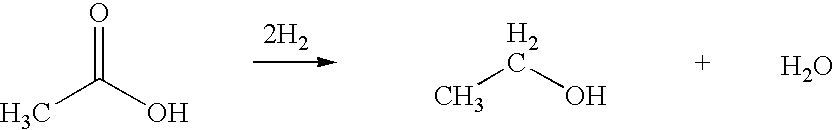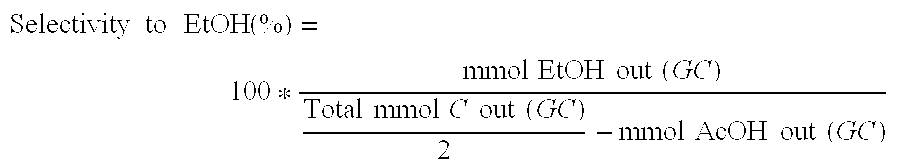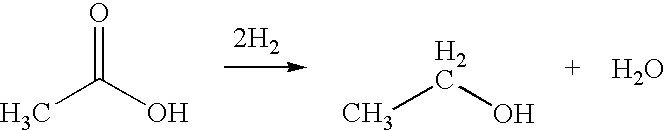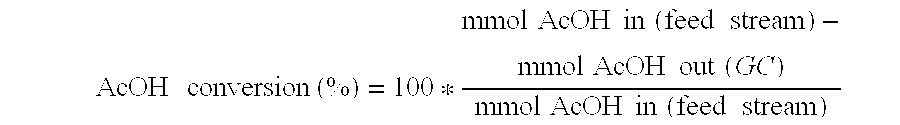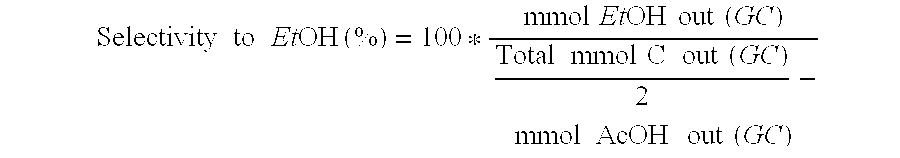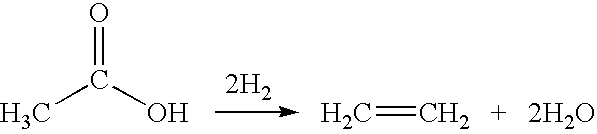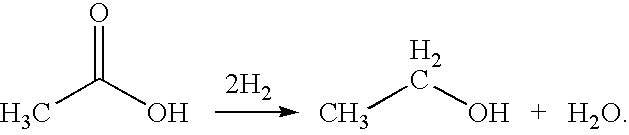Patents
Literature
28756 results about "Gas phase" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Gaseous phase (plural gaseous phases) (physics) One of the three fundamental structural phases of matter in which the thermal mobility of molecules or atoms is strong enough to permit their free motion, significantly exceeding the cohesive force.
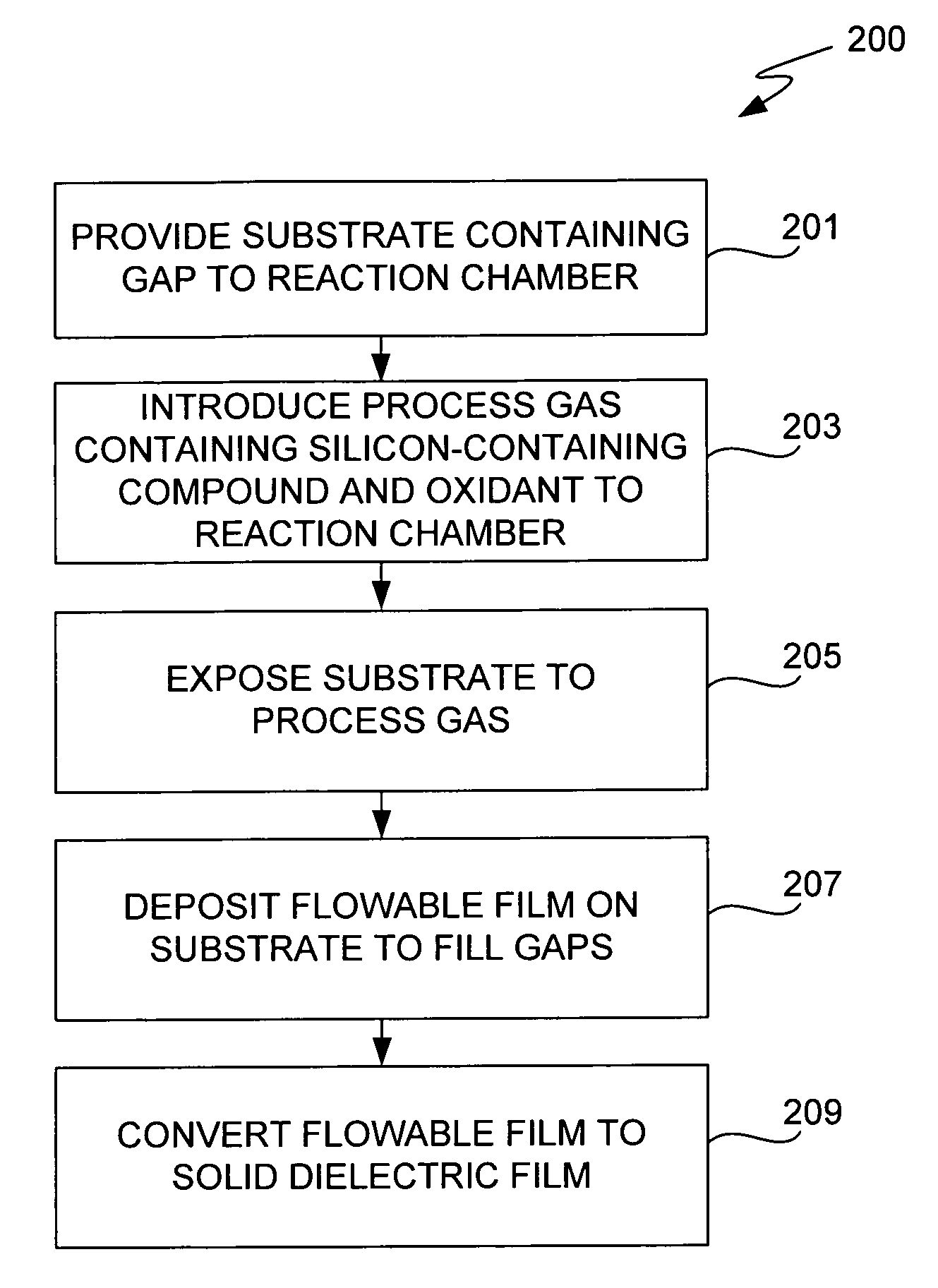
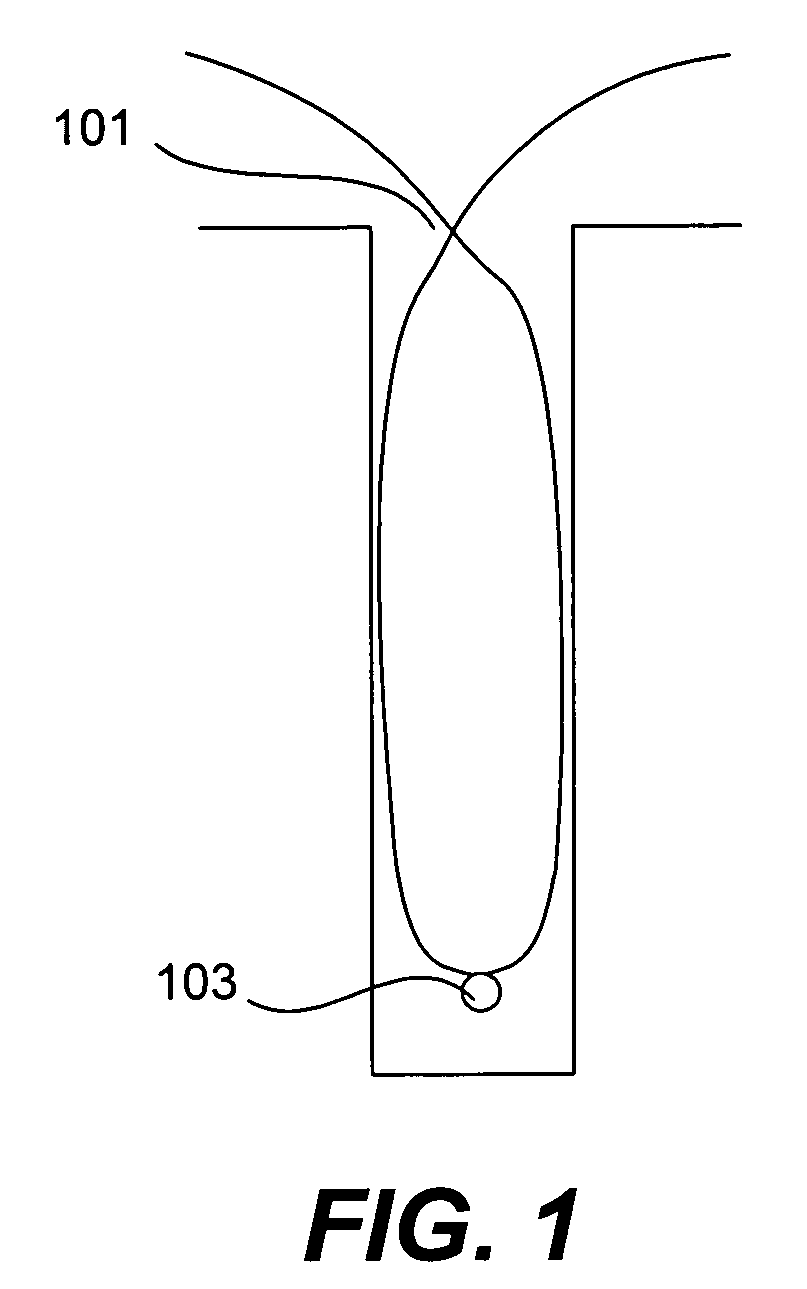
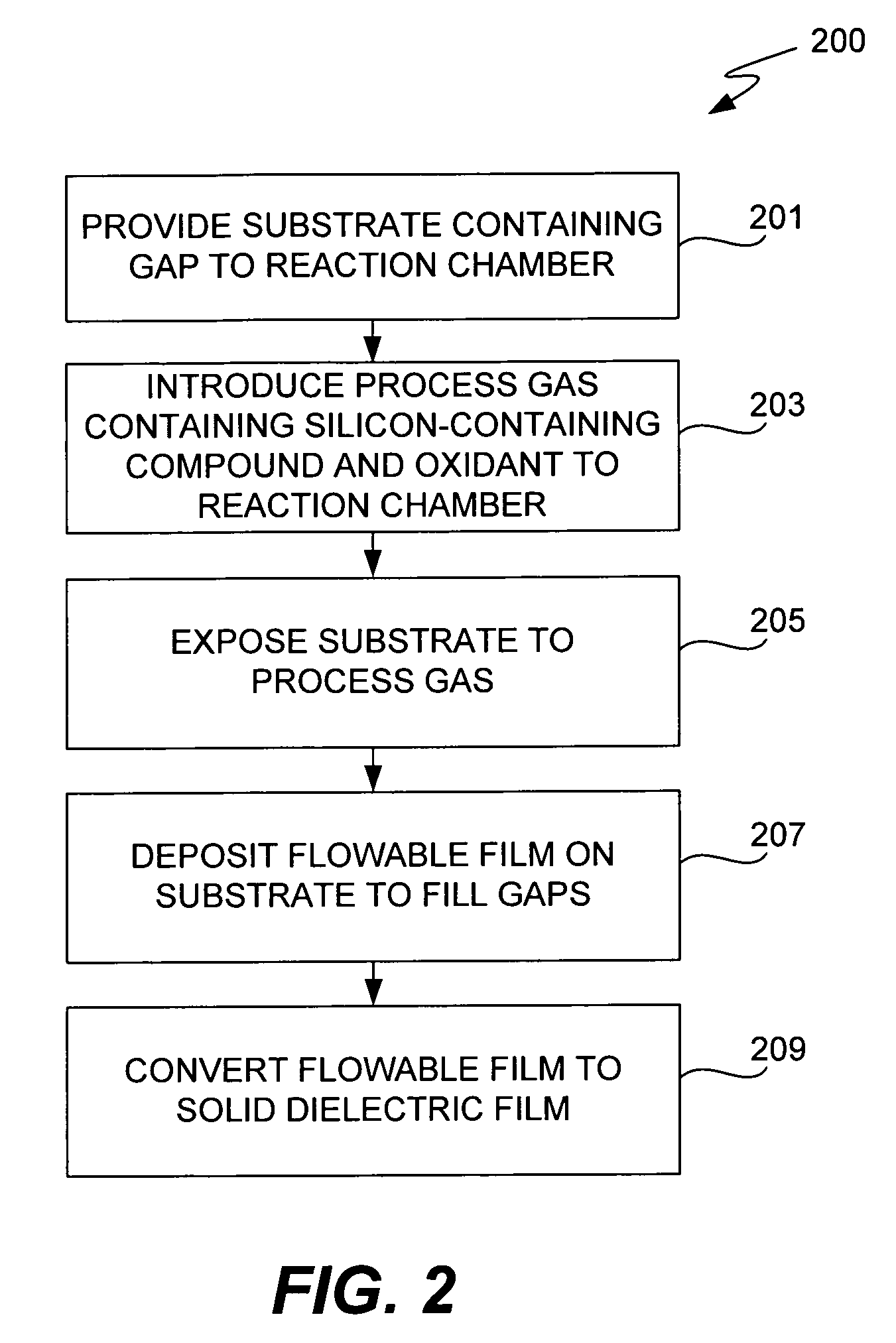
CVD flowable gap fill
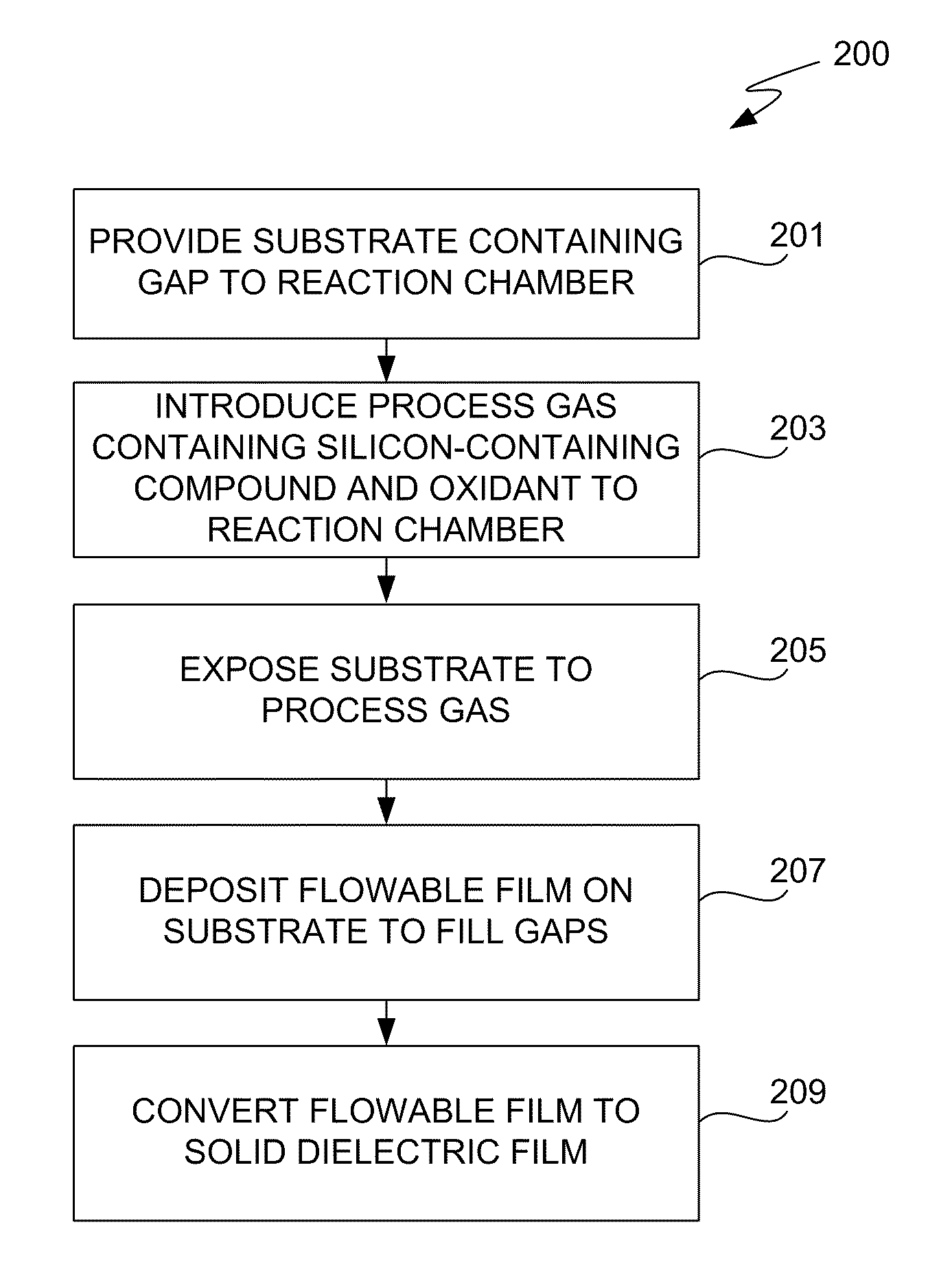
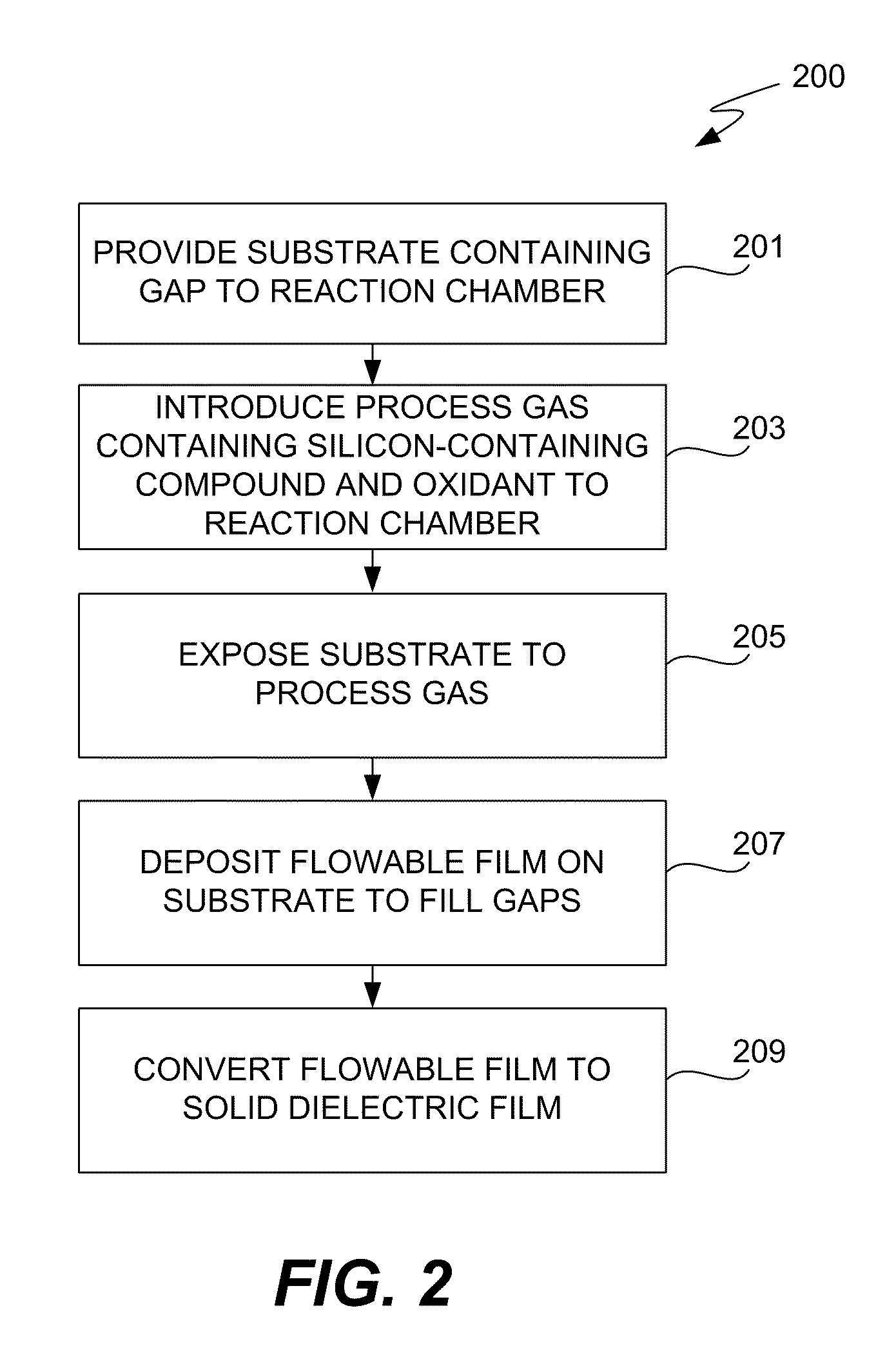
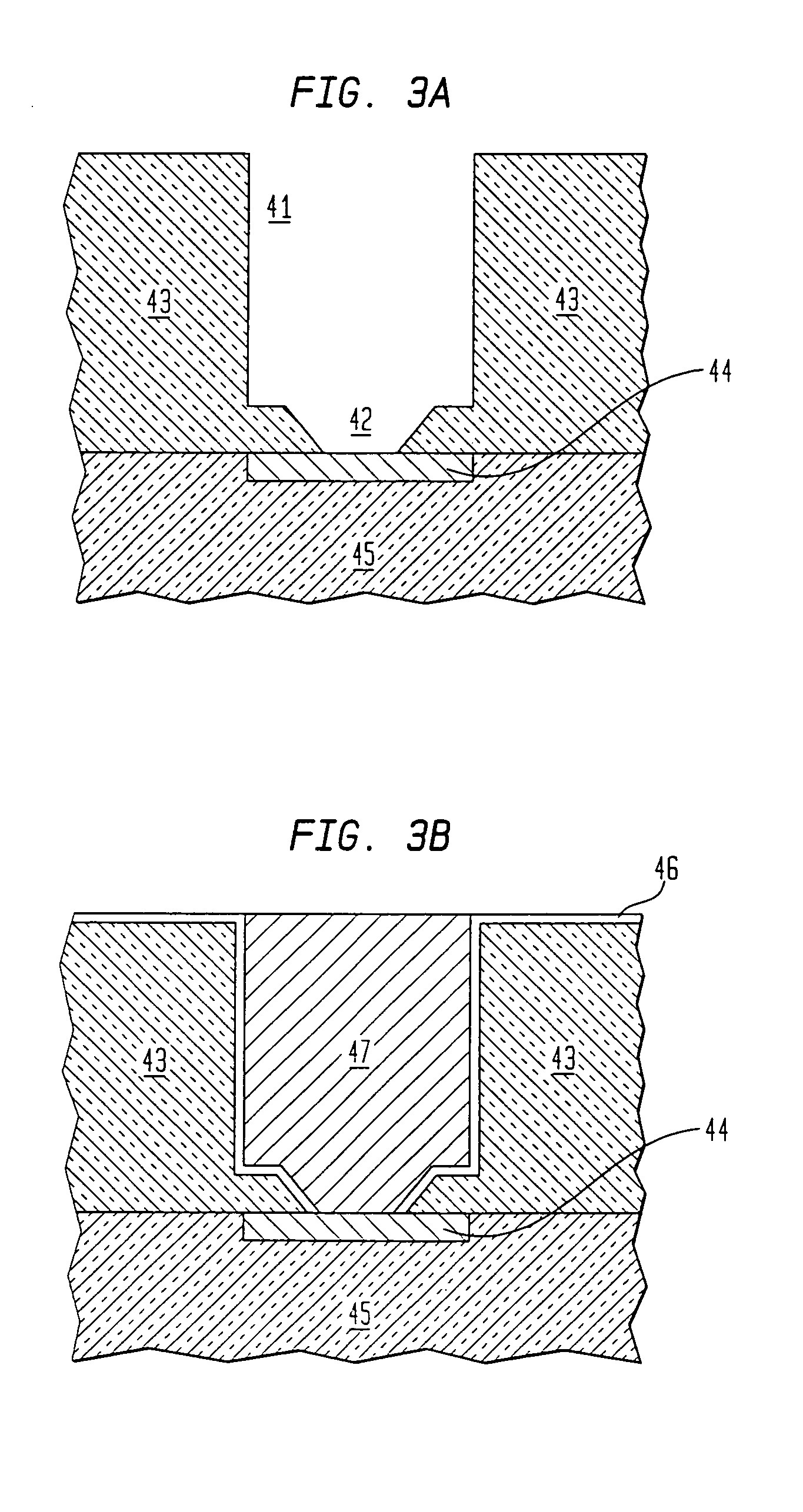
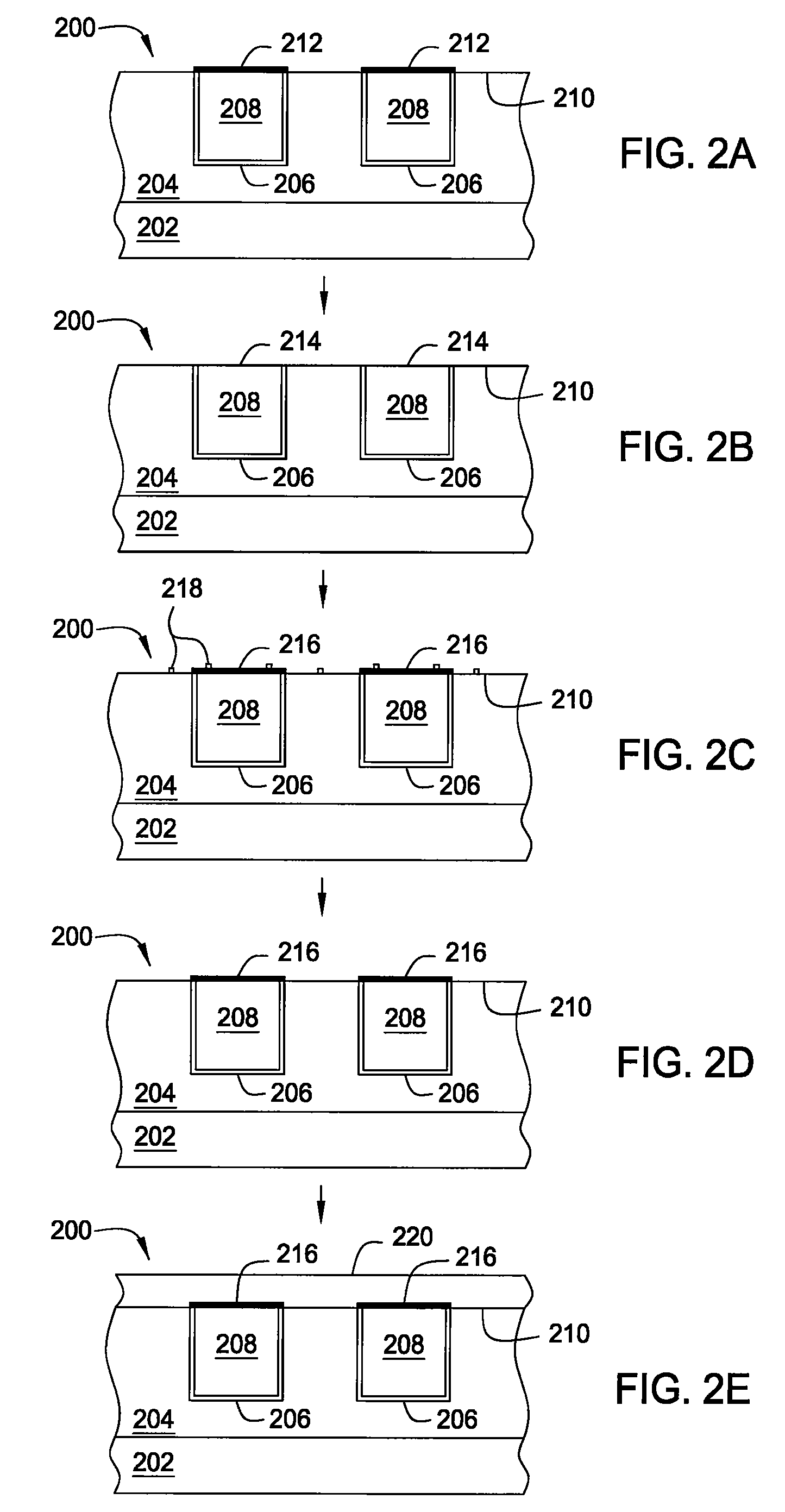
The present invention meets these needs by providing improved methods of filling gaps. In certain embodiments, the methods involve placing a substrate into a reaction chamber and introducing a vapor phase silicon-containing compound and oxidant into the chamber. Reactor conditions are controlled so that the silicon-containing compound and the oxidant are made to react and condense onto the substrate. The chemical reaction causes the formation of a flowable film, in some instances containing Si—OH, Si—H and Si—O bonds. The flowable film fills gaps on the substrates. The flowable film is then converted into a silicon oxide film, for example by plasma or thermal annealing. The methods of this invention may be used to fill high aspect ratio gaps, including gaps having aspect ratios ranging from 3:1 to 10:1.
Owner:NOVELLUS SYSTEMS
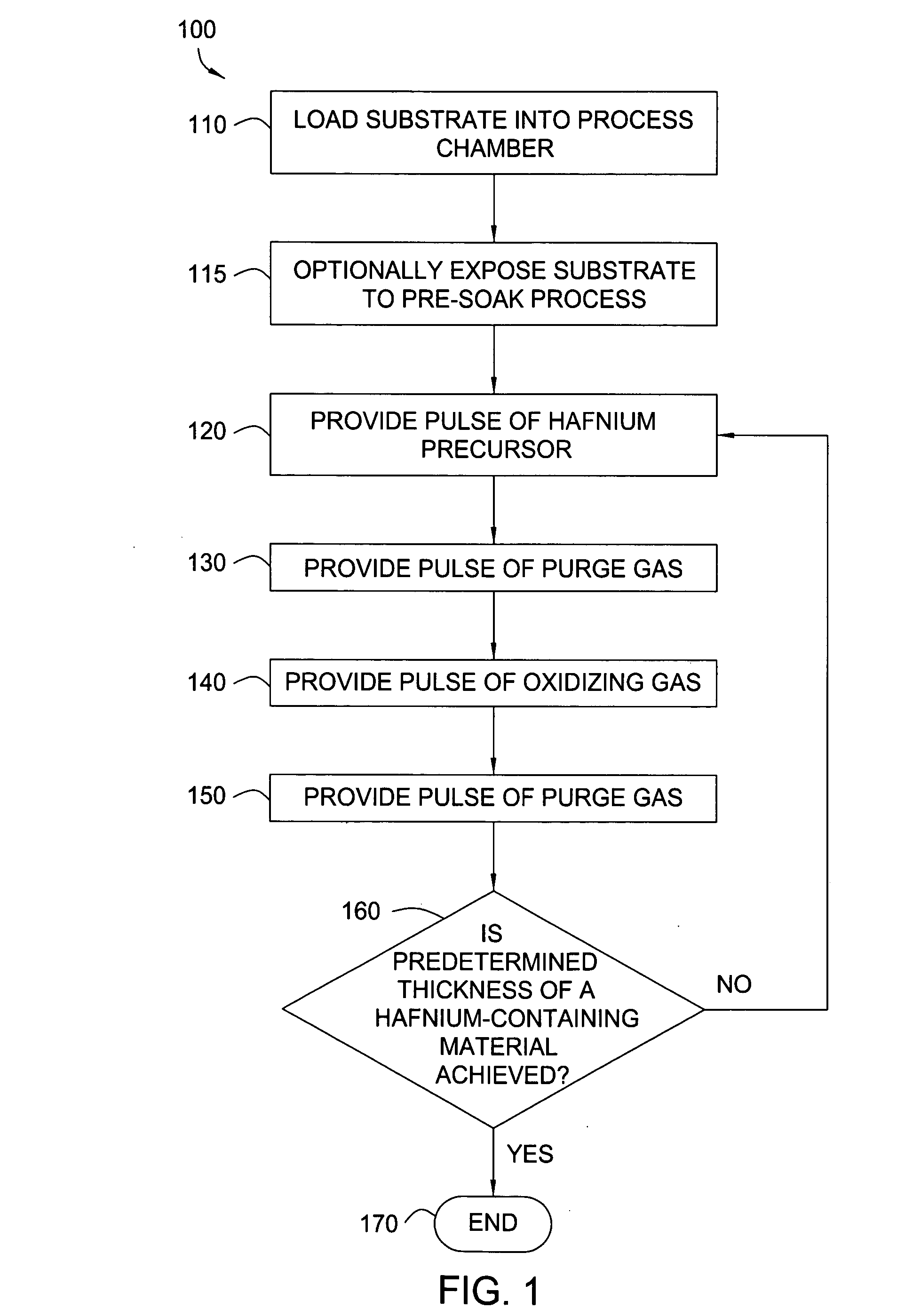
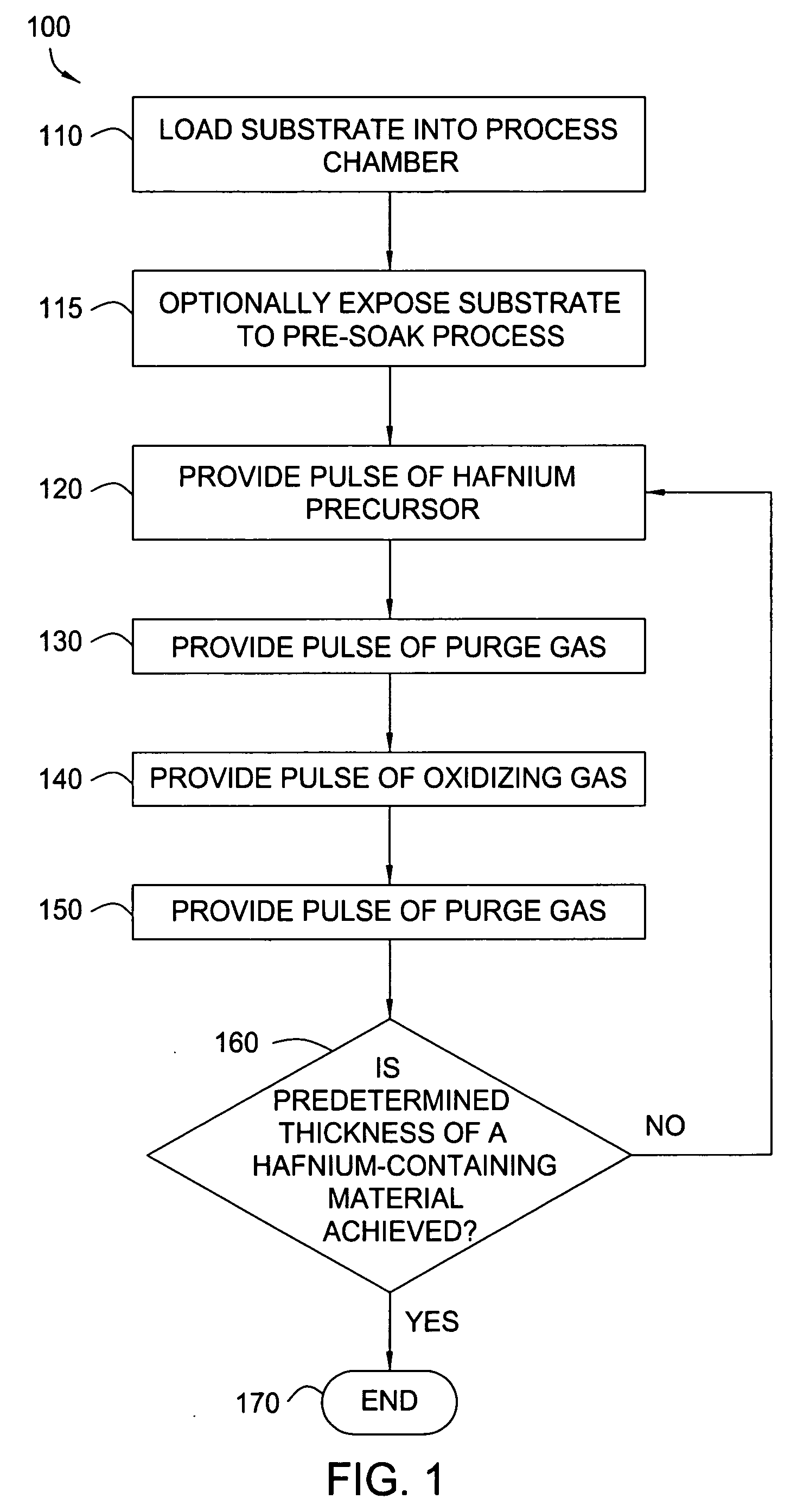
Apparatuses and methods for atomic layer deposition of hafnium-containing high-k dielectric materials
InactiveUS20050271813A1Steam generation heating methodsDecorative surface effectsGas phaseWater vapor
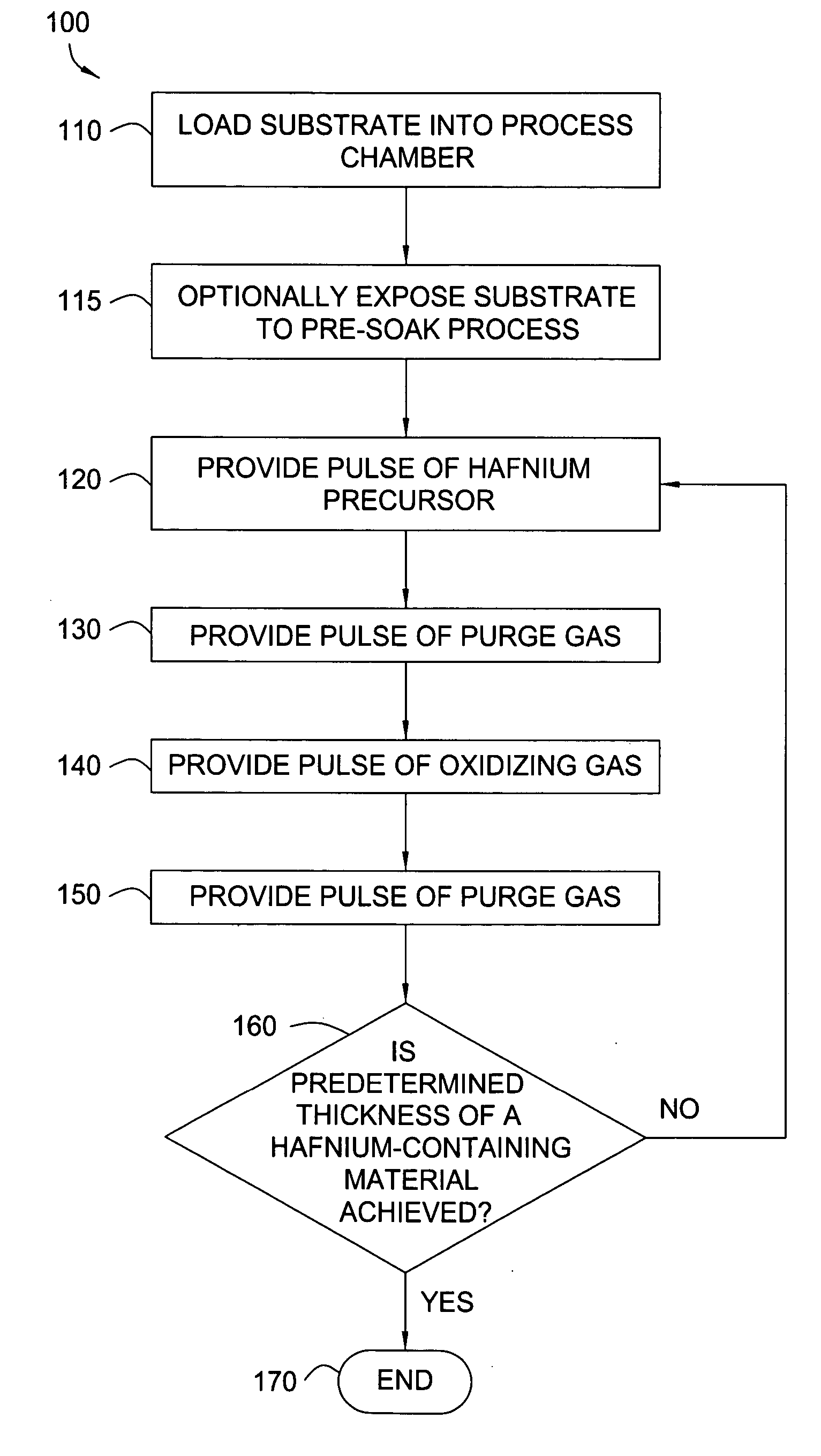
Embodiments of the invention provide methods for depositing dielectric materials on substrates during vapor deposition processes, such as atomic layer deposition (ALD). In one example, a method includes sequentially exposing a substrate to a hafnium precursor and an oxidizing gas to deposit a hafnium oxide material thereon. In another example, a hafnium silicate material is deposited by sequentially exposing a substrate to the oxidizing gas and a process gas containing a hafnium precursor and a silicon precursor. The oxidizing gas usually contains water vapor formed by flowing a hydrogen source gas and an oxygen source gas through a water vapor generator. In another example, a method includes sequentially exposing a substrate to the oxidizing gas and at least one precursor to deposit hafnium oxide, zirconium oxide, lanthanum oxide, tantalum oxide, titanium oxide, aluminum oxide, silicon oxide, aluminates thereof, silicates thereof, derivatives thereof or combinations thereof.
Owner:APPLIED MATERIALS INC
Precursor source mixtures
A precursor source mixture useful for CVD or ALD of a film comprising: at least one precursor composed of an element selected from the group consisting of Li, Na, K, Rb, Cs, Fr, Be, Mg, Ti, Zr, Hf, Sc, Y, La, V, Nb, Ta, Cr, Mo, W, Mn, Re, Fe, Ru, Os, Co, Rh, Ir, Ni, Pd, Pt, Cu, Ag, Au, Zn, Cd, Hg, B, Al, Ga, In, Tl, Si, Ge, Sn, Pb, As, P, Sb and Bi, to which is bound at least one ligand selected from the group consisting of hydride, alkyl, alkenyl, cycloalkenyl, aryl, alkyne, carbonyl, amido, imido, hydrazido, phosphido, nitrosyl, nitryl, nitrate, nitrile, halide, azide, alkoxy, siloxy, silyl, and halogenated, sulfonated or silyated derivatives thereof, which is dissolved, emulsified or suspended in an inert liquid selected from the group consisting of aliphatic hydrocarbons, aromatic hydrocarbons, alcohols, ethers, aldehydes, ketones, acids, phenols, esters, amines, alkylnitrile, halogenated hydrocarbons, silyated hydrocarbons, thioethers, amines, cyanates, isocyanates, thiocyanates, silicone oils, nitroalkyl, alkylnitrate, and mixtures thereof. The precursor source mixture may be a solution, emulsion or suspension and may consist of a mixture of solid, liquid and gas phases which are distributed throughout the mixture.
Owner:GLOBALFOUNDRIES INC
Gas distribution plate assembly for large area plasma enhanced chemical vapor deposition
InactiveUS6942753B2Semiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingChemical vapor deposition coatingGas phaseProduct gas
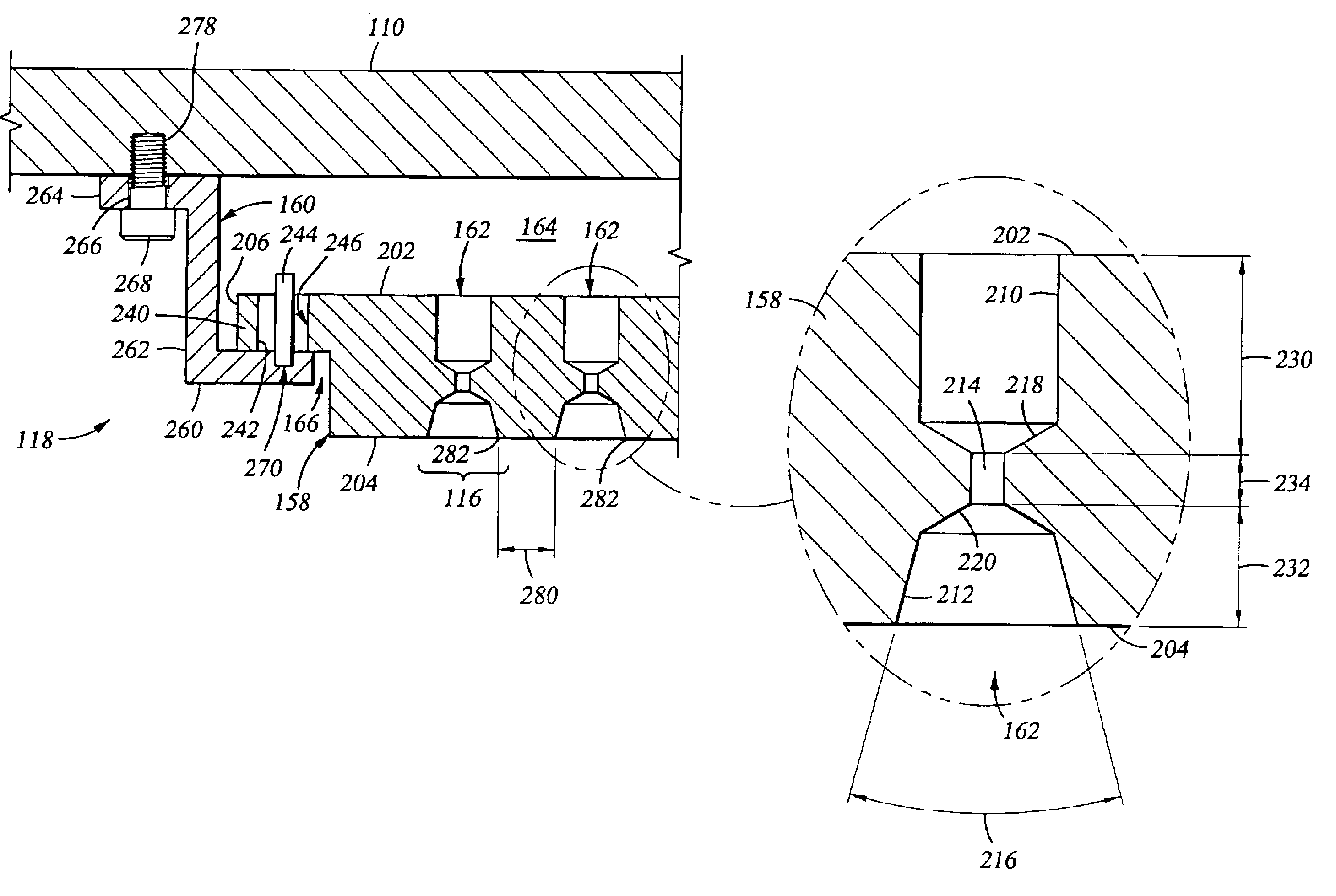
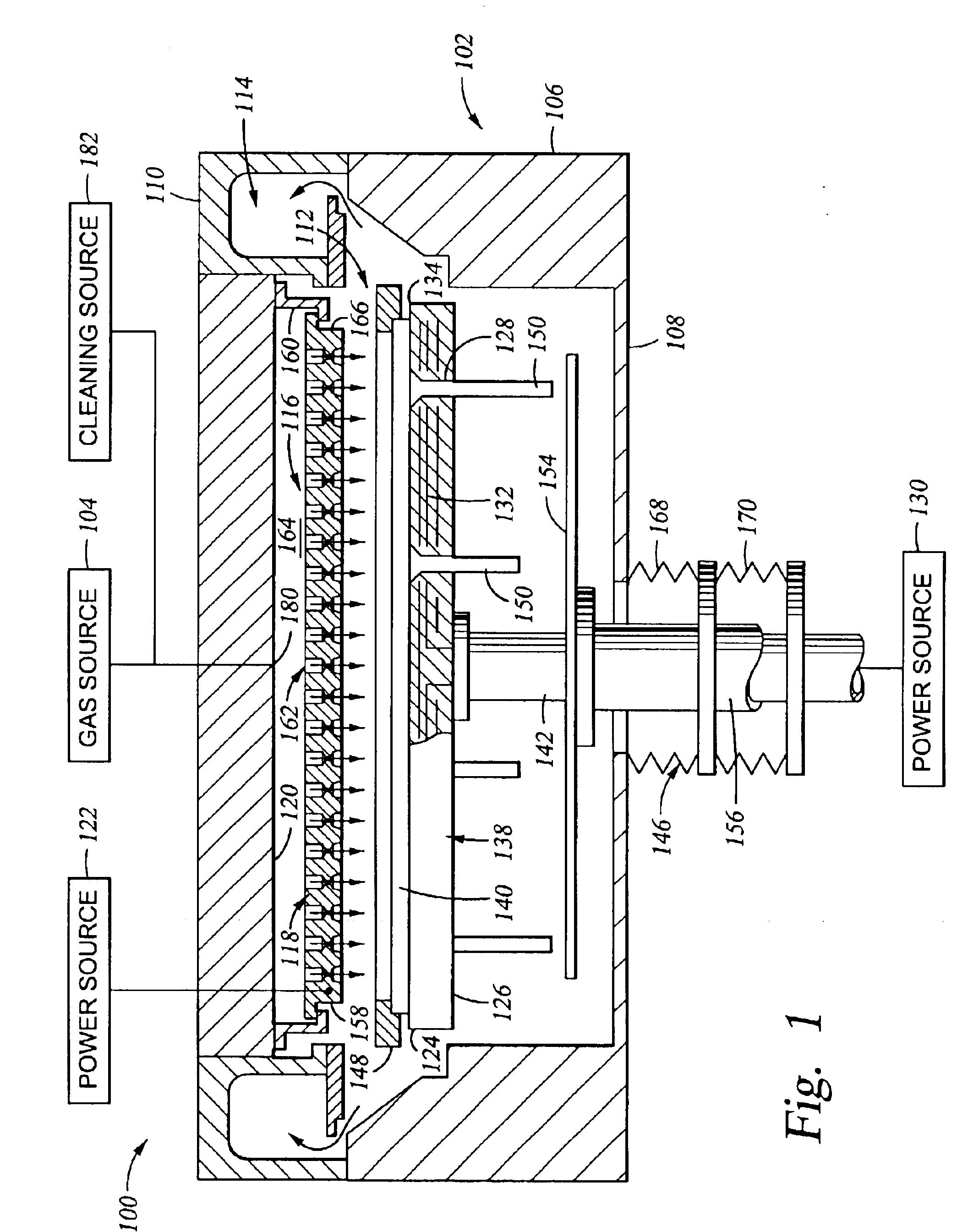
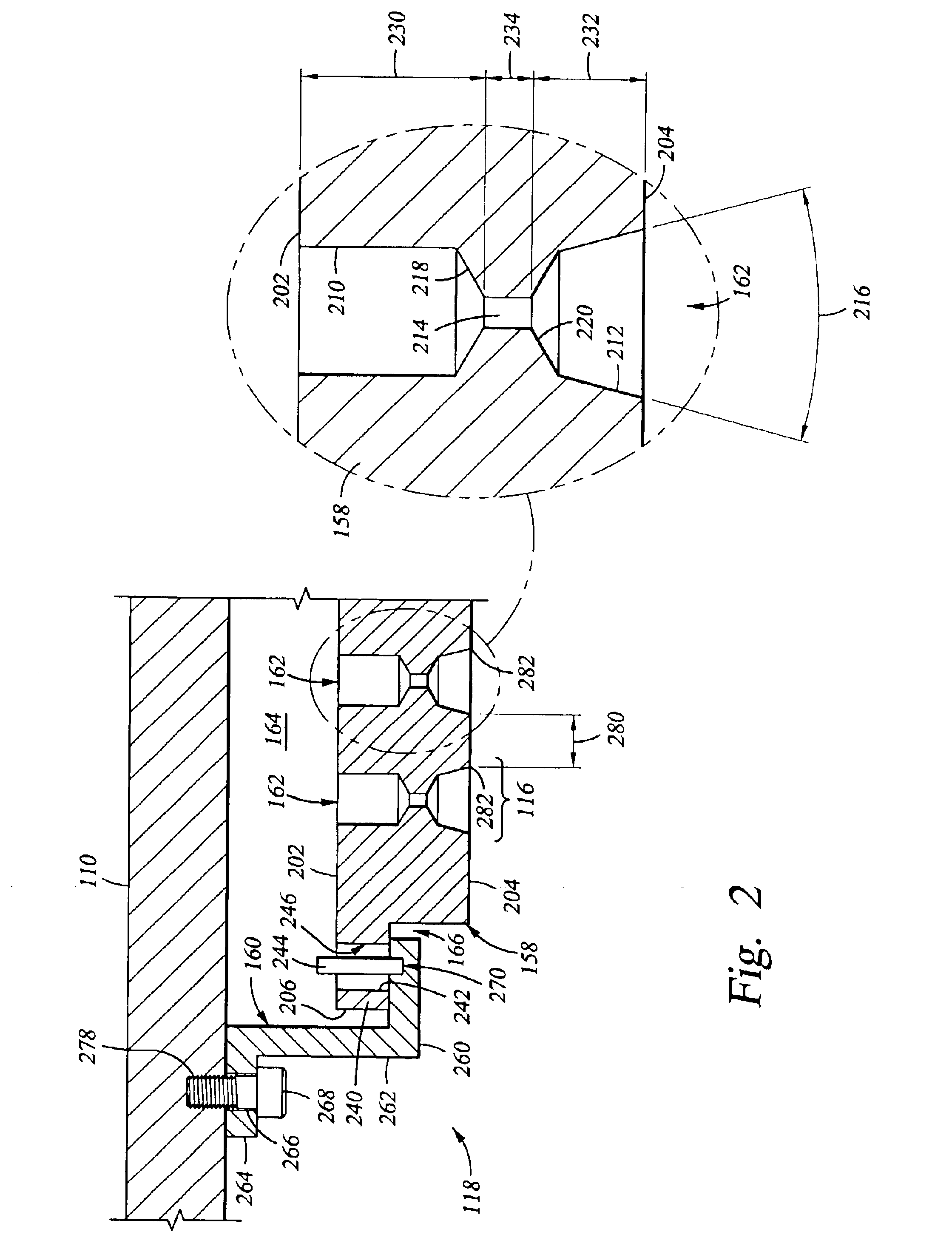
Embodiments of a gas distribution plate for distributing gas in a processing chamber are provided. In one embodiment, a gas distribution plate includes a diffuser plate having a plurality of gas passages passing between an upstream side and a downstream side of the diffuser plate. At least one of the gas passages includes a first hole and a second hole coupled by an orifice hole. The first hole extends from the upstream side of the diffuser plate while the second hole extends from the downstream side. The orifice hole has a diameter less than the respective diameters of the first and second holes.
Owner:APPLIED MATERIALS INC
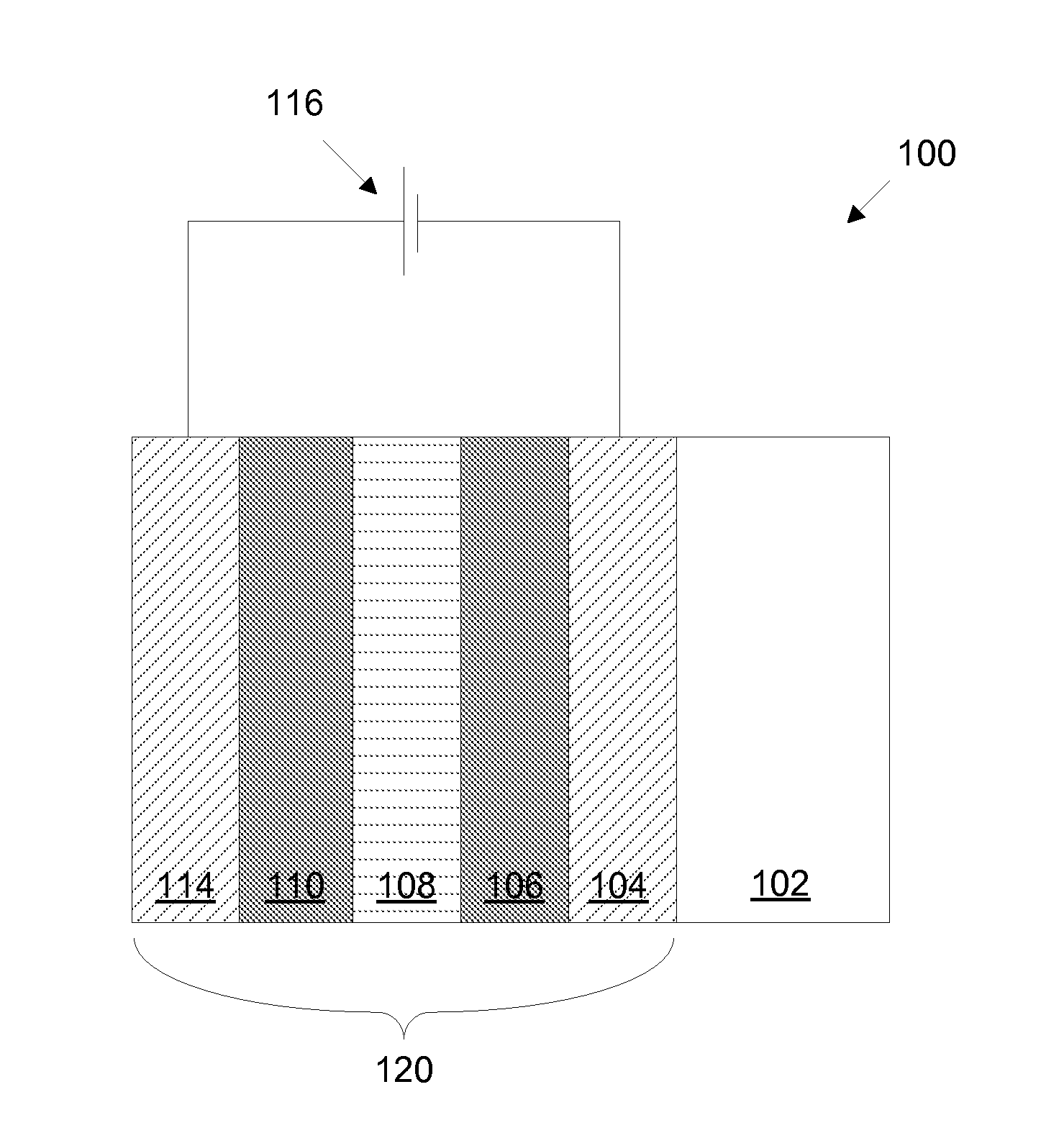
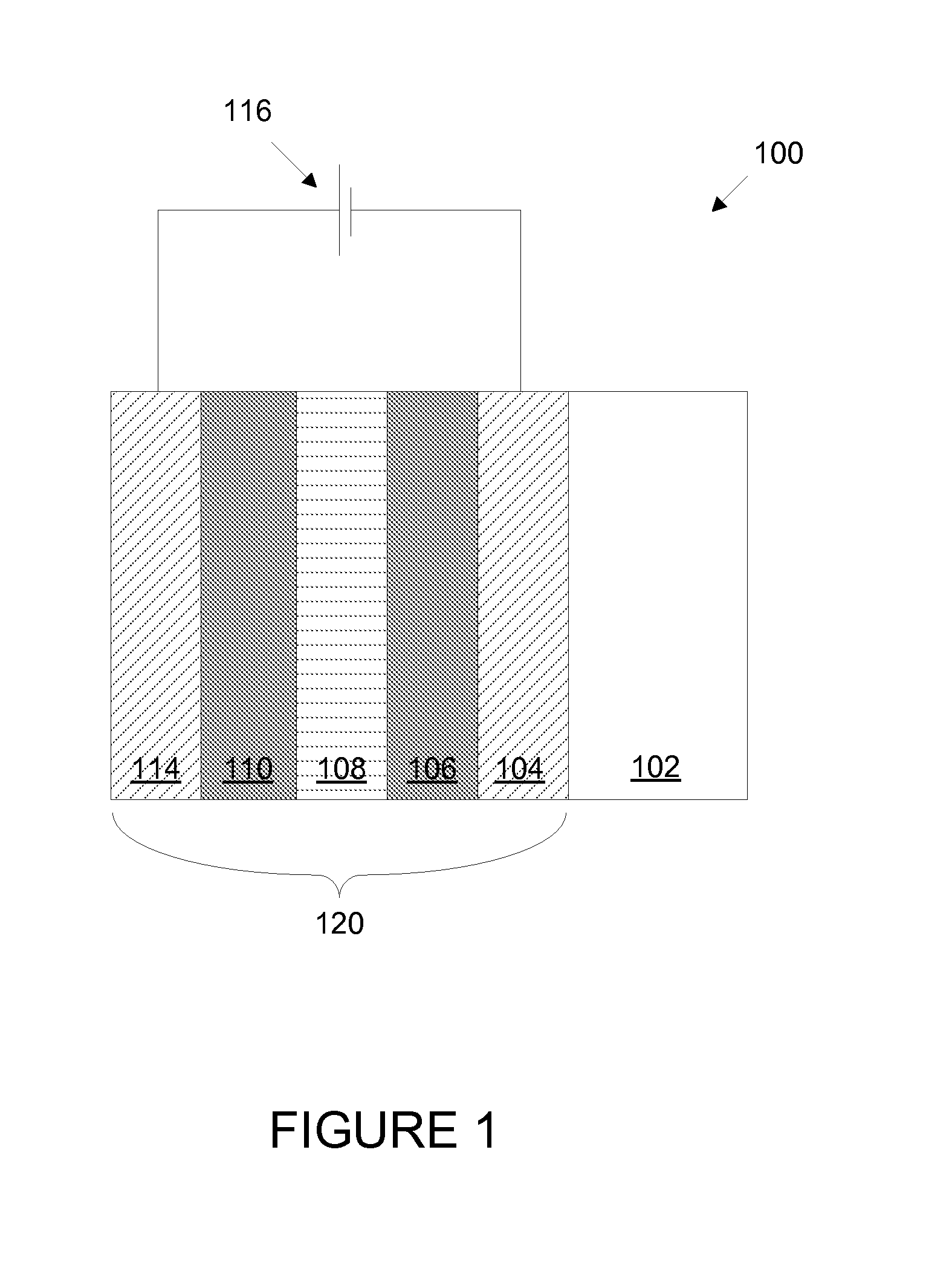
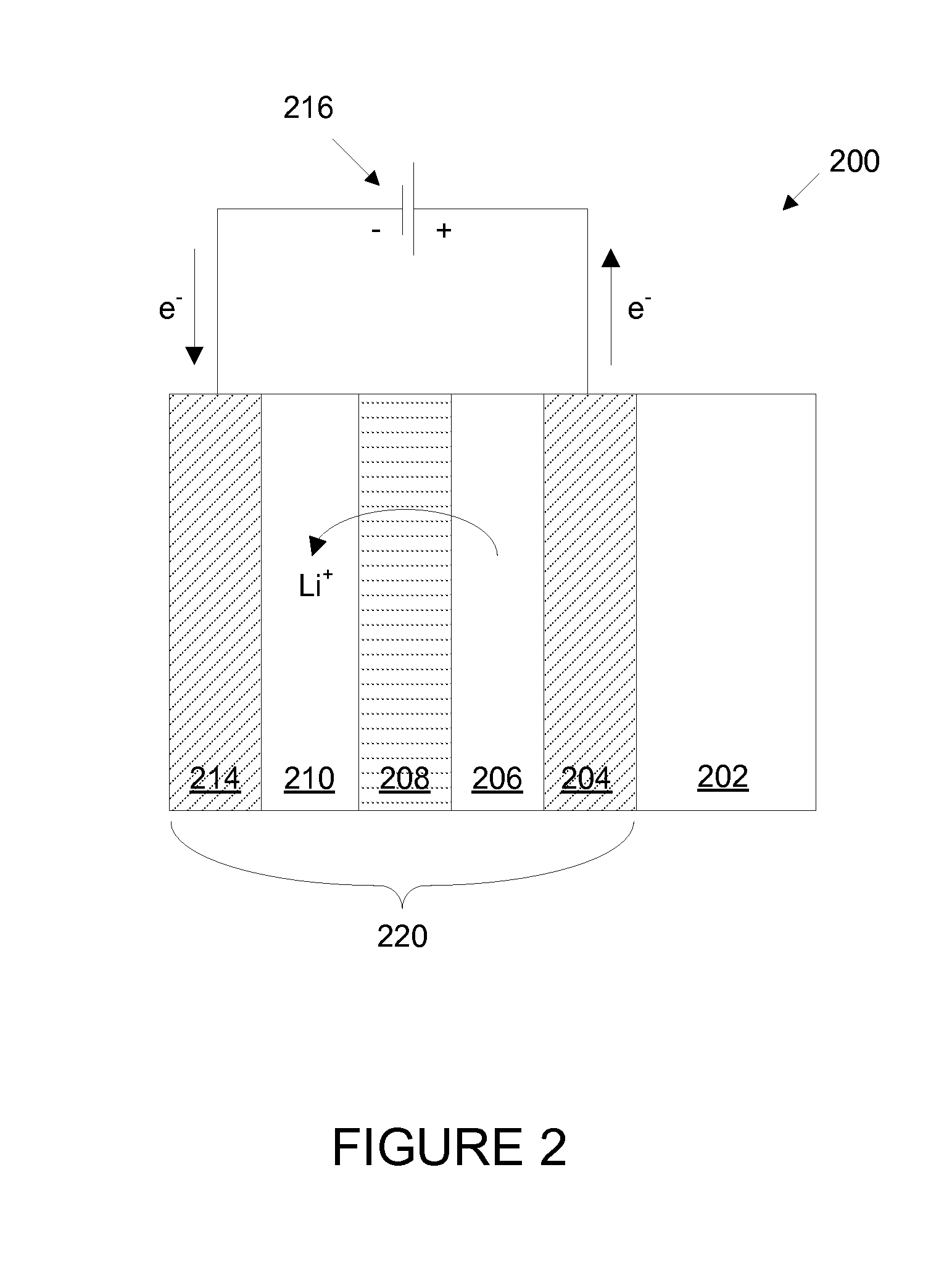
Fabrication of low defectivity electrochromic devices
ActiveUS20100243427A1High level of defectivityVacuum evaporation coatingSputtering coatingArchitectural glassGas phase
Prior electrochromic devices frequently suffer from high levels of defectivity. The defects may be manifest as pin holes or spots where the electrochromic transition is impaired. This is unacceptable for many applications such as electrochromic architectural glass. Improved electrochromic devices with low defectivity can be fabricated by depositing certain layered components of the electrochromic device in a single integrated deposition system. While these layers are being deposited and / or treated on a substrate, for example a glass window, the substrate never leaves a controlled ambient environment, for example a low pressure controlled atmosphere having very low levels of particles. These layers may be deposited using physical vapor deposition.
Owner:VIEW INC
Vapor deposition method for ternary compounds
InactiveUS20100102417A1High resistivitySolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingNitrogen plasmaGas phase
Embodiments provide a method for depositing or forming titanium aluminum nitride materials during a vapor deposition process, such as atomic layer deposition (ALD) or plasma-enhanced ALD (PE-ALD). In some embodiments, a titanium aluminum nitride material is formed by sequentially exposing a substrate to a titanium precursor and a nitrogen plasma to form a titanium nitride layer, exposing the titanium nitride layer to a plasma treatment process, and exposing the titanium nitride layer to an aluminum precursor while depositing an aluminum layer thereon. The process may be repeated multiple times to deposit a plurality of titanium nitride and aluminum layers. Subsequently, the substrate may be annealed to form the titanium aluminum nitride material from the plurality of layers. In other embodiments, the titanium aluminum nitride material may be formed by sequentially exposing the substrate to the nitrogen plasma and a deposition gas which contains the titanium and aluminum precursors.
Owner:APPLIED MATERIALS INC
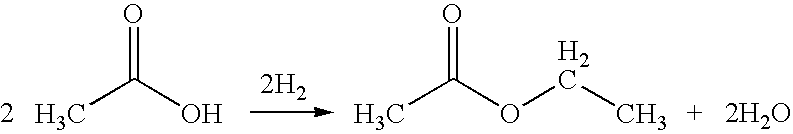
Ethanol production from acetic acid utilizing a cobalt catalyst
InactiveUS7608744B1High selectivityHigh yieldOrganic compound preparationOxygen compounds preparation by reductionAcetic acidPlatinum
A process for the selective production of ethanol by vapor phase reaction of acetic acid over a hydrogenating catalyst composition to form ethanol is disclosed and claimed. In an embodiment of this invention reaction of acetic acid and hydrogen over either cobalt and palladium supported on graphite or cobalt and platinum supported on silica selectively produces ethanol in a vapor phase at a temperature of about 250° C.
Owner:CELANESE INT CORP
Treatment processes for a batch ALD reactor
Embodiments of the invention provide treatment processes to reduce substrate contamination during a fabrication process within a vapor deposition chamber. A treatment process may be conducted before, during or after a vapor deposition process, such as an atomic layer deposition (ALD) process. In one example of an ALD process, a process cycle, containing an intermediate treatment step and a predetermined number of ALD cycles, is repeated until the deposited material has a desired thickness. The chamber and substrates may be exposed to an inert gas, an oxidizing gas, a nitriding gas, a reducing gas or plasmas thereof during the treatment processes. In some examples, the treatment gas contains ozone, water, ammonia, nitrogen, argon or hydrogen. In one example, a process for depositing a hafnium oxide material within a batch process chamber includes a pretreatment step, an intermediate step during an ALD process and a post-treatment step.
Owner:APPLIED MATERIALS INC
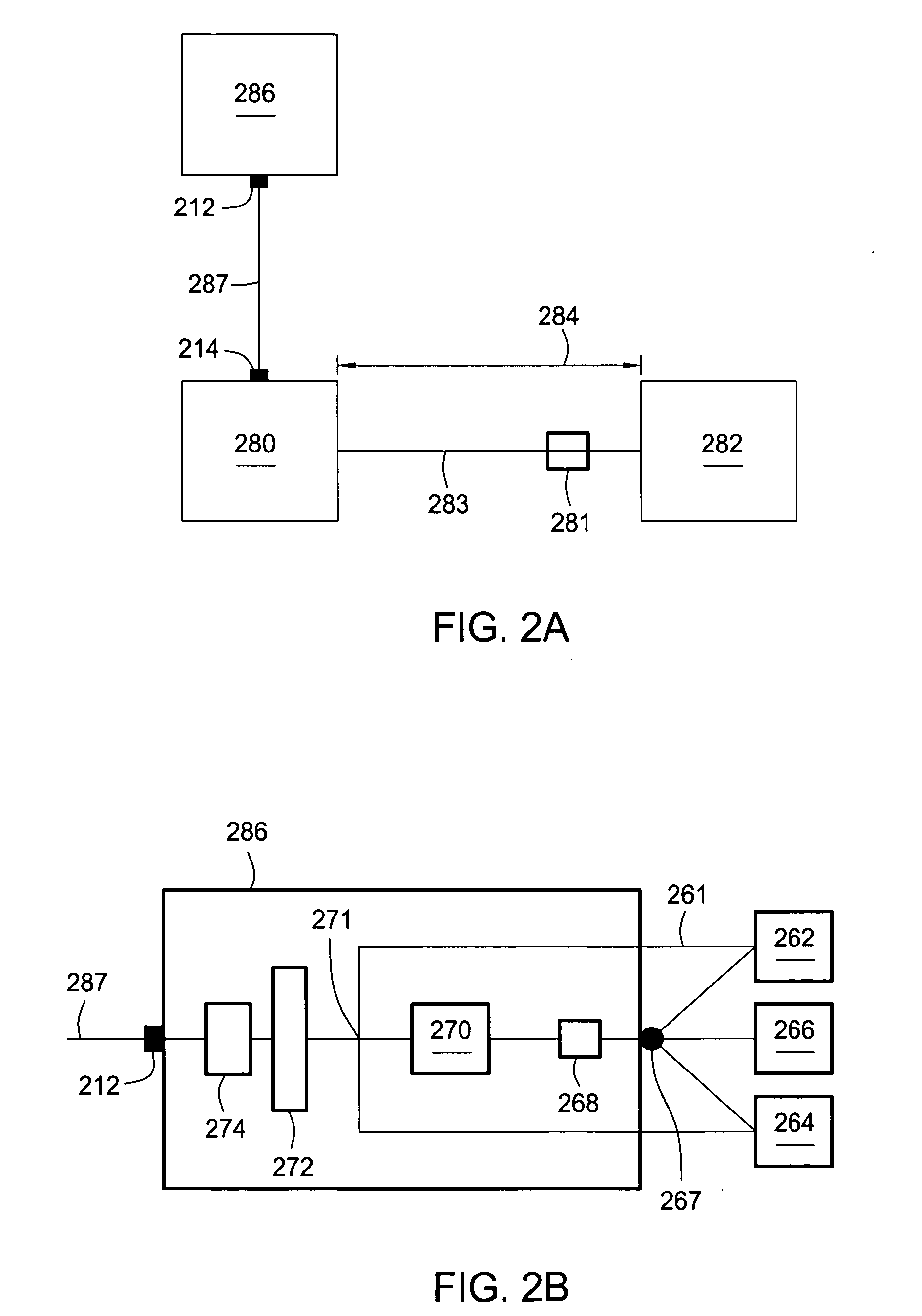
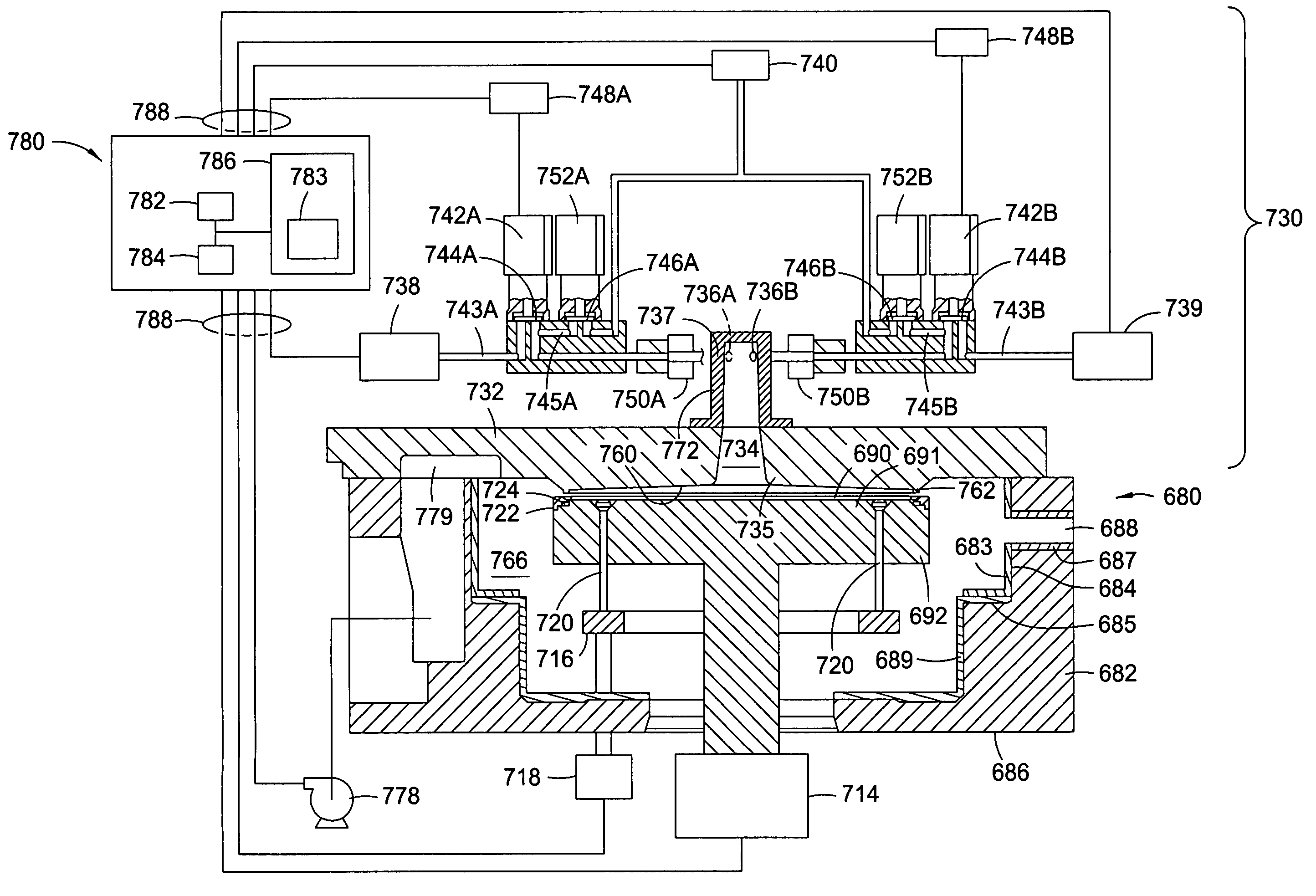
Apparatuses and methods for atomic layer deposition of hafnium-containing high-k dielectric materials
ActiveUS20050271812A1Steam generation heating methodsEfficient propulsion technologiesWater vaporGas phase
Embodiments of the invention provide apparatuses and methods for depositing materials on substrates during vapor deposition processes, such as atomic layer deposition (ALD). In one embodiment, a chamber contains a substrate support with a receiving surface and a chamber lid containing an expanding channel formed within a thermally insulating material. The chamber further includes at least one conduit coupled to a gas inlet within the expanding channel and positioned to provide a gas flow through the expanding channel in a circular direction, such as a vortex, a helix, a spiral or derivatives thereof. The expanding channel may be formed directly within the chamber lid or formed within a funnel liner attached thereon. The chamber may contain a retaining ring, an upper process liner, a lower process liner or a slip valve liner. Liners usually have a polished surface finish and contain a thermally insulating material such as fused quartz or ceramic. In an alternative embodiment, a deposition system contains a catalytic water vapor generator connected to an ALD chamber.
Owner:APPLIED MATERIALS INC
Direct and selective production of ethanol from acetic acid utilizing a platinum/tin catalyst
InactiveUS7863489B2High selectivityHigh yieldOrganic compound preparationOxygen compounds preparation by reductionCalcium silicateAcetic acid
A process for the selective production of ethanol by vapor phase reaction of acetic acid over a hydrogenating catalyst composition to form ethanol is disclosed and claimed. In an embodiment of this invention reaction of acetic acid and hydrogen over a platinum and tin supported on silica, graphite, calcium silicate or silica-alumina selectively produces ethanol in a vapor phase at a temperature of about 250° C.
Owner:CELANESE INT CORP
CVD flowable gap fill
The present invention meets these needs by providing improved methods of filling gaps. In certain embodiments, the methods involve placing a substrate into a reaction chamber and introducing a vapor phase silicon-containing compound and oxidant into the chamber. Reactor conditions are controlled so that the silicon-containing compound and the oxidant are made to react and condense onto the substrate. The chemical reaction causes the formation of a flowable film, in some instances containing Si—OH, Si—H and Si—O bonds. The flowable film fills gaps on the substrates. The flowable film is then converted into a silicon oxide film, for example by plasma or thermal annealing. The methods of this invention may be used to fill high aspect ratio gaps, including gaps having aspect ratios ranging from 3:1 to 10:1.
Owner:NOVELLUS SYSTEMS
Atomic layer deposition method of depositing an oxide on a substrate
The invention includes atomic layer deposition methods of depositing an oxide on a substrate. In one implementation, a substrate is positioned within a deposition chamber. A first species is chemisorbed onto the substrate to form a first species monolayer within the deposition chamber from a gaseous precursor. The chemisorbed first species is contacted with remote plasma oxygen derived at least in part from at least one of O2 and O3 and with remote plasma nitrogen effective to react with the first species to form a monolayer comprising an oxide of a component of the first species monolayer. The chemisorbing and the contacting with remote plasma oxygen and with remote plasma nitrogen are successively repeated effective to form porous oxide on the substrate. Other aspects and implementations are contemplated.
Owner:MICRON TECH INC
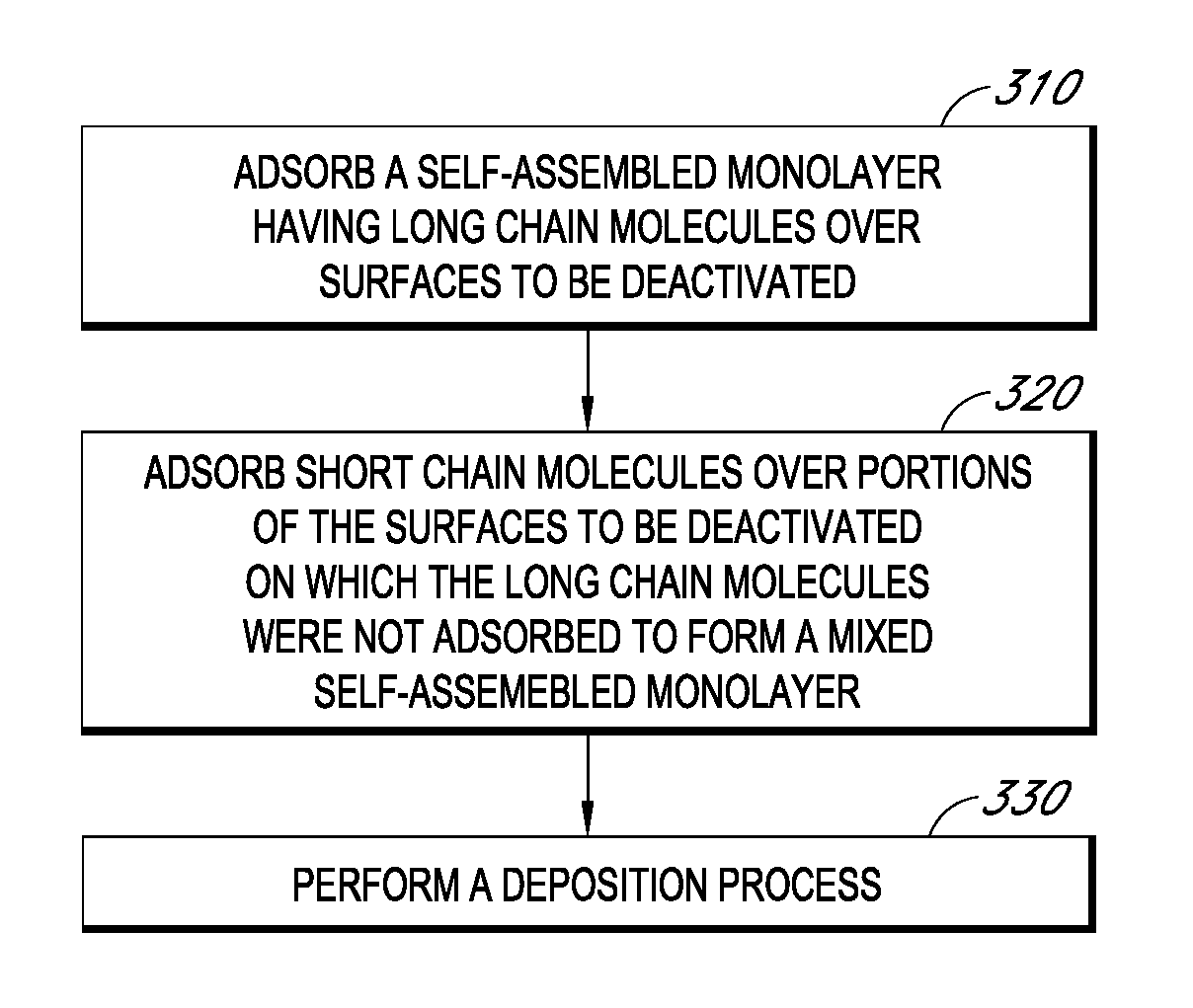
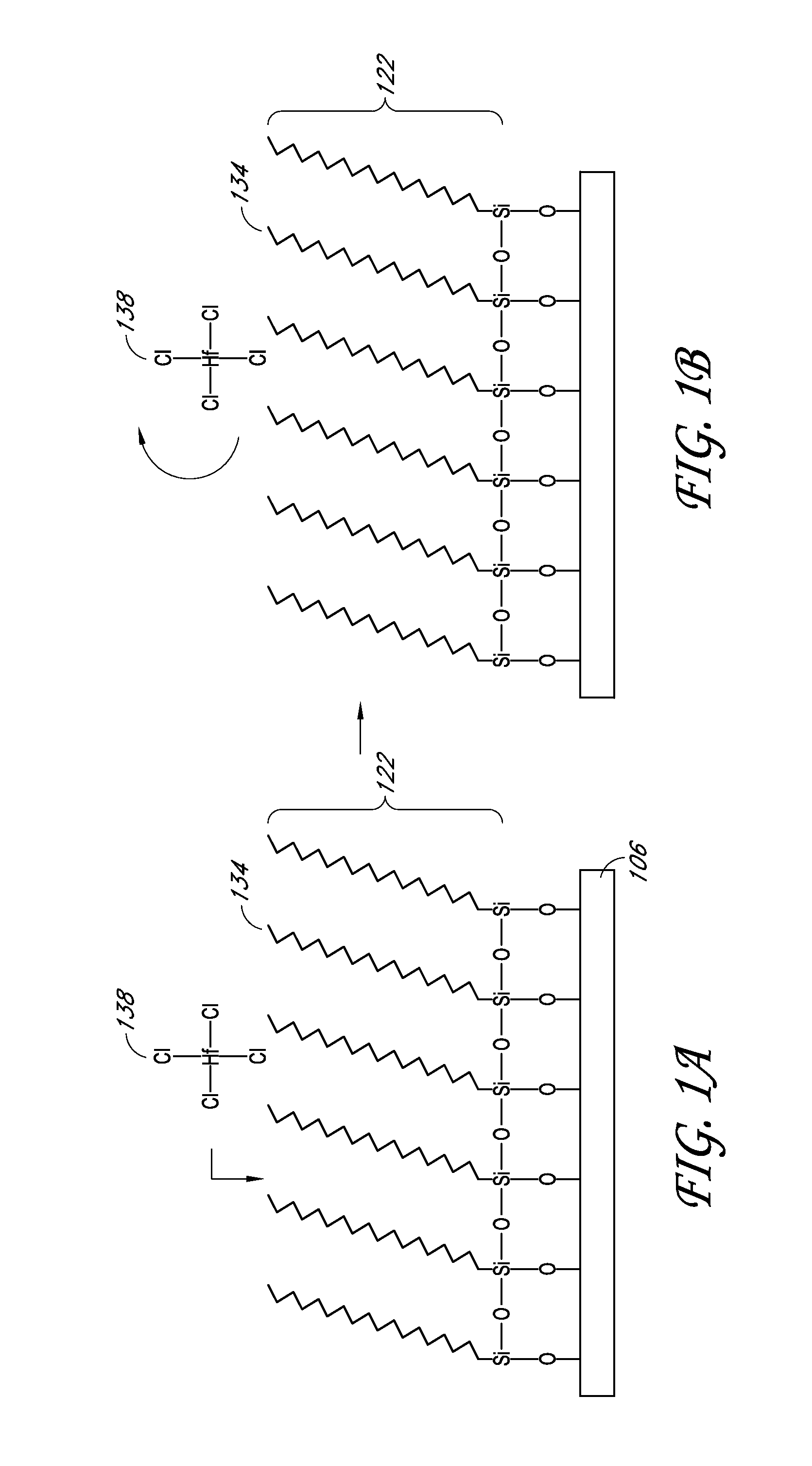
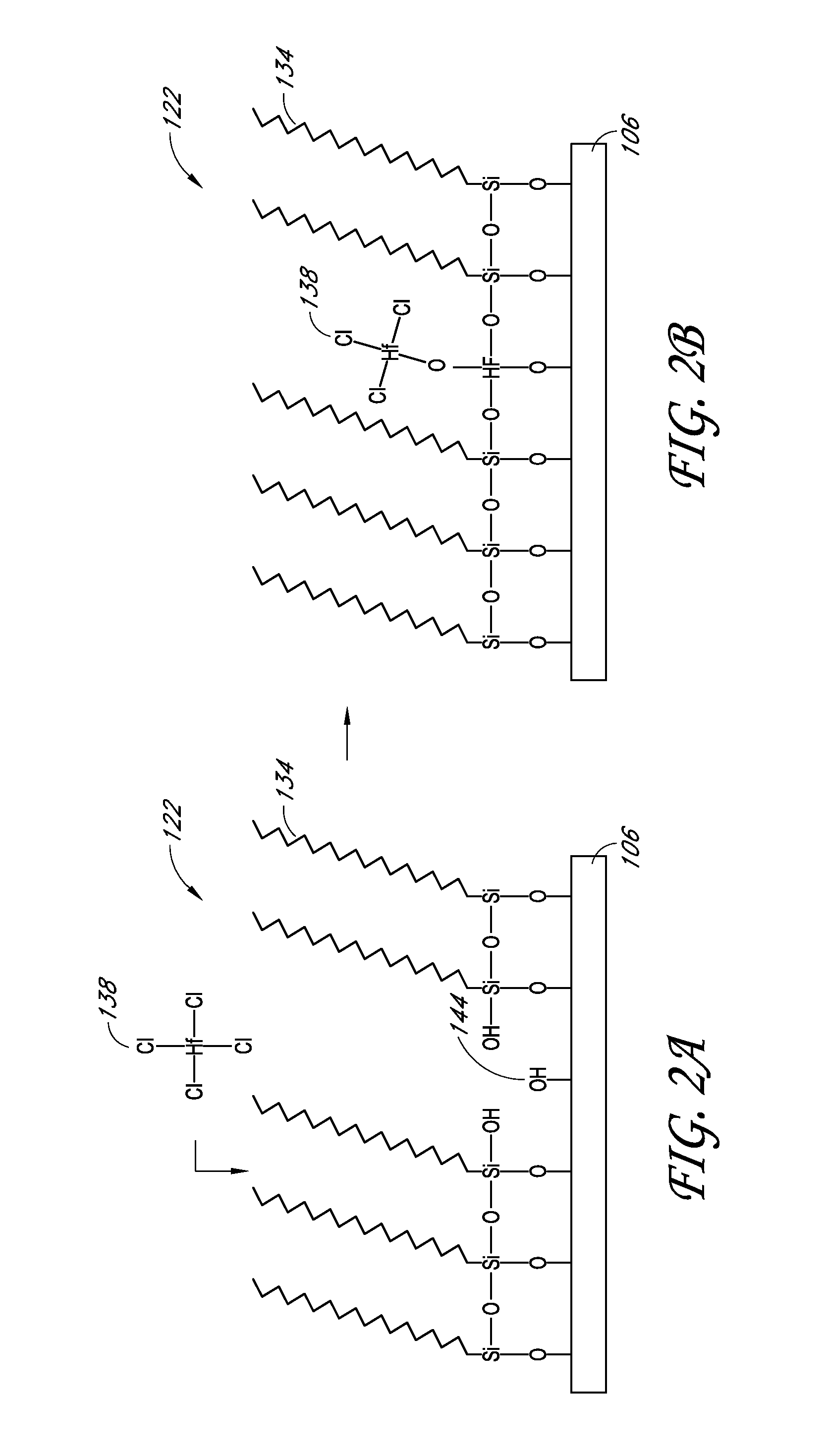
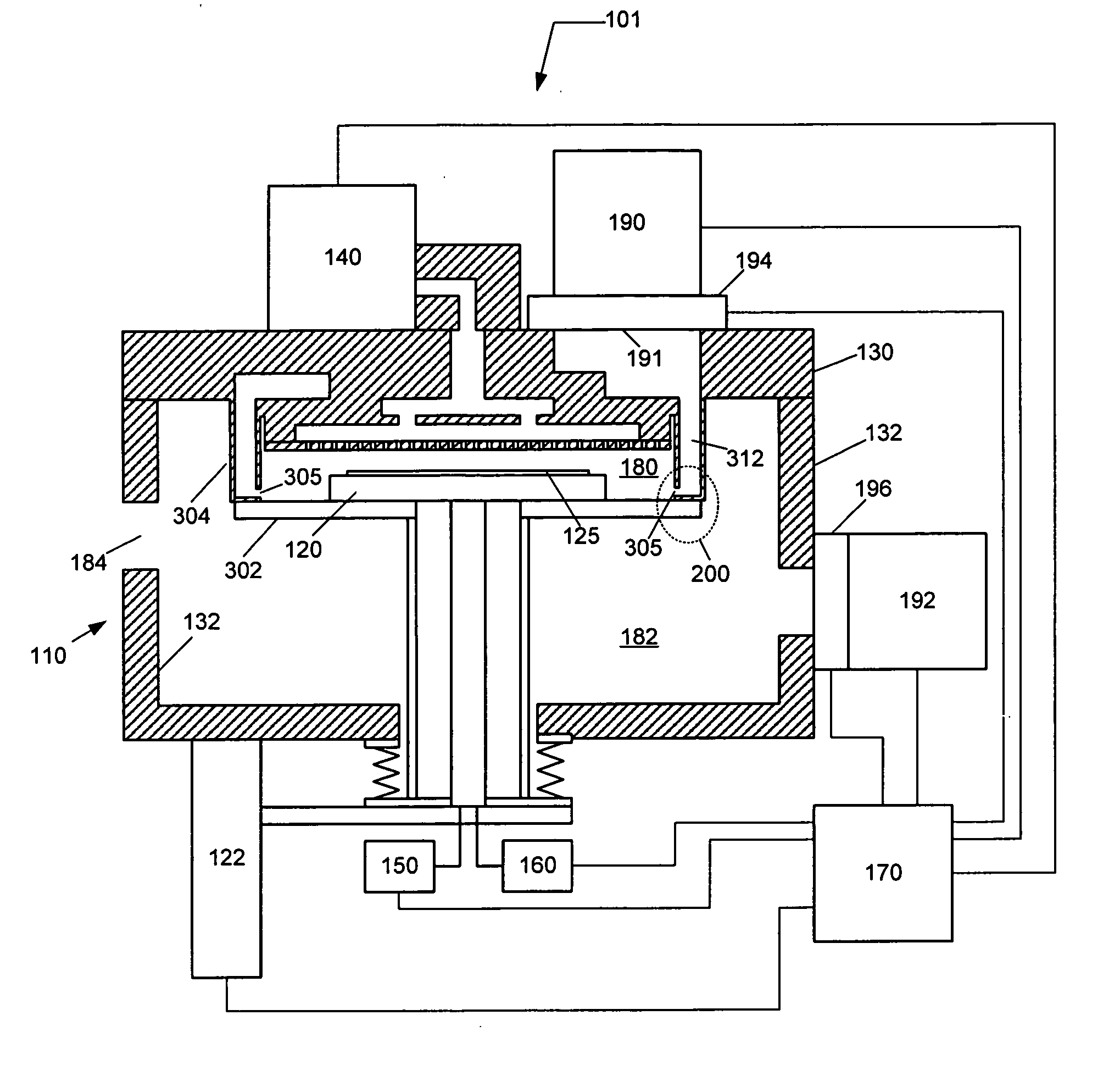
Reactive site deactivation against vapor deposition
Methods and structures relating to the formation of mixed SAMs for preventing undesirable growth or nucleation on exposed surfaces inside a reactor are described. A mixed SAM can be formed on surfaces for which nucleation is not desired by introducing a first SAM precursor having molecules of a first length and a second SAM precursor having molecules of a second length shorter than the first. Examples of exposed surfaces for which a mixed SAM can be provided over include reactor surfaces and select surfaces of integrated circuit structures, such as insulator and dielectric layers.
Owner:ASM IP HLDG BV
Apparatus for thermal and plasma enhanced vapor deposition and method of operating
InactiveUS20070116873A1Reduce pollutionElectric discharge tubesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingGas phaseProcess engineering
A method, computer readable medium, and system for vapor deposition on a substrate that maintain a first assembly of the vapor deposition system at a first temperature, maintain a second assembly of the vapor deposition system at a reduced temperature lower than the first temperature, dispose the substrate in a process space of the first assembly that is vacuum isolated from a transfer space in the second assembly, and deposit a material on the substrate. As such, the system includes a first assembly having a process space configured to facilitate material deposition, a second assembly coupled to the first assembly and having a transfer space to facilitate transfer of the substrate into and out of the deposition system, a substrate stage connected to the second assembly and configured to support the substrate, and a sealing assembly configured to separate the process space from the transfer space. The first assembly is configured to be maintained at a first temperature and the second assembly is configured to be maintained at a reduced temperature lower than the first temperature.
Owner:TOKYO ELECTRON LTD
Apparatus for chemical vapor deposition (CVD) with showerhead and method thereof
ActiveUS20060263522A1Unwanted chemical reactionFrom chemically reactive gasesChemical vapor deposition coatingSource materialGas phase
Owner:KOREA INST OF IND TECH +1
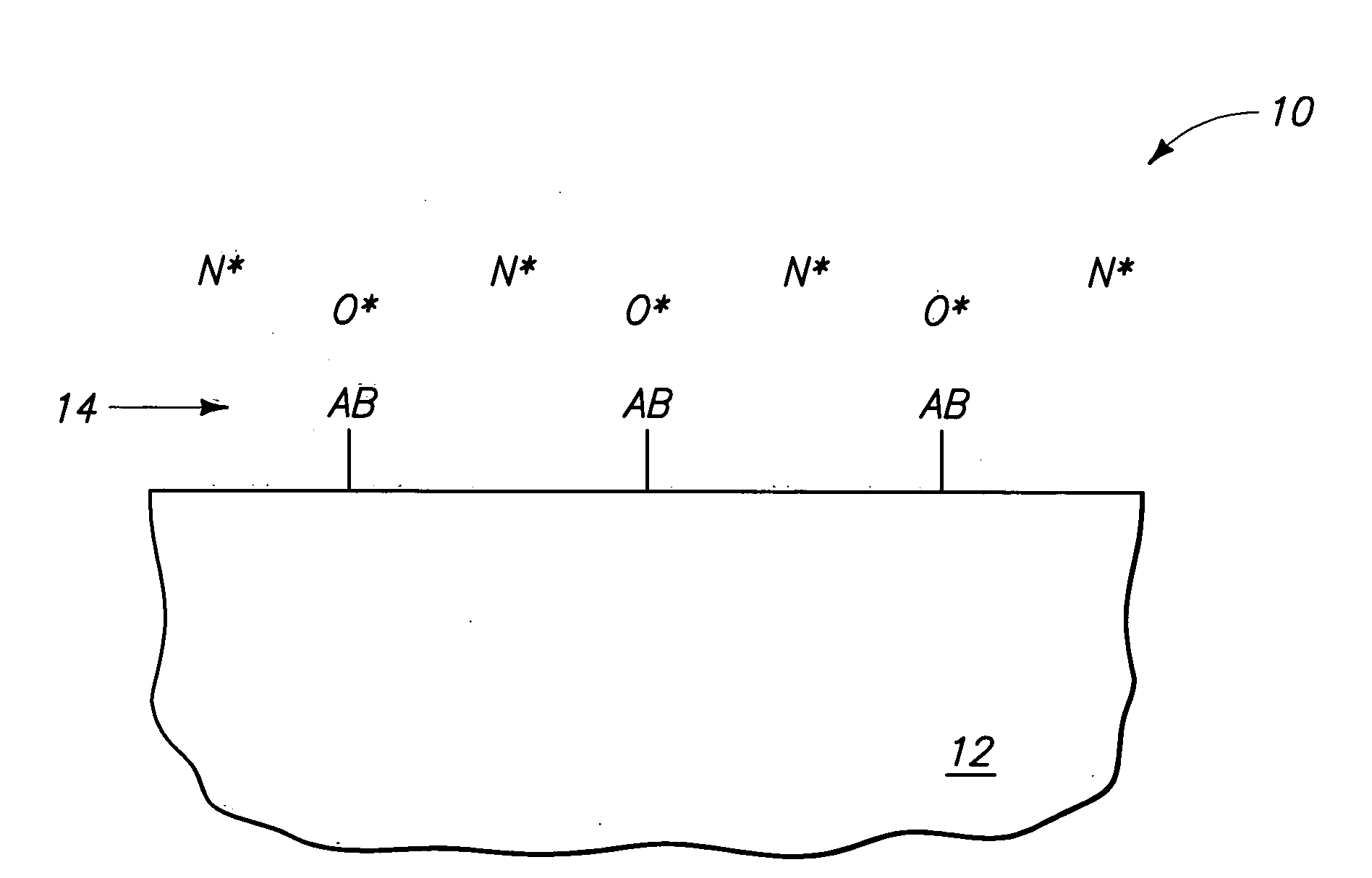
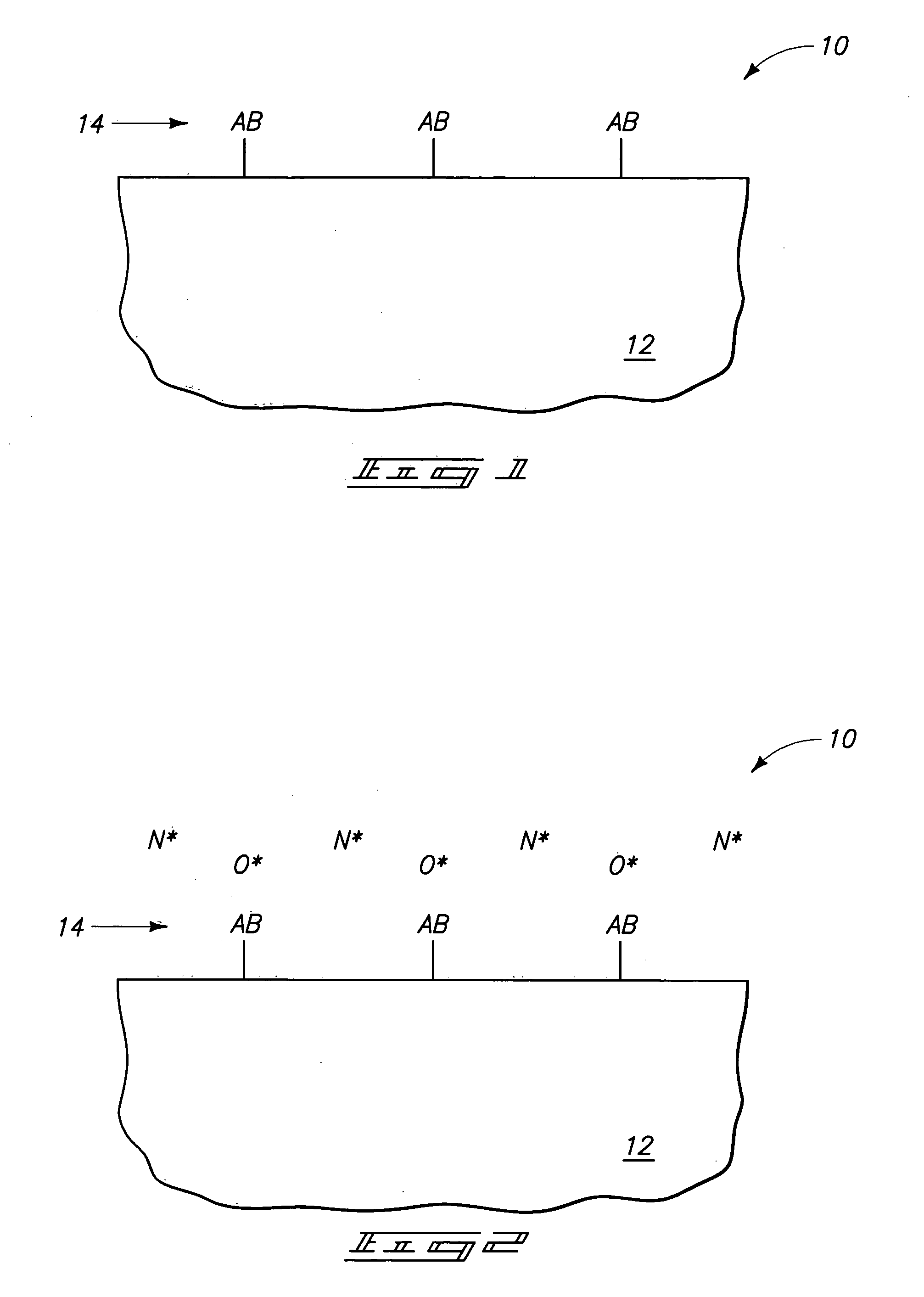
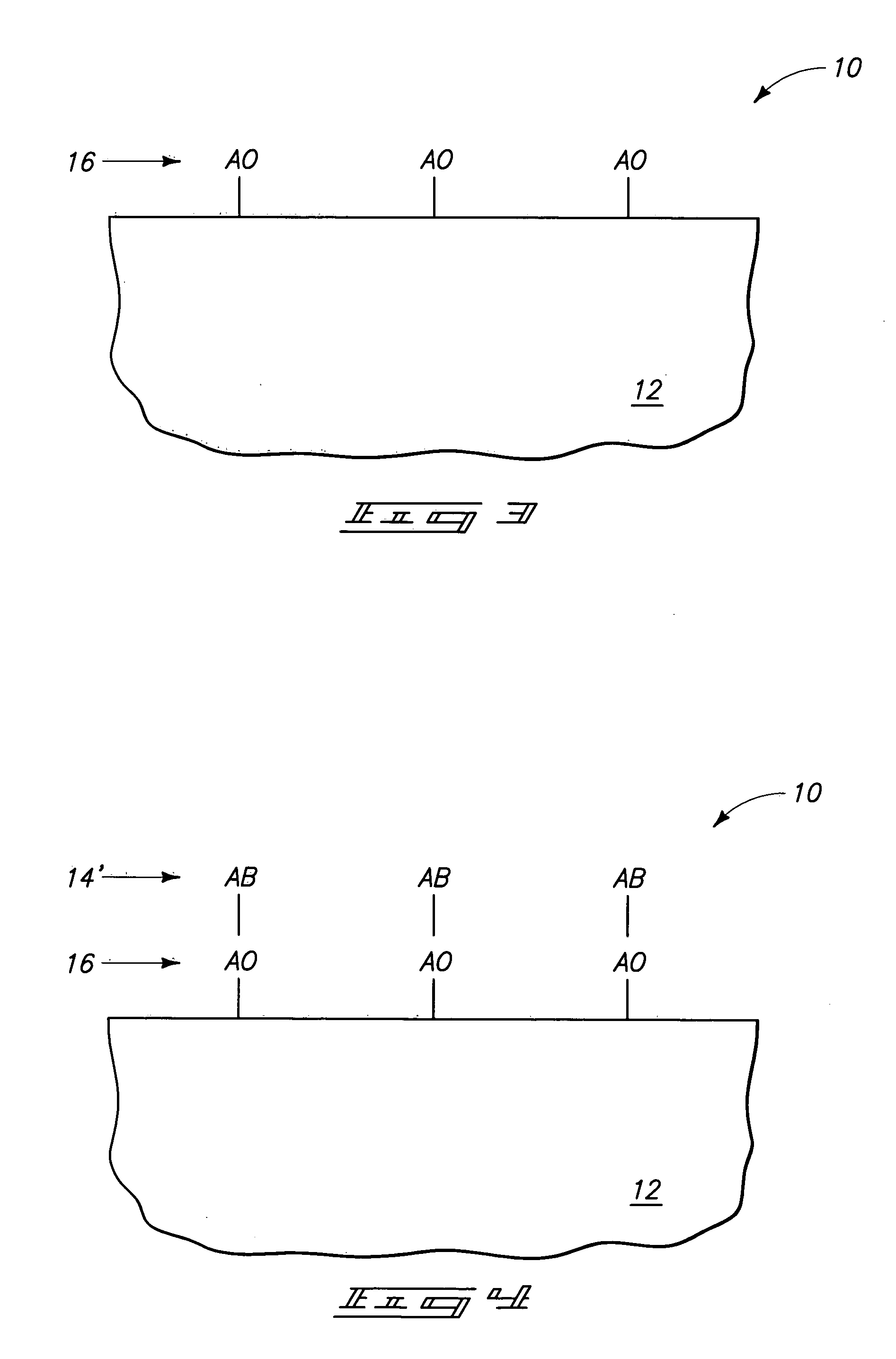
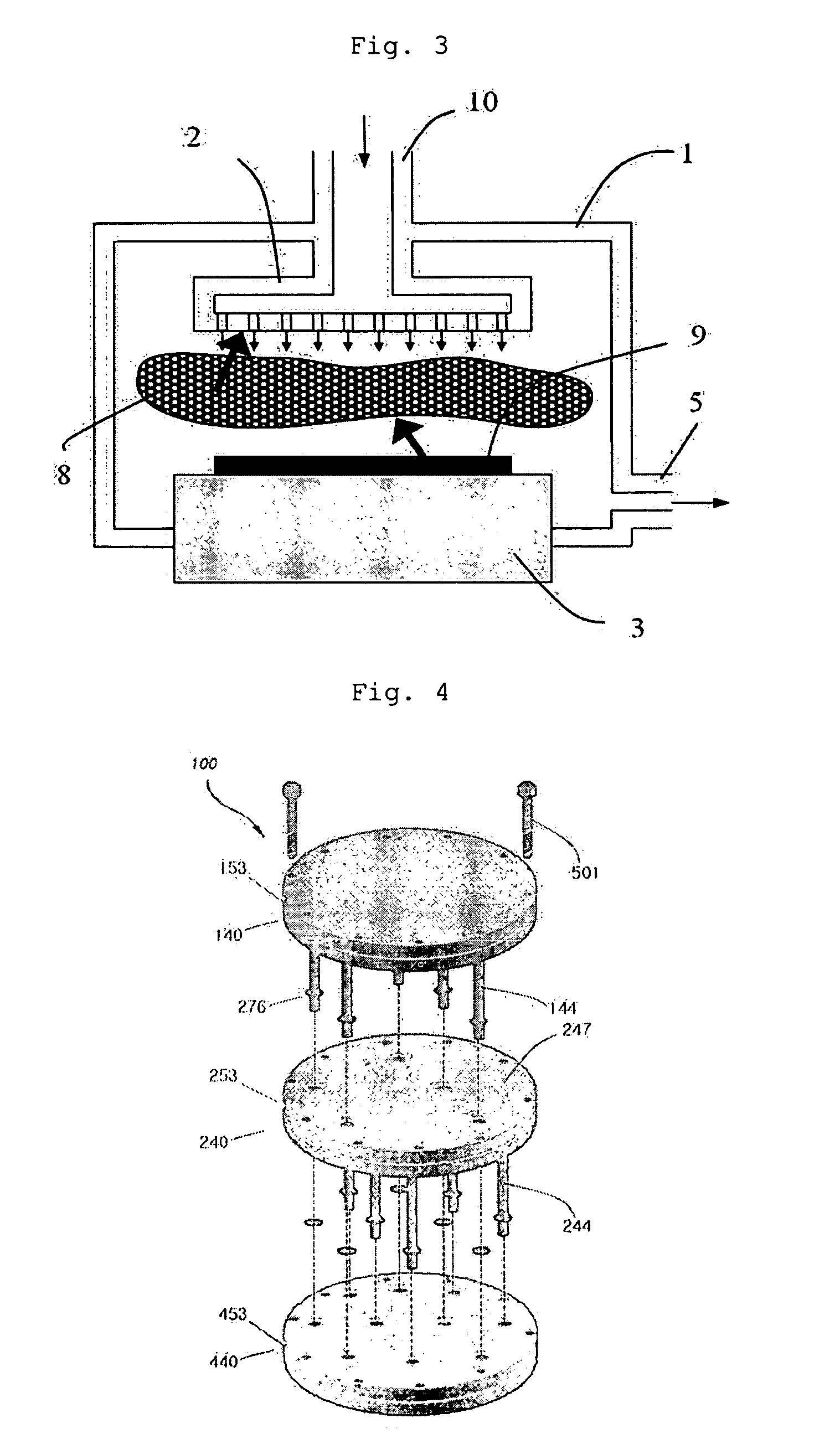
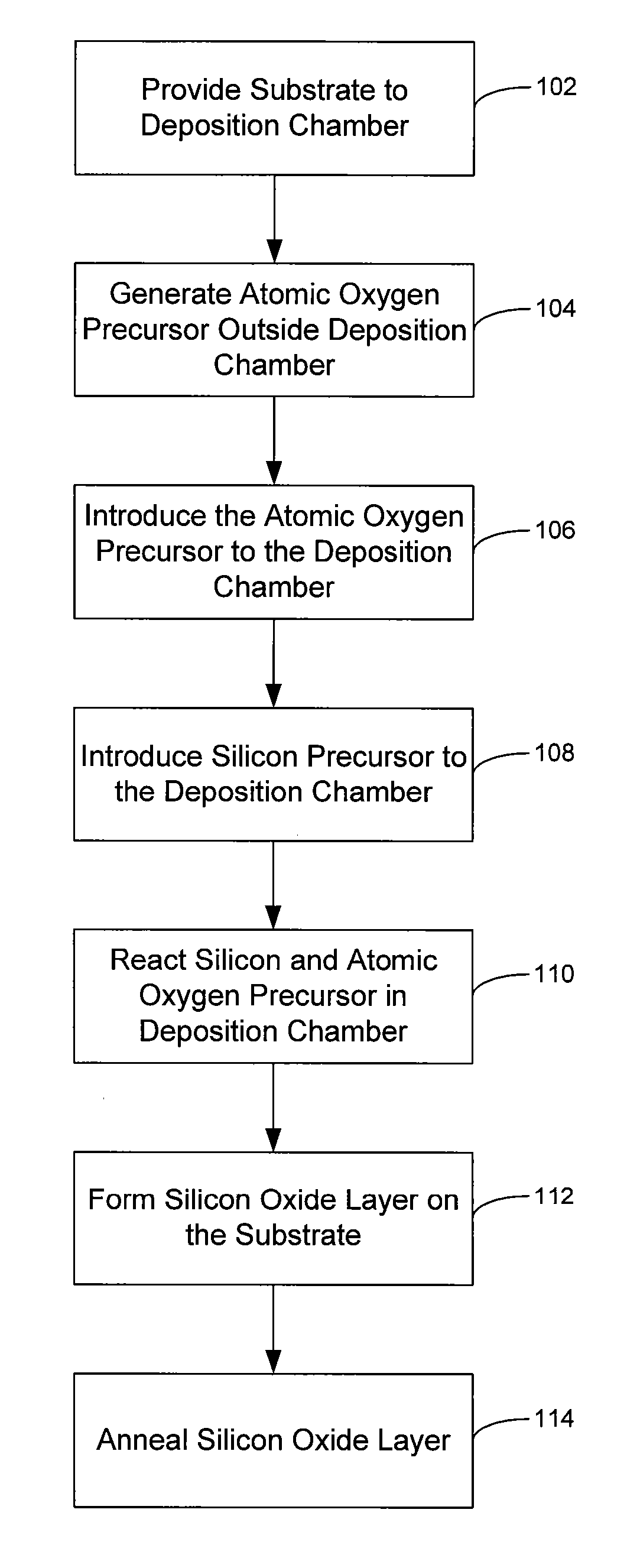
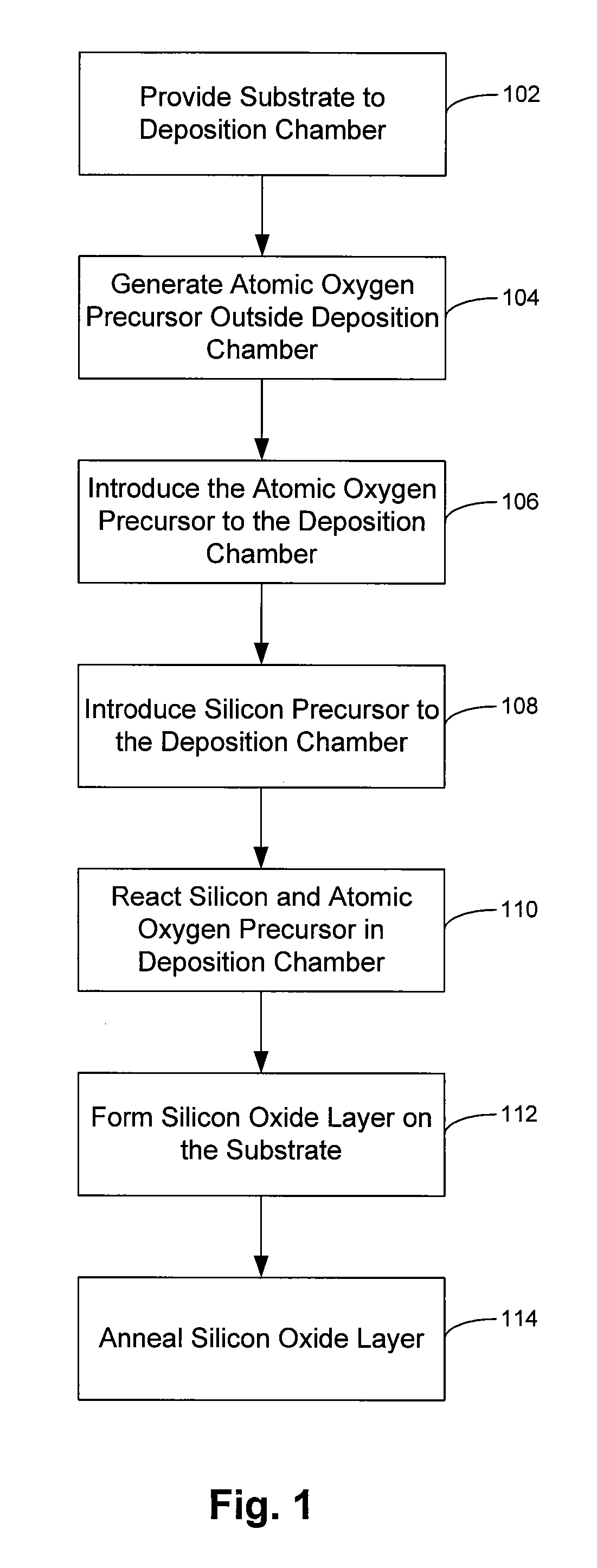
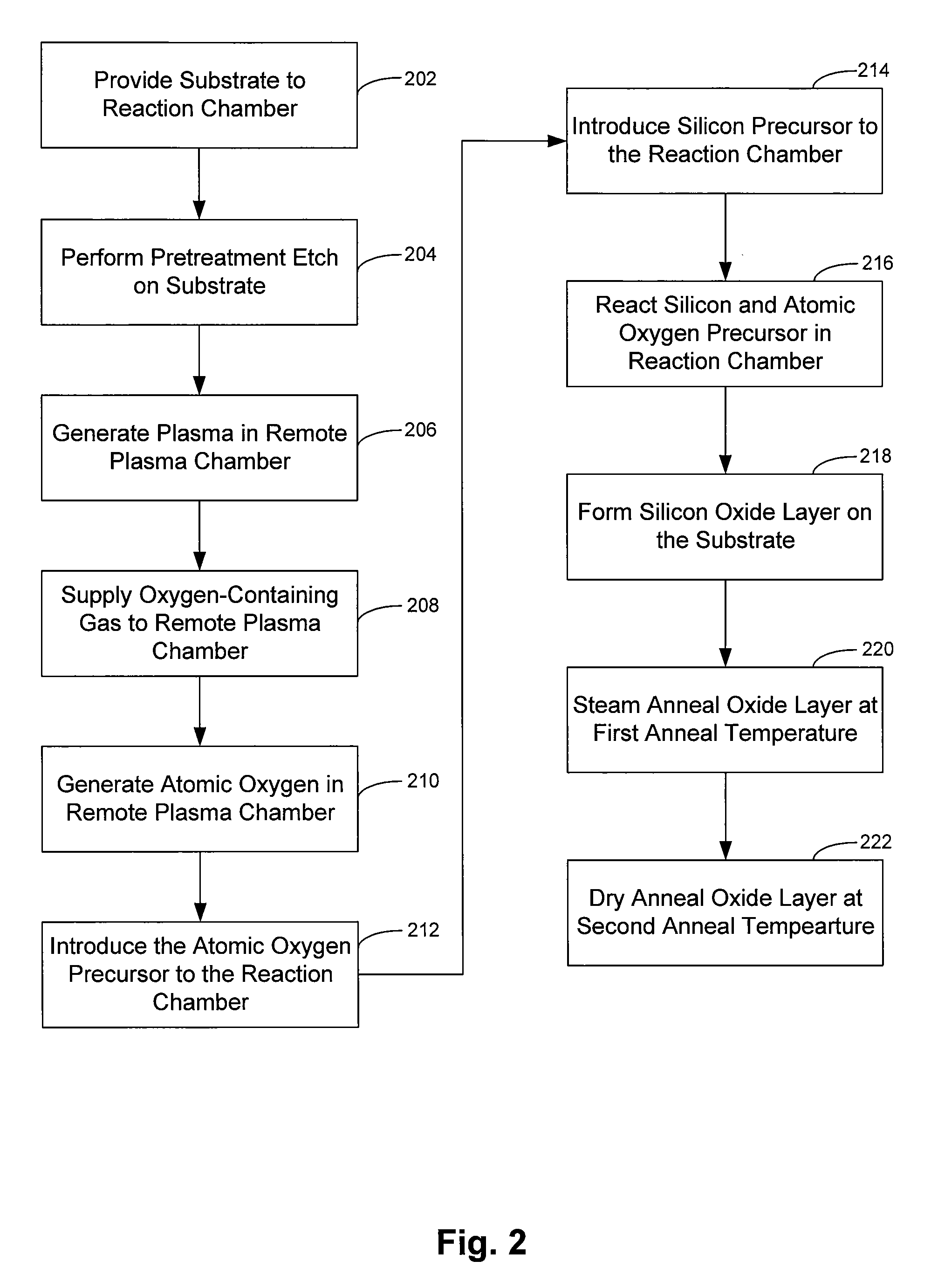
Chemical vapor deposition of high quality flow-like silicon dioxide using a silicon containing precursor and atomic oxygen
ActiveUS20070281496A1Semiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingChemical vapor deposition coatingGas phaseSilicon oxide
Methods of depositing a silicon oxide layer on a substrate are described. The methods may include the steps of providing a substrate to a deposition chamber, generating an atomic oxygen precursor outside the deposition chamber, and introducing the atomic oxygen precursor into the chamber. The methods may also include introducing a silicon precursor to the deposition chamber, where the silicon precursor and the atomic oxygen precursor are first mixed in the chamber. The silicon precursor and the atomic oxygen precursor react to form the silicon oxide layer on the substrate, and the deposited silicon oxide layer may be annealed. Systems to deposit a silicon oxide layer on a substrate are also described.
Owner:APPLIED MATERIALS INC
Free-standing and aligned carbon nanotubes and synthesis thereof
One or more highly-oriented, multi-walled carbon nanotubes are grown on an outer surface of a substrate initially disposed with a catalyst film or catalyst nano-dot by plasma enhanced hot filament chemical vapor deposition of a carbon source gas and a catalyst gas at temperatures between 300° C. and 3000° C. The carbon nanotubes range from 4 to 500 nm in diameter and 0.1 to 50 μm in length depending on growth conditions. Carbon nanotube density can exceed 104 nanotubes / mm2. Acetylene is used as the carbon source gas, and ammonia is used as the catalyst gas. Plasma intensity, carbon source gas to catalyst gas ratio and their flow rates, catalyst film thickness, and temperature of chemical vapor deposition affect the lengths, diameters, density, and uniformity of the carbon nanotubes. The carbon nanotubes of the present invention are useful in electrochemical applications as well as in electron emission, structural composite, material storage, and microelectrode applications.
Owner:THE RES FOUND OF STATE UNIV OF NEW YORK
Low Temperature Deposition of Silicon-Containing Films
ActiveUS20100304047A1Low deposition temperatureSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSpecial surfacesLow temperature depositionDeposition temperature
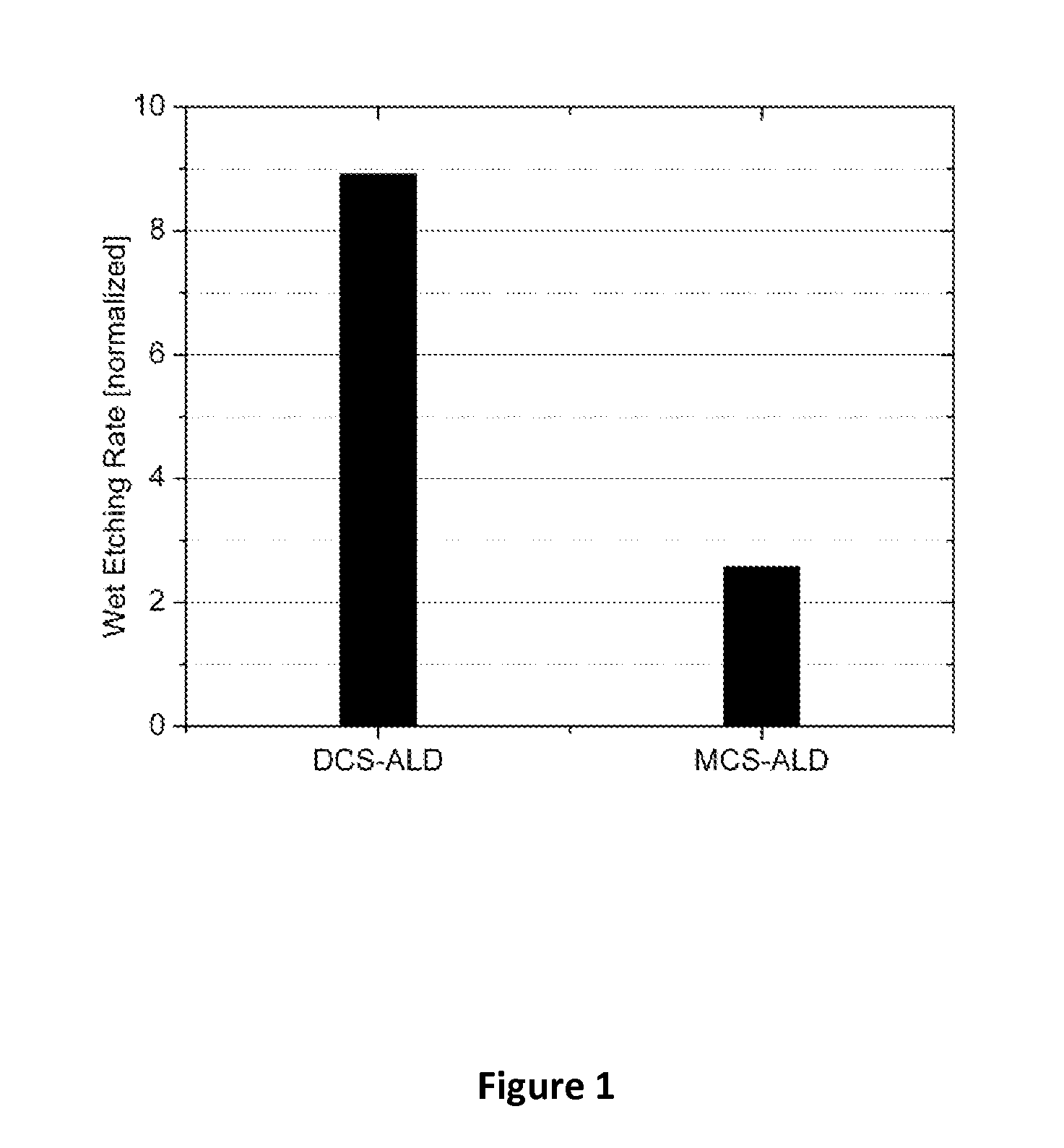
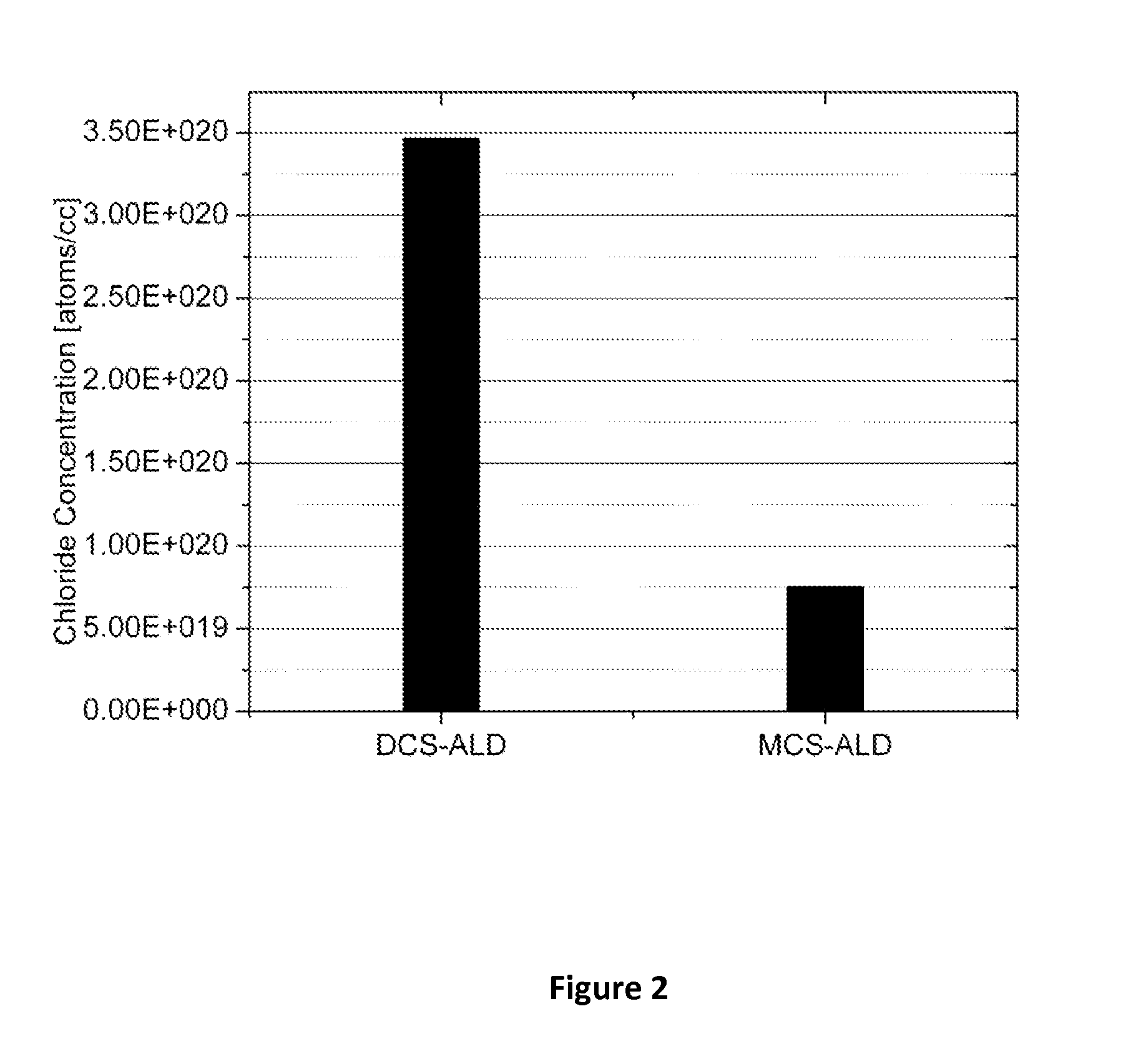
This invention discloses the method of forming silicon nitride, silicon oxynitride, silicon oxide, carbon-doped silicon nitride, carbon-doped silicon oxide and carbon-doped oxynitride films at low deposition temperatures. The silicon containing precursors used for the deposition are monochlorosilane (MCS) and monochloroalkylsilanes. The method is preferably carried out by using plasma enhanced atomic layer deposition, plasma enhanced chemical vapor deposition, and plasma enhanced cyclic chemical vapor deposition.
Owner:TOKYO ELECTRON LTD +1
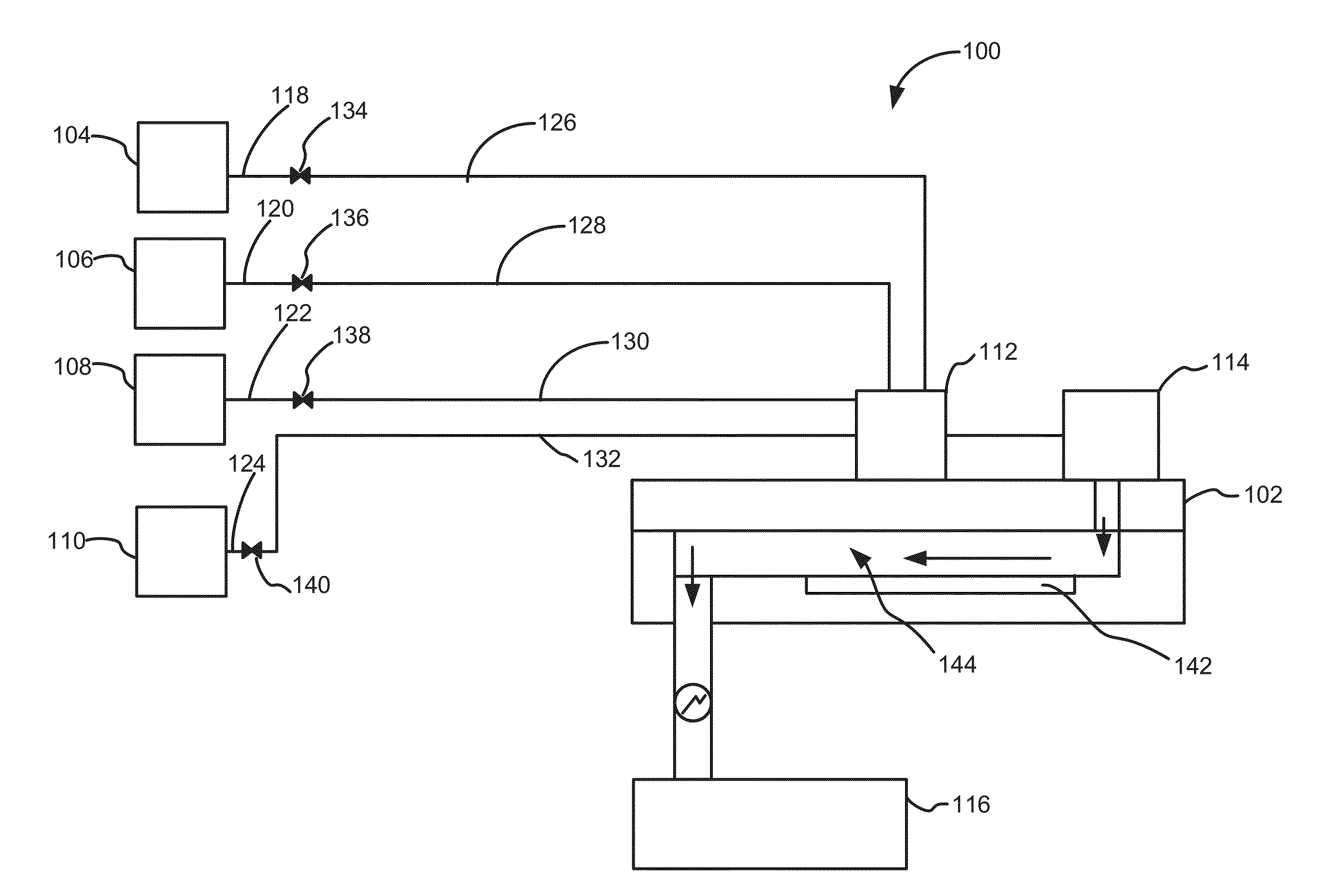
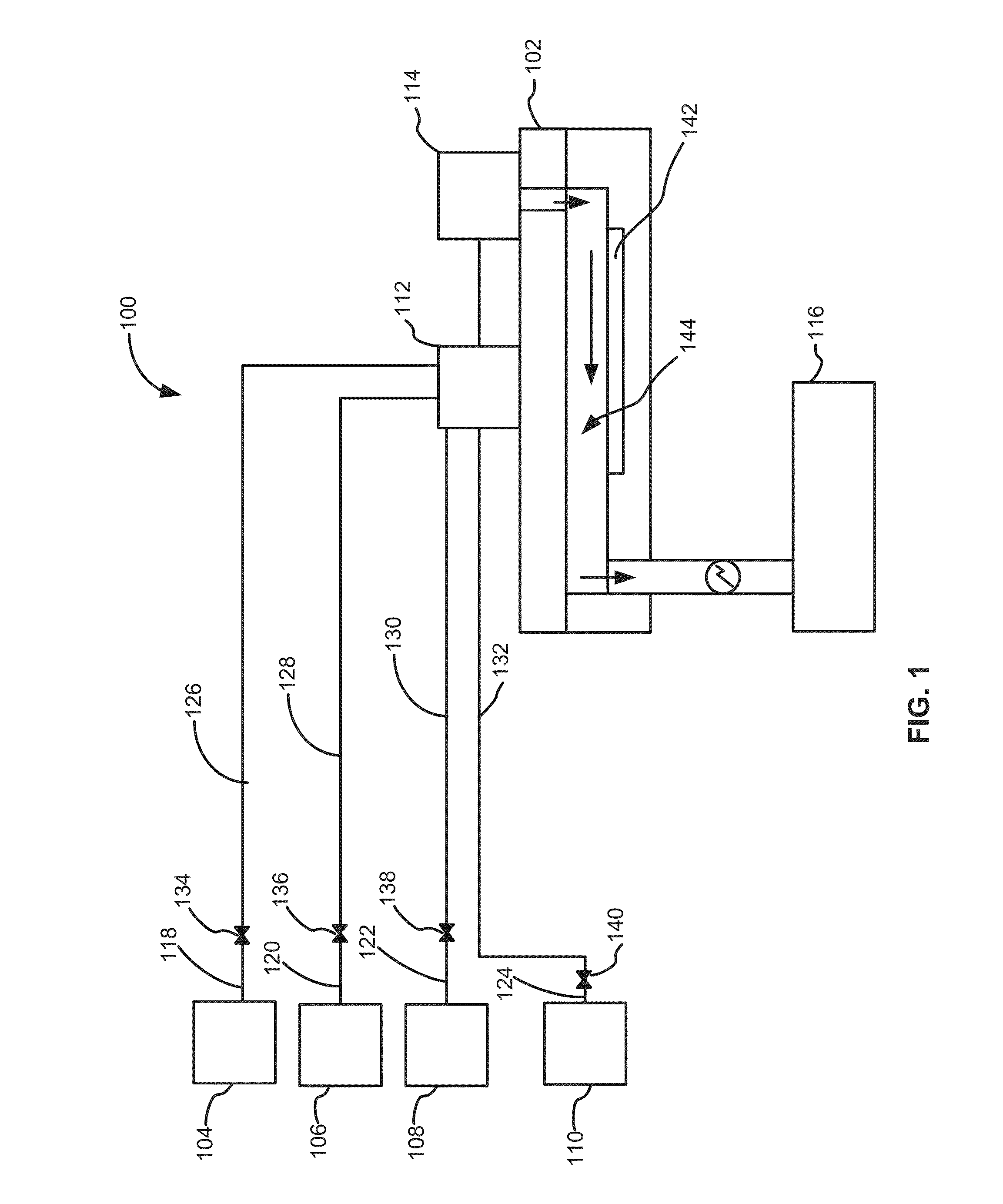
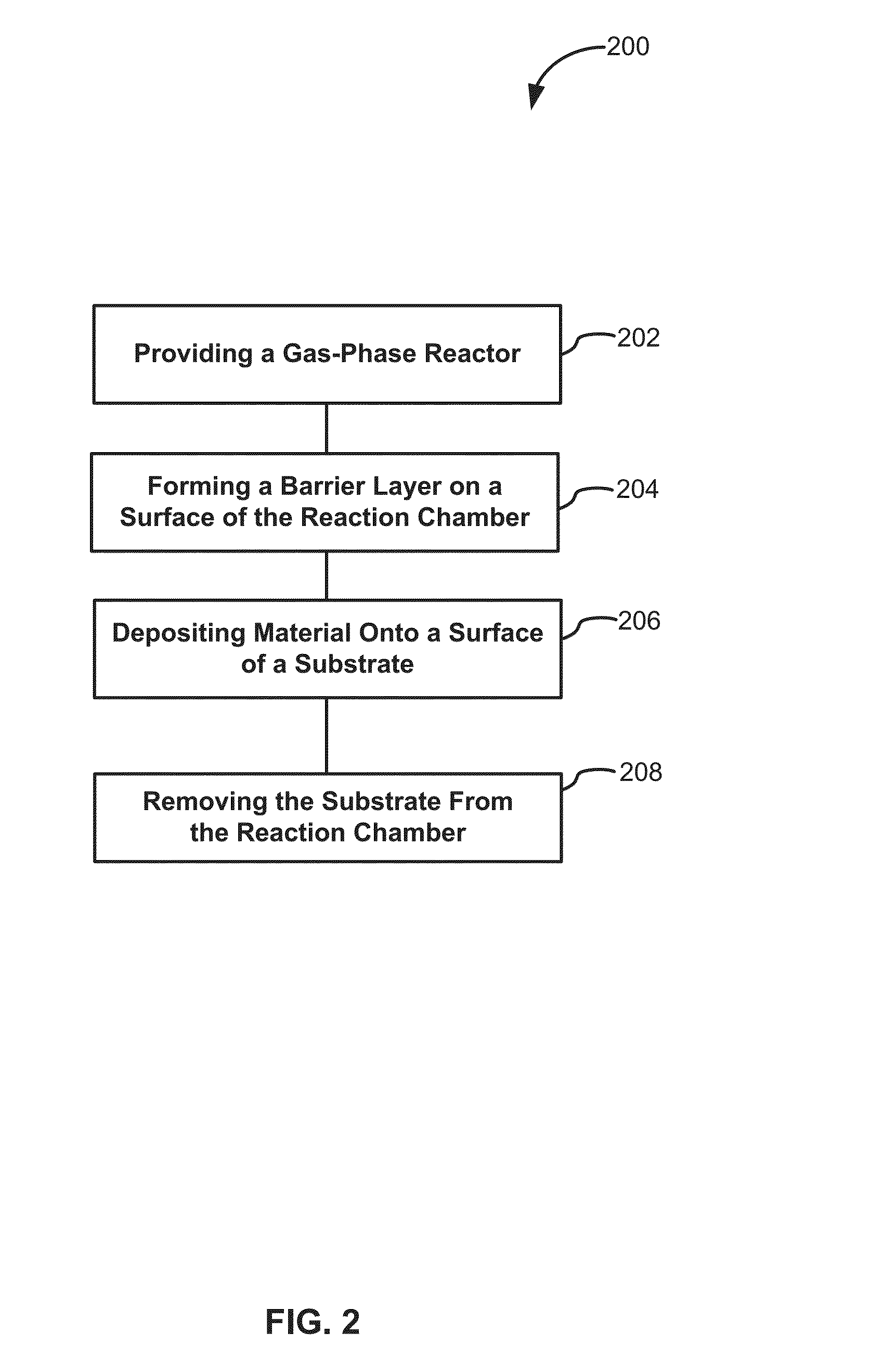
Method and system to reduce outgassing in a reaction chamber
ActiveUS20150140210A1Reduce outgassingImprove thickness uniformitySemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingChemical vapor deposition coatingOutgassingGas phase
Systems and methods of reducing outgassing of a substance within a reaction chamber of a reactor are disclosed. Exemplary methods include depositing a barrier layer within the reaction chamber and using a scavenging precursor to react with species on a surface of the reaction chamber. Exemplary systems include gas-phase deposition systems, such as atomic layer deposition systems, which include a barrier layer source and / or a scavenging precursor source fluidly coupled to a reaction chamber of the system.
Owner:ASM IP HLDG BV
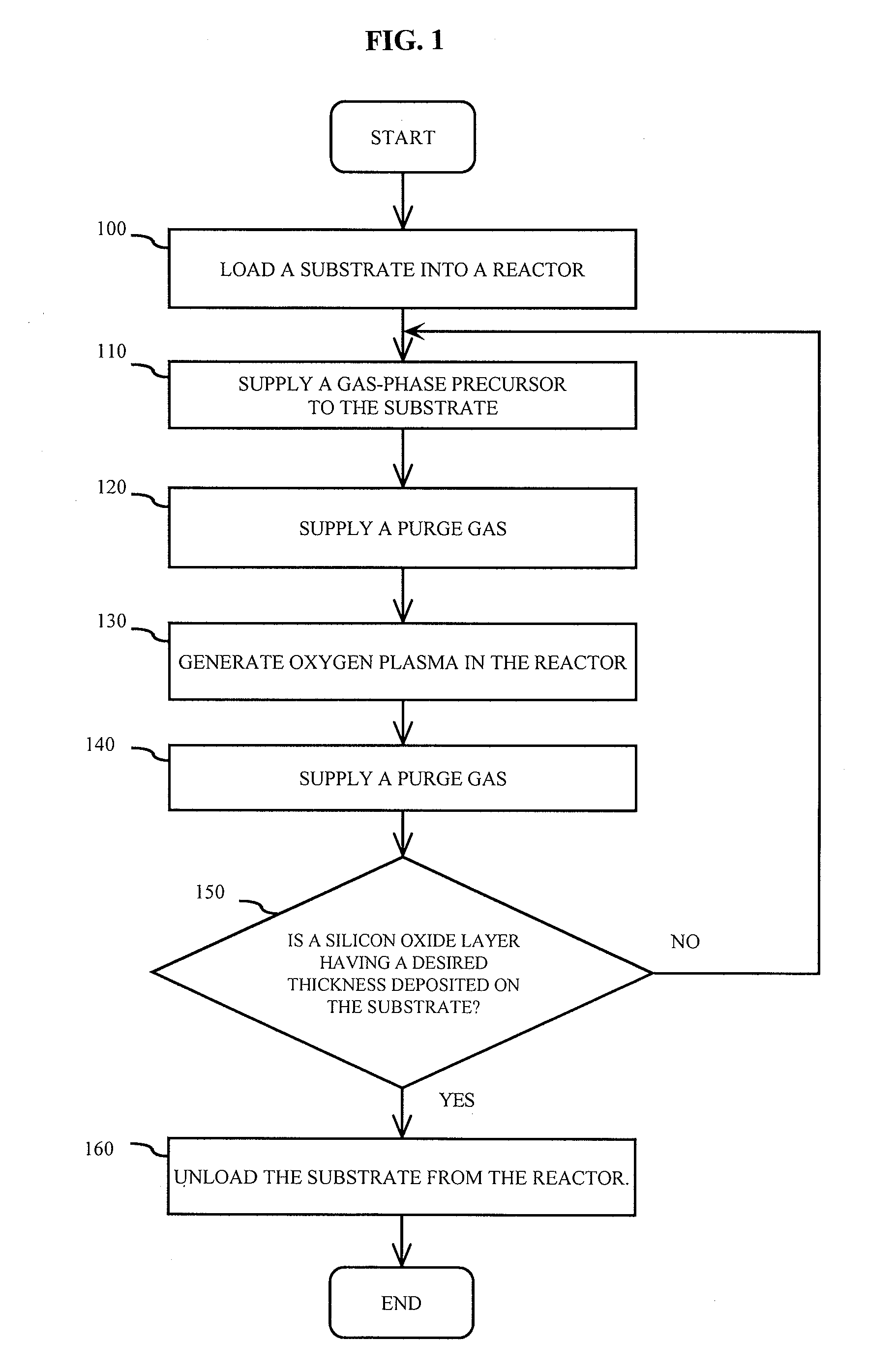
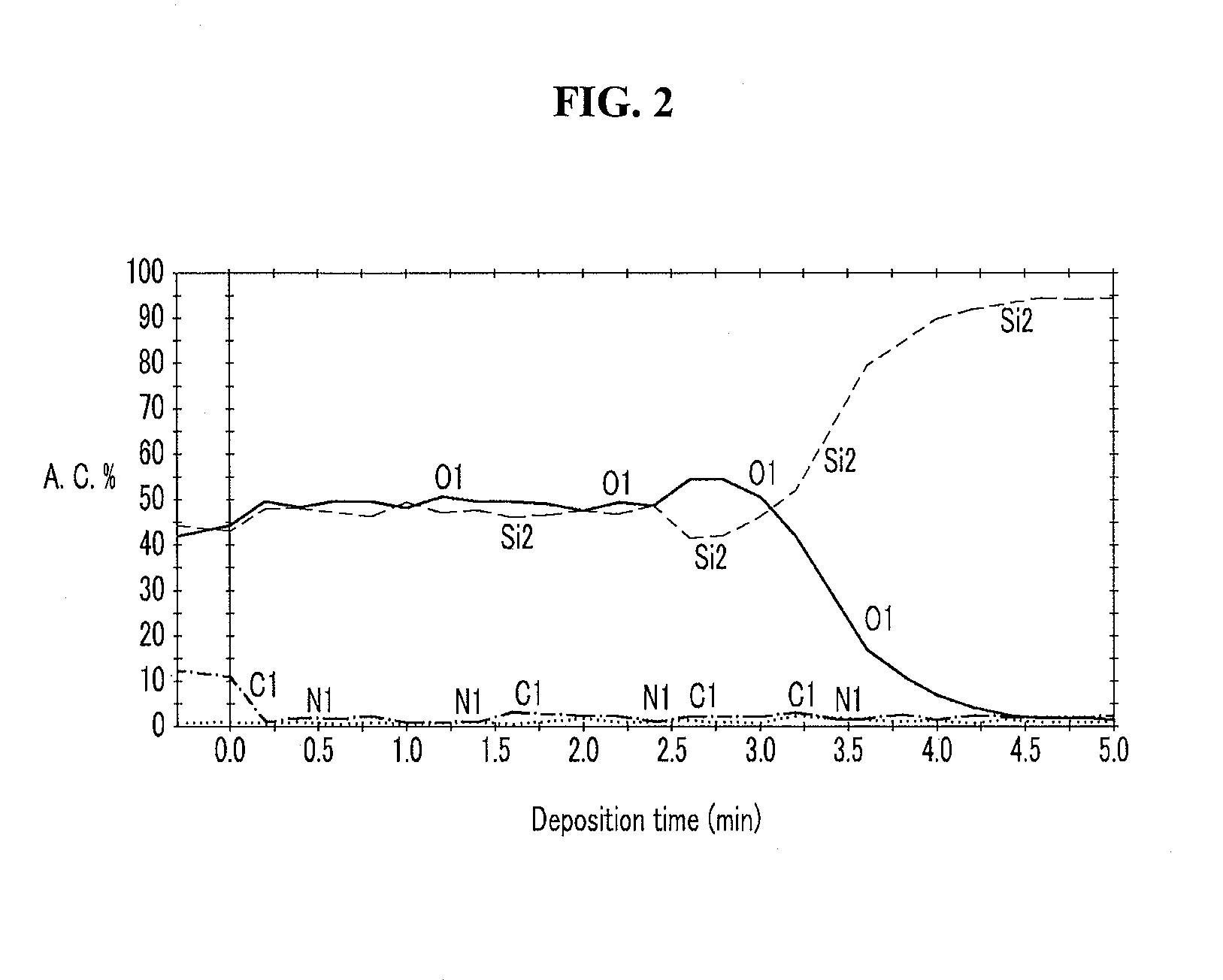
Method of depositing silicon oxide films
InactiveUS20090041952A1Semiconductor/solid-state device detailsSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingOxygen plasmaGas phase
Methods of depositing a silicon oxide film are disclosed. One embodiment is a plasma enhanced atomic layer deposition (PEALD) process that includes supplying a vapor phase silicon precursor, such as a diaminosilane compound, to a substrate, and supplying oxygen plasma to the substrate. Another embodiment is a pulsed hybrid method between atomic layer deposition (ALD) and chemical vapor deposition (CVD). In the other embodiment, a vapor phase silicon precursor, such as a diaminosilane compound, is supplied to a substrate while ozone gas is continuously or discontinuously supplied to the substrate.
Owner:ASM KOREA LTD
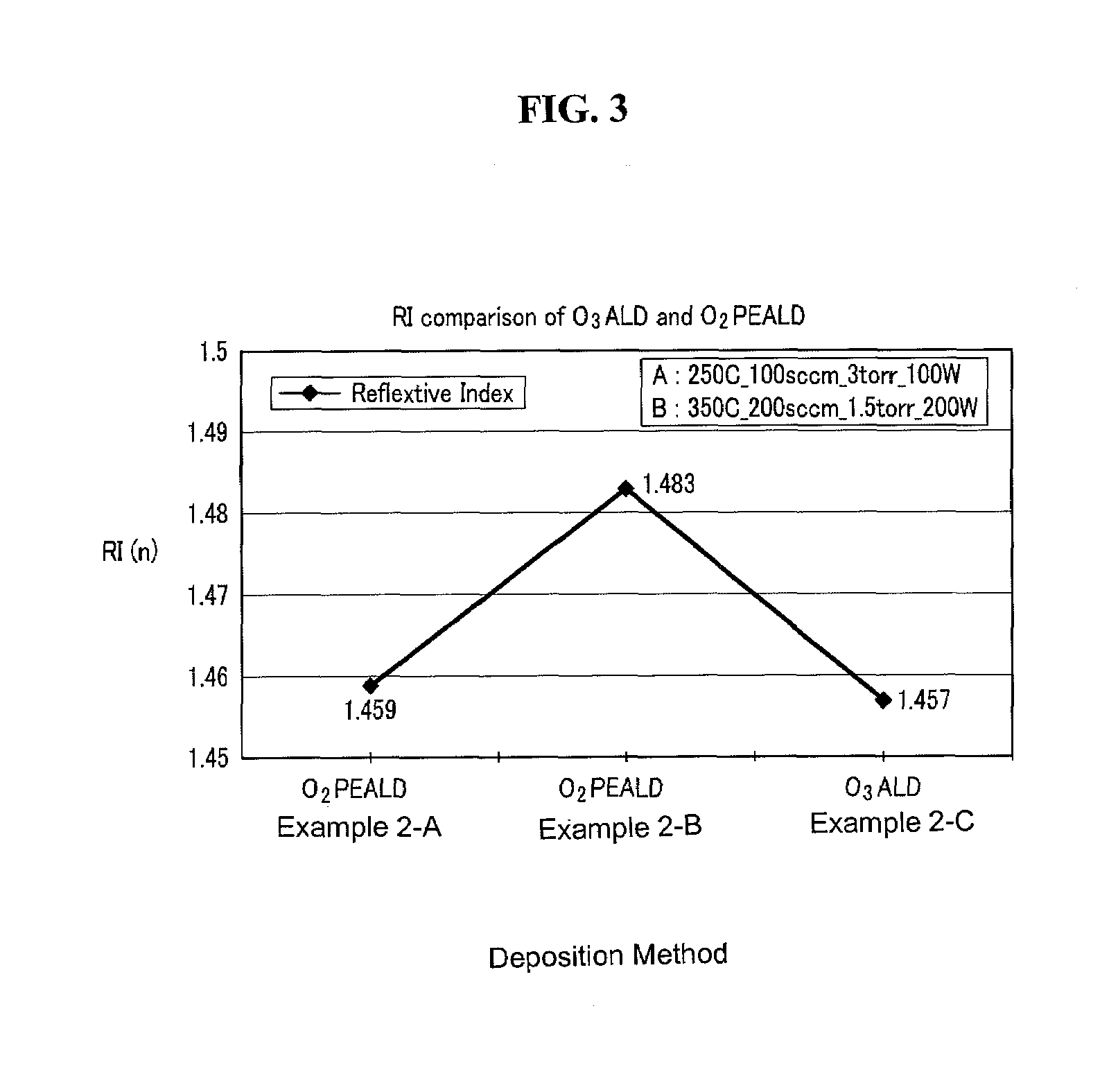
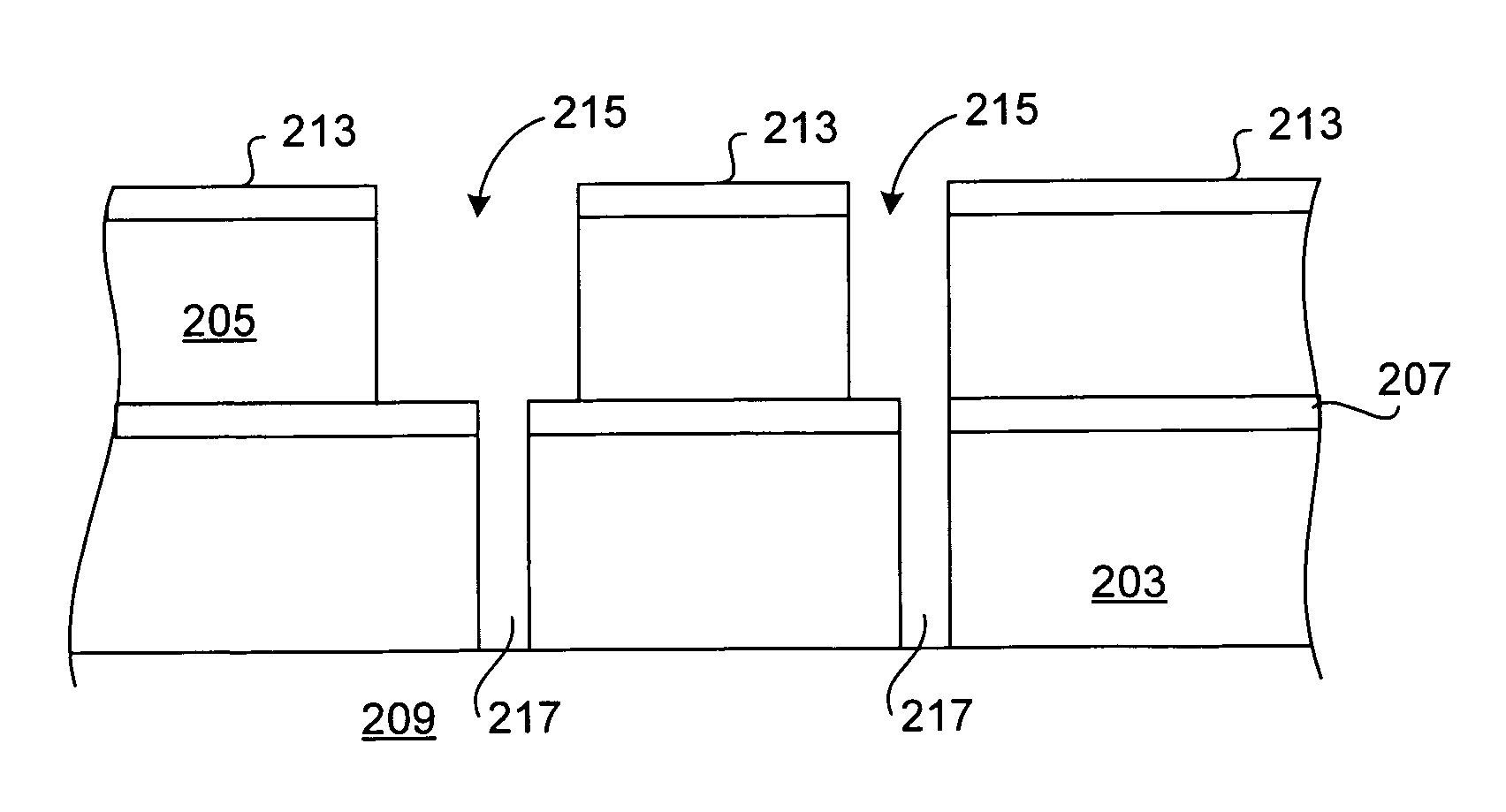
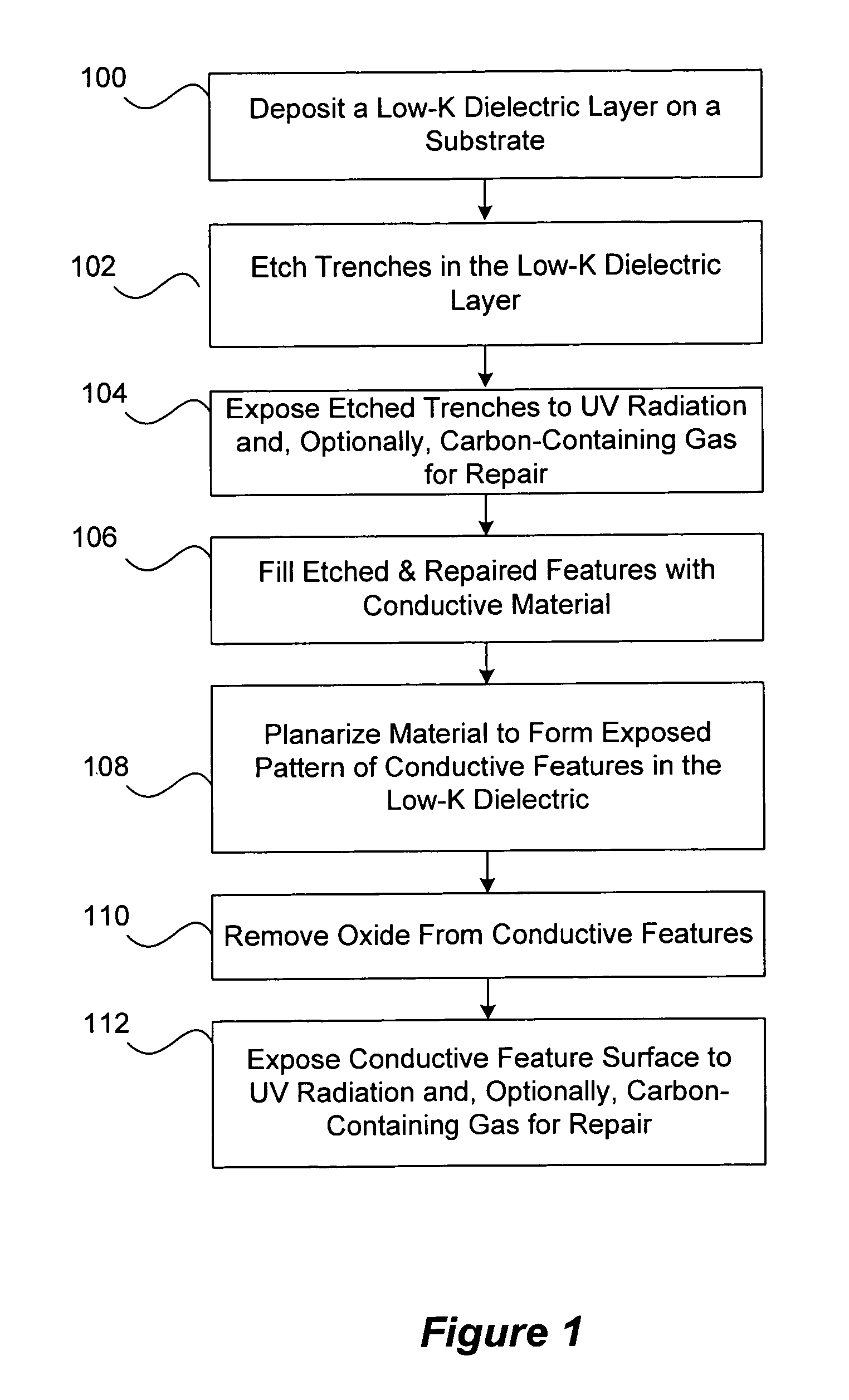
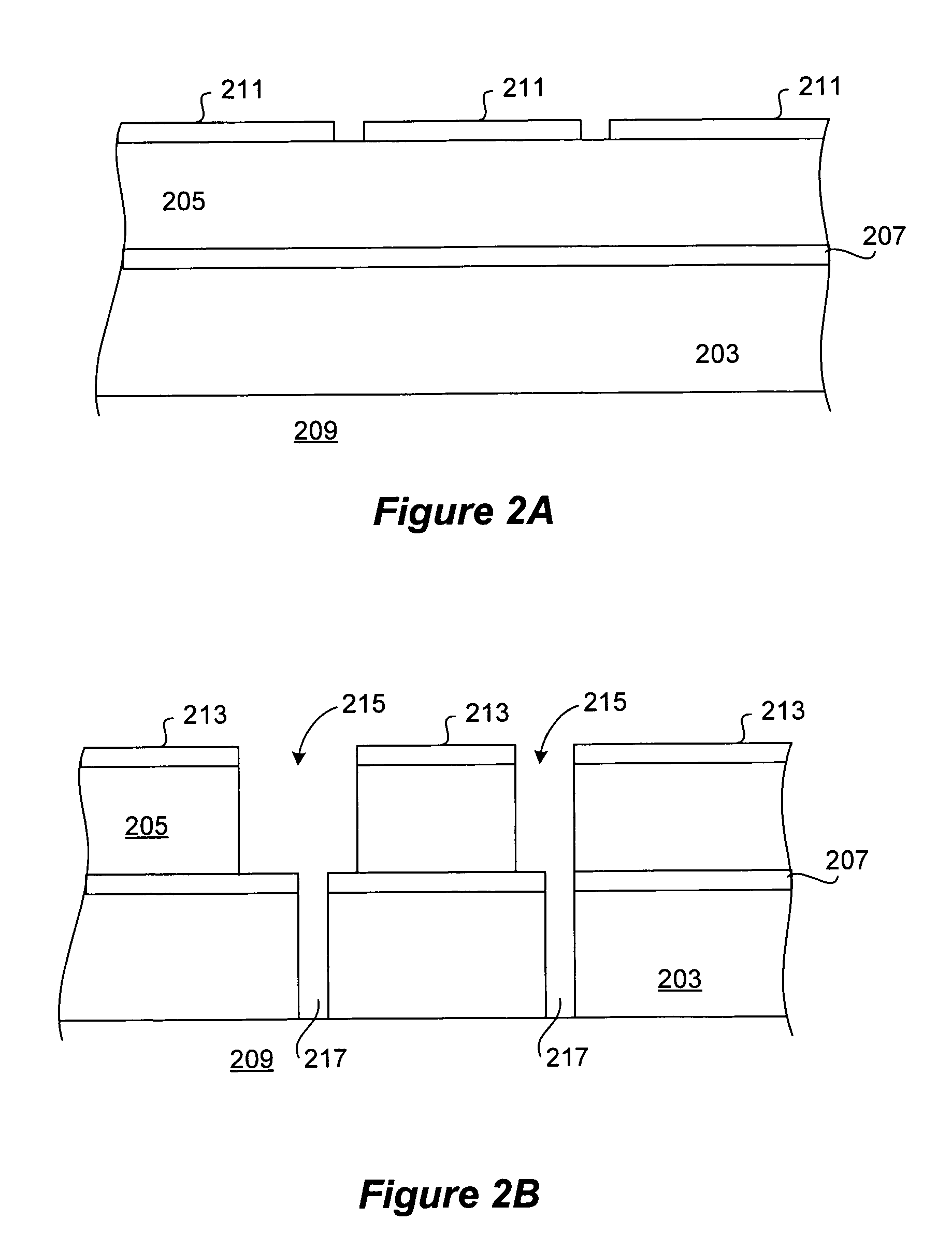
UV treatment for carbon-containing low-k dielectric repair in semiconductor processing
Owner:NOVELLUS SYSTEMS
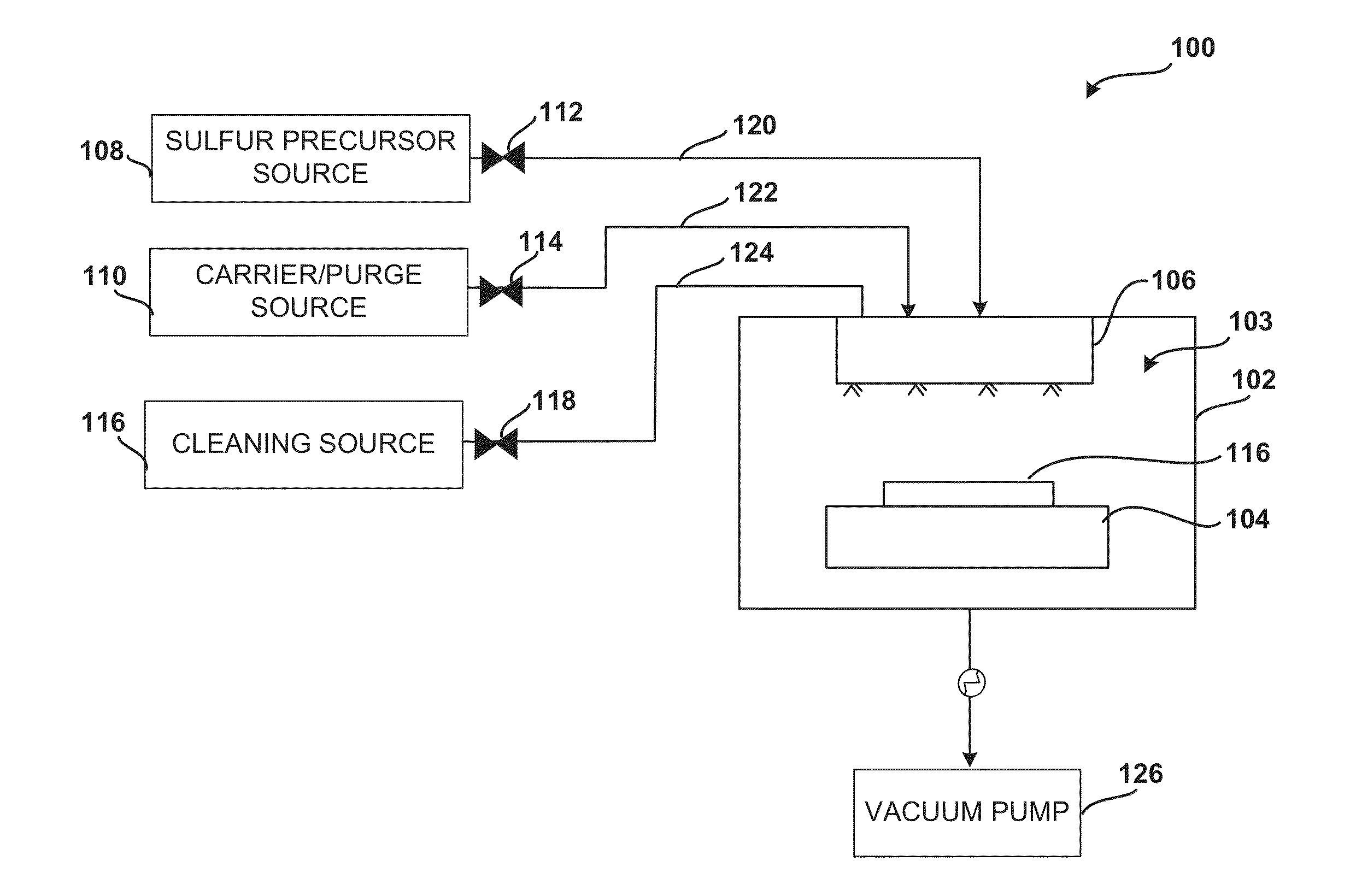
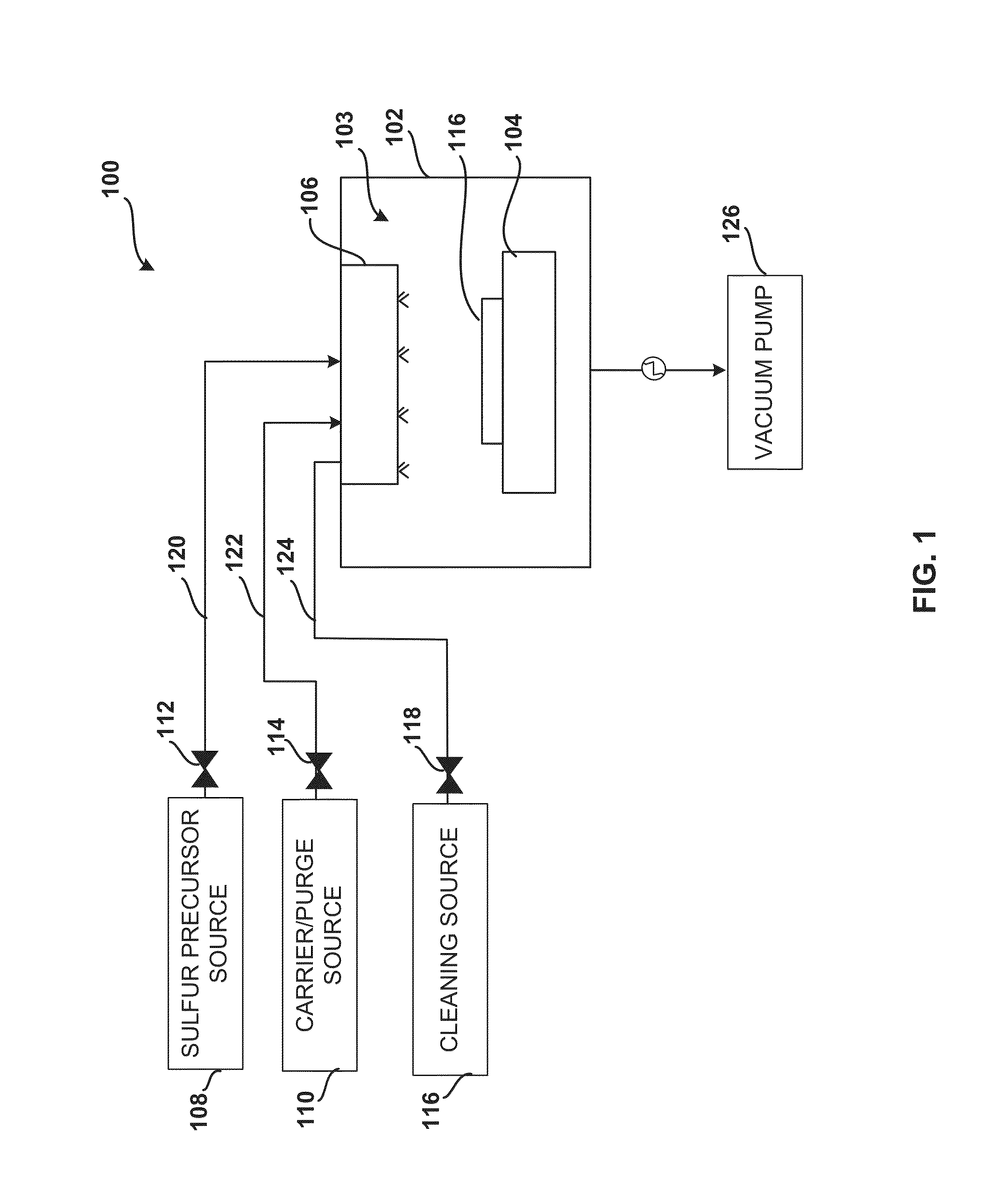
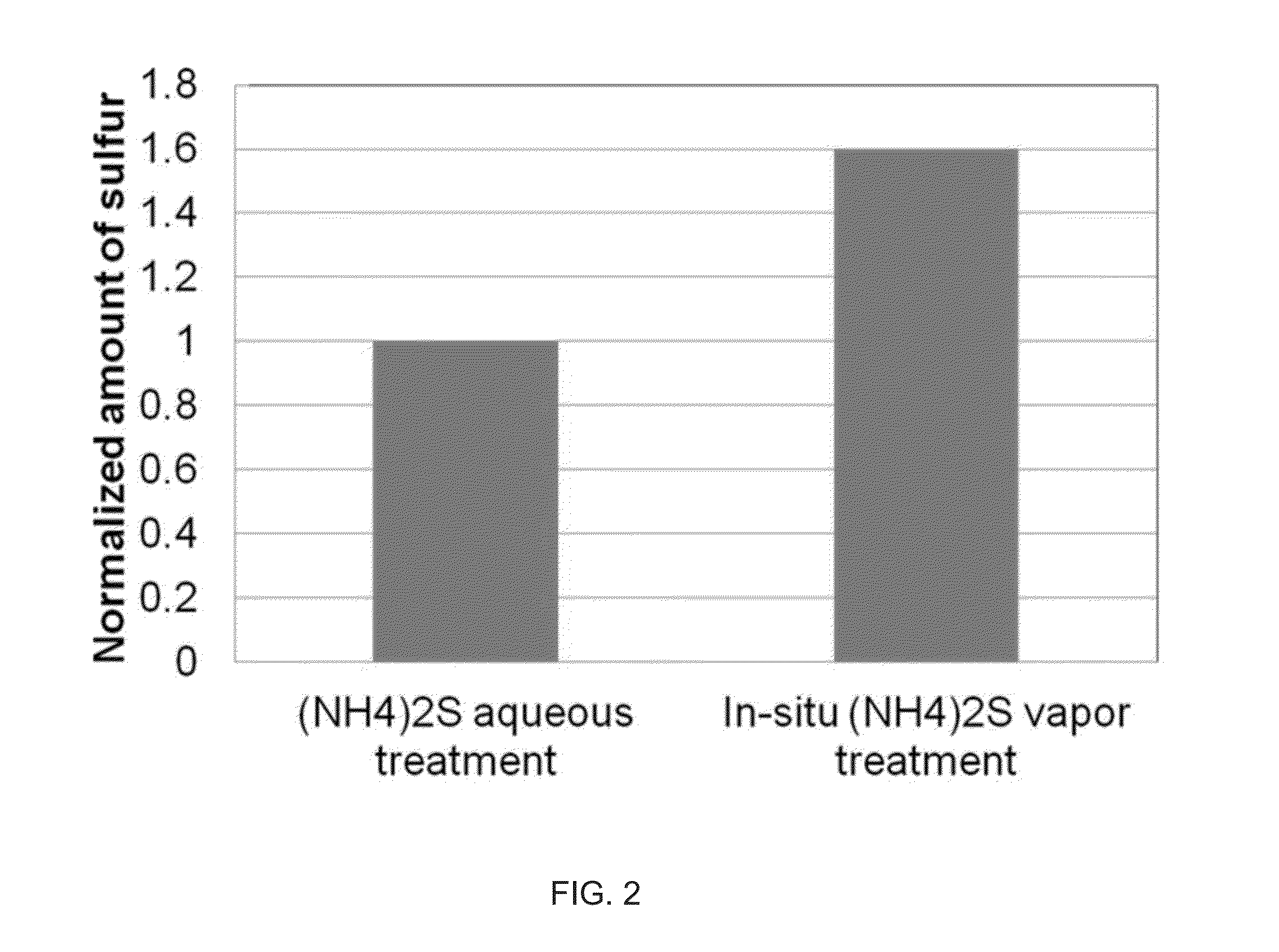
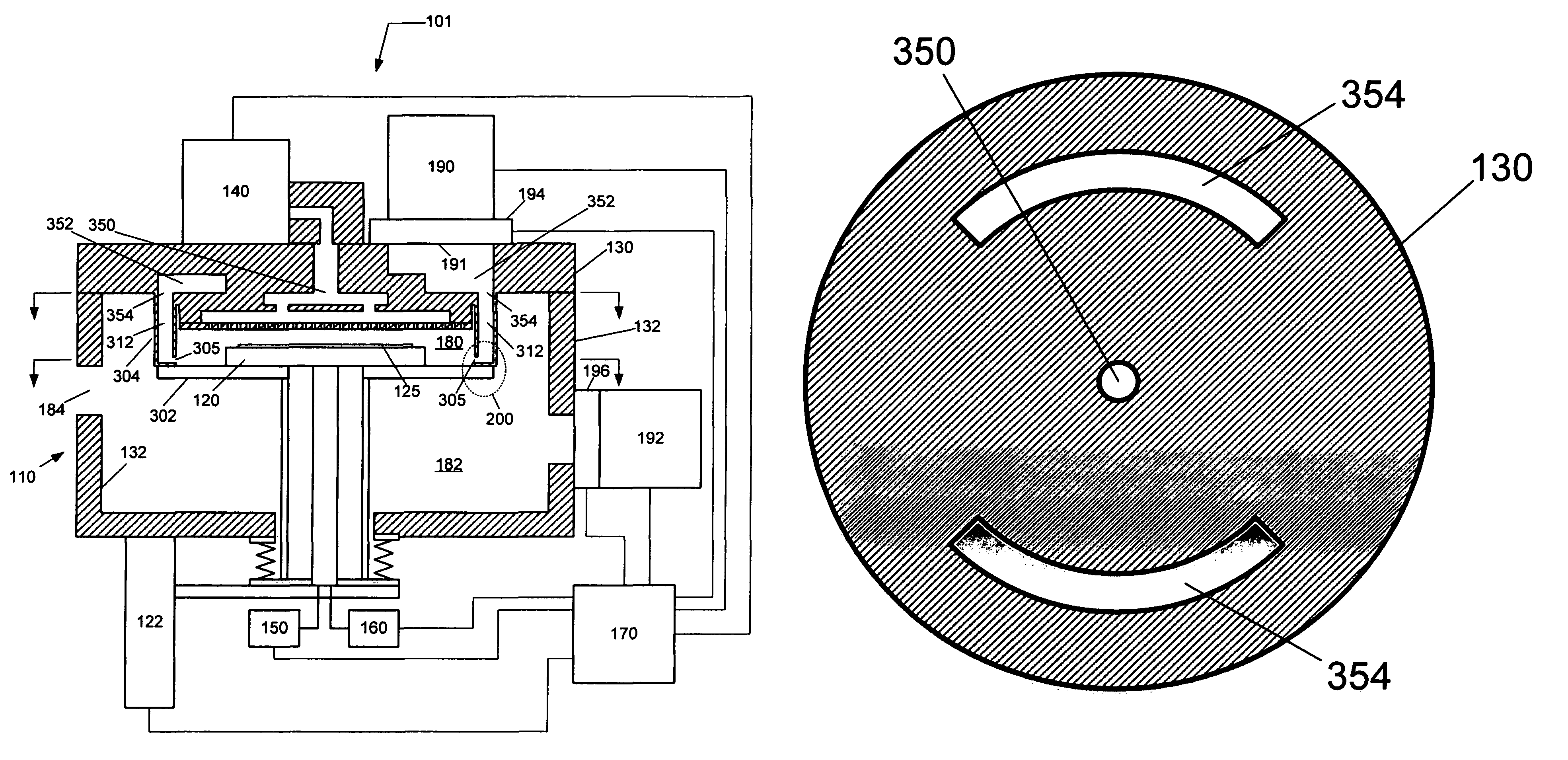
System and method for gas-phase sulfur passivation of a semiconductor surface
ActiveUS20140027884A1Semiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesGas phaseDevice form
Improved methods and systems for passivating a surface of a high-mobility semiconductor and structures and devices formed using the methods are disclosed. The method includes providing a high-mobility semiconductor surface to a chamber of a reactor and exposing the high-mobility semiconductor surface to a gas-phase sulfur precursor to passivate the high-mobility semiconductor surface.
Owner:ASM IP HLDG BV
Exhaust apparatus configured to reduce particle contamination in a deposition system
InactiveUS7740705B2Reduce pollutionUniform processingSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingChemical vapor deposition coatingGas phaseEngineering
Owner:TOKYO ELECTRON LTD
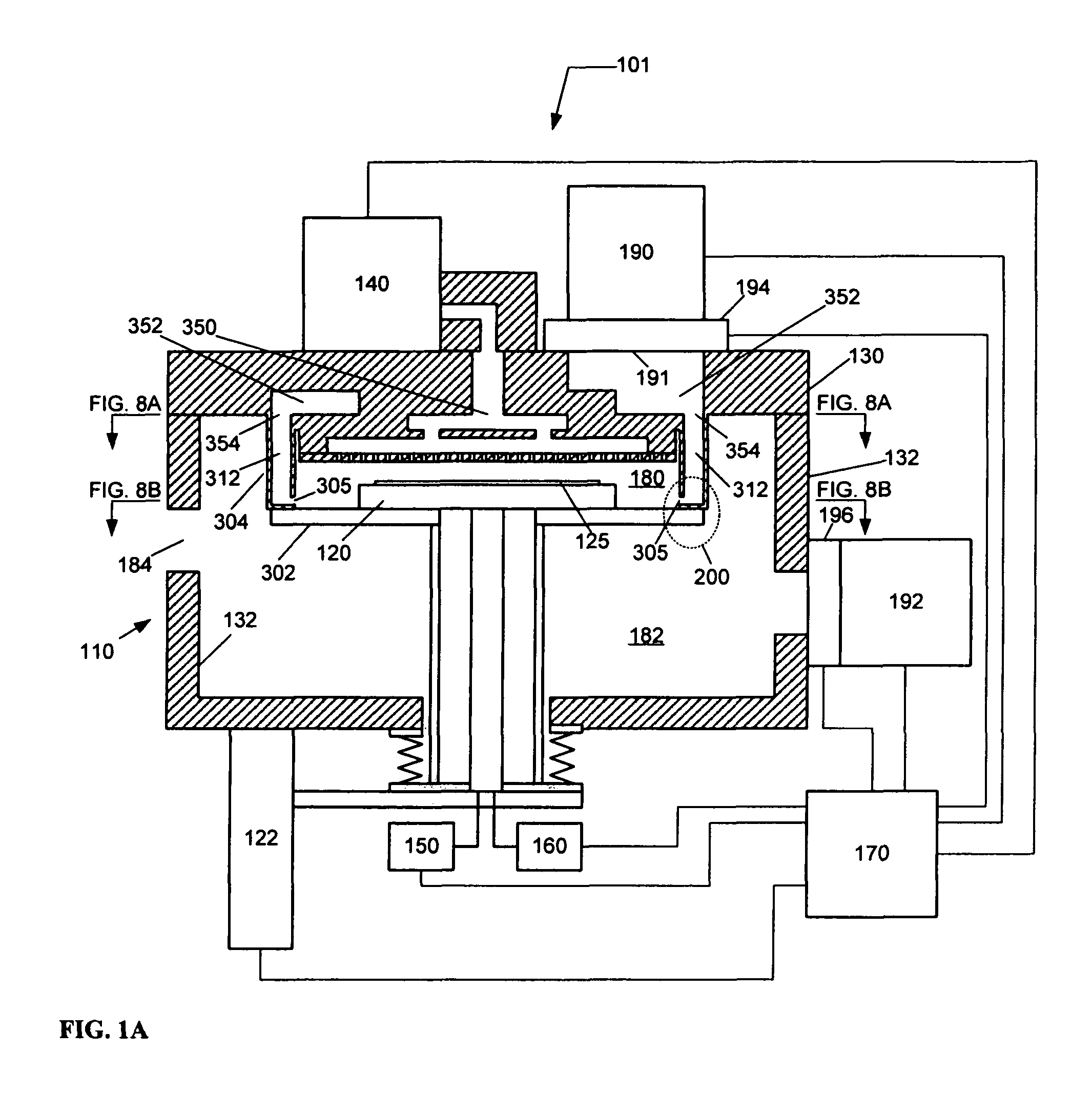
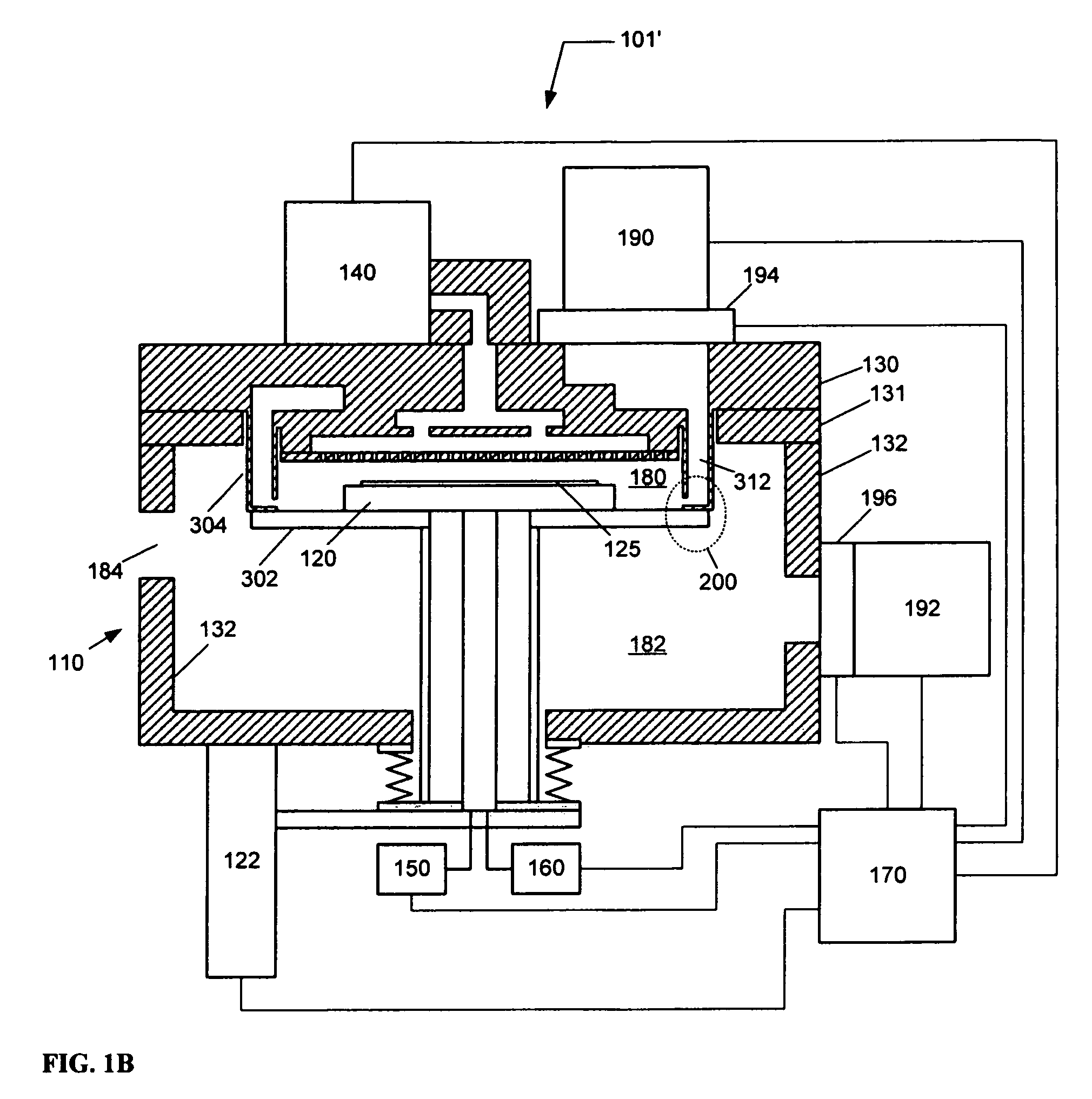
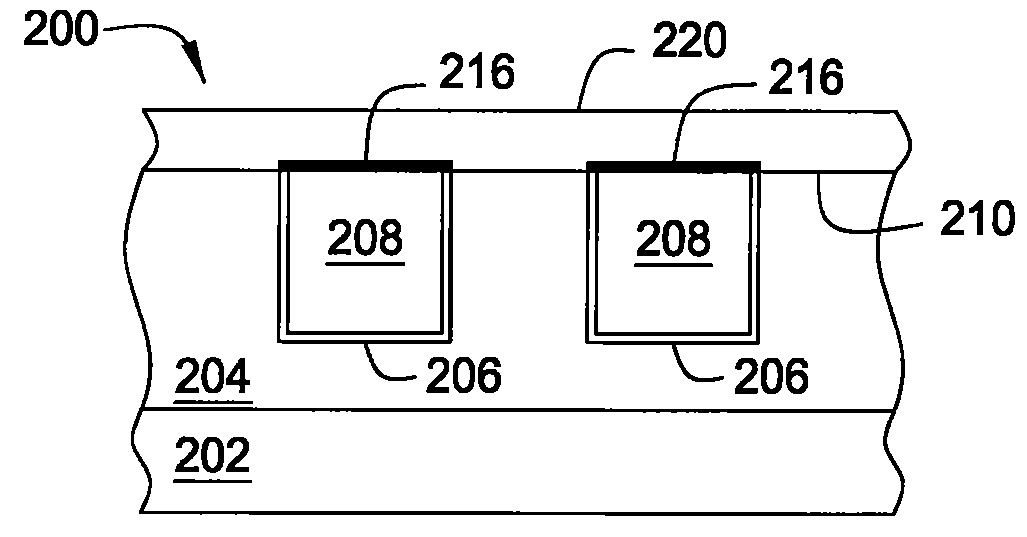
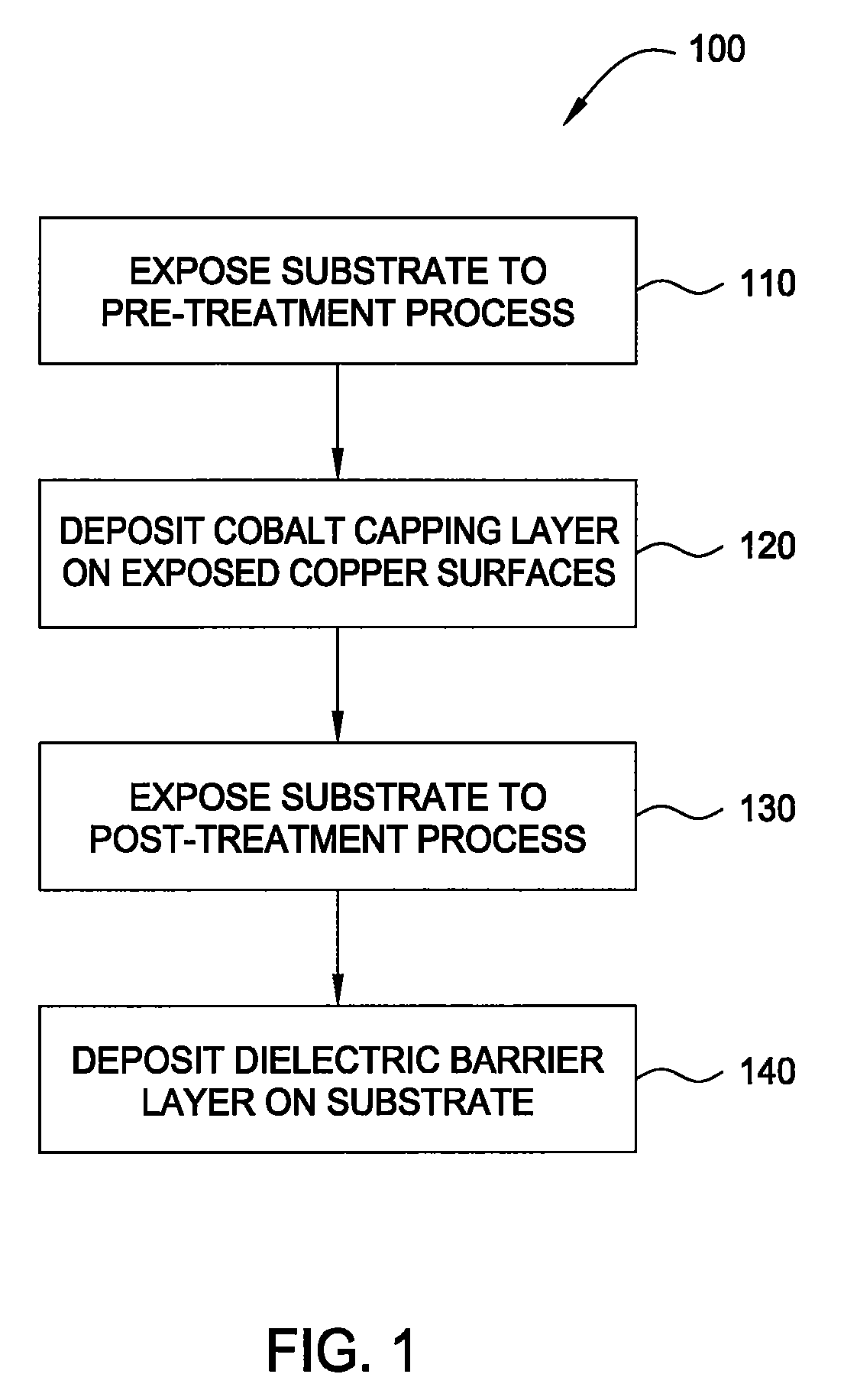
Selective cobalt deposition on copper surfaces
InactiveUS20090269507A1Pretreated surfacesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingGas phaseDielectric surface
Embodiments of the invention provide processes to selectively form a cobalt layer on a copper surface over exposed dielectric surfaces. In one embodiment, a method for capping a copper surface on a substrate is provided which includes positioning a substrate within a processing chamber, wherein the substrate contains a contaminated copper surface and a dielectric surface, exposing the contaminated copper surface to a reducing agent while forming a copper surface during a pre-treatment process, exposing the substrate to a cobalt precursor gas to selectively form a cobalt capping layer over the copper surface while leaving exposed the dielectric surface during a vapor deposition process, and depositing a dielectric barrier layer over the cobalt capping layer and the dielectric surface. In another embodiment, a deposition-treatment cycle includes performing the vapor deposition process and subsequently a post-treatment process, which deposition-treatment cycle may be repeated to form multiple cobalt capping layers.
Owner:APPLIED MATERIALS INC
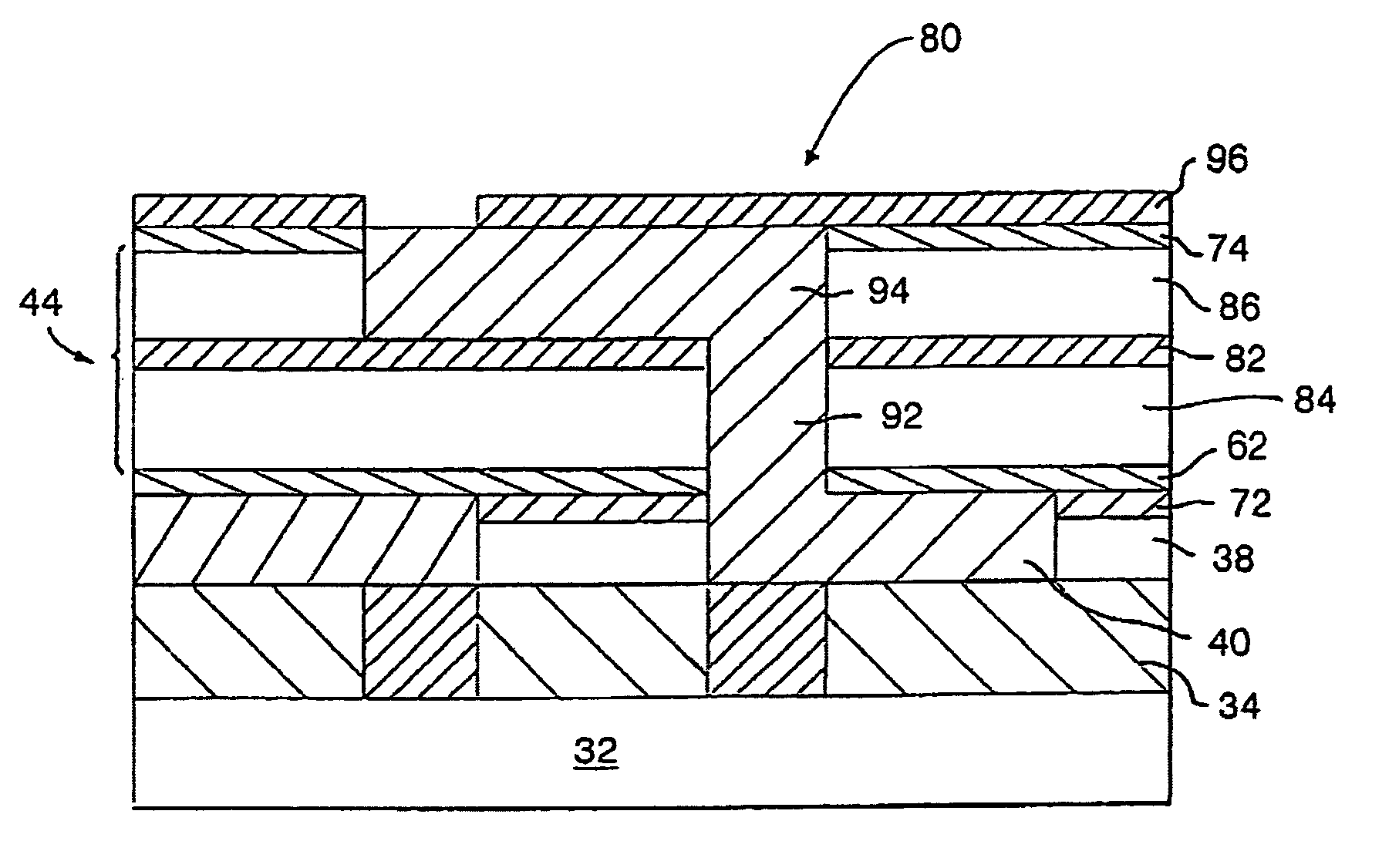
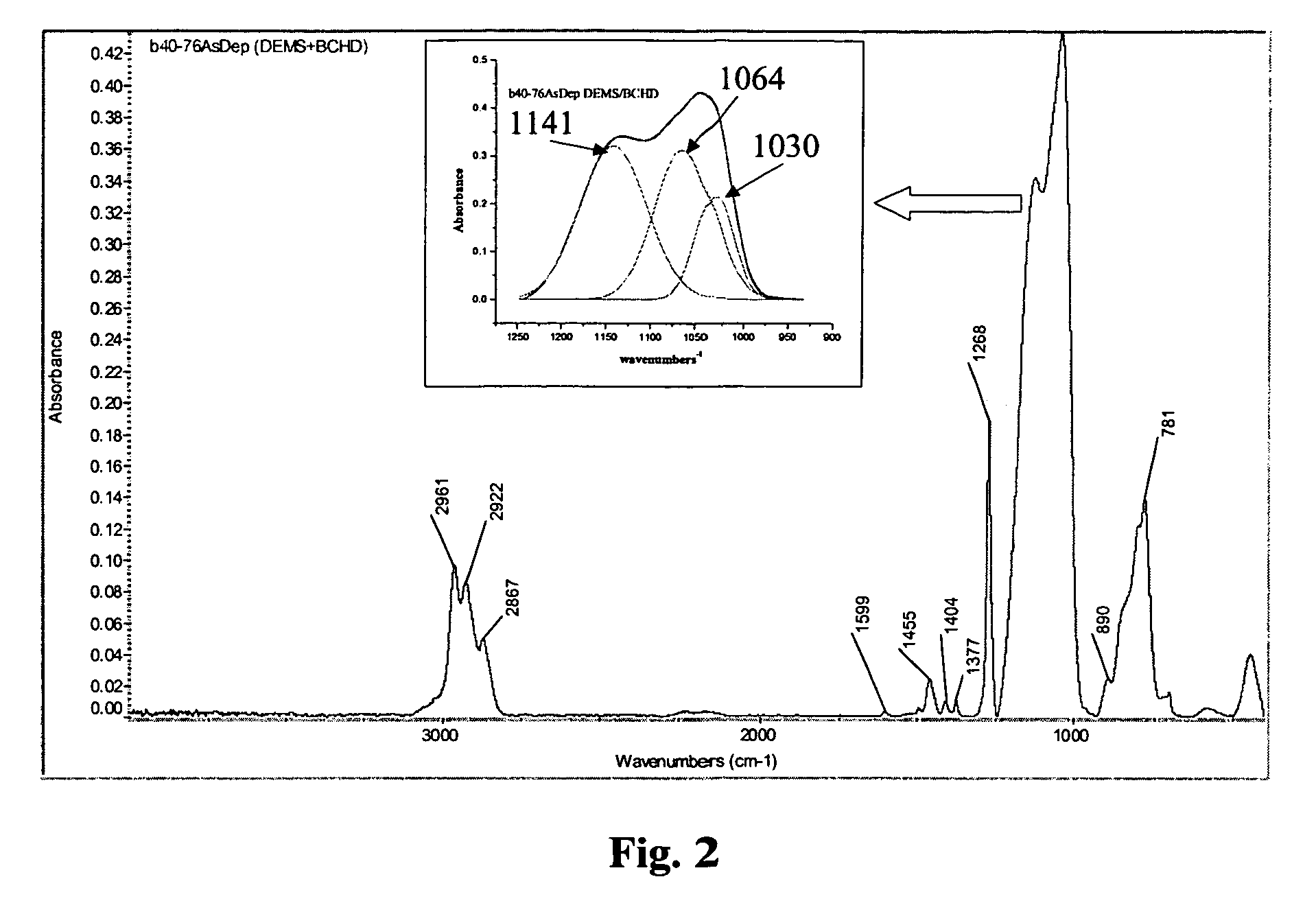
Method for fabricating an ultralow dielectric constant material as an intralevel or interlevel dielectric in a semiconductor device and electronic device made
InactiveUS7049247B2Low costReduce tensile stressSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingChemical vapor deposition coatingGas phaseParallel plate
A method for fabricating a thermally stable ultralow dielectric constant film comprising Si, C, O and H atoms in a parallel plate chemical vapor deposition process utilizing a plasma enhanced chemical vapor deposition (“PECVD”) process is disclosed. Electronic devices containing insulating layers of thermally stable ultralow dielectric constant materials that are prepared by the method are further disclosed. To enable the fabrication of a thermally stable ultralow dielectric constant film, specific precursor materials are used, such as, silane derivatives, for instance, diethoxymethylsilane (DEMS) and organic molecules, for instance, bicycloheptadiene and cyclopentene oxide.
Owner:INTEL CORP
Process for catalytically producing ethylene directly from acetic acid in a single reaction zone
InactiveUS20100030001A1High selectivityHigh yieldHydrocarbonsBulk chemical productionAcetic acidHydrogen
A process for the selective production of ethylene by vapor phase reaction of acetic acid over a hydrogenating catalyst composition to form ethylene in a single reaction zone is disclosed and claimed. In an embodiment of this invention reaction of acetic acid and hydrogen over either a copper supported on iron oxide, copper-aluminum catalyst, cobalt supported on H-ZSM-5, ruthenium-cobalt supported on silica or cobalt supported on carbon selectively produces ethylene in a vapor phase at a temperature in the range of about 250° C. to 350° C.
Owner:CELANESE INT CORP
Multi-component particles comprising inorganic nanoparticles distributed in an organic matrix and processes for making and using same
Multi-component particles comprising inorganic nanoparticles distributed in an organic matrix and processes for making and using same. A flowing aerosol is generated that includes droplets of a precursor medium dispersed in a gas phase. The precursor medium contains a liquid vehicle and at least one precursor. At least a portion of the liquid vehicle is removed from the droplets of precursor medium under conditions effective to convert the precursor to the nanoparticles or the matrix and form the multi-component particles.
Owner:CABOT CORP
Method of depositing nanolaminate film for non-volatile floating gate memory devices by atomic layer deposition
Disclosed herein is a method of depositing a nanolaminate film for next-generation non-volatile floating gate memory devices by atomic layer deposition. The method includes the steps of: introducing a substrate into an atomic layer deposition reactor; forming on the substrate a first high-dielectric-constant layer by alternately supplying an oxygen source and a metal source selected from among an aluminum source, a zirconium source and a hafnium source; forming on the first high-dielectric-constant layer a nickel oxide layer by alternately supplying a nickel source and an oxygen source; and forming on the nickel oxide layer a second high-dielectric-constant layer by alternately supplying an oxygen source and a metal source selected from among an aluminum source, a zirconium source and a hafnium source. The nanolaminate film deposited according to the method shows good memory window characteristics compared to those of memory devices fabricated using nanocrystal floating gates according to the prior physical vapor deposition methods, and thus can be applied to non-volatile floating gate memory devices.
Owner:KOREA RES INST OF CHEM TECH
Solid organometallic compound-filled container and filling method thereof
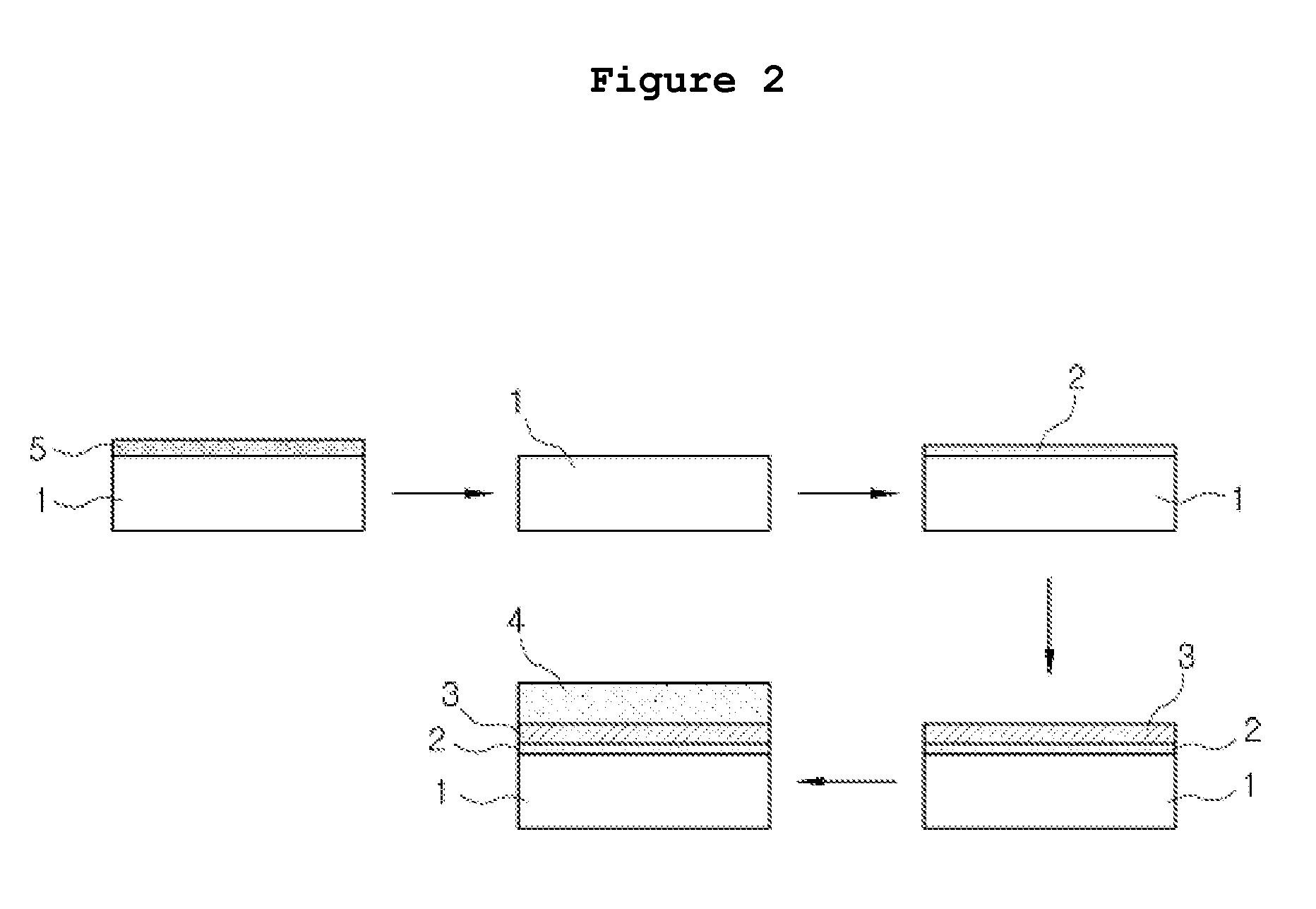
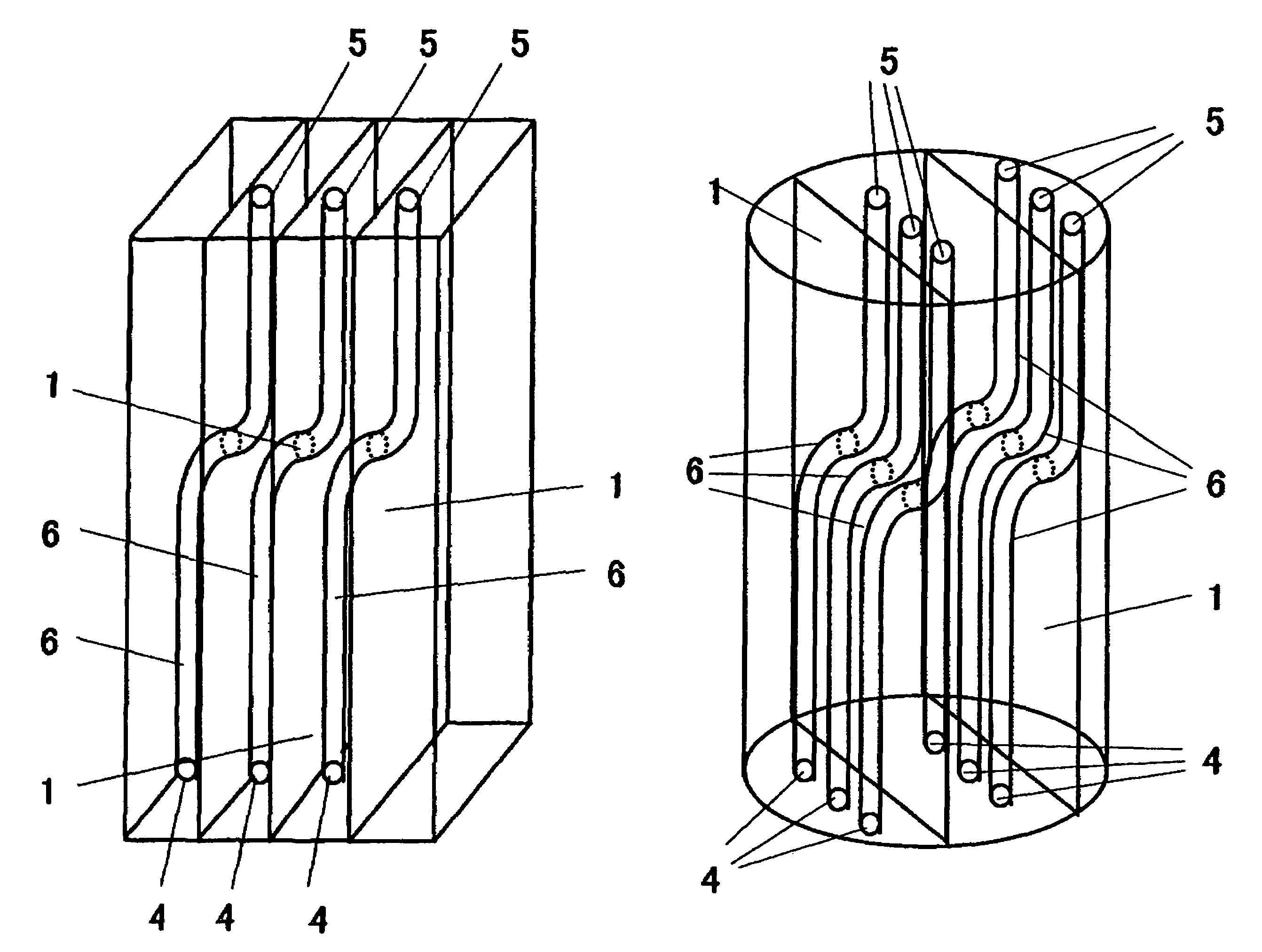
InactiveUS7547363B2Increasing outer sizeExtended maintenance periodEnvelopes/bags making machineryLayered productsGas phaseEngineering
A solid organometallic compound novel filled container stably supplies an apparatus for vapor phase epitaxial growth such as an MOCVD apparatus with a solid organometallic compound over a long term. The solid organometallic compound-filled container has a carrier gas inlet and a carrier gas outlet. The interior of the filled container is separated into a plurality of vertical compartments. A carrier gas introduced via the carrier gas inlet flows through each of the vertical compartments and is then discharged via the carrier gas outlet.
Owner:TOSOH FINECHEM CORP
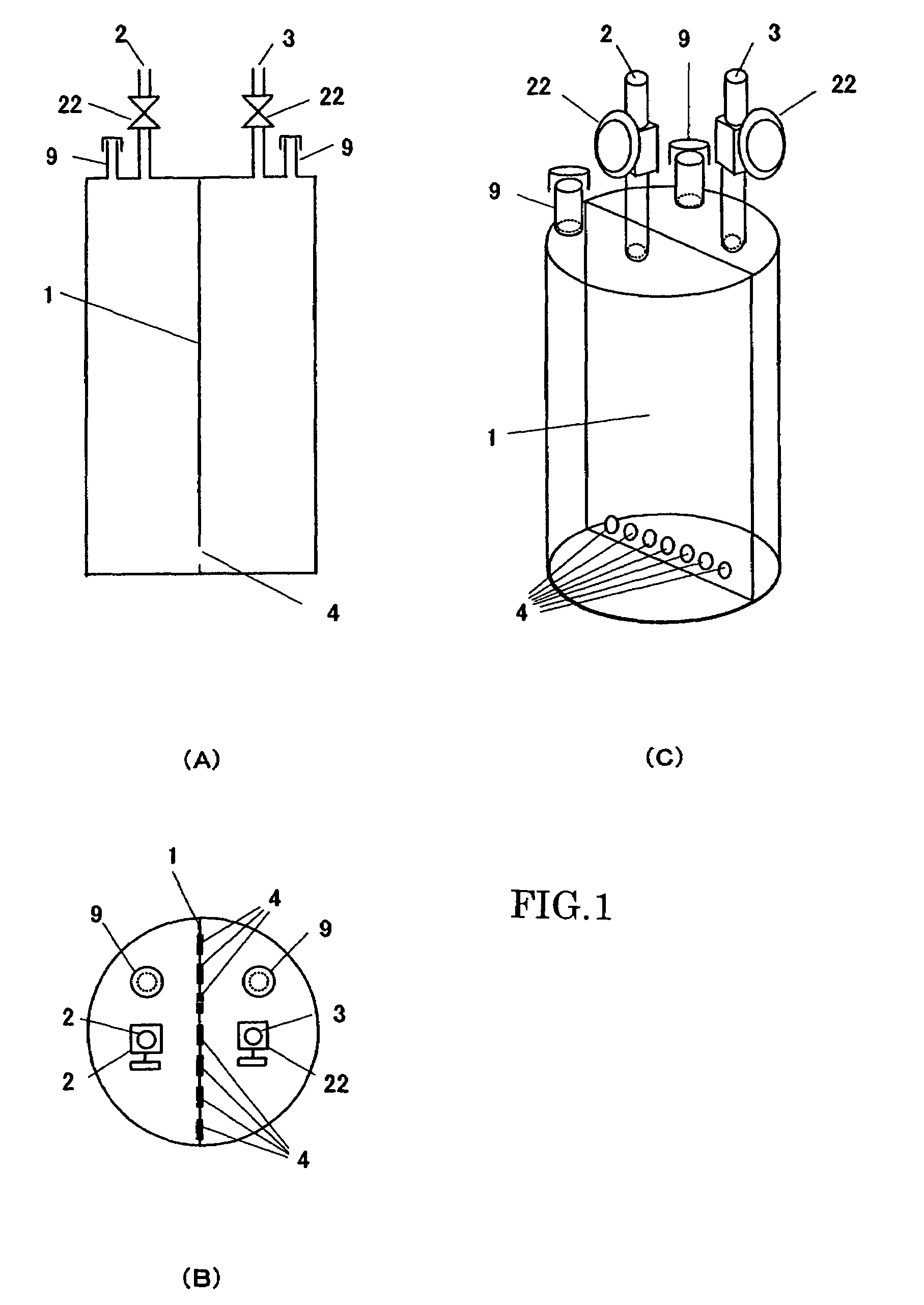
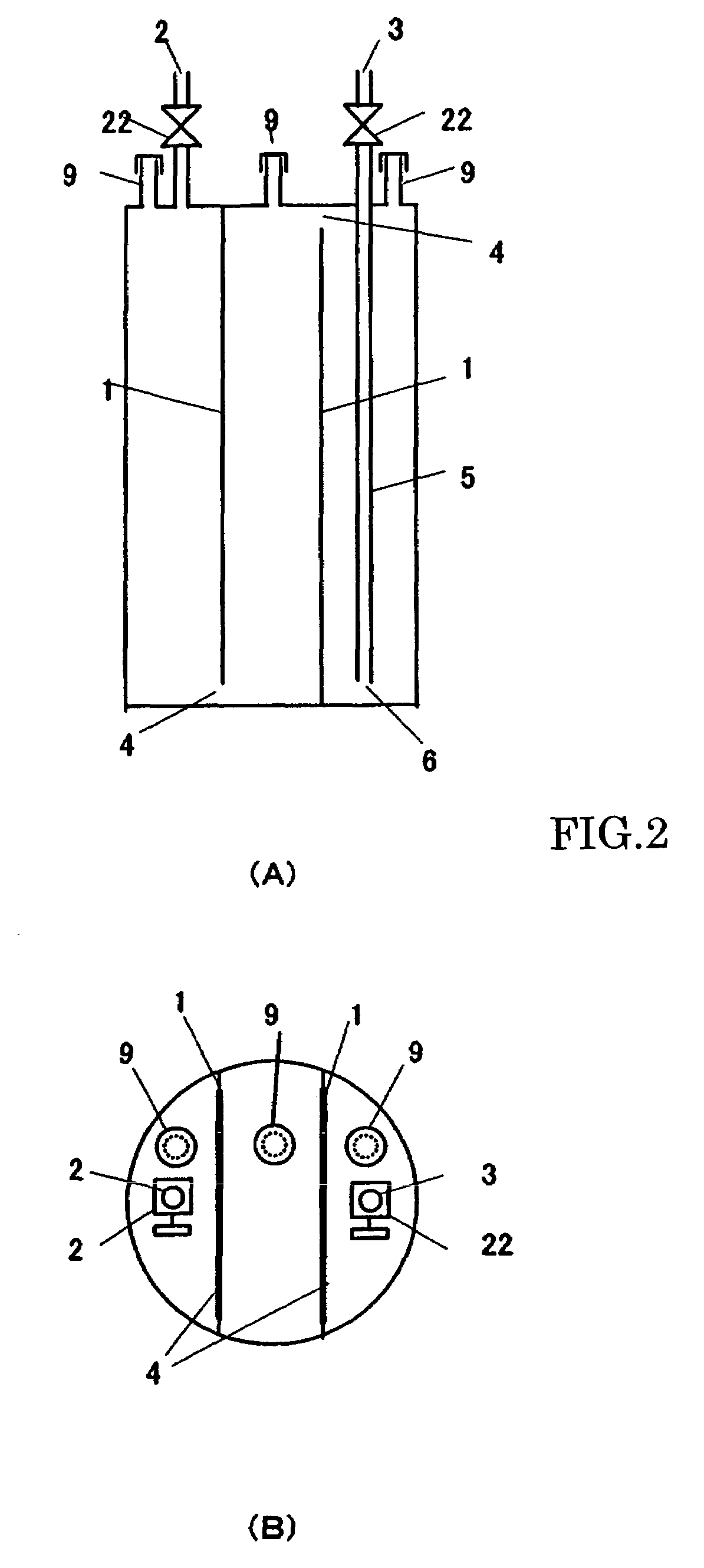
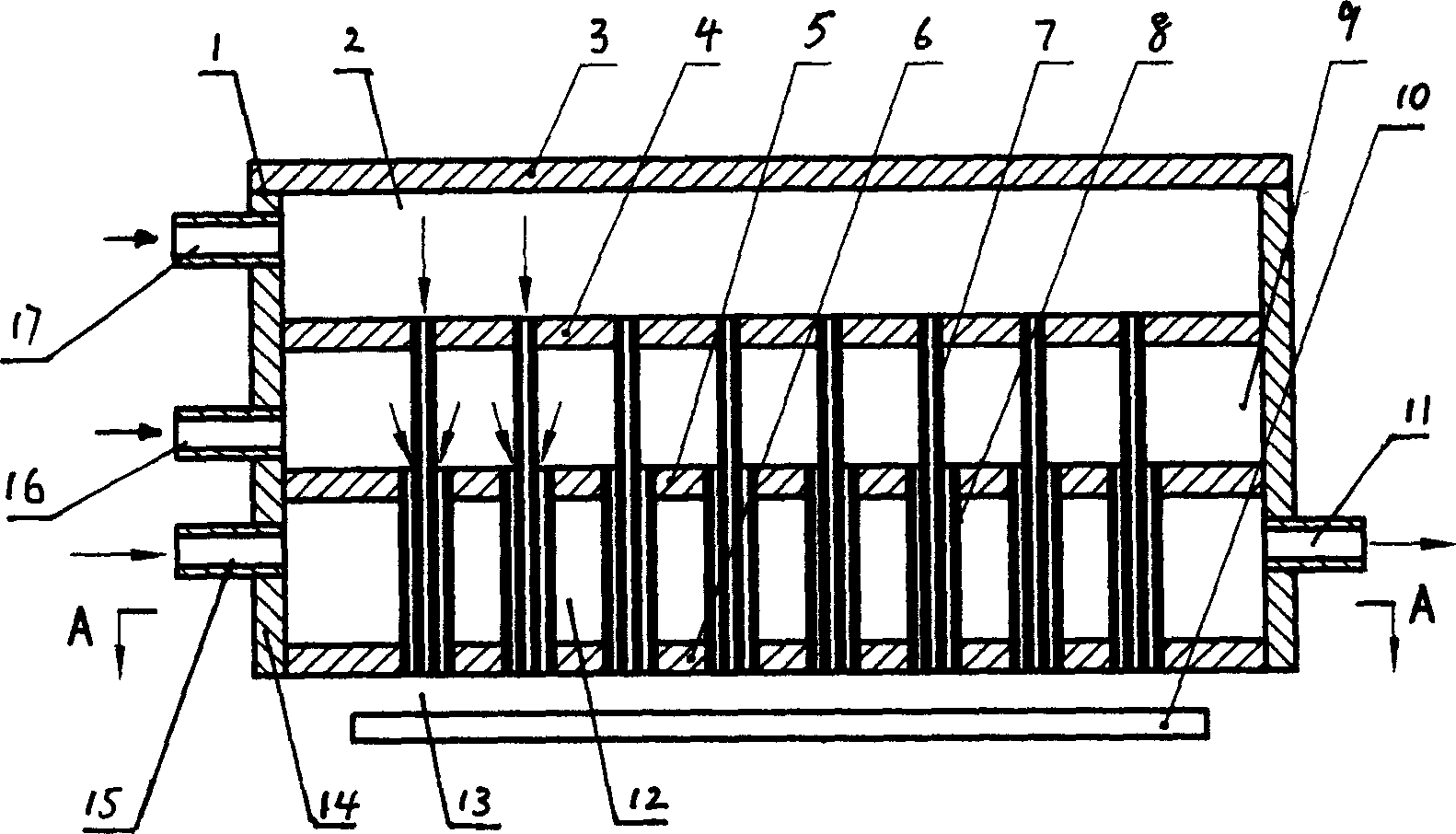
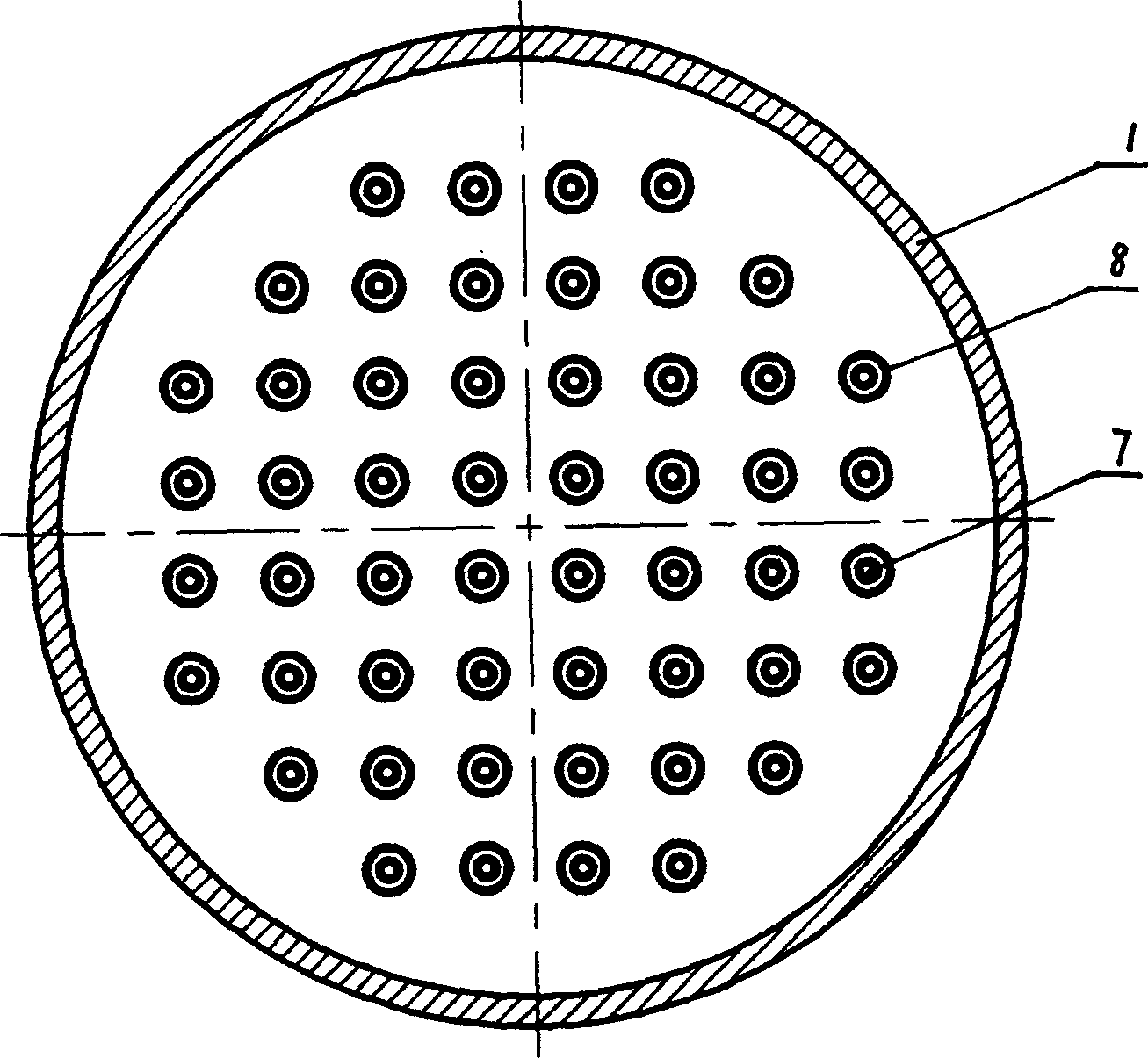
Bilayer inlet gas spray nozzle in use for metal-organic chemical vapor deposition device
This invention discloses a two-layer gas inlet blow head of a metal organic chemical gas phase deposit device including a closed shell having an upper gas inlet cavity and a lower gas inlet cavity, an upper escape pipe communicating with the upper gas cavity and reaction chamber is set between the upper-middle and the base plate and a lower escape pipe communicating with a lower gas inlet cavity and the reaction chamber is set between the lower plate and base plate characterizing that diameter of the lower escape pipe is layer than the upper and the upper is put in the lower. A cooling cavity is designed, the first reaction gas enters into the reaction chamber at the substrate surface from the upper and lower escape pipes separately.
Owner:南昌硅基半导体科技有限公司
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com