Patents
Literature
2696results about "Laser surgery" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
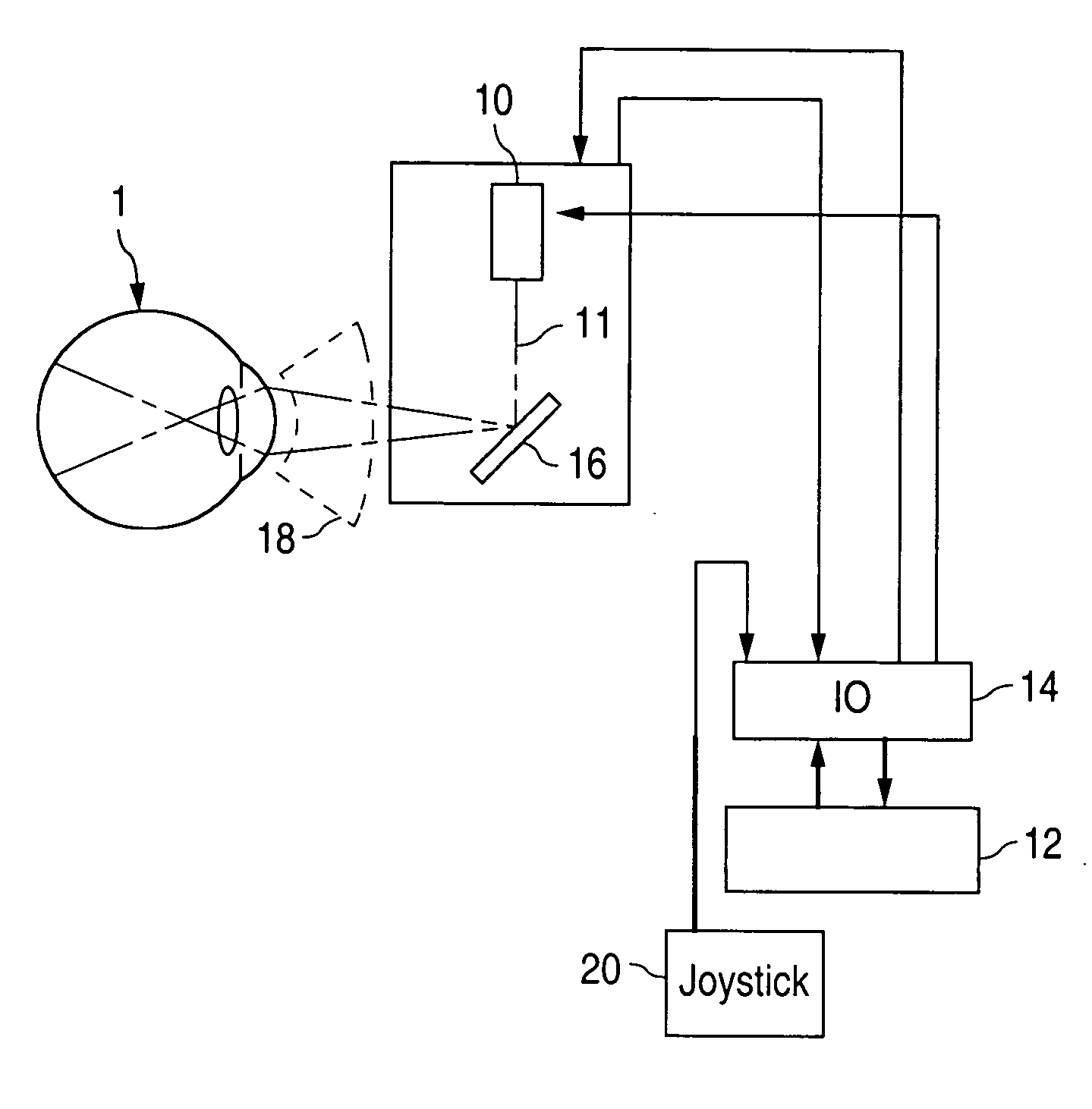
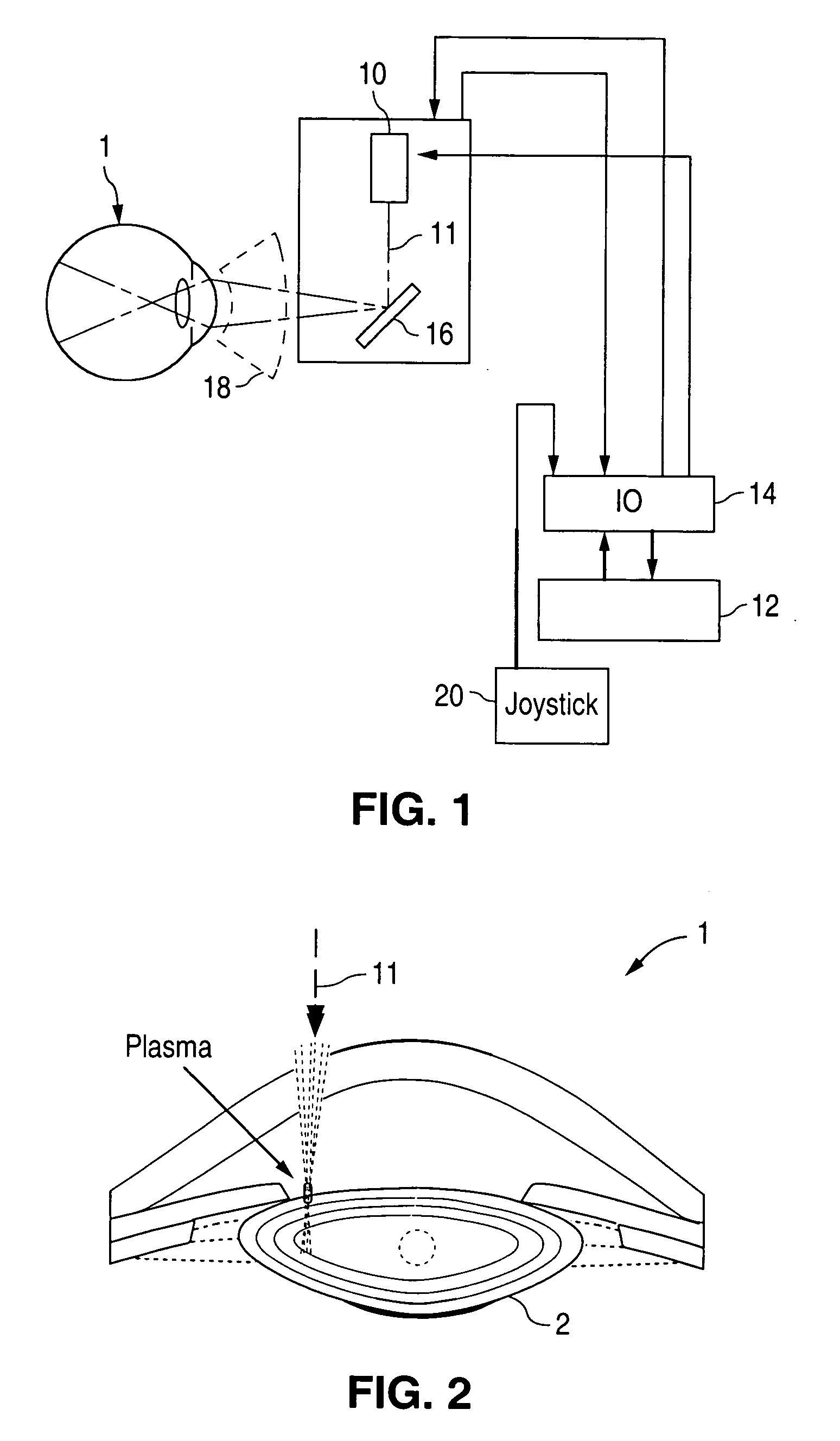
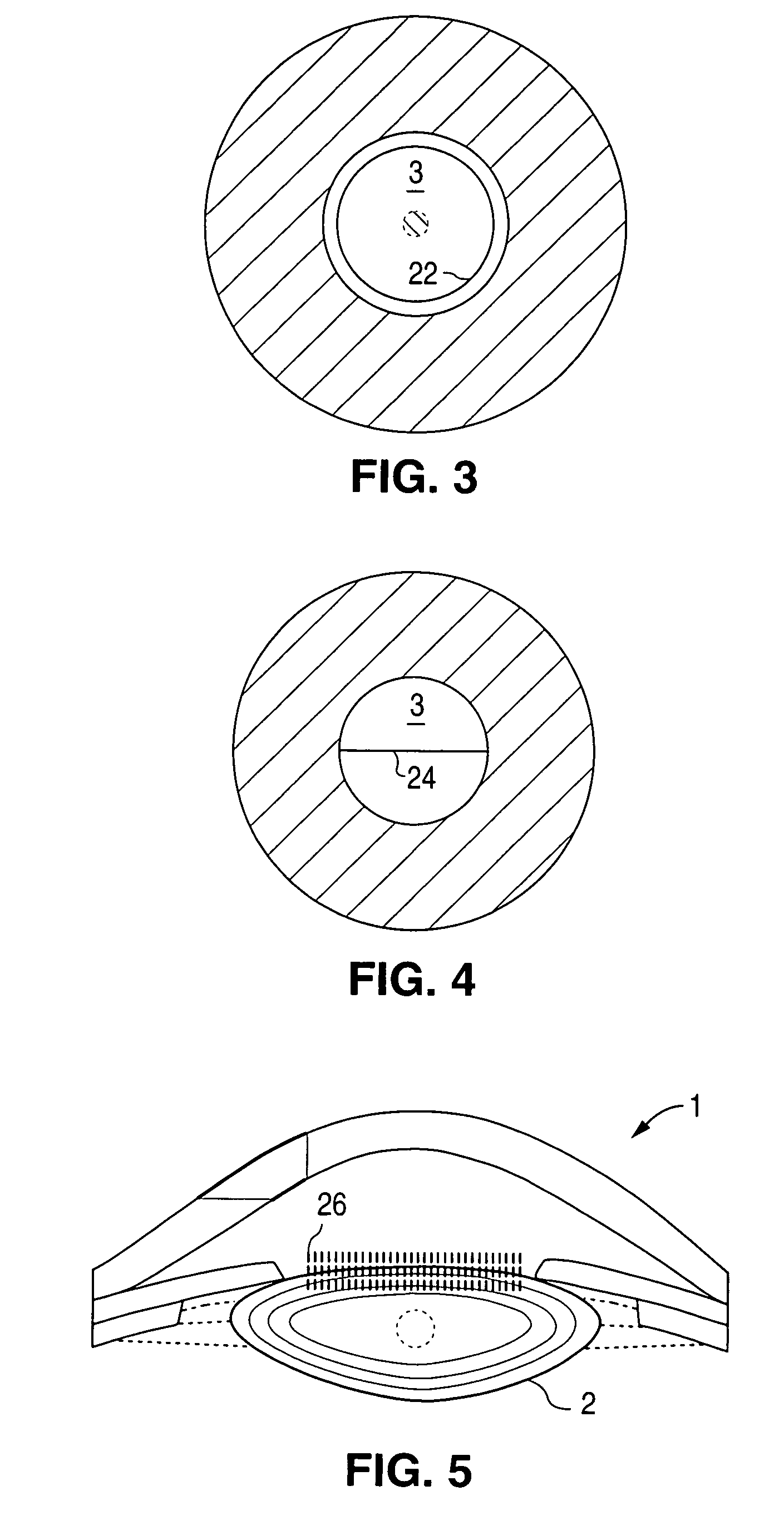
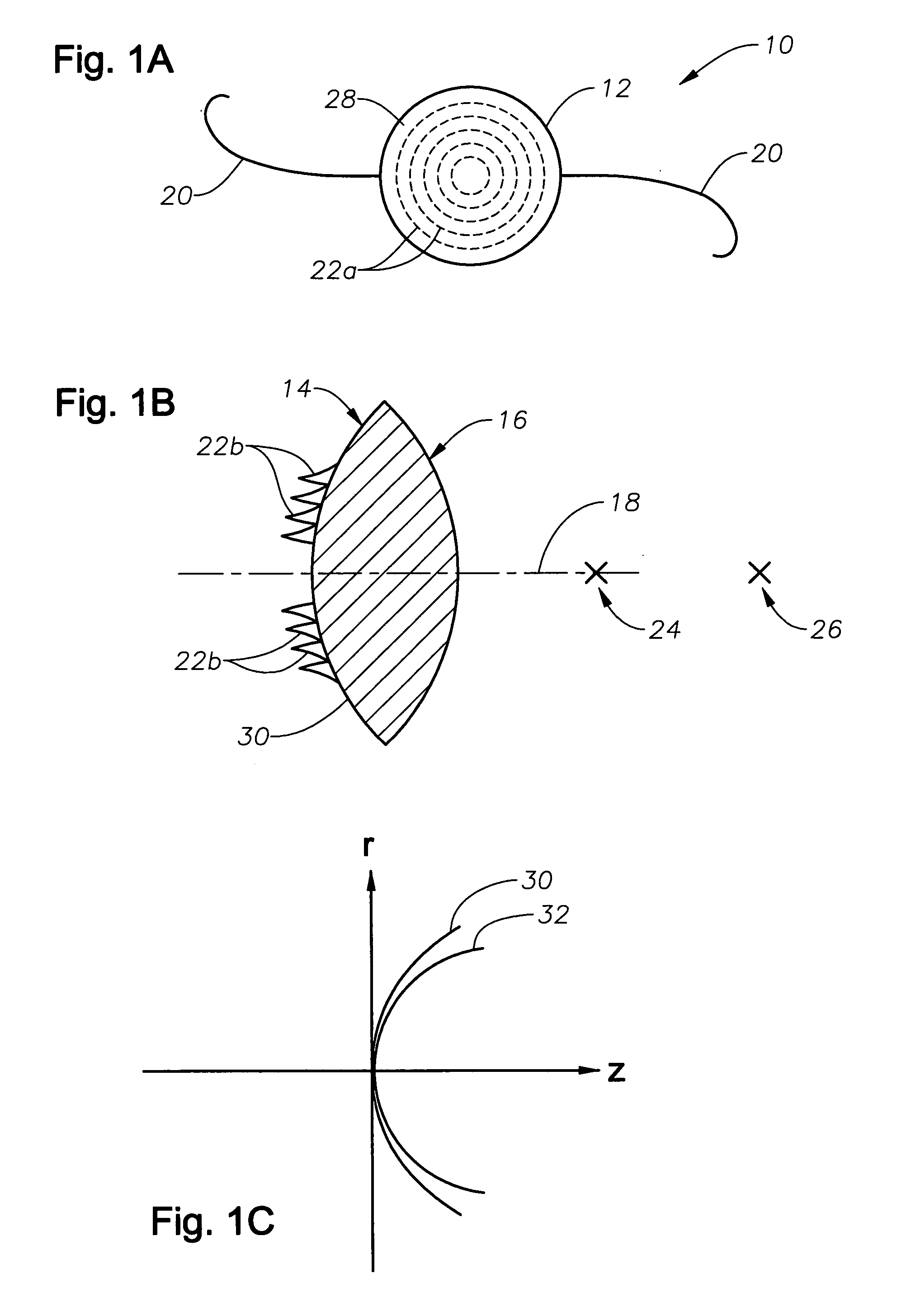
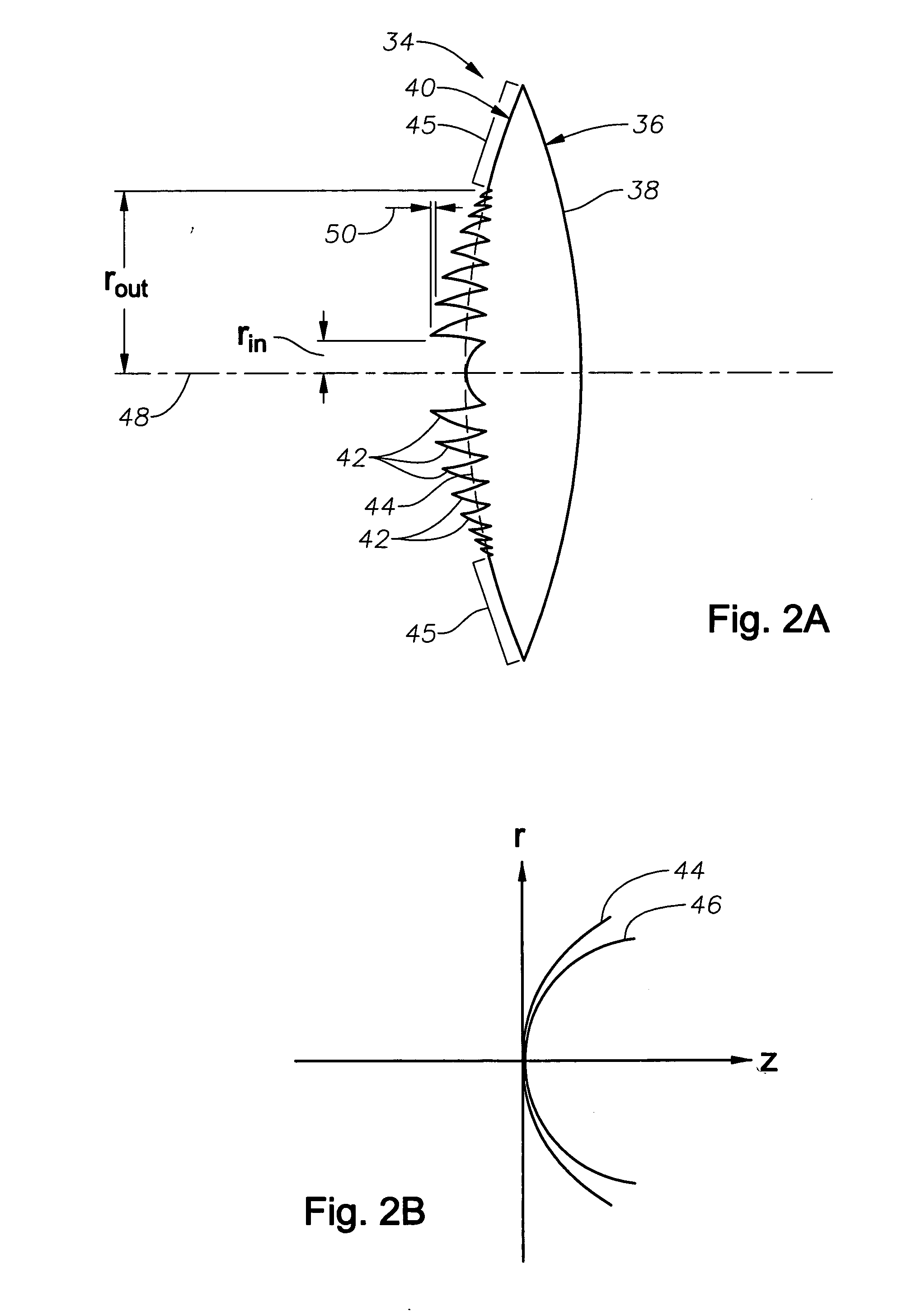
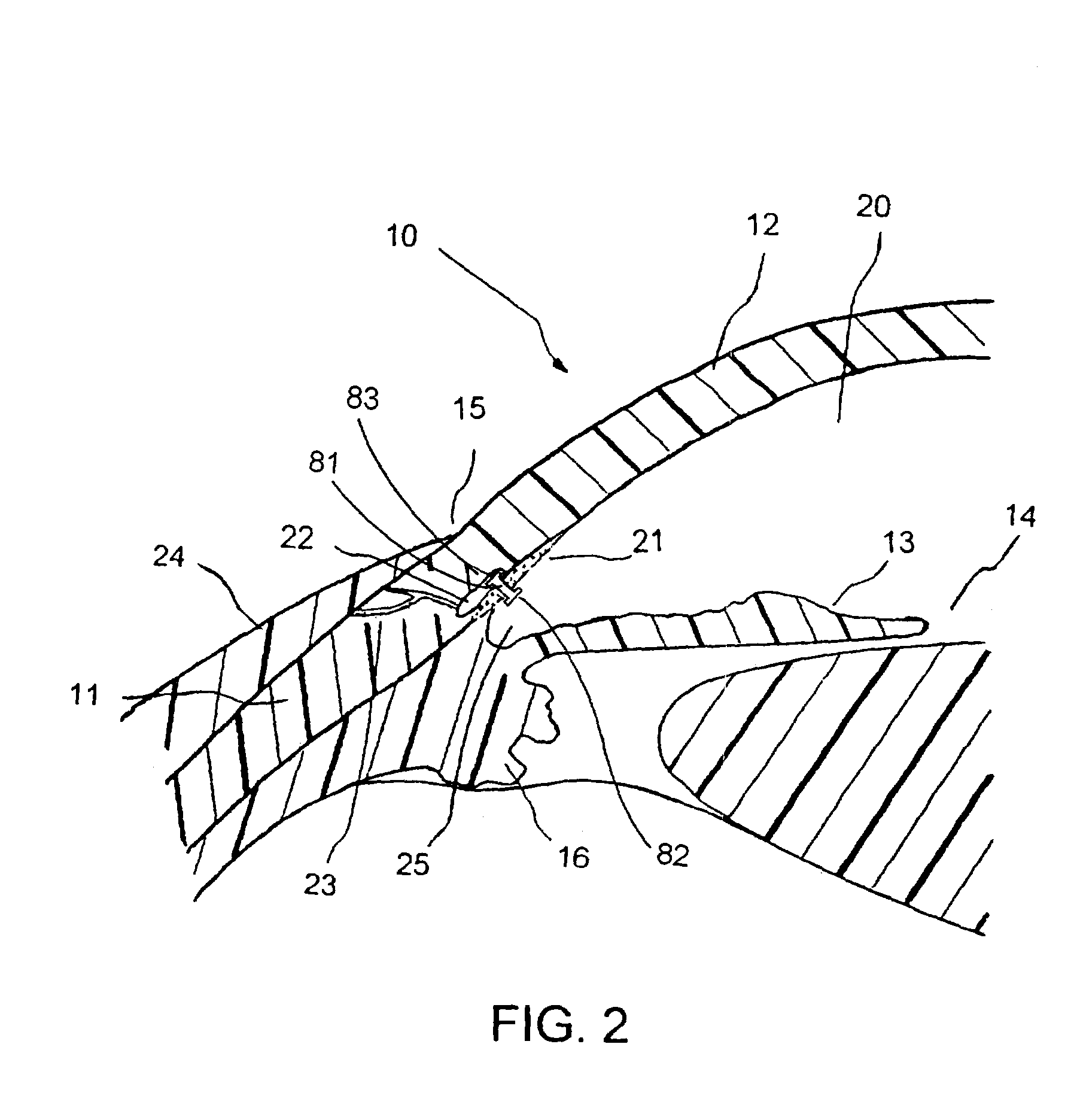
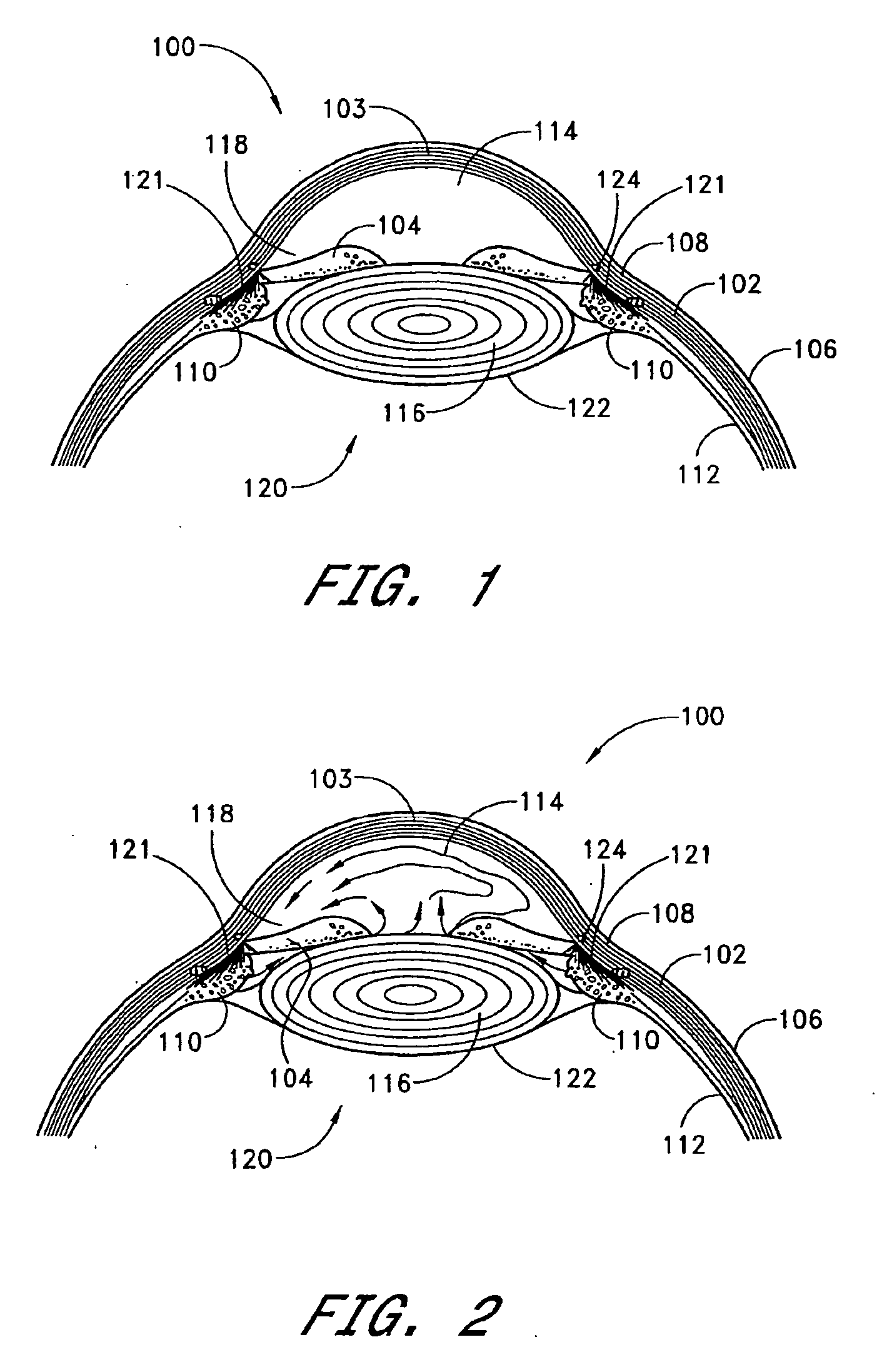
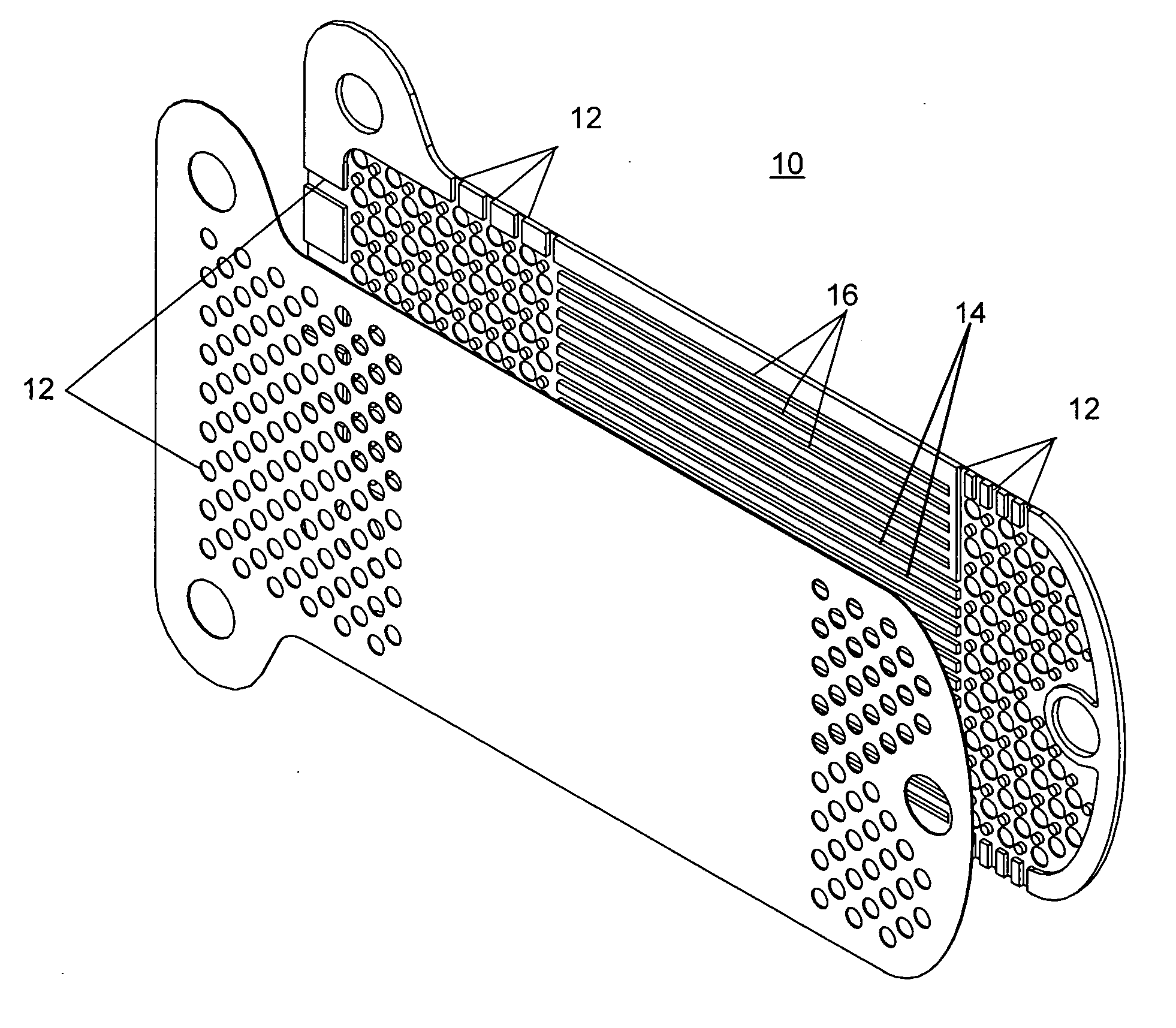
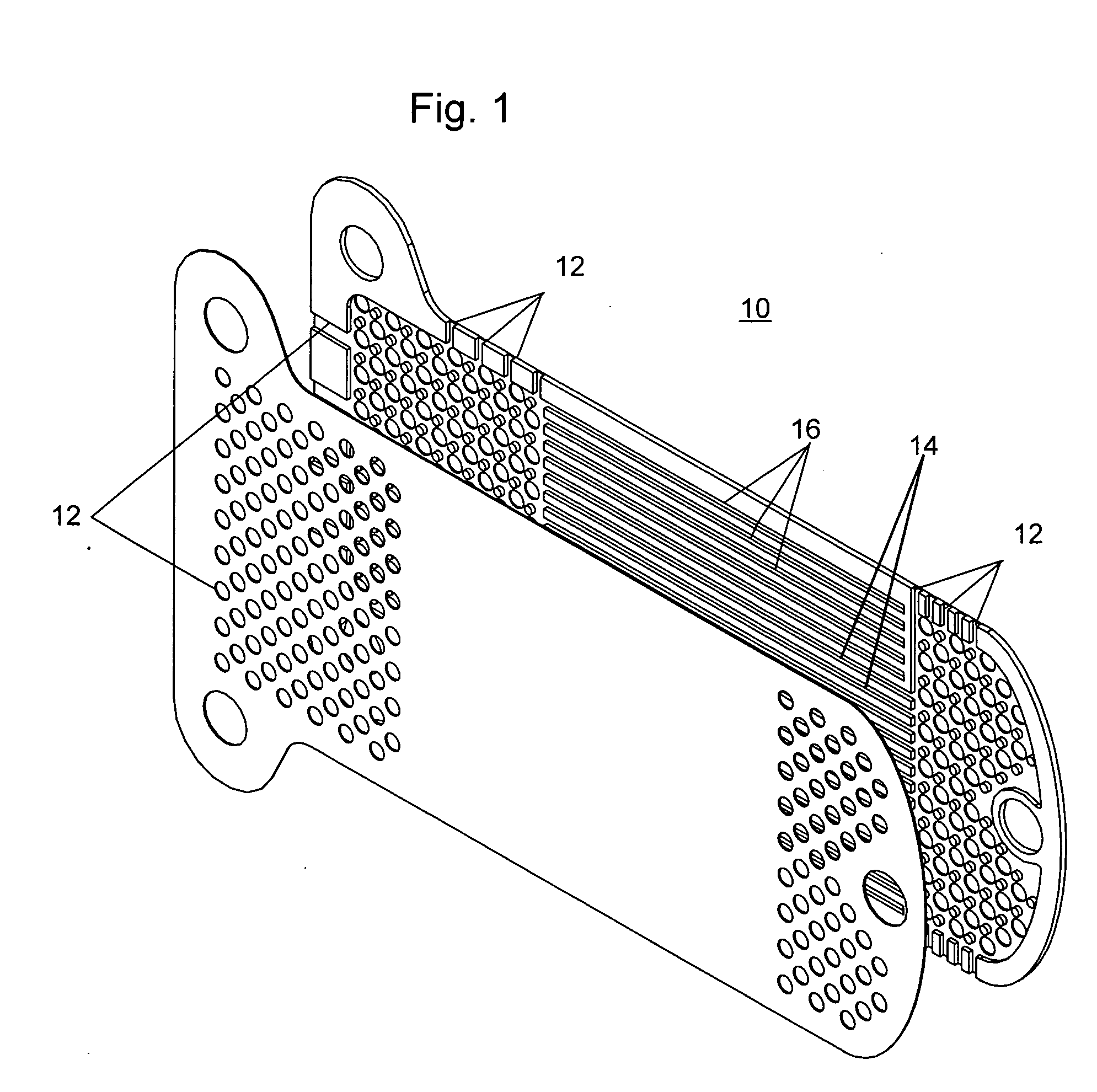
Method and apparatus for patterned plasma-mediated laser trephination of the lens capsule and three dimensional phaco-segmentation
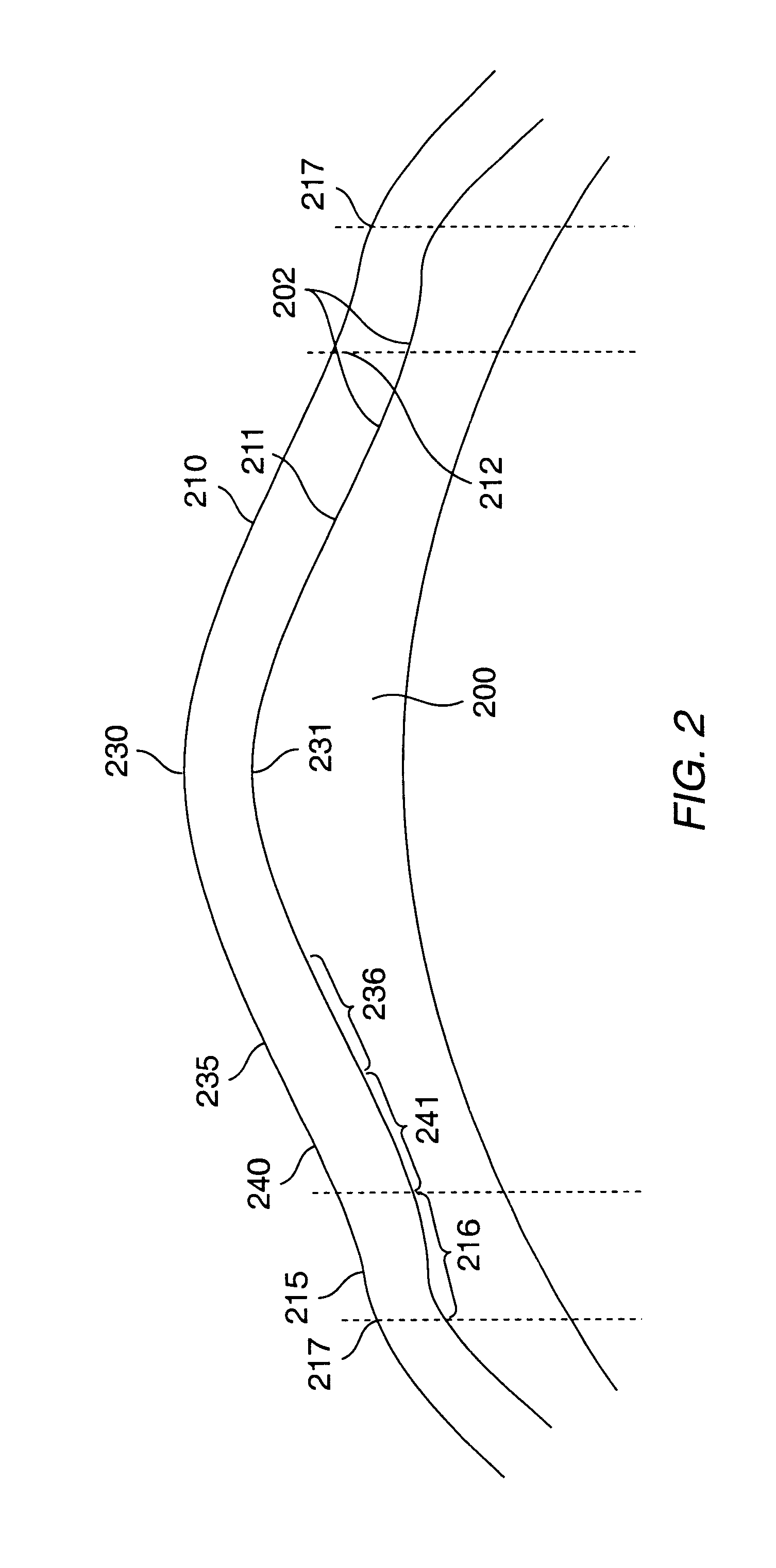
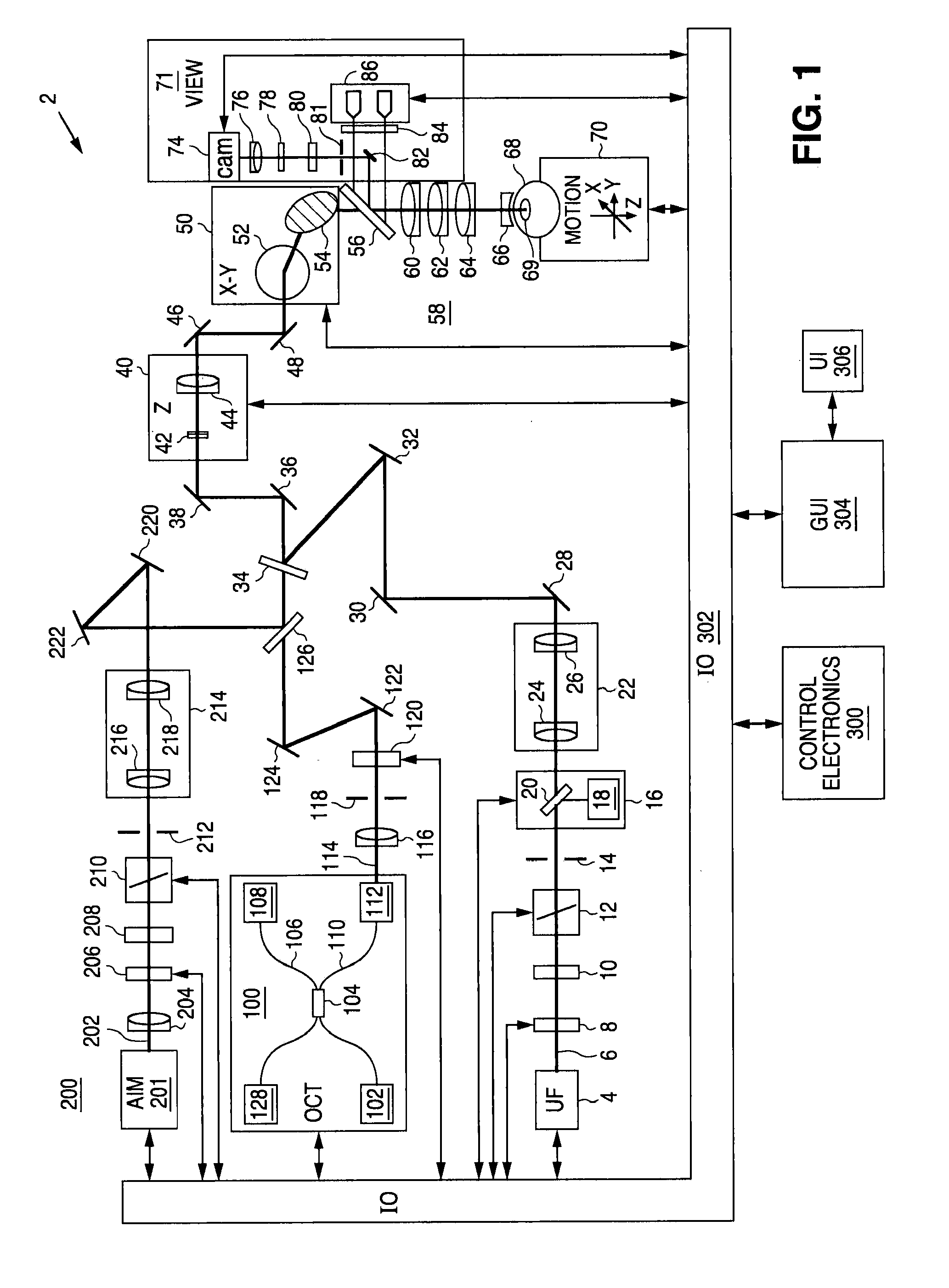
System and method for making incisions in eye tissue at different depths. The system and method focuses light, possibly in a pattern, at various focal points which are at various depths within the eye tissue. A segmented lens can be used to create multiple focal points simultaneously. Optimal incisions can be achieved by sequentially or simultaneously focusing lights at different depths, creating an expanded column of plasma, and creating a beam with an elongated waist.
Owner:AMO DEVMENT
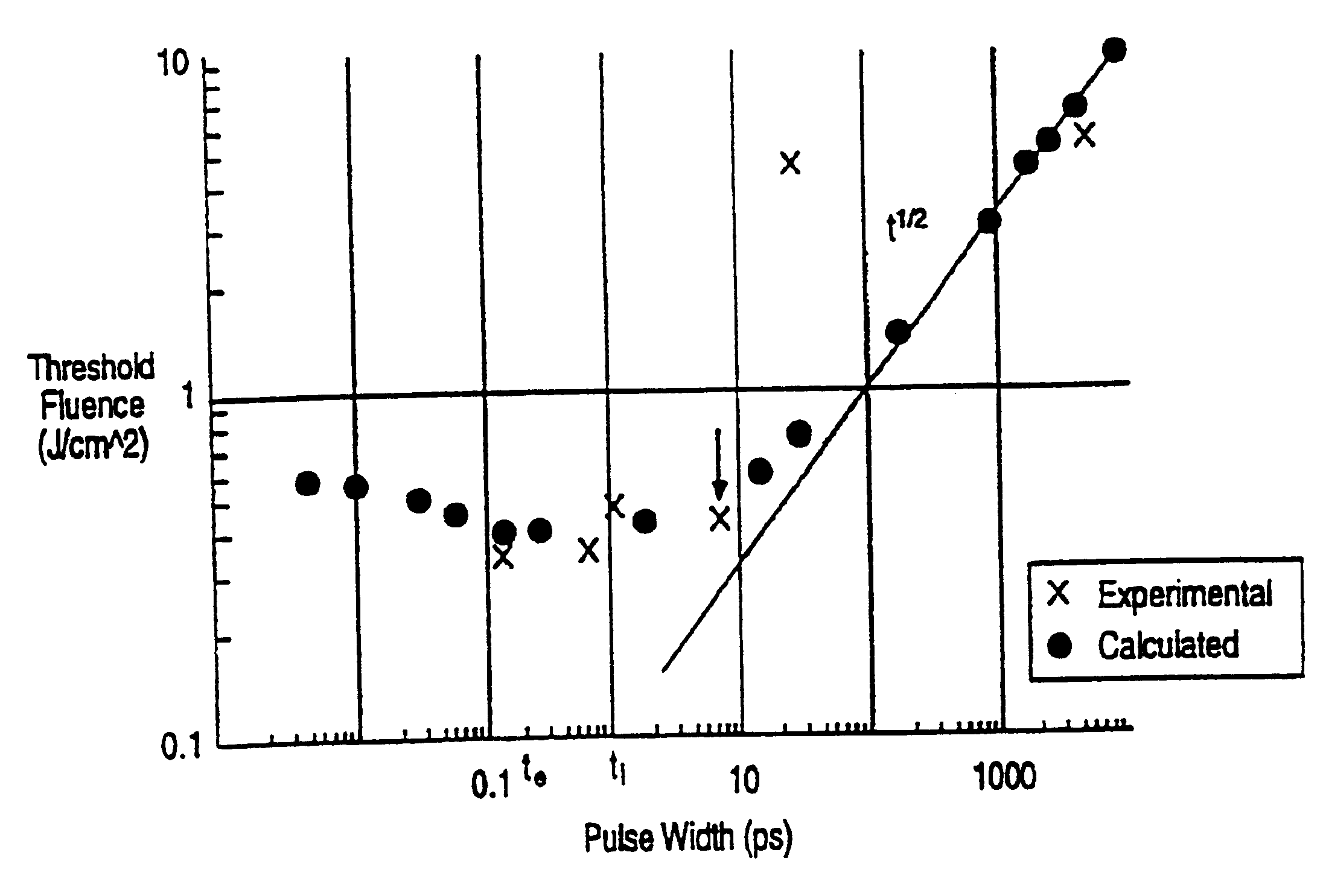
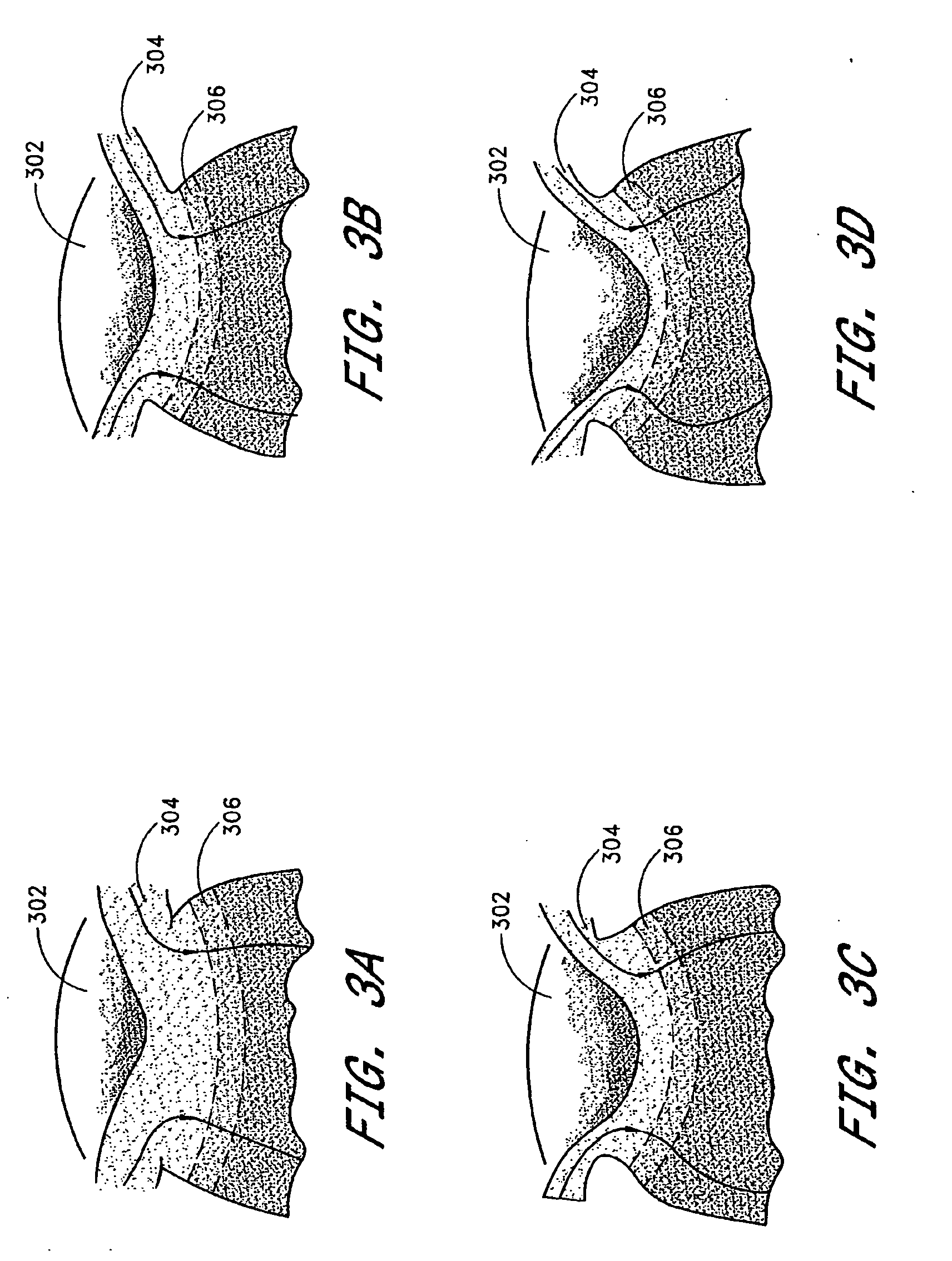
Method for controlling configuration of laser induced breakdown and ablation
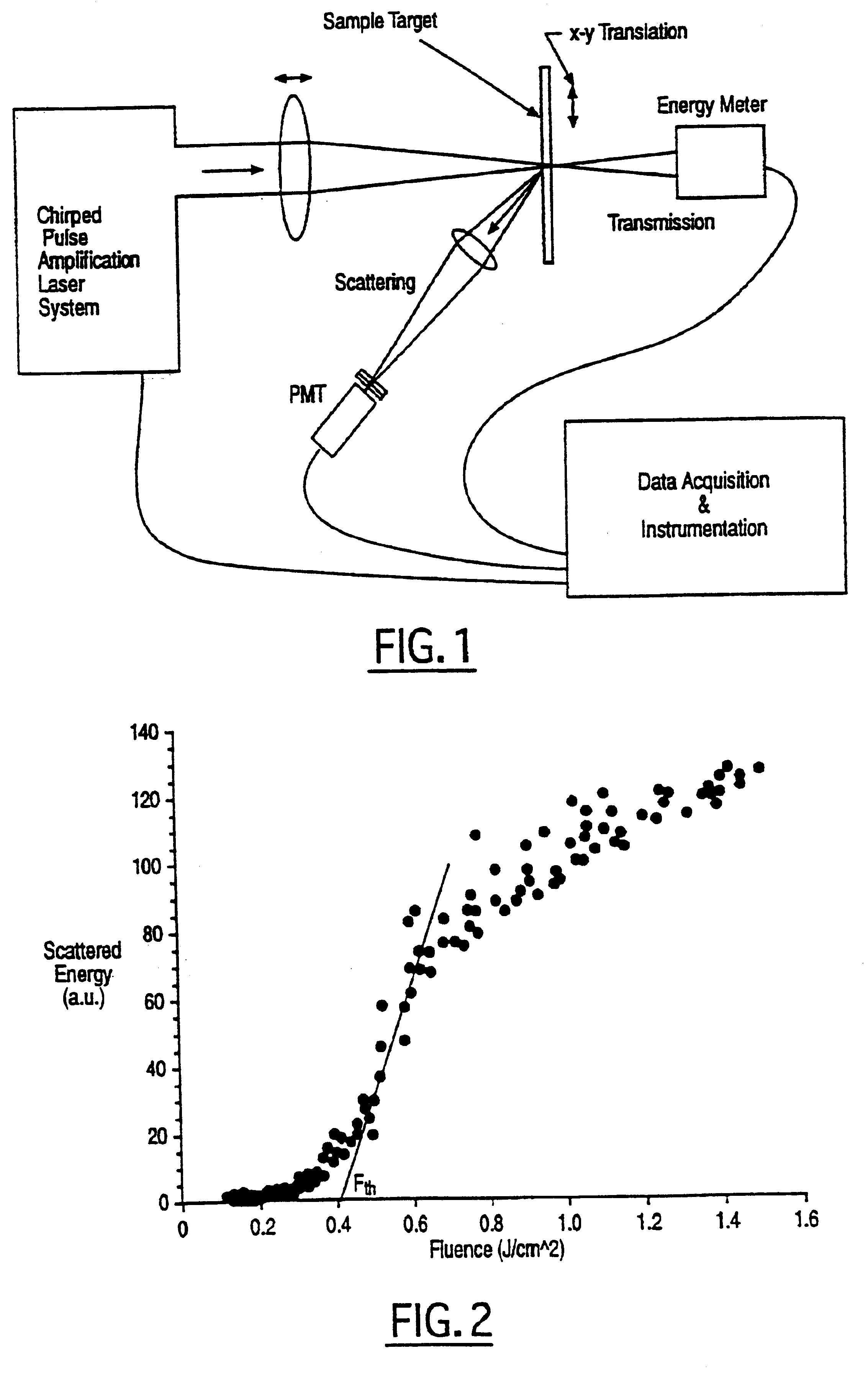
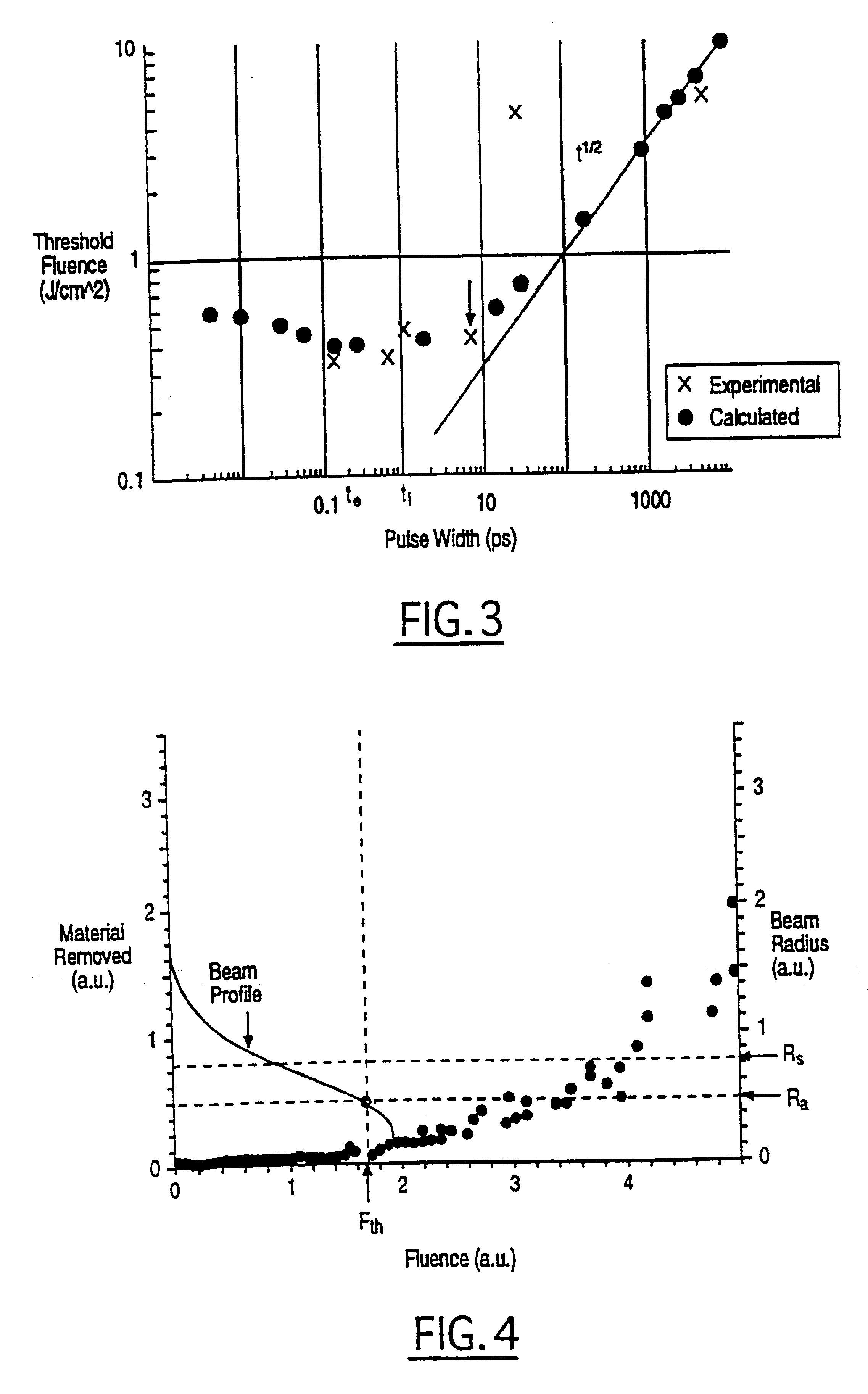
In one aspect the invention provides a method for laser induced breakdown of a material with a pulsed laser beam where the material is characterized by a relationship of fluence breakdown threshold (Fth) versus laser beam pulse width (T) that exhibits an abrupt, rapid, and distinct change or at least a clearly detectable and distinct change in slope at a predetermined laser pulse width value. The method comprises generating a beam of laser pulses in which each pulse has a pulse width equal to or less than the predetermined laser pulse width value. The beam is focused to a point at or beneath the surface of a material where laser induced breakdown is desired.The beam may be used in combination with a mask in the beam path. The beam or mask may be moved in the x, y, and Z directions to produce desired features. The technique can produce features smaller than the spot size and Rayleigh range due to enhanced damage threshold accuracy in the short pulse regime.
Owner:AMO DEVMENT
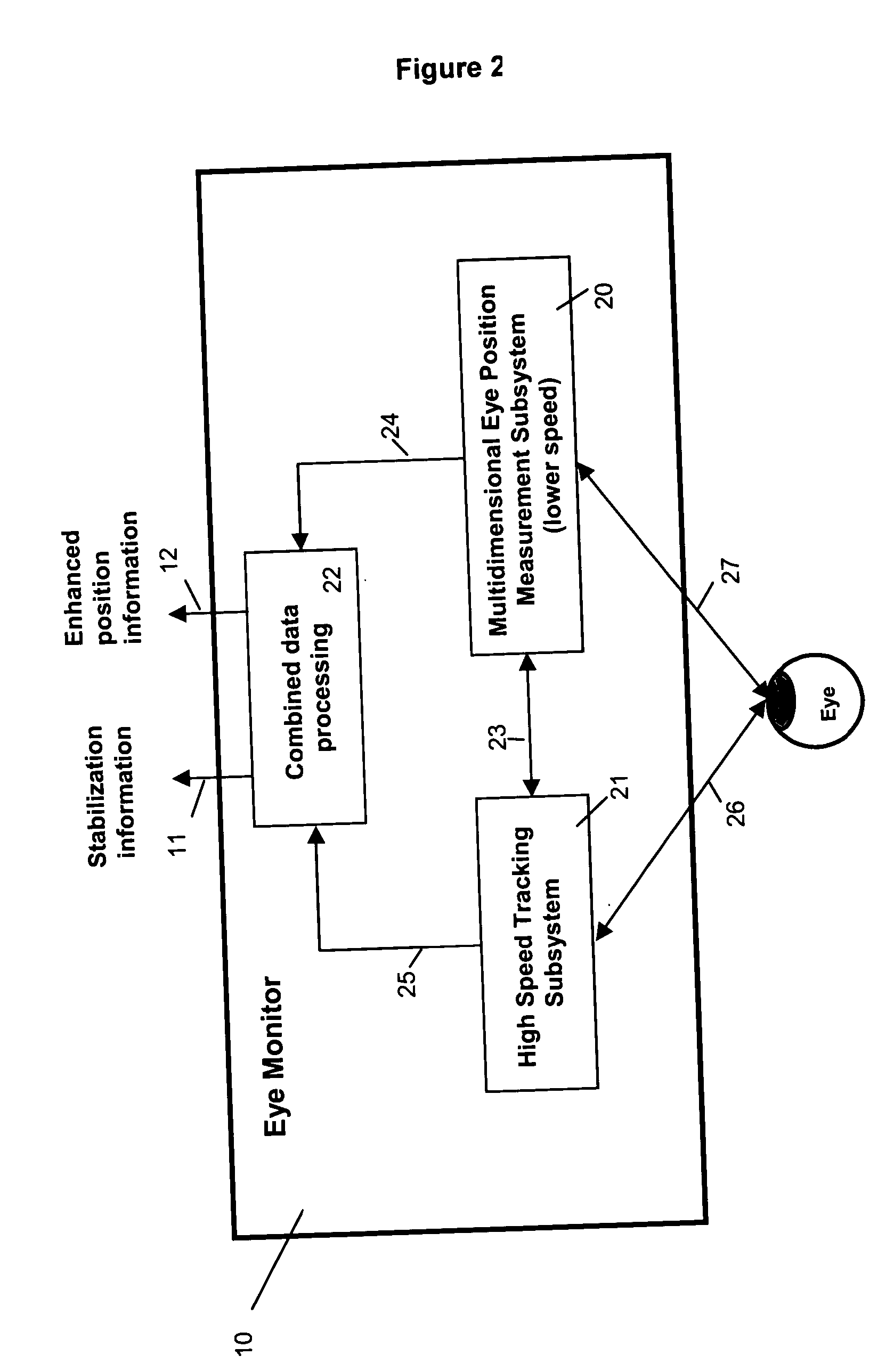
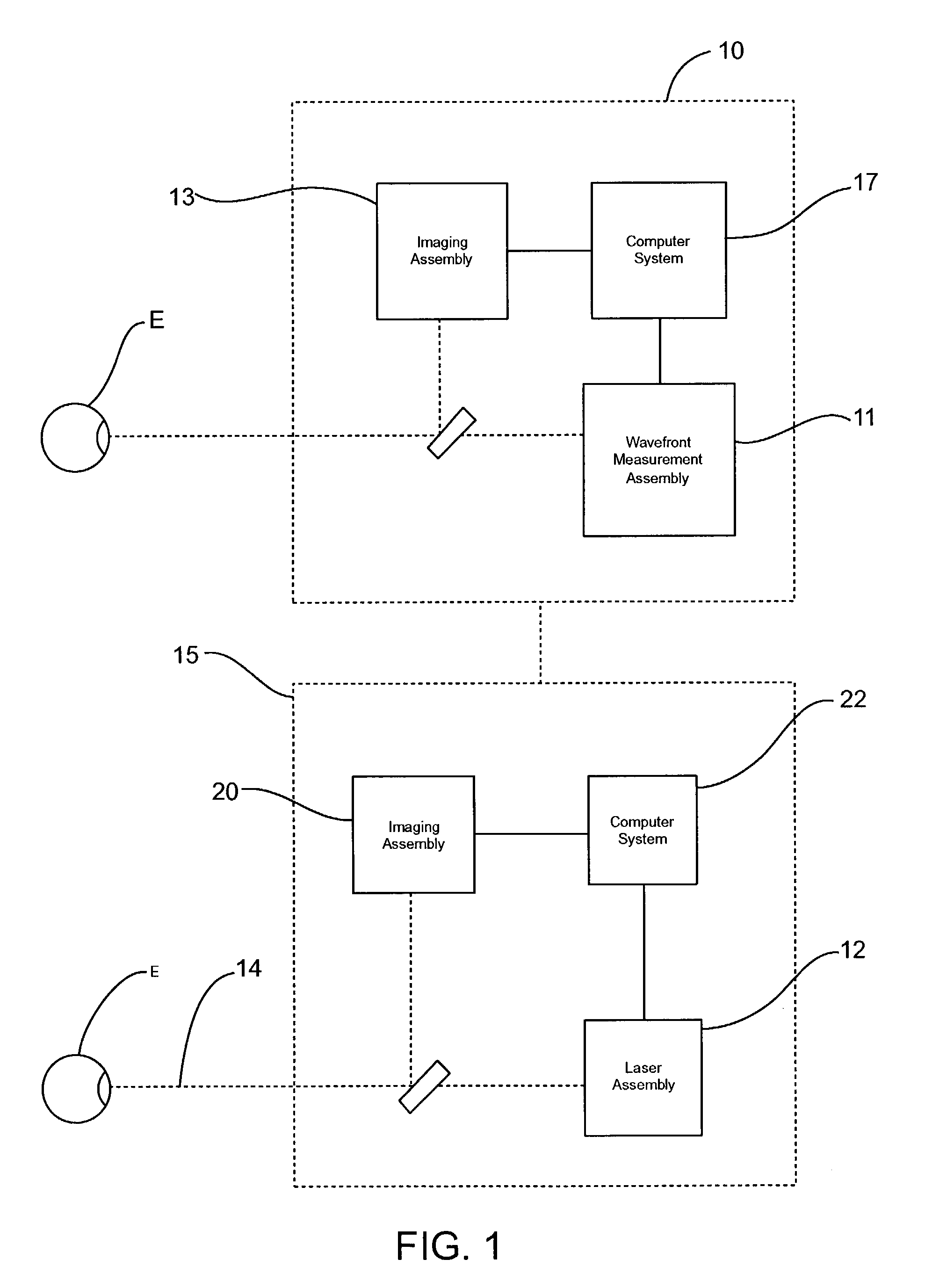
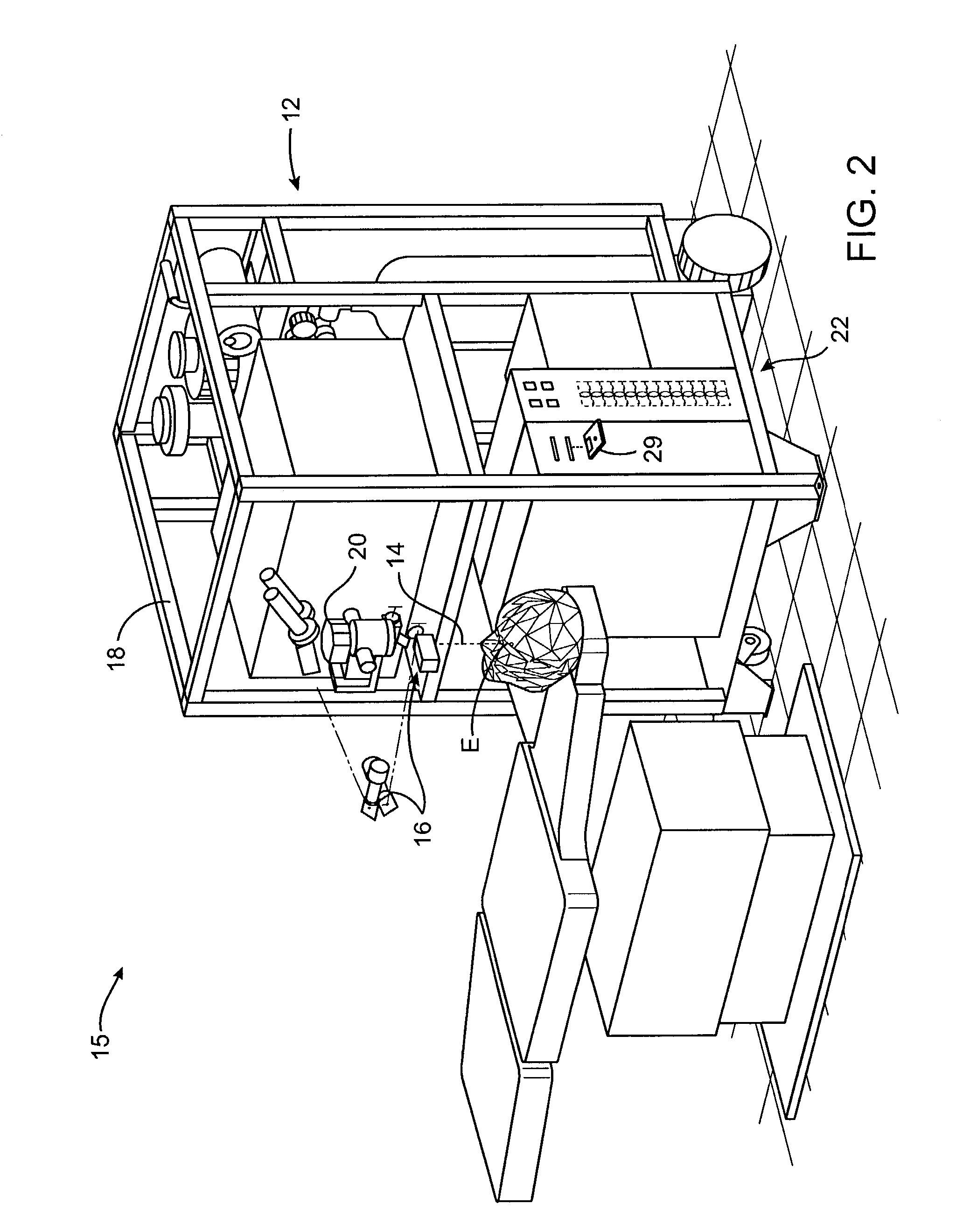
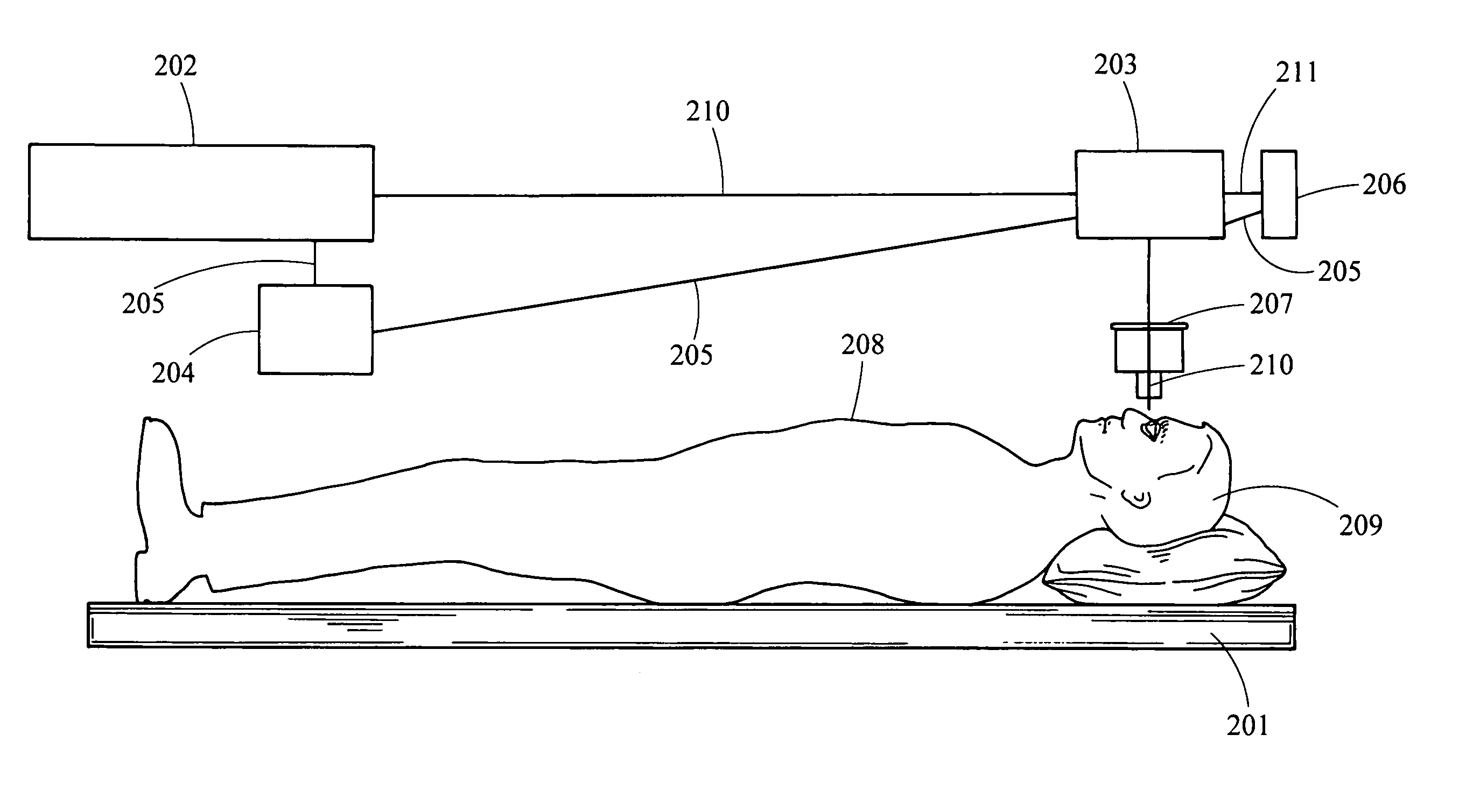
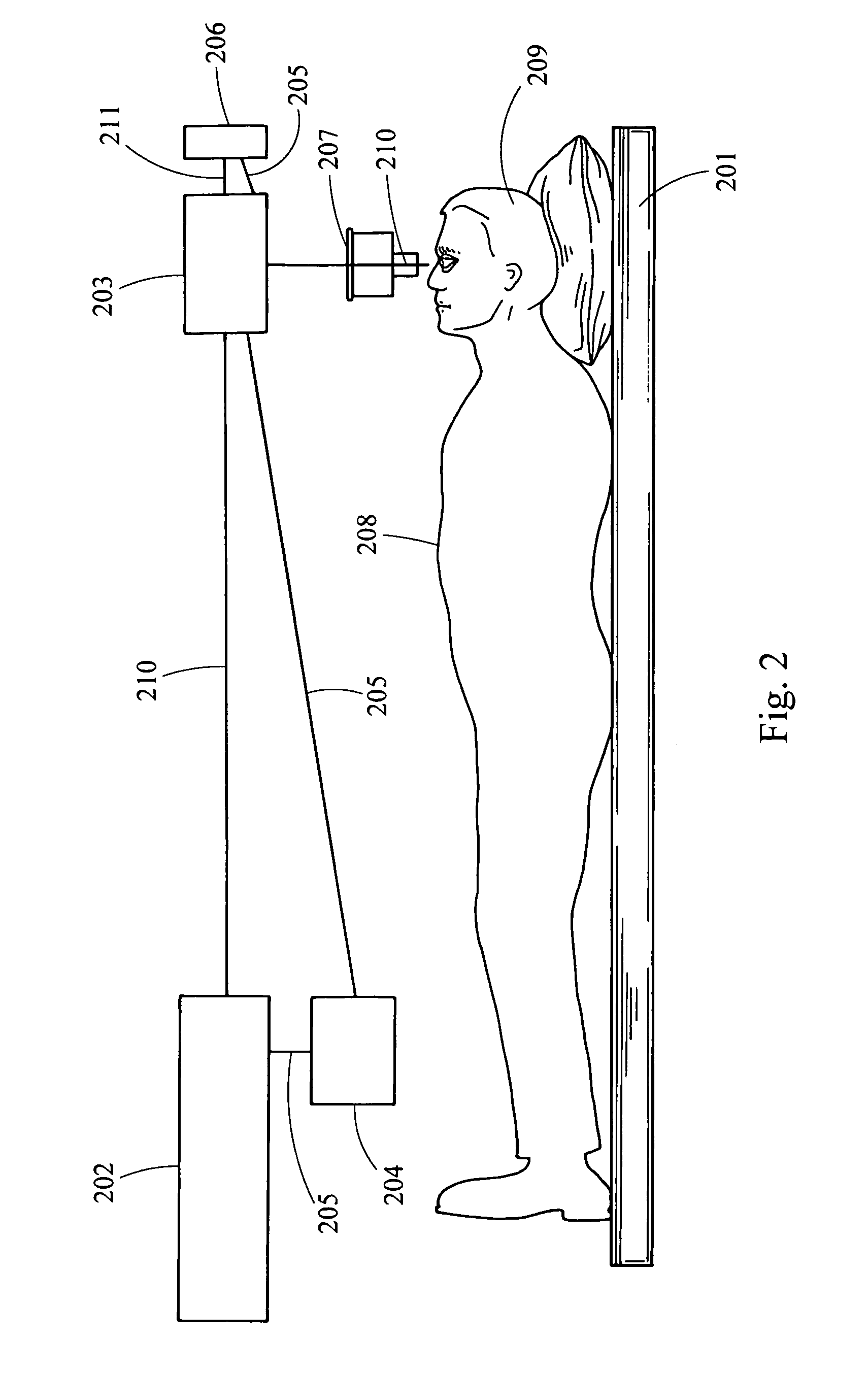
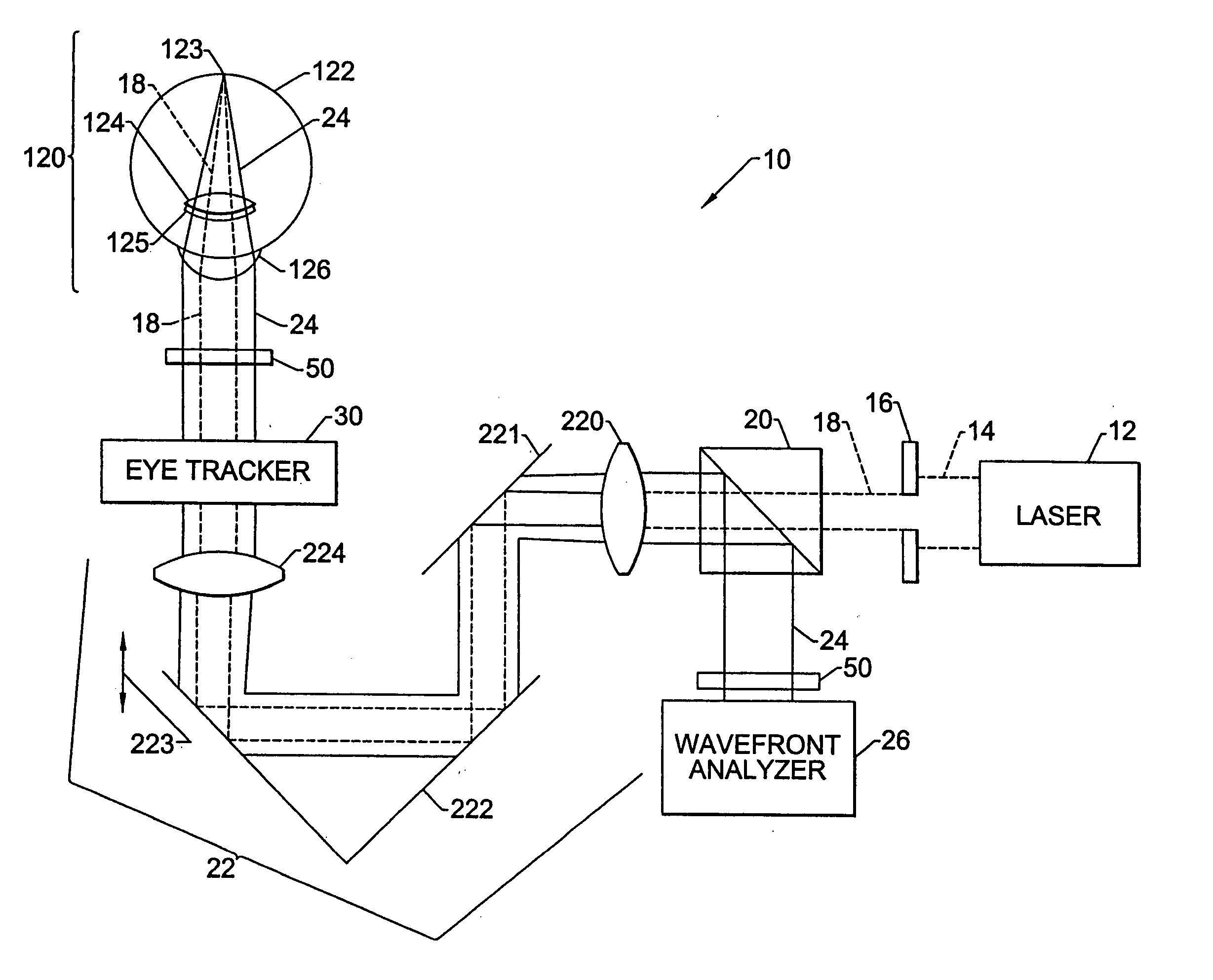
Multidimensional eye tracking and position measurement system for diagnosis and treatment of the eye
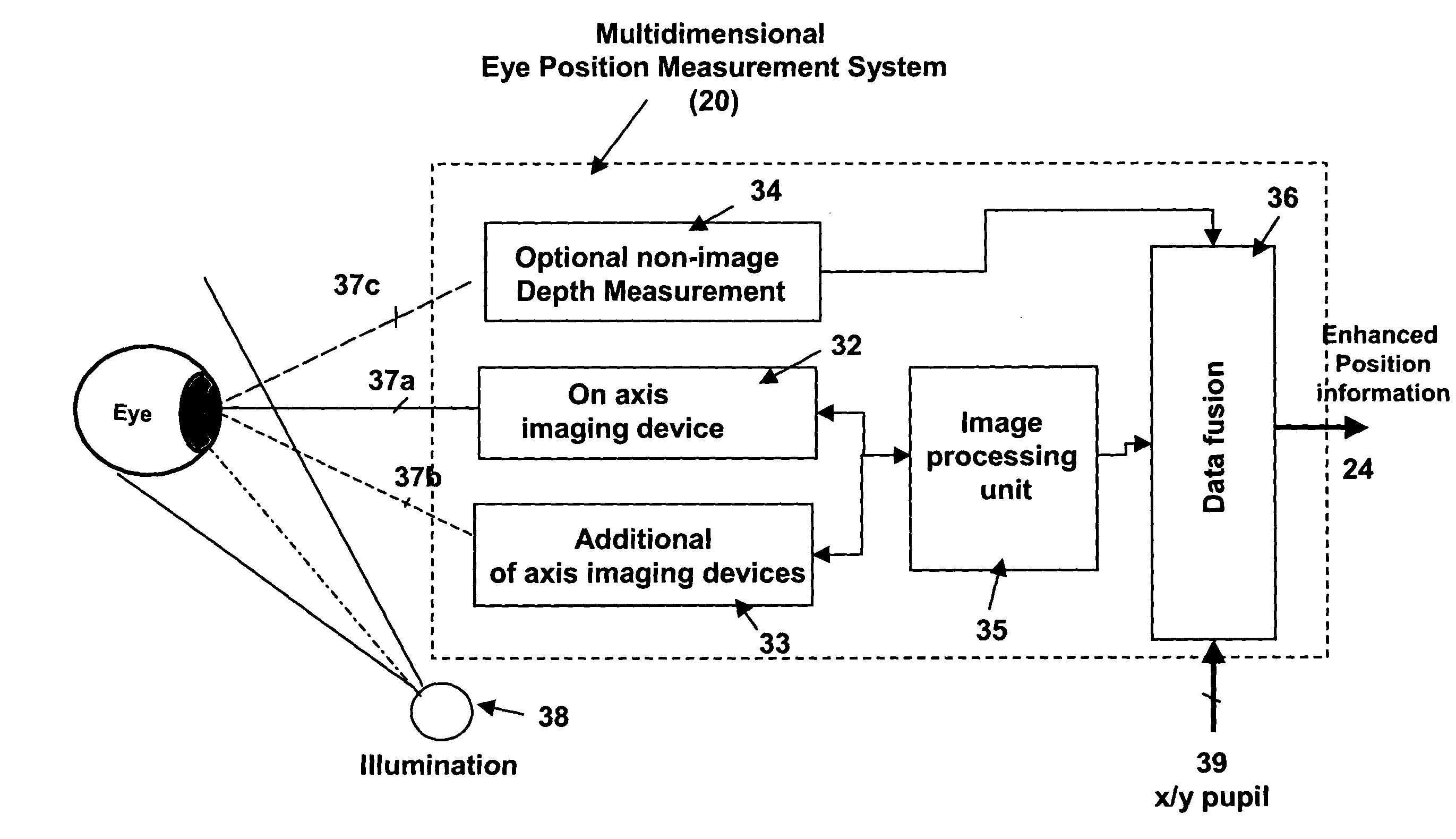
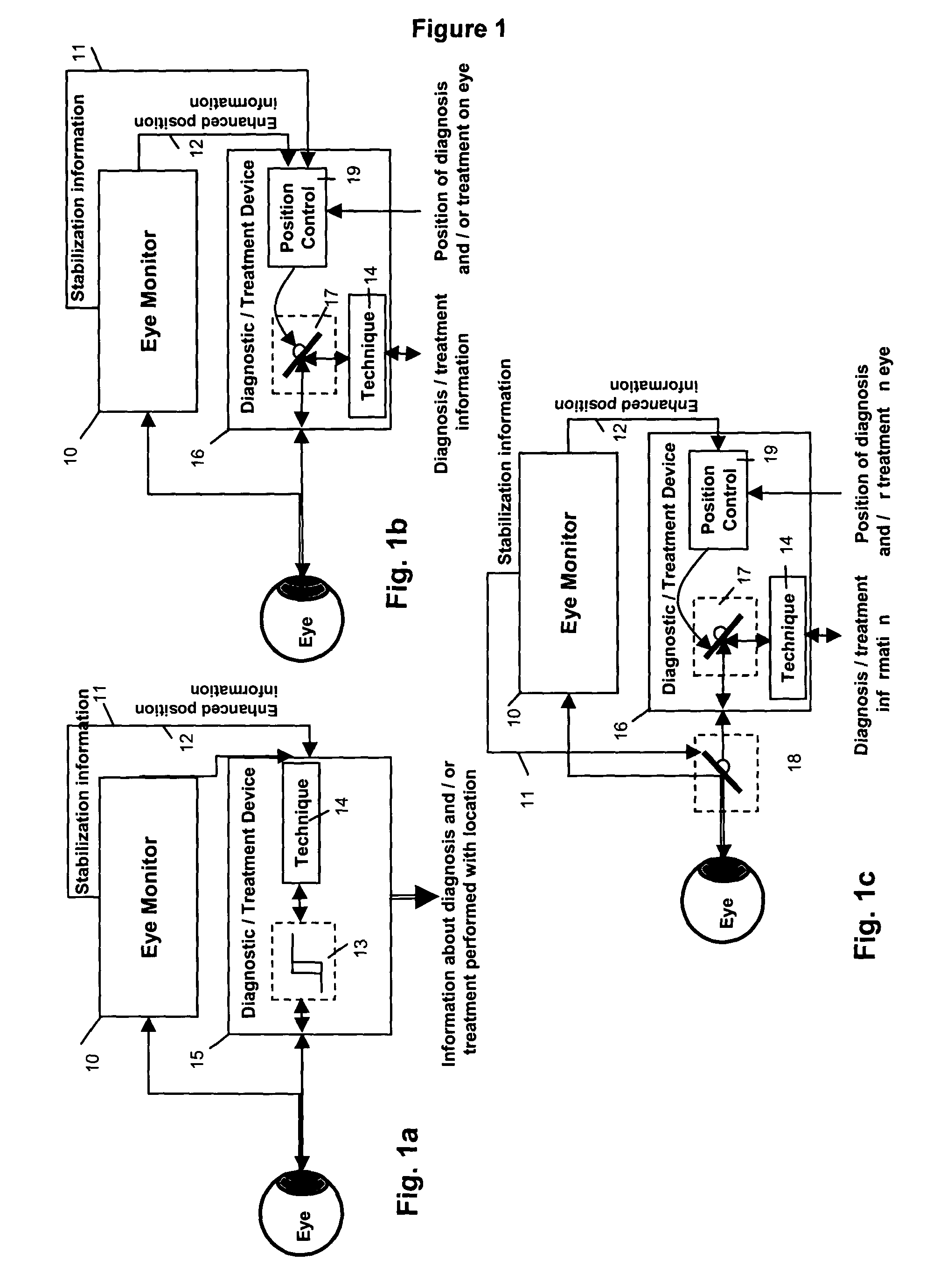
ActiveUS20050024586A1Improve spatial resolutionLess field of viewLaser surgeryCharacter and pattern recognitionMeasurement deviceSaccadic movements
The present invention relates to improved ophthalmic diagnostic measurement or treatment methods or devices, that make use of a combination of a high speed eye tracking device, measuring fast translation or saccadic motion of the eye, and an eye position measurement device, determining multiple dimensions of eye position or other components of eye, relative to an ophthalmic diagnostic or treatment instrument.
Owner:SENSOMOTORIC INSTR FUR INNOVATIVE SENSORIK MBH D B A SENSOMOTORIC INSTR
Drug delivery device
Drug delivery devices, and methods of delivering pharmaceutically active agents to a target tissue within a body using such devices, are disclosed. One drug delivery device includes a body having an internal surface for placement proximate a target tissue and a well having an opening to the internal surface. An inner core comprising a pharmaceutically active agent is disposed in the well.
Owner:NOVARTIS AG
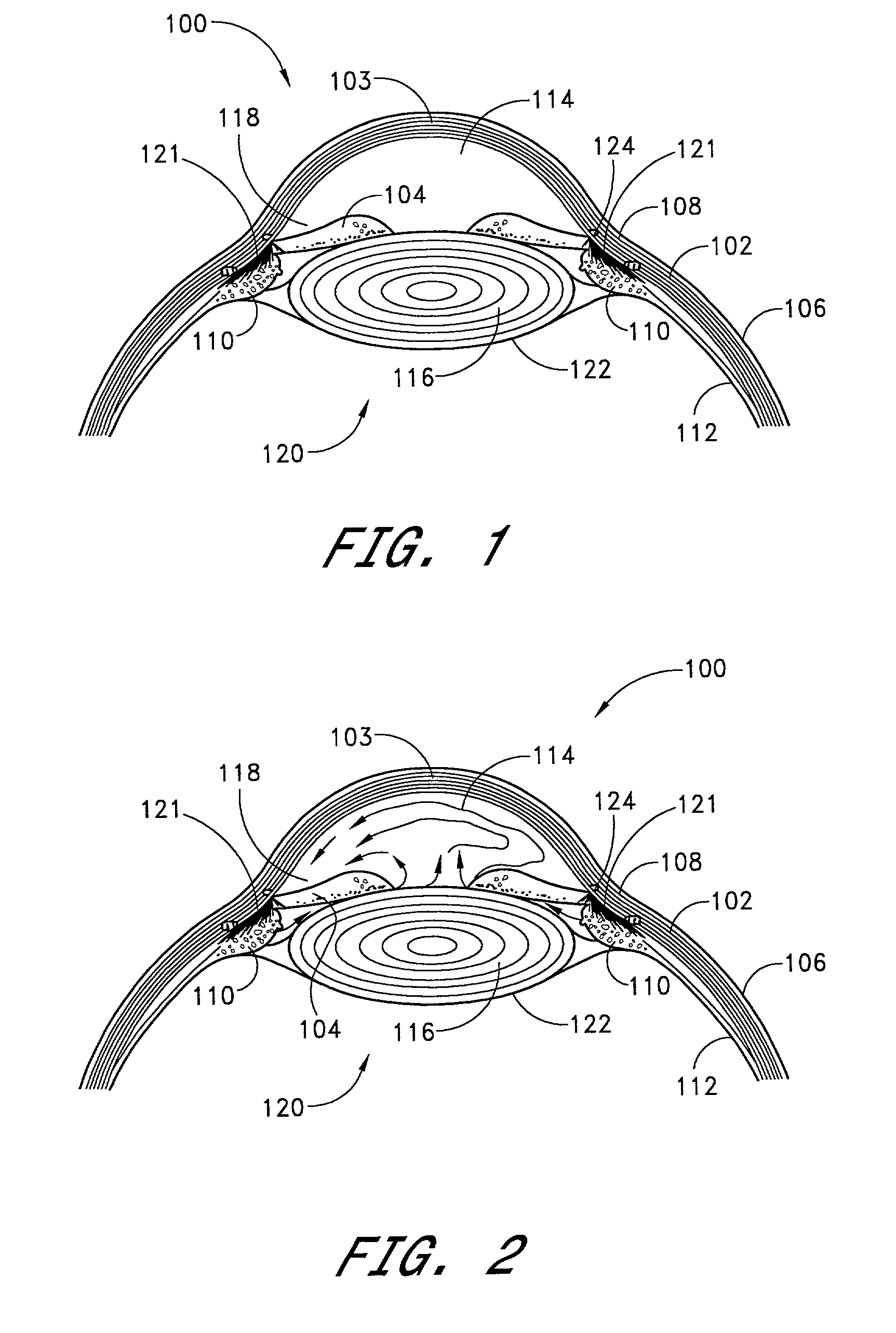
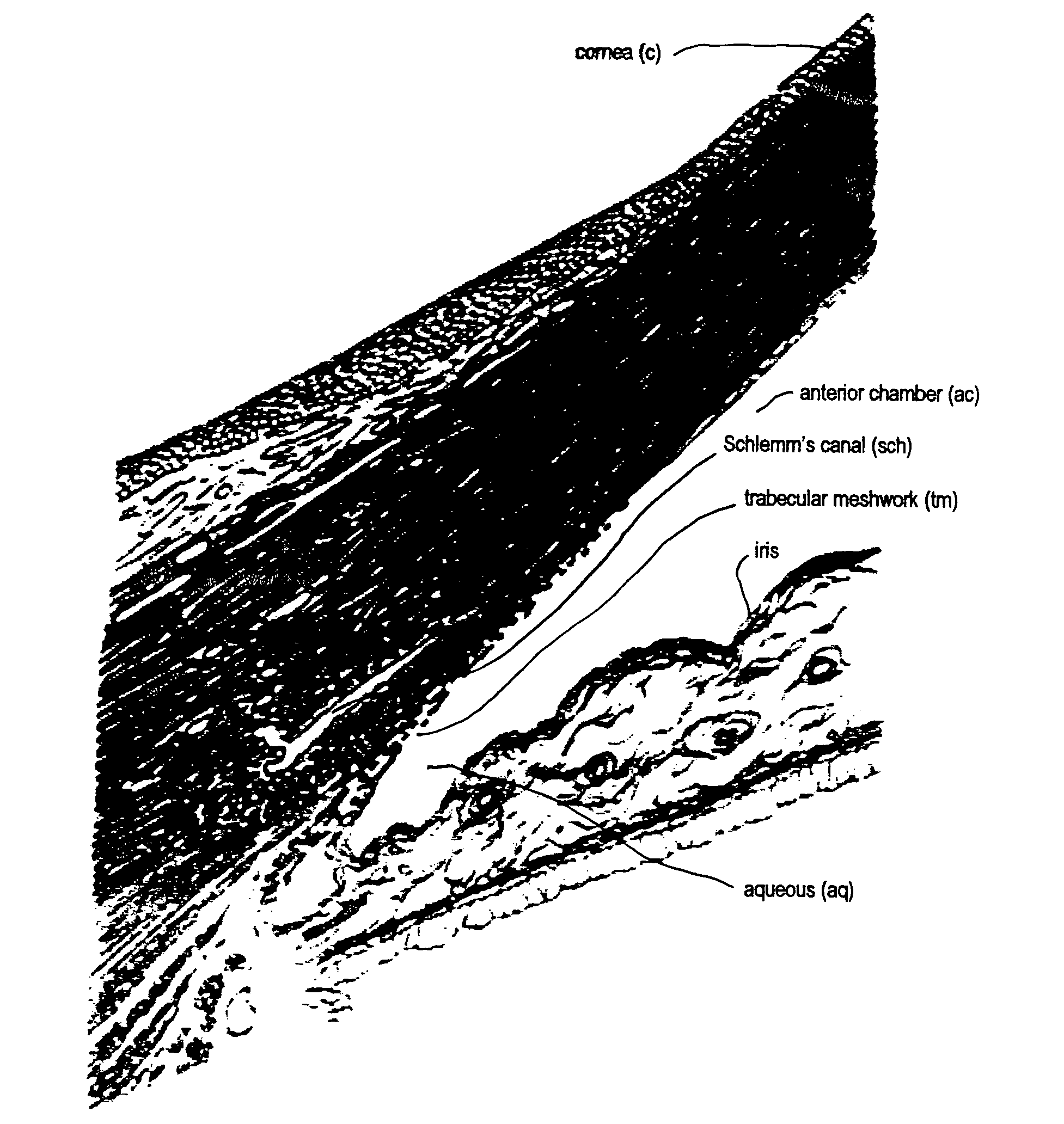
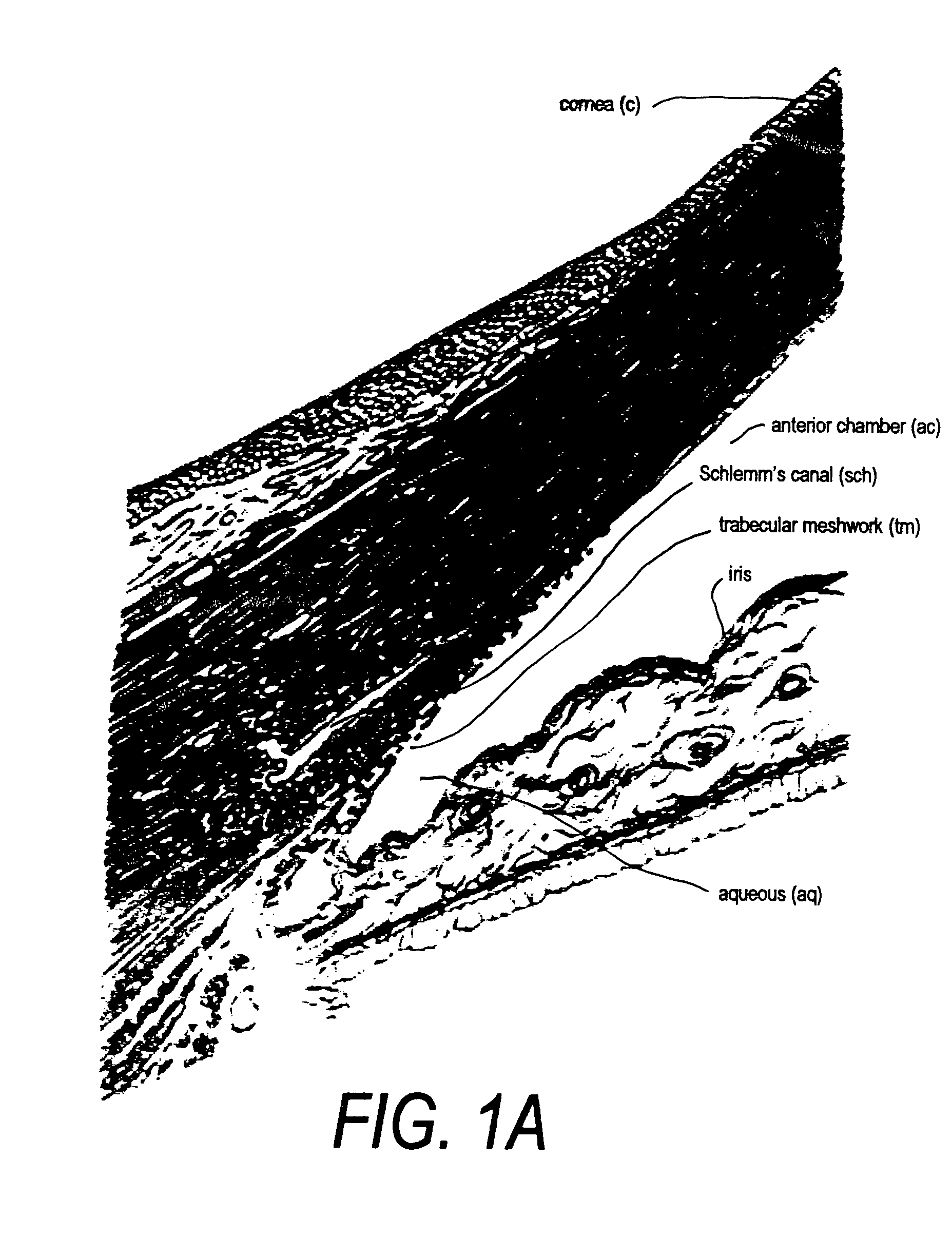
Apparatus and method for treating glaucoma
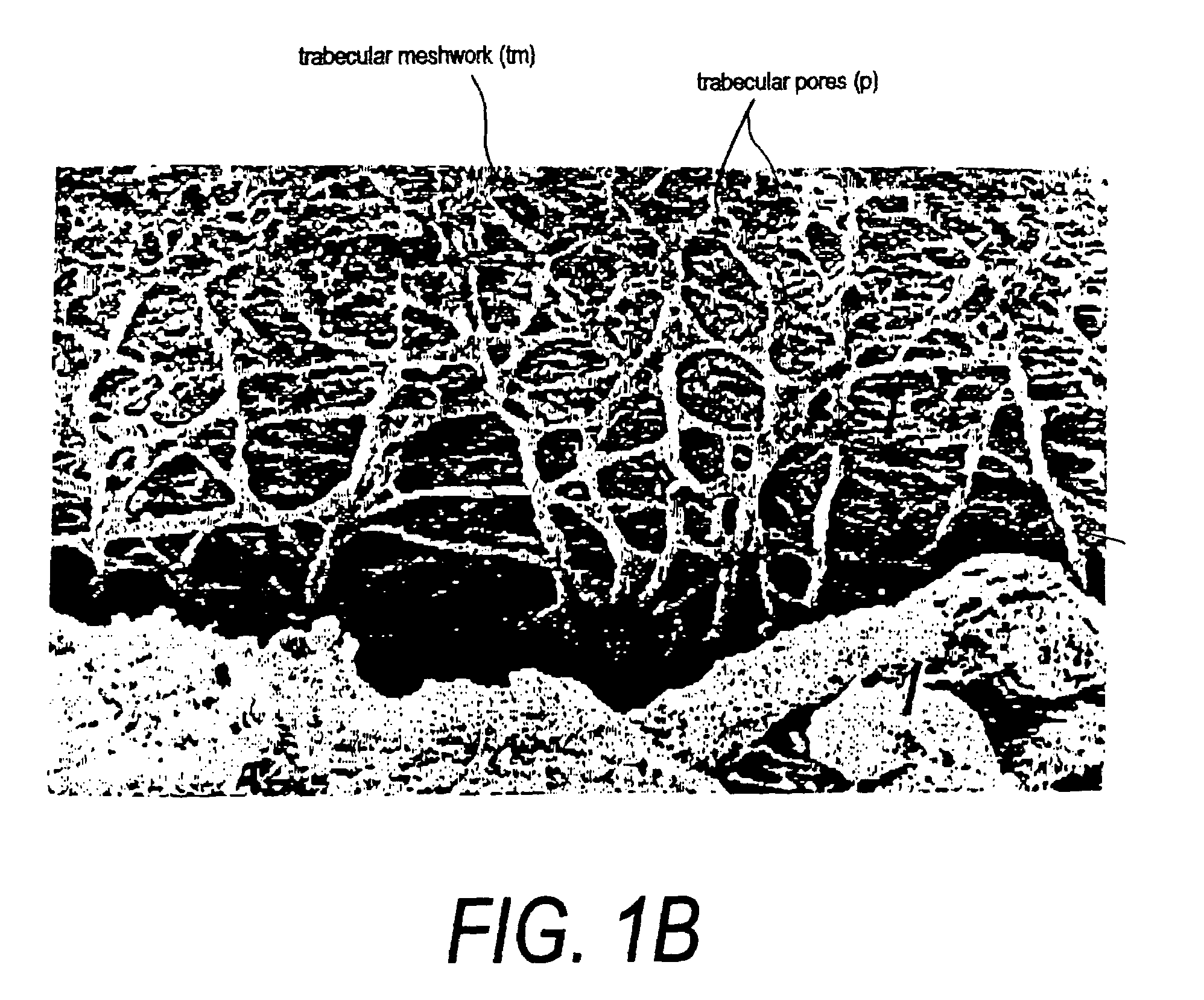
Surgical methods and related medical devices for treating glaucoma are shown. The method includes trabecular bypass surgery, which involves bypassing diseased trabecular meshwork with the use of a seton implant. The seton implant is used to prevent a healing process known as filling in, which has a tendency to close surgically created openings in the trabecular meshwork. The surgical method and novel implant are addressed to the trabecular meshwork, which is a major site of resistance to outflow in glaucoma. In addition to bypassing the diseased trabecular meshwork at the level of the trabecular meshwork, existing outflow pathways are also used or restored. The seton implant is positioned through the trabecular meshwork so that an inlet end of the seton implant is exposed to the anterior chamber of the eye and an outlet end is positioned into fluid collection channels at about an exterior surface of the trabecular meshwork or up to the level of aqueous veins.
Owner:GLAUKOS CORP
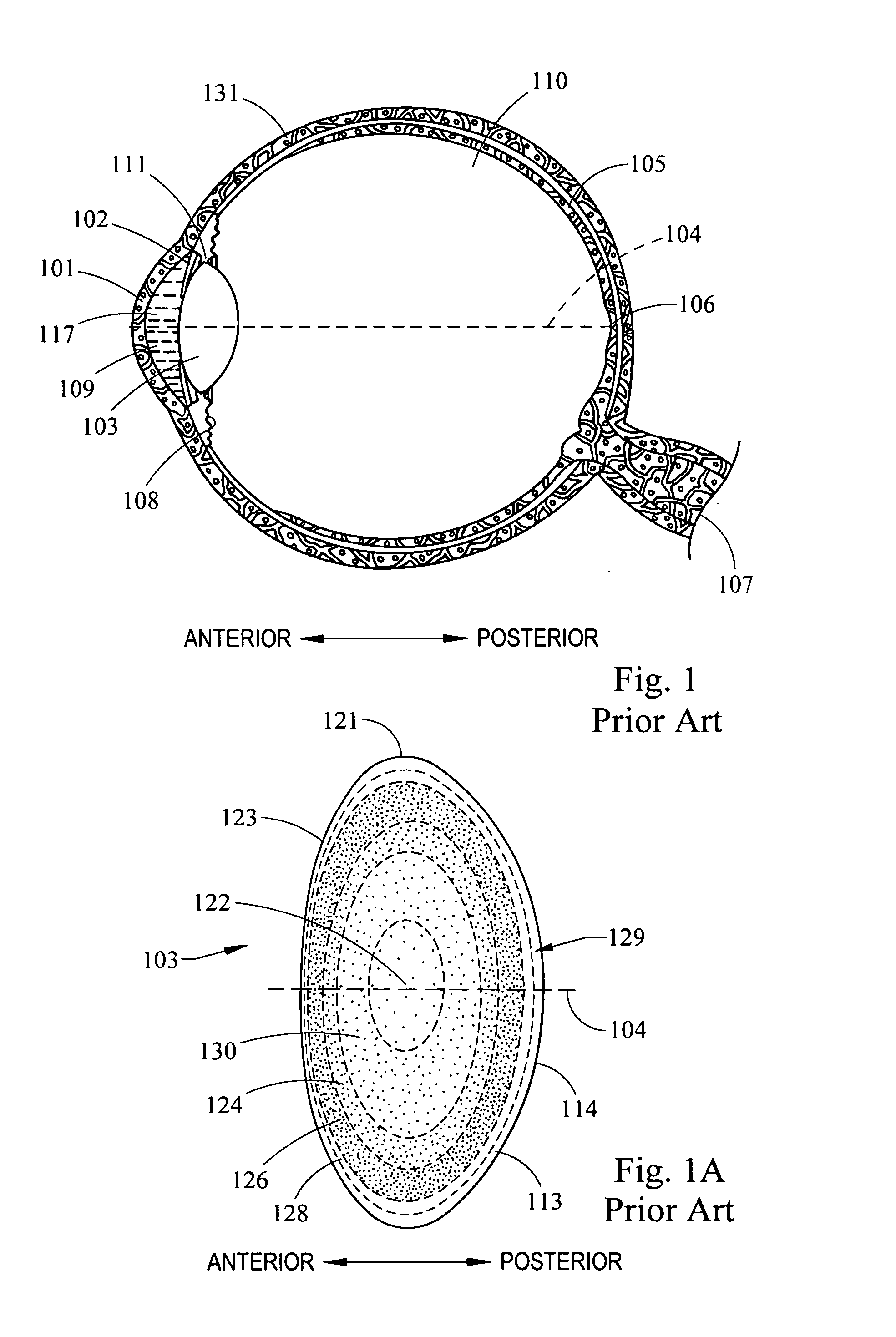
Apodized aspheric diffractive lenses
InactiveUS20060116764A1Improve image contrastSpectales/gogglesLaser surgeryCamera lensImage contrast
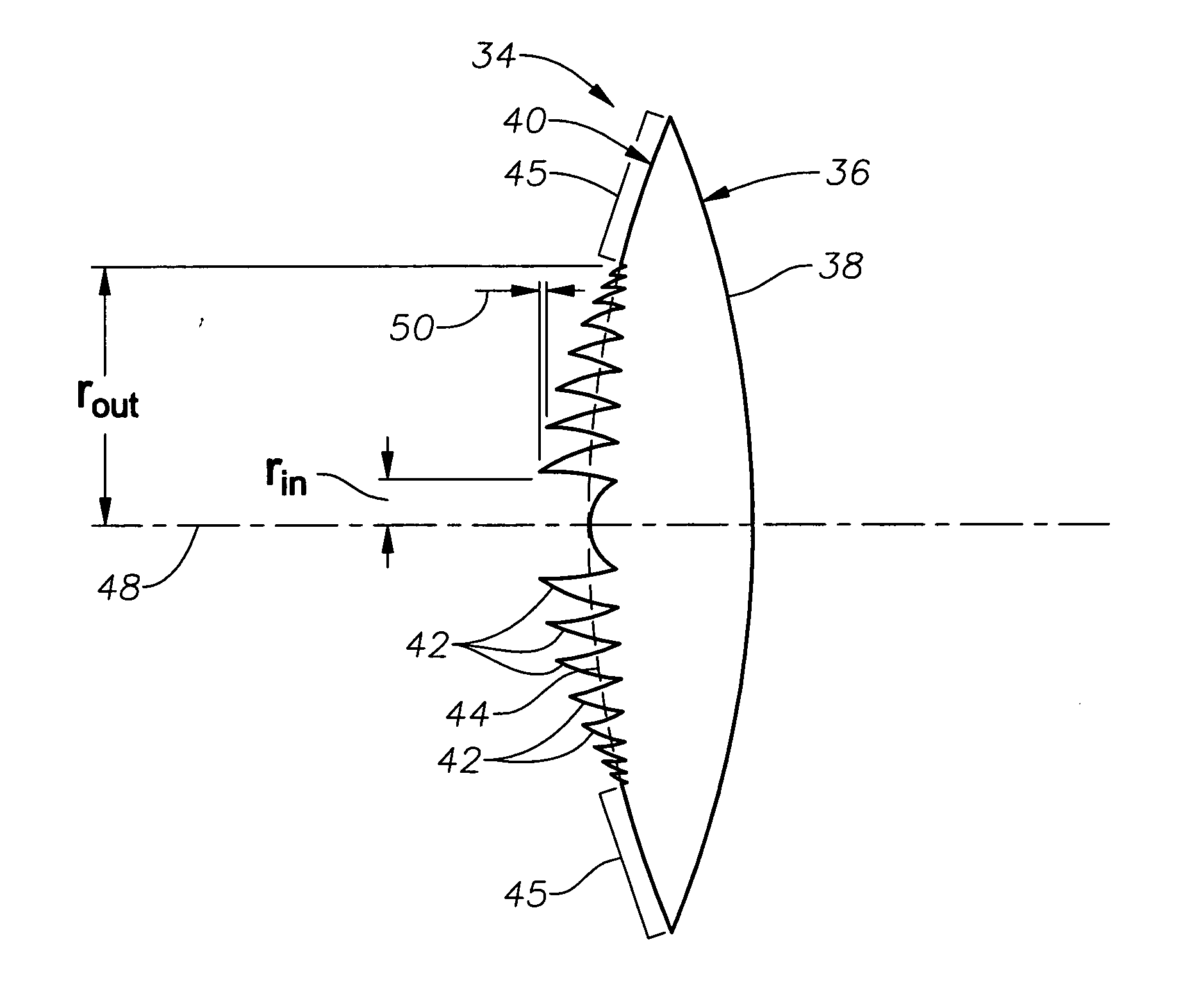
Aspheric diffractive lenses are disclosed for ophthalmic applications. For example, multifocal intraocular lens (IOLs) are disclosed that include an optic having an anterior surface and a posterior surface, at least one of which surfaces includes an aspherical base profile on a portion of which a plurality of diffractive zones are disposed so as to generate a far focus and a near focus. The aspherical base profile enhances image contrast at the far focus of the lens relative to that obtained by a substantially identical IOL in which the respective base profile is spherical.
Owner:ALCON INC
Fluid infusion methods for glaucoma treatment
The invention relates to methods of treating glaucoma, such as a method that includes inserting a stent through an incision in an eye; the stent having an inflow portion that is in fluid communication with an outflow portion of the stent; transporting the stent from the incision through the anterior chamber of the eye to an aqueous cavity of the eye, such that the inflow portion of the stent is positioned in the anterior chamber and the outflow portion of the stent is positioned at the aqueous cavity; and infusing fluid from the inflow portion to the outflow portion of the stent.
Owner:GLAUKOS CORP
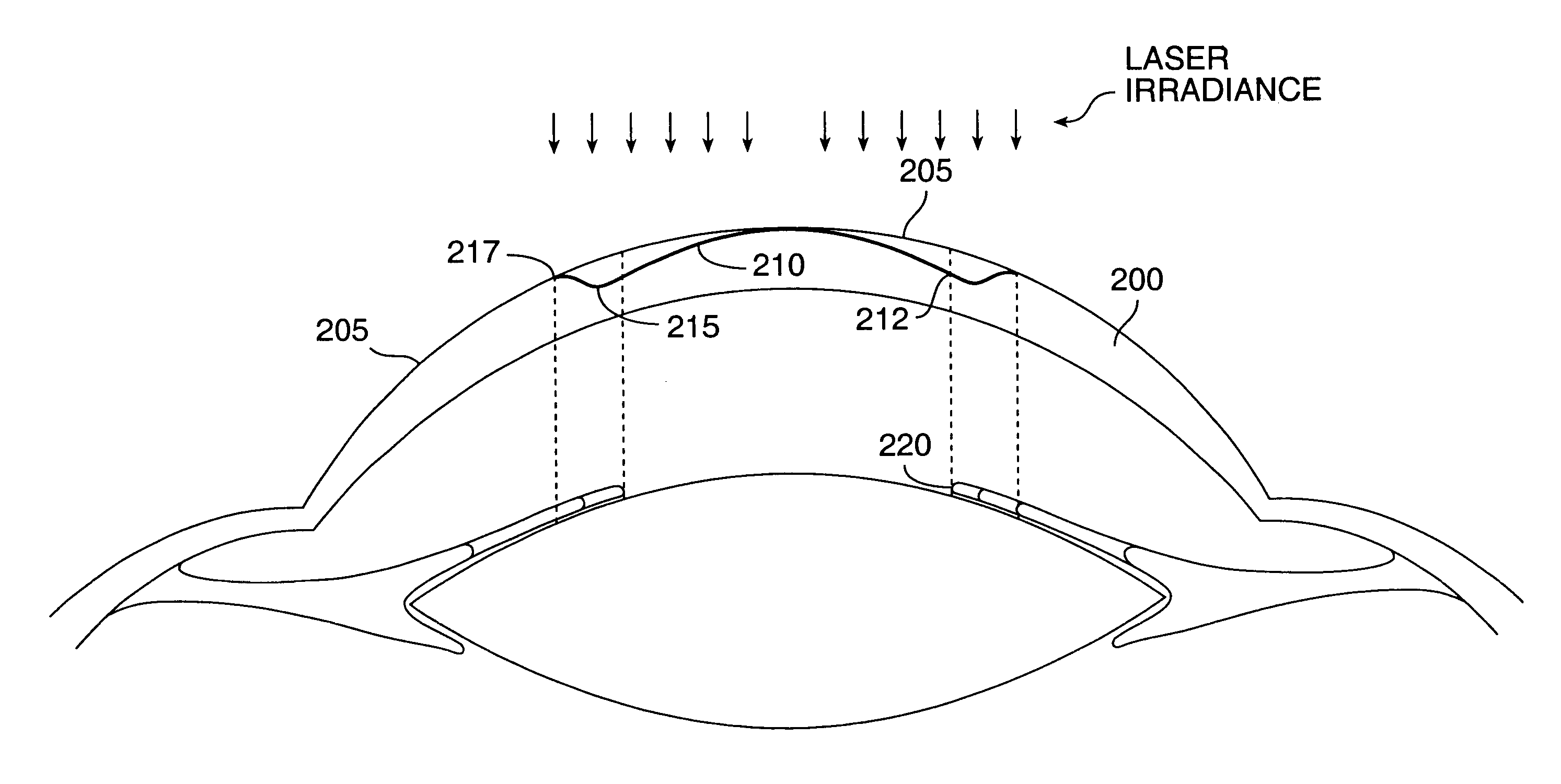
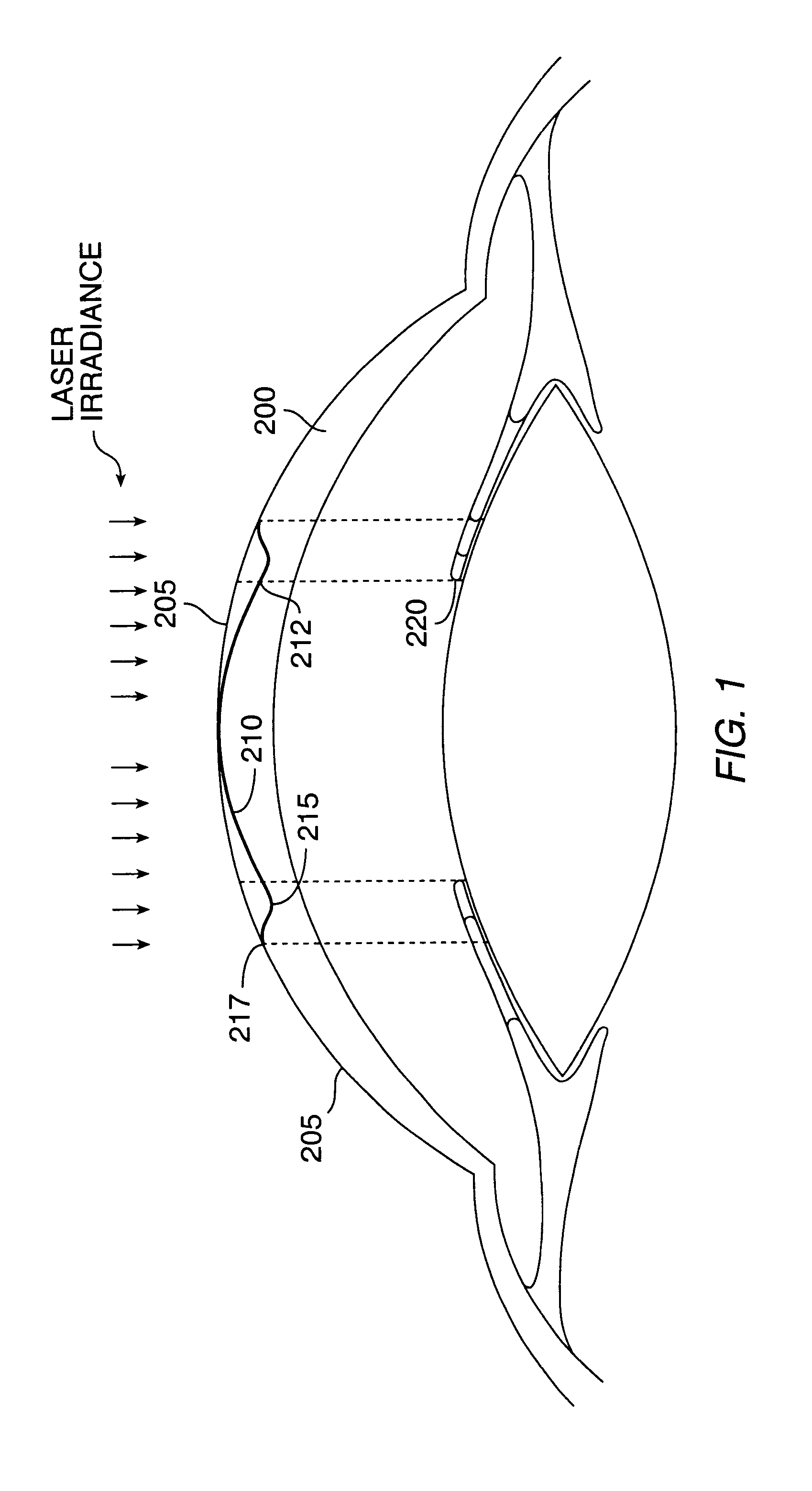
System and method for providing the shaped structural weakening of the human lens with a laser
ActiveUS8262646B2Increase amplitudeImprove errorLaser surgeryDiagnosticsRefractive errorLens materials
A system and method for increasing the amplitude of accommodation and / or changing the refractive power of lens material of a natural crystalline lens is provided. Generally, there is provided methods and systems for delivering a laser beam to a lens of an eye in a plurality of sectional patterns results in the shaped structural weakening of the lens. There is also provided a method and system for determining adjustments to refractive errors in the lens of an eye relating to the treatment of presbyopia. The change to refractive error can be a predicted error or an actual error that has been determined.
Owner:LENSAR LLC
Lenticular refractive surgery of presbyopia, other refractive errors, and cataract retardation
InactiveUS7655002B2Impaired growthReduce decreaseLaser surgerySurgical instrument detailsFluid transportRefractive error
Methods for the creation of microspheres treat the clear, intact crystalline lens of the eye with energy pulses, such as from lasers, for the purpose of correcting presbyopia, other refractive errors, and for the retardation and prevention of cataracts. Microsphere formation in non-contiguous patterns or in contiguous volumes works to change the flexure, mass, or shape of the crystalline lens in order to maintain or reestablish the focus of light passing through the ocular lens onto the macular area, and to maintain or reestablish fluid transport within the ocular lens.
Owner:SECOND SIGHT LASER TECH
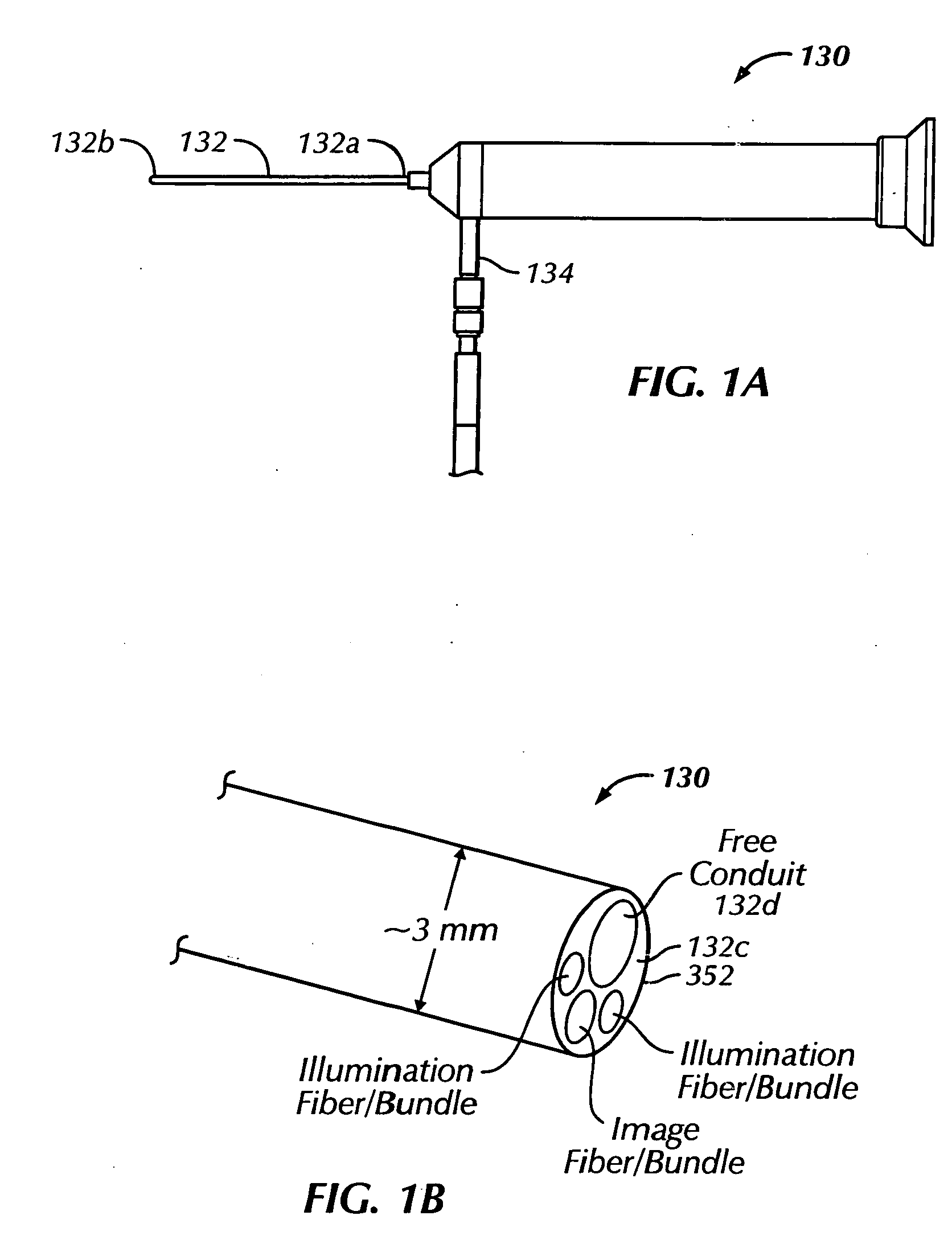
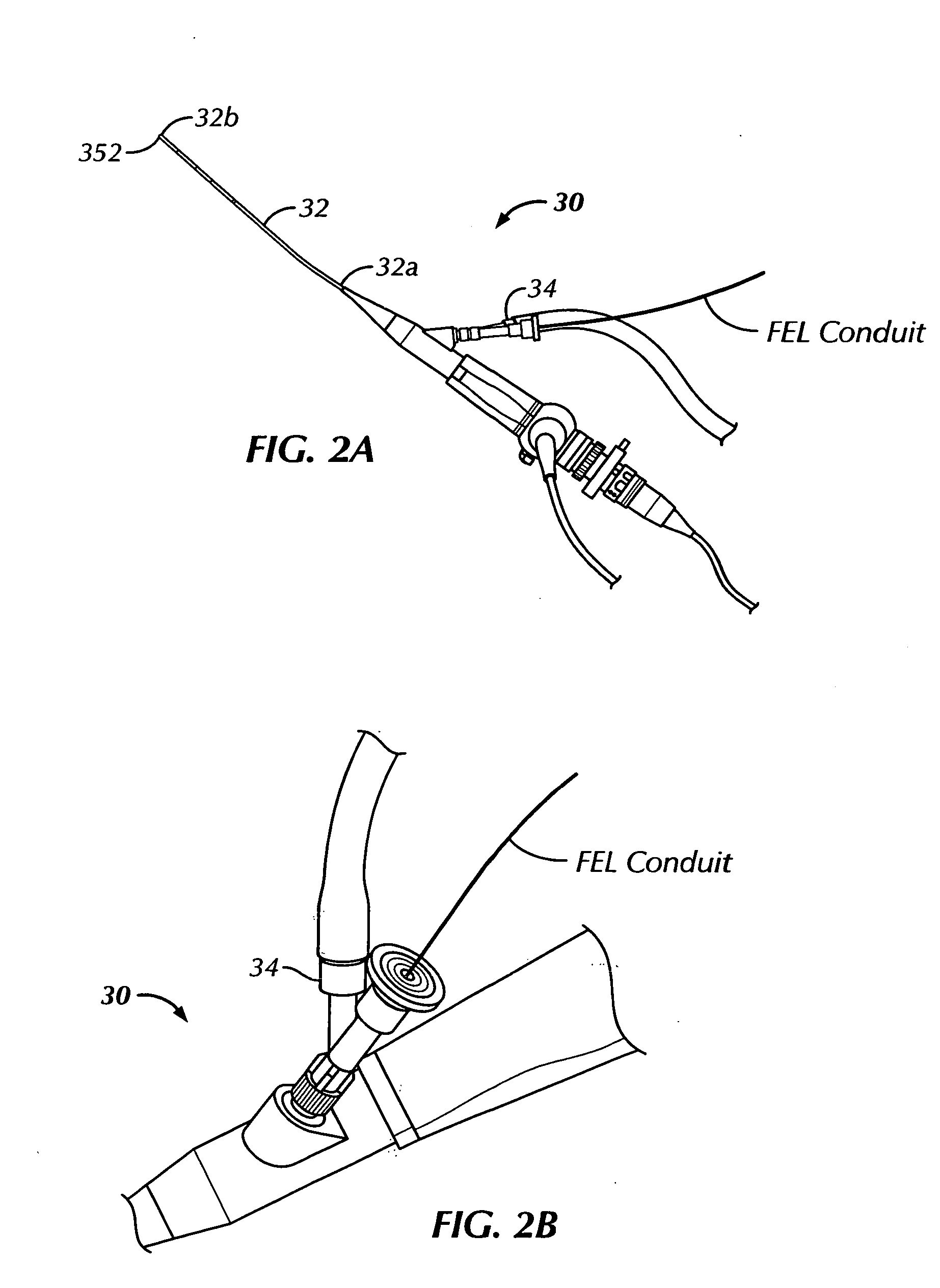
Ophthalmic orbital surgery apparatus and method and image-guided navigation system
A flexible endoscope for ophthalmic orbital surgery includes a flexible probe housing having a proximal end, a distal end and a lumen extending between the proximal end and the distal end. The endoscope also includes an image fiber disposed in the lumen that communicates image information from the distal end of the flexible probe, a purge fluid / gas port disposed at the proximal end of the flexible probe that accepts purge fluid / gas and a purge fluid / gas conduit disposed in the lumen and in fluid communication with the purge fluid / gas port. The fluid / gas conduit delivers purge fluid / gas to the distal end of the endoscope. The endoscope also includes an access conduit disposed in the lumen that receives one of an ablation instrument, a coagulating instrument and a medication delivery instrument.
Owner:VANDERBILT UNIV
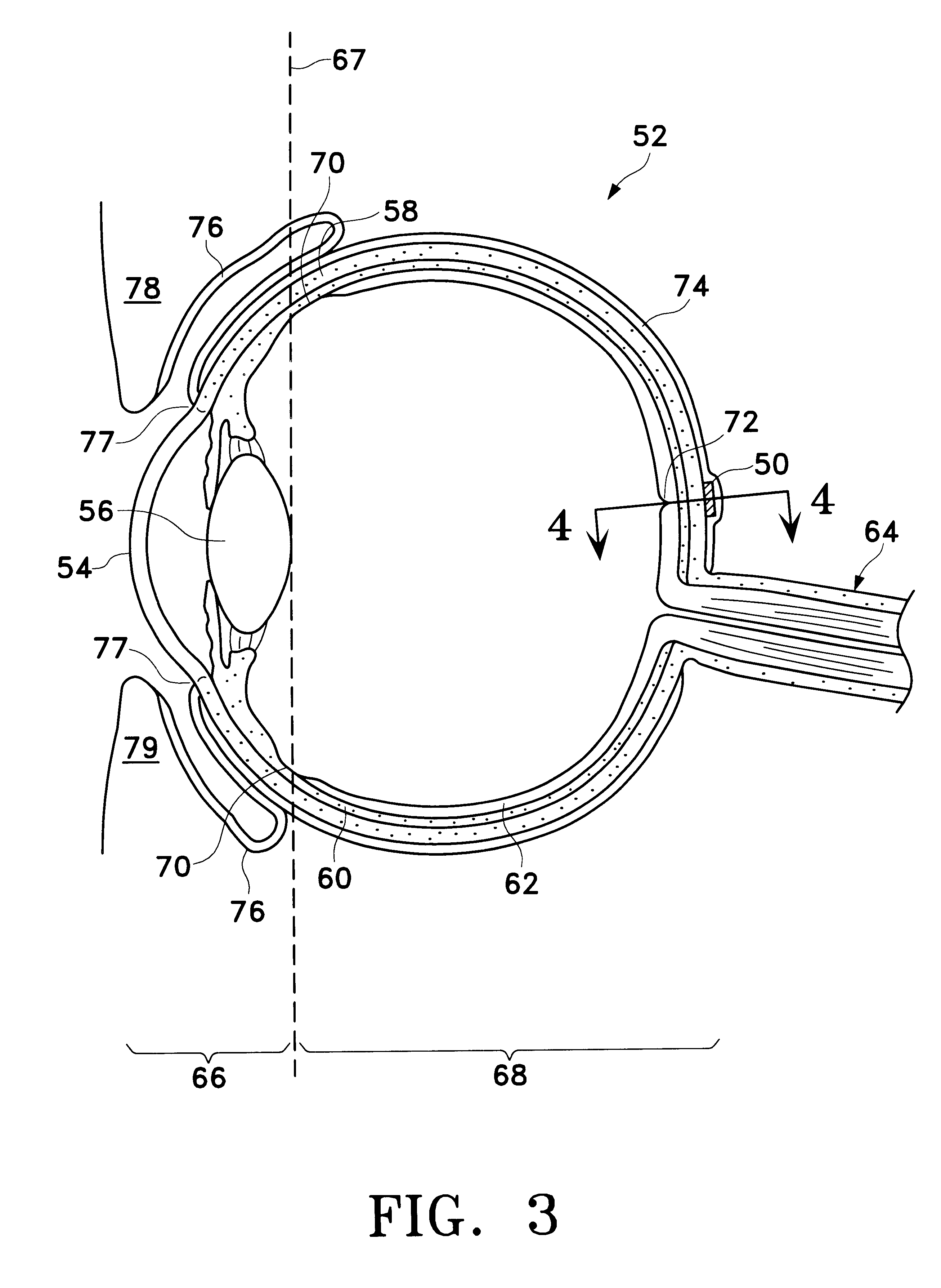
Minimally invasive glaucoma surgical instrument and method
InactiveUS6979328B2Easy to solveEasy accessSurgical needlesDiagnostic recording/measuringSchlemm's canalSurgical instrumentation
A surgical instrument and methods for the treatment of glaucoma are provided. The instrument uses either cauterization, a laser to ablate, sonic or ultrasonic energy to emulsify, or mechanical cutting of a portion of the trabecular meshwork. The instrument may also be provided with irrigation, aspiration, and a footplate. The footplate is used to enter Schlemm's canal, serves as a guide, and also protects Schlemm's canal.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Apparatus and Method for Ocular Treatment
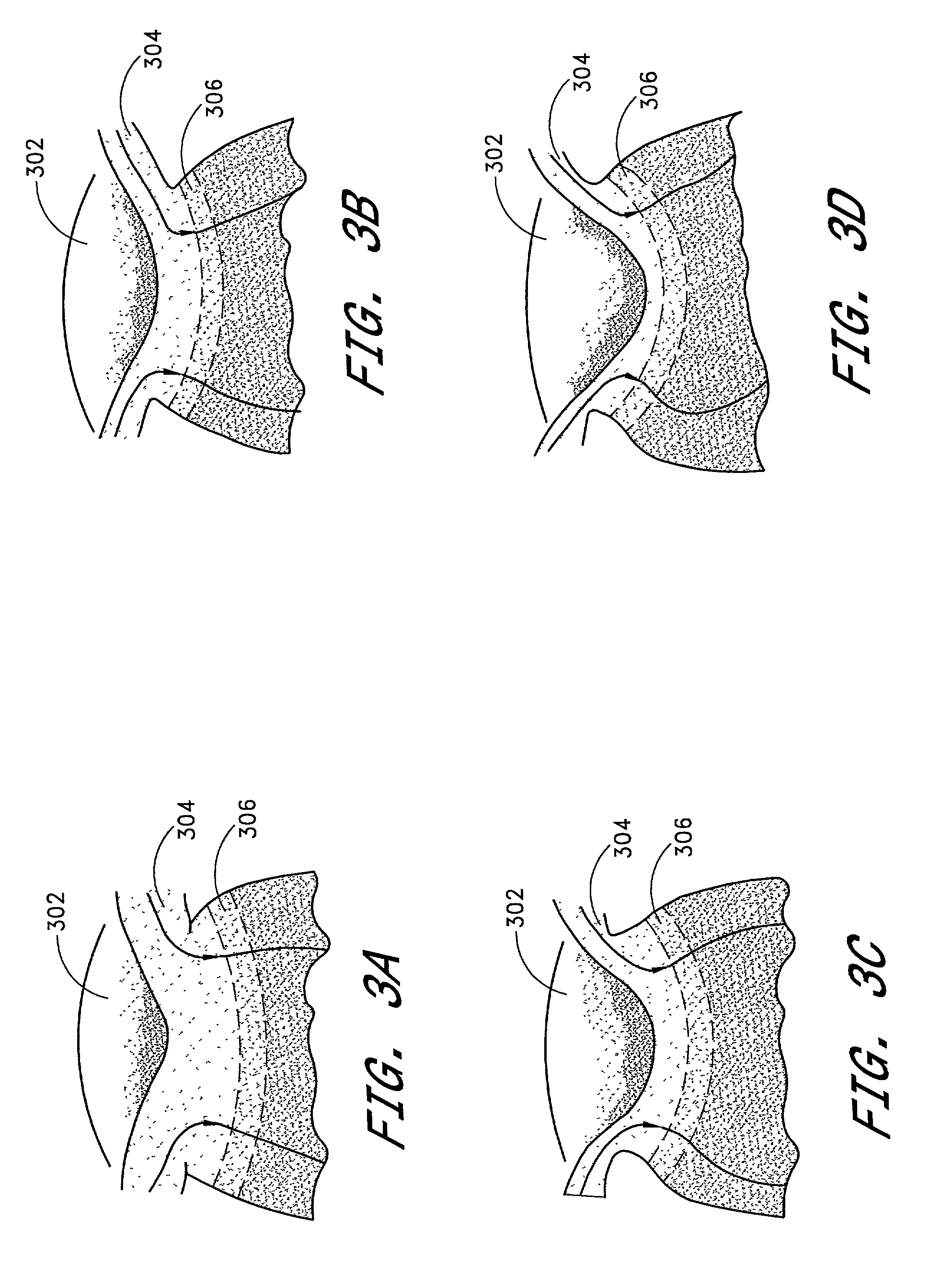
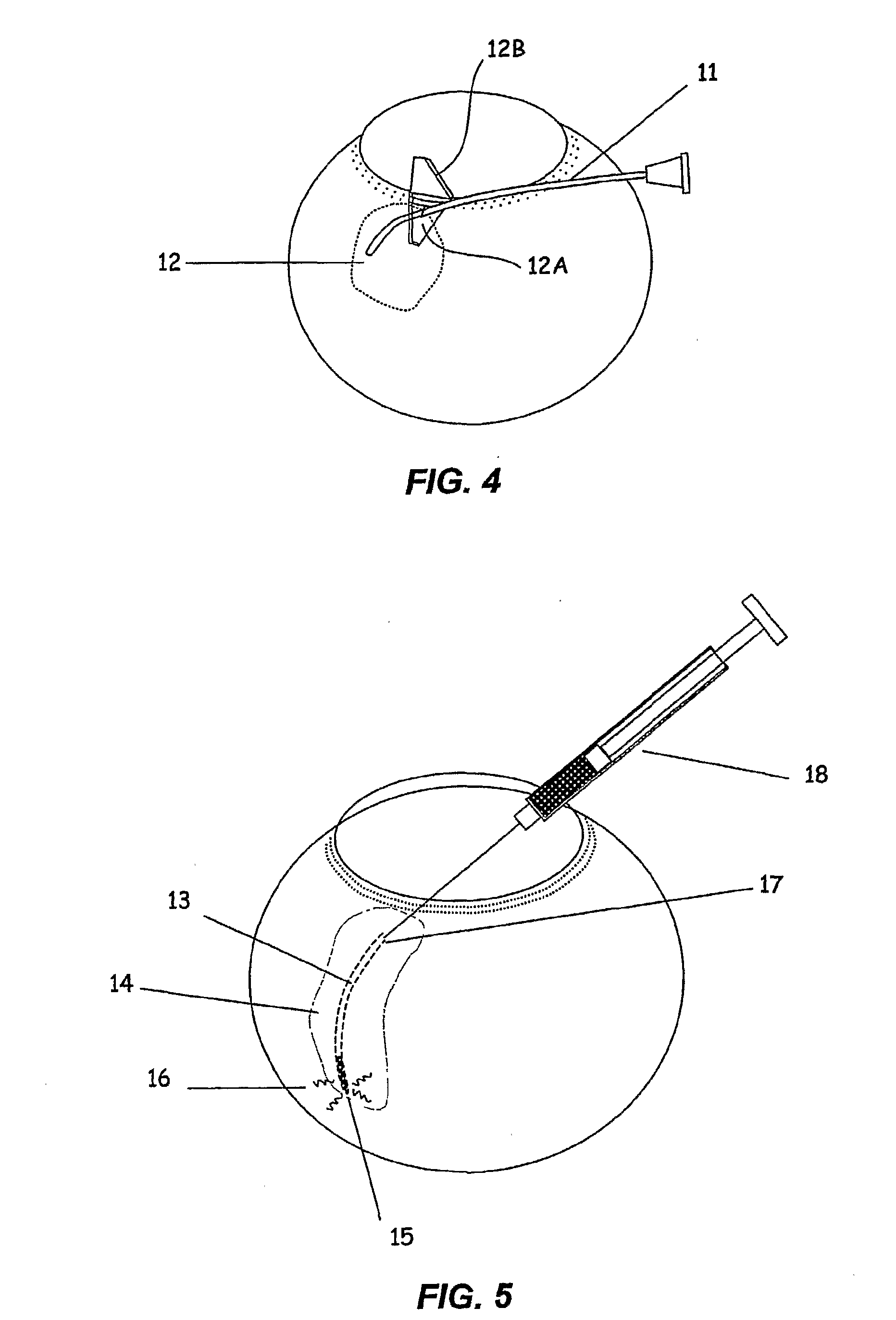
InactiveUS20080058704A1Reduce releaseFacilitate tissue targetingUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsLaser surgeryLess invasive surgerySuprachoroidal space
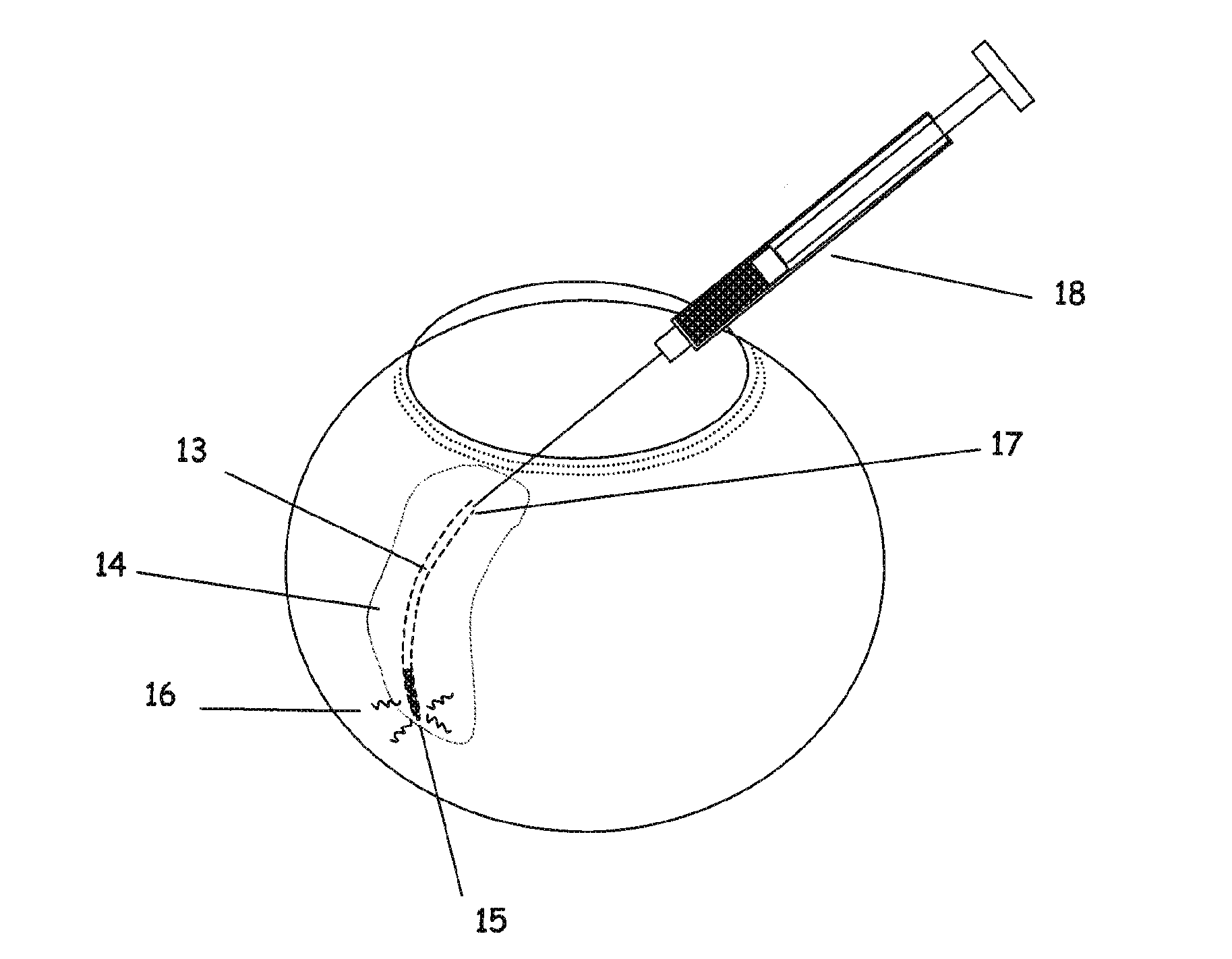
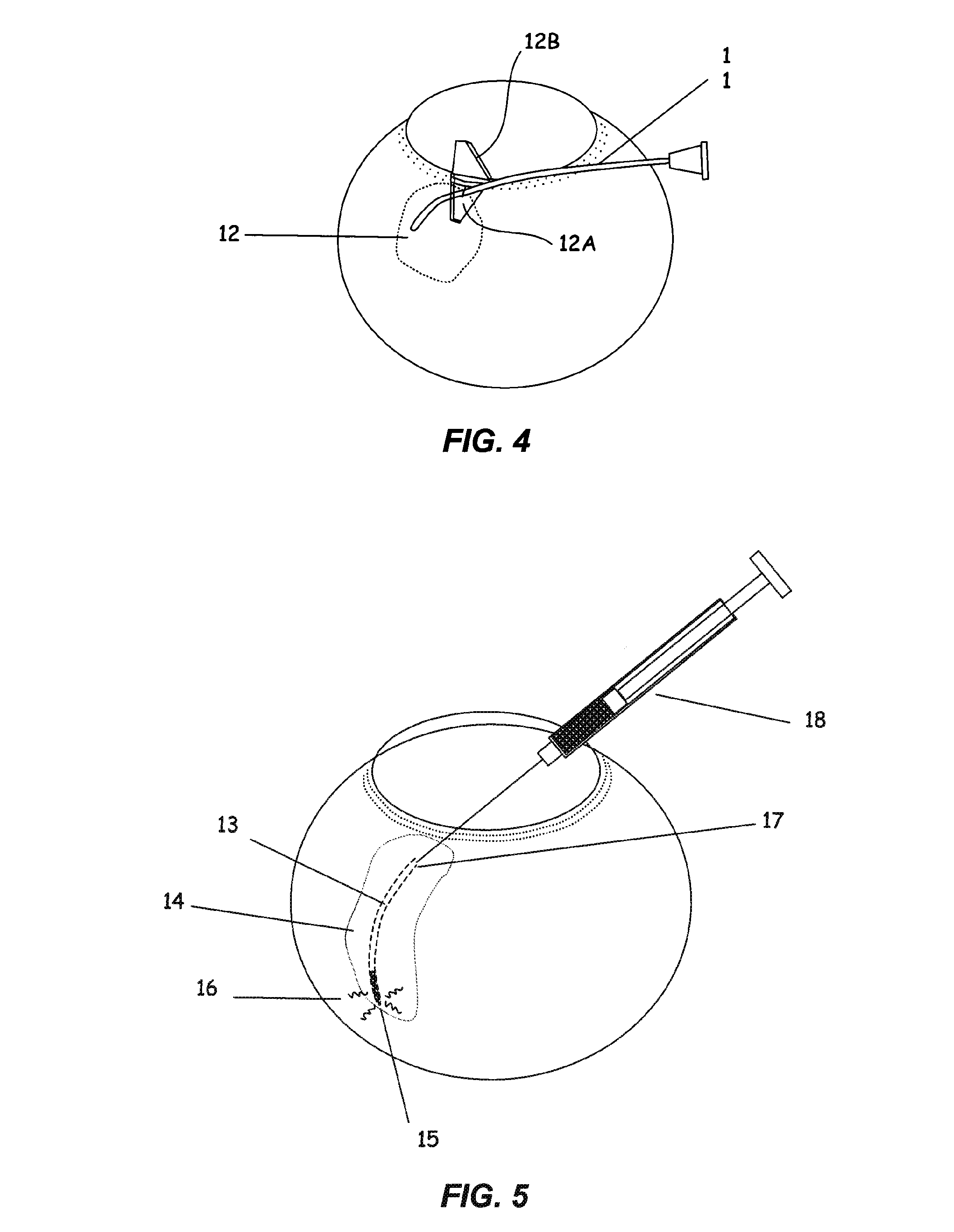
The invention provides tools, materials and related methods to surgically access the suprachoroidal space of an eye for the purpose of performing minimally invasive surgery or to deliver drugs to the eye. The invention provides a flexible microcannula device (11, 13) that may be placed into the suprachoroidal space (12, 14) through a small incision (12A) of the overlying tissues, maneuvered into the appropriate region of the space, and then activated to treat tissues adjacent to the distal tip of the device.
Owner:ISCI INTERVENTIONAL CORP
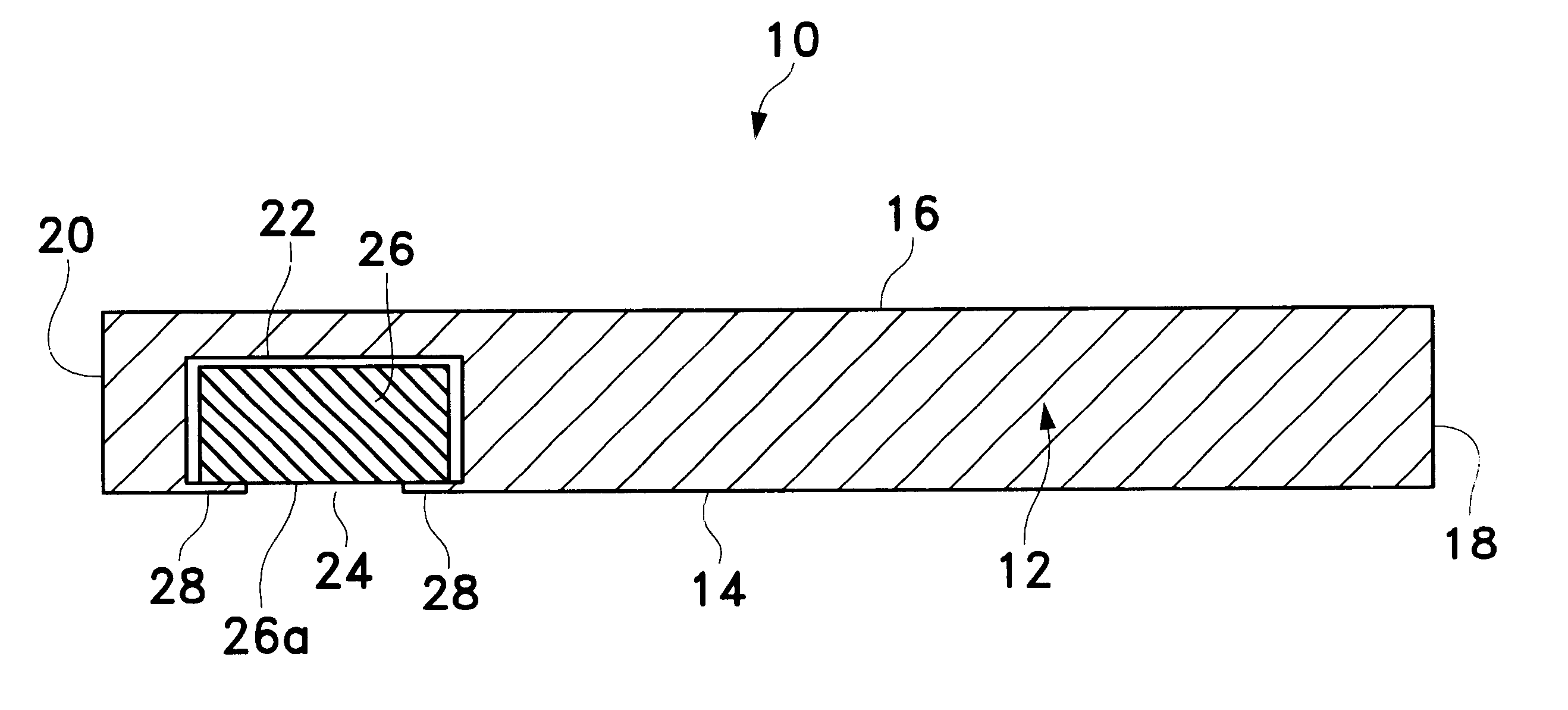
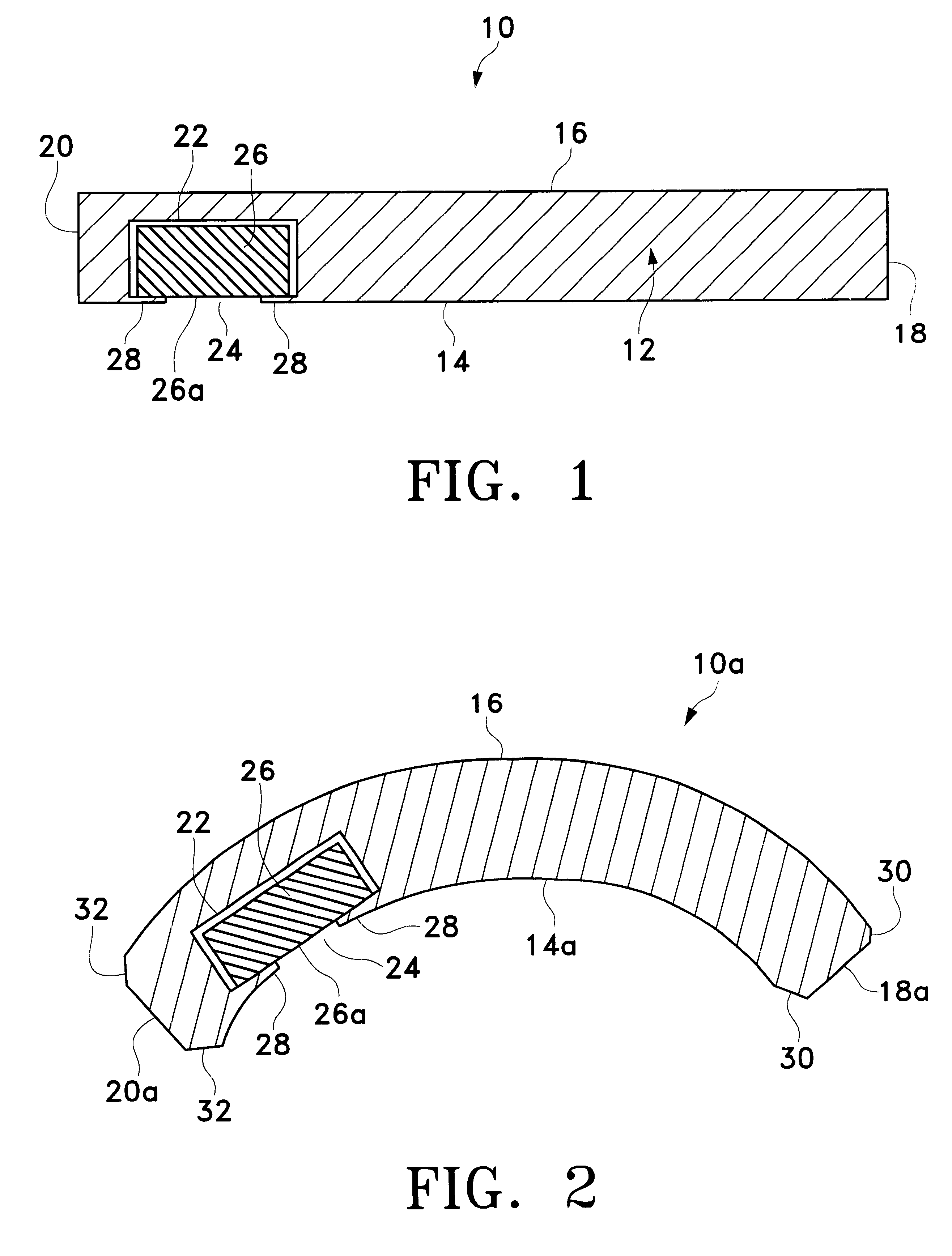
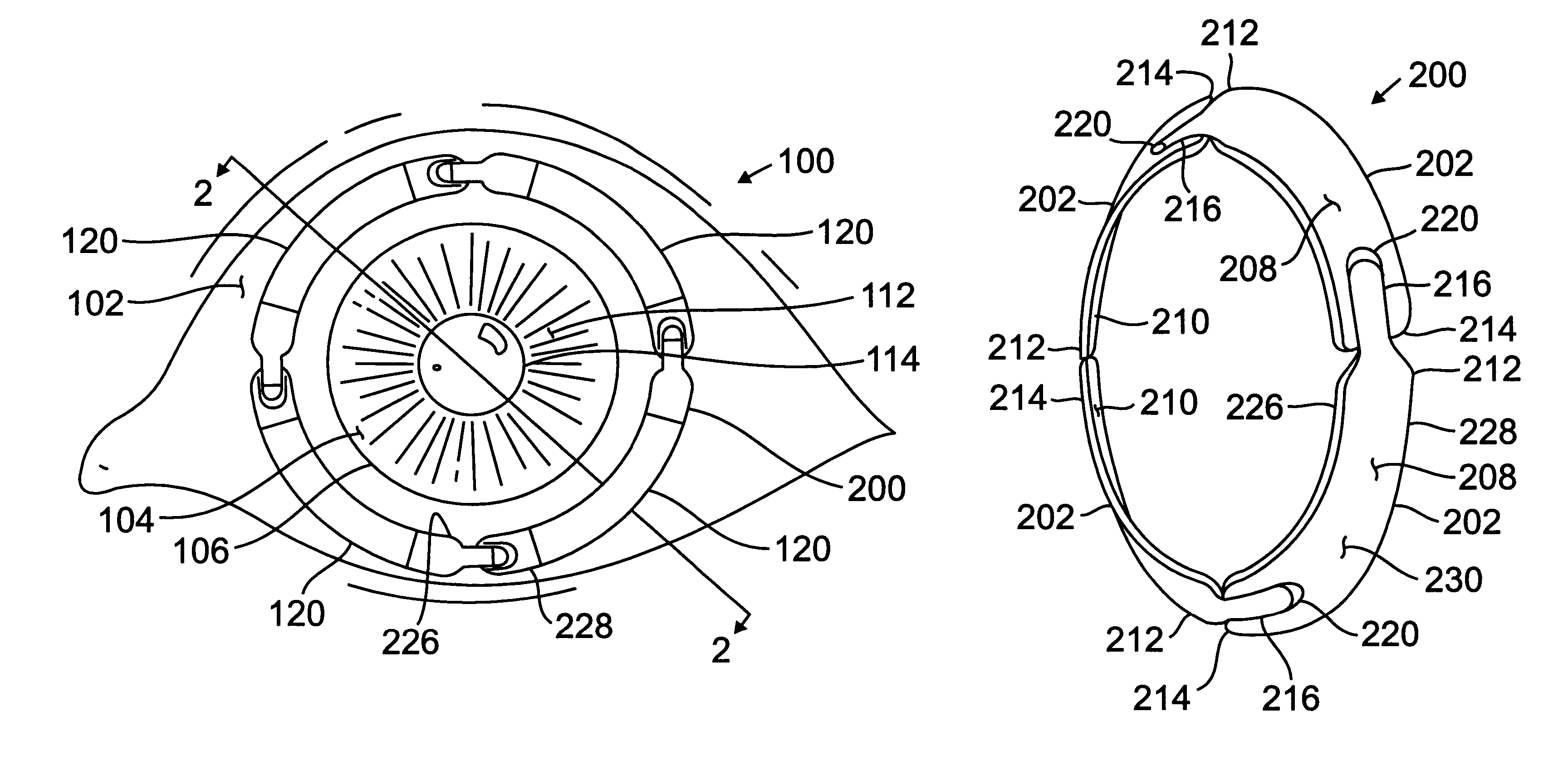
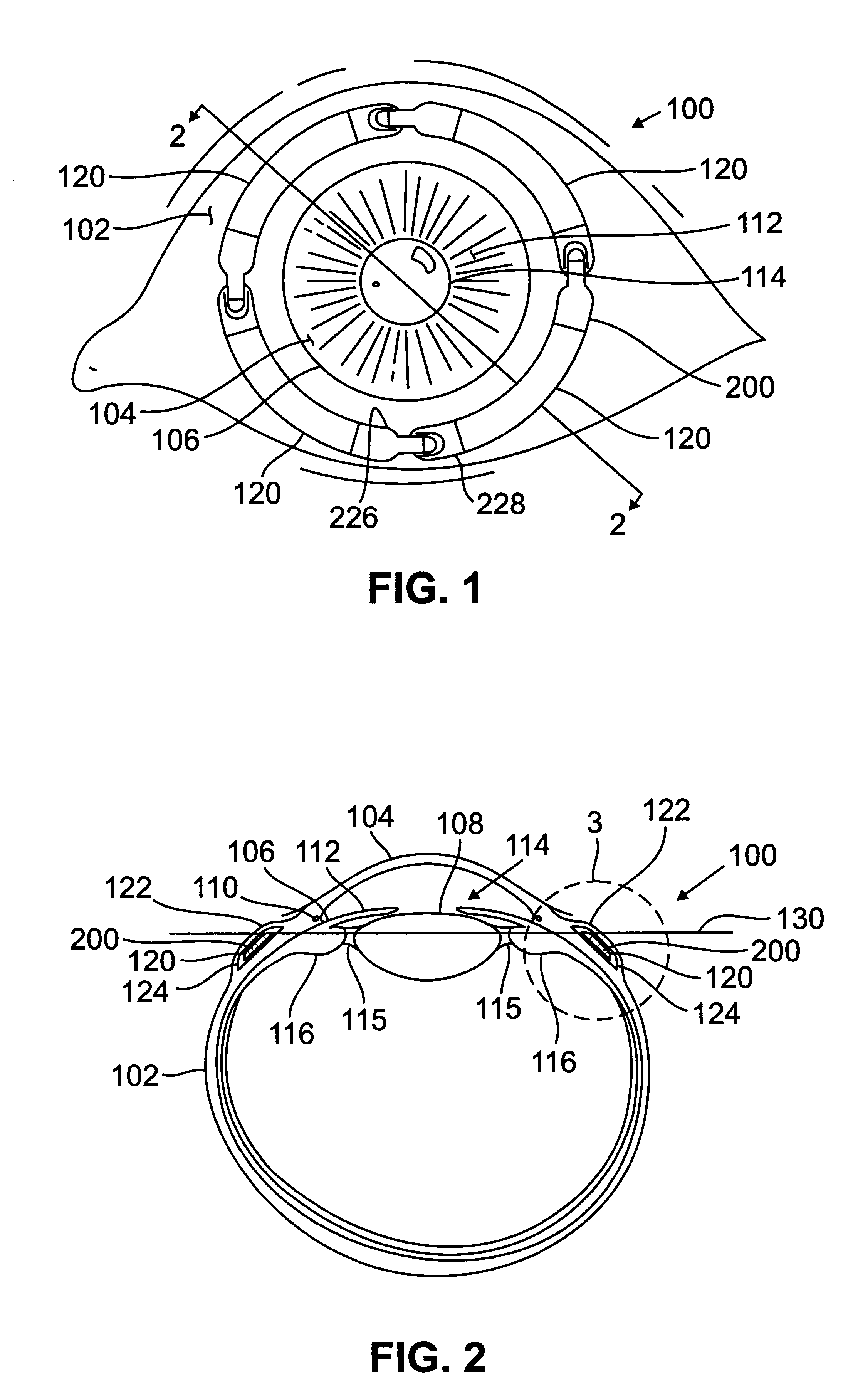
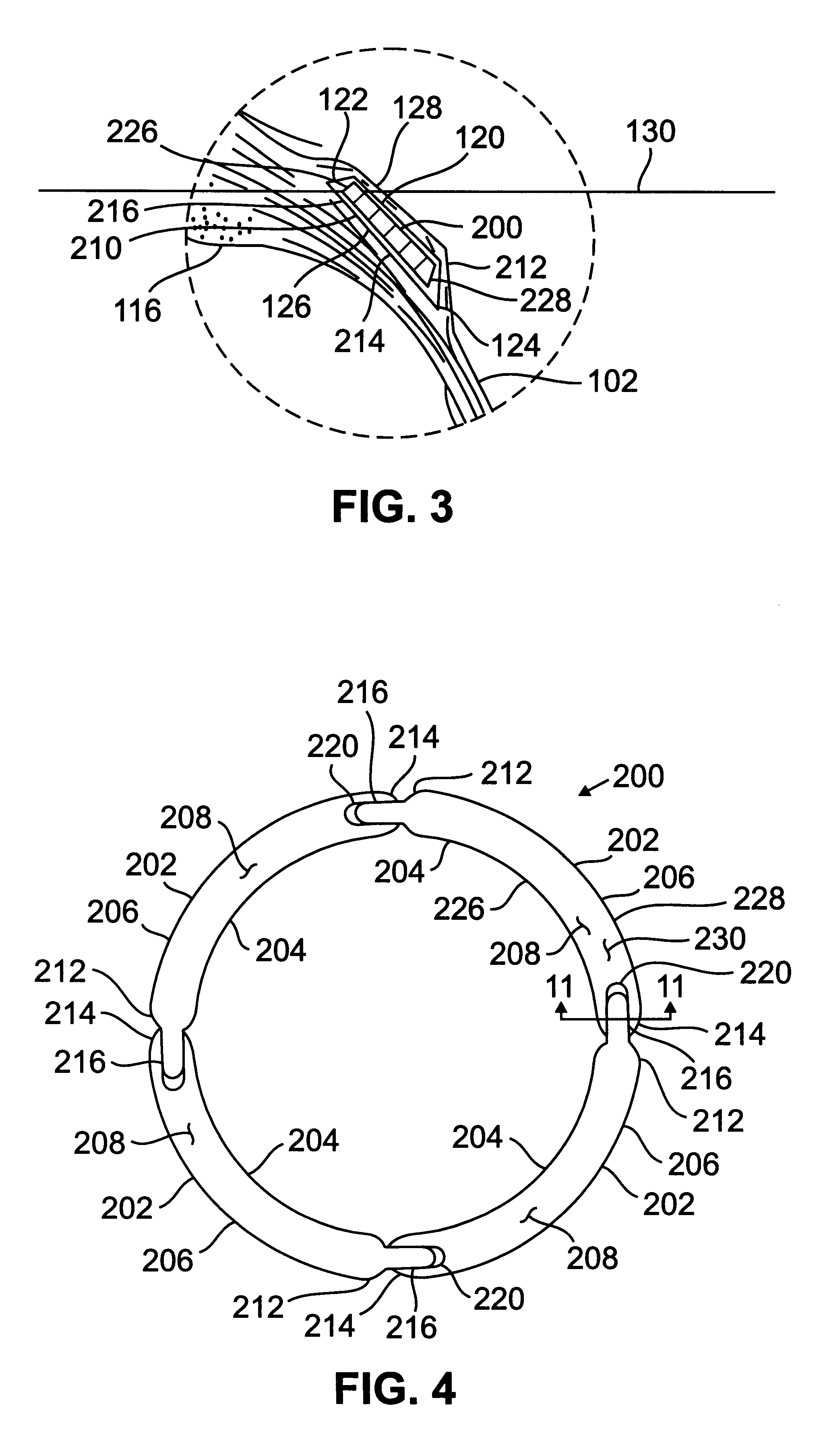
Segmented scleral band for treatment of presbyopia and other eye disorders
InactiveUS6197056B1Increase the effective working distanceLaser surgeryEye implantsDiseaseCiliary body
A segmented scleral expansion band adapted for implantation within or fastening to a segment of the sclera of an eye lying outside of and adjacent to the ciliary body of the eye, is formed from a number of arcuate segments, curved to match the curvature of the globe of the eye, and joined together at each end to form a complete scleral expansion band. The band is implanted in the sclera of the eye by forming circumferential tunnels, inserting the band segments through the tunnels, and joining the ends of the segments to form a complete scleral expansion band. The scleral expansion band is useful in treating presbyopia and other ocular disorders.
Owner:REFOCUS OCULAR INC
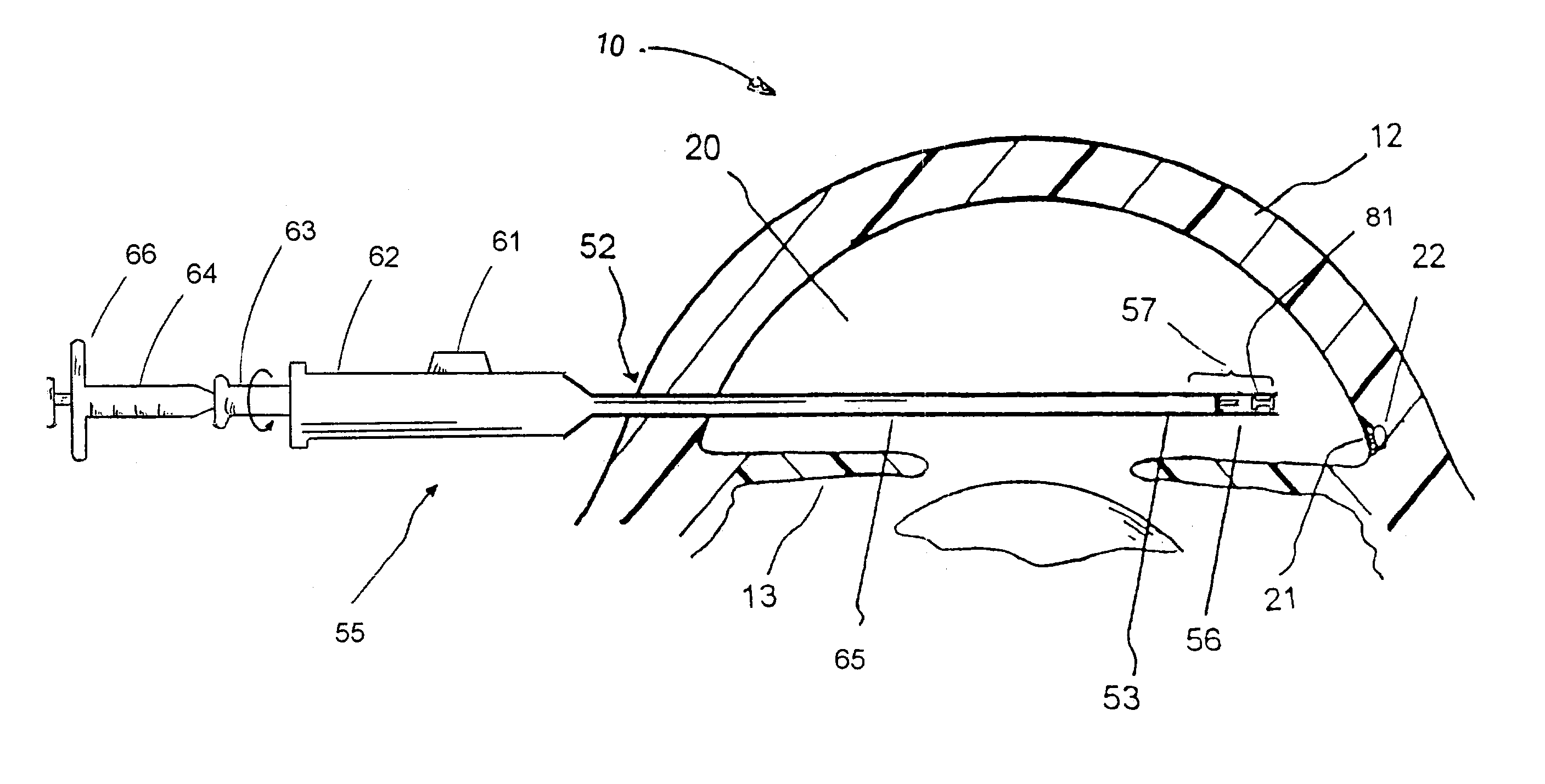
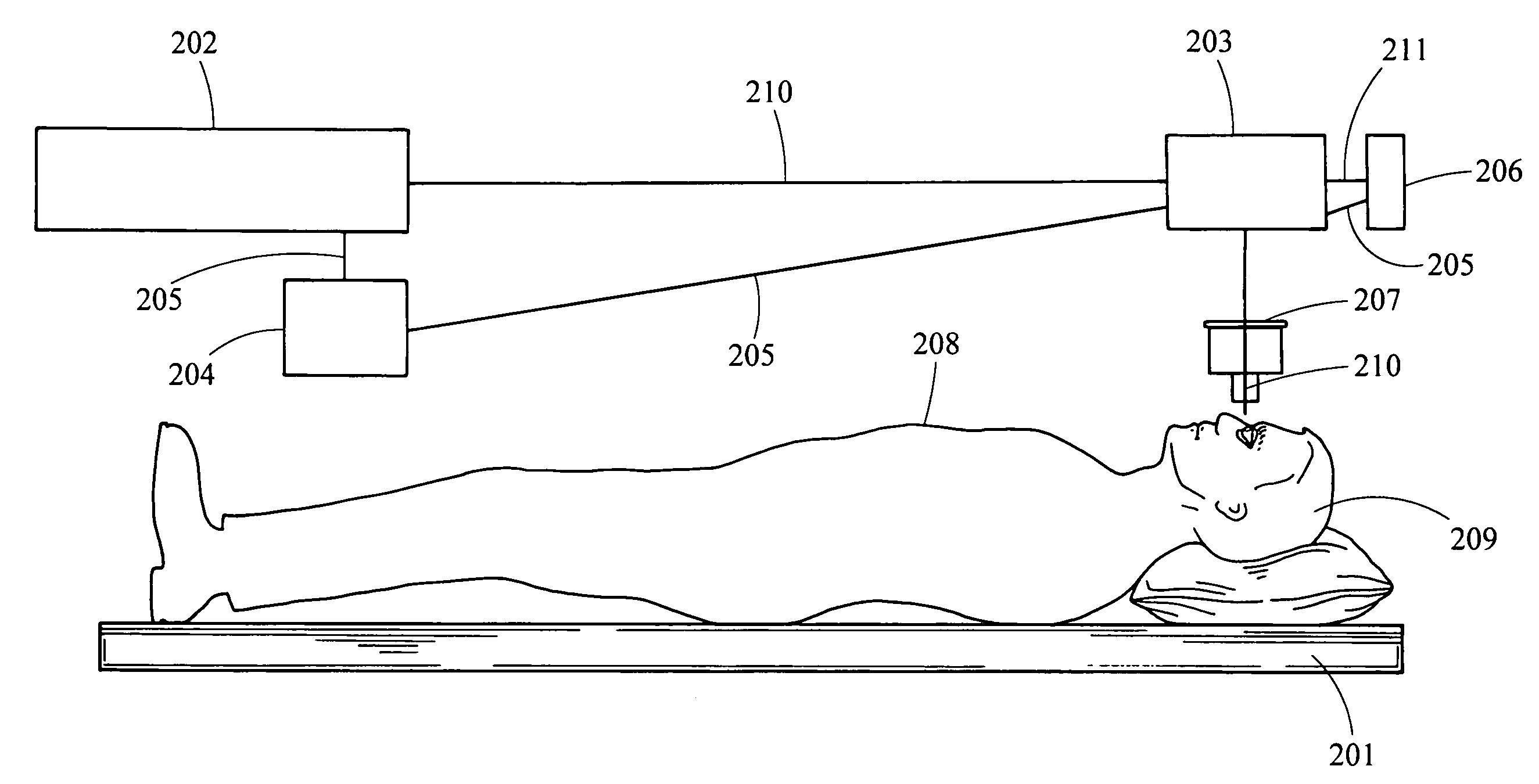
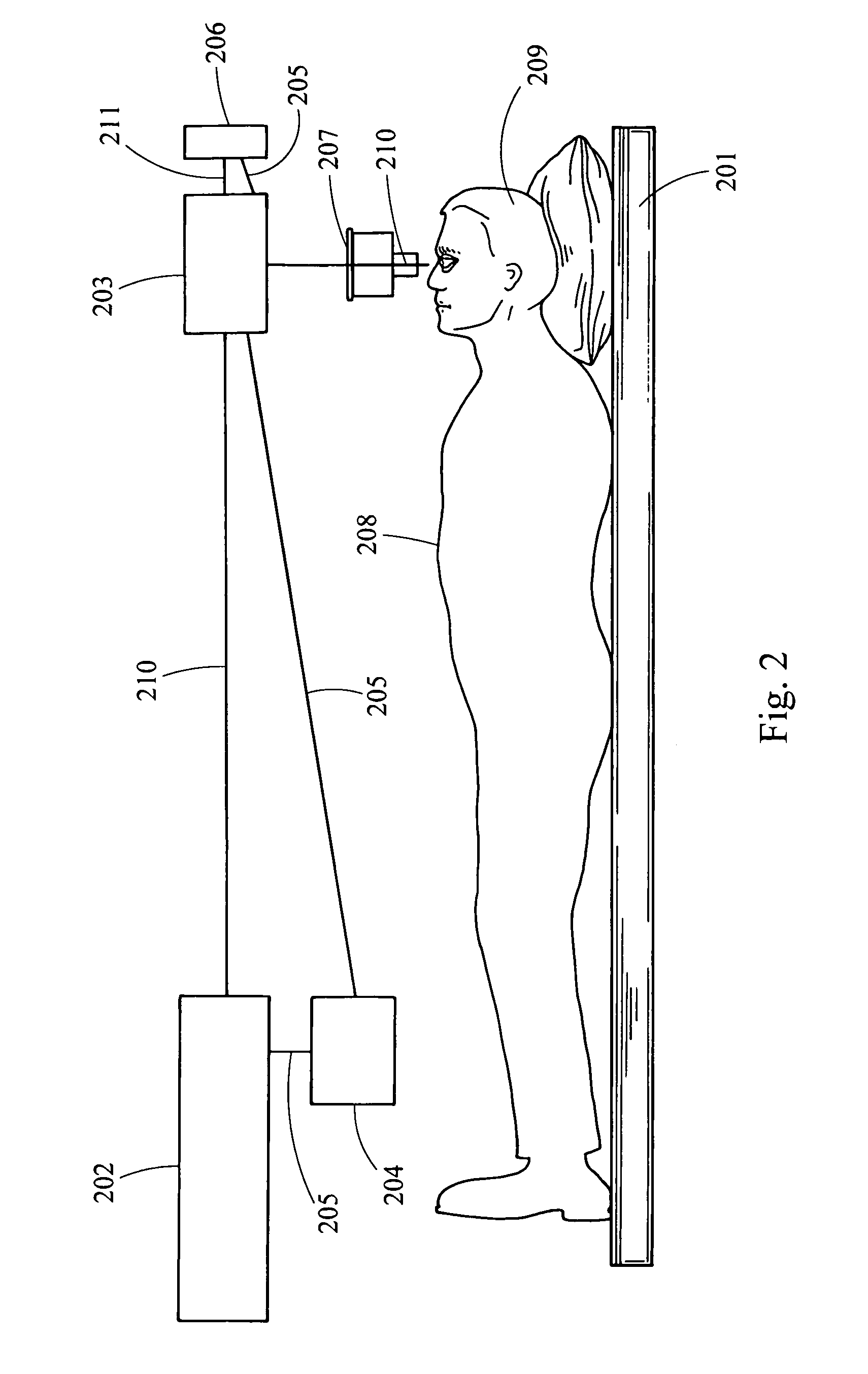
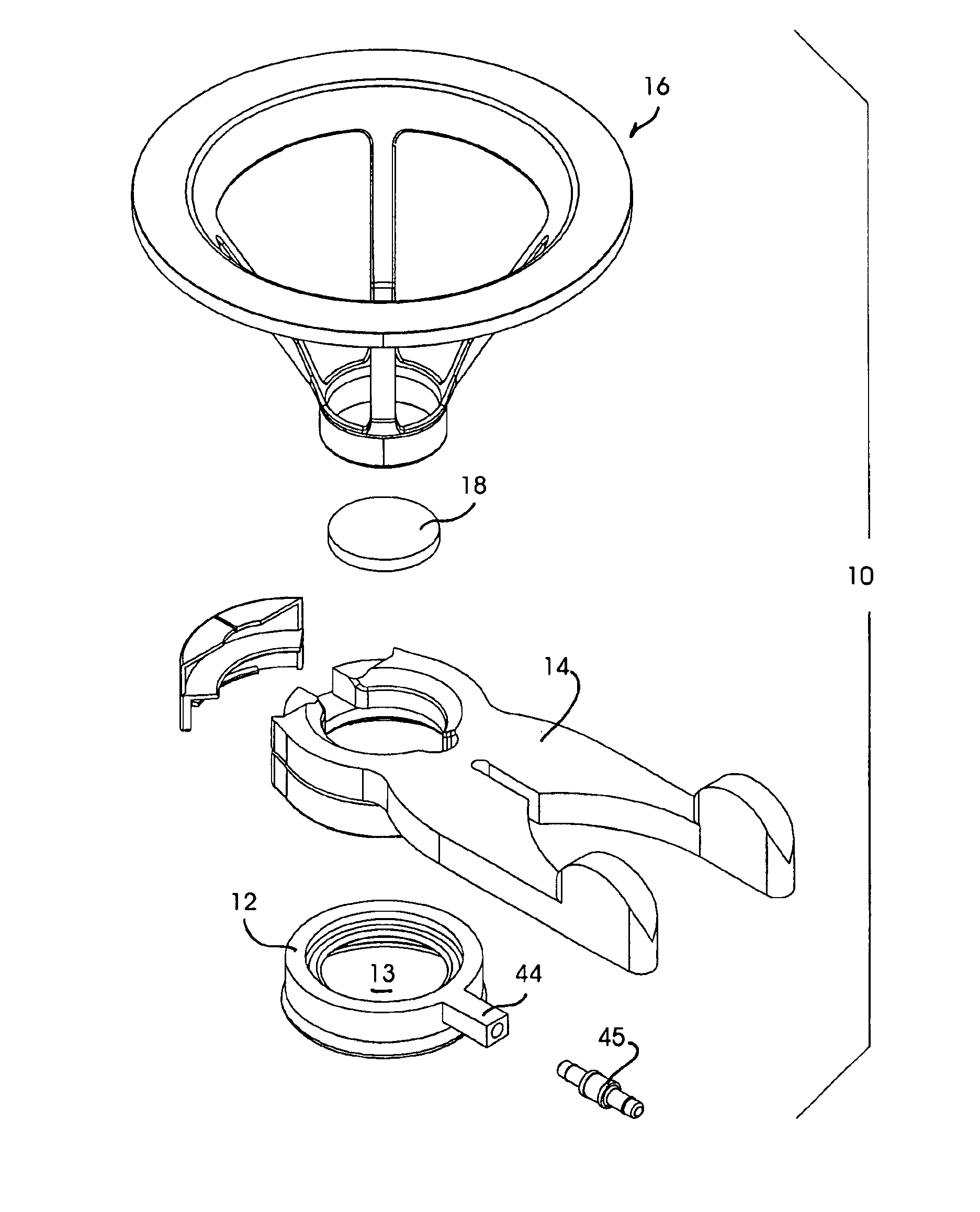
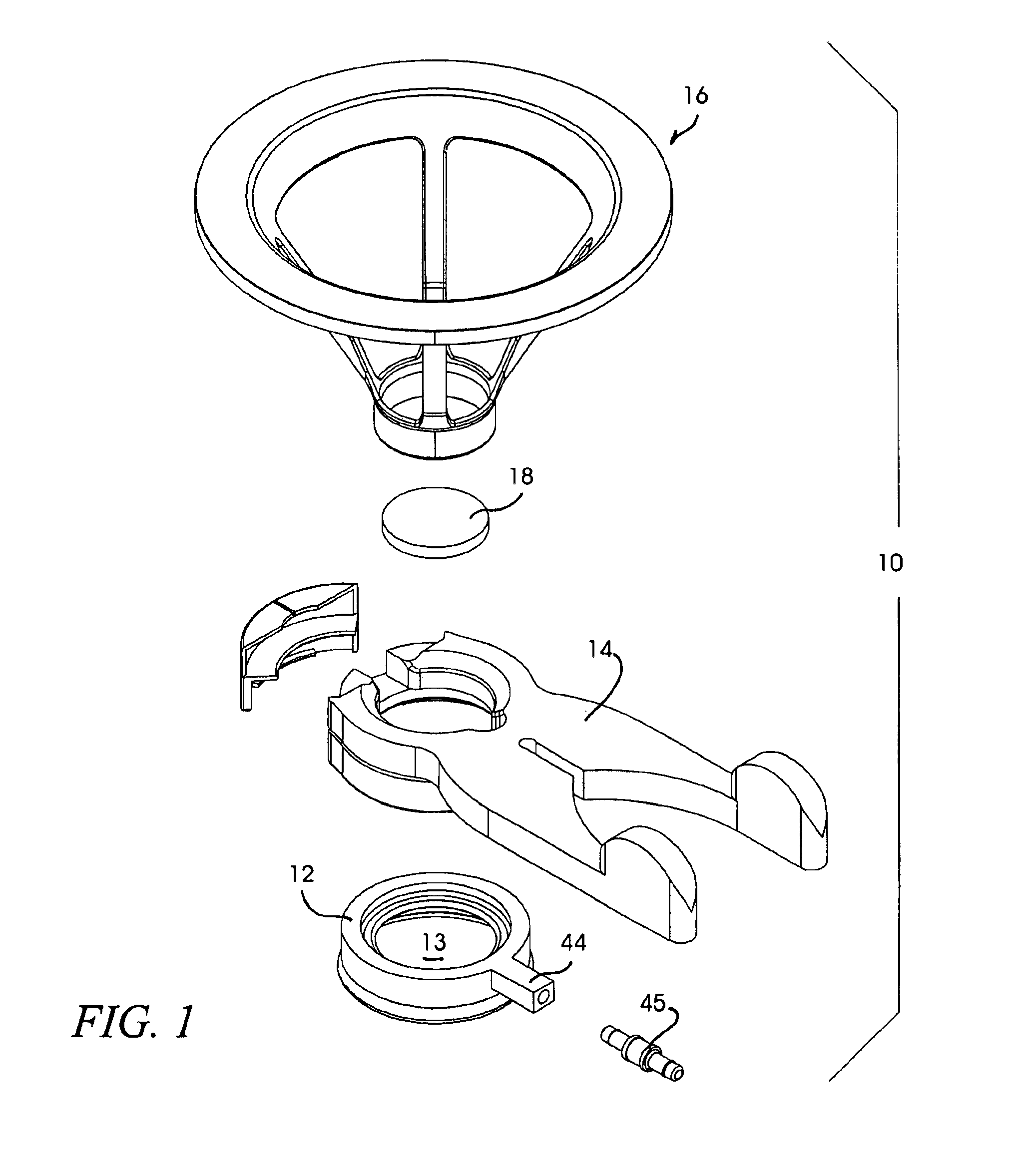
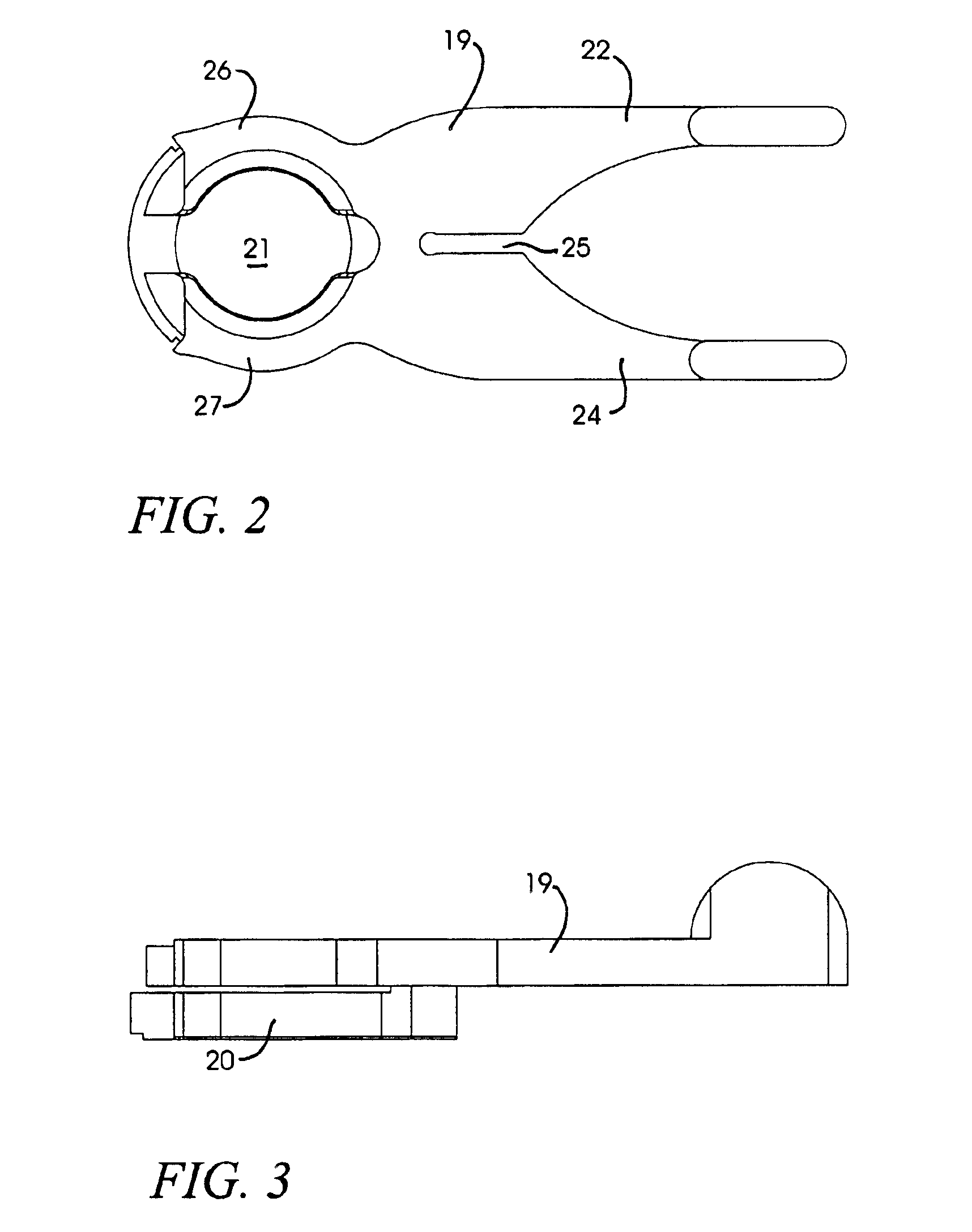
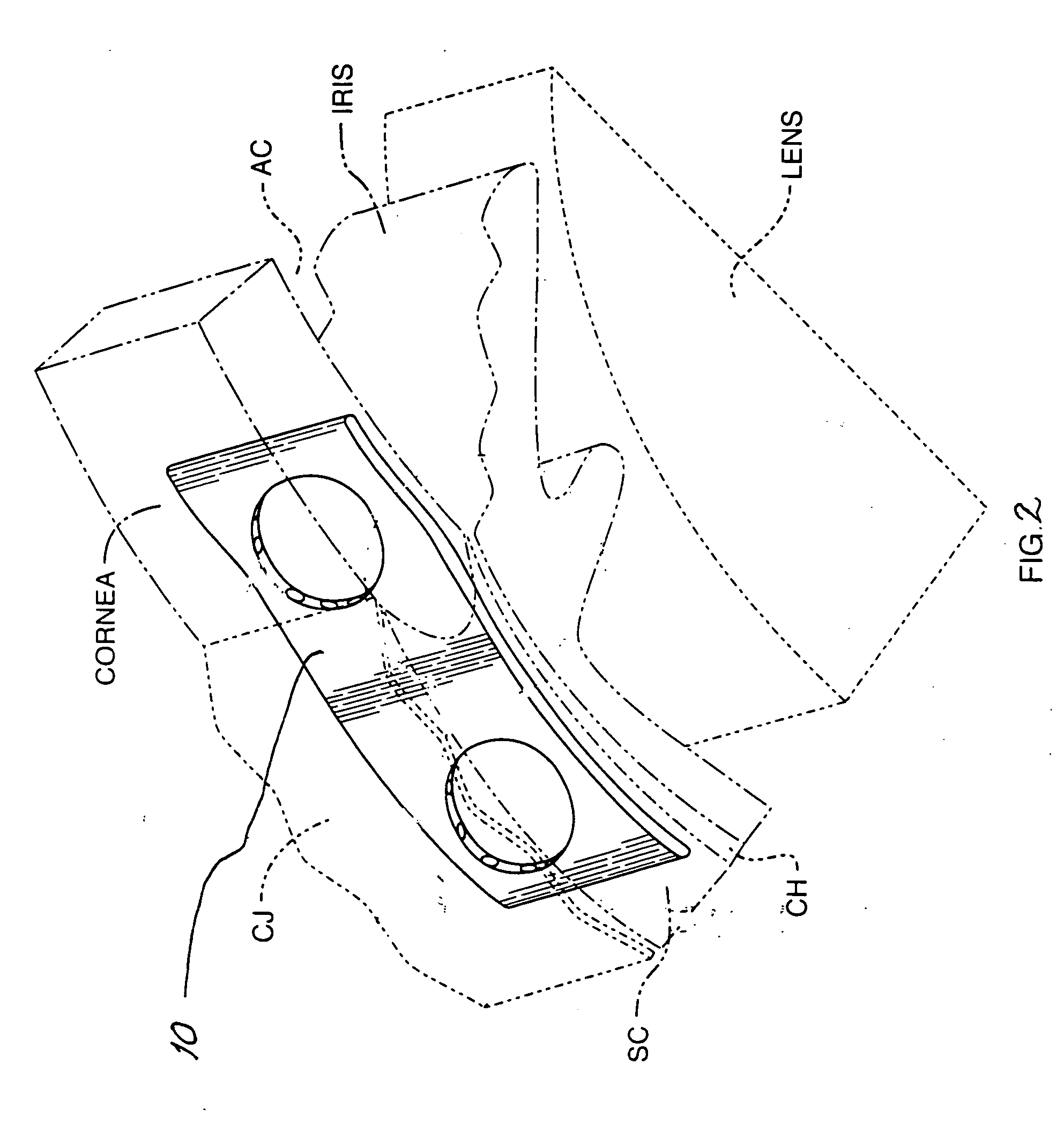
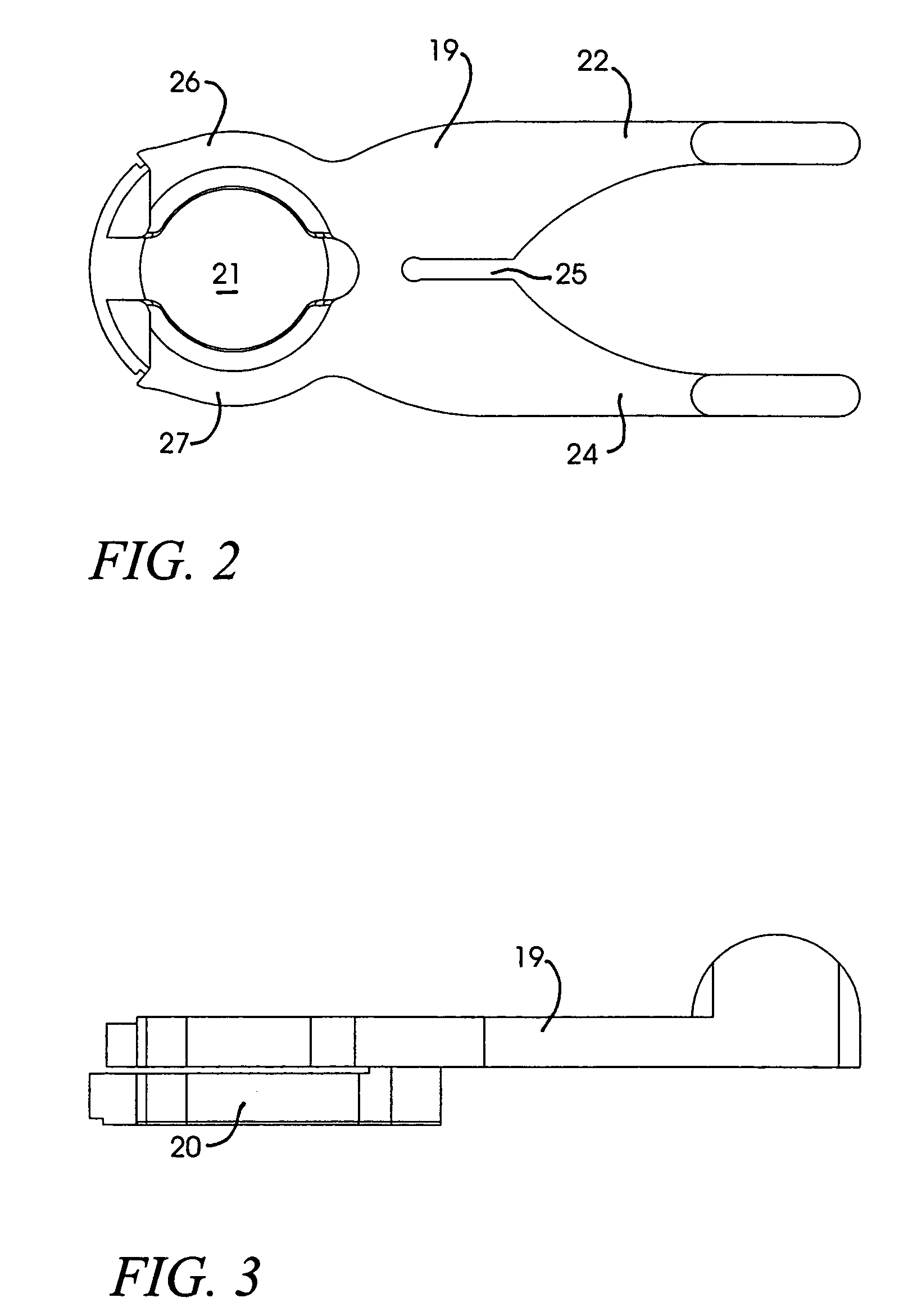
Ocular fixation and stabilization device for ophthalmic surgical applications
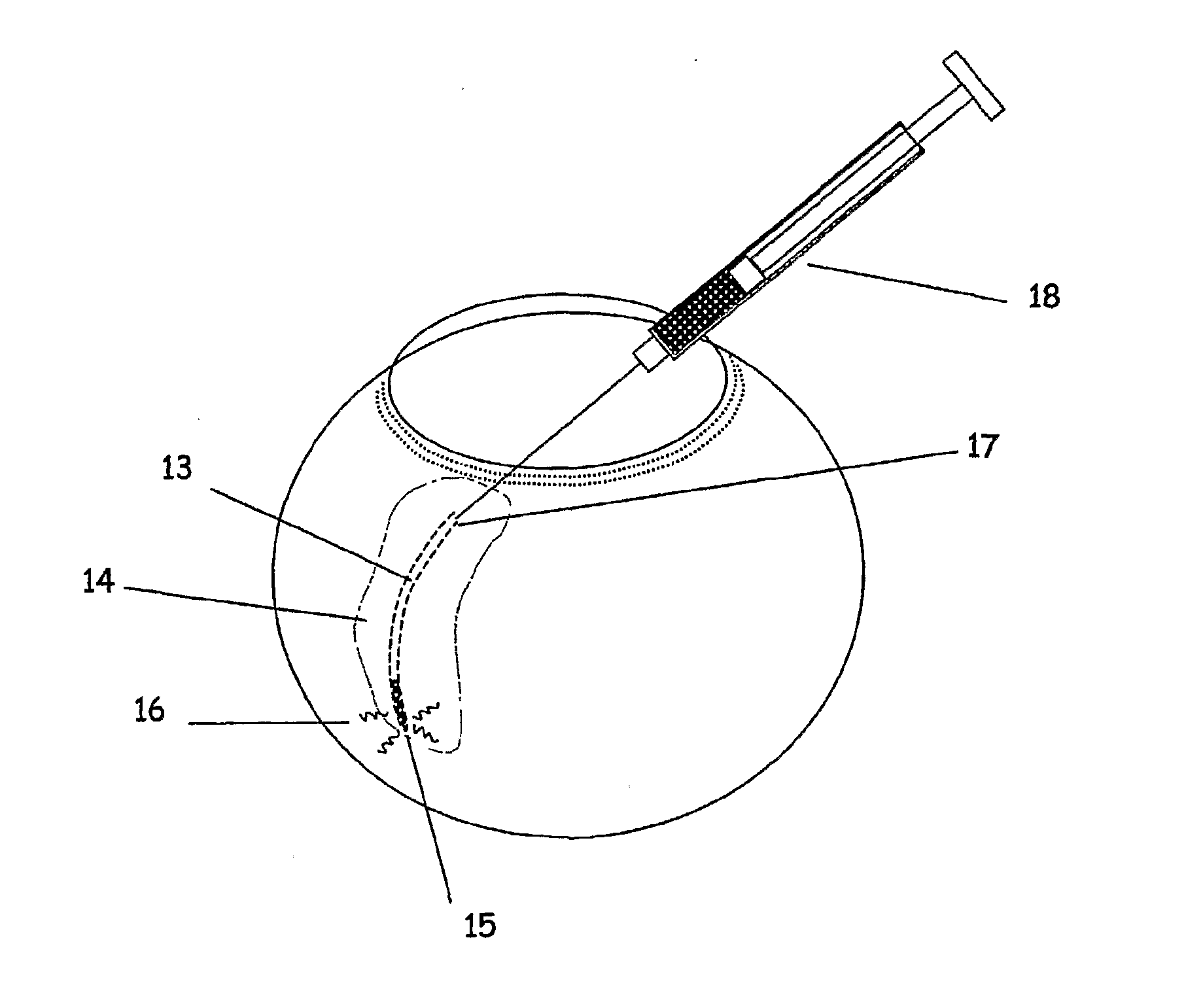
InactiveUS6863667B2Position stabilityLaser surgerySurgical instrument detailsEye laser surgeryCorneal surface
A disposable stabilization and applanation device for reconfiguring the cornea of an eye for ophthalmic laser surgery, includes an applanation lens that is disposed in a particular spatial position with respect to an incident laser beam. The applanation lens is inserted into the central opening of an attachment ring and applanates the eye in response to pressure from a lens cone. The attachment ring is coupled to the eye and includes a skirt which surrounds the applanation lens and extends outwardly therefrom to define a chamber. The skirt is formed with a groove which defines a suction channel between the attachment ring skirt and the corneal surface of an eye. A vacuum source is connected and fluid communication with the suction channel and is selectively activated to create a partial vacuum in the channel.
Owner:AMO DEVMENT
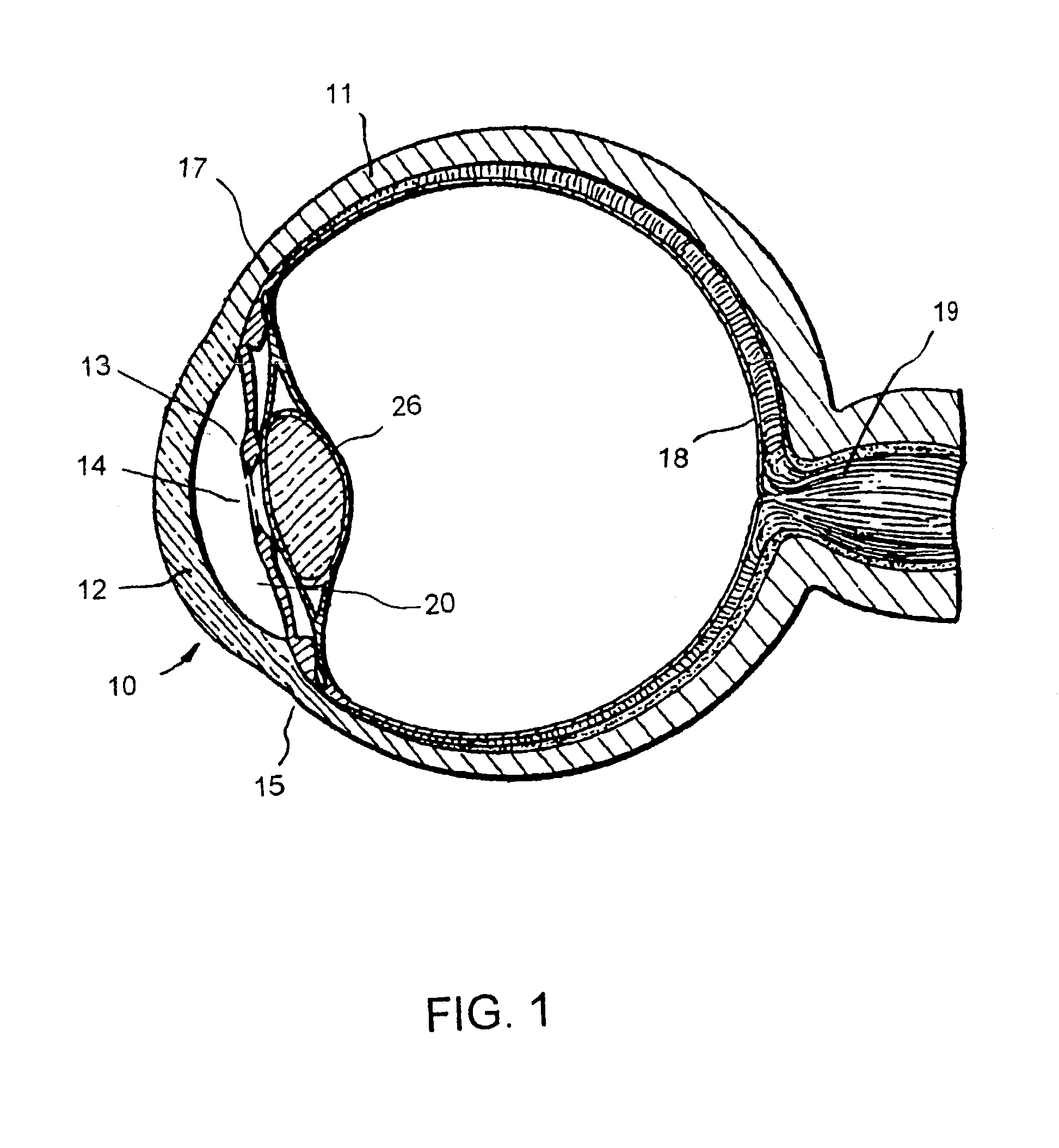
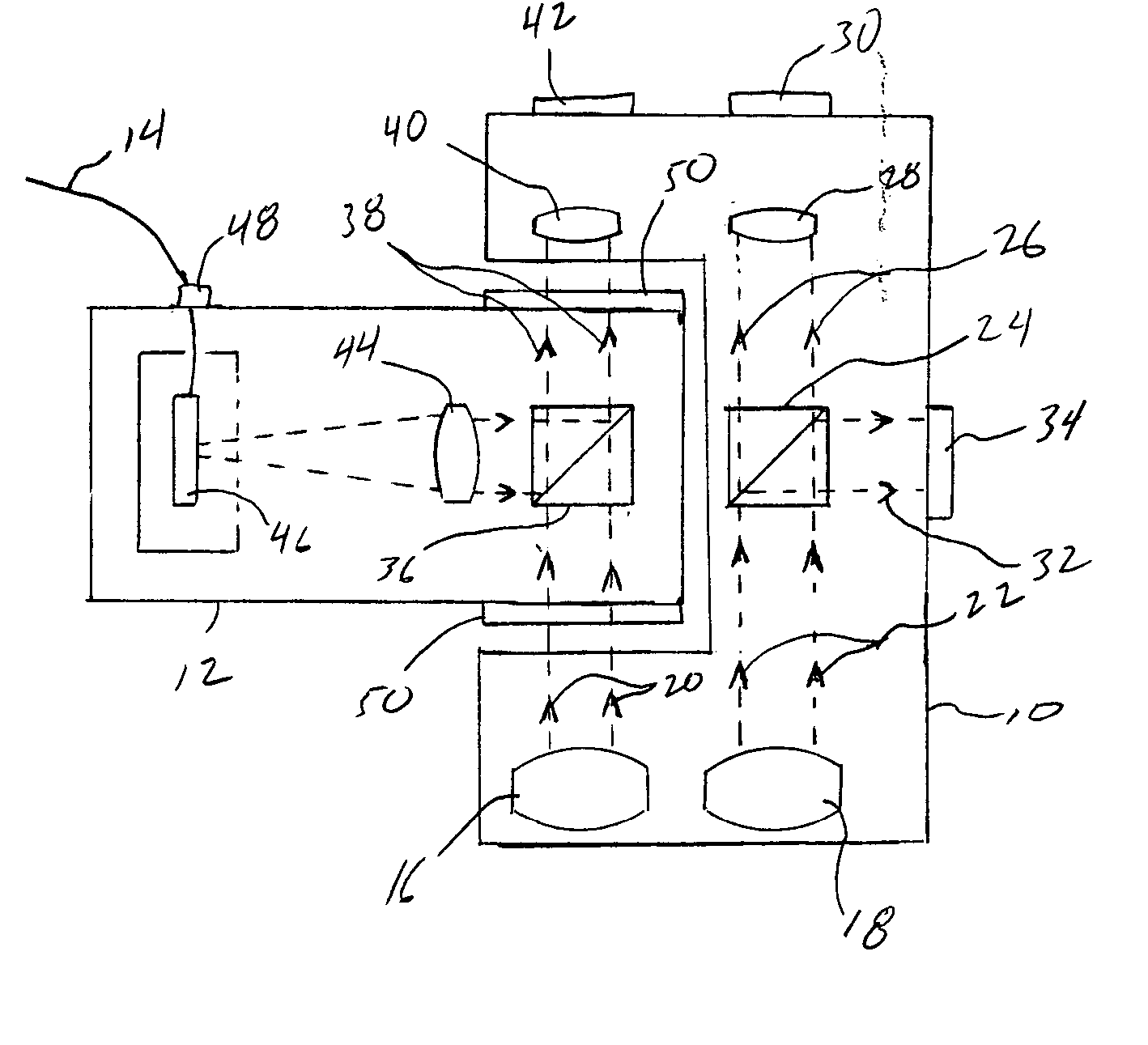
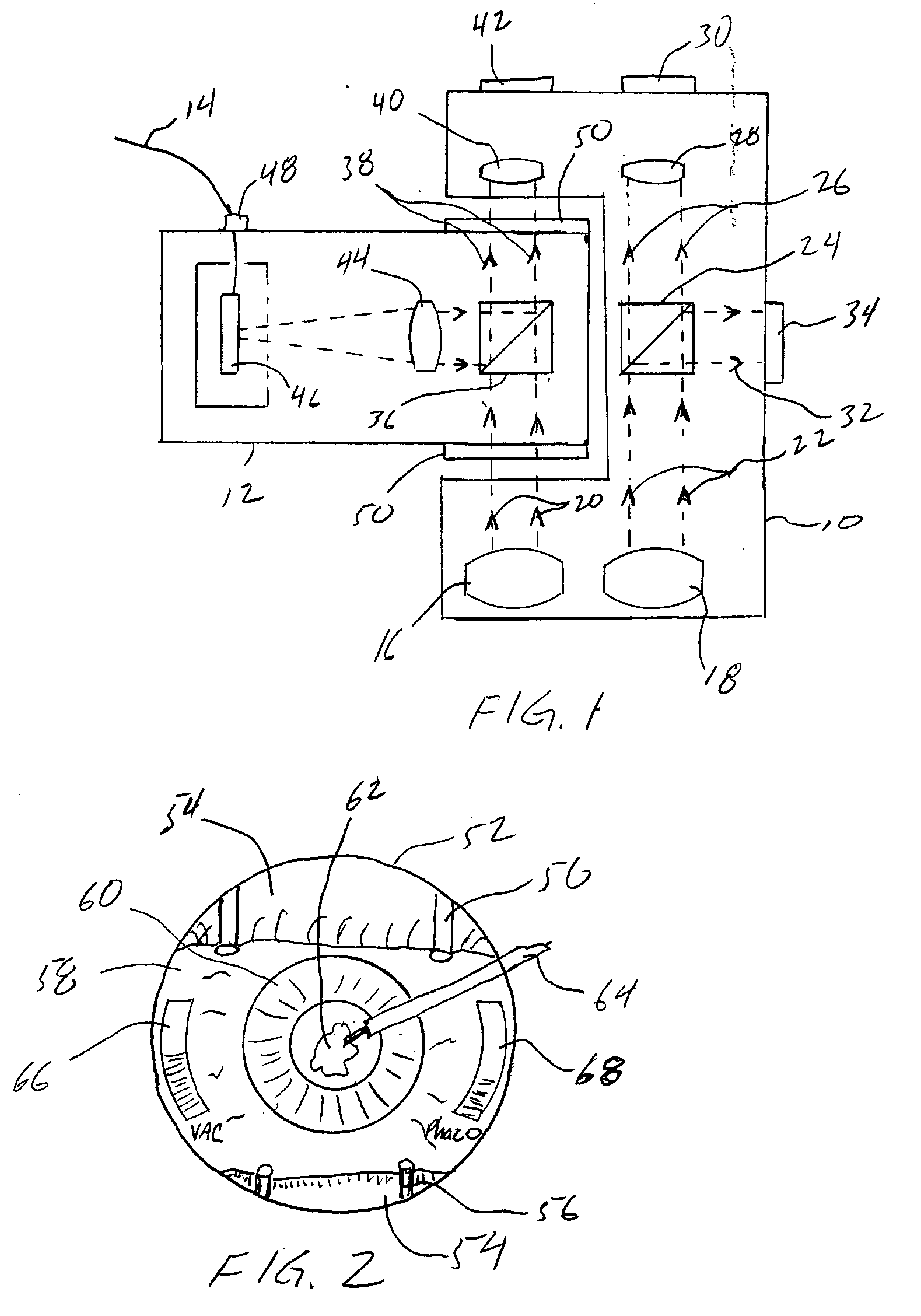
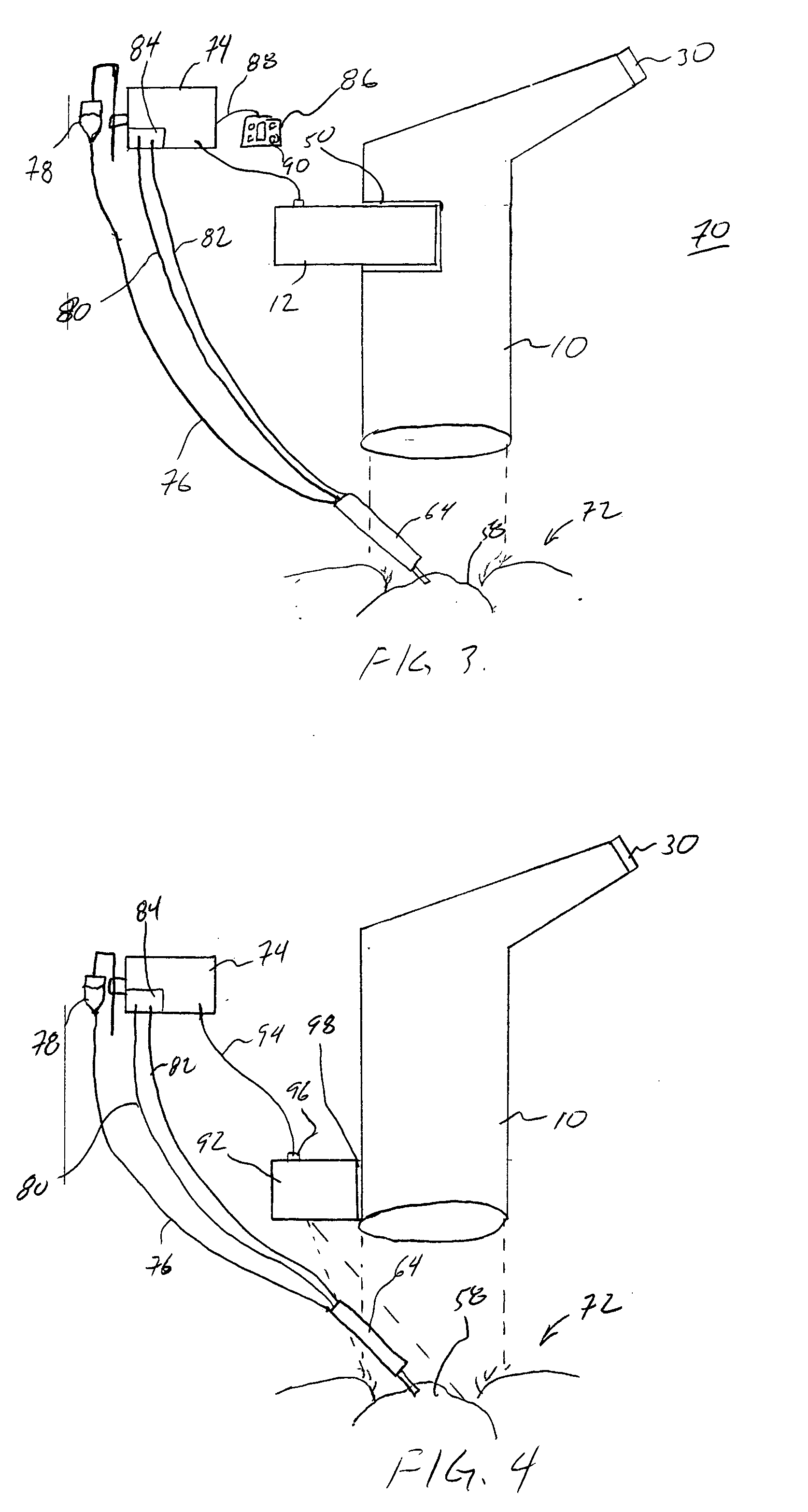
Heads-up display for displaying surgical parameters in a surgical microscope
An ophthalmic surgical system 70 includes a surgery-viewing device 10 for observing a surgical site 72. A surgical console 74 controls at least one surgical instrument 64. The surgical console 74 detects certain surgical parameters during surgery. A heads-up display 12 is connected to each of the surgery-viewing device 10 and the surgical console 74 for displaying at least one of the surgical parameters to a user through the surgery-viewing device 10.
Owner:BAUSCH & LOMB INC
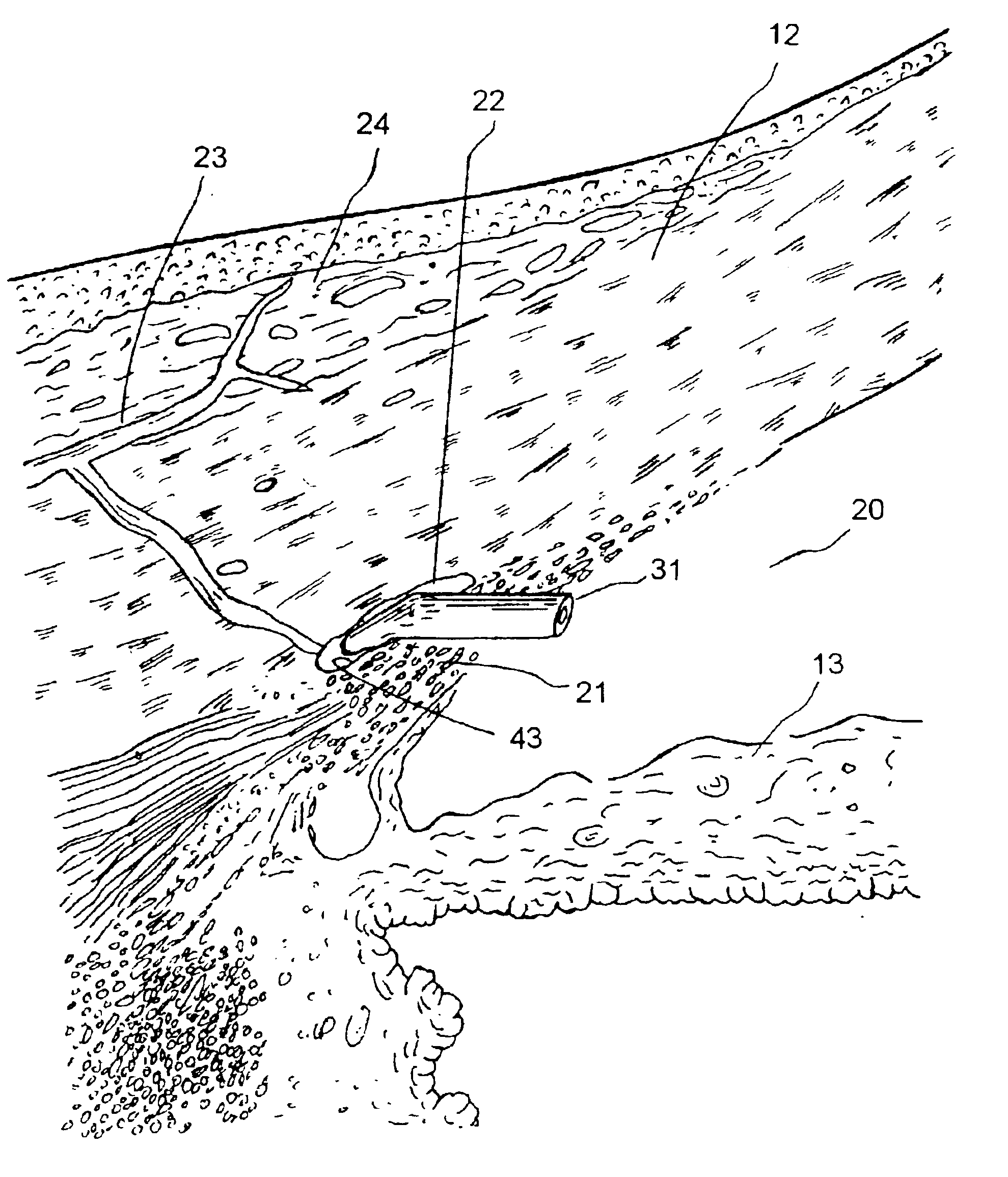
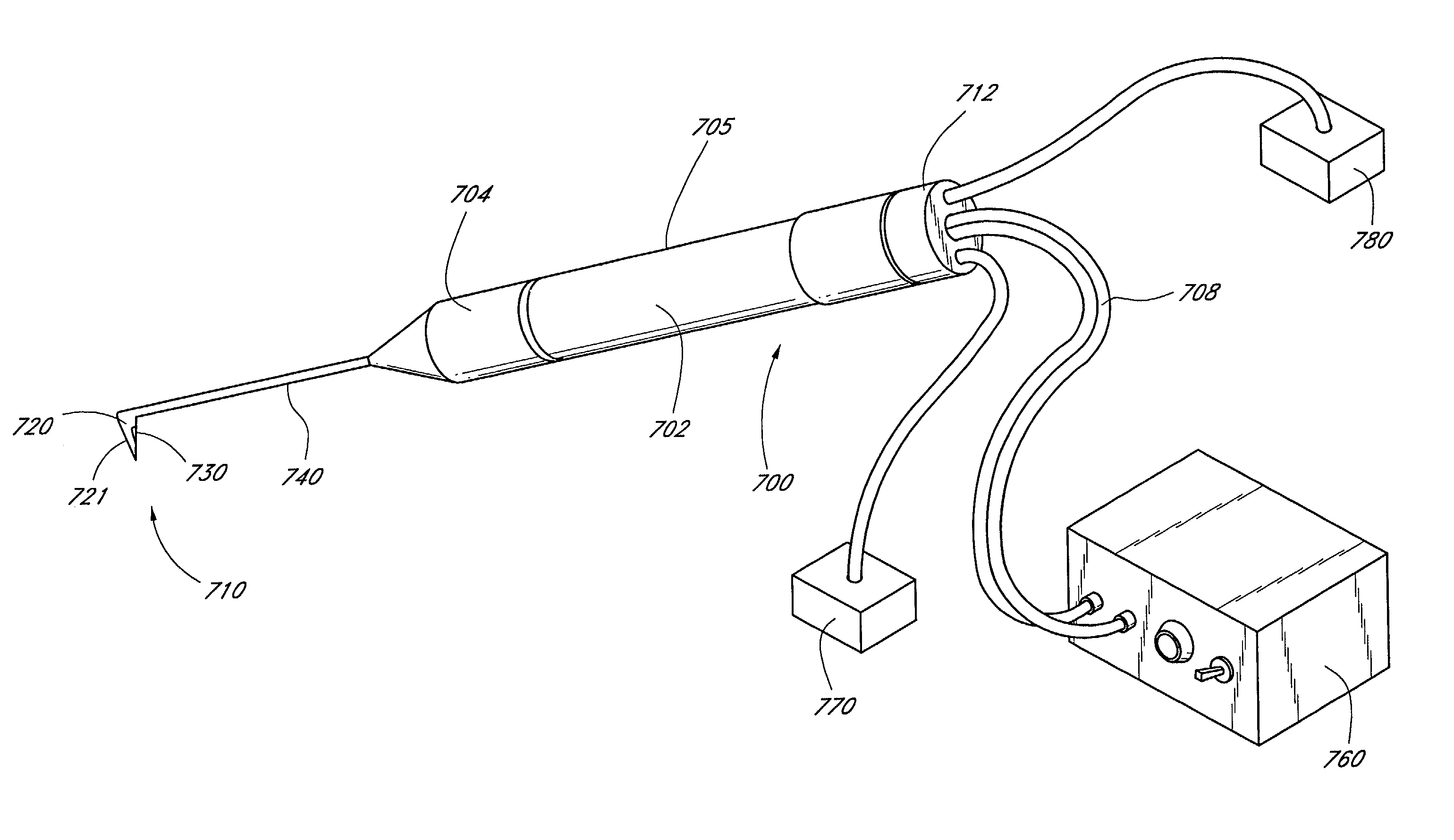
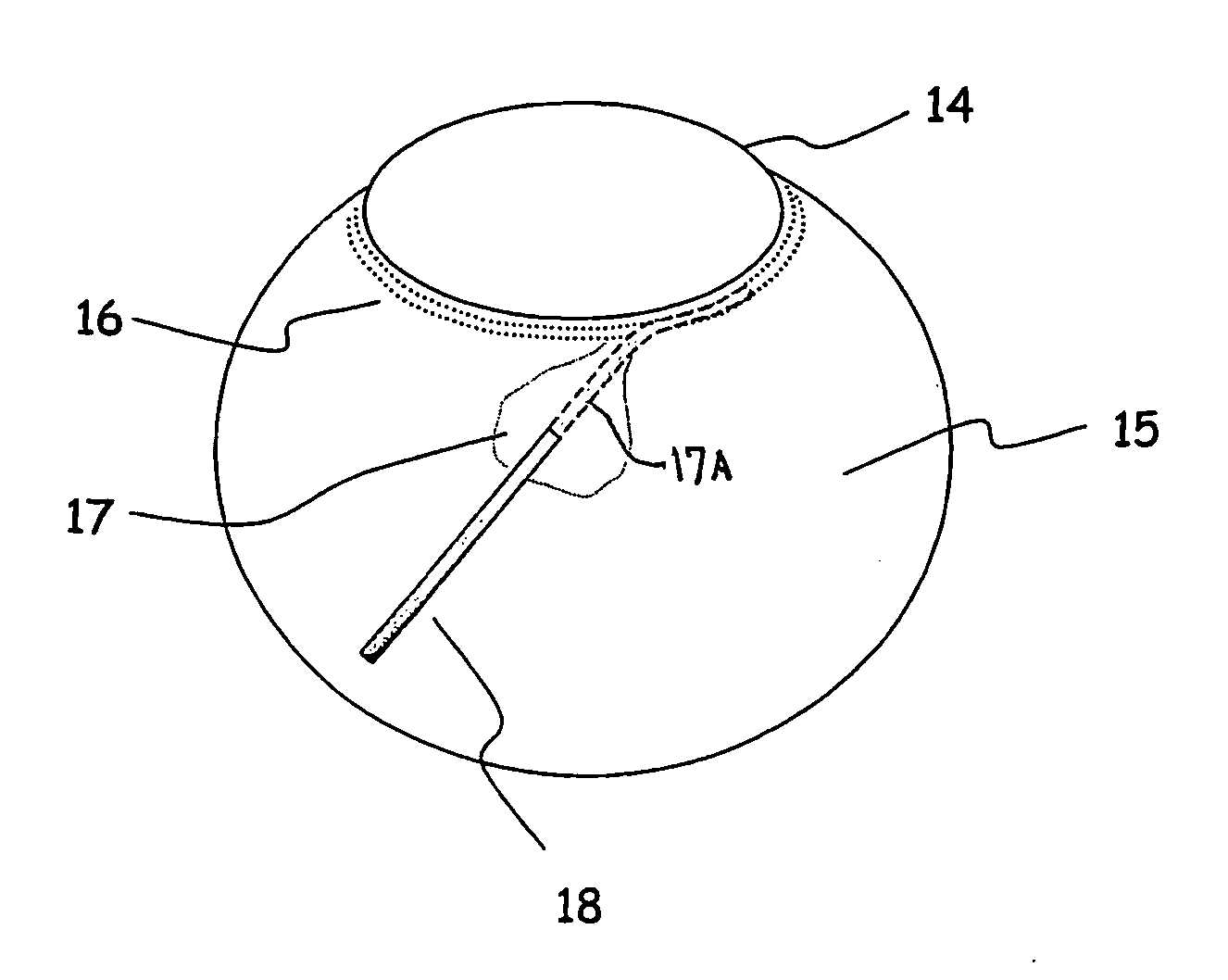
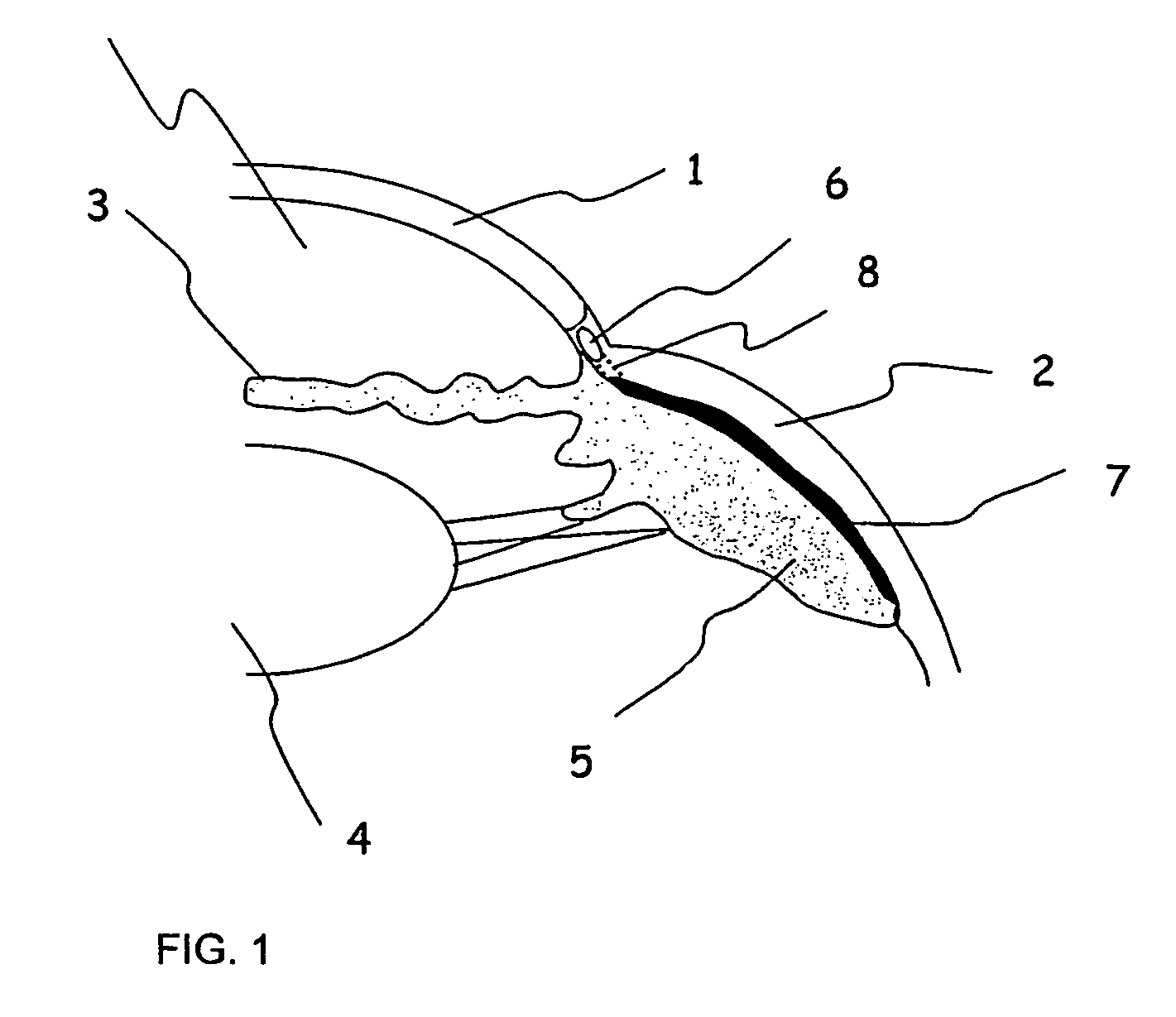
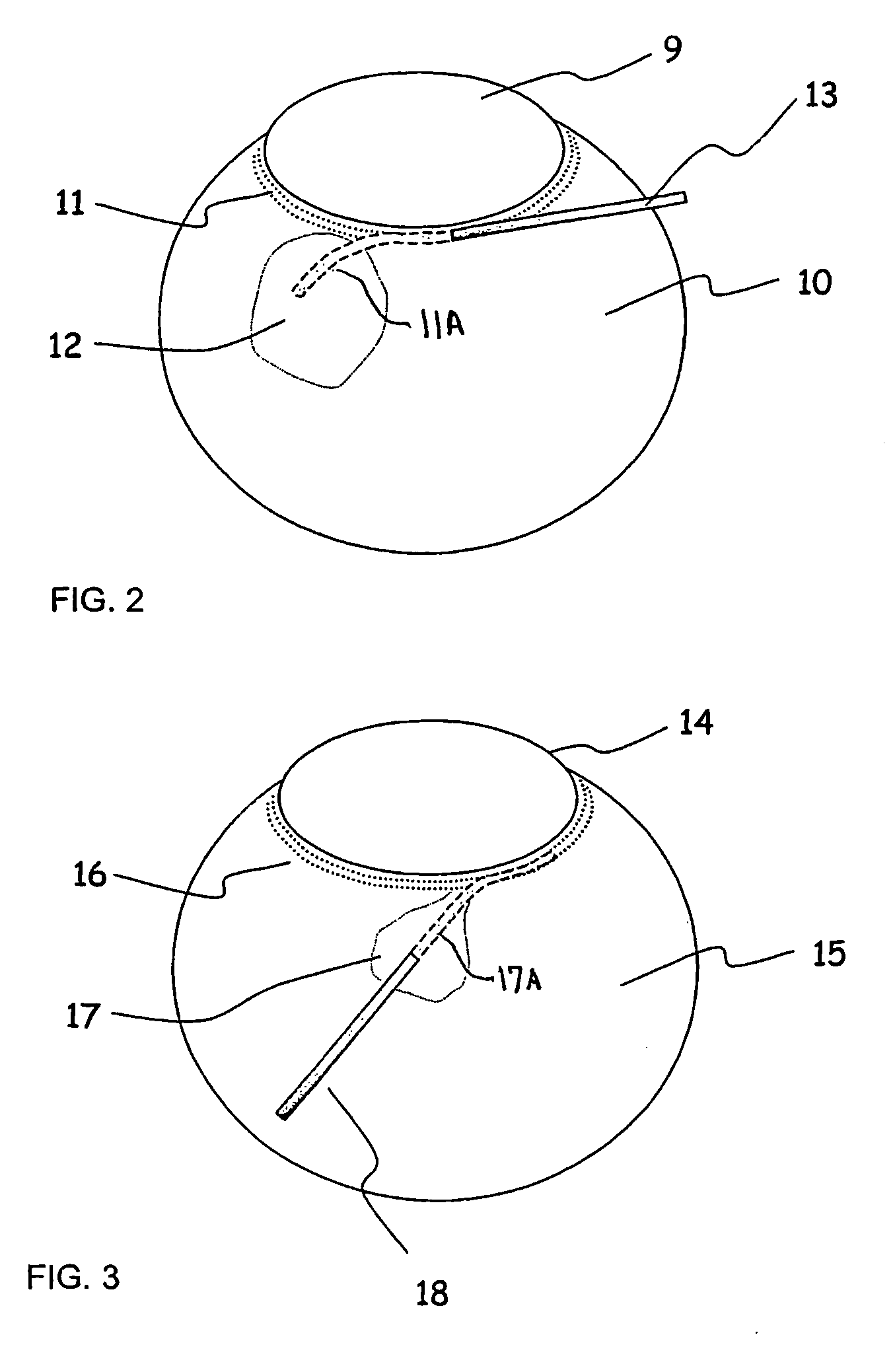
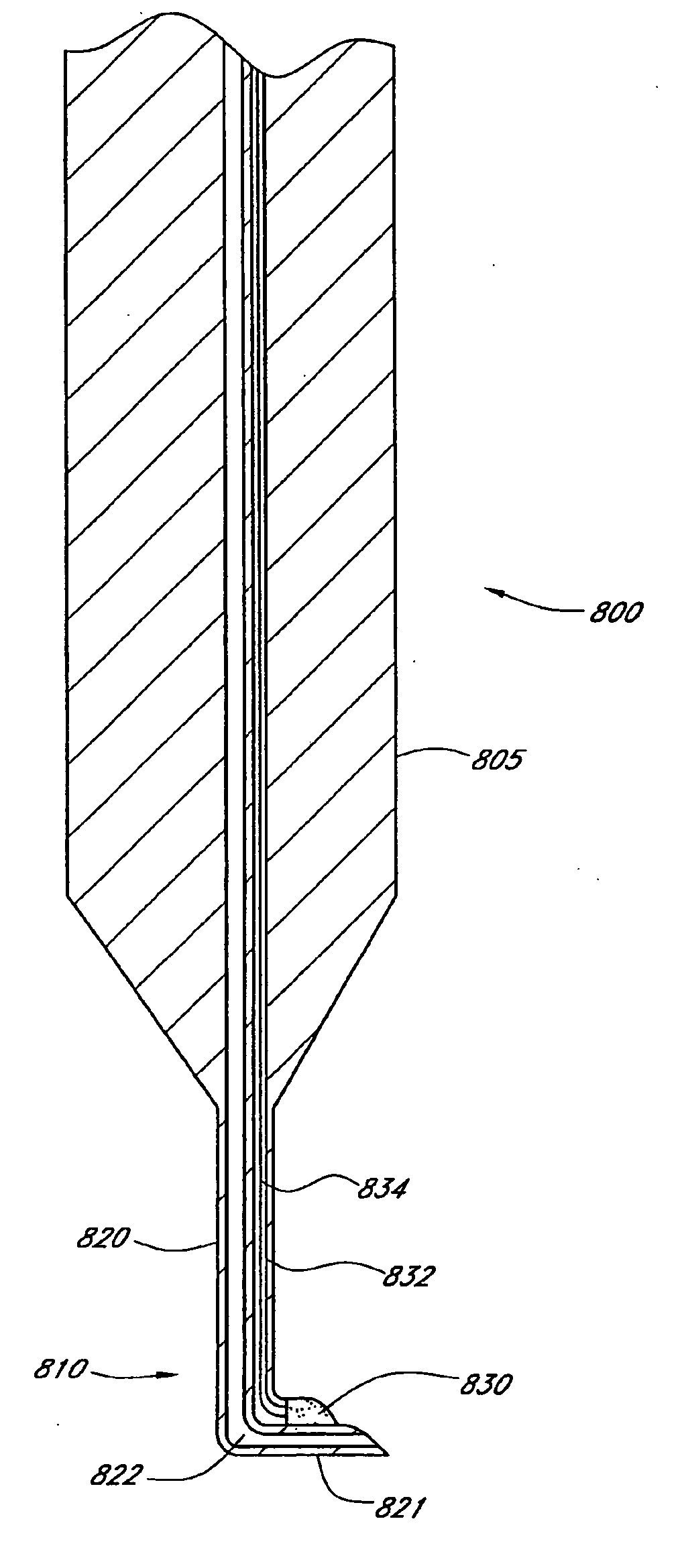
Apparatus And Method For Surgical Enhancement Of Aqueous Humor Drainage
An apparatus is provided for forming a tissue tract (8, 11A, 17A) from within a first passageway of an eye (11, 17) connecting to a second passageway in the eye (12, 16) comprising an elongated tool with a proximal end and distal end. The tool has an outer diameter in the range of about 50 to about 1000 microns. Methods of using the tool are provided for creating a fluid path for aqueous humor of an eye from a first passageway of the eye, such as the Schlemm's Canal, to a second passageway, such as the suprachoroidal space
Owner:ISCI INTERVENTIONAL CORP
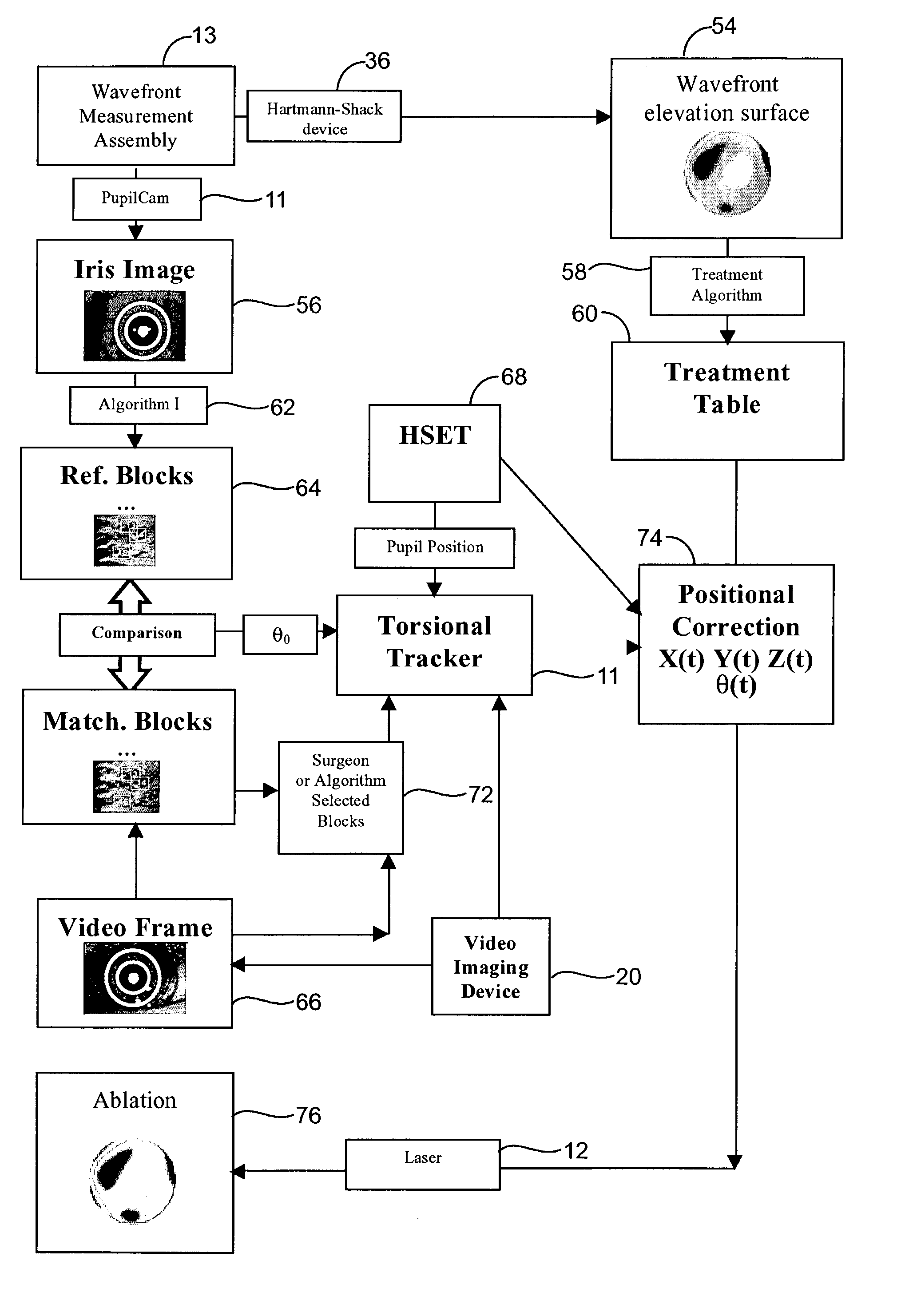
Methods and systems for tracking a torsional orientation and position of an eye
Methods and systems for tracking a position and torsional orientation of a patient's eye. In one embodiment, the present invention provides methods and software for registering a first image of an eye with a second image of an eye. In another embodiment, the present invention provides methods and software for tracking a torsional movement of the eye. In a particular usage, the present invention tracks the torsional cyclorotation and translational movement of a patient's eye so as to improve the delivery of a laser energy to the patient's cornea.
Owner:AMO MFG USA INC
Minimally invasive glaucoma surgical instrument and method
InactiveUS20060106370A1Easy accessEasy to solveLaser surgeryDiagnosticsSchlemm's canalMinimally invasive glaucoma surgery
Apparatuses and methods for the treatment of glaucoma are provided. The instrument uses either cauterization, a laser to ablate, sonic or ultrasonic energy to emulsify, or mechanical cutting of a portion of the trabecular meshwork. The instrument may also be provided with irrigation, aspiration, and a footplate. The footplate is used to enter Schlemm's canal, serves as a guide, and also protects Schlemm's canal.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Method and systems for laser treatment of presbyopia using offset imaging
InactiveUS6280435B1Less attractiveReduce discontinuityLaser surgerySurgical instrument detailsWide areaHyperopic astigmatism
Owner:AMO MFG USA INC
Multiple beam laser sculpting system and method
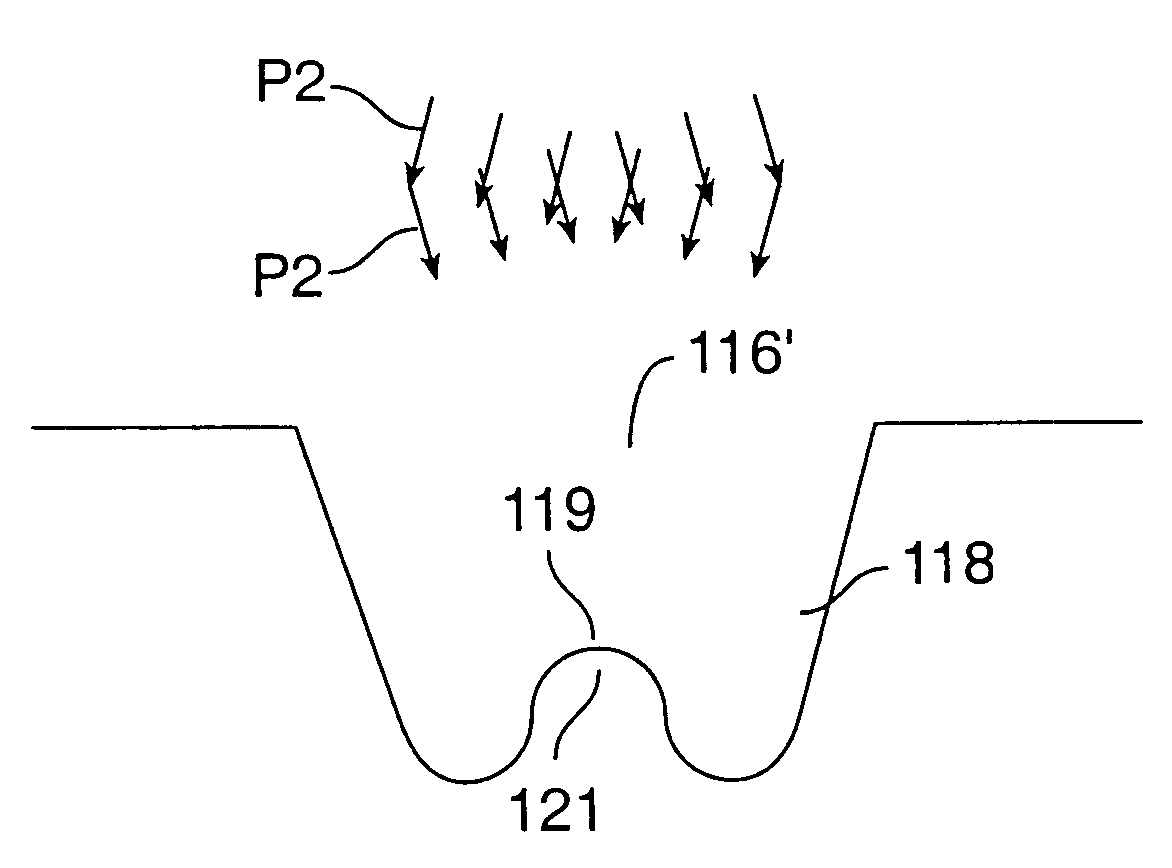
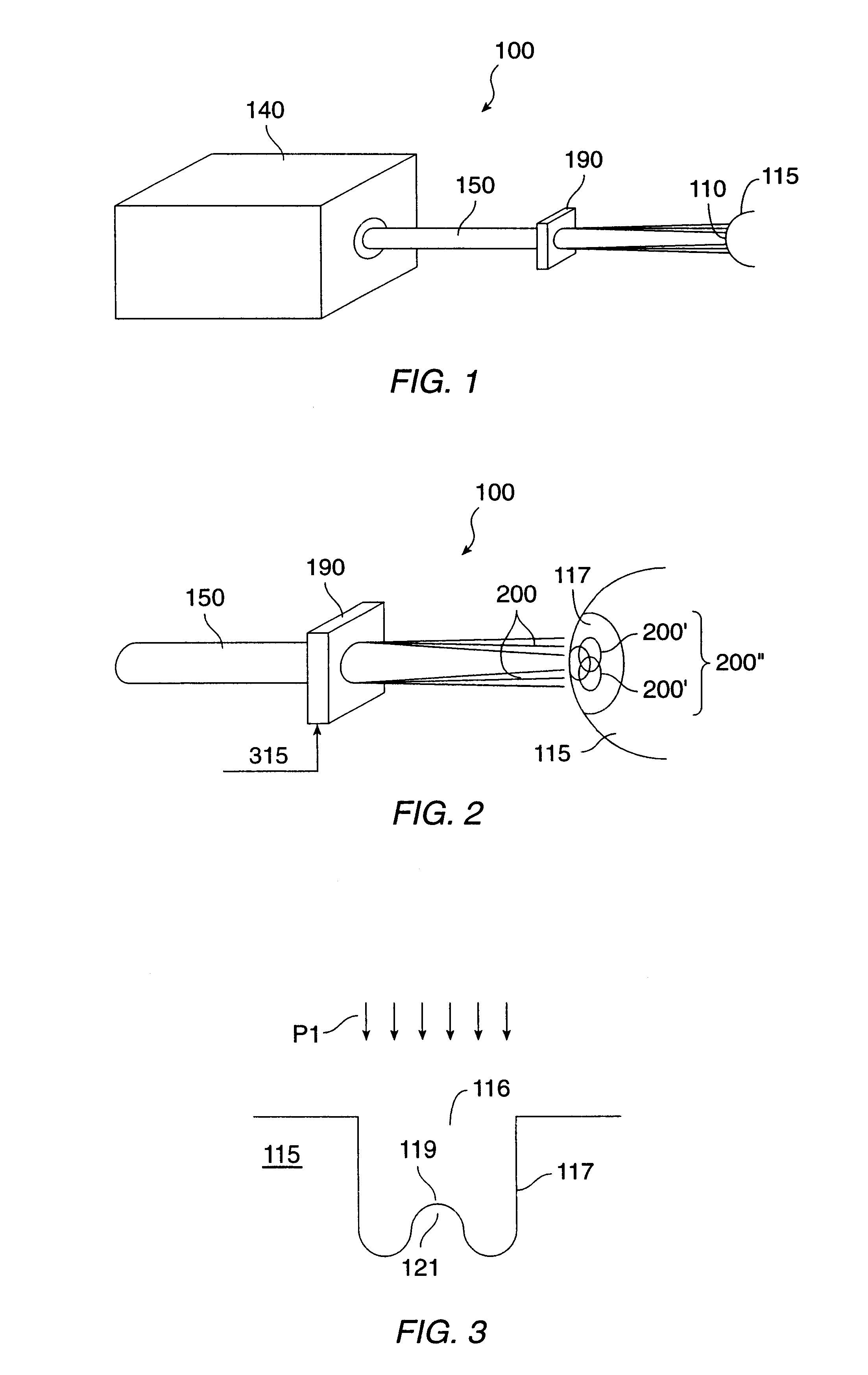
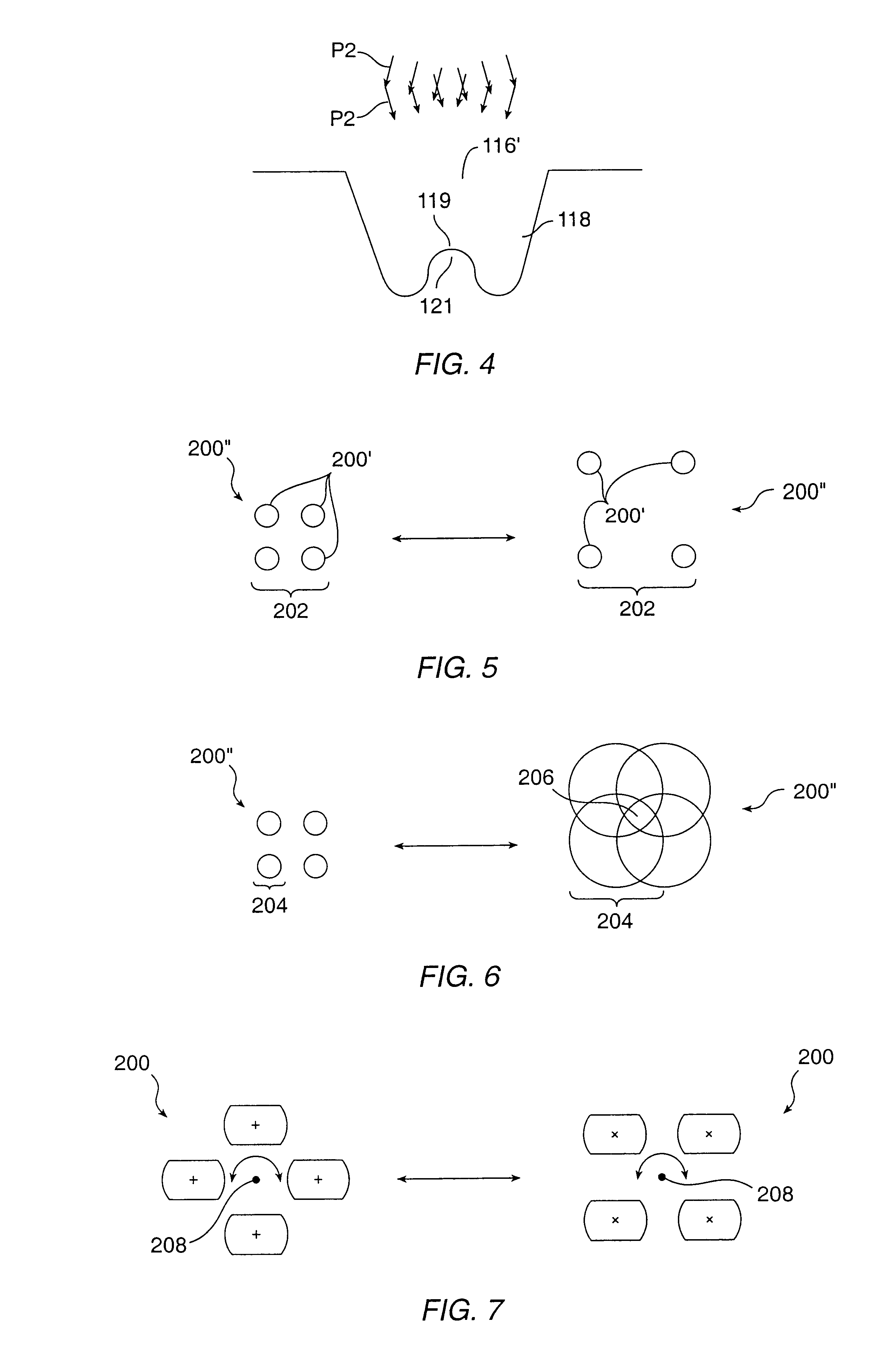
The invention improves the laser sculpting of a region of a material to a predetermined shape by improving the smoothness and accuracy of surfaces formed by the sculpting technique. The technique includes projecting plurality of partially overlapping beams toward the region. The invention includes blurring an edge of an ablation to smooth an internal portion of the ablation that is separate from the edge. The blurred edge may be formed by the partially overlapping beams. Using a computer controlled laser delivery system, the position and shape of the overlapping beams may be precisely controlled to sculpt the material to a desired shape according to a laser treatment table.
Owner:AMO MFG USA INC
Shunt for the treatment of glaucoma
InactiveUS20060069340A1Reducing ocular hypertensionLaser surgeryEye implantsIntraocular pressureFlow diverter
A system is provided for reducing intraocular pressure, the system having: an implantable shunt, the implantable shunt with a planar member, at least one microchannel disposed within that planar member, and a laser whereby at least one fenestration may be introduced into the microchannel.
Owner:SOLX
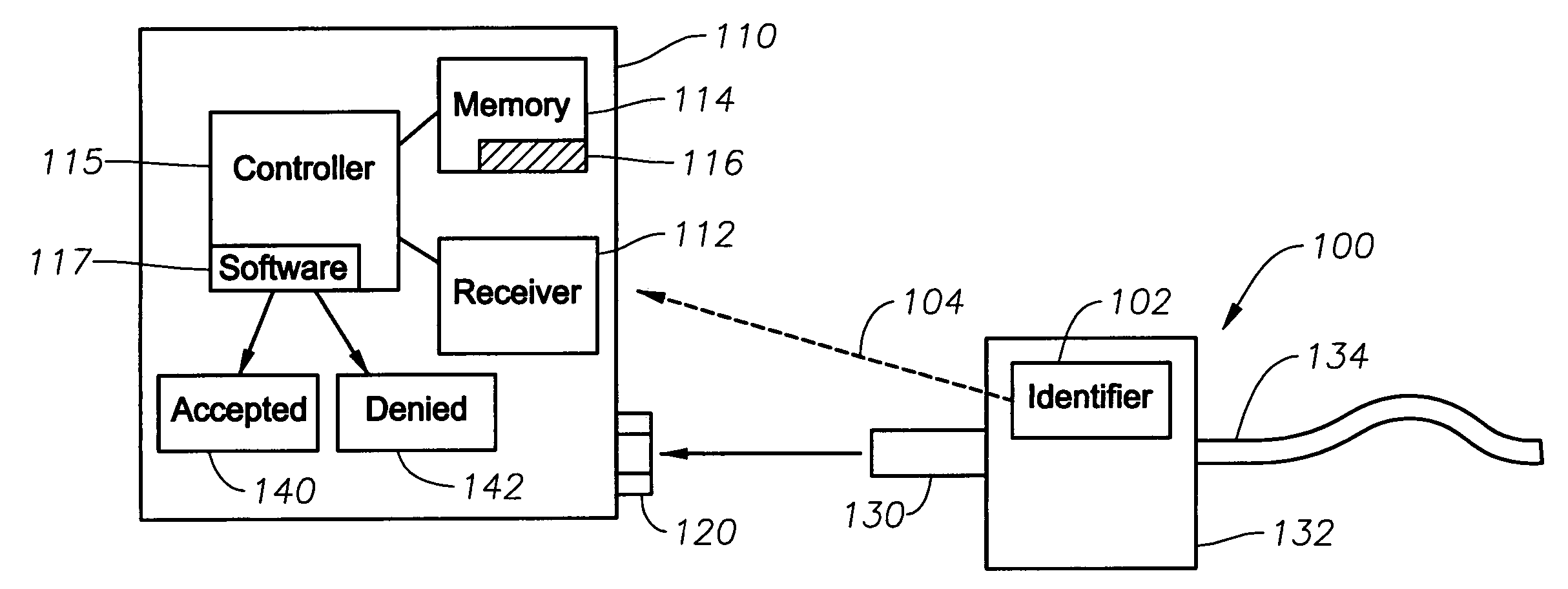
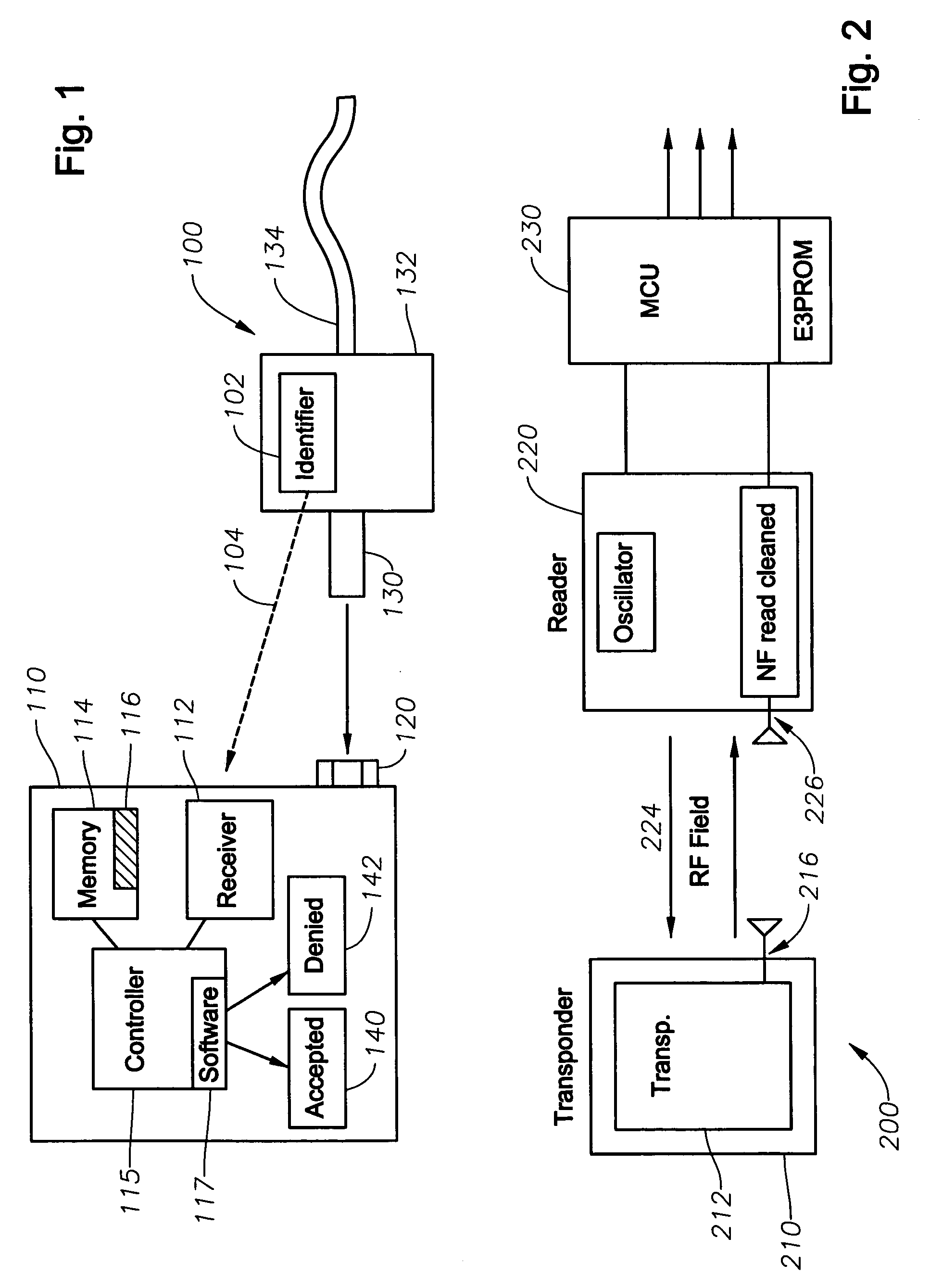
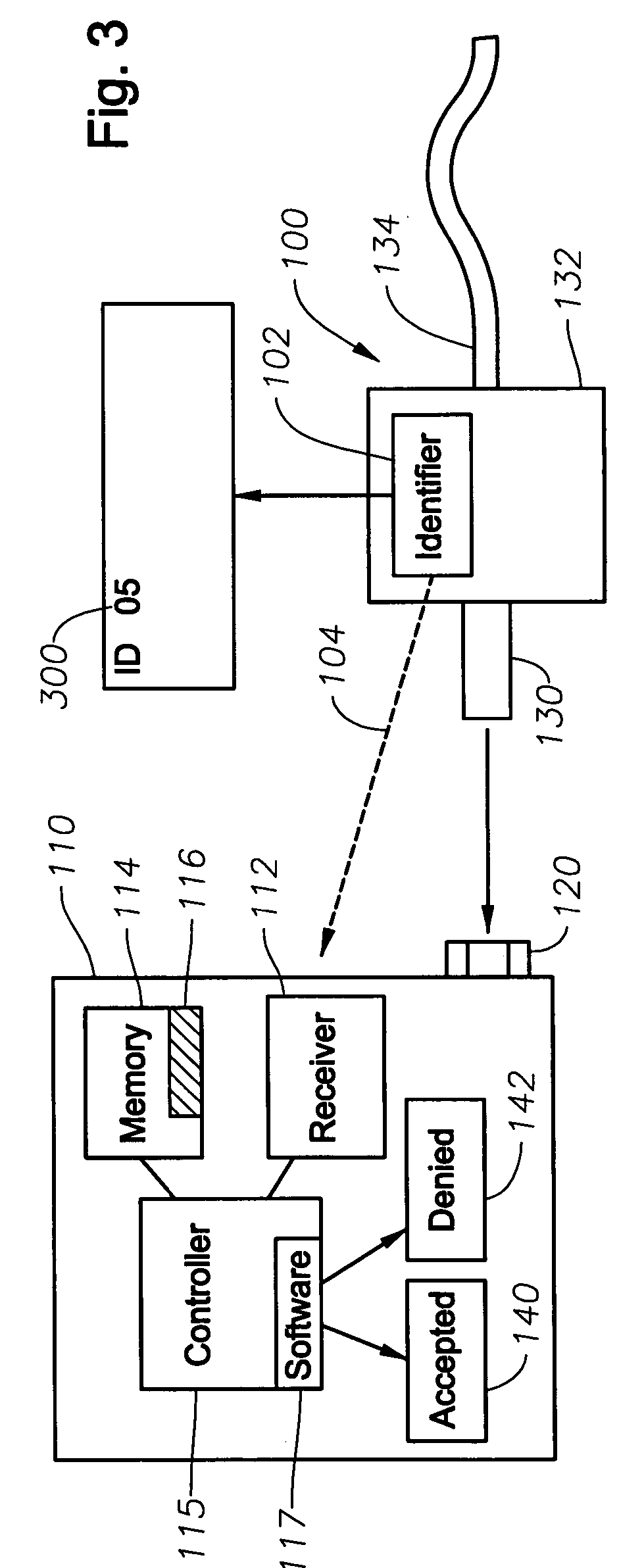
System and method for identifying and controlling ophthalmic surgical devices and components
System and method for identifying a component, such as an optical probe or pneumatic scissors, of an ophthalmic surgical device. A component of a surgical device includes an identifier, such as a RFID tag. Data from the RFID tag is transmitted to a RFID reader in the device. A controller determines whether the component corresponding to the received data is operable with the surgical device based on criteria, such as whether the received data is an authorized code that matches data stored in memory or whether the received data solves or satisfies an algorithm. The authorized codes are selected from a larger set of available codes. The controller enables or disables the operation of the device with the component based on whether the criteria is satisfied, the number of uses of the component, an amount of time that has passed since the component has been used, or a geographic location. The RFID data can also be used to calibrate the surgical device for use with the particular component and for inventory and monitoring purposes.
Owner:ALCON INC
Ocular fixation and stabilization device for ophthalmic surgical applications
A method for applanating an anterior surface of a cornea and coupling the eye to a surgical laser is disclosed. A interface is provided which has a central orifice and top and bottom surfaces. A suction ring is removably coupled to the bottom surface of the interface. The interface is positioned over an operative area of an eye, such that the suction ring comes into proximate contact with the surface of the eye. A suction is applied to the suction ring to stabilize the position of the interface relative to the operative area of the eye. An applanation lens is positioned in proximate contact with the operative area of the eye. Finally, the applanation lens is coupled to the interface to stabilize the position of the lens relative to the operative area of the eye.
Owner:AMO DEVMENT
System and method for providing the shaped structural weakening of the human lens with a laser
ActiveUS20070185475A1Increase amplitudeImprove errorLaser surgeryDiagnosticsRefractive errorRefraction errors
A system and method for increasing the amplitude of accommodation and / or changing the refractive power of lens material of a natural crystalline lens is provided. Generally, there is provided methods and systems for delivering a laser beam to a lens of an eye in a plurality of sectional patterns results in the shaped structural weakening of the lens. There is also provided a method and system for determining adjustments to refractive errors in the lens of an eye relating to the treatment of presbyopia. The change to refractive error can be a predicted error or an actual error that has been determined.
Owner:LENSAR LLC
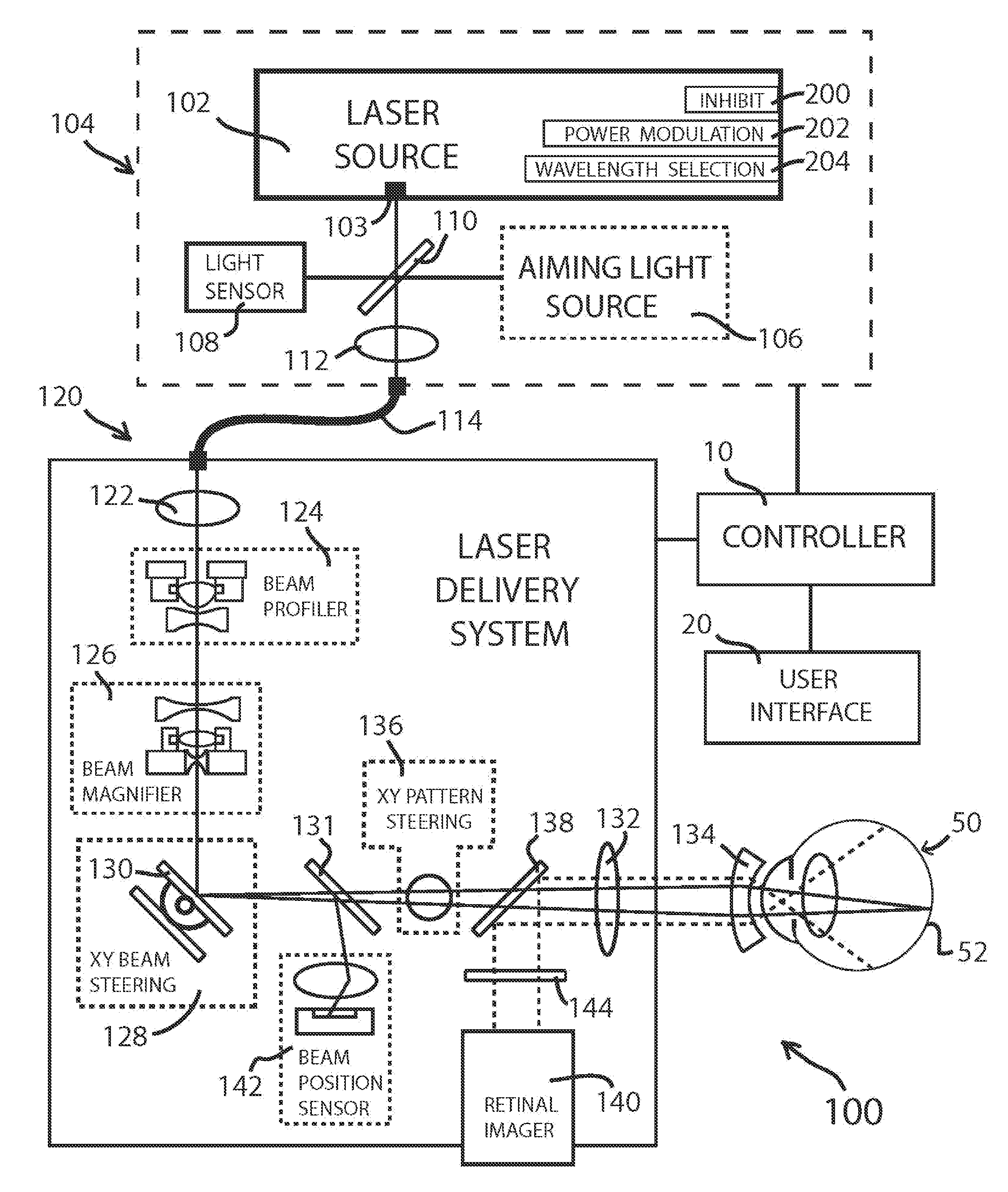
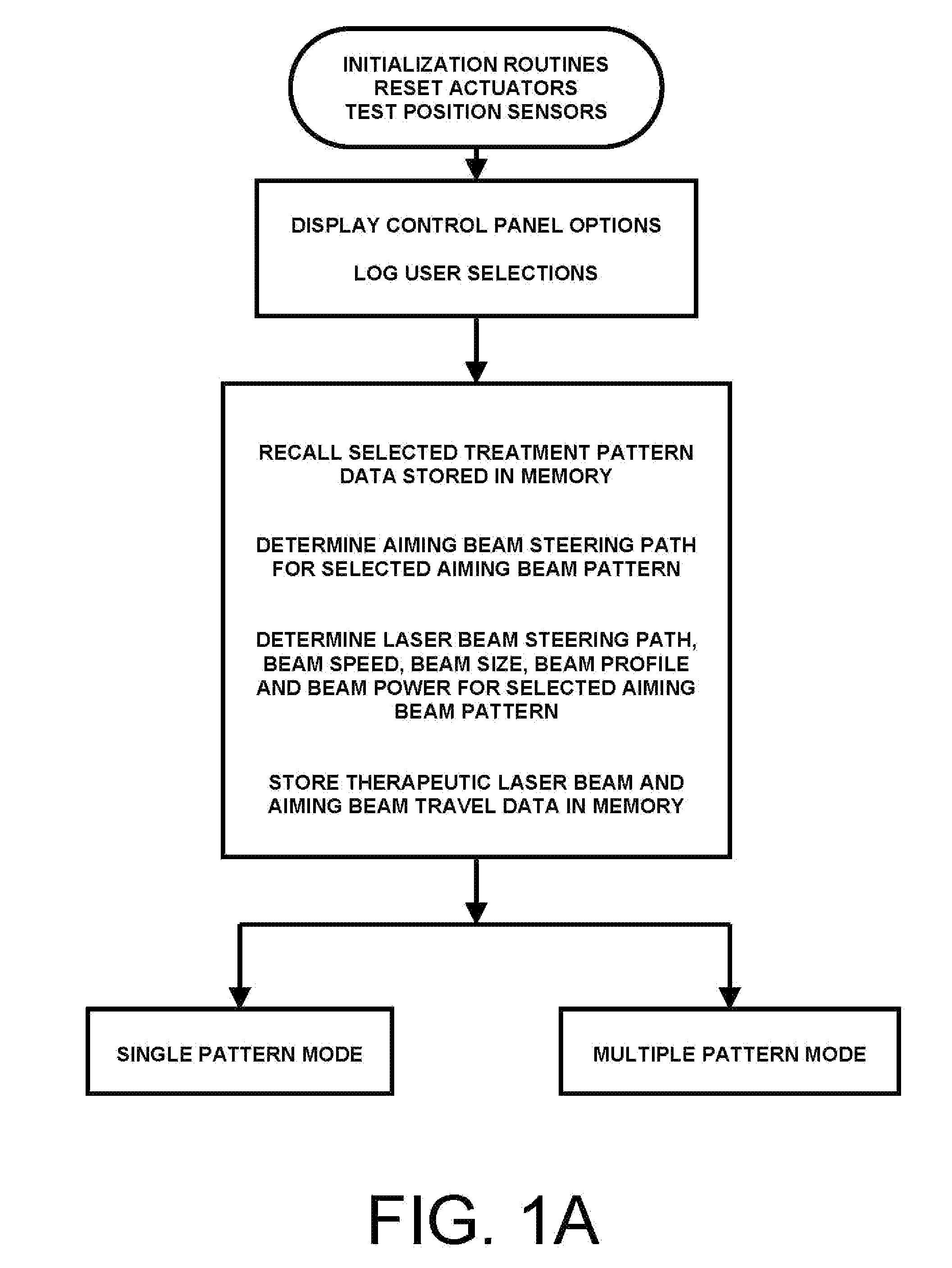
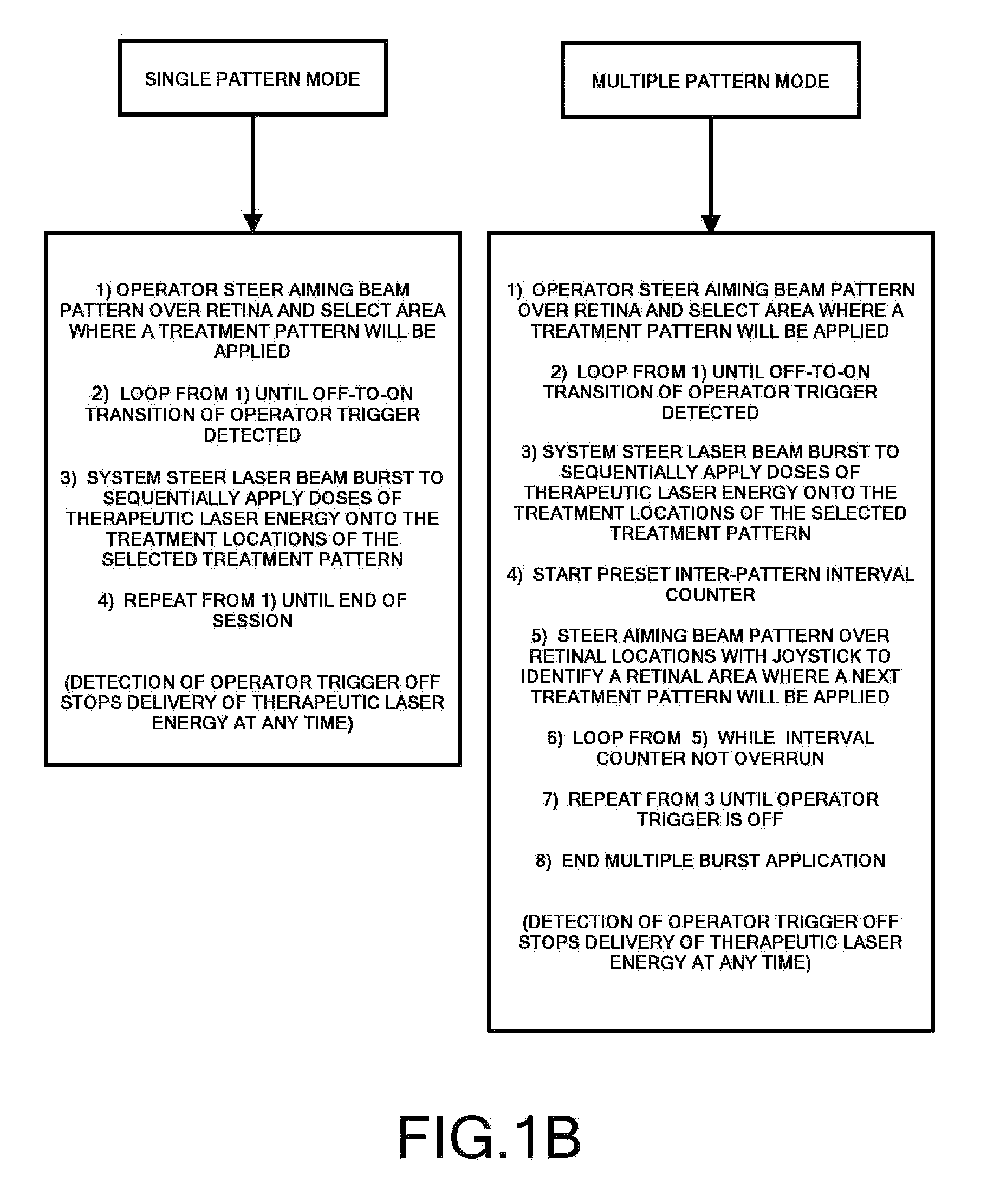
Steering laser treatment system and method of use
A system and method for delivering therapeutic laser energy onto selected treatment locations of the retina following a predetermined spatial distribution pattern using one single laser beam. A beam steering mechanism and control system delivers the laser energy sequentially to treatment locations forming a pre-selected treatment layout pattern. The invention allows time consuming therapeutic laser procedures such as pan-retinal photo-coagulation and segmental photocoagulation to be performed with increased accuracy and in a fraction of the time currently required for such procedures.
Owner:MOTOROLA MOBILITY LLC
Method for patterned plasma-mediated modification of the crystalline lens
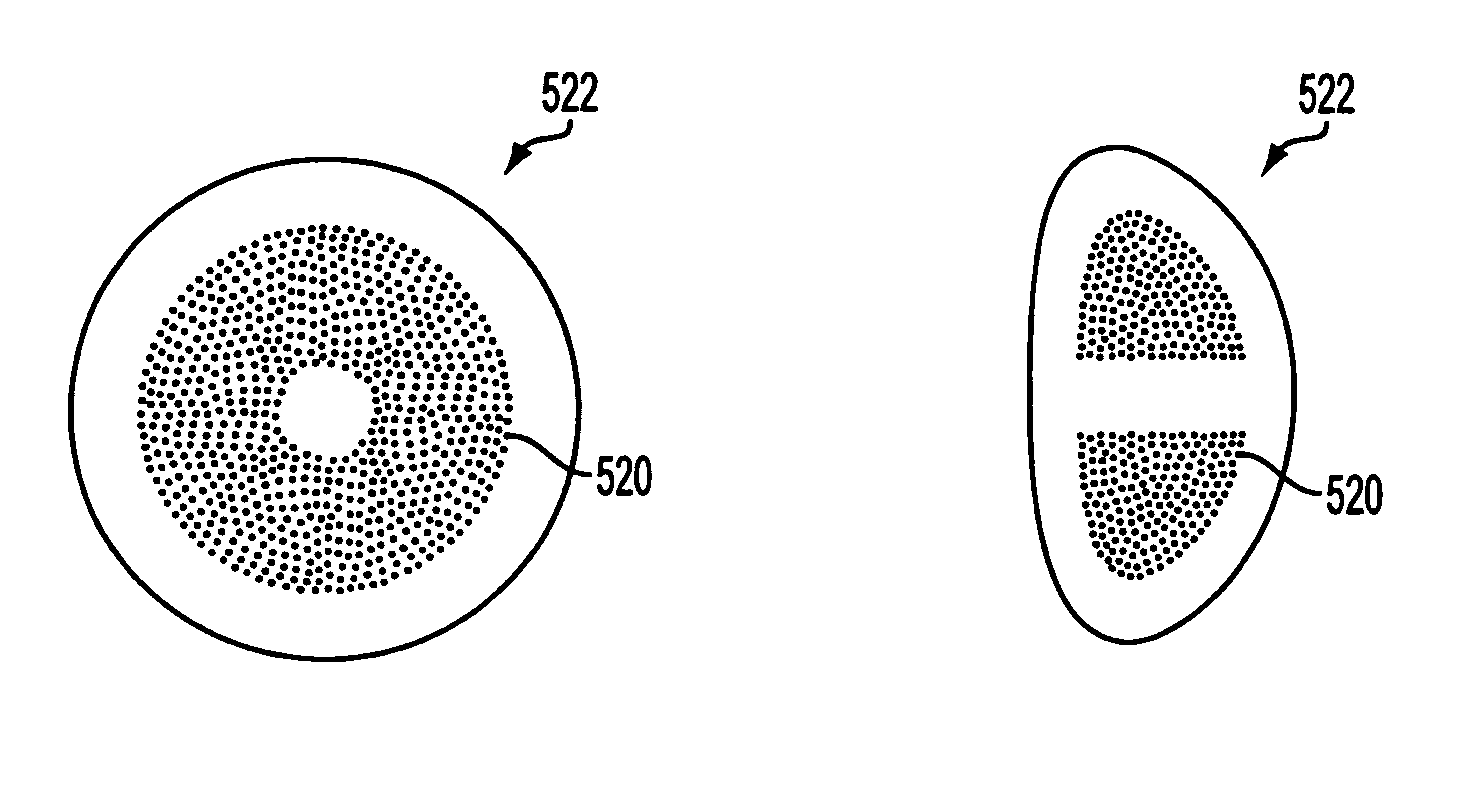
A method of treating a lens of a patient's eye includes generating a light beam, deflecting the light beam using a scanner to form a treatment pattern of the light beam, delivering the treatment pattern to the lens of a patient's eye to create a plurality of cuts in the lens in the form of the treatment pattern to break the lens up into a plurality of pieces, and removing the lens pieces from the patient's eye. The lens pieces can then be mechanically removed. The light beam can be used to create larger segmenting cuts into the lens, as well as smaller softening cuts that soften the lens for easier removal.
Owner:AMO DEVMENT
Devices and techniques for treating glaucoma
InactiveUS6989007B2Improve facilitiesGood mannersLaser surgeryDiagnosticsOpen angle glaucomaAqueous outflow
A system for non-invasive treatment of a patient's trabecular meshwork to treat primary open-angle glaucoma. The system and technique applies energy directly to media within clogged spaces in a patient's trabecular meshwork to increase aqueous outflow facility by (i) localization of microimplantable bodies carrying a selected exogenous chromophore, such as particles with a gold surface, in deeper regions of the trabecular meshwork, and (ii) irradiation of the microimplantables with a selected coherent wavelength having a power level and pulse duration that is strongly absorbed by the surfaces of the microimplantables.
Owner:OCCULOGIX CORP
Apparatus and method for ocular treatment
InactiveUS20100173866A1Facilitate tissue targetingSafely reachedLaser surgeryOrganic active ingredientsLess invasive surgerySuprachoroidal space
The invention provides tools, materials and related methods to surgically access the suprachoroidal space of an eye for the purpose of performing minimally invasive surgery or to deliver drugs to the eye. The invention provides a flexible microcannula or microcatheter device (11, 13) that may be placed into the suprachoroidal space (12, 14) through a small incision (12A) of the overlying tissues, maneuvered into the appropriate region of the space, and then activated to treat tissues adjacent to the distal tip of the device.
Owner:ISCI INTERVENTIONAL CORP
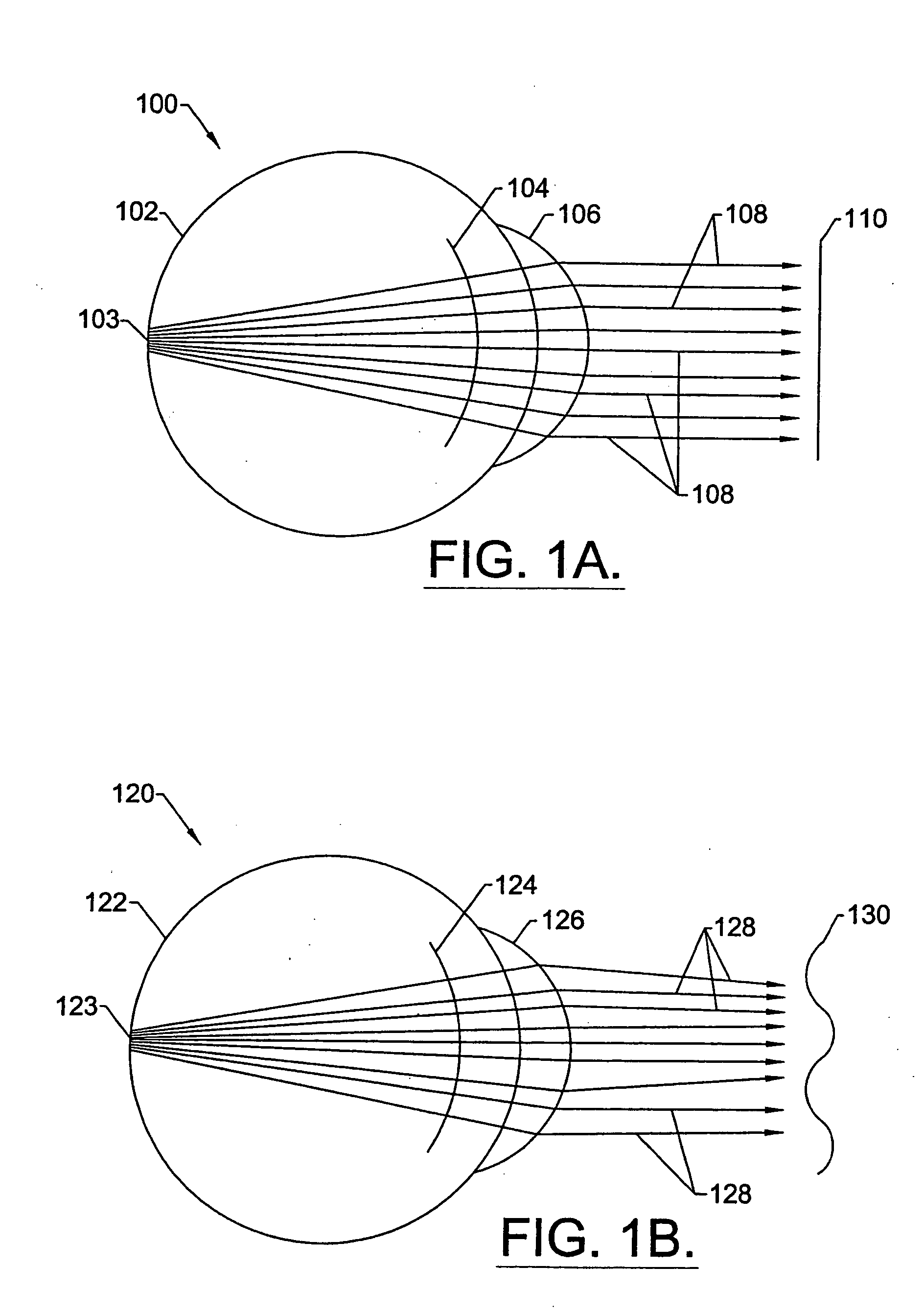
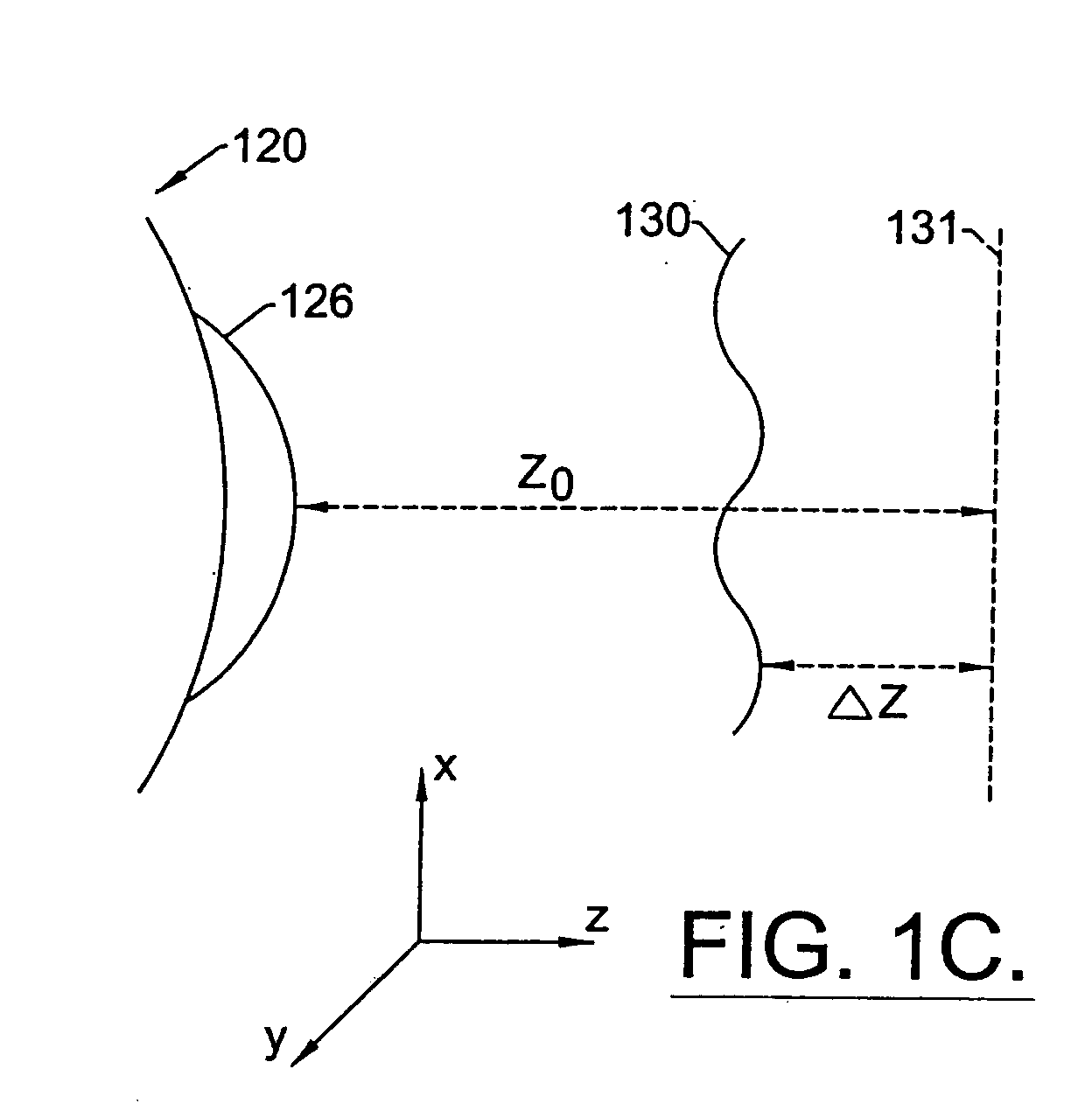
Method for determining and correcting vision
InactiveUS20050124983A1Simple and inexpensive designImprove visual effectsLaser surgerySurgical instrument detailsRefractive indexOptical path length
A method for enhancing vision of an eye includes a laser delivery system having a laser beam for ablating corneal material from the cornea of the eye. Measurements are made to determine an optical path difference between a plane wave and a wavefront emanating from the retina of the eye for a location at a surface of the cornea. An optical correction is provided to the laser delivery system for the location based on the optical path difference and refractive indices of media through which the wavefront passes. The optical correction includes dividing the optical path difference by a difference between an index of refraction of corneal material and an index of refraction of air. The laser beam is directed to the location on the surface of the cornea and corneal material ablated at the location in response to the optical correction to cause the wavefront to approximate the shape of the plane wave at that location.
Owner:FREY RUDOLPH W +4
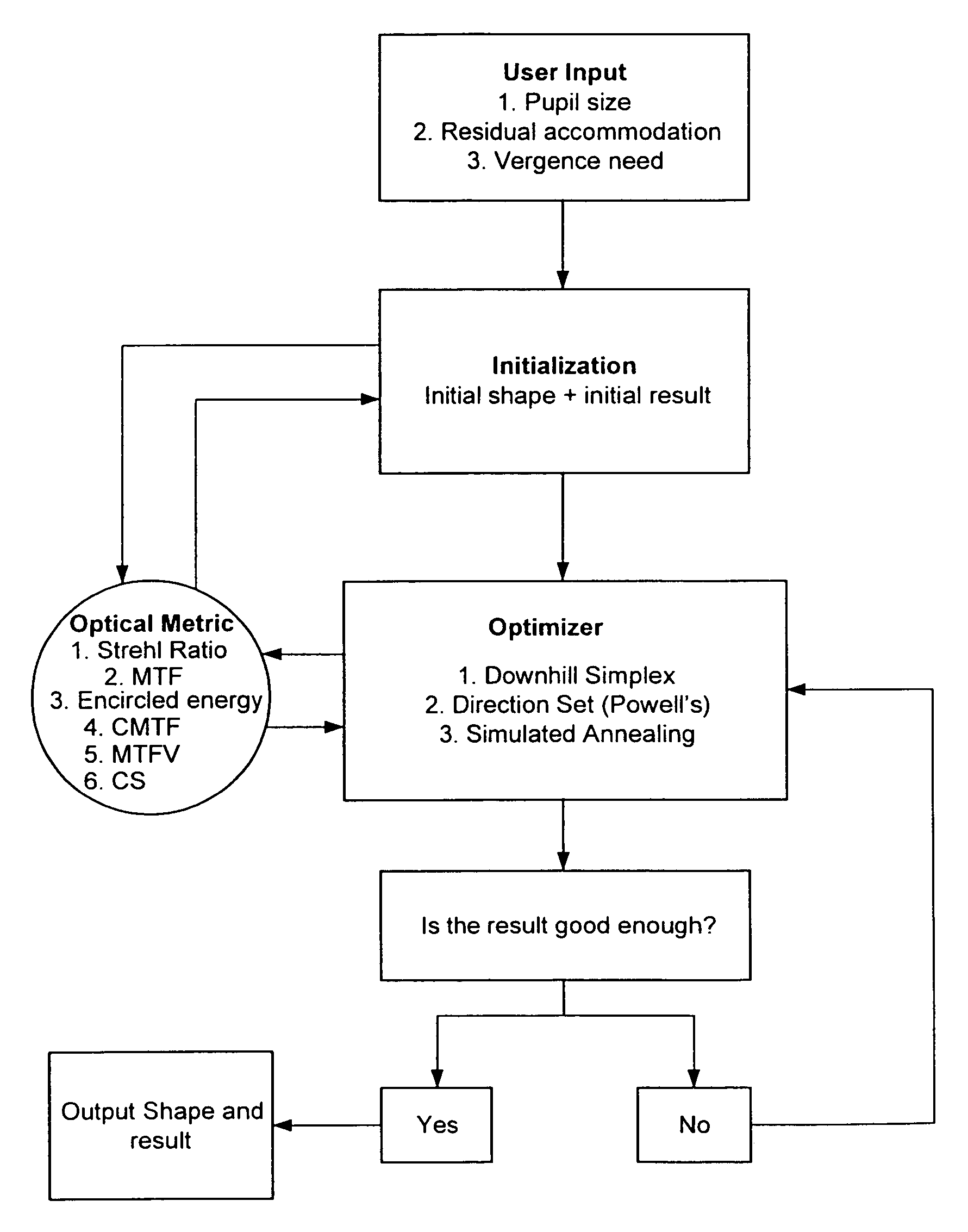
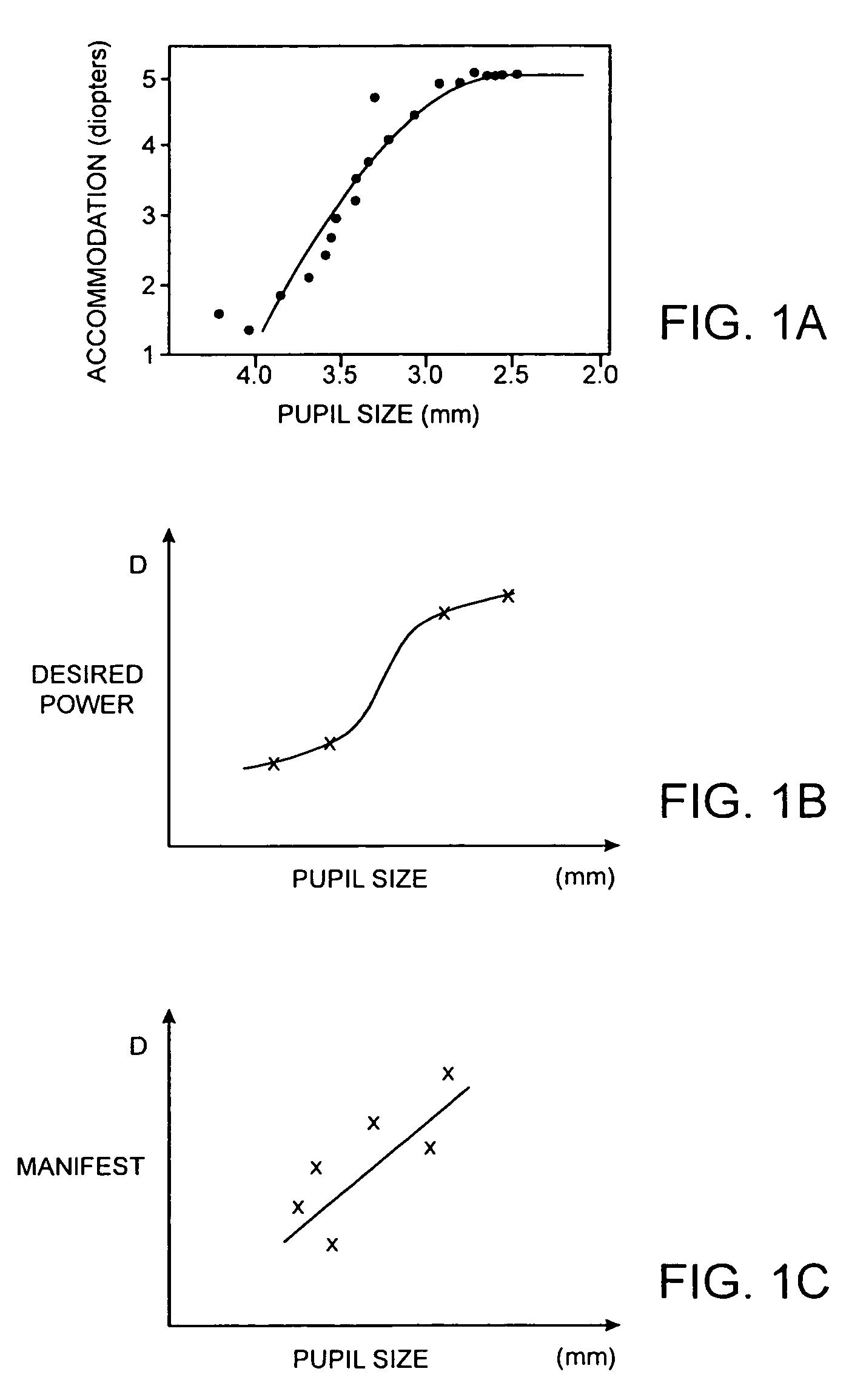
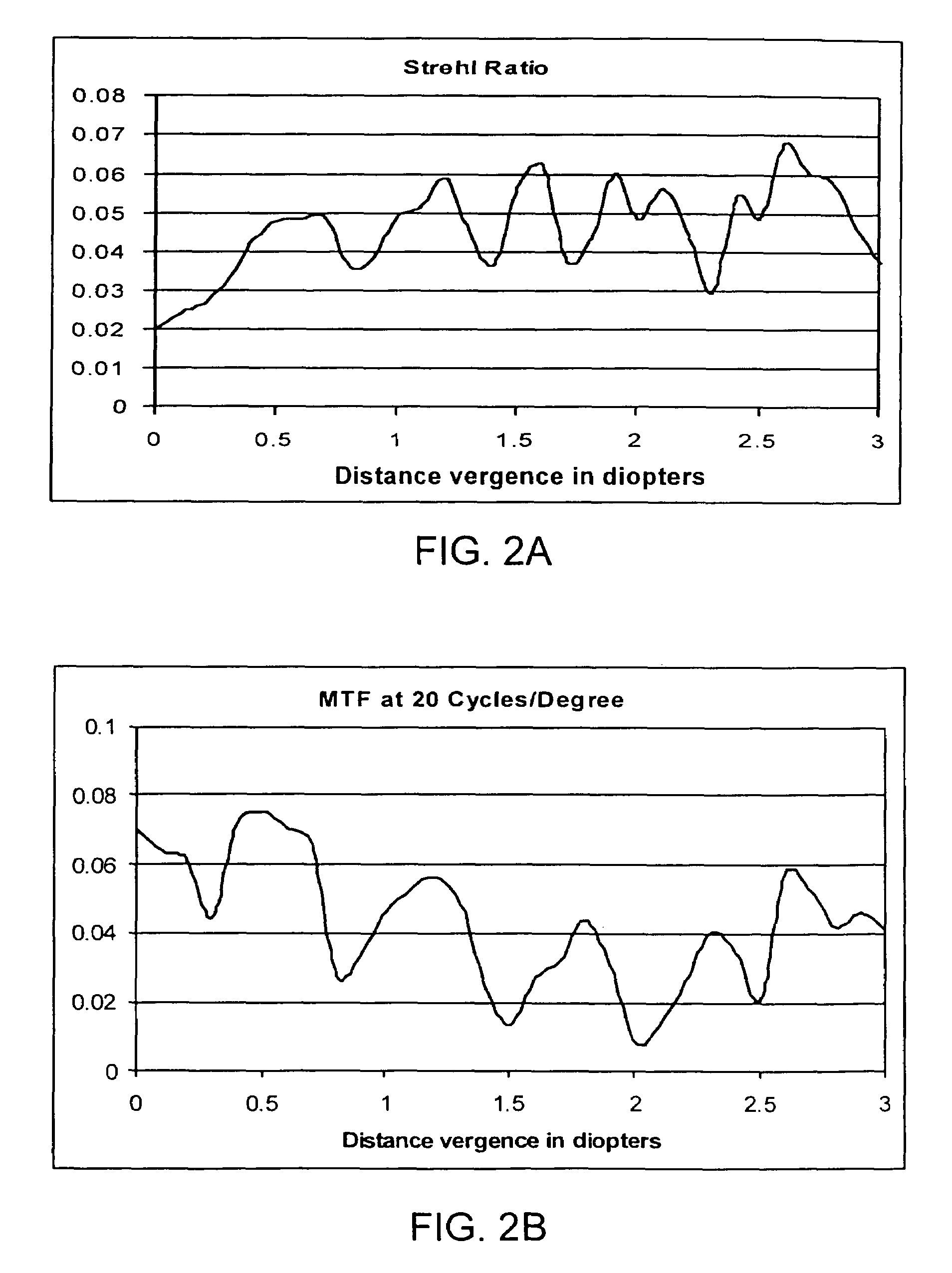
Presbyopia correction using patient data
Methods, devices, and systems establish an optical surface shape that mitigates or treats presbyopia in a particular patient. The combination of distance vision and near vision in a patient can be improved, often based on input patient parameters such as pupil size, residual accommodation, and power need. Iterative optimization may generate a customized corrective optical shape for the patient.
Owner:AMO MFG USA INC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com