Patents
Literature
50 results about "Eye laser surgery" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
High energy light source that uses light emitted by the natural vibrations of atoms (of a gas or solid material) to cut, burn or dissolve tissues to treat various diseases or disorders of the eye; includes surgeries, such as Laser Intrastromal Keratomileusis (LASIK), for vision disorders.
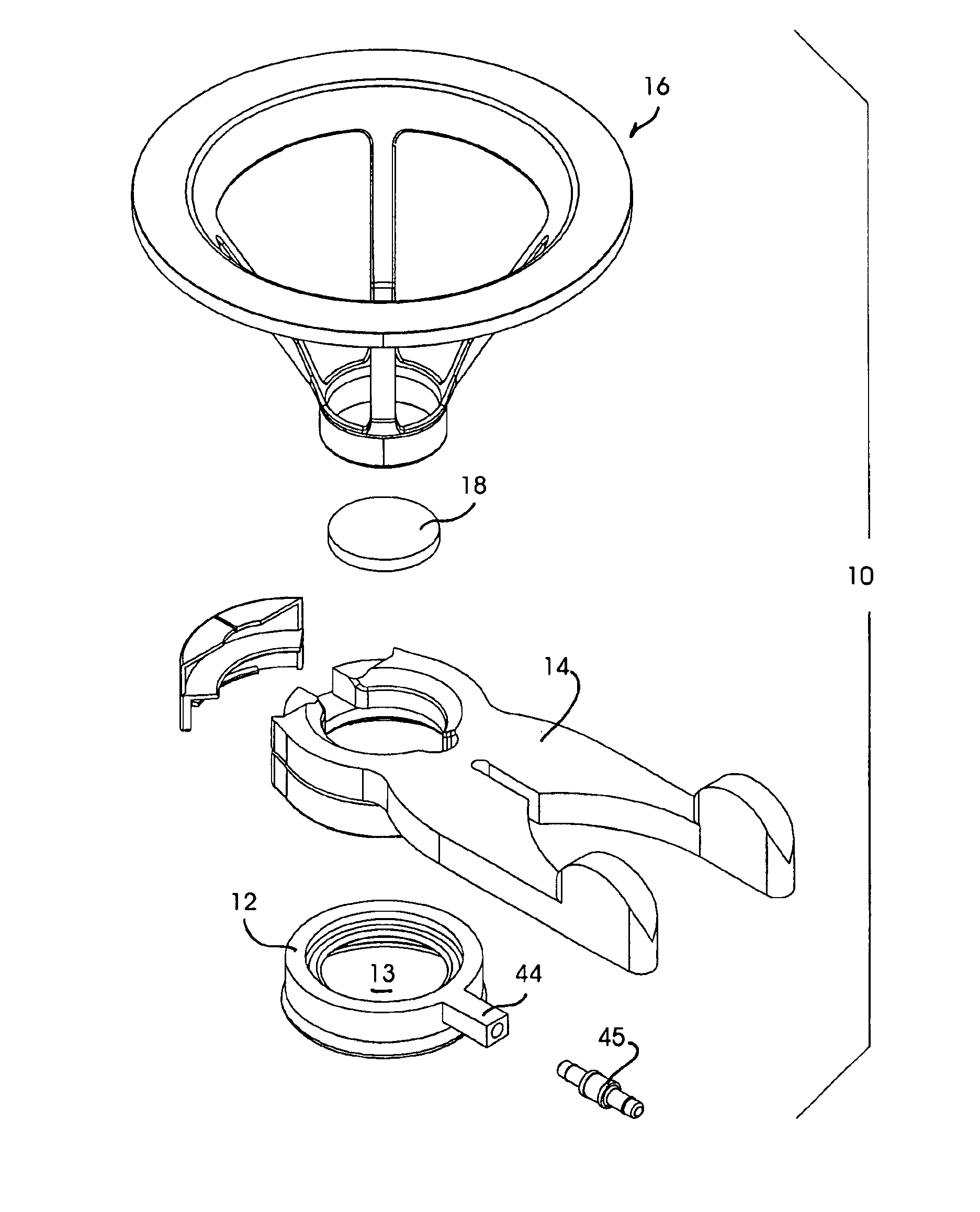
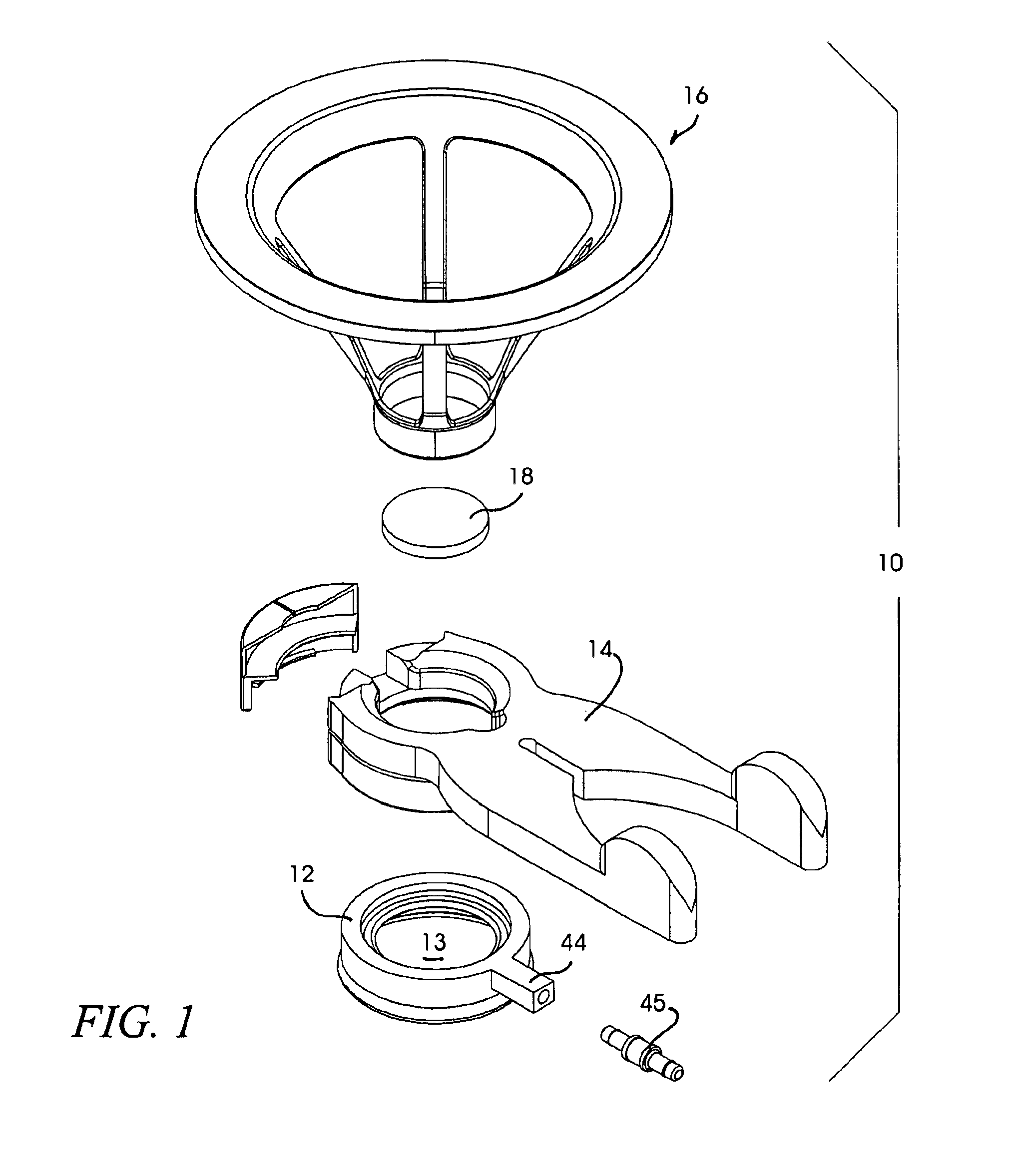
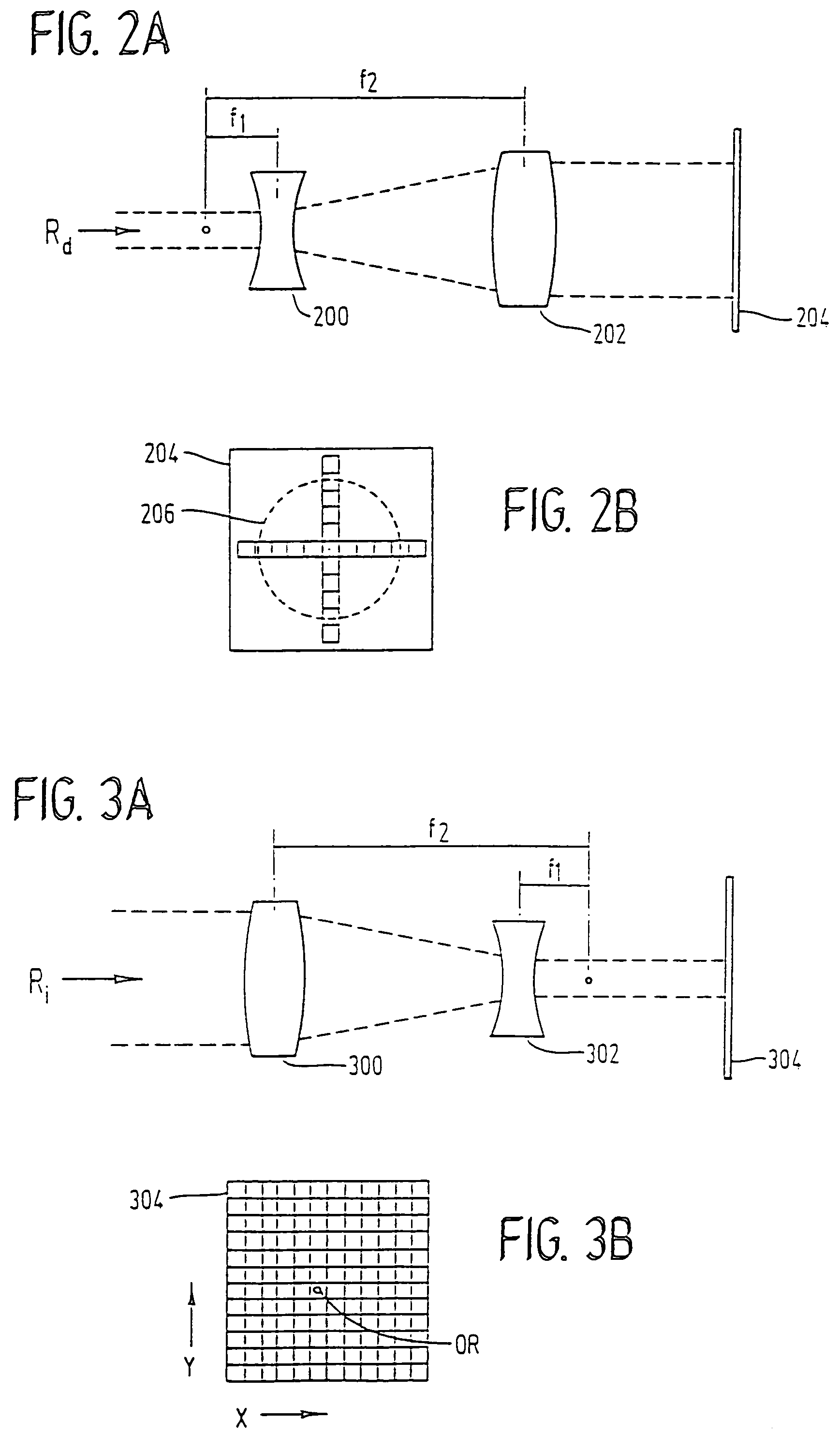
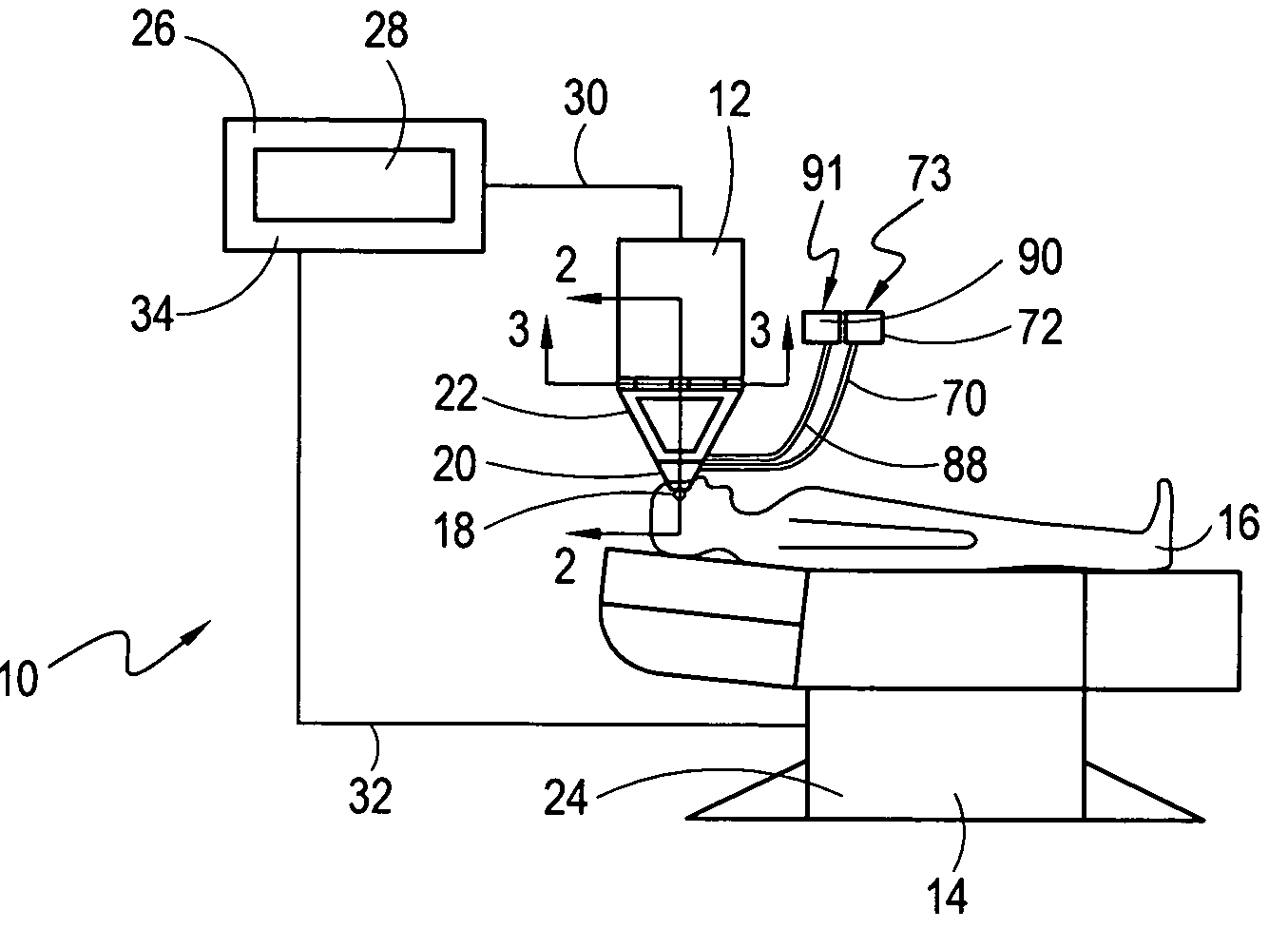
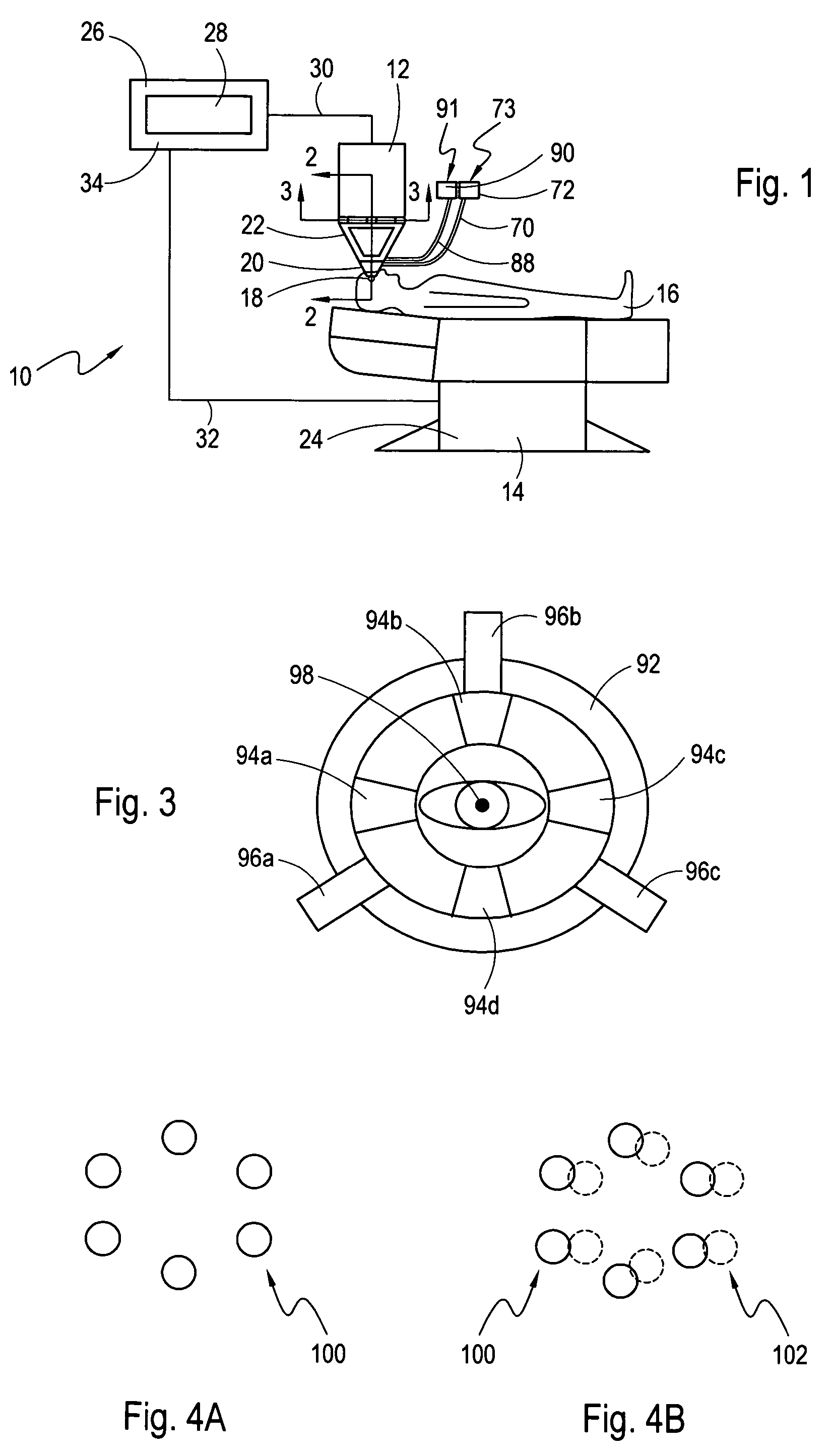
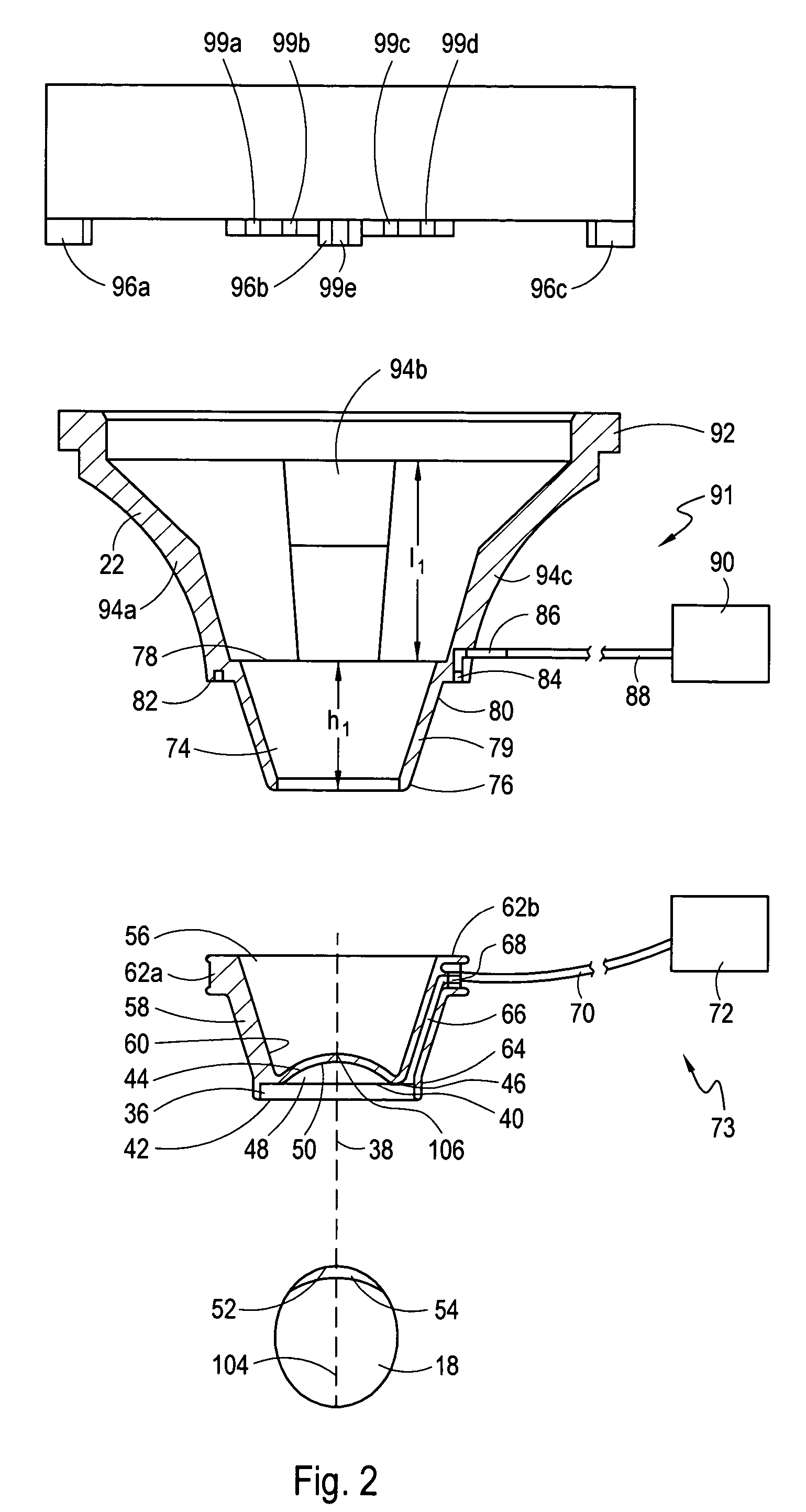
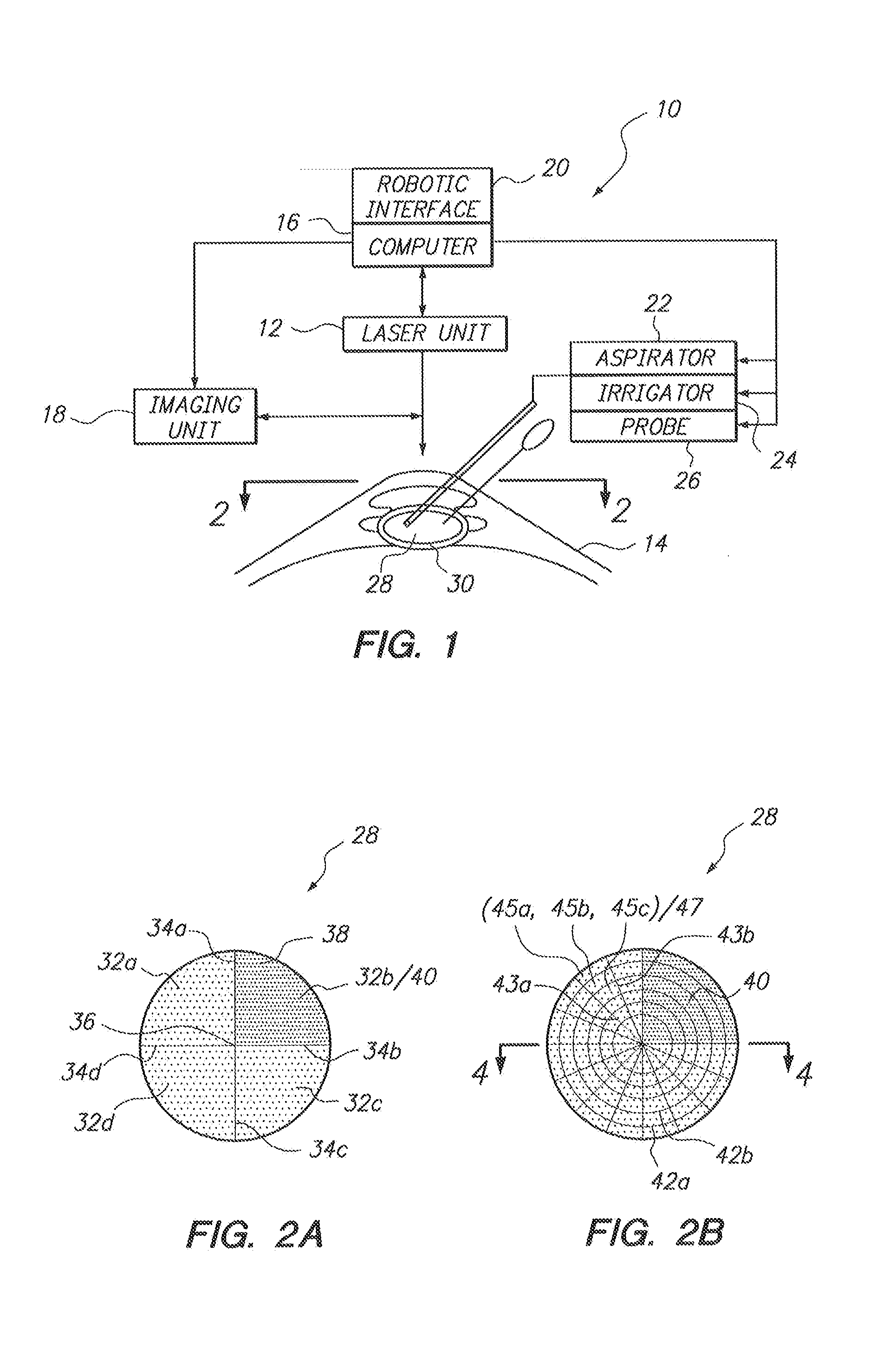
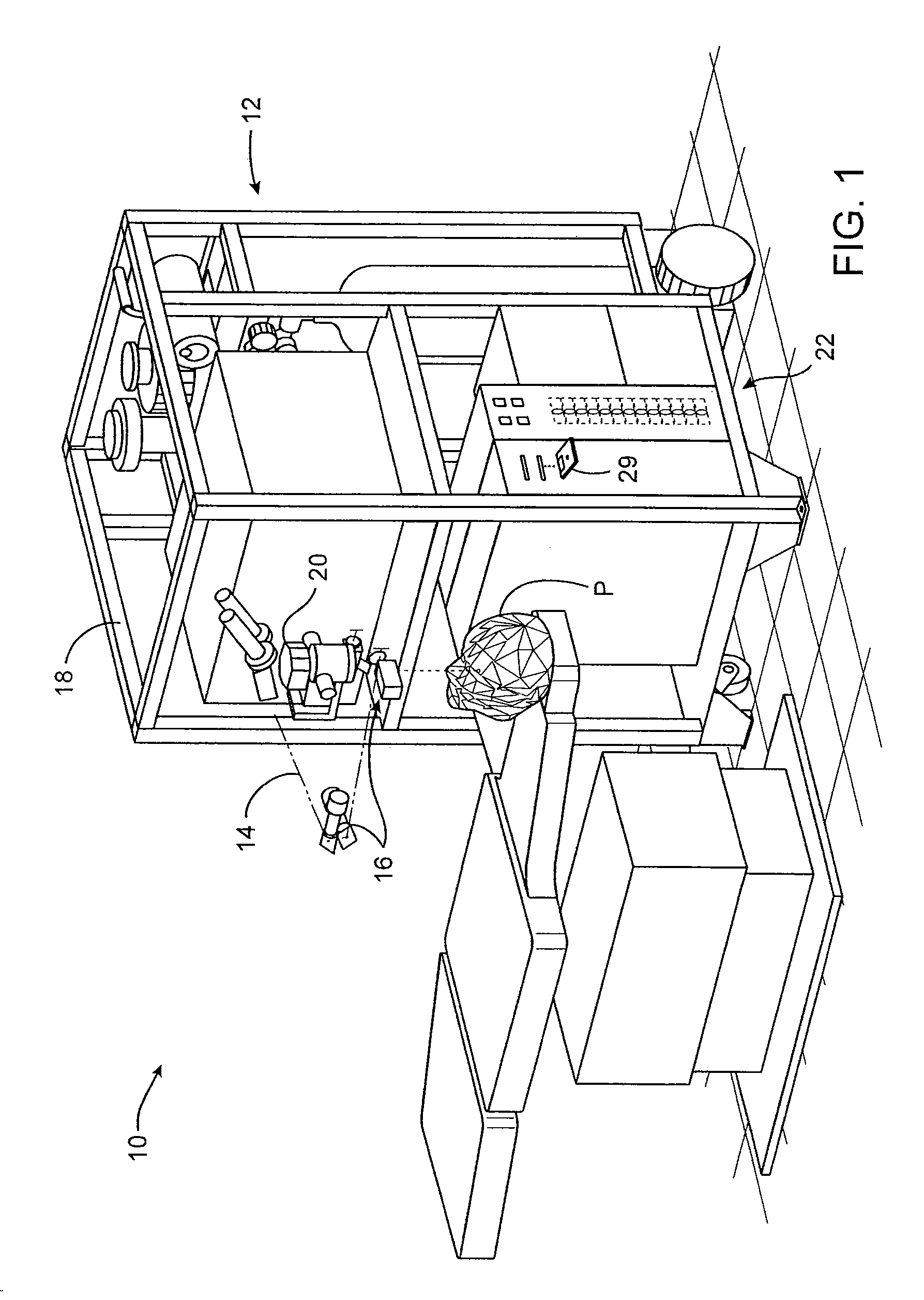
Ocular fixation and stabilization device for ophthalmic surgical applications
InactiveUS6863667B2Position stabilityLaser surgerySurgical instrument detailsEye laser surgeryCorneal surface
A disposable stabilization and applanation device for reconfiguring the cornea of an eye for ophthalmic laser surgery, includes an applanation lens that is disposed in a particular spatial position with respect to an incident laser beam. The applanation lens is inserted into the central opening of an attachment ring and applanates the eye in response to pressure from a lens cone. The attachment ring is coupled to the eye and includes a skirt which surrounds the applanation lens and extends outwardly therefrom to define a chamber. The skirt is formed with a groove which defines a suction channel between the attachment ring skirt and the corneal surface of an eye. A vacuum source is connected and fluid communication with the suction channel and is selectively activated to create a partial vacuum in the channel.
Owner:AMO DEVMENT
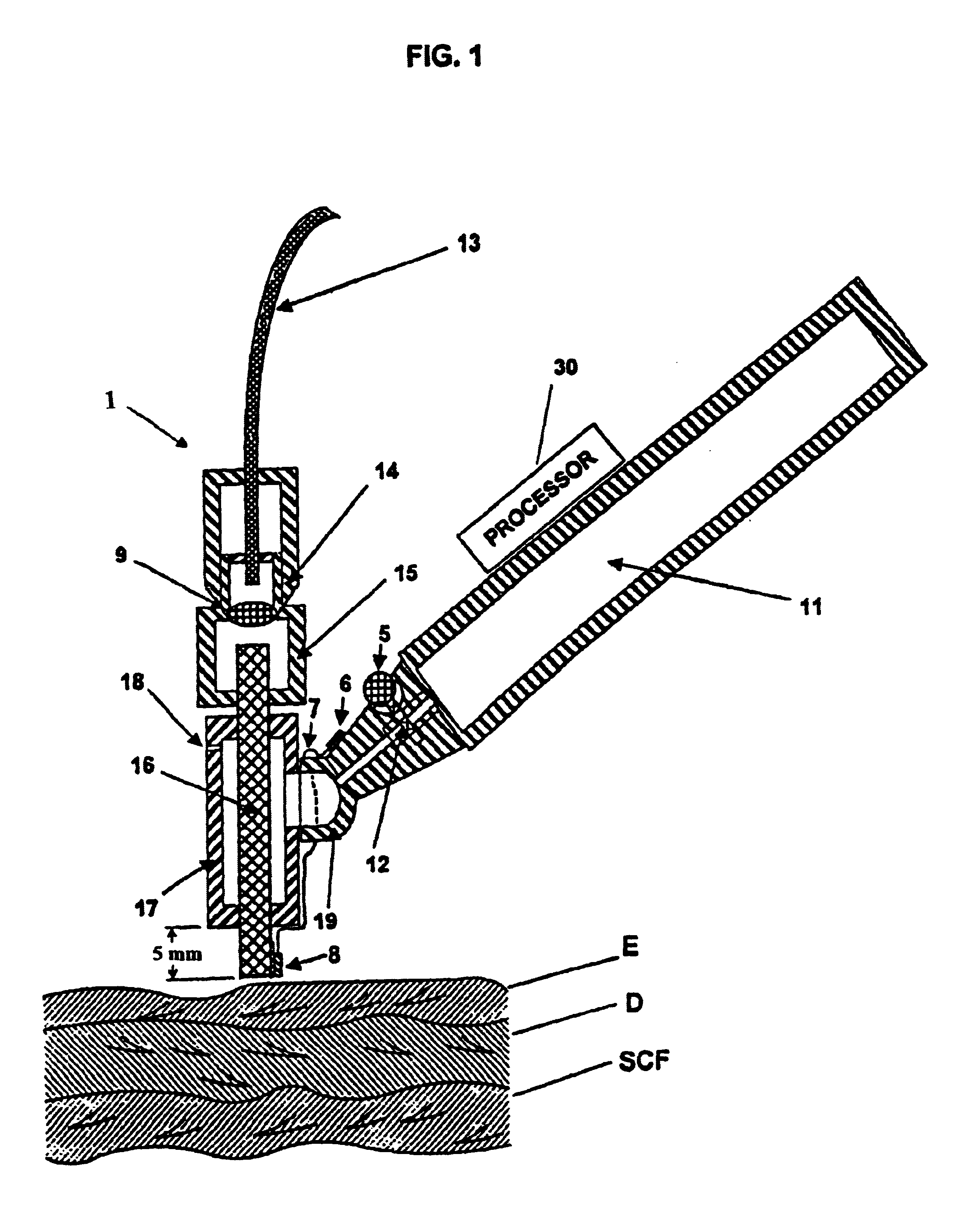
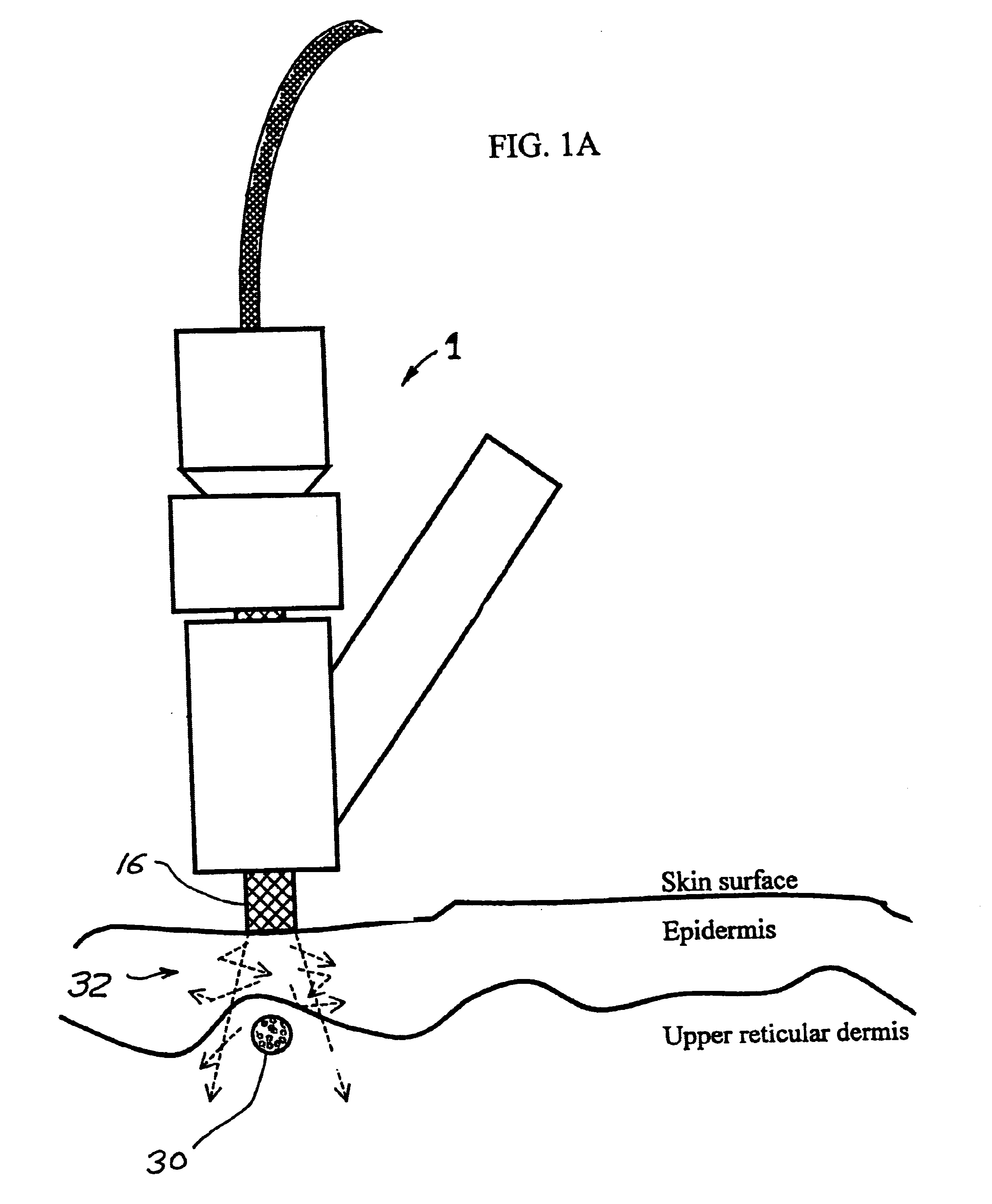
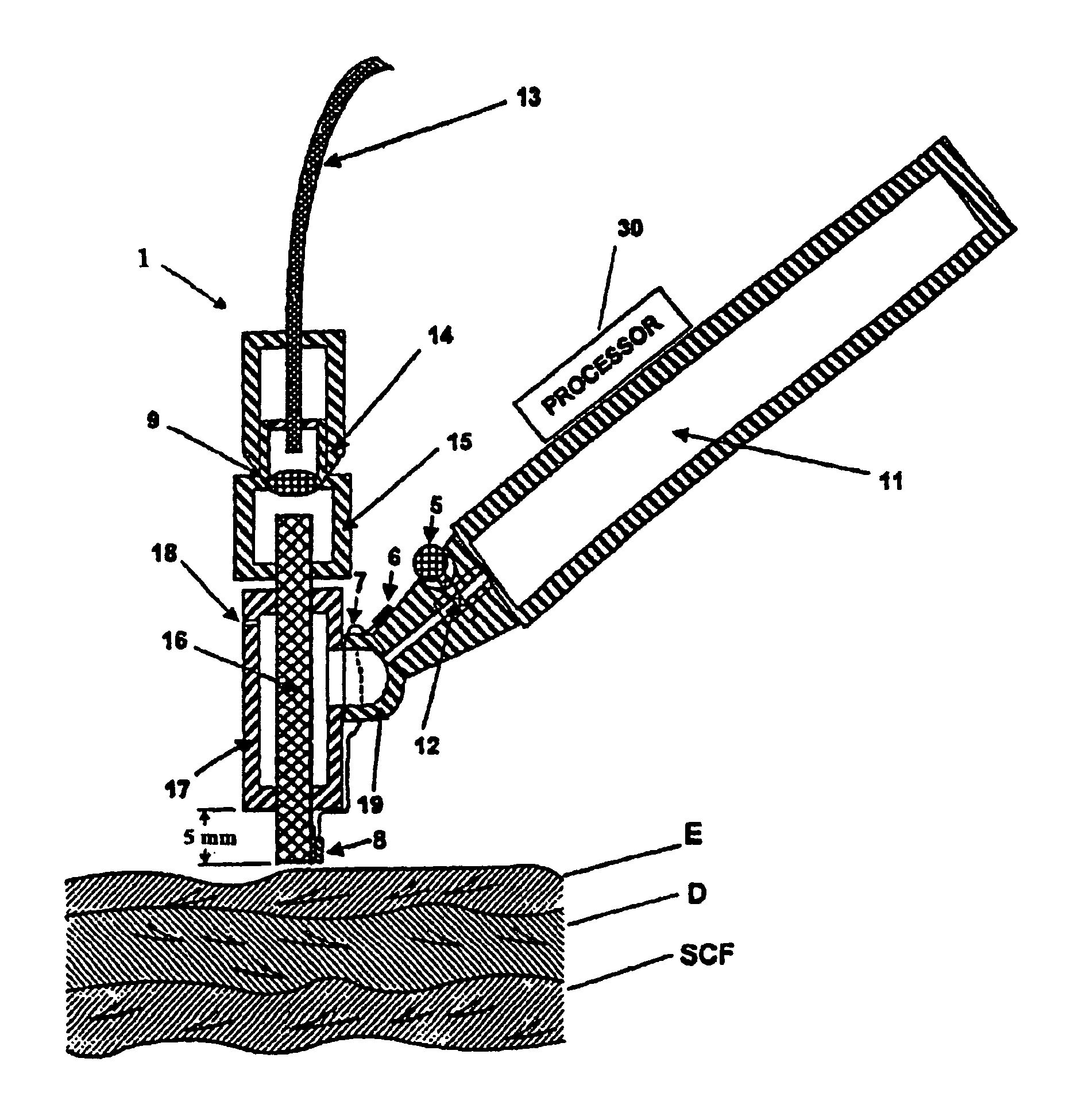
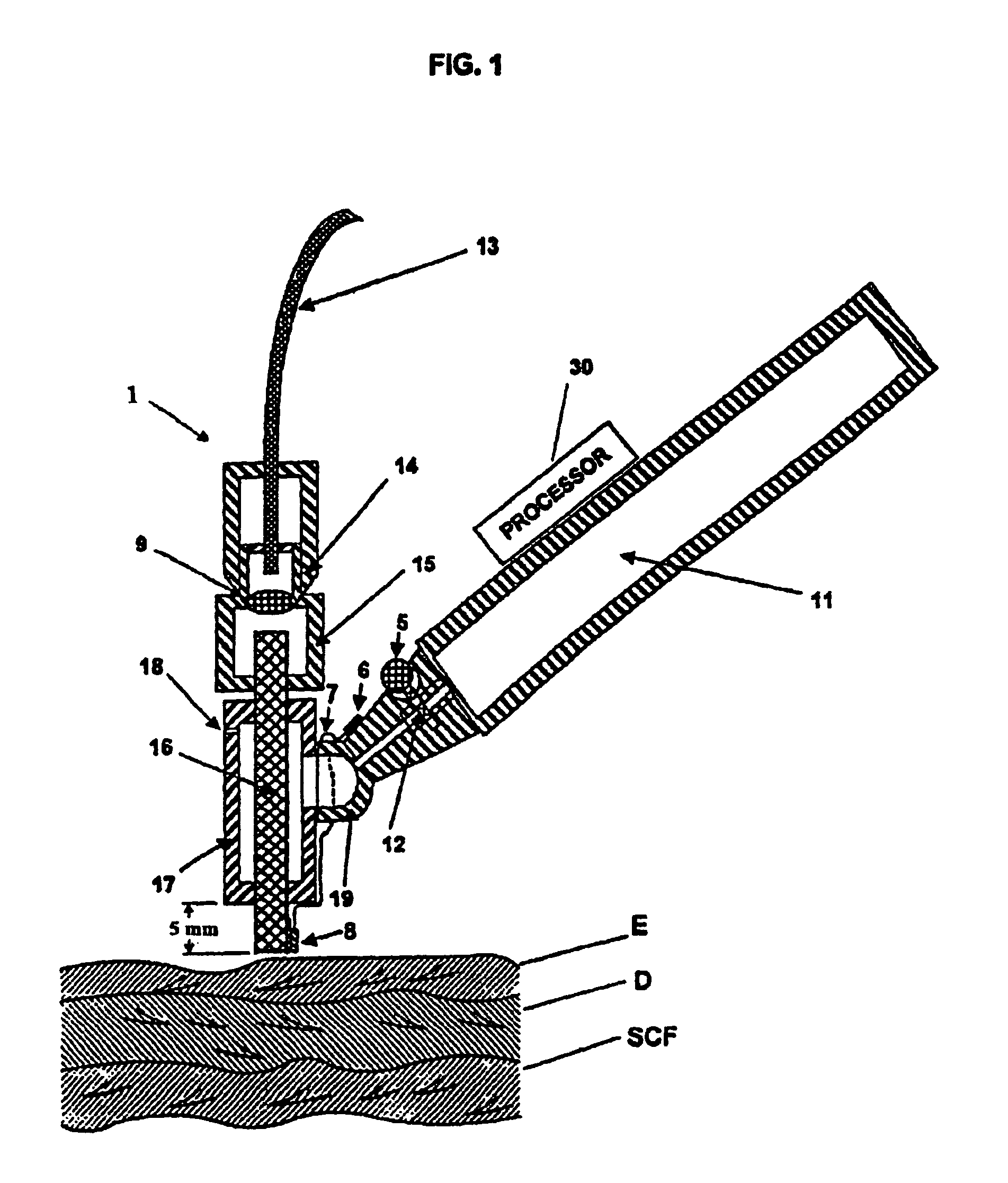
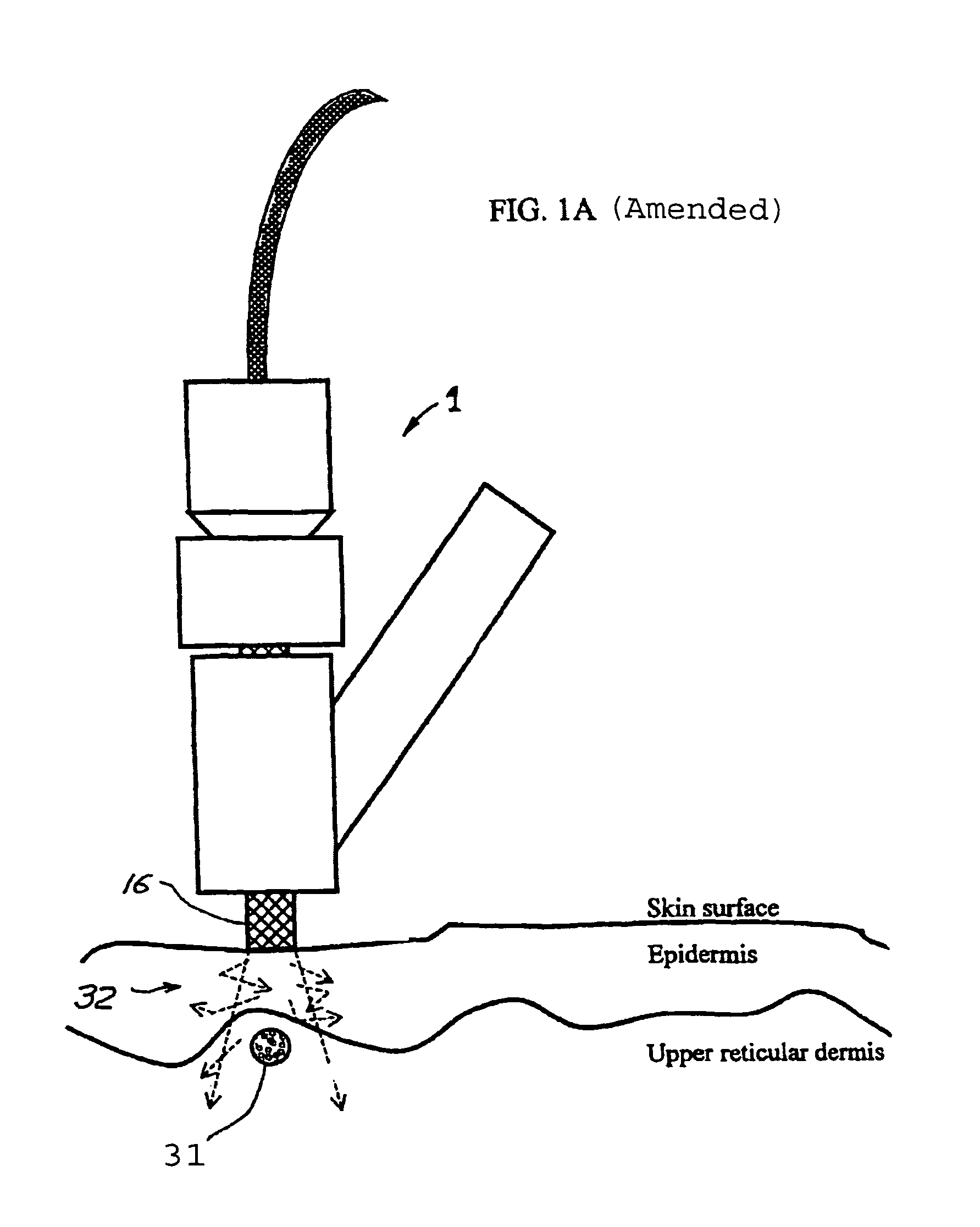
Tissue cooling rod for laser surgery
A laser treatment device and process with controlled cooling. The device contains a cooling element with high heat conduction properties, which is transparent to the laser beam. A surface of the cooling element is held in contact with the tissue being treated while at least one other surface of the cooling element is cooled by the evaporation of a cryogenic fluid. The cooling is coordinated with the application of the laser beam so as to control the temperatures of all affected layers of tissues. In a preferred embodiment useful for removal of wrinkles and spider veins, the cooling element is a sapphire plate. A cryogenic spray cools the top surface of the plate and the bottom surface of the plate is in contact with the skin. In preferred embodiments the wavelength of the laser beam is chosen so that absorption in targeted tissue is low enough so that substantial absorption occurs throughout the targeted tissue. In a preferred embodiment for treating large spider veins with diameters in the range of 1.5 mm, Applicants use an Er:Glass laser with a wavelength of 1.54 microns.< / PTEXT>
Owner:RELIANT TECH INC
Method and apparatus for laser surgery of the cornea
InactiveUS7220255B2Easy to controlIncrease powerLaser surgerySurgical instrument detailsCorneal ablationSurgical lasers
A laser-based method and apparatus for corneal surgery. The present invention is intended to be applied primarily to ablate organic materials, and human cornea in particular. The invention uses a laser source which has the characteristics of providing a shallow ablation depth (0.2 microns or less per laser pulse), and a low ablation energy density threshold (less than or equal to about 10 mJ / cm2), to achieve optically smooth ablated corneal surfaces. The preferred laser includes a laser emitting approximately 100–50,000 laser pulses per second, with a wavelength of about 198–300 nm and a pulse duration of about 1–5,000 picoseconds. Each laser pulse is directed by a highly controllable laser scanning system. Described is a method of distributing laser pulses and the energy deposited on a target surface such that surface roughness is controlled within a specific range. Included is a laser beam intensity monitor and a beam intensity adjustment means, such that constant energy level is maintained throughout an operation. Eye movement during an operation is corrected for by a corresponding compensation in the location of the surgical beam. Beam operation is terminated if the laser parameters or the eye positioning is outside of a predetermined tolerable range. The surgical system can be used to perform surgical procedures including removal of corneal scar, making incisions, cornea transplants, and to correct myopia, hyperopia, astigmatism, and other corneal surface profile defects.
Owner:LAI SHUI T
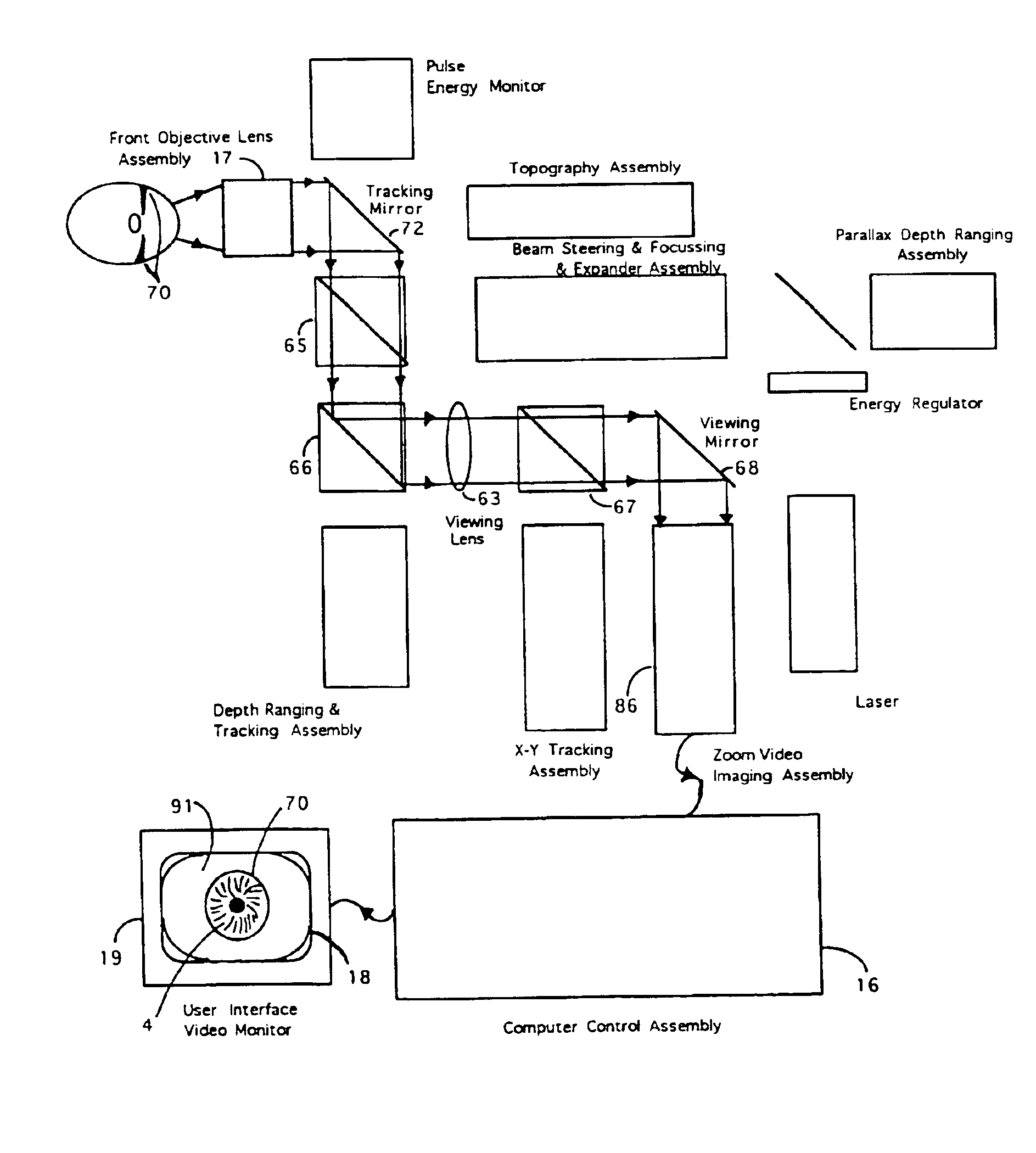
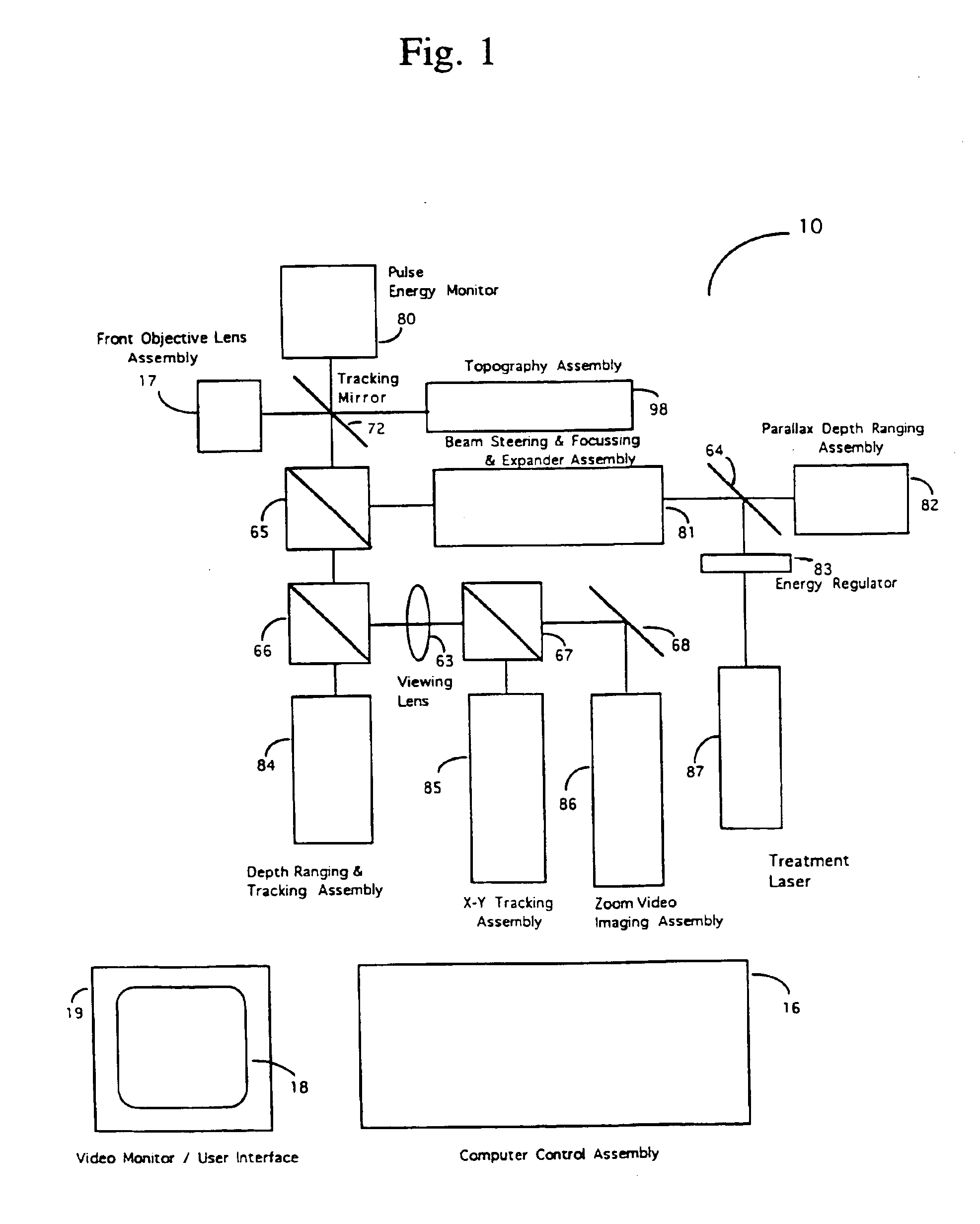
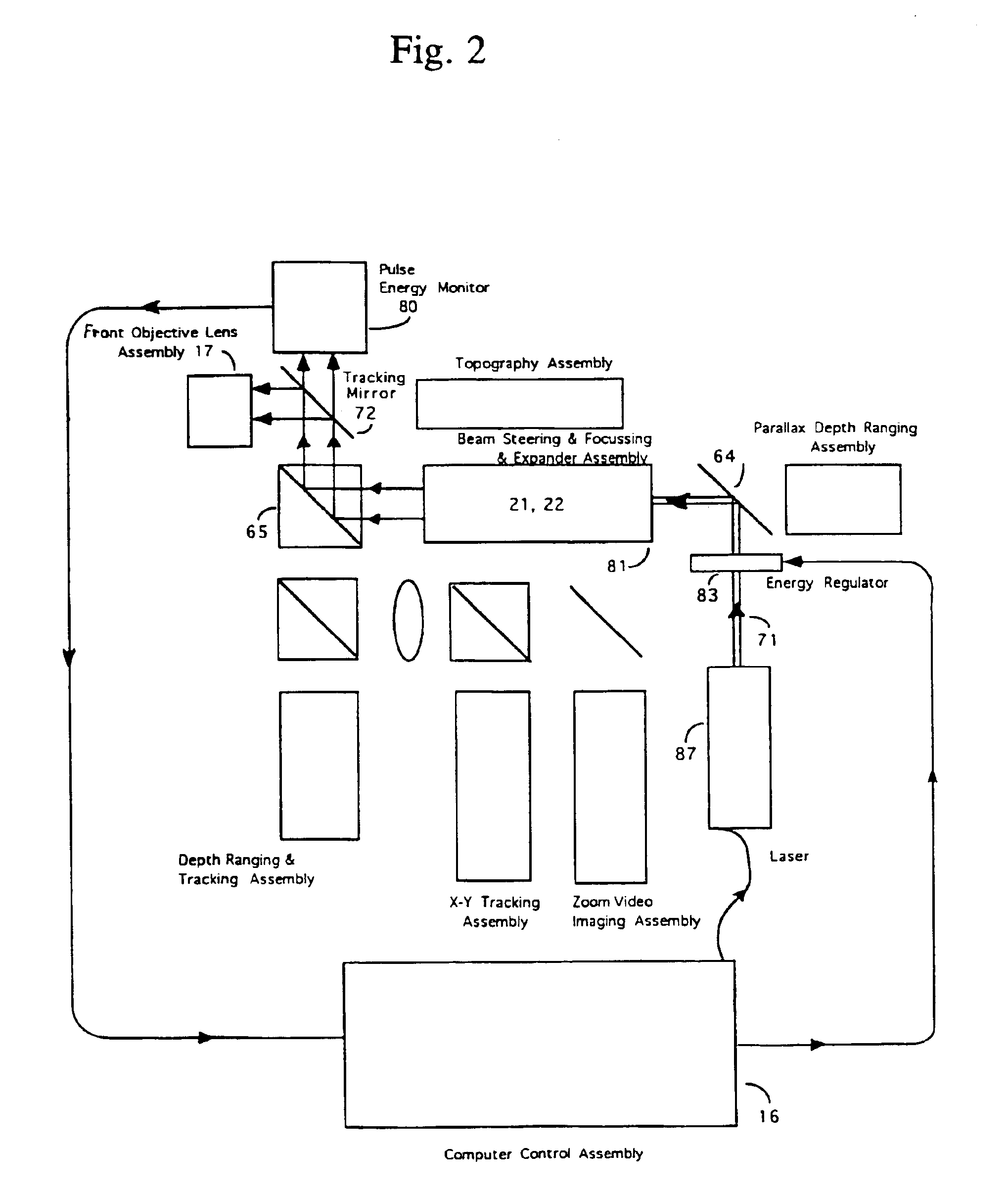
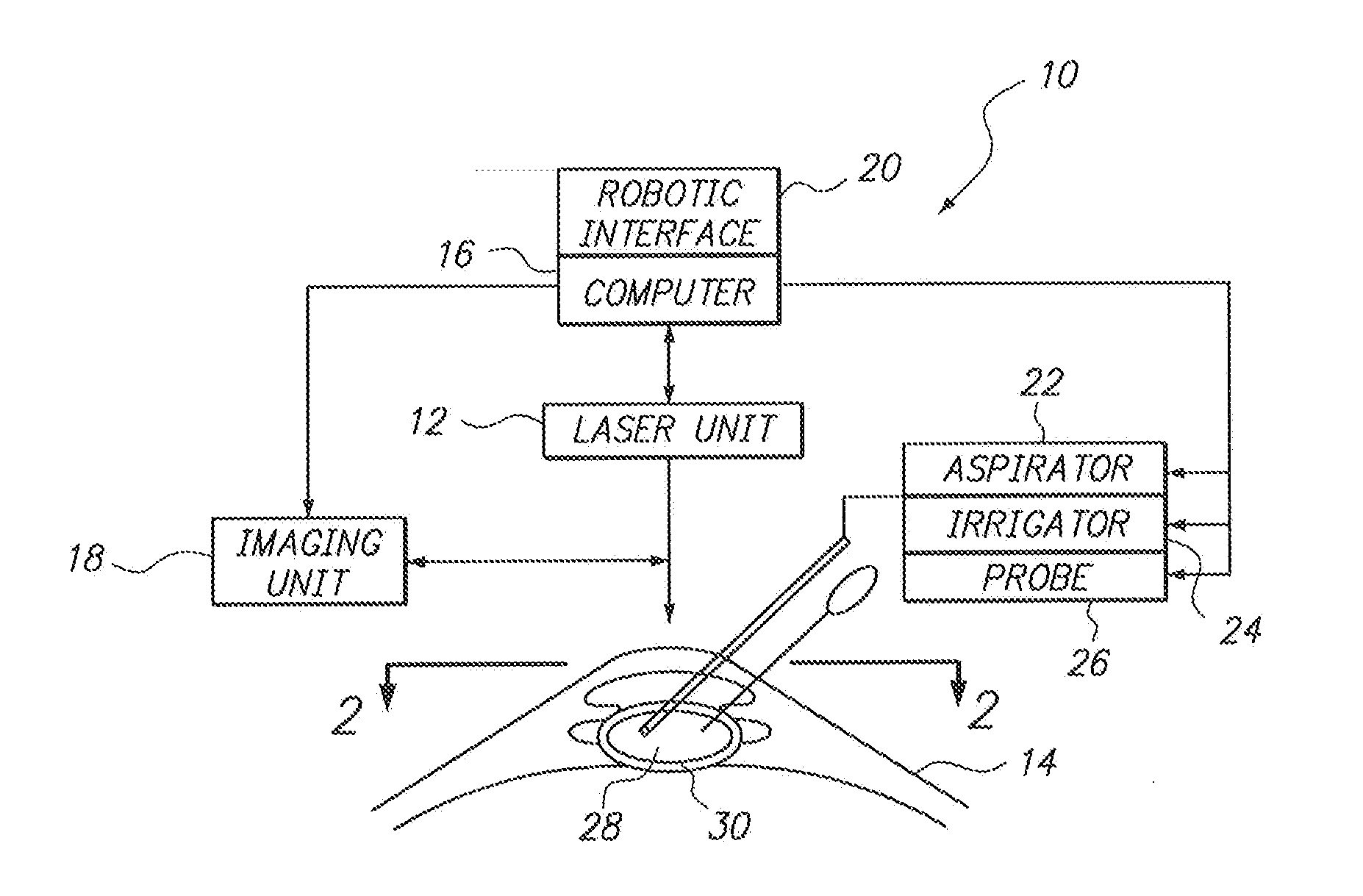
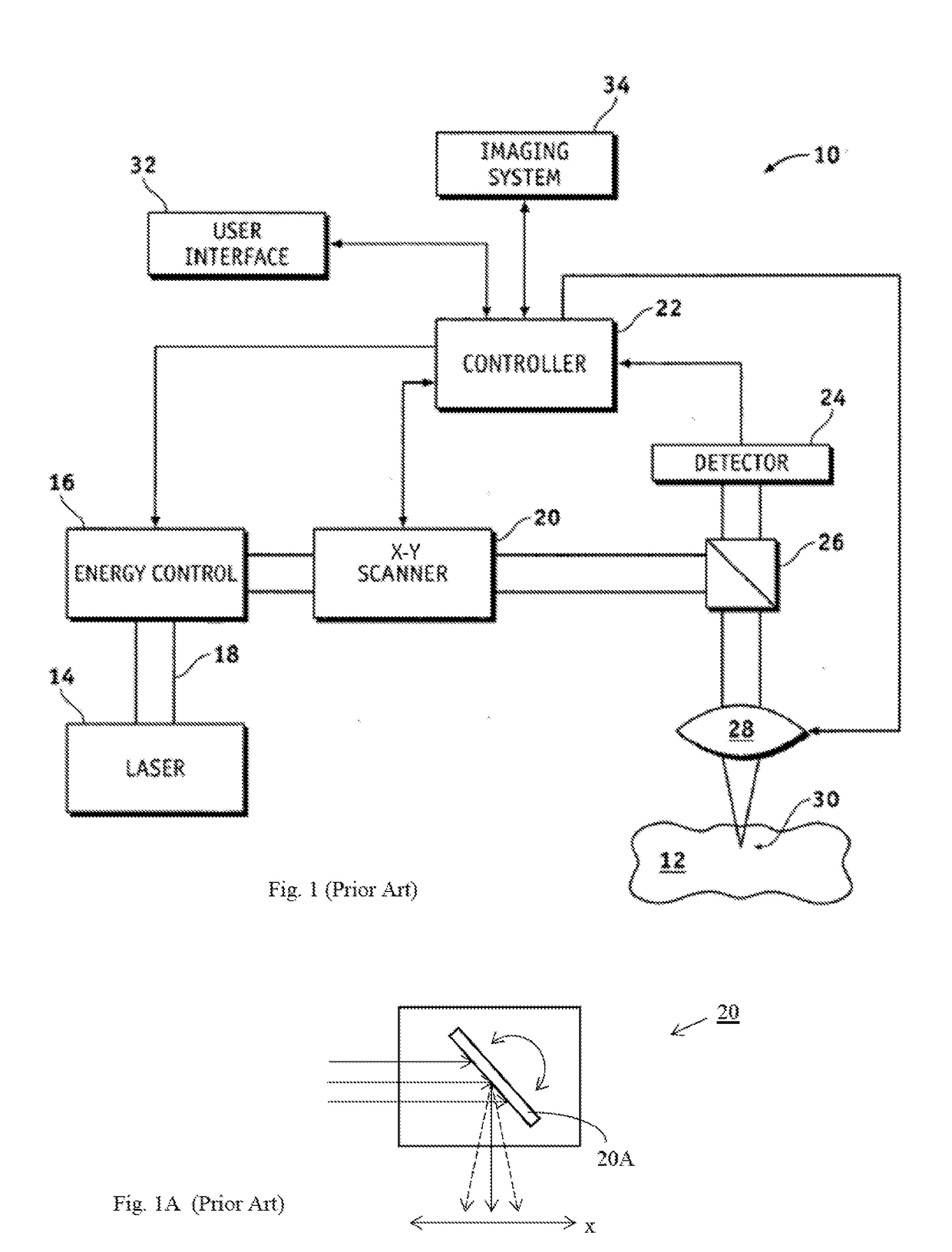
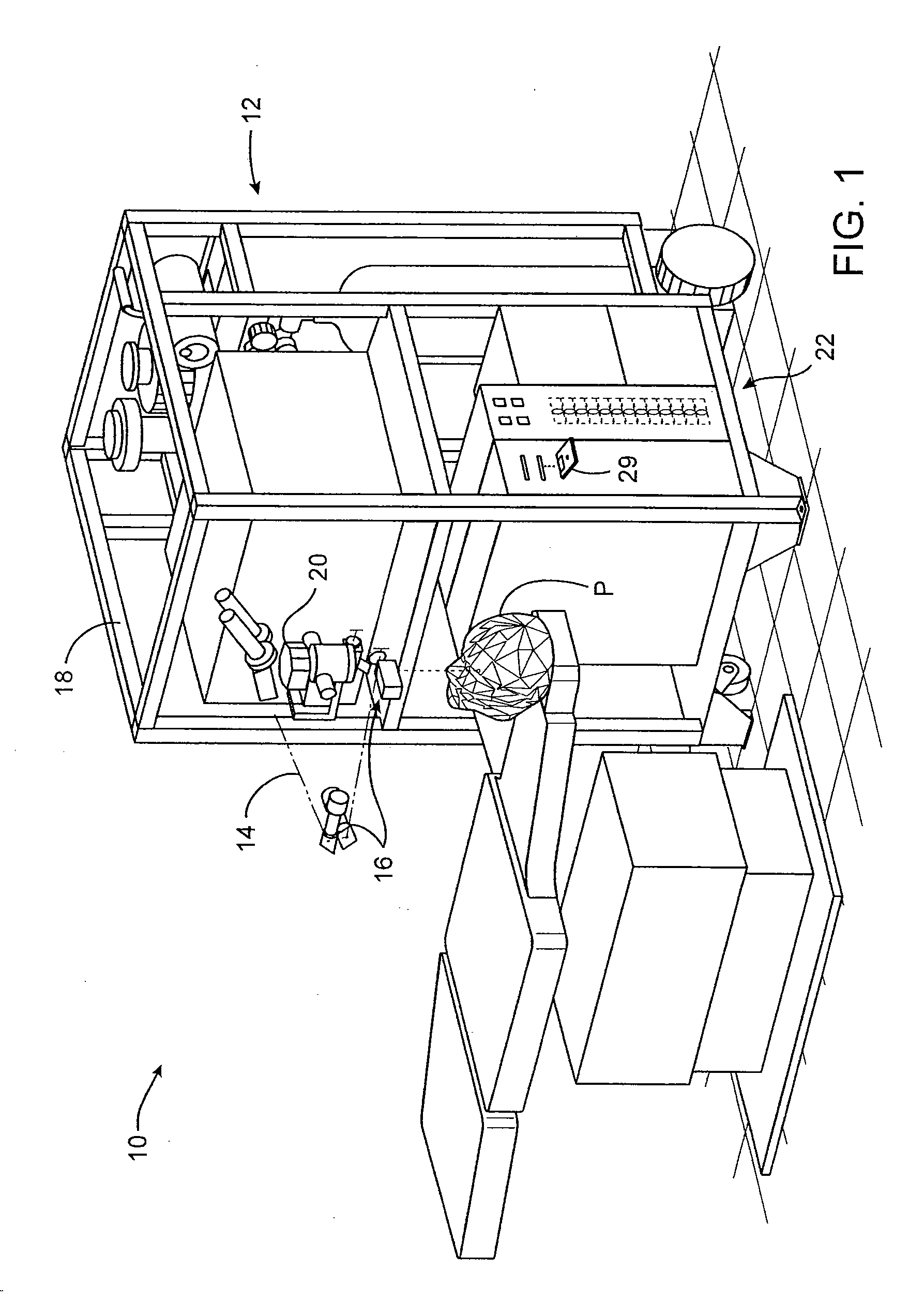
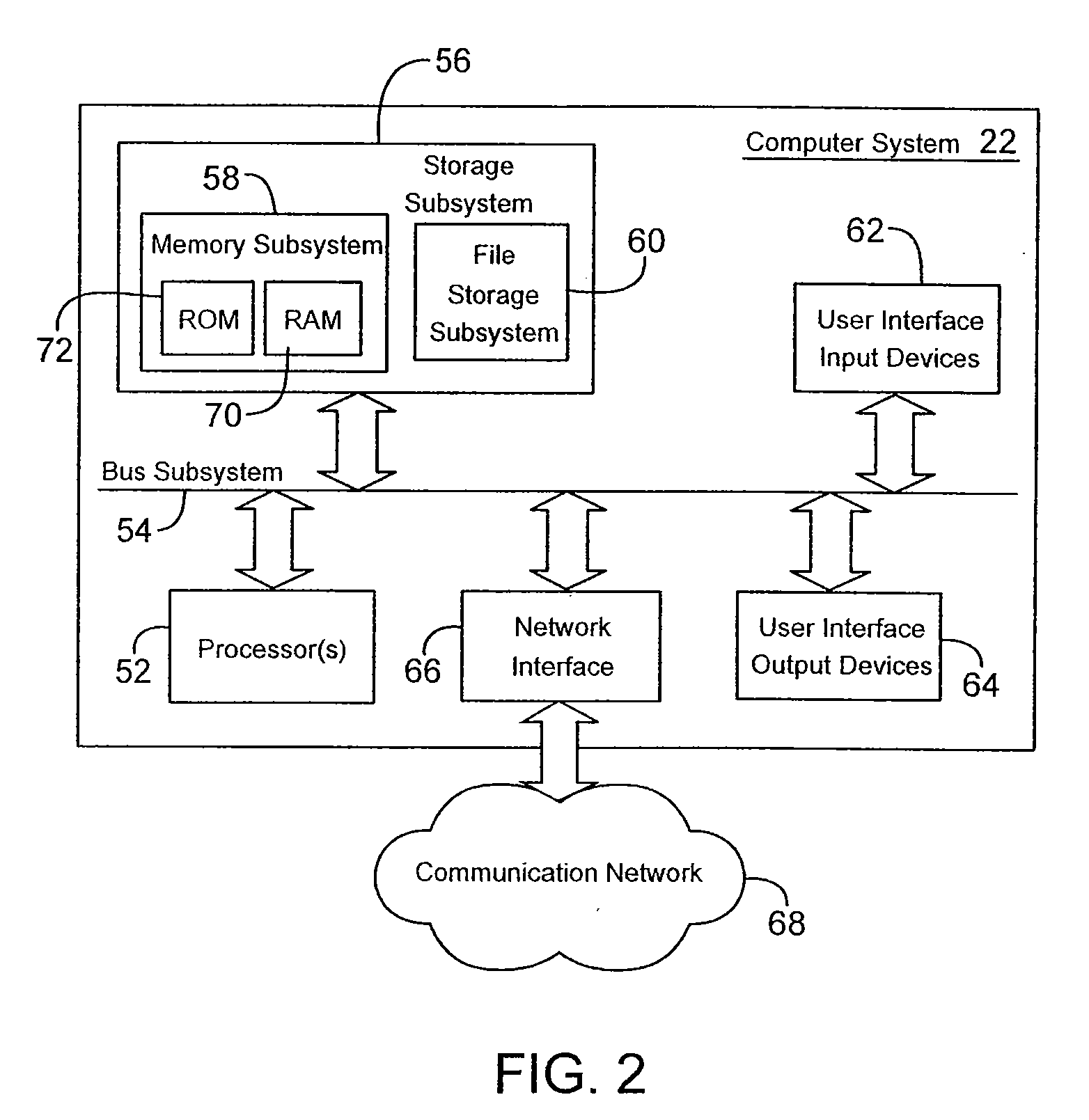
Automated laser workstation for high precision surgical and industrial interventions
InactiveUS6913603B2Speed of surgeryAvoid injuryLaser surgerySurgical instrument detailsEye laser surgerySurgical microscope
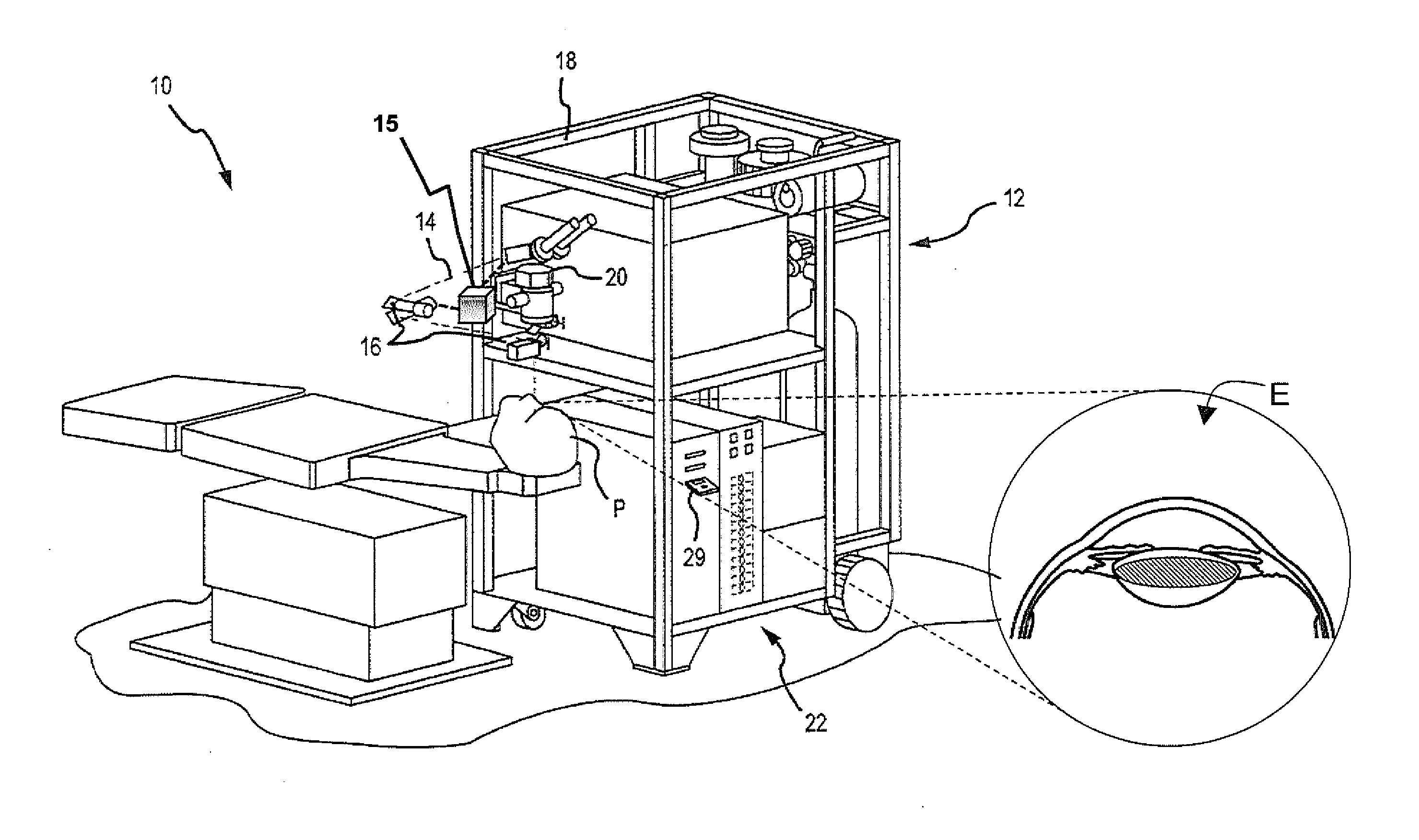
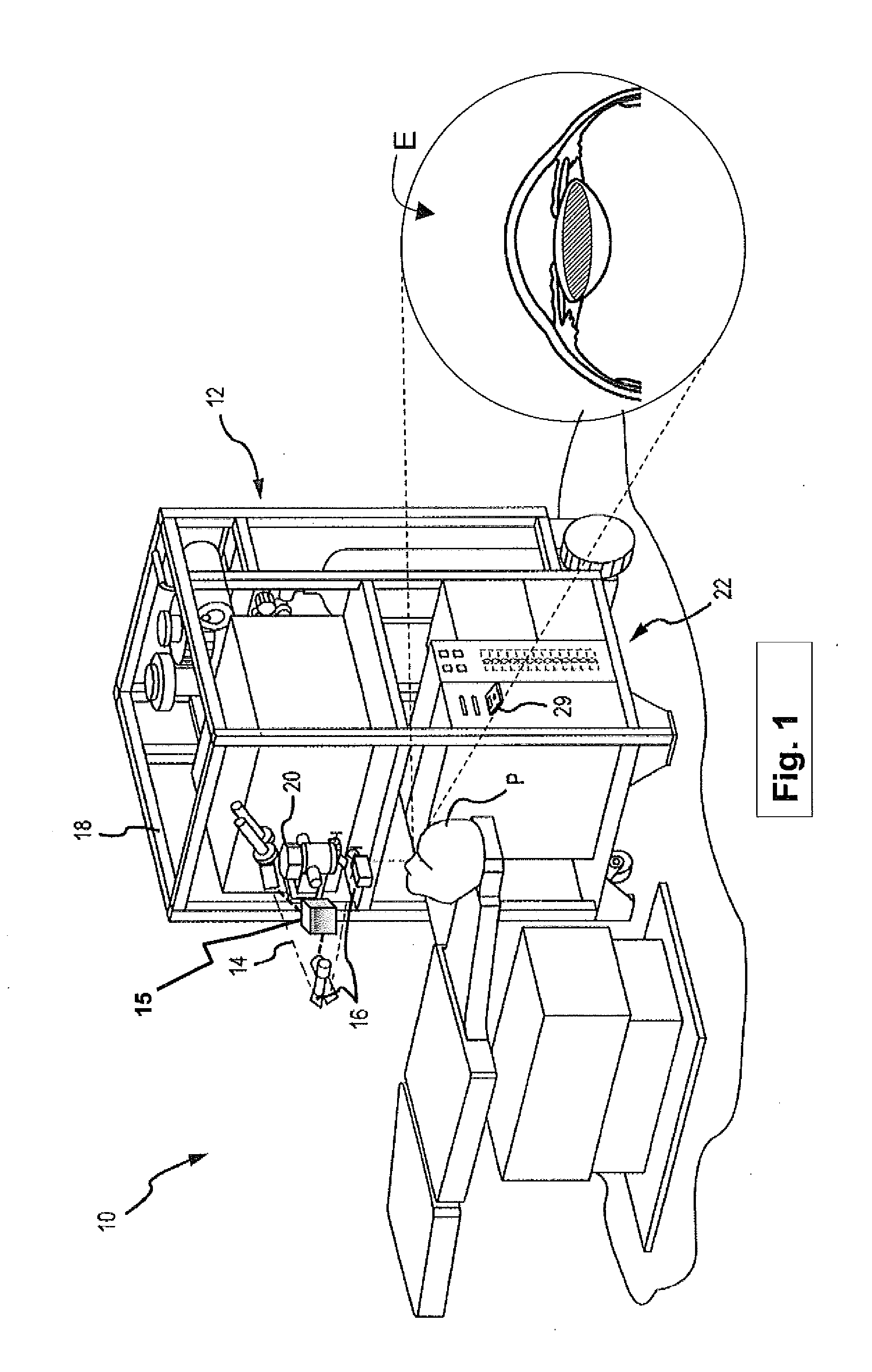
A method and system is described that greatly improves the safety and efficacy of ophthalmic laser surgery. The method and system are applicable to precise operations on a target subject to movement during the procedure. The system may comprise the following elements: (1) a user interface, (2) an imaging system, which may include a surgical microscope, (3) an automated tracking system that can follow the movements of an eye, (4) a laser, (5) a diagnostic system, and (6) a fast reliable safety means, for automatically interrupting the laser firing.
Owner:AMO MFG USA INC
System and method for positioning a patient for laser surgery
A system for positioning the eye of a patient, relative to a stationary surgical laser unit, includes a chair for moving the patient. An eye stabilizing element is held against the eye, with a tapered receptacle extending outwardly therefrom. Also, an alignment device with a tapered tip is mounted on the surgical laser unit. In operation, the patient is moved to engage the receptacle of the eye stabilizing element with the tip of the alignment device, to thereby align the patient's eye with the surgical laser unit for laser surgery.
Owner:TECHNOLAS PERFECT VISION +1
System and Method for Performing Lens Fragmentation
ActiveUS20120259320A1Easy accessEasily manipulatedLaser surgerySurgical instrument detailsCamera lensEye laser surgery
A system and method are provided for fragmenting a crystalline lens, to facilitate its removal from the lens bag during an ophthalmic laser surgery. First, a predetermined pattern is used to make Laser Induced Optical Breakdown (LIOB) cuts that section the lens into asymmetrical, operational segments. At least one operational segment is then selected and softened with a plurality of compact LIOB cuts. Once softened, the selected segment is aspirated. The remaining operational segments are then subsequently removed. During a procedure, an imaging unit can monitor movements of the lens bag to ensure proper placement of the LIOB cuts on the lens.
Owner:BAUSCH & LOMB INC +1
Device and method for reducing corneal induced aberrations during ophthalmic laser surgery
InactiveUS6991629B1Reduces and eliminates optical aberrationFacilitate strong sealLaser surgerySurgical instrument detailsEye laser surgeryAnterior surface
A disposable lens for reconfiguring the cornea of an eye for ophthalmic laser surgery includes a lens which has a flat anterior surface that is formed opposite a contact surface. A skirt surrounds the contact surface and extends outwardly therefrom to define a chamber. The skirt is formed with a groove which creates a suction channel between the skirt and the contact surface in the chamber. In its operation, the lens is positioned over the cornea and a vacuum pump is selectively activated to create a partial vacuum in the suction channel. Due to this partial vacuum, the cornea is drawn into the chamber where it is urged against the contact surface of the lens. The result of this is that the cornea is flattened into a configuration where the introduction of spherical aberration and coma into a light beam passing into the cornea is reduced or eliminated.
Owner:AMO DEVMENT
Compound modulation transfer function for laser surgery and other optical applications
InactiveUS7320517B2Mitigates and treats vision conditionMitigates presbyopiaLaser surgeryRefractometersEye laser surgeryLaser surgery
Methods, devices, and systems establish an optical surface shape that mitigates or treats a vision condition in a patient. An optical surface shape for a particular patient can be determined using a set of patient parameters for the specific patient by using a compound modulation transfer function (CMTF). The compound modulation transfer function can include a combination of modulation transfer functions (MTF's) at a plurality of distinct frequencies.
Owner:AMO MFG USA INC
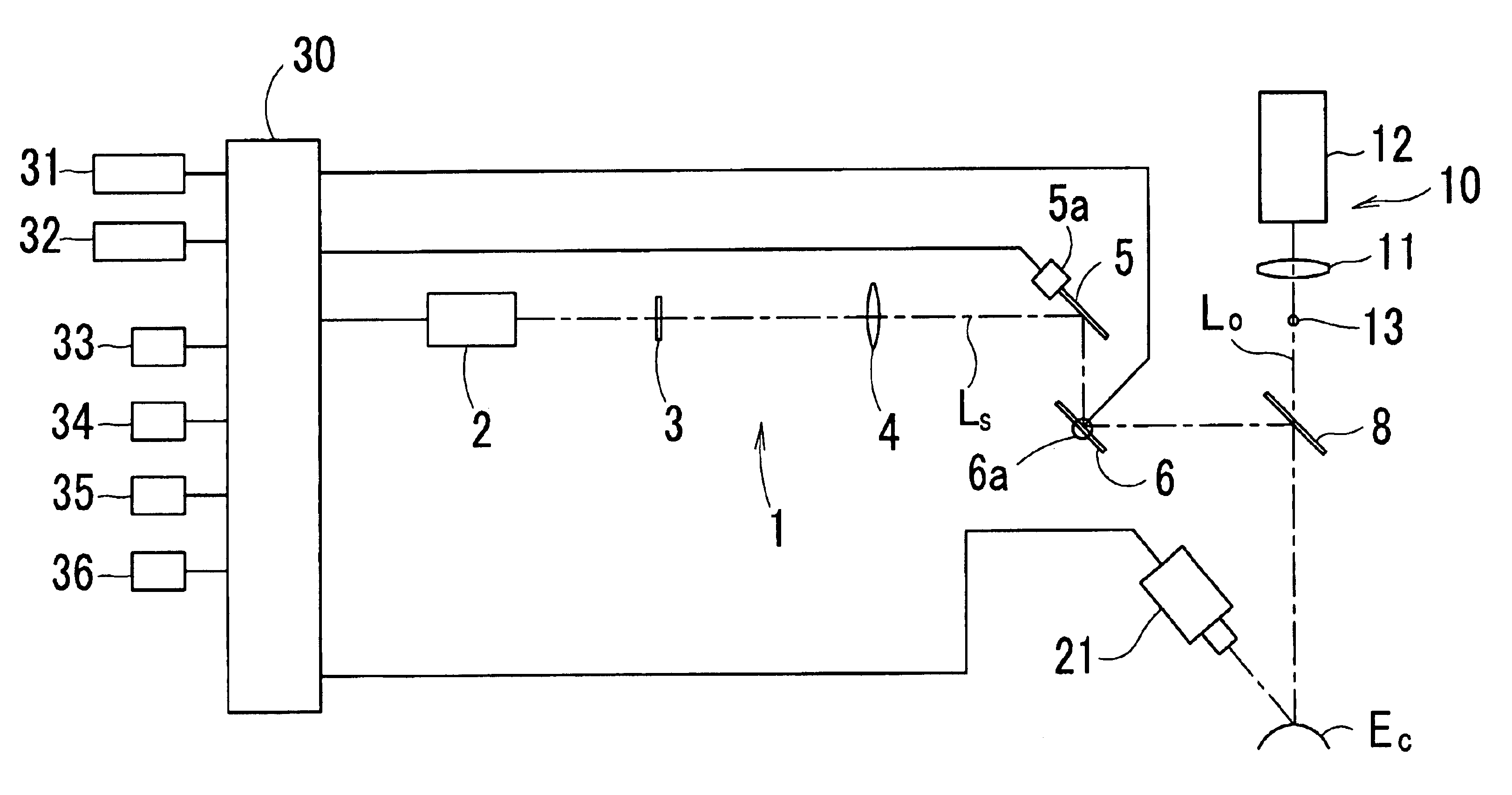
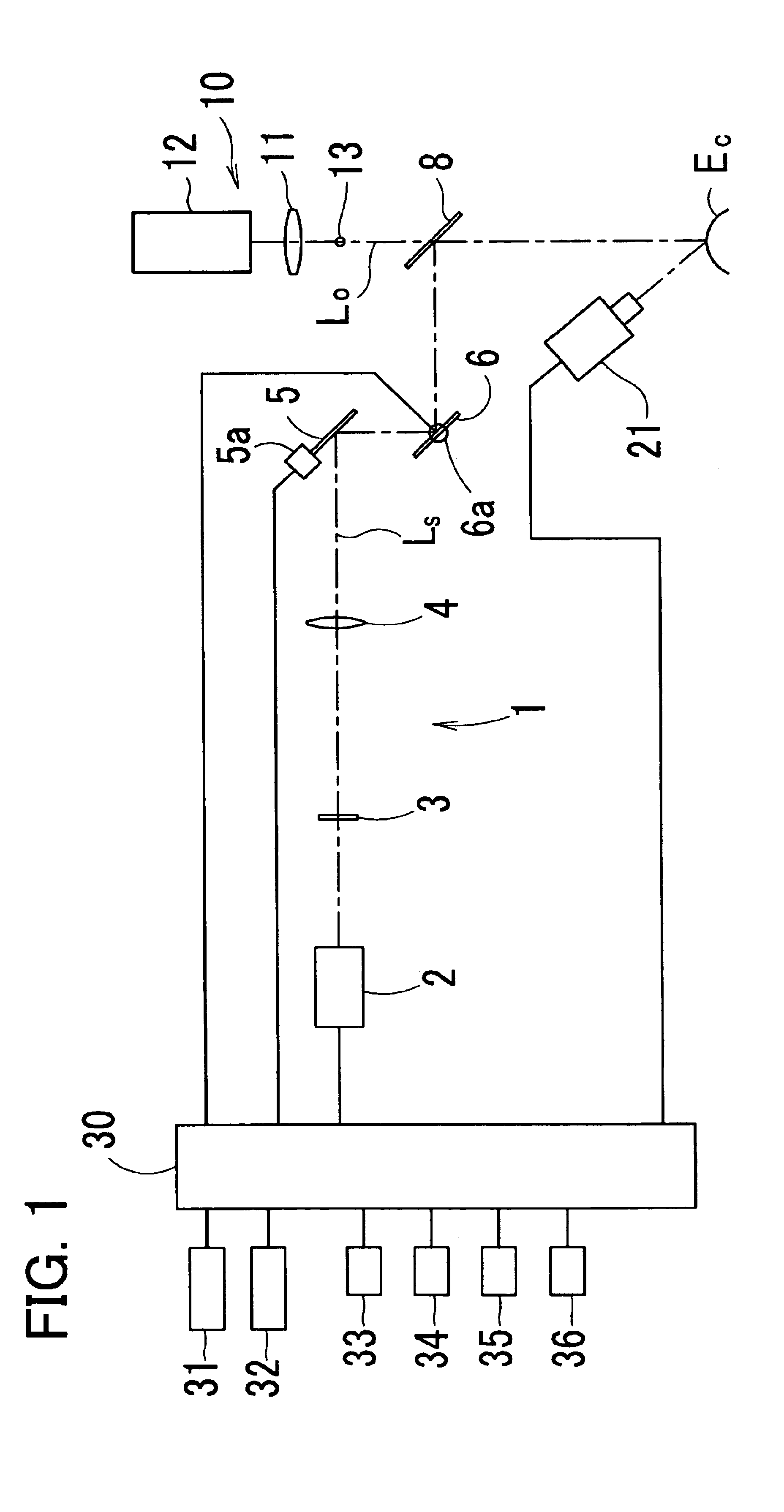
Ophthalmic laser surgical apparatus
InactiveUS6939343B2Reduce errorsLaser surgerySurgical instrument detailsEye laser surgeryOphthalmology
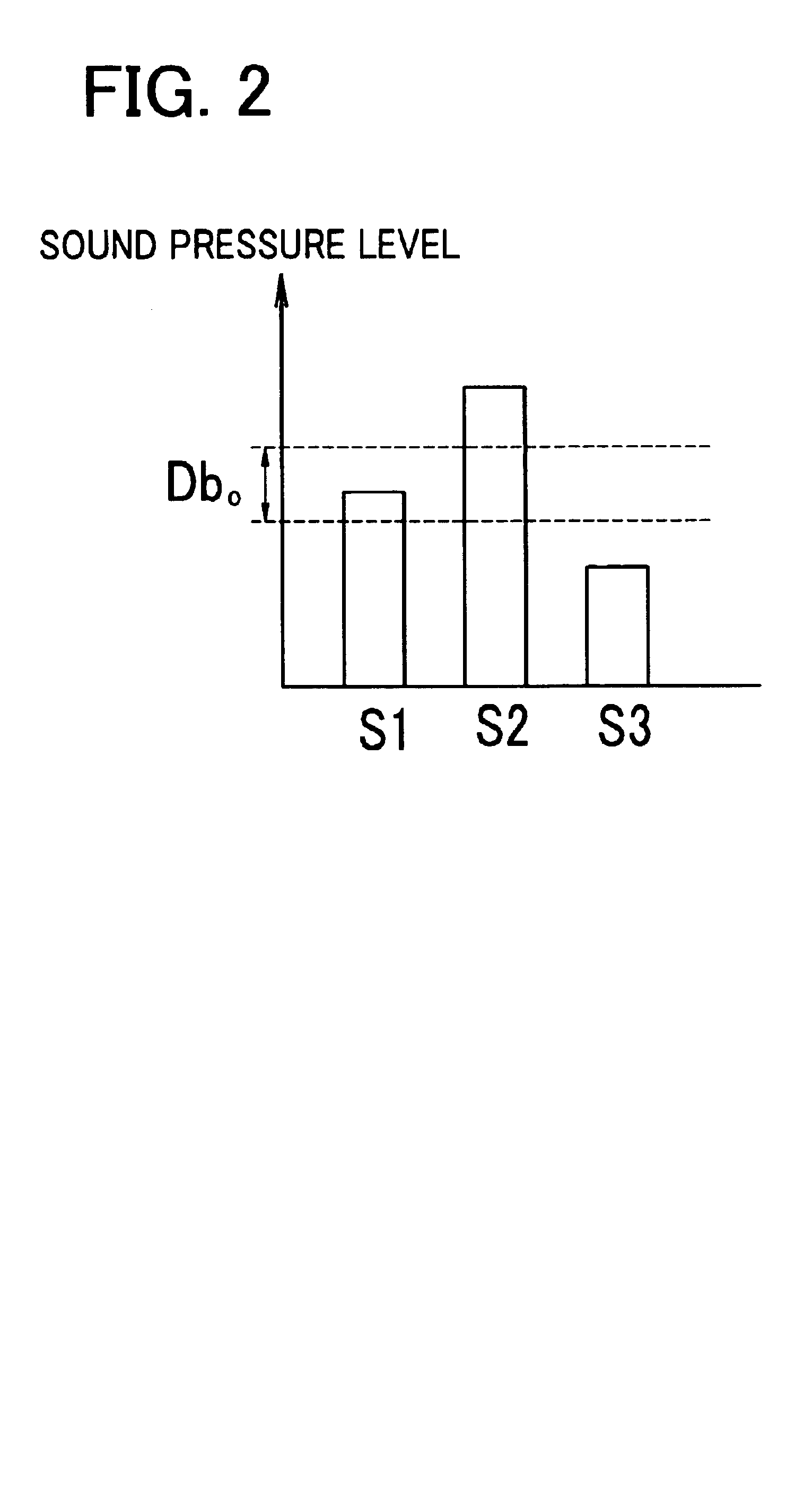
An ophthalmic laser surgical apparatus includes a laser irradiation optical system which irradiates a laser beam which causes ablation on tissue of an eye; a sound collecting unit which receives a shock sound which is generated during the ablation of the eye tissue; and a monitor unit which is connected to the sound collecting unit and detects a degree of dryness of the eye tissue during the ablation based on a sound pressure level of a sound signal from the sound collecting unit.
Owner:NIDEK CO LTD
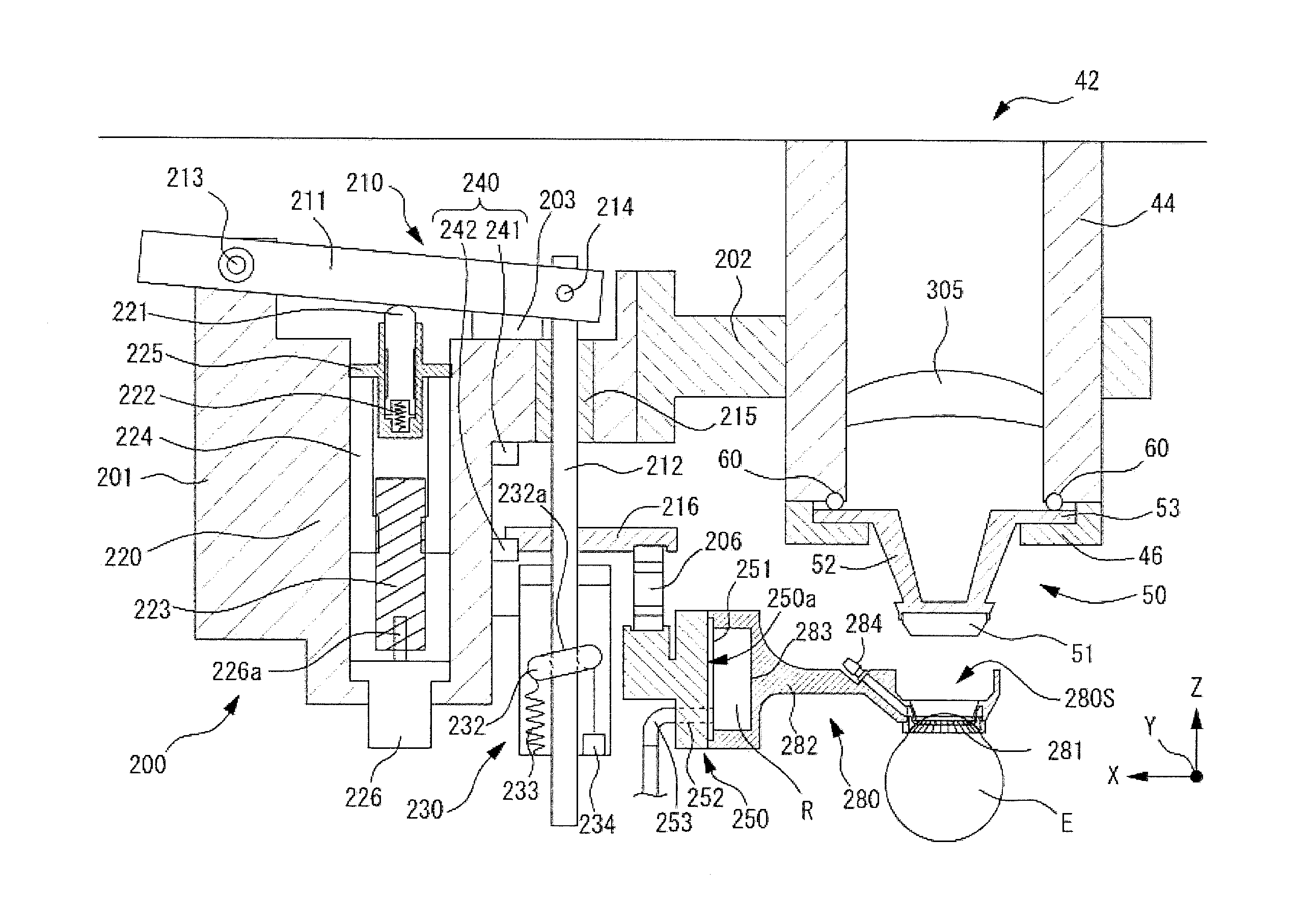
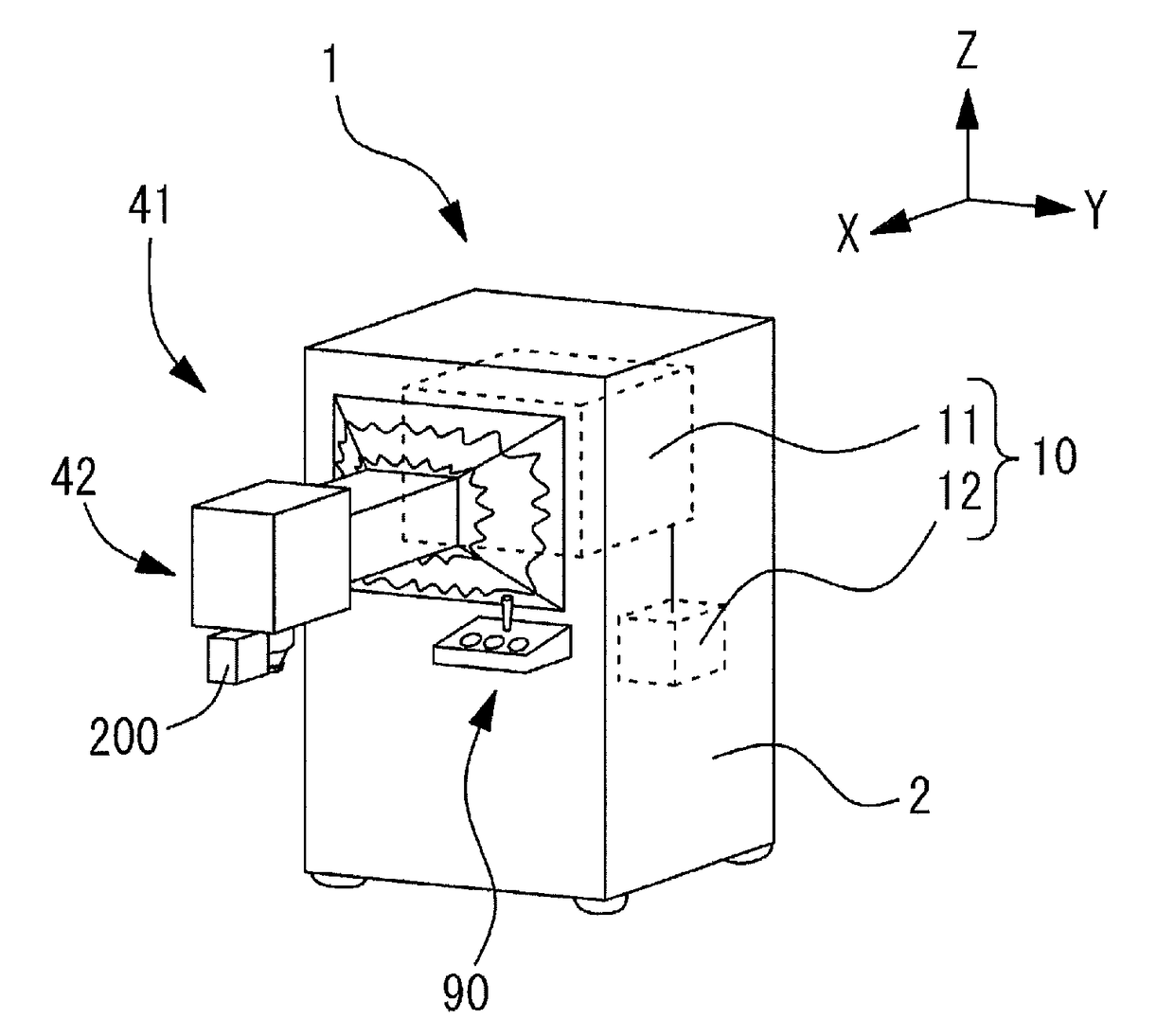
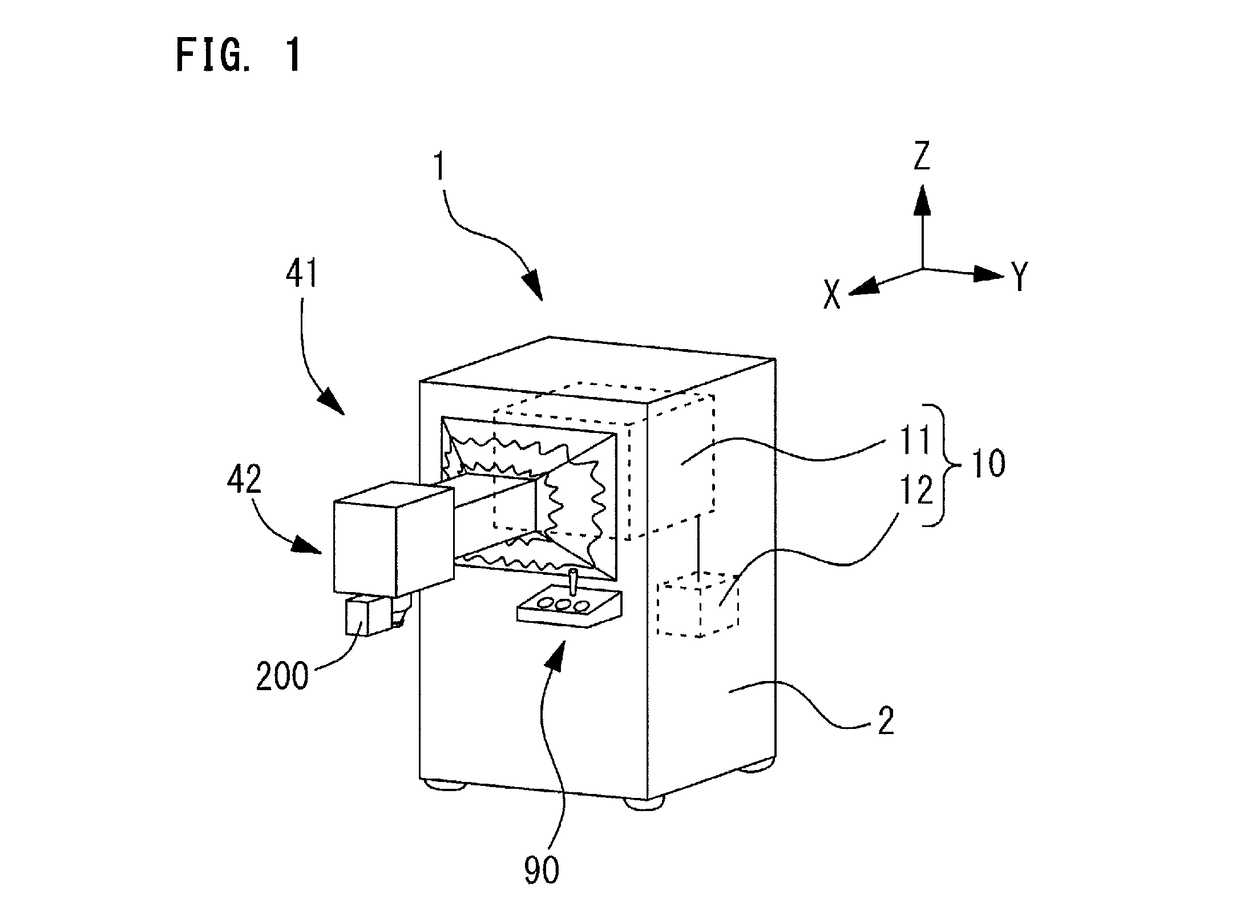
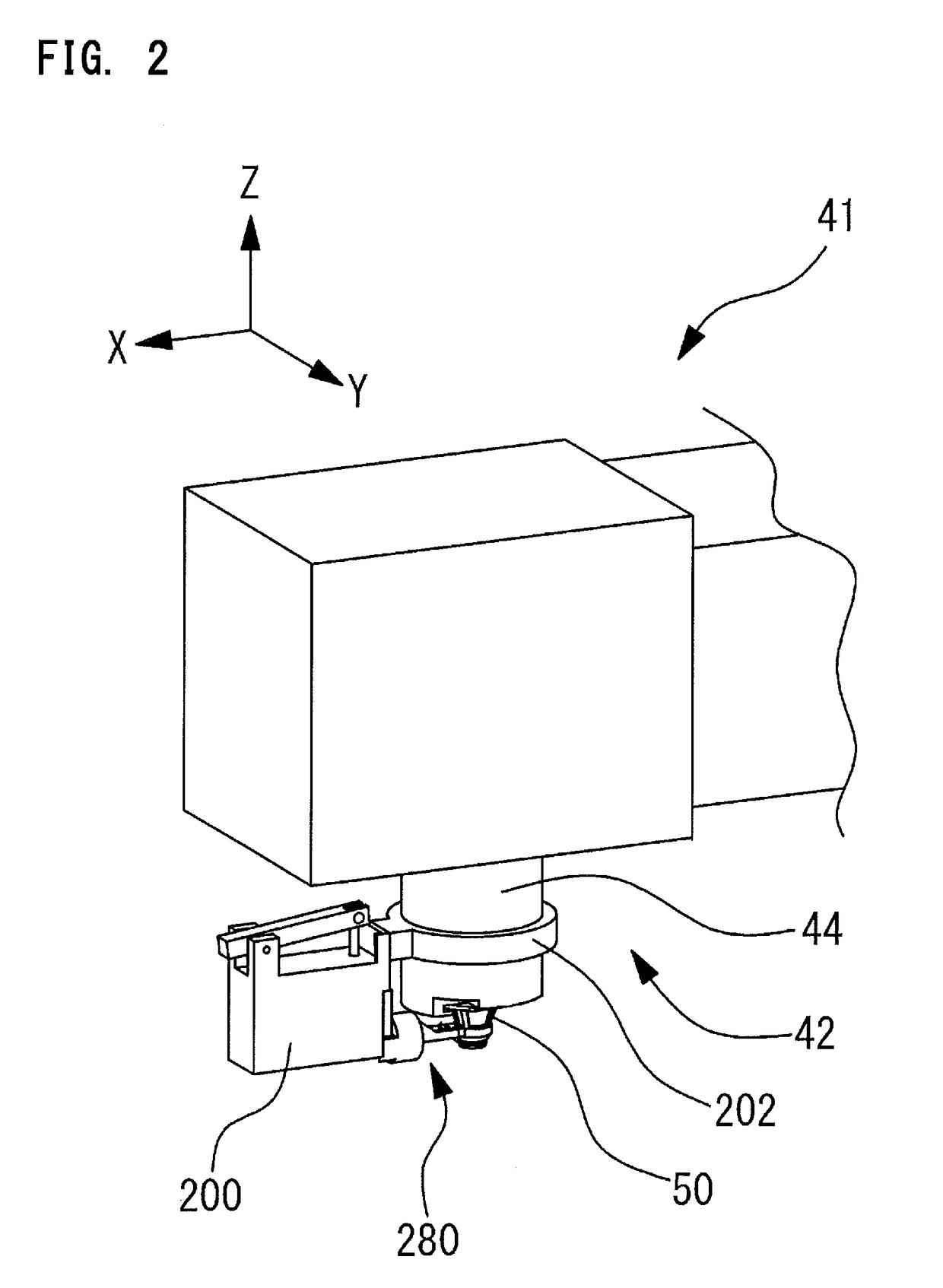
Ophthalmic laser surgery apparatus, and eyeball fixing portion movement unit and eyeball fixing unit used in the same
An ophthalmic laser surgery apparatus includes an irradiation optical system and including an objective lens, and treats a patient's eye by using a laser beam. The ophthalmic laser surgery apparatus includes a delivery unit that includes an irradiation end unit, includes at least a portion of the irradiation optical system, and optically guides the laser beam, a first movement unit that includes a first drive section and integrally moves the irradiation end unit and an eyeball fixing unit which is connected to the delivery unit and fixes the patient's eye, a second movement unit that includes a second drive section and moves the eyeball fixing unit by driving the second drive section, and drive control means for controlling driving of the first drive section and driving of the second drive section, and individually moving the first movement unit and the second movement unit.
Owner:NIDEK CO LTD
Compound modulation transfer function for laser surgery and other optical applications
InactiveUS20080129962A1Mitigates and treats vision conditionMitigates presbyopiaLaser surgeryRefractometersEye laser surgeryLaser surgery
Methods, devices, and systems establish an optical surface shape that mitigates or treats a vision condition in a patient. An optical surface shape for a particular patient can be determined using a set of patient parameters for the specific patient by using a compound modulation transfer function (CMTF). The compound modulation transfer function can include a combination of modulation transfer functions (MTF's) at a plurality of distinct frequencies.
Owner:AMO MFG USA INC
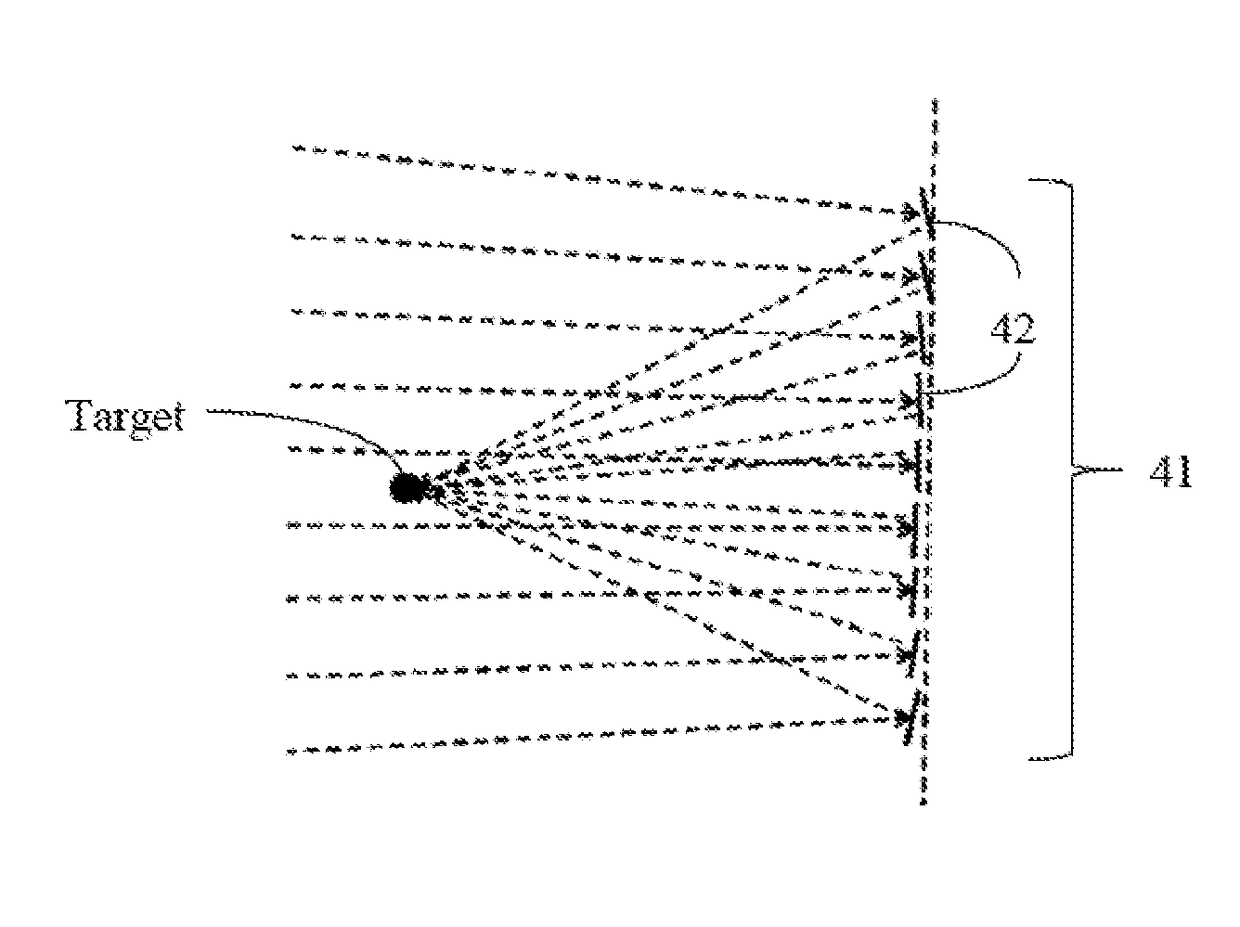
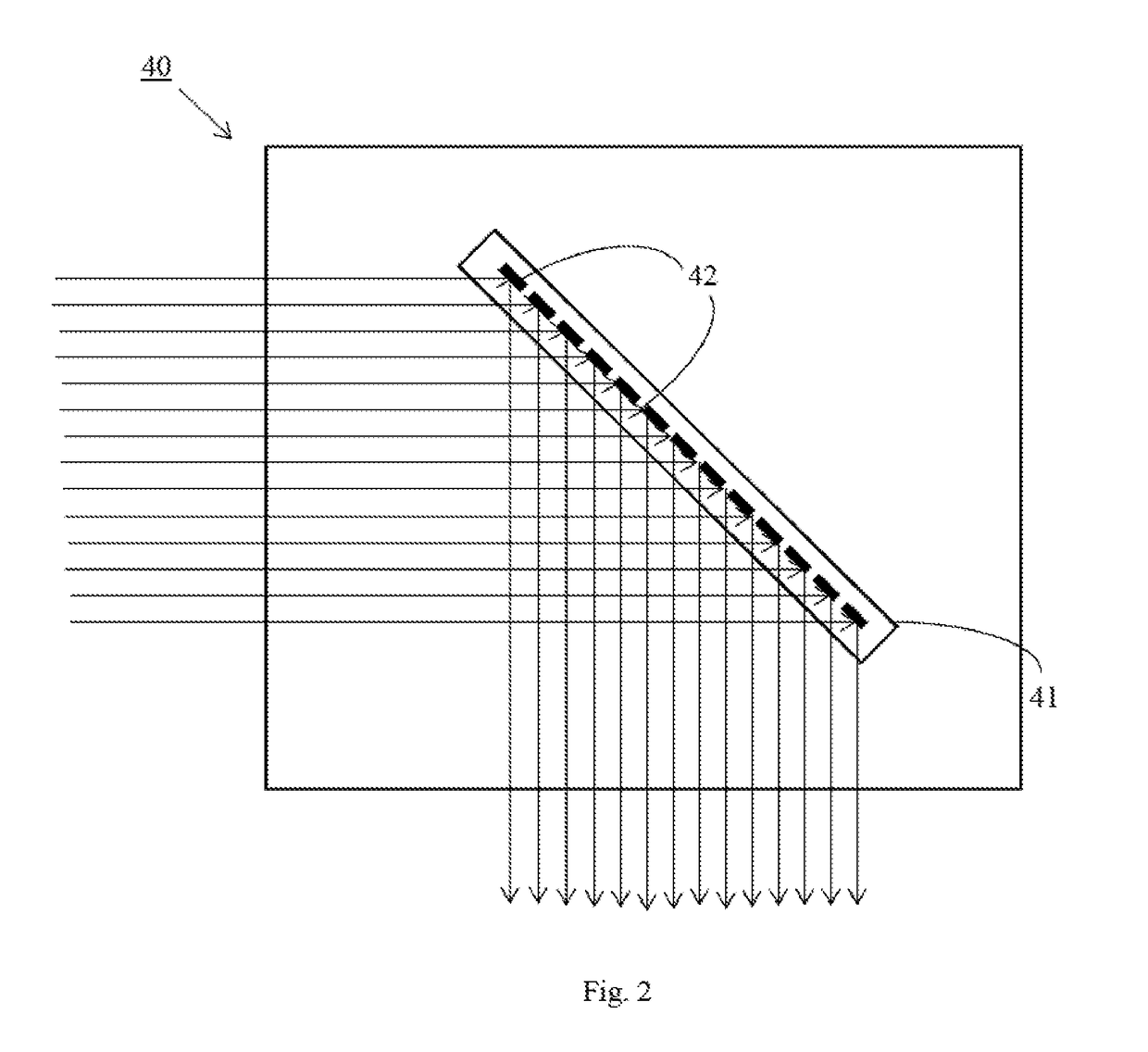
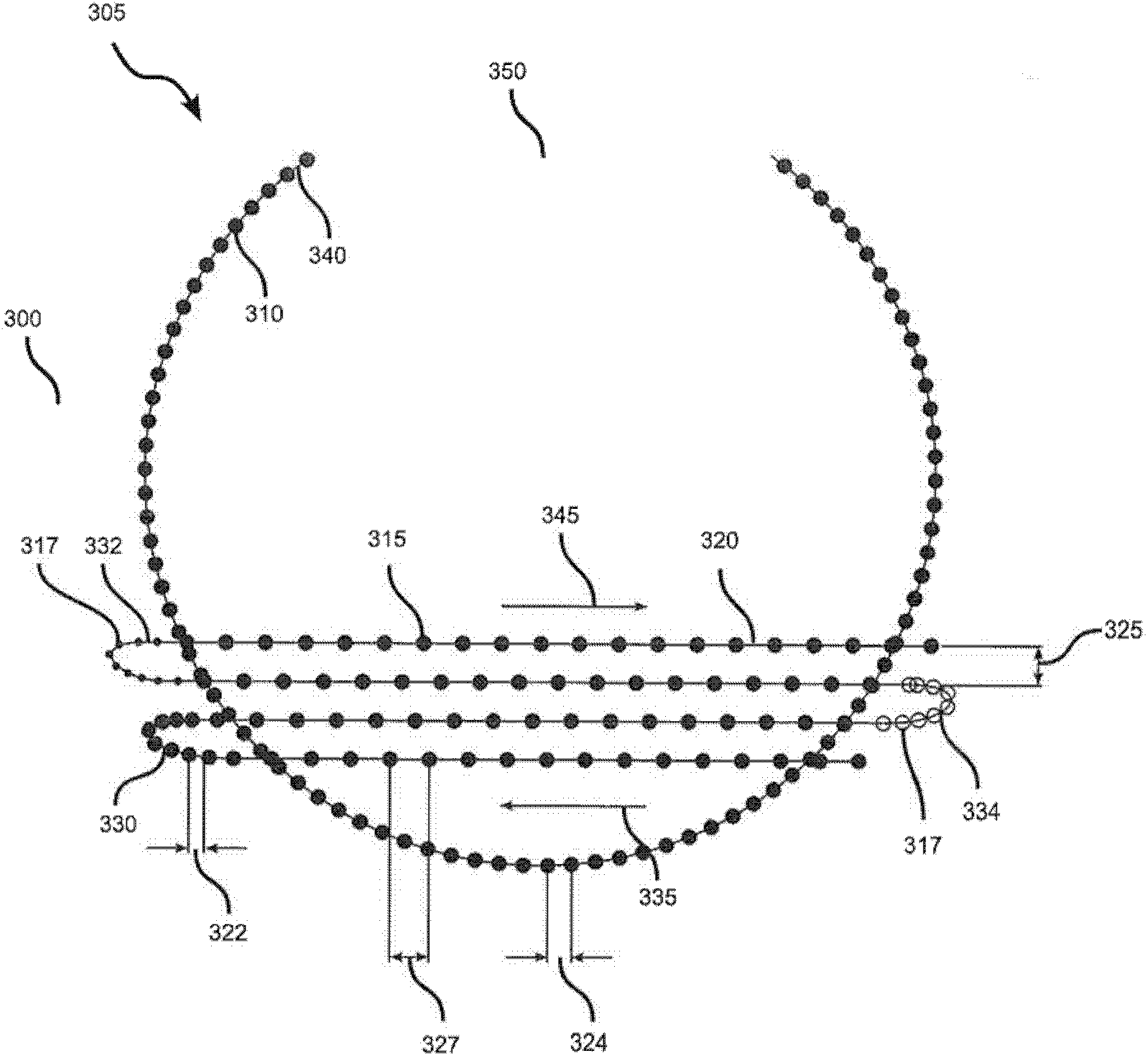
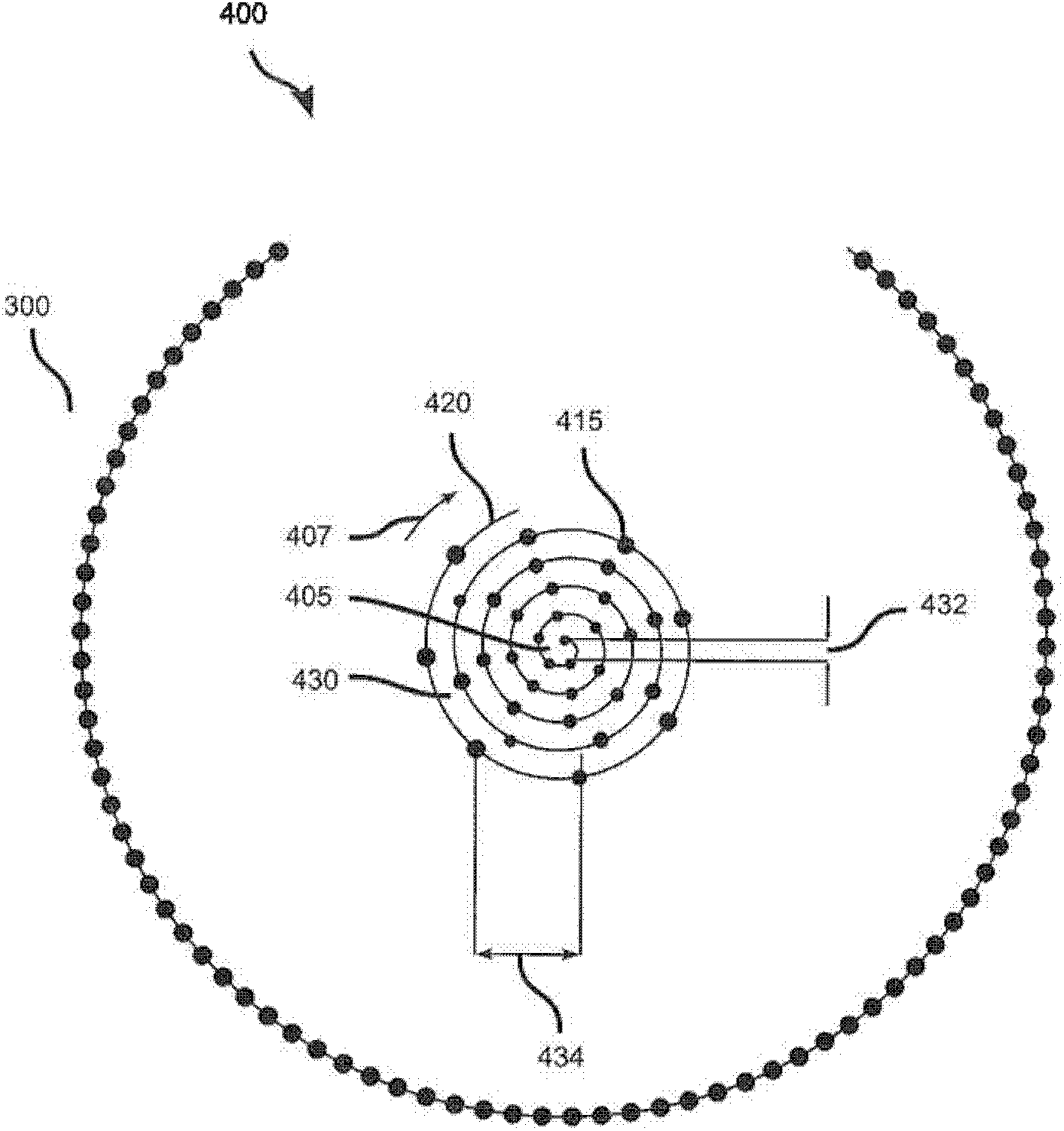
System and method for photoablation using multiple focal points using cyclical phase modulation
InactiveUS20080287935A1Faster angular speedIncrease ωLaser surgerySurgical instrument detailsEye laser surgeryPhotoablation
A system and method for performing ophthalmic laser surgery requires directing a laser beam through a stationary beam splitter to create a pattern of multi-focal spots. Also, a beam scanner is used to move this pattern along a substantially spiral path in a target area of tissue. To compensate for cyclical changes in orientation of the pattern relative to its spiral path, a computer is used to phase modulate pattern movement. Specifically, this phase modulation is expressed as:v′=v(1+F sin(nθ))where v is a variable (e.g. angular speed, line spacing, or z-spacing), v′ is the phase modulated variable, F is a magnitude factor for phase modulation control, n is an integer, and θ is an angular position of the pattern during phase modulation.
Owner:TECHNOLAS PERFECT VISION
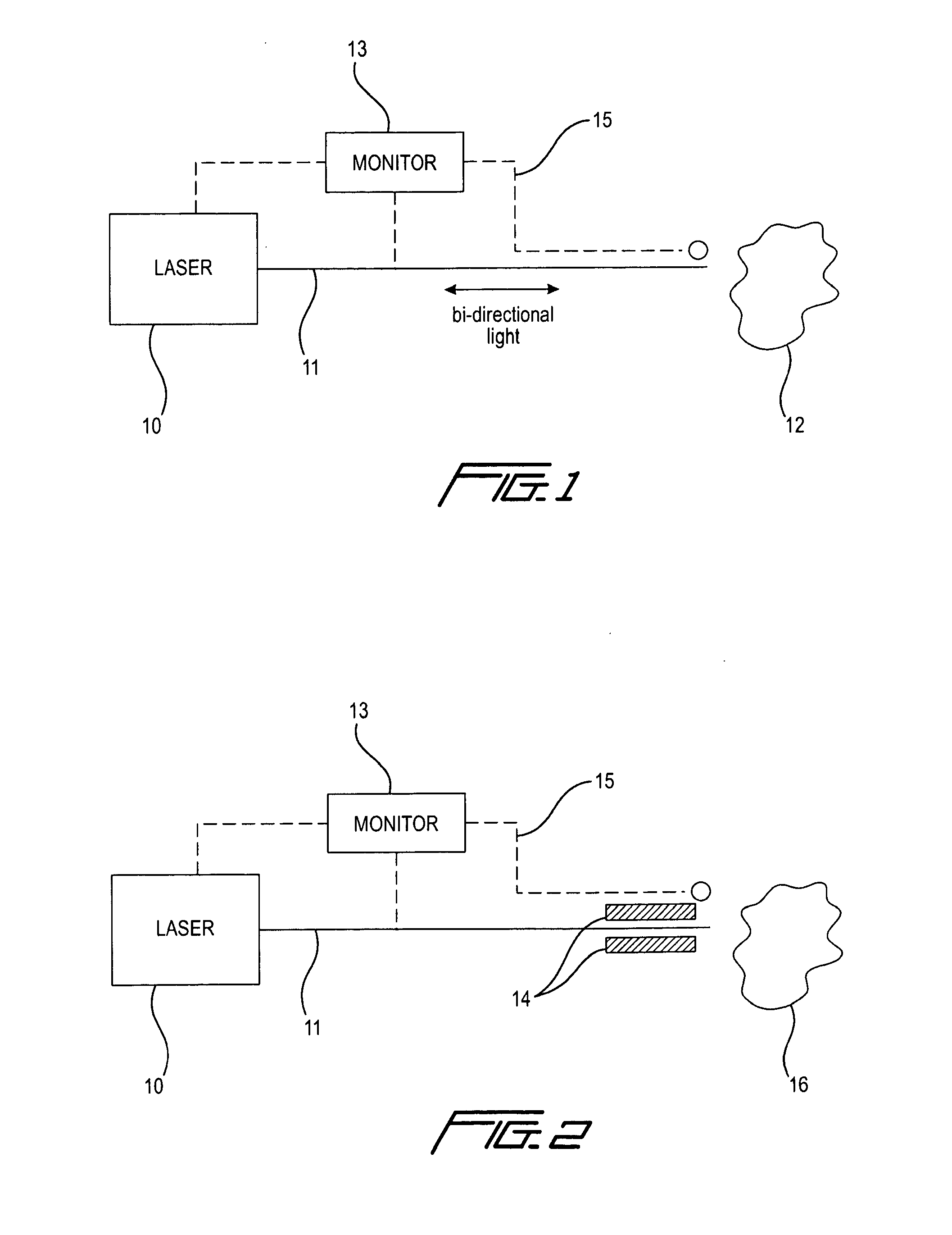
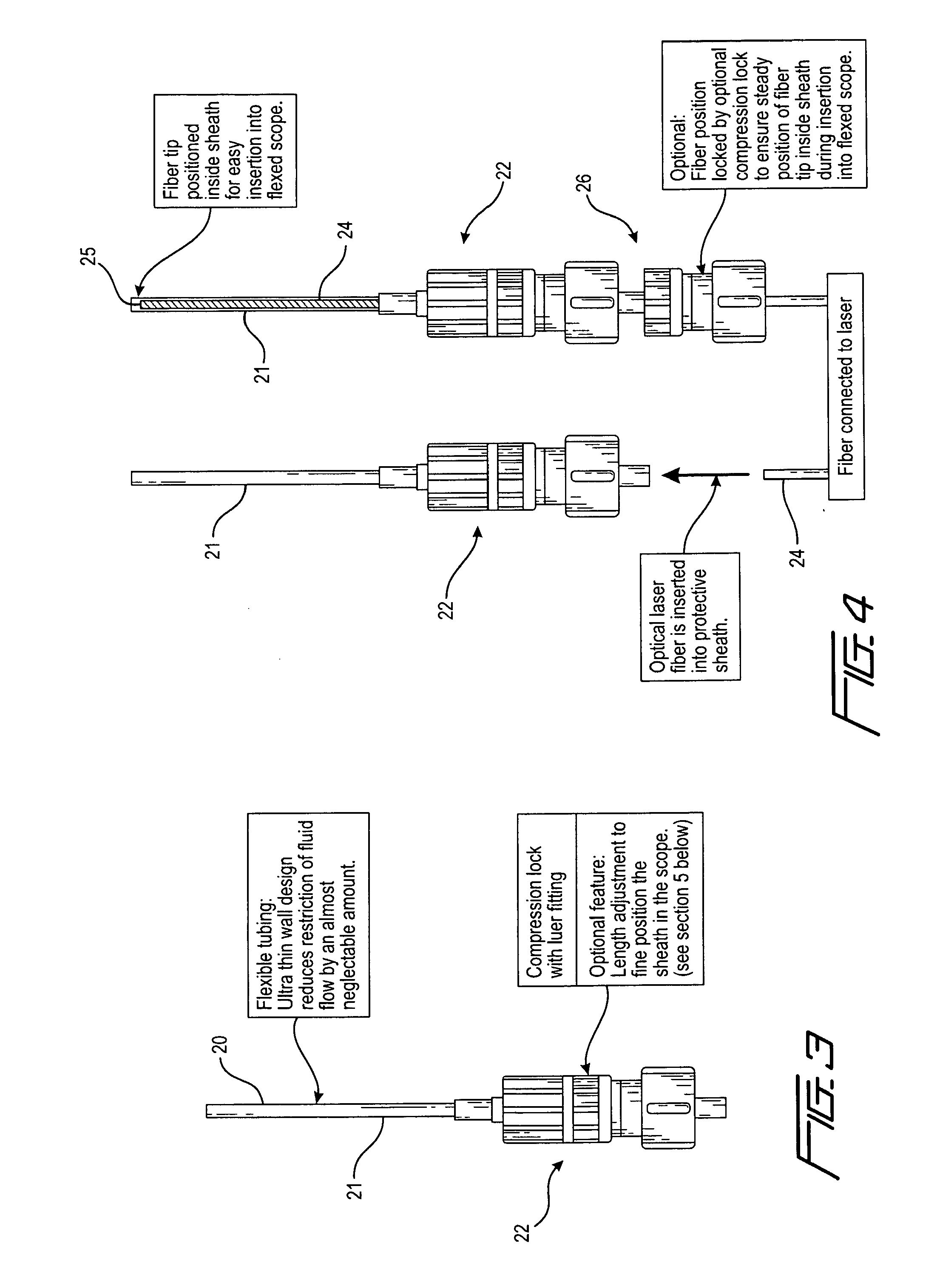
Apparatus and method for detecting overheating during laser surgery
InactiveUS20110213349A1Minimize damageRapidly and reliably detecting any overheatingPhotometryLight therapyInfraredFiber
A method and apparatus for improving the safety of a surgical procedure involving delivery of laser energy to a tissue, involves enhancing or increasing the detectability of radiation emitted by the tissue or any portion of a surgical instrument or device by providing a sacrificial material that absorbs radiation emitted during the surgical procedure, increasing the temperature of a surface on which the material is disposed and / or causing damage radiation to be emitted in a way that can be detected by monitoring the temperature of the surface and / or radiation, including infrared and / or visible light, emitted by the surface. In a preferred embodiment of the invention, the radiation absorbing material is a sheath arranged to surround the fiber.
Owner:BROWN JOE DENTON
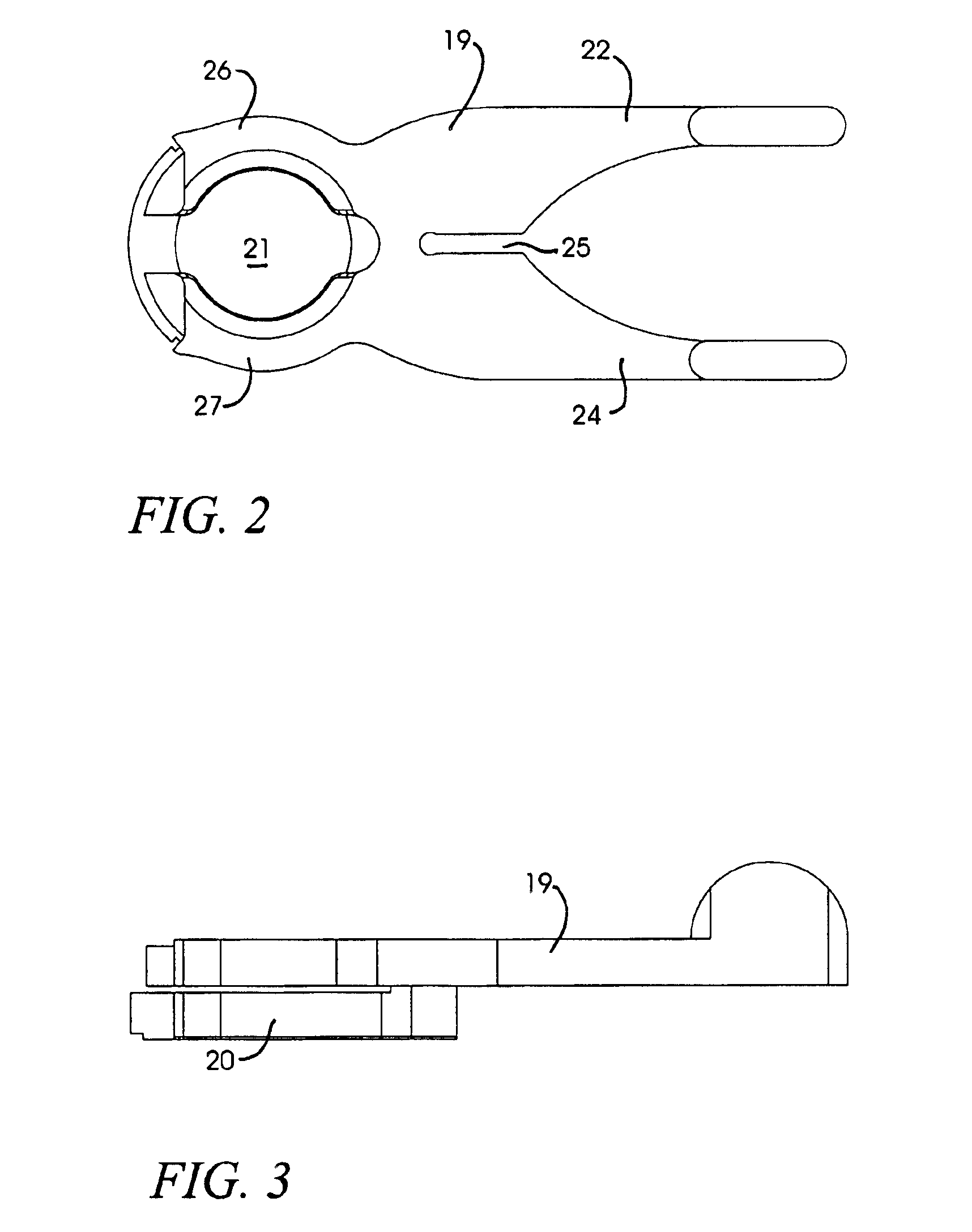
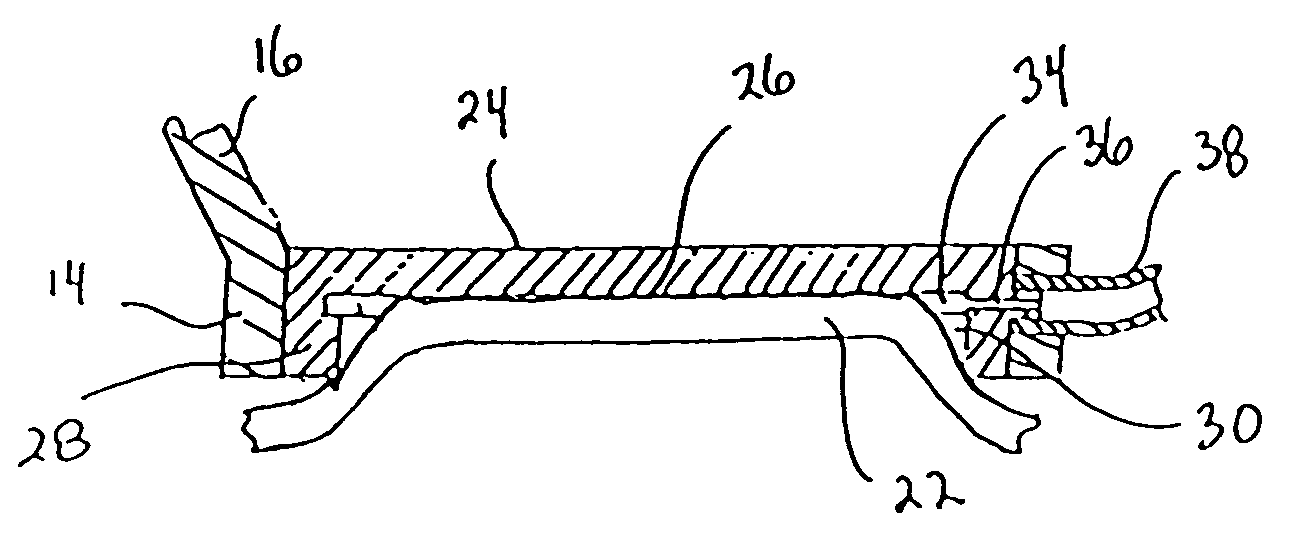
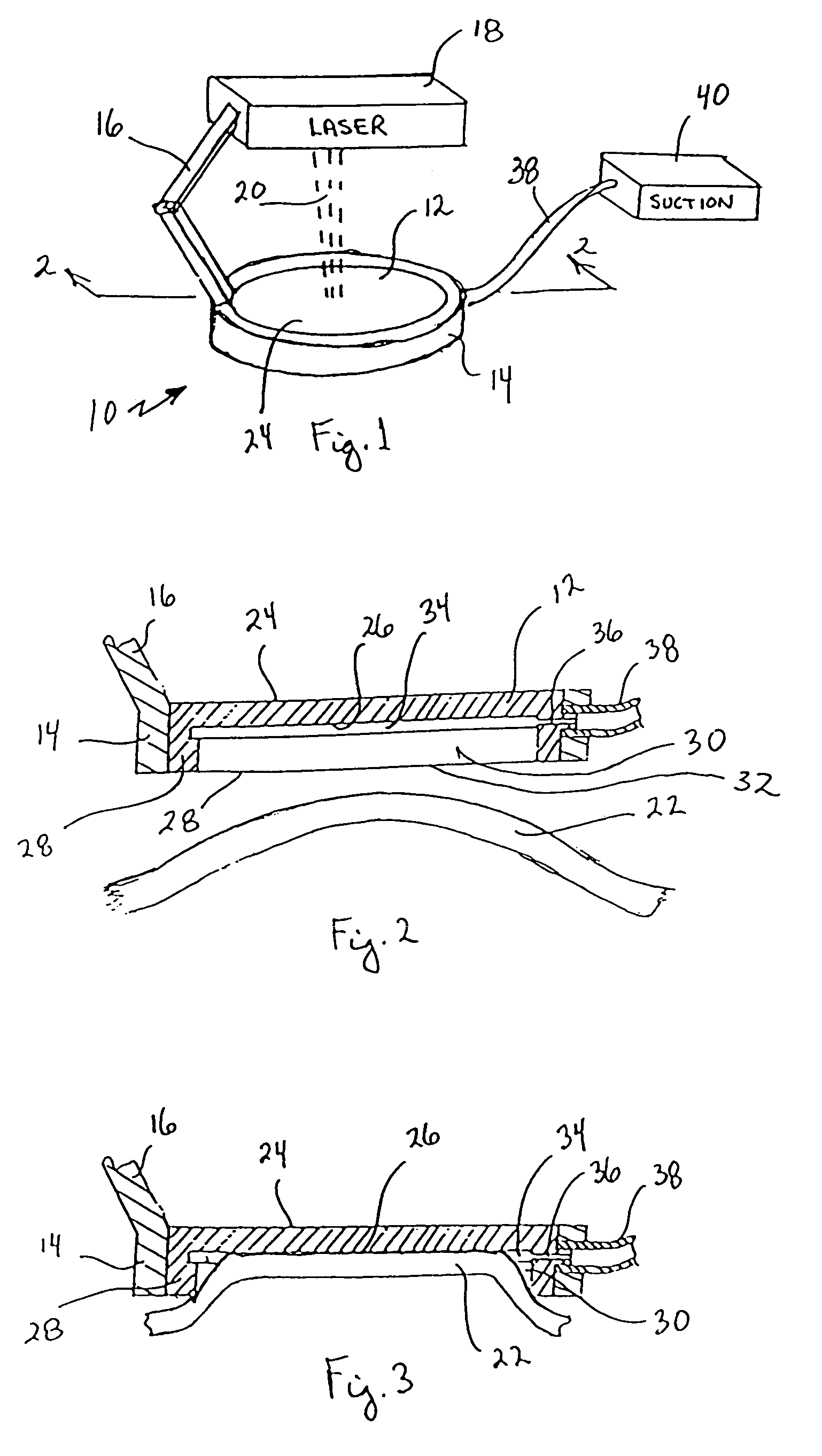
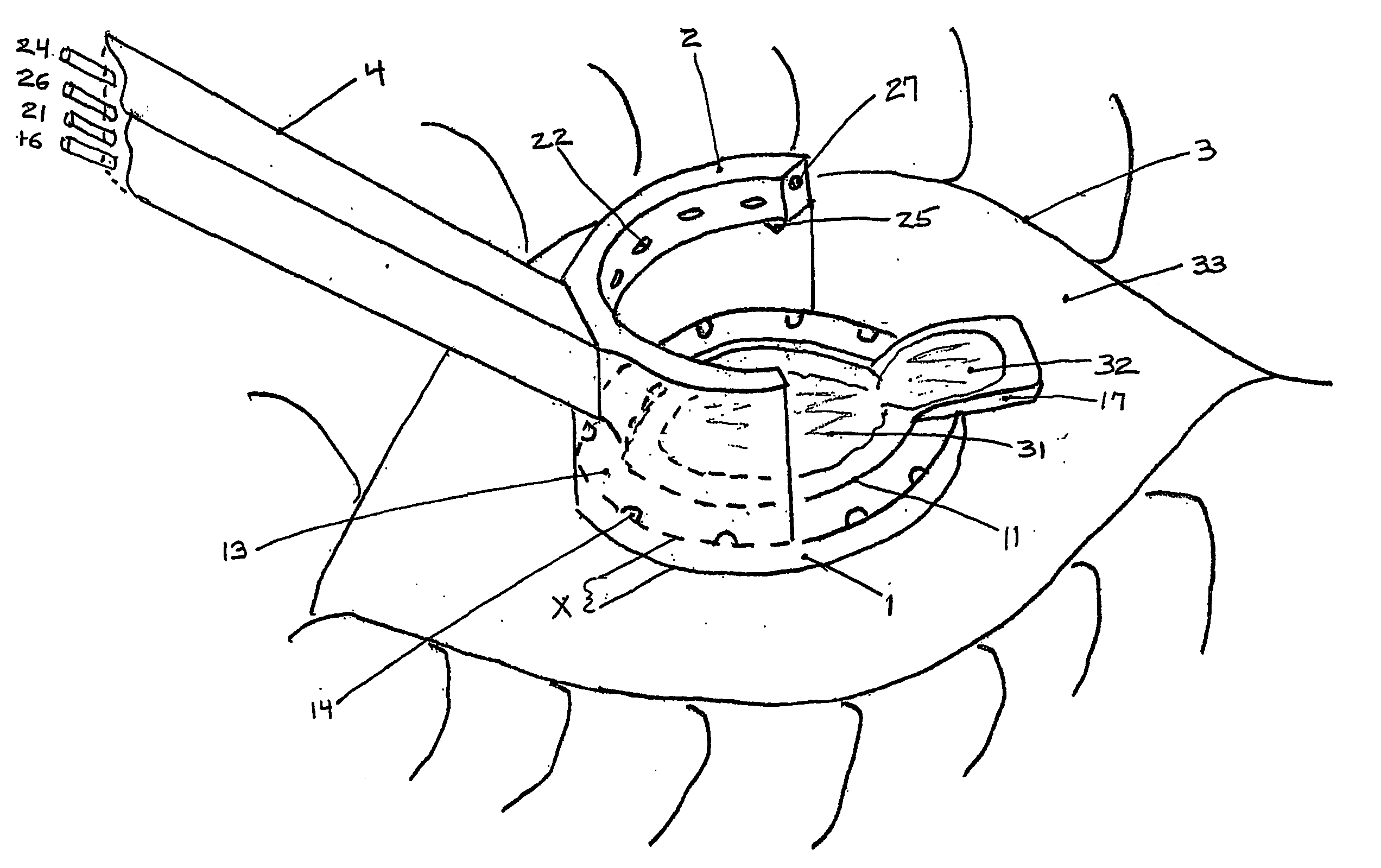
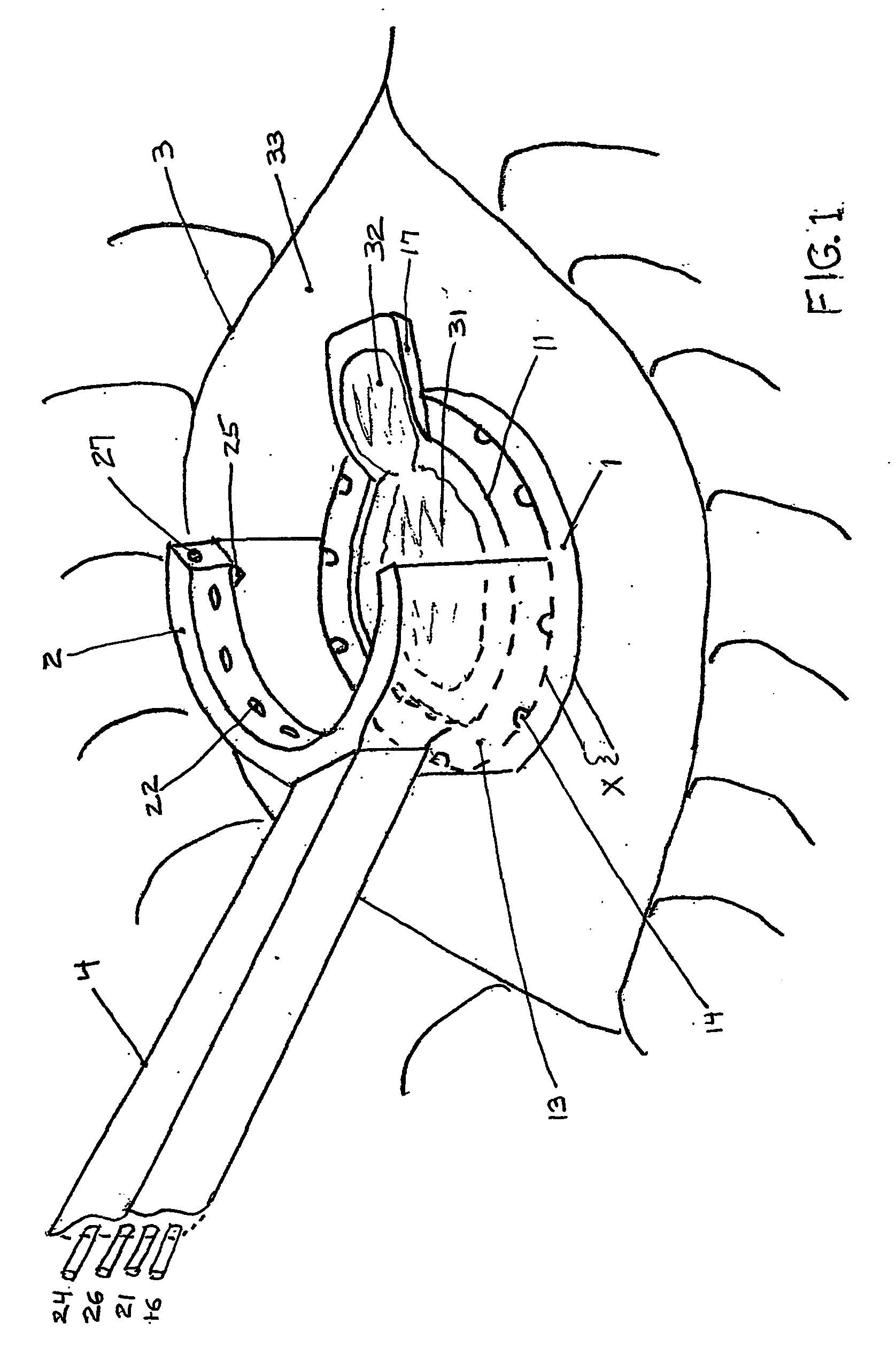
Multi-function surgical instrument for facilitating ophthalmic laser surgery
Owner:LAHAYE LEON C
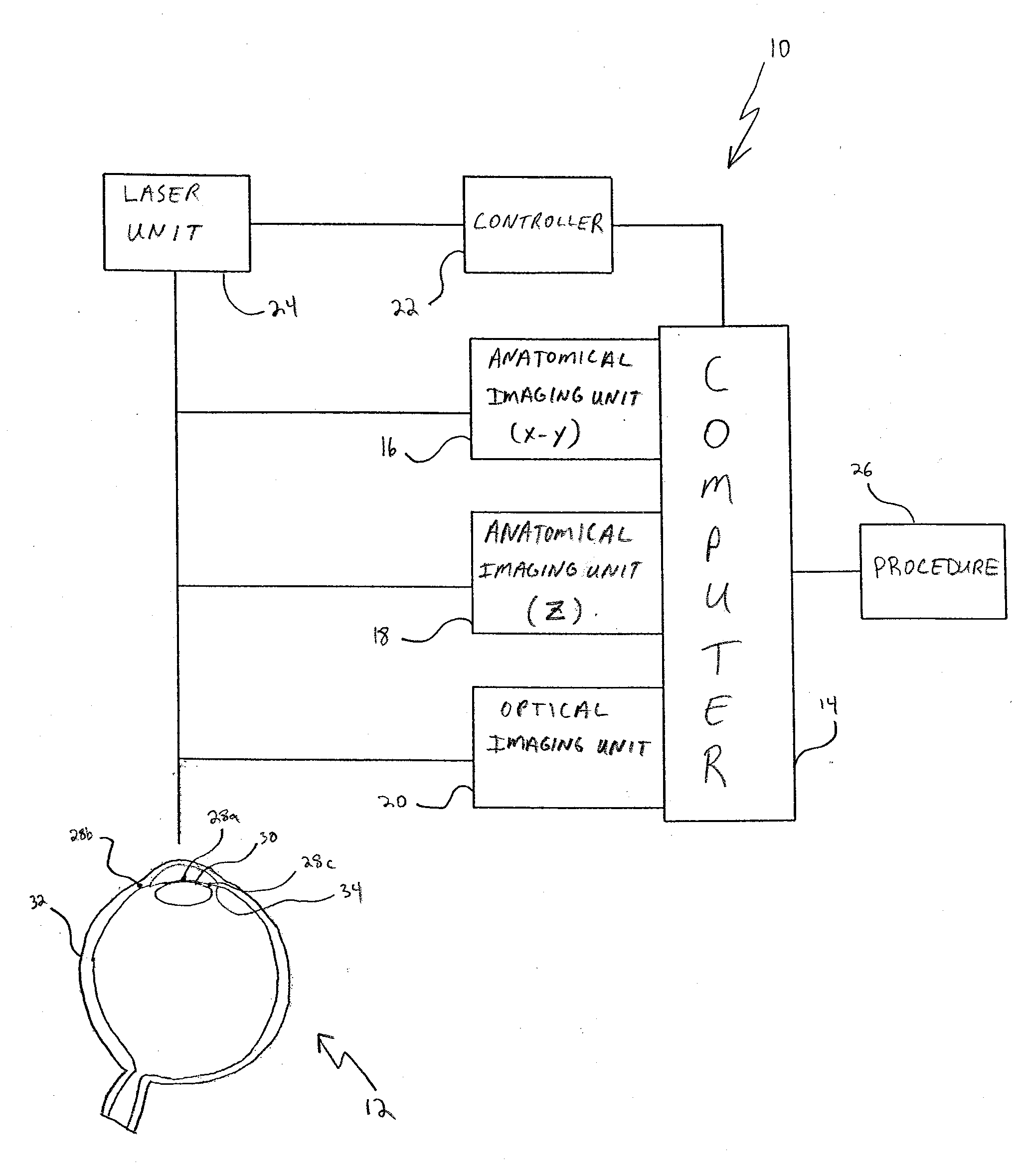
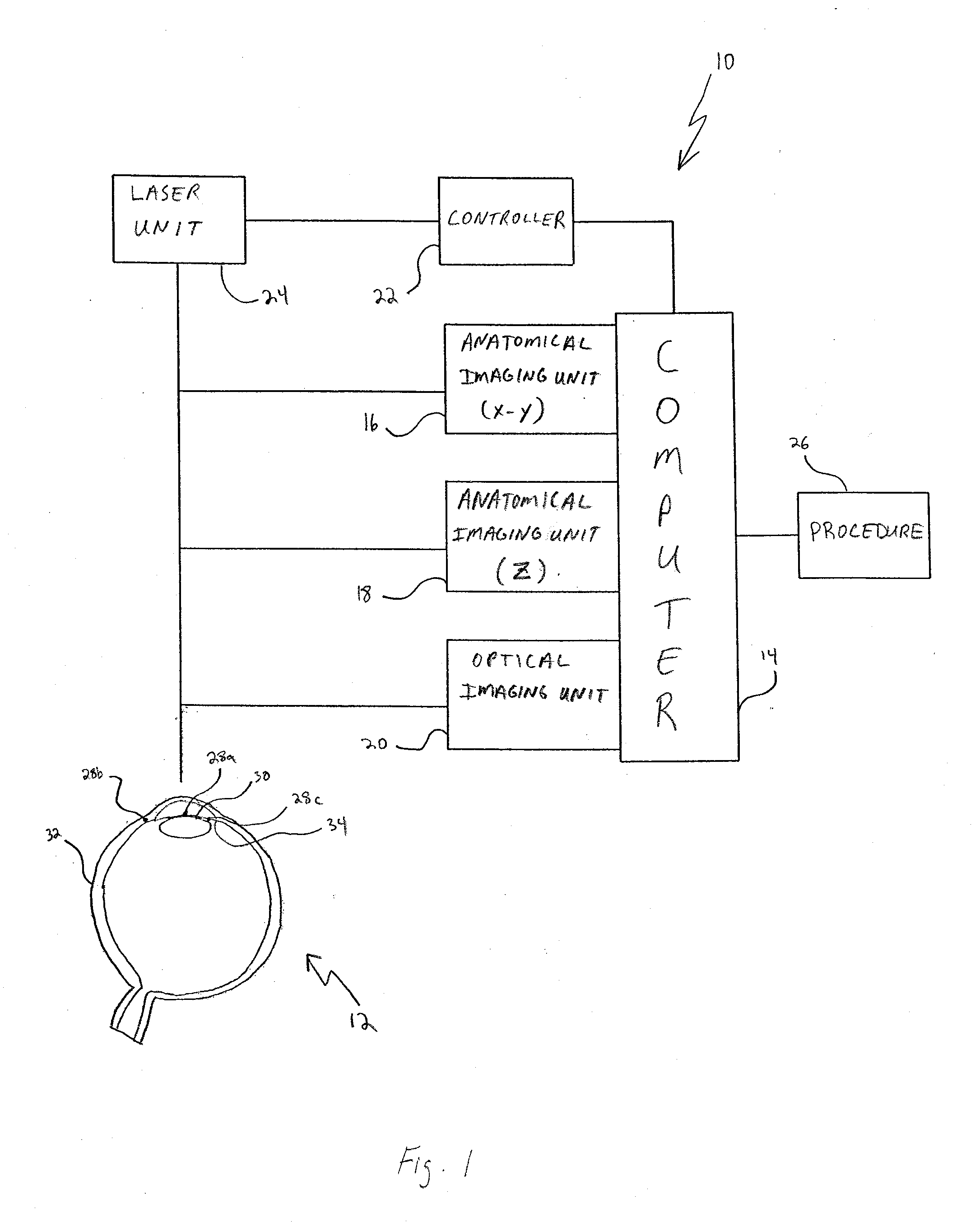
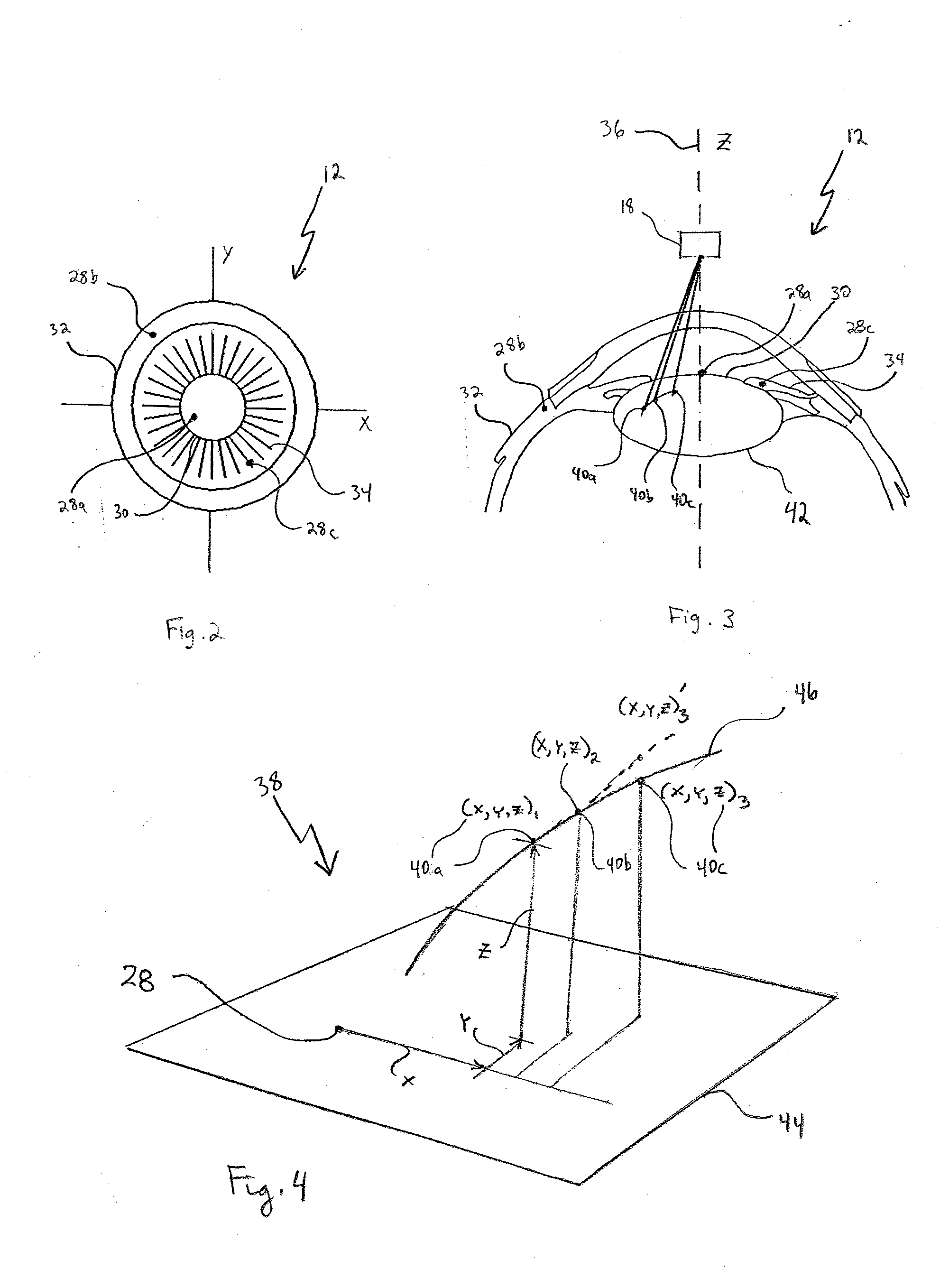
System and Method for Using Multiple Detectors
A system and method are provided for using multiple detectors to create a frame of reference for performing ophthalmic laser surgery. Anatomical detectors generate data sets and a computer program receives these data sets to create the frame of reference. The frame of reference is then used with a selected procedure for conducting ophthalmic laser surgery. An additional detector can measure refractive data of the eye for use as a data set that will refine the frame of reference.
Owner:TECHNOLAS PERFECT VISION
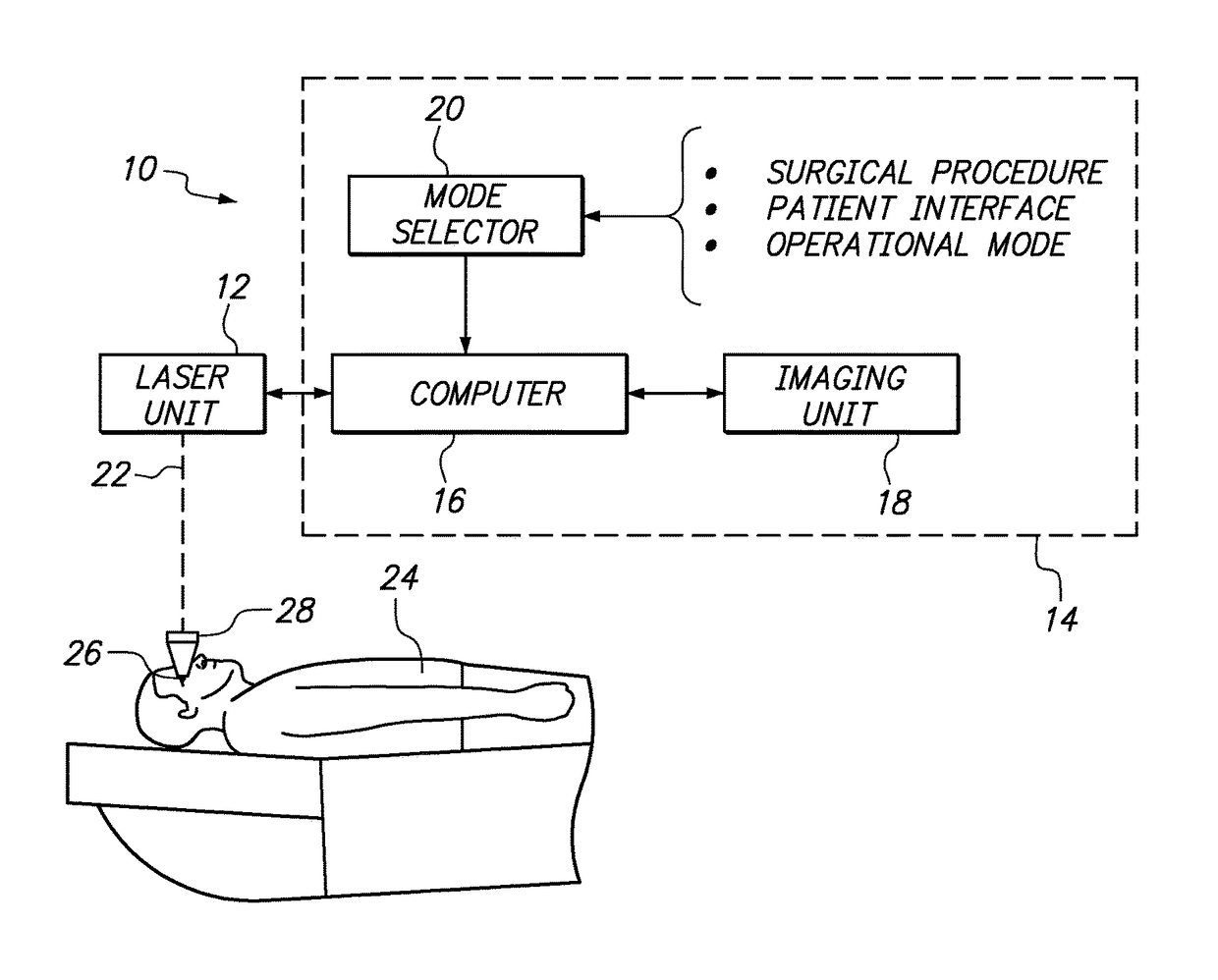
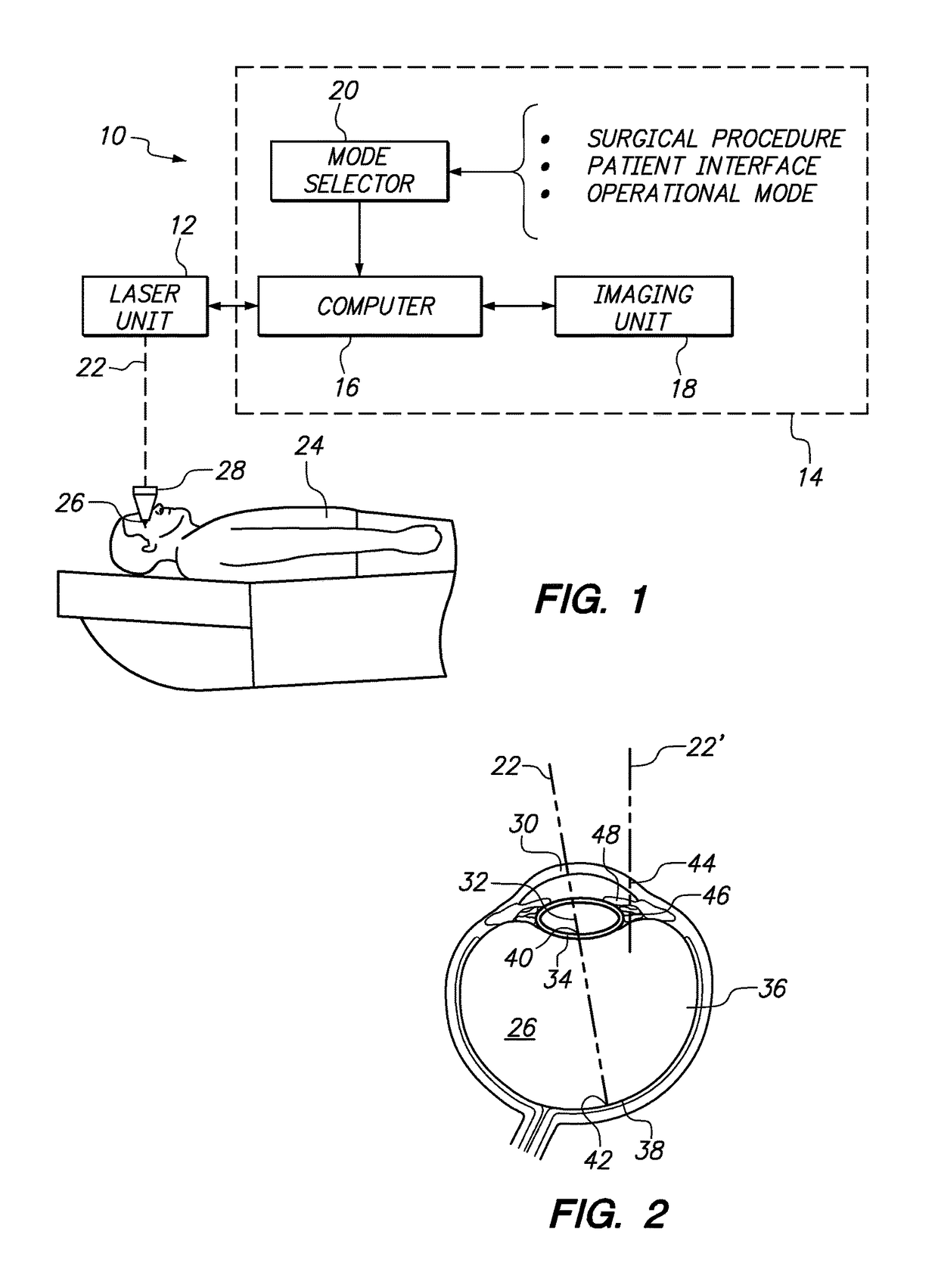
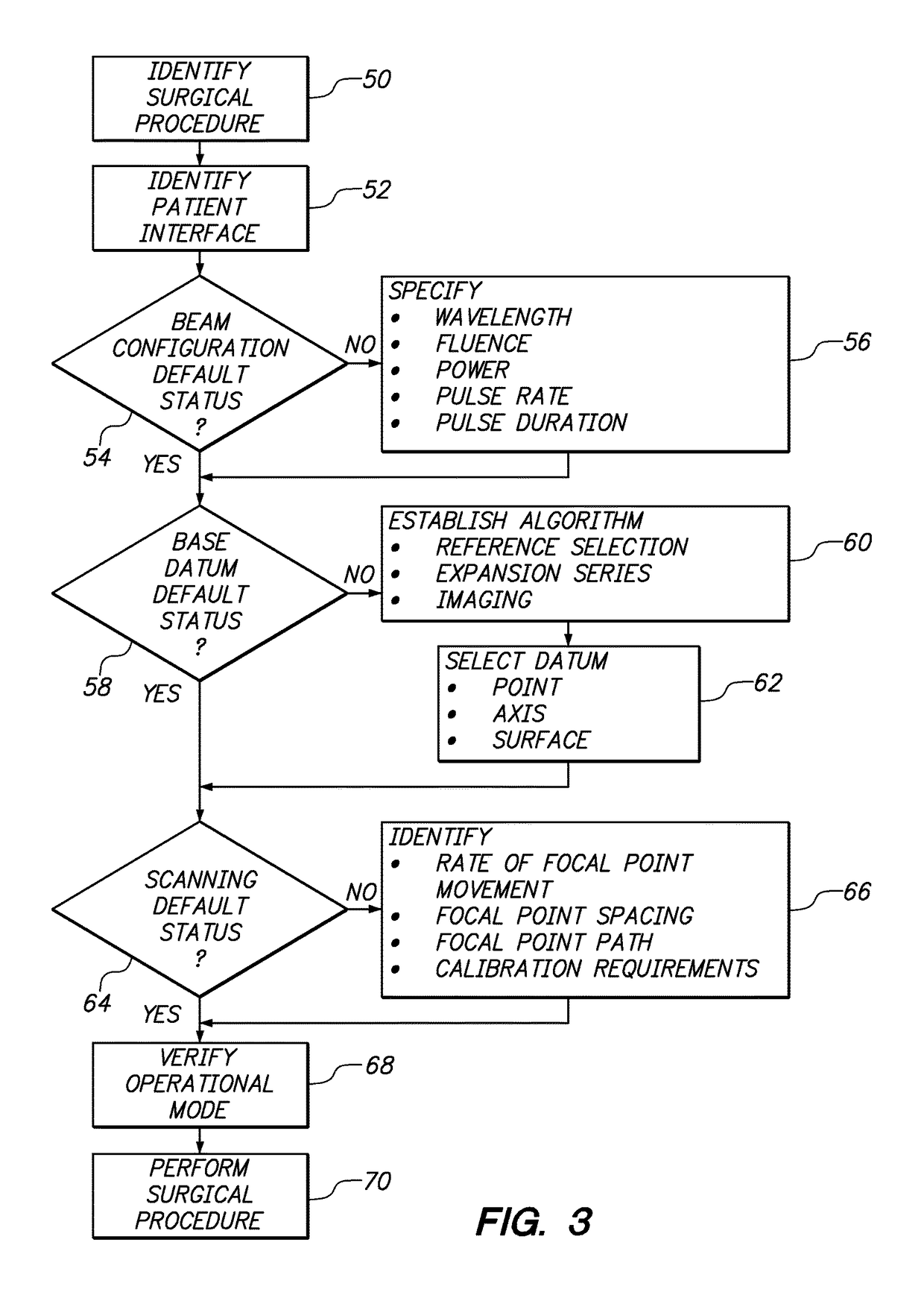
Surgical laser unit with variable modes of operation
A comprehensive multi-mode system for performing ophthalmic laser surgery on selected tissue inside an eye includes a laser unit for generating and focusing a laser beam to perform Laser Induced Optical Breakdown (LIOB) at a focal point in selected tissue. Also included is a selector for defining an operational mode according to characteristics of the tissue to be altered by LIOB. In combination, the operational mode specifies value ranges for configuration parameters for a pulsed femtosecond laser beam, establishes a base reference datum in the eye, and identifies a scanning procedure for the focal point of the laser beam to customize the system for a particular surgical procedure. A computer that is connected to the laser unit is responsive to the selector for implementing the operational mode.
Owner:TECHNOLAS PERFECT VISION
Iterative Fourier reconstruction for laser surgery and other optical applications
Methods, systems and software for determining an optical surface model for an optical tissue system using Fourier transformation algorithms. A method of reconstructing optical tissues of an eye comprises transmitting an image through the optical tissues of the eye. The surface gradients from the transmitted image are measured across the optical tissues of the eye. A Fourier transform algorithm is applied to the surface gradients to reconstruct an optical surface model that corresponds to the optical tissues of the eye.
Owner:AMO MFG USA INC
Apparatus for laser surgical ophthalmology
The invention relates to an apparatus for laser surgical ophthalmology, comprising a source of pulsed femtosecond laser radiation, components for guiding and focusing the laser radiation onto or into a tissue of an eye to be treated, a control unit controlling the source, which has been set up to switch the source between at least two operating modes with respectively differing radiation properties of the laser radiation, wherein in a first operating mode the radiation properties of the laser radiation are matched to the placement of an incision in the tissue, and in a second operating mode the radiation properties of the laser radiation are matched to a welding or cross-linking of the tissue.
Owner:WAVELIGHT GMBH
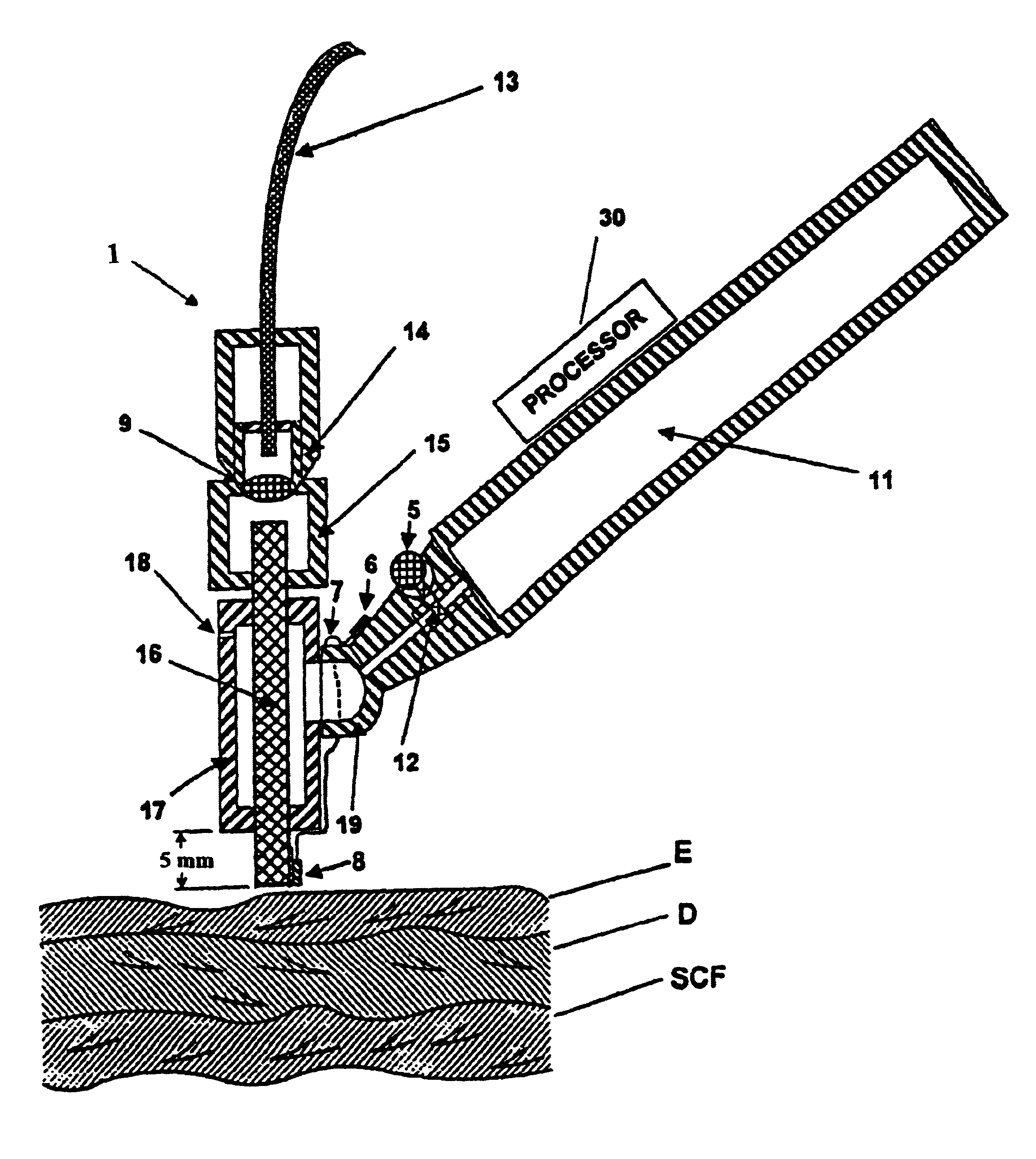
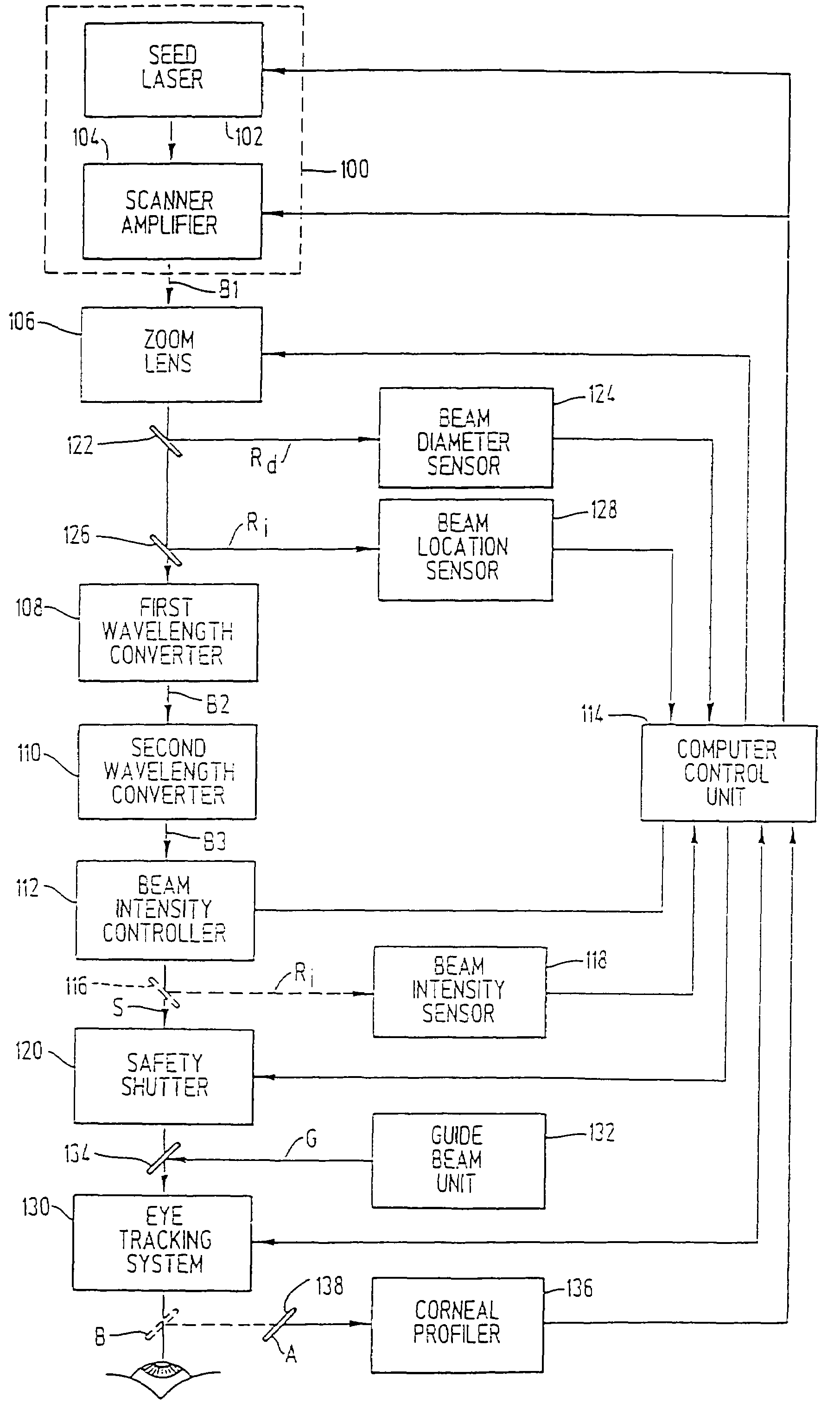
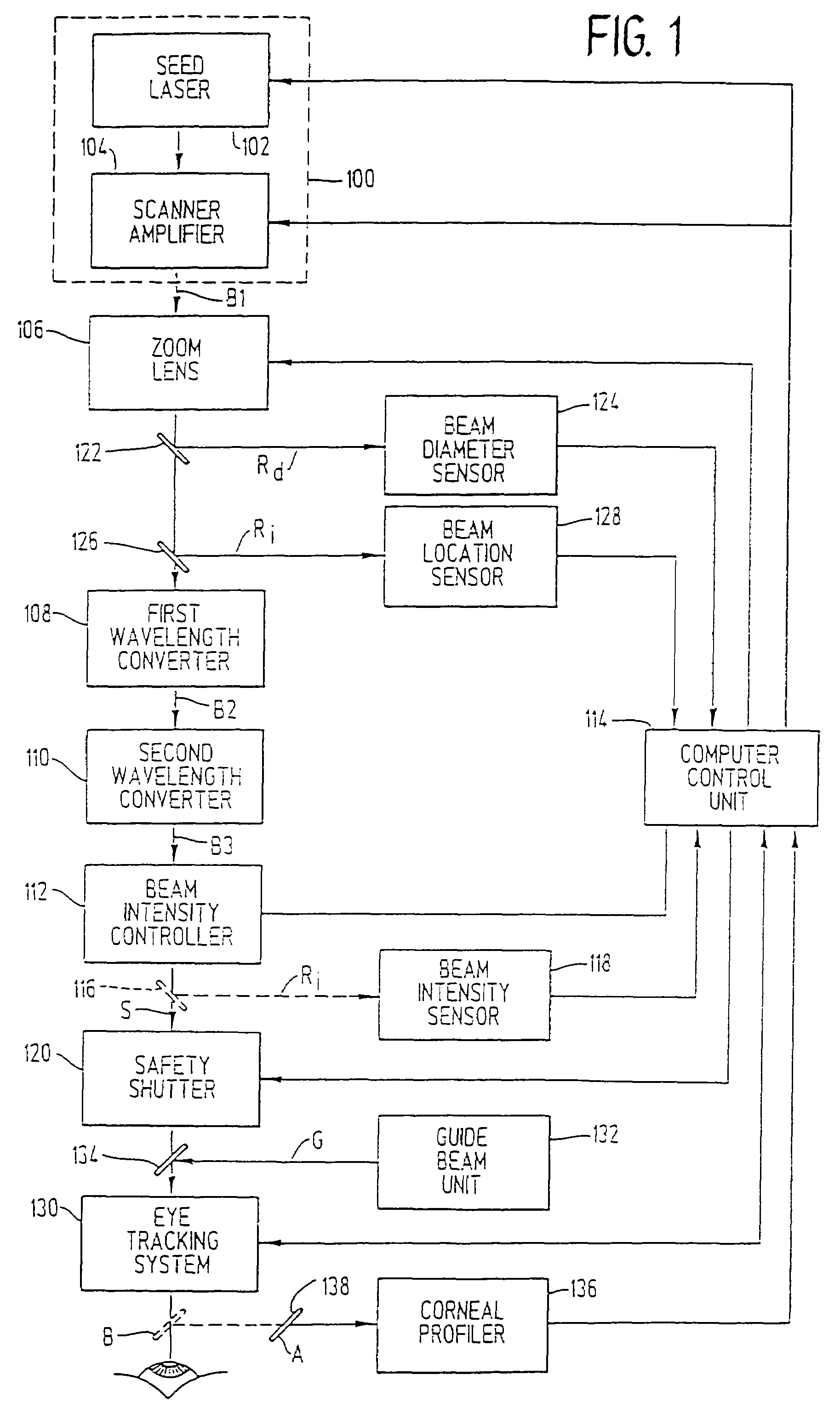
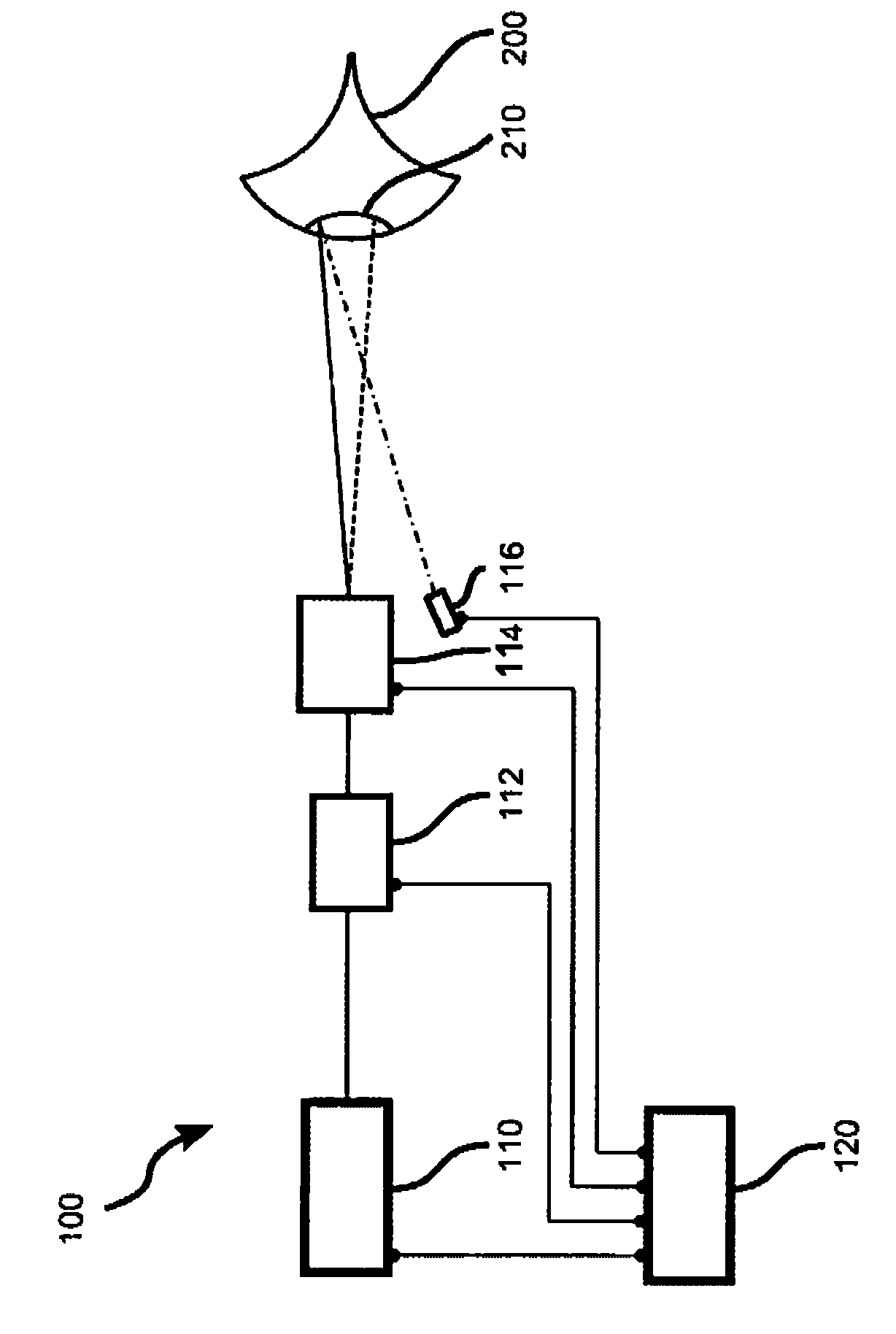
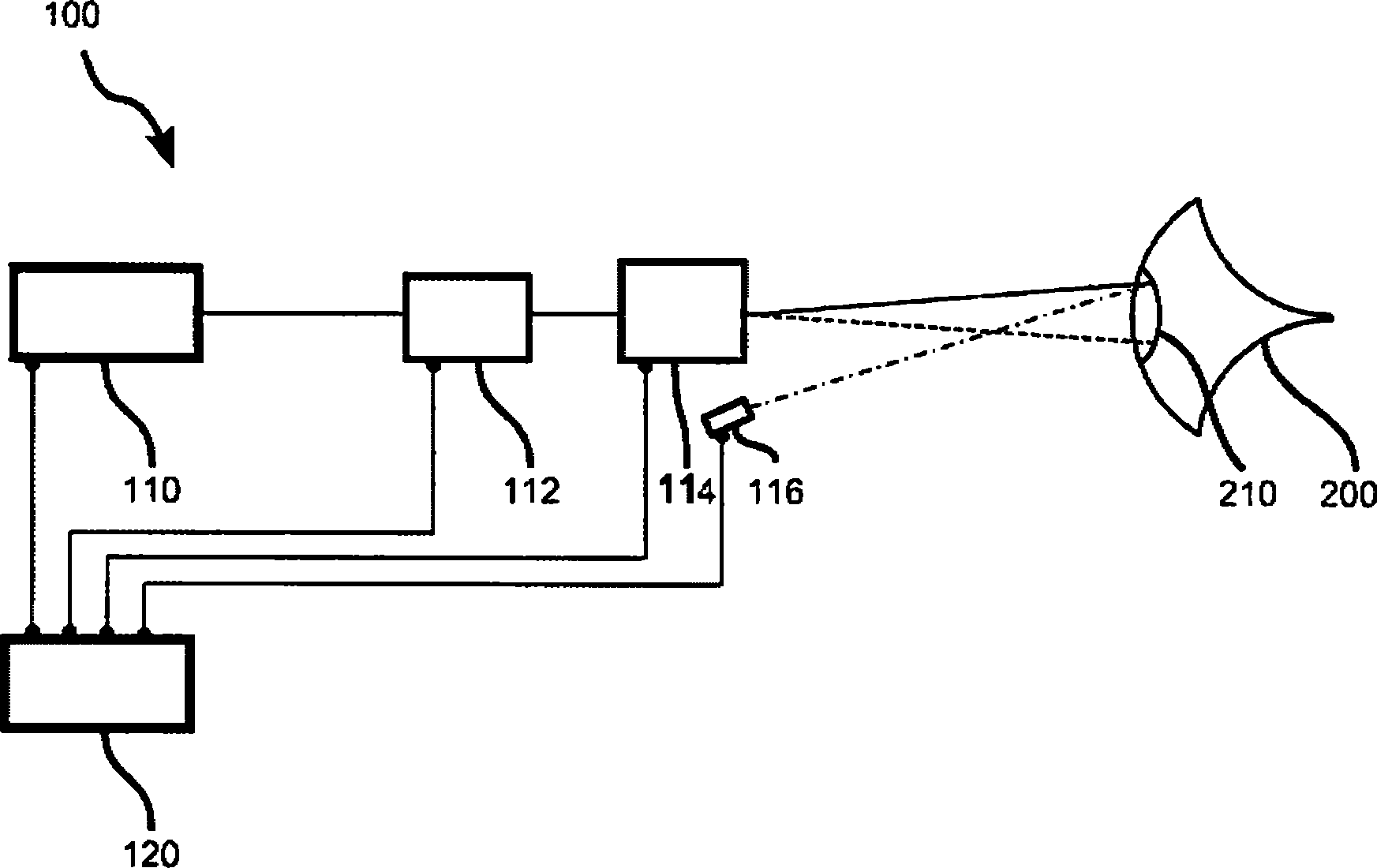
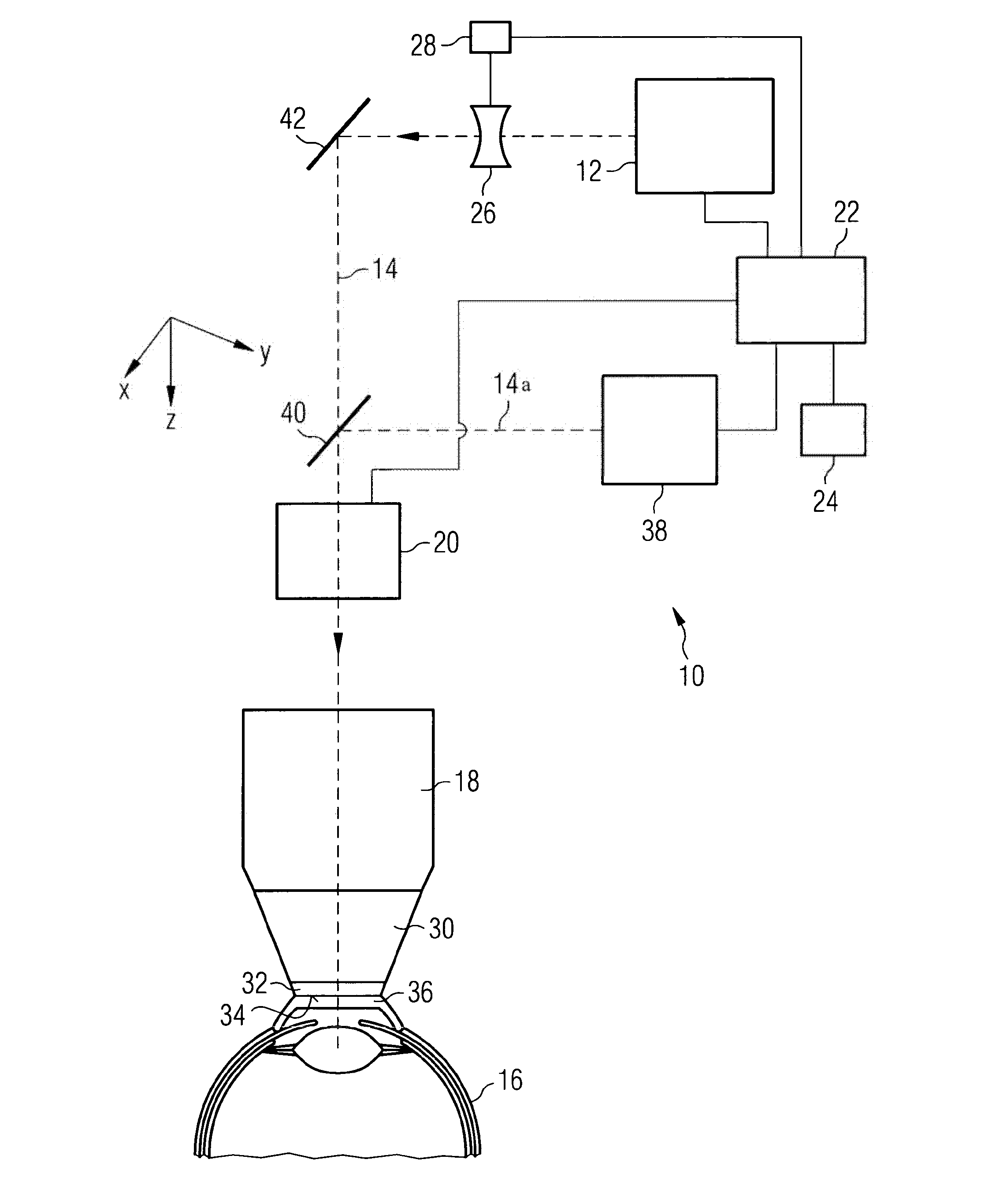
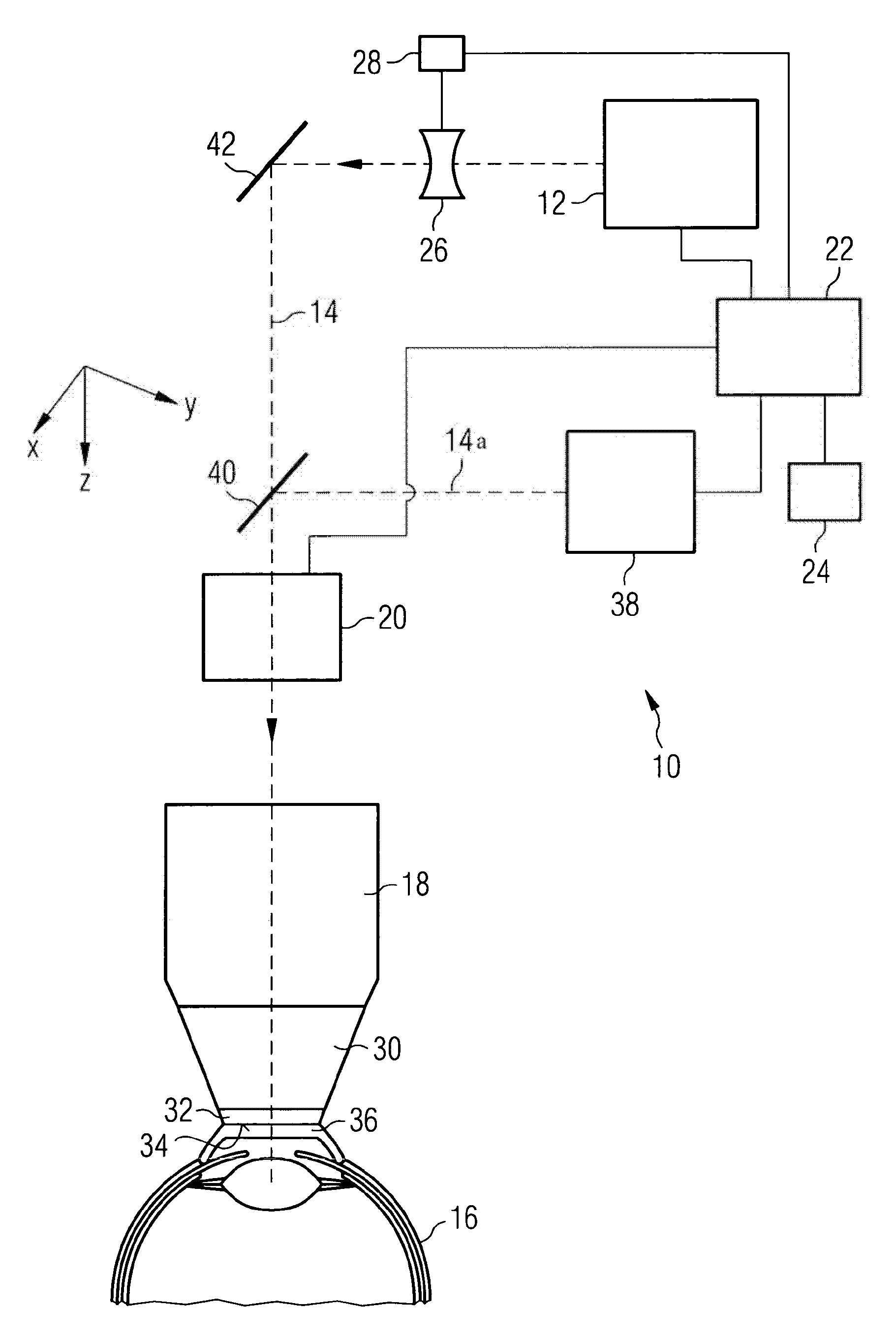
Device for ophthalmologic, particularly refractive, laser surgery
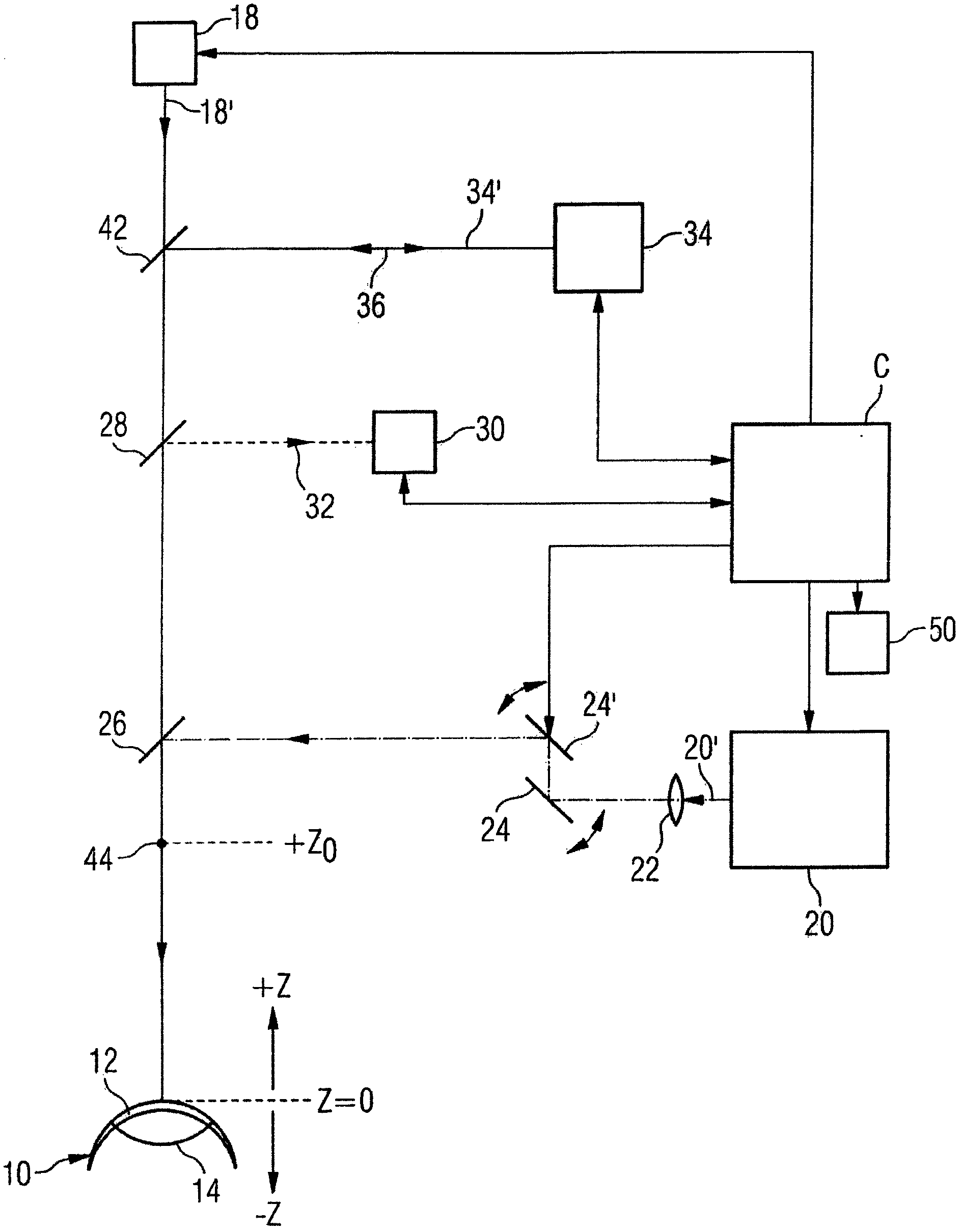
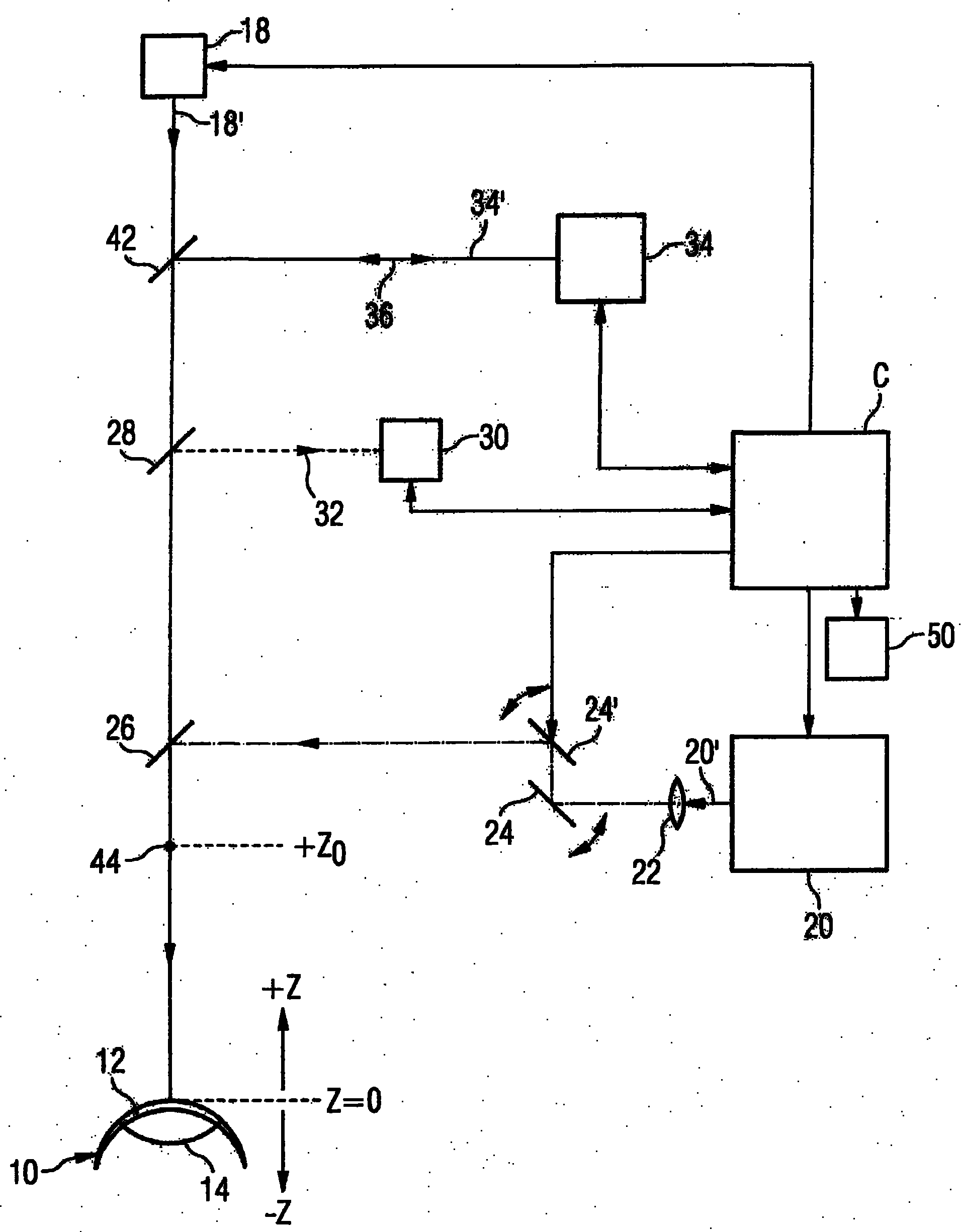
A device for ophthalmologic, particularly refractive, laser surgery comprises a laser beam source (20) for emitting a focused treatment laser beam (200) and an optical coherence interferometric measuring apparatus (34), for example an OLCR pachymeter, for measuring the z-position of a predetermined point of an eye to be treated in the coordinate system of the laser surgery device. A processor (C) used as an evaluation and control unit is equipped to assess on the basis of the measured z-position as to whether a desired treatment location of the eye in the z-direction coincides with the focal plane of the treatment laser beam or is offset therefrom. Depending on whether or not the patient is correctly positioned with respect to the focal plane, the processor (C) can cause a series of reactions.
Owner:ALCON INC
Device for laser-surgical ophthalmology
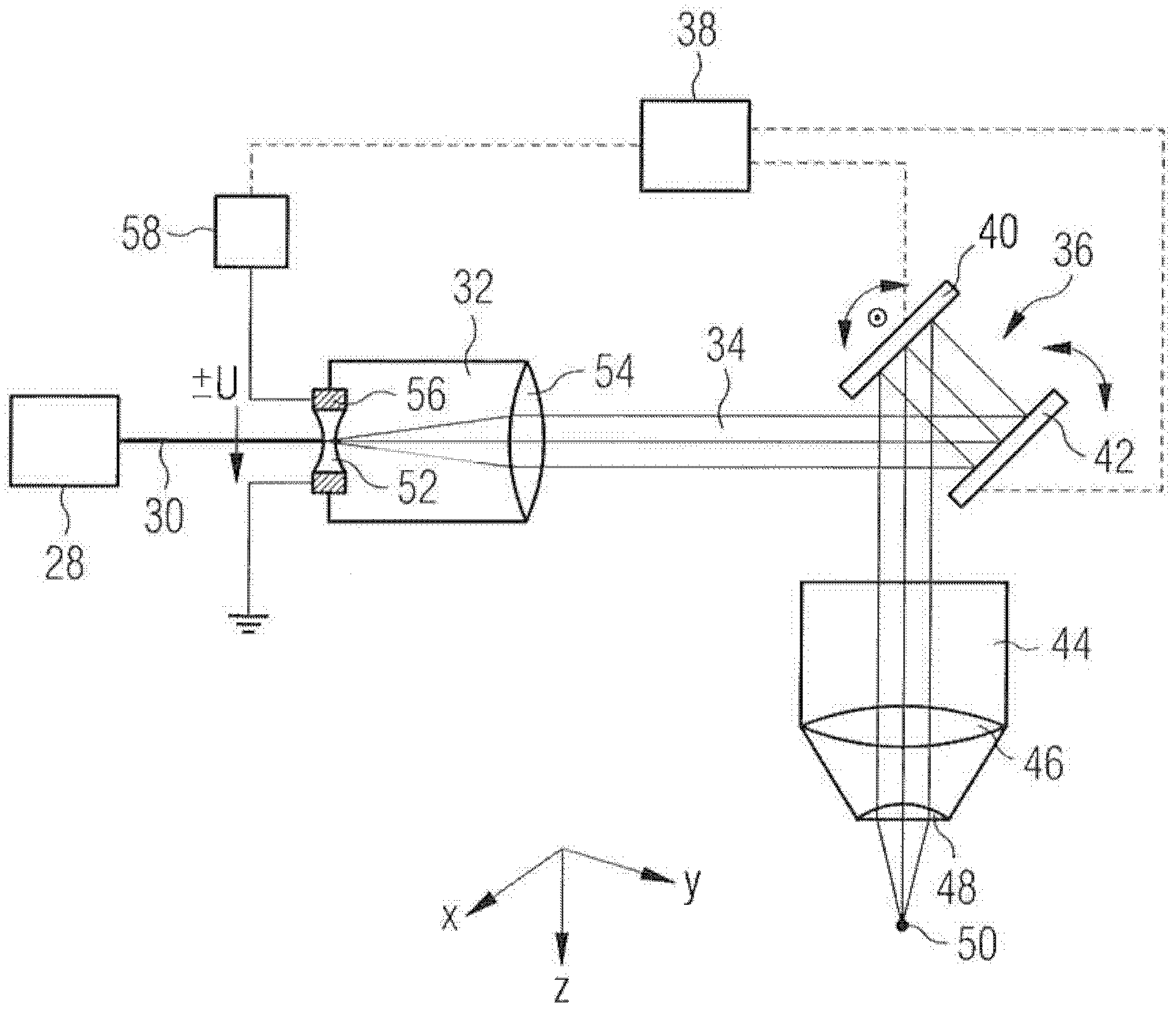
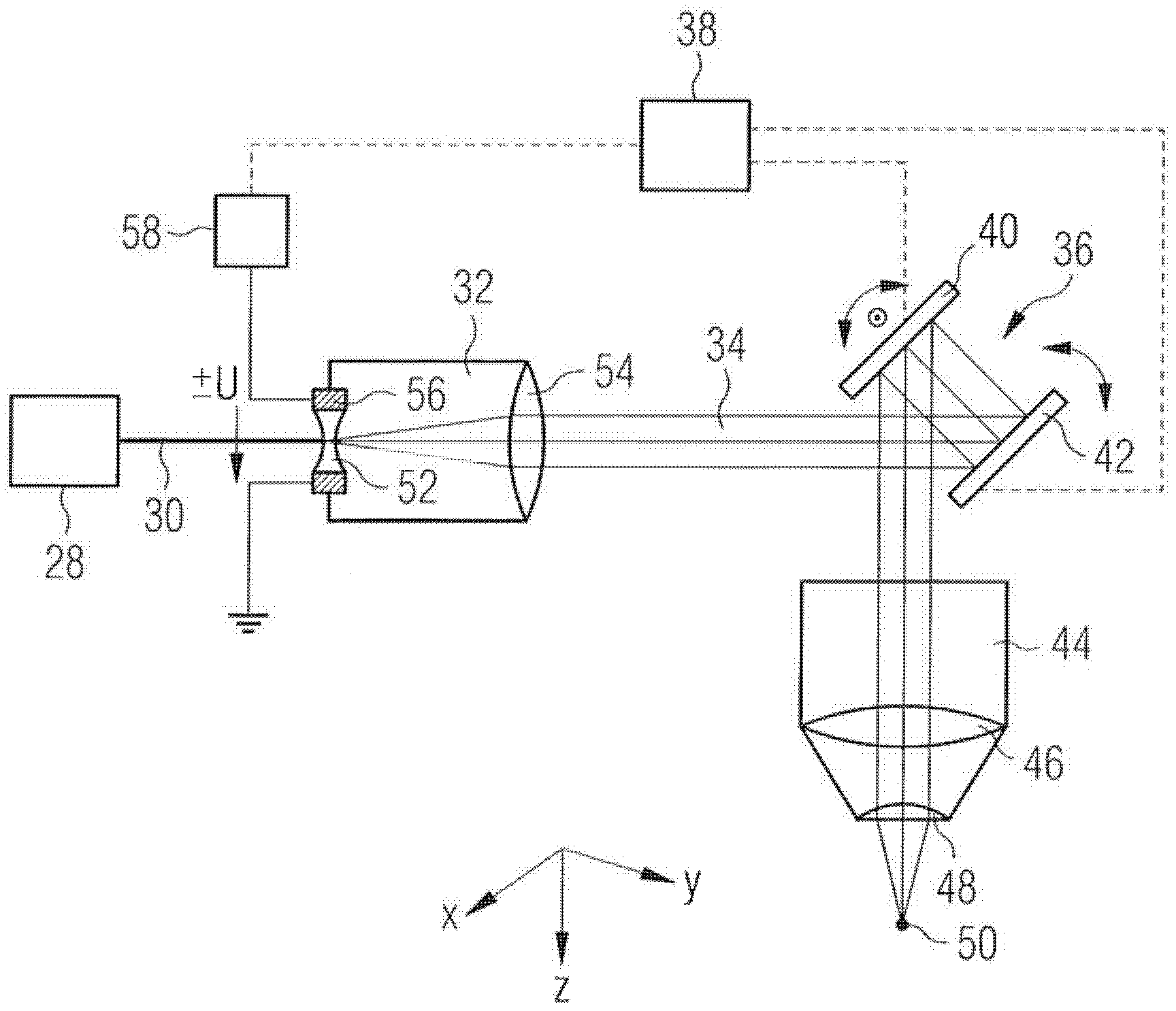
ActiveCN102458322AAccurate Matching of Vision DefectsLaser surgeryLaser beam welding apparatusEye laser surgeryLight beam
The invention relates to a device for laser-surgical ophthalmology comprising a source (28) for a pulsed femtosecond laser beam, a telescope (32) expanding the laser beam, a scanner (36) connected downstream of the telescope for deflecting the laser beam in a plane that is perpendicular to the beam path, and an F-theta lens system (44) connected downstream of the scanner for focusing the laser beam. According to the invention, an entrance lens (52) of the telescope (32) is designed as a controllable lens having variable refractive power. The entrance lens (52) is preferably formed by an electrically controllable liquid lens or liquid crystal lens.
Owner:ALCON INC
Ophthalmic laser delivery apparatus using MEMS micromirror arrays for scanning and focusing laser beam
ActiveUS20180110651A1High inertiaControl speedLaser surgeryOptical elementsEye laser surgeryEnergy control
In a laser delivery system for an ophthalmic laser surgery system, a laser beam scanner employs a single or two MEMS micromirror arrays. Each micromirror in the array is capable of being independently actuated to rotate to desired angles. In one embodiment, one or two micromirror arrays are controlled to scan a laser beam in two directions. In another embodiment, a micromirror array is controlled to both correct optical aberrations in the laser beam and scan the laser beam in two directions. In yet another embodiment, a micromirror array is controlled to cause the laser beam to be focused to multiple focal spots simultaneously and to scan the multiple focal spot simultaneously. The ophthalmic laser surgery system also includes an ultrashort pulse laser, a laser energy control module, focusing optics and other optics, and a controller for controlling the laser beam scanner and other components of the system.
Owner:AMO DEVMENT
Tissue cooling rod for laser surgery
A laser treatment device and process with controlled cooling. The device contains a cooling element with high heat conduction properties, which is transparent to the laser beam. A surface of the cooling element is held in contact with the tissue being treated while at least one other surface of the cooling element is cooled by the evaporation of a cryogenic fluid. The cooling is coordinated with the application of the laser beam so as to control the temperatures of all affected layers of tissues. In a preferred embodiment useful for removal of wrinkles and spider veins, the cooling element is a sapphire plate. A cryogenic spray cools the top surface of the plate and the bottom surface of the plate is in contact with the skin. In preferred embodiments the wavelength of the laser beam is chosen so that absorption in targeted tissue is low enough so that substantial absorption occurs throughout the targeted tissue. In a preferred embodiment for treating large spider veins with diameters in the range of 1.5 mm, Applicants use an Er:Glass laser with a wavelength of 1.54 microns.
Owner:RELIANT TECH INC
Iterative fourier reconstruction for laser surgery and other optical applications
Methods, systems and software for determining an optical surface model for an optical tissue system using Fourier transformation algorithms. A method of reconstructing optical tissues of an eye comprises transmitting an image through the optical tissues of the eye. The surface gradients from the transmitted image are measured across the optical tissues of the eye. A Fourier transform algorithm is applied to the surface gradients to reconstruct an optical surface model that corresponds to the optical tissues of the eye.
Owner:AMO MFG USA INC
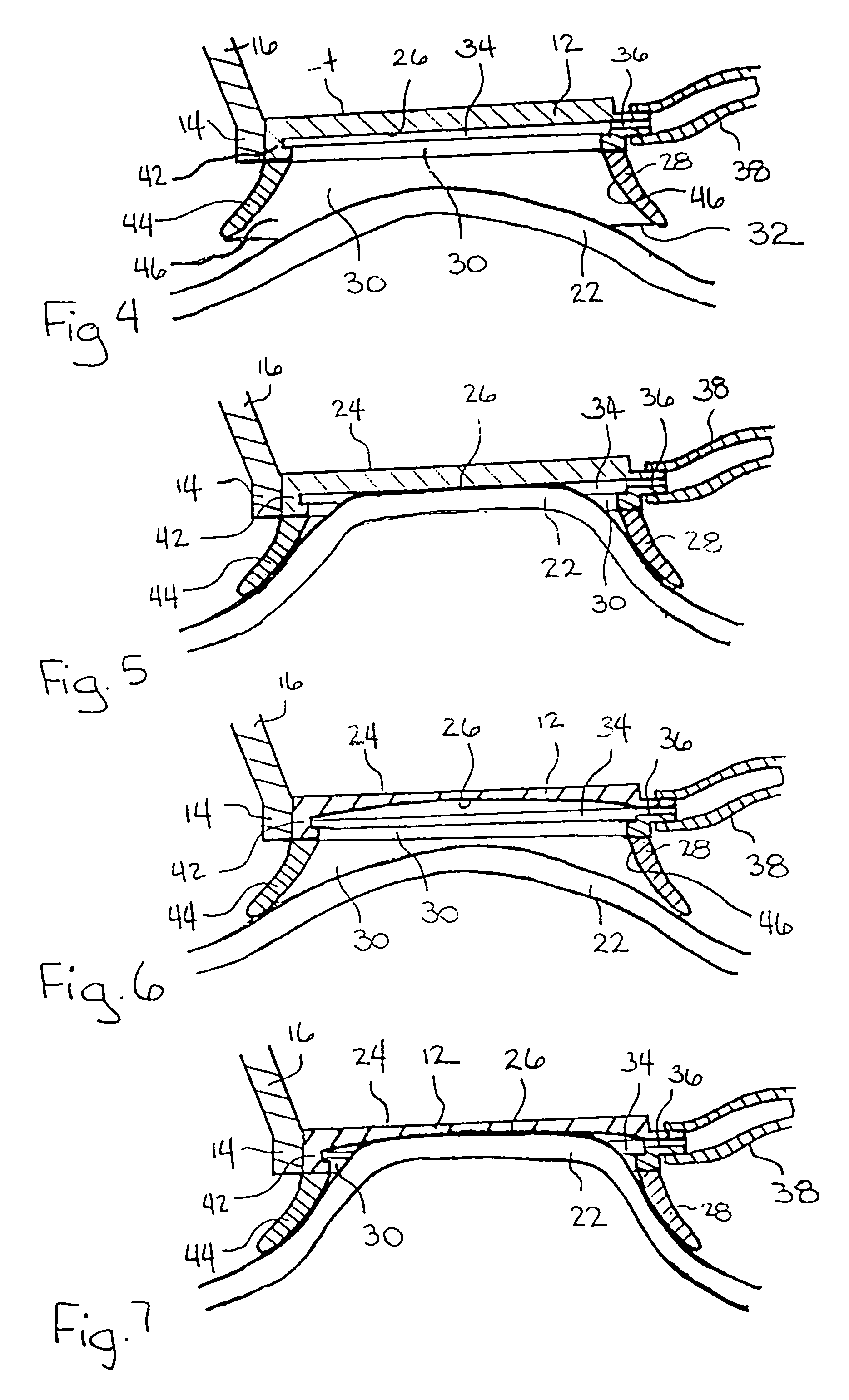
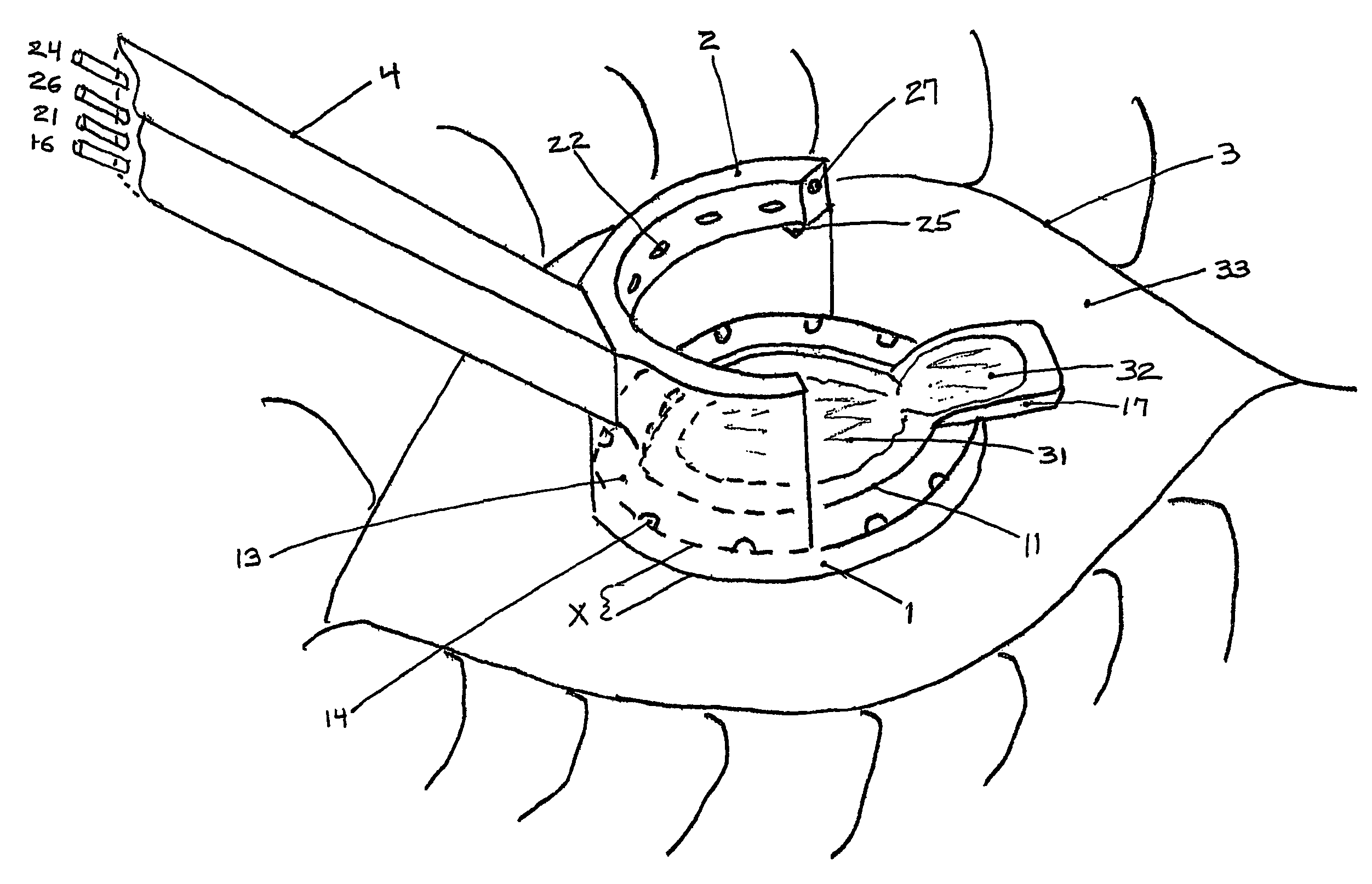
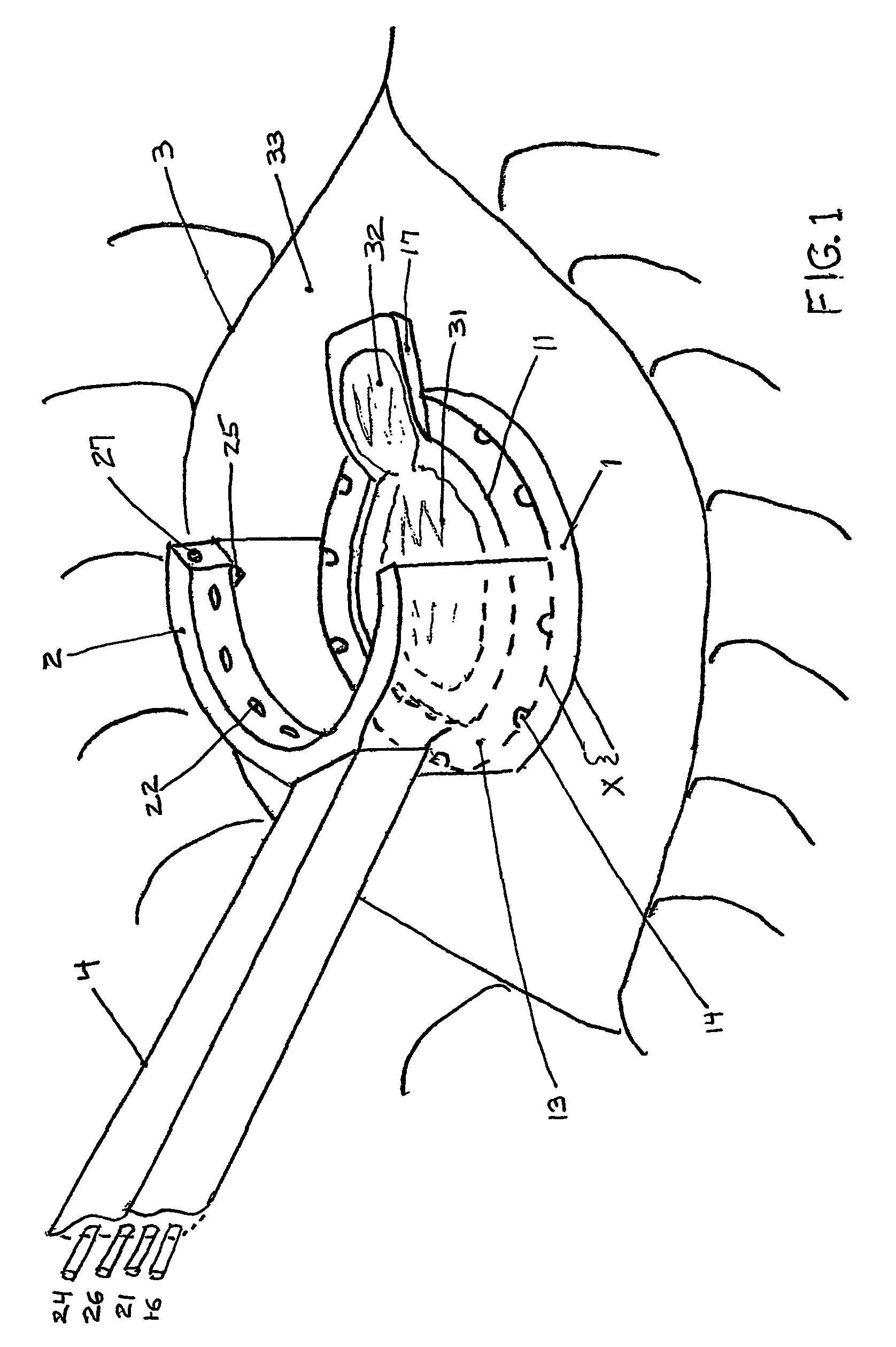
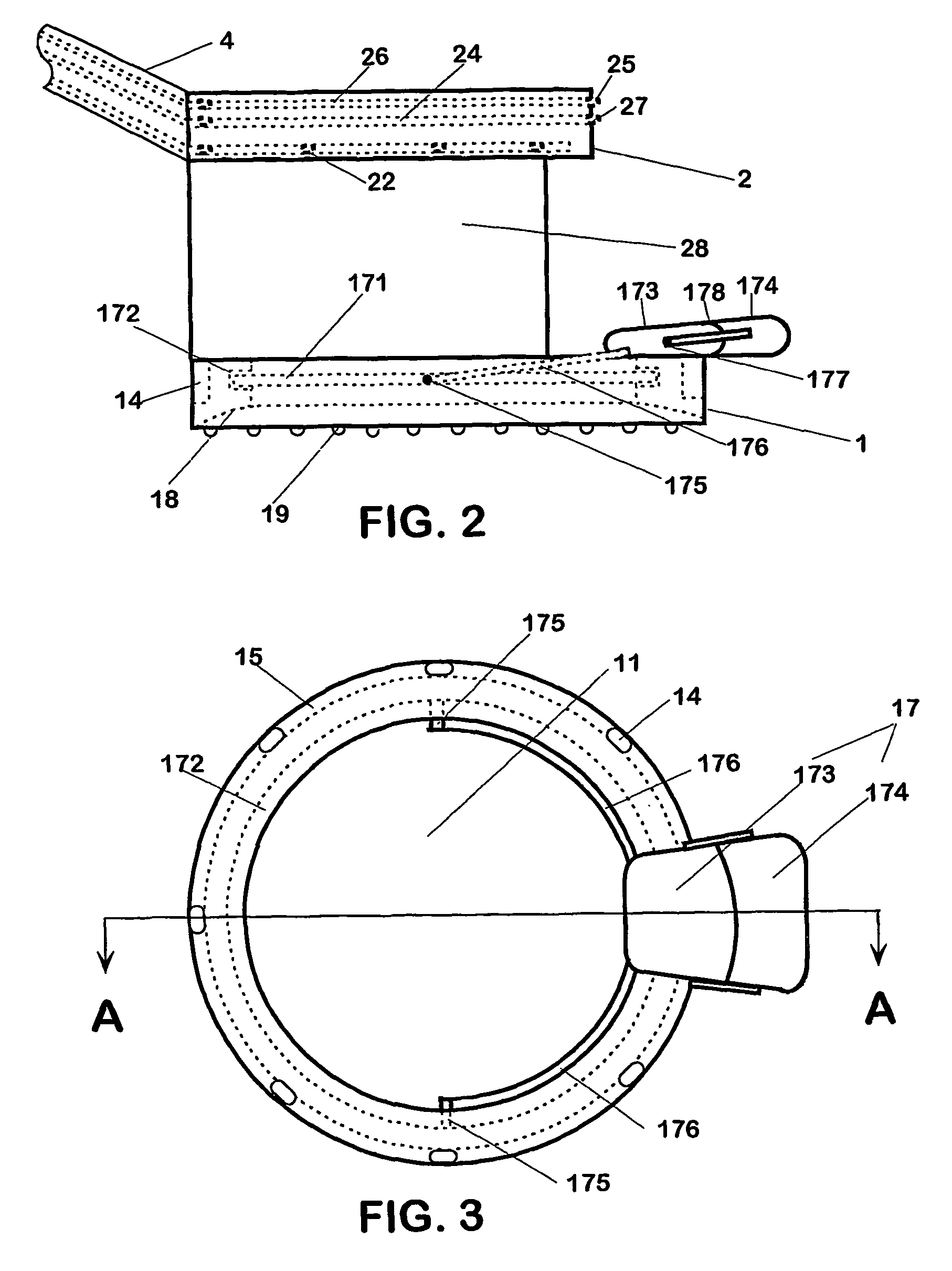
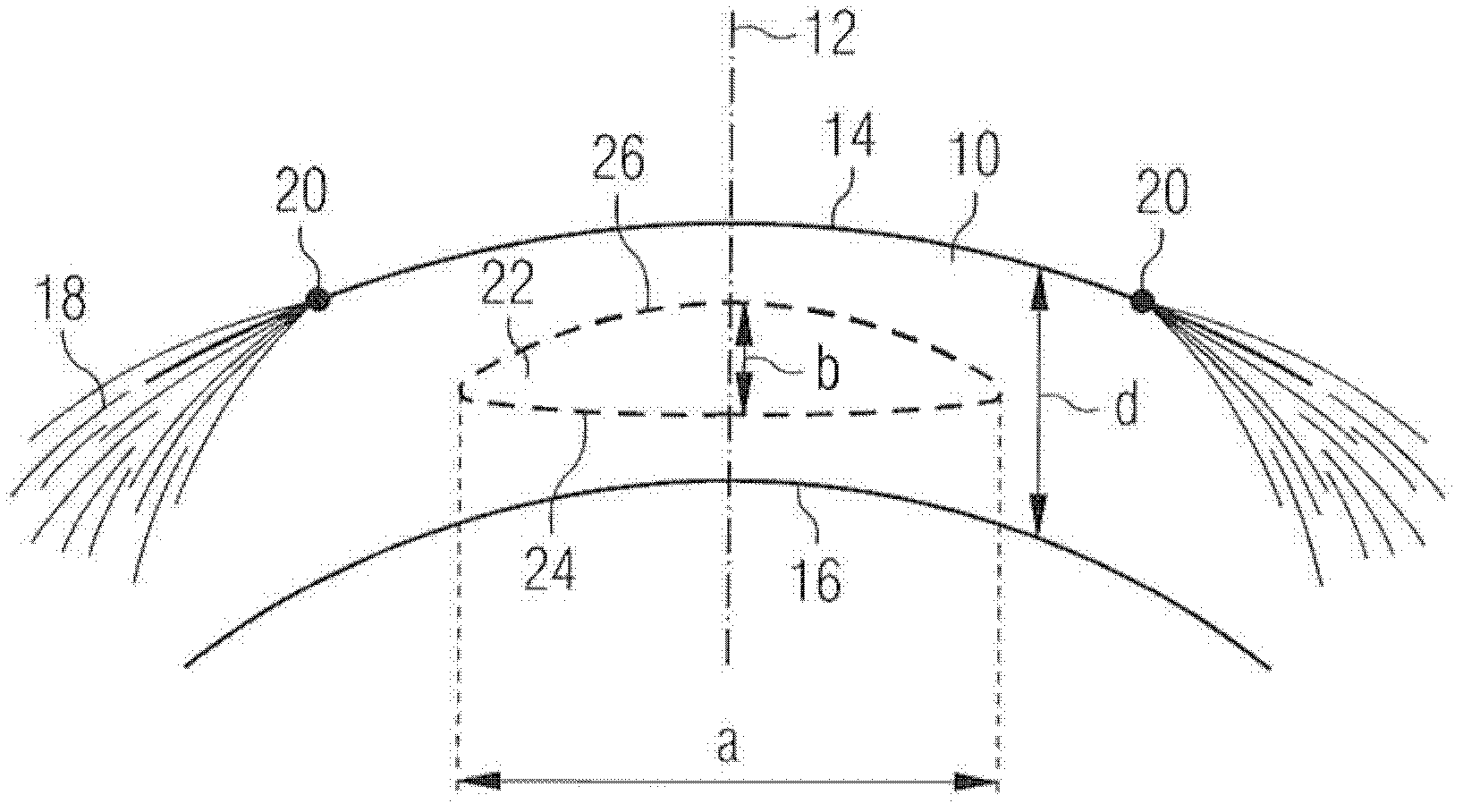
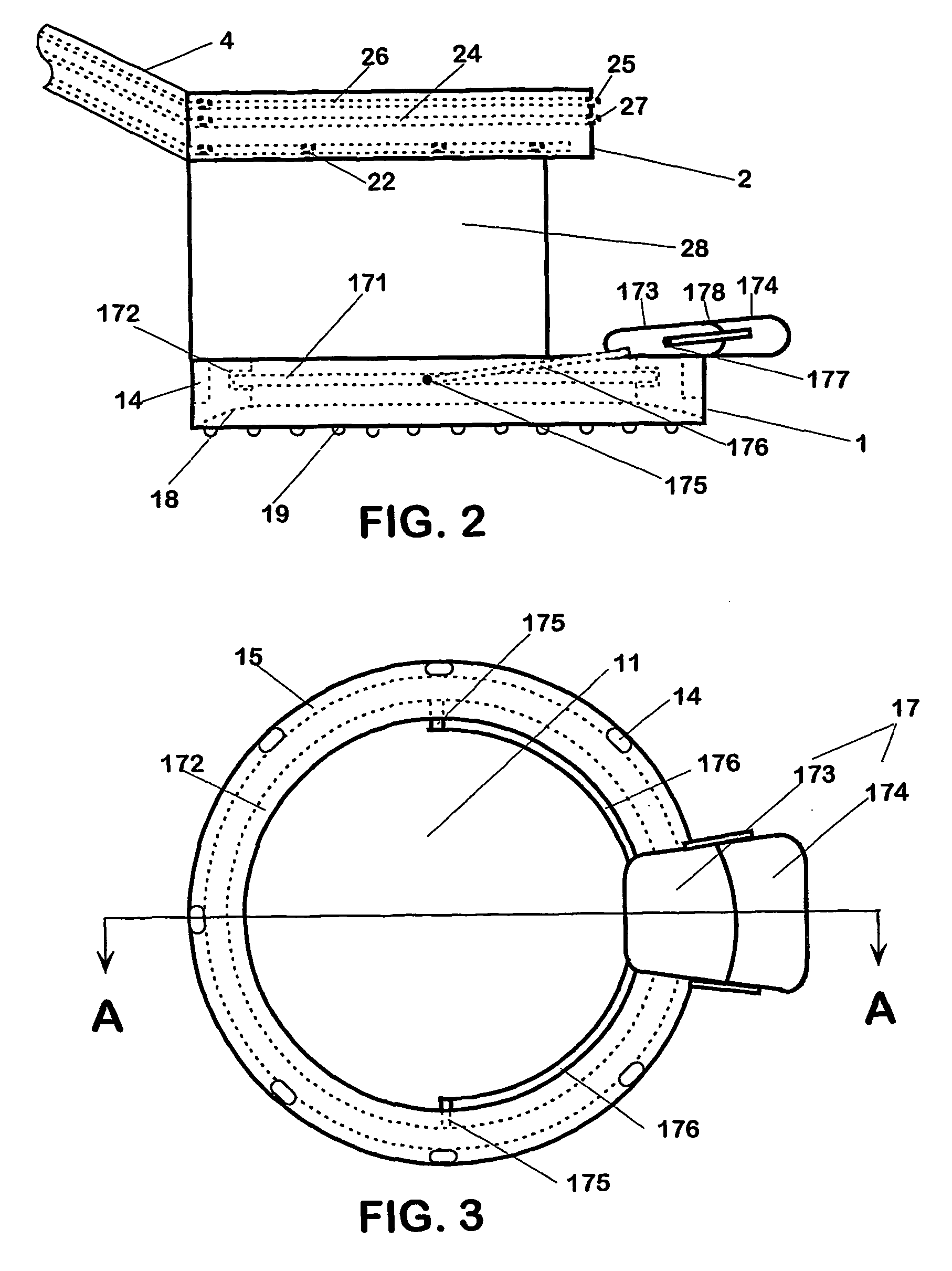
Multi-function surgical instrument for facilitating opthalmic laser surgery
A multi-function surgical instrument for facilitating ophthalmic surgery of the eye (3) by laser means, included are a lower ring (1) and an upper ring (2). One or two intermediate rings may also be included. The lower ring (1) includes a central aperture (11) to capture the limbus and aid in positioning of the eye (3). Protuberances on the lower surface (18) of said ring (1), application of vacuum between the lower surface (18) of the ring (1) and the eye (3), or both may be used to more firmly grip the eye (3). Ports (14) disposed on the upper surface (13) of the lower ring (1) and connected to a vacuum source may be used to control hydration of the surgical field. Attached to structures of the lower ring (1) is a sterile platform (17) for reposing temporarily removed tissues (32) during the administration of laser pulses to other tissues. The upper ring (2) is disposed above the surgical bed. Ports (22) disposed along said upper ring (2) and connected to a vacuum source may be used to control smoke and splatters resulting from the ablative procedure and create additional airflow to further control hydration of the surgical field.
Owner:LAHAYE LEON C
Ophthalmic laser surgery apparatus, and eyeball fixing portion movement unit and eyeball fixing unit used in the same
An ophthalmic laser surgery apparatus includes an irradiation optical system and including an objective lens, and treats a patient's eye by using a laser beam. The ophthalmic laser surgery apparatus includes a delivery unit that includes an irradiation end unit, includes at least a portion of the irradiation optical system, and optically guides the laser beam, a first movement unit that includes a first drive section and integrally moves the irradiation end unit and an eyeball fixing unit which is connected to the delivery unit and fixes the patient's eye, a second movement unit that includes a second drive section and moves the eyeball fixing unit by driving the second drive section, and drive control means for controlling driving of the first drive section and driving of the second drive section, and individually moving the first movement unit and the second movement unit.
Owner:NIDEK CO LTD
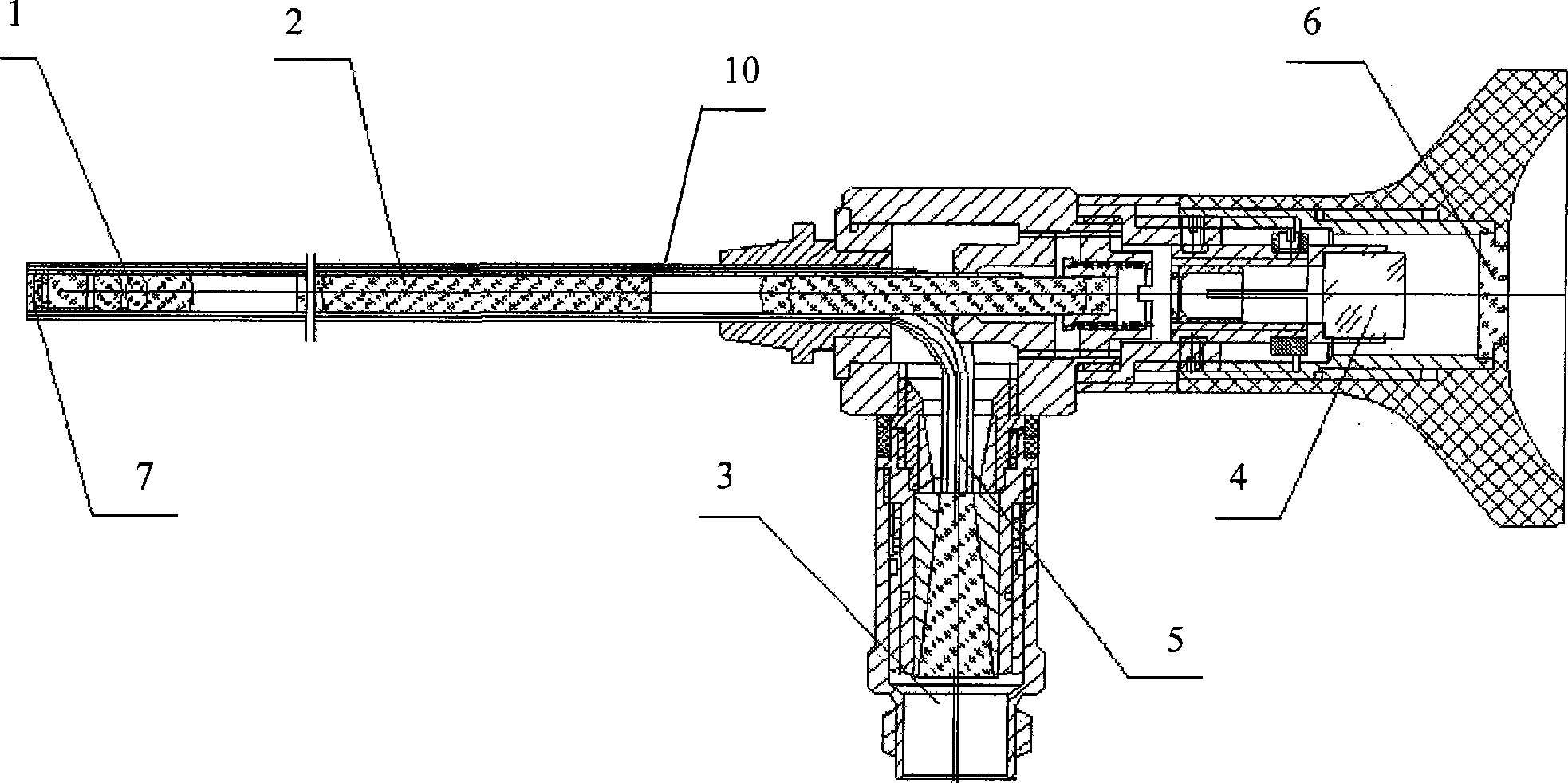
Laser surgery endoscope
InactiveCN101390776AAvoid damageGuaranteed image qualitySurgical instrument detailsEye laser surgeryImage transfer
The invention discloses a laser surgical endoscope, comprising a sealed drawtube, a field lens part, an image transferring system, a light intake part, an ocular part, a lead beam, a laser protecting lens and a window plate. The field lens part, the image transferring system, the light intake part, the ocular part, the lead beam and the laser protecting lens are arranged inside the sealed drawtube sequentially from left to right. The window plate is installed at the front end of the field lens part, and the laser protecting lens is arranged at the back end of the ocular. The lead beam is arranged inside the sealed drawtube between the window plate and the light intake part. One end of the lead beam is connected with the light intake part and the other end of the lead beam is connected with the window plate. Adopting the new design of arranging the laser protecting lens inside, the laser surgical endoscope can avoid injuries and damages to the operators and back end equipment such as a video camera and can ensure the quality of the acquired image so that the medical operators can directly carry out laser surgery under the endoscope. Therefore, the laser surgical endoscope has great practical significance for production.
Owner:TIANJIN BOLANG SCI TECH DEV
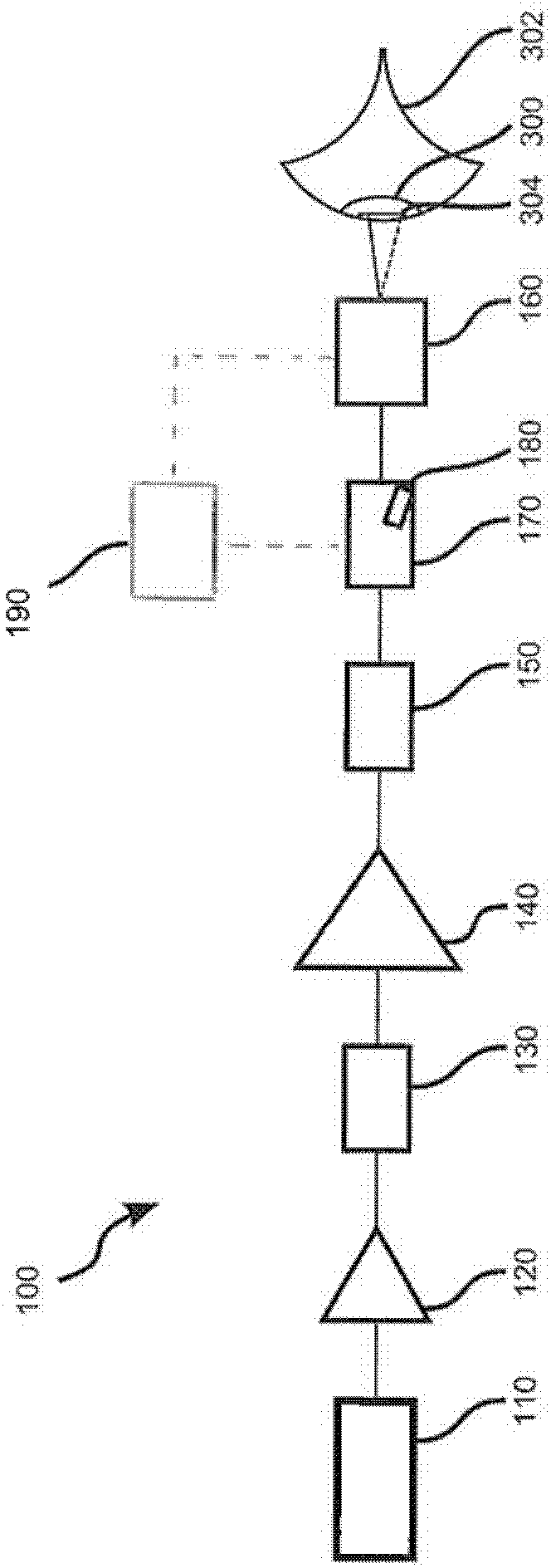
System for laser surgical ophthalmology
ActiveCN102448413AReduced pulse energyConstant pulse energyLaser surgeryLaser beam welding apparatusEye laser surgeryPulse energy
The invention relates to a system for laser surgical ophthalmology, comprising a source (110) of pulsed laser radiation having radiation parameters tuned for applying an incision in an eye tissue, particularly in the cornea, a scanner (160) for deflecting the laser radiation, and electronic control unit (190) set up for controlling the scanner according to a prescribed cut geometry, and a modulator unit (170) for modulating the laser pulse emitted by the source (110). The control unit (190) is further set up for controlling the modulator unit (170) according to a radiation deflection pattern determined for the cut geometry, such that at least one part of the laser pulse has a reduced pulse energy or is suppressed in predetermined parts of the radiation deflection pattern.
Owner:ALCON INC
System and methods for depth detection in laser-assisted ophthalmic procedures
Embodiments of this invention relate to systems and methods for automatic depth (or Z) detection before, during, or after laser-assisted ophthalmic surgery. When performing ophthalmic laser surgery, the operator (or surgeon) needs to make accurate and precise incisions using the laser beam. With the automatic depth detection systems and methods, the same laser used for the surgical procedure may be used for depth measurement of the surgical incisions. The surgical laser system may include a laser delivery system for delivering a pulsed laser beam to photoalter an eye, a mirror to transmit at least a portion of reflected light of the pulsed laser beam, a lens positioned to focus the transmitted reflected lighted on to a detector, (such as a CCD), and a depth encoder configured to automatically detect depth according to one or more of color, intensity, or shape of the focused spot on the CCD.
Owner:AMO DEVMENT
Ophthalmological surgery technique with active patient data card
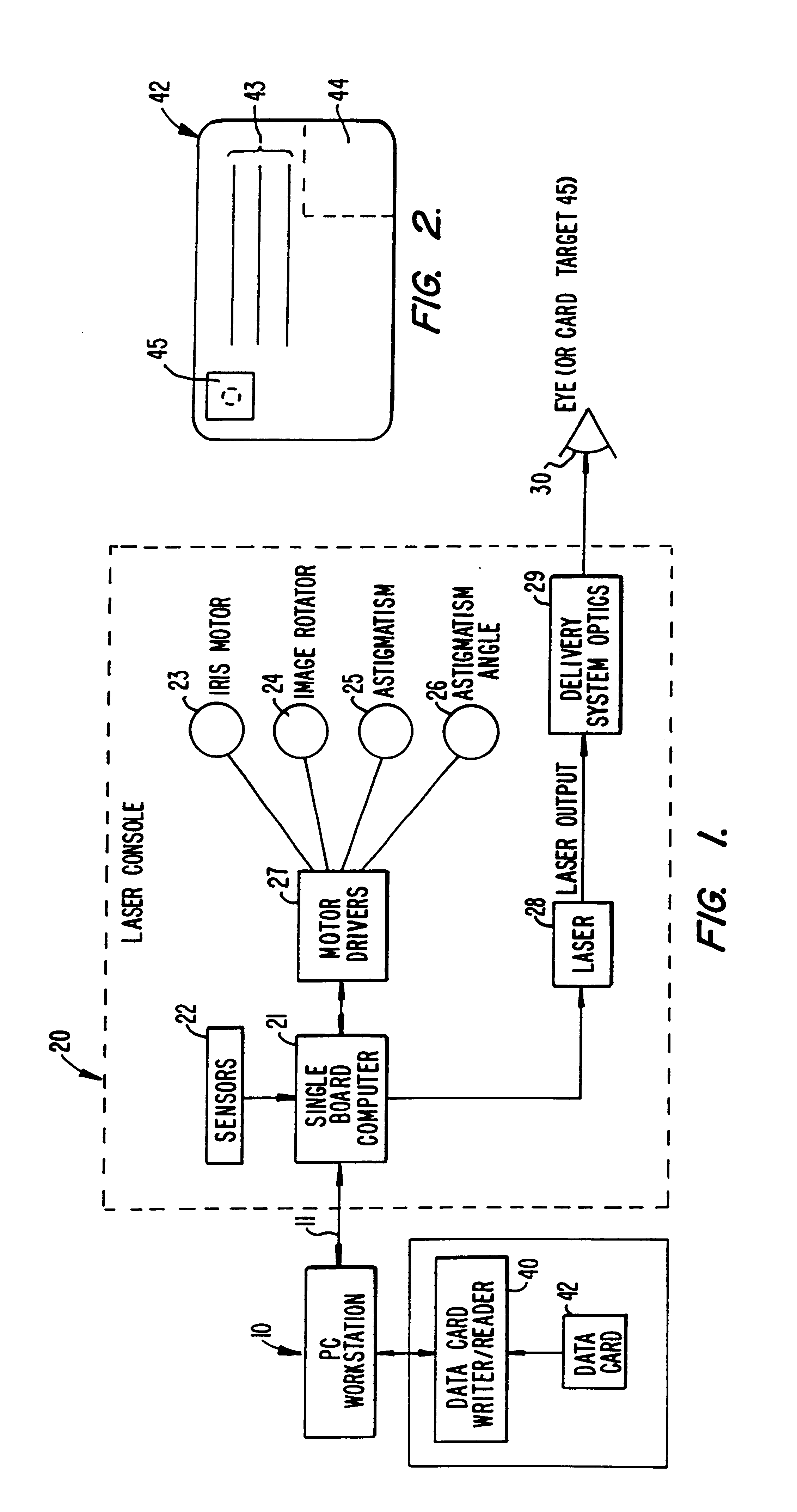
InactiveUS6846310B2Low implementation costReliable trackingLaser surgeryDiagnosticsEye laser surgeryOutput device
An ophthalmological laser surgery system having a laser, associated elements for delivering an optical beam from the laser to a patient eye location, a control unit for controlling the operation of the system and a system input / output device, is enabled by a patient data card. The data card originally contains both patient background and system control information, which is transferred to the control unit via the input / output device. During system operation, newly generated information, such as laser beam power, is stored in the data card to provide an independent record of the surgical procedure actually performed. After one use, the data card is invalidated to prevent further use.
Owner:AMO MFG USA INC
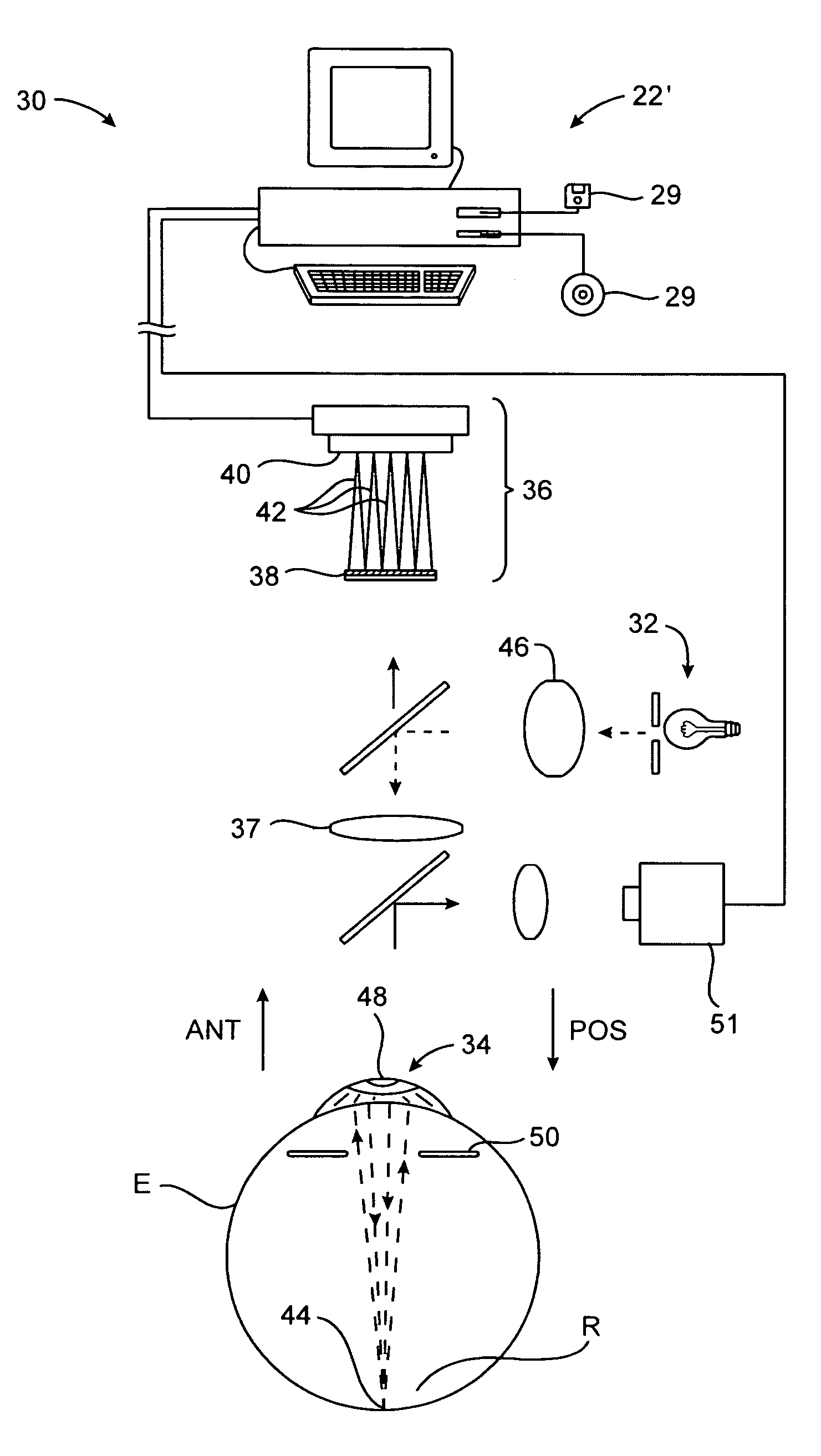
Apparatus for ophthalmological laser surgery
An apparatus for ophthalmological laser surgery comprises a contact surface (34), which bears with a shaping action on an eye (16) that is to be treated, components (12, 18, 20, 26, 40, 42) for providing focussed, pulsed laser treatment radiation and for directing the latter through the contact surface onto the eye, a measurement device (38) for measuring the position of the contact surface relative to the direction of propagation of the laser treatment radiation, wherein the measurement device provides position measurement data representative of the measured position of the contact surface at at least one location thereof, and an electronic evaluation and control arrangement (22), which is connected to the measurement device and which is designed to adjust the focal spot of the laser treatment radiation depending on the position measurement data. By measuring the position of the contact surface (34), the laser surgery apparatus permits compensation of unavoidable manufacturing tolerances of a contact element (32) forming the contact surface and therefore permits precise referencing of the anterior surface of the eye in relation to the laser surgery apparatus.
Owner:WAVELIGHT GMBH
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com