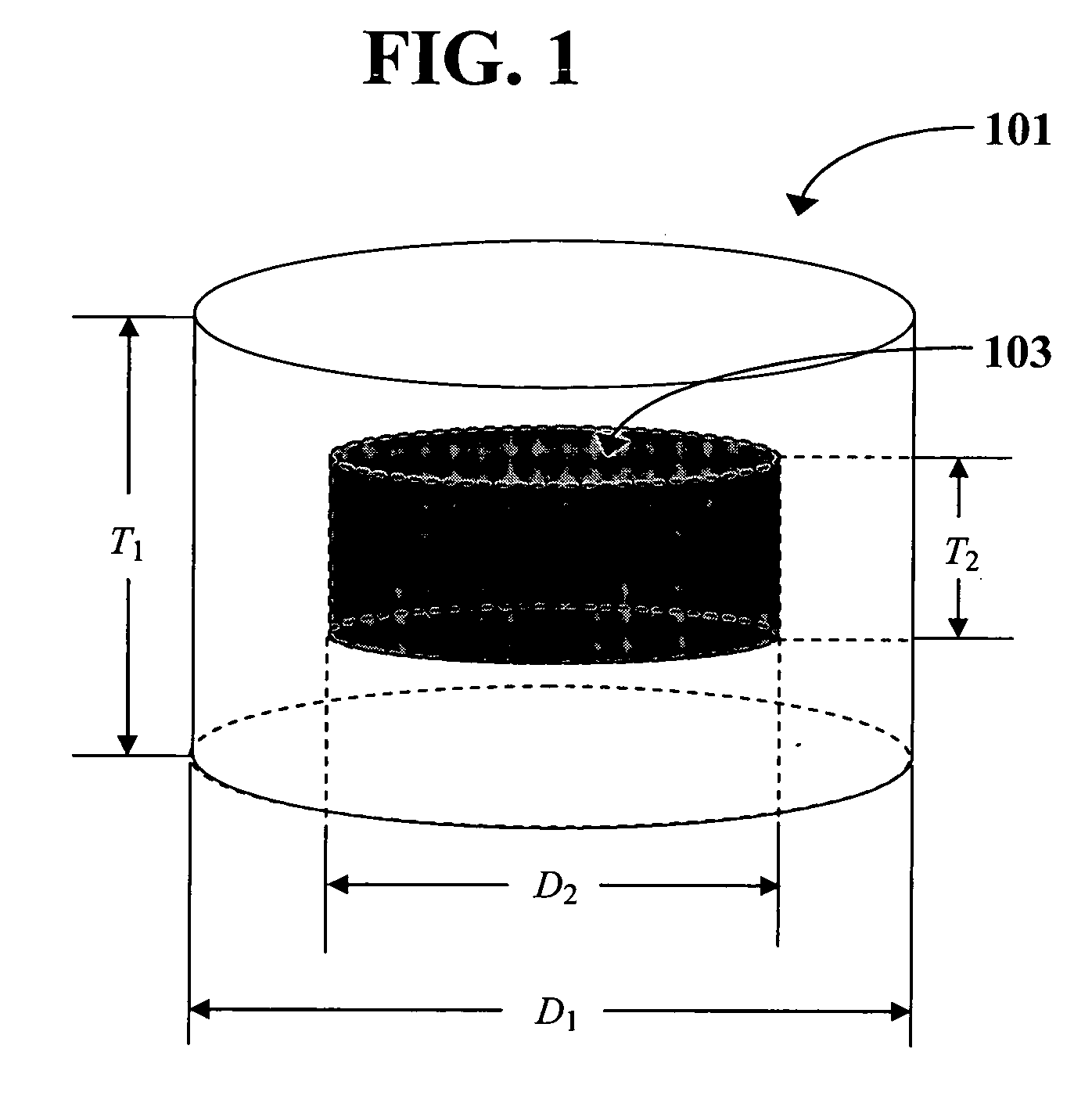
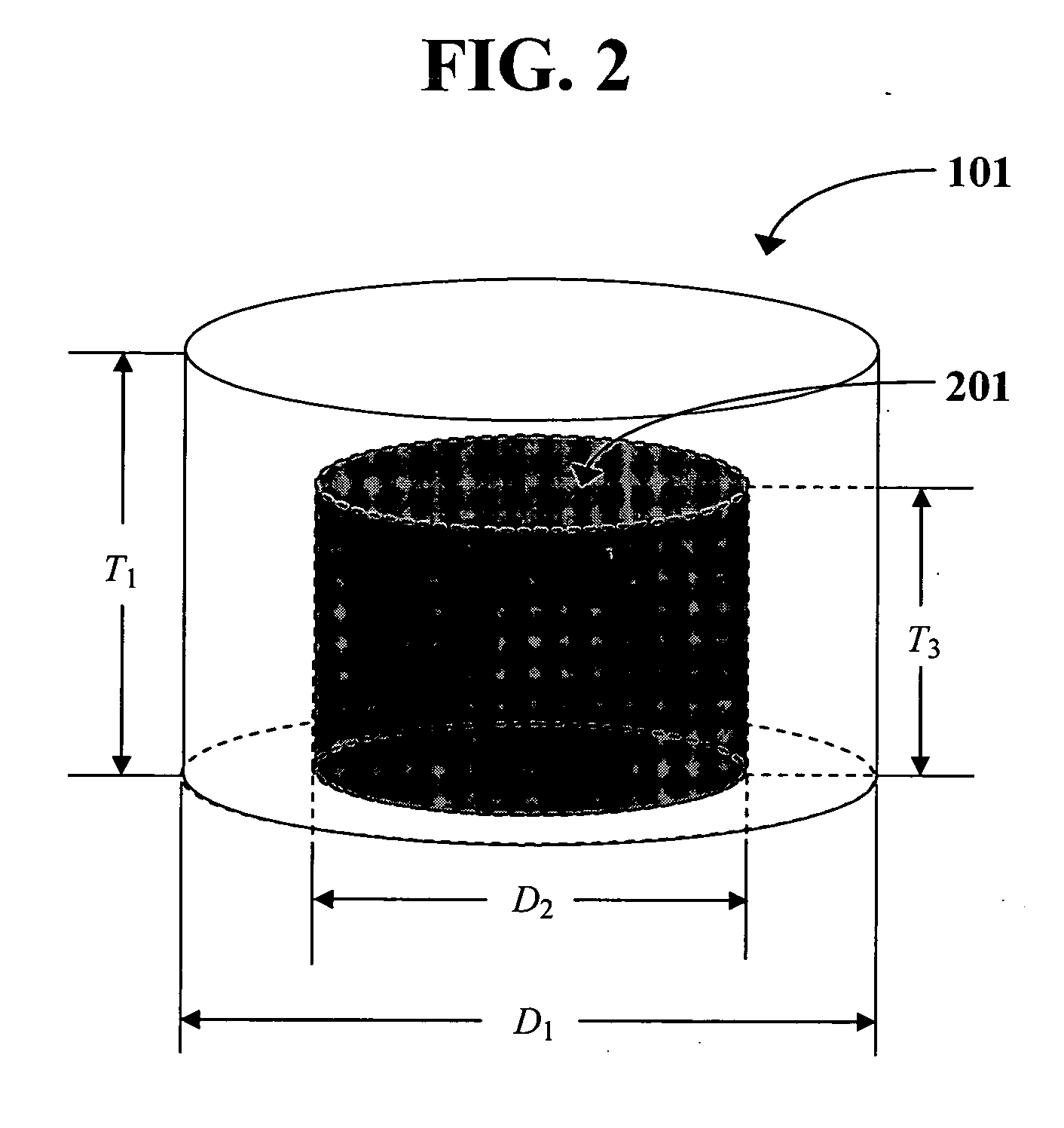
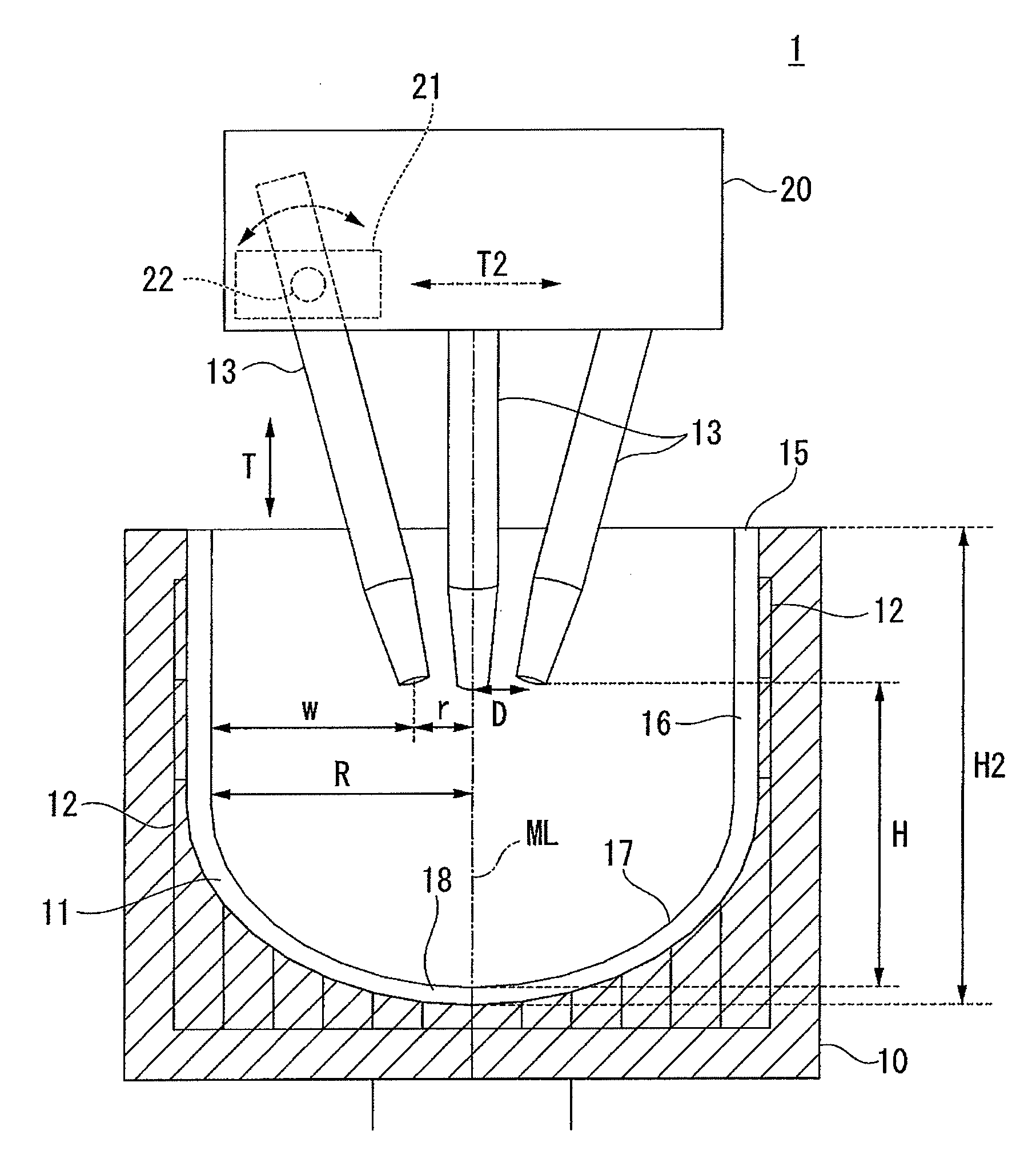
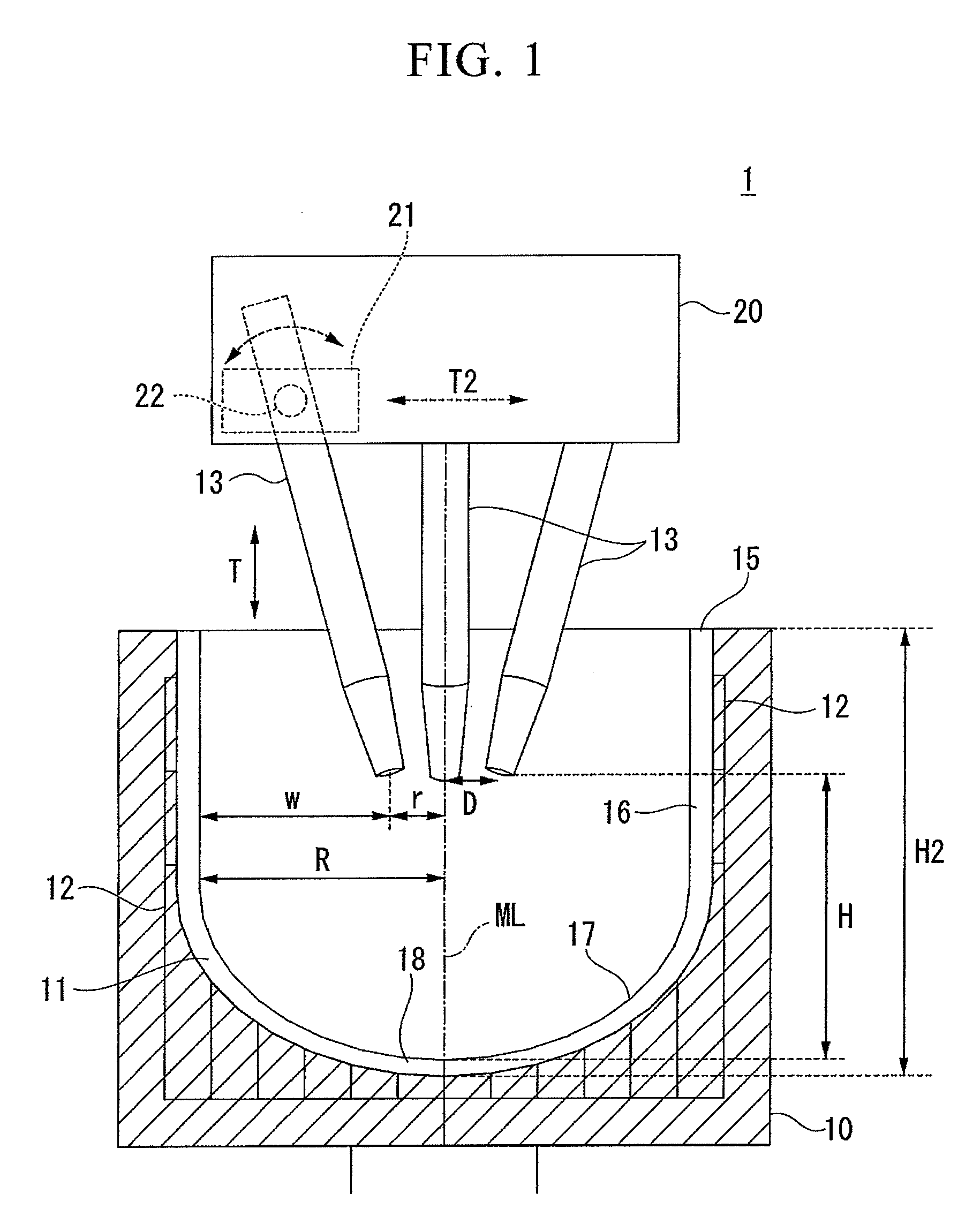
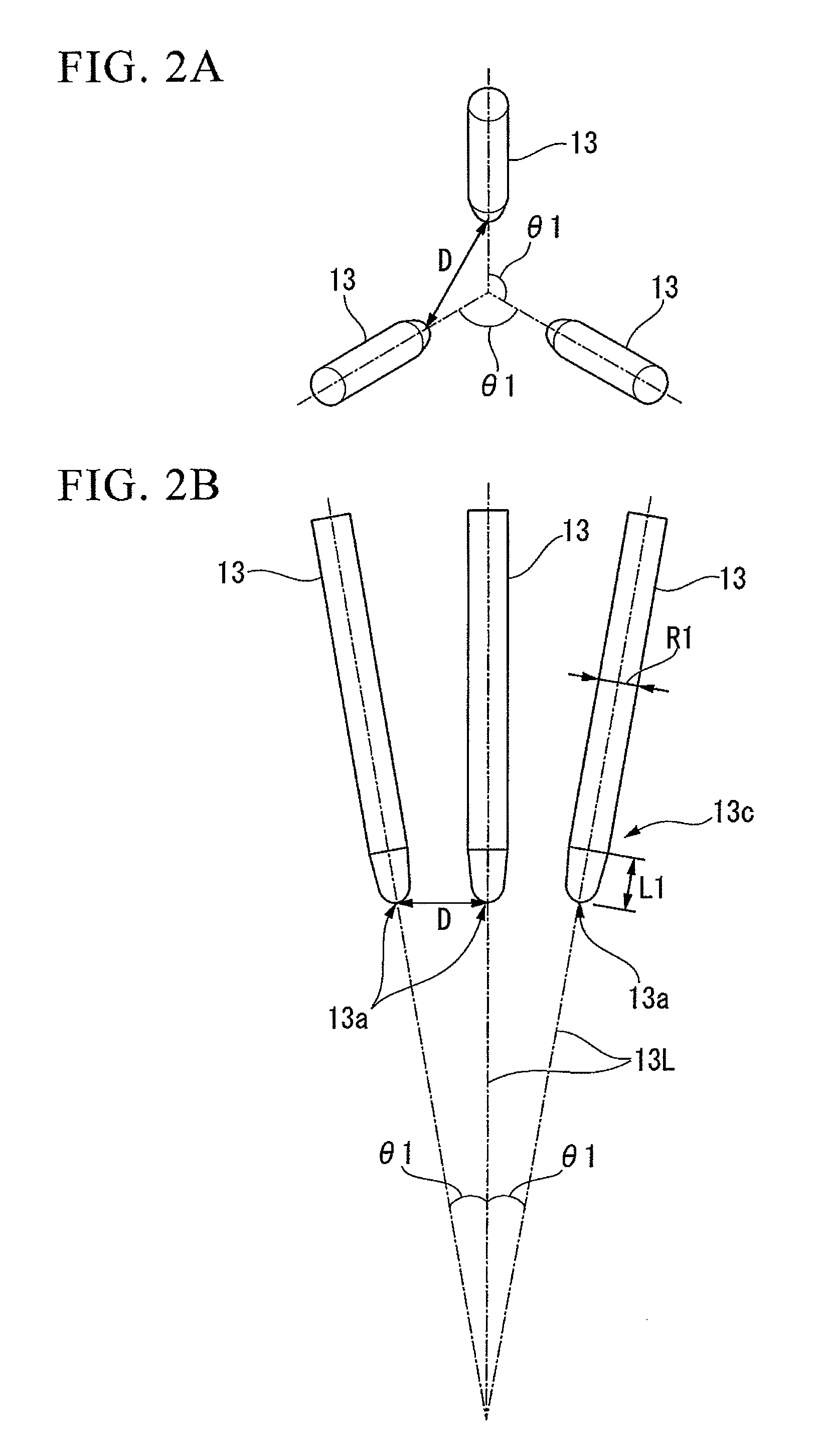
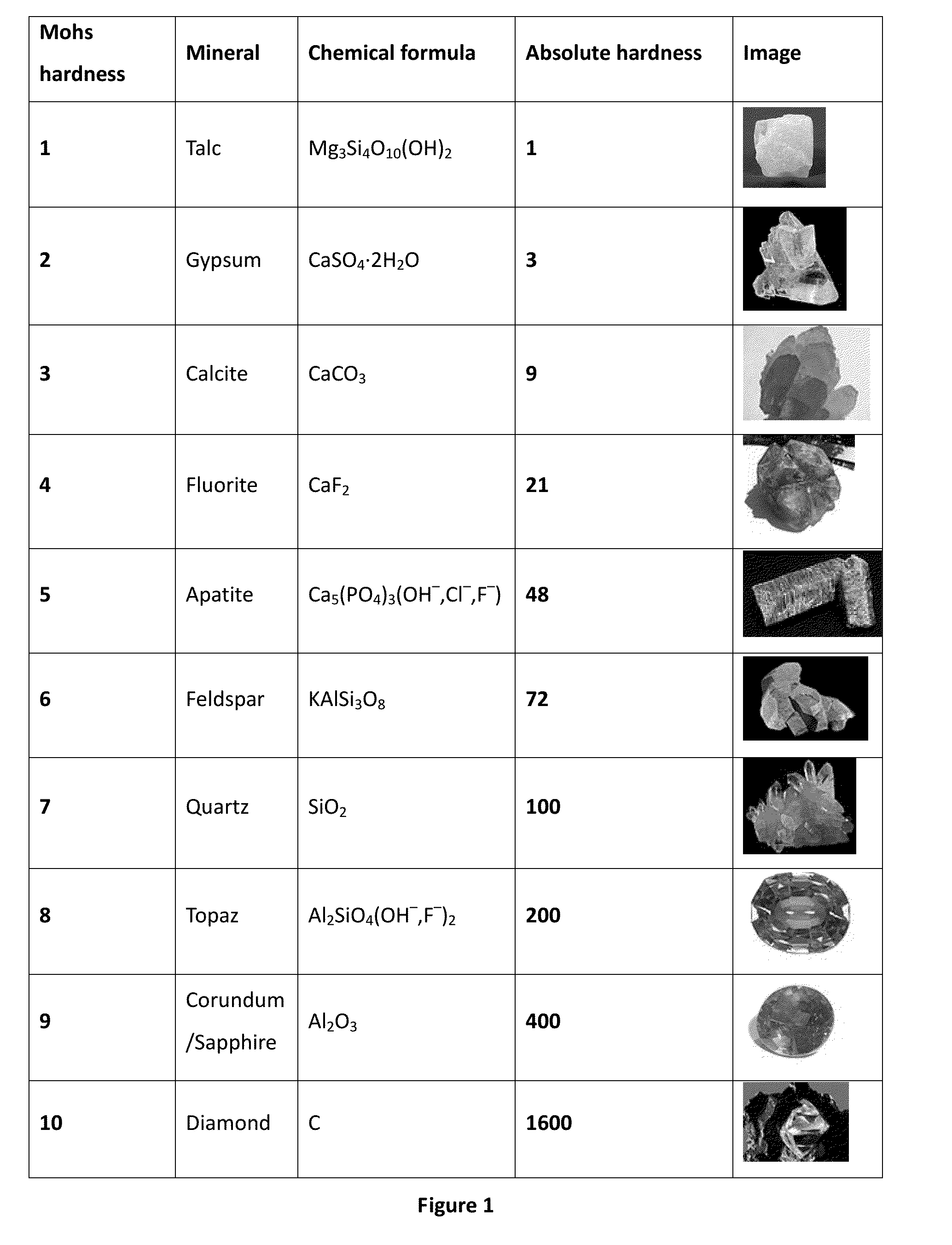
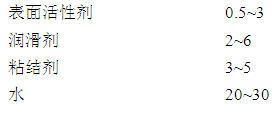Patents
Literature
946 results about "Fused quartz" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Fused quartz or fused silica is glass consisting of silica in amorphous (non-crystalline) form. It differs from traditional glasses in containing no other ingredients, which are typically added to glass to lower the melt temperature. Fused silica, therefore, has high working and melting temperatures. Although the terms fused quartz and fused silica are used interchangeably, the optical and thermal properties of fused silica are superior to those of fused quartz and other types of glass due to its purity. For these reasons, it finds use in situations such as semiconductor fabrication and laboratory equipment. It transmits ultraviolet better than other glasses, so is used to make lenses and optics for the ultraviolet spectrum. The low coefficient of thermal expansion of fused quartz makes it a useful material for precision mirror substrates.
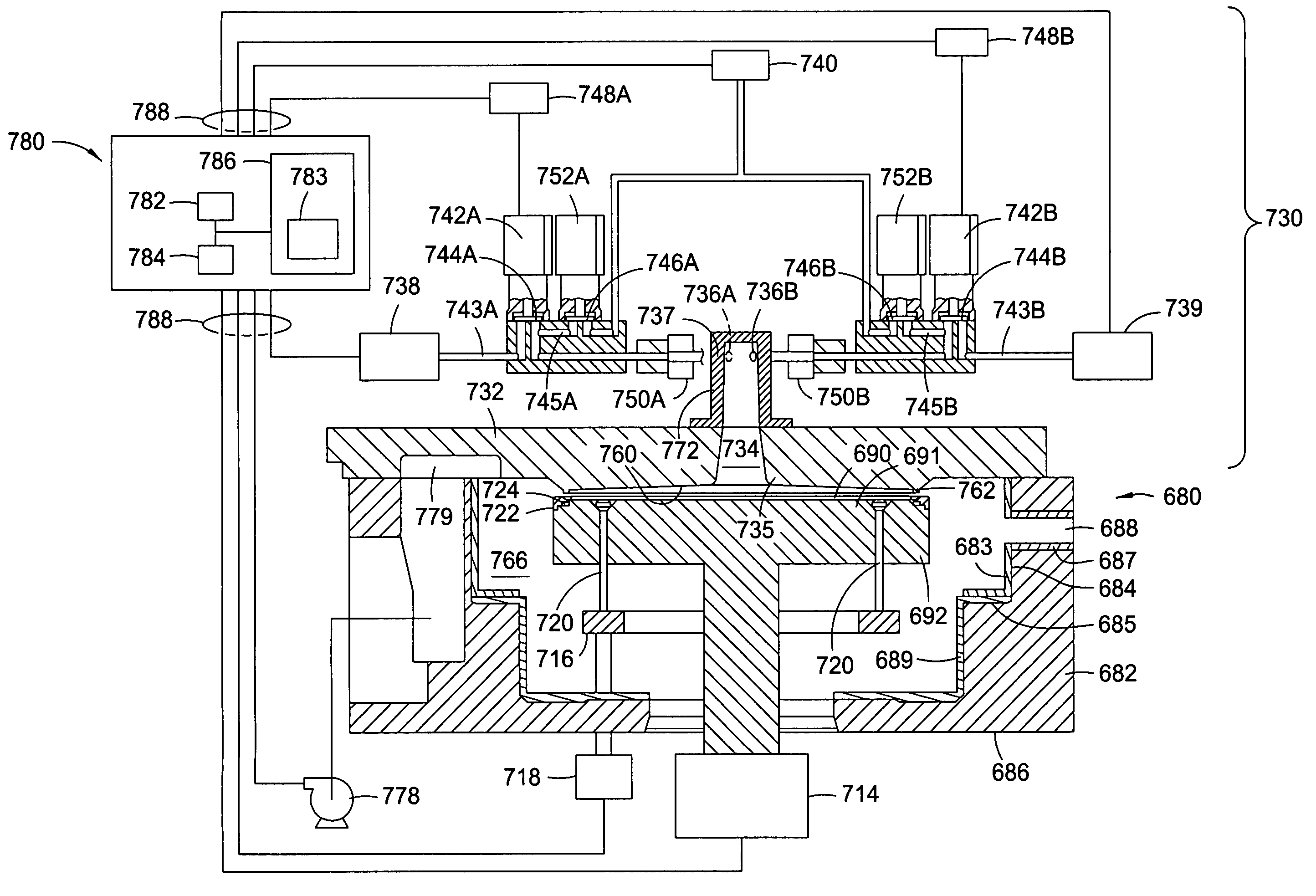
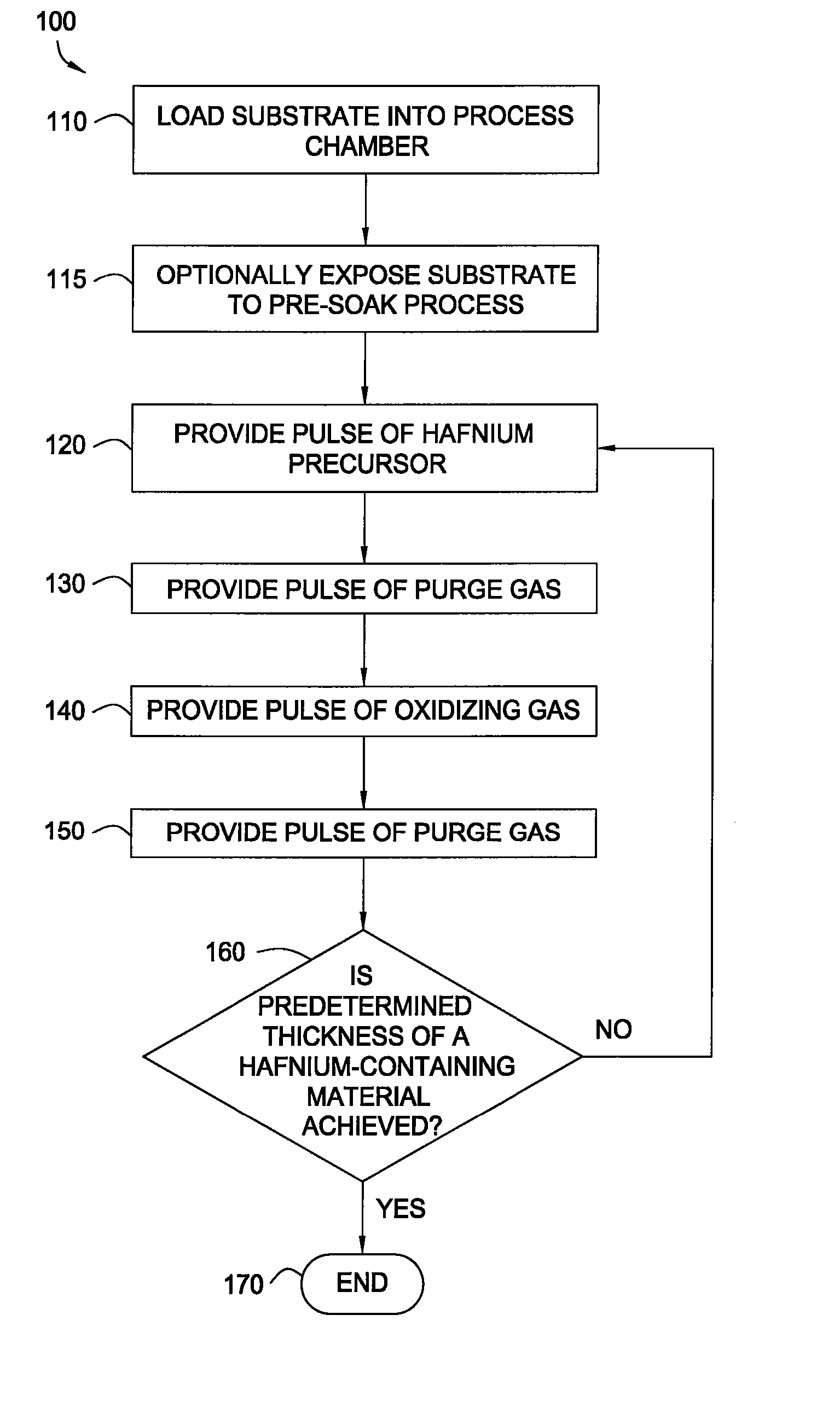
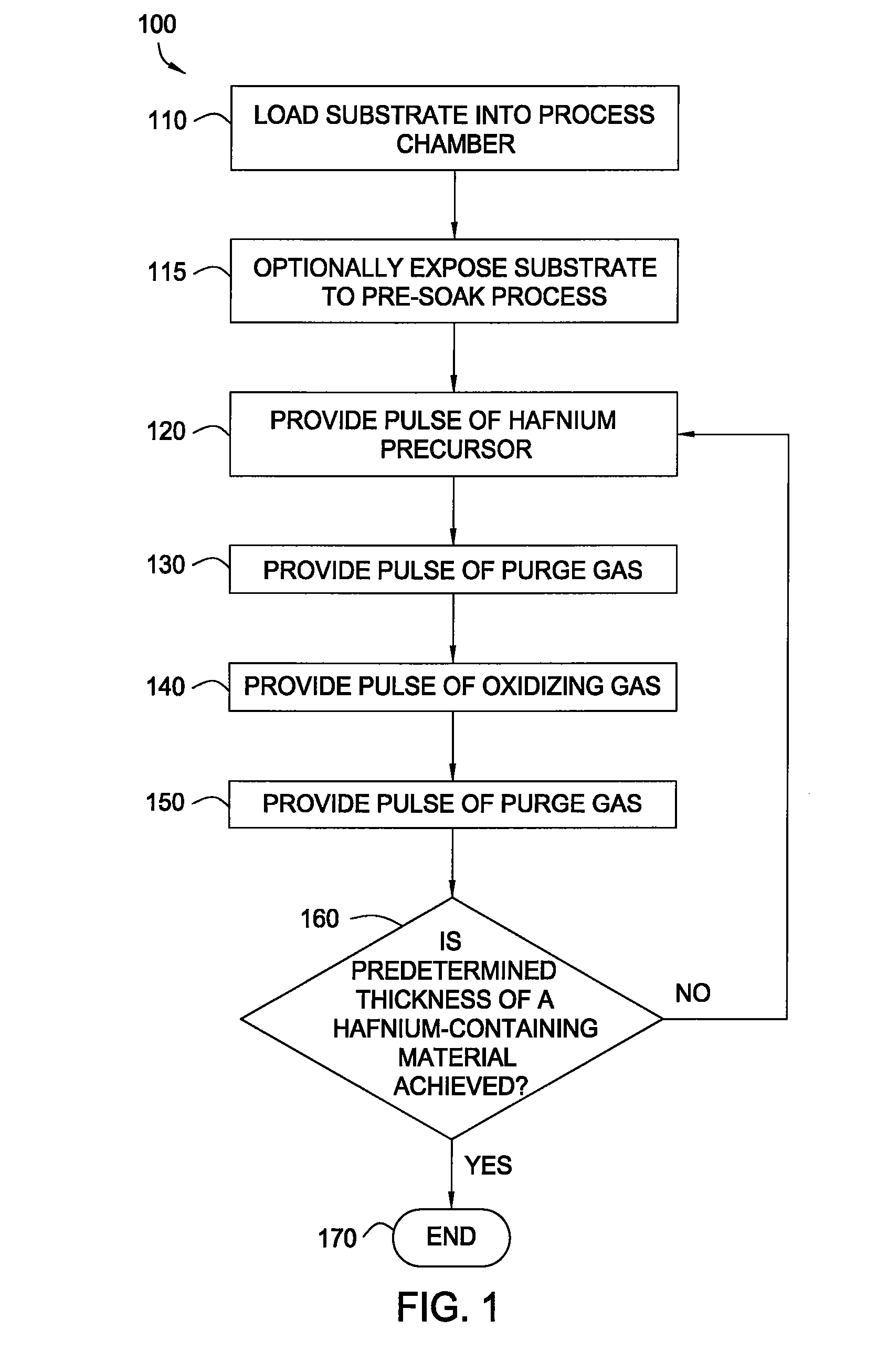
Apparatuses and methods for atomic layer deposition of hafnium-containing high-k dielectric materials
ActiveUS20050271812A1Steam generation heating methodsEfficient propulsion technologiesWater vaporGas phase
Embodiments of the invention provide apparatuses and methods for depositing materials on substrates during vapor deposition processes, such as atomic layer deposition (ALD). In one embodiment, a chamber contains a substrate support with a receiving surface and a chamber lid containing an expanding channel formed within a thermally insulating material. The chamber further includes at least one conduit coupled to a gas inlet within the expanding channel and positioned to provide a gas flow through the expanding channel in a circular direction, such as a vortex, a helix, a spiral or derivatives thereof. The expanding channel may be formed directly within the chamber lid or formed within a funnel liner attached thereon. The chamber may contain a retaining ring, an upper process liner, a lower process liner or a slip valve liner. Liners usually have a polished surface finish and contain a thermally insulating material such as fused quartz or ceramic. In an alternative embodiment, a deposition system contains a catalytic water vapor generator connected to an ALD chamber.
Owner:APPLIED MATERIALS INC
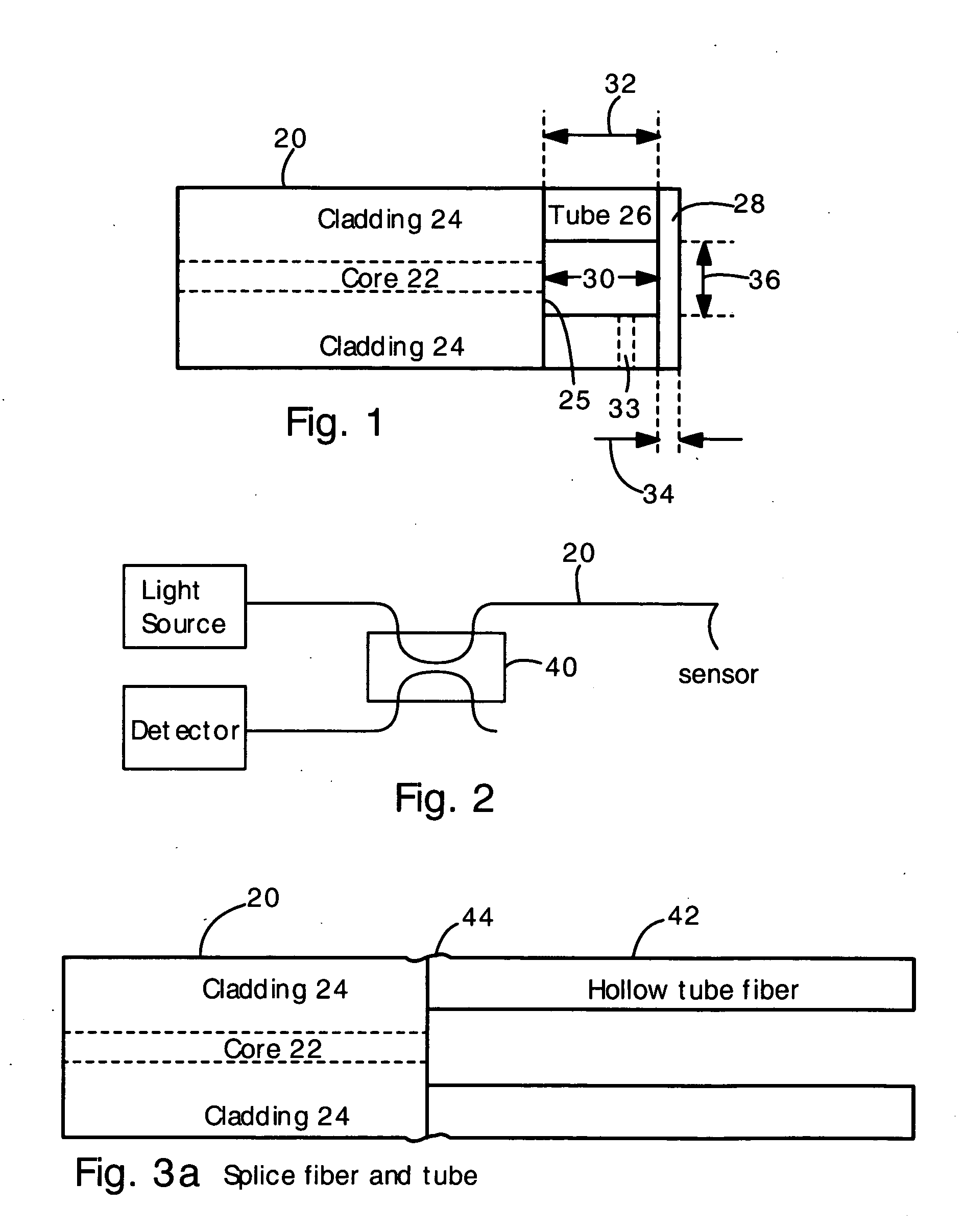
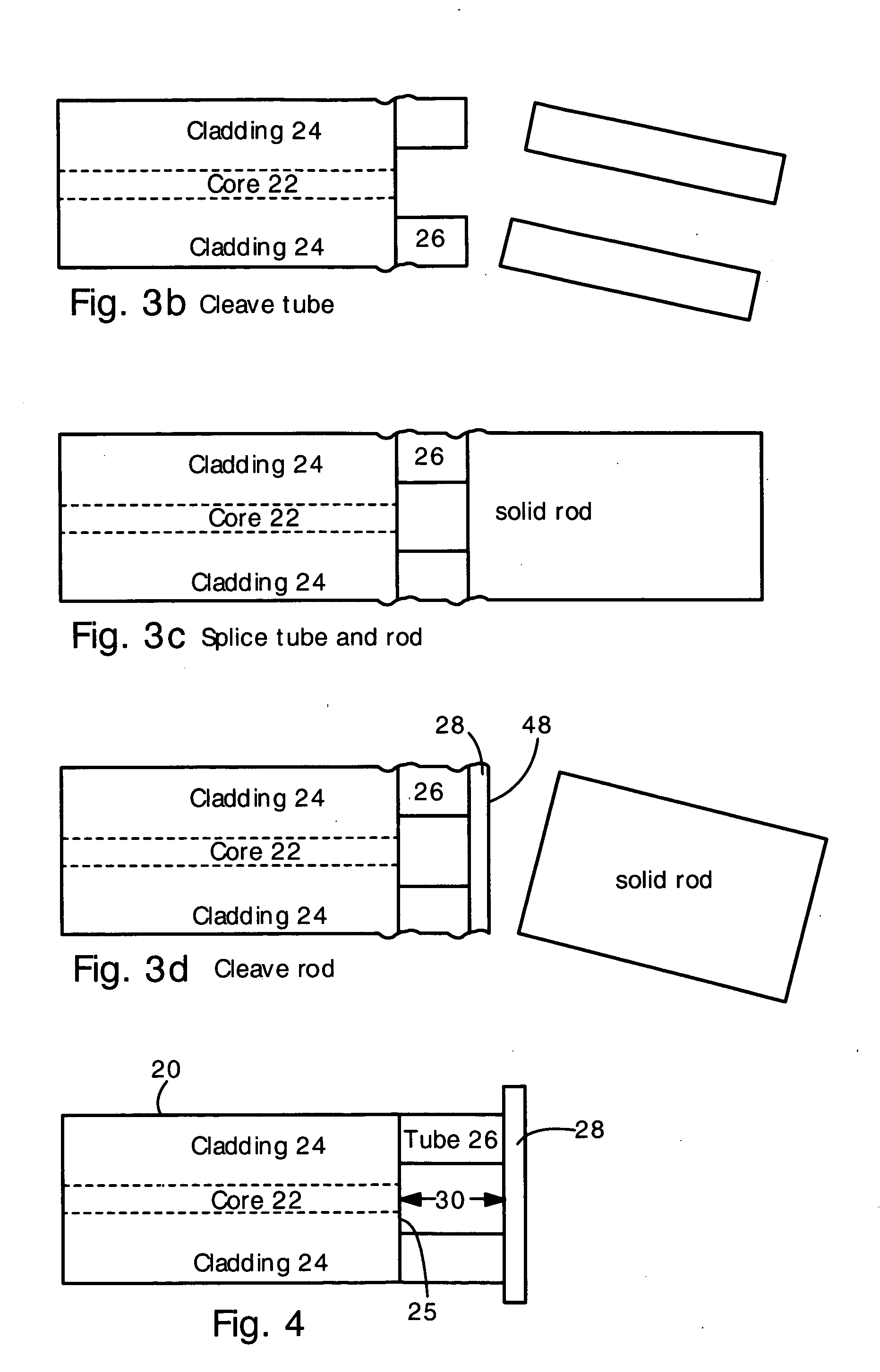
Optical fiber pressure and acceleration sensor fabricated on a fiber endface
InactiveUS20050062979A1Subsonic/sonic/ultrasonic wave measurementFluid pressure measurement by electric/magnetic elementsJet engineClassical mechanics
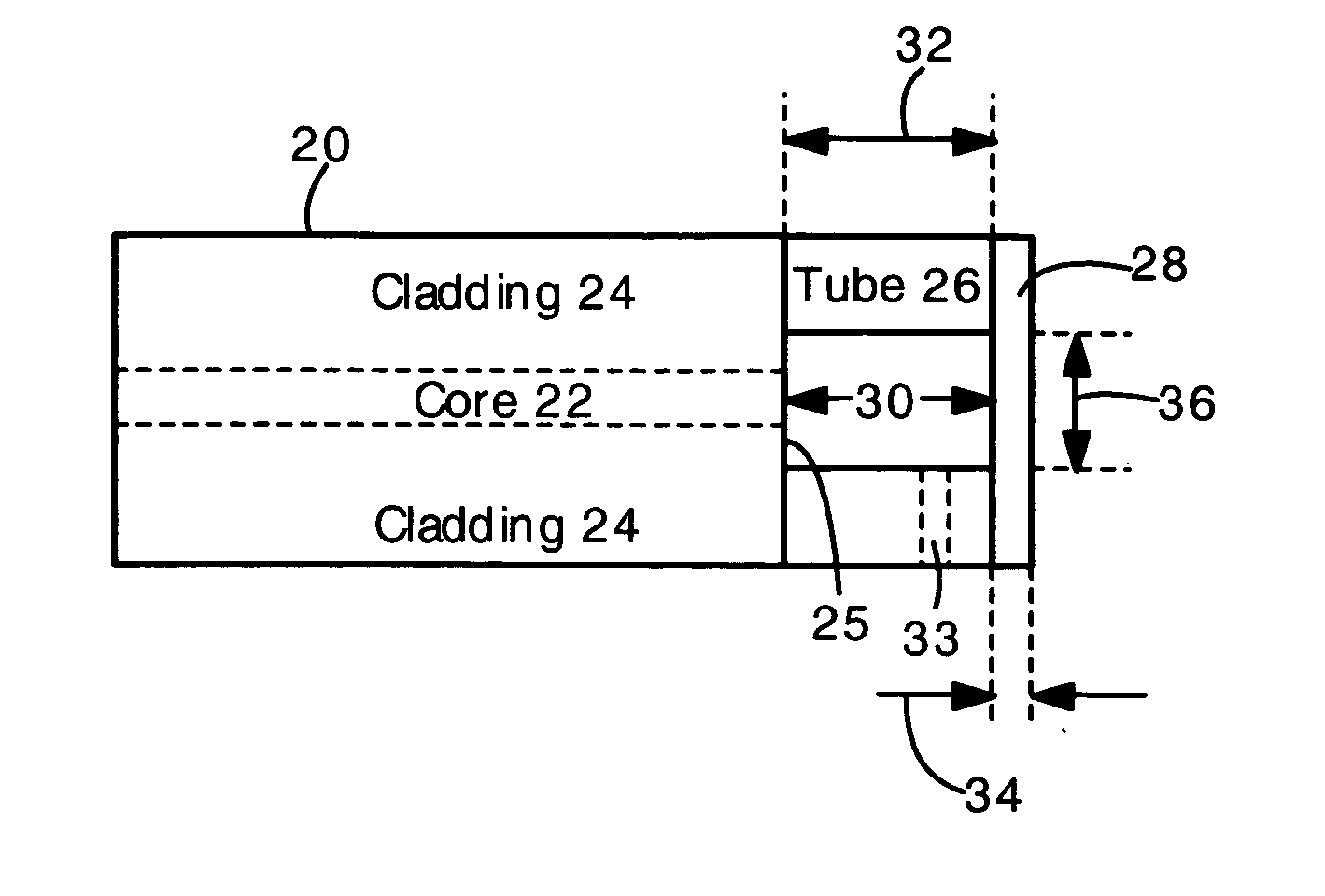
A fiber optic sensor has a hollow tube bonded to the endface of an optical fiber, and a diaphragm bonded to the hollow tube. The fiber endface and diaphragm comprise an etalon cavity. The length of the etalon cavity changes when applied pressure or acceleration flexes the diaphragm. The entire structure can be made of fused silica. The fiber, tube, and diaphragm can be bonded with a fusion splice. The present sensor is particularly well suited for measuring pressure or acceleration in high temperature, high pressure and corrosive environments (e.g., oil well downholes and jet engines). The present sensors are also suitable for use in biological and medical applications.
Owner:VIRGINIA TECH INTPROP INC
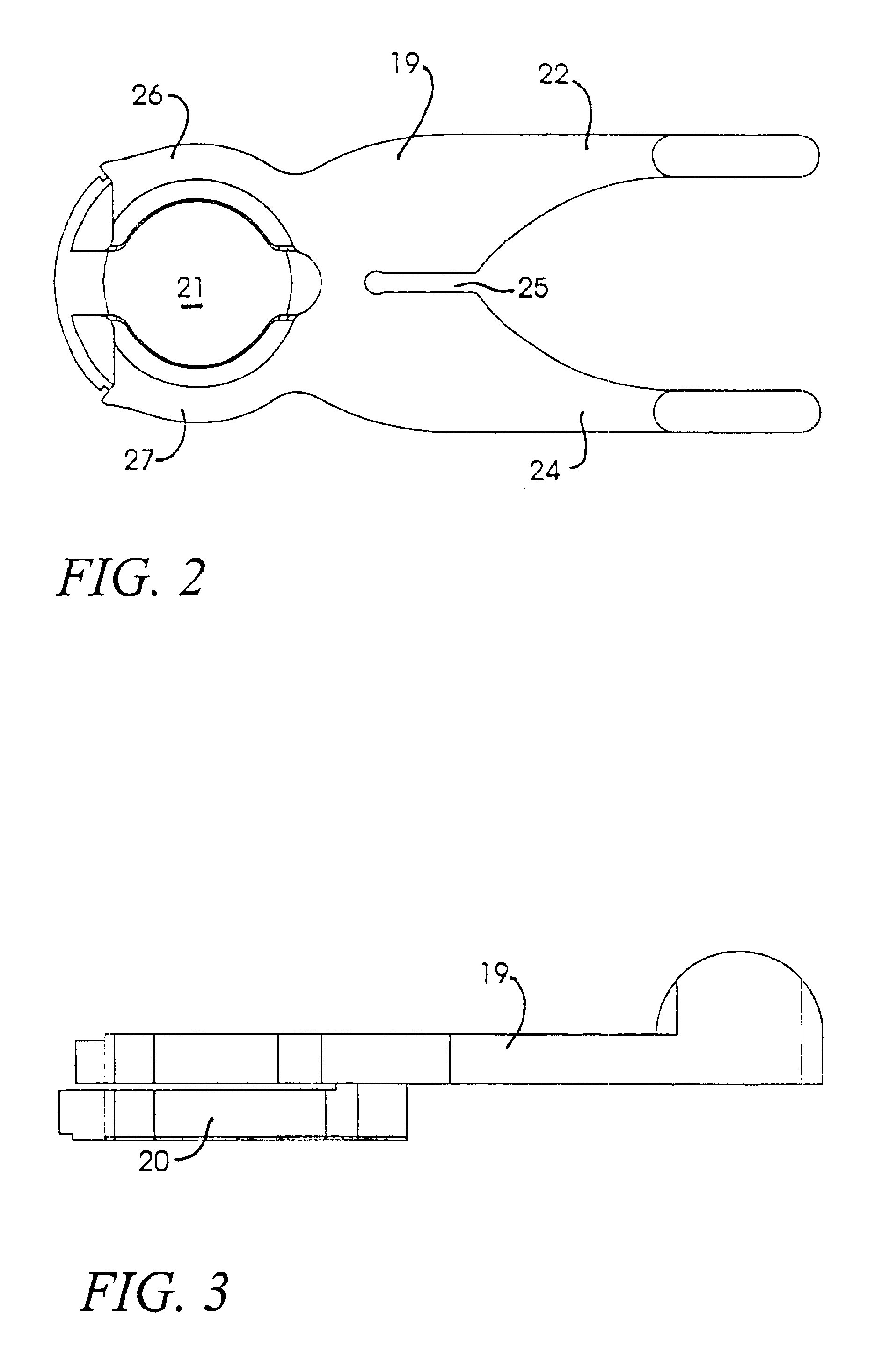
Applanation lens and method for ophthalmic surgical applications
InactiveUS6899707B2Guaranteed stable engagementResist discolorationLaser surgeryDiagnosticsHigh energyTransmittance
An improved applanation lens and method for use in an interface between a patient's eye and a surgical laser system does not discolor or lose light transmittance when subjected to gamma radiation. The improved applanation lens has an applanation surface configured to contact the eye upon application of a pressure. The lens is formed of high purity silicon dioxide (SiO2) with purity great enough to resist discoloration upon prolonged irradiation by high-energy radiation such as UV, x-rays, gamma rays or neutrons, and is preferably a fused silica.
Owner:AMO DEVMENT
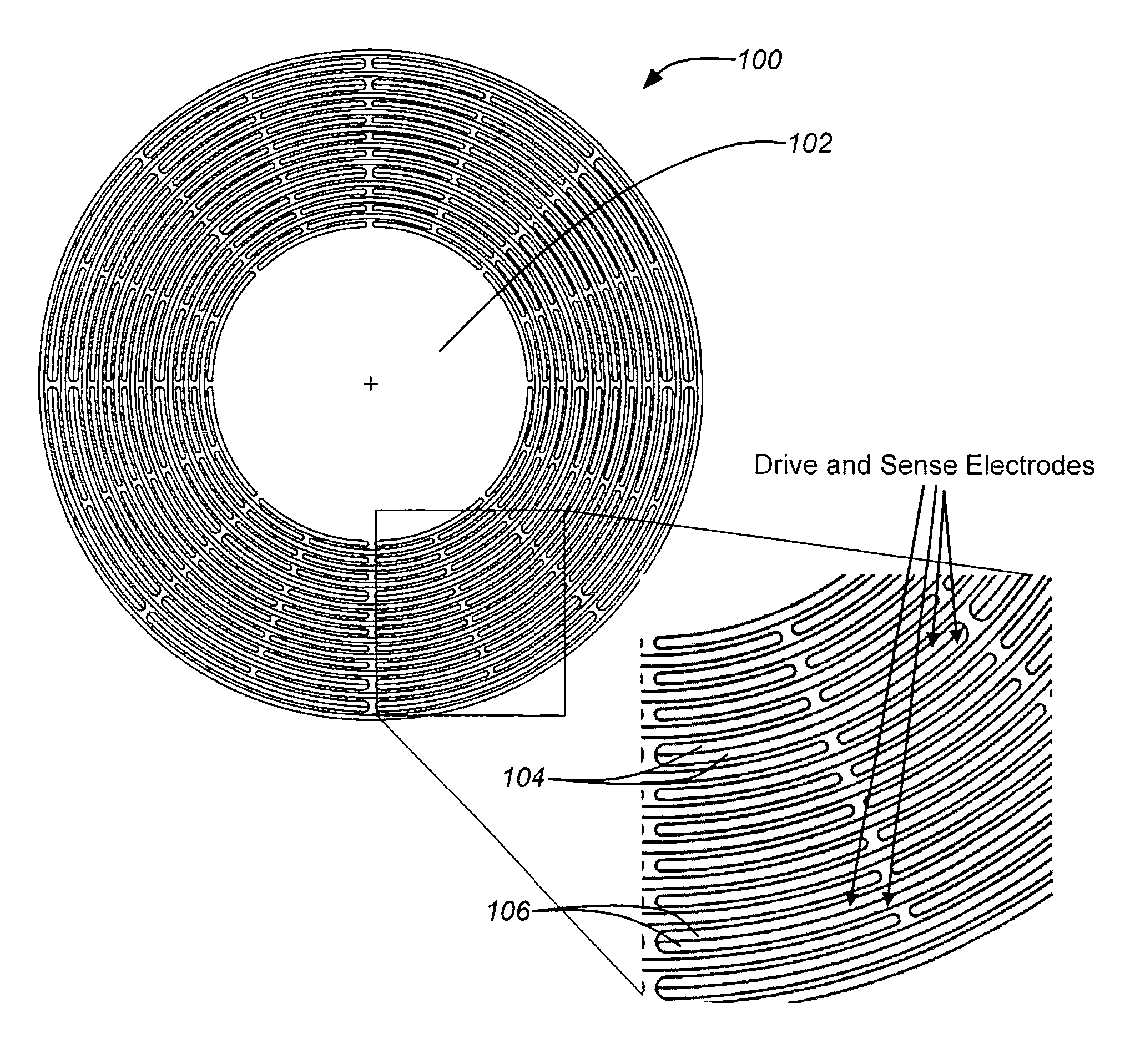
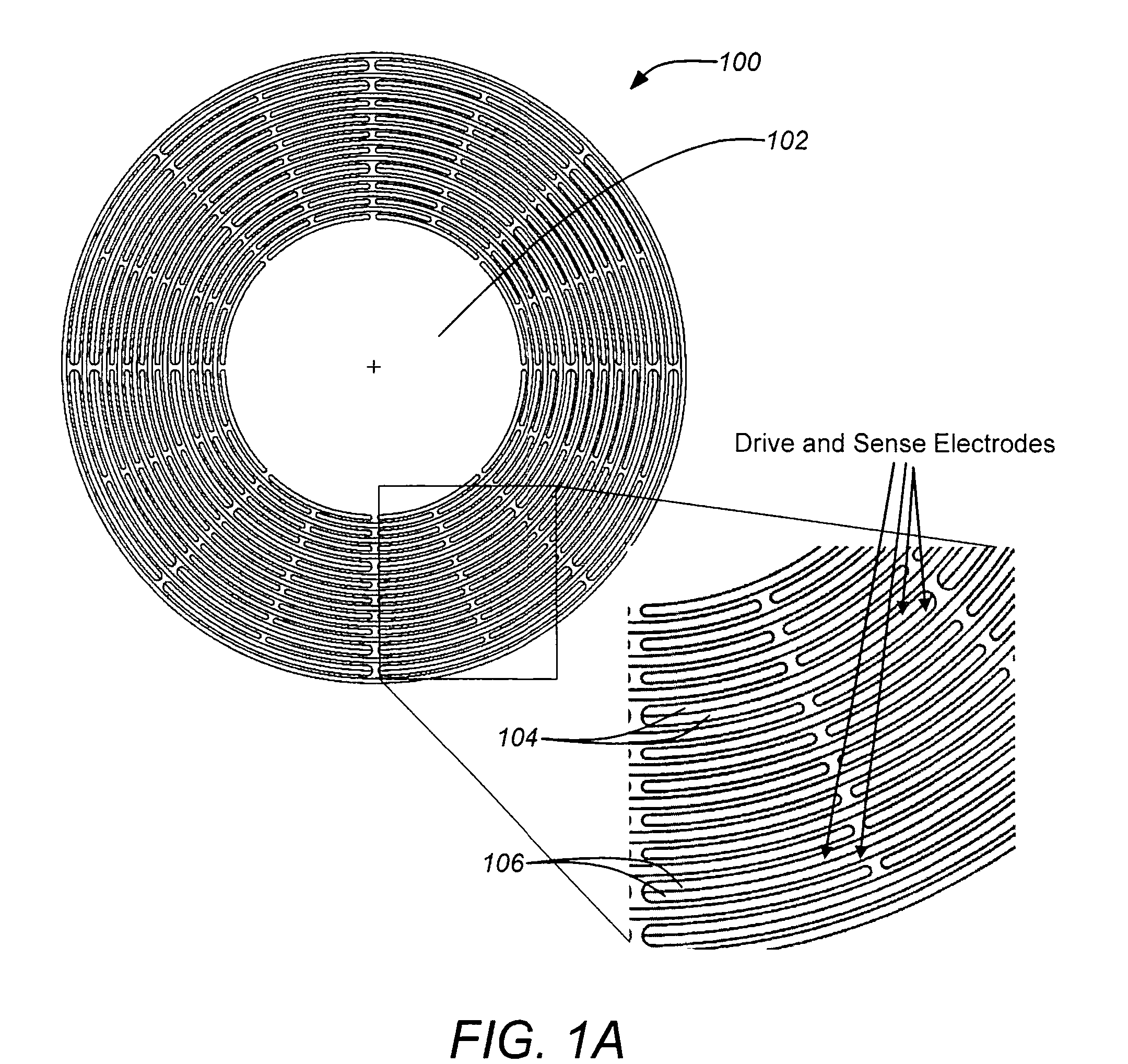
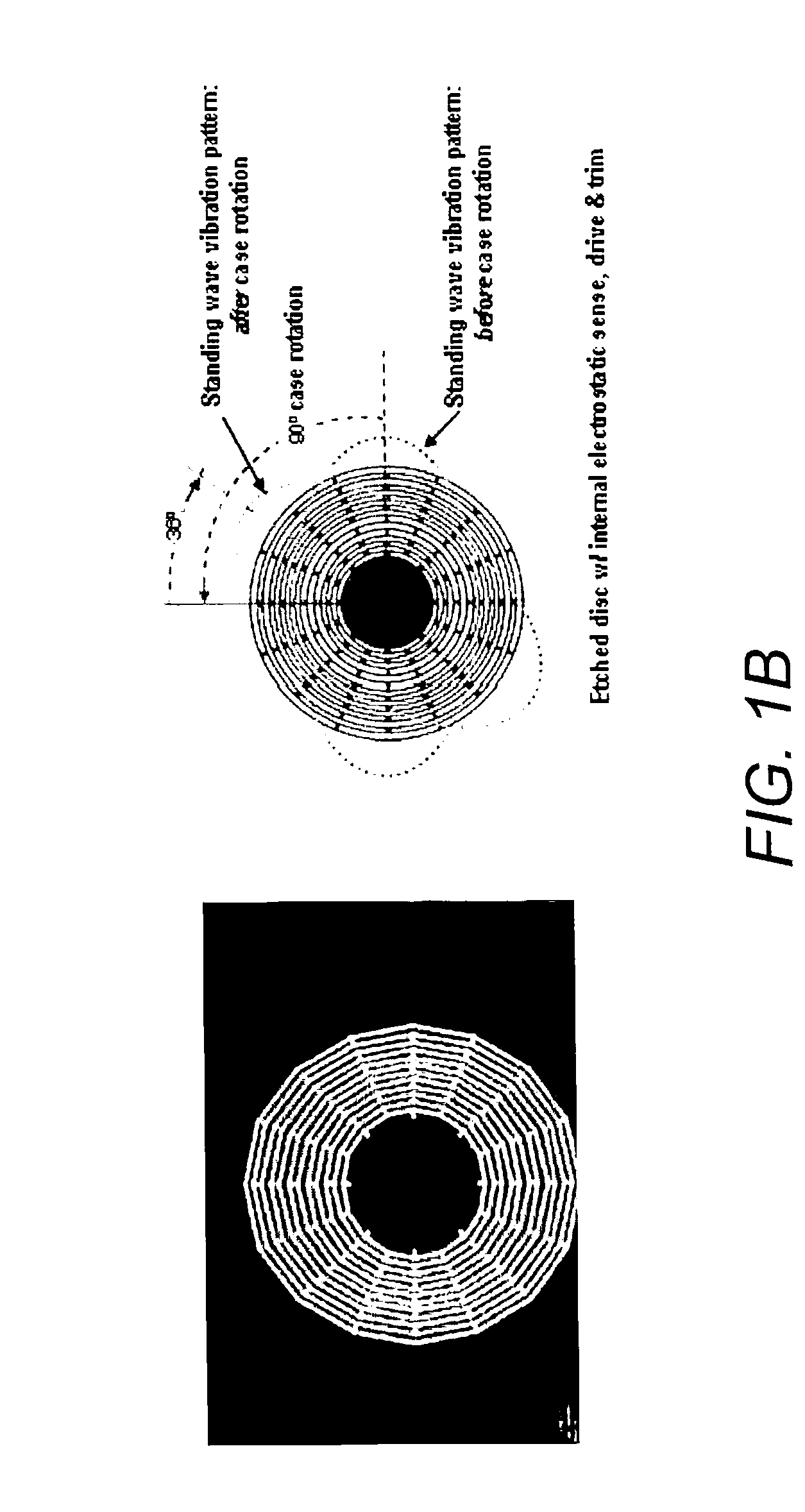
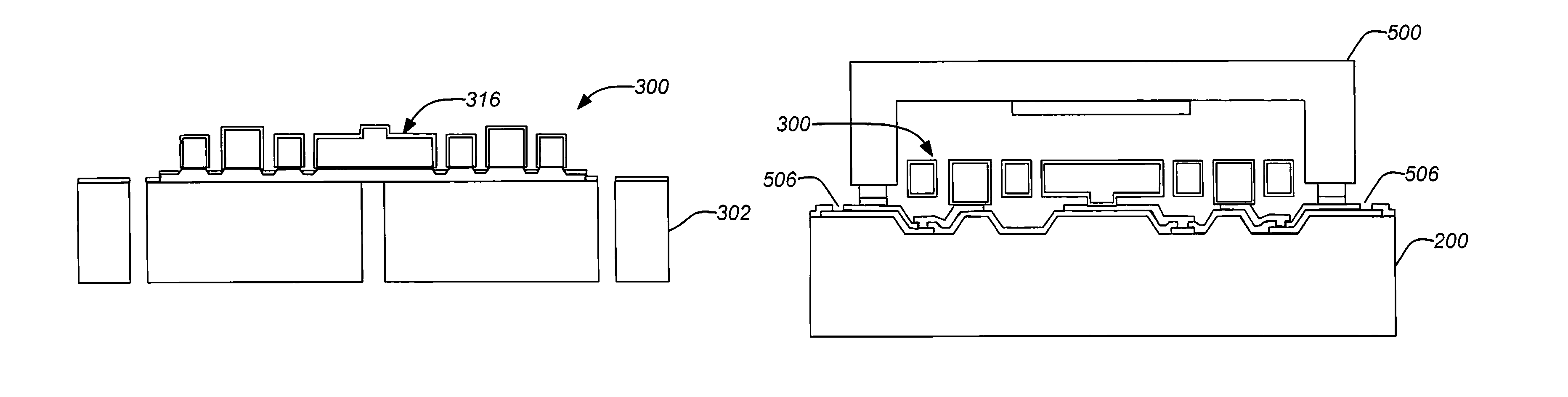
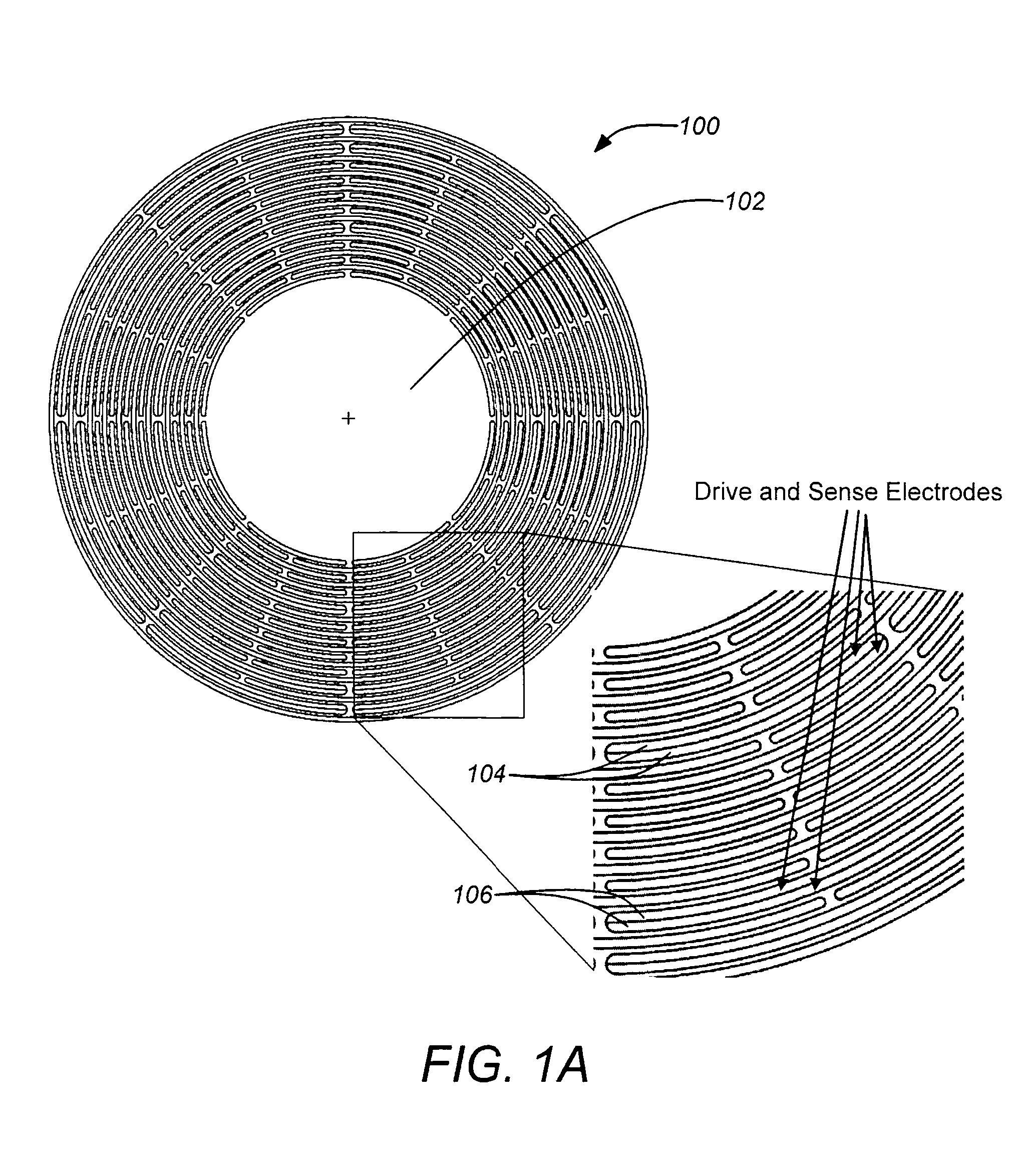
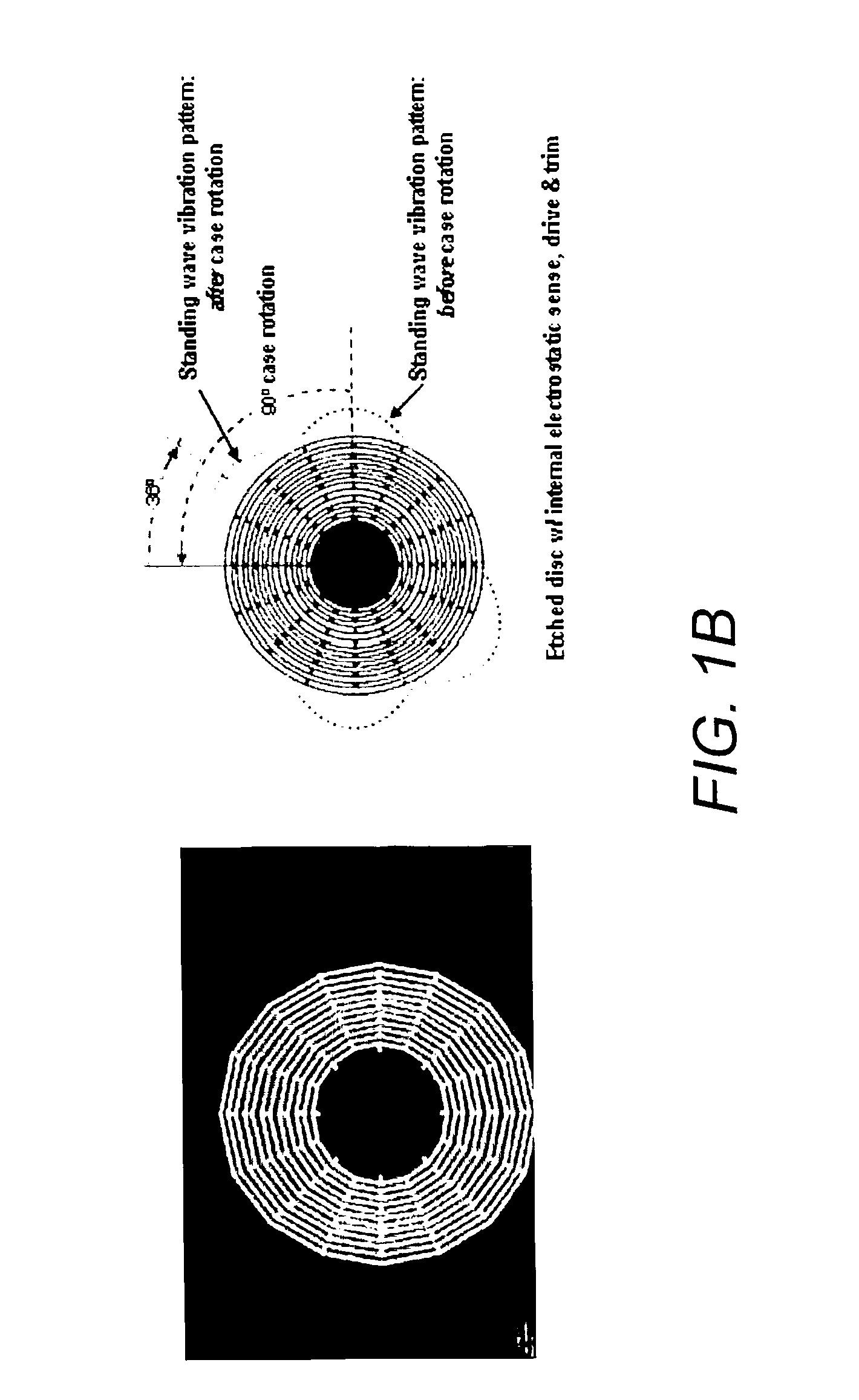
Disc resonator gyroscopes
ActiveUS20070017287A1Low anchor lossHigh QAcceleration measurement using interia forcesSpeed measurement using gyroscopic effectsCapacitanceCircular disc
Embodiments of the present invention are directed to apparatuses and methods of making a micromachined resonator gyroscope, e.g. a disc resonator gyro (DRG), including one or more of the following novel features. Embodiments of the invention may comprise a triple-wafer stack gyroscope with an all fused quartz (or all silicon) construction for an electrical baseplate, resonator and vacuum cap. This can yield superior thermal stability over prior art designs. A typical resonator embodiment may include a centrally anchored disc with high aspect-ratio in-plane electrostatic drive and sense electrodes to create large capacitance. A silicon sacrificial layer may be employed for attaching a quartz resonator wafer to a quartz handle wafer for high aspect-ratio etching. In addition, embodiments of the invention may comprise a low thermal stress, wafer-level vacuum packaged gyroscope with on-chip getter. An ultra-thin conductive layer deposited on the quartz resonator may also be utilized for high Q.
Owner:THE BOEING CO
Disc resonator gyroscopes
ActiveUS7581443B2Low anchor lossHigh QAcceleration measurement using interia forcesSpeed measurement using gyroscopic effectsCapacitanceGyroscope
Embodiments of the present invention are directed to apparatuses and methods of making a micromachined resonator gyroscope, e.g. a disc resonator gyro (DRG), including one or more of the following novel features. Embodiments of the invention may comprise a triple-wafer stack gyroscope with an all fused quartz (or all silicon) construction for an electrical baseplate, resonator and vacuum cap. This can yield superior thermal stability over prior art designs. A typical resonator embodiment may include a centrally anchored disc with high aspect-ratio in-plane electrostatic drive and sense electrodes to create large capacitance. A silicon sacrificial layer may be employed for attaching a quartz resonator wafer to a quartz handle wafer for high aspect-ratio etching. In addition, embodiments of the invention may comprise a low thermal stress, wafer-level vacuum packaged gyroscope with on-chip getter. An ultra-thin conductive layer deposited on the quartz resonator may also be utilized for high Q.
Owner:THE BOEING CO
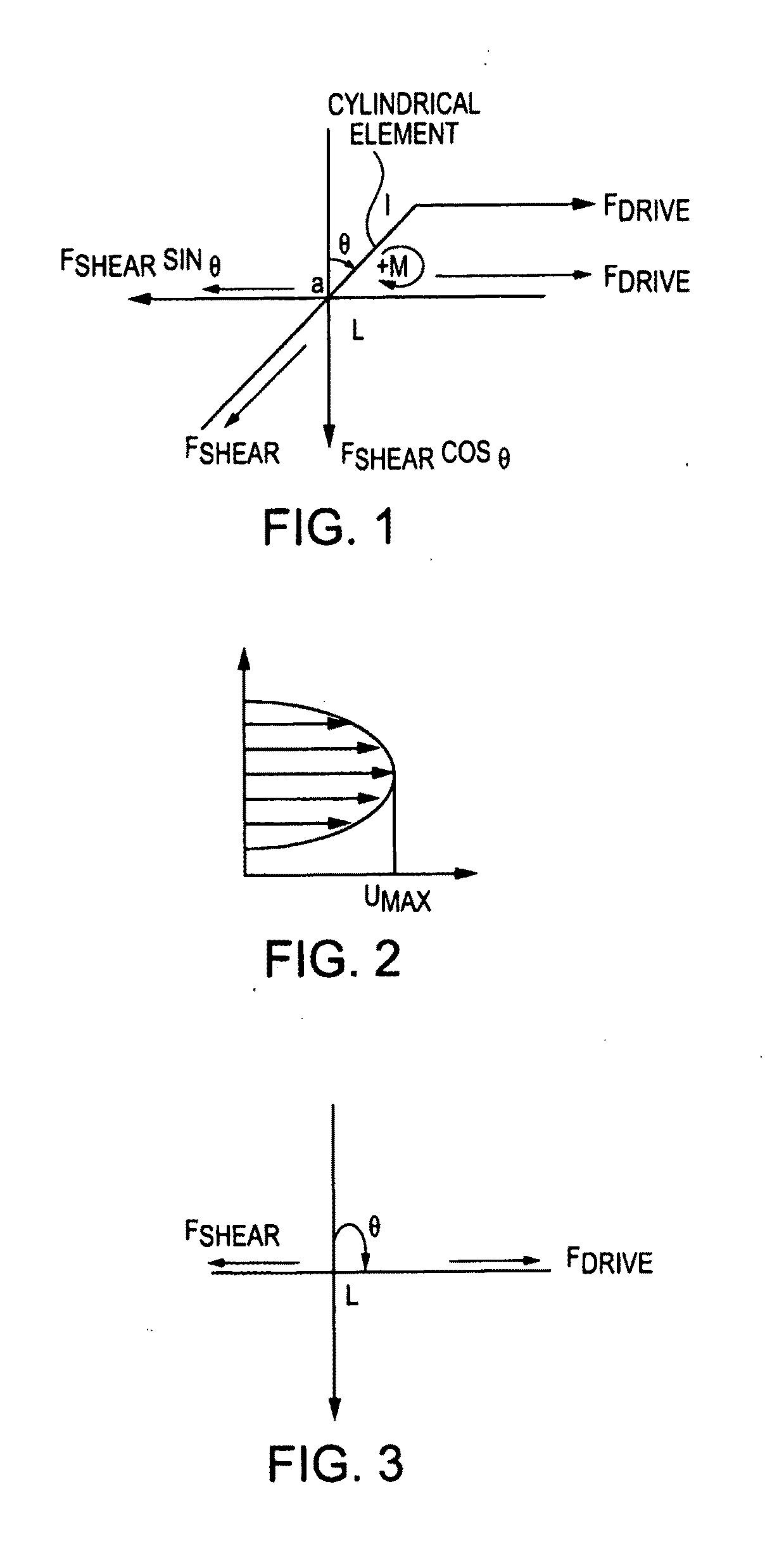
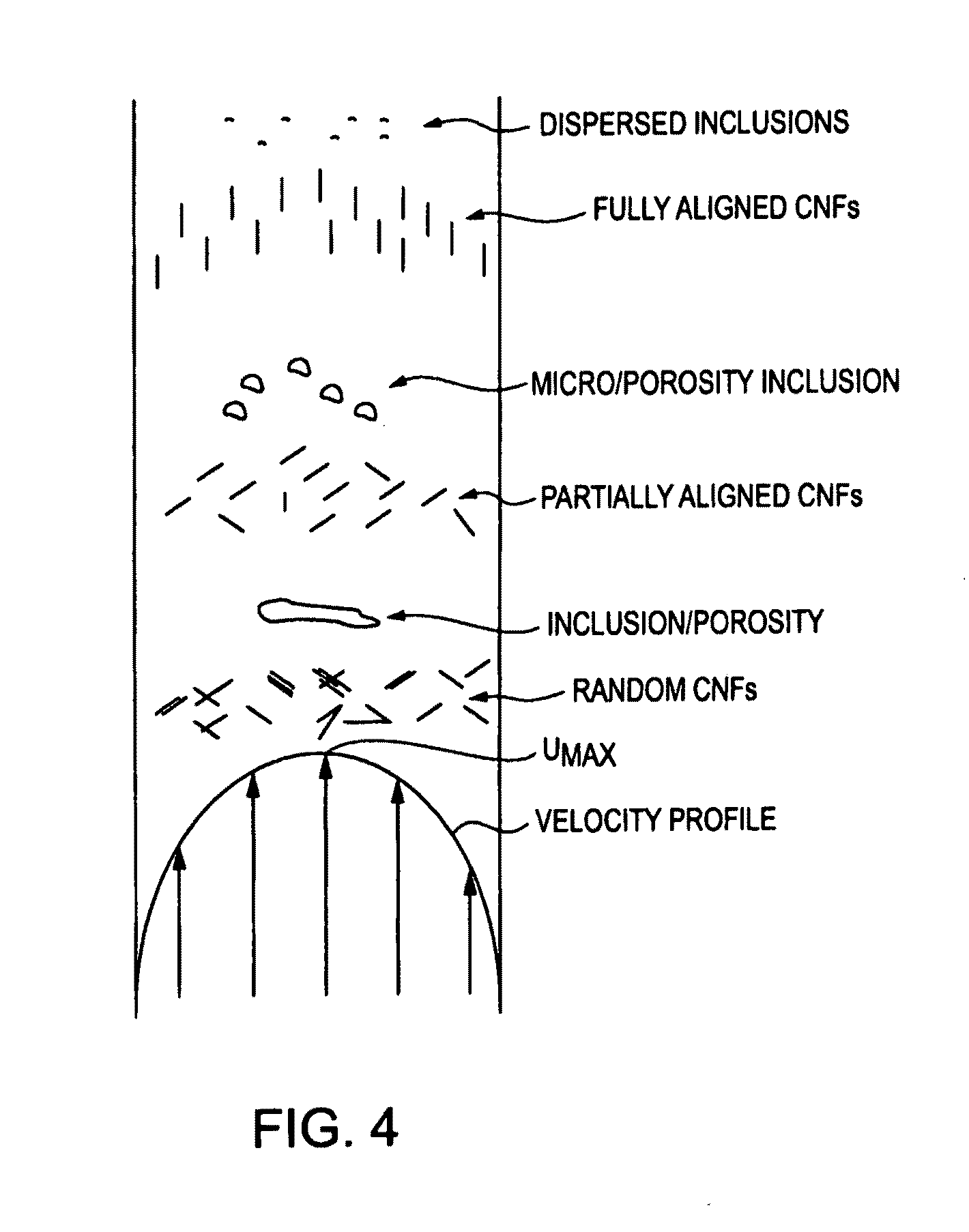
High strength composite materials and related processes
InactiveUS20100203351A1High strengthGlass making apparatusCeramic layered productsNanofiberHigh intensity
Composite materials exhibiting very high strength properties and other characteristics are disclosed. The materials comprise one or more nanomaterials dispersed within one or more matrix materials. The nanomaterials can be in a variety of forms, such as for example, carbon nanotubes and / or nanofibers. The matrix material can be glass, fused silicas, or metal. Also disclosed are various processes and operations to readily disperse and uniformly align the nanotubes and / or nanofibers in the flowing matrix material, during production of the composite materials.
Owner:CLEVELAND STATE UNIVERSITY
Methods for atomic layer deposition of hafnium-containing high-k dielectric materials
InactiveUS20080044569A1Steam generation heating methodsEfficient propulsion technologiesWater vaporGas phase
Embodiments of the invention provide methods for depositing materials on substrates during vapor deposition processes, such as atomic layer deposition (ALD). In one embodiment, a chamber contains a substrate support with a receiving surface and a chamber lid containing an expanding channel formed within a thermally insulating material. The chamber further includes at least one conduit coupled to a gas inlet within the expanding channel and positioned to provide a gas flow through the expanding channel in a circular direction, such as a vortex, a helix, a spiral, or derivatives thereof. The expanding channel may be formed directly within the chamber lid or formed within a funnel liner attached thereon. The chamber may contain a retaining ring, an upper process liner, a lower process liner or a slip valve liner. Liners usually have a polished surface finish and contain a thermally insulating material such as fused quartz or ceramic. In an alternative embodiment, a deposition system contains a catalytic water vapor generator connected to an ALD chamber.
Owner:APPLIED MATERIALS INC
Fused quartz tubing for pharmaceutical packaging
InactiveUS20120148770A1Reduce softeningLow working point temperatureLayered productsPharmaceutical containersRare earthWorking temperature
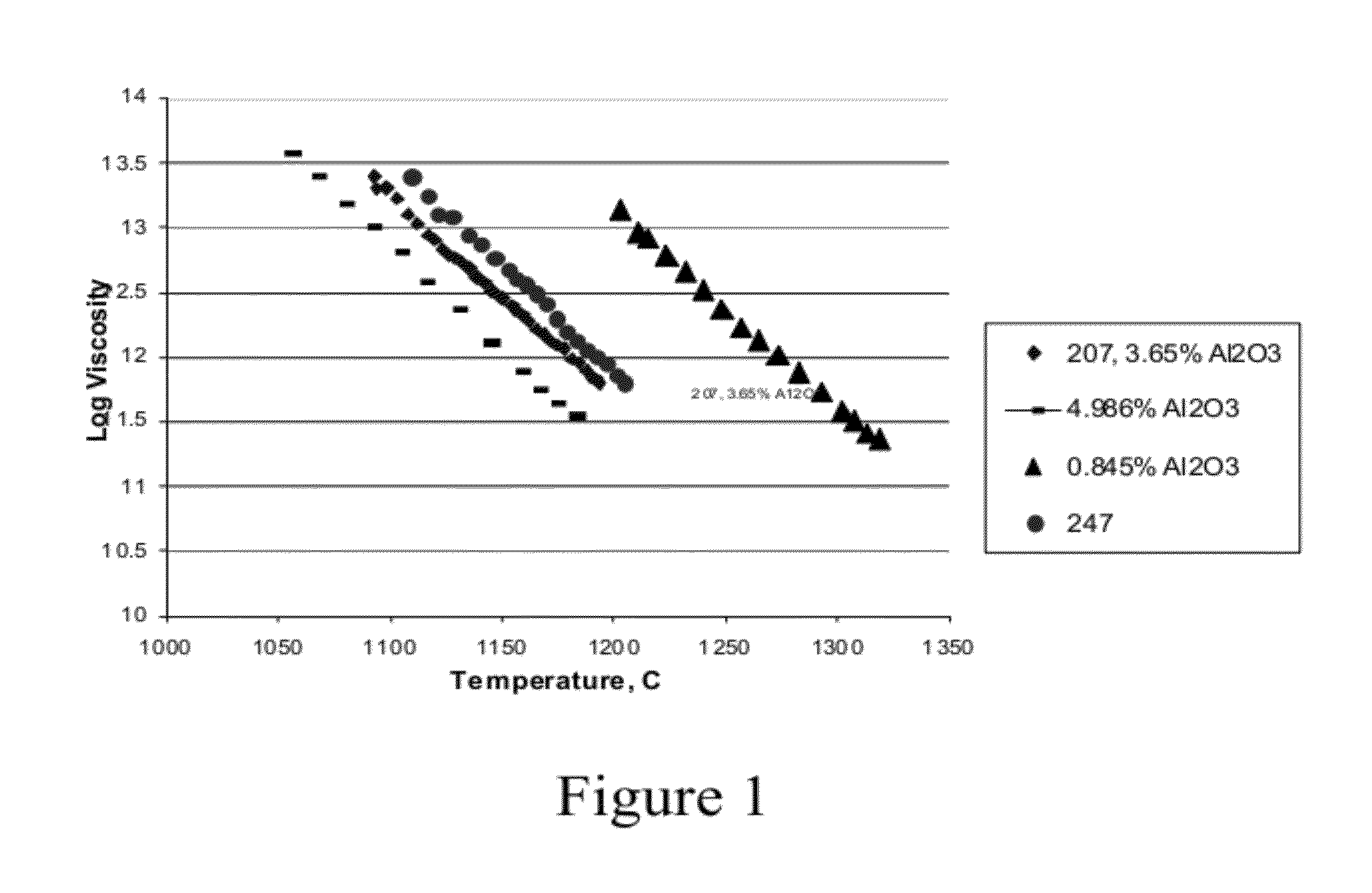
A high silica glass composition comprising about 82 to about 99.9999 wt. % SiO2 and from about 0.0001 to about 18 wt. % of at least one dopant selected from Al2O3, CeO2, TiO2, La2O3, Y2O3, Nd2O3, other rare earth oxides, and mixtures of two or more thereof. The glass composition has a working point temperature ranging from 600 to 2,000° C. These compositions exhibit stability similar to pure fused quartz, but have a moderate working temperature to enable cost effective fabrication of pharmaceutical packages. The glass is particularly useful as a packaging material for pharmaceutical applications, such as, for example pre-filled syringes, ampoules and vials.
Owner:MOMENTIVE PERFORMANCE MATERIALS INC
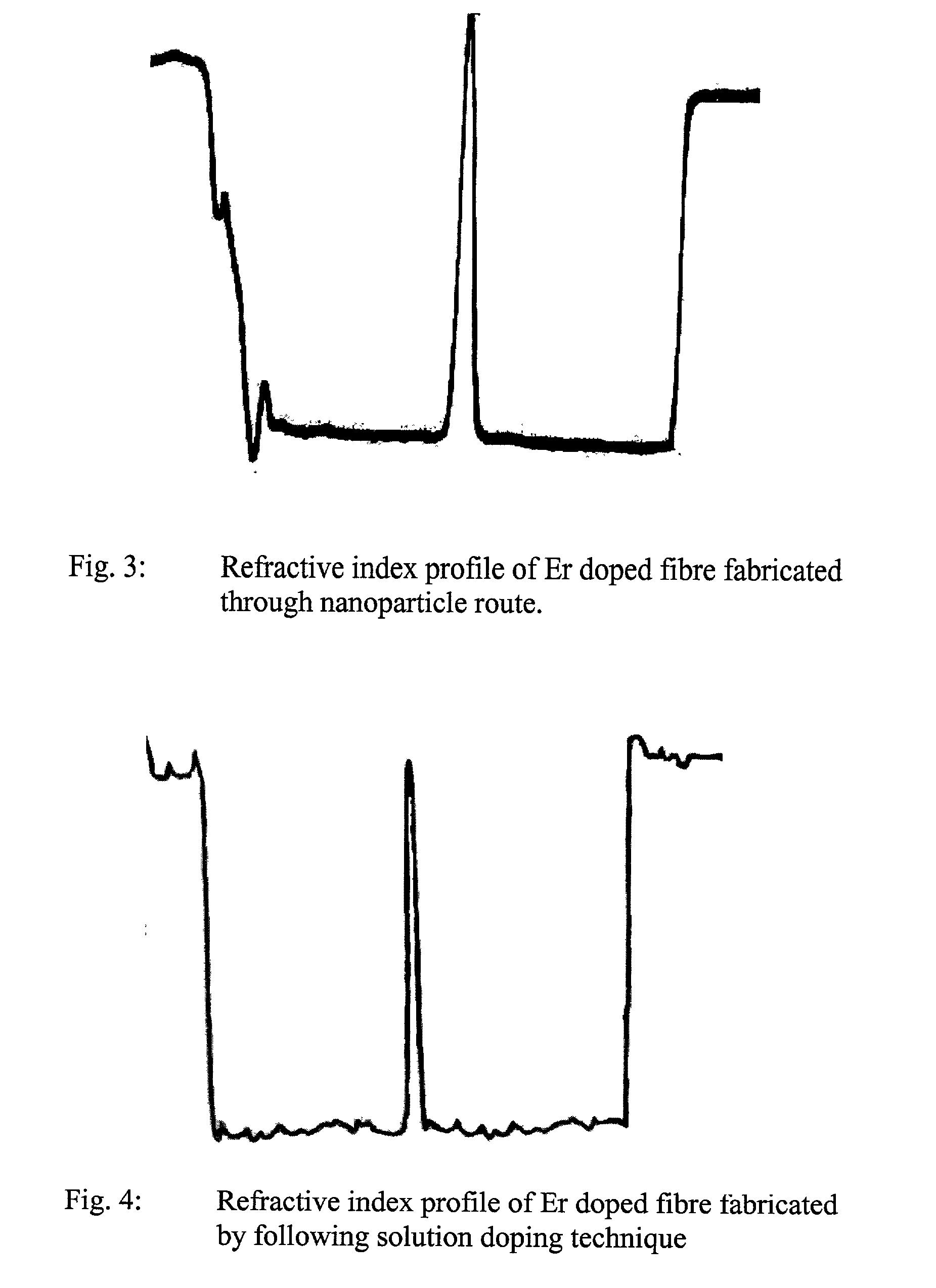
Process of making rare earth doped optical fibre
InactiveUS20040187524A1Reduce in quantityNumber of step involvedMaterial nanotechnologyCladded optical fibreDip-coatingSoot
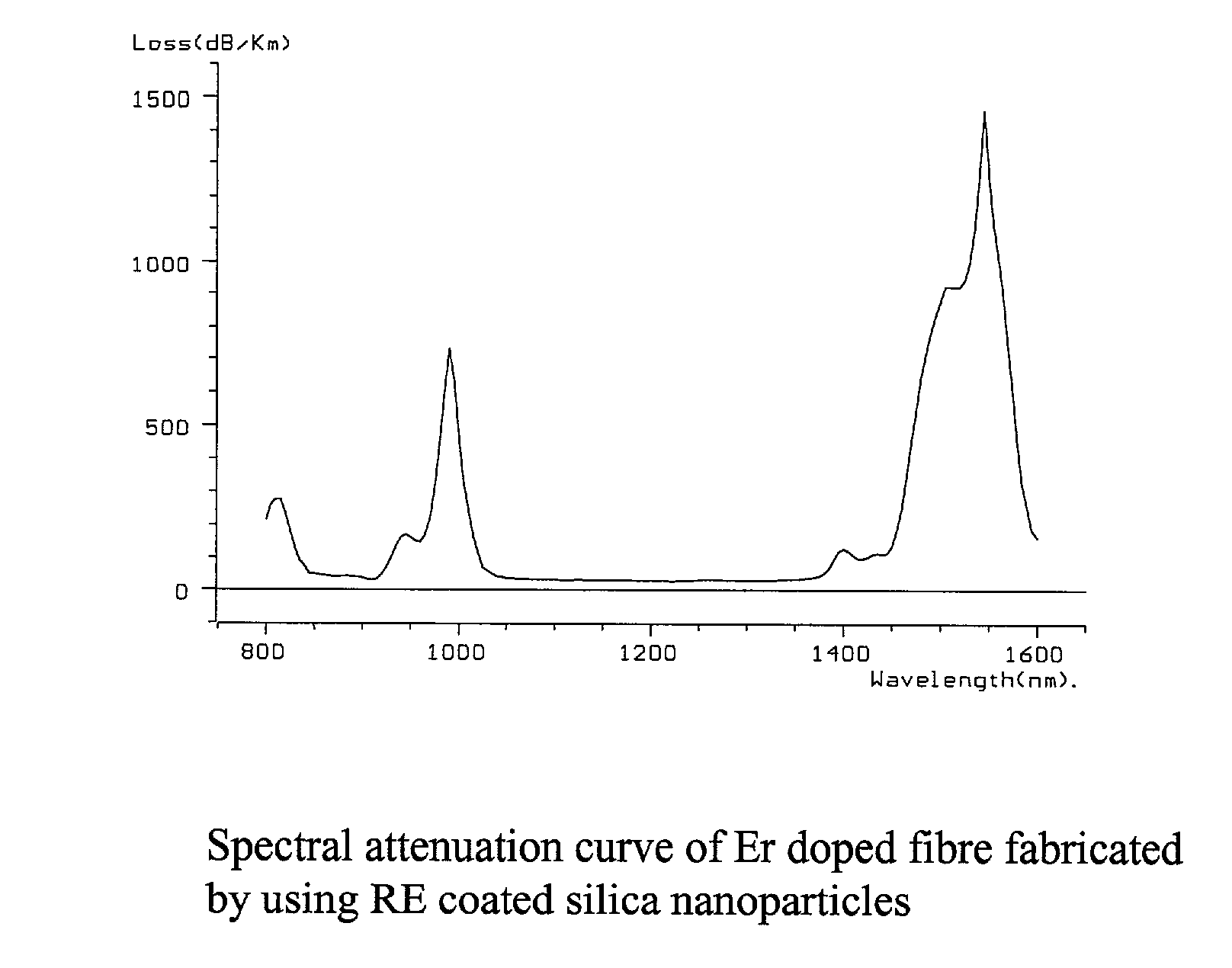
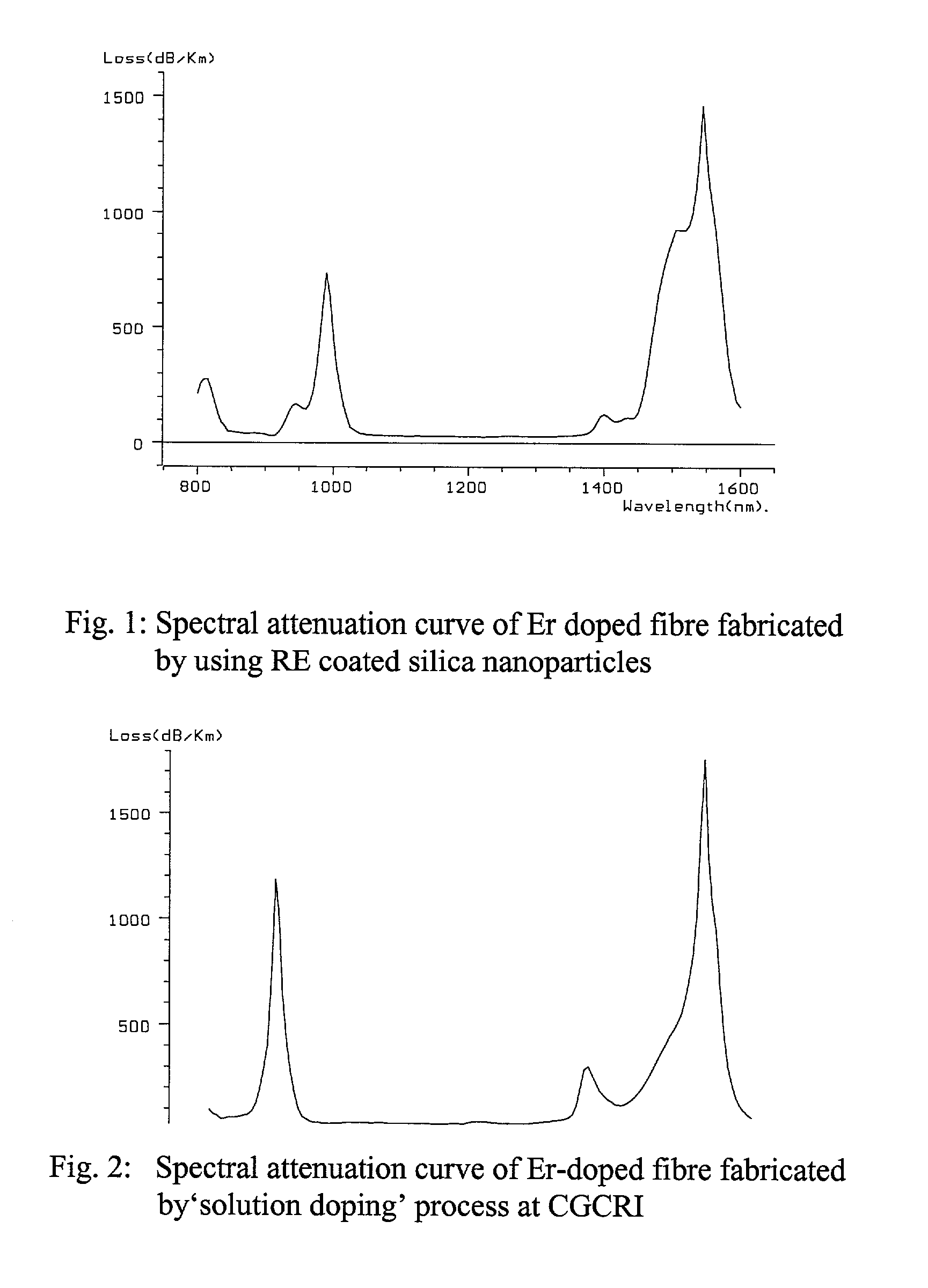
The present invention discloses a process for making rare earth (RE) doped optical fibre by using RE oxide coated silica nanoparticles as the precursor materia, more particularly the method of the present invention involves preparation of stable dispersions (sol) of RE oxide coated silica nanoparticles at ambient temperature and applying a thin coating on the inner surface of silica glass tube following dip coating technique or any other conventional methods, of the said silica sol containing suitable dopants selected from Ge, Al, P, etc., the coated tubes were further processed into optical preforms by following MCVD technique and fiberised in desired configuration, the novelty lies in eliminating the step of the formation of porous soot layer at high temperature by CVD process inside a fused silica glass tube for formation of the core and also in the elemination of the incorporation of the rare earth ions into the porous soot layer following the solution doping technique or other conventional methods, the direct addition of RE oxides in the sol eliminates the formation of microcrystalites and clusters of rare earth ions and prevents change in composition including variation of RE concentration in the core which results in increase in the reproducibility and reliability of the process to a great extent, further the addition of Ge(OET)4 at ambient temperature in the silica sol reduces the quantity of GeCl4 which is required at high temperature to achieve the desired Numerical Aperture.
Owner:COUNCIL OF SCI & IND RES +1
Fused quartz tubing for pharmaceutical packaging
ActiveUS20130095261A1Low working point temperatureHigh wt % contentDiagnosticsLayered productsDopantWorking temperature
A high silica glass composition comprising about 92 to about 99.9999 wt. % SiO2 and from about 0.0001 to about 8 wt. % of at least one dopant selected from Al2O3, CeO2, TiO2, La2O3, Y2O3, Nd2O3, other rare earth oxides, and mixtures of two or more thereof. The glass composition has a working point temperature ranging from 600 to 2,000° C. These compositions exhibit stability similar to pure fused quartz, but have a moderate working temperature to enable cost effective fabrication of pharmaceutical packages. The glass is particularly useful as a packaging material for pharmaceutical applications, such as, for example pre-filled syringes, ampoules and vials.
Owner:MOMENTIVE PERFORMANCE MATERIALS QUARTZ INC
Method for manufacturing composite multi-stage fused quartz powder ceramic crucible
InactiveCN101580339AGuaranteed in-situ curing moldingSmall coefficient of thermal expansionBy pulling from meltGlass shaping apparatusPorosityCrucible
The invention belongs to the field of inorganic non-metallic materials, and relates to the improvement of technology for preparing a fused quartz ceramic crucible. The method for preparing the fused quartz ceramic crucible comprises the steps of mixing-pulping-adding catalyst and initiator-gelatinating-drying- sintering. In the method, multi-stage fused quartz powder is taken as a raw material to prepare the quartz ceramic crucible by gel casting. The quartz ceramic crucible can realize even mixing of multiple dimensioned materials; furthermore, the prepared crucible has uniform structure, controllable porosity as well as excellent thermal shock resistance and high temperature resistance and can meet the requirements of technique and production of polysilicon. In addition, the technique has simple process and no environmental pollution, and is suitable for commercial process.
Owner:王迎奎
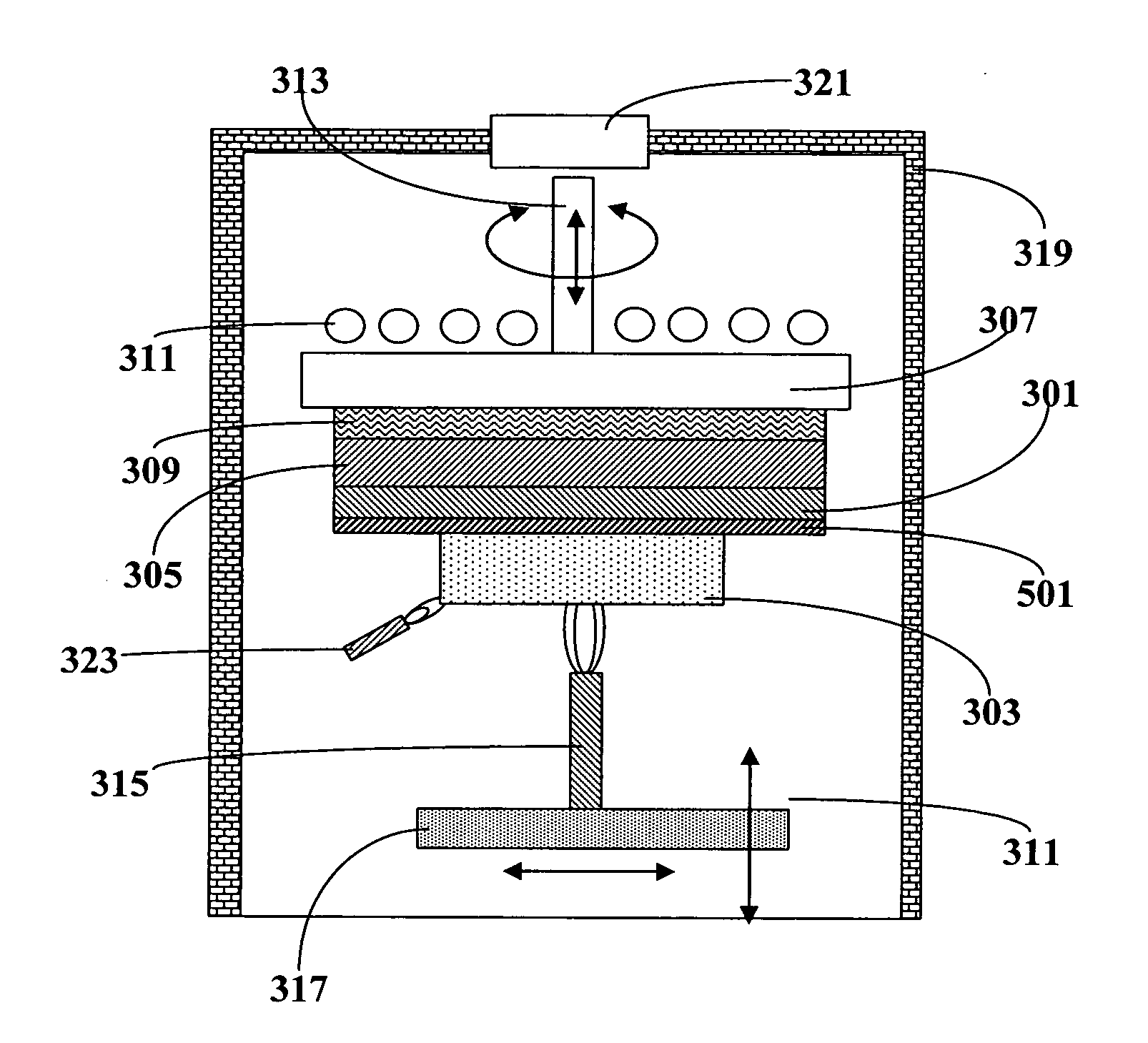
Method and apparatus for making fused silica
ActiveUS20070130995A1High purityHigh OH concentration uniformityGlass furnace apparatusMaterial analysis by optical meansBrickDeposition process
Disclosed are process and apparatus for making high purity fused silica glass materials. The process involves depositing soot particles onto an essentially planar deposition supporting surface and modulation of motion of the soot-generating device relative to the deposition supporting surface to result in a low local soot density variation. The apparatus is designed to implement the planar deposition process. The invention makes it possible to produce fused silica glass without the use of potentially contaminating refractory bricks.
Owner:CORNING INC
Preparation method of large quartz ceramic crucible
The invention discloses a preparation method of a large quartz ceramic crucible, which is formed based on the method of gel casting molding, and particularly comprises the following steps: a) taking fused quartz with purity of 99.0-99.9% according to the mass percent as a raw material, and carrying out granular grading on the grains of the fused quartz; b) uniformly mixing the raw material proportioned by the step a), adding gel solution, preparing into pulp in a ball mill or a blender; c) injecting or pressure-injecting the prepared pulp prepared by the step b) into a preheated metal mold, and taking out from the metal mold after the pulp is solidified into green bodies; d) naturally drying the green bodies; and e) putting the dried green bodies into a high-temperature furnace, baking toobtian the large quartz ceramic crucible. Raw material grain proportioning and the preparation method, optimized by the invention, can product the quartz ceramic crucible with larger overall dimension and thin wall for fusion of special glass, casting of polycrystalline and calcining of rear earth material.
Owner:洛阳北苑新材料技术有限公司
Preparation method of fused silica refractory casting material unwetted by aluminum liquid
The invention belongs to the field of refractory materials and discloses a preparation method of a fused silica refractory casting material unwetted by an aluminum liquid, which comprises the following step of: enhancing a ground substance by adopting 10-20wt% of white alundum powder, 4-8wt% of calcium aluminate cement, 3-5wt% of hydrated alumina compound binding agent, 4-10wt% of silicon oxide micropowder and 3-6wt% of alumina micropowder, wherein 60-70wt% of fused silica is used as a main material, BaSO4 and Na3AlF6 is adopted as a compound aluminum liquid anti-wetting agent with the addition of 1-6wt%, and additional 0.12wt% of trimeric sodium phosphate and additional 0.03wt% of sodium hexametahposphate are adopted as dispensing agents. The casting material prepared by using the method has high strength, is unwetted by the aluminum liquid, has the highest use temperature of 1000 DEG C and can be used as the refractory materials, such as an aluminum flowing groove of an aluminum smelting furnace and the like.
Owner:SINOSTEEL LUOYANG INST OF REFRACTORIES RES
Method for preparing heat insulation tile of shuttle
The invention relates to a method for preparing heat insulation tiles of a shuttle, which is mainly used in heat insulation of shuttles and aircraft heat insulation protecting field such as other aerospace, aviation, guided missile and the like, belonging to the special technical field. The method comprises the steps of matrix batching, shaping, sintering and implementing coating, and the matrix batching is prepared from the following components by weight percent: 50-95% of fused quartz glass fiber, 5-50% of alumina fiber, 0-5% of boron nitride and 0-3% of matrix assistant. The heat insulation tile in the invention has the advantages of high-temperature resistance, high strength, low density, low heat conduction and fine heat insulation effect.
Owner:ZHONGCAI HIGH NEW MATERIAL +1
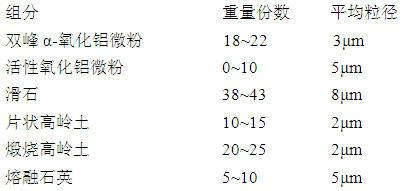
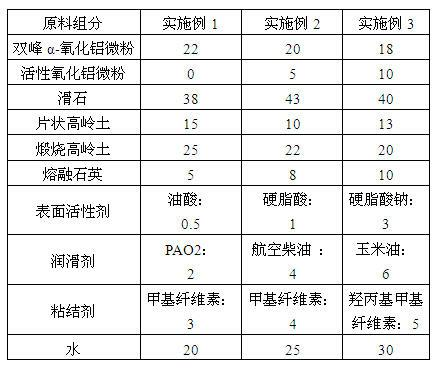
Thermal shock resistant thin-walled cordierite honeycomb ceramics and preparation method thereof
The invention relates to a thermal shock resistant thin-walled cordierite honeycomb ceramics. The components of the thermal shock resistant thin-walled cordierite honeycomb ceramics comprise, by weight, 18-22 parts of bimodal alpha-alumina micro powder with the particle size of 3 mum, 0-10 parts of activated alumina micro powder with the particle size of 5 mum, 38-43 parts of talc with the particle size of 8 mum, 10-15 parts of flake kaolin with the particle size of 2 mum, 20-25 parts of calcined kaolin with the particle size of 2 mum, and 5-10 parts of fused quartz with the particle size of 5 mum. The preparation method comprises the following steps: (1) uniformly mixing the bimodal alpha-alumina micro powder and the activated alumina micro powder; (2) uniformly mixing the resulting mixture from the step (1) and a surfactant; (3) uniformly mixing the resulting mixture from the step (2) and the talc; (4) uniformly mixing the resulting mixture from the step (3) with the flake kaolin, the calcined kaolin, the fused quartz, a binder, a lubricant and water; (5) carrying out treatments of forming, drying, sintering and thermal insulation, and then cooling to the room temperature to obtain the thermal shock resistant thin-walled cordierite honeycomb ceramics. The thermal shock resistant thin-walled cordierite honeycomb ceramics of the present invention has advantages of high mechanical strength, moderate porosity, and low expansion coefficient. The thermal shock resistance of the thermal shock resistant thin-walled cordierite honeycomb ceramics is that: the thermal shock resistant thin-walled cordierite honeycomb ceramics does not crack in three tests at the temperature of 750 DEG C. The thermal shock resistant thin-walled cordierite honeycomb ceramics meets the European IV emission standard.
Owner:JIANGSU PROVINCE YIXING NONMETALLIC CHEM MACHINERY FACTORY
High strength composite materials and related processes
InactiveCN101484397AIndividual molecule manipulationMetallic material coating processesNanofiberHigh intensity
Composite materials exhibiting very high strength properties and other characteristics are disclosed. The materials comprise one or more nanomaterials dispersed within one or more matrix materials. The nanomaterials can be in a variety of forms, such as for example, carbon nanotubes and / or nanofibers. The matrix material can be glass, fused silicas, or metal. Also disclosed are various processes and operations to readily disperse and uniformly align the nanotubes and / or nanofibers in the flowing matrix material, during production of the composite materials.
Owner:CLEVELAND STATE UNIVERSITY
Phosphate-silicon dioxide low-dielectric high temperature-resistant coating and preparation thereof
The invention discloses a low-dielectric high-temperature-resistant phosphate-silicon dioxide coating, with the mass percentage content between the components and the raw material as follows: 50-80% of percentage content of inorganic compound binder, 15-50% of high-temperature filler, 0.5-1.5 wt% of curing agent, 2-5 wt% of thickener, and 0.3-1.5wt% of surfactant; the inorganic compound binder is the mixture of aluminum phosphate or aluminium-chromium phosphate and silicon collosol; the high-temperature resistant filler is the mixture of fused quartz powder and refined quartz powder or alpha-Al2O3 power; the curing agent is MgO; the thickener is fumed silica; the surfactant is non-ionic surfactant. The phosphate binder is firstly prepared, followed by phosphate / silicon collosol compound binder; then the non-ionic surfactant and the high-temperature resistant filler are added to the compound binder, followed by the thickener and the curing agent, then the mixture is evenly mixed. The invention can be used for the surface protection of porous inorganic materials or non-porous inorganic materials and is typically used as wave-transparent material for aerospace crafts.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV
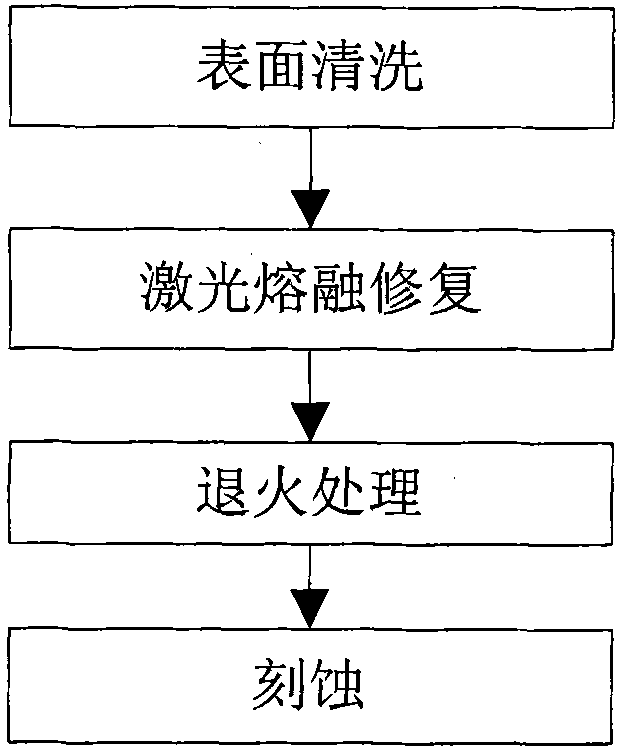
Method for repairing fused quartz optical damage component
The invention discloses a method for repairing a fused quartz optical damage component, which belongs to the technical field of the optical material and the optical component, in particular to a method for repairing and processing laser damage of a fused quartz optical component. The method comprises the following steps: firstly adopting infrared carbon dioxide laser to carry out laser fusion repair on the damage part of the fused quartz optical damage component; and then carrying out annealing treatment on the fused quartz optical damage component subjected to laser fusion repair. The method can carry out complete repair on the fused quartz optical damage component and eliminate residual stress caused by the laser fusion repairing process. The fused quartz optical component repaired by the method can revert to the state of the ideal fused quartz optical component. And the method also can inhibit the increase of the damage points of the fused quartz optical component. The method can prolong the service life of the fused quartz optical component, greatly reduces operation cost and has the characteristics of strong process controllability, high repetitiveness and stable performance.
Owner:UNIV OF ELECTRONICS SCI & TECH OF CHINA +1
Processing of fine silicon powder to produce bulk silicon
InactiveUS20080295294A1Reduce pressureQuality improvementPolycrystalline material growthSiliconIngotArgon gas
A method for using substantial quantities of silicon powders as charge and processing it to produce a high quality silicon ingots suitable for photovoltaic use is disclosed. In a fused silica crucible, silicon feedstock containing more than about 5% by weight silicon powder is charged. The crucible with the charged silicon feedstock is placed into a furnace chamber and a vacuum is drawn to remove air. The vacuum is applied slowly. Then, the furnace chamber is backfilled with argon gas and heated to form molten silicon. Afterward, the molten silicon is solidified and annealed to form a multicrystalline silicon ingot.
Owner:GT SOLAR INC
Method for preparing magnesia carbon brick non-aluminum antioxidant coating
InactiveCN101928480AHigh strengthAvoid enteringAlkali metal silicate coatingsCarboxymethyl celluloseBrick
The invention more particularly relates to a method for preparing magnesia carbon brick non-aluminum antioxidant coating, which has the technical scheme of comprising the steps of: firstly mixing 40-60wt% of boron glass, 5-20wt% of SiC, 20-35wt% of fused quartz, 1-5wt% of MgO, 5-10wt% of CaO and 0.1-0.3% of carboxymethyl cellulose, and additionally adding ludox accounting for 20-40wt% of the mixed material or liquid water glass accounting for 40-60wt% of the mixed material, then additionally adding water accounting for 50-60wt% of the mixed material, carrying ball-milling for 20-40min, and preparing antioxidant paint; then, evenly painting the prepared antioxidant paint on the surface of a magnesia carbon brick, naturally drying and stoving at 110 DEG C; and finally, putting the stoved magnesia carbon brick in a high temperature furnace, heating up to 1150-1250 DEG C, carrying out heat preservation for 20-40min, and preparing the magnesia carbon brick non-aluminum antioxidant coating. The invention has the characteristics of simple technique and low cost, and can be glazed at the temperature range of 500-1200 DEG C; and the prepared magnesia carbon brick non-aluminum antioxidant coating has good anti-oxidation performance.
Owner:WUHAN UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Thin wall cordierite carrier for ceramic honeycomb catalyst and method for preparing the same
InactiveCN1827217AEasy alignmentSmall expansion coefficientCatalyst carriersCeramicwarePorosityCordierite
The invention relates to the improvement on the ceramic beehive catalyst carrier, especially providing a ceramic beehive catalyst carrier with high mechanical strength and lower expansion parameter and preparing method. The invention is characterized in that: said beehive catalyst carrier is the alumina micro powder in 12-15%WT whose average particle diameter is less than 2 micron; the sheet kaolin and / or clay micro powder in 43-47% whose average particle diameter is less than 2 micron, the sheet steatite micro powder in 33-37% whose average particle diameter is 5-15 micron, and the fuse quartz in 6-12% whose average particle diameter is less than 2 micron to be mixed, molded and baked to attain the cordierite whose total amount is 92-96%, wherein, the Al203, MgO and SiO2 are each in 36-37%, 13.0-14.0% and 50-52%. The invention adds surface active agent in the mixture when in preparation. The prepared beehive cordierite total amount with 600 hole / square inch can reach 92-96%, the expansion parameter can reach 0.8X10-6 / Deg. C (800Deg. C to room temperature), and the factor of porosity can reach 39-40%. The invention can reduce the ignition temperature 25-40Deg. C, and reduce the tail gas discharge of nitrogen oxygen compound and carbon monoxide of vehicle 5-10% to meet the demand of Europe III standard.
Owner:JIANGSU PROVINCE YIXING NONMETALLIC CHEM MACHINERY FACTORY +1
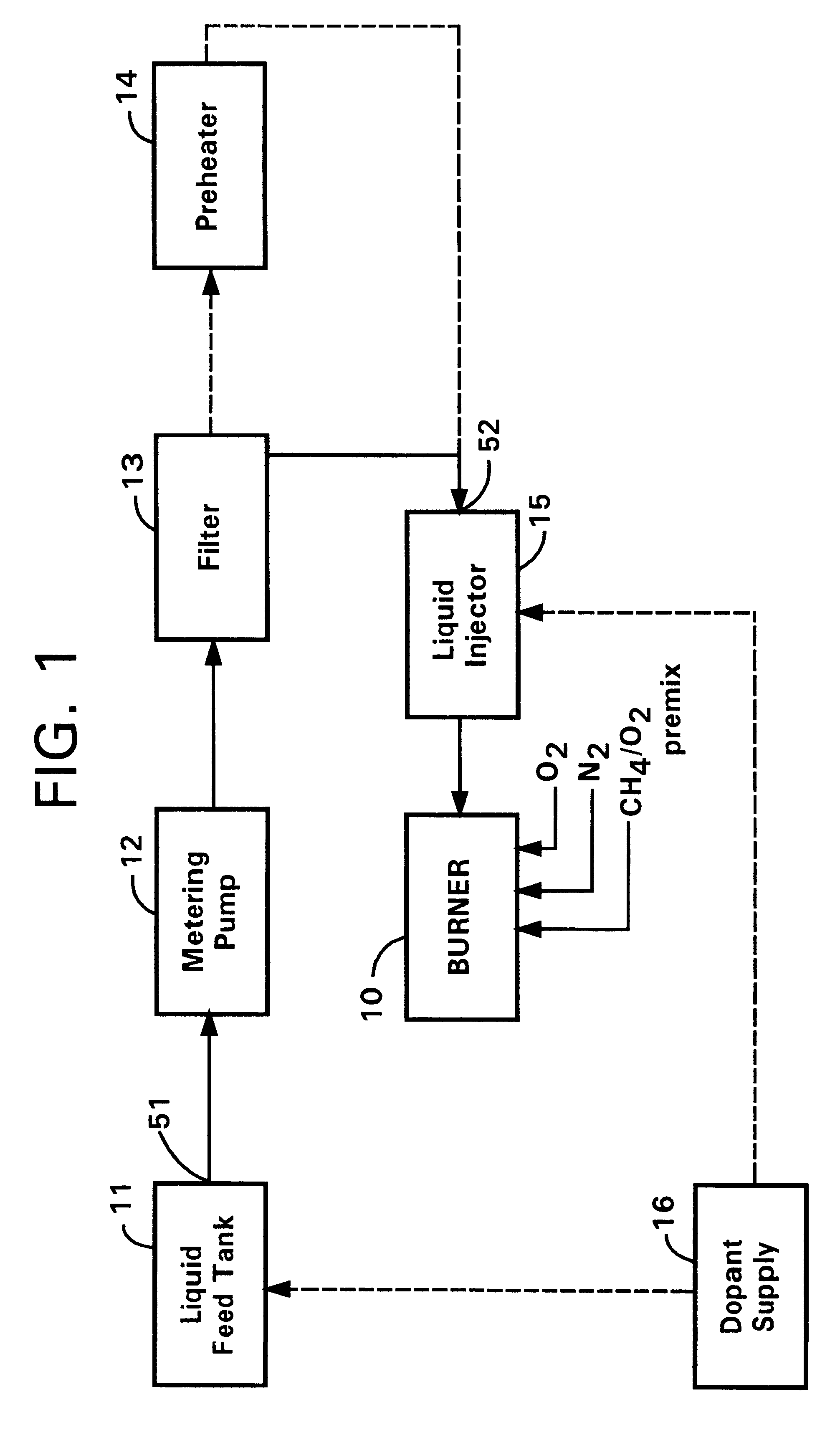
Method and apparatus for forming fused silica by combustion of liquid reactants
InactiveUS6565823B1High concentricityPrevents burner buildupSilicaSpray nozzlesCombustorDecomposition
The present invention is directed to a method for making fused silica glass. A liquid, preferably halide-free, silicon-containing compound capable of being converted by thermal oxidative decomposition to SiO2 is provided and introduced directly into the flame of a combustion burner, thereby forming finely divided amorphous soot. The amorphous soot is deposited on a receptor surface where, either substantially simultaneously with or subsequently to its deposition, the soot is consolidated into a body of fused silica glass. The invention further relates to an apparatus for forming fused silica from liquid, preferably halide-free, silicon-containing reactants which includes: a combustion burner which, in operation, generates a flame; an injector for supplying a liquid silicon-containing compound to the flame to convert the compound by thermal oxidative decomposition to a finely divided amorphous soot; and a receptor surface on which the soot is deposited.
Owner:CORNING INC
Preparation method of heat-resisting alloy sliding-block shell by investment casting
InactiveCN103600030AImprove room temperature strengthImprove pass rateFoundry mouldsFoundry coresAlloySurface coating
The invention discloses a preparation method of a heat-resisting alloy sliding-block shell by investment casting. The preparation method is characterized in that: the method comprises a first step of preparing coating, wherein surface coating comprises silica sol and a refractory powder material is fused alumina; and transition layer coating and back layer coating comprise the silica sol and a refractory powder material is one selected from the fused quartz, kaolin clinker and bauxite clinker; a second step of coating a wax mould with the surface coating, scattering the sand material of the fused alumina, drying and repeating for 2 times; coating the surface layer with the transistion layer coating, scattering one of the fused quartz, the kaolin clinker and the bauxite clinker, drying, and repeating for 5 times; and finally coating with a back layer coating, scattering one of the fused alumina, the kaolin clinker and the bauxite clinker and drying; and a third step of dewaxing and calcinating; and the shell produced by the method has advantages of high room-temperature strength and high-temperature strength, good internal surface quality, high percent of pass, low production cost and good economic benefit.
Owner:泰州枫叶冶金设备有限公司
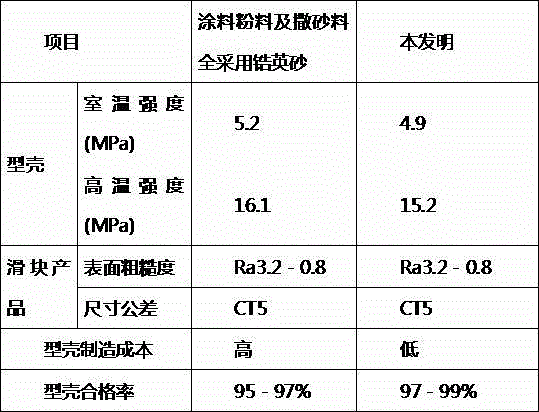
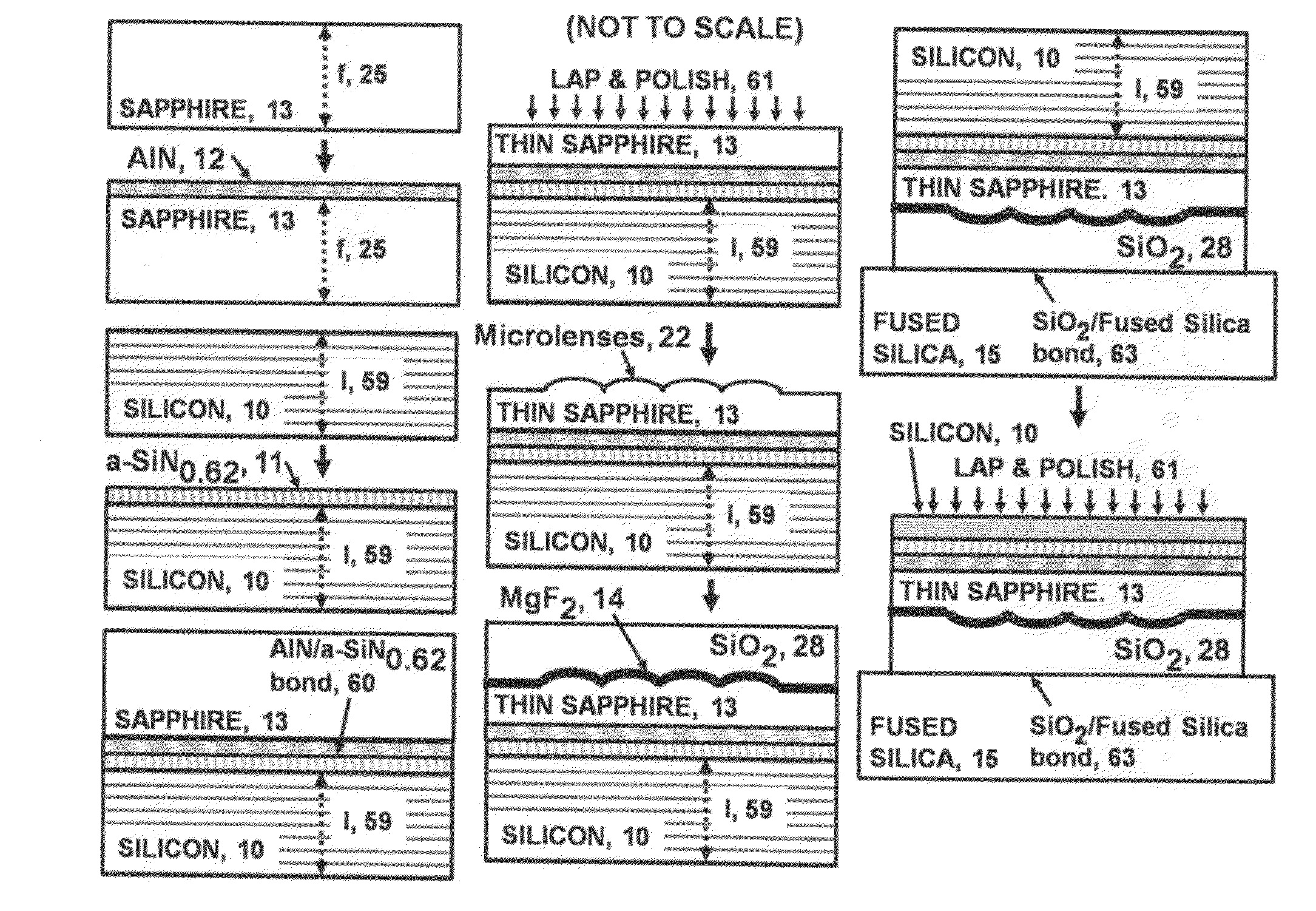
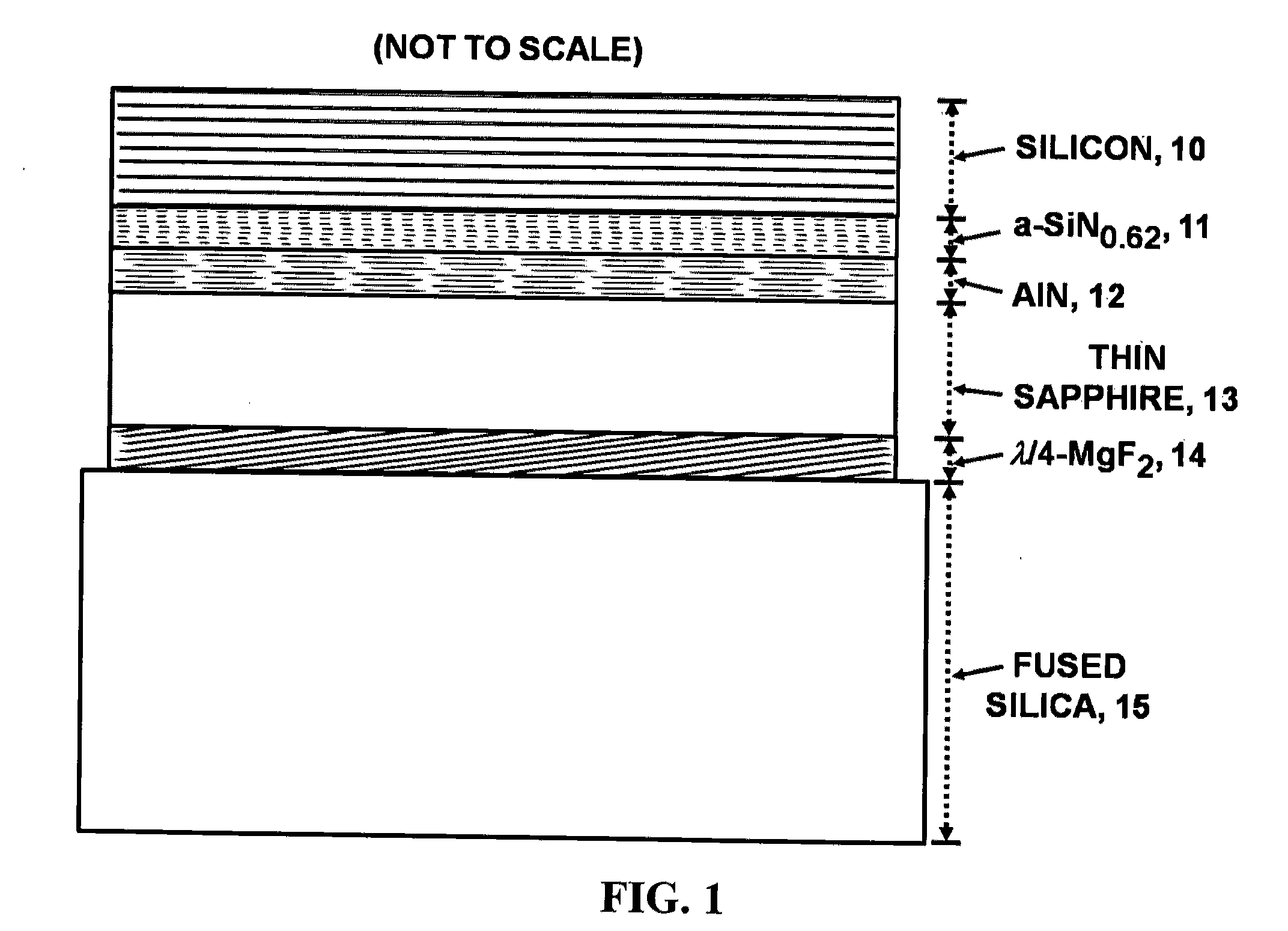
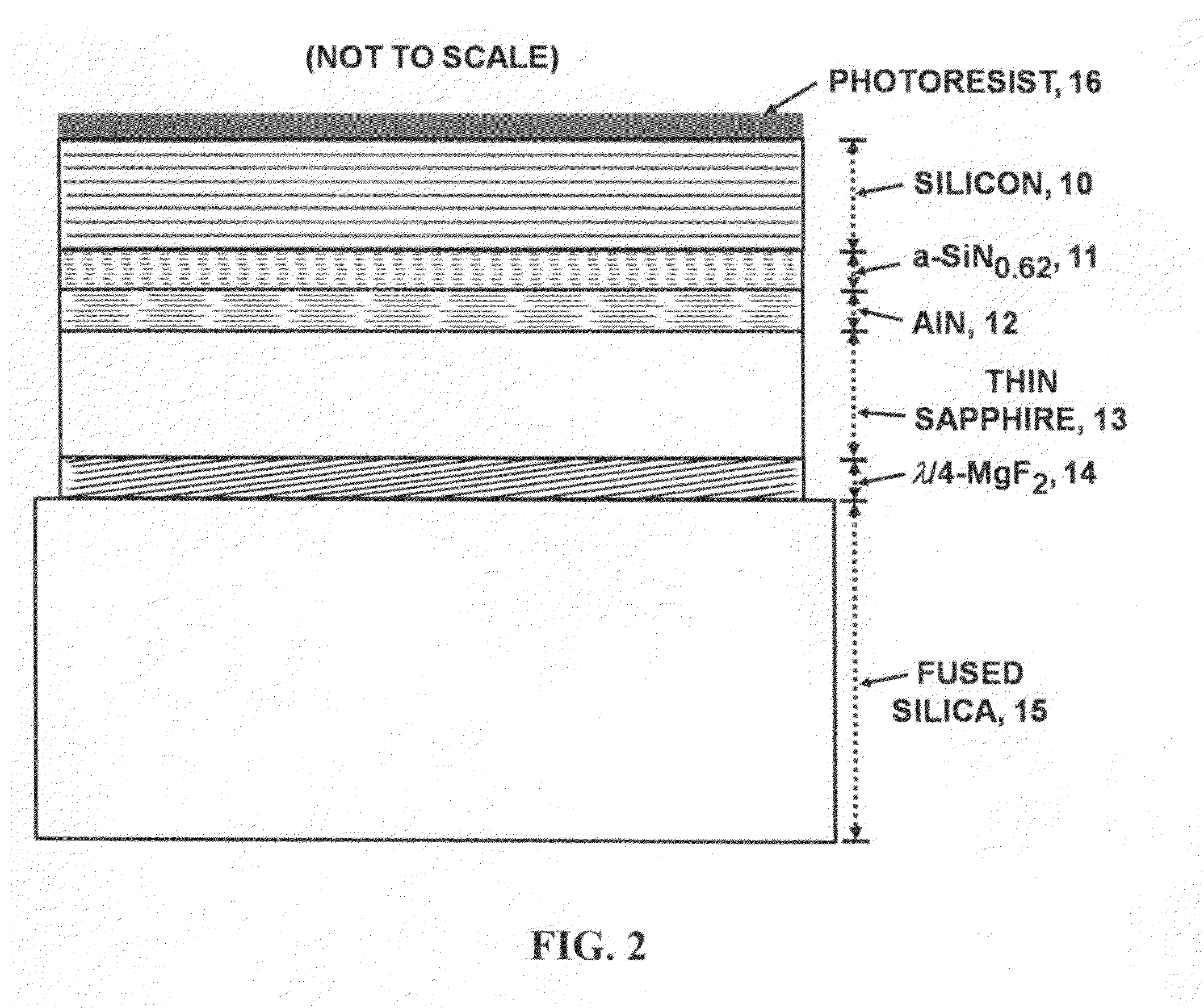
Thin, very high transmittance, back-illuminated, silicon-on-saphire semiconductor substrates bonded to fused silica
InactiveUS20120299143A1High light transmittanceSuppression problemSolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSingle crystalSilicon dioxide
A very high transmittance, back-illuminated, silicon-on-thin sapphire-on-fused silica wafer substrate design is presented for enabling high quantum efficiency and high resolution, silicon or silicon-germanium avalanche photodiode detector arrays with improved indirect optical crosstalk suppression. The wafer substrate incorporates a stacked antireflective bilayer between the sapphire and silicon, comprised of single crystal aluminum nitride (AlN) and non-stoichiometric, silicon rich, amorphous silicon nitride (a-SiNX<1.33), as well as a one quarter wavelength, magnesium fluoride (λ / 4-MgF2) back-side antireflective layer which is bonded to a fused silica wafer. The fused silica provides mechanical support, allowing the sapphire to be thinned to optimal thickness below 50 μm, for improved optical transmittance and in conjunction with monolithic sapphire microlenses, suppression of indirect optical crosstalk from multiple reflections of APD emitted light. After solid-state device fabrication, the silicon can be coated with photoresist and the fused silica dissolved in buffered hydrogen fluoride (HF) to recover the thin Si—(AlN / a-SiNX<1.33)-sapphire-(MgF2).
Owner:STERN ALVIN GABRIEL
Method and apparatus for manufacturing fused silica crucible, and the fused silica crucible
ActiveUS20100071613A1Good transparent glass layerAvoid overall overheatingAfter-treatment apparatusPolycrystalline material growthCrucibleMaterials science
A method of manufacturing a fused silica crucible by heating and melting a vitreous silica powder compact shaped into a mold using arc discharge of electrodes arranged around a rotation shaft of the mold, includes the steps of: arranging the electrodes in a ring shape, and setting a ratio W / R of a horizontal distance W between the electrode front end and the surface of the vitreous silica powder compact to a vitreous silica powder compact opening radius R, for at least a predetermined time during arc heating, to be in the range of 0.002 to 0.98.
Owner:SUMCO CORP
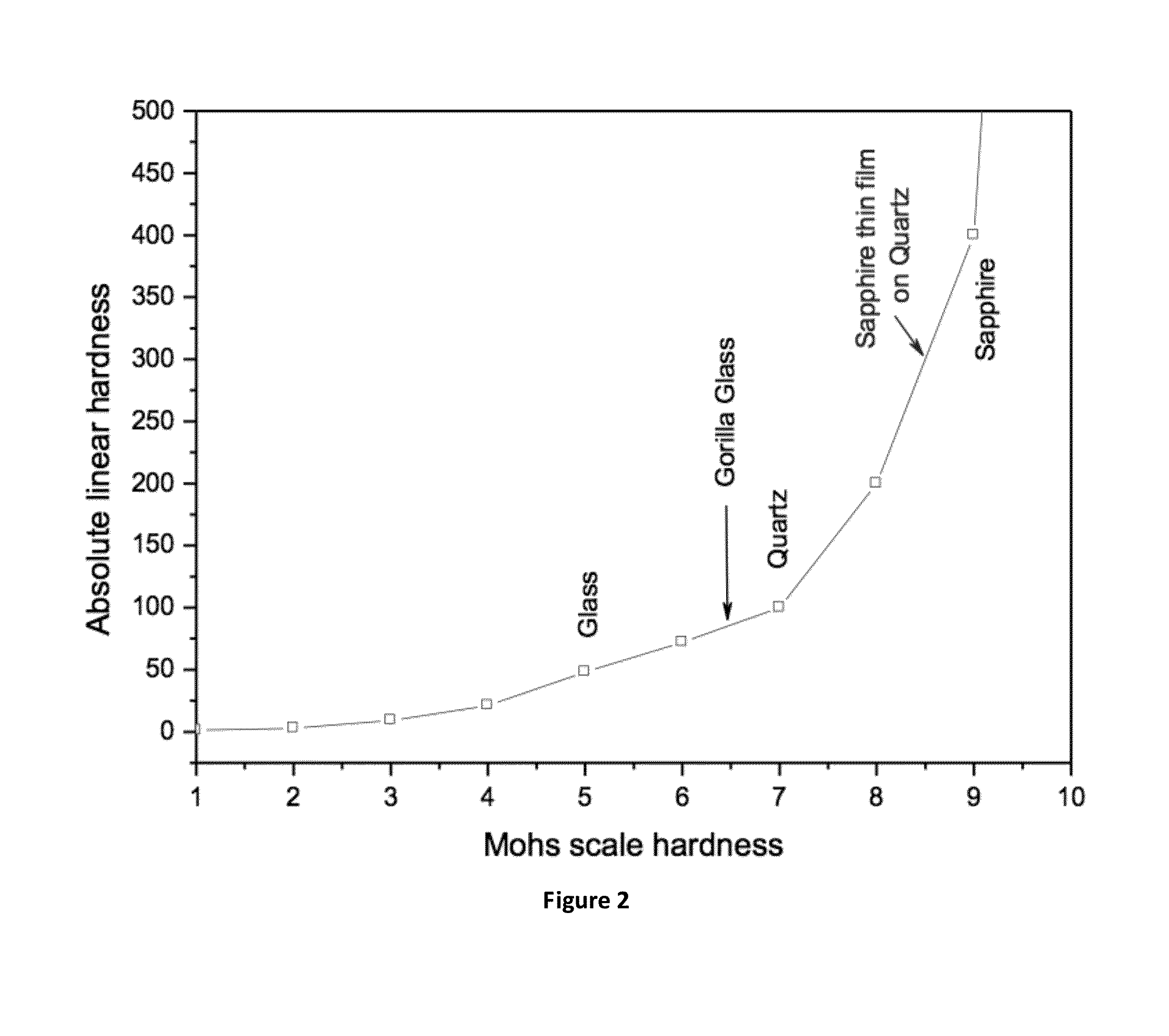
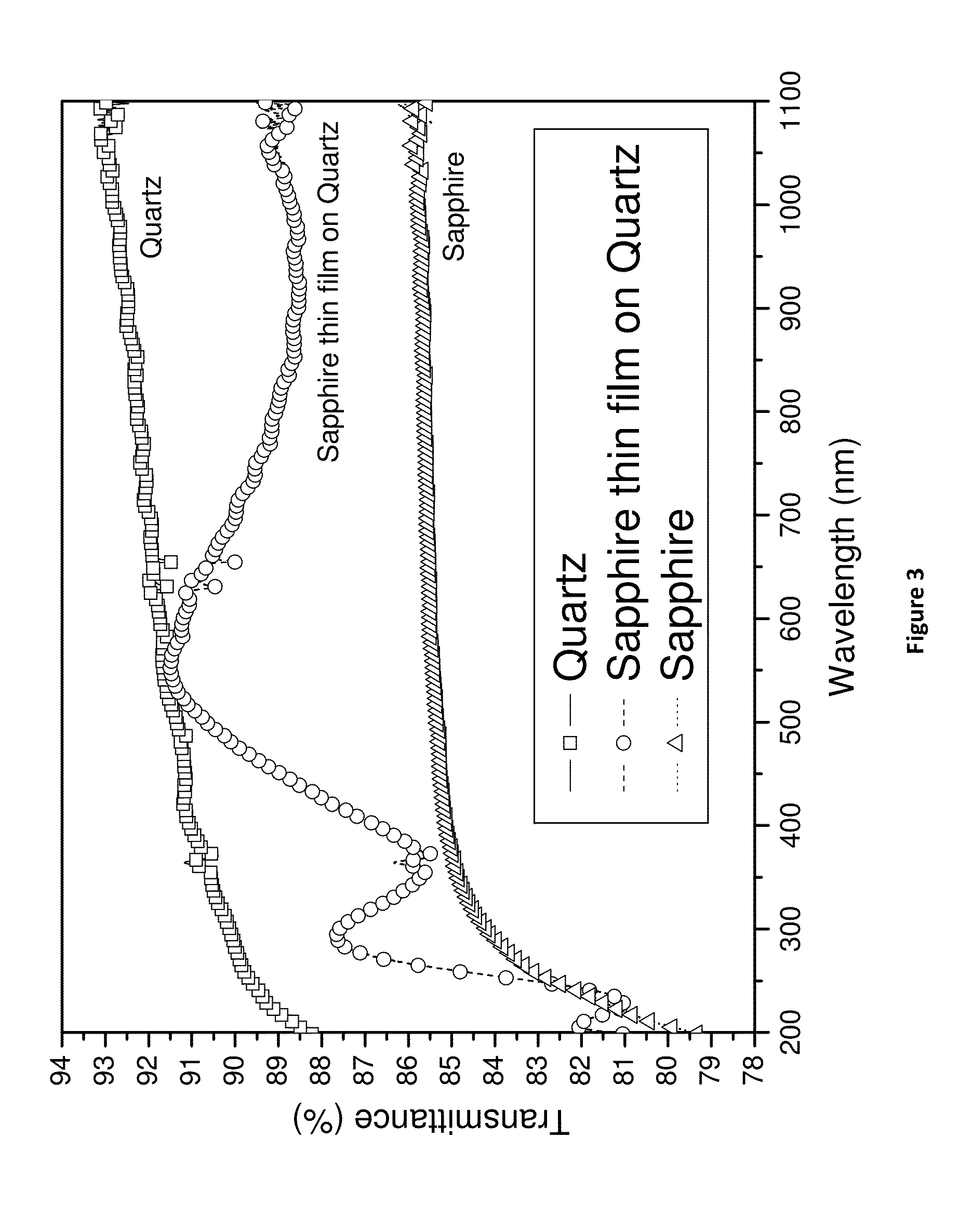
Sapphire thin film coated substrate
A method to deposit a layer of harder thin film substrate onto a softer substrate. In particular, the present invention provides a method to deposit a layer of sapphire thin film on to a softer substrate e.g. quartz, fused silica, silicon and (toughen) glass. This combination is better than pure sapphire substrate.
Owner:HKBU R&D LICENSING LTD
Low dielectric, low expansion and low temperature co-fired ceramic material and preparation method thereof
The invention relates to a low dielectric, low expansion and low temperature co-fired ceramic material and a preparation method thereof. The method comprises the steps of a, mixing (60-80)wt% of borosilicate glass powder with (20-40)wt% of spherical fused quartz micro powder to obtain low-temperature co-fired ceramic powder, b, adding a solvent, an adhesive agent, a plasticizer and a dispersing agent to the low temperature co-fired ceramic powder, obtaining casting slurry, and preparing the casting ceramic slurry into a green ceramic tape, and c, placing the green ceramic tape into an electric furnace for sintering to form the low temperature co-fired ceramic material. According to the low dielectric, low expansion and low temperature co-fired ceramic material and the preparation method thereof, a high-purity superfine spherical fused quartz material is added to representative borosilicate glass, so that the dielectric constant and the thermal expansion coefficient of an LTCC (low temperature co-fired ceramic) substrate material are reduced, and the low temperature sintering of the spherical fused quartz material is achieved. The prepared low temperature co-fired ceramic material has the dielectric constant of 5.1(1MHz) and the thermal expansion coefficient of 4.2*10<-6>K<-1>, and has a good application prospect.
Owner:(CNBM) BENGBU DESIGN & RES INST FOR GLASS IND CO LTD +1
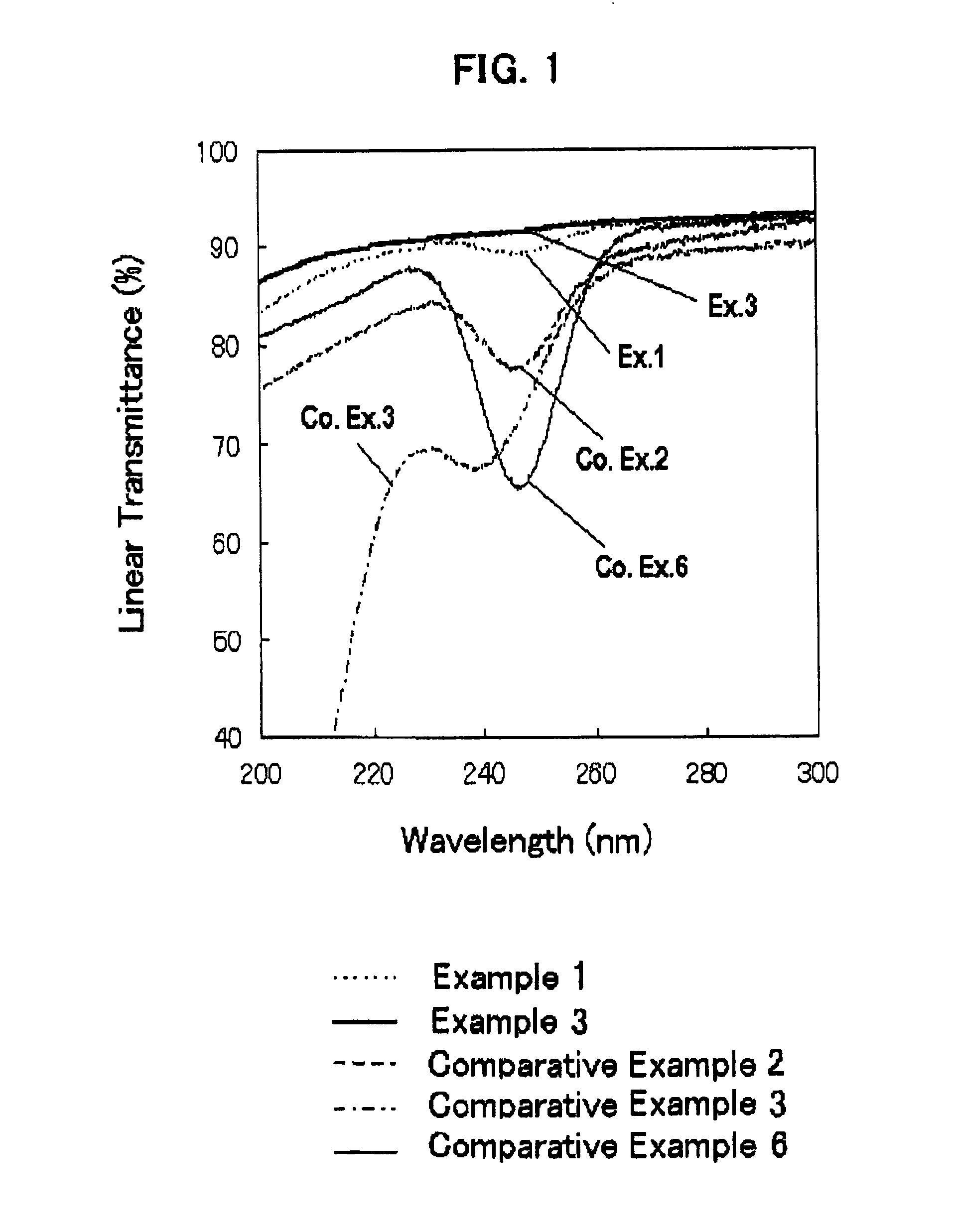
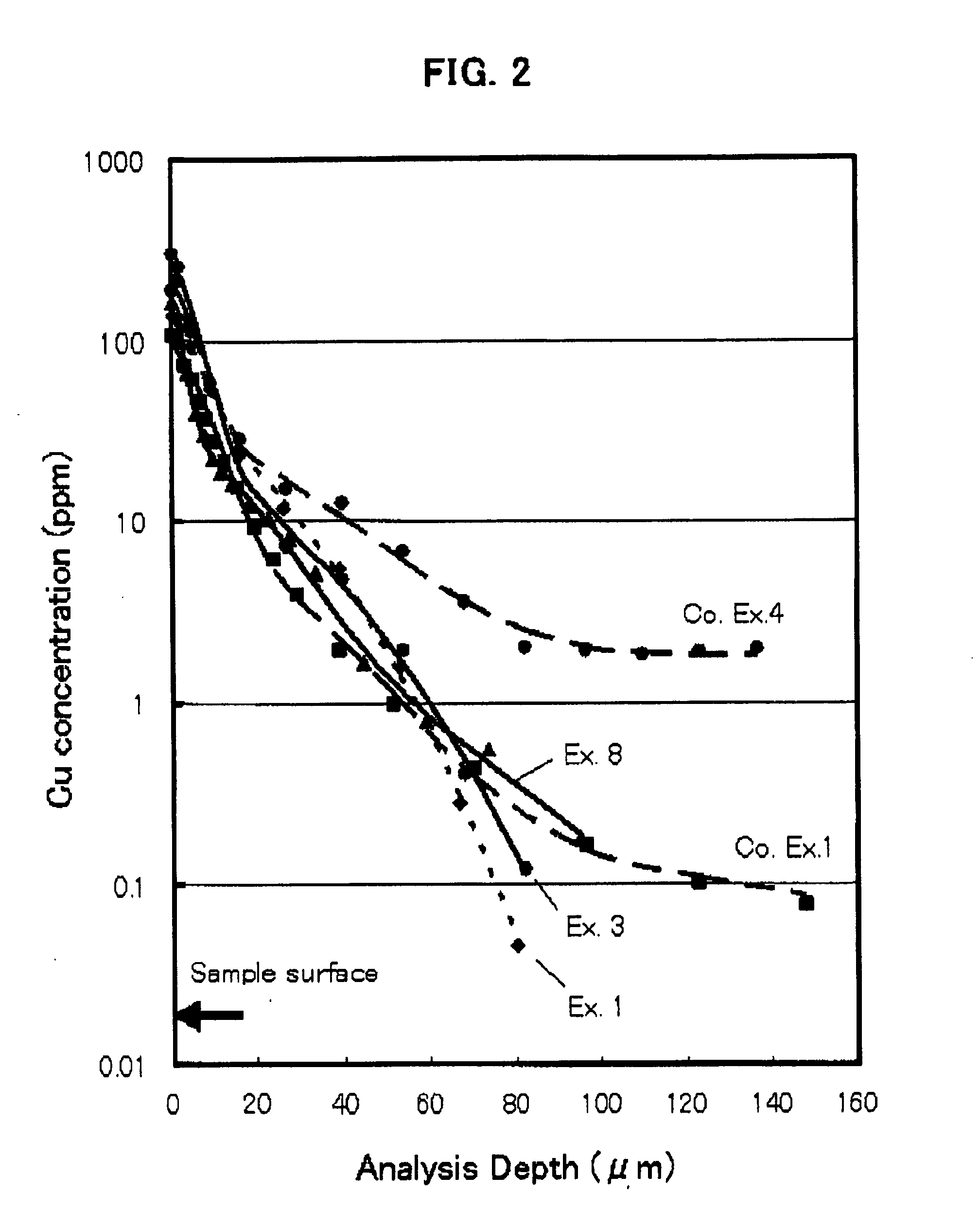
Fused silica glass and process for producing the same
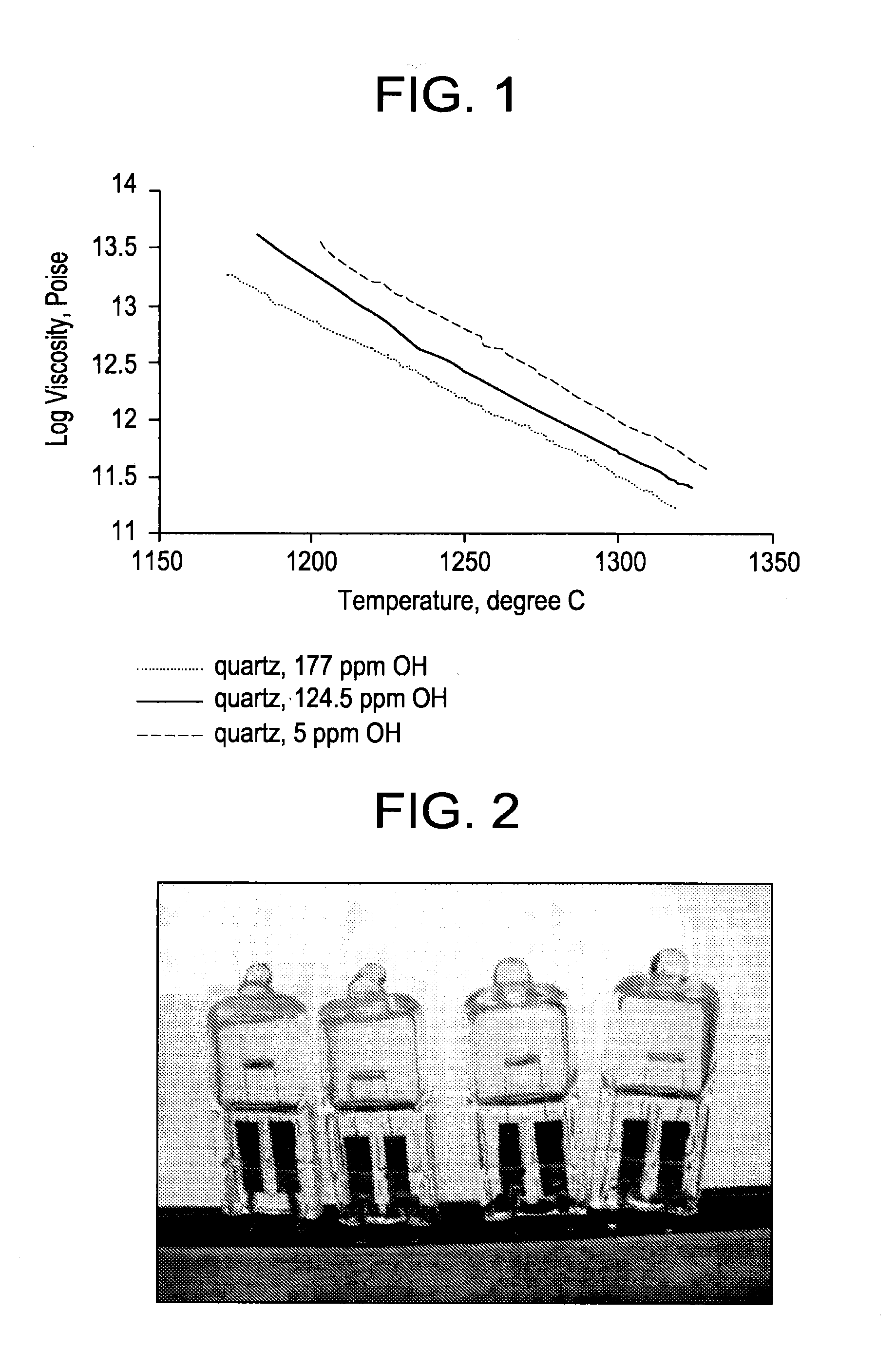
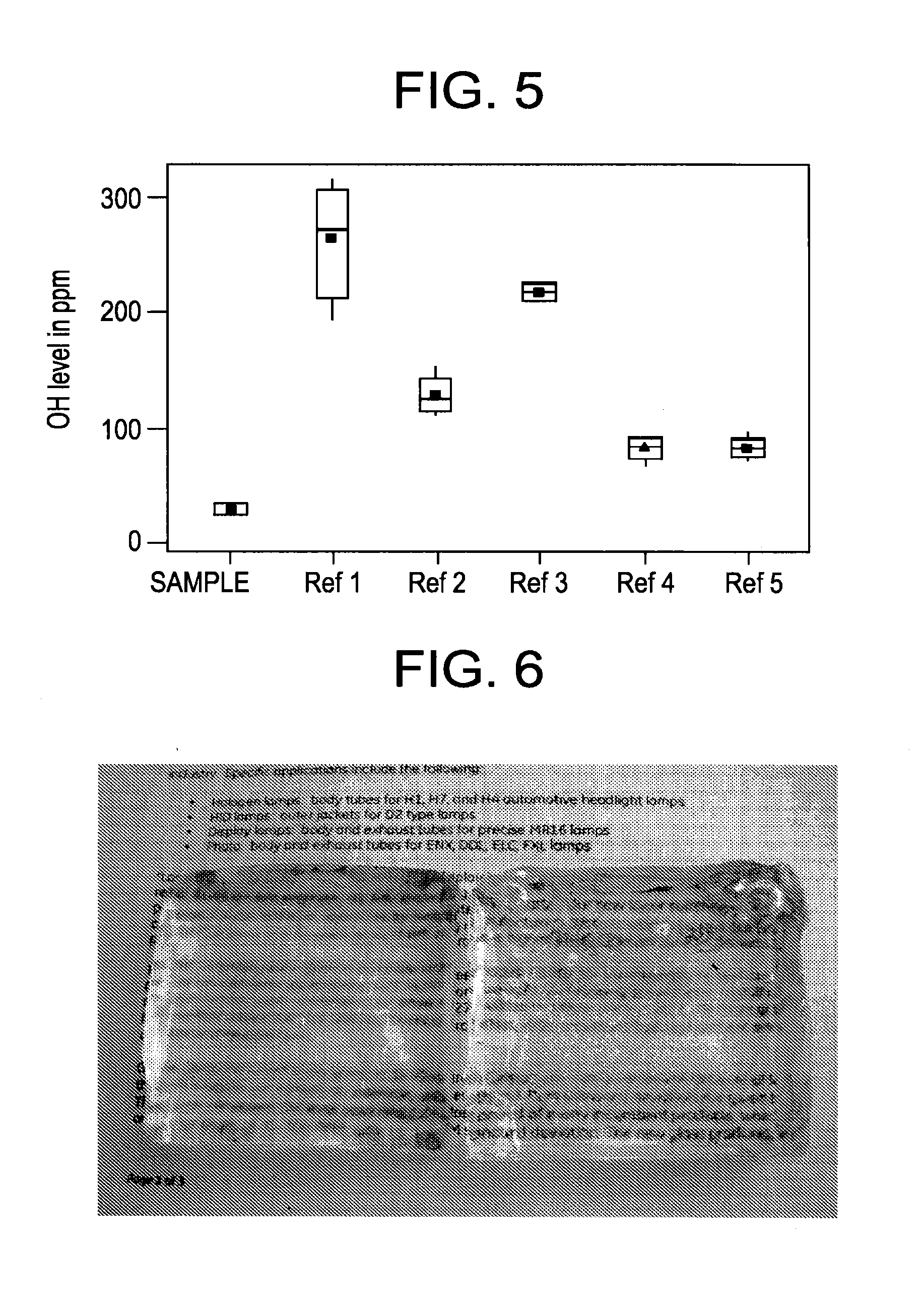
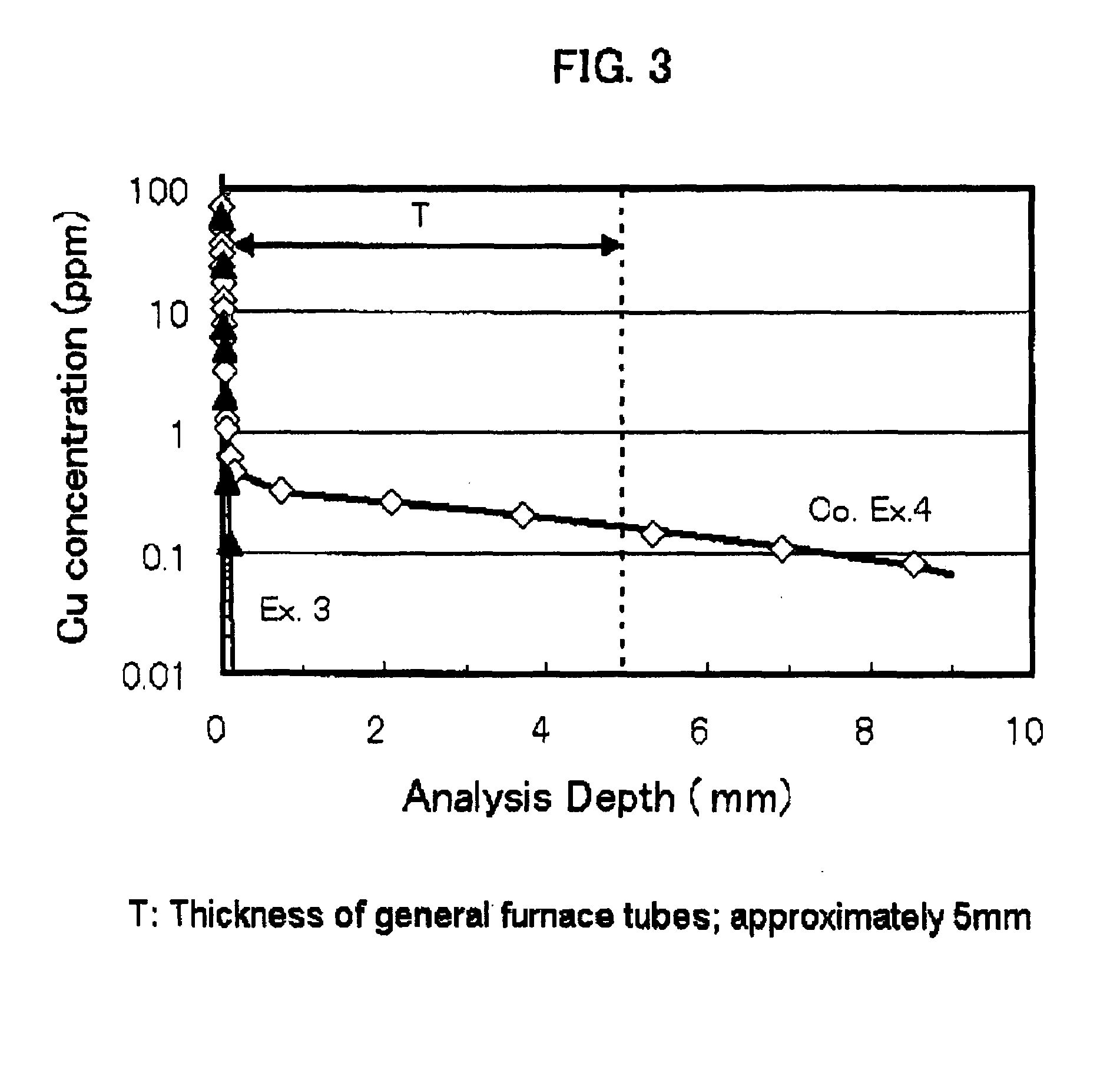
ActiveUS20100041538A1High transparencyReduce the probability of spreadingGlass shaping apparatusGlass tempering apparatusMetal impuritiesUltraviolet
Fused silica glass having an internal transmittance of UV with 245 nm wavelength, being at least 95% at 10 mm thickness, a OH content of not larger than 5 ppm, and a content of Li, Na, K, Mg, Ca and Cu each being smaller than 0.1 ppm. Preferably the glass has a viscosity coefficient at 1215° C. of at least 1011.5 Pa·s; and a Cu ion diffusion coefficient of not larger than 1×10−10 cm2 / sec in a depth range of greater than 20 μm up to 100 μm, from the surface, when leaving to stand at 1050° C. in air for 24 hours. The glass is made by crystobalitizing powdery silica raw material; then, fusing the crystobalitized silica material in a non-reducing atmosphere. The glass exhibits a high transmittance of ultraviolet, visible and infrared rays, has high purity and heat resistance, and exhibits a reduced diffusion rate of metal impurities, therefore, it is suitable for various optical goods, semiconductor-production apparatus members, and liquid crystal display production apparatus members.
Owner:TOSOH CORP +1
Composite combining silica thermal repairing material and preparation method thereof
The invention discloses a composite bonded silicious hot repair material, which belongs to the technical field of refractory materials. The repair material comprises the following compositions in percentage by weight: 45 to 55 percent of silicious clinker aggregate, 8 to 12 percent of silicious clinker powder, 20 to 30 percent of natural silica powder, 8 to 12 percent of complex binder, 3 to 5 percent of plasticizer, and 1 to 1.5 percent of dispersant. The silicious clinker aggregate and the silicious clinker powder are waste main crown silica bricks (SiO2 is more than or equal to 95 percent) and fused quartz tubes or fused quartz wedges (SiO2 is more than or equal to 98 percent), SiO2 is more than or equal to 96 percent in natural silica, the complex binder is formed by compounding an SiO2 ceramic bond and a phosphorous acid (phosphate) chemical bond, the plasticizer is white clay or bentonite, and the dispersant is silica fume. The repair material is processed according to the particle size. The invention can satisfy various conditions proposed by hot repair of a kiln to the repair material, can also realize the aims of saving energy sources and increasing the service life of the kiln, and can also be used for filling or building positions which are not suitable for silica brick masonry during the cold repair at the same time.
Owner:山西高科耐火材料股份有限公司
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com