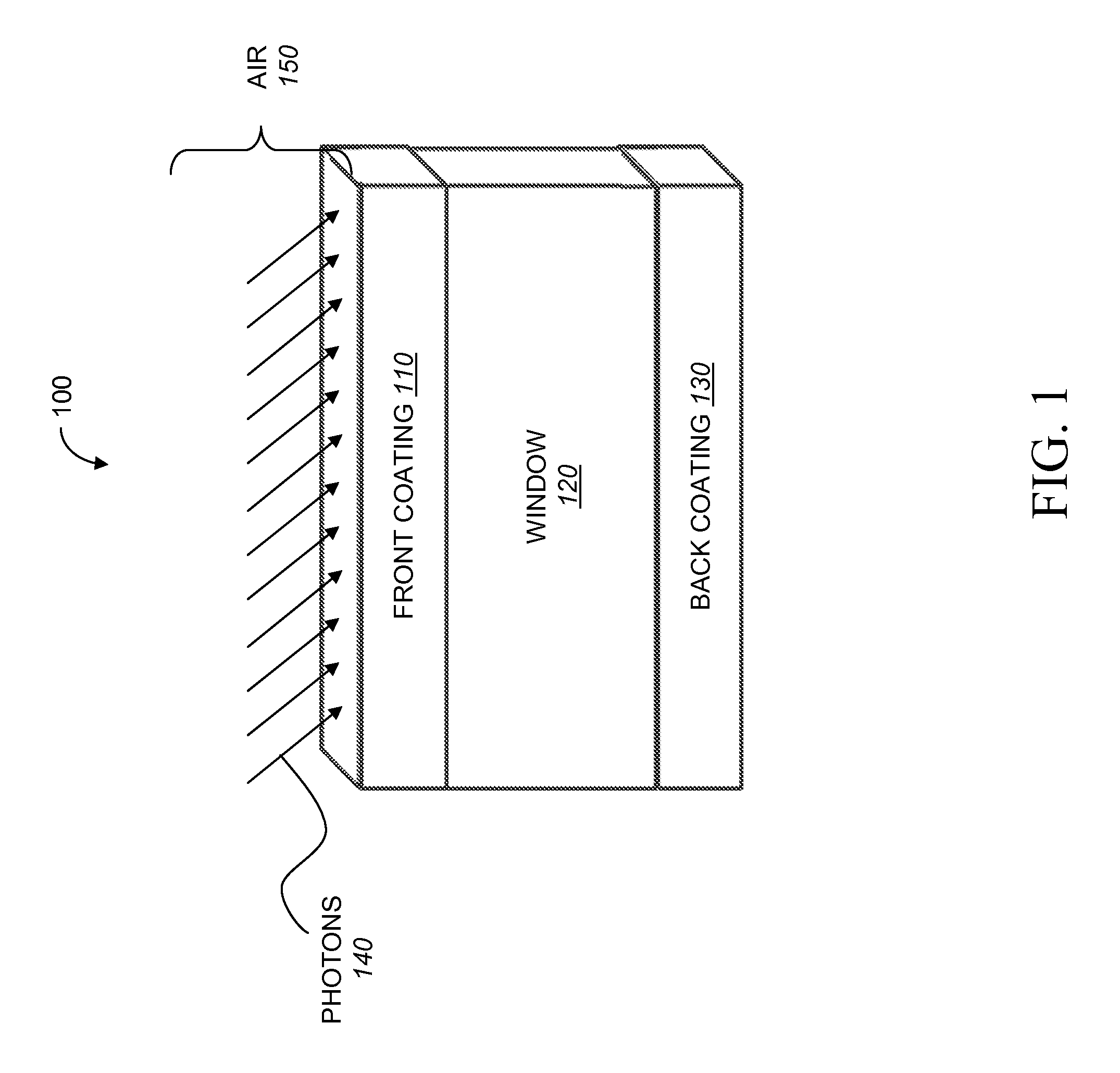
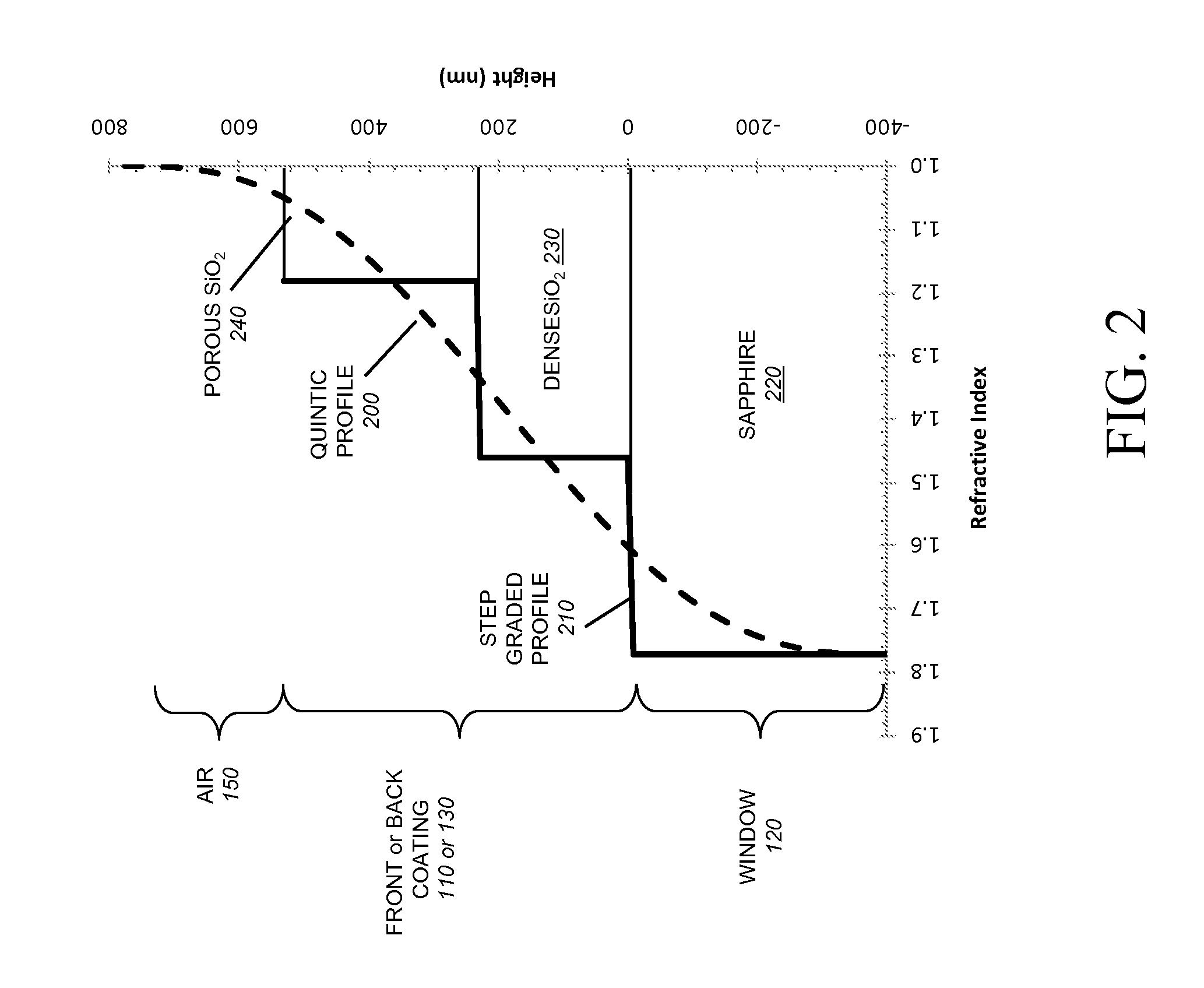
High transmittance optical windows and method of constructing the same
InactiveUS20110168261A1Avoid reflectionsHigh light transmittanceSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingPhotovoltaic energy generationOptical coatingMaterial synthesis
Designs for ultra-high, broadband transmittance through windows over a wide range of incident angles are disclosed. The improvements in transmittance result from coating the windows with a new class of materials consisting of porous nanorods. A high transmittance optical window comprises a transparent substrate coated on one or both sides with a multiple layer coating. Each multiple layer coating includes optical films with a refractive index intermediate between the refractive index of the transparent substrate and air. The optical coatings are applied using an oblique-angle deposition material synthesis technique. The coating can be performed by depositing porous SiO2 layers using oblique angle deposition. The high transmittance window coated with the multiple layer coating exhibits reduced reflectance and improved transmittance, as compared to an uncoated transparent substrate.
Owner:MAGNOLIA OPTICAL TECH +1
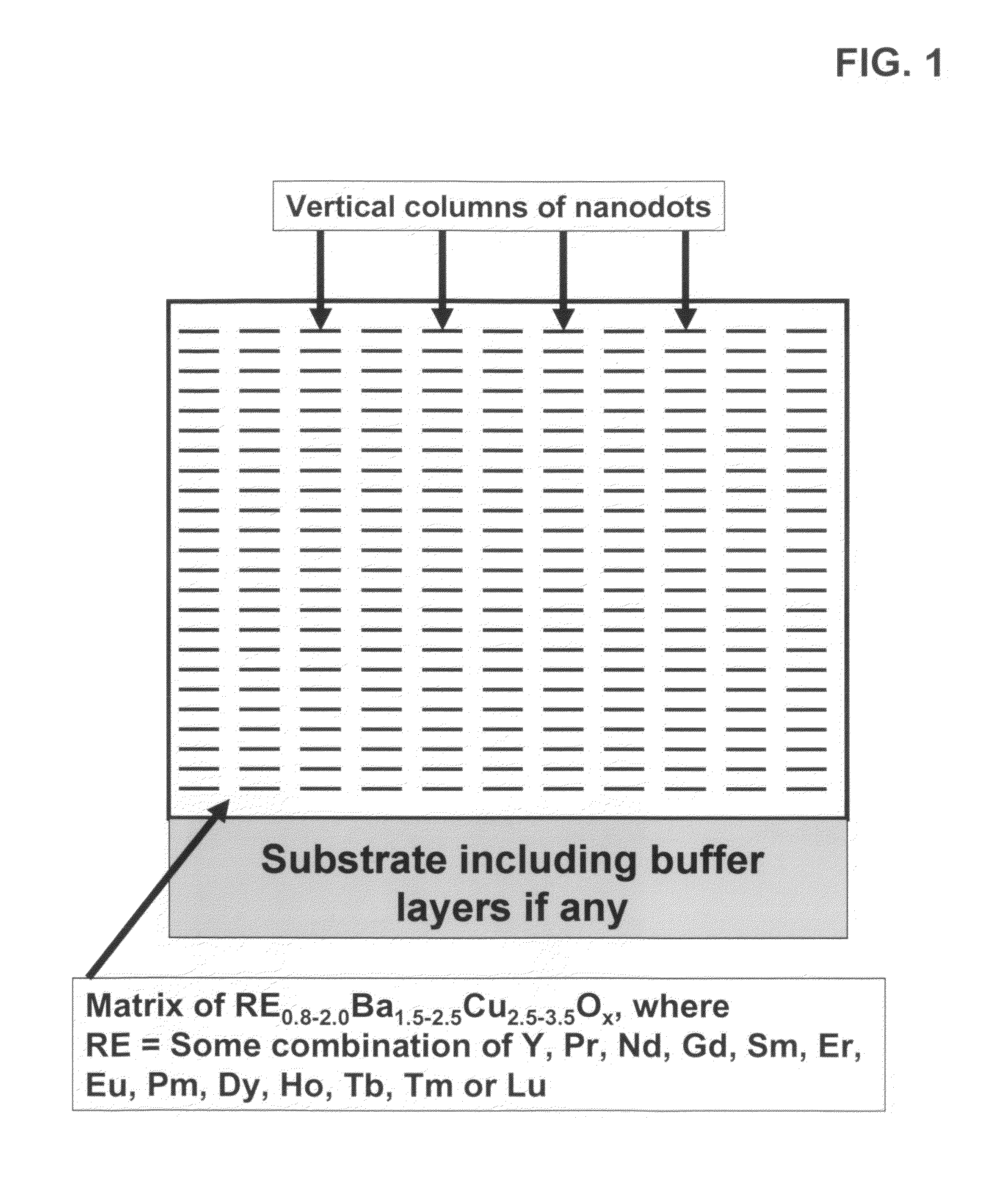
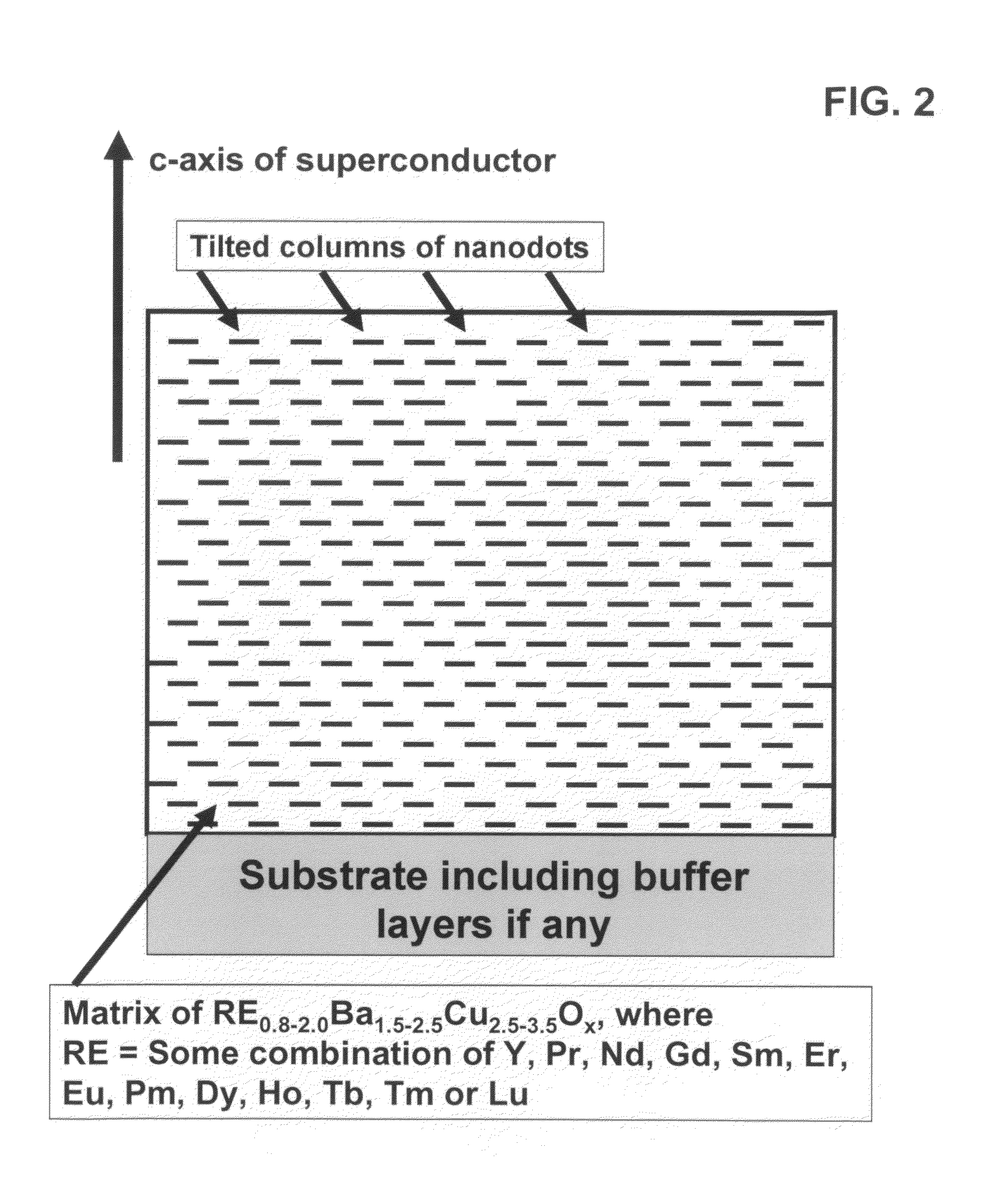
High performance devices enabled by epitaxial, preferentially oriented, nanodots and/or nanorods
ActiveUS20080176749A1Improve performanceSuperconductors/hyperconductorsGalvano-magnetic material selectionNanodotPhotoluminescence
Novel articles and methods to fabricate same with self-assembled nanodots and / or nanorods of a single or multicomponent material within another single or multicomponent material for use in electrical, electronic, magnetic, electromagnetic, superconducting and electrooptical devices is disclosed. Self-assembled nanodots and / or nanorods are ordered arrays wherein ordering occurs due to strain minimization during growth of the materials. A simple method to accomplish this when depositing in-situ films is also disclosed. Device applications of resulting materials are in areas of superconductivity, photovoltaics, ferroelectrics, magnetoresistance, high density storage, solid state lighting, non-volatile memory, photoluminescence, thermoelectrics and in quantum dot lasers.
Owner:GOYAL AMIT
Nanostructure Having a Nitride-Based Quantum Well and Light Emitting Diode Employing the Same
ActiveUS20080157057A1Increase brightnessReduce impactNanostructure manufactureSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingQuantum efficiencyNanostructure
Disclosed are a nanostructure with an indium gallium nitride quantum well and a light emitting diode employing the same. The light emitting diode comprises a substrate, a transparent electrode and an array of nanostructures interposed between the substrate and the transparent electrode. Each of the nanostructures comprises a core nanorod, and a nano shell surrounding the core nanorod. The core nanorod is formed substantially perpendicularly to the substrate and includes a first nanorod of a first conductivity type, an (AlxInyGa1-x-y)N (where, 0≦x≦1, 0≦y≦1 and 0≦x+y≦1) quantum well, and a second nanorod of a second conductivity type, which are joined in a longitudinal direction. The nano shell is formed of a material with a bandgap greater than that of the quantum well, and surrounds at least the quantum well of the core nanorod. Meanwhile, the second nanorods are connected in common to the transparent electrode. Accordingly, with the nano shells, it is possible to provide a light emitting diode capable of improving external quantum efficiency by preventing non-radiative recombination on a surface of the (AlxInyGa1-x-y)N quantum well.
Owner:SEOUL VIOSYS CO LTD
Method of manufacture of colloidal rod particles as nanobar codes
InactiveUS7045049B1Speed up the processMaterial nanotechnologyNanomagnetismNanoparticleSynthesis methods
Owner:SICPA HLDG SA +1
Titanium dioxide nanorod and preparation method thereof
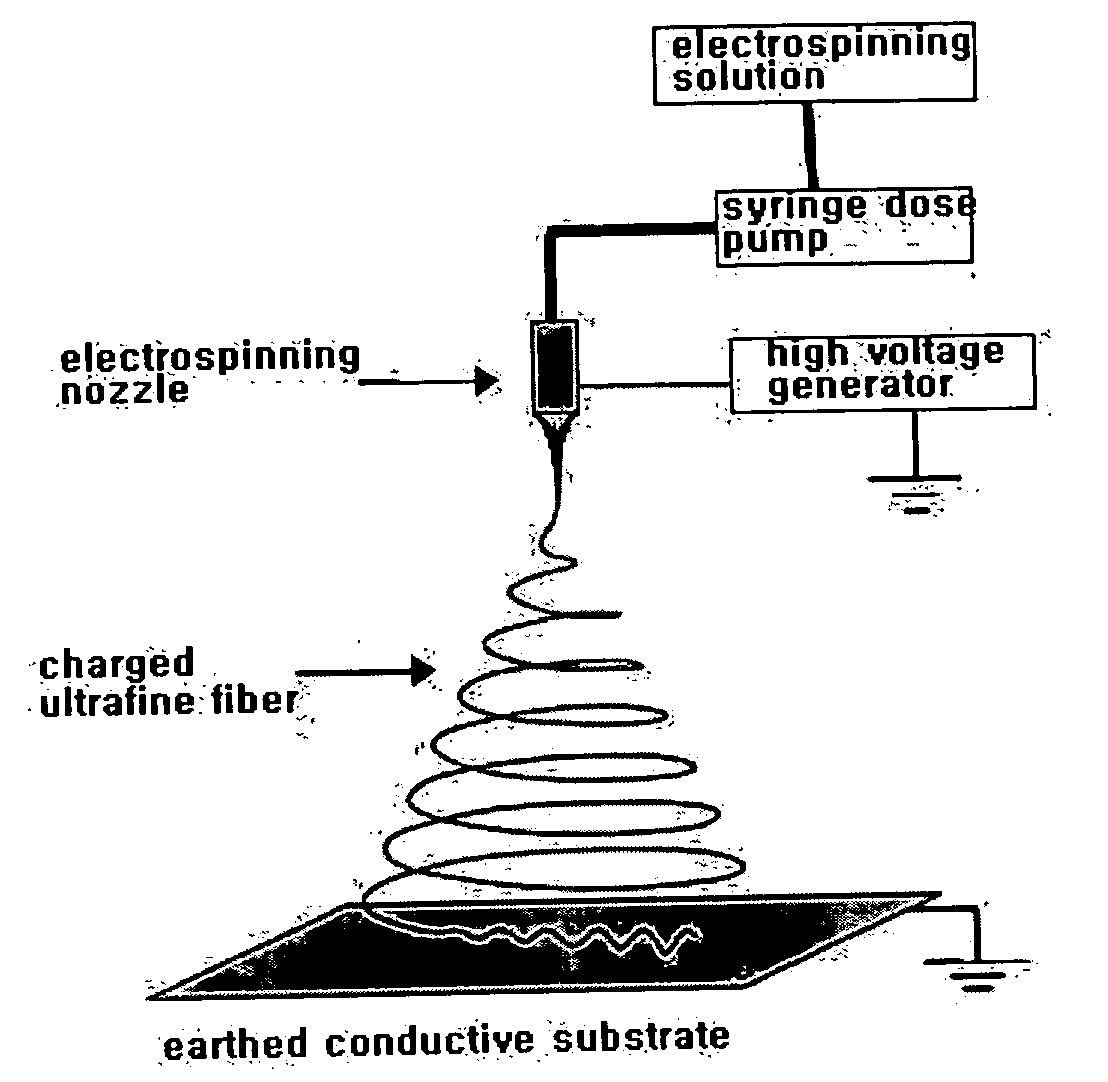
InactiveUS20070116640A1Easy to prepareMaterial nanotechnologyPigmenting treatmentFiberSingle crystal
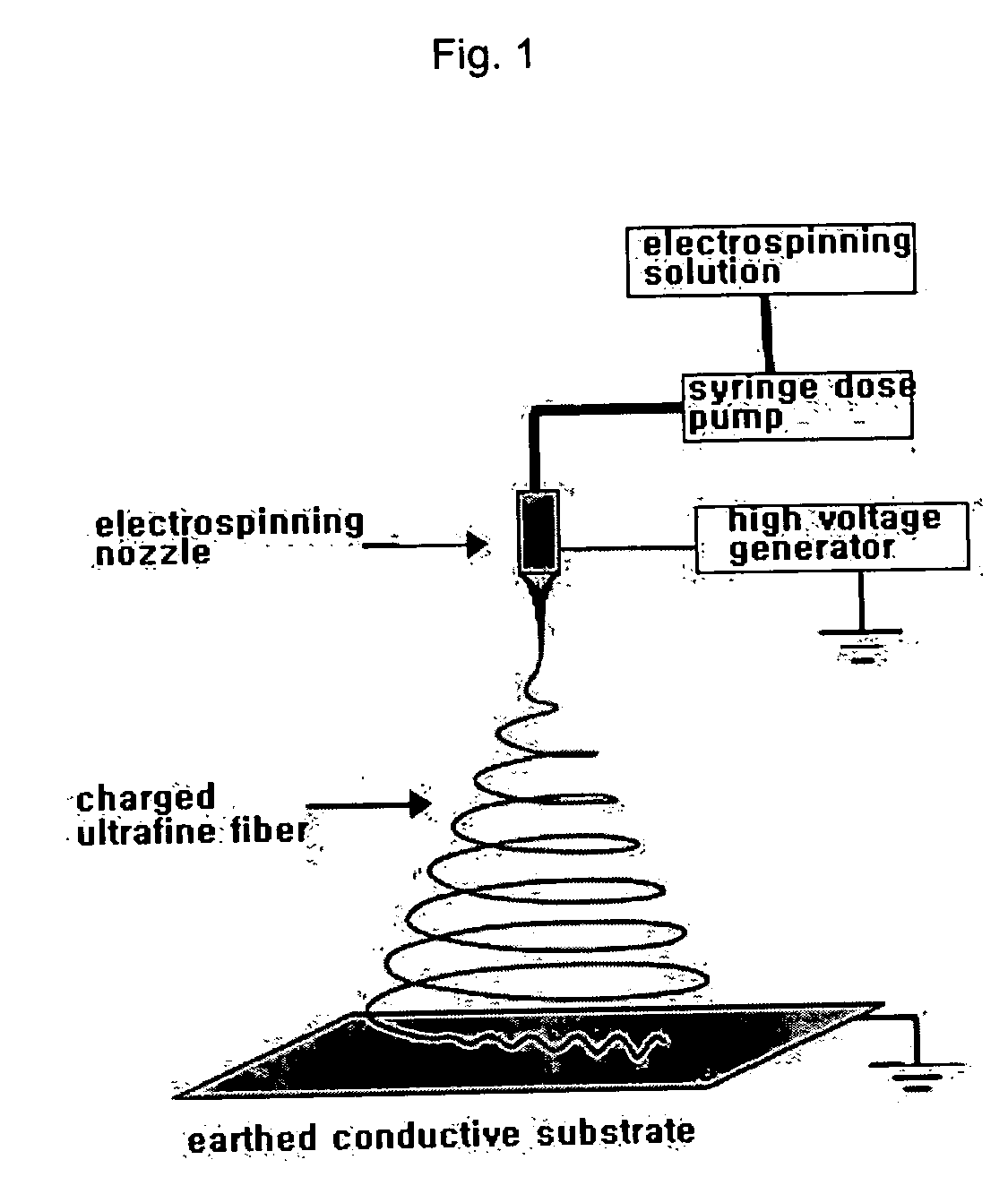
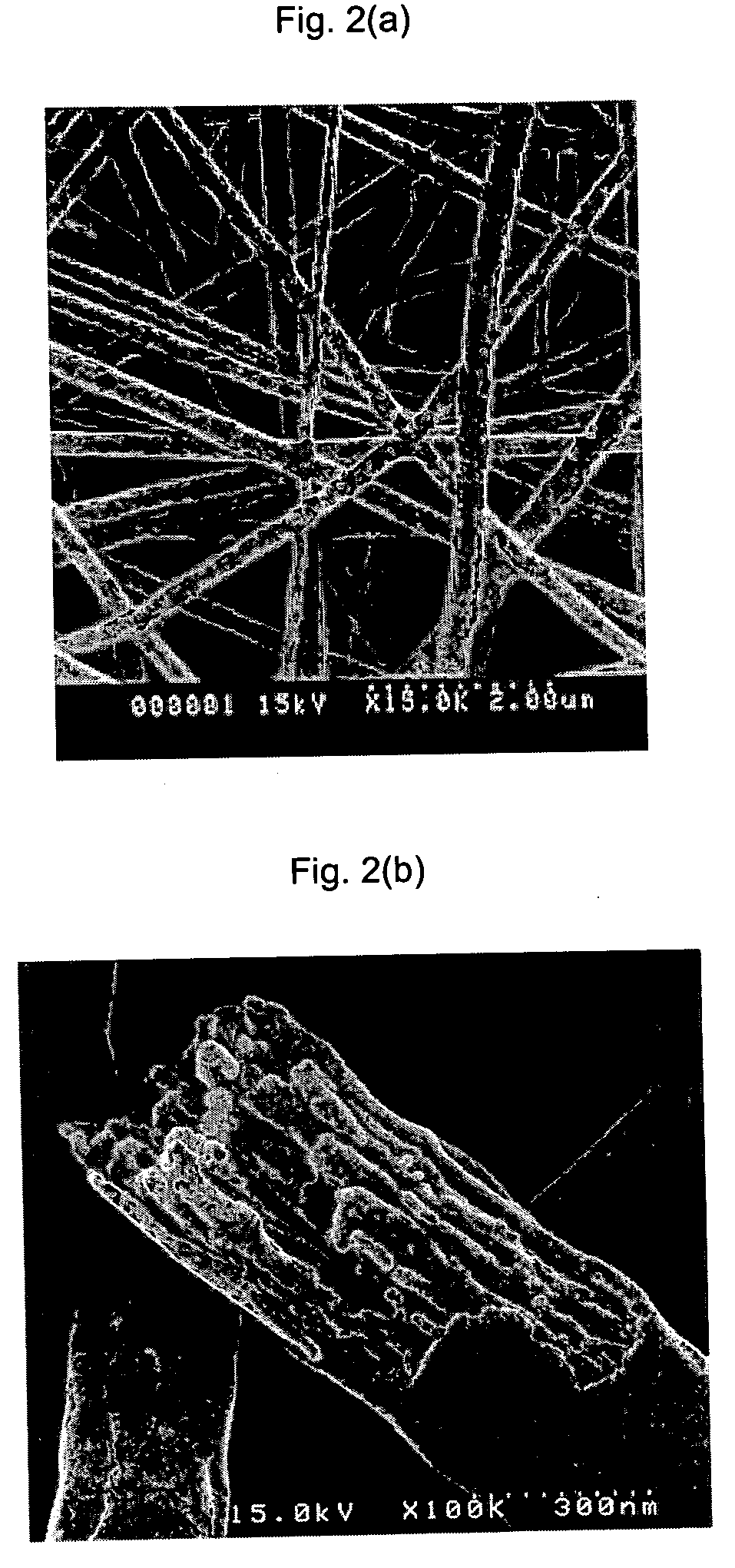
A titanium dioxide nanorod having anisotropy and a preparation method thereof in which, particularly, an ultrafine composite fiber of polymer and titanium dioxide precursor and a single crystal titanium dioxide nanorod using a phase separation are prepared, wherein a mixed solution containing titanium dioxide precursor, polymer which is compatible with the precursor and solvent is prepared, the mixed solution is electrospun to form titanium dioxide polymer composite fiber containing ultrafine fibril structure therein by the phase separation between the titanium dioxide precursor and the polymer, the composite fiber is heat-pressed, and the polymer material is removed from the composite fiber, so as to obtain titanium dioxide nanorod, which can be used as dye-sensitized solar cells, various sensors, and photocatalysts.
Owner:KOREA INST OF SCI & TECH
Printable compositions having anisometric nanostructures for use in printed electronics
Compositions and methods for production of conductive paths can include a printable composition including a liquid carrier and a plurality of nanostructures. The plurality of nanostructures can have an aspect ratio of at least about 5:1 within the liquid carrier. Examples of nanostructures include nanobelts, nanoplates, nanodiscs, nanowires, nanorods, and mixtures of these materials. These printable compositions can be used to form a conductive path on a substrate. The printable composition can be applied to a substrate using any number of conventional printing techniques. Following application of the printable composition, at least a portion of the liquid carrier can be removed such that the nanostructures can be in sufficient contact to provide a conductive path. The nanostructures arranged in a conductive path can be sintered or used as a conductive material without sintering.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Group iii nitride nanorod light emitting device and method of manufacturing thereof
ActiveUS20120068153A1Three-dimensional structure is improvedImprove luminous efficiencySemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSemiconductor devicesNitrogenPulsed mode
A group III nitride nanorod light emitting device and a method of manufacturing thereof. The method includes preparing a substrate, forming an insulating film including one or more openings exposing parts of the substrate on the substrate, growing first conductive group III nitride nanorod seed layers on the substrate exposed through the openings by supplying a group III source gas and a nitrogen (N) source gas thereto, growing first conductive group III nitride nanorods on the first conductive group III nitride nanorod seed layers by supplying the group III source gas and an impurity source gas in a pulse mode and continuously supplying the N source gas, forming an active layer on a surface of each of the first conductive group III nitride nanorods, and forming a second conductive nitride semiconductor layer on the active layer.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com